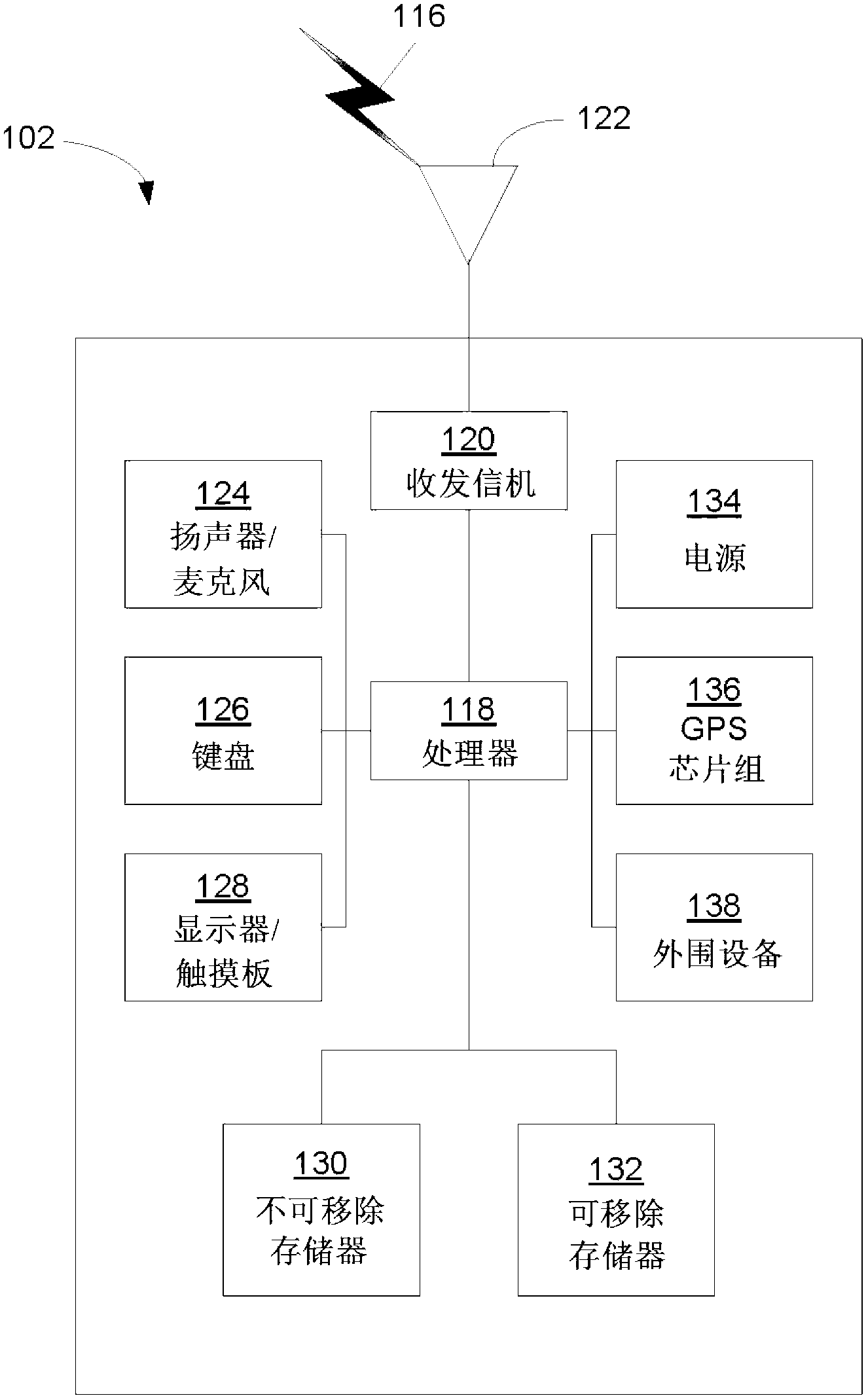
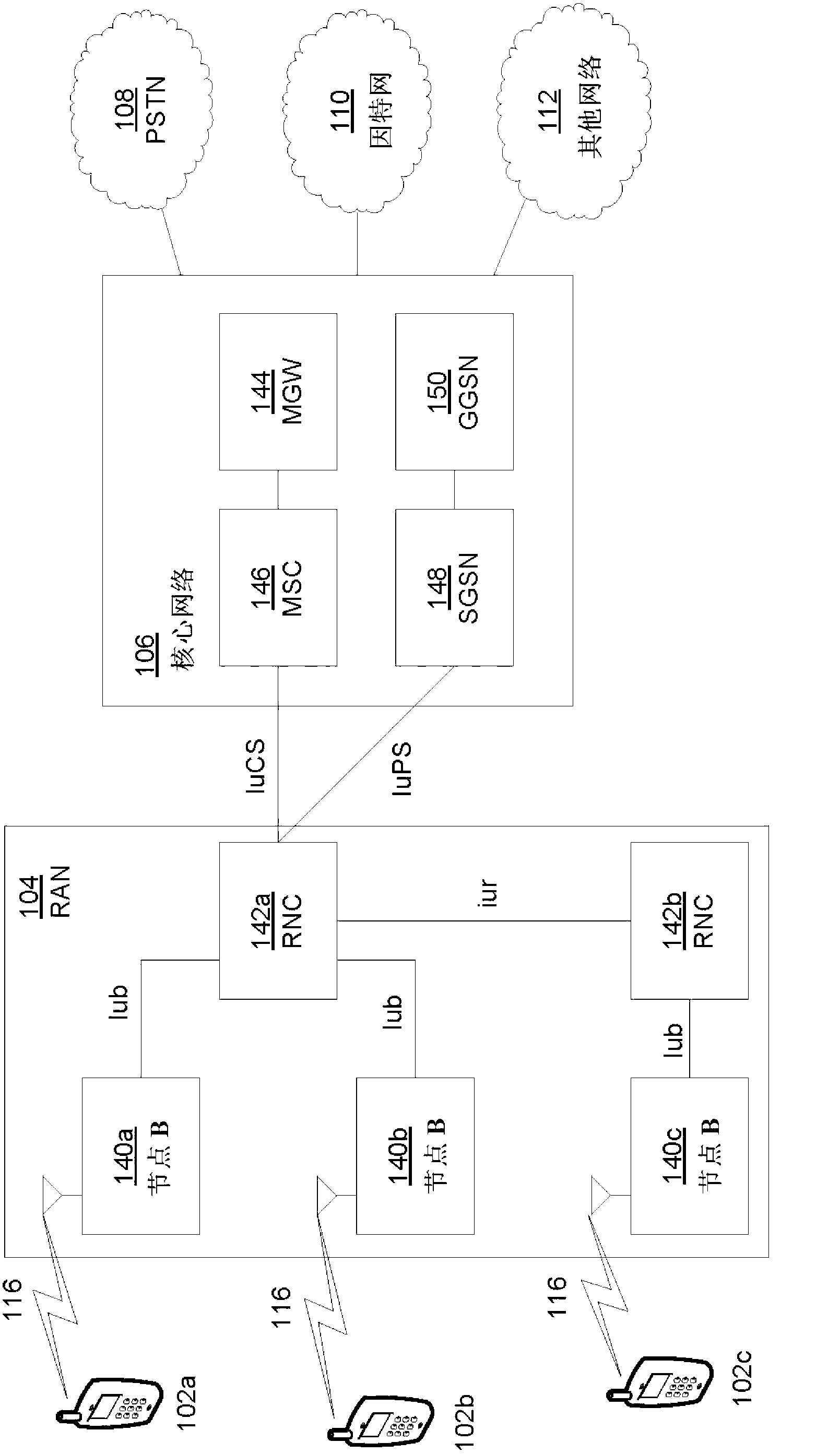
Patents
Literature
213 results about "Common pilot channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
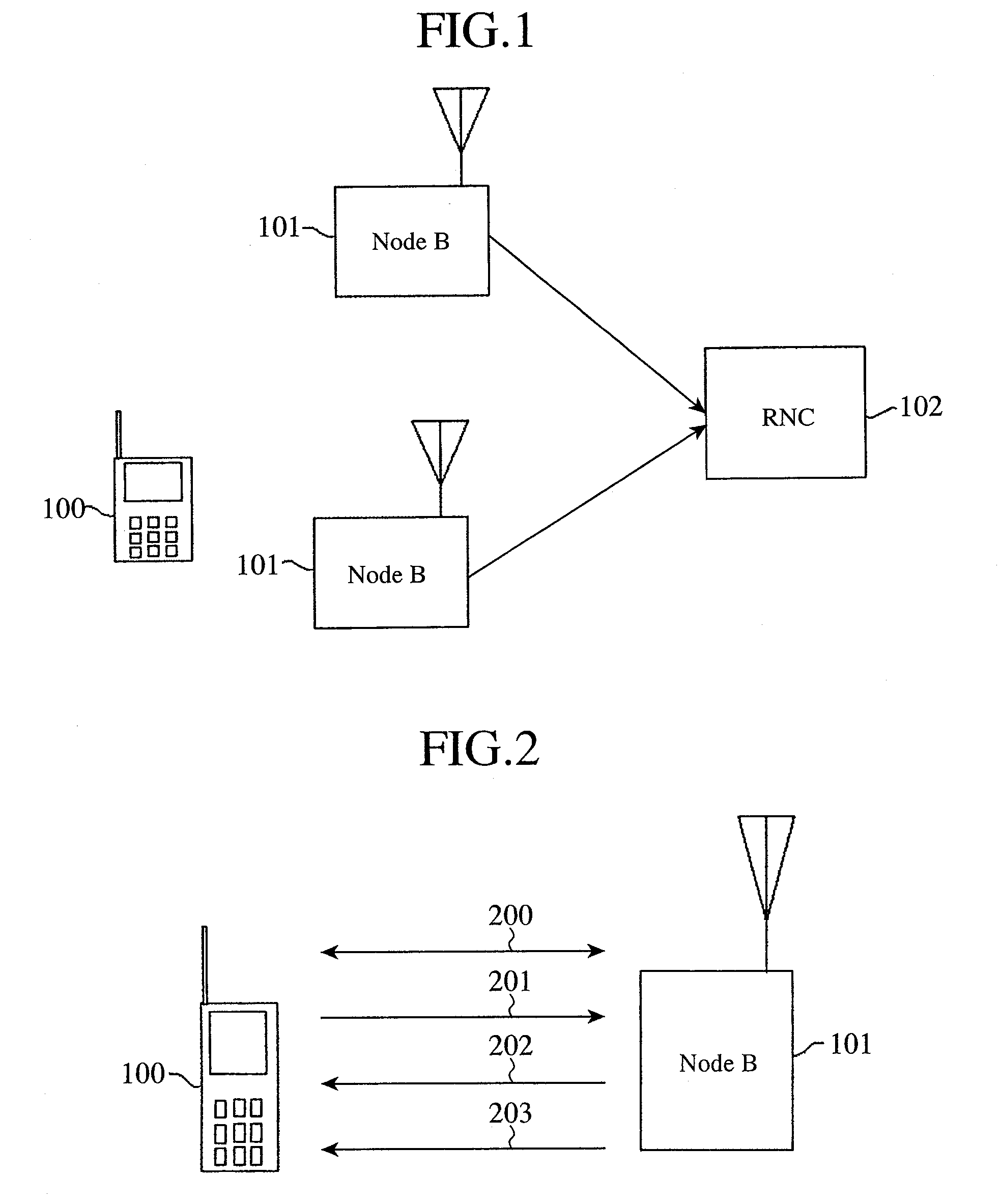
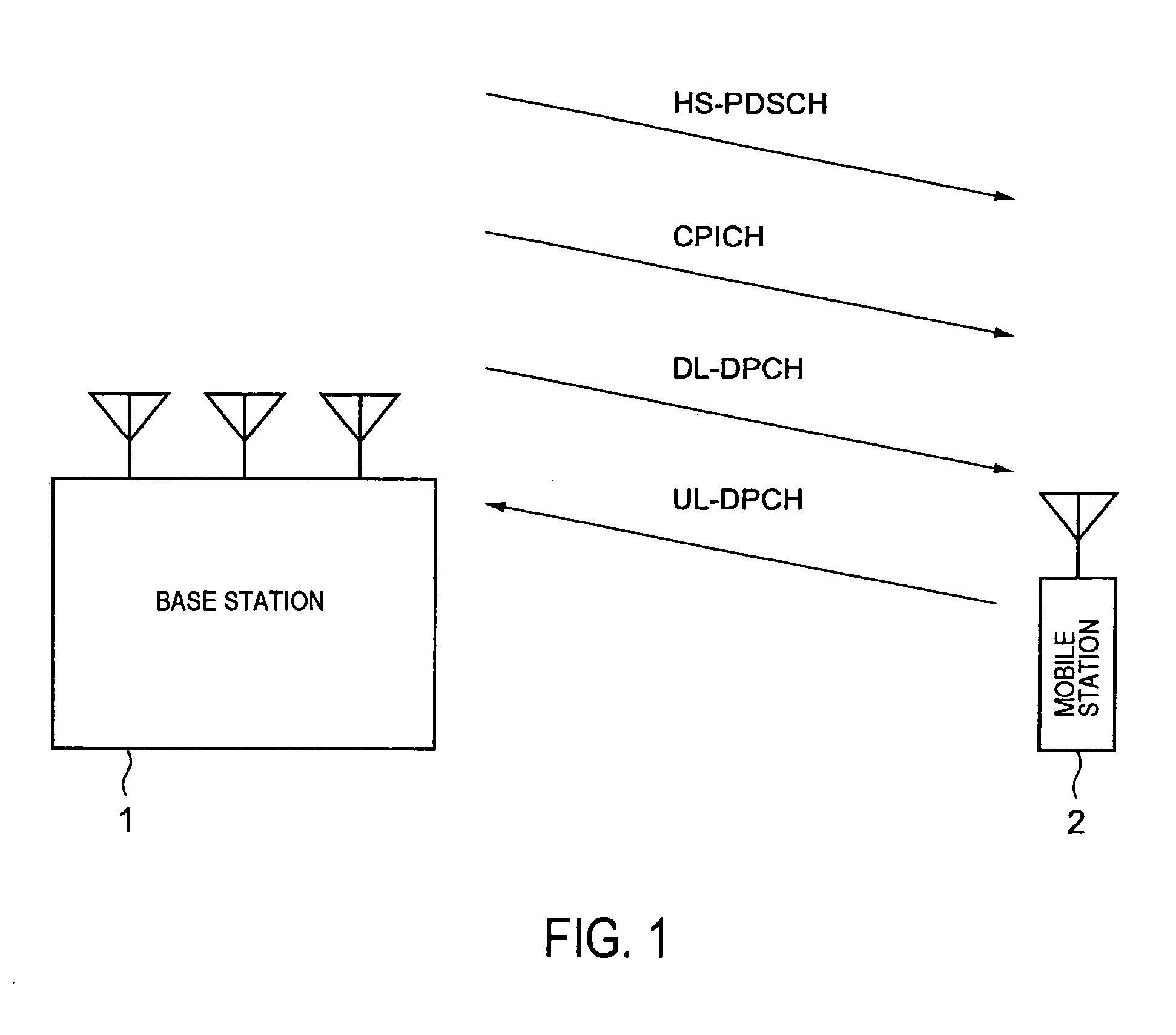
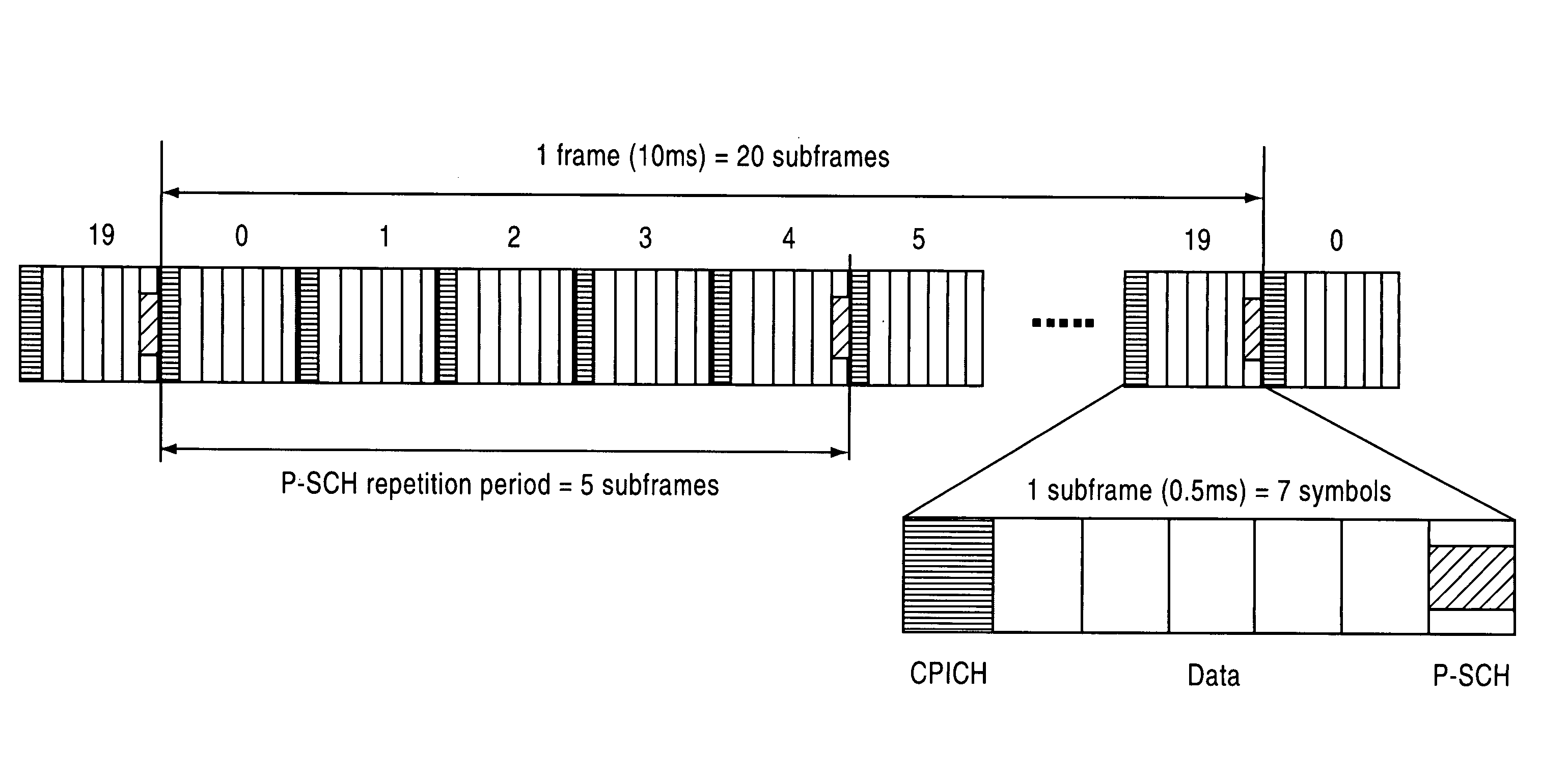
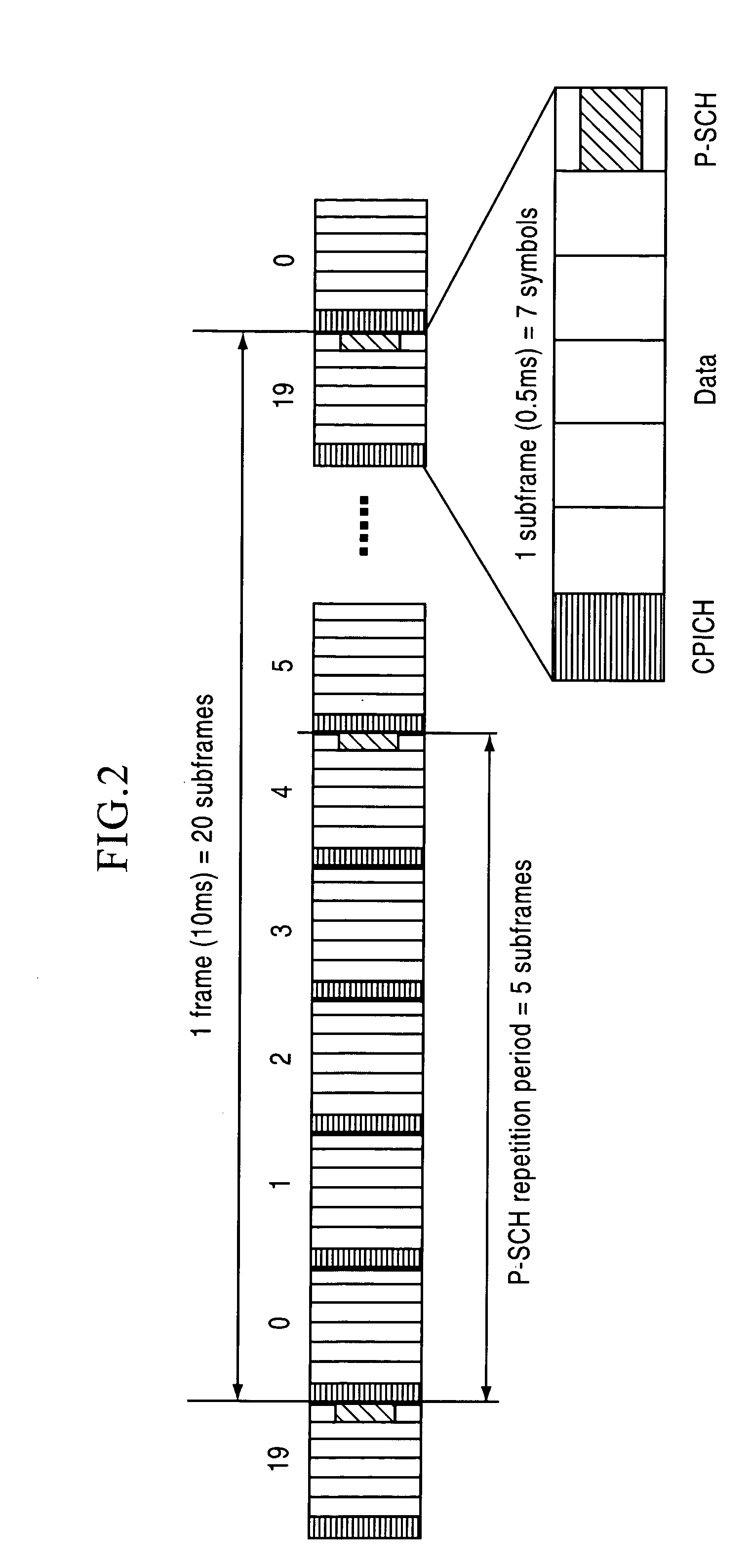
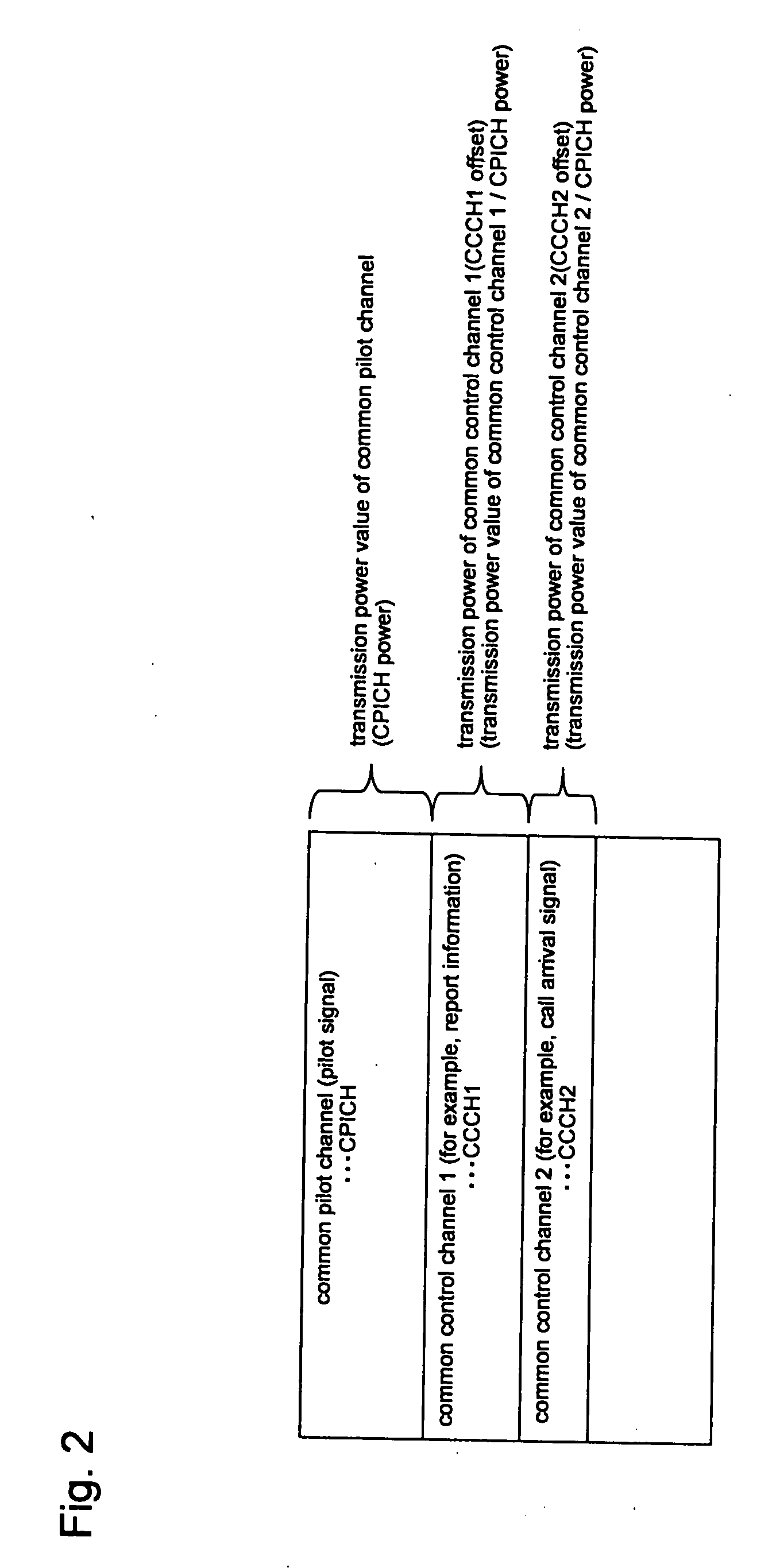
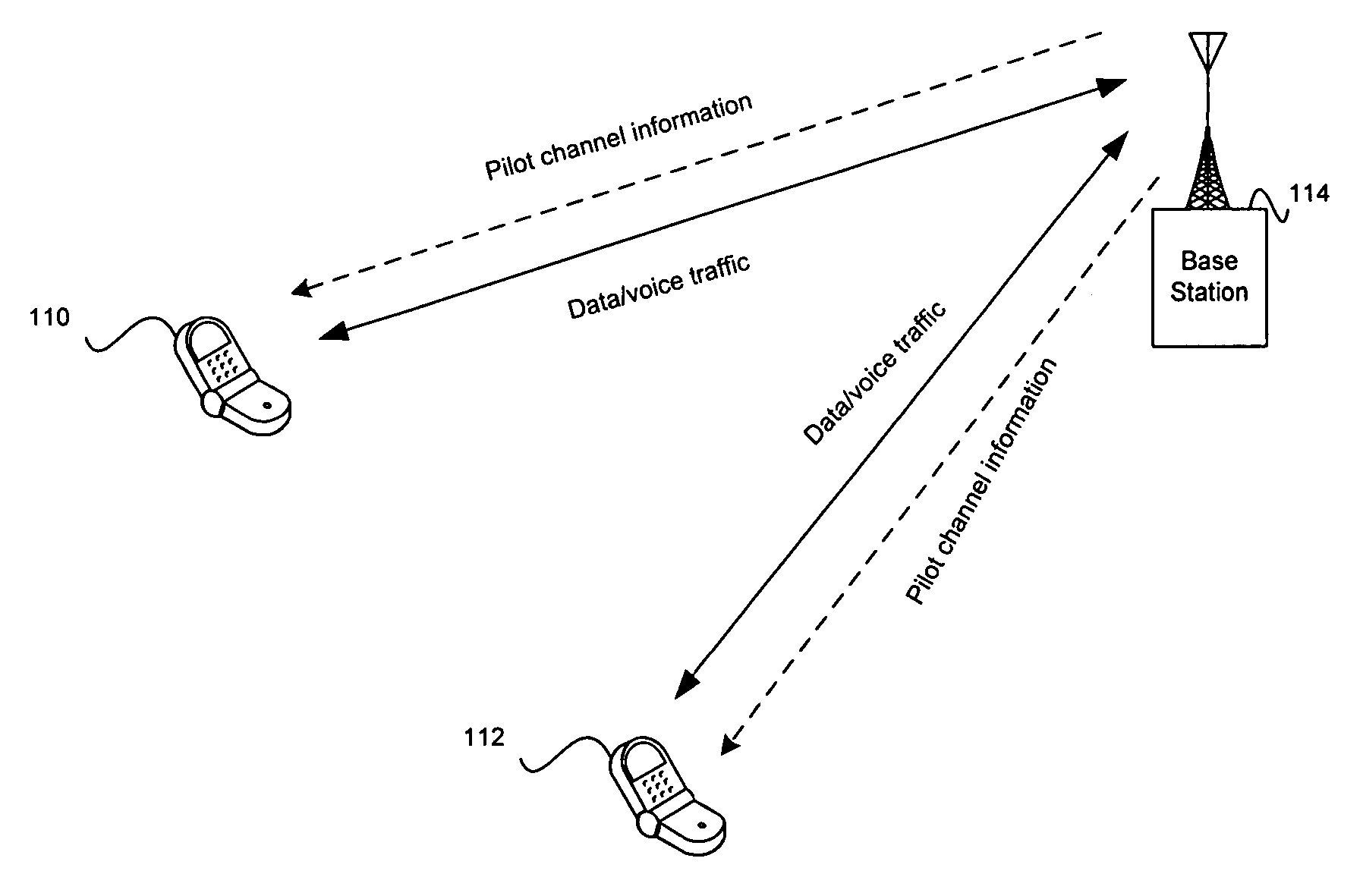
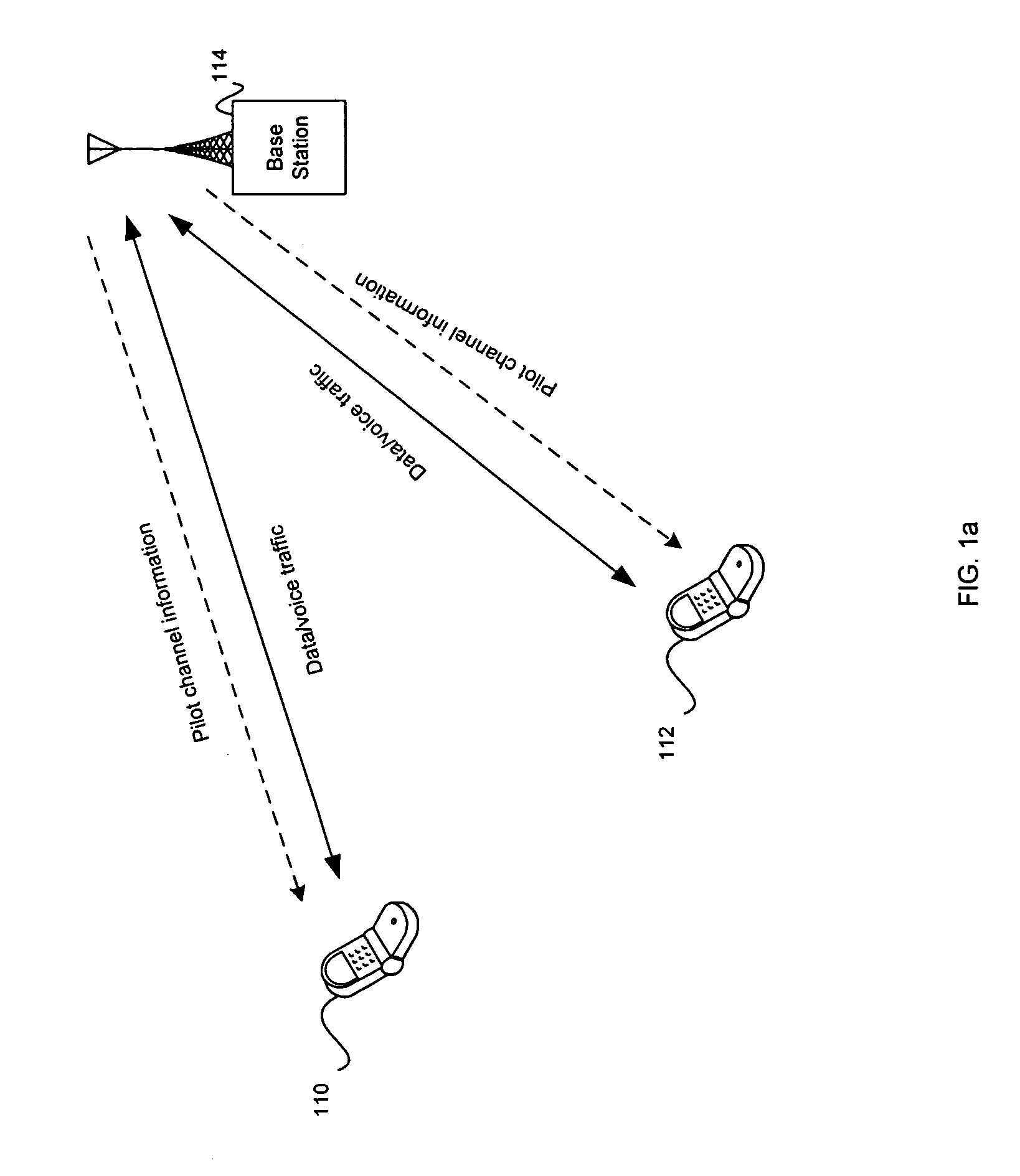
CPICH stands for Common Pilot Channel in UMTS and some other CDMA communications systems. In WCDMA FDD cellular systems, CPICH is a downlink channel broadcast by Node Bs with constant power and of a known bit sequence. Its power is usually between 5% and 15% of the total Node B transmit power. Commonly, the CPICH power is 10% of the typical total transmit power of 43 dBm. The Primary Common Pilot Channel is used by the UEs to first complete identification of the Primary Scrambling Code used for scrambling Primary Common Control Physical Channel (P-CCPCH) transmissions from the Node B. Later CPICH channels provide allow phase and power estimations to be made, as well as aiding discovery of other radio paths.
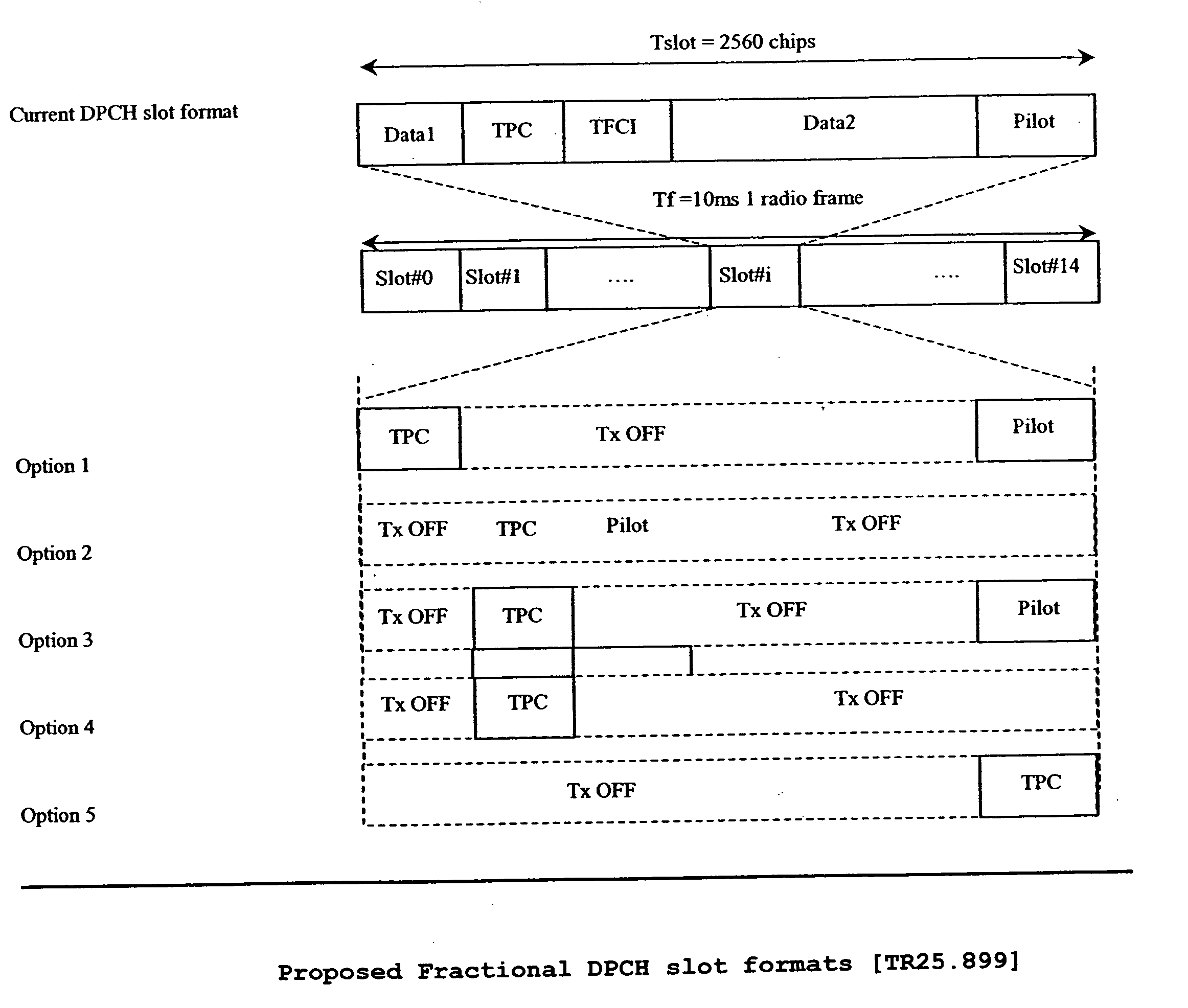
Recovery method for lost signaling connection with HSDPA/fractional DPCH
ActiveUS20050281222A1Connection be loseAssess restrictionConnection managementRecovery methodTelecommunications
A method and apparatus are provided for defining terminal behavior in a case where the terminal detects that it cannot receive the HS-DSCH from a serving cell reliably when the DCCH is mapped to HS-DSCH (e.g. does not receive any radio link control (RLC) acknowledged mode feedback for the uplink measurement reports or in general the common pilot channel (CPICH) level drops too low in the serving HS-DSCH cell). The terminal is autonomously moved to a cell forward access channel (CELL_FACH) state and uplink signaling is initiated on a random access channel (RACH) to inform a network node and ask for HS-DSCH re-establishment in a suitable cell (preferably in the one being strongest one in the active set or according to the measurements done prior the connection from the serving HS-DSCH cell was lost), or setting up a regular R′99 / R′5 DPCH in order to restore the RRC signaling connection in the CELL_DCH state.
Owner:SISVEL INT
Communication Quality Judgment Method, Mobile Station, Base Station, and Communications System
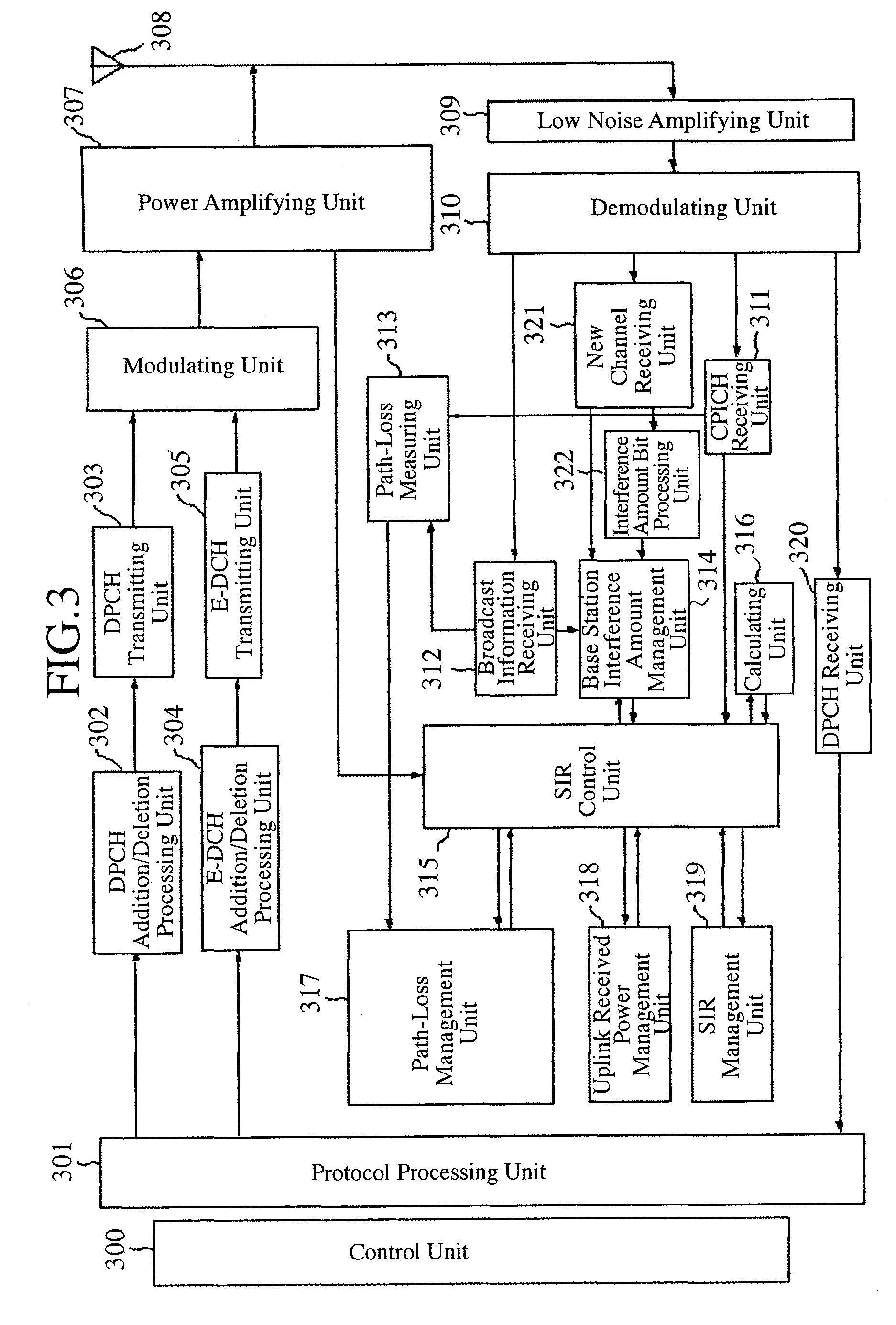
In order to carry out high-speed packet communications using a large-volume transmission channel like an E-DCH, uplink communication quality must be good. However, in a state in which a link imbalance occurs, a mobile station cannot estimate the uplink communication quality from downlink communication quality. Therefore, the mobile station calculates a path loss from the setting power of a common pilot channel which is notified from a base station, and the received power of the common pilot channel received thereby, and also estimates the received power in the base station on the basis of this path loss. The mobile station further judges the uplink communication quality by estimating the SIR in the base station by using the interference power notified from the base station and the estimated received power.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Incremental pilot insertion for channnel and interference estimation
ActiveUS20060013338A1Improve abilitiesIncrease resourcesMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationCommunications systemDynamic resource
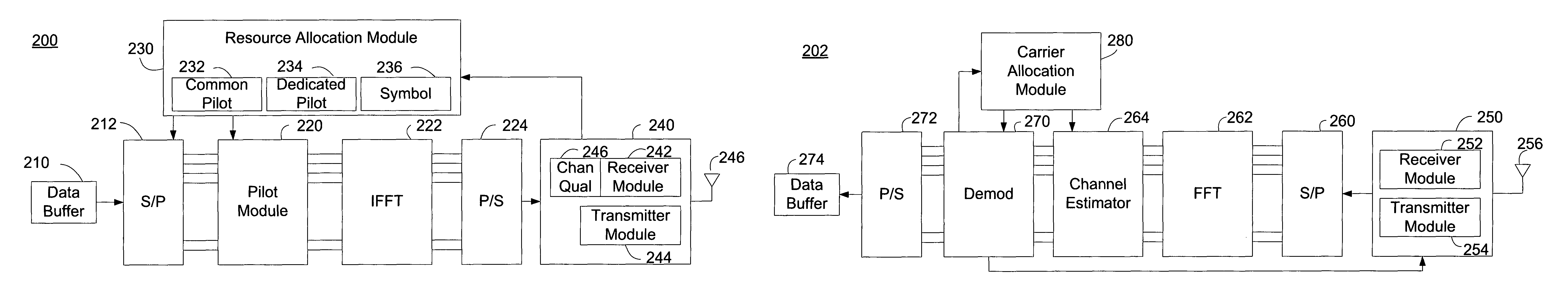
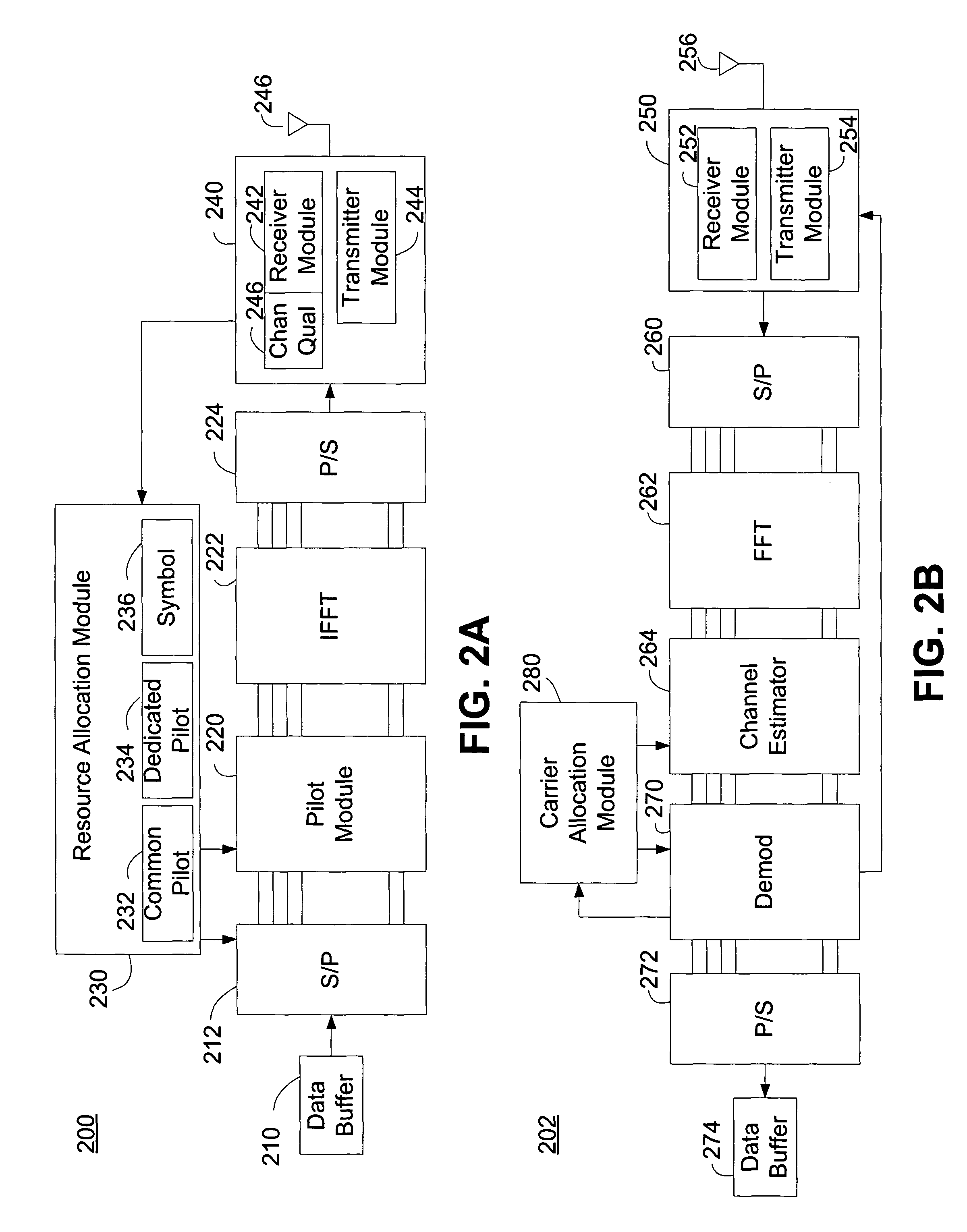
Dynamic resource allocation systems, apparatus, and methods are disclosed for selectively improving the ability of a receiver to determine a channel estimate in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) system. A wireless communication system can use a common pilot channel configuration to aid channel estimation in one or more receivers in communication with the system. A receiver in communication with the system may be unable to demodulate received data due to an inaccurate channel estimate. The receiver can communicate to a transmitter in the system a request for additional channel estimation resources. The wireless communication system can provide additional channel estimation resources by inserting dedicated pilot channels into one or more of the frequencies allocated to symbols for the receiver. If the receiver is still unable to demodulate received data, the wireless communication system can incrementally insert additional pilot channels in the symbol associated with the receiver.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
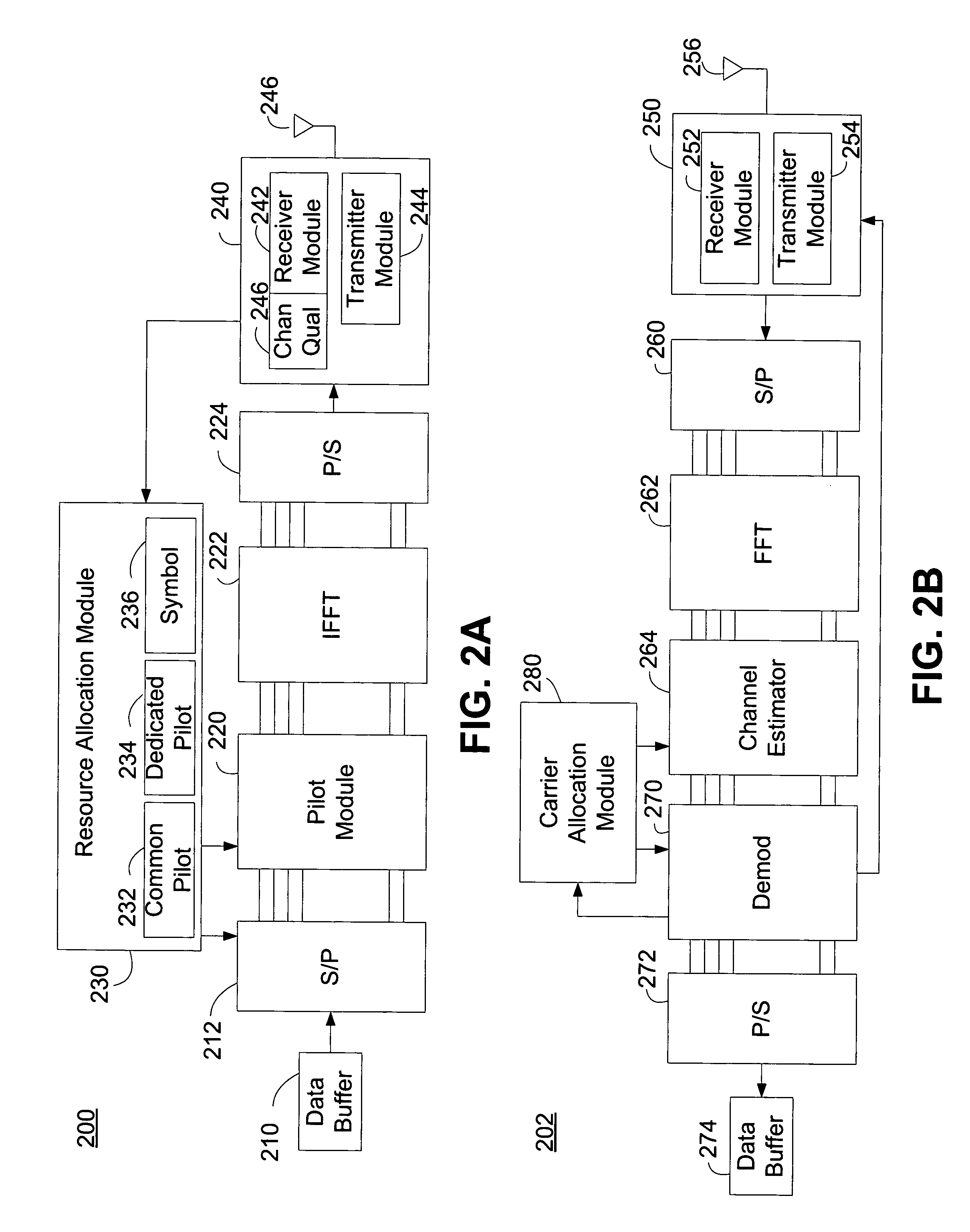
Selection of user-specific transmission parameters for optimization of transmit performance in wireless communications using a common pilot channel
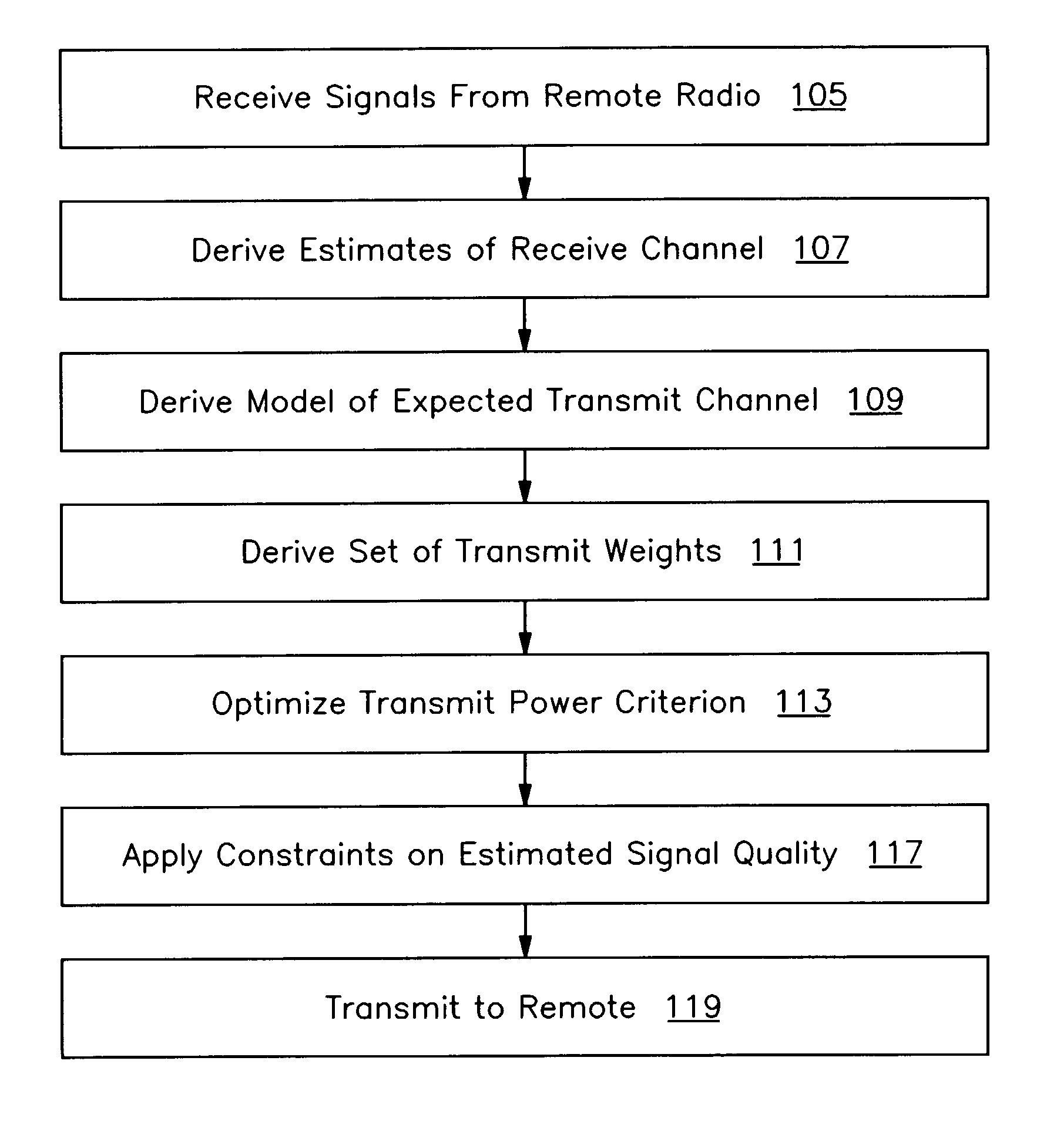
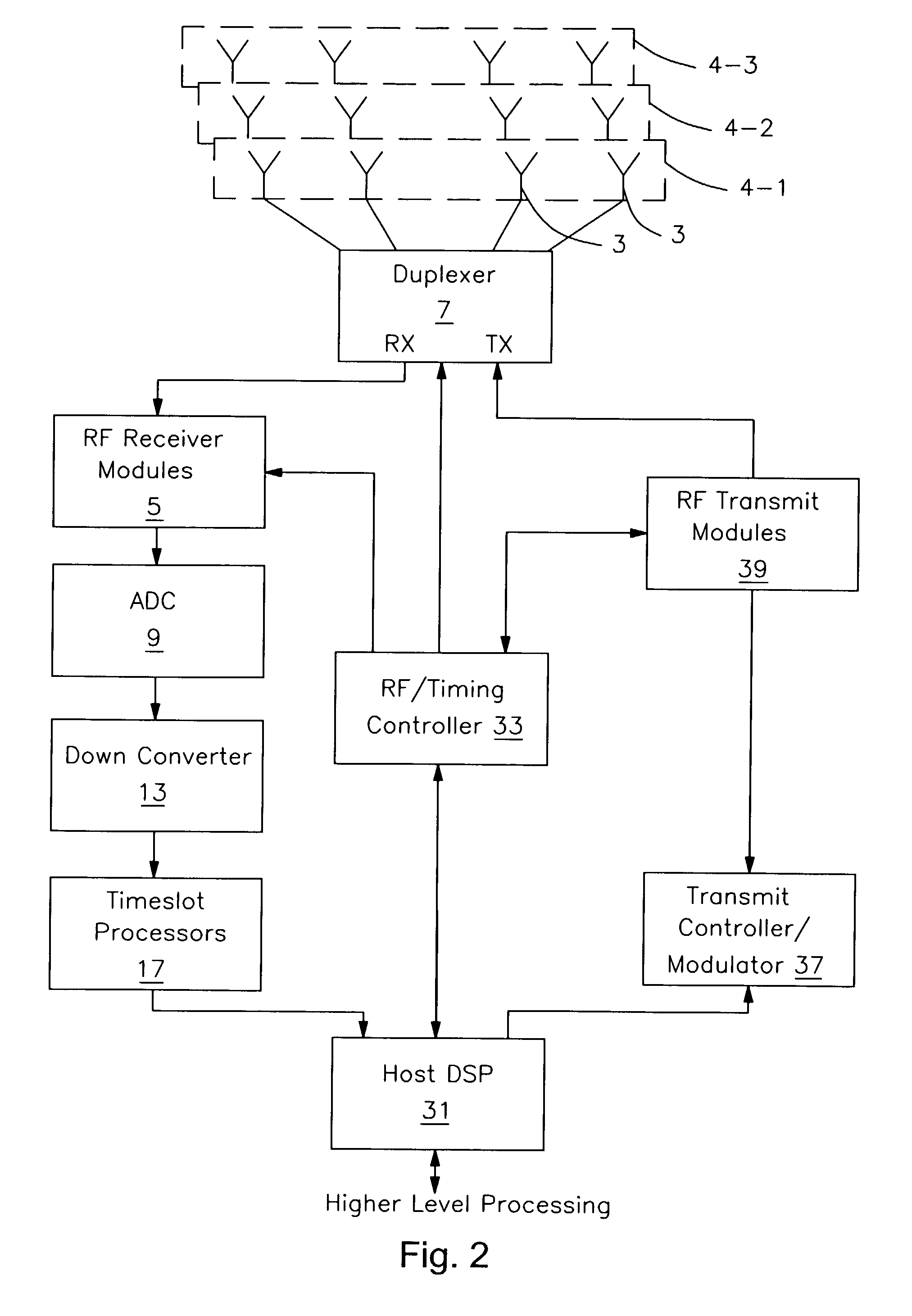
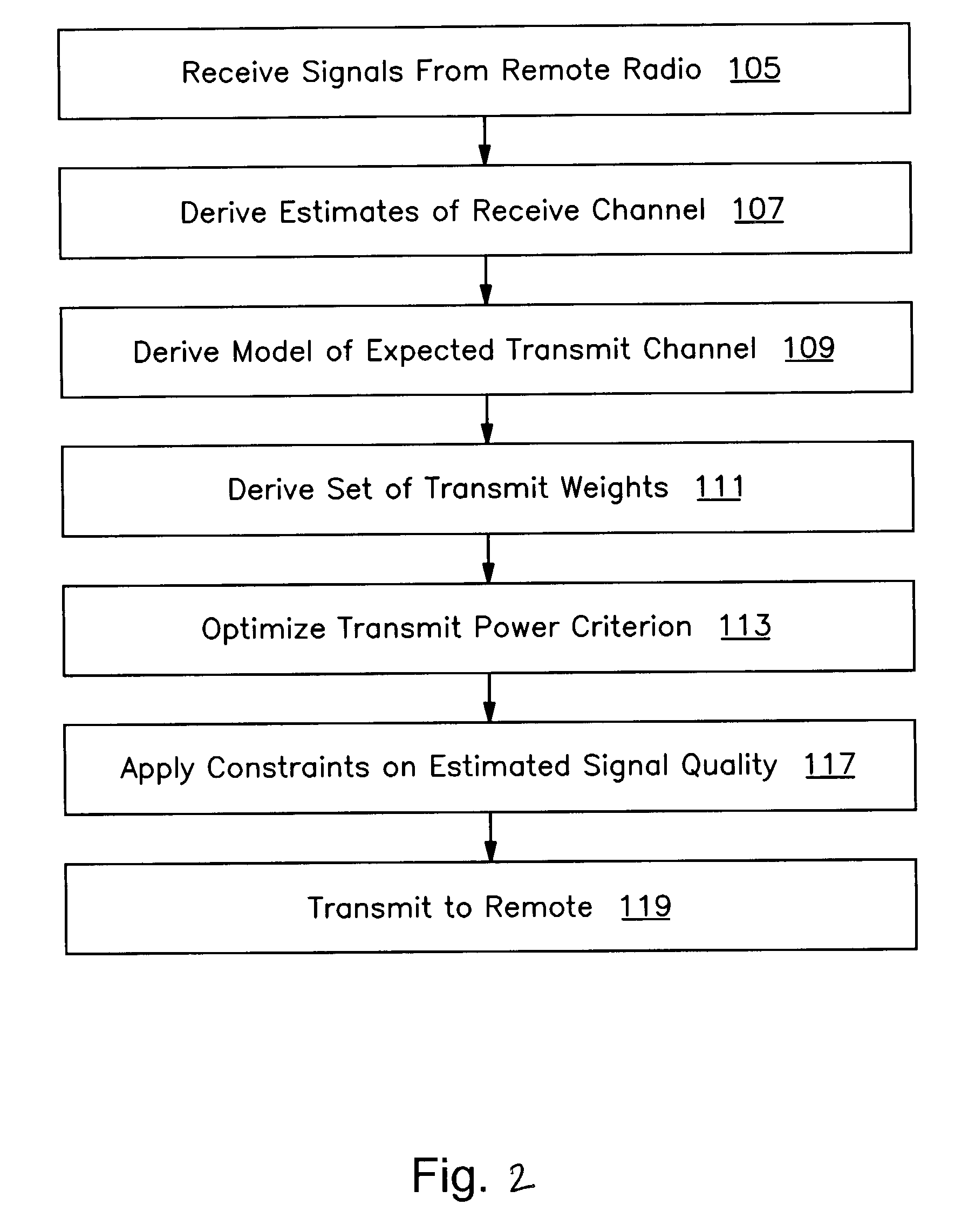
A method and apparatus are provided that optimizes a transmitted user-specific signal. In one embodiment, the invention includes receiving signals from a remote radio, deriving estimates of receive channels corresponding to the received signals using the received signals, deriving a model of an expected transmit channel to the remote radio based on the receive channel estimates, deriving a set of transmit parameters to be applied to an array of transmit antennas to transmit a signal to the remote radio by optimizing a transmit power criteria using the model of the expected transmit channel and constraints on the estimated quality of a signal transmitted over the expected transmit channel, and transmitting to the remote radio by applying the derived set of transmit parameters to the transmit antenna array.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
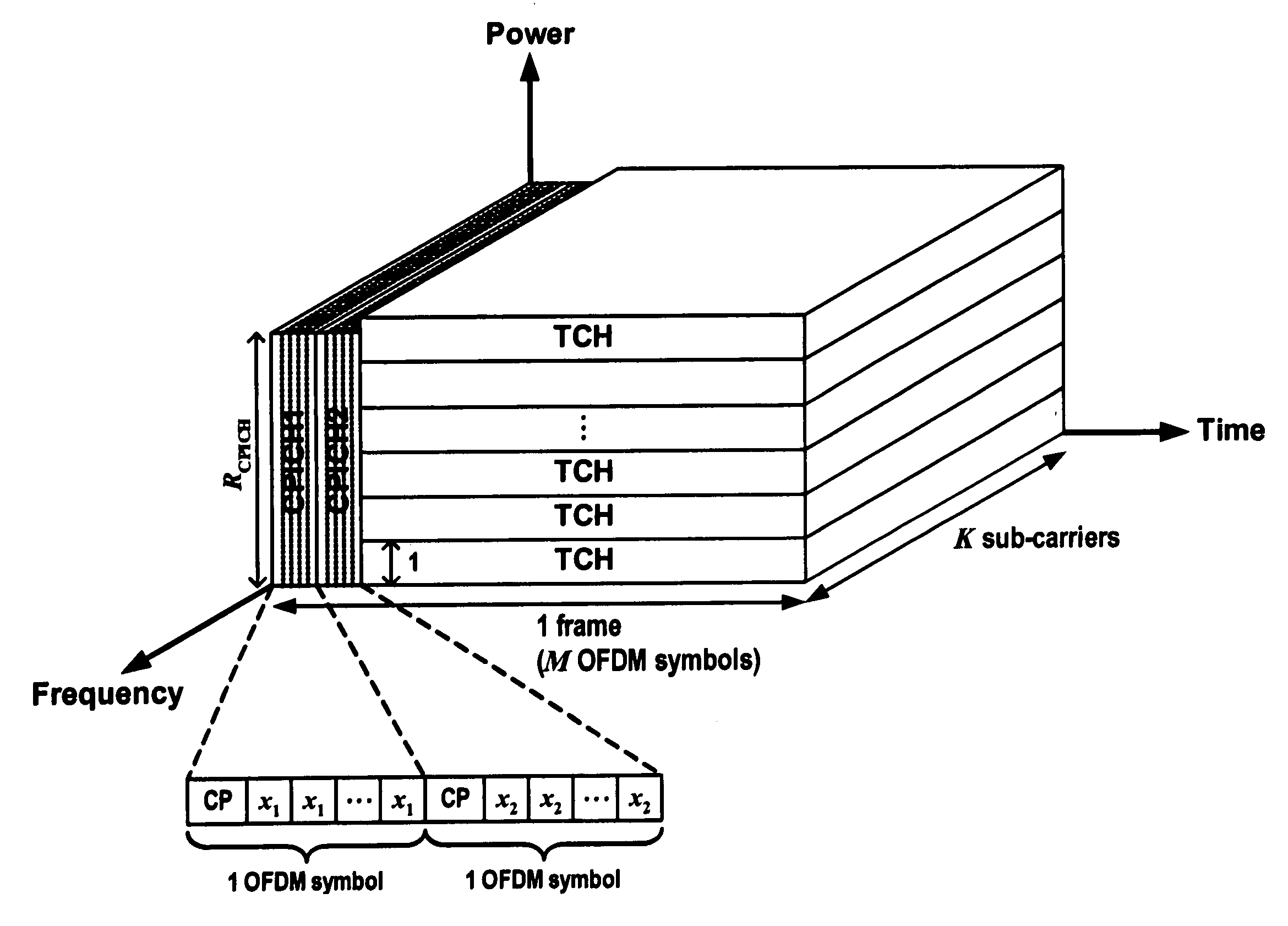
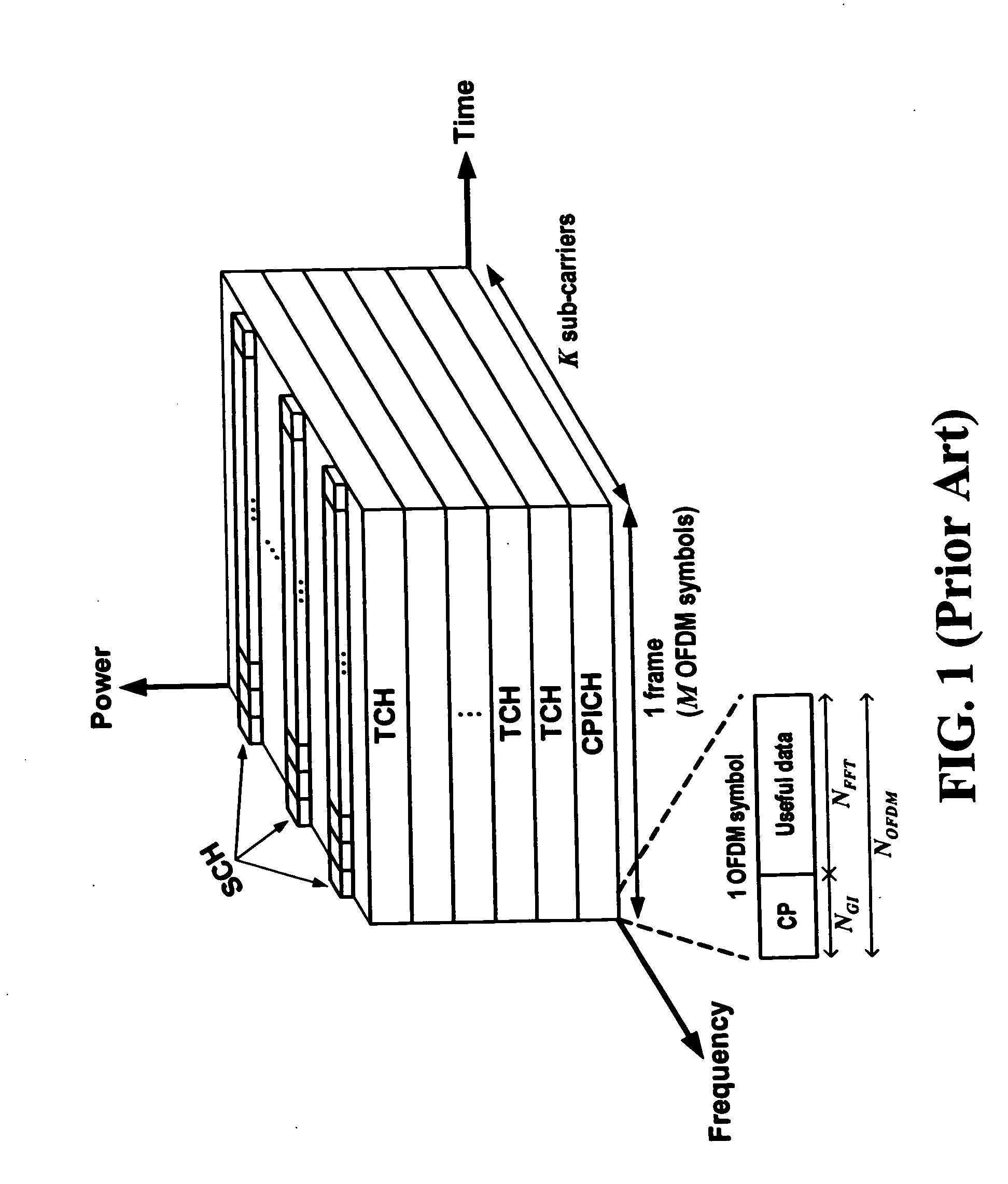
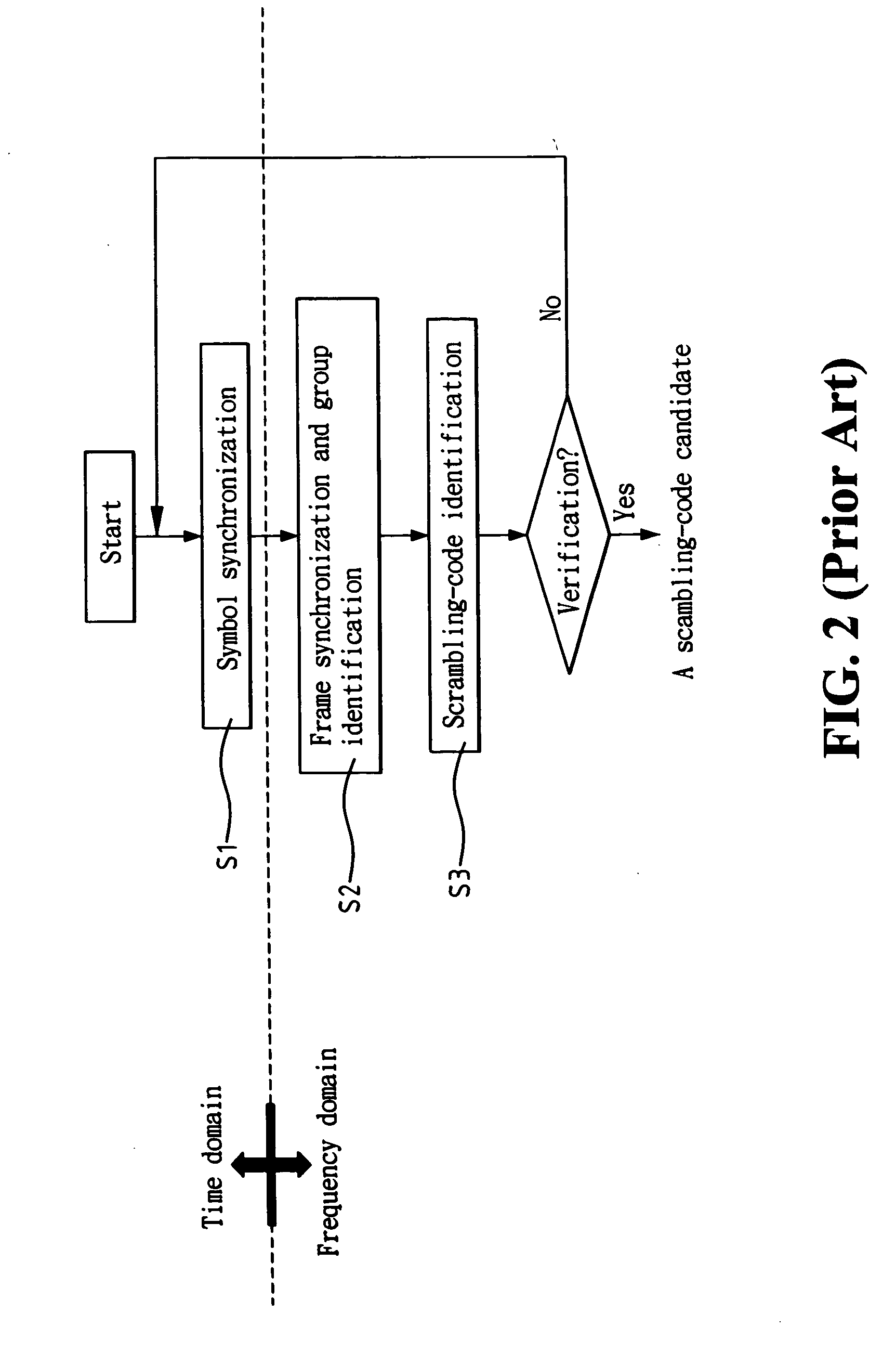
Cell search method for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing based cellular communication system
ActiveUS20050157637A1Overcomes shortcomingRobust against channel effectSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementCell searchCellular communication systems
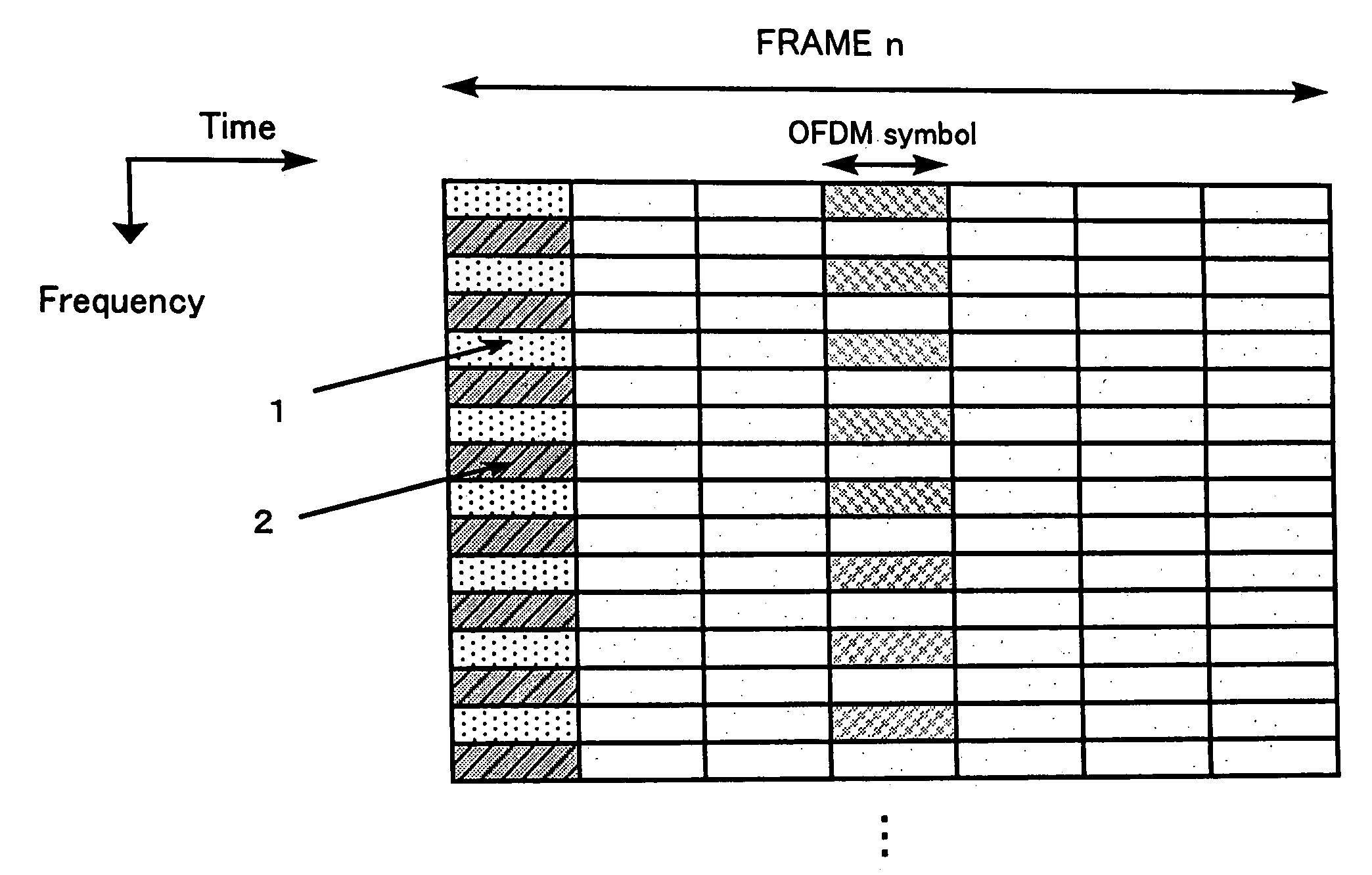
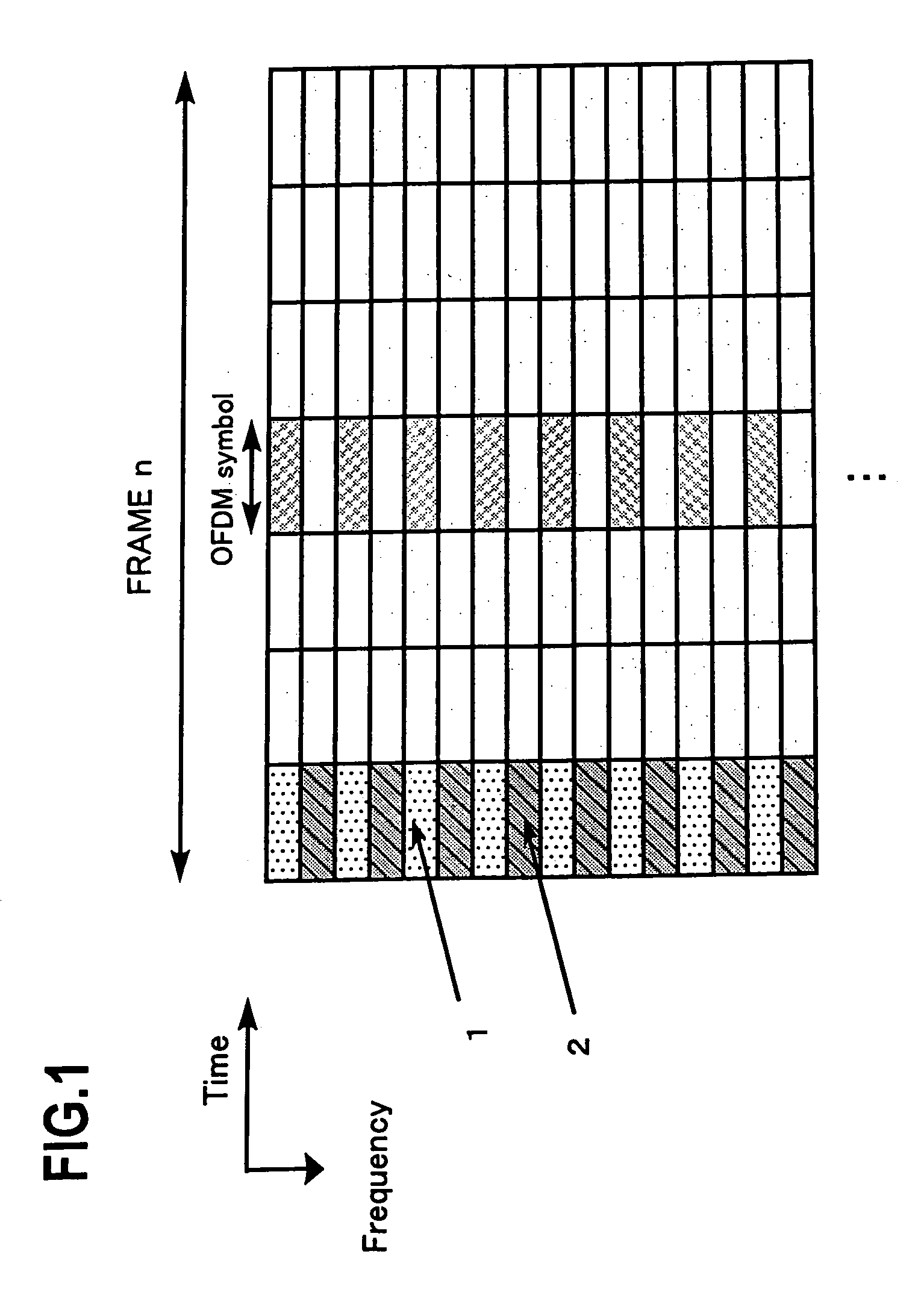
A method for synchronizing and identifying the cell code (scrambling code) of a cell in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) based cellular communication system is provided. In this method, desired cell is found by utilizing a frame structure of OFDM symbols and through a corresponding cell search procedure, where the frame structure has periodic signal pattern and contains the information about the cell code of the desired cell in common pilot channel (CPICH) signal. And, the cell search method utilizes the periodic property of the frame structure to detect frame timing, and the correlation property of CPICH signal to identify the cell code. The cell search method of the present invention offers the advantages of good link quality, fast acquisition, and low power consumption.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Transmit diversity with formed beams in a wireless communications system using a common pilot channel
InactiveUS7206554B1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsTransmission monitoringTraffic signalCommunications system
A method and apparatus are provided that allows beamforming to be used on a user-specific signal together with a sector-wide pilot signal in a communication system, such as a CDMA system. In one embodiment, the invention includes transmitting a pilot signal with a wide beamwidth to a remote terminal from a first array, transmitting a first traffic signal with a narrow beamwidth directed to the remote terminal from the first array, and transmitting a second diversity traffic signal with a second narrow beamwidth directed to the remote terminal from a second array. In some examples, the invention may also include transmitting a second pilot signal from the second antenna array.
Owner:INTEL CORP
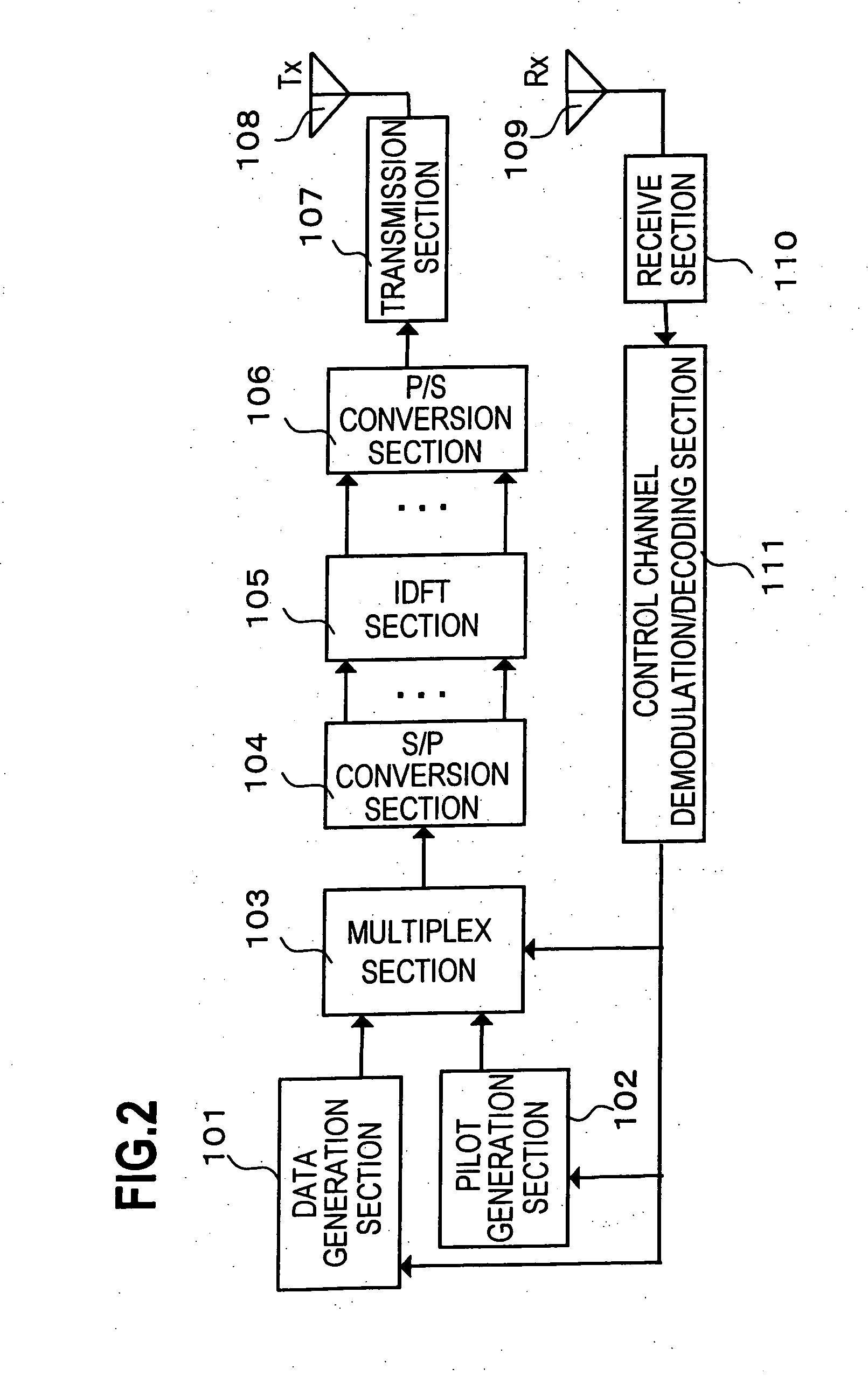
Transmitting and receiving apparatuses and methods
ActiveUS20090196165A1Improve reception qualityTransmission path divisionBroadcast transmission systemsMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCommon pilot channel
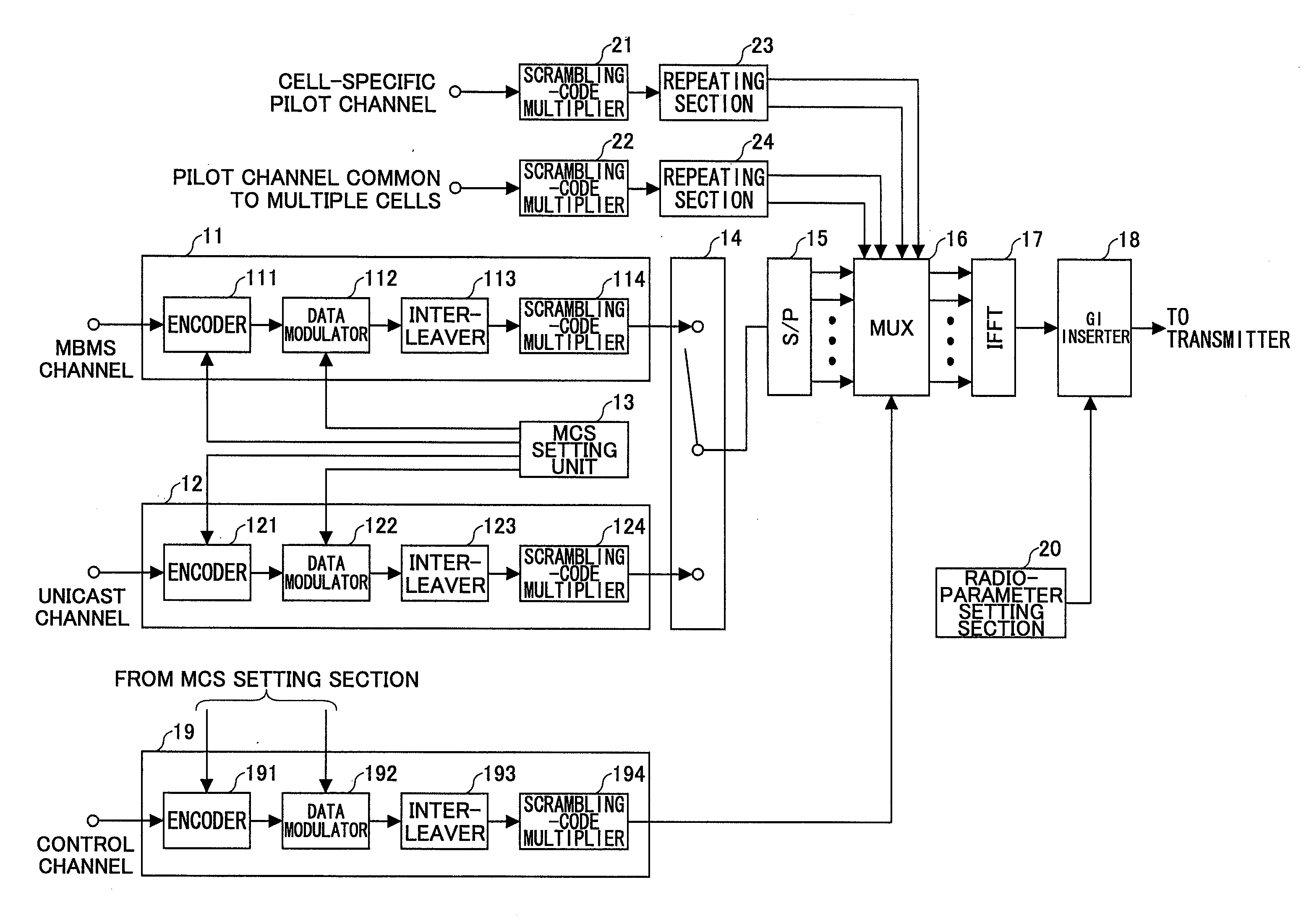
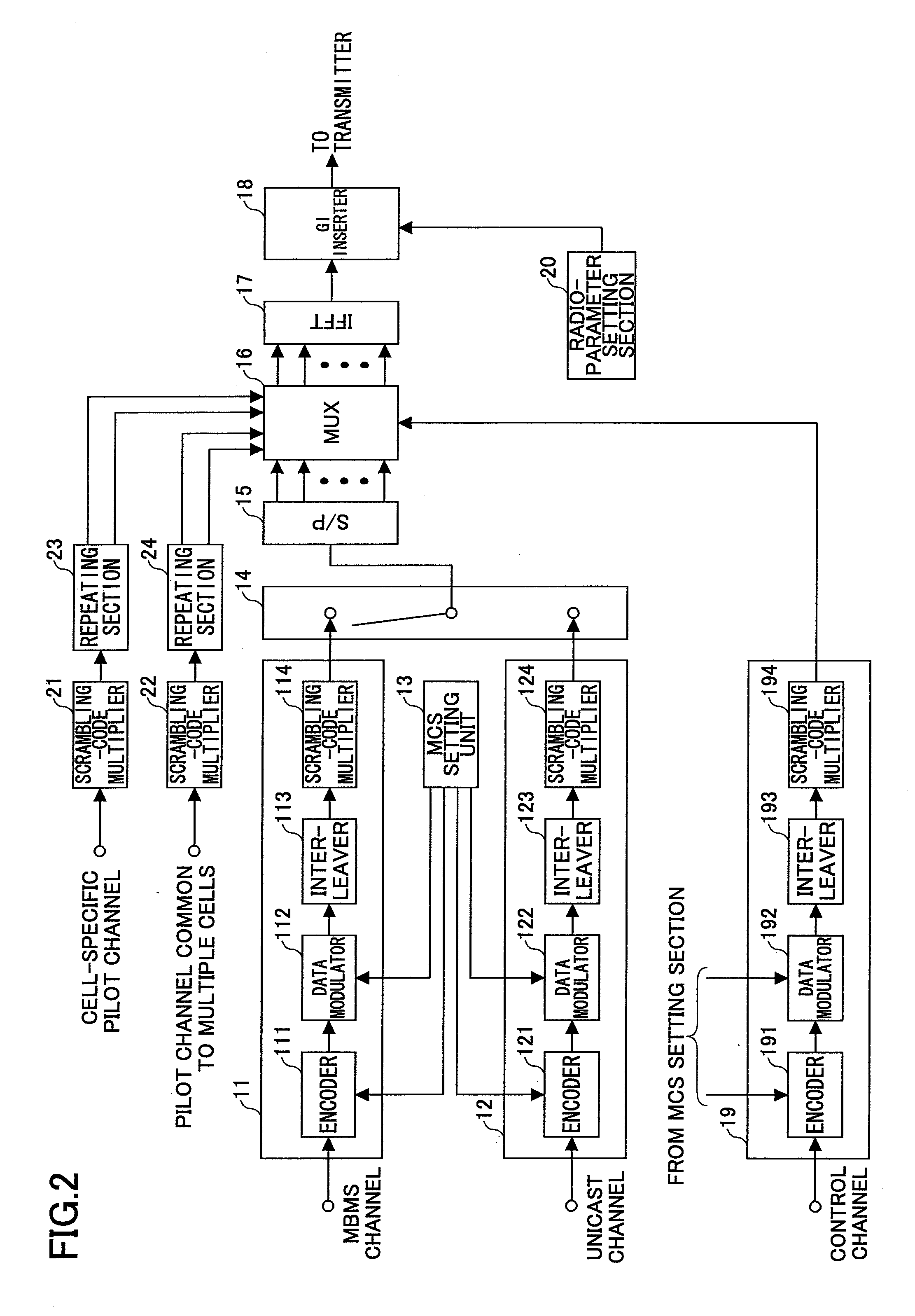
A transmitting apparatus which transmits a transmit symbol in orthogonal-frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) is disclosed. The transmitting apparatus includes a unit which provides a unicast channel; a unit which provides a multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS) channel; a unit which provides a specific pilot channel which is specific to a specified cell; a unit which provides one or more common pilot channels common to a plurality of cells; and a multiplexing unit which multiplexes the unicast channel, the MBMS channel, the specific pilot channel, and the one or more common pilot channels, and creates the transmit symbol, wherein the multiplexing unit time-division multiplexes, in the same frequency band, a unicast frame which includes the unicast channel, and an MBMS frame which includes the MBMS channel, and wherein an insertion density of the common pilot channel included in the MBMS frame is larger than an insertion density of the specific pilot channel included in the unicast frame.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Mobile communication system, mobile station, base station, communication path quality estimation method used for the same
InactiveUS20050181832A1Increase speedImprove accuracyError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorBroadcast transmission systemsEstimation methodsControl channel
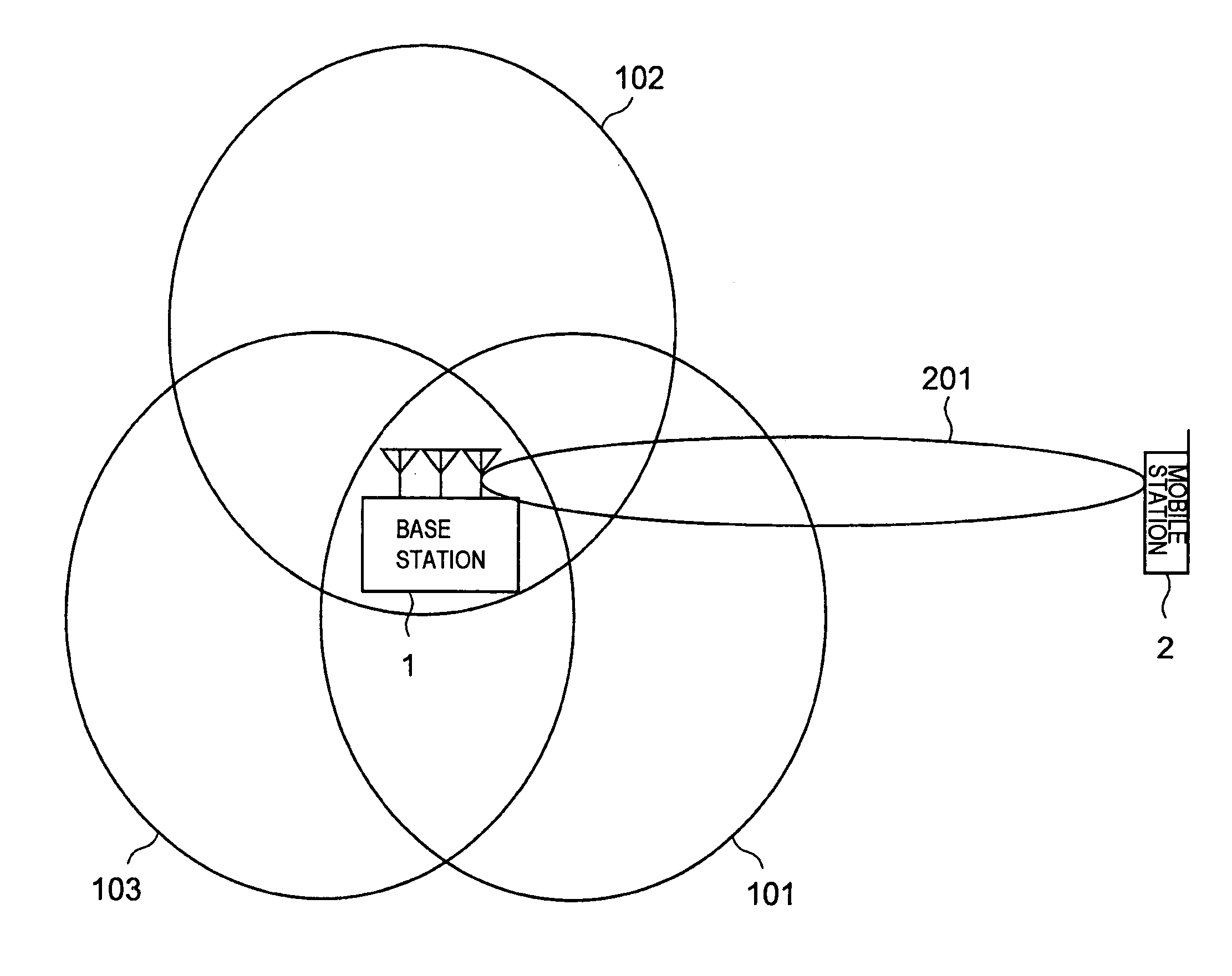
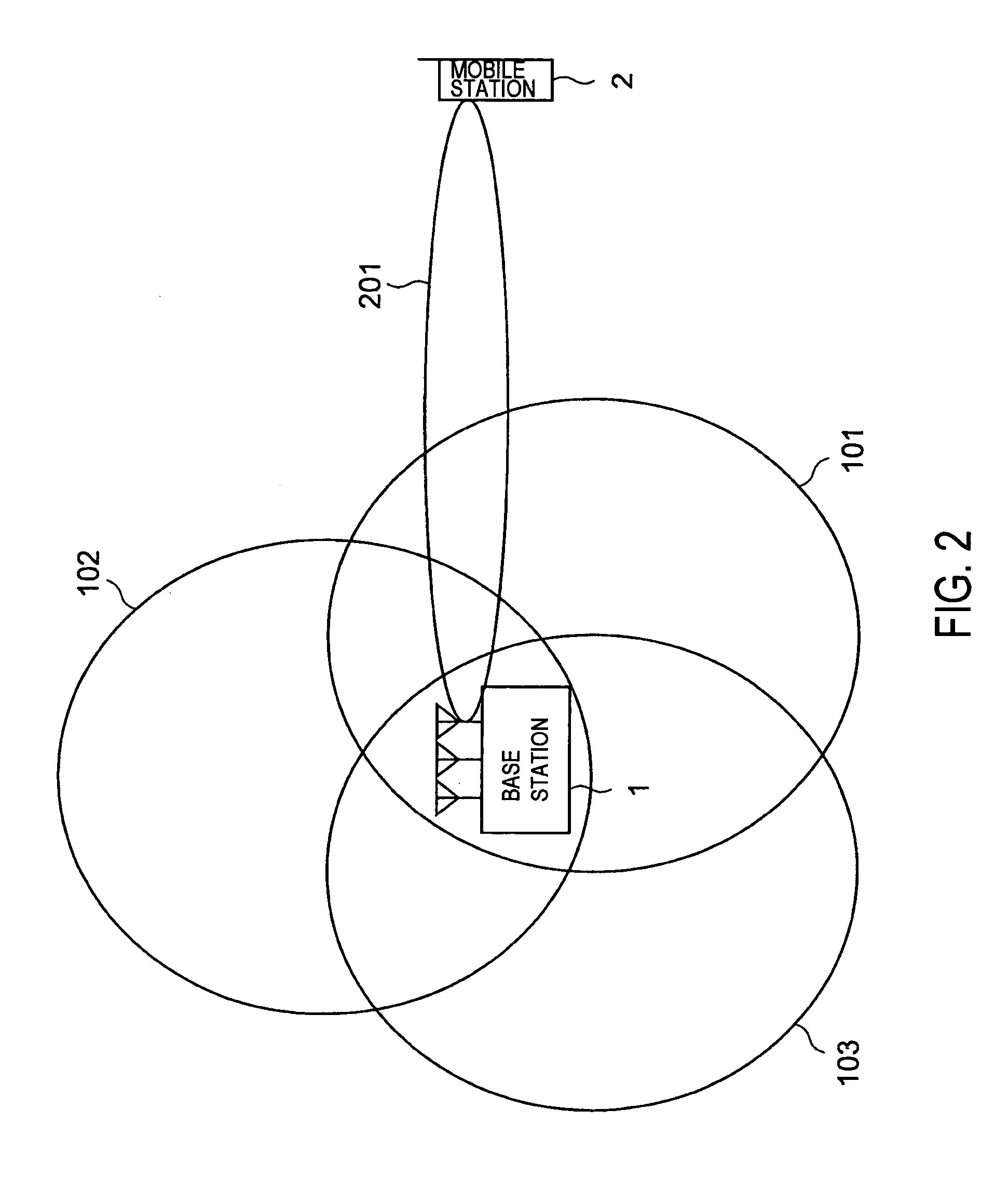
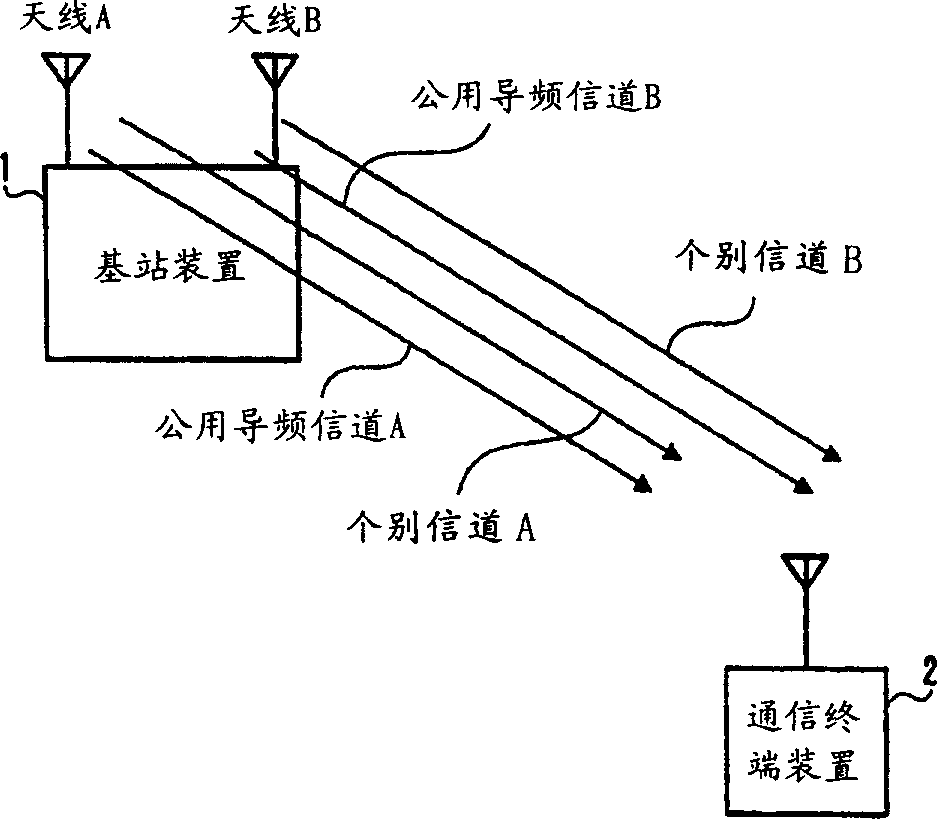
A mobile communication system capable of improving the system throughput. A base station (1) divides one cell into three sectors. A common pilot channel is transmitted to a plurality of mobile stations in the sectors by beams (101-103) whose directivity is controlled by an adaptive antenna for each of the sectors. On the other hand, when a mobile station (2) communicates data with the base station (1), the base station transmits a data channel and an individual control channel to the mobile station (2) by using a beam (201) whose directivity is controlled individually. The mobile station (2) switches between the common pilot channel and the individual control channel from the base station (1) for estimating the communication path quality.
Owner:NEC CORP
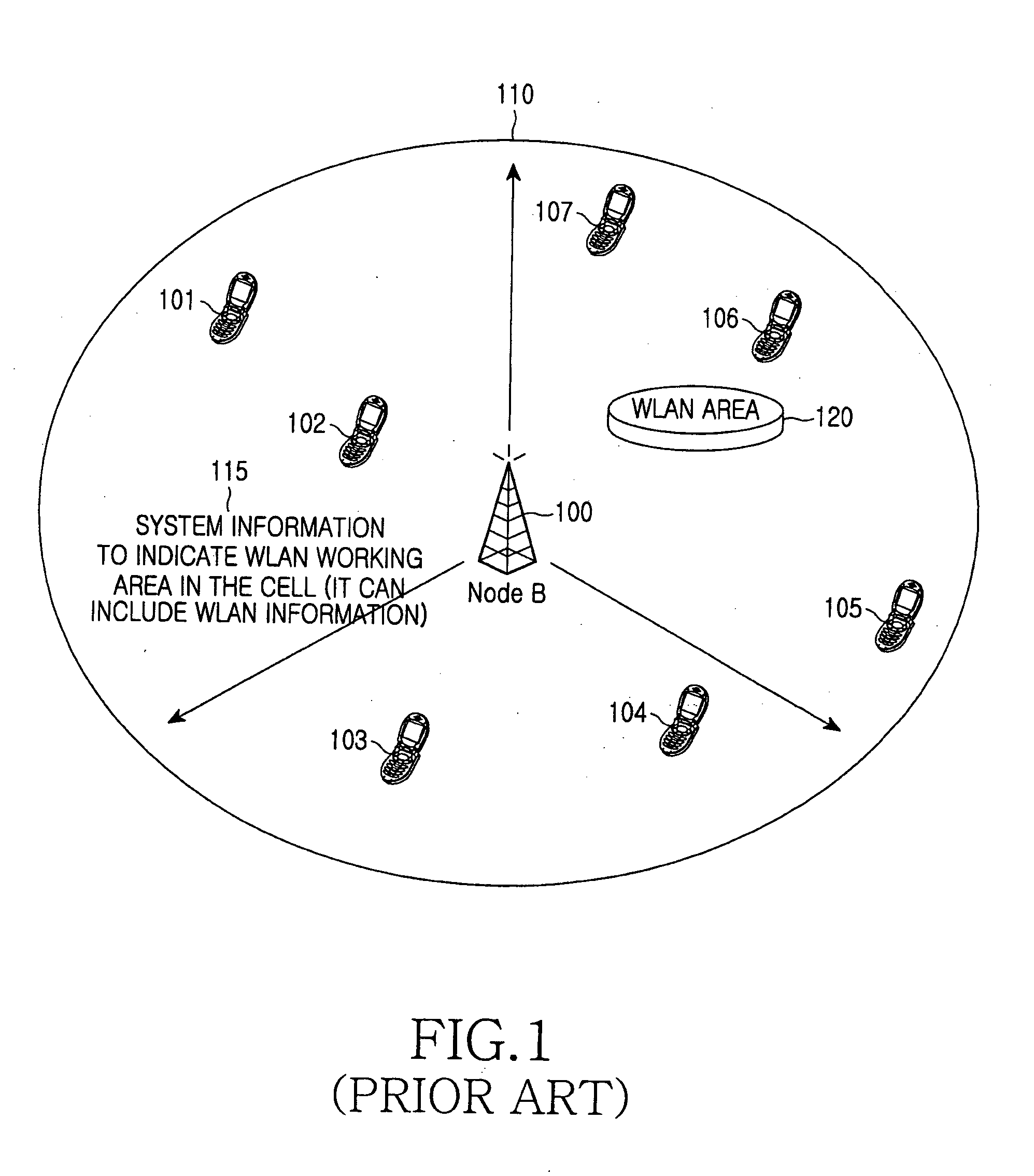
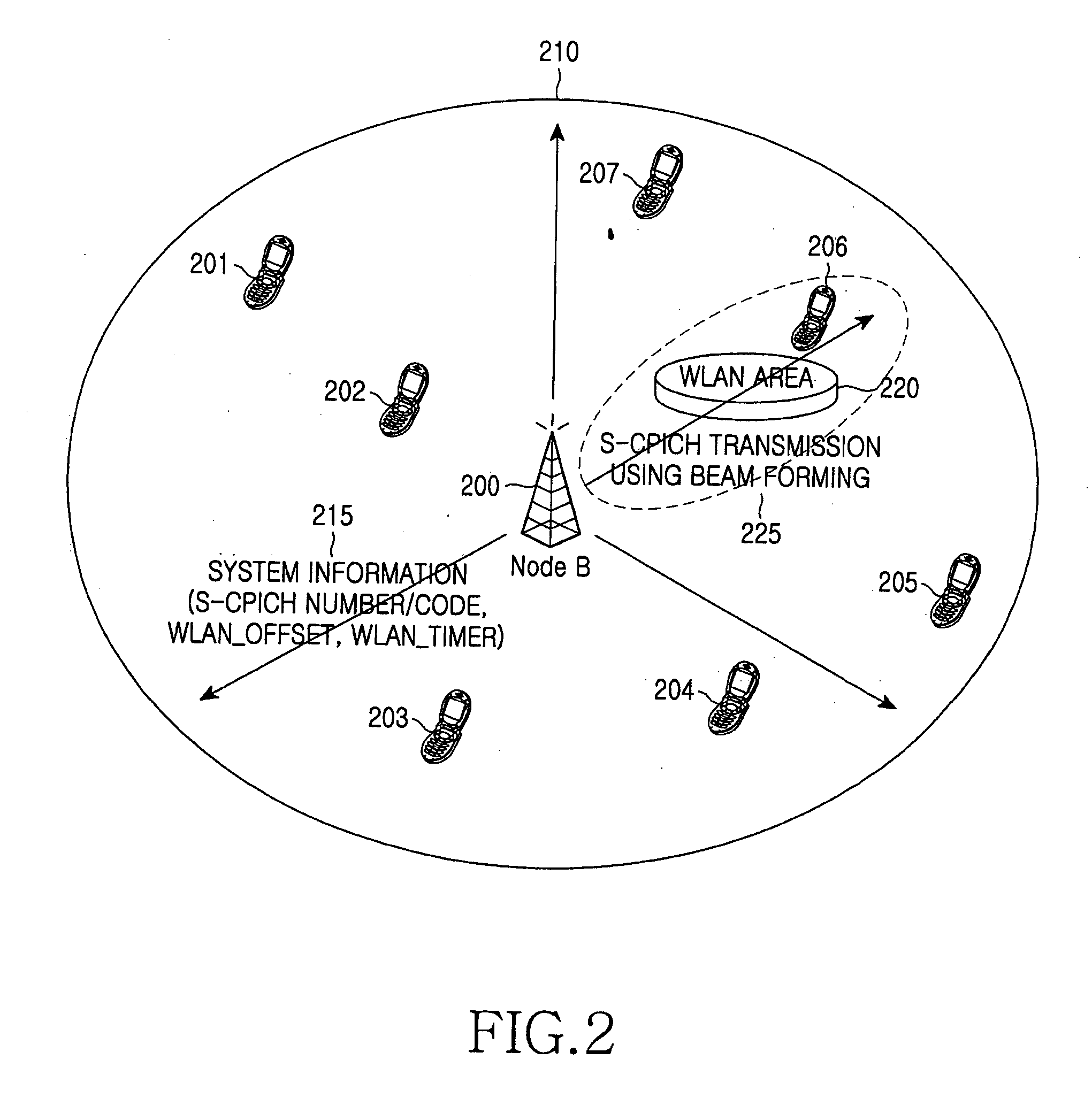
Apparatus and method for transmitting wireless LAN information in mobile communication network for wireless LAN interworking
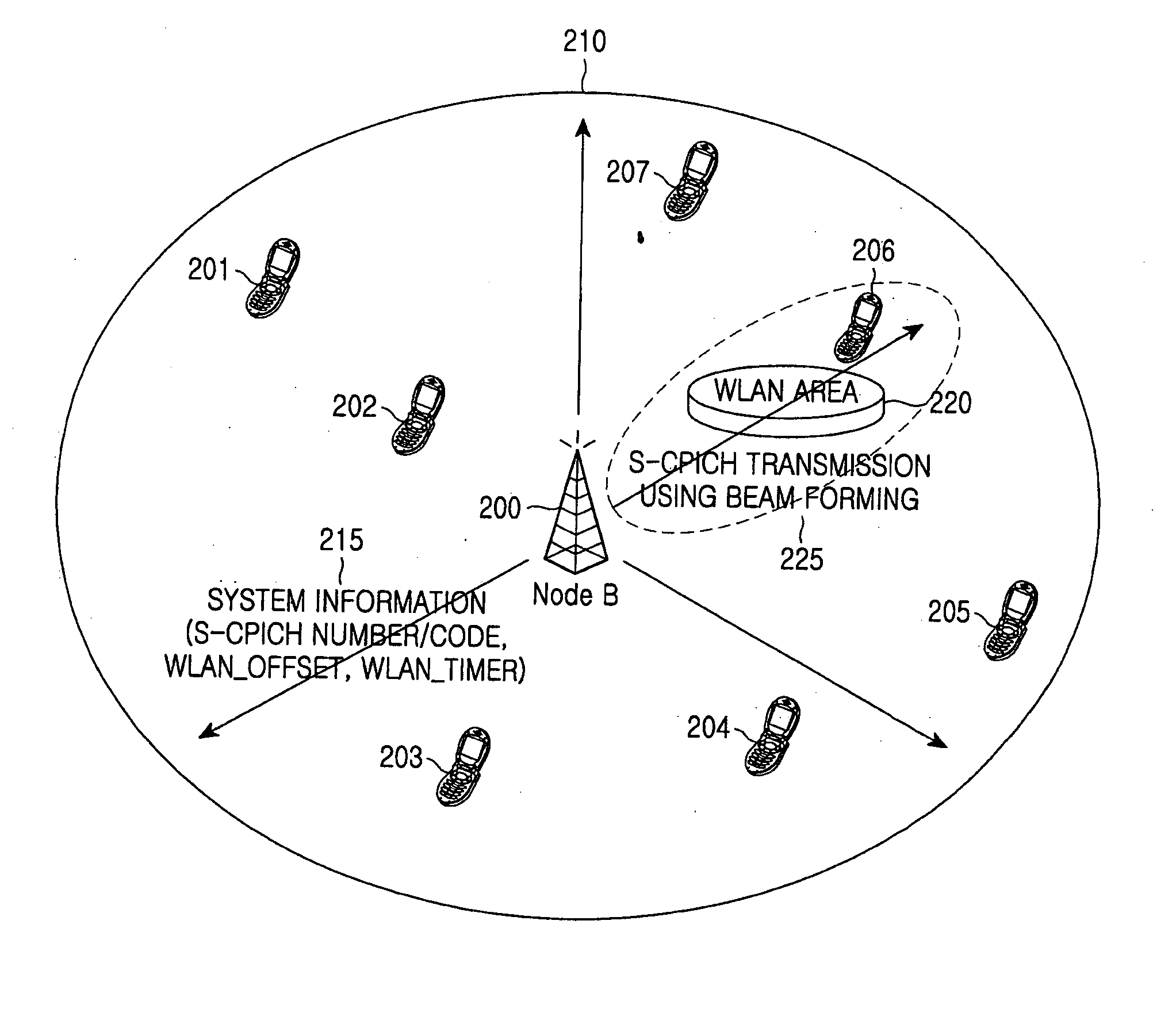
ActiveUS20060034236A1Guaranteed normal transmissionWithout unnecessarily wasting power consumption in the mobile terminalAssess restrictionData switching by path configurationWireless lanCommon pilot channel
An apparatus and a method are provided for transmitting wireless local area network (WLAN) information in a mobile communication network for WLAN-interworking. The method includes the steps of setting a WLAN threshold value, which is used for determining if a WLAN area is present in a cell, and a measurement period in system information, broadcasting the system information in the cell, and transmitting a common pilot channel, which indicates that the WLAN area is present in the cell, in a predetermined direction with predetermined transmission power to cover the WLAN area by using beam forming.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
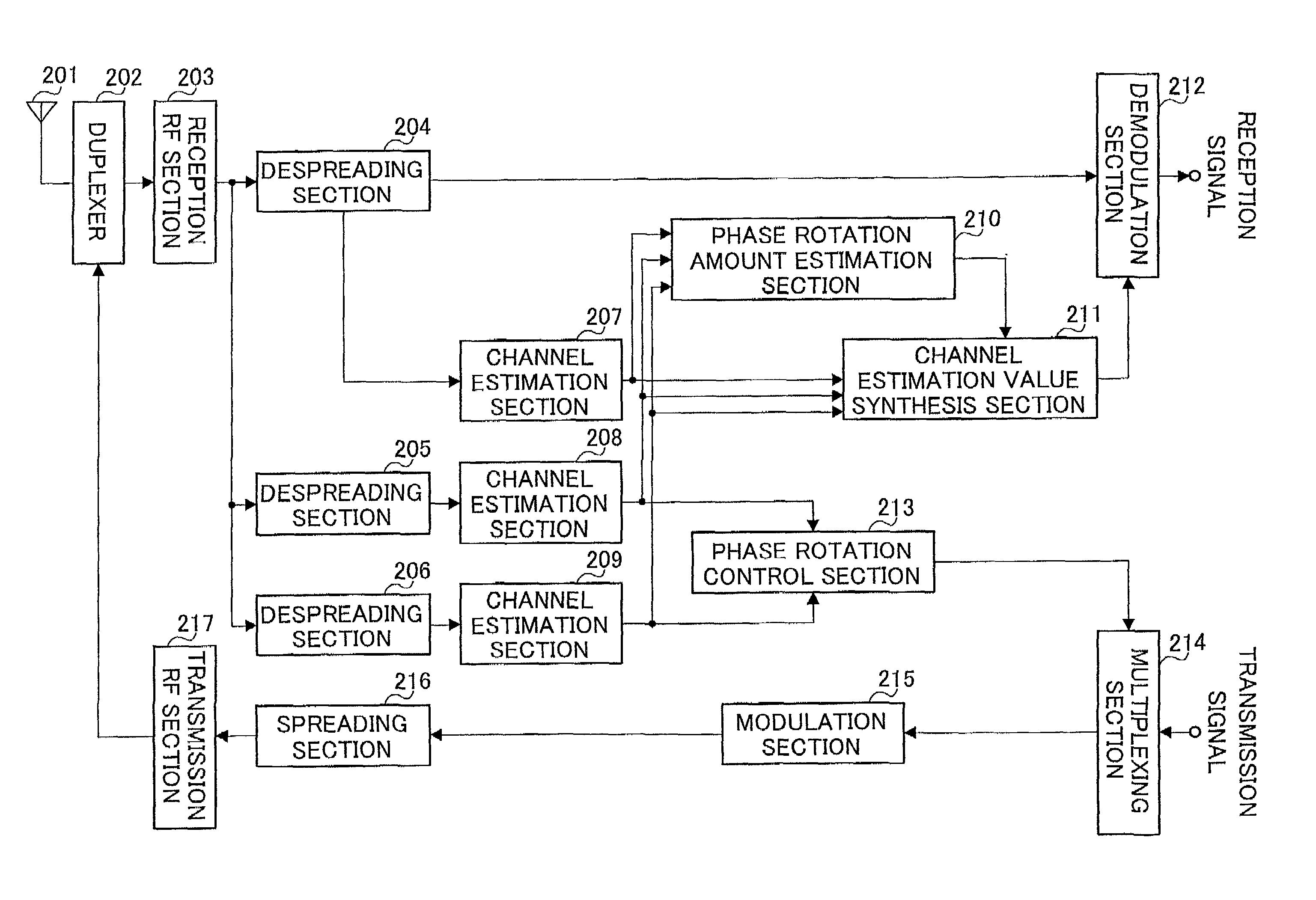
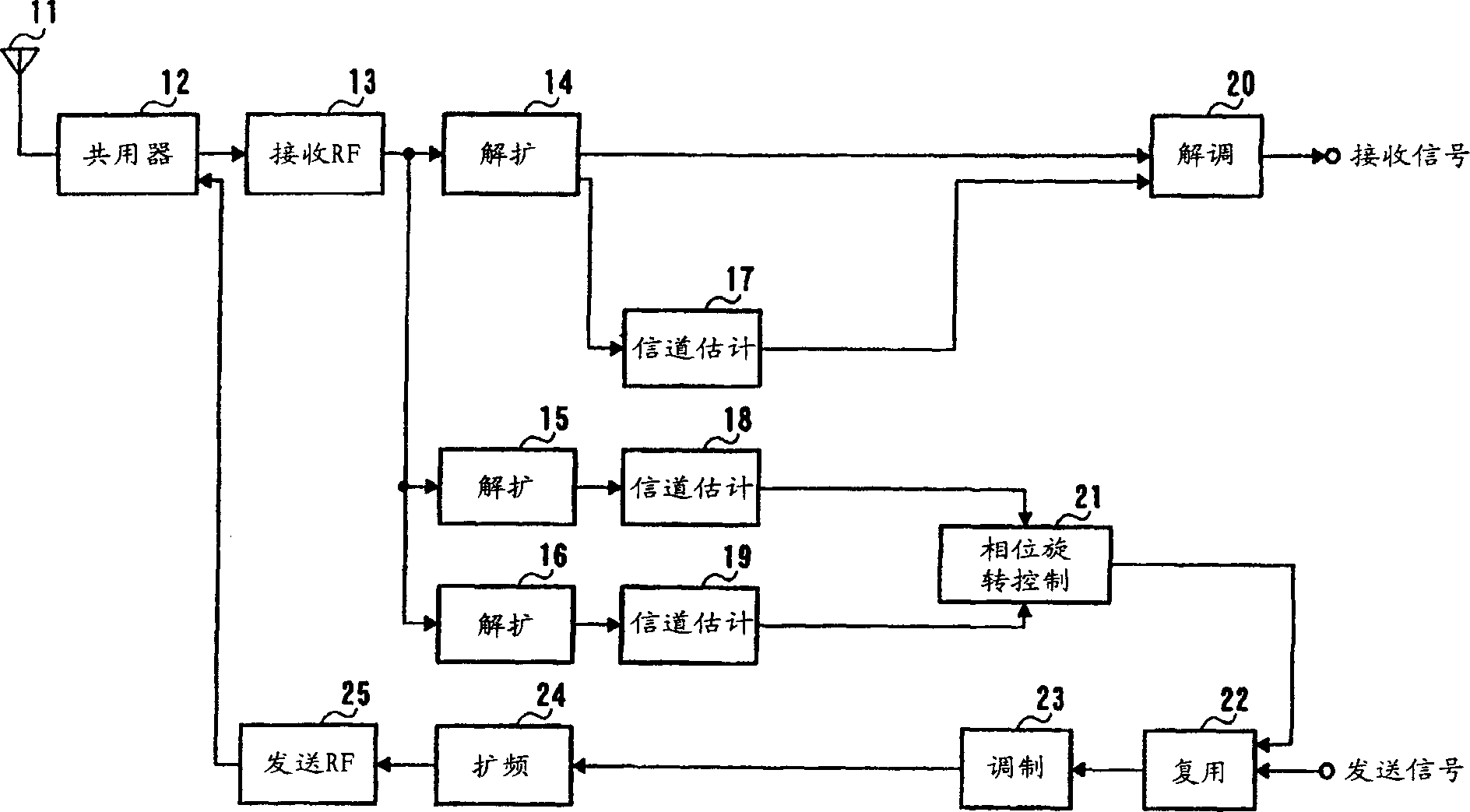
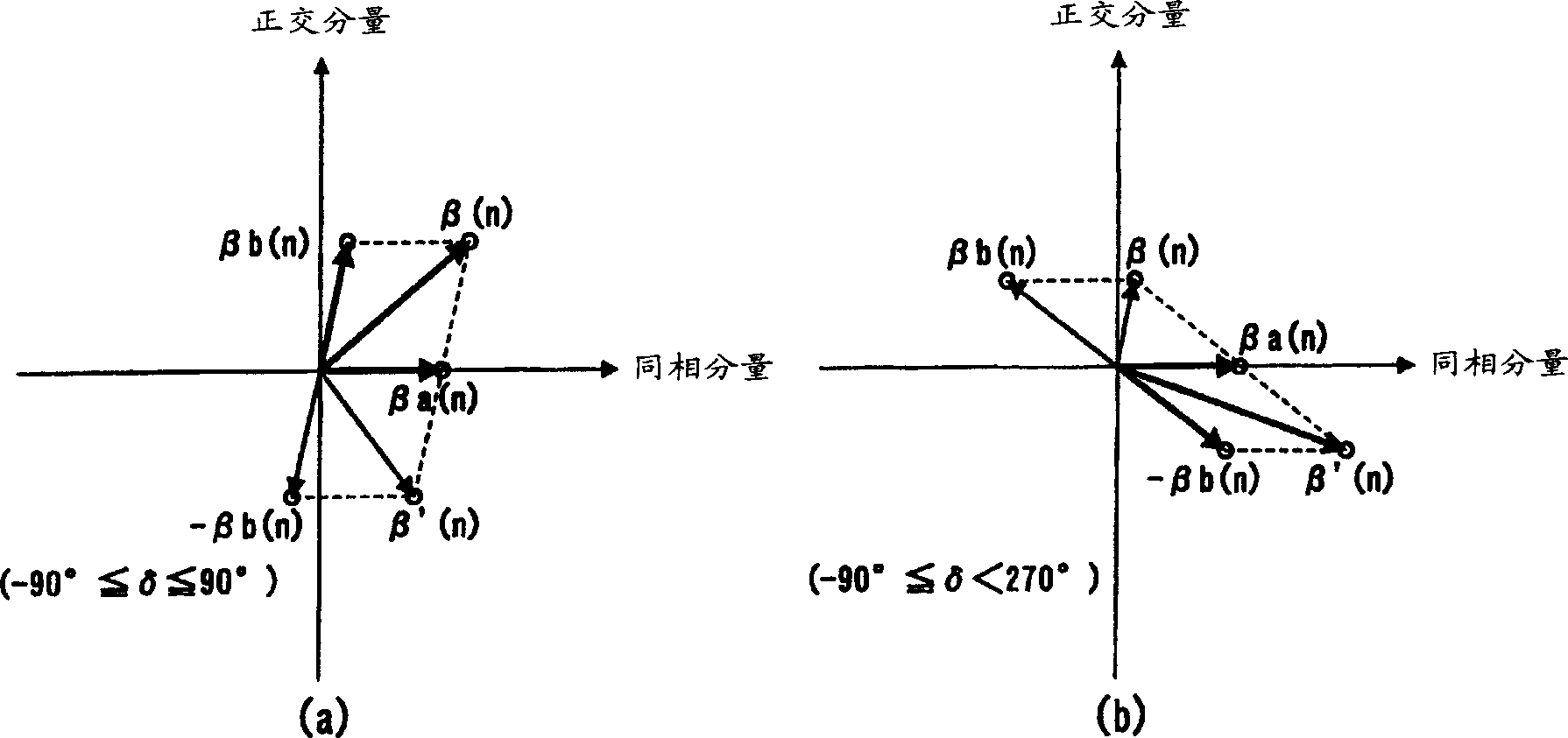
Communication terminal device and channel estimating method
InactiveUS7002939B1Improve reliabilitySpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemTerminal equipment
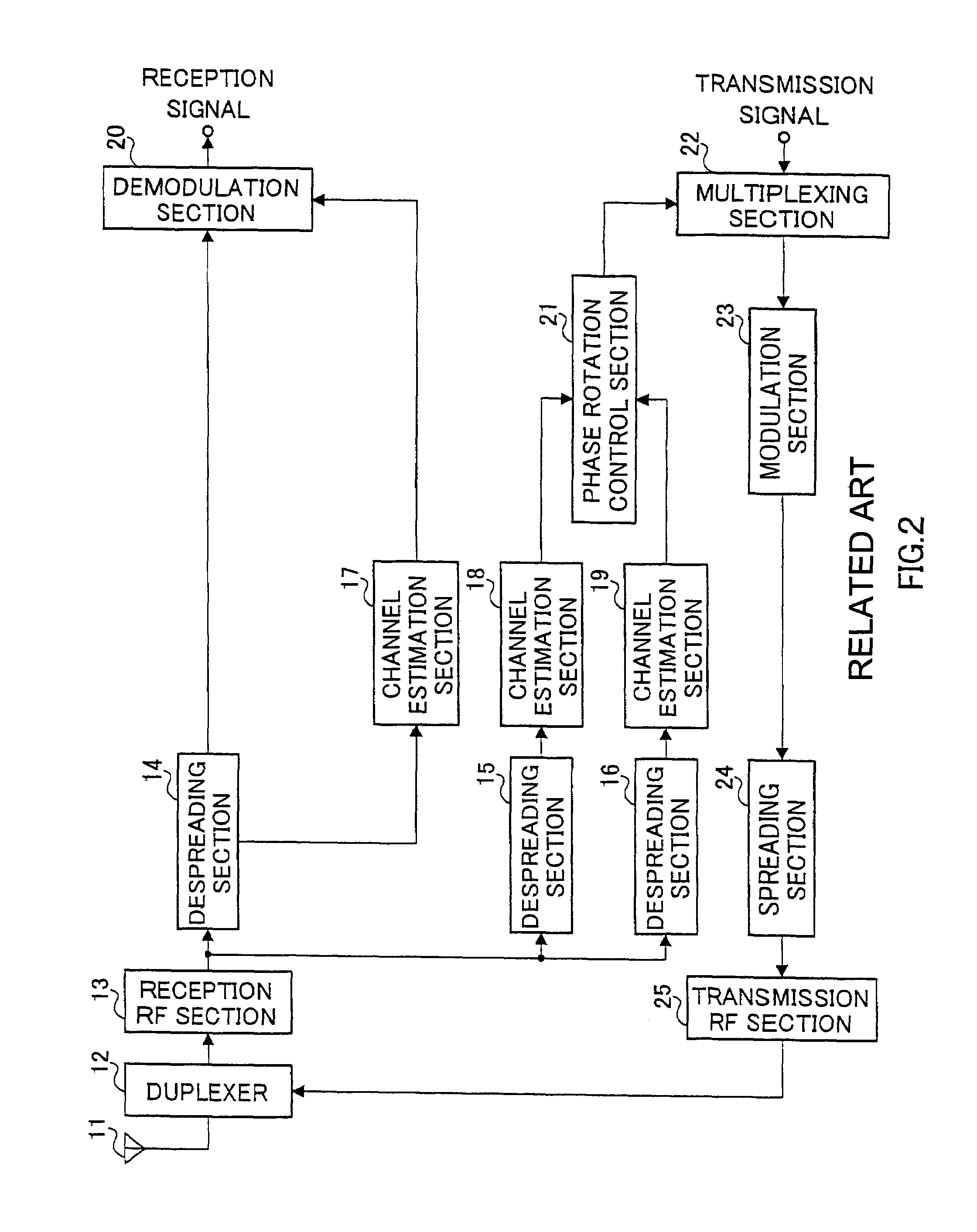
A phase rotation amount estimating unit (210) rotates a channel estimation value of a signal in a common pilot channel (B) through a candidate phase rotation amount θ (θ=0, 180) for synthesizing with a channel estimation value of a signal in a common pilot channel (A). A phase rotation is estimated based on the highest one of orthogonalities between this synthesis result and channel estimation values of signals in individual channels. A channel estimation value synthesis unit (211) synthesizes a value obtained by rotating a channel estimation value of a signal in the common pilot channel (B) through a phase rotation amount θ with a channel estimation value of a signal in the common pilot channel (A), whereby the reliability of a channel estimation value can be enhanced in a transmission diversity-introduced radio communication system.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for improving noise power estimate in a wcdma network
Method and apparatus for improving a noise power estimate in a wideband CDMA (WCDMA) network are disclosed and may include calculating a total noise power estimate for a downlink channel based on a plurality of control channel bits from a plurality of different types of control channels. The plurality of control channel bits may include at least two of: dedicated physical channel (DPCH) transmit power control (TPC) bits, DPCH pilot bits, and common pilot channel (CPICH) bits. A first noise power estimate may be calculated for the downlink channel based on a plurality of the DPCH TPC bits. A value of at least one of the plurality of DPCH TPC bits may not be known when the at least one of the plurality of DPCH TPC bits is received.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Resolving user-specific narrow beam signals using a known sequence in a wireless communications system with a common pilot channel
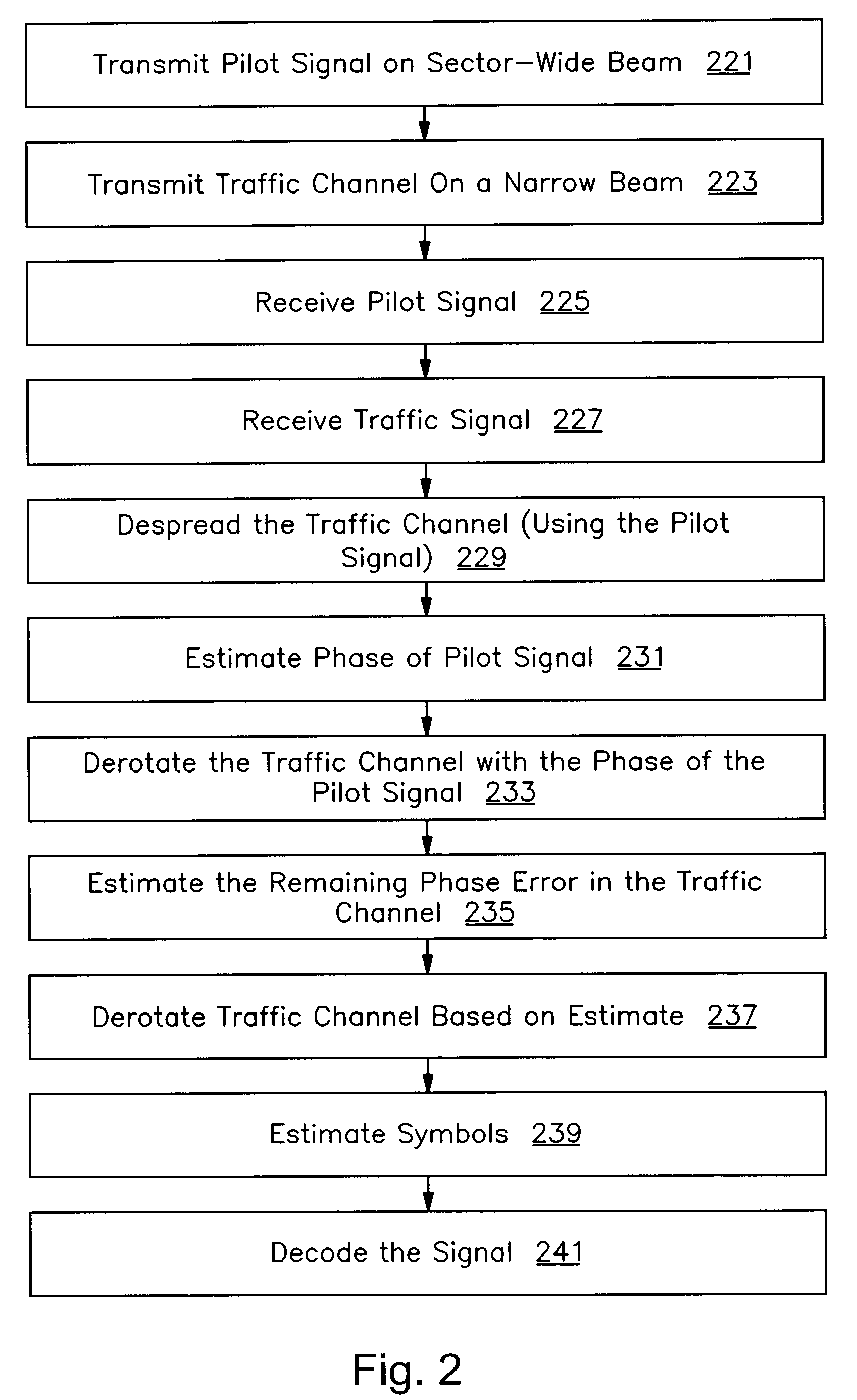
A method and apparatus are provided that corrects for differences in reception between a user-specific signal and a common signal. In one embodiment, the invention includes receiving a common pilot signal transmitted on a wide beam at a remote terminal, receiving a user-specific signal transmitted on a directed narrow beam at the remote terminal, demodulating the user-specific signal using the common pilot signal for channel estimation, estimating a phase error in the demodulated user-specific signal using known symbols in the user-specific signal, and correcting for the phase error in the demodulated user-specific signal using the phase error estimates.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Incremental pilot insertion for channnel and interference estimation
ActiveUS8085875B2Improve abilitiesIncrease resourcesSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsCommunications systemDynamic resource
Dynamic resource allocation systems, apparatus, and methods are disclosed for selectively improving the ability of a receiver to determine a channel estimate in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) system. A wireless communication system can use a common pilot channel configuration to aid channel estimation in one or more receivers in communication with the system. A receiver in communication with the system may be unable to demodulate received data due to an inaccurate channel estimate. The receiver can communicate to a transmitter in the system a request for additional channel estimation resources. The wireless communication system can provide additional channel estimation resources by inserting dedicated pilot channels into one or more of the frequencies allocated to symbols for the receiver. If the receiver is still unable to demodulate received data, the wireless communication system can incrementally insert additional pilot channels in the symbol associated with the receiver.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
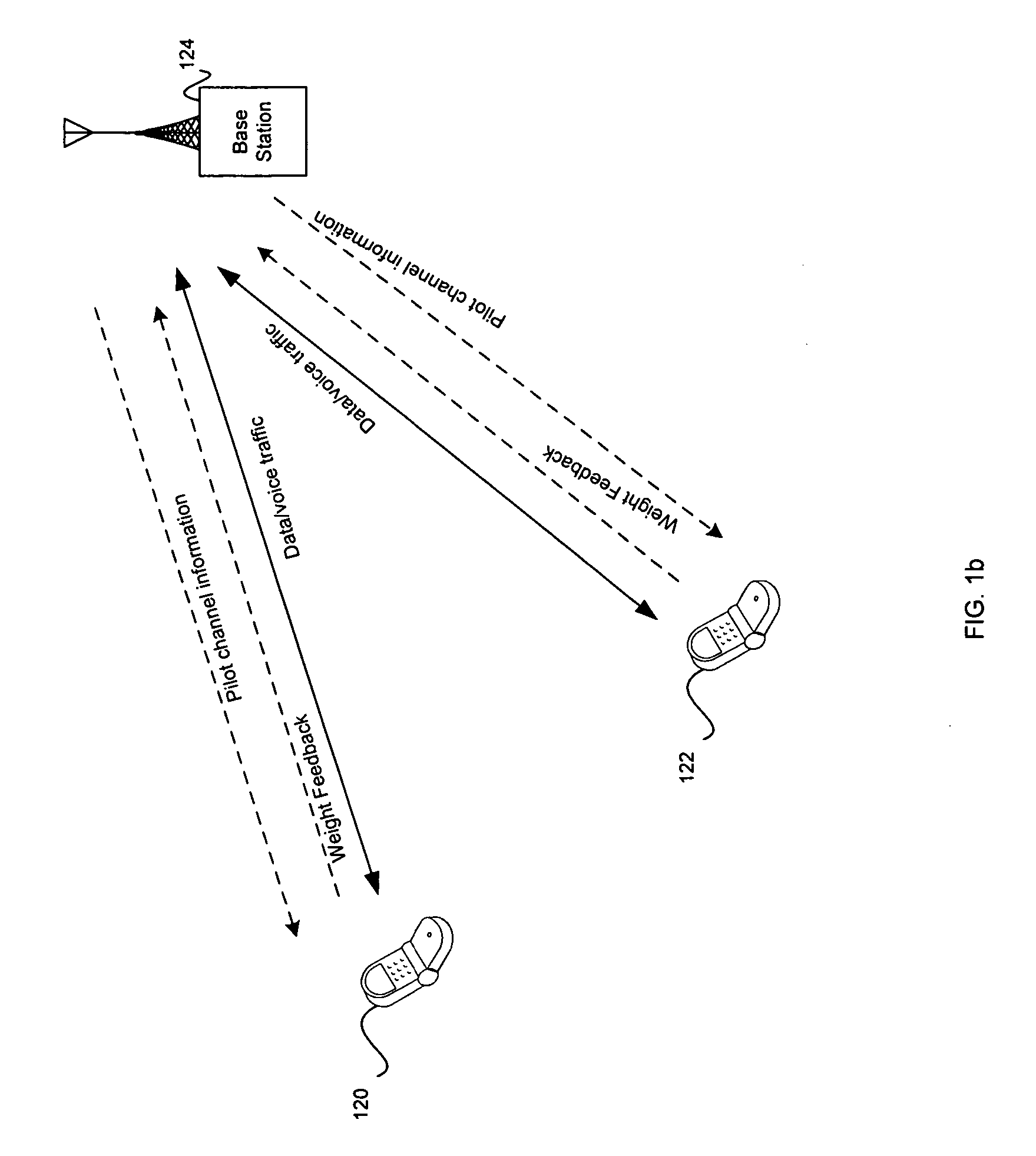
Method and apparatus for down-link feedback multiple antenna transmission in wireless communication system
ActiveUS7236478B2Simple structureImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityRadio transmission for post communicationMultiplexingCommunications system
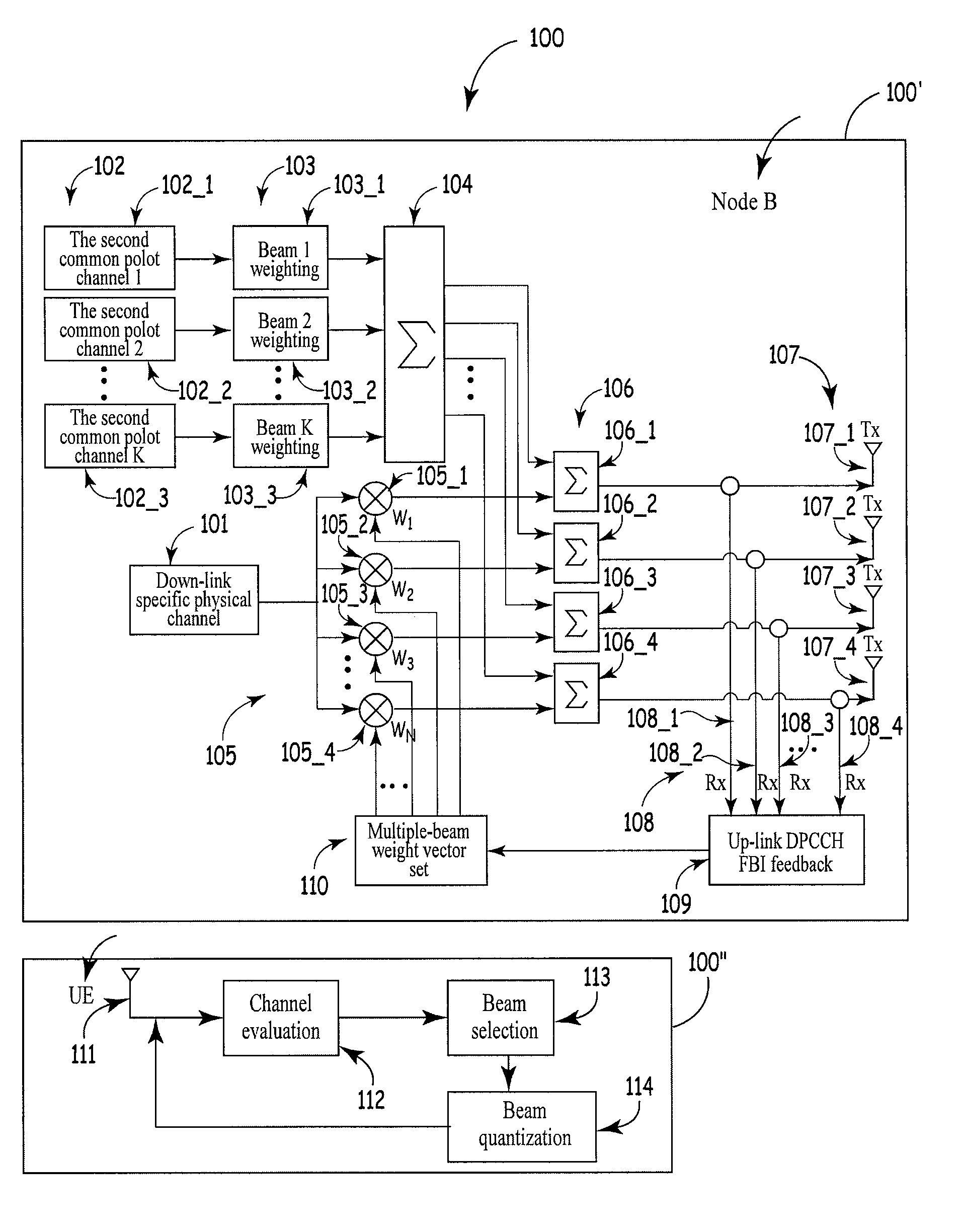
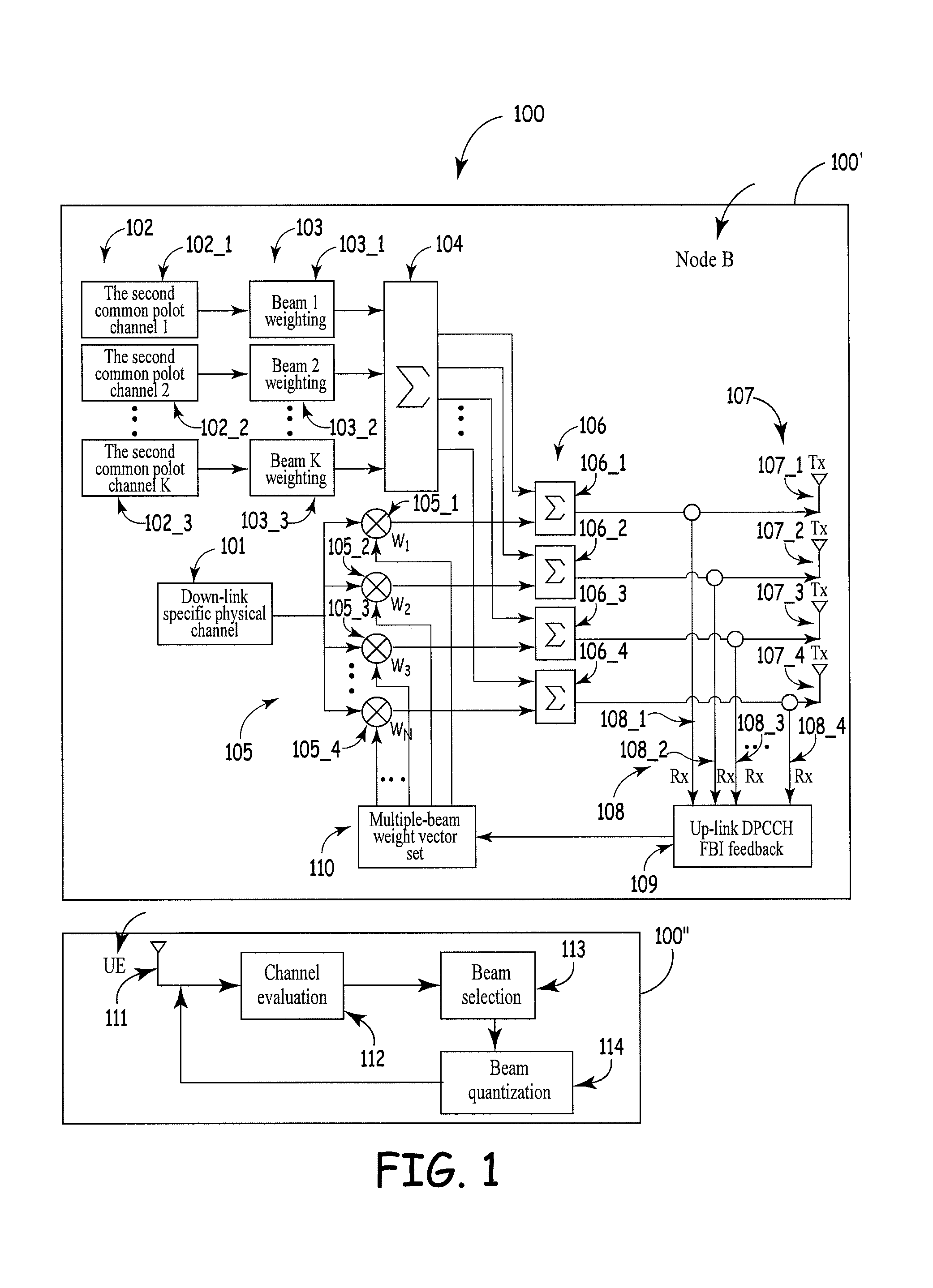
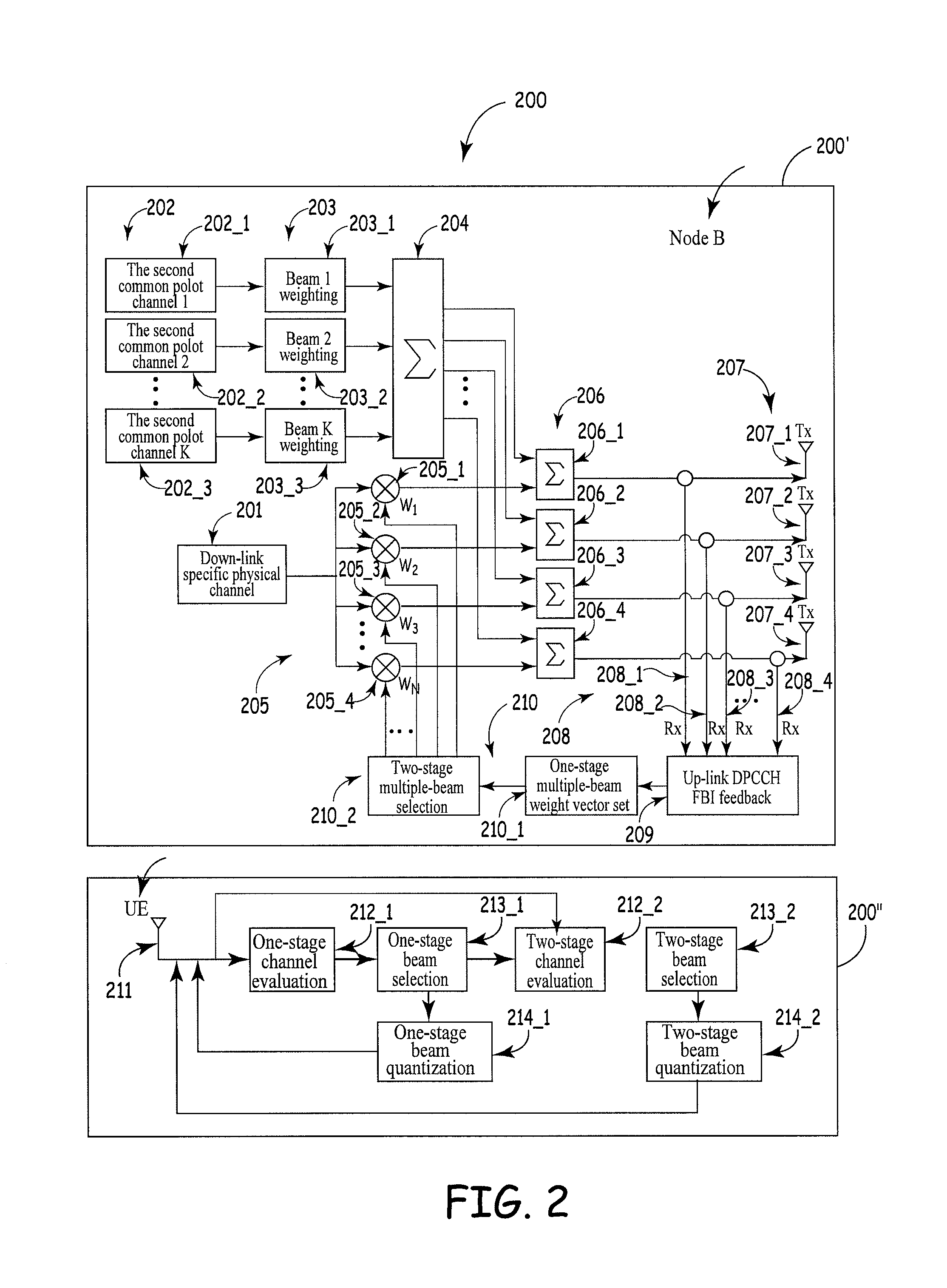
An apparatus and method for down-link multiple-antenna transmission in a wireless communication system is provided wherein a base station section comprises: a down-link specific physical channel unit, a second common pilot channel unit, a beam weighting unit of common pilot channels, a multiplexing and summing unit, a down-link specific physical channel weighting unit, a specific physical channel and second common pilot channel multiplexing unit, an antenna array unit, a multiple-beam weight vector set unit, up-link specific physical channels, and a feedback bit information unit; and a service cell section or mobile station section comprises: an antenna unit, a channel evaluating unit, a beam selection unit, and a beam quantizing unit. The space characteristics of the physical channels are utilized reasonably. Accordingly, a beam gain is obtained, interference is suppressed effectively, and the apparatus is easy to operate.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
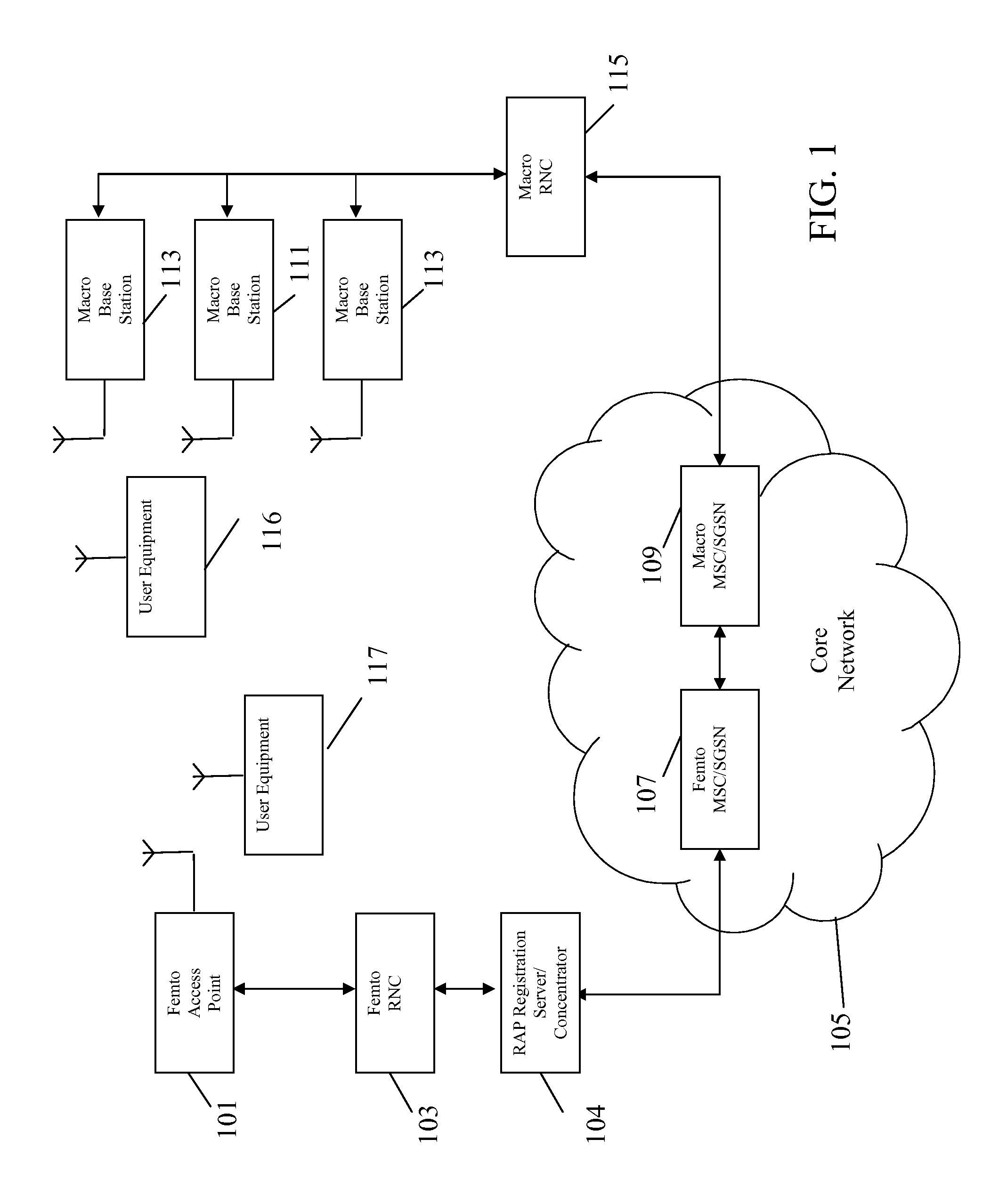
Managing power consumption in base stations and remote access points
InactiveCN102714812APower managementEnergy efficient ICTBroadcast channelsCommon control physical channel
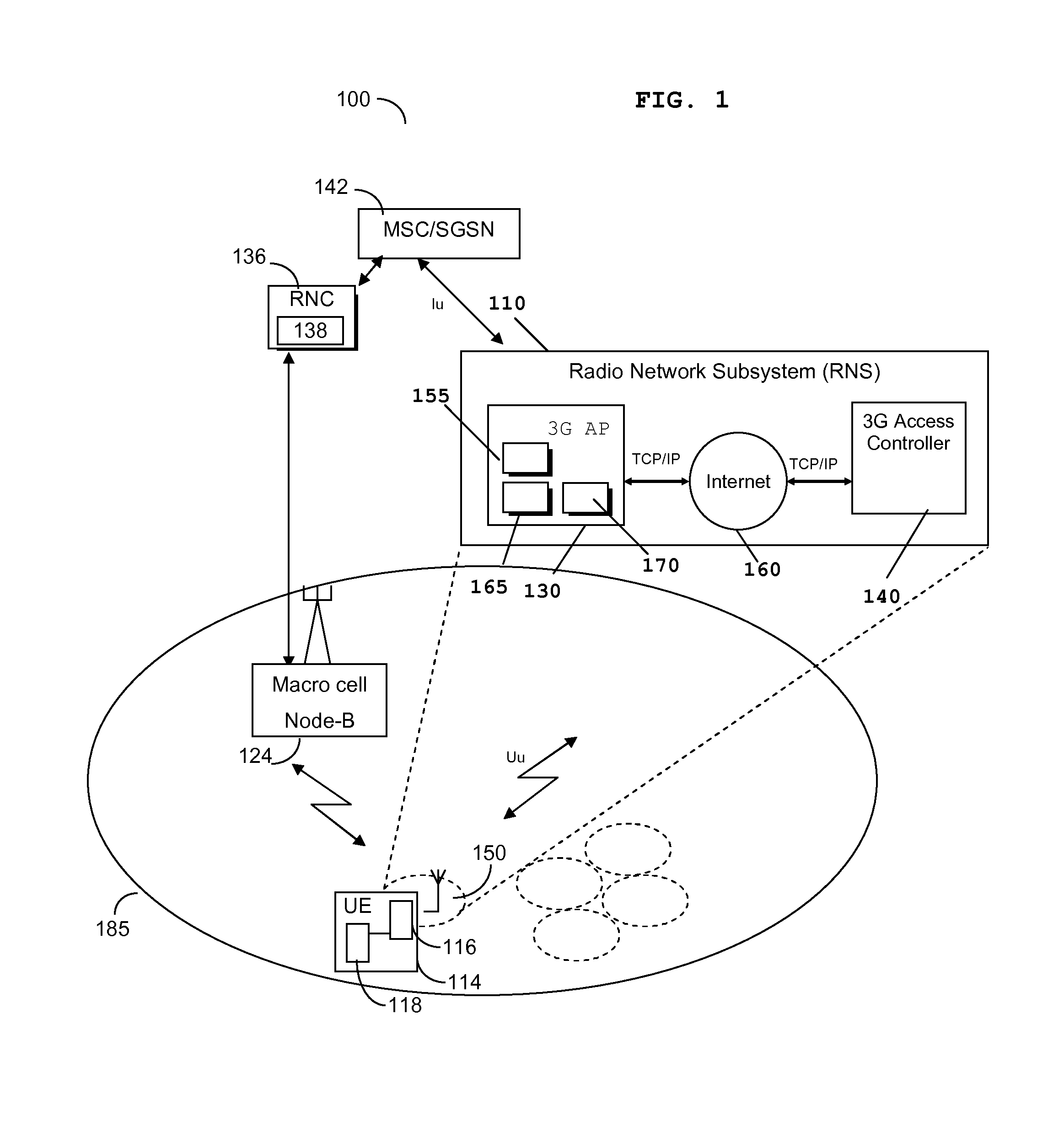
A wireless transmit / receive unit (WTRU) in communication with a wireless network that may include a base station (or base node) and a cell that may be in a dormant mode is contemplated. The WTRU may determine that the WTRU may be within a vicinity of the cell and may generate a report that includes one or more measurements related to a location of the WTRU. The WTRU may transmit the report to the network and may receive an indication to perform one or more measurements related to the cell. The one or more measurements related to the cell may be based on a Common Pilot Channel (CPICH), a Synchronization Channel (SCH), and / or a Broadcast Channel (Primary Common Control Physical Channel) (BCH P-CCPCH) that may be transmitted by the cell upon a command from a base node.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
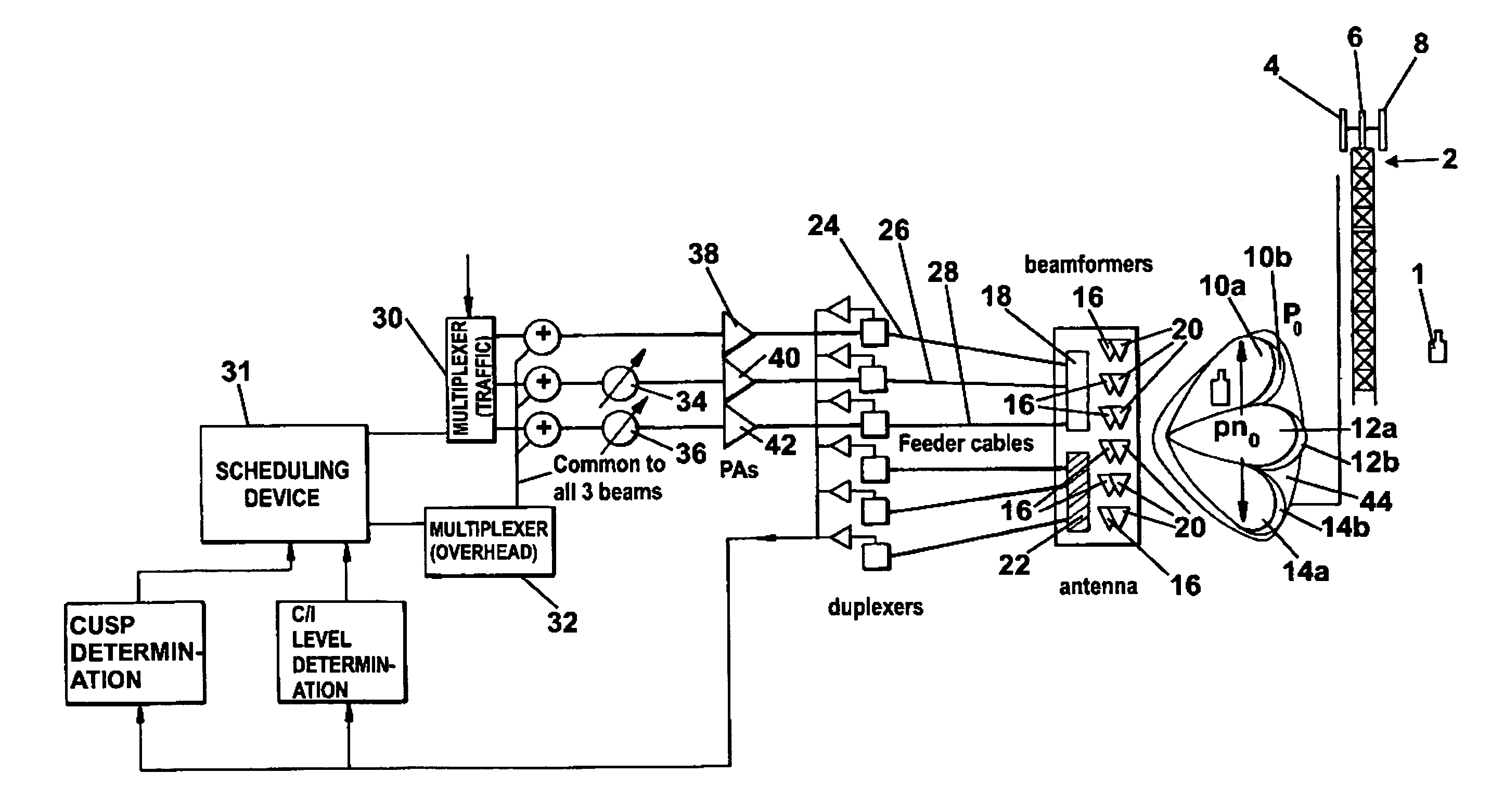
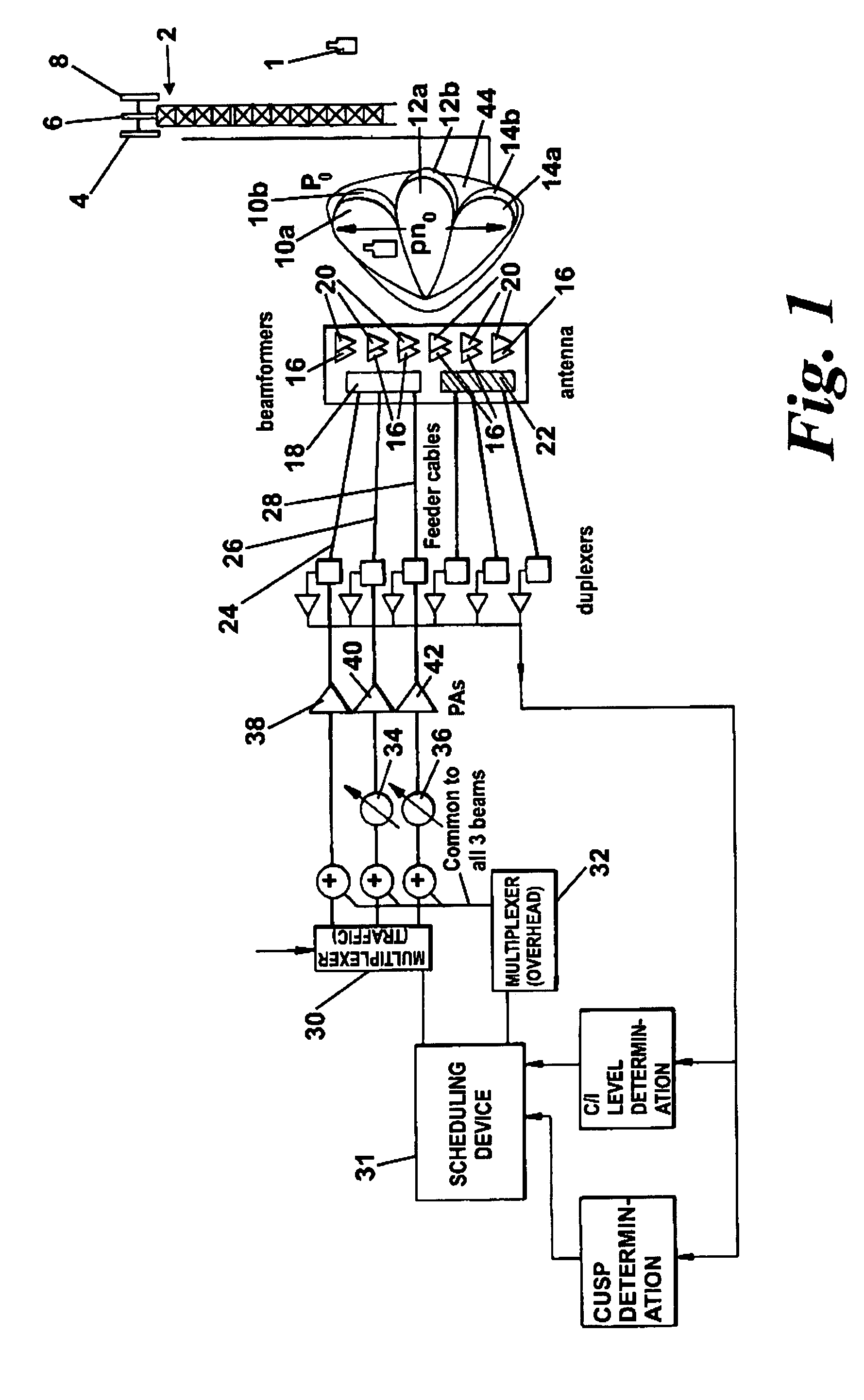
Multi-beam cellular communication system
ActiveUS7826471B2Reduce lossesStable interference environmentPower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemCellular communication systems
A cellular communication system comprising a plurality of geographically spaced base stations (2) each of which comprises an antenna arrangement (4, 6, 8) per base station sector, each of which antenna arrangements has an antenna element for generating an array of narrow beams (10, 12, 14) covering the sector. Timeslots are simultaneously transmitted over each of the beams so as to generate successive sets of simultaneously transmitted timeslots per sector. The timeslots are each split into multiple orthogonal codes, for example Walsh codes. The communication system additionally comprising a scheduling device (31) for allocating for successive sets of timeslots common overhead channels, including a common pilot channel, which are allocated to the same sub-set of codes of each timeslot in the set. For successive sets of timeslots different data traffic is allocated to the same sub-set of codes of each timeslot in the set. This effectively generates a sector wide antenna beam carrying the common overhead channels and a plurality of narrow beams each of which carry different data traffic. Inter-beam interference is addressed by the application of Adaptive Modulation and Coding and by an inter-beam handoff scheme. The handoff scheme ensures that when an end user equipment is located in a cusp region between adjacent beams the antenna arrangement simultaneously transmits data traffic to that mobile station on at least both of the adjacent beams.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Communication quality judgment method, mobile station, base station, and communications system
InactiveUS20110021239A1Site diversityTransmission monitoringPacket communicationCommunication quality
In order to carry out high-speed packet communications using a large-volume transmission channel like an E-DCH, uplink communication quality must be good. However, in a state in which a link imbalance occurs, a mobile station cannot estimate the uplink communication quality from downlink communication quality. Therefore, the mobile station calculates a path loss from the setting power of a common pilot channel which is notified from a base station, and the received power of the common pilot channel received thereby, and also estimates the received power in the base station on the basis of this path loss. The mobile station further judges the uplink communication quality by estimating the SIR in the base station by using the interference power notified from the base station and the estimated received power.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Pilot scrambling enabling direct pilot sequence detection in initial acquisition in evolved UTRA
ActiveUS20070116166A1Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexUser equipmentCommon pilot channel
A communications network and method thereof include a base station controller configured to provide a repetition period of a primary synchronization channel to be equal to a predetermined integer value times a scrambling code length of the scrambling code of a common pilot channel. A user equipment in the network is configured to search for a known sequence comprising the primary synchronization channel to select a cell and a corresponding sub-frame / symbol timing from the selected cell.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Method and apparatus for setting a transmit power level
InactiveUS20120028629A1Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one orEfficient qualityPower managementWireless commuication servicesTransceiverCommunication unit
An access point for supporting communication in a femto cell of a cellular communication network. The access point comprises transceiver circuitry arranged to enable communication with at least one cell subscribed wireless communication unit located within the femto cell, and signal processing logic module. The signal processing logic is arranged to configure a transmit power level of a Common Pilot CHannel (CPICH) for transmission based at least on cell subscribed wireless communication unit information.
Owner:IP ACCESS LTD
CDMA-Based Mobile Terminal, CDMA-Based Mobile Communication Method, and Communication Quality Estimating Method
InactiveUS20090052403A1Avoid failurePower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementInformation processingCommunication quality
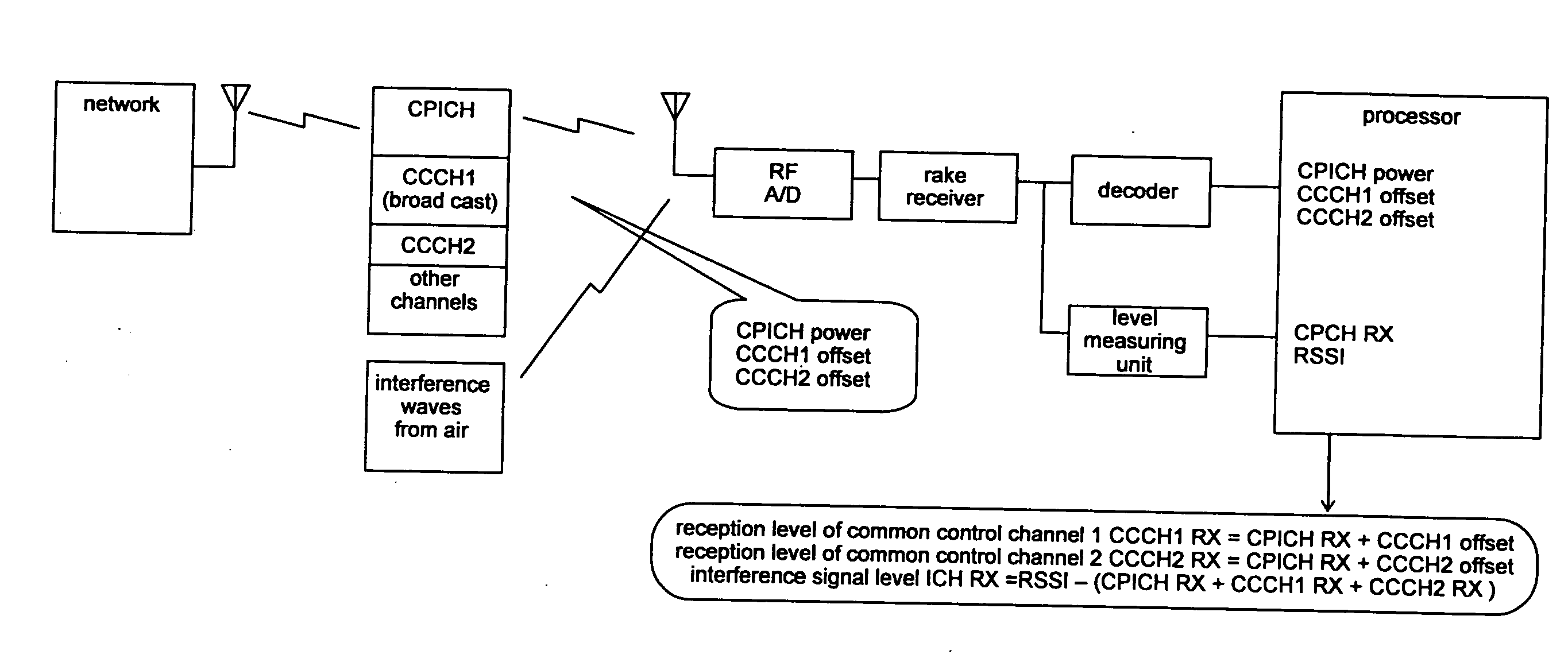
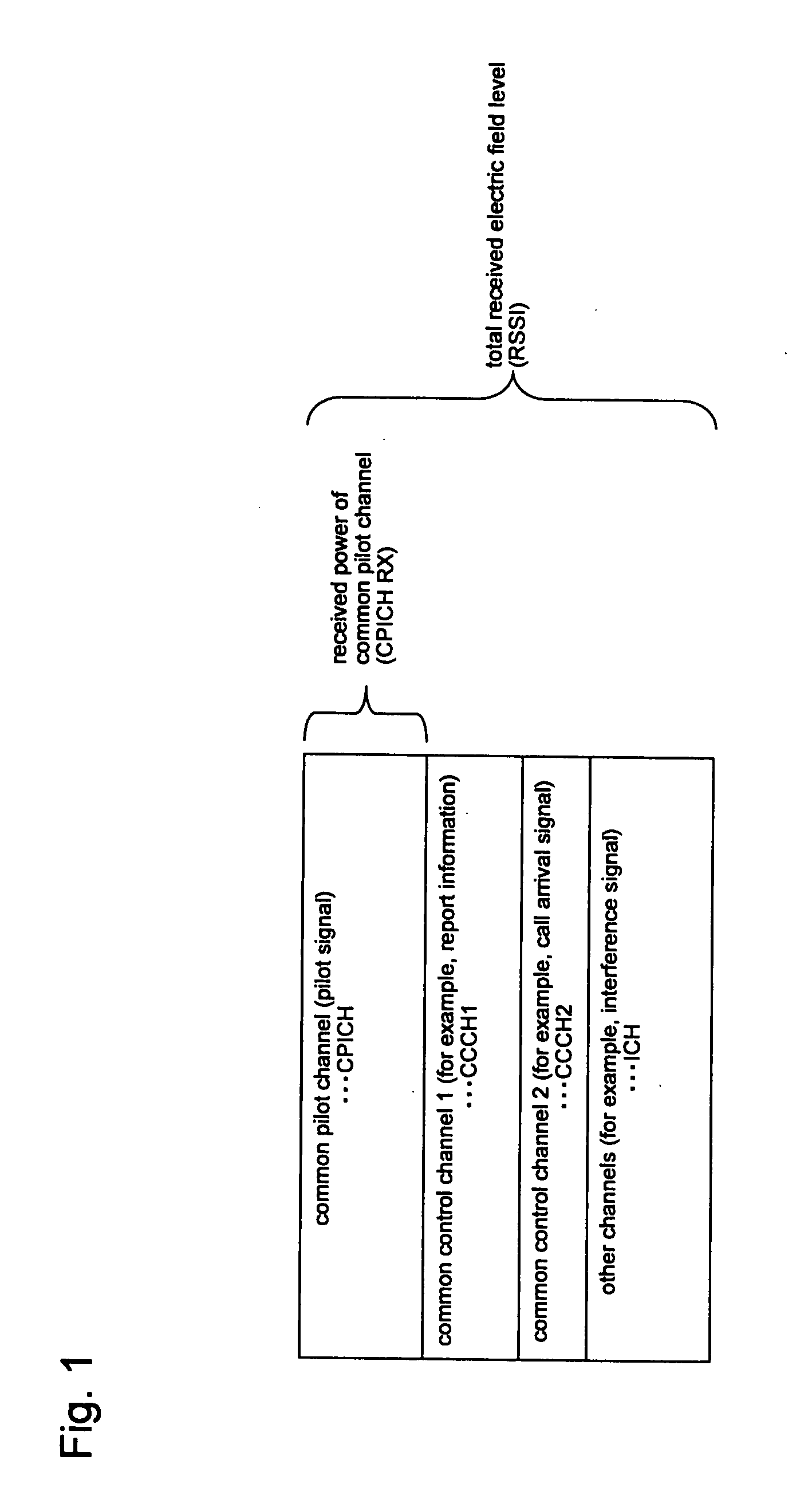
A mobile terminal (100) comprises antenna (102), radio unit (104), signal processing unit (110), signal analyzer unit (120), received signal information storage unit (150), and reception quality storage unit (160). Signal processing unit (110) comprises received signal processing unit (112) and notified information processing unit (114), while received signal information storage unit (150) comprises common pilot channel information storage unit (152) and common control channel information storage unit (154). Received signal processing unit (112) measures the reception quality of a common pilot channel and stores it in common pilot channel information storage unit (152). Notified information processing unit (114) extracts transmission power of the common pilot channel and common control channel from report information, and then stores them in common control channel information storage unit (154). Signal analyzer unit (120) calculates the reception quality of the common control channel and the interference signal level, based on the information stored in received signal information storage unit (150).
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
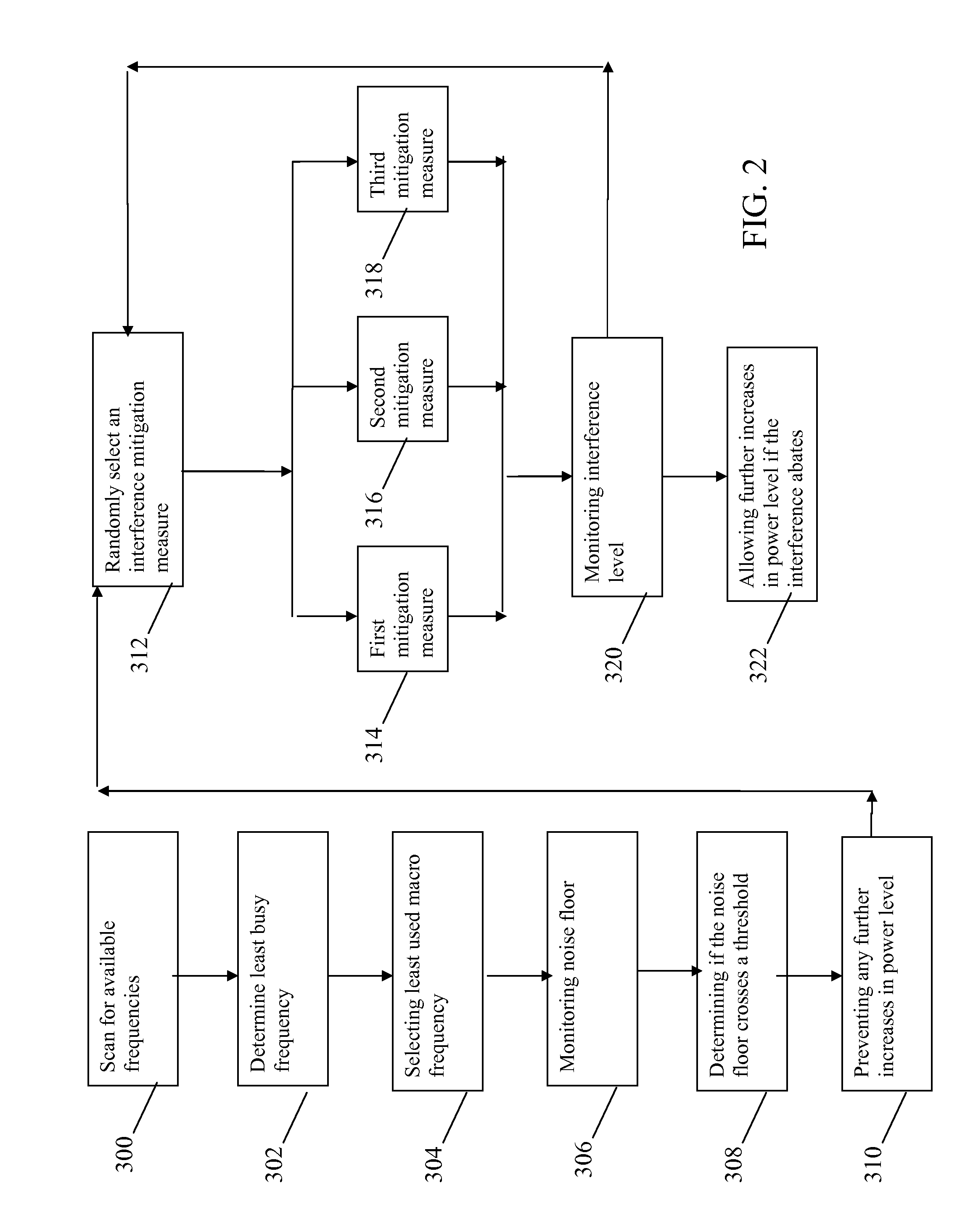
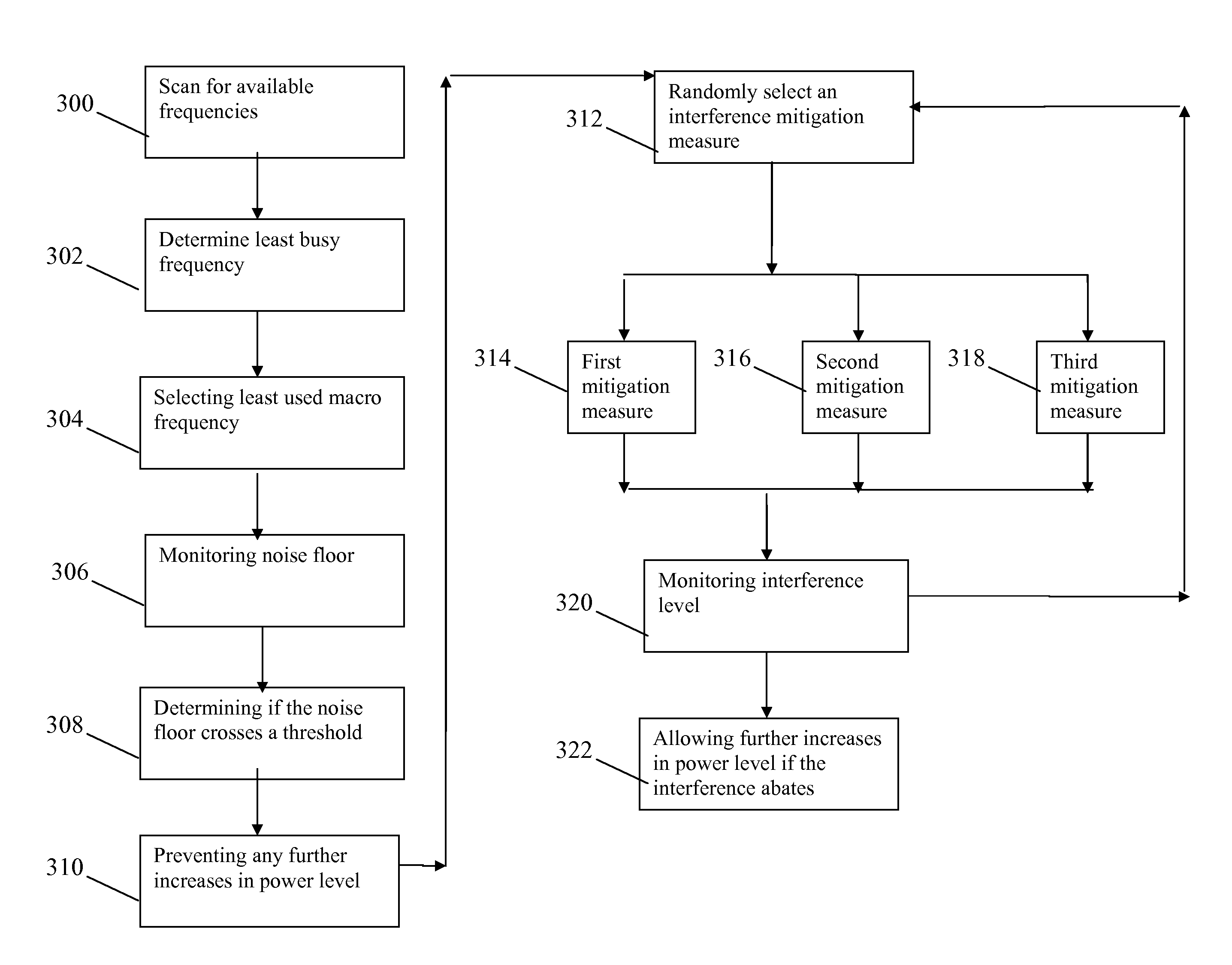
Optimizing power settings in a communication system to mitgate interference
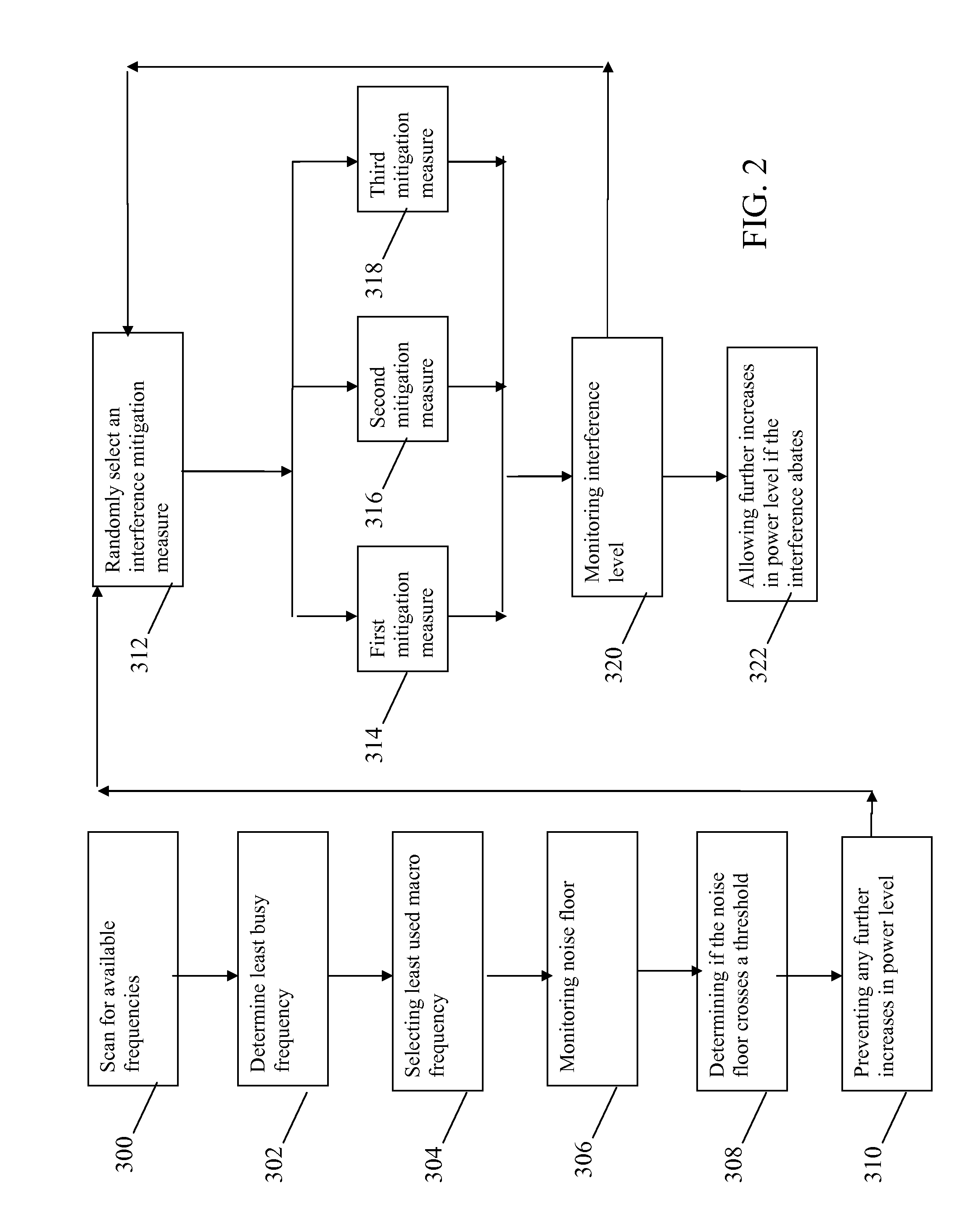
InactiveUS20090104912A1Improved and facilitated operationReduce distractionsPower managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemEngineering
A method and apparatus for optimizing power settings in a communication system includes a first step (306) of monitoring a noise floor. A next step (308) includes determining if the noise floor crosses a threshold level. A next step (310) includes preventing any further increases in a Common Pilot Channel power level. A next step (312) includes randomly selecting and performing an interference mitigation measure. A next step (320) includes monitoring an interference level. A next step (322) and allowing further increases in a Common Pilot Channel power level if the interference abates by more than a predetermined amount.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method, equipment and system for saving energy for base station
ActiveCN101959292ARealize energy savingReduce transmit powerPower managementEnergy efficient ICTHigh probabilityCommon pilot channel
The invention discloses a method, equipment and a system for saving energy for a base station, relating to the communication field and solving the problem of higher probability of dropped call of a user in a process of energy saving of the base station in the prior art. In the method, if detectiong that a cell in a normal working state meets a cell energy saving condition, base station energy saving control equipment sends an indication message of closing the cell to base station energy saving executing equipment, wherein the indication message comprises adjusting step length and / or adjusting time interval for gradually adjusting transmission power of a main common pilot channel; and the base station energy saving executing equipment receives the indication message for closing the cell and reduces the transmission power of the cell main common pilot channel according to the adjusting step length and / or adjusting time interval in the indication message. The embodiment of the invention is mainly used in the process of energy saving of the base station, effectively realizes the energy saving of the base station and reduces the probability of dropped call of the user.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
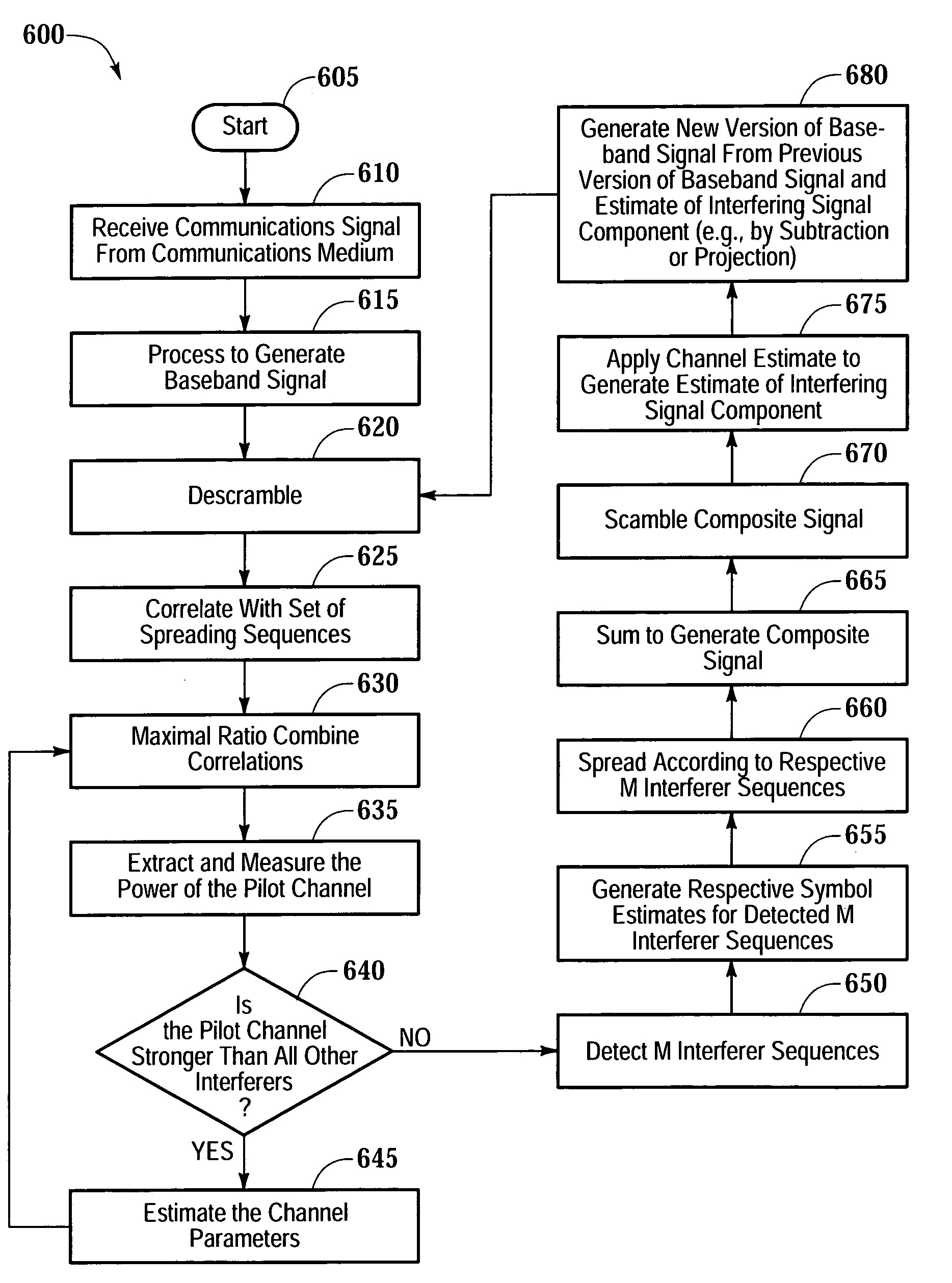
System, method and apparatus for wireless channel parameter estimation in spread spectrum communication systems
ActiveUS7012977B2Accurate estimateEliminate the effects ofError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemChannel parameter
The present invention provides a system, method and apparatus for estimating channel parameters in spread spectrum communication systems. A first method is accomplished by receiving a base station signal and then demodulating the base station signal. After demodulating the base station signal, a maximum signal is selected from the base station signal. If the maximum signal is the common pilot channel, then the channel parameters are estimated directly from the common pilot channel. If the maximum signal is not the common pilot channel, then the demodulated base station signal is iteratively fed back for further demodulation and re-selection of the maximum signal until the maximum signal is the common pilot channel. A second method is accomplished by incorporating channel estimates made from the interfering signals in a constructive manner to the first method.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
CDMA communication system and channel estimating method used in the same
InactiveUS20010043642A1Total current dropPower managementModulated-carrier systemsChannel dataCommon pilot channel
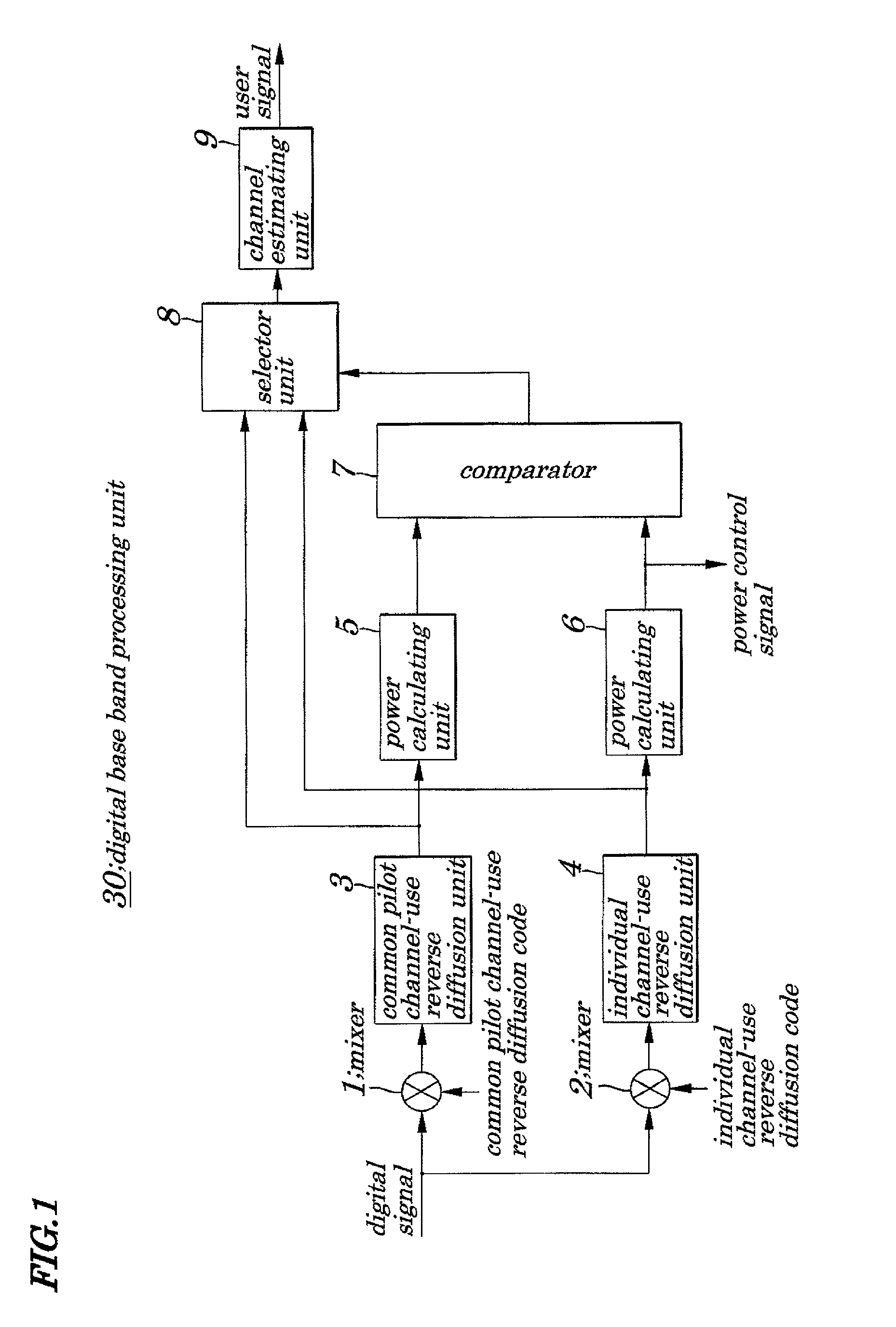
A common pilot channel-use reverse diffusion unit generates common pilot data using a received digital signal and a common pilot channel-use reverse diffusion code, while an individual channel-use reverse diffusion unit generates individual channel data using the received digital signal and an individual channel-use reverse diffusion code. Power calculating unit converts respective output data items of the common pilot channel-use reverse diffusion unit and the individual channel-use reverse diffusion unit into power values, a larger one of which is then determined by a comparator. A selector unit selects the data item having thus determined larger power value of those output data items of those reverse diffusion units. A channel estimating unit estimates the channel using data symbols of the data item thus selected by the selector unit.
Owner:NEC CORP
Communication terminal device and channel estimating method
InactiveCN1320308AImprove reliabilitySpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemTerminal equipment
Phase rotation amount estimation section 210 rotates a channel estimation value of the common pilot channel B signal by a candidate amount of phase rotation [theta] ([theta]=0, 180) and synthesizes the rotated channel estimation value and the channel estimation value of the common pilot channel A signal. Then, phase rotation amount estimation section estimates an amount of phase rotation having this synthesis result most orthogonal to the channel estimation value of the individual channel signal as the amount of phase rotation. Channel estimation value synthesis section 211 synthesizes a value obtained by rotating the channel estimation value of the common pilot channel B signal by an amount of phase rotation [theta] and the channel estimation value of the common pilot channel A signal. This allows a radio communication system using transmission diversity to improve the reliability of channel estimation values.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optimizing power settings in a communication system to mitigate interference
InactiveUS8050629B2Improved and facilitated operationReduce distractionsPower managementRadio transmissionCommunications systemEngineering
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Optimum radio communication method with radio frame variable control and radio communication system using the same
InactiveUS20080123762A1Flexible high-speed data transmissionReduce controlError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemControl channel
Not only pilot channel symbols but also control channel symbols can be flexibly decreased in a radio communication system, which includes a transmission side apparatus transmitting a data frame where a plurality of continuous or discontinuous frequency areas are assigned to one transfer time block and a frame is formed of a predetermined number of transfer time blocks; and a reception side apparatus receiving a data frame from the transmission side apparatus, The transmission side apparatus transmits to the reception side apparatus a data frame which has a common pilot channel and a control channel in the beginning of the frame, the reception side apparatus measures a received quality of the data frame, decides a frame type based on the measured received quality and notifies the decided frame type to the transmission side apparatus. The transmission side apparatus sends subsequent frame data to the reception side apparatus in use of a frame format corresponding to the notified frame type.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for broadcasting system information wireless packed data transmission
InactiveCN1416231AEfficient use ofAssess restrictionCode division multiplexPacket data transmissionMobile station
The base station broadcasts the system information within the subzone range. Besides the general information of the system information block, the system information includes following information: the available code resources in the downward shared channel used by the adjacent subzone to transmit packet data; the power bias between the public pilot channel and the downward shared channel in the adjacent subzone. The method reduces the possibility that the mobile station soon switches to another subzone from the subzone just switching in since too high load and the poor channel quality. Moreover, the mobile station can use these system informations, combining own measured value to choose best subzone, in order not to waste the system resources.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and system for diversity processing including using dedicated pilot method for closed loop
Methods and systems for diversity processing including using dedicated pilot method for closed loop may include combining a plurality of received WCDMA / HSDPA multipath signals for each diversity transmit antenna to at least one processed diversity signal. The received WCDMA / HSDPA multipath signals may originate from diversity transmit antennas at a base station that may be transmitting information via a closed loop or open loop diversity transmission mode. The closed loop diversity transmission mode may be closed loop 1 or closed loop 2. Estimations may be made of the closed loop transmit weights used by the base station for transmission of the symbols. Closed loop symbols transmitted by the diversity transmit antennas may then be estimated based on received diversity signals and at least one dedicated pilot channel. Open loop symbols may be estimated using information from at least one common pilot channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
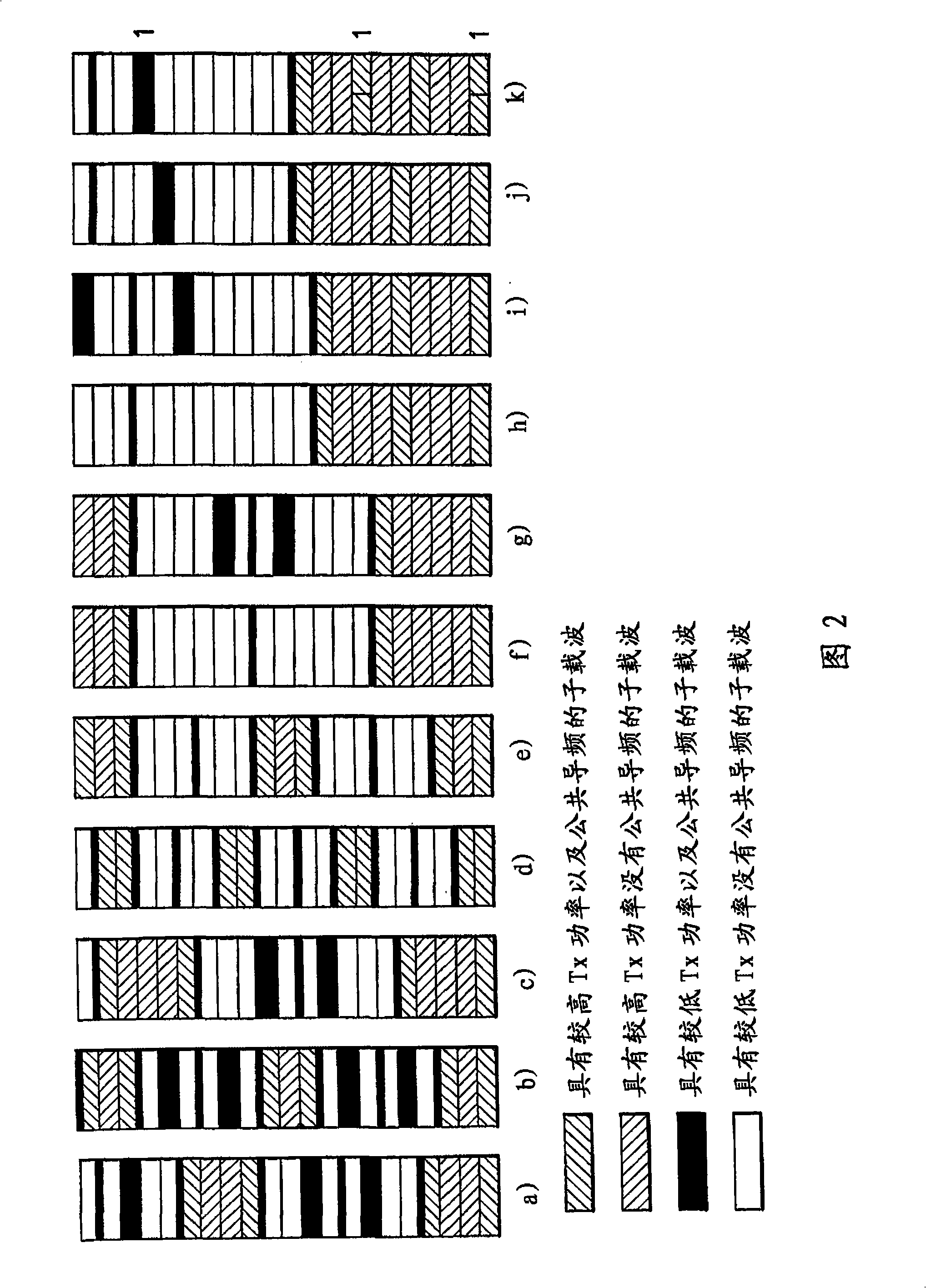
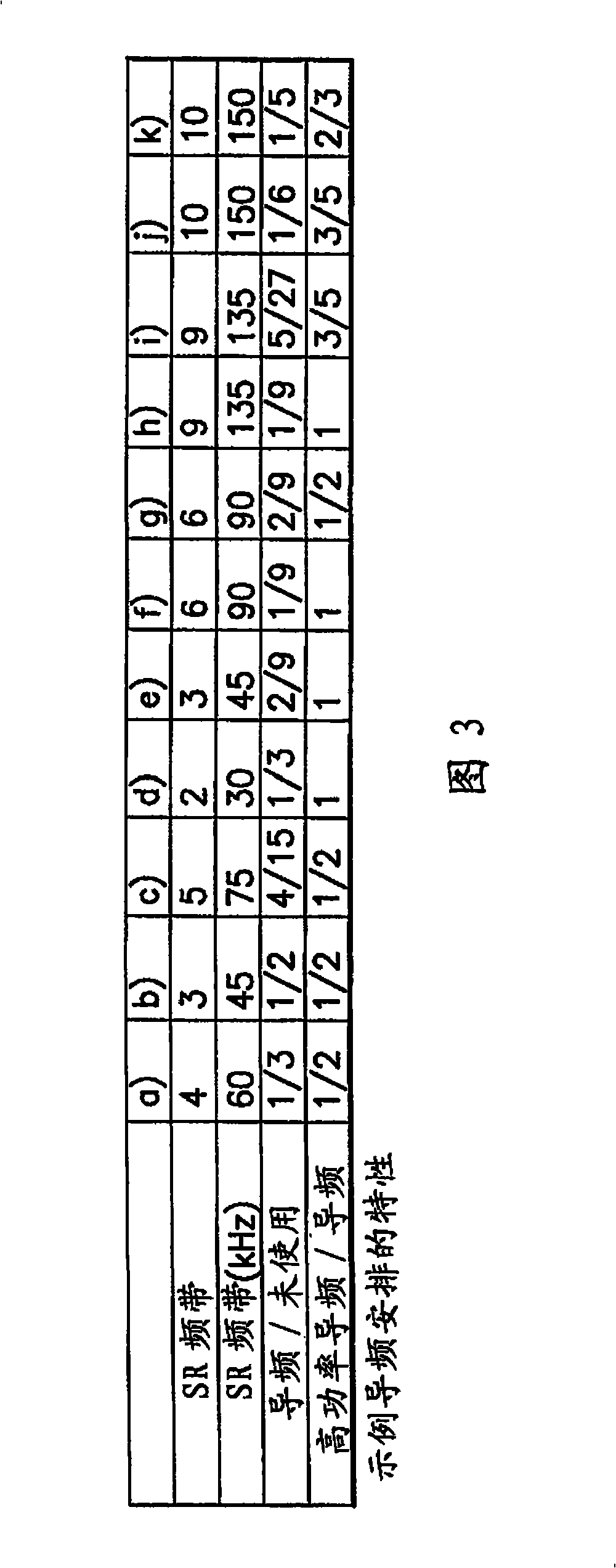
Apparatus, method and computer program product providing common pilot channel for soft frequency reuse
ActiveCN101305529AImprove estimation performanceIncrease transmit powerPower managementTransmission control/equalisingTelecommunicationsCommunications system
A method for operating a wireless communication system in a cell includes allocating a first plurality of pilot resources to a first frequency sub-band comprising a plurality of high power sub-carriers, allocating a second plurality of pilot resources to a second frequency sub-band comprising a plurality of low power sub-carriers, signaling a power offset between the plurality of pilot resources in the plurality of high power sub-carriers and the plurality of pilot resources in the plurality of low power sub-carriers, and transmitting the first and the second plurality of pilot resources overthe first and the second frequency sub-bands.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com