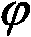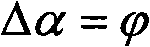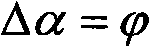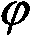Patents
Literature
351 results about "Phase Code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
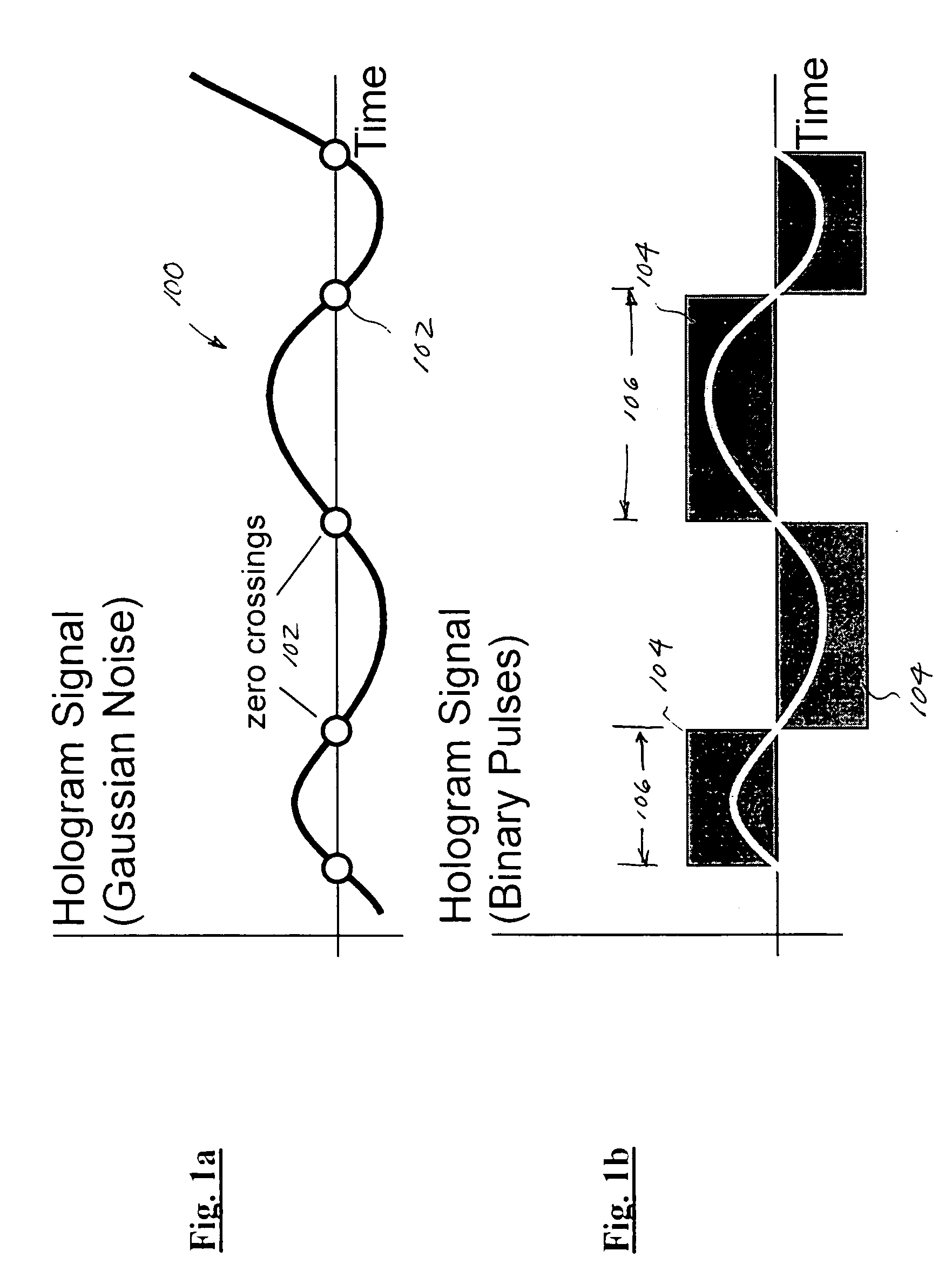
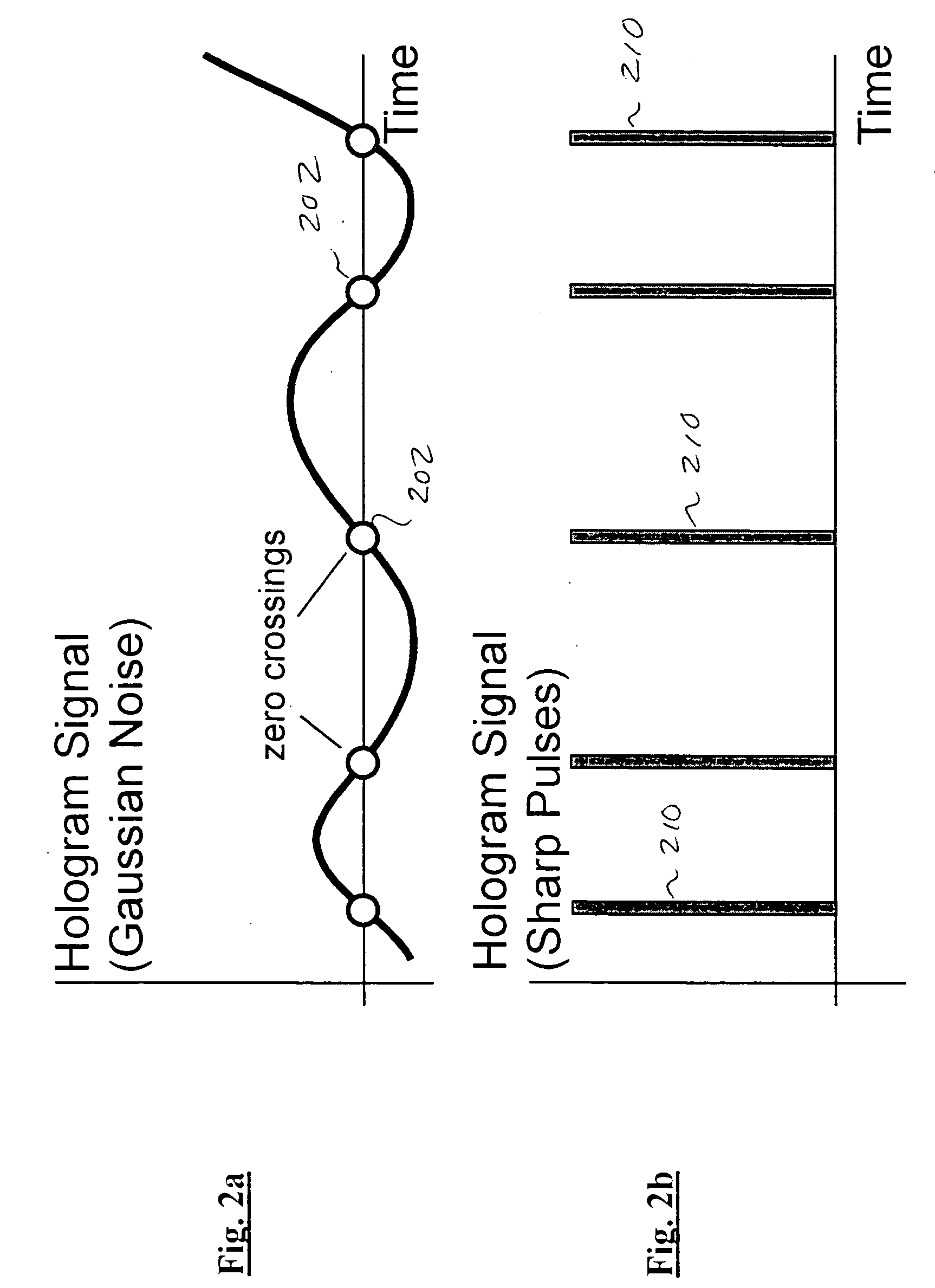
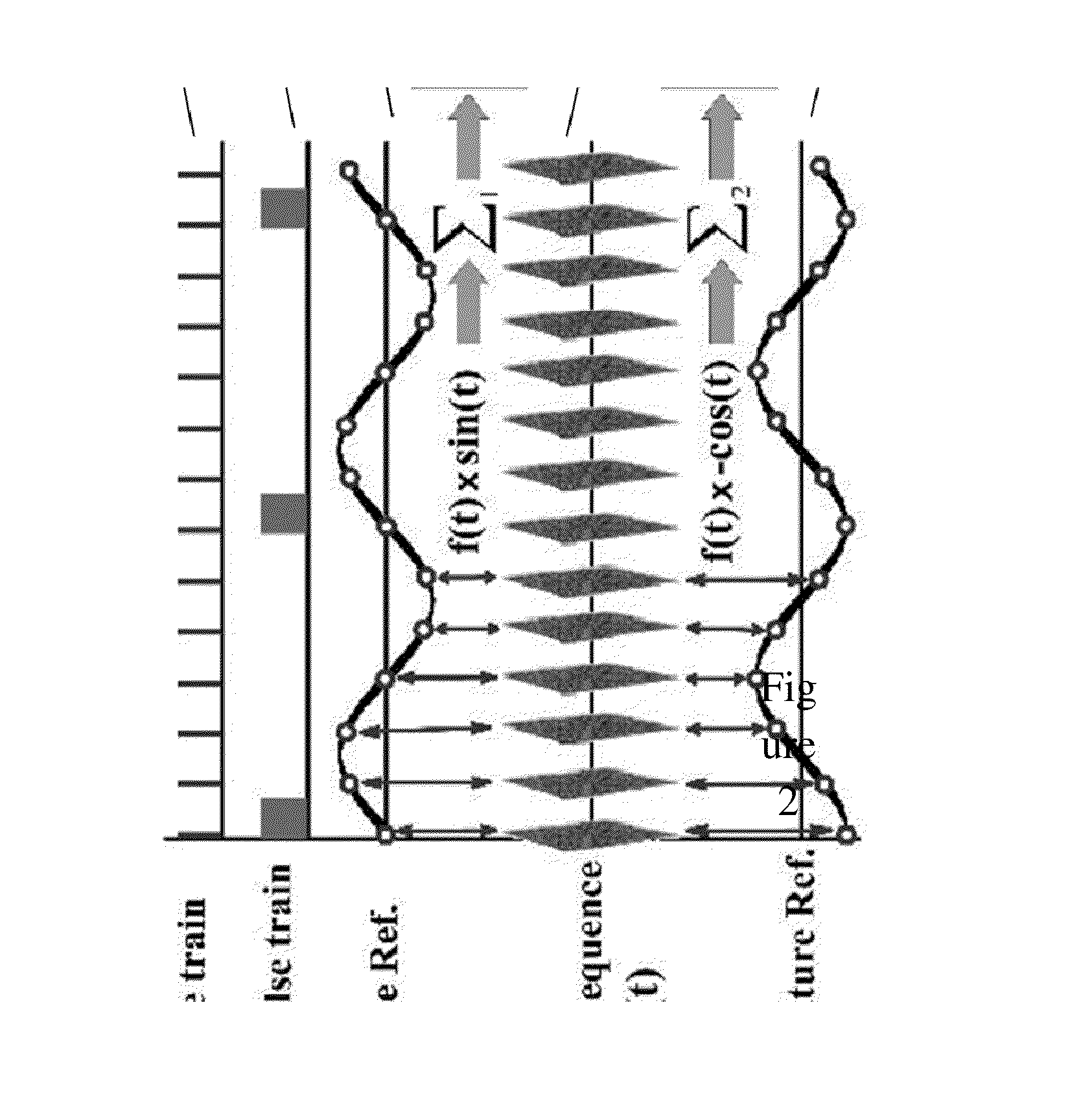
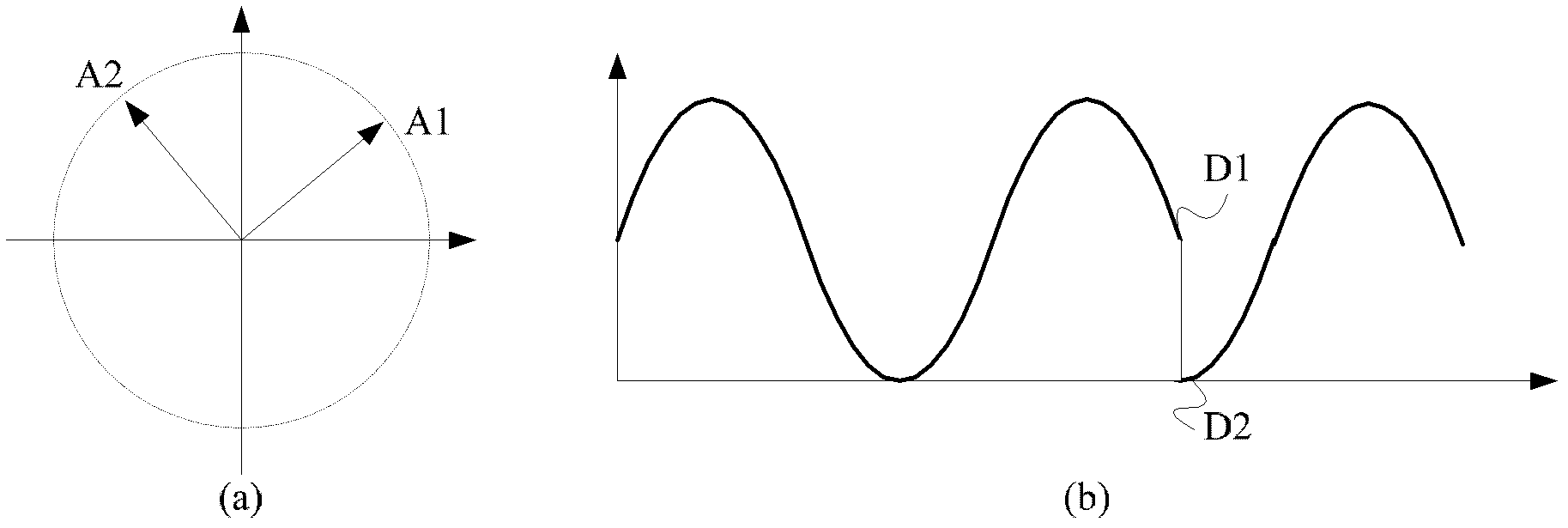
A coded value specifying the phase for a study.
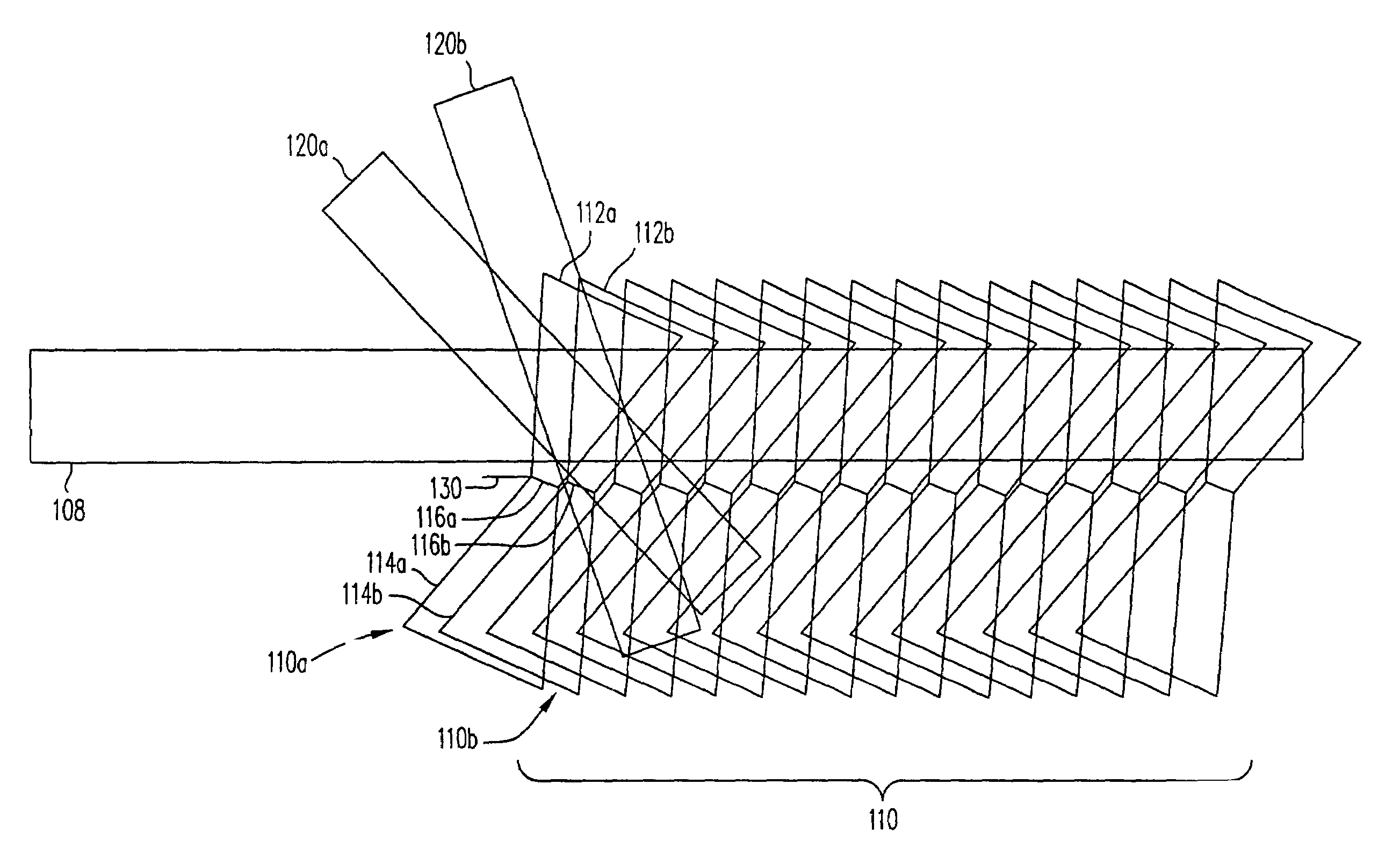
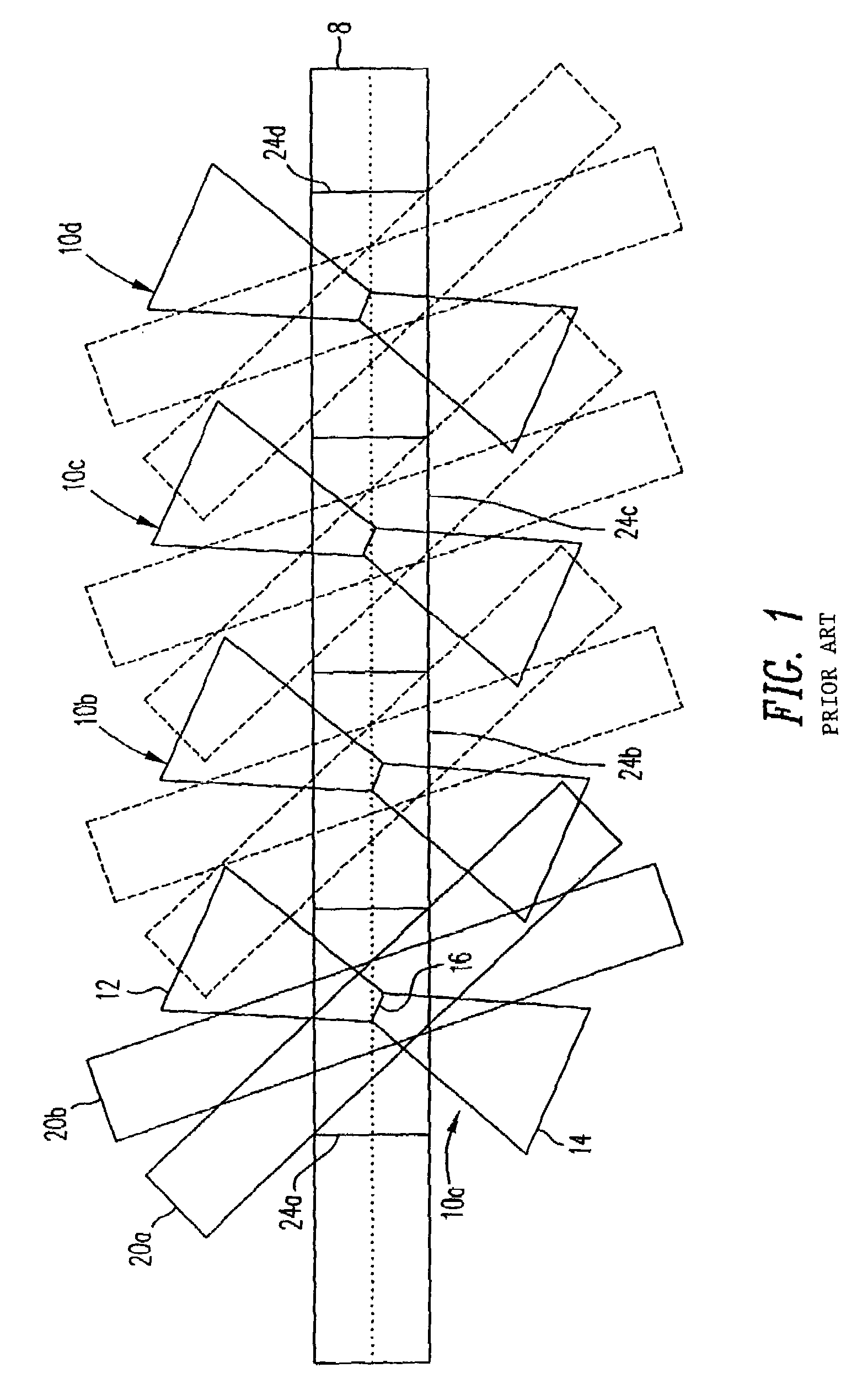
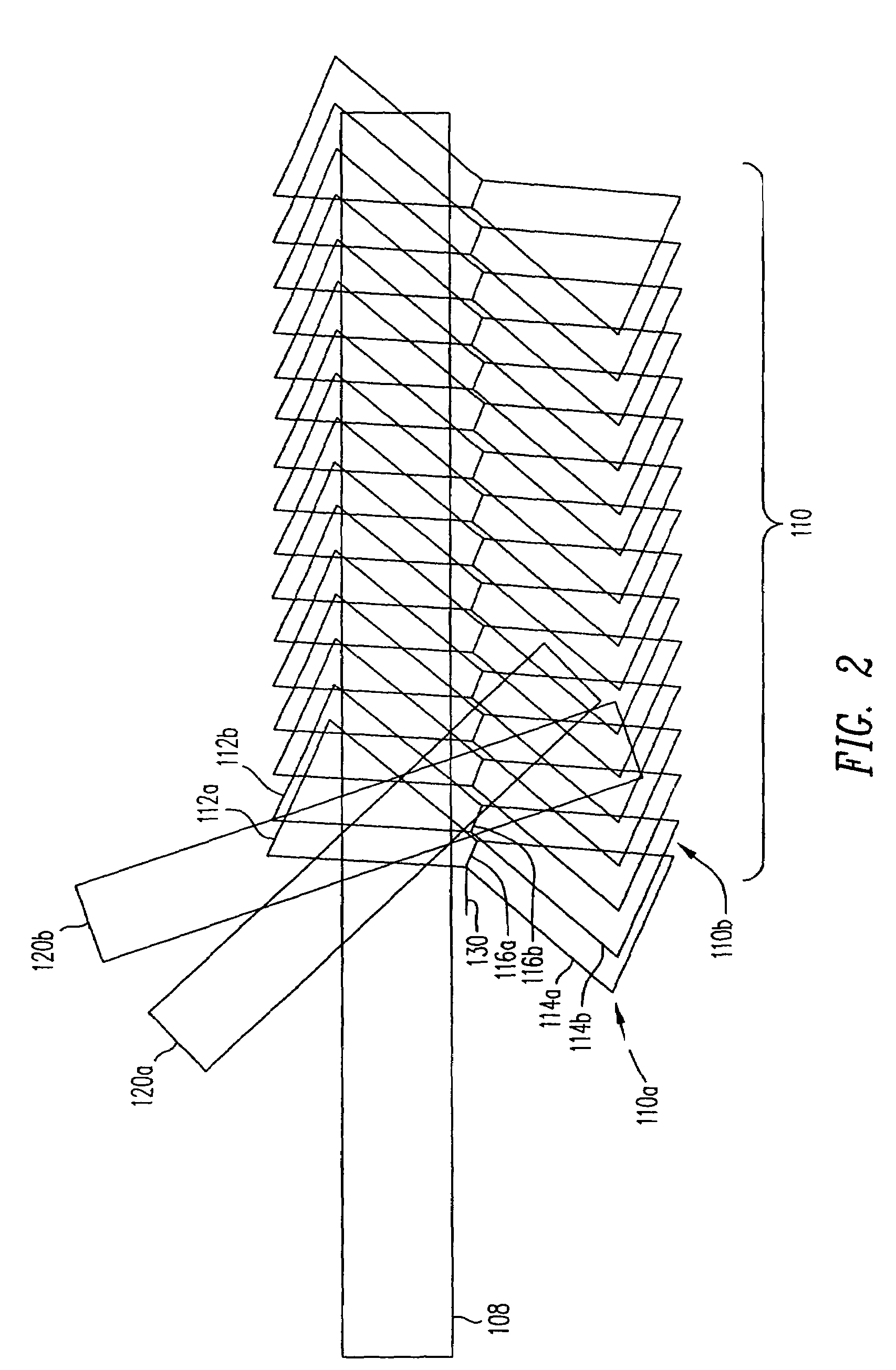
Polytopic multiplex holography
ActiveUS7092133B2Treatment using aerobic processesTransportation and packagingMultiplexingLight beam
Disclosed is a multiplexing method and apparatus that allows holograms to be spatially multiplexed with partial spatial overlap between neighboring stacks of holograms. Each individual stack can additionally take full advantage of an alternate multiplexing scheme such as angle, wavelength, phase code, peristrophic, or fractal multiplexing, for example. An amount equal to the beam waist of the signal beam writing a hologram separates individual stacks of holograms. Upon reconstruction, a hologram and its neighbors will all be readout simultaneously. An filter is placed at the beam waist of the reconstructed data such that the neighbors that are read out are not transmitted to the camera plane. Alternatively, these unwanted reconstructions can be filtered out with an angular filter at an intermediate plane in the optical system that has a limited angular passband.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy method and device based on tangential polarization
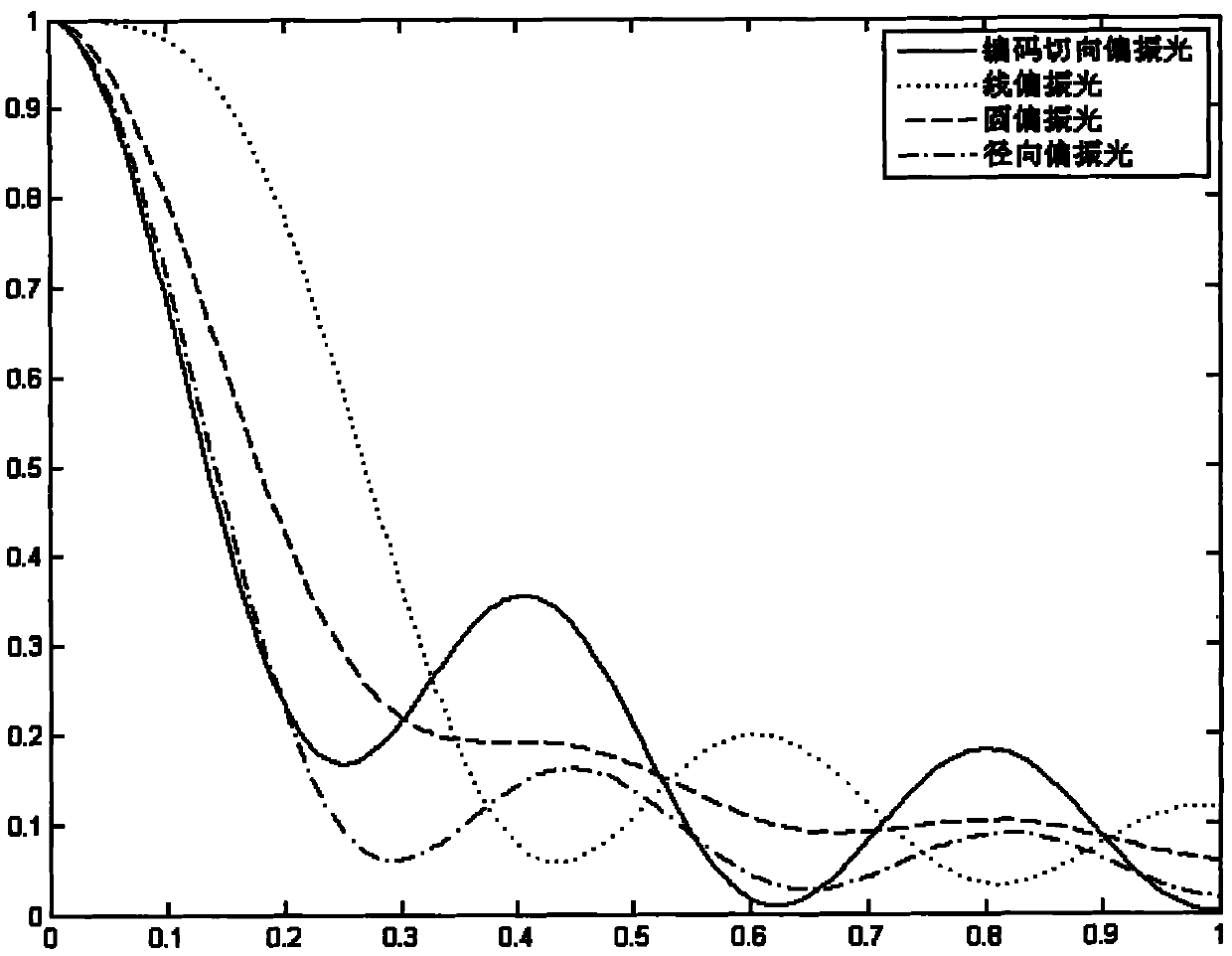
InactiveCN101907766ALow powerReduce bleachingMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageImage resolution
The invention discloses a super-resolution fluorescence microscopy method based on tangential polarization, comprising the following steps: carrying out 0-2pi vortex phase coding focus on tangential polarization exciting light, and obtaining an exciting spot below a diffraction limit on a fluorescence sample; adjusting tangential polarization STED laser and the phase coding tangential polarization exciting light to realize confluence and co-axis, focusing on the fluorescence sample to form a circle bread-shaped focusing spot the central point of which coincides with the central point of the exciting spot; adjusting the operating power of the STED laser to cause the area of a luminous point in the exciting spot to reach the super-resolution ratio; and collecting fluorescence emitted from the luminous point and carrying out detection processing to obtain a microimage with the super-resolution ratio. The invention also discloses a device for realizing the super-resolution fluorescence microscopy method based on tangential polarization. In the invention, on the premise of ensuring the super-resolution ratio, the working power of the STED is reduced greatly, thereby lowering bleaching of the sample and avoiding damage for the sample.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Autocalibrating parallel imaging reconstruction method from arbitrary k-space sampling with reduced noise
ActiveUS20120092009A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionParallel imagingReconstruction method
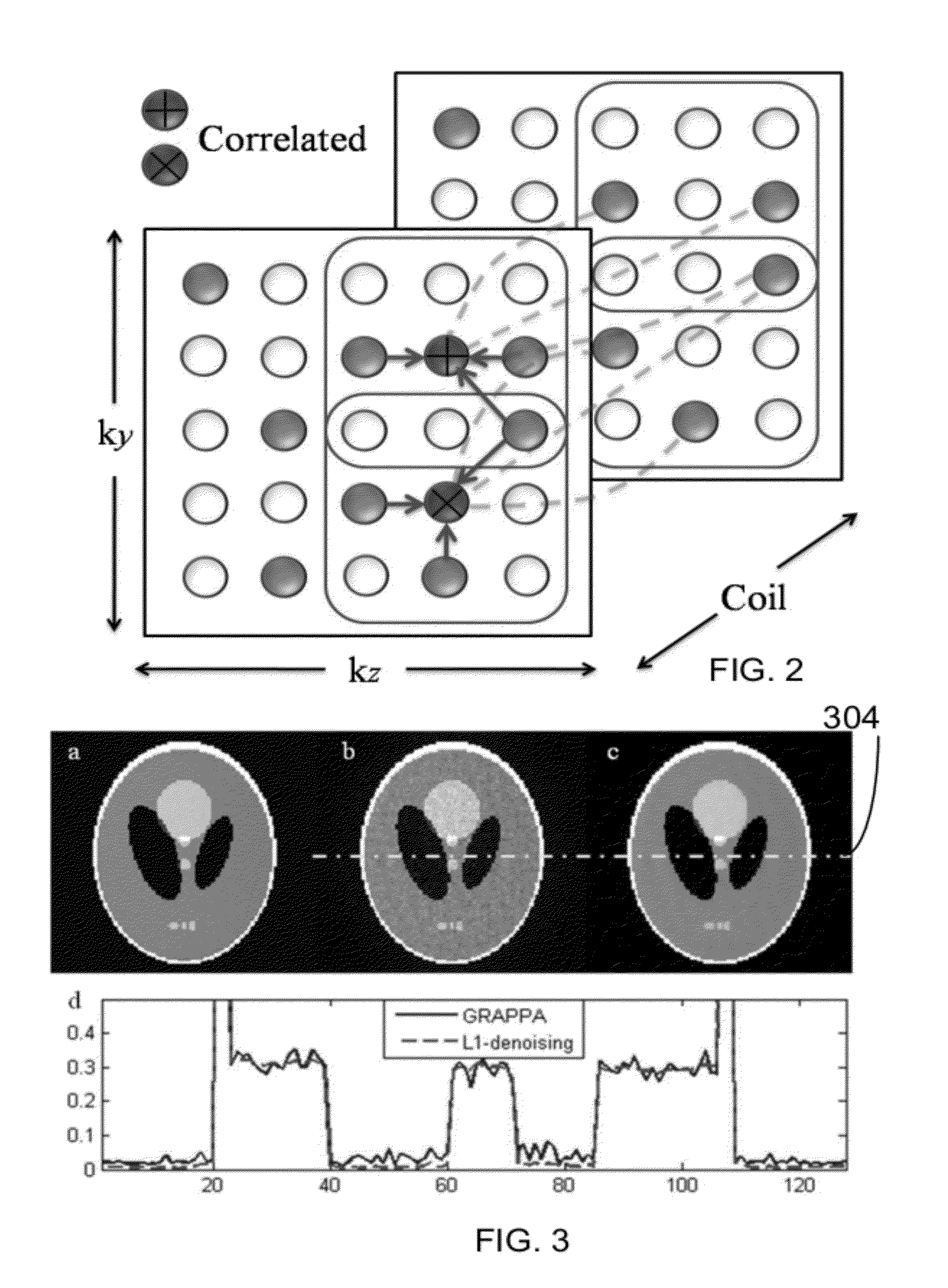
A computer implemented method for magnetic resonance imaging is provided. A 3D Fourier Transform acquisition is performed with two phase encode directions, wherein phase code locations are chosen so that a total number of phase encodes is less than a Nyquist rate, and closest distances between phase encode locations takes on a multiplicity of values. Readout signals are received through a multi-channel array of a plurality of receivers. An autocalibrating parallel imaging interpolation is performed and a noise correlation is generated. The noise correlation is used to weight a data consistency term of a compressed sensing iterative reconstruction. An image is created from the autocalibration parallel imaging using the weighted data consistency term. The image is displayed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Optical element, device, method, and applications
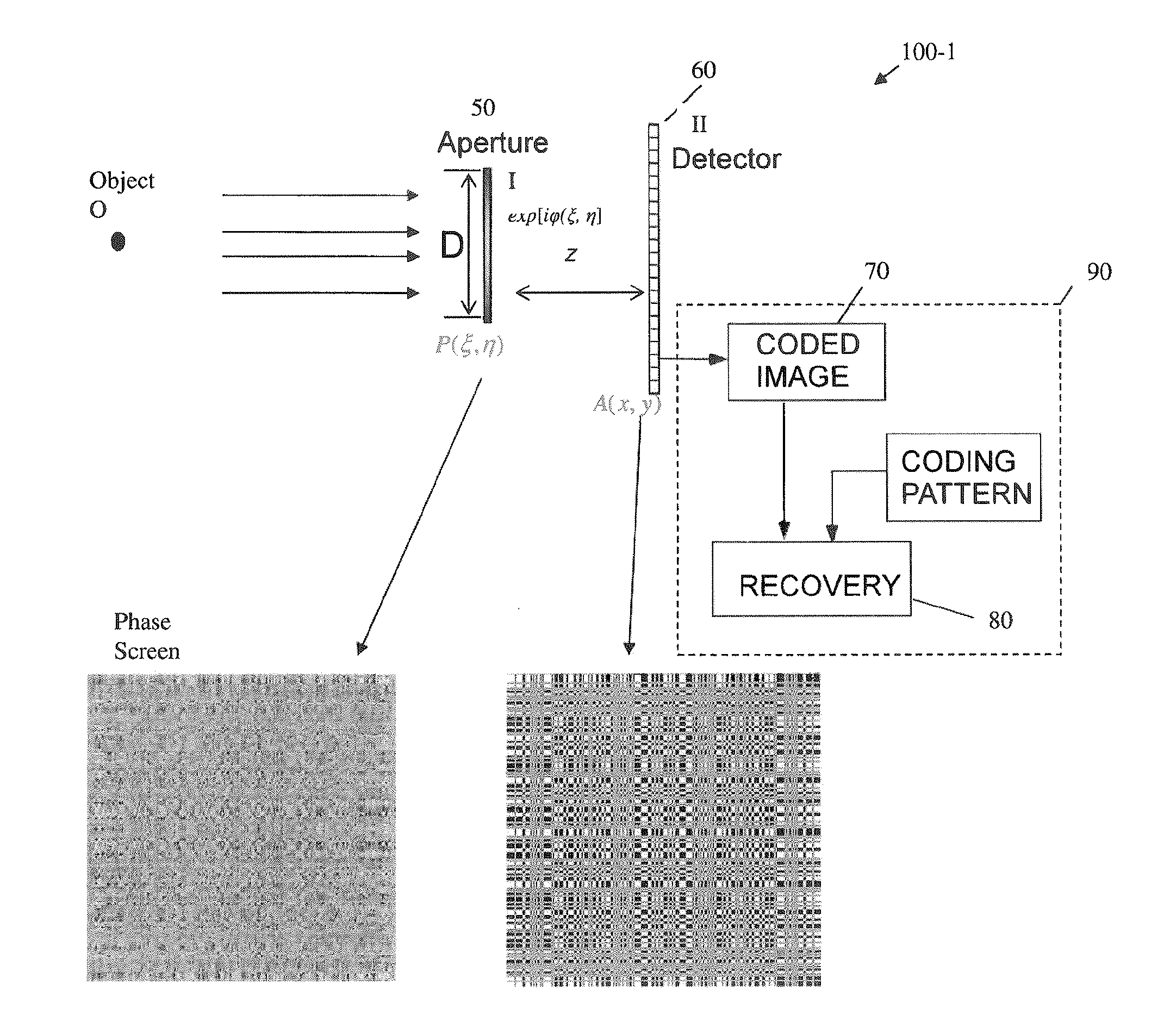
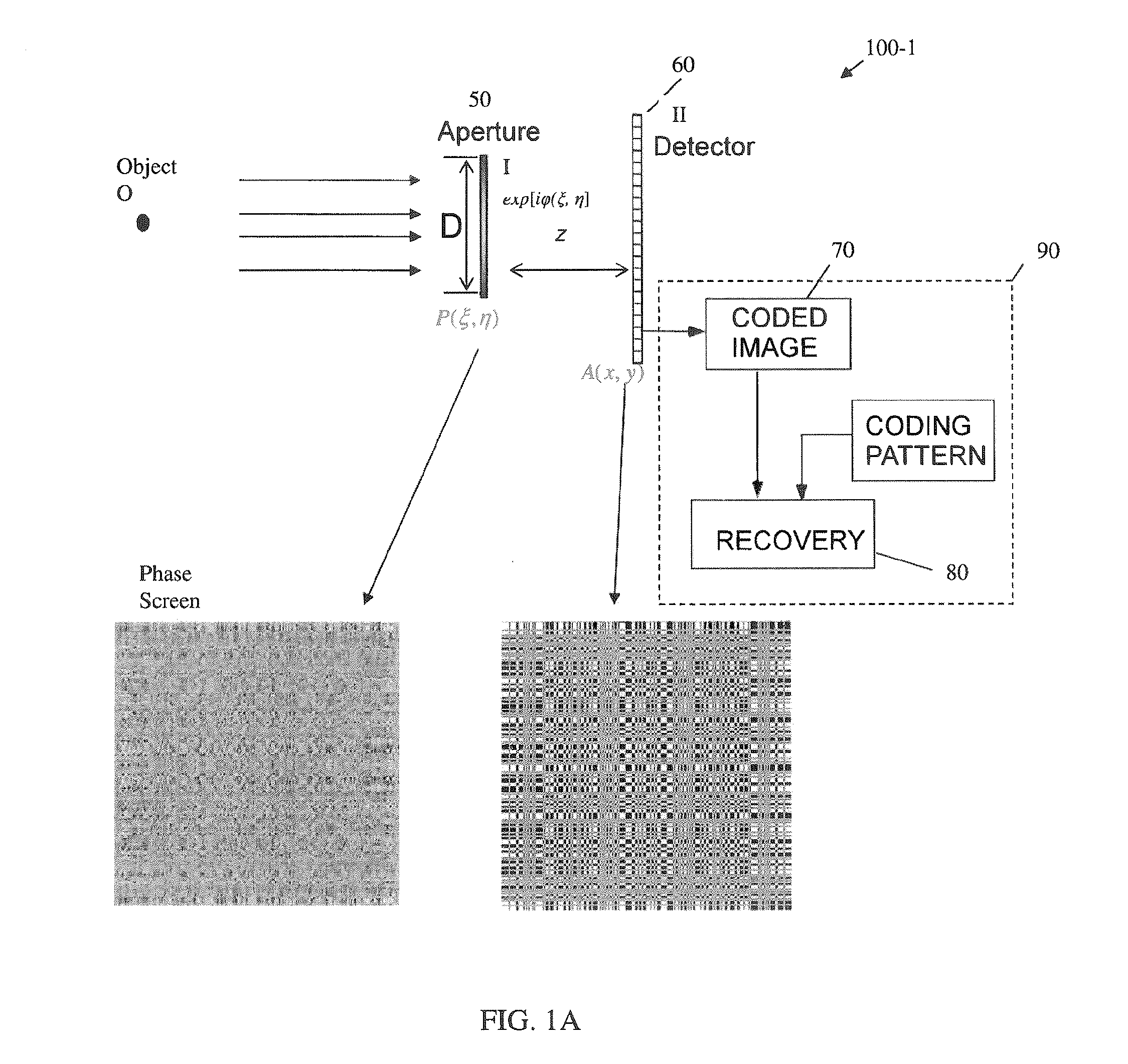
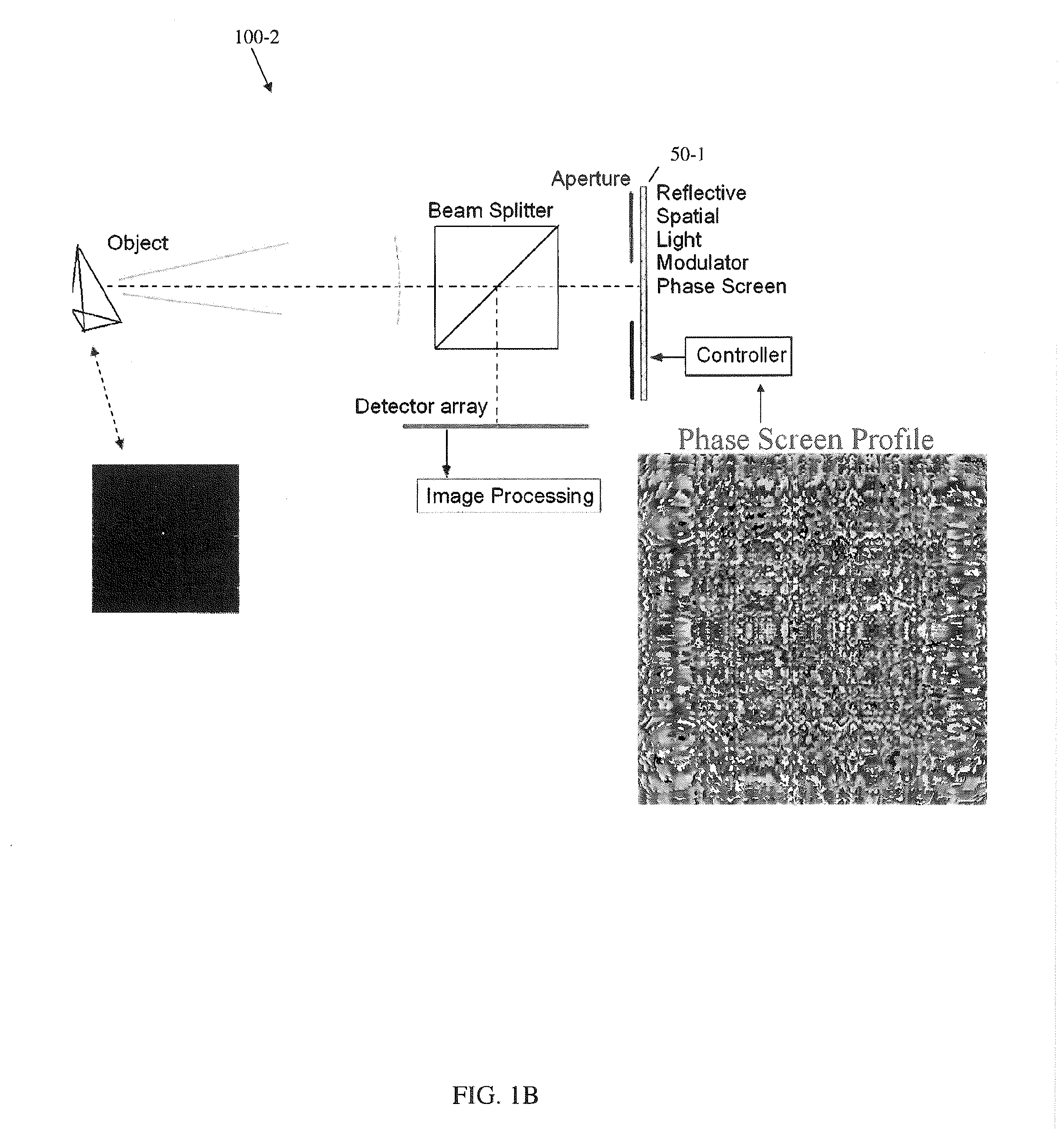
A novel phase-coded aperture, associated imaging system, and design method is disclosed. The optical imaging system includes a coded-aperture followed optically by a detector array and includes an image processor. A diffraction pattern in the form of a band-limited uniformly redundant array is formed on the detector array when focusable radiation from a point source in object space is modulation by the transmission function of the coded-aperture. Since diffraction effects cannot be ignored in the optical regime, an iterative phase retrieval method is used to calculate the phase-coded aperture transmission function. Correlation type processing can be applied for the image recovery.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
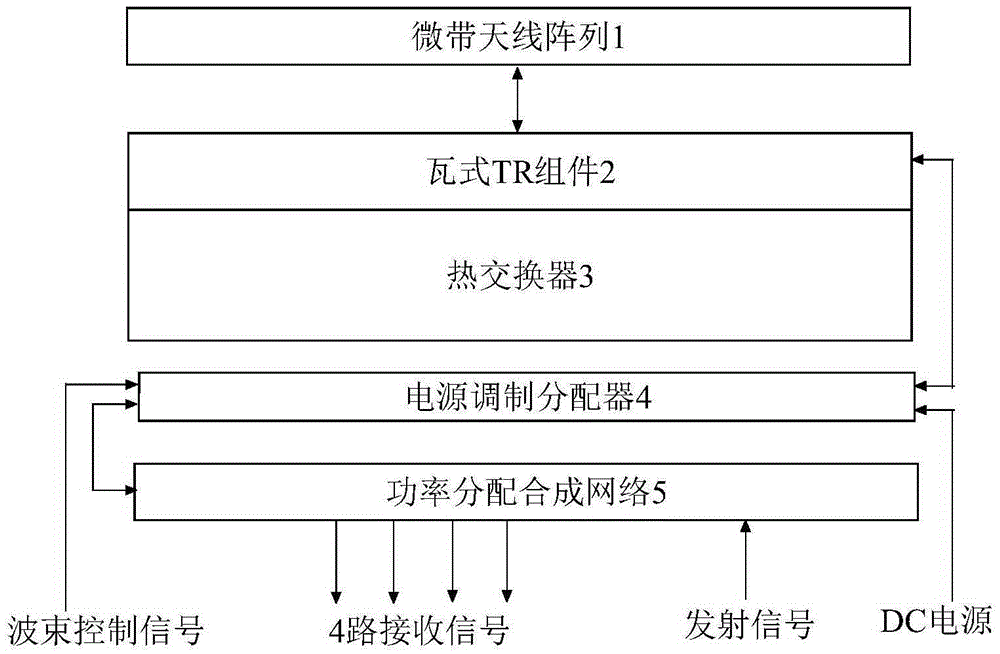
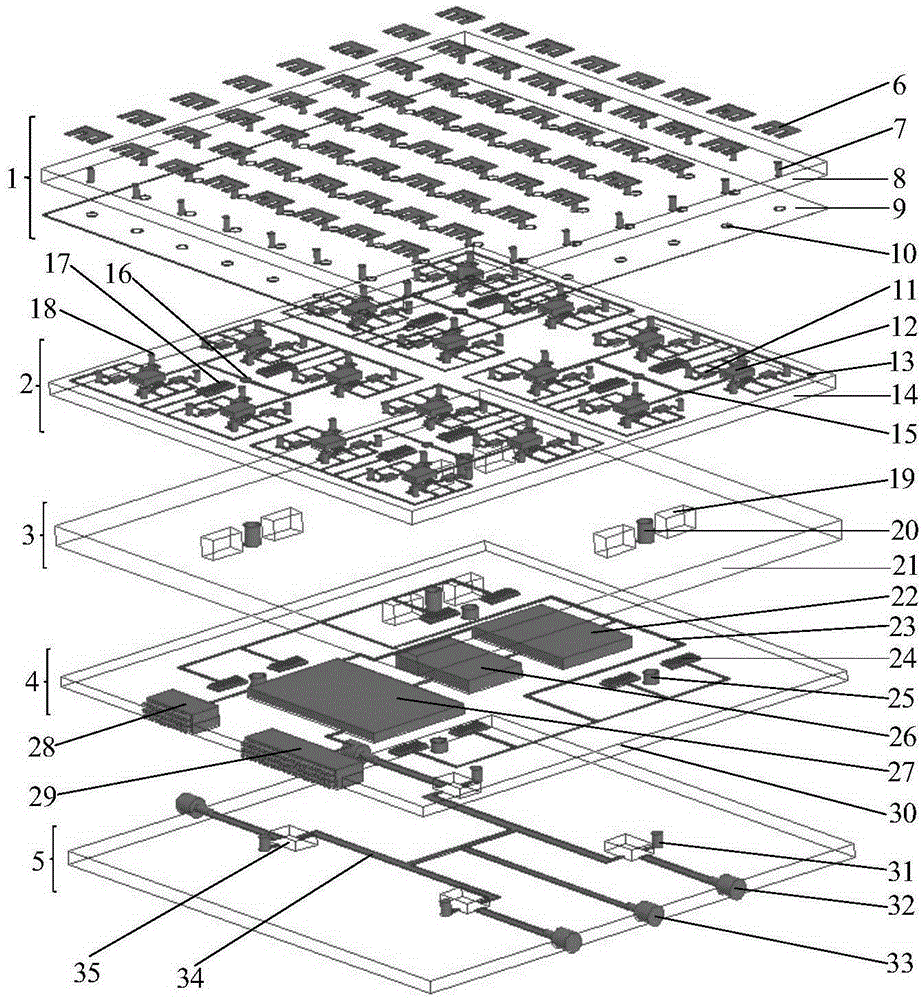
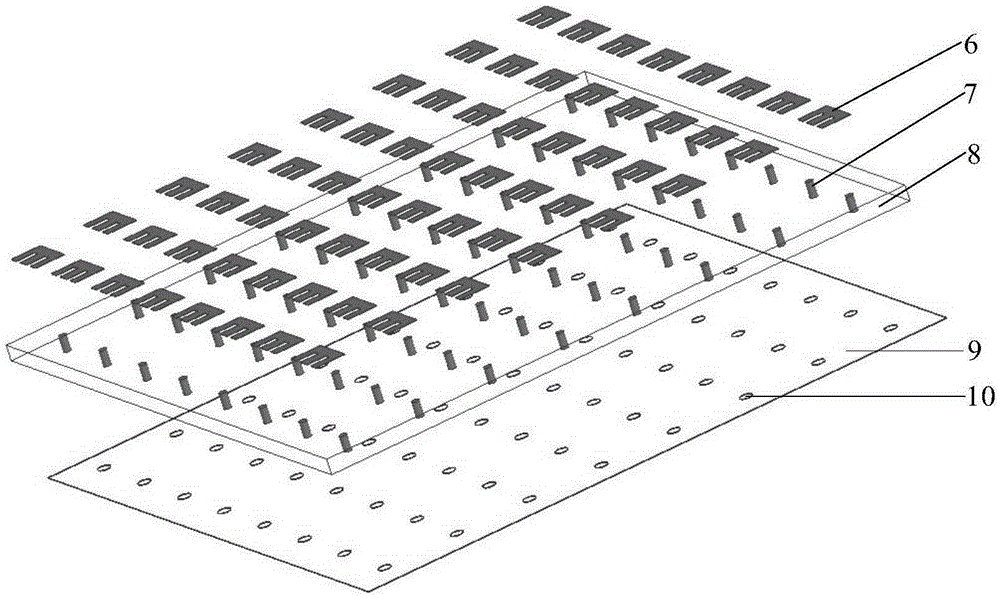
High-power seeker tile type active phased array antenna
ActiveCN105356051AReduce volumeReduce weightAntenna arraysAntennas earthing switches associationMicrostrip antenna arrayControl signal
The invention discloses a high-power seeker tile type active phased array antenna, and aims at providing an active phased array antenna which is small in size and low in weight and can reliably work with no requirement for temperature compensation. The high-power seeker tile type active phased array antenna is realized by the following scheme that E-type patches act as radiation array elements of a microstrip antenna array which can be extended according to integral multiples of 4x4 array scale, rectangular grid arrays are distributed on an antenna dielectric substrate, and a tile type TR component is closely connected with a heat exchanger integrally; and the microstrip antenna array is connected with the high-power transmit-receive chips of the tile type TR component to form transmit-receive channels through integration, every four high-power transmit-receive chips are connected with one TR multifunctional chip simultaneously, four TR multifunctional chips form one 4x4 subarray circuit module together, and then subsequent connection with a power distribution synthesis network is performed. Power supply, high-power pulse power modulation and amplitude-phase code control of a DC power supply and wave beam control signals are realized via a power supply modulation distributor so that directional diagram scanning of the high-power tile type active phased array antenna can be realized.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Epoch-variant holographic communications apparatus and methods
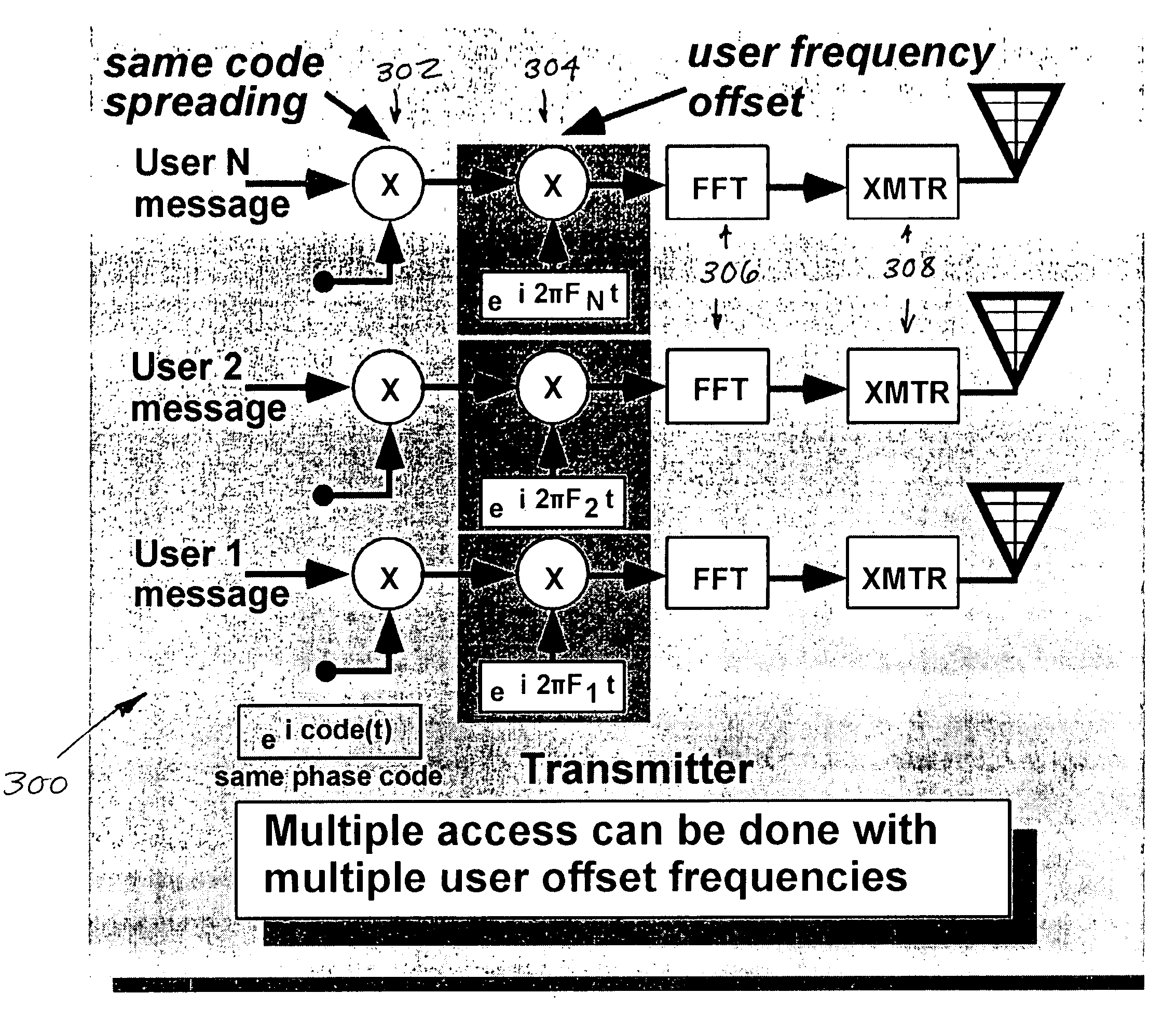
Improved apparatus and methods for utilizing holographic waveforms for a variety of purposes including communication, ranging, and detection. In one exemplary embodiment, the holographic waveforms are transmitted over an RF bearer medium to provide, inter alia, highly covert communications, radar systems, and microwave data links. The bearer (i.e., carrier) is optionally frequency-hopped, and various pulse modulation techniques (including variation of the phase-coding clock epoch) applied in order to further increase communications efficiency and covertness. Methods of providing multiple access and high bandwidth data transmission are also disclosed. Improved apparatus utilizing these features; e.g., a wireless miniature covert transceiver / locator, are also disclosed.
Owner:HOLOWAVE
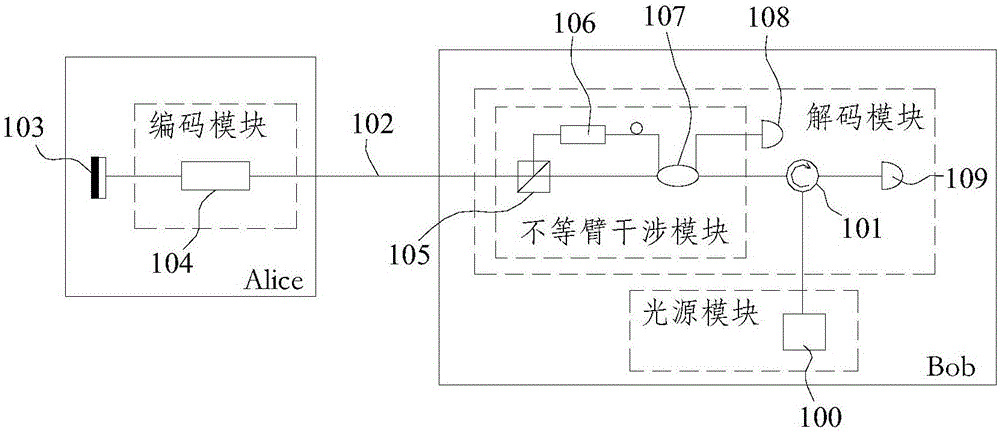
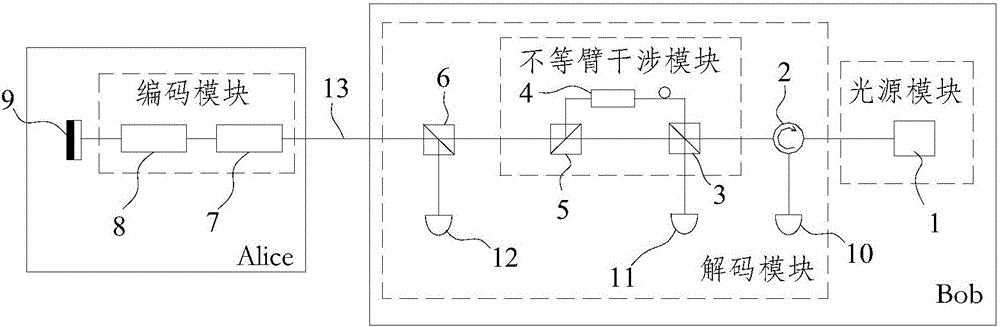
Plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution system and method based on time-phase encoding, transmitting end and receiving end
ActiveCN106161011AImprove bit rateKey distribution for secure communicationCode moduleComputer architecture
The invention discloses a plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution system and method based on time-phase encoding, a transmitting end and a receiving end. The plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution system comprises the transmitting end and the receiving end which are in mutually optical connection, a coding module in the transmitting end comprises a Z basis vector time coding module coding optical signals according to any sequence and a phase coding module which is an X basis vector phase coding module, and a decoding module in the receiving end is matched with the coding module. The plug-and-play quantum secret key distribution method includes: after an Alice end receives and reflects optical signals from a Bob end, performing Z basis vector time coding and phase coding; sending the optical signals after going through Z basis vector time coding and phase coding to the Bob end for decoding and detecting, wherein phase coding refers to X basis vector phase coding. Improved time-phase coding is used, so that ultrahigh-contrast coding and decoding can be realized, and code generating rate can be increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENZHOU QUANTUM NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Apparatus for and method of determining quadrature code timing from pulse-shape measurements made using an in-phase code
ActiveUS20070058700A1Eliminate associated biasDecrease in levelSatellite radio beaconingTransmissionCorrelation filterPhase Code
A receiver employs a pre-correlation filter to determine the precise timing of, for example, a PRN code on the quadrature channel of a received signal, using an image of the average chip shape that the filter forms for a PRN code on the in-phase channel. The image is expressed as a time series of complex power measurements along the length of a single chip. The averaging process retains the detail of the composite in-phase signal (direct plus multipath signals) while reducing the level of signal noise by an amount proportional to the length of the averaging process. An analysis of the image reveals that there is, in the in-phase channel signal that is averaged, information from the quadrature channel signal. The quadrature channel signal information produces, in the image of the average chip shape of the in-phase channel PRN code, a “wiggle” that corresponds to the timing of the chips of the quadrature channel PRN code. The receiver detects the chip edges of the quadrature PRN code directly from an analysis of the high frequency phase modulations of the complex vector of samples that represents the average chip shape. Using GPS signals, the receiver detects the P-code transitions by synchronizing to the 10.23 MHz phase modulations in the complex vector of samples that represent the averaged chip shape. The receiver uses the detected P-code transitions and, more particularly, the P-code transitions that are closest to the C / A code transitions, to produce P-code phase information that the receiver uses pseudorange calculations to remove biases associated with timing differences between the transmission of the in-phase and quadrature PRN codes.
Owner:NOVATEL INC
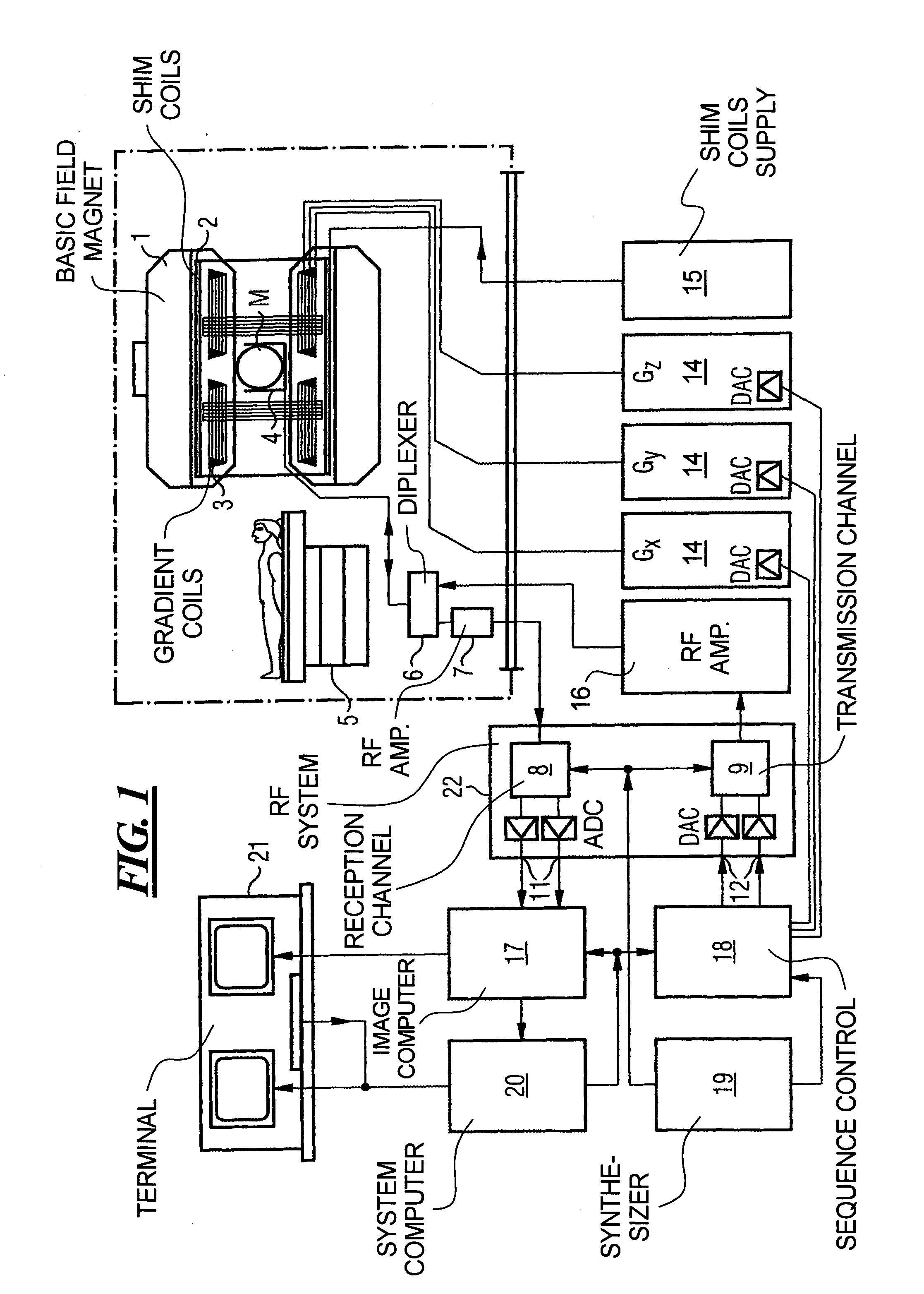
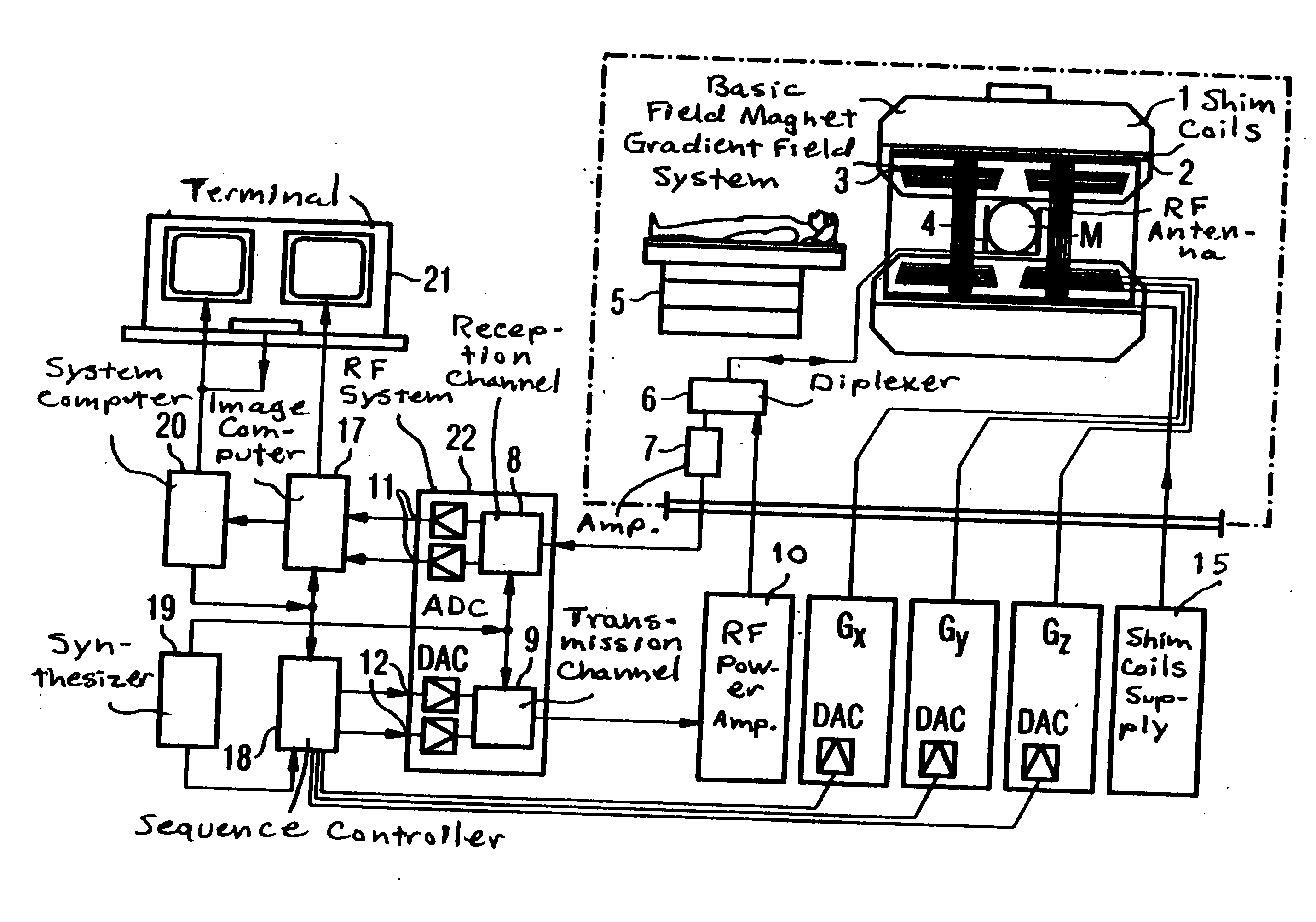
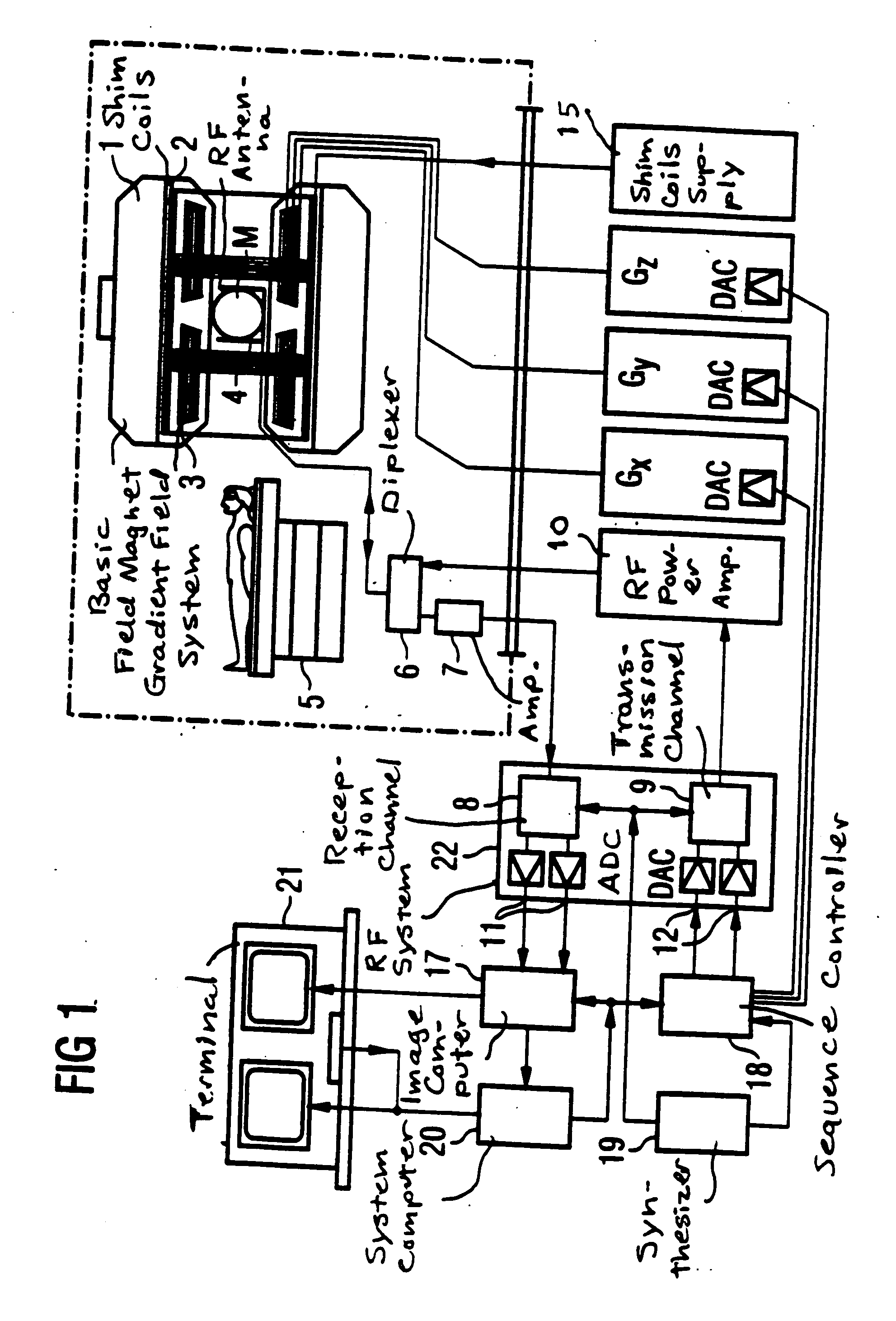
Magnetic resonance tomography apparatus and method employing a true FISP sequence with improved off-resonant behavior of two spin ensembles
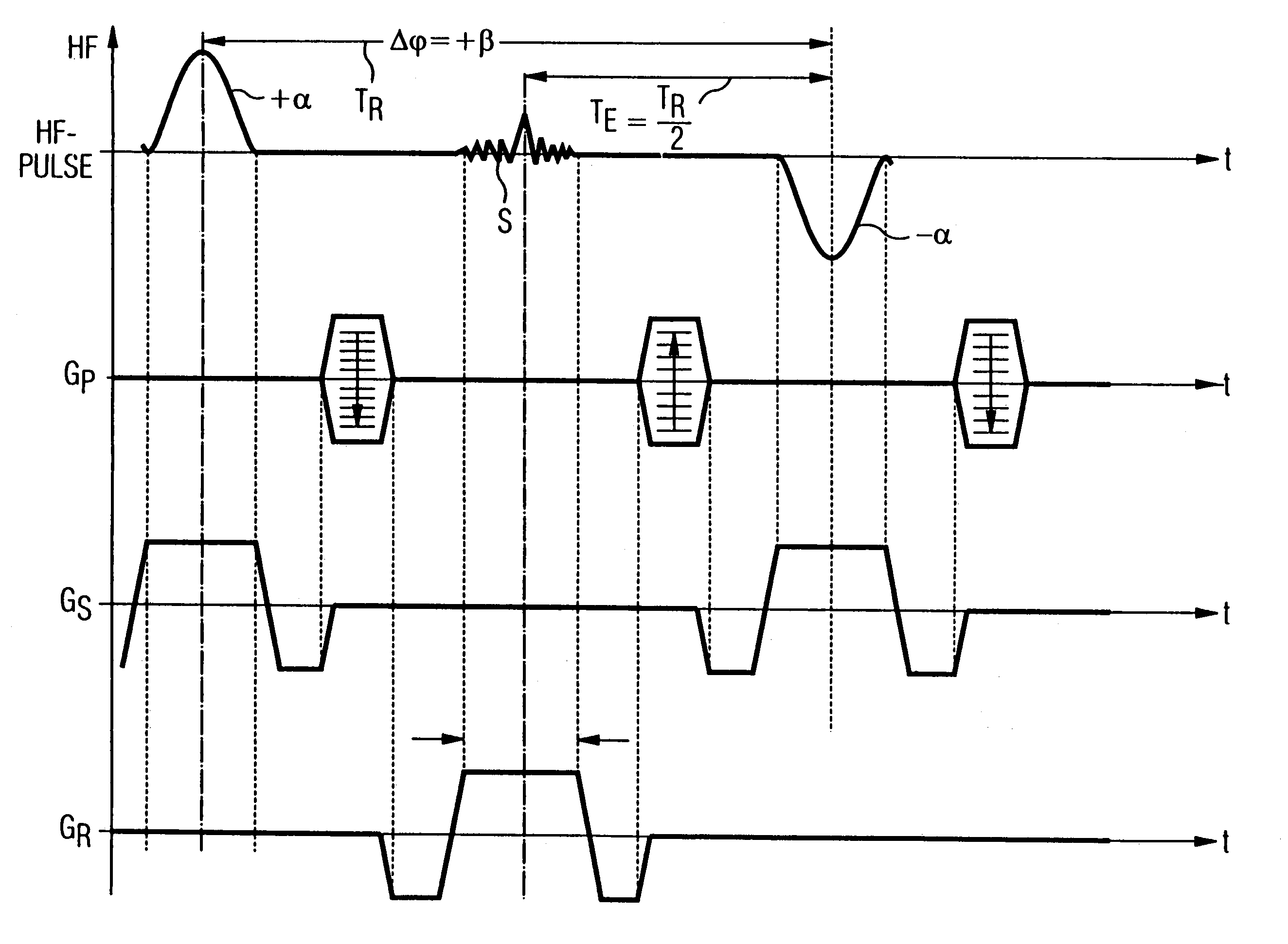
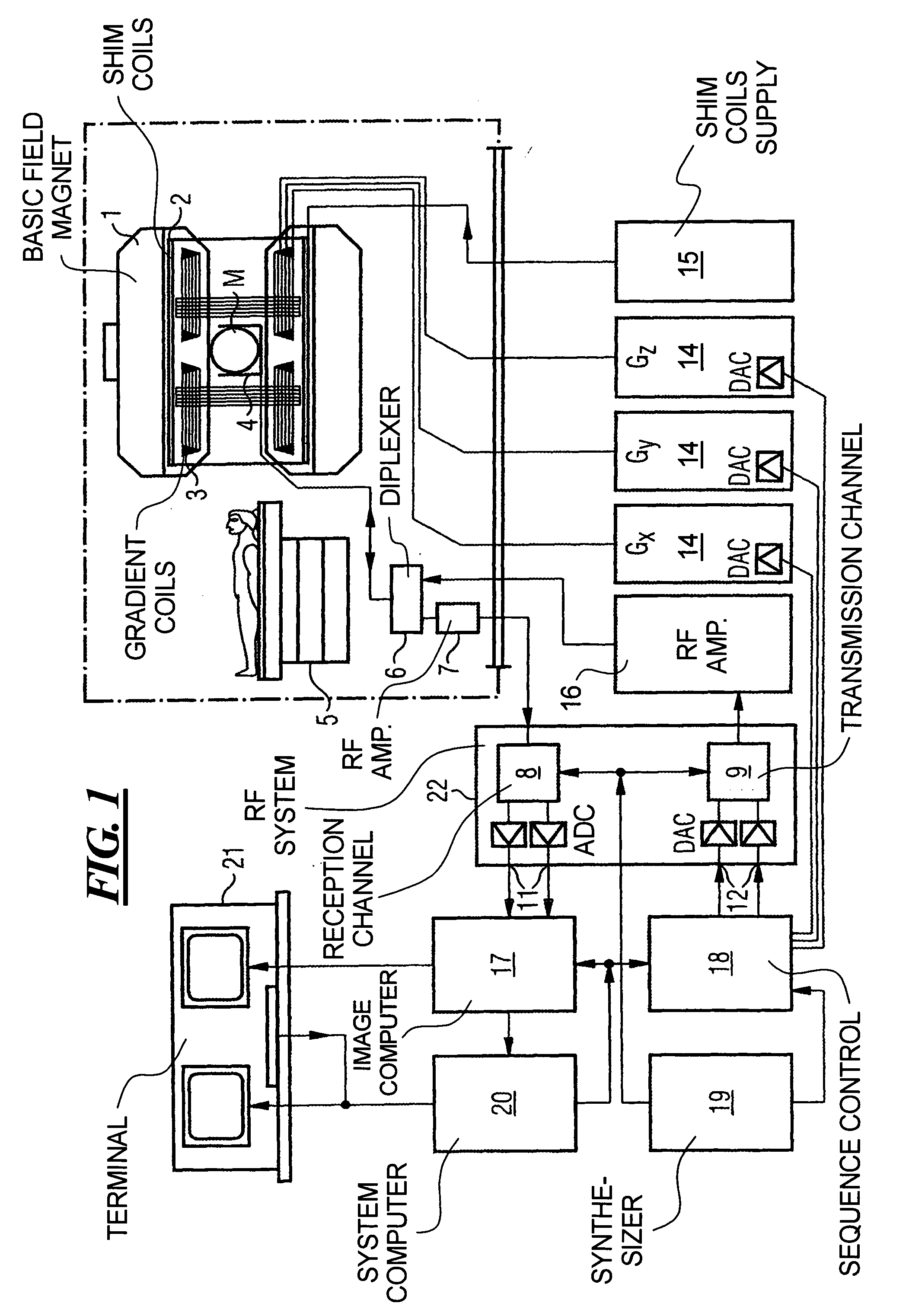
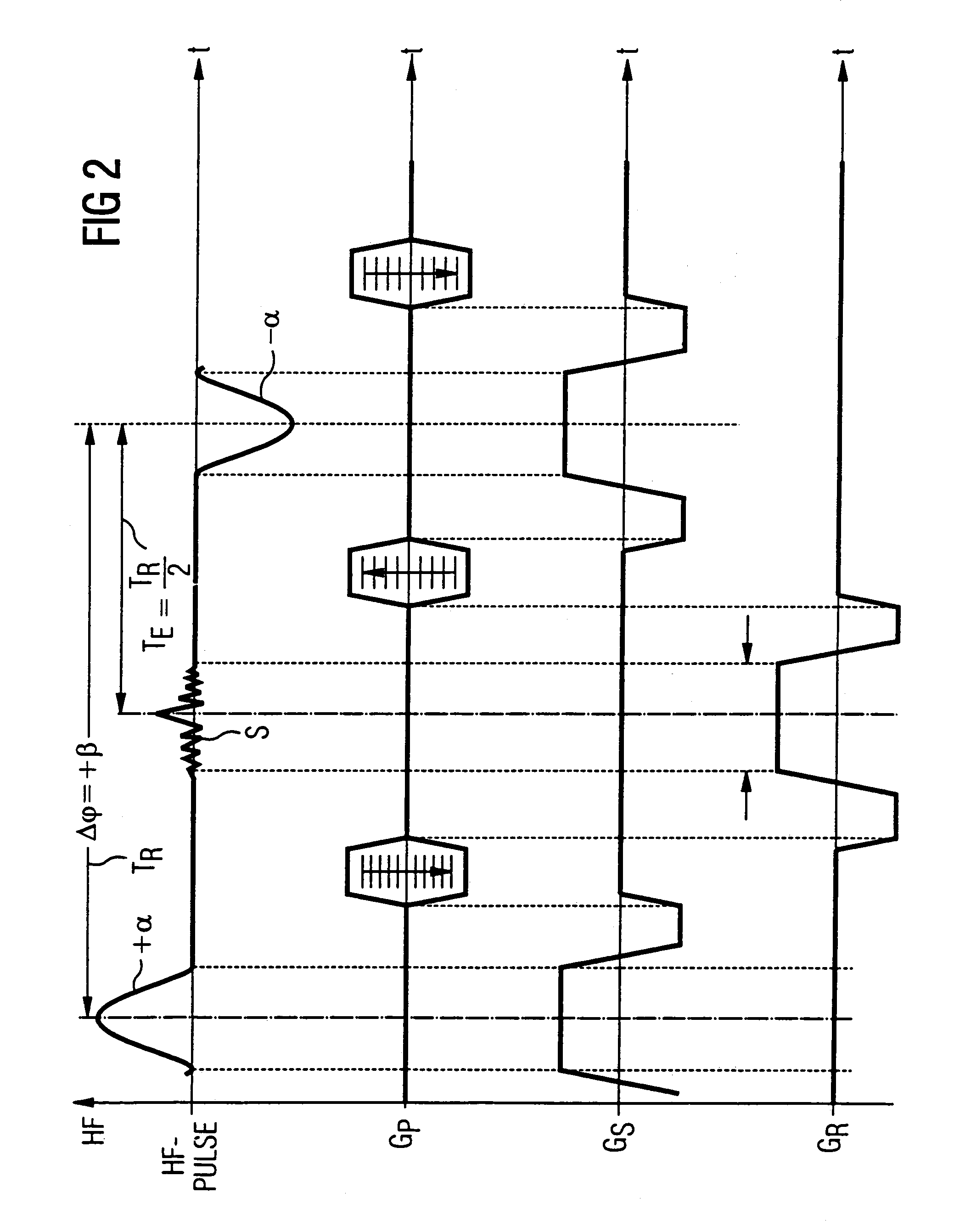
InactiveUS7020509B2Significant differenceImprove stabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData setPhase Code
In a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus employing a FISP pulse sequence, the pulse sequence is repeated with a repetition time TR with different phase-coding gradient directions and with an alternating operational sign of the flip angle α. The gradient pulse trains are thereby completely balanced. A phase increment ΔΦ=β is generated in addition to the alternating operational sign of the flip angle α between successive excitation pulses, so that the steady state signals for a first and a second spin ensemble optionally have either identical or reversed signal polarities. A first dataset on the basis of identical signal polarities and a second dataset on the basis of reversed signal polarities are obtained by means of the free selection of the mutual signal polarities. A pure image of the first and the second spin ensembles is thus obtained by the addition and / or subtraction of the first and second datasets.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
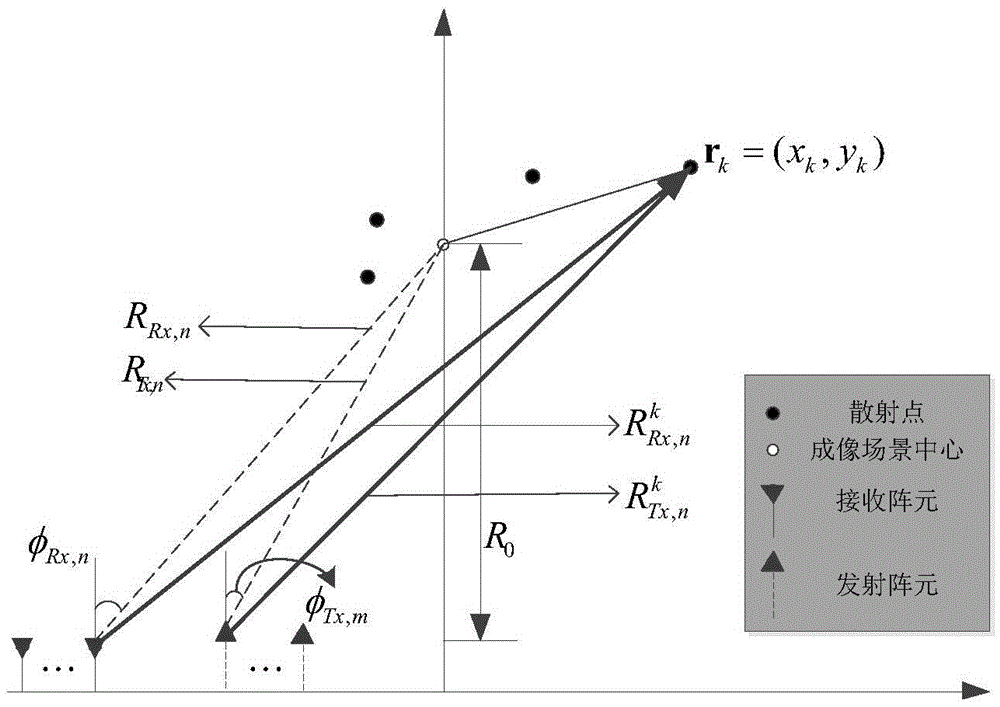
Multi-target positioning method of bistatic multi-input multi-output radar
InactiveCN102135617AAvoid decompositionFast convergenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMulti inputComputation complexity
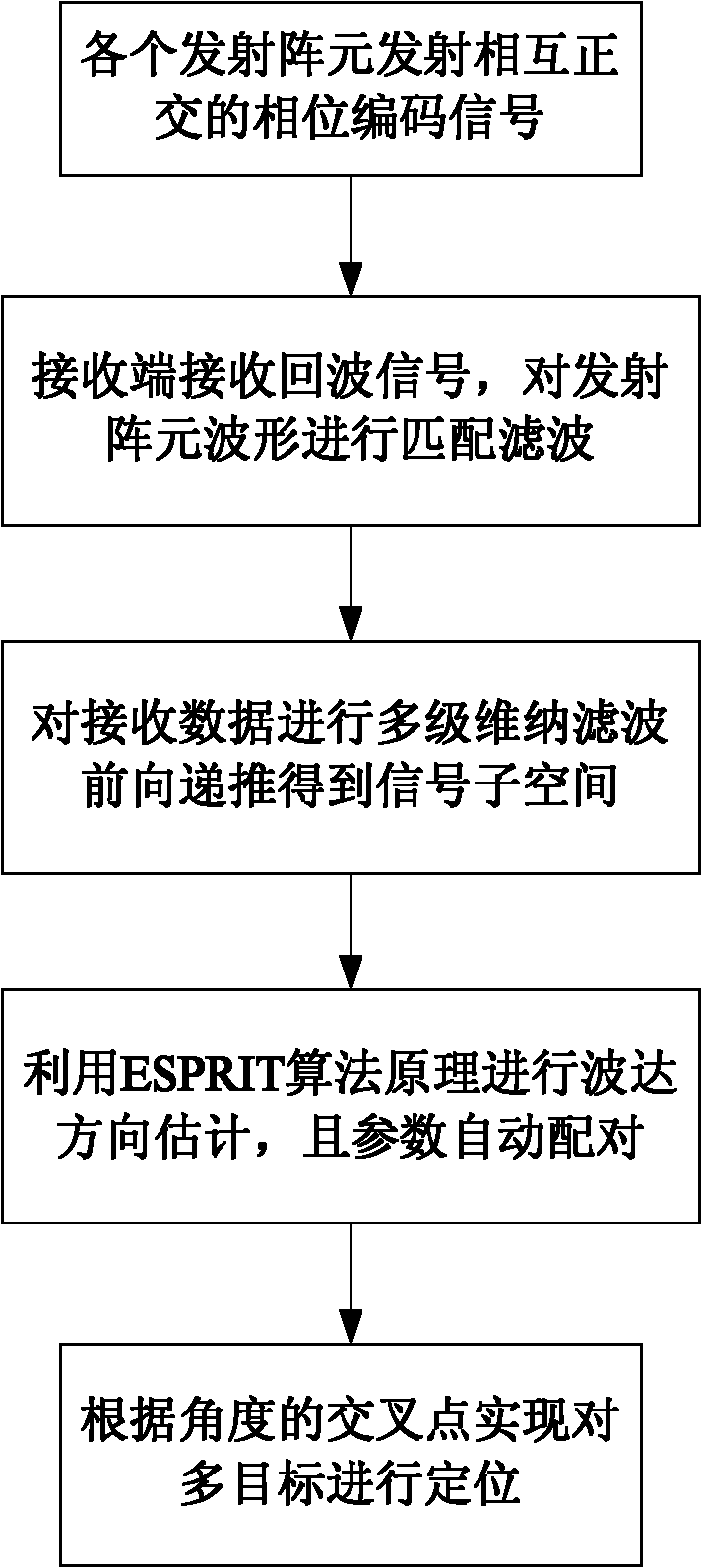
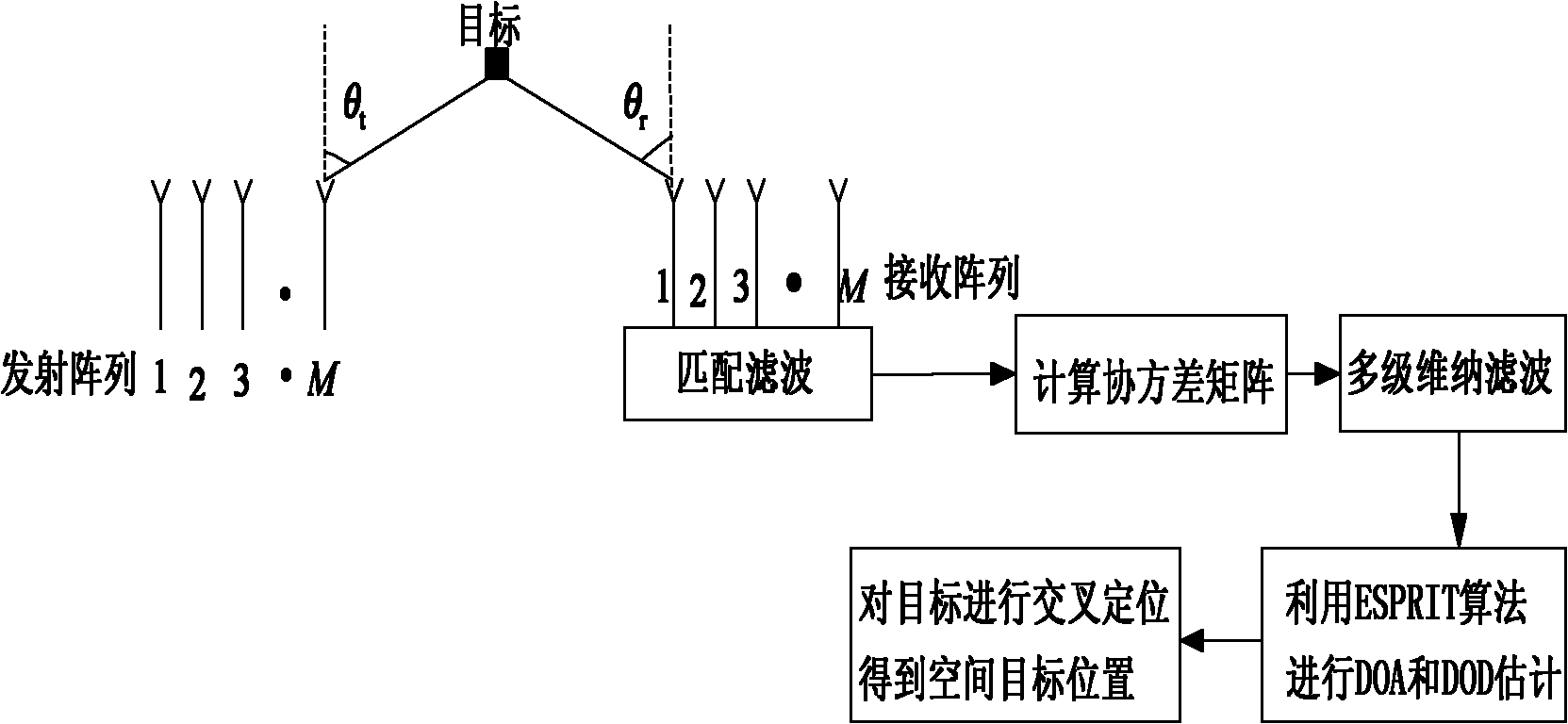
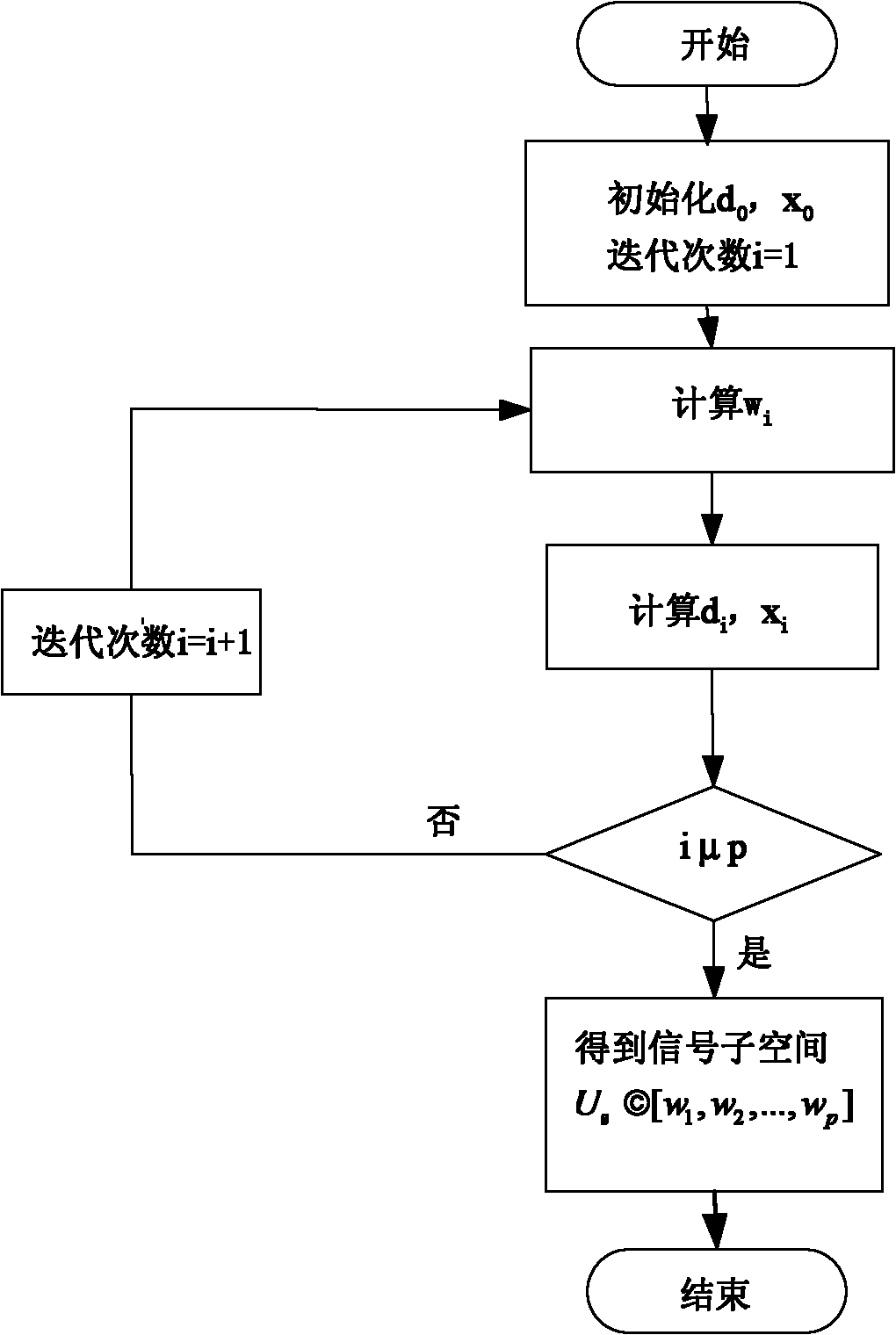
The invention provides a multi-target positioning method of a bistatic multi-input multi-output radar, comprising the following steps of: (1) transmitting mutually orthogonal phase-coded signals by M transmitting array elements, and receiving the phase-coded signals by N receiving array elements, wherein the distances of the M transmitting array elements and the N receiving array elements are all of half wavelengths; (2) carrying out matched filtering on the received phase-coded signals by a matched filter of a receiver of each receiving array element; (3) carrying out multistage Wiener filtering on a matched signal data covariance matrix space, and carrying out forward recursion to obtain a signal subspace; (4) carrying out high-resolution DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation by using an ESPRIT algorithm, wherein a pairing algorithm is used for carrying out the automatic pairing on two-dimensional parameters; and (5) realizing multi-target positioning according to cross points at two angles so as to obtain the positions of space targets. The multi-target positioning method provided by the invention has the advantages of low computation complexity, high computation speed, high estimation accuracy and can be used for positioning the sea-surface or low-altitude targets during tracking and guidance.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
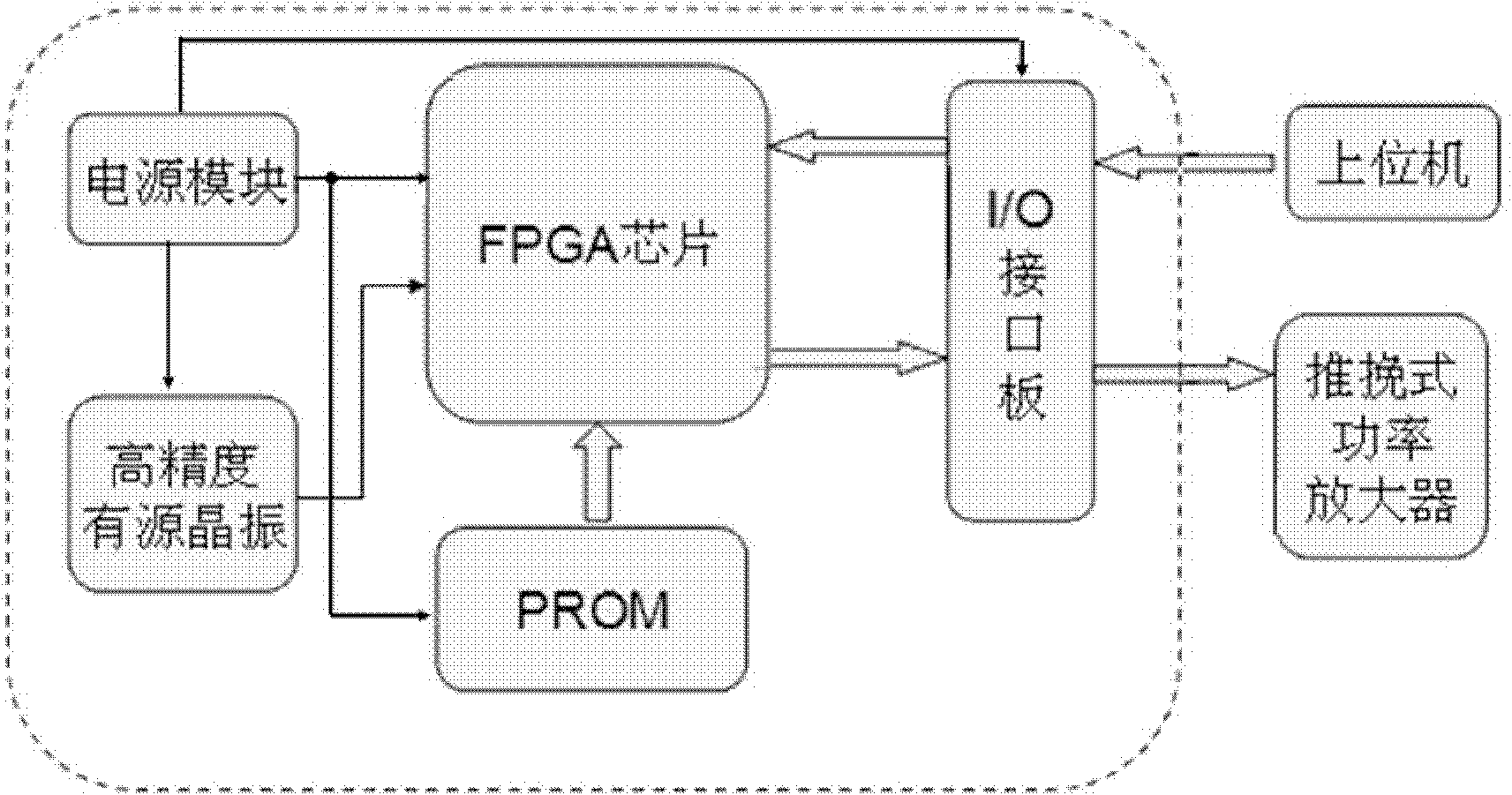
Multi-channel high precision phase control signal generation device
ActiveCN101862511AIncrease the number of channelsHigh precisionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyFpga field programmable gate arrayProgrammable read-only memory
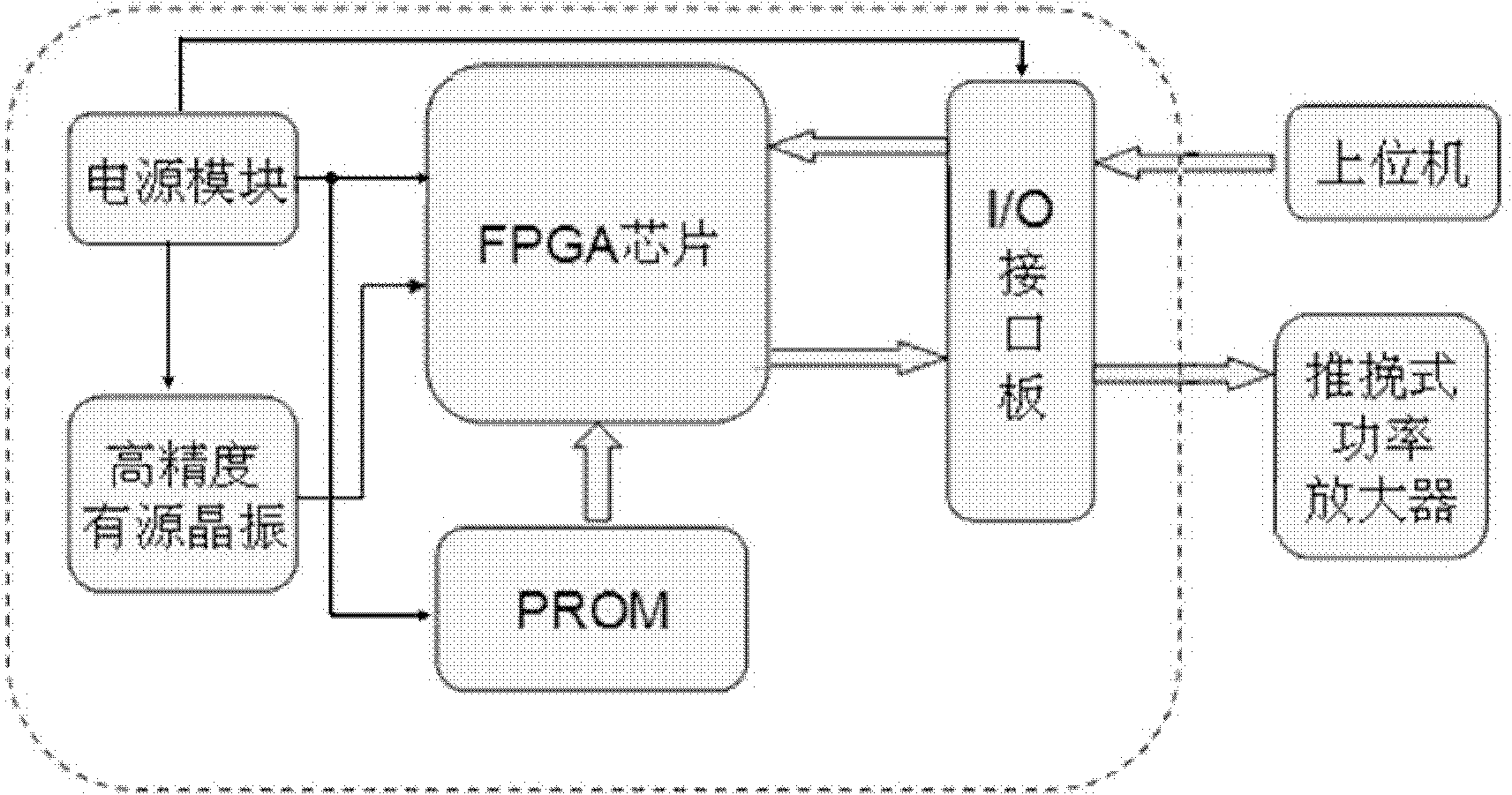
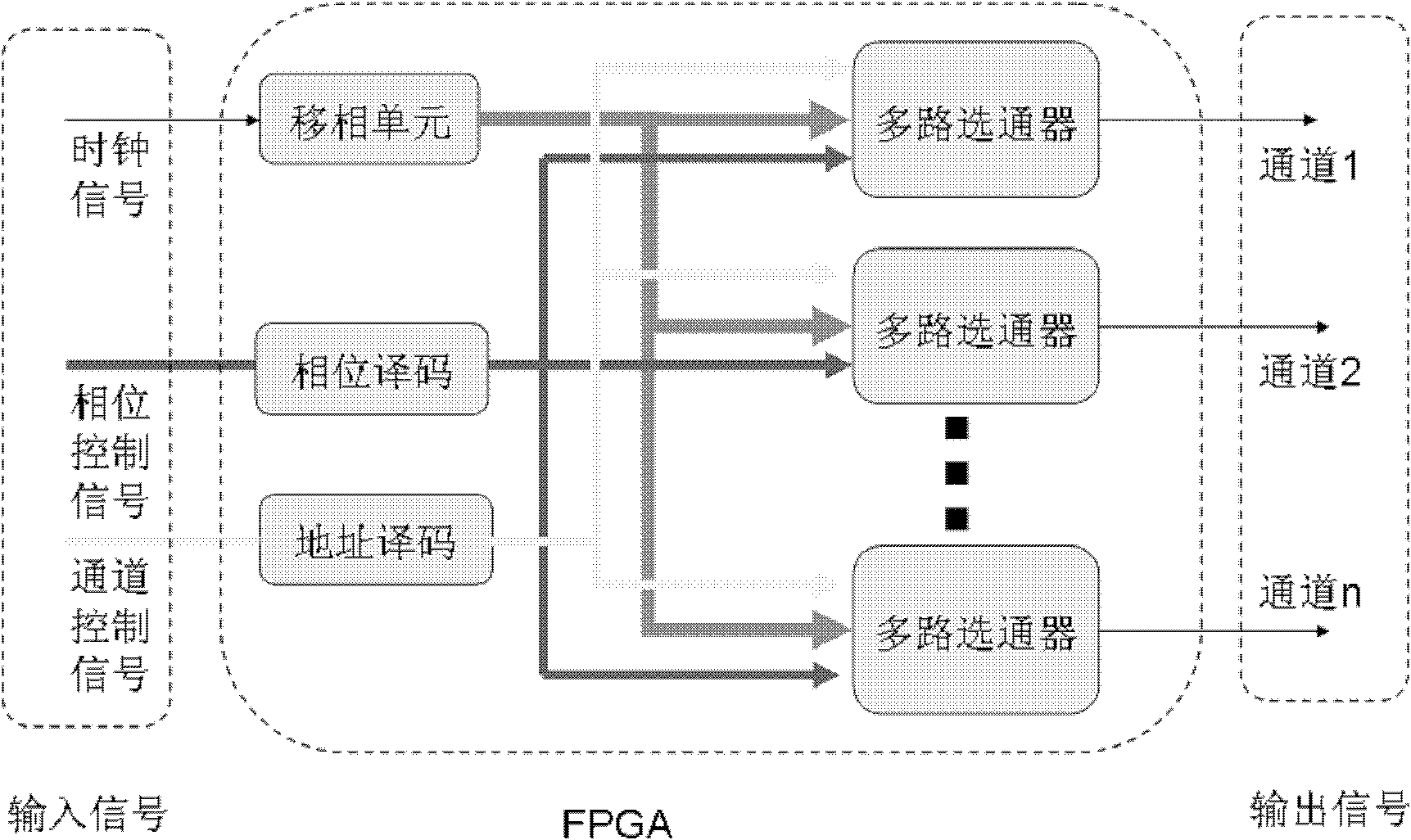
The invention relates to a multi-channel high precision phase control signal generation device which utilizes a programmable read-only memory to generate a customized special circuit in an FPGA (Filed Programmable Gate Array) circuit through a VHDL (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Hardware Description Language) language programming. The multi-channel high precision phase control signal generation device comprises a phase shift module, a phase coding module, an address coding module and a plurality of multi-channel gates. By taking a high precision active crystal oscillator as an information source, all multi-channel gates works in parallel to receive phase control signals of a host computer and output square wave signals of a multi-channel special phase. The output square wave signals access resonance of a power amplifier to generate sine wave signals with the same frequency and phase with the traditional output signals and the sine wave signals are used for excitation signals of an ultrasonic transducer array element in a phase control type high intensity focusing ultrasonic treatment system; and the frequency of the crystal oscillator is determined by the resonance frequency and the phase control precision requirements of the ultrasonic transducer array element. The invention dramatically increases the channel amount of the phase control signals and enhances the precision of the phase control signals, thereby satisfying the needs of the high intensity focusing ultrasonic treatment system.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHENDE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
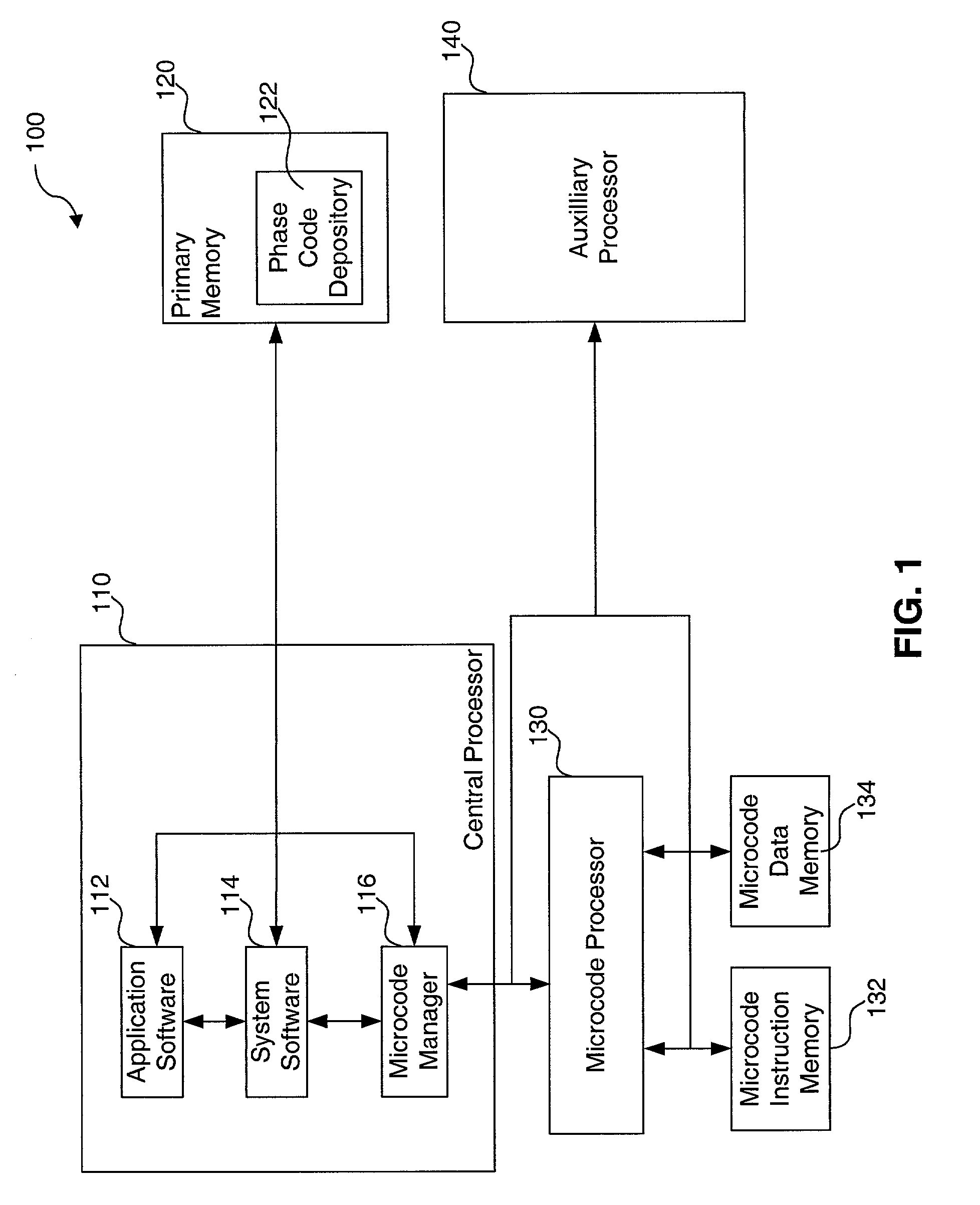
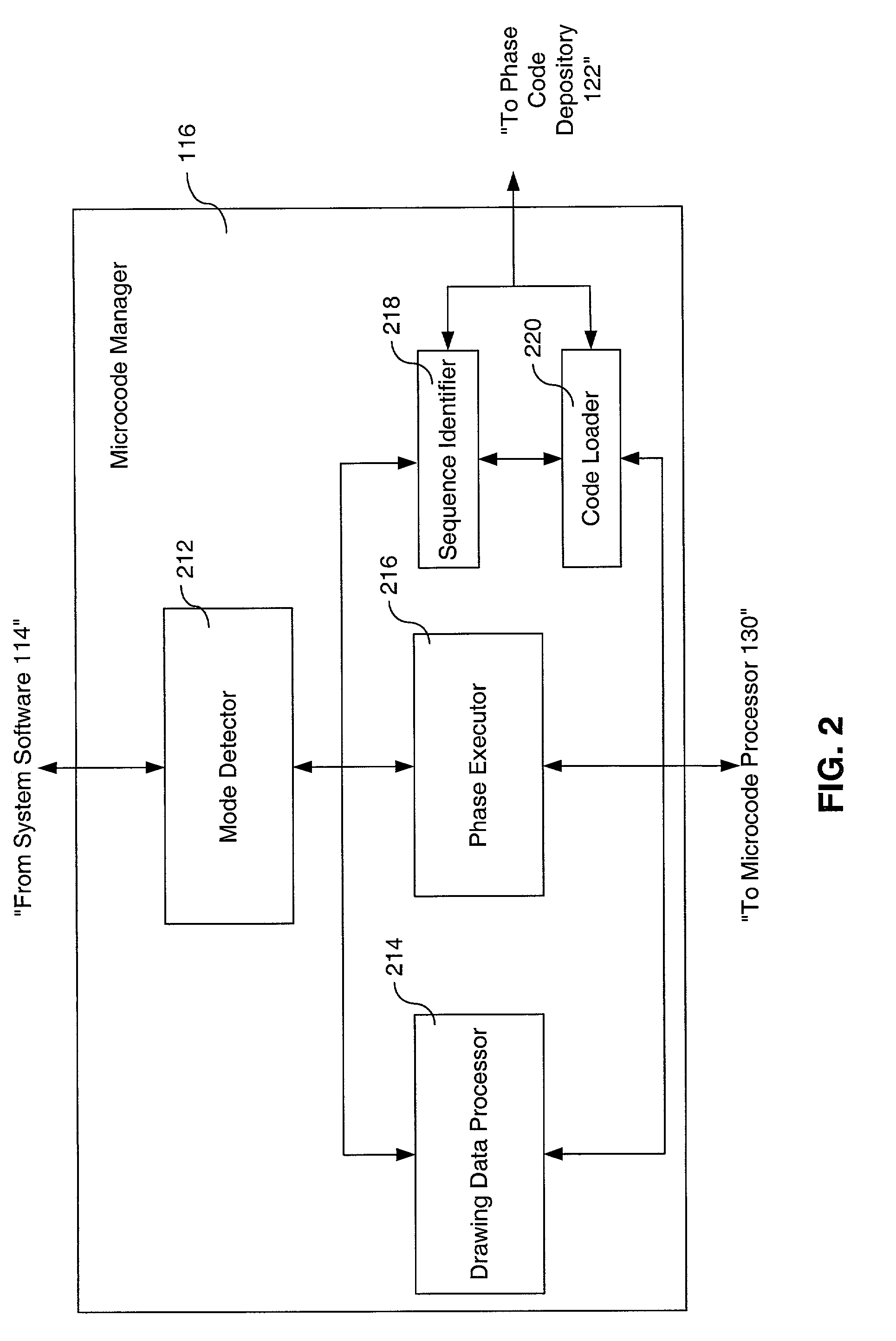
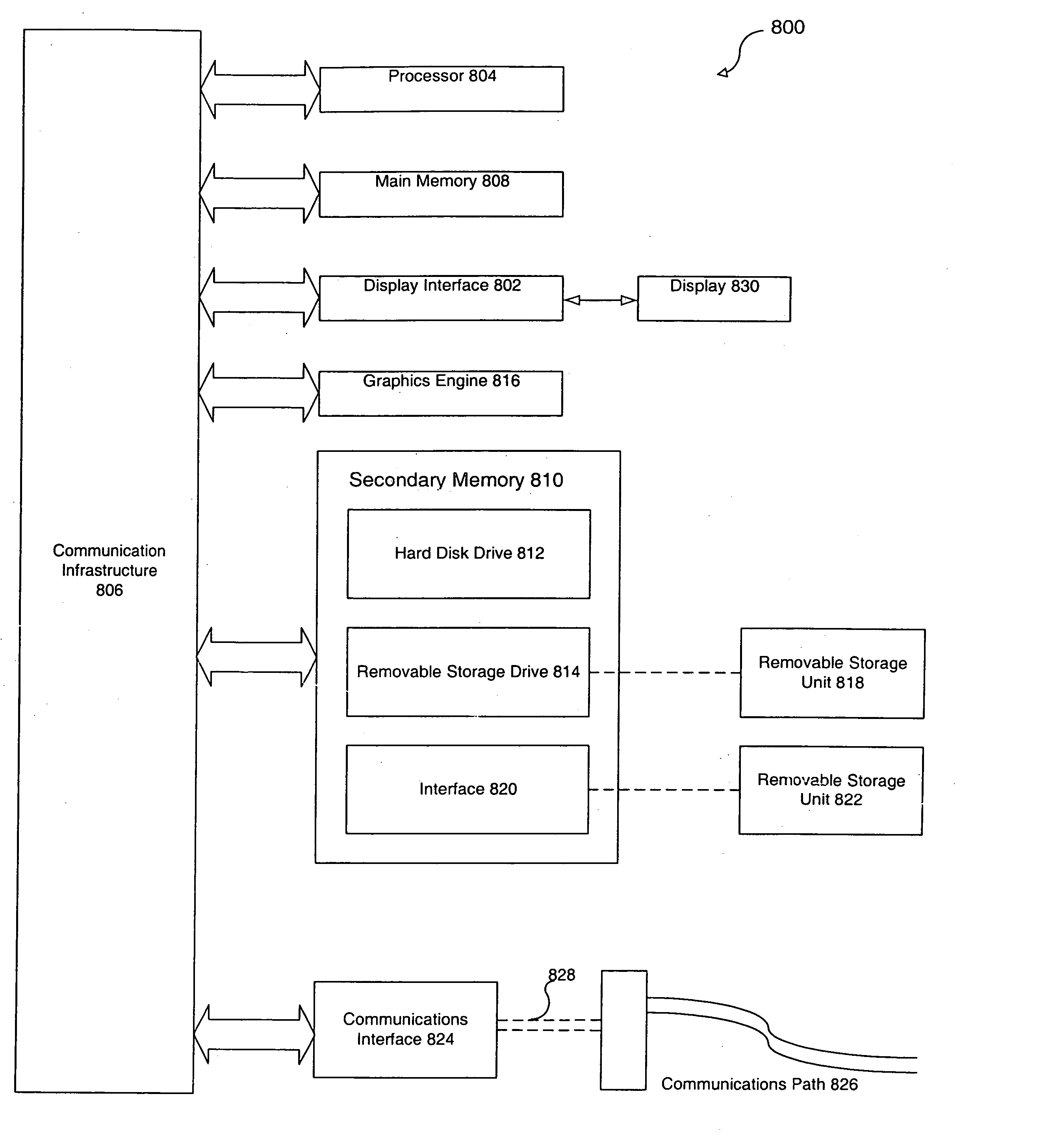
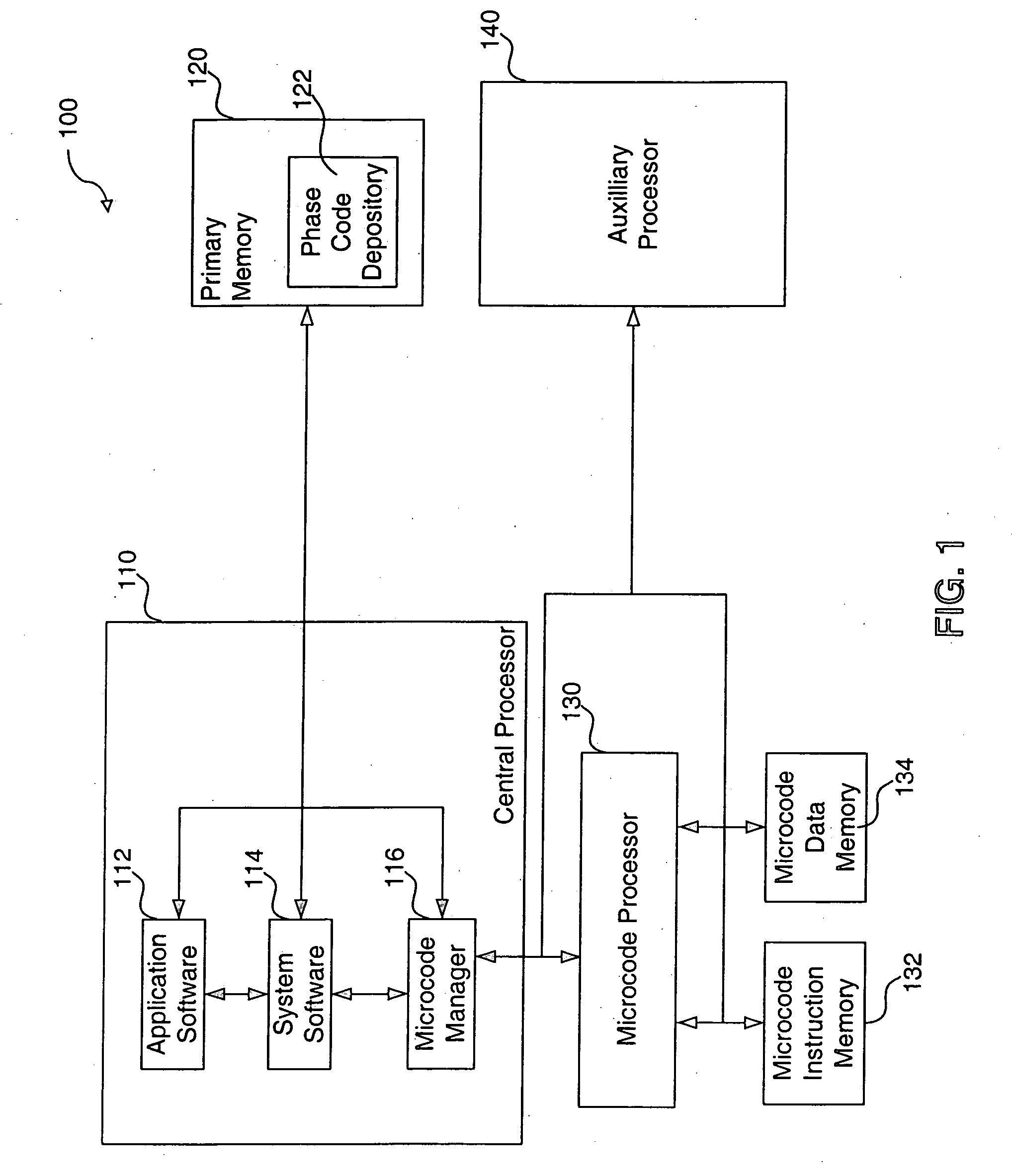
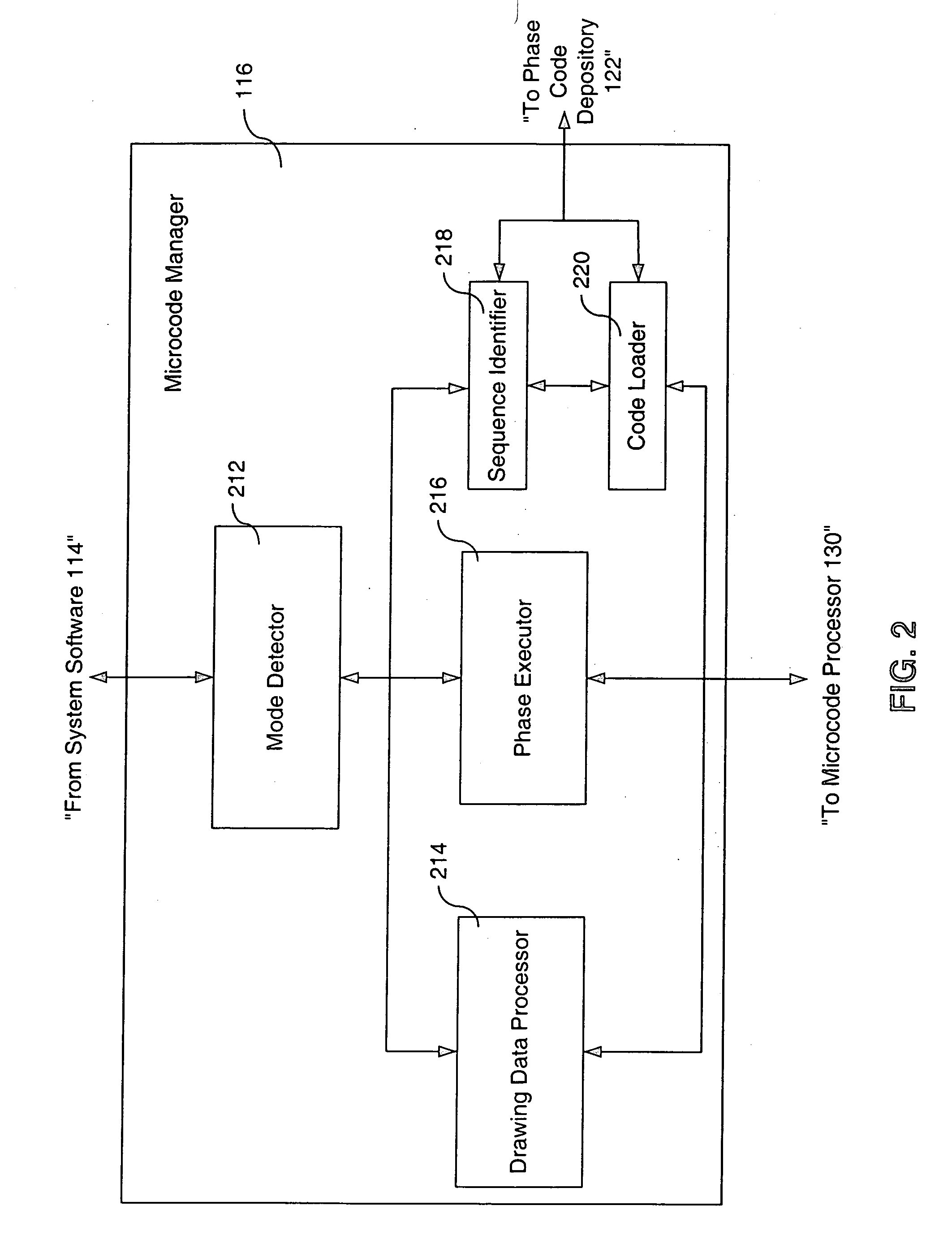
Method, system and computer program product for efficiently utilizing limited resources in a graphics device
InactiveUS7098921B2Improve performanceImprove abilitiesDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionInstruction memoryMemory address
A memory management system provides microcode instructions that are divided into multiple tuned phases and stored as separate modules inside a phase code depository. A microcode manager, containing a mode detector, sequence identifier, code loader, drawing data processor and phase executor, interacts with a microcode processor and the phase code depository. The mode detector evaluates a user request for a desired mode. In response to a command from the mode detector, the sequence identifier selects a correct phase sequence that is needed to implement the desired mode. The code loader transfers the phase sequence from the phase code depository to the microcode processor where it is stored in a microcode instruction memory. The memory address for each module within the phase sequence is written to a microcode data memory. The drawing data for the graphics mode is sent from the drawing data processor to the microcode processor, and the phase executor instructs the microcode processor to execute the phase sequence to render the desired mode by processing the drawing data. The resulting data is forwarded to another processor for additional microcode processing, vector processing, rasterization, or the like. The ability to select interchangeable phase modules to implement a desired mode reduces microcode memory requirements and allows easy integration and reuse of previously developed features among different games and other graphics software developers without having to rely on the type of platform.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
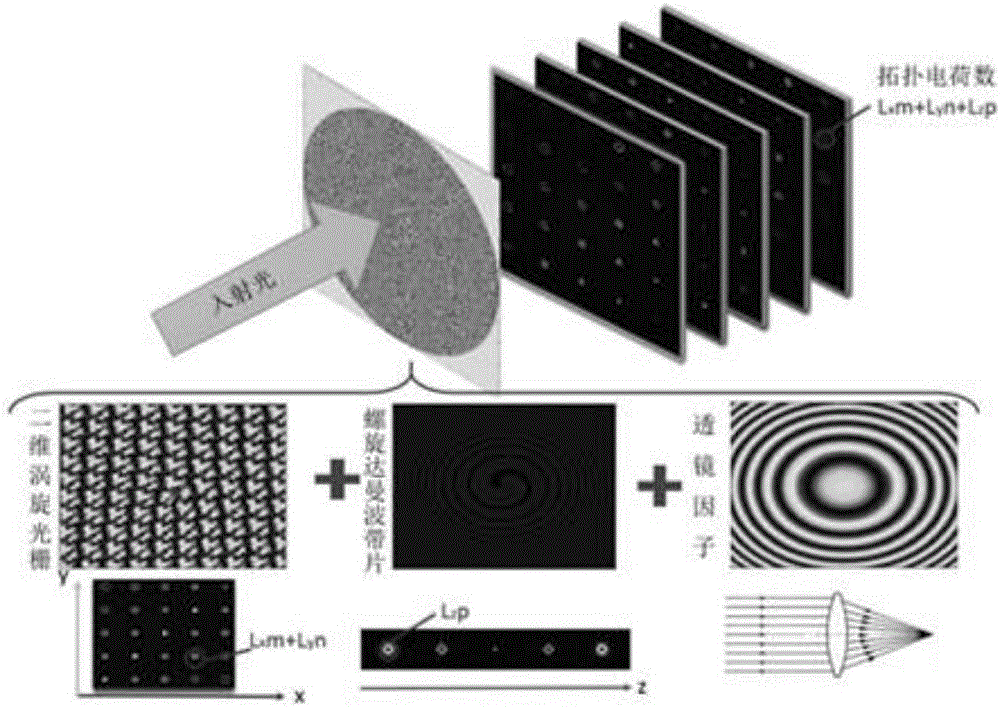
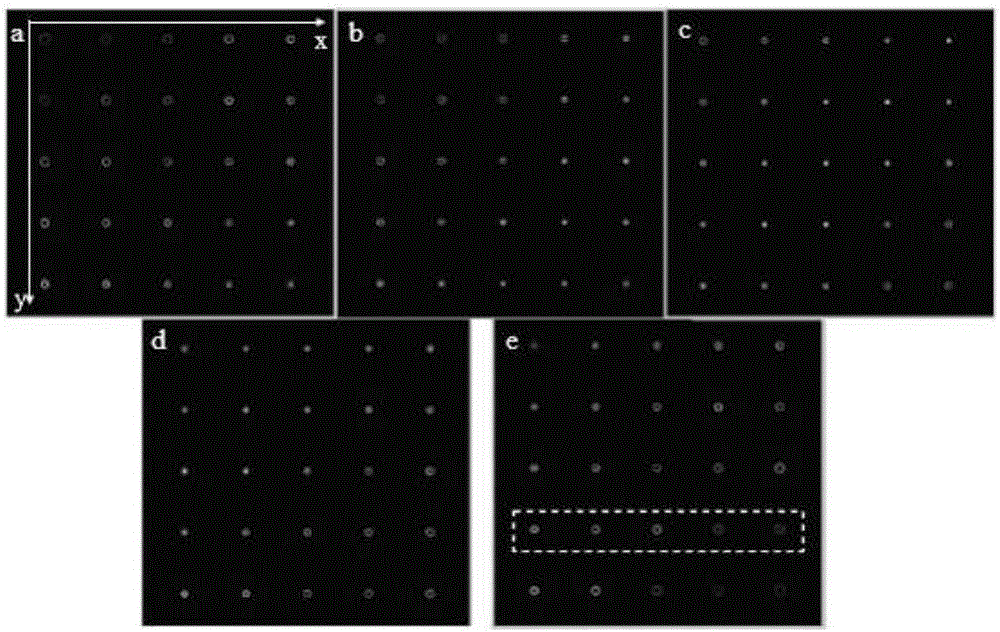
Integrating method of three-dimensional spatial distribution vortex arrays
ActiveCN106199800AEqual light intensityReduce complexityDiffraction gratingsSpatial light modulatorGrating
The invention relates to an integrating method of three-dimensional spatial distribution vortex arrays, and belongs to the field of diffraction optics. A pure-phase code of a two-dimensional uniform-strength vortex optical grating and a pure-phase code of a spiral Dammam wave zone plate are obtained through analytic operation and an optimization algorithm respectively, phase information of the pure-phase codes is overlaid, a lens factor is introduced, discretized phase values are loaded to a spatial light modulator according to the pixel number and the pixel size of the spatial light modulator, and then the corresponding three-dimensional vortex arrays can be obtained. According to the method, the equal-strength and regular-distribution three-dimensional vortex arrays can be obtained, and each vortex beam in the arrays has the specific topological charge number.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
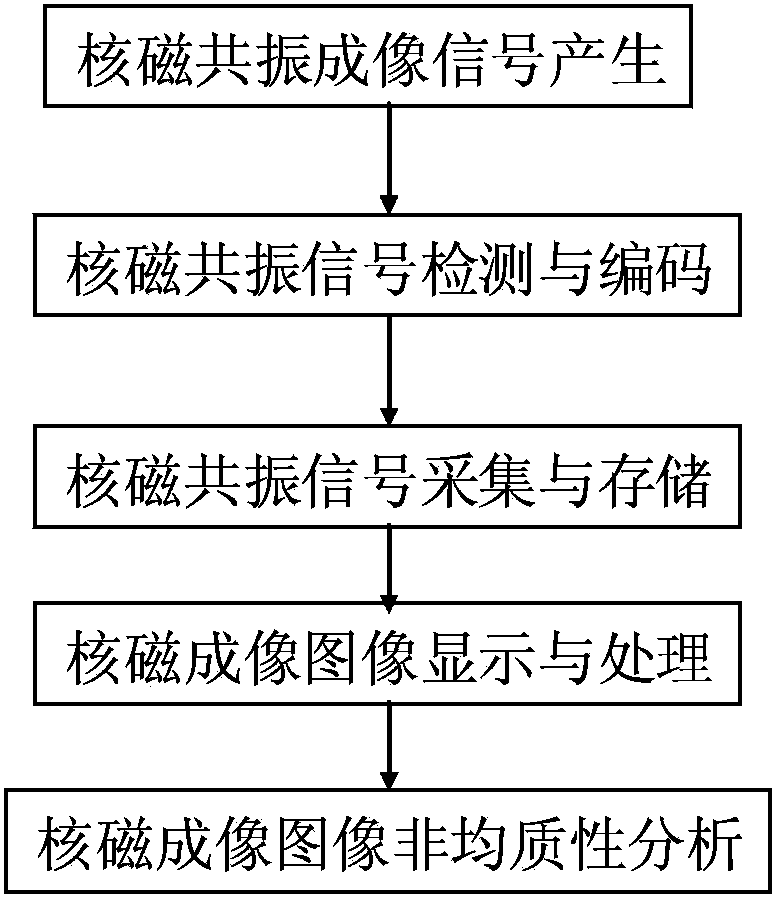
Rock heterogeneous quantitative evaluation method based on magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN103353462AOvercoming the Difficulties of Unrepresentative SamplingSimple processing capacityAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePorosityPhase Code
The invention discloses a rock heterogeneous quantitative evaluation method based on magnetic resonance imaging. Three-dimensional space orientation of rock can be realized by layer selection pulse, phase coded pulse and frequency coded pulse. An imaging signal can be obtained by applying a spin-echo sequence, and optimization selection of imaging experimental parameters can be carried out through experimental scale. On the basis, a nuclear magnetic imaging signal obtained by experimental measurement is subjected to digital image processing so as to generate a pseudo color graph. By means of the relationship between the porosity and nuclear magnetic imaging signal intensity of a stand sample, the total porosity and porosity and distribution spectrum of a single layer can be obtained. Multi-layer imaging results are compared and a porosity heterogeneous coefficient is defined, so that the longitudinal porosity distribution characteristic and heterogeneity of rock can be obtained. In addition, by applying a first-order spherical variation function model and a grid search method, characteristic parameters of a variation function can be obtained. Heterogeneous coefficients and relative heterogeneous coefficients can be defined to realize longitudinal and horizontal heterogeneous quantitative characterization of rock.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
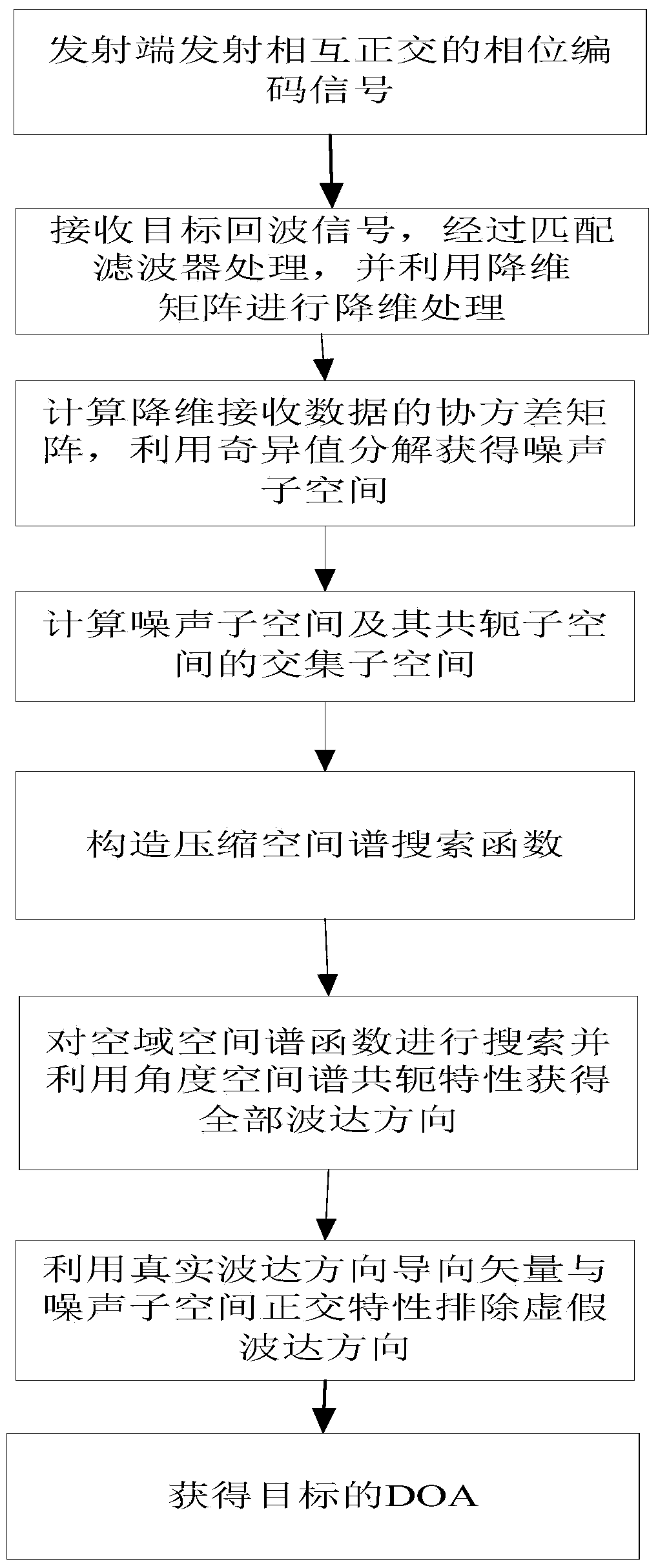
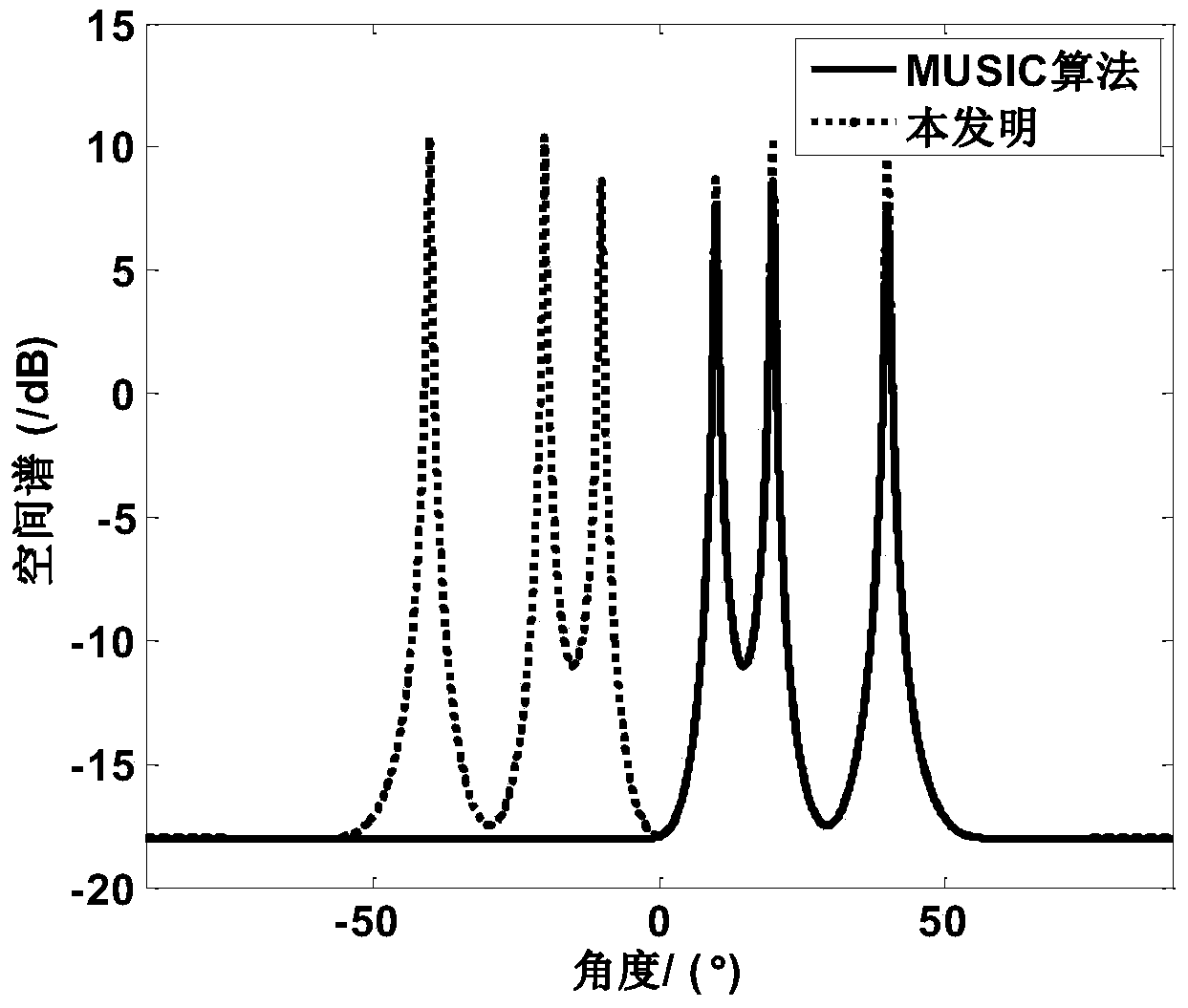
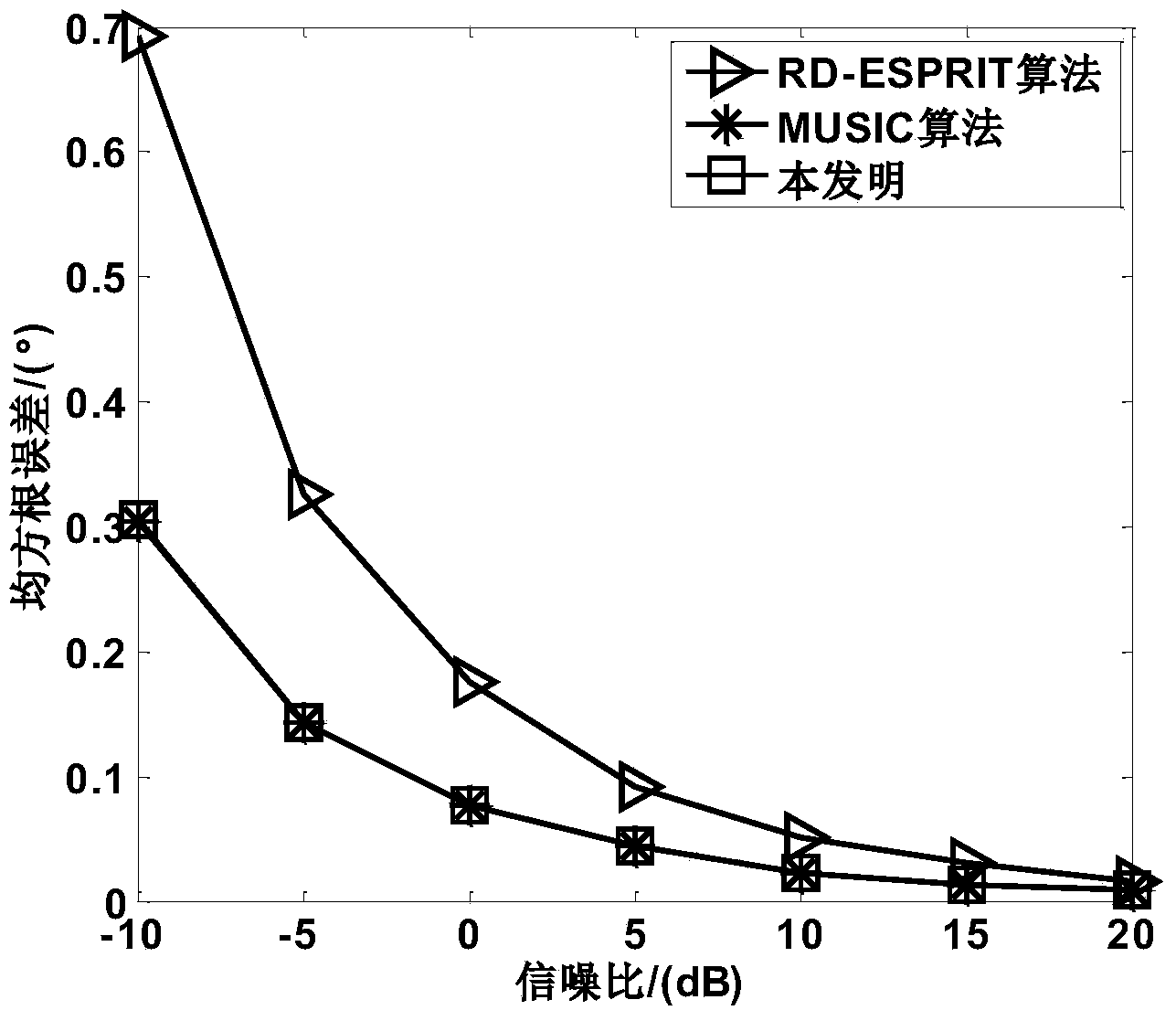
Compression spatial spectrum-based single base MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) radar target DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation method
ActiveCN104251989AAvoid federated searchReduce operational complexityDirection findersSpecial data processing applicationsRadar systemsMultiple signal classification
The invention relates to the technical field of radars, in particular to the application of a single base MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) radar system and a compression spatial spectrum-based single base MIMO radar target DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation method. The compression spatial spectrum-based single base MIMO radar target DOA estimation method comprises the steps of enabling an emission array to emit phase-coded signals which are mutually orthorhombic and enabling a receiving terminal to perform matched filtering processing through a receiving array matching filter; performing dimensionality reduction processing on J receiving data subjected to snapshotting matched filtering through a dimensionality reduction array; calculating a covariance matrix R of the receiving data Y subjected to dimensionality reduction processing and working out an intersection subspace of a noise subspace and a conjugate subspace thereof; constructing a compression spatial spectrum function and searching the compression spatial spectrum function; excluding a false DOA and obtaining a real DOA of a target. The compression spatial spectrum-based single base MIMO radar target direction of arrival estimation method avoids a combined search of a two-dimension DOA of a traditional MUSIC algorithm when searches the airspace DOA, and only needs one-dimensional space search and the algorithm complexity is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Polytopic multiplex holography
InactiveUS20060238841A1Treatment using aerobic processesTransportation and packagingMultiplexingPhase Code
Disclosed is a multiplexing method and apparatus that allows holograms to be spatially multiplexed with partial spatial overlap between neighboring stacks of holograms. Each individual stack can additionally take full advantage of an alternate multiplexing scheme such as angle, wavelength, phase code, peristrophic, or fractal multiplexing, for example. An amount equal to the beam waist of the signal beam writing a hologram separates individual stacks of holograms. Upon reconstruction, a hologram and its neighbors will all be readout simultaneously. An filter is placed at the beam waist of the reconstructed data such that the neighbors that are read out are not transmitted to the camera plane. Alternatively, these unwanted reconstructions can be filtered out with an angular filter at an intermediate plane in the optical system that has a limited angular passband.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
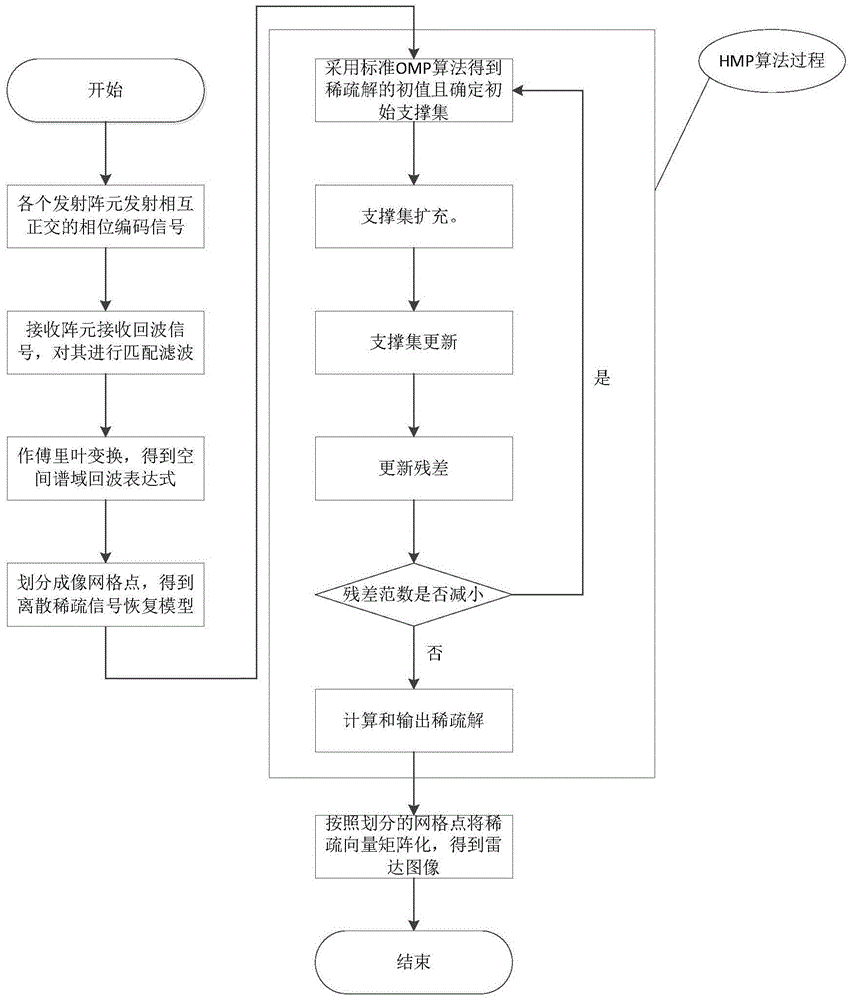
MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) radar sparse imaging algorithm based on hybrid matching pursuit algorithm
ActiveCN105652273AOvercoming resolutionOvercoming the disadvantage of high sidelobesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase CodeArray element
The invention belongs to the radar technology field and the signal processing field, and relates to application of a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) type system, in particular to an MIMO radar sparse imaging algorithm based on a hybrid matching pursuit algorithm. The MIMO radar sparse imaging algorithm comprises the steps that firstly, M emitting array elements emit orthometric phase-coded signals, and N receiving array elements receive the phase-coded signals; secondly, a matched filter of a receiver of each receiving array element conducts matched filtering on the received phase-coded signals; thirdly, fourier transform is conducted on the matched-filtered signals, and a spatial spectral domain echo expression is obtained. Index selection of each time in the HMP algorithm is realized through an OMP algorithm, orthogonality of base signal selection is guaranteed through the operation, and spatial surface elements which are very close to one another can be distinguished when fourier similar characteristics exist in a dictionary matrix; meanwhile, backtracking selection operation in the HMP algorithm is the same as that in an SP algorithm.
Owner:江苏和正特种装备有限公司
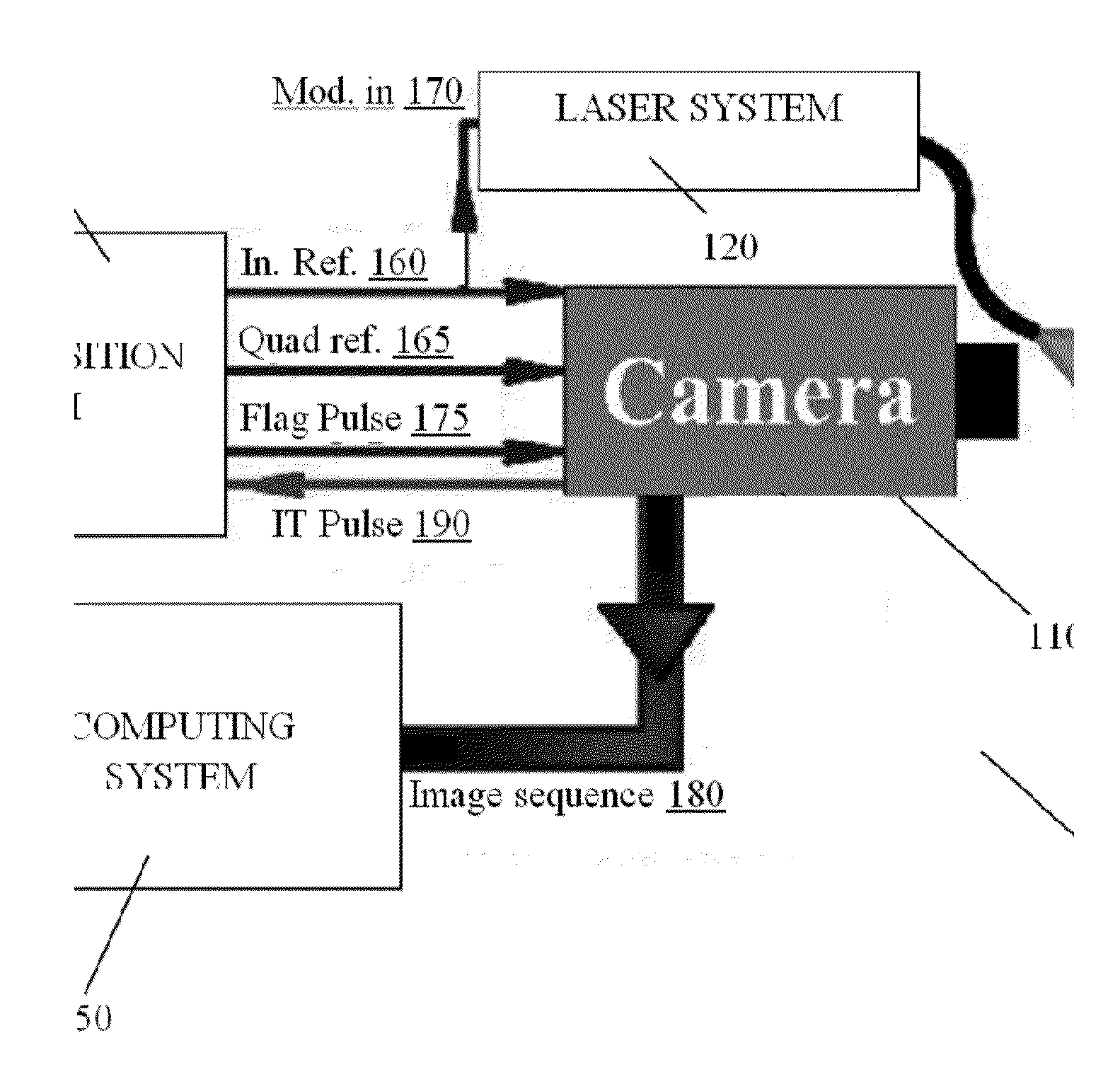
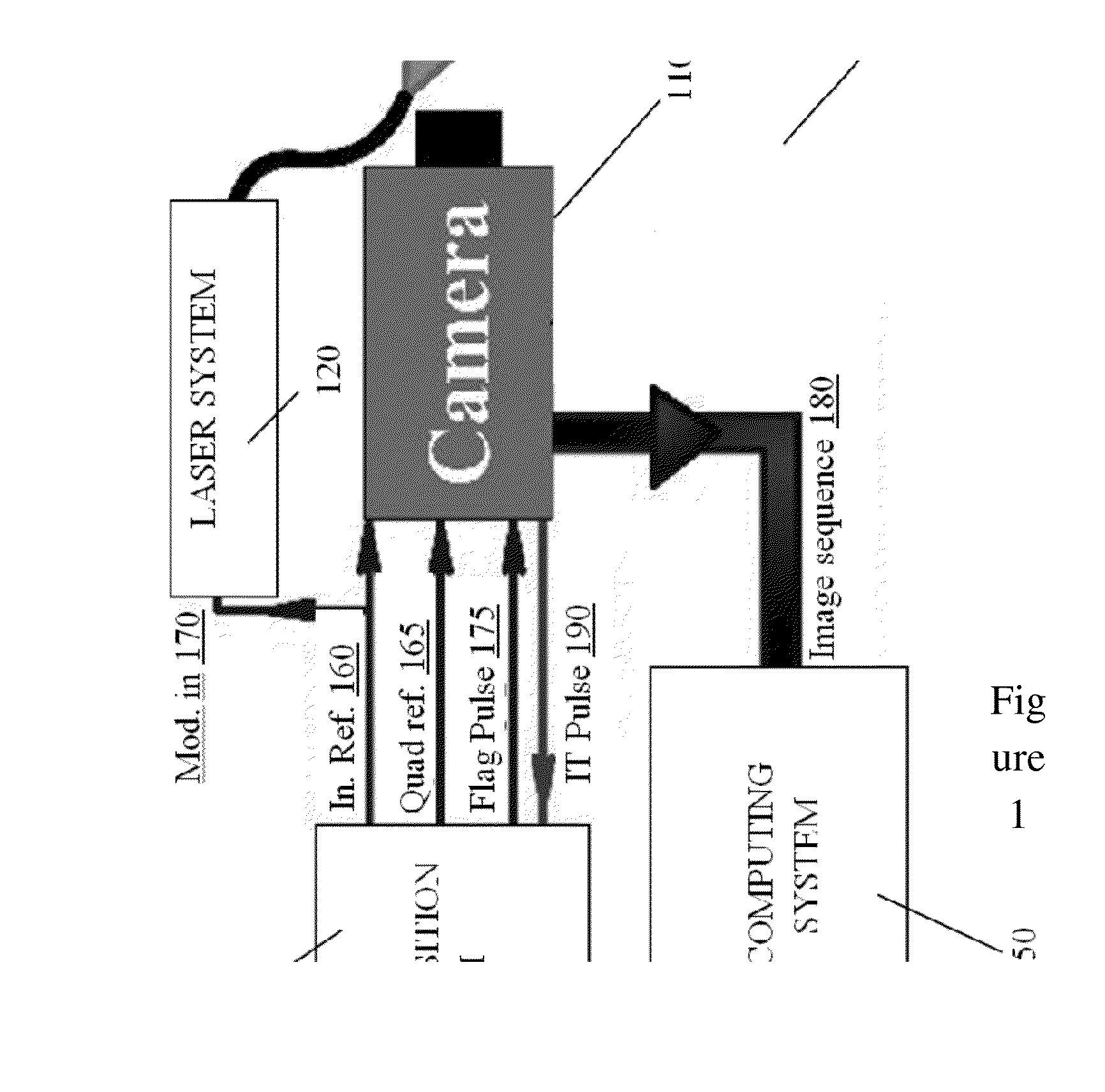
Systems and methods for thermophotonic dynamic imaging
ActiveUS20140085449A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioAnalysis by thermal excitationColor television detailsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPhase Code
Systems and methods for improved thermophotonic imaging are provided in which both amplitude and phase image information is obtained with a high signal to noise ratio and depth-resolved capabilities. Image data obtained from an imaging camera is dynamically averaged and subsequently processed to extract amplitude and / or phase image data. The system may be configured for a wide range of imaging modalities, including single frequency modulation (thermophotonic lock-in imaging), Thermal-Wave Radar imaging or Thermophotonic Radar imaging involving chirp modulation, and Binary Phase Coded Modulation. Such imaging modalities may find application in many diverse areas, including non-destructive testing and biomedical diagnostic imaging including the imaging of teeth and monitoring changes in the tooth over time which are due to pathology such as dental caries or erosion.
Owner:MANDELIS ANDREAS +2
Method and device for realizing far field super-resolution focus
The invention discloses a method for realizing far field super-resolution focus, which comprises the following steps: modulating an incident light ray emitted by a laser to a tangential polarized light; carrying out 0-2pi vortex phase coding on the tangential polarized light; and carrying out the far field super-resolution focus on the tangential polarized light which is subject to the 0-2pi vortex phase coding, thus realizing far field focus and horizontal super-resolution and meeting demands of visible light super-resolution focus, especially a scanning confocal microscope. The invention also discloses a relevant device which is applied to the method for realizing the far field super-resolution focus. The invention has simple method and wide application; the horizontal focus effect of the invention is superior to that of the prior art; and the device of the invention has simple system structure, low cost and universality, in particular being suitable for being applied in measuring equipment for precise or ultraprecise microcosmic observation, especially the scanning cofocal microscope.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method, system and computer program product for efficiently utilizing limited resources in a graphics device
InactiveUS20070273700A1Improve performanceImprove abilitiesConcurrent instruction executionProcessor architectures/configurationMemory addressInstruction memory
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
Method and magnetic resonance tomography apparatus for producing phase-coded flow images
In a method and MR apparatus for the automatic segmentation of flow images acquired by magnetic resonance tomography for the depiction of tissue or organs traversed with fluid such as blood, at least one phase image of a selected region of the subject is acquired by magnetic resonance tomography, and fluid-traversed regions in the at least one phase image are automatically segmented.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
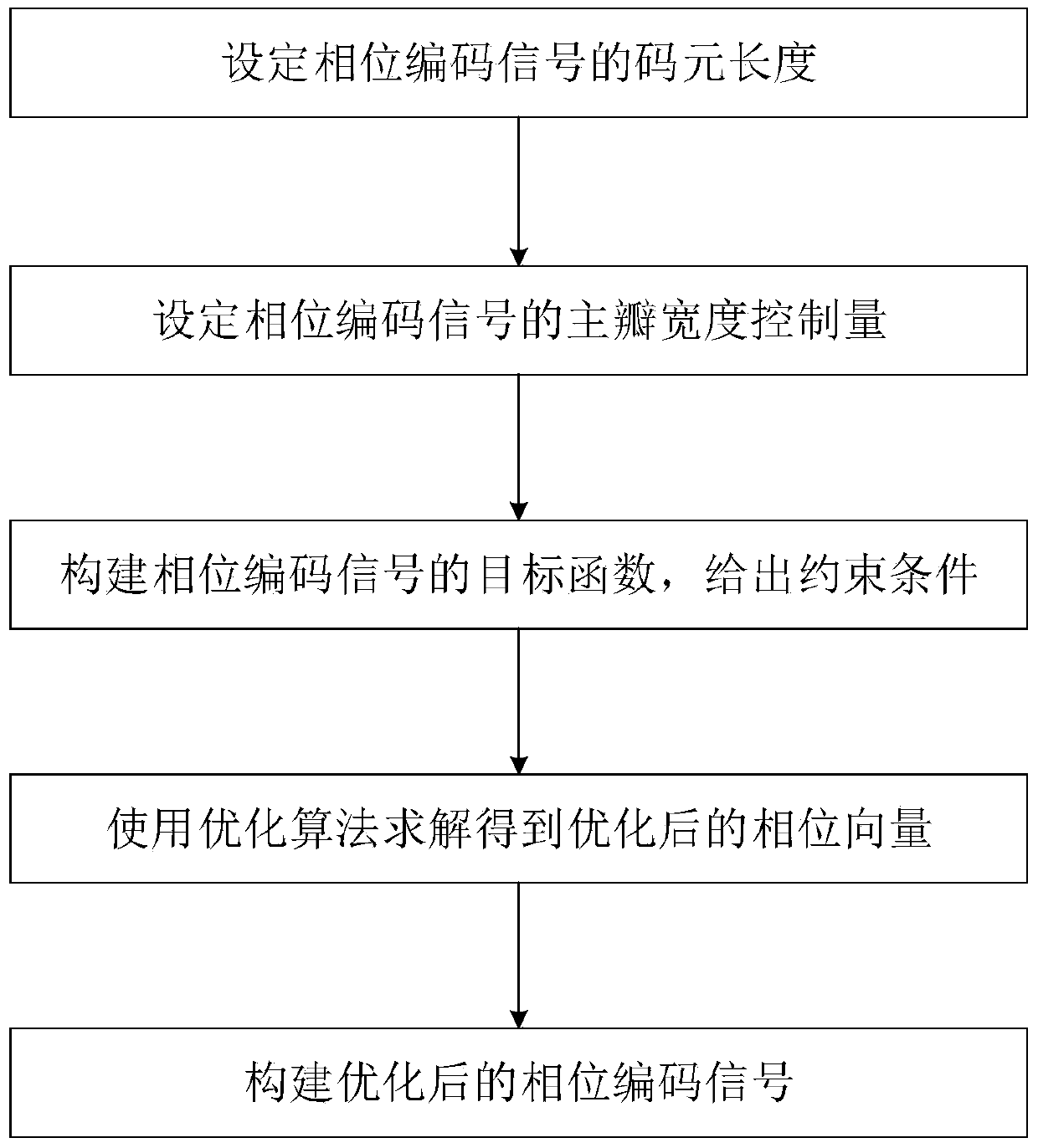
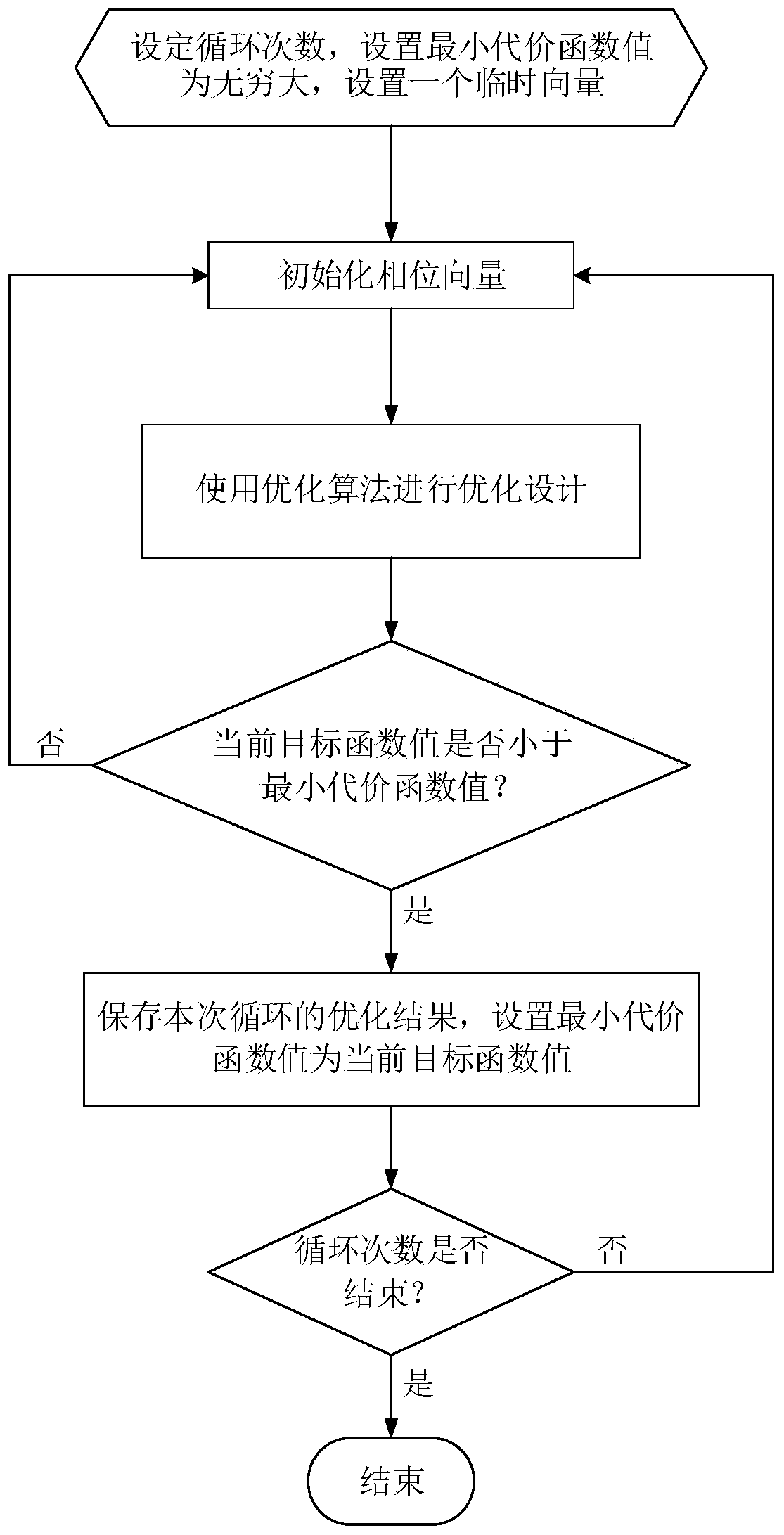
High bit rate and low range resolution of low sidelobe phase coded signal design method
ActiveCN104198996AIncrease firing rateIncrease code lengthRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImage resolutionPhase Code
The invention discloses a high bit rate and low range resolution of low sidelobe phase coded signal design method which mainly aims at solving the problems that the range sidelobe of a phase coded signal cannot be further reduced by the existing method and the existing phase coded signal is easy to identify. The implementation process of the high bit rate and low range resolution of low sidelobe phase coded signal design method comprises step 1, setting the code element length of a phase coded signal; step 2, setting a value of the main lobe width control quantity of the phase coded signal; step 3, building an objective function of the phase coded signal according to the code element length and the main lobe width control quantity of the phase coded signal; step 4, building constraint conditions of the phase coded signal; step 5, solving the objective function by an optimization algorithm under the constraint conditions to obtain an optimized phase coded signal. According to the high bit rate and low range resolution of low sidelobe phase coded signal design method, the range sidelobe of the phase coded signal can be further reduced, the identified difficulty of the phase coded signal can be increased, and the high bit rate and low range resolution of low sidelobe phase coded signal design method can be applied to the design of the phase coded signal.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Structured light three-dimensional measurement method based on segment quantization phase coding
ActiveCN107036556AImprove accuracyHigh precisionUsing optical meansThree dimensional measurementPhase Code
The present invention discloses a structured light three-dimensional measurement method based on segment quantization phase coding. The method comprises three key portions consisting of the quantization phase coding principle, the segment phase coding principle and the three-dimensional measurement principle. The method is characterized in that: (1) compared to a traditional sine fringe and phase coding fringe projection method, the method provided by the invention perform modulation of quantization coding phases through a special coding sequence, and the decoding accuracy of a special coding rule is greatly improved; (2) the method allows the modulated quantization coding phases to be embedded into 3 coding fringes, and uses continuous 3-bit code words to determine the level of the current period fringe to greatly improve the accuracy of the fringe level and the three-dimensional measurement precision; and (3) according to the actual measurement precision, the method can generate many code words, is high in measurement precision and good in robustness, and has potential application prospects and practical values in the three-dimensional measurement of a complex object, a large object and an object with single color.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
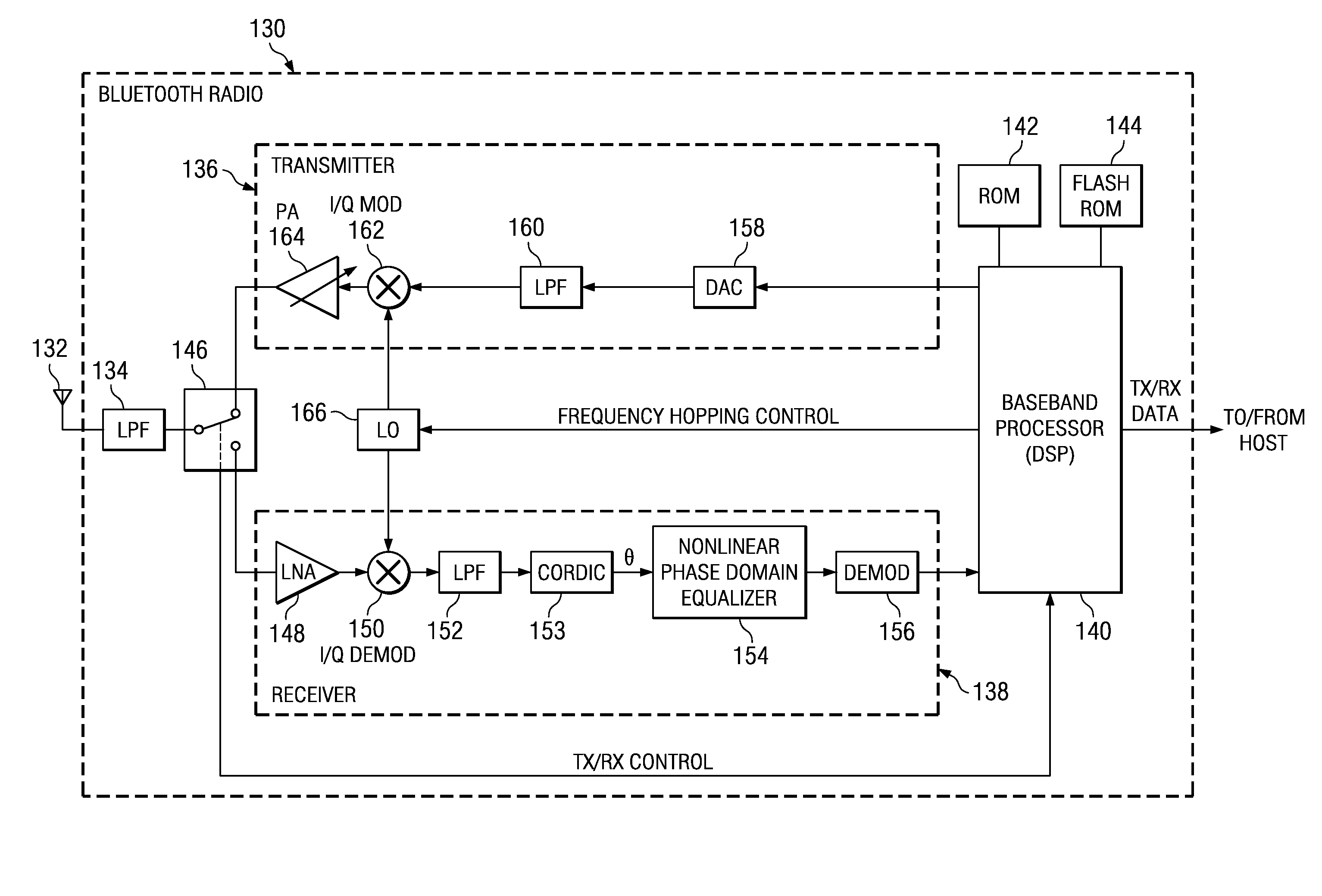
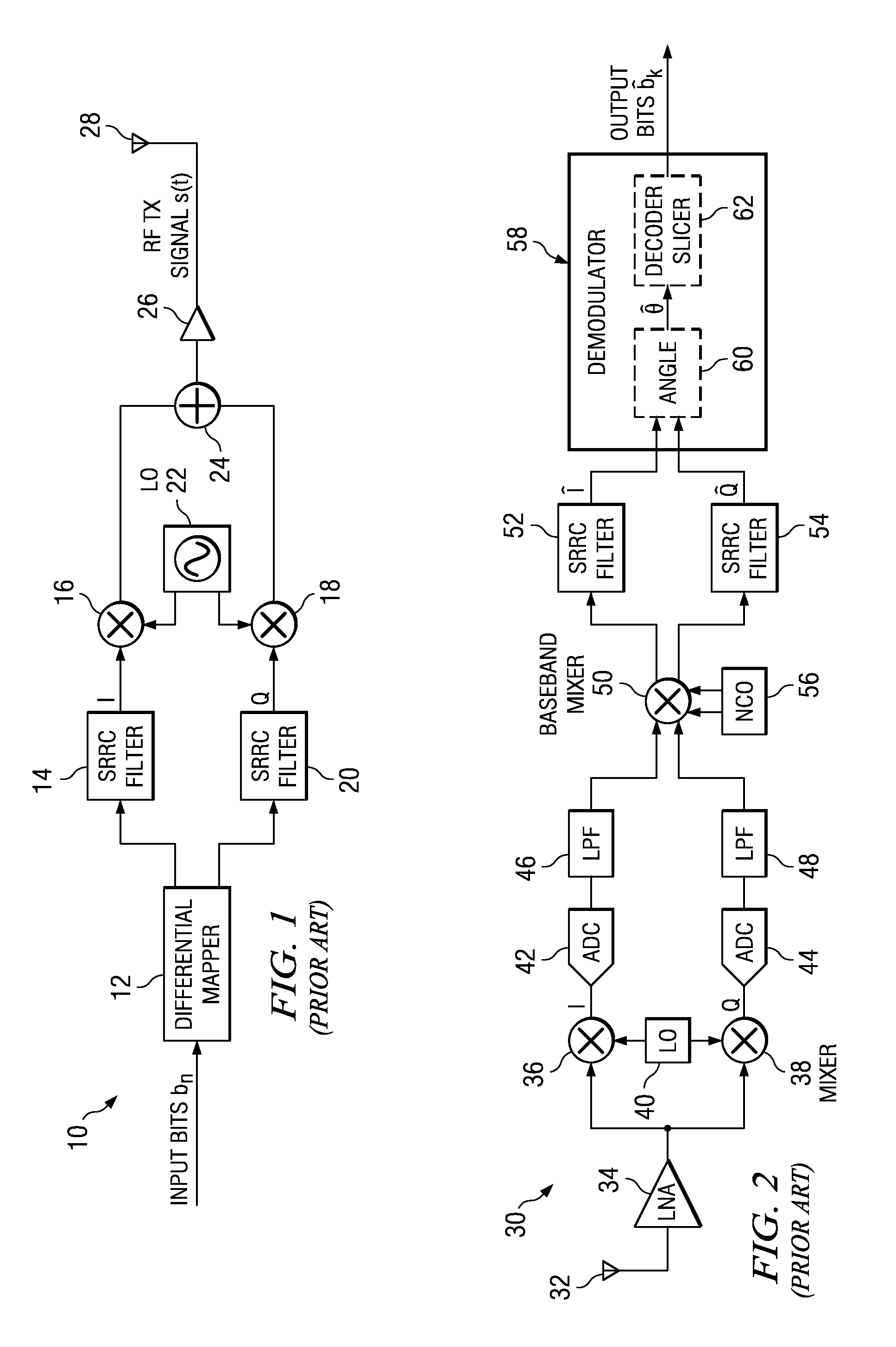
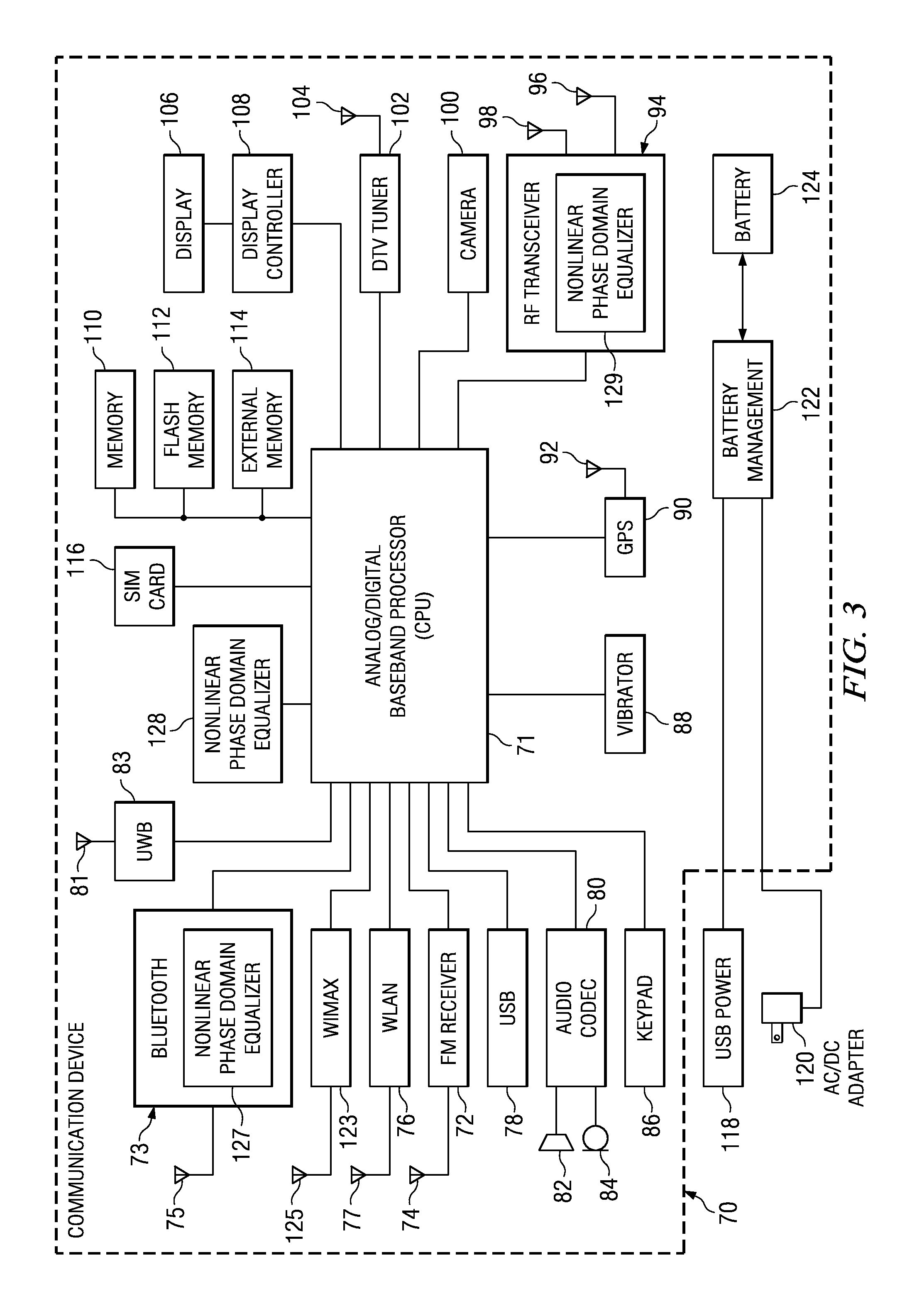
Nonlinear adaptive phase domain equalization for multilevel phase coded demodulators
ActiveUS20080298453A1Simple designImprove immunityMultiple-port networksError preventionSoftware engineeringCarrier frequency offset
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of nonlinear adaptive phase domain equalization for multilevel phase coded demodulators. The invention improves the immunity of phase-modulated signals (PSK) to intersymbol interference (ISI) such as caused by transmitter or receiver impairments, frequency selective channel response filtering, timing offset or carrier frequency offset. The invention uses phase domain signals (r, □ rather than the classical Cartesian quadrature components (I, Q) and employs a nonlinear adaptive equalizer on the phase domain signal. This results in significantly improved ISI performance which simplifies the design of a digital receiver.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Mono-static MIMO radar distribution type target angle estimation method based on fourth-order cumulant
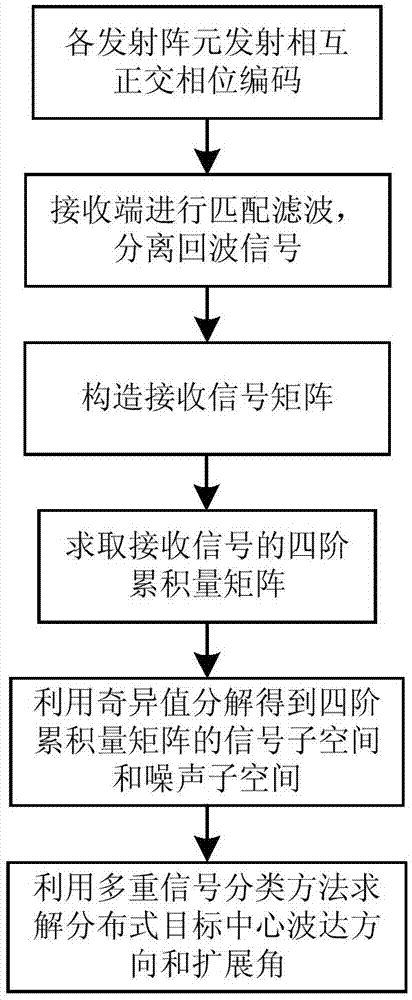
ActiveCN103926573AImprove estimation accuracyLarge apertureWave based measurement systemsSignal classificationDecomposition
The invention provides a mono-static MIMO radar distribution type target angle estimation method based on a fourth-order cumulant. M transmit-receive antenna arrays are provided, a transmitting end transmits mutually orthogonal phase-coded signals, and a receiving end receives mutually orthogonal phase-coded signals. A matching filter of each receiving array of the receiving end carries out matching filtering on the received orthogonal signals and then carries out separation, and a distribution type target receive signal matrix is obtained. A fourth-order cumulant matrix of the receive signals is calculated by using the distribution type target receive signal matrix. Eigenvalue decomposition is carried out on the fourth-order cumulant matrix, a mutually orthogonal signal subspace and a noise subspace are obtained, and a spatial spectrum function is constructed by using a multi-signal classification algorithm. The distribution type target angle is calculated through a two-dimensional spectral peak searching method. Even when in a colored-noise environment, the mono-static MIMO radar distribution type target angle estimation method based on the fourth-order cumulan still has high estimation accuracy for a central direction-of-arrival angle, can estimate an expansion angle of a distribution type target, and achieves automatic matching between the direction-of-arrival angle and the expansion angle.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Wake-up signal detection method for underwater acoustic communication MODEM
InactiveCN104243369ASmall carrier leakageLow intercept capabilityBaseband system detailsModem deviceClock rate
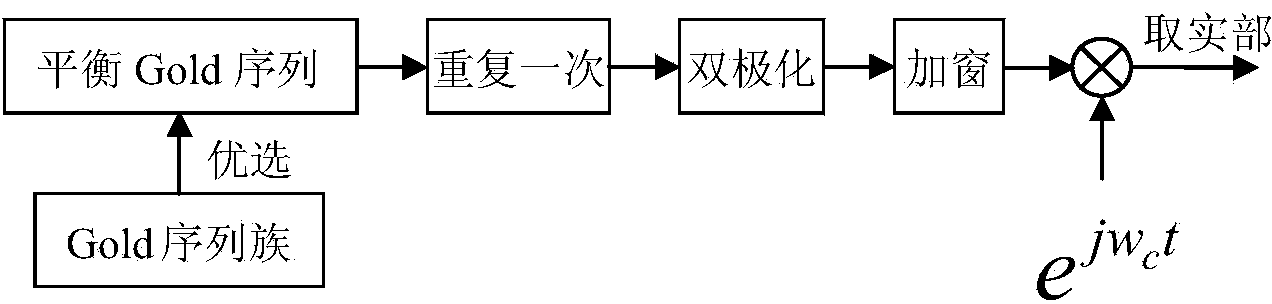
The invention provides a wake-up signal detection method for an underwater acoustic communication MODEM. The method includes the steps that two repeated two-phase code signals generated by a balanced Gold sequence are selected as wake-up signals, sliding correlation treatment between adjacent data block pairs different in length is adopted in a receiving end, a data block start moment corresponding to the maximum correlation value is wake-up signal arrival time, the difference between the length of a data block corresponding to the maximum correlation value and the length of each sent wake-up signal is the Doppler time stretching length, and therefore the wake-up signal arrival time and the Doppler time stretching length are jointly estimated; a current correlation value is obtained in the mode that a product of start data of the currently adjacent data block pairs at last time is subtracted from the sum of a former correlation value and a product of tail data of the currently adjacent data block pairs, the calculation amount is far smaller than that of multiple sliding copy correlation devices, and the method can be conducted in real time under the conditions of dormancy of the underwater acoustic communication MODEM and the low clock frequency of a processor and is high in practicality.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
Photonic-channeled x-ray detector array
ActiveUS20170038481A1Imaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationOptical radiationGrating
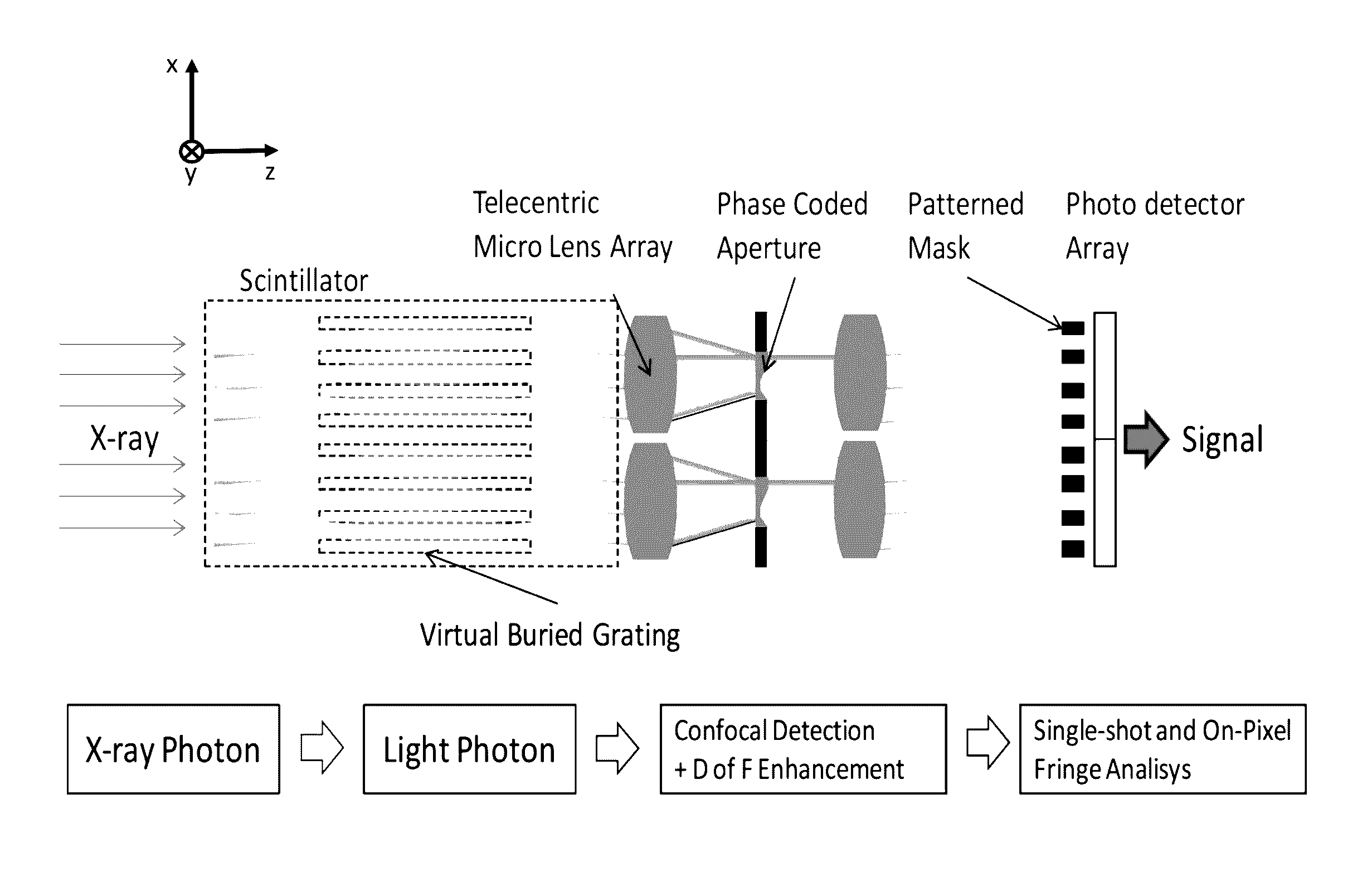
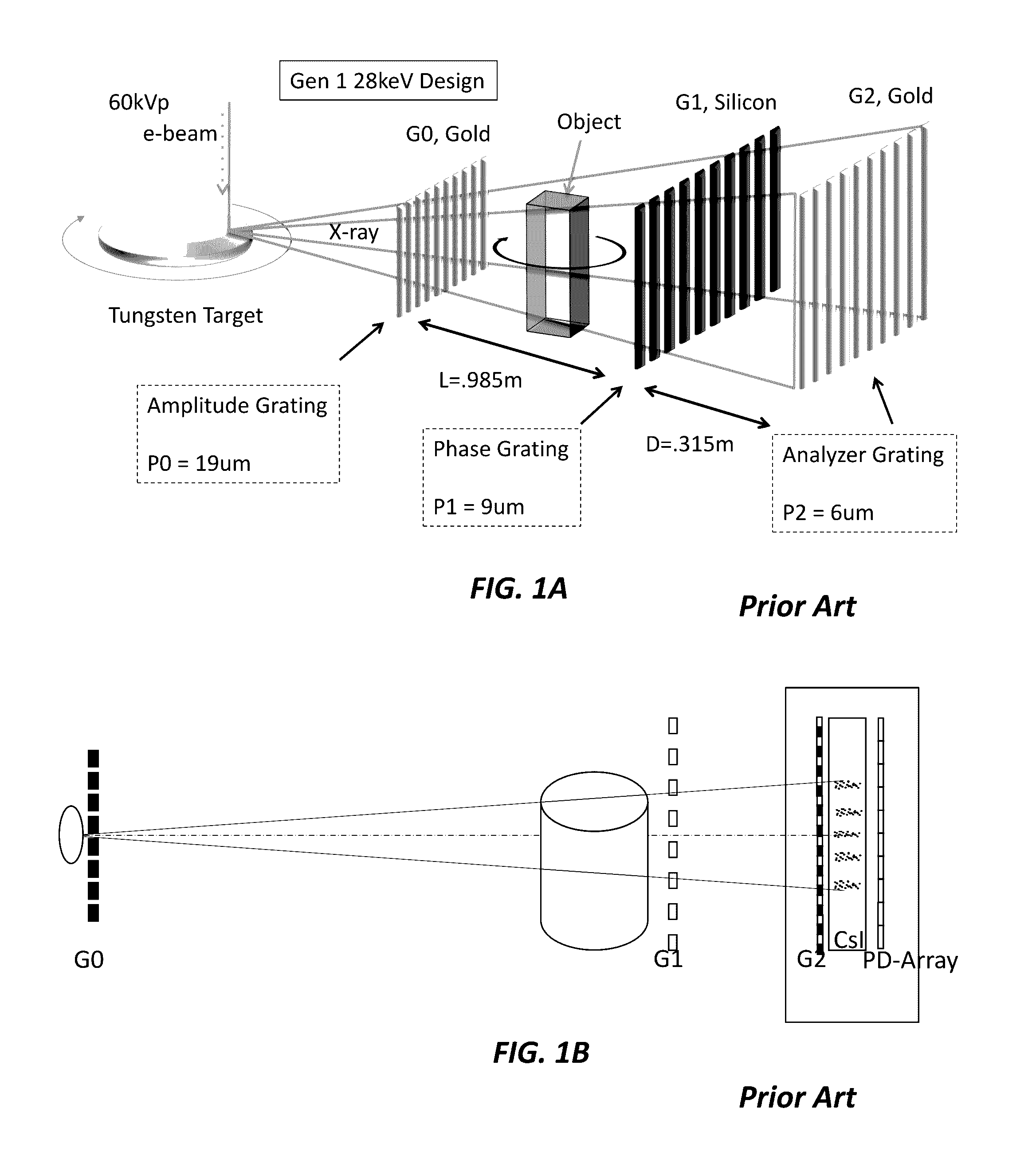
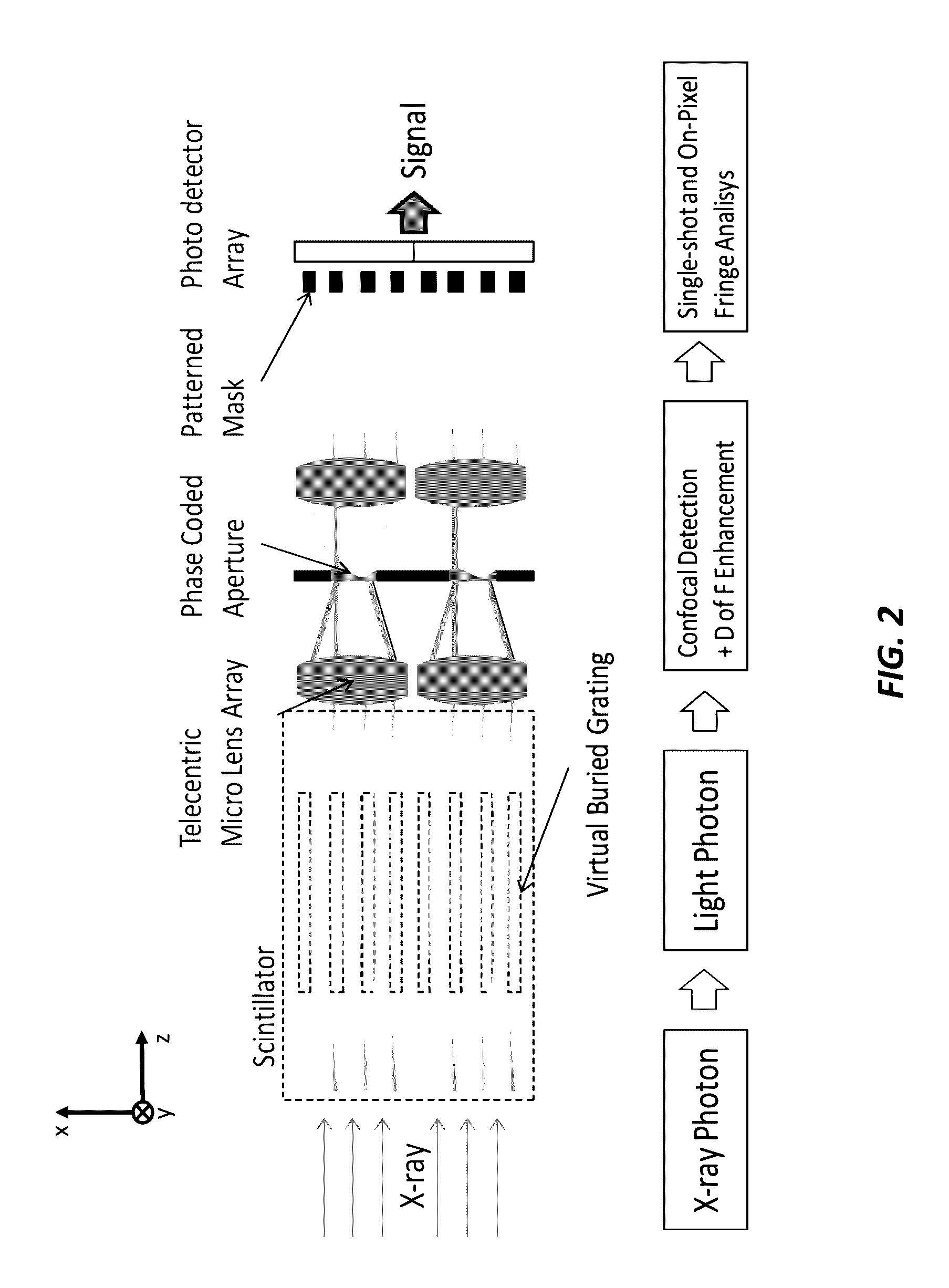
An X-ray detector array includes a scintillator that converts input X-ray radiation to secondary optical radiation output from the scintillator, a first telecentric micro lens array that array receives the secondary optical radiation, a phase coded aperture, where the first telecentric micro lens array directs the secondary optical radiation on the phase coded aperture, a second telecentric micro lens array, where the secondary optical radiation output from the phase coded array is directed to the second telecentric micro lens array, a patterned grating mask, where the second telecentric micro lens array directs the optical beam on the patterned mask, and a photodetector array, where the patterned mask outputs the optical beam in a pattern according to the patterned mask to the photodetector array, where the photodetector array outputs a signal, where a photon fringe pattern is imaged and sampled in the wavelength domain of the radiation from the scintillator.
Owner:UNIV ARIZONA +1
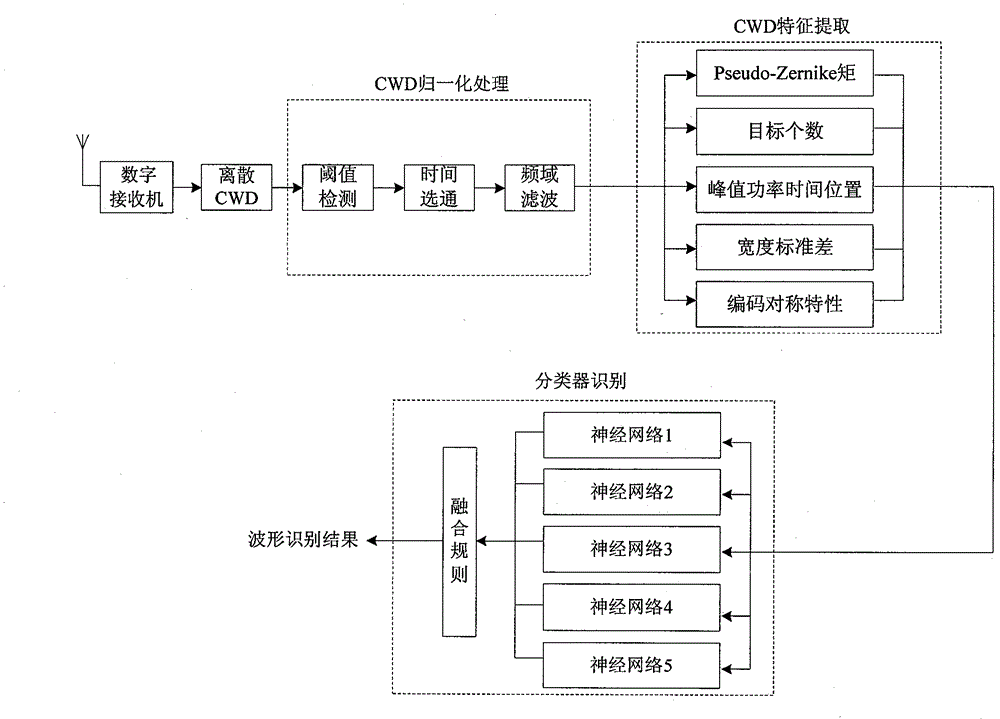
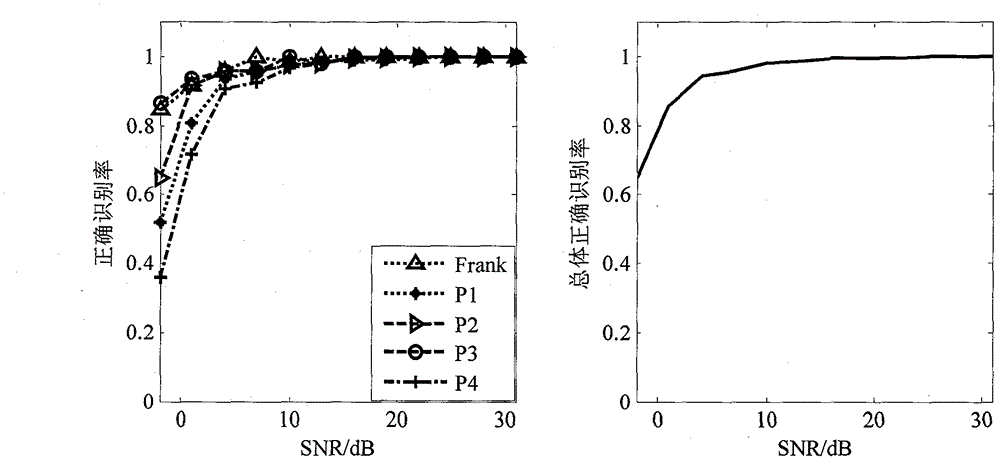
Poly-phase code radar signal waveform automatic identification method based on continuous wave Doppler (CWD) feature
InactiveCN103064063ARealize identificationImprove accuracyWave based measurement systemsPhase CodePeak value
The invention relates to a poly-phase code radar signal waveform automatic identification method based on continuous wave Doppler (CWD) feature and belongs to the technical field of information countermeasures. According to the poly-phase code radar signal waveform automatic identification method based on CWD feature, a discrete sampling type Choi-Williams conversion is used as a basic tool, a CWD image of poly-phase code pulse compression radar signal is used as a feature extraction object, a Pseudo-Zernike moment of the CWD image, a target number of an image, a time position of a peak power in a CWD and a poly-phase code waveform symmetrical property are taken as features to identify a poly-phase code pulse compression radar waveform, and a neural network which is composed of 10 perceptrons and stops in advance of overall average is set up for automatic waveform identification. The poly-phase code radar signal waveform automatic identification method based on CWD feature has the advantages that the identification precision of the poly-phase code radar signal waveform is improved, the requirement of a signal to noise ratio is further decreased, and a new way can be developed for the design of radar signal identification and sorting by popularized and used in a poly-phase code continuous wave radar signal.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
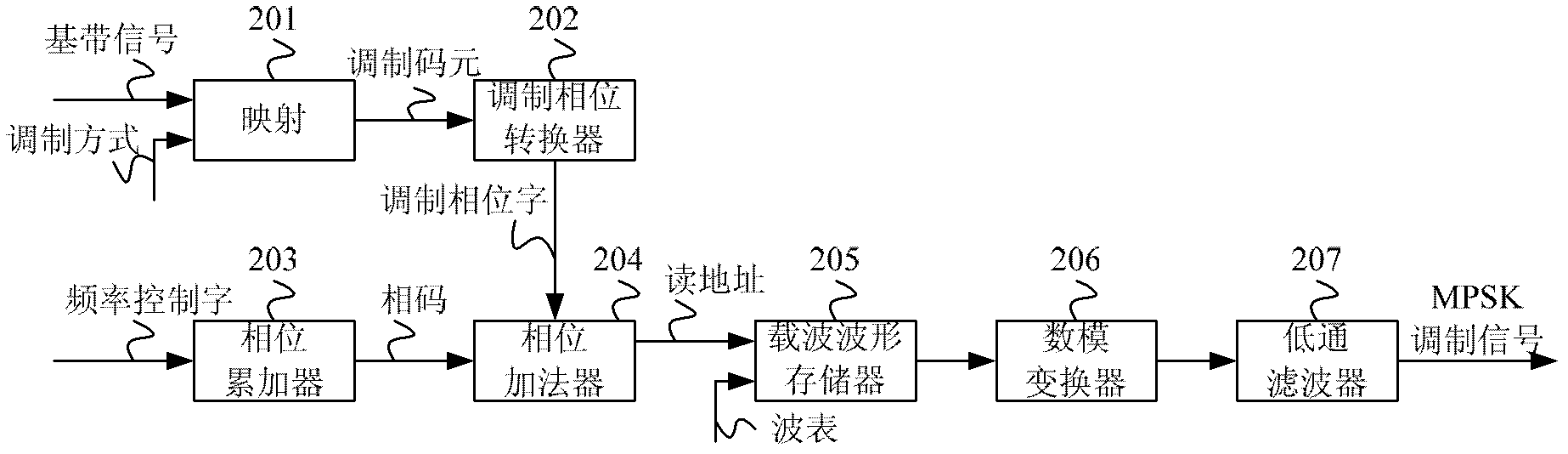
Multi-system phase shifting keying (MPSK) modulation method, MPSK modulation device and function signal generator
ActiveCN103179066ASimplify hardware designAvoid Orthogonal CarriersPhase-modulated carrier systemsData translationWave shape
An embodiment of the invention provides a multi-system phase shifting keying (MPSK) modulation method, an MPSK modulation device and a function signal generator. The MPSK modulation device comprises a mapping module used for converting serial base band signals to be modulated into modulation code elements according to the modulation mode, a modulation phase converter used for converting the modulation code elements into phase words, a phase accumulator used for accumulating frequency control words to obtain a phase code, a phase summator used for summating the phase code and the modulation phase words to obtain a reading address, a carrier wave form storage used for reading carrier wave form data stored in the storage according to the reading address and a digital-to-analog converter used for converting the carrier wave form data into MPSK modulation signals in analog form. The MPSK modulation device has the advantages of being capable of achieving full digital achieving mode, free of a multiplying unit, free of quadrature carrier, good in expandability, simple to achieve and especially suitable for the function signal generator.
Owner:RIGOL
MRI method and apparatus with elimination of the ambiguity artifact
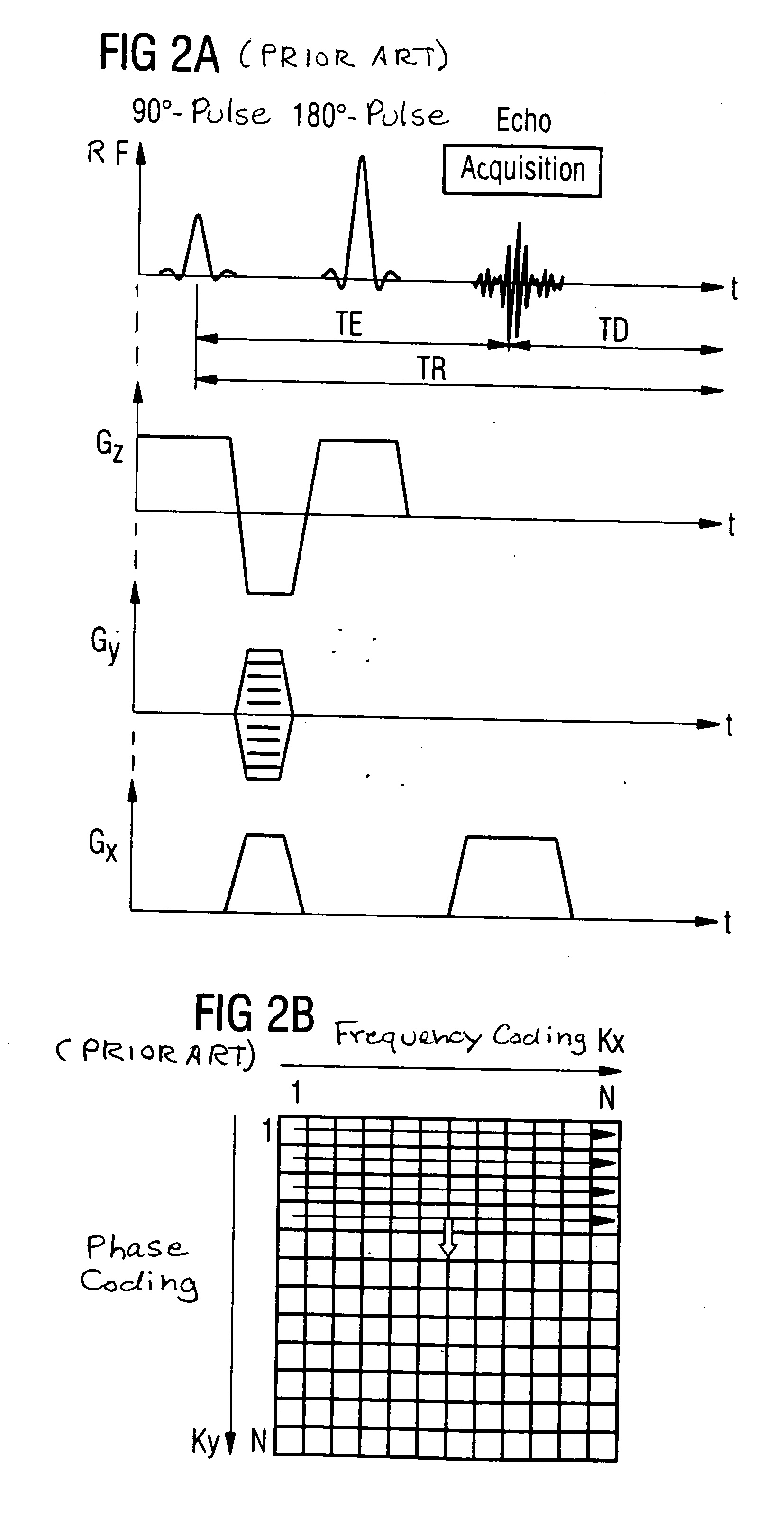
InactiveUS20050001619A1Avoid it happening againMagnetic measurementsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesAmbiguityFourier transform on finite groups
In a method for magnetic resonance imaging, by combined switching of radio-frequency excitation pulses, slice selection gradient pulses, phase-coding gradient pulses and readout gradient pulses, a matrix in the k-space is scanned row-by-row and transformed using a Fourier transformation into a matrix in the spatial domain, with the polarity of the slice selection gradient being inverted during the scanning of the k-matrix, allowing elimination of the ambiguity artifact.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com