Patents
Literature
106 results about "Merit function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
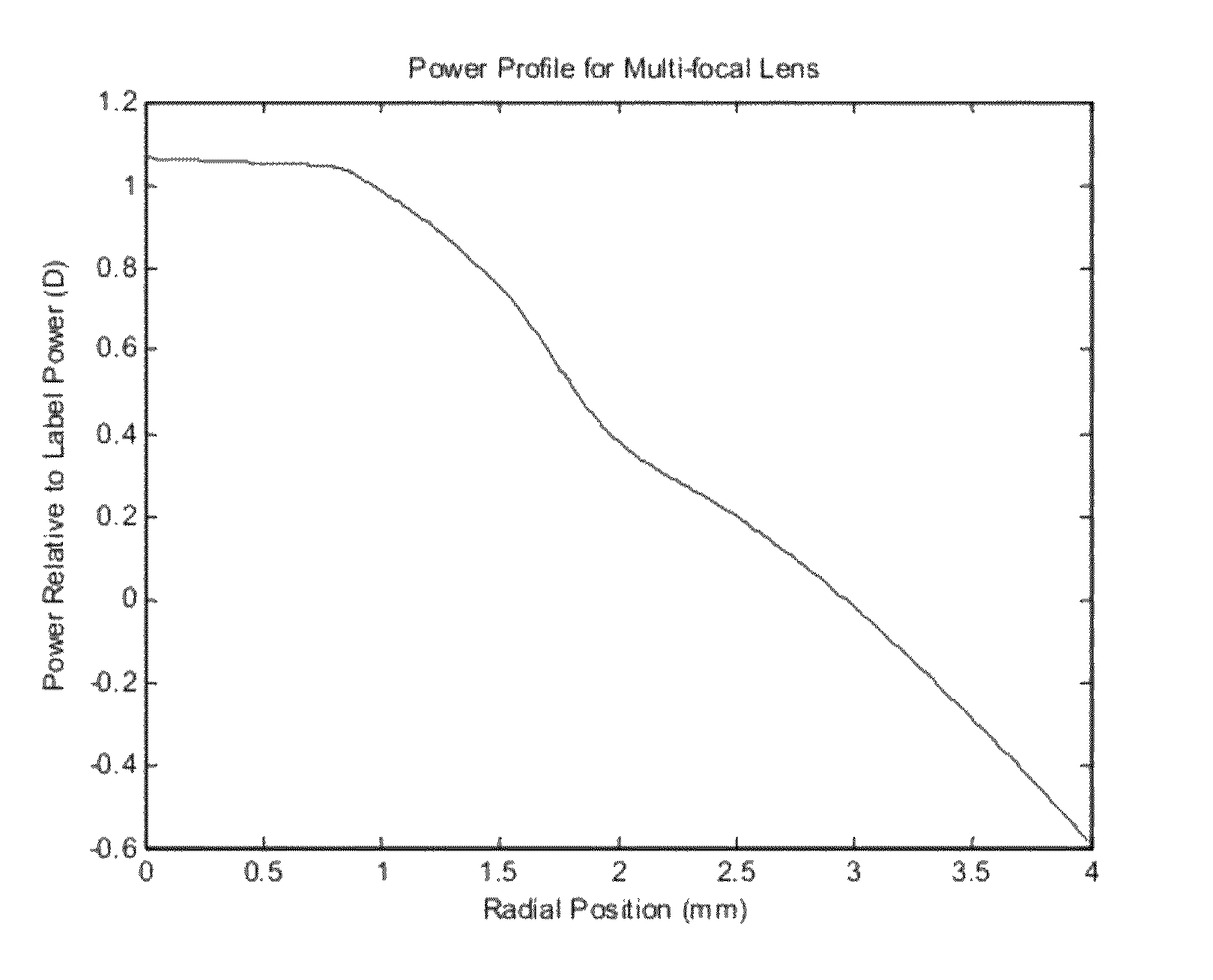
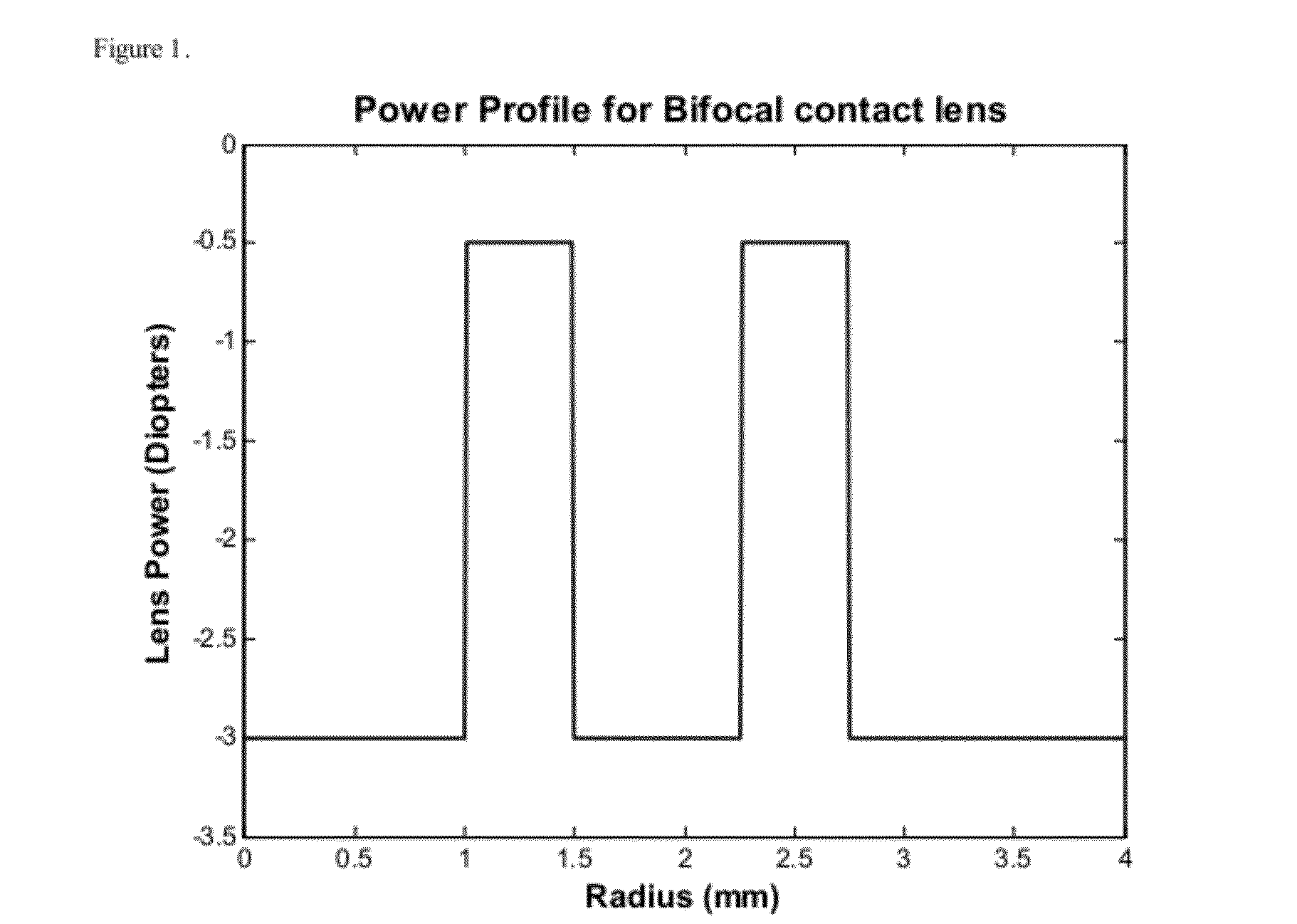
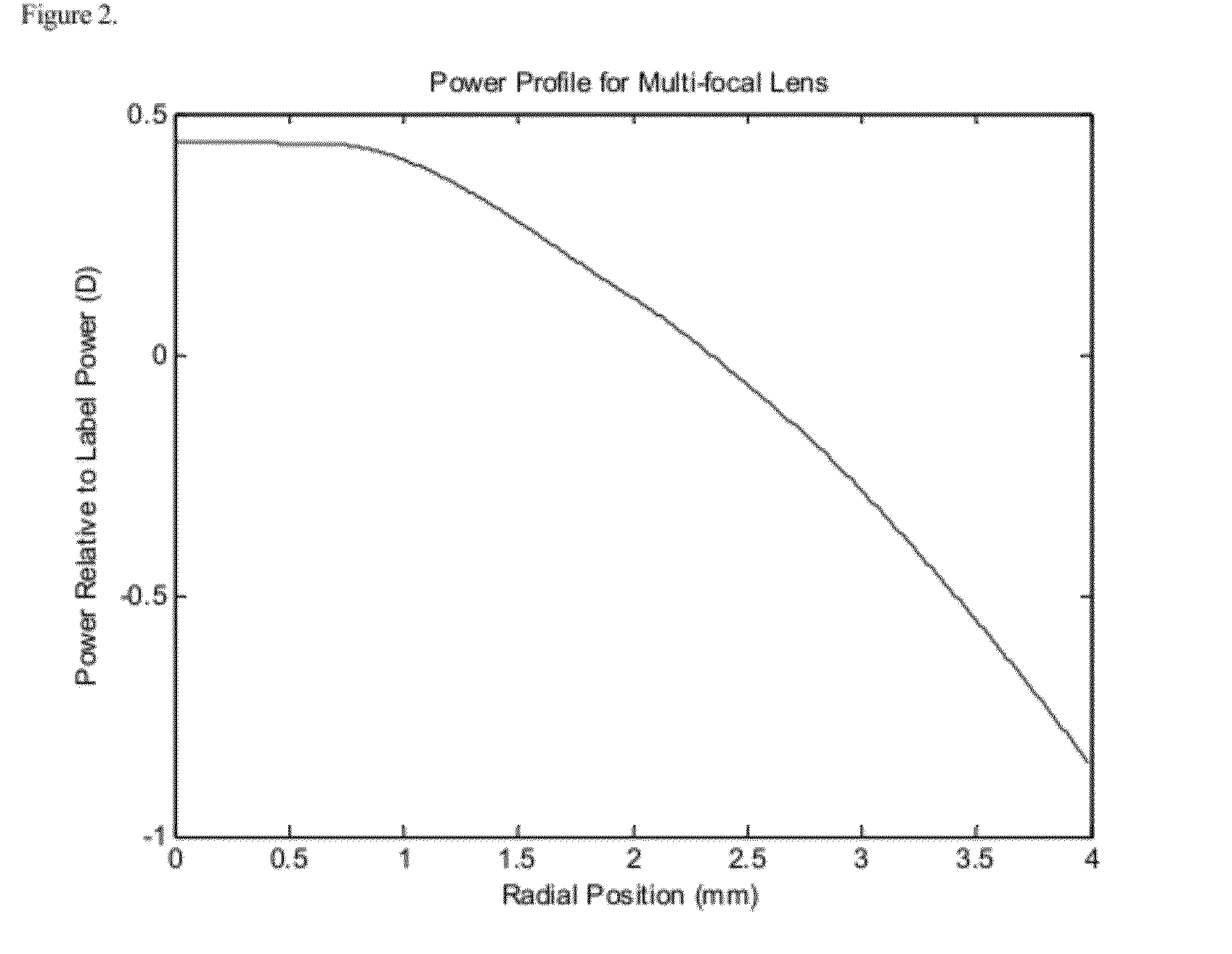
Method for designing progressive addition lenses
InactiveUS6956682B2Total lens maximum astigmatism can be reducedElectromagnetic transmissionOptical partsOphthalmologyProgressive addition lenses
The invention provides a method for designing progressive surfaces and lenses produced using image blur to construct a merit function. The shape of a lens surface, or surfaces, is arbitrarily defined and optimized to minimize the image blur based merit function.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
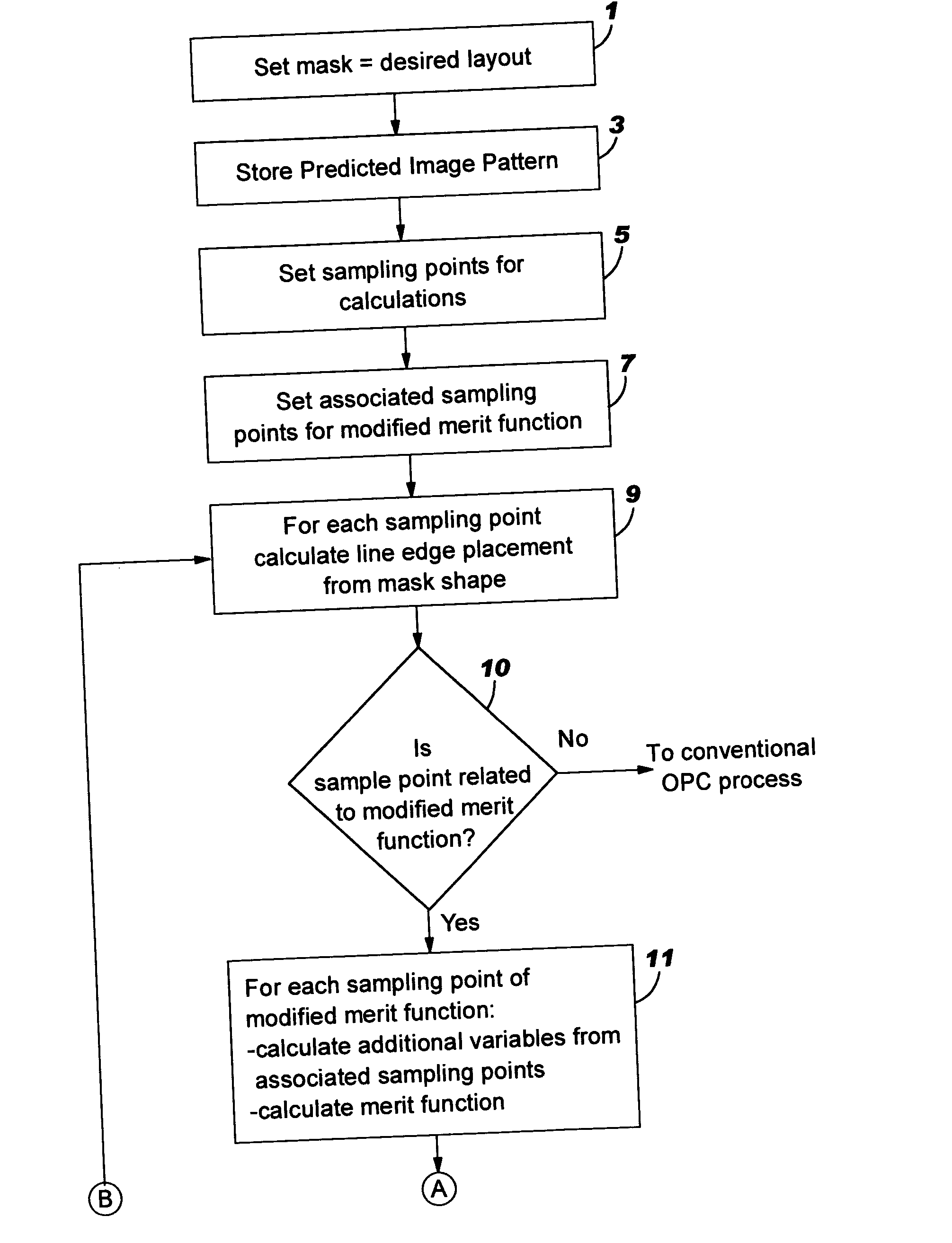
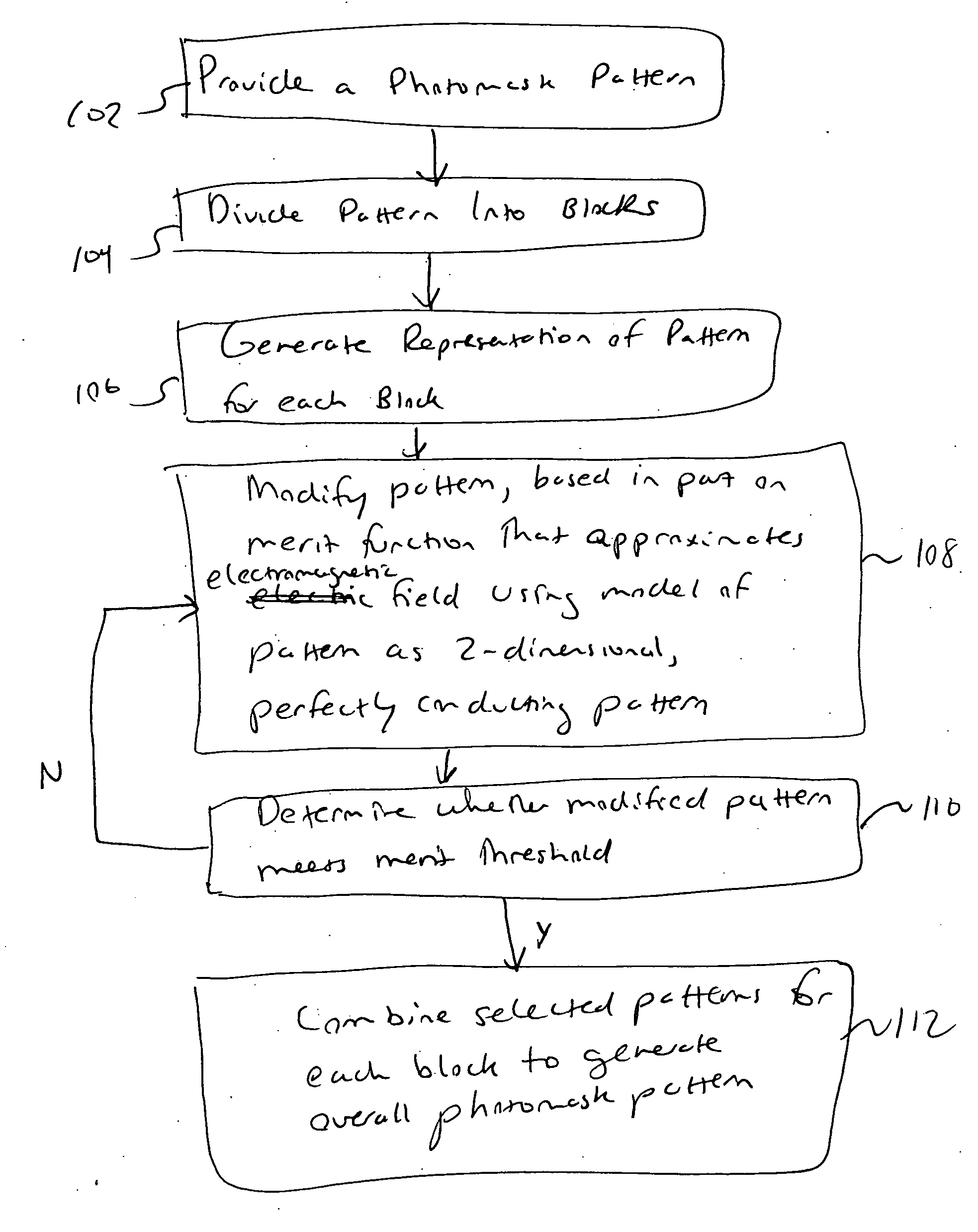
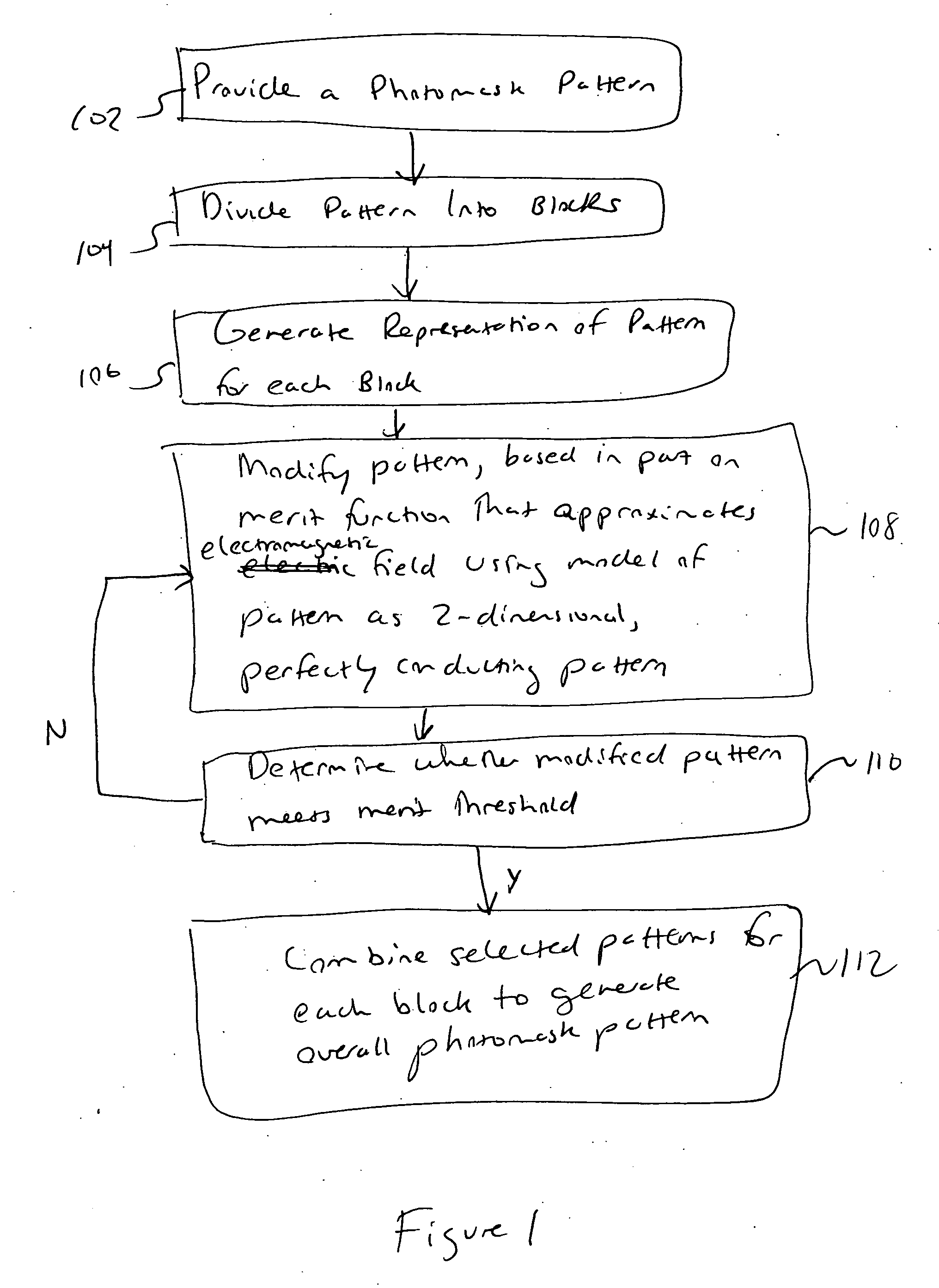
Method for time-evolving rectilinear contours representing photo masks
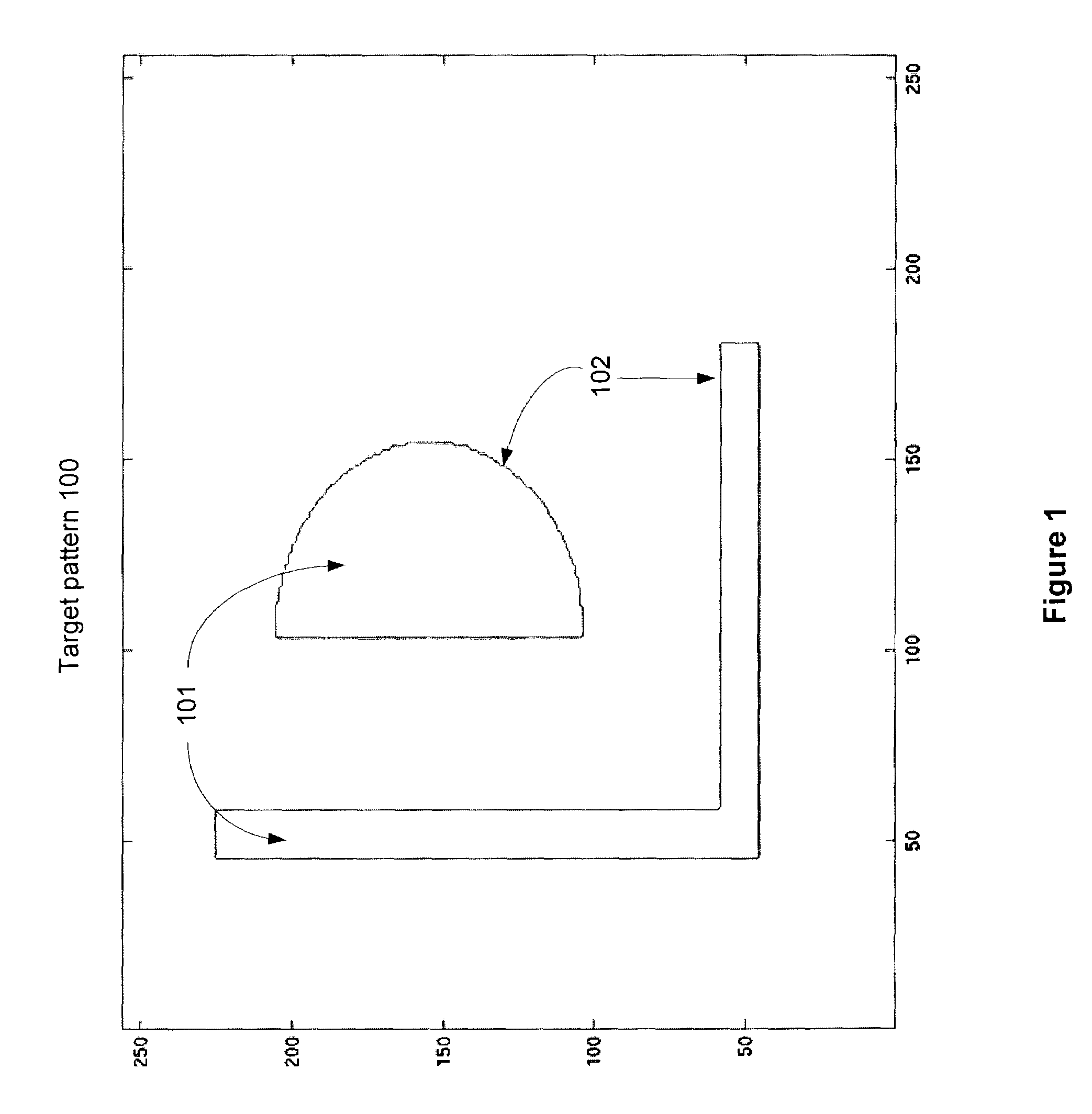
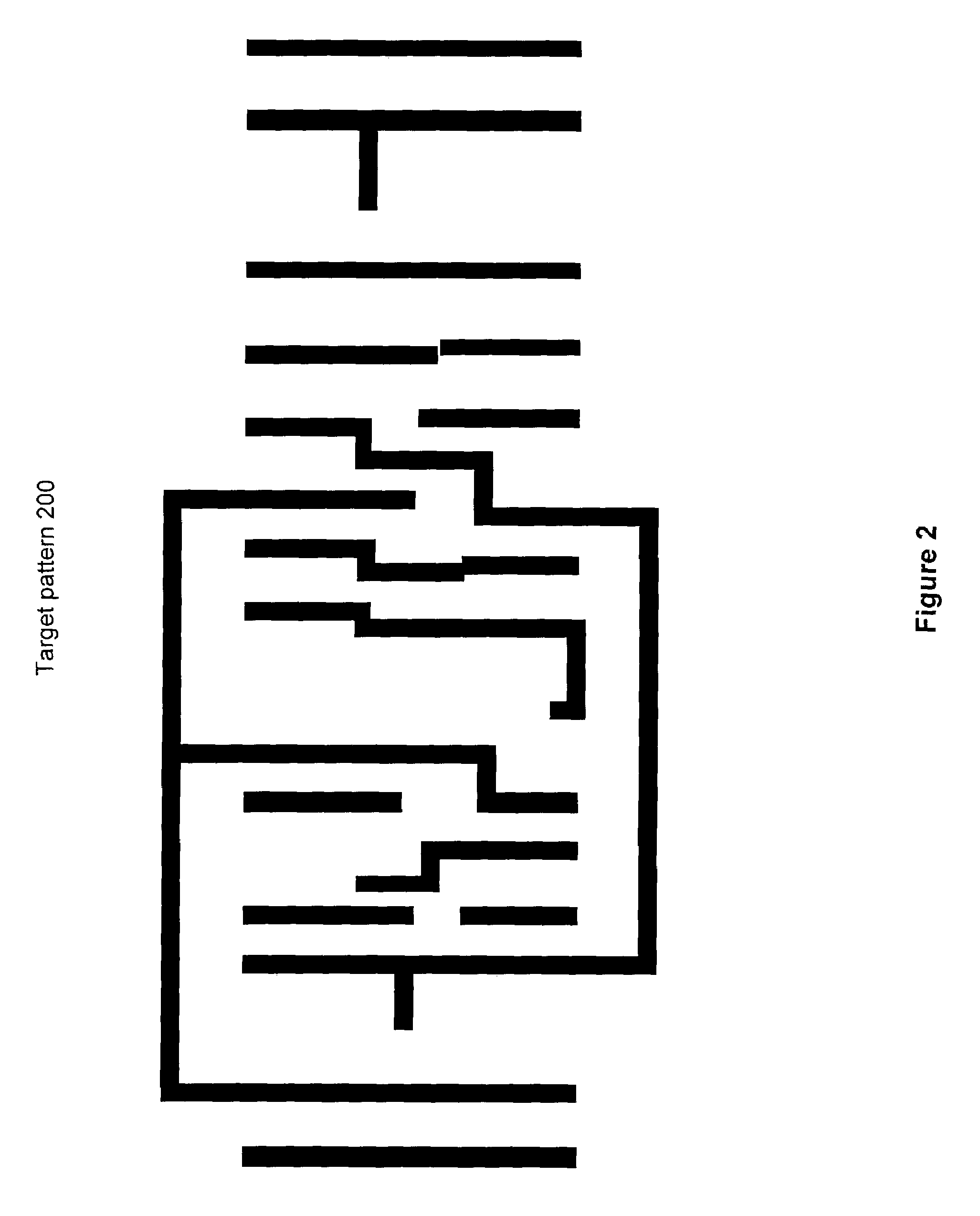
InactiveUS7124394B1Originals for photomechanical treatmentSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPattern recognitionMerit function
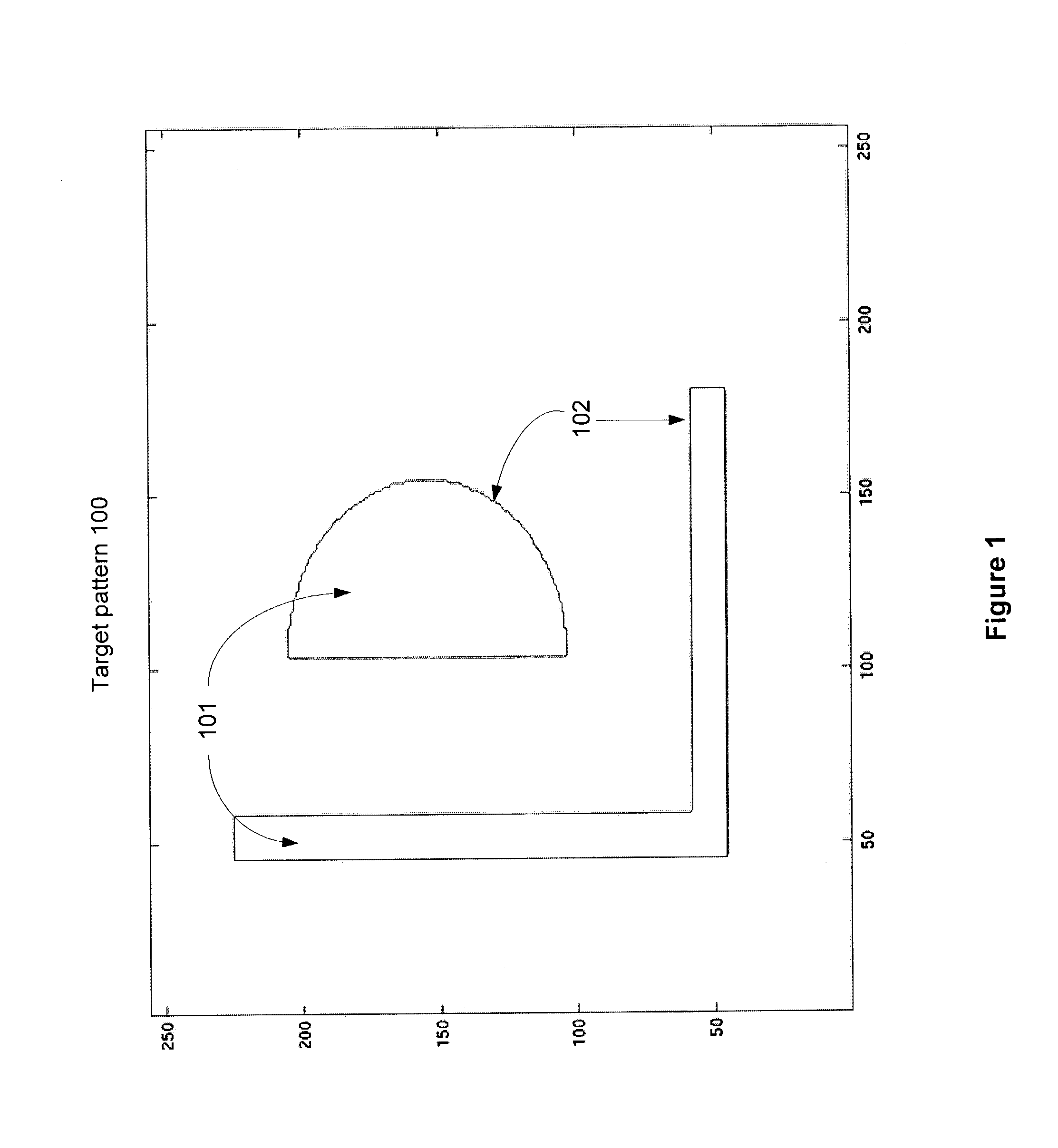
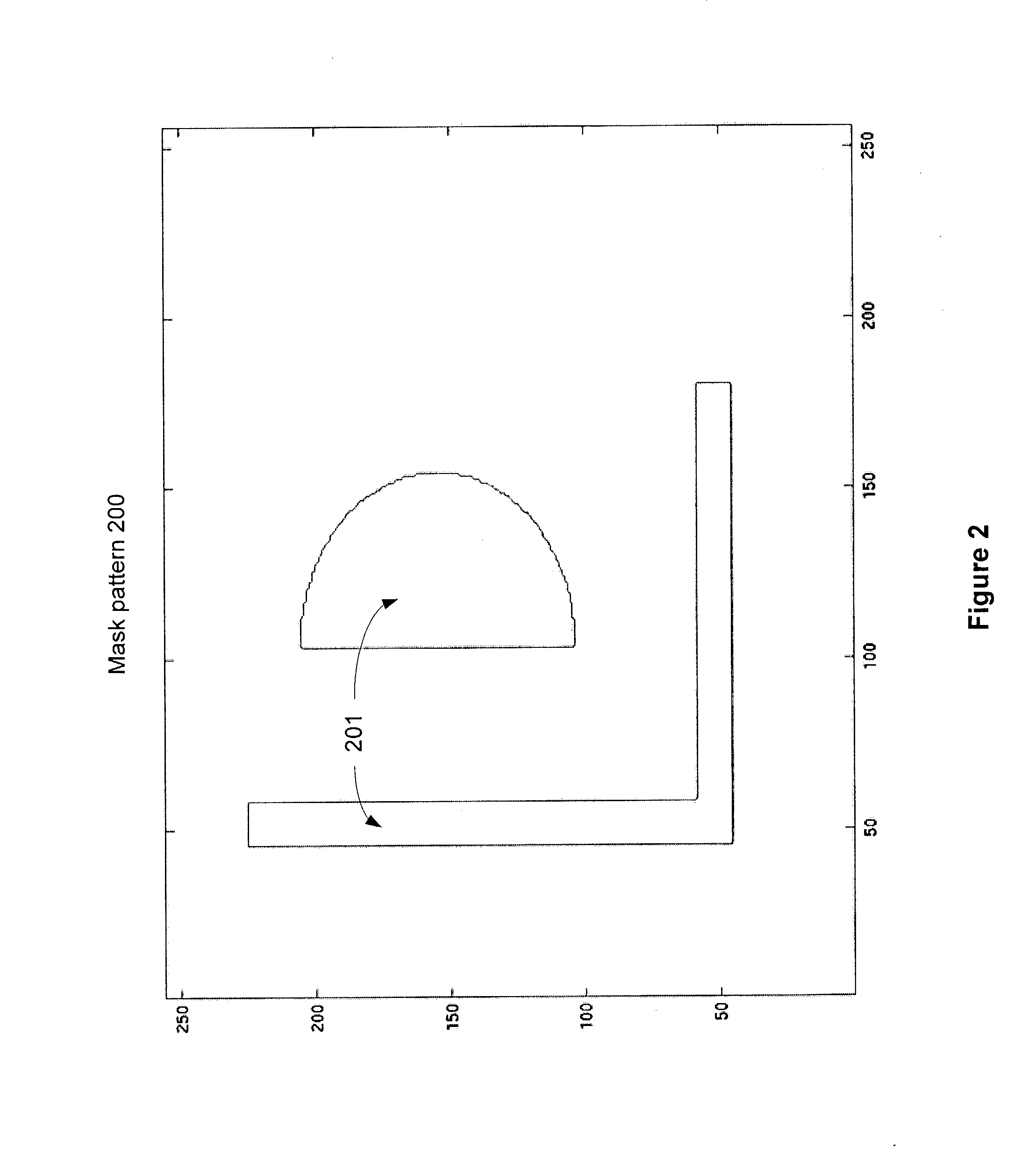
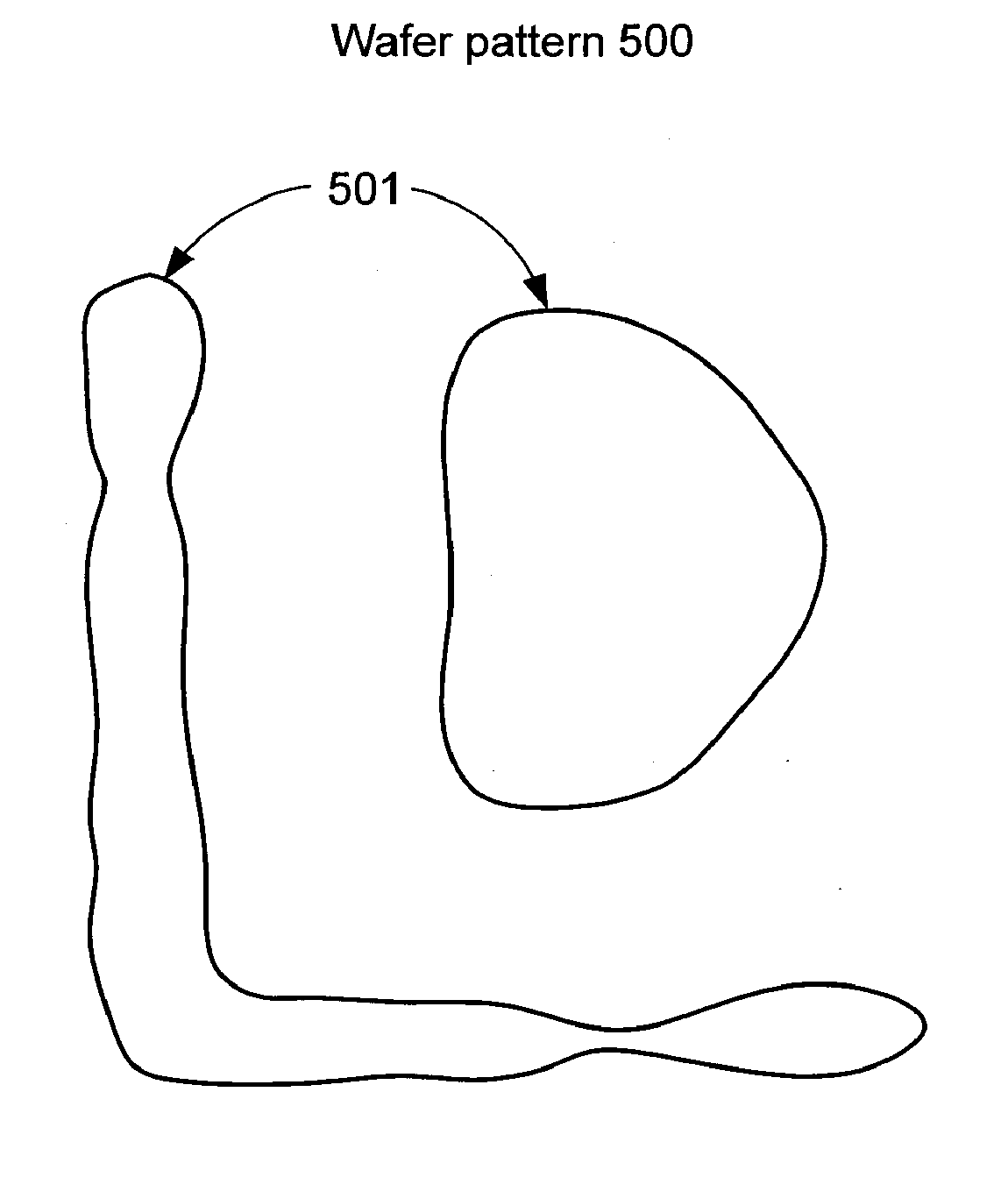
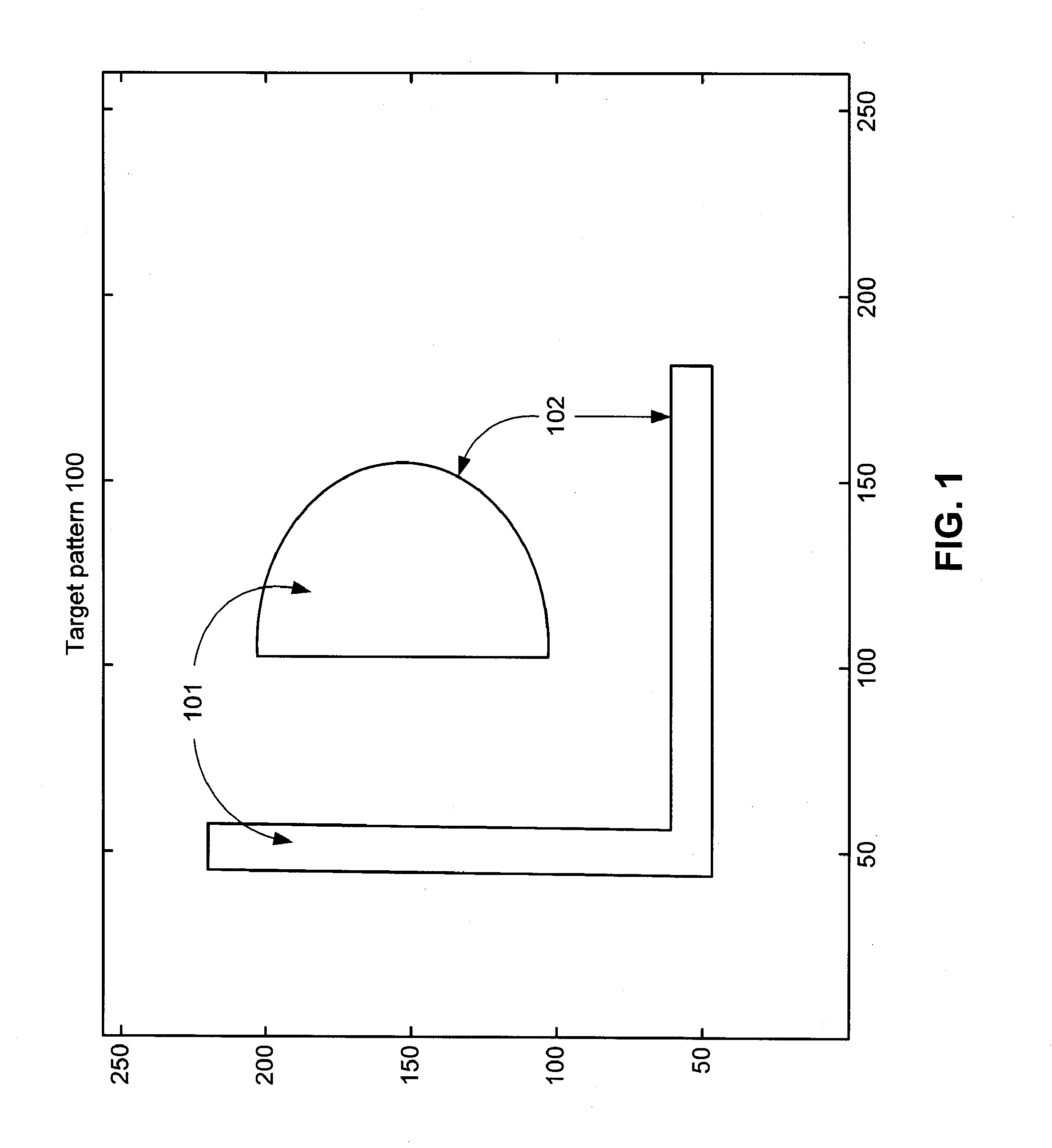
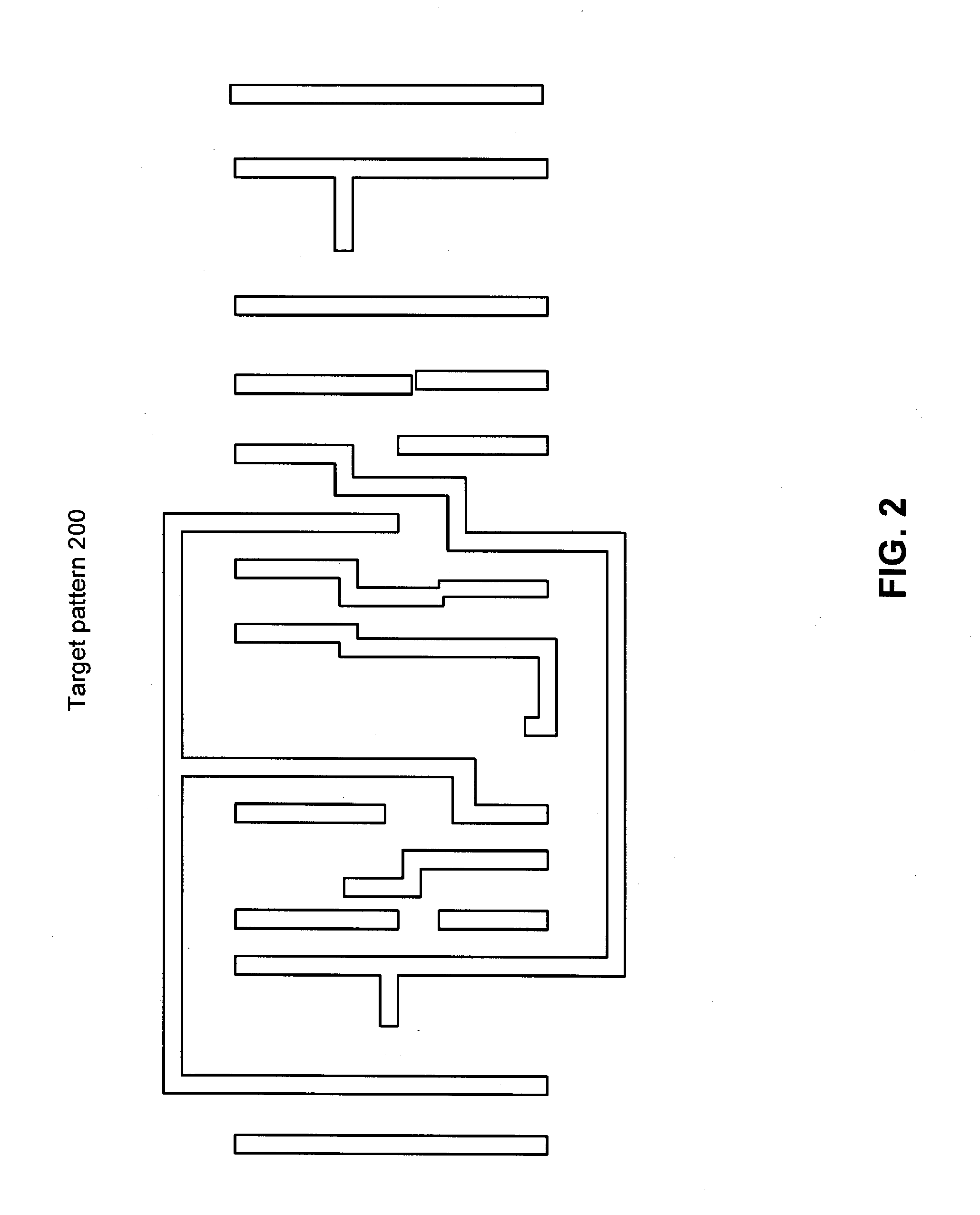
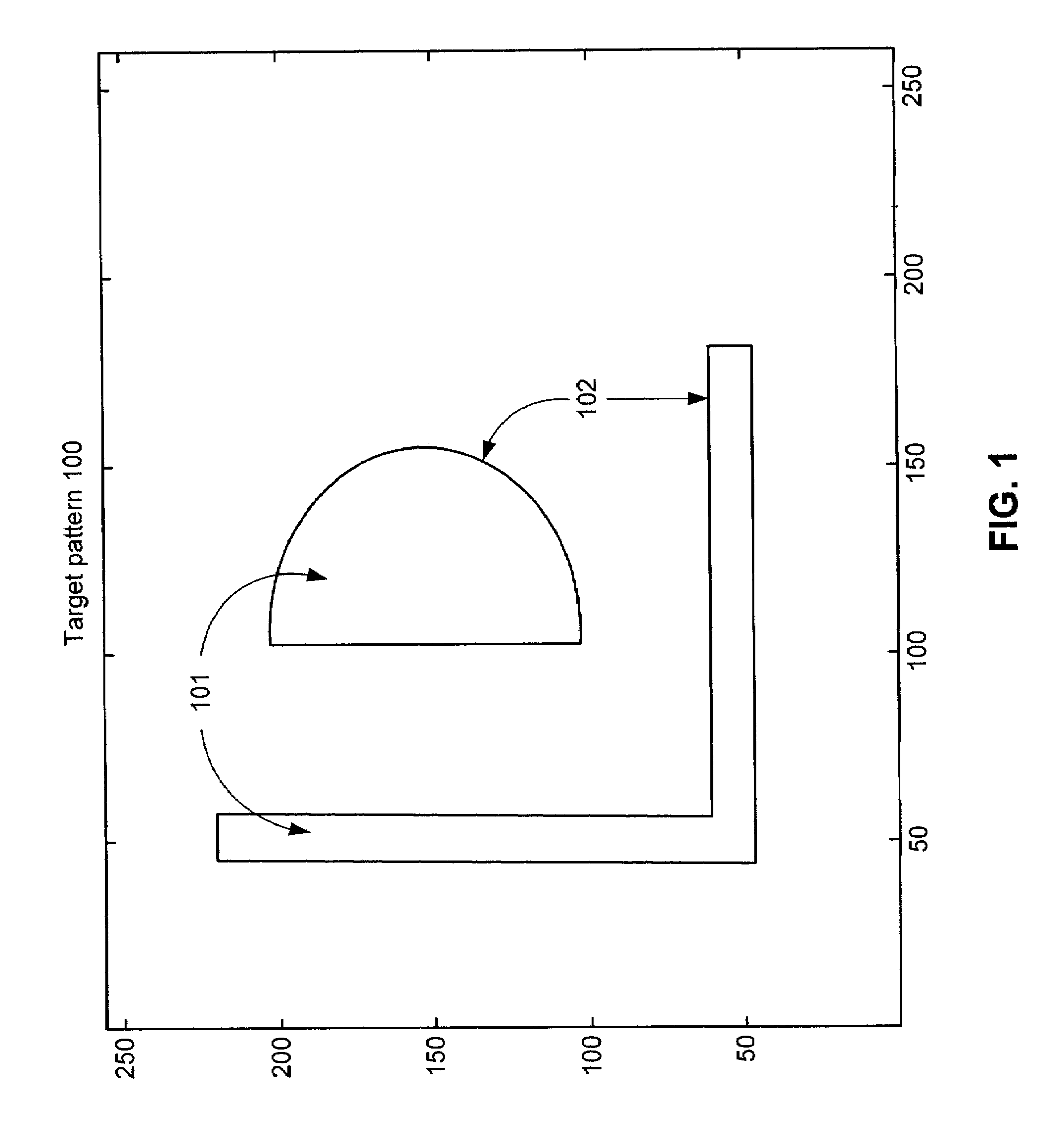
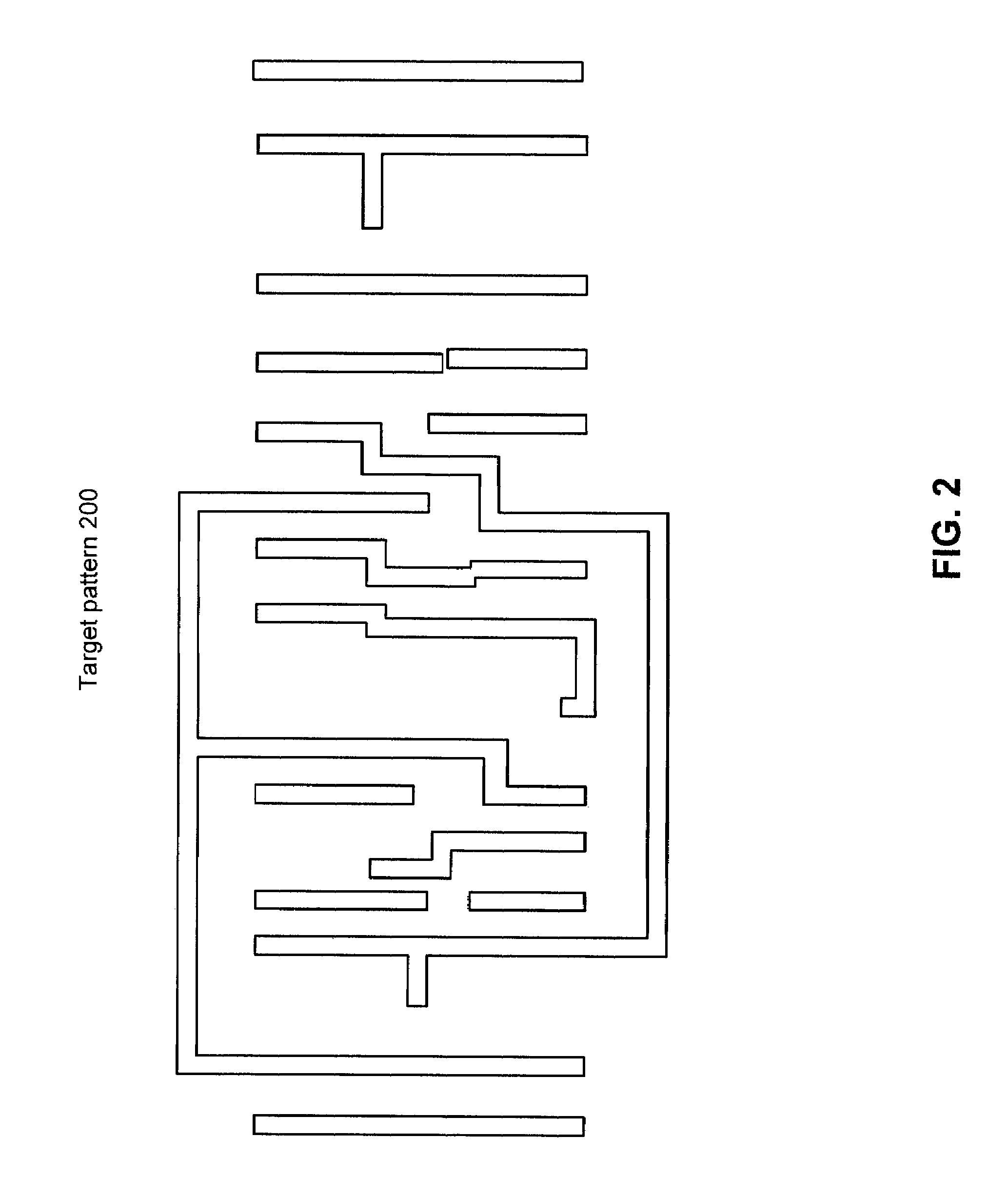
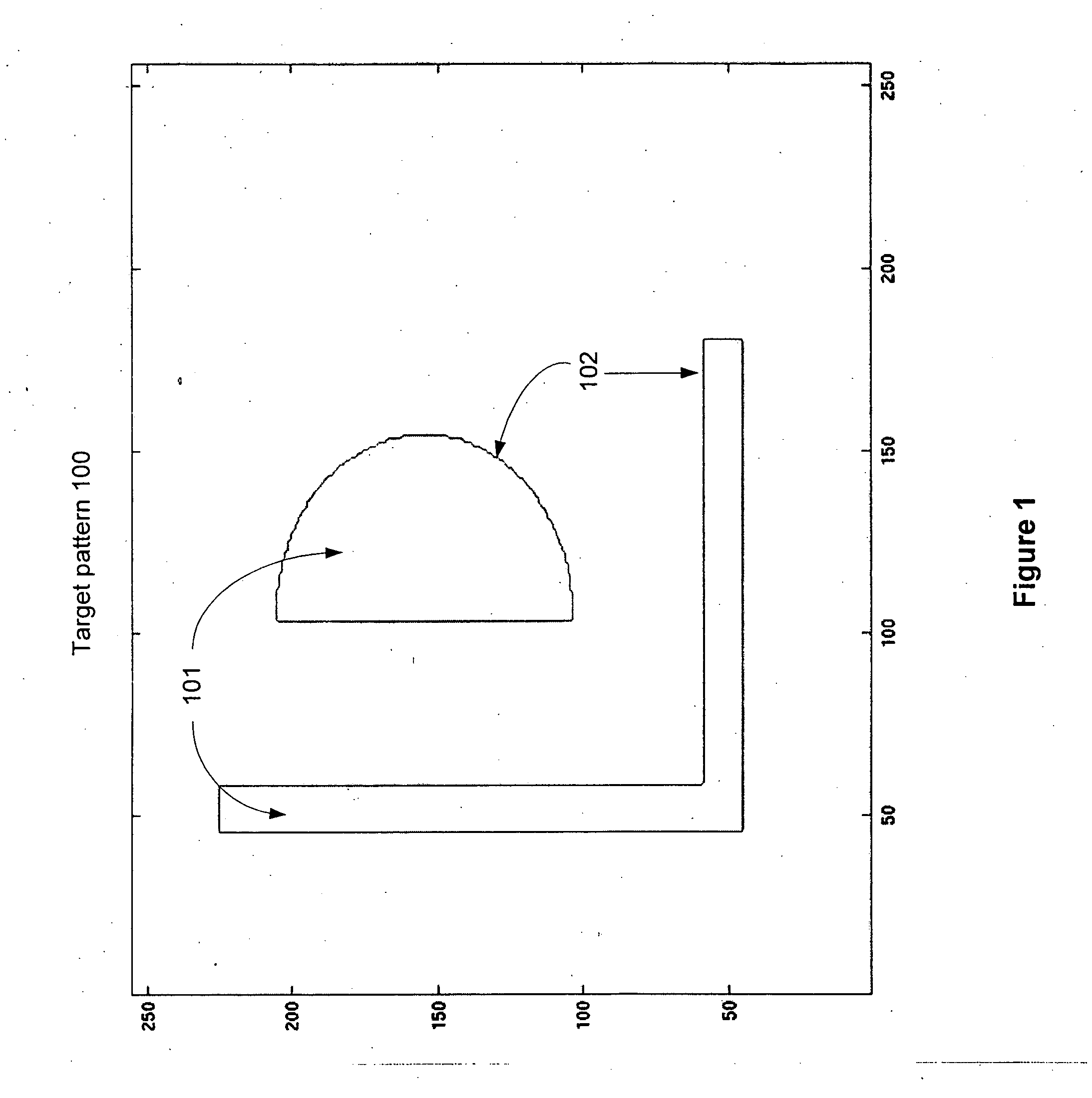
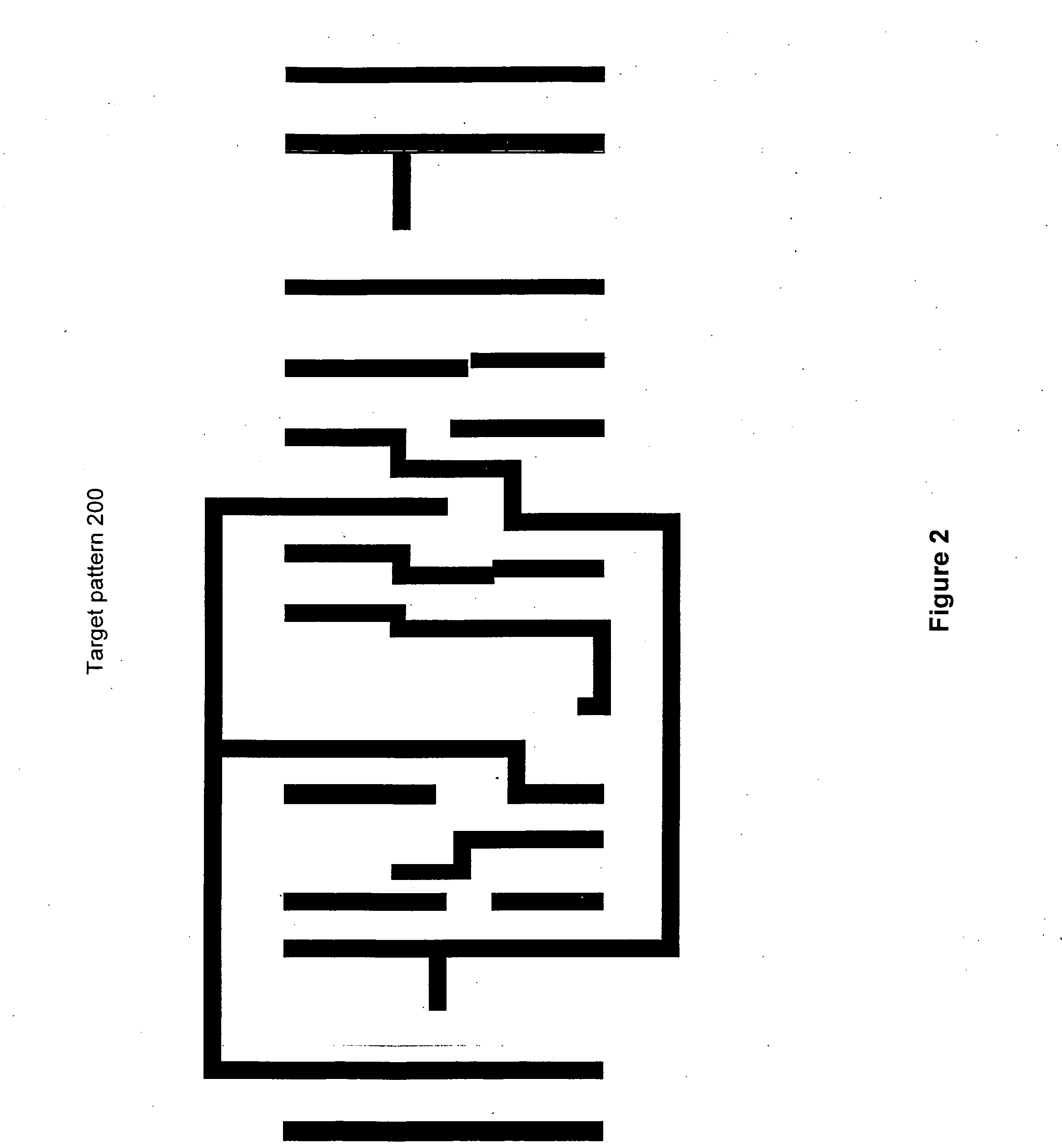
Photomask patterns are represented using contours defined by level-set functions. Given target pattern, contours are optimized such that defined photomask, when used in photolithographic process, prints wafer pattern faithful to target pattern. Optimization utilizes “merit function” for encoding aspects of photolithographic process, preferences relating to resulting pattern (e.g. restriction to rectilinear patterns), robustness against process variations, as well as restrictions imposed relating to practical and economic manufacturability of photomasks.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for optimizing optical system and recording medium with program for optimizing optical system
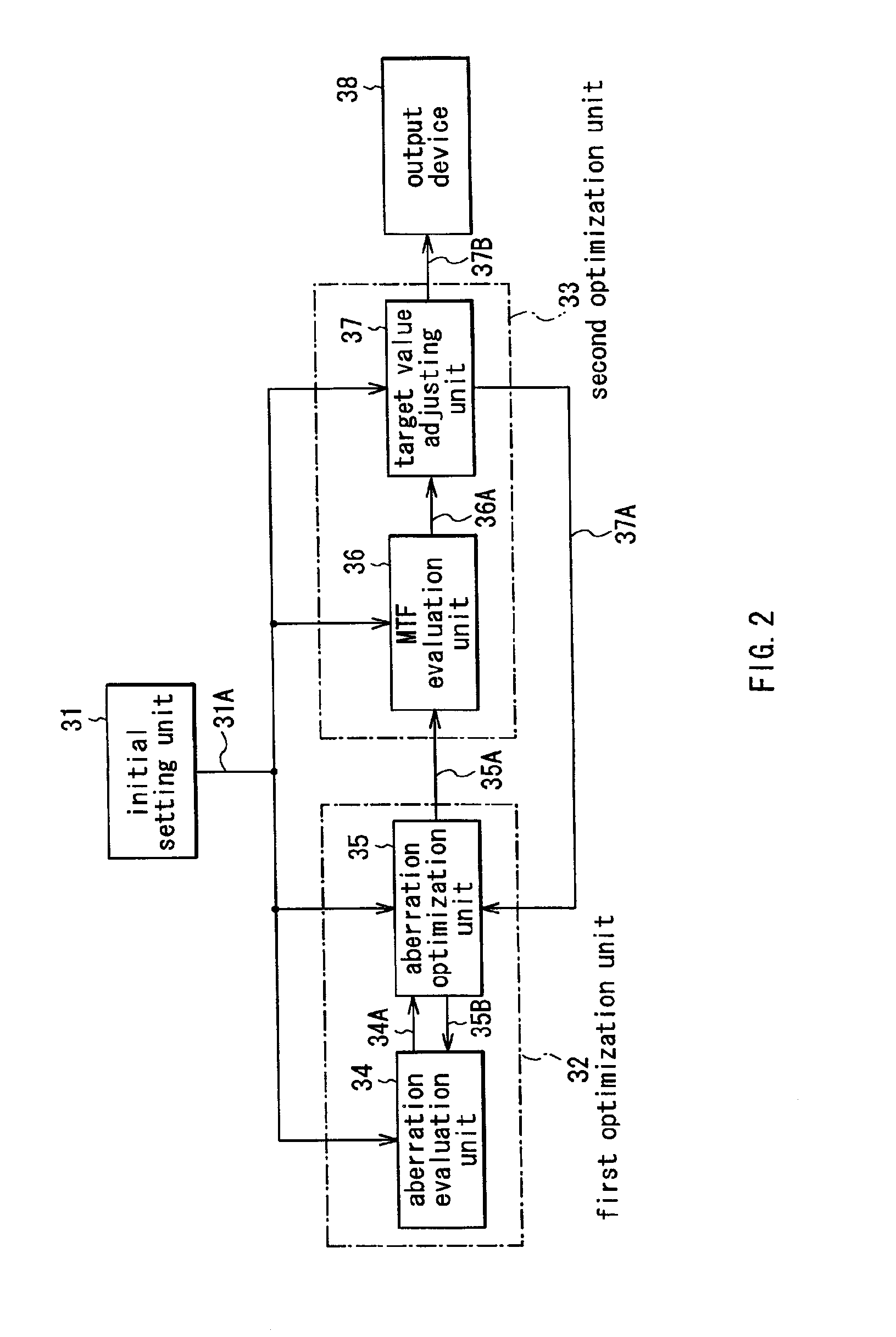
InactiveUS6895334B2Electric/magnetic detectionGravitational wave measurementOptical propertyOptic system
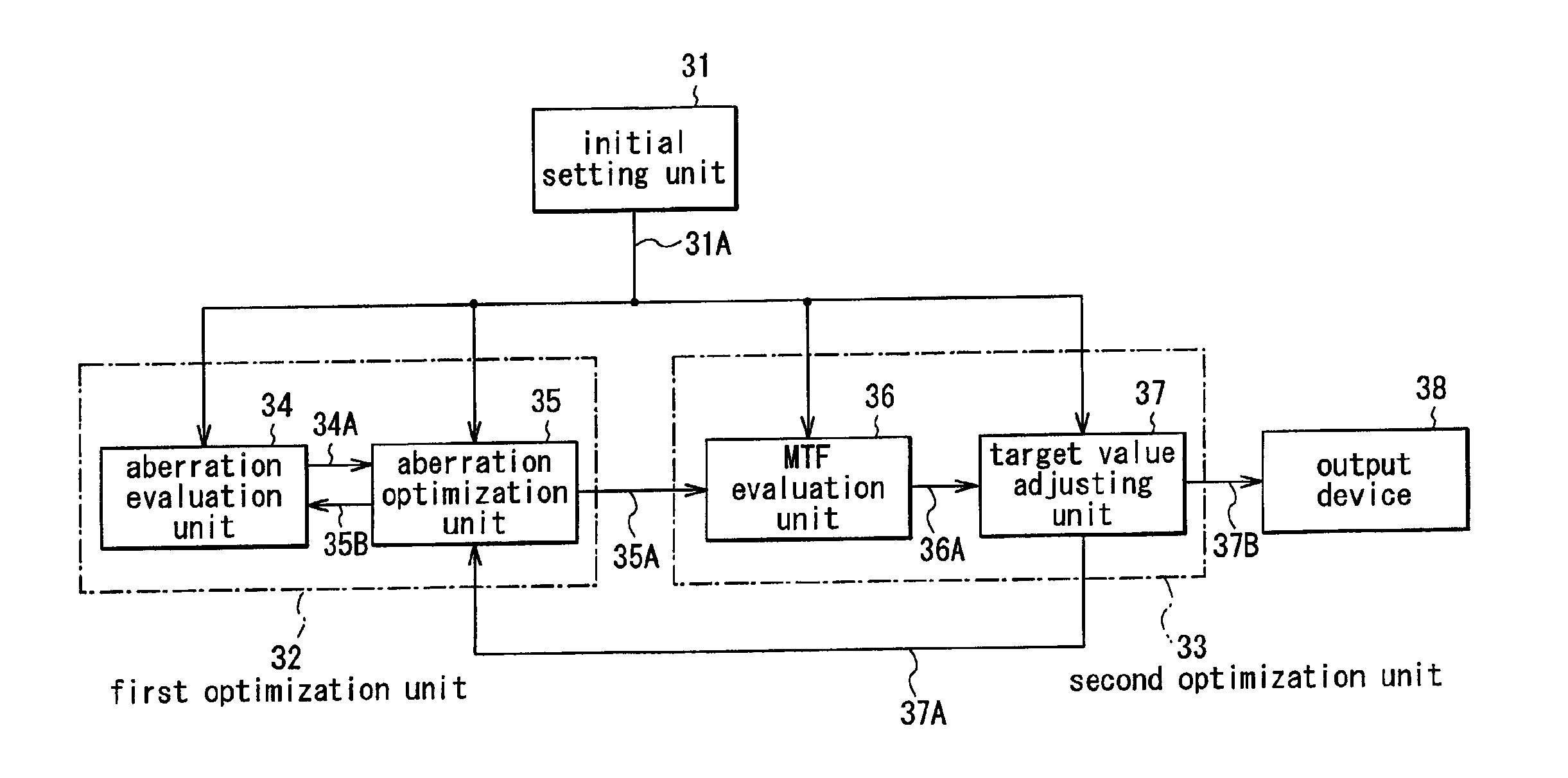
Optical properties with high non-linearity such as a modulation transfer function (MTF) are efficiently optimized at high speed compared to conventional methods. An optimal solution of an optical system is obtained in a first optimization unit using a merit function on aberration. Weights or target values of the merit function on aberration is automatically adjusted in a second optimization unit in a manner that an evaluated value of the MTF or the like approaches a desired value. The first optimization unit re-optimizes the optical system using the weights or target values which have been automatically adjusted. Thus, automated is a function equivalent to the operation which has been conducted by a designer such as adjustment to weights or target values.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
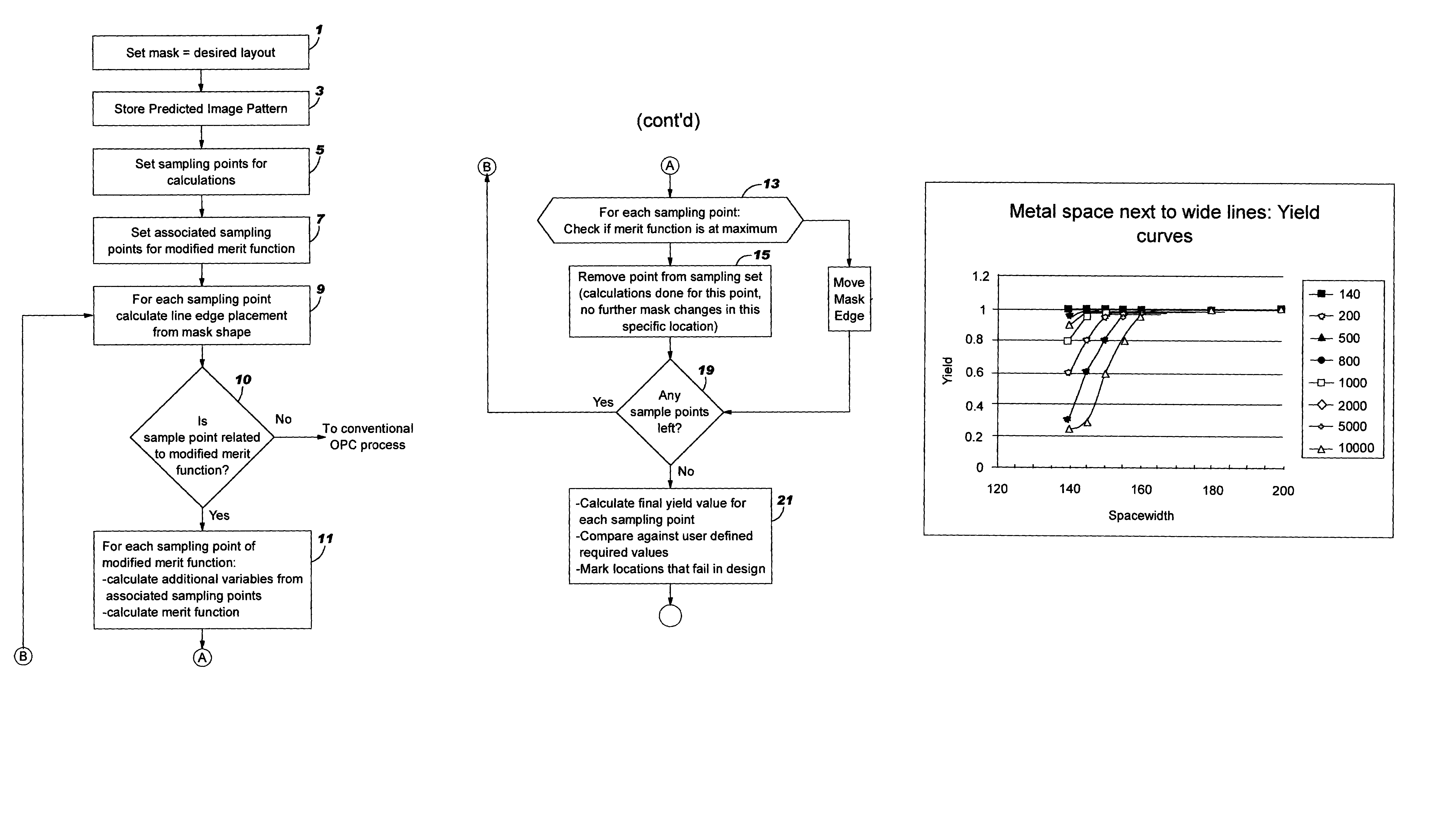
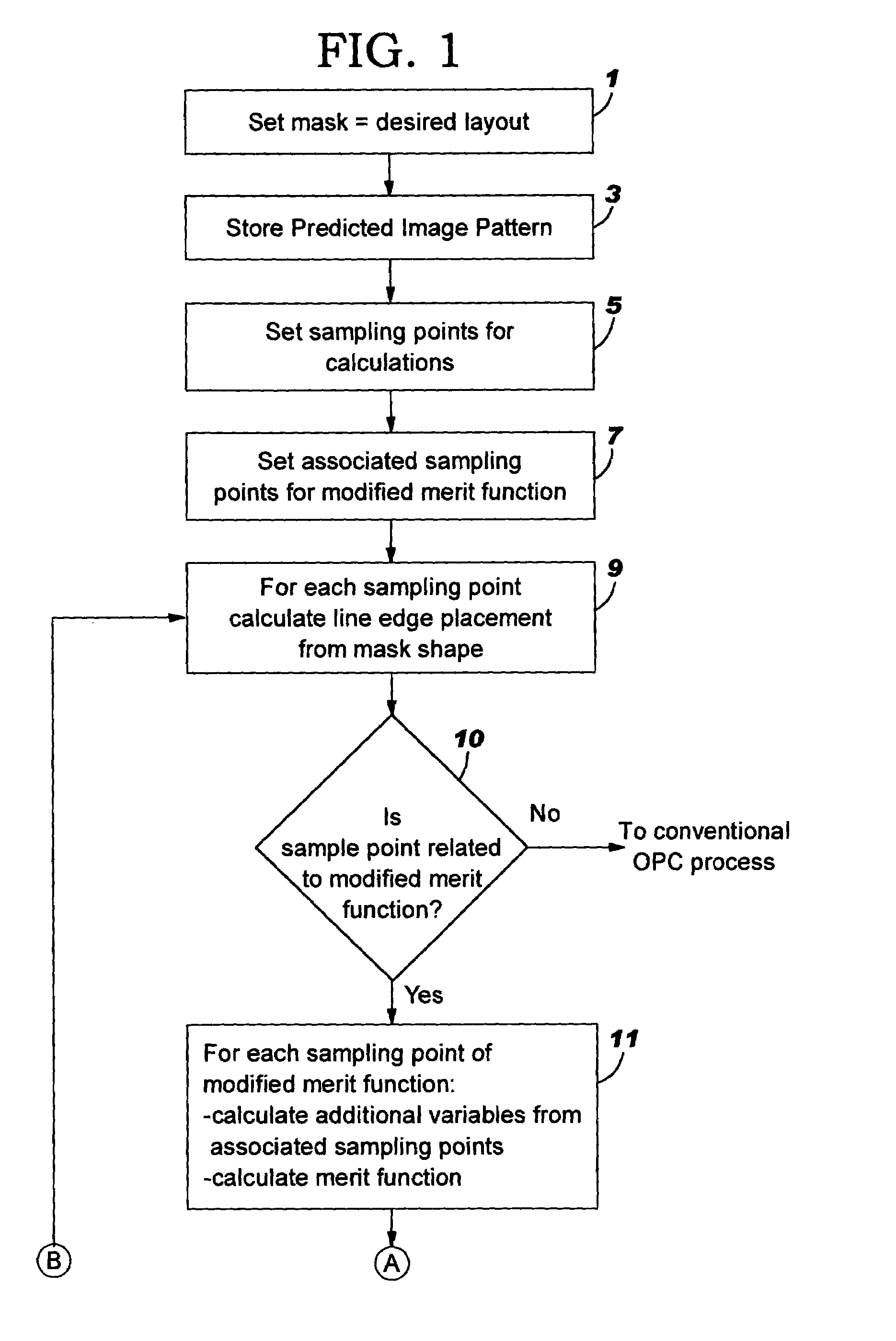
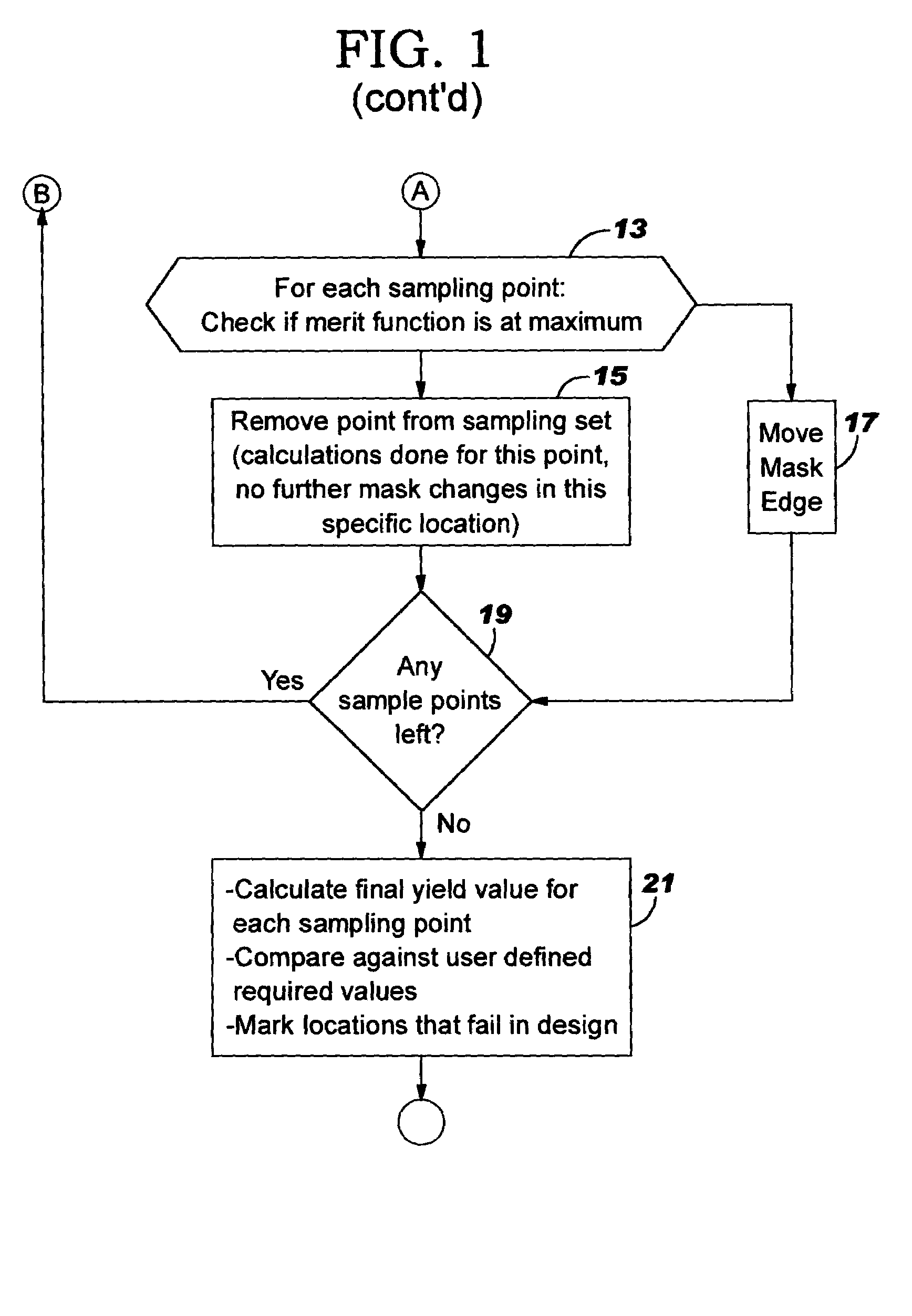
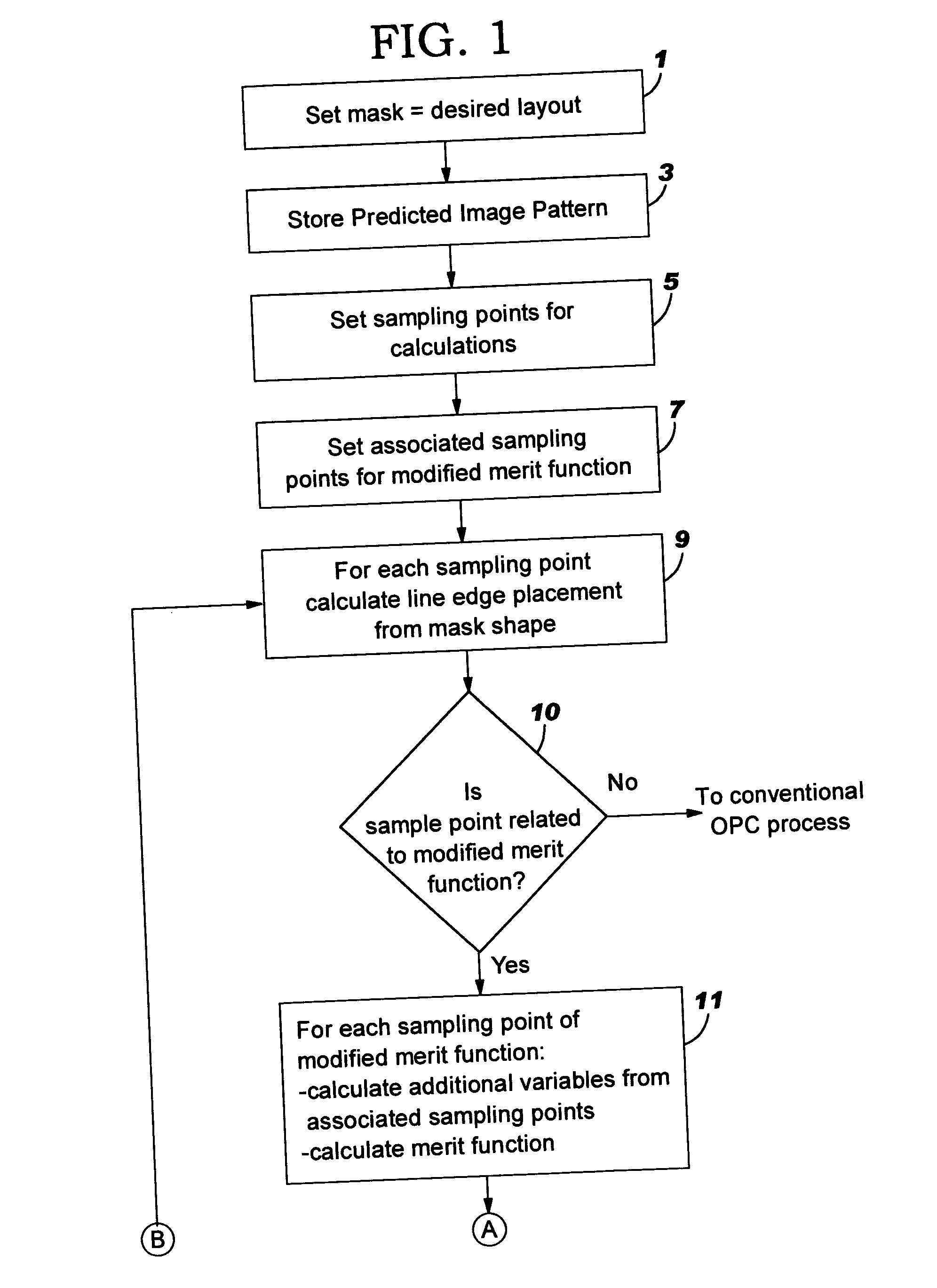
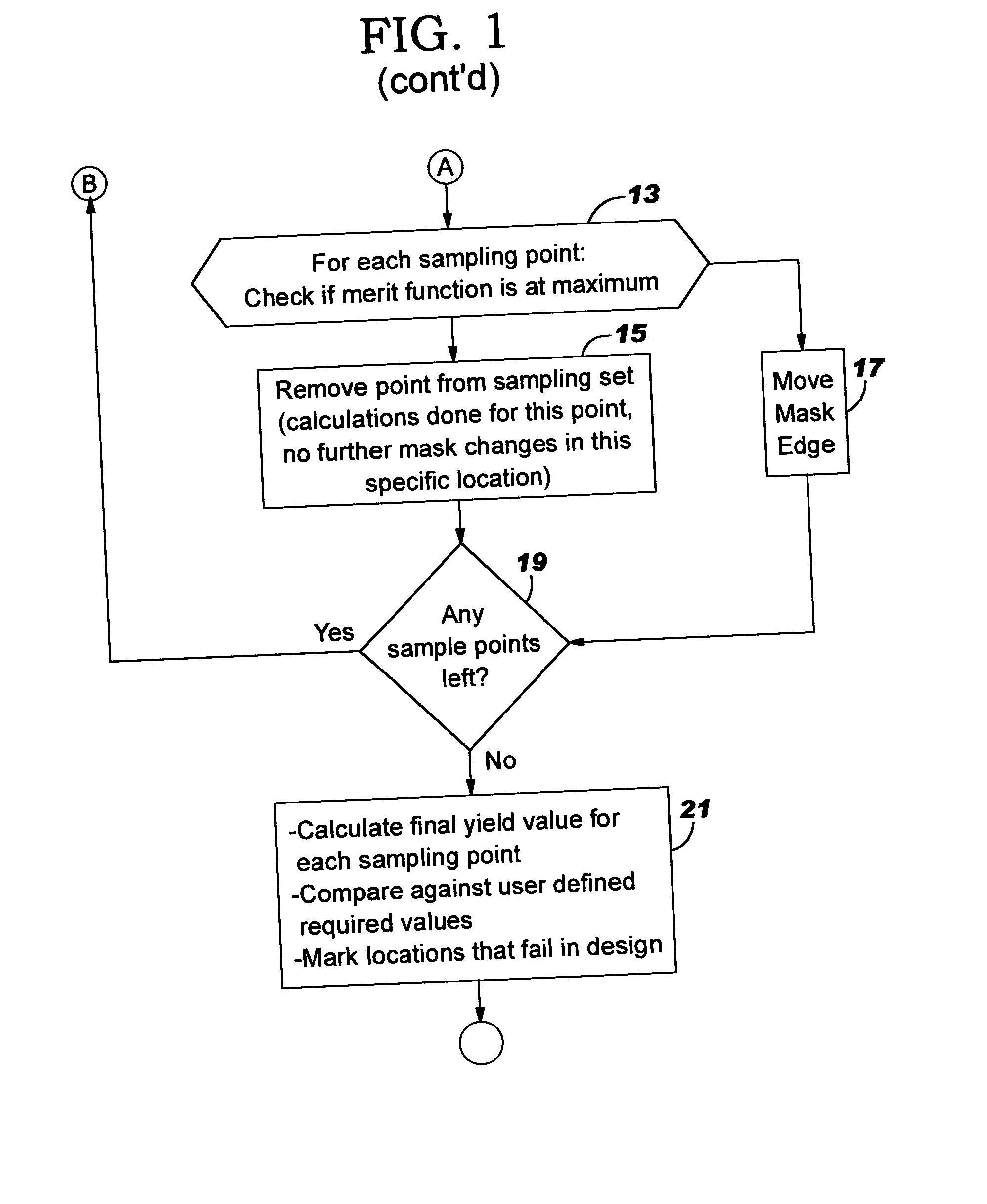
Method for interlayer and yield based optical proximity correction
InactiveUS6961920B2Improve lithographic processIncrease proximityPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMerit function
An optical proximity correction method is provided using a modified merit function based upon yield. Known failure mechanisms related to layout geometries are used to derive yield functions based upon distance values between layout features, such as, edge features. In comparing the edge points on the predicted layout pattern with the corresponding point on the design layout pattern, a yield test is first undertaken before movement of the points on the predicted layout pattern to a position of higher yield. Where yield is acceptable, no further movement is made. Where incremental movement of points results in coming within acceptable proximity before acceptable yield is reached, the point is flagged for further consideration.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Systems, Masks, and Methods for Photolithography
ActiveUS20070184357A1Improve efficiencyPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentPattern recognitionLithography process
Photomask patterns are represented using contours defined by mask functions. Given target pattern, contours are optimized such that defined photomask, when used in photolithographic process, prints wafer pattern faithful to target pattern. Optimization utilizes “merit function” for encoding aspects of photolithographic process, preferences relating to resulting pattern (e.g. restriction to rectilinear patterns), robustness against process variations, as well as restrictions imposed relating to practical and economic manufacturability of photomasks.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Optimized photomasks for photolithography
InactiveUS7480889B2Character and pattern recognitionCAD circuit designPattern recognitionComputer science
Owner:KLA CORP
Ophthalmic lenses capable of reducing chromatic aberration
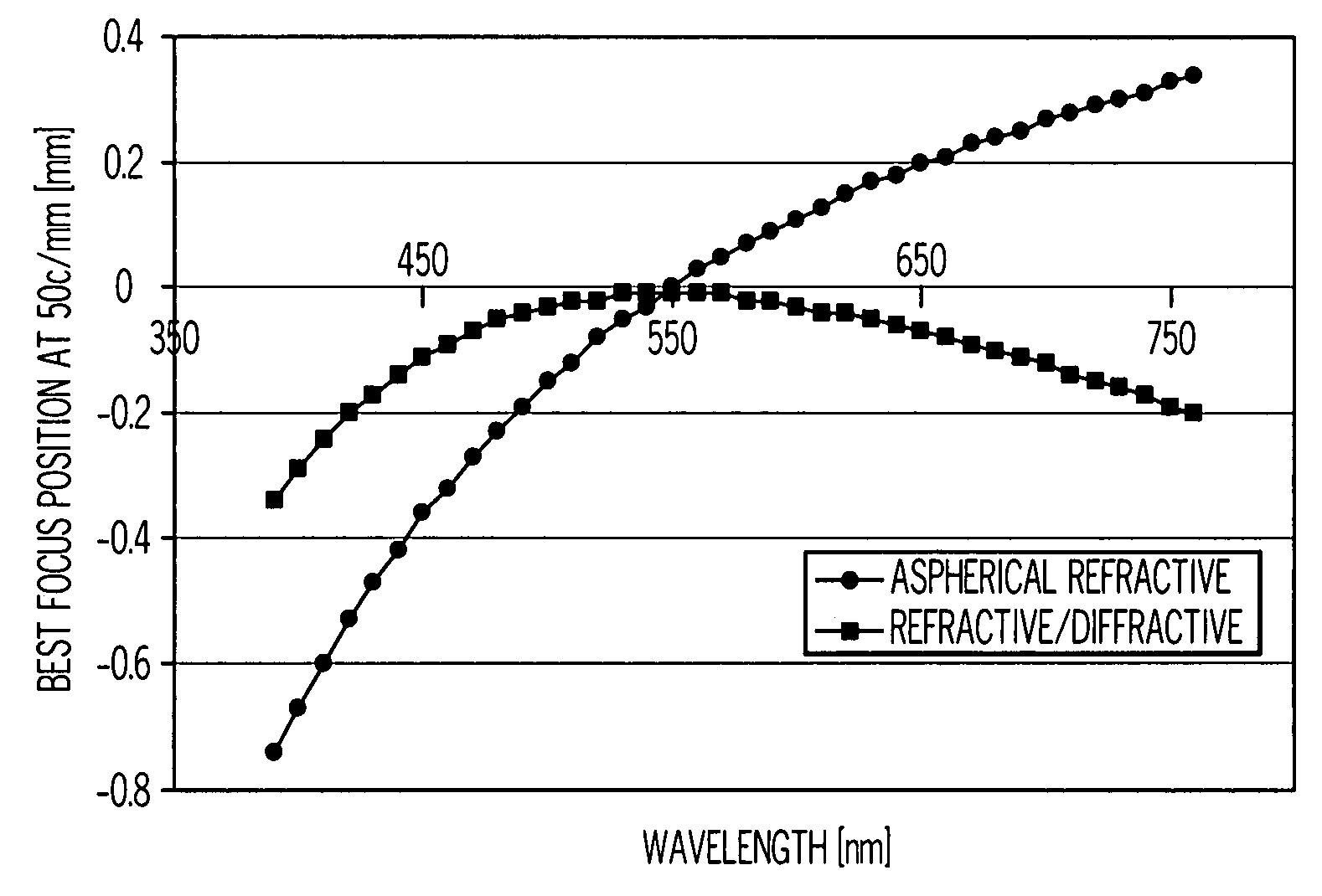
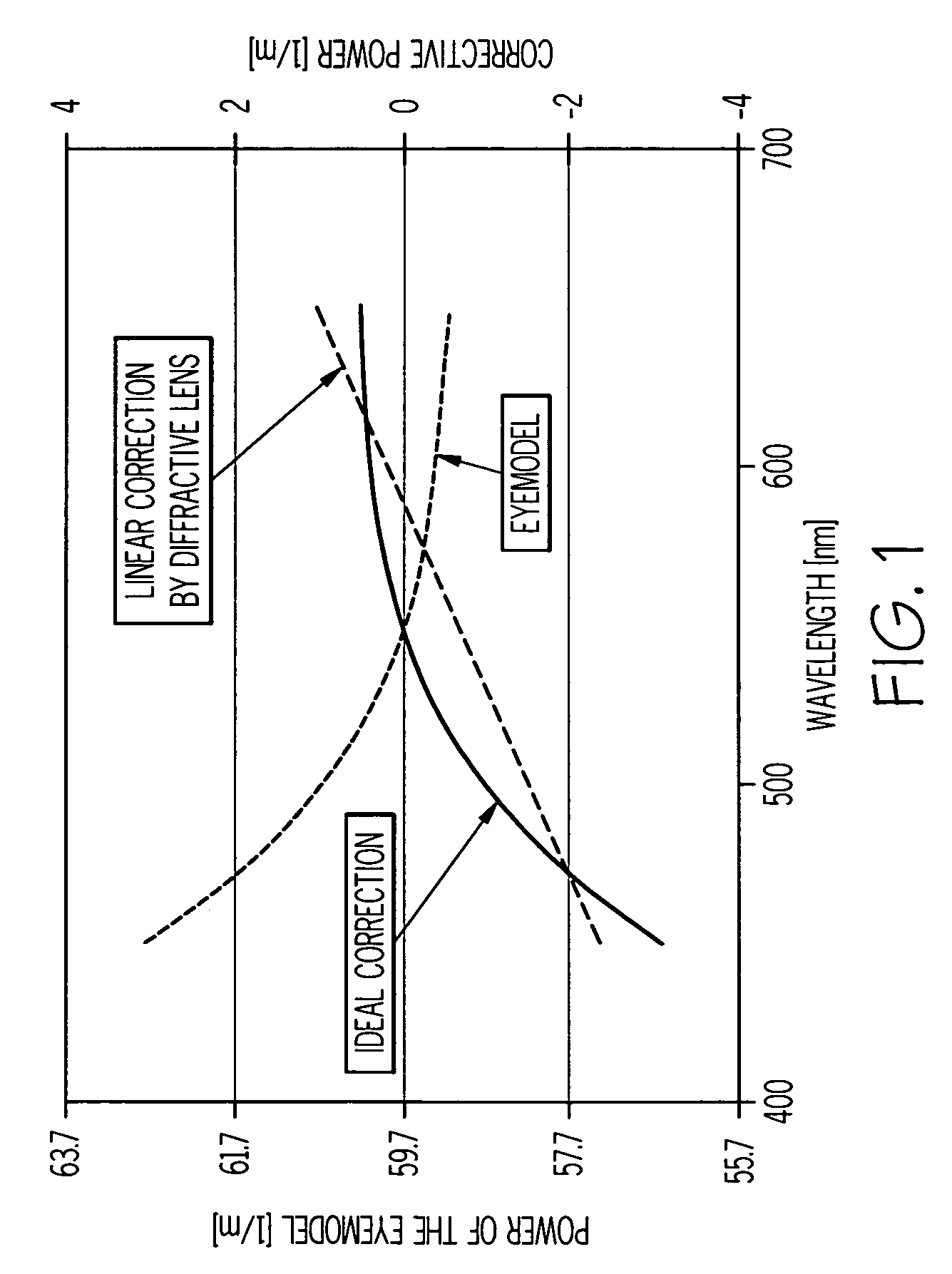
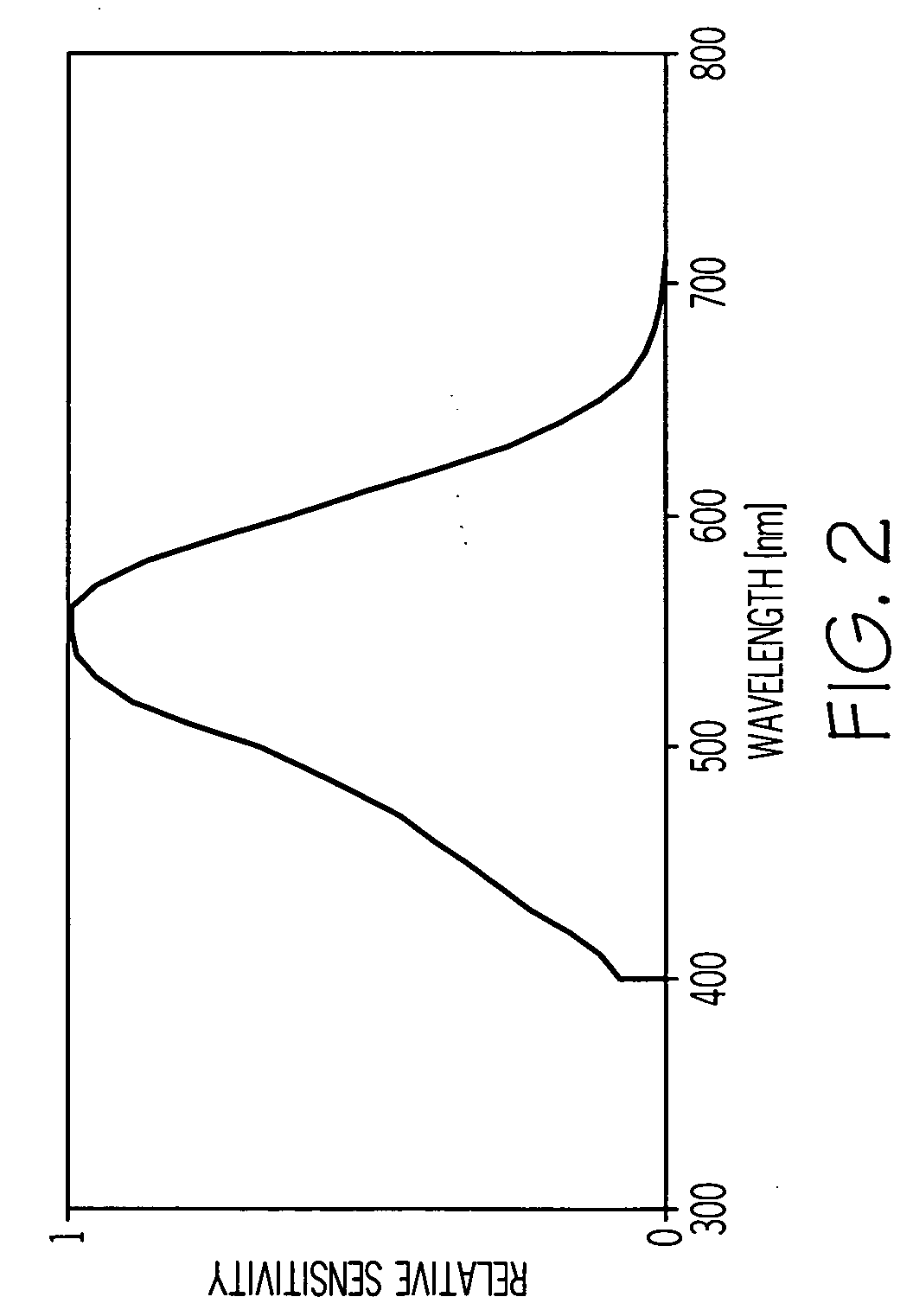
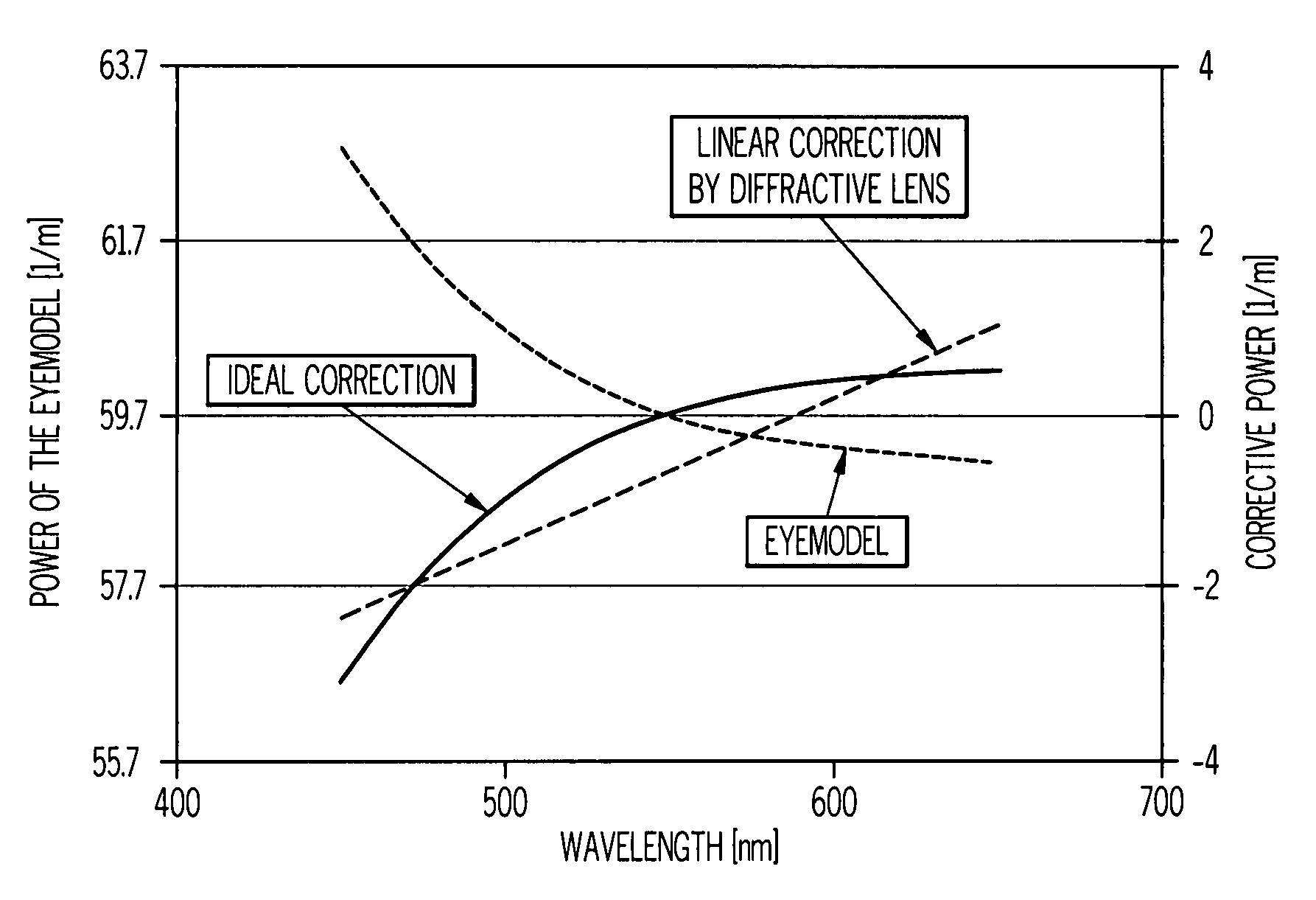
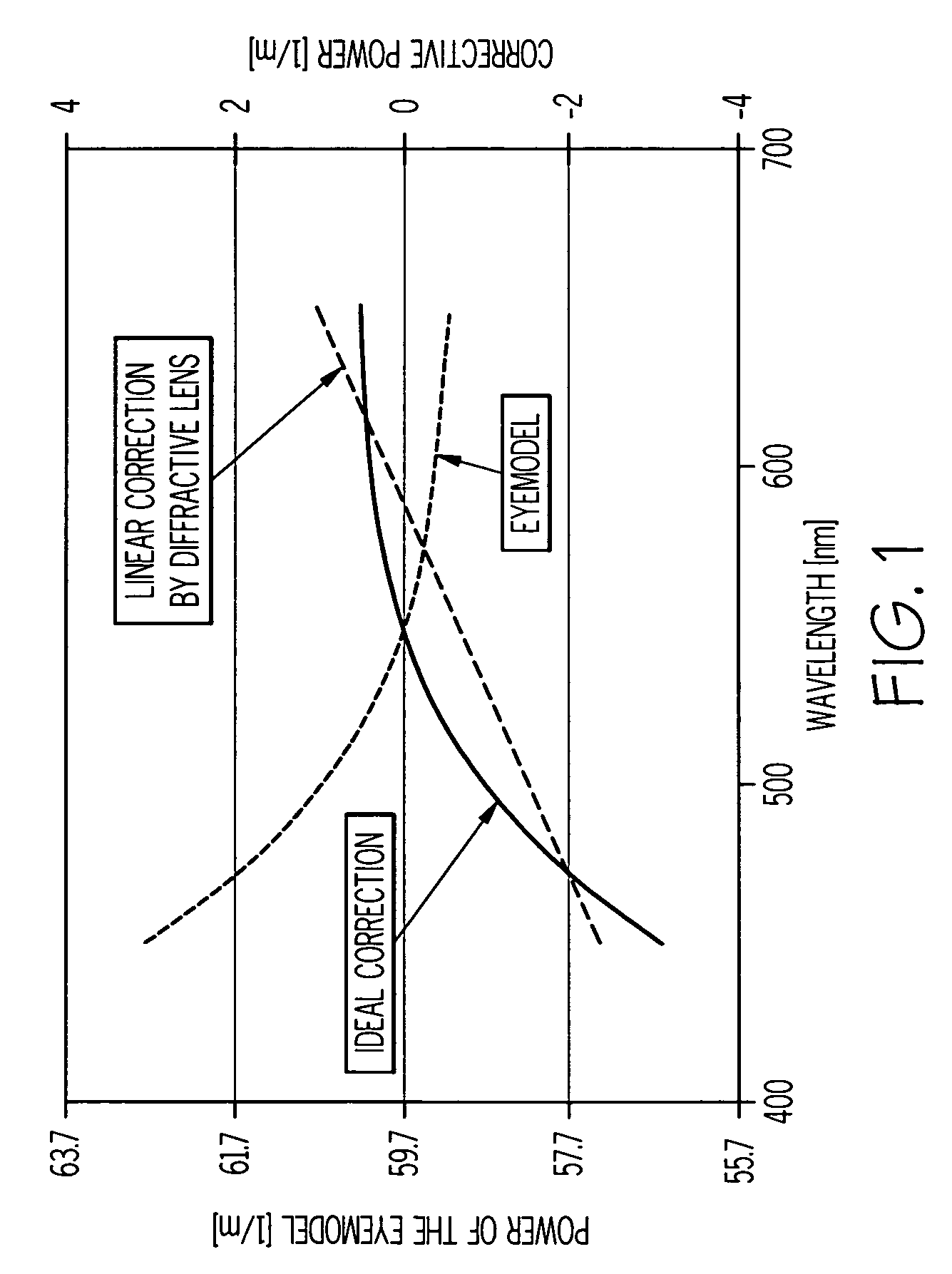
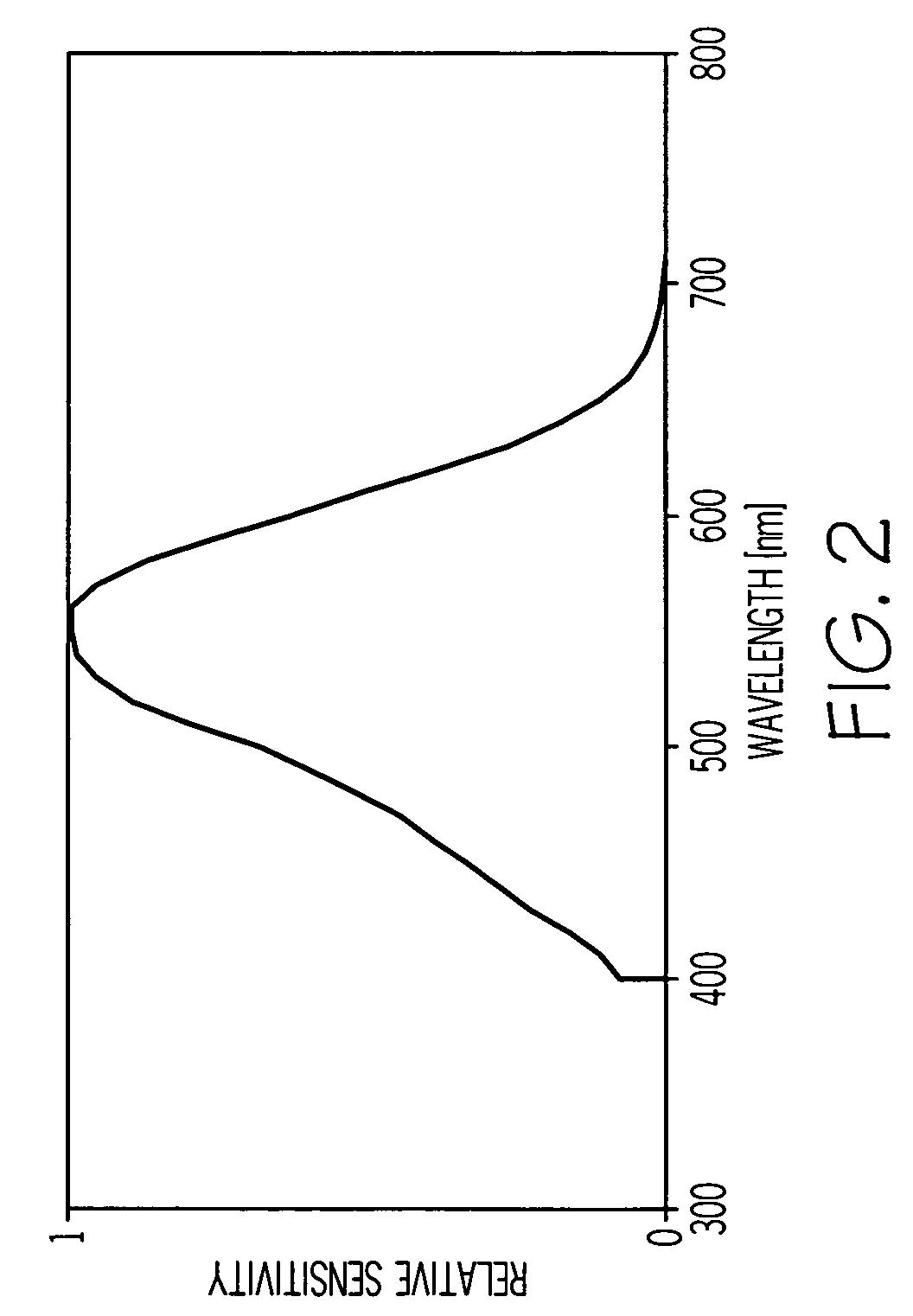
ActiveUS20070002444A1Improve visual qualityIncrease capacitySpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsImaging qualityEye lens
A method of designing an aspheric ophthalmic lens with both refractive and diffractive powers that is capable of reducing chromatic aberration and at least one monochromatic aberration of an eye comprises combining aspherical refractive and diffractive surfaces, selecting an appropriate eye model, establishing a design lens having at least one aspheric surface with a capacity to reduce monochromatic aberration in said eye model, establishing a diffractive lens element that corrects for chromatic aberration of the model eye; and adjusting the lens surface design in order to obtain a suitably high polychromatic image quality in a form that is weighted to comply with a spectral merit function.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Ophthalmic lenses capable of reducing chromatic aberration
ActiveUS7677725B2Improve visual qualityIncrease capacitySpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsImaging qualityEye lens
A method of designing an aspheric ophthalmic lens with both refractive and diffractive powers that is capable of reducing chromatic aberration and at least one monochromatic aberration of an eye comprises combining aspherical refractive and diffractive surfaces, selecting an appropriate eye model, establishing a design lens having at least one aspheric surface with a capacity to reduce monochromatic aberration in said eye model, establishing a diffractive lens element that corrects for chromatic aberration of the model eye; and adjusting the lens surface design in order to obtain a suitably high polychromatic image quality in a form that is weighted to comply with a spectral merit function.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Optimized intraocular lens
InactiveUS20090292354A1Improve visual acuityImproved peripheral visionSurgeryEye diagnosticsCamera lensIntraocular lens
An optimized aspheric lens has improved optics when implanted into a patient having a curved retina. Light entering the optimized aspheric lens on-axis or at an angle to the optical axis is properly focused by the lens, reducing aberrations and producing a much smaller spot size of light on the retina. A method of selecting the optimized values for variables of the lens design, such as base radii of the front and back surface of the lens, conic constants of the front and back surfaces, and / or center thickness of the lens, among other possible parameters is provided. The method includes calculating changes in a merit function while changing the various values for the variables and selecting an optimized merit function.
Owner:STAAR SURGICAL COMPANY INC
Shaped non-corrective eyewear lenses and methods for providing same
ActiveUS20050122470A1Simplify mathematical constructionGood optical performanceOptical partsAxis of symmetryEyeglass lenses
The disclosure relates to shaped ophthalmic lenses and methods for providing such lenses, including non-powered lenses having non-quadratic surfaces of complementary curvature. Such lenses may have a curvature maximum away from an axis of symmetry and a substantially constant wall thickness. Equations describing and methods of designing such lenses are disclosed including embodiments where two spheres of substantially different curvature are merged in accordance with a weighting function, and adjusted using merit functions.
Owner:CARL ZEISS VISION AUSTRALIA HO
System, masks, and methods for photomasks optimized with approximate and accurate merit functions
ActiveUS7703049B2CAD circuit designOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputer scienceMerit function
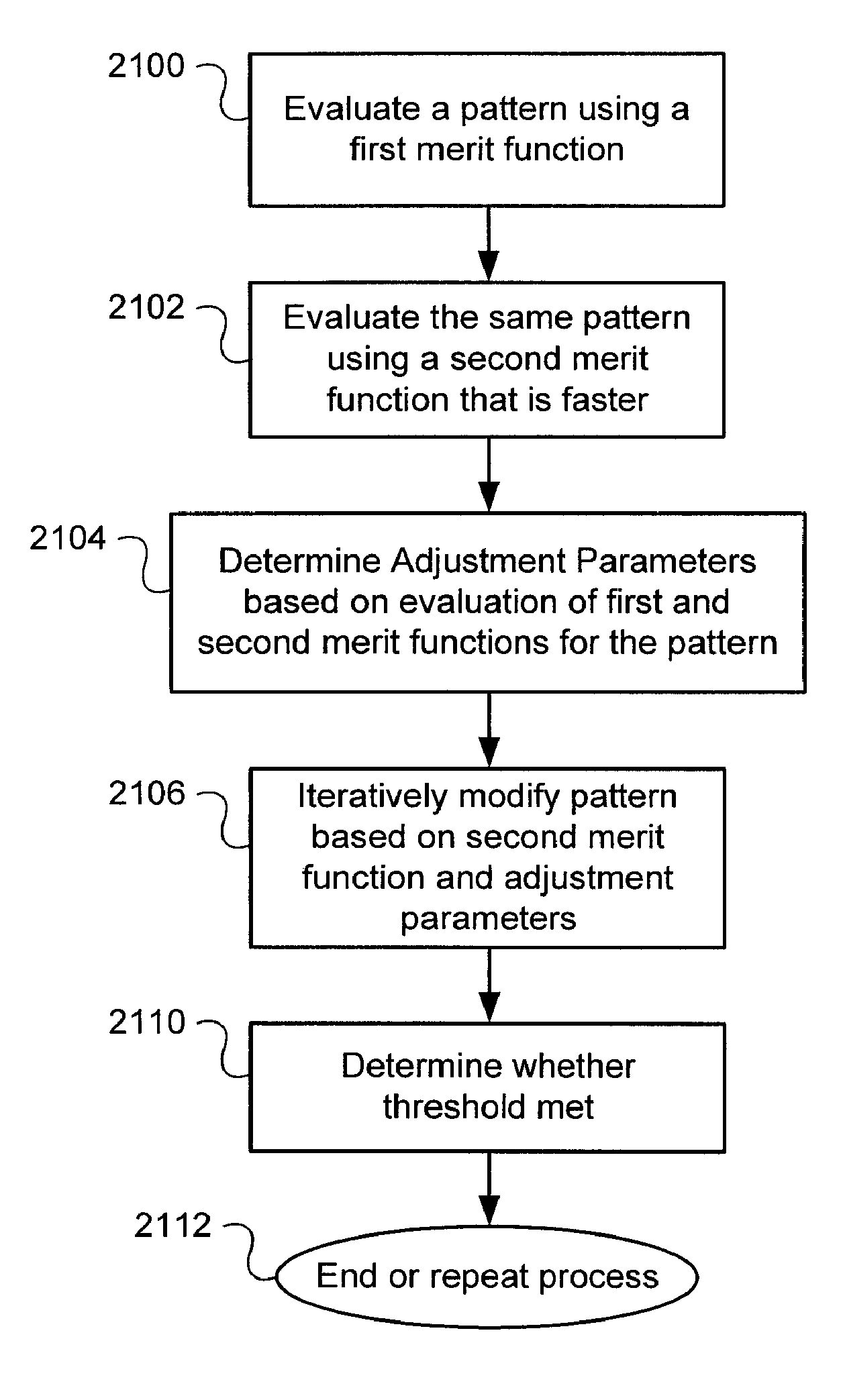
Photomask patterns are represented using contours defined by mask functions. Given target pattern, contours are optimized such that defined photomask, when used in photolithographic process, prints wafer pattern faithful to target pattern. Optimization utilizes “merit function” for encoding aspects of photolithographic process, preferences relating to resulting pattern (e.g. restriction to rectilinear patterns), robustness against process variations, as well as restrictions imposed relating to practical and economic manufacturability of photomasks. An accurate, slower merit function may be used to determine adjustment parameters for a faster, approximate merit function. The faster merit function may be used for iteration and adjusted based on the adjustment parameters.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
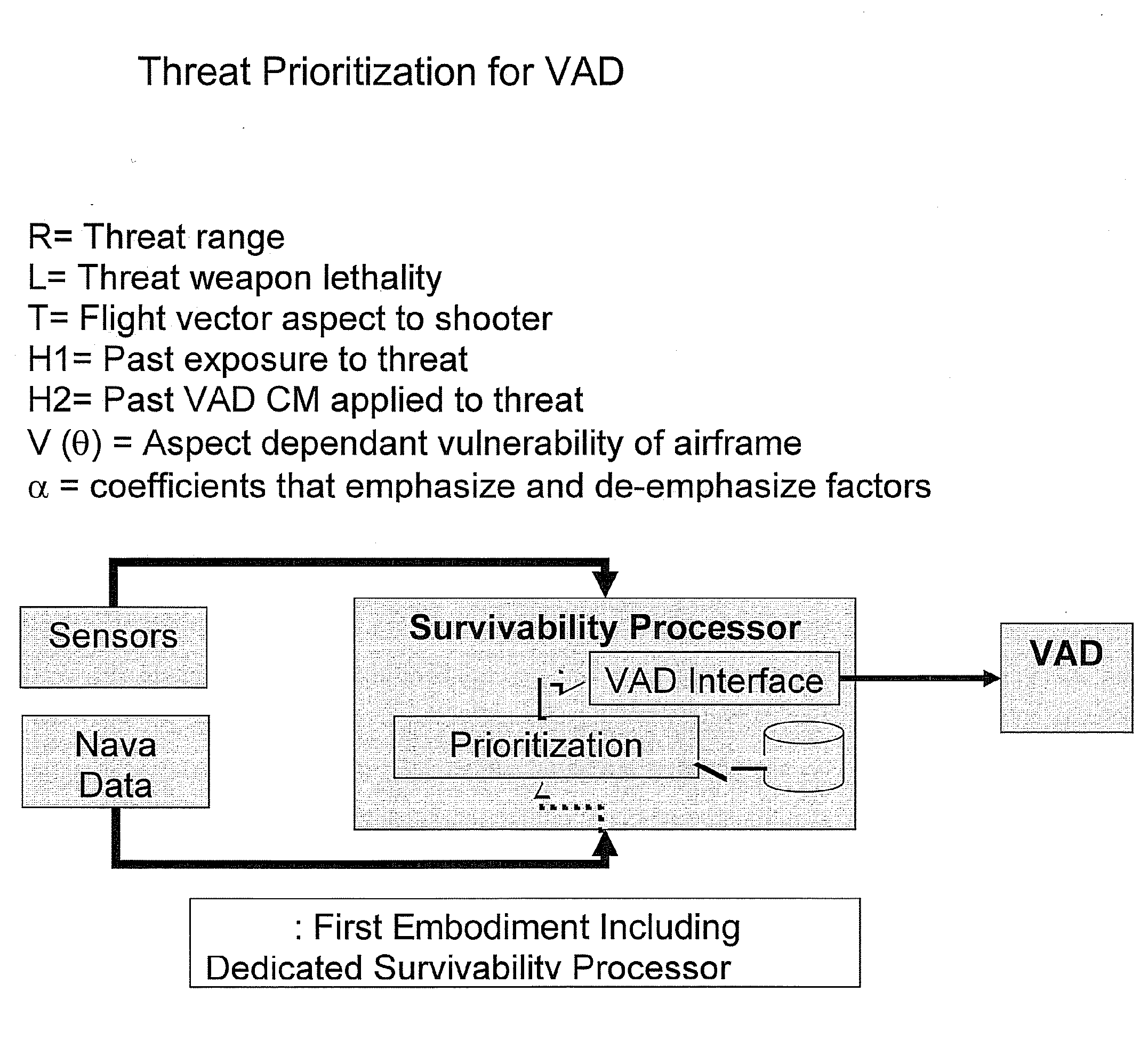
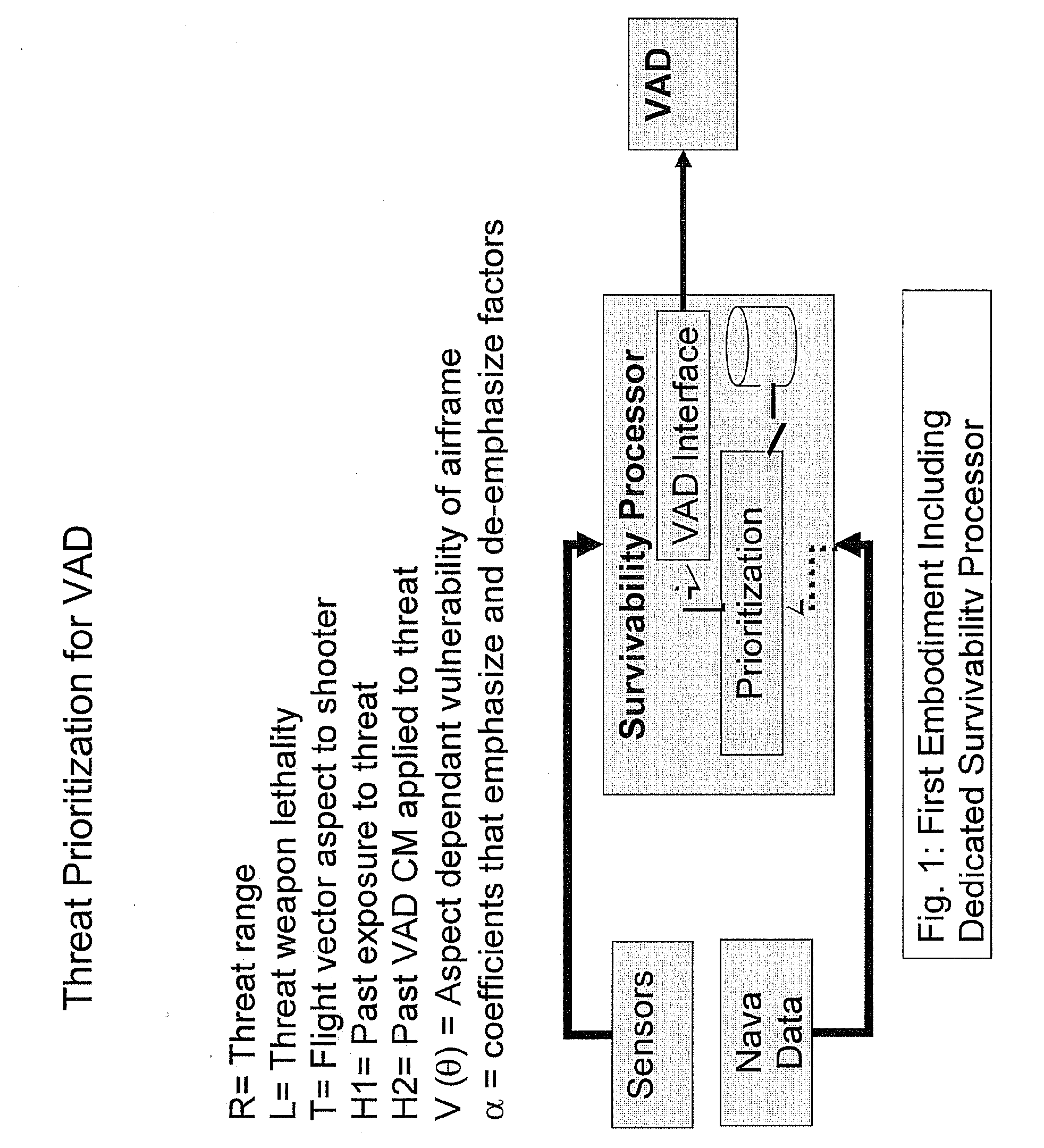
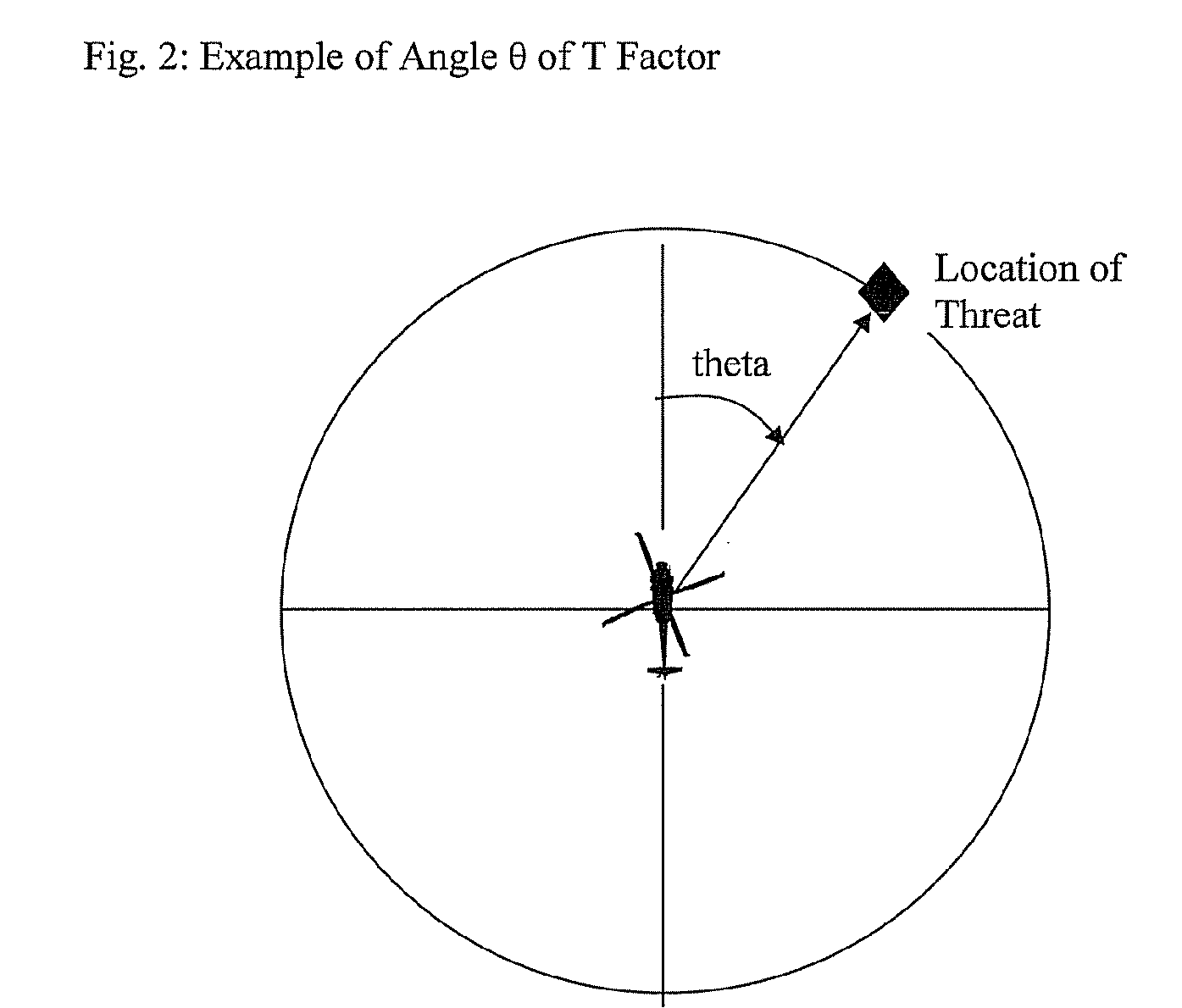
System and method for prioritizing visually aimed threats for laser-based countermeasure engagement
ActiveUS20090173788A1Improve efficiencyImprove survivabilityDefence devicesAiming meansCountermeasureSurvivability
The present invention increases the survivability of a helicopter by prioritizing a threat engagement sequence for a laser-based countermeasure system based on the determined relative lethality of each detected visually trained threat (e.g., small arms fire). The system and method defines a plurality of threat effectiveness merit factors, or lethality factors, that are determinable from available helicopter navigation and sensor data, to quantify the danger associated with each detected threat. The system and method then combines the defined lethality factors using a mathematical function, such as a merit function, to numerically quantify the level of threat posed by each threat. The calculated threat values for each of the detected threats are compared to prioritize the threats for engagement by a laser-based countermeasure system, such as a Visual Acquisition Disrupter (VAD) system.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Lens systems for presbyopia
A family of ophthalmic lenses for correcting presbyopia meets constraints for distance vision, near vision, and disparity and may be designed according to a process that incorporates a merit function accounting for binocular visual performance.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Method for interlayer and yield based optical proximity correction
InactiveUS20050066300A1Improve lithographic processEasy to optimizePhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMerit function
An optical proximity correction method is provided using a modified merit function based upon yield. Known failure mechanisms related to layout geometries are used to derive yield functions based upon distance values between layout features, such as, edge features. In comparing the edge points on the predicted layout pattern with the corresponding point on the design layout pattern, a yield test is first undertaken before movement of the points on the predicted layout pattern to a position of higher yield. Where yield is acceptable, no further movement is made. Where incremental movement of points results in coming within acceptable proximity before acceptable yield is reached, the point is flagged for further consideration.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
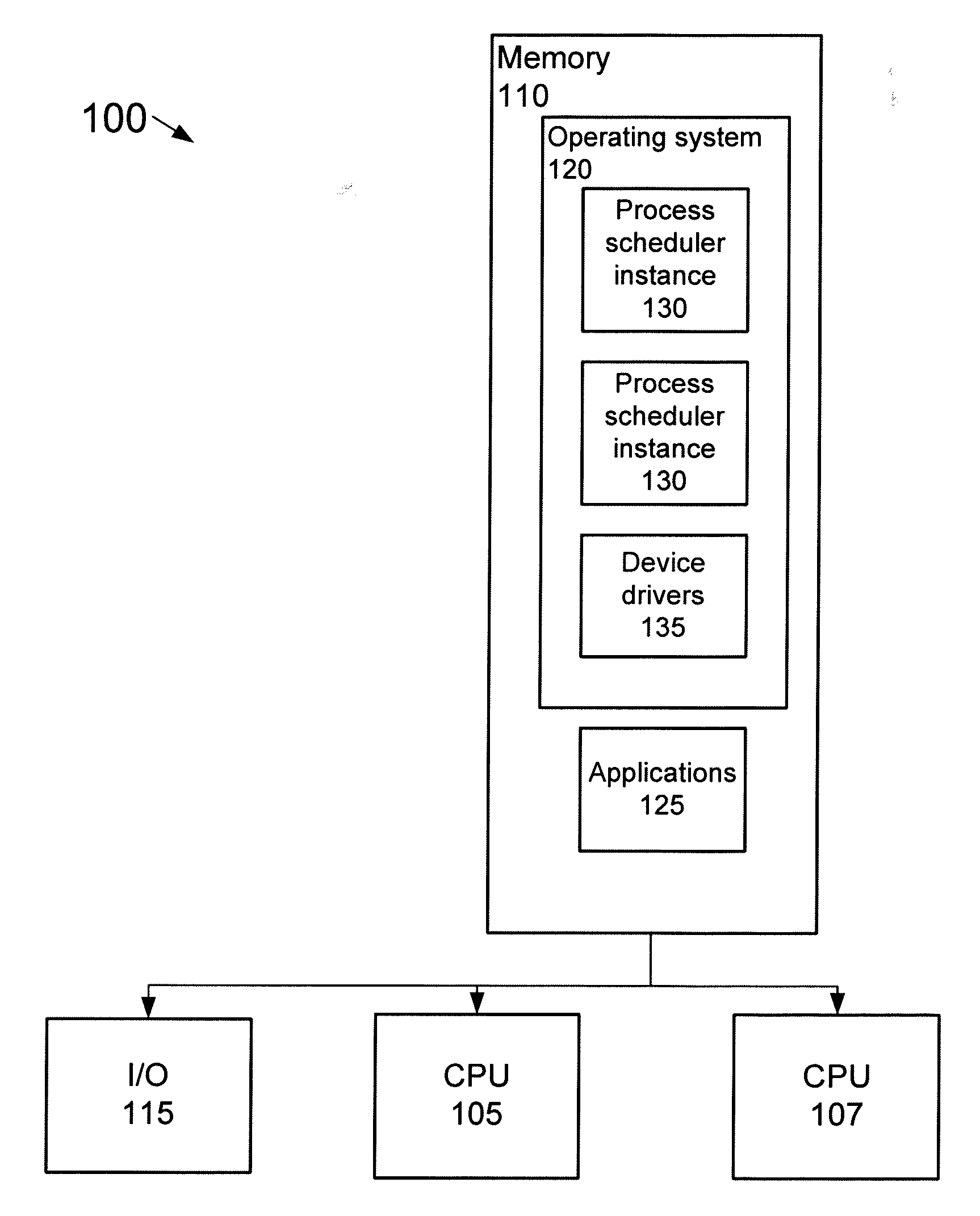
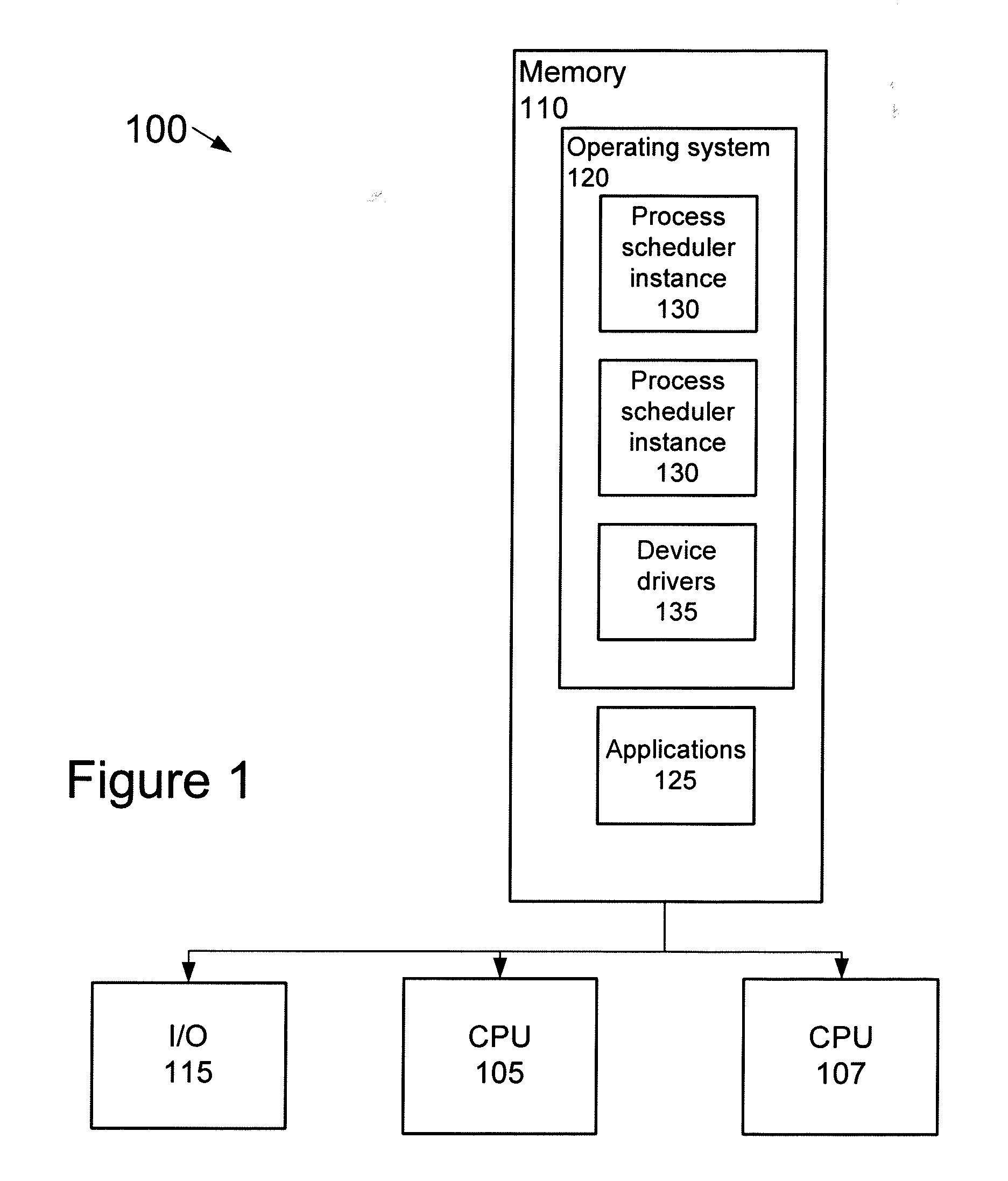
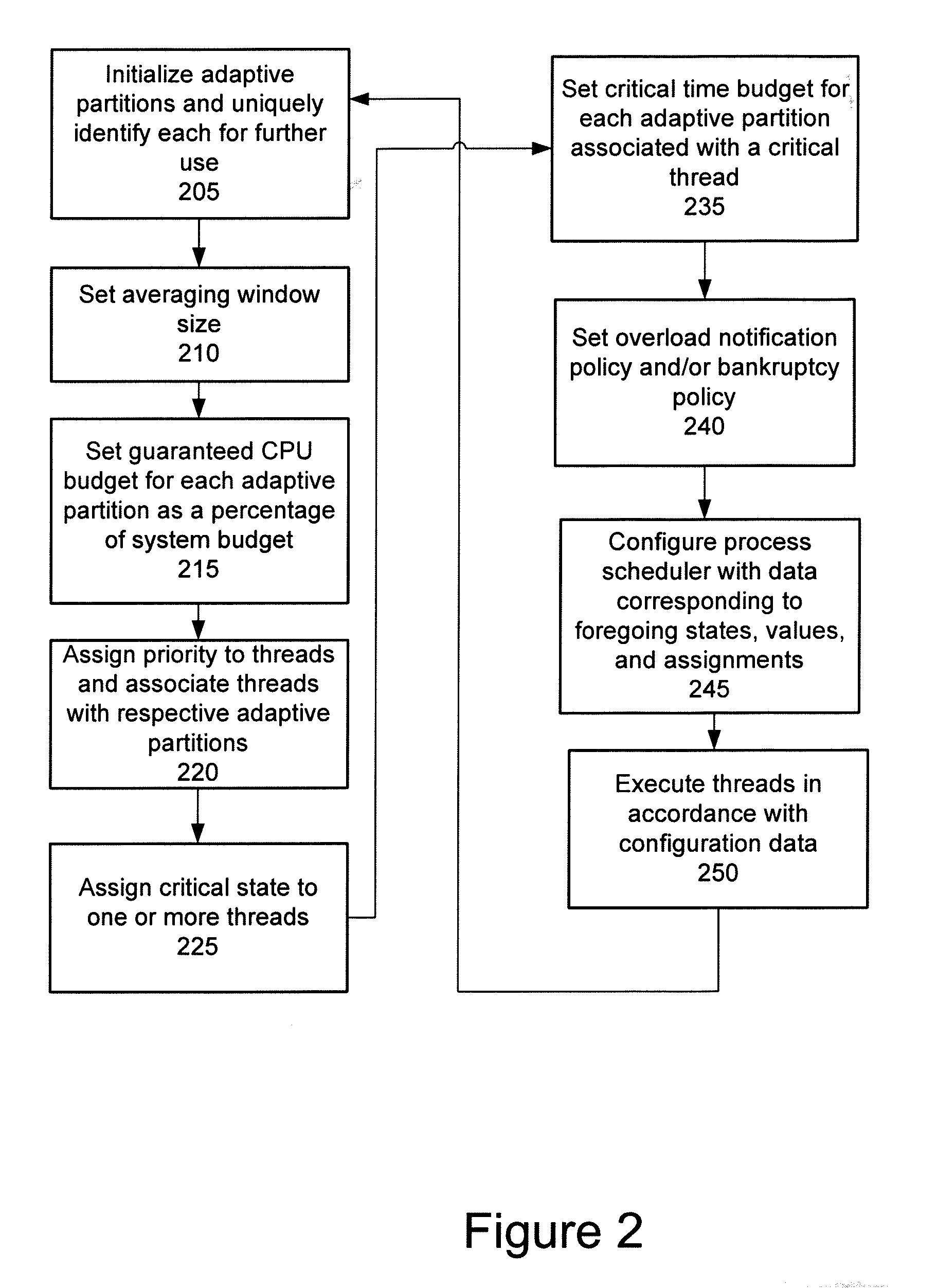
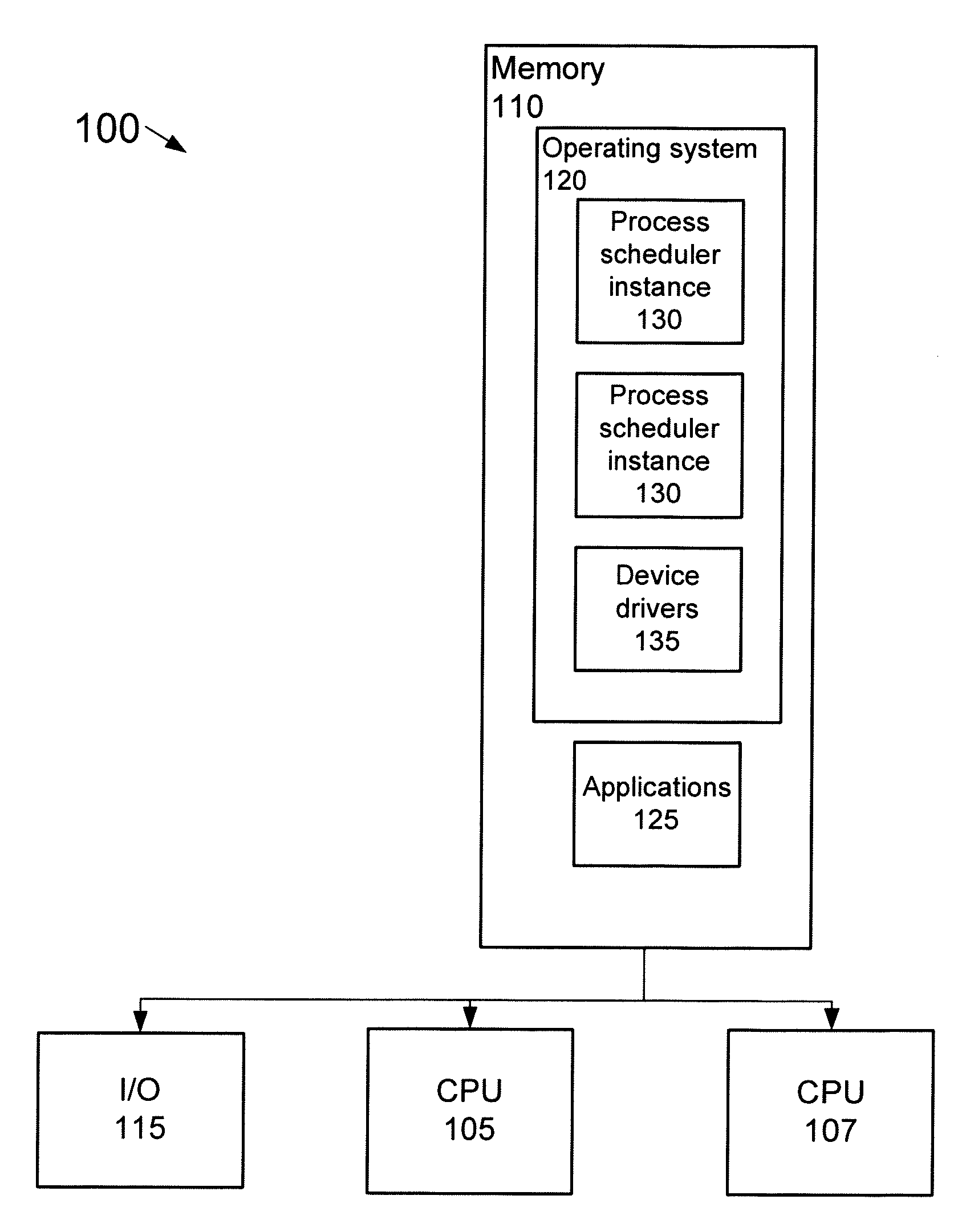
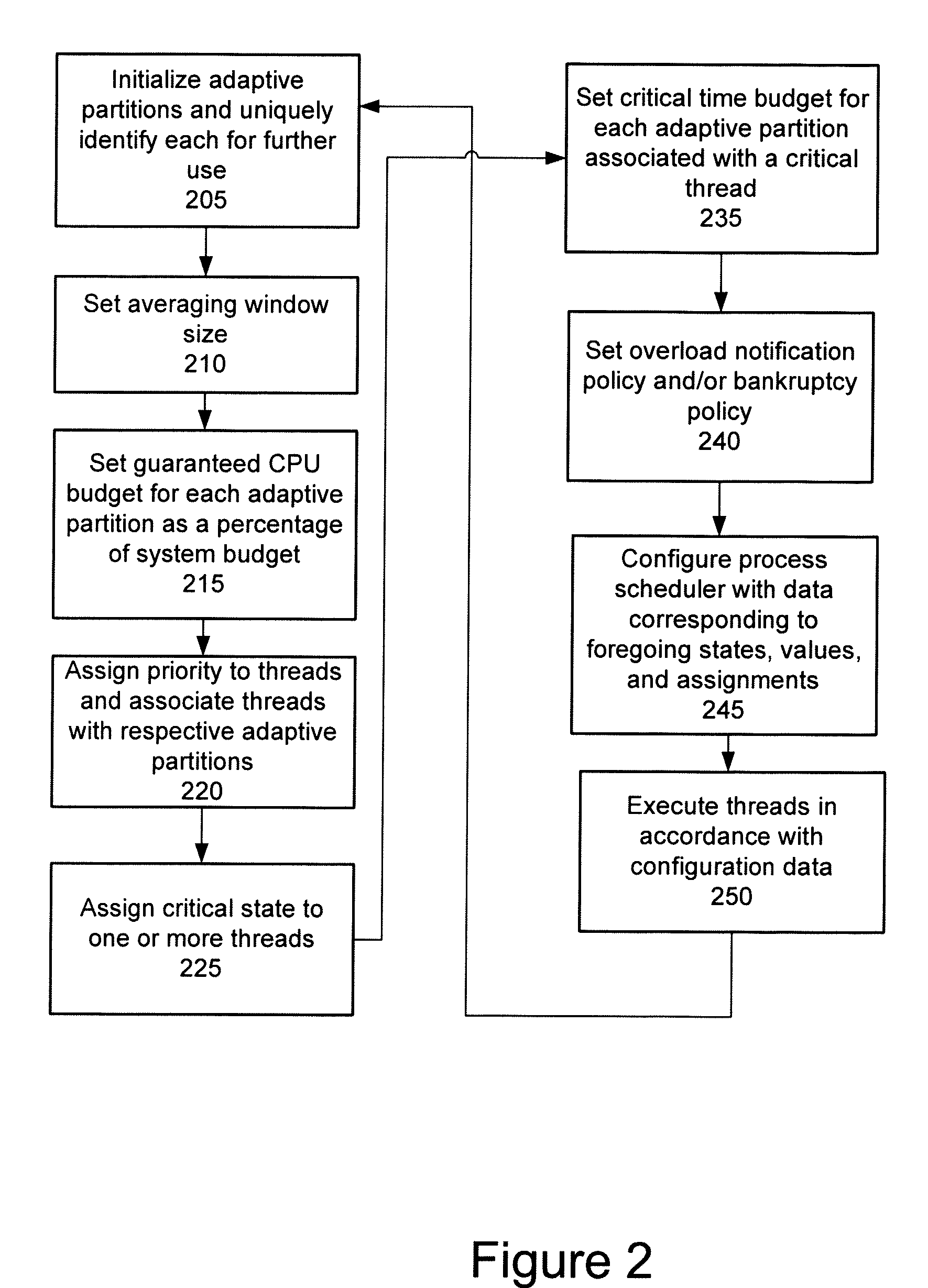
Adaptive partitioning scheduler for multiprocessing system
A symmetric multiprocessing system includes multiple processing units and corresponding instances of an adaptive partition processing scheduler. Each instance of the adaptive partition processing scheduler selectively allocates the respective processing unit to run process threads of one or more adaptive partitions based on a comparison between merit function values of the one or more adaptive partitions. The merit function for a particular partition of the one or more adaptive partitions may be based on whether the adaptive partition has available budget on the respective processing unit. The merit function for a particular partition associated with an instance of the adaptive partition scheduler also, or in the alternative, may be based on whether the adaptive partition has available global budget on the symmetric multiprocessing system.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
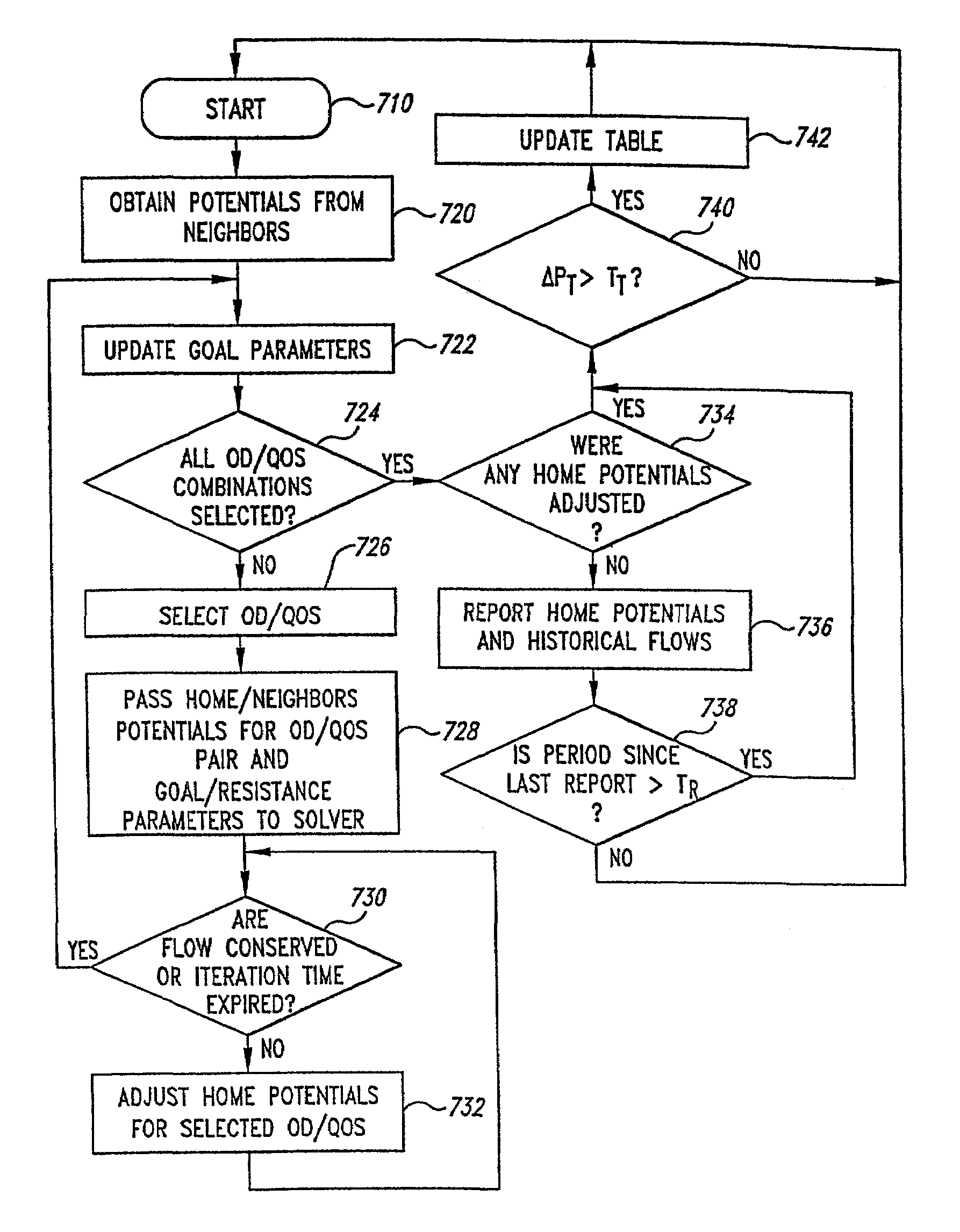
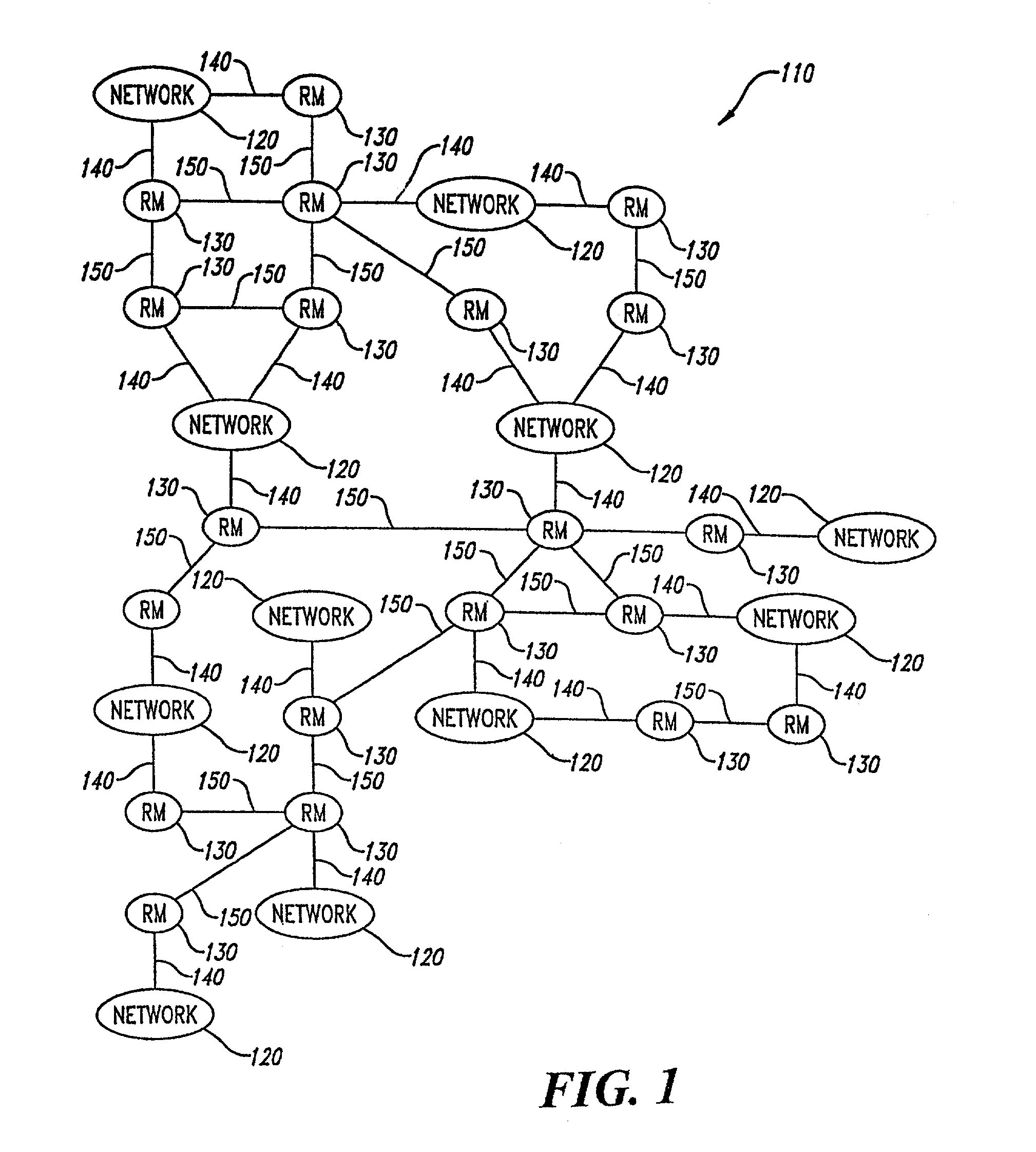
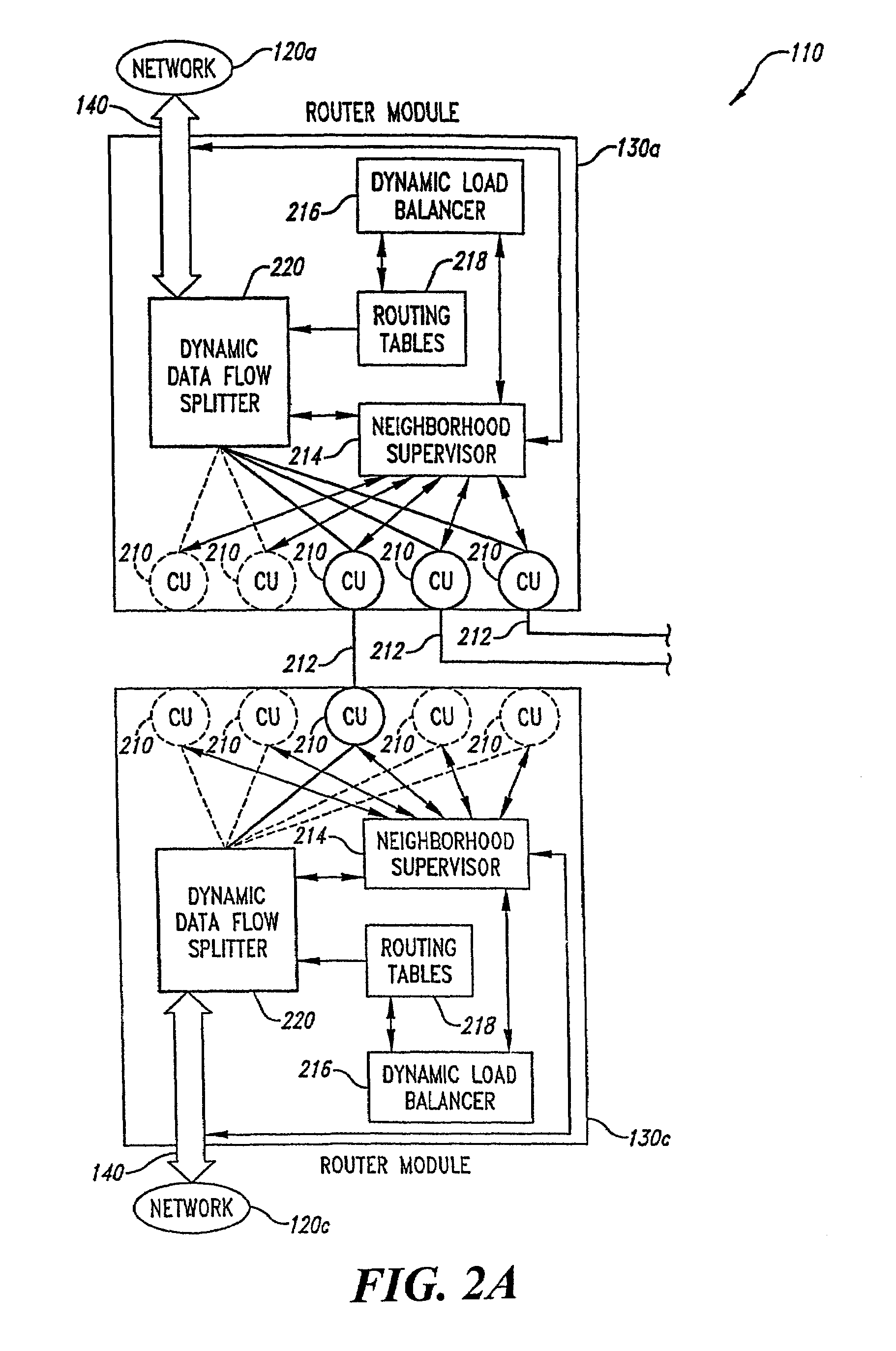
Network traffic director system having modules that implement merit or penalty functions involving stochastic changes in network topology
ActiveUS7020147B1Antenna adaptation in movable bodiesWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemTransceiver
A spontaneous data communication network includes antenna / transceiver sets located in mobile (e.g., vehicles such as cars, buses, trucks, ferries, etc.) or stationary units (e.g., computers, manufacturing equipment, office furniture, office equipment, road signs, overpasses, bridges, etc.). Each antenna / transceiver set directs network traffic based on optimizing a merit function or penalty function to reduce costs of congestion for stochastically changing demands and flows in a data communication system. The routers exchange values with neighboring routers. Based on the exchanged values and values local to a router, flow conditions are checked and if necessary the local values are adjusted until the flow conditions are satisfied or a time period expires. Adjustments are associated with optimizing a merit function or penalty function. Based on the adjusted values, the router adjusts parameters to be used to direct packets of the network traffic flows to other routers or other destinations within the data communication system. An aggregation scheme is used for reducing the number of values stored in a single router module.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
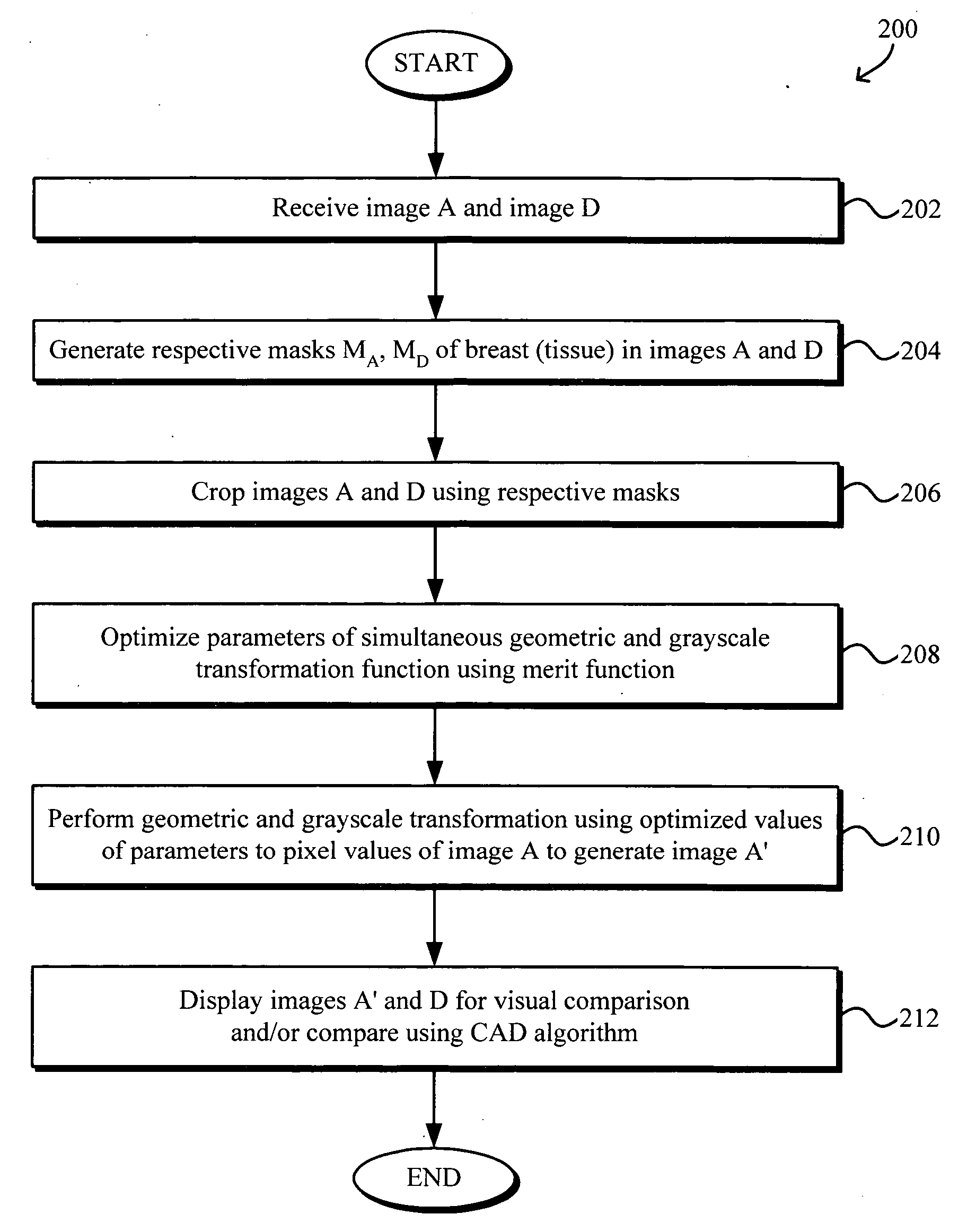
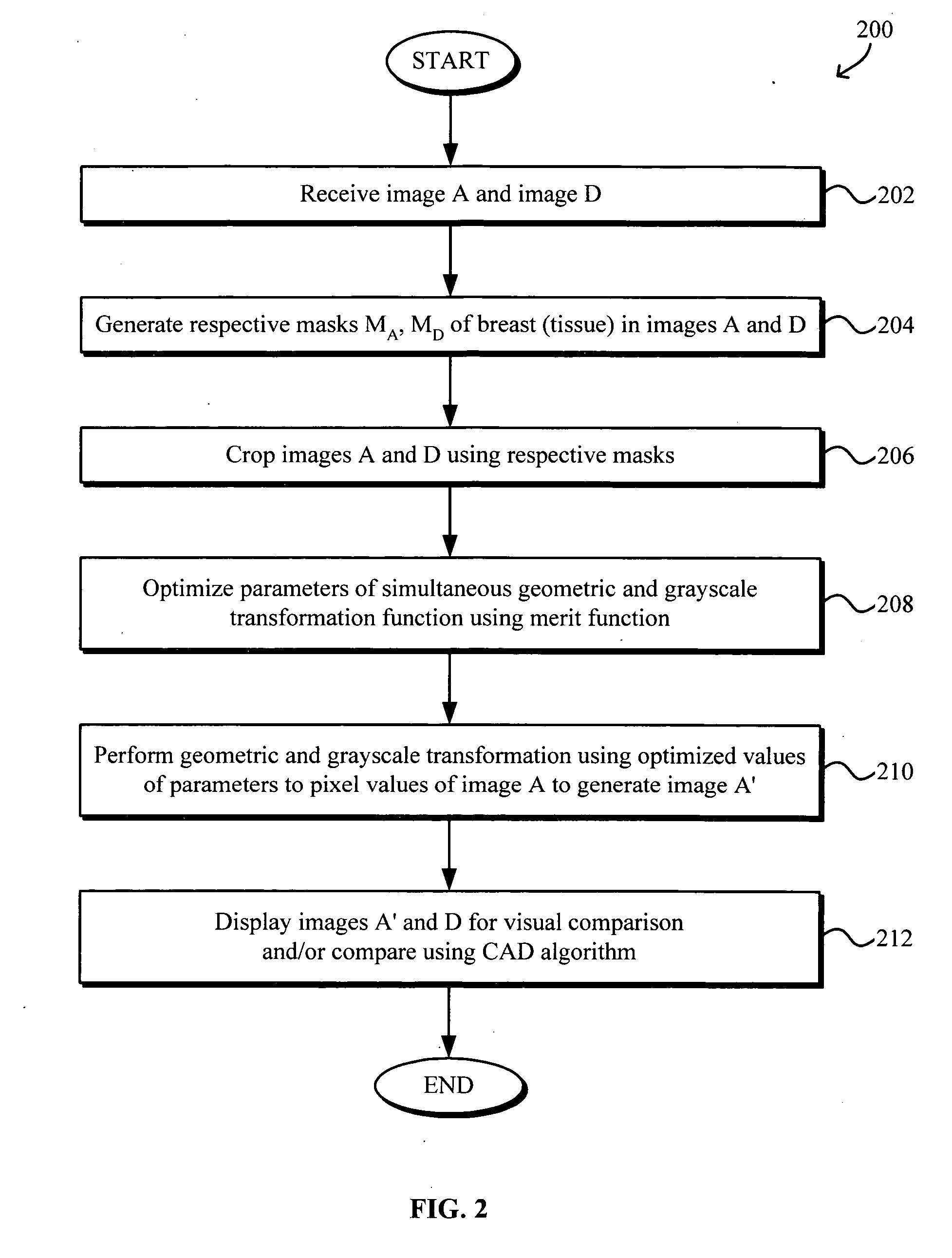
Simultaneous grayscale and geometric registration of images
InactiveUS20050163360A1Improve reliabilityIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionAlgorithm
Simultaneous grayscale and geometric registration of images, such as mammograms, facilitates temporal comparison and enhances the speed and reliability of computer aided diagnosis (CAD) detection of medical abnormalities. The method generally includes optimizing a merit function, e.g., sum of squared errors, containing parameters associated with a transformation function for simultaneous geometric and grayscale registering of the images, the optimizing of the merit function being performed by determining optimal values of the parameters using data in the images and registering one image to the other by applying the geometric and grayscale transformation function using the optimal values of the parameters. The optimizing may be performed iteratively from coarse to fine resolutions using a modified Levenberg-Marquardt method for optimizing nonlinear parameters with linear regression for optimizing linear parameters. A final iteration may be performed after removing pixel value pairs from the images that correspond to outliers of a joint pixel value histogram.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
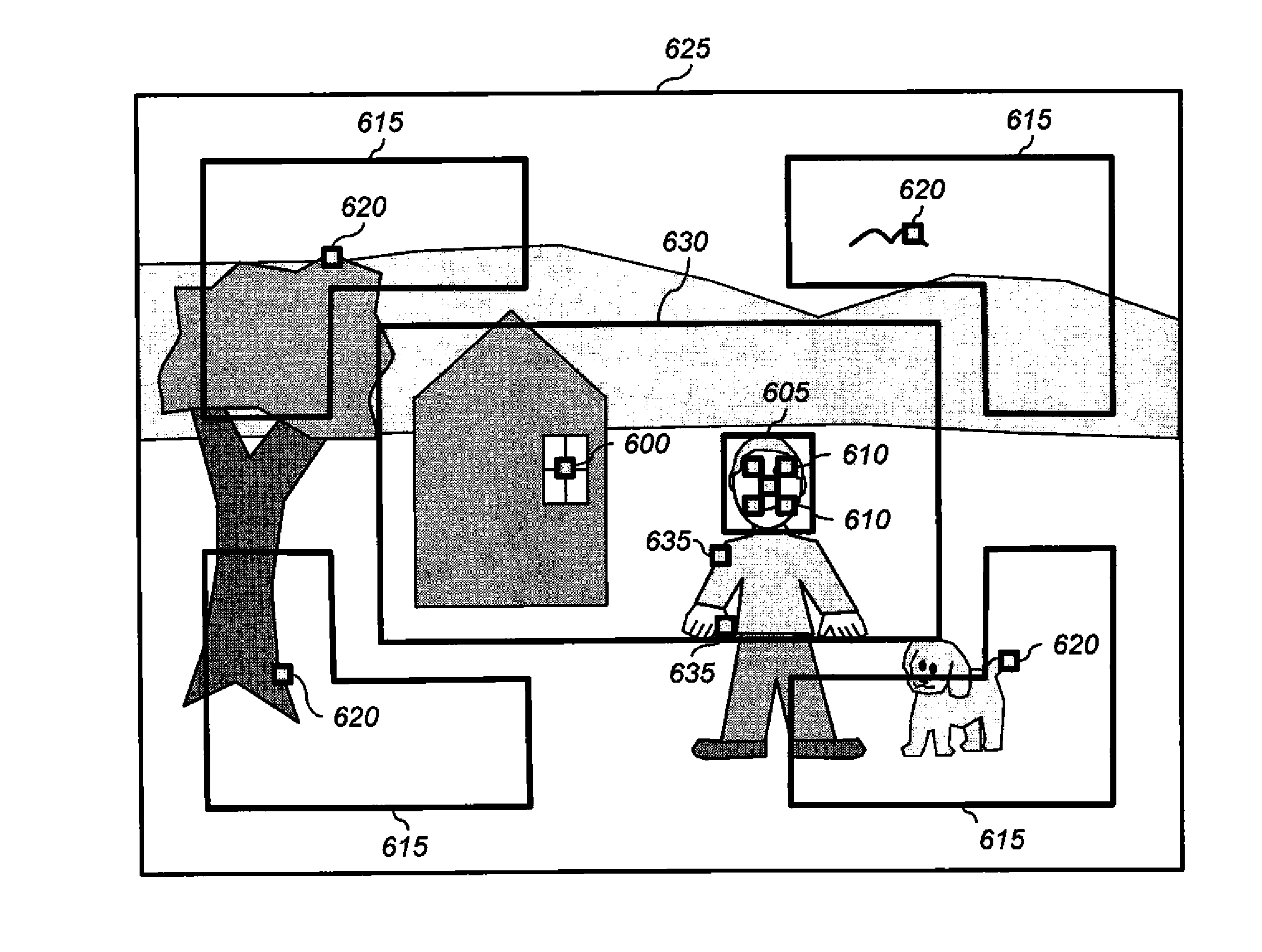
Estimating subject motion between image frames
InactiveUS20120201427A1High movement precisionImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionWeight coefficientDigital image
A method for determining a motion estimate, comprising: capturing at least two digital images of a scene at different capture times; designating one of the digital images as a reference digital image; designating a plurality of image regions; determining motion estimates for each image region by shifting the image regions within the non-reference digital images according to each of a plurality of spatial offsets relative to the image region within the reference digital image, computing merit function values for each spatial offset providing an indication of a difference between the image region in the reference digital image and the shifted image regions, computing a fitting function that provides an estimated merit function value as a function of spatial offset; and determining the motion estimate responsive to the determined non-integer spatial offset. A combined motion estimate is determined using weighting coefficients determined responsive to the shapes of the fitting functions.
Owner:APPLE INC
Optimized photomasks for photolithography
ActiveUS20070011644A1Character and pattern recognitionCAD circuit designPattern recognitionPhotolithography
Photomask patterns are represented using contours defined by level-set functions. Given target pattern, contours are optimized such that defined photomask, when used in photolithographic process, prints wafer pattern faithful to target pattern. Optimization utilizes “merit function” for encoding aspects of photolithographic process, preferences relating to resulting pattern (e.g. restriction to rectilinear patterns), robustness against process variations, as well as restrictions imposed relating to practical and economic manufacturability of photomasks.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Omnidirectional reflector
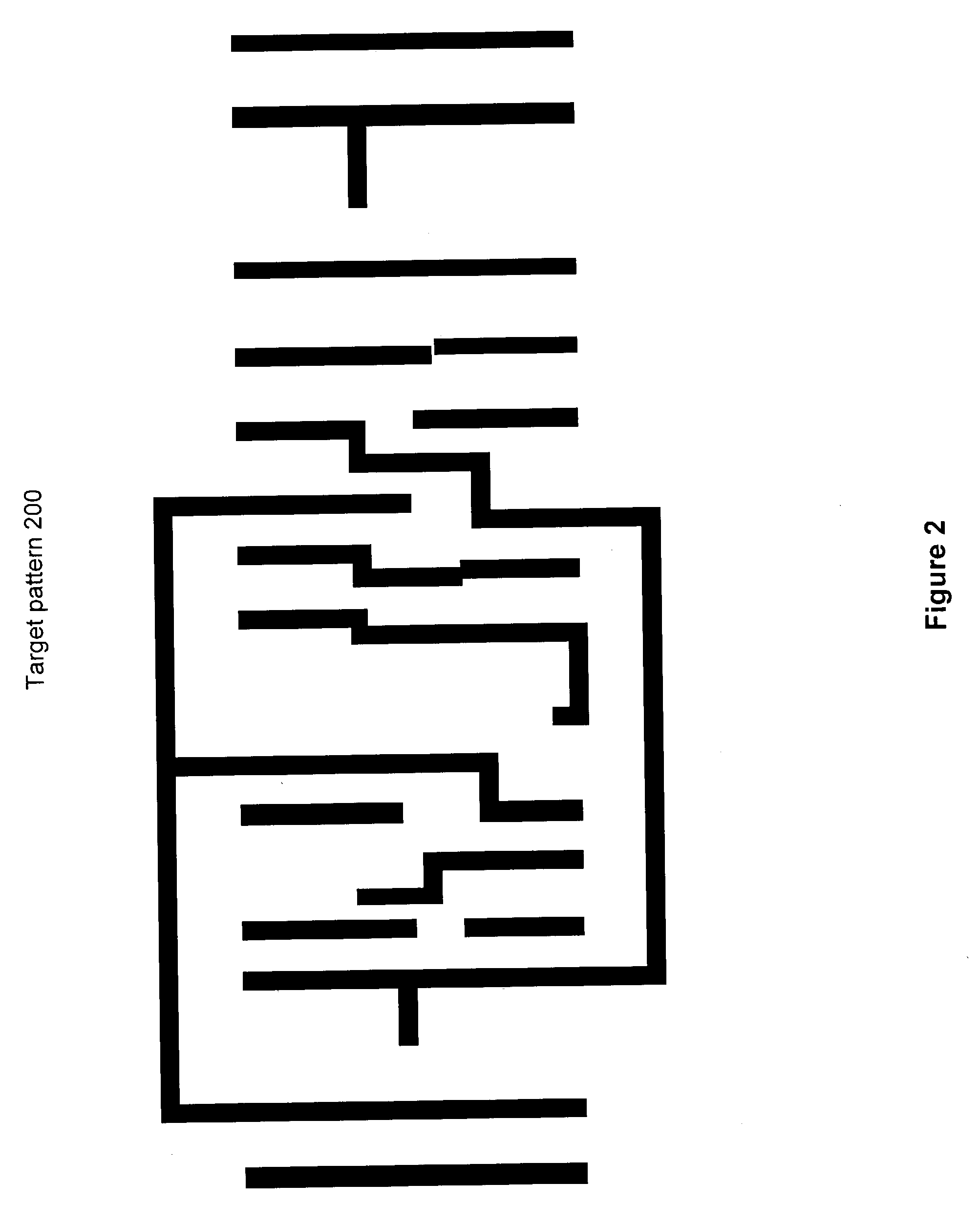
InactiveUS20120307369A1Increasing the thicknessSpecial data processing applicationsOptical elementsRefractive indexMerit function
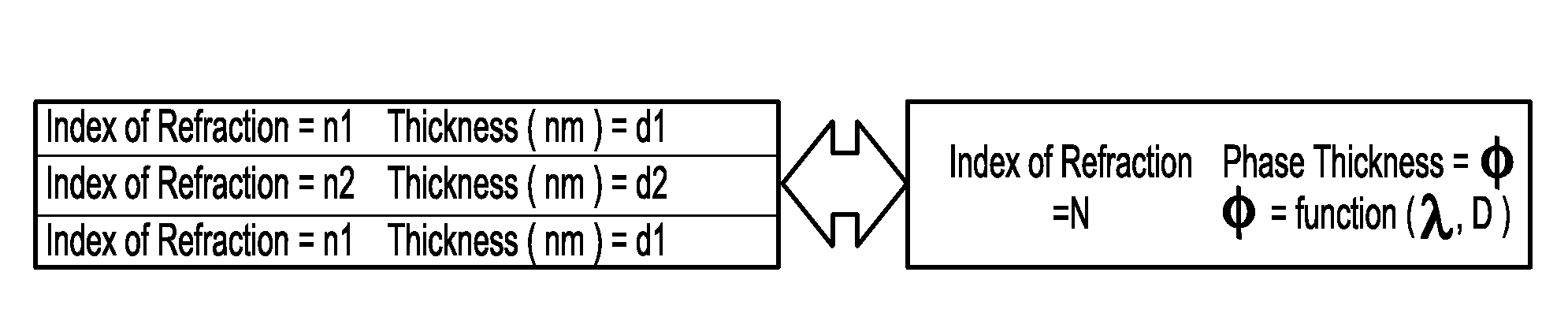
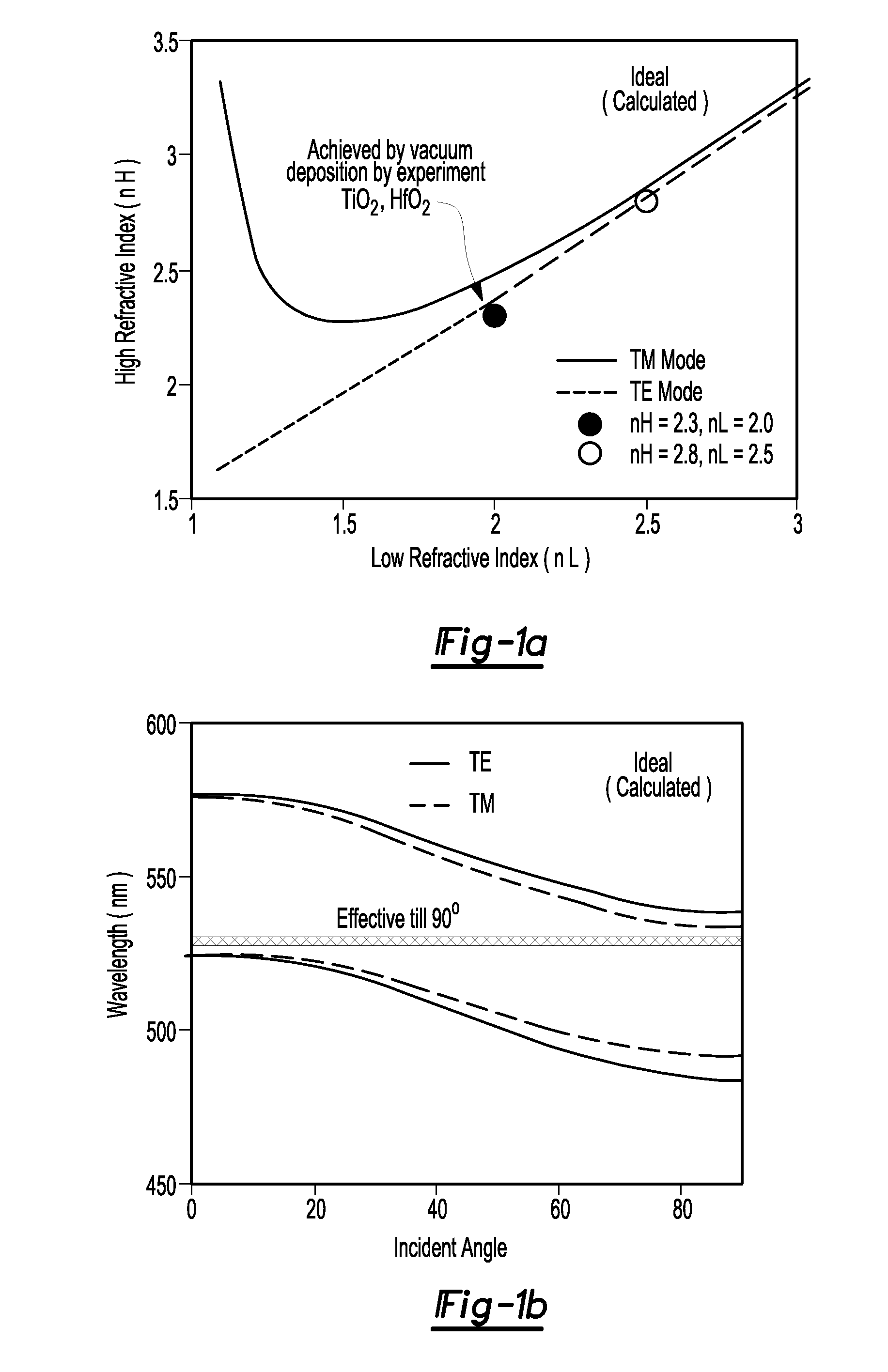
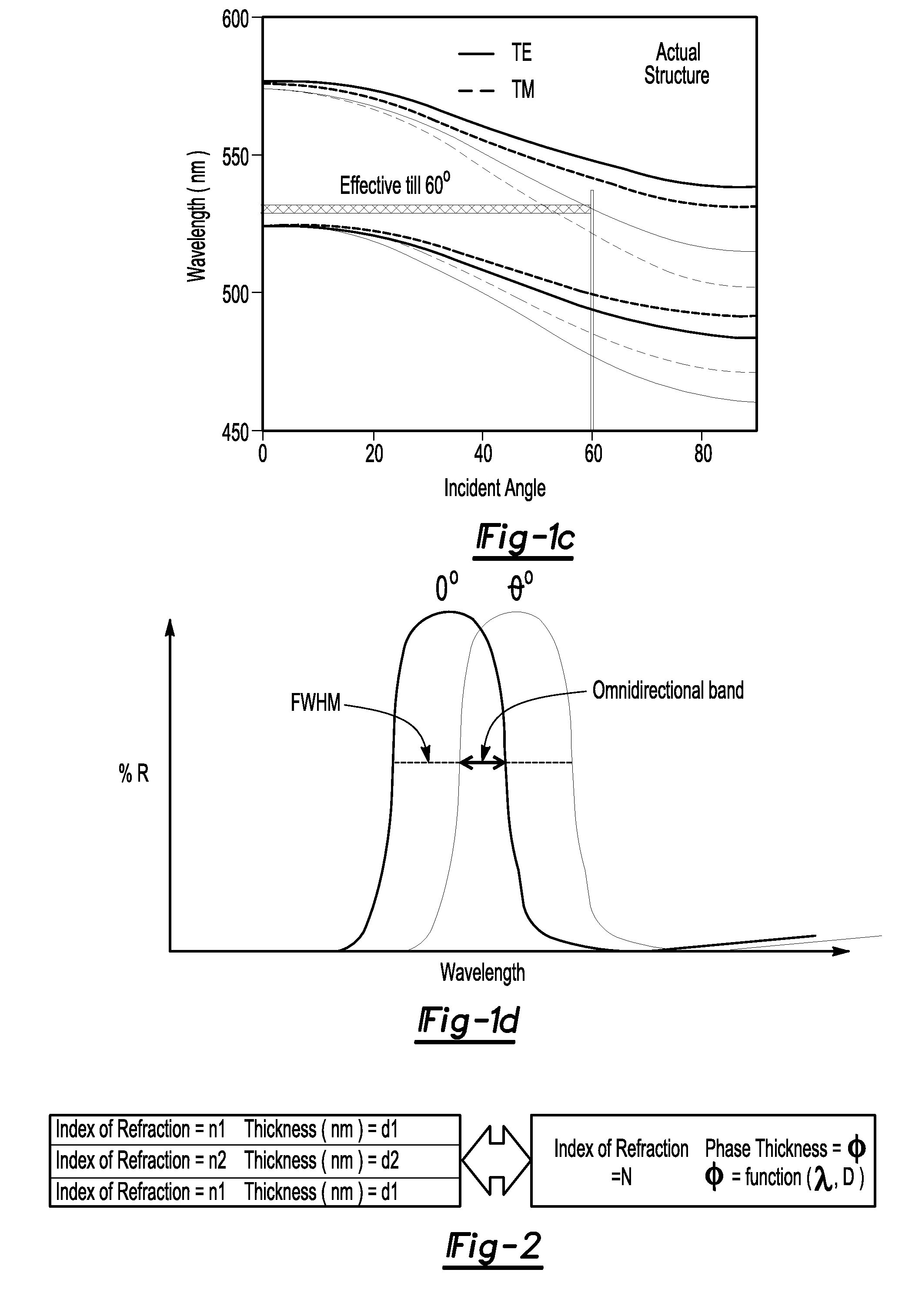
A process for designing and manufacturing an omnidirectional structural color (OSC) multilayer stack. The process can include providing a digital processor operable to execute at least one module and a table of index of refraction values corresponding to different materials that are usable for manufacturing an OSC multilayer stack. An initial design for the OSC multilayer stack can be provided and at least one additional layer is added to the initial design OSC multilayer stack to create a modified OSC multilayer stack. In addition, the thickness of each layer of the modified OSC multilayer stack is calculated using a merit function module until an optimized OSC multilayer stack has been calculated.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR ENGINEERING & MANUFACTURING NORTH AMERICA +1
System and method for in-situ monitor and control of film thickness and trench depth
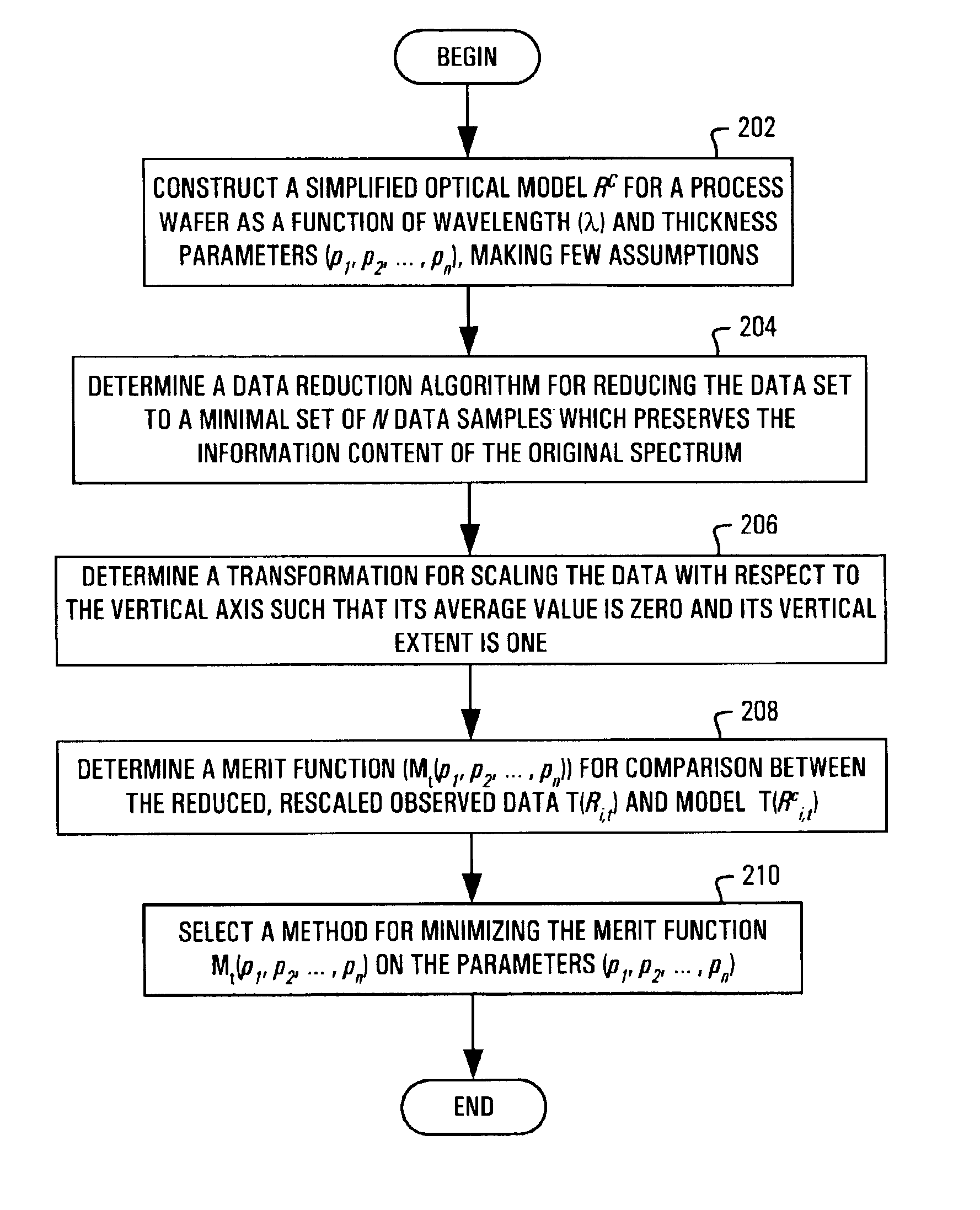
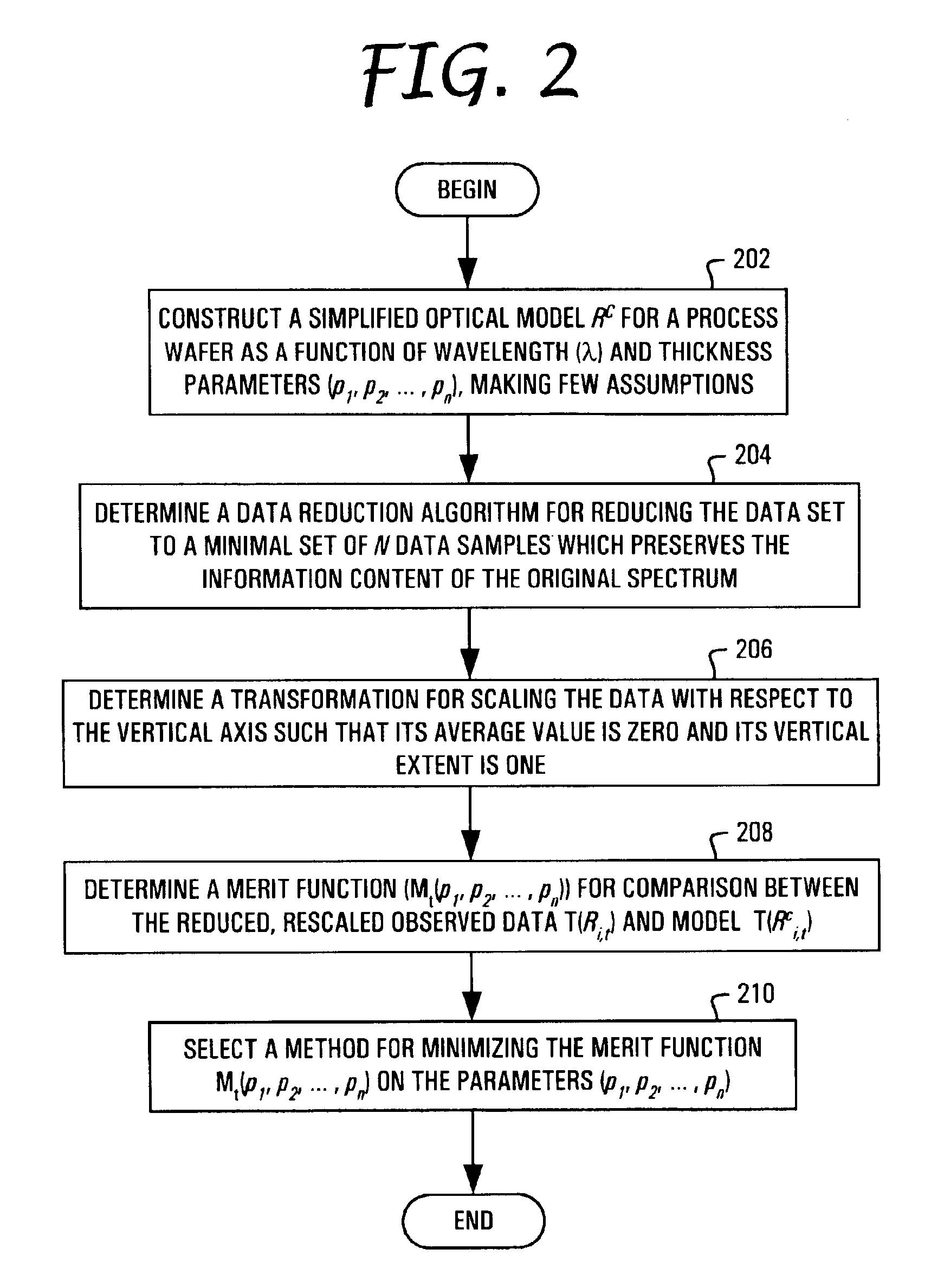
ActiveUS7049156B2Accurate calculationReduce settingsTesting sensing arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPresent methodLayer thickness
The present invention is directed to a system, method and software program product for calculating metrological data (e.g. layer thicknesses and depths of recesses and trenches) on a surface or structure, such as a semiconductor wafer. The present method does not require knowledge of the reflectivity or transmissivity of the surface or structure, but only a quantity related to the reflectivity or transmissivity linear transformation needs to be known. Initially, a simplified optical model for the process is constructed using as many parameters as necessary for calculating the surface reflectivity of the discrete regions on the wafer. Reflectivity data are collected from the surface of a wafer using, for instance, in-situ monitoring, and nominal reflectivity is determined from the ratio of the current spectrum to a reference spectrum. The reference spectrum is taken from a reference wafer consisting entirely of a material in which the reflection properties are well characterized. Both the observed and calculated data are transformed such that their vertical extents and spectrally averaged values coincide. By transforming both the observed data and calculated model such that their vertical extents and spectrally averaged values coincide, large errors in both the data and the model can be tolerated. A merit function is employed which measures the agreement between observed data and the model with a particular choice of parameters. The merit function may be minimized using a standard numerical technique for finding a deep minimum in the merit function at the correct values of the parameters.
Owner:VERITY INSTR
Optimized photomasks for photolithography
InactiveUS20070011647A1Character and pattern recognitionComputation using non-denominational number representationPattern recognitionPhotolithography
Photomask patterns are represented using contours defined by level-set functions. Given target pattern, contours are optimized such that defined photomask, when used in photolithographic process, prints wafer pattern faithful to target pattern. Optimization utilizes “merit function” for encoding aspects of photolithographic process, preferences relating to resulting pattern (e.g. restriction to rectilinear patterns), robustness against process variations, as well as restrictions imposed relating to practical and economic manufacturability of photomasks.
Owner:DINO TECH ACQUISITION
Adaptive partitioning scheduler for multiprocessing system
A symmetric multiprocessing system includes multiple processing units and corresponding instances of an adaptive partition processing scheduler. Each instance of the adaptive partition processing scheduler selectively allocates the respective processing unit to run process threads of one or more adaptive partitions based on a comparison between merit function values of the one or more adaptive partitions. The merit function for a particular partition of the one or more adaptive partitions may be based on whether the adaptive partition has available budget on the respective central processing unit. The merit function for a particular partition associated with an instance of the adaptive partition scheduler also, or in the alternative, may be based on whether the adaptive partition has available global budget on the symmetric multiprocessing system.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Method of manufacturing projection objectives and set of projection objectives manufactured by that method
InactiveUS20070013882A1Improve standardsCost-effective manufacturingProjectorsPhotomechanical apparatusOptical ModuleComputer science
In a method of manufacturing projection objectives including defining an initial design for a projection objective and optimizing the design using a merit function, a set of related projection objectives including a first projection objective and at least one second projection objective is defined. Further, a plurality of merit function components, each of which reflects a particular quality parameter, is defined. One of these merit function components defines a common module requirement requiring that the first projection objective and the second projection objective each include at least one common optical module that is constructed to be substantially identical for the first and the second projection objective. The method results in a set of projection objectives having at least one common optical module. Employing the method in the manufacturing of complex projection objectives, such as projection objectives for microlithography, facilitates the manufacturing process and allows substantial cost savings.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
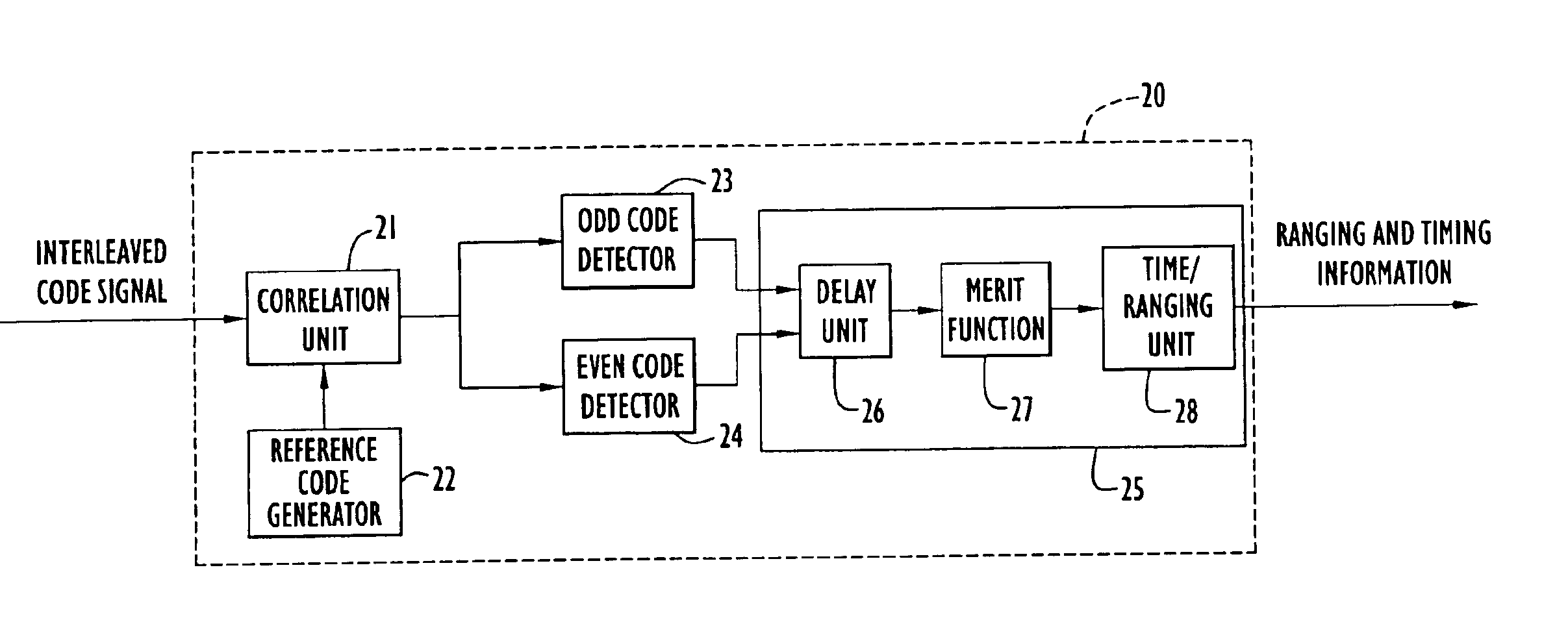
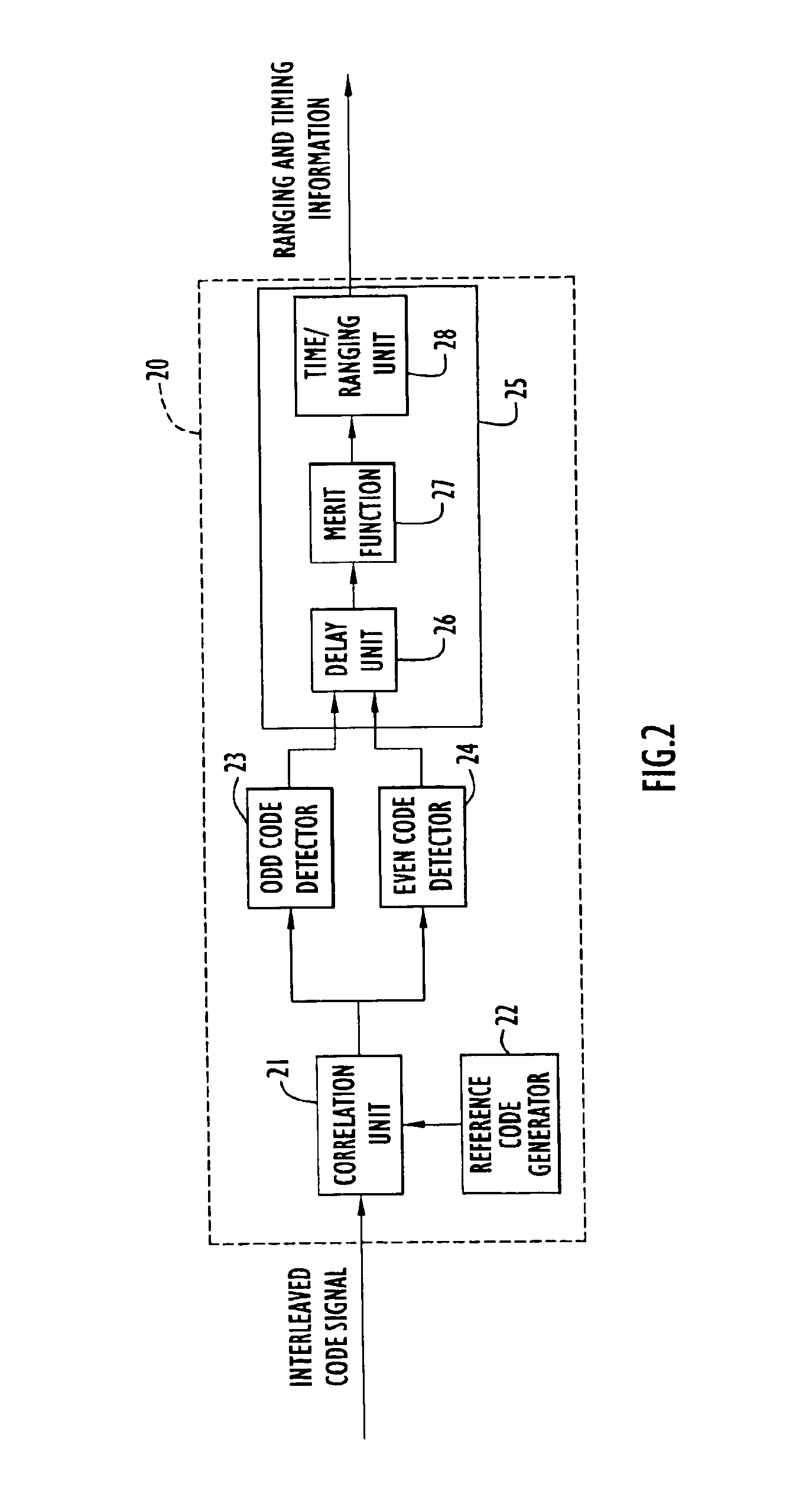
Method and apparatus for detecting an interleaved code
InactiveUS6873664B1Inexpensively detectingLower requirementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCode division multiplexEven codeComputer science
A receiver that receives a long pseudonoise (PN) code signal composed of two shorter codes interleaved with one another, includes a correlator unit that correlates the received signal with one or more reference codes corresponding to the two interleaved codes, respectively, and generates correlation signals. The receiver also includes an even code detector coupled to the correlator unit, for detecting from the correlation signals one of the two shorter codes, and an odd code detector coupled to the correlator unit, for detecting from the correlation signals the short code that is not detected by the even detector. A delay unit is coupled to the even and odd code detectors, and delays the even or the odd correlation signals so as to align the correlation signals. The aligned signals are combined and evaluated by a merit function. If the combined signals exceed a threshold value the short codes are determined to be aligned, the phase of each code can be determined, and the phase of the longer code can be determined from the determined phases of the shorter codes. The receiver can detect two short PN codes that have been combined, such as by interleaving the short codes, to create a long PN code. Hence, the receiver can inexpensively detect the two short codes which allows the receiver to detect the long code with high gain.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
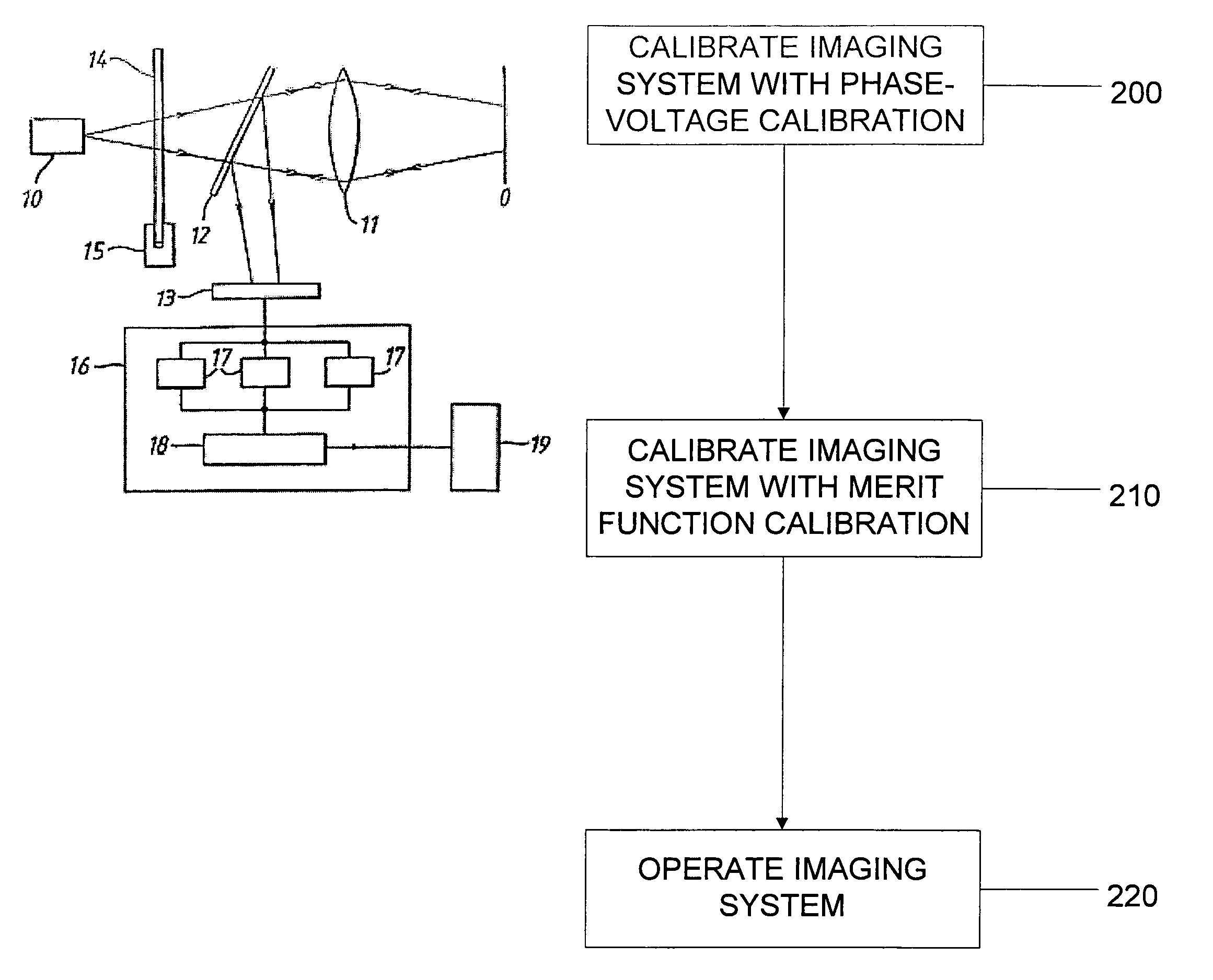
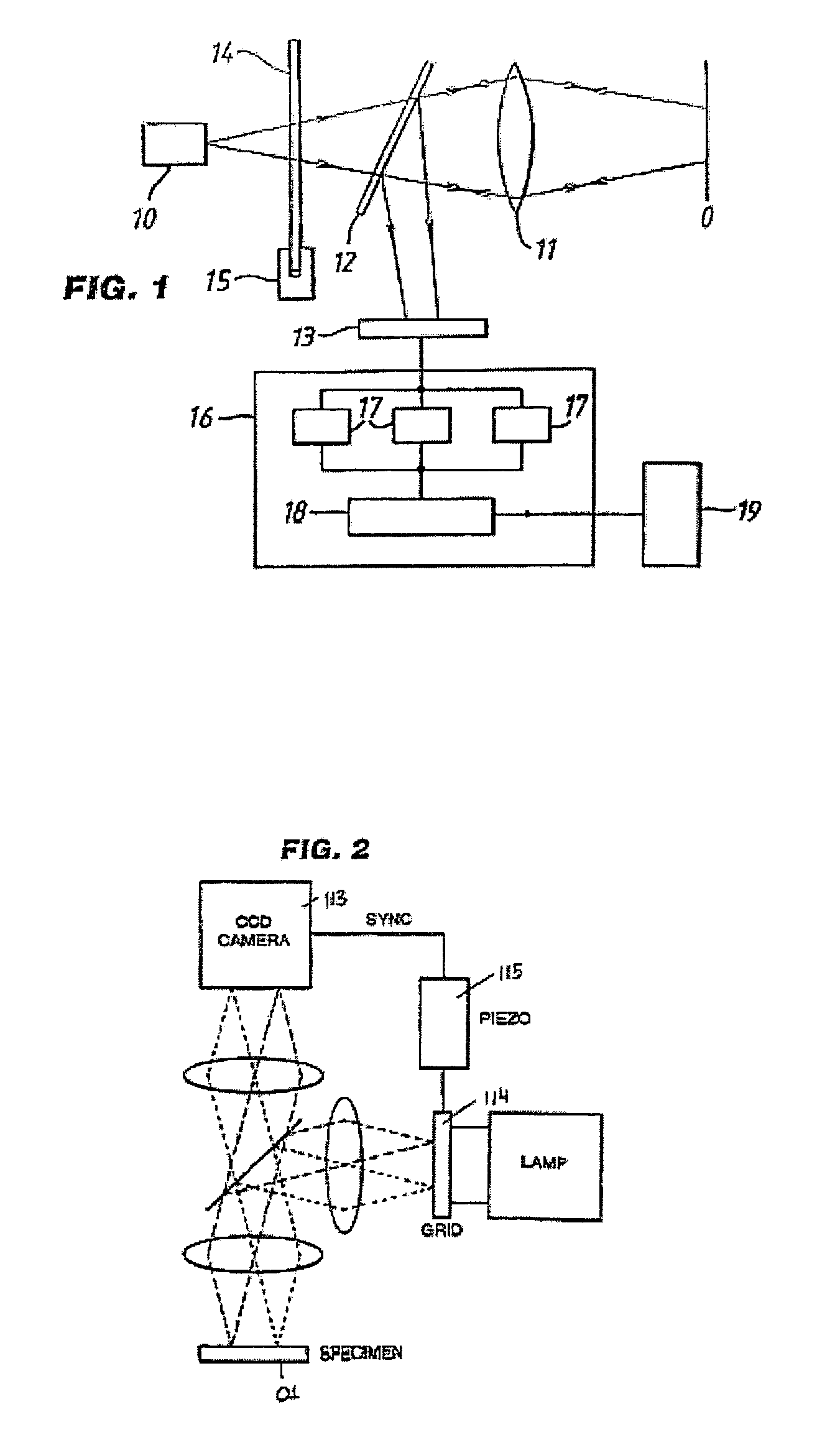
Methods, systems and computer program products for calibration of microscopy imaging devices
An imaging system on which a calibration method is practiced includes: a light source; a substrate for supporting an object; a patterning mask that generates a substantially periodic spatial pattern on the object; a phase shifter that adjusts the relative position of the patterning mask and object to shift the position of the pattern on the object; a detector that detects images of the object; and an analyzer that analyzes at least three images of the object, each of which represents a different spatial shift of the pattern, the analyzer being configured to remove the spatial pattern from the images to generate an optically sectioned image of the object. The calibration method includes: calibrating the position of the mask relative to the substrate via a phase-voltage technique; calibrating the position of the mask relative to the substrate via a merit function technique; and operating the calibrated imaging system.
Owner:THALES SA
Fast systems and methods for calculating electromagnetic fields near photomasks
InactiveUS20070011648A1Effective calculationPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentElectromagnetic fieldComputer science
Photomask patterns are represented using contours defined by mask functions. Given target pattern, contours are optimized such that defined photomask, when used in photolithographic process, prints wafer pattern faithful to target pattern. Optimization utilizes “merit function” for encoding aspects of photolithographic process, preferences relating to resulting pattern (e.g. restriction to rectilinear patterns), robustness against process variations, as well as restrictions imposed relating to practical and economic manufacturability of photomasks. Merit function may approximate electromagnetic field using model of mask pattern as infinitely thin, perfectly conducting pattern. Model may also be used for other lithographic methods, including simulation and verification.
Owner:LUMINESCENT TECH
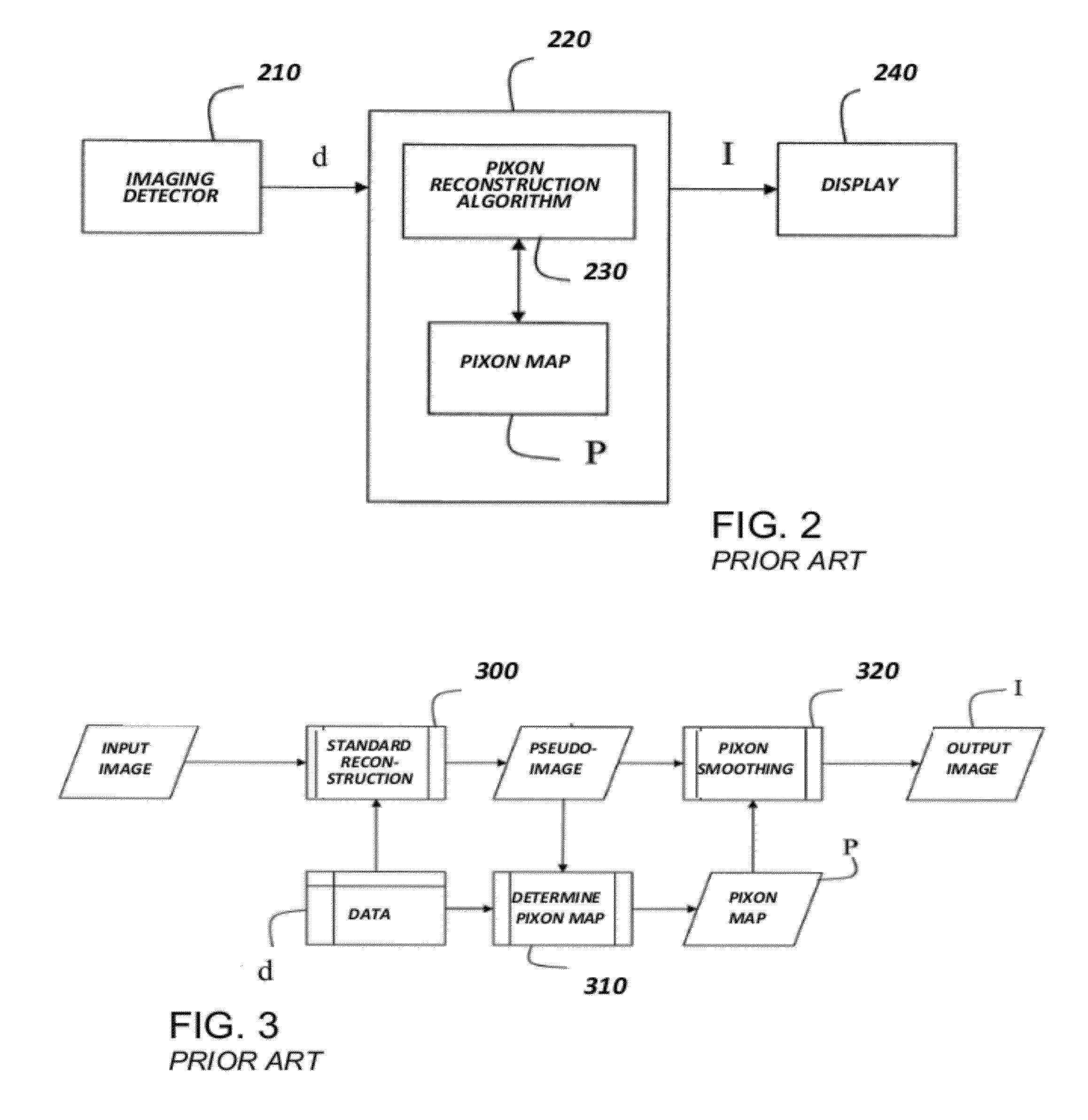
Method to Determine A Pixon Map in Interactive Image Reconstruction and Spectral Analysis
A method for iterative reconstruction of an object containing noise using the pixon method determines the pixon map from a variable that is used to update the object in the iteration. The updating variable is based on an optimized merit function, and smoothes the updating variable during each iteration. The updating variable depends on the reconstruction method, but is typically a gradient of a merit function or a multiplicative update factor. The updated object can optionally also be further smoothed at the end of the iteration, using the pixon map determined during the iteration.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
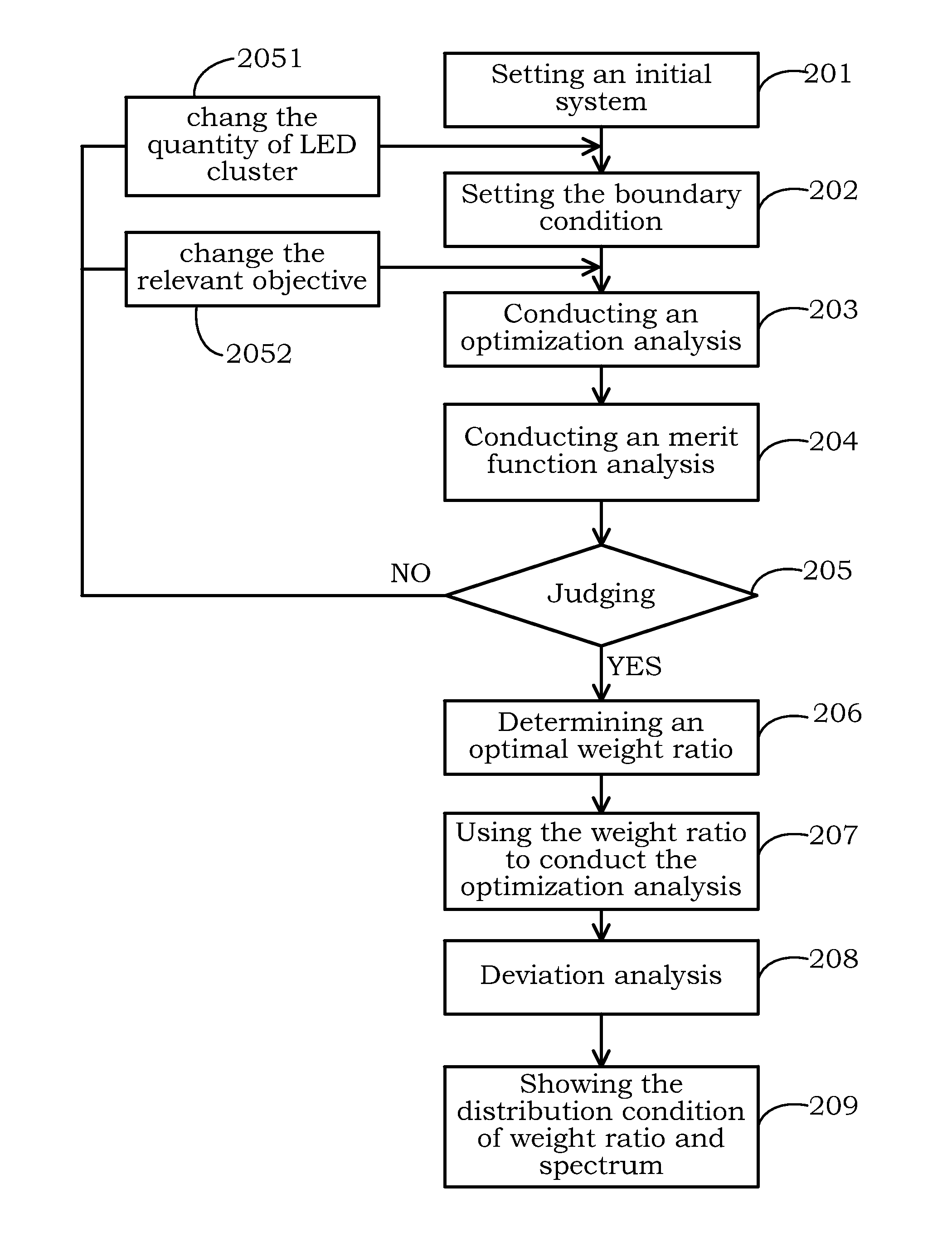
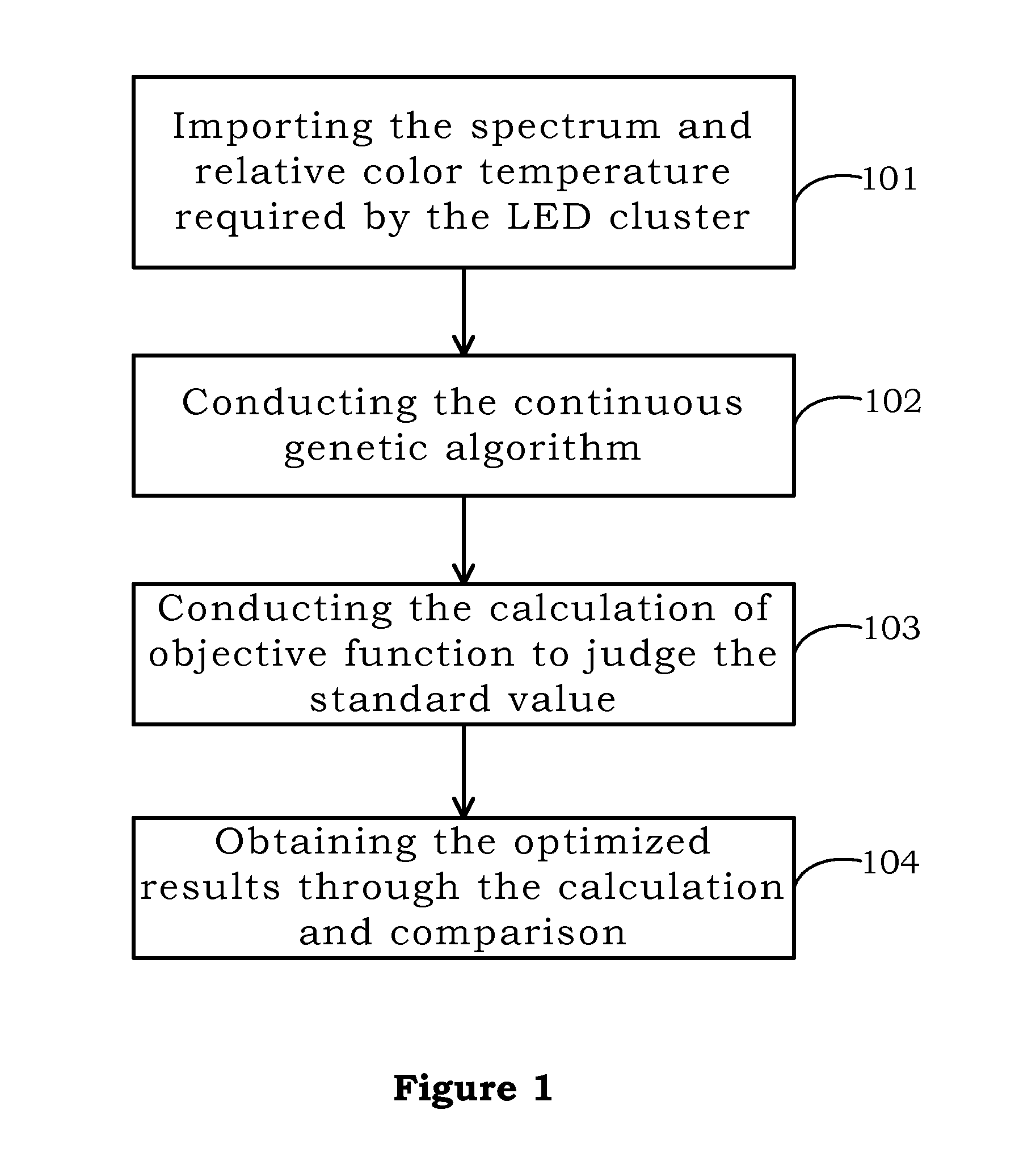
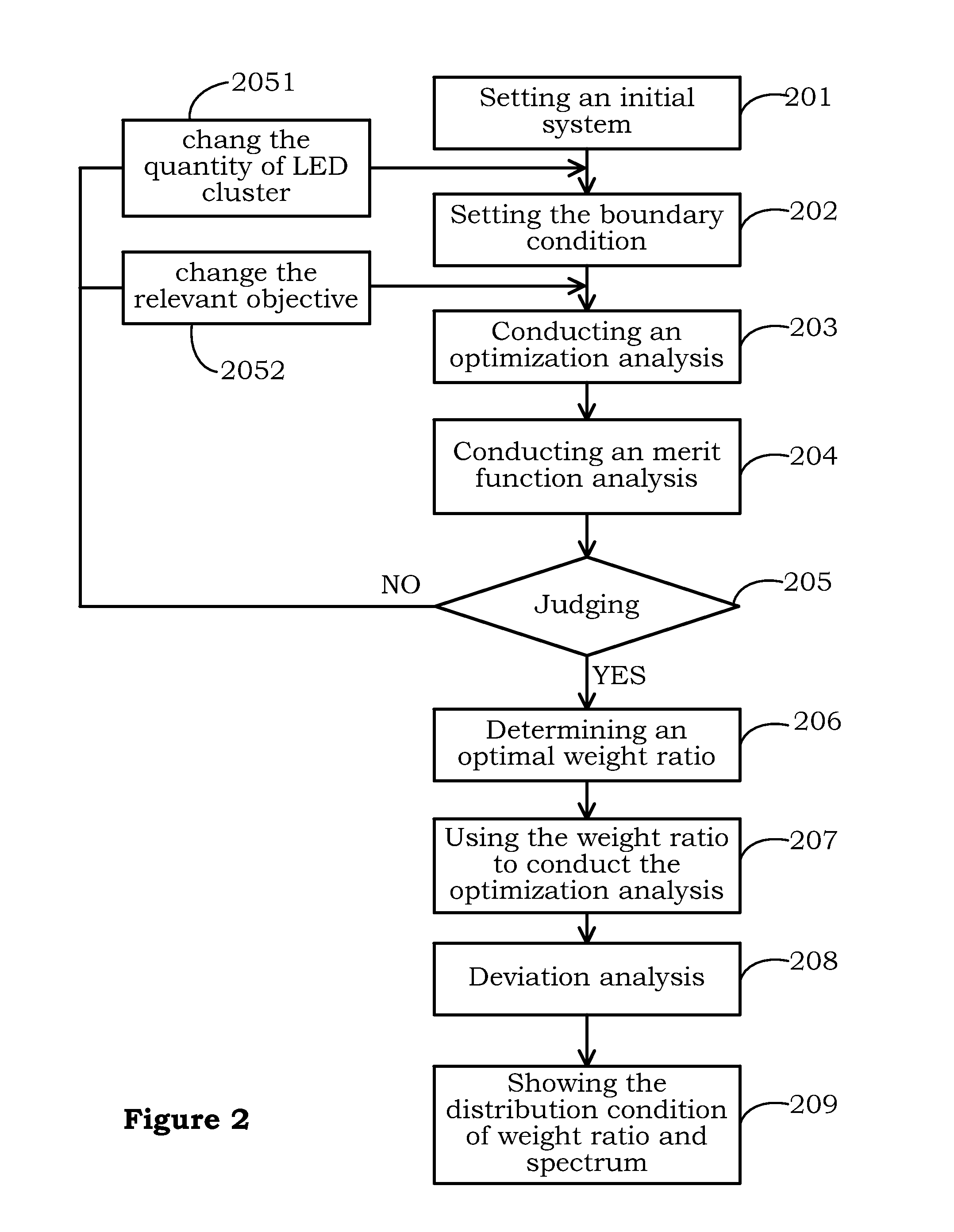
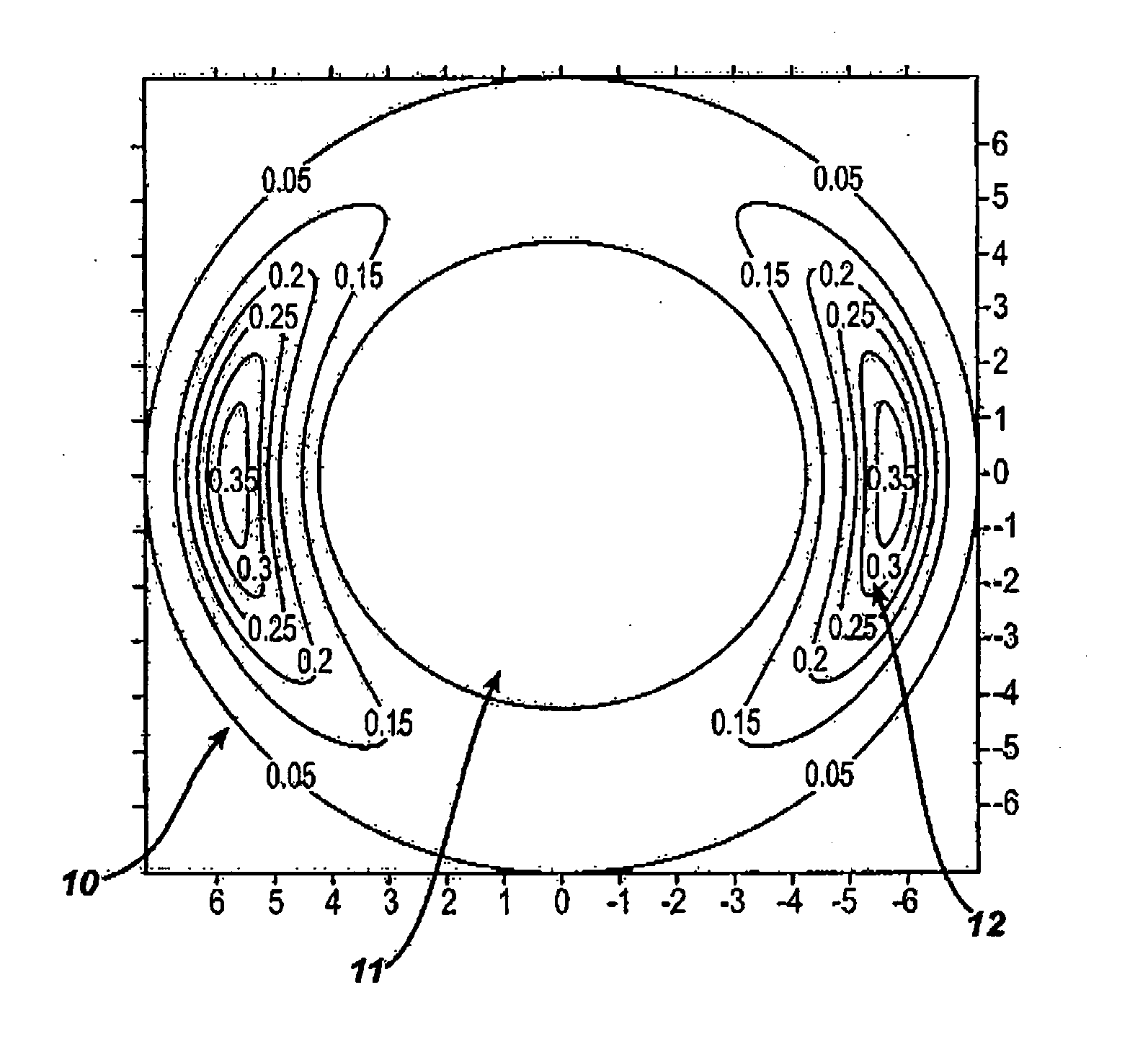
Method for mixing light of LED cluster
ActiveUS20130082622A1High indexHigh luminous efficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesFluorescenceGenetic algorithm
The method for mixing light of LED cluster is disclosed. Firstly, a plurality of LED cluster are provided, then the step is importing the related data, then the step for the continuous genetic algorithm and the merit function are respectively carried out, finally the step for exporting data is achieved. The applied field of the invention is able to comprise LED cluster, fluorescence light source array, and fluorescence lamp array, as well as the other light source field etc.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
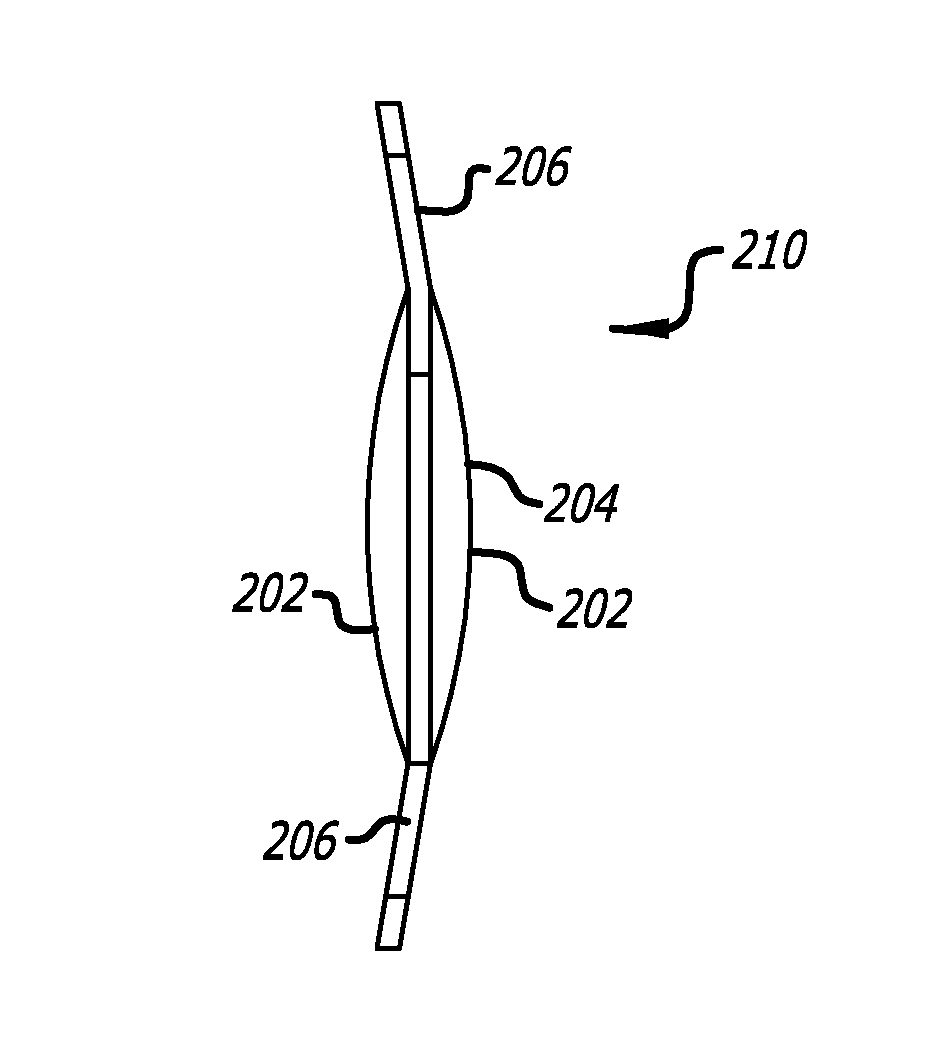
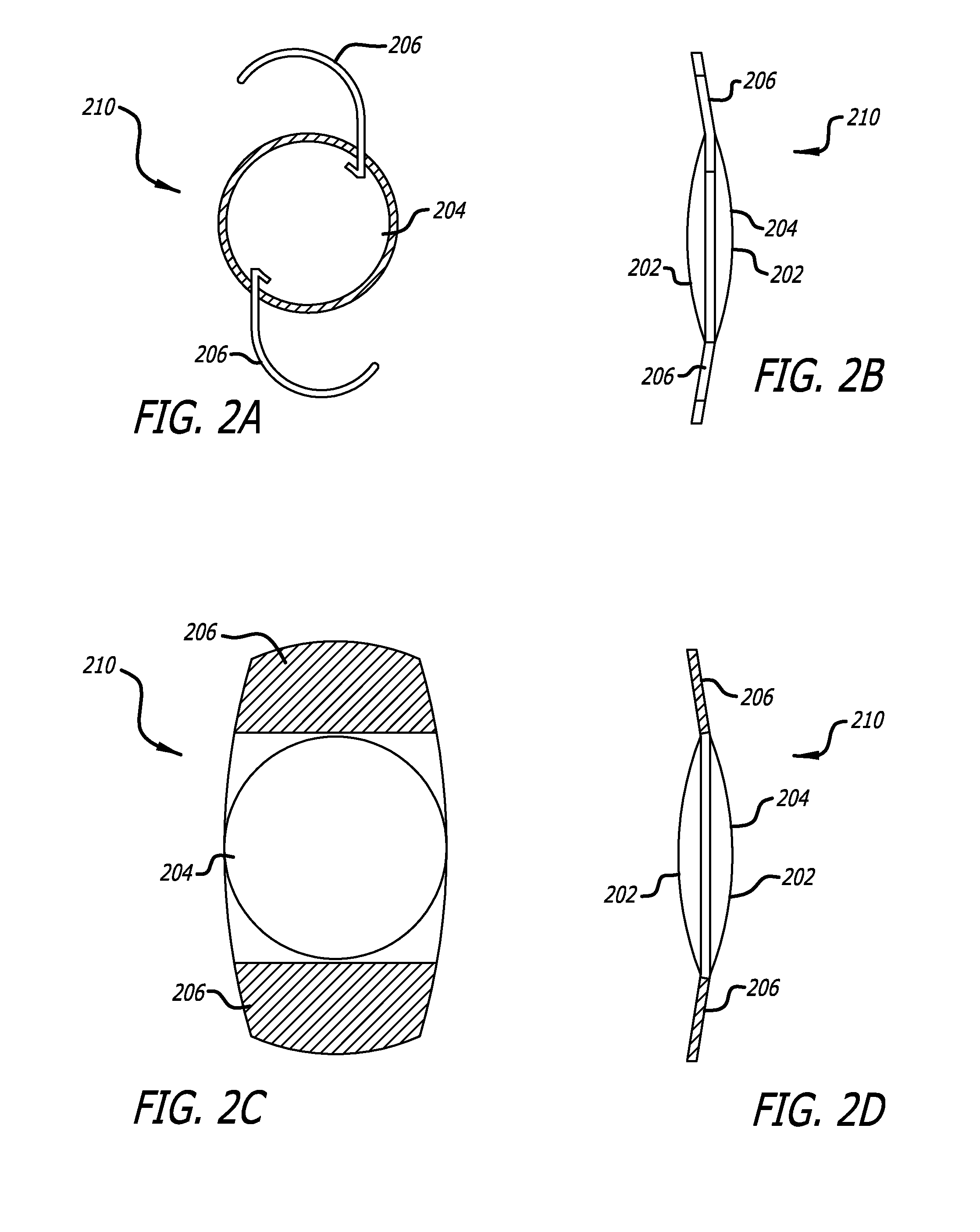
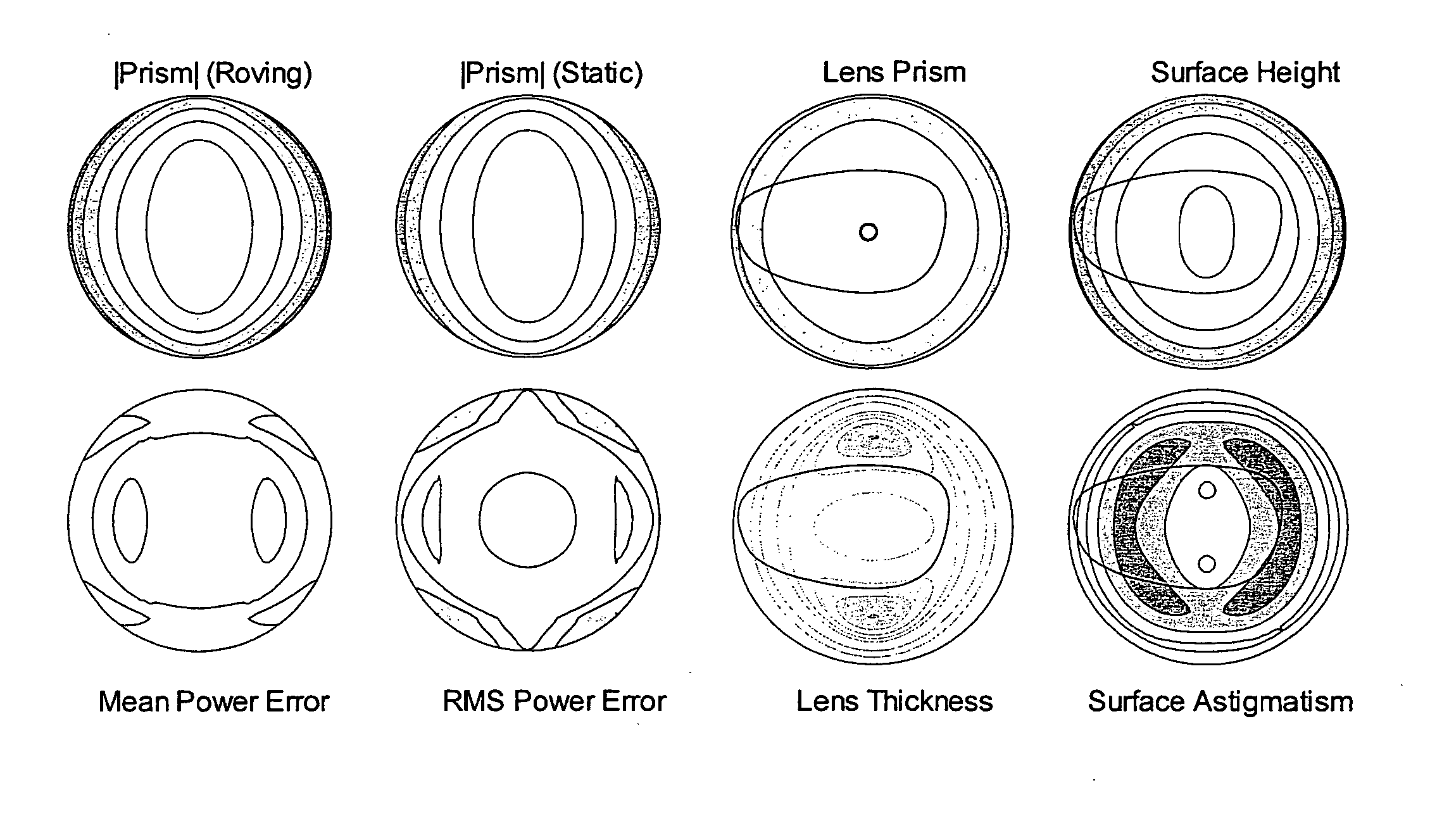
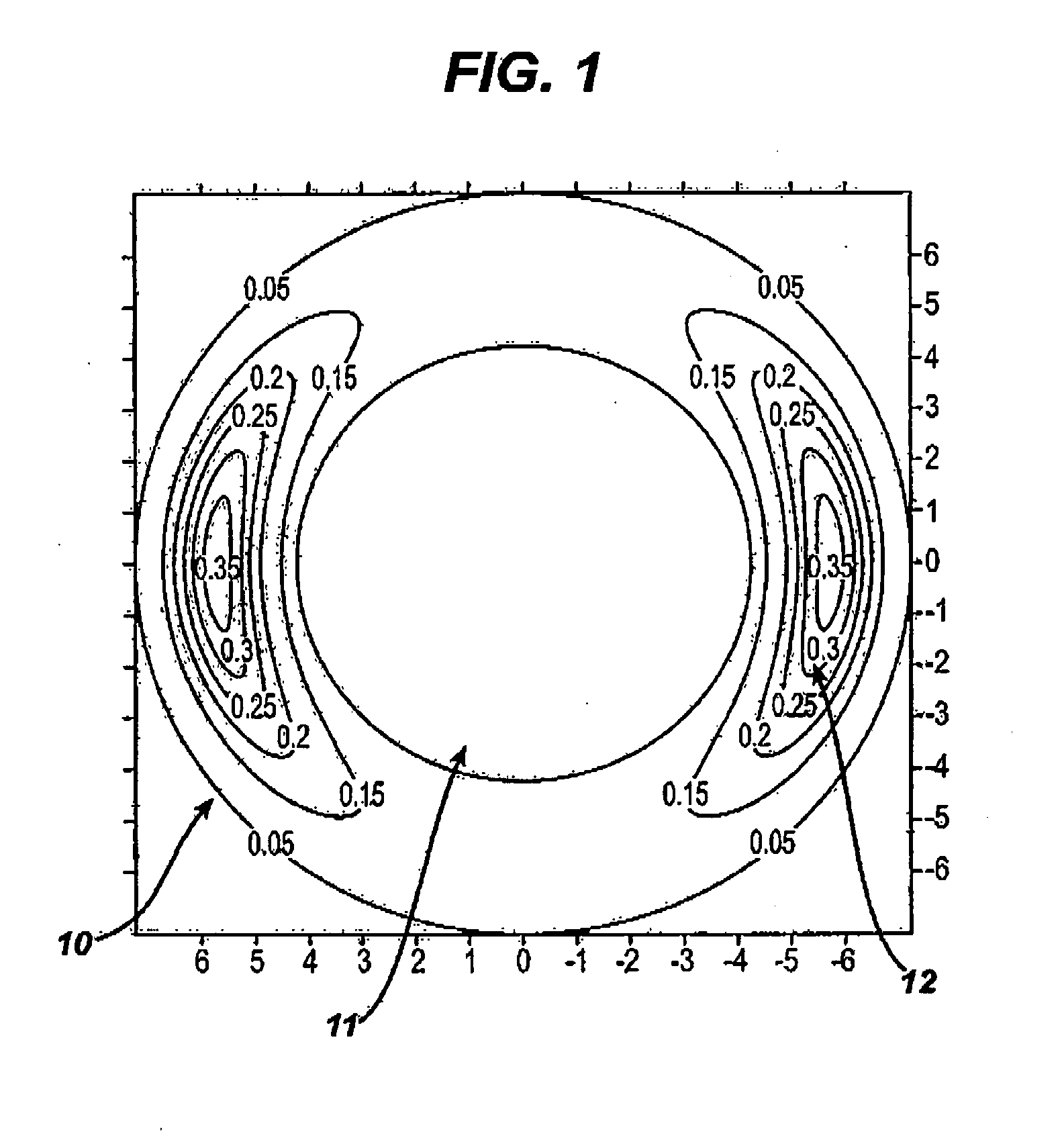
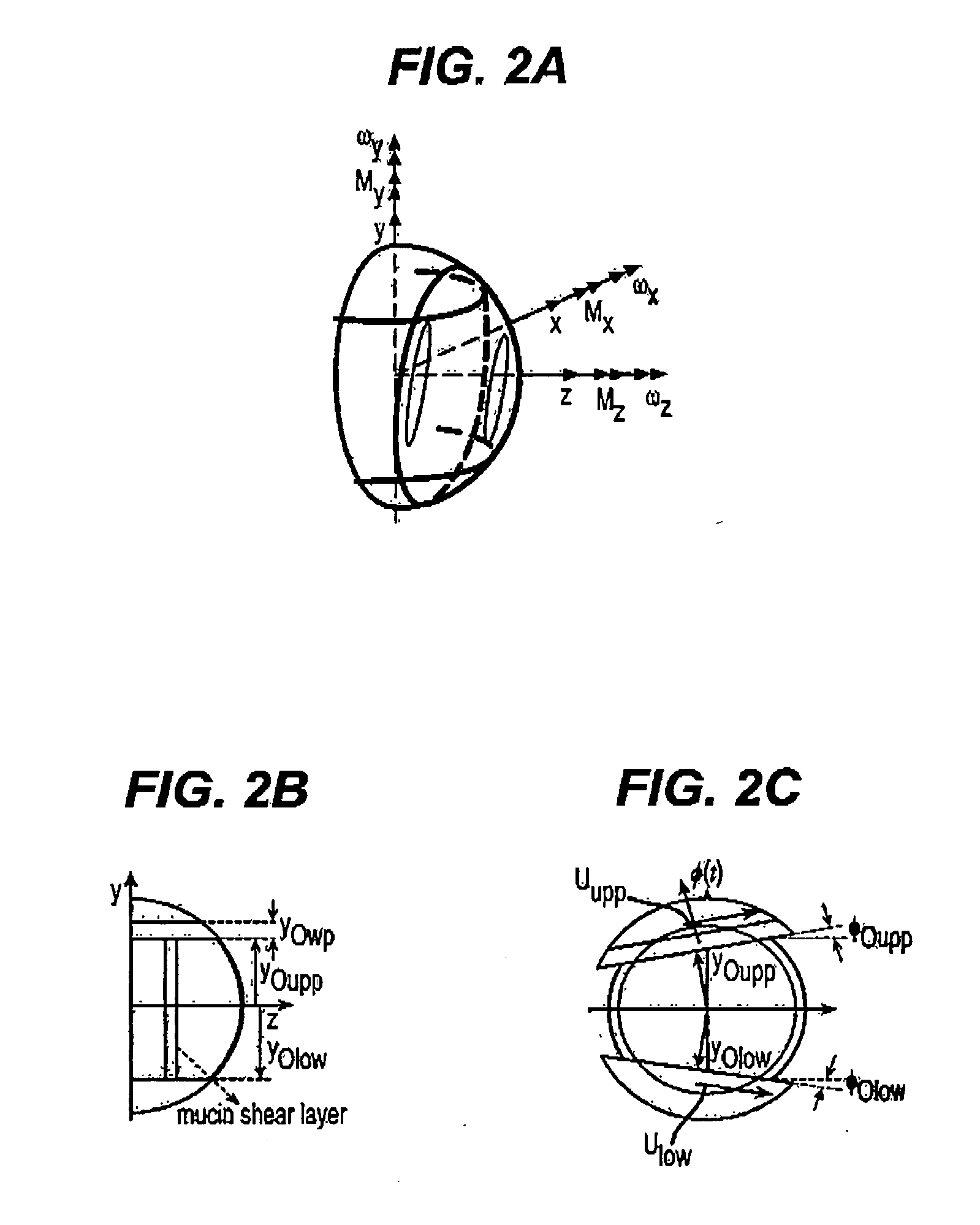
Method for stabilizing contact lenses
A method for stabilizing contact lenses includes providing a lens design with a nominal set of stabilization zone parameters, applying a merit function to the lens design based on balancing moments of momentum, and creating a contact lens design with improved stabilization based on the application of the merit functions to the lens design with a nominal set of stabilization zone parameters.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com