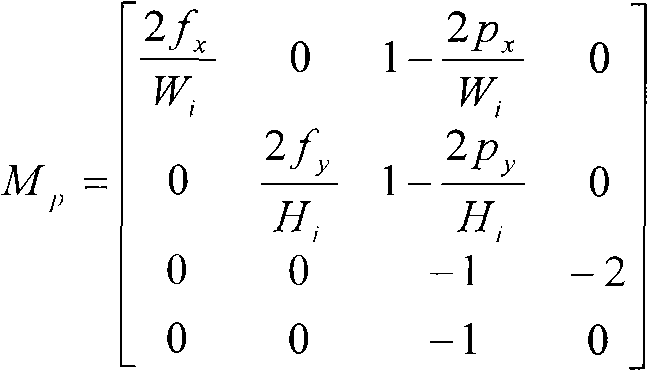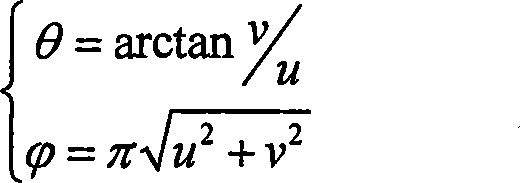Patents
Literature
2538 results about "Iterative reconstruction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Iterative reconstruction refers to iterative algorithms used to reconstruct 2D and 3D images in certain imaging techniques. For example, in computed tomography an image must be reconstructed from projections of an object. Here, iterative reconstruction techniques are usually a better, but computationally more expensive alternative to the common filtered back projection (FBP) method, which directly calculates the image in a single reconstruction step. In recent research works, scientists have shown that extremely fast computations and massive parallelism is possible for iterative reconstruction, which makes iterative reconstruction practical for commercialization.
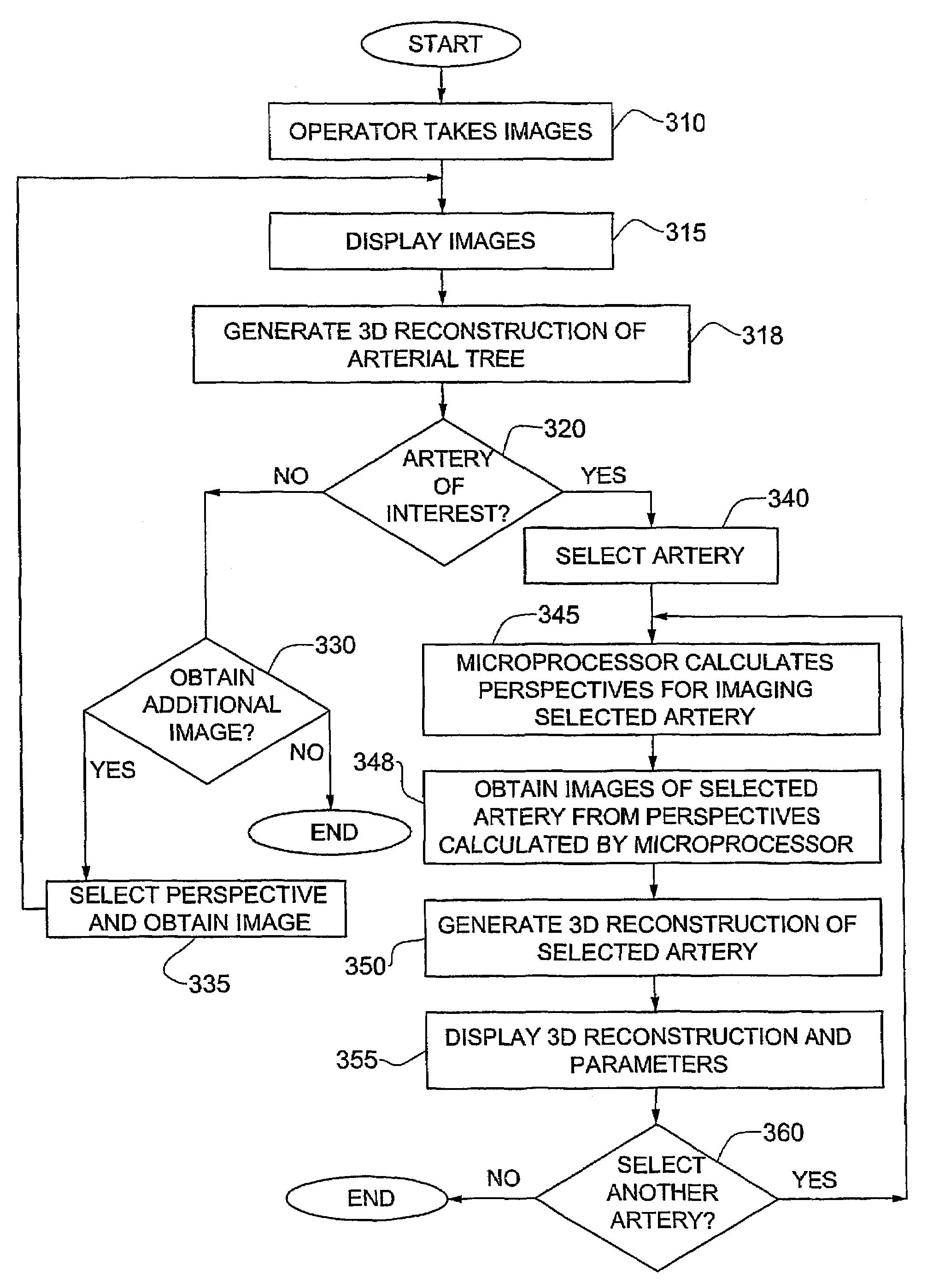
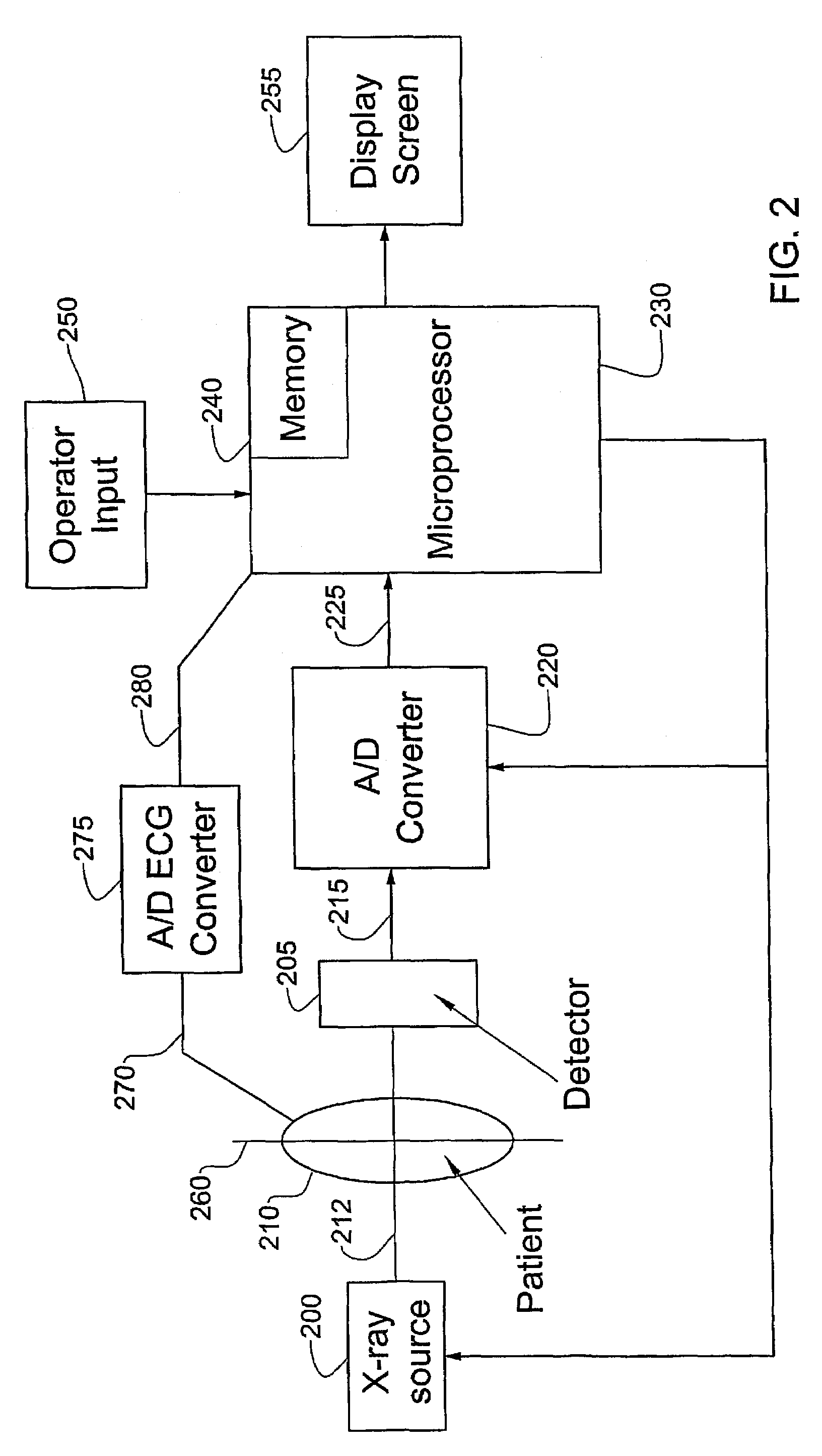
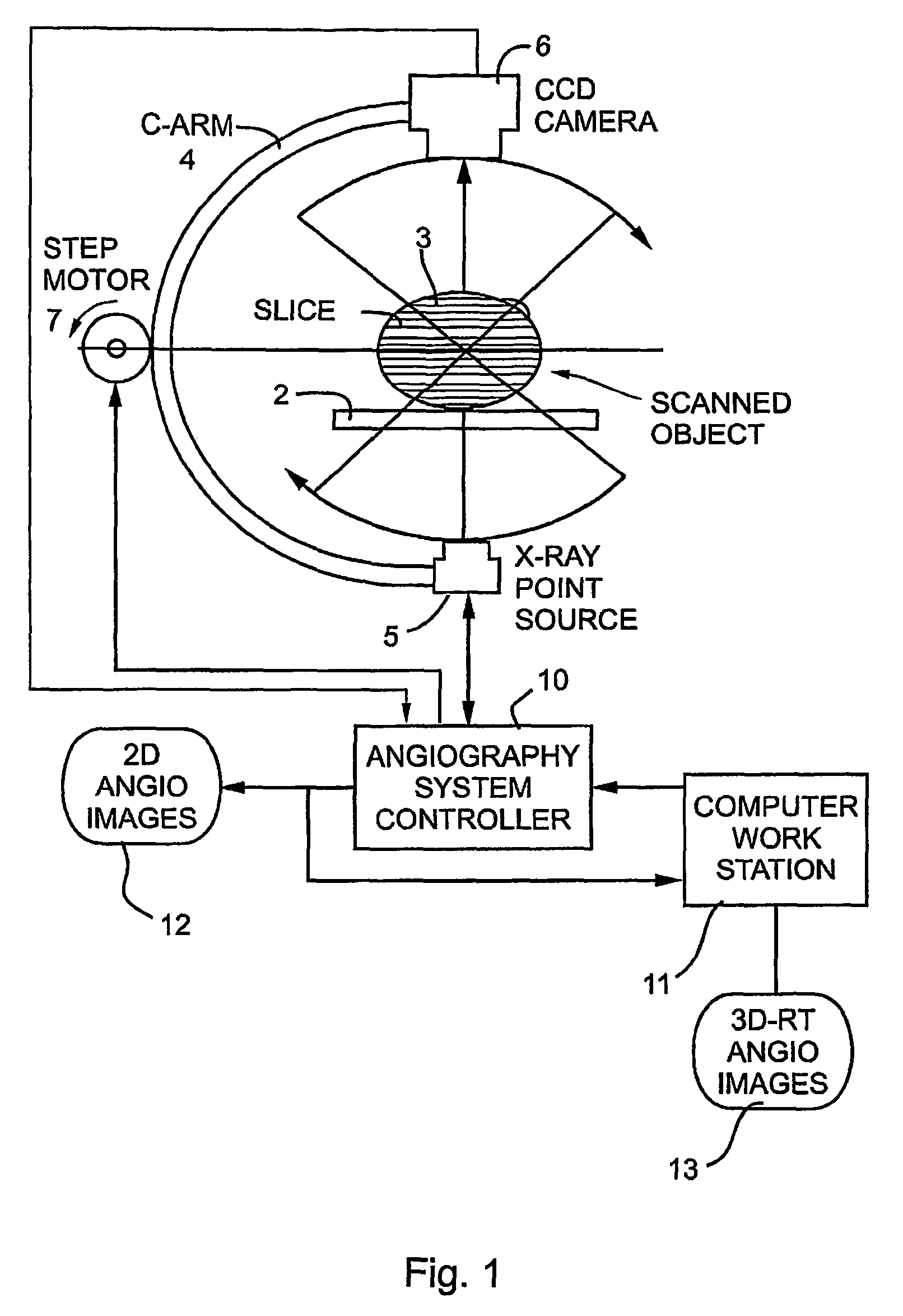
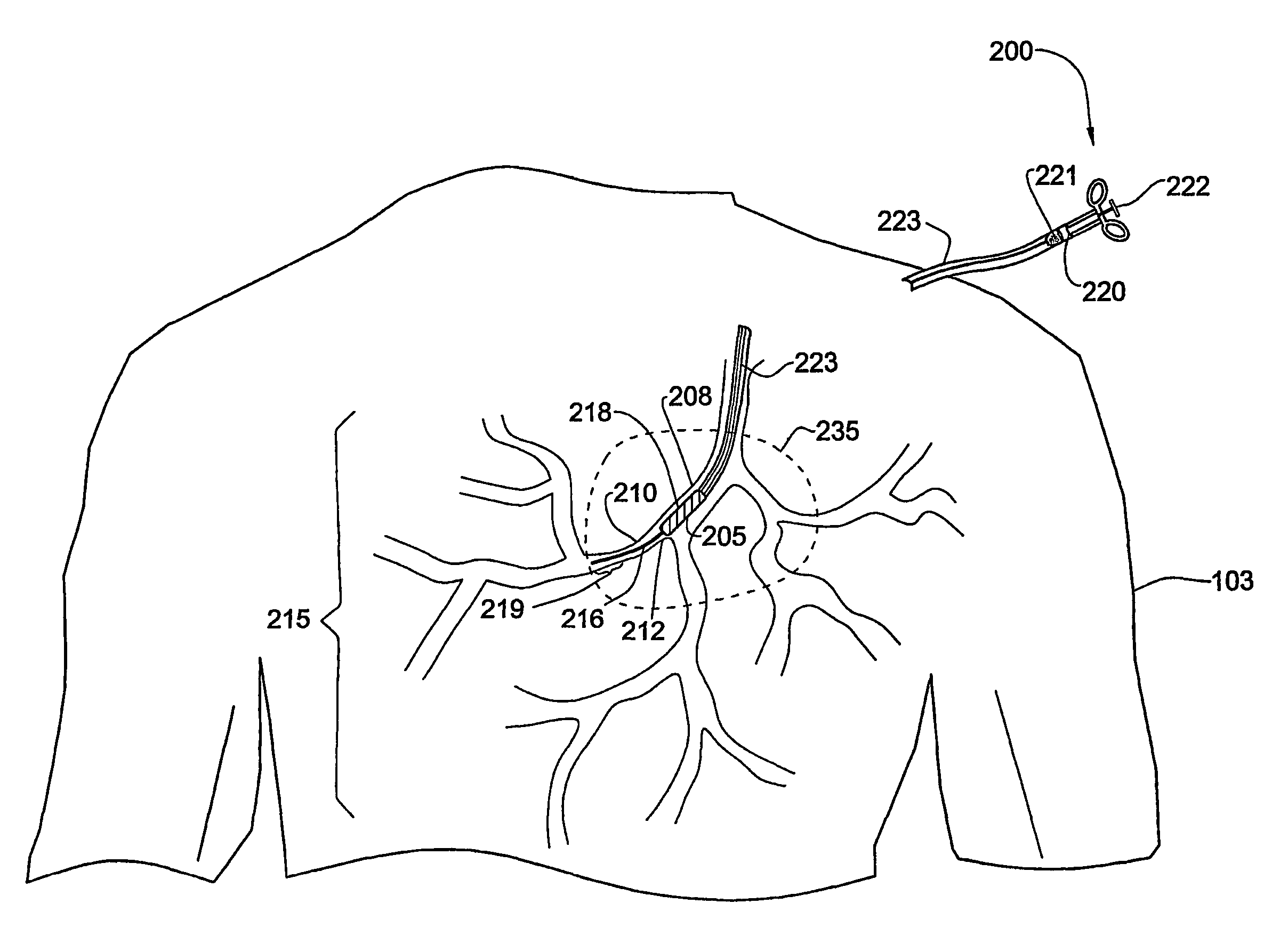
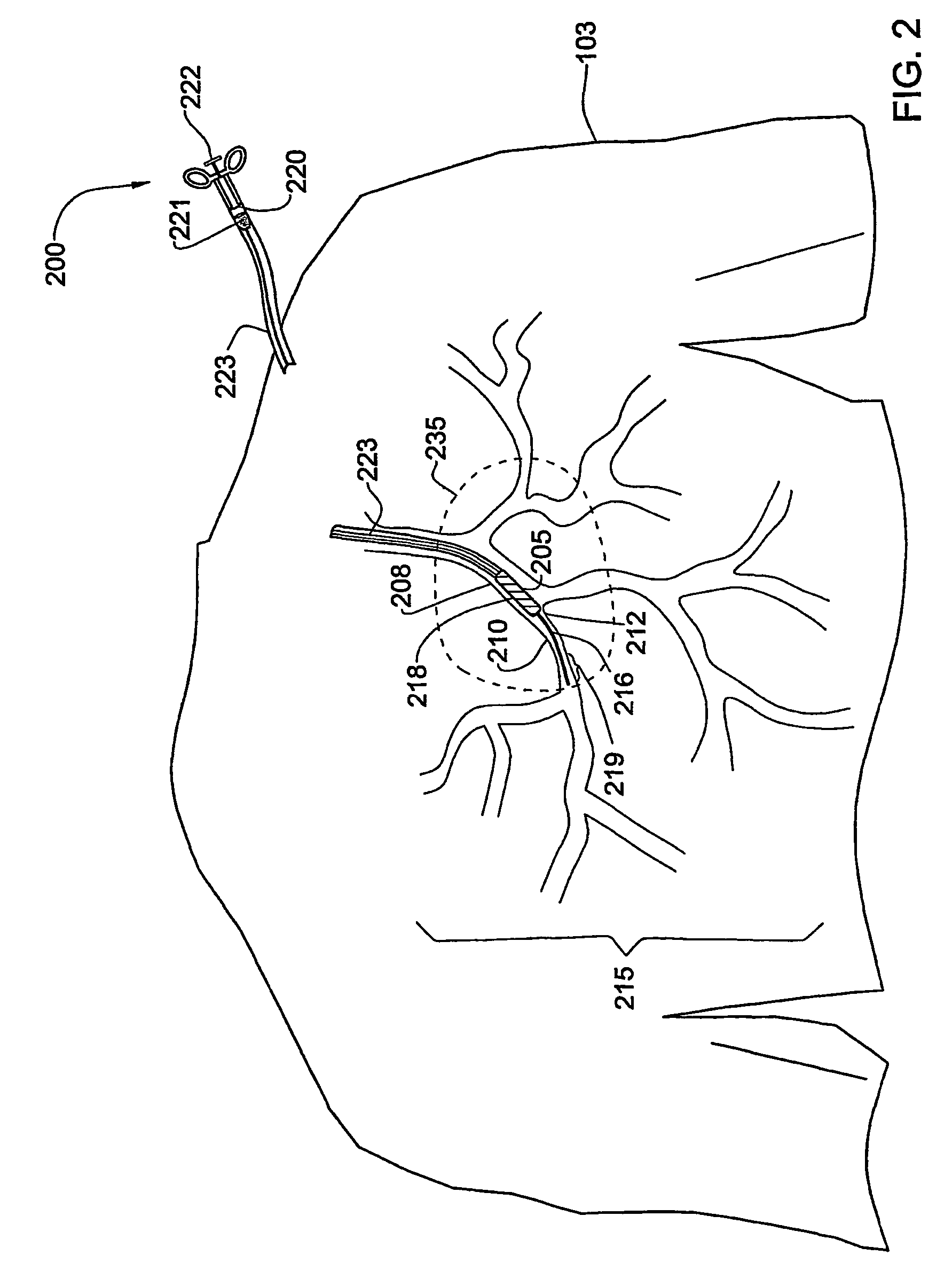
System and method for three-dimensional reconstruction of an artery
InactiveUS7321677B2Reduce exposureEasy accessBlood flow measurement devices2D-image generationArterial treeBlood vessel
A method and system for imaging an artery contained in an arterial tree. A microprocessor generates a three-dimensional reconstruction of the arterial tree from two or more angiographic images obtained from different perspectives. The orientation of the axis of the artery in the arterial tree is then determined, and a perspective of the artery perpendicular to the axis of the artery is determined. A three dimensional reconstruction of the artery from angiographic images obtained from the determined perspective is then generated.
Owner:PAIEON INC
System and method for three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular organ
InactiveUS7742629B2Easy to useEliminate potential incorrect distortionImage analysisOptical rangefindersOptical densityDensitometry
Embodiments of the present invention include methods and systems for three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular organ (for example, coronary artery) using a plurality of two-dimensional images. Some of the embodiments may include displaying a first image of a vascular network, receiving input for identifying on the first image a vessel of interest, tracing the edges of the vessel of interest including eliminating false edges of objects visually adjacent to the vessel of interest, determining substantially precise radius and densitometry values along the vessel, displaying at least a second image of the vascular network, receiving input for identifying on the second image the vessel of interest, tracing the edges of the vessel of interest in the second image, including eliminating false edges of objects visually adjacent to the vessel of interest, determining substantially precise radius and densitometry values along the vessel in the second image, determining a three dimensional reconstruction of the vessel of interest and determining fused area (cross-section) measurements along the vessel and computing and presenting quantitative measurements, including, but not limited to, true length, percent narrowing (diameter and area), and the like.
Owner:PAIEON INC
Videotactic and audiotactic assisted surgical methods and procedures
InactiveUS20080243142A1Medical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesAnatomical structuresSurgical operation
The present invention provides video and audio assisted surgical techniques and methods. Novel features of the techniques and methods provided by the present invention include presenting a surgeon with a video compilation that displays an endoscopic-camera derived image, a reconstructed view of the surgical field (including fiducial markers indicative of anatomical locations on or in the patient), and / or a real-time video image of the patient. The real-time image can be obtained either with the video camera that is part of the image localized endoscope or with an image localized video camera without an endoscope, or both. In certain other embodiments, the methods of the present invention include the use of anatomical atlases related to pre-operative generated images derived from three-dimensional reconstructed CT, MRI, x-ray, or fluoroscopy. Images can furthermore be obtained from pre-operative imaging and spacial shifting of anatomical structures may be identified by intraoperative imaging and appropriate correction performed.
Owner:GILDENBERG PHILIP L
System and method for three-dimensional reconstruction of an artery
InactiveUS20050008210A1Precise processingReduce exposureBlood flow measurement devices2D-image generationArterial treeBlood vessel
Owner:PAIEON INC
Method and system for positioning a device in a tubular organ
InactiveUS7778685B2Accurate measurementImprove assessmentDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsComputer scienceAngle of view
A system and method for positioning a device at a desired location in a tubular organ such as an artery. A three-dimensional reconstruction of the organ is obtained, and the desired location is marked in the reconstruction. The device is inserted into the organ and an image is obtained of the device and organ. The reconstruction with the marked location is projected onto a plane from the perspective of the image and the projection and image are superimposed. If the device is not at the desired location, the device is repositioned in the organ and an additional image of the device is obtained. The reconstruction is then projected onto a plane from the perspective of the additional image and the additional image and the projection are superimposed. This process is repeated, as required, until the device is in the desired location.
Owner:PAIEON INC
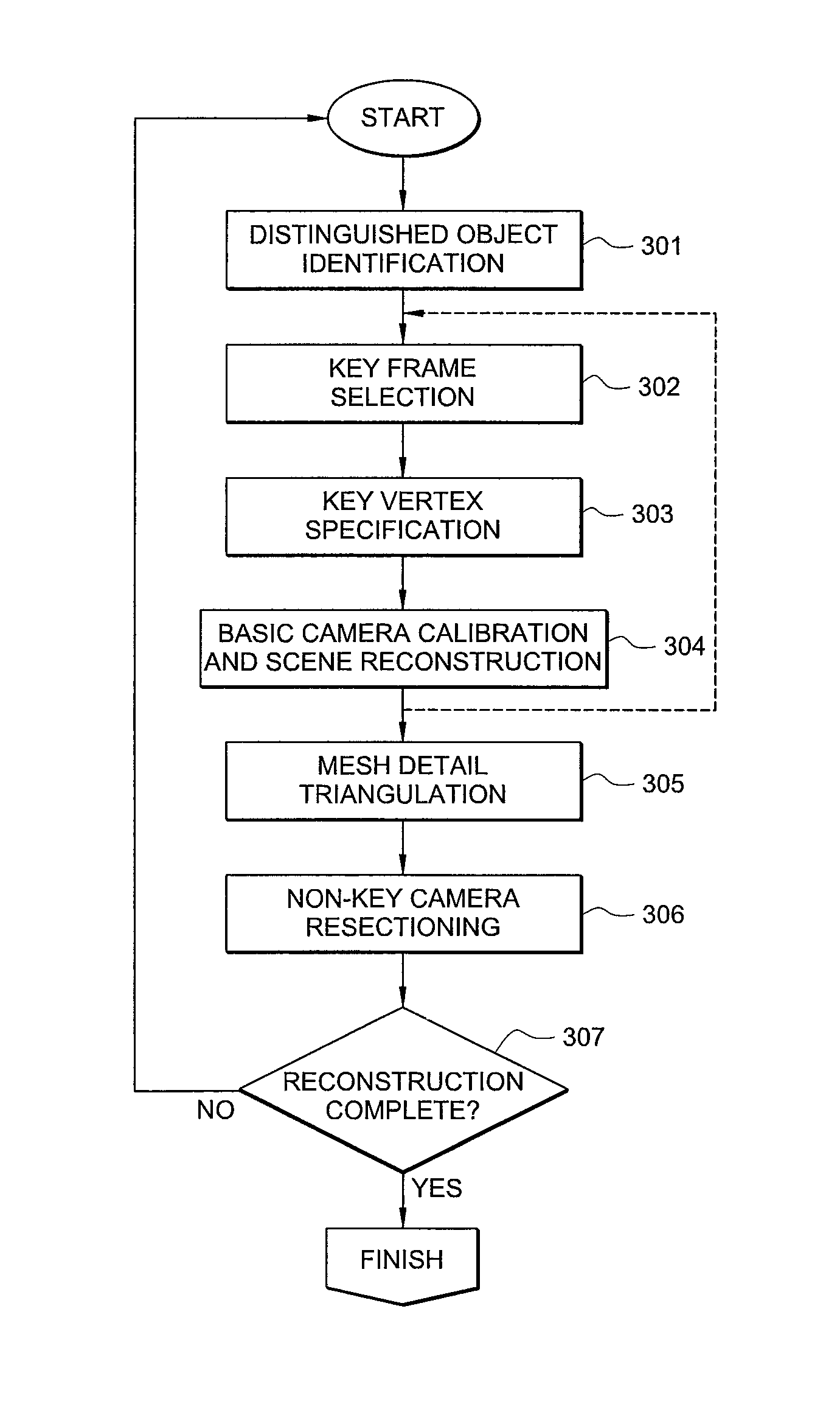
Methodology for 3D scene reconstruction from 2D image sequences
ActiveUS8655052B2Lower requirementReduce computational demand of reconstruction processImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognition3D reconstruction2d images
The present invention is directed to a system and method for interactive and iterative reconstruction in a manner that helps to reduce computational requirements by generating a model from a subset of the available data, and then refining that model using additional data. Example embodiments directed to scene reconstruction, reconstruct a 3D scene from a plurality of 2D images of that scene by first generating a model of the 3D scene from a subset a of the 2D images. The model can then be refined using specific characteristics of each image in the subset that are calculated using the other images in the subset. The model is further refined using images not in the original subset.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
Color translating UV microscope
A color translating UV microscope for research and clinical applications involving imaging of living or dynamic samples in real time and providing several novel techniques for image creation, optical sectioning, dynamic motion tracking and contrast enhancement comprises a light source emitting UV light, and visible and IR light if desired. This light is directed to the condenser via a means of selecting monochromatic, bandpass, shortpass, longpass or notch limited light. The condenser can be a brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast or DIC. The slide is mounted in a stage capable of high speed movements in the X, Y and Z dimensions. The microscope uses broadband, narrowband or monochromat optimized objectives to direct the image of the sample to an image intensifier or UV sensitive video system. When an image intensifier is used it is either followed by a video camera, or in the simple version, by a synchronized set of filters which translate the image to a color image and deliver it to an eyepiece for viewing by the microscopist. Between the objective and the image intensifier there can be a selection of static or dynamic switchable filters. The video camera, if used, produces an image which is digitized by an image capture board in a computer. The image is then reassembled by an overlay process called color translation and the computer uses a combination of feedback from the information in the image and operator control to perform various tasks such as optical sectioning and three dimensional reconstruction, coordination of the monochromater while collecting multiple images sets called image planes, tracking dynamic sample elements in three space, control of the environment of the slide including electric, magnetic, acoustic, temperature, pressure and light levels, color filters and optics, control for microscope mode switching between transmitted, reflected, fluorescent, Raman, scanning, confocal, area limited, autofluorescent, acousto-optical and other modes.
Owner:RICHARDSON TECH
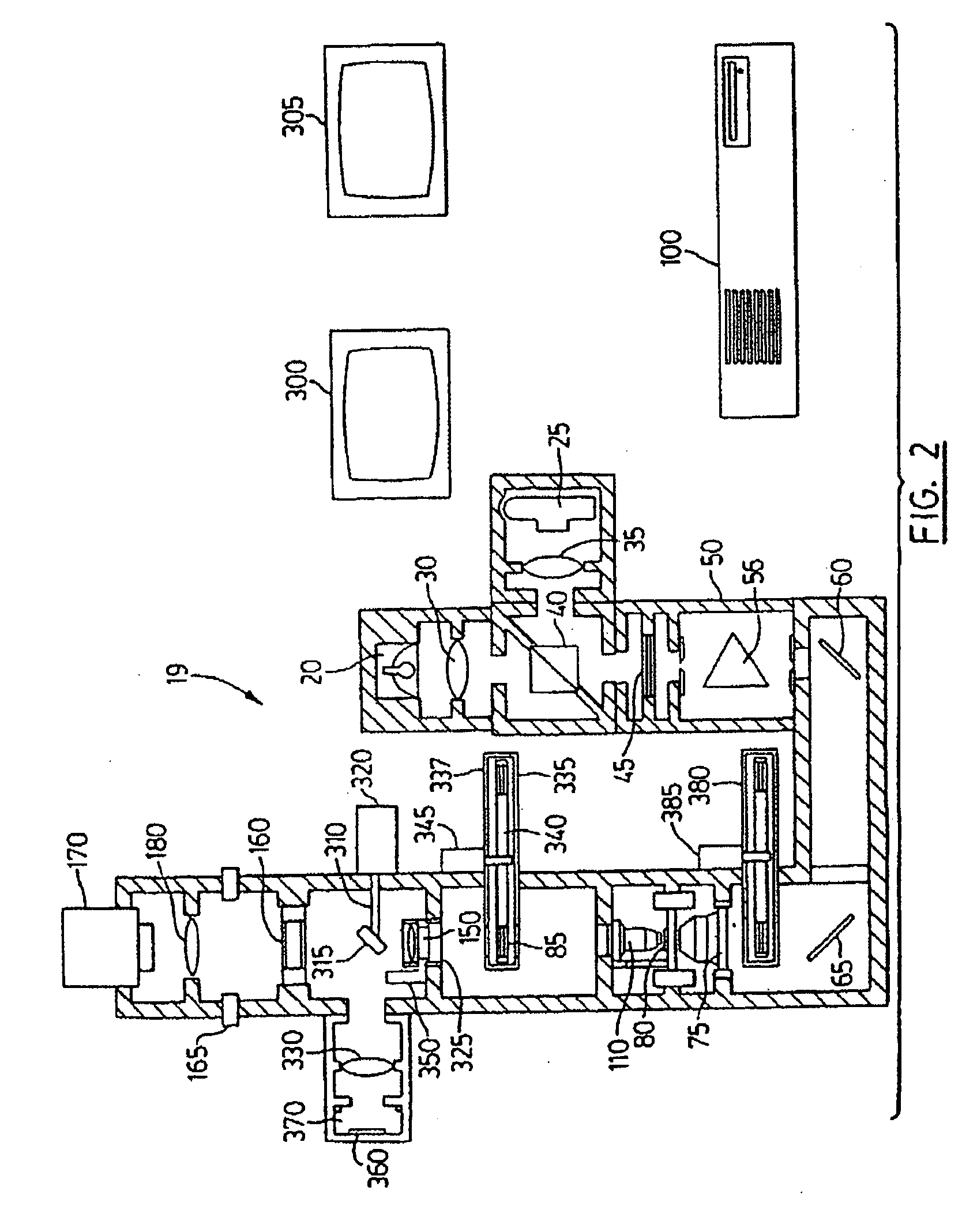
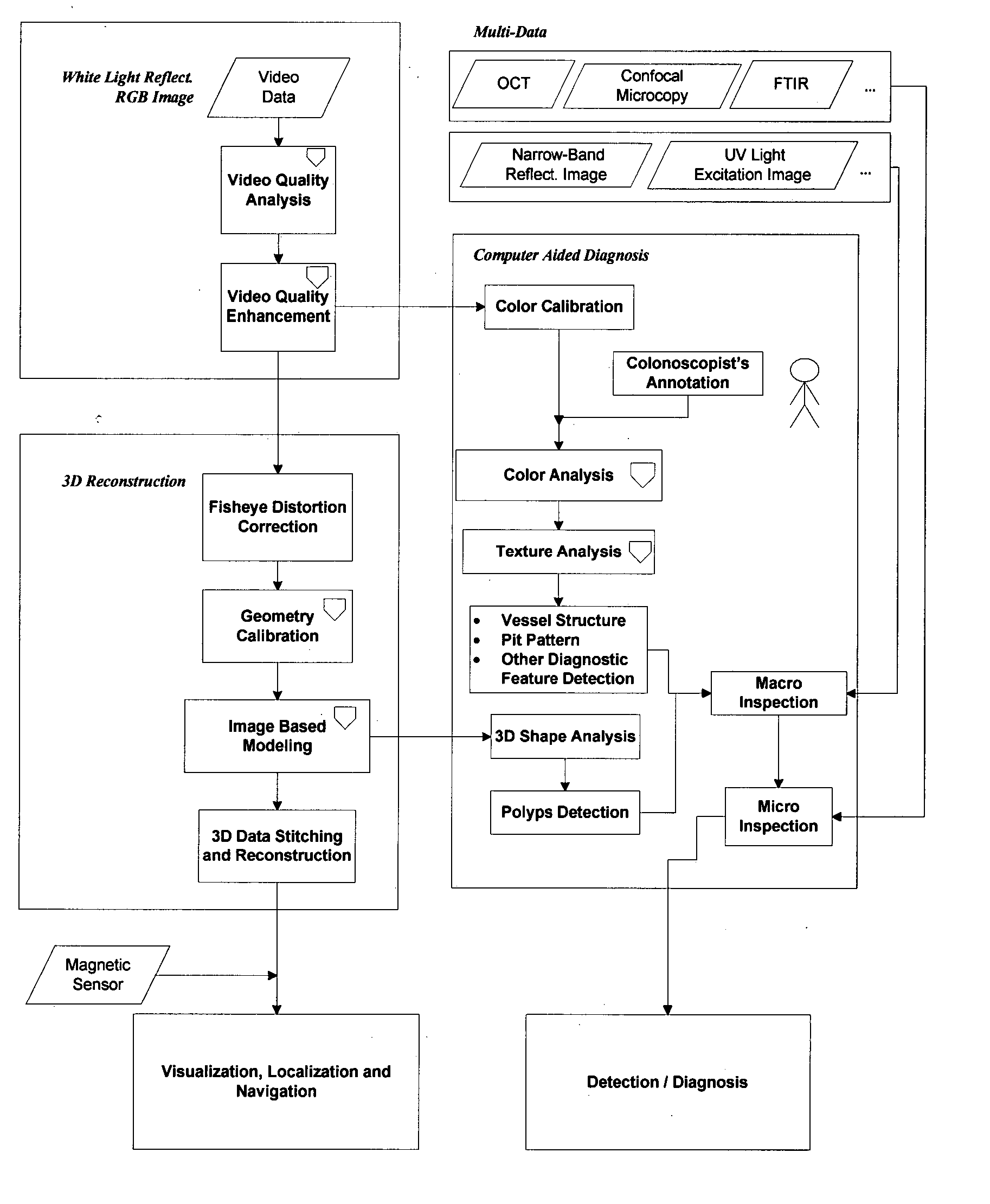
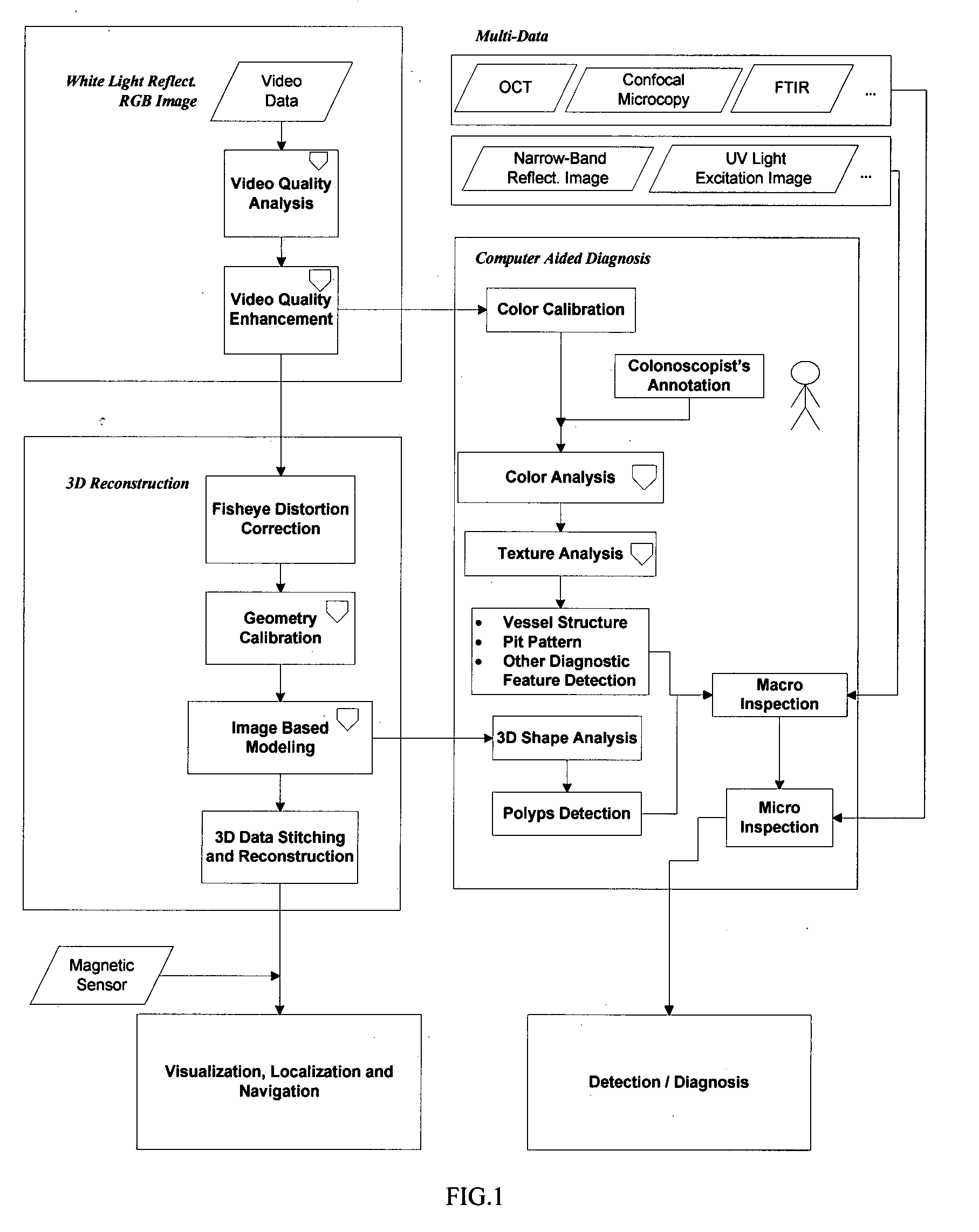
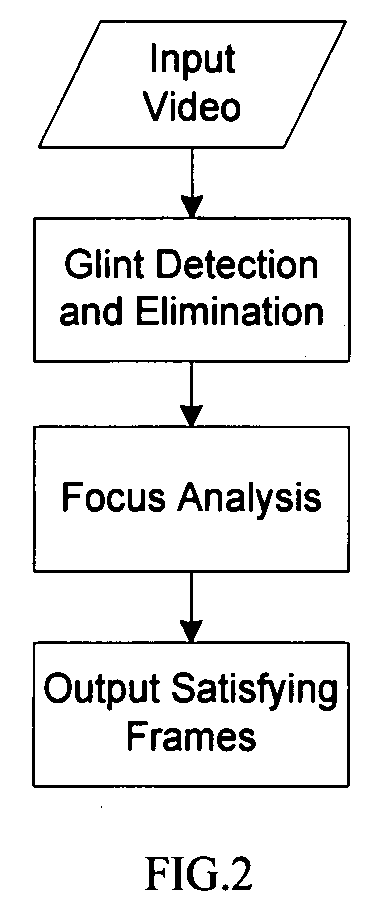
Computer aided diagnosis using video from endoscopes
A process for providing computer aided diagnosis from video data of an organ during an examination with an endoscope, comprising analyzing and enhancing image frames from the video and detecting and diagnosing any lesions in the image frames in real time during the examination. Optionally, the image data can be used to create a 3 dimensional reconstruction of the organ.
Owner:CADES SCHUTTE A LIMITED LIABILITY LAW PARTNERSHIP
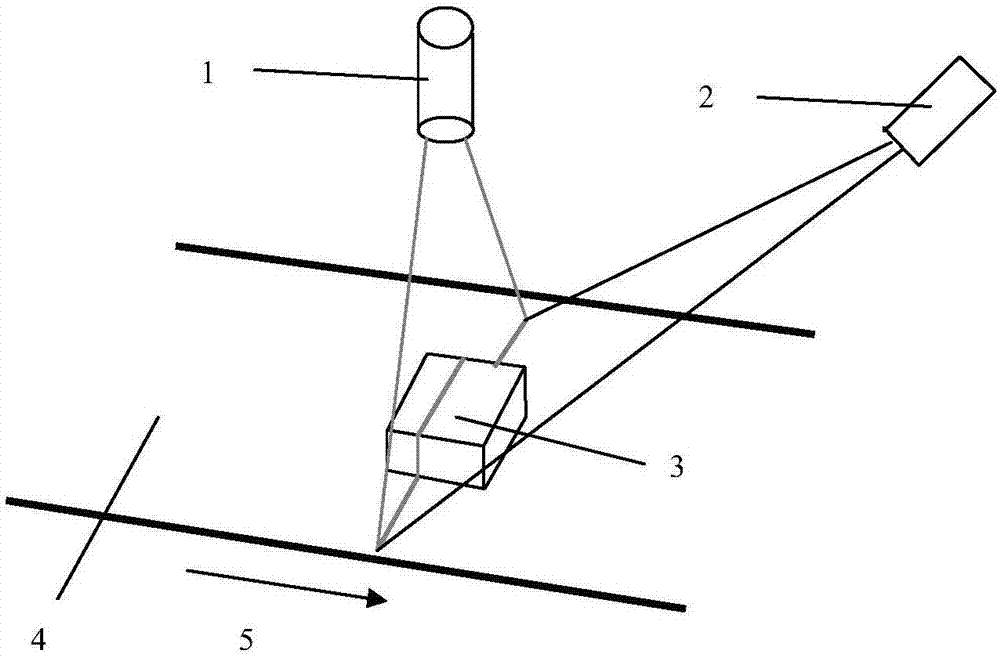
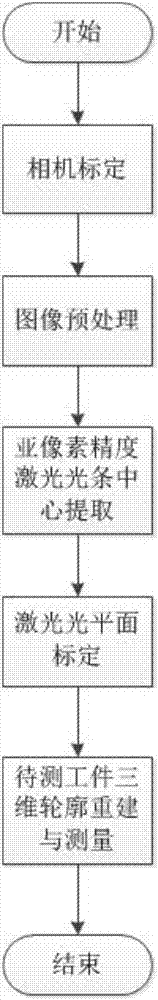
A method of 3D contour measurement of a workpiece on a conveyor belt based on line laser scanning
ActiveCN107578464AHigh measurement accuracyAccurate measurementImage analysisUsing optical meansMobile laser scanningLaser light
The invention discloses a method of 3D contour measurement of a workpiece on a conveyor belt based on line laser scanning. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining camera internal and external parameters through camera calibration, carrying out filtering and laser light strip center position initial extraction through an image preprocessing step, carrying out sub-pixel precision refinement on the center coordinates of a light bar, obtaining a light plane equation through the laser light plane calibration and finally carrying out reconstruction and measurement of the three-dimensional contour information of a workpiece to be measured. The workpiece 3D contour measurement brought forward by the invention has the following advantages: a high measurement precision which means thethree-dimensional contour information of the workpiece to be measured can be accurately obtained through the laser light bar extraction with sub-pixel precision and 3D reconstruction; a fast measurement speed which means real-time measurement of 3D contour information of the workpiece to be tested can be realized to improve the efficiency of industrial production site operations; and low hardwarecosts which is realized in a hardware implementation mode in which laser is combined with a monocular camera. Accordingly, the technical method of the application has advantages such as being in a non-contact mode, high in measurement precision, fast in speed and low in cost, and can be applied to an industrial automation production process to realize accurate measurement of the 3D contour information of the workpiece on the conveyor belt.
Owner:CHANGSHA XIANGJI HAIDUN TECH CO LTD
Two-dimensional method and system enabling three-dimensional user interaction with a device
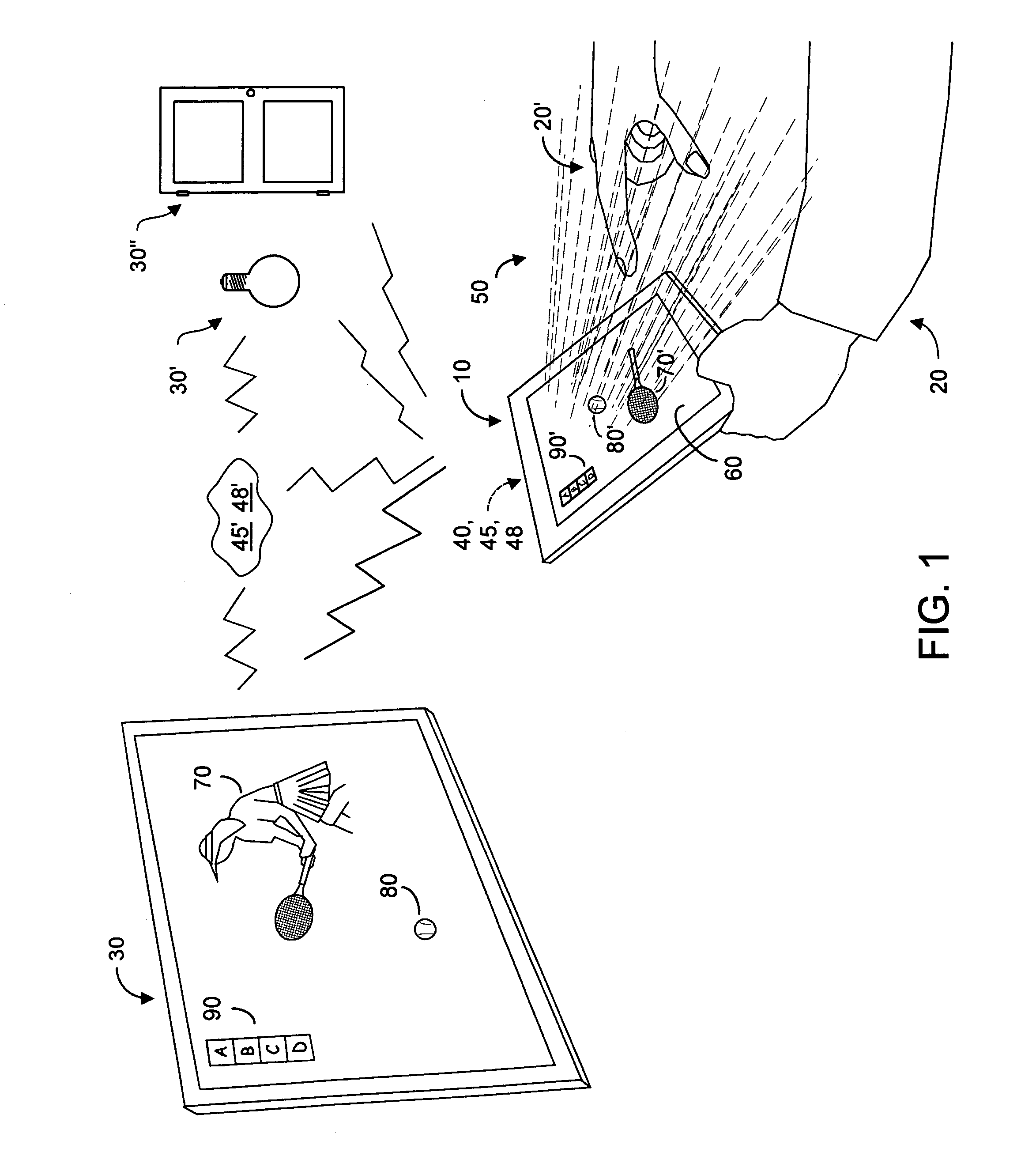
InactiveUS8686943B1Low costLow form factor requirementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsVideo gamesPinhole cameraDisplay device
Owner:KAYA DYNAMICS LLC
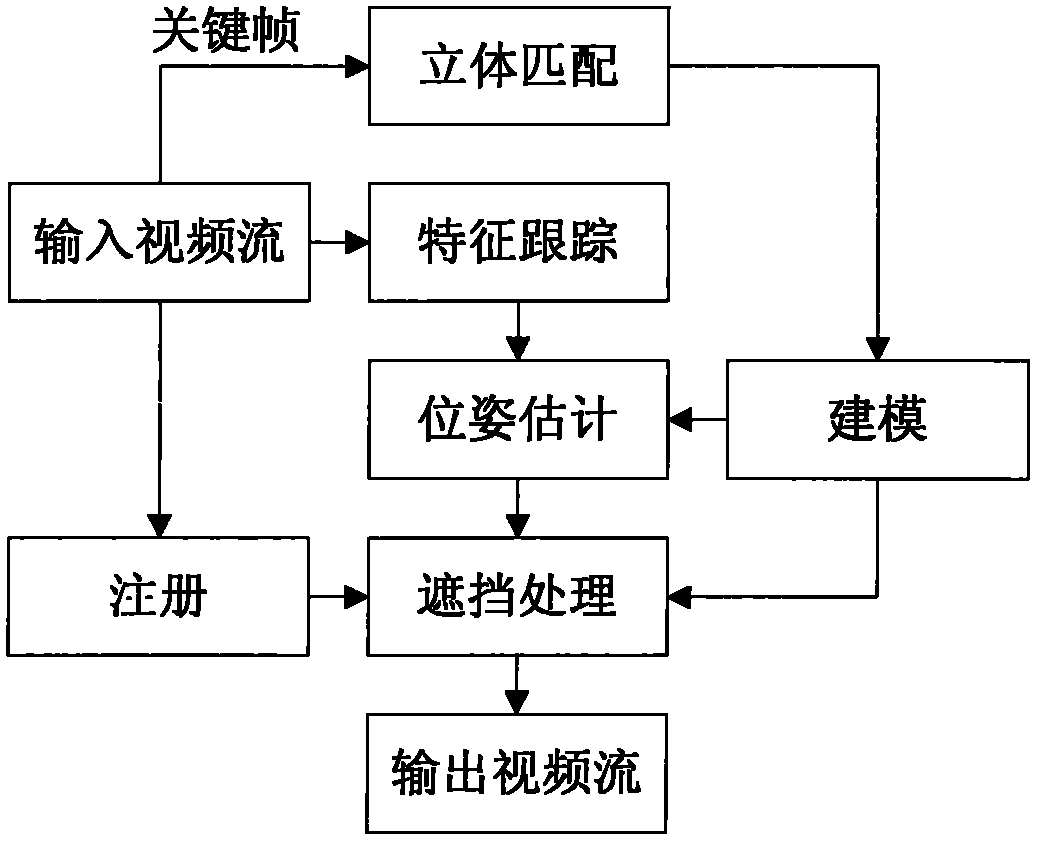
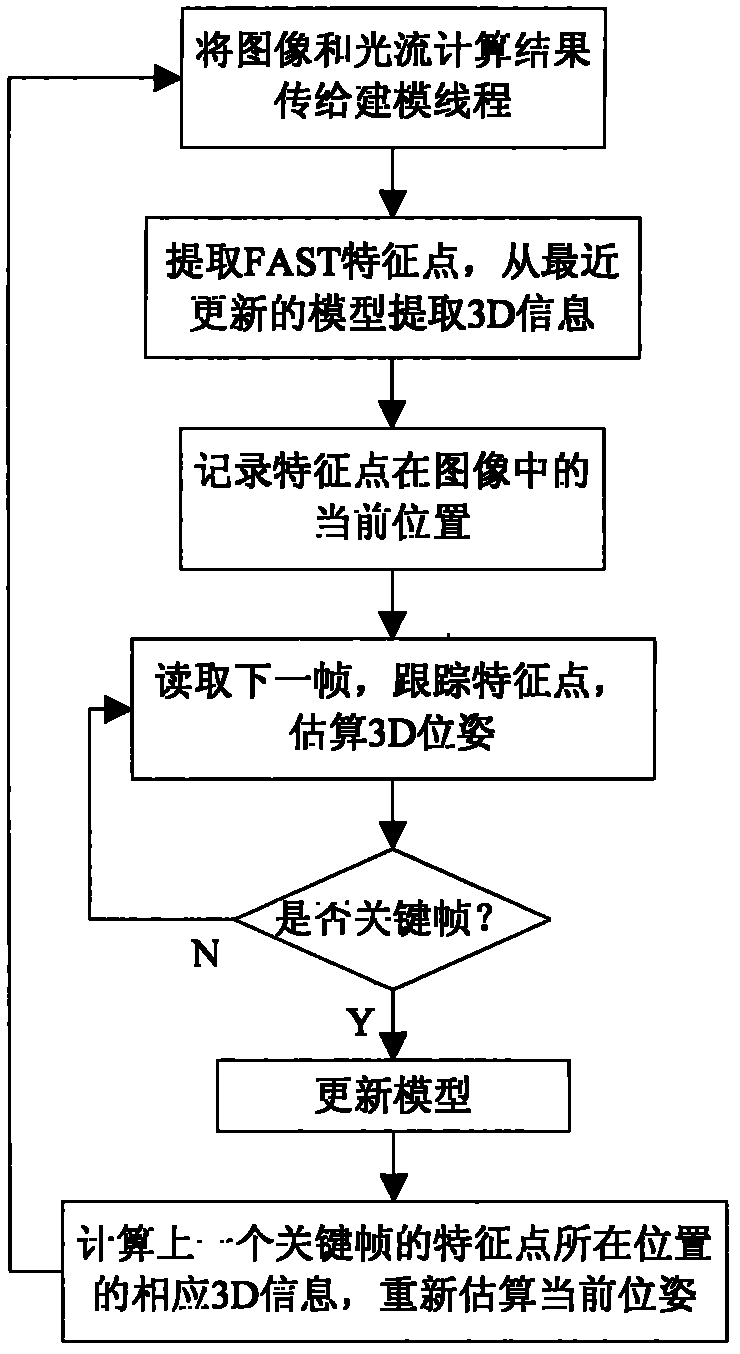
Fast multilevel imagination and reality occlusion method at actuality enhancement environment
InactiveCN102129708AMeet real-time requirementsStrengthen the occlusionSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingDimensional modelingParallel processing
The invention relates to a fast multilevel imagination and reality occlusion method at an actuality enhancement environment, comprising the following steps of: acquiring videos of a real scene by using a two-path video camera; extracting a pair of keyframes from a two-path video stream at set intervals to carry out the resolving of a dense depth map, building a three-dimensional model of a real object participating in occlusion, and extracting sparse feature points; tracking the sparse feature points of all middle frames of the two-path video stream, and estimating the posture of a current camera by combining with the positions of the sparse feature points in an image; acquiring the three-dimensional information of the real object according to a model built for the last time; moving and rotating the model of the real object according to the posture of the current camera; carrying out depth relation comparison by utilizing the three-dimensional information of the recently regulated real object with a registered three-dimensional virtual object; and respectively processing the three-dimensional tracking of the middle frames and the three-dimensional reconstruction of the keyframes in parallel at different threads. The invention is suitable for unknown and variable environments without modeling in advance and can meet the requirements for real time.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Three-dimensional reconstruction method based on coding structured light
ActiveCN101667303ASimple calculationImprove matching accuracyImage analysisUsing optical meansTemplate matchingFeature vector
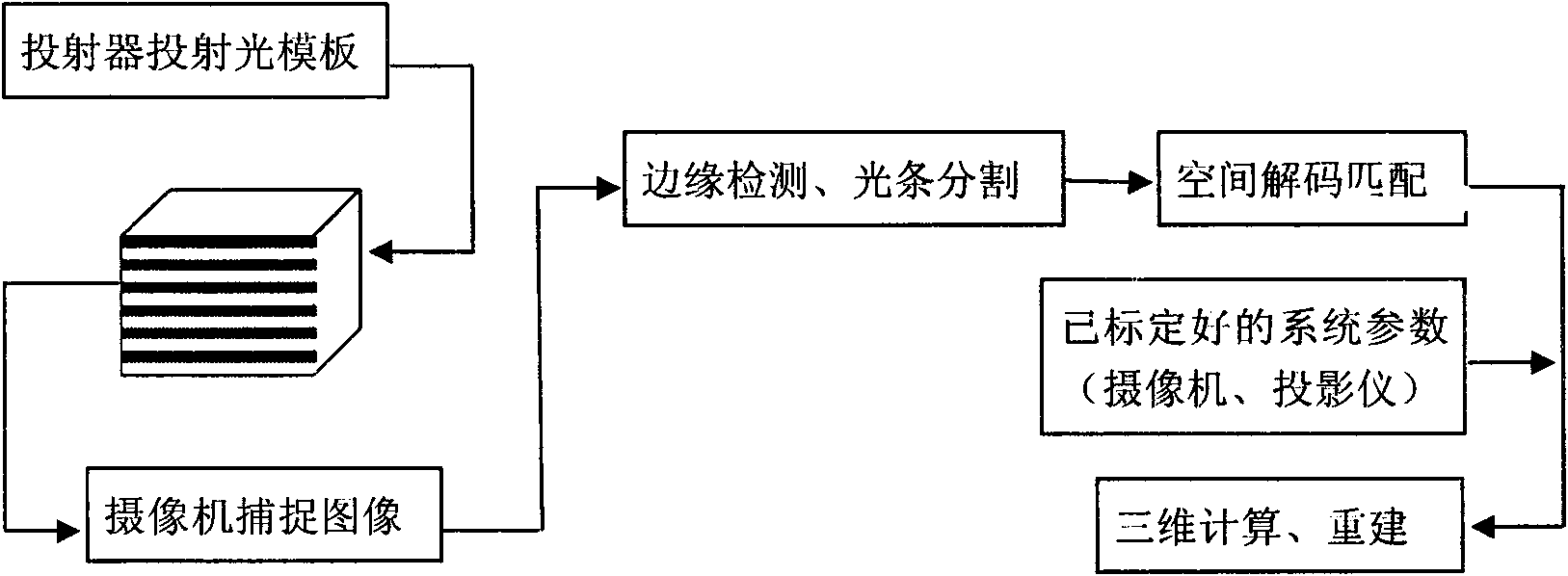
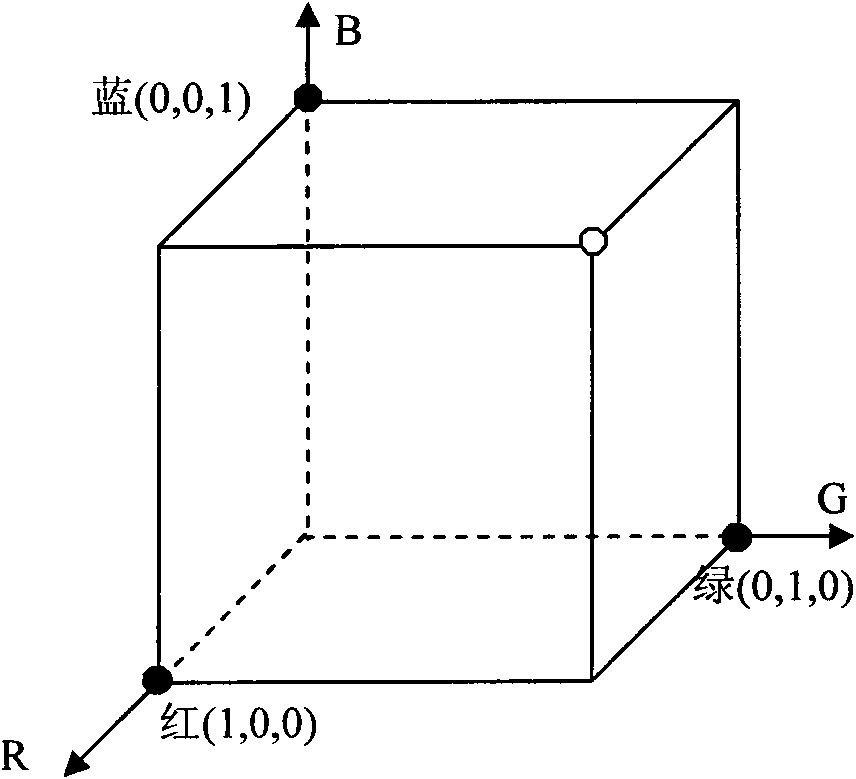
The invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method based on coding structured light, comprising the following steps: 1) projecting structured light to an object to be measured, and capturing an image modulated by the object to be measured by a camera; 2) matching an optical template, comprising: (2.1) positioning the optical strip boundary, scanning along each row of the image, determining a pixel point with strong gray variation as a candidate marginal point, and searching a local domain; and (2.2) matching the optical strip: adopting a color cluster method to build a color matching proper vector, comparing image color with a projected color, and defining Euclidean distance between the color proper vector and the cluster center to distribute the colors of red, green, blue and white of the candidate optical strip; and 3) using a calibrated system parameter for three-dimensional reconstruction of the object to be measured, determining the relation between a space point coordinate and the image coordinate point thereof by the calibrated conversion matrix parameter; and restoring three-dimensional spatial coordinate from the image coordinate of a feature point. The invention can simplify calculation process and has high matching precision and high reconstruction precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
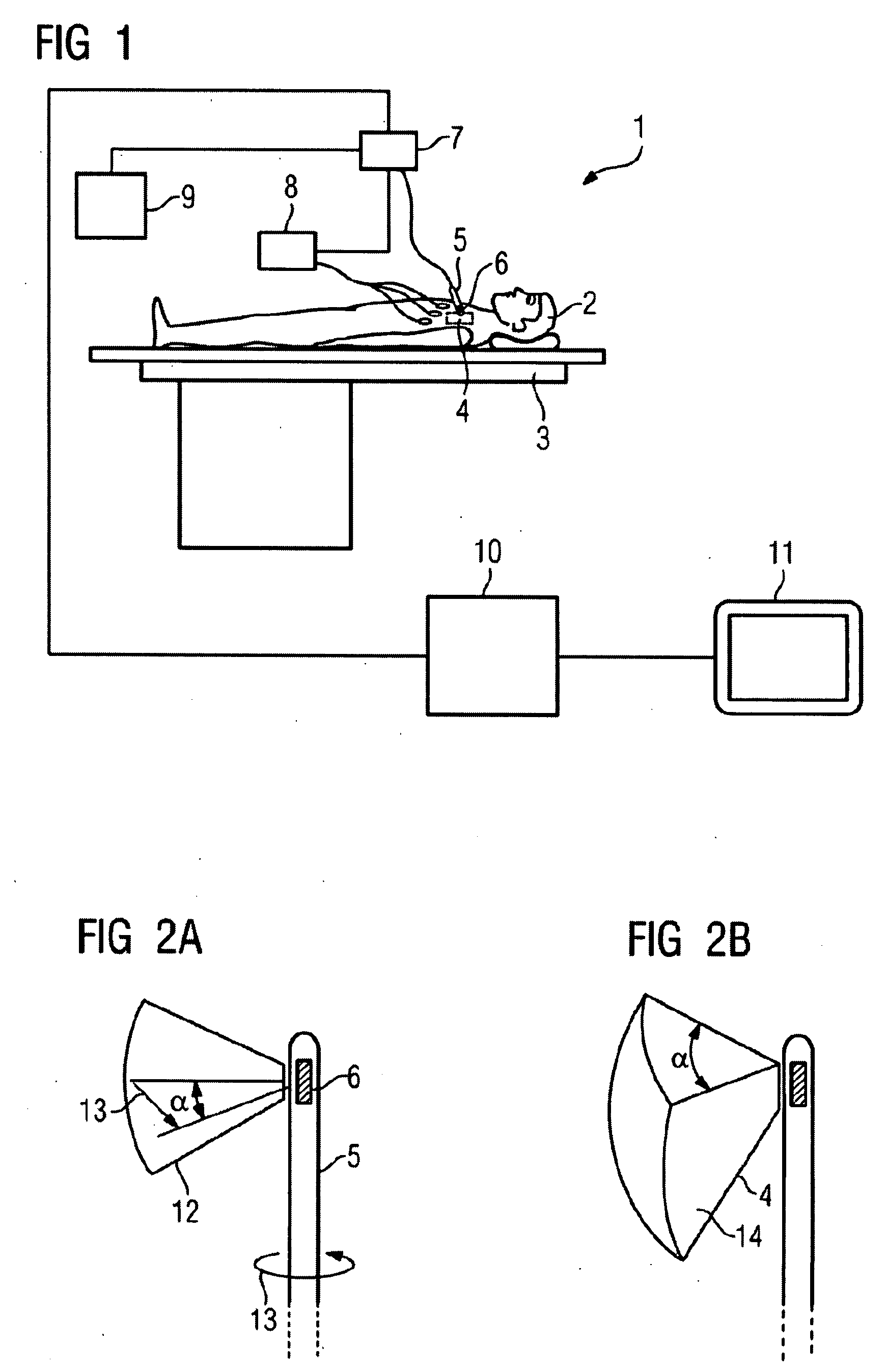
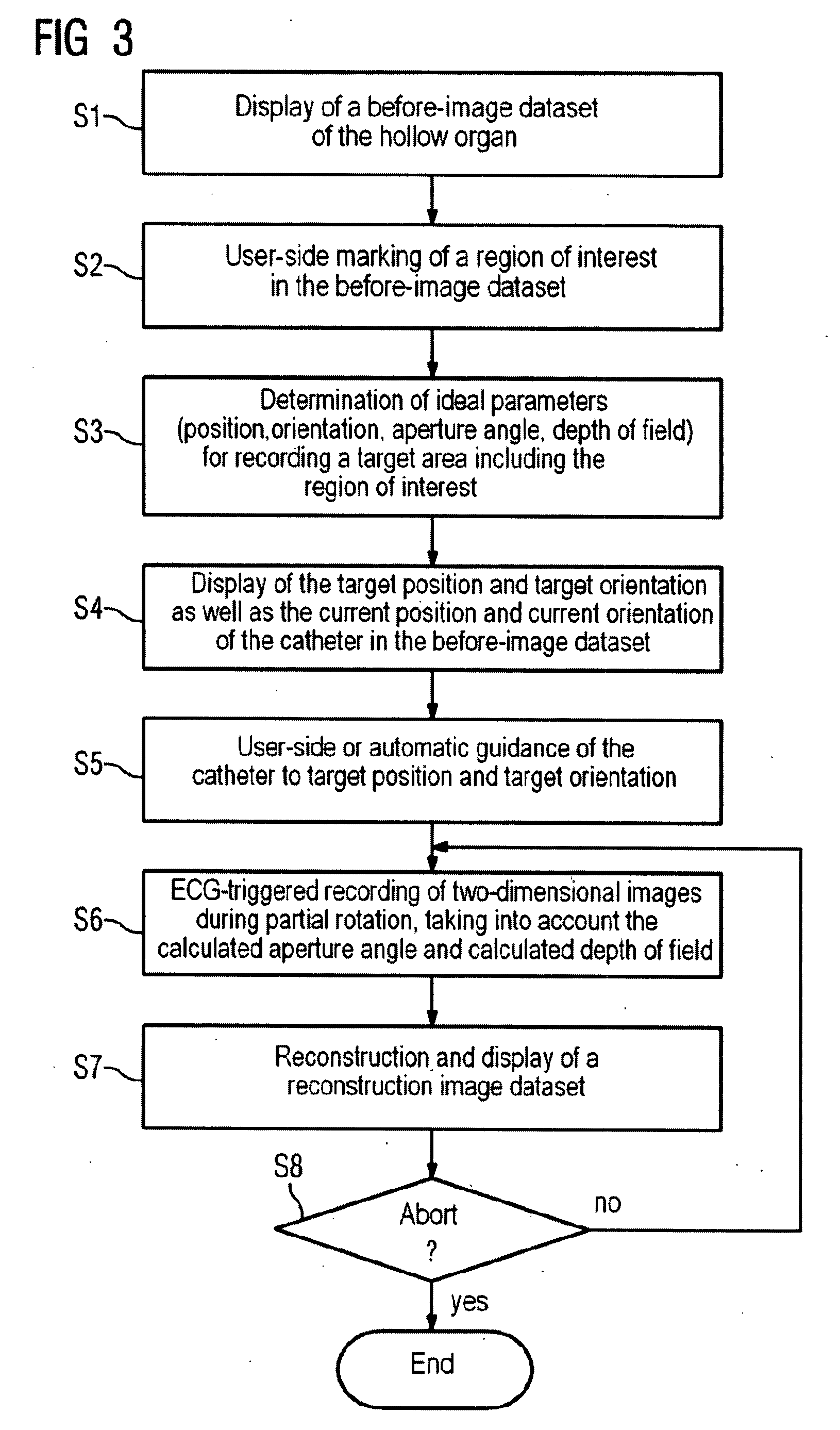
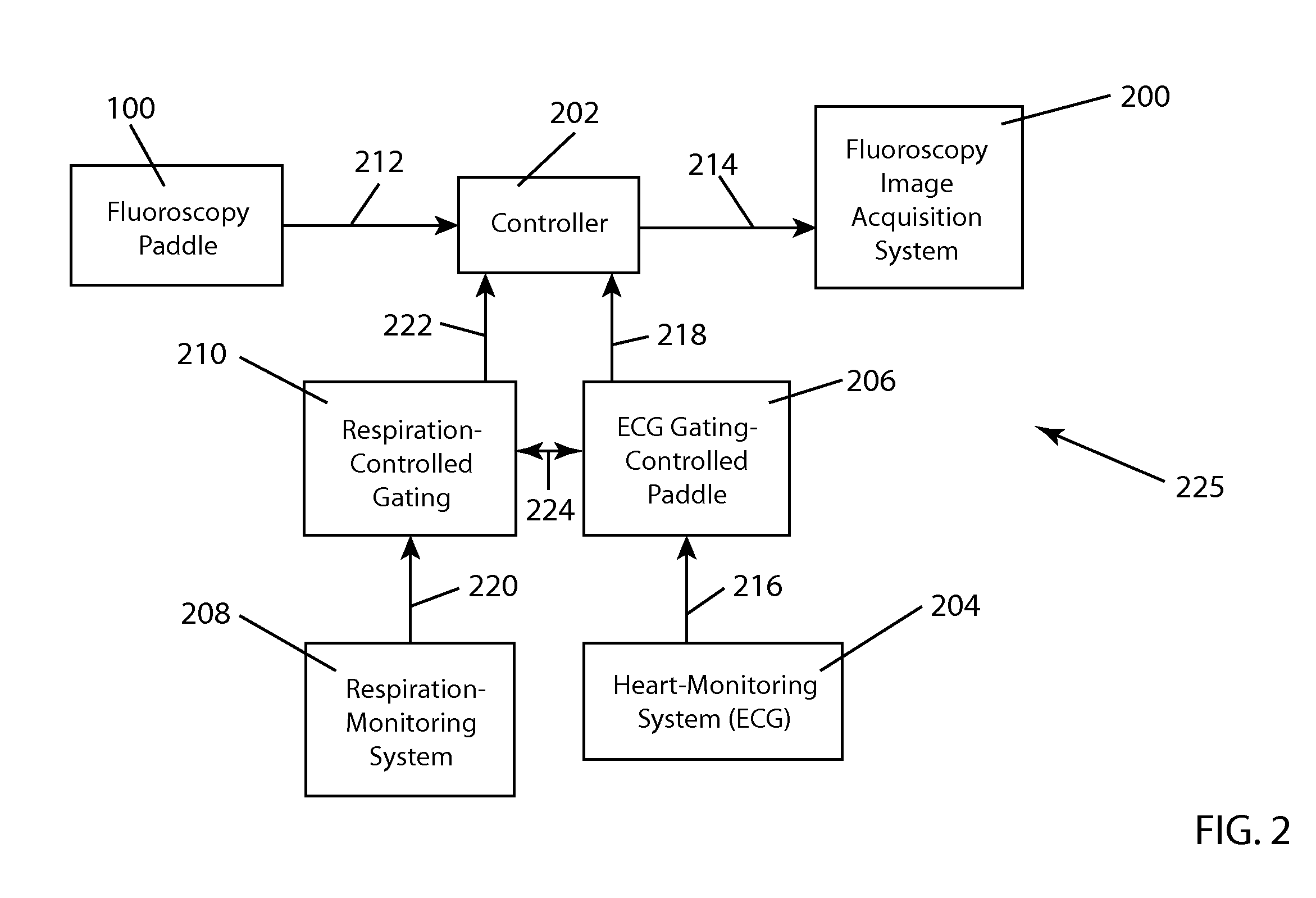
Two-dimensional or three-dimensional imaging of a target region in a hollow organ
InactiveUS20080177172A1Fast rebuildElectrocardiographyCharacter and pattern recognitionData setImage recording
A two-dimensional or three-dimensional imaging of a target region in a hollow organ is provided. A two- or three-dimensional reconstruction image dataset is reconstructed from two-dimensional images from the inside of the hollow organ that are recorded by via a rotating image recording device and displayed, with images covering the entire target region being recorded during a partial rotation of the image recording device through a rotation angle.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
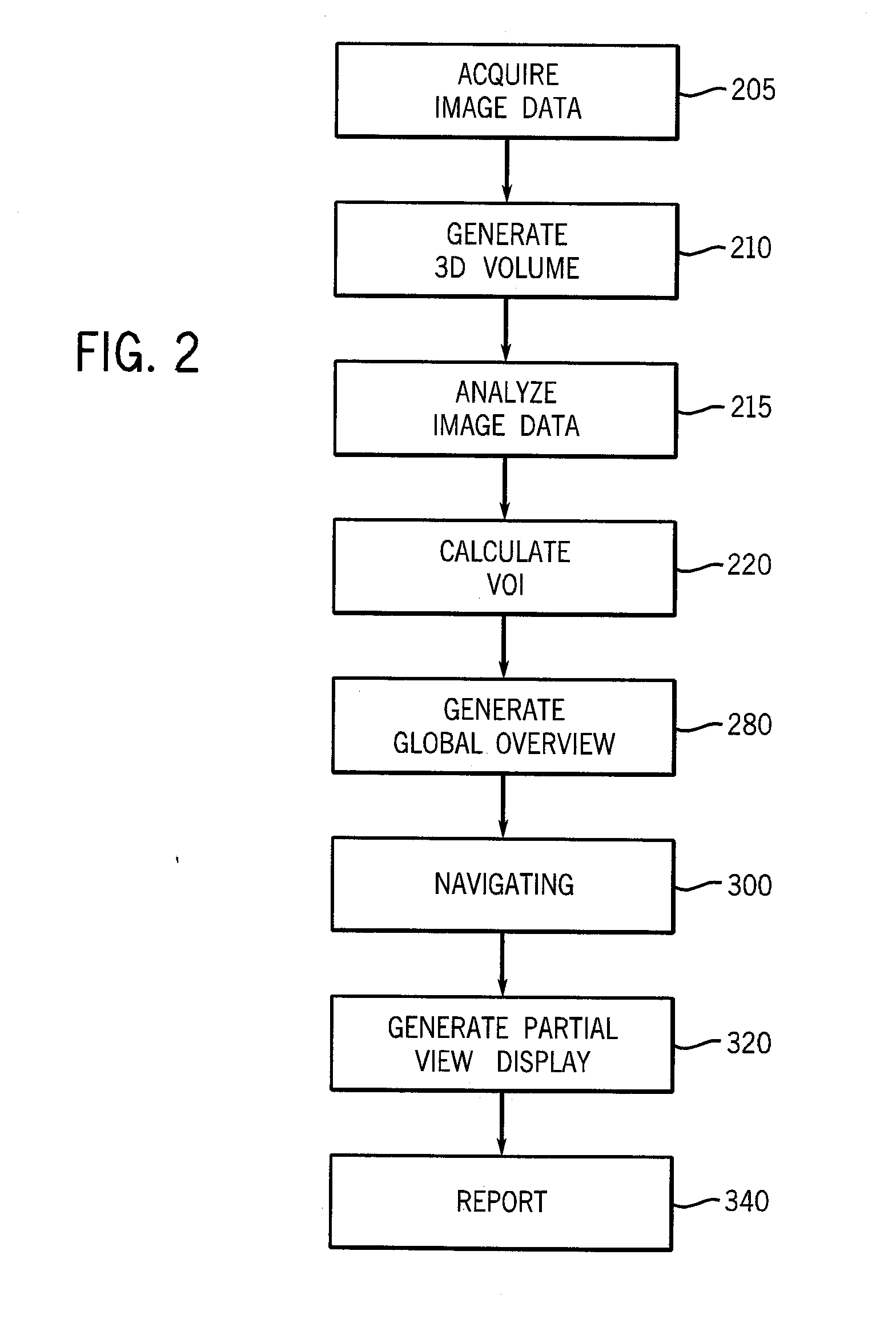
System and method to generate a selected visualization of a radiological image of an imaged subject
ActiveUS20090080765A1Shorten the timeImprove efficiencyReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionProgram instructionOutput device
A system to illustrate image data of an imaged subjected is provided. The system comprises an imaging system, an input device, an output device, and a controller in communication with the imaging system, the input device, and the output device. The controller includes a processor to perform program instructions representative of the steps of generating a three-dimensional reconstructed volume from the plurality of two-dimensional, radiography images, navigating through the three-dimensional reconstructed volume, the navigating step including receiving an instruction from an input device that identifies a location of a portion of the three-dimensional reconstructed volume, calculating and generating a two-dimensional display of the portion of the three-dimensional reconstructed volume identified in the navigation step, and reporting the additional view or at least one parameter to calculate and generate the additional view.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
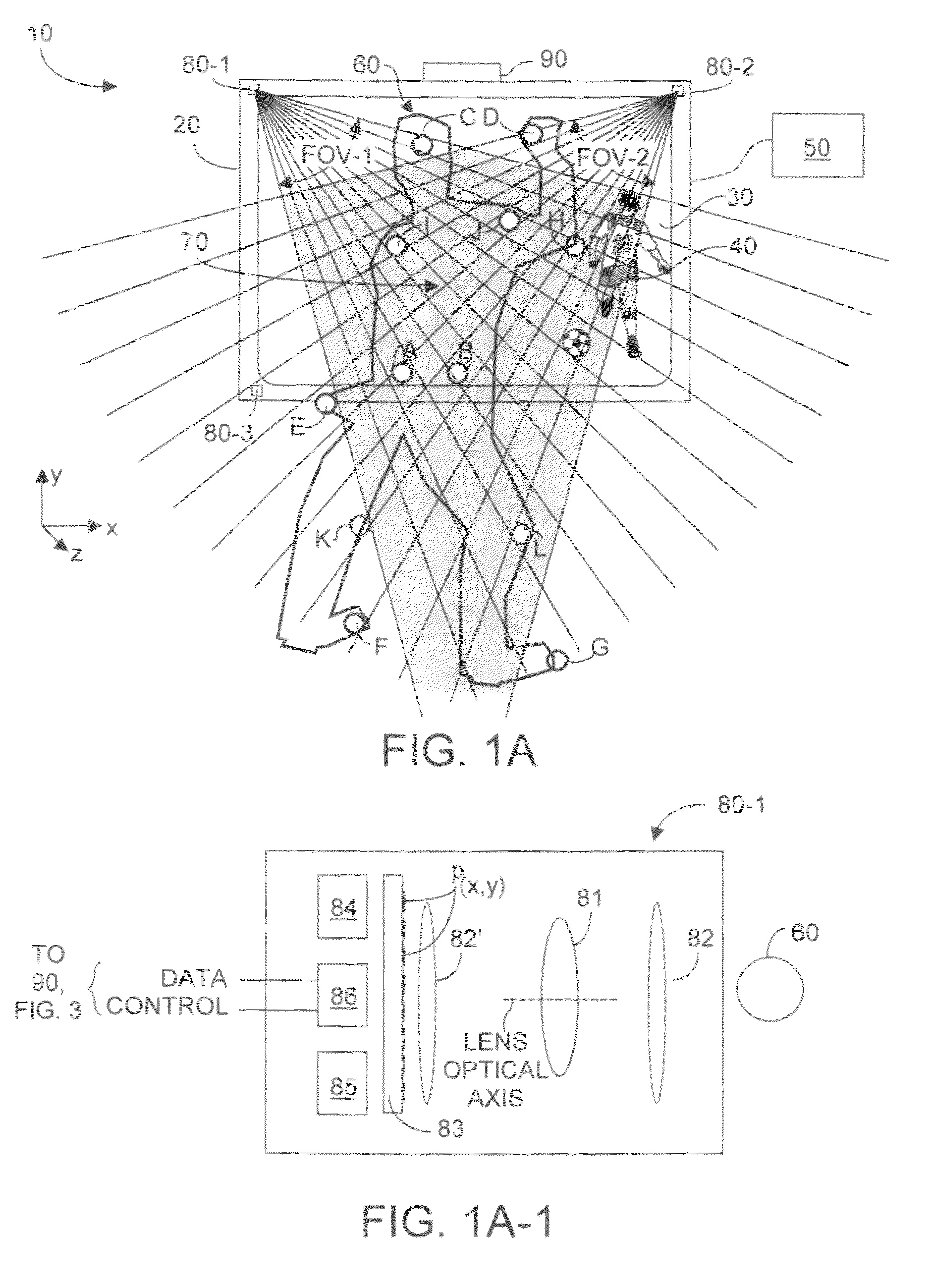
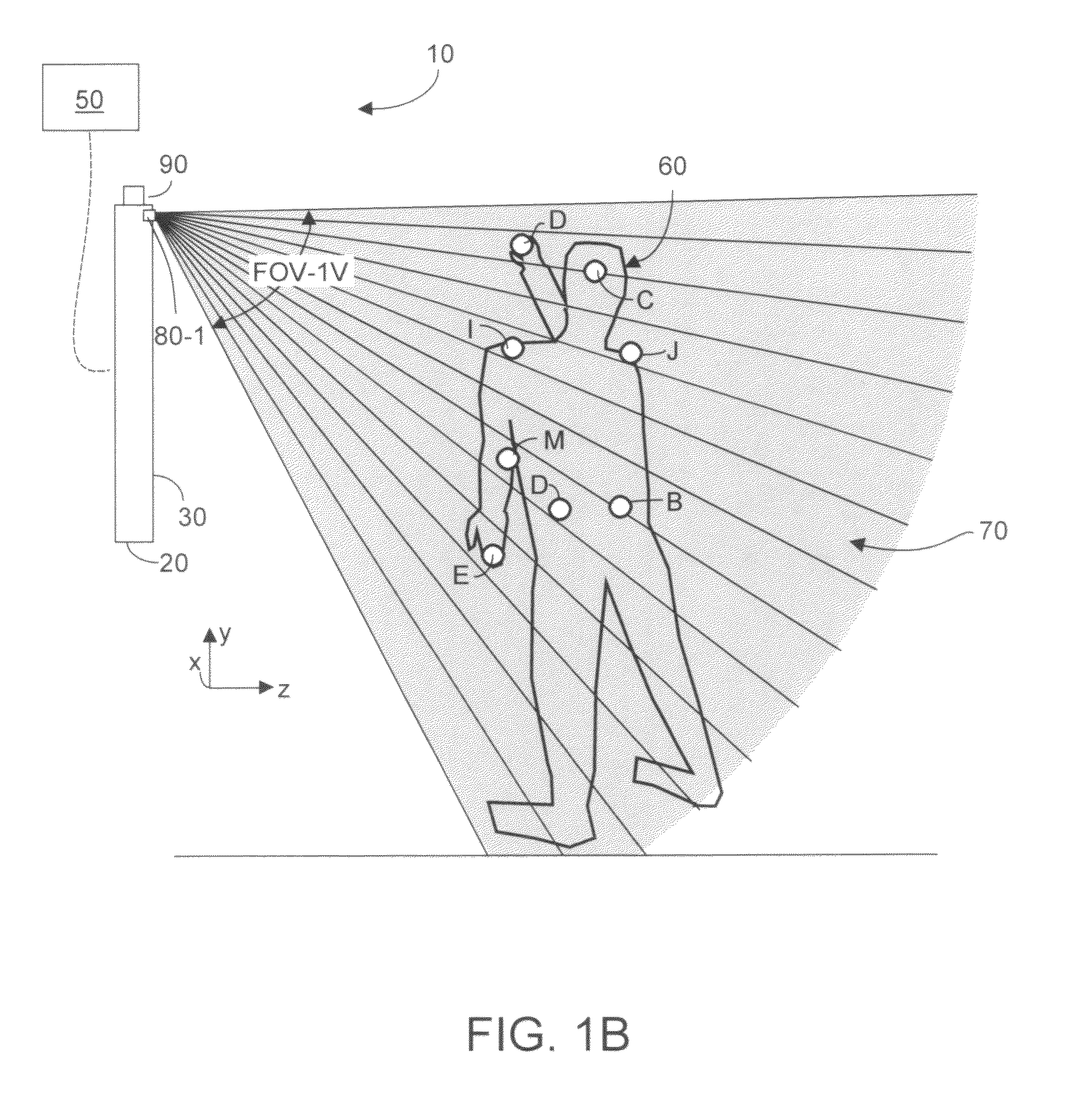
Portable remote control device enabling three-dimensional user interaction with at least one appliance
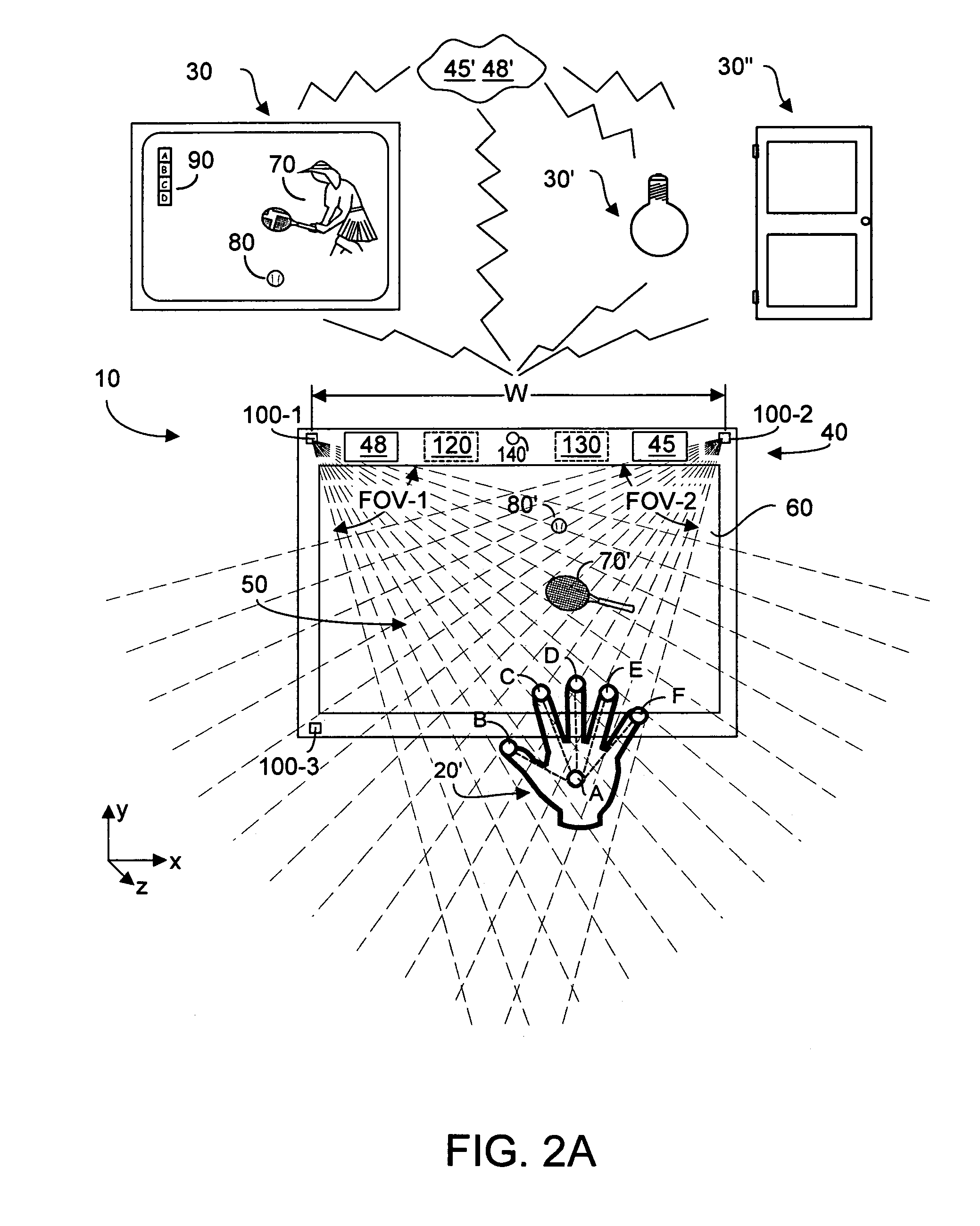
ActiveUS8773512B1Quick eliminationFast dataInput/output for user-computer interactionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPinhole cameraRemote control
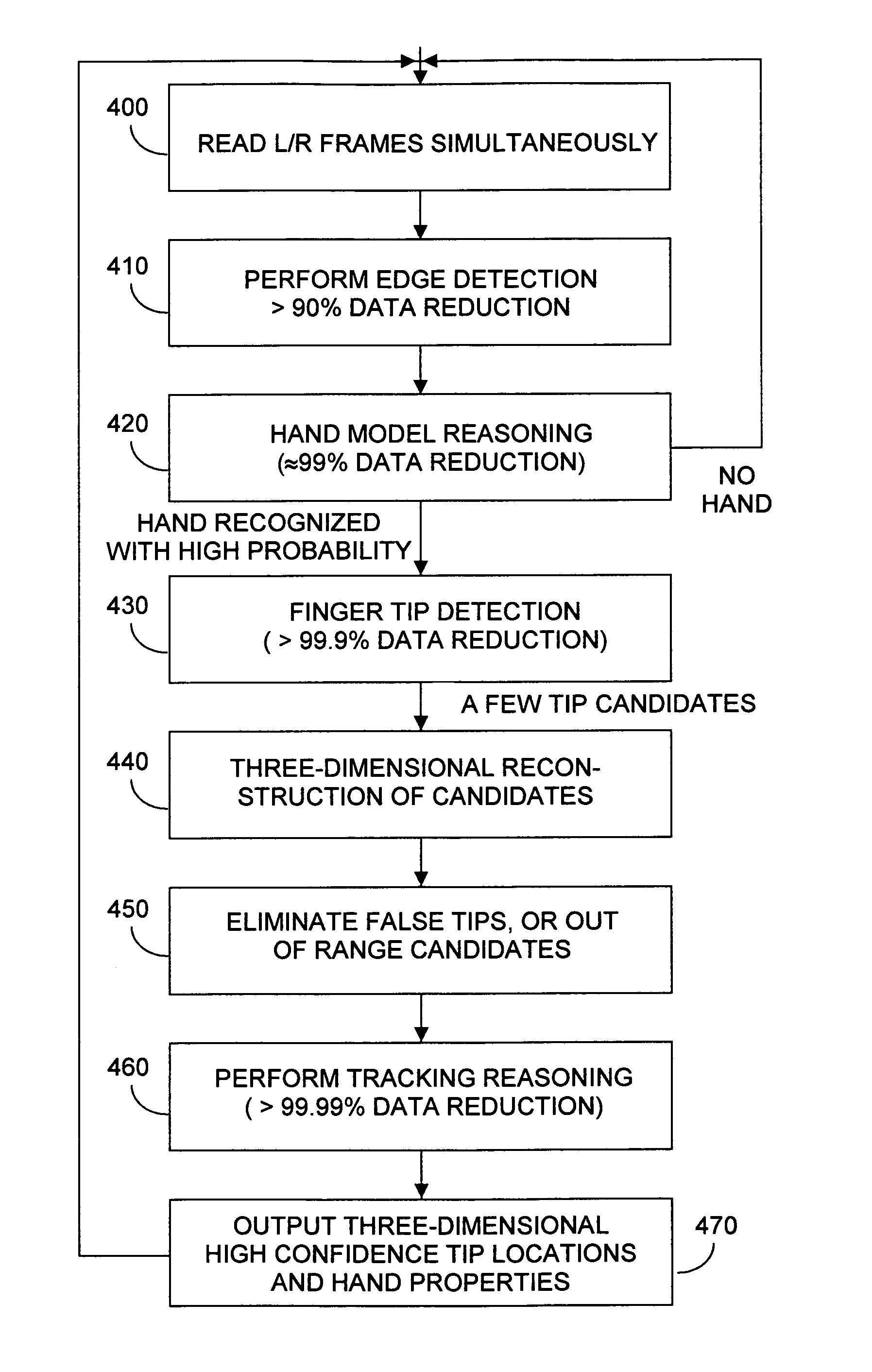
A portable remote control device enables user interaction with an appliance by detecting user gestures made in a hover zone, and converting the gestures to commands that are wirelessly transmitted to the appliance. The remote control device includes at least two cameras whose intersecting FOVs define a three-dimensional hover zone within which user interactions are imaged. Separately and collectively image data is analyzed to identify a relatively few user landmarks. Substantially unambiguous correspondence is established between the same landmark on each acquired image, and a three-dimensional reconstruction is made in a common coordinate system. Preferably cameras are modeled to have characteristics of pinhole cameras, enabling rectified epipolar geometric analysis to facilitate more rapid disambiguation among potential landmark points. As a result processing overhead and latency times are substantially reduced. Landmark identification and position information is convertible into commands that alter the appliance behavior as intended by the user's gesture.
Owner:KAYA DYNAMICS LLC
Regional depth edge detection and binocular stereo matching-based three-dimensional reconstruction method
ActiveCN101908230AStable matching costReduce mistakesImage analysis3D modellingObject pointReconstruction method
The invention discloses a regional depth edge detection and binocular stereo matching-based three-dimensional reconstruction method, which is implemented by the following steps: (1) shooting a calibration plate image with a mark point at two proper angles by using two black and white cameras; (2) keeping the shooting angles constant and shooting two images of a shooting target object at the same time by using the same camera; (3) performing the epipolar line rectification of the two images of the target objects according to the nominal data of the camera; (4) searching the neighbor regions of each pixel of the two rectified images for a closed region depth edge and building a supporting window; (5) in the built window, computing a normalized cross-correlation coefficient of supported pixels and acquiring the matching price of a central pixel; (6) acquiring a parallax by using a confidence transmission optimization method having an acceleration updating system; (7) estimating an accurate parallax by a subpixel; and (8) computing the three-dimensional coordinates of an actual object point according to the matching relationship between the nominal data of the camera and the pixel and consequently reconstructing the three-dimensional point cloud of the object and reducing the three-dimensional information of a target.
Owner:江苏省华强纺织有限公司 +1
Image processing method and mobile terminal
ActiveCN105825544ASolve the situationSolve the problem of saving light and shadow effect images generated by different 3D lighting3D-image rendering3D modellingImaging processingPoint cloud
The present invention provides an image processing method. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a visible light image and the depth information through shooting the same scene; according to the acquired visible light image and the depth information, obtaining the three-dimensional point cloud data of the scene based on a preset algorithm; according to the three-dimensional point cloud data of the scene obtained through calculation, conducting the three-dimensional reconstruction of the scene, generating a three-dimensional geometric model and constructing a virtual scene; and conducting the rendering treatment on the constructed virtual scene. The embodiment of the present invention also provides a corresponding mobile terminal. According to the image processing method provided in the embodiment of the present invention, images of different lighting effects in different 3D illumination conditions can be obtained, and the user experience is improved. The problem in the prior art that the images of different lighting effects in different 3D illumination conditions cannot be pre-viewed and stored without changing the physical scene by means of the mobile terminal can be solved.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Radiotherapeutic apparatus in operation
InactiveCN1537657AReduce Multidimensional Motion DirectionReduce angle requirementsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiation Dosages3d image
A radiotherapeutic apparatus using high-energy electron beams to radiate the bed of removed tumor and the residual tumor tissue in excision operation features that the CT or MRI 3D imaging software is used to determine the position of tumor focal, an analog technique is used to determine the incident direction, angle and position of electron beam, a radiotherapeutic plan system is used to calculate the radiation dosage, and a laser locator on the radiating head with straight-line electron accelerator is used to align the electron beam to the tumor focal.
Owner:高春平
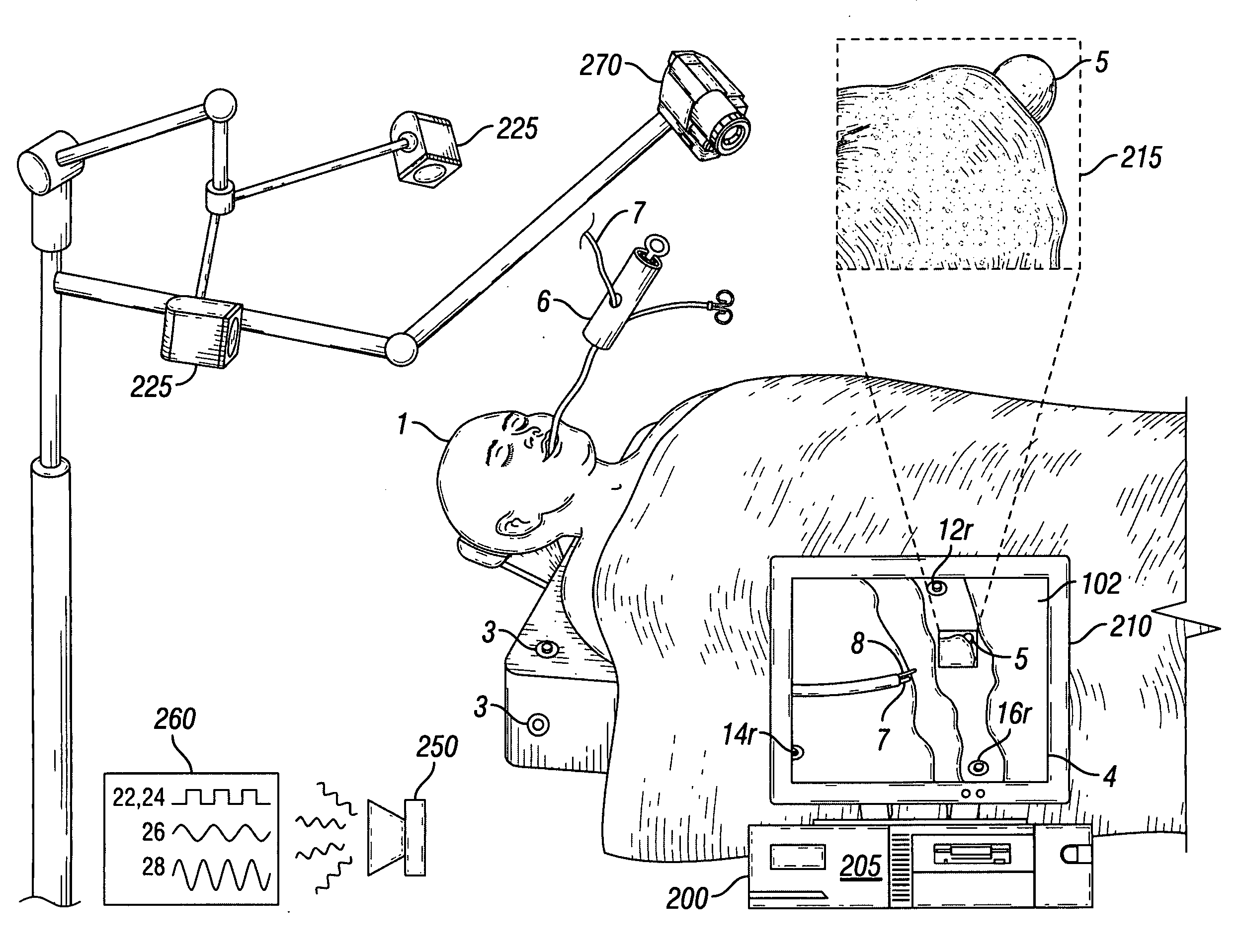
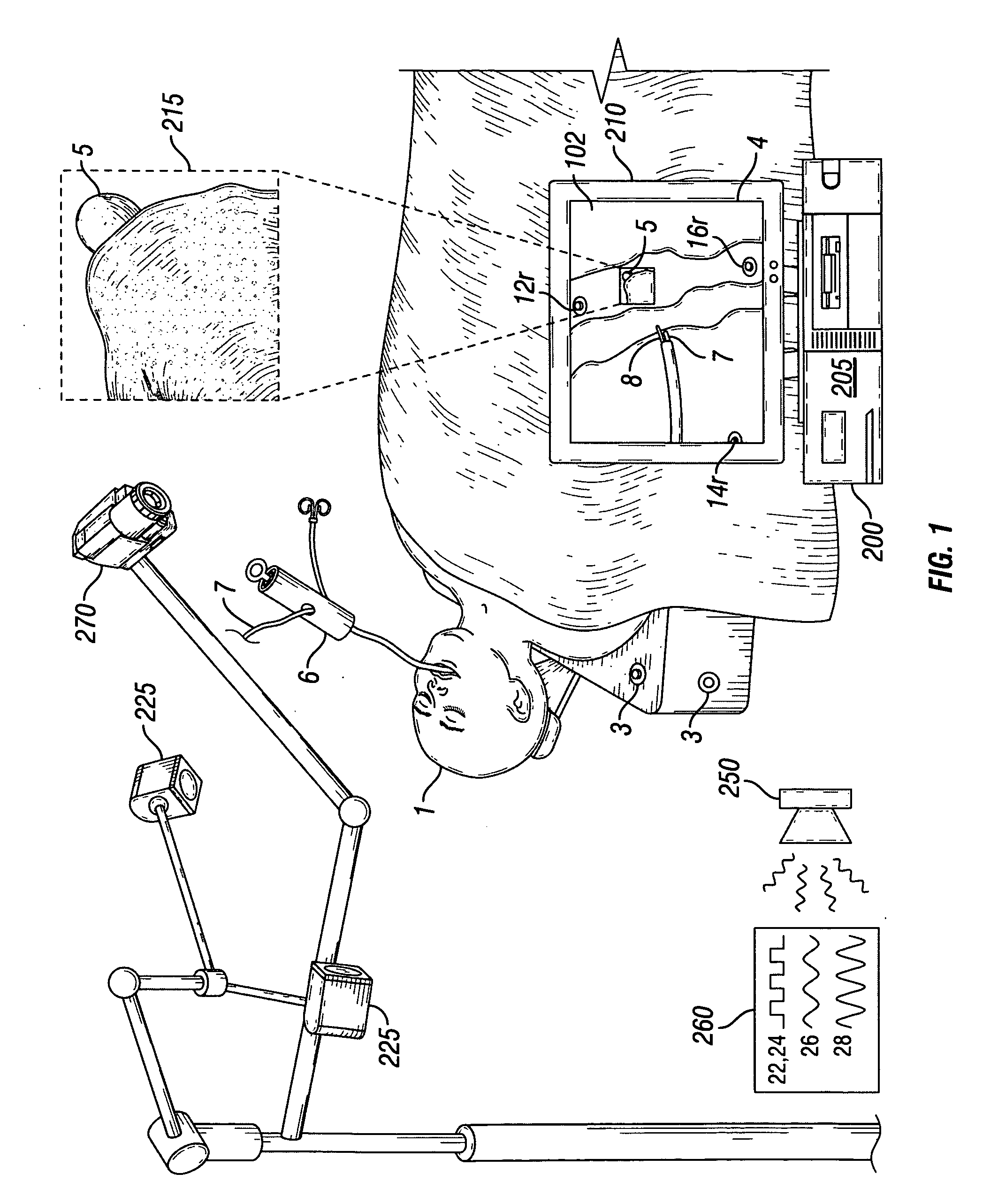
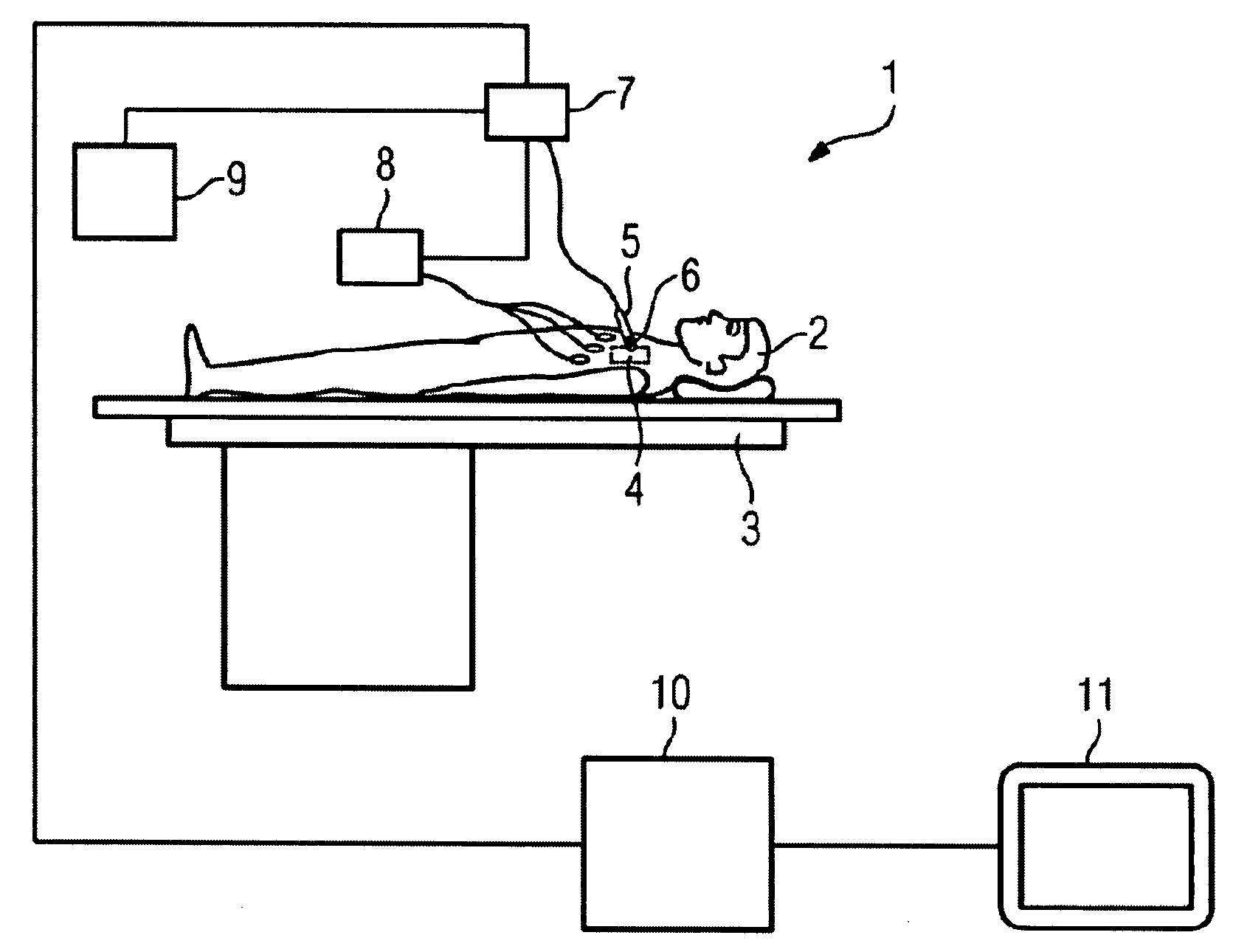
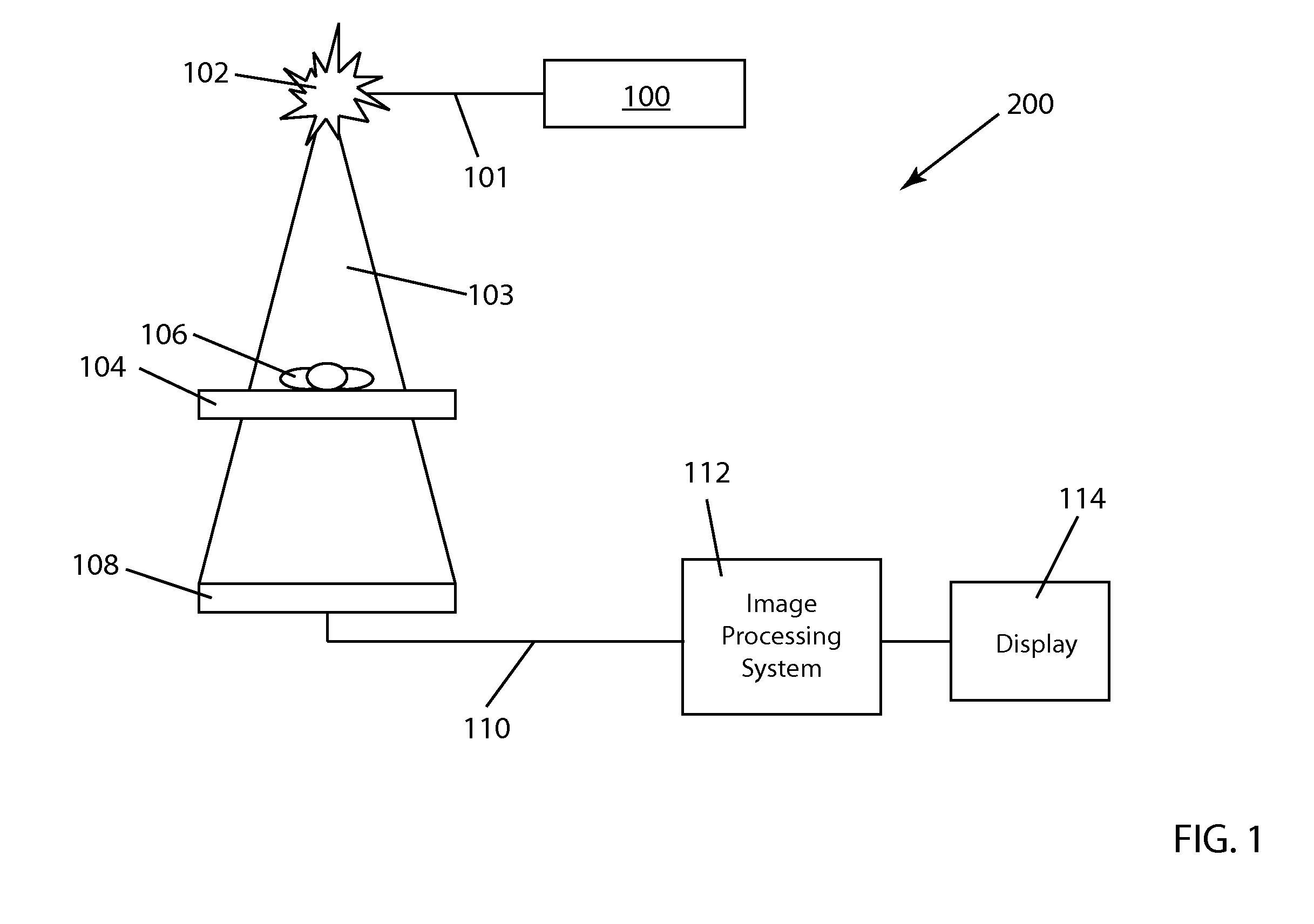
3D Model Creation of Anatomic Structures Using Single-Plane Fluoroscopy
ActiveUS20120071751A1Improve accuracyImprove effectivenessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnatomical structuresFluoroscopic image
A method for 3D reconstruction of the positions of a catheter as it is moved within a region of the human body, comprising: (a) ascertaining the 3D position of a point on a catheter for insertion in the body region; (b) acquiring a fixed angle, single-plane fluoroscopic image of the body region and of the catheter; (c) transferring the image data and catheter-point position to a computer; (d) determining the 2D image coordinates of the point on the catheter; (e) changing the length of catheter insertion by a measured amount; (f) thereafter acquiring a further single-plane fluoroscopic image of the body region and the catheter from the same angle, transferring the length change and additional image data to the computer, and determining the 2D image coordinates of the point on the catheter; (g) computing the 3D position of the catheter point; and (h) repeating steps e-g plural times. A 3D model is constructed by assembling the plural 3D positions of the point within the body region into a 3D model of the region.
Owner:APN HEALTH
Contact network three-dimensional reconstruction method based on SIFT and LBP point cloud registration
InactiveCN104299260ASolve the problem of high configuration requirementsImprove registration speedImage renderingSpecial data processing applicationsContact networkSomatosensory system
The invention provides a contact network three-dimensional reconstruction method based on SIFT and LBP point cloud registration. The method comprises the first step of obtaining initial three-dimensional point cloud data of the environment where parts of a contact network to be reconstructed are located through motion-sensing peripheral Kinect for Windows, and conducting denoising, simplifying, partitioning clustering, fusing and other preprocessing operations on the initial three-dimensional point cloud data to obtain single-view-angle point cloud data of the parts of the contact network to be reconstructed, the second step of extracting key points through an SIFT algorithm, constructing description vectors of the key points by means of LBP features of uniform patterns and determining the corresponding relations between the key points in different point clouds according to the distances between the vectors, the third step of completing point cloud registration through a rough registration method and an ICP fine registration method and obtaining the complete three-dimensional point cloud data of the parts of the contact network to be reconstructed, and the fourth step of completing three-dimensional reconstruction through the Poisson surface reconstruction method and obtaining a three-dimensional model. According to the method, the key factor is point cloud registration which is the key step influencing the three-dimensional reconstruction speed; the description vectors of the key points are constructed by means of the LBP features of the uniform patterns, so that vector dimensions are reduced, the matching speed of the corresponding relations is increased, registration is accelerated, and the three-dimensional reconstruction speed is increased.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
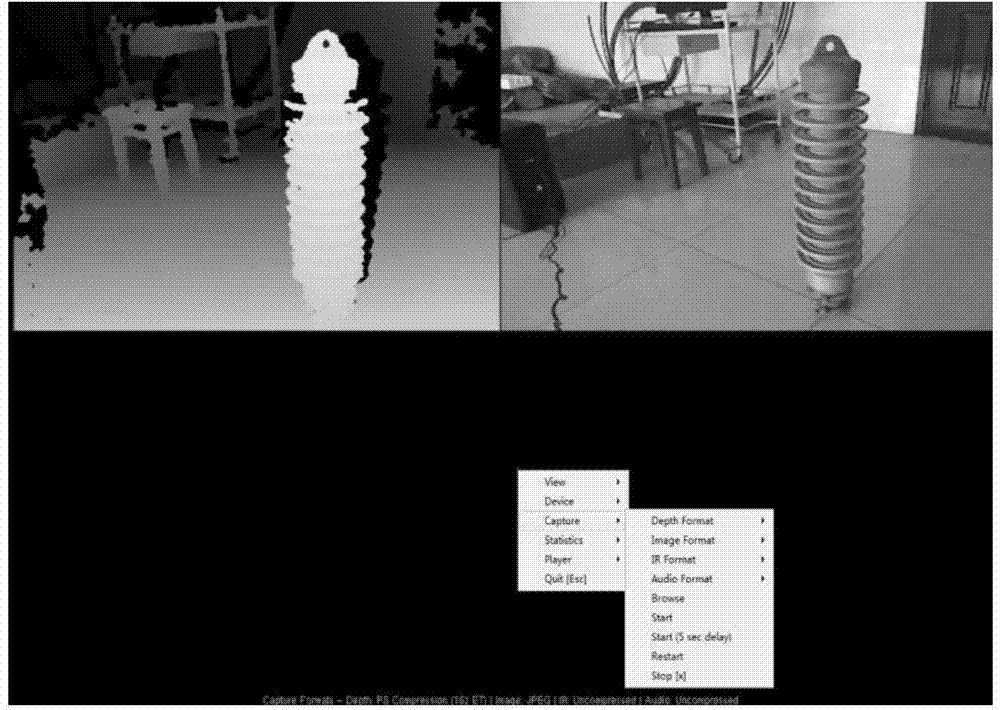
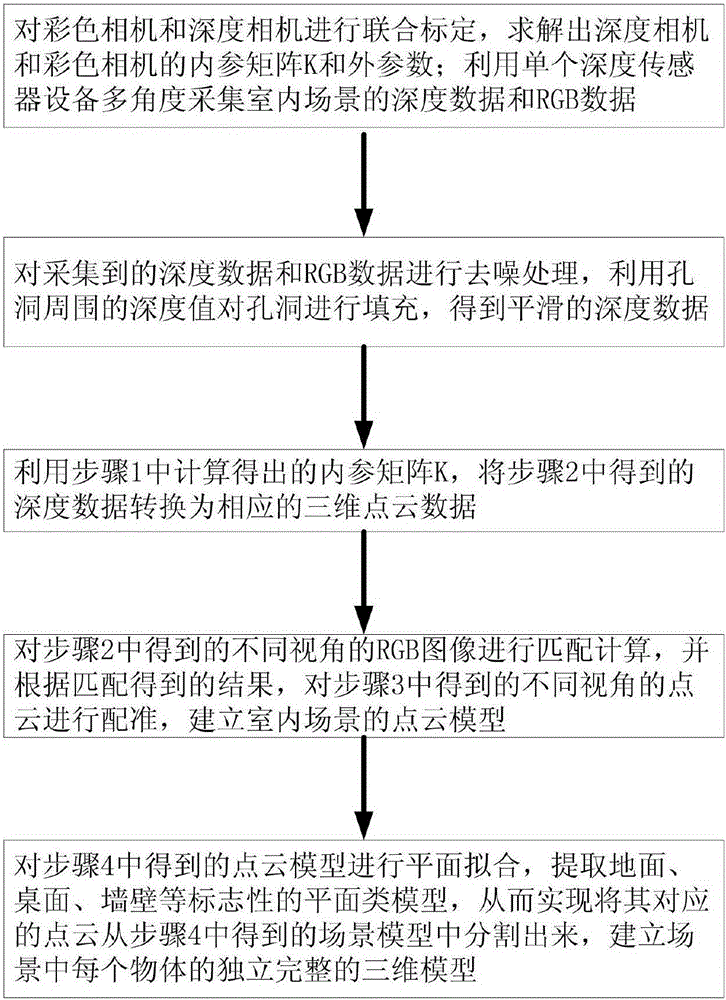
Indoor scene 3D reconstruction method based on Kinect
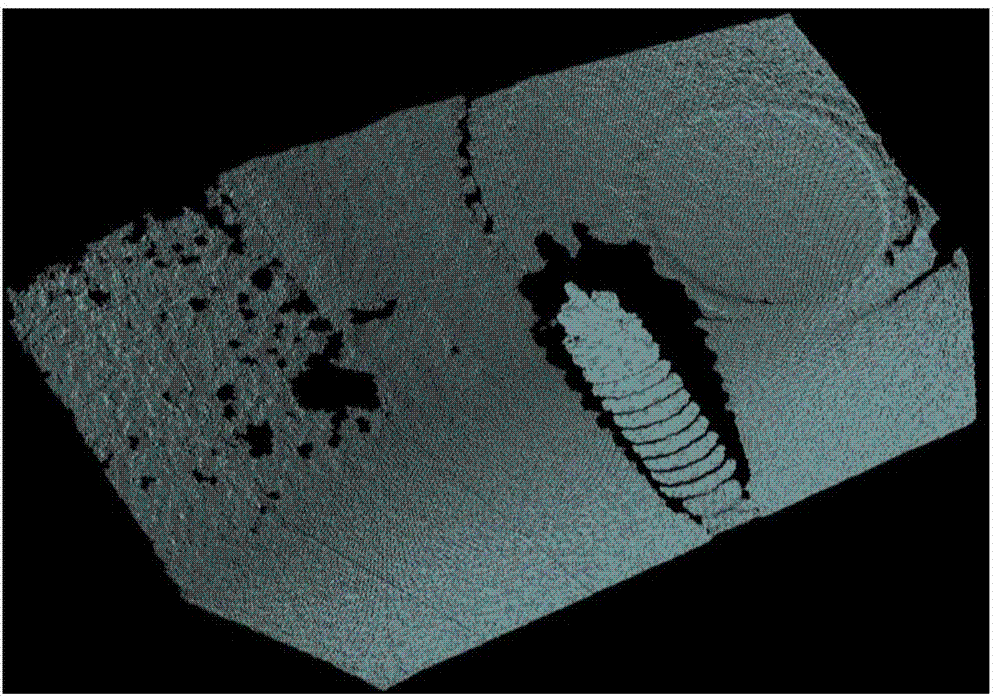
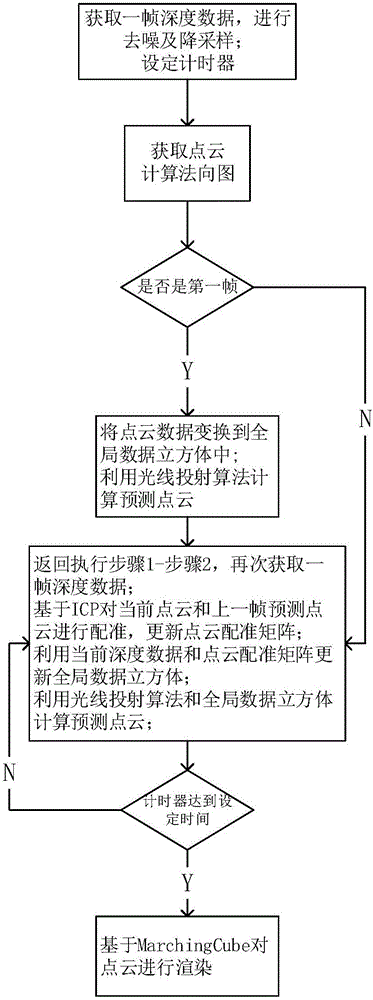
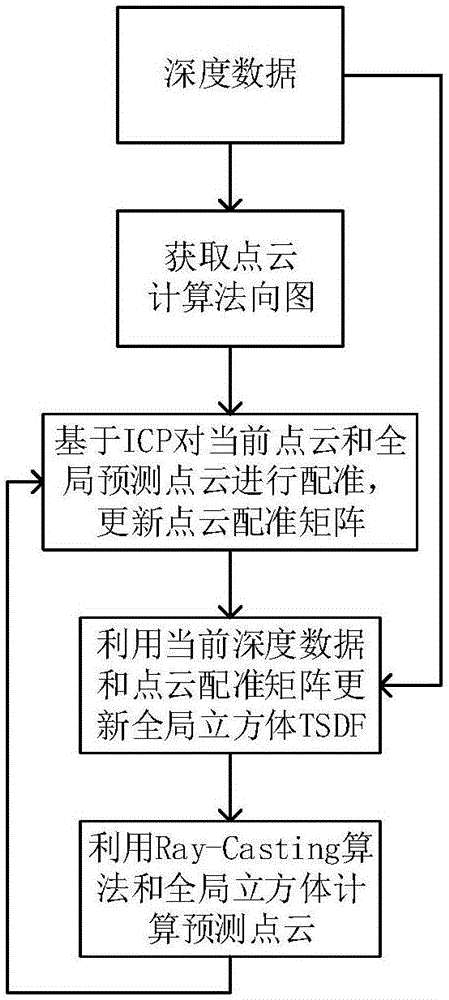
ActiveCN106803267ALess redundancyImprove real-time performanceDetails involving processing stepsImage enhancementPoint cloudRay casting
The invention discloses an indoor scene 3D reconstruction method based on Kinect and solves the technical problem of the real-time reconstruction of an indoor scene 3D model and avoidance of excessive redundant points. The method comprises steps of: obtaining the depth data of an object by using Kinect and de-nosing and down-sampling the depth data; obtaining the point cloud data of a current frame and calculating the vector normal of each point in the frame; using a TSDF algorithm to establish a global data cube, and using a ray casting algorithm to calculate predicted point cloud data; calculating a point cloud registration matrix by using an ICP algorithm and the predicted point cloud data, fusing the obtained point cloud data of each frame into the global data cube, and fusing the point cloud data frame by frame until a good fusion effect is obtained; rendering the point cloud data with an isosurface extraction algorithm and constructing the 3D model of the object. The method improves the registration speed and the registration precision, is fast in fusion speed and few in redundancy points, and can be used for real-time reconstruction of the indoor scene.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
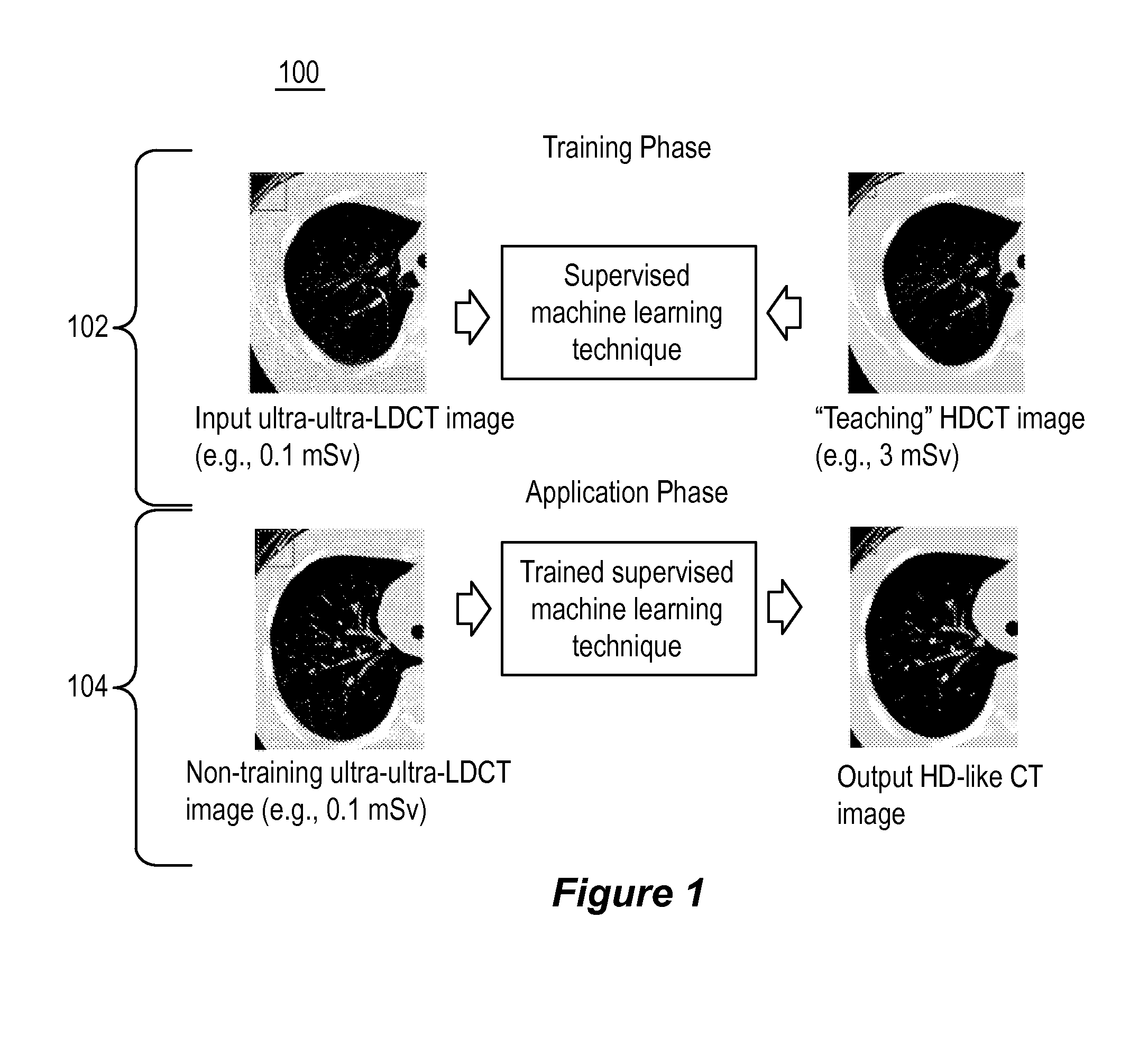
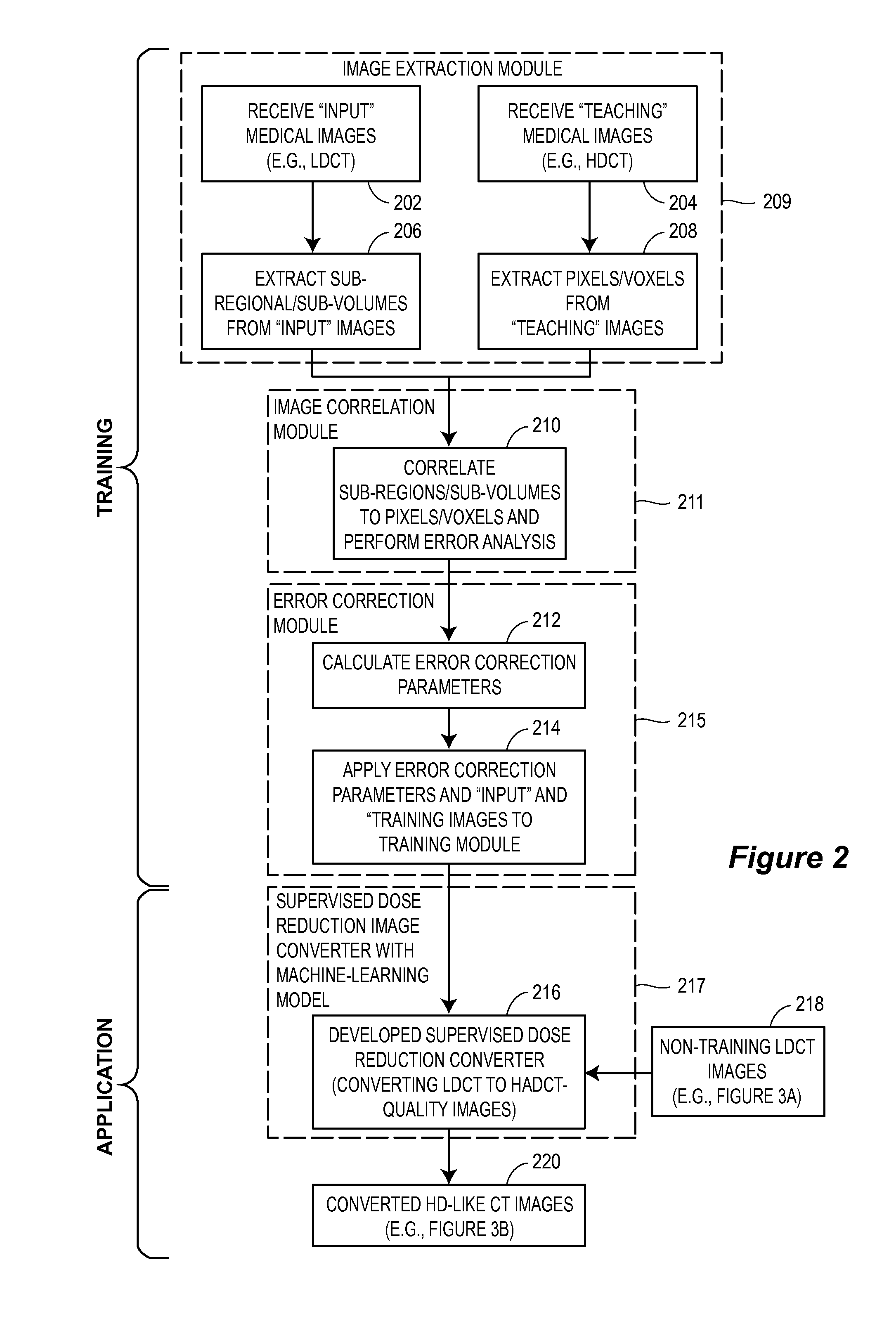
Supervised machine learning technique for reduction of radiation dose in computed tomography imaging
ActiveUS20150201895A1Quality improvementReduce noiseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionComputed tomographyDose reduction
Substantial reduction of the radiation dose in computed tomography (CT) imaging is shown using a machine-learning dose-reduction technique. Techniques are provided that (1) enhance low-radiation dosage images, beyond just reducing noise, and (2) may be combined with other approaches, such as adaptive exposure techniques and iterative reconstruction, for radiation dose reduction.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
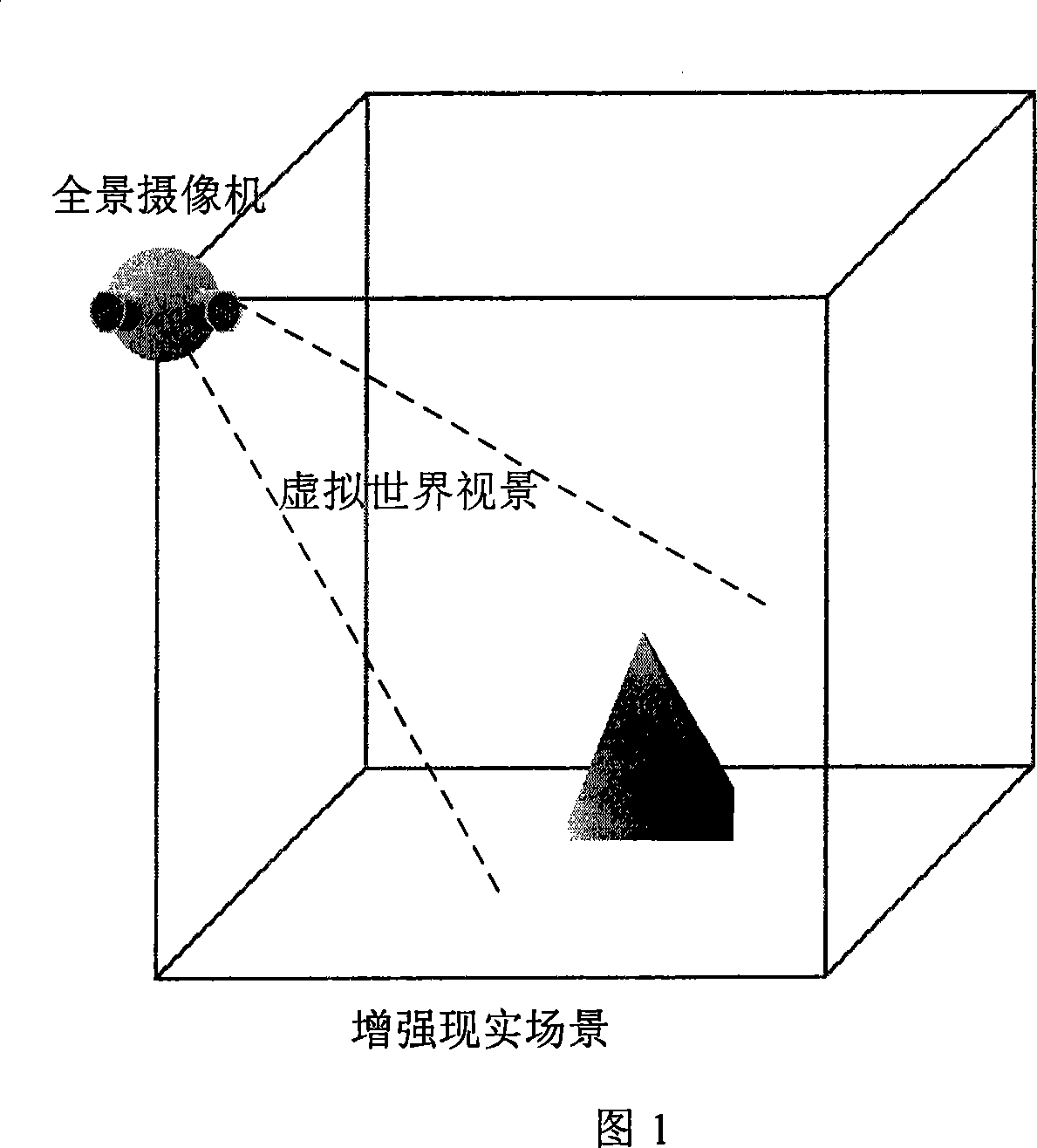
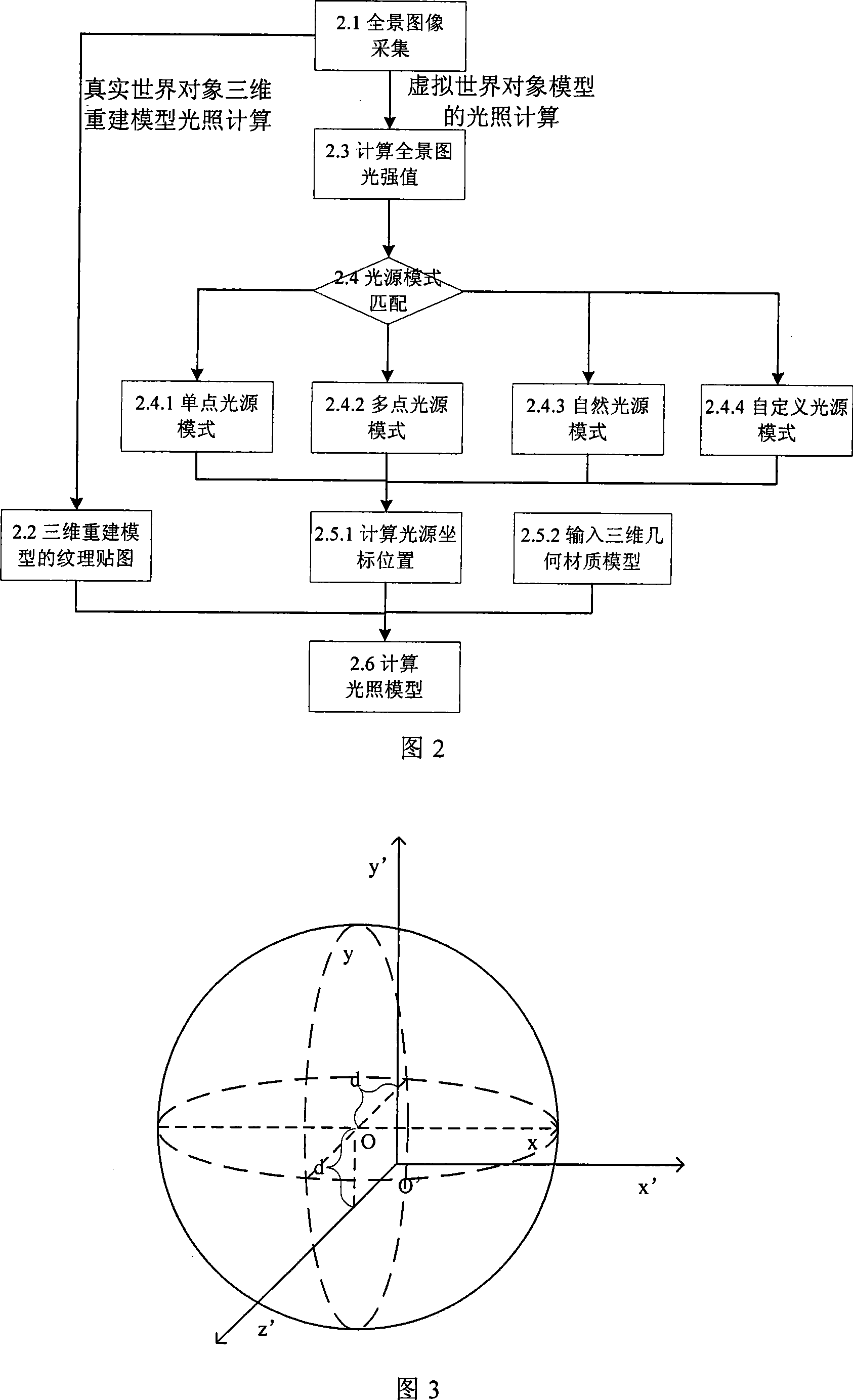
Method for real-time generating reinforced reality surroundings by spherical surface panoramic camera
InactiveCN101246600AReal-time generationEnhance real-time dynamic interaction3D-image renderingOptical propertyPattern matching
The present invention provides a method of generating augmented reality surroundings illumination model by a spherical panoramic camera real time, including: (1) placing the spherical panoramic camera in the augmented reality surroundings, placing in the viewport of the virtual worlds, real-time collecting panoramic picture; (2) processing the texture map having optical property aimed at the real world object after being collected panoramic picture of the step 1; (3) calculating collected panoramagram light intensity value aimed at the virtual world object after being collected the panoramic picture of the step 1, processing illumination model pattern matching, generating virtual world illumination model by the calculation; (4) calculating the illumination model of the augmented reality site under the condition of interactive local impact of the consideration reconstruction model and the virtual object model. The invention real-time generates illumination model in the complex photoenvironment, having advantage of support augmented reality site real time interactive.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
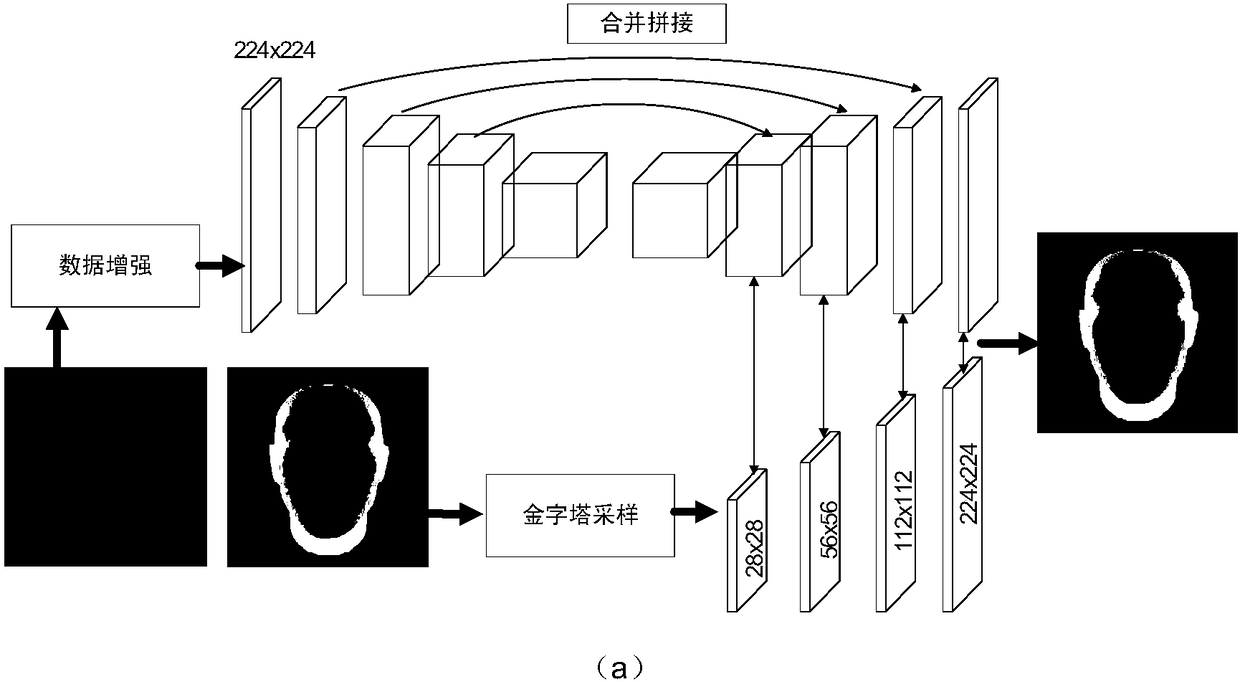
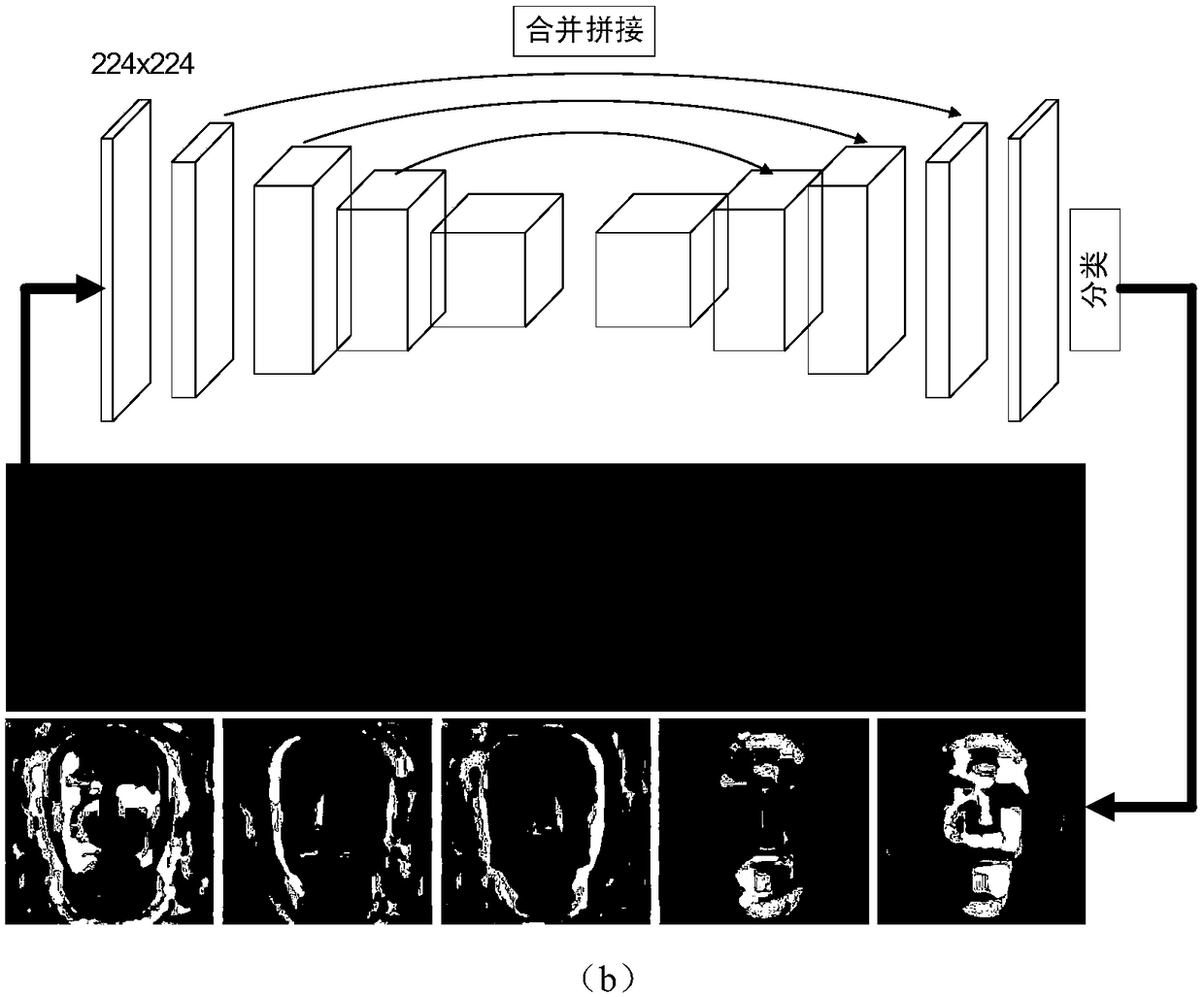
Deep learning-based multiview face three-dimensional model reconstruction method
ActiveCN108510573AHigh speedSimple data entryNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsLearning basedDeep integration
The invention discloses a deep learning-based multiview face three-dimensional model reconstruction method, and belongs to the field of computer vision. The method comprises the following steps of: generating a multi-illumination multiview virtual face image; generating a depth map of a face front view; training a plurality of independent and parallel convolutional neural networks; training a neural network in which weights of various views are distributed; and restoring depth maps output by the networks into a face three-dimensional grid model and carrying out peak coloring. According to themethod, multiview images are independently trained to restore depth maps, and each view weight distribution map is trained to carry out deep integration, so that the face three-dimensional model reconstruction precision is improved under the premise of ensuring the efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Iterative reconstruction methods for multi-slice computed tomography
InactiveUS6907102B1Avoid warpingError minimizationReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHelical scanMulti slice
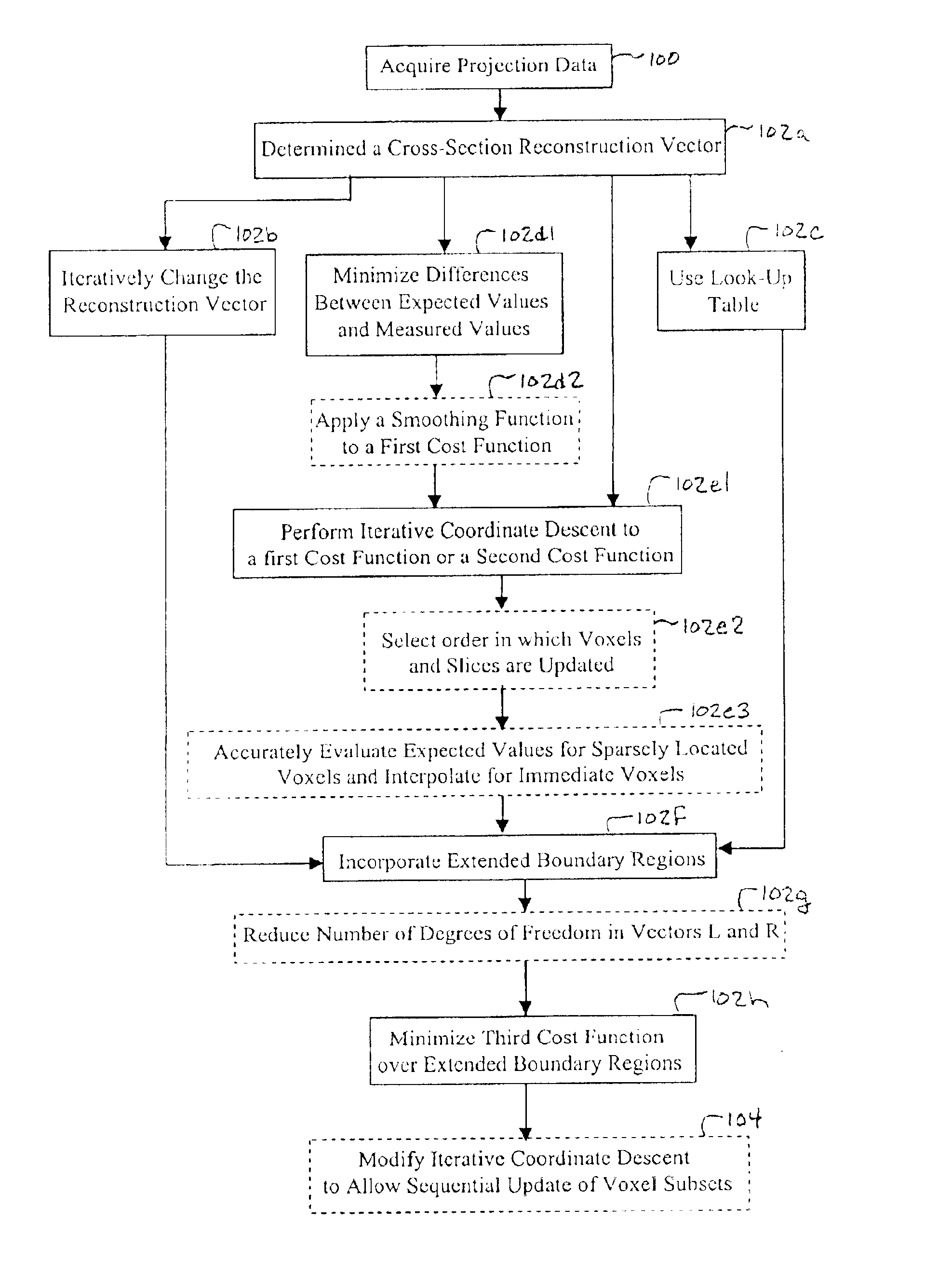
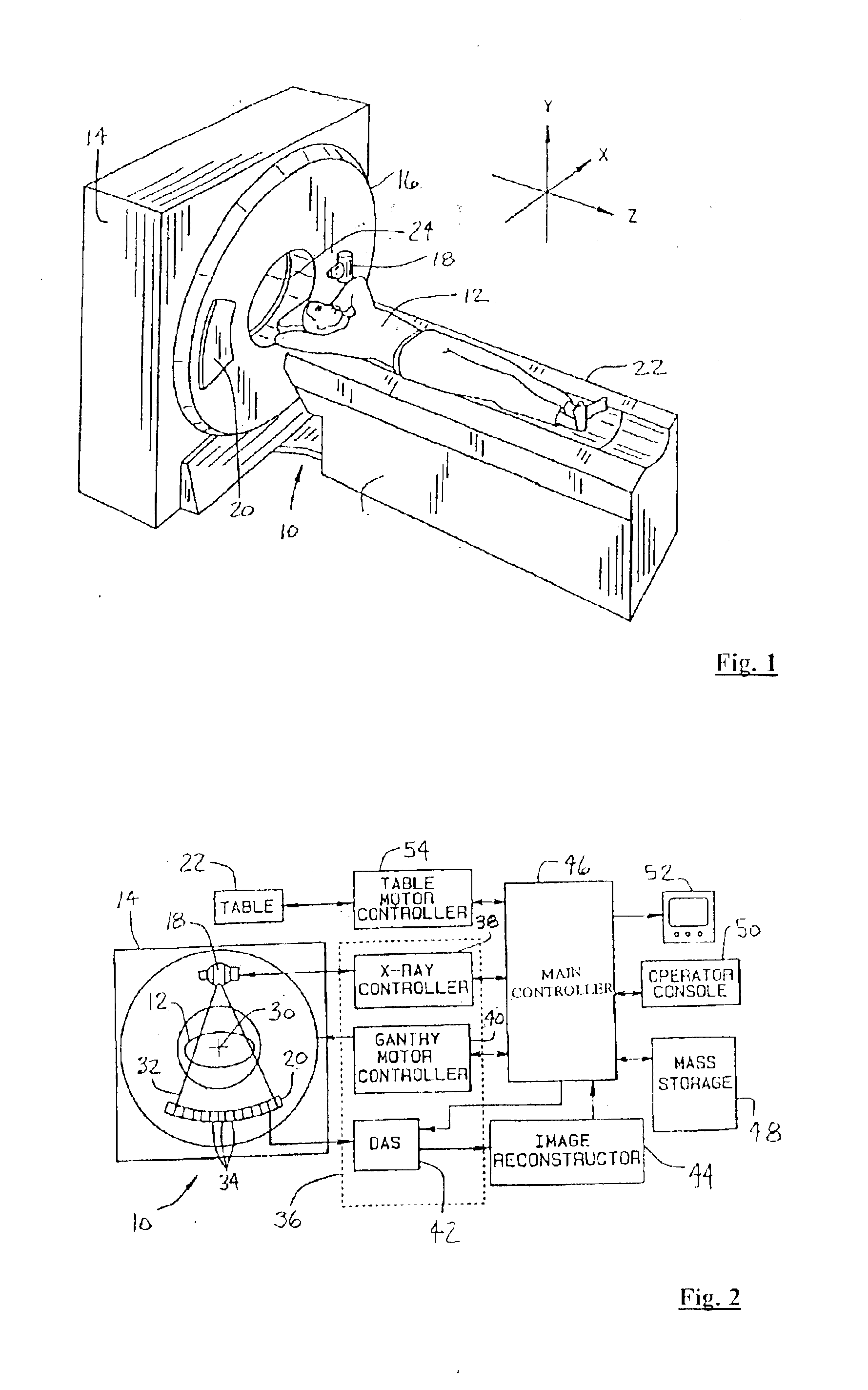
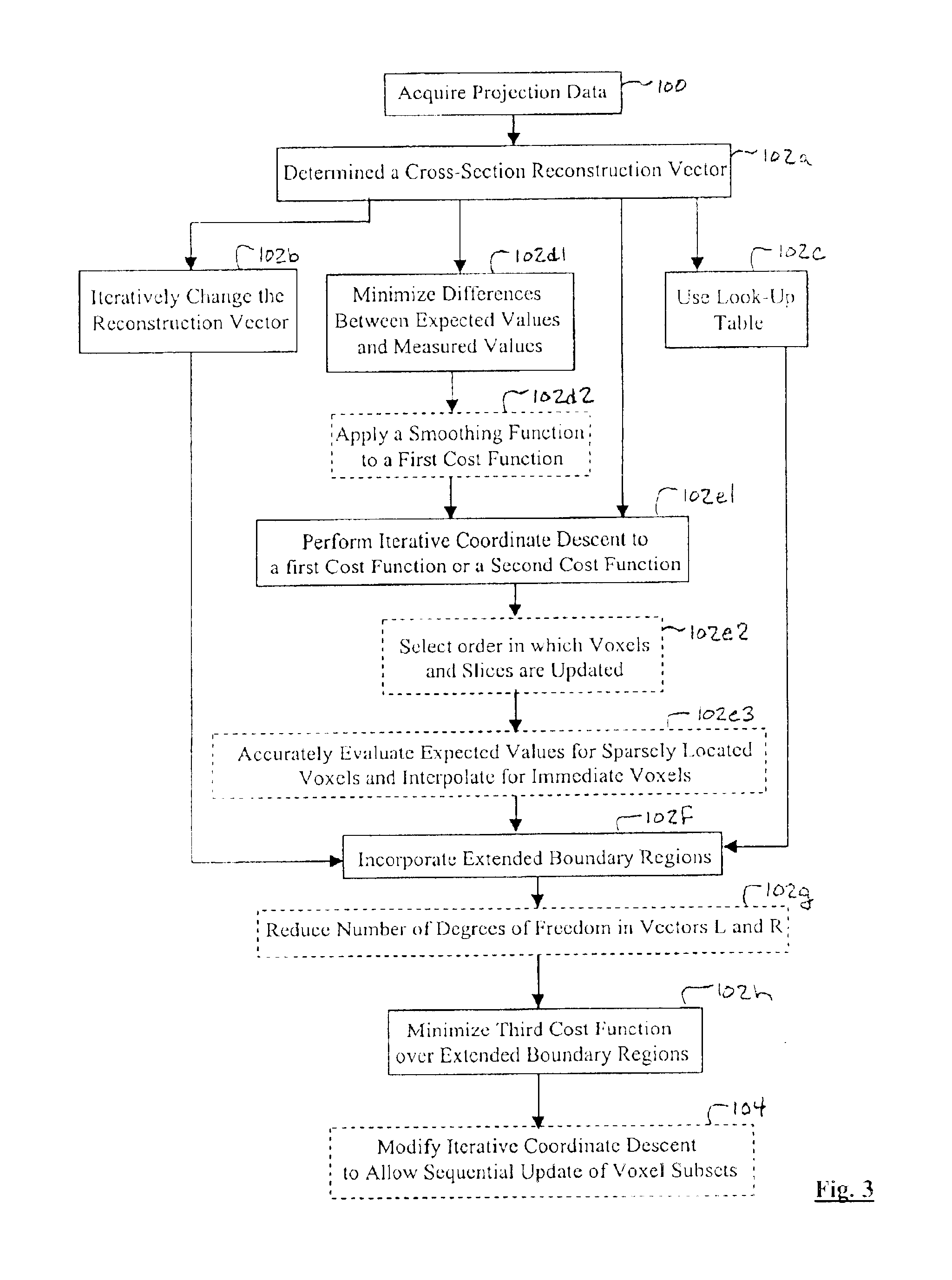
A multi-slice computed tomography imaging system is provided including a source that generates an x-ray beam and a detector array that receives the x-ray beam and generates projection data. A translatable table has an object thereon and is operable to translate in relation to the source and the detector array. The source and the detector array rotate about the translatable table to helically scan the object. An image reconstructor is electrically coupled to the detector array and reconstructs an image in response to the projection data using a computed tomography modeled iterative reconstruction technique. The iterative reconstruction technique includes determining a cross-section reconstruction vector, which approximately matches the projection data via a computed tomography model. Methods for performing the same are also provided including accounting for extended boundary regions.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +2
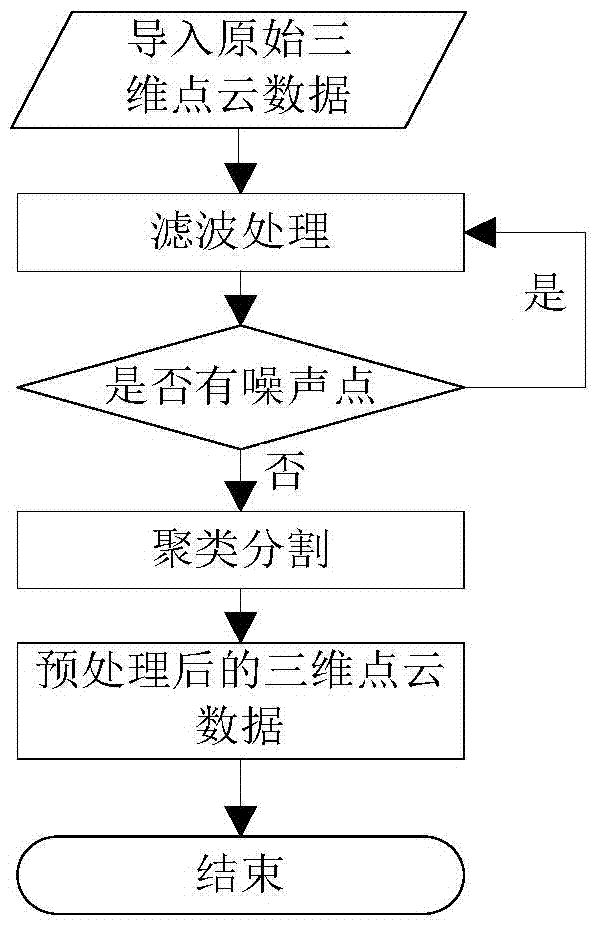
Indoor scene three-dimensional reconstruction method based on single depth vision sensor
InactiveCN105205858ASimplify the scanning processShort scan timeImage analysis3D modellingViewpointsData information
The invention relates to an indoor scene three-dimensional reconstruction method based on a single depth vision sensor. The method is technically characterized by including the following steps of firstly, continuously scanning a whole indoor scene through the single depth vision sensor; secondly, conducting preprocessing including denoising, hole repairing and the like on collected depth data to obtain smooth depth data; thirdly, calculating point cloud data corresponding to the current depth frame according to the depth data collected in the second step; fourthly, conducting registration on point cloud obtained through different viewpoint depth frames to obtain complete point cloud of the indoor scene; fifthly, conducting plane fitting, achieving segmentation of the special point cloud, and establishing an independent and complete three-dimensional model of each object in the indoor scene. Scanning devices used by the method are simple; scanned data information is comprehensive, and the point cloud registration accuracy calculation efficiency is effectively improved; finally, a complete and high-quality three-dimensional model set with a geographic structure and a color map can be established for the indoor scene.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Dynamically reconfigurable optical pattern generator module useable with a system to rapidly reconstruct three-dimensional data
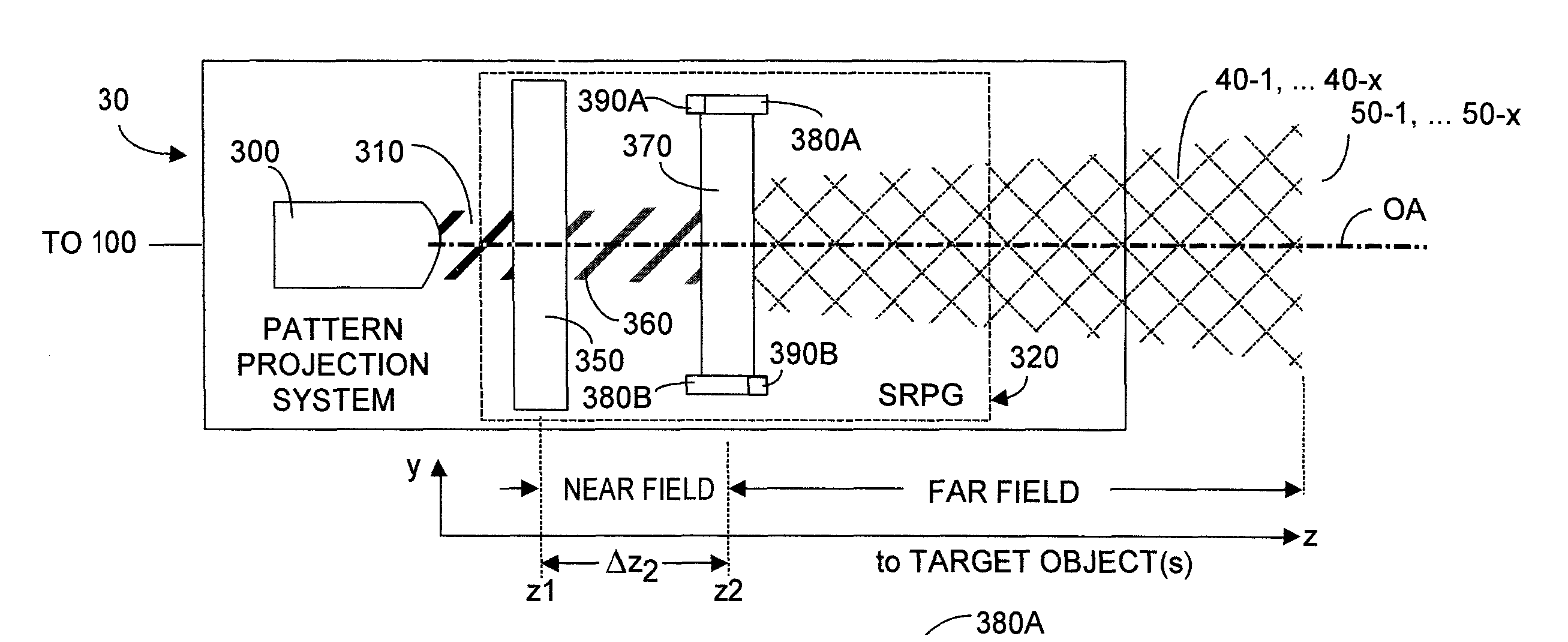
ActiveUS9325973B1Augment parallax informationRobust and efficient detectionImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxComputer module
Dynamic projection of at least first and second patterns contributes detectable disparity onto a scene that includes a target object. The scene is imaged with two-dimensional cameras whose acquired imagery includes disparity contributions whose presence enable a three-dimensional reconstruction depth map to be rapidly and accurately generated. In one embodiment coherent light is input to a first DOE within whose near range output is disposed a second DOE, whose far range output projects an image. Electronically varying effective optical distance between the two DOEs varies the pattern projected from the second DOE. A processor system and algorithms enable dynamic intelligent selection of projected patterns to more readily discern target object characteristics: shape, size, velocity. Patterns can implement spatio-temporal depth reconstruction, spatio-temporal depth reconstruction, and even single-camera spatio-temporal light coding reconstruction. Target objects may be scanned or may make gestures that are rapidly detected and recognized by the system and method.
Owner:PACKSIZE
3D scene model from video
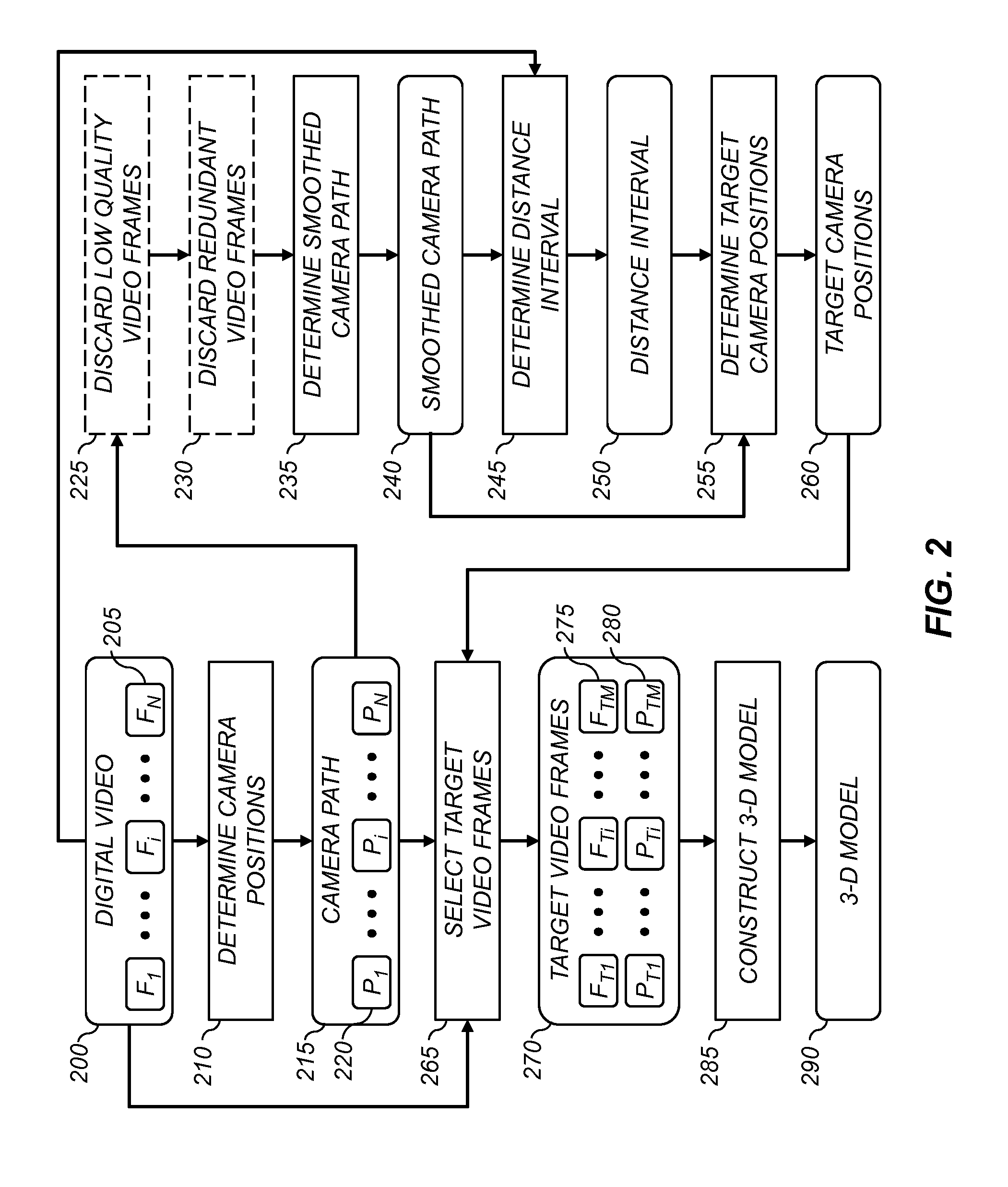
InactiveUS20130215239A1Reduce in quantityImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisDigital videoThree dimensional model
A method for determining a three-dimensional model of a scene from a digital video captured using a digital video camera, the digital video including a temporal sequence of video frames. The method includes determining a camera position of the digital video camera for each video frame, and fitting a smoothed camera path to the camera positions. A sequence of target camera positions spaced out along the smoothed camera path is determined such that a corresponding set of target video frames has at least a target level of overlapping scene content. The target video frames are analyzed using a three-dimensional reconstruction process to determine a three-dimensional model of the scene.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC
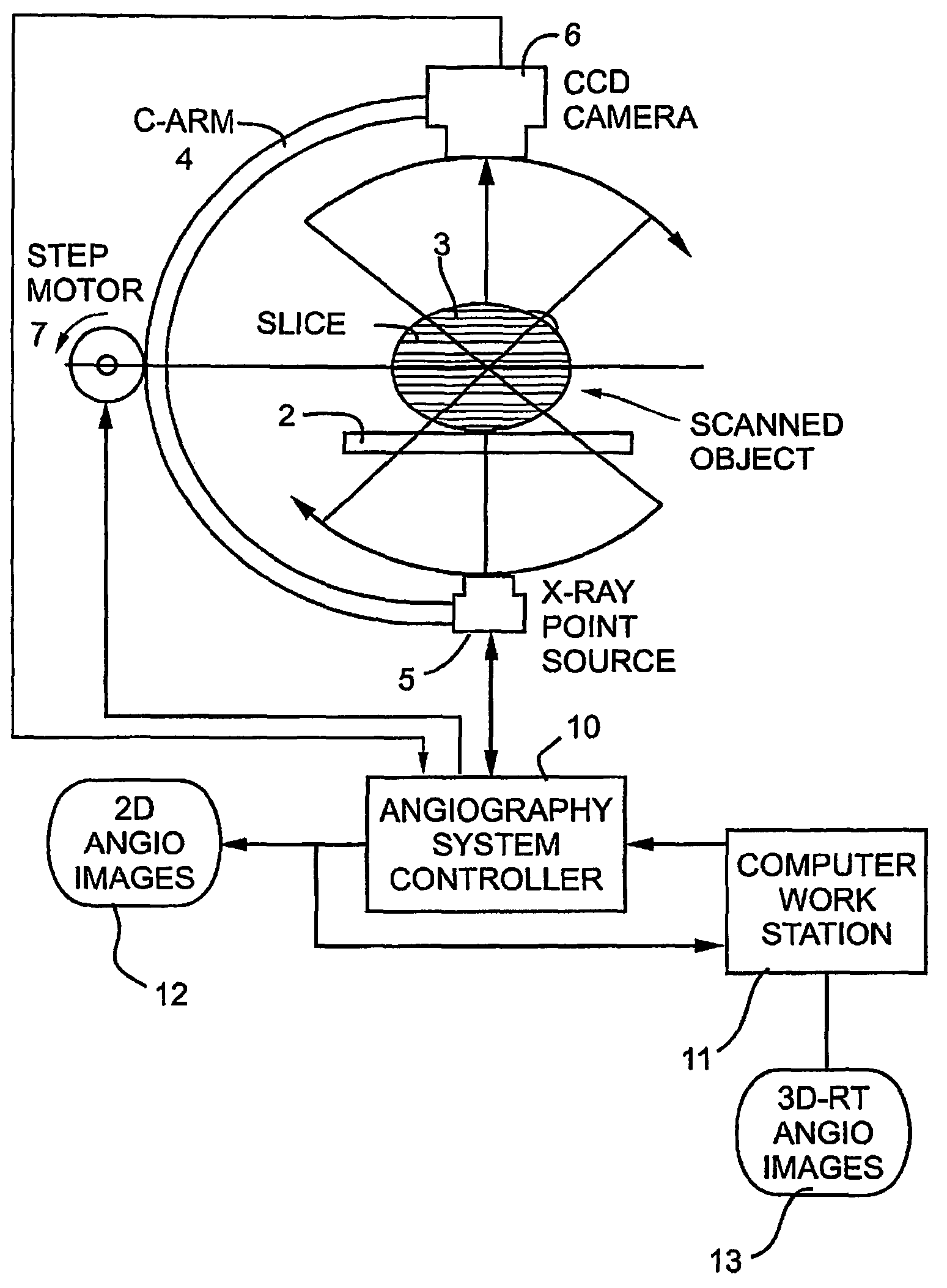
Vascular angiography three-dimensional rebuilding method under dynamic model direction
InactiveCN101301207AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityImage analysisComputerised tomographsDynamic modelsReconstruction method
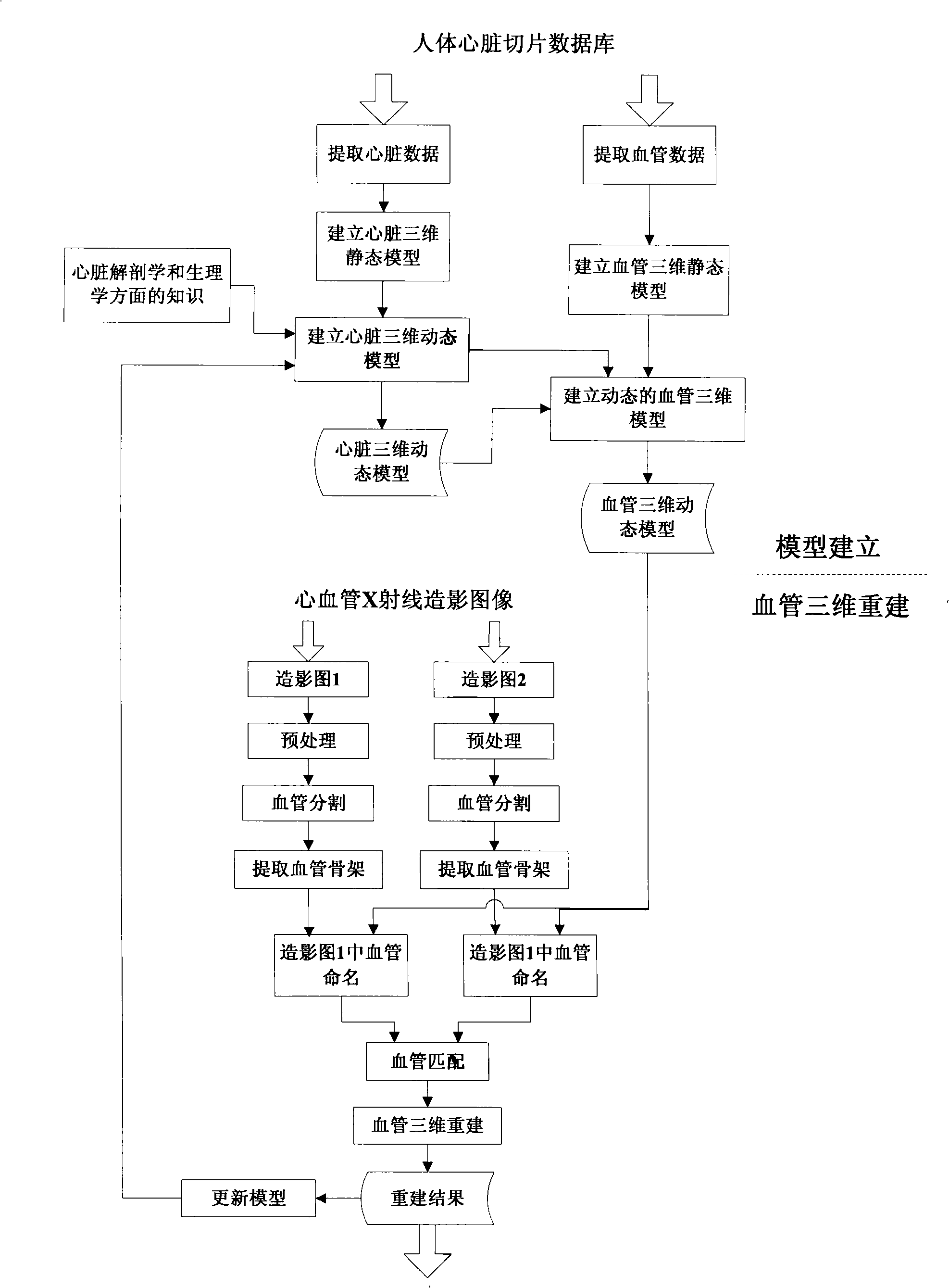
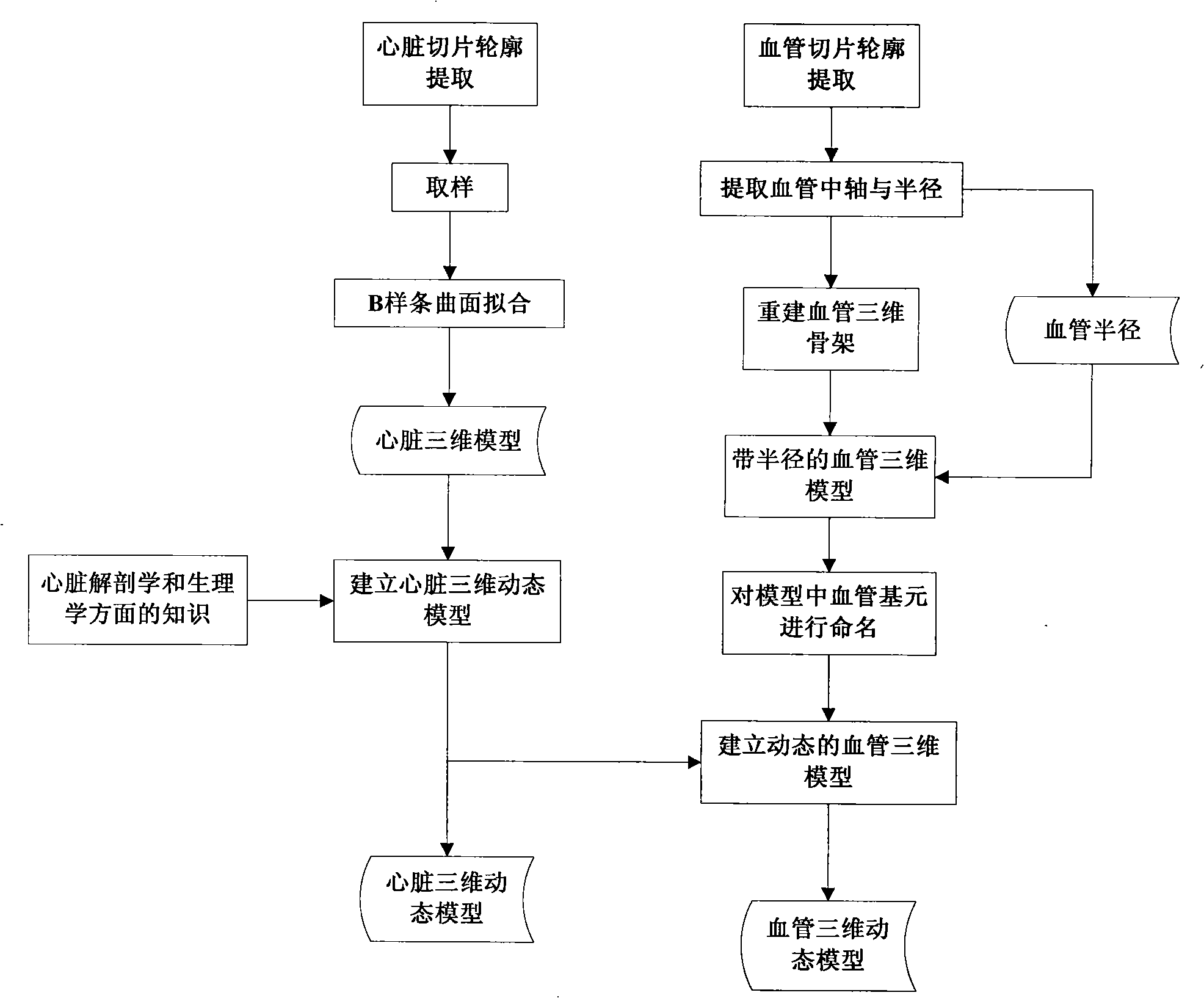
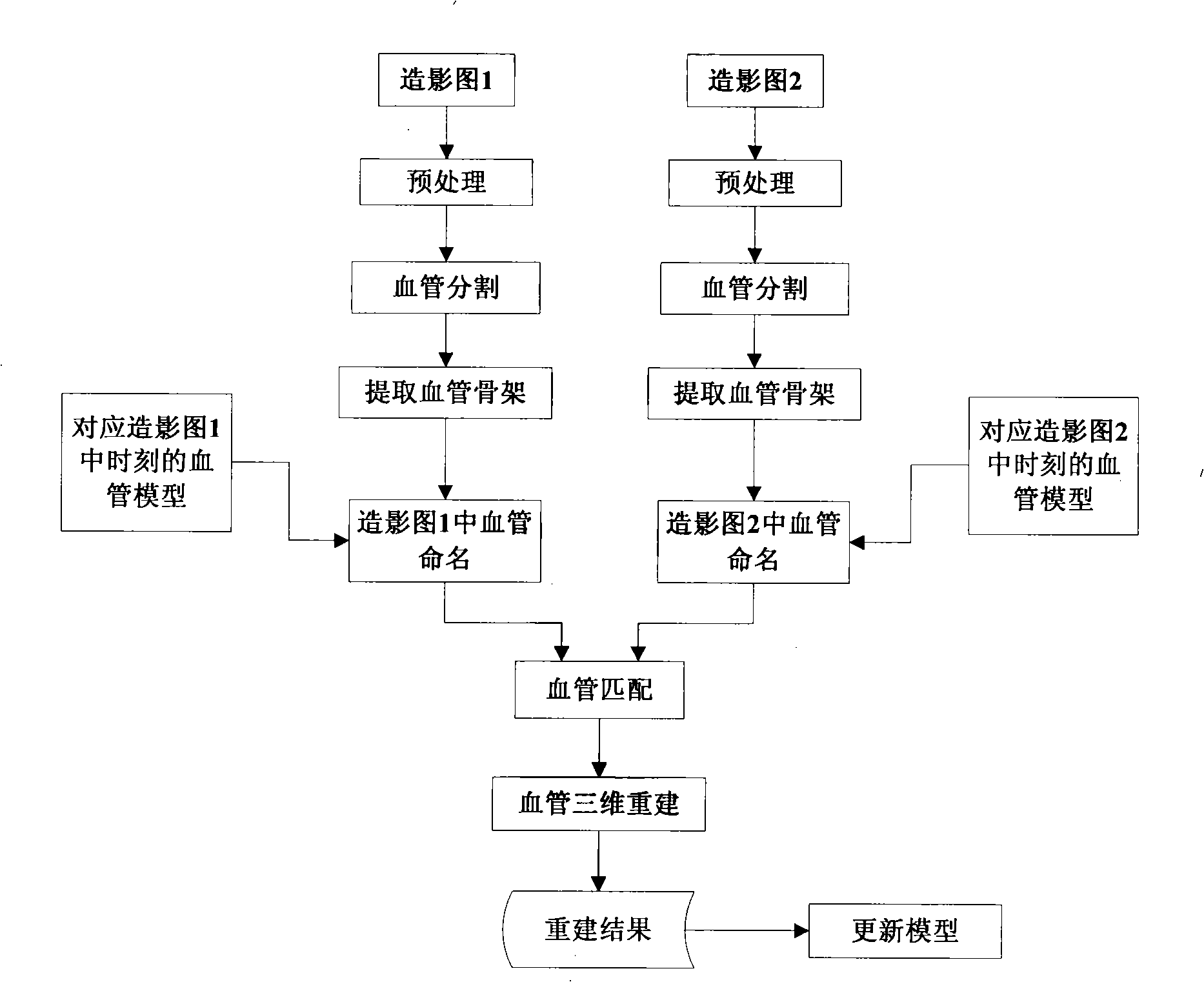
The present invention provides a dynamic model directed angiography three-dimensional reconstruction method, pertaining to an intersectional field of digital image processing and medicine imaging, for satisfying special requests of auxiliary detection and surgery guidance for cardiovascular disease in clinical medicine. The invention includes steps of angiography image preprocessing, vascellum segmentation, vascellum skeleton and radii extraction, model directed vascellum base element recognition, vascellum matching and vascellum three-dimensional reconstruction. The invention also provides a cardiovascular dynamic model construction method including steps of cardiovascular slice data extraction, cordis static and dynamic model building, and static and dynamic model building. According to the invention, good angiography three-dimensional reconstruction result may be obtained, which effectively assists detection and surgery guidance for cardiovascular disease, thereby satisfying clinical requests.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Autocalibrating parallel imaging reconstruction method from arbitrary k-space sampling with reduced noise
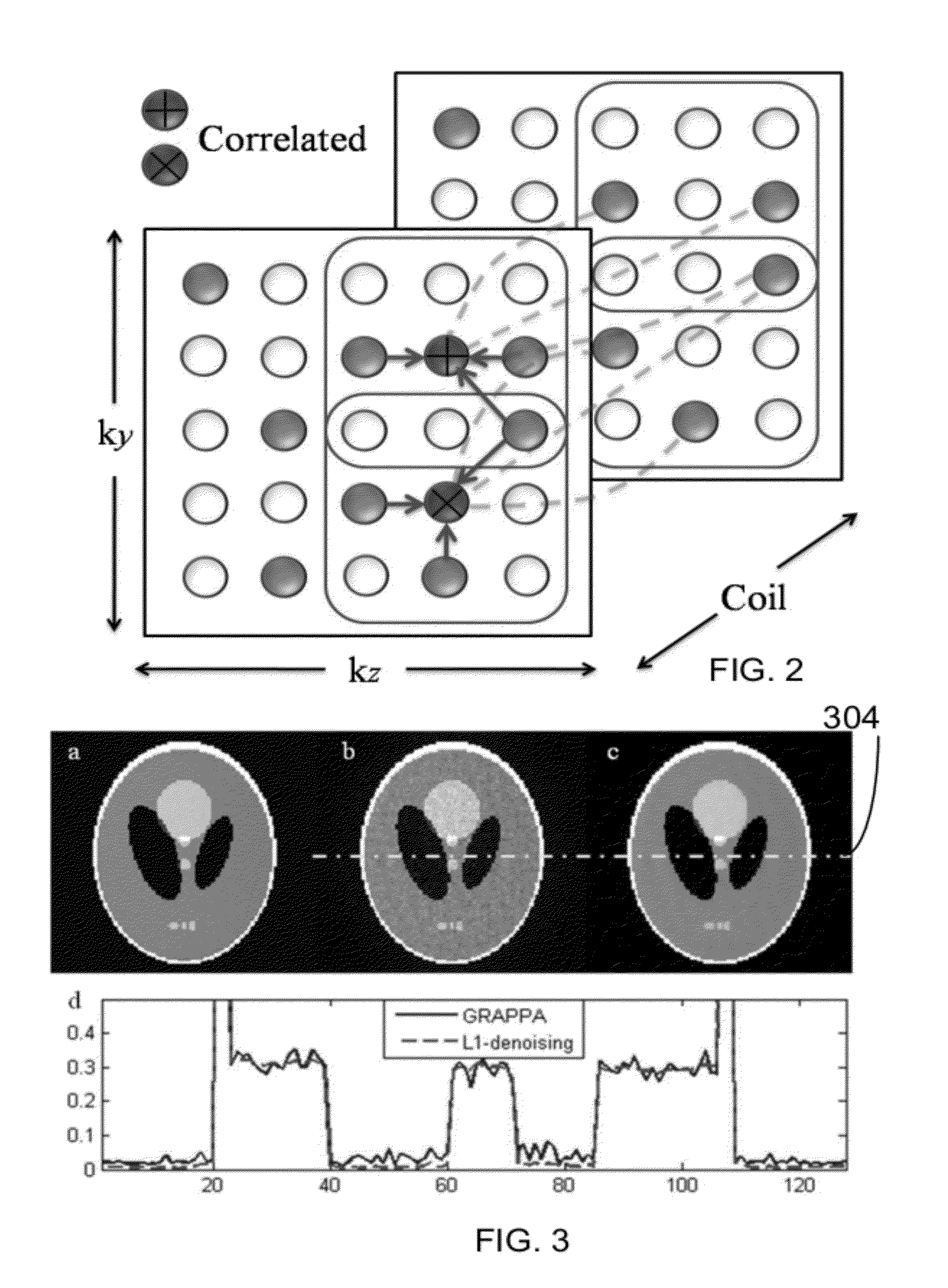
ActiveUS20120092009A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionParallel imagingReconstruction method
A computer implemented method for magnetic resonance imaging is provided. A 3D Fourier Transform acquisition is performed with two phase encode directions, wherein phase code locations are chosen so that a total number of phase encodes is less than a Nyquist rate, and closest distances between phase encode locations takes on a multiplicity of values. Readout signals are received through a multi-channel array of a plurality of receivers. An autocalibrating parallel imaging interpolation is performed and a noise correlation is generated. The noise correlation is used to weight a data consistency term of a compressed sensing iterative reconstruction. An image is created from the autocalibration parallel imaging using the weighted data consistency term. The image is displayed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com