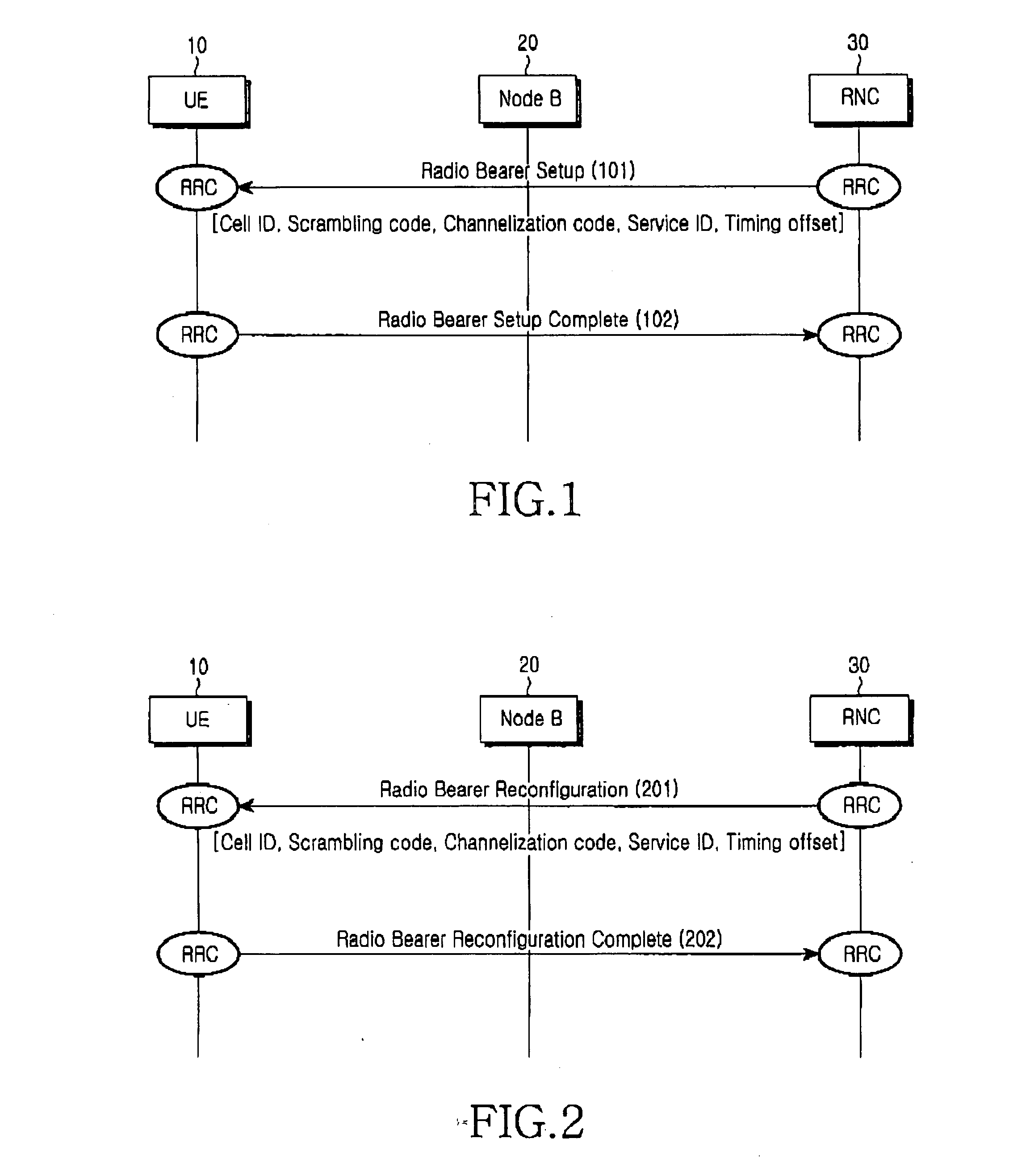
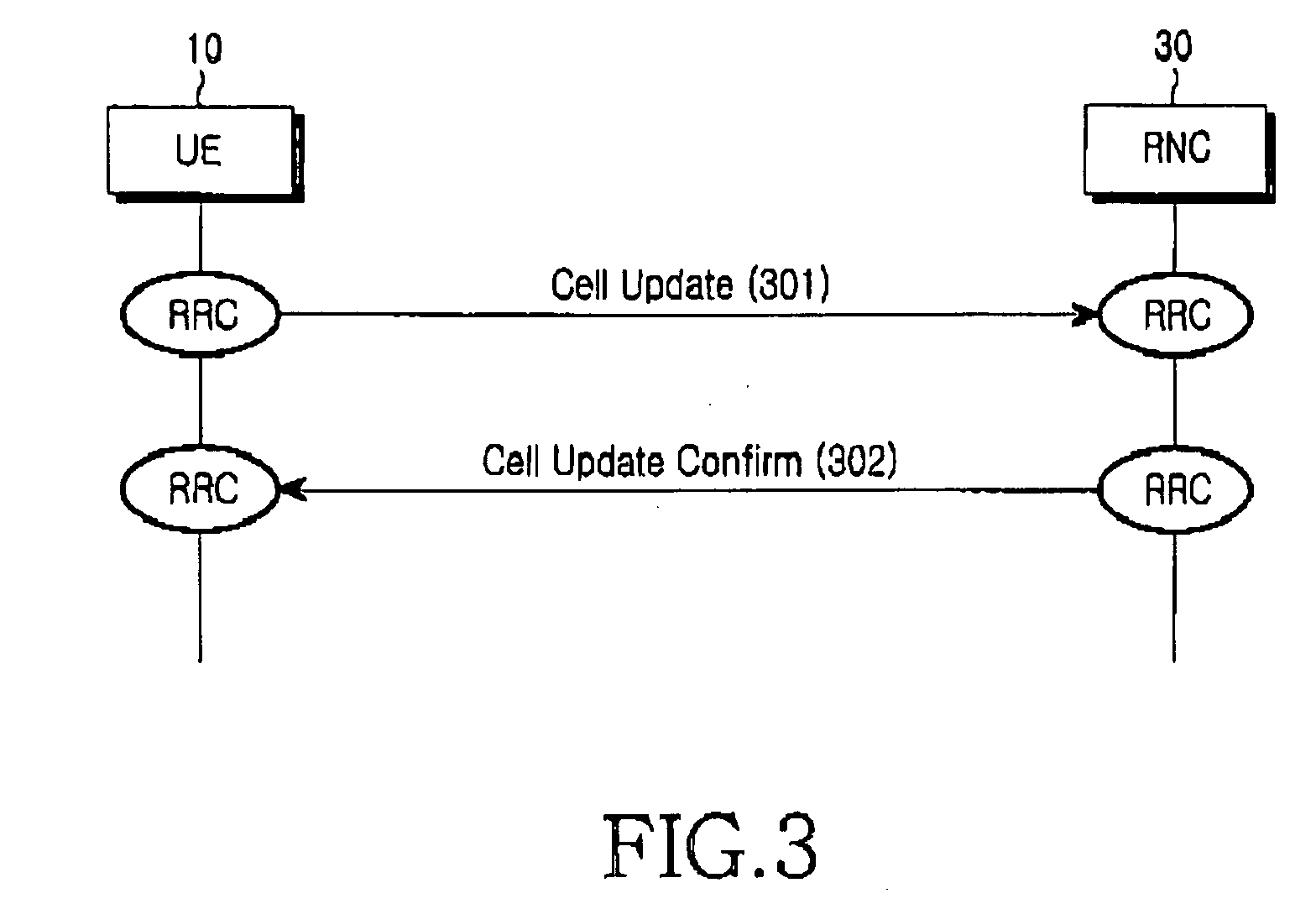
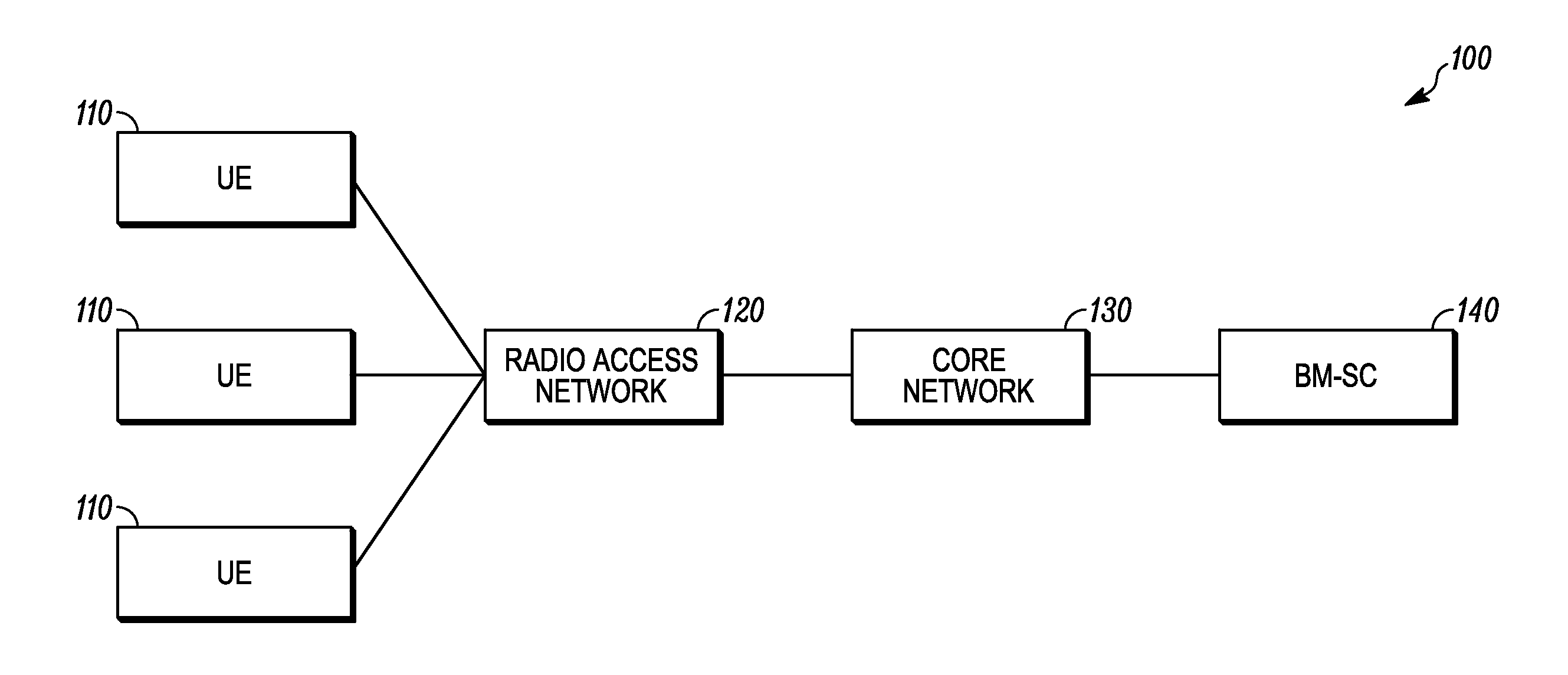
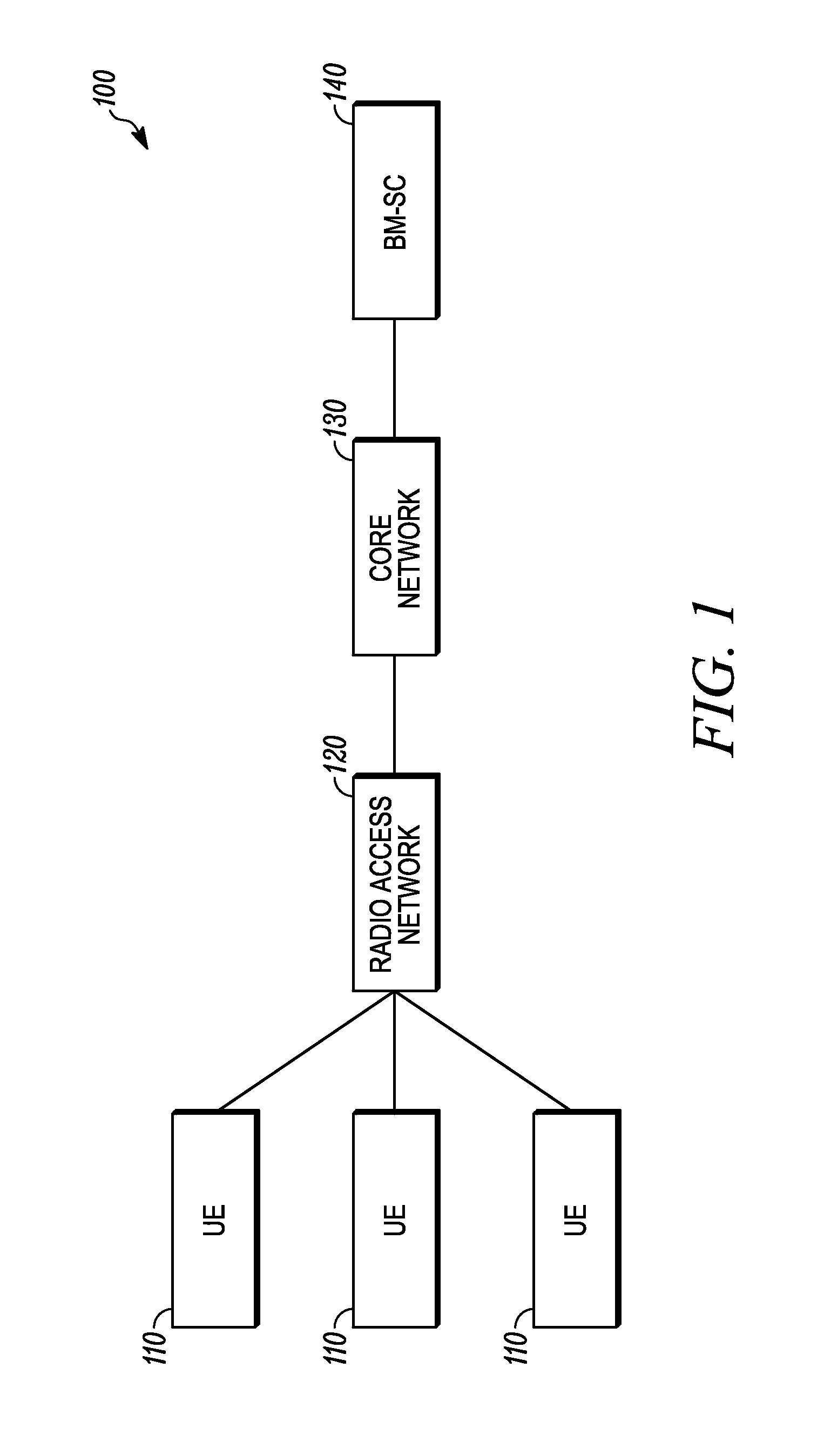
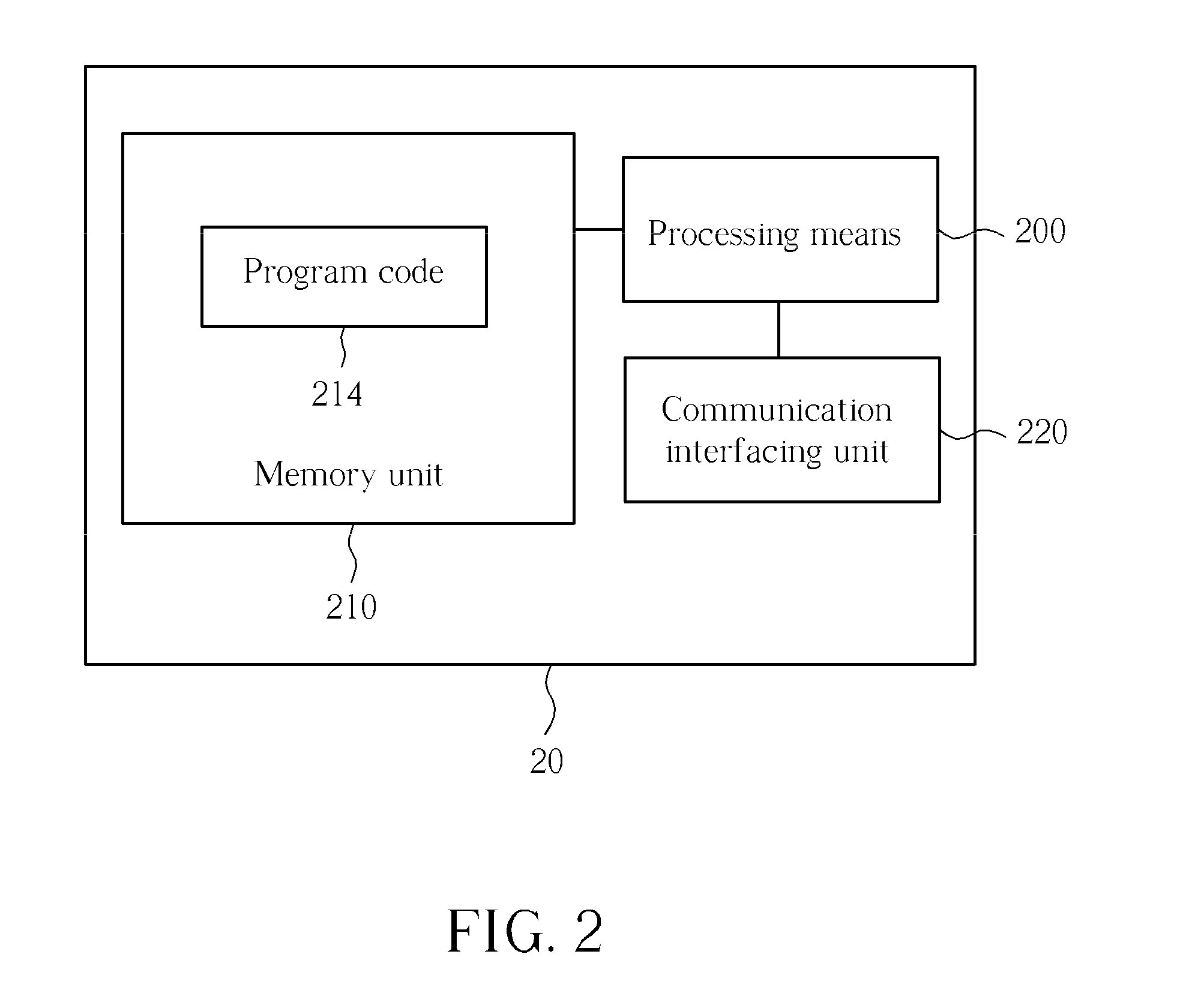
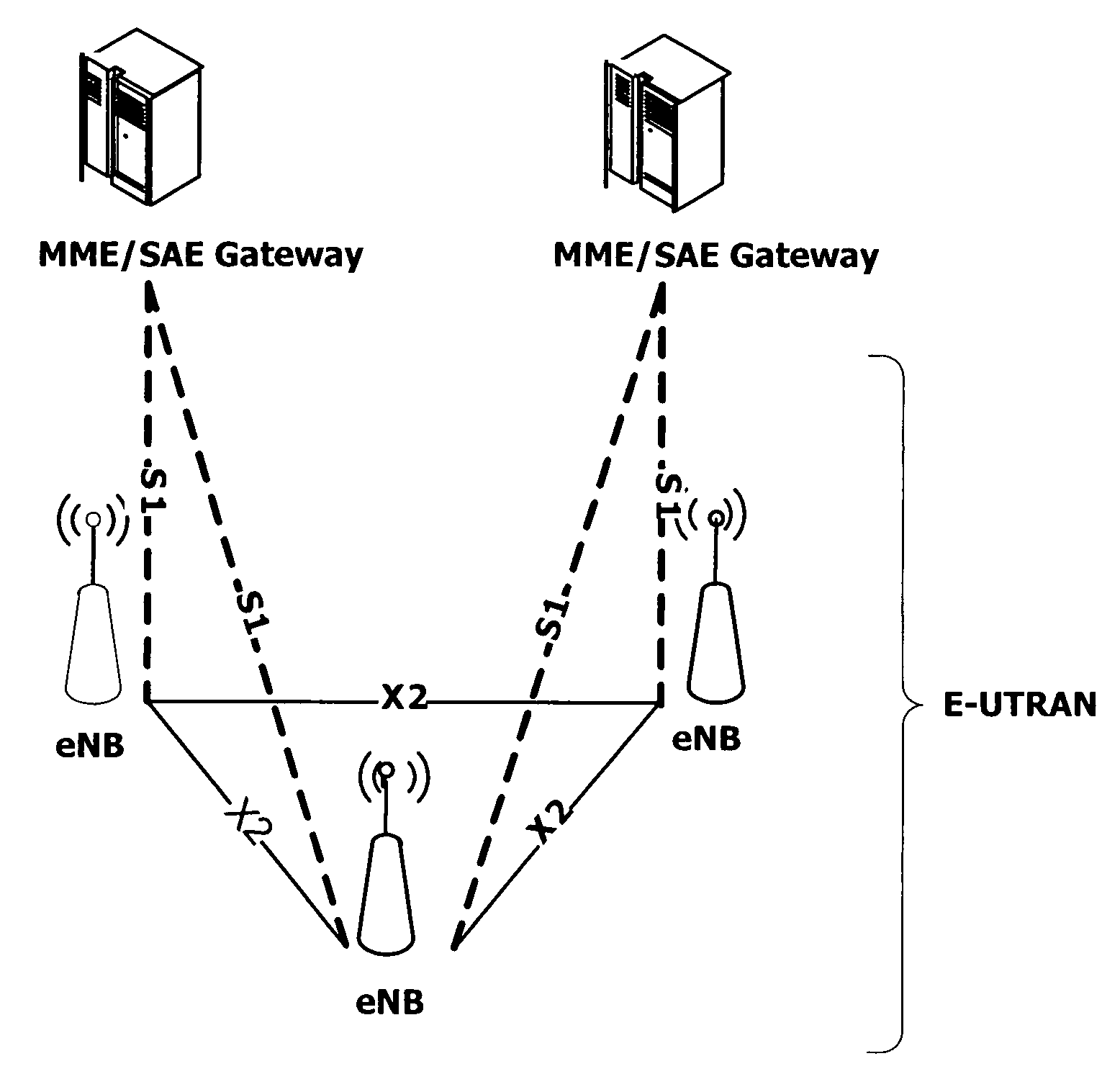
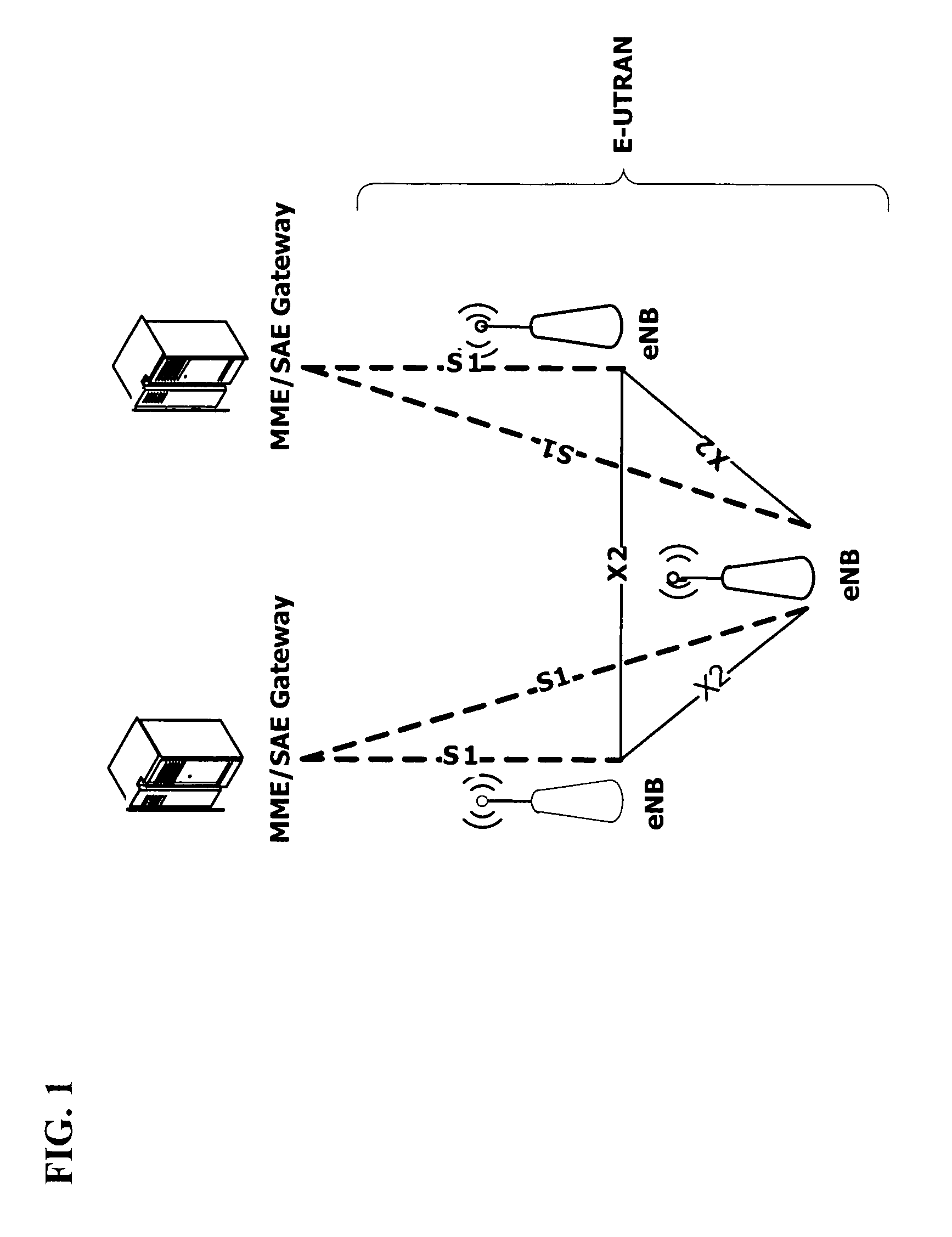
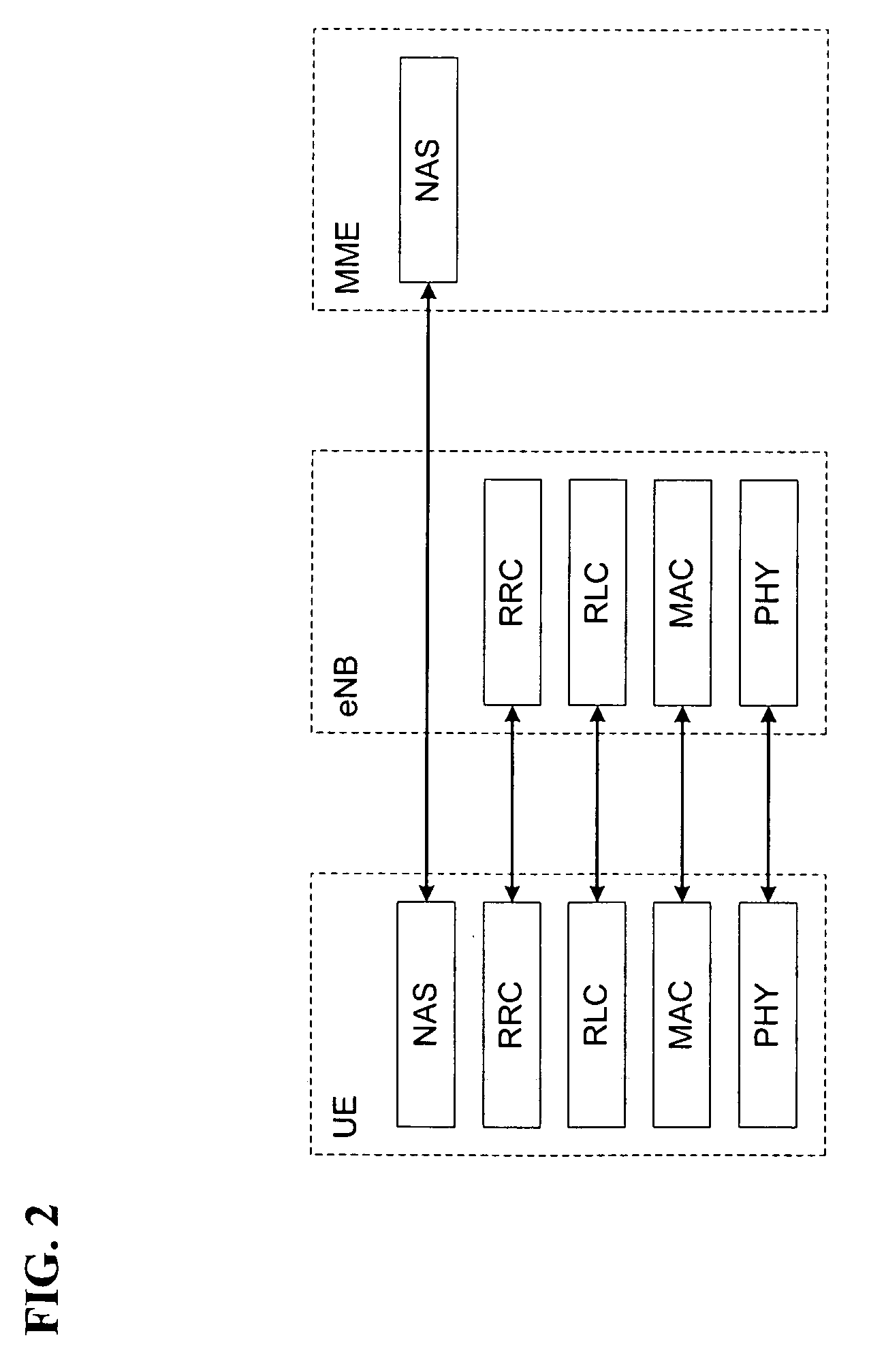
Patents
Literature
1005 results about "Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
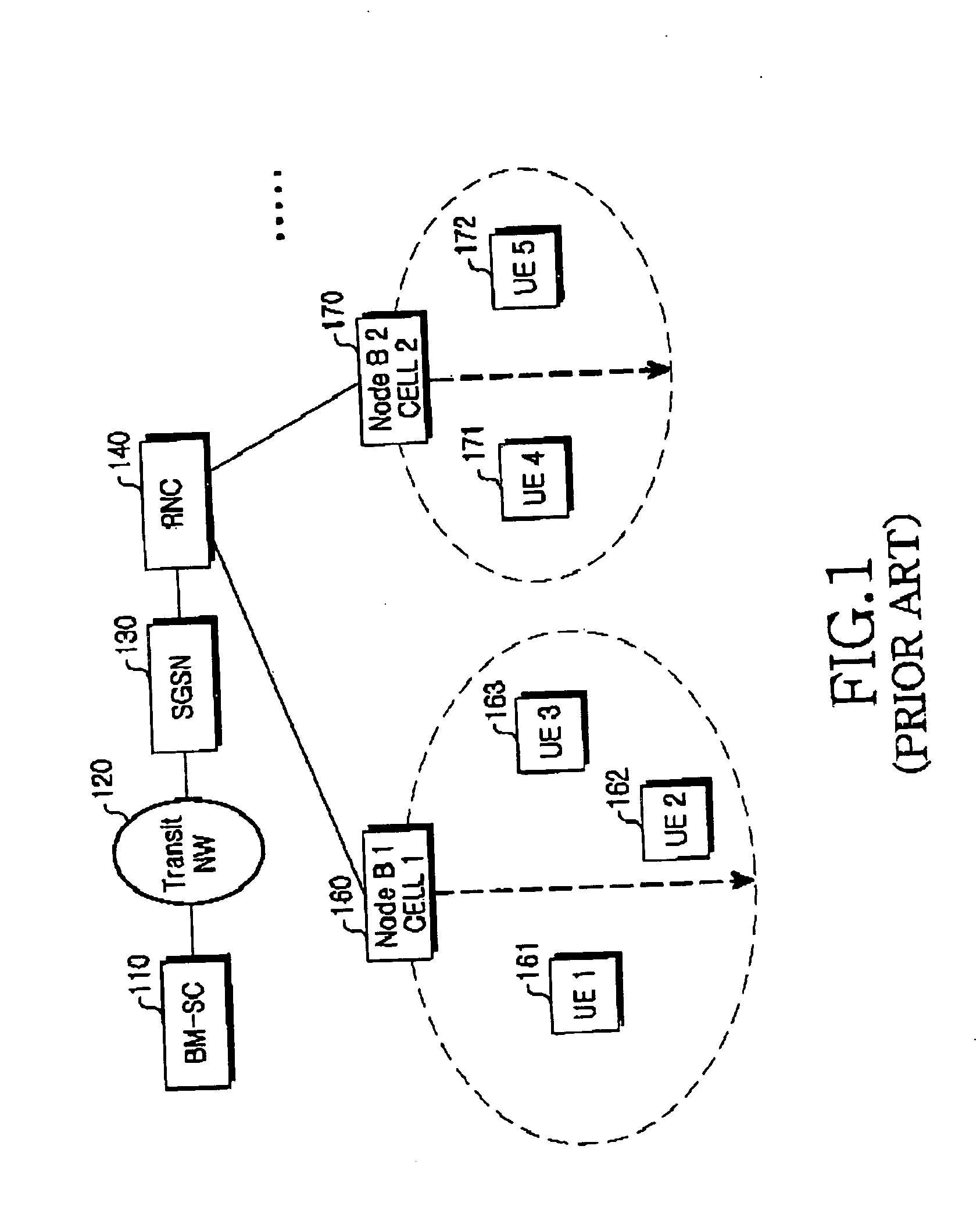
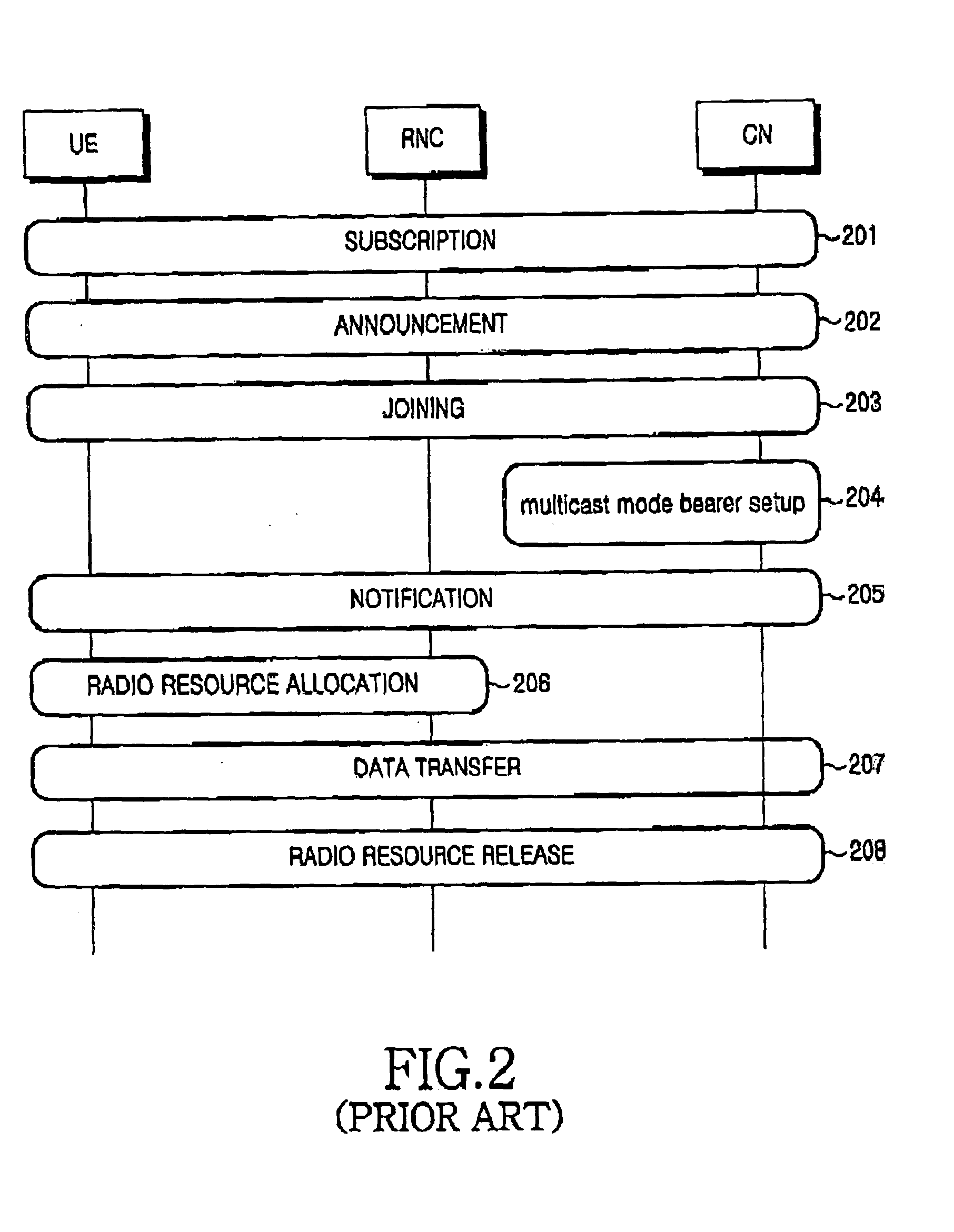
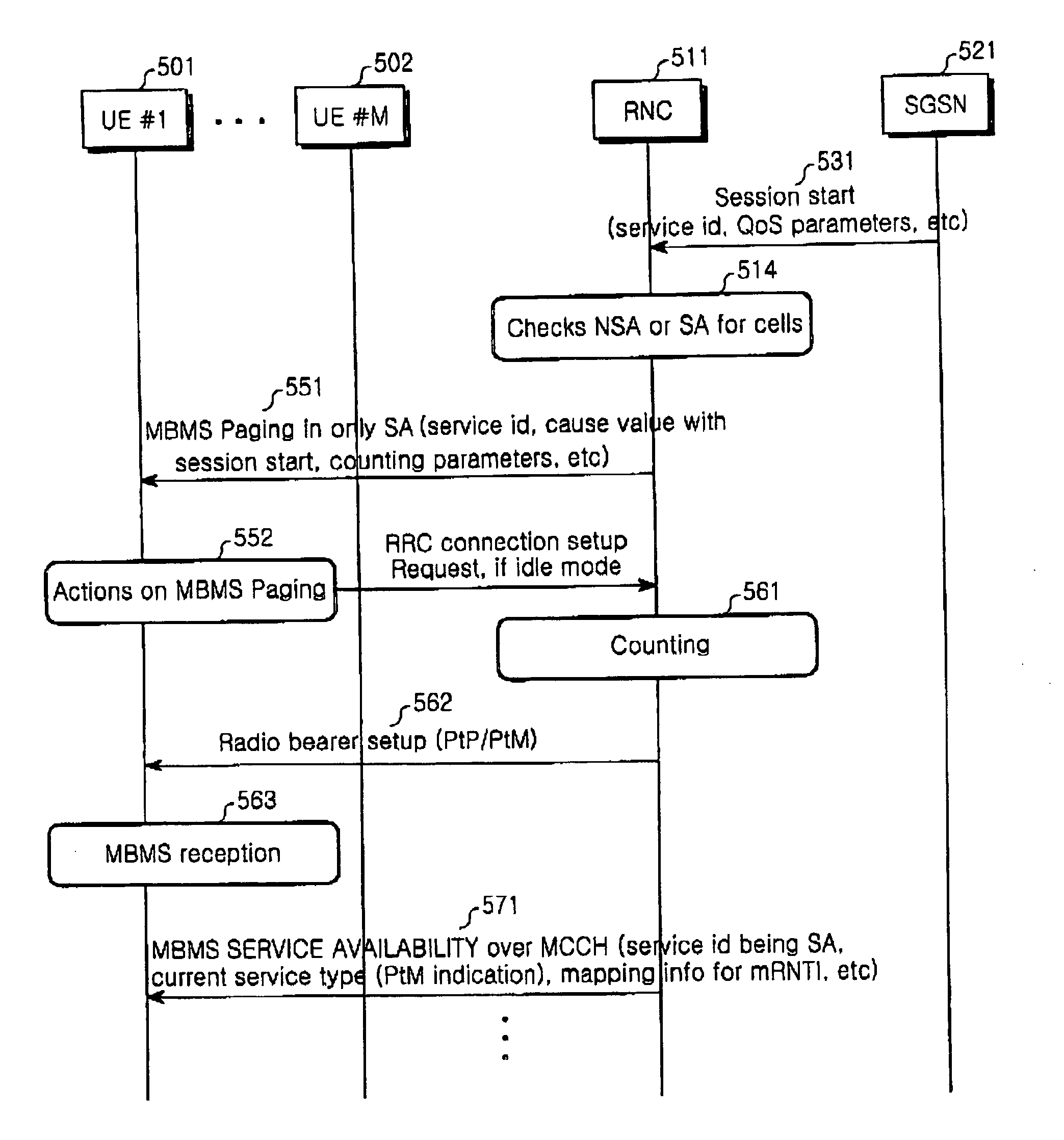
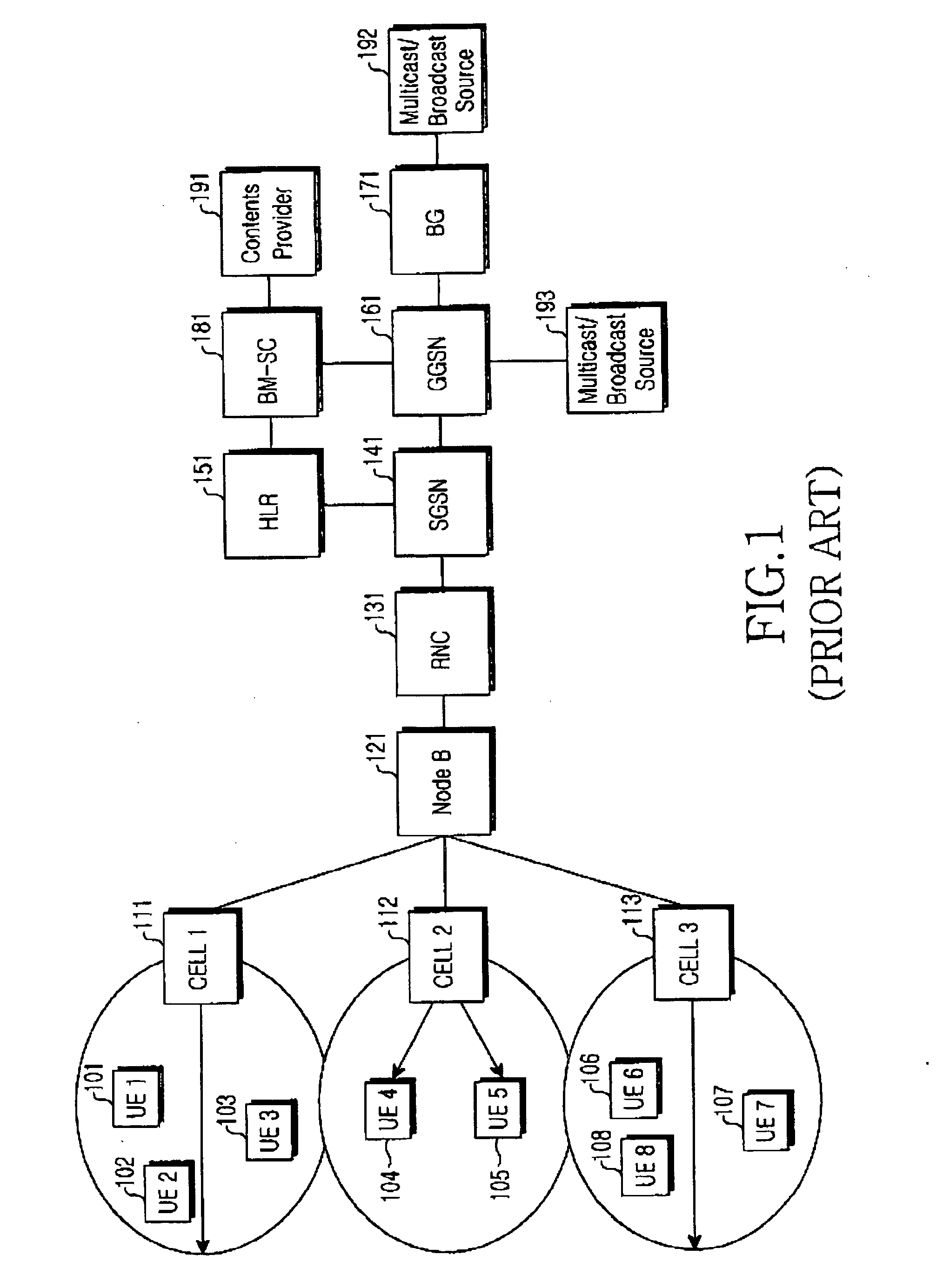
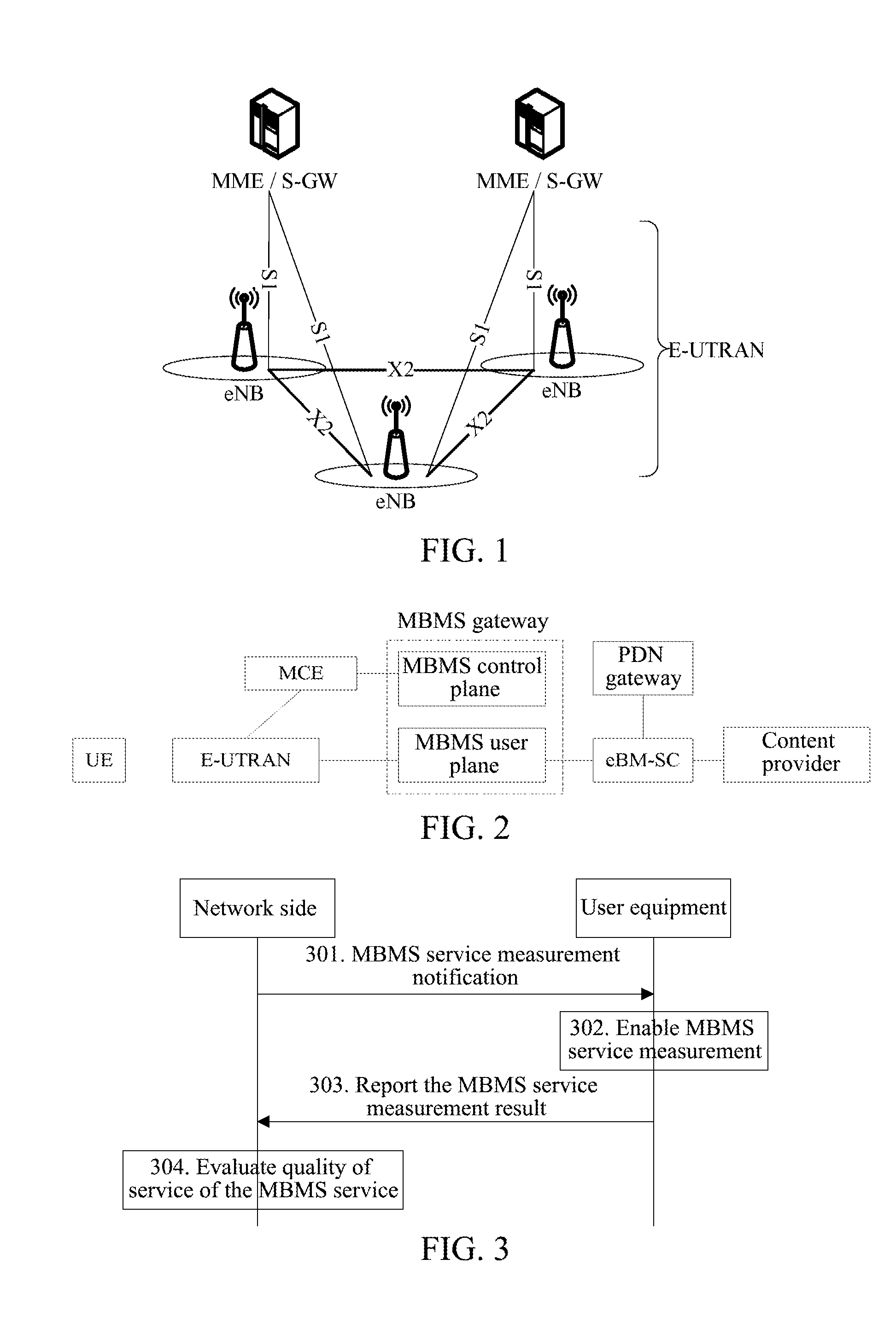
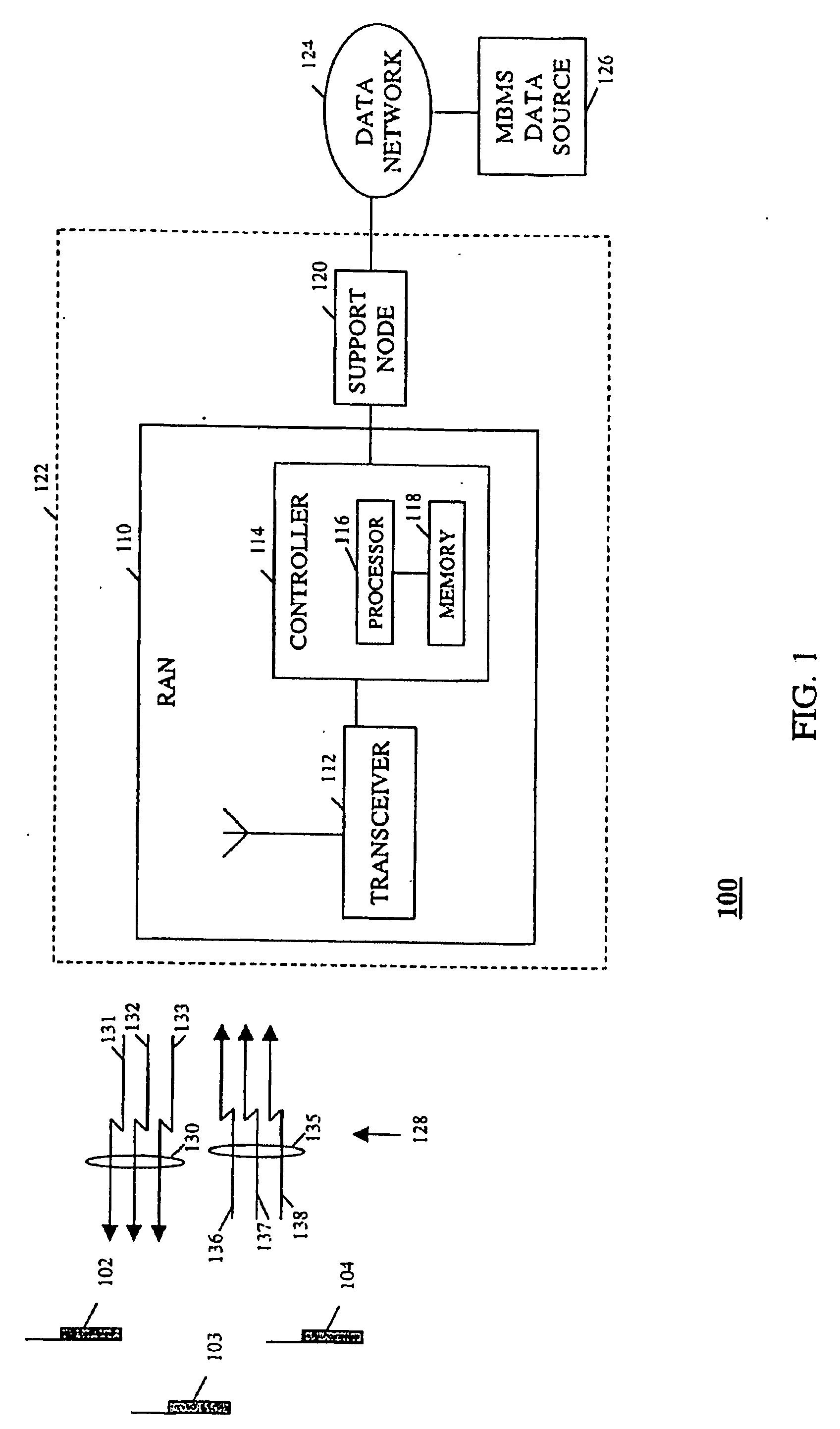
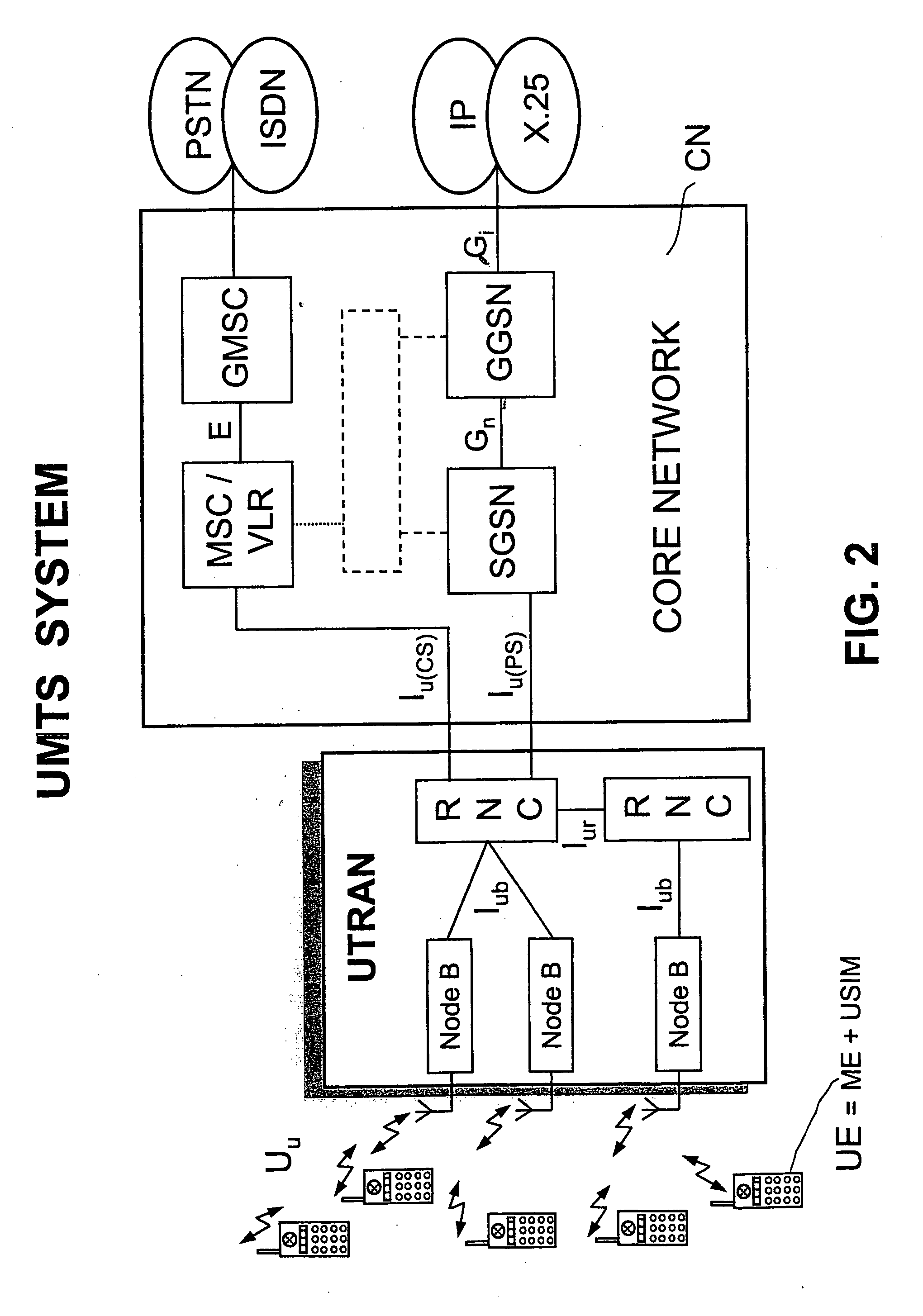
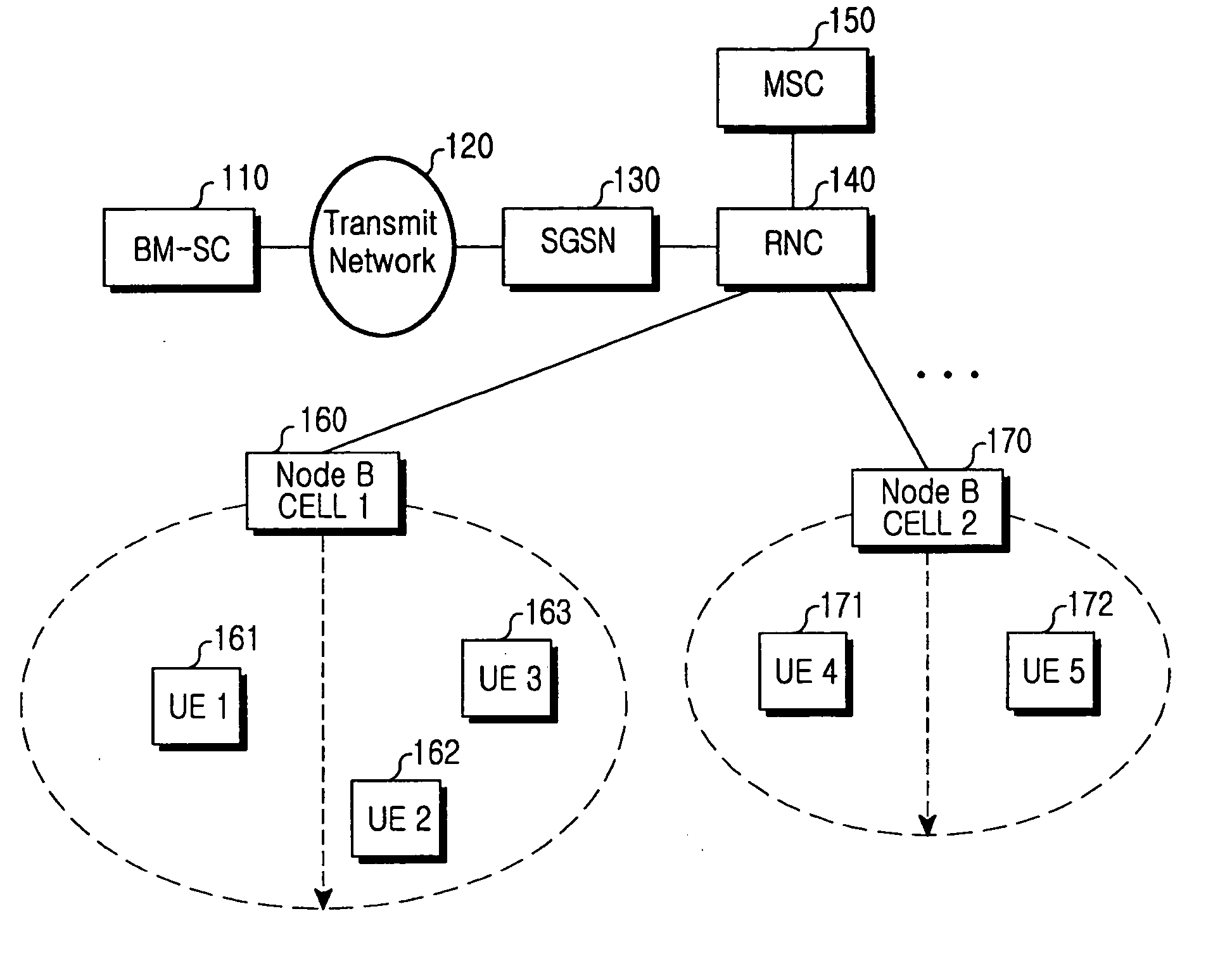
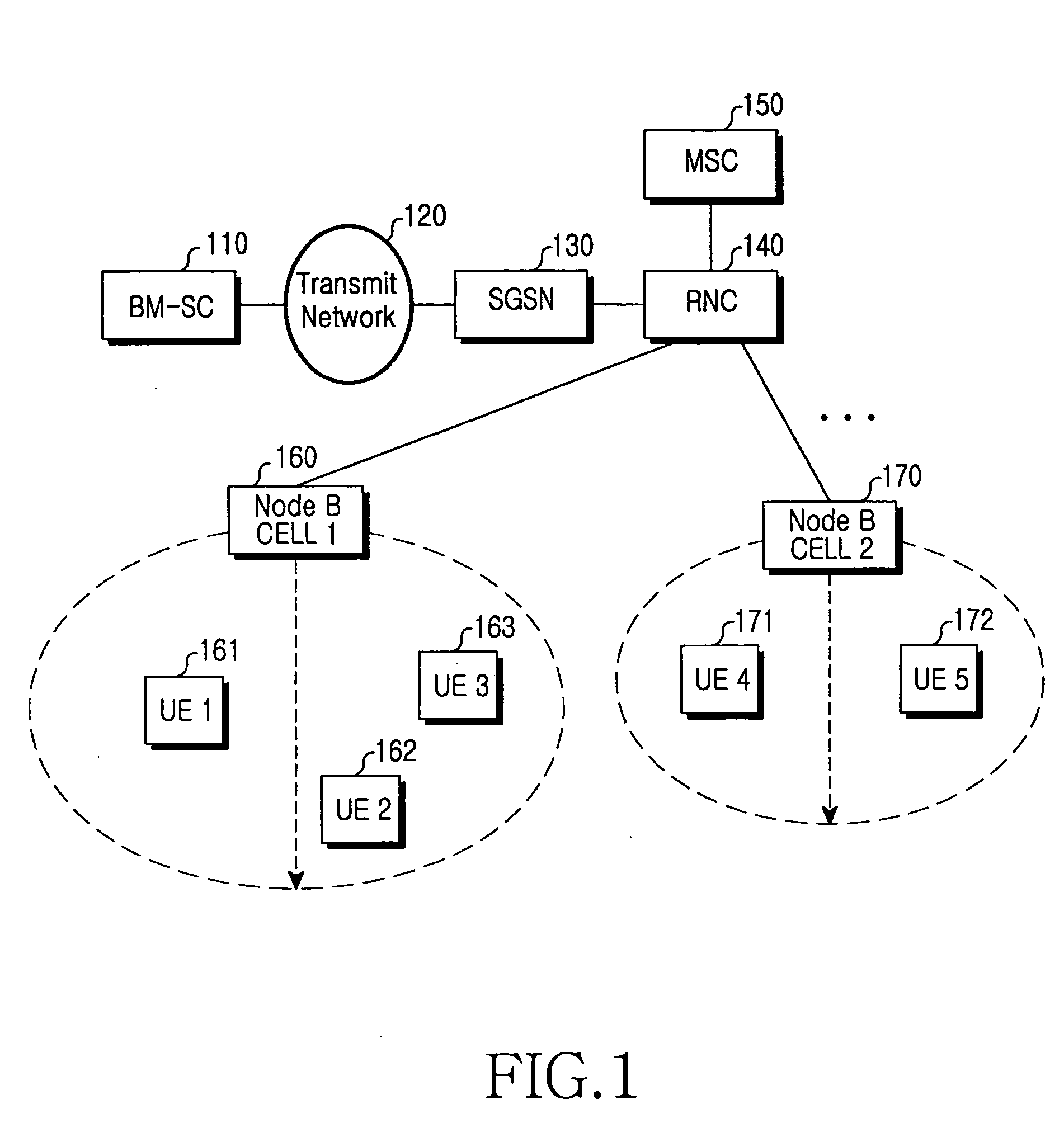
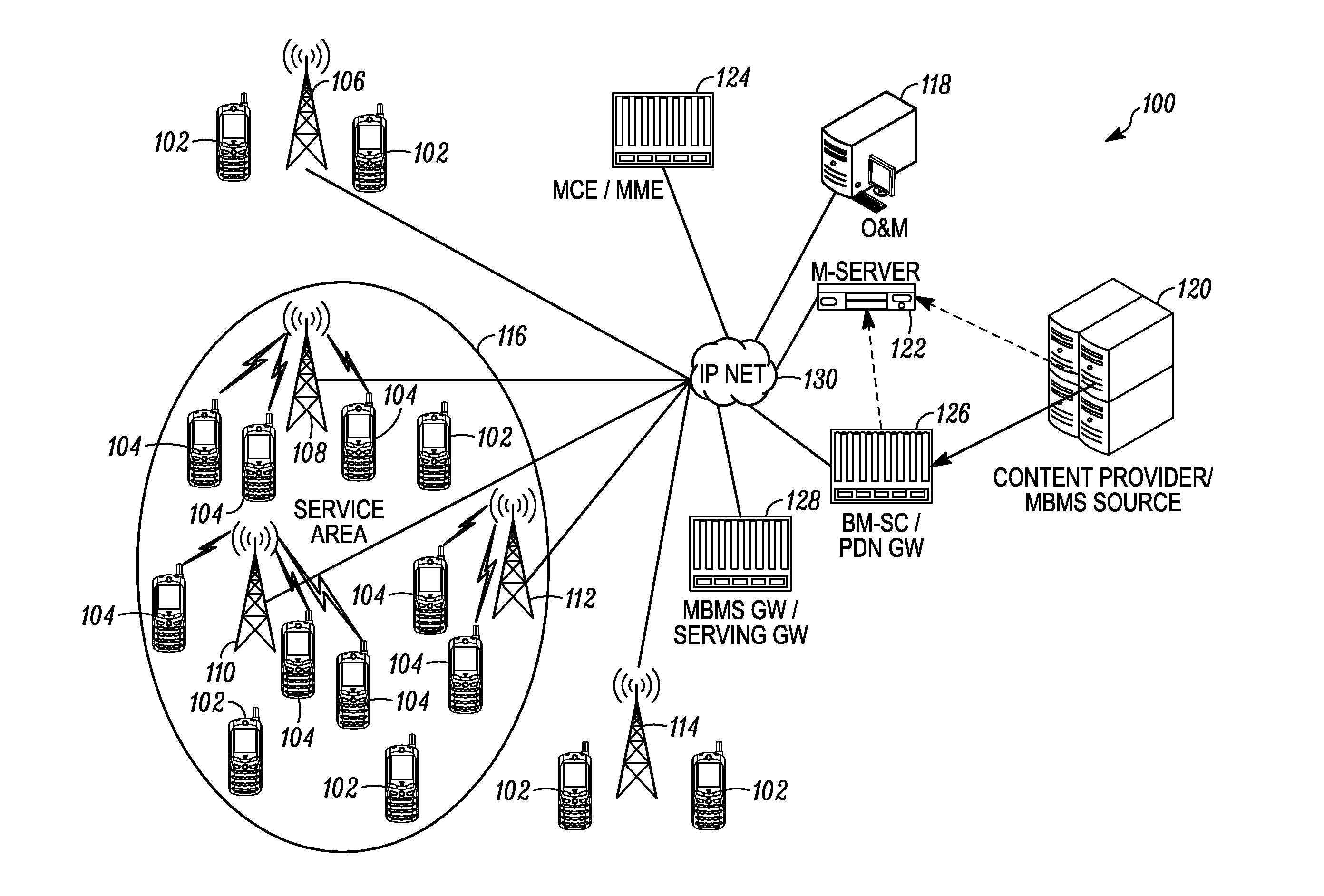
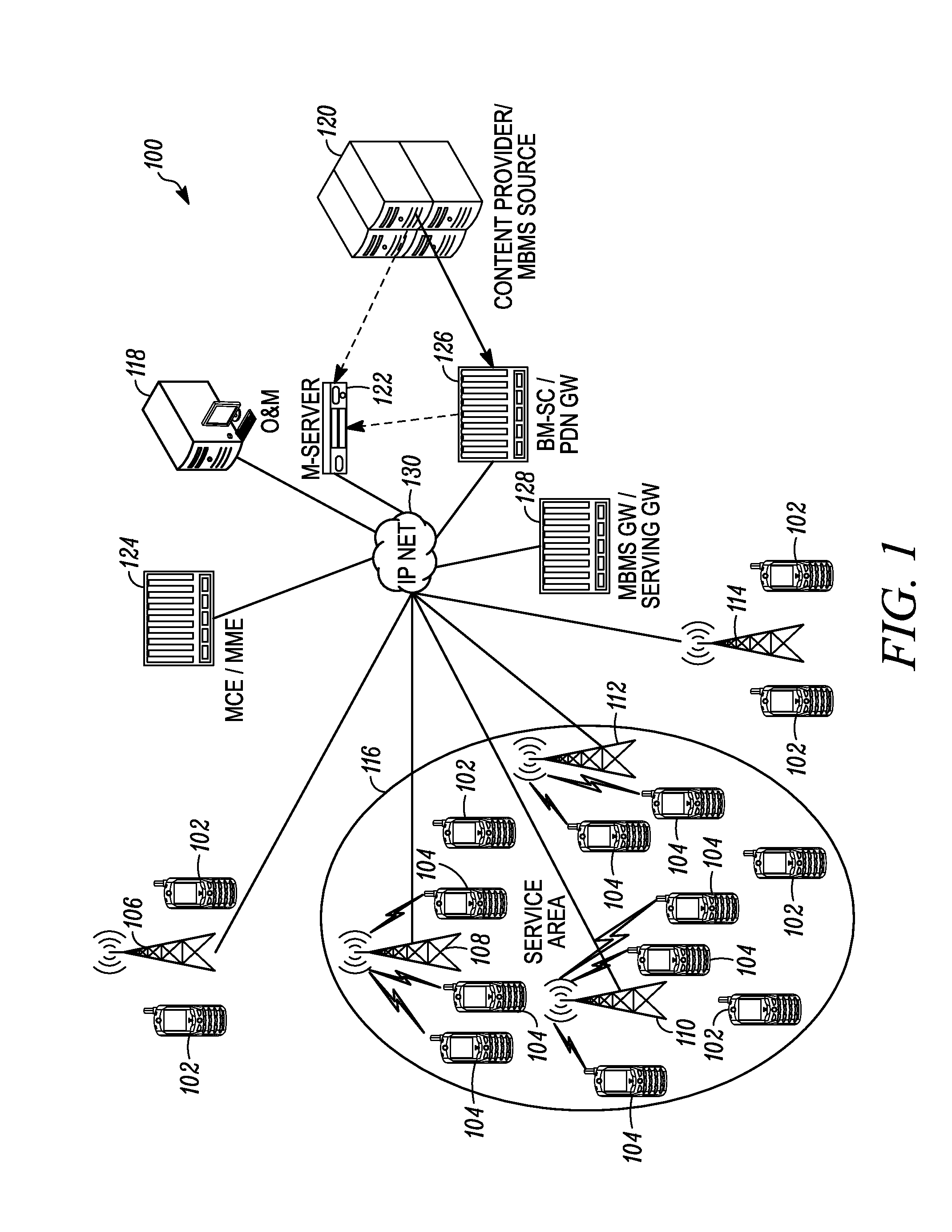
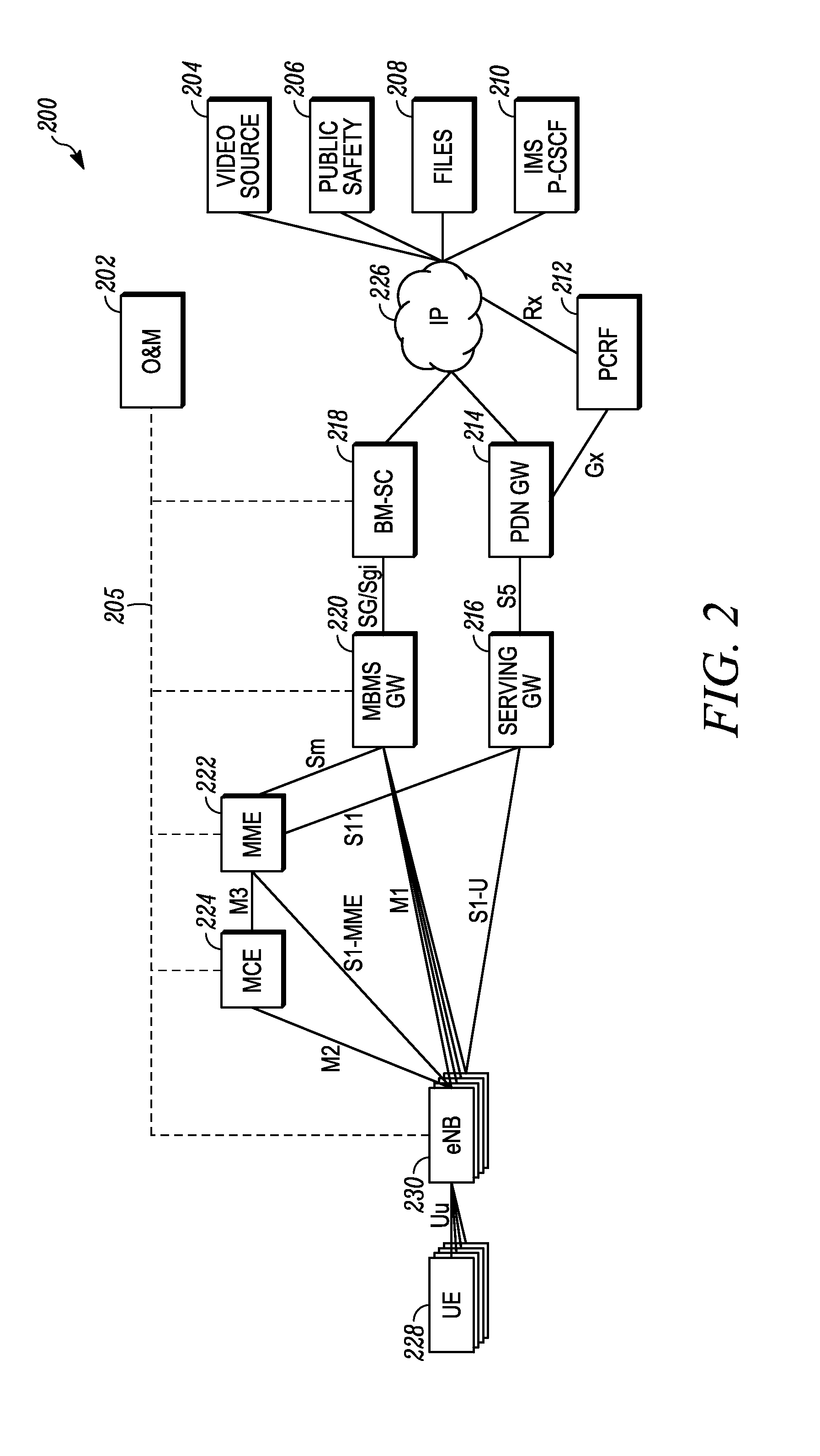
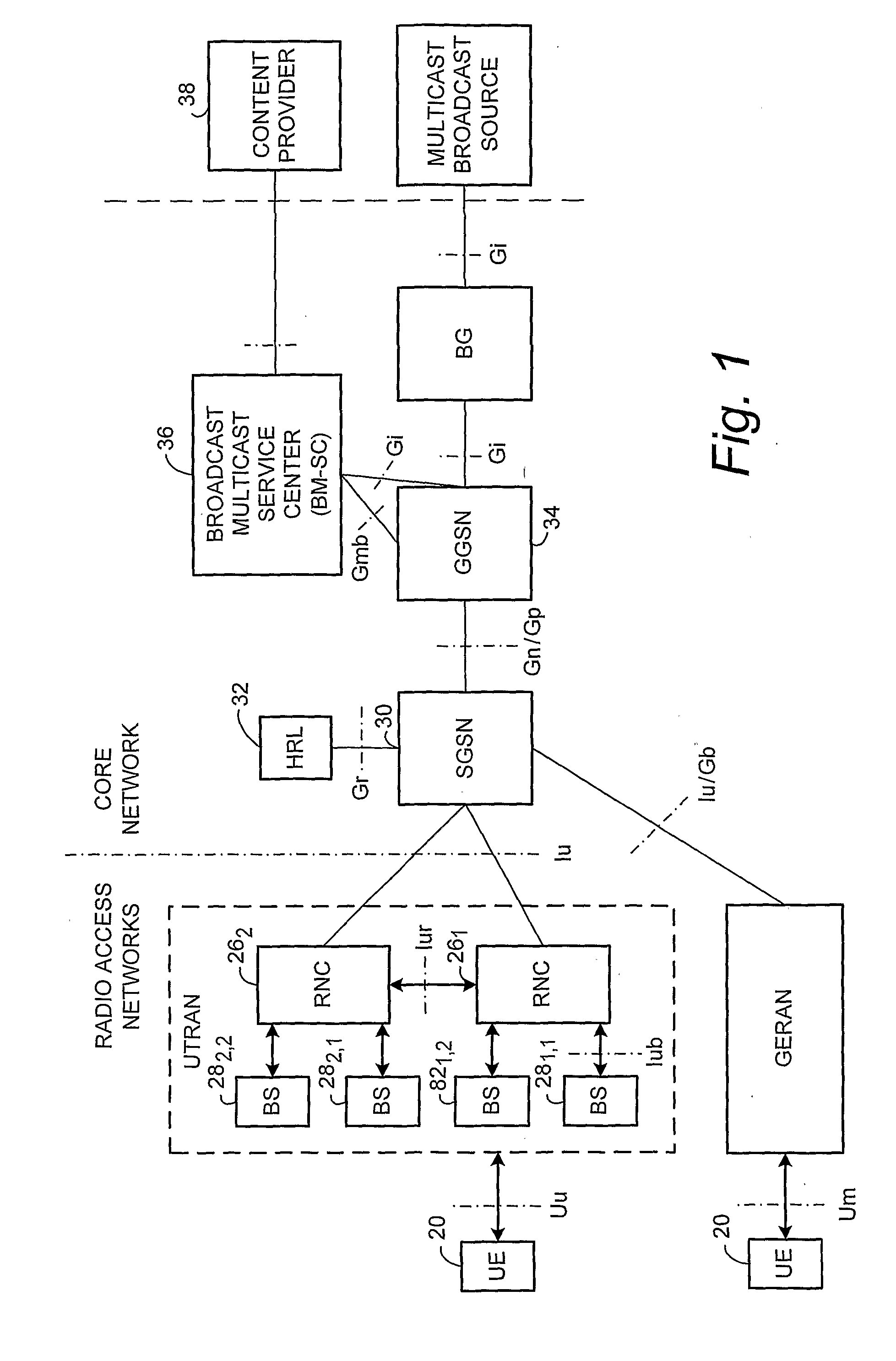
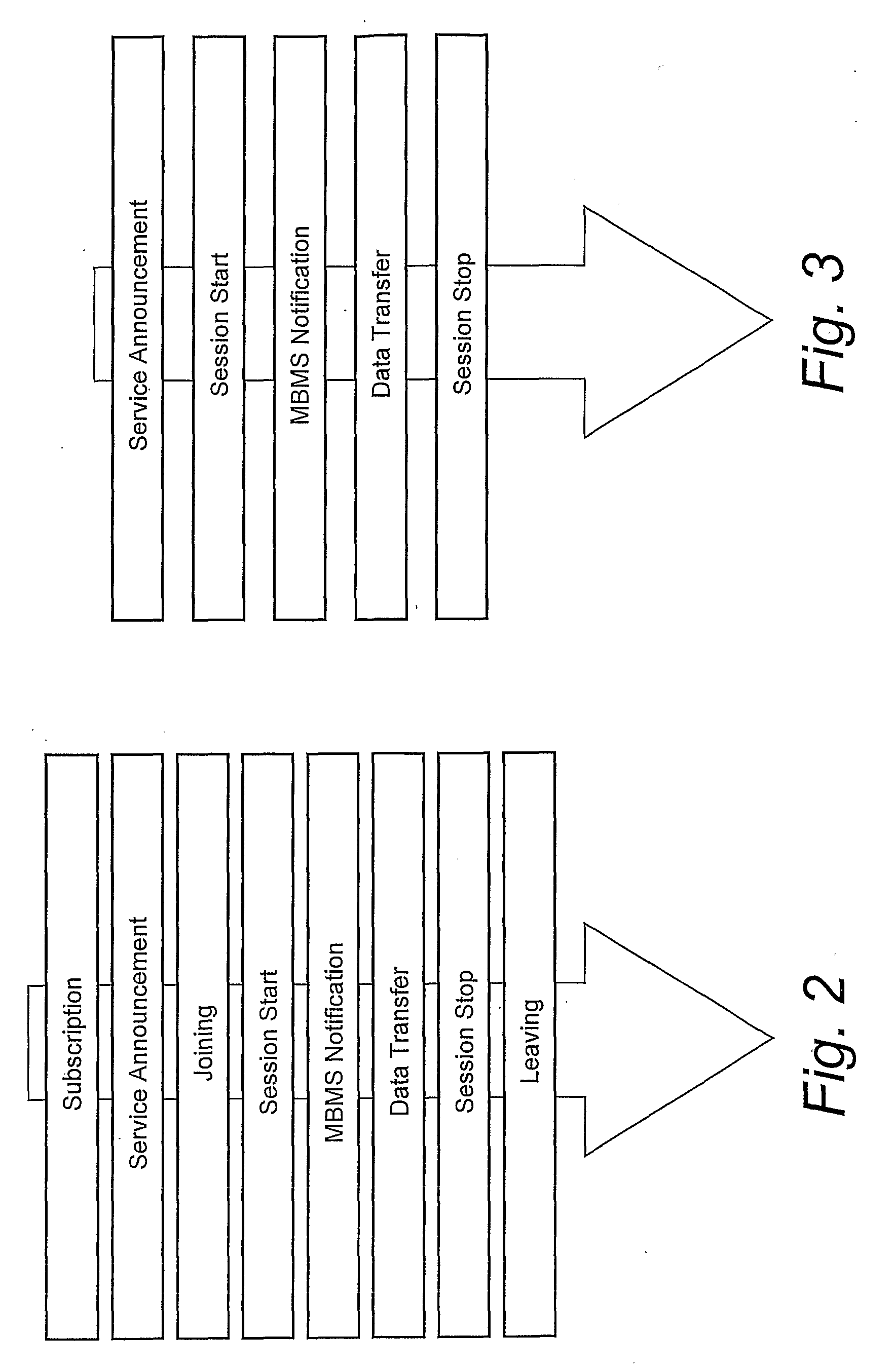
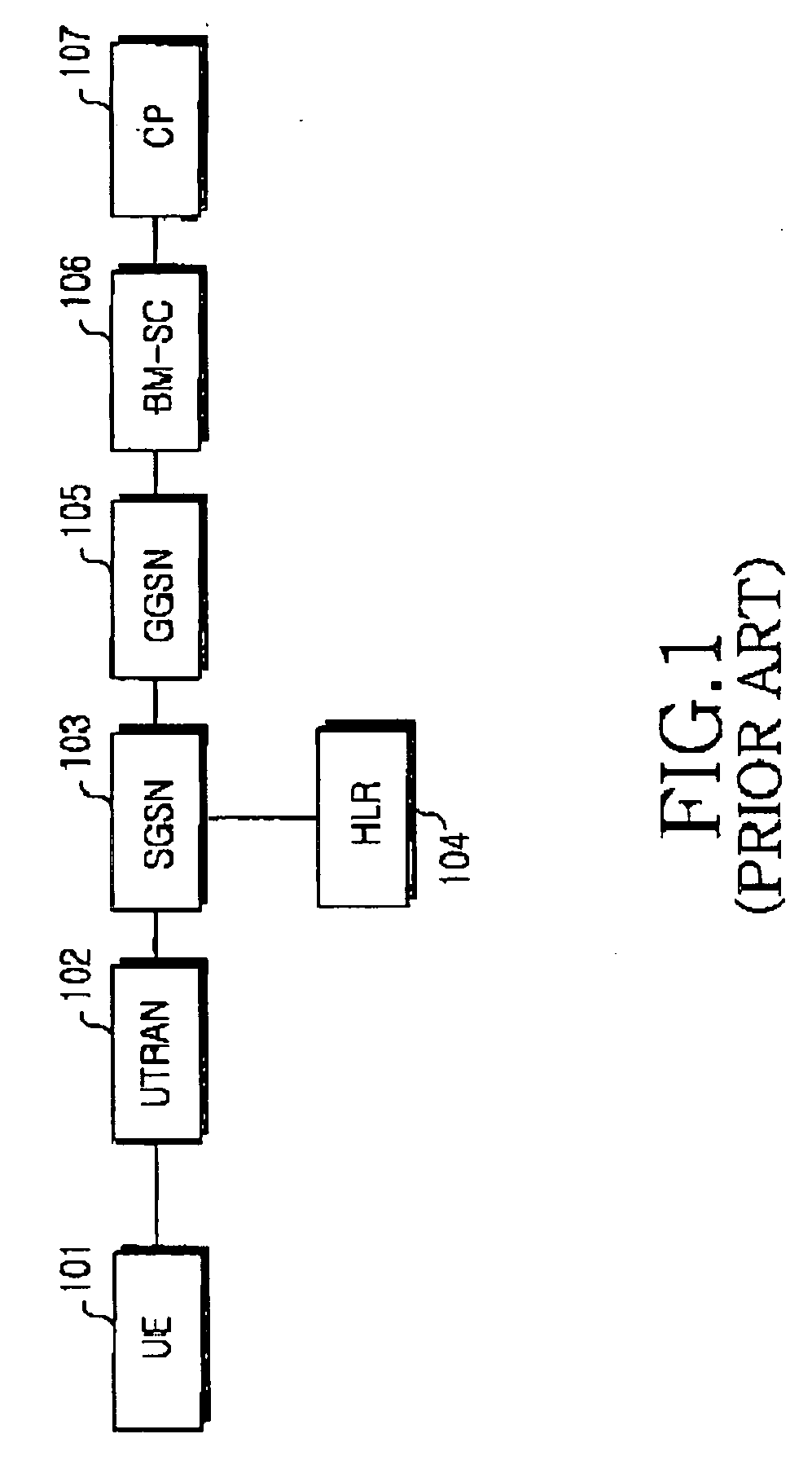
Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Services (MBMS) is a point-to-multipoint interface specification for existing and upcoming 3GPP cellular networks, which is designed to provide efficient delivery of broadcast and multicast services, both within a cell as well as within the core network. For broadcast transmission across multiple cells, it defines transmission via single-frequency network configurations. The specification is referred to as Evolved Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Services (eMBMS) when transmissions are delivered through an LTE (Long Term Evolution) network. eMBMS is also known as LTE Broadcast.
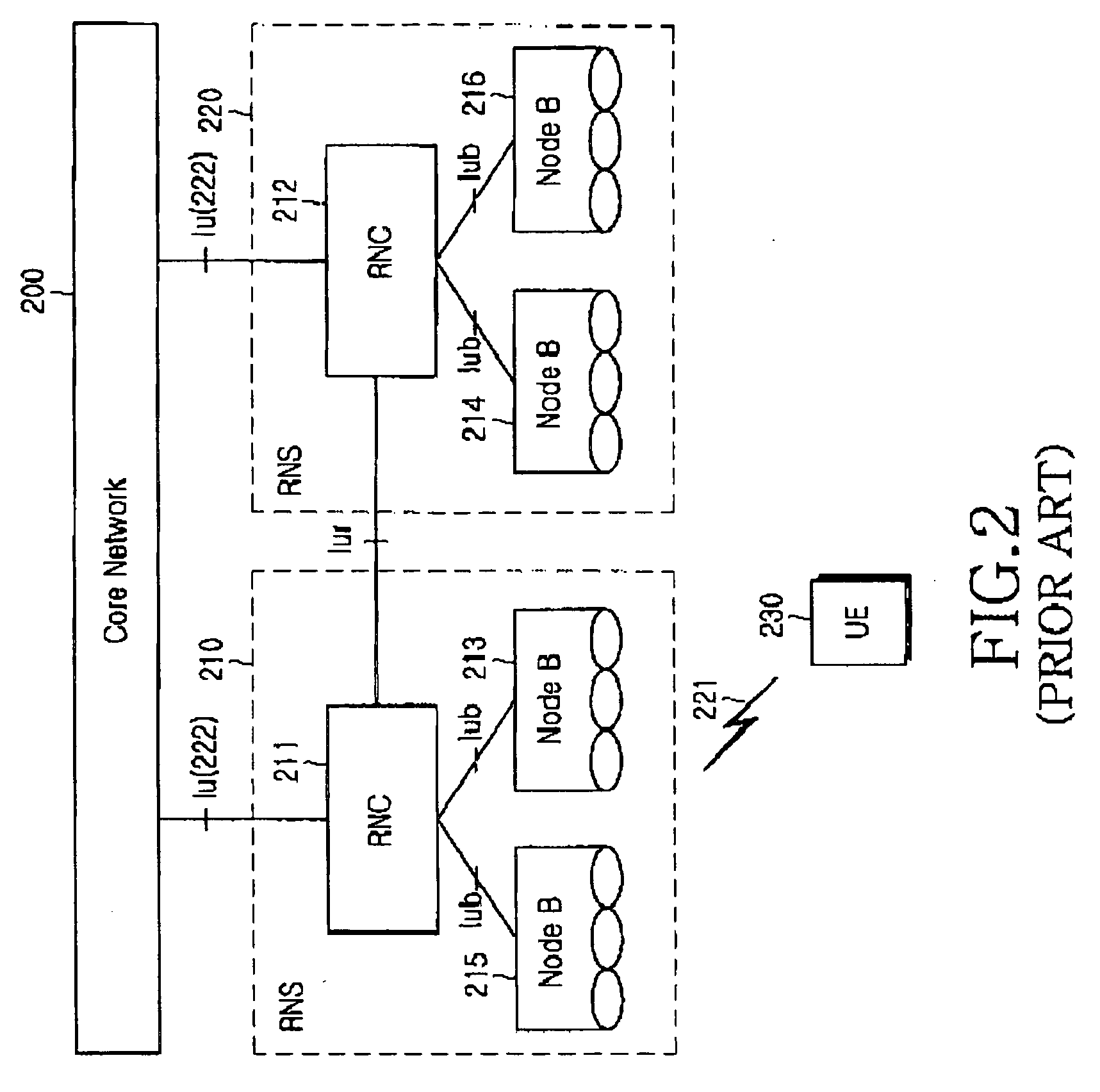
Cell reselection method for receiving packet data in a mobile communication system supporting MBMS
ActiveUS20050090278A1Assess restrictionBroadcast service distributionMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceTelecommunications
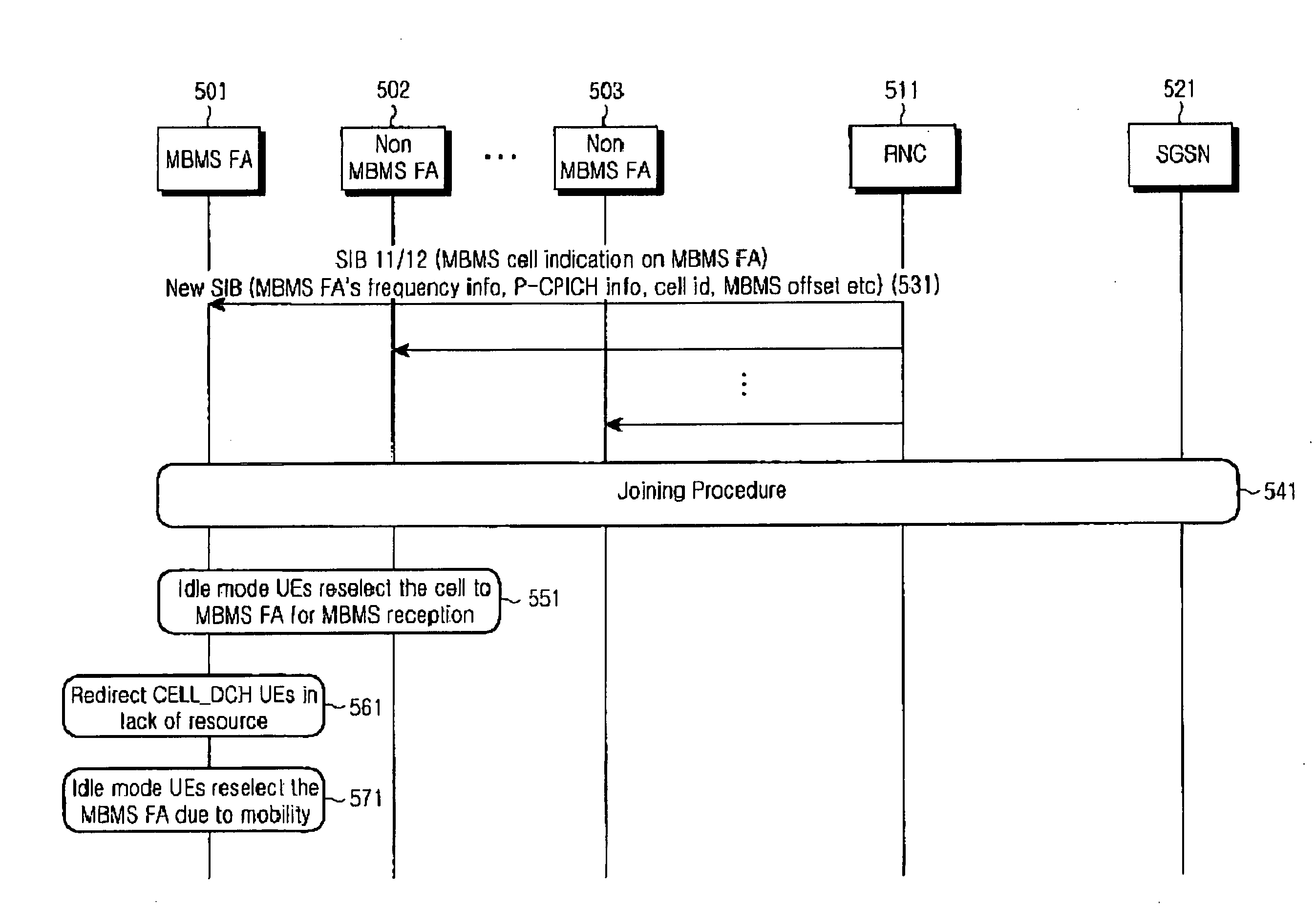
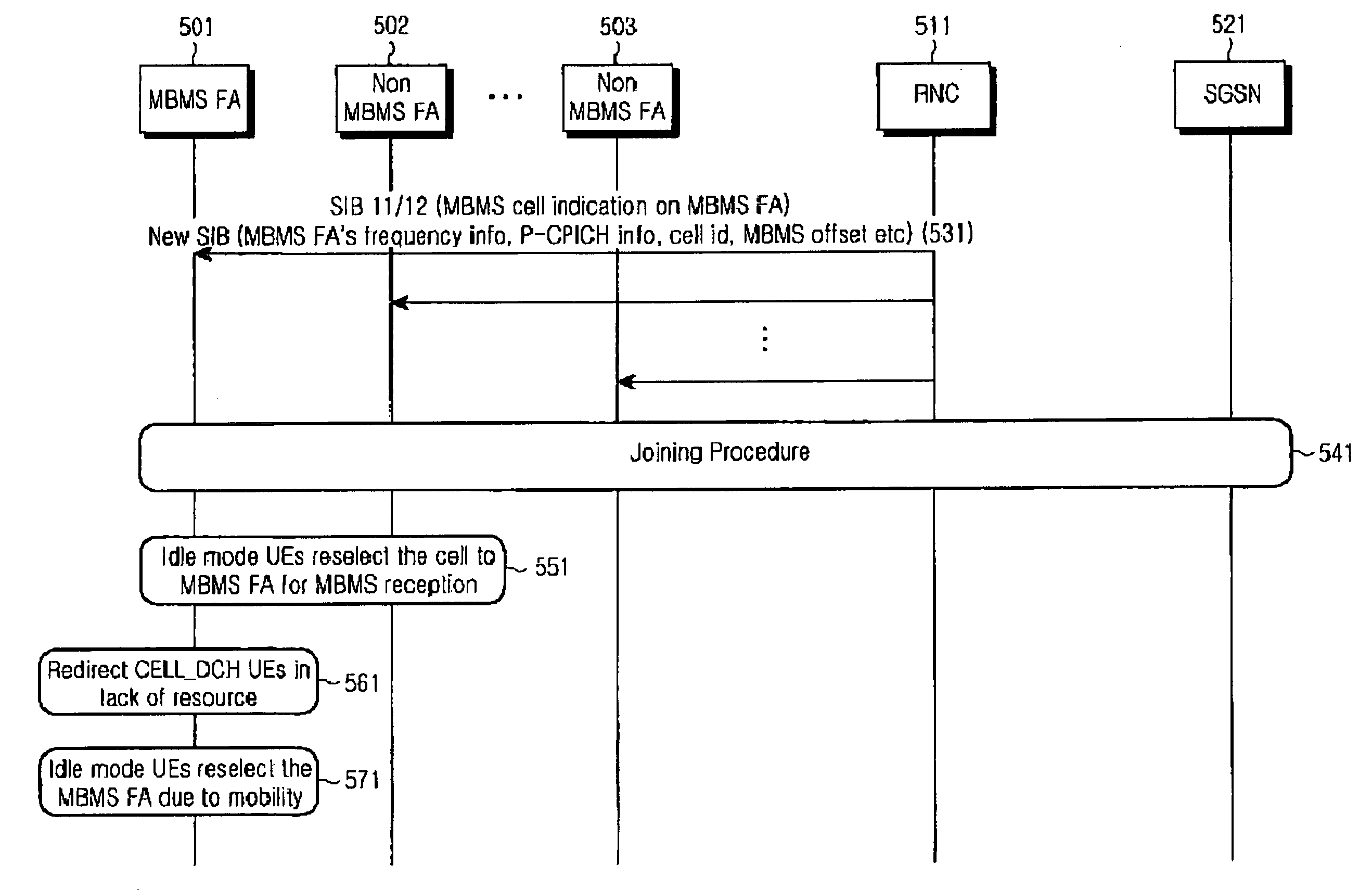
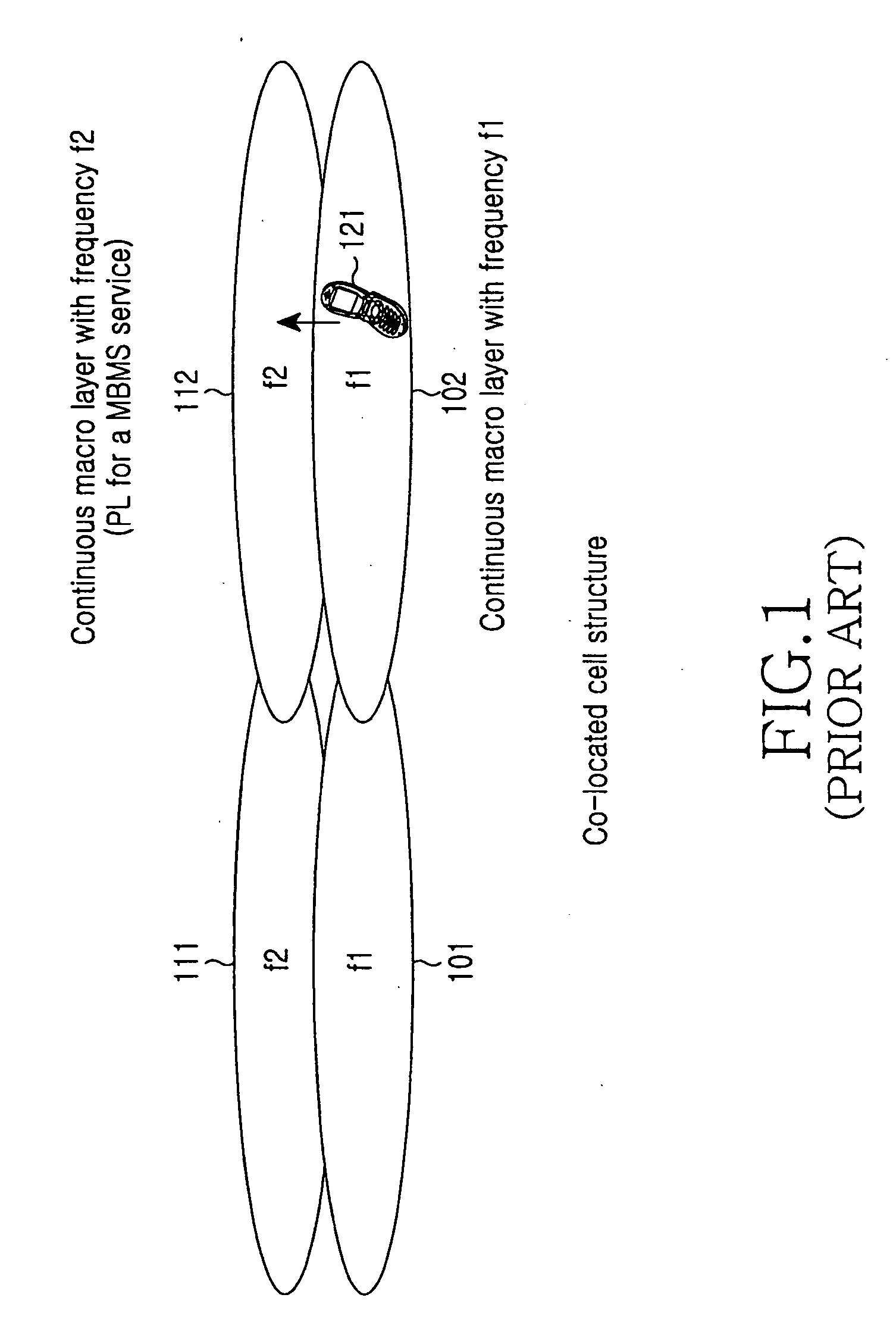
A method for selecting a cell by a user equipment (UE) to receive a Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service (MBMS) service in a mobile communication system which supports the MBMS service with different frequency allocations (FAs) in the same area. In the method, a radio network controller (RNC) transmits information on an MBMS cell to the UE, and the MBMS cell information includes an MBMS offset for guaranteeing priority for cell reselection to the MBMS cell. The UE performs cell reselection using the MBMS cell information and receives the MBMS service from the reselected cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of transmitting/receiving control message in a mobile communication system providing multimedia broadcast/ multicast service
ActiveUS20040087320A1Affect performance of systemNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceTelecommunications
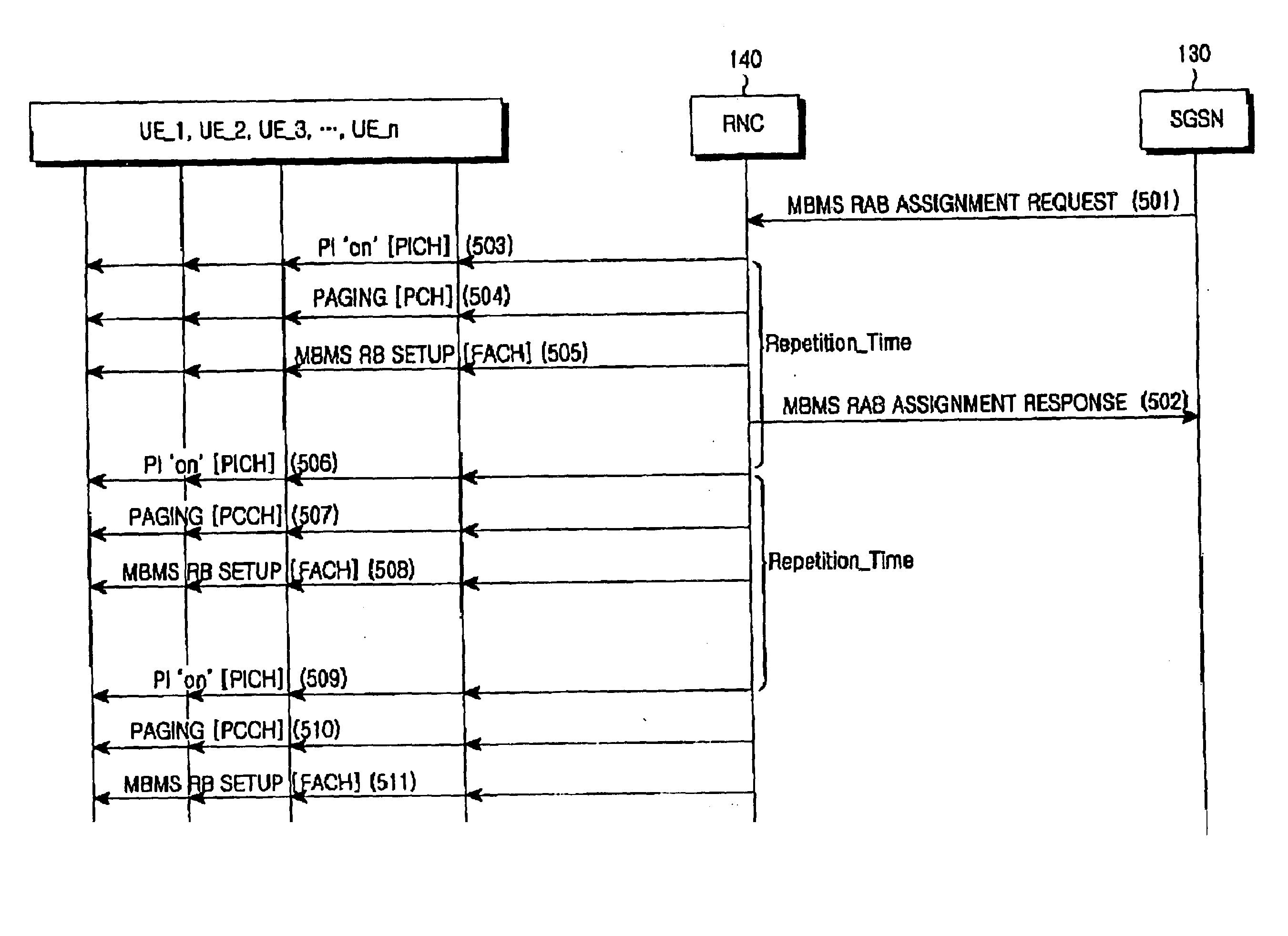
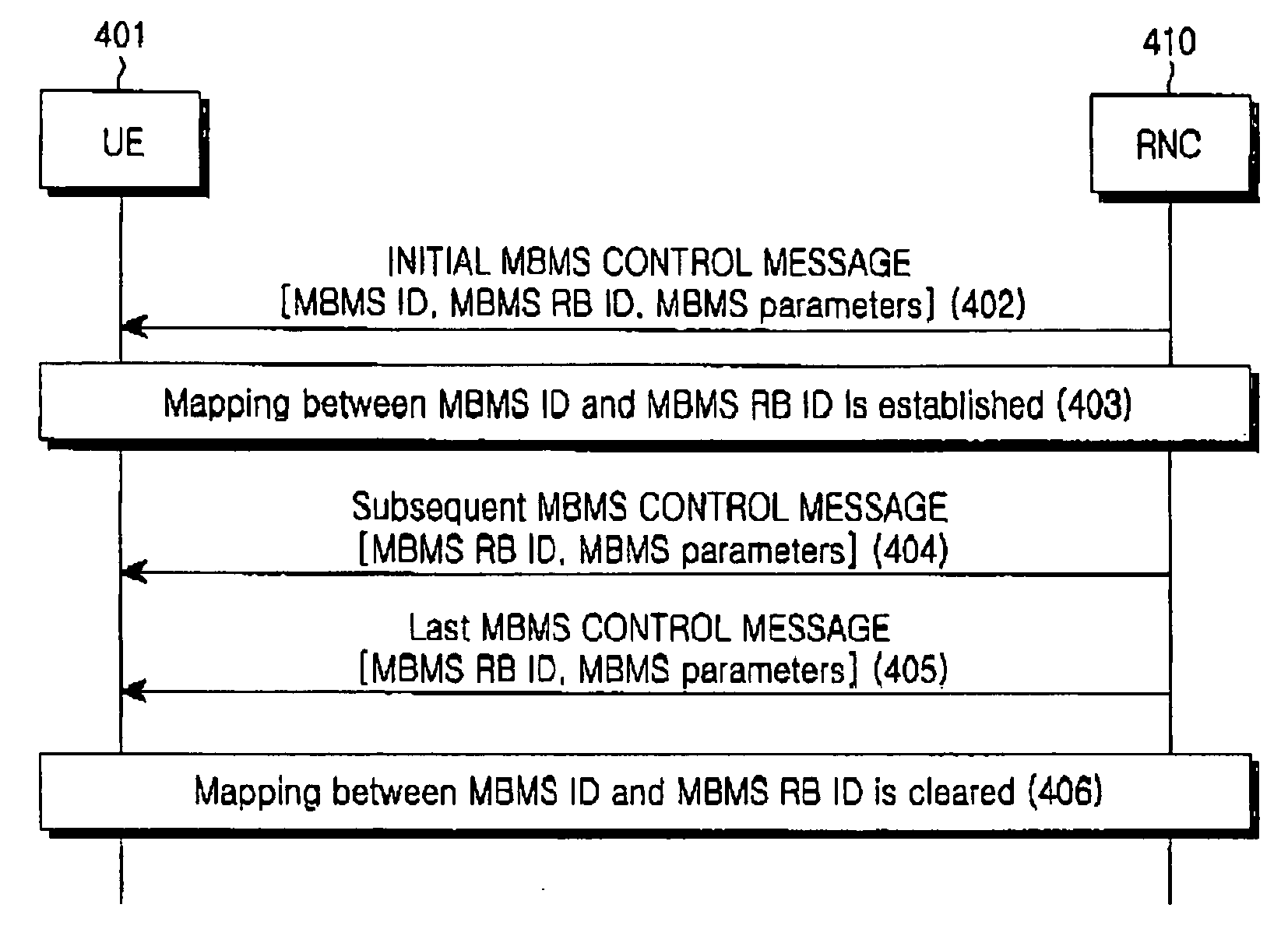
A control message transmitting / receiving method in an MBMS-supporting mobile communication system. In the present invention, an RNC periodically transmits control messages related to MBMS RB setup to UEs. Thus, although a UE initially fails to receive an intended MBMS service, it can set up an MBMS RB by receiving a related retransmitted control message. Also, the RNC periodically provides information about ongoing MBMS services on a cell basis so that a UE can decide whether its requested MBMS service is in progress and request information required to set up an MBMS RB for the MBMS service to the RNC by individual signaling.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for transmitting/receiving service availability information of multimedia broadcasting/multicast service
ActiveUS20050111393A1Broadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexCurrent cellMultimedia Broadcast Multicast Service
Disclosed is a mobile communication system for providing a number of User Equipment (UEs) positioned in a plurality of cells with Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service (MBMS) using CDMA technology. A Radio Network Controller (RNC) transmits a MBMS availability message to each of the plurality of cells under management regarding at least one MBMS which is available in a corresponding cell in order to support the mobility of the UE which receives the MBMS. The UE decides whether it can receive a desired MBMS in the current cell, after receiving the MBMS availability message, and requests the desired MBMS or reselects another cell. The continuity of MBMS reception is improved while UEs using the MBMS are moving and the overhead of RRC connection setup for unnecessary MBMS request is reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
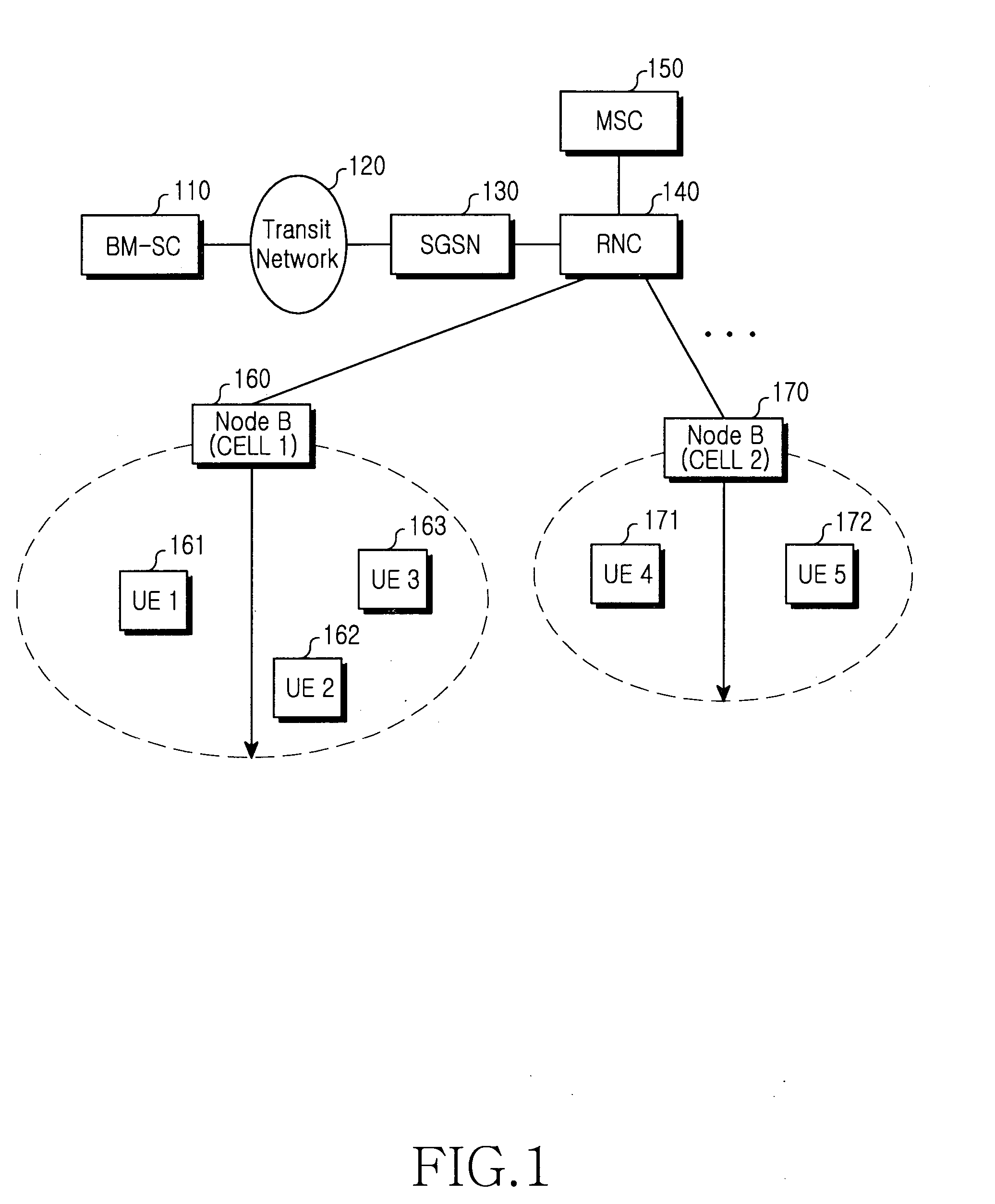
Method and apparatus for providing multimedia broadcast multicast service data to a subscriber to a multimedia broadcast multicast service
InactiveUS20050043035A1Special service provision for substationBroadcast with distributionMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCommunications system
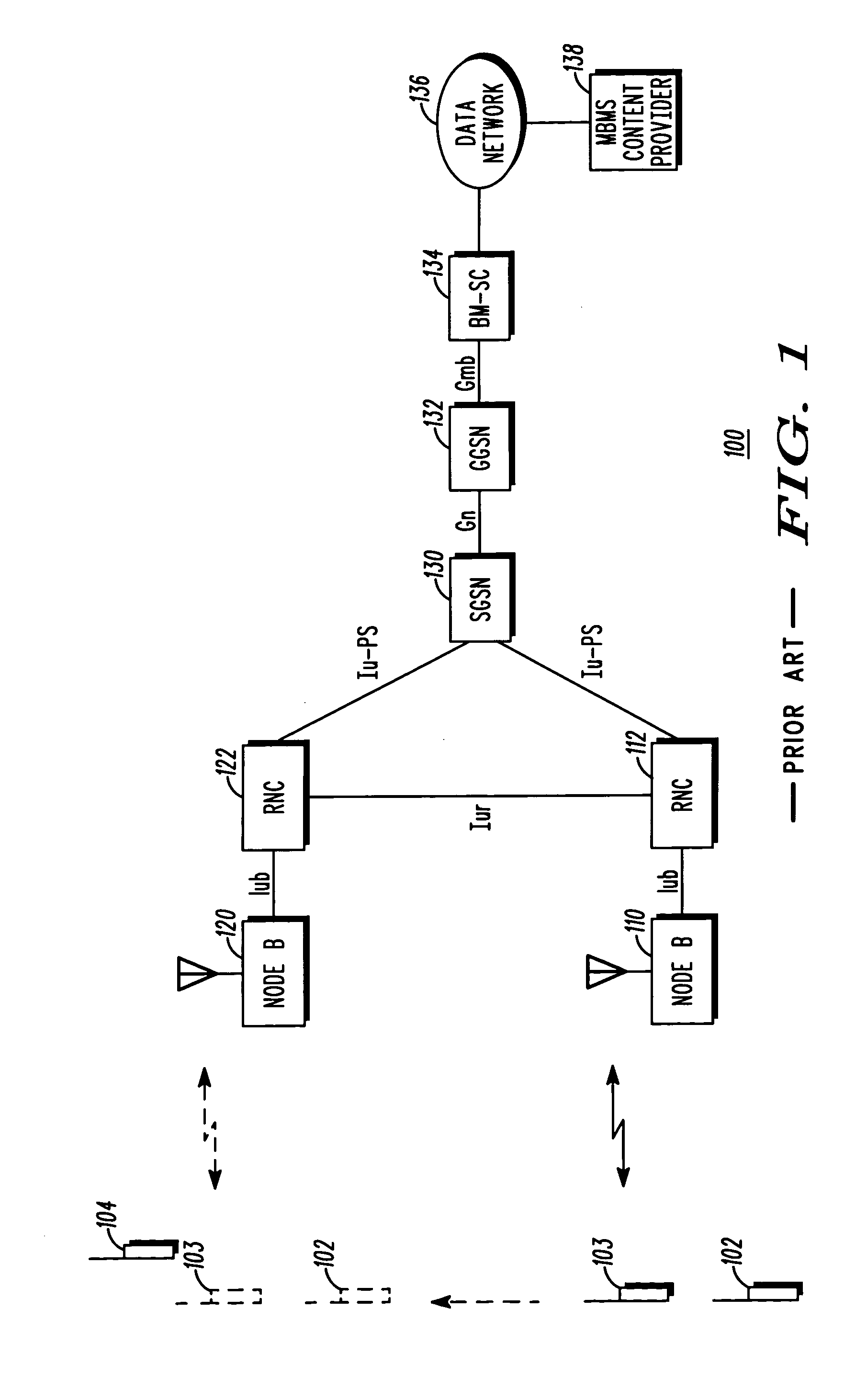
A communication system conveys Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service (MBMS) data to multiple mobile stations (MSs) subscribing to an MBMS service while minimizing possible congestion over an Iub interface. A network controller receives at least one MBMS data packet comprising an MBMS payload. In response to receiving the at least one data packet, the network controller establishes communication channels to the multiple MSs for conveyance of MBMS data and conveys to a downstream network element, via an Iub interface, a single copy of the payload. The downstream network element replicates the received payload to produce a copy of the payload for each established communication channel. The downstream network element then assembles, in association with each established communication channel, a set of one or more data packets for conveyance via the established communication channel, wherein each set of data packets includes a copy of the payload.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
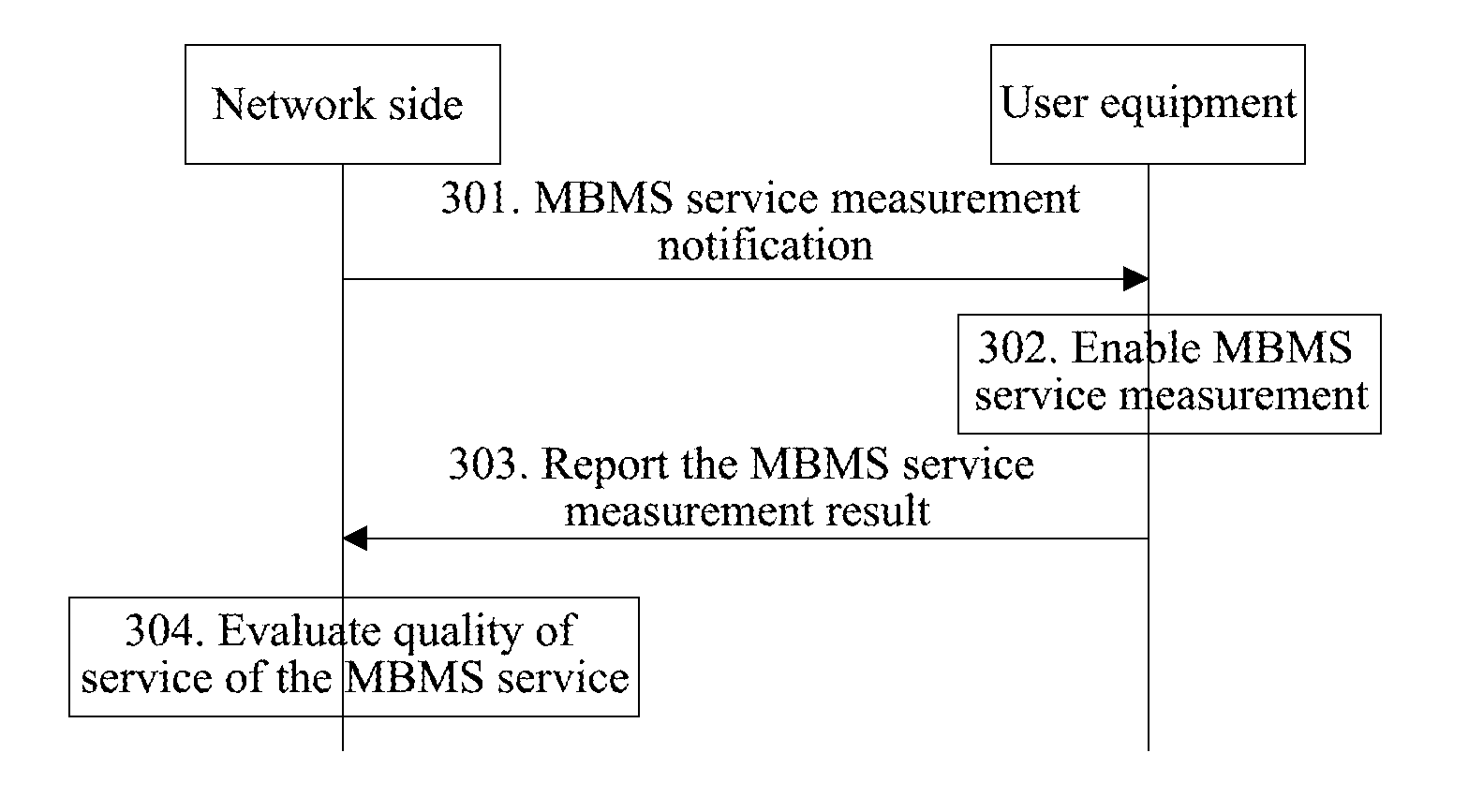
Method and system for reporting multimedia broadcast multicast service measurement
InactiveUS20130010624A1Efficiency problemError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCurrent cellMultimedia Broadcast Multicast Service
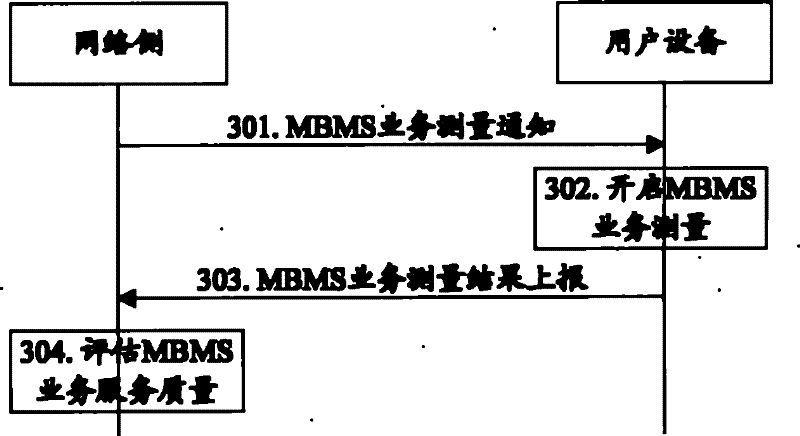
The present invention discloses a method and system for measuring and reporting a multimedia broadcast multicast service, for solving the technical problem of how to measure and report a measurement result reflecting MBMS performance by the UE. In the present invention, the UE measures the MBMS according to a measurement configuration, and when a measurement reporting norm is met, the UE reports a measurement result or a measurement log of the measured MBMS measurement quantity to a network side. By the method, the operators can be assisted to timely understand the MBMS service performance of the current cell and can timely find the potential problems according to the measurement reporting result, and then resolve the problems as soon as possible; furthermore, the efficiency and cost problems caused by previous drive test can be effectively saved, and the service performance is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
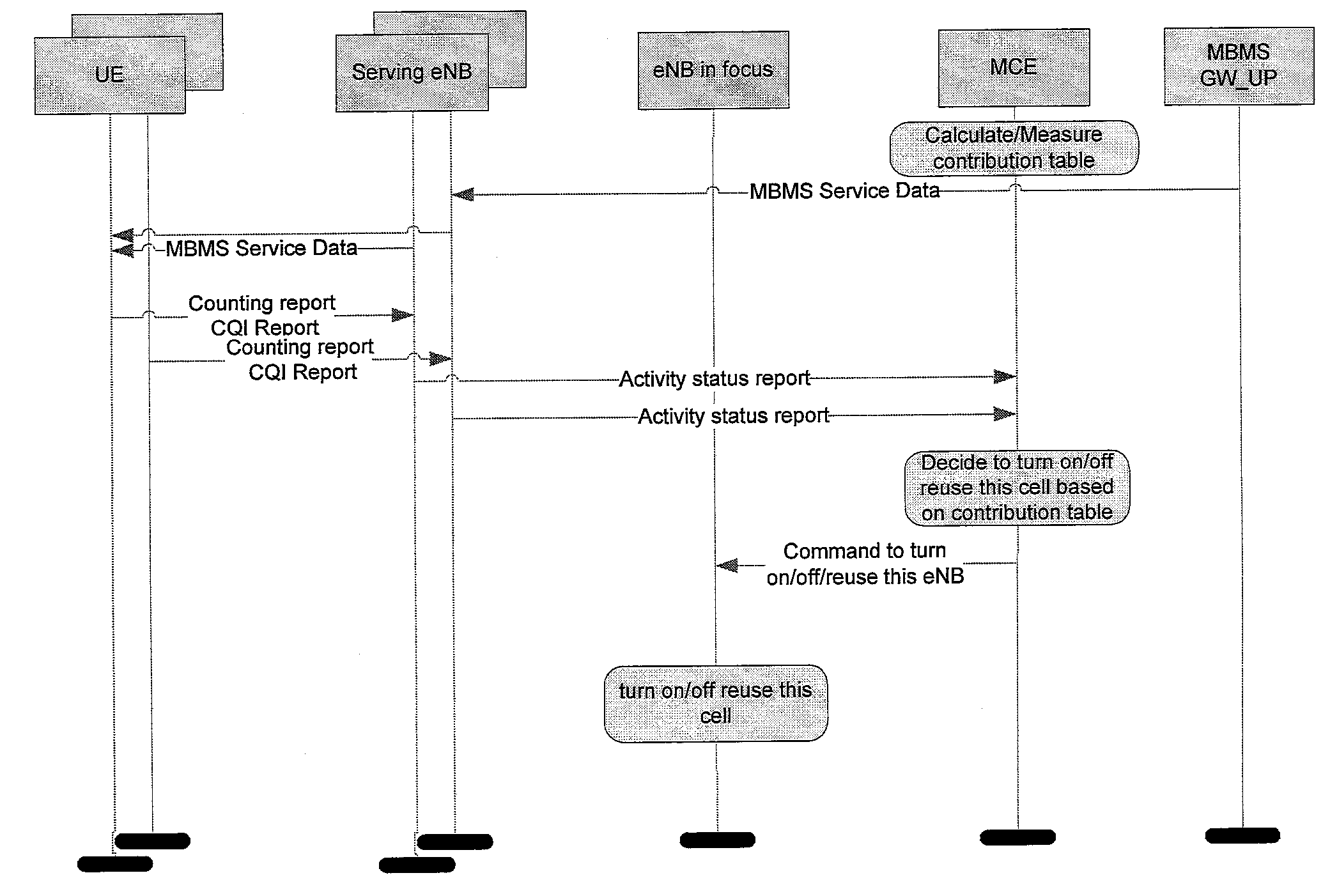
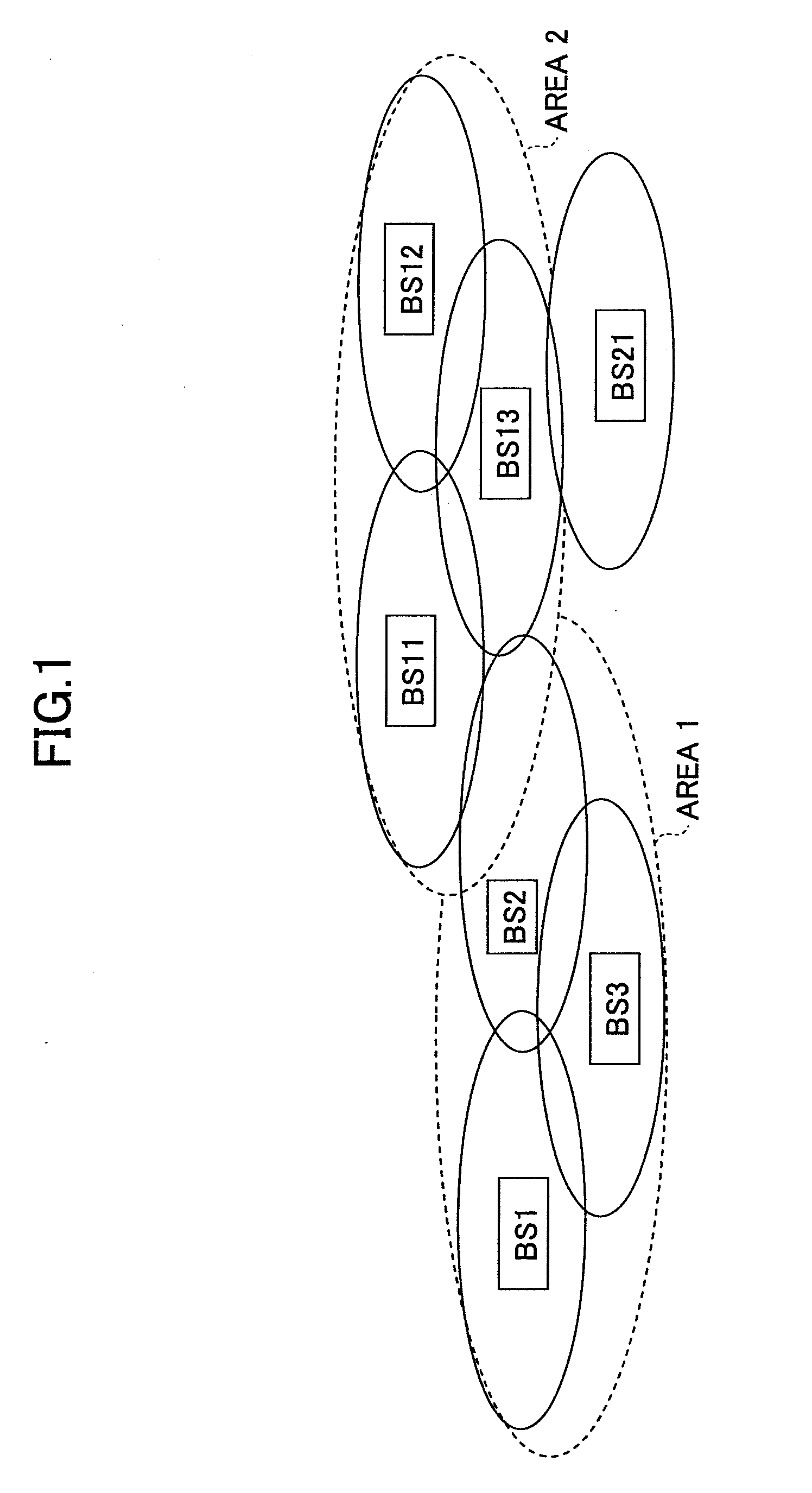
System and Method for Controlling Base Stations for Multimedia Broadcast Communications
InactiveUS20080274759A1Broadcast service distributionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCommunications system
A method, apparatus and system are provided for controlling base stations for multimedia broadcast communications. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a reporting subsystem configured to compile an activity status report based on a counting report and a channel quality indicator report received from user equipment and to send the activity status report to an entity of the communication system. The apparatus also includes a dynamic single-frequency network subsystem configured to control a multimedia broadcast and multimedia multicast service provided by the apparatus as a function of a static contribution table associated therewith and the activity status report.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
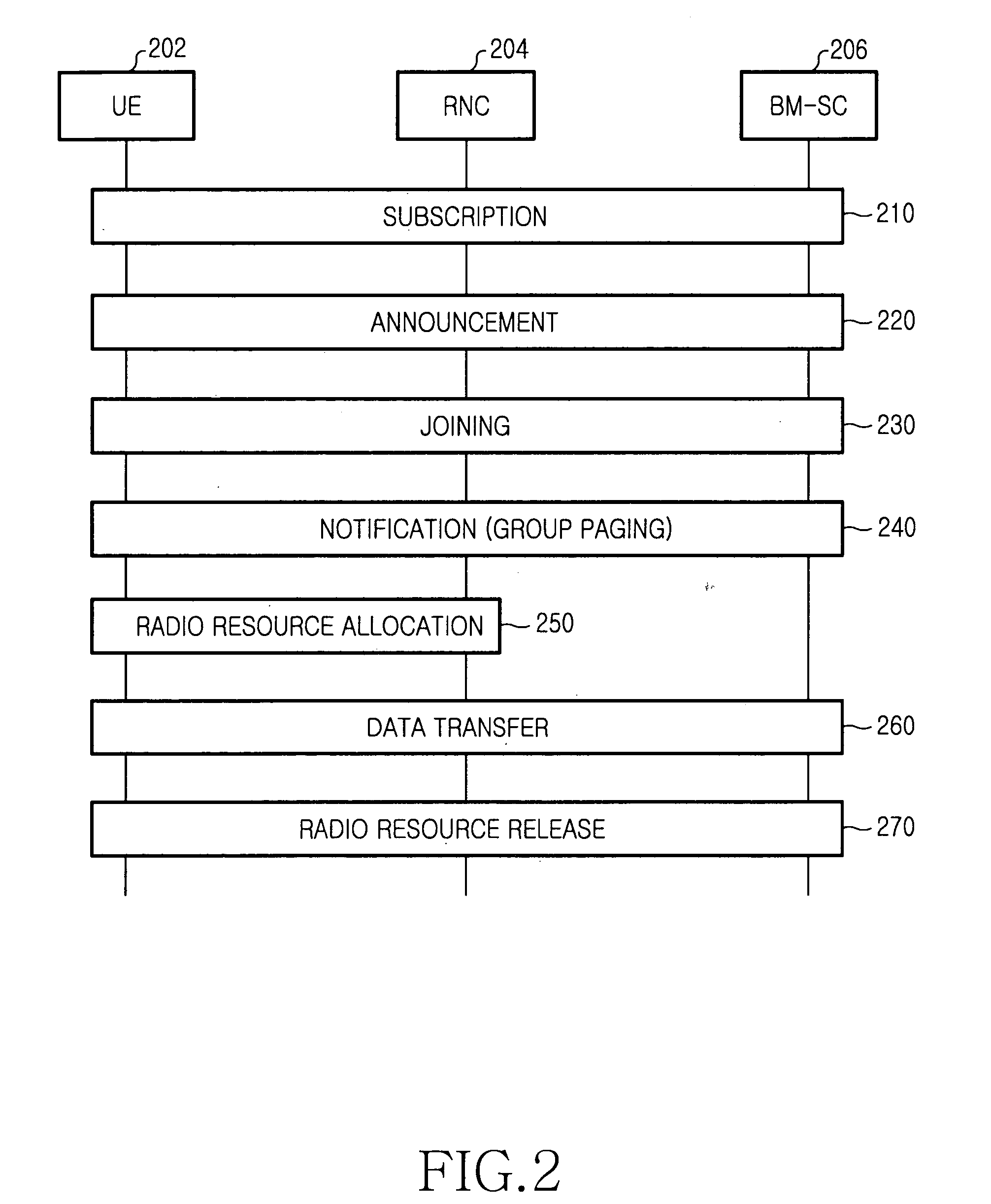
Method and apparatus for providing session data to a subscriber to a multimedia broadcast multicast service
ActiveUS20050030966A1Special service provision for substationTelevision system detailsMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCommunications system
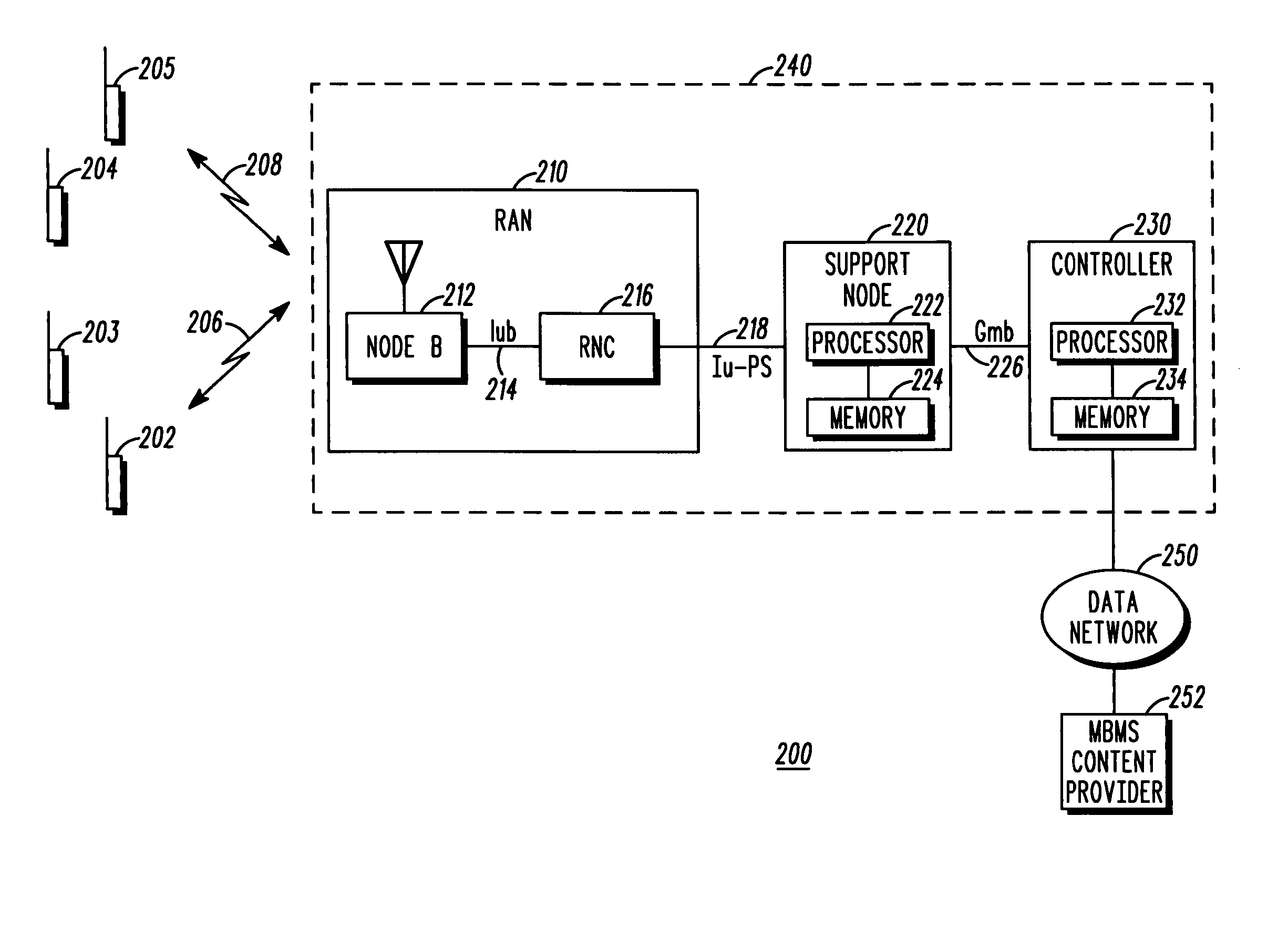
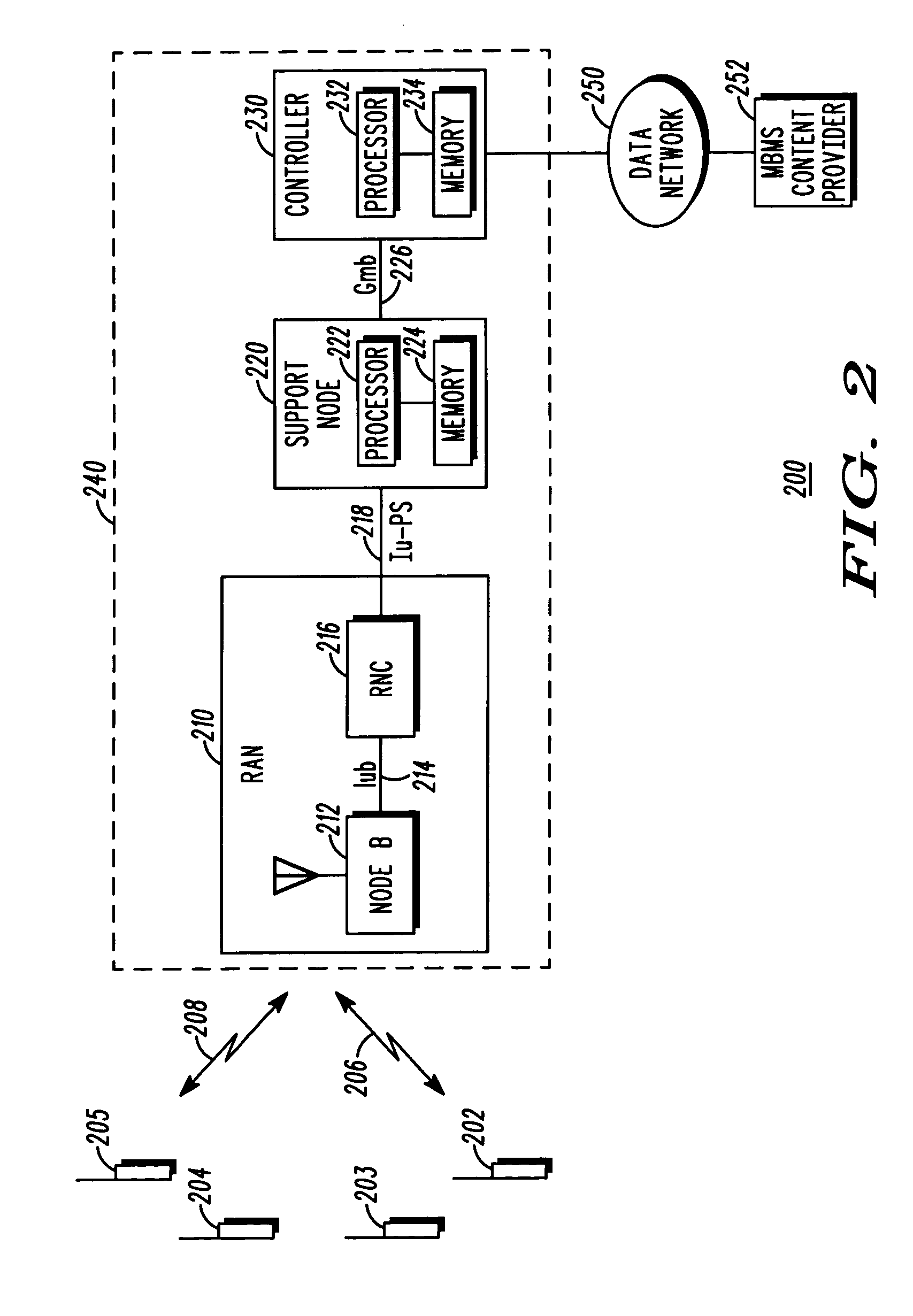
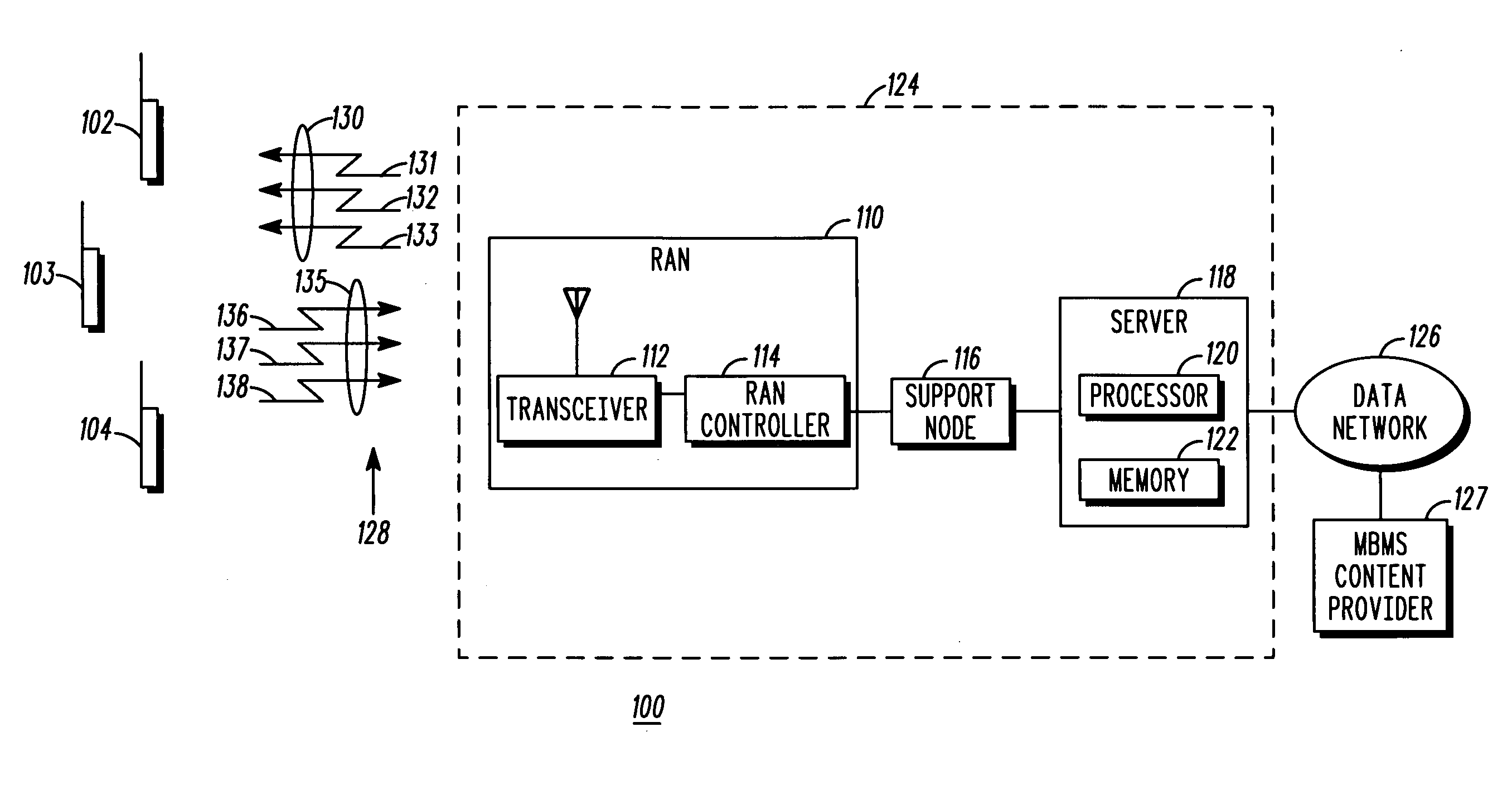
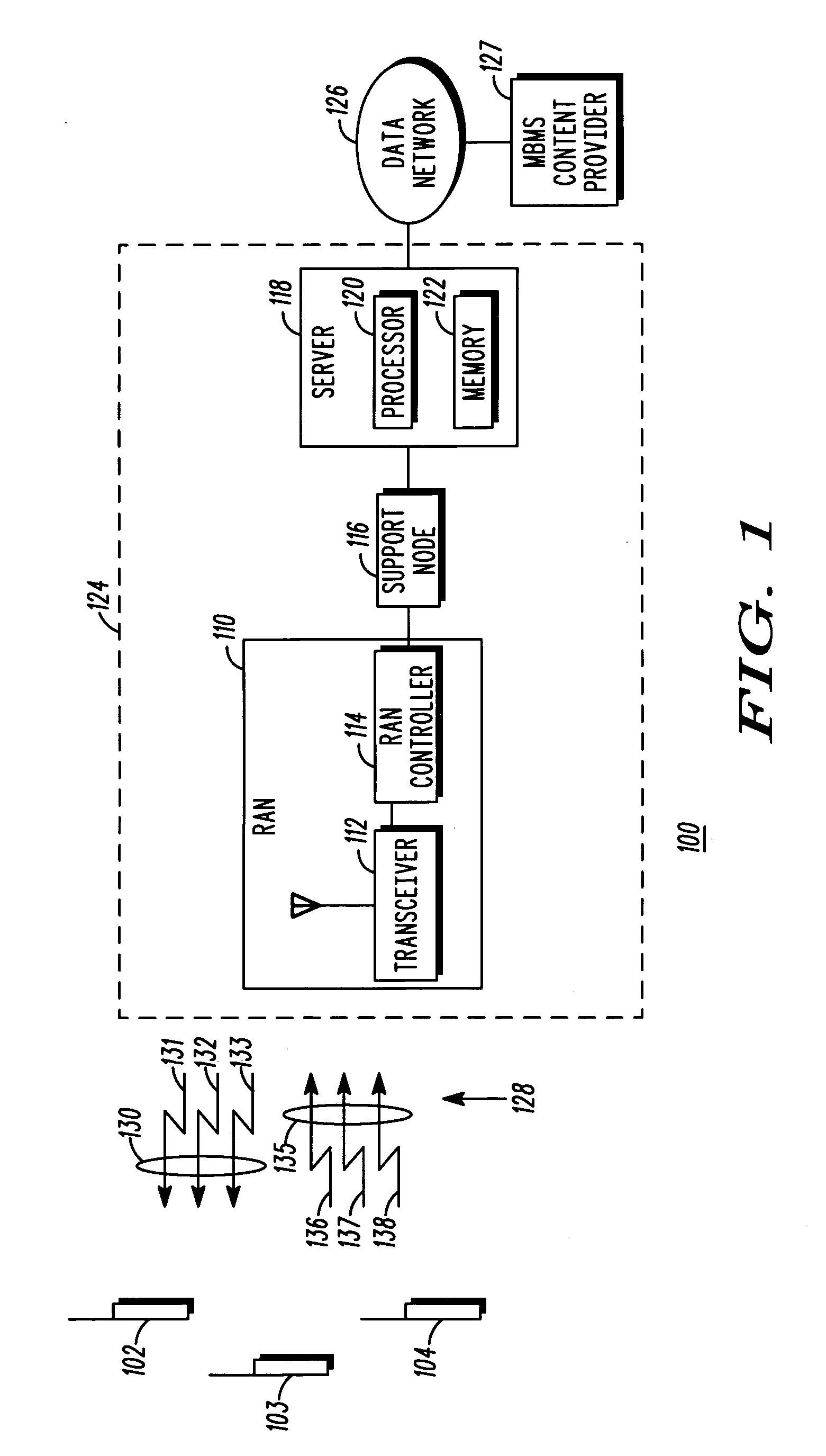
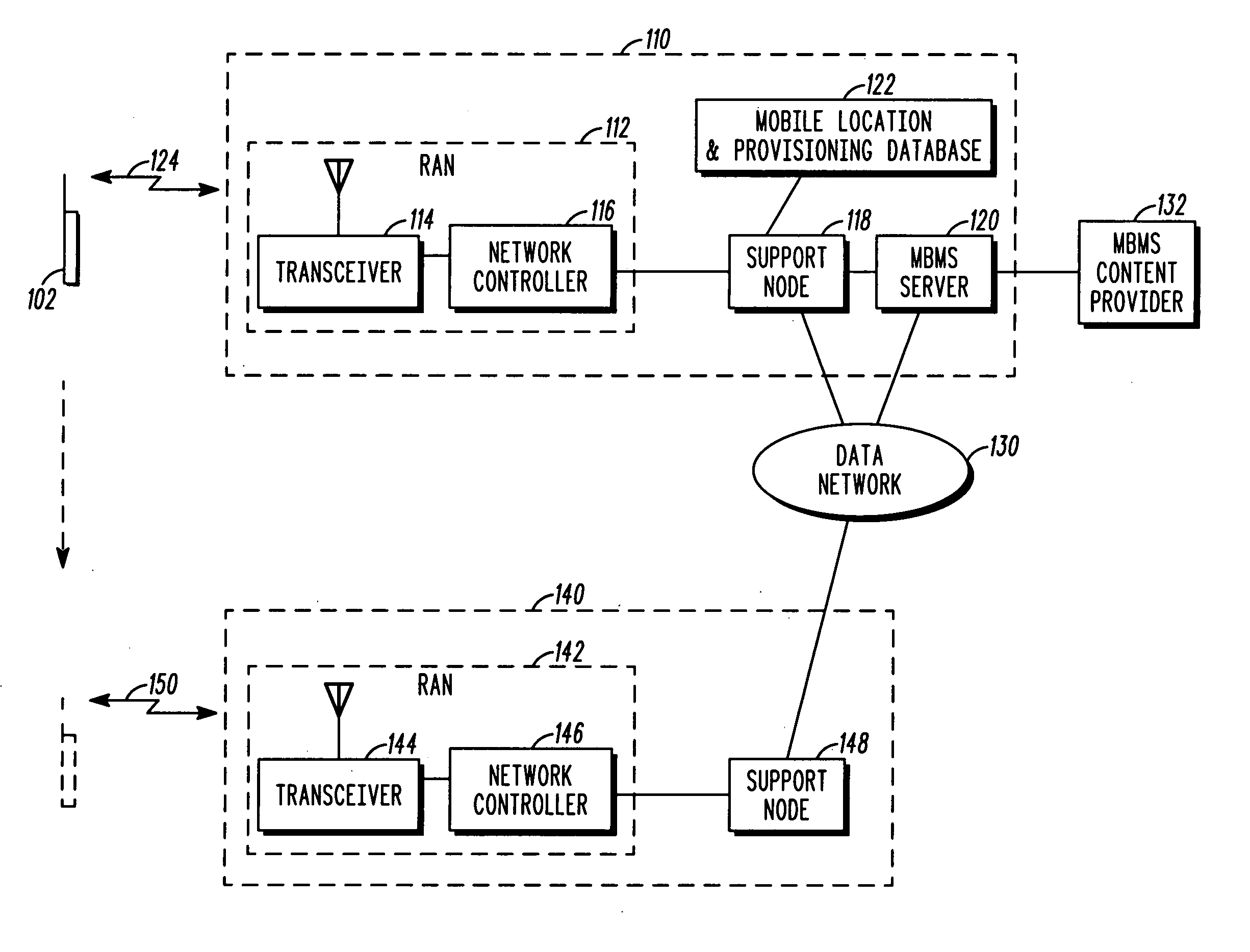
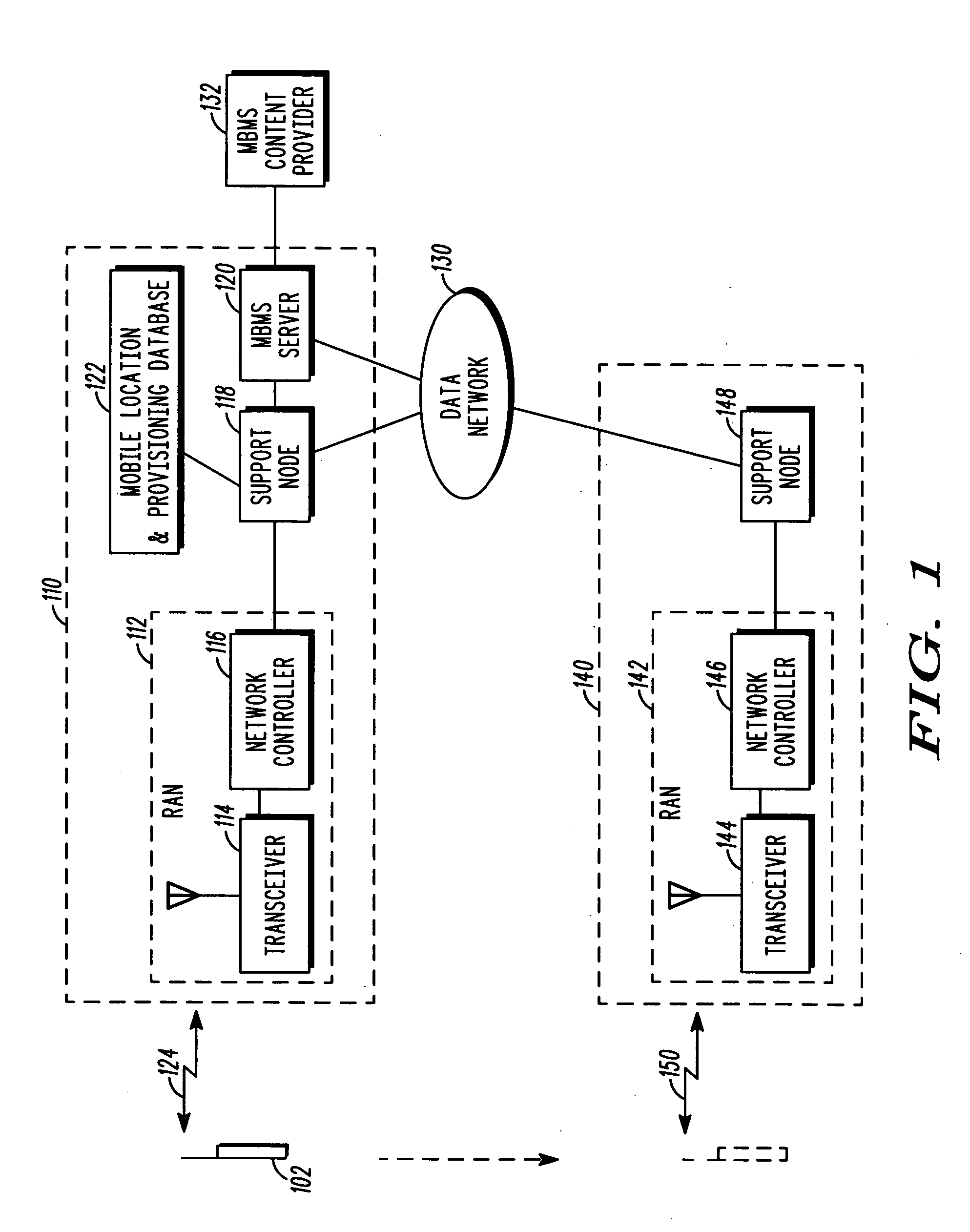
A communication system that includes a Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service (MBMS) service provides re-broadcasts of an event to subscribers to the MBMS service. An infrastructure included in the communication system and comprising a server coupled to a RAN controller via a support node receives a first set of MBMS data from an MBMS content provider and conveys the first set of MBMS data along with an associated first Session Description to a subscribed mobile station. The infrastructure then receives a second set of MBMS data from the MBMS content provider, wherein the second set of MBMS data comprises a re-conveyance of the first set of MBMS data, and conveys an MBMS notification along with an associated second Session Description to the mobile station. The mobile station may then determine whether to receive the re-conveyance based on the first and second Session Descriptions.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
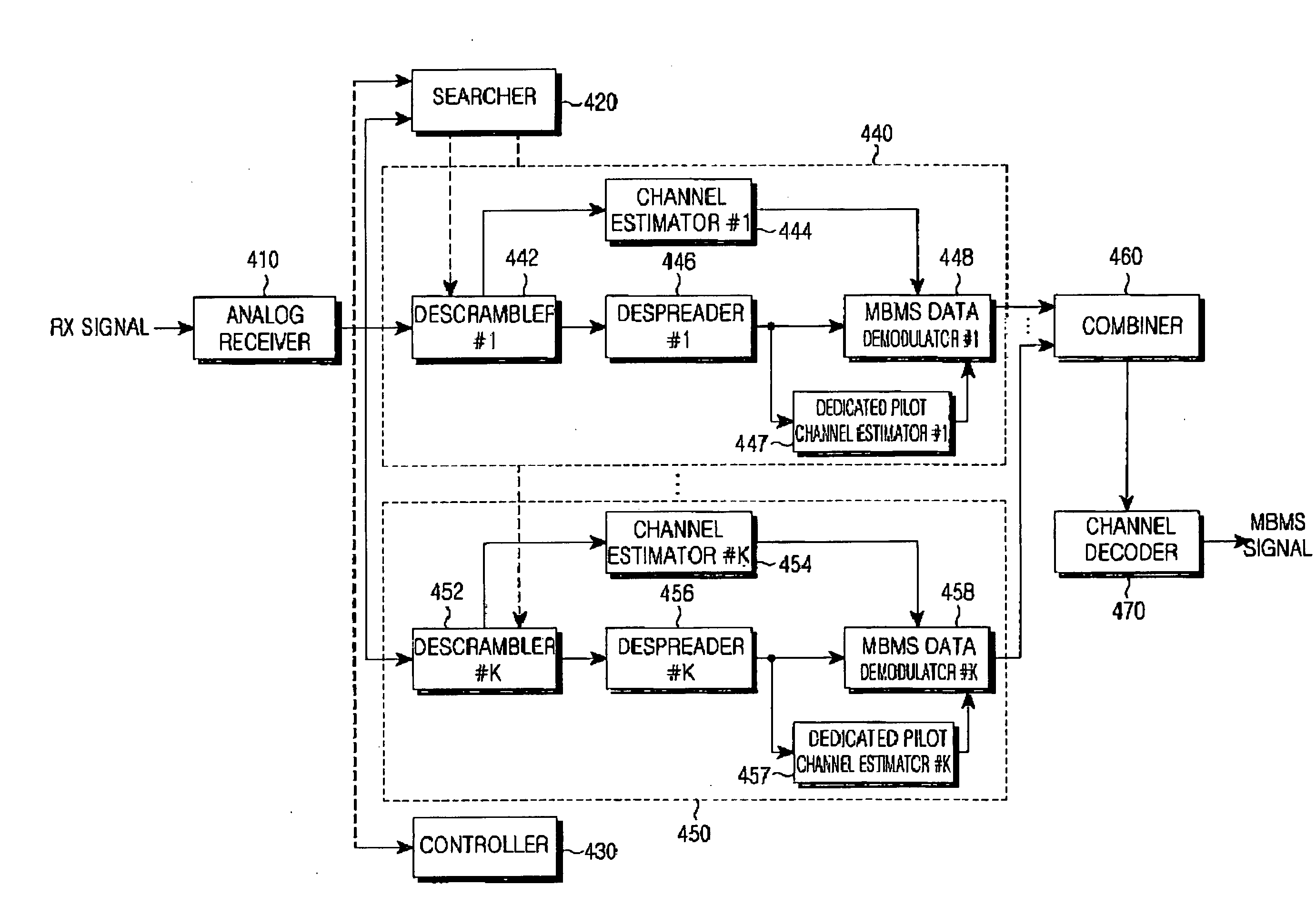
Soft combining apparatus and method in a CDMA mobile communication system providing MBMS service
ActiveUS7203512B2Ensure correct executionSite diversityBroadcast service distributionAsynchronous cdmaMultimedia Broadcast Multicast Service
A method and apparatus for determining soft handover in a CDMA mobile communication system supporting Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service (MBMS) is provided. In the asynchronous CDMA mobile communication system supporting MBMS, when a UE moves to a region where it can receive data from a plurality of Node Bs, the UE determines whether to perform soft combining using a measurement value of a dedicated pilot channel signal, in performing soft handover. In this way, the UE can determine whether to perform soft combining on MBMS data received from a plurality of Node Bs by itself. Therefore, even though an MBMS user moves from a current or existing cell to a new cell, a stable MBMS service is provided to the user, thereby contributing to the user's convenience.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
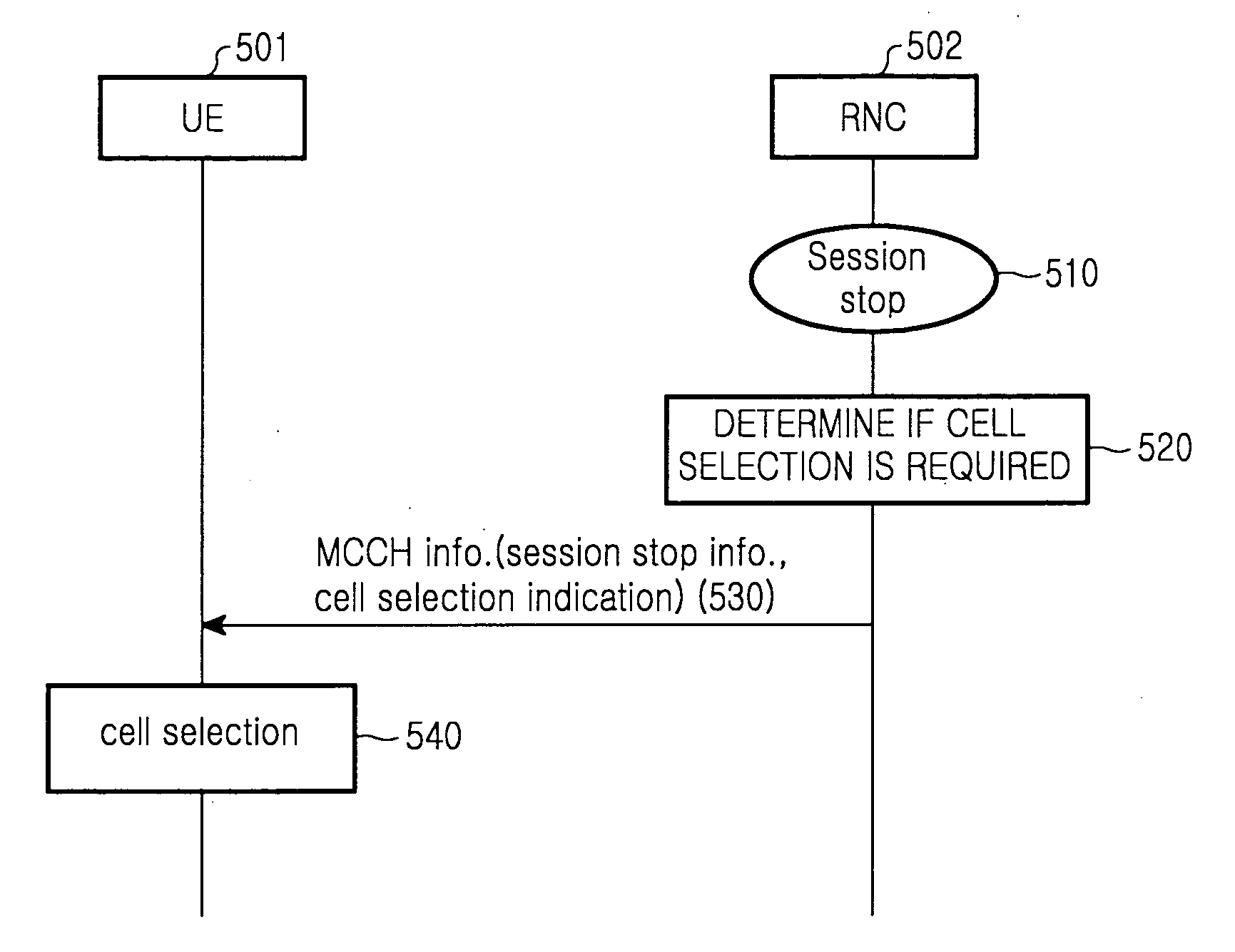
Method and apparatus for indicating cell selection when a session is stopped in a multimedia broadcast/multicast service system
ActiveUS20060056347A1Assess restrictionBroadcast service distributionMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCurrent cell
A multimedia broadcast / multicast service (MBMS) service and a method and apparatus for maintaining congestion and a signal transfer load of a cell at a suitable level when a session of the MBMS service is terminated in a frequency layer convergence (FLC) situation in which the MBMS service is provided in a preferred frequency layer (PL). When a session of the MBMS service is terminated, a radio network controller (RNC) determines if a cell selection is required in UEs, desiring to receive the MBMS service located in the PL cell, by using a start time of a new session and load levels of a current cell and other cells, and sends, to the UEs, explicit cell selection indication information along with session stop information according to a determination result. Therefore, the congestion and signal transfer load of the cell can be maintained in the suitable level.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
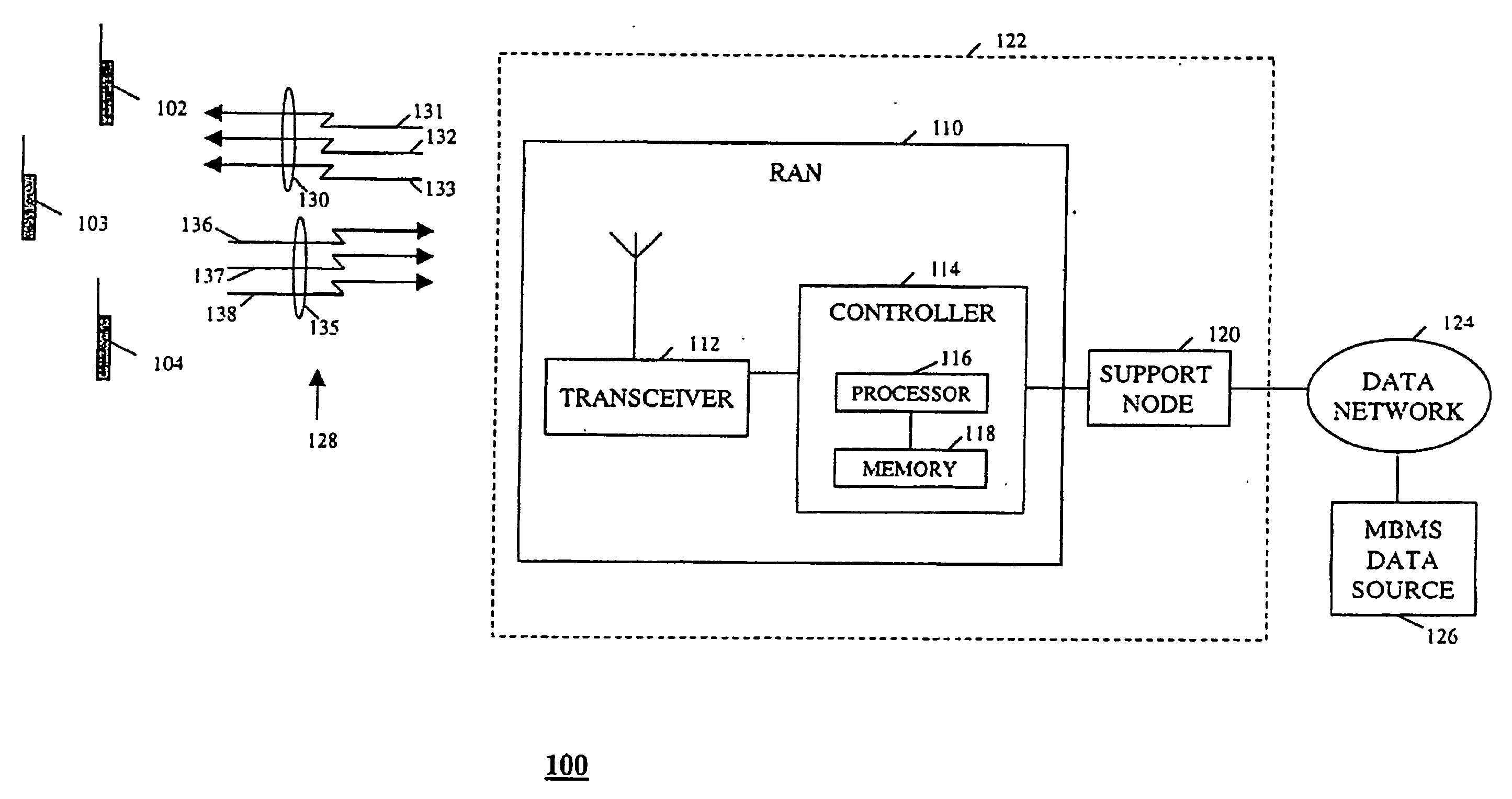
Method and apparatus for controlling access to a multimedia broadcast multicast service in a packet data communication system
InactiveUS20060252439A1Network traffic/resource managementConnection managementMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceFactor base
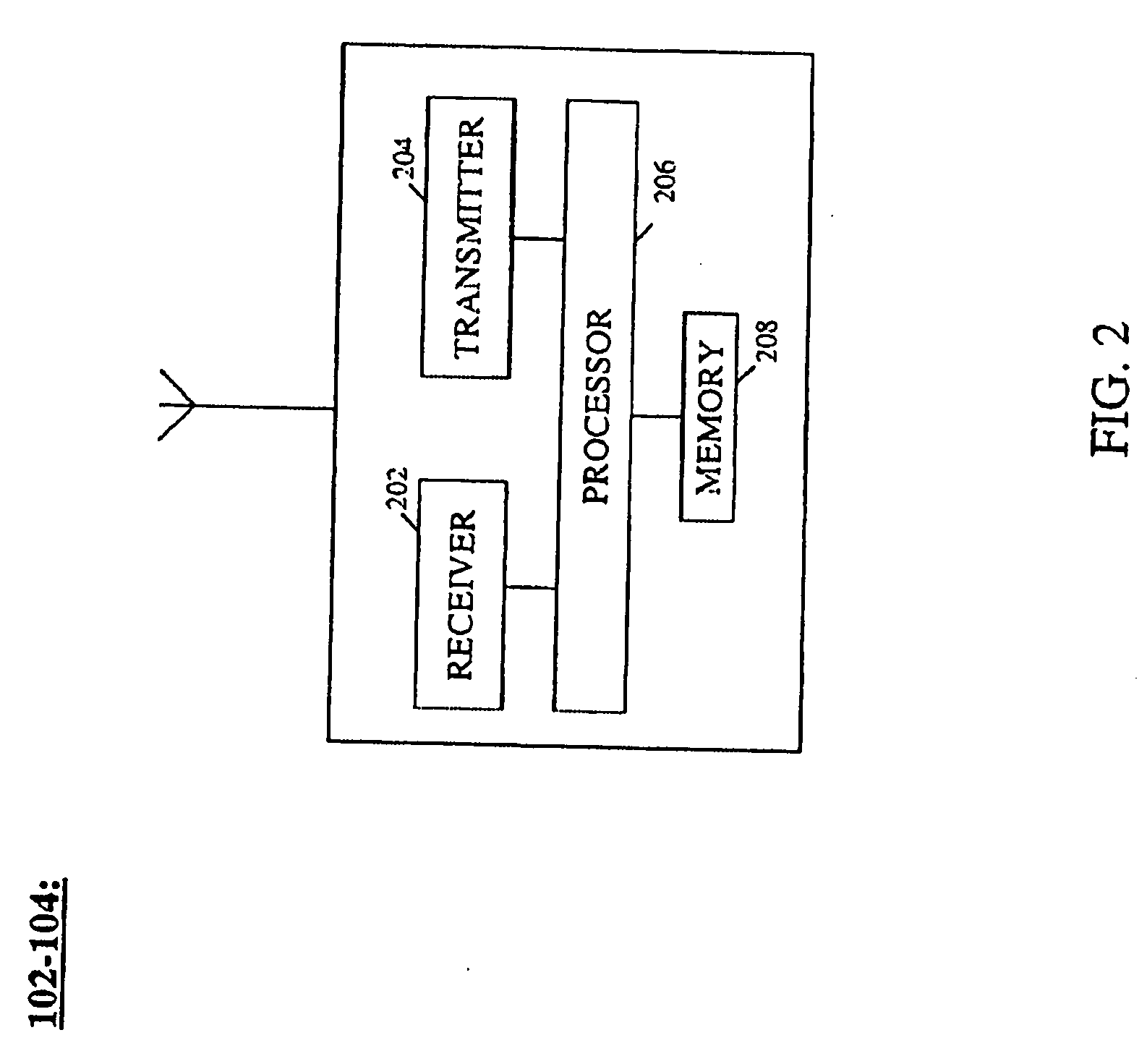
A communication system (100) determines whether to establish a point-to-multipoint communication or a point-to-point communication for conveyance of Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service (MBMS) data based on a number of mobile stations (MSs) (102-104), both idle mode and maintaining an active connection, serviced by the system and subscribed to an MBMS service. The system, broadcasts (306) a control message that includes an access probability factor. In order to avoid overloading the system with responses to the control message, MSs maintaining an active connection ignore (506, 508) the control message while idle mode MSs determine (506, 512) whether to respond based on the access probability factor. The system compares (310) a number of received responses to a threshold and determines whether to establish a point-to-multipoint communication (312) or a point-to-point communication (322) based on the comparison. The system also adjusts (314, 330) the access probability factor based on the number of responses.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
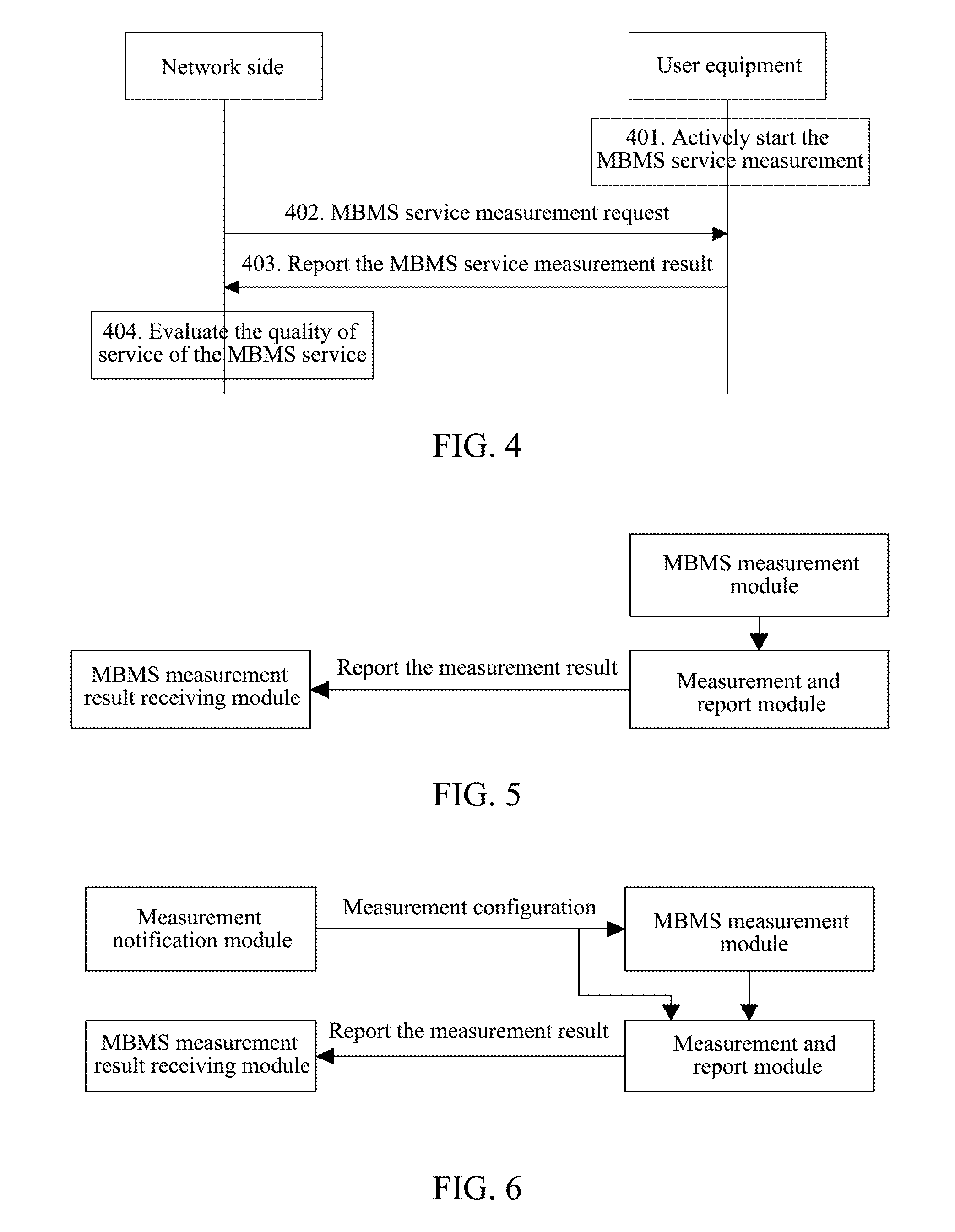
Realization method and system for receiving state report by user equipment in multimedia broadcast multicast service
ActiveCN101883327AAchieve statisticsMeet activityNetwork traffic/resource managementBroadcast service distributionMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceTelecommunications
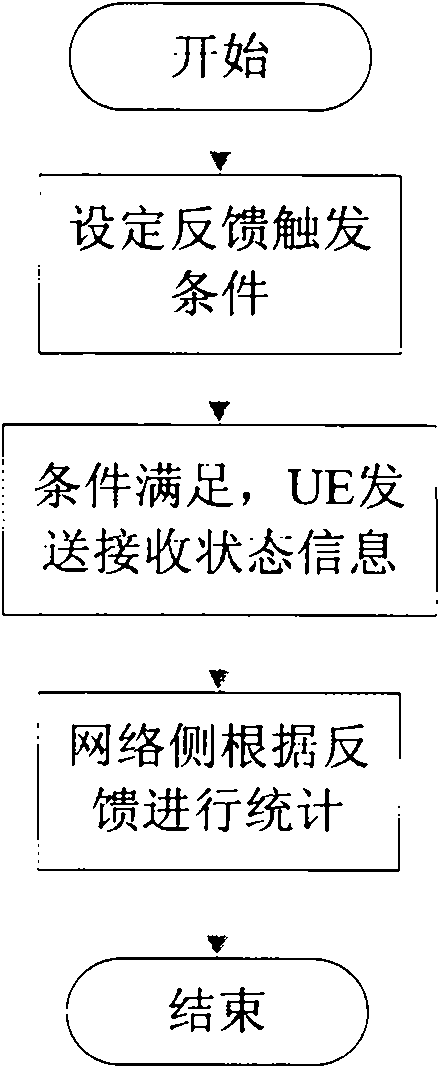
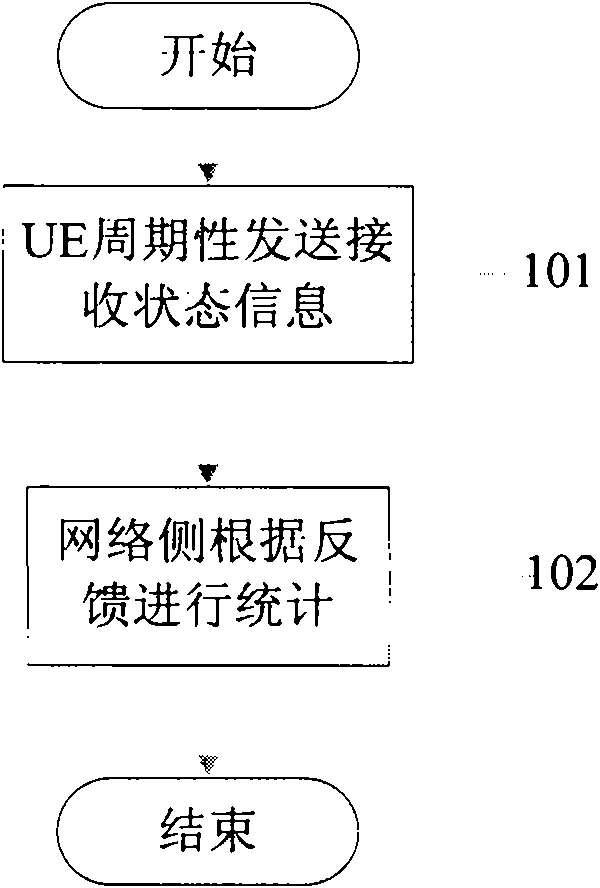
The invention discloses a realization method and a system for sending and receiving a state report by a UE (User Equipment) in an MBMS (Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service). The realization method comprises the following steps of: actively initiating a feedback process by the UE or sending a feedback request indication to the UE by a network side within a certain period or at the occurrence of a trigger event; sending feedback information to the network side by the UE according to such indication; and counting a UE receiving state by the network side according to the feedback information of the UE. The invention also discloses a system for sending the MBMS and receiving the state report by the UE. In the invention, the UE can send and receive the state report under the condition of a plurality of MCCHs (Multiple Control Channel), the correct statistics on the number of the UE is realized, and requirements on activating or deactivating MBSFN (Multimedia Broadcast System Frame Number) transmission by the network side are satisfied.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and apparatus for receiving data in user equipment of supporting multimedia broadcast multicast service
ActiveUS20120257562A1Effectively receiving dataData efficientPower managementBroadcast transmission systemsMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceControl channel
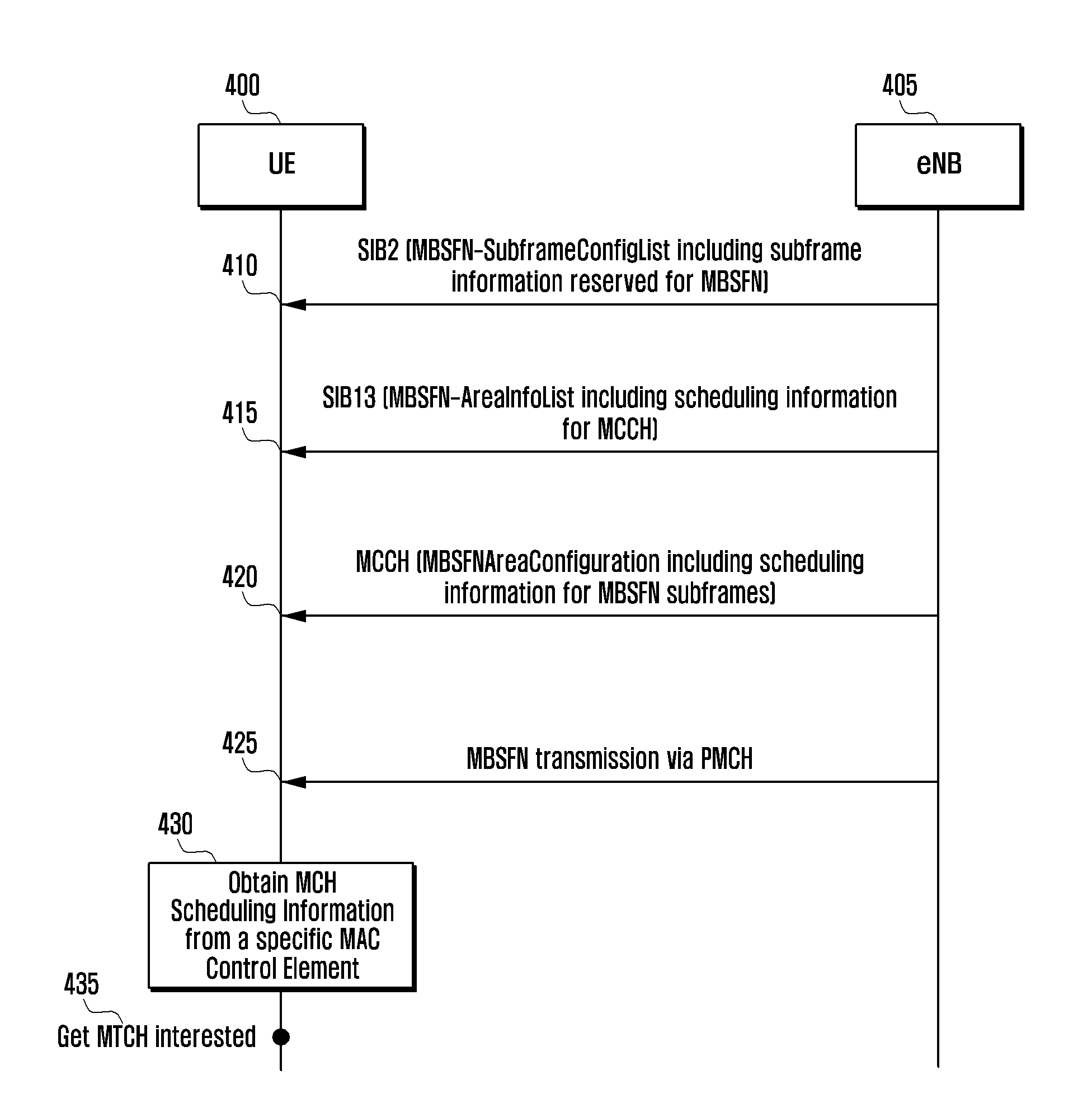
A method and an apparatus for receiving data in a User Equipment (UE) supporting a Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service (MBMS) are provided. A method of receiving data by a UE which supports an MBMS includes obtaining first indication information indicating a Multicast / Broadcast over a Single Frequency Network (MBSFN) subframe reserved for an MBSFN, obtaining second indication information indicating a subframe in the MBSFN subframe, the subframe decoding a Physical Multicast CHannel (PMCH), and when although a first subframe is indicated as the MBSFN subframe, the first subframe is not indicated to decode a PMCH and is not of a subframe for a Positioning Reference Signal (PRS), receiving a Physical Downlink Control CHannel (PDCCH) of the first subframe and decoding a corresponding Physical Downlink Shared CHannel (PDSCH).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cell reselection method for receiving packet data in a mobile communication system supporting MBMS
ActiveUS7437178B2Assess restrictionBroadcast service distributionMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceTelecommunications
A method for selecting a cell by a user equipment (UE) to receive a Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service (MBMS) service in a mobile communication system which supports the MBMS service with different frequency allocations (FAs) in the same area. In the method, a radio network controller (RNC) transmits information on an MBMS cell to the UE, and the MBMS cell information includes an MBMS offset for guaranteeing priority for cell reselection to the MBMS cell. The UE performs cell reselection using the MBMS cell information and receives the MBMS service from the reselected cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for transmitting multimedia services in the UMTS networks by immediate multicasting of a streaming subset
ActiveUS20040223513A1Fast deliveryEliminate delaysSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceReal time services
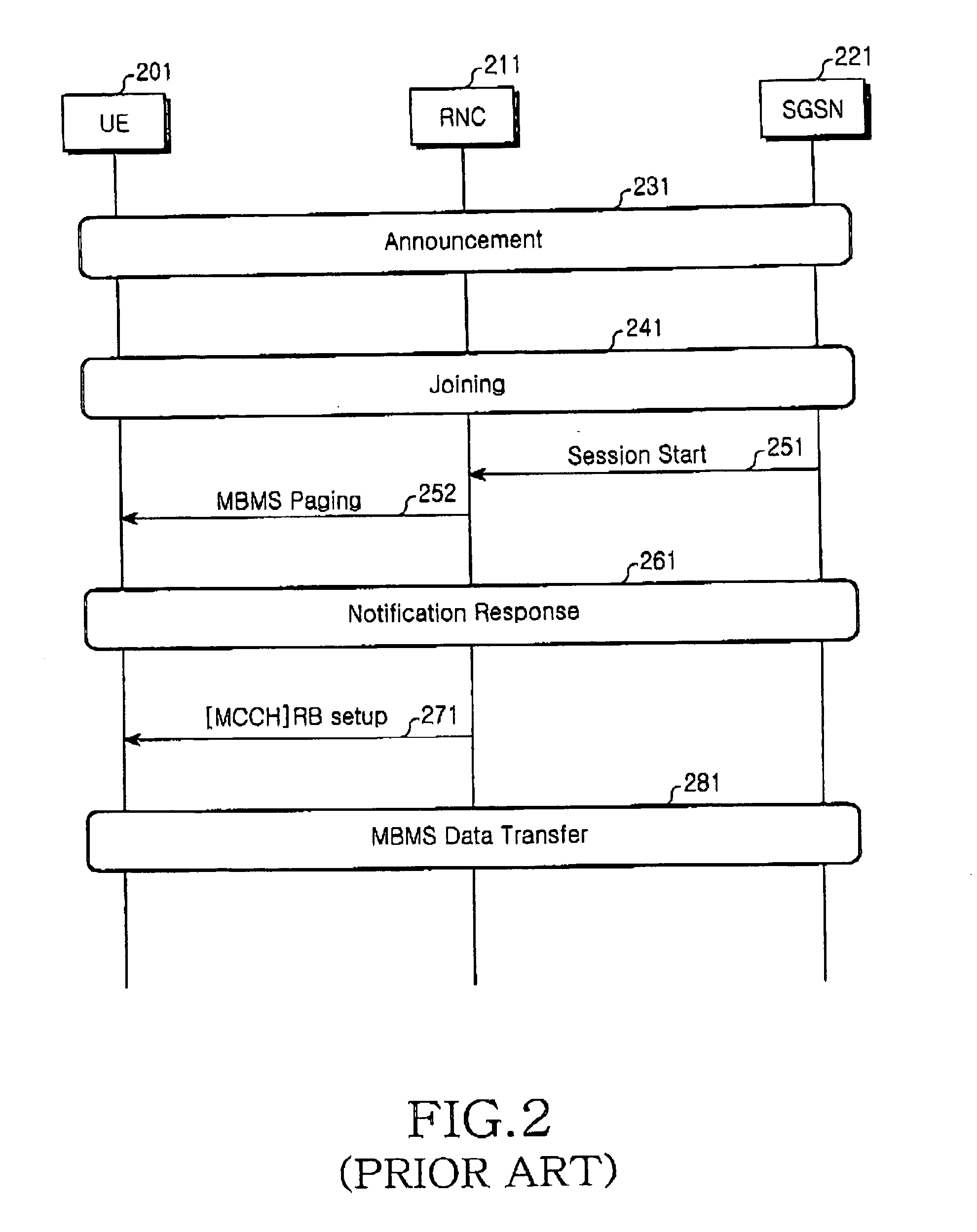
The method concerns multicast service delivering through the UMTS and GSM networks. For this aim is given higher priority to an opportune subset of all the real-time services with guaranteed bandwidth transmissible by the network. This subset is named IS-MBMS (Immediate Streaming-Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service). A certain amount of physical resources is reserved in all the system for the IS-MBMS services; not real-time services can be transmitted on the reserved resources when not used by the IS-MBMS ones. The reserved resources allow for transmitting the IS-MBMS services with minimum bit-rate, at least. The network announces in the service area that an IS-MBMS content becomes available; in reply one or more subscribed users transmit a request for joining a multicast group for that service. The network transmits a notification message on a multicast channel to give to the joined users useful information of how get the announced service, i.e.: Service-Id, RB parameters, etc. The IS-MBMS content is transmitted immediately on a point-to-multipoint channel set-up in each involved cells, even if there are zero recipients in the cell. Content is transmitted in parallel in different cells, leading to service continuity, and the mobile station can perform soft combining. During the IS-MBMS content delivery the network can count in each involved cell the number of subscribed users joined to the transmitted IS-MBMS service. The network switches from point-to-multipoint to point-to-point or to no transmission depending on the result of counting and on a fixed threshold. Alternatively the network, parallel to the content delivery, can execute a checking procedure to see if there are joined users in a cell: in this case the point-to-multipoint channel is switched to no transmission (fig. 3).
Owner:HMD GLOBAL
Method and apparatus of transmitting data in mbsfn subframe in wireless communication system
InactiveUS20110299449A1Efficient use ofBroadcast transmission systemsPilot signal allocationMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCommunications system
A method and apparatus of transmitting data in a Multimedia Broadcast multicast service Single Frequency Network (MBSFN) subframe in a wireless communication system is provided. A base station (BS) transmits a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) to a user equipment in a first orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) symbol, transmits reference signals for a plurality of extended antenna ports to the user equipment in a second OFDM symbol by mapping the reference signals to subcarriers, and transmits a physical downlink shared channel (PDSCH) to the user equipment in the second OFDM symbol by mapping the PDSCH to the remaining subcarriers other than the subcarriers to which the reference signals are mapped.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
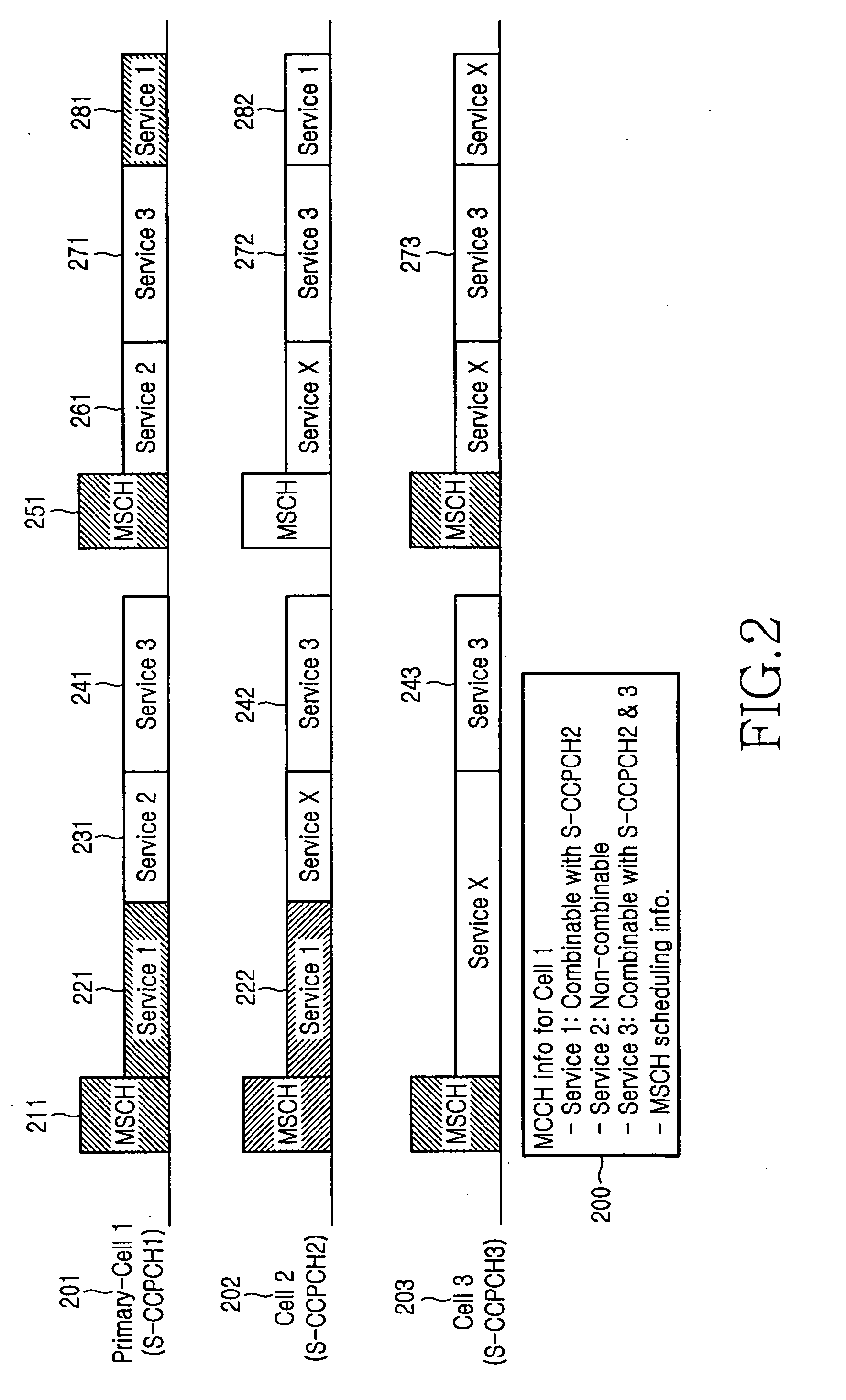
Partial combining method and apparatus for multimedia broadcast/multicast service
ActiveUS20060067281A1Time-division multiplexConnection managementCurrent cellMultimedia Broadcast Multicast Service
A method and apparatus for enabling partial combining on a Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service (MBMS) service are provided where a radio network controller (RNC) specifically informs a user equipment (UE) whether an MBMS service signal of the current cell is combinable with the same MBMS service signals received from different cells for each individual service or timing, through an MCCH or an MSCH, which is a type of a logical channel for an MBMS service, in a Uu interface. The UE combines the MBMS service signals transmitted from the different cells, thereby obtaining a gain in terms of utilization of transmission power and radio resources.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Soft combining apparatus and method in a CDMA mobile communication system providing MBMS service
ActiveUS20050063339A1Ensure correct executionSite diversityBroadcast service distributionAsynchronous cdmaMultimedia Broadcast Multicast Service
A method and apparatus for determining soft handover in a CDMA mobile communication system supporting Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service (MBMS) is provided. In the asynchronous CDMA mobile communication system supporting MBMS, when a UE moves to a region where it can receive data from a plurality of Node Bs, the UE determines whether to perform soft combining using a measurement value of a dedicated pilot channel signal, in performing soft handover. In this way, the UE can determine whether to perform soft combining on MBMS data received from a plurality of Node Bs by itself. Therefore, even though an MBMS user moves from a current or existing cell to a new cell, a stable MBMS service is provided to the user, thereby contributing to the user's convenience.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method to control a multimedia broadcast multicast service(MBMS) mode of a MBMS session in a communication system
InactiveUS20110116433A1Broadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCommunications system
A method to control a multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS) mode of a MBMS session in a communication system is provided herein. In operation, a first network element that is located outside a radio access network determines to use one of a single frequency network MBMS mode and a single cell MBMS mode for the MBMS session based on a property of the MBMS session. The first network element then transmits a session control signaling message to a second network element that is located inside the radio access network. The session control signaling message instructs the second network element that user plane data for the MBMS session shall be transmitted using the determined MBMS mode. The base stations then transmit the user plane data to one or user equipments in a target service area according to the determined MBMS mode.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and System for Receiving Multimedia Broadcast/Multicast Service Control Information, and UE Thereof
InactiveUS20070133456A1Precise processingData switching by path configurationBroadcast service distributionBroadcast channelsMultimedia Broadcast Multicast Service
A method for receiving Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service (MBMS) control information includes: a network side transfers a system information block in a broadcast channel, the system information block includes Radio Link Control Layer (RLC) configuration information; a User Equipment (UE) selects a new cell, and obtains the available RLC configuration information which is available to the new cell, and re-establishes an RLC receiving entity according to the available RLC configuration information. A method for receiving MBMS control information, includes: a network side transferring a system information block in a broadcast channel, the system information block including RLC configuration information; receiving, a UE, the RLC configuration information, and if there is out-of-sequence delivery configuration information within the RLC configuration information, configuring an RLC receiving entity according to the received out-of-sequence delivery configuration information. The invention also provides a system for receiving MBMS control information, and a UE thereof.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
System and method in a communication network of dynamically assigning a multimedia broadcast/multicast service bearer to a multicast channel
ActiveUS20120155282A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceTelecommunications
Methods for dynamically assigning a multimedia broadcast / multicast service (MBMS) bearer to a Multicast Channel (MCH) in a communication network include a logical server: receiving a MBMS configuration for the communication network; receiving a request for a MBMS bearer within a service area, wherein the request specifies a QoS requirement for the MBMS bearer; inspecting the MBMS configuration to determine if an existing MCH in the service area meets the QoS requirement for the MBMS bearer; based on the inspecting, assigning the MBMS bearer to the existing MCH or assigning the MBMS bearer to a new MCH.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
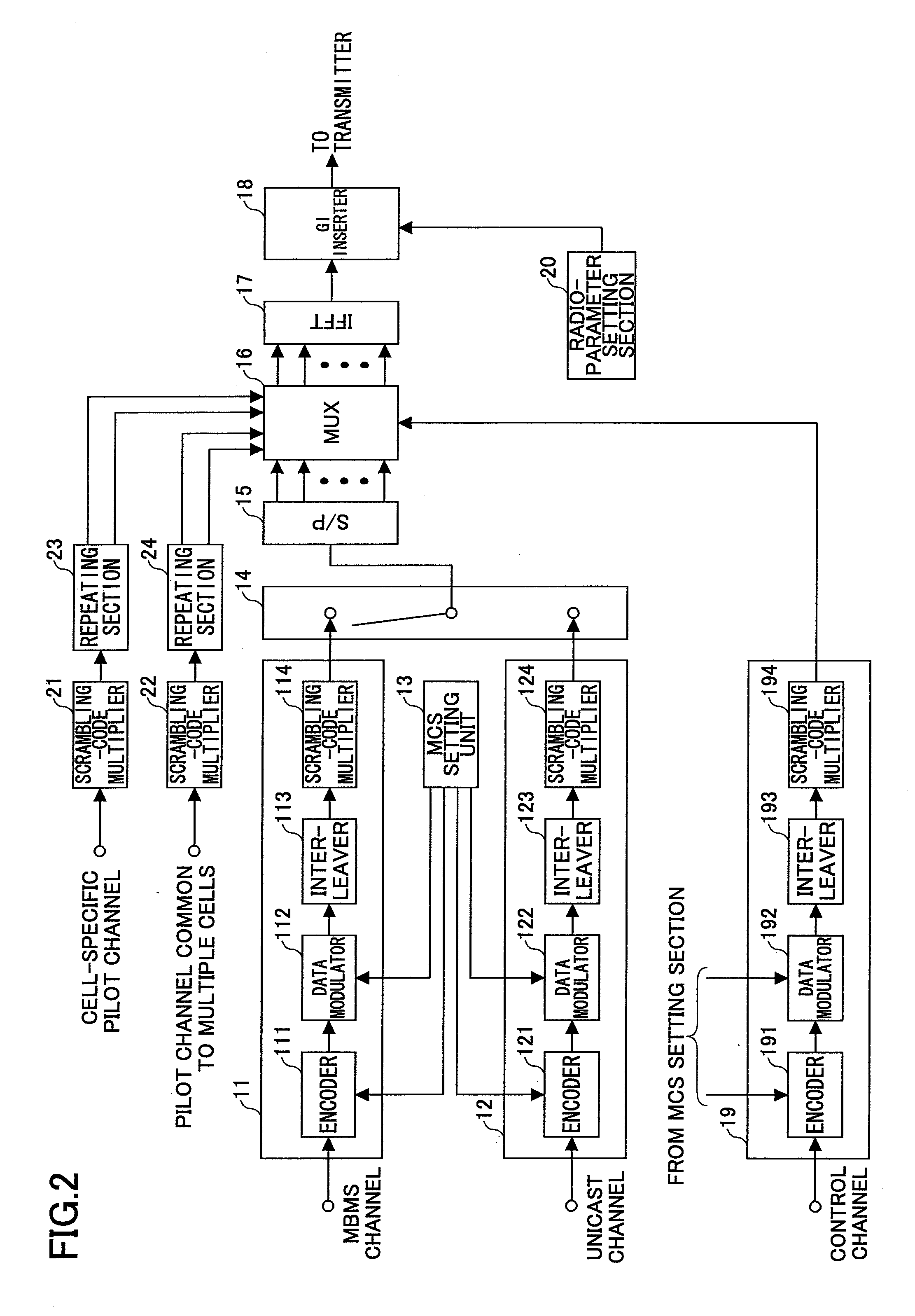
Transmitting and receiving apparatuses and methods
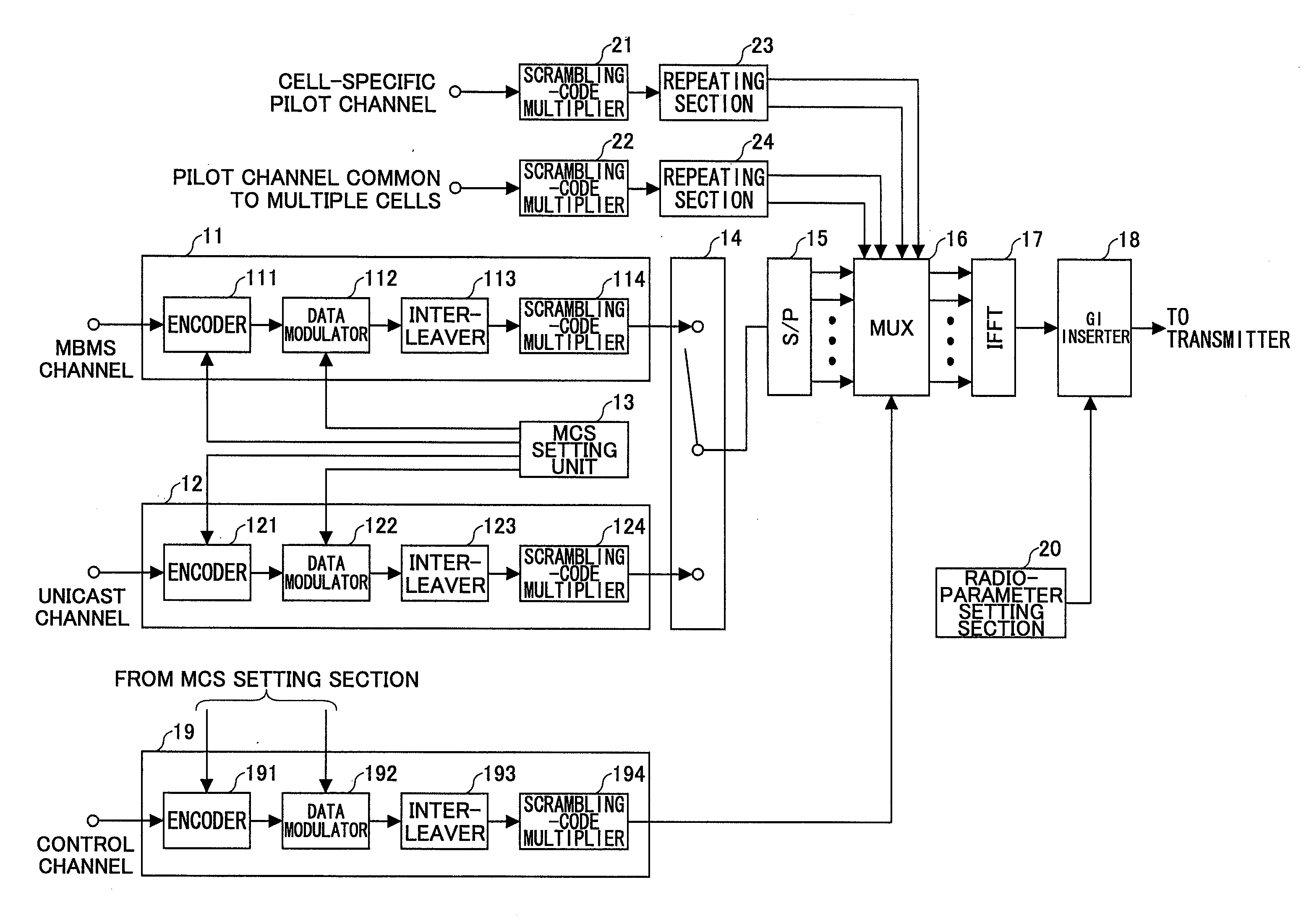
ActiveUS20090196165A1Improve reception qualityTransmission path divisionBroadcast transmission systemsMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCommon pilot channel
A transmitting apparatus which transmits a transmit symbol in orthogonal-frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) is disclosed. The transmitting apparatus includes a unit which provides a unicast channel; a unit which provides a multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS) channel; a unit which provides a specific pilot channel which is specific to a specified cell; a unit which provides one or more common pilot channels common to a plurality of cells; and a multiplexing unit which multiplexes the unicast channel, the MBMS channel, the specific pilot channel, and the one or more common pilot channels, and creates the transmit symbol, wherein the multiplexing unit time-division multiplexes, in the same frequency band, a unicast frame which includes the unicast channel, and an MBMS frame which includes the MBMS channel, and wherein an insertion density of the common pilot channel included in the MBMS frame is larger than an insertion density of the specific pilot channel included in the unicast frame.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method of handling mobility in multimedia broadcast multicast service single frequency network in a wireless communication system and related communication device
InactiveUS20110077006A1Wireless commuication servicesWireless communicationMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCommunications system
A method of handling mobility in multimedia broadcast multicast service single frequency network (MBSFN) for a user equipment of a wireless communication system includes when the user equipment proceeds with an MBMS service and performs handover from a source cell to a target cell, checking whether a target MBSFN area which the target cell belongs to is the same as a source MBSFN area which the source cell belongs to, when the target MBSFN area is different from the source MBSFN area, receiving a multicast control channel (MCCH) corresponding to the target MBSFN area, checking whether the MBMS service is provided in the target MBSFN area, and when the MBMS service is provided in the target MBSFN area, sending a service join request to a target network of the wireless communication system, for continuing to receive the MBMS service.
Owner:HTC CORP
Method and terminal for performing handover in mobile communications system of point-to-multipoint service
InactiveUS20080273503A1Prevent service delaysTime-division multiplexBroadcast service distributionMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCommunications system
A method for performing a handover in a mobile communications system of a Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service (MBMS), wherein when a terminal having subscribed (joined) a point-to-multipoint service moves from a first base station to a second base station, the terminal is commanded (indicated) by the first base station to transfer point-to-multipoint service information, and then transfers to the second base station a point-to-multipoint service list subscribed (joined) by the terminal or information on the point-to-multipoint service received from the first base station, whereby a service delay which may occur during the handover can be effectively avoided.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Multimedia broadcast multicast service measurement and reporting method and system
InactiveCN102215455AImprove performanceBroadcast service distributionLocation information based serviceCurrent cellMultimedia Broadcast Multicast Service
The invention discloses a multimedia broadcast multicast service measurement and reporting method and a multimedia broadcast multicast service measurement and reporting system, which are used for solving the technical problem of how to measuring multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS) performance and reporting measurement results reflecting the MBMS performance by user equipment (UE). The method comprises that: the UE measures an MBMS according to measurement configuration; and when measurement reporting criterions are met, the UE reports the obtained measurement results or measurement logs of the MBMS measurement to a network side. By the method provided by the invention, a help in timely knowing the MBMS performance of a current cell can be provided for an operator, and possible problems can be timely discovered and solved as early as possible according to the reported measurement results; in addition, the problems of efficiency and cost caused by drive tests can be effectively solved, and the service performance is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and apparatus for providing a multimedia broadcast/multicast service in a visited network
ActiveUS20050170842A1Special service provision for substationBroadcast service distributionMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCommunications system
A communication system provides a Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service (MBMS) to a roaming user equipment (UE) by receiving, at a first network, a request from the UE to subscribe to an MBMS service and, in response to receiving the request, conveying to the UE a Temporary Mobile Group Identity (TMGI) that is uniquely associated with the MBMS service and the first network. When the first network receives information associated with a registration of the UE with a second network and further receives MBMS data associated with the MBMS service, the first network conveys the MBMS data and the TMGI to the UE via the second network. By using a TMGI that is unique to the MBMS service and the first network, the UEs subscribed to an MBMS service at the second network ignore a notification conveyed to the UE by the second network, thereby preserving a battery life of such UEs.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Hard handover method and apparatus for user equipment (UE) using frequency layer convergence (FLC) in a multimedia broadcast/multicast system (MBMS) system
InactiveUS20060058047A1Efficient executionBroadcast service distributionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceFrequency shift
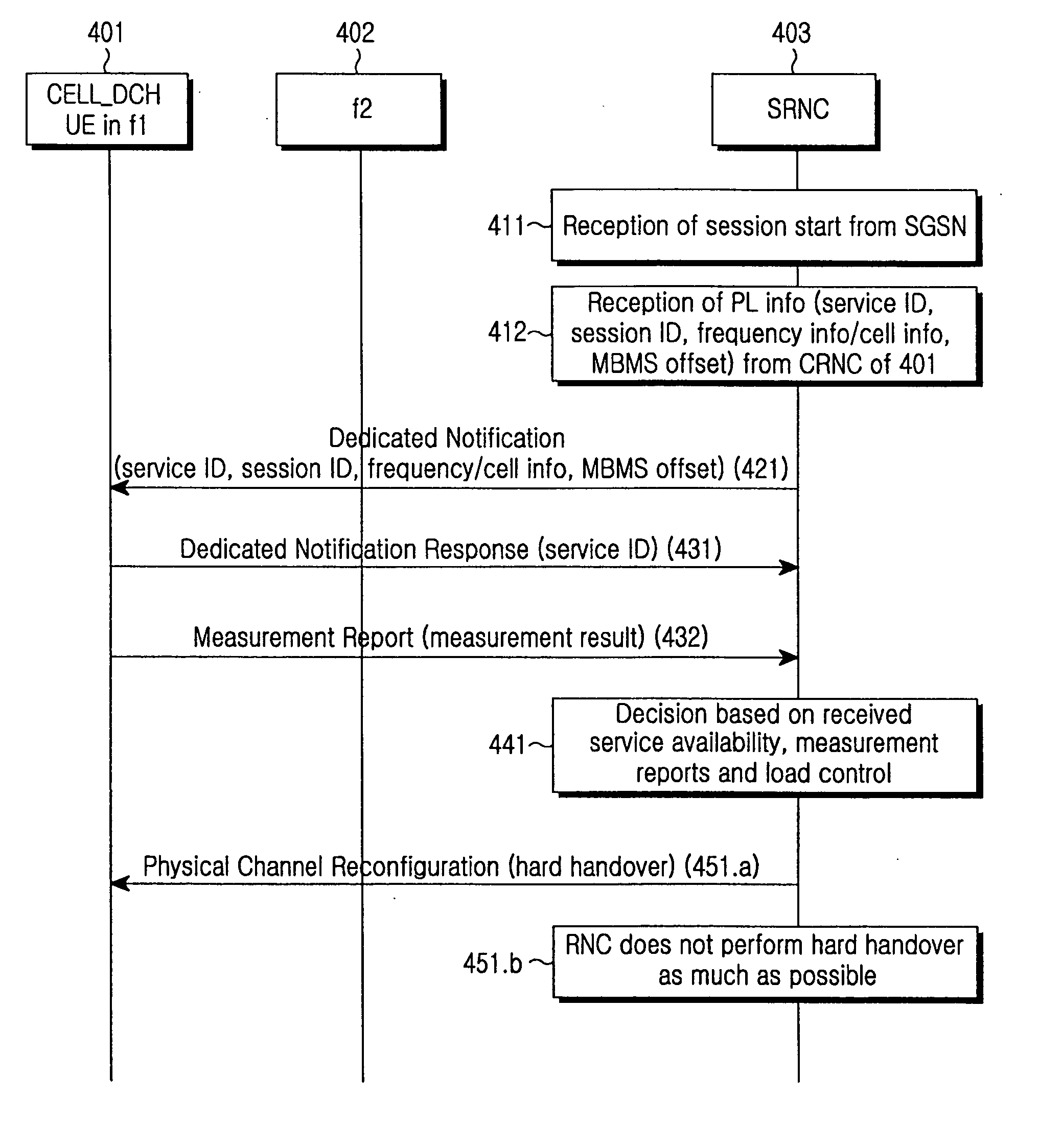
Disclosed a method for efficiently performing a frequency shift when a User Equipment (UE) intends to receive at least one service through at least one preferred frequency in a system for providing a Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service (MBMS) service. The method comprises the steps of inserting information for a preferred frequency of a service into a message and transmitting the message to the UE, the service being indicated by the message, the message reporting a start of the service which the UE has joined, receiving a response message including request information representing the indicated service or at least one different service, which has been selected by the UE, and determining if the UE is to perform hard handover to the preferred frequency according to the request information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Evolved multimedia broadcast multicast service on enhanced component carriers
ActiveUS20160205664A1Transmission path divisionBroadcast transmission systemsMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceComputer network
Methods, systems, and devices are described for evolved multimedia broadcast multicast service (eMBMS) utilizing enhanced component carriers (eCCs). A wireless system may send unicast data using resources allocated for multicast transmissions (e.g., eMBMS transmissions). The presence of unicast data in a transmission time interval (TTI) scheduled for multicast transmission may be indicated by a control region within the TTI. A UE may monitor the control region to identify the presence of unicast information. A TTI scheduled for multicast transmission may also include reference signals to aid in the demodulation of multicast or unicast data. In some cases, the reference signals may be front-loaded at the beginning or embedded within the TTI. The embedded reference signals may be configured based on the type of data carried by the TTI scheduled for multicast transmission, or by length of the cyclic prefix used by the TTI scheduled for multicast transmission.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method of implementing multicasting service
InactiveUS20070136759A1Satisfy the demandAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceComputer network
The present invention discloses a method for implementing Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service (MBMS), wherein multiple service modes are set for the MBMS and each service mode is corresponding to a path, a user equipment (UE) activates at least one service mode supported by the current network and receives the MBMS data in the corresponding path of the activated service mode from the network side. This method guarantees that UE covered by networks of multiple types can safely receive the subscribed MBMS data. When the current network covering UE fails to support the activated service mode, the UE will activate a service mode that the current network supports such that the UE can receive the MBMS data in this service mode. Therefore, it is ensured that UE can receive the subscribed MBMS data in any network environments, thus satisfying subscribers' demands to a larger extent.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Radio access node registration for multimedia broadcast multicast service
InactiveUS20070105557A1Reduce in quantitySpecial service provision for substationPower managementMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceCommunications system
A radio network control node acts across an Iur interface as a drift radio network control node (262) for a user equipment unit (UE) in a communications system supporting a multimedia broadcast multicast service (MBMS). The drift radio network control node (262) maintains a first counter for counting a number of events occurring at the drift radio network control node (262). Registration of the drift radio network control node (262) with a core network node (30) is advantageously delayed until the counter has exceeded a first threshold value. In one example mode, the number of events occurring at the drift network control node (262) which is counted by the counter is a number of user equipment units for which a Iur linking procedure is performed for the MBMS session. In another example mode, the number of events occurring at the drift network control node (262) which is counted by the counter are time periods elapsed since an Iur linking procedure for the MEMS session has been performed for a predetermined user equipment unit.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method of using service identifier for transmitting control information in mobile communication system providing multimedia broadcast/multicast service
InactiveUS20050037768A1Efficient receptionSpecial service provision for substationBroadcast service distributionMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceMobile communication systems
Disclosed is a method for using an identifier for an MBMS in a CDMA mobile communication system providing the MBMS. The method assigns by a radio network controller a cell identifier related to the MBMS available in a cell that includes the user equipment. The cell identifier is different from an identifier used in an upper layer. The method also transmits to the user equipment a control message that includes the cell identifier.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com