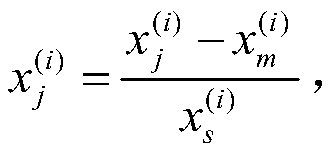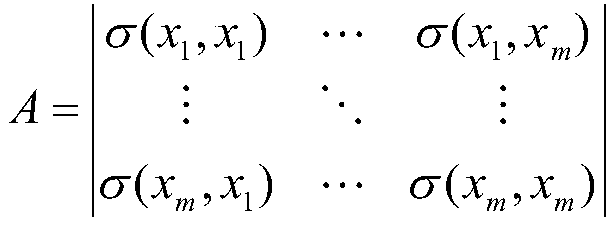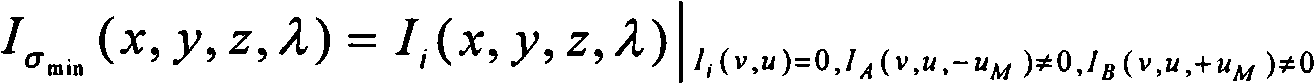Patents
Literature
800 results about "Spatial spectrum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
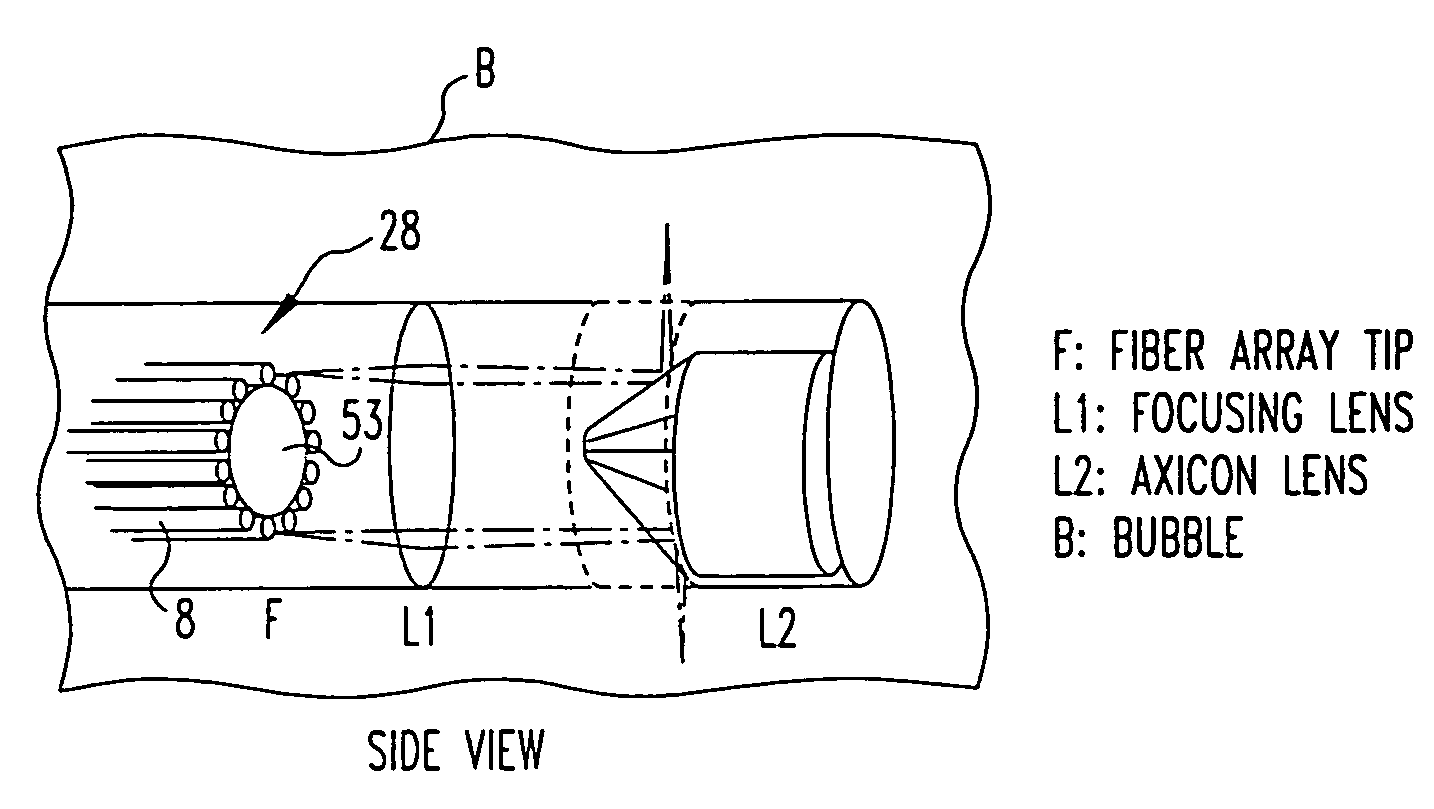
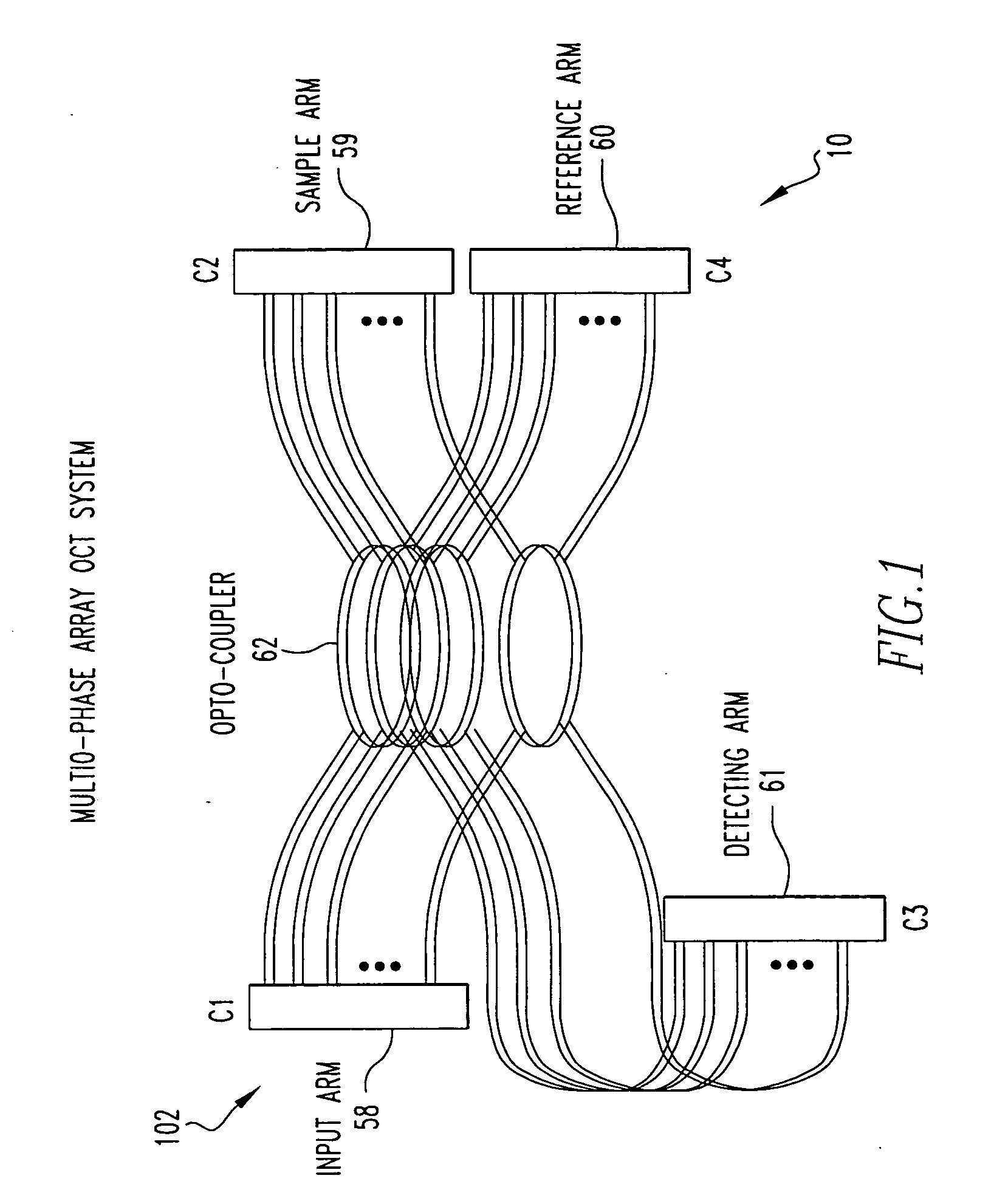
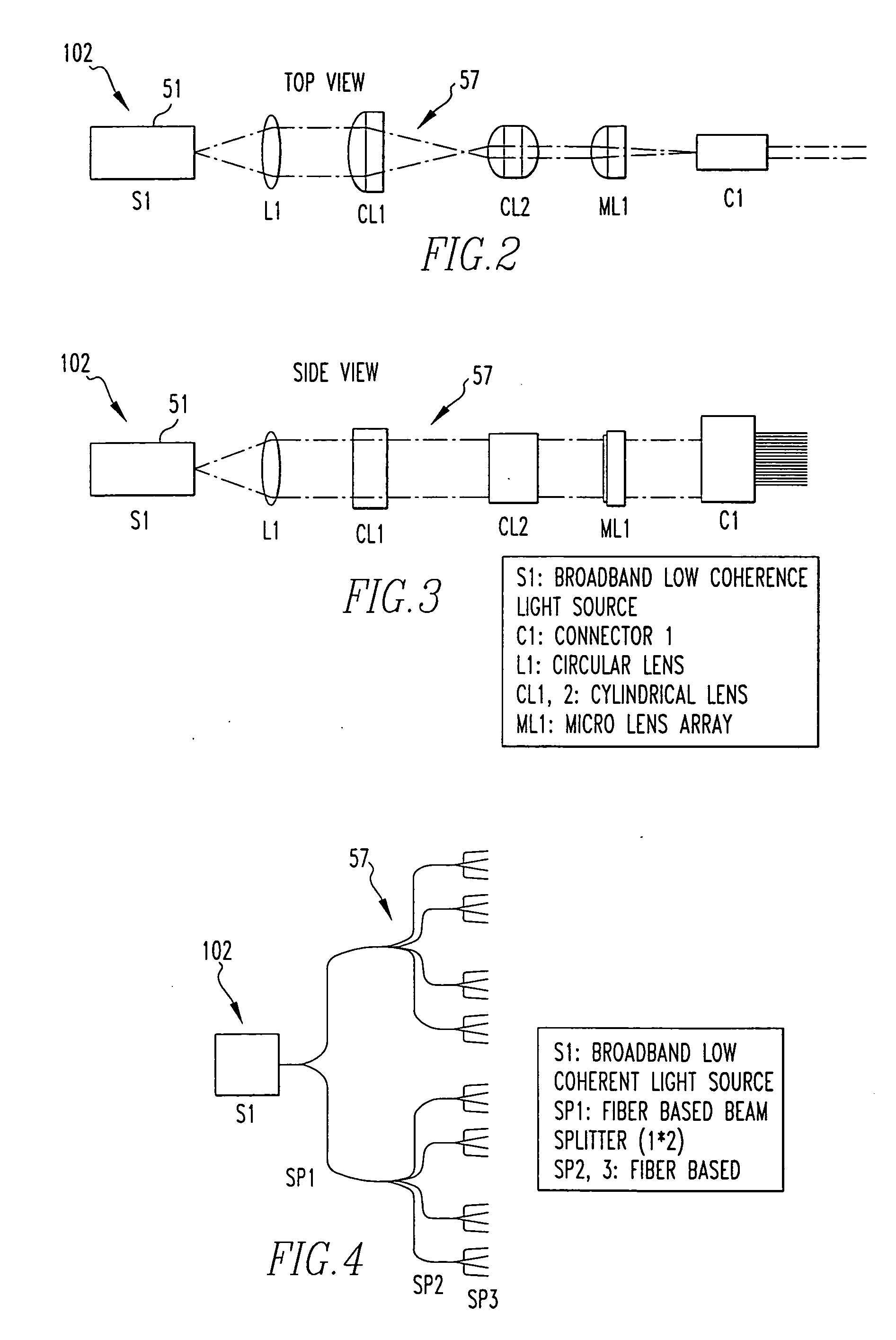
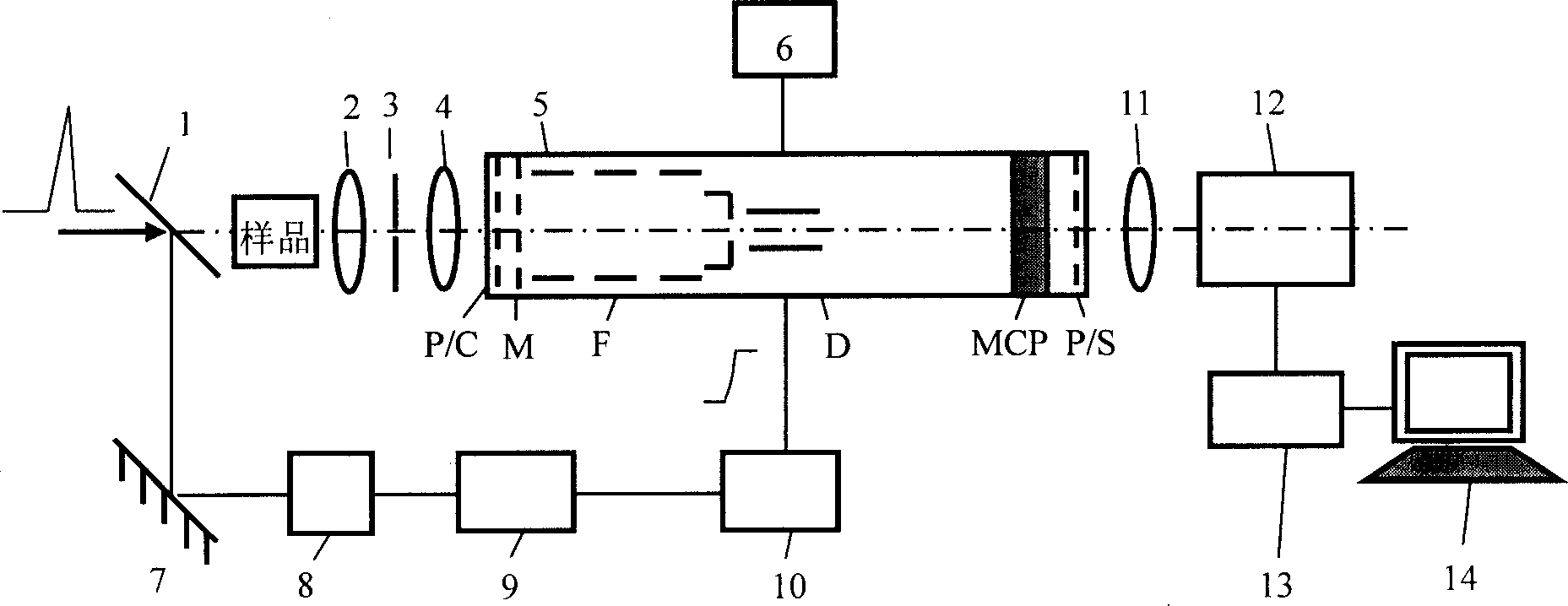
OCT using spectrally resolved bandwidth
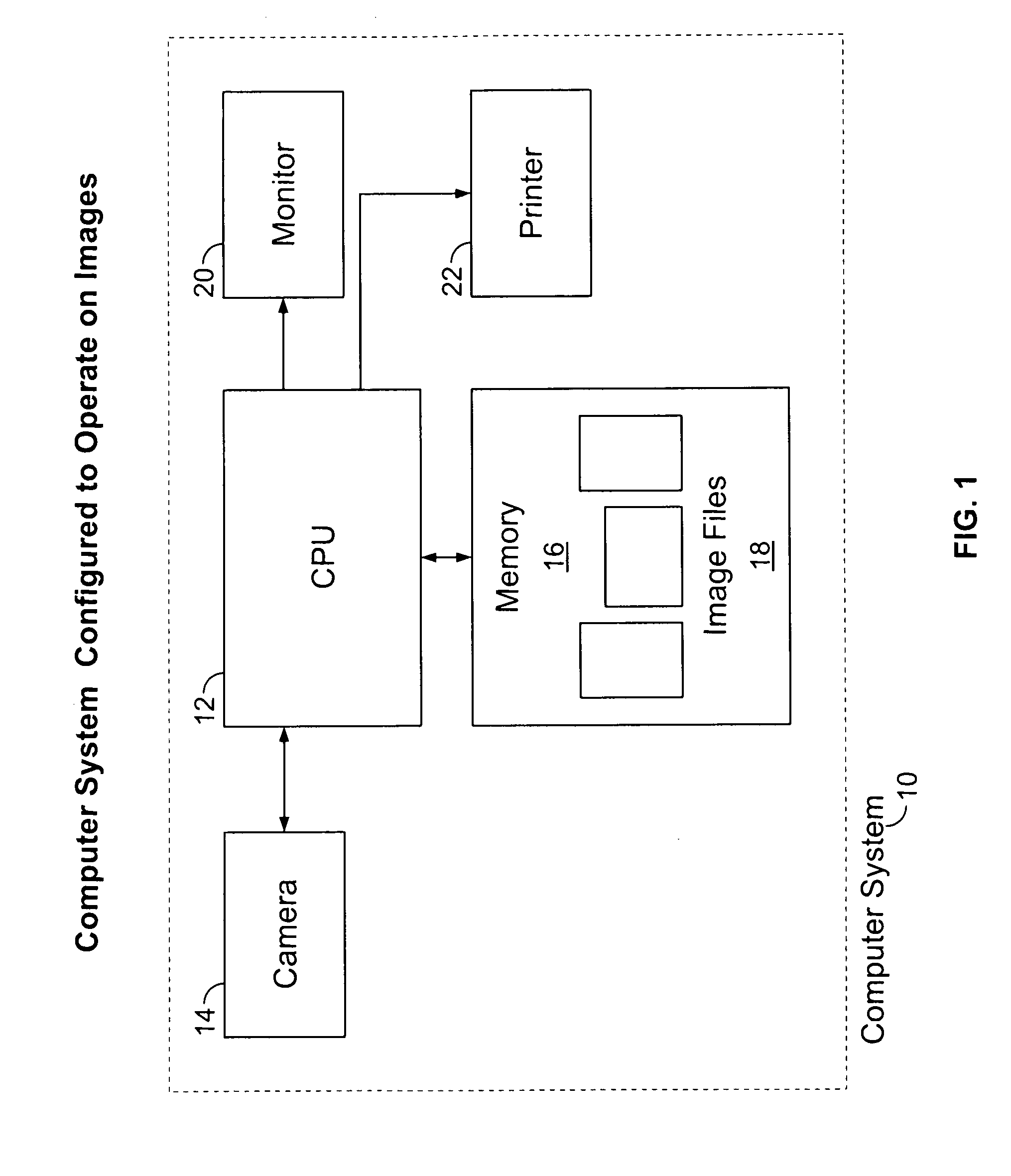
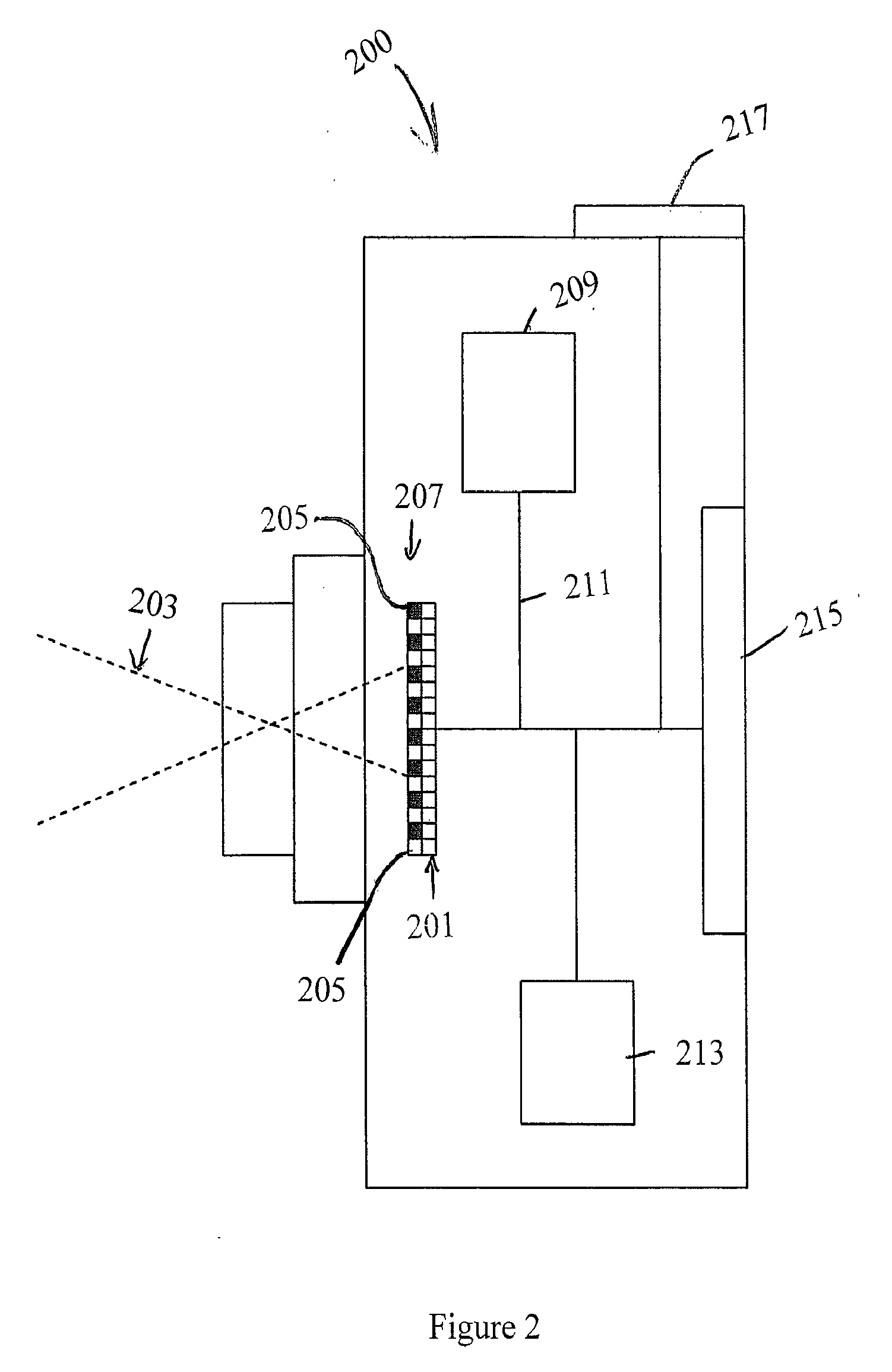
The present invention is related to a system for optical coherence tomographic imaging of turbid (i.e., scattering) materials utilizing multiple channels of information. The multiple channels of information may be comprised and encompass spatial, angle, spectral and polarization domains. More specifically, the present invention is related to methods and apparatus for utilizing optical sources, systems or receivers capable of providing (source), processing (system) or recording (receiver) a multiplicity of channels of spectral information for optical coherence tomographic imaging of turbid materials. In these methods and apparatus the multiplicity of channels of spectral information that can be provided by the source, processed by the system, or recorded by the receiver are used to convey simultaneously spatial, spectral or polarimetric information relating to the turbid material being imaged tomographically. The multichannel optical coherence tomographic methods can be incorporated into an endoscopic probe for imaging a patient. The endoscope comprises an optical fiber array and can comprise a plurality of optical fibers adapted to be disposed in the patient. The optical fiber array transmits the light from the light source into the patient, and transmits the light reflected by the patient out of the patient. The plurality of optical fibers in the array are in optical communication with the light source. The multichannel optical coherence tomography system comprises a detector for receiving the light from the array and analyzing the light. The methods and apparatus may be applied for imaging a vessel, biliary, GU and / or GI tract of a patient.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
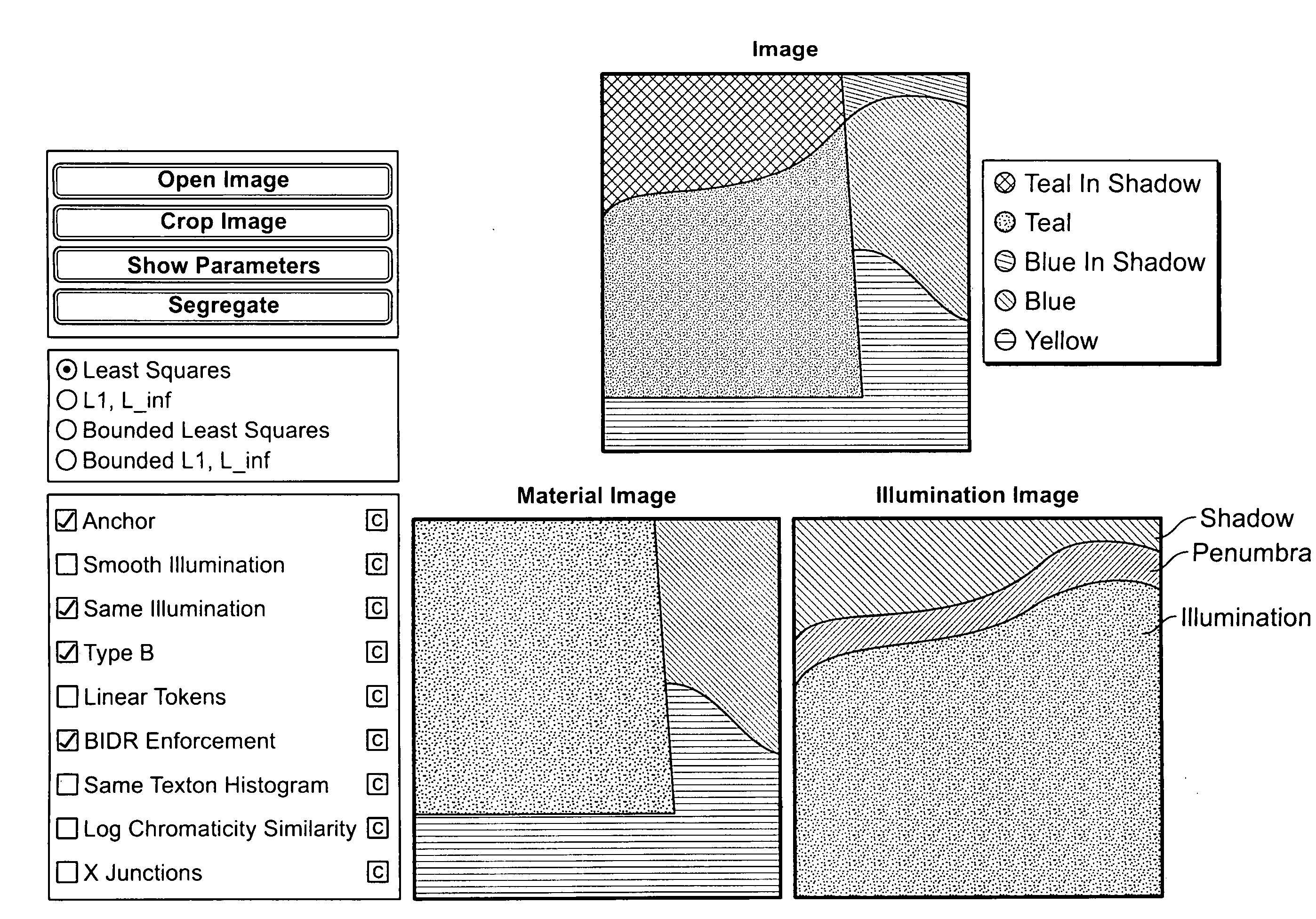
Image segregation system architecture
ActiveUS20100142825A1Accurately correctly identifyRecognisation of pattern in signalsSpatial spectrumImage generation
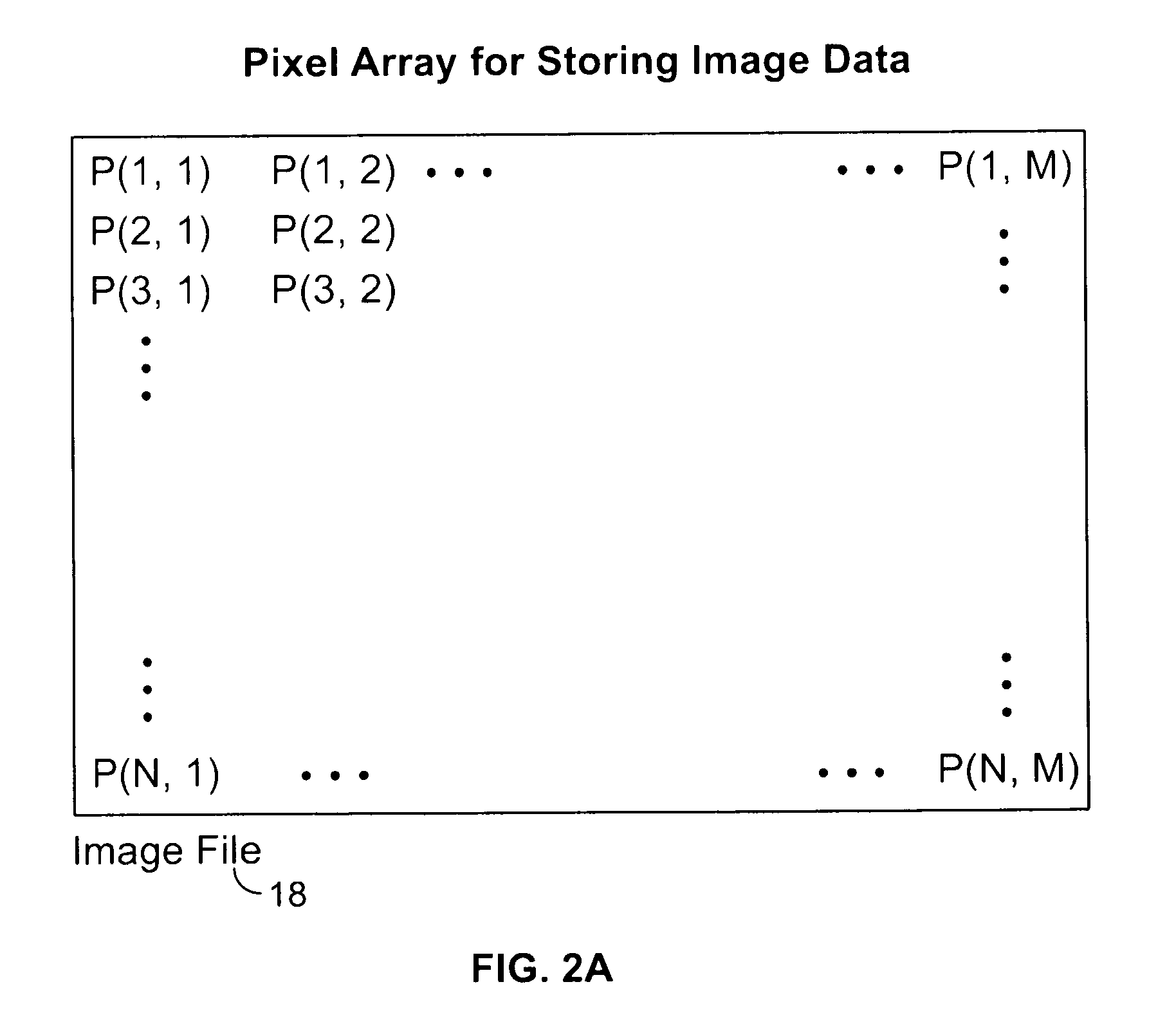
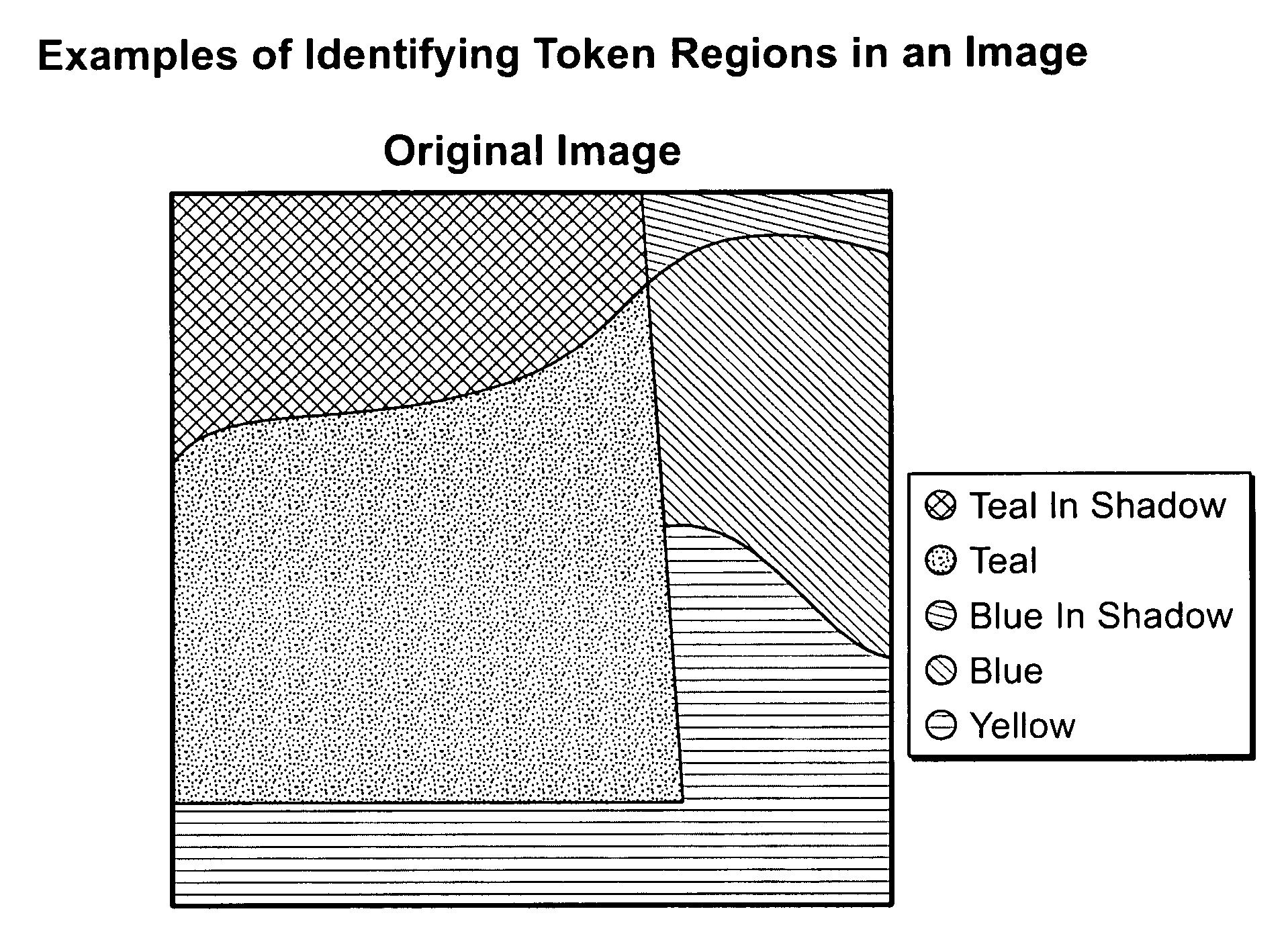
In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, an automated, computerized method is provided for processing an image. According to a feature of the present invention, the method comprises the steps of generating spatio-spectral information for the image, defining a constraint as a function of the spatio-spectral information, and performing an optimization operation as a function of the constraint to generate an intrinsic image corresponding to the image.
Owner:INNOVATION ASSET COLLECTIVE
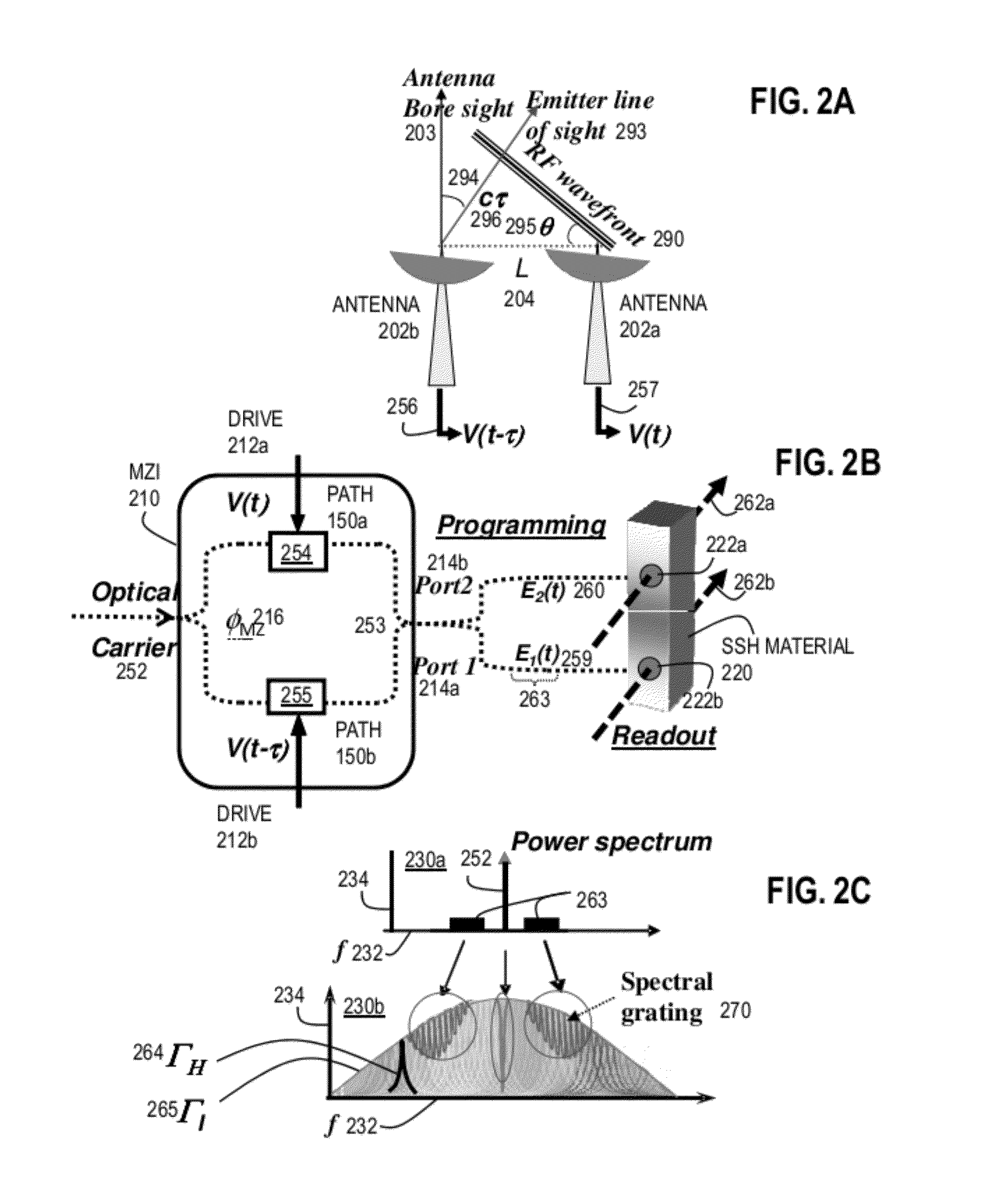
Spatial Spectral Photonic Receiver for Direction Finding via Wideband Phase Sensitive Spectral Mapping
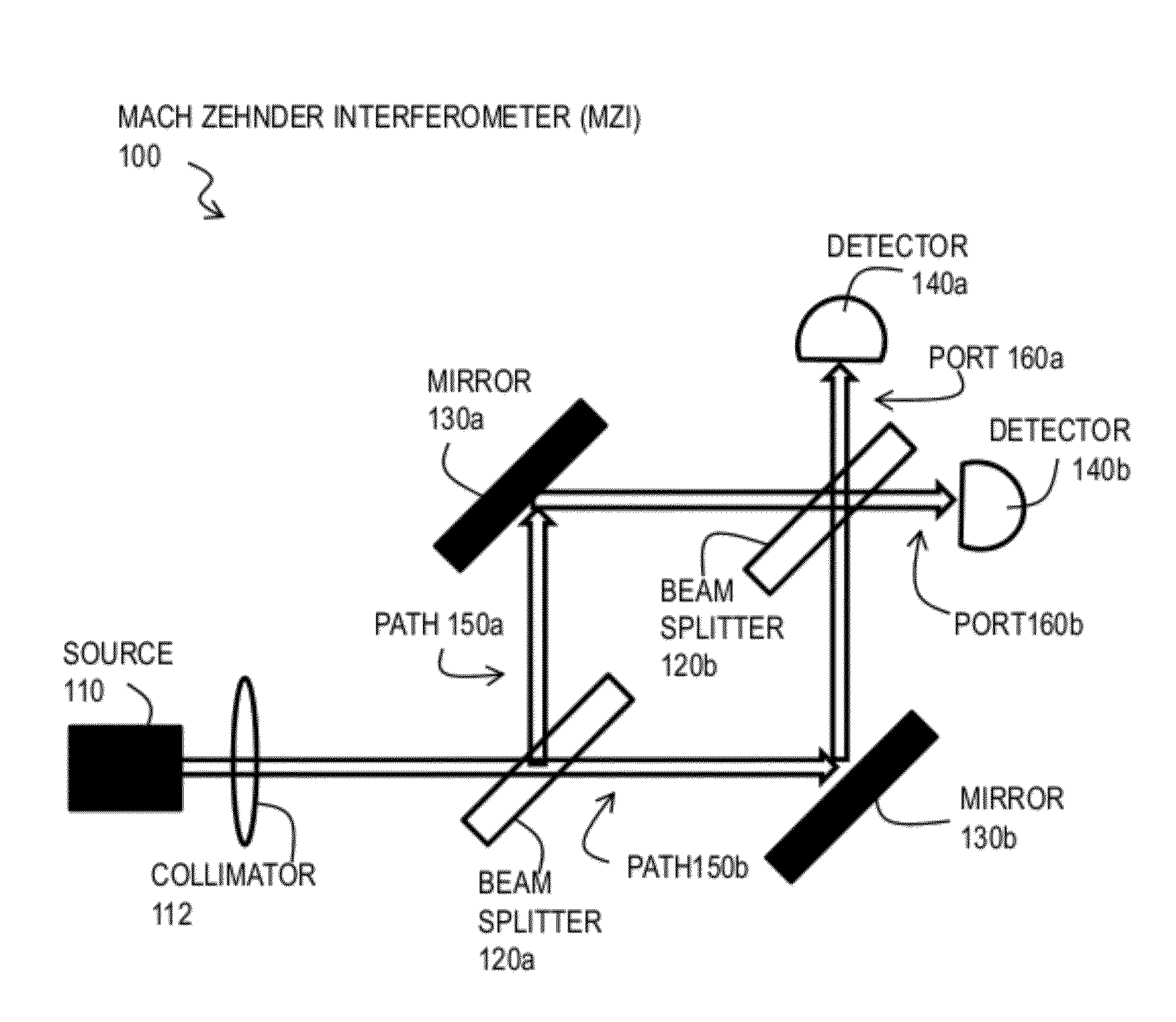
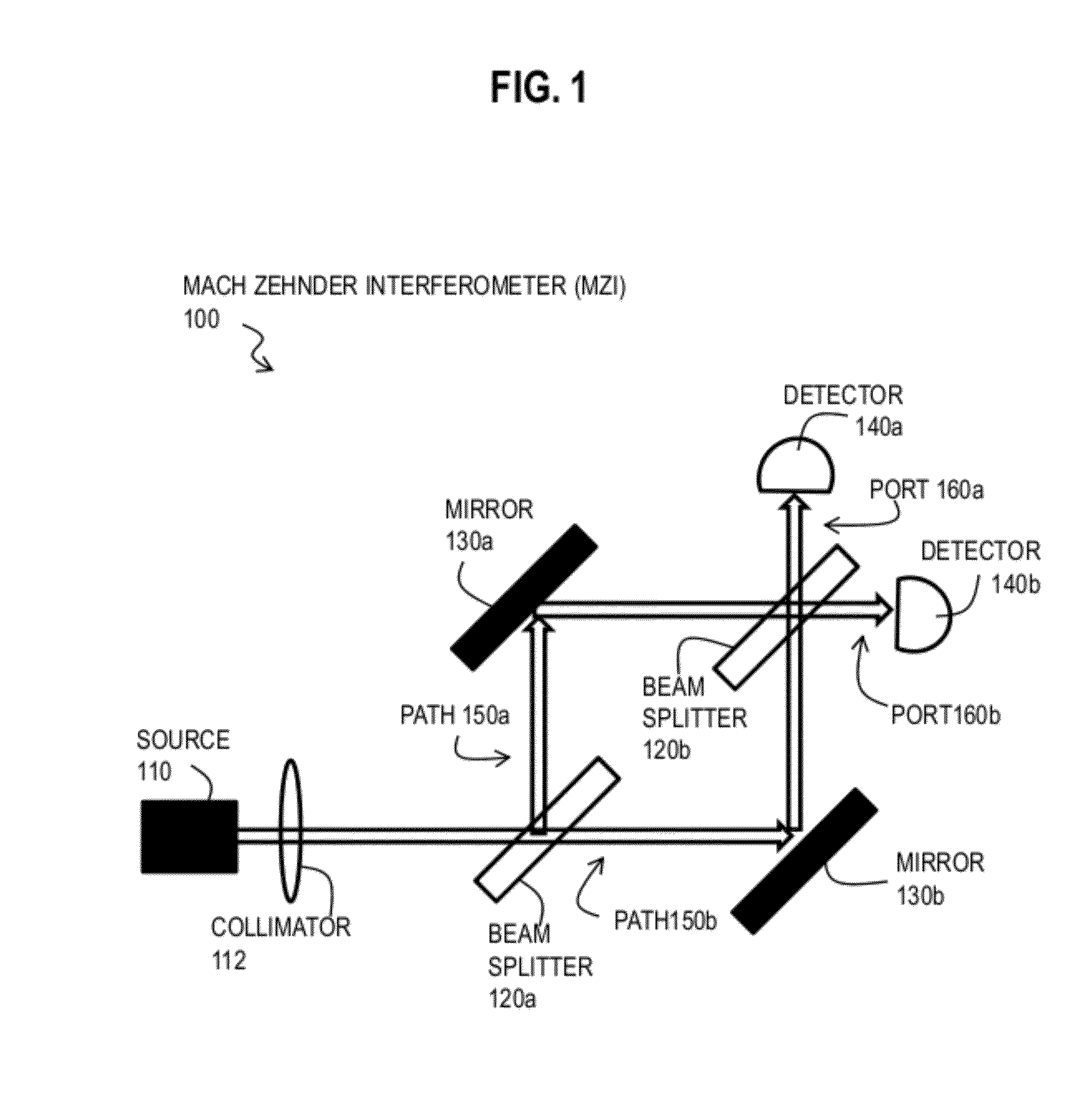
InactiveUS20120140236A1Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFrequency spectrumSpectrum analyzer
An apparatus includes a single or dual output port, dual-drive Mach-Zehnder Interferometer configured to generate a first optical signal in one path, and to generate a second optical signal in a different path. The apparatus also includes an optical spectrum analyzer configured to receive output from at least one port of the dual-drive Mach-Zehnder Interferometer. A method includes causing radio frequency signals from two different antennae to modulate an optical carrier at a corresponding drive of a dual-drive Mach-Zehnder Interferometer, and causing output from at least one port of the Mach-Zehnder Interferometer to be directed to an optical spectrum analyzer. The method further comprises determining arrival angle at each of a plurality of frequencies in the radio frequency signals based on output from the optical spectrum analyzer.
Owner:S2 CORP +1
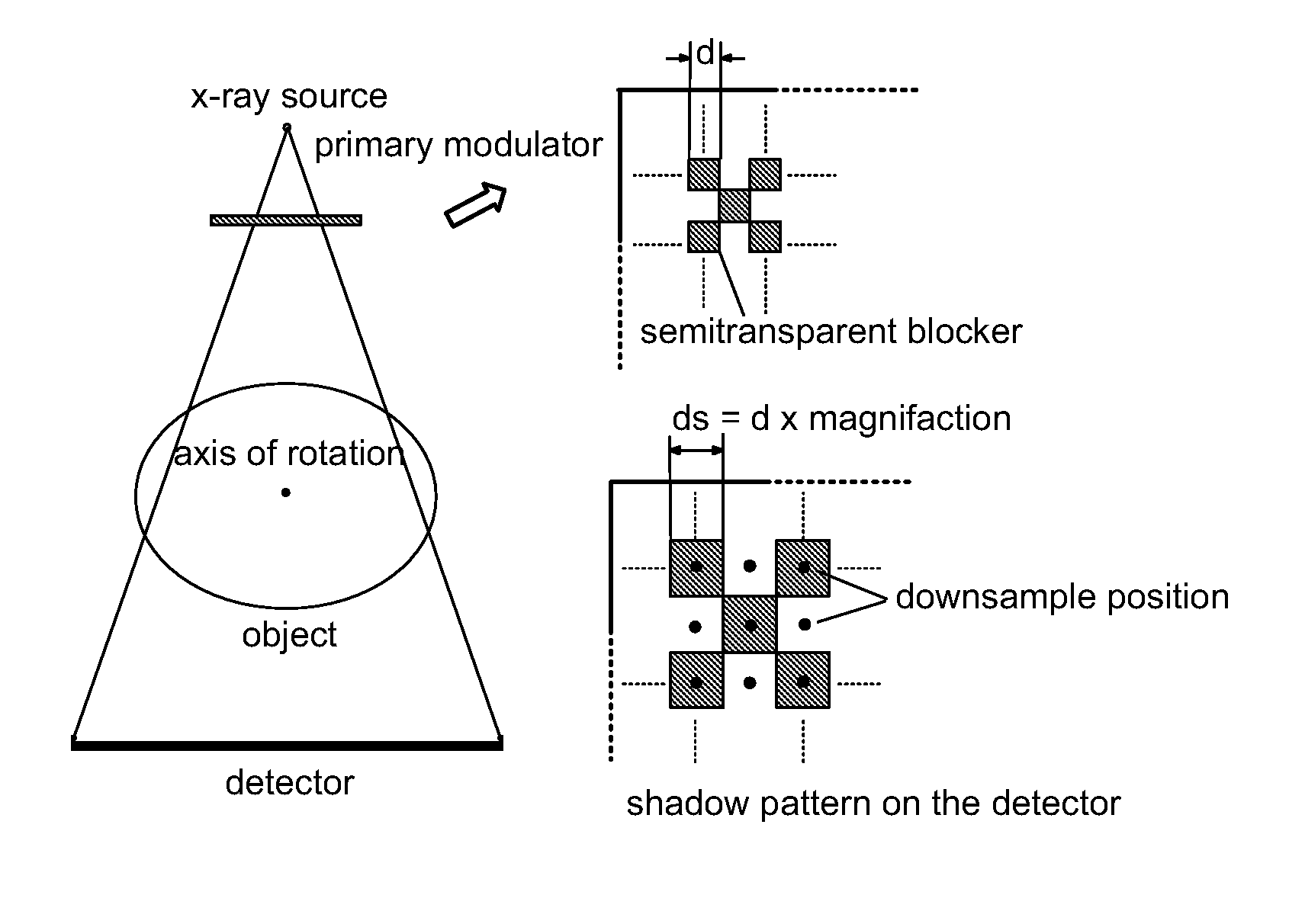
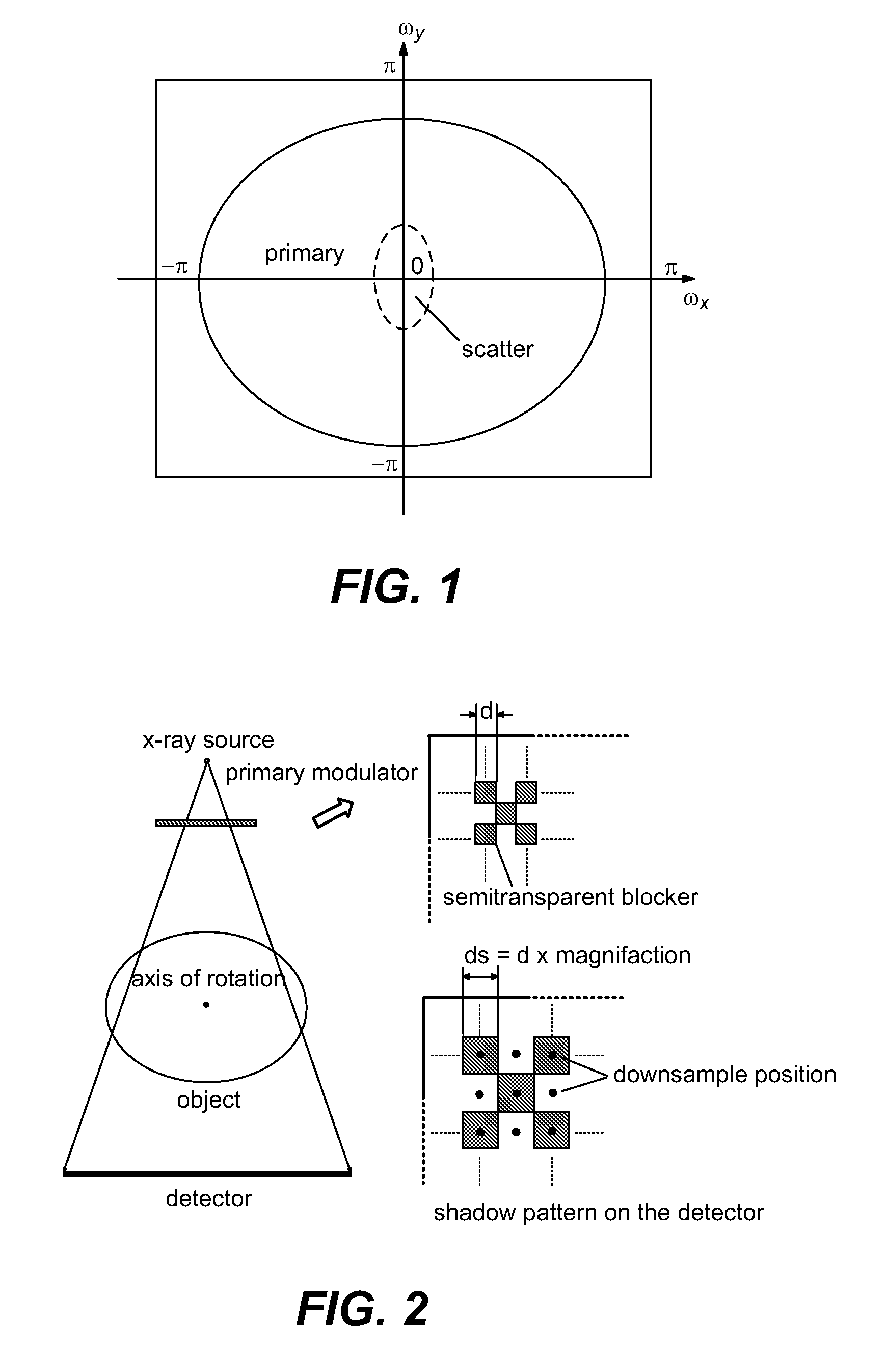
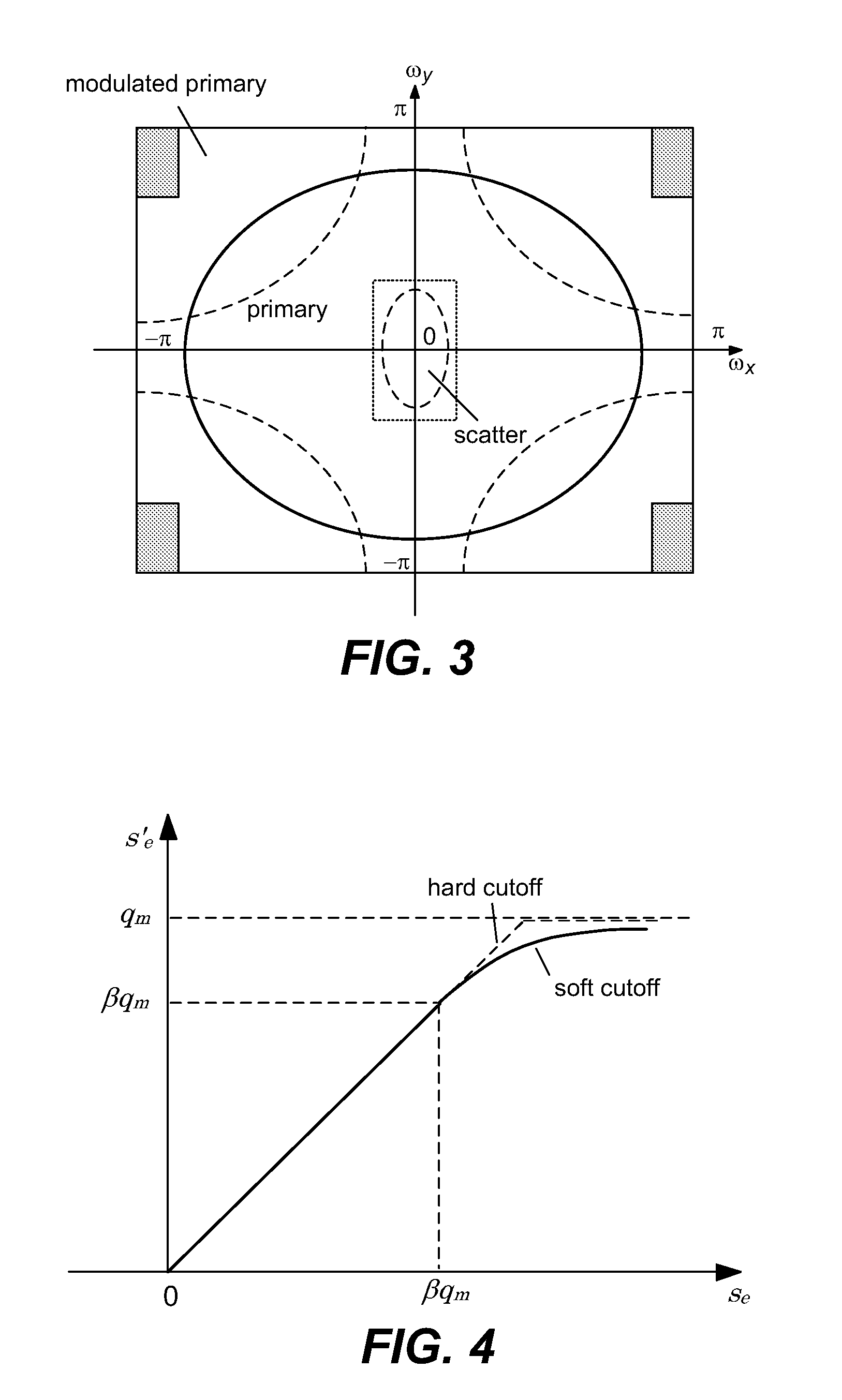
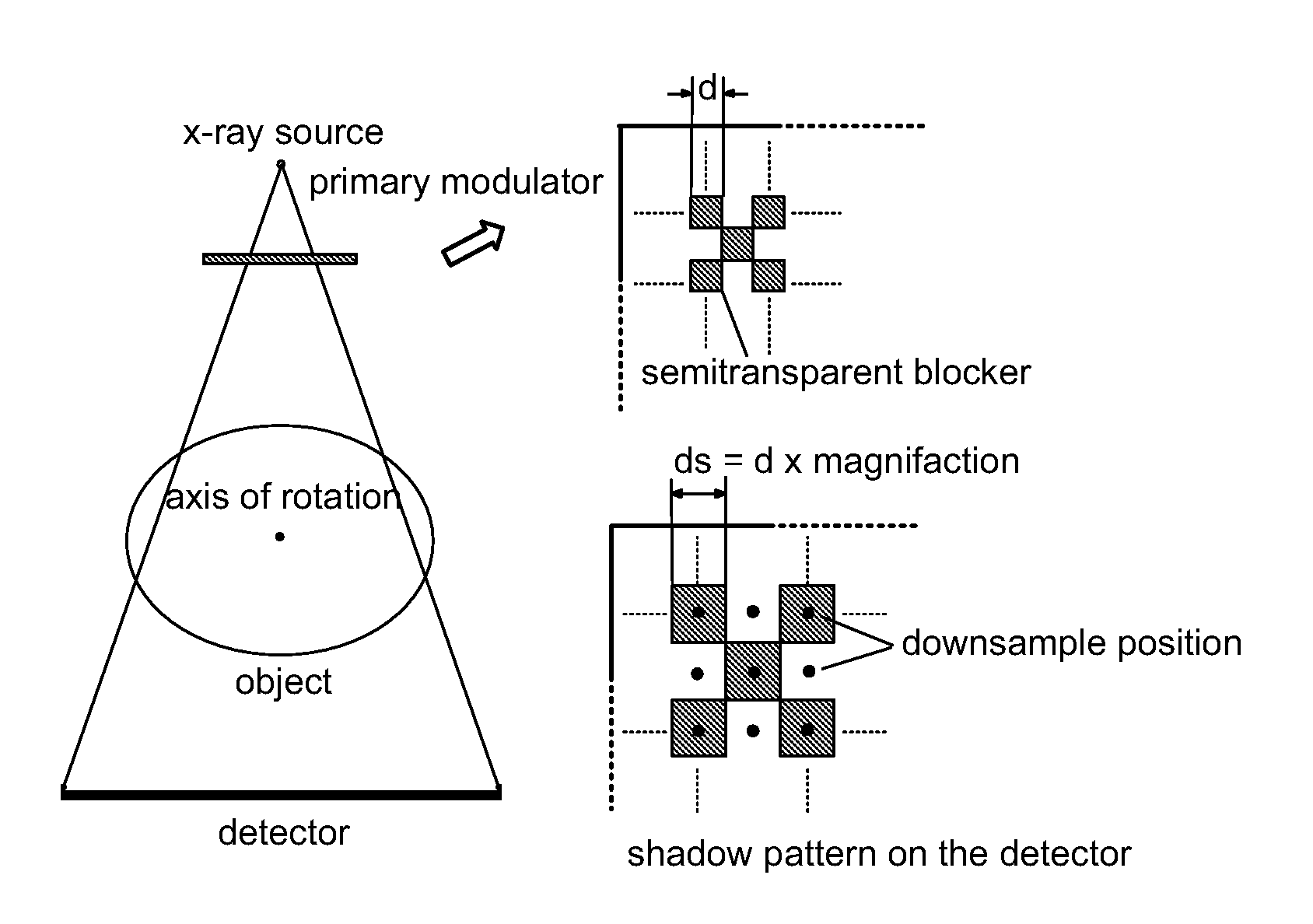
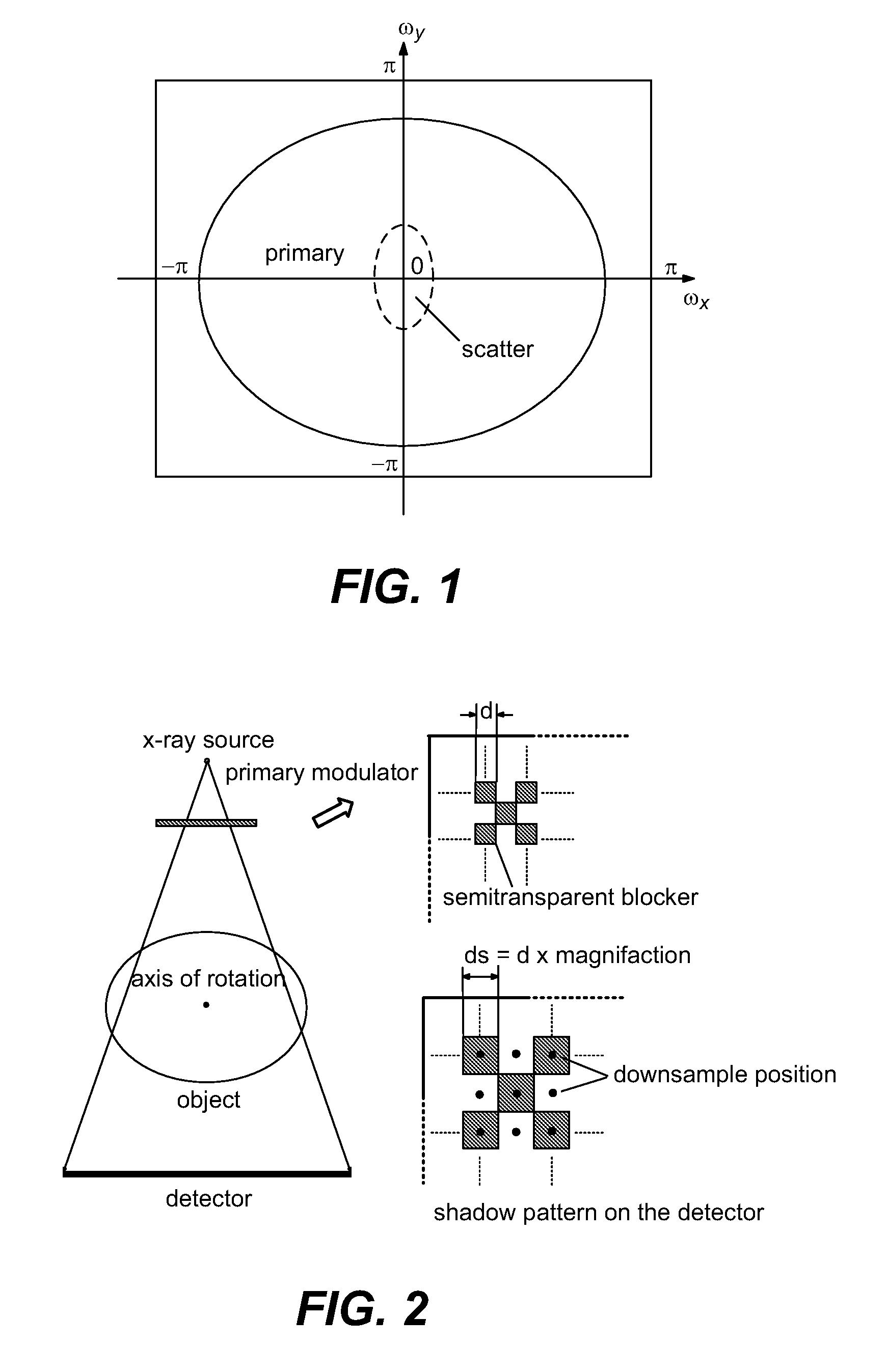
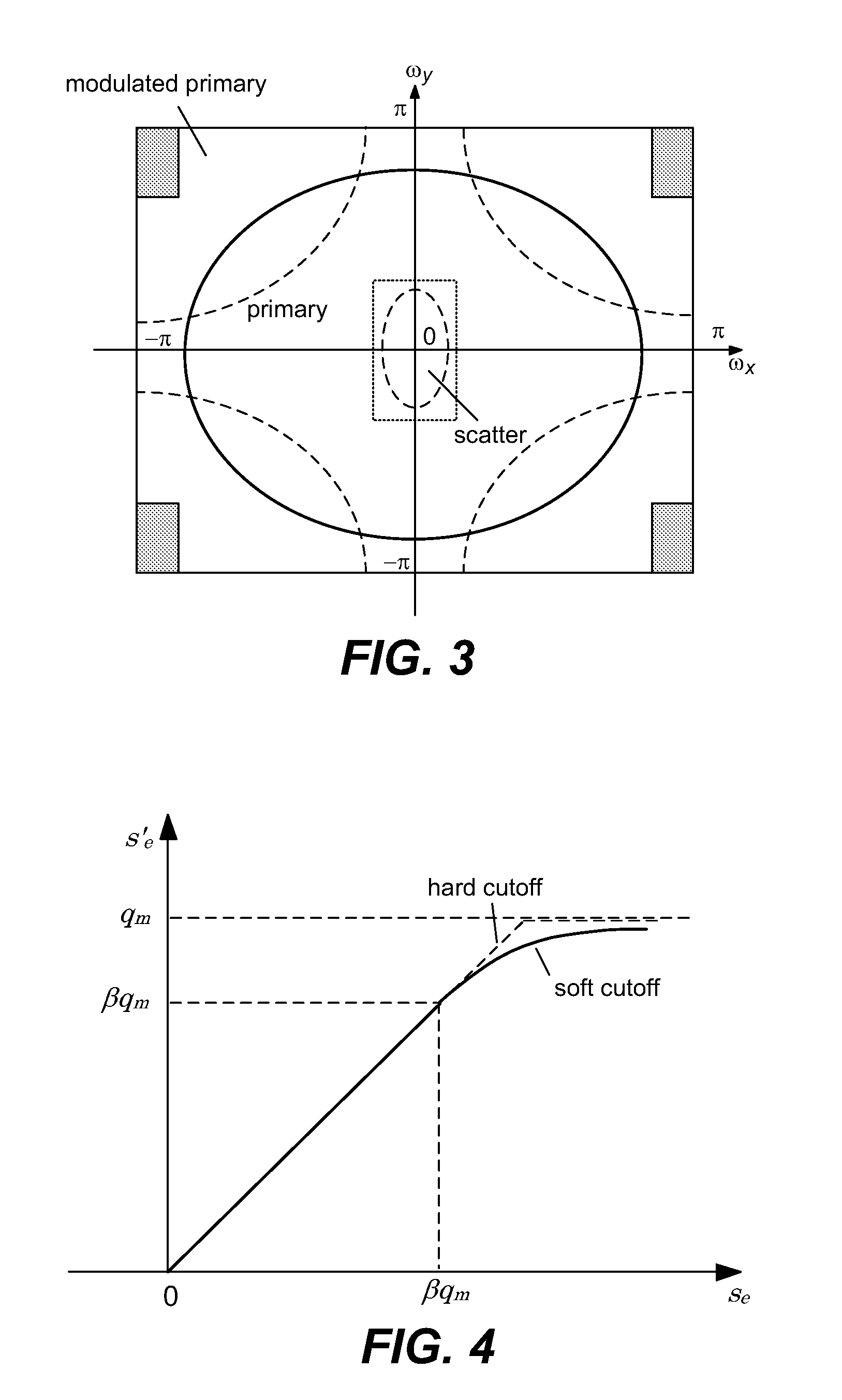
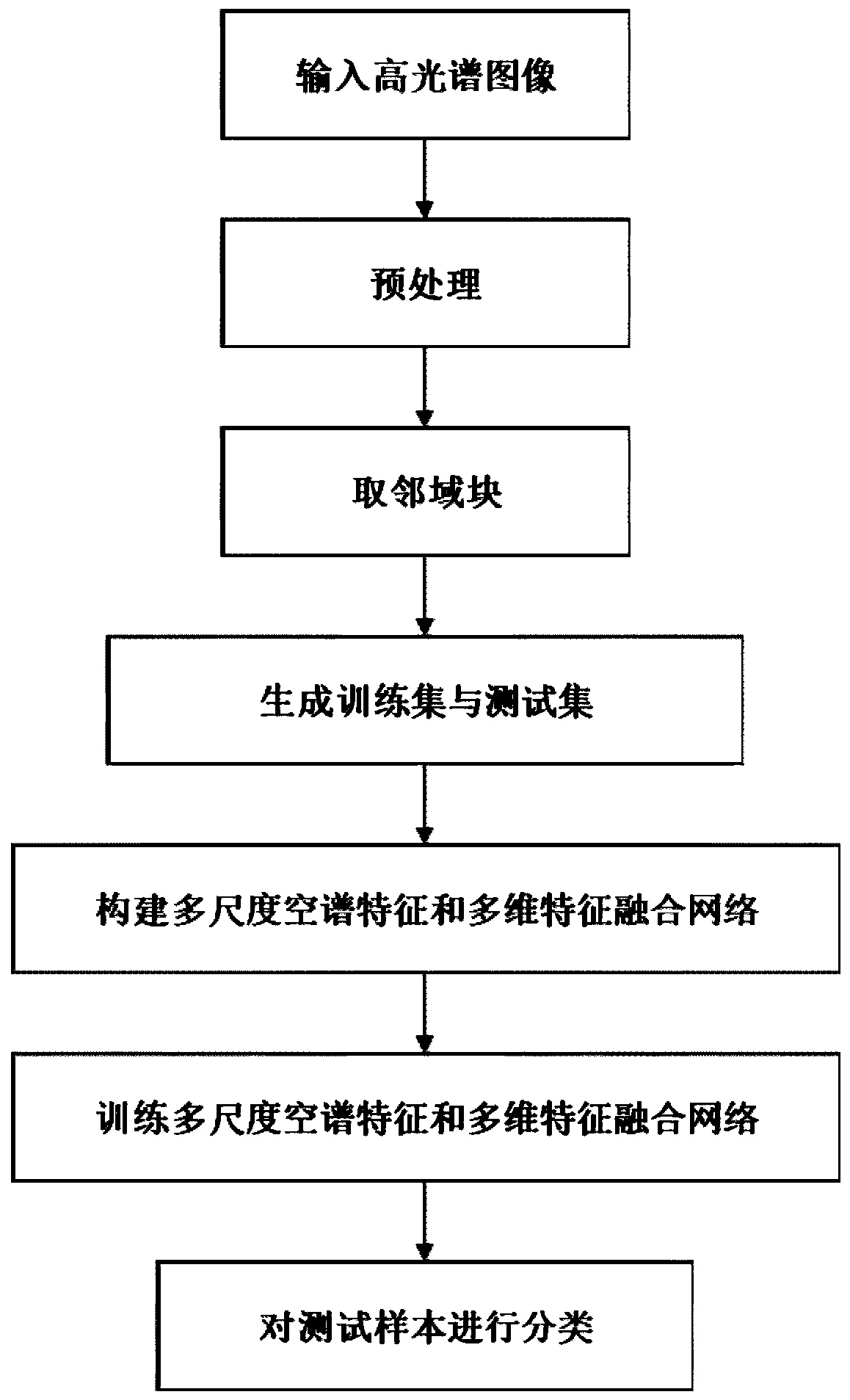
Scatter correction for x-ray imaging using modulation of primary x-ray spatial spectrum
ActiveUS7463712B2Efficient transferMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayX ray image
Scatter radiation in an x-ray imaging system including an x-ray source and an x-ray detector is separated by using amplitude modulation to translate the spatial frequency of a detected x-ray beam to a higher frequency and provide separation from low frequency scatter signal. The low frequency content of the detected x-ray beam is then obtained by demodulating the detected modulated signal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
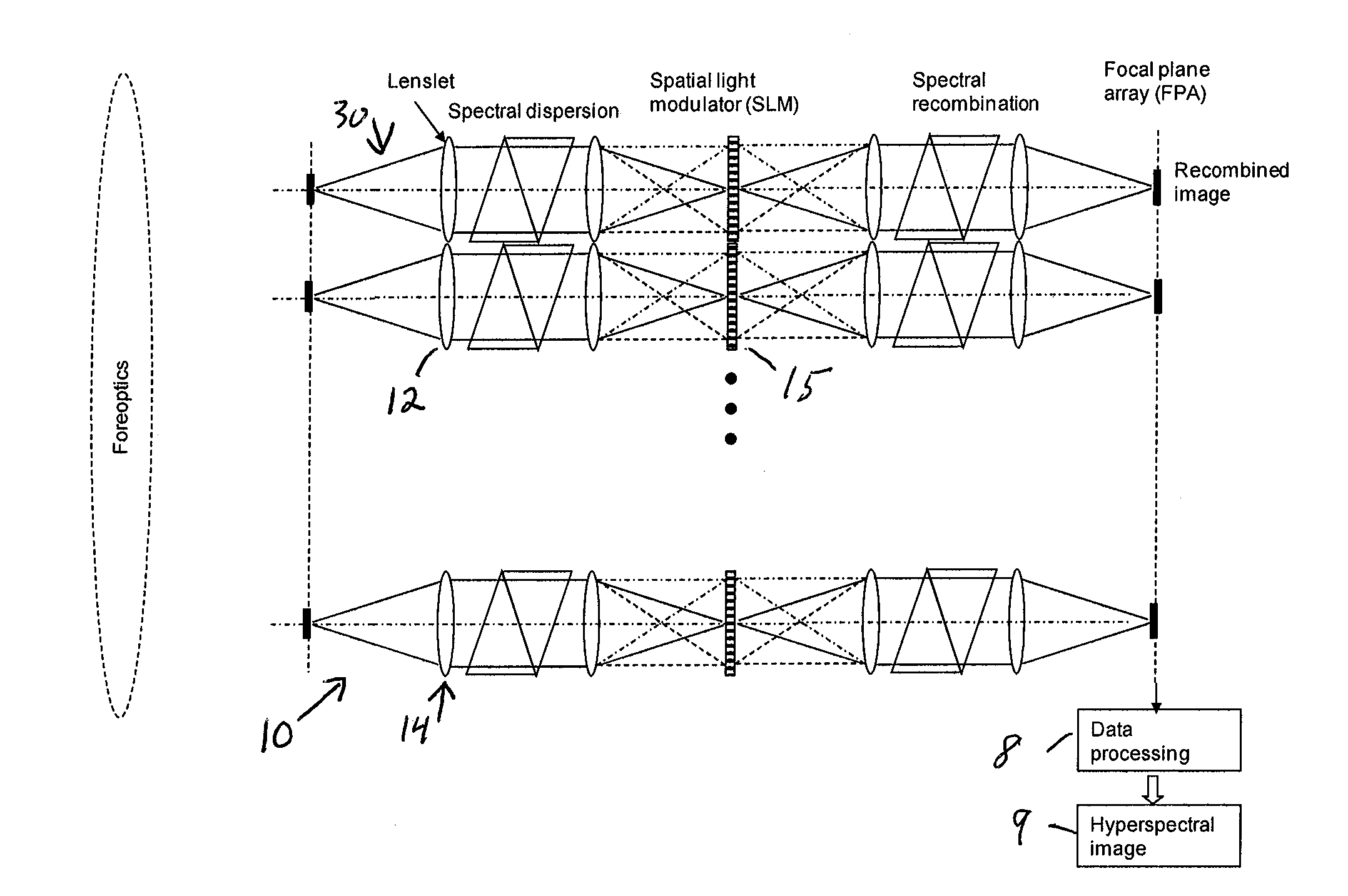
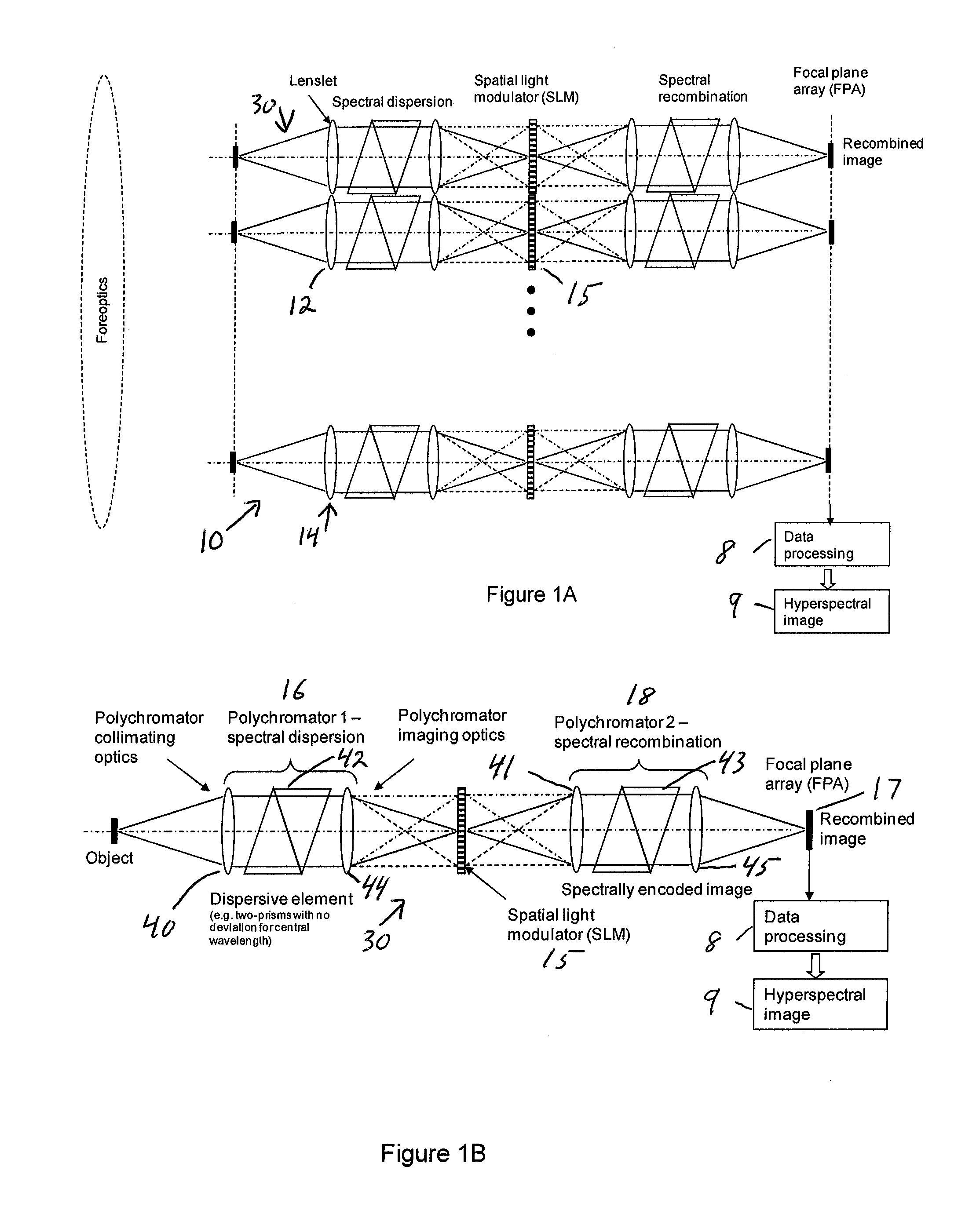
Single-Shot Spectral Imager
ActiveUS20100309467A1Improve spatial resolutionEasy to useRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using refracting elementsMultiplexingSpatial light modulator
A single-shot spectral imager or imaging system which acquires multiplexed spatial and spectral data in a single snapshot with high optical collection efficiency and with the speed limited only by the readout time of the detector circuitry. The imager uses dispersive optics together with spatial light modulators to encode a mathematical transform onto the acquired spatial-spectral data. A multitude of encoded images is recorded simultaneously on a focal plane array and subsequently decoded to produce a spectral / spatial hypercube.
Owner:SPECTRAL SCI
Method and arrangement for analyzing samples
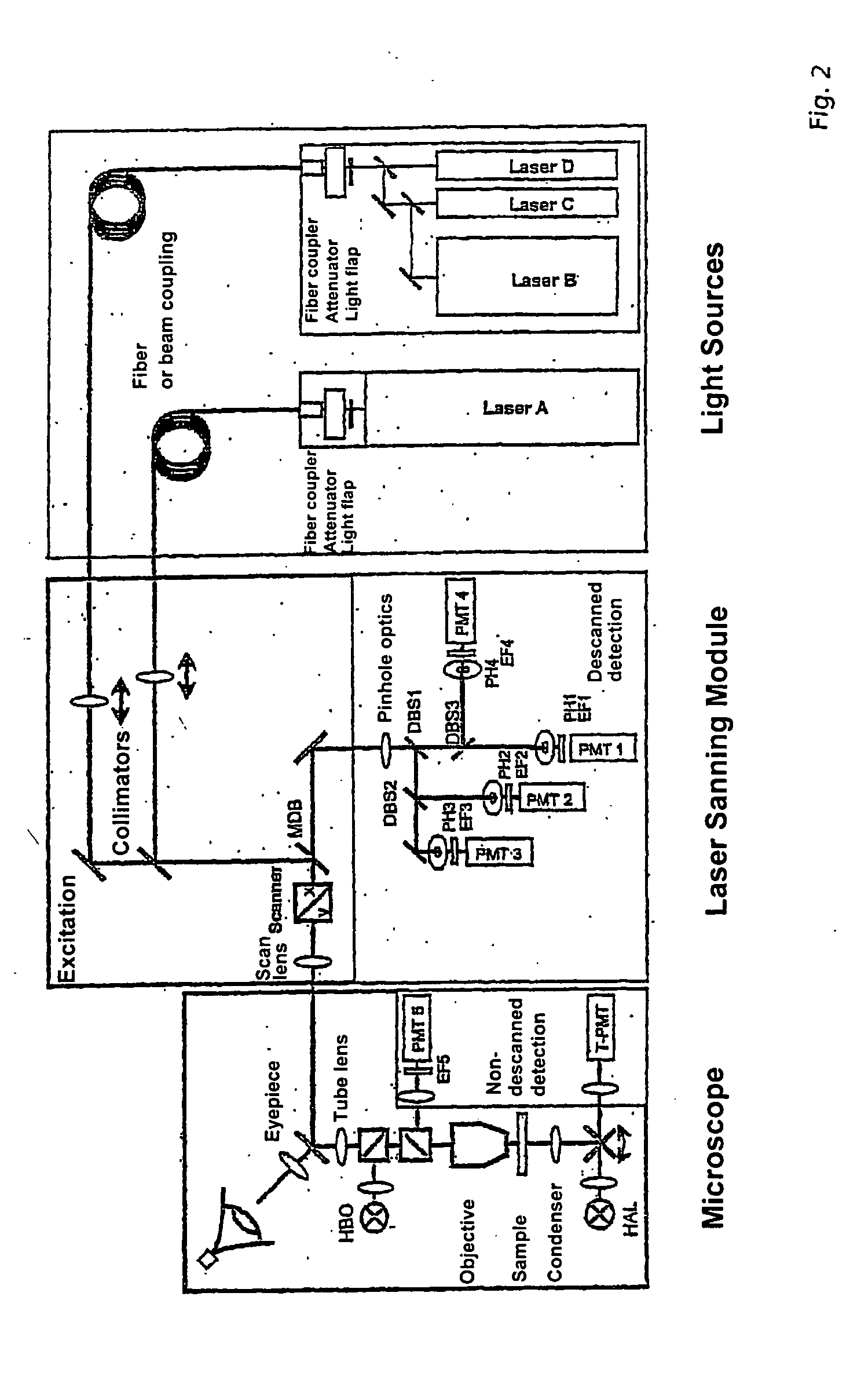
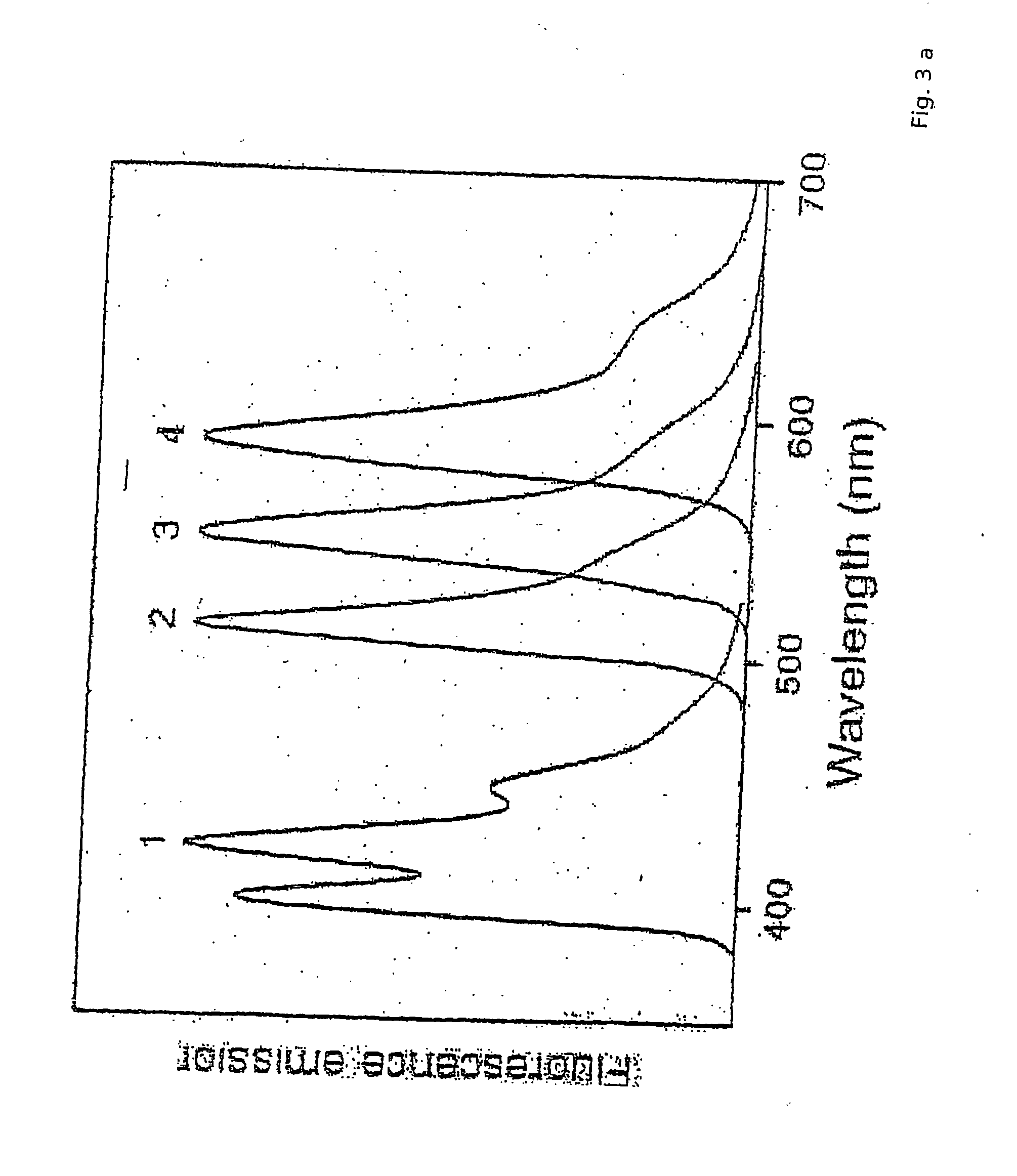
InactiveUS20050179892A1Increase the number ofAccurate assessmentRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLaser scanning microscopeImaging processing
A method and / or arrangement for the analysis of fluorescing samples in an image-generating microscope system, preferably a laser scanning microscope, wherein the sample is scanned point-by-point or line-by-line in at least one surface section and a dispersive splitting of the radiation coming from the sample is carried out during the scanning, wherein the split radiation is detected by at least one line of detector elements in a wavelength-dependent manner, a selection of two-dimensional or three-dimensional sample parts which correspond to pre-stored two-dimensional or three-dimensional geometric objects or the like is carried out based on the recorded and stored intensity distribution of at least one of these detection elements and / or at least one other detection element for the radiation reflected from the sample by image processing, and an analysis of the spectral signature and / or spatial spectral sequence is carried out for at least a portion of these sample regions with respect to the fluorescence markers arranged thereon.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
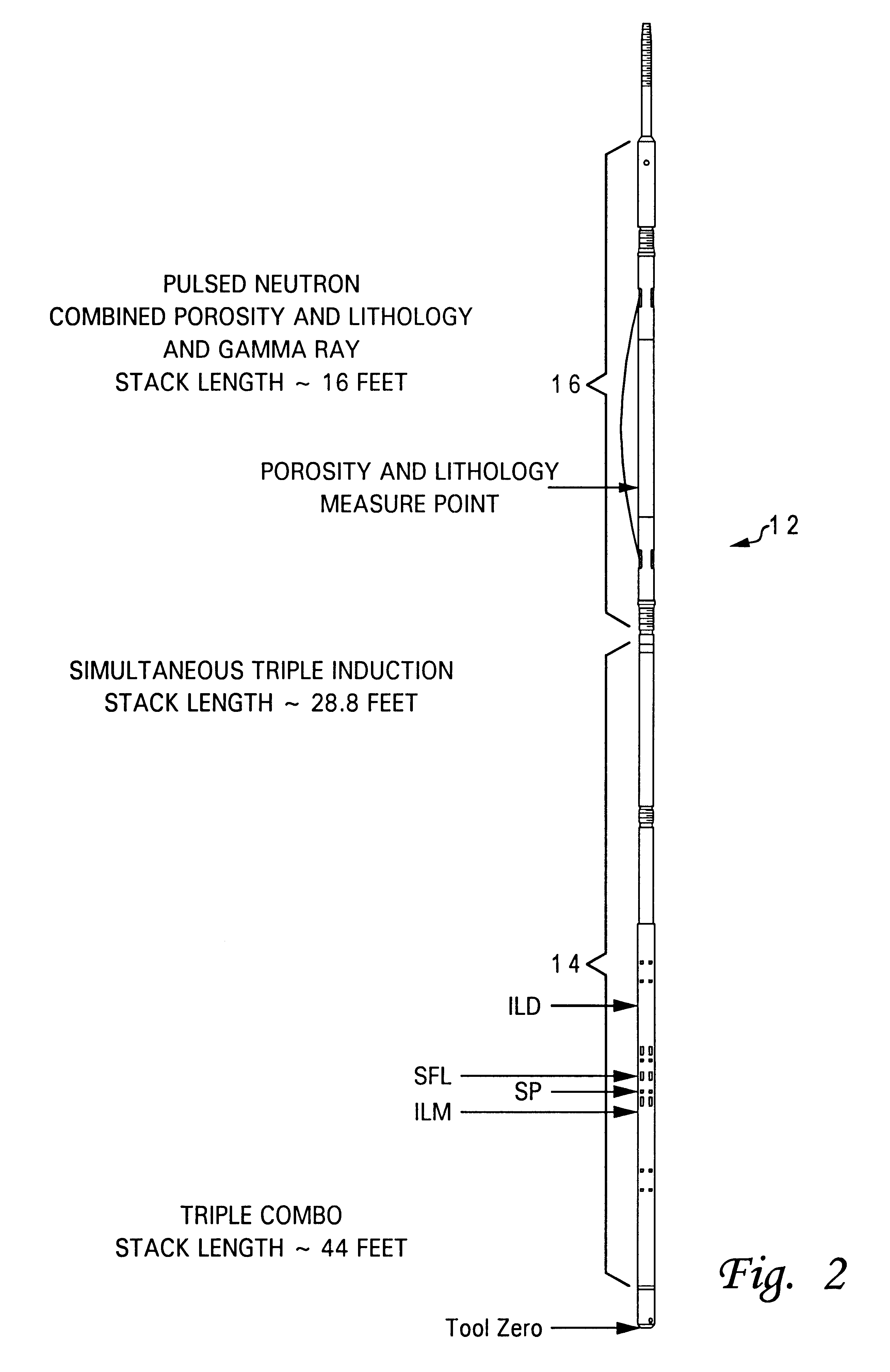
Formation evaluation combination system for petrophysical well log analysis
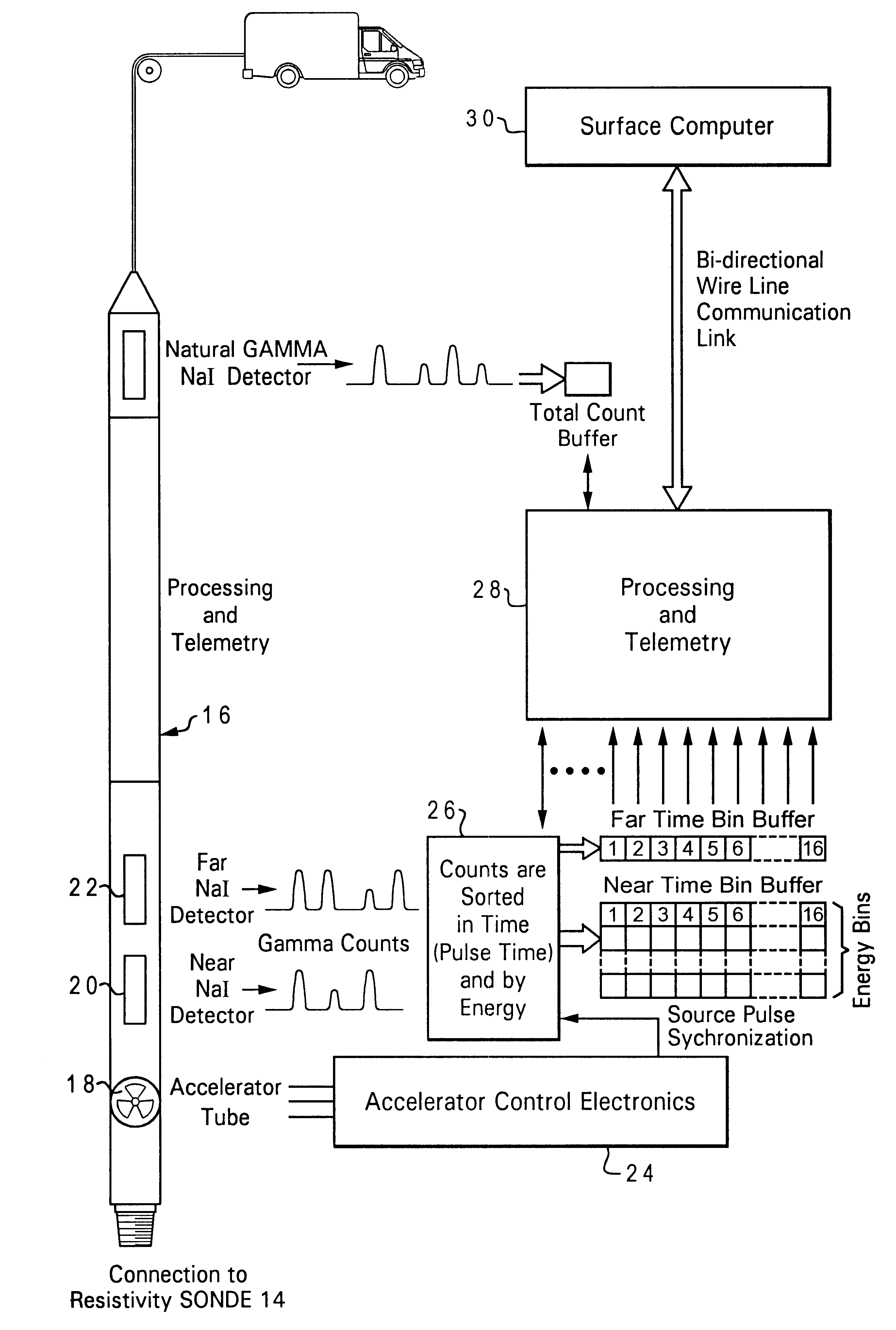
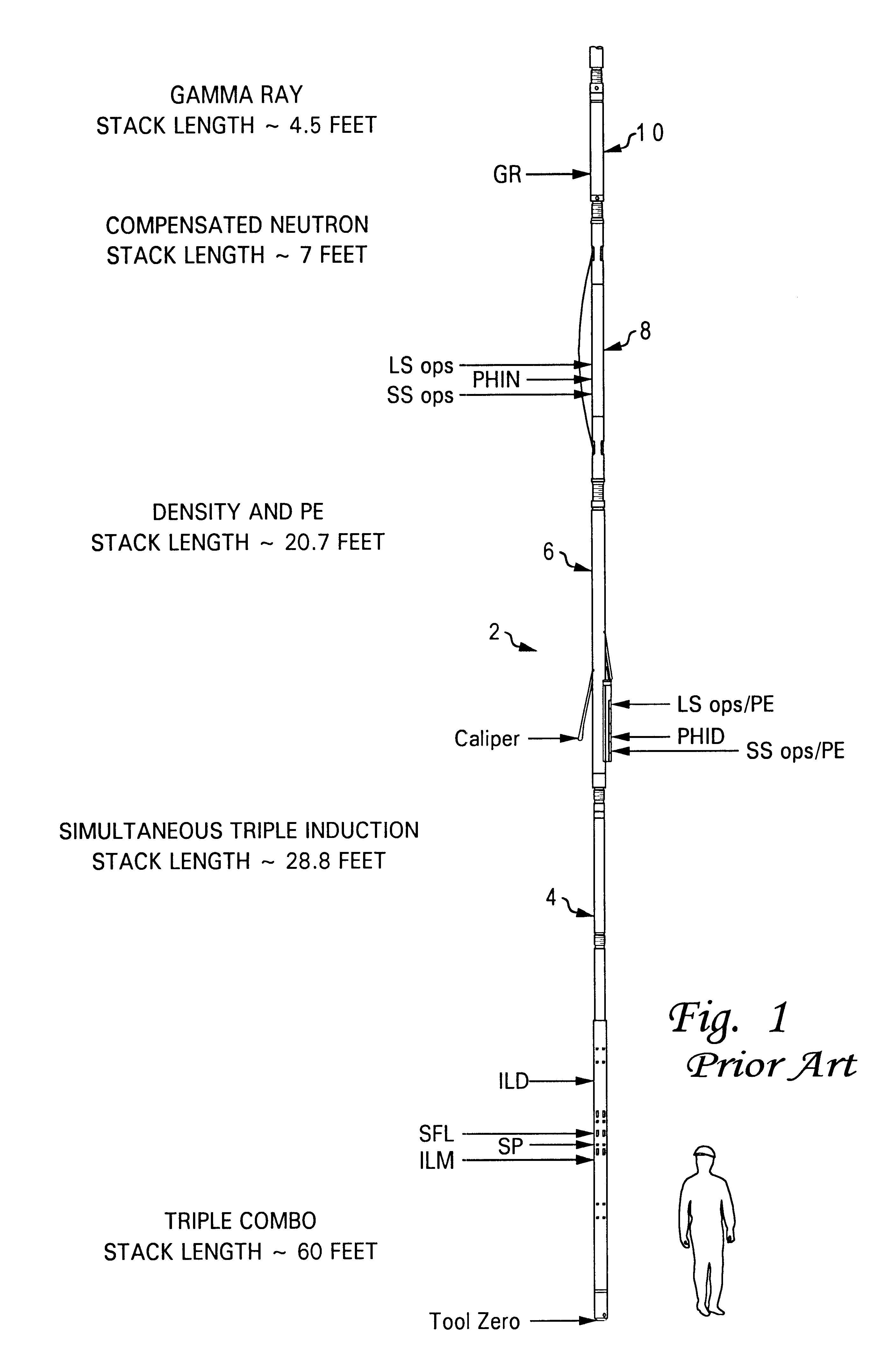
InactiveUS6376838B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationGamma ray detectionNeutron porosity
A method of measuring characteristics of a geologic formation, using the time, energy and spatial spectra of gamma rays induced by an accelerator, which allows (i) the measurement of the photoelectric absorption (Pe) factor of the formation using a gamma-ray spectrum detected from gamma rays induced in the formation, (ii) the calculation of a neutron porosity of the formation using the gamma-ray spectrum, and (iii) the determination of a bulk density of the formation using the spectroscopic measurements. The Pe factor may be inferred by directly mapping the spectroscopic measurements. The porosity may be calculated by relating the gamma-ray spectrum to a hydrogen content of the formation. The density may be determined by computing a gamma diffusion length of the formation based on the gamma-ray spectrum. In addition to these measurements, the resistivity of the formation and its spontaneous potential may also be measured using an electromagnetic induction system.
Owner:PRECISION ENERGY SERVICES
Holographic projection real-time 3D display system and method
ActiveUS20110254916A1Achieve normal displayRestore complex wavefrontsStereoscopic photographyHolographic writing meansWavefrontSpatial spectrum
A real-time color holographic three-dimensional (3D) display system and method realized by using principles of digital holographic display and a common photographing / projection device array system are provided. For an object O to be displayed, an array of M×N cameras which are anchored to a certain reference point R in a space corresponding to the object O is used to perform spatial spectrum sampling and capturing on any spatial spectrum surface S of the object O with a sampling density being a spatial sampling angle ωmn. Each acquired spatial spectrum view image Imn is projected by a corresponding array of M×N projectors in each spatial spectrum capturing direction to a reference surface PR necessary for restoring 3D information of the original object O. Output of full spatial spectrums of the object O is realized through a spatial spectrum limited stretching function of a holographic functional screen placed on the reference surface PR which is used on discrete spatial spectrum input image information, thereby achieving digital holographic display intended to restore complex wavefronts.
Owner:AFC TECH
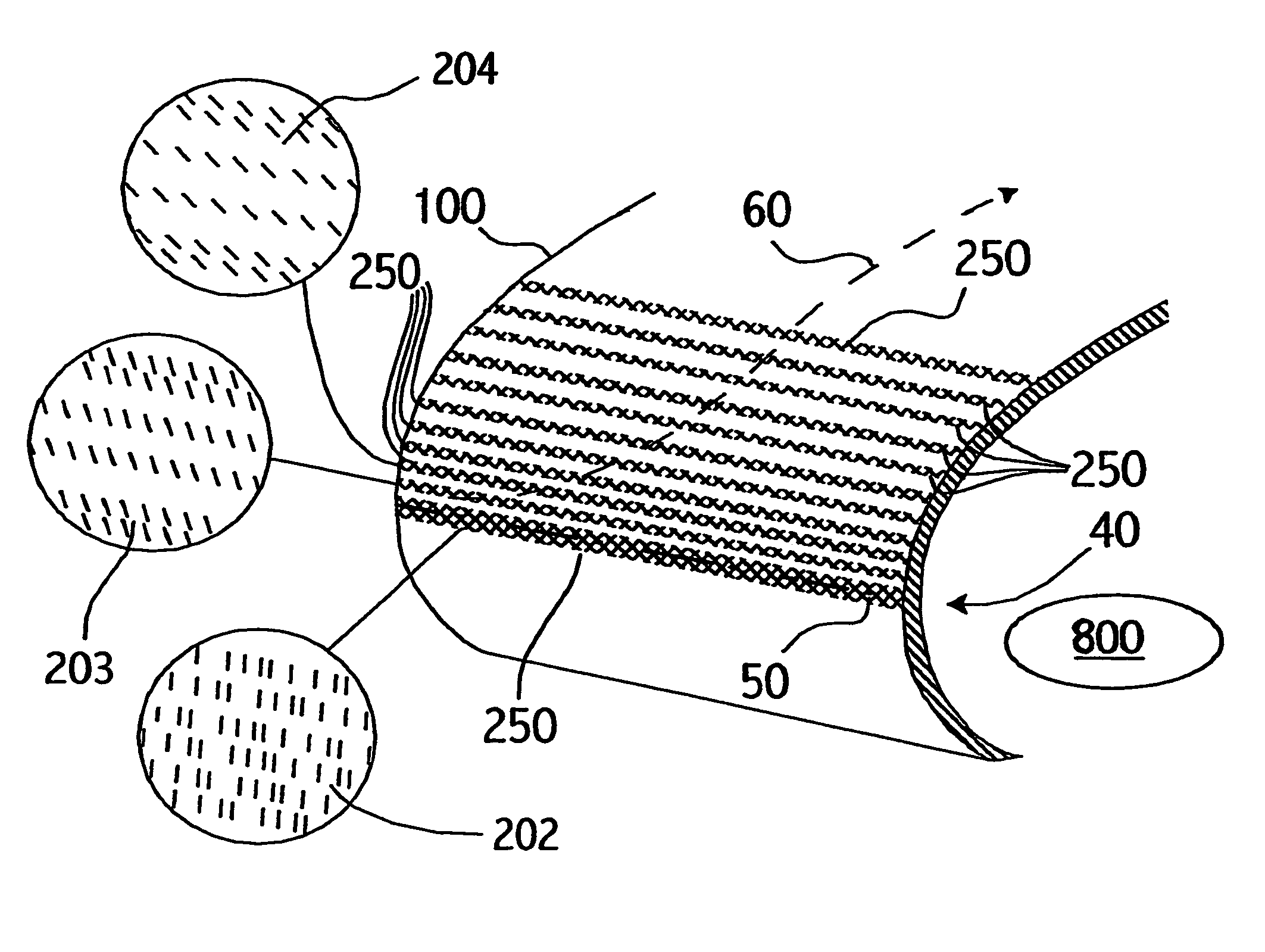
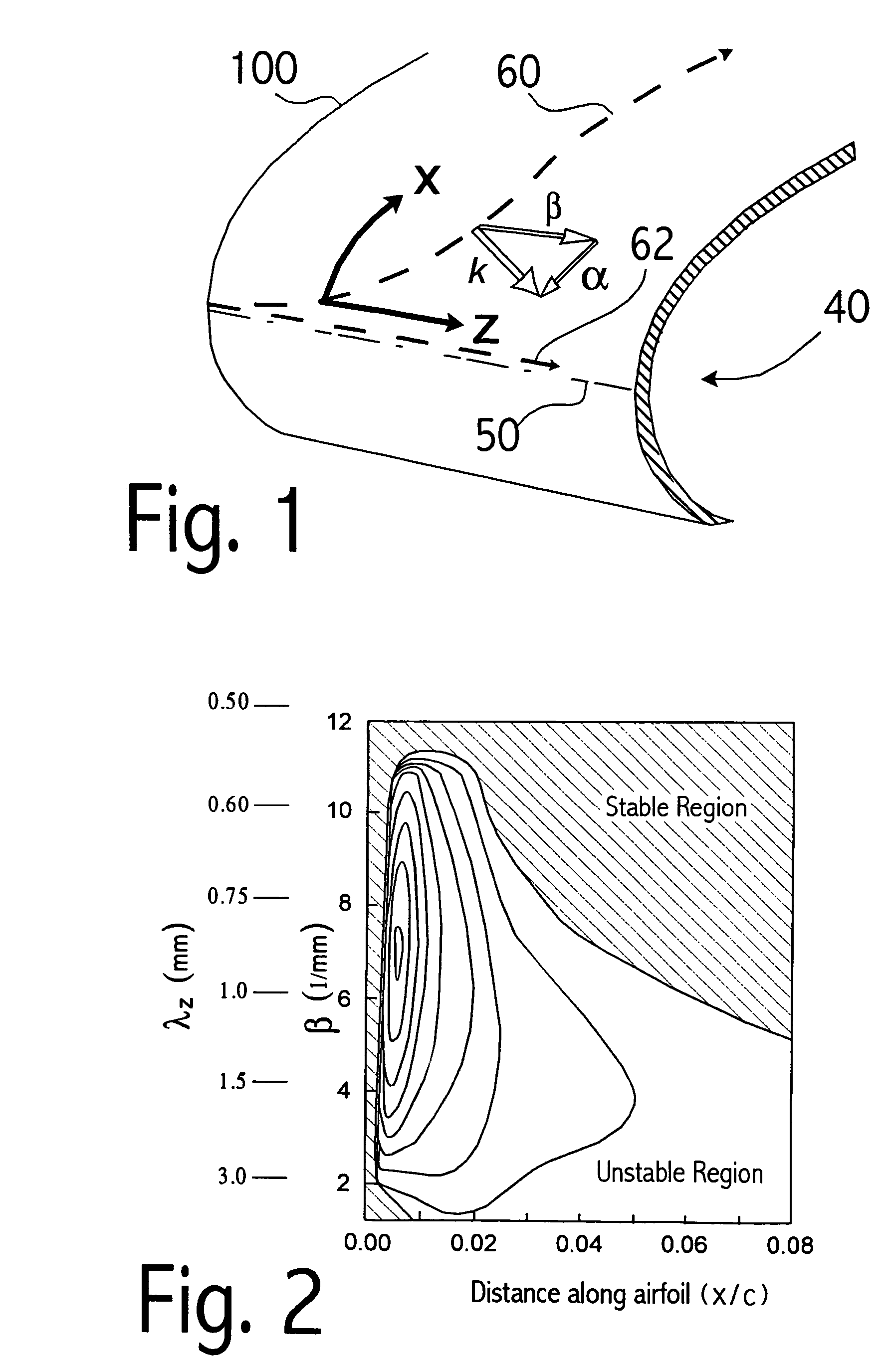
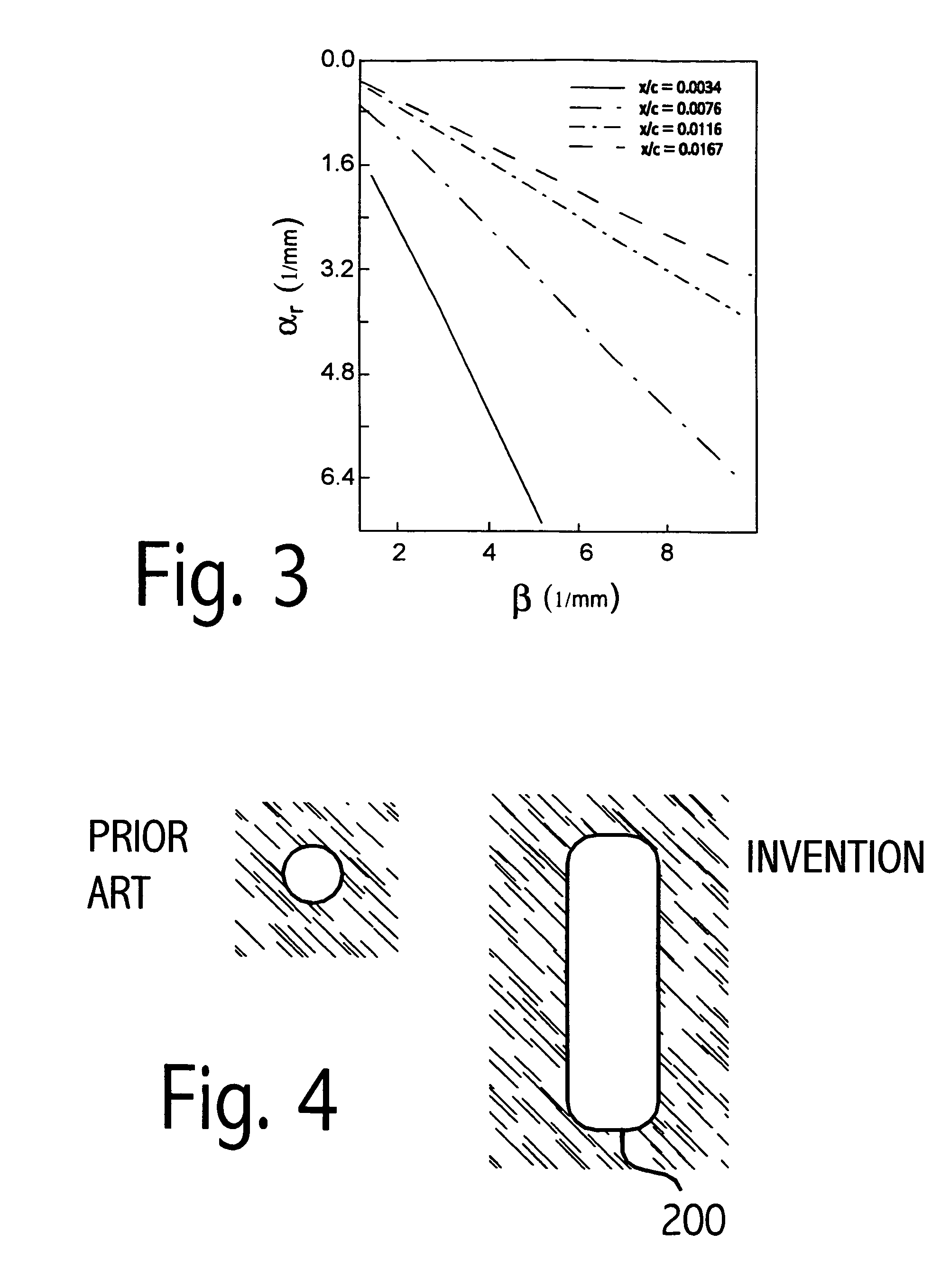
Perforated skin structure for laminar-flow systems
InactiveUS7152829B2Improve thermal conductivityBoundary layer controlsWingsThrottle controlStreaming instability
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Scatter correction for x-ray imaging using modulation of primary x-ray spatial spectrum
ActiveUS20070268997A1Efficient transferMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayX ray image
Scatter radiation in an x-ray imaging system including an x-ray source and an x-ray detector is separated by using amplitude modulation to translate the spatial frequency of a detected x-ray beam to a higher frequency and provide separation from low frequency scatter signal. The low frequency content of the detected x-ray beam is then obtained by demodulating the detected modulated signal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
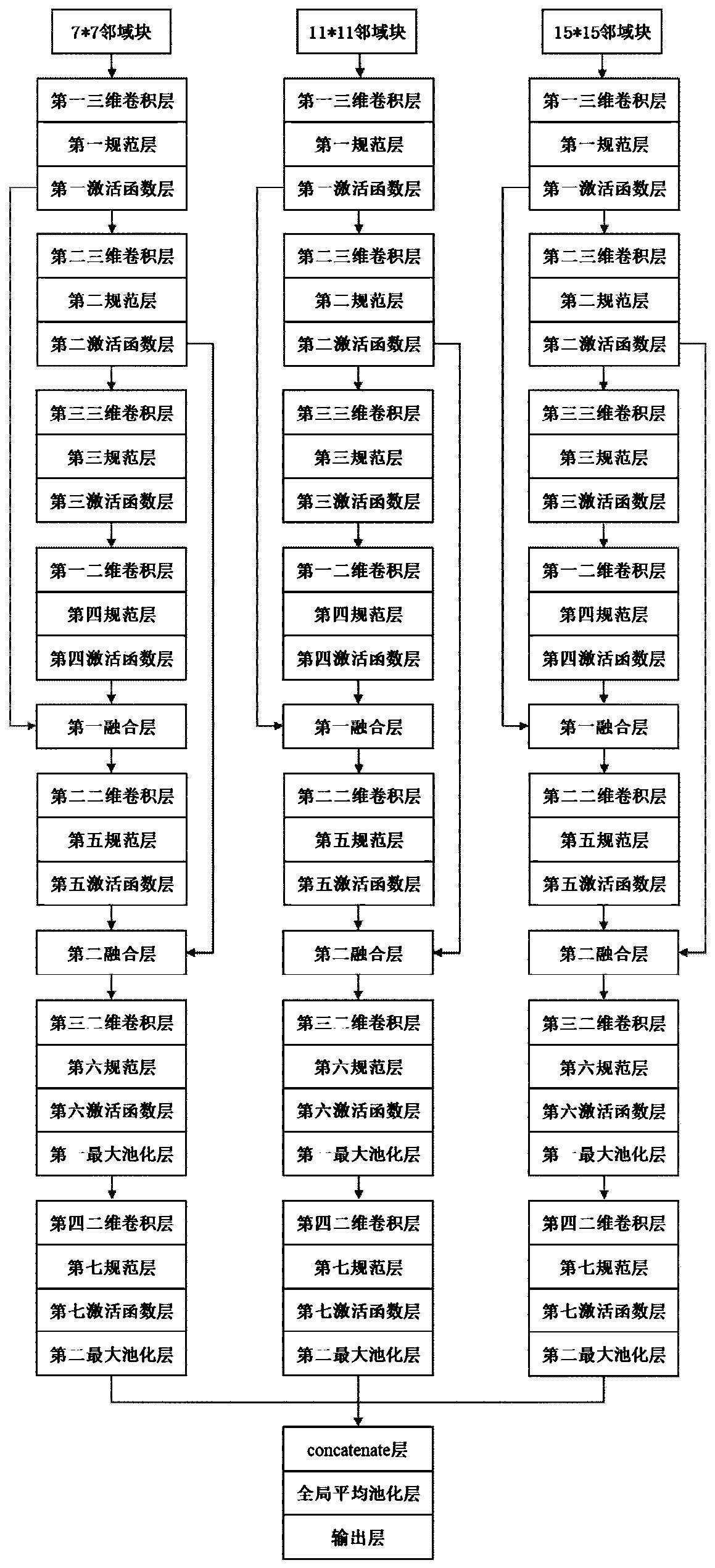
Hyperspectral image classification method based on fusion of multi-scale and multi-dimensional spatial-spectral characteristics
ActiveCN110321963AImprove classification accuracyEasy to identifyScene recognitionSmall sampleTest sample
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification method based on fusion of multi-scale and multi-dimensional spatial spectral characteristics. The method comprises the following steps: (1)inputting a hyperspectral image; (2) preprocessing the hyperspectral images to be classified; (3) tracking neighborhood blocks; (4) generating a training set and a test set; (5) constructing a multi-scale spatial spectrum feature and multi-dimensional feature fusion network; (6) training a multi-scale spatial spectrum feature and multi-dimensional feature fusion network; and (7) classifying the test samples. The method provided by the invention can effectively solve the problems of too single feature and too single scale of the convolutional neural network during training, can solve the problem of low average classification precision AA during hyperspectral classification, can maintain the recognition capability of small sample number categories while realizing high classification precision, and is good in classification performance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Constraint generation for use in image segregation
ActiveUS20100142805A1Accurately correctly identifyImage enhancementImage analysisSpatial spectrumImage separation
In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, an automated, computerized method is provided for processing an image. According to a feature of the present invention, the method comprises the steps of providing an image, organizing spatio-spectral information for the image in a matrix equation expressed by: [A][x]=[b], wherein [A] expresses values determined by a constraining relationship imposed upon the spatio-spectral information, [b] expresses recorded information for the image, and [x] expresses an unknown material / illumination component of the image, and utilizing the matrix equation in an image segregation operation.
Owner:INNOVATION ASSET COLLECTIVE
High-spectrum image classification method based on combined loss enhanced network
InactiveCN107180248AEnhanced Supervised Learning ProcessReduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsNetwork structureClassification methods
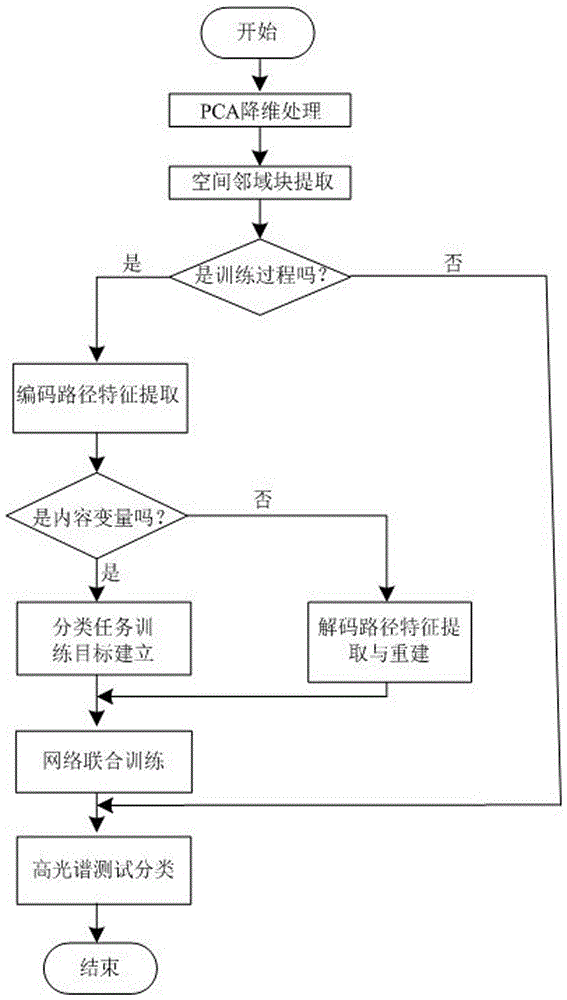
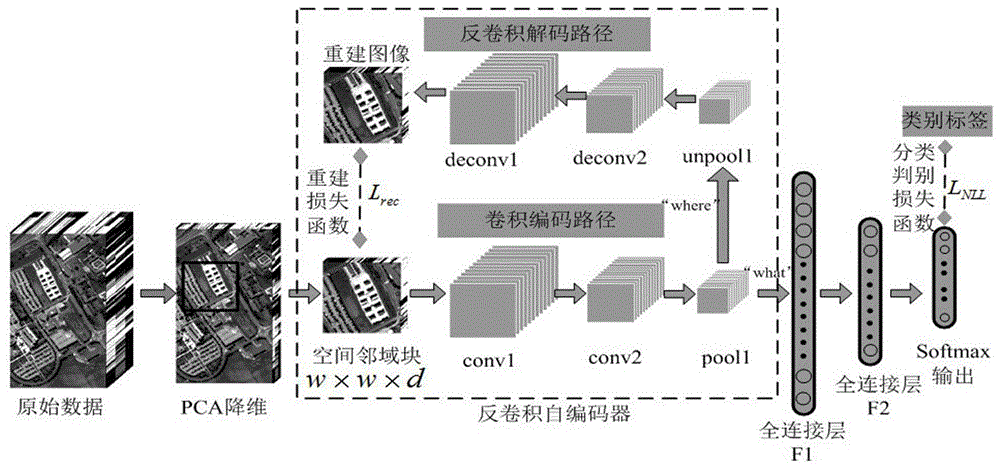
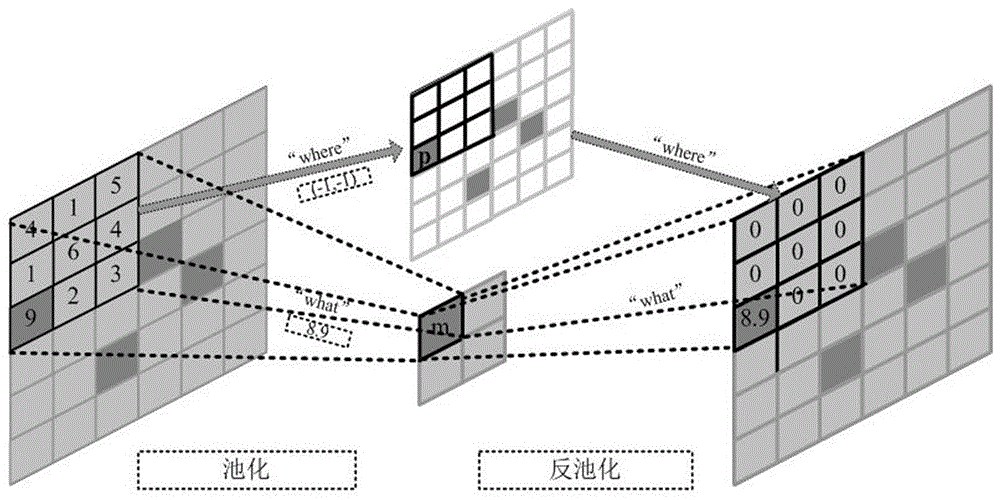
The invention discloses a high-spectrum image classification method based on a combined loss enhanced network, and the method is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: 1), PCA dimension reduction; 2), spatial domain block extraction; 3), coding path feature extraction; 4), classification task training target building; 5), decoding path feature extraction and reconstruction; 6), network combined training; 7), high-spectral testing classification. The method can achieve the combination of learning reconstruction loss and classification discrimination loss functions in the same network structure in a mode of end-to-end training, so the spatial spectrum information of a high-spectral image is used efficiently, and the learning of CNN for unimportant feature variables is automatically weakened, so as to reduce the complexity of a high-spectral classification model. Meanwhile, the dependence of a high-spectrum image classification method on a label sample is reduced, and the classification precision is improved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Temporal-spatial joint filtering high-resolution DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation method based on compressed sensing technology
InactiveCN103399312ALower the input SNR thresholdEffective estimateWave based measurement systemsCompressed sensingNarrowband
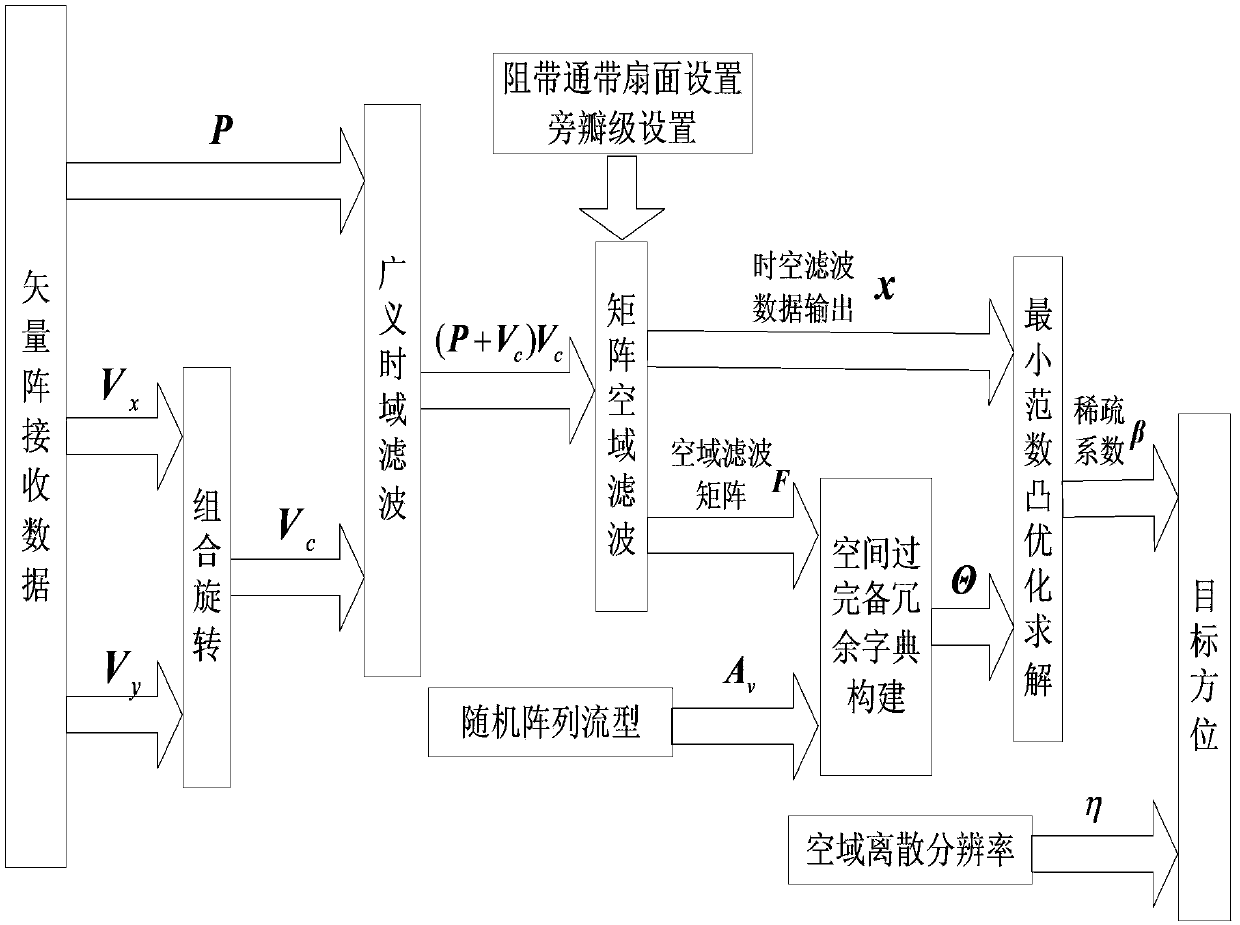
The invention provides a temporal-spatial joint filtering high-resolution DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation method based on a compressed sensing technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acoustic pressure vibration velocity joint temporal filtering, to be specific, carrying out rotating combination on the data of an acoustic vector sensor, and utilizing differences in the corresponding properties of a signal and noise to carry out denoising processing; (2) matrix spatial filtering, to be specific, carrying out spatial filtering on the temporally filtered data by a matrix spatial filter of which the maximum value of the mean square error of attenuation in a stop-band and a passband is minimum; and (3) compressed sensing DOA estimation by the array of the acoustic vector sensor, to be specific, receiving data and a manually formed spatial over-complete redundance dictionary via an input array preprocessed by temporal filtering, and seeking the sparse representation of the signal to carry out vector spatial spectrum estimation. The method has great spectral resolution capability in the high-resolution DOA estimation problem of a high-speed motion target under single snapshot conditions and is insensitive to the wideband and narrowband properties and coherent properties of the signal.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
New spatio-spectral sampling paradigm for imaging and a novel color filter array design
InactiveUS20100085452A1Minimize overlapMinimize luminance deviationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageDisplay device
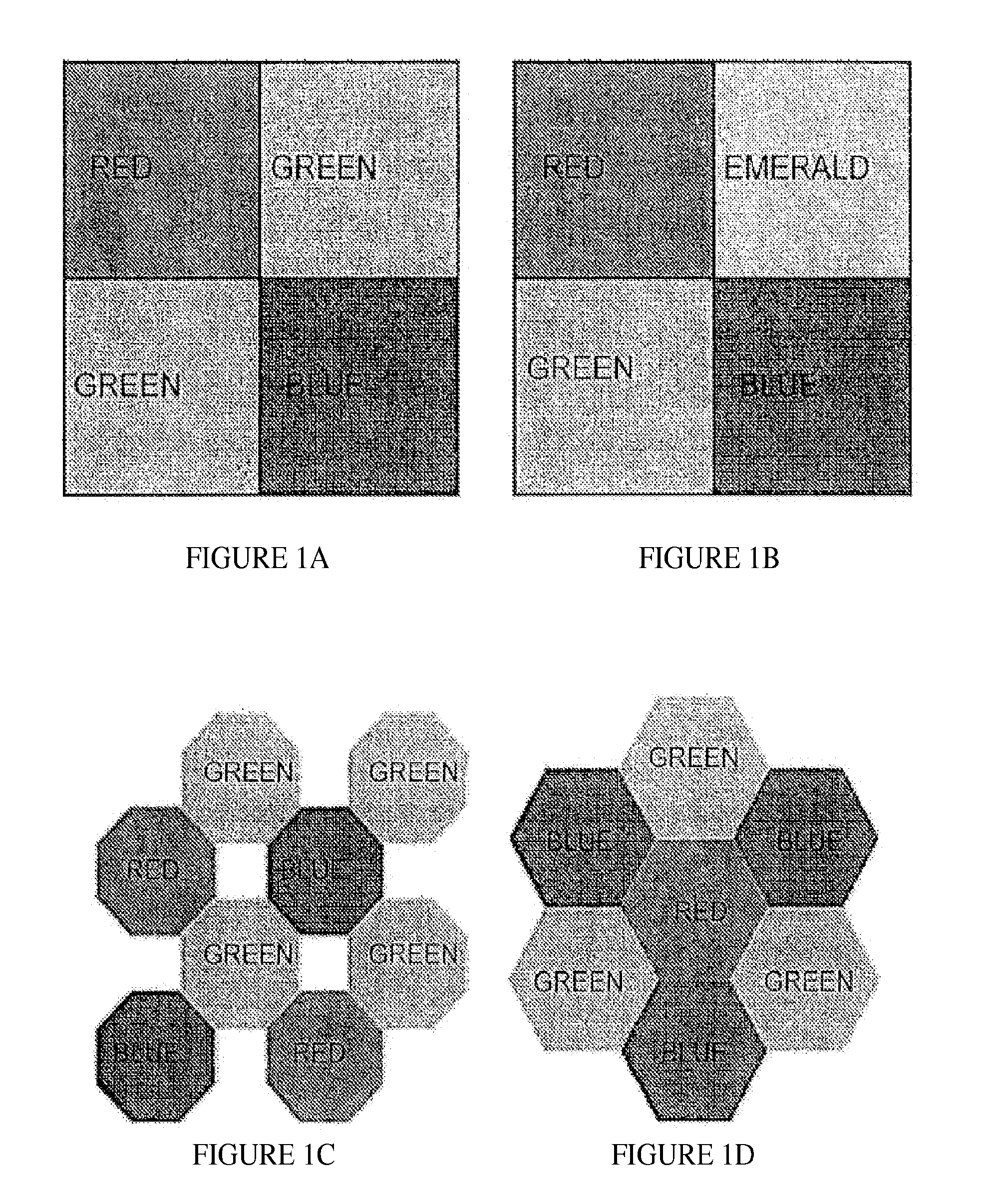
One aspect of the present invention relates to a new alternative to the Bayer pattern for spatial subsampling in color imaging applications. One aspect of the present invention relates to a new design paradigm for spatio-spectral sampling, which is also described. The proposed scheme offers the potential to significantly reduce hardware complexity in a wide variety of applications, while at the same time improving output color image quality. According to another aspect, it is realized that conventional processing techniques are subject to diminishing returns, and with the exception of the most sophisticated processing techniques generate imperfections perceptible to a practiced eye. According to one aspect, a framework for CFA design in presented. In one embodiment the physical characteristics of the CFA are generated so that the spectral radii of luminance and chrominance channels are maximized. In another embodiment, the CFA designed to subject to the conditions of perfect reconstruction. In one aspect, the physical characteristics of CFA design are constrained to require physically realizable CFA(s). Alternatively, certain physical characteristics can be emphasized to generate easier to manufacture CFA(s). According to another aspect, conventional methods and systems are evaluated, confirming shortcomings regarding aliasing in imaging and bandwidth, against which certain embodiments are benchmarked, showing improved performance under at least some embodiments of proposed designs and methods. According to another aspect, a display device CFA is evaluated in terms of throughput of stimuli as limited by aliasing. It is shown the spectral replicas of the chrominance signals induced by existing CFA patterns are centered around frequencies that are not sufficiently far from the DC, consequently overlapping with the luminance signal spectrum and reducing the throughput of the stimuli. By reinterpreting the interactions between the stimuli, display CFA, and CSF in terms of amplitude modulation, an alternative CFA coding scheme that modulates the chrominance signals to a higher frequency relative to common schemes is provided in some embodiments.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Characteristic testing system of semiconductor laser
ActiveCN102109571ARealize measurementAchieving precise measurementsLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPower semiconductor deviceTemperature control
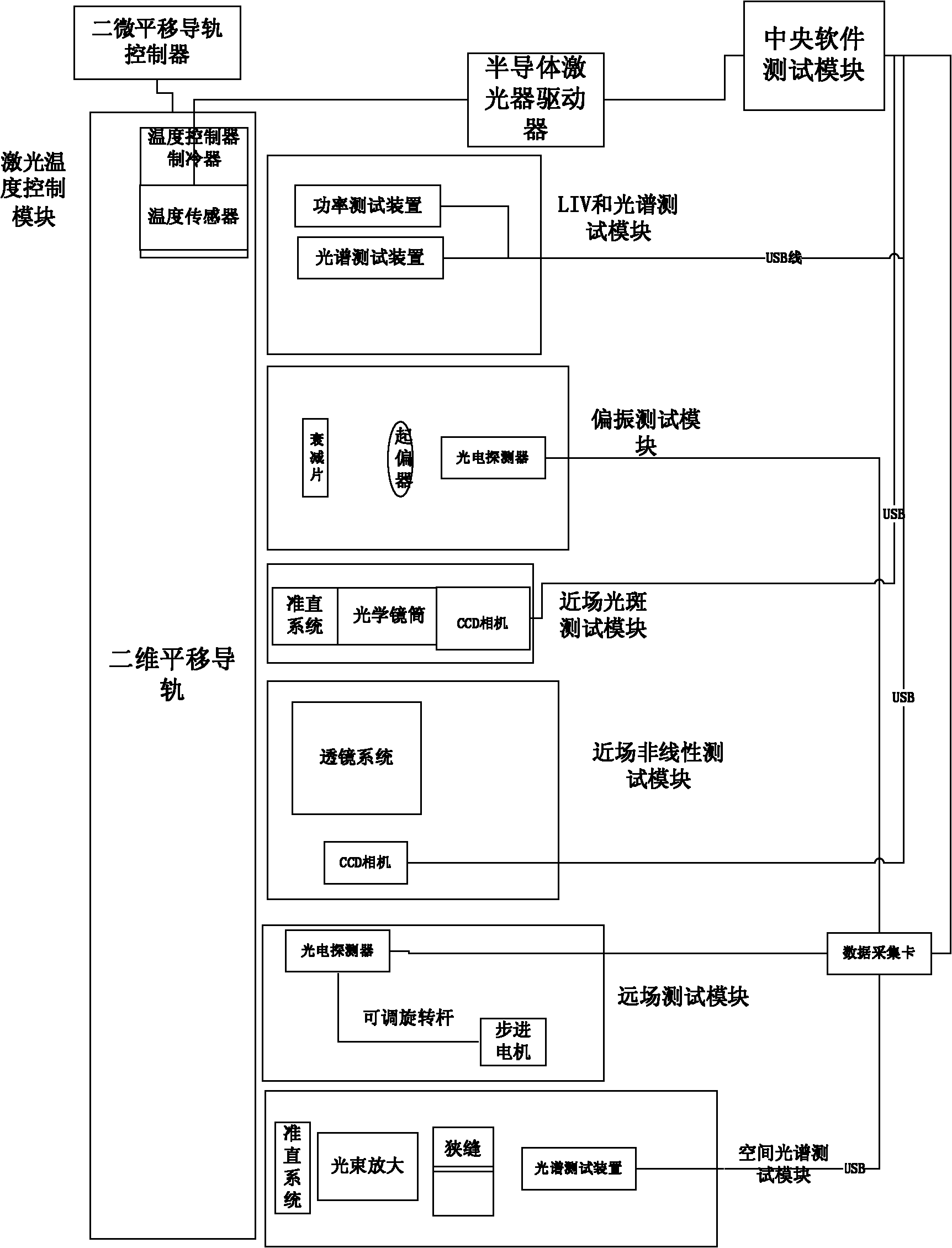
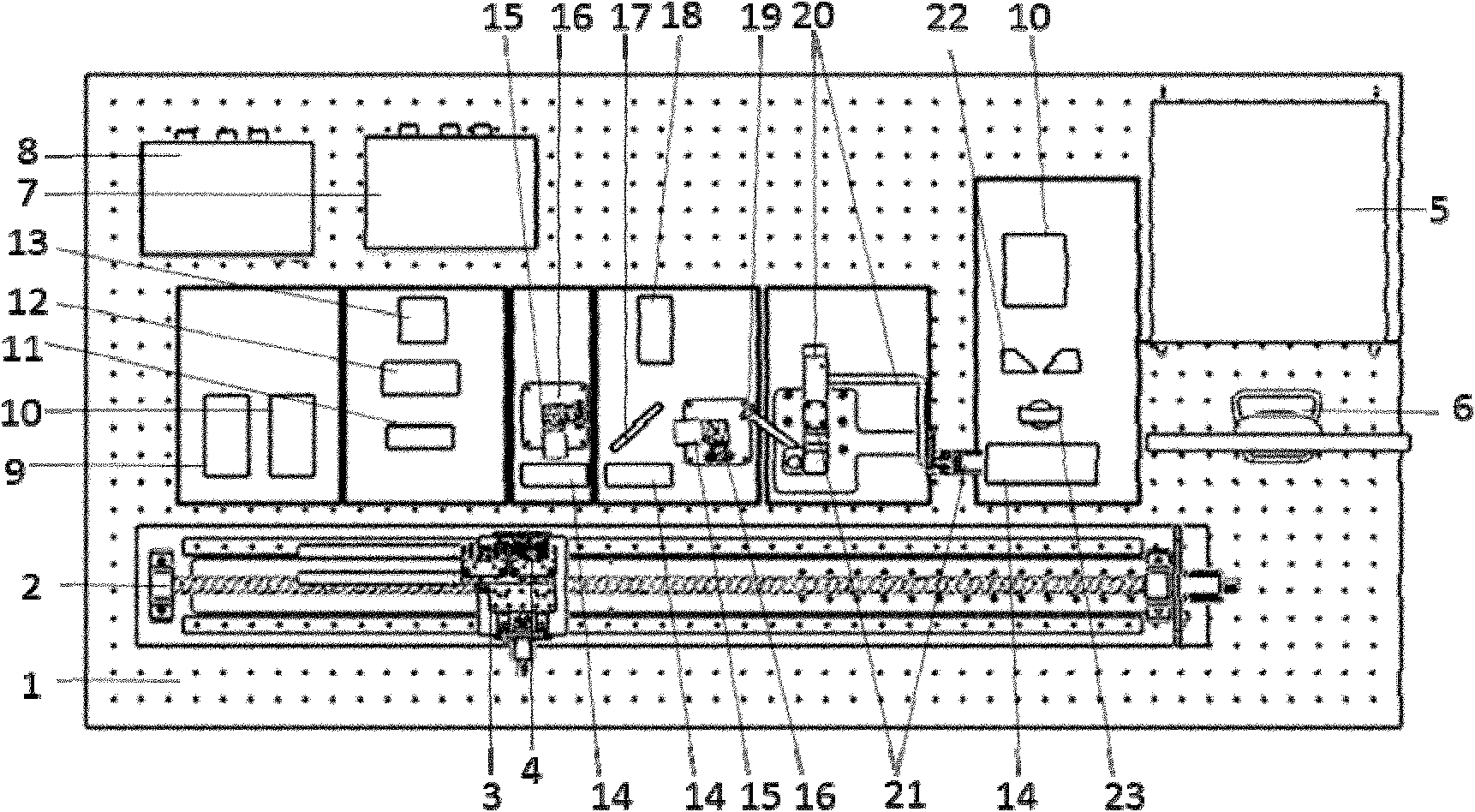
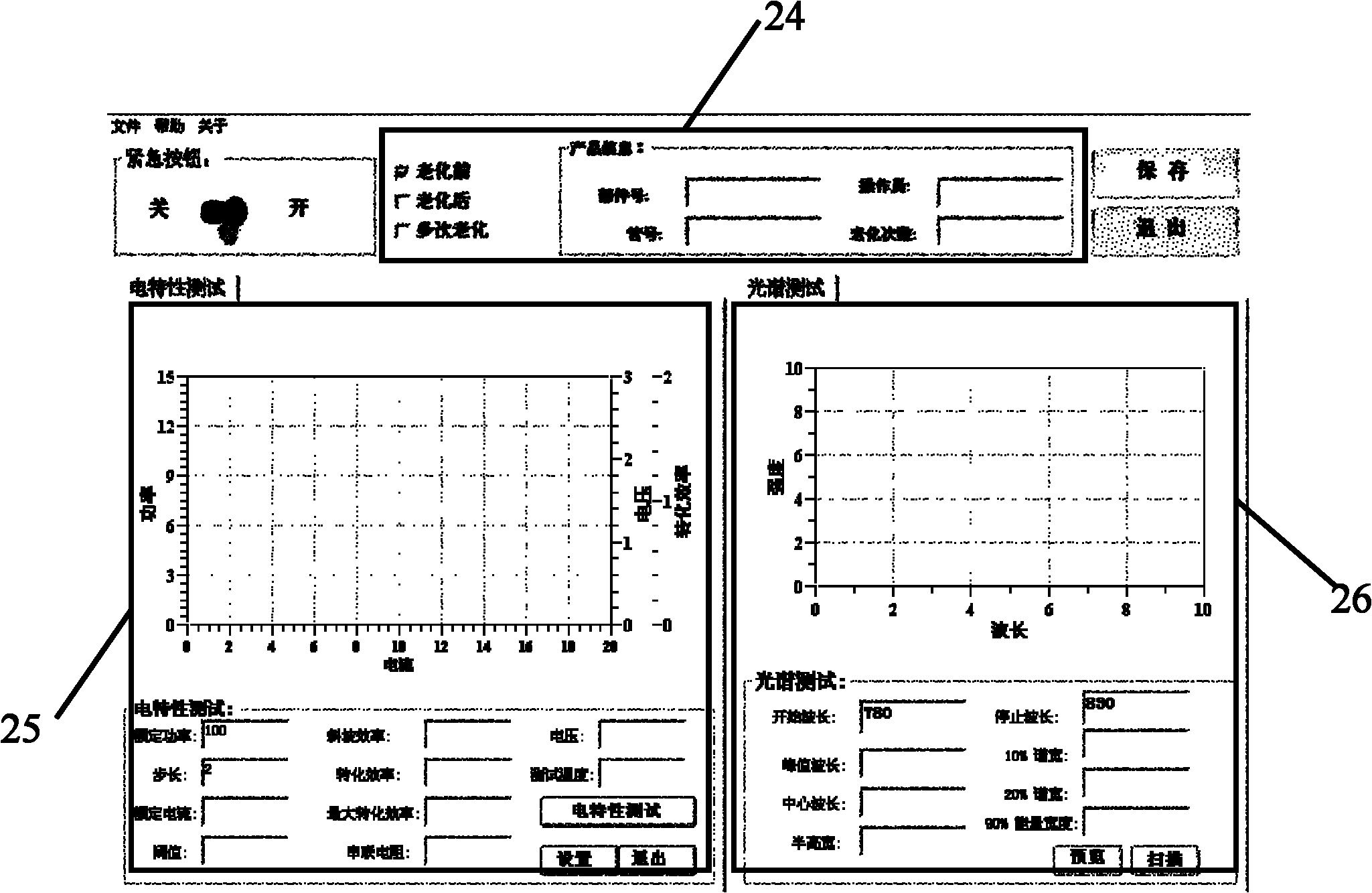
The invention discloses a characteristic testing system of a semiconductor laser, comprising a semiconductor laser driver, three-dimensional parallel guide rails, a laser temperature control module, an LIV (power-current-voltage) and spectrum test module, a polarization test module, a near-field light spot test module, a near-field nonlinear test module, a far-field test module, a space spectrum test module and a center software processing module. Working modules can be selected according to needs simultaneously. The characteristic testing system is used for high-accuracy and automation test of the semiconductor laser, especially for a high-power semiconductor laser, so that the cost for detection and manufacture of the semiconductor laser is reduced.
Owner:FOCUSLIGHT TECH
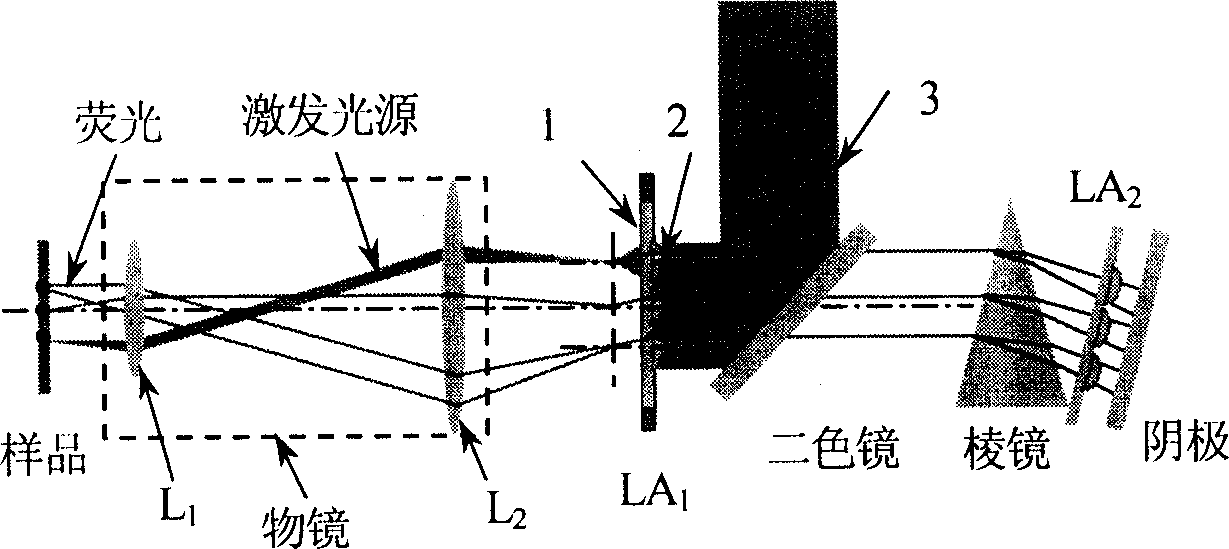
Five-dimensional fluorescent microscope imaging technique
InactiveCN1737536AMeasurable fluorescence lifetimeImprove spatial resolutionColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageFluorescence
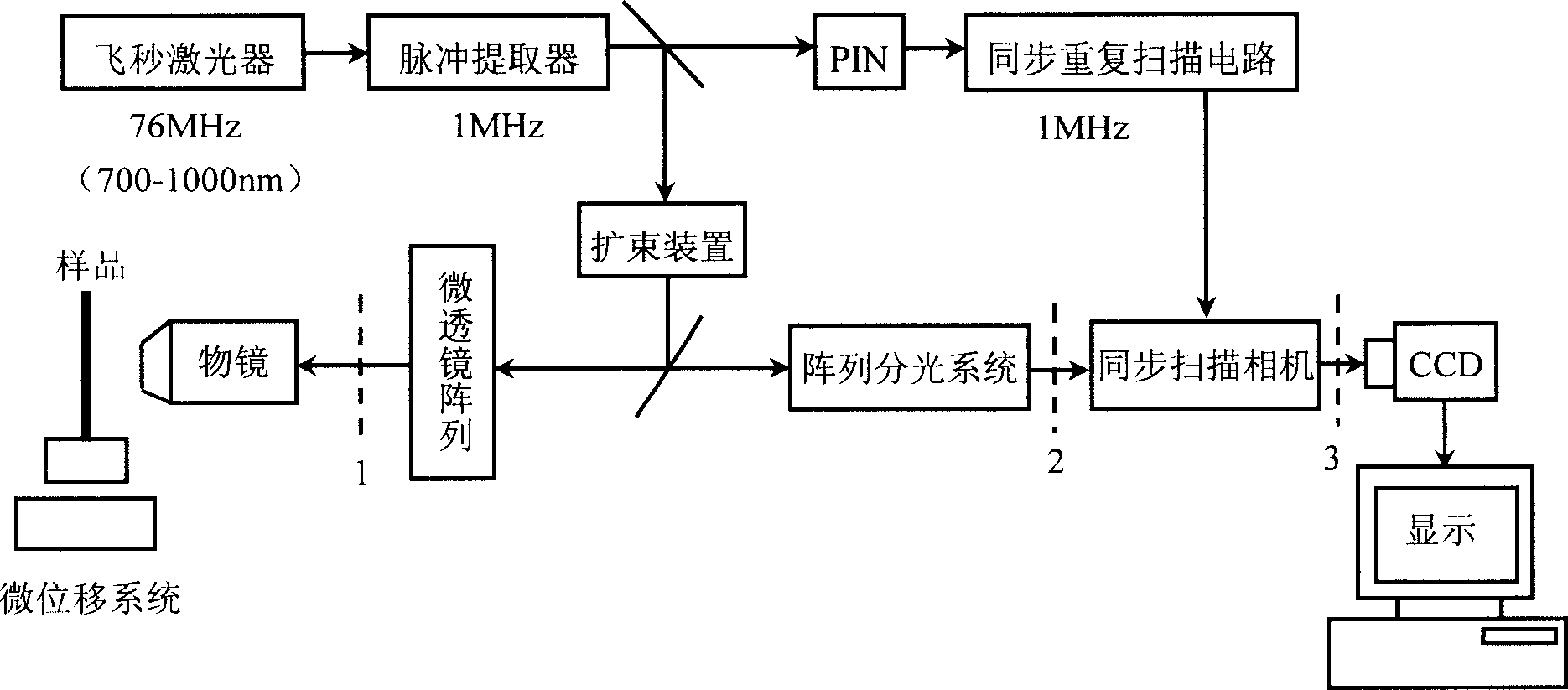
This invention relates to one method to acquire biology spectrum information and life information and to realize three-dimensional imaging. The invention is characterized by the following: getting multi-photon or single photon triggering of five-dimensional fluorescent microscope imaging information, that is three-dimensional space, one dimensional time and spectrum. This multi-parameter compound measurement and technique, which can satisfy the needs of different layers in study and can realize the flexible made three-dimensional spectrum for measurement.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
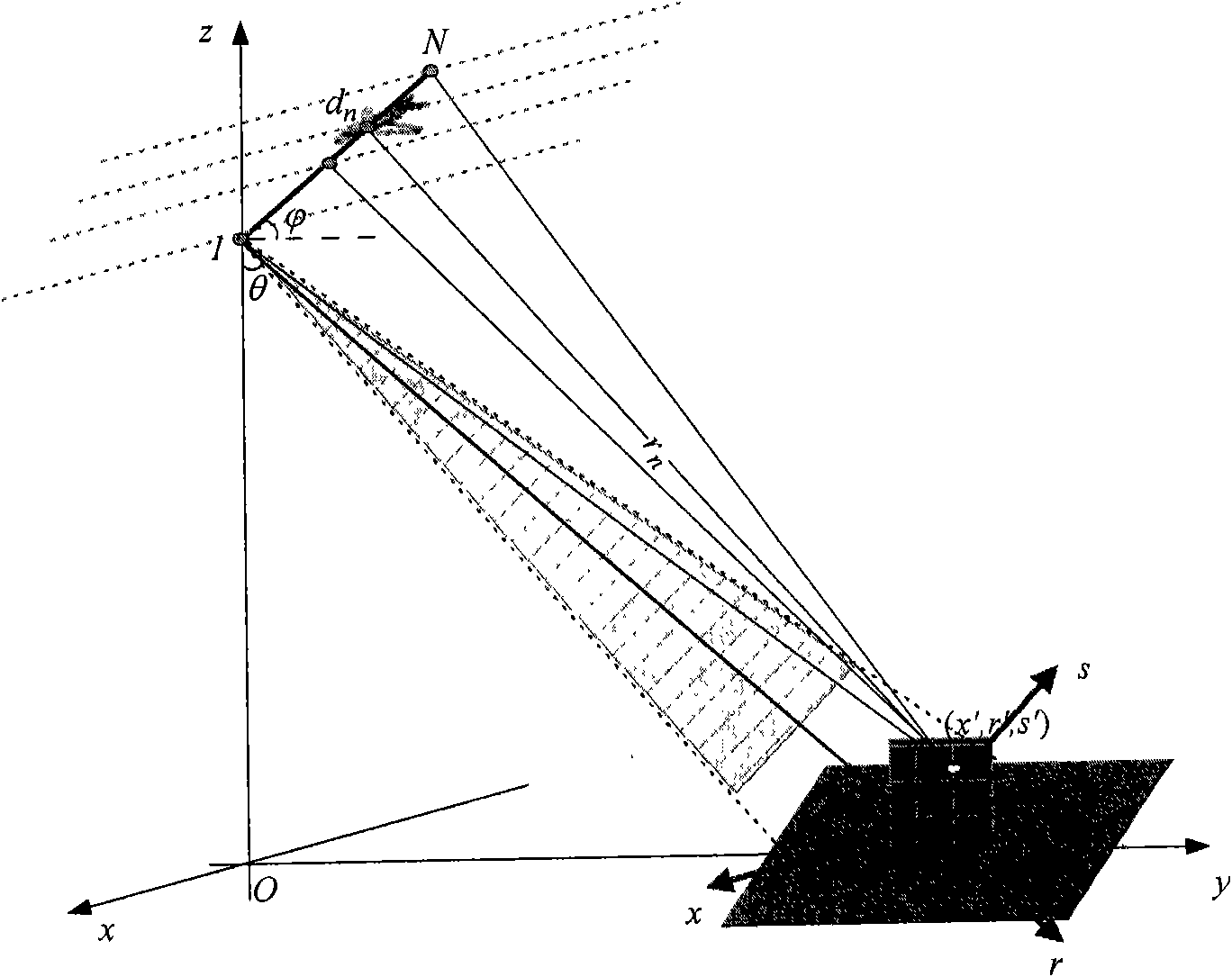
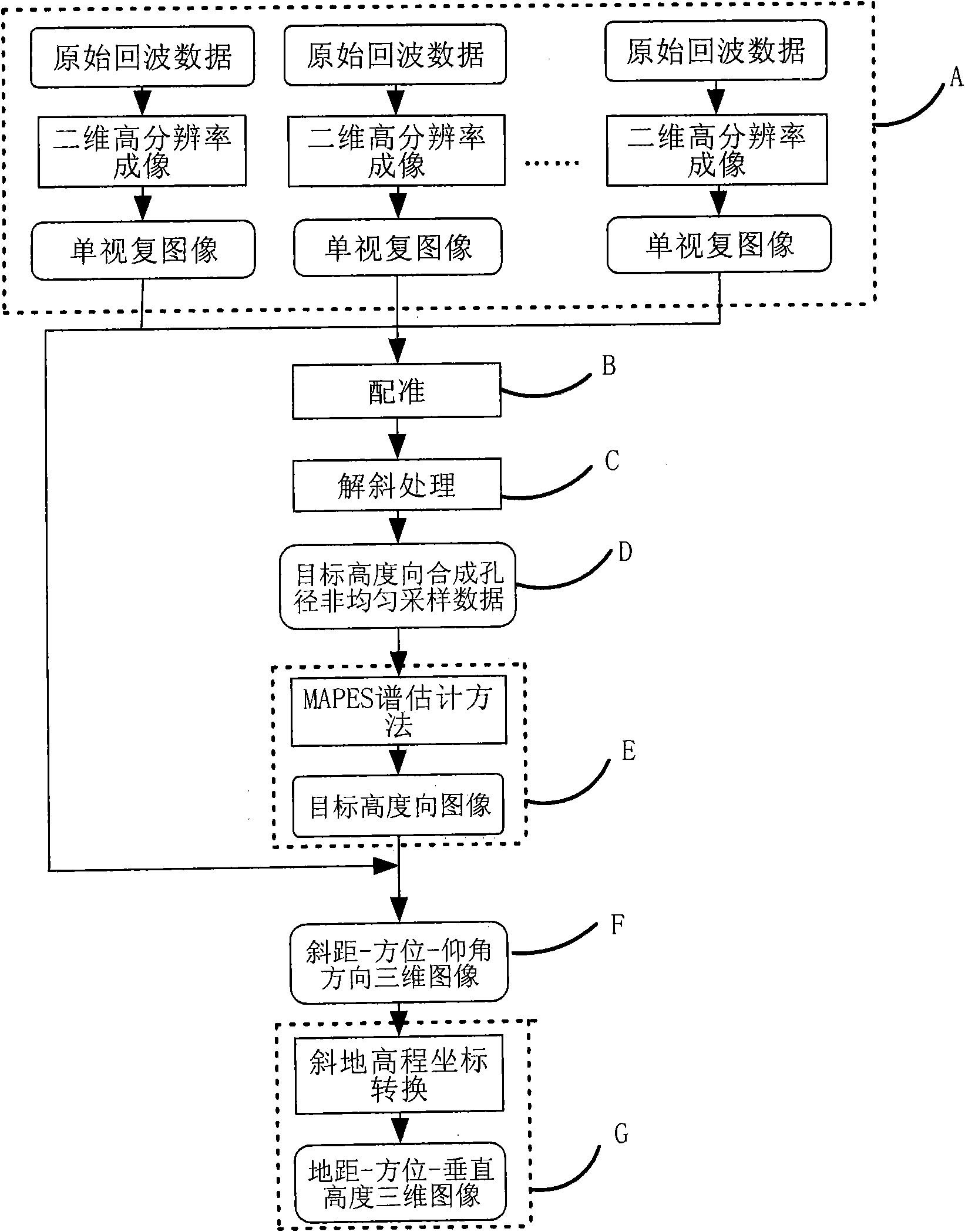
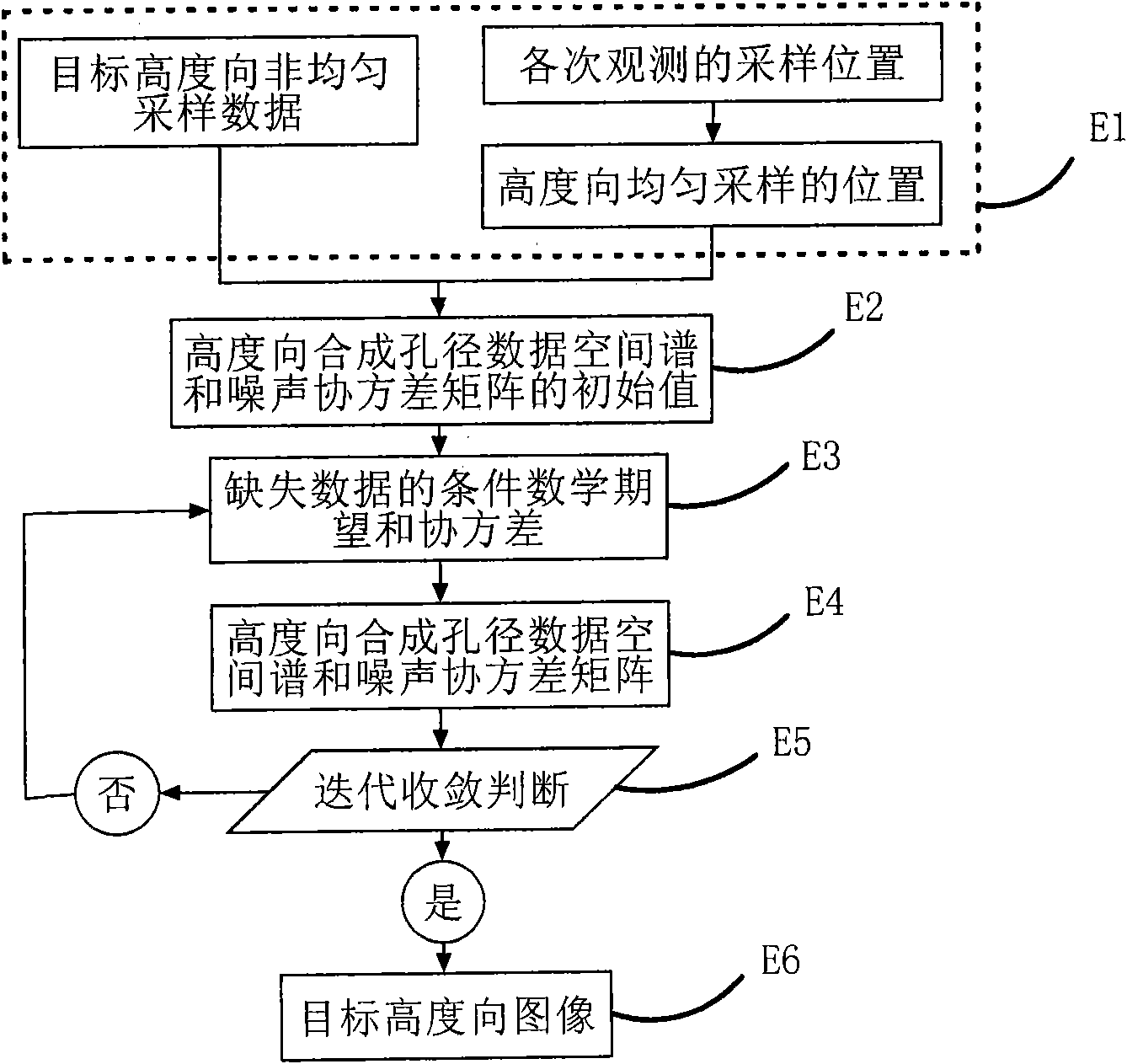
Non-uniform distributed multi-baseline synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging method
The invention discloses a non-uniform distributed multi-baseline synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging method, and relates to the three-dimensional imaging technology. The method comprises the following steps of: performing two-dimensional focusing on primary echo data obtained by flying observation at each time to obtain single-look complex images; registering sequences of the single-look complex images to acquire non-uniform sampling data of an observation target under different visual angles; removing inclination aiming at the non-uniform sampling data to perform phase modulation; then estimating a spatial spectrum of the primary uniform sampling data by using a missing data-based amplitude phase estimation method and maximizing mathematically expected iterative operation of observation data so as to implement imaging of a target height direction; and finishing three-dimensional imaging of the target by combining a two-dimensional target image obtained in two-dimensional imaging of each track. The method for performing the imaging of the height direction based on the amplitude phase estimation method reduces elevation blur caused by multi-baseline non-uniform distribution and acquires clear high-resolution target three-dimensional imaging results.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for encoded spatio-spectral information processing
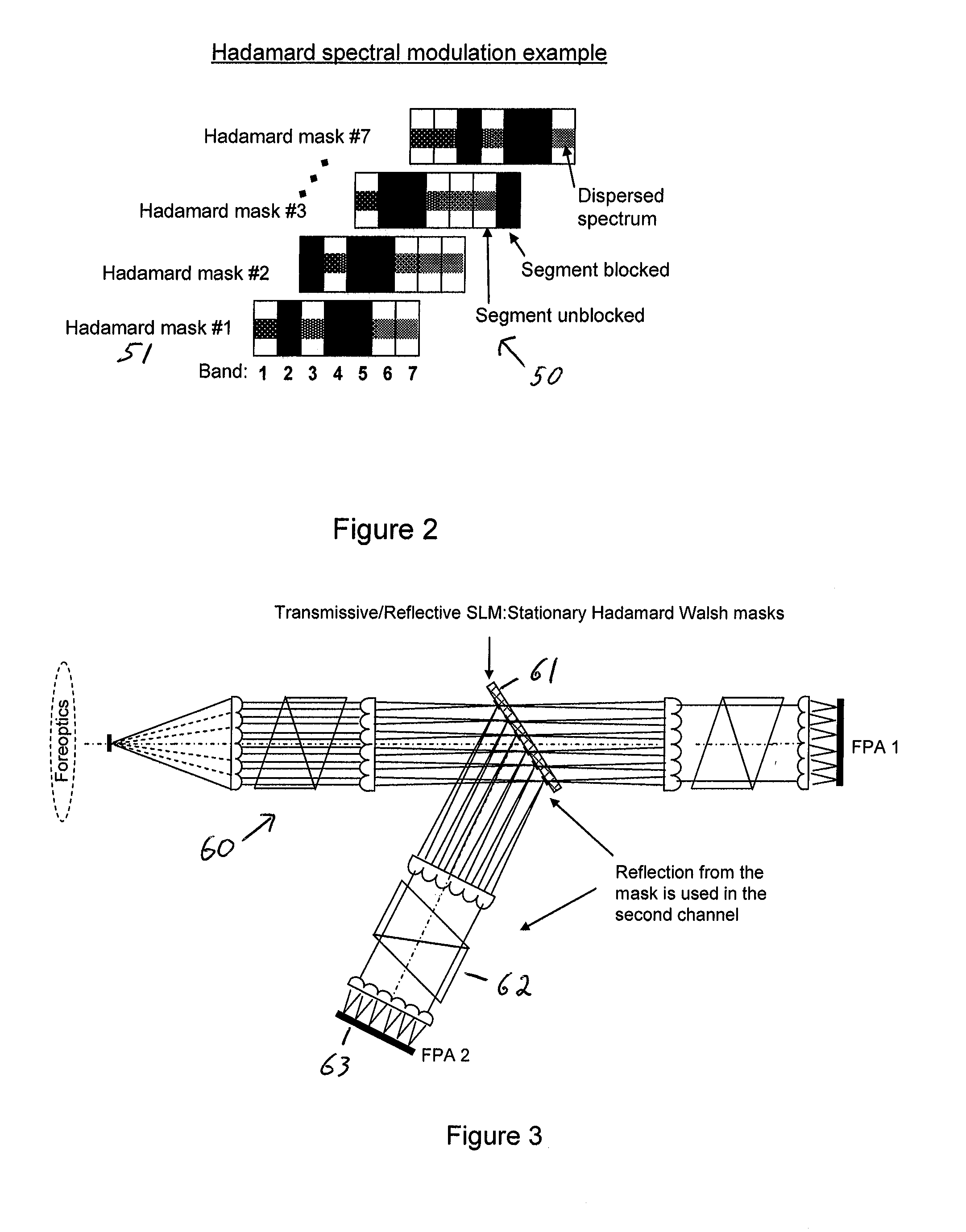
InactiveUS20050024640A1Less sensitive to ambient noiseEasy to operateRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsInformation processingFrequency spectrum
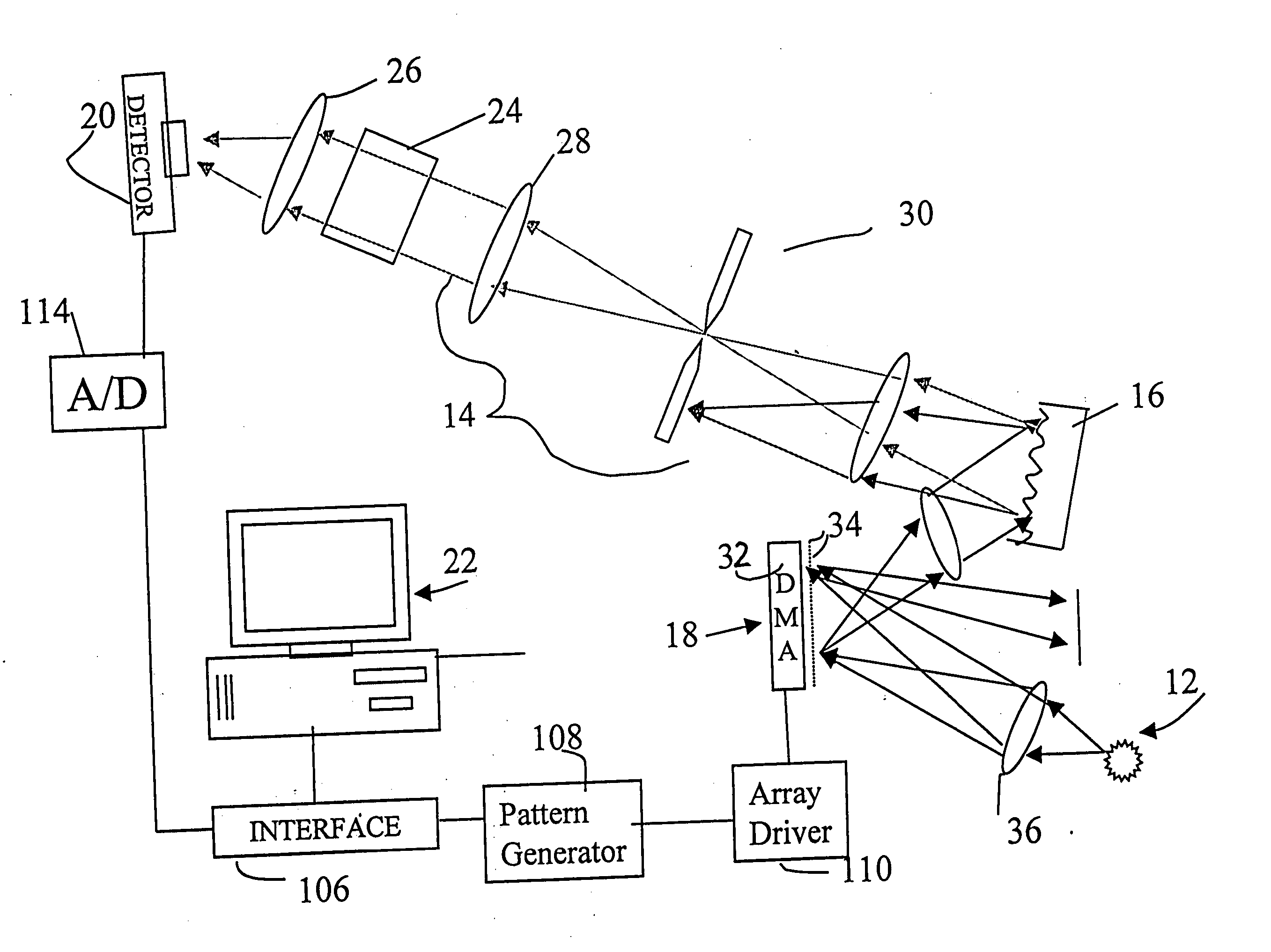
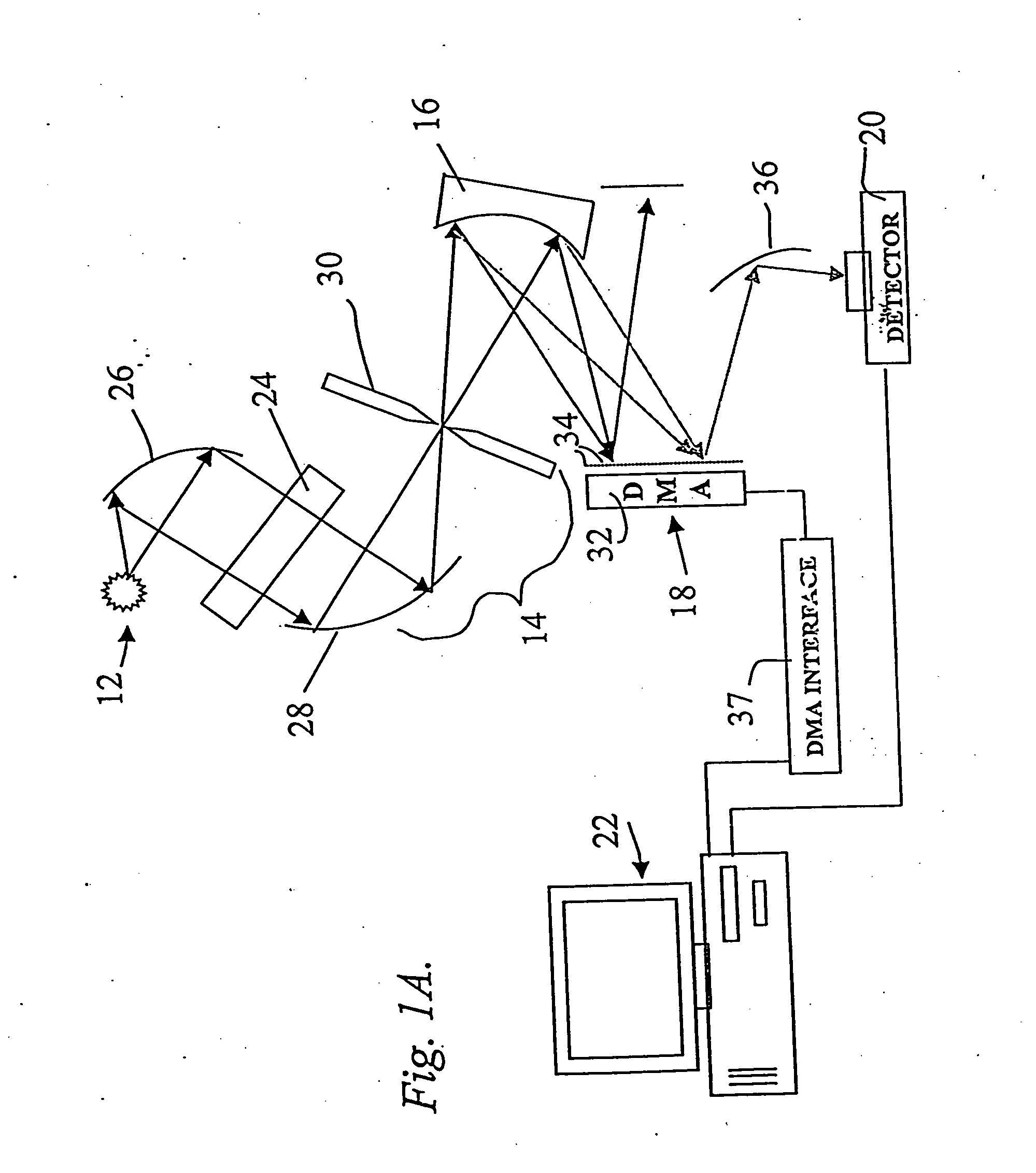
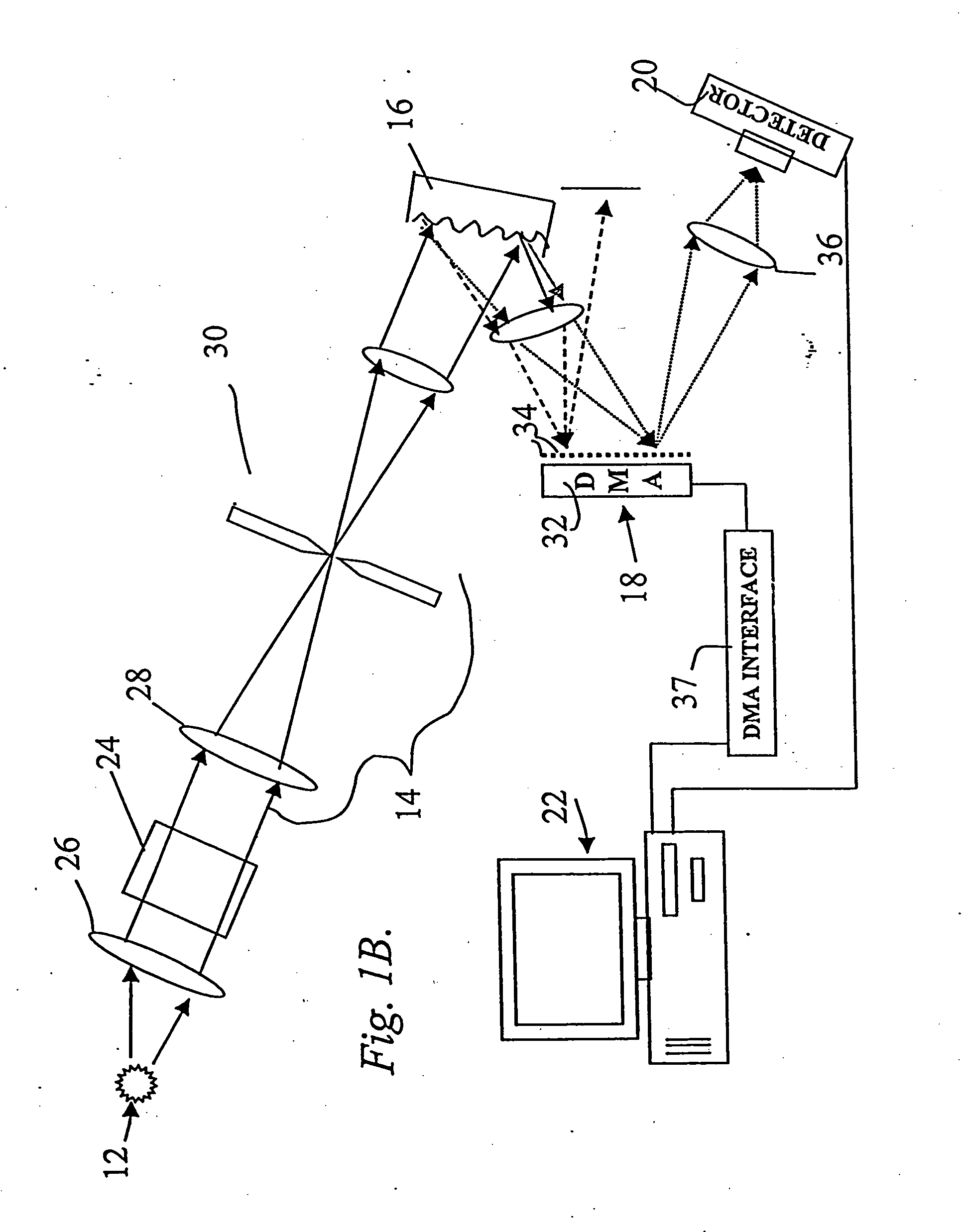
Encoded spatio-spectral information processing is performed using a system having a radiation source, wavelength dispersion device and two-dimensional switching array, such as digital micro-mirror array (DMA). In one aspect, spectral components from a sample are dispersed in space and modulated separately by the switching array, each element of which may operate according to a predetermined encoding pattern. The encoded spectral components can then be detected and analyzed. In a different aspect, the switching array can be used to provide a controllable radiation source for illuminating a sample with radiation patterns that have predetermined characteristics and separately encoded components. Various applications are disclosed.
Owner:FATELEY WILLIAM G +3
Hyperspectral image classification method based on convolutional neural network and spatial spectrum information fusion
InactiveCN107909015AEfficient extractionReduce complexityScene recognitionNeural learning methodsImage resolutionSpectral dimension
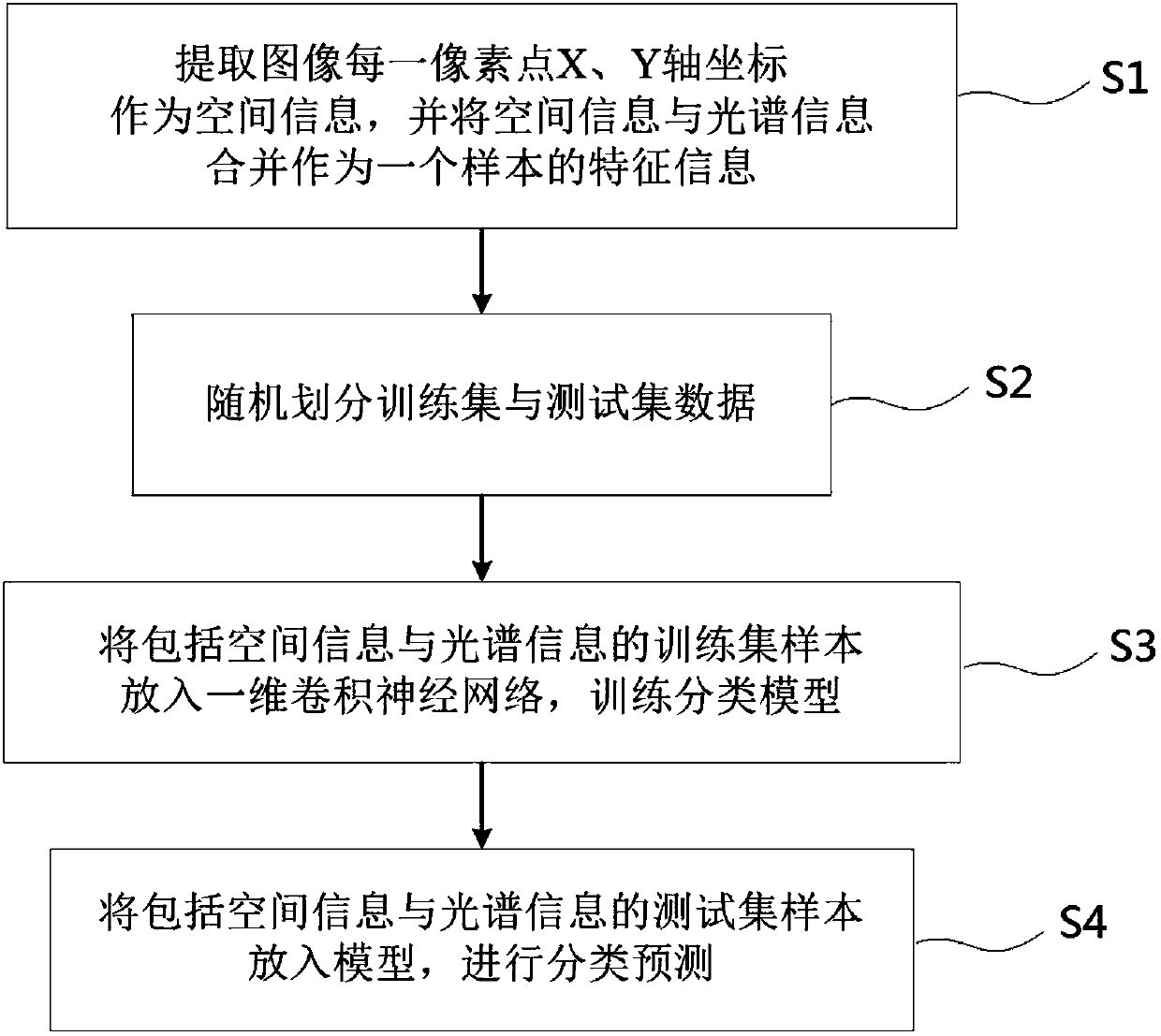
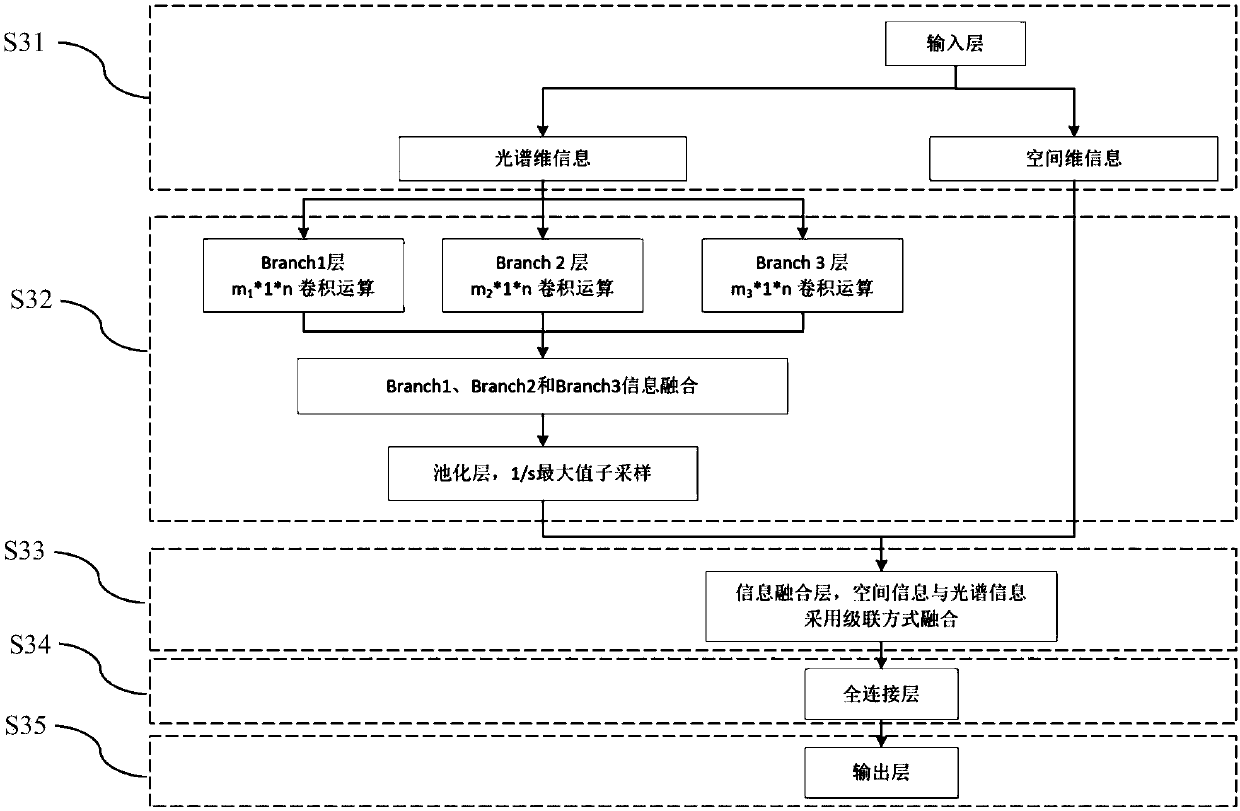
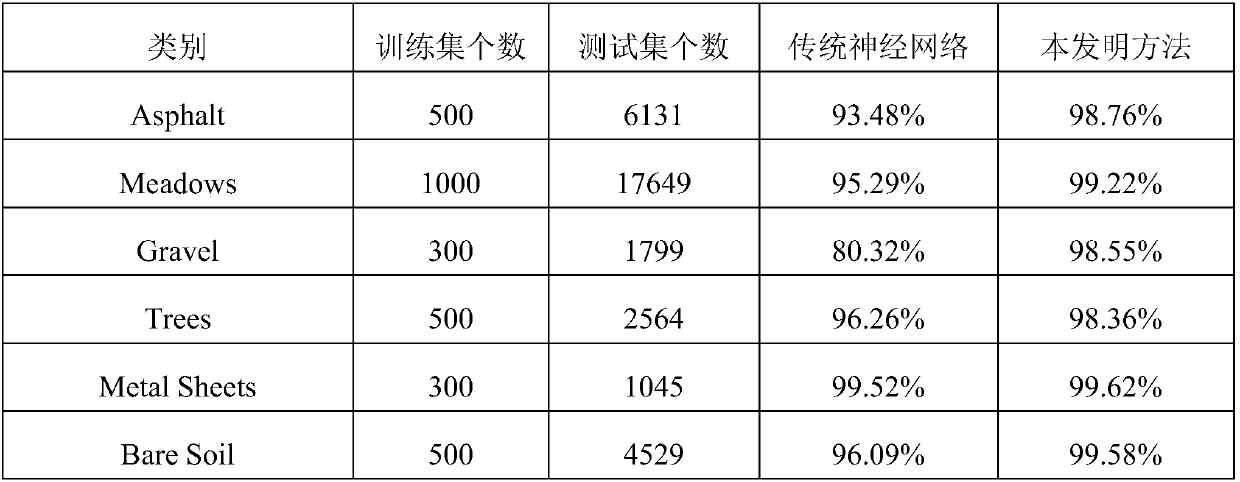
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification method based on a convolutional neural network and spatial spectrum information fusion. The method comprises the steps that S1 X and Y axiscoordinates of each pixel point of a hyperspectral image are extracted as spatial information, and the spatial information and spectral information are combined as the feature information of a sample; S2 training set and test set data are randomly divided; S3 training set samples including the spatial information and the spectral information are put into a one-dimensional convolutional neural network to train a classification model; and S4 the training set samples including the spatial information and the spectral information are put into the classification model for classification prediction. The convolutional neural network uses convolution kernels of different sizes to carry out convolution operation, which can effectively extract feature information with different resolutions in the spectral dimension of a hyperspectrum. In addition, the spectral dimension information and the spatial dimension information are input into the neural network to learn simultaneously. The feature of dual high resolutions of the hyperspectrum is fully used. The algorithm structure is simple, and the classification accuracy can be significantly improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF INTELLIGENT MFG
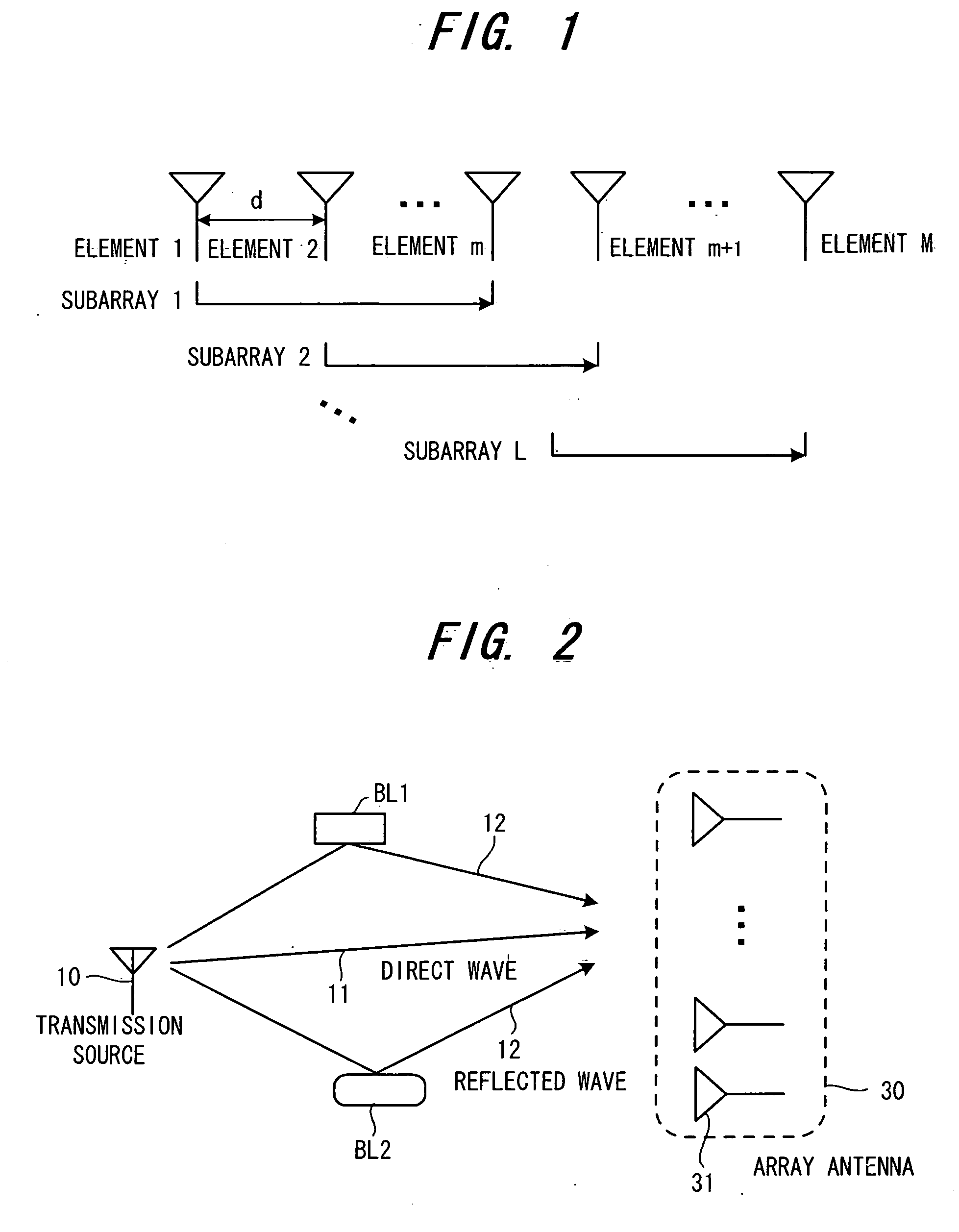
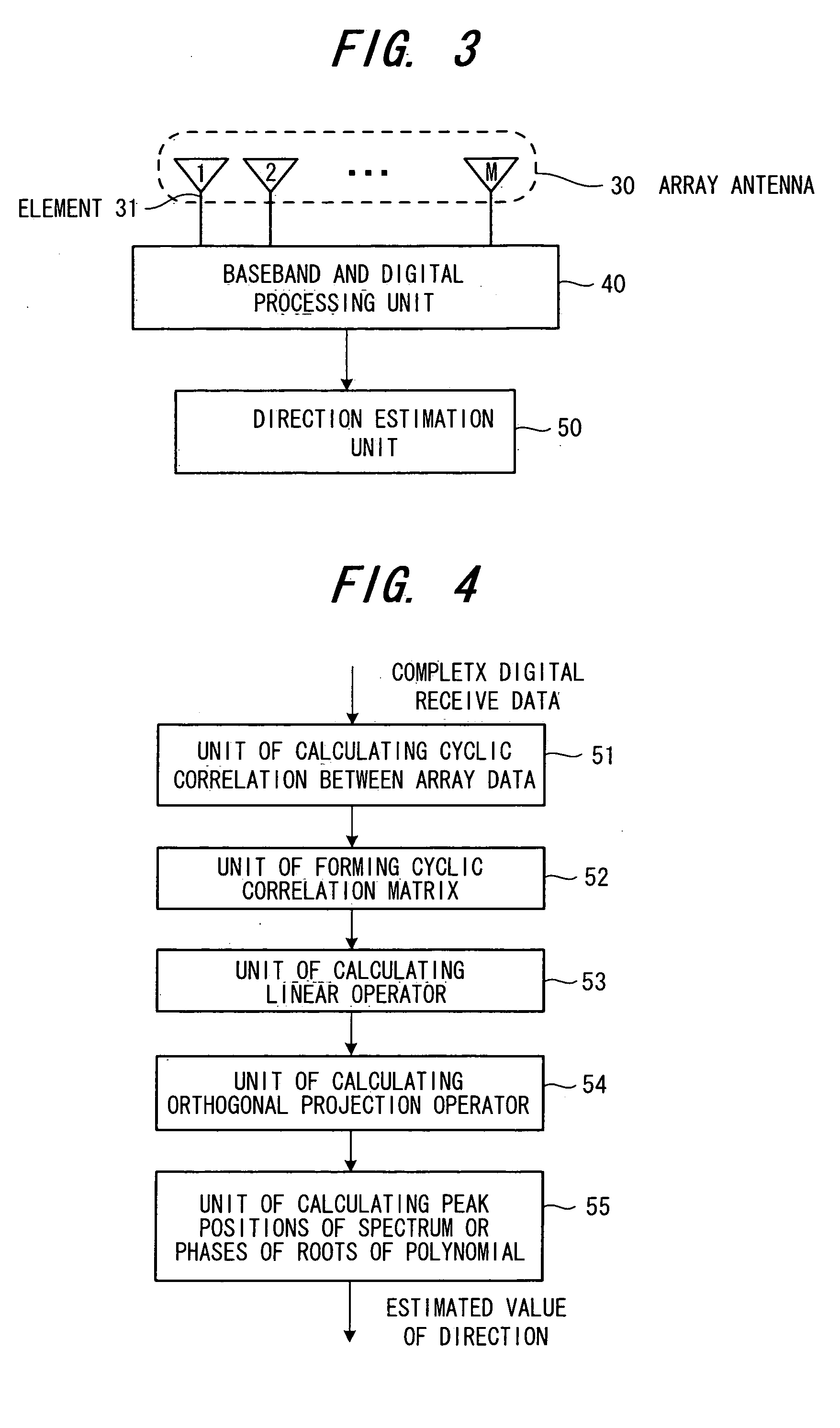
Method and device for tracking the directions-of-arrival of radio waves
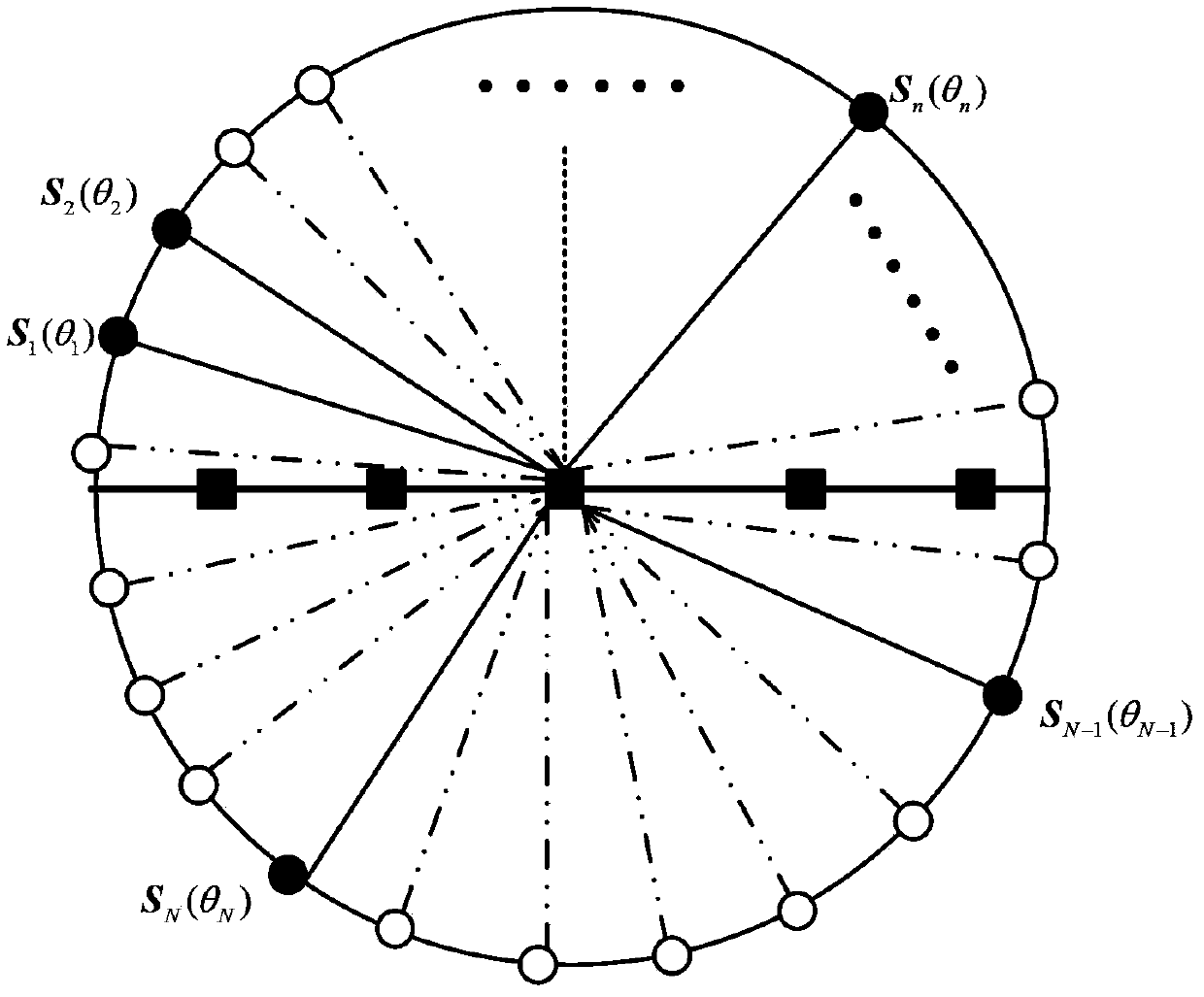
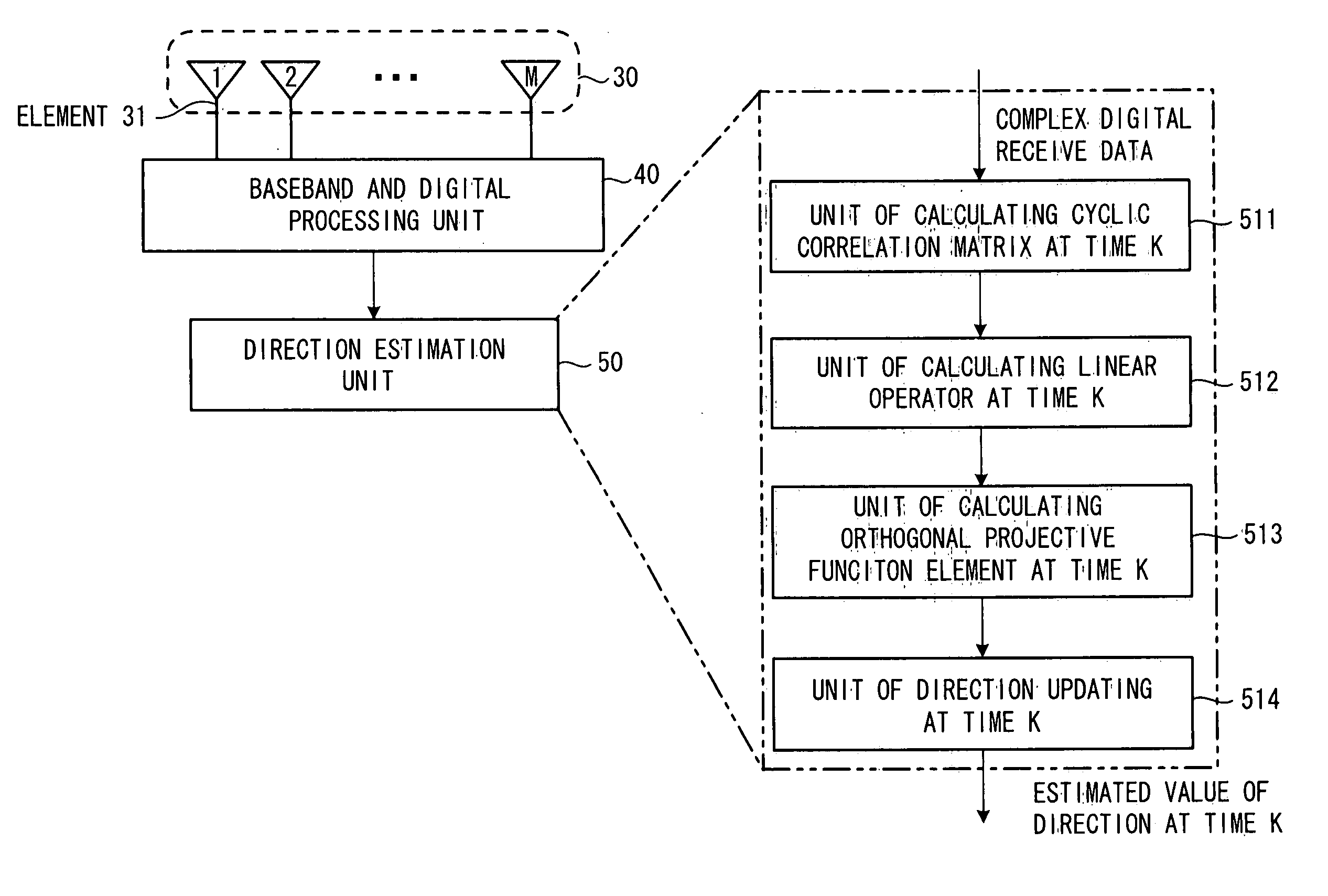
InactiveUS20060007043A1Reduce computing loadSpatial transmit diversityMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesEngineeringSpatial spectrum
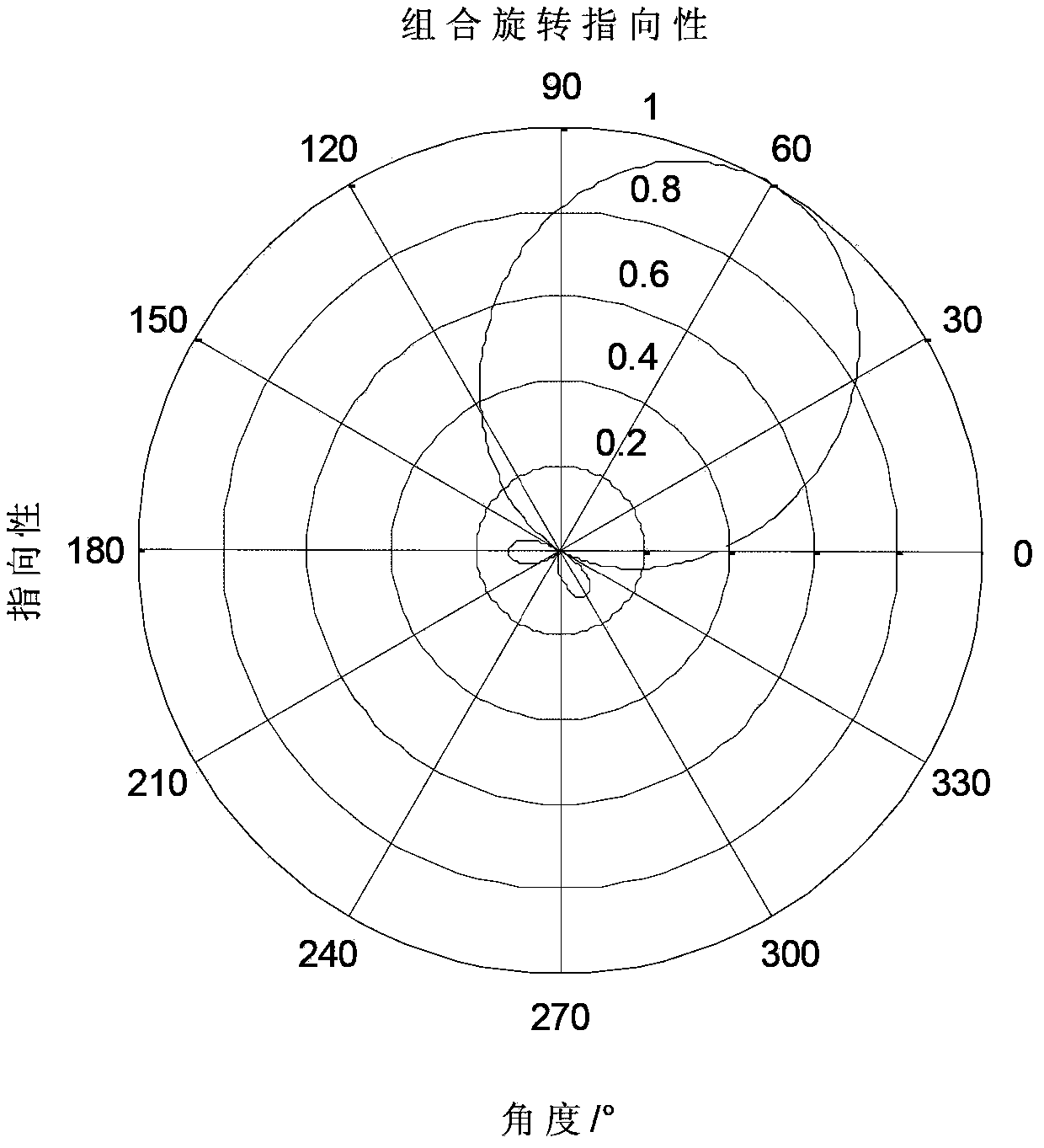
L overlapping forward subarrays with {overscore (q)} (≧q) antenna elements are formed with, where q is the number of desired signals, a cyclic correlation matrix is formed from the cyclic correlations between the received signals of L forward subarrays and a received signal of the first predetermined antenna element, the cyclic correlated matrix is divided into two upper and lower submatrices, an orthogonal projection operator in the noise subspace is calculated by performing a linear operation on these two upper and lower cyclic correlation matrices, then by calculating a spatial spectrum or a polynomial by using the estimated orthogonal projection operator, the directions are estimated from of the position of q highest peaks of the spatial spectrum or the phases of q roots of the polynomial closest to the unit circle in z-plane.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
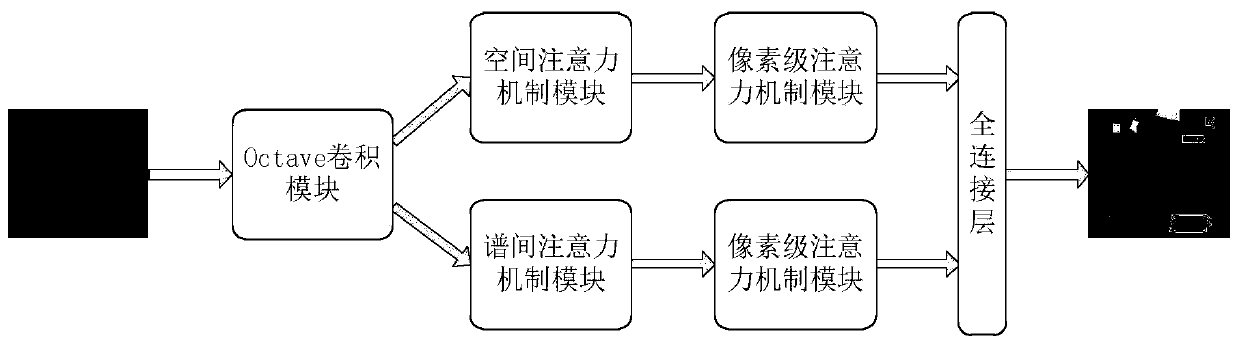
Spatial spectrum attention hyperspectral image classification method based on Octave convolution
ActiveCN110516596AResolve accuracyAddressing weak robustnessClimate change adaptationScene recognitionOctaveHyperspectral image classification
The invention discloses a spatial spectrum attention hyperspectral image classification method based on Octave convolution, and solves the problems of large class spacing, small different class spacing and low classification accuracy in the prior art. The scheme is as follows: inputting images to be classified and preprocessing data, dividing a training set and a test set, constructing an Octave convolutional neural network, determining a loss function of the Octave convolutional neural network, training and updating the Octave convolutional neural network, testing the data of the test set, and completing hyperspectral image classification. According to the method, Octave convolution operation is used to reinforce feature representation, and a spatial attention mechanism and a spectral attention mechanism are introduced, so that the network can more accurately find an area which is more beneficial to classification and contains more comprehensive and detailed information. The method ishigh in classification precision and strong in robustness, and can be applied to analysis and management of hyperspectral image data.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
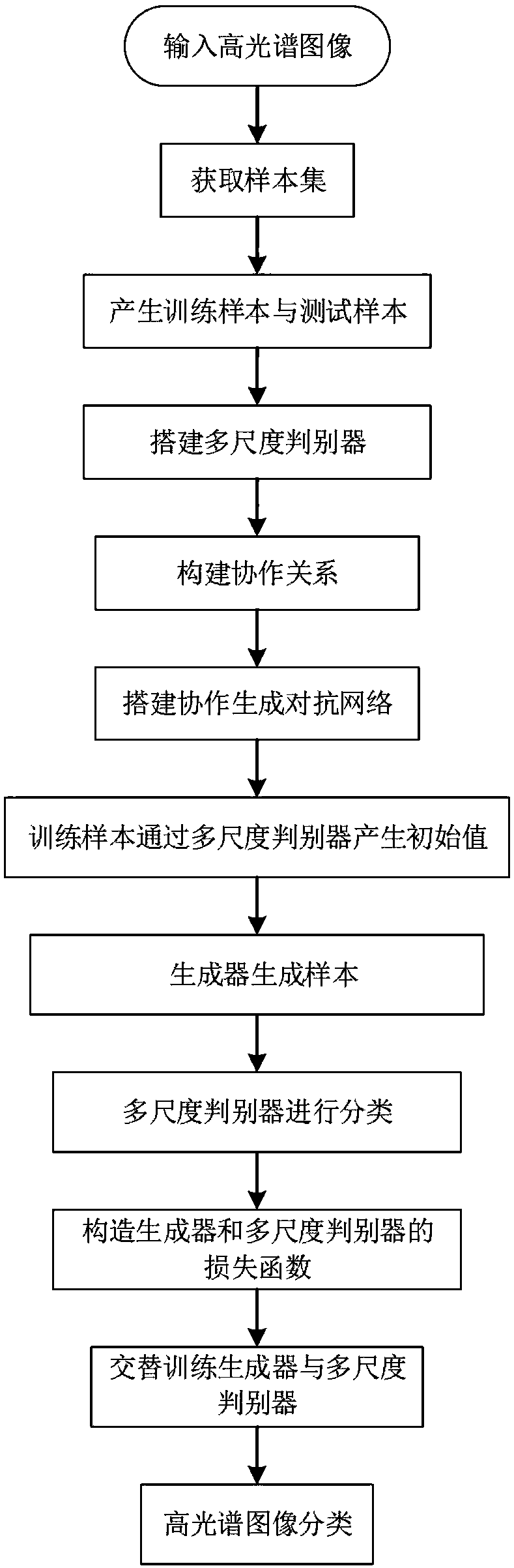
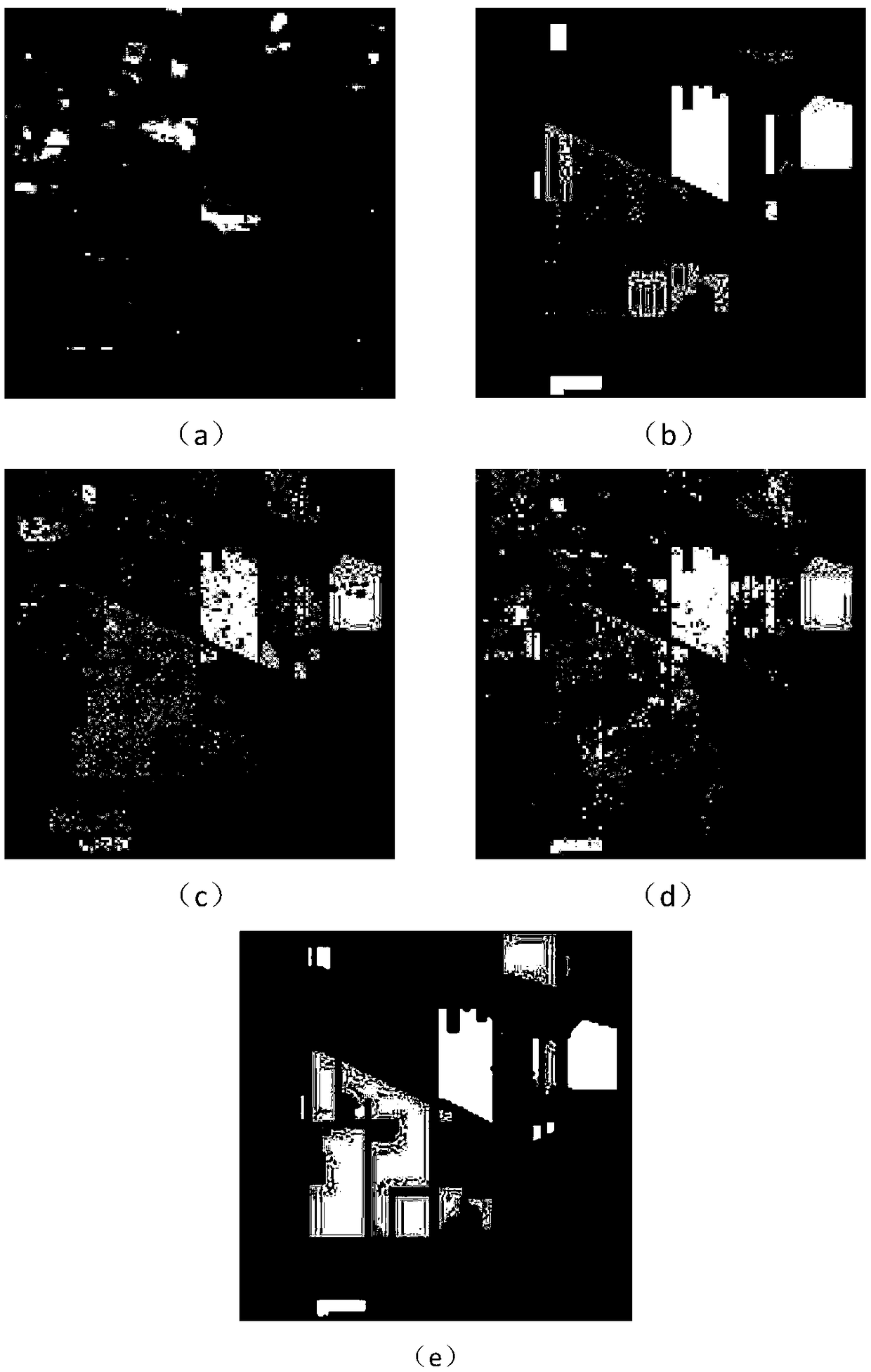
A hyperspectral image classification method based on a cooperative generation antagonistic network and a space spectrum combination
ActiveCN109145992AImprove accuracyAlleviate the fitting phenomenonCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesDiscriminatorPattern recognition
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification method based on a cooperative generation antagonistic network and a space spectrum combination. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a hyperspectral image; obtaining a sample set; generating training samples and test samples; building a multi-scale discriminator; constructing cooperative relationship; building a cooperative generation countermeasure network; the initial value of the training sample being generated by the multi-scale discriminator; the generator generating samples; a multi-scale discriminator perfromingclassification; constructing the loss function of generator and multiscale discriminator; alternatively training the generator and the multi-scale discriminator; hyperspectral images being classified. The invention utilizes the established cooperation to generate the antagonistic network, extracts the spatial spectrum combined characteristics of pixels, generates more realistic samples, increasesthe number of samples, alleviates the problems of over-fitting the network and slow convergence speed of the network, and improves the accuracy of the hyperspectral image classification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
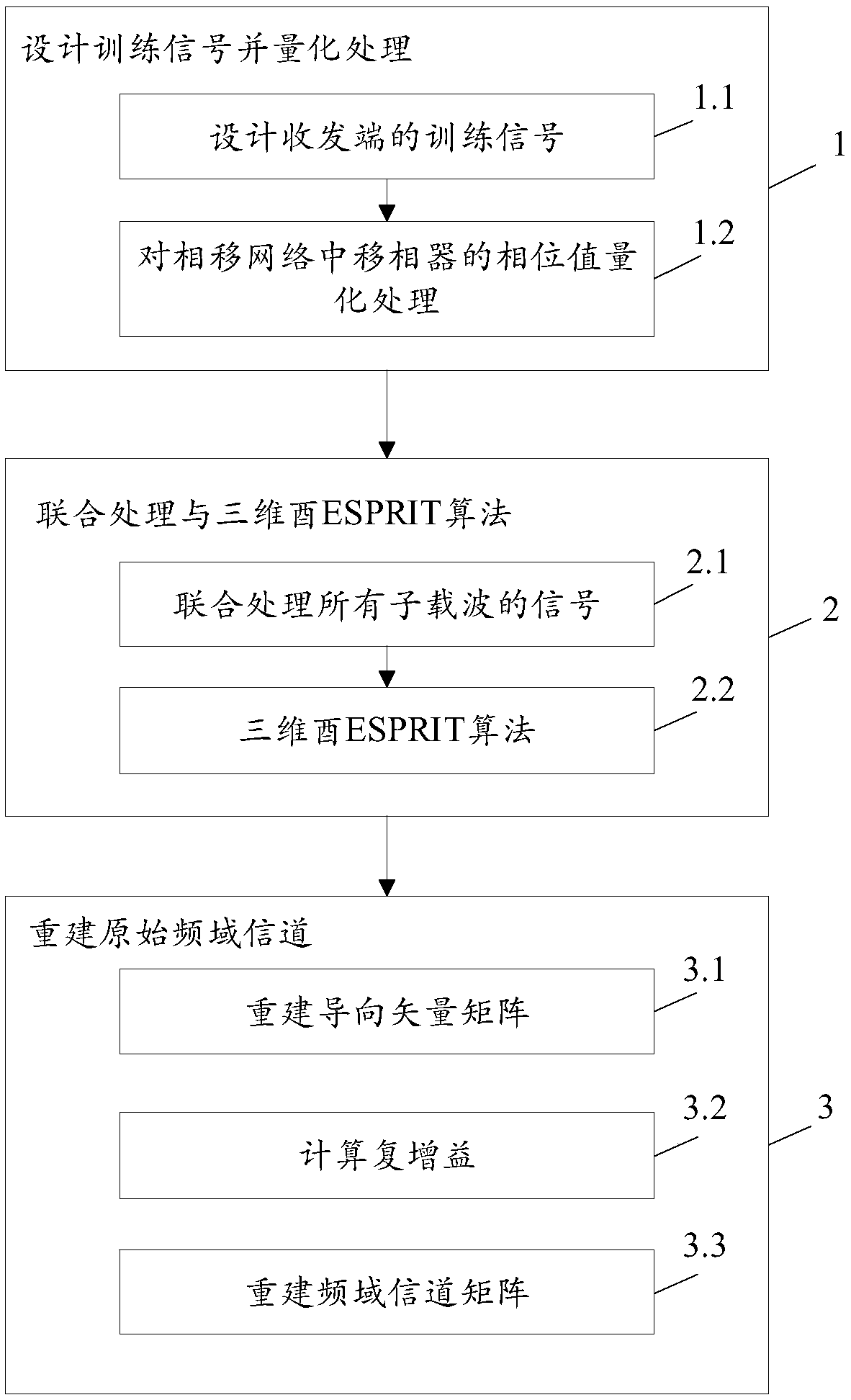
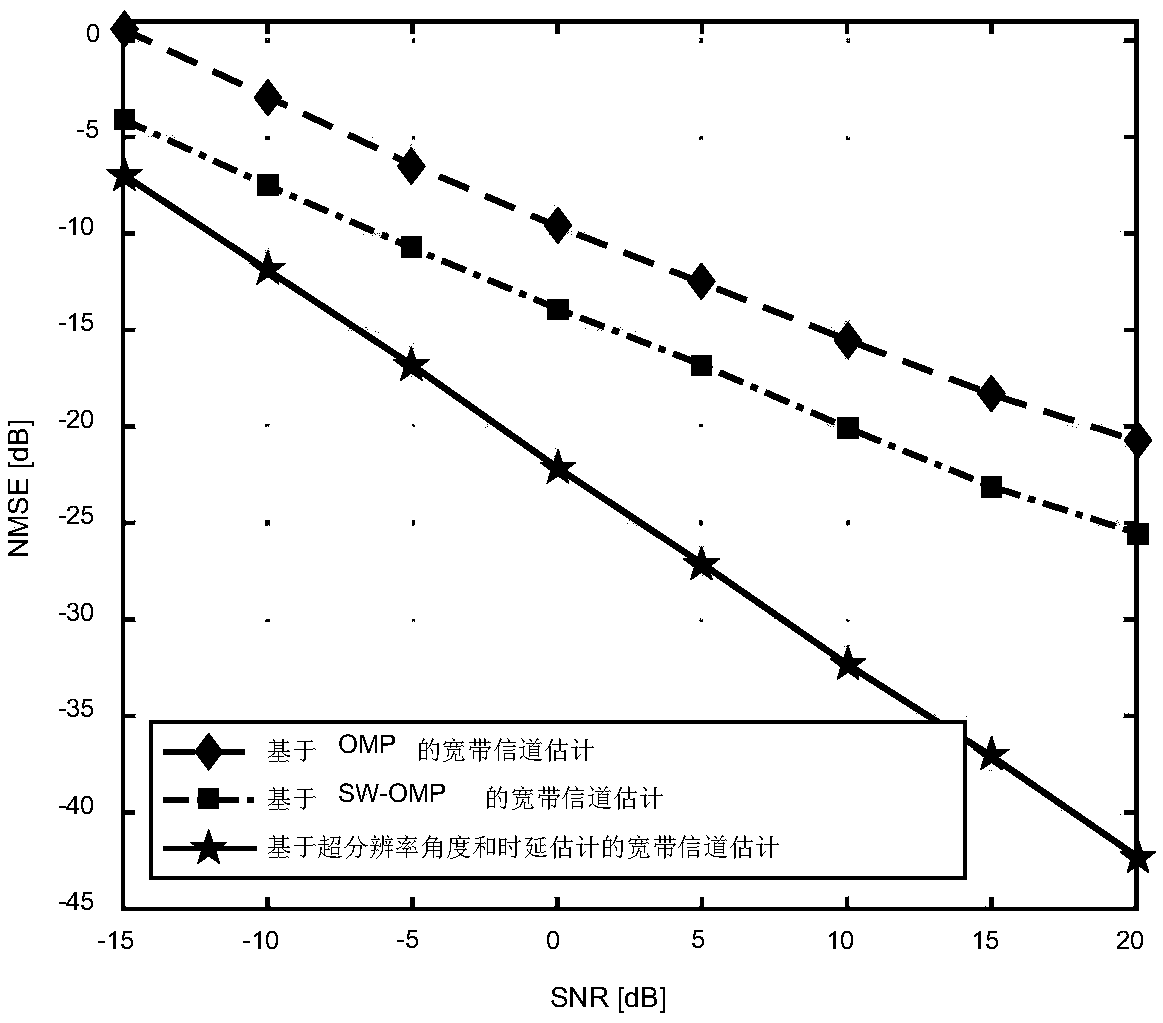
Super-resolution angle and time delay estimation based broadband channel estimation method
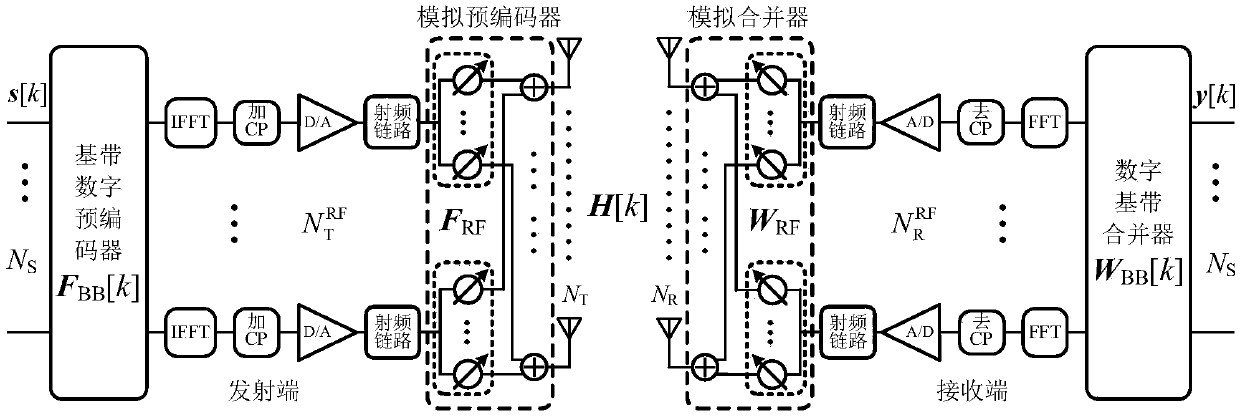
ActiveCN108933745AReduce overheadReduce the difficulty of implementationRadio transmissionChannel estimationCompressed sensingEncoder
The invention discloses a super-resolution angle and time delay estimation based broadband channel estimation method. According to the invention, aiming at a millimeter wave large scale MIMO system ina hybrid analog-digital coding architecture, in order to solve a problem of quantization error influence due to limited quantization angle grid resolution in a traditional compression sensing based broadband channel estimation method, sparsity of a millimeter wave channel it utilized, through designing training signals of a transceiving end, a classical spatial spectrum estimation method is introduced, so that pilot frequency expenditure required by channel estimation can be reduced substantially and an arrival angle and a leaving angle of the millimeter wave channel and a super resolution estimation value of corresponding multi-path time delay can be acquired with high accuracy. Therefore, channel estimation accuracy can be improved distinctively. Besides, according to the invention, phases of a phase shifter in a phase shift network corresponding to an analog pre-encoder and an analog combiner to limited quantization bits, so that practical system implementation is facilitated.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Differential confocal Raman spectra test method
InactiveCN101290293AImproved microspectral detection capabilitiesImprove detection performanceRaman scatteringLight beamAbsolute measurement
The invention belongs to the micro-spectrum imaging technical field and relates to a differential confocal raman spectral test method. The method integrates the technical characteristics of the differential confocal detection method and the raman spectral detection method, forms a test method capable of realizing sample microarea spectral detection, precisely catches focus positions of excitation light beams through the differential confocal technology, detects raman spectra of corresponding positions, simultaneously adopts a designed pupil filter, sharpens Airy disc major lobes of a differential confocal raman spectral system, improves the microarea raman spectral detectability and precisely acquires microarea space spectrum information which comprises spectral information and position information of microarea samples. The method obviously improves the microarea spectral detectability of a confocal raman spectromicroscope, has absolute tracking zero points and bipolar tracking characteristics, realizes absolute measurement of physical dimension, can be widely applied in the technical fields such as biomedicine, life sciences, biophysics, biochemistry, industrial precision detection and so on to perform high-precision detection of geometric positions and spectral characteristics of microareas, and has very important application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
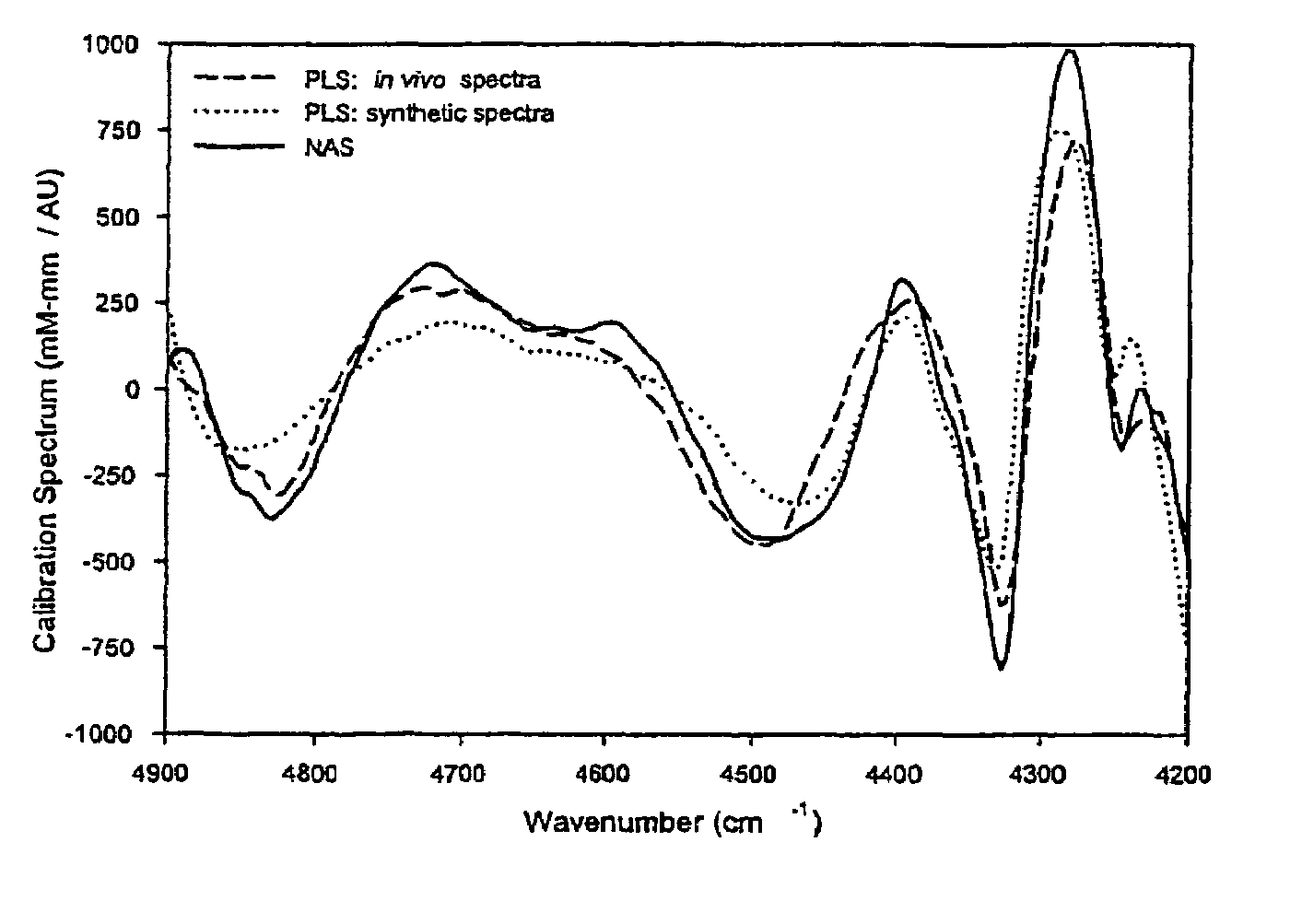
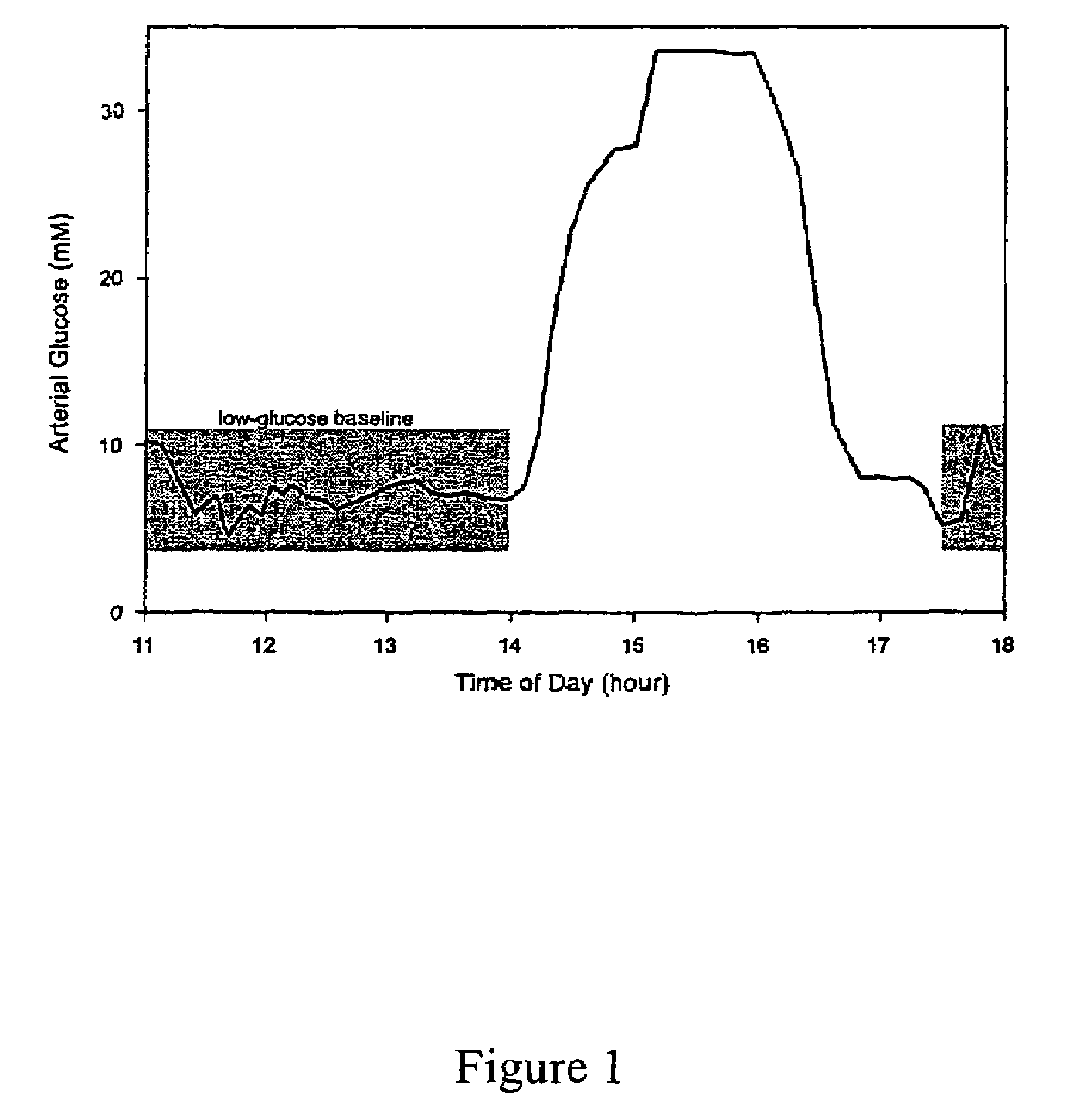
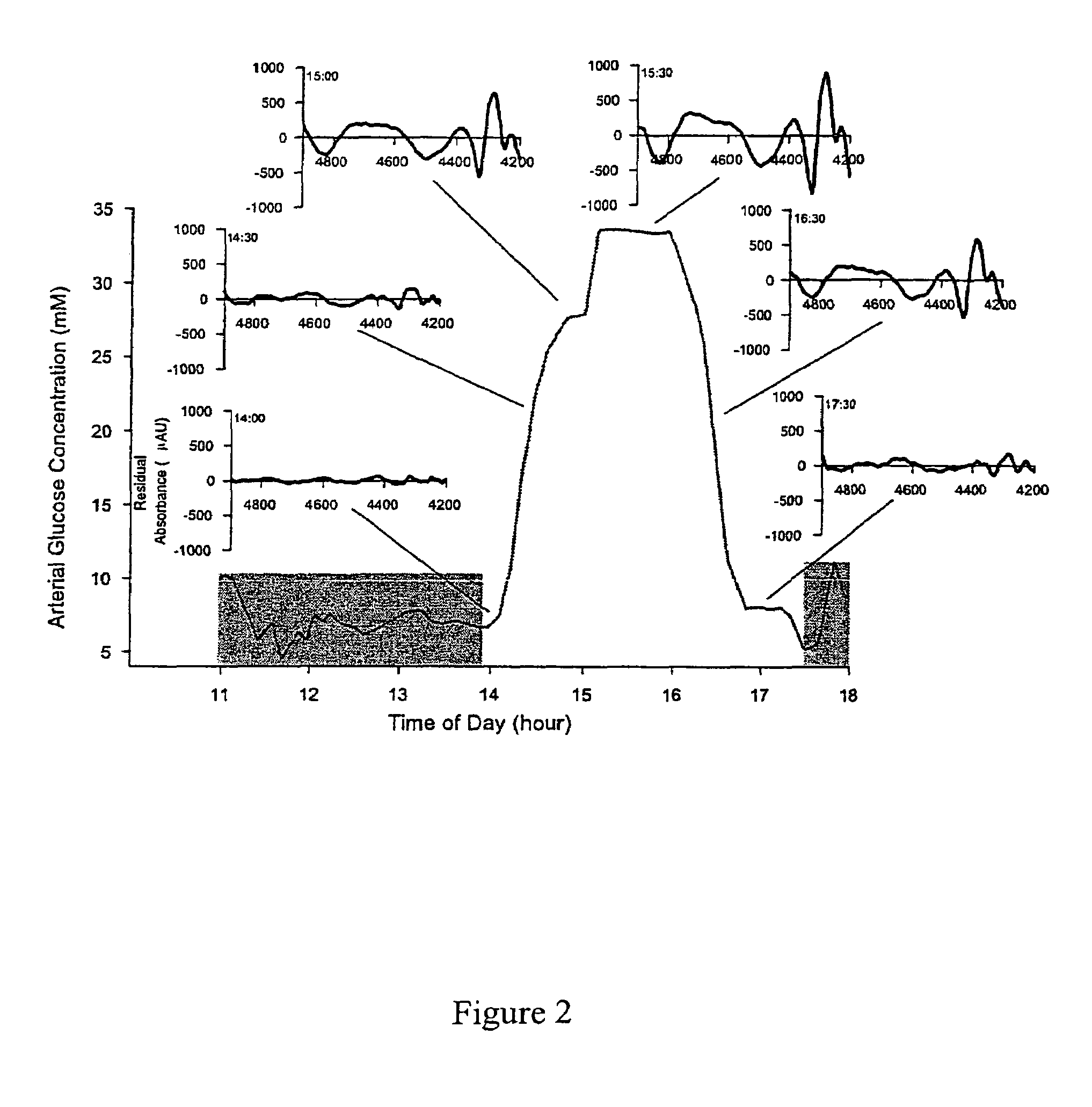
Method for generating a net analyte signal calibration model and uses thereof
Owner:IOWA RES FOUND UNIV OF
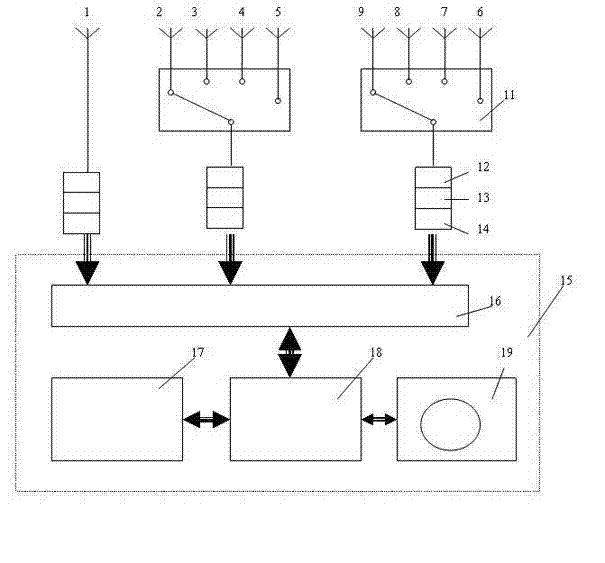
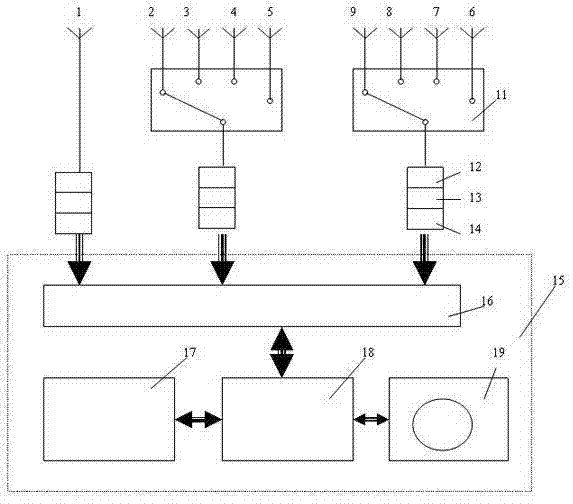
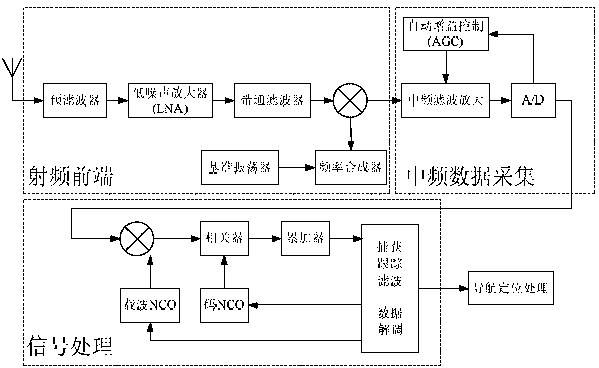
Direction finding method for three-channel spatial spectrum estimation direction finding system
InactiveCN102445679ALow costReduce the receive channelRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSpatial spectrumFIND Technology
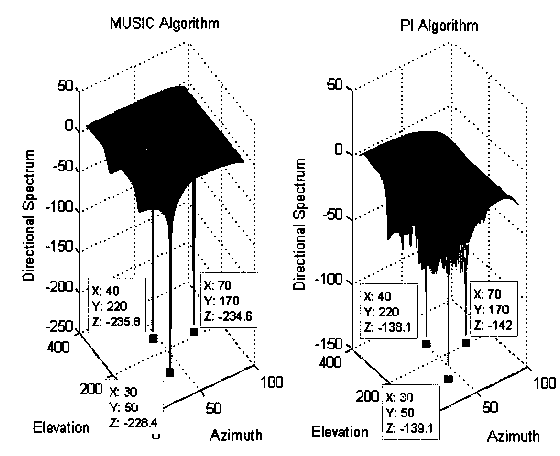
The invention discloses a direction finding method for a three-channel spatial spectrum estimation direction finding system. The system comprises a direction finding antenna array, three common-frequency multi-channel receivers and a direction finding algorithm processor, wherein the direction finding antenna array is a 9-element uniform circular array and is provided with an antenna select switch for selecting different antenna elements in the antenna array; three antennas are selected by the antenna select switch each time, wherein the No. 1 antenna is required to be selected each time; 1, 2 and 9, 1, 3 and 8, 1, 4 and 7, and 1, 5 and 6 are selected, wherein each number represents the number of the selected antenna, and the four groups of antennas are alternately selected; the direction finding receivers are of three-channel; and three antennas selected by the antenna switch each time are connected with the three common-frequency multi-channel receivers respectively. By researching the spatial spectrum estimation direction finding technology and improving an MUSIC direction finding algorithm, receiving channels are reduced under the condition of not reducing the antenna elements; meanwhile, the direction finding performance is guaranteed to be unchanged; and the aims of lowering the cost of the direction finding equipment and improving the reliability of the equipment are fulfilled.
Owner:成都中安频谱科技有限公司
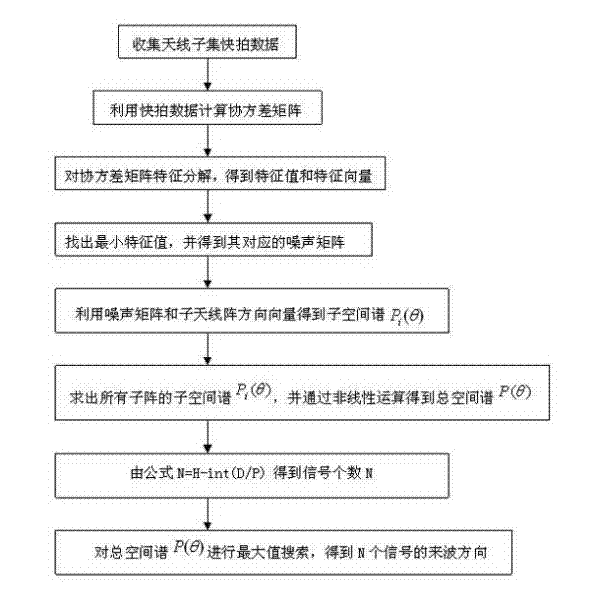
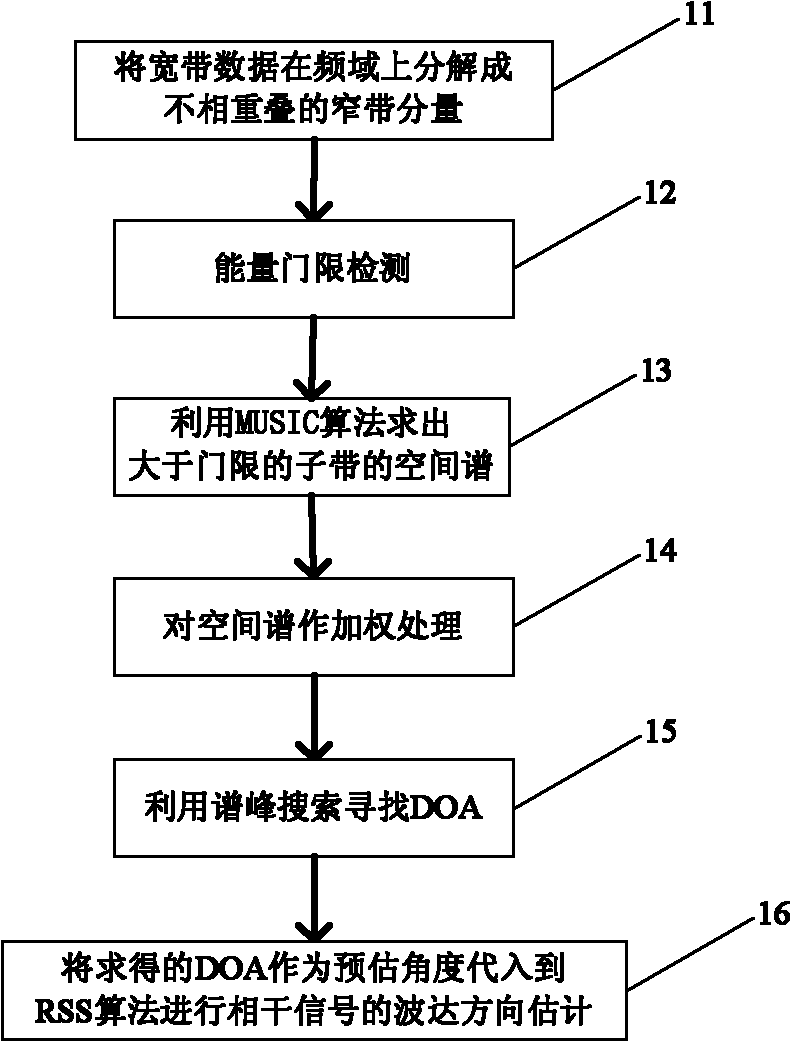
Broadband signal direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method based on threshold detection
InactiveCN102013911AThe estimate is accurateReduce computationSpatial transmit diversityEstimation methodsSignal subspace
The invention provides a broadband signal direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method based on threshold detection. The method comprises the following steps: by means of energy threshold detection, abandoning subbands the energy of which is smaller than the threshold, and carrying out narrow-band spatial spectrum treatment on subbands the energy of which is larger than the threshold; and then solving DOA angles by adopting a spectrum weighing method. By means of the method, accurate estimation results can be obtained for incoherent signals; and in terms of coherent signals, the estimation results obtained by the method is taken as estimated angles for a Coherent Signal-Subspace Method (CSM), and then accurate DOA information is solved by utilizing a focus transformation method. Compared with the traditional method, the method has the advantages that the theory is simple, the estimation is accurate, the computation amount is less, and the hardware cost can be greatly lowered in practical application.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for using image depth information in identifying illumination fields
ActiveUS20080089576A1Correct and accurateImage enhancementImage analysisSpatial spectrumComputer vision
Owner:INNOVATION ASSET COLLECTIVE
Anti-interference method of GNSS (global navigation satellite system) receiver equipment
InactiveCN103630910AEnhanced inhibitory effectObvious advantagesSatellite radio beaconingMultiple signal classificationSpatial spectrum
The invention provides an anti-interference method of GNSS (global navigation satellite system) receiver equipment. The anti-interference method adopts spatial spectrum estimation MUSIC (multiple signal classification) algorithm, thus having good anti-interference effect. Different from traditional power inversion algorithm, the spatial spectrum estimation MUSIC algorithm distributes banded nulls near an interference source. The anti-interference method can accurately find the interference direction and can effectively restrain the interference; even if the signal to interference ratio is reduced to be 20dB, the anti-interference method can also restrain the interference.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com