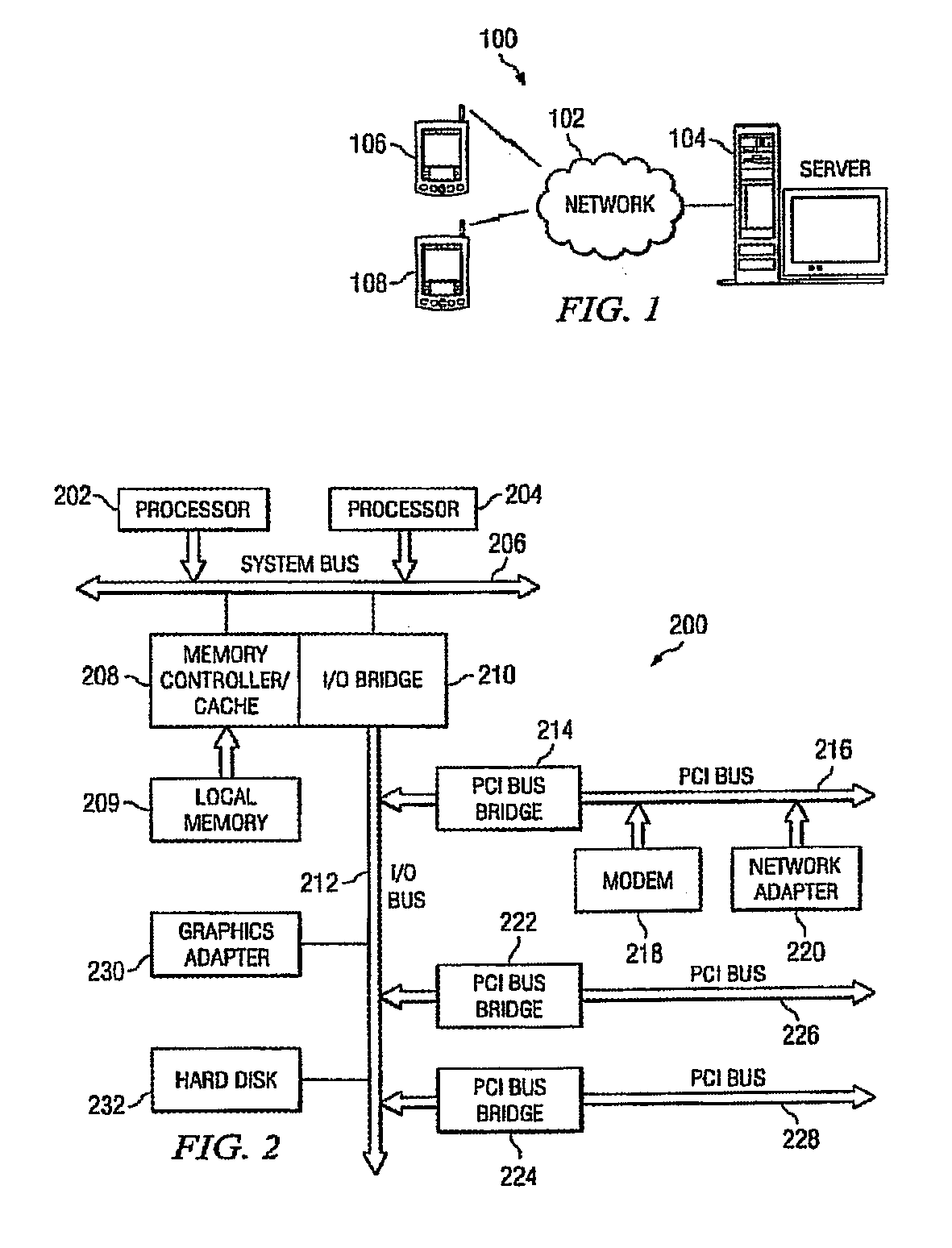
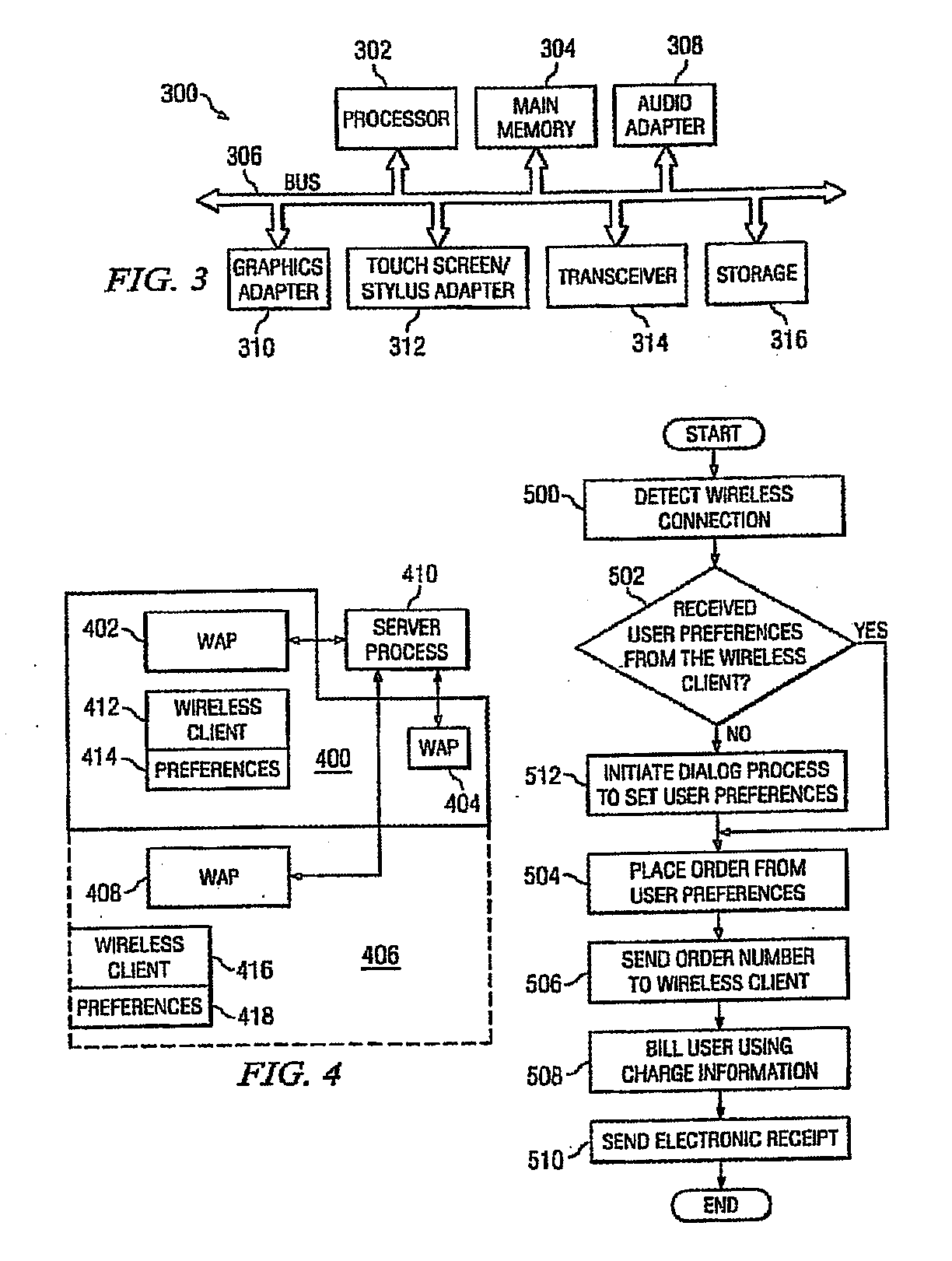
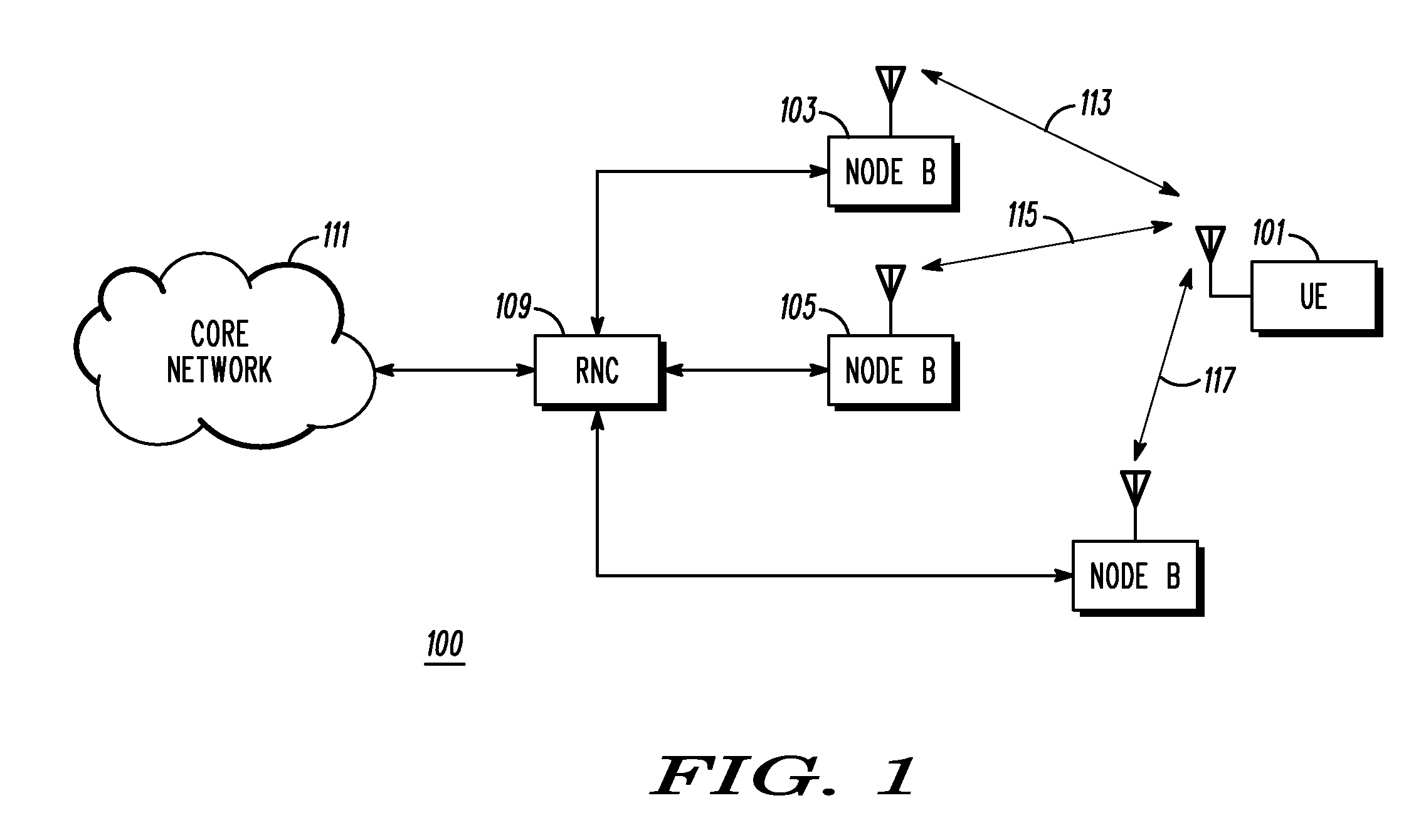
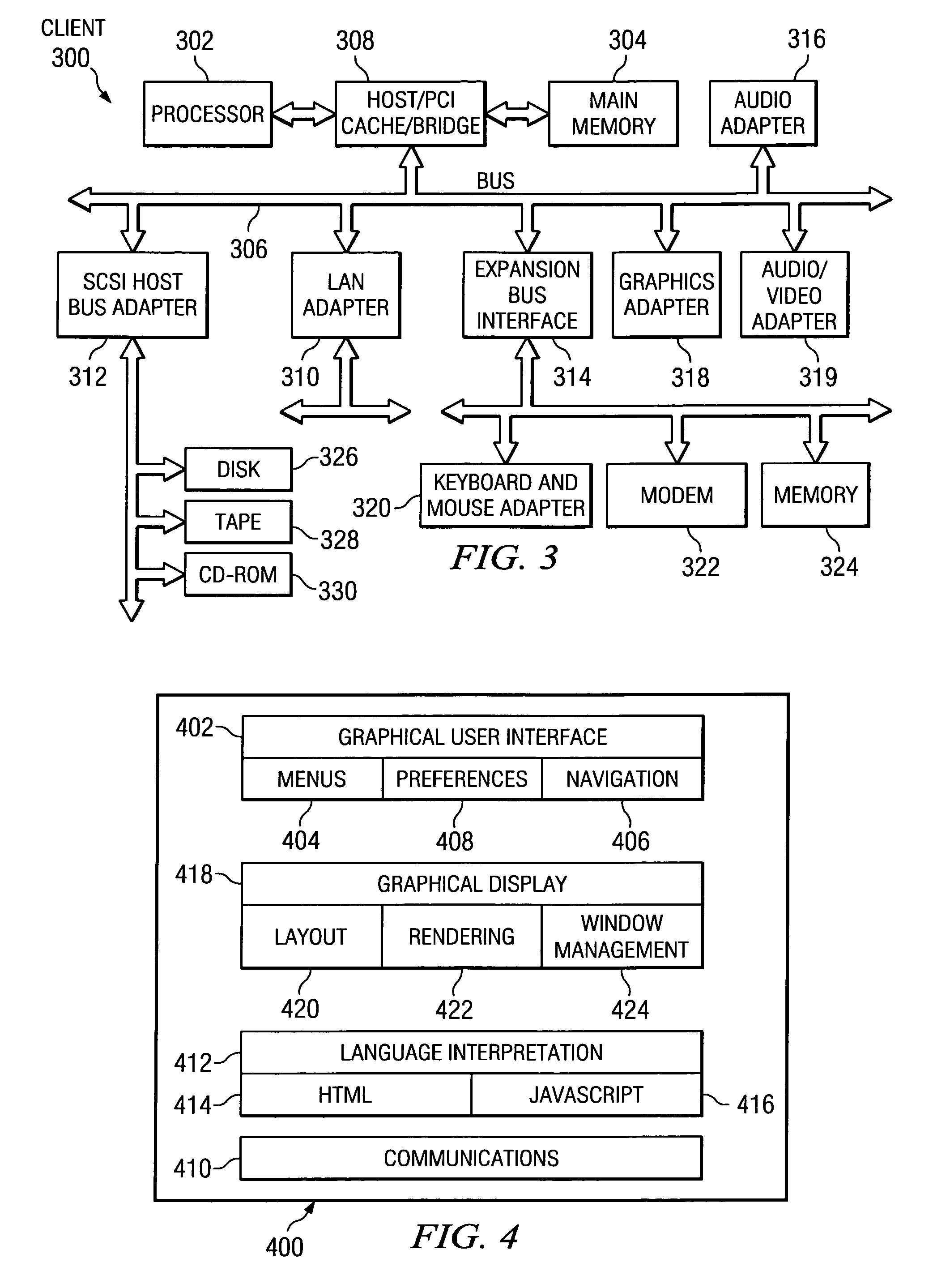
Patents
Literature
686 results about "Real time services" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
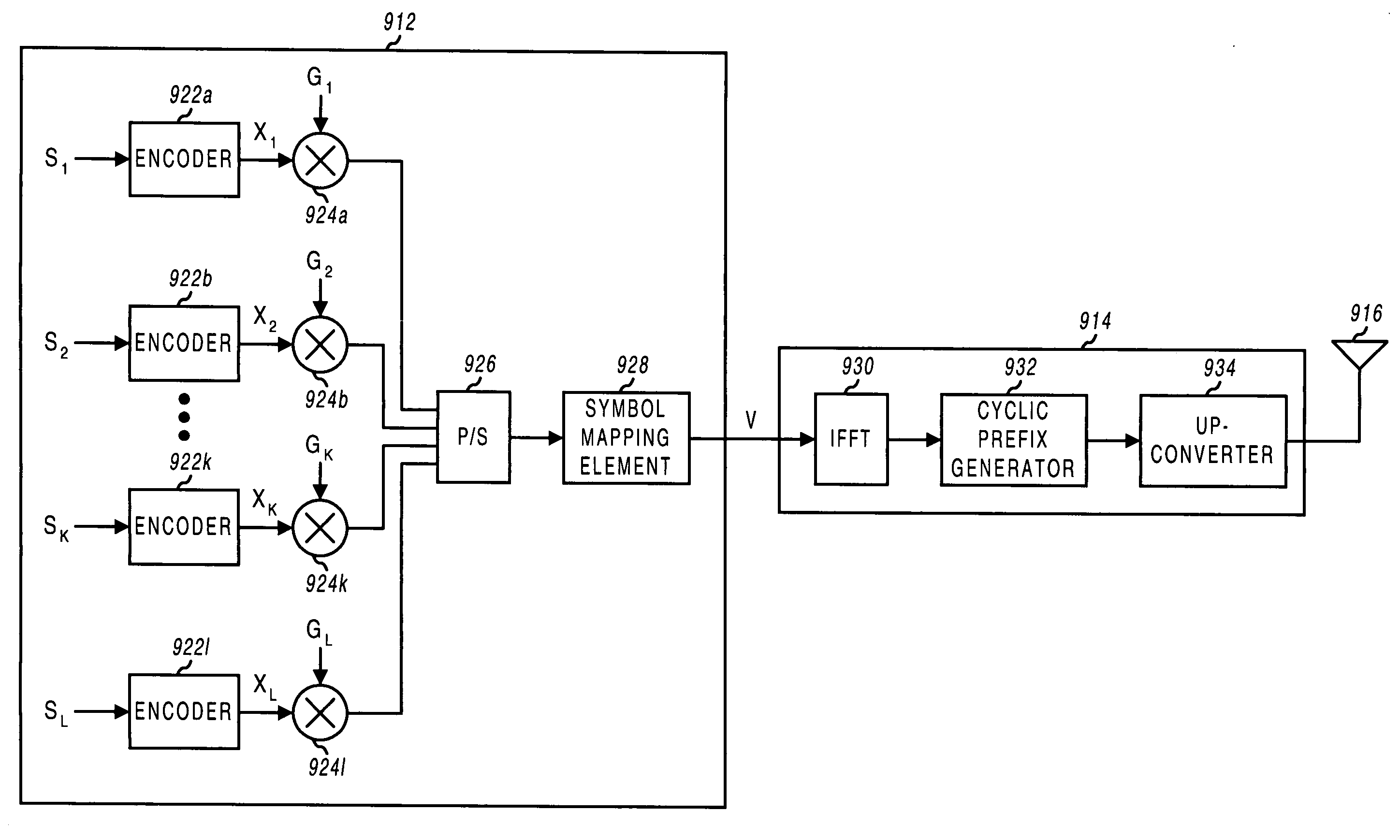
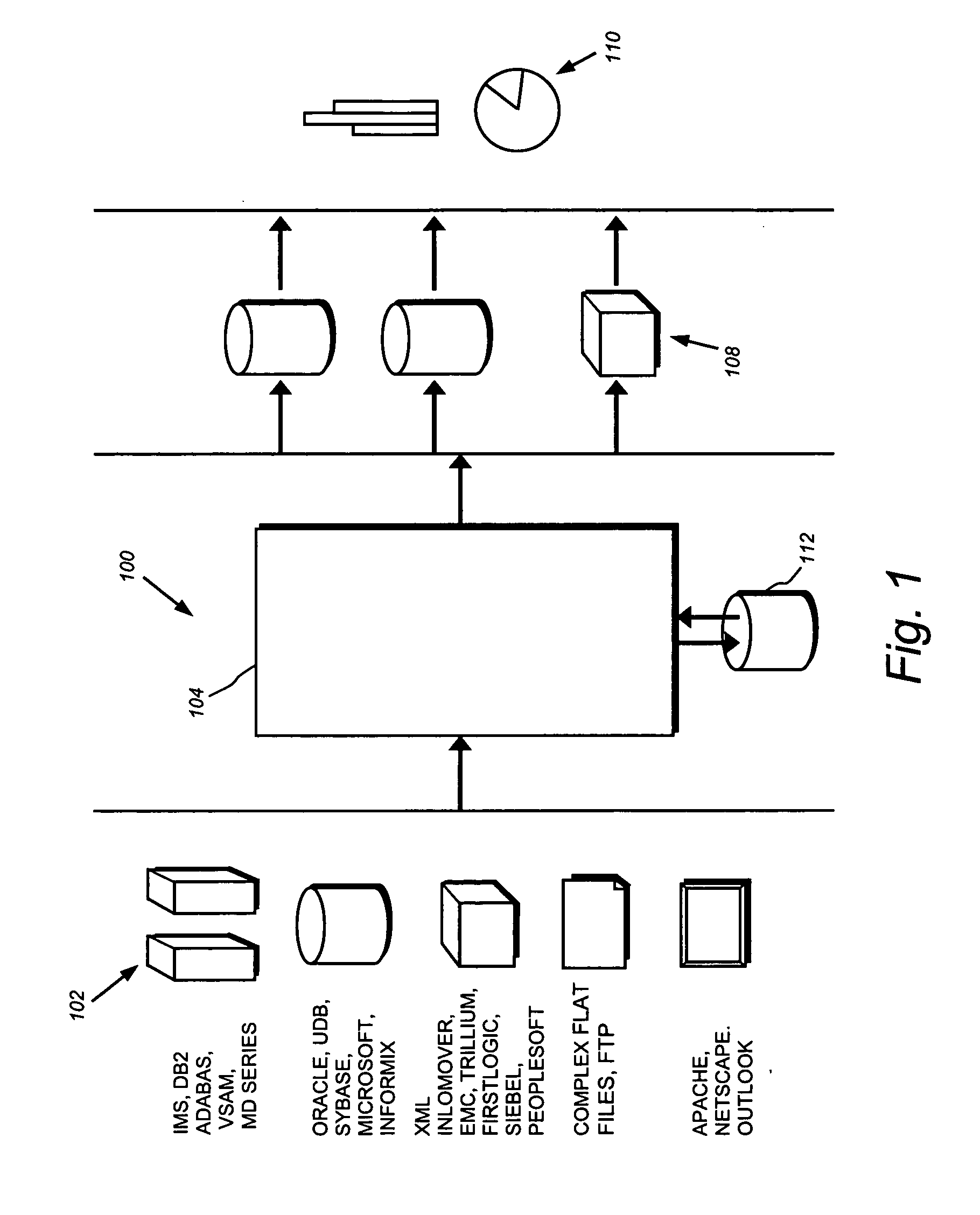
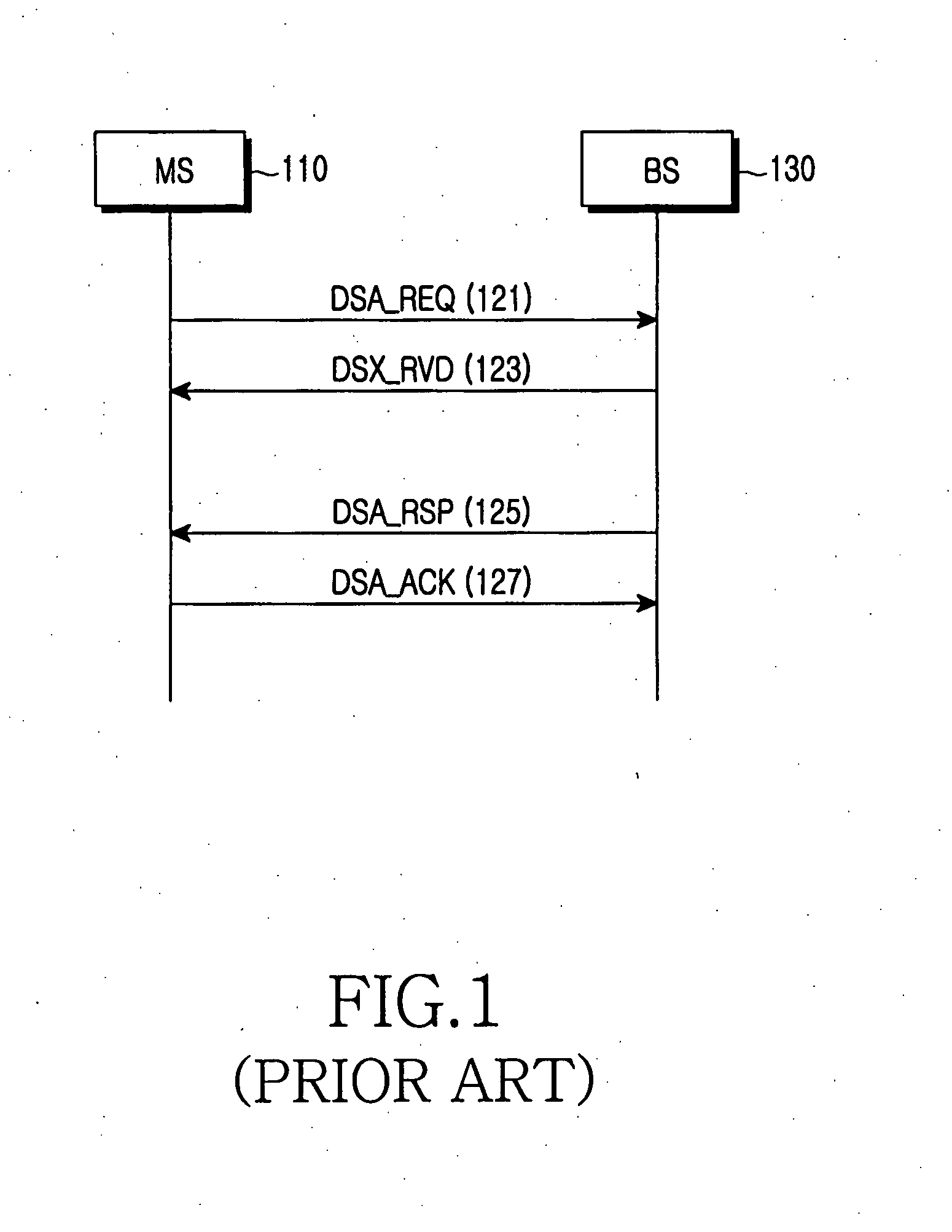
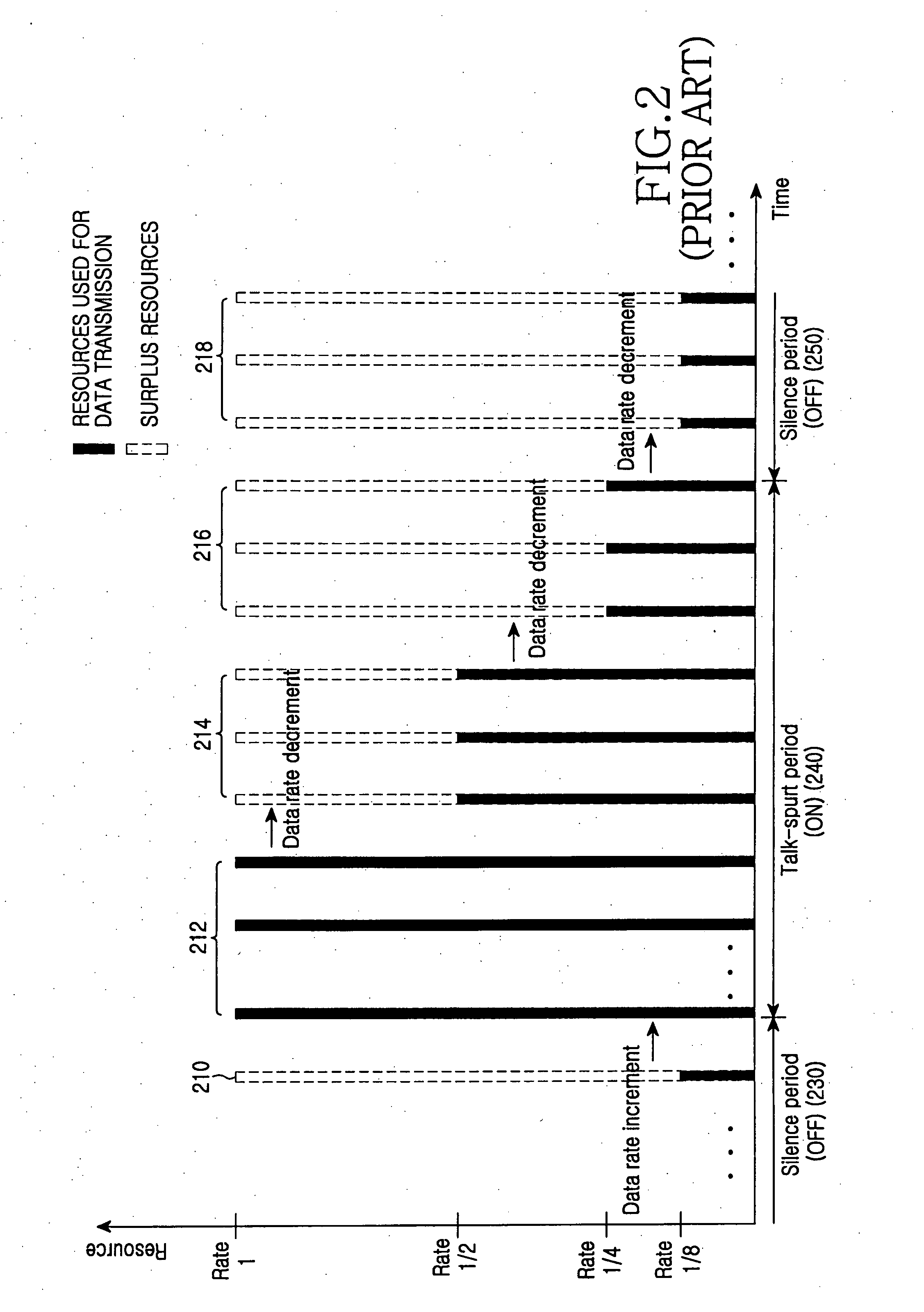
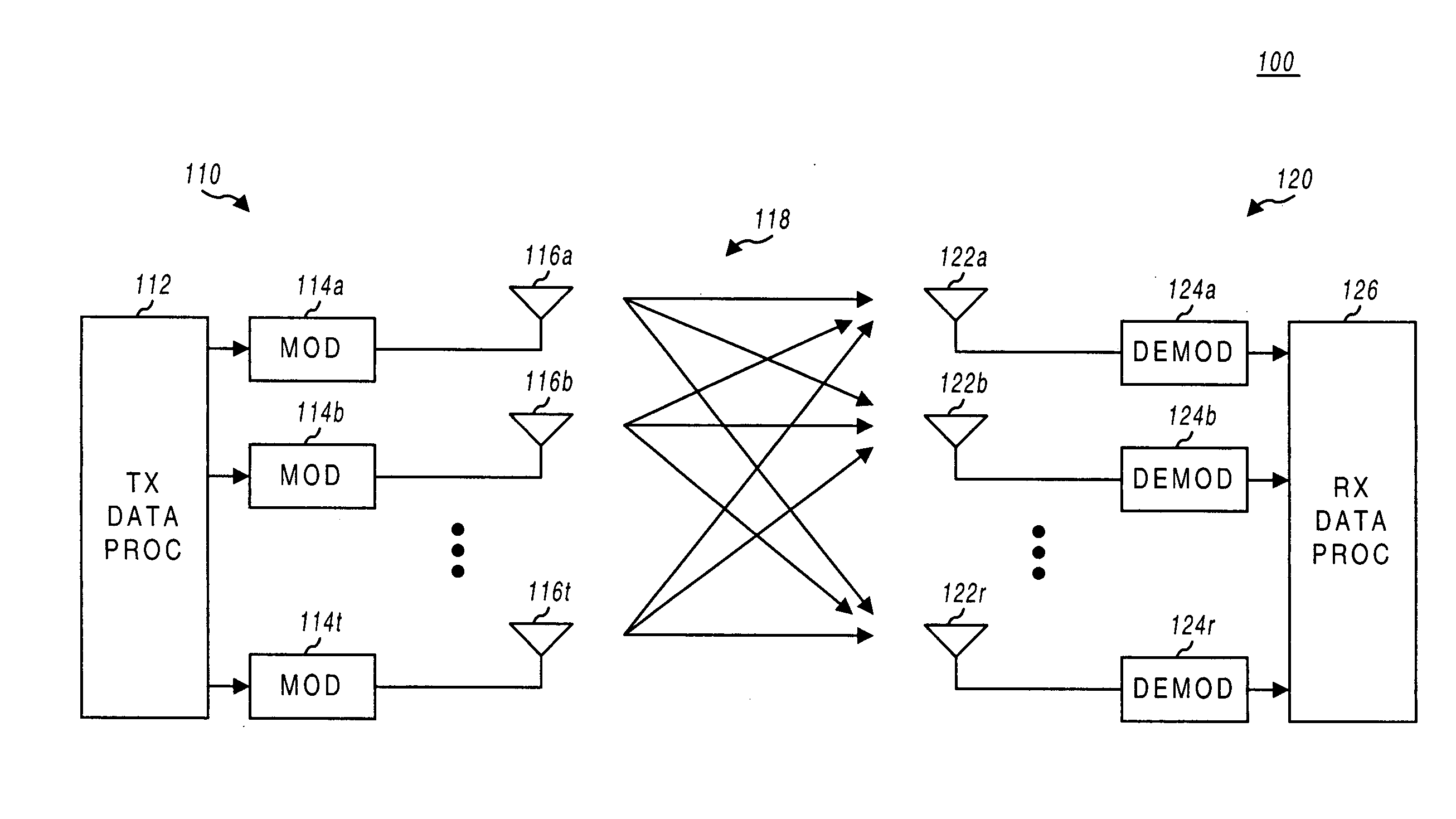
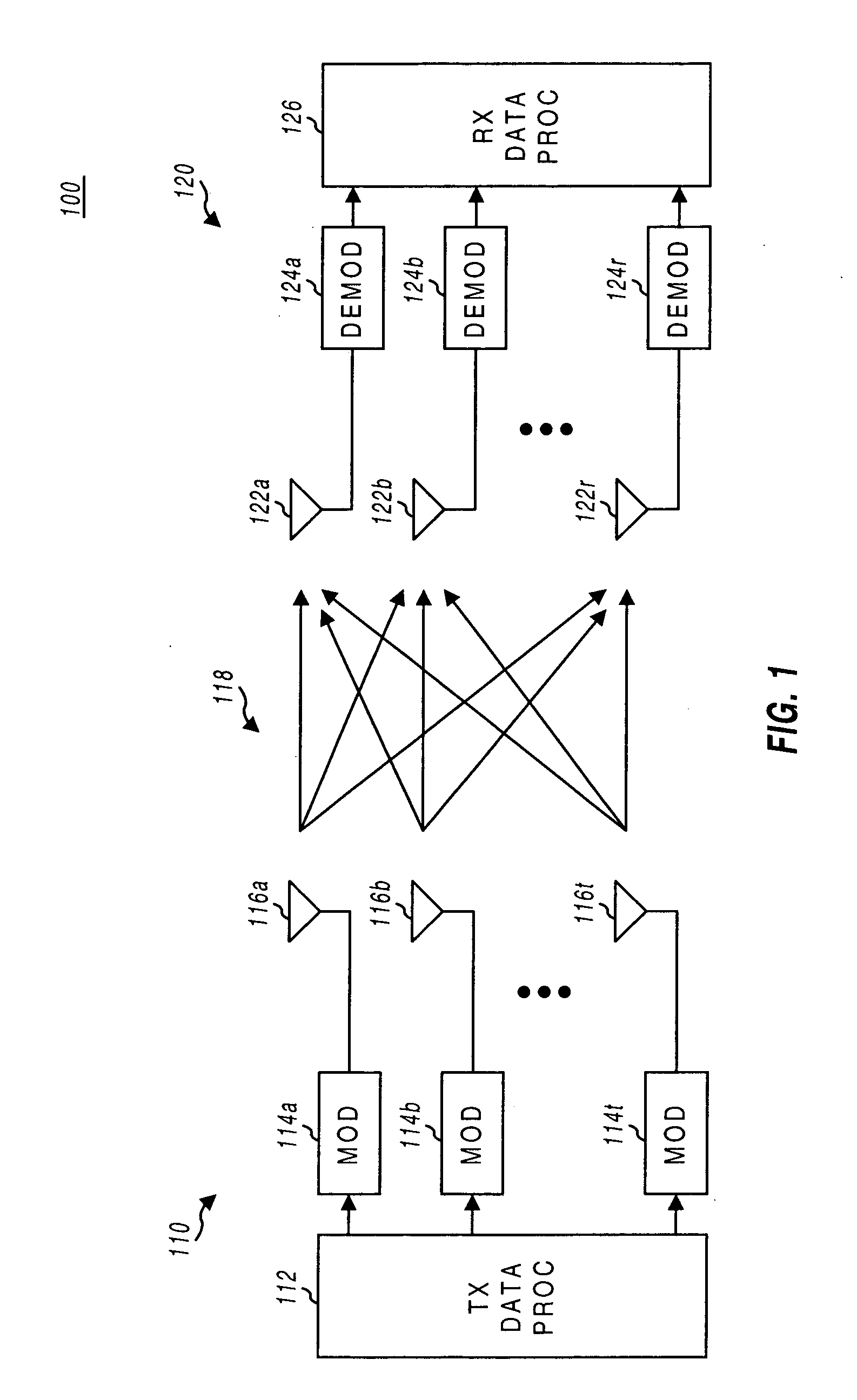
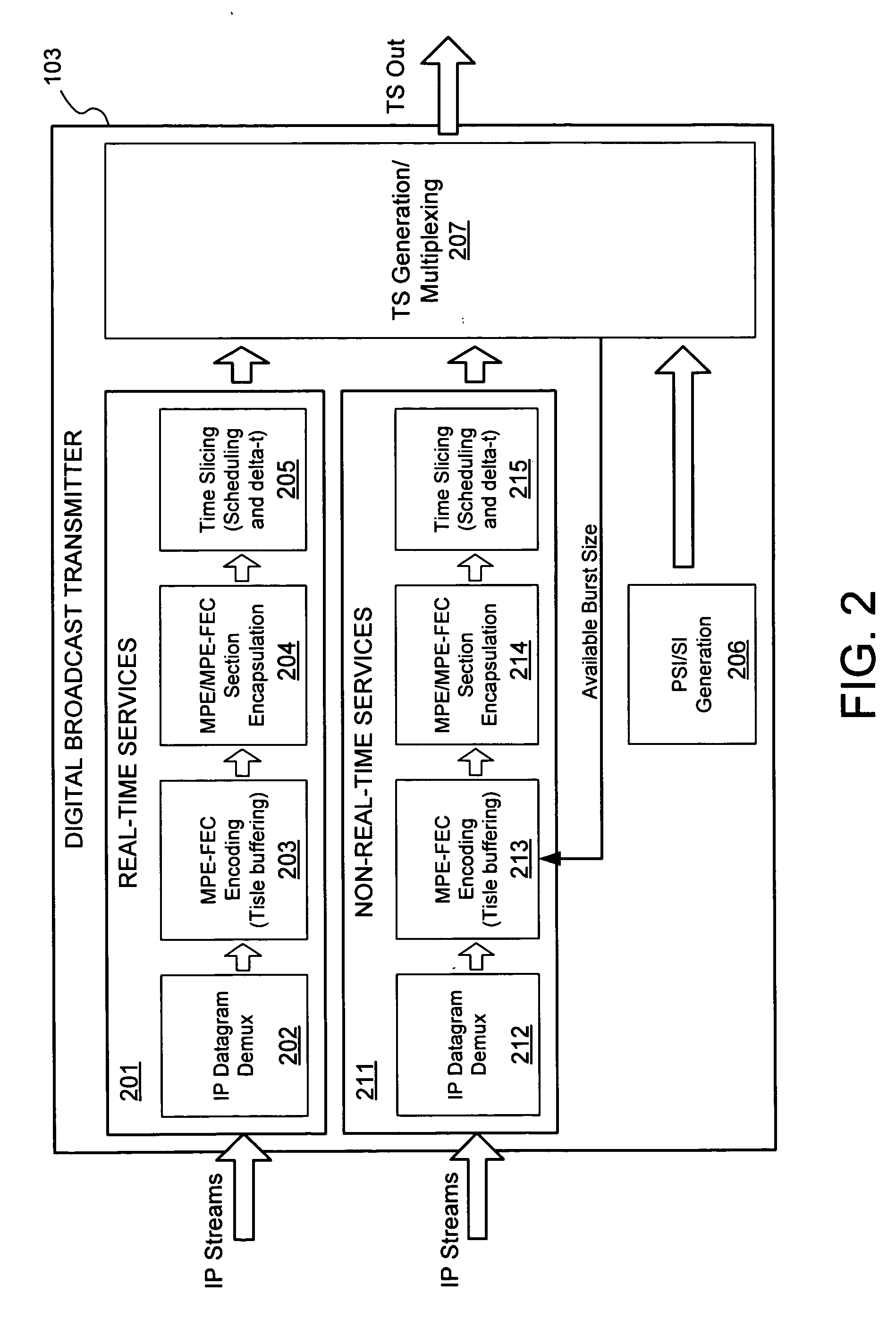
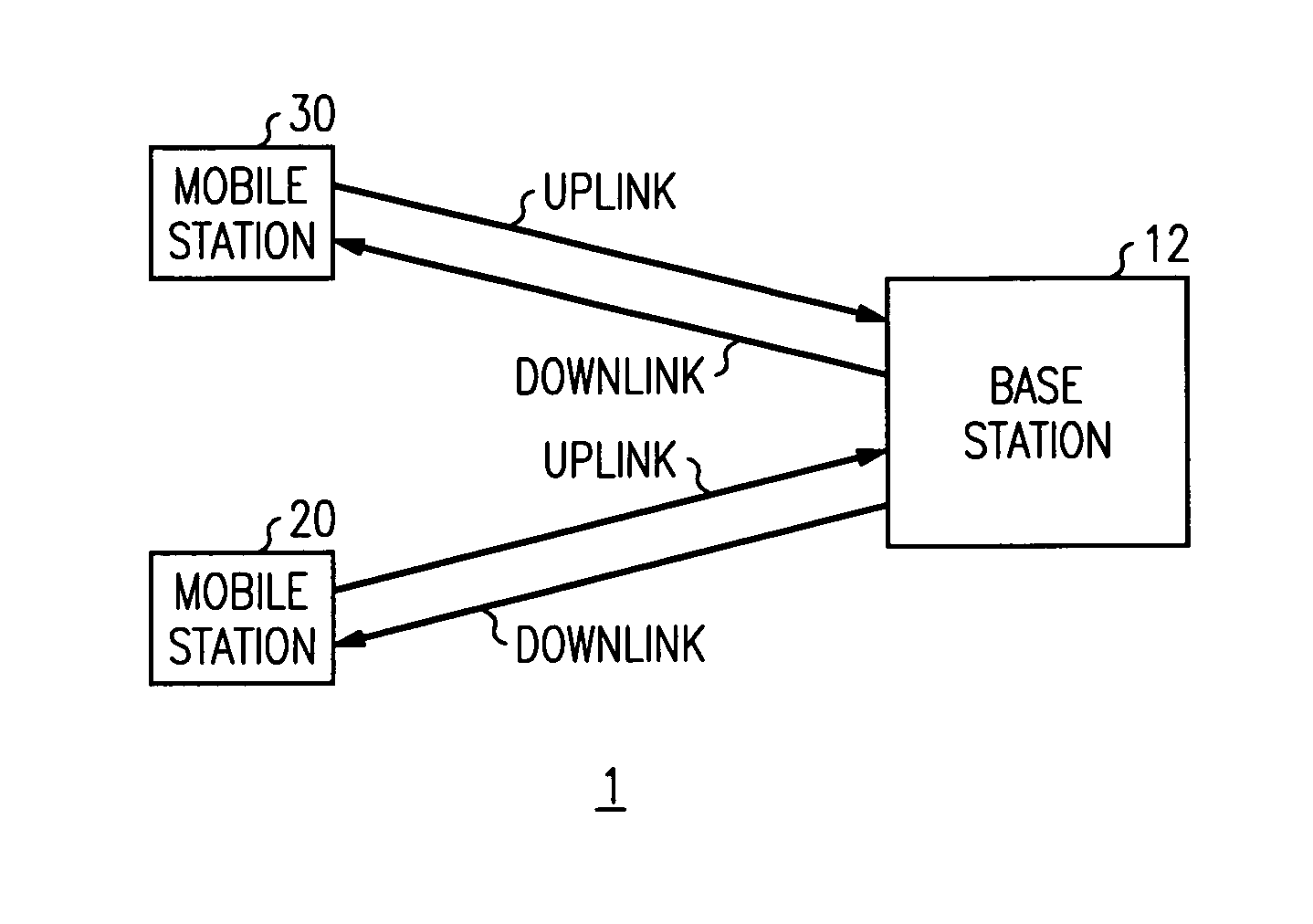
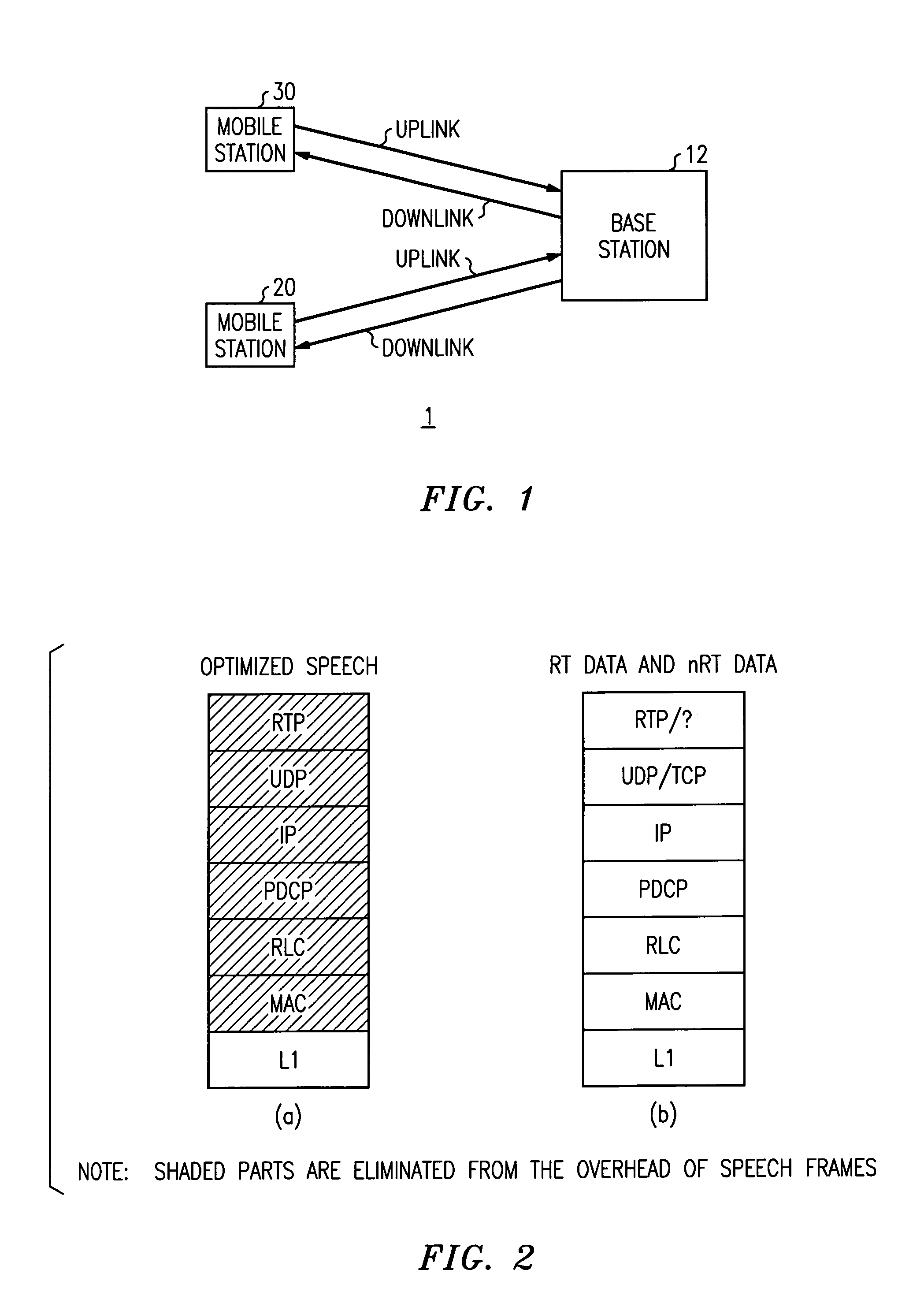
Multiplexing of real time services and non-real time services for OFDM systems
InactiveUS6952454B1Guaranteed normal transmissionImprove efficiencyFrequency-division multiplex detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsData streamFull Rate
Transmitter and receiver units for use in an OFDM communications system and configurable to support multiple types of services. The transmitter unit includes one or more encoders, a symbol mapping element, and a modulator. Each encoder receives and codes a respective channel data stream to generate a corresponding coded data stream. The symbol mapping element receives and maps data from the coded data streams to generate modulation symbol vectors, with each modulation symbol vector including a set of data values used to modulate a set of tones to generate an OFDM symbol. The modulator modulates the modulation symbol vectors to provide a modulated signal suitable for transmission. The data from each coded data stream is mapped to a respective set of one or more “circuits”. Each circuit can be defined to include a number of tones from a number of OFDM symbols, a number of tones from a single OFDM symbol, all tones from one or more OFDM symbols, or some other combination of tones. The circuits can have equal size or different sizes. Different circuits can be used for full rate data (e.g., active speech) and low rate data (e.g., silence periods).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
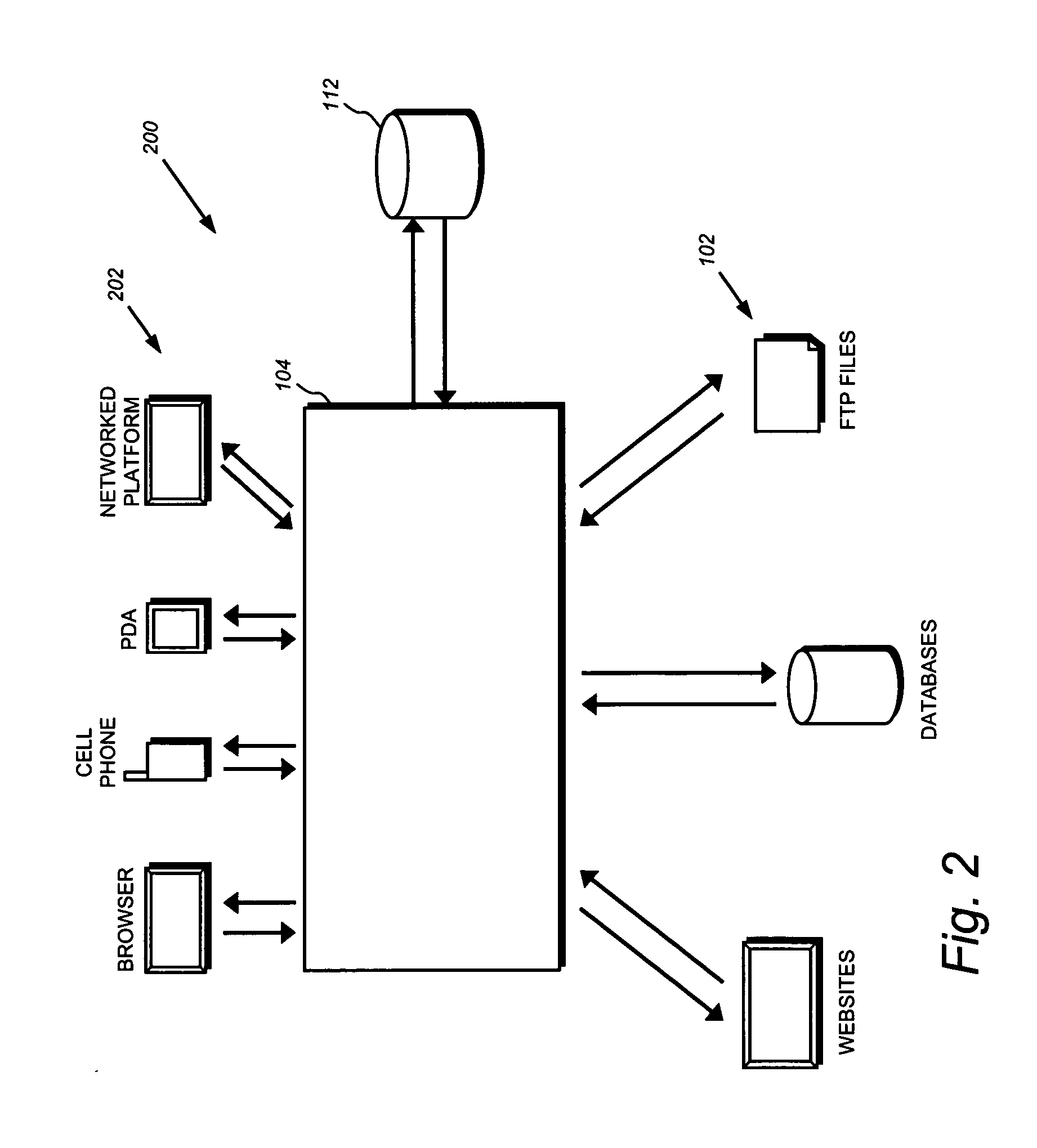
Data integration through a services oriented architecture
InactiveUS20050223109A1Simple interfaceConvenient data synchronizationDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsReal time servicesService-oriented architecture
Services such as product services, real-time services, and common services are deployed in a services oriented architecture. These services may, for example, be deployed for use in a variety of enterprise data integration functions.
Owner:IBM CORP
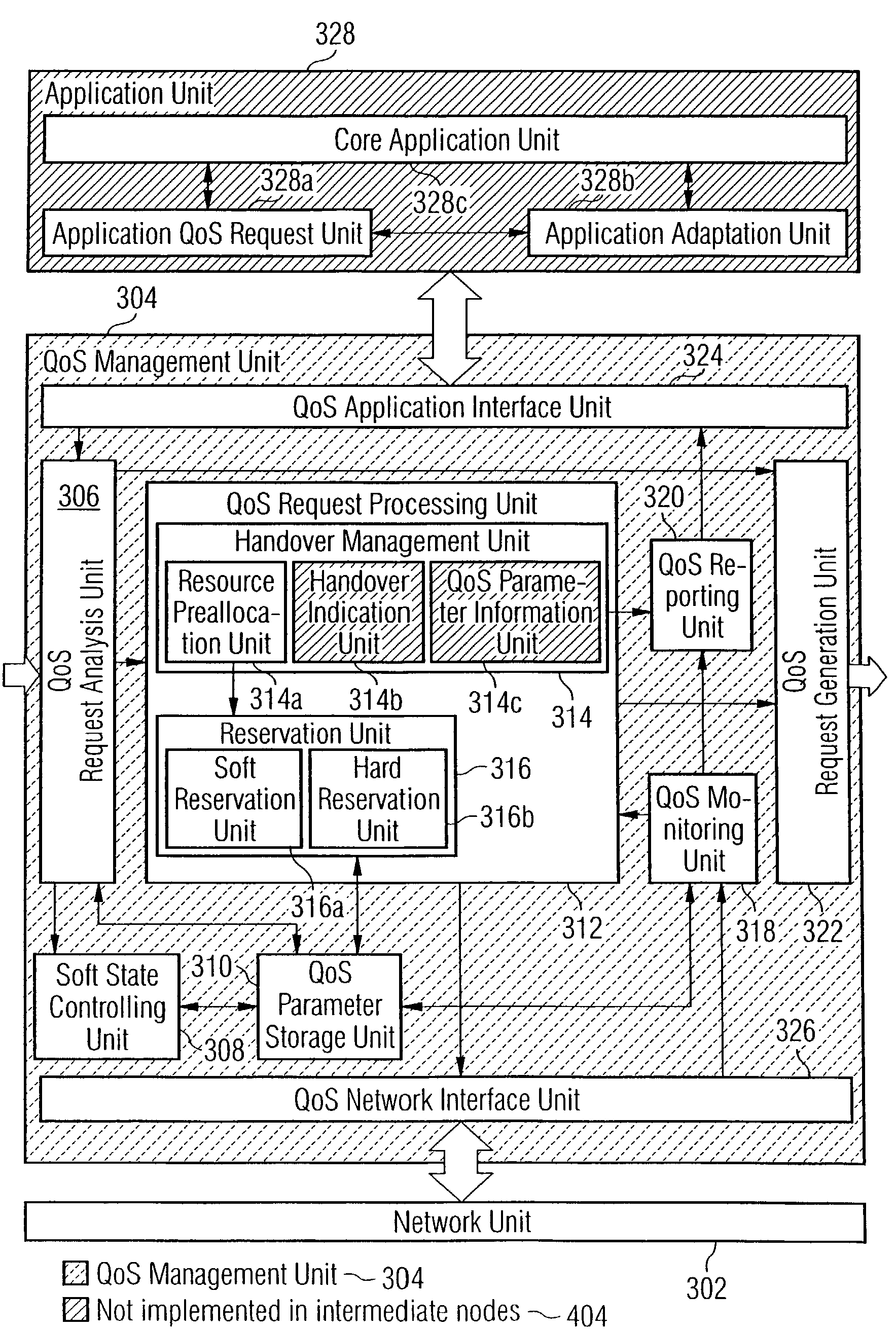
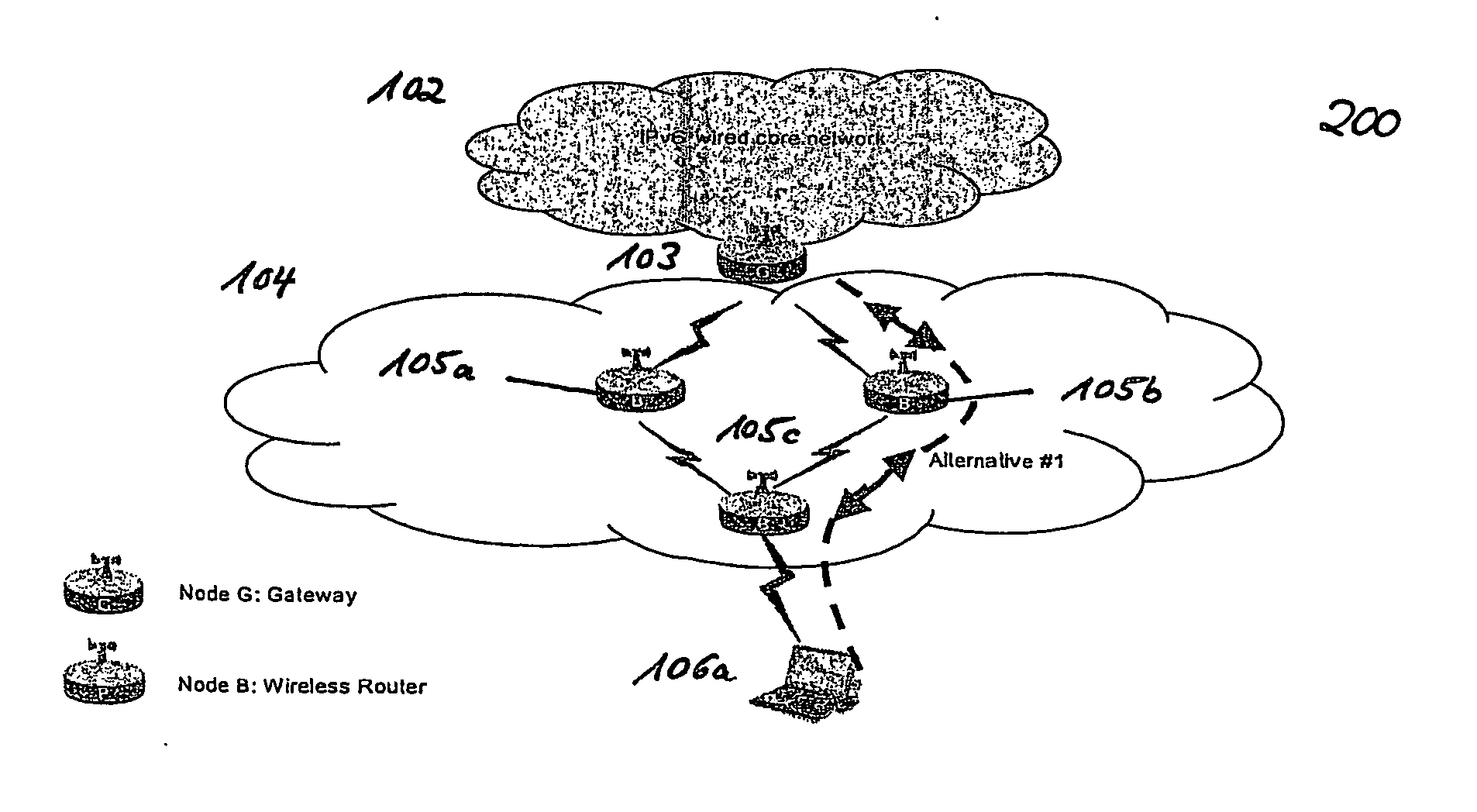
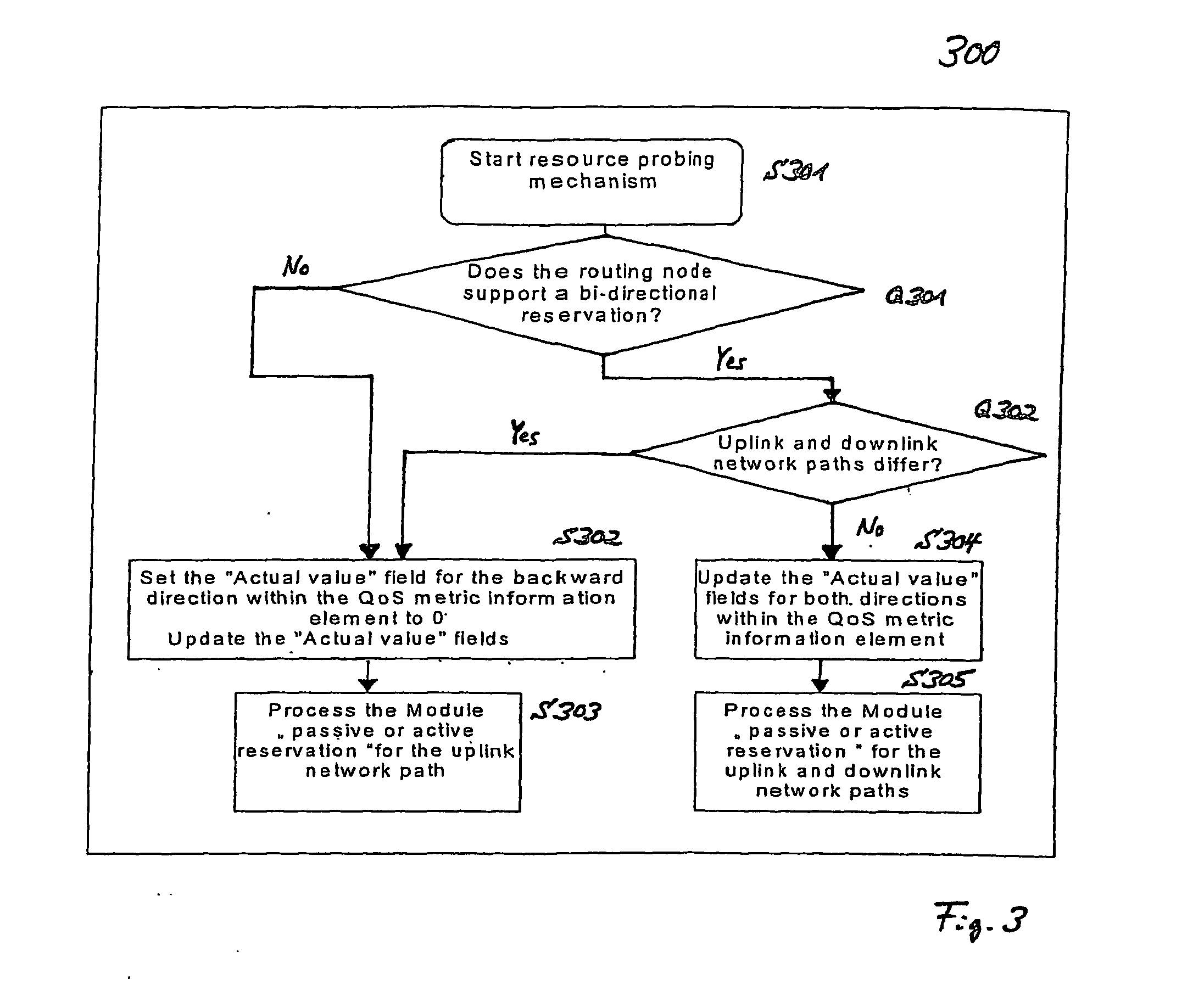
Adaptive quality-of-service reservation and pre-allocation for mobile systems
ActiveUS7289453B2Minimize impactDelay minimizationError preventionTransmission systemsAdaptive servicesQos management
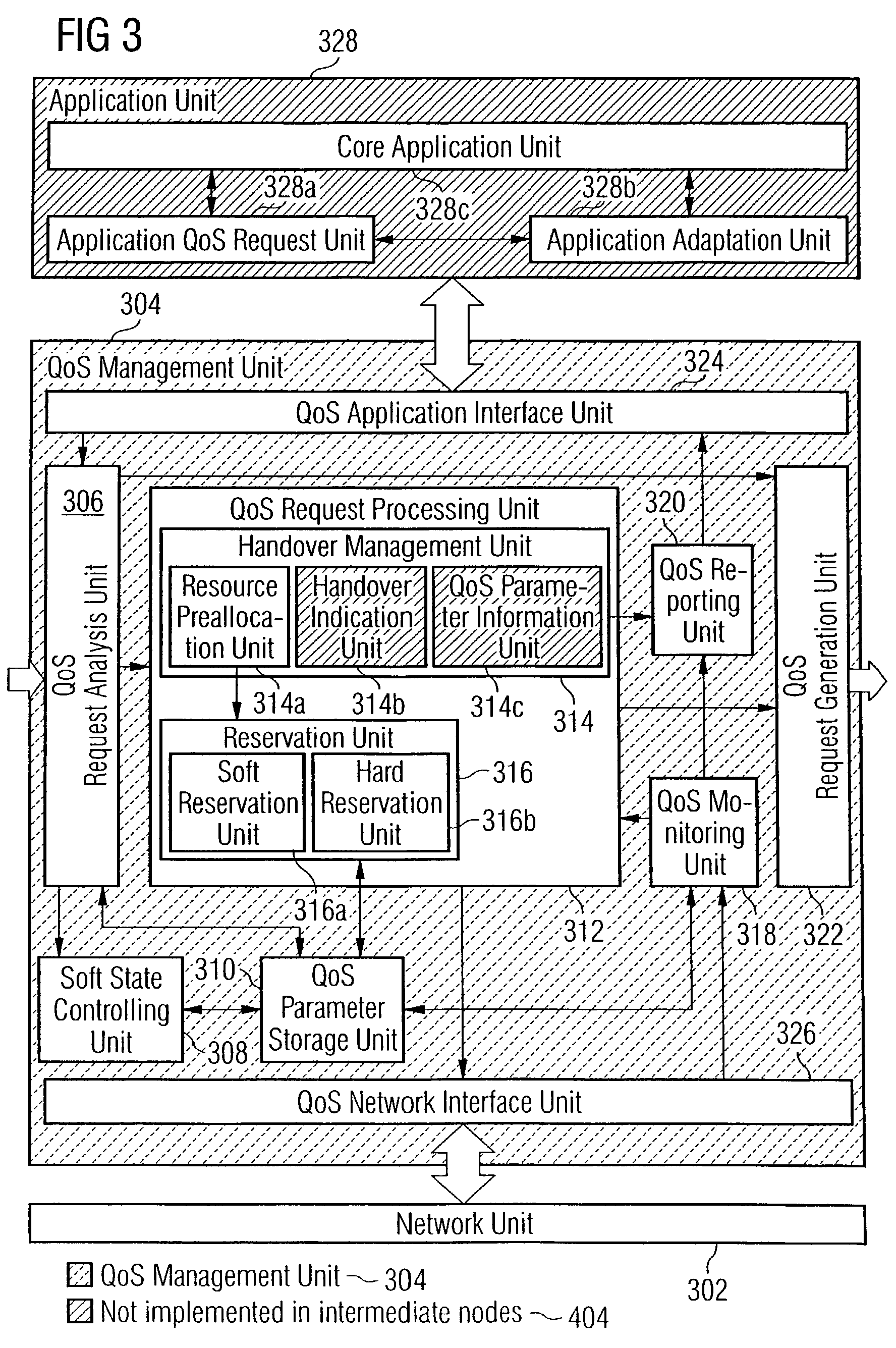
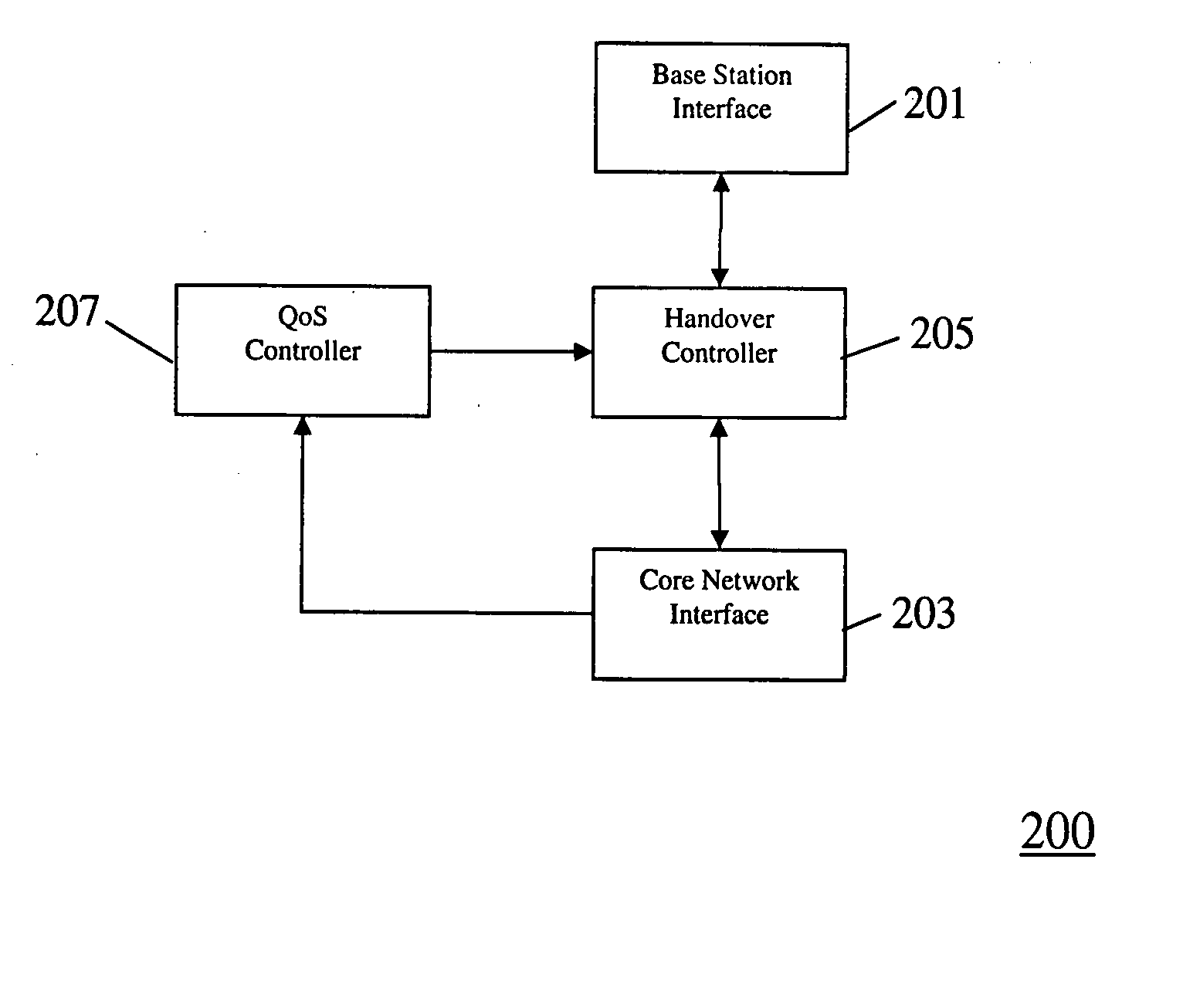
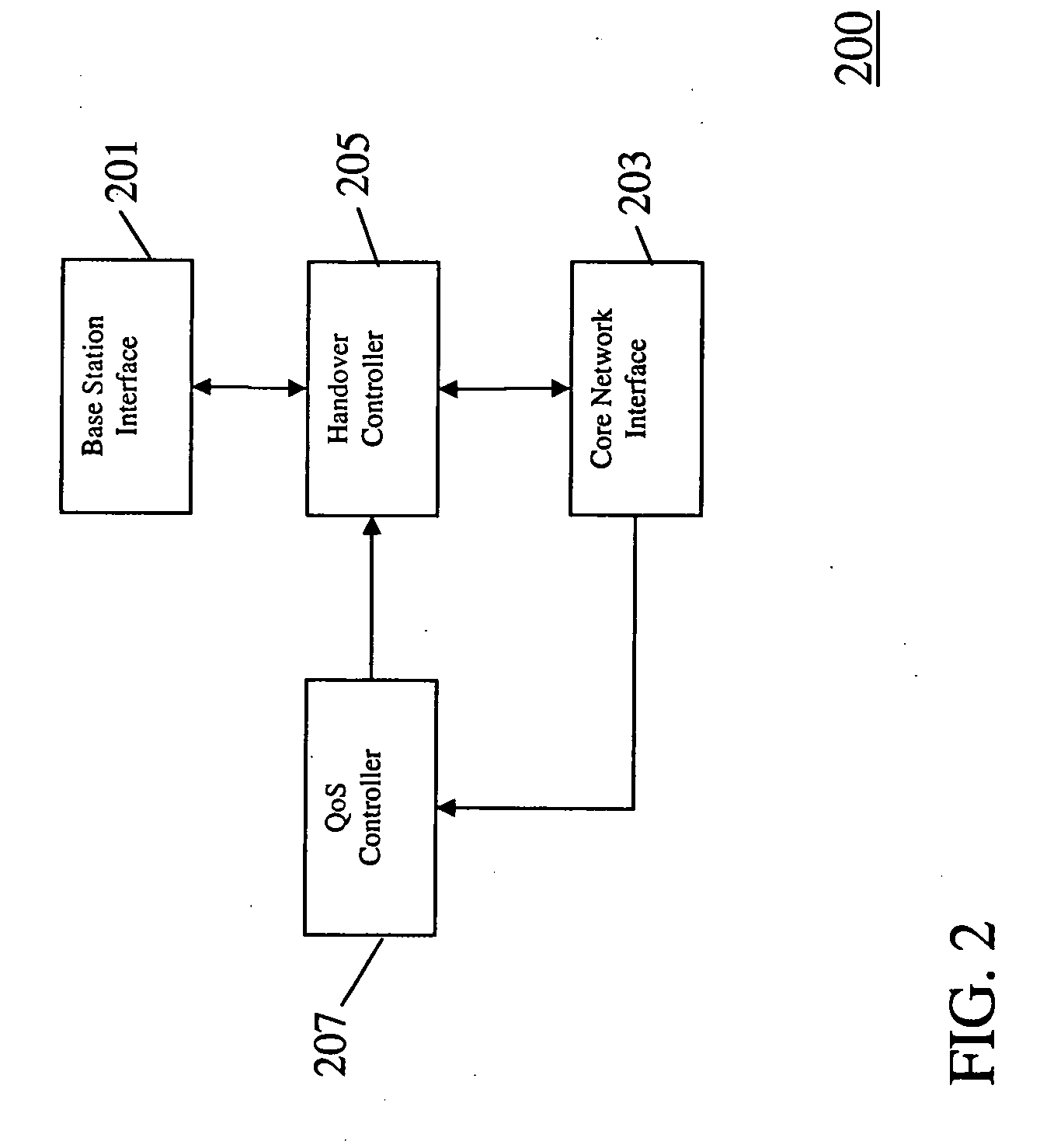
In the field of Quality-of-Service (QoS) management for adaptive real-time services running on mobile devices which support different access technologies in dynamic wireless Internet Protocol (IP) networks, the connectivity of the applied nodes is unpredictable time-varying. In this context, a QoS management unit (304) is proposed that allows adaptive applications with real-time requirements in typical mobile wireless scenarios—e.g. a radio link with a changing transmission quality and handover procedures (2900)—to adaptively and responsively react to a time-varying network topology and different radio link characteristics. Said QoS management unit (304) provides methods of pre-allocating, reserving, monitoring and adapting QoS-related parameters in a dynamic mobile environment.The QoS management unit (304) comprises at least one analysis unit (306) which evaluates QoS requests received from other nodes (402a / b, 404) to inform the application unit (328) of said mobile terminal (208) about the current QoS situation, at least one processing unit (312) that manages request messages (1200, 2000, 2400) for each type of QoS request, at least one monitoring unit (318) which monitors the current QoS situation within said mobile node (208) and initiates requests by activating the processing unit (312), and at least one generation unit (322) which is responsible for generating QoS requests or passing them on to the QoS management units (304) of other nodes (402a+b, 404).
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
Method and system for model-based heterogeneous server configuration management
ActiveUS20030233431A1Error detection/correctionInterprogram communicationReference modelingReal time services
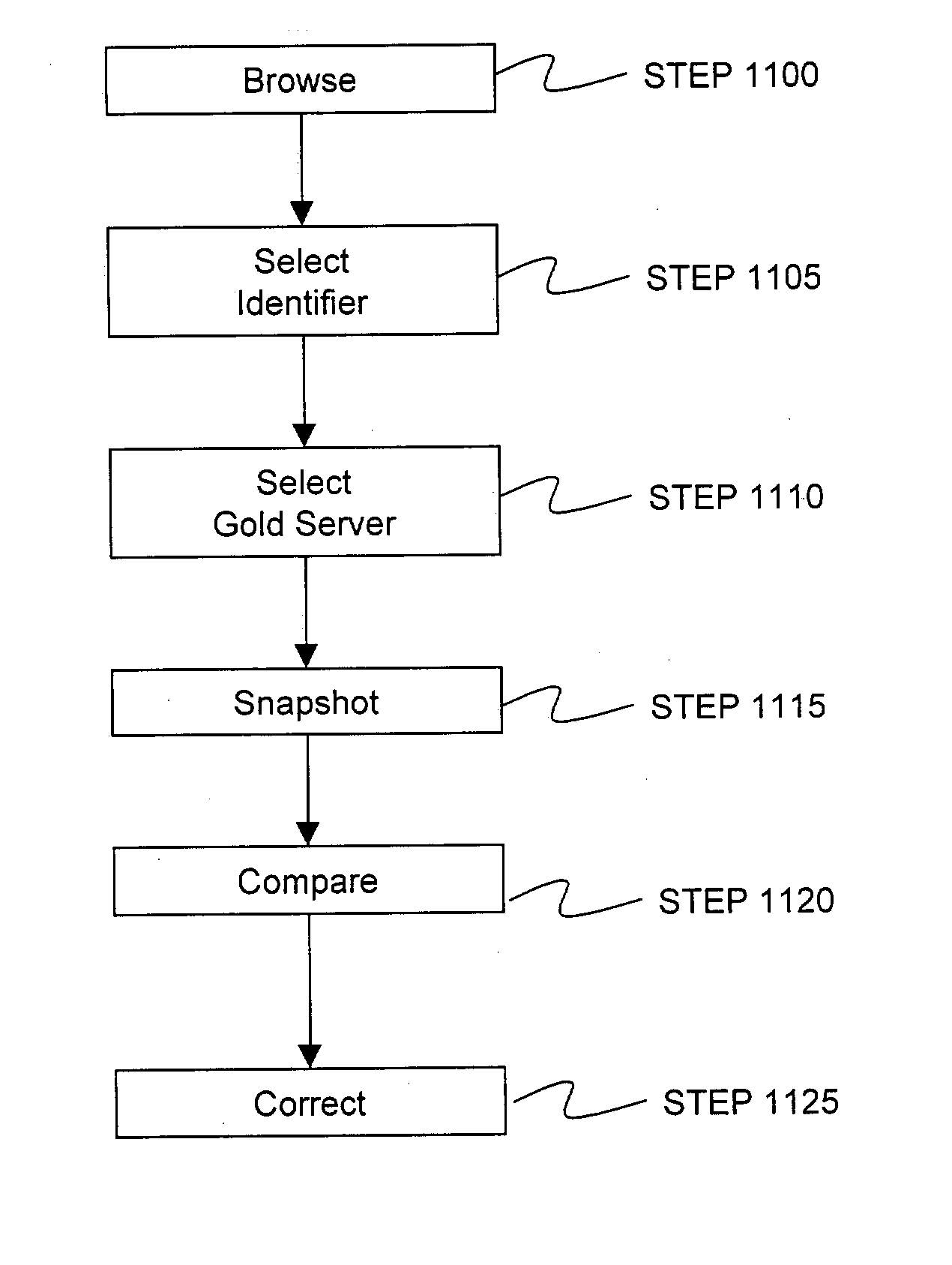
A method and system for configuring heterogeneous servers across a network through modules that can browse, snapshot, track changes, track compliance, correct server objects on each of the servers, and provision new servers is provided. In one embodiment, server objects on multiple servers can be browsed in real time. While browsing, a collection of server object identifiers can be selected and collected in a template. The values of the server objects identified in the template can be recorded for a "gold server" through a "snapshot" process, which collects the values and saves them in a reference model. By comparing other live servers to the reference model, discrepancies in configuration of the other live servers can be identified and corrected. The reference models can also be used to provision a new server. Alternative to the reference model, an arbitrary snapshot or scheduled snapshots of a server can be used to track change and compliance in that server.
Owner:BLADELOGIC
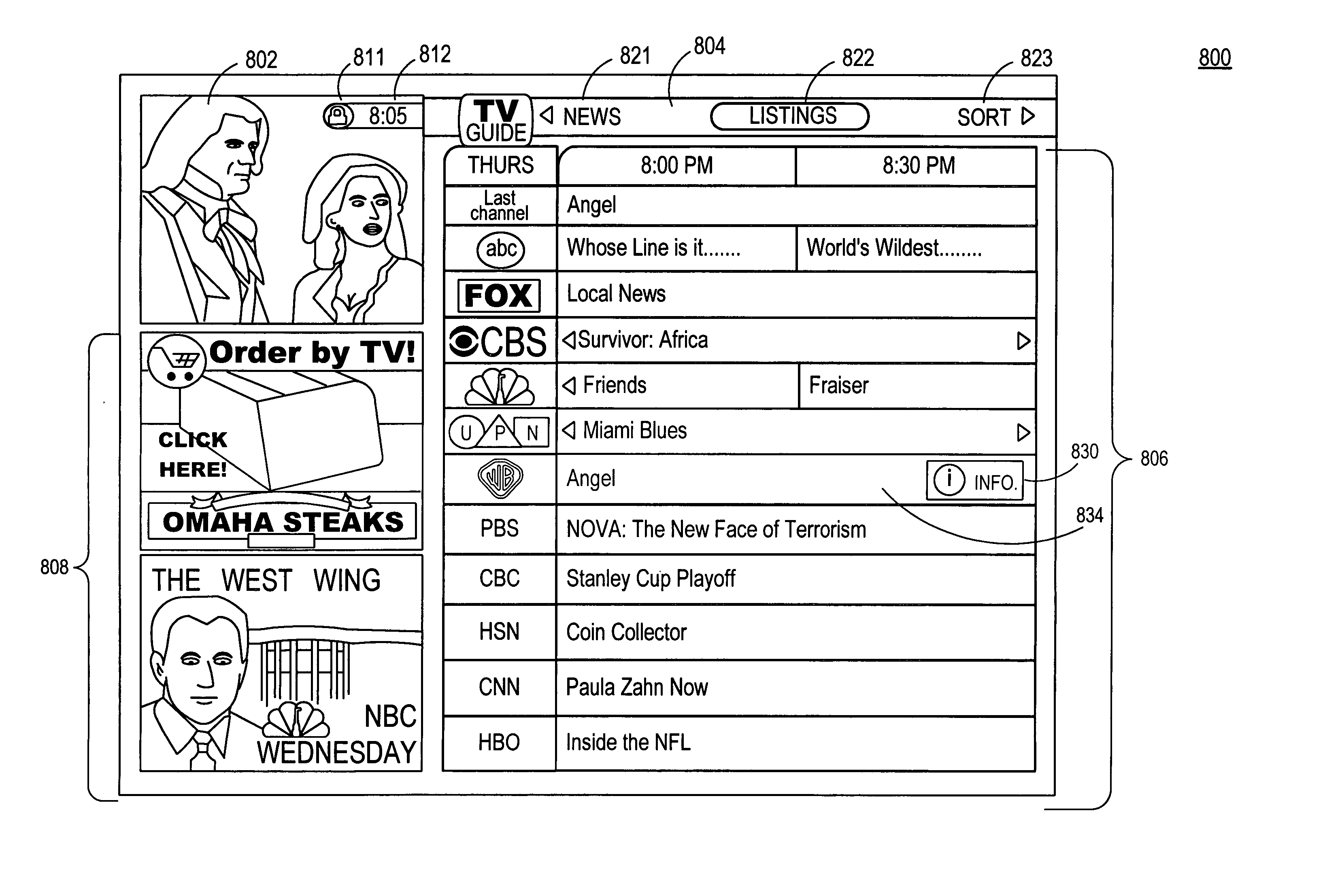
Systems and methods for providing real-time services in an interactive television program guide application
InactiveUS20050015803A1Improve the display effectTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTime informationReal time services
An interactive television program guide application is provided that displays real-time information to a user. The interactive television program guide application may display alerts for indicating to the user the availability of real-time information. The interactive television program guide application may also display program listings with real-time information. In response to the user selecting a program listing, the interactive television program guide application may provide the user with an indication that real-time content related to the selected listing is available. In some embodiments, the real-time content is not the program corresponding to the selected program listing.
Owner:UNITED VIDEO PROPERTIES
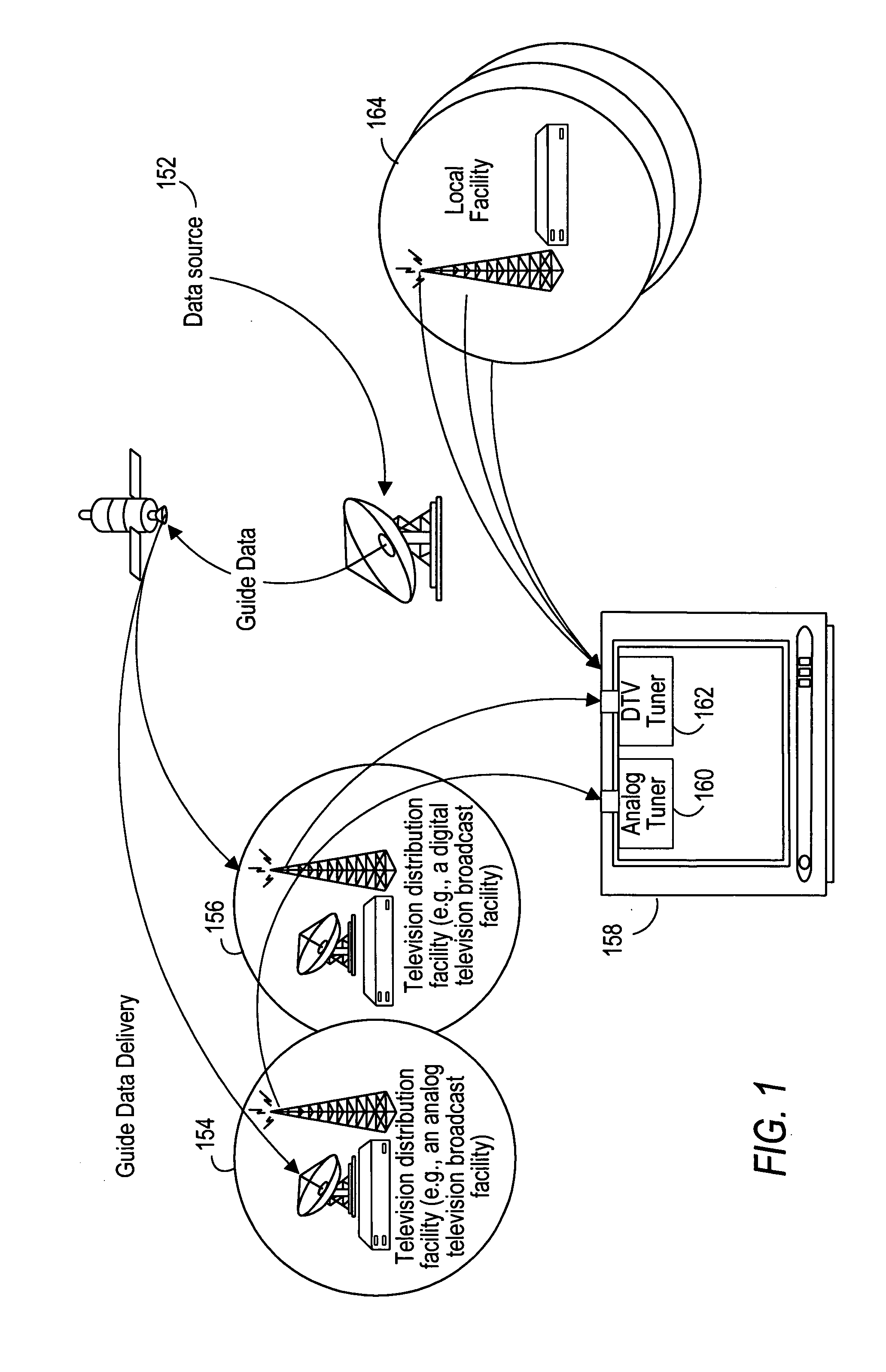
Method and system for transmitting/receiving data in a communication system
InactiveUS20070206561A1Effective distributionReduce overhead informationModulated-carrier systemsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemReal time services
A method for transmitting and receiving data in a communication system. The method includes grouping, by a Base Station (BS), Mobile Stations (MSs) using a real-time service, into groups, allocating burst blocks to the groups, and allocating data bursts of burst blocks to the MSs; and determining, by each MS, whether its own uplink burst is allocated, and transmitting data to the BS through a sub-burst of a burst block allocated to a group to which each MS belongs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
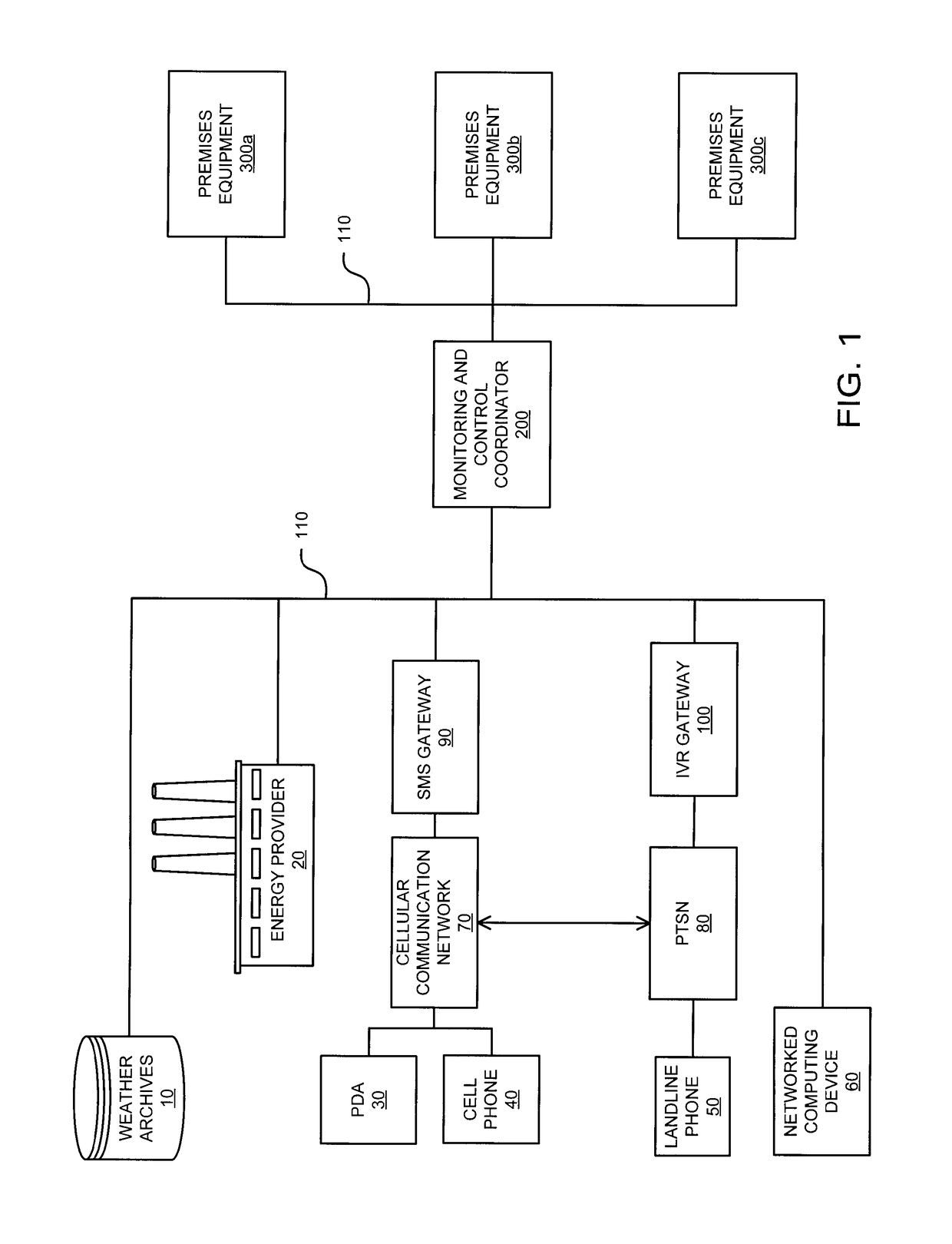
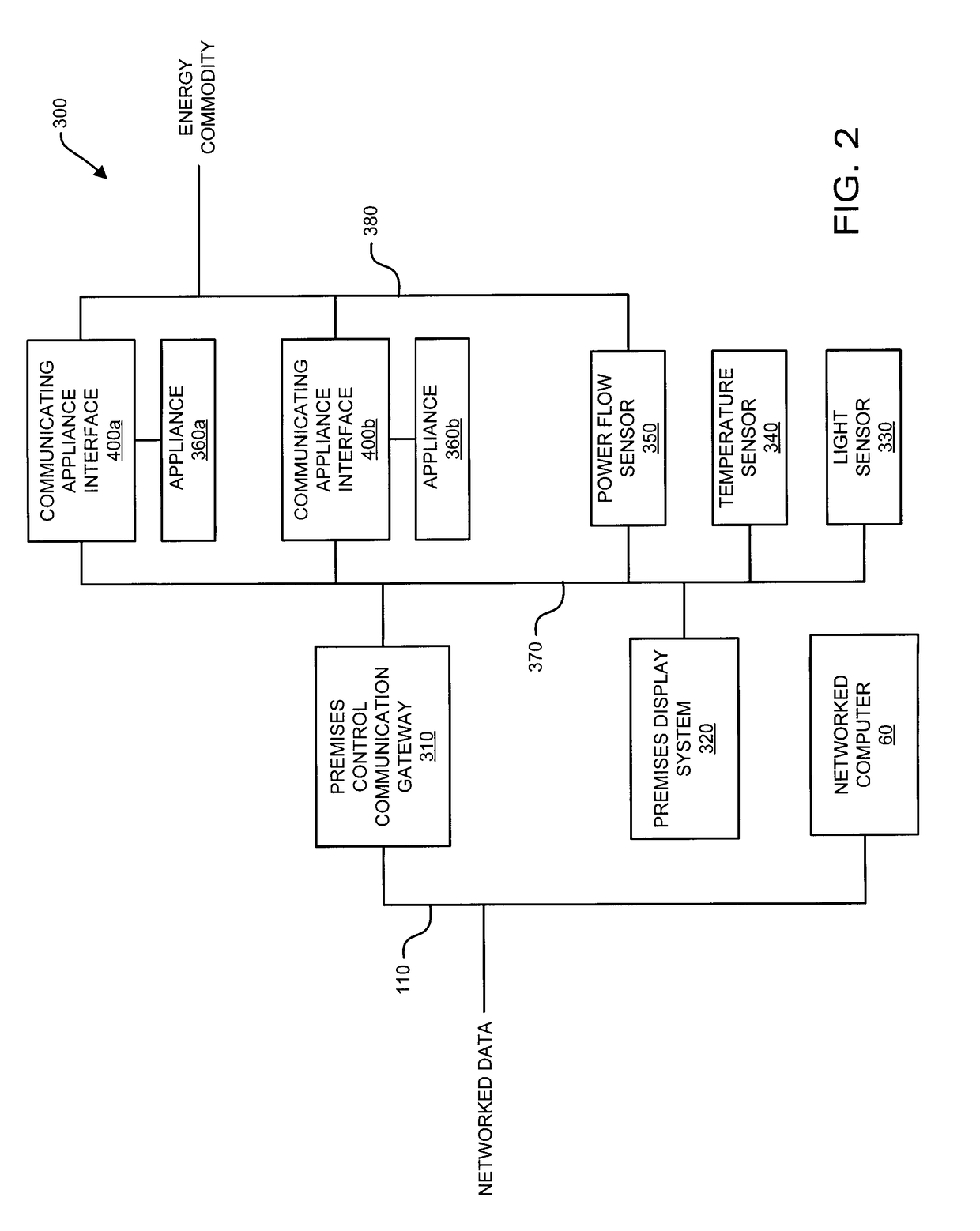
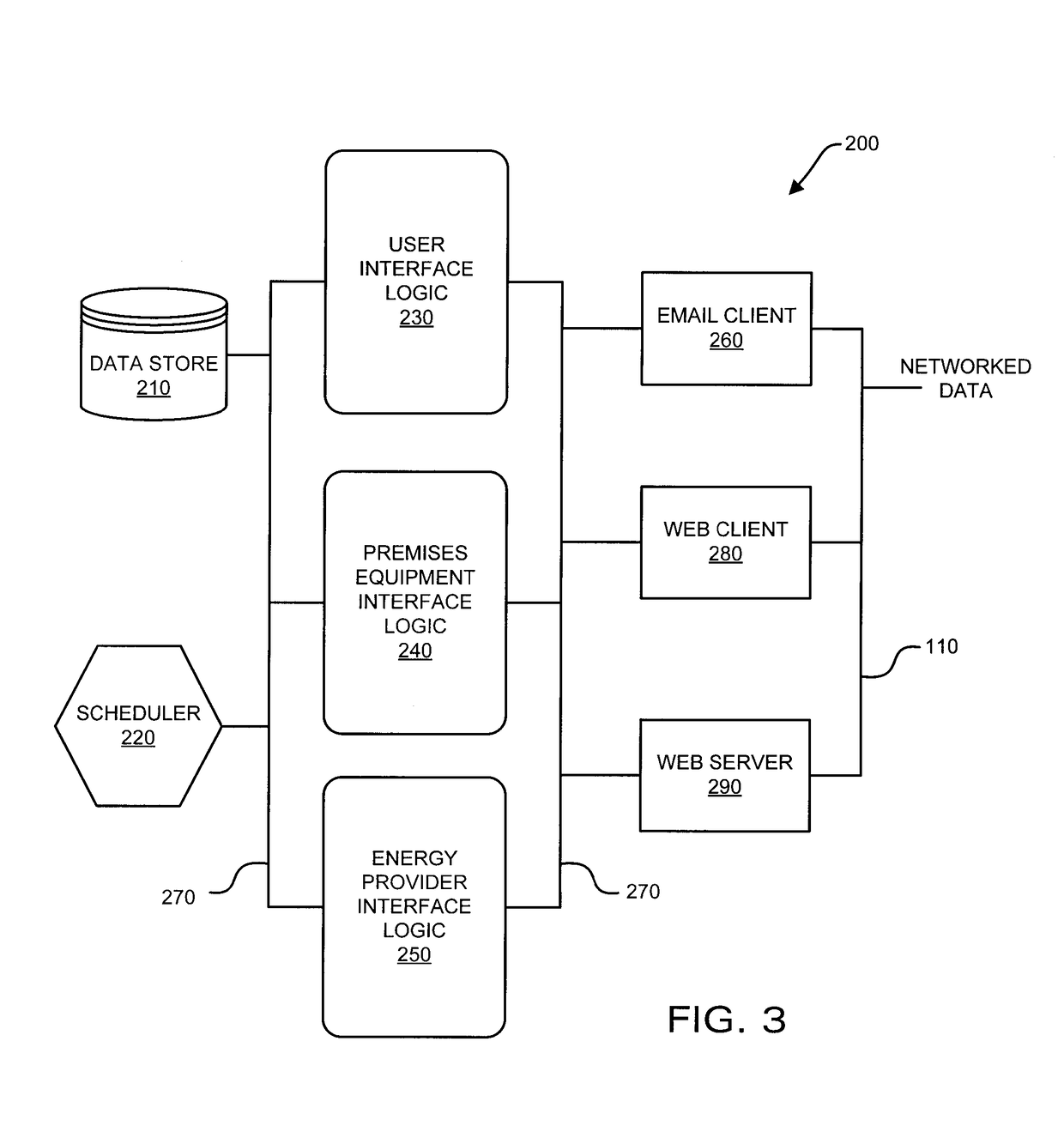
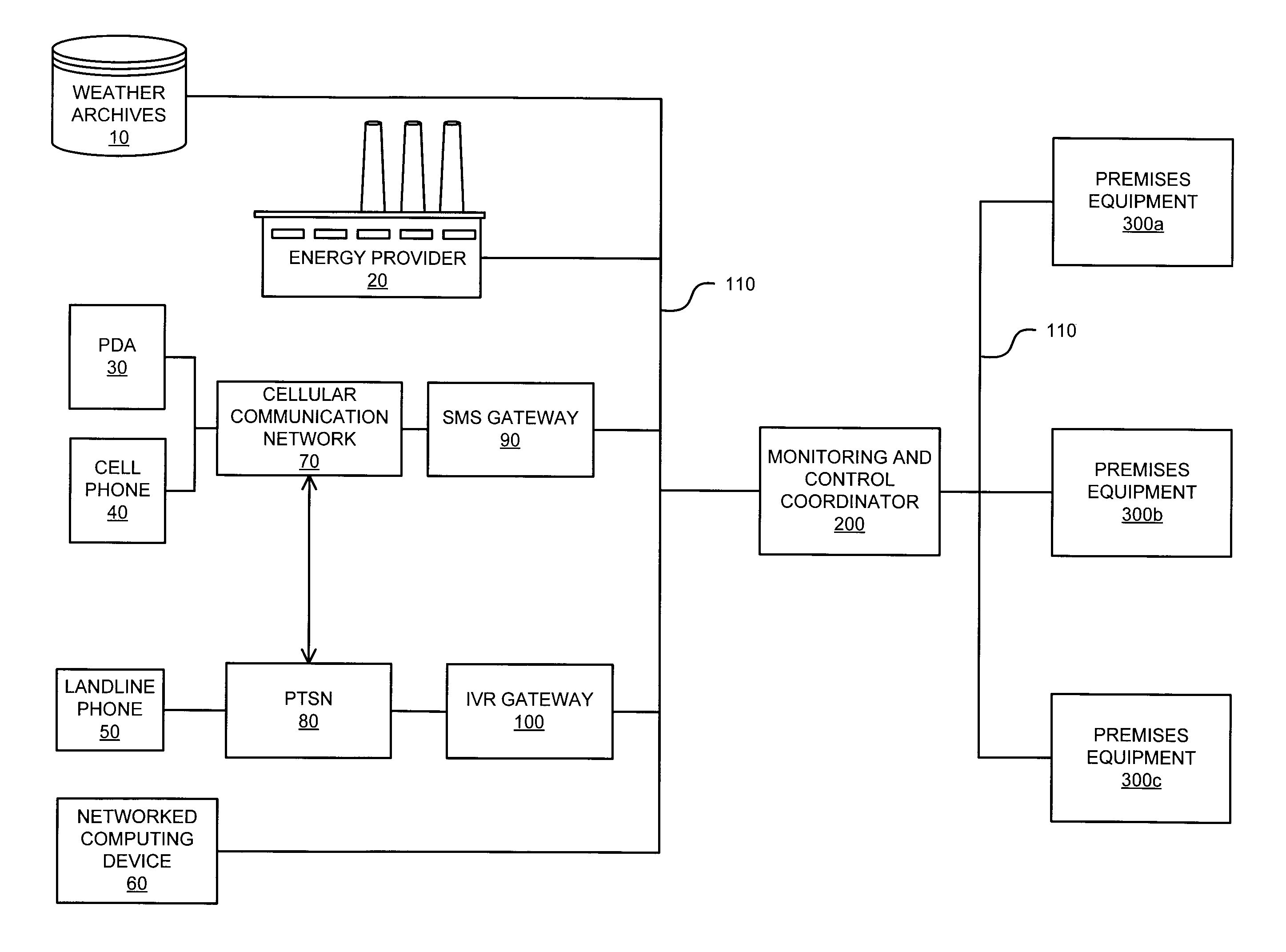
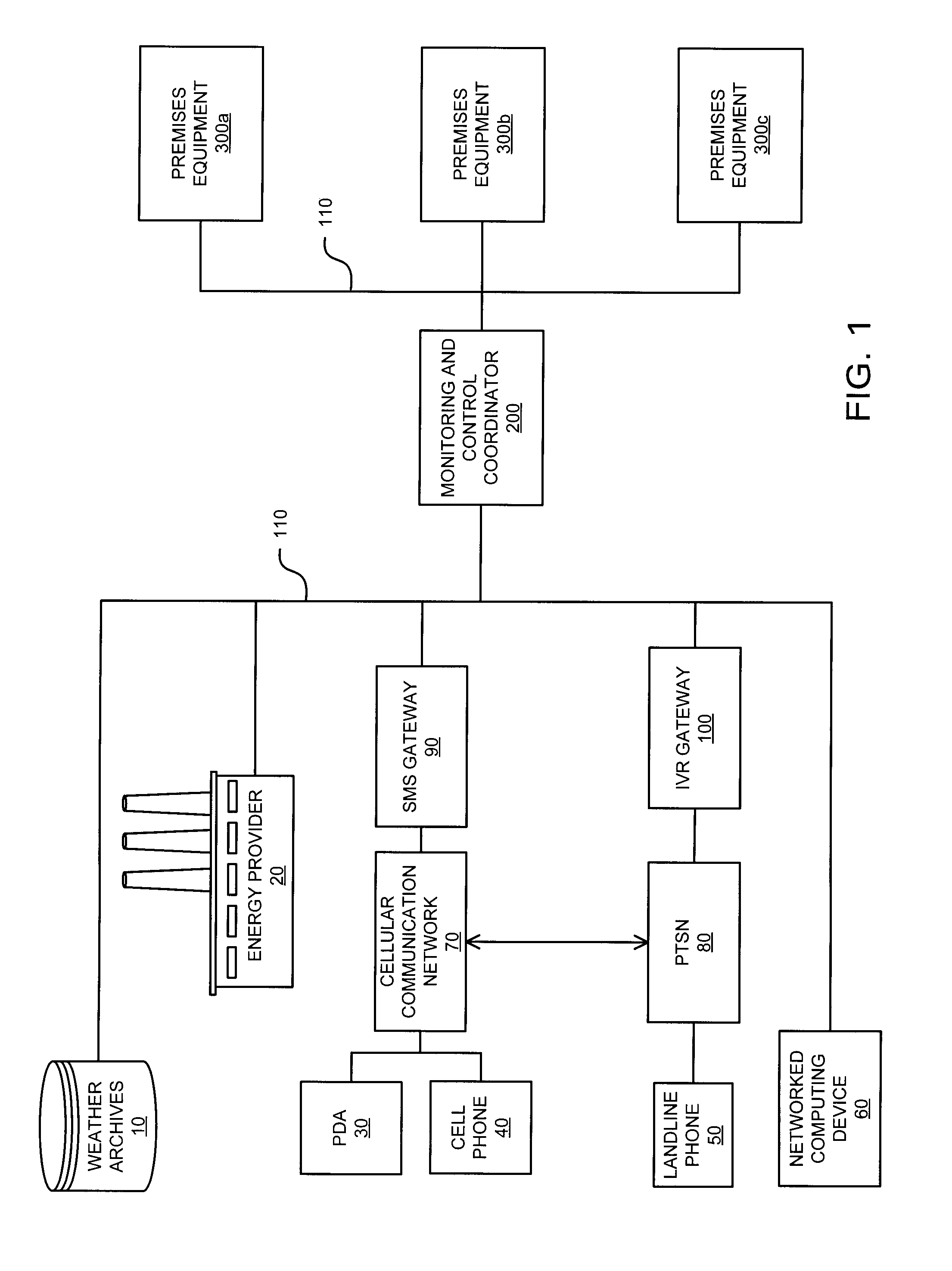
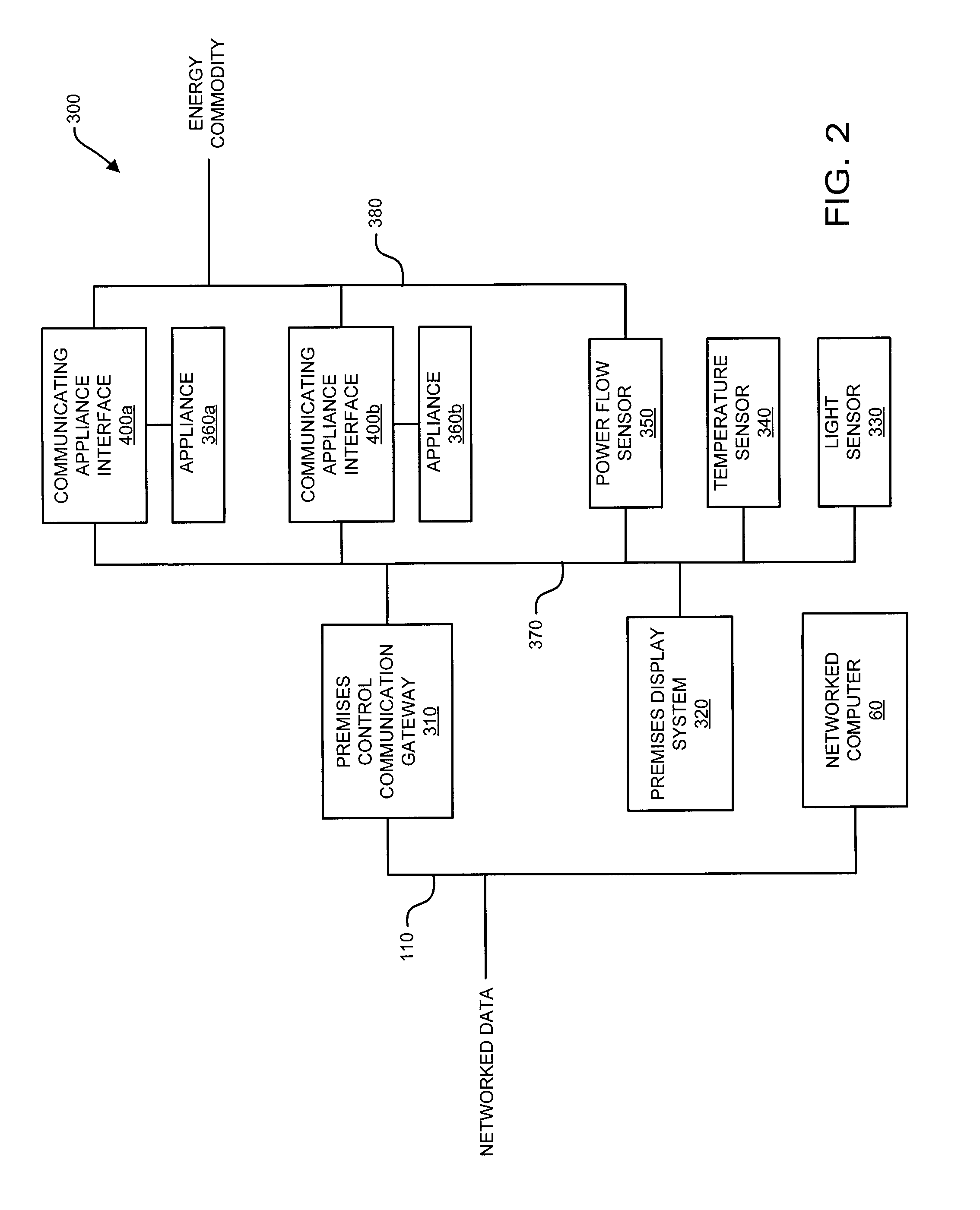
Interconnected premises equipment for energy management
Energy commodities in the form of electricity and combustible fuel (e.g. natural gas, propane) are used by appliances in a fashion which is monitored and controlled through a Premises Energy Management System (PEMS). The system facilitates direct monitoring and control of energy-consuming appliances, in real time, utilizing automated programmatic control and a plurality of human interfaces including local display and control, email, web browser, text messaging, and integrated voice response (IVR). A Monitoring and Control Coordinator (MCC) provides centralized coordination of functions and one or more Communicating Appliance Interfaces (CAI) interacting with energy consuming appliances are interconnected via wired and wireless communication networks and protocols. The system may retrieve information from third parties, such as weather services, for optimizing energy usage. An interface may be provided to the energy provider / purveyor to enhance the provision of energy by providing additional real-time services such as demand management and service outage management.
Owner:PATTON ELECTRONICS
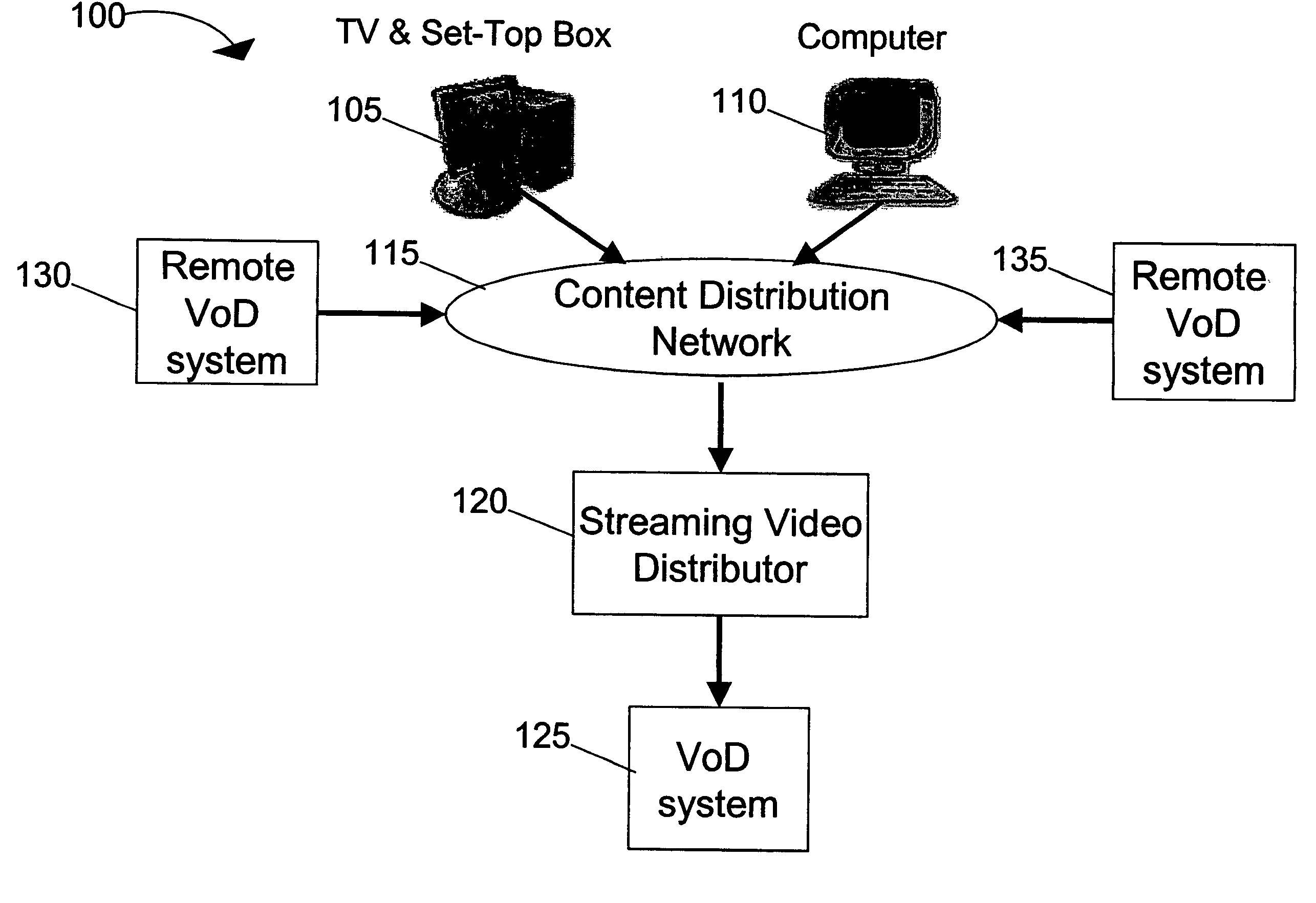
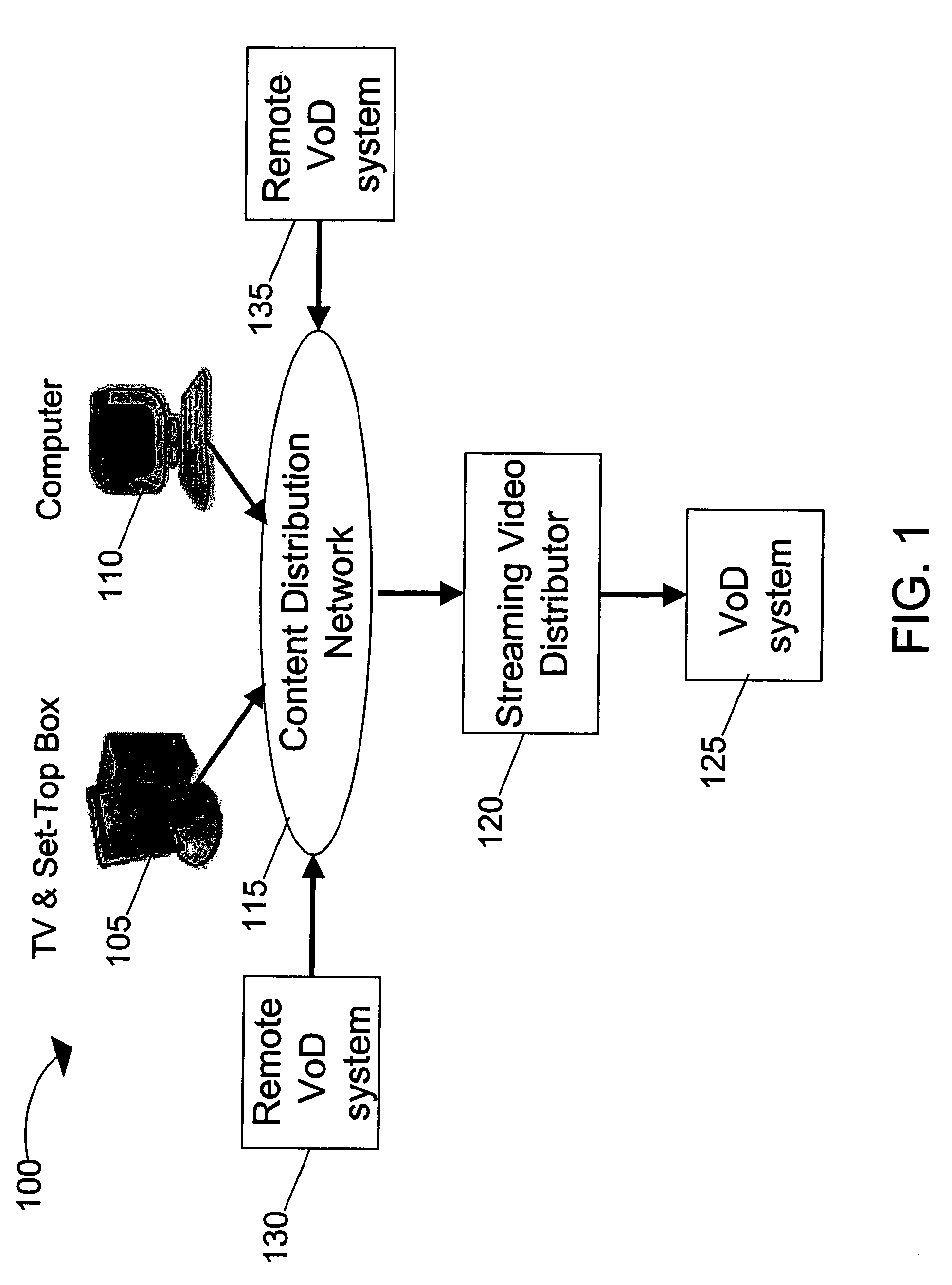
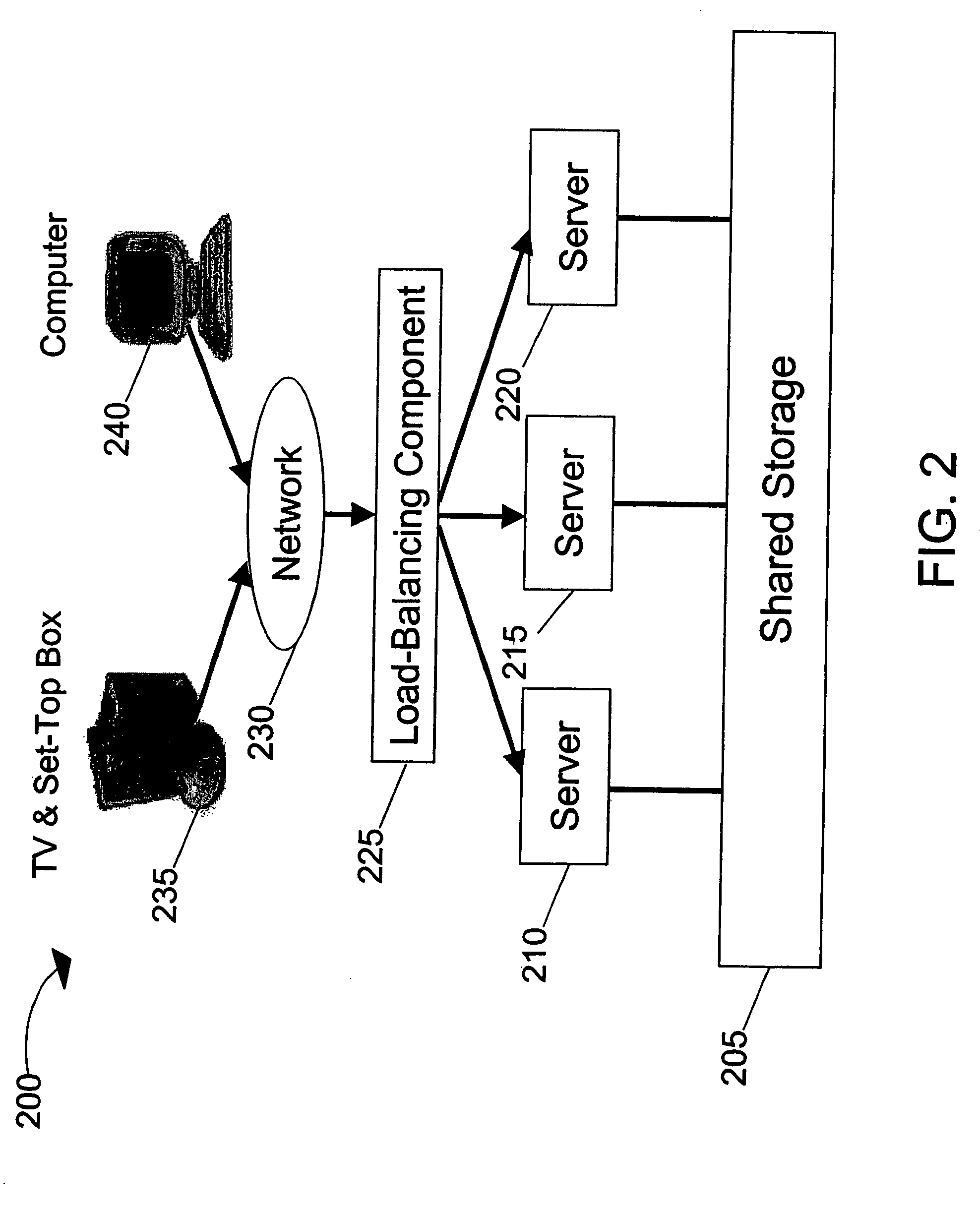
Systems and methods for load balancing storage and streaming media requests in a scalable, cluster-based architecture for real-time streaming
InactiveUS20050262246A1Large capacityCost-effectivelyTelevision system detailsDigital computer detailsReal time servicesCluster based
A scalable, cluster-based VoD system implemented with a multi-server, multi-storage architecture to serve large scale real-time ingest and streaming requests for content assets is provided. The scalable, cluster-based VoD system implements sophisticated load balancing algorithms for distributing the load among the servers in the cluster to achieve a cost-effective and high streaming and storage capacity solution capable of serving multiple usage patterns and large scale real-time service demands. The VoD system is designed with a highly-scalable and failure-resistant architecture for streaming content assets in real-time in various network configurations.
Owner:KASENNA
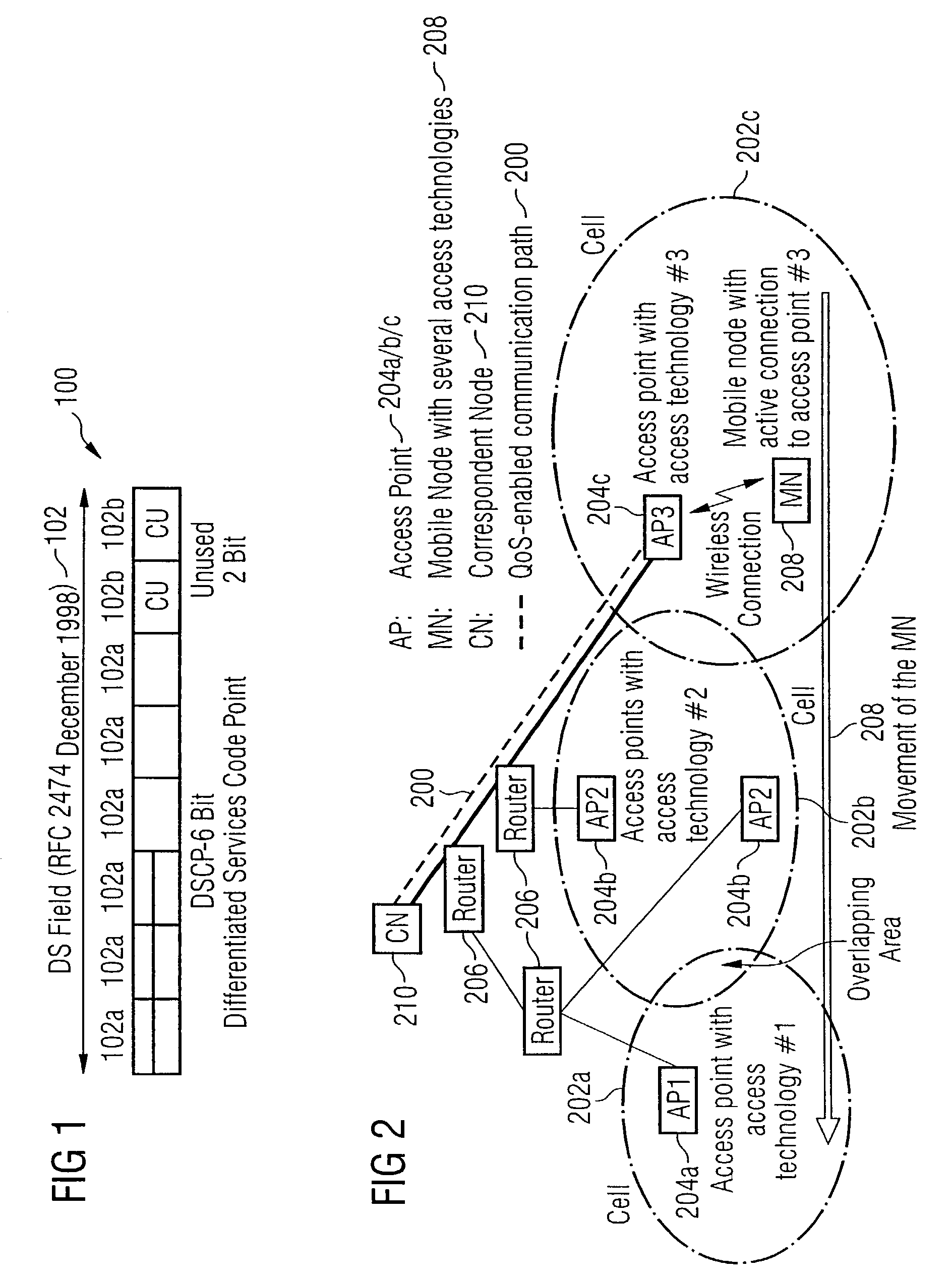
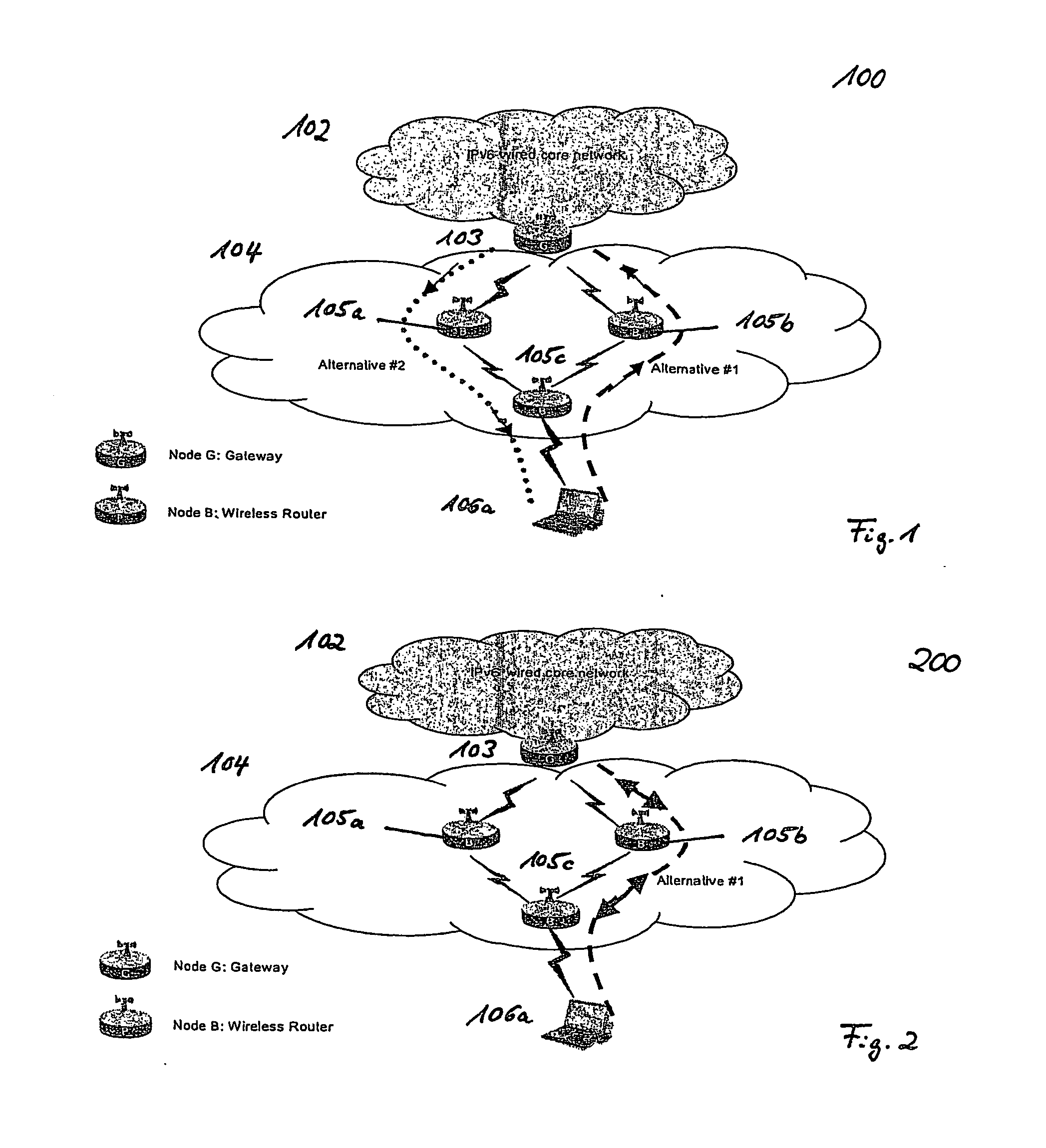
Bidirectional Qos Reservation Within an in-Band Signaling Mechanism
InactiveUS20070217406A1Optimize networkImprove network utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesReal time servicesWireless ad hoc network
A mechanism for a bidirectional reservation procedure within an in-band signaling mechanism gives symmetric real-time services running on mobile devices, which are used to support different access technologies in dynamic, mobile, wireless IP networks where the quality of the node connectivity can sometimes be unpredictably time-varying, the possibility to mutually reserve, monitor and adapt resources and service parameters for upstream and downstream direction along a communication path. The mechanism optimizes reservation mechanisms, especially for adaptive real-time services in wireless and wireless ad-hoc networks, by making use of a dynamic bidirectional reservation in-band signaling approach.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG +1
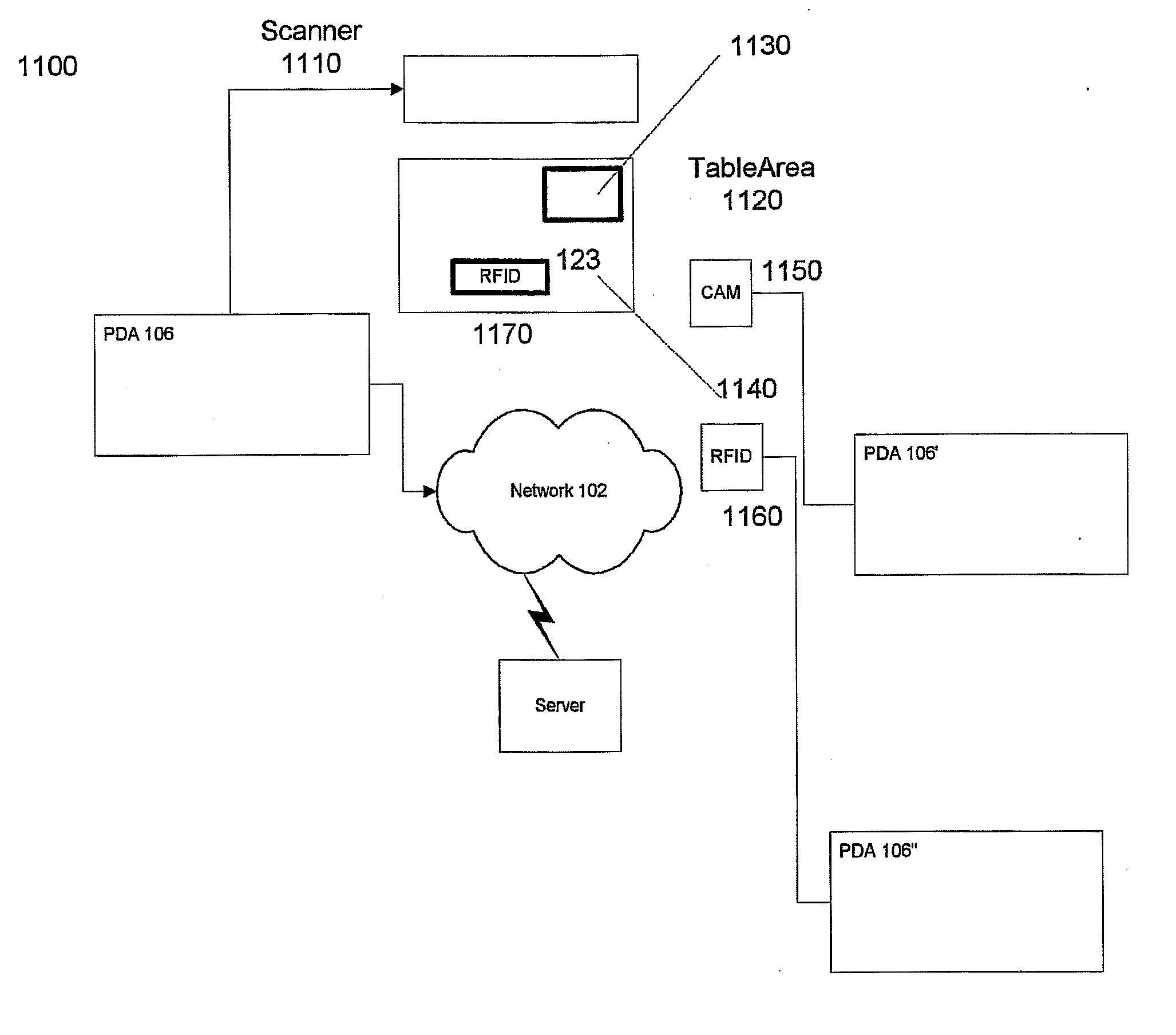
Method and apparatus for wireless customer interaction with the attendants working in a restaurant
InactiveUS20060186197A1CommerceSpecial data processing applicationsWaiters/waitressesReal time services
An apparatus and method are disclosed of a wireless system for customers to interact with attendants (e.g waiters) in restaurants. The system provides for a computing system that transmits electronic menus to wireless portable digital assistants (PDA's) and enables customers to place orders and make real-time service requests. For example, the customer is able to select food items from the menus, indicate preparation instructions for each food item, send comments to the attendants, and request drink refills. The customer is able to check on the status of food preparation via the PDA and observe the food being prepared by a camera link. Upon finishing the meal the restaurant can transmit an electronic bill to the customer.
Owner:OUTLAND RES
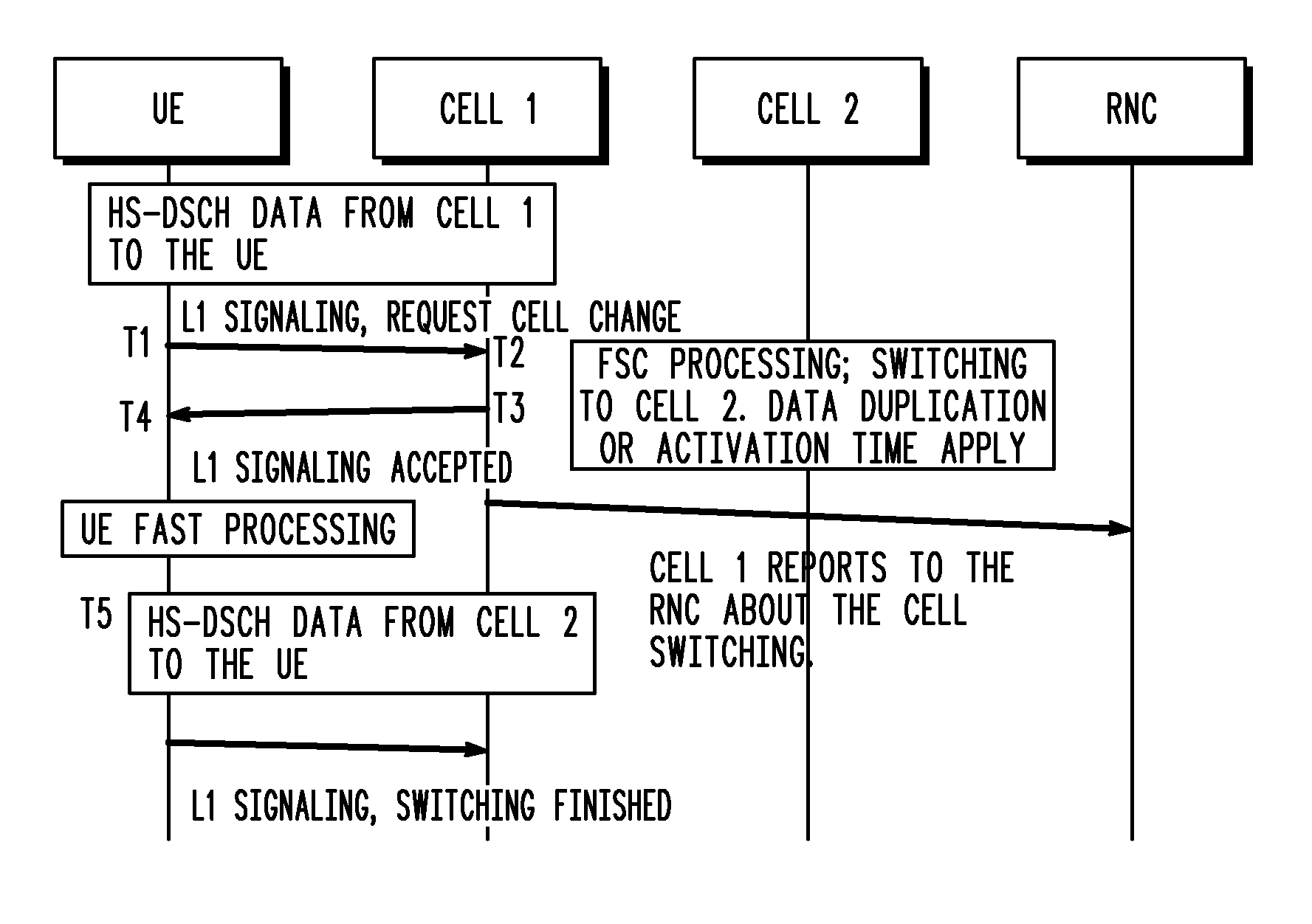
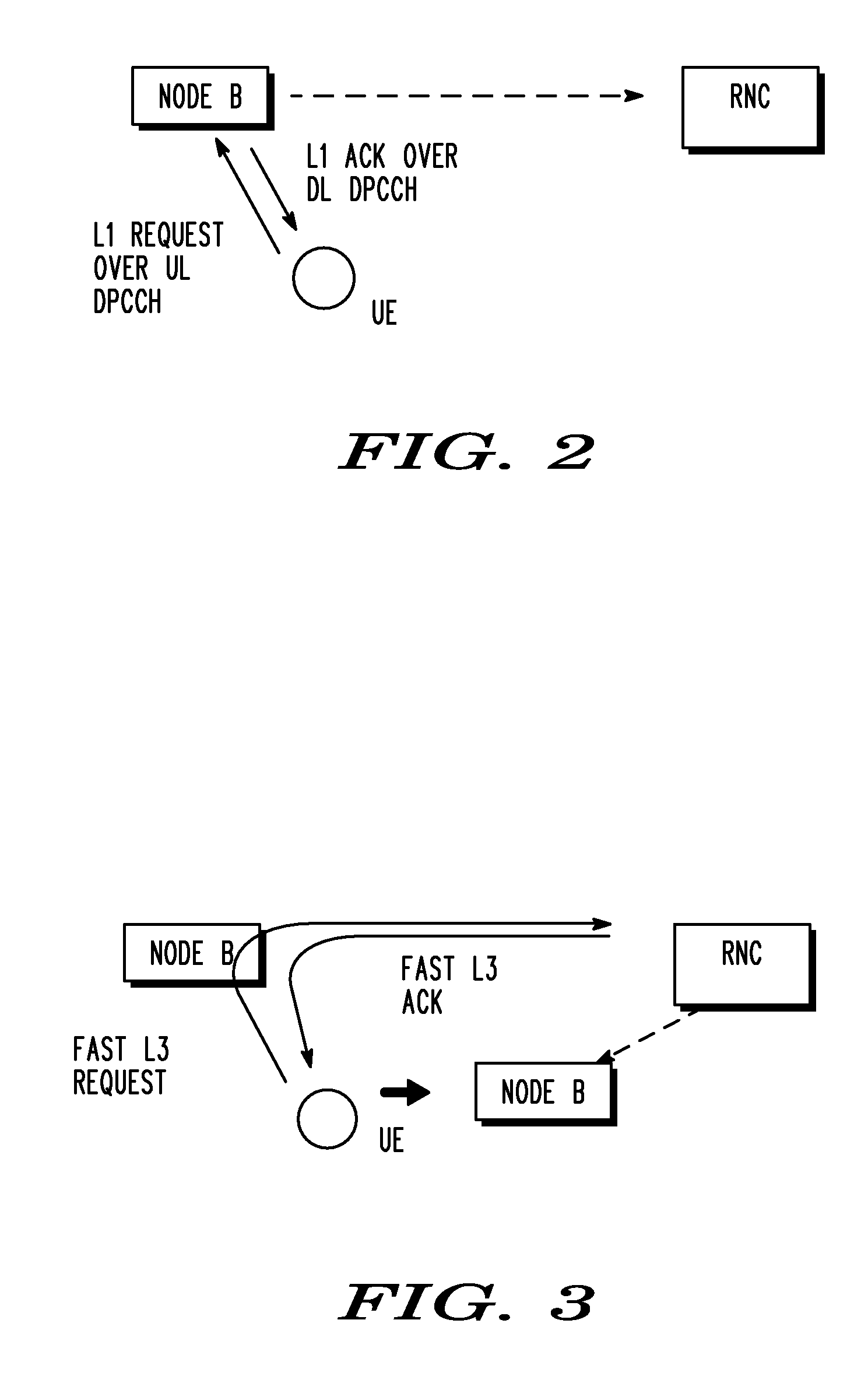
Mobility enhancement for real time service over high speed downlink packet access (HSDPA)
ActiveUS20070097918A1Data switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsReal time services
A system and method for enhancing service over a high-speed downlink packet access (HSDPA) service in a cellular communication network includes informing a UE of the cells in an HSDPA active subset of cells. The US makes a measurement of the cells and selects a best cell for switching. The UE determines whether the best cell is an intra-node B cell or inter-node B cell with the serving cell from the network. If the best cell is an intra-node B cell, the UE signals the node B of the best cell, the node B switches to the best cell directly and UE receives the data from the target cell directly, and then Node B reports the switch to a radio network controller (RNC) that completes the final switching to the best cell by the RNC. If the best cell is an inter-node B cell, the UE signals the RNC of the best cell directly, whereupon the RNC sends the UE an acknowledgment without waiting for the completeness of the network configurations. The RNC re-routes data to the best cell, and the UE switches to the best cell after receiving the acknowledgment.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Multiplexing of real time services and non-real time services for OFDM systems
InactiveUS20060023666A1Guaranteed normal transmissionImprove efficiencyFrequency-division multiplex detailsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsData streamFull Rate
Transmitter and receiver units for use in an OFDM communications system and configurable to support multiple types of services. The transmitter unit includes one or more encoders, a symbol mapping element, and a modulator. Each encoder receives and codes a respective channel data stream to generate a corresponding coded data stream. The symbol mapping element receives and maps data from the coded data streams to generate modulation symbol vectors, with each modulation symbol vector including a set of data values used to modulate a set of tones to generate an OFDM symbol. The modulator modulates the modulation symbol vectors to provide a modulated signal suitable for transmission. The data from each coded data stream is mapped to a respective set of one or more “circuits”. Each circuit can be defined to include a number of tones from a number of OFDM symbols, a number of tones from a single OFDM symbol, all tones from one or more OFDM symbols, or some other combination of tones. The circuits can have equal size or different sizes. Different circuits can be used for full rate data (e.g., active speech) and low rate data (e.g., silence periods).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Specification of a software architecture for capability and quality-of-service negotiations and session establishment for distributed multimedia applications
InactiveUS20060294112A1Efficiently and timely reactError preventionTransmission systemsExtensible markupMiddleware
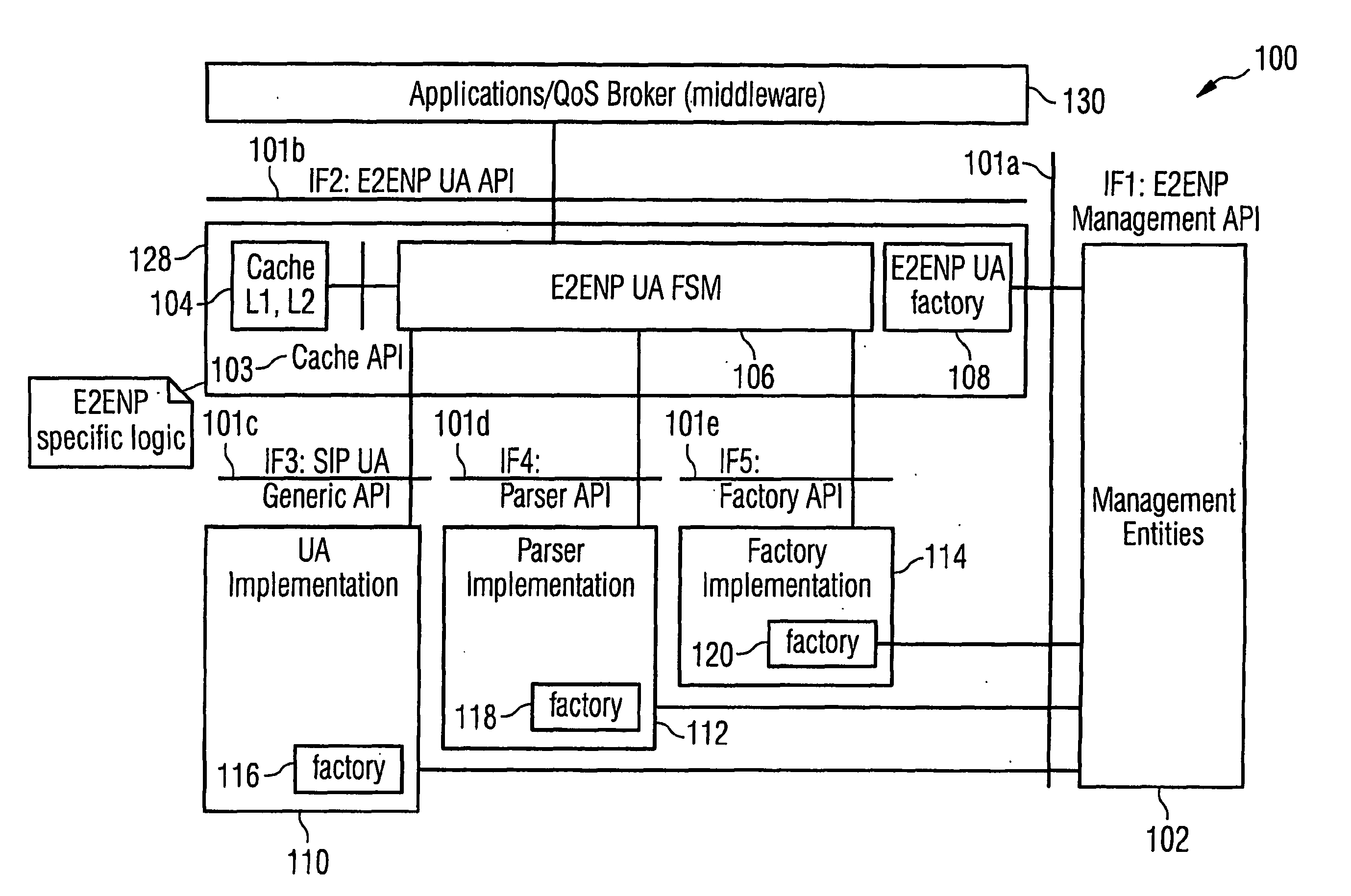
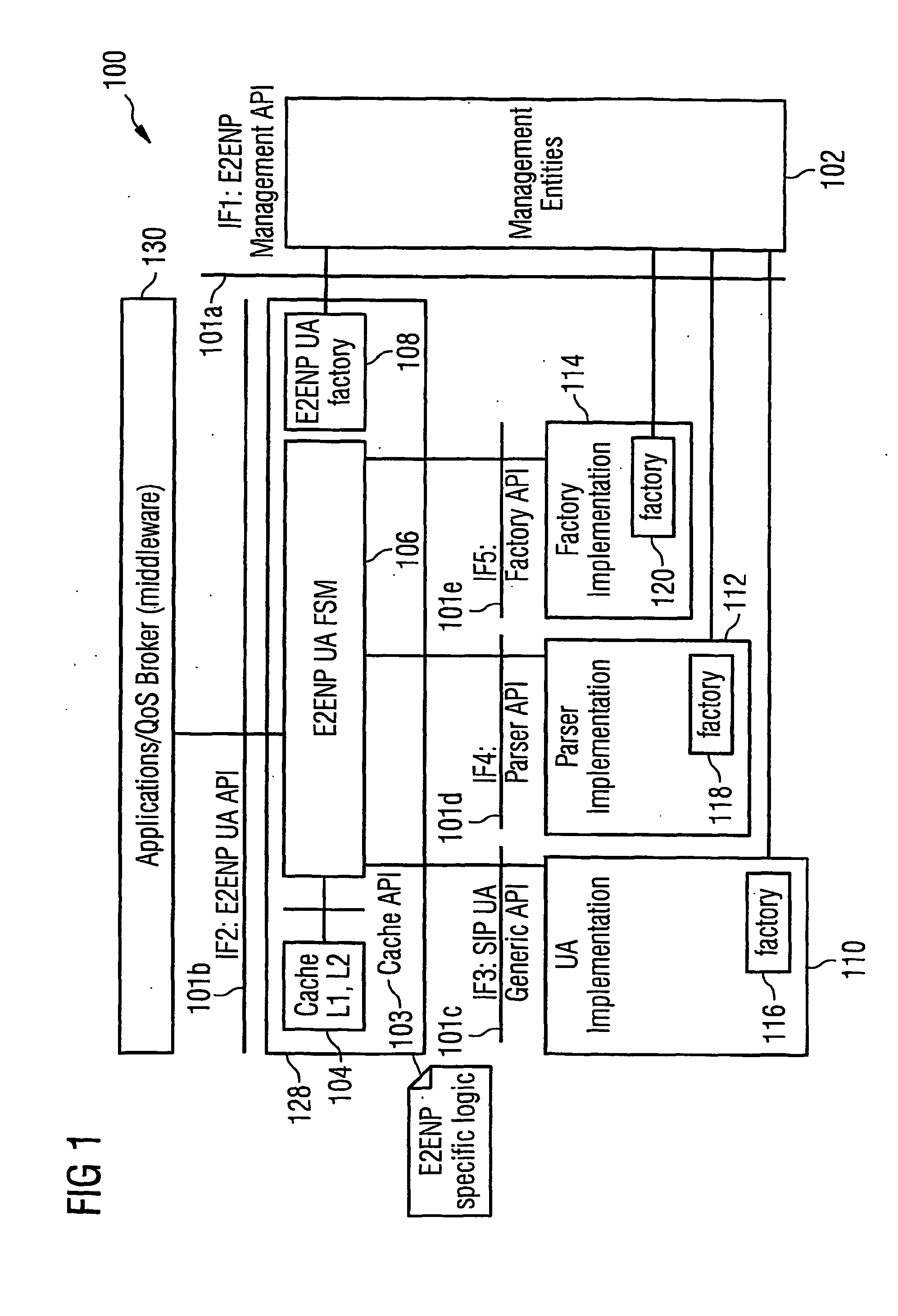
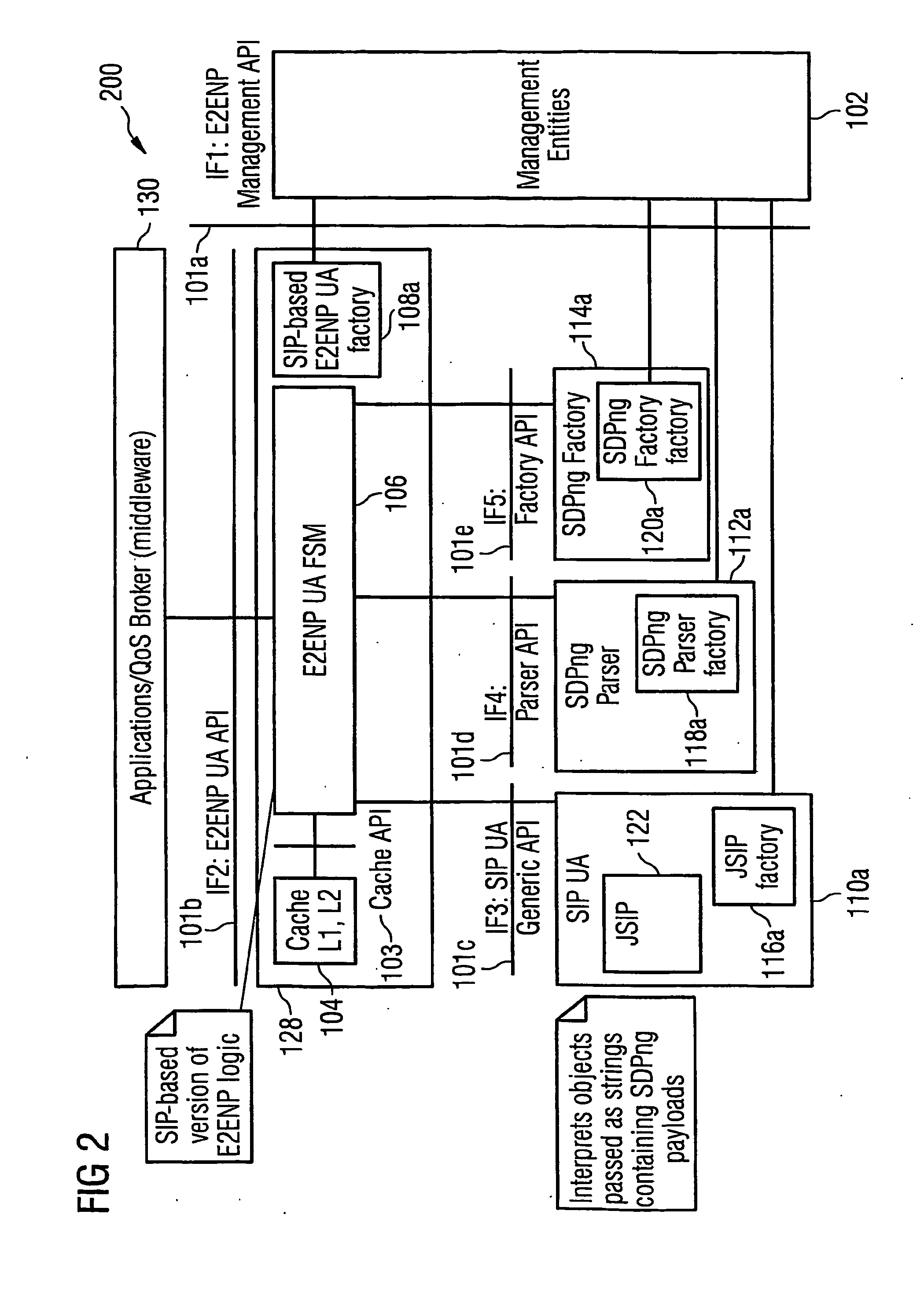
The underlying invention generally relates to the field of mobile computing in a wireless mobile networking environment with distributed multimedia applications (130). More specifically, it is directed to the field of Quality-of-Service (QOS) management for adaptive real-time services running on mobile devices and an End-to-End Negotiation Protocol (E2ENP) based on a novel usage of a session-layer protocol (SIP) in conjunction with extensions of a session description protocol implementation (SDP, SDPng) and the Extensible Markup Language (XML) for defining user profile and terminal capability information which allow to enforce and use hierarchical QOS Contract specifications. Thereby, said End-to-End Negotiation Protocol (E2ENP) is applied to derive negotiable information, which enables a prenegotiation, fast negotiation and a fast, dynamic re-negotiation of the end-to-end quality and capabilities for a telecommunication session, for multiple configurations of two or a multiplicity of end peers and / or middleware in a consistent, reliable, and incremental way by enabling the mobile applications to efficiently and timely react to QoS violations. Furthermore, the invention pertains to the concept and realization of a novel E2ENP User Agent (128) which encapsulates the signaling part of E2ENP and expresses the information to be negotiated in an interchangeable format in such a way that heterogeneous applications (130) can easily agree on a reference model applied to orchestrate local, peer, and network resources according to the preferences and profiles of the respective user in a coordinated manner. According to one embodiment of the invention, the employed E2ENP sessionlayer protocol Application Programming Interfaces (101a-e) are independent of the actually used session-layer protocol and session description protocol implementations.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG +1
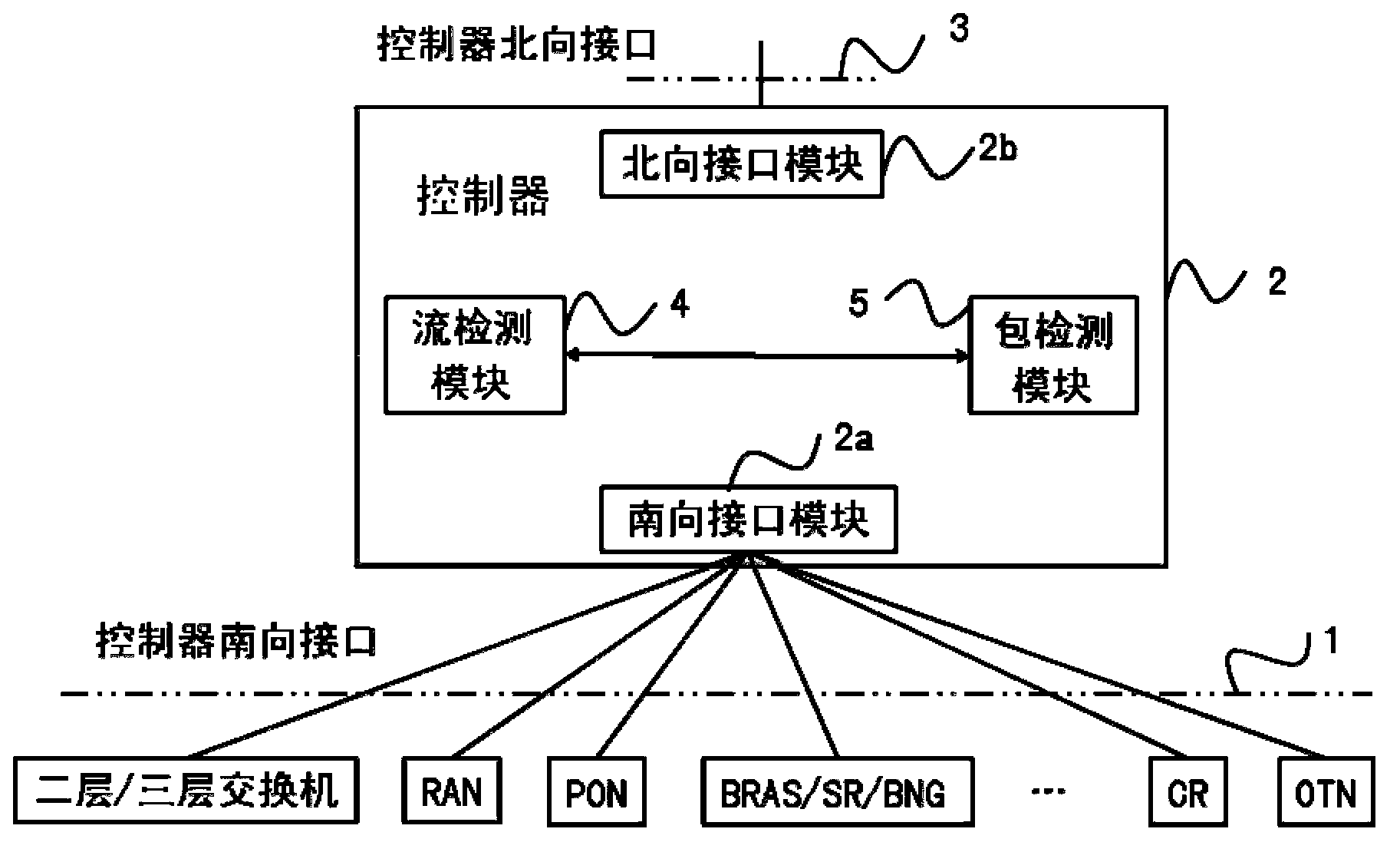
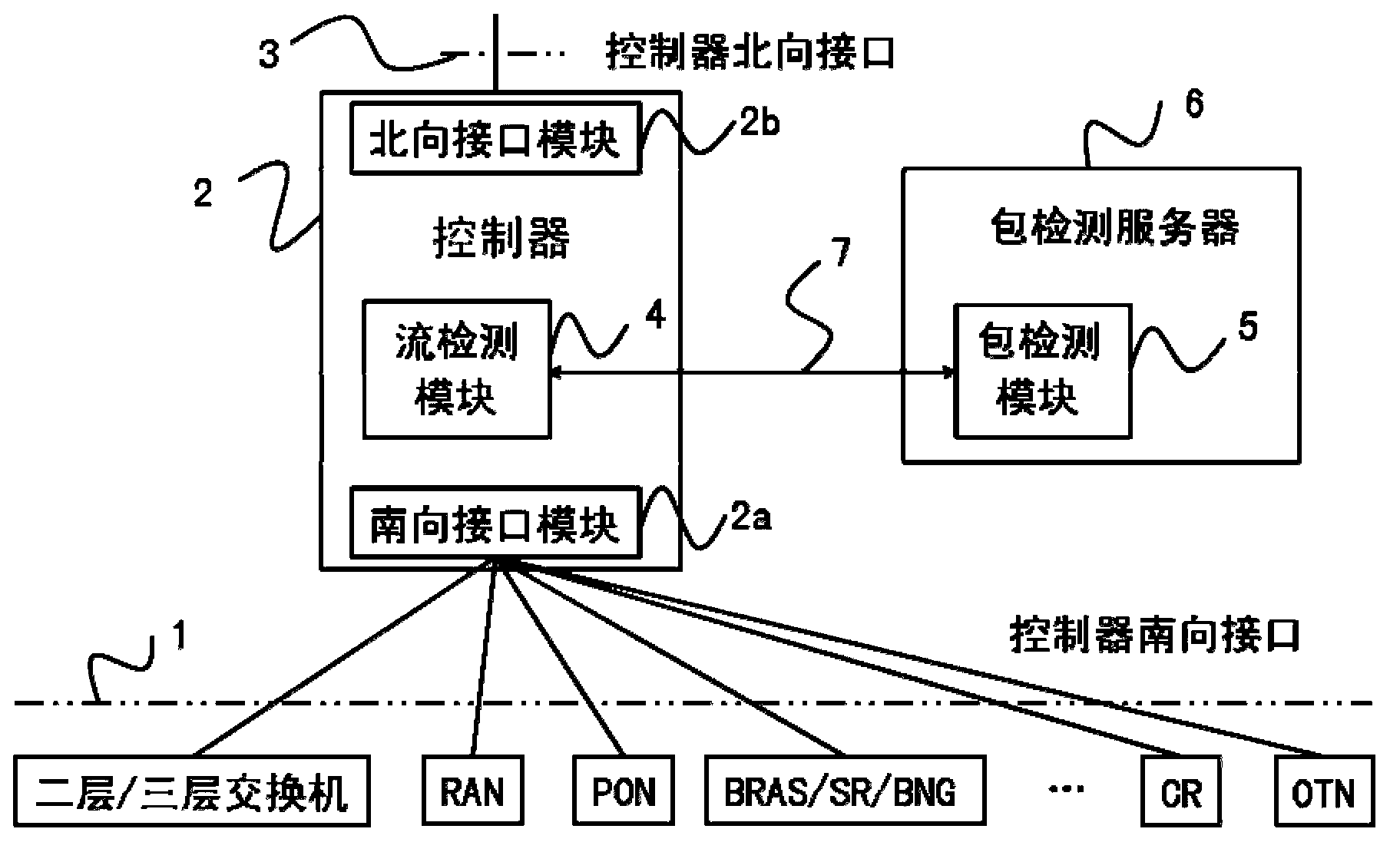
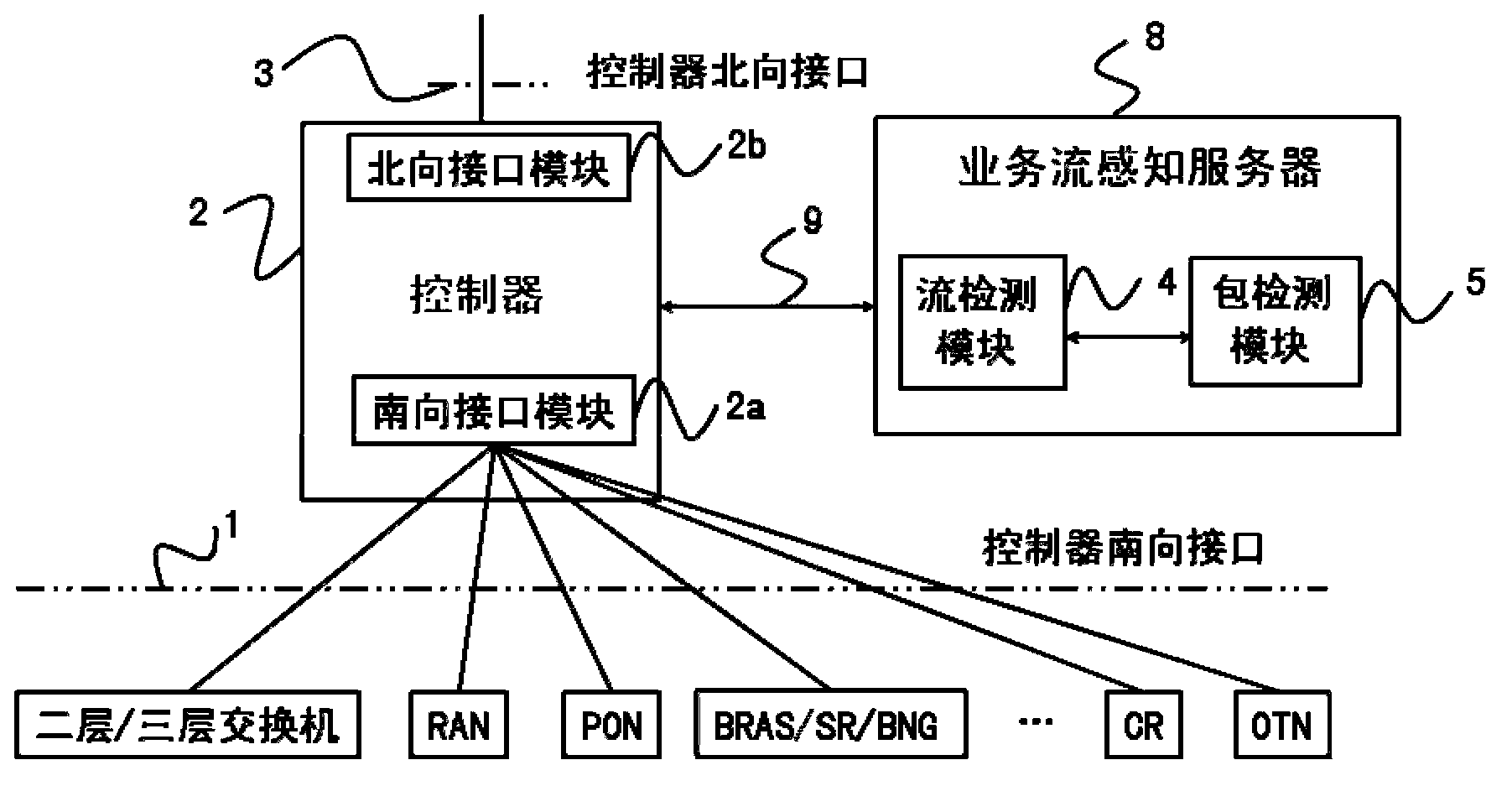
Service flow aware system and method combining flow detection and package detection in SDN
The invention discloses a service flow aware system and method combining flow detection and package detection in the SDN, and relates to the field of the SDN. The service flow aware method includes the steps that when an initial novel service flow enters the SDN, table items not matched with the novel service flow in an equipment flow table are forwarded, the novel service flow is forwarded to a controller, a flow detection module carries out flow detection, a package detection module carries out package detection to recognize the service type and the service characteristics of the novel service flow, the controller triggers the awareness of a specific service according to the characteristics of the service flow, flow signs, flow statistics and package statistics, for current continuous service flow, the controller samples a real-time service flow, the dynamic variation of the real-time service is discovered through service awareness, and network strategies are adjusted correspondingly. The service flow aware system and method combining flow detection and package detection in the SDN combines the flow detection technology and the package detection technology, expands the southing port of the controller in the SDN, and can completely obtain the states of network flows of different industries and different applications in the current network.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
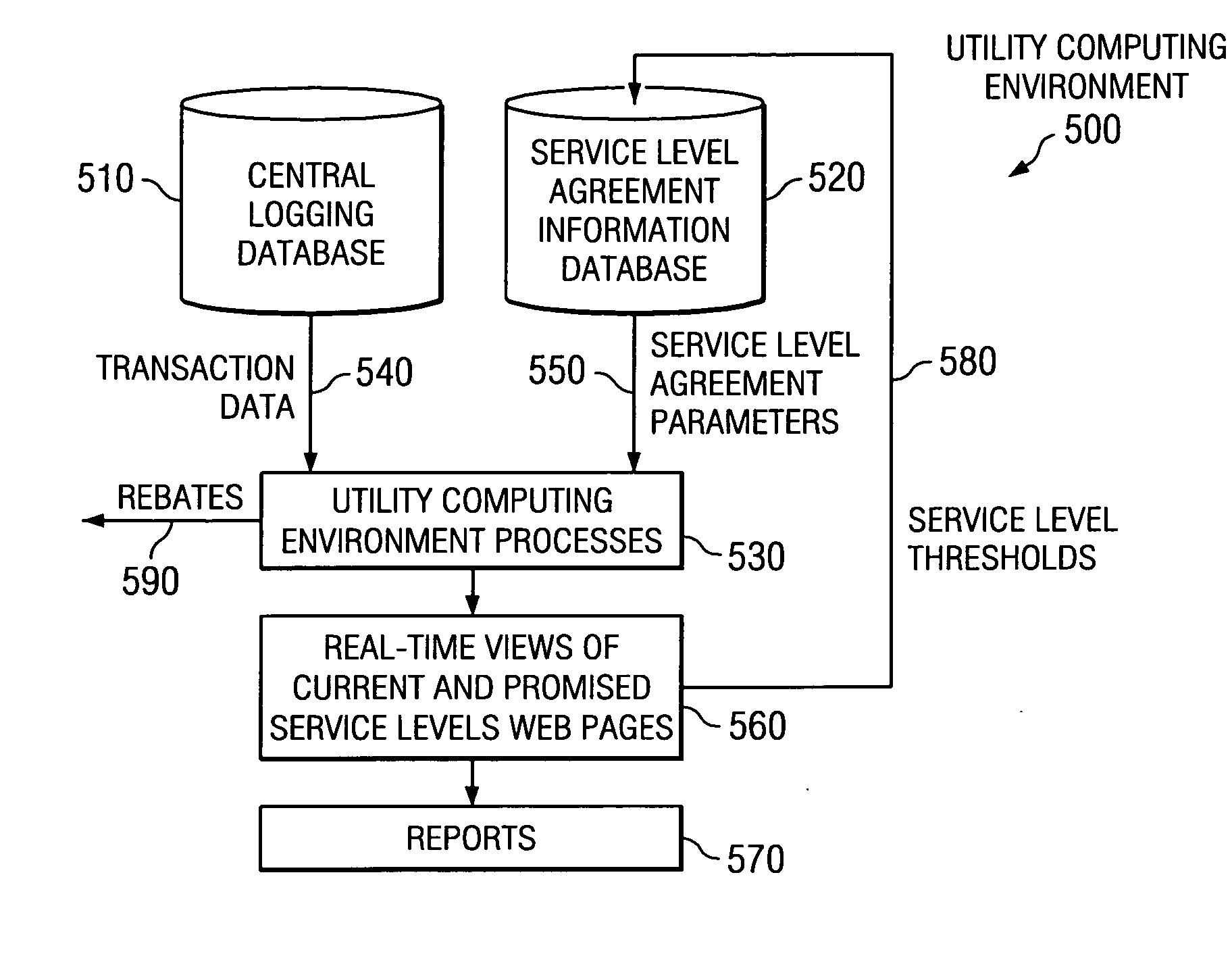
Method of displaying real-time service level performance, breach, and guaranteed uniformity with automatic alerts and proactive rebating for utility computing environment
InactiveUS20050066026A1Eliminate the potential discrepancyMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsUtility computingService-level agreement
The present invention provides a method, apparatus, and computer program product for displaying real-time service level performance, breach, and guaranteed uniformity with automatic alerts and proactive rebating for a utility computing environment. Service level agreement parameters, based on a service level agreement between a customer and a service provider, are used to identify discrepancies in a promised service level for the utility computing environment. A real-time view of a current service level and the promised service level for the customer are displayed. When a discrepancy between the promised service level and the current service level occurs, a rebate is generated for the customer. Alerts identifying the discrepancy and its root cause are provided to the customer and the service provider for the discrepancy. Alerts may also be provided prior to the occurrence of the discrepancy so that an action may be performed to eliminate the potential discrepancy.
Owner:IBM CORP
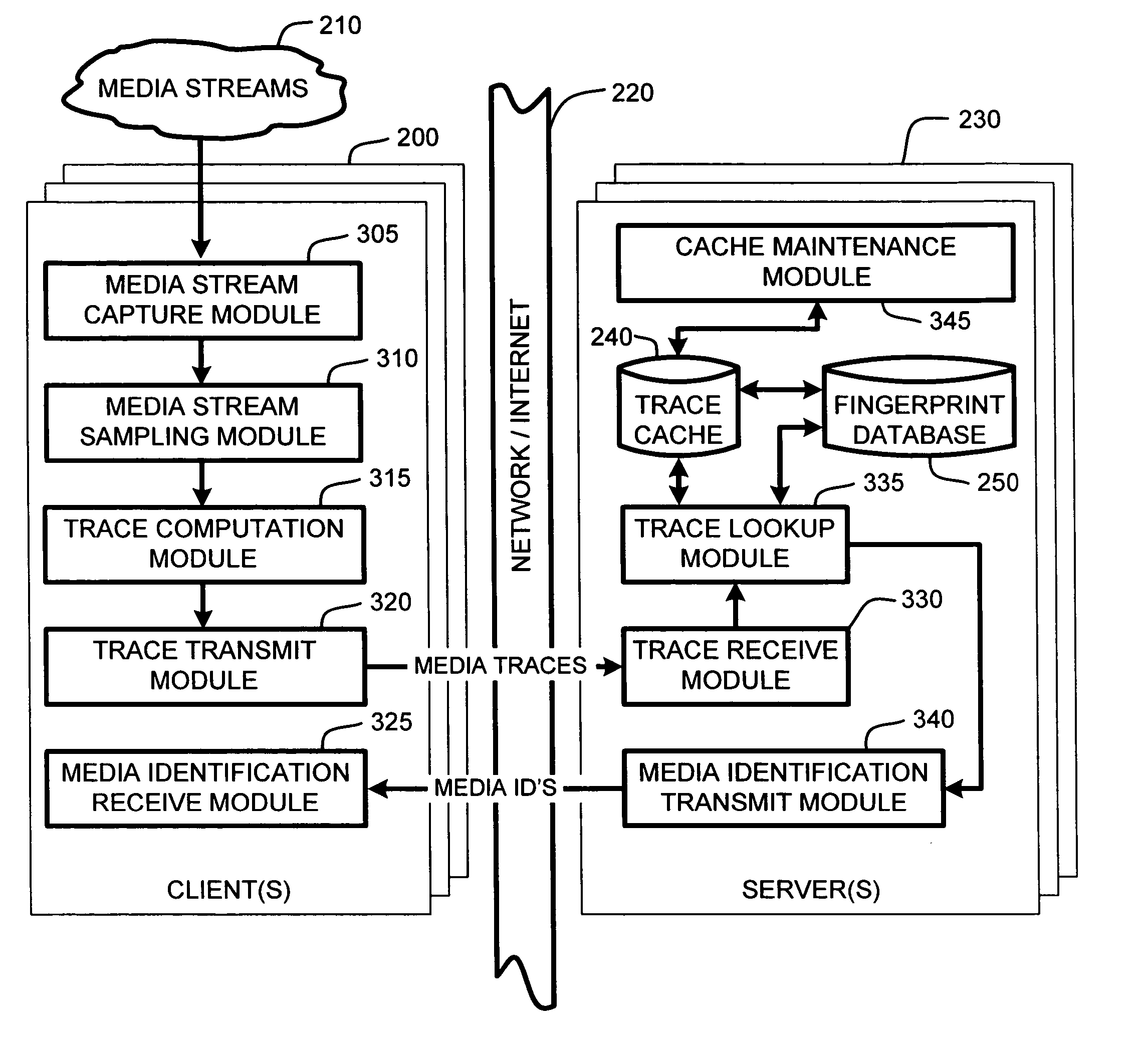
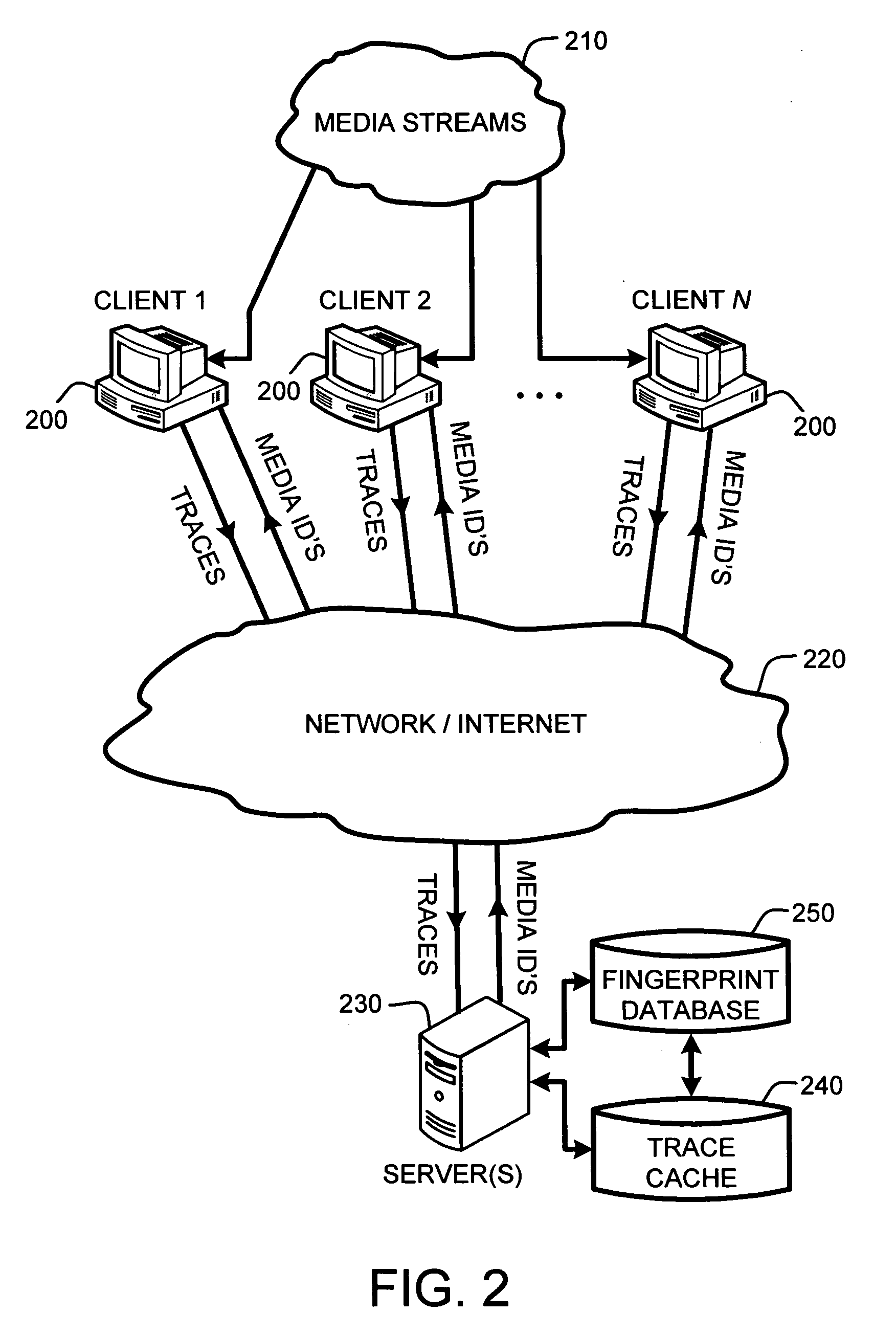
System and method for speeding up database lookups for multiple synchronized data streams
InactiveUS20060106867A1Increase loadImprove accuracyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData streamReal time services
A “Media Identifier” operates on concurrent media streams to provide large numbers of clients with real-time server-side identification of media objects embedded in streaming media, such as radio, television, or Internet broadcasts. Such media objects may include songs, commercials, jingles, station identifiers, etc. Identification of the media objects is provided to clients by comparing client-generated traces computed from media stream samples to a large database of stored, pre-computed traces (i.e., “fingerprints”) of known identification. Further, given a finite number of media streams and a much larger number of clients, many of the traces sent to the server are likely to be almost identical. Therefore, a searchable dynamic trace cache is used to limit the database queries necessary to identify particular traces. This trace cache caches only one copy of recent traces along with the database search results, either positive or negative. Cache entries are then removed as they age.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Failure detection and fault tolerance method and failure detection and fault tolerance system for real-time cloud platform
ActiveCN103716182ANo loss of stateComprehensive detection effectData switching networksFault toleranceReal time services
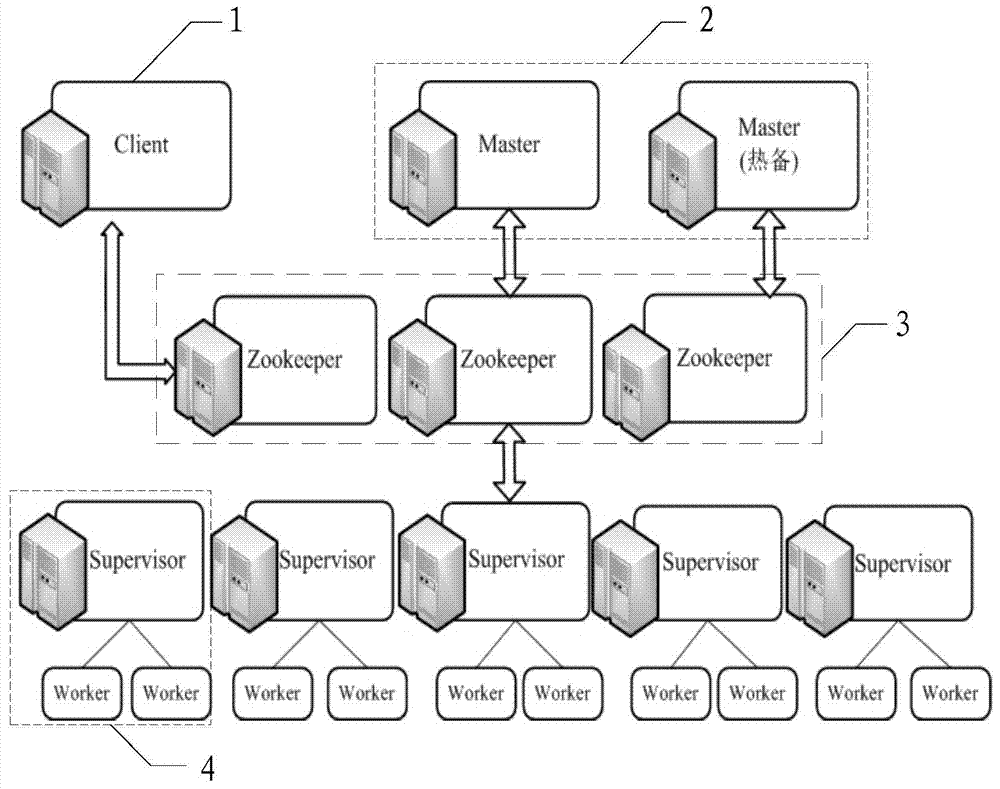
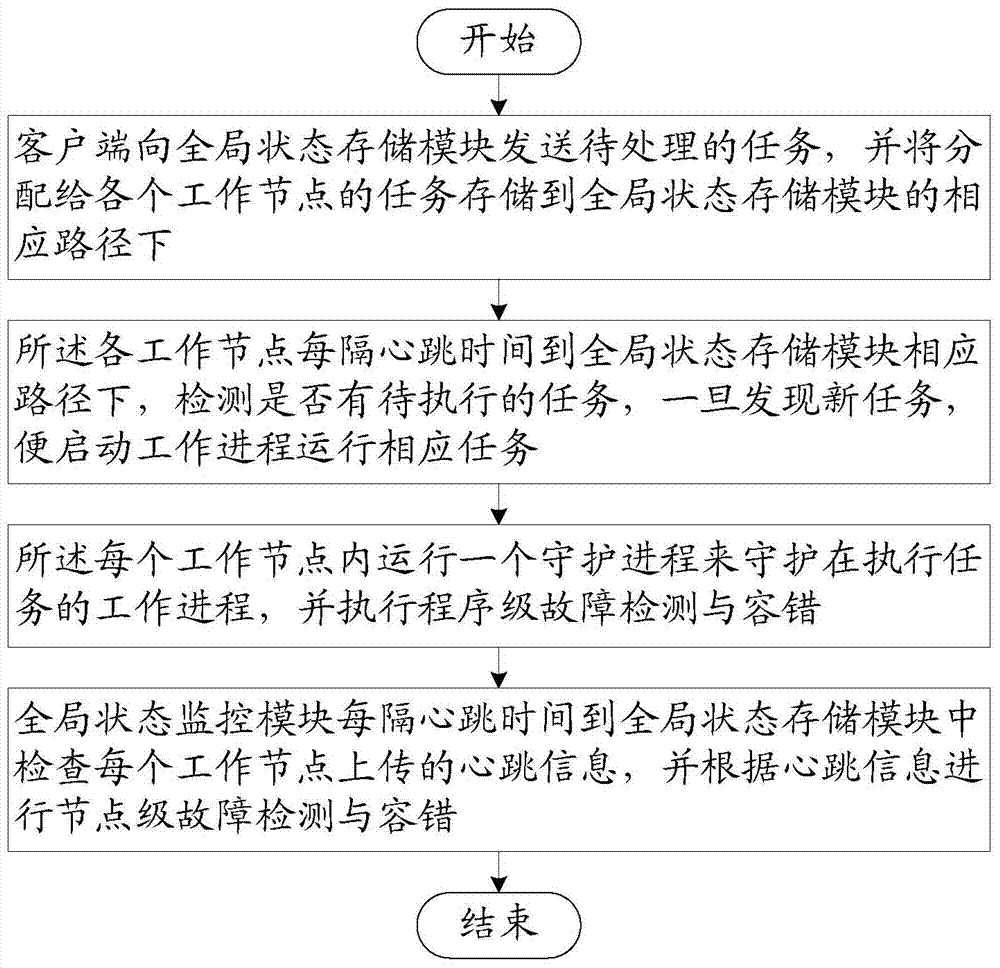
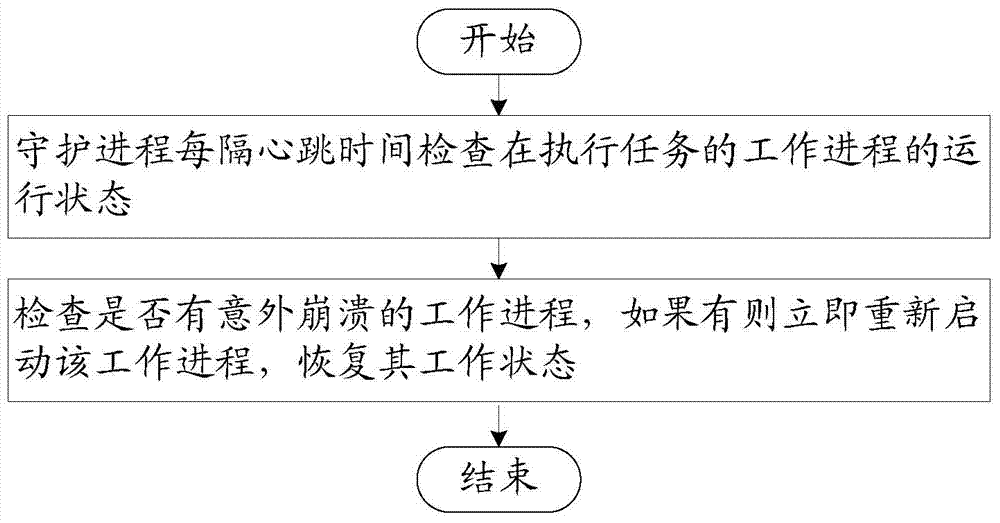
The invention relates to a failure detection and fault tolerance method and a failure detection and fault tolerance system for a real-time cloud platform. The system comprises a client used for sending a command, summiting a task and storing tasks assigned to working nodes in corresponding paths, a global state monitoring module used for monitoring the operation state of the working nodes, carrying out node-level failure detection and fault tolerance according to heartbeat information uploaded by the working nodes and performing migration of a task in a failure node, a global state storage module used for storing the working state and heartbeat information of the global state monitoring module and the working nodes, and working nodes used for performing a task, running a daemon process to guard a work process and performing program-level failure detection and fault tolerance. State information of a whole cluster is all stored in a Zookeeper system, a stateless architecture of the nodes is realized, a node failure does not cause state loss, the system has a perfect failure detection and fault tolerance mechanism, multilevel fault tolerance is realized, and uninterrupted operation of real-time services is guaranteed.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Systems, methods, and computer program products facilitating real-time transactions through the purchase of lead options
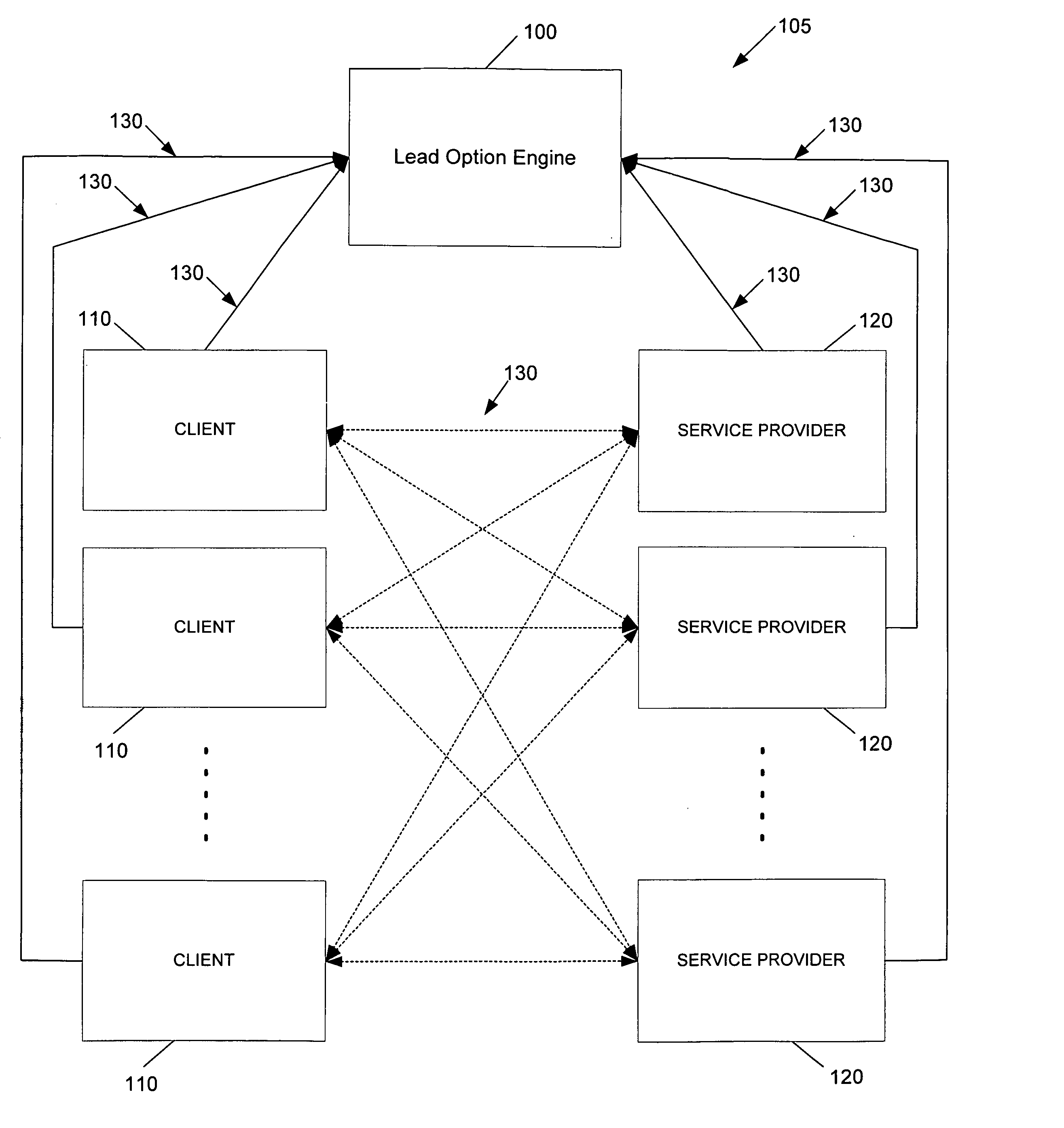
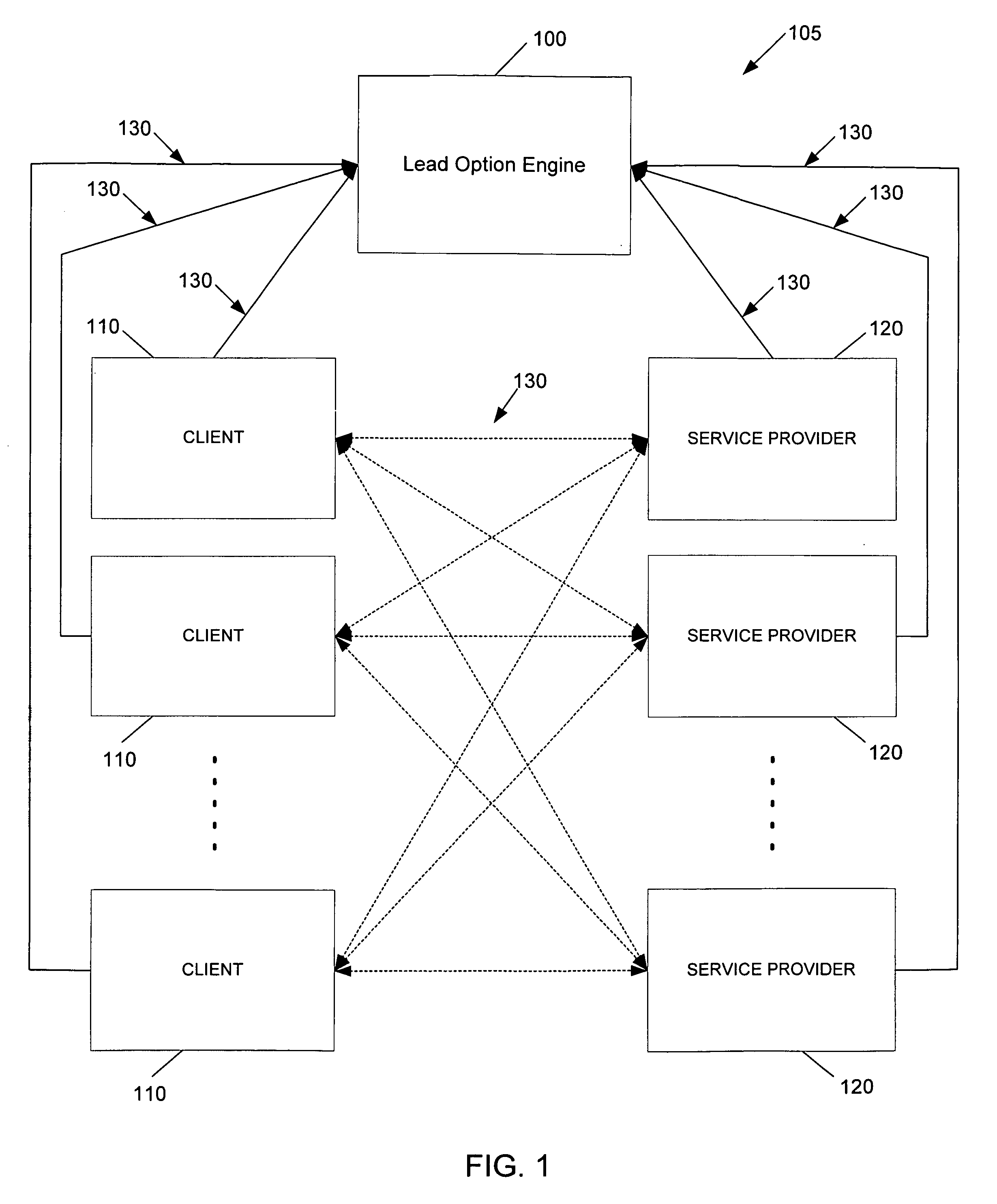
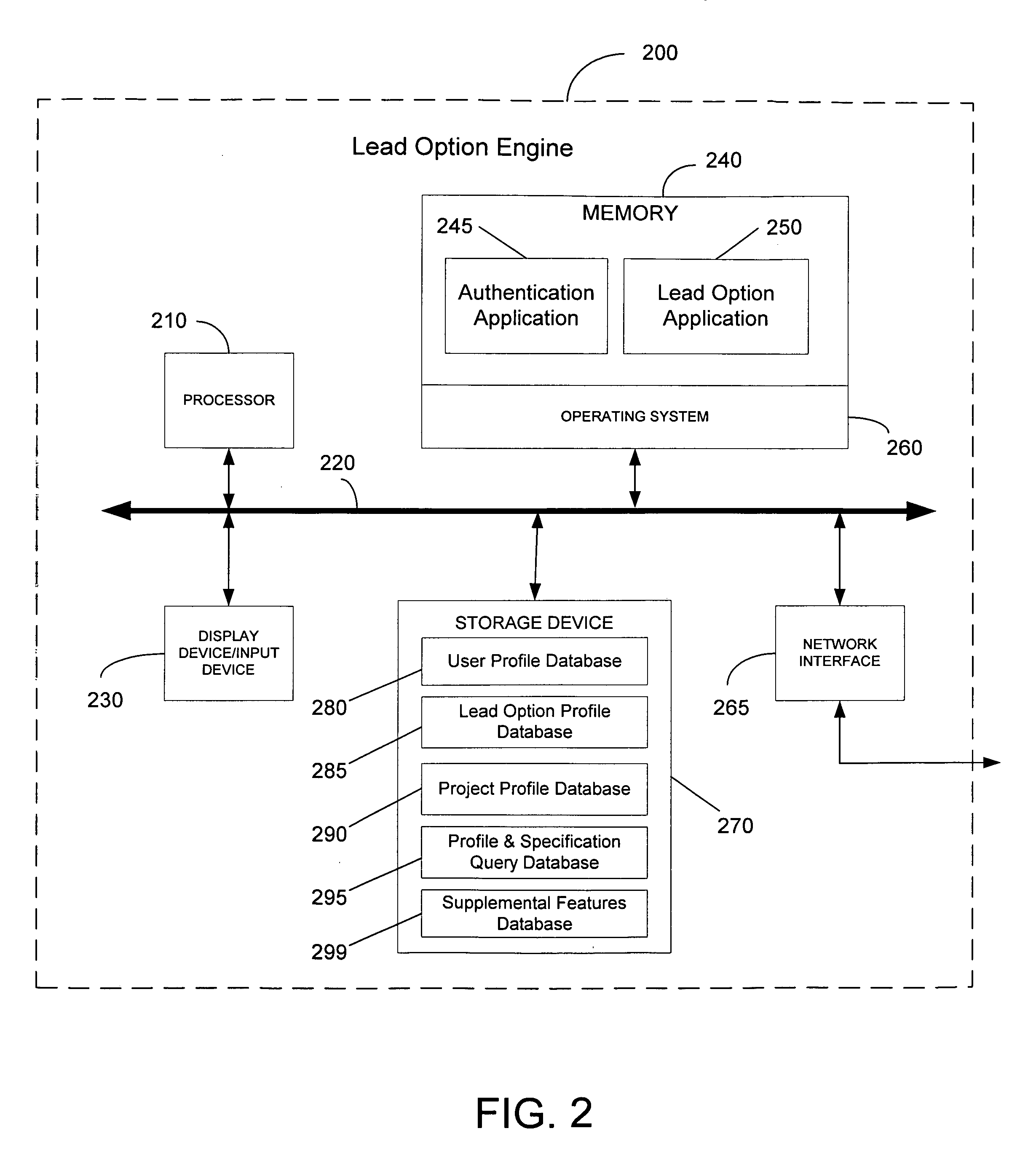
InactiveUS7139732B1Facilitate real-time service transactionConvenient transactionFinanceElectronic credentialsReal time servicesService provision
Systems, methods and computer program products facilitating real-time service transactions between two or more users, including at least one client and at least one service provider. Service providers complete project profiles identifying projects they wish to work on, and clients complete project profiles identifying projects they would like to pay service providers to complete. The project profiles including identifying parameters such as the type of service or project, start date, completion date, skills required for completion, and the like. Both the clients and service providers may then purchase lead options to identify their desire for obtaining a matching user. The lead options can be a sum of money a user wishes to pay for a lead. The systems, methods and computer products then determine matching clients and service providers based upon the project profiles, and identifies to one or more lead option submitting users the immediately available users that match the project profile submitted by the user. In this manner, clients and service providers can utilize the present invention to locate immediately appropriate and available users with which to transact with.
Owner:ROGER MARX DESENBERG +1
Padding time-slice frames with useful data
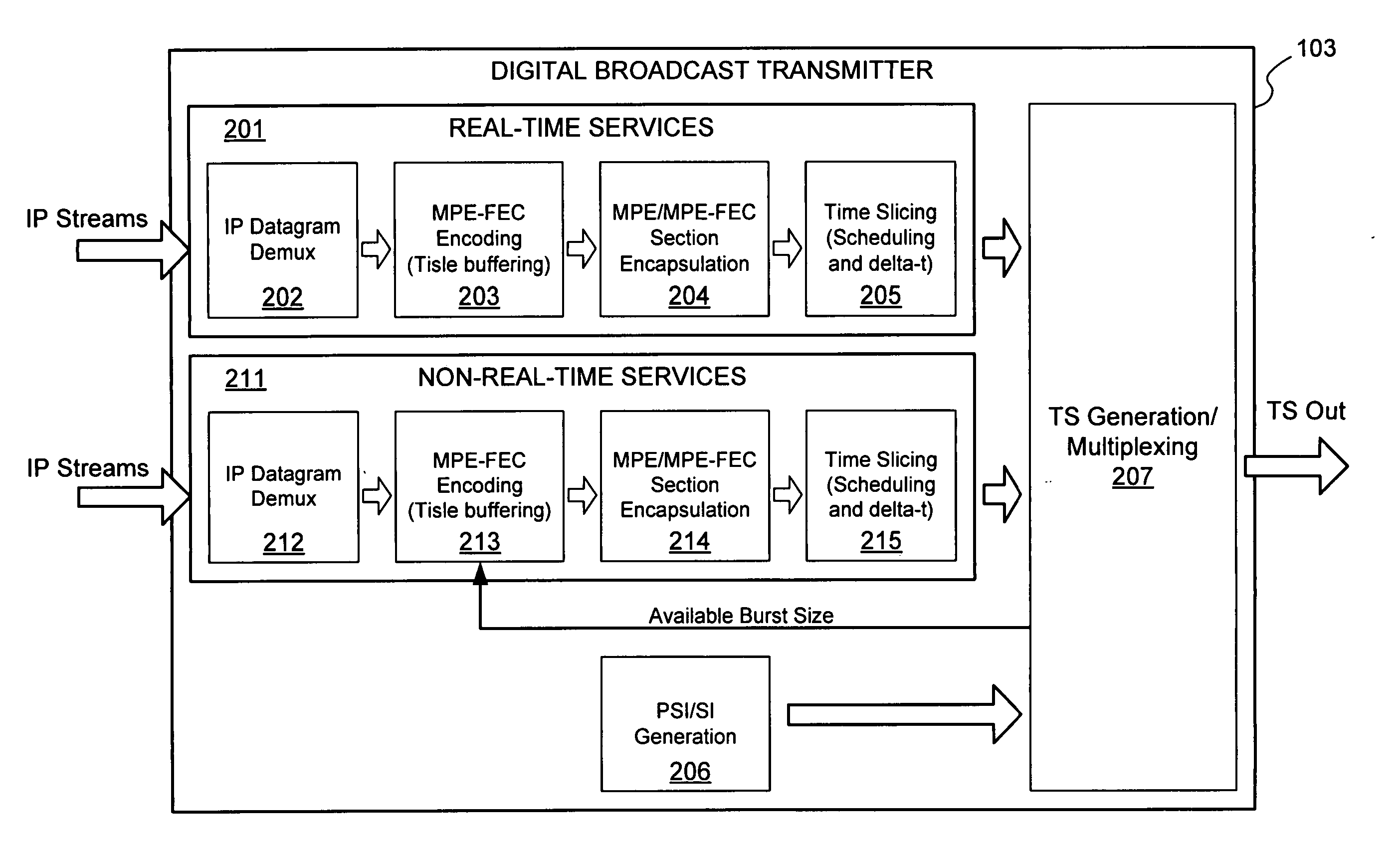
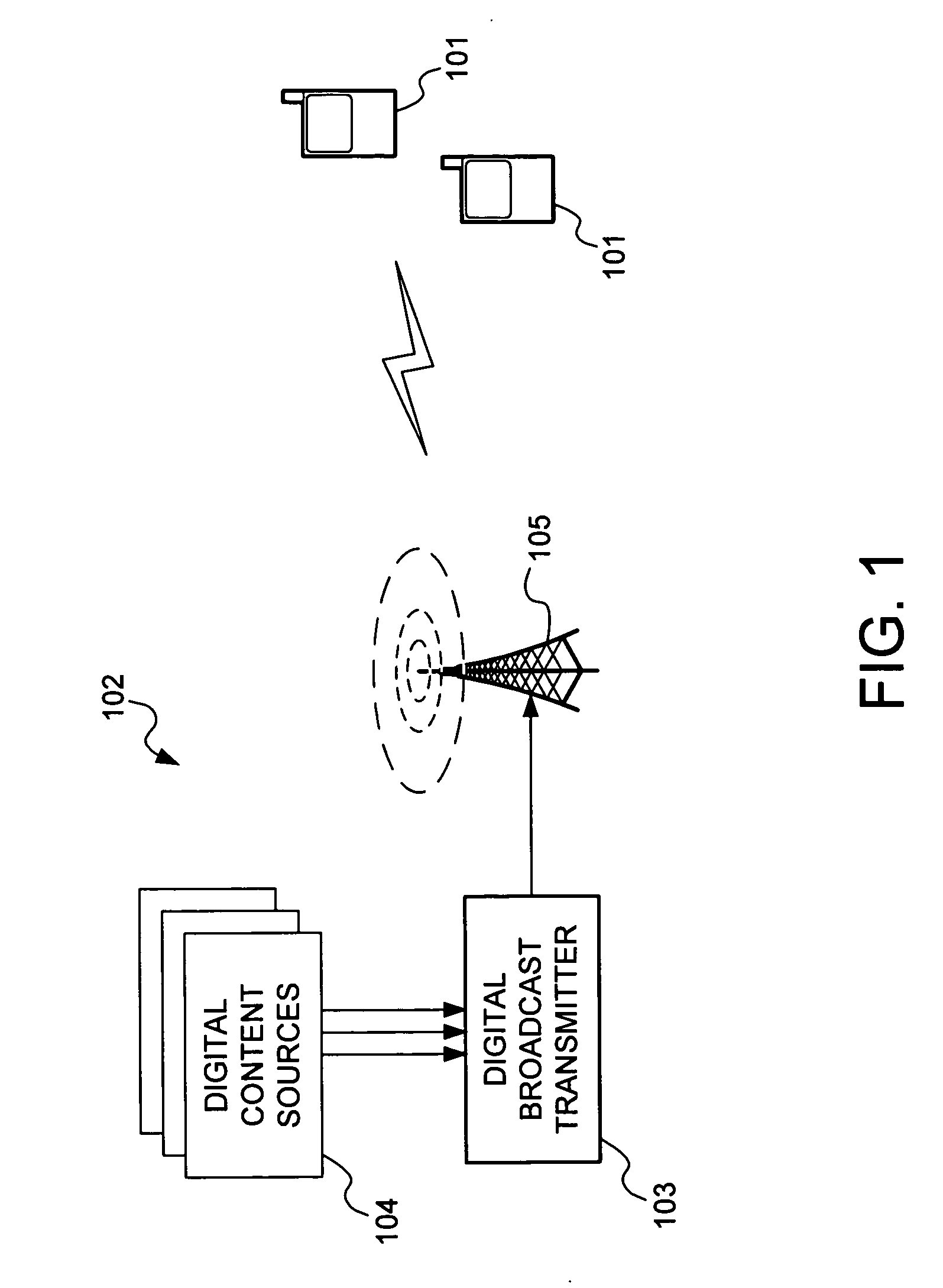
InactiveUS20070002871A1Maximizes interleaving lengthQuantity maximizationNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationNon real timeReal time services
Provided are apparatuses and methods for padding a series of real-time service time-slice bursts with related non-real-time service data in a digital broadcast transmission system. Real-time services (e.g., streaming video) are formed into a series of bursts or slots as a single frame. Available capacity within each slot of the frame is filled using related non-real-time service data (e.g., a file download). Receivers may receive individual bursts from within the frame and / or may receive the entire frame in order to receive the related non-real-time service data.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
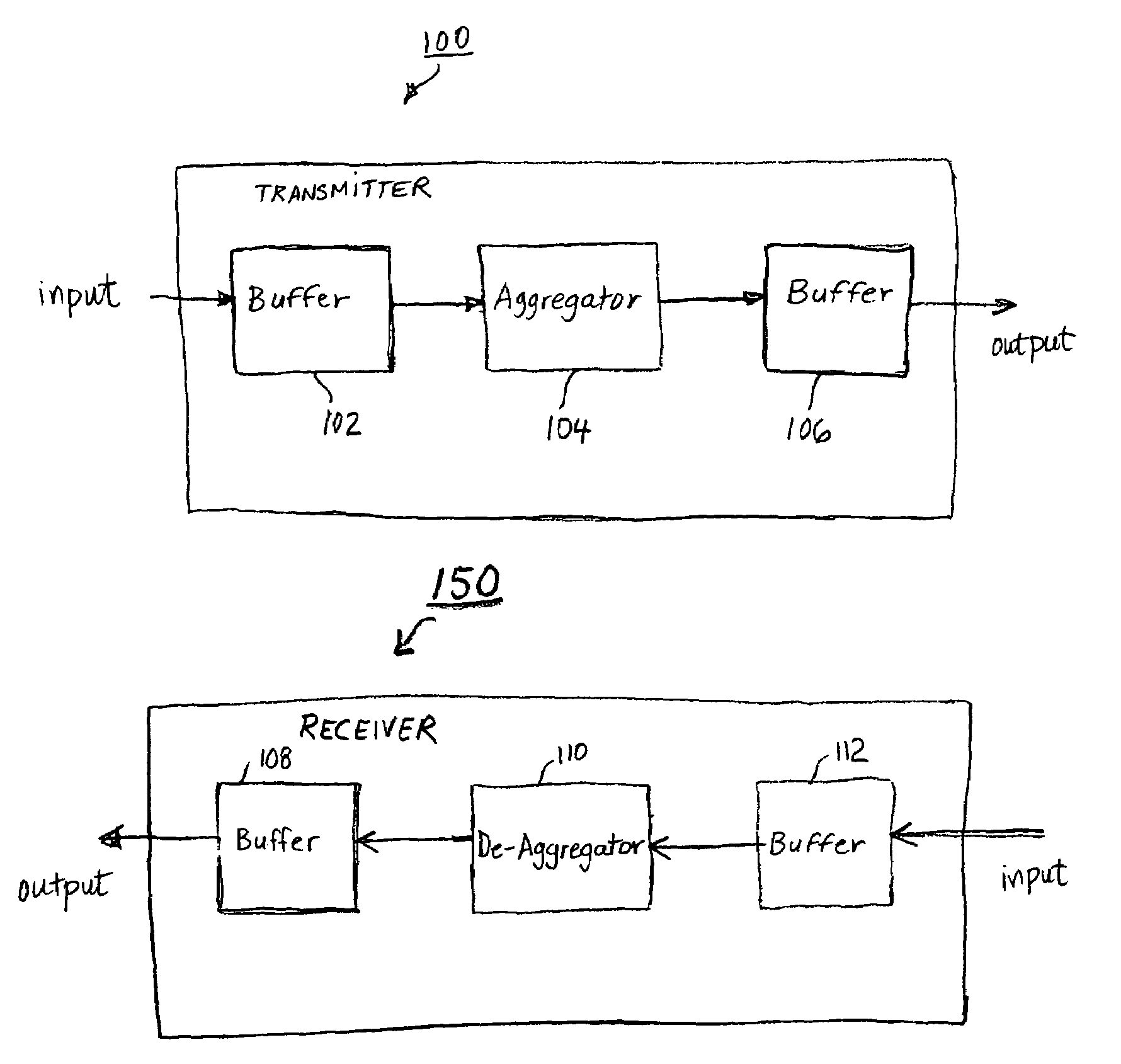
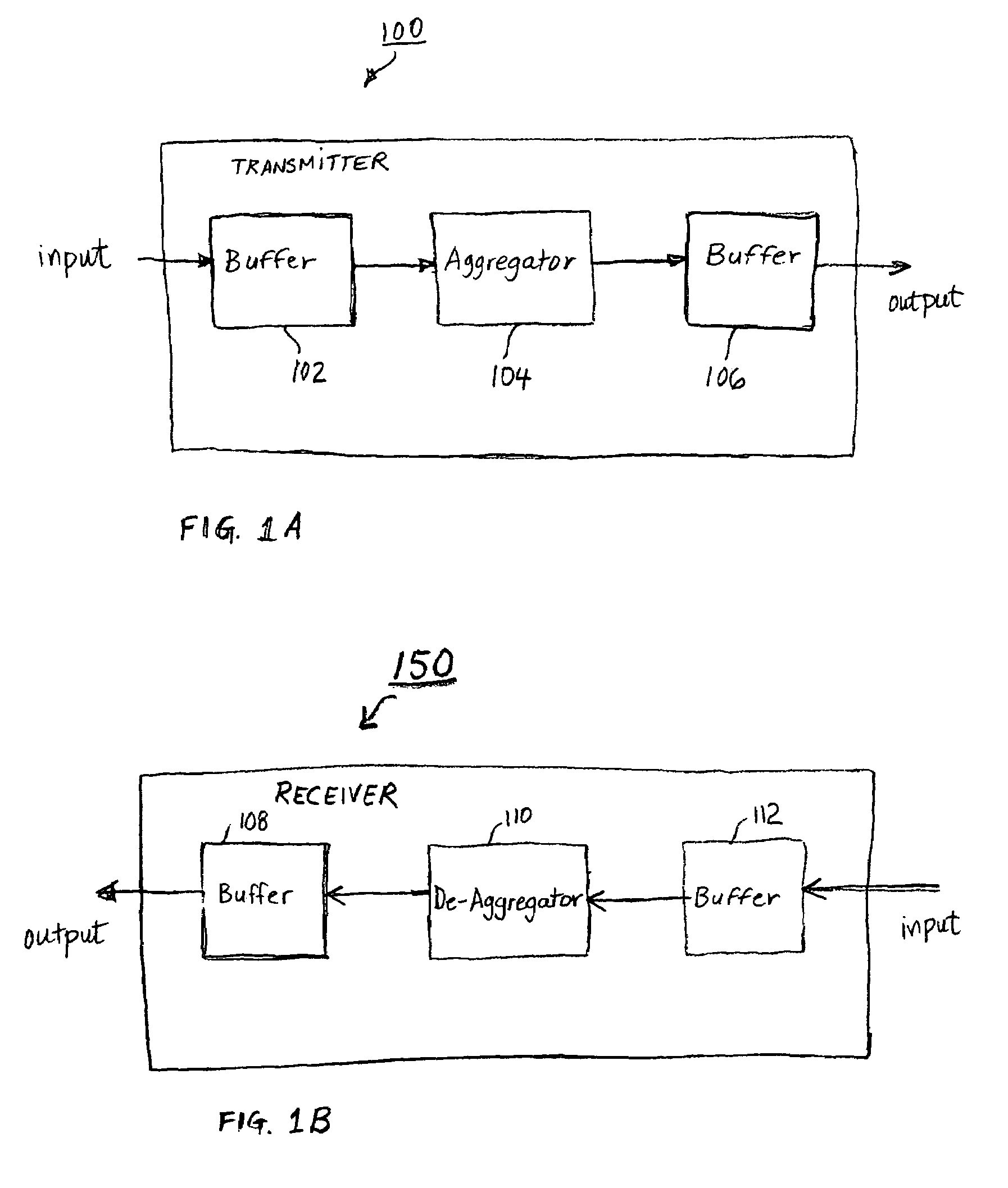
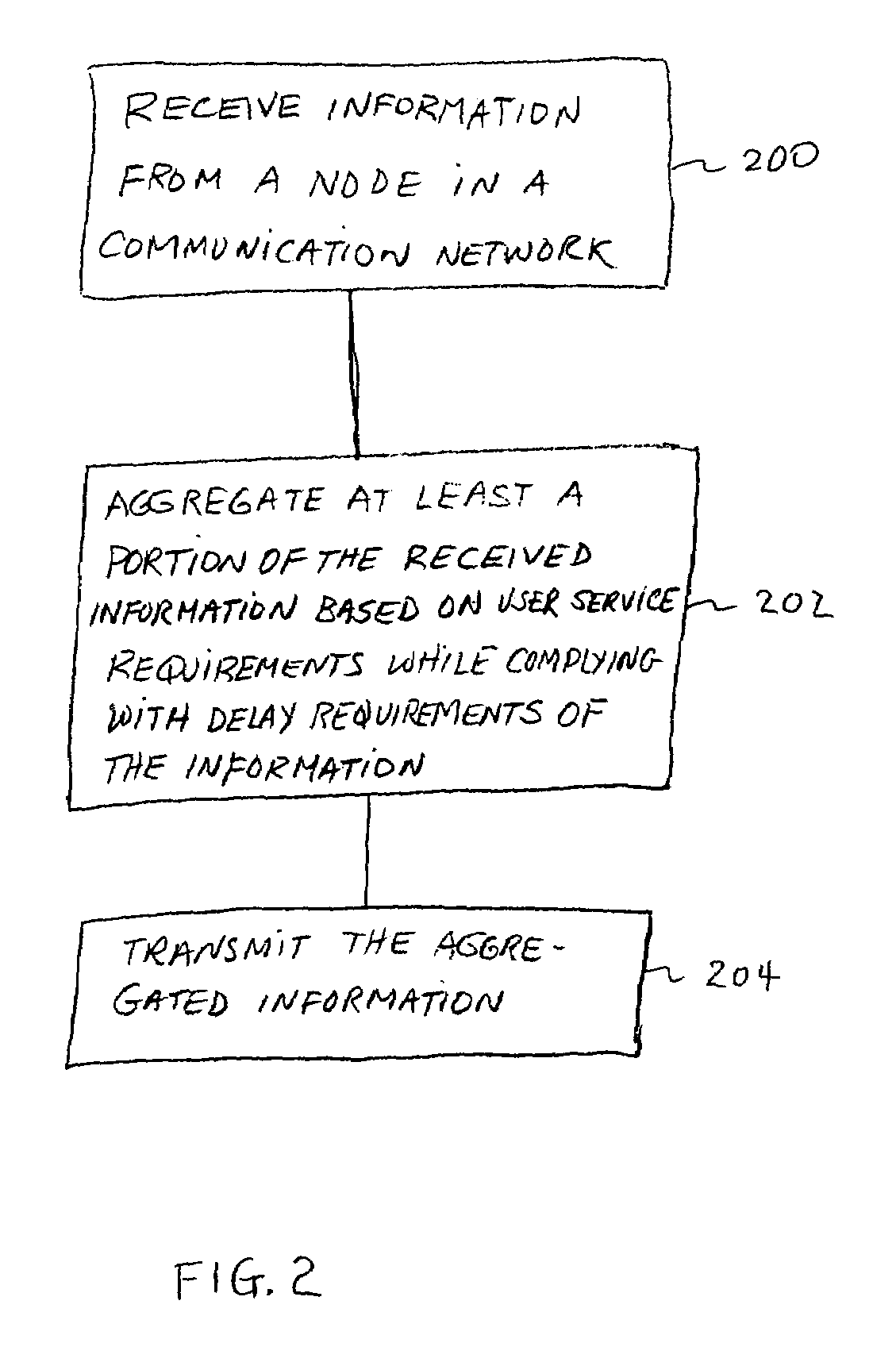
Packet aggregation for real time services on packet data networks
ActiveUS7391769B2Improve efficiencyIncrease system capacitySpecial service provision for substationHybrid switching systemsData packCommunications system
A method and equipment is used to transmit and / or receive time delay-intolerant information over a communication system. The information is transmitted in aggregated form. A plurality of packets representing time delay-intolerant information is combined to form an aggregate packet. The aggregate packet is formed based on user service requirements while maintaining time delay requirements of the information. The size of the aggregated is formed from a negotiation between the transmitting equipment and receiving equipment. Because of the use of an aggregated packet less scheduling of packets is done and the aggregated packet can be transmitted at a rate different than the fixed rate of the time delay-intolerant information. The equipment comprises transmit equipment and receive equipment. The transmit equipment contains an aggregator that combines a plurality of packets based on user service requirements. The packets to be transmitted are retrieved at the fixed rate of the time delay-intolerant information. The size of the aggregate packet can be determined on a static or dynamic basis. The receiving equipment contains a de-aggregator circuit that receives aggregated packets and generates individual packets from the received aggregated packet. The generated individual packets are retrieved from the de-aggregator at the fixed rate of the time delay-intolerant information.
Owner:GEMPLU
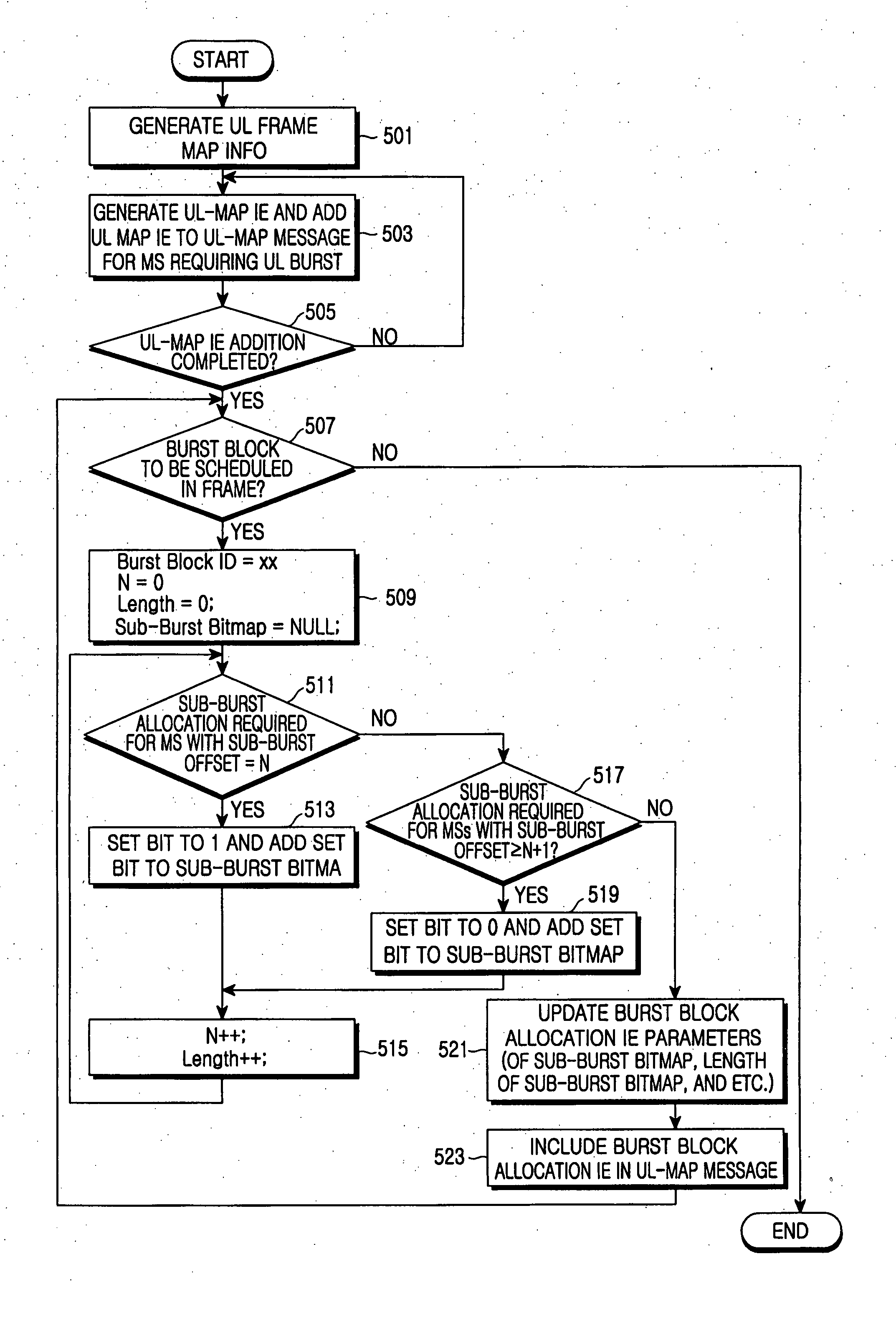
Burst based access and assignment method for providing real-time services
InactiveUS6996083B1Efficient and flexible multiplexingTime-division multiplexRadio transmission for post communicationTime efficientReal time services
A method and system for reducing delay in wireless communications by use of a burst based access and assignment system. The method for setting up a communication channel uses short burst(s) (essentially a slot of a time frame). Time is saved by keeping the uplink and downlink channels flexible and independent of each other. Thus less time is used trying to fit all requests and responses into constrained choices as in previous protocols. The result is less delay to the mobile user and greater usage density for the wireless service provider.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
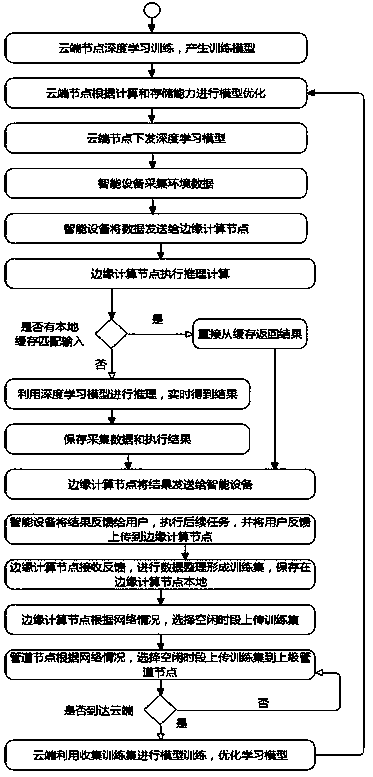
Deep learning computing system and method for cloud terminal edge computing fusion
ActiveCN107766889AImprove real-time performanceImprove recognition rateInterprogram communicationCharacter and pattern recognitionPersonalizationReal time services
The invention discloses a deep learning computing system and method for cloud terminal edge computing fusion and relates to the fields of cloud computing, edge computing and artificial intelligence technology. According to the method, deep learning computing is distributed to a cloud terminal, a pipeline and an edge side, the cloud terminal is responsible for basic model training of a large historical data computing quantity, personalized model distribution is performed according to the demand of the edge side, nodes from the cloud terminal to the edge side deploy a deep learning model after learning, the deep learning model is used for completing inference, the edge side continuously feeds back an inference result, and then the inference result is uploaded to the cloud terminal to continuously optimize the model. Compared with the traditional mode that training and inference are both performed on the cloud terminal, in the whole deep learning computing process, the computing model iscontinuously optimized, personalized model distribution is performed according to the demand of the edge side, bandwidth is effectively utilized, network transmission efficiency is guaranteed, and real-time service execution efficiency is improved.
Owner:INSPUR GROUP CO LTD
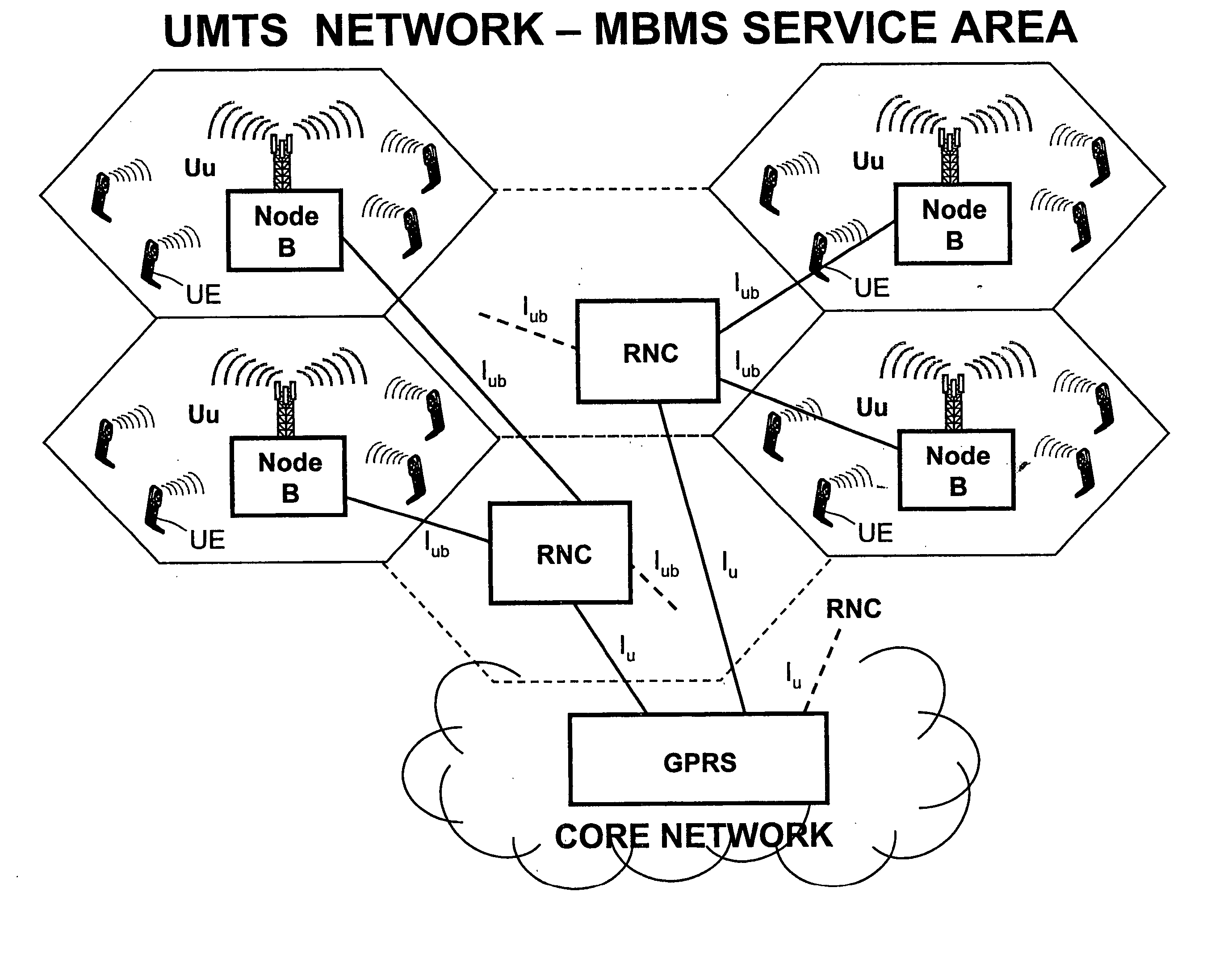
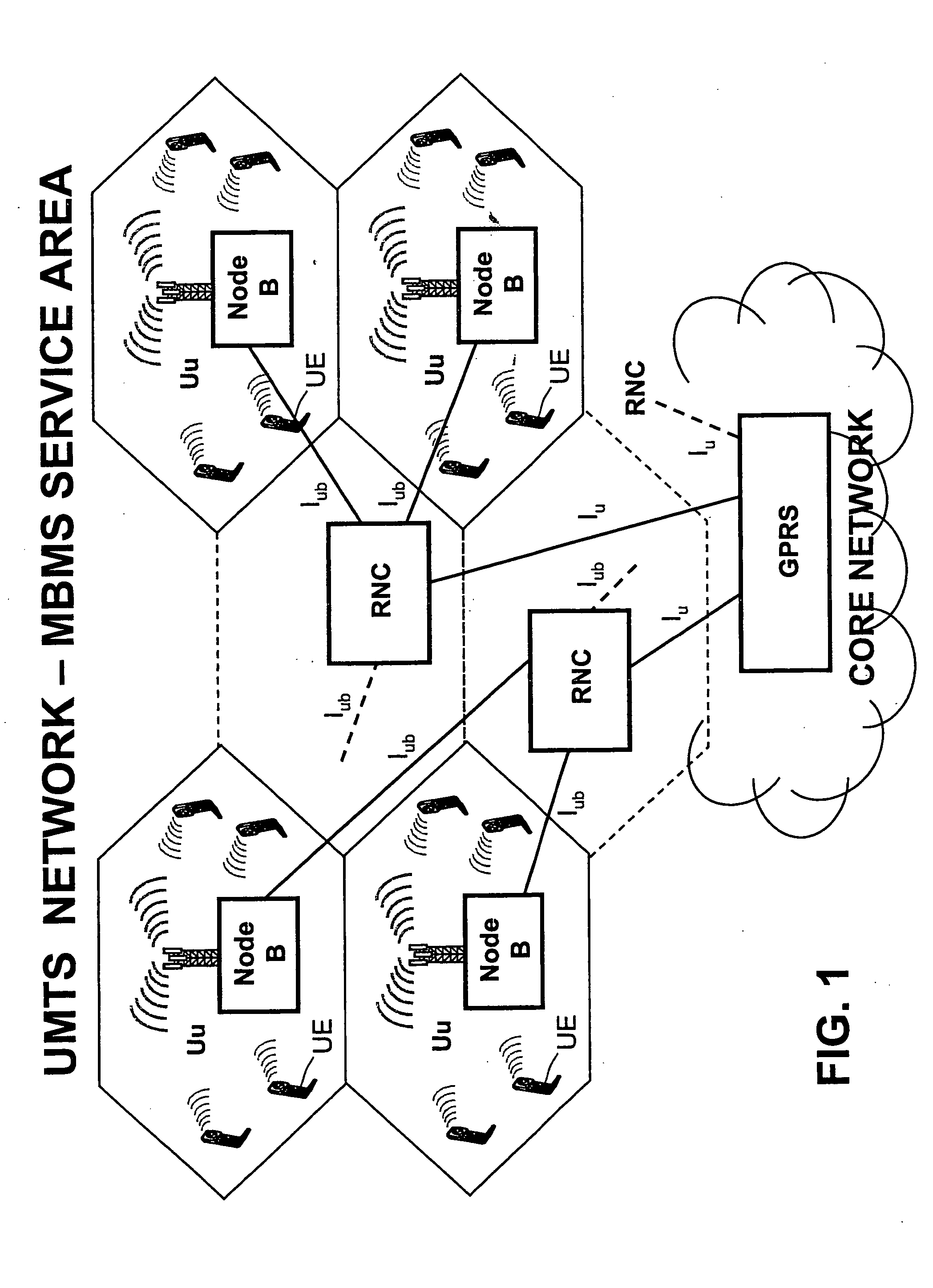
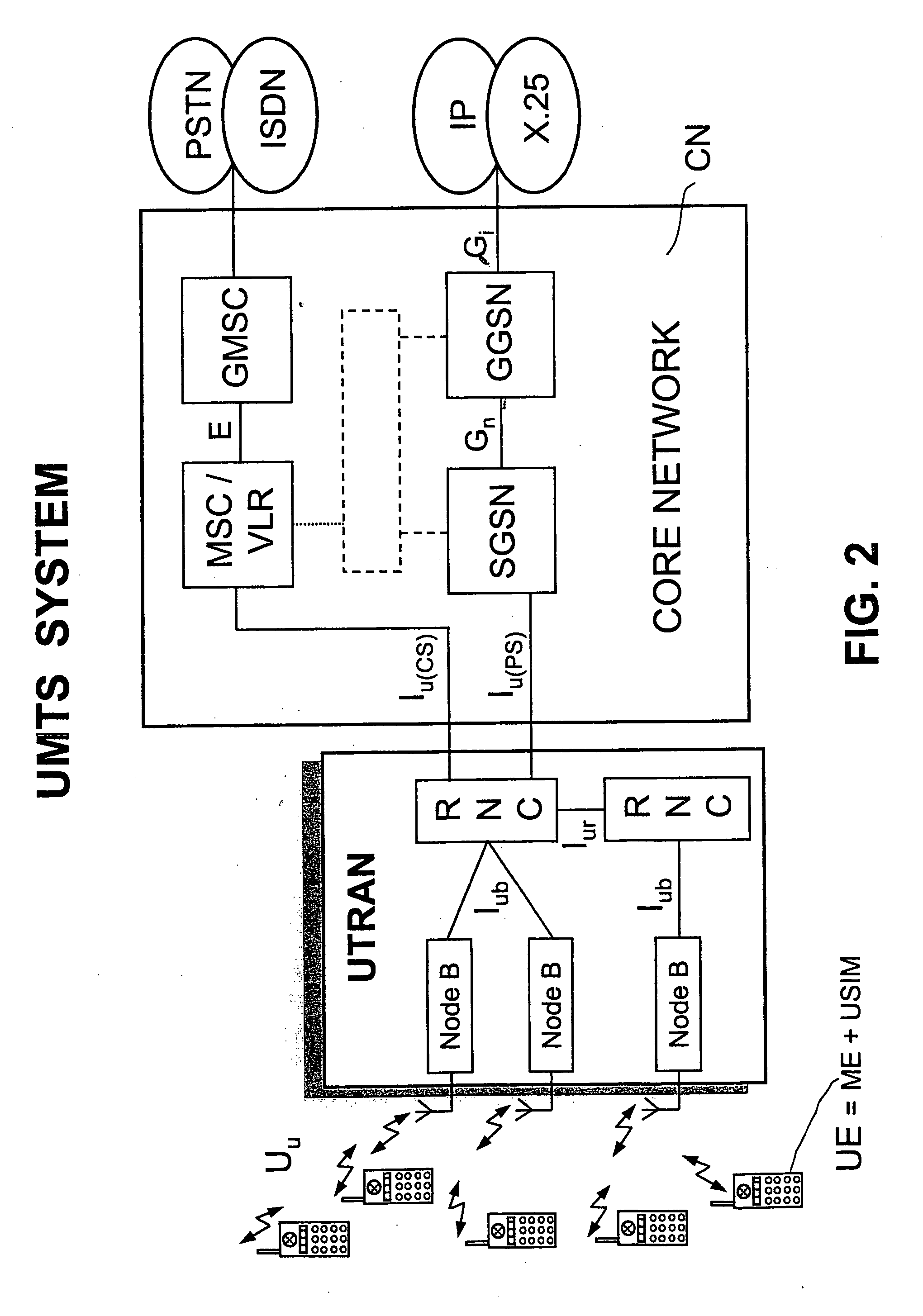
Method for transmitting multimedia services in the UMTS networks by immediate multicasting of a streaming subset
ActiveUS20040223513A1Fast deliveryEliminate delaysSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementMultimedia Broadcast Multicast ServiceReal time services
The method concerns multicast service delivering through the UMTS and GSM networks. For this aim is given higher priority to an opportune subset of all the real-time services with guaranteed bandwidth transmissible by the network. This subset is named IS-MBMS (Immediate Streaming-Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service). A certain amount of physical resources is reserved in all the system for the IS-MBMS services; not real-time services can be transmitted on the reserved resources when not used by the IS-MBMS ones. The reserved resources allow for transmitting the IS-MBMS services with minimum bit-rate, at least. The network announces in the service area that an IS-MBMS content becomes available; in reply one or more subscribed users transmit a request for joining a multicast group for that service. The network transmits a notification message on a multicast channel to give to the joined users useful information of how get the announced service, i.e.: Service-Id, RB parameters, etc. The IS-MBMS content is transmitted immediately on a point-to-multipoint channel set-up in each involved cells, even if there are zero recipients in the cell. Content is transmitted in parallel in different cells, leading to service continuity, and the mobile station can perform soft combining. During the IS-MBMS content delivery the network can count in each involved cell the number of subscribed users joined to the transmitted IS-MBMS service. The network switches from point-to-multipoint to point-to-point or to no transmission depending on the result of counting and on a fixed threshold. Alternatively the network, parallel to the content delivery, can execute a checking procedure to see if there are joined users in a cell: in this case the point-to-multipoint channel is switched to no transmission (fig. 3).
Owner:HMD GLOBAL
Real-time media stream insertion method and apparatus
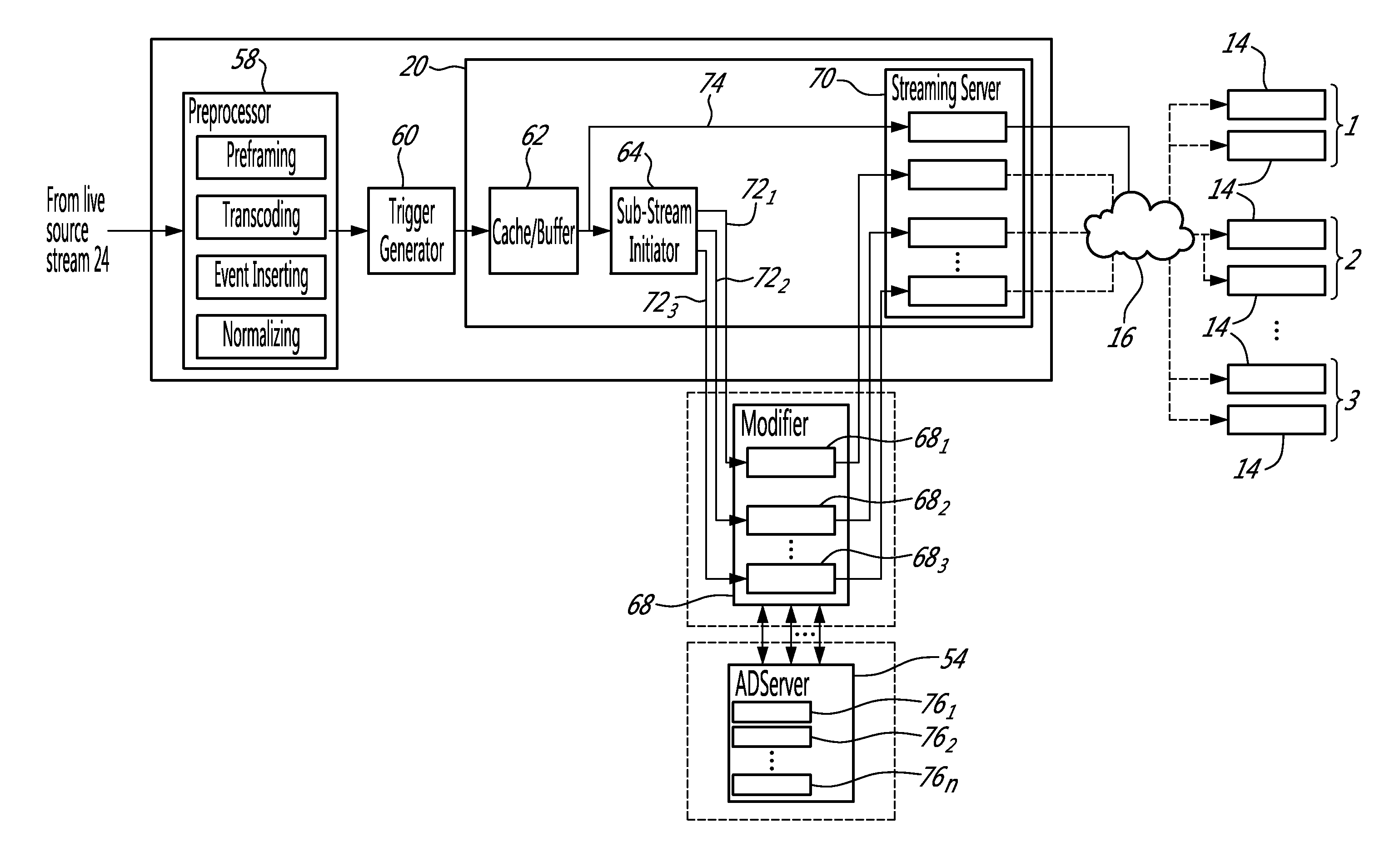
InactiveUS20120166289A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionReal time servicesMedia server
There is disclosed a system and method for real time server side per stream insertion of strategic media and per-stream delivery. In one aspect of the invention the system comprises a media server for modifying a plurality of live media sub-streams based upon the categorizations of a group of connected media clients. In a further aspect of the invention, the live source media sub-streams are modified by overlaying delimited media content segments within the plurality of sub-streams with media assets, inserting media assets into the plurality of sub-streams, removing one or more of the media content segments from the sub-streams, and adjusting encoded markers within the plurality of sub-streams to compensate for the modifications.
Owner:MACQUARIE SIERRA INVESTMENT HLDG INC
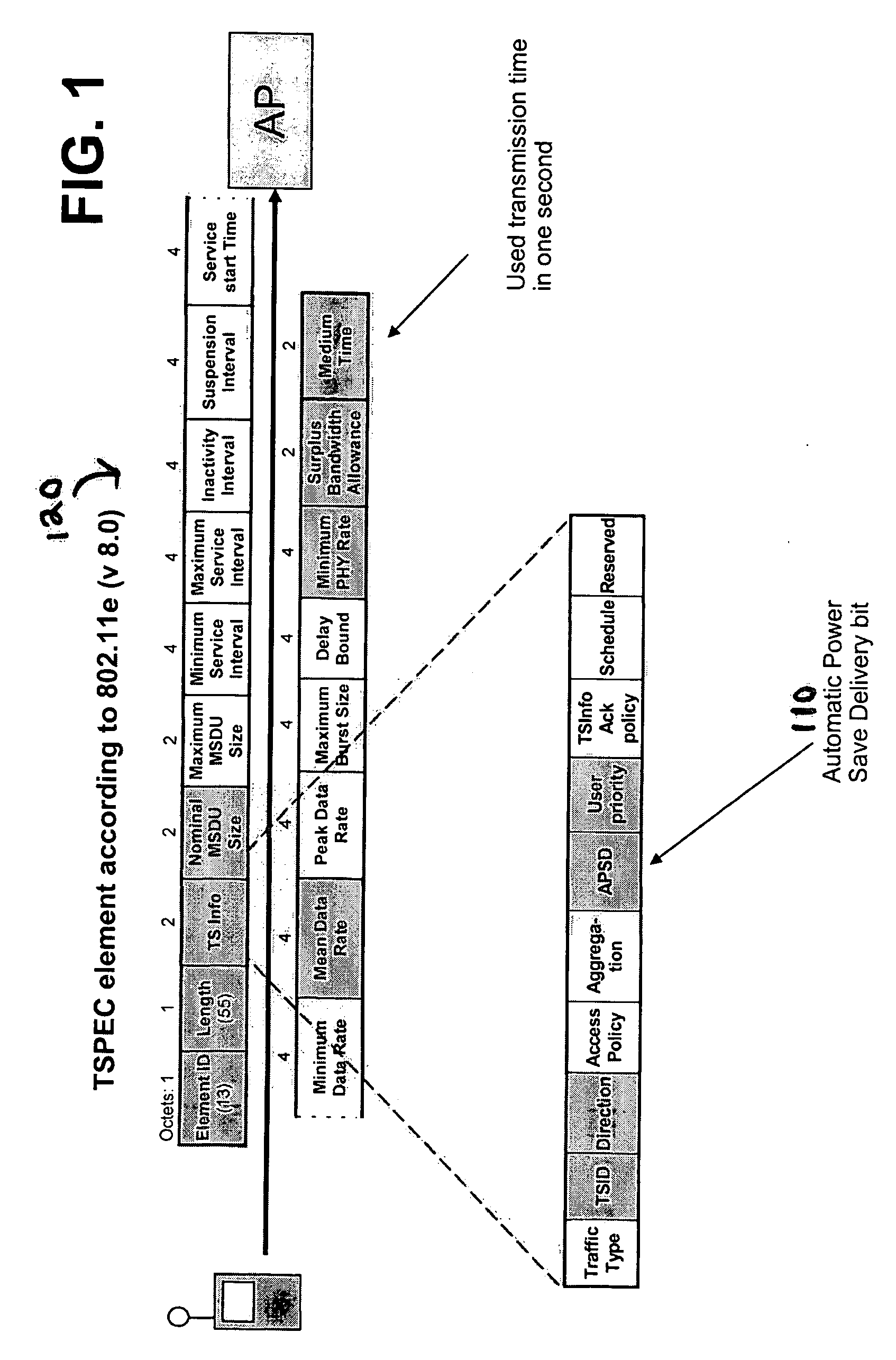
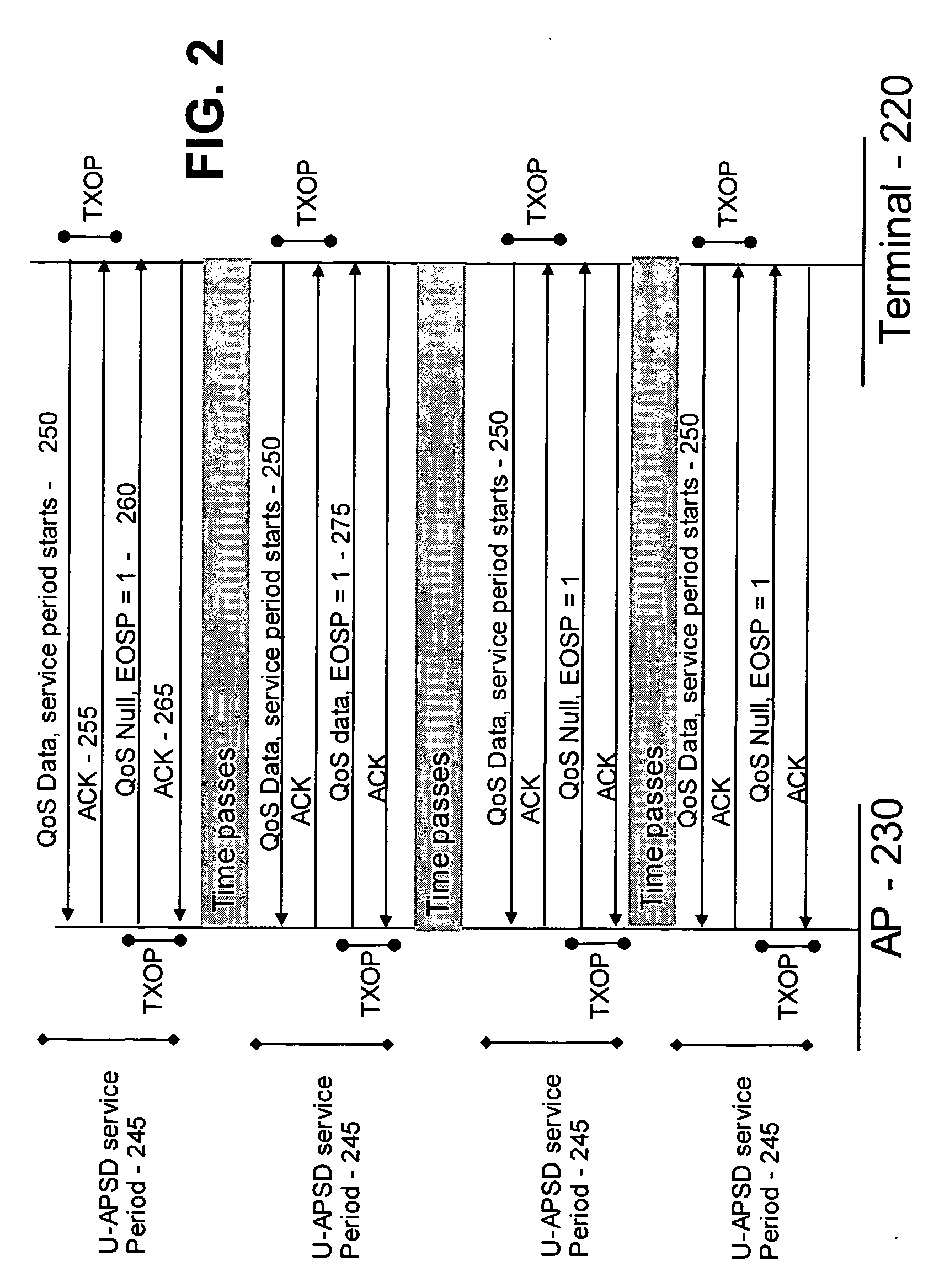
Power consumption reduction logic for unscheduled APSD and real time services
ActiveUS20070004374A1Reduce power consumptionReduce the amount requiredEnergy efficient ICTPower managementFrame basedReal time services
A system and method for more efficiently scheduling and implementing unscheduled automatic power save delivery service periods between a terminal and an access point. An triggering interval is set for an untrigger flag, the untrigger flag not permitting the implementation of an automatic power save delivery period. Automatic triggering is used unless a plurality of criteria are met, in which case the triggering interval is calculated based upon a plurality of variables. Untrigger flags are set for selected frames based upon the triggering interval, and unscheduled automatic power save delivery service periods are implemented for frames for which the untrigger flag is not set and for which the terminal receives an indication of additional data from a remote source such as an access point.
Owner:RPX CORP
Interconnected premises equipment for energy management
ActiveUS8095233B1Power network operation systems integrationClimate change adaptationRequirements managementEngineering
Energy commodities in the form of electricity and combustible fuel (e.g. natural gas, propane) are used by appliances within a residence or commercial premises in a fashion which is monitored and controlled through a Premises Energy Management System (PEMS). The system facilitates direct monitoring and control of energy-consuming appliances, in real time, utilizing automated programmatic control and a plurality of human interfaces including local display and control, email, web browser, text messaging, and integrated voice response (IVR). A Monitoring and Control Coordinator (MCC) provides centralized coordination of functions and one or more Communicating Appliance Interfaces (CAI) interact with energy consuming appliances are interconnected via wired and wireless communication networks and protocols. The system may retrieve information from third parties, such as from weather services, for optimizing energy usage. An interface may be provided to the energy provider / purveyor to enhance the provision of energy by providing additional real-time services such as demand management and service outage management.
Owner:PATTON ELECTRONICS
Method For Selecting Real-Time Service Data Transmission Path
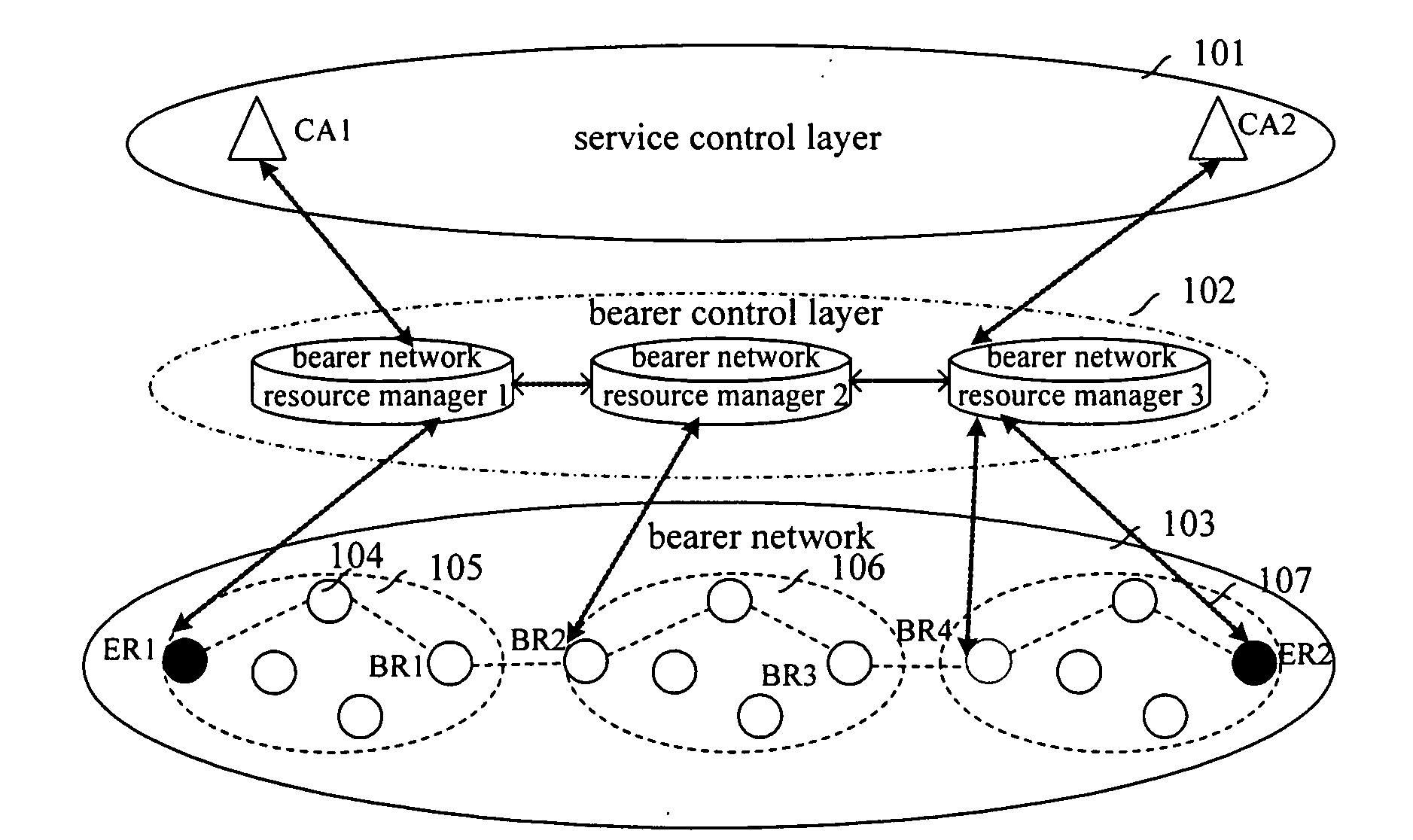
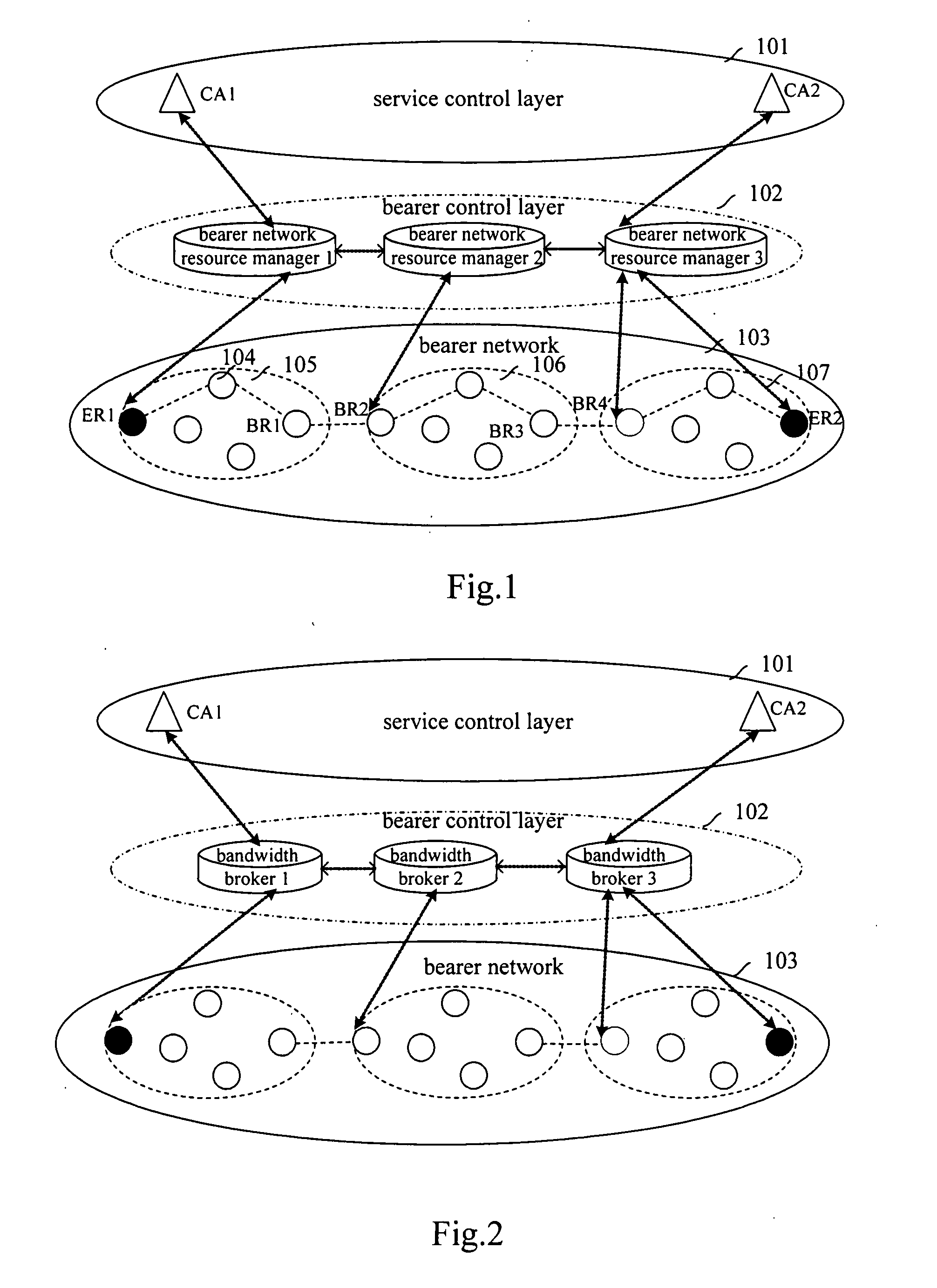
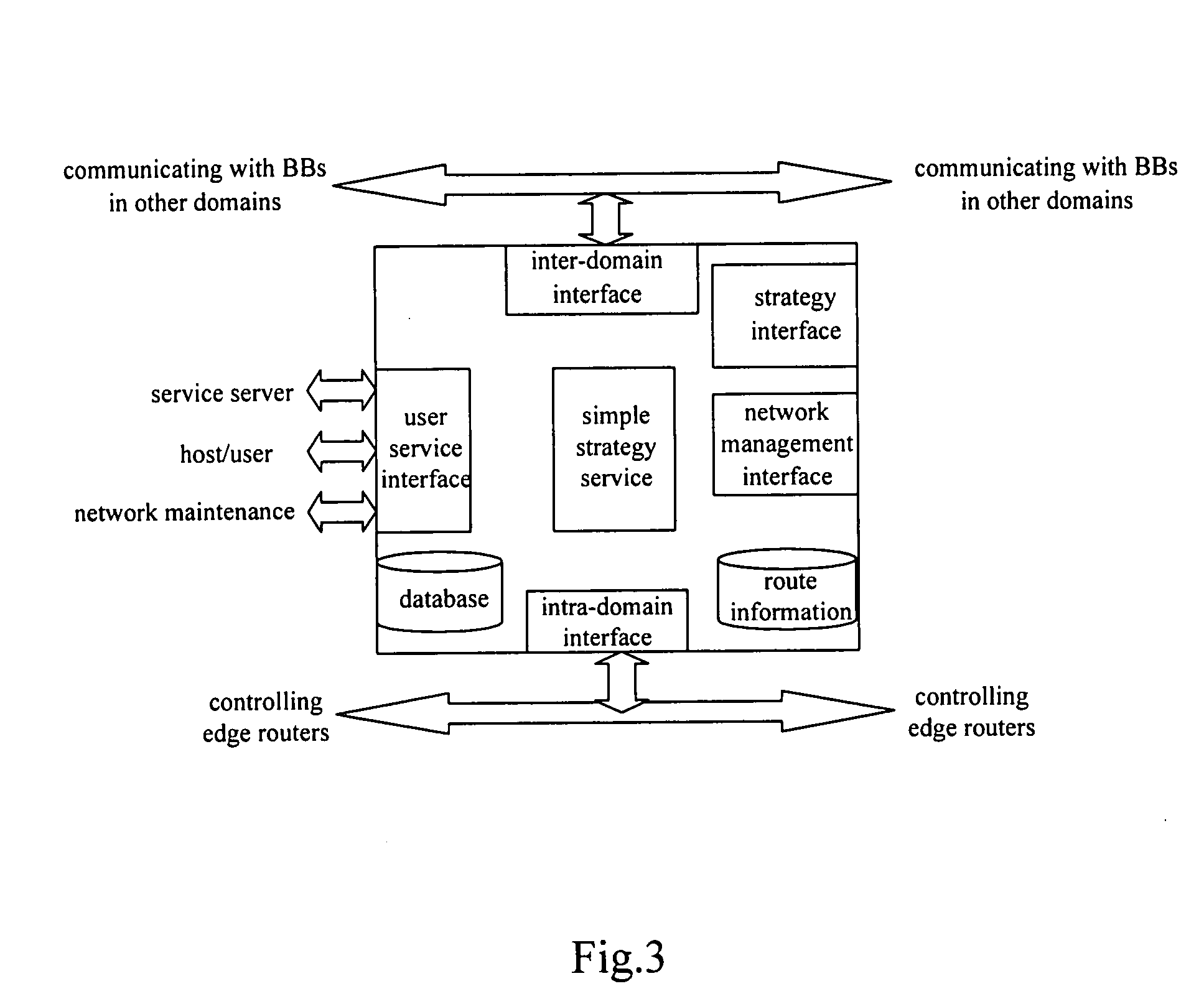
ActiveUS20080130627A1Easy to implementEasy maintenanceData switching by path configurationNetwork resource managementControl layer
The present invention discloses a method for selecting a real-time service data transmission path, comprising establishing an independent bearer control layer comprising more than one bearer network resource manager between a service control layer and a bearer network. The method further comprises: after a source bearer network resource manager which is connected to the service control layer receives a connection request for a real-time service, orderly selecting and determining, from the source bearer network resource manager towards a destination bearer network resource manager, an intra-domain route path for the real-time service in a management domain corresponding to each bearer network resource manager, and an inter-domain route path between adjacent management domains corresponding to adjacent bearer network resource managers. In addition, the present invention discloses six methods for selecting a real-time service data transmission path based on different strategies. The methods according to the present invention can increase success ratio of routing, and can obtain an optimal route in simple and flexible manners, thus can guarantee reasonable allocation of resources.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Sensor network medium access control (MAC) system for multihop communication
ActiveUS20100034159A1Avoid transmission delaysImprove energy consumptionEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationReal time servicesNetwork media
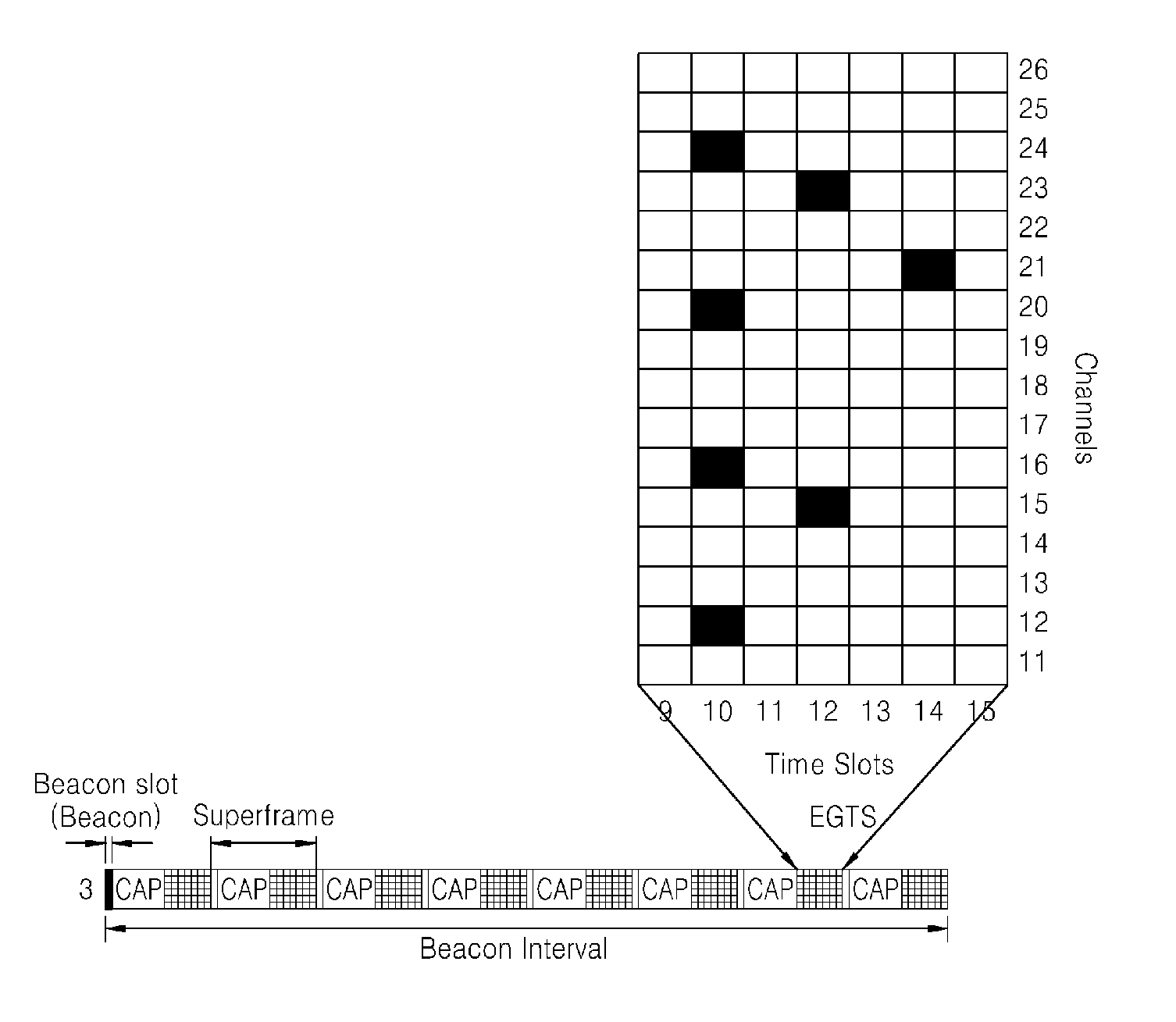
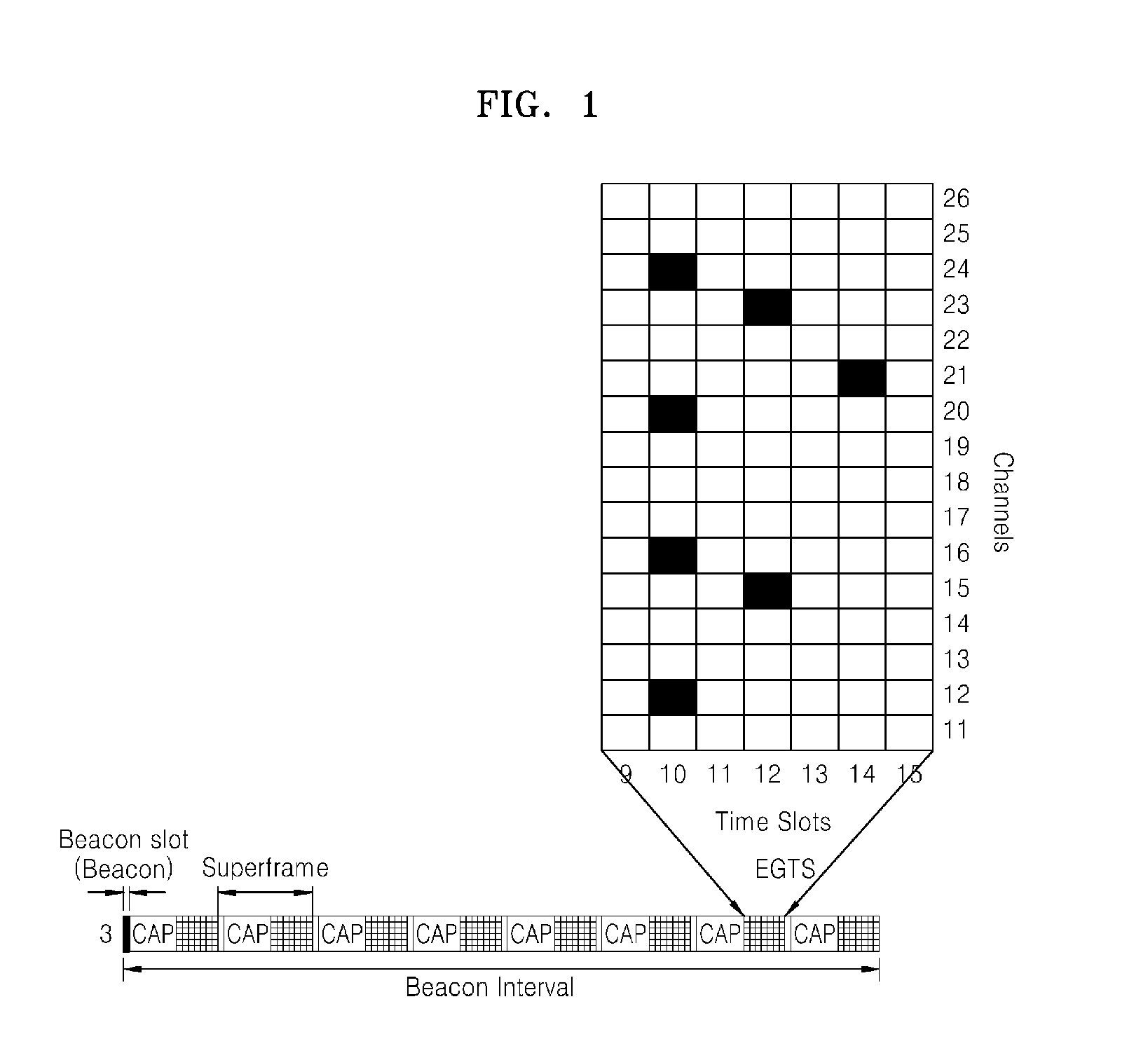
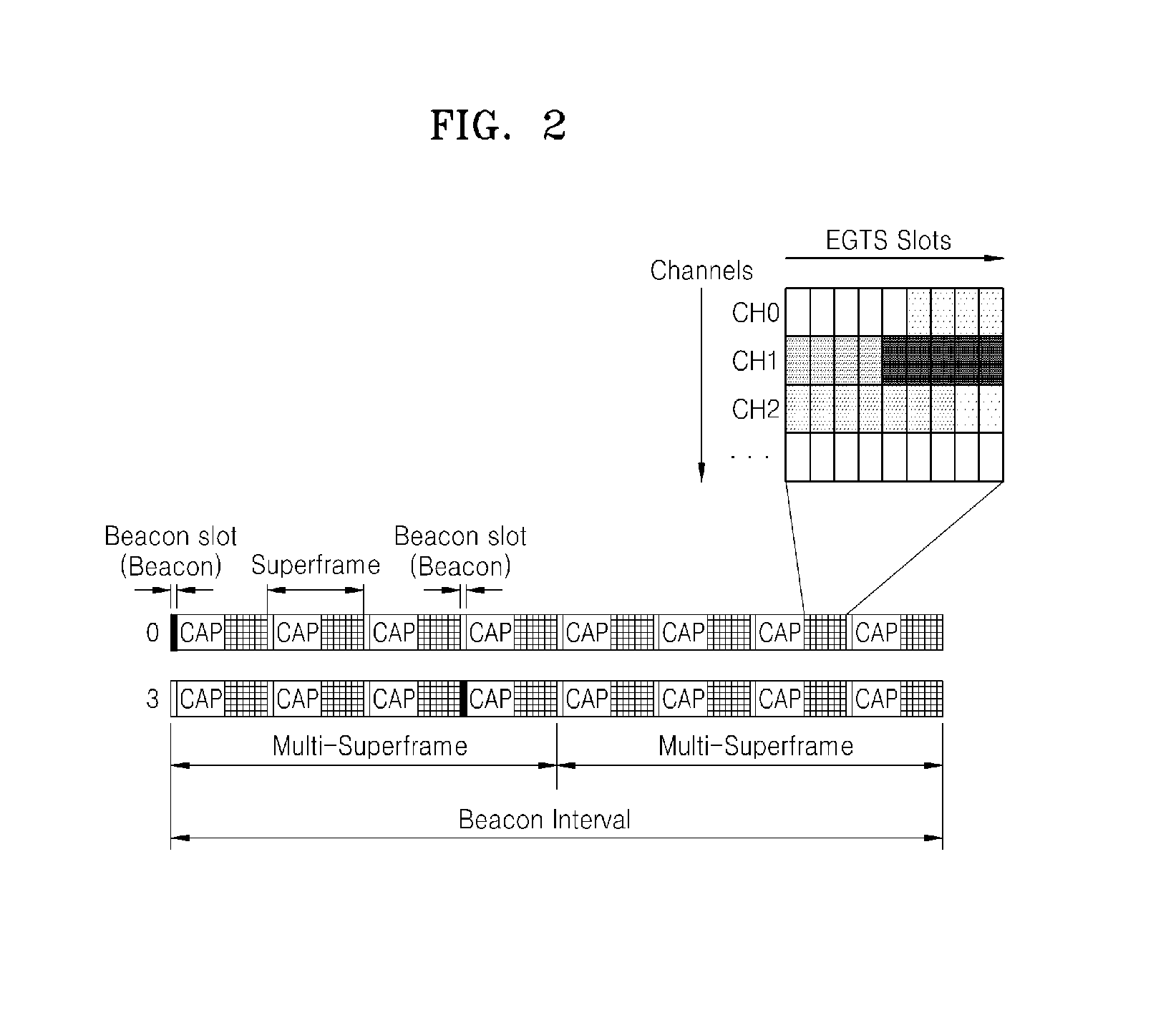
A medium access control (MAC) technique of a multihop sensor network. In the multihop sensor network, the MAC technique may contribute to significantly reducing transmission delay, and allow real-time services to be provided to all nodes by extending a guaranteed time slot (GTS) restricted to one hop in a personal area network (PAN) coordinator (PNC) to all nodes. Furthermore, the MAC technique may allow the number of available GTSs to be significantly increased, by using all 16 frequency band channels instead of using only a single frequency band and setting a multi-superframe.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Handover in a cellular communication system
ActiveUS20070123267A1Improve performanceGood switching effectNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNon real timeReal time services
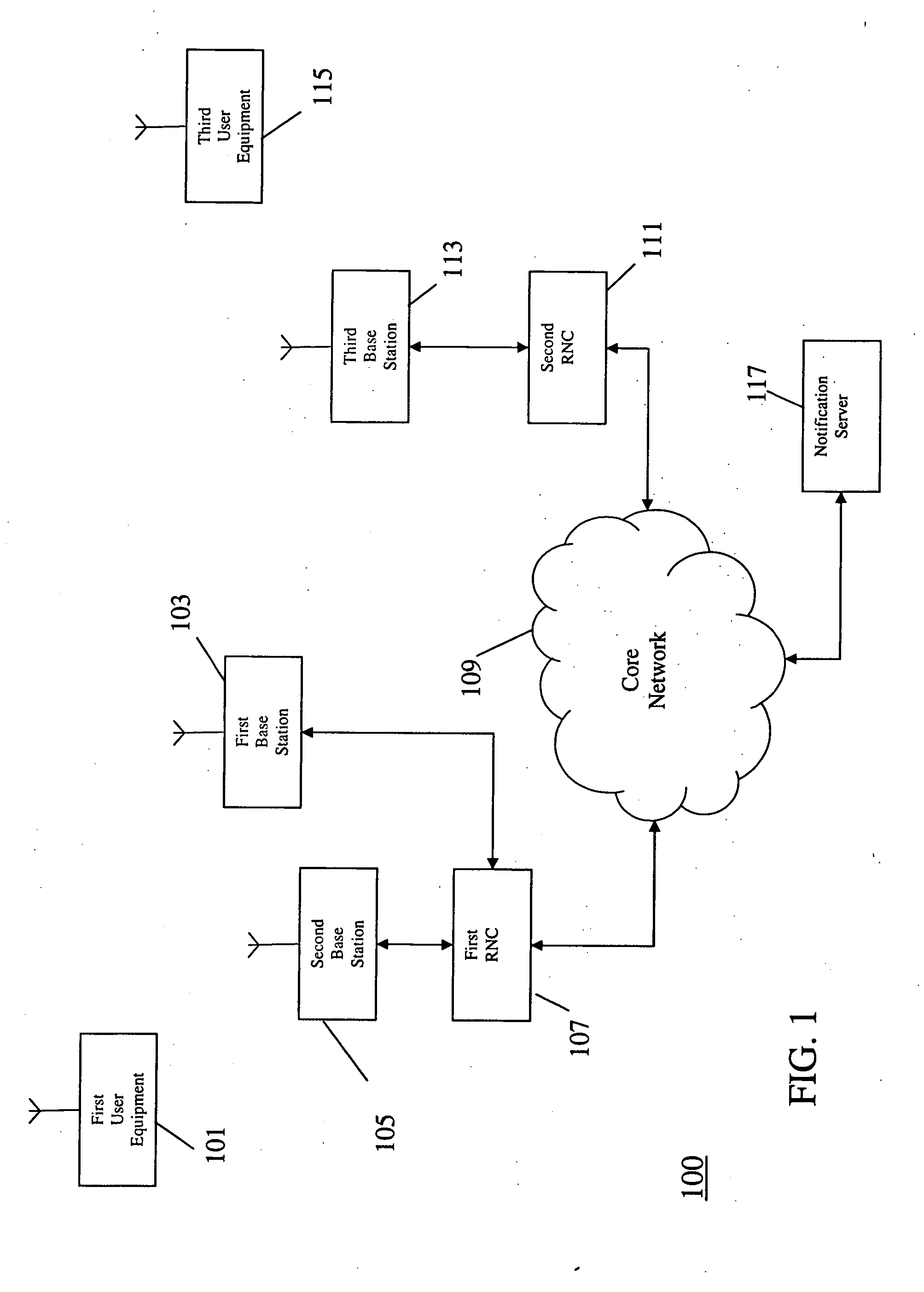
A cellular communication system includes first and second base stations and a user equipment. A Radio Network Controller controls a handover of the user equipment between the base stations by either forwarding data of the communication to both the first and second base stations or to only one of the first and second base stations dependent on a Quality of Service (QoS) characteristic of the communication of the user equipment. The QoS characteristic can specifically be an indication of a delay constraint for the communication service such as an indication of whether the service is a real-time service or a non-real time service.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method for improving quality of service (QoS) of real-time service in wireless local area network based on service differentiation
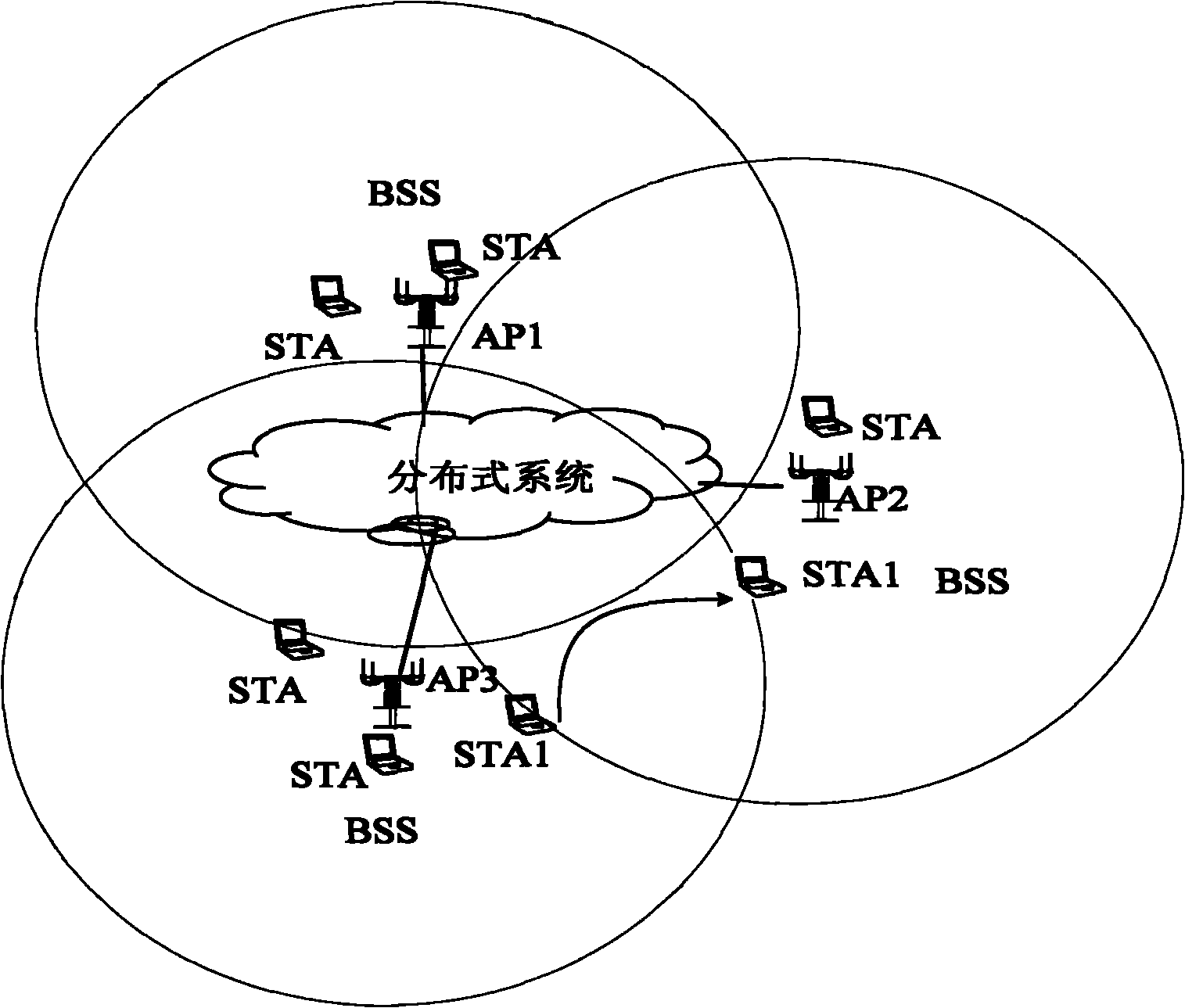
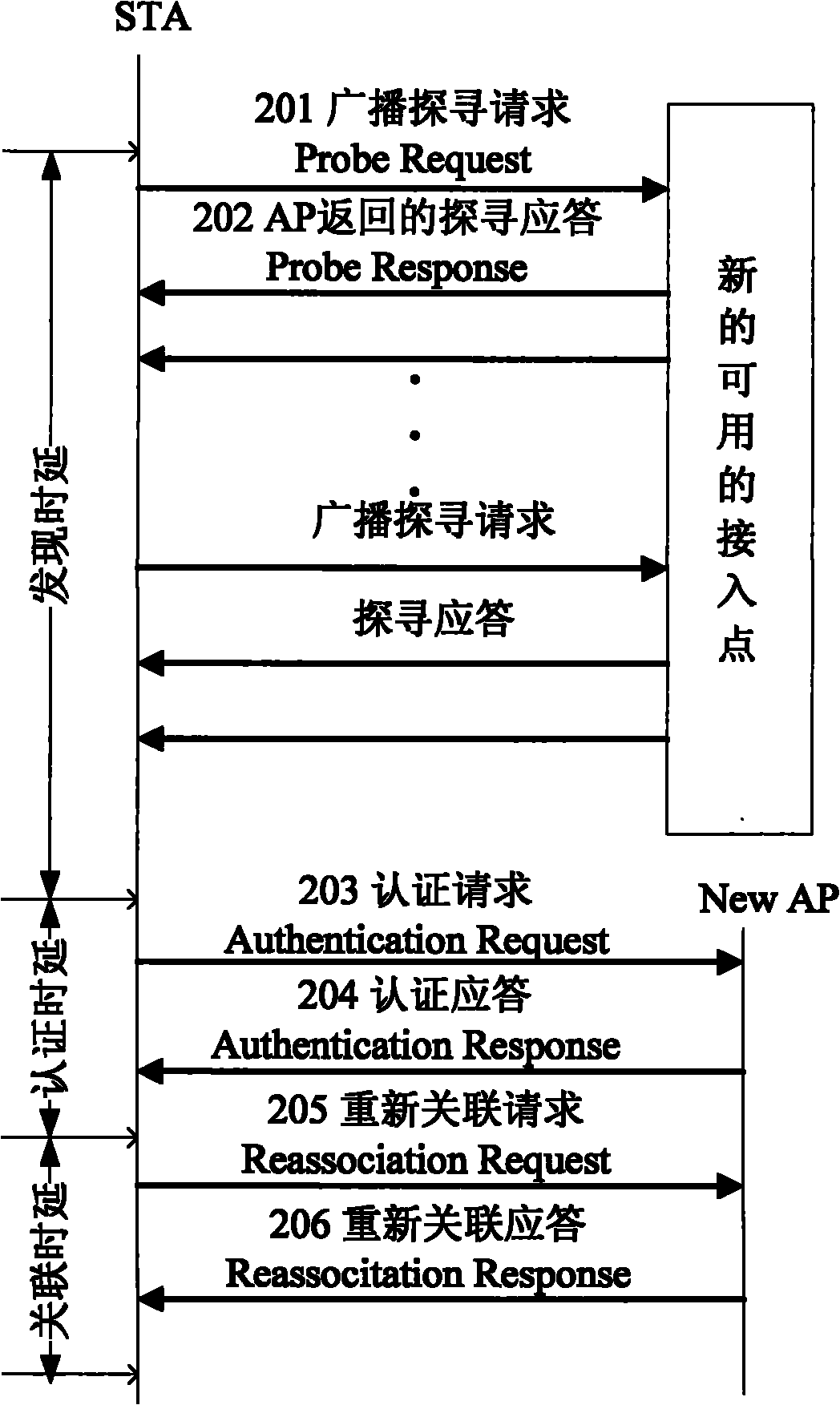
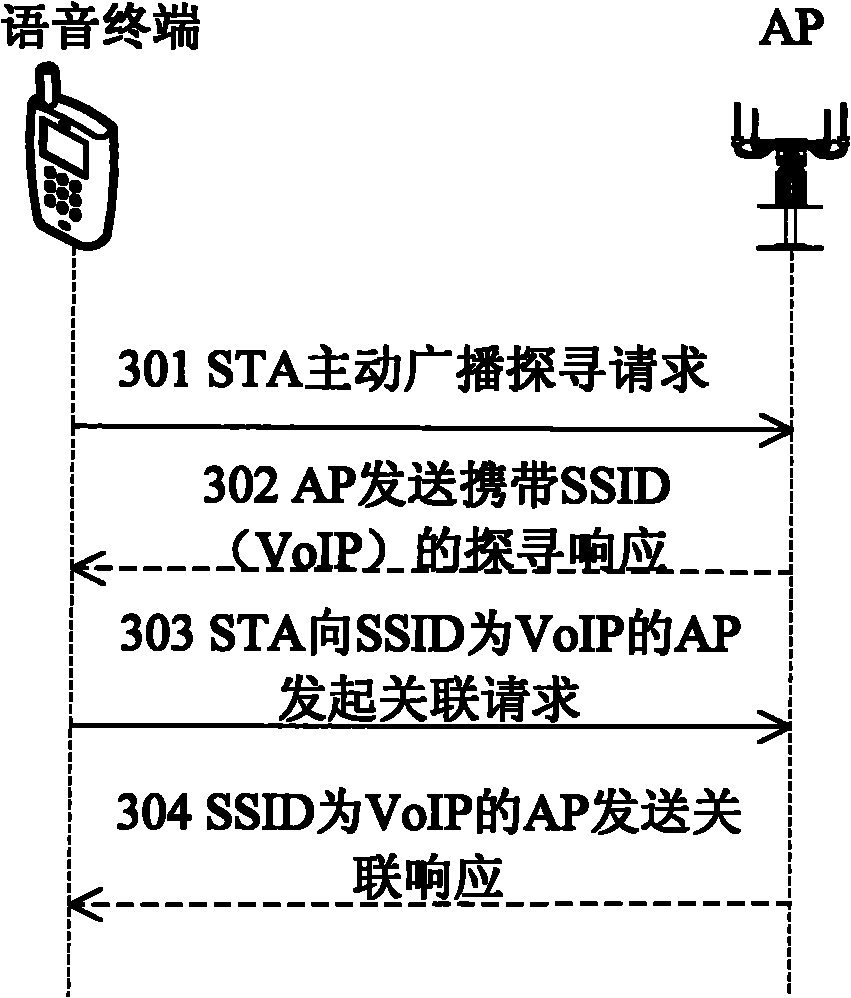
ActiveCN101931954ANetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesNon real timeReal time services
The invention relates to a method and a system for improving the quality of service (QoS) of a real-time service in a wireless local area network based on service differentiation. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a plurality of virtual contacts at one access point (AP) and allocating different service set identifiers (SSID) to each virtual contact, wherein the SSIDs correspond to service types and corresponding relation information of the service types and authentication modes is also allocated at the AP; when a mobile terminal is associated / reassociated to the AP, acquiring each SSID allocated by the AP from the AP and carrying the SSID corresponding to the service type currently applied by the mobile terminal in an authentication request; selecting a corresponding authentication mode for authentication by the AP according to the service type corresponding to the received SSID, wherein the authentication of the real-time service is quicker than that of a non-real-time service. The method preferentially ensures the QoS of the real-time service based on service type differentiation.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGXING SOFTWARE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com