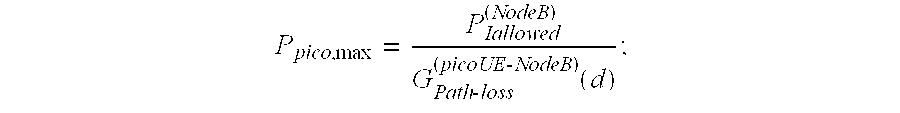Patents
Literature
1664 results about "Path loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
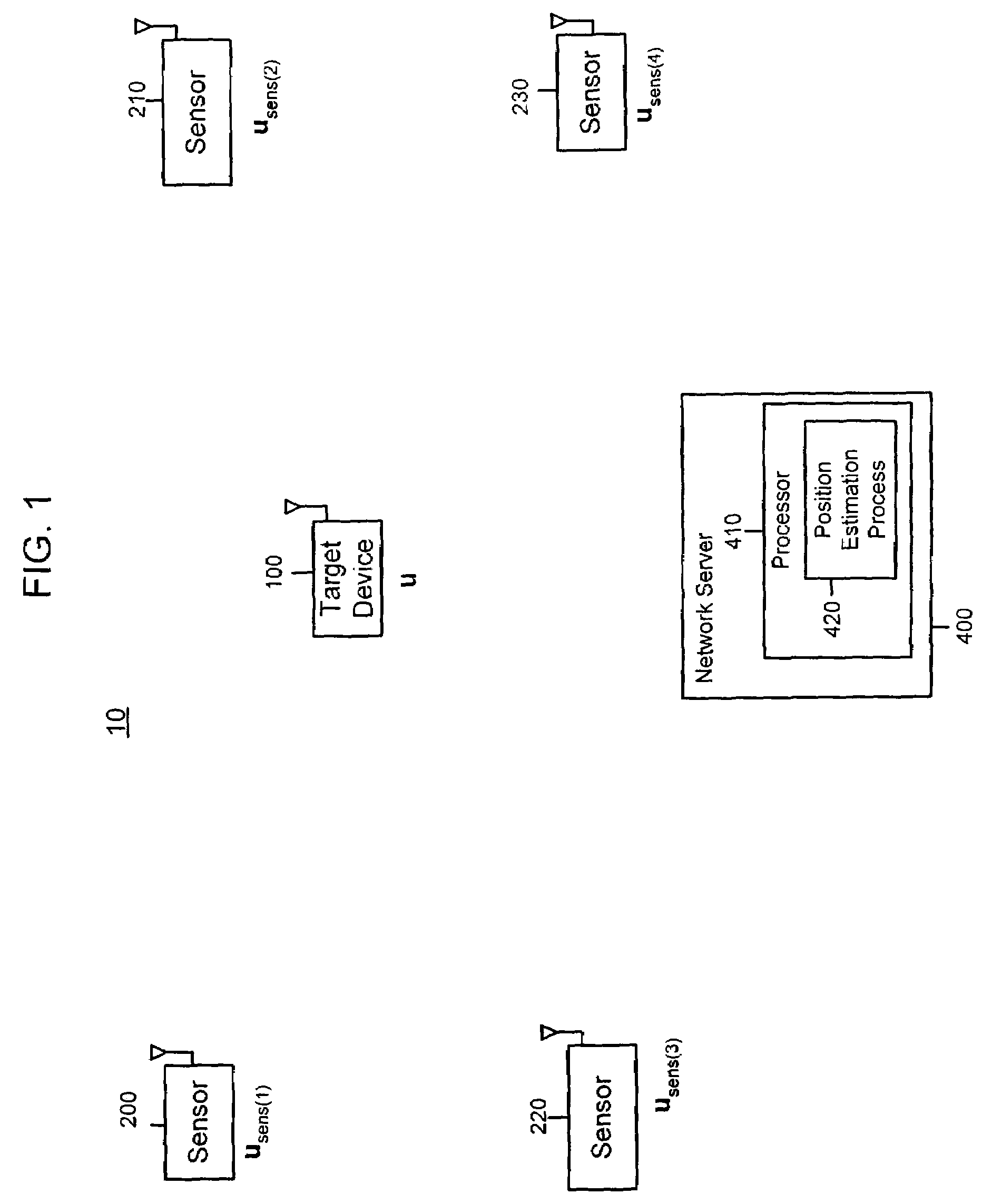
Path loss, or path attenuation, is the reduction in power density (attenuation) of an electromagnetic wave as it propagates through space. Path loss is a major component in the analysis and design of the link budget of a telecommunication system.
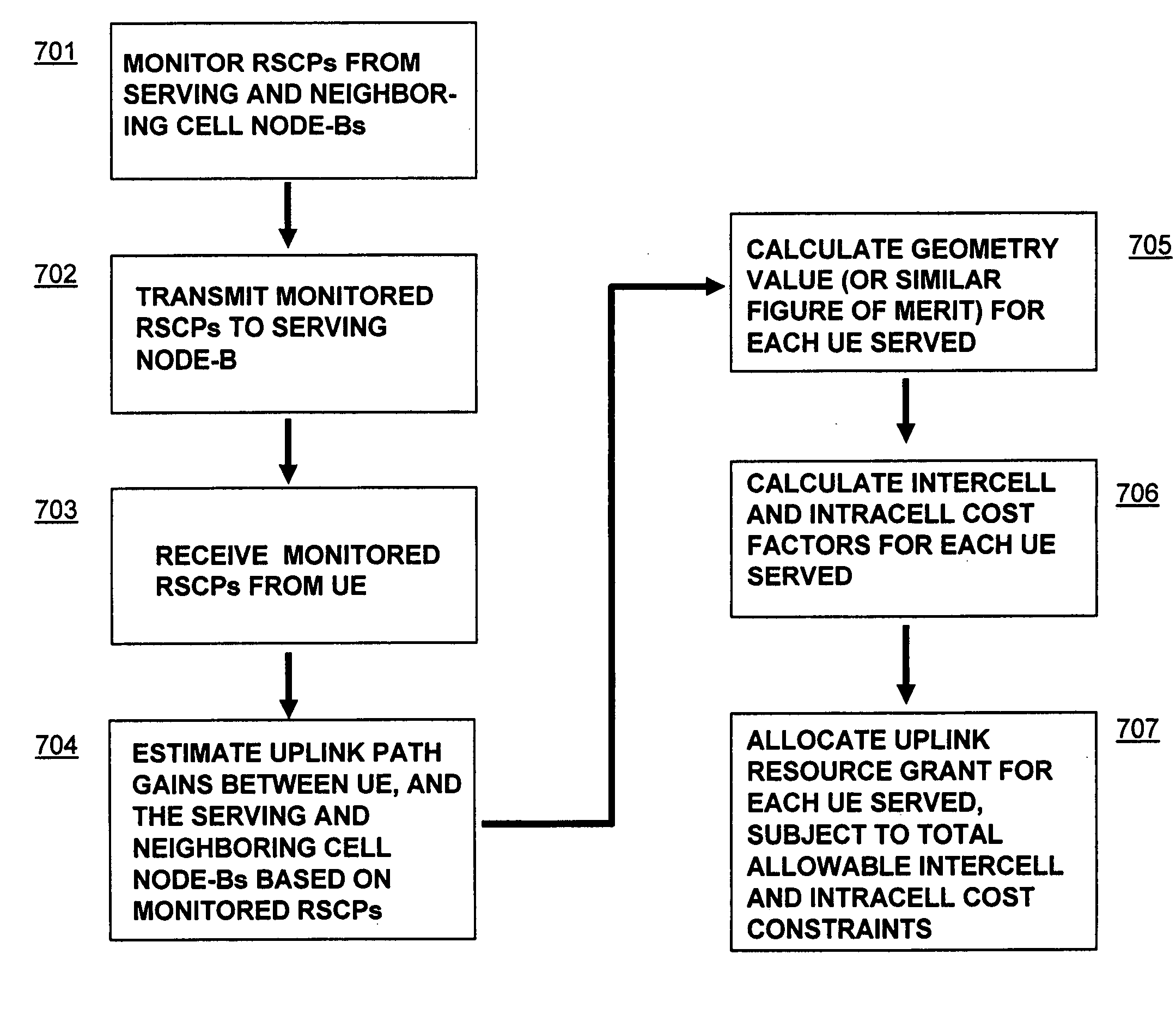
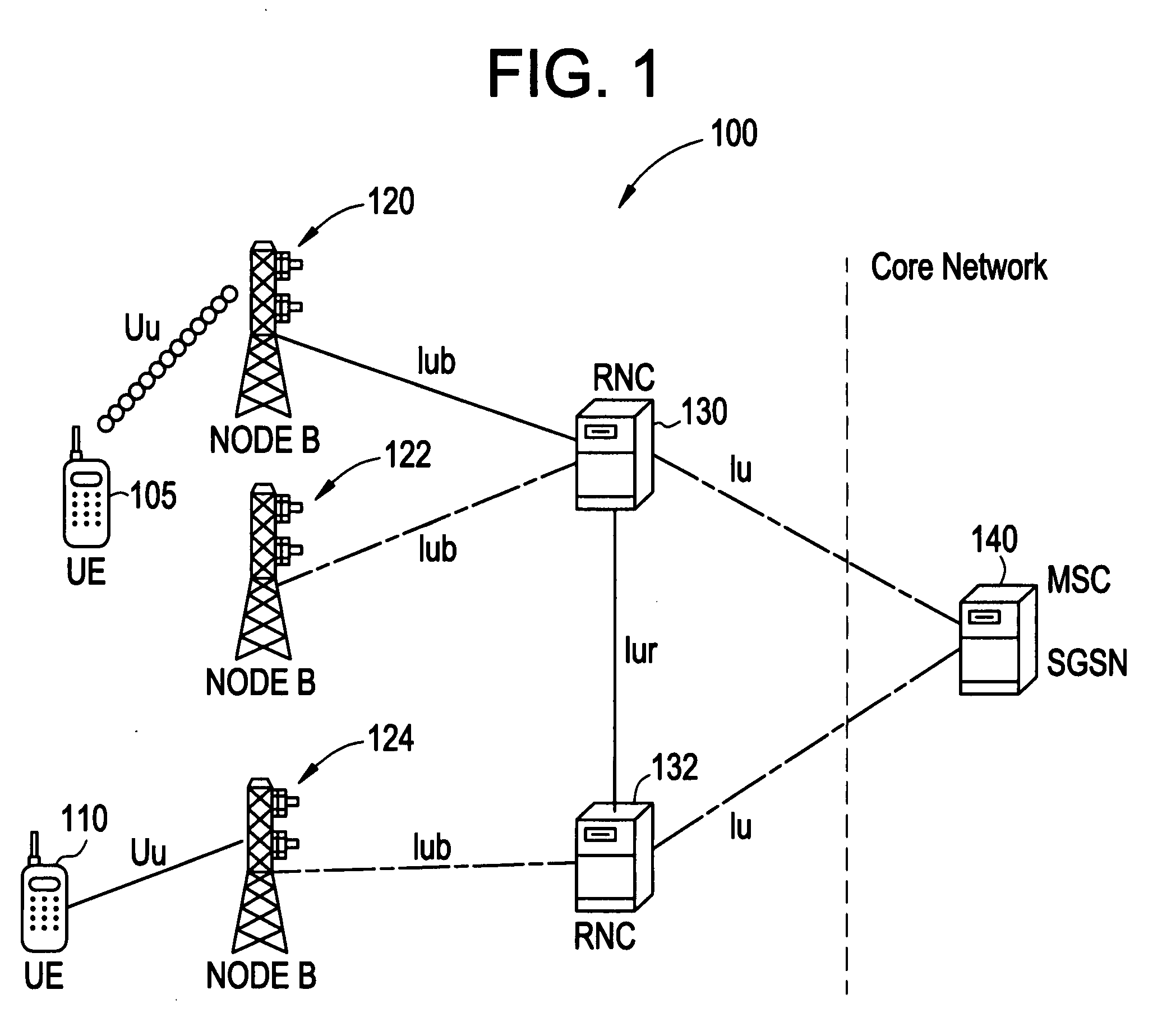
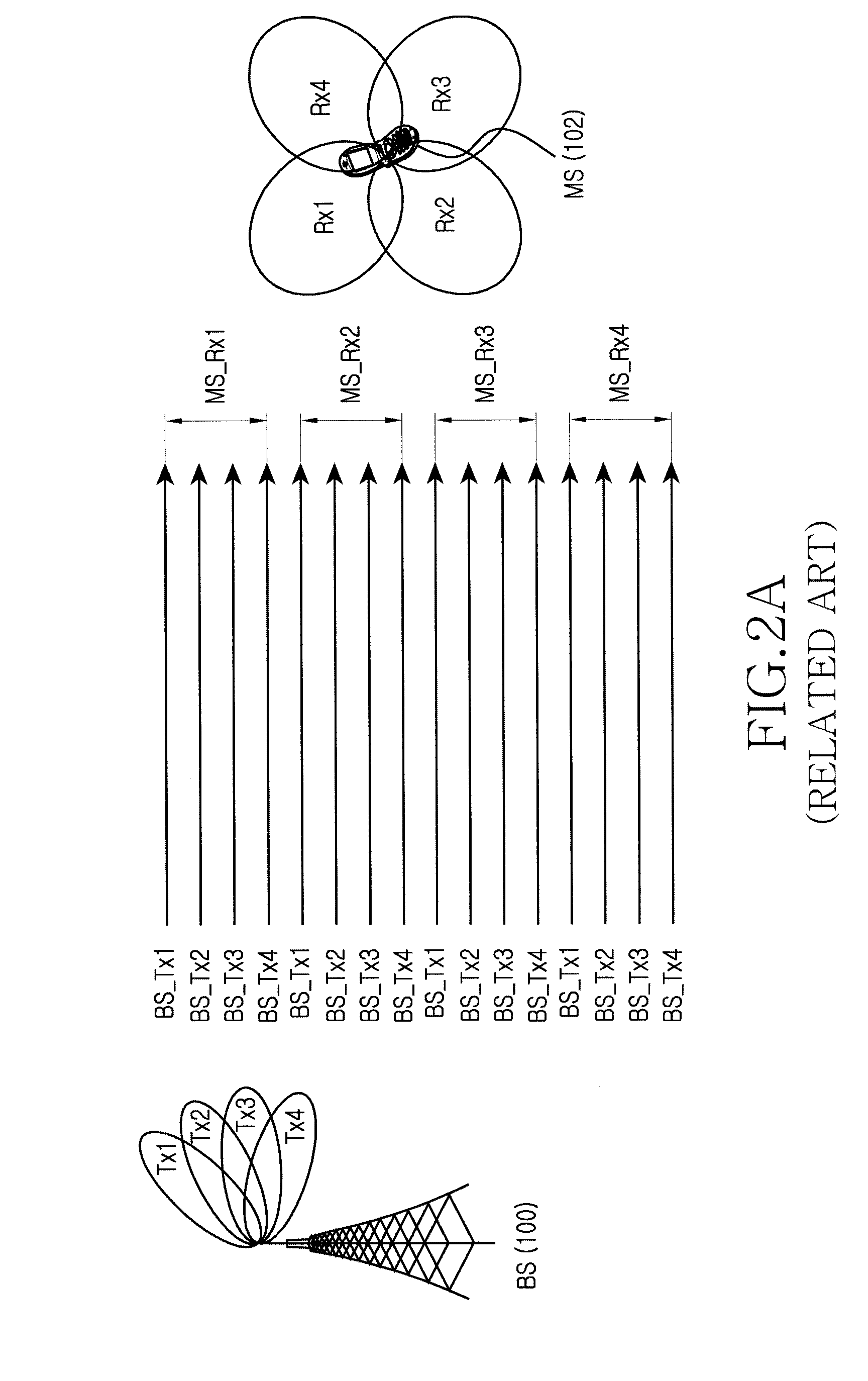
Uplink resource allocation to control intercell interference in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20070042784A1Avoid elevationSuitable characteristicPower managementReceivers monitoringCommunications systemUplink transmission
Embodiments of the present invention exploit the reciprocity of radio channels in TDD, and longer-term correlation between average uplink and downlink path losses in FDD wireless communication systems to enable distributed schedulers in an enhanced uplink system to allocate uplink transmission resources while preemptively managing intercell interference levels. Each cell's base station transmits a downlink reference signal at a known transmission power level. A mobile station monitors the received signal strength of the downlink reference signals from multiple base stations. The transmitted and received signal strength levels can be used by the mobile station to estimate the amount of intercell interference that the mobile station's uplink transmissions cause, and the mobile station's uplink transmission parameters are adjusted accordingly. In further embodiments, the received reference signal power levels, or values derived therefrom, are transmitted by the mobile station to its serving base station, where a scheduling algorithm uses the information to adjust one or more transmission parameters relating to a grant of uplink transmission resources to the UE, thereby controlling the intercell interference generated by the mobile station's uplink transmissions.
Owner:SONY CORP
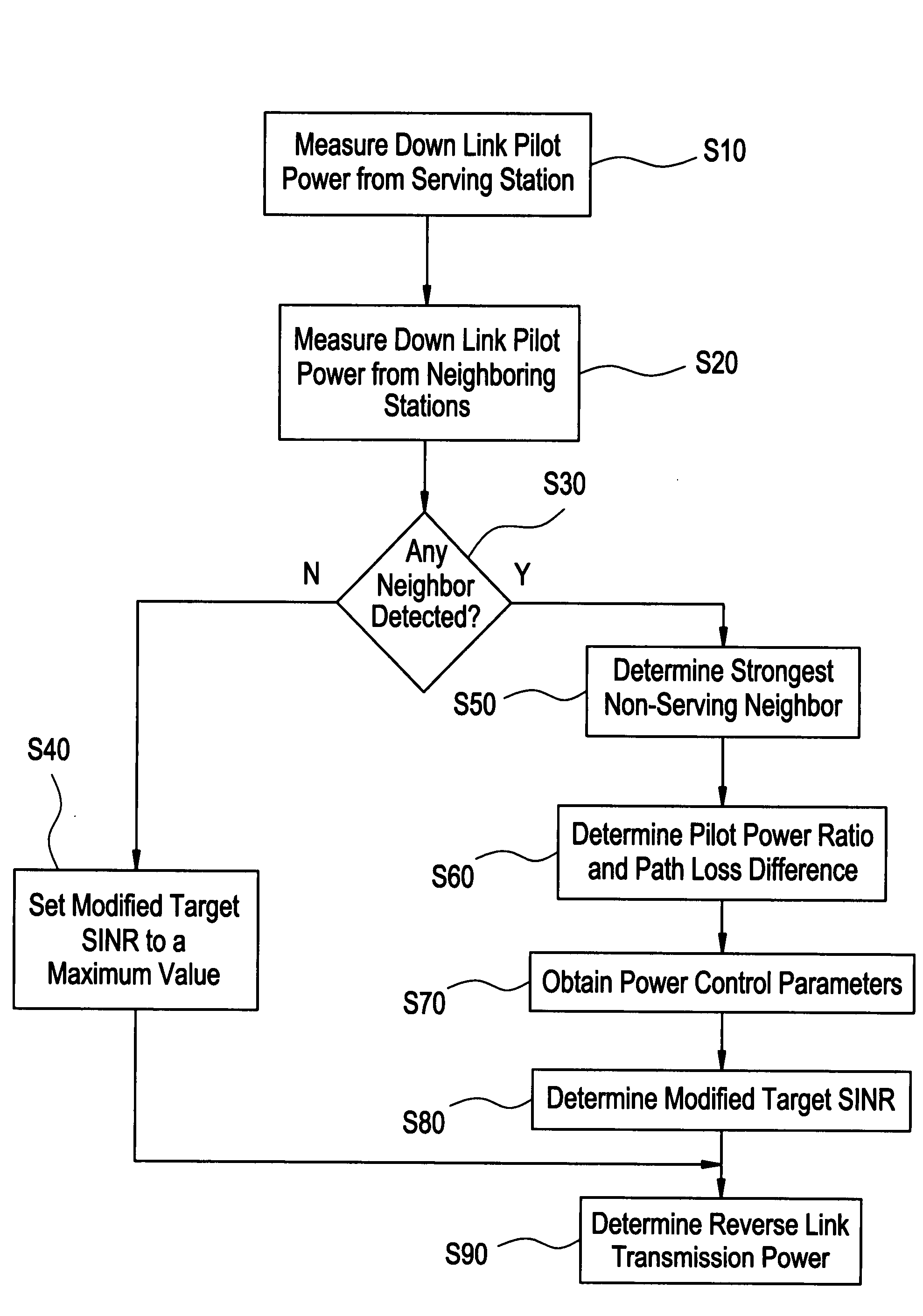
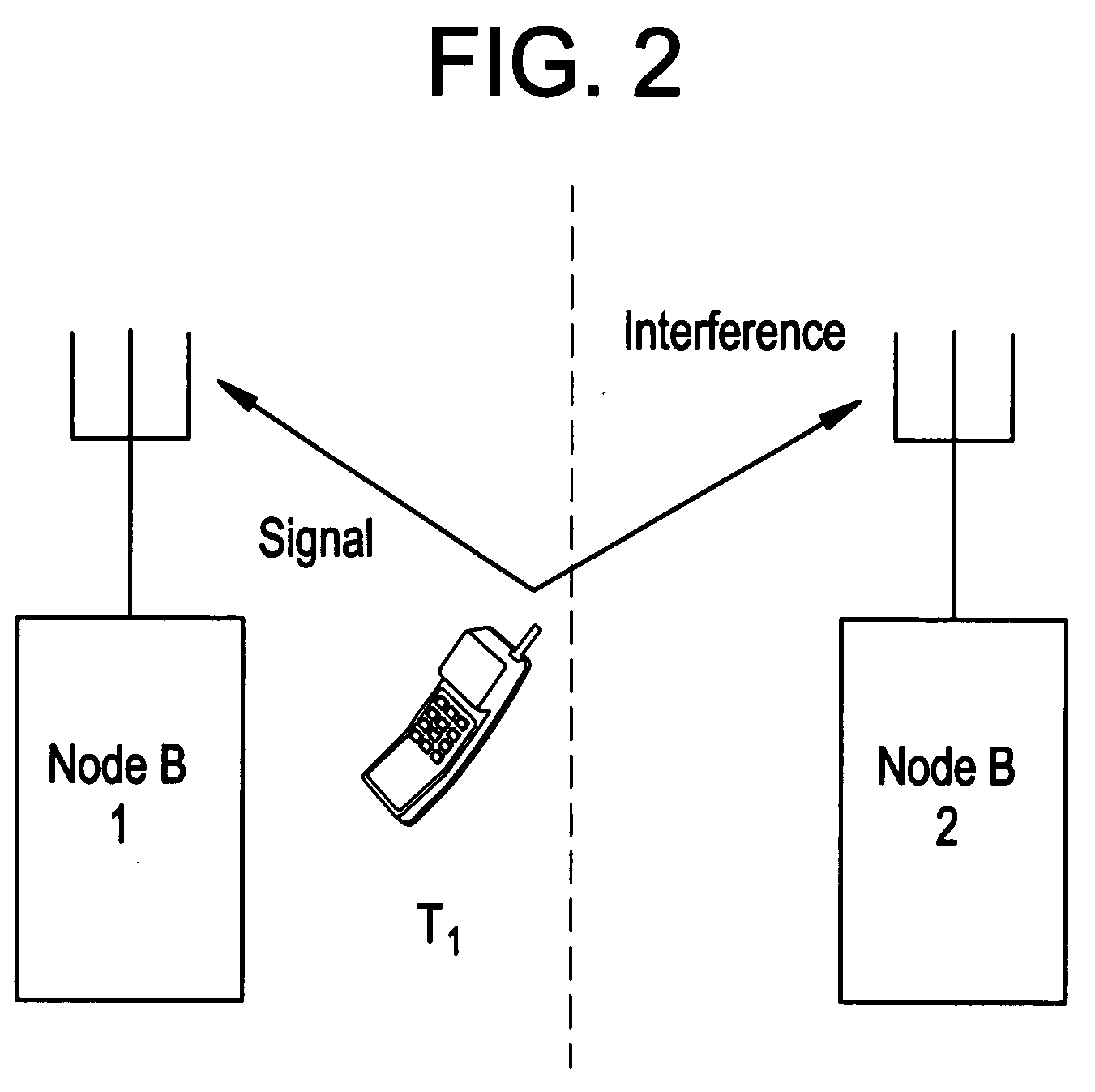
Reverse link power control
InactiveUS20080166976A1Little varianceImprove throughputPower managementRadio transmissionUser equipmentPower control
In one embodiment, a reverse link transmission power for a user equipment is determined based on a first path loss and a second path loss. The first path loss is path loss between a serving station and the user equipment, and the serving station serves the communication needs of the user equipment. The second path loss is path loss between a neighboring station and the user equipment, and the neighboring station neighbors the serving station.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
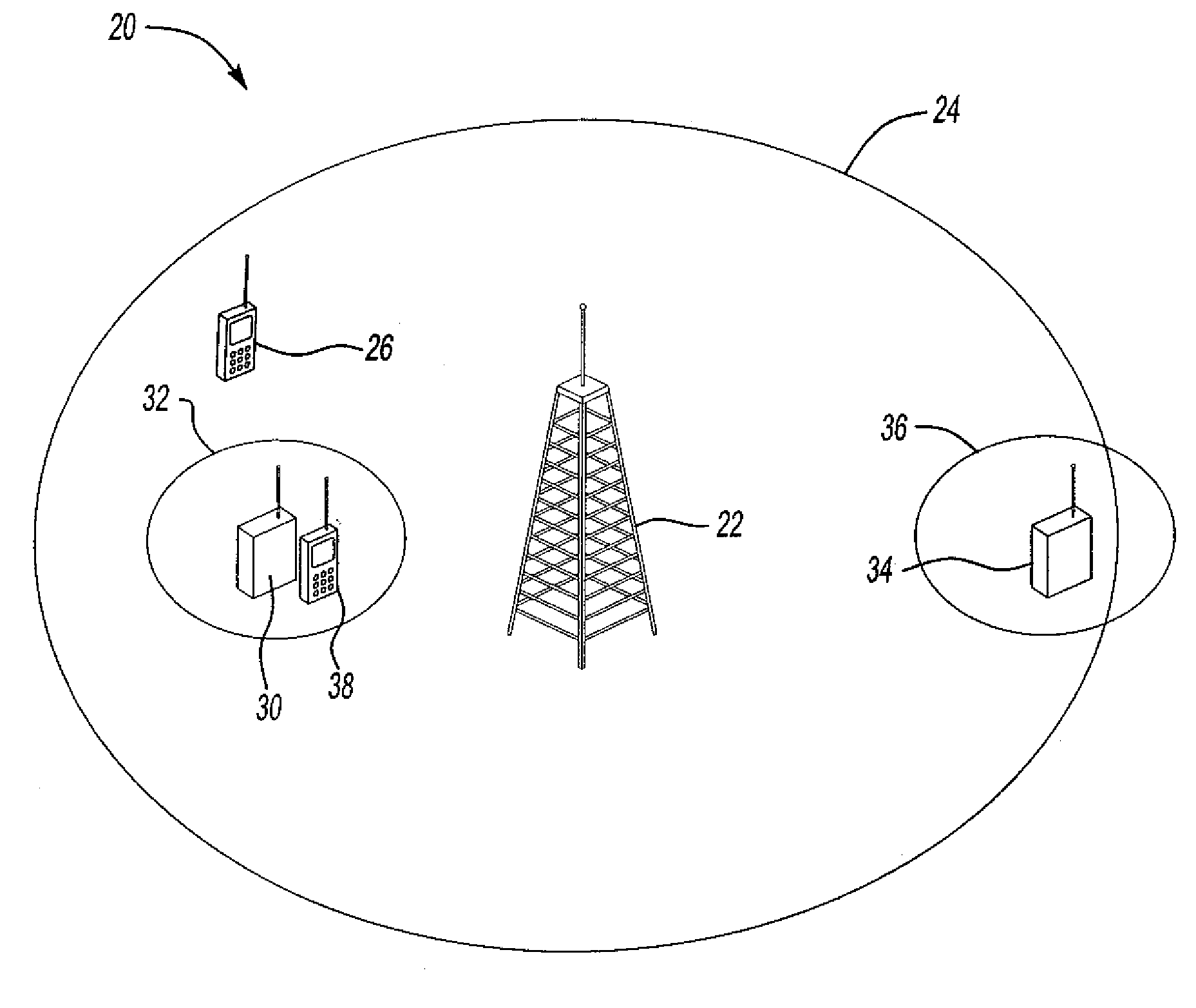
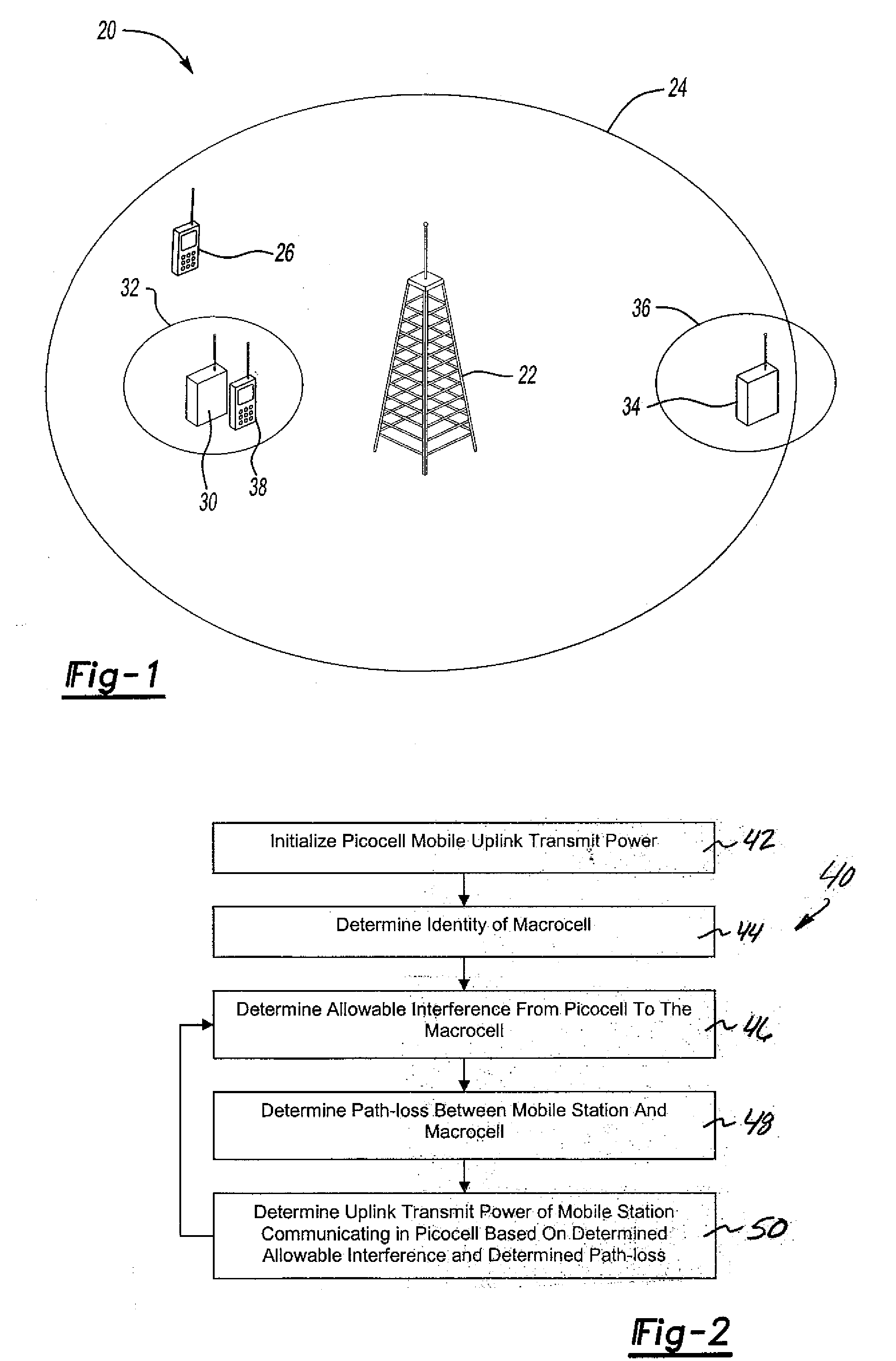
Controlling uplink power for picocell communications within a macrocell
InactiveUS20080146154A1Power managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsTransmitted power
A method of communicating in a picocell within a macrocell includes automatically setting an uplink transmit power of a mobile station to avoid uplink interference between the picocell and the macrocell. A disclosed example includes determining an allowable interference from the picocell to the macrocell. A path-loss between a mobile station and a macrocell is determined. An uplink transmit power of the mobile station for communicating in the picocell is determined based upon the determined allowable interference and the determined path-loss.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
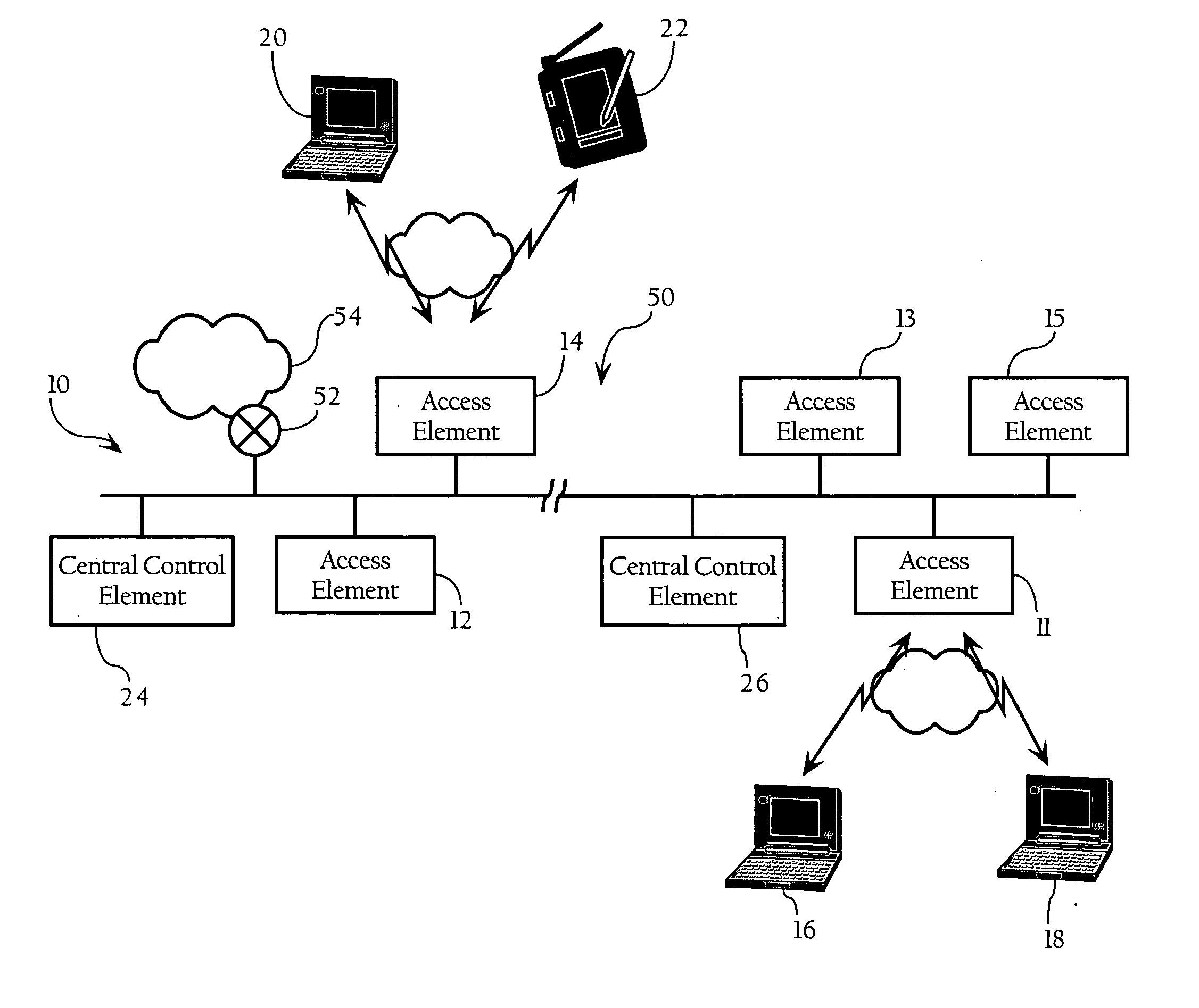
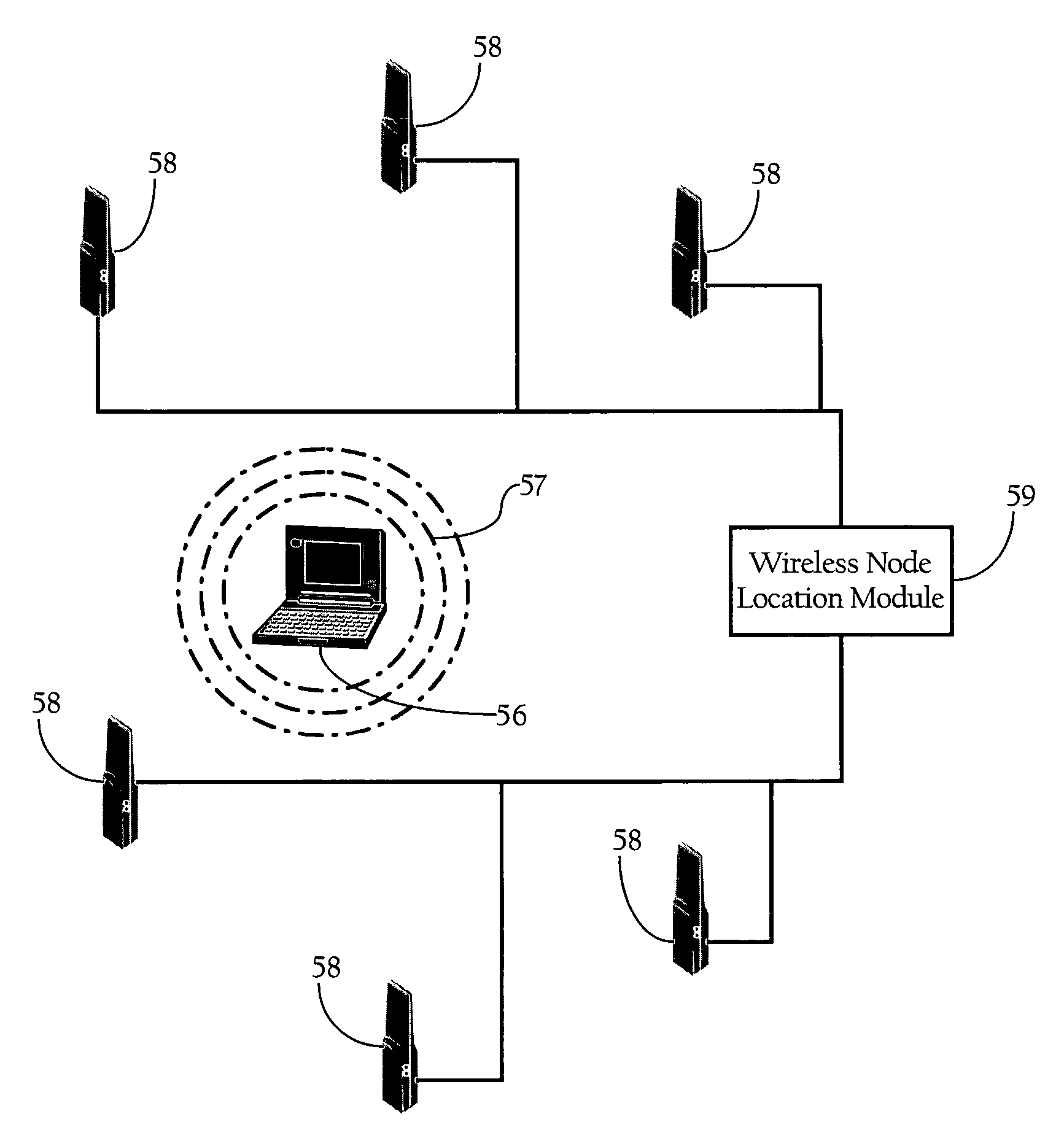
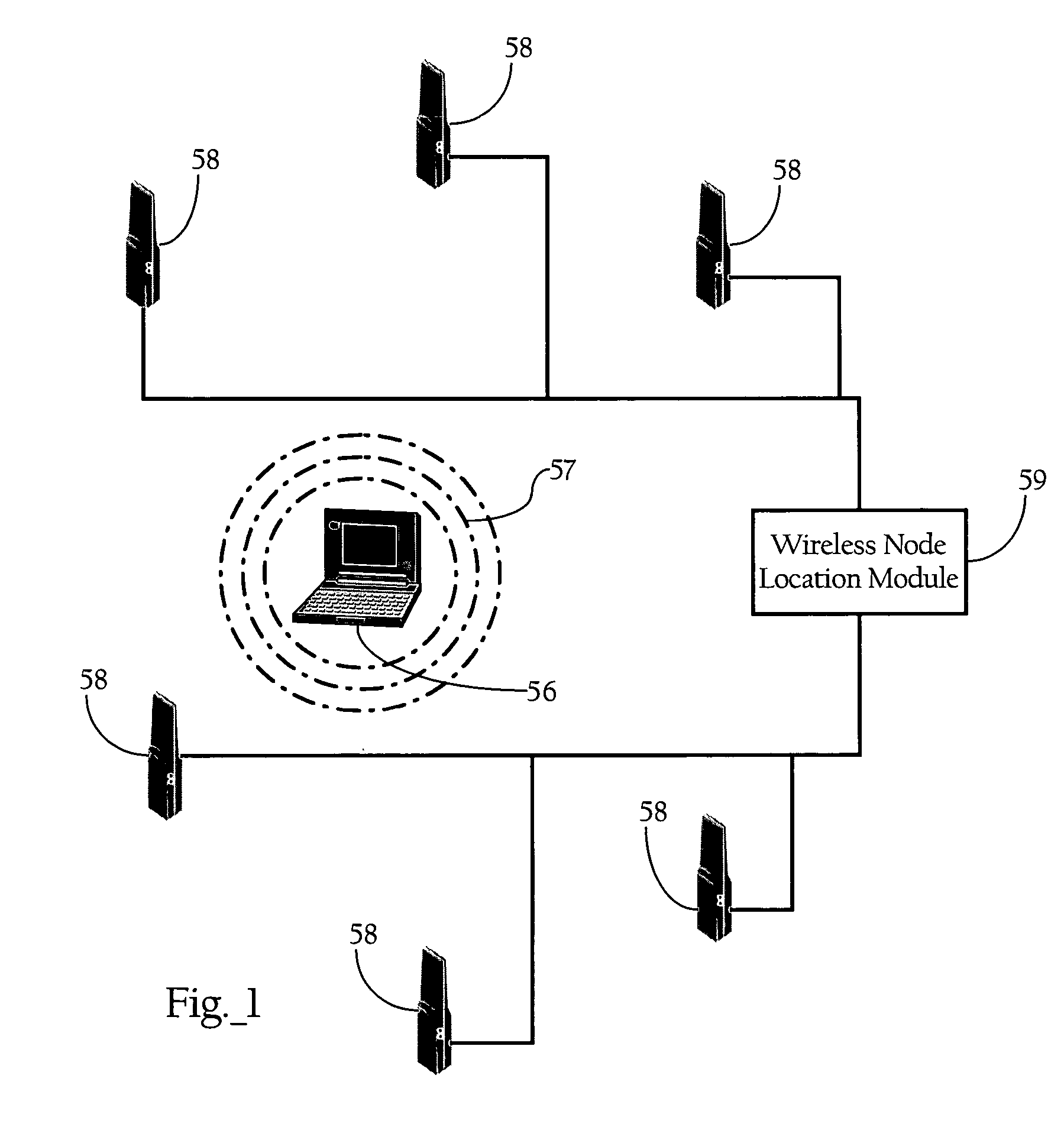
Tag location,client location, and coverage hole location in a wireless network
InactiveUS20060075131A1Reduce power consumptionEfficient methodNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionRadiolocationPublic infrastructure
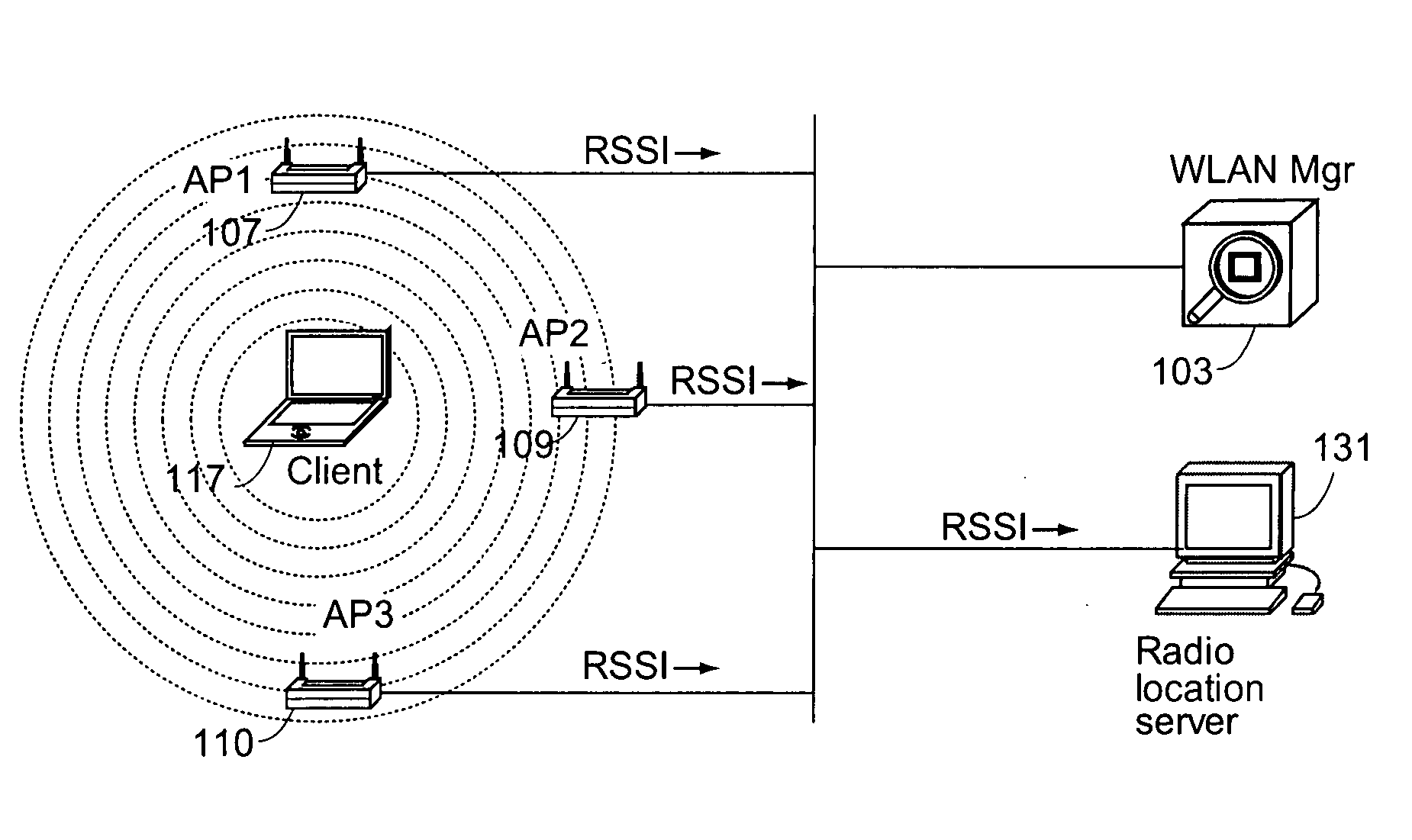
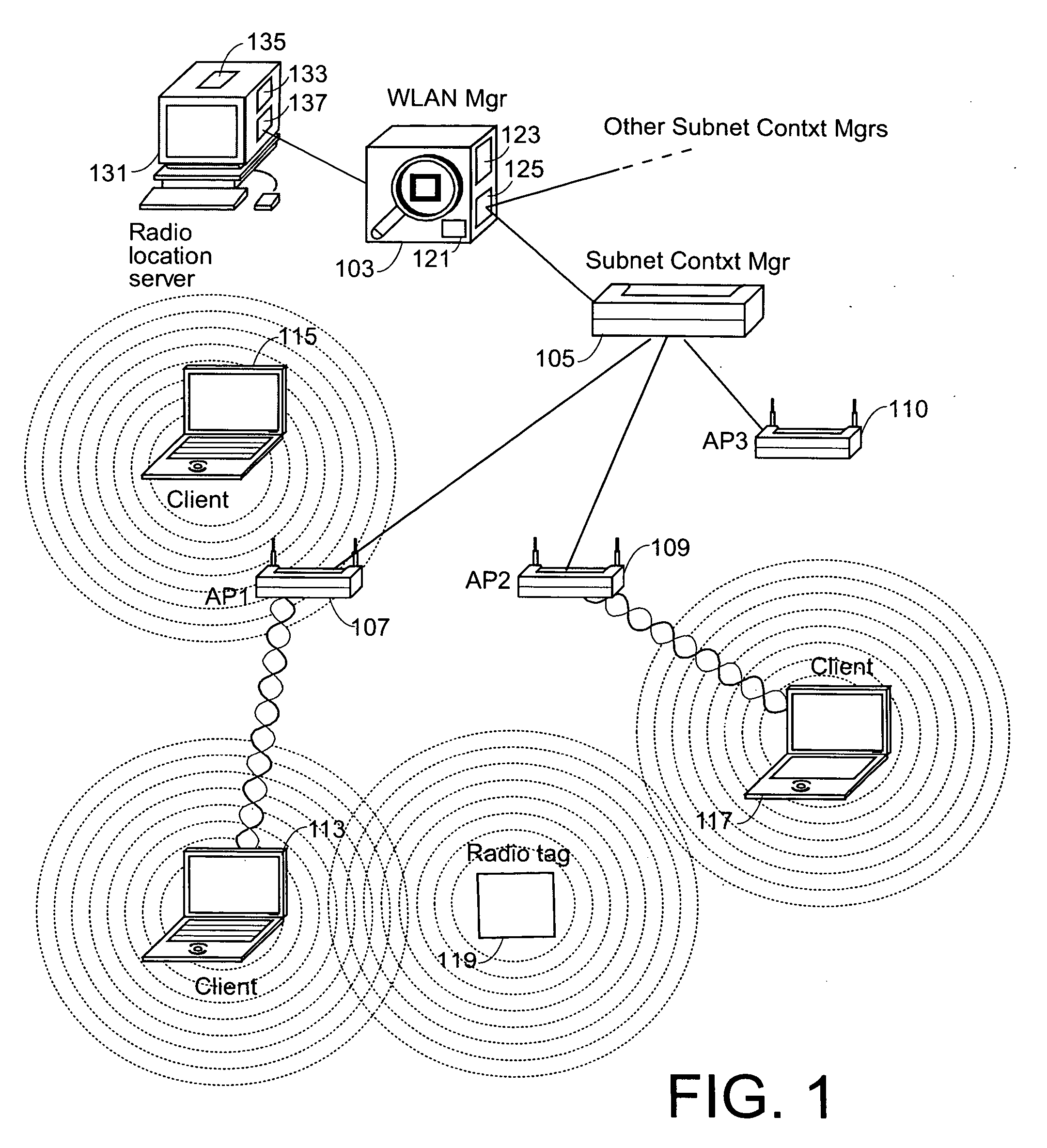
Determining the location of a radio tag or client station of a wireless network, and the location of coverage holes by receiving from a plurality of wireless stations of the wireless network path loss information of the path loss of one or more location frames received at the respective wireless stations. The location frames transmitted by the radio tag or client station having a pre-defined frame structure. The radio tags and client stations use a common infrastructure for transmitting a location frame configured for radiolocation by path loss measurement. The common infrastructure includes a pre-defined protocol common for both radio tags and client stations for transmitting information for reception by the plurality of stations of the wireless network for radiolocation. The pre-defined protocol includes using the location frame having the pre-defined frame structure.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
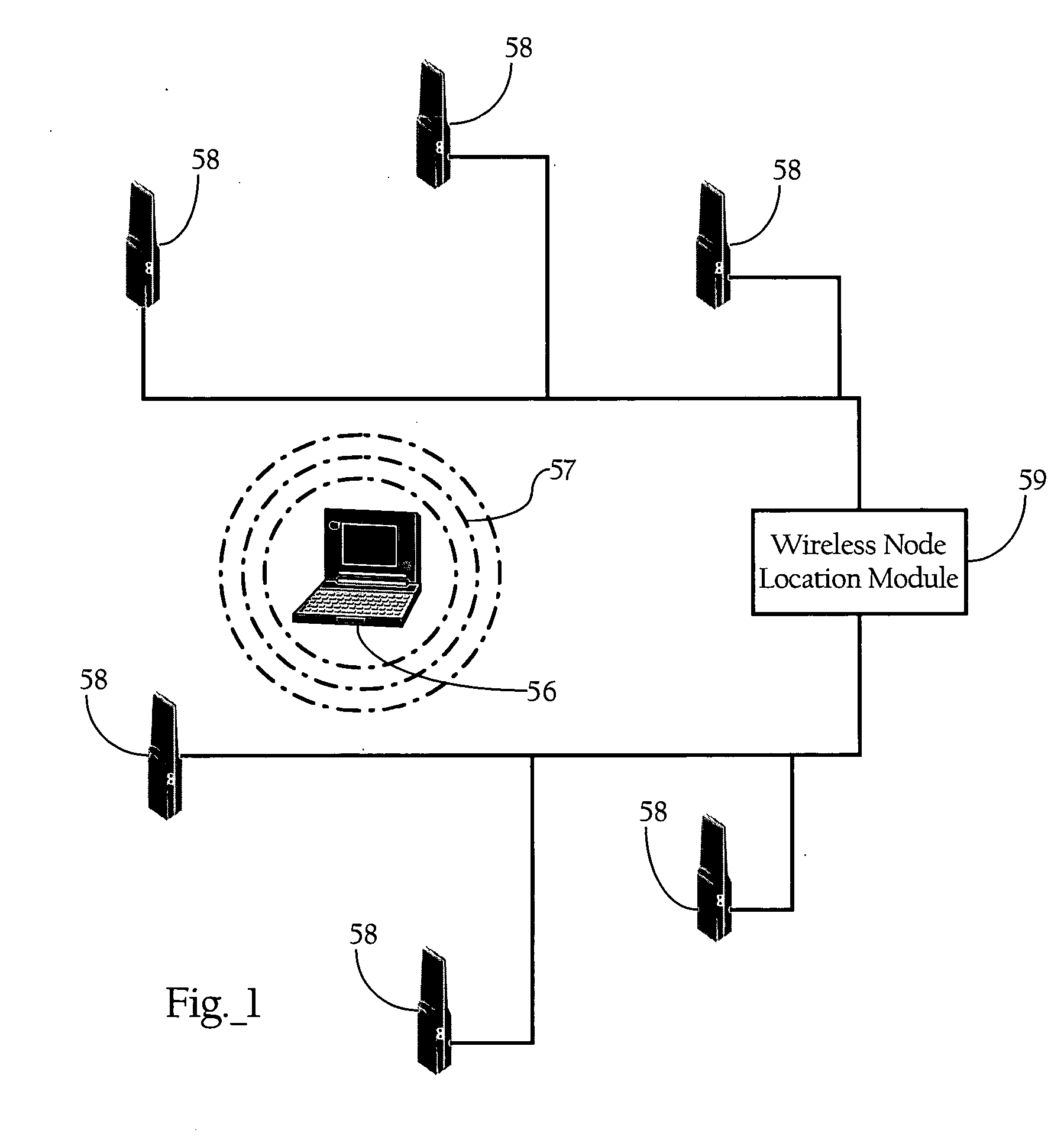
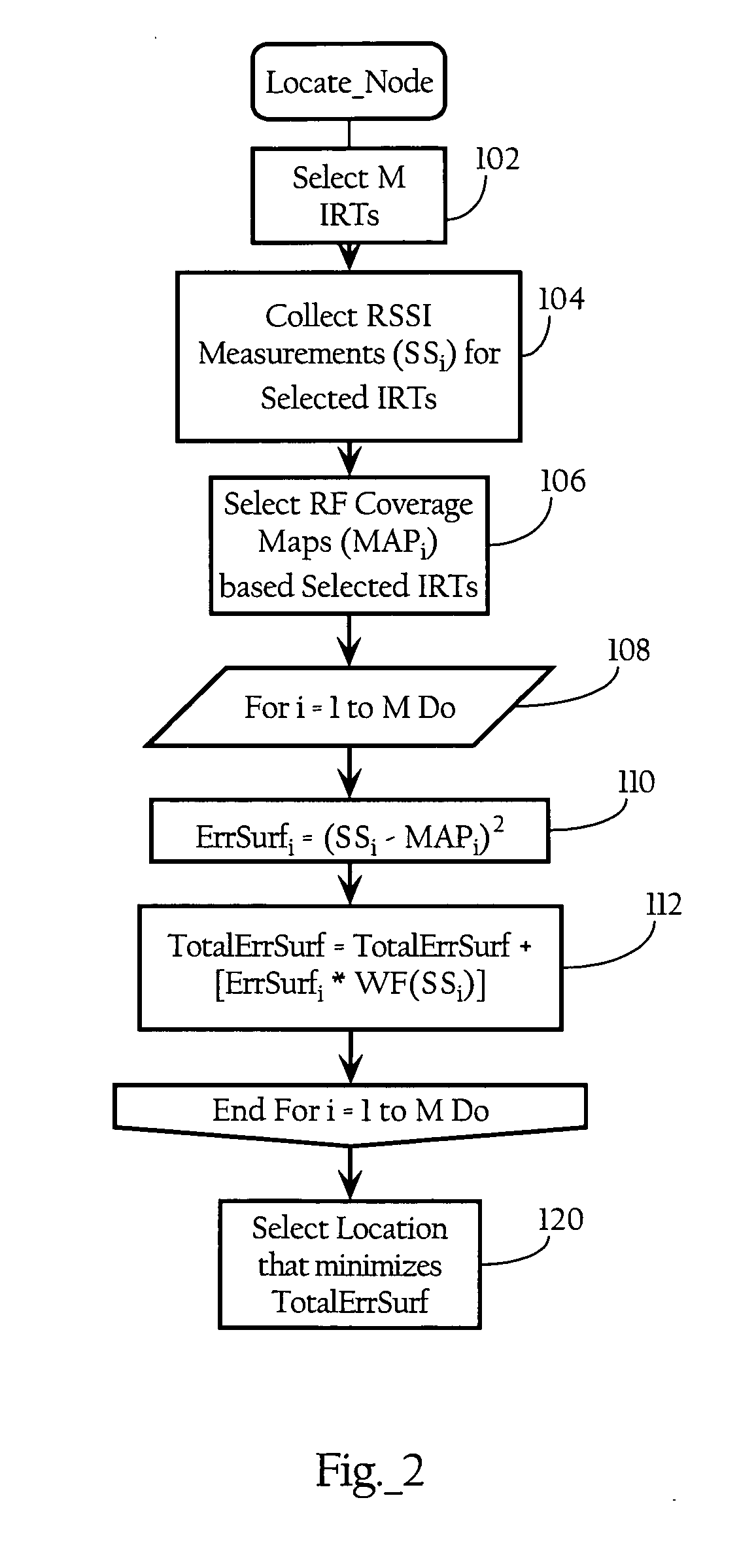
Location of wireless nodes using signal strength weighting metric
ActiveUS20050208952A1Improve estimation accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationTransceiverRadio reception
Methods, apparatuses, and systems directed to a wireless node location mechanism that uses a signal strength weighting metric to improve the accuracy of estimating the location of a wireless node based on signals detected among a plurality of radio transceivers. In certain implementations, the wireless node location mechanism further incorporates a differential signal strength metric to reduce the errors caused by variations in wireless node transmit power, errors in signal strength detection, and / or direction-dependent path loss. As opposed to using the absolute signal strength or power of an RF signal transmitted by a wireless node, implementations of the present invention compare the differences between signal strength values detected at various pairs of radio receivers to corresponding differences characterized in a model of the RF environment. One implementation of the invention searches for the locations in the model between each pair of radio receivers where their signal strength is different by an observed amount.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
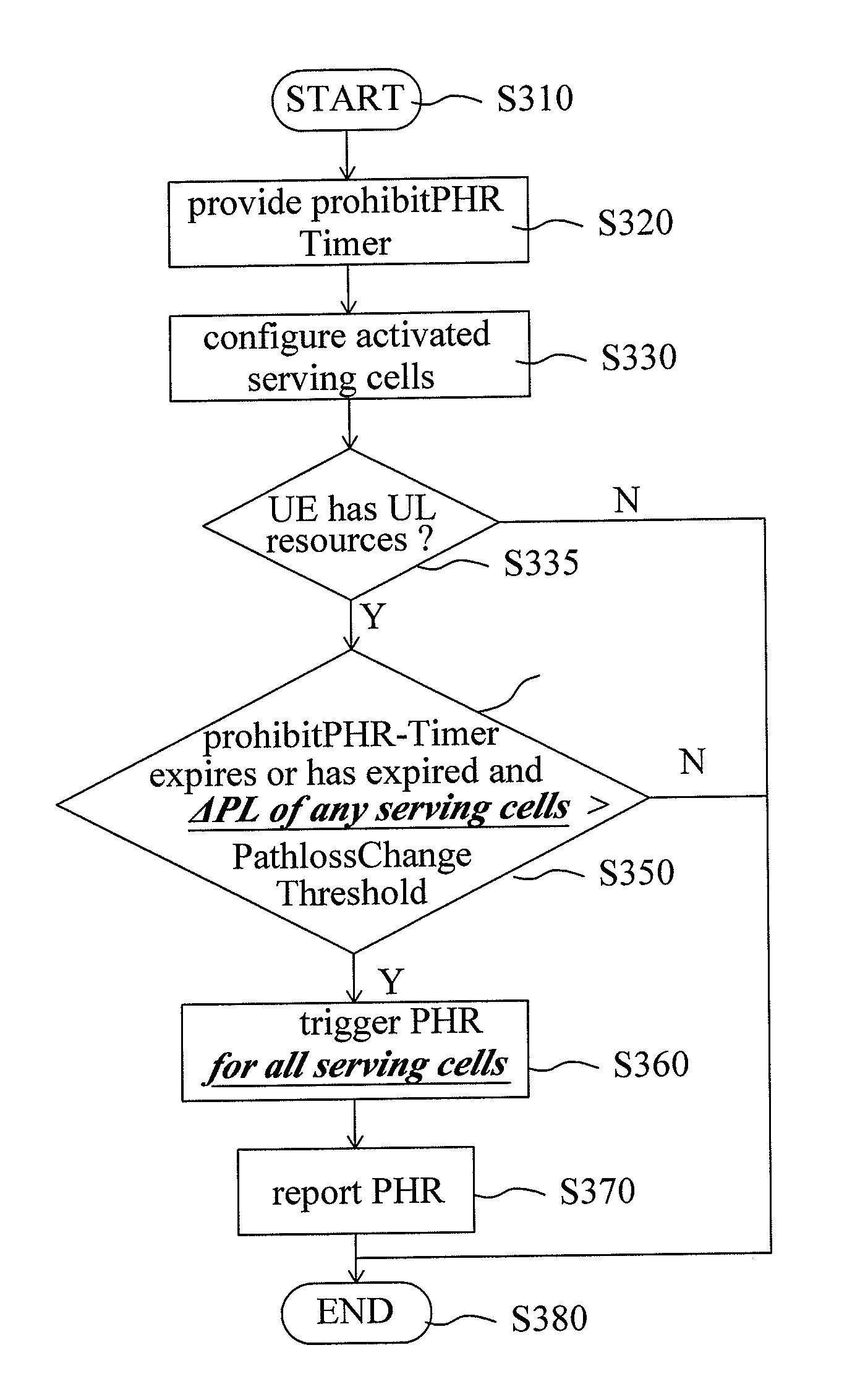
Method for performing power headroom reporting procedure and phr mac control element
ActiveUS20110243016A1Information obtainImprove communication qualityPower managementError preventionComputer networkEngineering
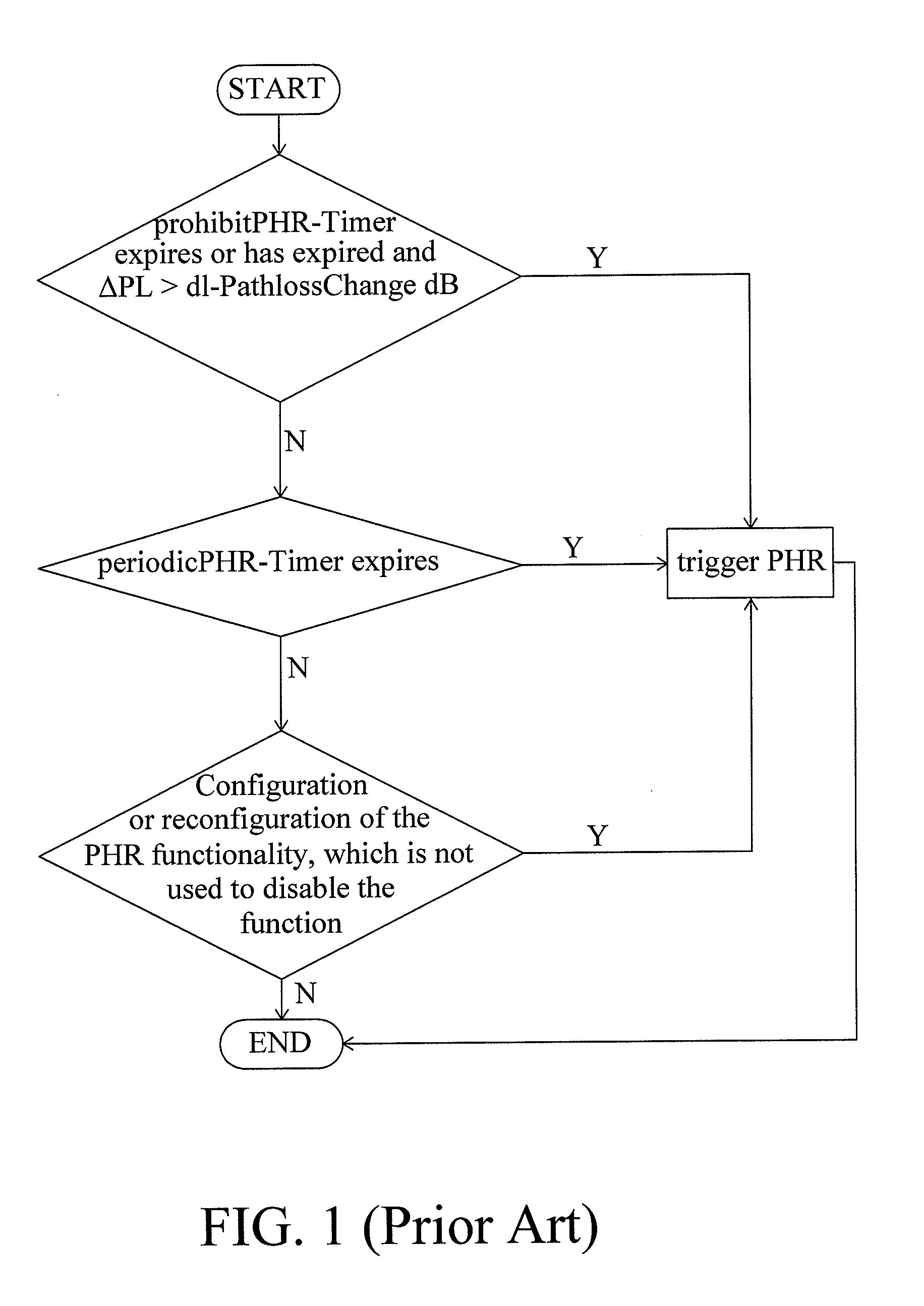
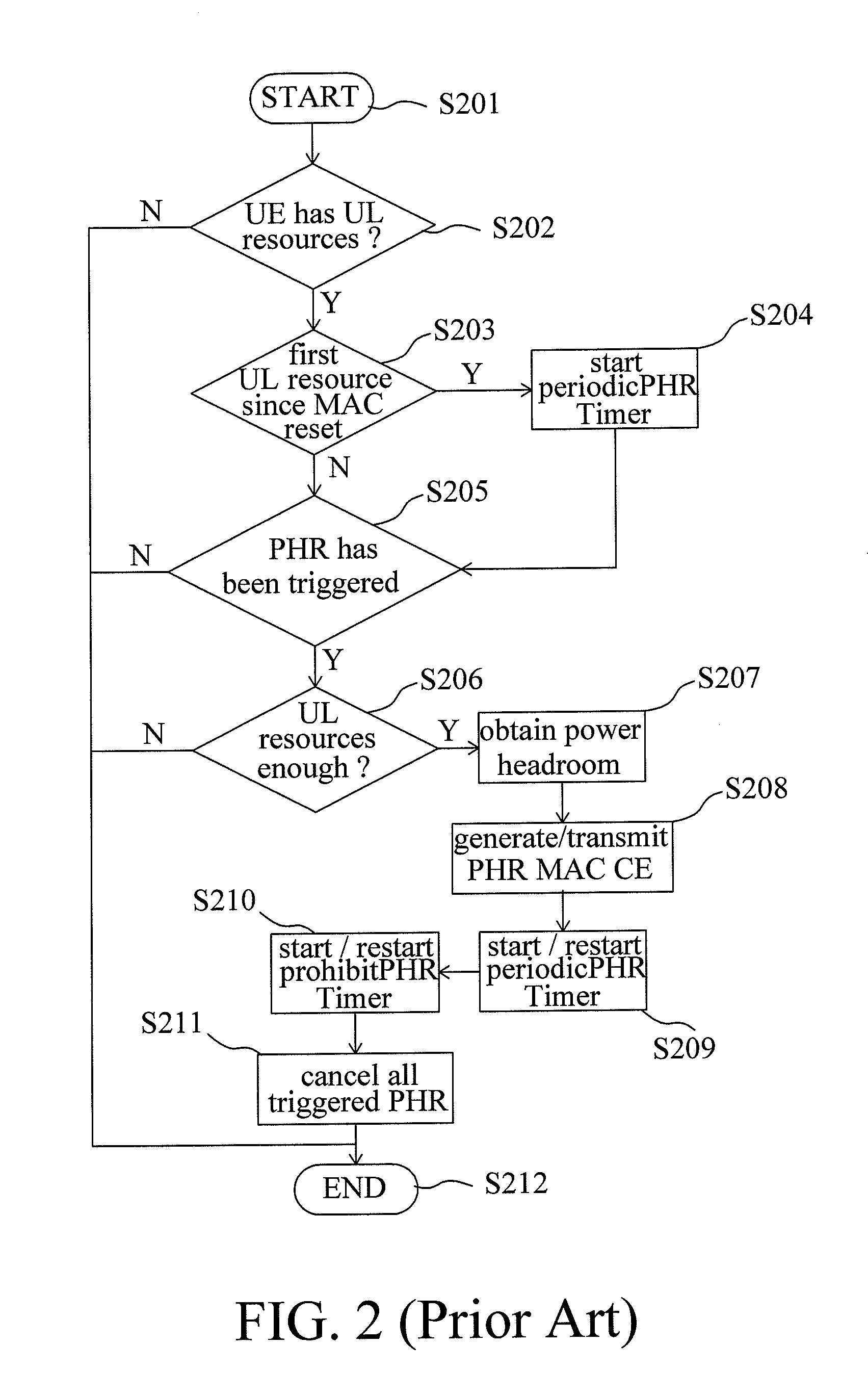
This invention relates to a method for performing Power Headroom reporting procedure, adapted for a user equipment, wherein the user equipment is operated in a plurality of activated serving cells, the method includes the steps of: providing a prohibitPHR-Timer; obtaining a plurality of downlink path loss values respectively corresponding to the activated serving cells; triggering a power headroom report when the prohibitPHR-Timer expires or has expired and at least one of the downlink path loss values has changed more than a PathlossChange threshold since the last transmission of a PHR; and reporting the power headroom report.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
Uplink control method and apparatus in wireless communication system
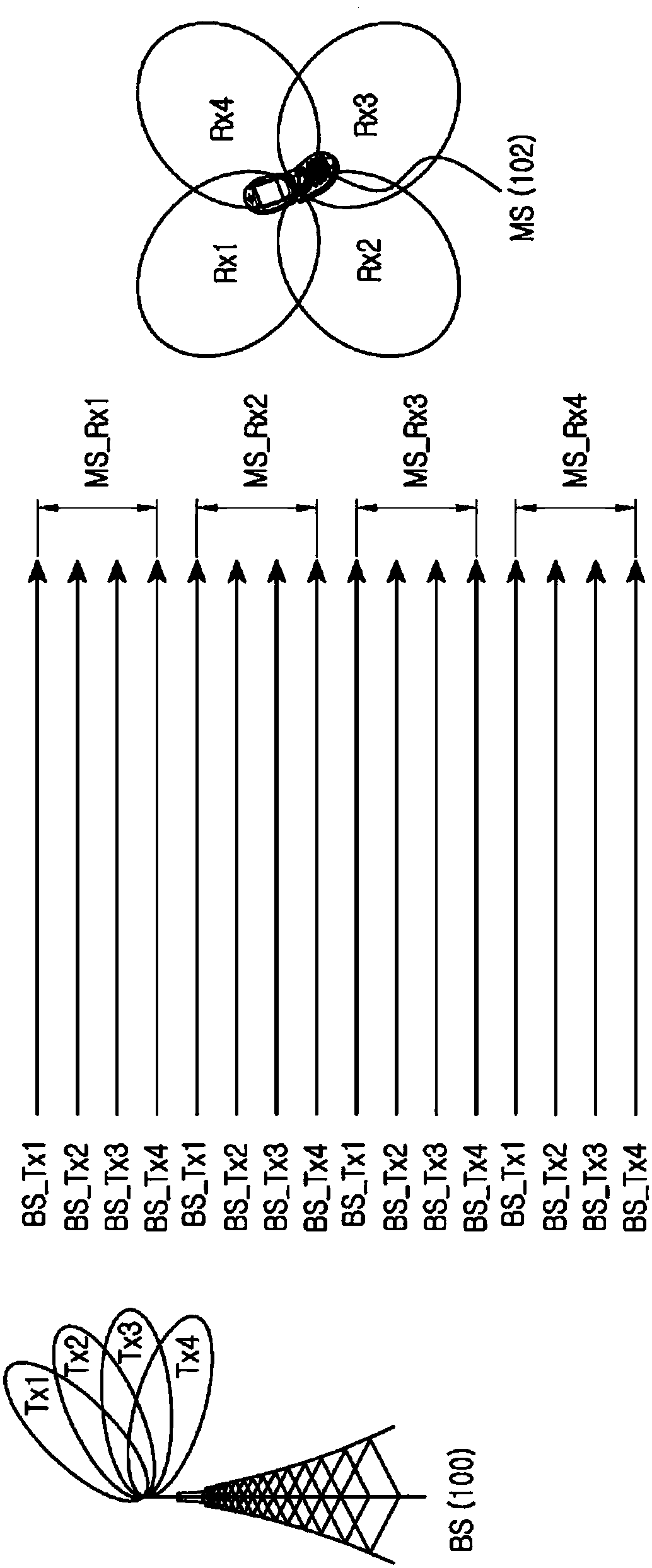
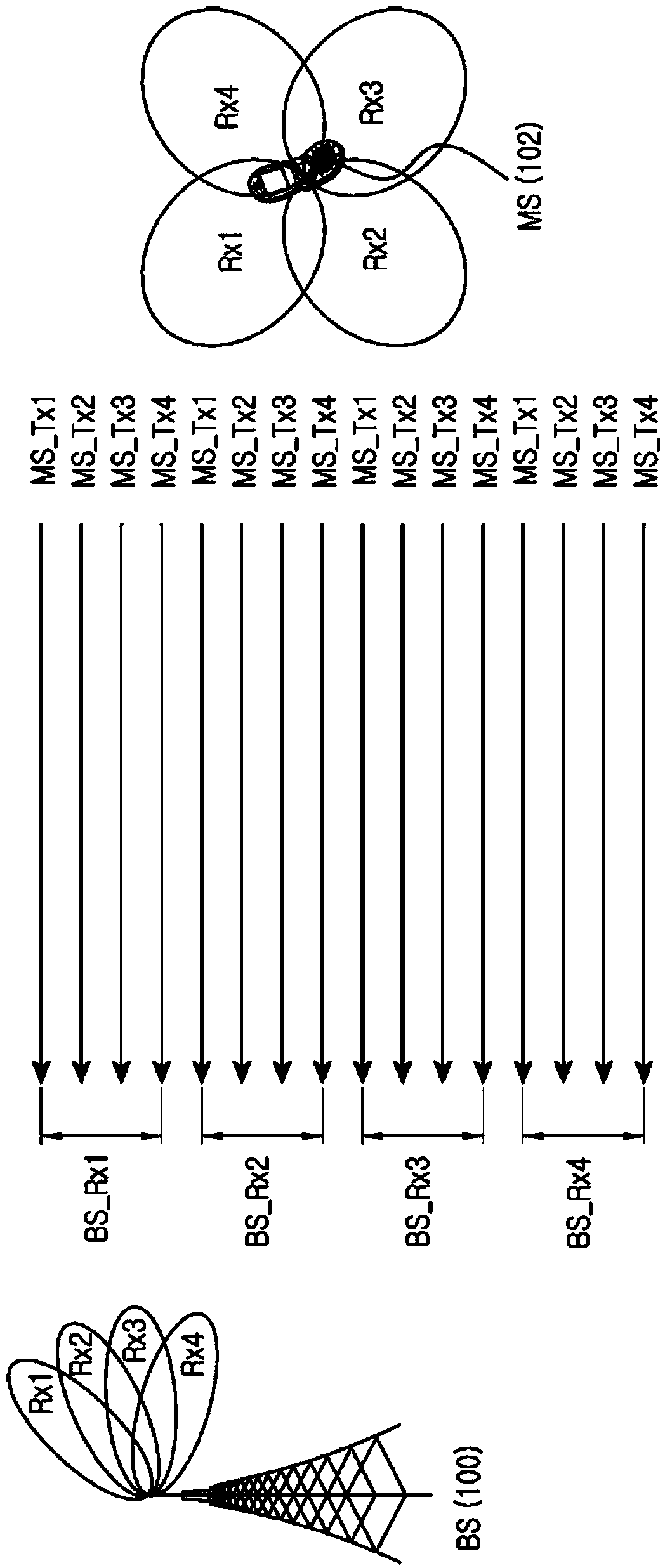
An UpLink (UL) control method and apparatus for in a wireless communication system supporting beamforming are provided. A method of a Mobile Station (MS) for UL control in the wireless communication system supporting the beamforming includes receiving a plurality of DownLink (DL) reference signals from a plurality of Base Station (BS) transmission beams using a plurality of MS reception beams having different directivity, measuring a path loss based on a reception signal strength of each of the plurality of DL reference signals received through different transmission / reception beams, selecting an MS transmission beam for uplink based on the path loss value measured for each of the plurality of DL reference signals, and transmitting a UL signal to a BS using the selected MS transmission beam.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Location of wireless nodes using signal strength weighting metric
ActiveUS7116988B2Improve estimation accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationTransceiverRadio reception
Methods, apparatuses, and systems directed to a wireless node location mechanism that uses a signal strength weighting metric to improve the accuracy of estimating the location of a wireless node based on signals detected among a plurality of radio transceivers. In certain implementations, the wireless node location mechanism further incorporates a differential signal strength metric to reduce the errors caused by variations in wireless node transmit power, errors in signal strength detection, and / or direction-dependent path loss. As opposed to using the absolute signal strength or power of an RF signal transmitted by a wireless node, implementations of the present invention compare the differences between signal strength values detected at various pairs of radio receivers to corresponding differences characterized in a model of the RF environment. One implementation of the invention searches for the locations in the model between each pair of radio receivers where their signal strength is different by an observed amount.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
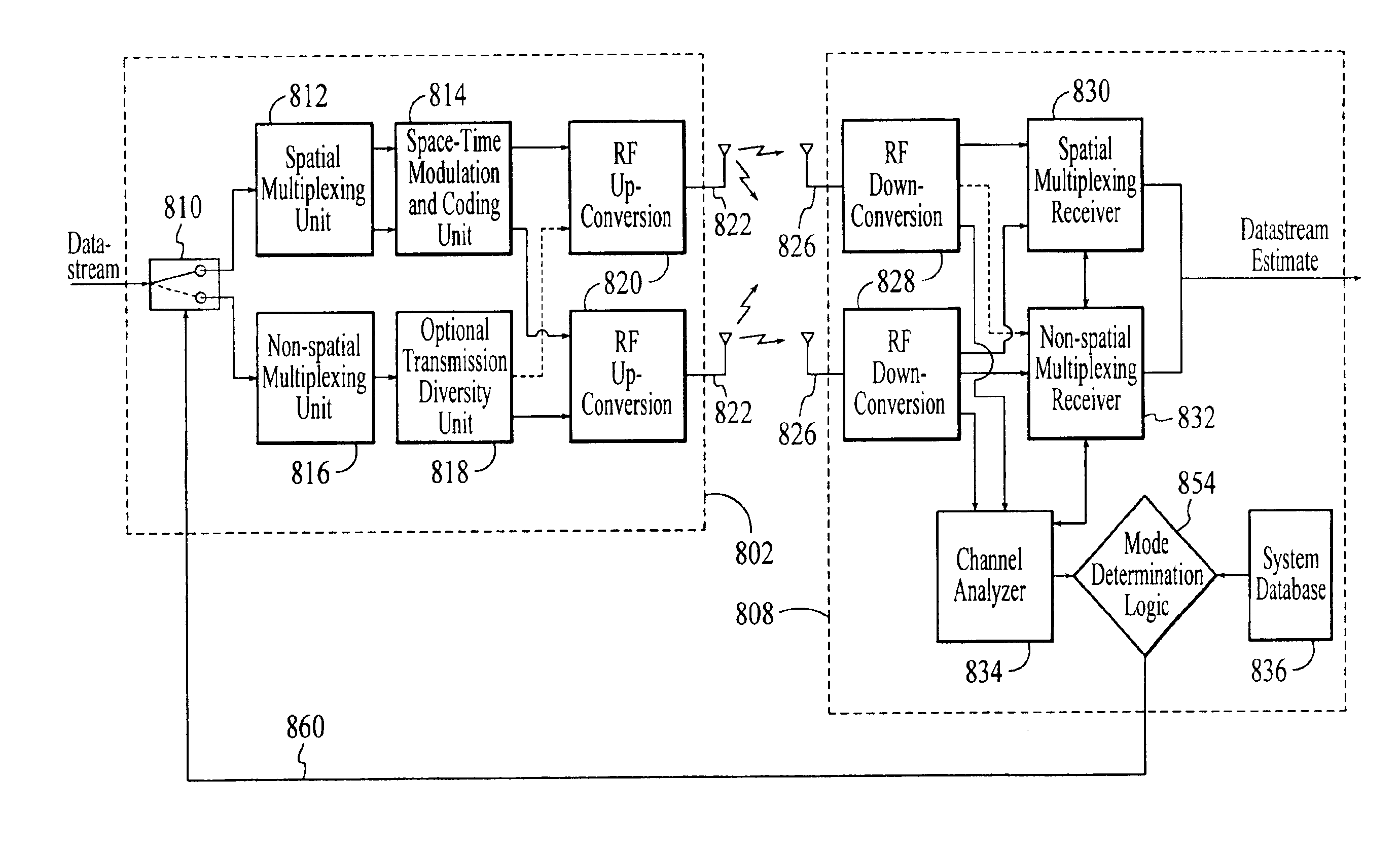
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS20050174981A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTransceiverMultiple modes
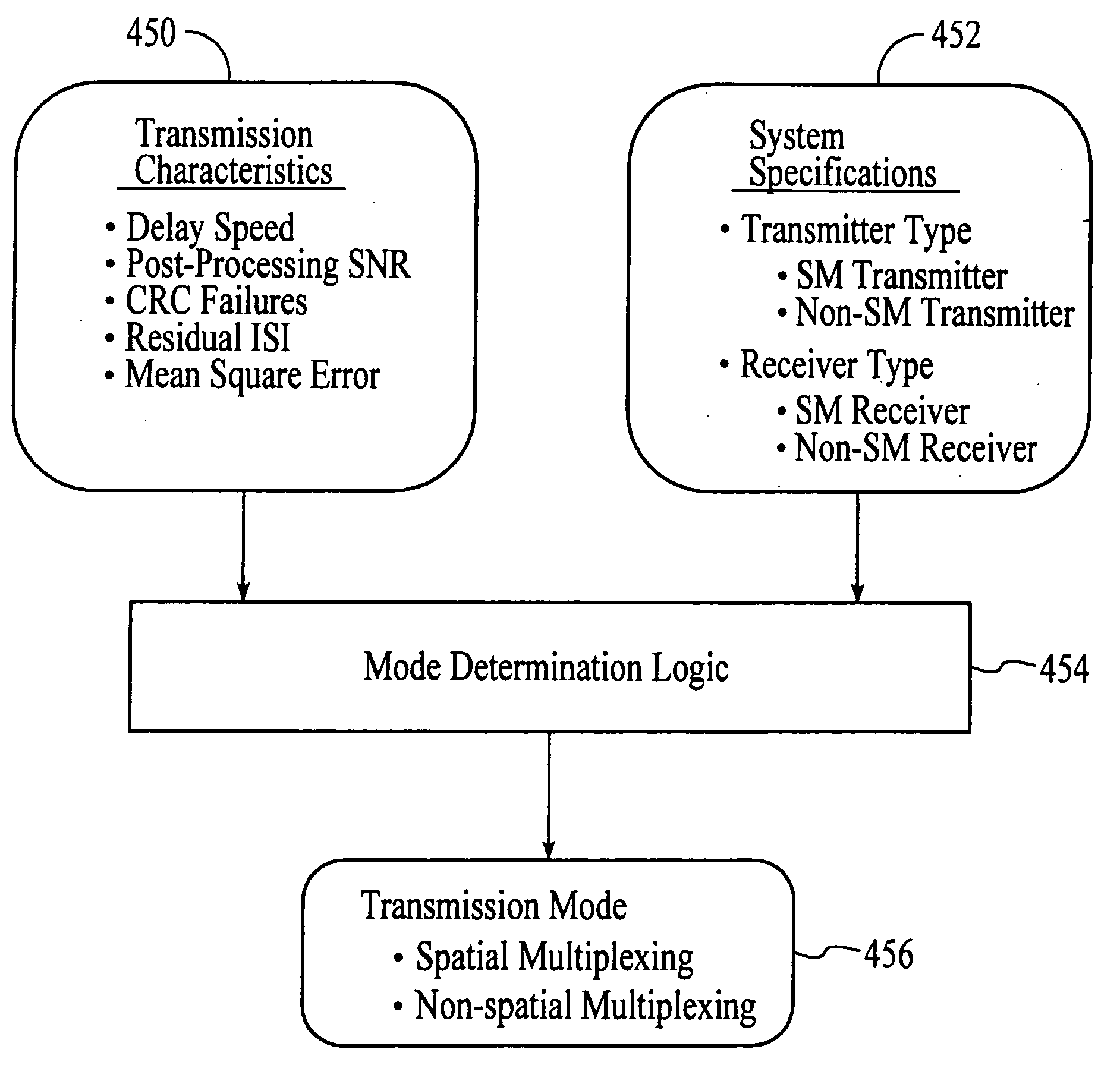
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
Power headroom reporting for non-scheduled uplink component carriers
ActiveUS20130010720A1Efficient and robust (de)activationMinimize signaling overheadPower managementEnergy efficient ICTTransmitted powerResource block
This invention relates to a proposal for power headroom reporting for uplink component carriers for which no uplink resource allocation is scheduled by the eNodeB. The user equipment (UE) calculates a virtual power headroom for the non-scheduled uplink component carrier, based on a virtual uplink resource assignment pre-configured by the UE and eNodeB. According to one embodiment the maximum transmit power of the UE is set to a pre-configured fixed value. Alternatively, the maximum transmit power is calculated by the UE considering the power reduction, while the uplink transmission power is set to zero. The virtual power headroom is then transmitted to the eNodeB, which in turn can infer therefrom the pathloss and / or power-per-resource-block for the non-scheduled uplink component carrier and may also infer the power reduction used by the UE. This allows a more accurate scheduling of future uplink transmissions on said non-scheduled uplink component carrier.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
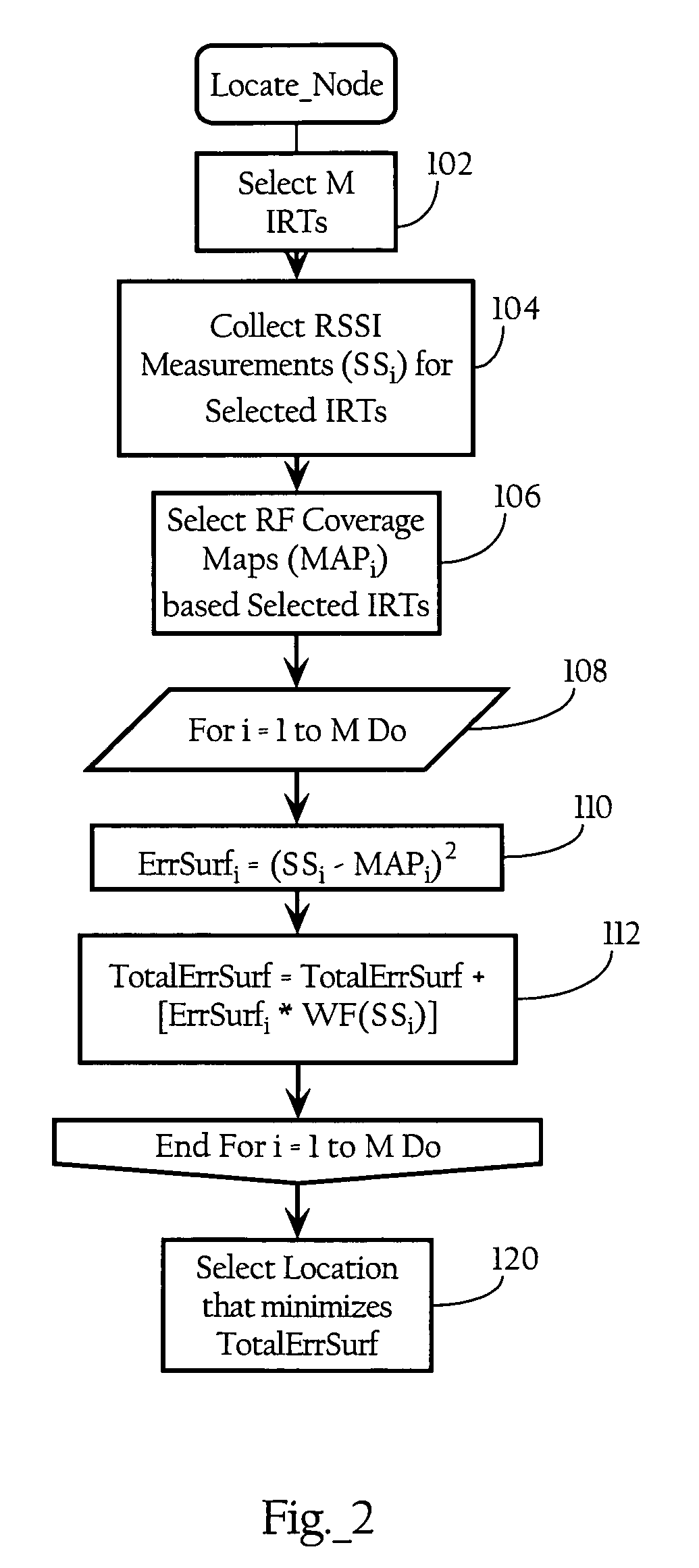
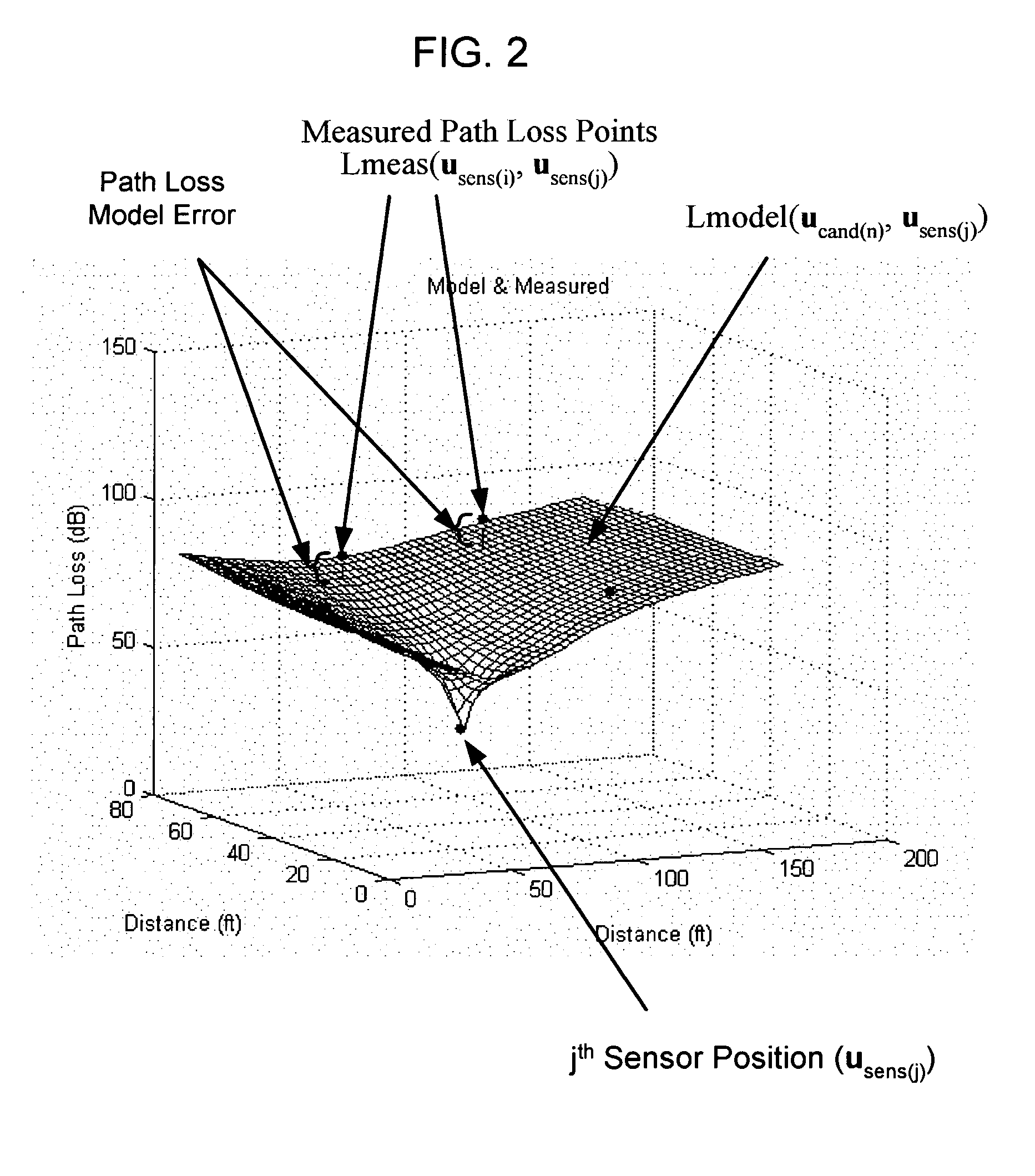
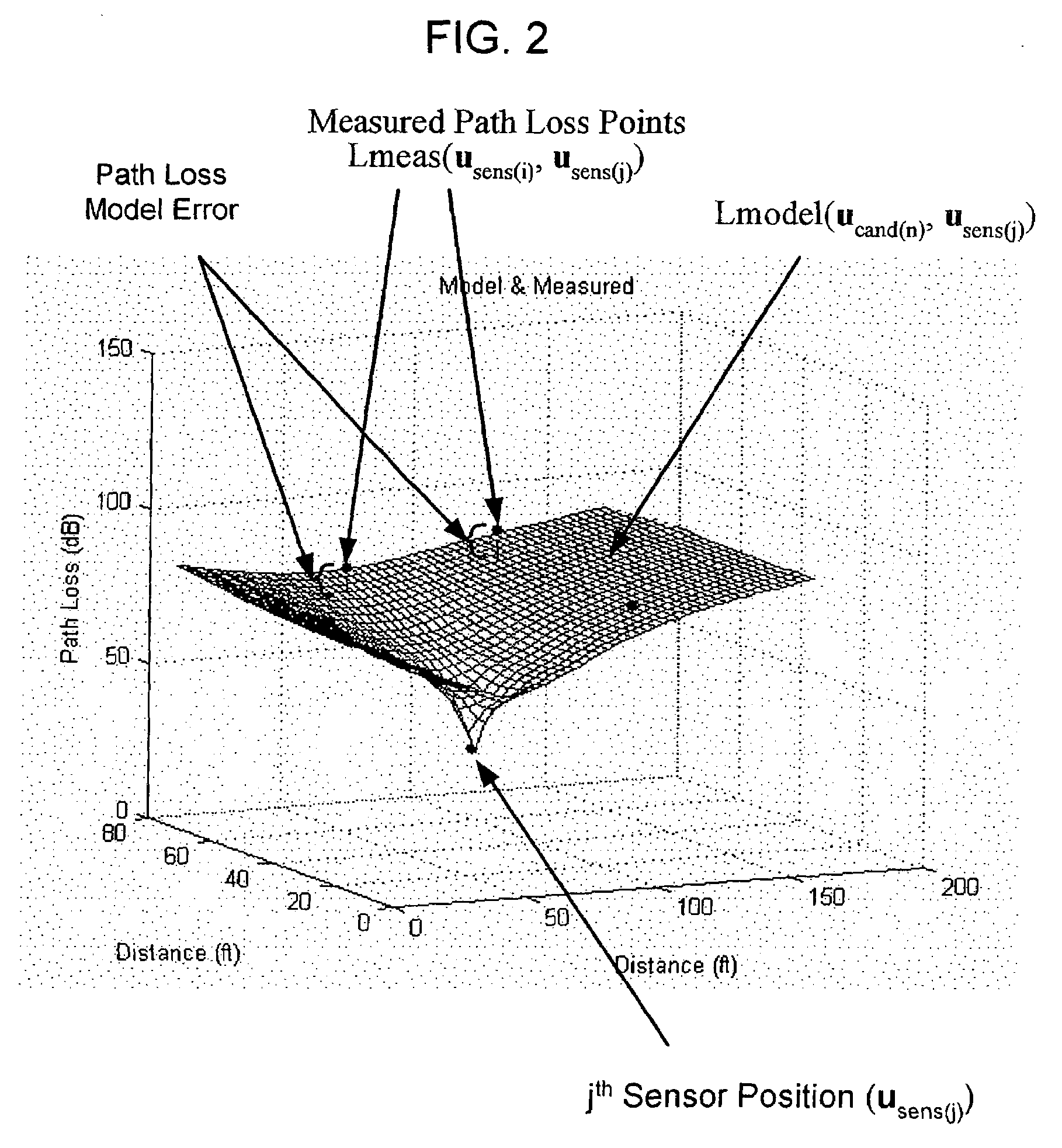
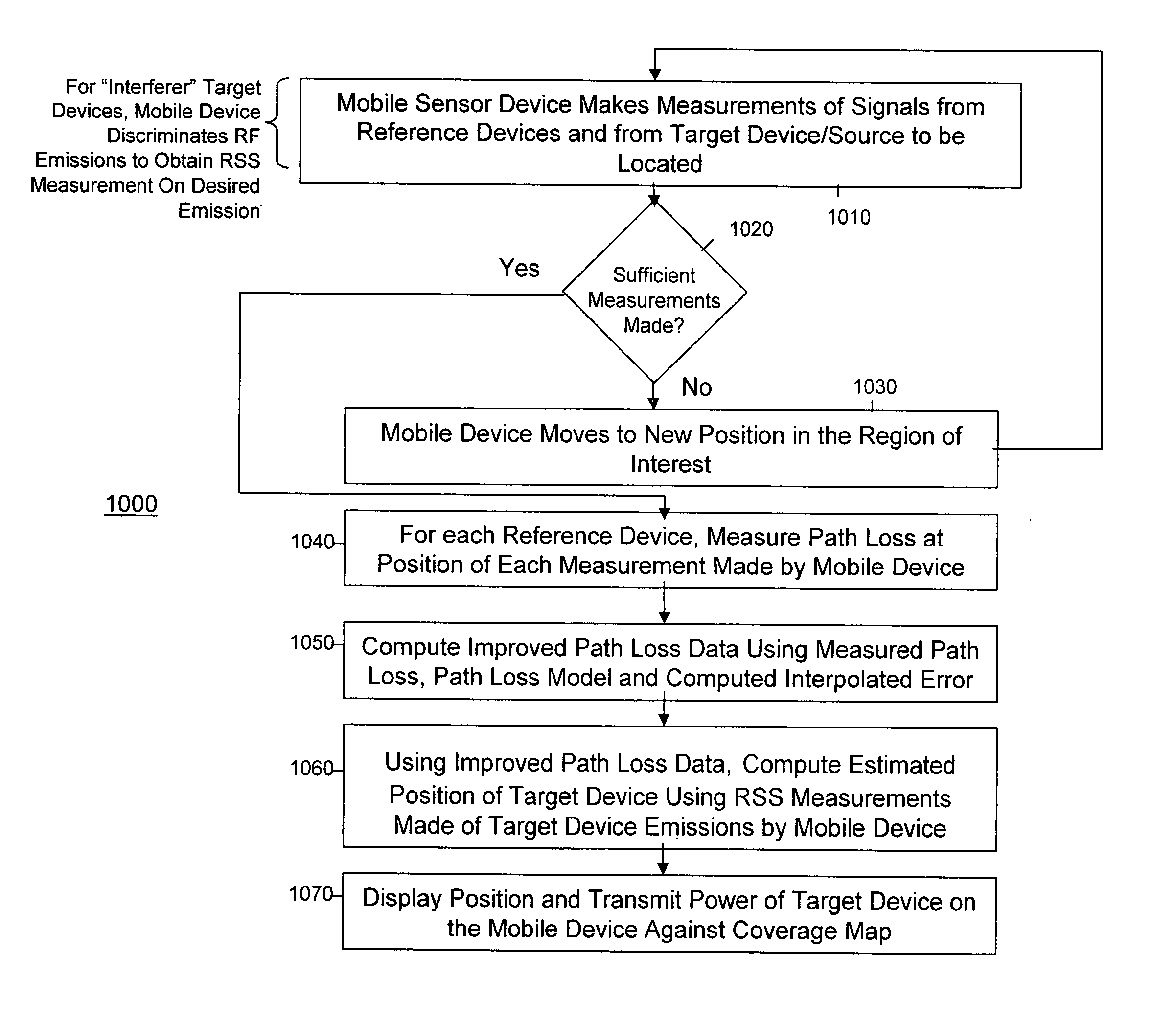
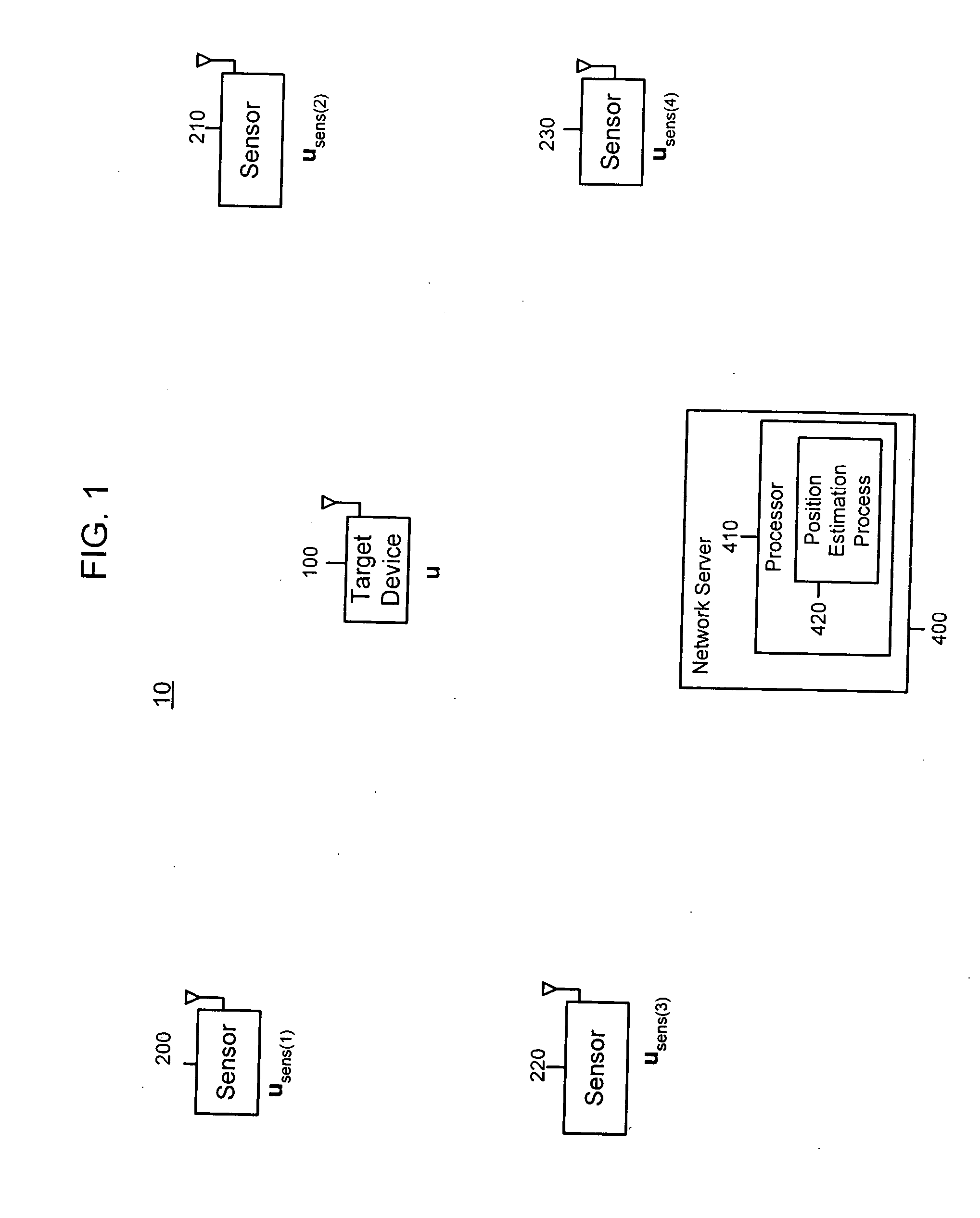
System and method for locating radio emitters using self-calibrated path loss computation
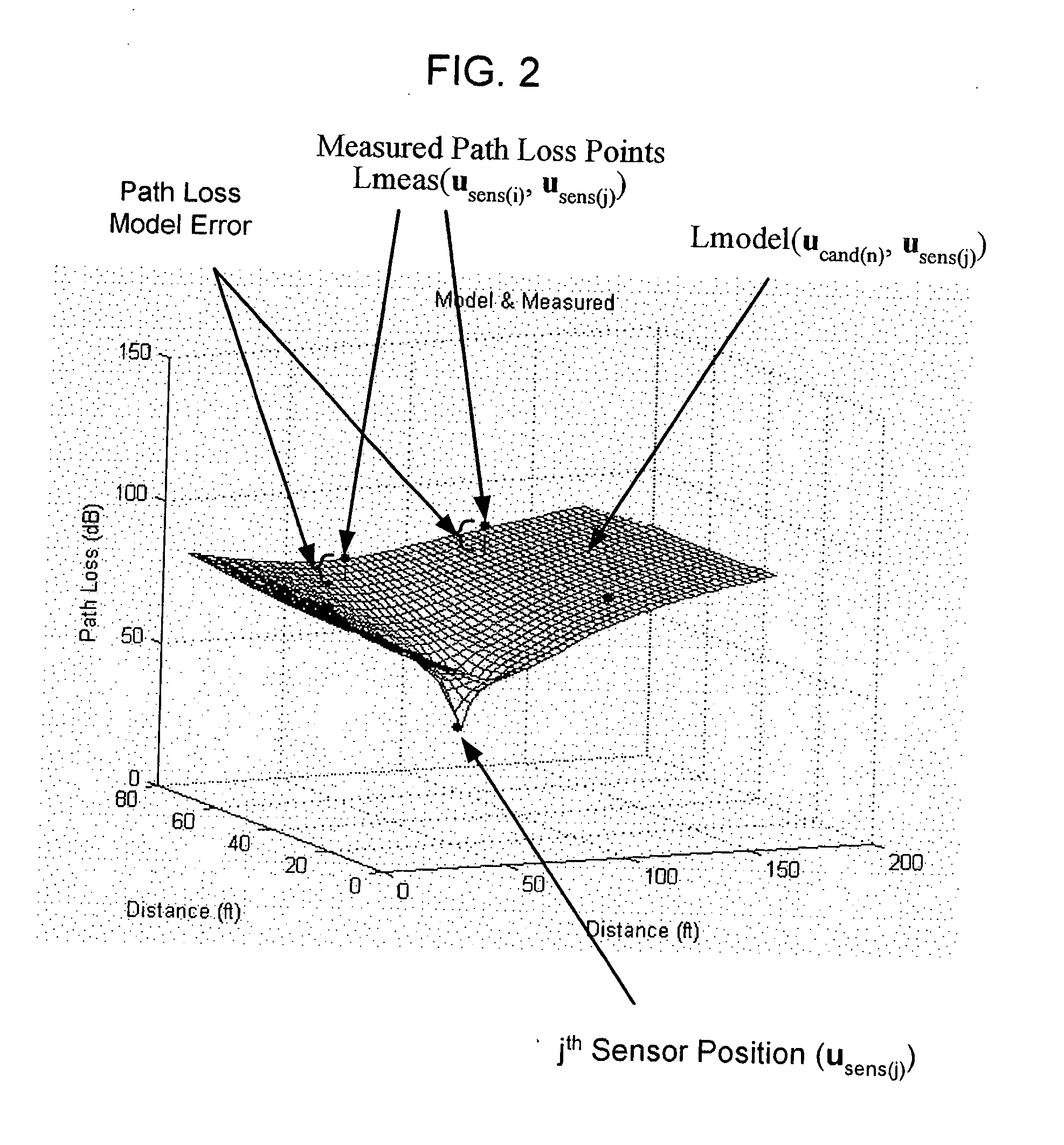
ActiveUS20050285792A1Reduce complexityImprove accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationRadiotransmitterDevice placement
Techniques for reducing the complexity and improving the accuracy of receive signal strength based location systems. The system comprises a plurality of radio sensor devices placed at known positions within a space in which devices are to be located. According to one technique, the path loss is measured between all combinations of pairs of radio sensor devices based on a test signal transmitted by each radio sensor device. A path loss model is evaluated to compute modeled path loss data between all combinations of pairs of radio sensor devices. For each measured path loss, a path loss error relative to each radio sensor device is computed by taking the difference between the measured path loss and the modeled path loss. The path loss error relative to each radio sensor device at any candidate position is interpolated from the computed path loss errors. A path loss estimate between a candidate position and each radio sensor device is computed by adding the interpolated path loss error relative to that radio sensor device at the candidate position and path loss data obtained by evaluating the path loss model based on the distance between at each candidate position and the corresponding radio sensor device. When determining the position of a device emitting radio signals (called a target device), the improved path loss estimate is used. According to another technique, for each radio sensor device, parameters are derived for a path loss model function from the measured path loss between that radio sensor device and each of the other radio sensor devices using a minimization computation. Then, a path loss estimate between a position and each radio sensor device is computed by evaluating the path loss model function using the parameters derived for each radio sensor device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
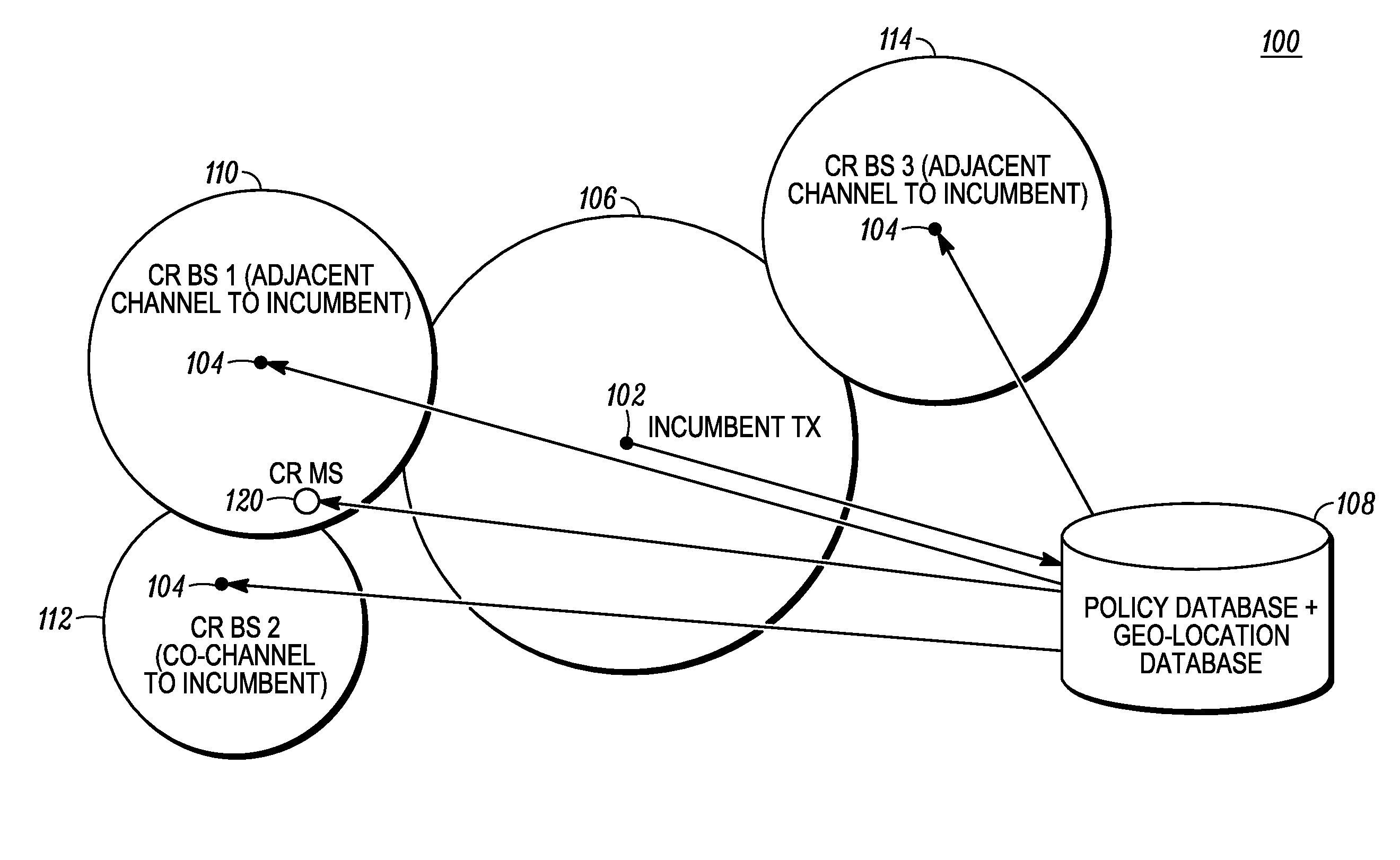
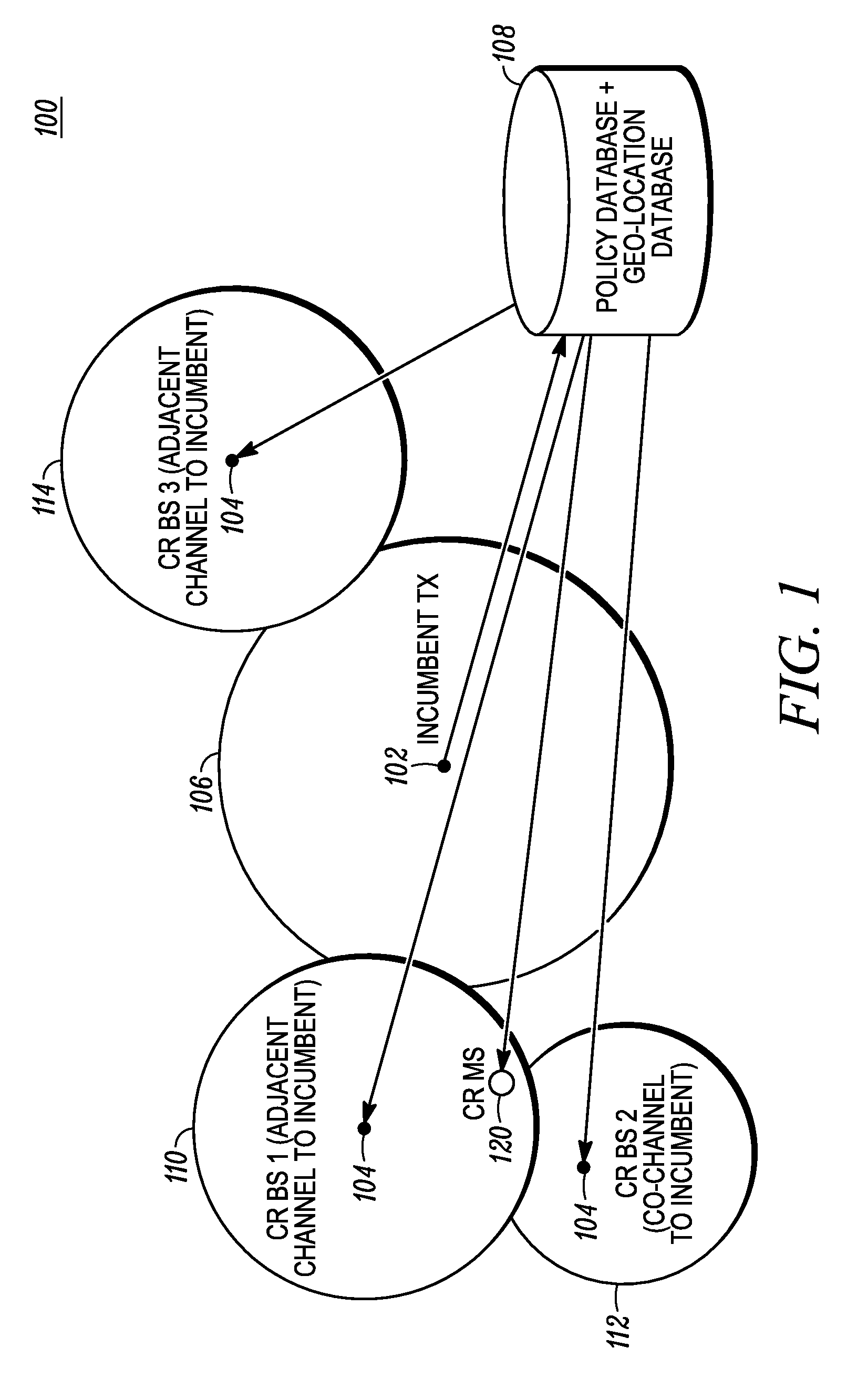
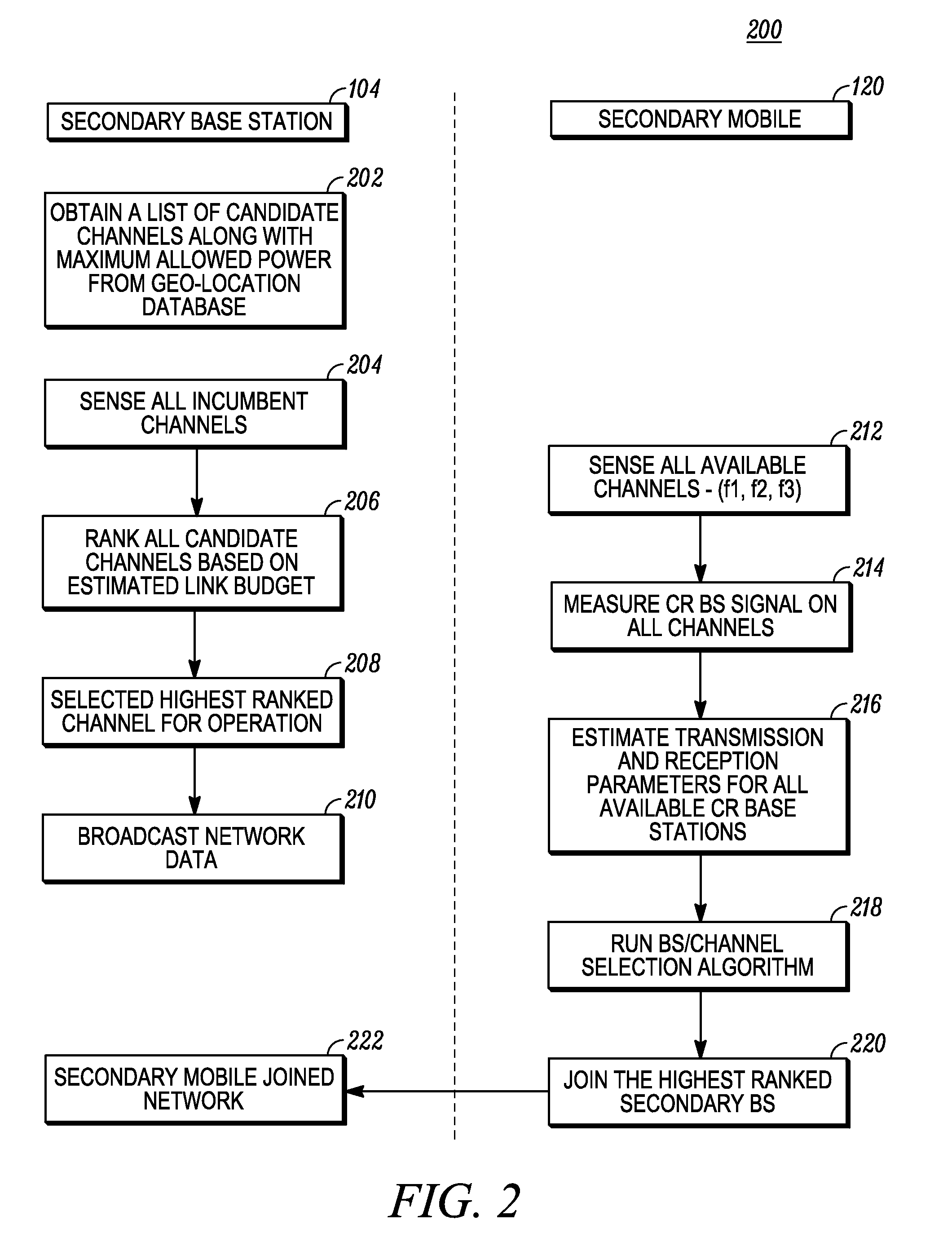
Method and apparatus for optimizing spectrum utilization by a cognitive radio network
ActiveUS20100081449A1Spectral gaps assessmentAssess restrictionCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
A technique for a secondary communication system to utilize spectrum designated to another (or primary) communication system is provided. By ranking a plurality of secondary base stations based on base station transmit power, calculated required transmit power and path loss, a set of criteria is developed for selecting a highest ranked secondary base station for operation within a primary's spectrum. The ranking may be adapted based on mobility of the secondary's subscriber; and as such the secondary system communicates within the primary's spectrum using the adaptively ranked base stations. Channel selection may also be ranked. The technique and apparatus allows a cognitive radio (CR) network to operate within an incumbent network's spectrum.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS6937592B1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionOperation modeMultiple modes
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
Uplink control method and apparatus in wireless communication system
An UpLink (UL) control method and apparatus for in a wireless communication system supporting beamforming are provided. A method of a Mobile Station (MS) for UL control in the wireless communication system supporting the beamforming includes receiving a plurality of DownLink (DL) reference signals from a plurality of Base Station (BS) transmission beams using a plurality of MS reception beams having different directivity, measuring a path loss based on a reception signal strength of each of the plurality of DL reference signals received through different transmission / reception beams, selecting an MS transmission beam for uplink based on the path loss value measured for each of the plurality of DL reference signals, and transmitting a UL signal to a BS using the selected MS transmission beam.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for determining service availability
A method of determining the availability of at least one of a plurality of different services in a wireless communication network comprising at least a first station and a second station which are in communication has the following steps. The pathloss between said first station and said second station is estimated, and based on the pathloss and the requirements of at least one of said services, the power with which said first station is required to transmit to said second station is determined. The required power is compared with the maximum power with which the first station is capable of transmitting.
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
Mechanism for performing energy-based routing in wireless networks
A method is provided to operate a communications node (2) in a network including a plurality of nodes. The communications node (2) includes a transceiver (6) to transmit and receive messages. The communications node (2) has at least one communications link with a first node of the plurality of nodes. The method includes the steps of: (i) determining path loss information across the at least one communications link by evaluating power data corresponding to a received signal from the first node; (ii) distributing the path loss information to the network; and (iii) routing messages to the network based on path loss information.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
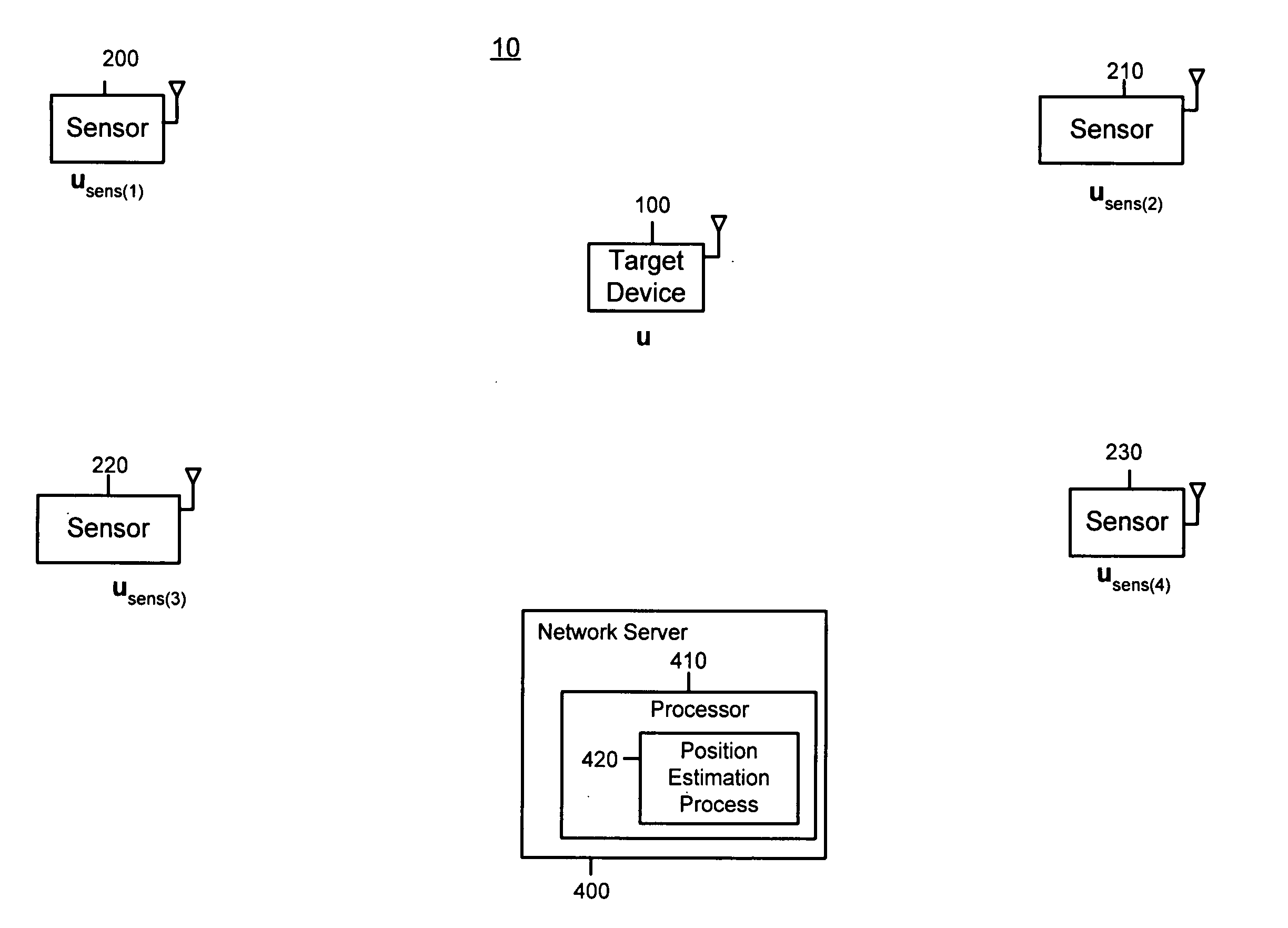
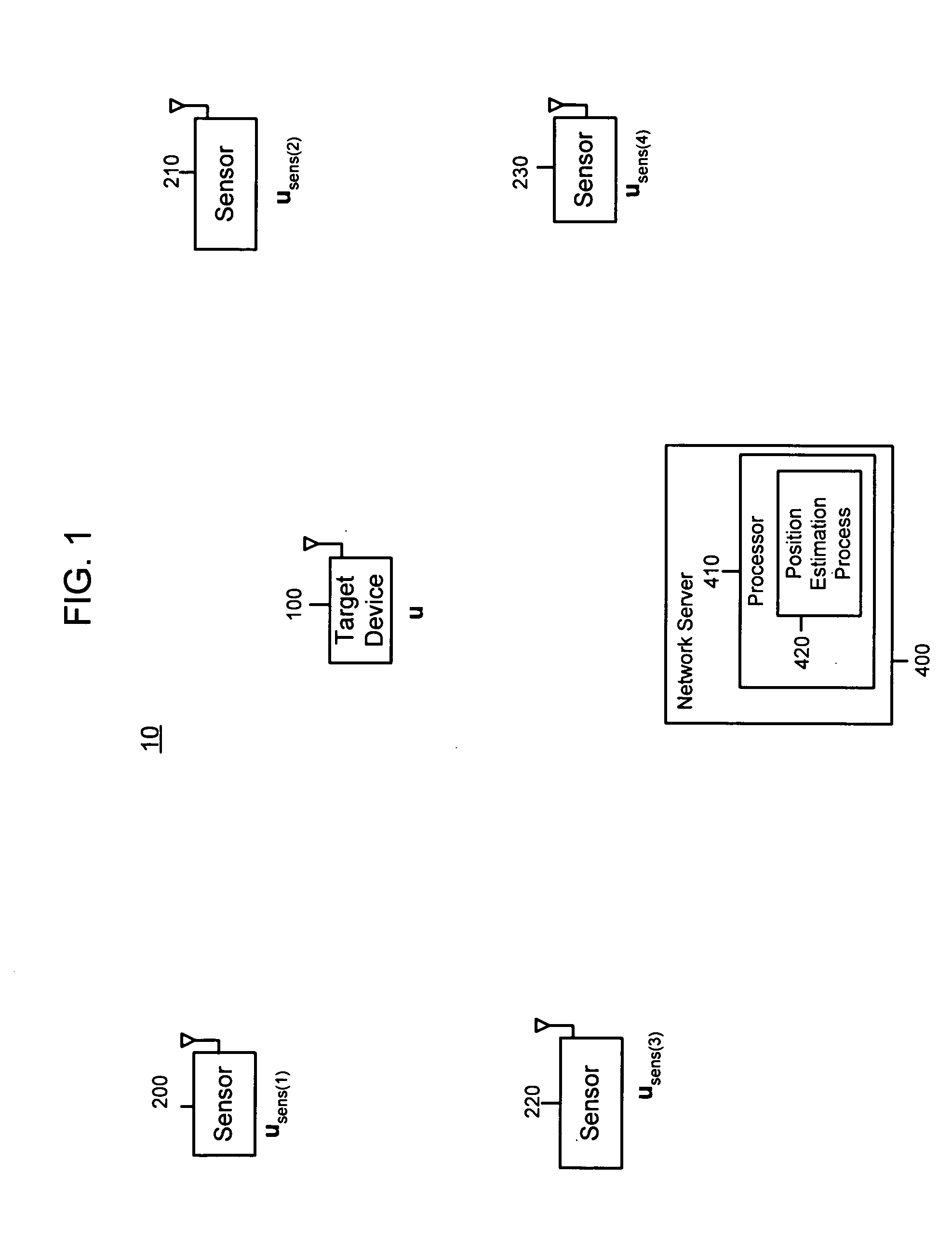
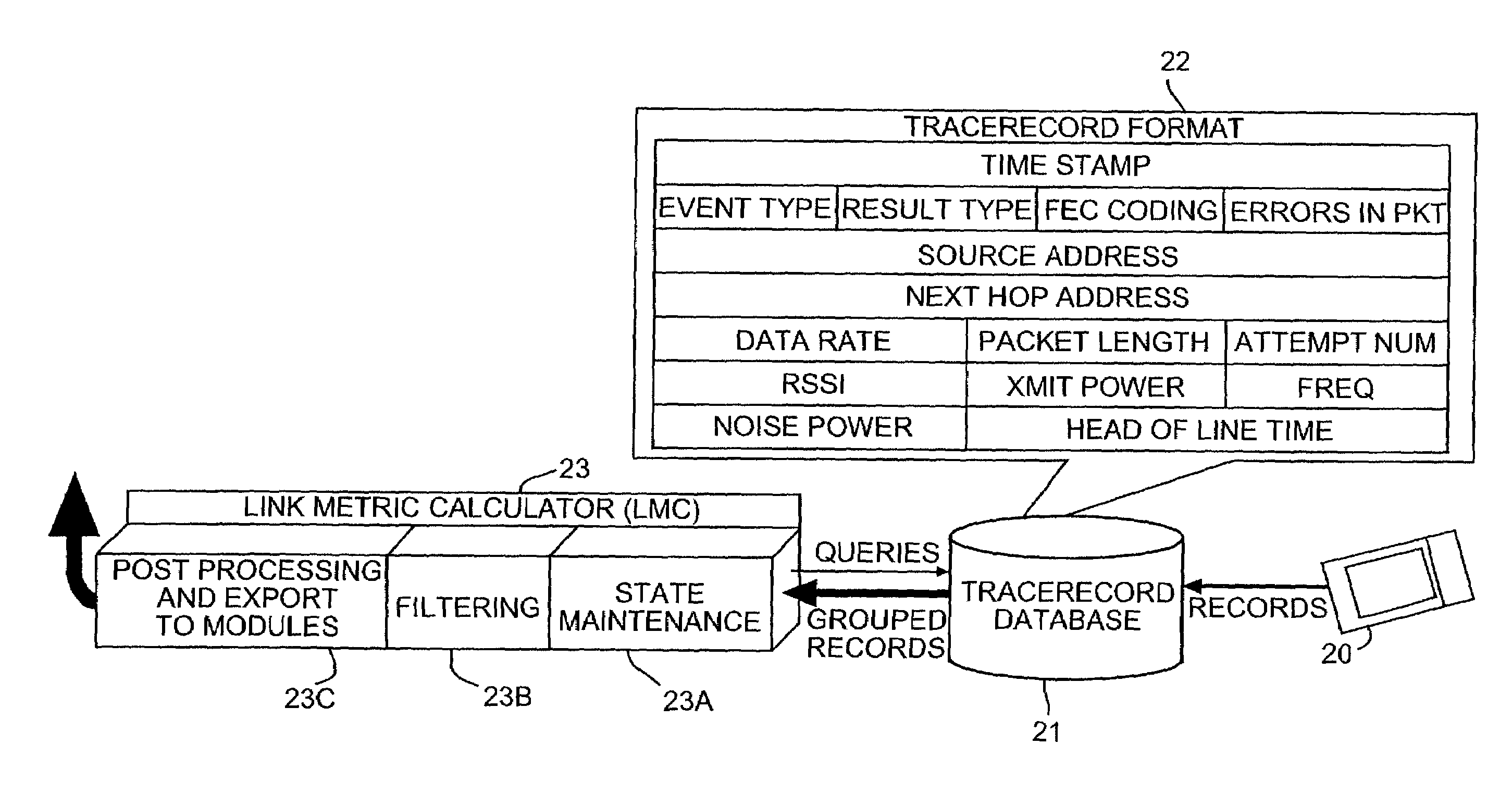
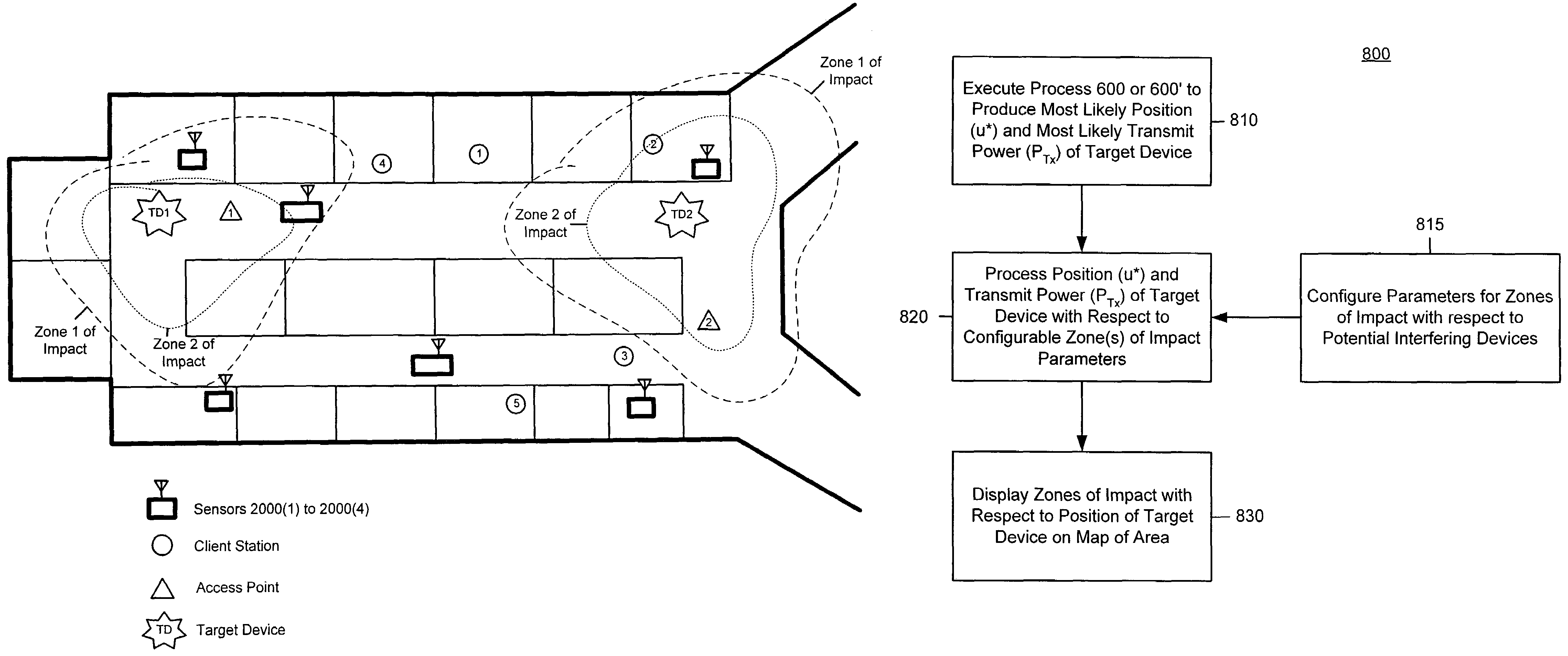
Self-calibrated path loss position estimation and zone of impact determination
A device and method are provided for estimating a position of a target device (e.g., a device emitting radio frequency energy) based on data pertaining to strength of an emission received from the target device. At a mobile device, emissions are received from the target device when the mobile device is at each of a plurality of positions to produce receive signal strength data representative thereof. The mobile device, also recieves signals from each of a plurality of reference devices at a corresponding known position when the mobile device is at each of the plurality of positions. The position of the target device is estimated based on receive signal strength data associated with received emissions from the target device and from the reference devices. Using the estimated position and estimated transmit power of the target device, a zone of impact of the target device is determined with respect to other wireless activity based on the estimated position and estimated transmit power of the target device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
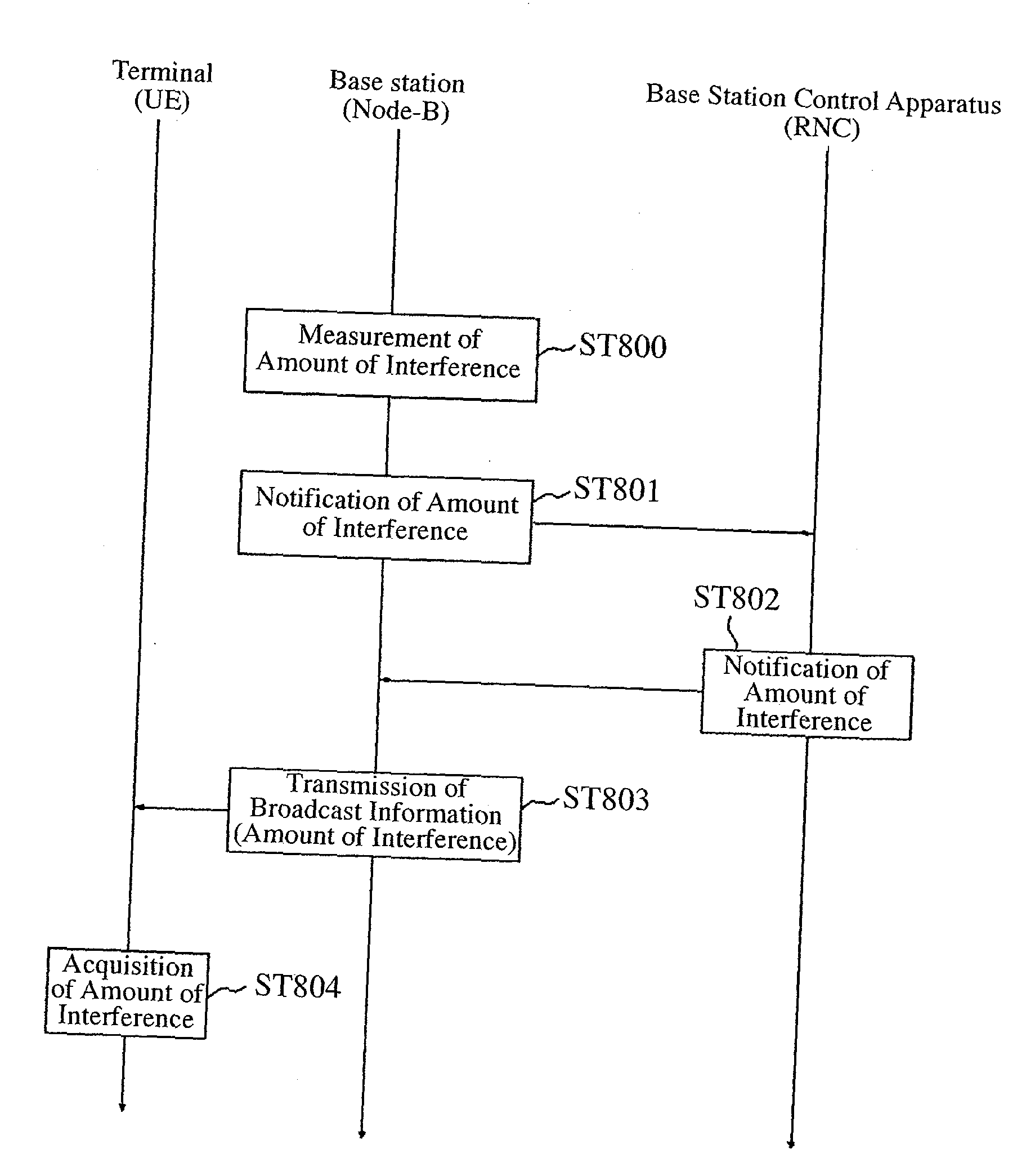
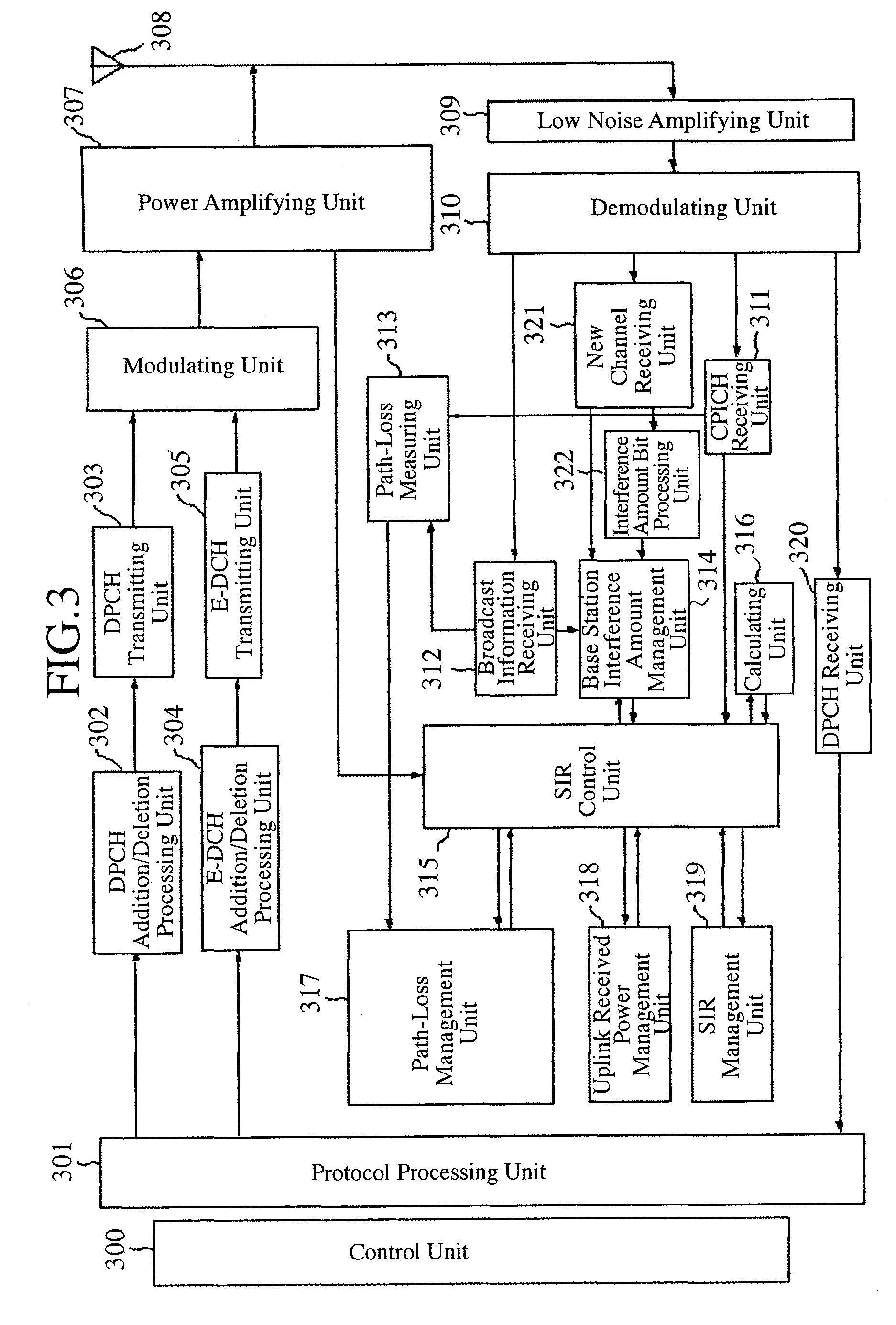
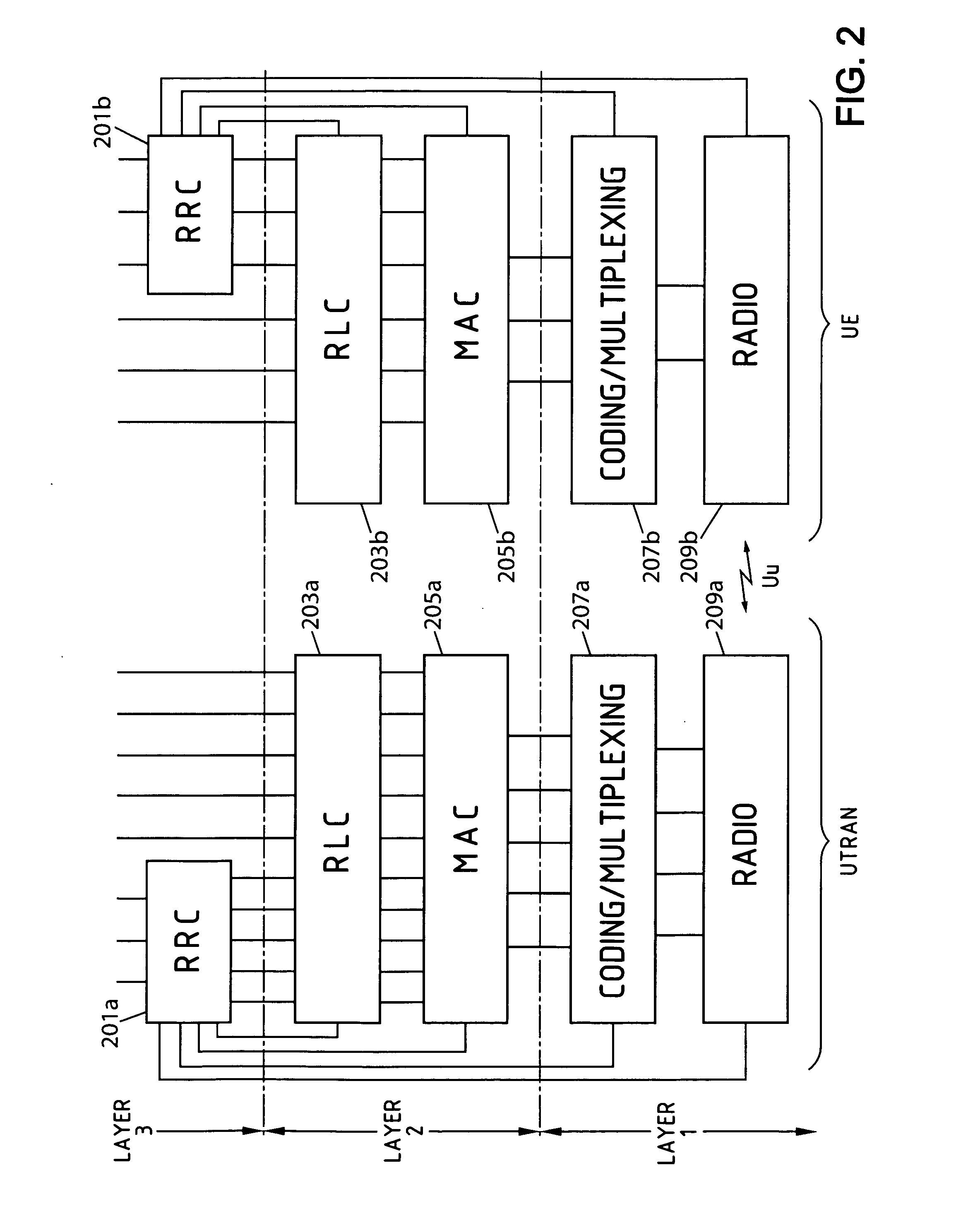
Communication Quality Judgment Method, Mobile Station, Base Station, and Communications System
In order to carry out high-speed packet communications using a large-volume transmission channel like an E-DCH, uplink communication quality must be good. However, in a state in which a link imbalance occurs, a mobile station cannot estimate the uplink communication quality from downlink communication quality. Therefore, the mobile station calculates a path loss from the setting power of a common pilot channel which is notified from a base station, and the received power of the common pilot channel received thereby, and also estimates the received power in the base station on the basis of this path loss. The mobile station further judges the uplink communication quality by estimating the SIR in the base station by using the interference power notified from the base station and the estimated received power.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
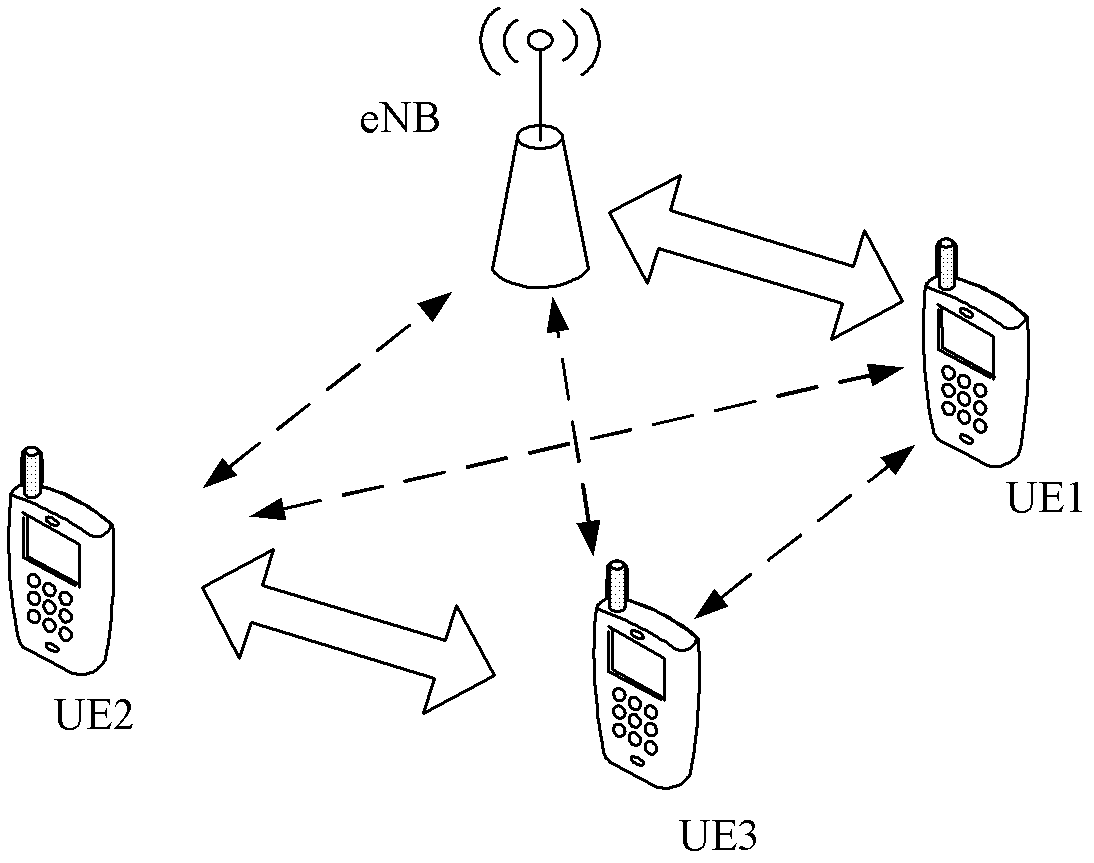
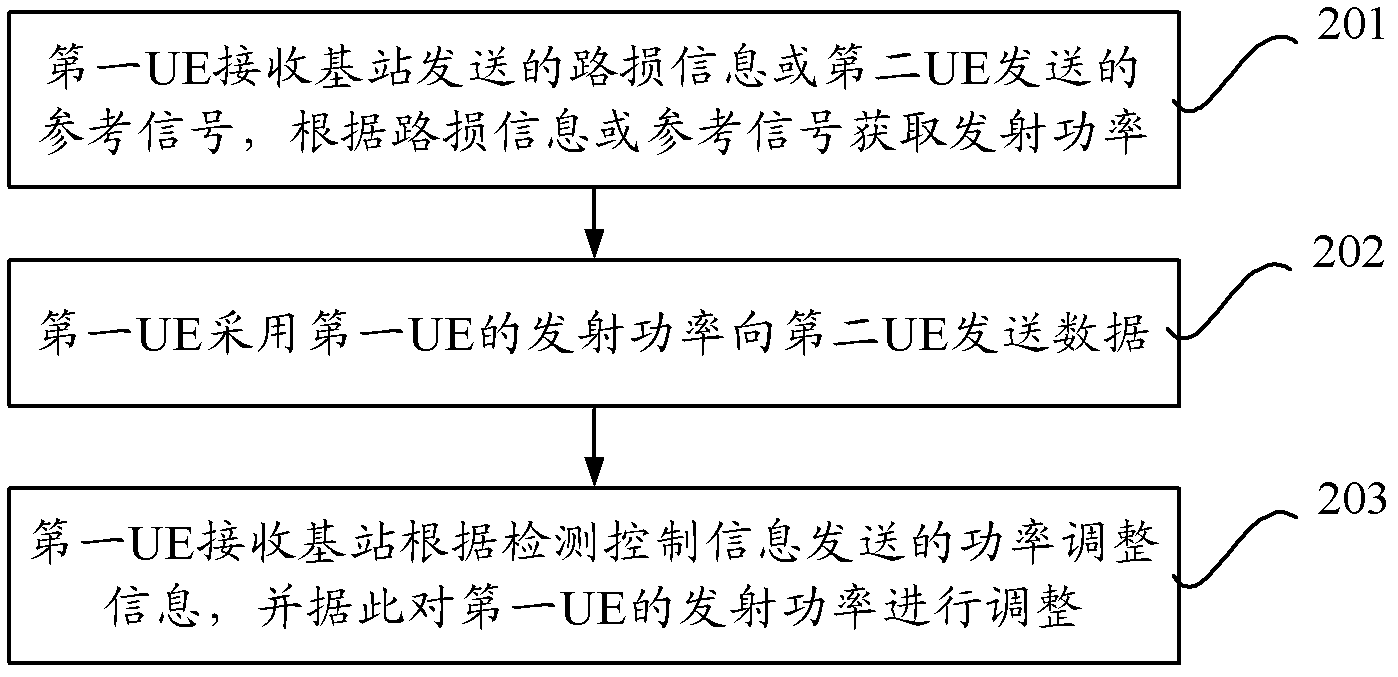
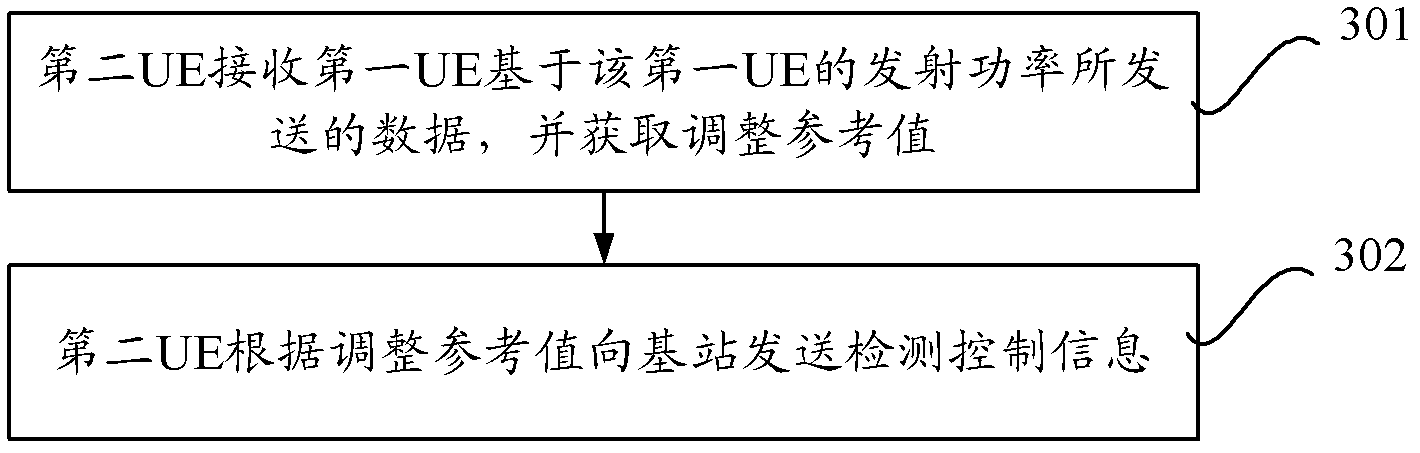
Power control method, user equipment, base station and communication system of dimension to dimension (D2D)
ActiveCN103139889AImplement power controlSolve the problem that the transmit power of the first UE cannot be adjustedPower managementCommunications systemE communication
The invention provides a power control method, user equipment, a base station and a communication system of dimension to dimension (D2D). The power control method comprises that a first user equipment (UE) receives path loss information sent by the base station or reference signals sent by a second UE, transmission power of the first UE is obtained through the path loss information or the reference signals, data is sent to the second EU based on the transmission power of the first UE so that the second EU obtains adjustment reference value according to the data and sends detection control information to the base station according to the adjustment reference value, and the first UE receives the power adjustment information sent by the base according to the detection control information and adjusts the transmission power of the first UE according to the power adjustment information. The power control method, the user equipment, the base station and the communication system of the D2D achieve power control of a transmitting end device in the D2D.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving signal in communication system
InactiveUS20130217404A1Easy to set upGuaranteed normal transmissionPower managementAssess restrictionCommunications systemComputer science
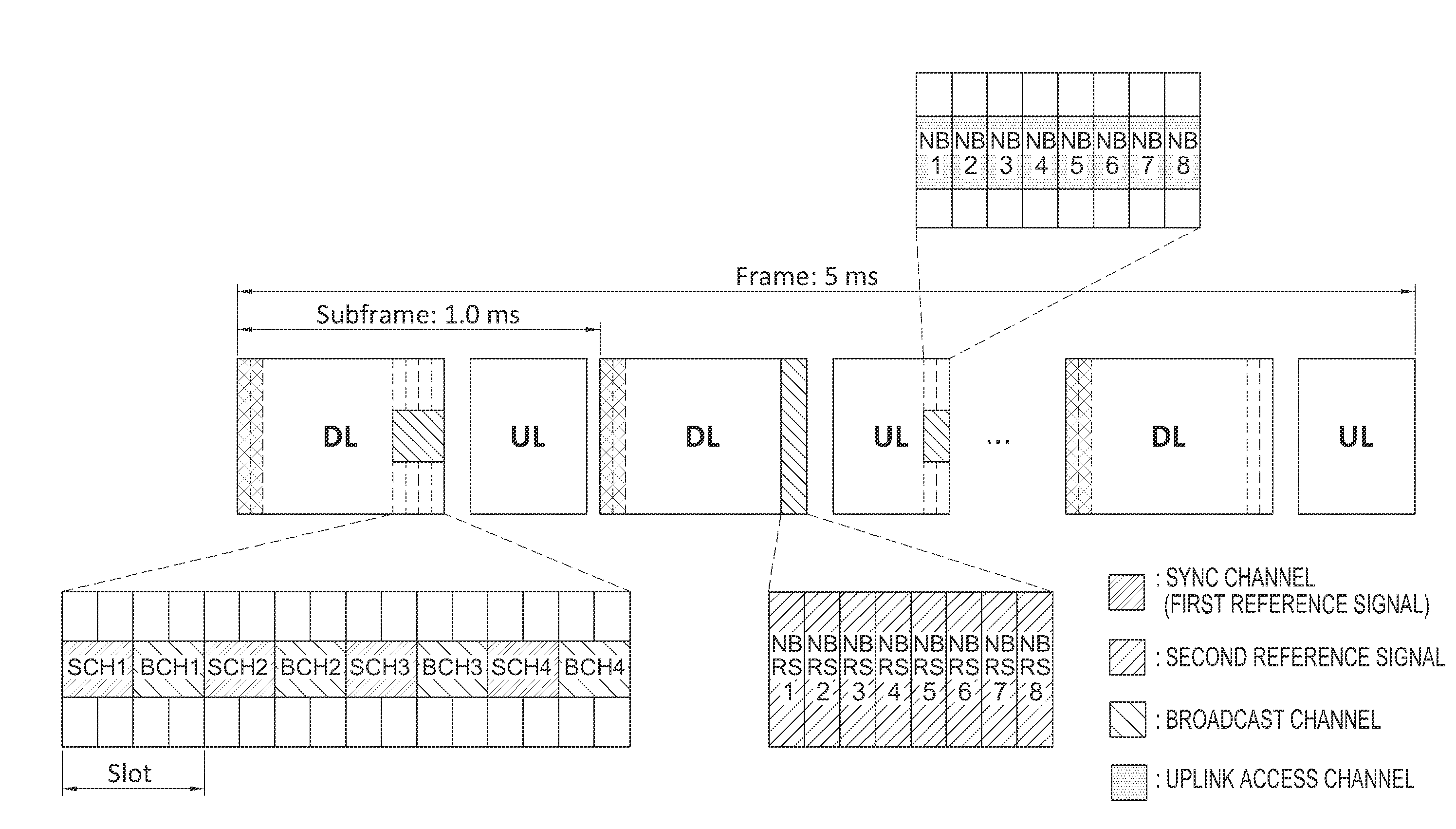
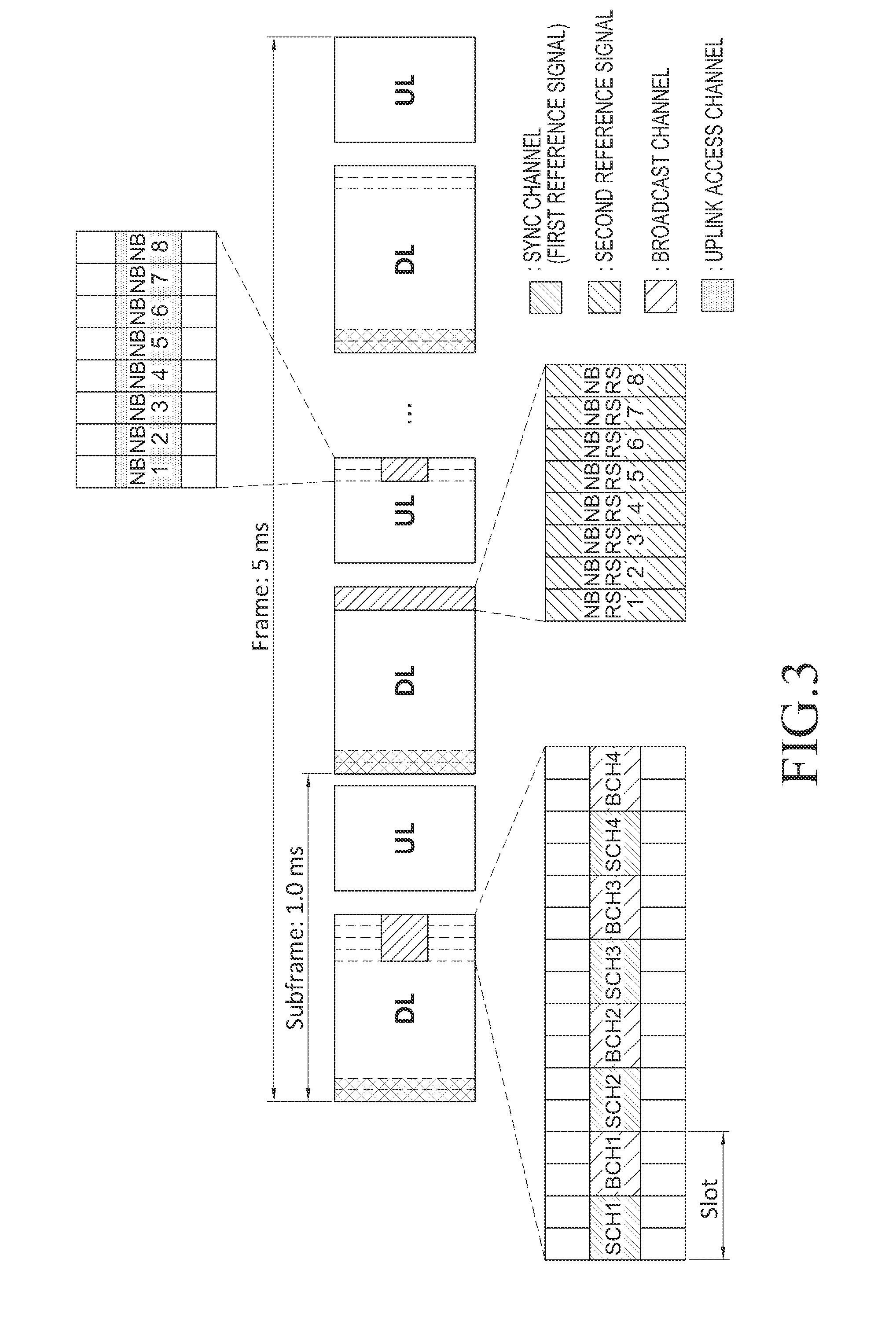
A method of transmitting / receiving signals at a terminal in a communication system is provided. The method includes determining at least one first reception path with a lowest path loss from among first reception paths that receive a first reference signal from a base station, receiving a second reference signal through second paths set up based on the at least one first reception path, and transmitting an uplink access signal with a second uplink transmitting beam that corresponds to a second downlink receiving beam corresponding to a second path having a lowest path loss.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Extending wireless communication RF coverage inside building
ActiveUS20060025072A1High possible repeater gainAvoiding base station receiver desensitizationPower managementResonant long antennasCommunications systemTransceiver
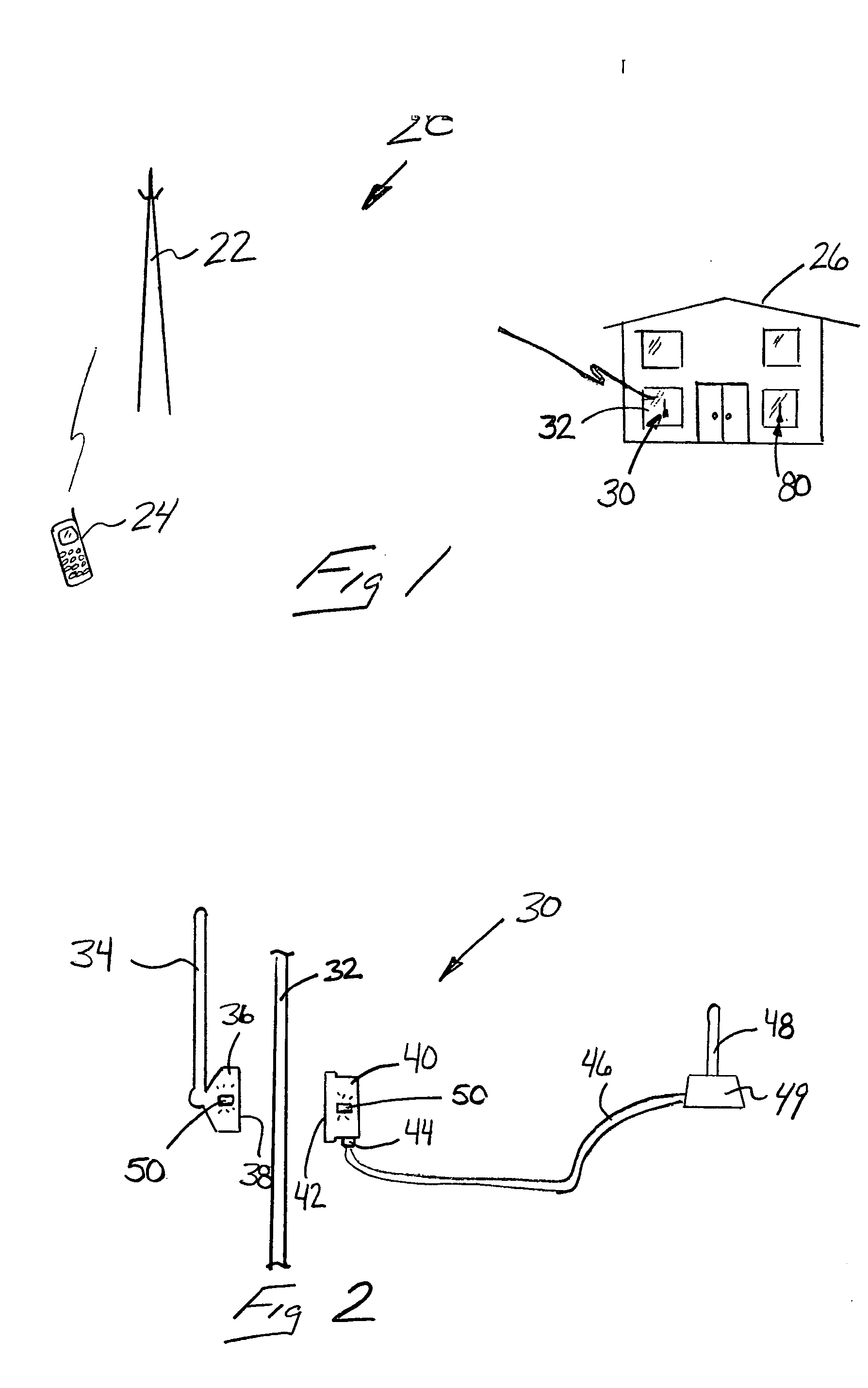
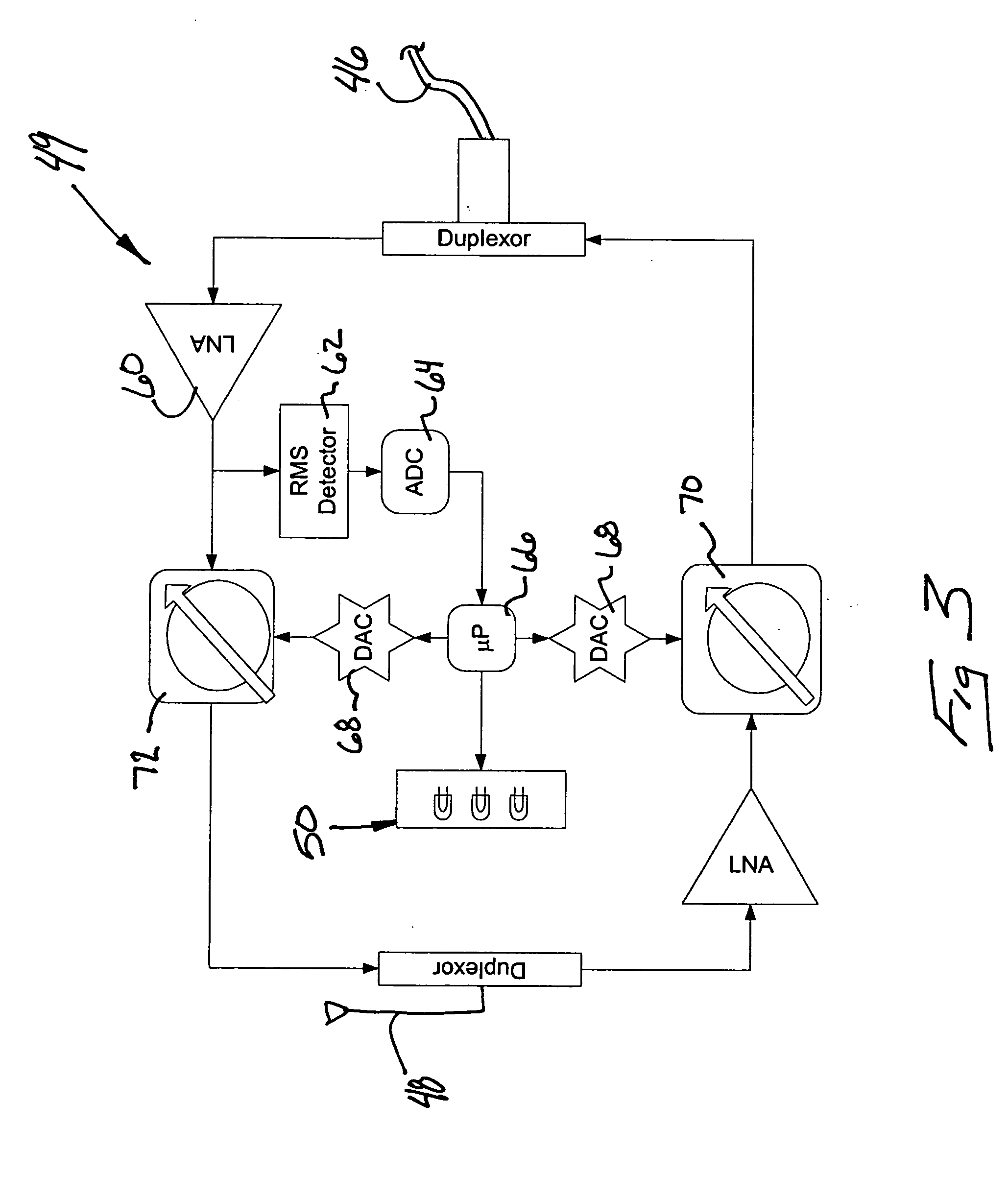
A wireless communication system includes at least one repeater antenna assembly for providing adequate RF coverage within a building, such as a home. An example repeater antenna assembly has an automatically adjustable gain that is controlled responsive to a pathloss associated with a received signal to avoid base station transceiver desensitization and positive feedback. A disclosed assembly avoids base station desensitization and positive feedback. Another disclosed technique maintains a selected minimum link budget within the building.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Transmission power management
InactiveUS20080084848A1Improve network performanceQuality improvementPower managementBroadcast transmission systemsCommunications systemRadio channel
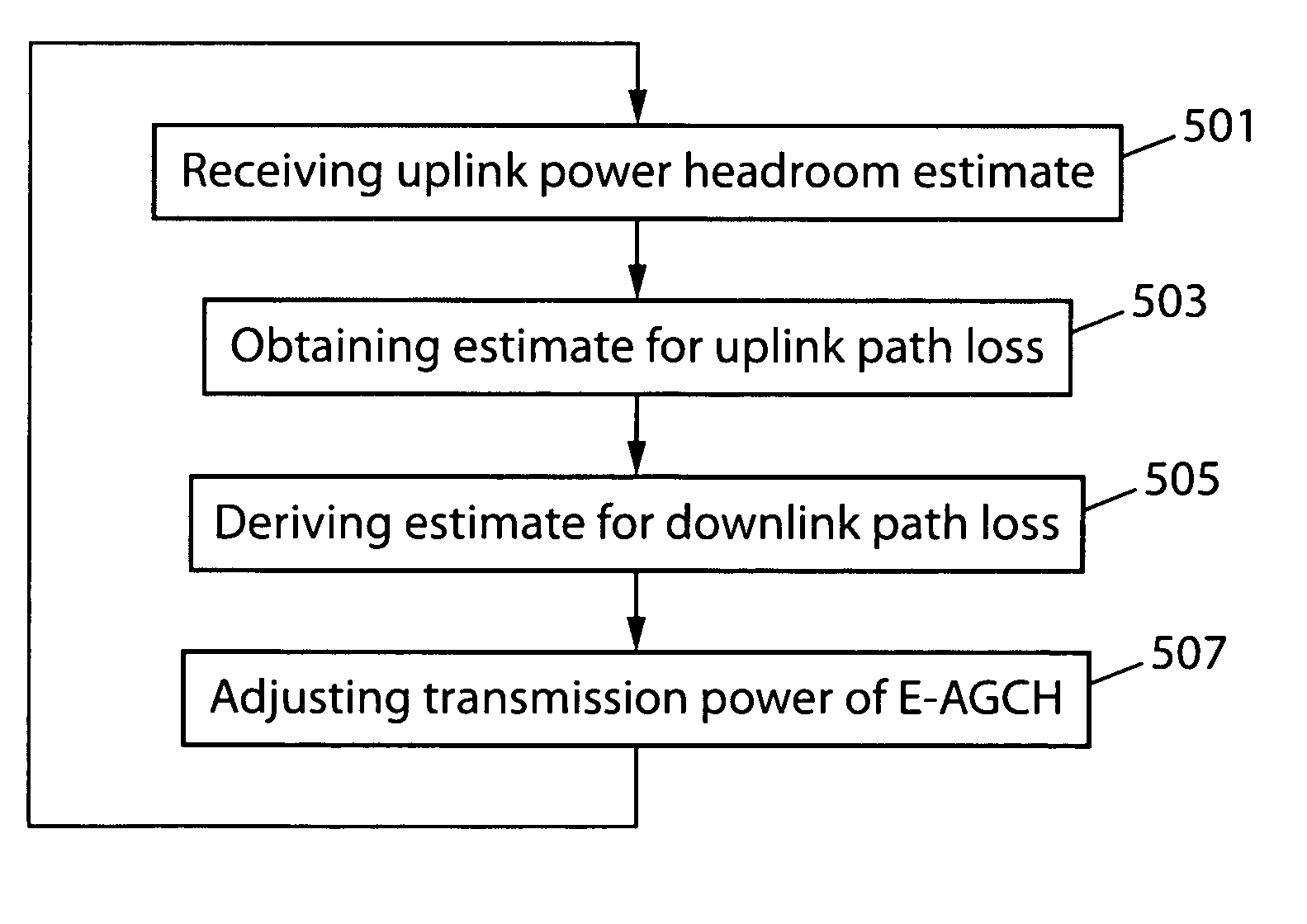
The present invention relates to a method of adjusting transmission power on a downlink radio channel in a communication system comprising a user equipment and a base station. In the method uplink power headroom is determined by dividing a maximum transmission power of the user equipment by a transmission power of a control channel of the user equipment and the determined uplink power headroom value is sent to the base station. Then uplink path loss estimate is determined between the user equipment and the base station based on the uplink power headroom. Then an estimate for the downlink path loss is derived and finally the transmission power of the downlink radio channel is adjusted taking into account the downlink path loss estimate.
Owner:ROCKSTAR BIDCO +1
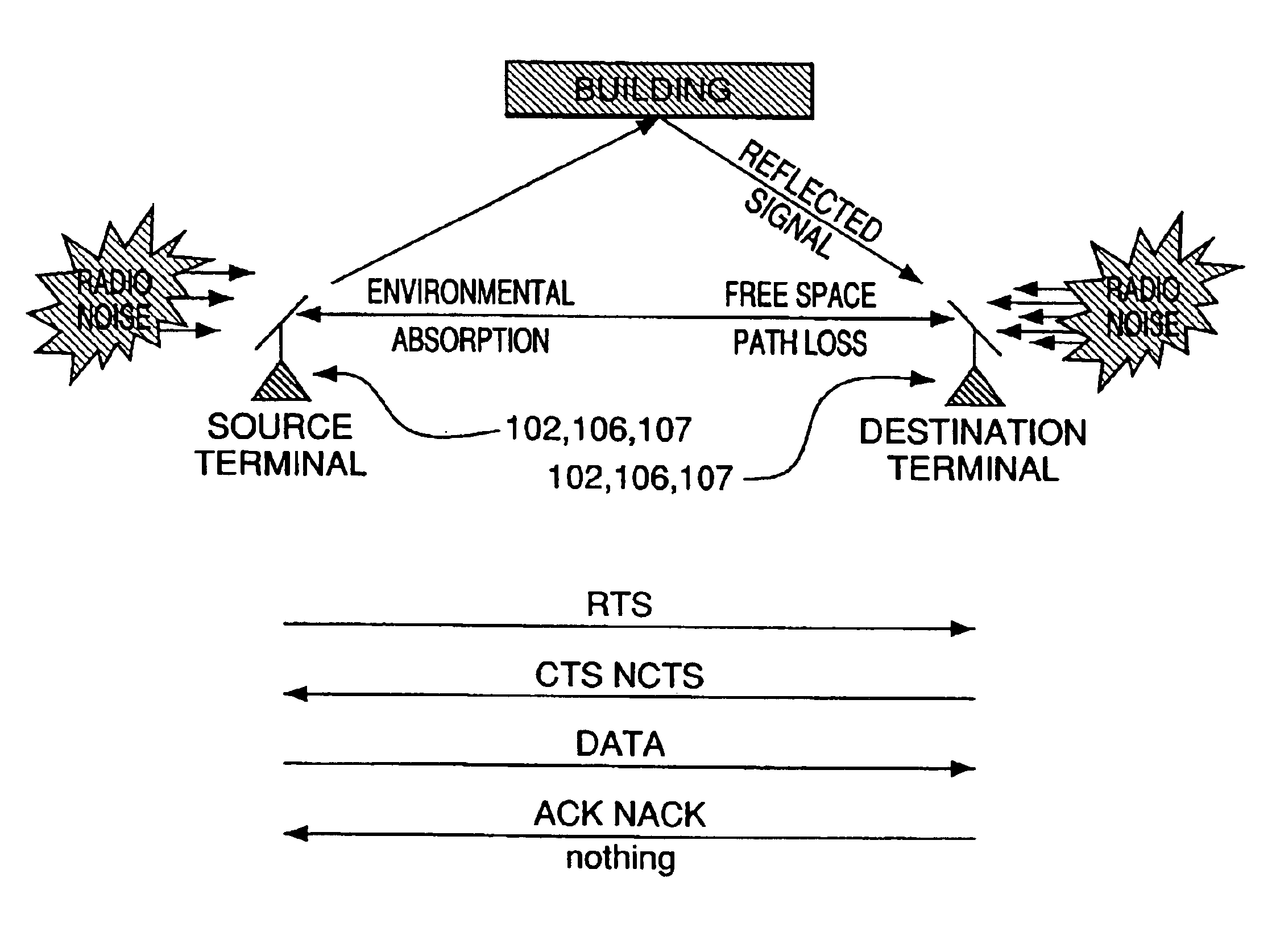
System and method for providing adaptive control of transmit power and data rate in an ad-hoc communication network
A system and method for selecting an appropriate transmit power and data rate at which a communication signal is transmitted over a link between nodes in a wireless ad-hoc communication network based on factors such as variations in path loss in the link, fading conditions, noise level estimation and overall link quality. The system and method perform the operations of computing path loss in the link based on information provided to the source node from the destination node pertaining to characteristics of a message that was transmitted by the source node and received by the destination node, determining a noise factor at the destination node, and calculating the power level and rate at which the data is transmitted over the link from the source node to the destination node based on the path loss and the noise factor. More specifically, the method calculates the power level based on the path loss, the noise factor and signal fading, and determines the rate based on the calculated power level. Furthermore, the path loss is computed dynamically as conditions of said link change over time. Accordingly, the system and method are capable of determining the proper level of transmit power and data rate for assuring that the destination node will receive the data transmitted by the source node at a reliability of at least 90%.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
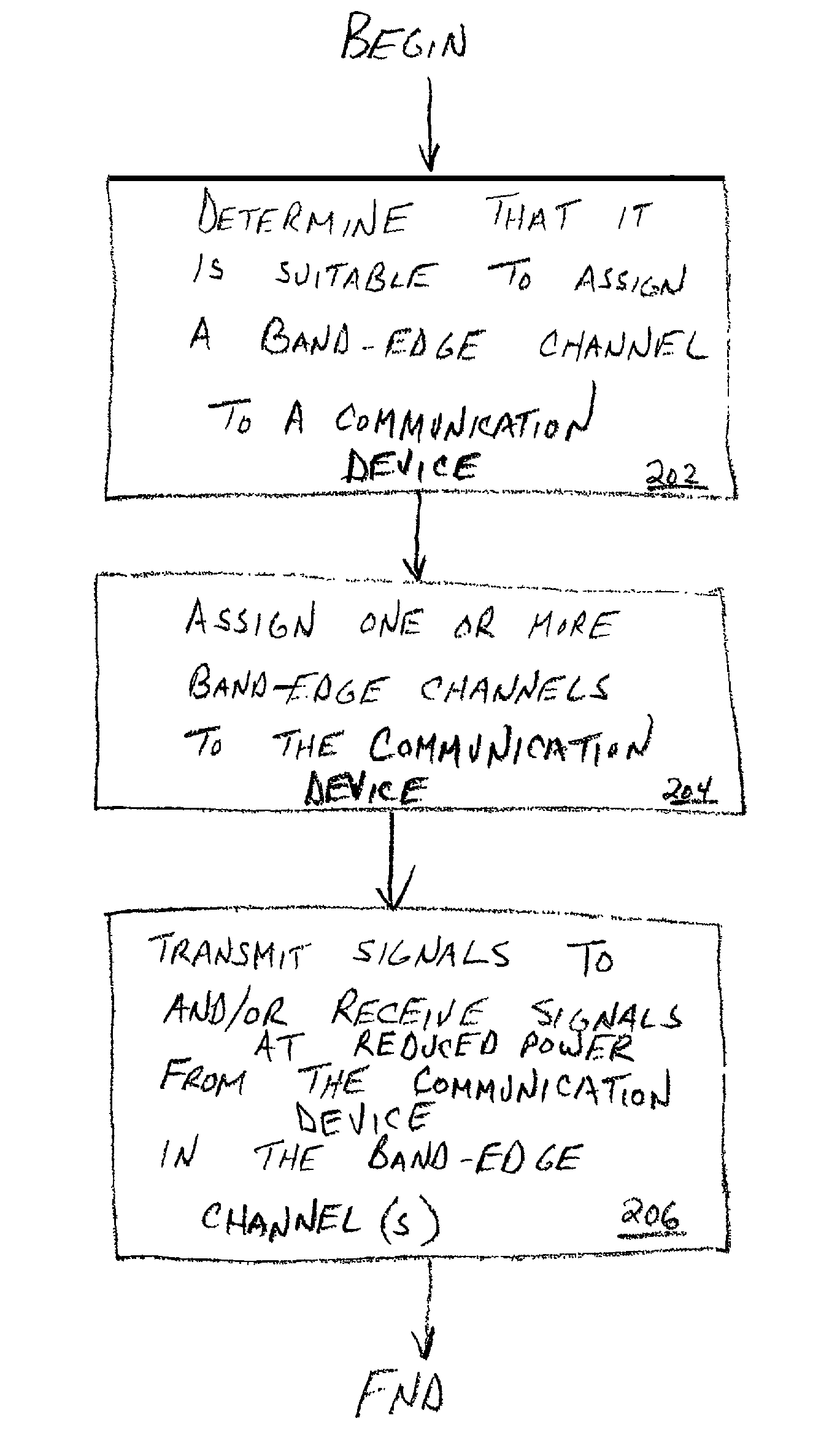
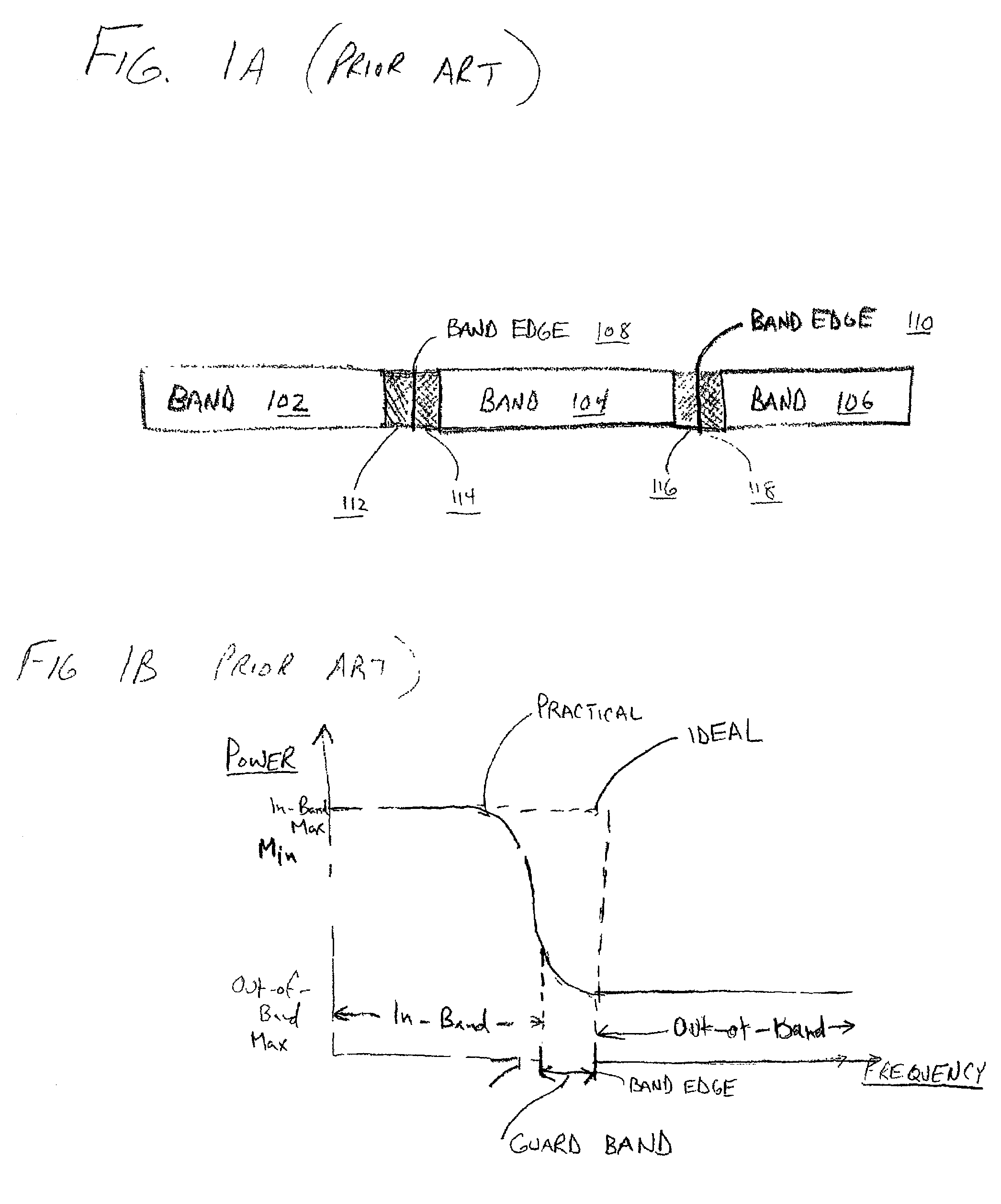
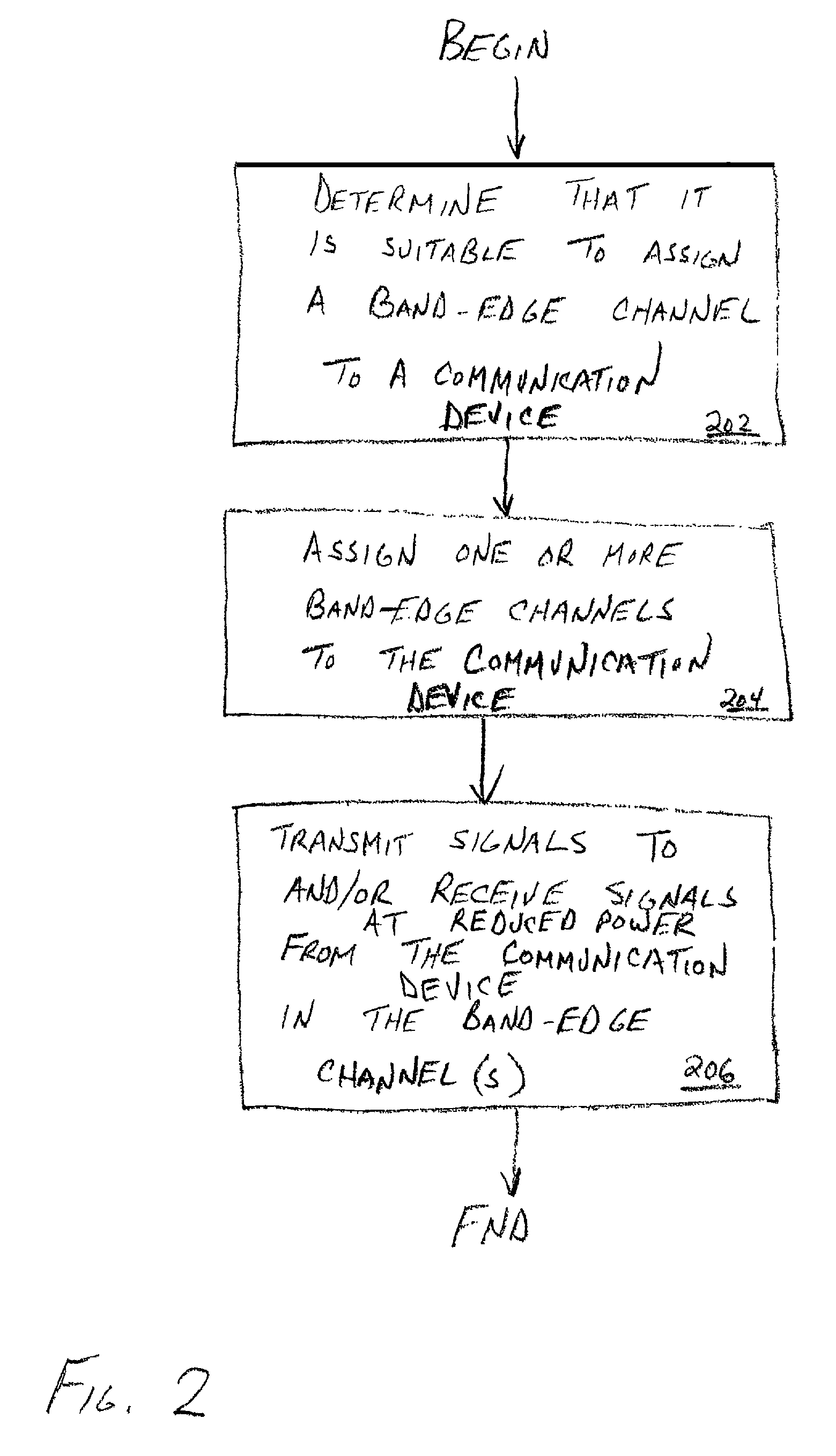
Method and apparatus for increasing spectral efficiency using mitigated power near band-edge
ActiveUS7151795B1Improve spectral efficiencyReduce power levelPower managementEnergy efficient ICTFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A method and apparatus for increasing the spectral efficiency of communications systems by employing portions of the spectrum, which portions might otherwise be reserved as all or part of guard bands and not utilized (i.e., effectively wasted), for communicating at reduced power levels between devices that are determined to experience relatively high performance (e.g., relatively little path loss, etc.). In a communication system having a first predefined maximum system transmission power level for in-band transmissions, a method is provided for determining that communication performance between a first communication device and a second communication device exceeds a performance threshold. Based on the determination, a first band-edge channel for communication between the first communication device and the second communication device (i.e., transmission from the first device to the second device and / or visa versa) is assigned. Finally, the first communication device and / or the second communication device utilize one or more band-edge channels (each may use a different band-edge channel) for transmitting a relatively reduced power level.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Self-calibrated path loss position estimation and zone of impact determination
ActiveUS20050285793A1Direction finders using radio wavesPosition fixationRadio frequency energyTransmitted power
A device and method are provided for estimating a position of a target device (e.g., a device emitting radio frequency energy) based on data pertaining to strength of an emission received from the target device. At a mobile device, emissions are received from the target device when the mobile device is at each of a plurality of positions to produce receive signal strength data representative thereof. In addition, at the mobile device, signals are received from each of a plurality of reference devices at a corresponding known position (and transmitted with known transmit powers) when the mobile device is at each of said plurality of positions to produce receive signal strength data representative thereof. The position of the target device is estimated based on receive signal strength data associated with received emissions from the target device and receive signal strength data associated with received signals from the reference devices. Using the estimated position and estimated transmit power of the target device, a zone of impact of the target device is determined with respect to other wireless activity based on the estimated position and estimated transmit power of the target device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for determining organization parameters in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS7043254B2Avoid complexityAvoids labor intensive recordingPower managementTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemRSS
Automated adjustment of system organization parameters in a wireless communication system is provided by determining the parameter settings using a characterization of signal propagation of the system's coverage area. This characterization is based on measurements of path loss-related characteristics by the system's base stations and wireless terminals. An exemplary path loss-related characteristic is path loss as determined by measuring received signal strength (RSS) at wireless terminals based on signals transmitted at known powers by a plurality of the system's base stations. It is possible for the wireless terminals to take measurement while operating in the coverage area, whether idle or during communication with the system, and for such terminals to be associated with the system's subscribers. A resulting characterization of signal propagation in the coverage area based on the measured path loss-related characteristic can then be used to determine a variety of parameter settings.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Apparatus and method for uplink power control for a wireless transmitter/receiver unit utilizing multiple carriers
A method and apparatus for determining uplink power in a wireless transmit receive unit (WTRU). The WTRU operates in a carrier aggregated system. The WTRU is configured to receive a plurality of uplink power parameters indexed to one of a plurality of uplink carriers and receive a transmit power control command indexed to the one of the plurality of uplink carriers. The WTRU is configured to determine a pathloss of the one of the plurality of uplink carriers and determine a transmit power for the one of the plurality of uplink carriers based on the plurality of power parameters, the transmit power control command, and the pathloss.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
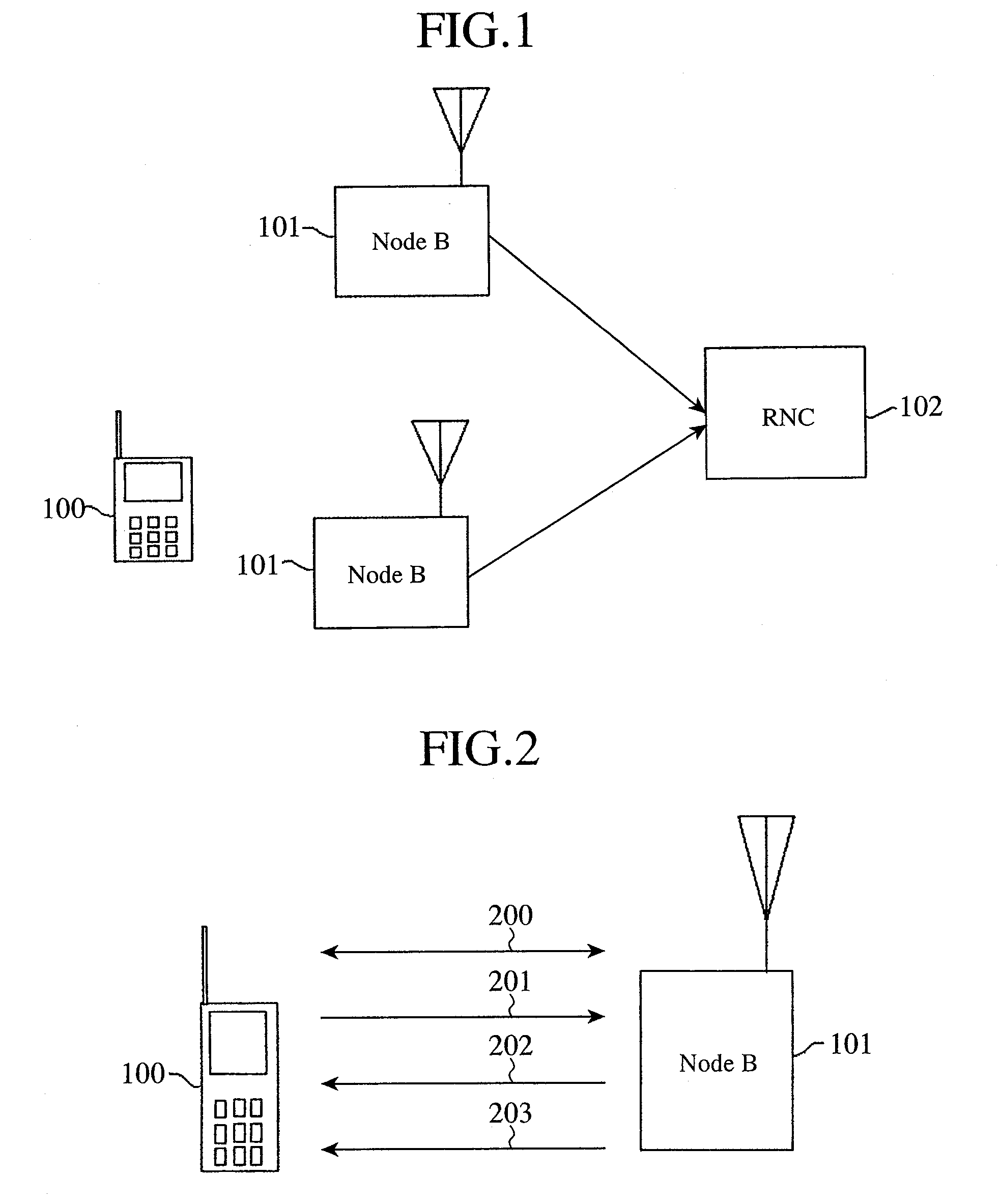
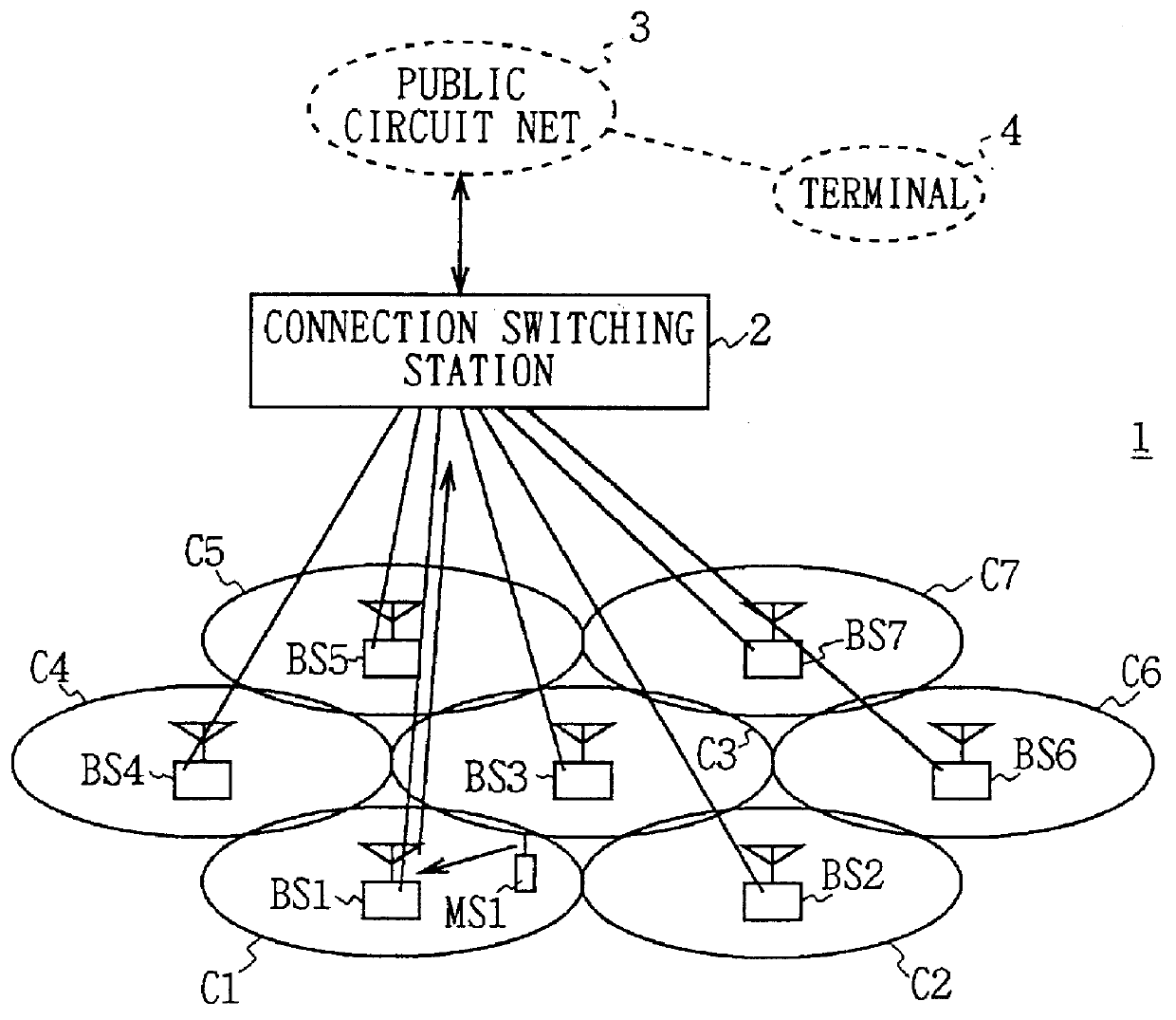
Cellular wireless communications system and base station
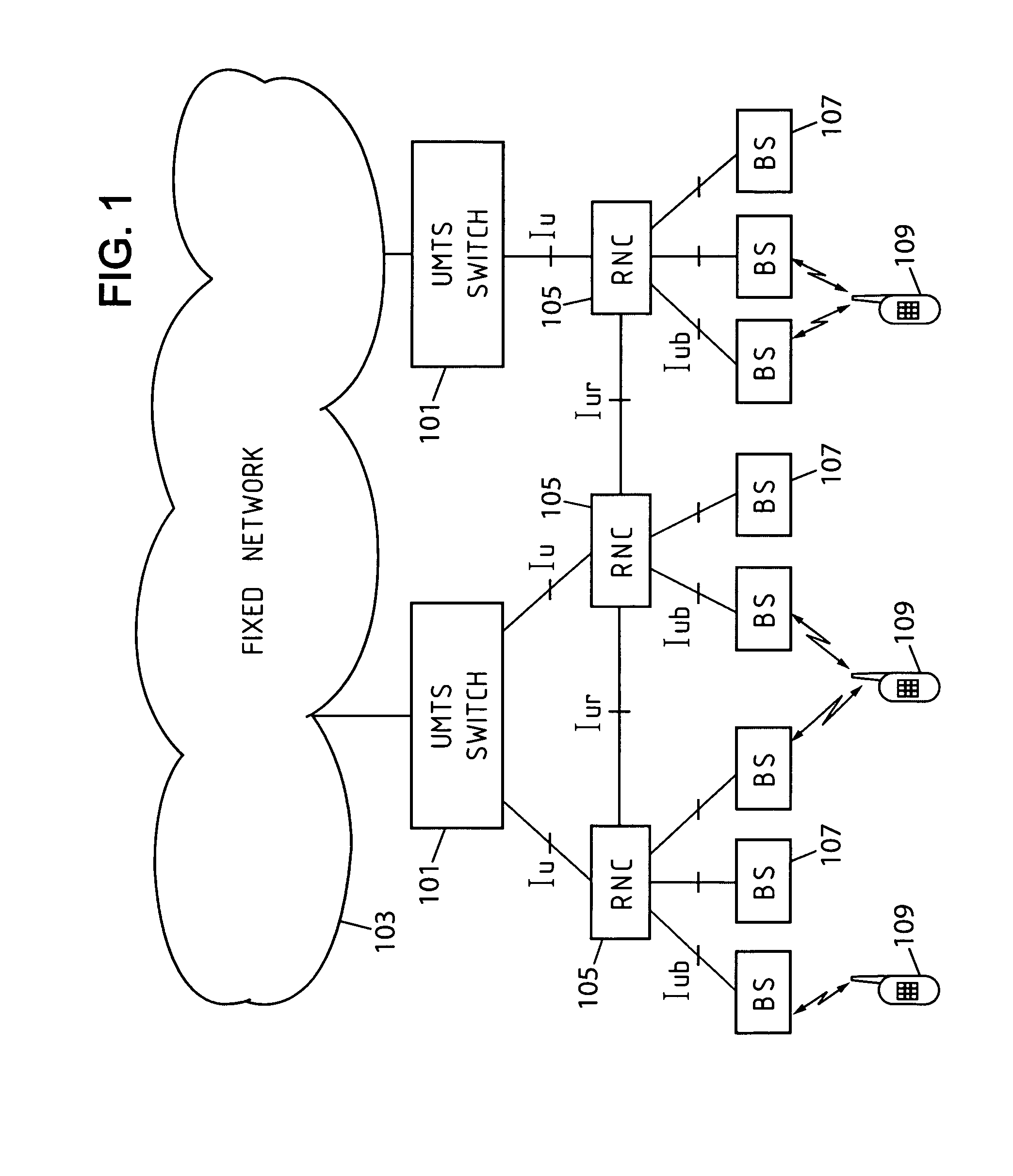
InactiveUS6021125ATelephonic communicationTime-division multiplexCommunications systemMobile station
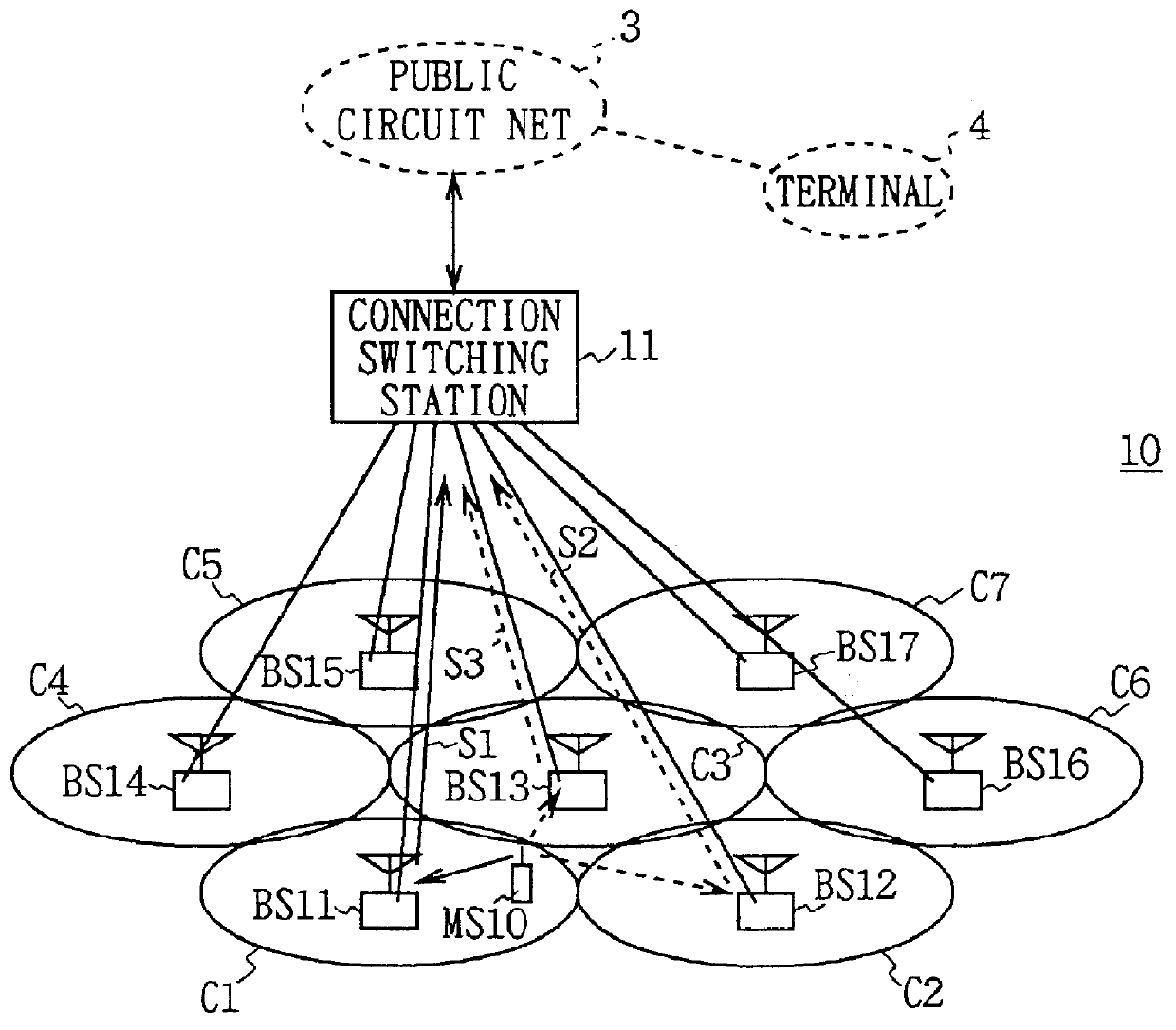
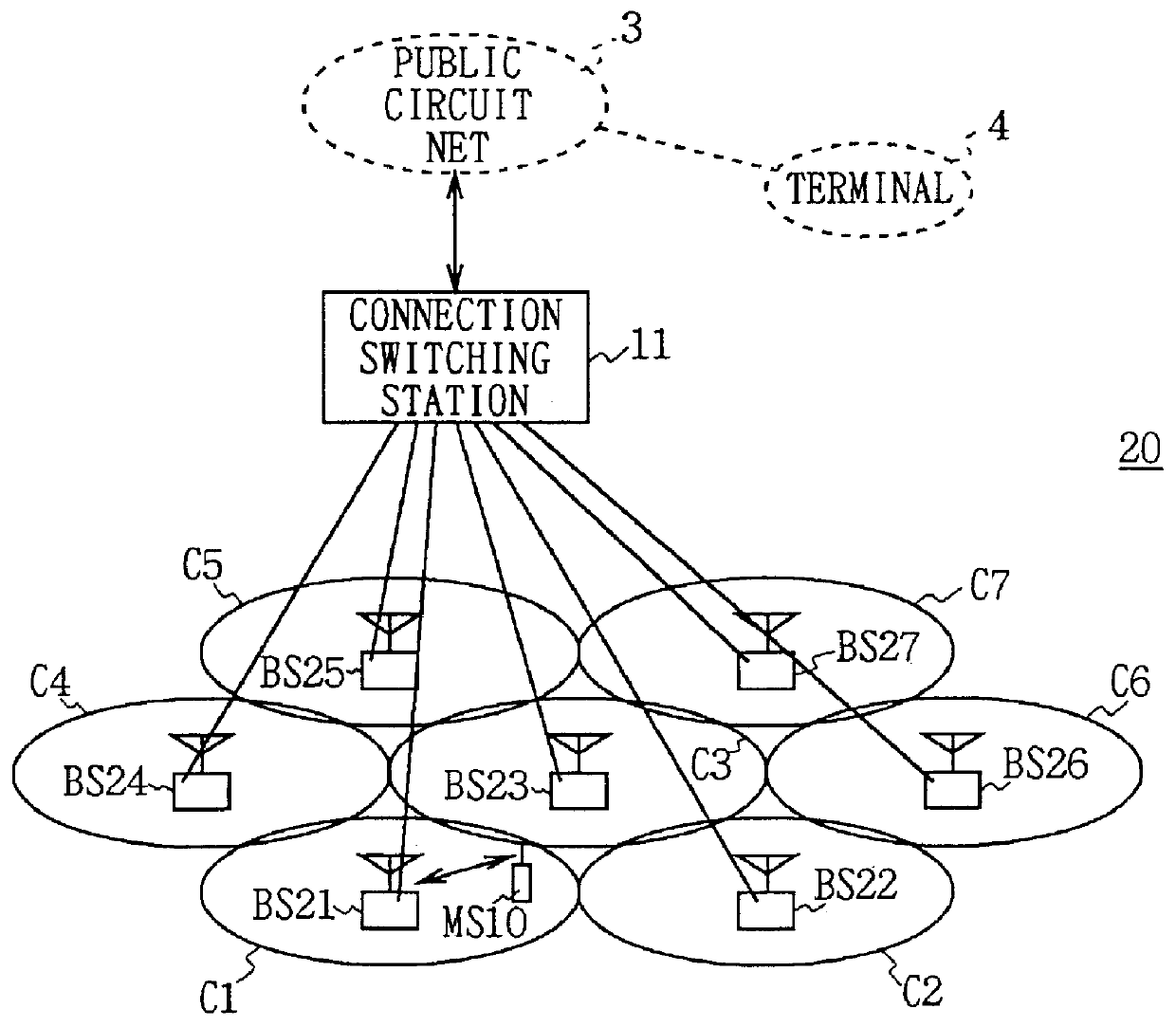
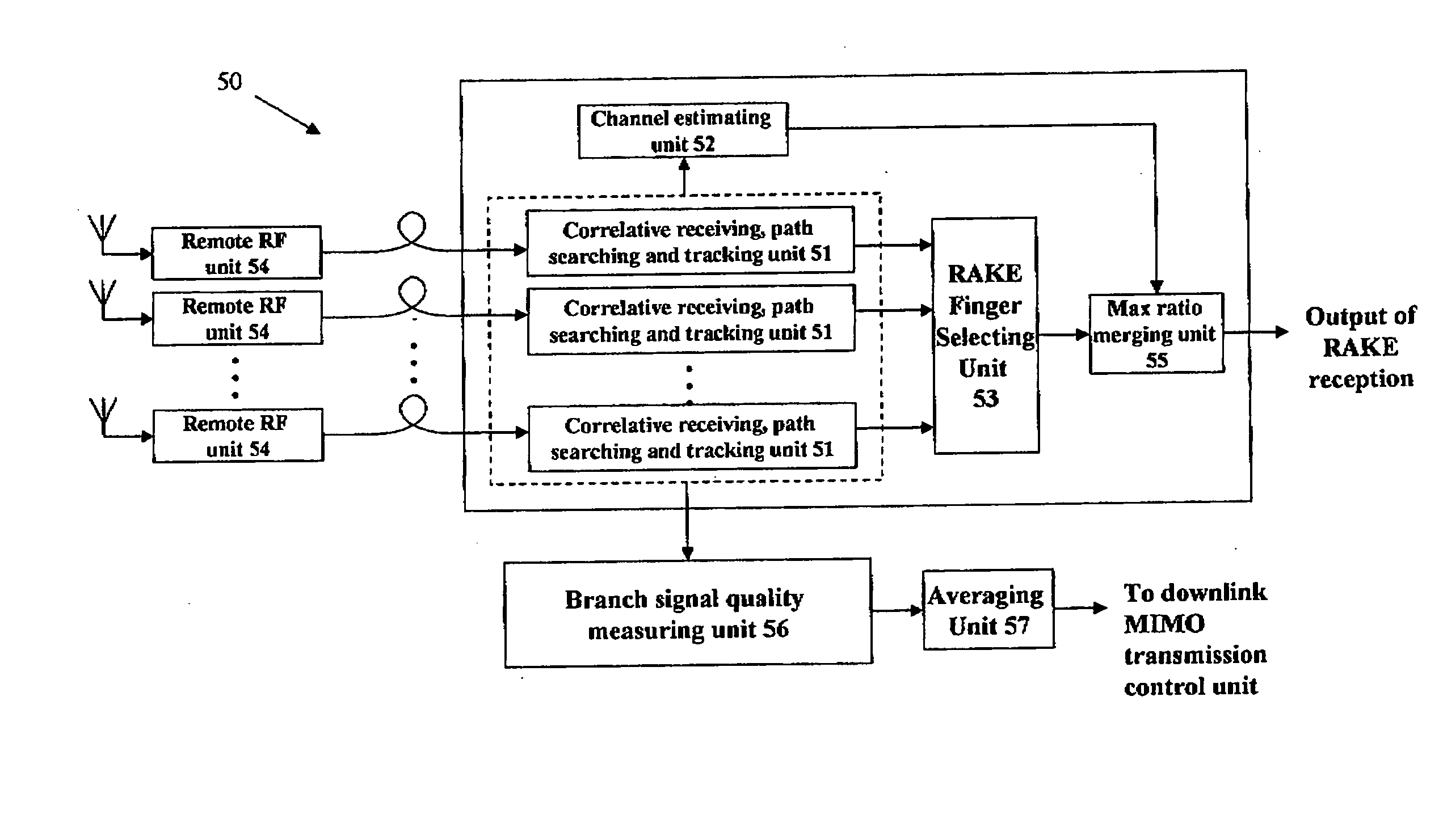
A cellular wireless communication system for further improving the quality of communications. The base station (BS11) notifies the communication channel which the mobile station (MS10) is using, to the base stations (BS12, BS13) having the lower pathloss than the own station, the base stations receive said communication channel and transmit the reception signals (S2, S3) to the connection switching station (11), and the connection switching station combines respective reception signals (S1-S3) to be transmitted so as to restore the data transmitted from the mobile station, and thereby the reception signal received at the base station having the satisfactory receiving condition can be combined and the diversity reception using the whole system can be conducted, so that the quality of communications from the mobile station to the base station can be easily improved.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and arrangement for power control
InactiveUS20050003846A1Power managementResonant long antennasCommunications systemWireless transmission
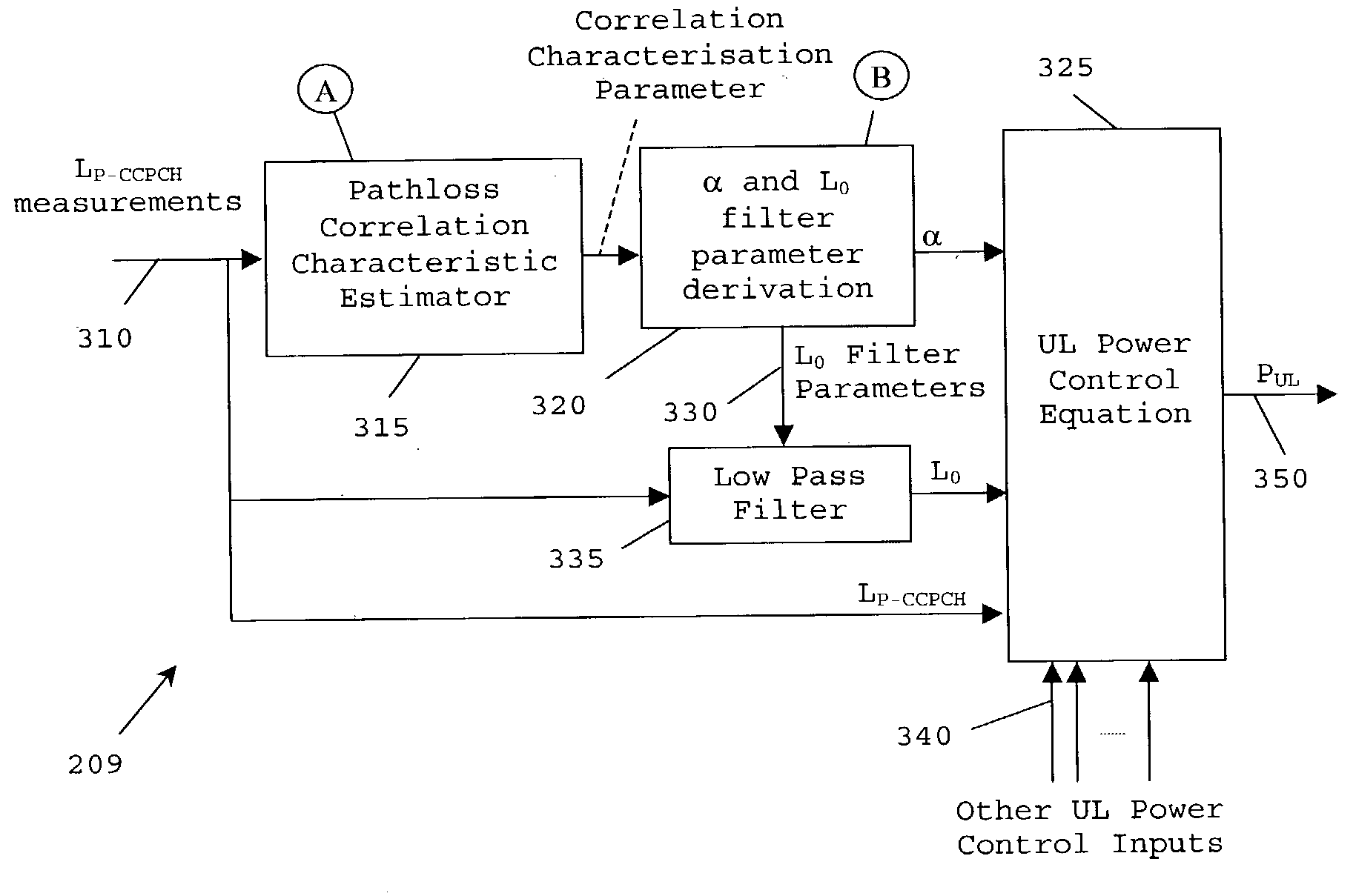
A method for performing power control in a wireless communication unit (112) operating in a wireless communication system (100), includes the steps of: determining (315) a path loss correlation metric to derive one or more parameters pertaining to a wireless transmission; and adjusting an output power level of said wireless communication unit in response to said one or more parameters. Basing power control calculations on a path loss correlation metric provides the advantage of improved power control performance particularly for slow moving subscriber equipment without compromising power control performance at high speed.
Owner:SISVEL INT
Multiple input/multiple output communication method based on distributed transmission sources
InactiveUS20070280370A1High speed downlink packet accessIncrease downlink speedSite diversitySpatial transmit diversitySignal qualityData stream
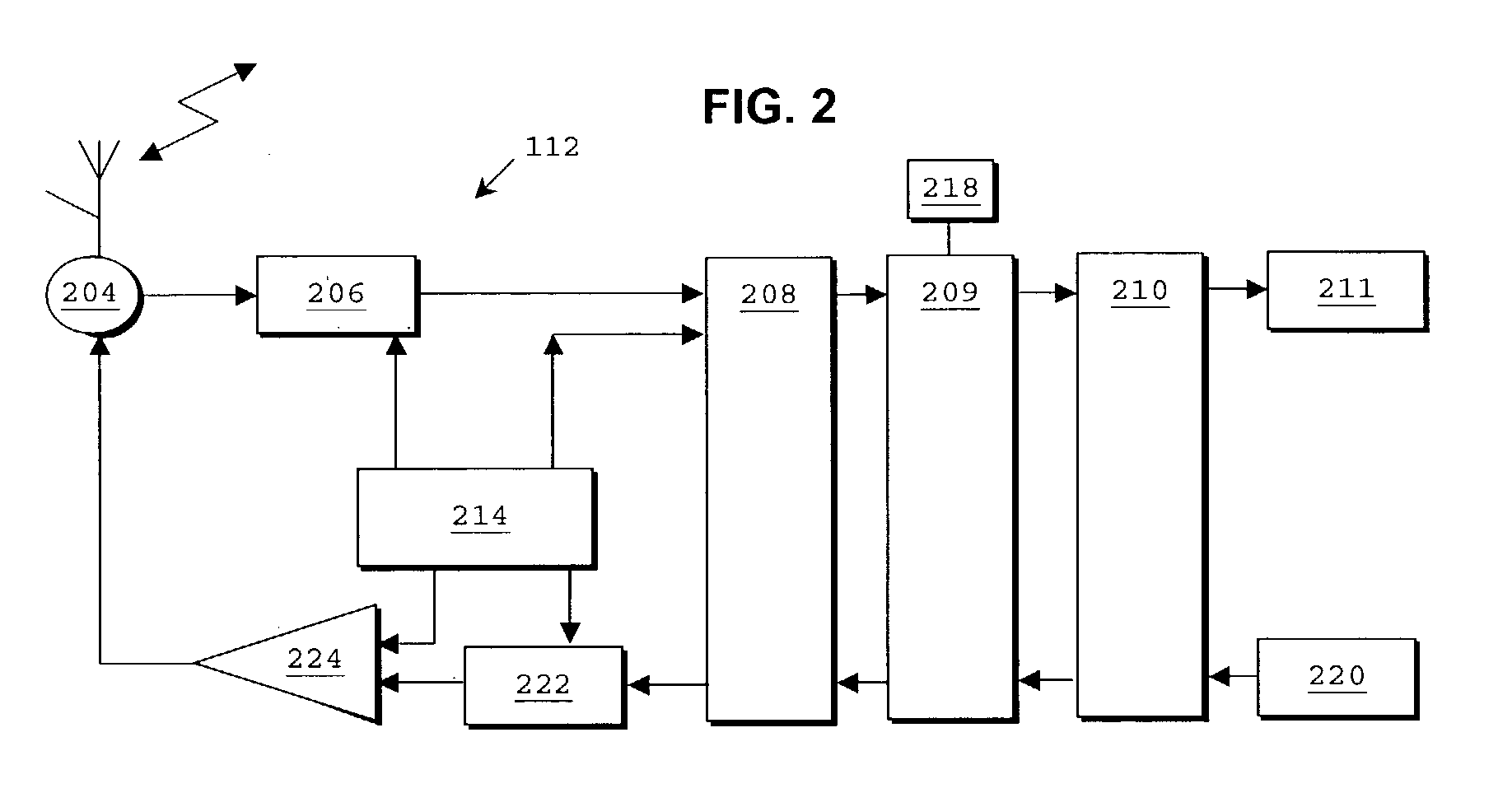
A MIMO method based on distributed transmission sources for transmitting a downlink data stream between M transmitting antennas and a mobile terminal having P receiving antennas, M and P>1, channels from at least two transmitting antennas to one of receiving antennas have different multipath distributions, said method comprises transmitting corresponding M substreams to the mobile terminal by using the same spreading code; estimating the multipath channel matrix; and processing the signal according to the multipath channel matrix to restore the downlink data stream, the estimating including measuring the total number of actual multipath received components having different delays in the transmitted signals; constructing the multipath channel matrix by taking the number as the multipath number, so that if the signal transmitted by one of the transmitting antennas to the receiving antenna has no multipath component corresponding to one of the delays, the channel parameter corresponding to the transmitting antenna, the receiving antenna and the delay is set as 0, the transmitting comprises adjusting the gain of said M sub-data streams based on the average signal quality measurement of uplink signals from the mobile terminal to said M transmitting antennas, so that average path losses of respective downlink channels are substantially equal.
Owner:UTSTARCOM TELECOM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com