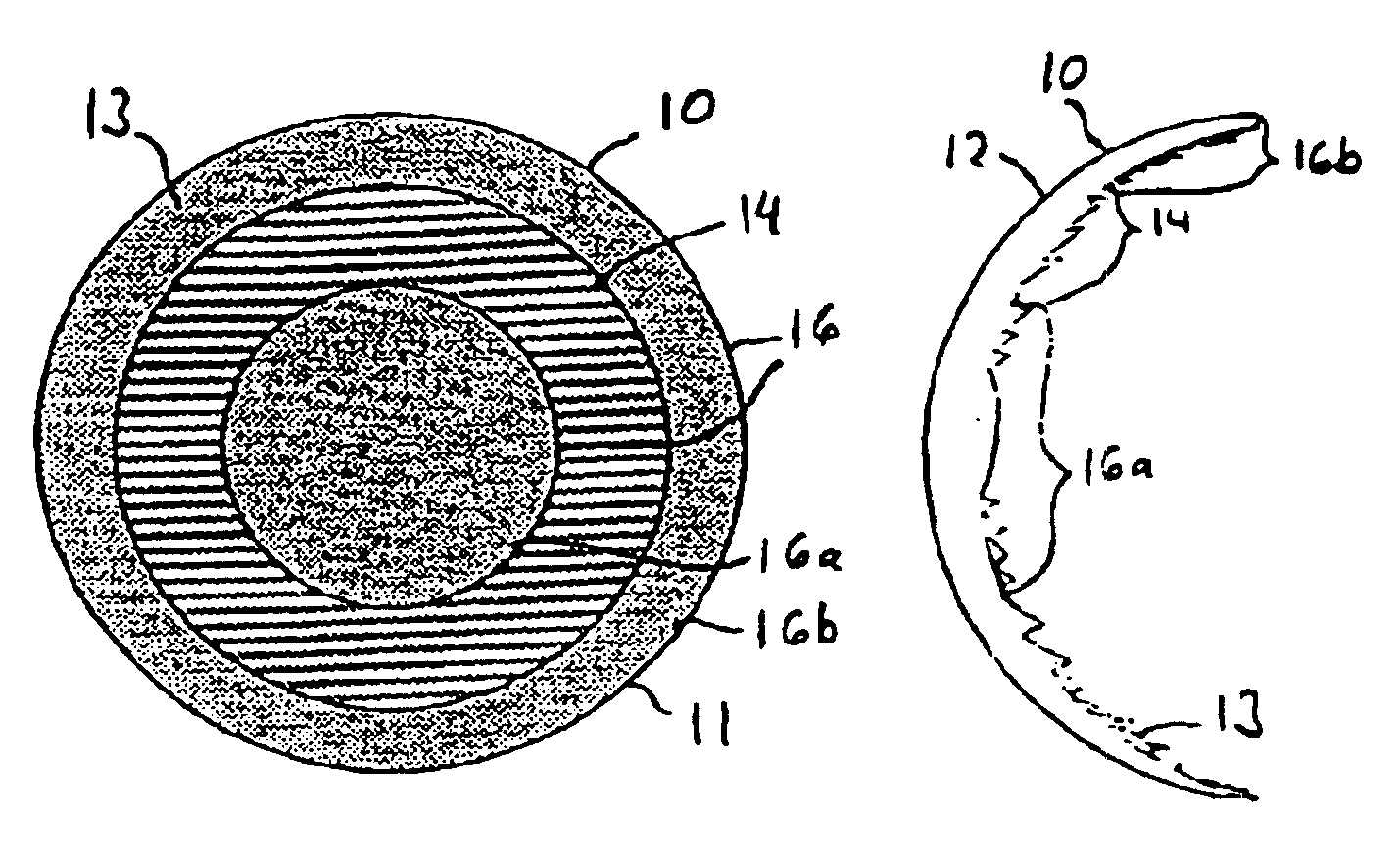
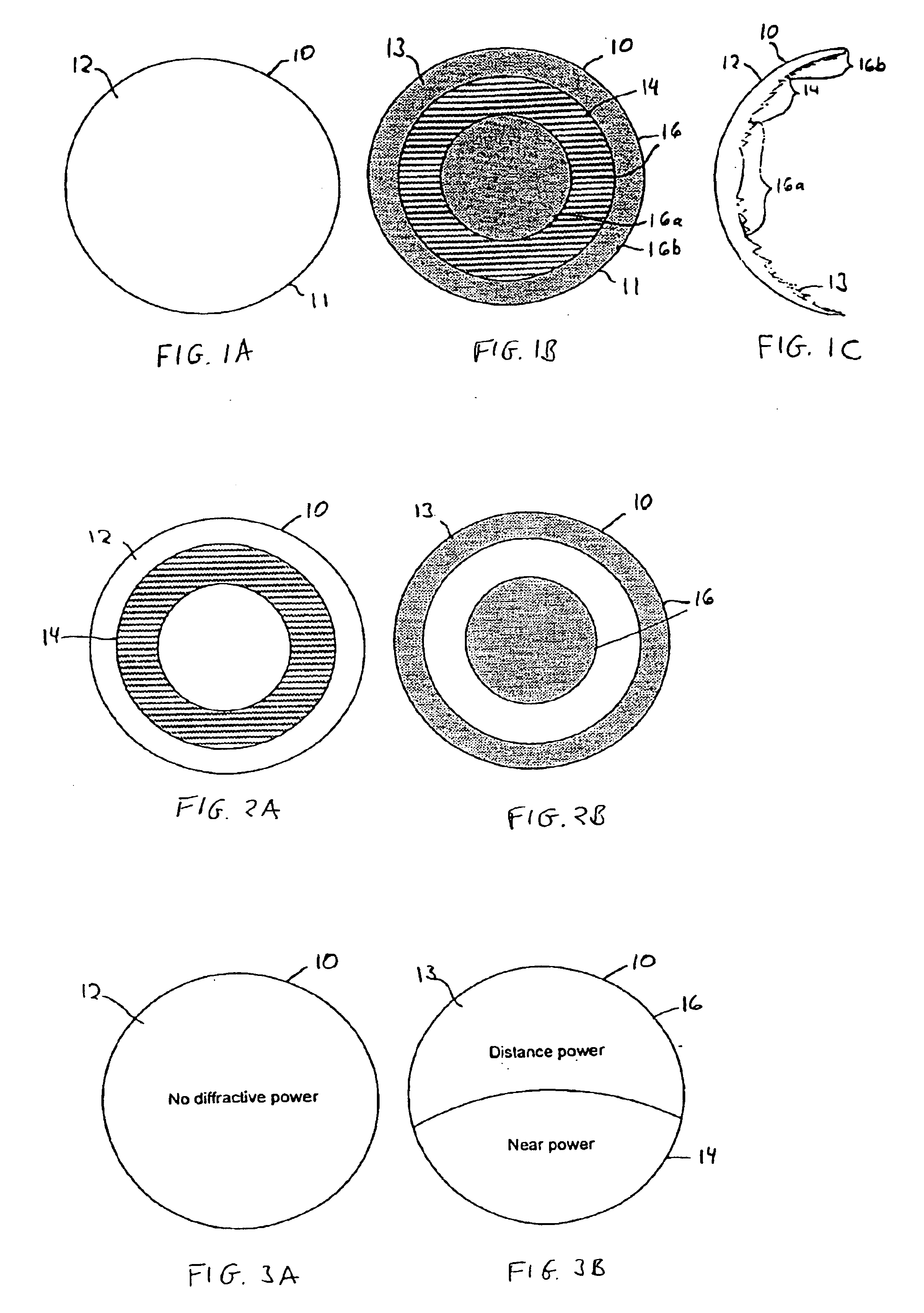
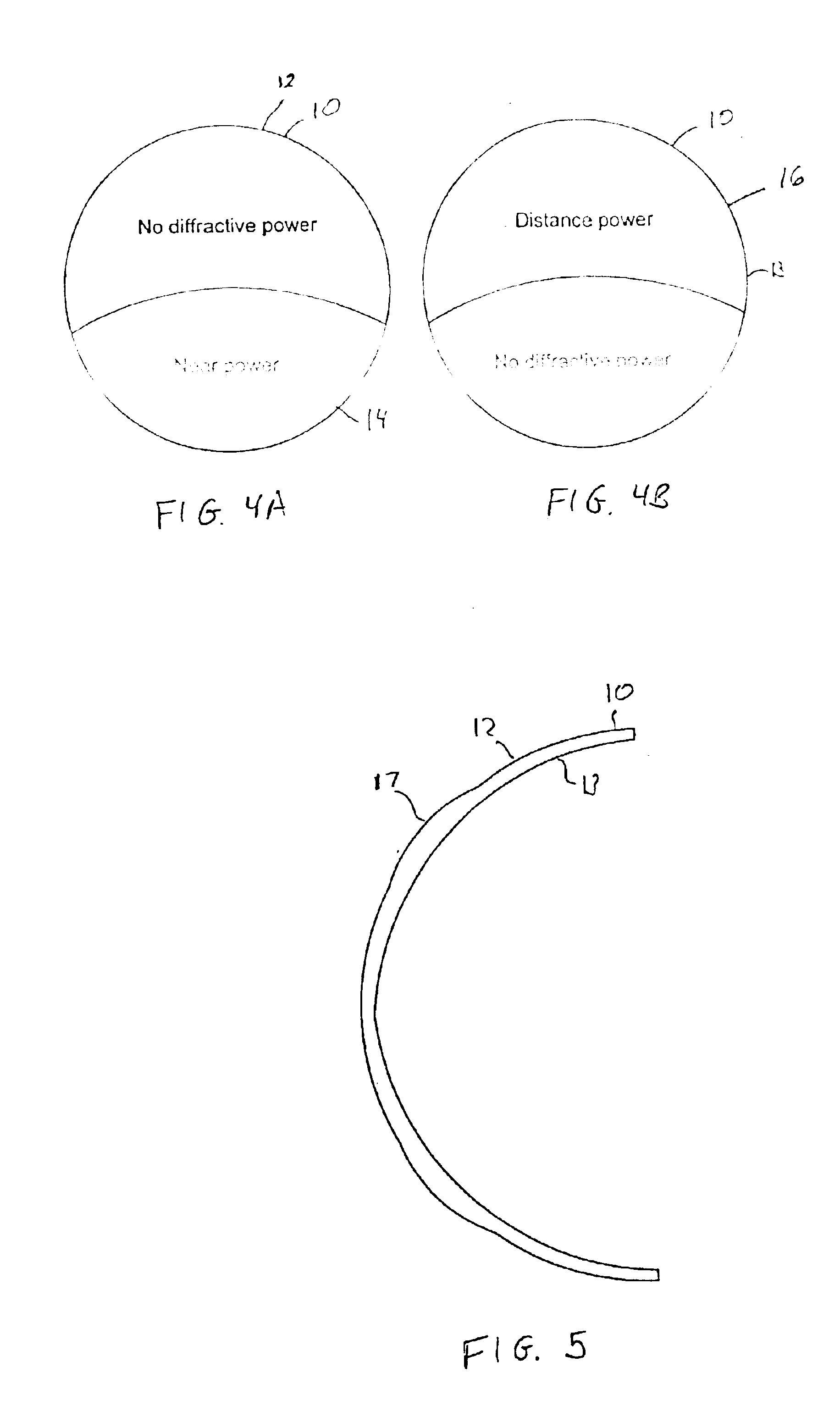
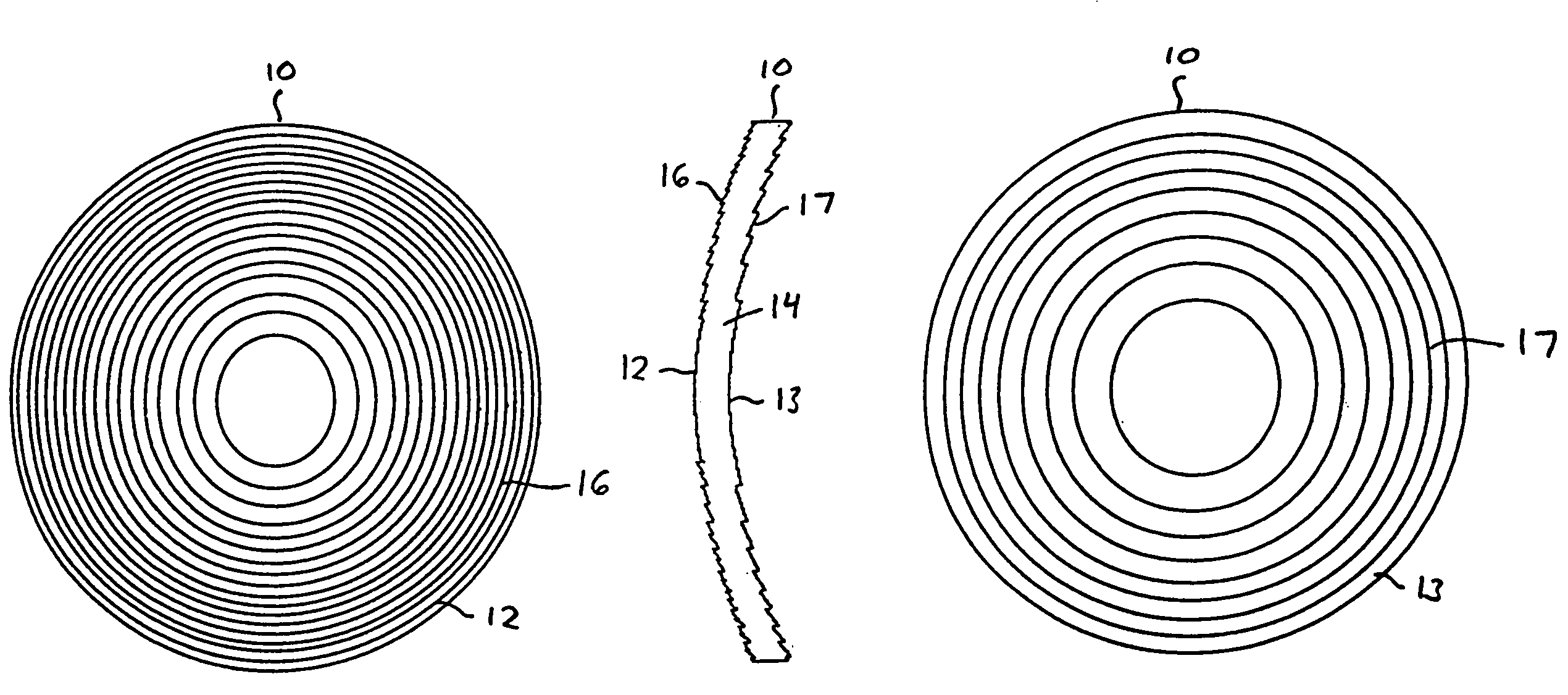
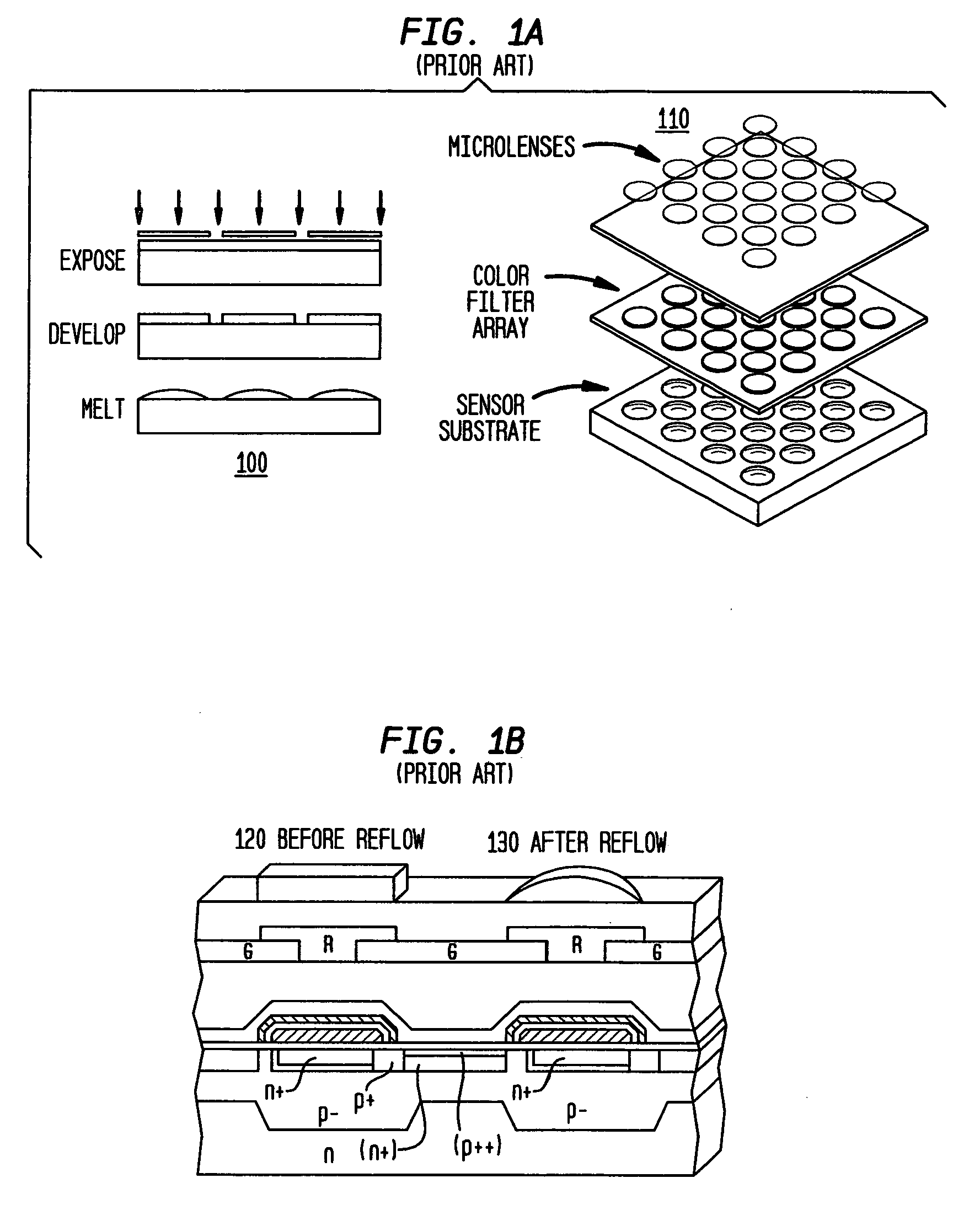
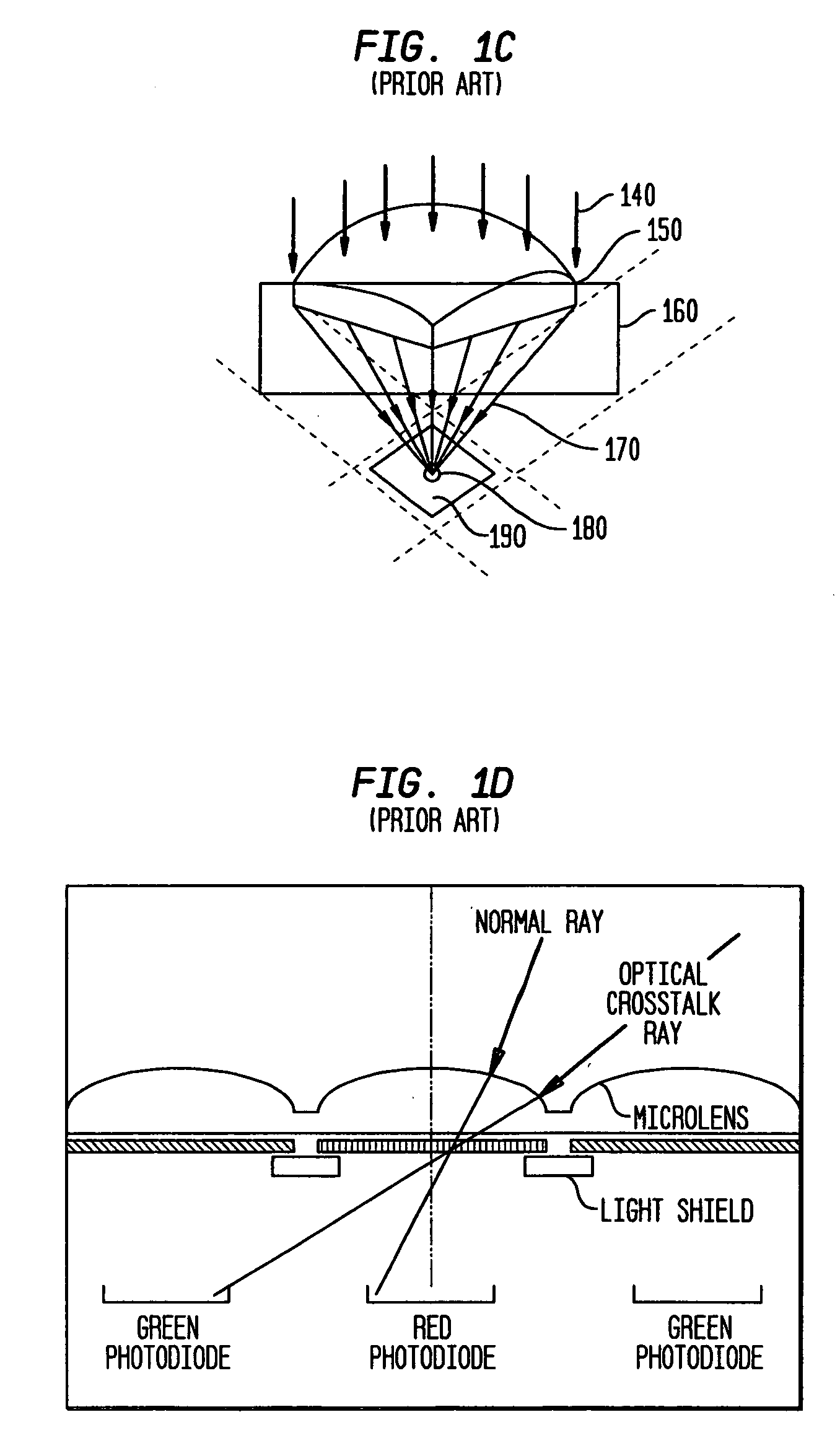
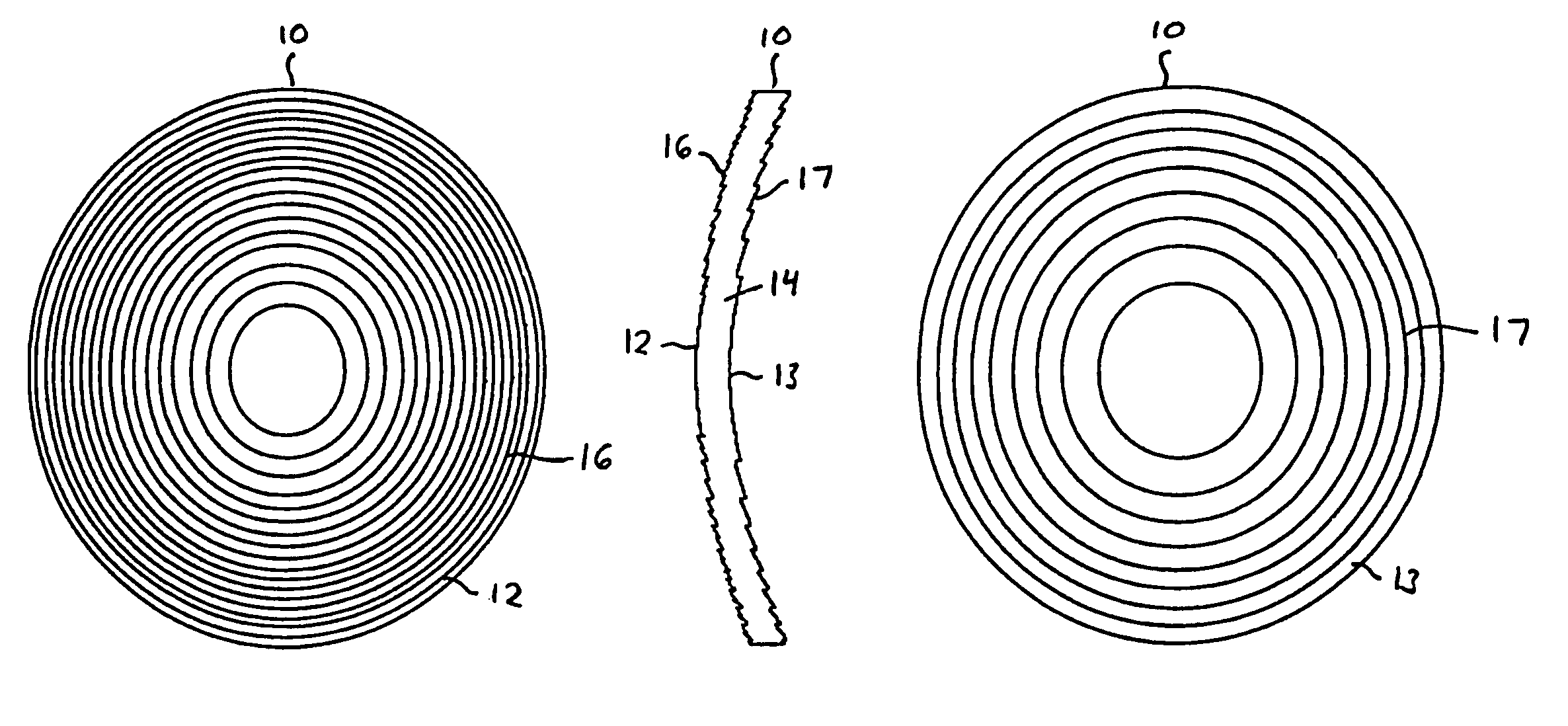
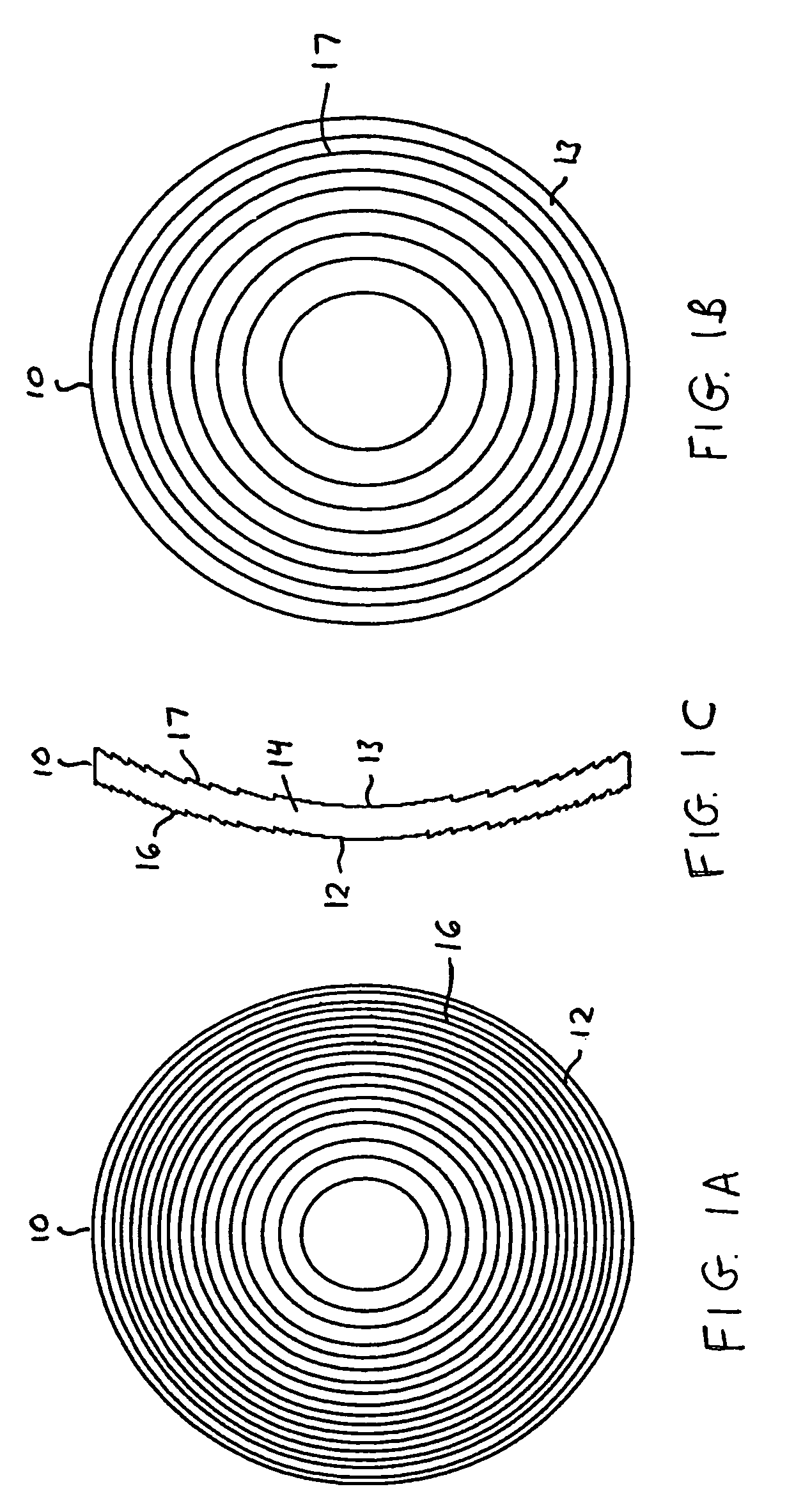
Patents
Literature
204 results about "Diffractive lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
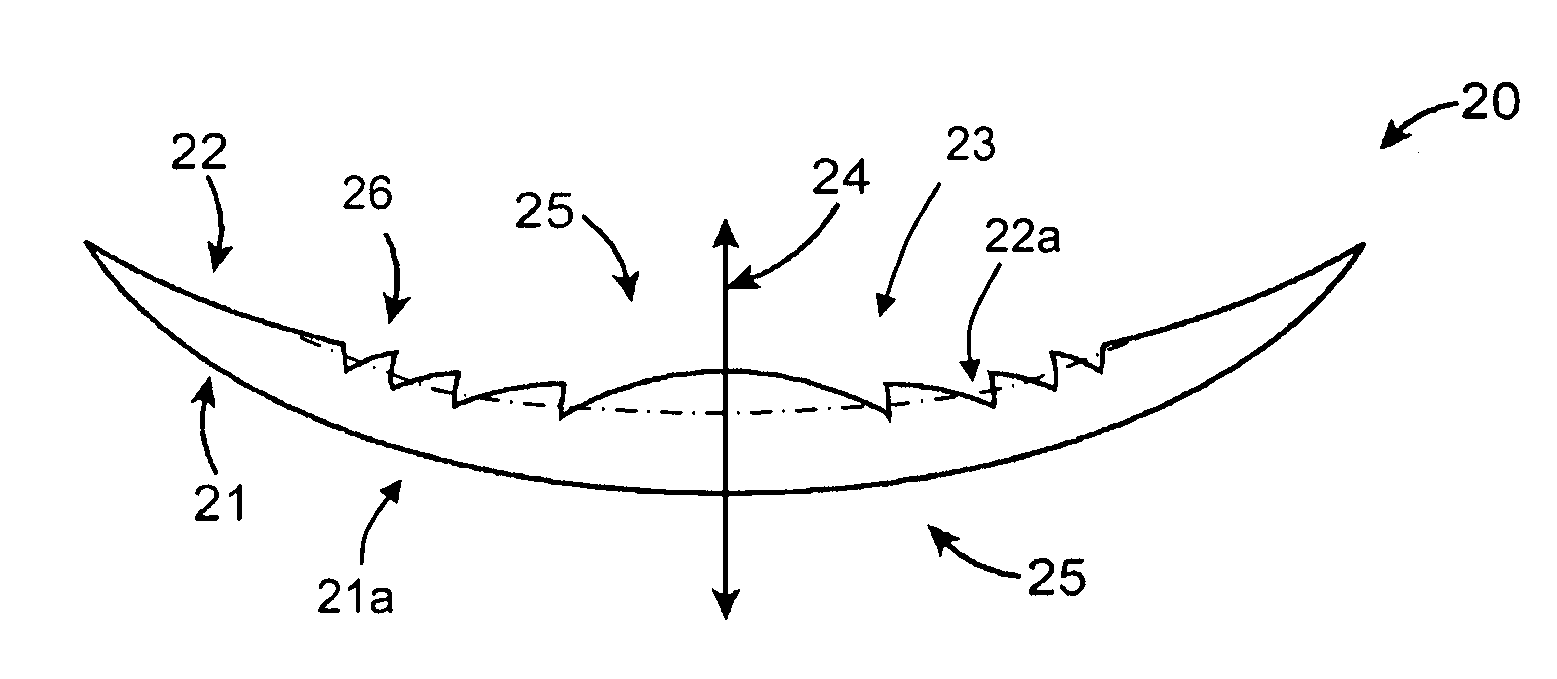
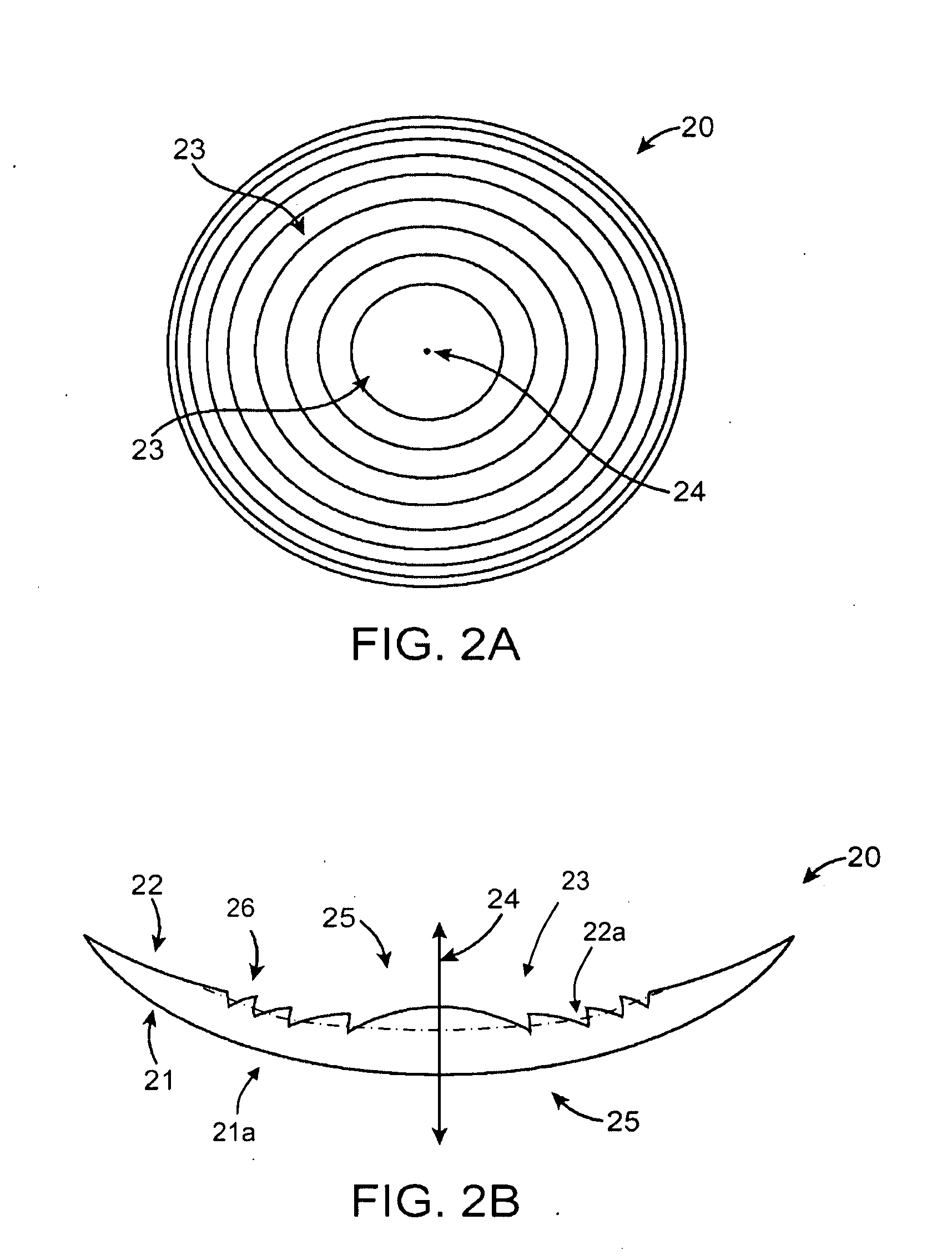
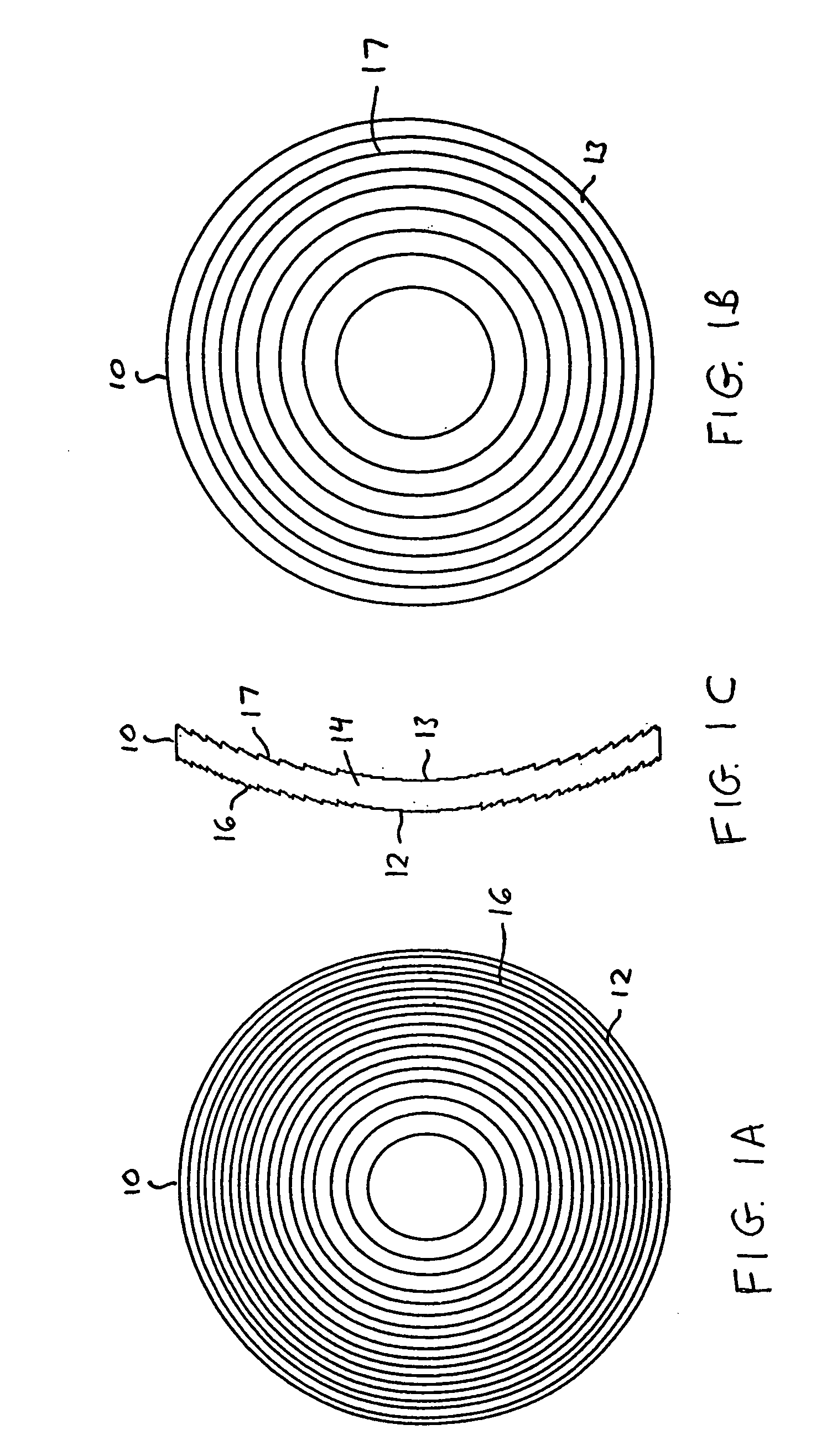
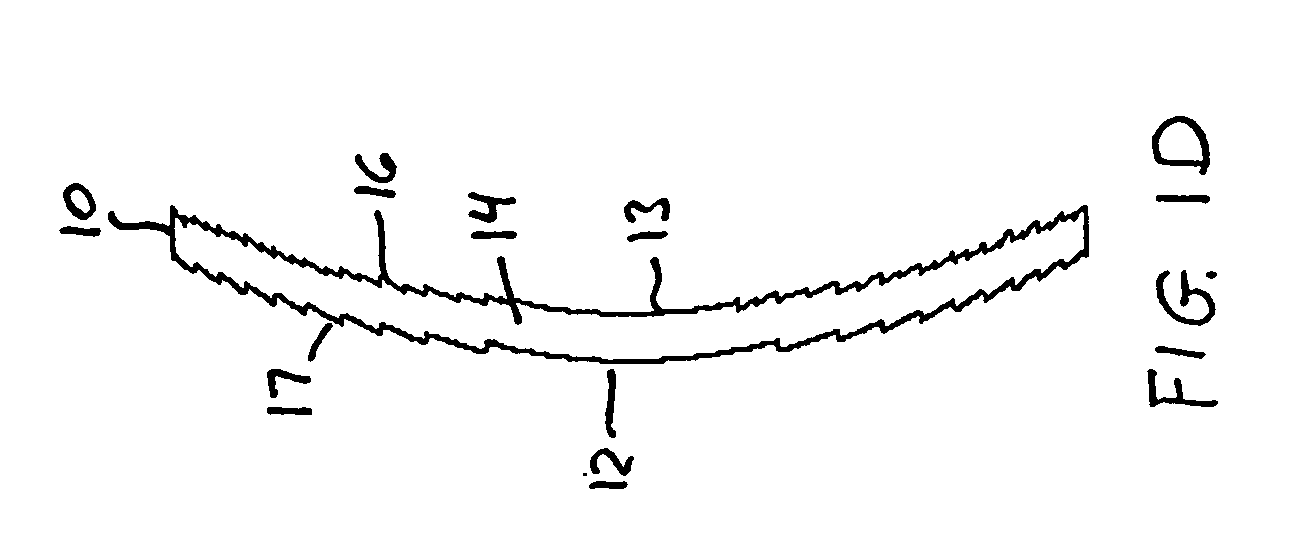
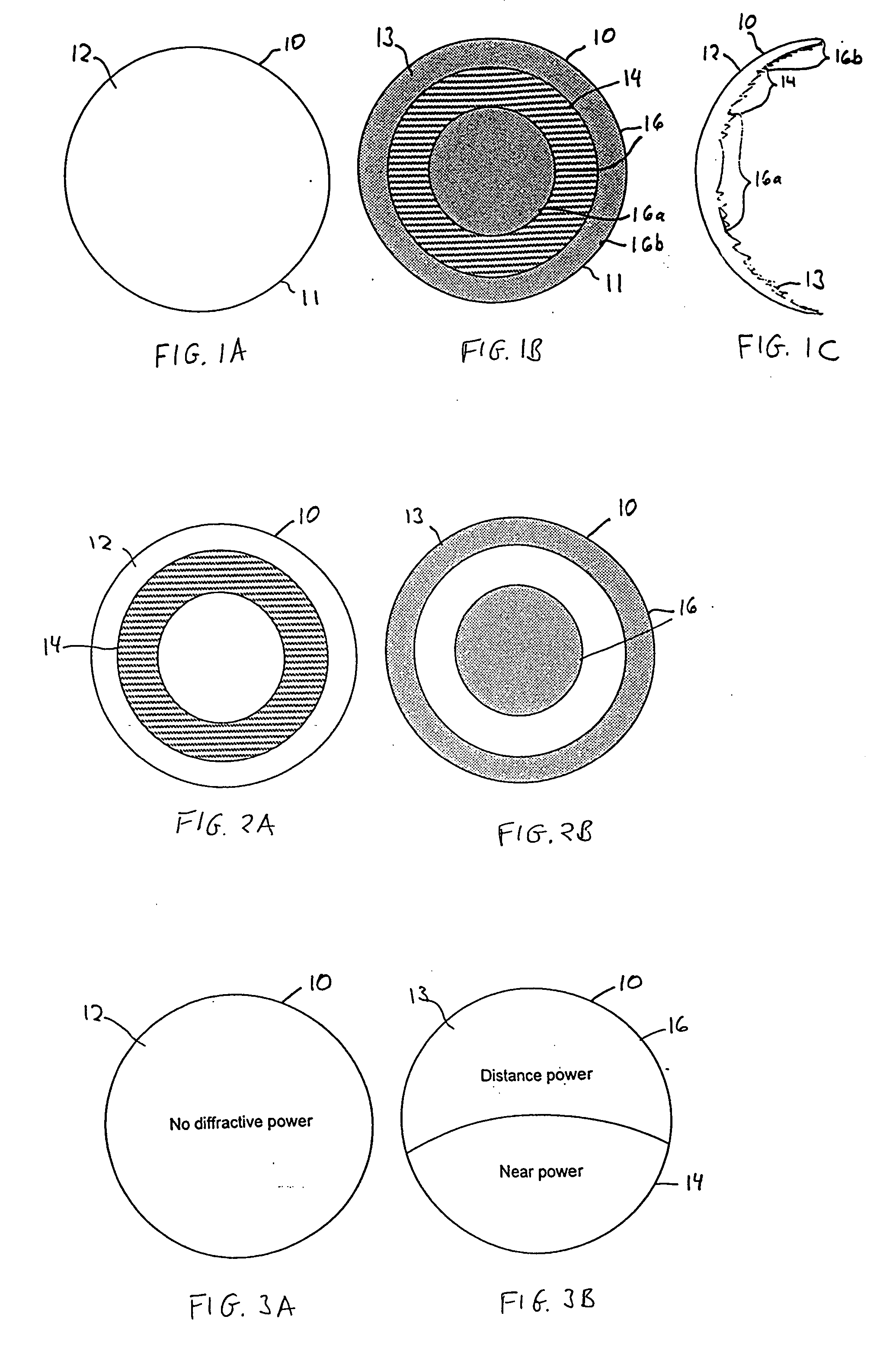
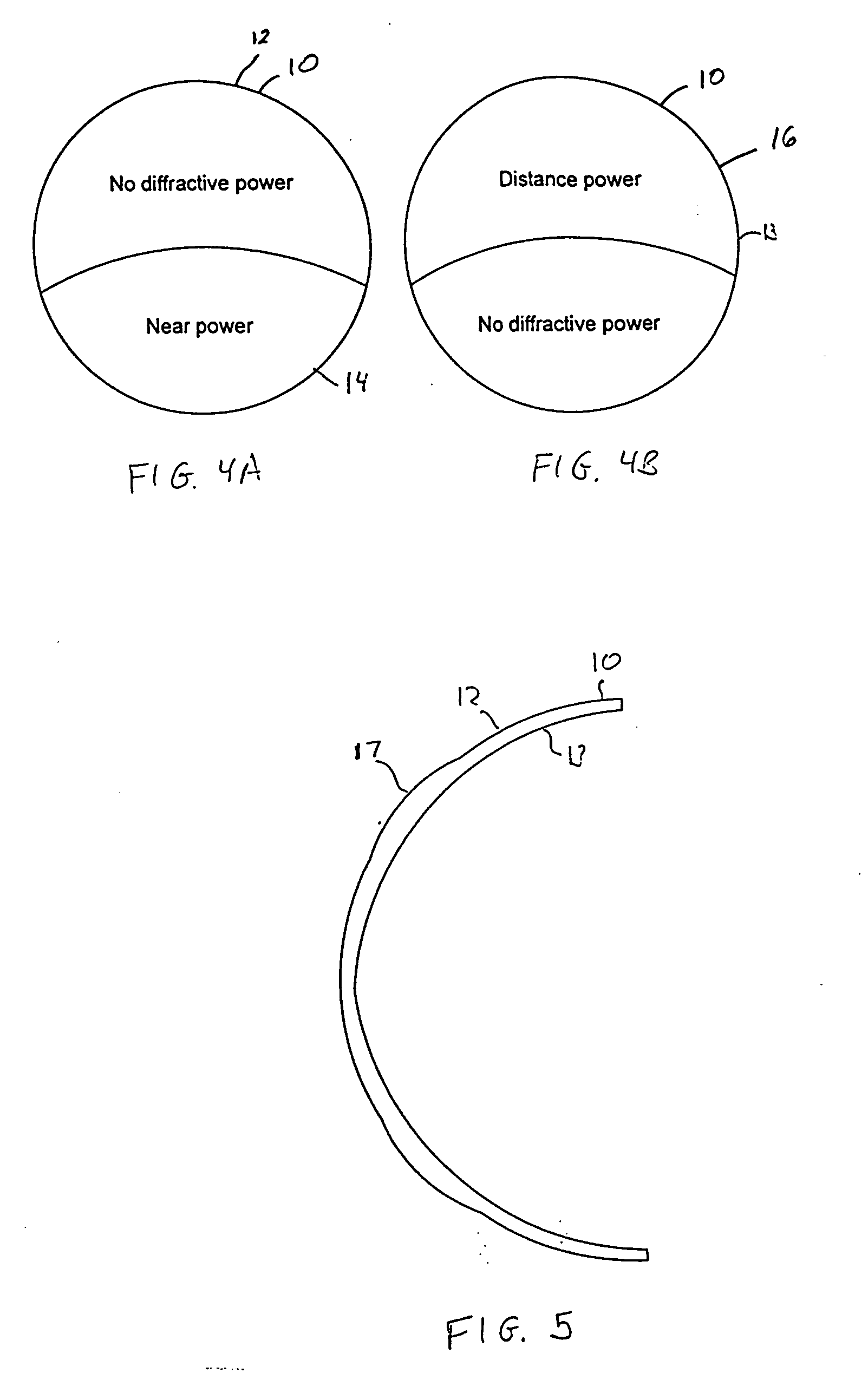
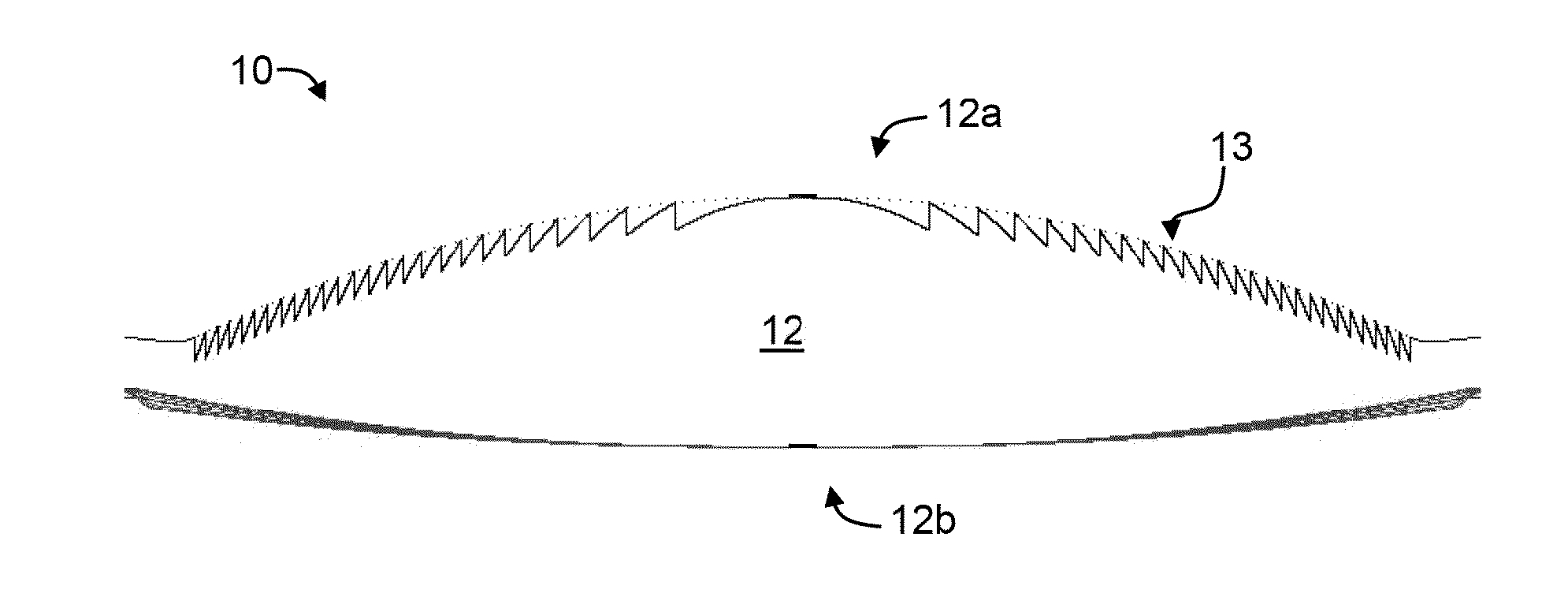
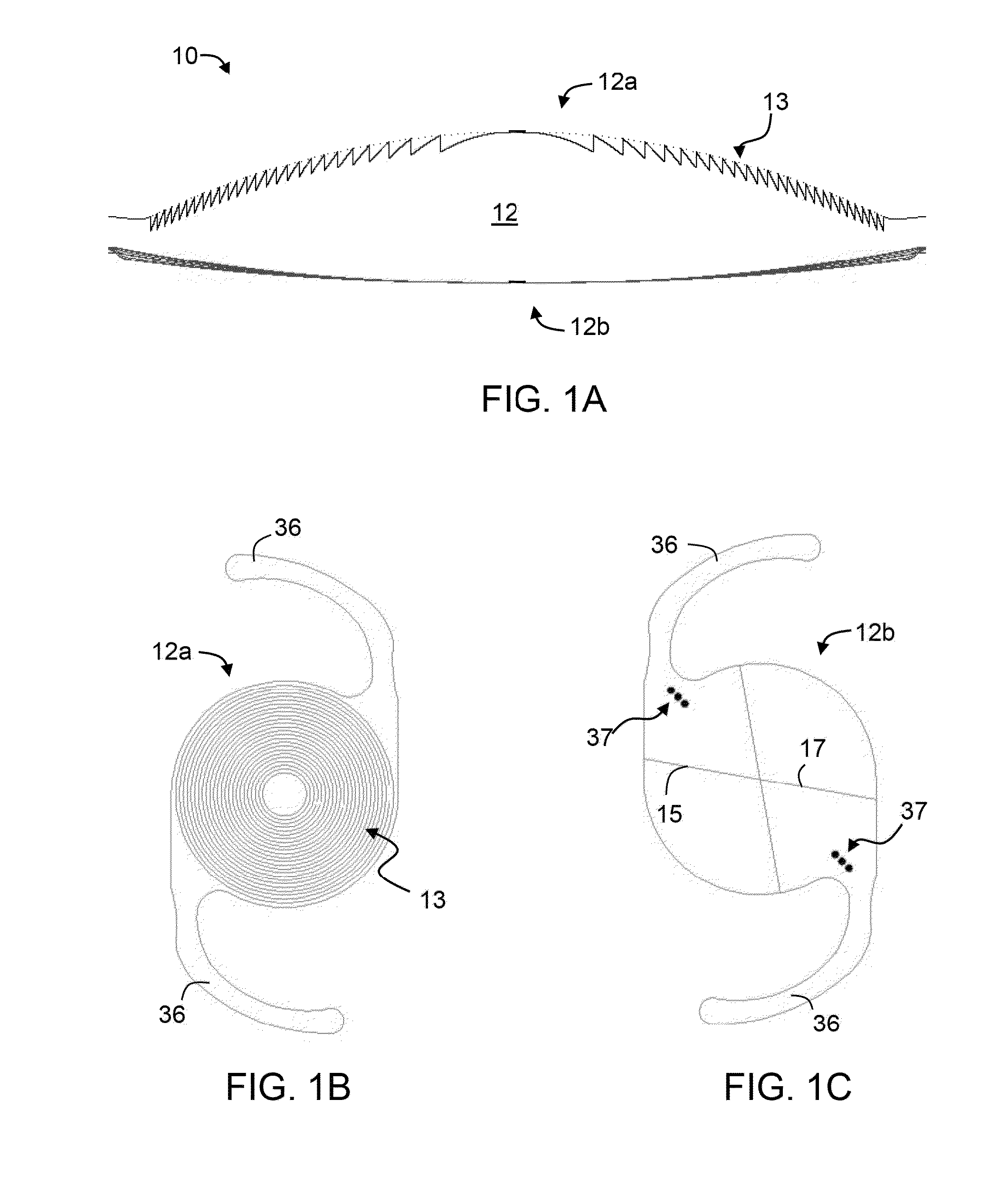
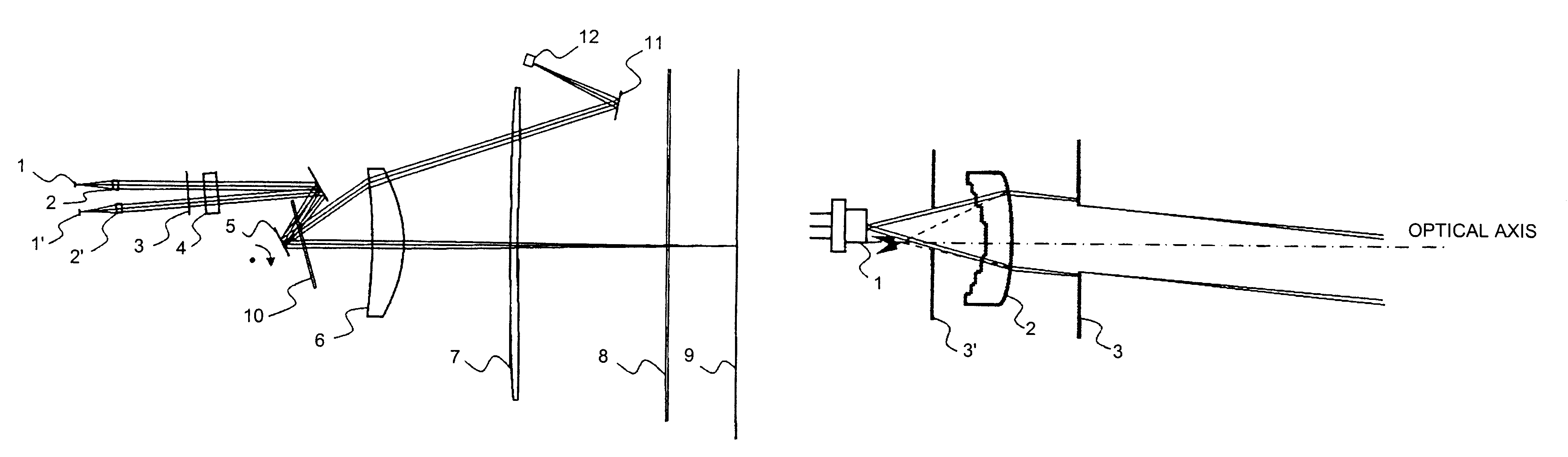
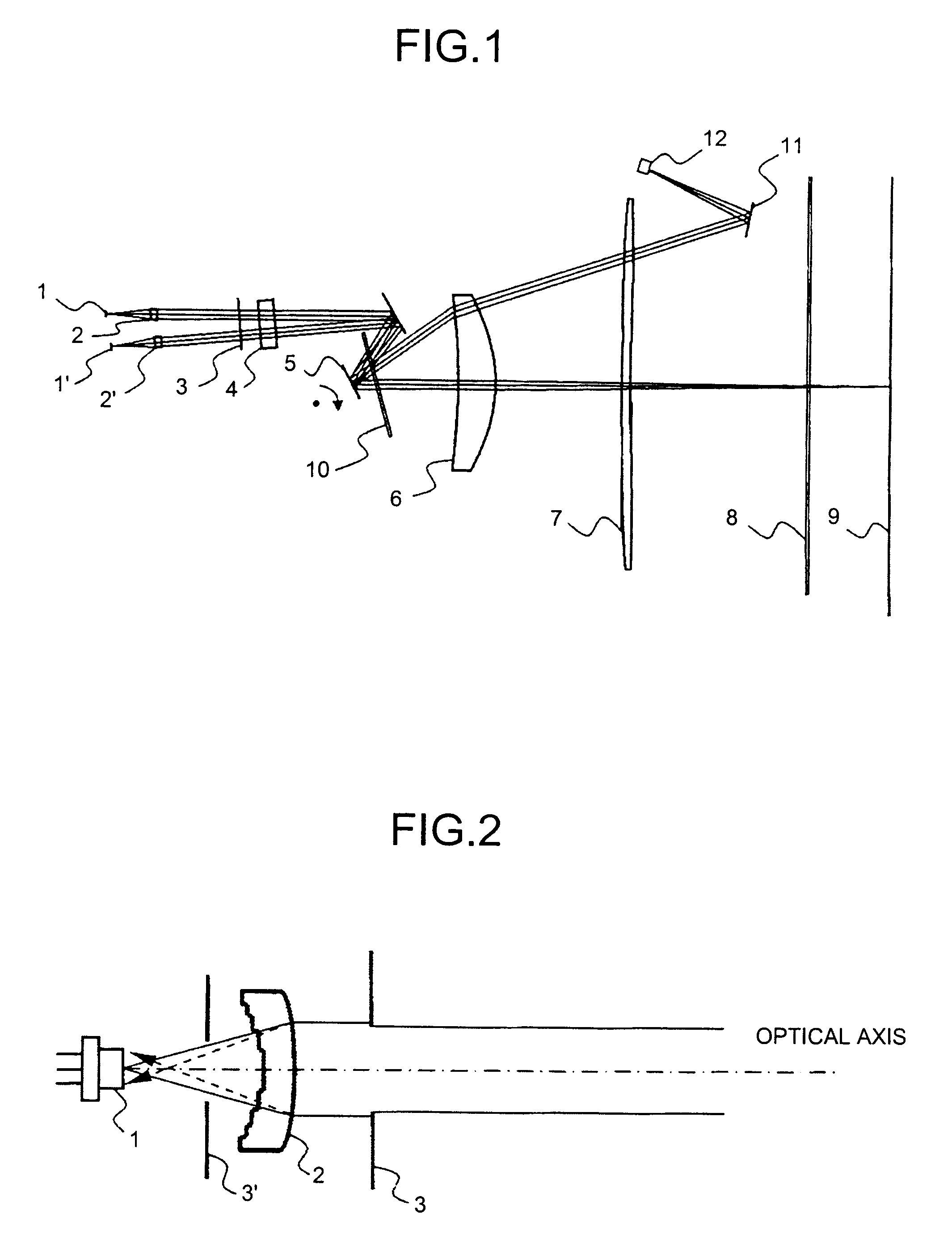
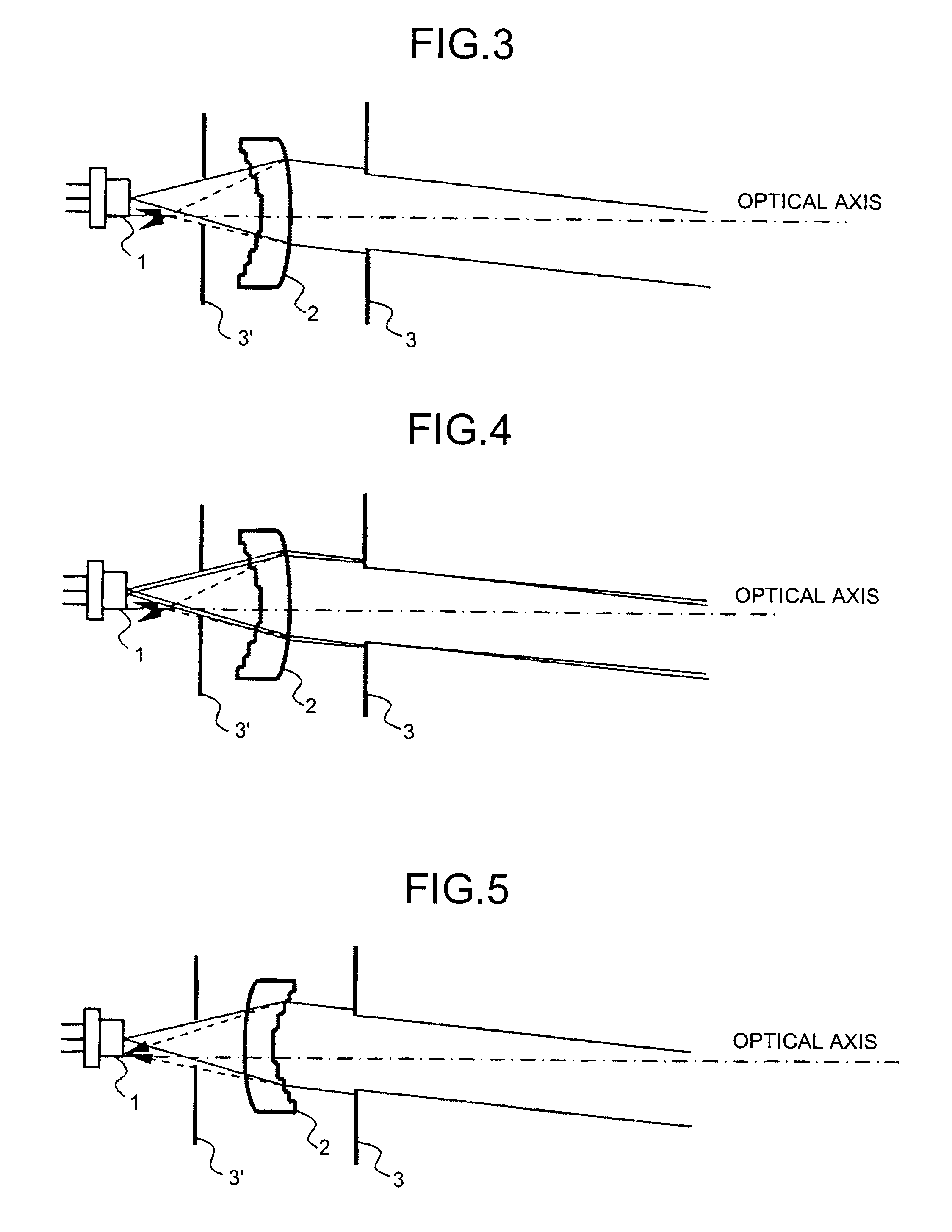
Apodized aspheric diffractive lenses
InactiveUS20060116764A1Improve image contrastSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryCamera lensImage contrast
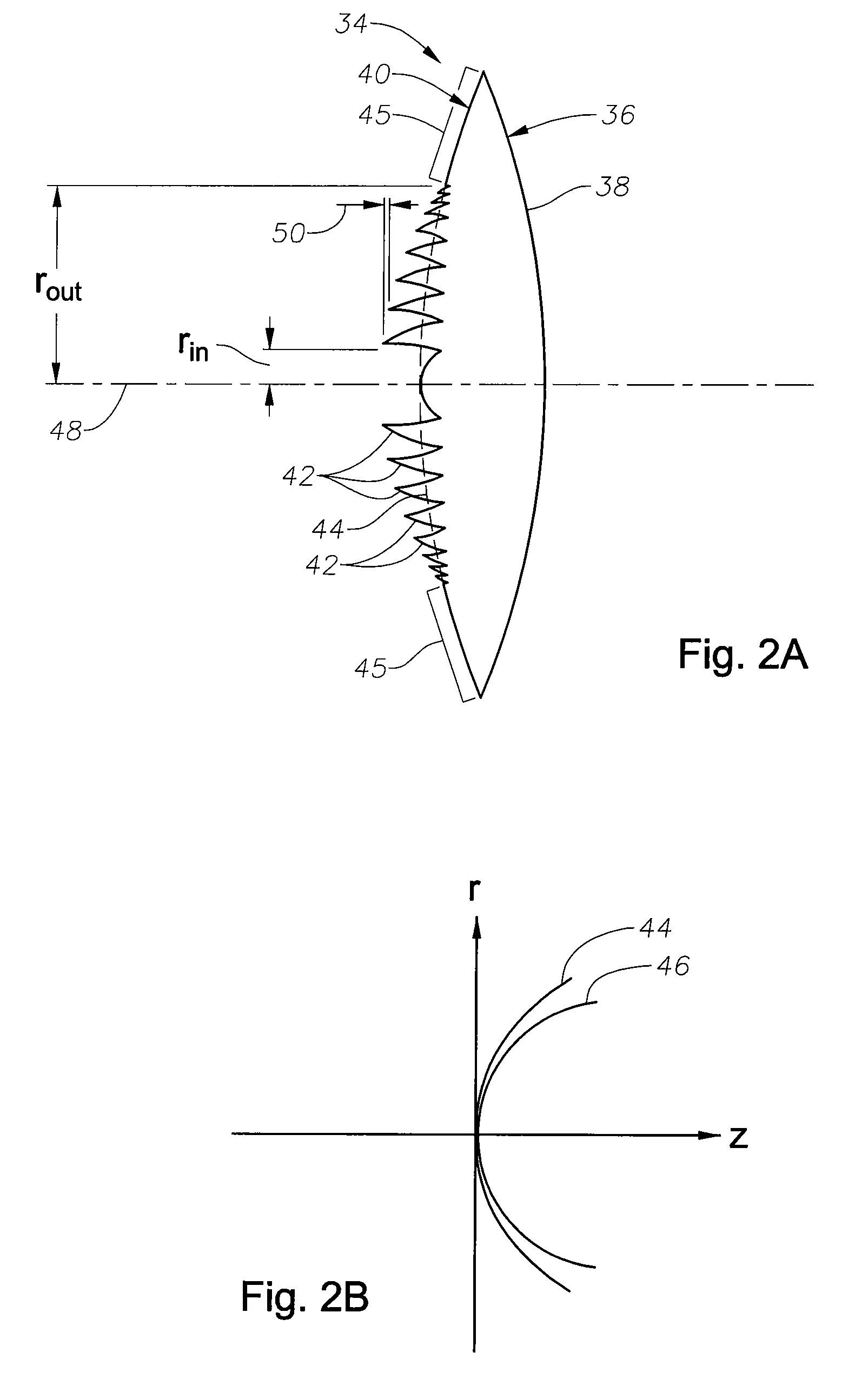
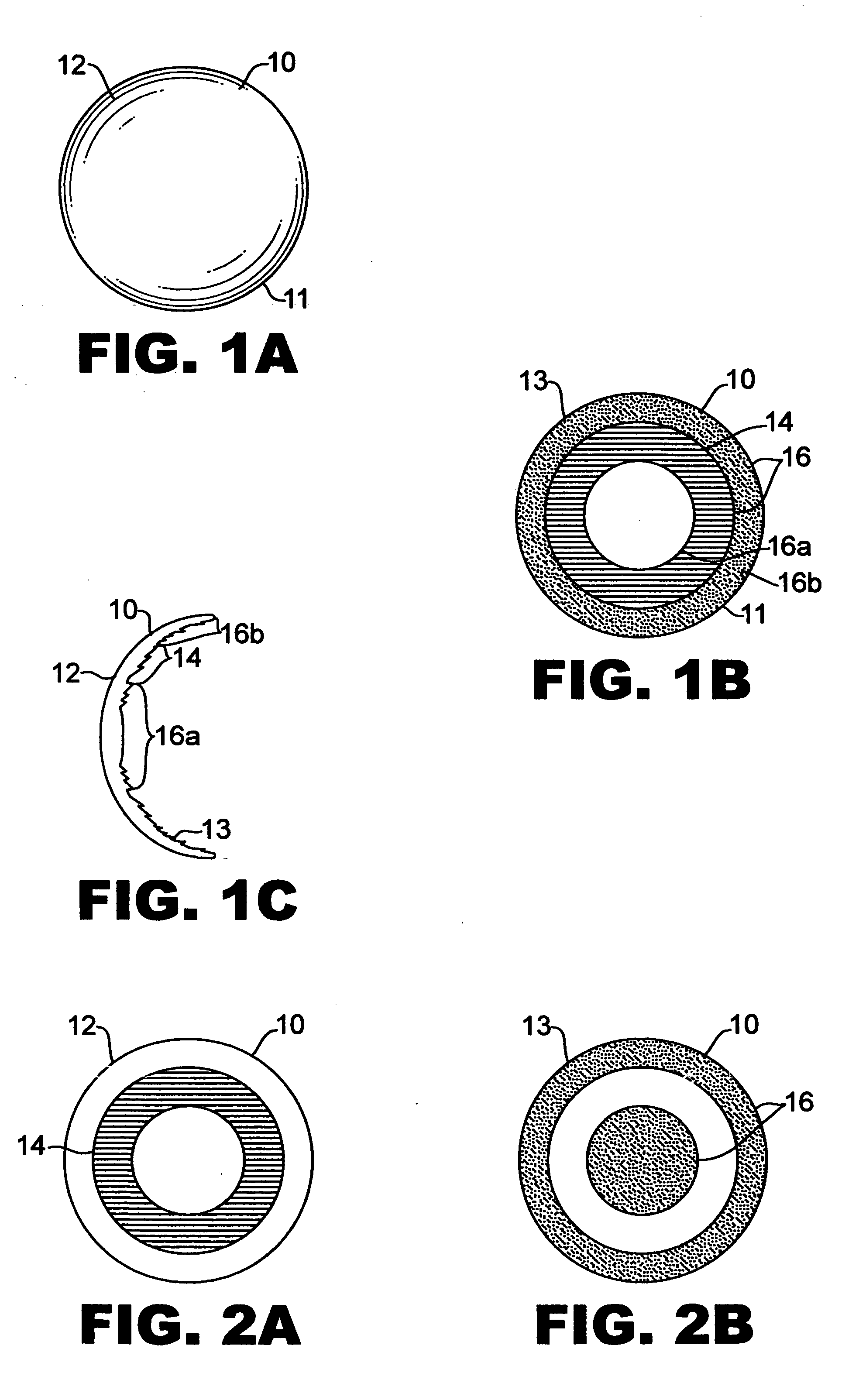
Aspheric diffractive lenses are disclosed for ophthalmic applications. For example, multifocal intraocular lens (IOLs) are disclosed that include an optic having an anterior surface and a posterior surface, at least one of which surfaces includes an aspherical base profile on a portion of which a plurality of diffractive zones are disposed so as to generate a far focus and a near focus. The aspherical base profile enhances image contrast at the far focus of the lens relative to that obtained by a substantially identical IOL in which the respective base profile is spherical.
Owner:ALCON INC
Electro-active diffractive lens and method for making the same
Aspects of the present invention provide an electro-active lens and method for manufacturing the same that encapsulates liquid crystal using solid transparent optical material using an improved liquid crystal seal feature. The seal feature greatly reduces the visibility of the liquid crystal seal feature in an assembled electro-active lens. The seal feature is also structurally robust such that the electro-active lens can be processed to fit a spectacle frame without disturbing containment of the liquid crystal and without disrupting electrical connectivity to the lens used to alter the refractive index of the liquid crystal, thereby ensuring fabrication of a commercially viable electro-active lens.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION INT GMBH
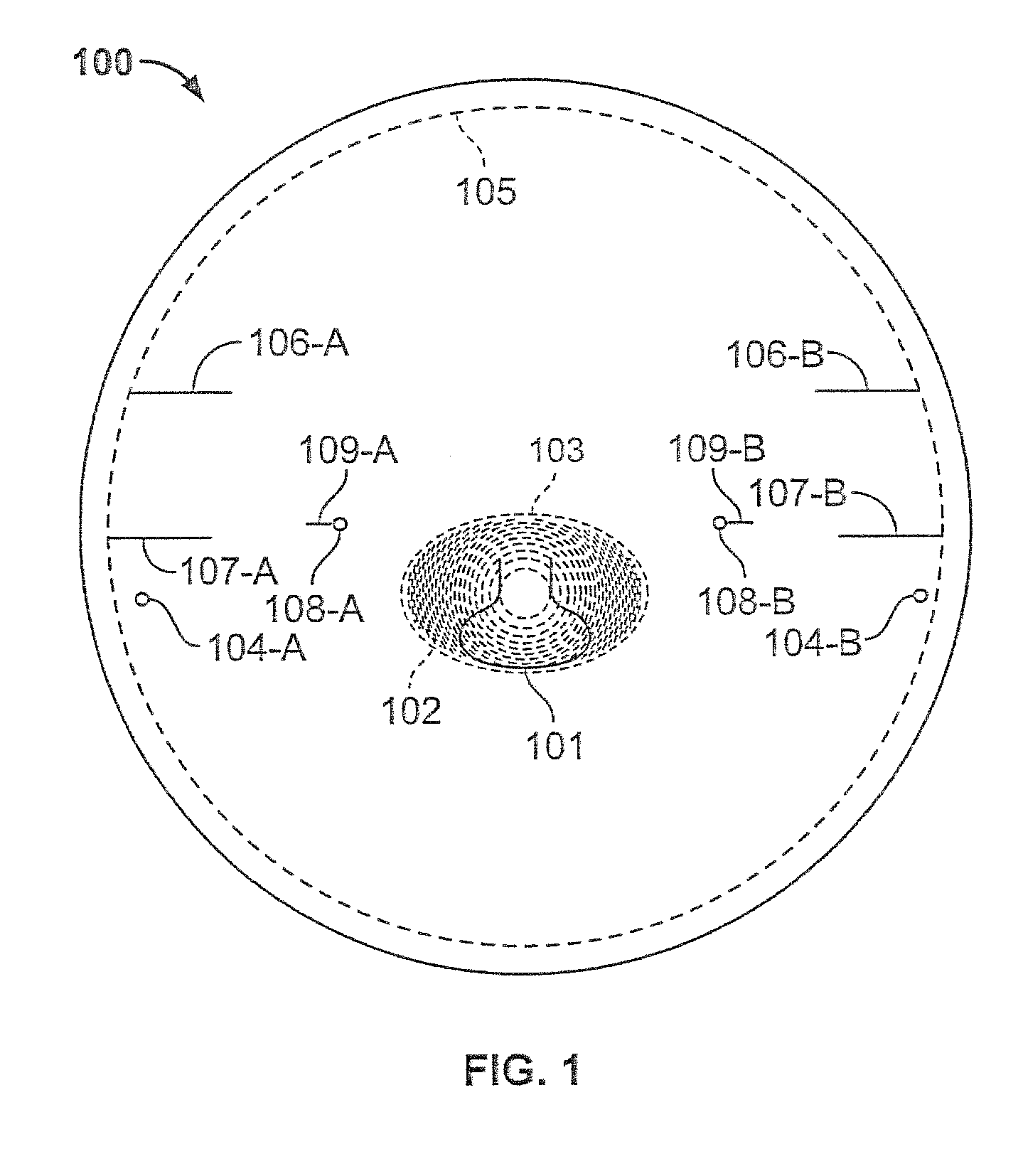
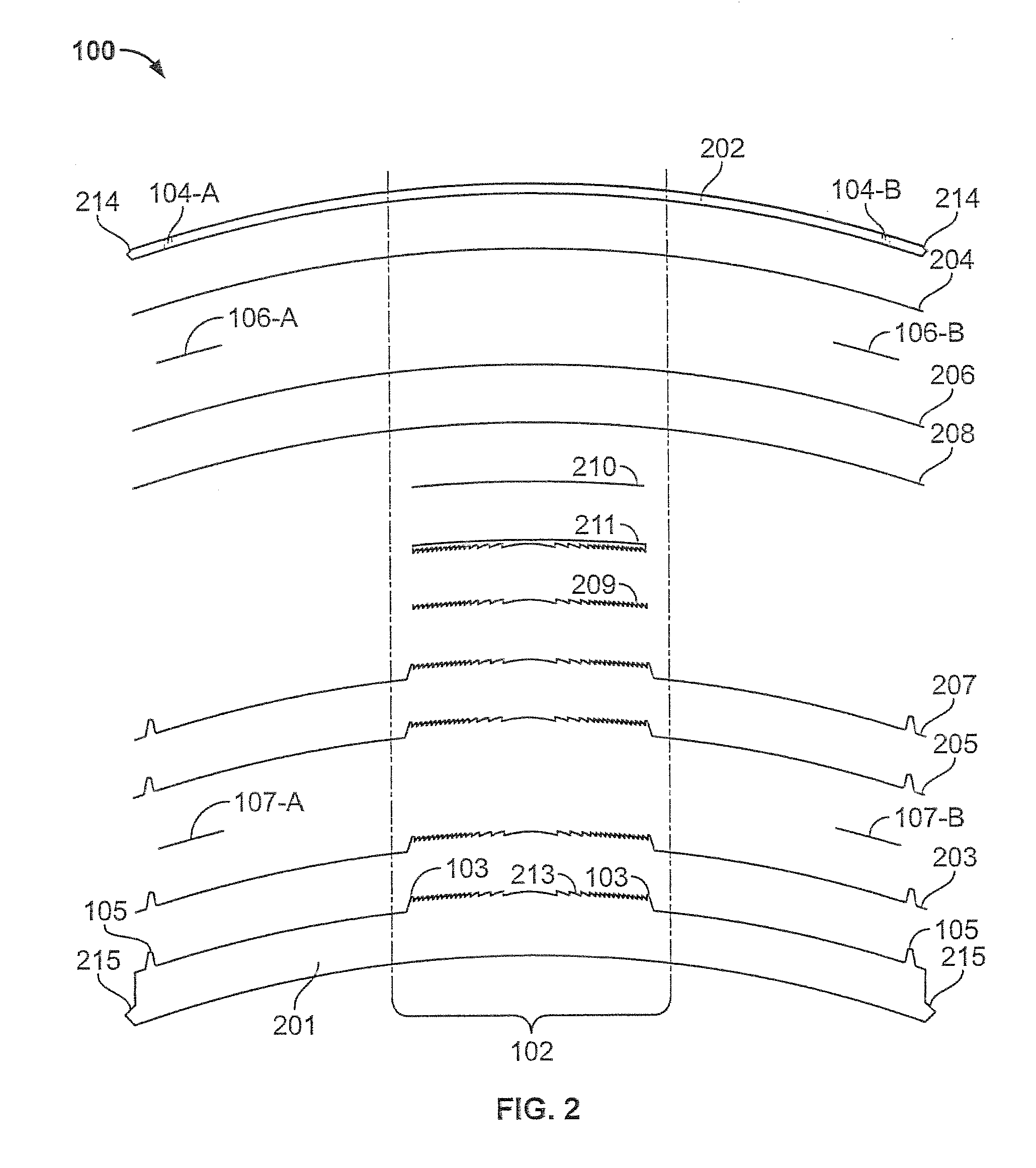
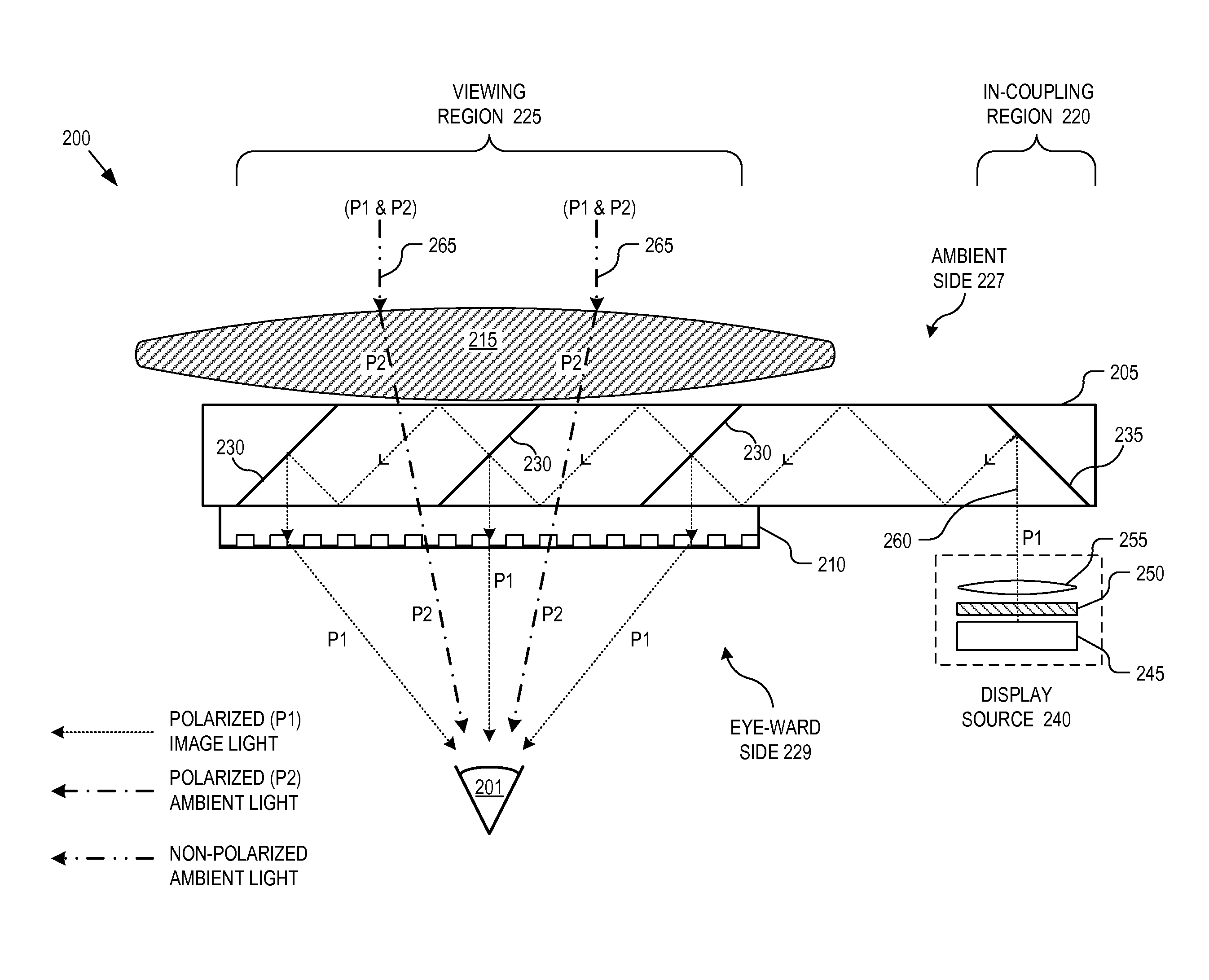
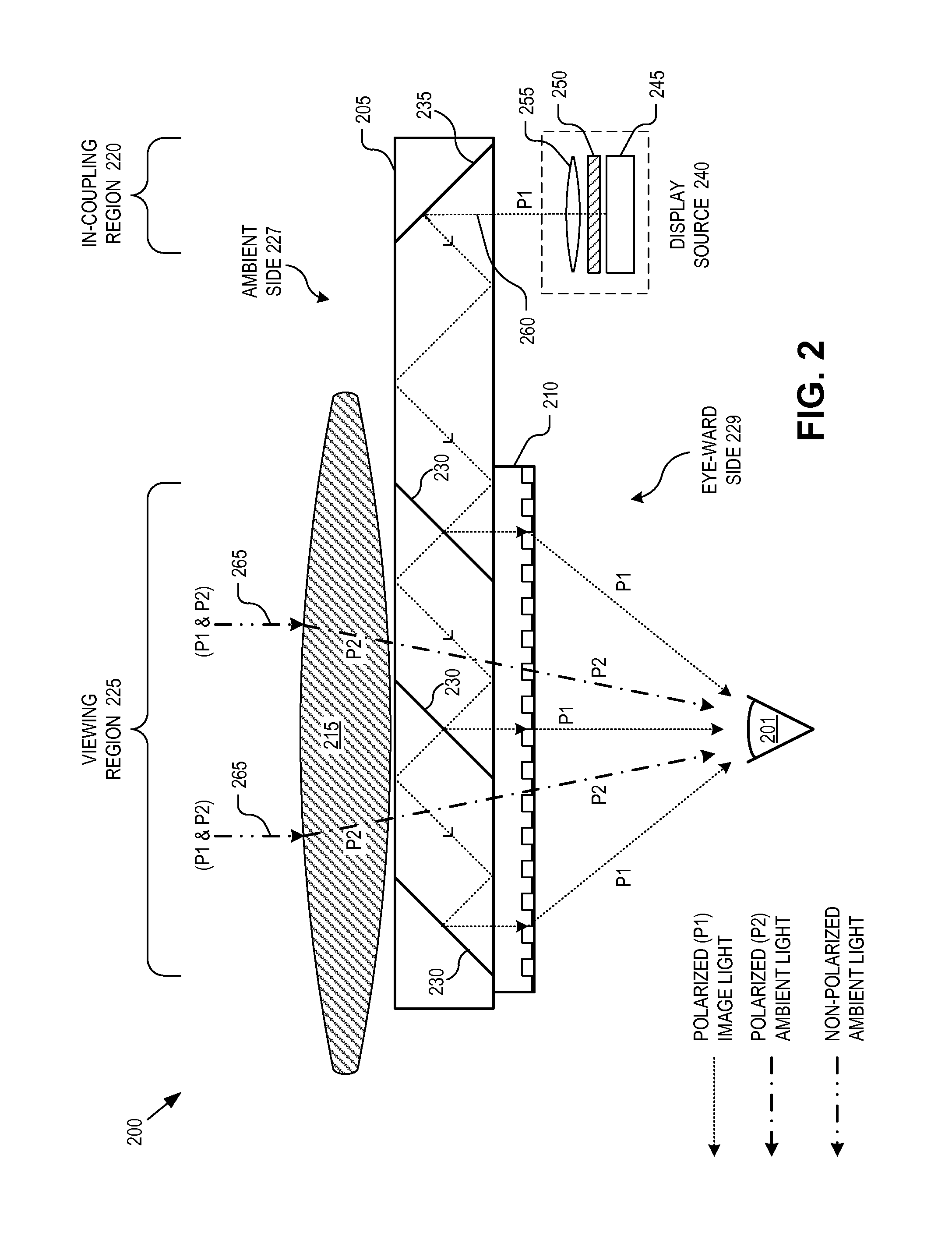
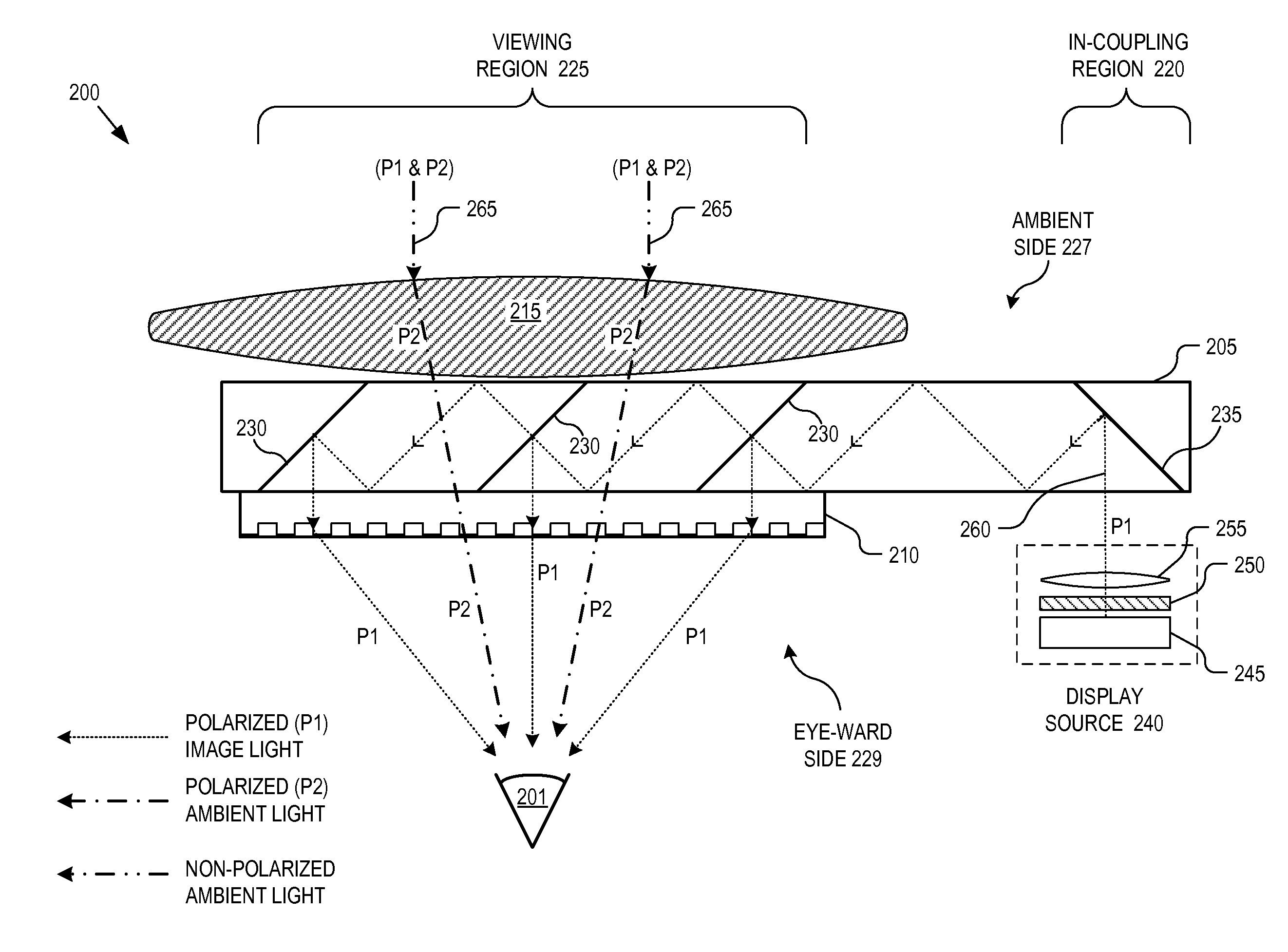
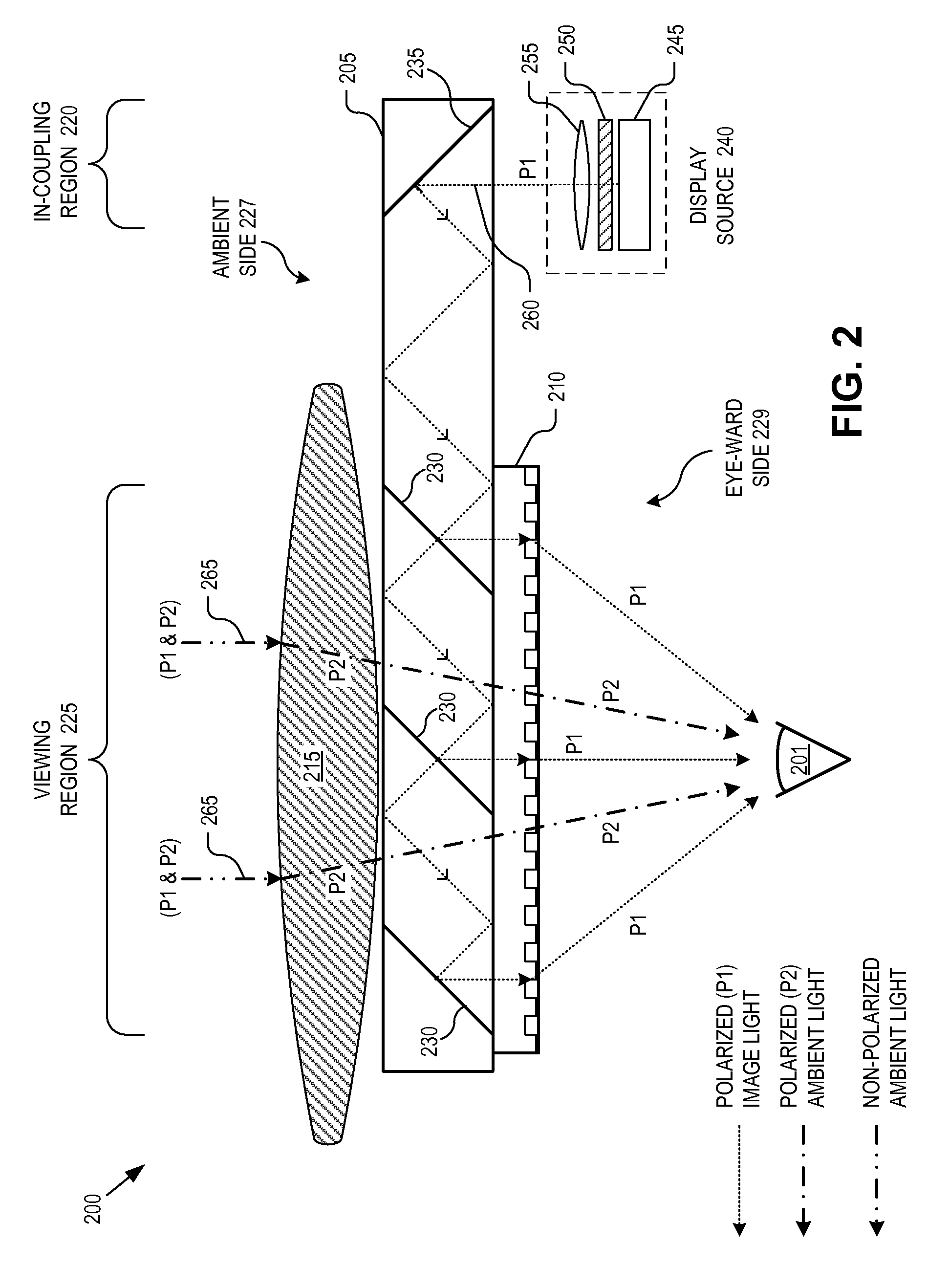
Near-to-eye display with diffractive lens
An eyepiece for a HMD includes a waveguide, an ambient light polarizer, and a wire grid polarizer with a diffraction lens having a lens function patterned into the wire grid polarizer. Polarized image light is guided between eye-ward and ambient sides of the waveguide from a display source to a viewing region of the waveguide where the polarized image light is directed out of the waveguide through the eye-ward side. The viewing region passes ambient light incident on the ambient side through to the eye-ward side. The ambient light polarizer is disposed adjacent to the ambient side to polarize the ambient light into polarized ambient light having a second polarization orthogonal to the first polarization. The wire grid polarizer is disposed adjacent to the eye-ward side along the viewing region. The wire grid polarizer is oriented to applying the lens function to the polarized image light via diffraction.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Diffractive lens exhibiting enhanced optical performance
ActiveUS20090268155A1Reduce light scatterOptimize light energy distributionSpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsLight energyDiffractive lens
The present invention provides improved ophthalmic lenses and methods for their design and use. Monofocal and multifocal diffractive ophthalmic lenses having reduced light scatter, improved light energy distribution properties, and / or other improvements in optical performance are provided. These properties are provided, at least in part, by the diffractive profiles of the invention, often having subtlety shaped echelettes with appropriately curving profiles. Smooth diffractive profiles may be used reduce light scatter. Diffractive profiles may be configured to limit the light energy in certain selected orders, thereby improving viewing quality and mitigating unwanted effects such as dysphotopsia. Diffractive profiles of may additionally or alternatively vary the light energy distributed between individual echelettes, providing additional advantages in various viewing situations.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Bifocal multiorder diffractive lenses for vision correction
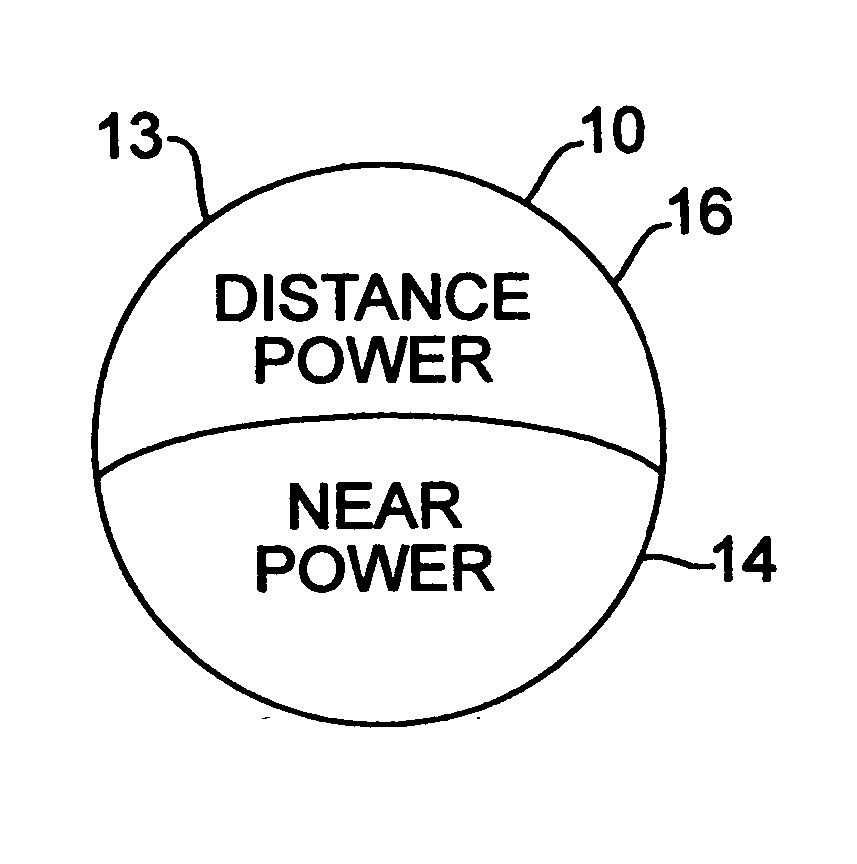
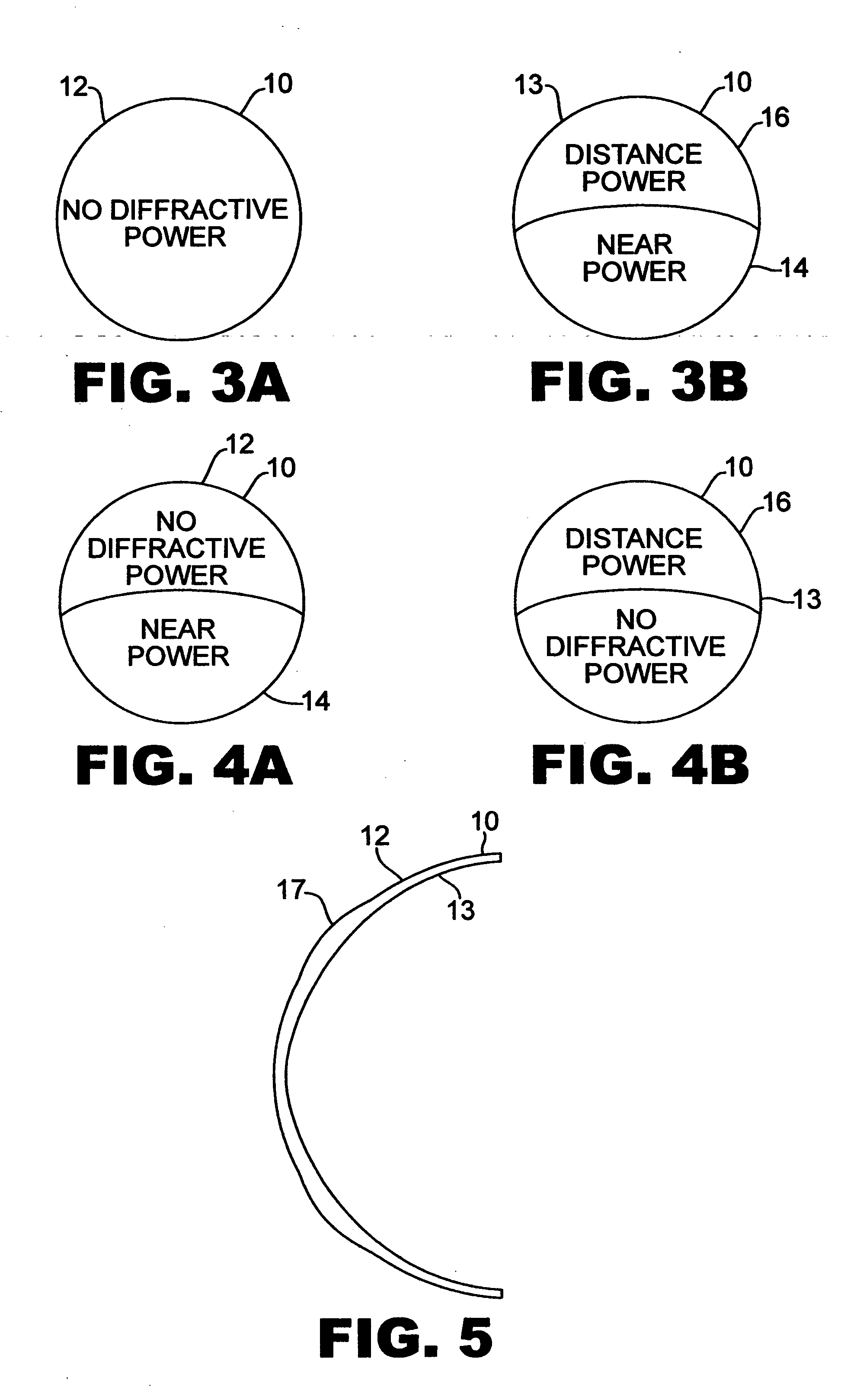
A bifocal multiorder diffractive lens having a lens body with one or more first regions having a first multiorder diffractive structure providing near vision correction, and one or more second regions having a second multiorder diffractive structure providing distance vision correction, in which the lens defines an aperture divided between the first and second regions. The lens body may be provided by a single optical element or multiple optical elements. In other embodiments, a bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided by a single or multiple element lens body having a multiorder diffractive structure for distance vision correction and one or more refractive regions to add power for near vision correction, or a single or multiple element lens body shaped for refractive power for distance vision correction and a multiorder diffractive structure for add power for near vision correction. Multiorder diffractive structures may be optimized for photopic and scotopic vision.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
Diffractive lenses for vision correction
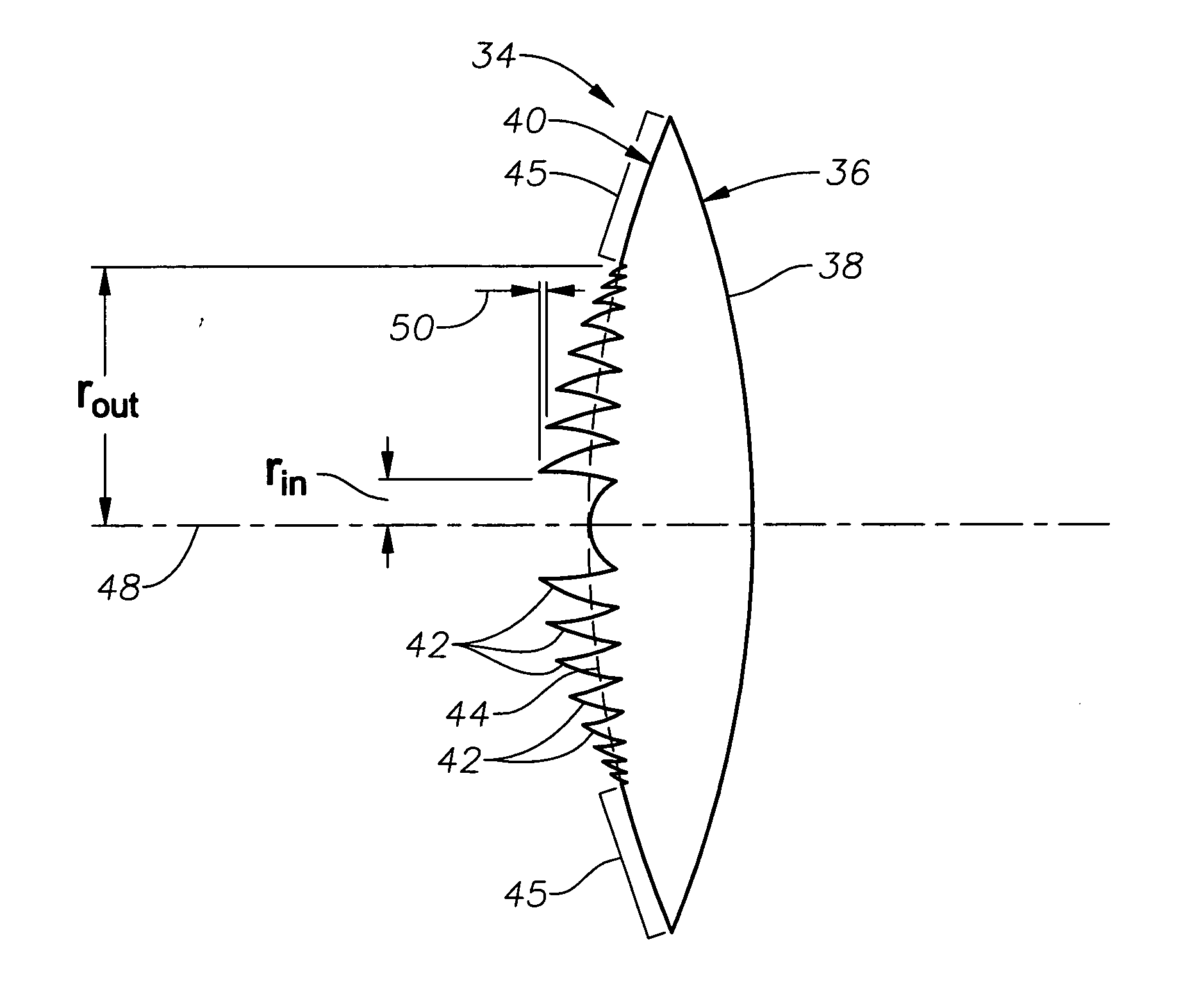
ActiveUS7156516B2Smooth edgesEasy to manufactureSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensSquare waveformDiffraction order
Diffractive lenses for vision correction are provided on a lens body having a first diffractive structure for splitting light into two or more diffractive orders to different focal distances or ranges, and a second diffractive structure, referred to as a multiorder diffractive (MOD) structure, for diffracting light at different wavelengths into a plurality of different diffractive orders to a common focal distance or range. In a bifocal application, the first and second diffractive structures in combination define the base power for distance vision correction and add power for near vision correction of the lens. The first and second diffractive structures may be combined on the same surface or located on different surfaces of the lens. The first diffractive structure may have blazed (i.e., sawtooth), sinusoidal, sinusoidal harmonic, square wave, or other shape profile. A sinusoidal harmonic diffractive structure is particularly useful in applications where smooth rather than sharp edges are desirable.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
Process for fabricating MEMS membrane with integral mirror/lens
InactiveUS7208333B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction gratingsOptical surfaceDiffractive lens
An optical membrane device and method for making such a device are described. This membrane is notable in that it comprises an optically curved surface. In some embodiments, this curved optical surface is optically concave and coated, for example, with a highly reflecting (HR) coating to create a curved mirror. In other embodiments, the optical surface is optically convex and coated with, preferably, an antireflective (AR) coating to function as a refractive or diffractive lens.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
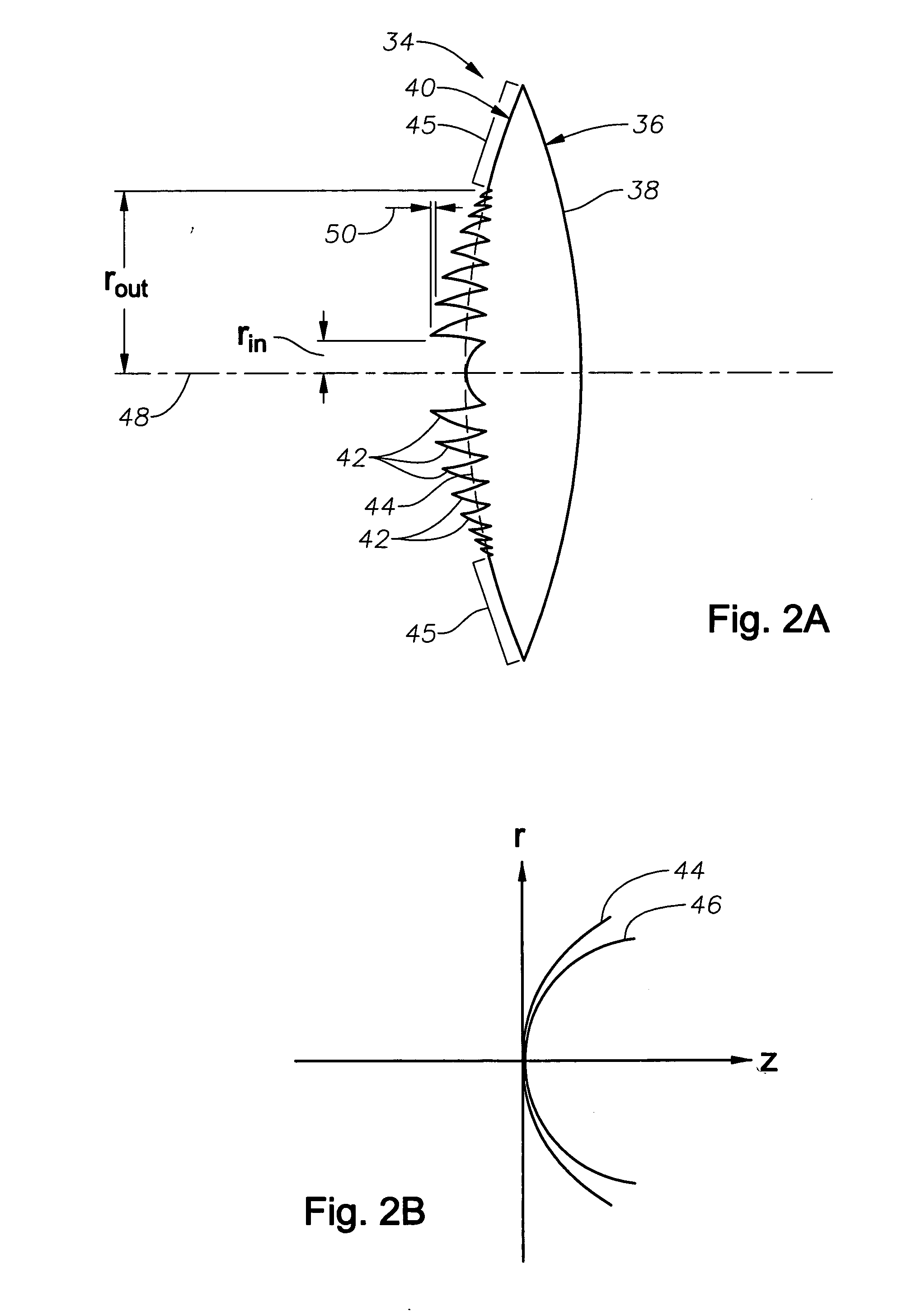
Diffractive multifocal lens having radially varying light distribution
ActiveUS7871162B2Reduce light scatterOptimize light energy distributionSpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsLight energyEye lens
The present invention provides improved ophthalmic lenses and methods for their design and use. Monofocal and multifocal diffractive ophthalmic lenses having reduced light scatter and / or improved light energy distribution properties are provided. These properties are provided by the diffractive profiles of the invention, often having subtlely shaped echelettes with appropriately curving profiles. Light scatter may be generated by the sharp corners associated with vertical steps between adjacent conventional diffractive echelettes. Smooth diffractive profiles of the invention reduce light scatter. Light energy directed towards non-viewing diffractive orders may have a unwanted effects on vision quality. Diffractive profiles of the invention may limit the light energy in certain, selected orders, thereby improving viewing quality and mitigating unwanted effects such as dysphotopsia. Diffractive profiles of the invention can also vary the light energy distributed between individual echelettes, providing additional advantages in various viewing situations.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Electrically focus-tunable lens
An electrically focus-tunable lens having a passive lens and a liquid crystal diffractive lens both sandwiched between a first transparent substrate with a first electrode applied to one surface and a second transparent substrate with a second electrode applied to one surface. The electrodes are operative to apply at least one voltage across the liquid crystal diffractive lens
Owner:DIGILENS
Injection molded microoptics
ActiveUS20070029277A1Minimizes number and task-timesReduces of semiconductor arraysMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesFiberTransformer
A wafer-scale apparatus and method is described for the automation of forming, aligning and attaching two-dimensional arrays of microoptic elements on semiconductor and other image display devices, backplanes, optoelectronic boards, and integrated optical systems. In an ordered fabrication sequence, a mold plate comprised of optically designed cavities is formed by reactive ion etching or alternative processes, optionally coated with a release material layer and filled with optically specified materials by an automated fluid-injection and defect-inspection subsystem. Optical alignment fiducials guide the disclosed transfer and attachment processes to achieve specified tolerances between the microoptic elements and corresponding optoelectronic devices and circuits. The present invention applies to spectral filters, waveguides, fiber-optic mode-transformers, diffraction gratings, refractive lenses, diffractive lens / Fresnel zone plates, reflectors, and to combinations of elements and devices, including microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and liquid crystal device (LCD) matrices for adaptive, tunable elements. Preparation of interfacial layer properties and attachment process embodiments are taught.
Owner:IBM CORP
Diffractive lenses for vision correction
Diffractive lenses for vision correction are provided on a lens body having a first diffractive structure for splitting light into two or more diffractive orders to different focal distances or ranges, and a second diffractive structure, referred to as a multiorder diffractive (MOD) structure, for diffracting light at different wavelengths into a plurality of different diffractive orders to a common focal distance or range. In a bifocal application, the first and second diffractive structures in combination define the base power for distance vision correction and add power for near vision correction of the lens. The first and second diffractive structures may be combined on the same surface or located on different surfaces of the lens. An optical element, such as a substrate or coating, may be integrated along one or both surfaces of the lens to provide the lens with smooth outer surface(s).
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
Ophthalmic lenses capable of reducing chromatic aberration
ActiveUS20070002444A1Improve visual qualityIncrease capacitySpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsImaging qualityEye lens
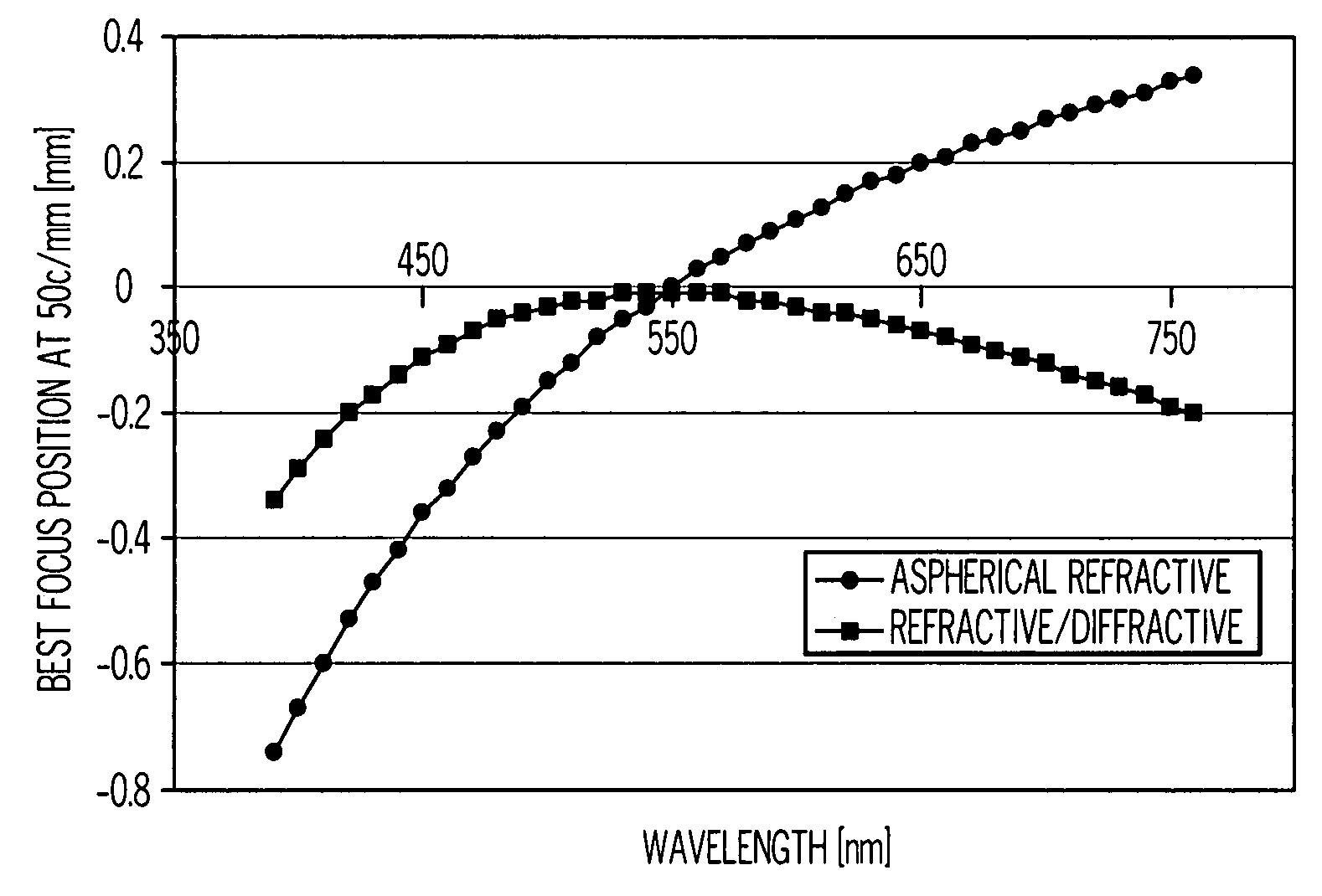
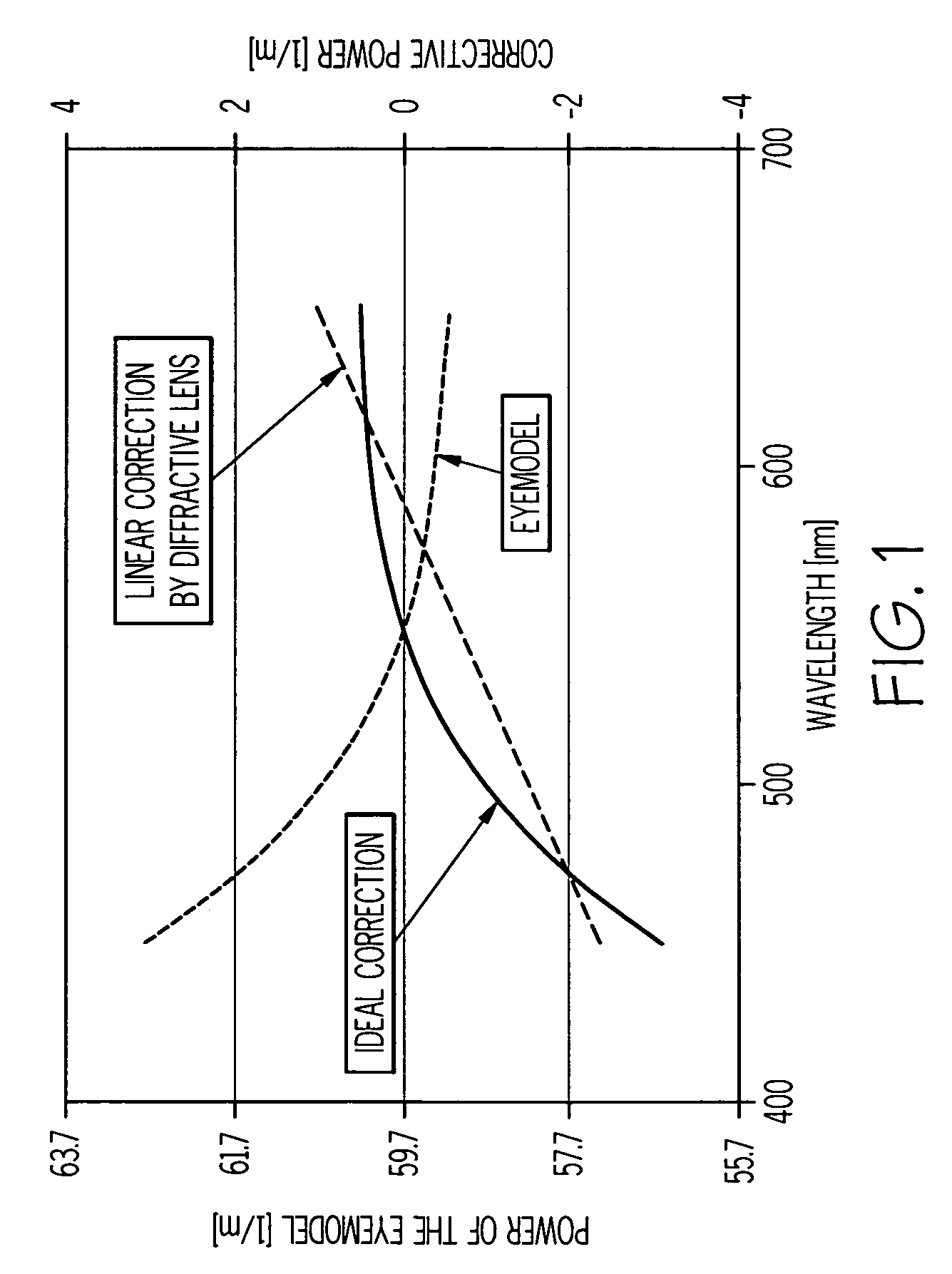
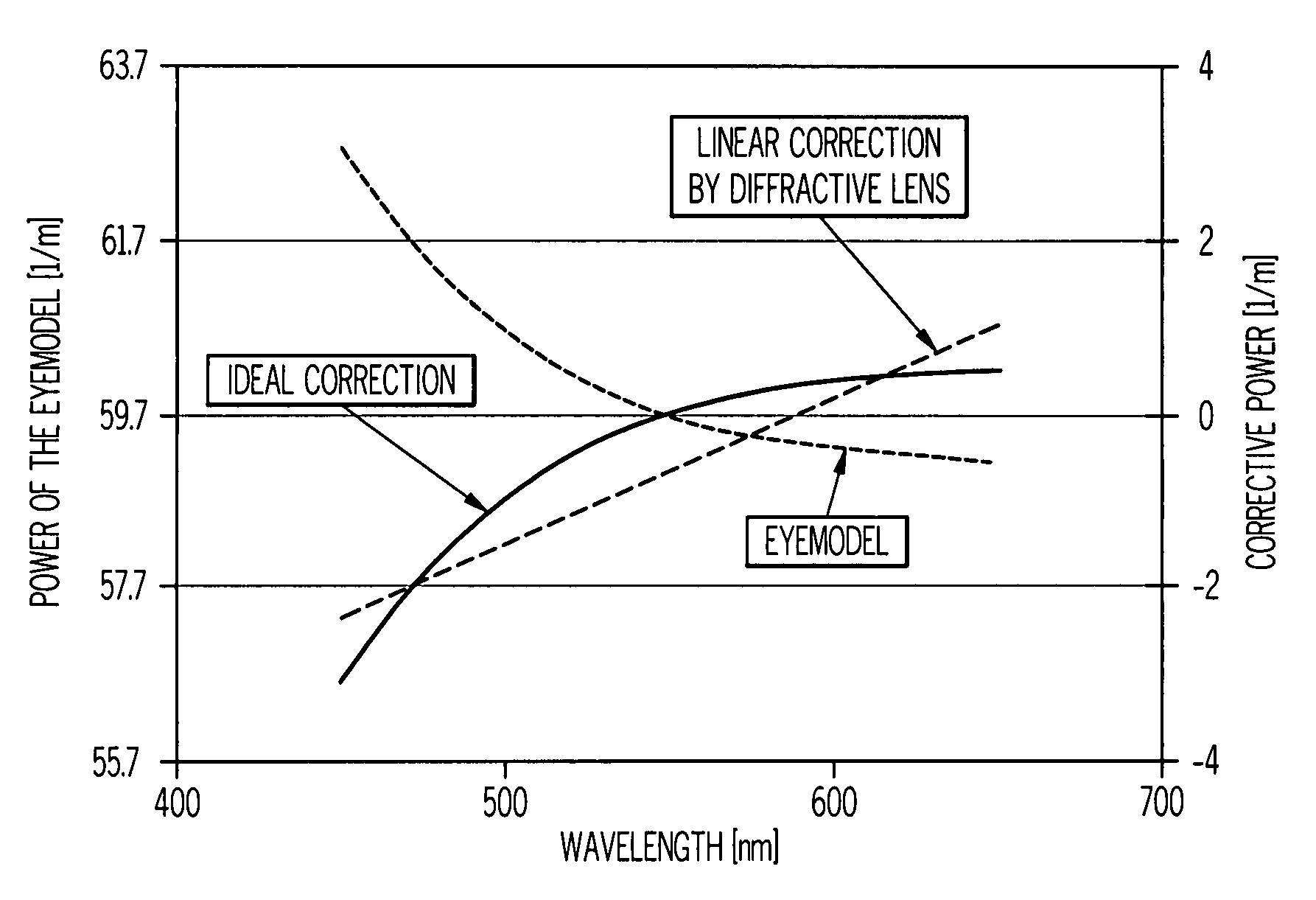
A method of designing an aspheric ophthalmic lens with both refractive and diffractive powers that is capable of reducing chromatic aberration and at least one monochromatic aberration of an eye comprises combining aspherical refractive and diffractive surfaces, selecting an appropriate eye model, establishing a design lens having at least one aspheric surface with a capacity to reduce monochromatic aberration in said eye model, establishing a diffractive lens element that corrects for chromatic aberration of the model eye; and adjusting the lens surface design in order to obtain a suitably high polychromatic image quality in a form that is weighted to comply with a spectral merit function.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
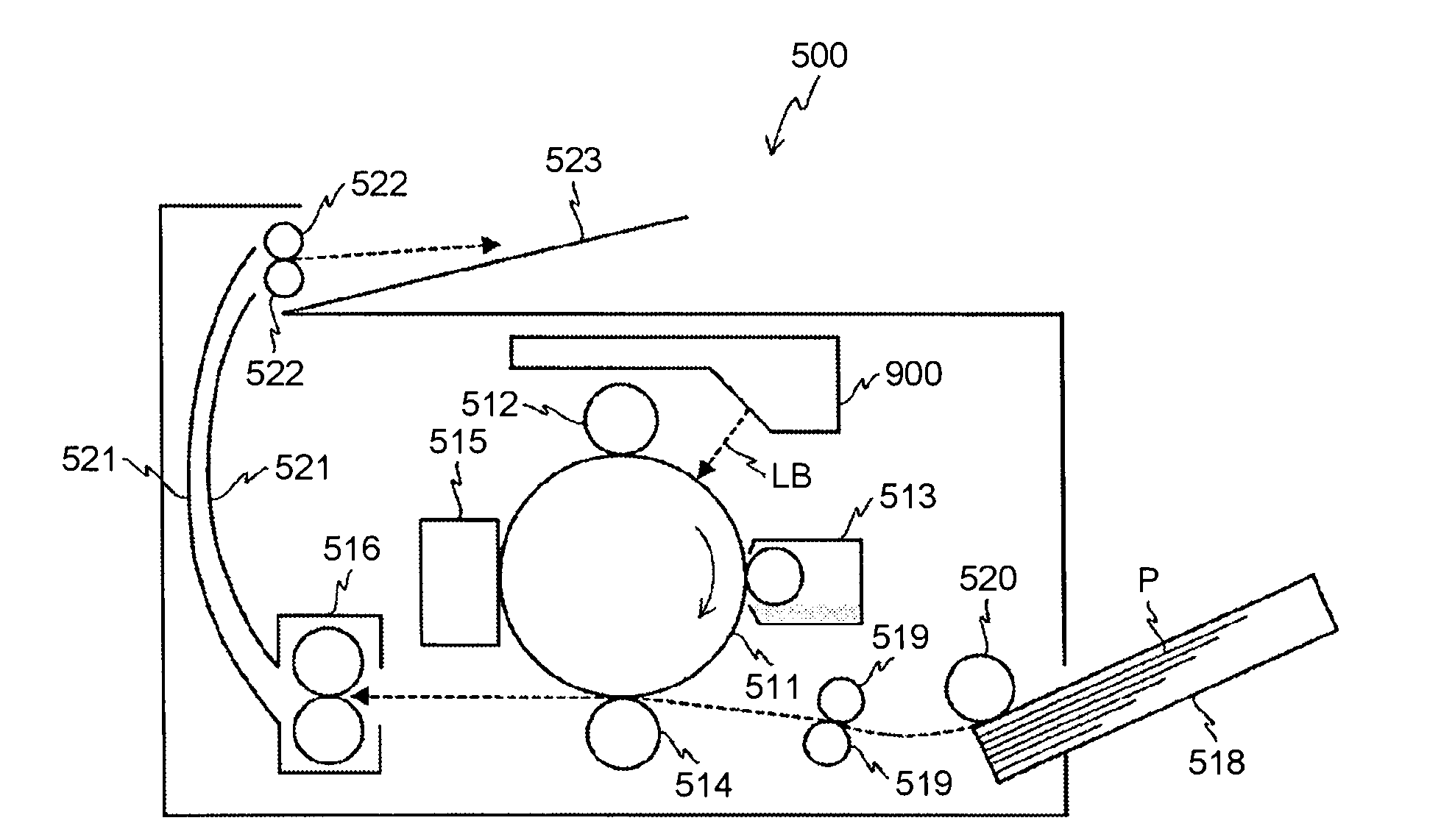
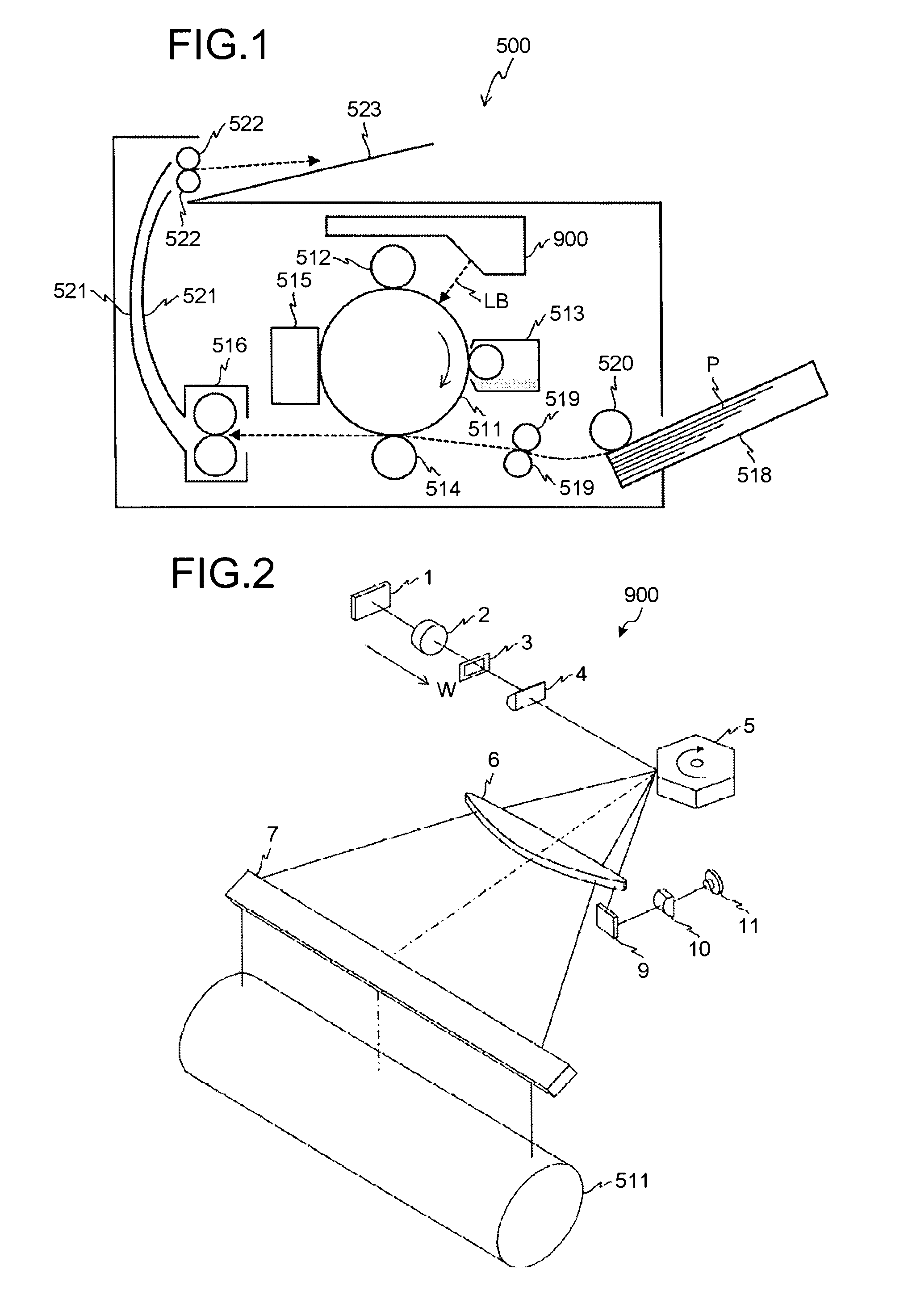
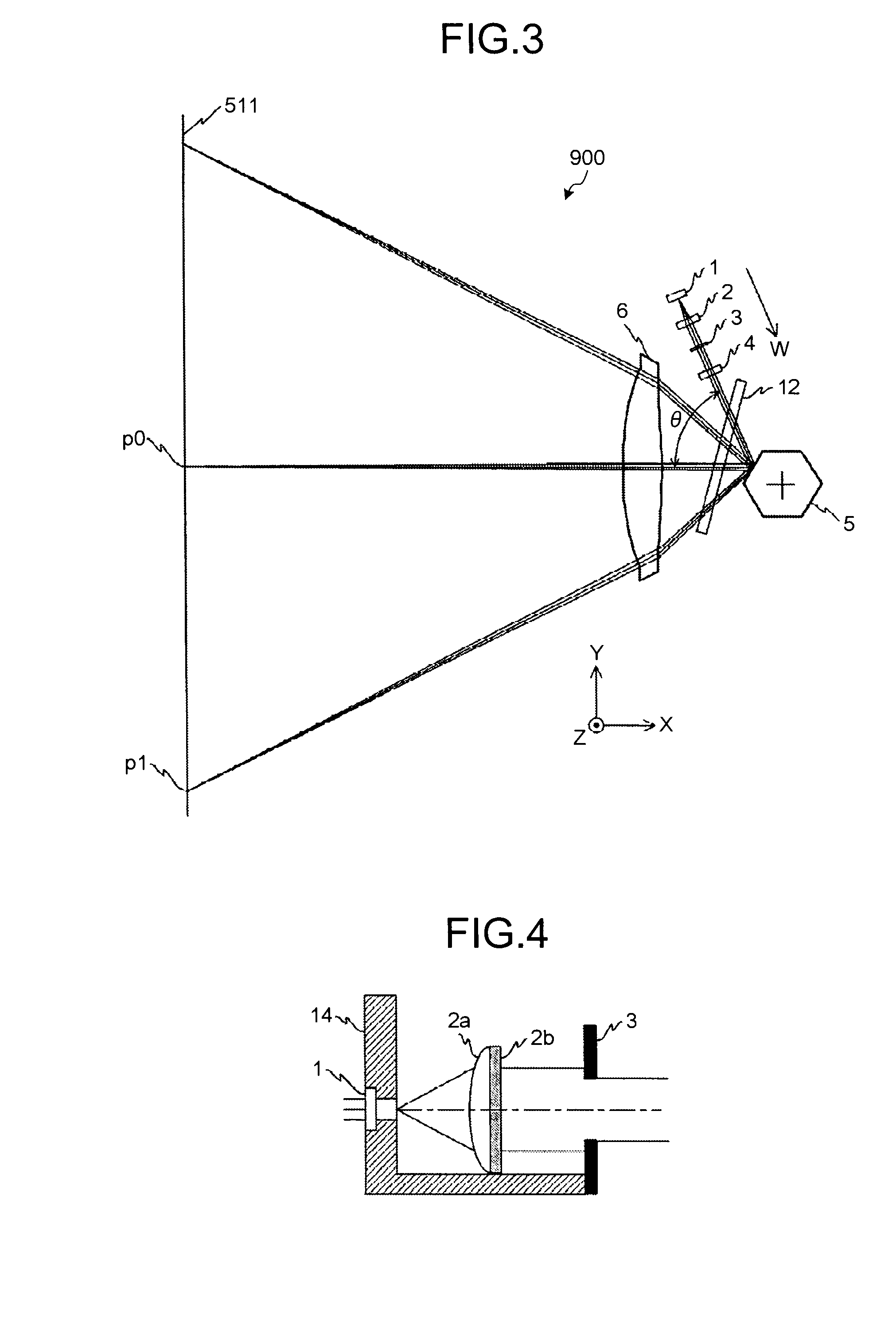
Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using optical scanner
An optical axis of at least one surface of a resin-made diffracting lens is shifted in a main scanning direction with respect to an incident beam. A synchronous detection can cancel a problem of a misalignment in the main scanning direction due to a temperature variation. A light reflected from a second surface of the resin-made diffractive lens condenses on a position that is displaced in an optical axis direction from an optical beam outgoing point of a semiconductor laser, and thereby the light reflected again from the semiconductor laser does not form an image on a scanned surface and an impact on the image becomes low.
Owner:RICOH KK
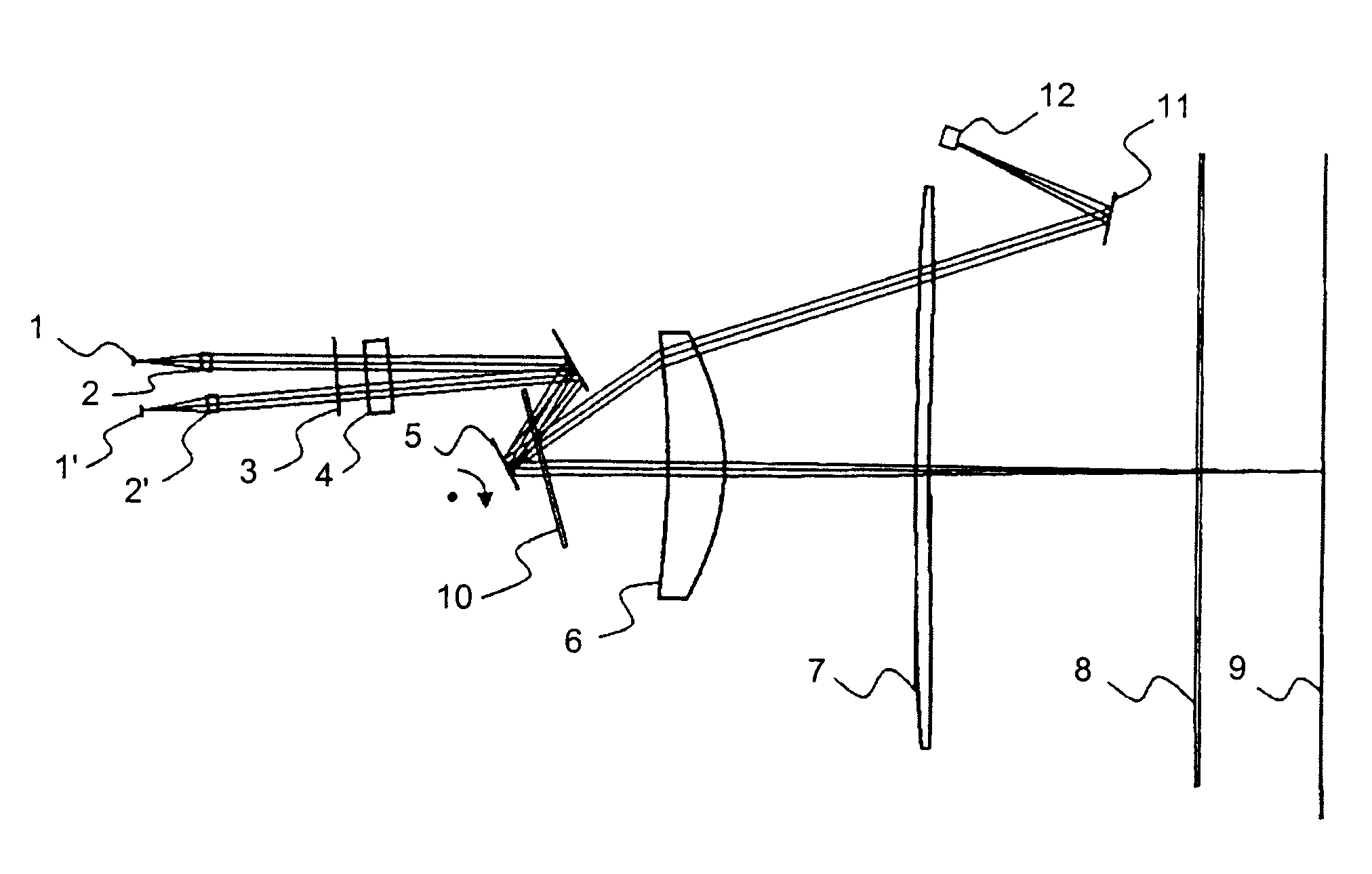
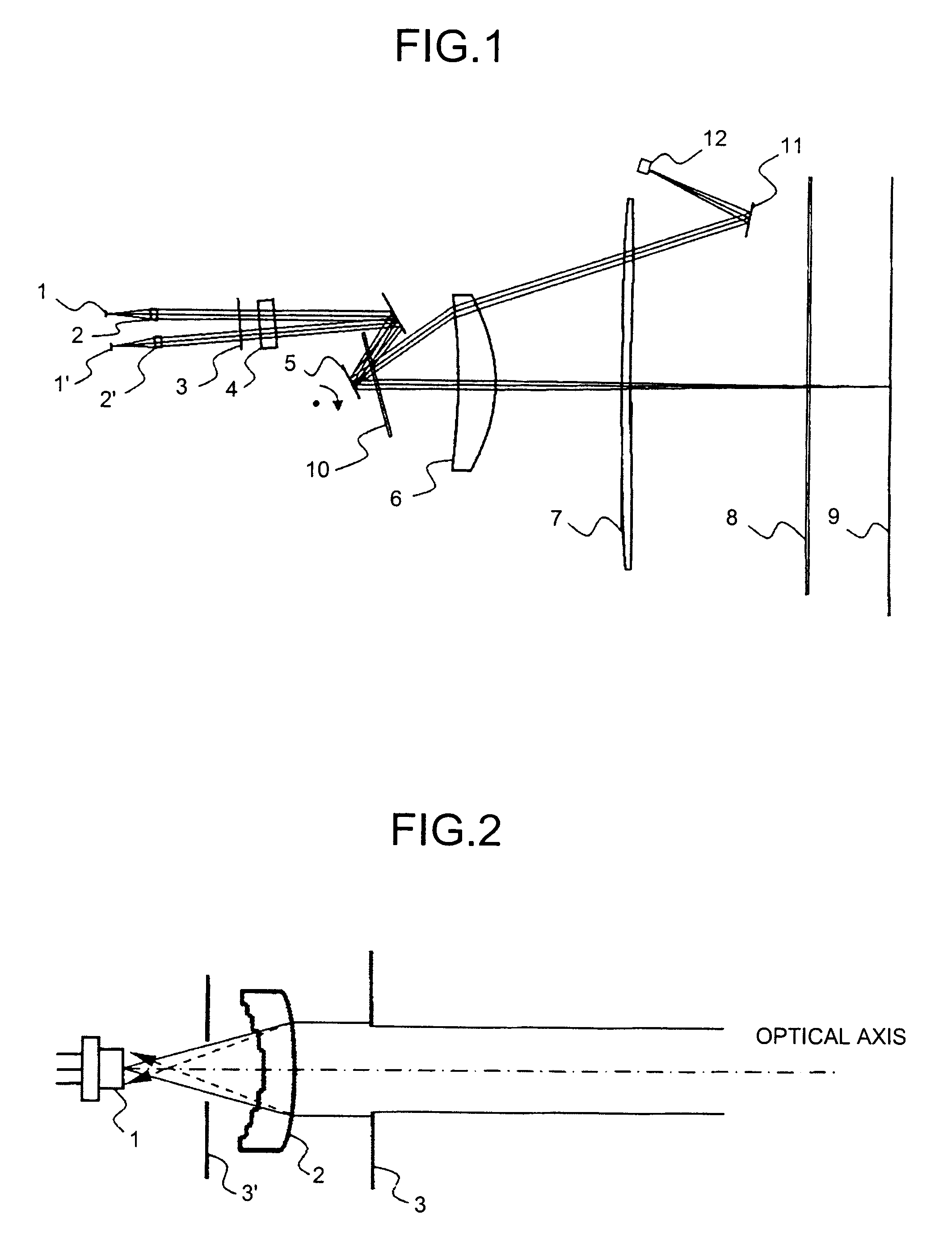
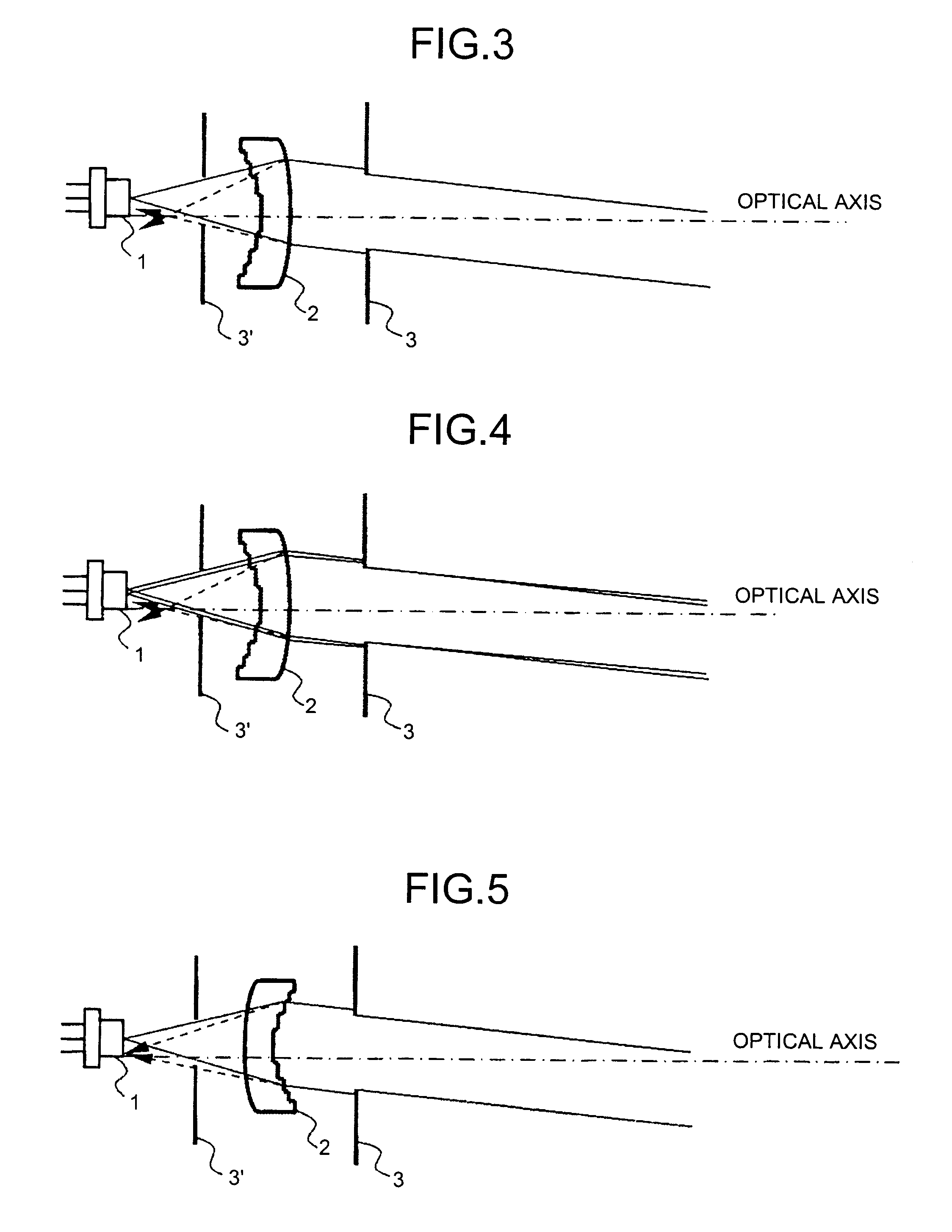
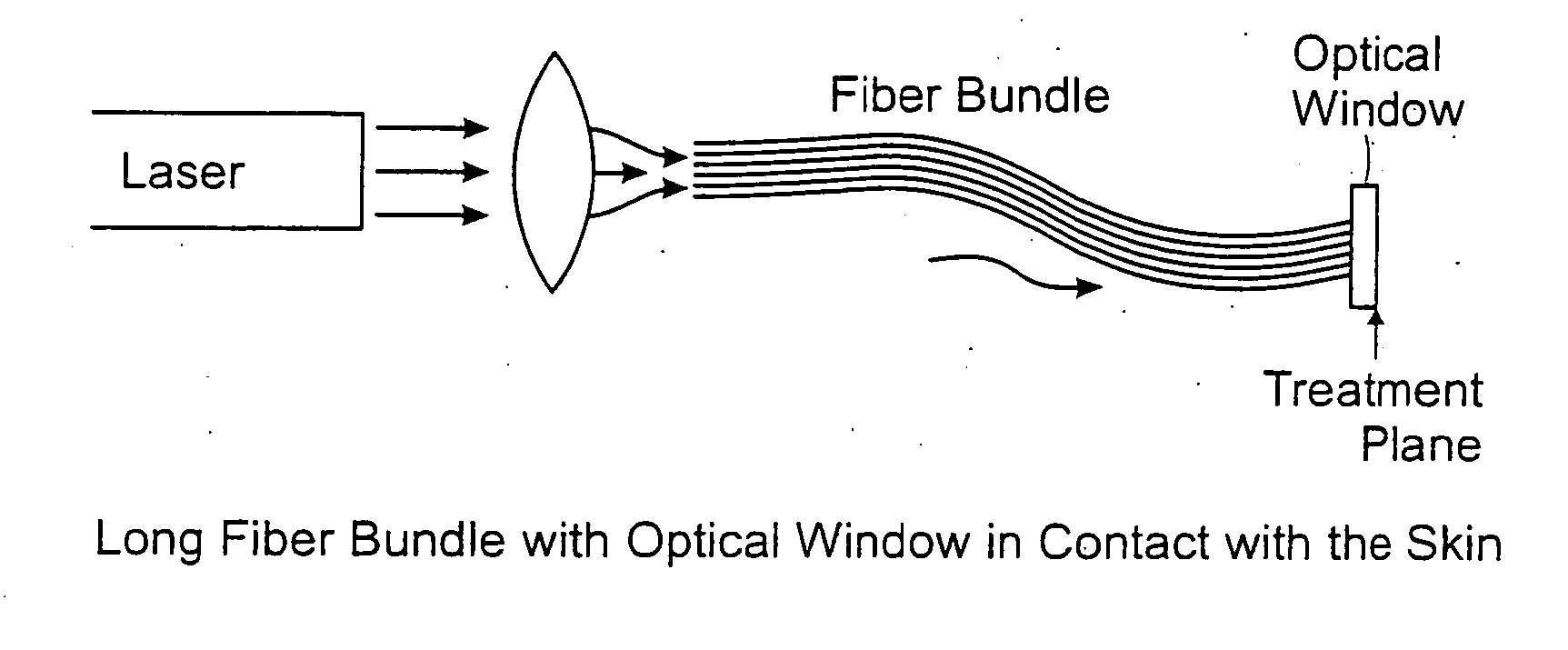
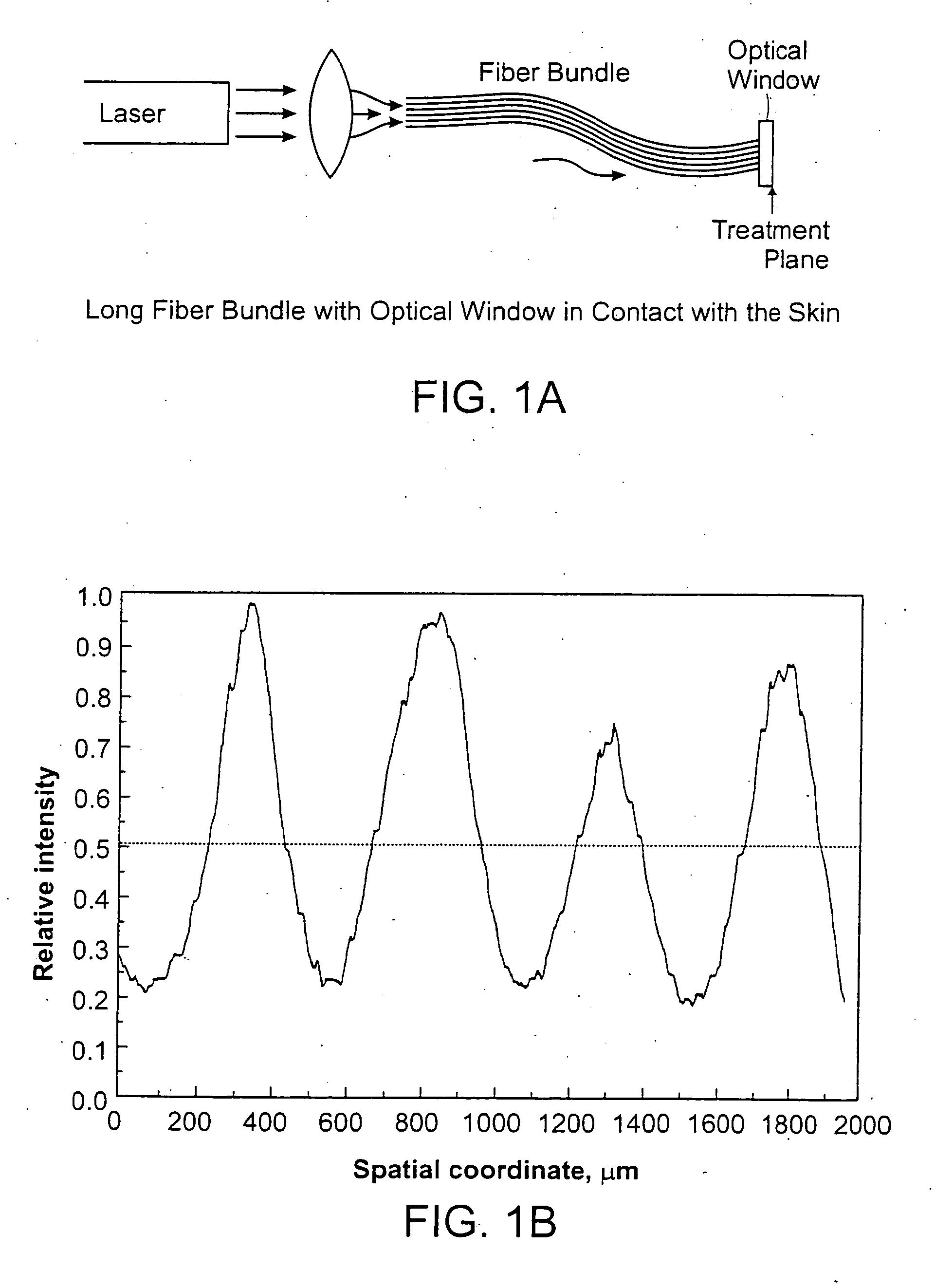
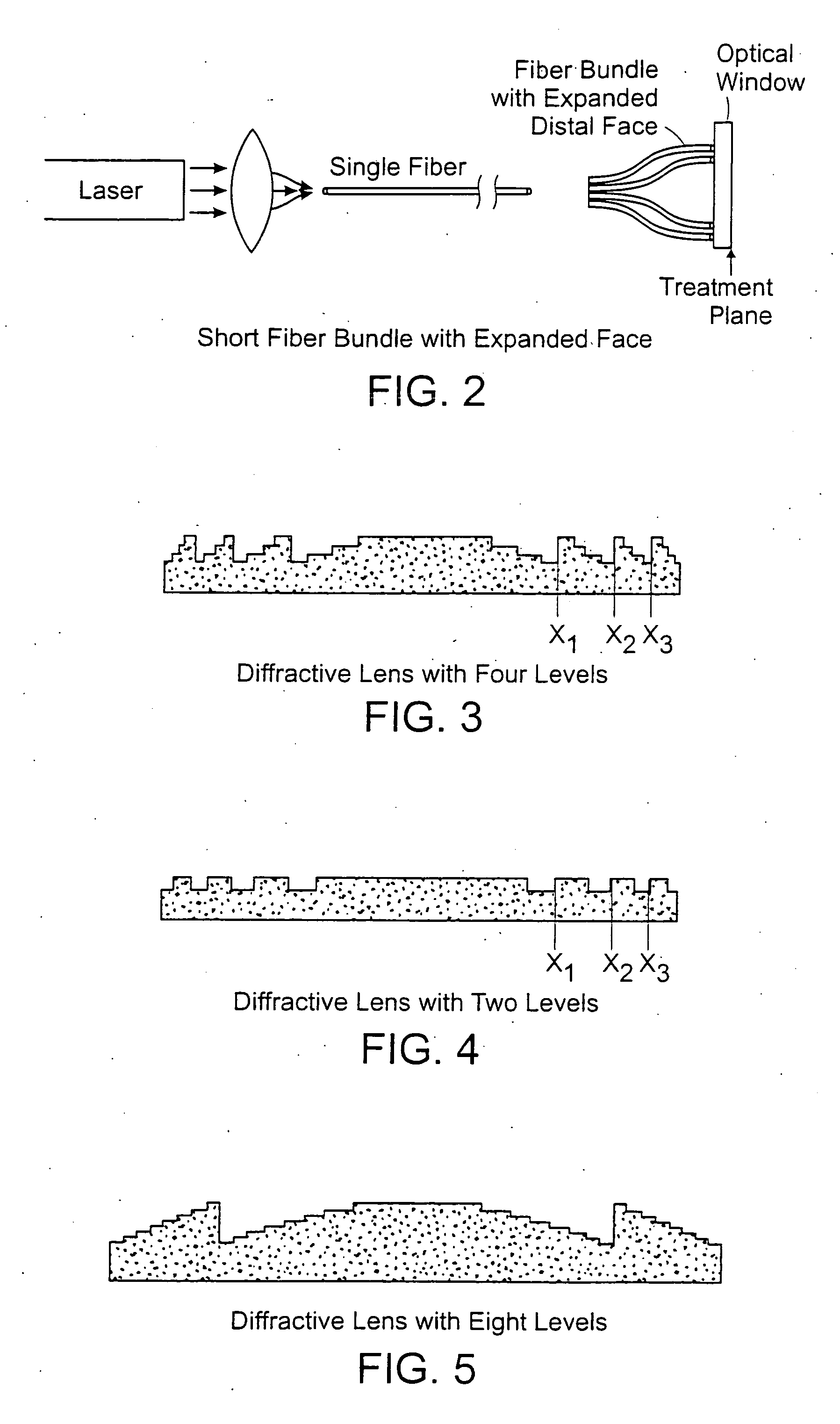
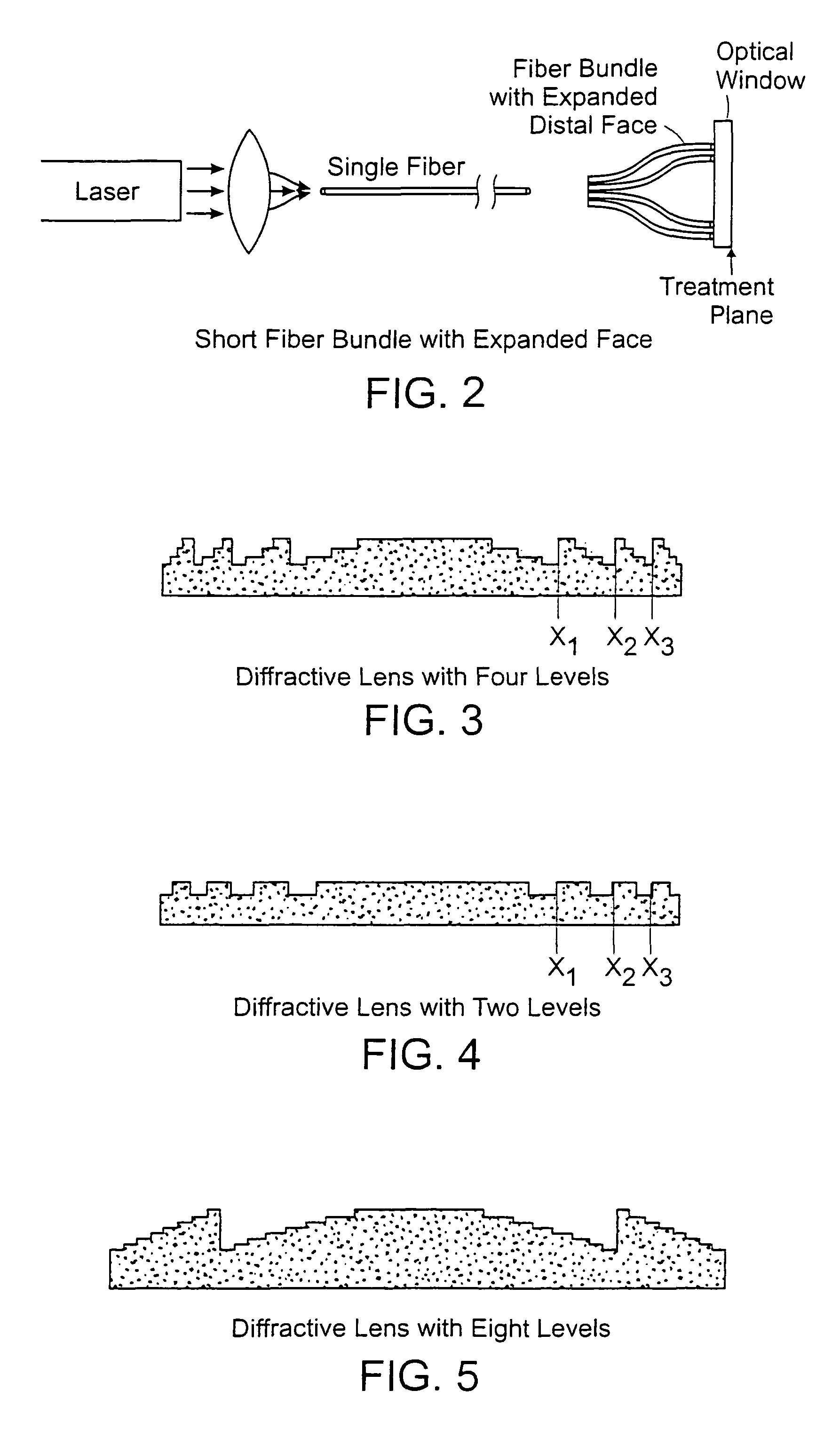
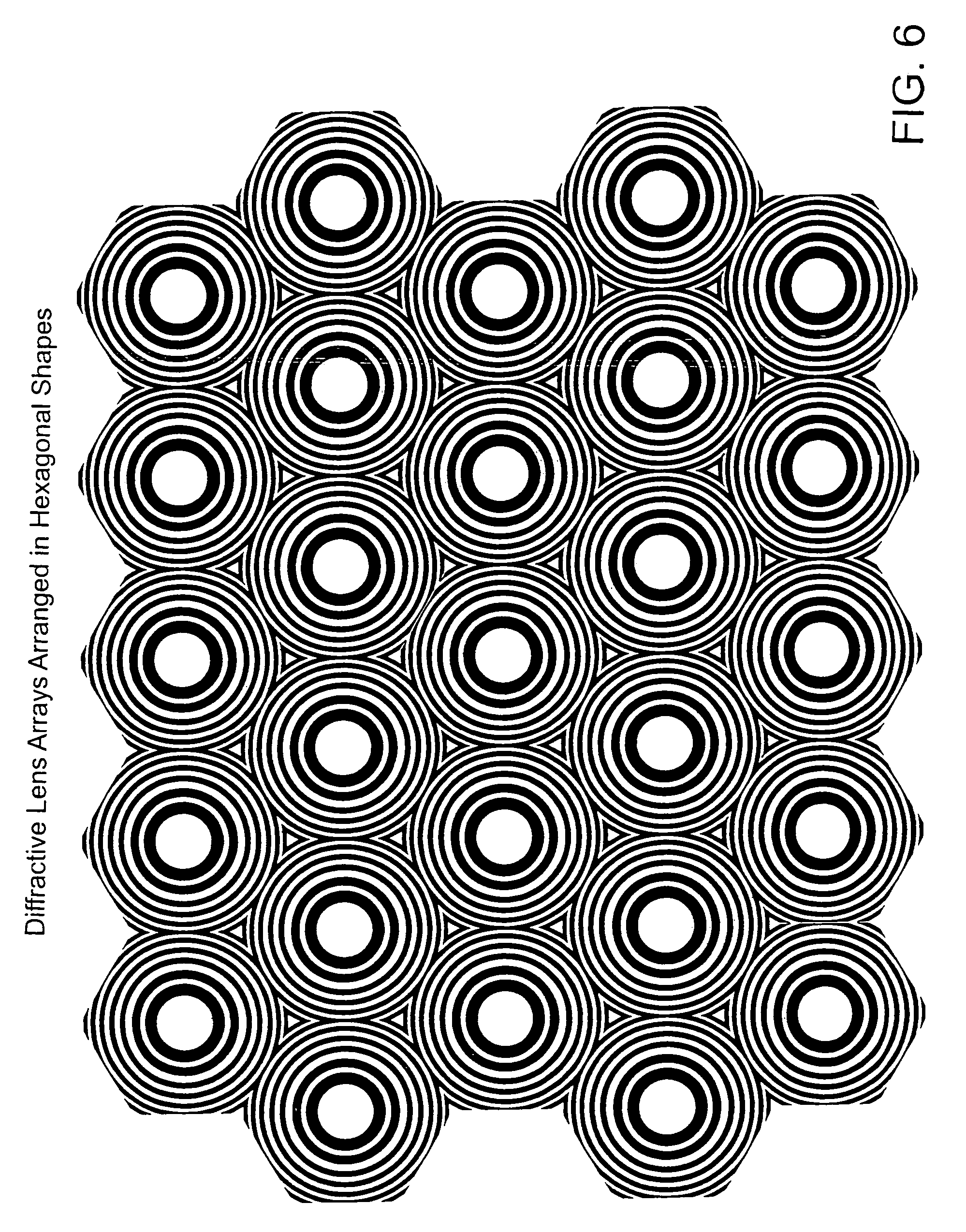
Methods and systems for laser treatment using non-uniform output beam
ActiveUS20060247609A1Increase the areaPromote absorptionDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsCollagen shrinkageNd:YAG laser
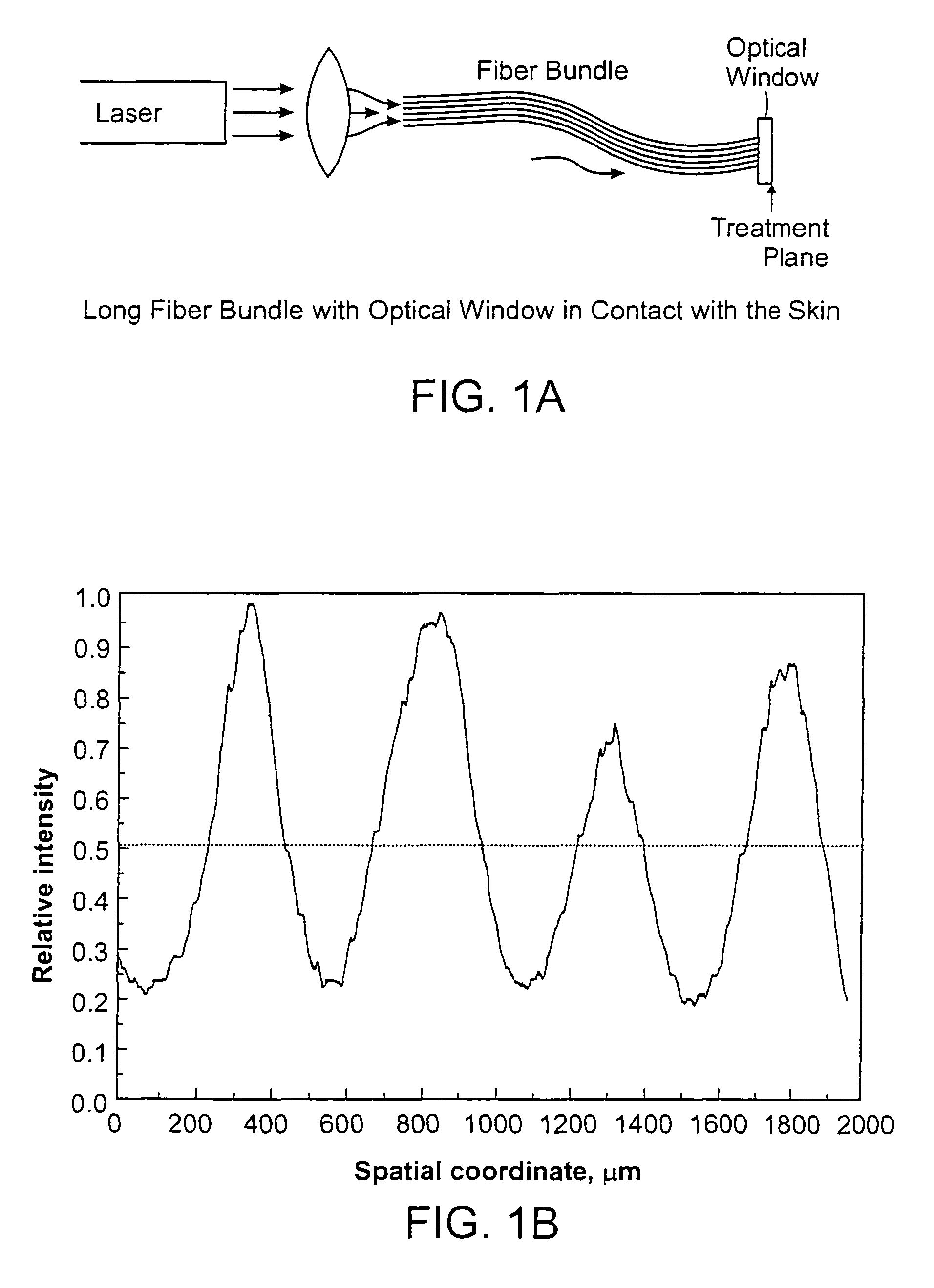
Methods and apparatus for treatment, such as skin rejuvenation treatment, using non-uniform laser radiation. A high-intensity portion of the laser radiation causes collagen destruction and shrinkage within select portions of the treatment area, while a lower-intensity portion of the radiation causes fibroblast stimulation leading to collagen production across other portions of the treatment area. An output beam from a laser source, such as an Nd:YAG laser, is coupled into an optical system that -modifies the beam to provide a large-diameter beam having a non-uniform energy profile, comprised of a plurality of high-intensity zones surrounded by lower-intensity zones within the treatment beam. The higher-intensity zones heat select portions of the target tissue to temperatures sufficient for a first treatment (e.g. collagen shrinkage), while the lower-intensity zones provide sufficient energy for a second treatment (e.g. stimulated collagen production). A large area of tissue, preferably 7-10 mm in diameter, can be treated simultaneously, while minimizing the risk of burning or other damage to the skin. In one embodiment, the invention uses a fiber bundle to provide a non-uniform energy output beam. In another embodiment, the invention uses a diffractive lens array to produce the non-uniform output beam. A cooling system can also be integrated with the laser treatment system.
Owner:CYNOSURE
Method of manufacturing diffraction lens
A novel manufacturing method for a diffraction lens, whereby aperture and eccentricity effects can be suppressed and any multi-focusing effect can also be obtained in a more stable manner. A synchronous structure is set up where at least two reliefs whose first order diffracted lights give respective focal distances different from one another are set to overlap with each other in at least a part of an area in a radial direction of a diffraction lens, and with respect to every grating pitches of one relief having the maximum grating pitch among the reliefs set up in overlap, grating pitches of another relief are overlapped periodically; and the resulting relief pattern is formed on a surface of an optical material.
Owner:MENICON CO LTD
Reflective lithography mask inspection tool based on achromatic Fresnel optics
InactiveUS6914723B2High resolutionEfficient use ofOptical filtersMaterial analysis by optical meansFresnel lensMask inspection
A mask blank inspection tool includes an AFO having a diffractive lens and a refractive lens formed on a common substrate. The diffractive lens is a Fresnel zone plate and the refractive lens is a refractive Fresnel lens. The AFO is used to image light from a defect particle on a multilayer mask blank or the surface of the multilayer mask blank to a detector.
Owner:XRADIA
Ophthalmic lenses capable of reducing chromatic aberration
ActiveUS7677725B2Improve visual qualityIncrease capacitySpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsImaging qualityEye lens
A method of designing an aspheric ophthalmic lens with both refractive and diffractive powers that is capable of reducing chromatic aberration and at least one monochromatic aberration of an eye comprises combining aspherical refractive and diffractive surfaces, selecting an appropriate eye model, establishing a design lens having at least one aspheric surface with a capacity to reduce monochromatic aberration in said eye model, establishing a diffractive lens element that corrects for chromatic aberration of the model eye; and adjusting the lens surface design in order to obtain a suitably high polychromatic image quality in a form that is weighted to comply with a spectral merit function.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Methods and systems for laser treatment using non-uniform output beam
ActiveUS7856985B2Minimizing risk of burning and other damagePromotes collagen productionDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsCollagen shrinkageNd:YAG laser
Owner:CYNOSURE
Apodized aspheric diffractive lenses
InactiveUS20100087921A1Improve image contrastSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryCamera lensAnterior surface
Aspheric diffractive lenses are disclosed for ophthalmic applications. For example, multifocal intraocular lens (IOLs) are disclosed that include an optic having an anterior surface and a posterior surface, at least one of which surfaces includes an aspherical base profile on a portion of which a plurality of diffractive zones are disposed so as to generate a far focus and a near focus. The aspherical base profile enhances image contrast at the far focus of the lens relative to that obtained by a substantially identical IOL in which the respective base profile is spherical.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method of fabricating diffractive lens array and UV dispenser used therein
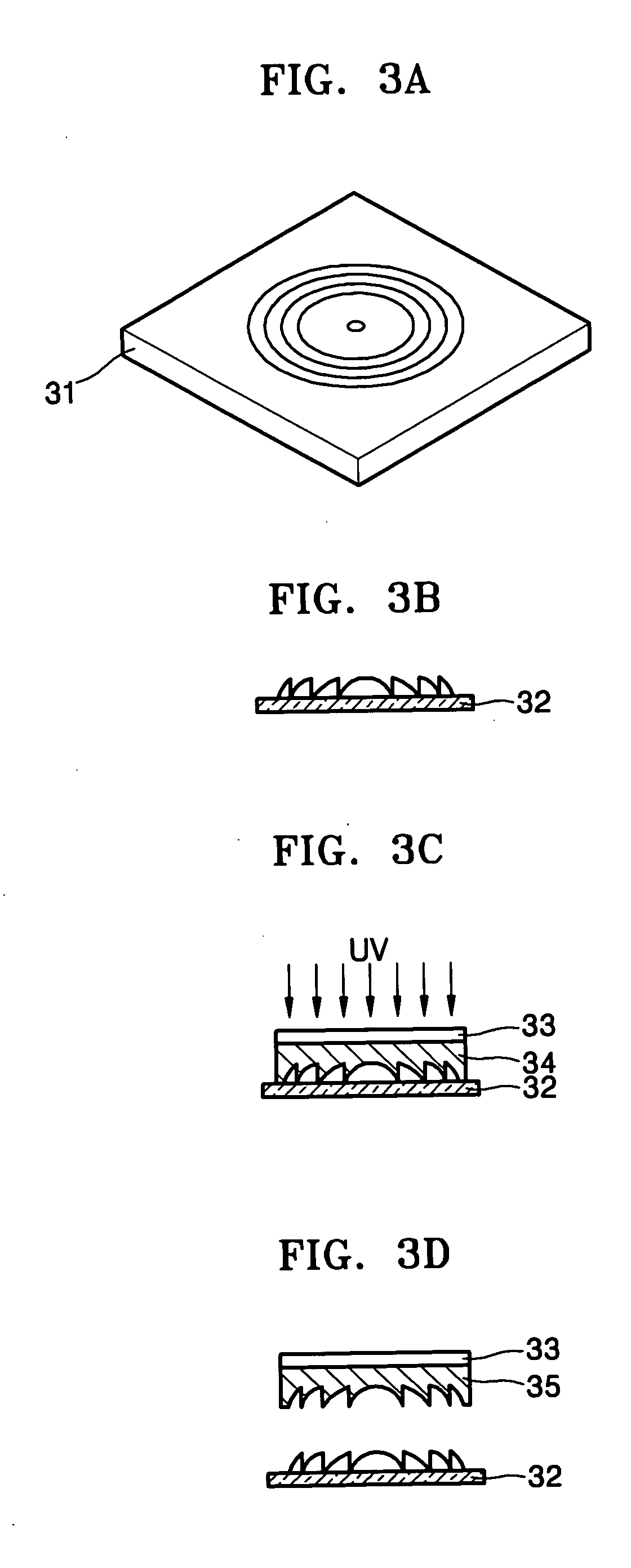
InactiveUS20050162733A1Eliminate alignment errorsIncrease production capacityOptical filtersOptical articlesUltravioletDiffractive lens
A method of fabricating a diffractive lens array mold and an ultraviolet (UV) dispenser for use in the same. The method includes the steps of (a) fabricating a single or array diffractive lens mold using a nickel (Ni) shim; (b) fabricating a first diffractive lens array mold using an ultraviolet (UV) dispenser including the single diffractive lens mold; and (c) fabricating a second diffractive lens array mold having an inverted profile of the first diffractive lens array mold.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Bifocal multiorder diffractive lenses for vision correction
A bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided having a lens body with one or more first regions having a first multiorder diffractive structure providing near vision correction, and one or more second regions having a second multiorder diffractive structure providing distance vision correction, in which the lens defines an aperture divided between the first and second regions. Such one or more first regions may represent one or more annular rings, or other portion of the lens, and the second region may occupy the portion of the lens aperture outside the first region. The lens body may be provided by a single optical element or multiple optical elements. When multiple optical elements are used, the multiorder diffractive structures may be located along an interior surface of the lens. In other embodiments, a bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided by a single or multiple element lens body having a multiorder diffractive structure for distance vision correction and one or more refractive regions to add power for near vision correction, or a single or multiple element lens body shaped for refractive power for distance vision correction and a multiorder diffractive structure for add power for near vision correction. The lens may represent a contact lens, a spectacle lens, or the optic portion of an intraocular implant (IOL). Multiorder diffractive structures may be optimized for performance for photopic and scotopic vision.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
LED light with a diffracting lens
InactiveUS20100002435A1Reduce the amount requiredSave resourcesPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesLed arrayOptoelectronics
The present invention is an underwater light for watertight installation under the waterline of a vessel, for example, within a thru-hull of the vessel, comprising a domed or plano convex diverging lens capable of diverging the light broadly through the water. In a preferred embodiment, the underwater light employs an LED array light source.
Owner:UNDERWATER LIGHTS USA
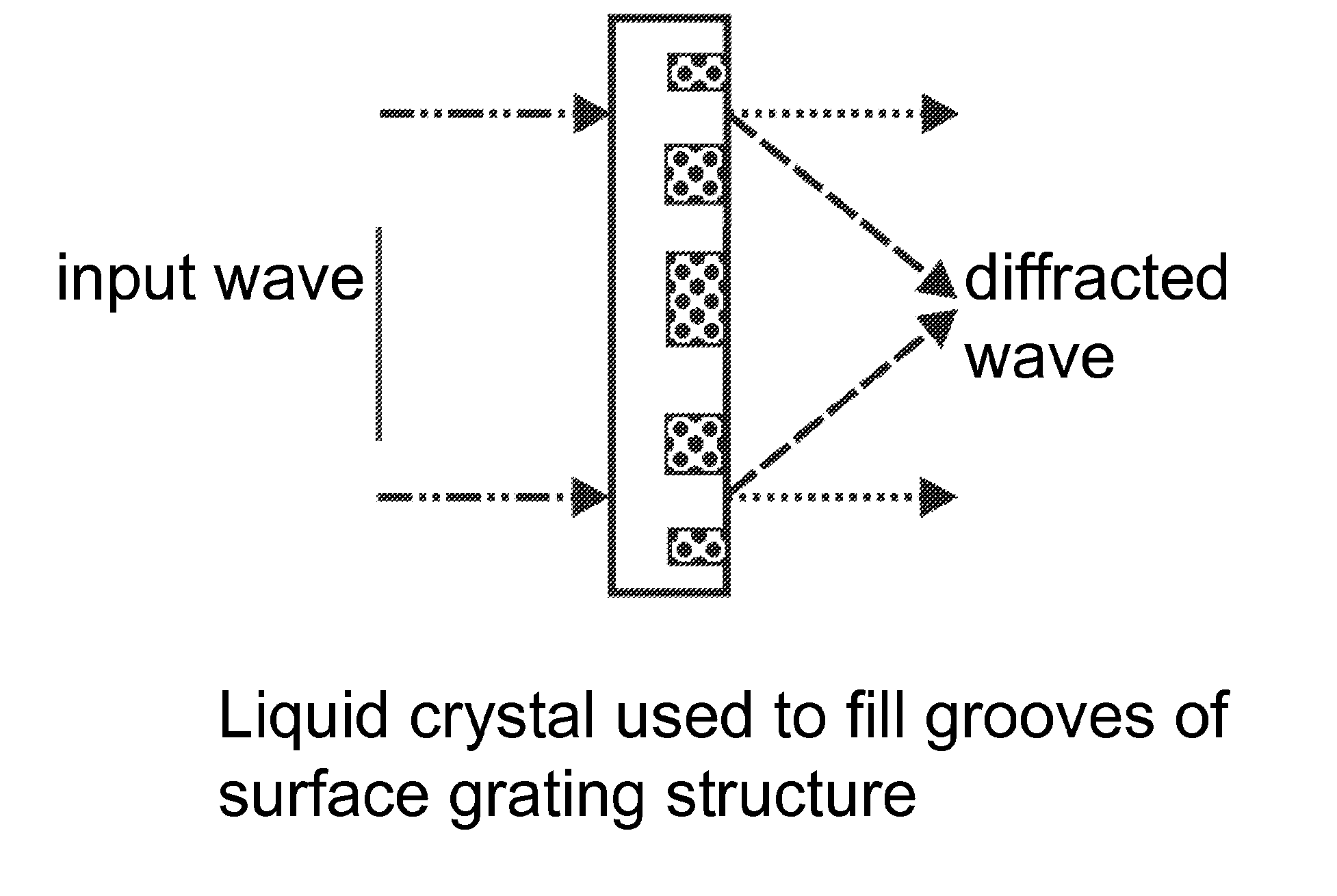
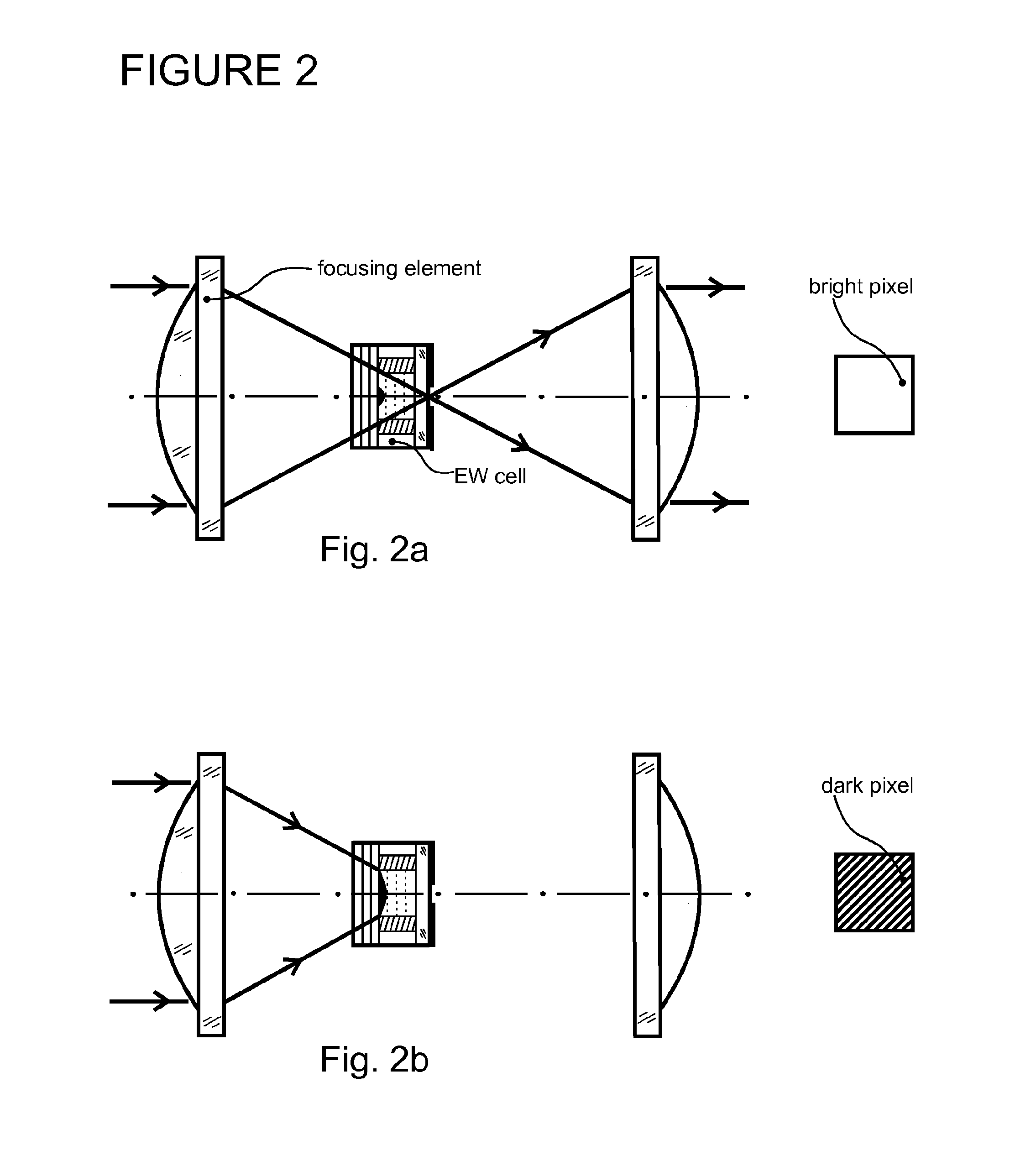
Spatial Light Modulator Using Electrowetting Cells
InactiveUS20100232000A1Increase contrastActive addressable light modulatorDiffraction gratingsSpatial light modulatorRefractive index
A spatial light modulator for modulating light field amplitude comprises a surface relief grating adapted to act as a diffractive lens, where a material is used to fill at least one groove of a surface grating structure, such that a controllable refractive index birefringence of the material inside the surface relief grating is controlled by an electric field, which leads to a controllable intensity at a fixed focal point.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
Diffractive lens exhibiting enhanced optical performance
ActiveUS8231219B2Reduce light scatterOptimize light energy distributionSpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsLight energyEye lens
The present invention provides improved ophthalmic lenses and methods for their design and use. Monofocal and multifocal diffractive ophthalmic lenses having reduced light scatter, improved light energy distribution properties, and / or other improvements in optical performance are provided. These properties are provided, at least in part, by the diffractive profiles of the invention, often having subtlety shaped echelettes with appropriately curving profiles. Smooth diffractive profiles may be used reduce light scatter. Diffractive profiles may be configured to limit the light energy in certain selected orders, thereby improving viewing quality and mitigating unwanted effects such as dysphotopsia. Diffractive profiles of may additionally or alternatively vary the light energy distributed between individual echelettes, providing additional advantages in various viewing situations.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Near-to-eye display with diffractive lens
An eyepiece for a HMD includes a waveguide, an ambient light polarizer, and a wire grid polarizer with a diffraction lens having a lens function patterned into the wire grid polarizer. Polarized image light is guided between eye-ward and ambient sides of the waveguide from a display source to a viewing region of the waveguide where the polarized image light is directed out of the waveguide through the eye-ward side. The viewing region passes ambient light incident on the ambient side through to the eye-ward side. The ambient light polarizer is disposed adjacent to the ambient side to polarize the ambient light into polarized ambient light having a second polarization orthogonal to the first polarization. The wire grid polarizer is disposed adjacent to the eye-ward side along the viewing region. The wire grid polarizer is oriented to applying the lens function to the polarized image light via diffraction.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Bifocal multiorder diffractive lenses for vision correction
A bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided having a lens body with one or more first regions having a first multiorder diffractive structure providing near vision correction, and one or more second regions having a second multiorder diffractive structure providing distance vision correction, in which the lens defines an aperture divided between the first and second regions. Such one or more first regions may represent one or more annular rings, or other portion of the lens, and the second region may occupy the portion of the lens aperture outside the first region. The lens body may be provided by a single optical element or multiple optical elements. When multiple optical elements are used, the multiorder diffractive structures may be located along an interior surface of the lens. In other embodiments, a bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided by a single or multiple element lens body having a multiorder diffractive structure for distance vision correction and one or more refractive regions to add power for near vision correction, or a single or multiple element lens body shaped for refractive power for distance vision correction and a multiorder diffractive structure for add power for near vision correction. The lens may represent a contact lens, a spectacle lens, or the optic portion of an intraocular implant (IOL). Multiorder diffractive structures may be optimized for performance for photopic and scotopic vision.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
Toric-diffractive lens
Owner:DAVE JAGRAT NATAVAR
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus
An optical scanning device includes a light source, a pre-deflection optical system, a polygon mirror, and a scanning optical system. The pre-deflection optical system includes a coupling lens and a diffraction lens. A light output surface of the coupling lens is a phase shifting surface, while a light output surface of the diffraction lens is a diffractive surface. The absolute value of the focal length of the diffraction lens is longer than the absolute focal length of the coupling lens.
Owner:RICOH KK
Mid-infrared hyperspectral spectroscopy systems and methods therefor
ActiveUS9518917B2High sensitivityEfficient emissionsSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyTest sampleHarmonic
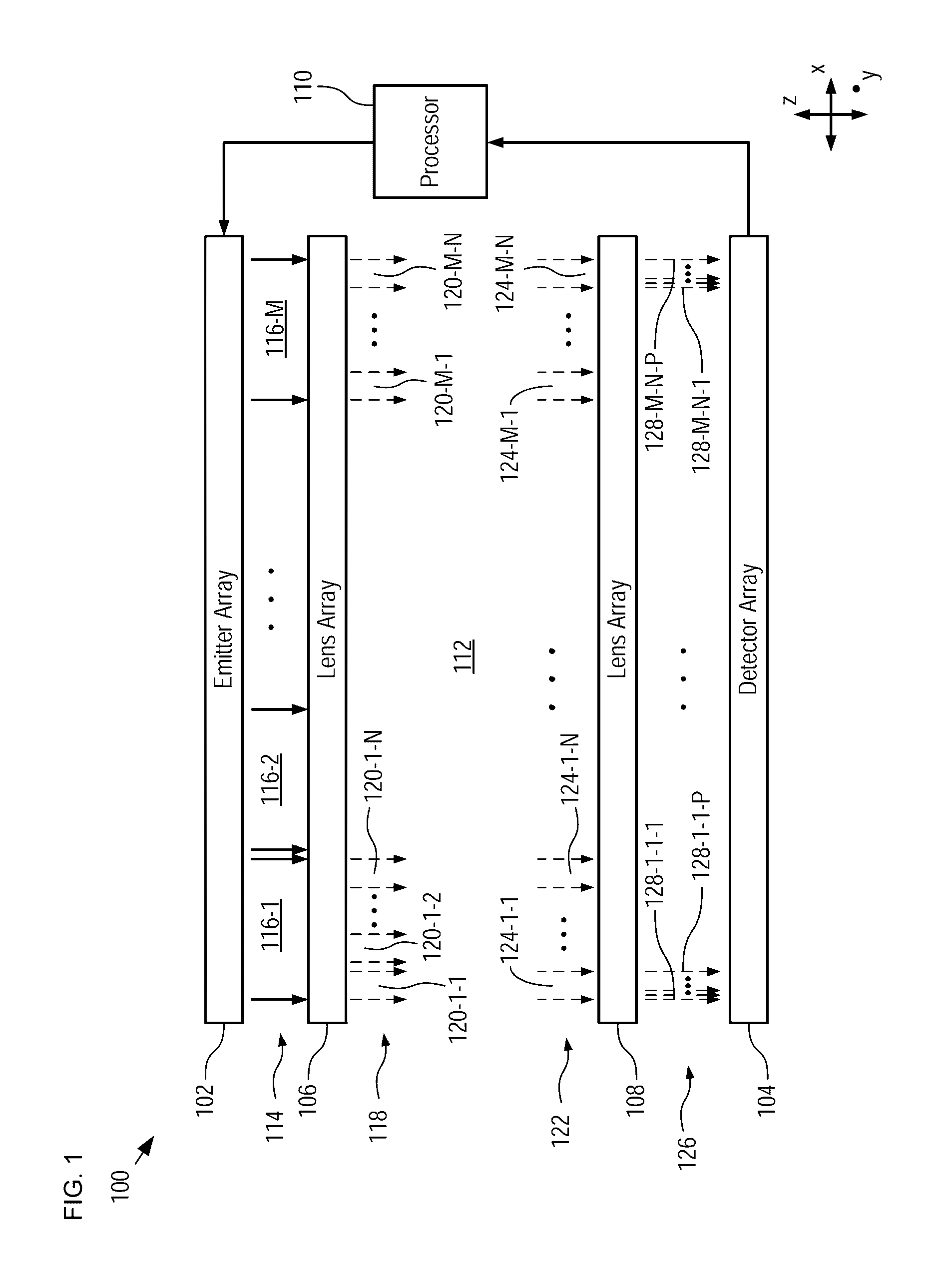
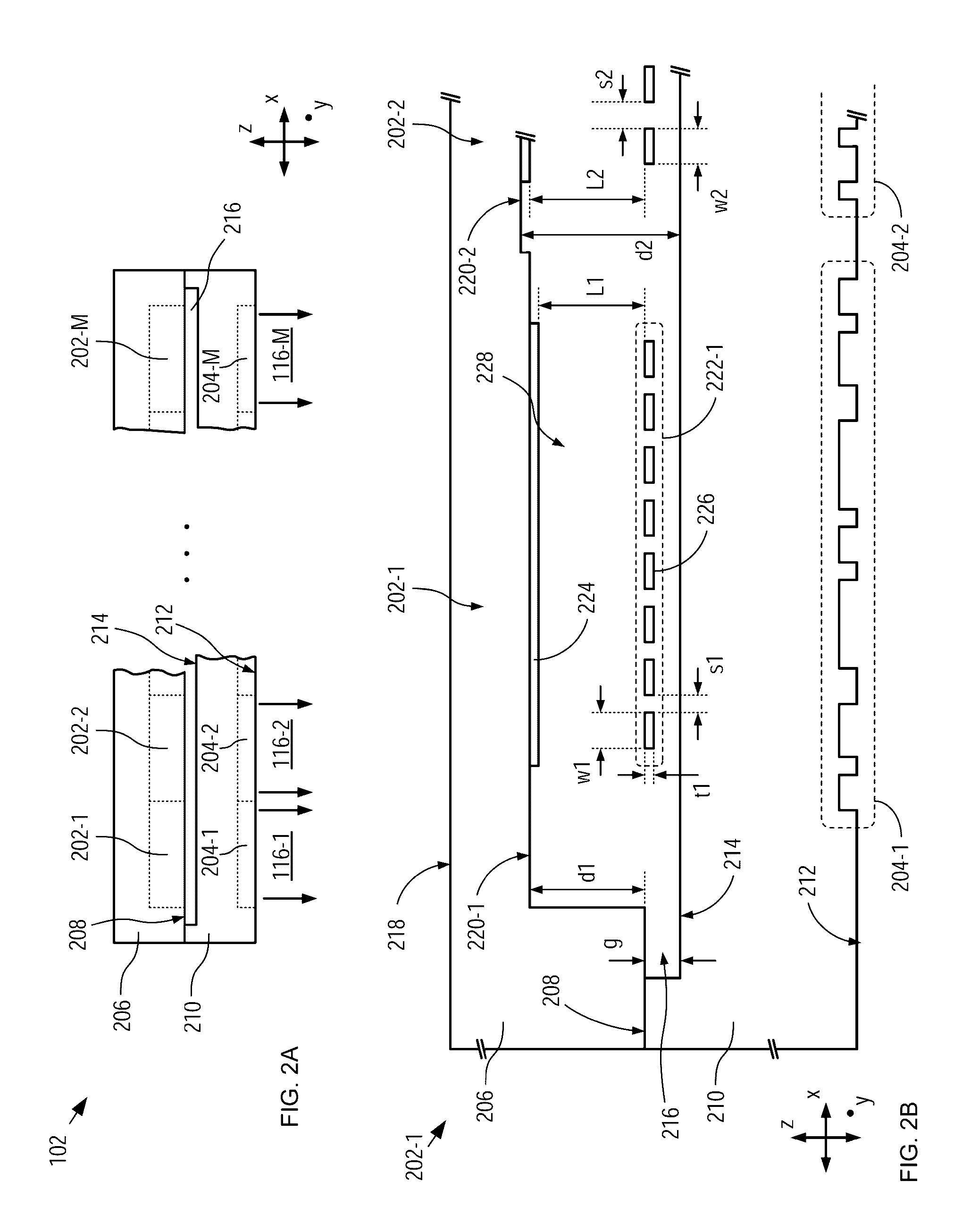
MIR spectroscopy systems comprising hierarchical spectral dispersion that enables fine spectral resolution and high sensitivity spectroscopy are disclosed. Hierarchical spectral dispersion is derived by employing at least two diffractive lens arrays, located on either side of a test sample, each receiving input radiation having an input spectral range and distributing the input radiation into a plurality of output signals, each having a fraction of the spectral range of the input radiation. As a result, the signal multiplication factor of the two arrays is multiplied in a manner that mitigates the propagation of wavelength harmonics through the system. In some embodiments, an emitter array comprising a plurality of spectrally selective emitters provides the input MIR radiation to a spectroscopy system. In some embodiments, spectrally selective detectors are used to detect narrow spectral components in the radiation after they have passed through the test sample.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com