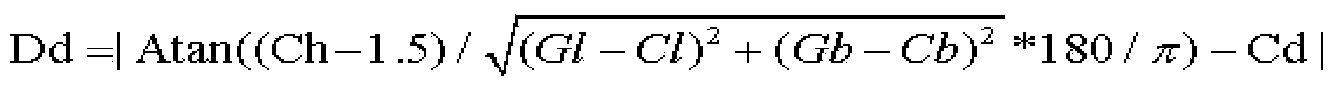Patents
Literature
414 results about "Interference ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
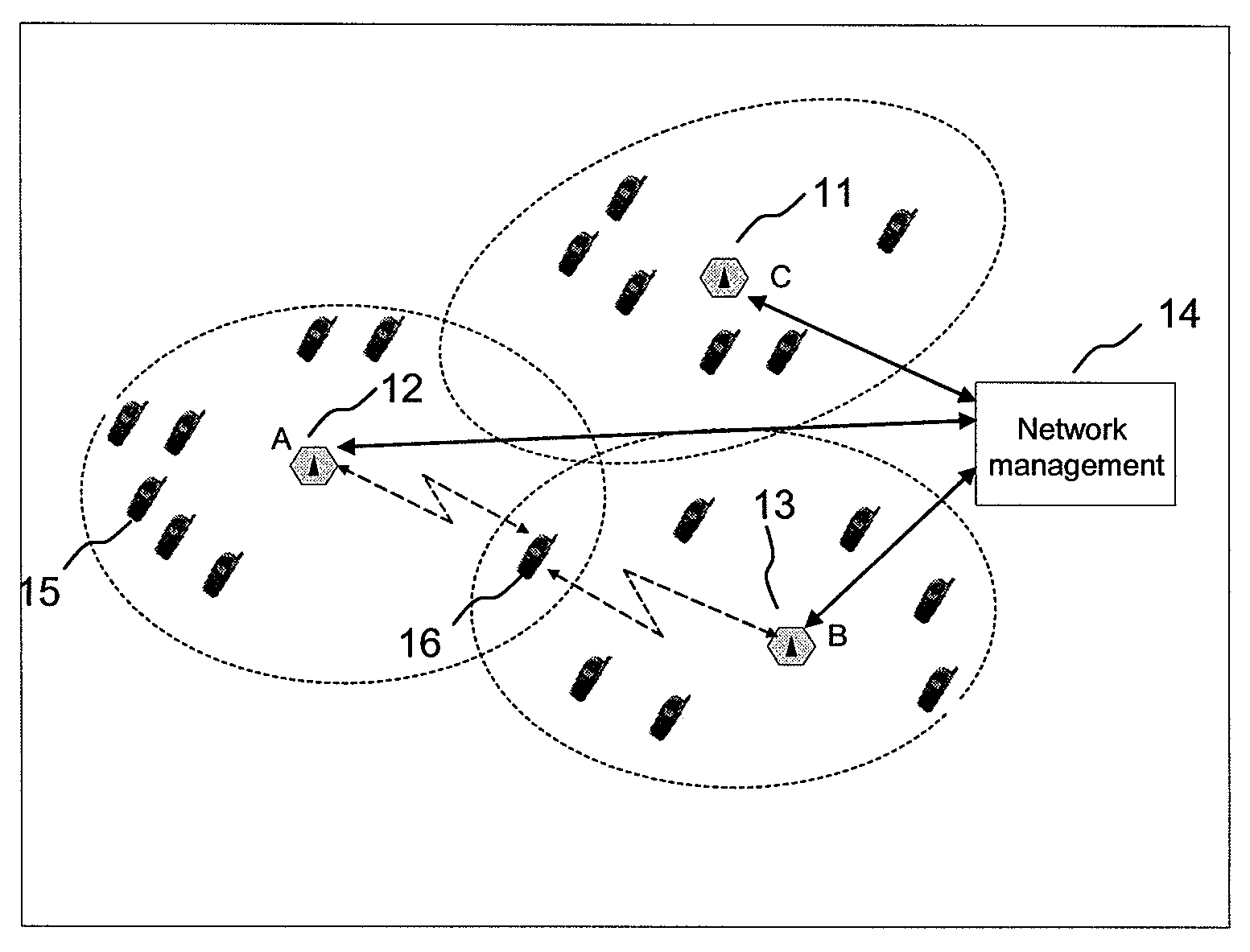
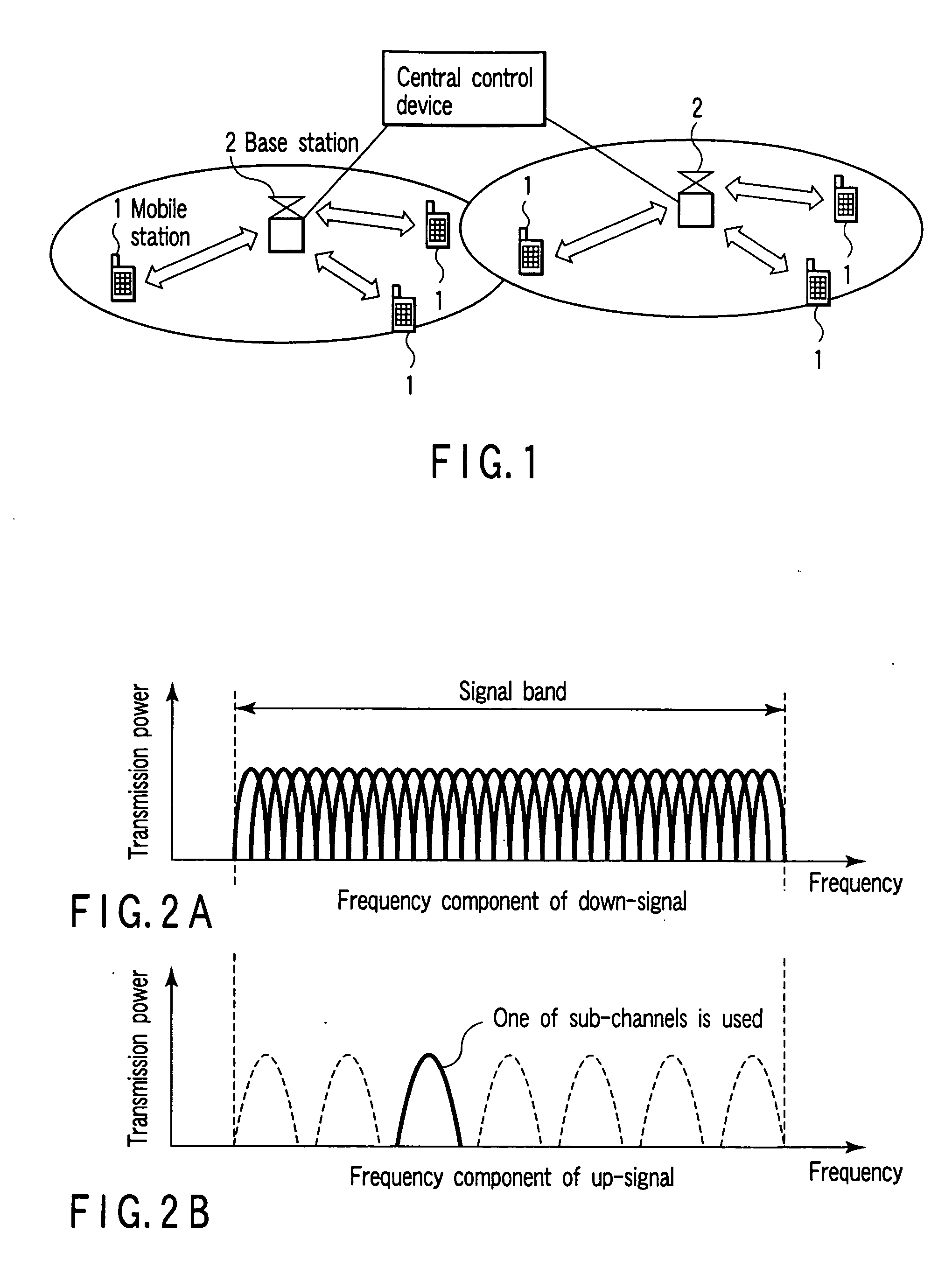
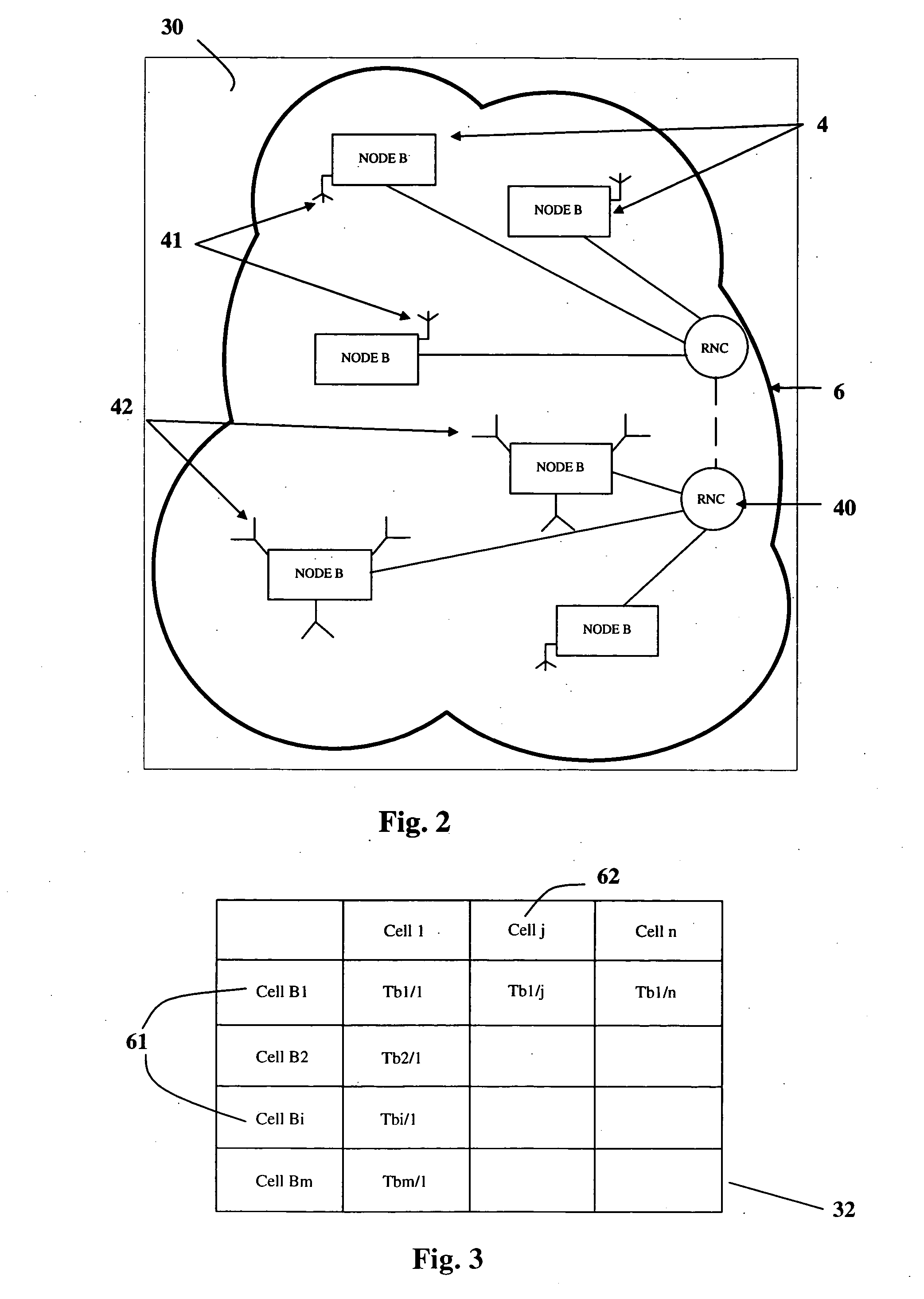
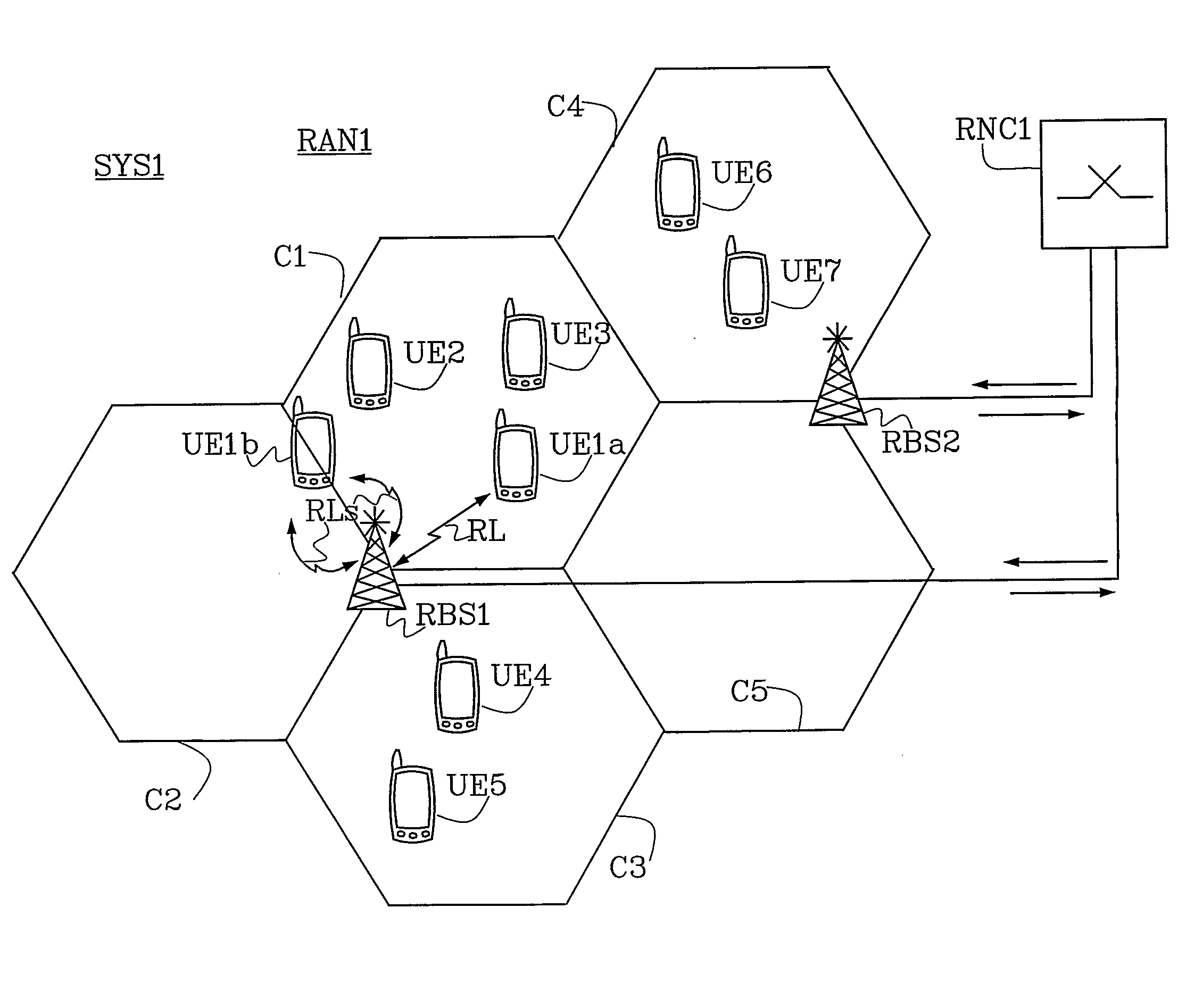
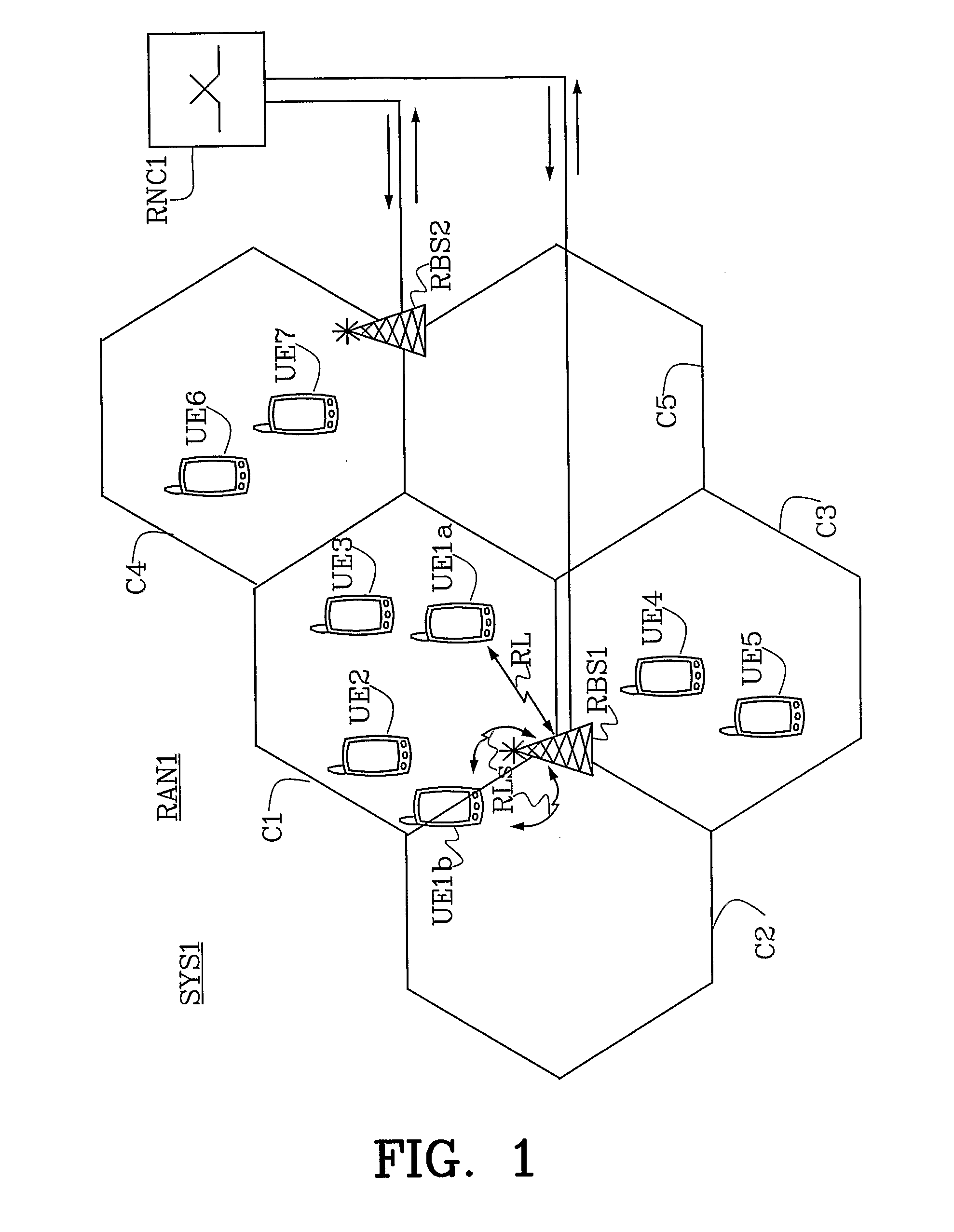
Capacity Optimisation in a Cellular Wireless Network
ActiveUS20090046665A1Network topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSignal qualityInterference ratio
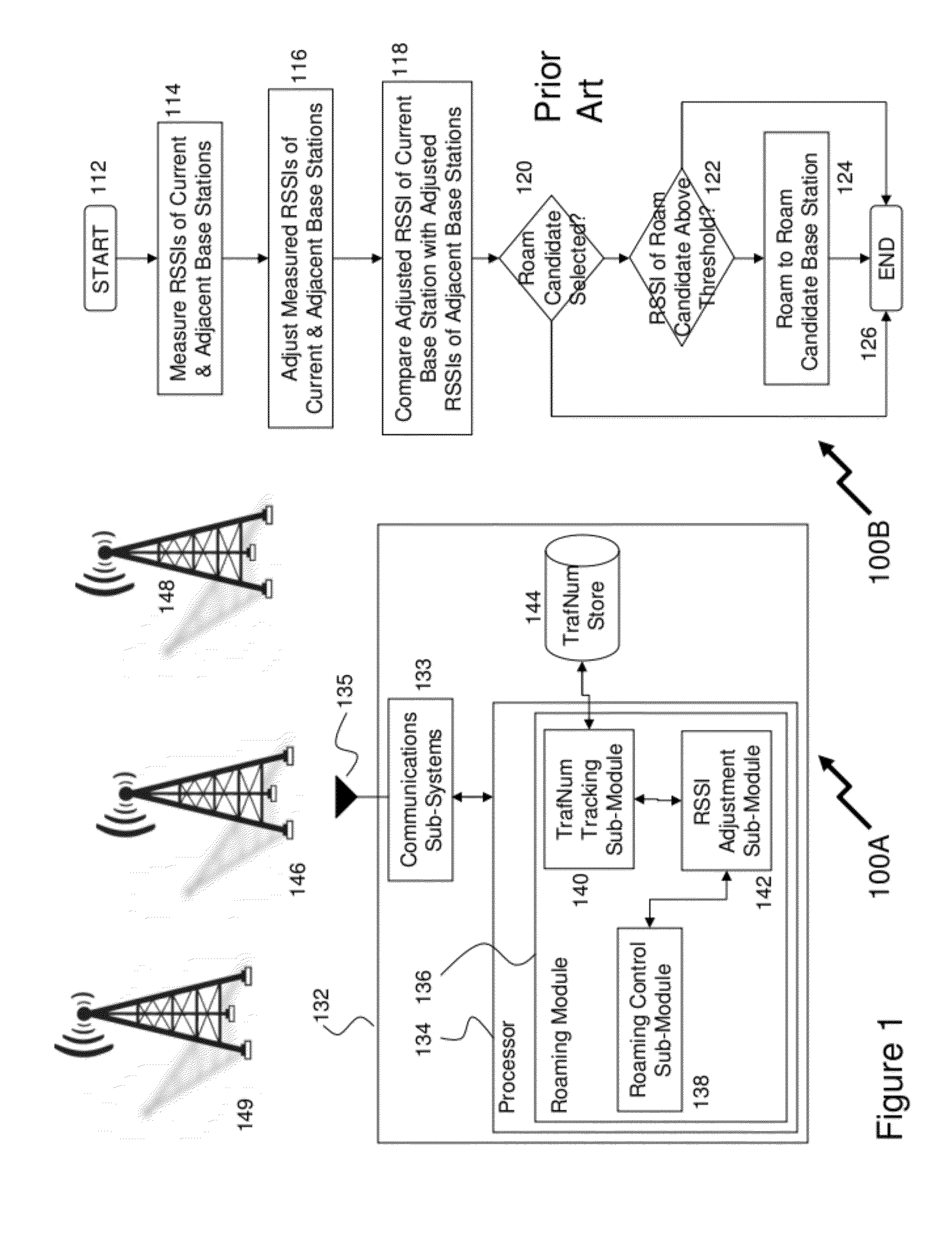
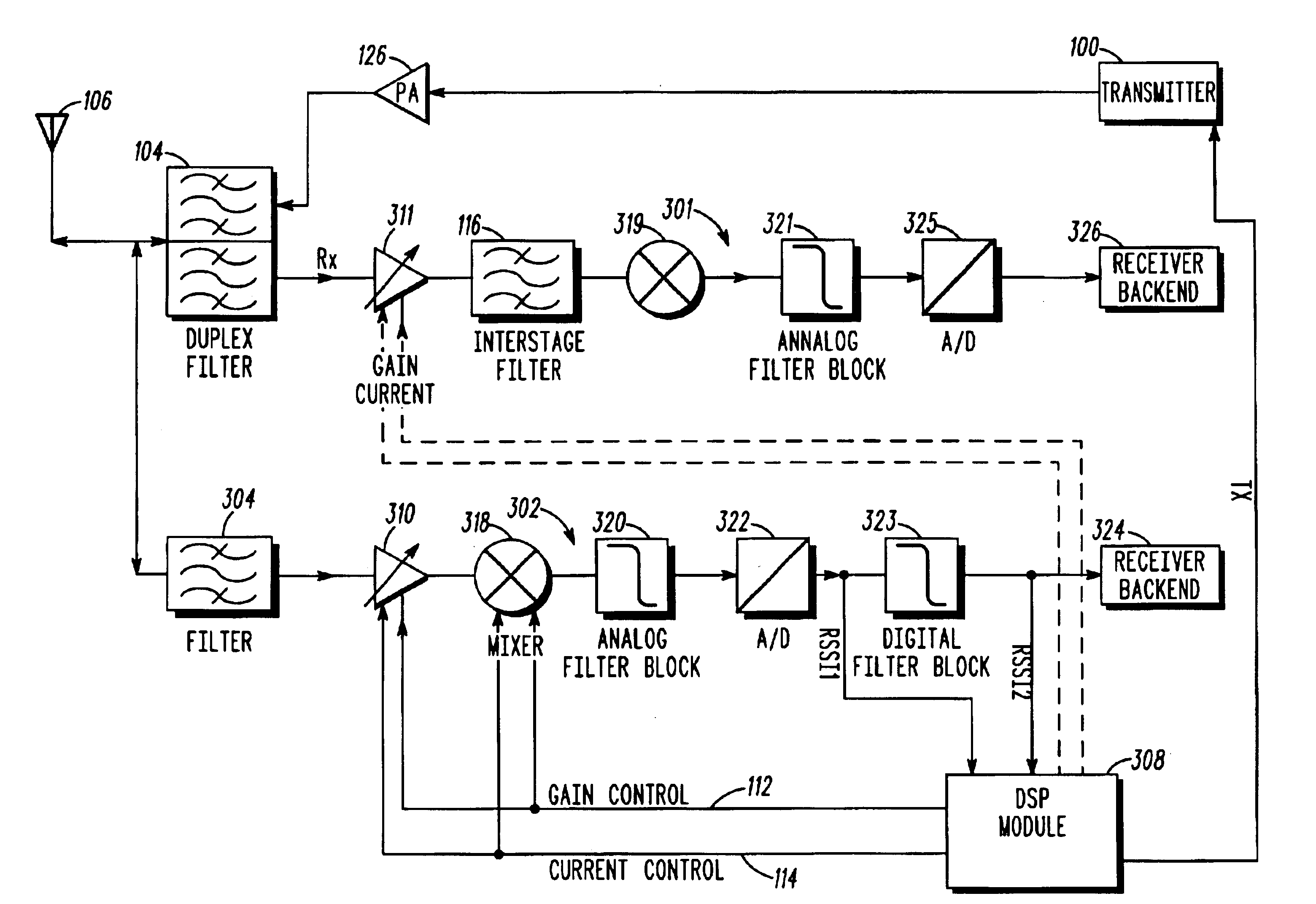
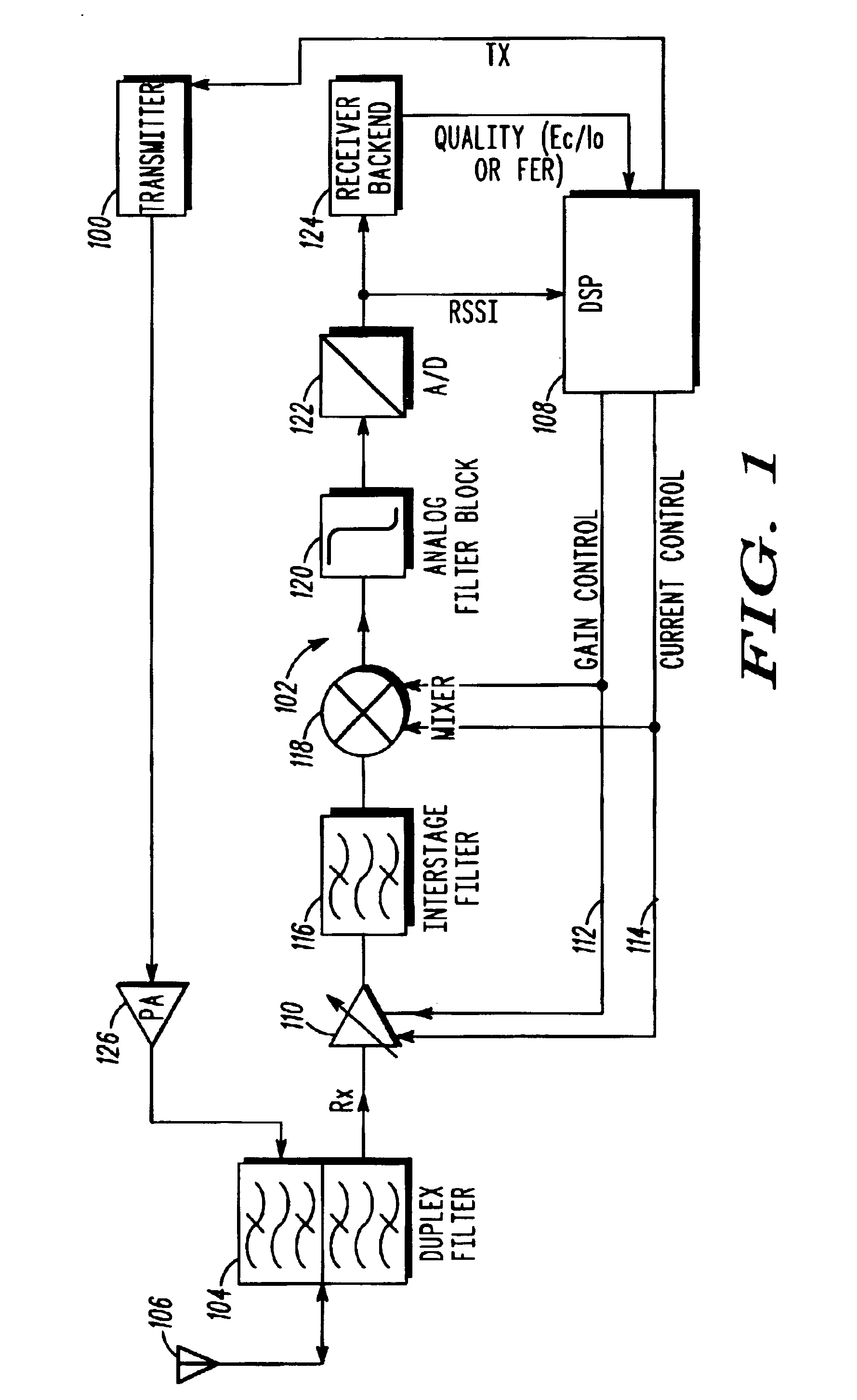
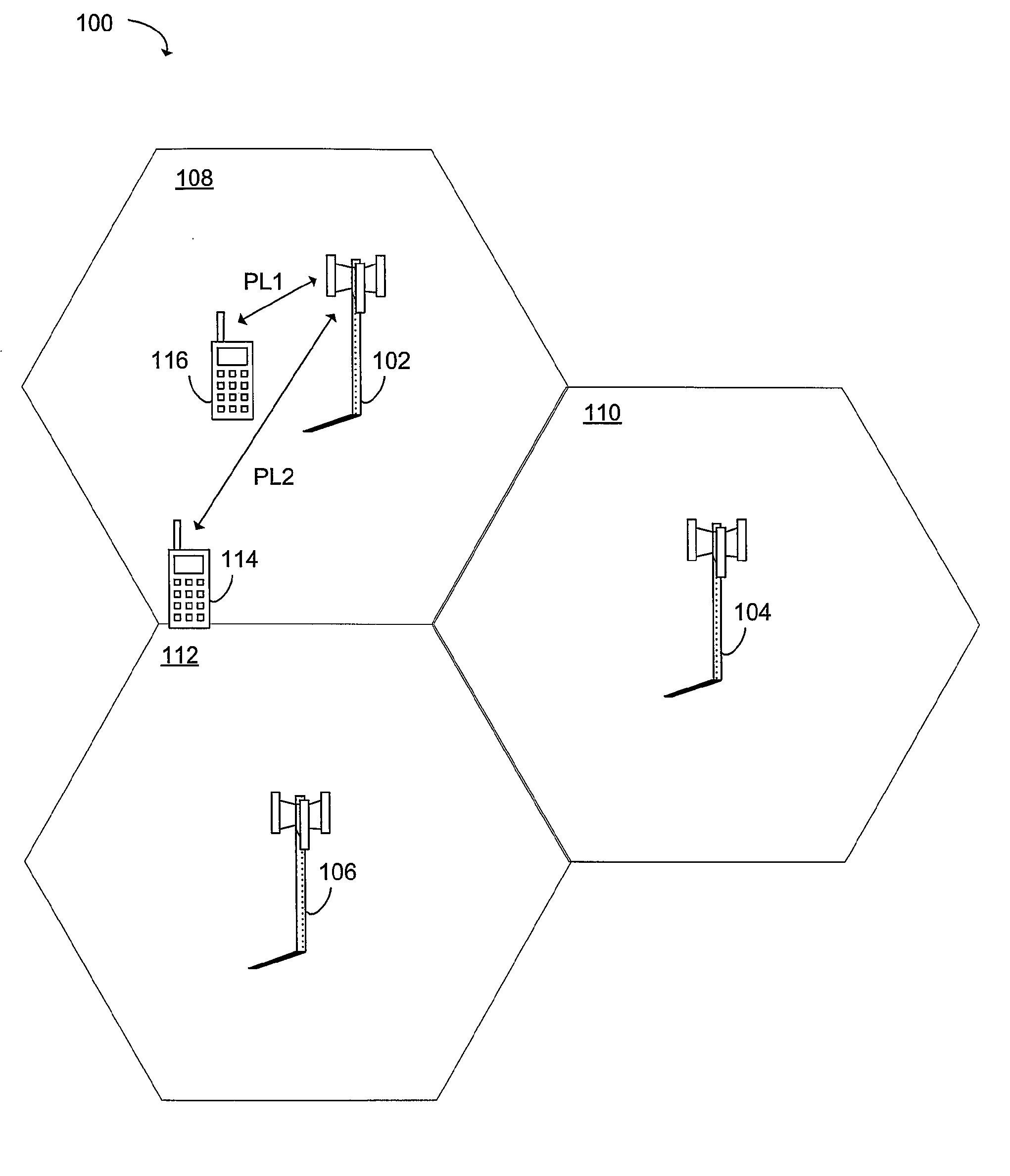
Embodiments of the invention relate to cellular wireless networks and are particularly suited to networks including different types of base stations. So-called femtocell base stations are typically deployed within a subscriber's premises and operate at low transmit power, providing a very limited area of wireless coverage. A femtocell is typically deployed within the area of wireless coverage of a conventional macrocell type of base station, and if handover from a macrocell is performed on the basis of the best signal to noise plus interference ratio, a connection is likely to be transferred to another macrocell rather than to a femtocell. However, in view of the low density of user equipments capable of transceiving with a femtocell, the femtocell could potentially provide a greater data rate to the user equipment terminal than is possible with a macrocell. A cellular wireless network according to an embodiment of the invention employs a method of handover algorithm that has dependence on both a measure of signal quality such as signal to noise plus interference ratio and on a measure of loading of the base station. The handover algorithm is thereby able to weight selection of a base station on the basis of data rate, and intelligently engineer handover to a femtocell.
Owner:APPLE INC
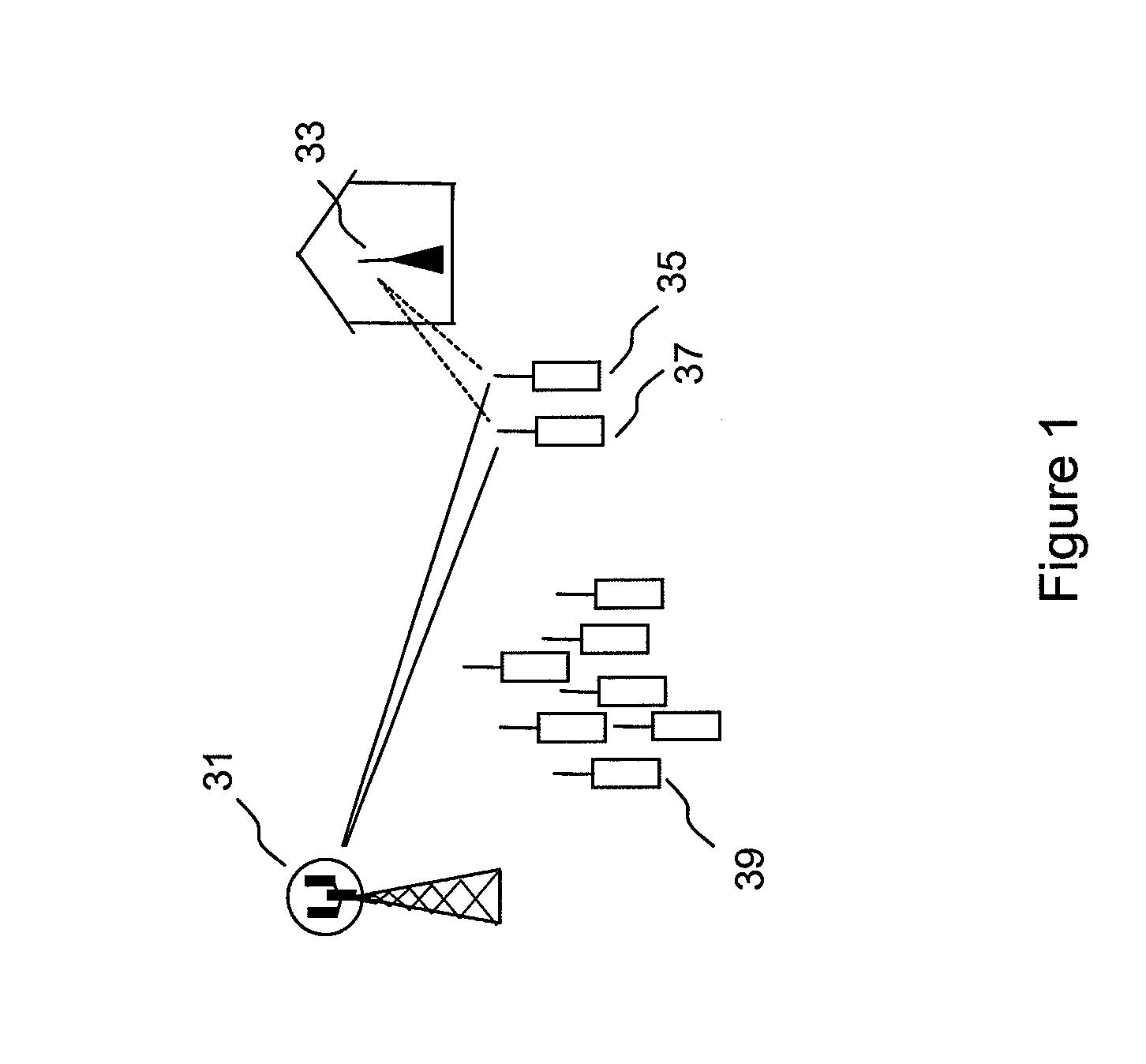
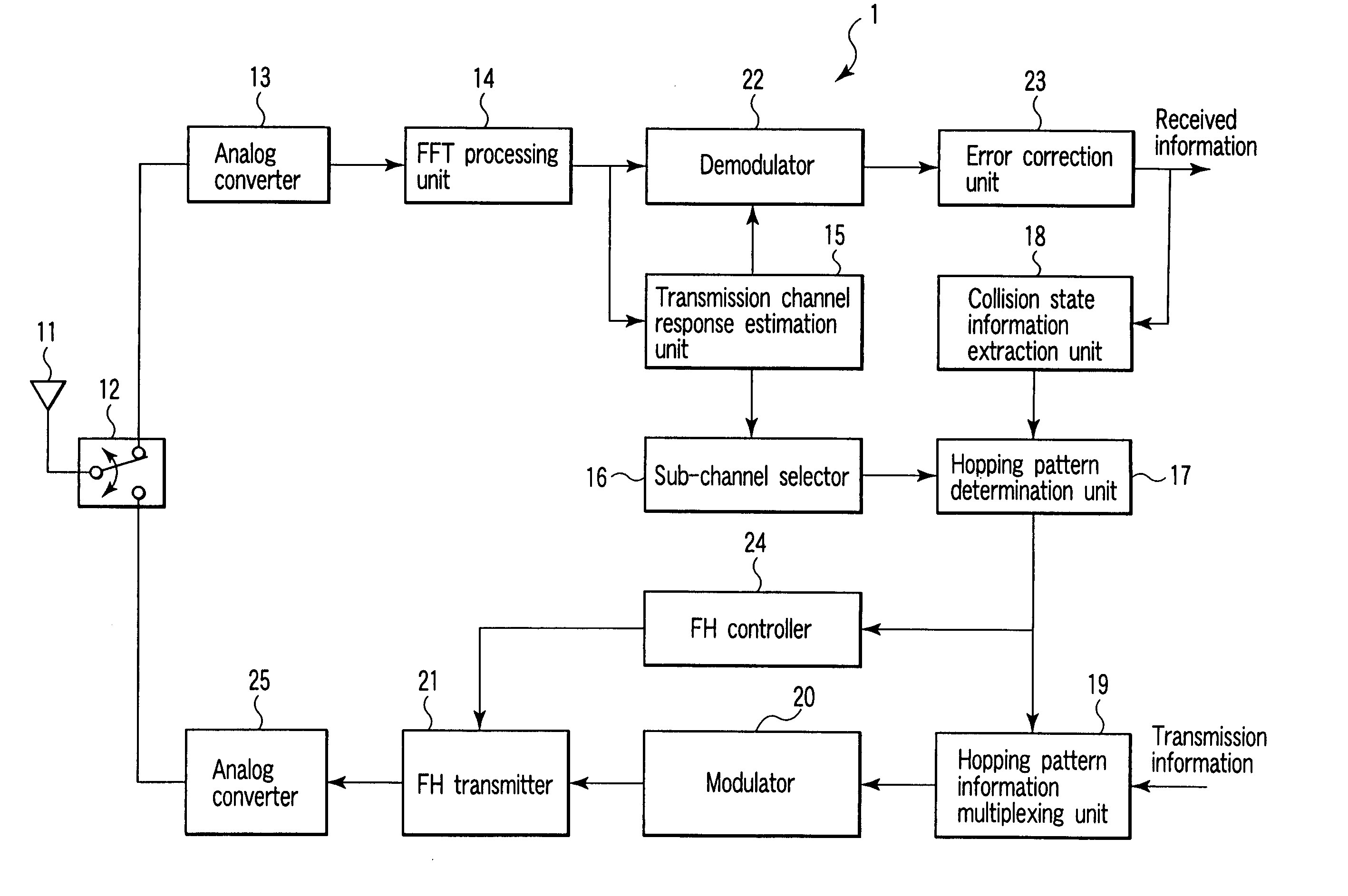
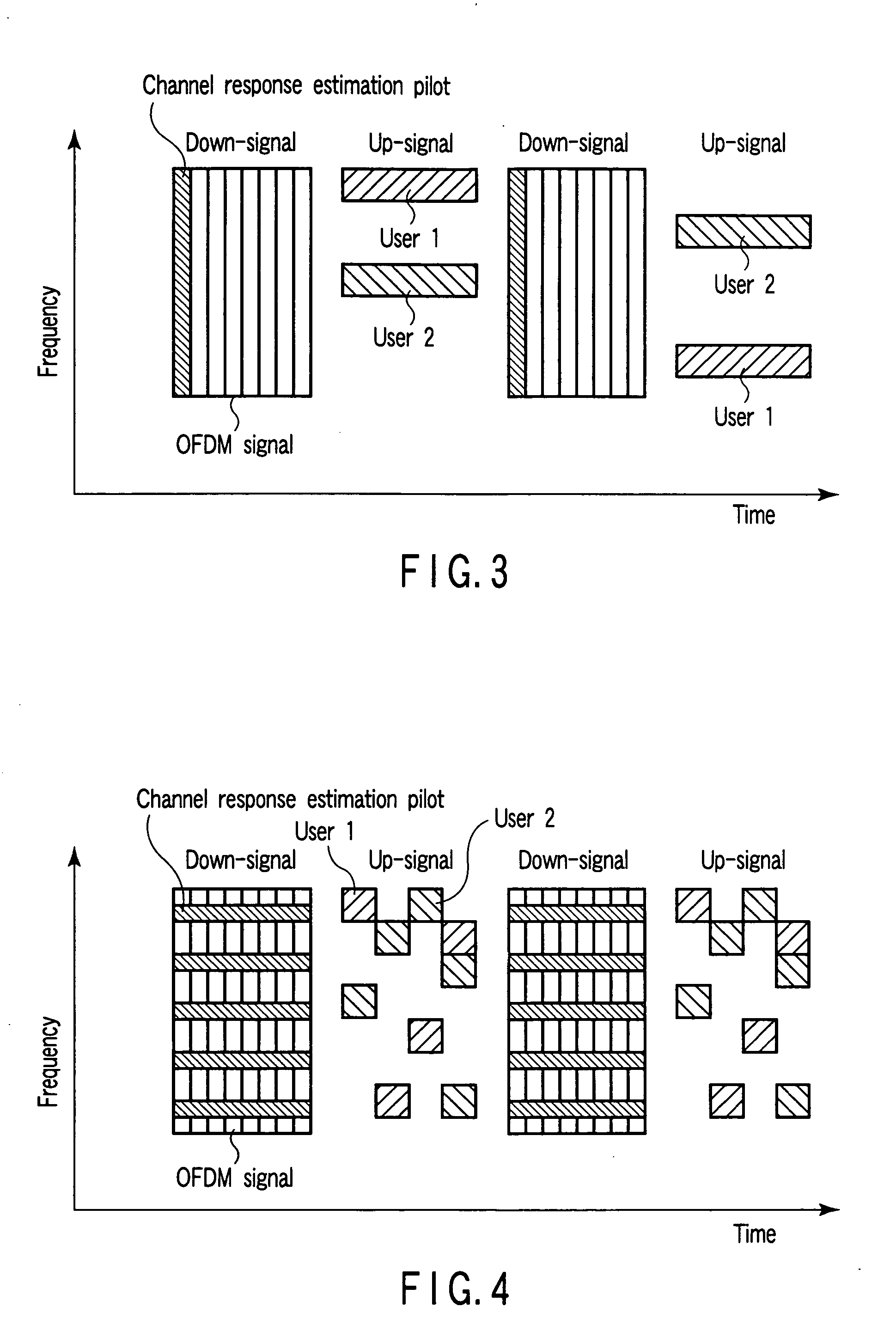
Radio communication apparatus, base station and system
InactiveUS20060013285A1Modulated-carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexSignal to noise power ratioTransmitter
Radio communication apparatus for receiving OFDM signal from base station and transmitting FH signal to base station, using sub-channels, base station comparing hopping pattern information items indicating hopping patterns from radio communication apparatuses including radio communication apparatus, and generating collision information when hopping patterns include colliding hopping patterns, includes estimation unit configured to estimate channel response values of sub-channels based on OFDM signal, selector which selects, from sub-channels, several sub-channels which have higher channel response values than a value, each of channel response values being expressed by power level, signal-to-noise power ratio, or signal-to-interference ratio, determination unit configured to determine hopping pattern from selected sub-channels, transmitter which transmits, to base station, hopping pattern information item indicating determined hopping pattern, receiver which receives collision information from base station, and correction unit configured to correct hopping pattern based on collision information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
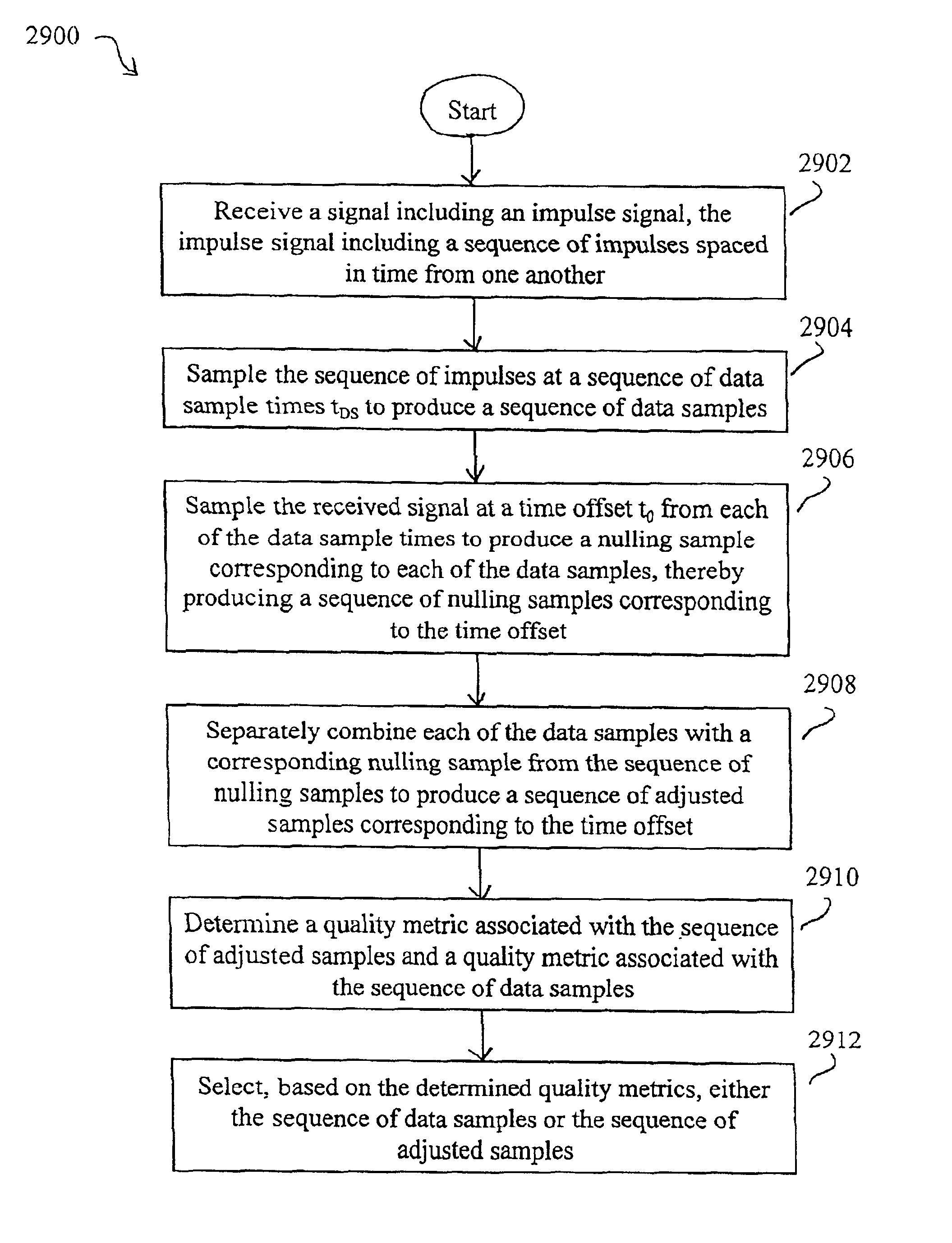
Method and system for reducing potential interference in an impulse radio
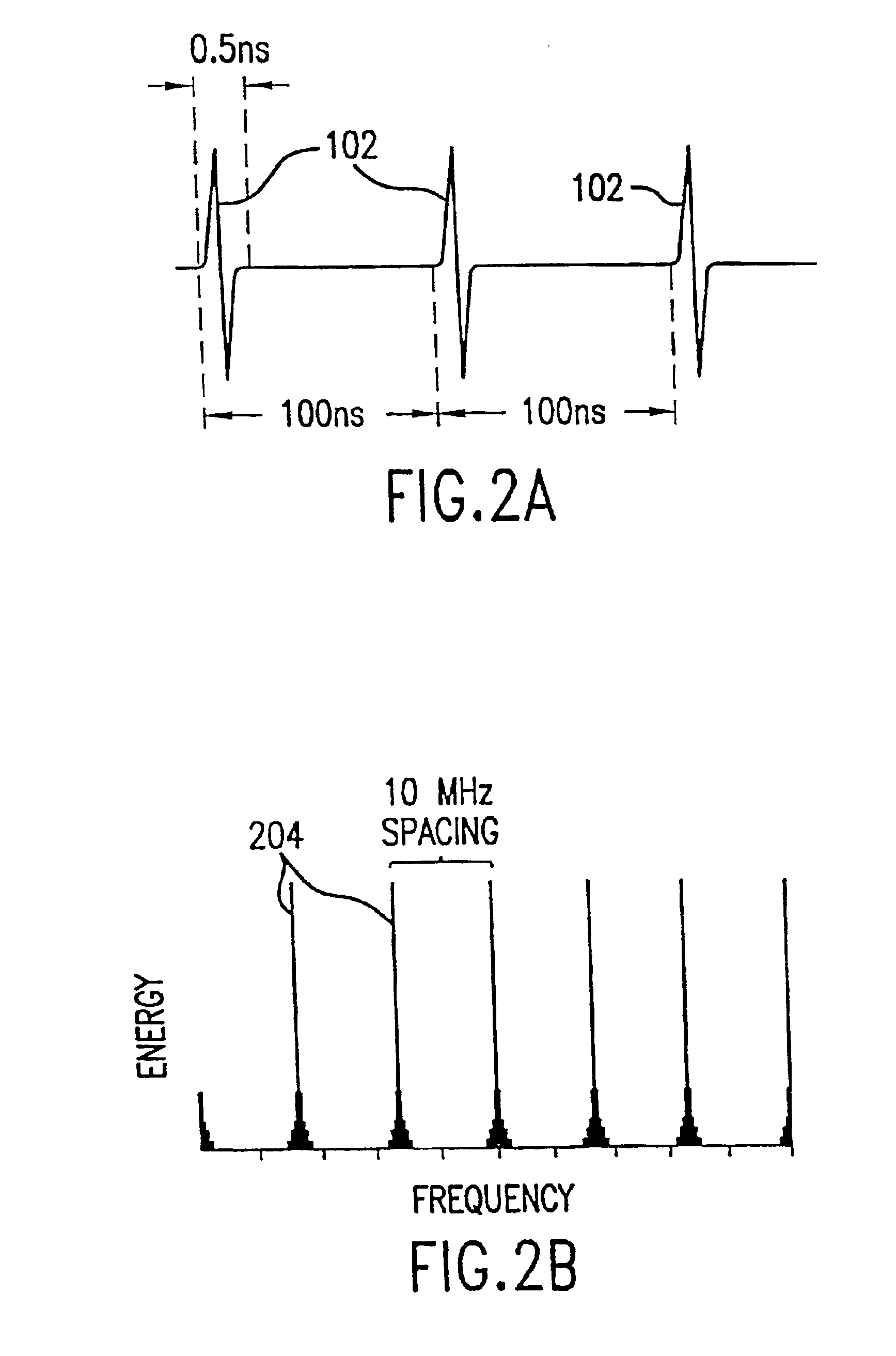
InactiveUS6914949B2Reduce distractionsReduce broadband noiseError preventionTransmission systemsInterference ratioRadio reception
Potential interference is reduced in an impulse radio. A signal including an impulse signal and potential interference is received by the impulse radio. The impulse signal includes a sequence of impulses. The sequence of impulses of the received signal is sampled at a sequence of data sample times to produce a sequence of data samples. The received signal is also sampled at a plurality of time offsets from each of the data sample times to produce a plurality of nulling samples corresponding to each of the data samples. A separate sequence of nulling samples for each of the time offsets is thereby produced. Each of the data samples is then separately combined with a corresponding nulling sample from each of the separate sequences of nulling samples to produce a separate sequence of adjusted samples corresponding to each of the time offsets. A separate quality metric, representative of a signal-to-interference level, is then determined for each of the separate sequences of adjusted samples. A preferred sequence of samples is selected for further signal processing based on the determined quality metrics. Alternatively or additionally, one of the plurality of time offsets is selected as the preferred time offset based on the determined quality metrics.
Owner:ALEREON
Traffic management in distributed wireless networks
InactiveUS20120224484A1Error preventionTransmission systemsService-level agreementInterference ratio
Wireless networks and devices are ubiquitous today. For service providers to offer customers QoS and Service Level Agreements (SLAs) means in part providing resilient connectivity of wireless devices with good signal strength, good Signal to Noise and Interference Ratio (SNIR), and adequate useable bandwidth. Doing so requires that devices transmitting and receiving packets use over-the-air bandwidth efficiently and manage over-the-air congestion. According to embodiments of the invention QoS measurements and controls are incorporated only in the network (i.e. APs or controllers) and therefore QoS and SLAs can be achieved with all deployed client stations versus standards based approaches that require additional capabilities in network nodes, client stations and in most cases modifications to the applications. SLAs can be provided exploiting embodiments of the invention for traffic prioritization, capacity improvements through load distribution, and adjacent channel interference mitigation discretely or in combination with standards based mechanisms.
Owner:3INOVA NETWORKS
Channel quality indicator for OFDM
ActiveUS20050041622A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorSecret communicationInterference ratioCarrier signal
The present invention provides an improved channel quality indicator indicia for OFDM communication environments. In addition to taking into consideration carrier-to-interference ratios, the present invention also takes into consideration the degree to which the channel response varies among the sub-carriers throughout the OFDM frequency band. The carrier-to-interference ratio and the degree of channel response variation are directly or indirectly used by a base station to select coding and modulation schemes for transmissions from the base station to the mobile terminal reporting these factors. Further, scheduling of data sent to the mobile terminal and other mobile terminals competing for the same channel resources may also be based in part on the carrier-to-interference ratio and the degree to which the channel response varies.
Owner:APPLE INC
Cellular system, mobile station, base station and transmission power control method as well as program to be executed for implementing the method
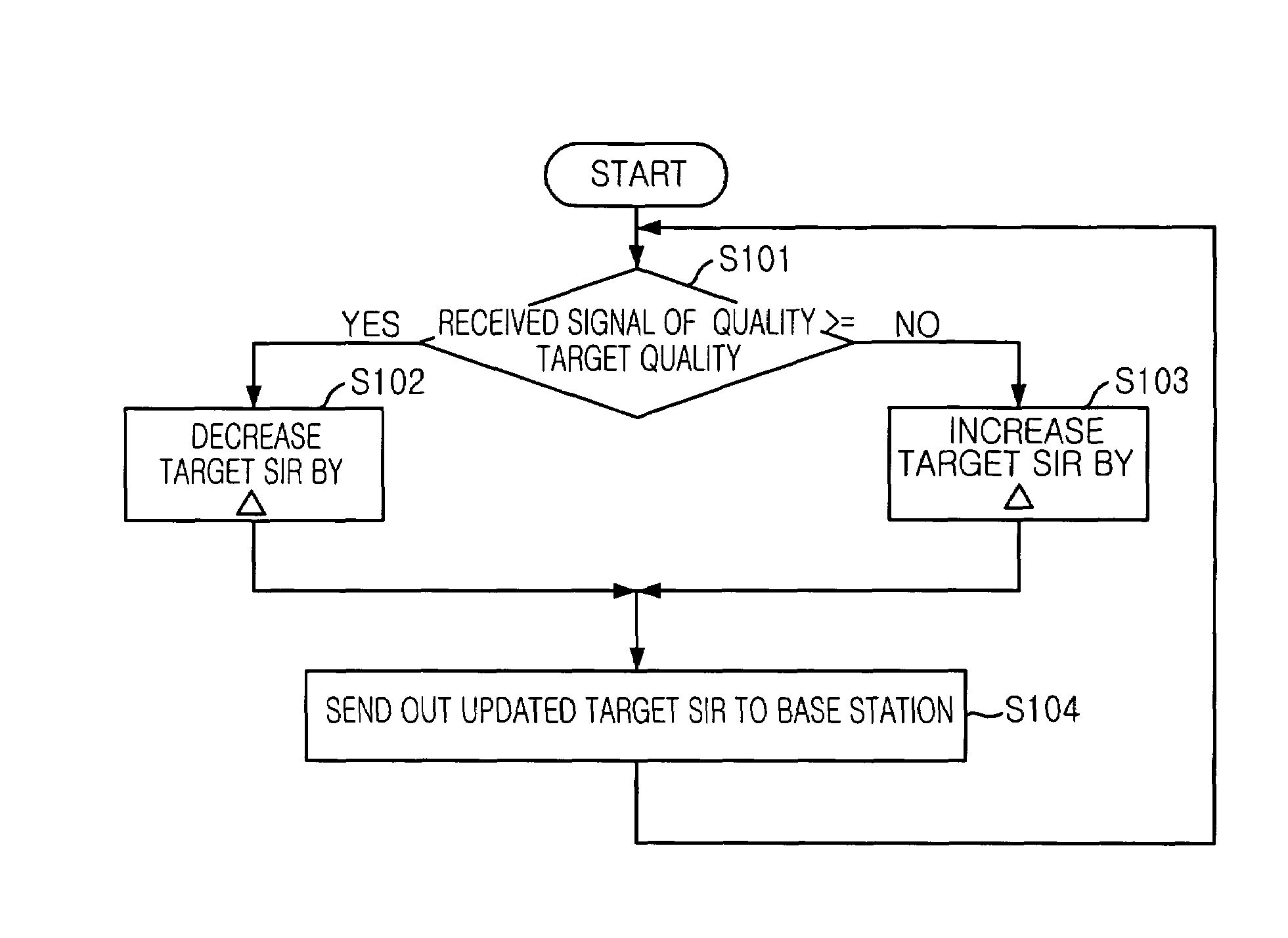
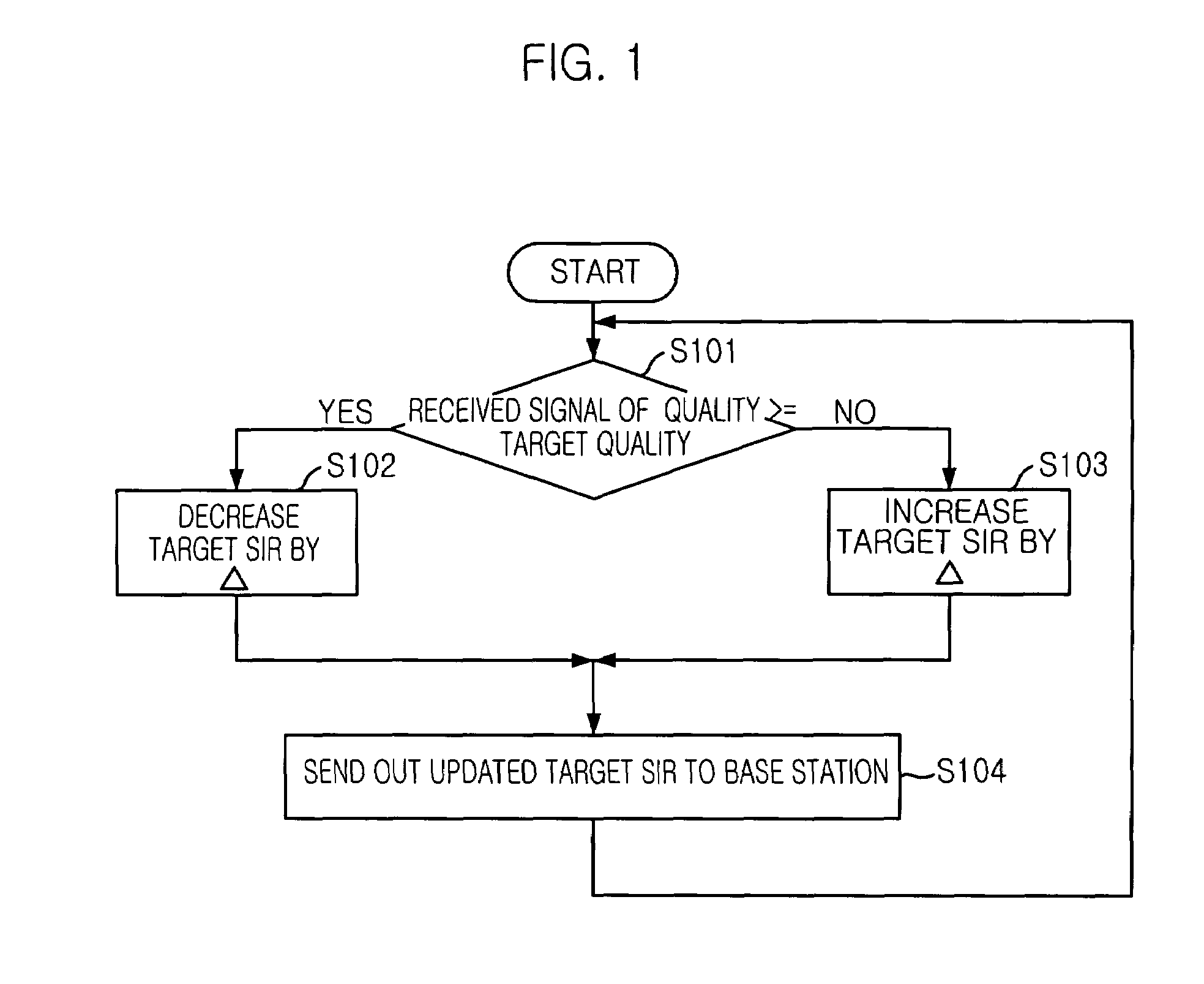
ActiveUS20050043051A1Quality is easy to controlQuality improvementPower managementTransmission control/equalisingInterference ratioTarget signal
In a cellular system, each mobile station concurrently linked to plural link base stations in soft handover state and receiving packet from the packet-transmitting base station controls a transmission power of an up-link dedicated physical channel based on a first transmission power control information included in down-link dedicated physical channels of the link base stations. In other state, the mobile station controls the transmission power based on a second transmission power control information included in a down-link dedicated physical channel of the packet-transmitting base station. This accelerates the power increase up to a target power level causing that the measured signal-to-interference-ratio at the packet-transmitting base station reaches a target signal-to-interference-ratio, thereby improving receiving quality of control signal from the mobile station at the packet-transmitting base station.
Owner:NEC CORP
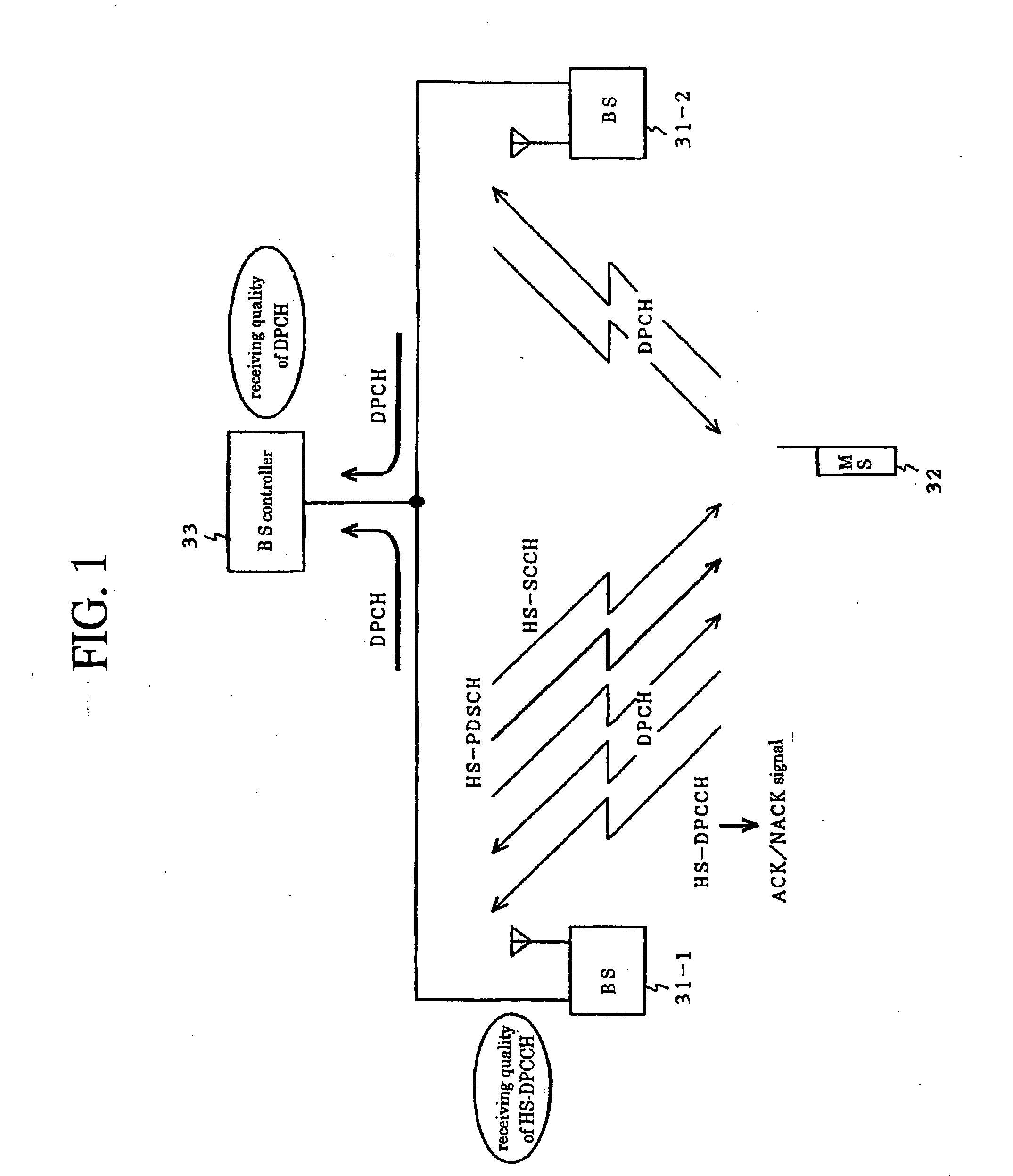
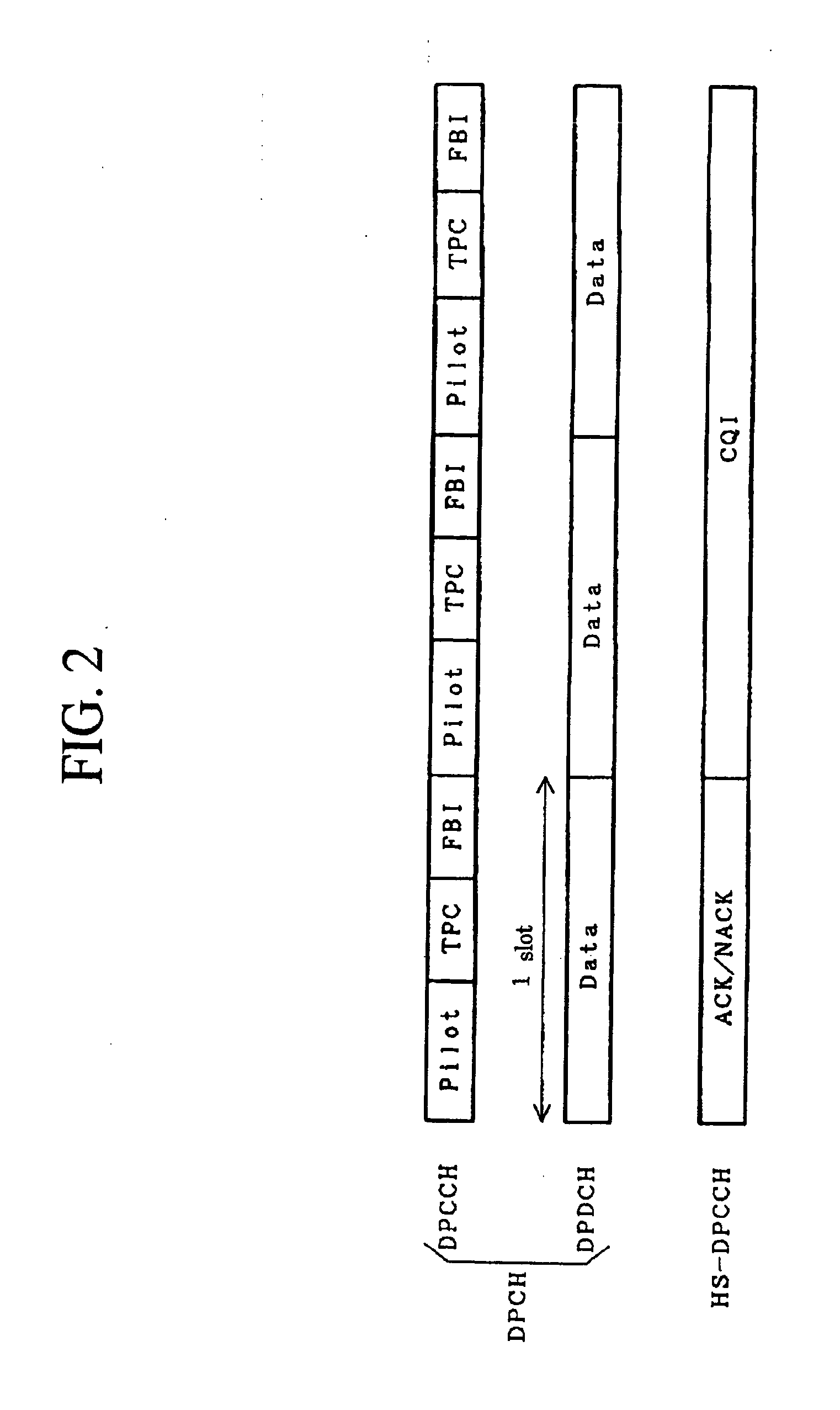
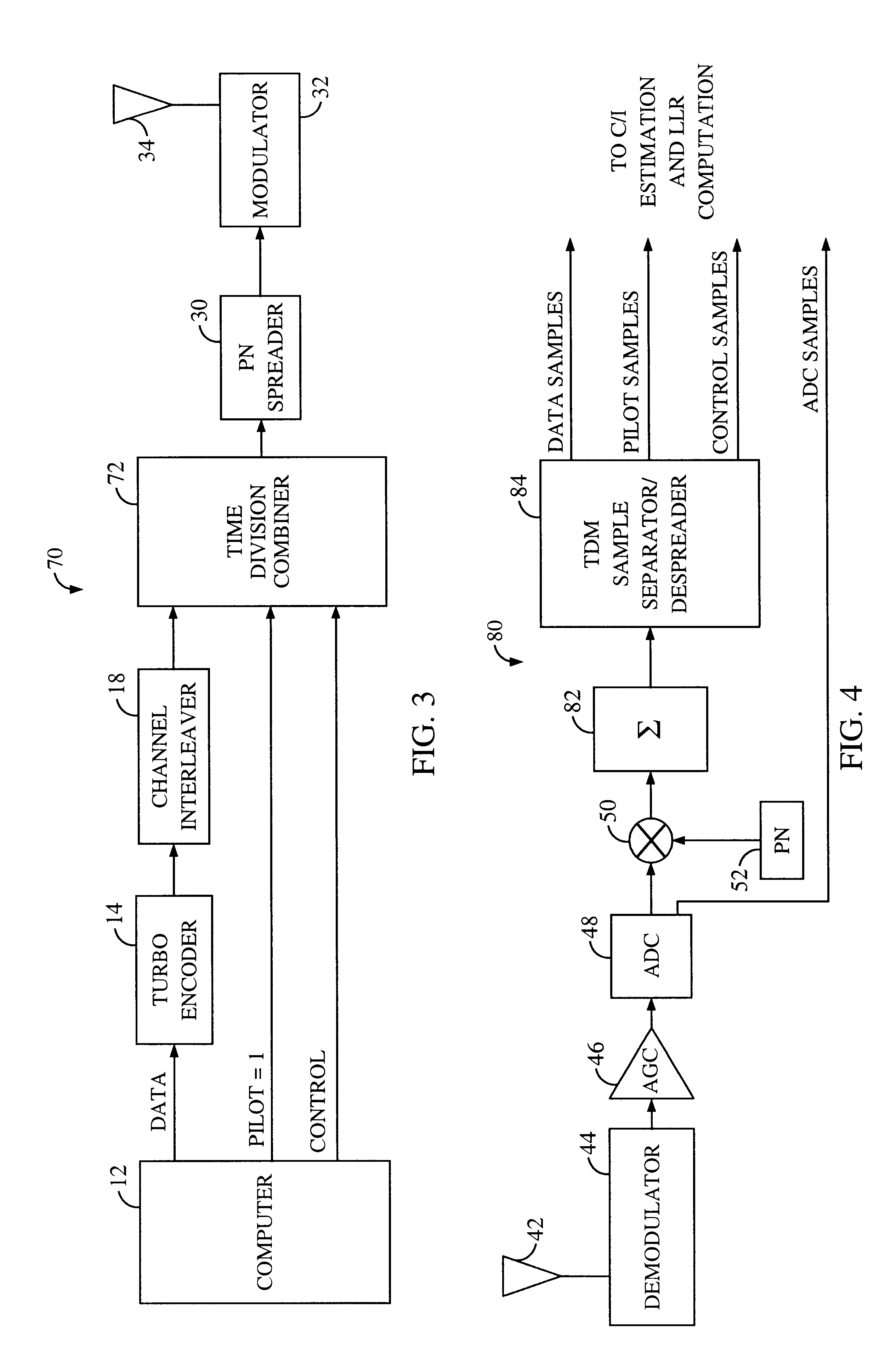
System and method for performing accurate demodulation of turbo-encoded signals via pilot assisted coherent demodulation
InactiveUS6377607B1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorError correction/detection using convolutional codesTransceiverInterference ratio
An efficient telecommunications receiver system for accurately decoding a received composite signal having a data signal component and a pilot signal component. The receiver system includes a first circuit for receiving the composite signal and extracting a pilot signal and a data signal from received composite signal. A second circuit calculates a log-likelihood ratio as a function of a channel estimate based on the pilot signal. A third circuit scales the log-likelihood ratio by a predetermined log-likelihood ratio scaling factor and provides an accurate log-likelihood value in response thereto. A fourth circuit decodes the received composite signal based on the accurate log-likelihood value and the data signal. In a specific embodiment, the pilot signal and the data signal comprise pilot samples and data samples, respectively. The third circuit includes a carrier signal-to-interference ratio circuit for computing a first signal-to-interference ratio and a second signal-to-interference ratio based partly on the pilot signal. The first signal-to-interference ratio is based on the data samples, and the second signal-to-interference ratio is based on the pilot samples. The first signal-to-noise ratio and the second signal-to-noise ratio provide input to a circuit for computing the predetermined log-likelihood ratio scaling factor that is included in the third circuit. In a more specific embodiment, the first circuit includes a despreader for despreading the received composite signal in accordance with a predetermined spreading function and providing a despread signal in response thereto. The spreading function is a pseudo noise sequence or a Walsh function. The first circuit further includes a decovering circuit that extracts the pilot signal and the data signal from the despread signal. In the illustrative embodiment, the accurate receiver system further includes a circuit for generating a rate and / or power control message and transmitting the rate and / or power control message to an external transceiver in communication with the efficient receiver system.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Wireless system
ActiveUS20100035620A1Avoid interferenceEasy to useModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionInterference ratioCarrier signal
The capacity of a cellular wireless system is increased by operation of base stations or base station sectors arranged to re-use radio resource elements that are used by neighbouring base stations or base station sectors, in conjunction with operation of relay stations, which are similarly arranged to re-use radio resource elements used by neighbouring relay stations, and where the radio resource elements re-used by the relay stations are different to those used by the base stations. The relay stations provide coverage, particularly in the areas at the boundaries between the areas of coverage of base stations that suffer from interference between signals transmitted from the respective base stations. In addition, the relay stations generally increase the average available carrier to interference ratio compared with a system in which base stations alone are deployed. The scheme for the allocation of radio resource elements ensures in particular that interference is avoided between signals transmitted from a base station and signals transmitted from a relay station in radio resource elements allocated to control data.
Owner:APPLE INC
Traffic management in distributed wireless networks
InactiveUS20120224481A1Error preventionTransmission systemsService-level agreementInterference ratio
Wireless networks and devices are ubiquitous today. For service providers to offer customers QoS and Service Level Agreements (SLAs) means in part providing resilient connectivity of wireless devices with good signal strength, good Signal to Noise and Interference Ratio (SNIR), and adequate useable bandwidth. Doing so requires that devices transmitting and receiving packets use over-the-air bandwidth efficiently and manage over-the-air congestion. According to embodiments of the invention QoS measurements and controls are incorporated only in the network (i.e. APs or controllers) and therefore QoS and SLAs can be achieved with all deployed client stations versus standards based approaches that require additional capabilities in network nodes, client stations and in most cases modifications to the applications. SLAs can be provided exploiting embodiments of the invention for traffic prioritization, capacity improvements through load distribution, and adjacent channel interference mitigation discretely or in combination with standards based mechanisms.
Owner:3INOVA NETWORKS
Scheduling of wireless packet data transmissions
InactiveUS20050063389A1Improve throughputChange the balanceError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceInterference ratio
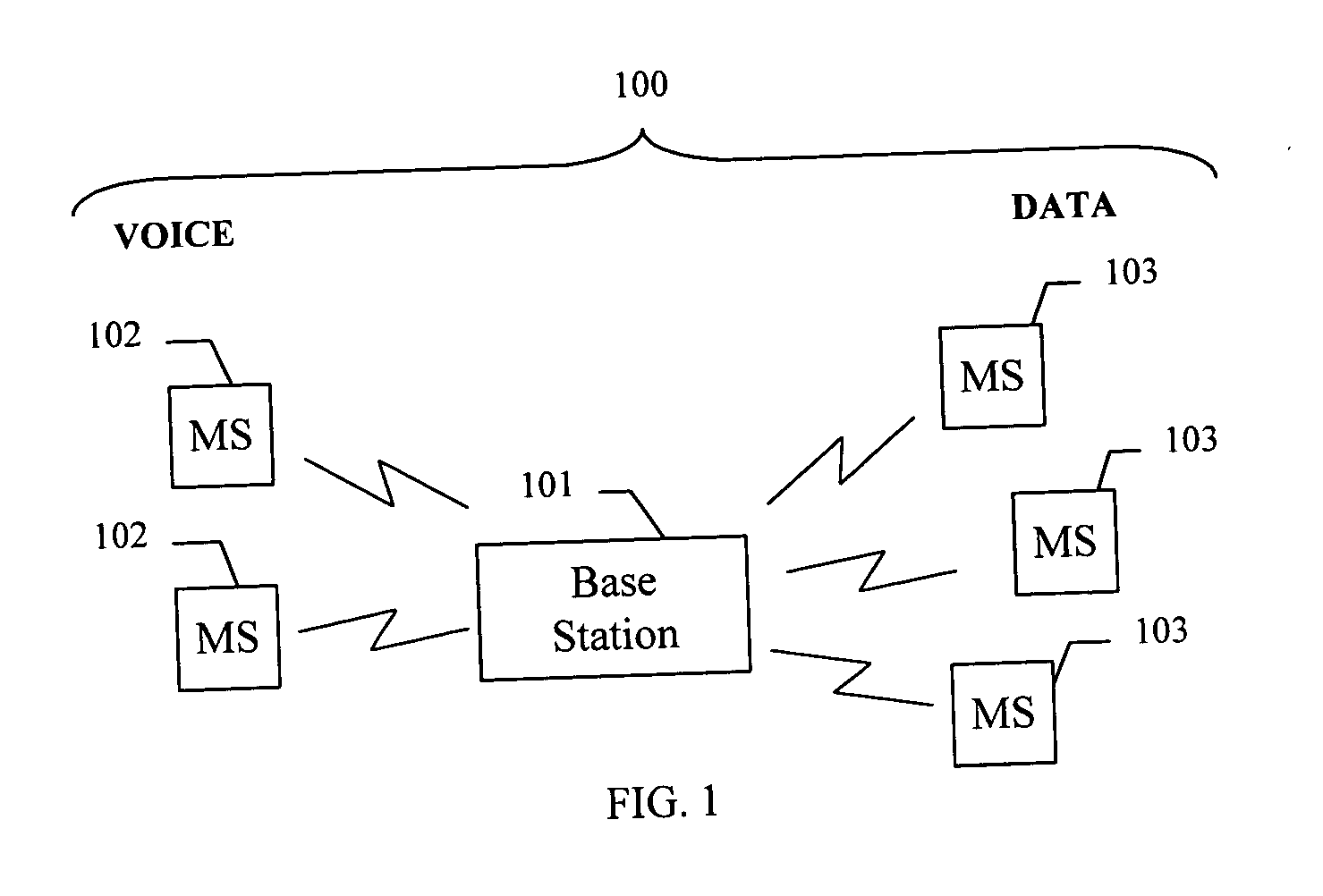
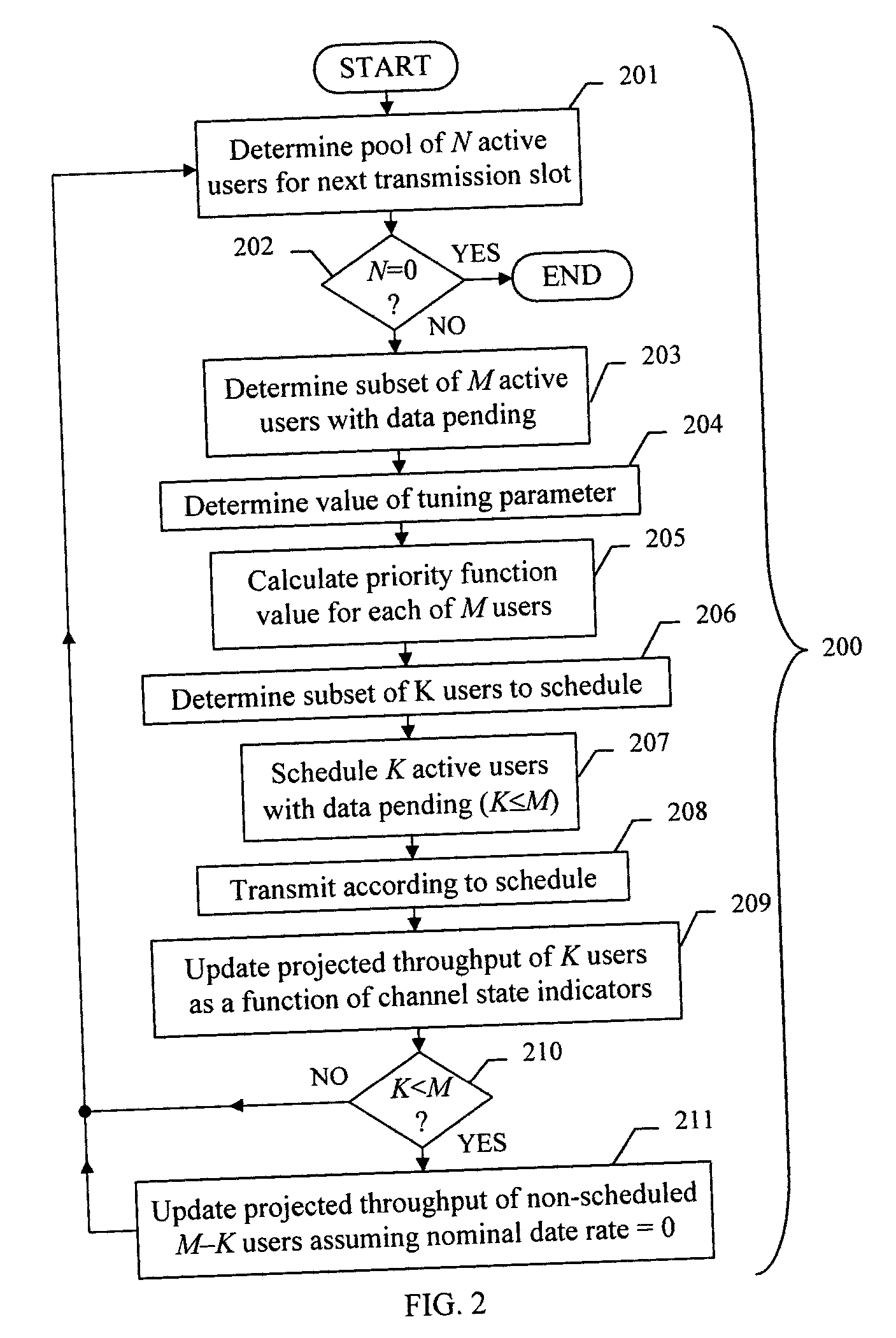
A method for scheduling packet data transmissions in a wireless communication system is described wherein a priority function is based on a channel state indicator (CSI), the projected average throughput of the users, and a tuning parameter designed to control the throughput and fairness characteristics of the scheduling algorithm. The method also considers fairness criteria dictated by predetermined Quality of Service (QoS) requirements. The channel state indicator may be a Requested Data Rate (RDR) or Carrier-to-Interference ratio (C / I) information. The base station calculates a priority function for the multiple mobile users. Each priority function is a function of the CSI, the projected average throughput of a given mobile user, the average projected throughput over a set of users, and the tuning parameter.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
Apparatus and method for estimating a channel condition of a forward link in a mobile communication system
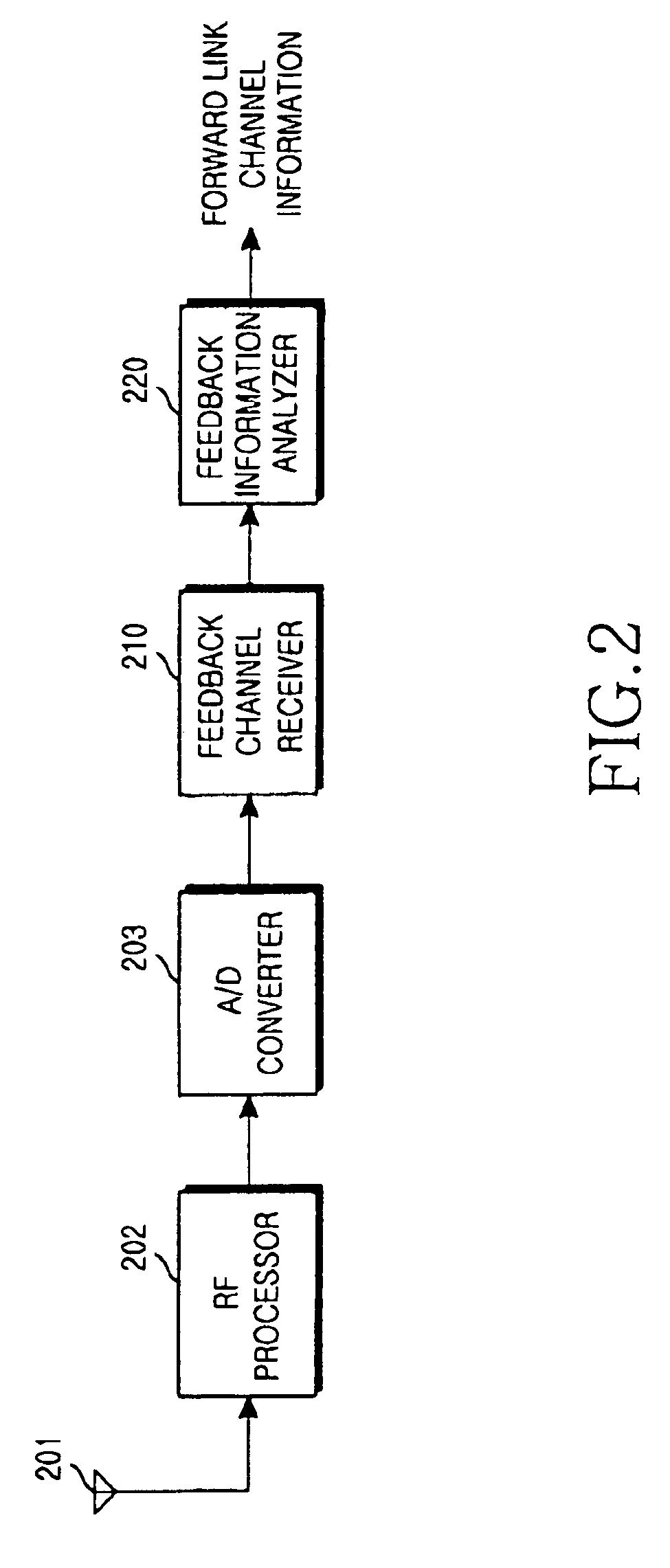
InactiveUS7321563B2Reduction in efficiency of reverseLow efficiencyUrinalsWater closetsCommunications systemInterference ratio
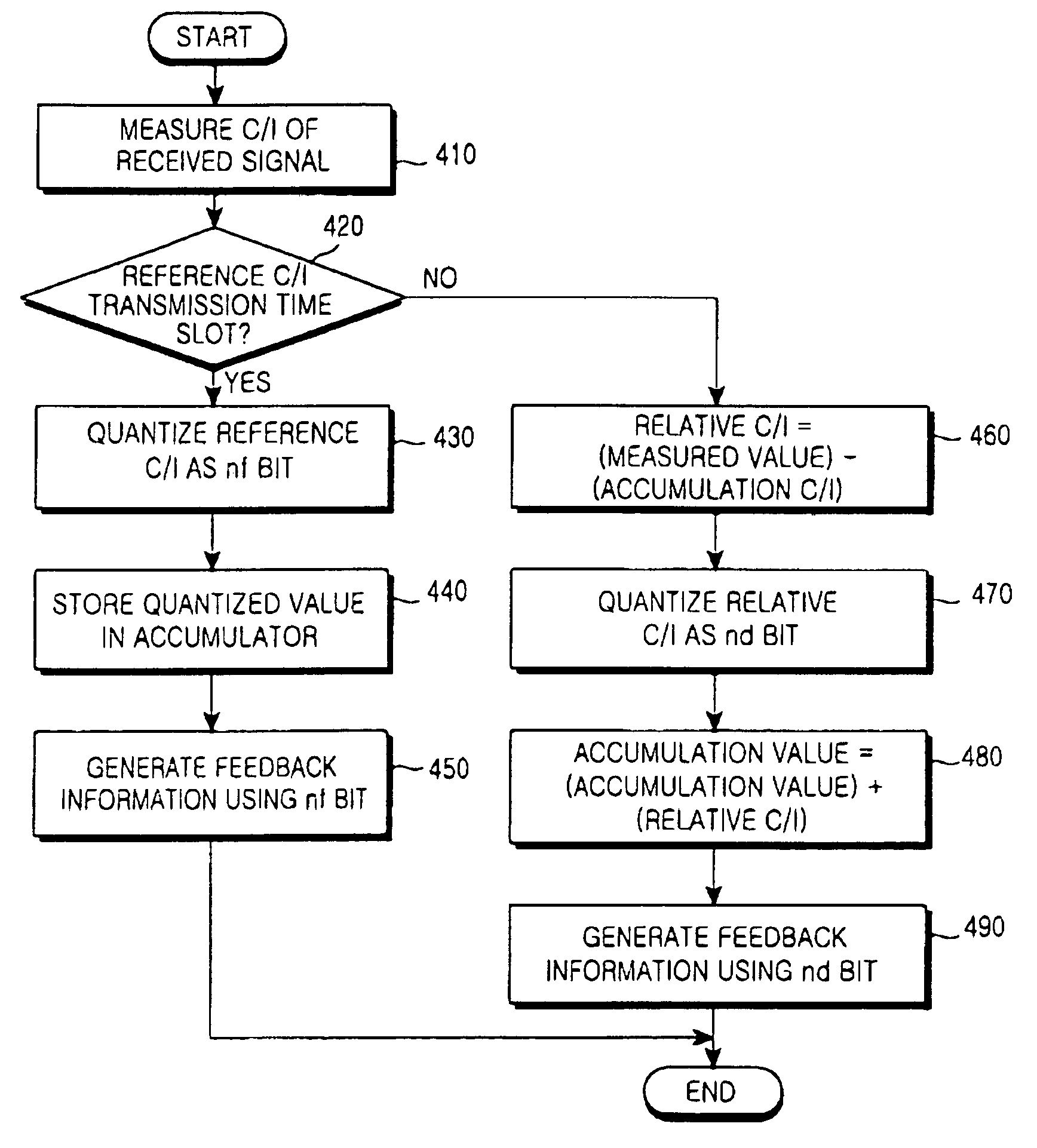
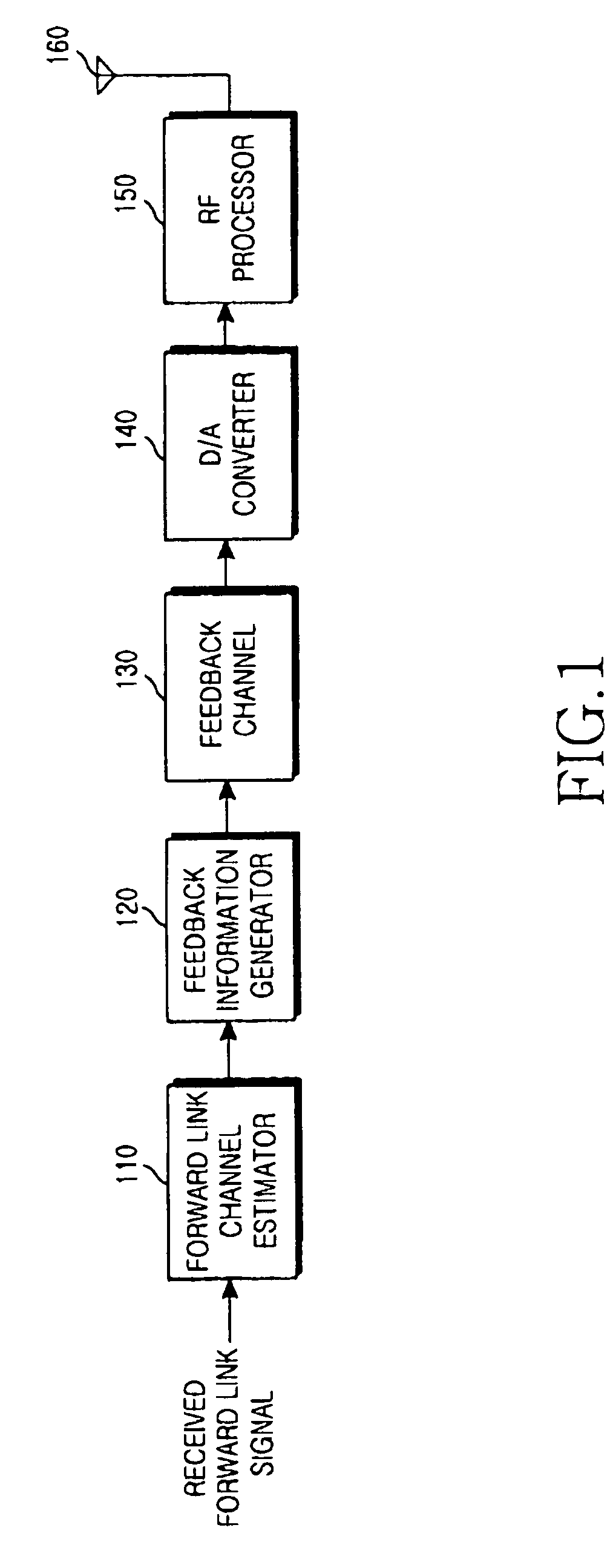
A apparatus and method for estimating a channel condition of a forward link by a mobile station in a mobile communication system including the mobile station and a base station for performing an operation of transmitting / receiving data using a plurality of subcarriers having mutual orthogonality. The method comprises measuring carrier-to-interference ratio (C / I) values of the subcarriers using a signal received from the base station; determining from the received signal a subcarrier for transmitting feedback information in a given coherence bandwidth; generating feedback information to be transmitted over the determined subcarrier; and transmitting the generated feedback information to the base station as information for estimating a channel condition of the forward link.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
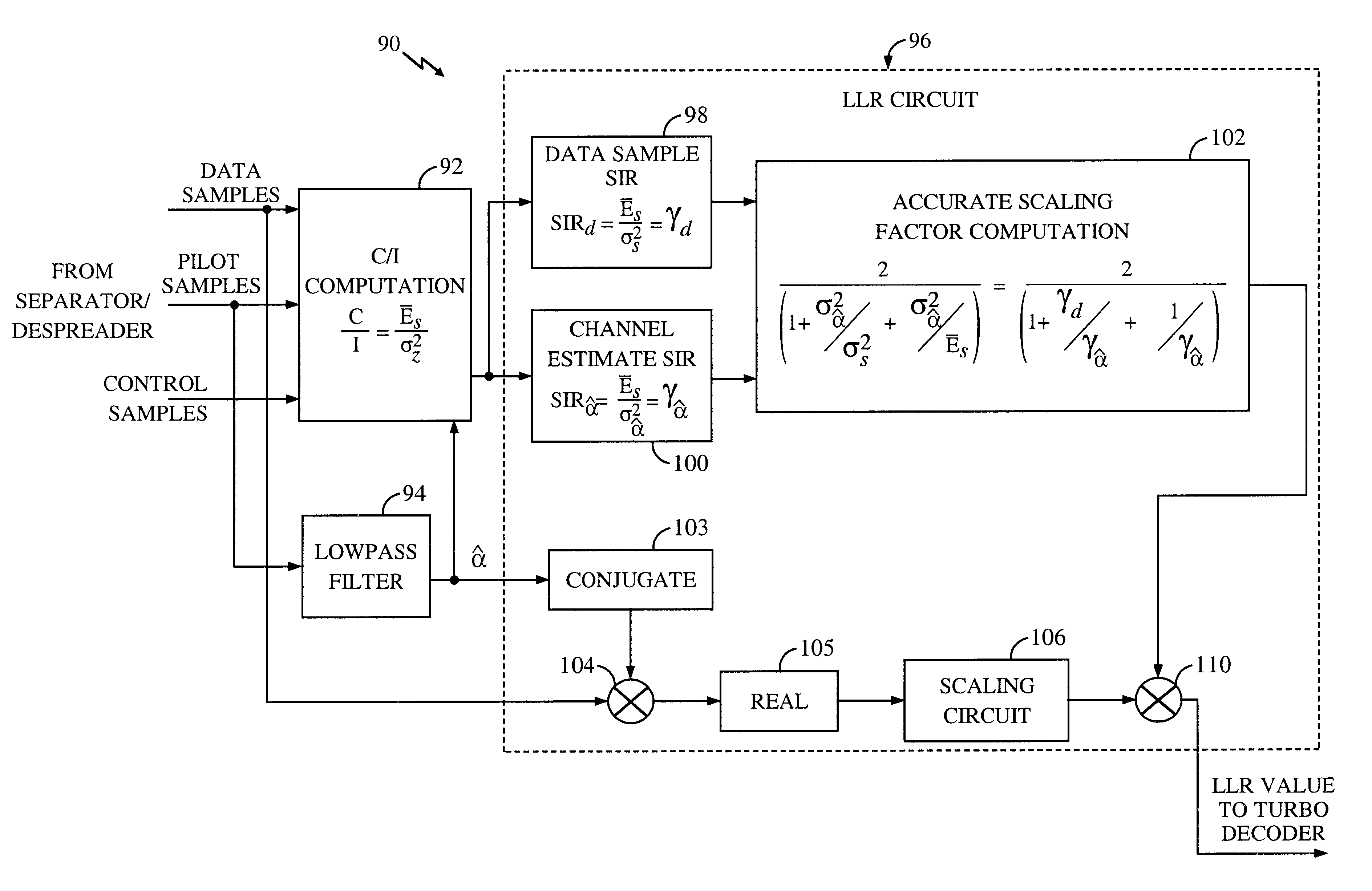
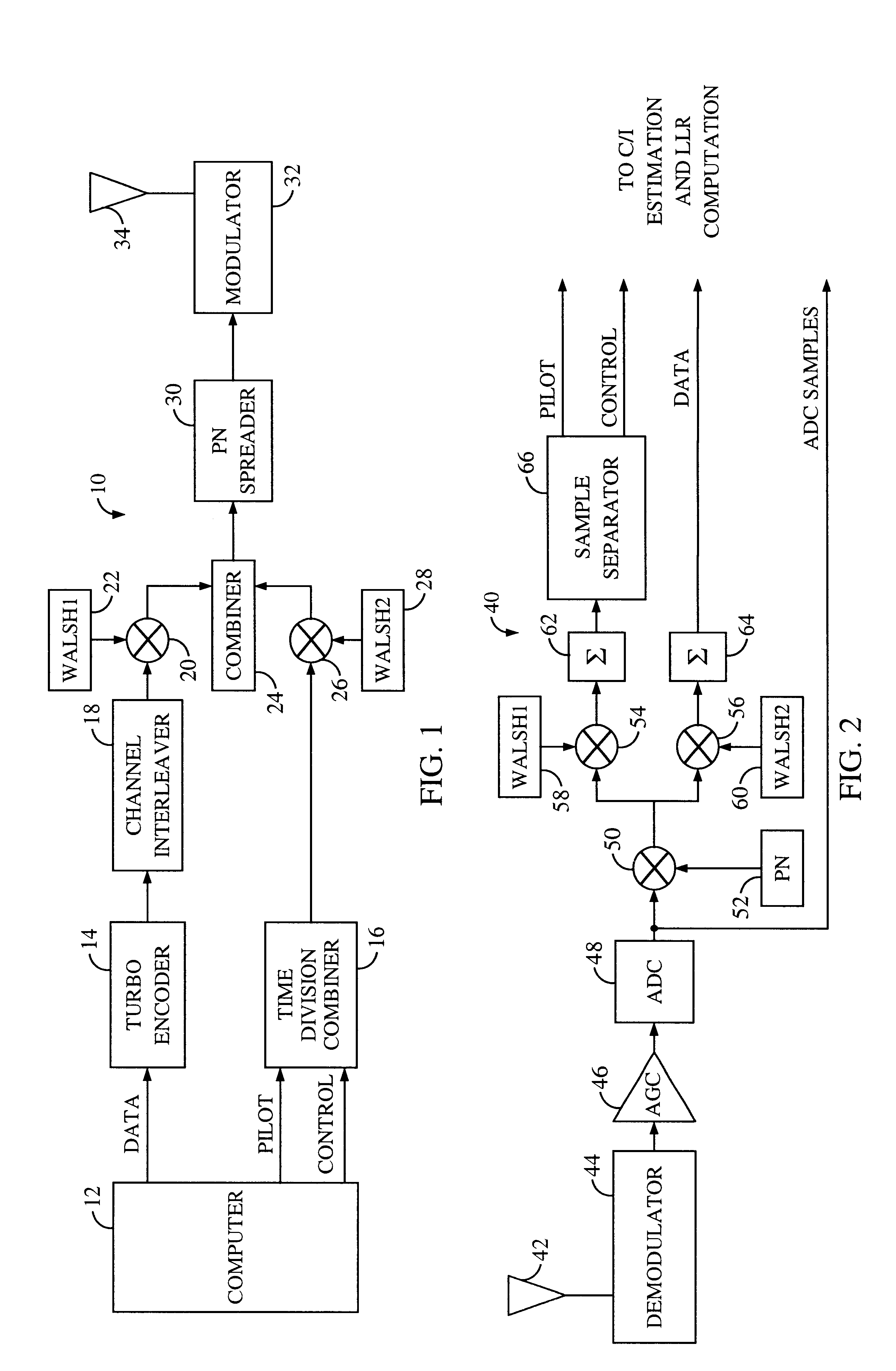
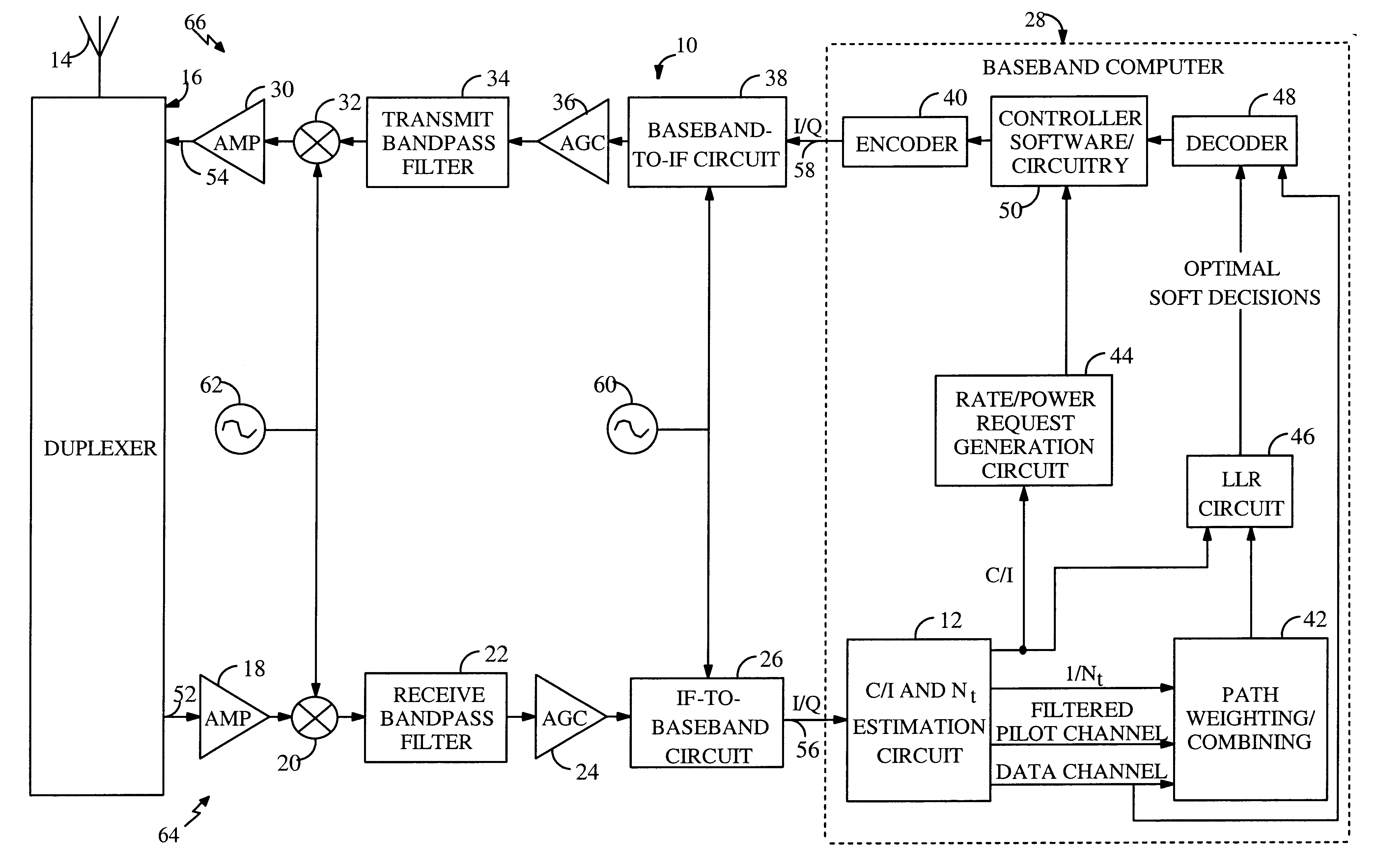
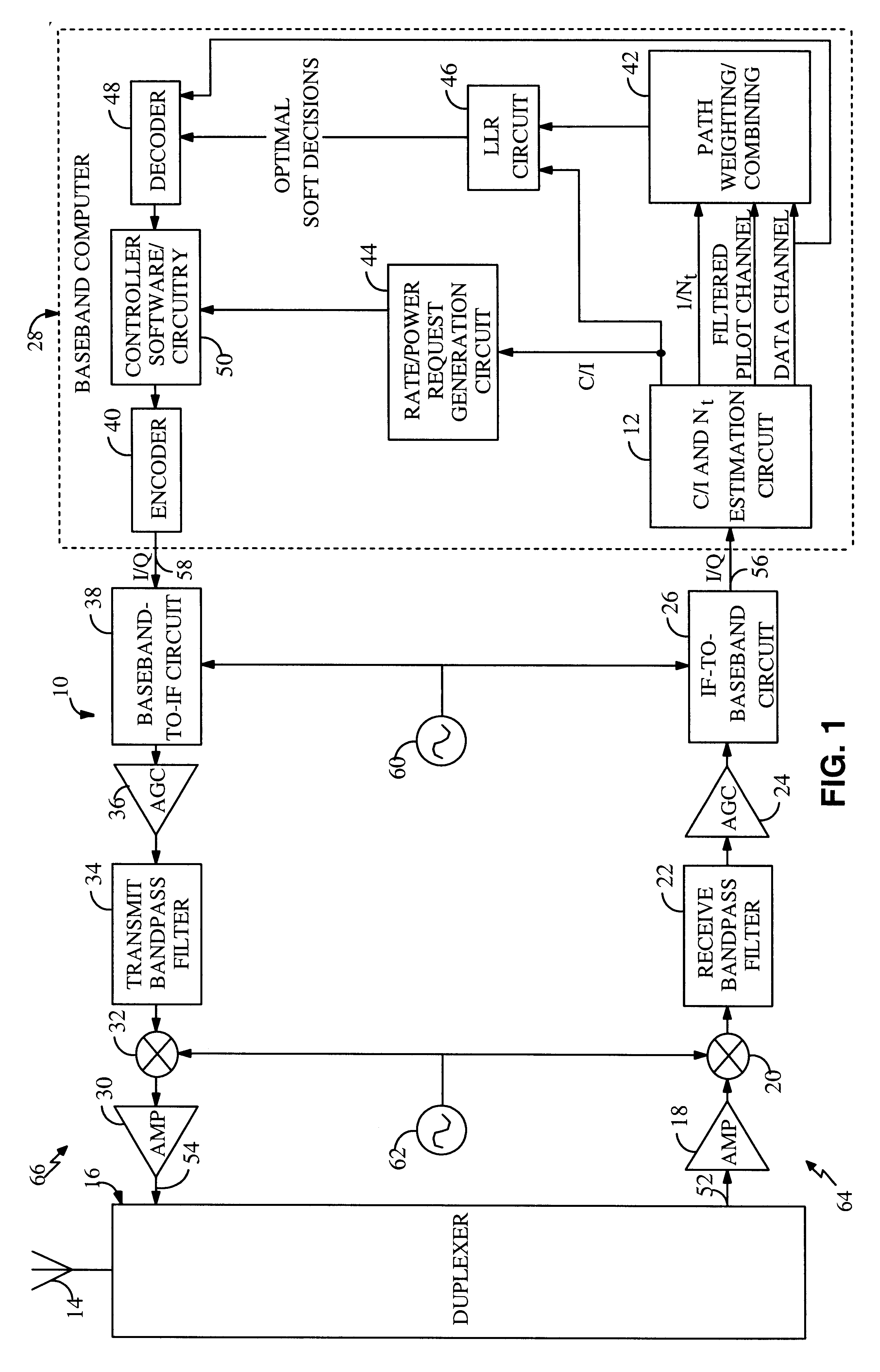
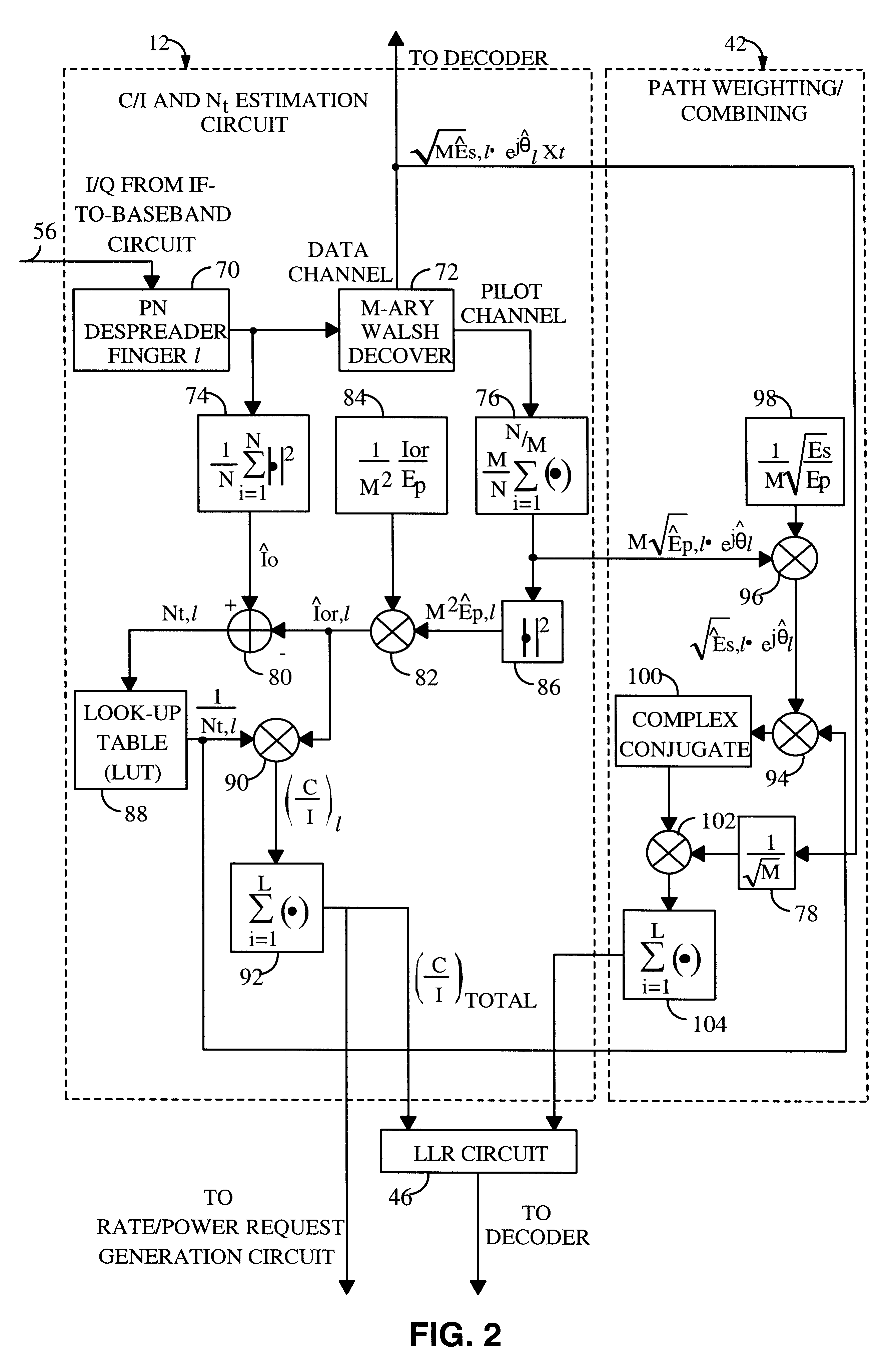
System and method for providing an accurate estimation of received signal interference for use in wireless communications systems
A system for providing an accurate interference value signal received over a channel and transmitted by an external transceiver. The system includes a first receiver section for receiving the signal, which has a desired signal component and an interference component. A signal extracting circuit extracts an estimate of the desired signal component from the received signal. A noise estimation circuit provides the accurate interference value based on the estimate of the desired signal component and the received signal. A look-up table transforms the accurate noise and / or interference value to a normalization factor. A carrier signal-to interference ratio circuit employs the normalization factor and the received signal to compute an accurate carrier signal-to-interference ratio estimate. Path-combining circuitry generates optimal path-combining weights based on the received signal and the normalization factor. In the illustrative embodiment, the system further includes a circuit for employing the accurate interference value to compute a carrier signal-to-interference ratio. An optimal path-combining circuit computes optimal path-combining weights for multiple signal paths comprising the signal using the accurate interference value and provides optimally combined signal paths in response thereto. A log-likelihood ratio circuit computes a log-likelihood value based on the carrier signal-to-interference ratio and the optimally combined signal paths. A decoder decodes the received signal using the log-likelihood value. An additional circuit generates a rate and / or power control message and transmits the rate and / or power control message to the external transceiver.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and device for estimating a carrier-to-interference ratio in a radio communication system
InactiveUS6650872B1Raise the ratioError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInterference ratioCommunications system
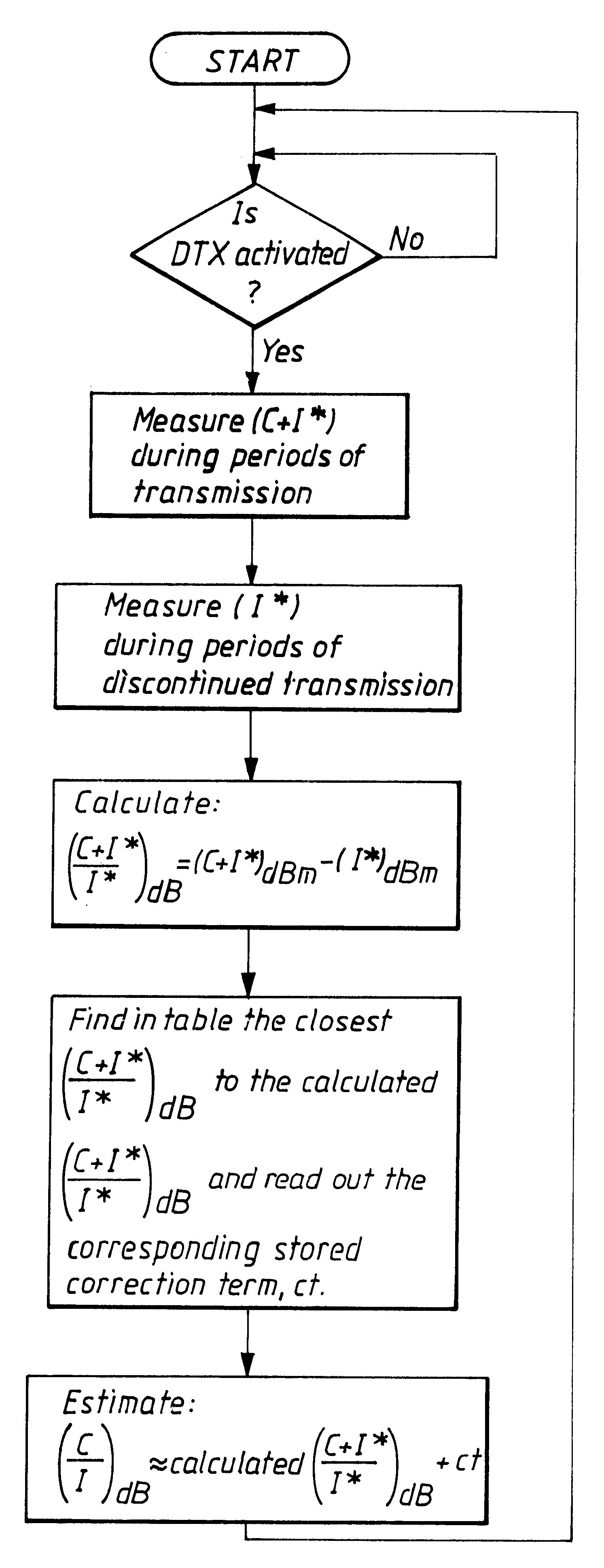
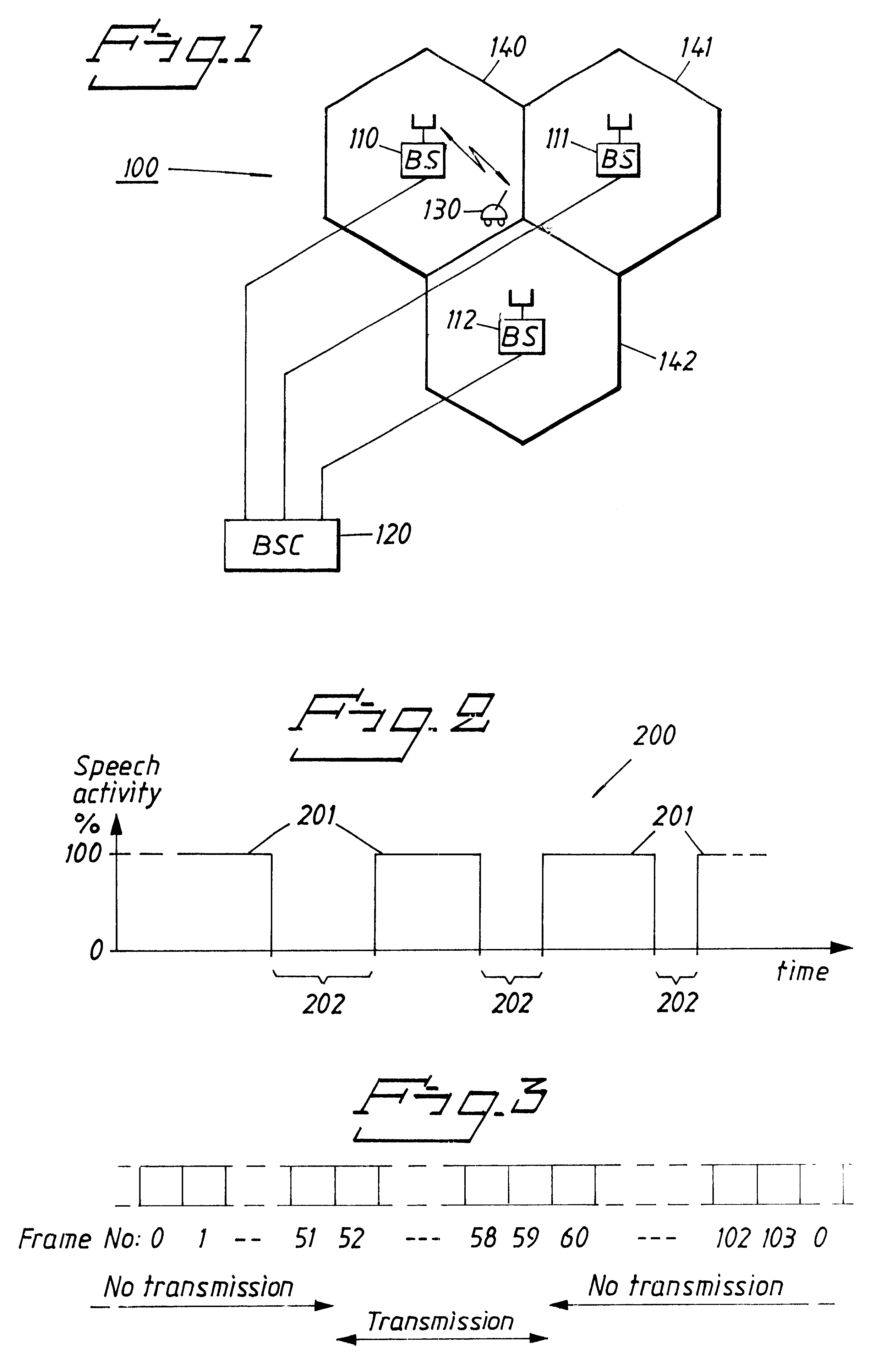
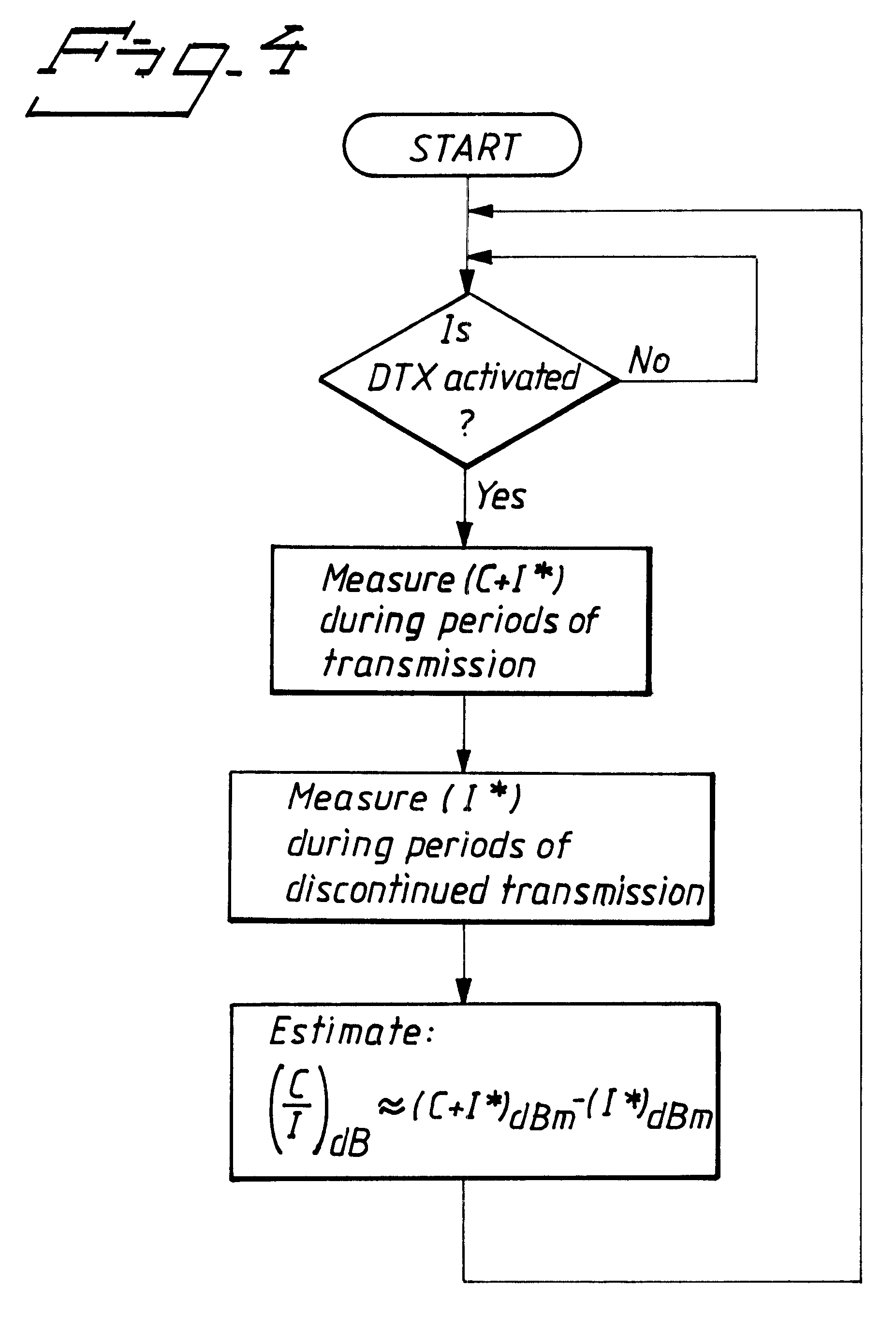
The carrier-to-interference ratio in a radio communication system is estimated by using measurements of the received signal strength in a communication channel within periods of time when transmission is discontinued and measurements of the received signal strength in the communication channel within periods of time with transmission.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Traffic management in distributed wireless networks
Wireless networks and devices are ubiquitous today. For service providers to offer customers QoS and Service Level Agreements (SLAs) means in part providing resilient connectivity of wireless devices with good signal strength, good Signal to Noise and Interference Ratio (SNIR), and adequate useable bandwidth. Doing so requires that devices transmitting and receiving packets use over-the-air bandwidth efficiently and manage over-the-air congestion. According to embodiments of the invention QoS measurements and controls are incorporated only in the network (i.e. APs or controllers) and therefore QoS and SLAs can be achieved with all deployed client stations versus standards based approaches that require additional capabilities in network nodes, client stations and in most cases modifications to the applications. SLAs can be provided exploiting embodiments of the invention for traffic prioritization, capacity improvements through load distribution, and adjacent channel interference mitigation discretely or in combination with standards based mechanisms.
Owner:3INOVA NETWORKS
Channel quality indicator for OFDM
ActiveUS7388847B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInterference ratioCarrier signal
Owner:APPLE INC
Adaptive power and data rate control for ad-hoc mobile wireless systems
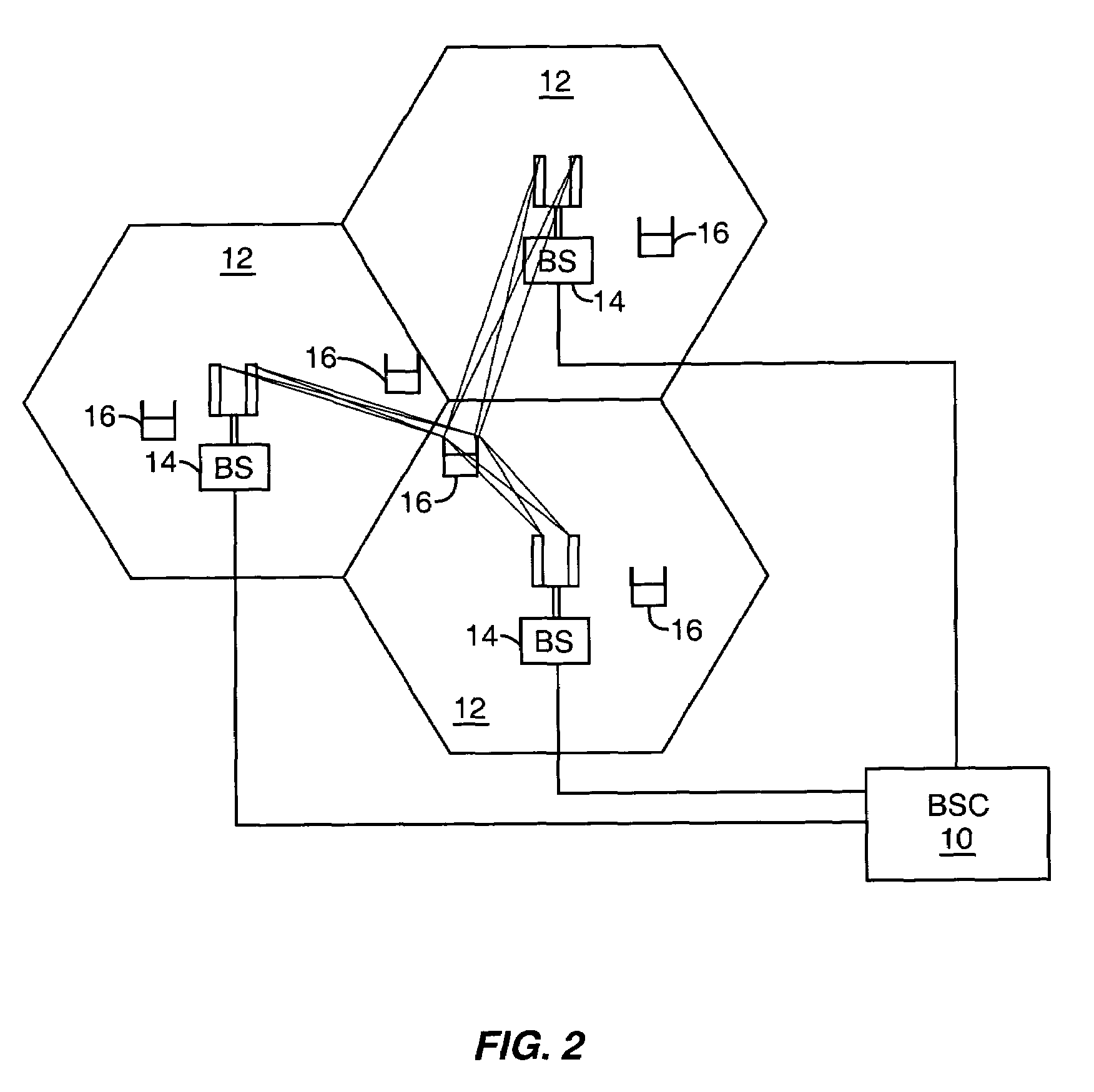
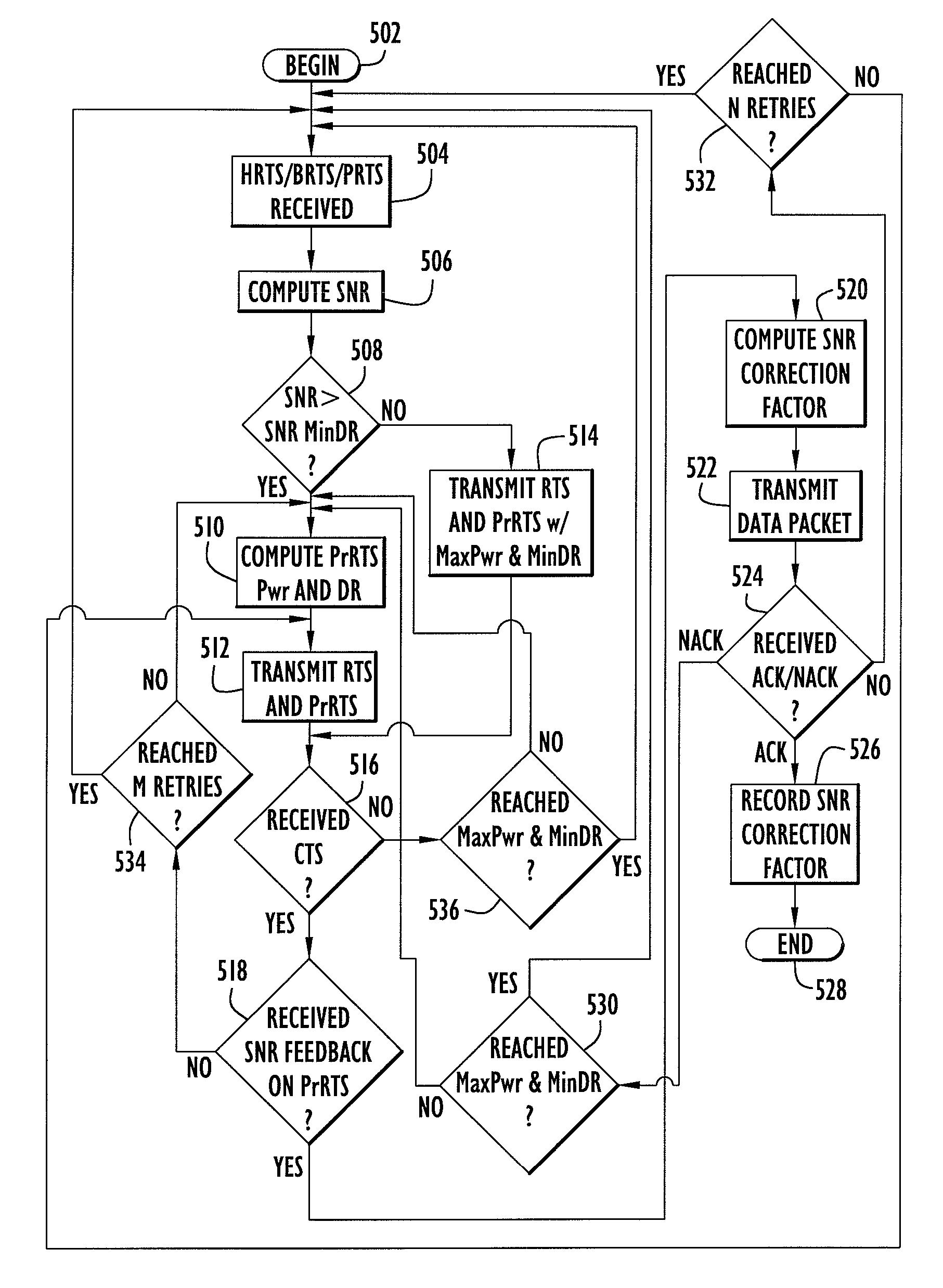
InactiveUS7983230B1Power managementNetwork traffic/resource managementClear to sendInterference ratio
A method for controlling transmit power of a node in wireless network, such as, e.g., an ad-hoc wireless network operating in accordance with a carrier sense multiple access (CSMA) protocol and where asymmetrical radio links may exist. During a request to send (RTS) and clear to send (CTS) exchange between a first node and a second node, both a request to send (RTS) packet and a probing request to send (PrRTS) packet are transmitted from the first node to the second node. The transmit power and data rate of the PrRTS packet may be different from the transmit power and data rate of the RTS packet. In response, the second node returns a CTS packet that includes a signal to noise ratio (SNR) for both the RTS packet and the PrRTS packet. A correction factor for data transmit power is then computed based in part on both the SNR for the RTS and the SNR for the PrRTS, and a data packet is thereafter transmitted at a power level that has been modified in accordance with the correction factor. The correction factor may further aid the estimation of the signal-to-noise-and-interference ratio (S / (N+I)) at a receiving node, which enables a sending node either to overcome the interference by adjusting the transmit power or avoid the interference by not accessing the channel until it hears the node again.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
Reduced crossmodulation operation of a multimode communication device
A method to reduce crossmodulation in a multimode radio communication device with a transmitter, a receiver, and a second receiver (400) that operates in a receiver channel bandwidth (402) includes a step of measuring a first signal strength in the receiver channel bandwidth (404), a second signal strength outside of the receiver channel bandwidth (406), and a power level of the transmitter. A next step (408) includes determining a signal-to-crossmodulation interference ratio (SCMIR). A next step (410) includes calculating a SCMIR threshold. A next step (412) includes comparing the ratio to the threshold. A next step (416,420) includes increasing the linearity of the receiver if the ratio is less than the threshold.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
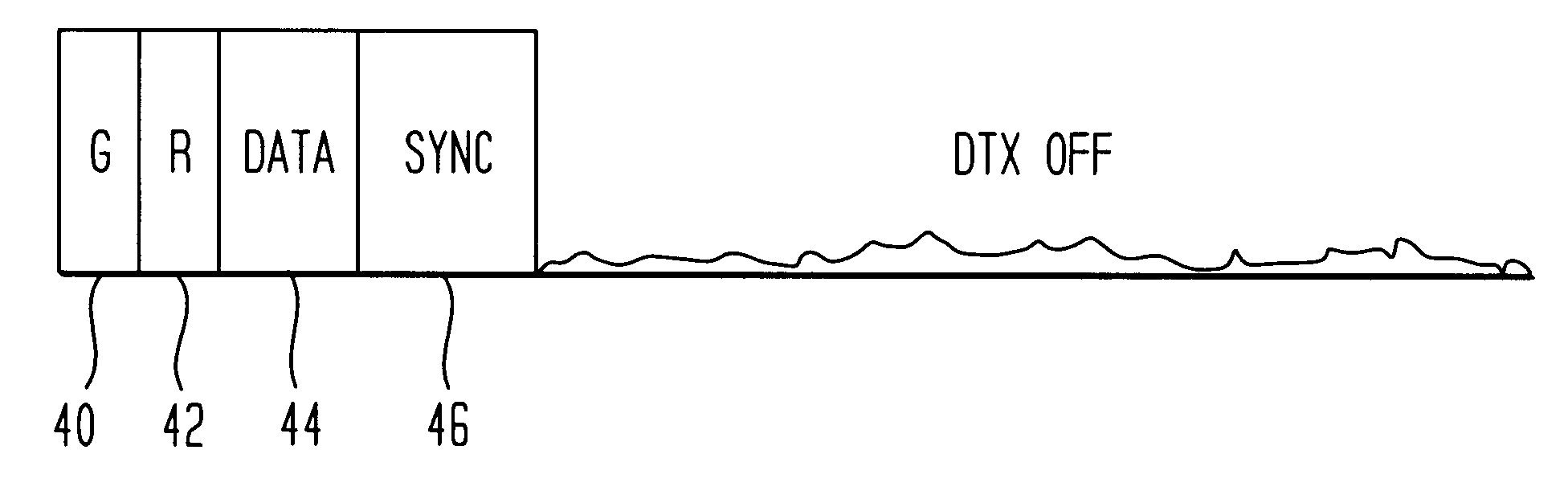
Method to dynamically determine interference and carrier-to-interference ration during TDMA calls
InactiveUS6842438B1Overcome disadvantagesPower managementTransmission control/equalisingInterference ratioActive time
In the method for dynamically determining interference and carrier-to-interference ratio, interference is measured during an active TDMA time slot. In one embodiment, a base station determines the interference level in an active time slot using power level measurement taken during a DTX OFF period, when a mobile station is transmitting in discontinuous transmission mode. In another embodiment, a base station orders a mobile station to cease transmission during a SACCH portion of the time slot, and determines an interference level I measurement using power level measurements taken during the inactive SACCH field. Another embodiment provides for the determination of an interference level I using power level measurements taken during the guard and ramp fields.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
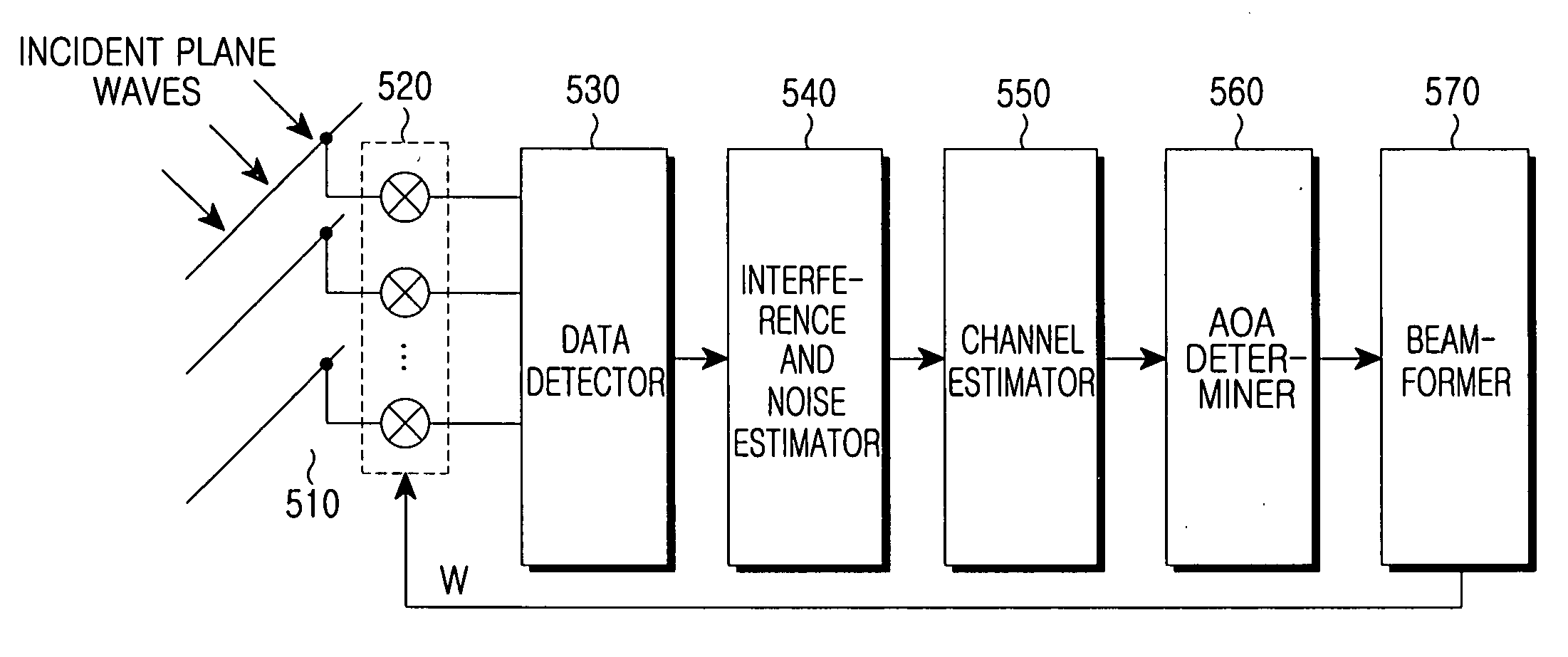
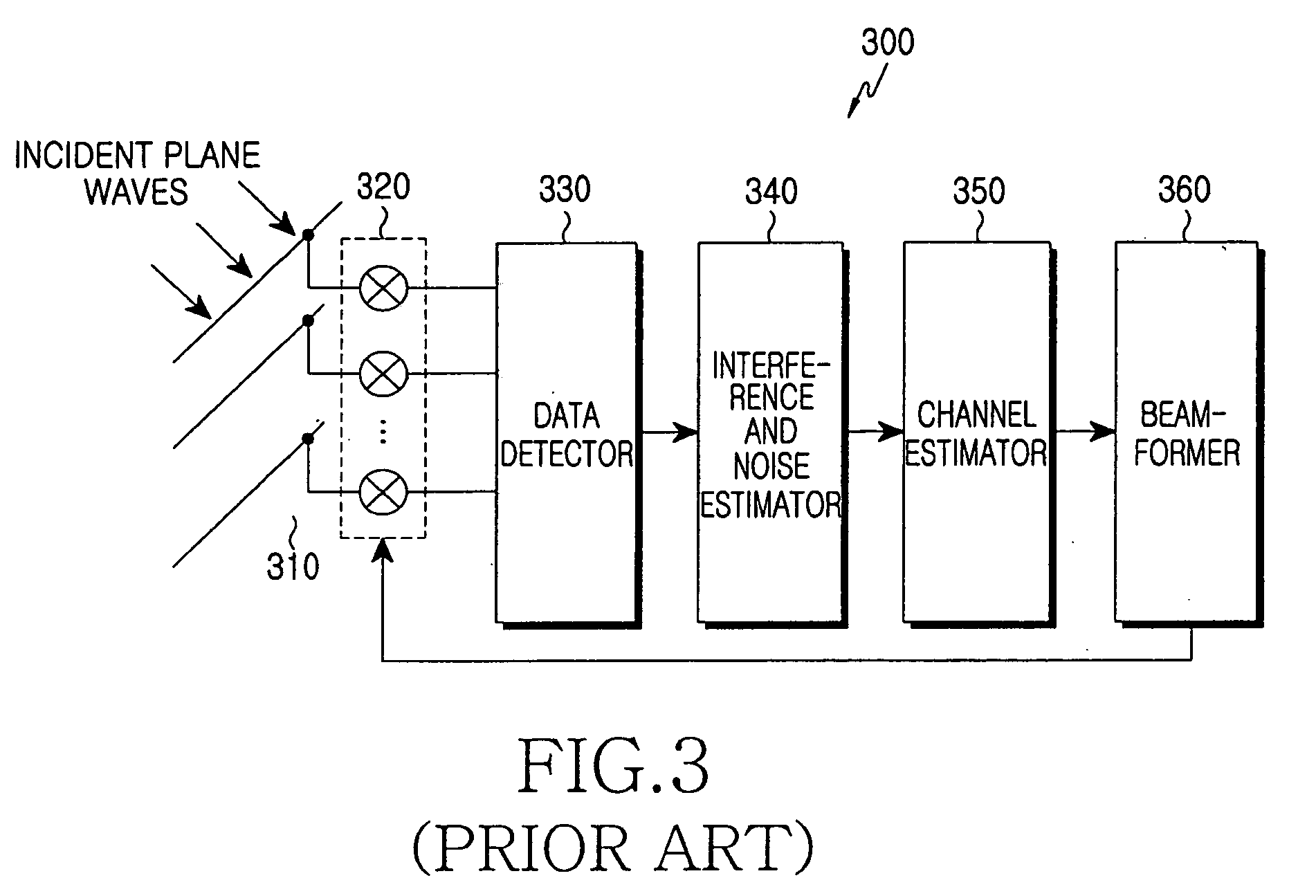
Beam-forming apparatus and method using a spatial interpolation based on regular spatial sampling
ActiveUS20060244660A1Reduce complexityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesBeam angleInterference ratio
A beam-forming apparatus and method for improving system performance using a spatial interpolation and at least one Angle of Arrival (AoA) in a system based on regular spatial sampling is provided. The AoA is estimated using a carrier-to-interference ratio. Beam-forming angles are distributed and steered in a predefined scheme such that an identical process is applied in all directions. According to this steering, a linear system model is computed based on regular spatial sampling using regular spatial separation at beam angles. Beam-forming performance is improved by compensating for a difference between adaptive and sector-type arrays. Only the steps of computing a spatial interpolation and determining an angle range for beam-forming using at least one AoA are added. The precision of estimating an AoA and the precision of beam-forming increase without an additional antenna. Because the system is simpler than that of an adaptive beam-forming system, significant gain is obtained.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
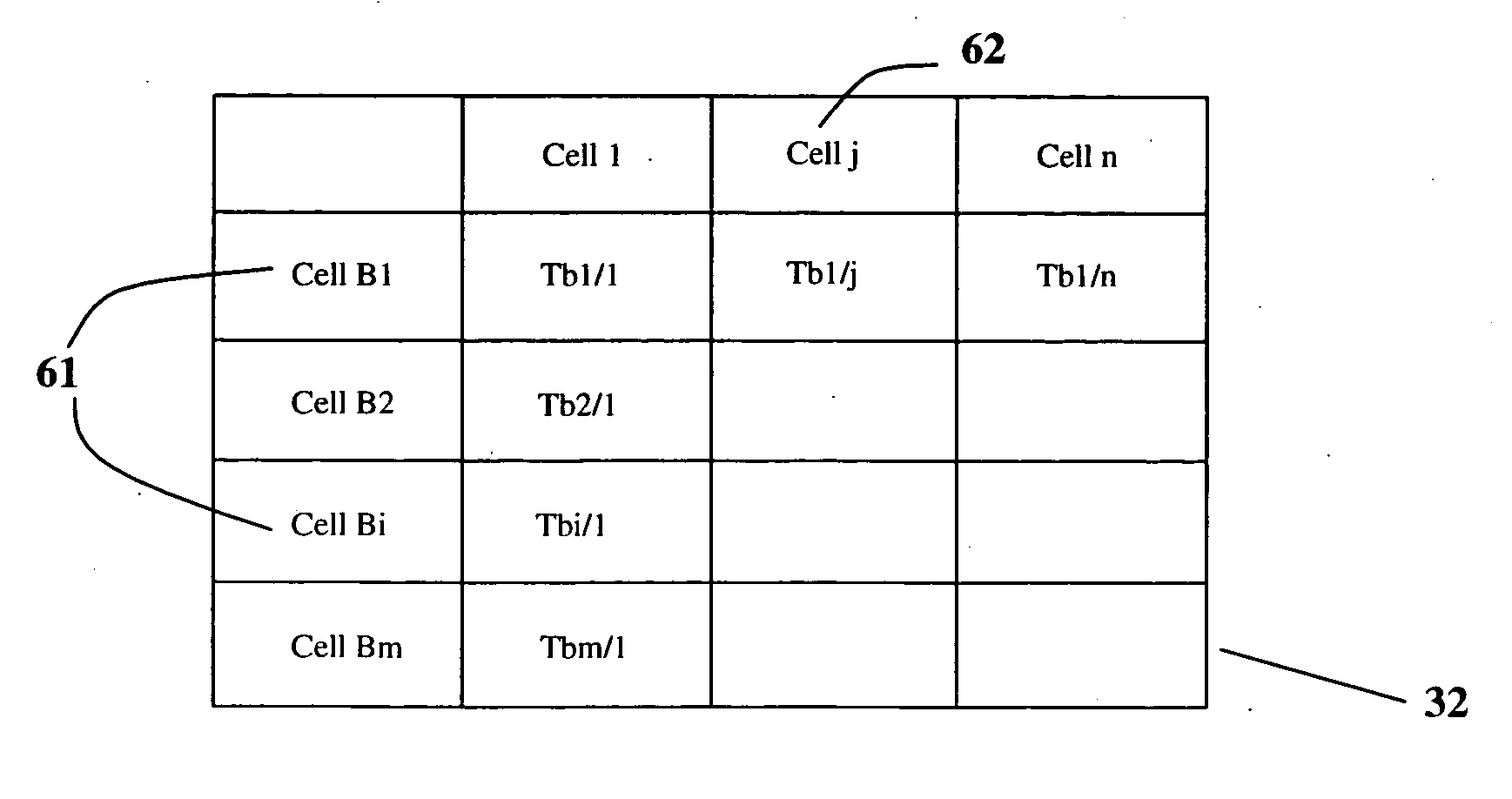
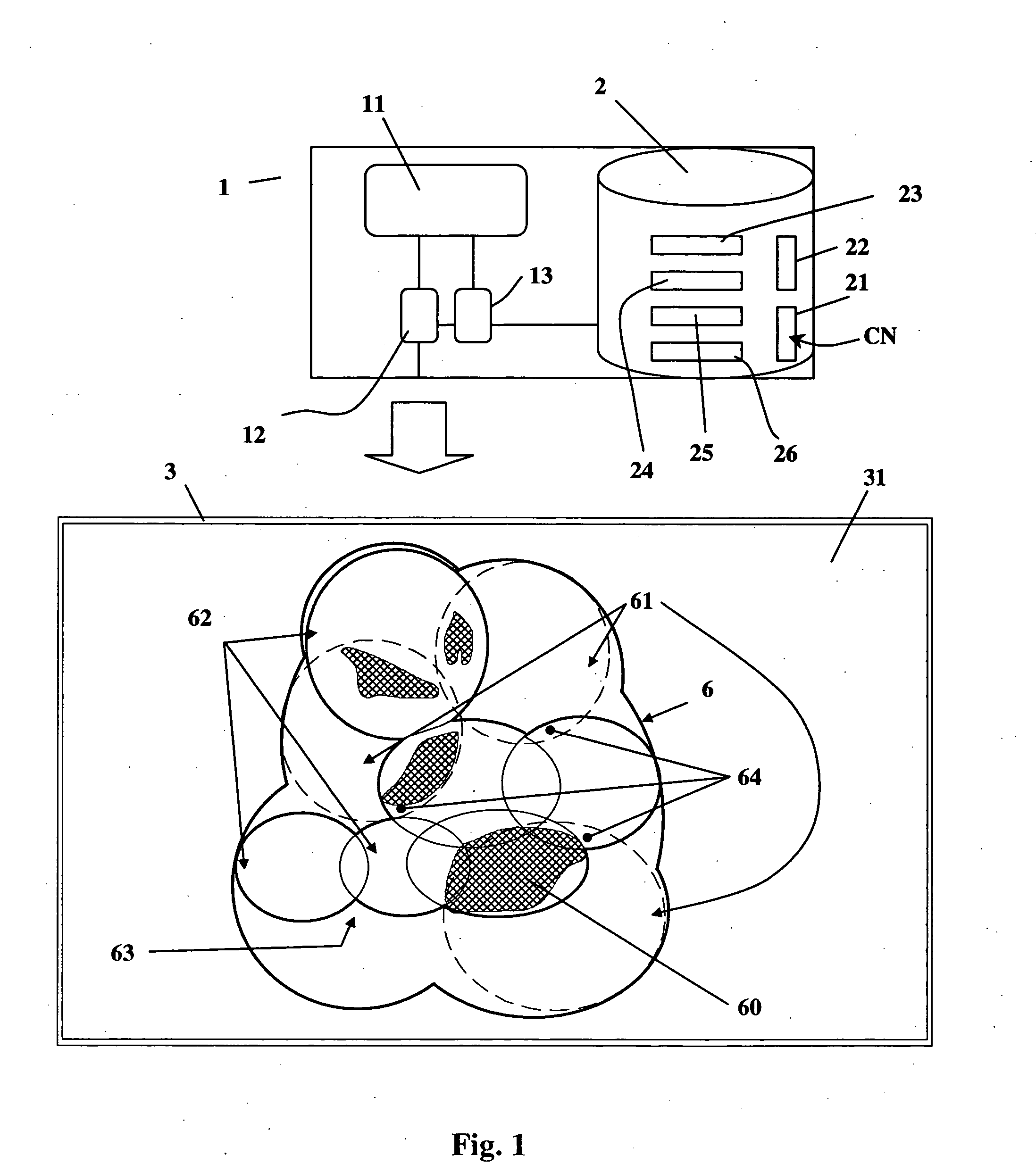
Method and apparatus for medium access control in a wireless broadband system with multiple-input multiple-output or multiple-input single-output technology with multiuser capabilities
InactiveUS20120082200A1Reduce resource requirementsIncrease available bandwidthTransmission monitoringSignalling characterisationInterference ratioBroadband
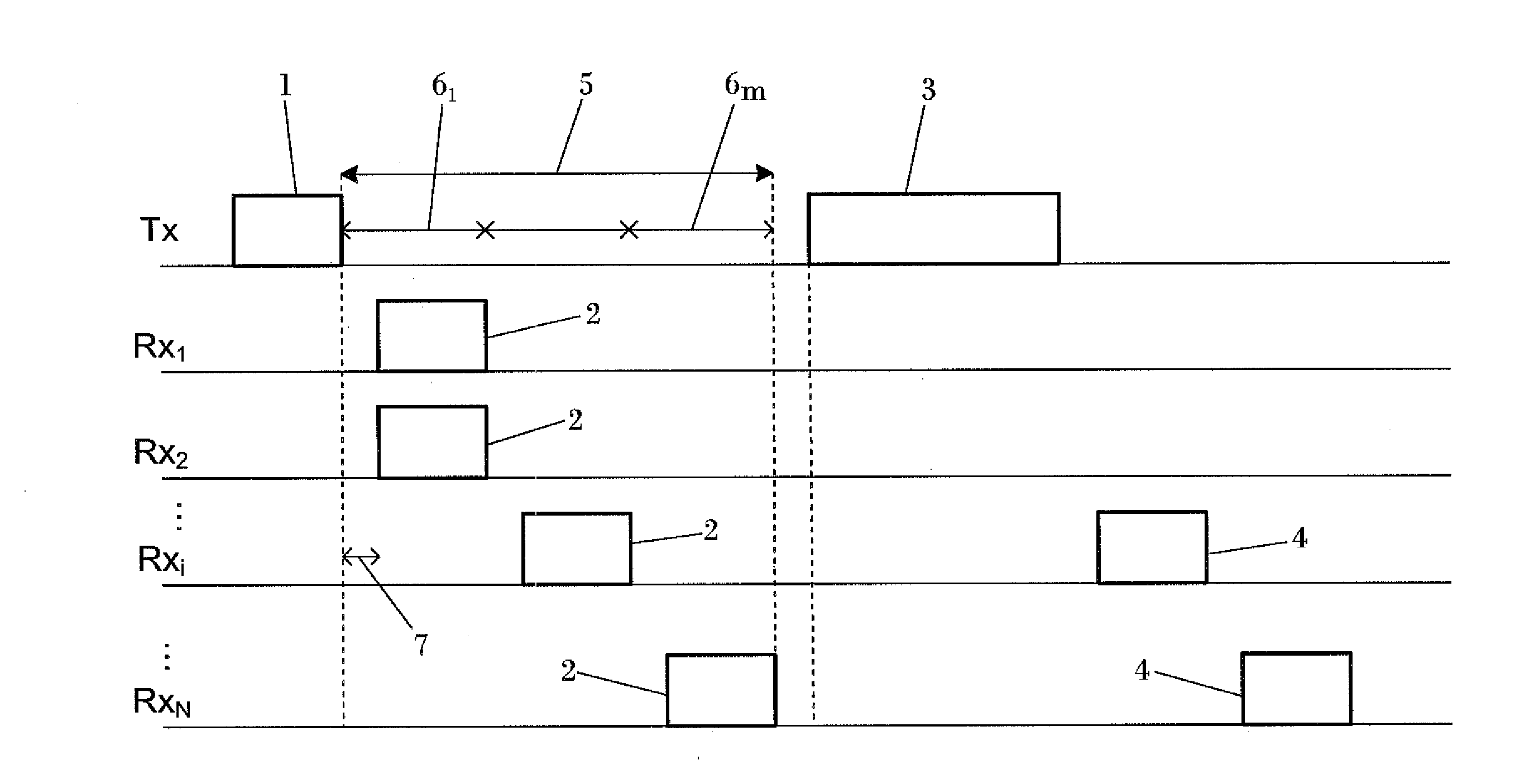
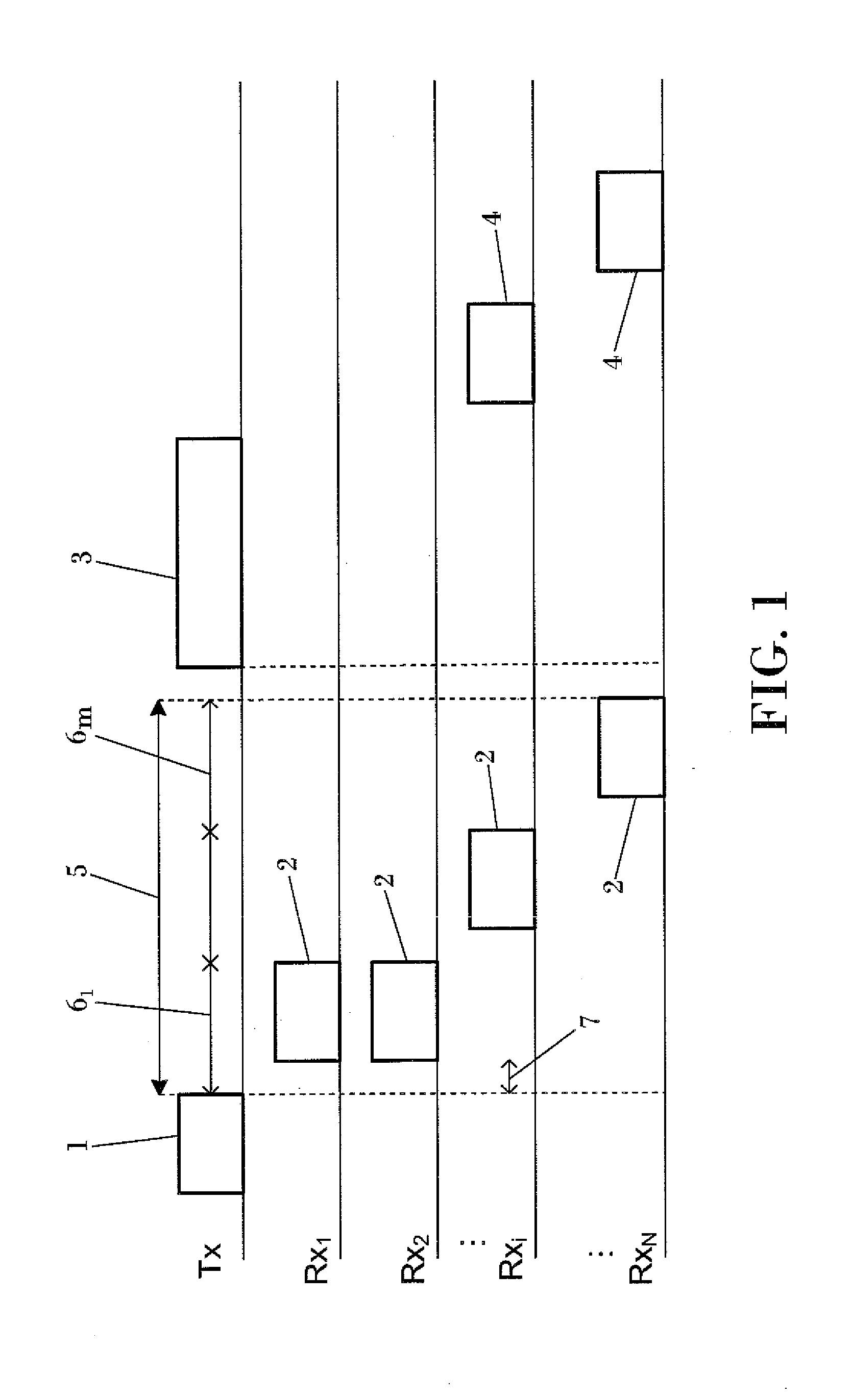
Method and apparatus for medium access control in a wireless broadband system with multiuser MIMO / MISO technology comprising the steps of a transmitter (Tx) broadcasting a polling message (1) to all the users (Rx1 . . . Rxi . . . RXN) associated to said transmitter (Tx); the users answering with reply messages (2) during a time slot (61 . . . 6m) randomly selected from a plurality of time slots in which a period of time dedicated to sending reply messages (5) is divided; the transmitter (Tx) performing a scheduling and transmission of data (3); and scheduled users sending Acknowledgment messages (4). Preferably, only users which measure a Signal to Noise plus Interference Ratio over a pre-defined threshold for a transmission beam send reply messages (2).
Owner:FUNDACIO PRIVADA CENT TECNOLOGIC DE TELECOMUNICACIONS DE CATALUNYA
System and method for constructing a carrier to interference matrix based on subscriber calls
InactiveUS20120270544A1Valuable bandwidthReduce expensesTransmission monitoringWireless commuication servicesTime informationInterference ratio
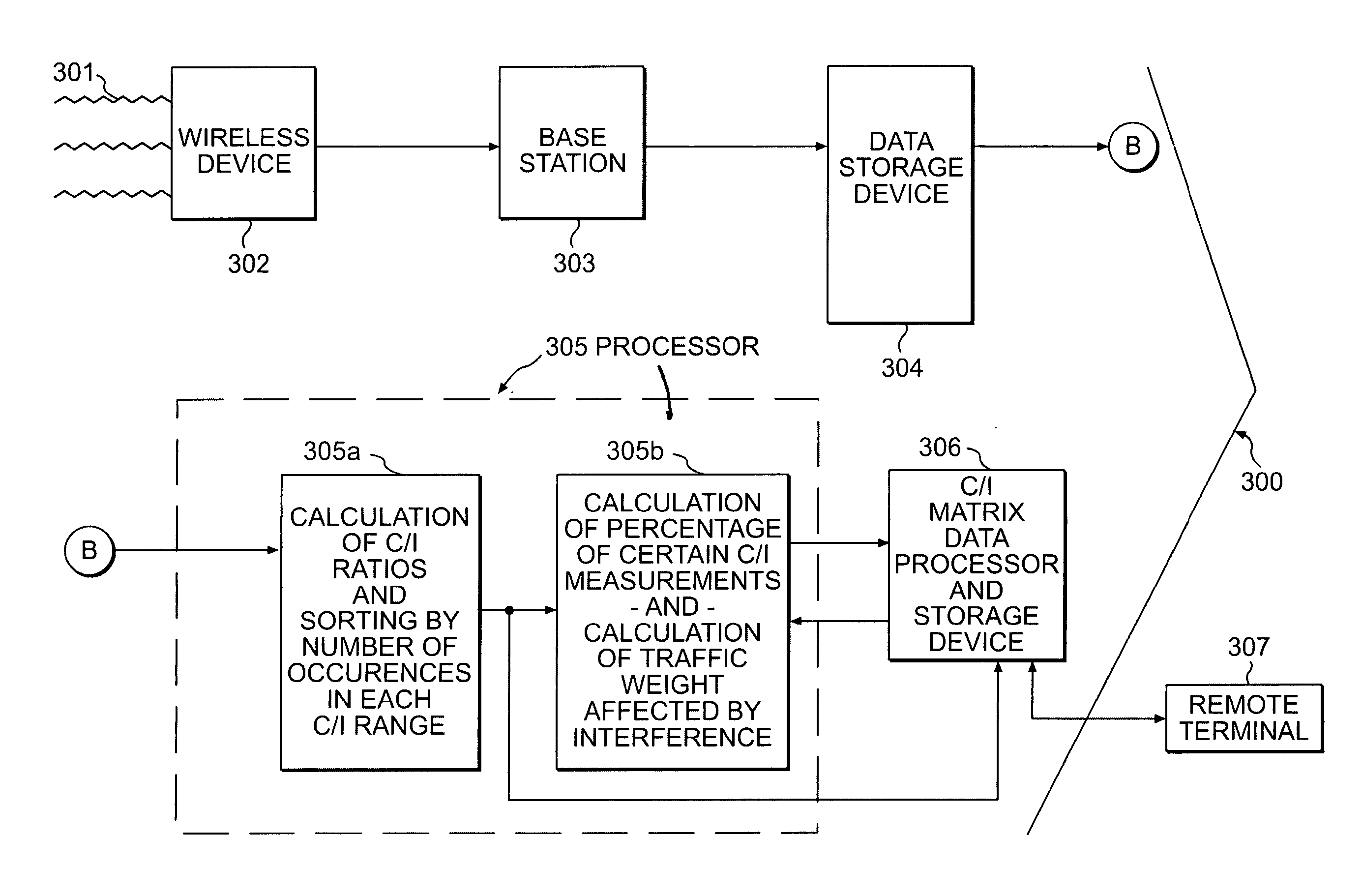
A conventional wireless device constantly measures the signal strength of its server base station and the strength of signals from surrounding base stations for handoff purposes. The wireless device transmits this information to its serving base station, which discards the information a short time afterward, following handoff. The present system and method store the formerly discarded information in one of several existing network elements or in a separate computer system. This information is used to generate a carrier to interference ratio, which indicates the level of interference between station pairs, and to also generate a carrier to interference matrix, including identifying potential interference for each station pair. The frequency of occurrences during predetermined desired periods of time and the volume of traffic affected by each level of interference may also be calculated. This provides comprehensive, continuous, real-time information for wireless frequency planning.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
Method of calculating and displaying mutual interference in the down direction in a cellular radiotelephone network with a W-CDMA type access
InactiveUS20040242158A1Required calculation powerGood precisionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission noise suppressionUltrasound attenuationInterference ratio
The process consists of selecting a sub-set of interfering cells and a sub-set of interfered cells among a set of a radio cells in a network, fixing a plurality of calculation parameters such as threshold levels for signal / interference ratios, parameters related to the power of interfering cells and the traffic channel, then determining the service area of the interfered cells and the area including inter-cell overlaps, then calculating the attenuation of the interfering cell and the attenuation of the serving interfered cell respectively, at each point or pixel in the overlap area. An estimate of the signal / interference ratio is made for each pixel starting from attenuations and parameters. The invention is used to isolate and identify interfering cells and interfered cells. The power in the interfering cells generating an excessive disturbance can thus be adjusted.
Owner:SOC FR DU RADIOTELEPHONE SFR
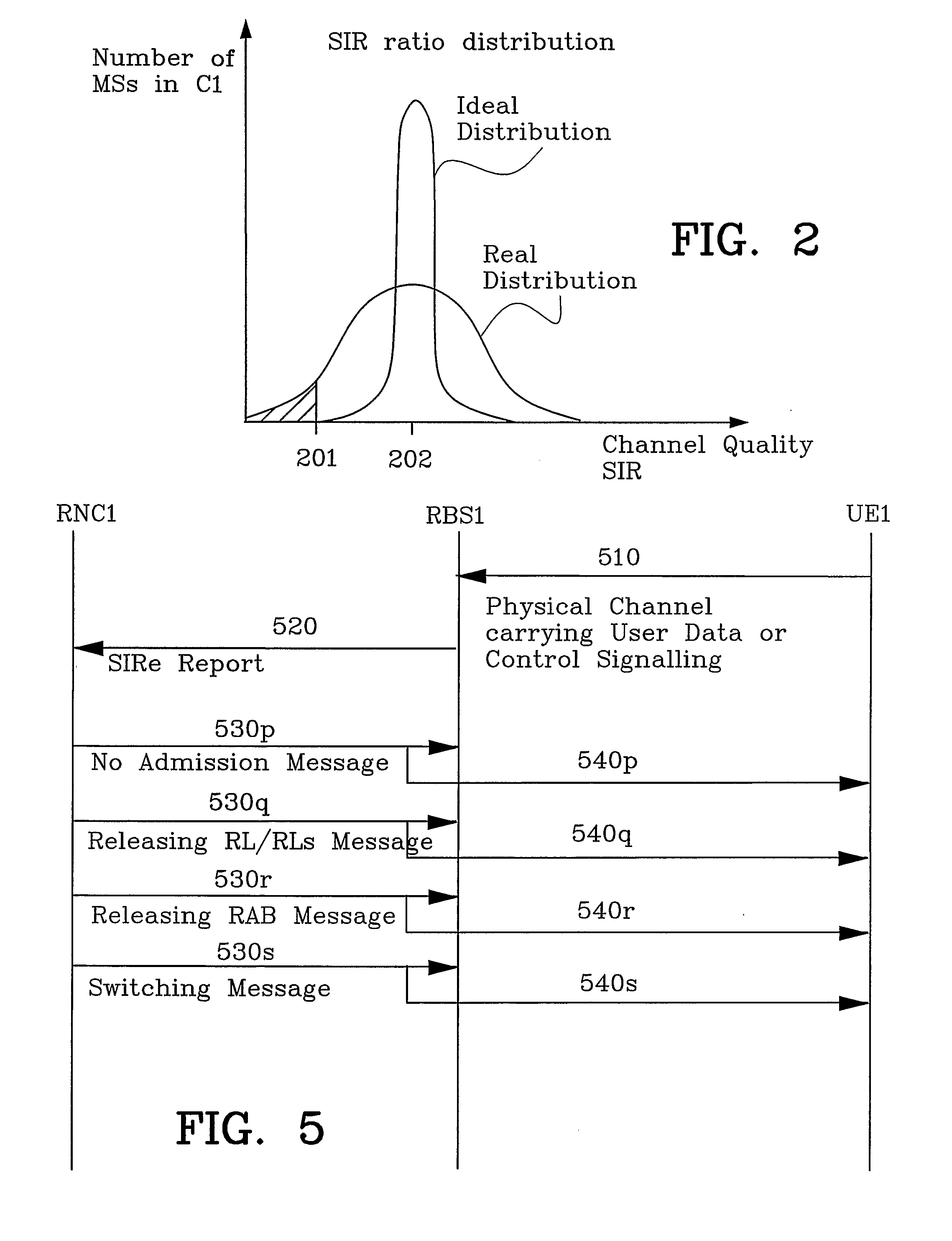
Method and Apparatus in a Telecommunication System
ActiveUS20080268864A1Improve accuracyAvoid congestionNetwork traffic/resource managementSubstation equipmentRadio networksTelecommunications
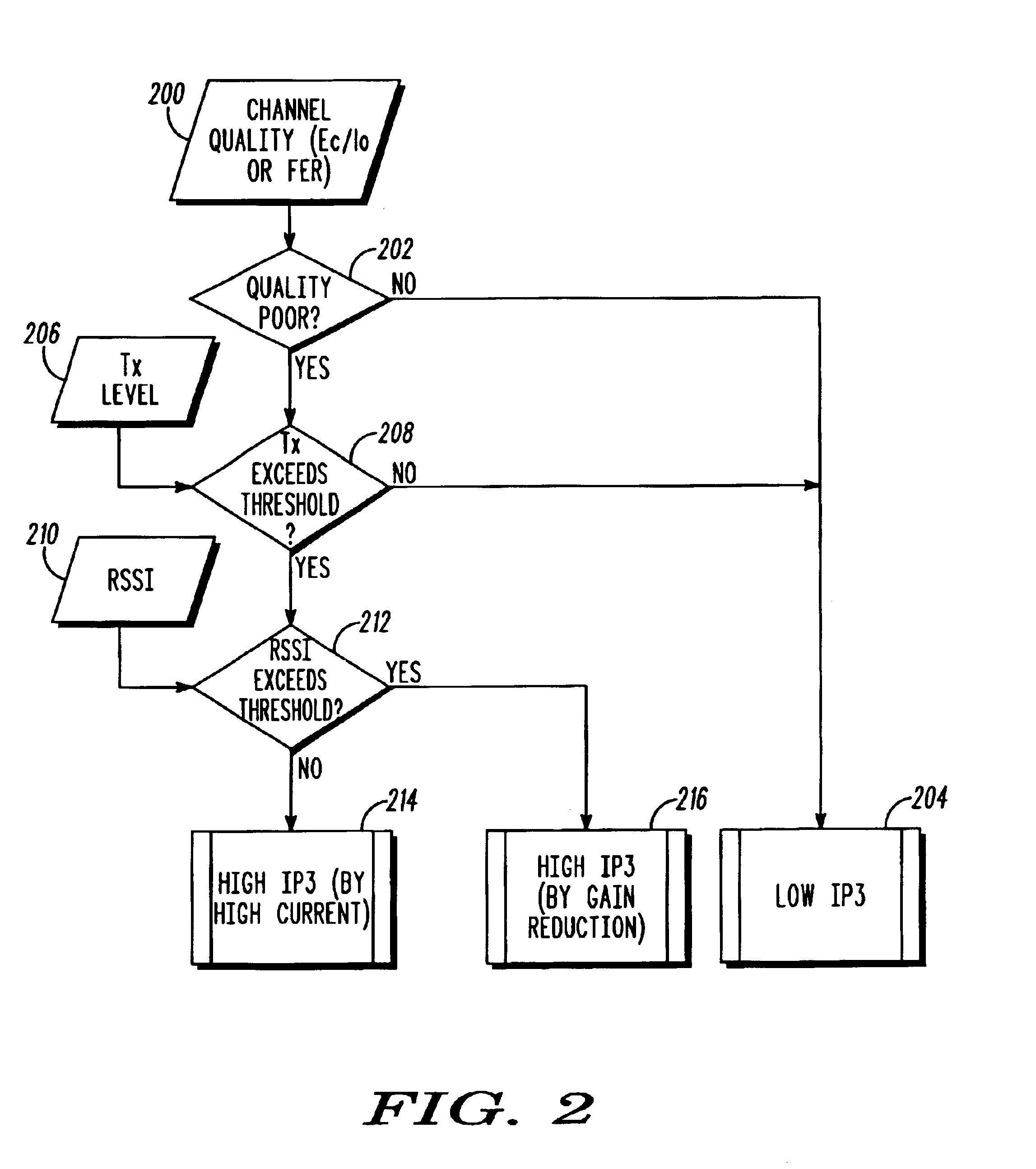
The present invention relates in general to the radio communications field and, in particular, to a method and apparatus for detecting congestion in a spread spectrum Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) cellular communication system. By measuring the number of Signal-to-Interference Ratio Error reports being received at the Radio Network Controller a potential congestion can be detected in the cell when the number of reports being received is above a threshold. Further can a differentiation be made between a potential or a serious congestion and different actions be performed dependant on if a potential or a serious congestion is detected.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and Method for Power Control
ActiveUS20110136533A1Easy to usePower managementTransmission control/equalisingInterference ratioTransmitted power
A method of operating base station includes determining a first transmit power of a user equipment (UE), which includes determining a serving base station receive power, determining a path loss of the UE to the base station, determining a downlink signal to noise and interference ratio (SNIR) at the UE, and forming the first UE transmit power. Forming the first UE transmit power comprises summing the serving base station receive power, the path loss of the UE to the base station and the downlink SNIR. The method further includes instructing the UE to transmit at the first UE transmit power.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
TD-SCDMA base station planning point automatic selection method based on coverage prediction
ActiveCN104378769AReduced precision requirementsImprove rationalityNetwork planningHigh signal intensityInterference ratio
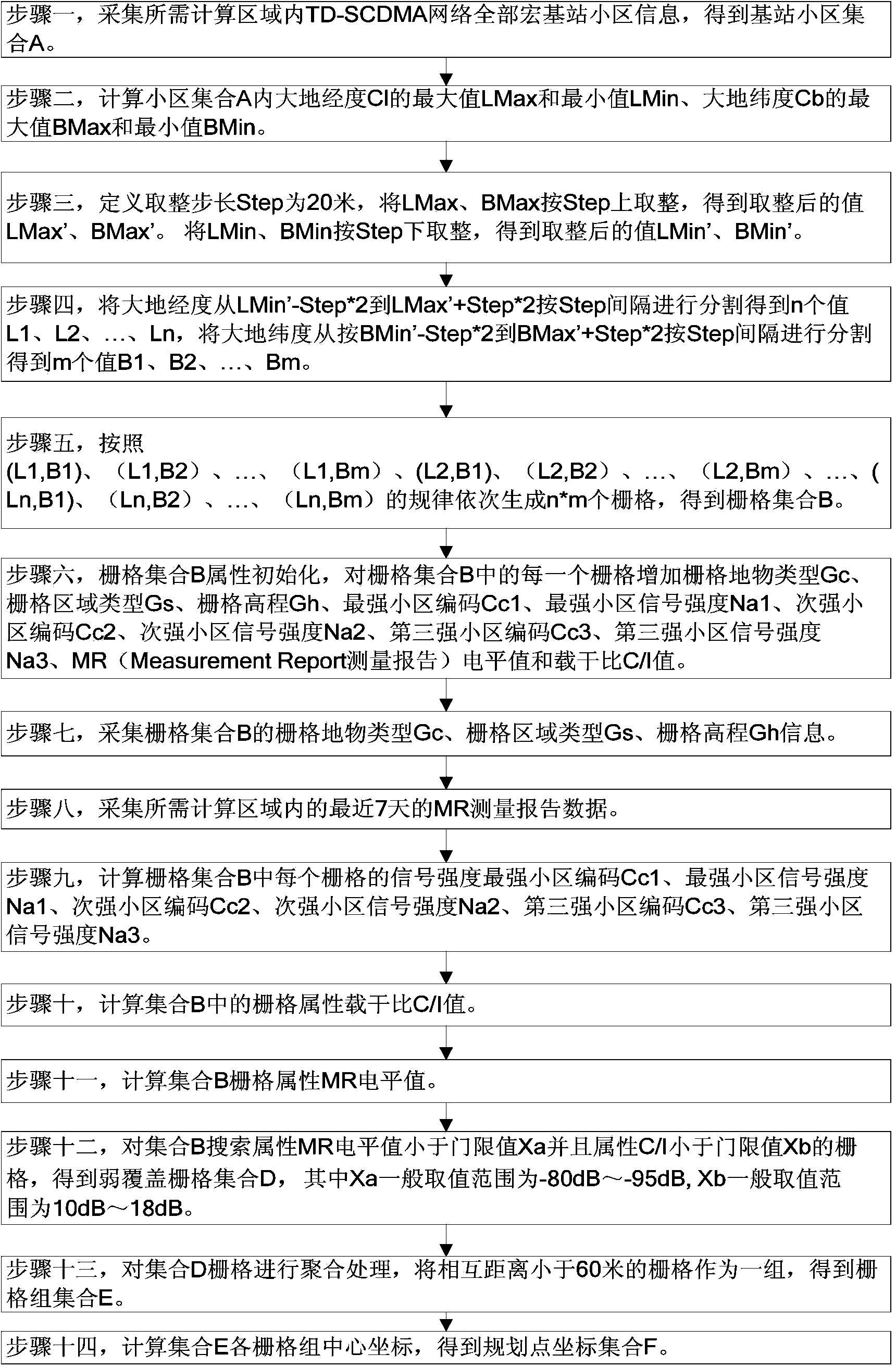
The invention discloses a base station planning point automatic selection method. The method comprises the core steps that cell information of macro base stations is acquired, and a set A is obtained; the maximum value and the minimum value of cell longitudes and latitudes in the set A are calculated, and the maximum value and the minimum value are rounded according to the step length; the longitudes and the latitudes are segmented according to the step length from the minimum value to the maximum value; according to pairing of the longitudes and the latitudes, a set B is obtained; the attributes of the set B are initialized; grid ground feature information of the set B is acquired; an MR level value is acquired; the signal intensity of each grid in the set B is calculated, and the first three cells with the first three high signal intensities are obtained; the carrier-to-interference ratio of the grids in the set B are calculated; the attribute MR level values of the grids in the set B are calculated; the grids with the attribute MR level values smaller than a threshold value Xa and the carrier-to-interference ratios smaller than a threshold value Xb are searched for in the set B, and a poor coverage set D is obtained; aggregation processing is carried out on the grids of the set D, and the grids with the distances smaller than a threshold value are arranged in one set, so that a grid group set E is obtained; the center coordinates of the grid groups of the grid group set E are calculated, and a planning point coordinate set F is obtained.
Owner:CHINA INFOMRAITON CONSULTING & DESIGNING INST CO LTD
Method and apparatus for open loop power control in frequency division multiple access system
ActiveUS20070189234A1Increase capacityReduce distractionsEnergy efficient ICTPower managementInterference ratioSystem capacity
A method and apparatus for efficient open loop power control in a packet data mobile communication system using Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) is disclosed. When a target Signal-to-Interference Ratio (SIR) required for the determination of transmission power using open loop power control is set, influence upon neighboring cells is considered. In other words, when a Mobile Station (MS) is located at a cell boundary and thus induces large interference with its neighboring cells, the target SIR is set low. In the other case, the target SIR is set high. Therefore, by adjusting transmission power according to the position of an MS and a relationship between the MS and the neighboring cells, support for high data rate can be provided to an MS that is located near a Base Station (BS) and interference induced by an MS that is located around a cell boundary can be minimized. In this way, the entire system capacity can also be improved.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and apparatus for beam switching in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS7400606B2Increase heightMaximized ratioTime-division multiplexSubstation equipmentCommunications systemSystem capacity
In a CDMA data communication system capable of variable rate transmission, utilization of beam switching techniques decreases the average interference caused by transmissions of a base station to subscriber stations within a cell, and in neighboring cells. Base stations utilize multiple transmit antennas, each transmitting signals at controlled amplitudes and phases, to form transmit signal corresponding to sector divisions. Data and reference signals are transmitted along sector division beams that alternate according to fixed time slots in order to increase system capacity and data rates by maximizing carrier-to-interference ratios (C / I) measured at subscriber stations.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
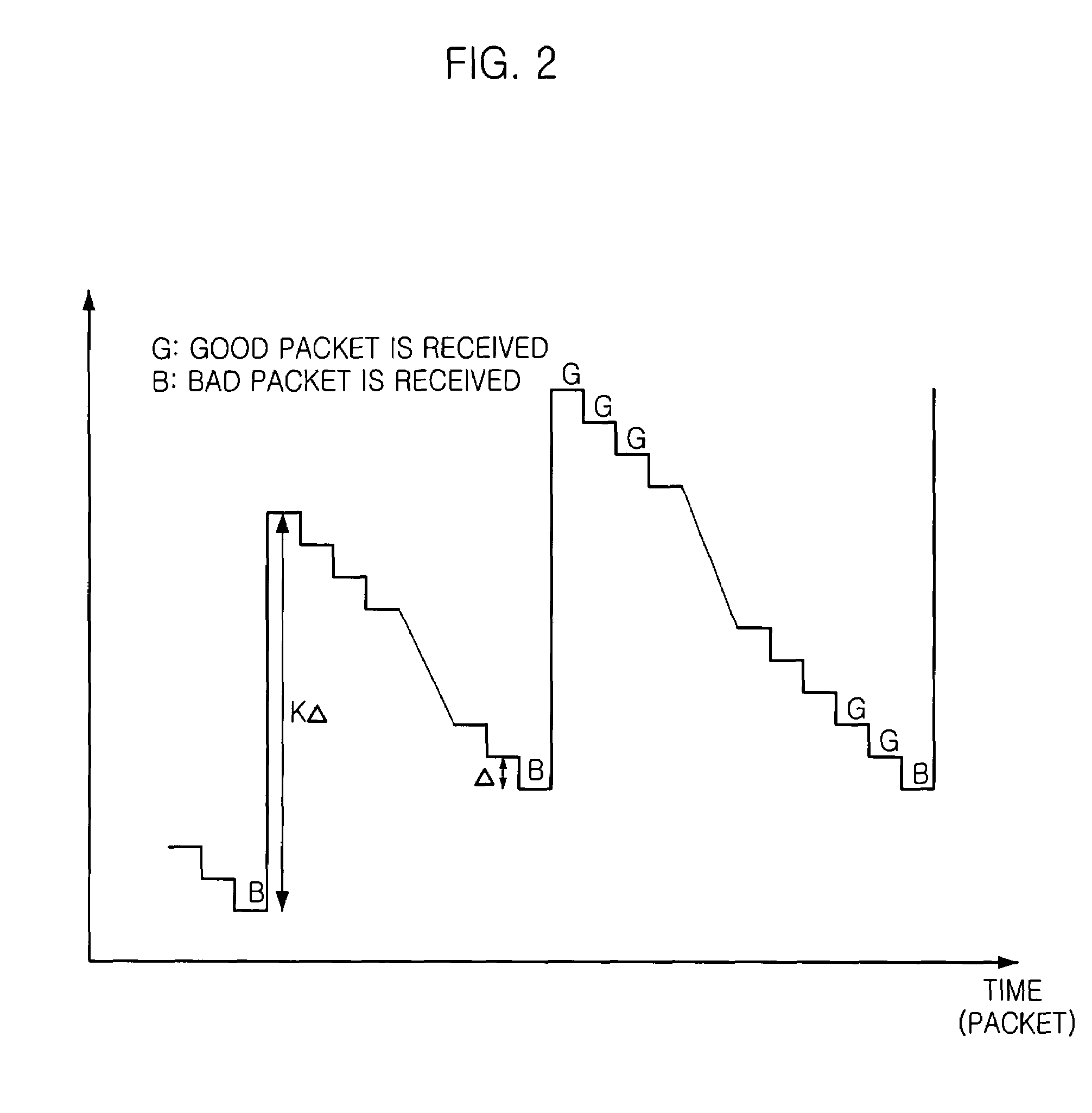
Method for controlling power level based on packet error rate in wireless personal area network system
InactiveUS7400899B2Securing of qualityPower managementResonant long antennasComputer networkInterference ratio
Disclosed is a method for controlling a power level based on a packet error rate (PER) in a wireless personal area network (WPAN) system. The method for controlling a power level based on a packet error rate (PER) in a wireless personal area network (WPAN) system, includes the steps of: a) at a receiver, computing a PER of a packet in an initial check duration of PER (DP) wherein a transmission power level of the packet is set by a piconet coordinator (PNC); b) at the receiver, determining whether the computed PER satisfies a target PER, adjusting a target signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) and requesting a transmitter to adjust the initial transmission power level; and c) at the receiver, determining whether the number (N) of successive G is larger than a power control threshold, wherein G denotes DP satisfying the target PER, changing the target SIR based on the determination result whether the number (N) of successive G is larger than the power control threshold, and requesting the transmitter to adjust the possible transmission power level.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for implementing selection of multiple-band multi-access technique district by wireless communication mobile equipment
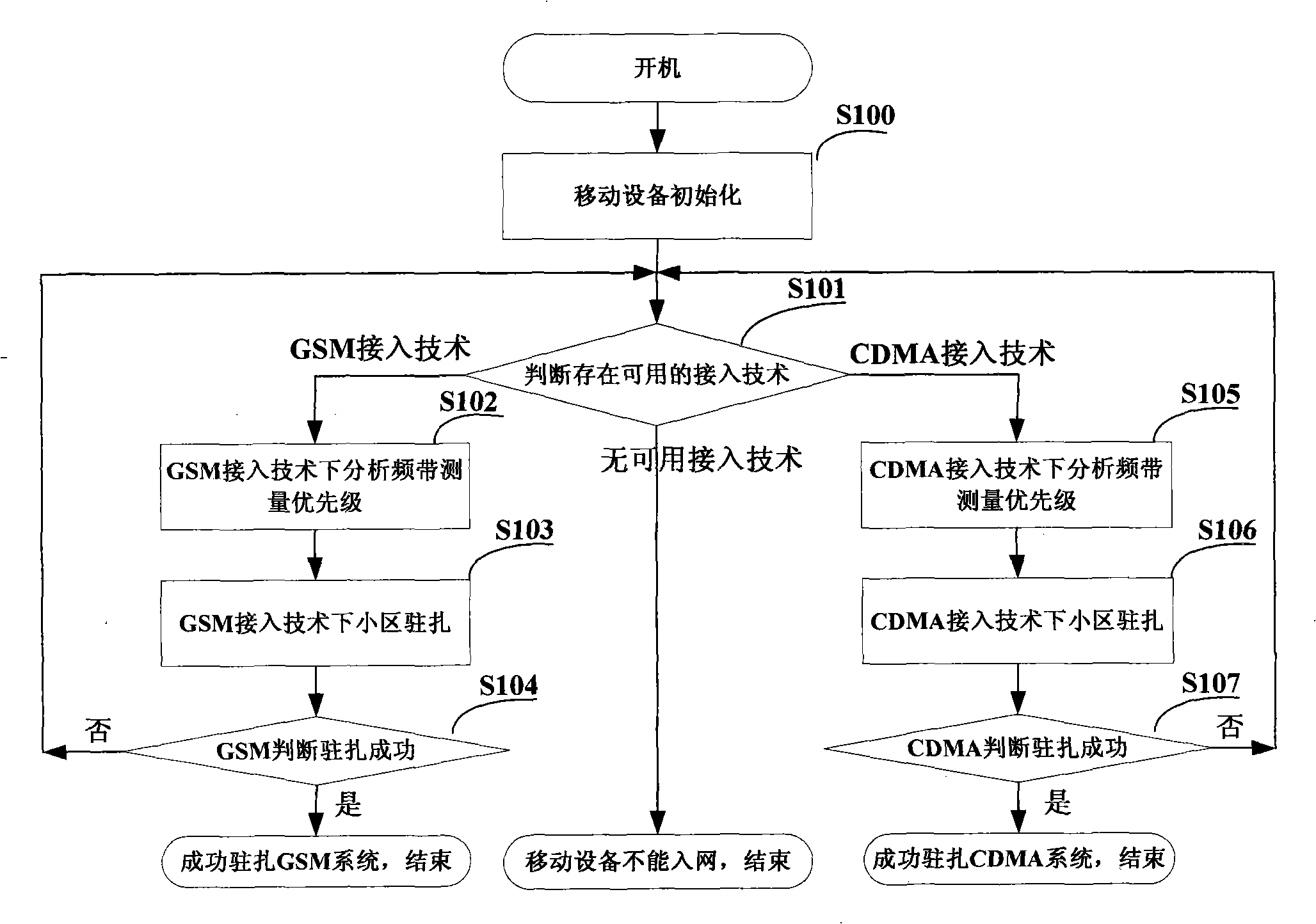
ActiveCN101325757APrecise positioningAccurate location serviceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsHigh level techniquesMulti bandInterference ratio
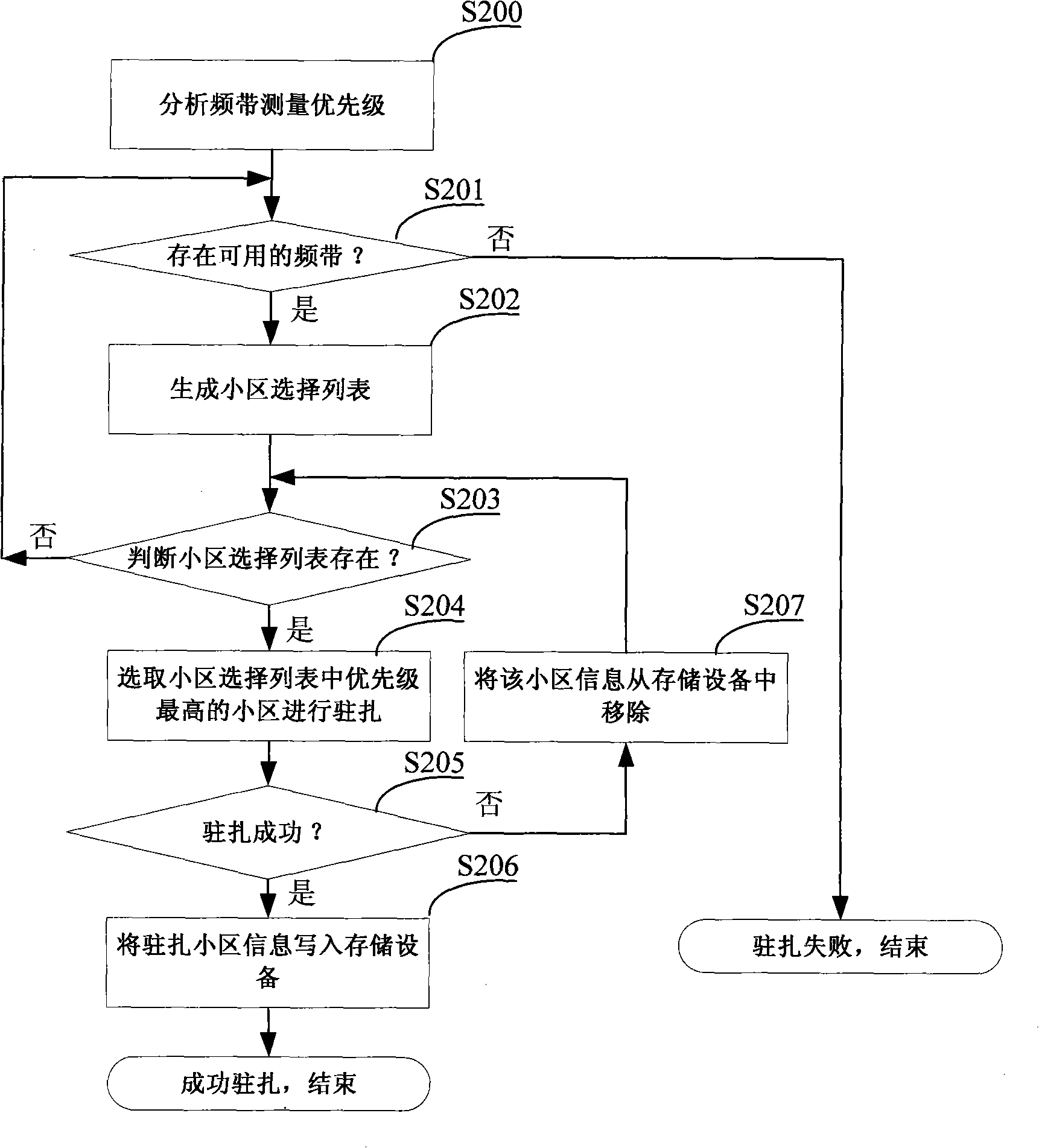
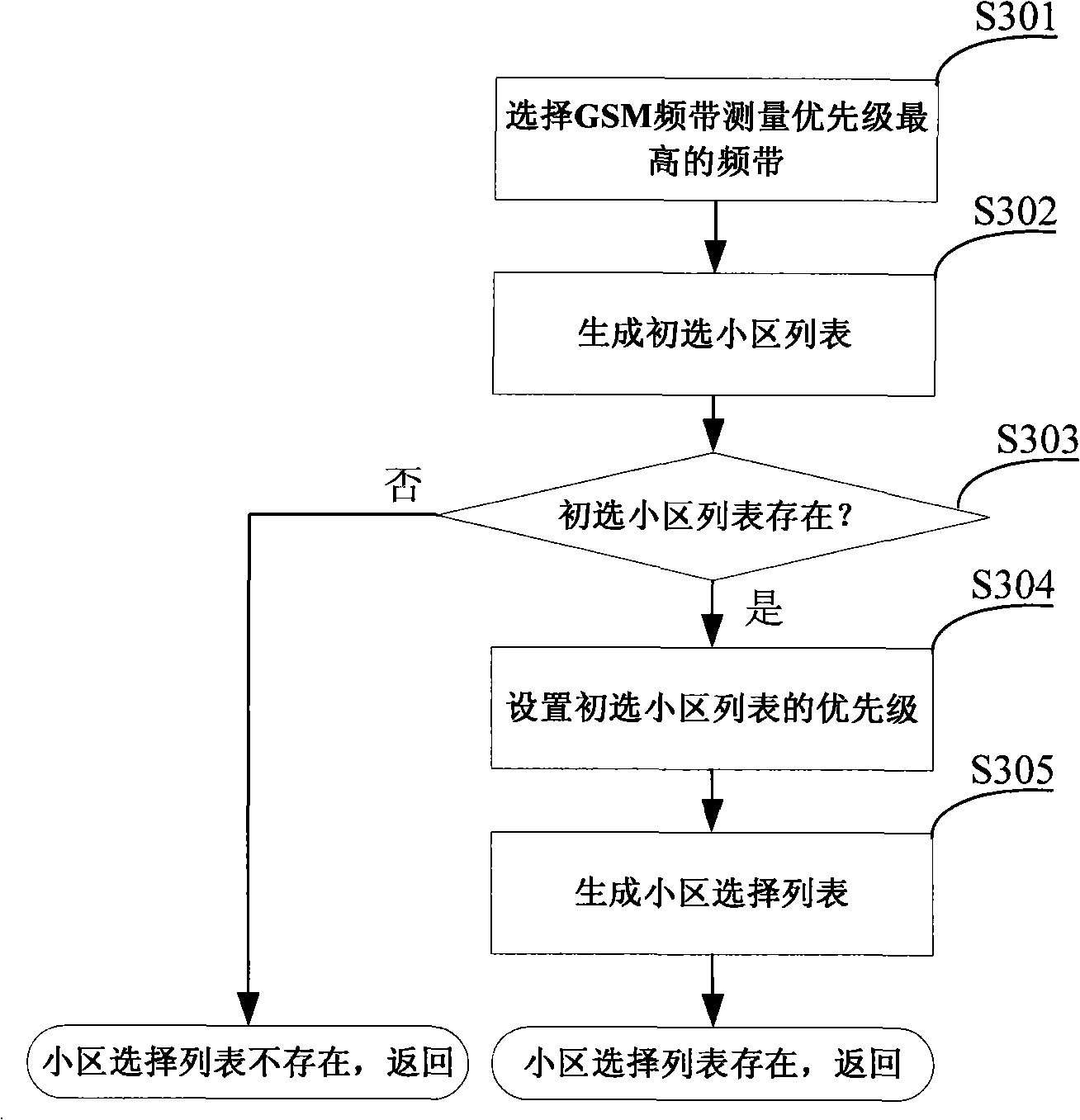
The invention relates to a method for a radio communication mobile device to implement cell selection with multi-band multi-access technology, comprising the steps of after starting the mobile device, confirming priority for band measurement according to information acquired from storage equipment, such as access technology selected by a user, a cell residence history table and a neighbor cell history table; confirming primary cell list of cell selection according to an indicated value of signal intensity of band measurement with highest priority, an intensity value of pilot channel, and carrier-to-interference ratio of pilot channel; confirming a cell selection list combined with the cell residence history table and the neighbor cell history table; the mobile device resides on the cell with the highest priority in the cell selection list. With the implement method of cell selection with multi-band multi-access technology for the radio communication mobile device, mobile device can reside cells fast, which reduces measurement number of frequency point effectively and reduces operation time, reduces power consumption of the system, and is capable of locating the service cells more accurately, and enhances efficiency of initial residence of cells.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Method and system to indicate a desired transmit power and soft power control in a wireless network
InactiveUS20100061317A1Well formedReduce transmit powerPower managementEnergy efficient ICTInterference ratioCommunications system
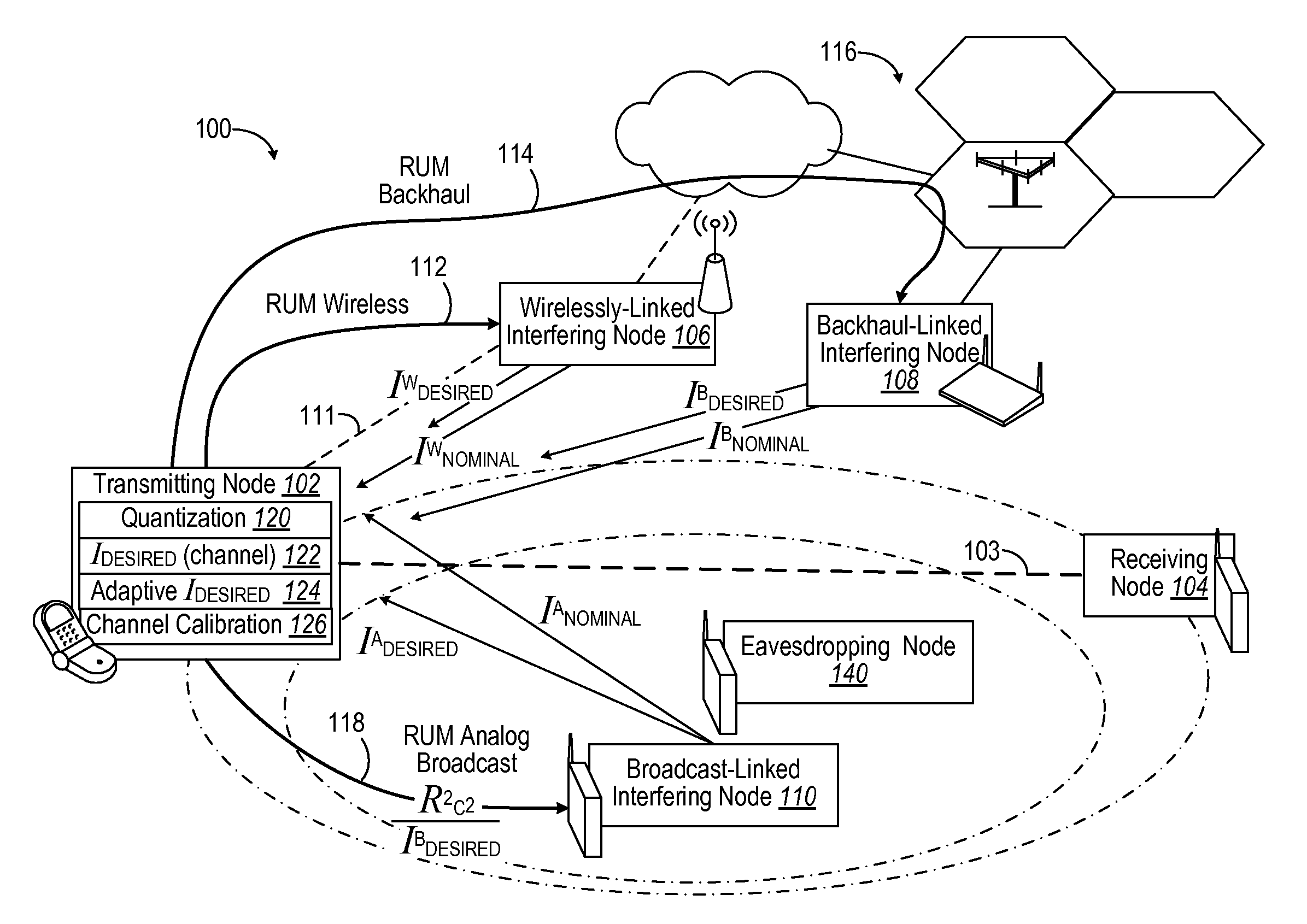
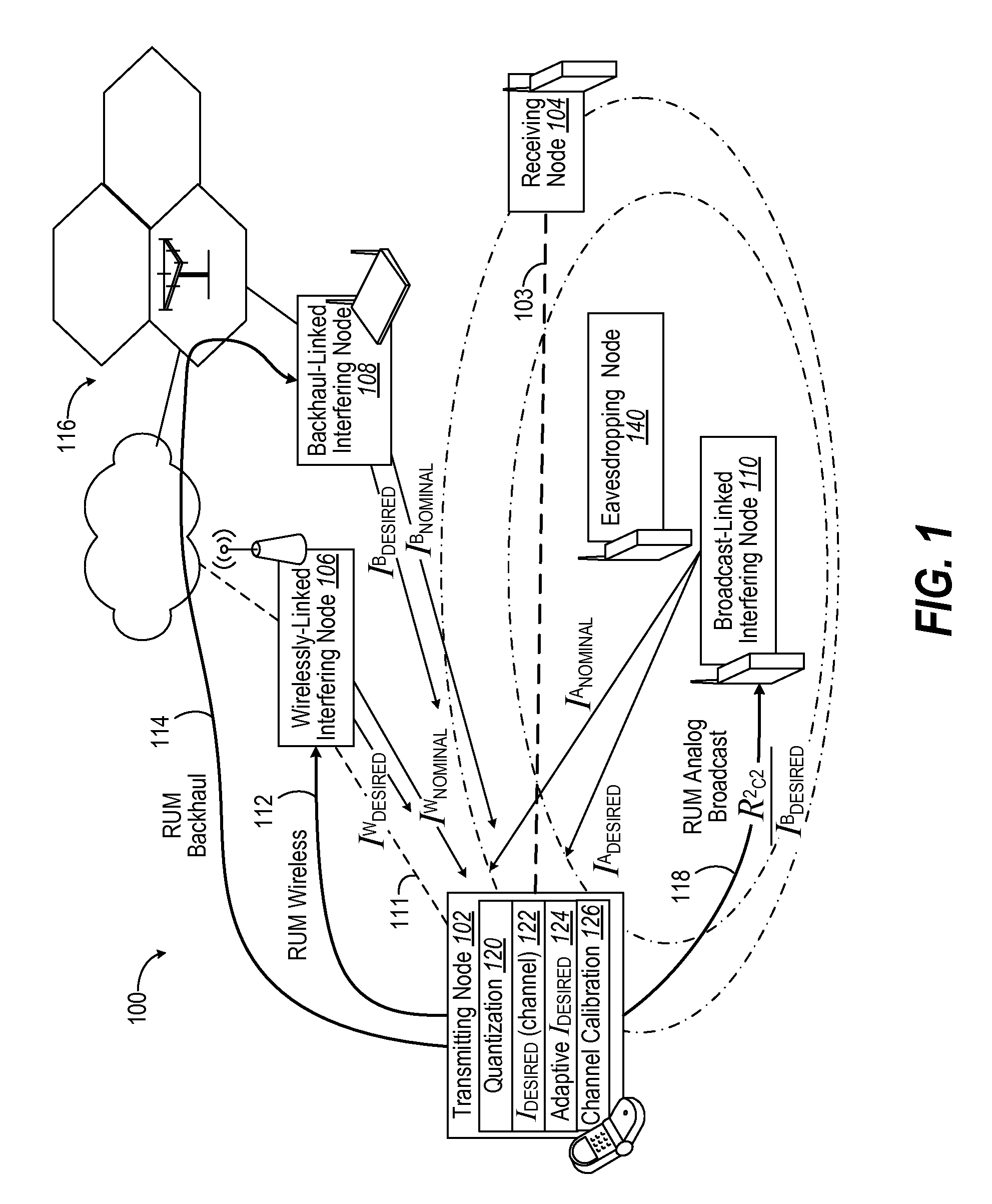
In a wireless communication system, short-term interference mitigation may be used to mitigate (e.g., to avoid or reduce) interference on a given link in order to improve performance of data transmission. The interference mitigation reduces transmit power of interfering transmissions so that a higher signal-to-noise-and-interference ratio (SINR) can be achieved for a desired data transmission. A node may observe high interference from an interfering node that degrades performance of data transmission sent on that link. By taking advantage of an communication path with the interfering node (e.g., wireless data / control channel, backhaul network connection, or analog broadcast signal), the transmitting node can successfully complete time critical communications while allowing the interfering node to also simultaneously communicate without reducing overall resources nor burdening any managing nodes.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com