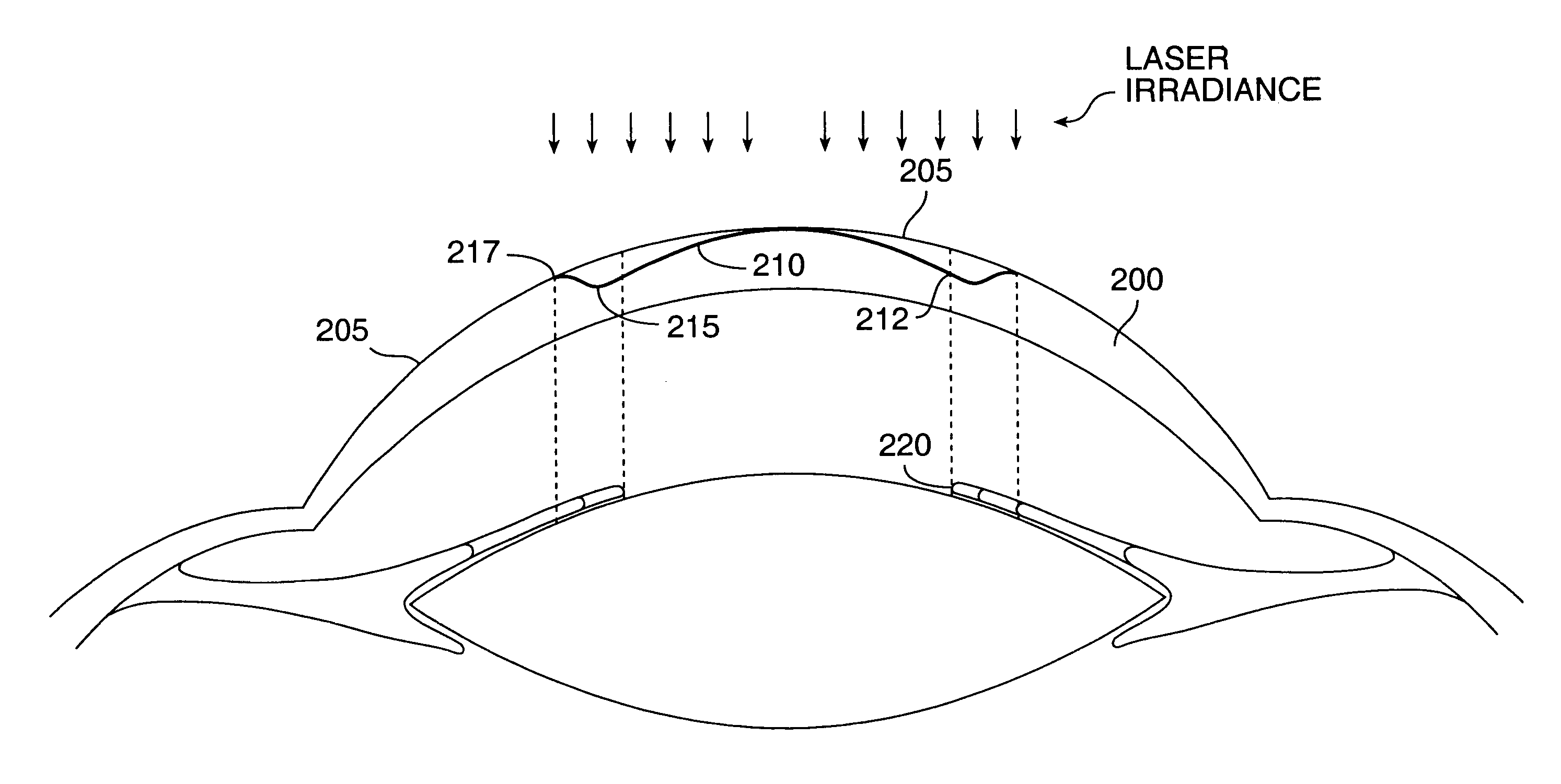
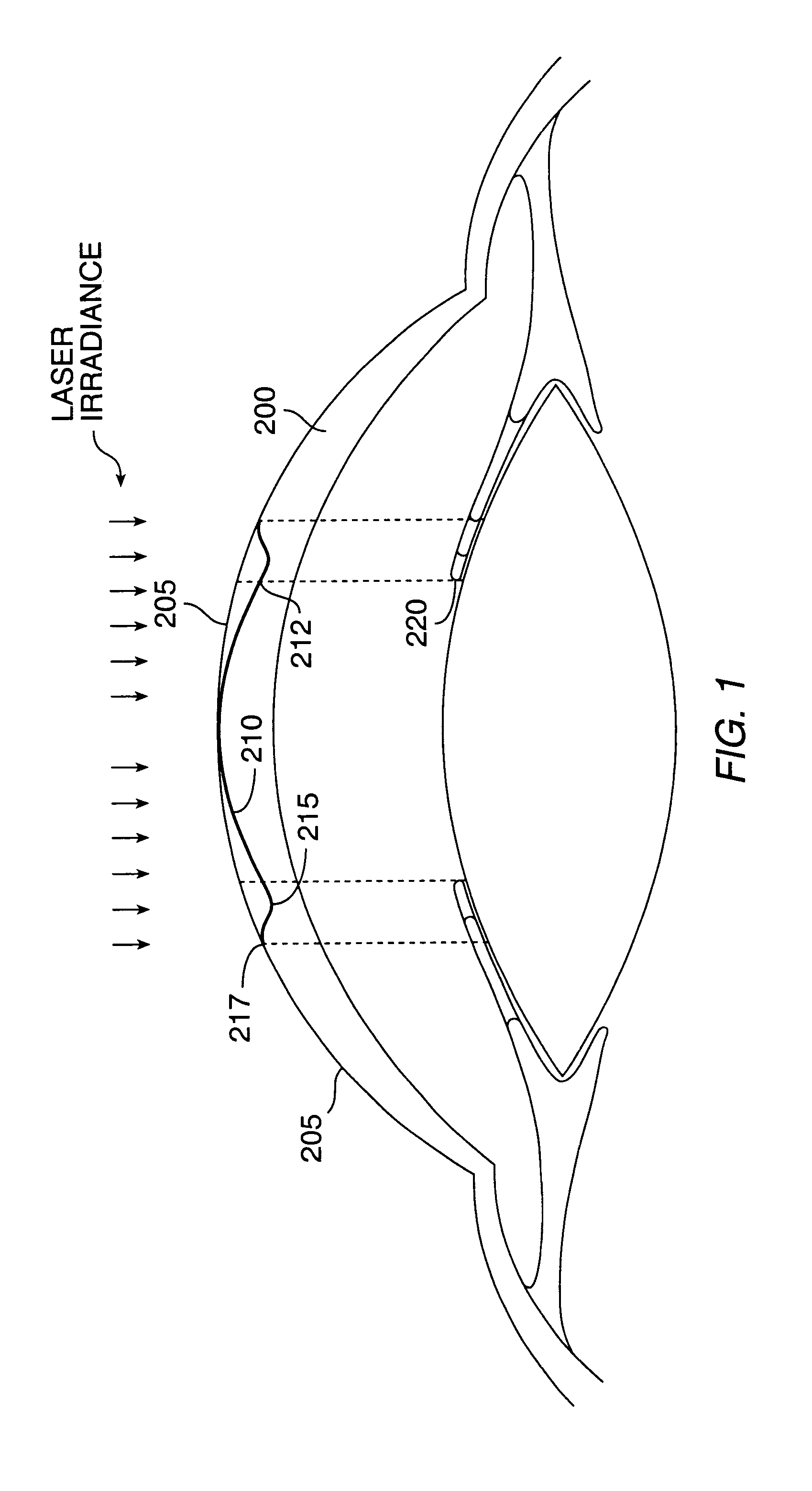
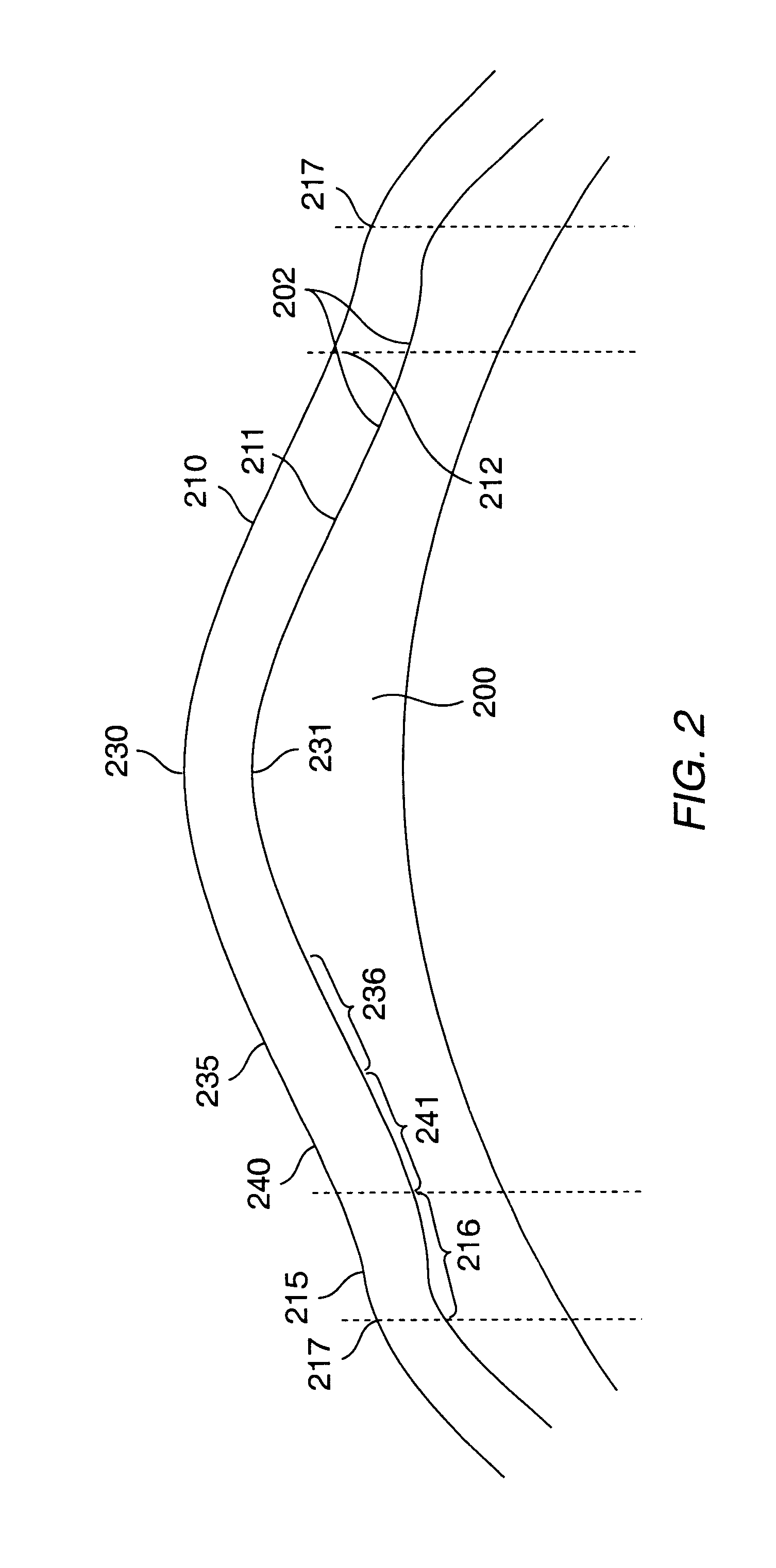
Patents
Literature
405 results about "Anterior surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
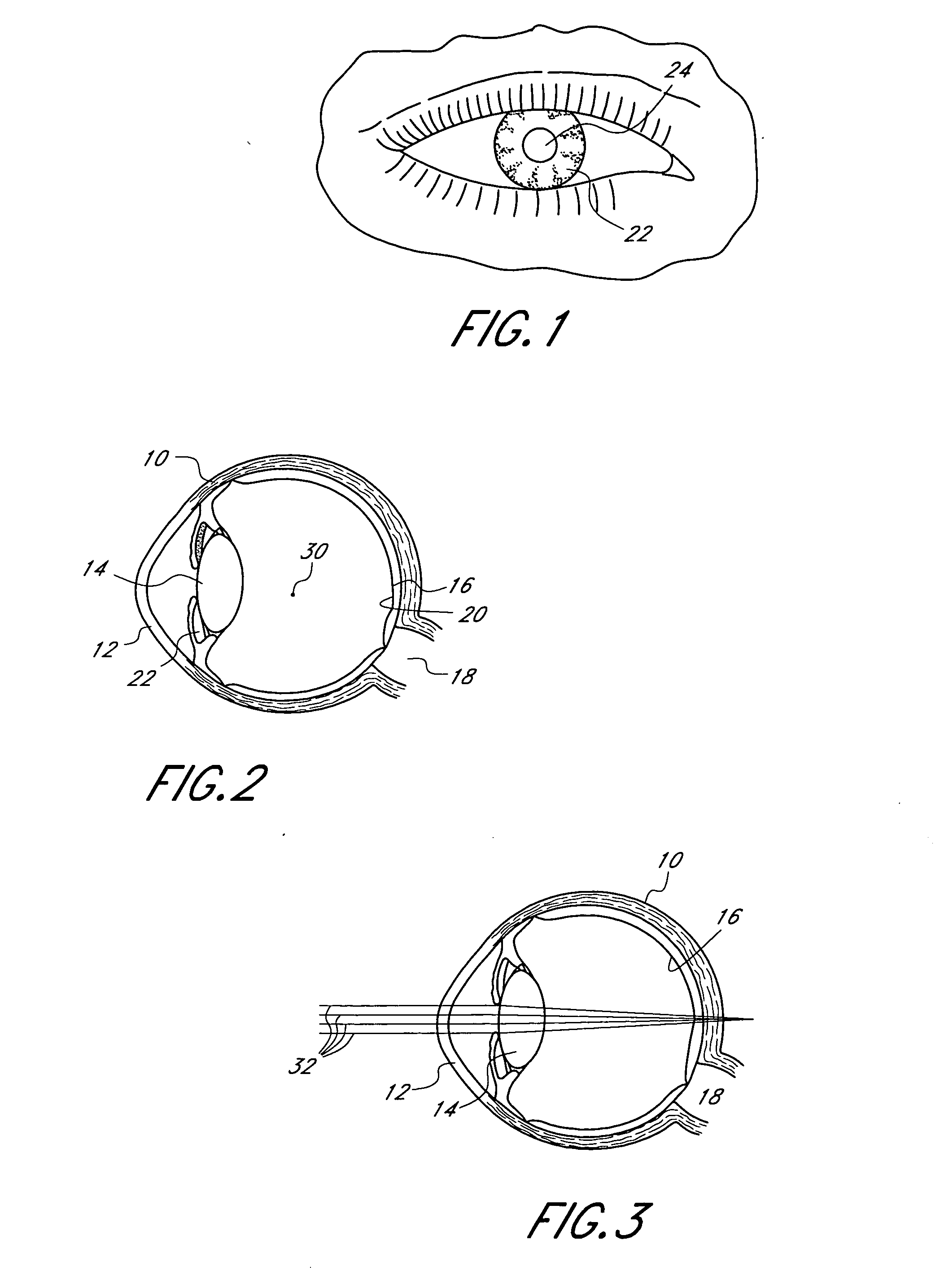
Anterior surface. Type:Term. Definitions. 1. the surface of a structure or part of the body that faces forward. TA recognizes an anterior surface (facies anterior ...) of the following structures: heart (... cordis [TA]); cornea (... corneae [TA]); body of maxilla (... corporis maxillae [TA]); lens (...
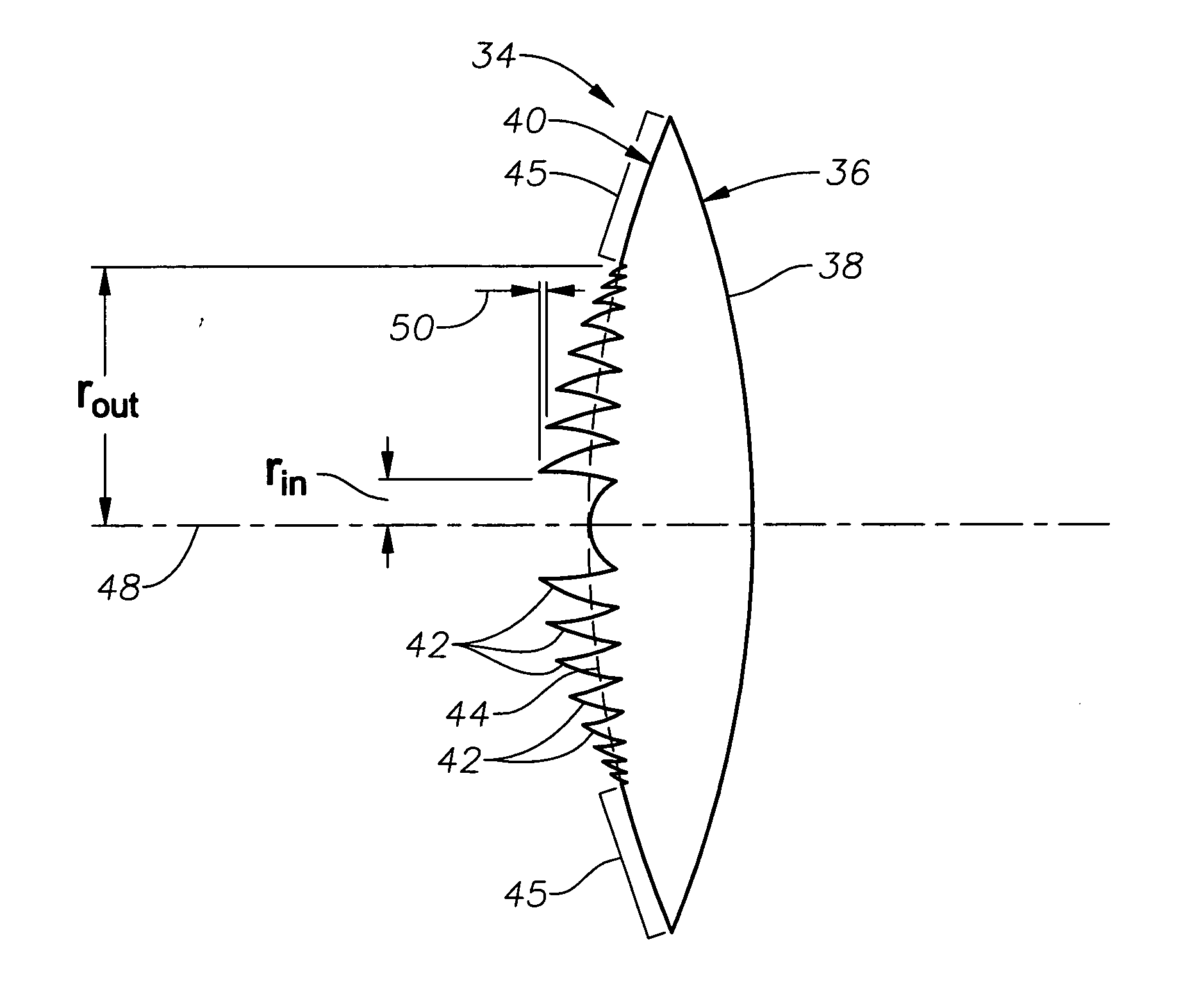
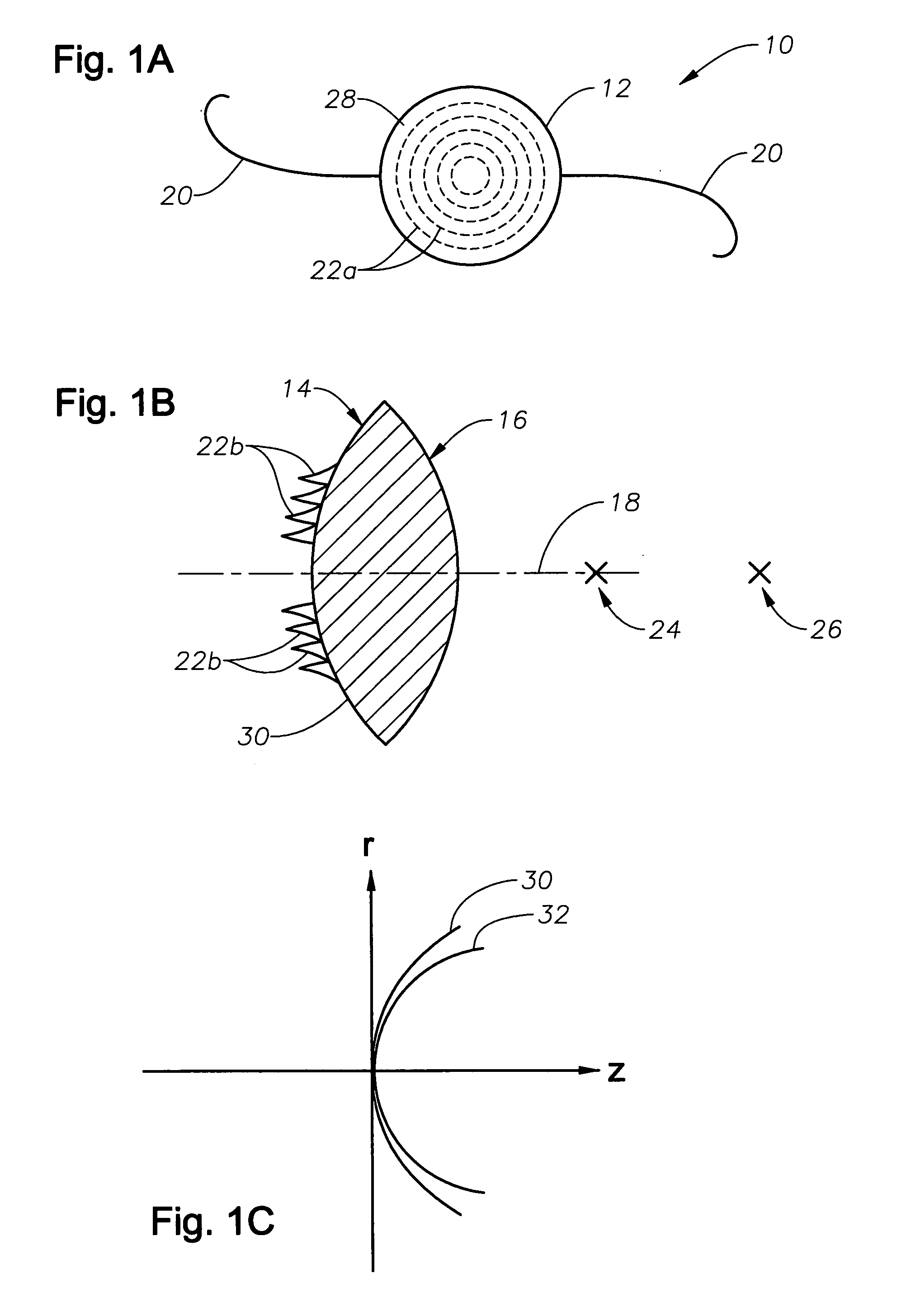
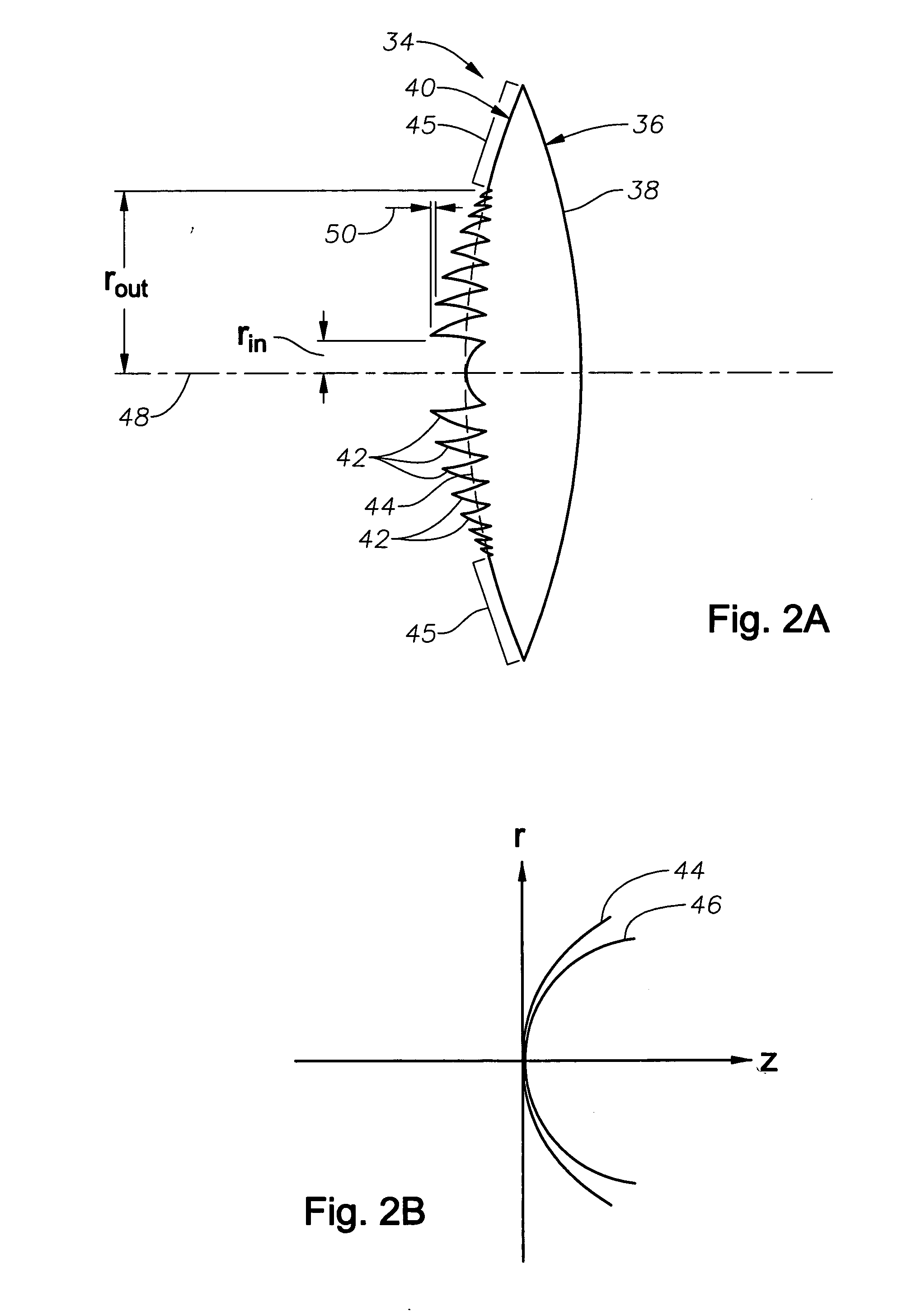
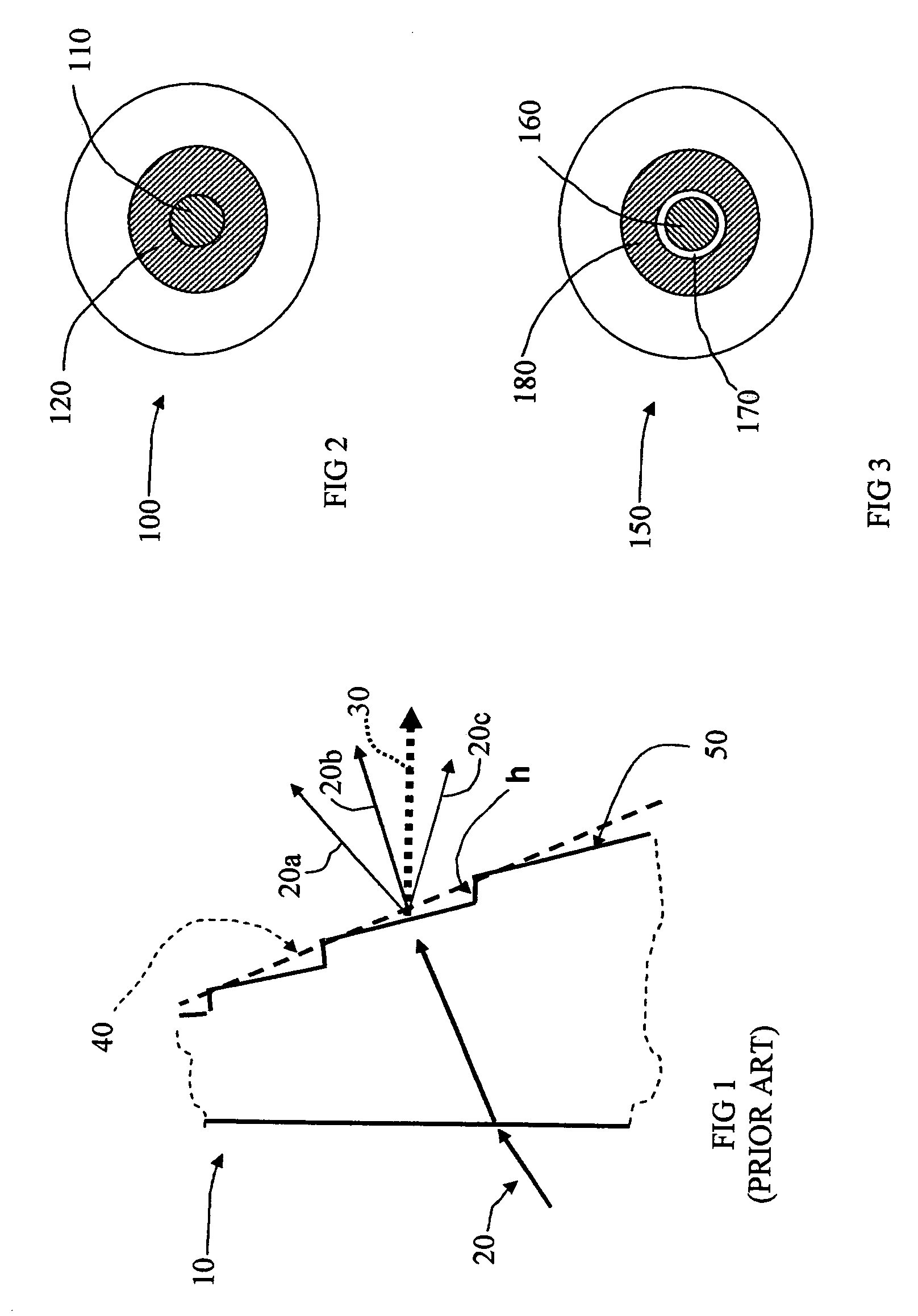
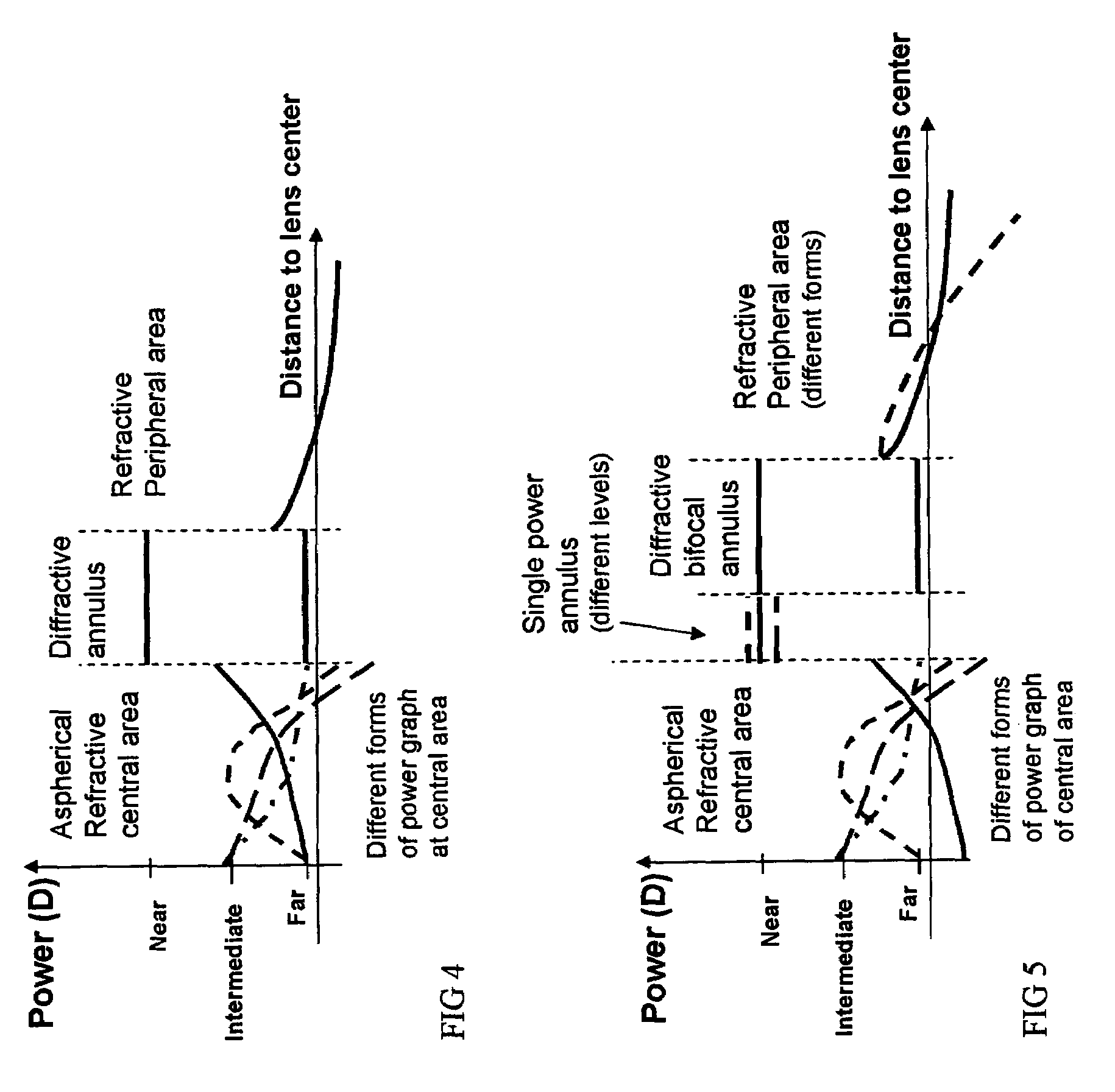
Apodized aspheric diffractive lenses
InactiveUS20060116764A1Improve image contrastSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryCamera lensImage contrast
Aspheric diffractive lenses are disclosed for ophthalmic applications. For example, multifocal intraocular lens (IOLs) are disclosed that include an optic having an anterior surface and a posterior surface, at least one of which surfaces includes an aspherical base profile on a portion of which a plurality of diffractive zones are disposed so as to generate a far focus and a near focus. The aspherical base profile enhances image contrast at the far focus of the lens relative to that obtained by a substantially identical IOL in which the respective base profile is spherical.
Owner:ALCON INC
Aspherical diffractive ophthalmic lens
ActiveUS7073906B1Limited amountIntermediate performanceSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensLens plateAnterior surface
A multifocal ophthalmic lens includes a lens element having anterior and posterior surfaces with a central aspherical refractive zone disposed on one of the anterior and posterior surfaces; and a diffractive bifocal zone disposed outside of the aspherical refractive zone. The central aspherical refractive zone may be disposed on the anterior surface and the diffractive bifocal zone may be disposed on the posterior surface.
Owner:VISION ADVANCEMENT LLC
Therapeutic device for pain management and vision
ActiveUS20100036488A1Increase moistureRelieve painSenses disorderEye implantsEpitheliumTherapeutic Devices
A therapeutic lens for the treatment of an epithelial defect comprises a layer of therapeutic material disposed over the stroma and / or Bowman's membrane to inhibit water flow from the tear liquid to the stroma and / or Bowman's membrane, such that corneal deturgescence can be restored to decrease corneal swelling and light scattering. The layer may cover and protect nerve fibers to decrease pain. The layer may comprise an index of refraction to inhibit light scatter from an anterior surface of the stroma and / or Bowman's membrane. The lens may comprise a curved anterior surface that provides functional vision for the patient when the epithelium regenerates. The layer of therapeutic material can be positioned on the eye in many ways, for example with a spray that is cured to adhere the layer to the exposed surface of the stroma and / or Bowman's membrane.
Owner:NEXIS VISION LIQUIDATING TRUST +2
Intraocular implant and an artificial lens device
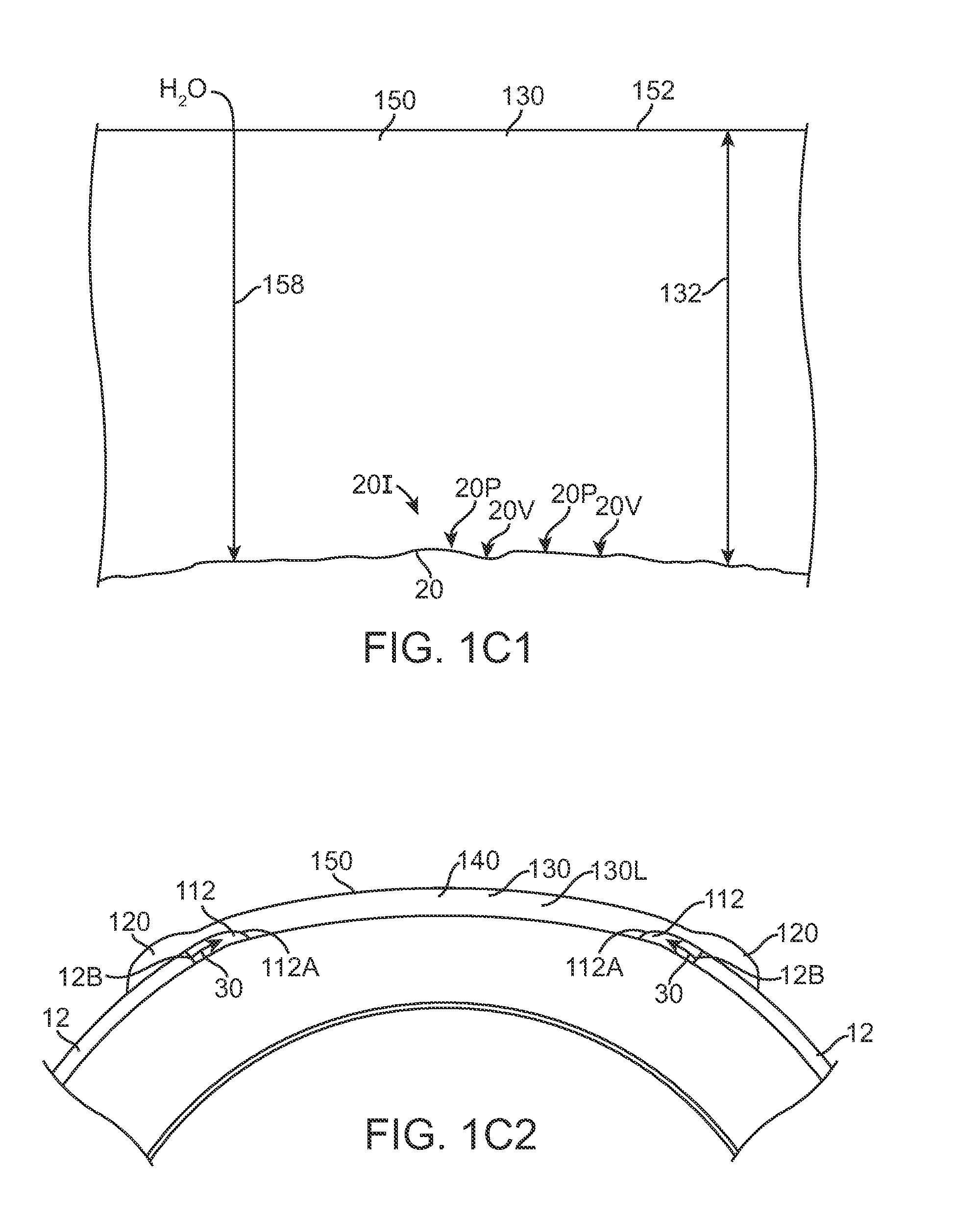
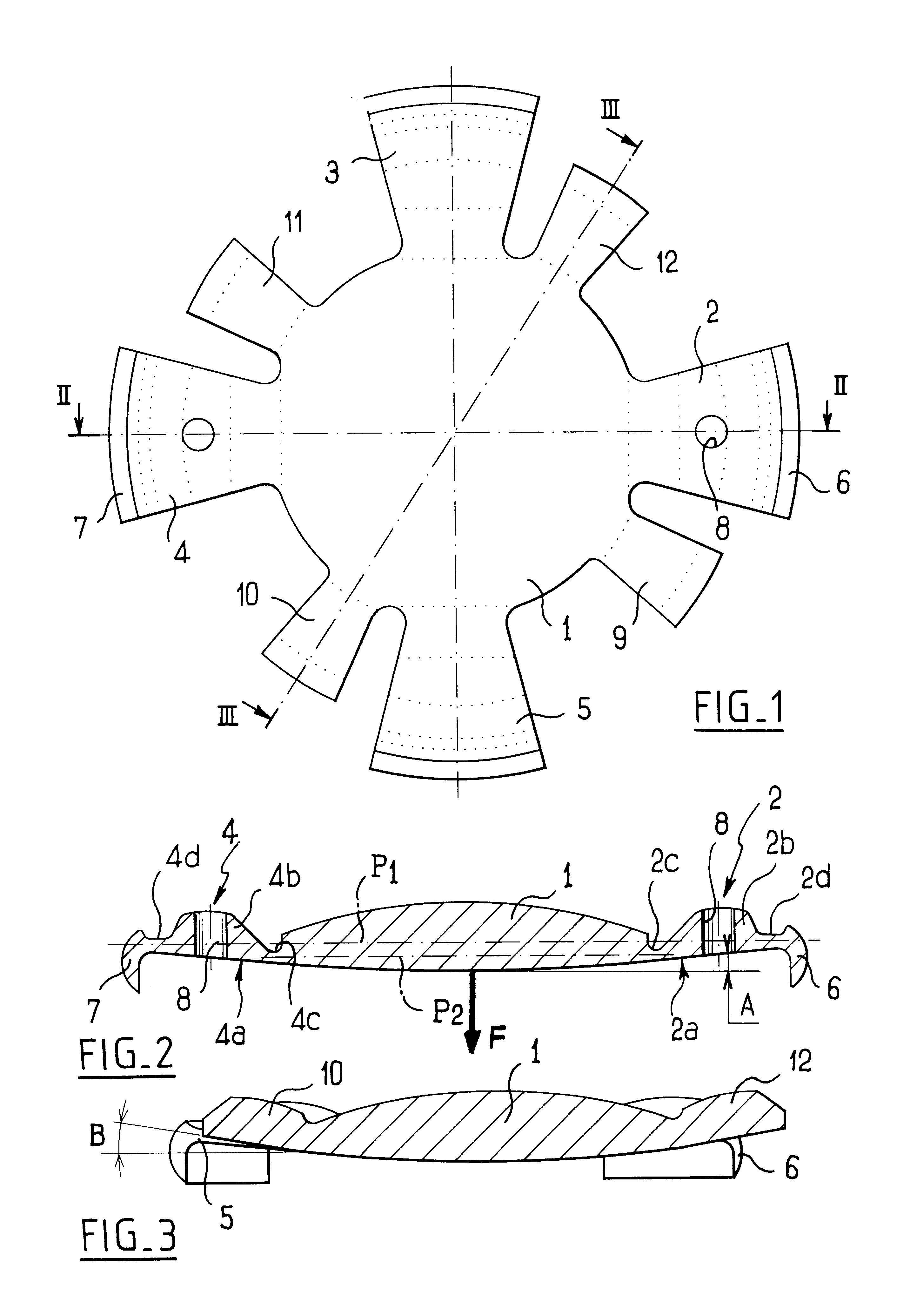
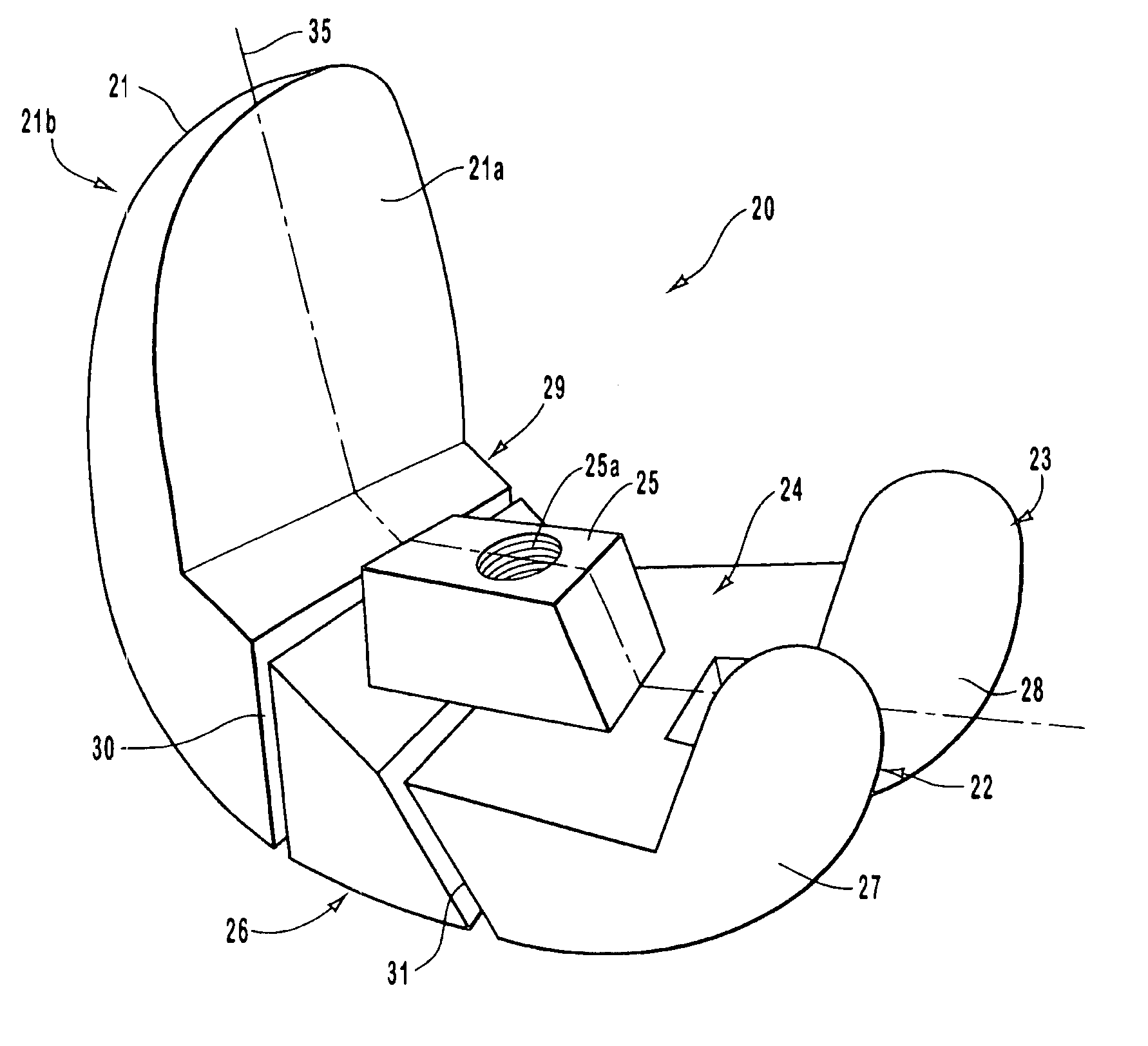
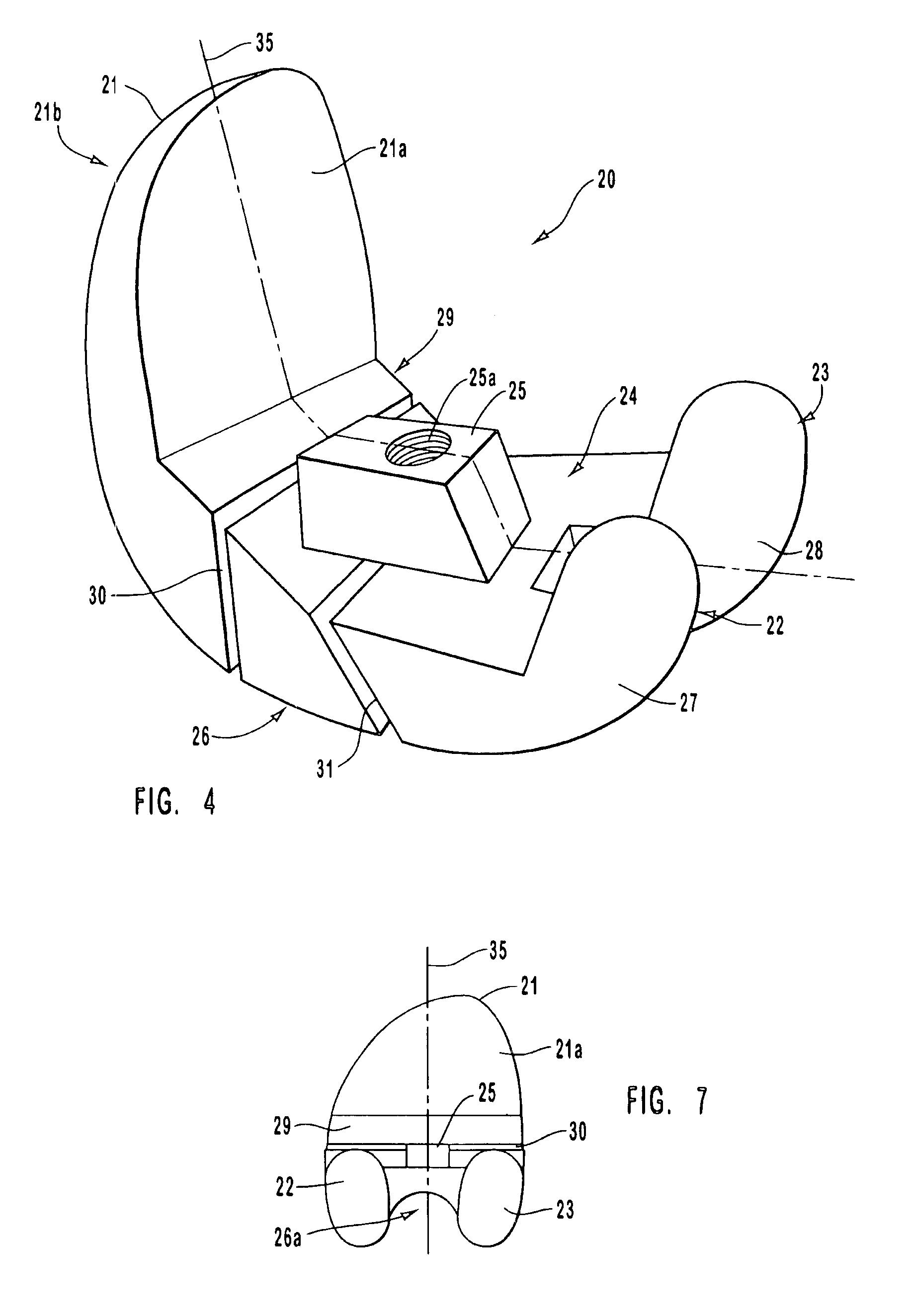
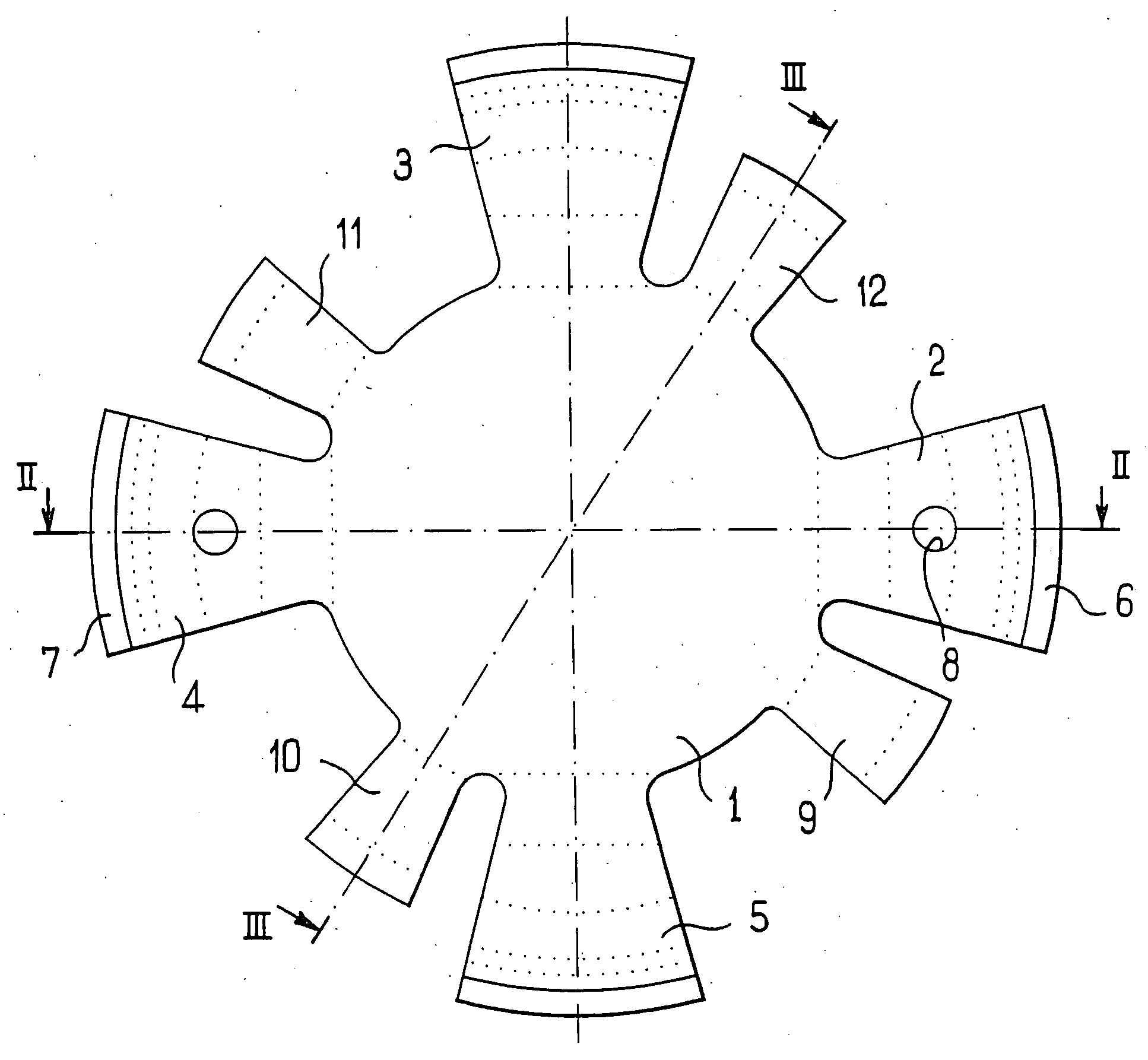
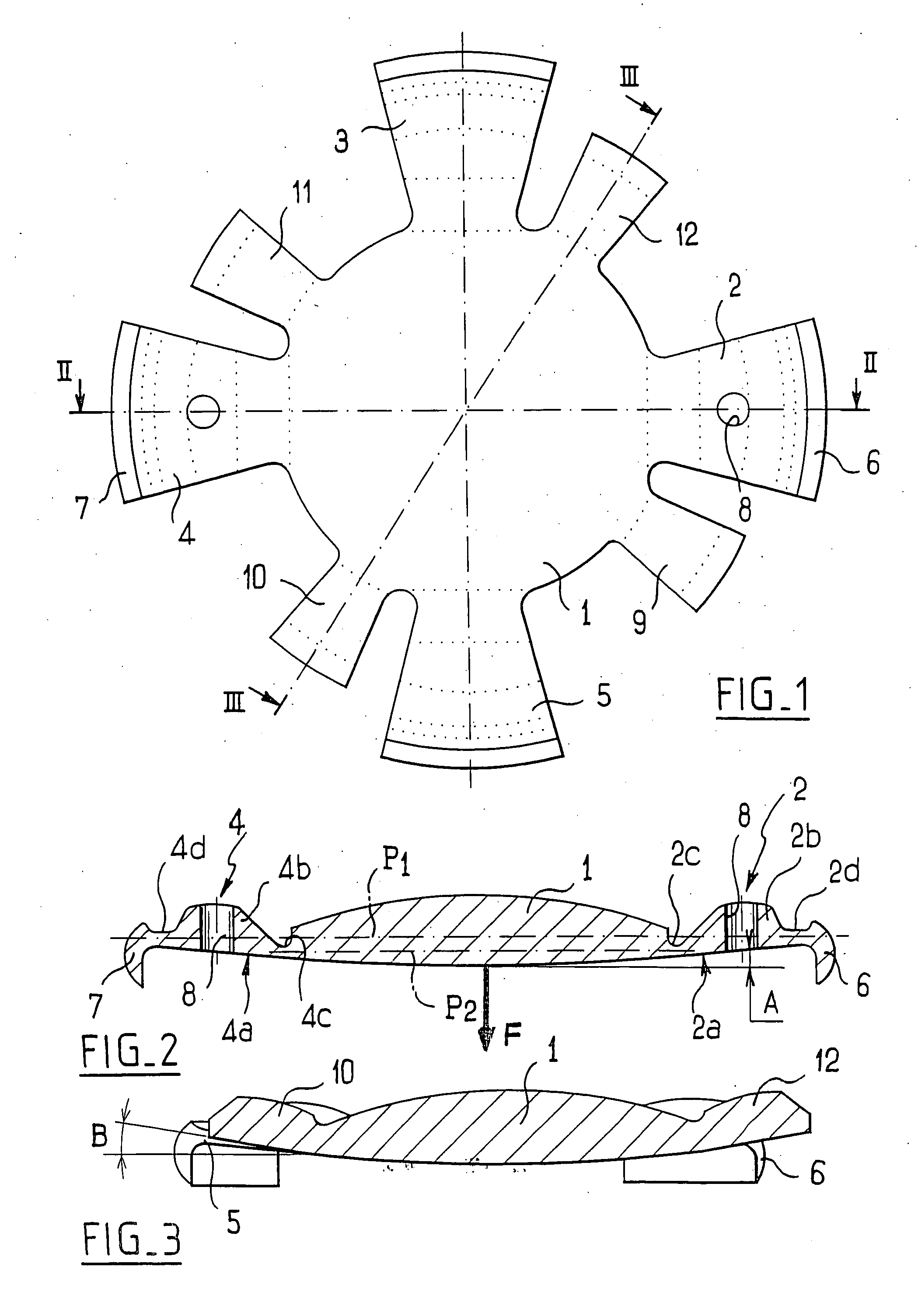
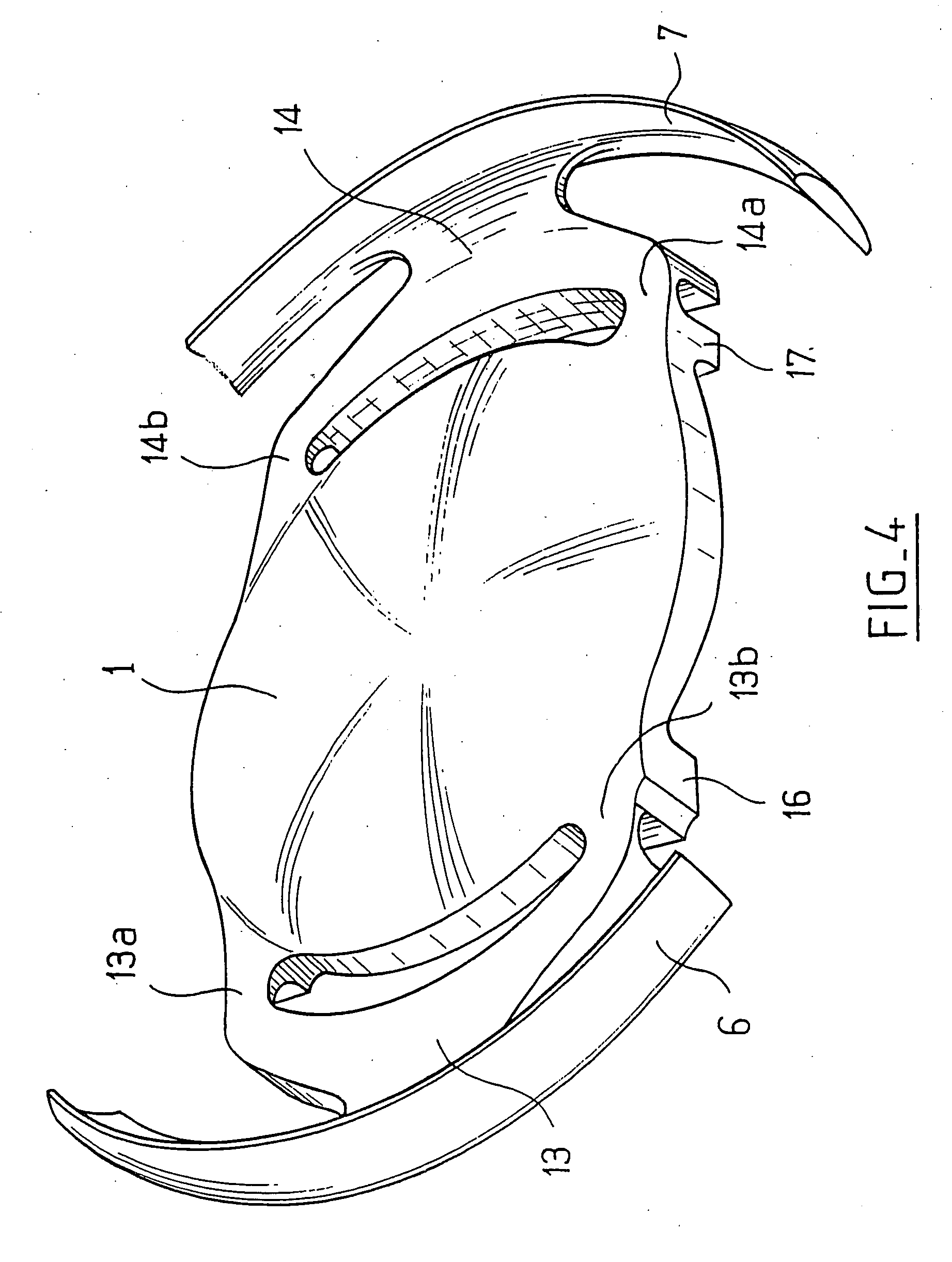
An accommodating intraocular implant for locating in the capsular bag, the implant comprising a single piece of elastically deformable material constituting a central lens (1) and at least two haptic portions (2, 4) in the form of radial arms for bearing via their free ends against the equatorial zone of the capsular bag, the free end of each radial arm (2, 4) being fitted with a shoe (6, 7) of substantially toroidal outside surface enabling the implant to bear against the equatorial zone of the bag, the connection between each shoe (6, 7) and the corresponding arm (2, 4) being of the hinge type situated in the vicinity of the posterior edge of the shoe (6, 7) and being formed by a first thin portion (2d, 4d) of the arm, while the connection between each arm and the lens is of the hinge type implemented at the anterior surface of the lens by a second likewise thin portion (2c, 4c) of the arm, the plane (P1) containing the first thin portions being situated behind the plane (P2) containing the second thin portions.
Owner:HANNA KHALIL PROF DR
Method and systems for laser treatment of presbyopia using offset imaging
InactiveUS6280435B1Less attractiveReduce discontinuityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsWide areaHyperopic astigmatism
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Computer aided contact lens design and fabrication using spline surfaces
A method of computer-aided contact lens design and fabrication uses spline-based mathematical surfaces without restrictions of rotational symmetry. The spline encompasses any piecewise function with any associated constraints of smoothness or continuity. The method comprises some or all of the following steps: data acquisition, three-dimensional mathematical surface model construction, posterior surface description, ray tracing for anterior surface, and peripheral edge system (PES) design. The result is a mathematical or algorithmic description of a contact lens. Based on the more powerful mathematical representation of splines, these contact lenses can have posterior surfaces that provide a good fit to corneas having complicated shapes. This enables the design and fabrication of lenses (including soft lenses) with good optics for irregularly shaped corneas.
Owner:BARSKY BRIAN A
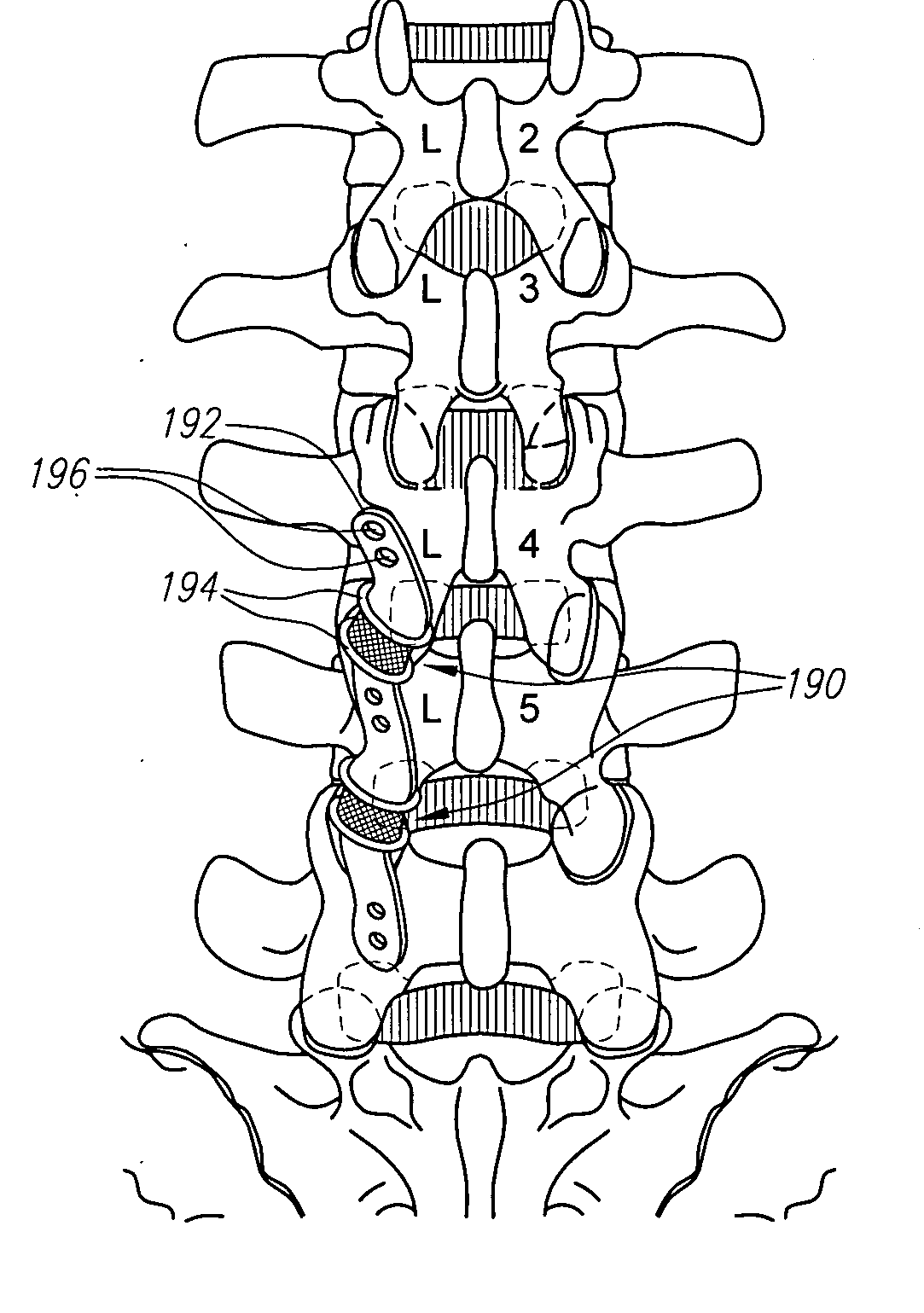
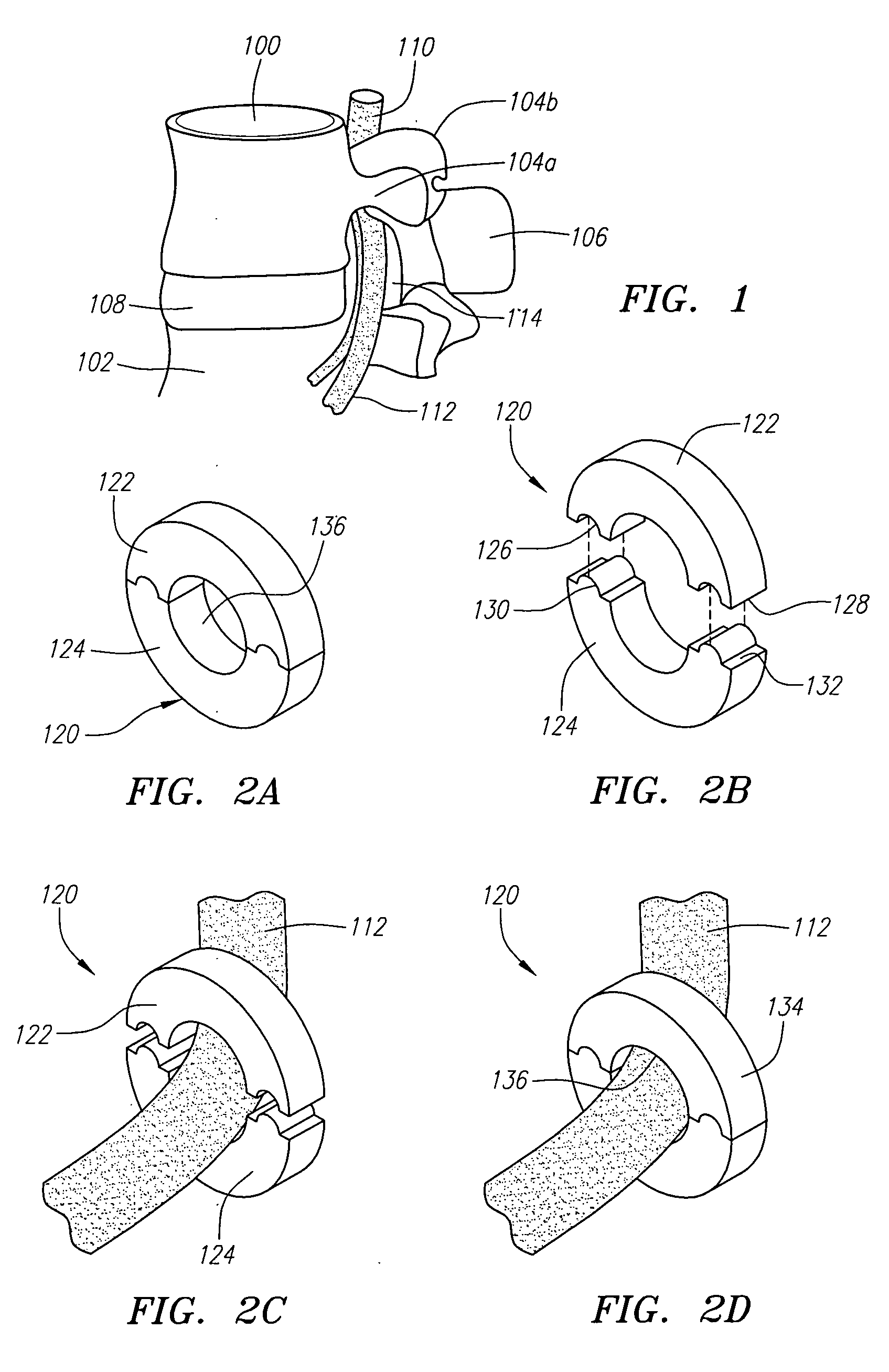
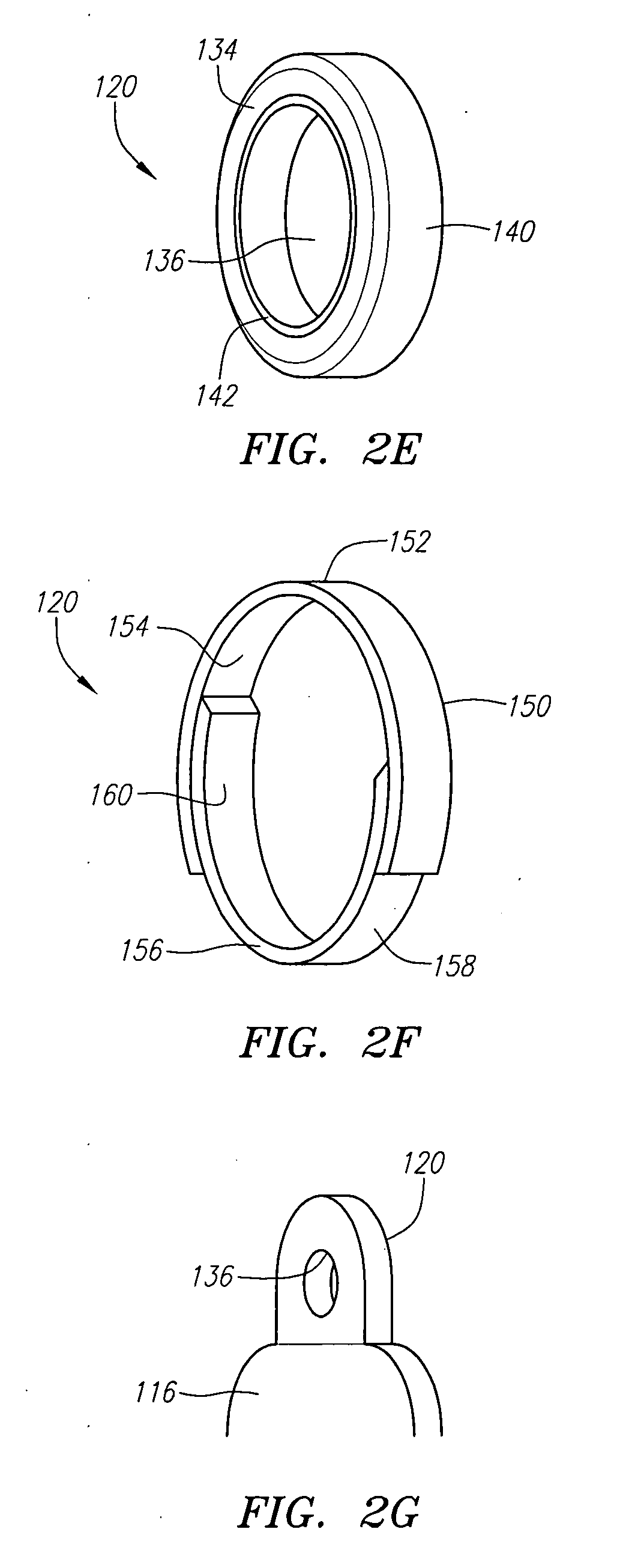
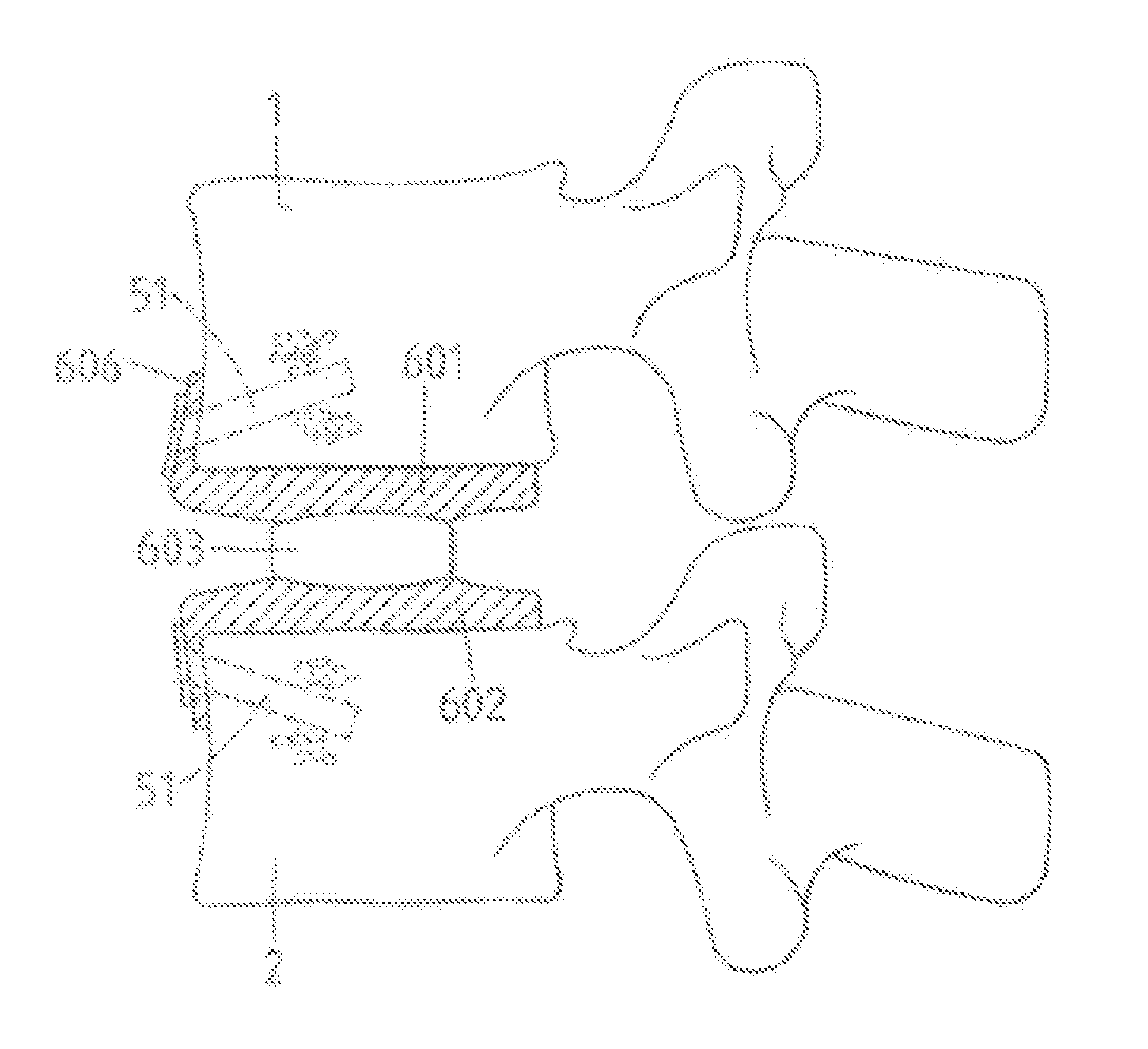
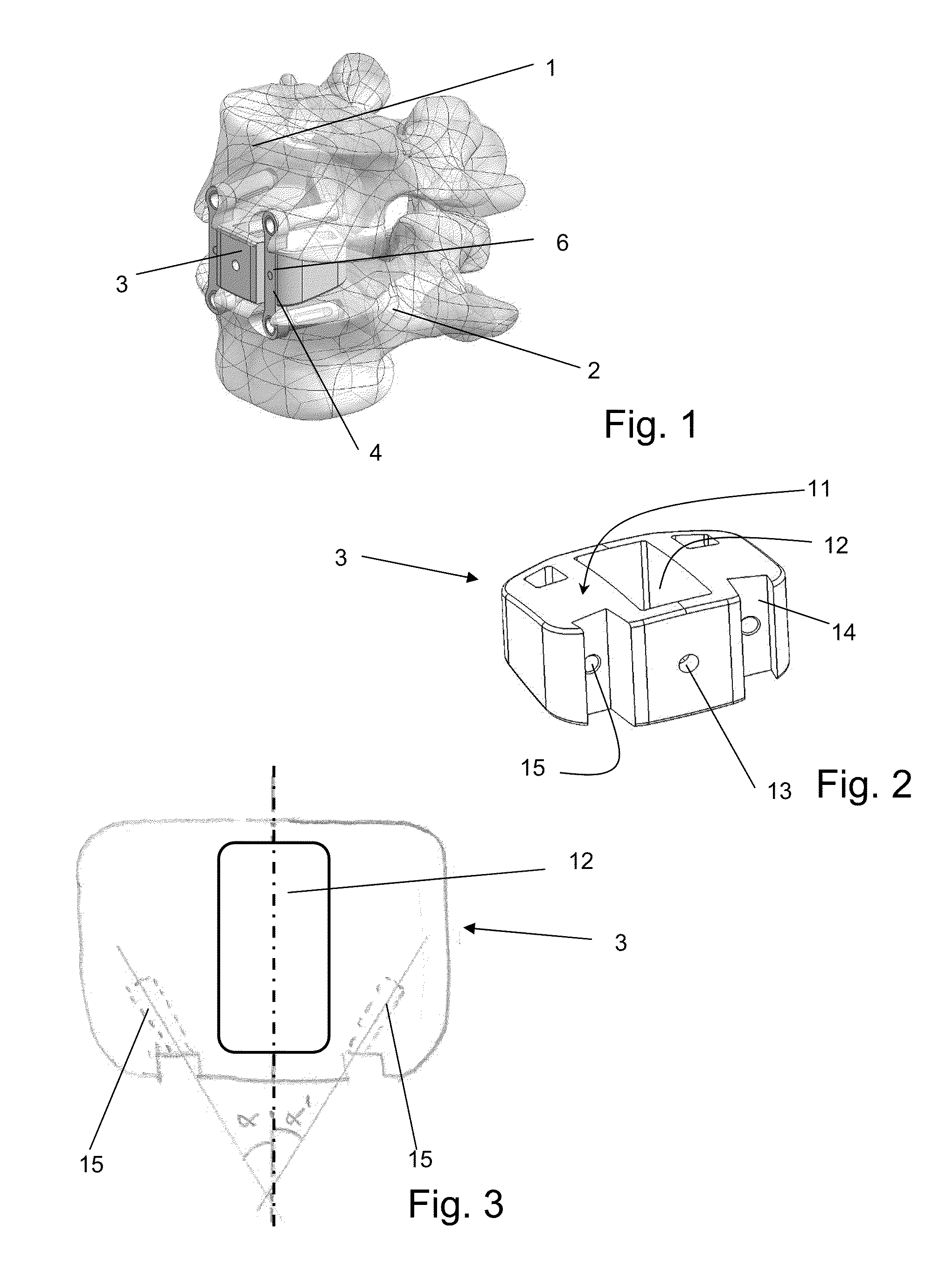
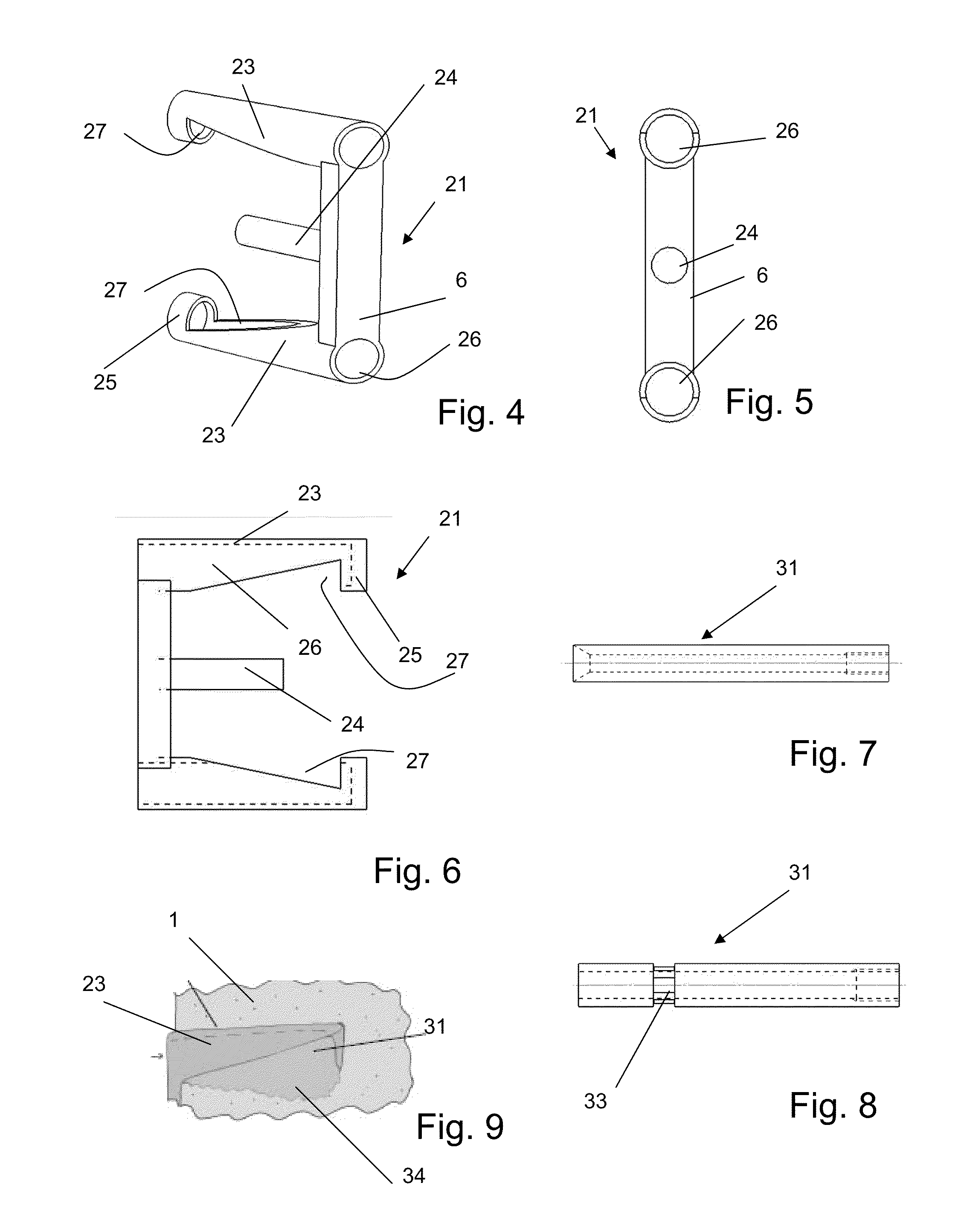
Apparatus for anterior intervertebral spinal fixation and fusion
Owner:INT SPINAL INNOVATIONS +2
Method and apparatus for preparing a glenoid surface
ActiveUS7294133B2Easy to implantEasy to installProsthesisOsteosynthesis devicesAnterior surfaceProsthesis
A method and apparatus for facilitating shoulder arthroplasty by providing a reference to establish version of the glenoid. In one form of the invention, a guide for positioning a guide pin to facilitate implantation of a glenoid prosthesis is provided. To properly position the guide pin, the guide is first oriented with respect to the scapula. A portion of the guide is positioned over the approximate center of the glenoid surface and another portion of the guide is positioned against the anterior surface of the scapula. After the guide is properly positioned, the guide pin is inserted through an aperture in the guide and anchored in the glenoid. Thereafter, the guide pin can serve as an alignment guide for other devices used to modify the glenoid surface. For example, a reamer having a cannulated central shaft can be placed over the guide pin and utilized to resurface the glenoid.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Method for resecting the knee using a resection guide and provisional prosthetic component
InactiveUSRE39301E1Properly balanceAccurate balanceDiagnosticsJoint implantsAnterior surfaceKnee Joint
A method and apparatus for knee replacement surgery wherein a femoral provisional component is provided which corresponds to a permanent component to be implanted in a human and which includes means for establishing the correct fit and position of such a component, prior to its implantation, in relation to the soft tissues of the knee before final resection of the anterior femoral surface. The provisional component further includes cutting guide means for such anterior surface resection such that accurate cuts may be made with the provisional component in place. The method involves preparing the distal femoral surface using the femoral intramedullary canal as a constant reference point for posterior and distal cutting guides followed by locating the provisional component by means of a provisional intramedullary stem so that the relationship with the soft tissues of the knee may be accurately established.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
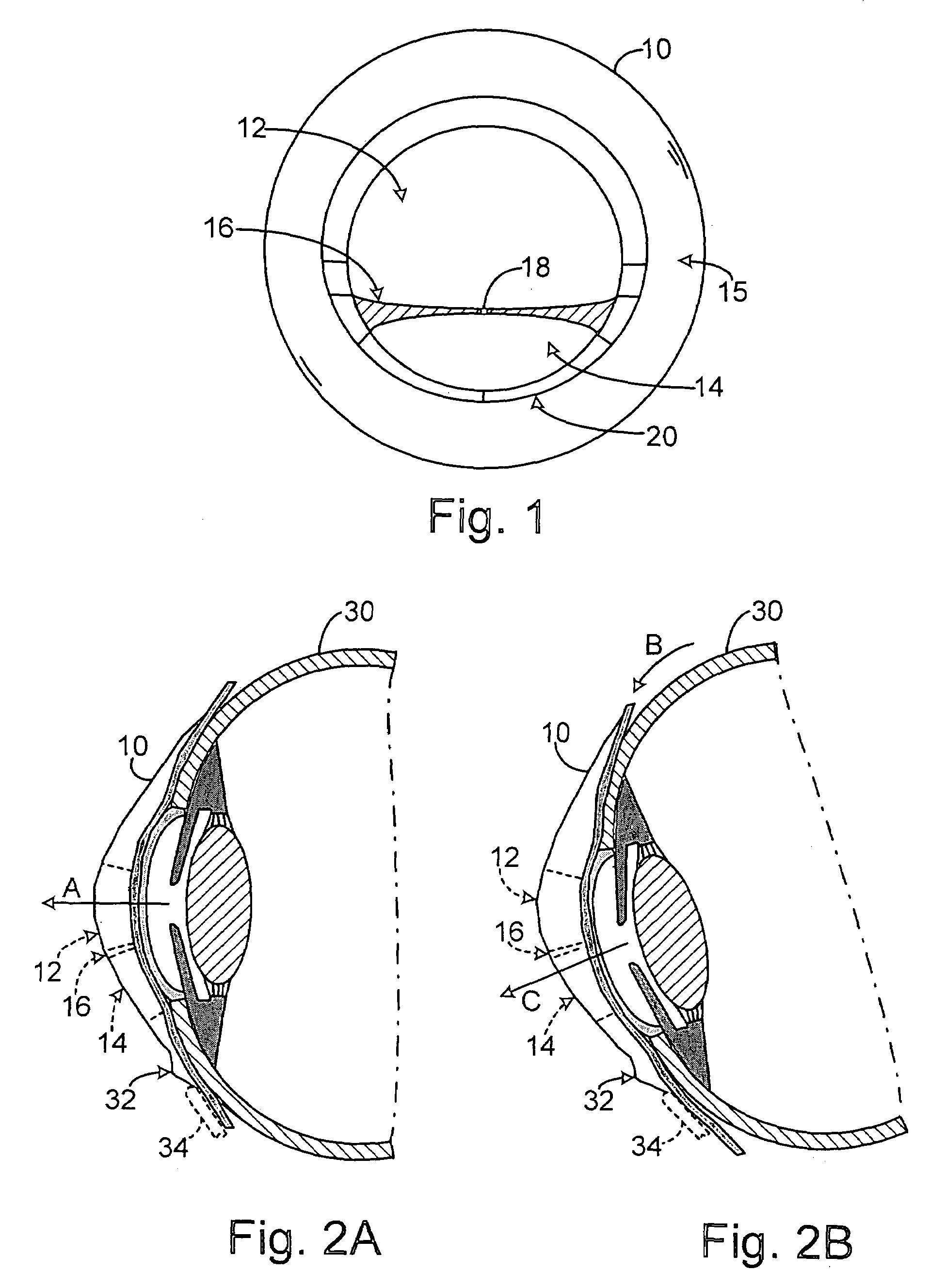
Ocular fixation and stabilization device for ophthalmic surgical applications
A method for applanating an anterior surface of a cornea and coupling the eye to a surgical laser is disclosed. A interface is provided which has a central orifice and top and bottom surfaces. A suction ring is removably coupled to the bottom surface of the interface. The interface is positioned over an operative area of an eye, such that the suction ring comes into proximate contact with the surface of the eye. A suction is applied to the suction ring to stabilize the position of the interface relative to the operative area of the eye. An applanation lens is positioned in proximate contact with the operative area of the eye. Finally, the applanation lens is coupled to the interface to stabilize the position of the lens relative to the operative area of the eye.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Method and apparatus for spinal distraction
ActiveUS20050137602A1Less immediate traumaConvenient amountInternal osteosythesisCannulasDistractionSpinal column
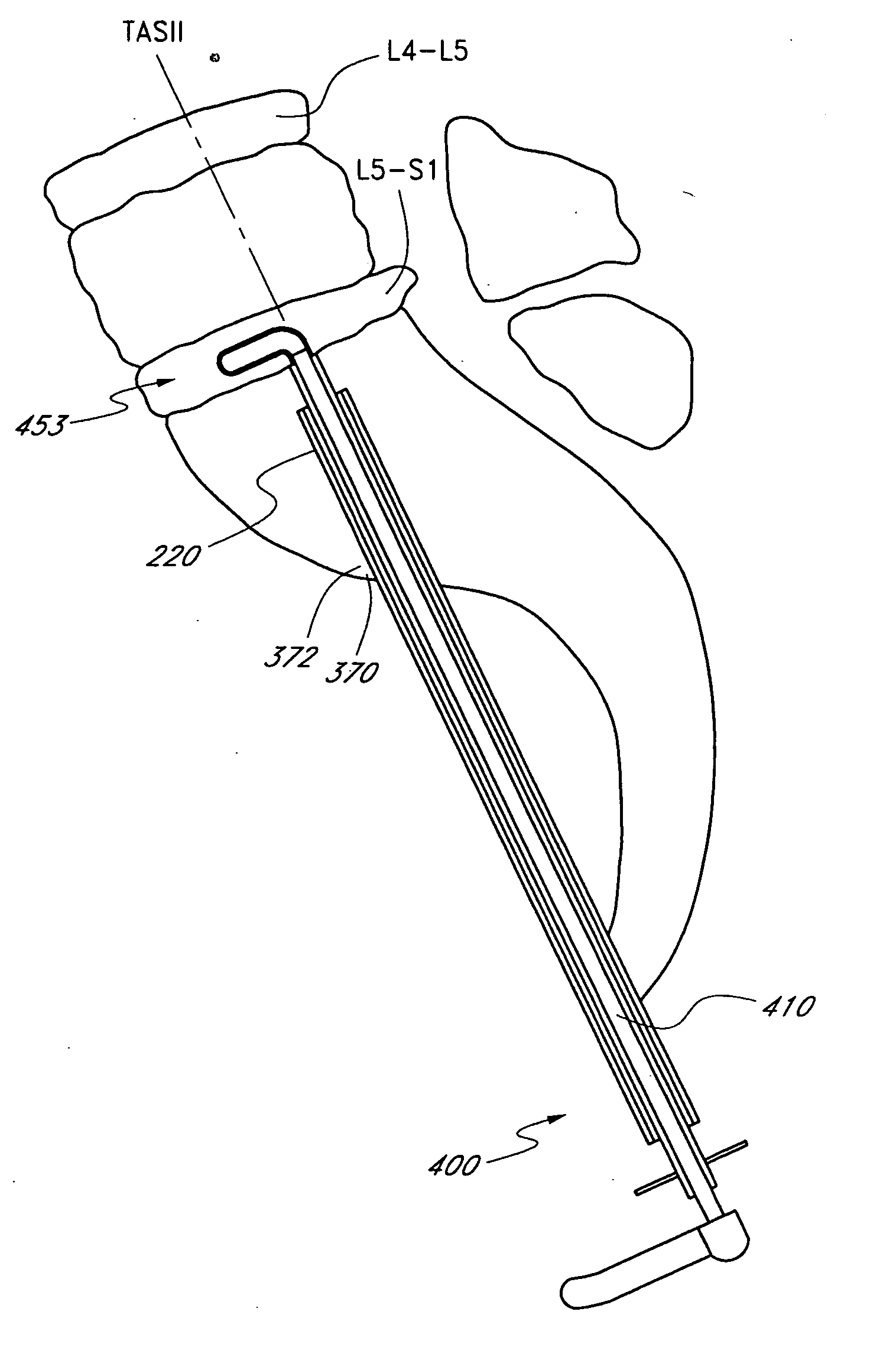
Disclosed are surgical tools, tool sets and methods for percutaneously accessing and preparing treatment sites within the spine for subsequent treatment procedures. The treatment site may be an inter-vertebral motion segments in the lumbar and sacral regions of the spine. The tool set may comprise introducer tools and bone dilators for accessing and tapping into a targeted site, such as, for example, the anterior surface of the S1 vertebral body. The tool set may also comprise cutters and extractors for preparing the treatment site for subsequent treatment procedures. The tool set may additionally comprise a bone graft inserter, an exchange system, and / or a temporary distraction tool for further preparing the treatment site for subsequent treatment procedures.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
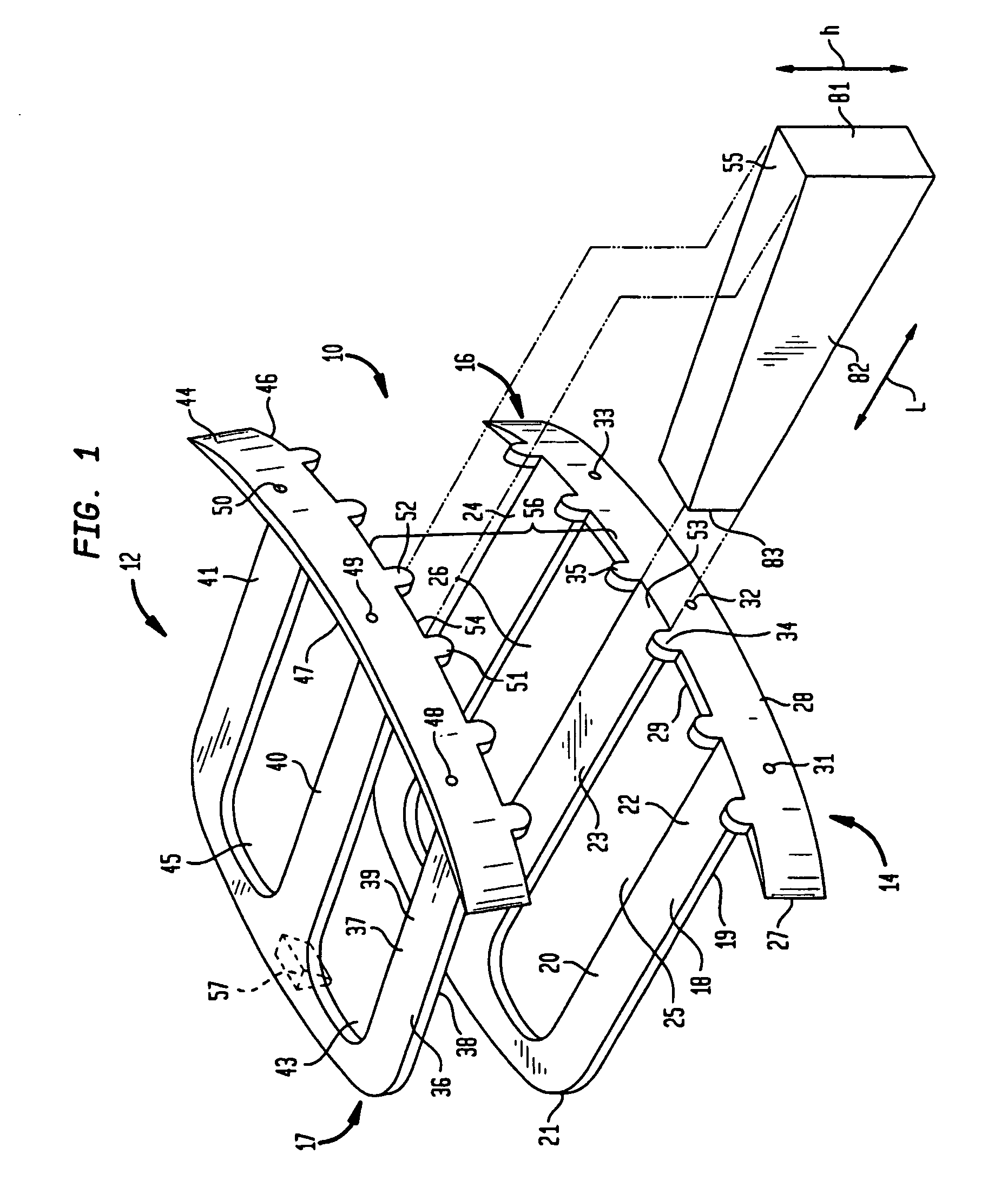
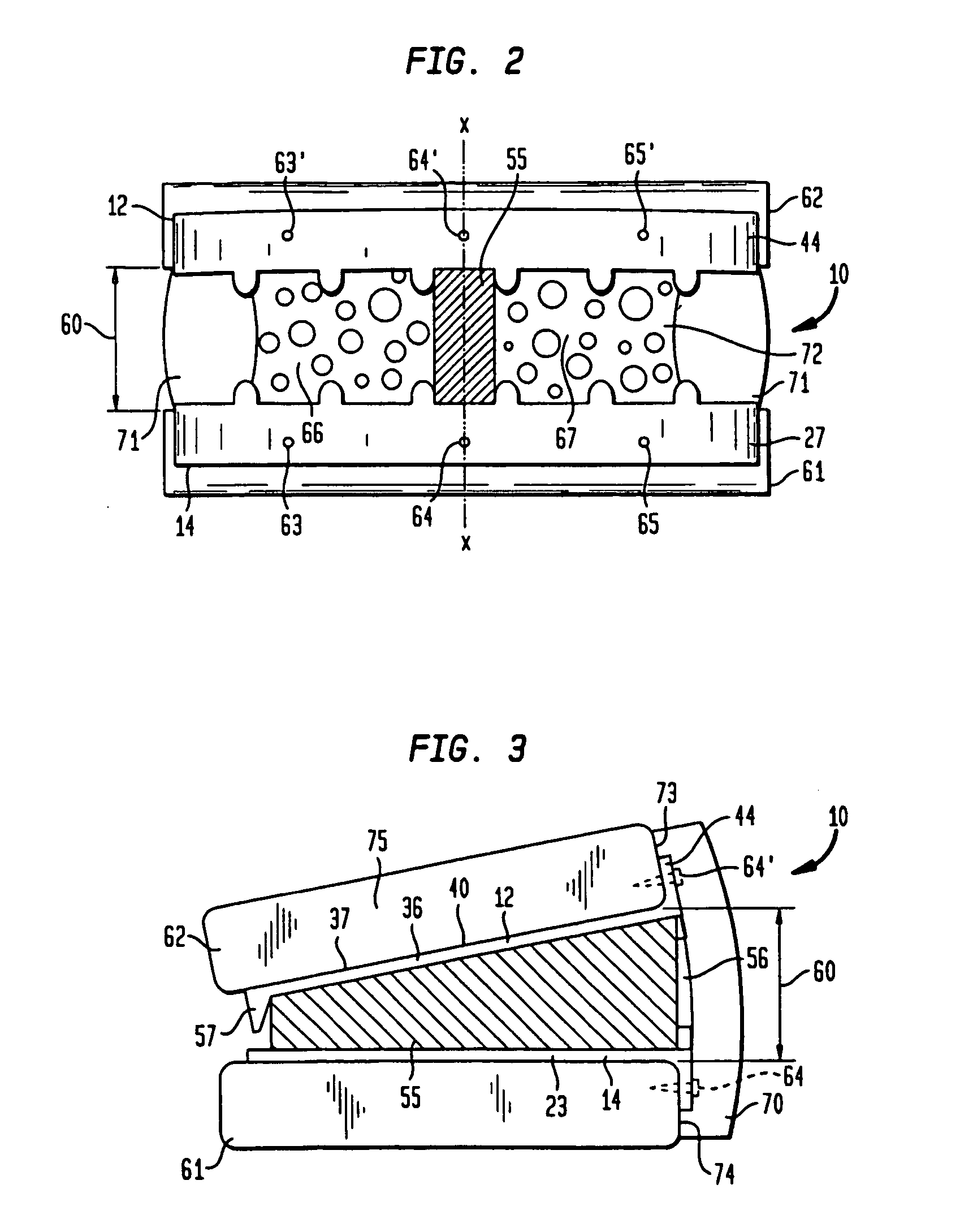
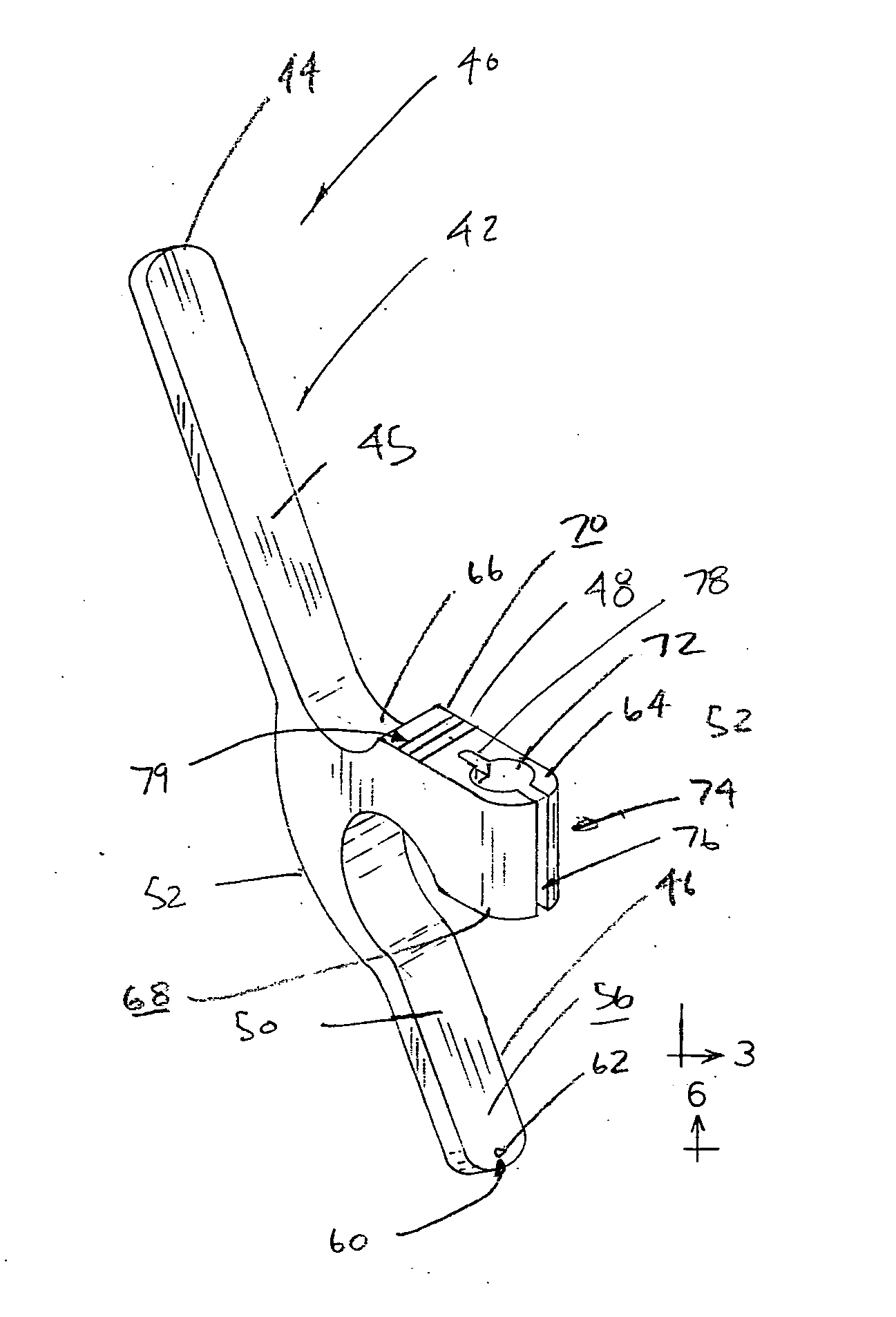
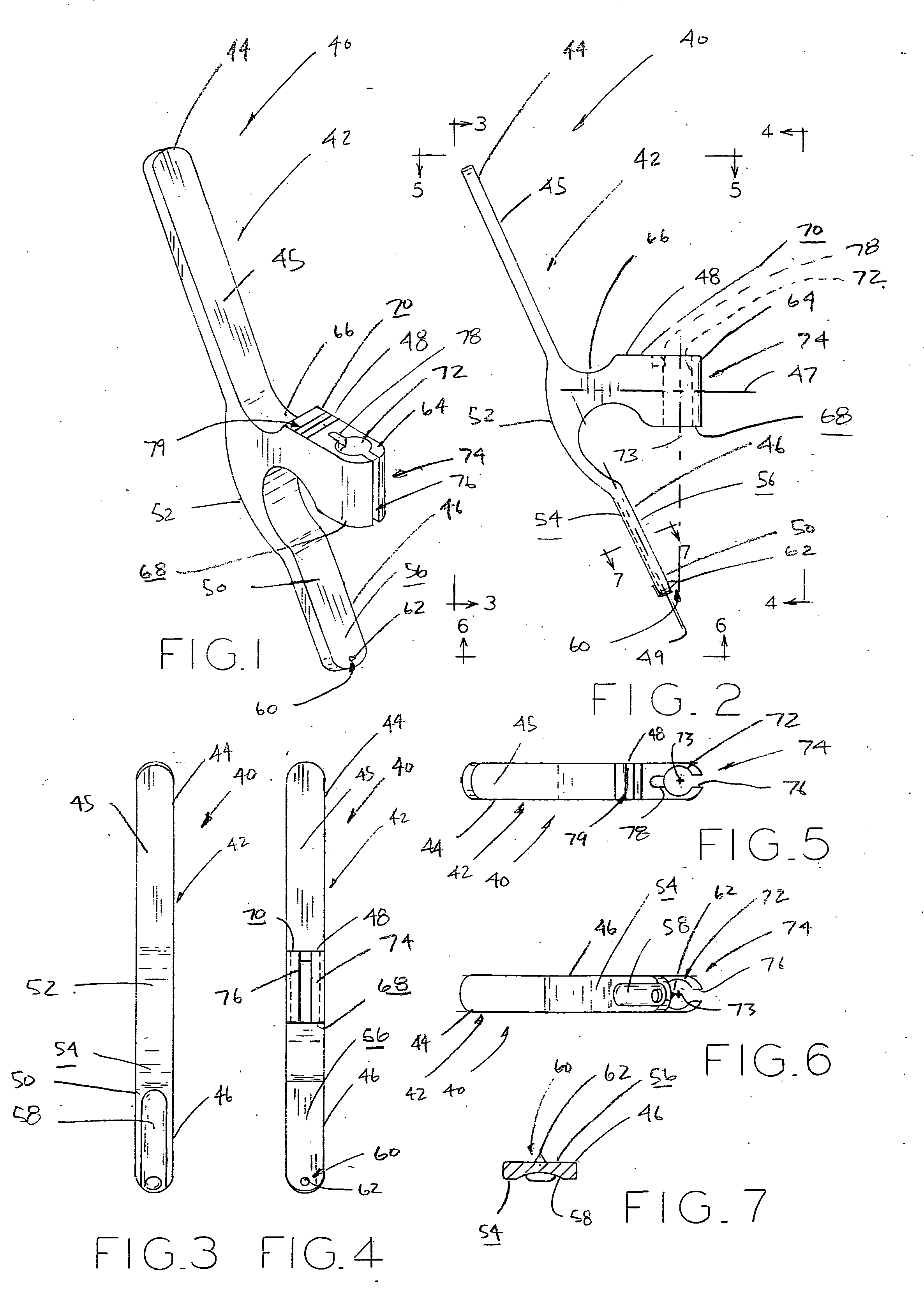
Modular patella instrument
A patella clamp has a first part including a reference surface engageable with the anterior surface of a patella. The first part includes a stop surface spaced from the reference surface. A second clamping part is provided which is moveable with respect to the first clamping part. A cutting element coupled to the first clamping part is moveable with respect to the first part. The cutting element includes a shaft with an adjustable collar mounted on the shaft for movement with respect to the longitudinal axis of the shaft and cutting element. The adjustable collar on the shaft is engageable with a stop surface on the first part for spacing the cutting element a desired distance from the reference surface. A pair of gages are provided for selectively setting the position of the adjustable collar with respect to either the amount of patella bone being removed or the amount of patella bone remaining.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Spinal stabilization systems and methods
InactiveUS20070083200A1Allows flexion and extension and lateral bendingReduce the possibilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsIntervertebral discAnterior surface
Spinal stabilization devices, systems, and methods are described. In a first aspect, a foramenal spacer includes a rigid member adapted to maintain the integrity of the foramenal space. In a second aspect, facet joint stabilizing members and prosthetic facet joints are provided to augment or replace the native facet joint. In a third aspect, lateral spinal stabilization systems are adapted to be attached to the lateral surfaces of adjacent vertebral bodies. In a fourth aspect, anterior spinal stabilization systems are adapted to be attached to the anterior surfaces of adjacent vertebral bodies. In a fifth aspect, several embodiments of dynamic spinal stabilization devices and systems are described. Each of the foregoing devices, systems, and methods is suitable for use independently, in combination with other devices, systems, and methods described herein, and / or in combination with prosthetic intervertebral discs known in the art.
Owner:SPINAL KINETICS
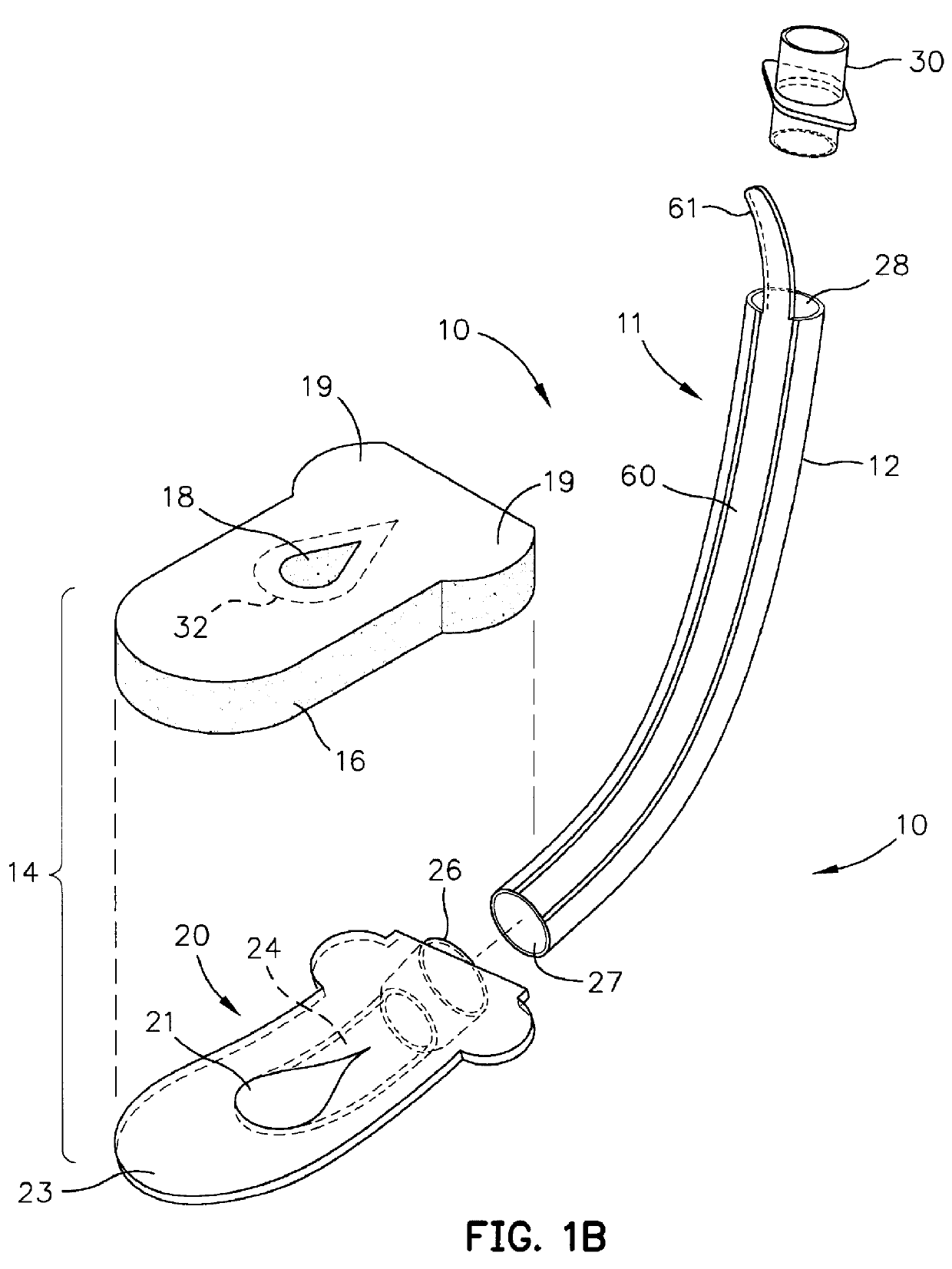
Laryngeal airway device
Owner:GEN ELECTRIC CAPITAL
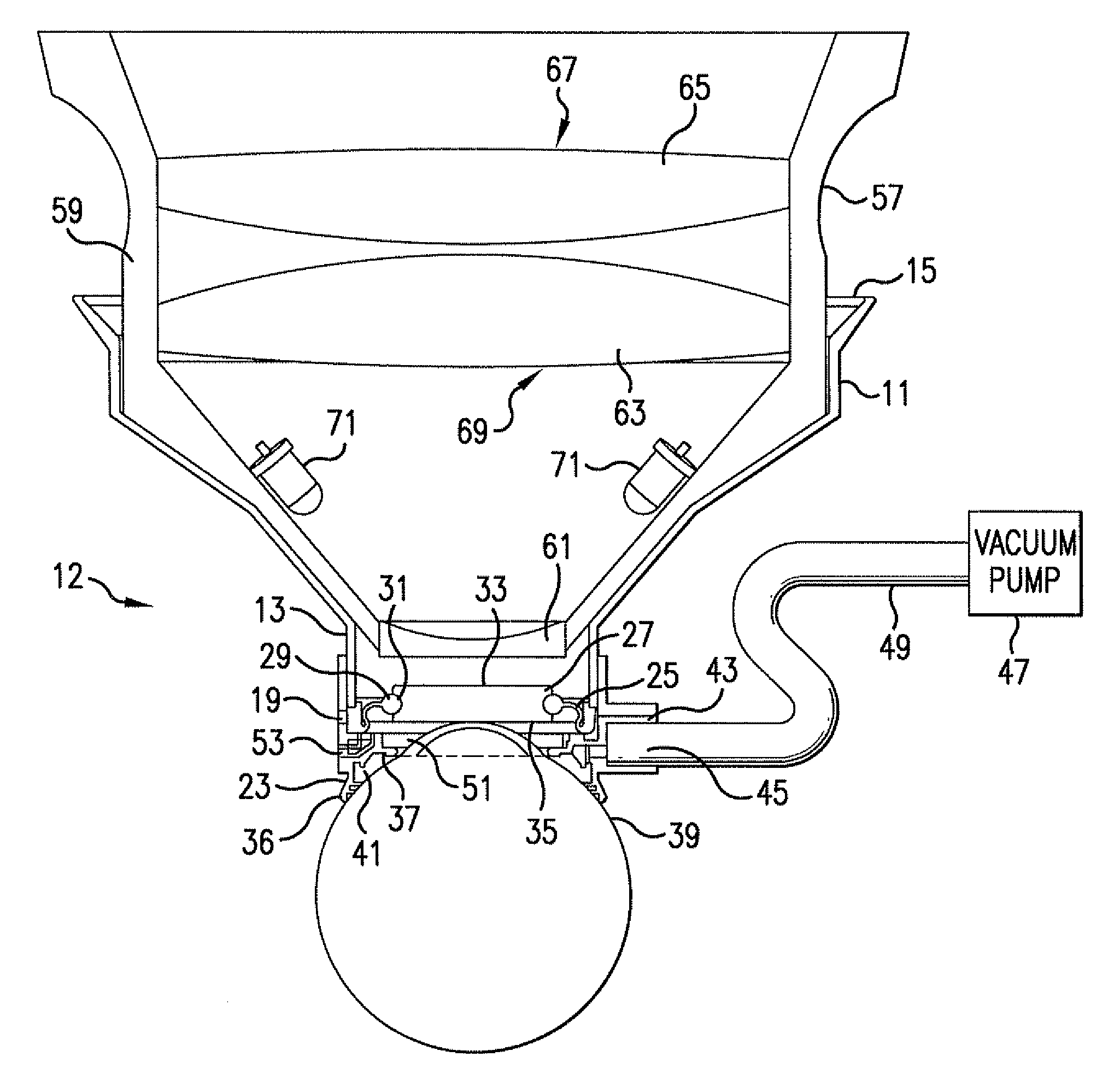
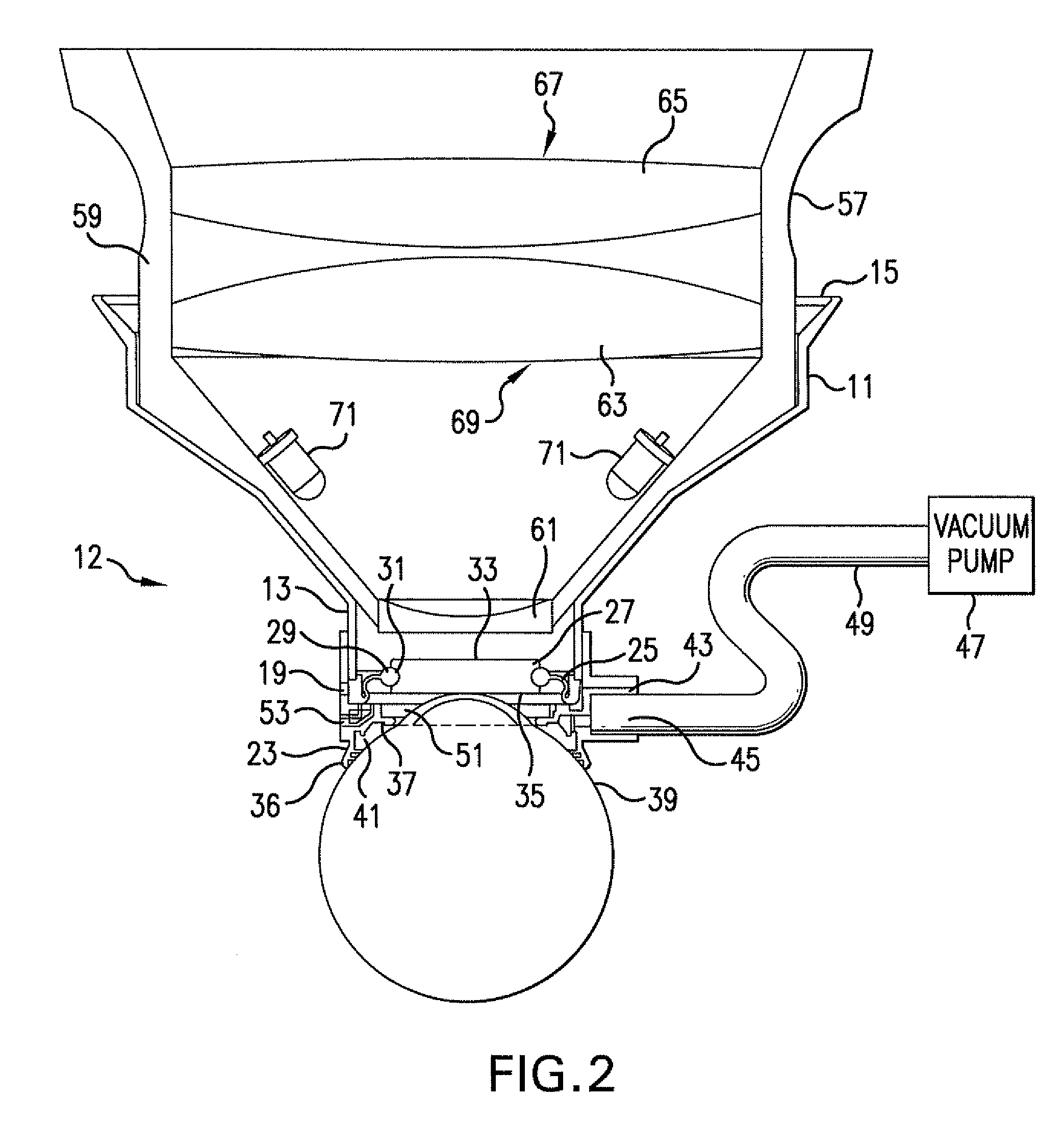
Ophthalmic interface apparatus and system and method of interfacing a surgical laser with an eye
An ophthalmic patient interface system includes an interface device and an ocular device. The interface device includes a frame having a first end and a second end, a lens disposed at the first end, and a skirt affixed to the first end. The second end is adapted to couple with a surgical laser system, and the skirt is adapted to seal against an anterior surface of an eye. The ocular device includes magnifying optics and is adapted to be removably seated within the second end. The magnifying optics image a region on a corneal side of the lens when the ocular device is seated within the second end.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Fenestrated contact lens for treating myopia
An improved corneal contact lens for use in orthokeratology wherein the lens has an anterior surface, posterior surface and includes a tear zone which defines a tear reservoir located on the posterior surface of the lens. The improvement involves providing at least one fenestration surface located in the tear zone which defines an opening extending through the contact lens from the anterior surface to the posterior surface. The openings in the tear zone relieve fluid pressure which was found to cause certain symptoms, such as lens adhesion, tightening and general wearing discomfort. The fenestrations in the tear zone provide enhanced wearing comfort without adversely affecting the cornea-shaping properties of the lens.
Owner:CONTEX
Devices and techniques for light-mediated stimulation of trabecular meshwork in glaucoma therapy
An apparatus and technique for transscleral light-mediated biostimulation of the trabecular plates of a patient's eye in a treatment for glaucoma or ocular hypertension. The apparatus includes; (i) a working end geometry for contacting the anterior surface of the sclera and cornea to insure that a laser emission reaches the trabecular meshwork from a particular location on the anterior surface of the sclera, (ii) a laser energy source providing a wavelength appropriate for absorption beneath the anterior scleral surface to the depth of the trabecular plates, and (iii) a dosimetry control system for controlling the exposure of the laser emission at the particular spatial locations. The device uses a light energy source that emits wavelengths in the near-infrared portion of the spectrum, preferably in the range of about 1.30 mum to 1.40 mum or from about 1.55 mum to 1.85 mum. The depth of absorption of such wavelength ranges will extend through most, if not all, of the thickness of the sclera (750 mum to 950 mum). In accordance with a proposed method of trabecular biostimulation, the targeted region is elevated in temperature to a range between about 40° C. to 55° C. for a period of time ranging from about 1 second to 120 seconds or more.
Owner:SOLX
Toric multifocal contact lenses
The present invention provides a toric multifocal contact lens having a cylindrical optical power to correct astigmatism vision errors and a multifocal power to compensate for presbyopia. A toric multifocal contact lens of the invention has a central axis, an anterior surface having a first central optical zone, and an opposite posterior surface having a second central optical zone. The first central optical zone and the second central optical zone combine to provide a cylindrical optical power to correct astigmatism vision errors and a multifocal power to compensate for presbyopia.
Owner:ALCON INC
Method and apparatus for manipulating material in the spine
InactiveUS20050149034A1Less immediate traumaConvenient amountInternal osteosythesisCannulasTreatments proceduresAnterior surface
Disclosed are surgical tools, tool sets and methods for percutaneously accessing and preparing treatment sites within the spine for subsequent treatment procedures. The treatment site may be an inter-vertebral motion segments in the lumbar and sacral regions of the spine. The tool set may comprise introducer tools and bone dilators for accessing and tapping into a targeted site, such as, for example, the anterior surface of the S1 vertebral body. The tool set may also comprise cutters and extractors for preparing the treatment site for subsequent treatment procedures. The tool set may additionally comprise a bone graft inserter, an exchange system, and / or a temporary distraction tool for further preparing the treatment site for subsequent treatment procedures.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
Mask configured to maintain nutrient transport without producing visible diffraction patterns
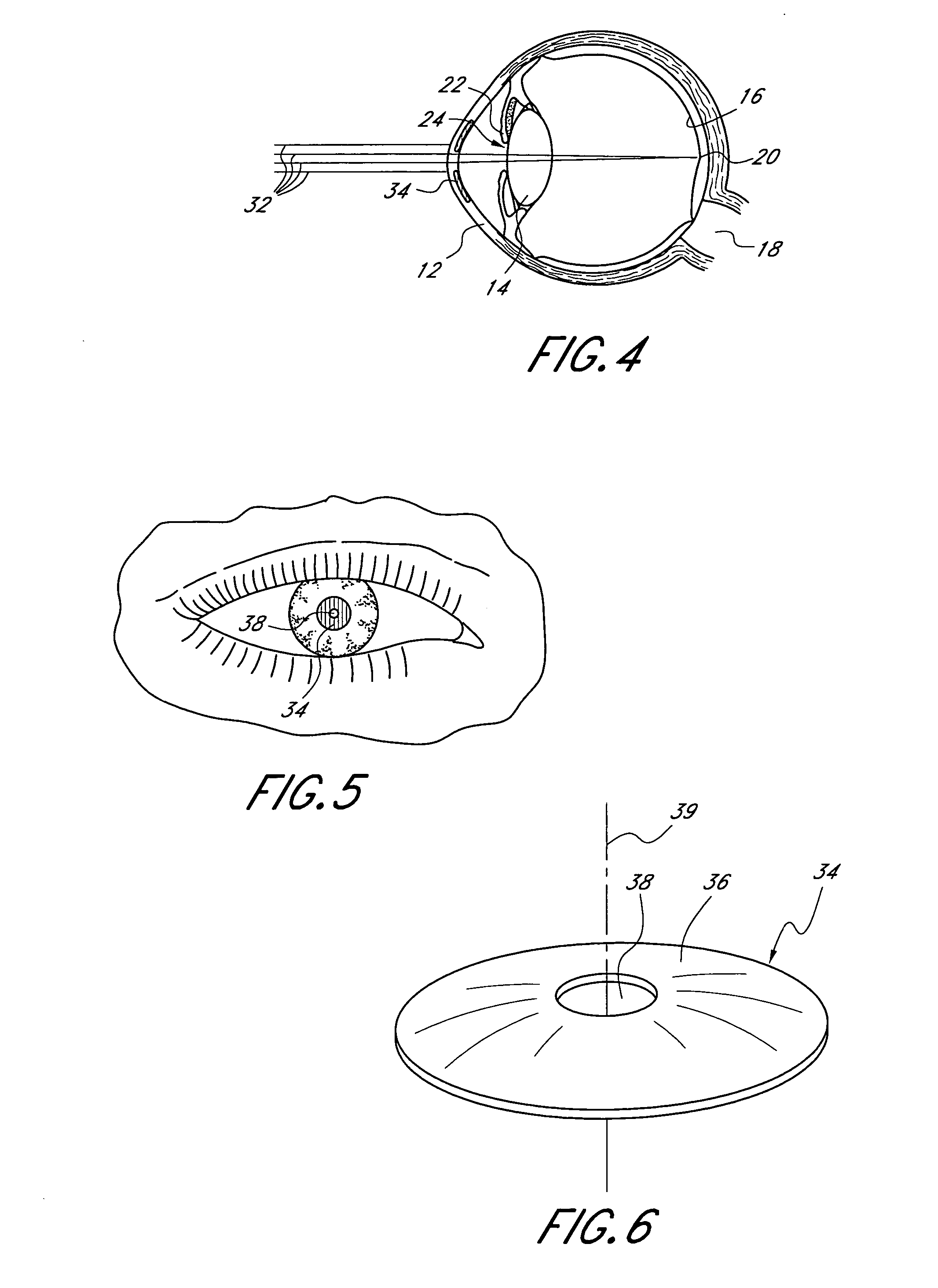
InactiveUS20050033420A1Increase depth of focusEliminate visible diffraction patternSpectales/gogglesSenses disorderAnterior surfaceCorneal layer
A mask configured to be implanted in a cornea of a patient to increase the depth of focus of the patient includes an anterior surface, a posterior surface, and a plurality of holes. The anterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a first corneal layer. The posterior surface is configured to reside adjacent a second corneal layer. The plurality of holes extends at least partially between the anterior surface and the posterior surface. The holes of the plurality of holes are configured to substantially eliminate visible diffraction patterns.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
Intraocular implant and an artificial lens device
InactiveUS20050085907A1Improve abilitiesReduce productionIntraocular lensAnterior surfaceIntraocular implant
An accommodating intraocular implant for locating in the capsular bag, the implant comprising a single piece of elastically deformable material constituting a central lens (1) and at least two haptic portions (2, 4) in the form of radial arms for bearing via their free ends against the equatorial zone of the capsular bag, the free end of each radial arm (2, 4) being fitted with a shoe (6, 7) of substantially toroidal outside surface enabling the implant to bear against the equatorial zone of the bag, the connection between each shoe (6, 7) and the corresponding arm (2, 4) being of the hinge type situated in the vicinity of the posterior edge of the shoe (6, 7) and being formed by a first thin portion (2d, 4d) of the arm, while the connection between each arm and the lens is of the hinge type implemented at the anterior surface of the lens by a second likewise thin portion (2c, 4c) of the arm, the plane (P1) containing the first thin portions being situated behind the plane (P2) containing the second thin portions.
Owner:HUMANOPTICS AG
Guide pin for guiding instrumentation along a soft tissue tract to a point on the spine
InactiveUS20050137605A1Less immediate traumaConvenient amountInternal osteosythesisCannulasDistractionTreatments procedures
Disclosed are surgical tools, tool sets and methods for percutaneously accessing and preparing treatment sites within the spine for subsequent treatment procedures. The treatment site may be an inter-vertebral motion segments in the lumbar and sacral regions of the spine. The tool set may comprise introducer tools and bone dilators for accessing and tapping into a targeted site, such as, for example, the anterior surface of the S1 vertebral body. The tool set may also comprise cutters and extractors for preparing the treatment site for subsequent treatment procedures. The tool set may additionally comprise a bone graft inserter, an exchange system, and / or a temporary distraction tool for further preparing the treatment site for subsequent treatment procedures.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
Bone screw retaining system
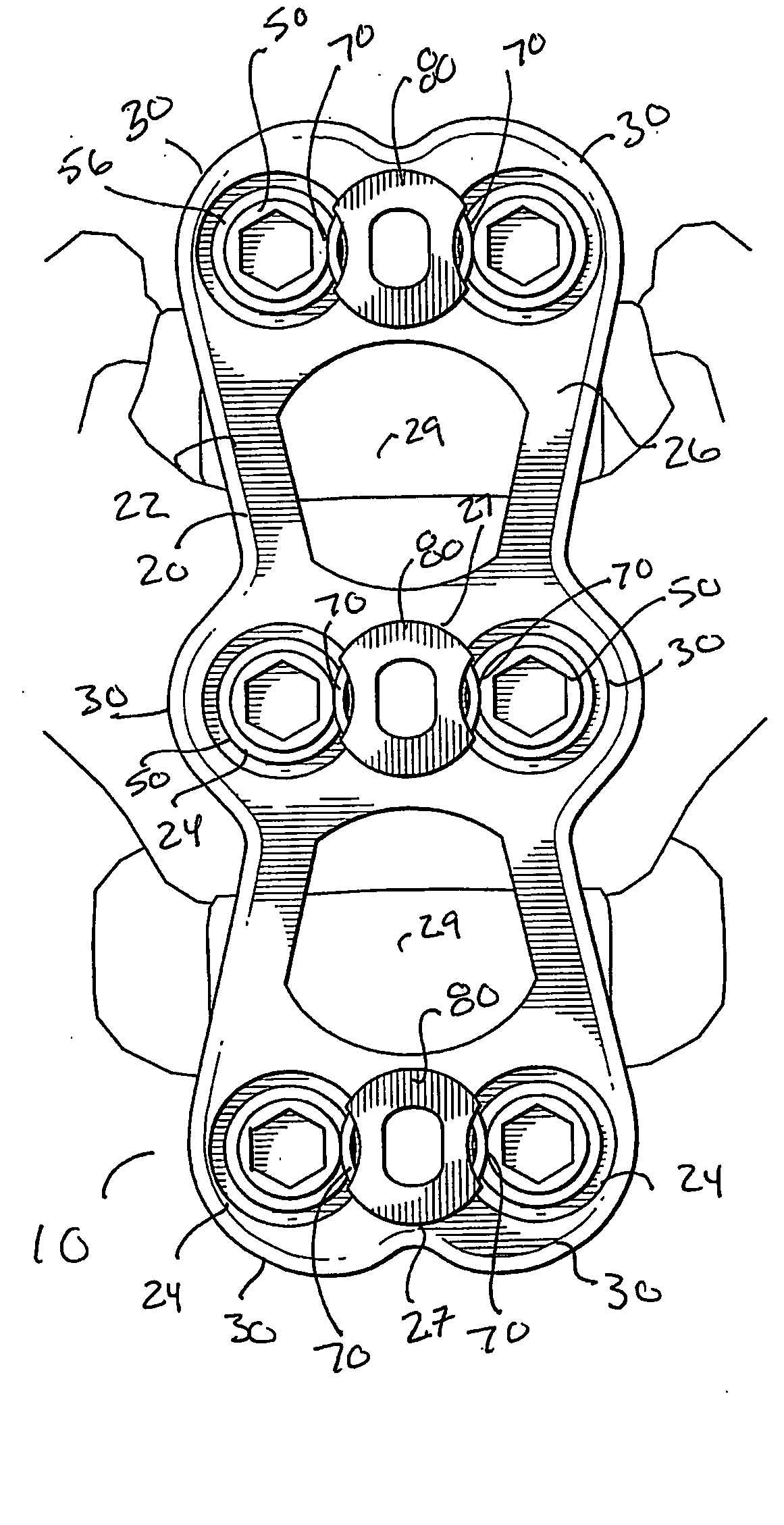
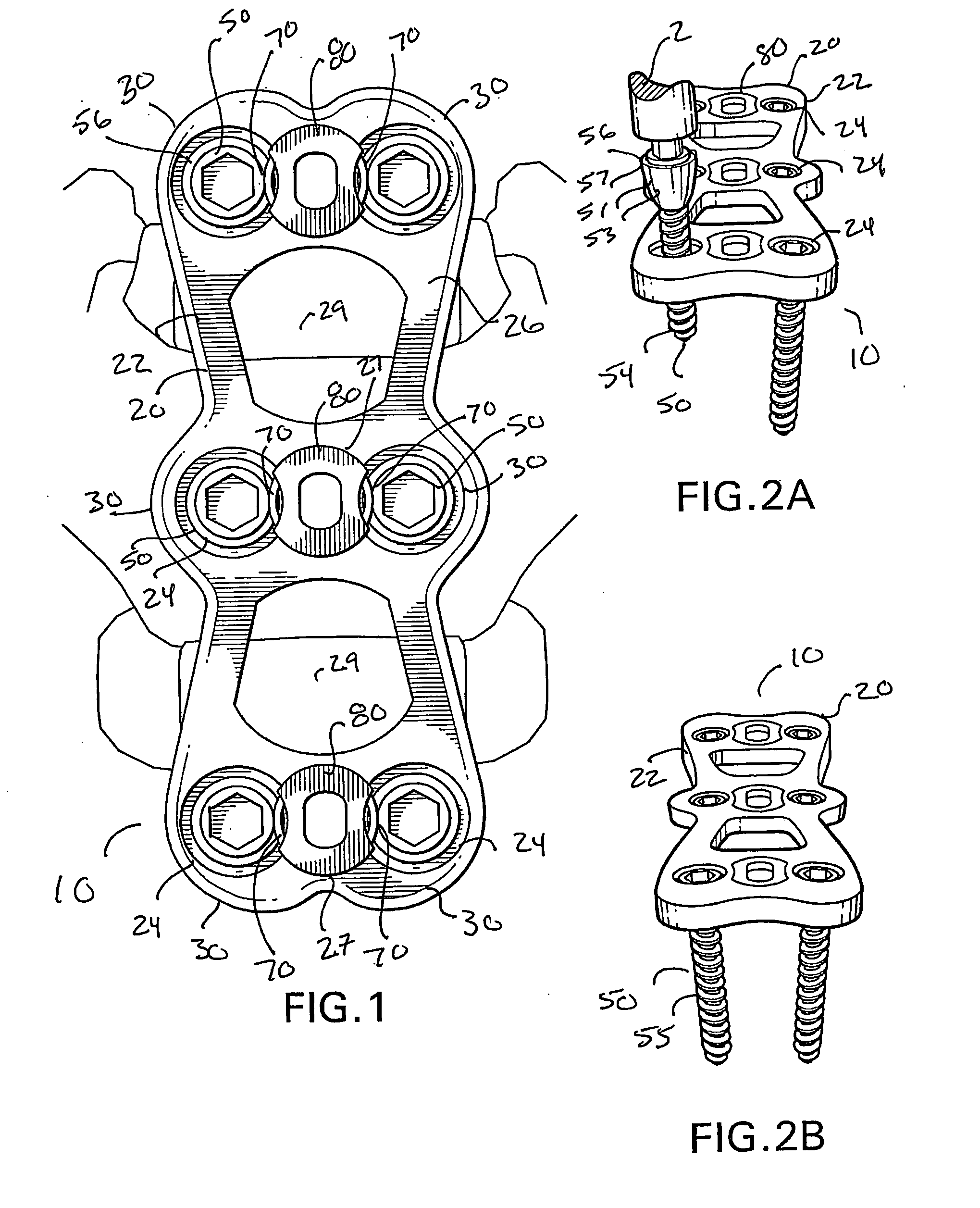
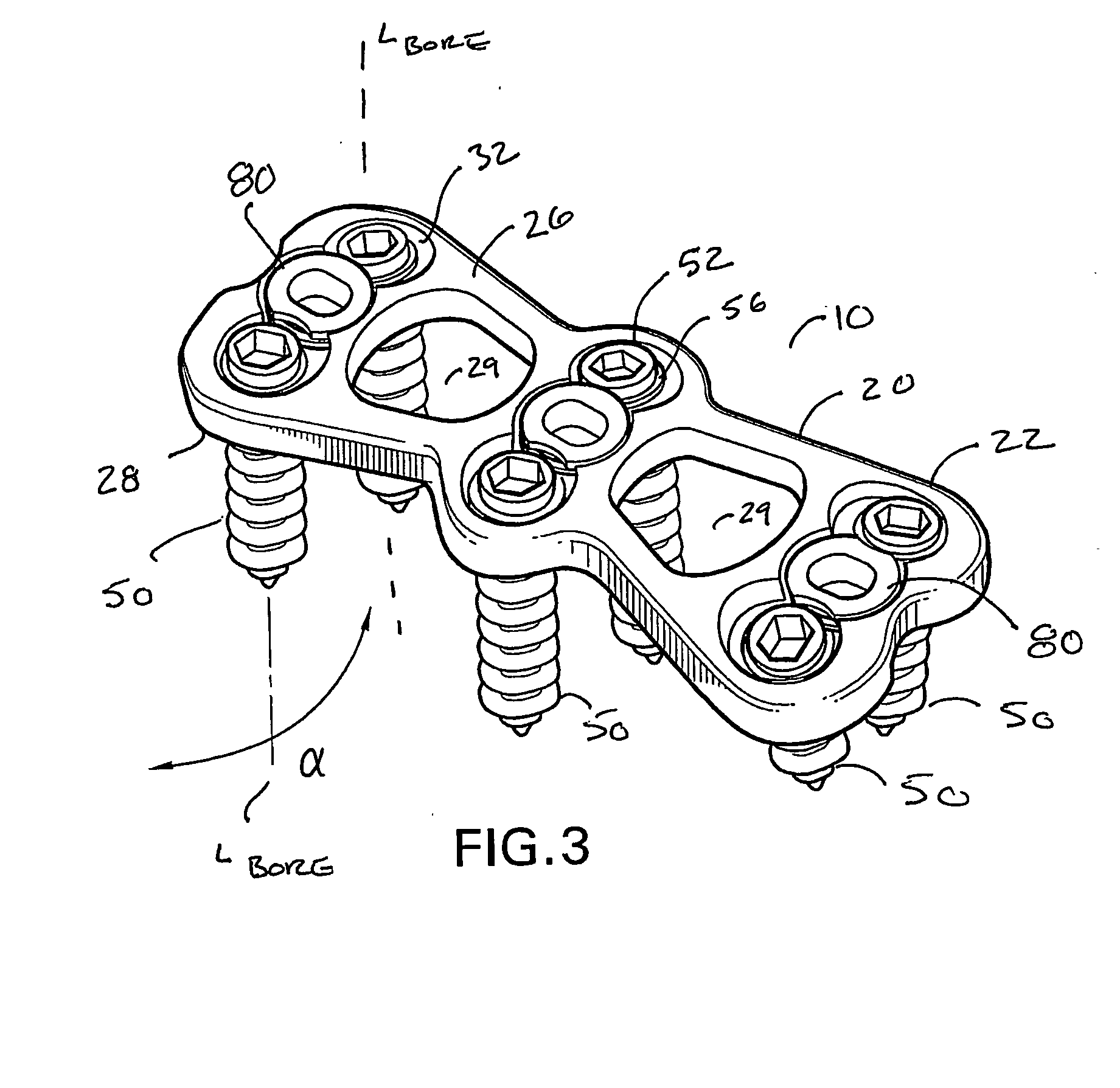
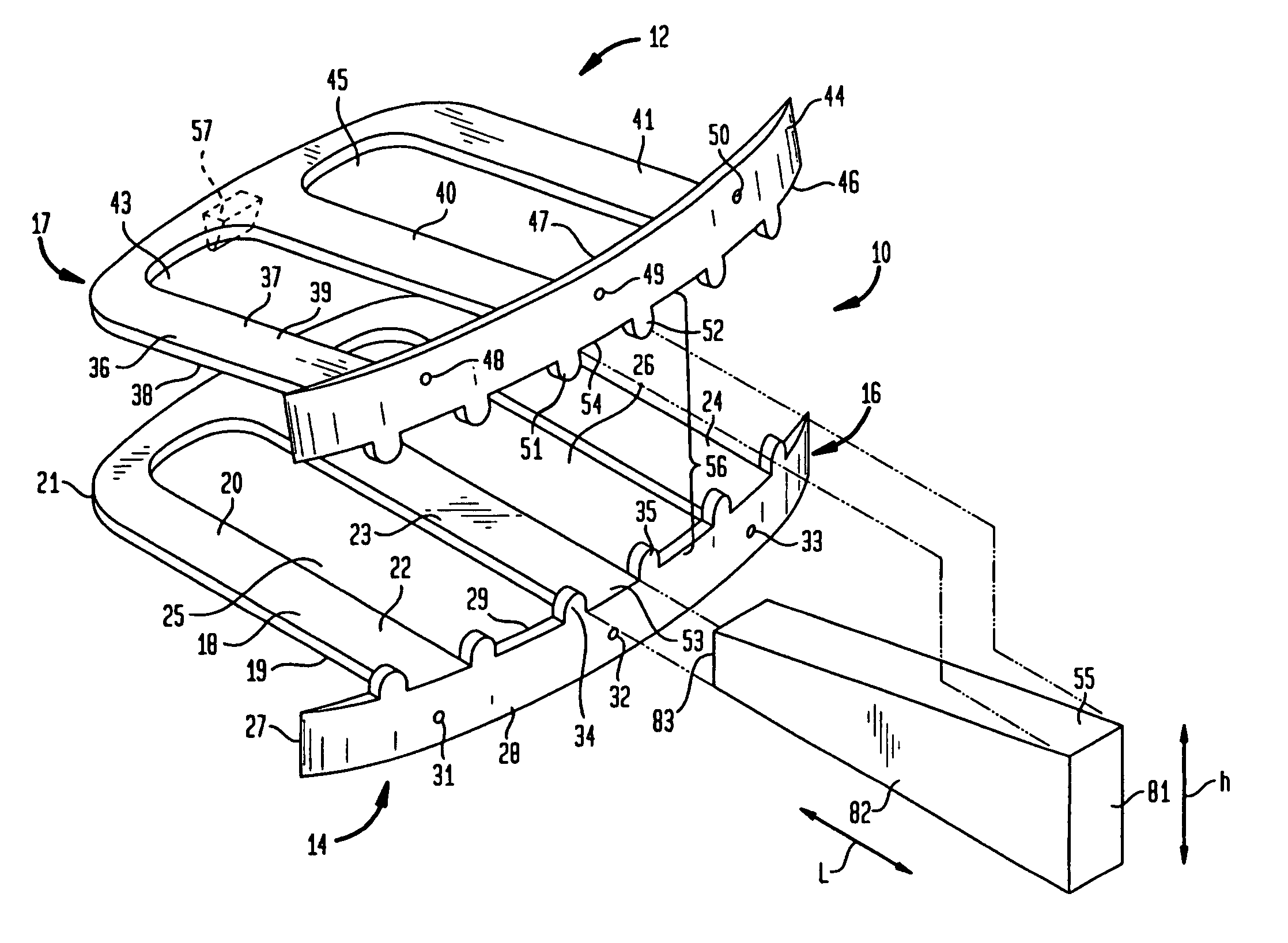
A bone screw retaining system including an implant adapted to be applied the anterior human cervical spine for contacting anterior aspects of at least two cervical vertebral bodies, the implant having a plate that defines a plurality of transversely extending bores that extend along a longitudinal axis between an anterior surface and a posterior surface, each bore being configured to receive a bone screw for engaging the plate to the cervical spine. An elastically deformable spring member positioned therein a cavity of the plate such that portions of the spring member can extend into a portion of an upper region of each of the bores of a pair of opposing bores, the spring member being movable between a first relaxed, expanded position and a second, compressed position. In the first relaxed position, at least a portion of the spring member extends outwardly substantially transverse to the longitudinal axis of the bore and into the upper region of the bore and, in the second position, portions of the spring member are medially biased away from the longitudinal axis of the bore toward the outer wall of upper region of the bore, which increases the effective inner diameter of the upper region of the bore.
Owner:ROBINSON JAMES C
Interbody spinal fusion device
InactiveUS20070276375A1Promote bone fusionEasy maintenanceInternal osteosythesisBone implantLamina terminalisAnterior surface
A pair of flat support plates in a spinal fusion implant device contact and rest against the softer, central cancellous bone portion of respective endplates of adjacent vertebrae. Each support plate has a front template that is orthogonal to the plate and is bent to communicate with the anterior surface of the hard cortical endplate the vertebrae. A wedge-shaped support strut in a central channel between the two plates is configured to vary the distance between the support plates such that the height of the device proximate the anterior end is greater than the height of the device at the posterior end to maintain the natural lordosis of the spine. Channels formed on either side of the support strut are filled with bone graft material and contact the endplates of the vertebrae through large openings in the flat support plates to facilitate fusion.
Owner:RAPP LAWRENCE G
Method and apparatus for preparing a glenoid surface
ActiveUS20060058809A1Easy to implantEasy to installProsthesisOsteosynthesis devicesAnterior surfaceProsthesis
A method and apparatus for facilitating shoulder arthroplasty by providing a reference to establish version of the glenoid. In one form of the invention, a guide for positioning a guide pin to facilitate implantation of a glenoid prosthesis is provided. To properly position the guide pin, the guide is first oriented with respect to the scapula. A portion of the guide is positioned over the approximate center of the glenoid surface and another portion of the guide is positioned against the anterior surface of the scapula. After the guide is properly positioned, the guide pin is inserted through an aperture in the guide and anchored in the glenoid. Thereafter, the guide pin can serve as an alignment guide for other devices used to modify the glenoid surface. For example, a reamer having a cannulated central shaft can be placed over the guide pin and utilized to resurface the glenoid.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
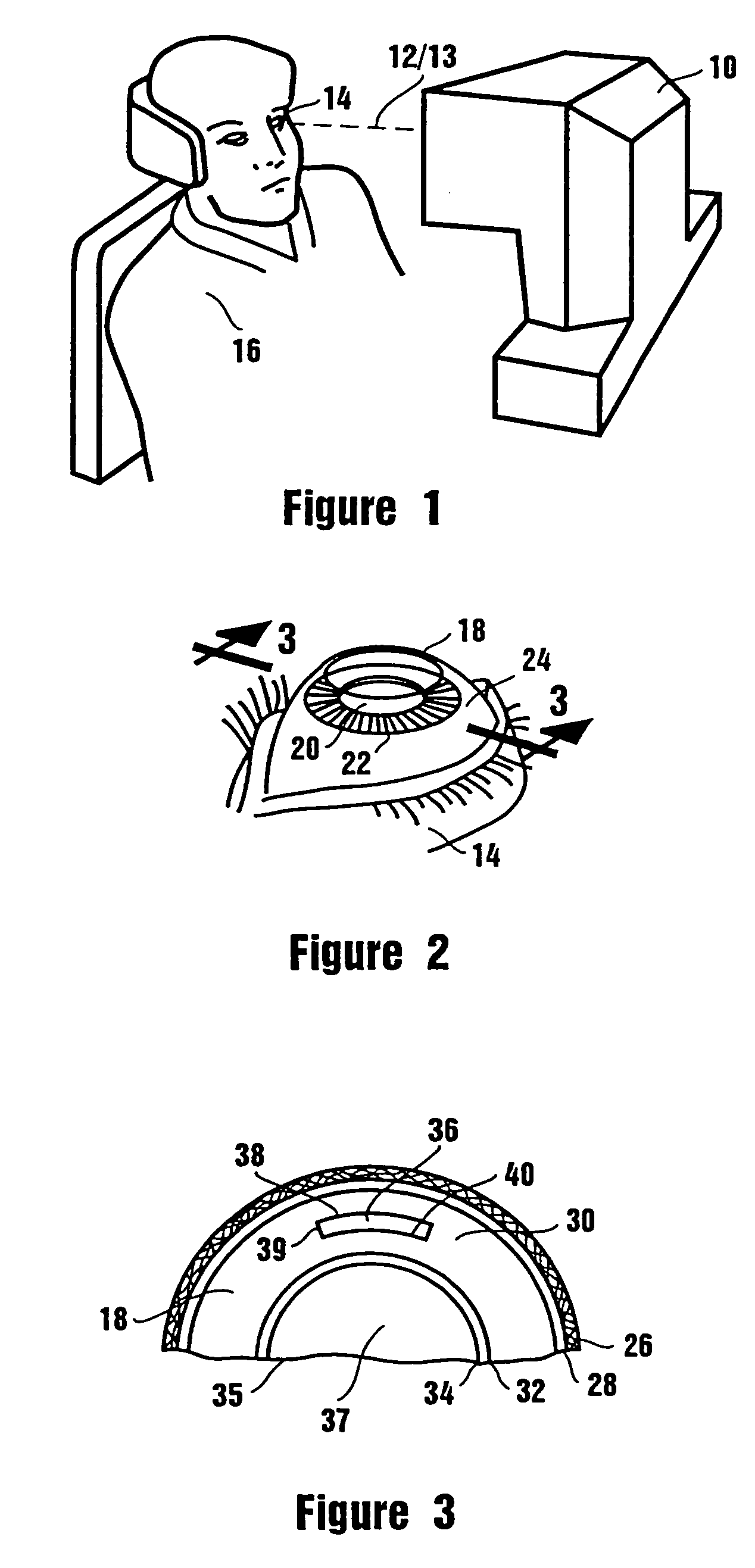
Adjustable universal implant blank for modifying corneal curvature and methods of modifying corneal curvature therewith
InactiveUS6949093B1Severe conditionImprove eyesightLaser surgeryEye implantsCorneal curvatureCorneal surface
A method for correcting the refractive error in a cornea of an eye, including the steps of positioning an inlay on the surface of the cornea, the inlay having a first surface and a second surface, and the second surface being adjacent the surface of the cornea. Energy is applied to the inlay to ablate a portion of the first surface of the inlay by an amount adapted to correct the refractive error in the eye. The inlay is removed from the surface of the cornea, and the cornea is separated into a first corneal surface and a second corneal surface, the first corneal surface facing in a posterior direction of the eye and the second corneal surface facing in an anterior surface of the eye. The inlay is then positioned adjacent at least one of the first corneal surface and the second corneal surface.
Owner:MINU
Spine stabilization device, and method and kit for its implantation
ActiveUS20100274358A1Good and reliable anchoringLimited surfaceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisLiquid stateAnterior surface
A spine stabilization device is provided, the spine stabilization device including an interbody spacer shaped to be inserted between a vertebral body of an upper vertebra and a vertebral body of a lower vertebra, and including a top surface oriented towards the lower endplate of the vertebral body of the upper vertebra and a bottom surface oriented towards the upper endplate of the vertebral body of the lower vertebra; and a fixation device to be inserted after placement of the interbody spacer, the fixation device including a support portion securing the interbody spacer against escaping from between the vertebral bodies of the upper and lower vertebra into a ventral direction, the support portion shaped to rest against a portion of an anterior surface of the interbody spacer, and further including an anchor, the anchor including an anchoring material portion that is configured to be inserted, in a liquid state, into cancellous bone tissue of at least one of the vertebral body of the upper vertebra and of the vertebral body of the lower vertebra, to thereby infiltrate the cancellous bone tissue, and to harden thereafter so as to fix the support portion to the vertebral body.
Owner:SPINEWELDING
Ophthalmic lens having an optical zone blend design
ActiveUS7004585B2Smooth transitionMinimize appearanceIntraocular lensOptical partsAnterior surfacePrimary gaze
An ophthalmic lens, such as multifocal contact lens, that is worn on the surface of the eye and has a blended design for a segmented optical zone. The lens has an anterior surface and an opposite posterior surface, wherein the anterior surface includes a vertical meridian, a horizontal meridian, a central optical zone having at least a first optical zone for primary gaze, a second optical zone for down-gaze and an optical blending zone between the first and second optical zones. The optical blending zone has a surface that ensures a smooth surface transition from the first optical zone to the second optical zone and that allows the first and second optical zone to be designed independently and optimally so that ghost images or blur from the transition between the first and second optical zones can be minimized or eliminated. Image blur from the blend zone that subtends the pupil is minimized by the magnitude of the curvature of the blend zone. The optical zones will have the optimal aberration parameters to control vision.
Owner:ALCON INC
Method of corneal surgery by laser incising a contoured corneal flap
A method of corneal laser surgery is disclosed. A first periphery is defined at an anterior surface of the cornea. This first periphery bounds a first planar area. A second periphery is defined within stromal tissue of the cornea. This second periphery bounds a second planar area. The second planar area is sized differently than the first planar area. A layer of stromal tissue which is bounded by the second periphery is subsequently incised. Stromal tissue between substantial portions of the first periphery and the second periphery is also incised, such that at least some corneal tissue disposed between the first and second peripheries remains connected to corneal tissue outside of the first and second peripheries.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Myopic corneal ring with central accommodating portion
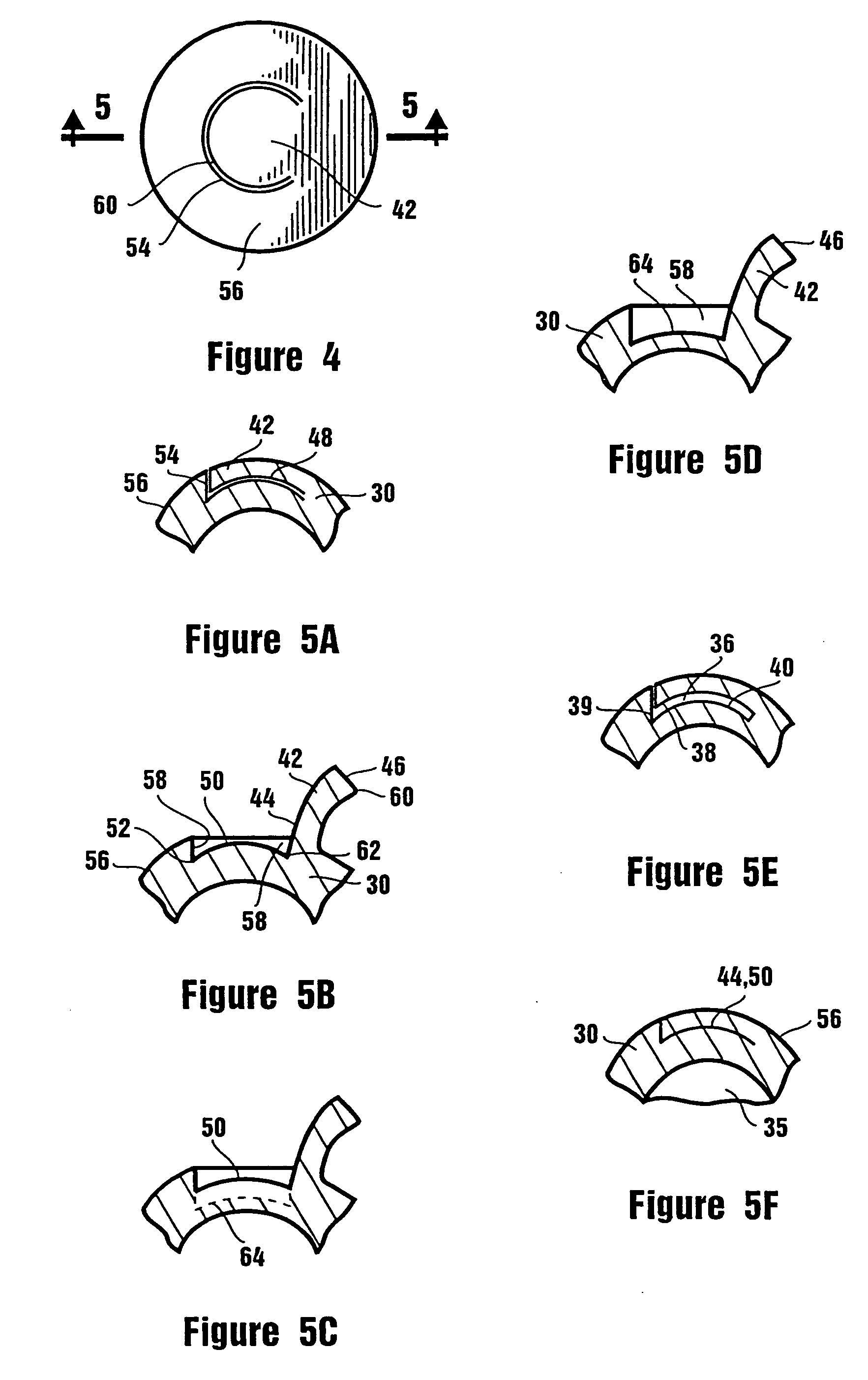
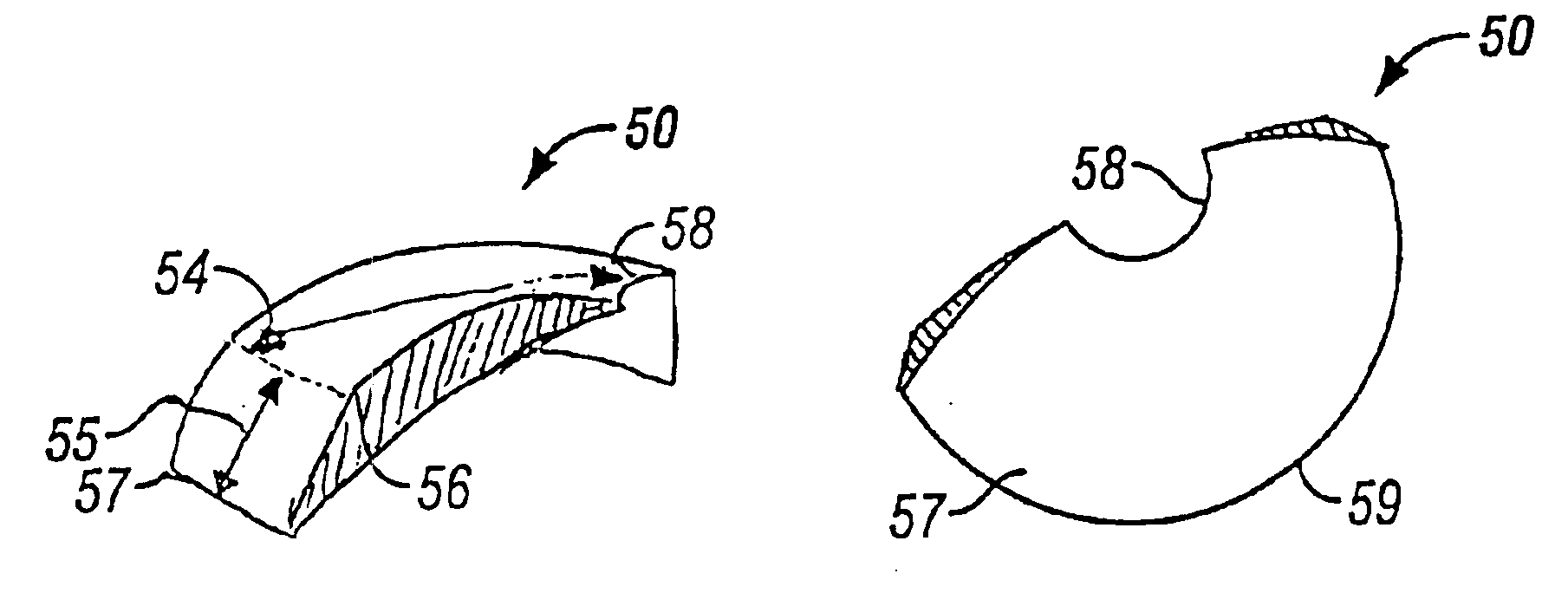
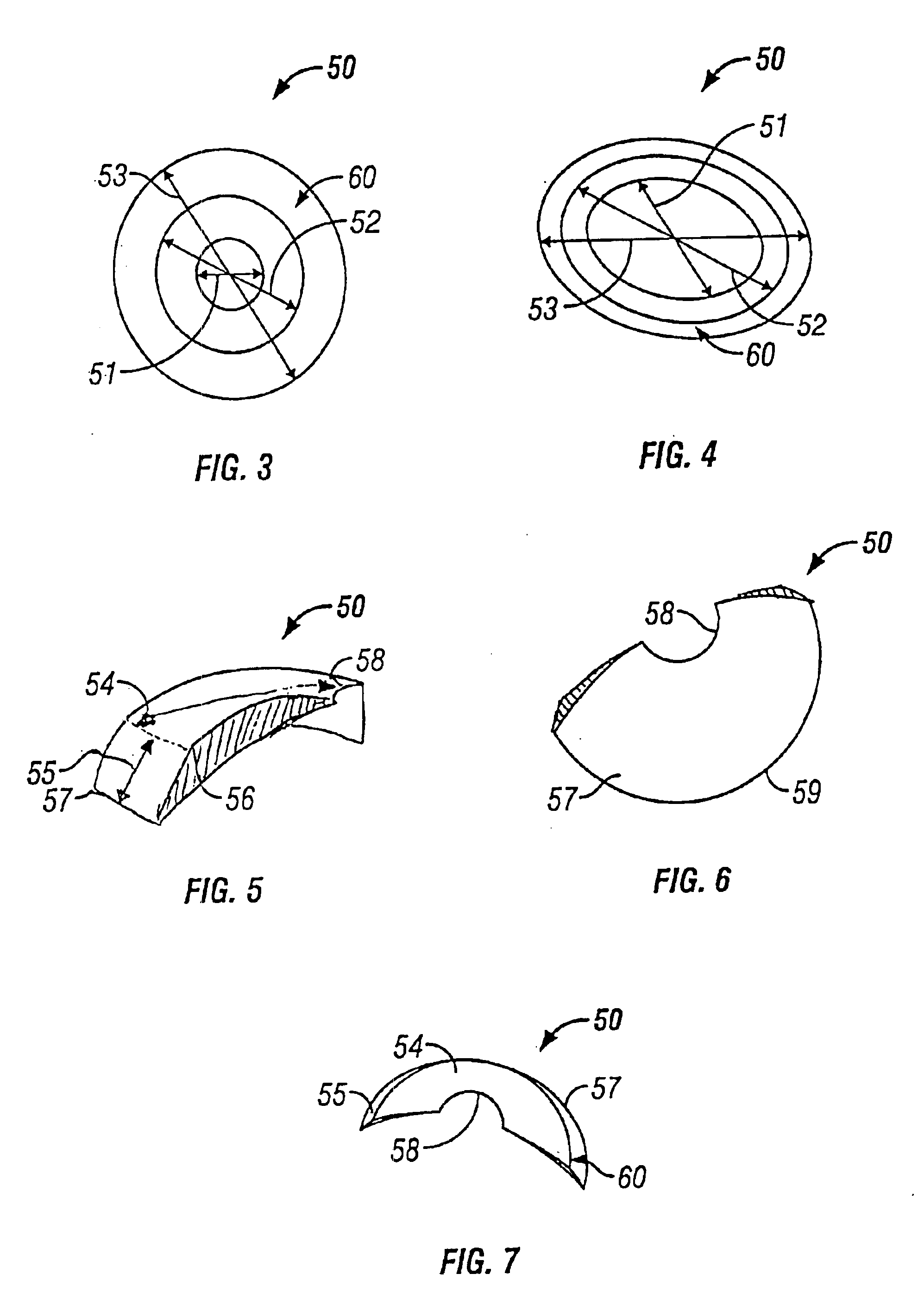
InactiveUS6849090B2Prevents optical aberrationReduce tensionEye implantsCorneal ringAnterior surface
A bio-compatible corneal ring for myopic correction and accommodation for presbyopia. The corneal ring is made from a bio-compatible material with a lens body having an inner and outer circular edge. The inner circular edge forms an opening in the lens body. The posterior surface of the lens body has a uniform radii of curvature between the inner and outer circular edges. The anterior surface has two radii of curvatures providing for correction of myopia. The first radii of curvature extends from near the outer circular edge to a junction point before the inner circular edge. The second radii of curvature extends from the junction point and continues to the inner circular edge. The inner and outer circular edges have a thickness of less than about 0.020 mm, but preferably are about 0.010 mm or less.
Owner:REVISION OPTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com