Patents
Literature
610 results about "Network media" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Network media refers to the communication channels used to interconnect nodes on a computer network. Typical examples of network media include copper coaxial cable, copper twisted pair cables and optical fiber cables used in wired networks, and radio waves used in wireless data communications networks.
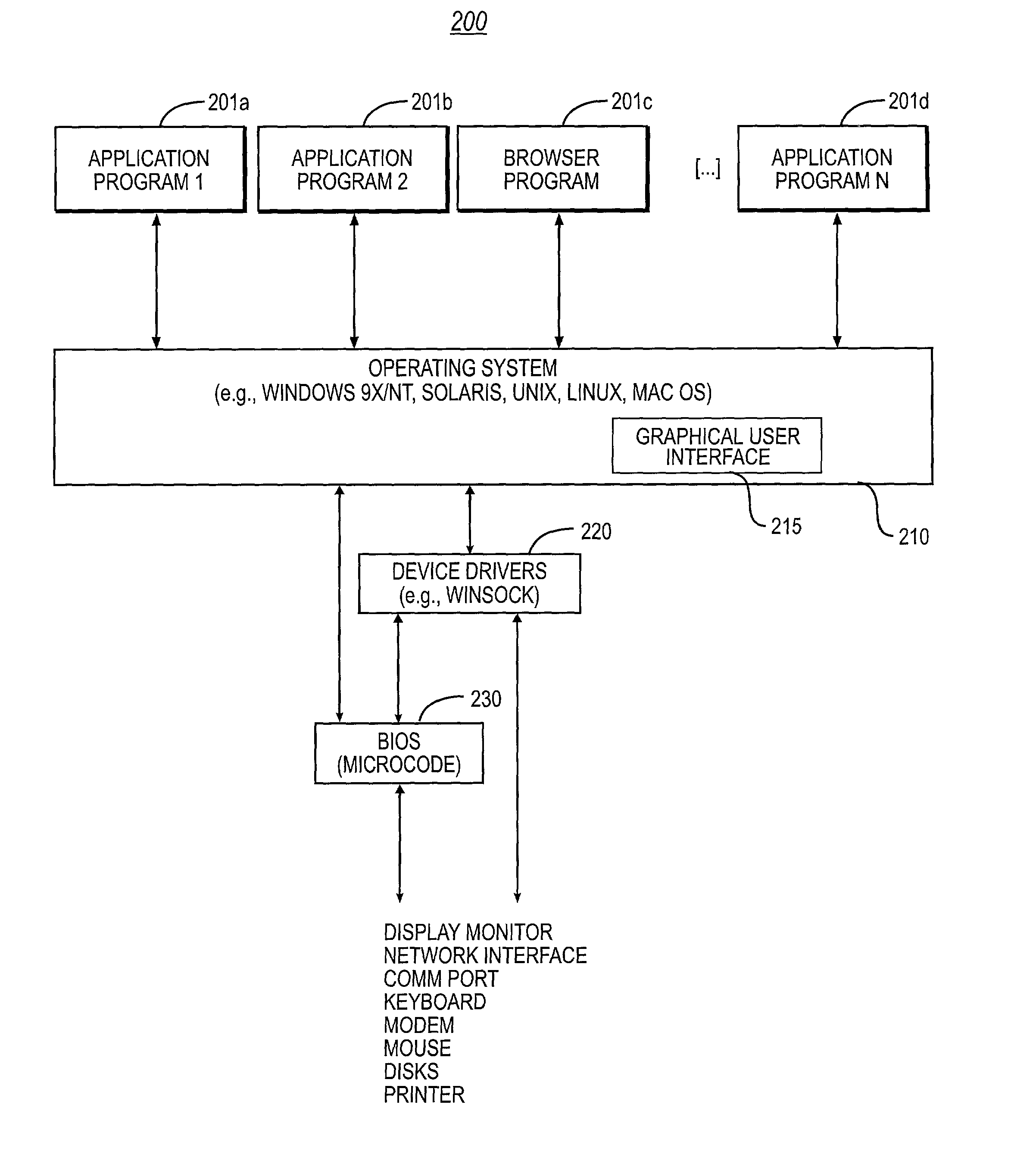
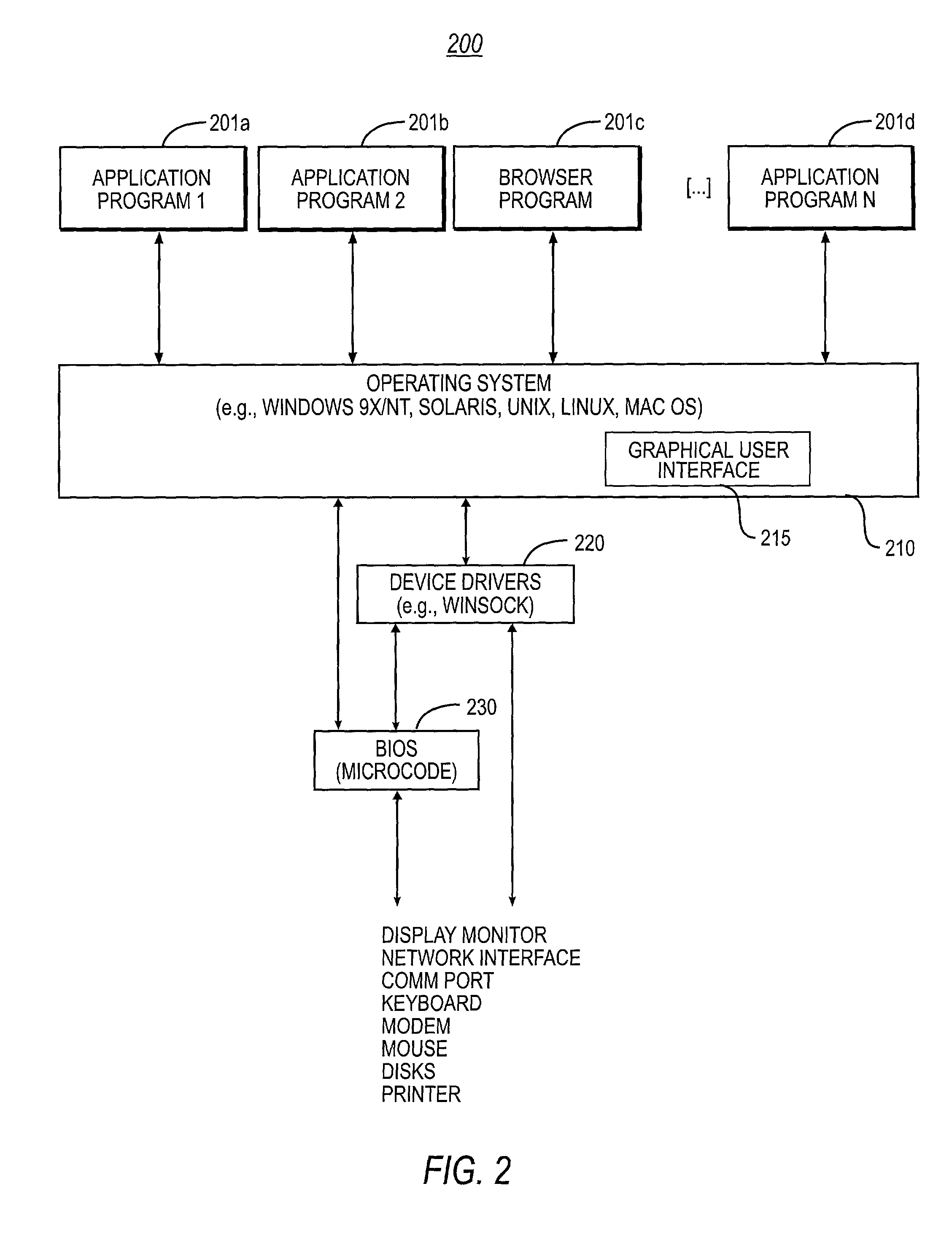
System and methodology for optimizing delivery of email attachments for disparate devices
InactiveUS20020016818A1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsDevice typeWireless handheld devices
An e-mail system that re-packages message attachments optimized for delivery to wireless handheld devices is described. The preferred embodiment provides an optimization of the e-mail deliveries to allow for the recipients to receive e-mail attachments at a time and in a size / format as desired. The preferred embodiment compares the size of attached images to the capabilities of the type of the recipient client device, and preempts delivery of the original format of those attachments if they are determined to be burdensome or overwhelming. In cases wherein these attachments would strain the capabilities of the recipient devices' wireless bandwidth and / or display features, the original attachments are removed from the messages and do not accompany the e-mail delivery. Any detached attachment is saved in a network media-sharing repository, and can be subsequently accessed via a link (e.g., URL) referencing that storage address. Recipients can specify their wireless handheld device types, and opt to receive transformations of this type of attachment as a default substitute in subsequent e-mail deliveries. In cases wherein the recipient has previously used multiple types of client devices when receiving messages from the system, the present invention applies a transformation on the current attachment that corresponds to the least capable in the set of those multiple devices. Recipients may also elect to receive the URL for the network storage address of copies of either the original and / or transformed attachments.
Owner:SYNIVERSE ICX CORP
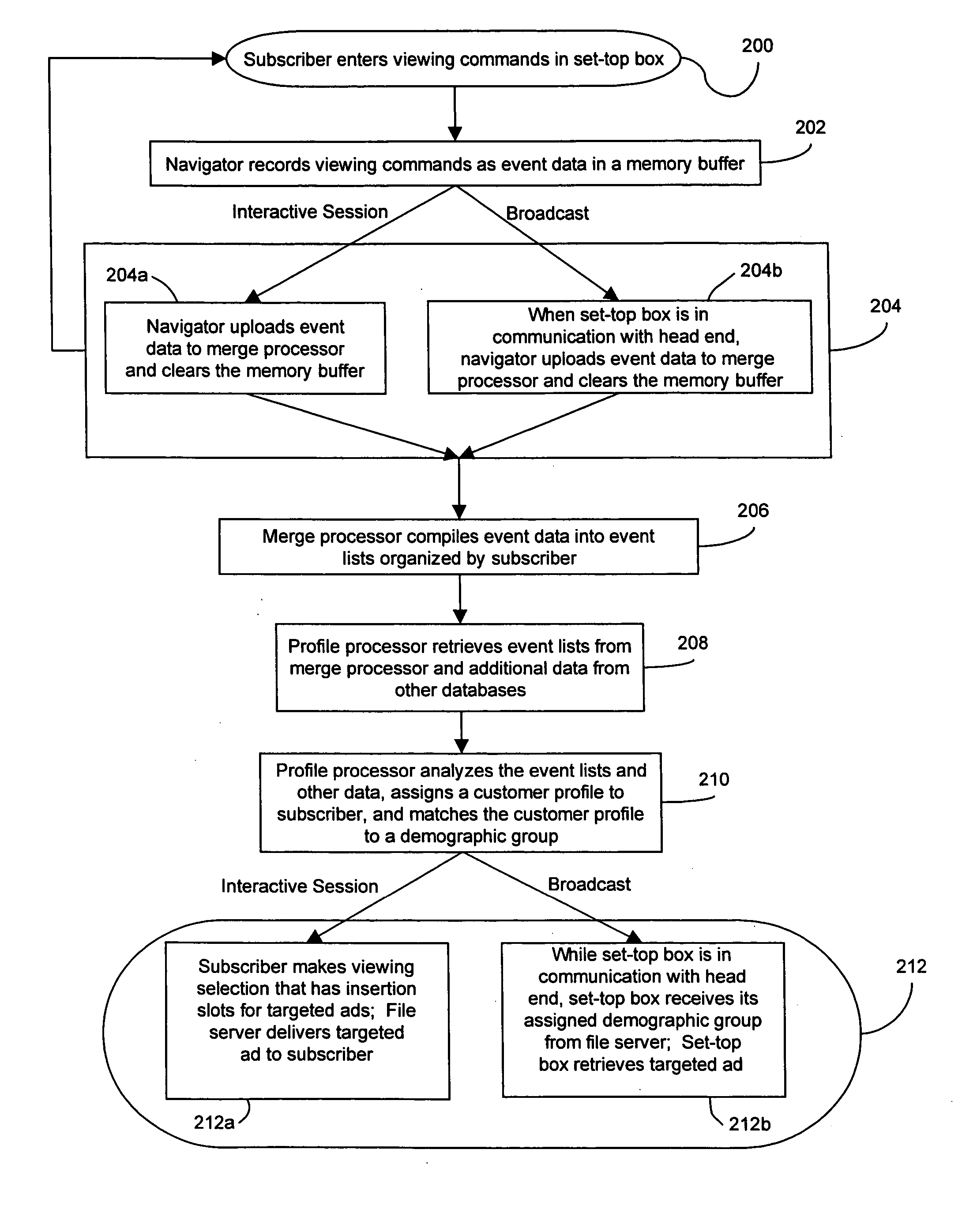
Method and system for providing targeted advertisements
InactiveUS20040163101A1Receiver side switchingAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInteractive televisionNetwork media
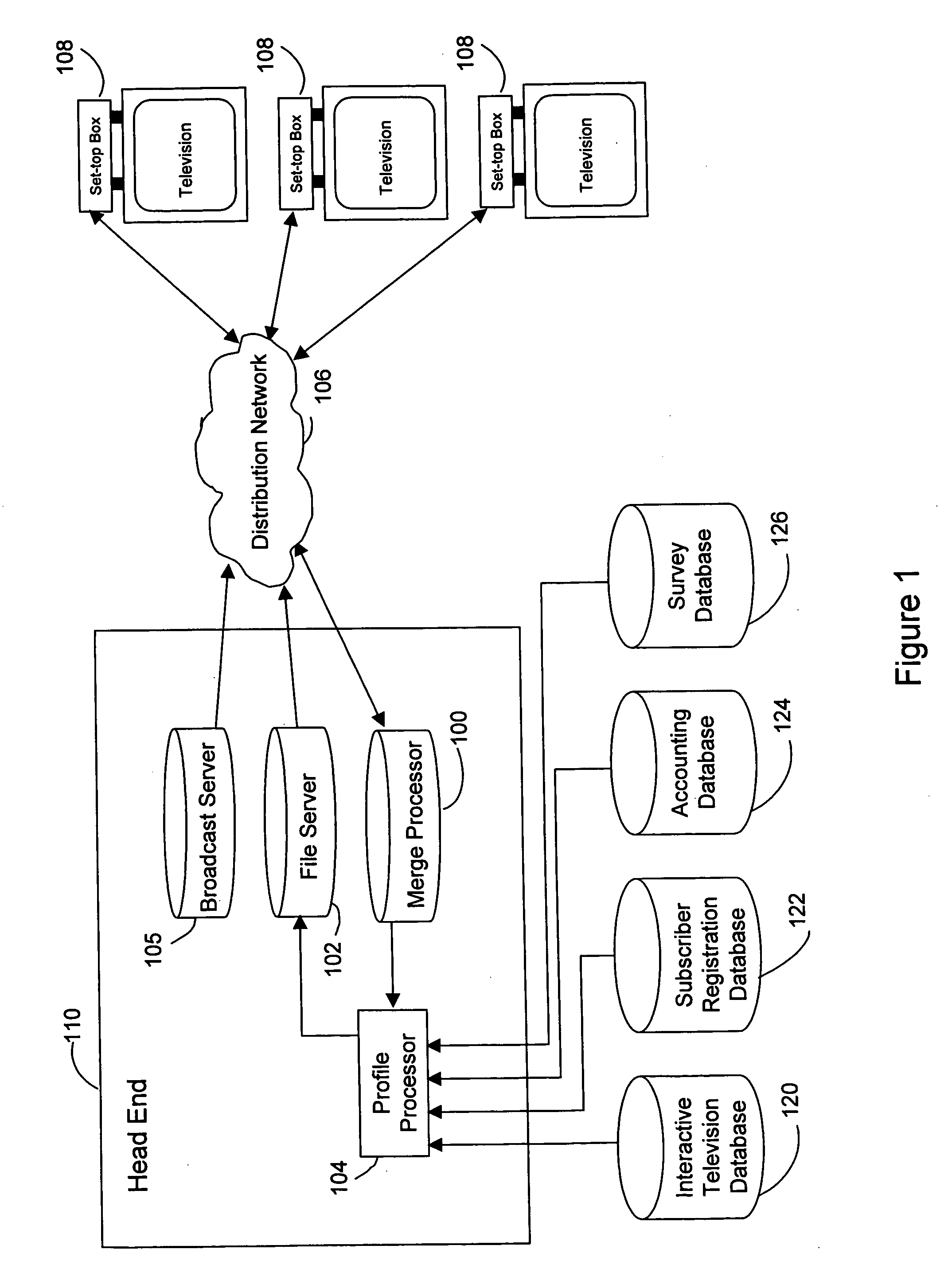
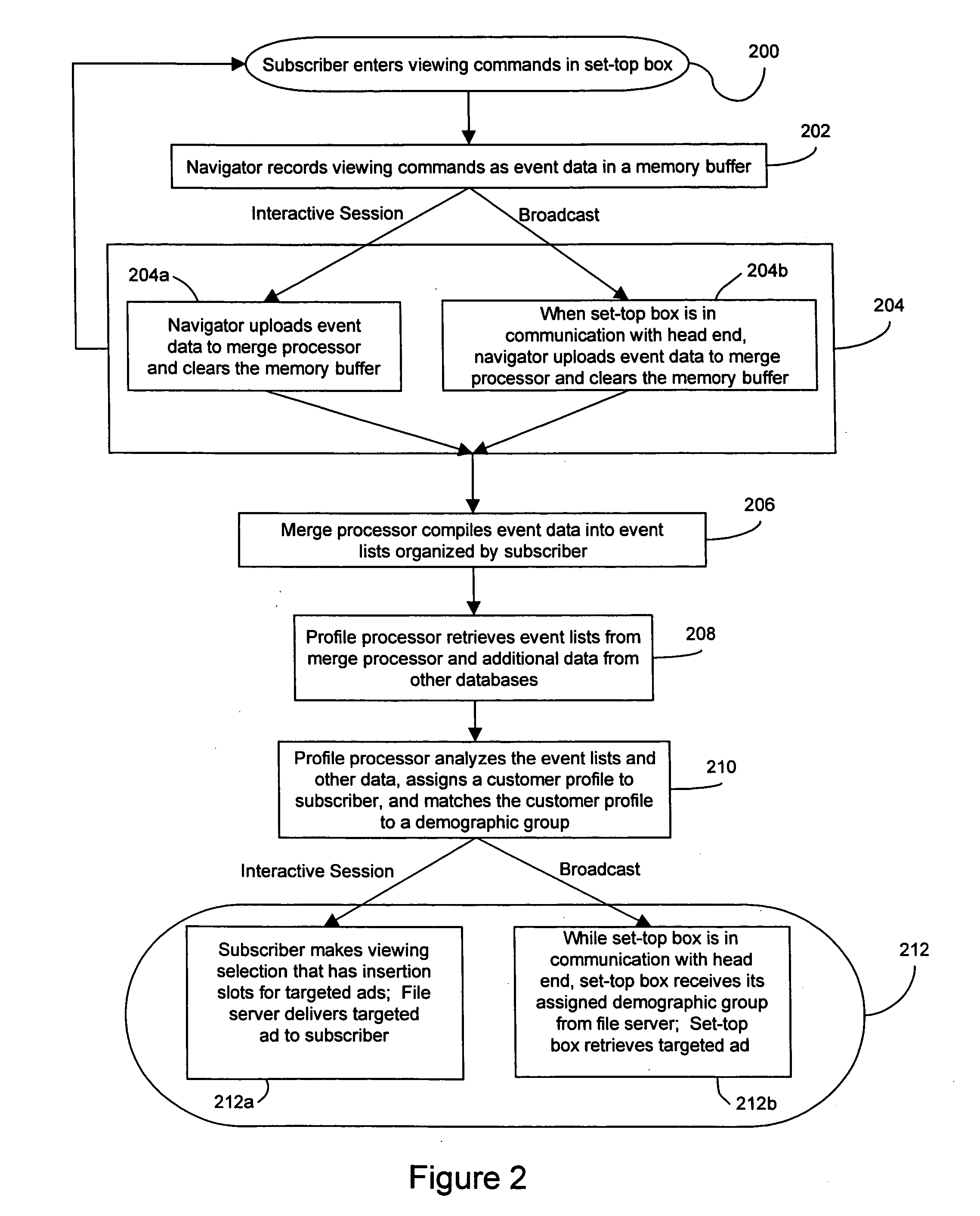
A method and system for providing targeted advertisements over a networked media delivery system, especially interactive television networks, the system comprising tracking and storing viewer selections, analyzing the selections, and delivering targeted advertisements that appeal to the particular subscriber making the selections, the system including a merge processor, a file server, a profile processor, and a broadcast server contained in a head end in communication with a plurality of set-top boxes through a distribution network. Based on a subscriber's viewing habits and account information, the present invention delivers different, customized advertisements to different viewers watching the same program or channel. The present invention delivers the advertisements as either still frame bit maps or as video streams advertisement insertion in a playlist or a broadcast media program.
Owner:ALPHONSO
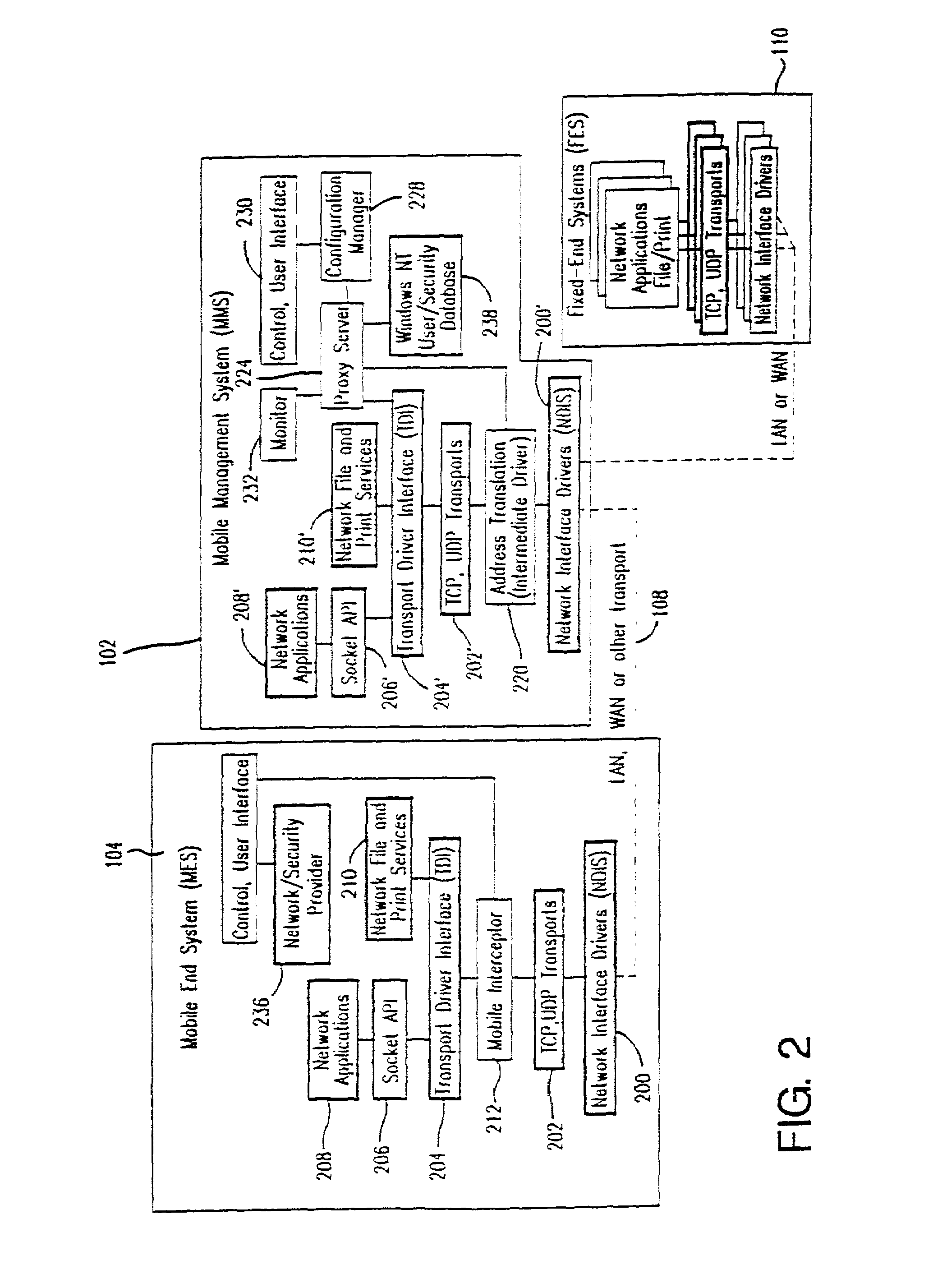
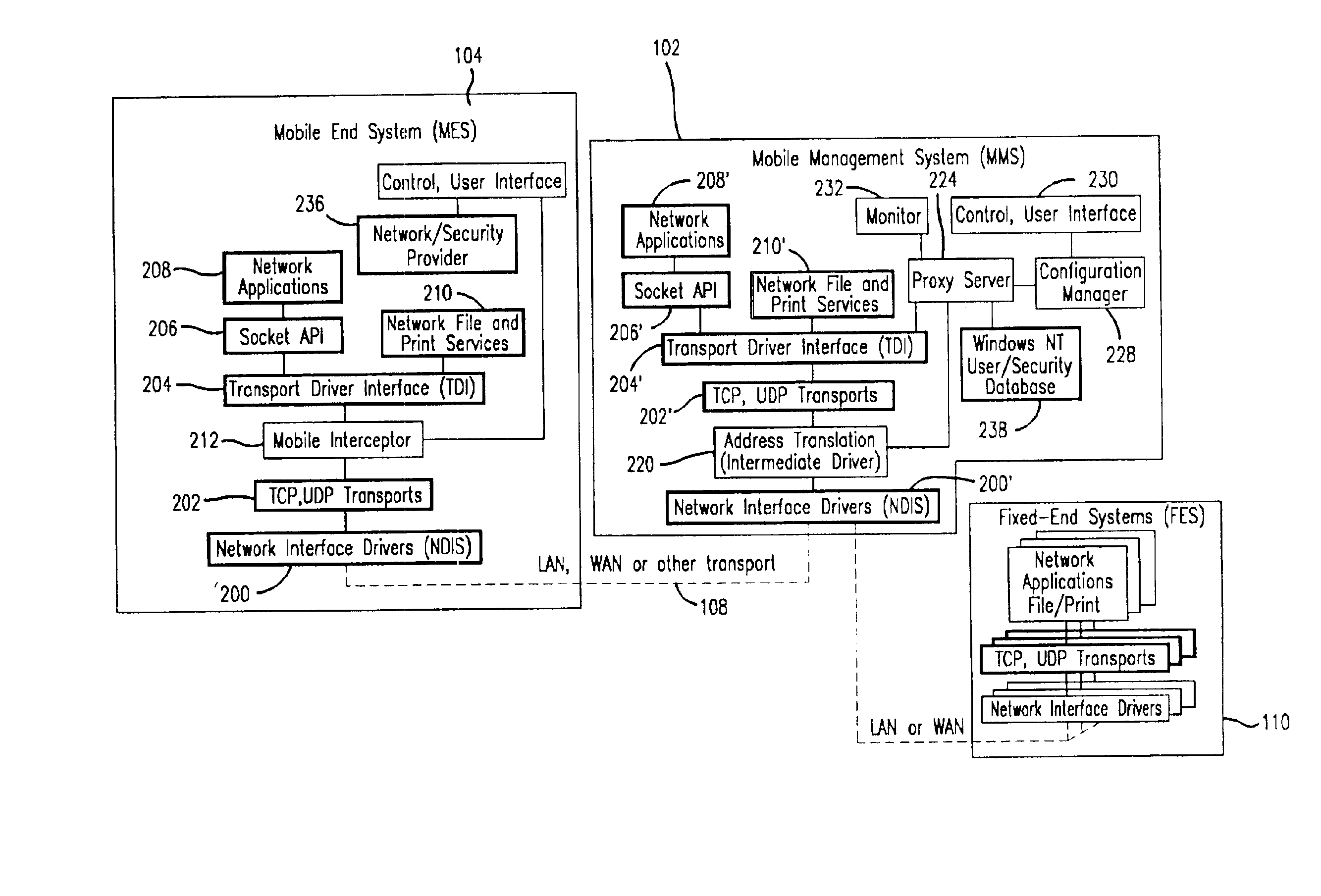
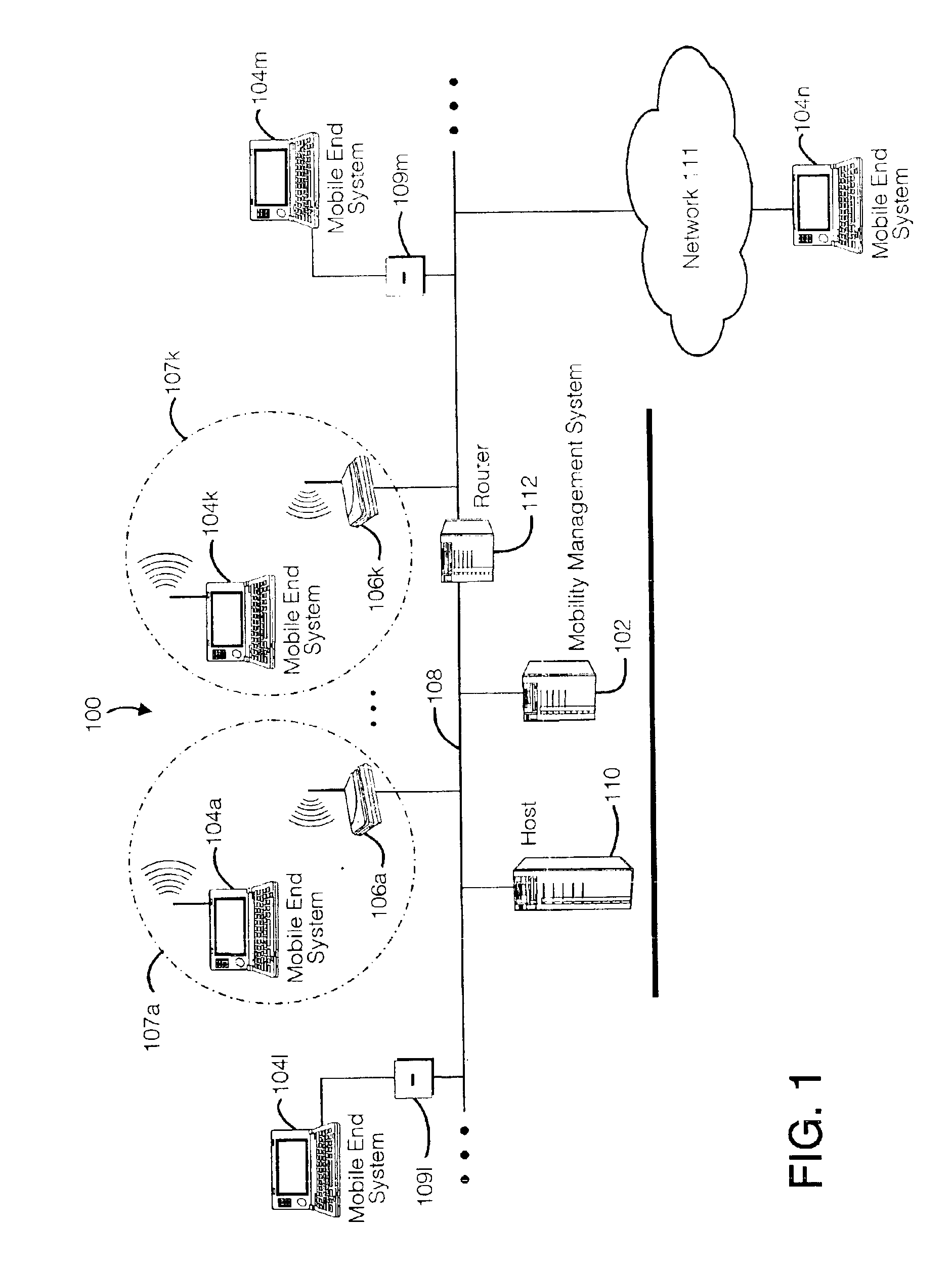
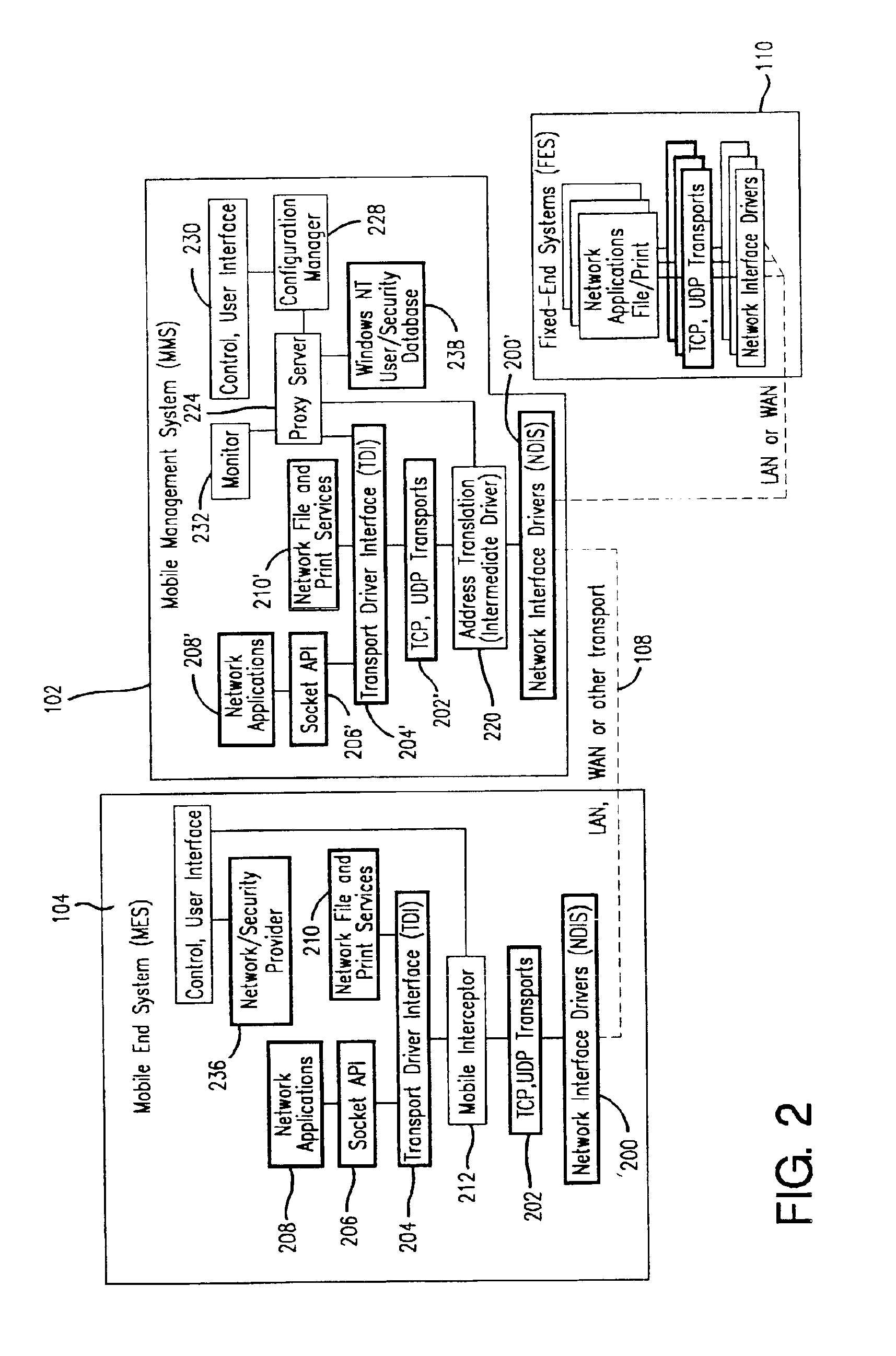
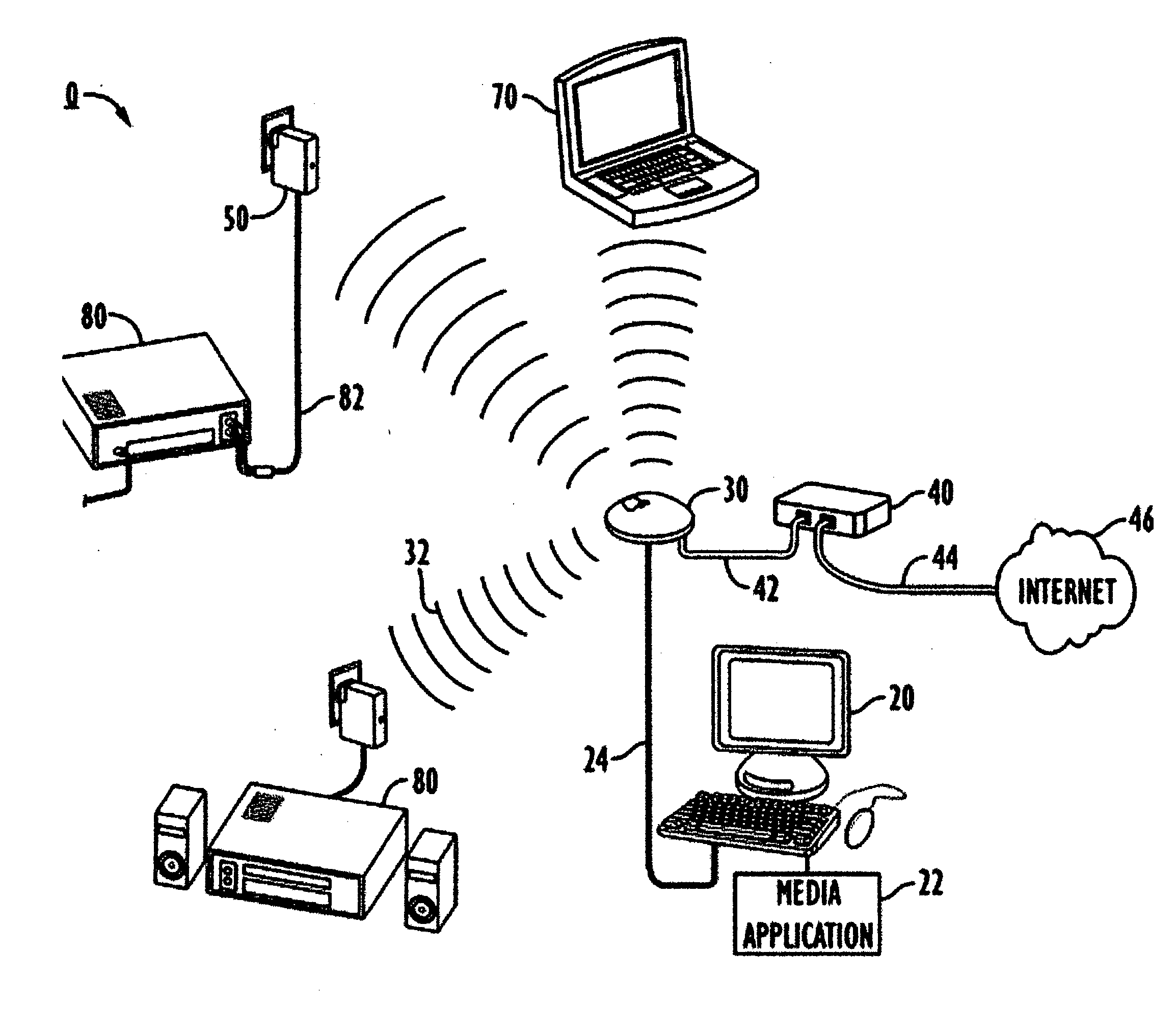
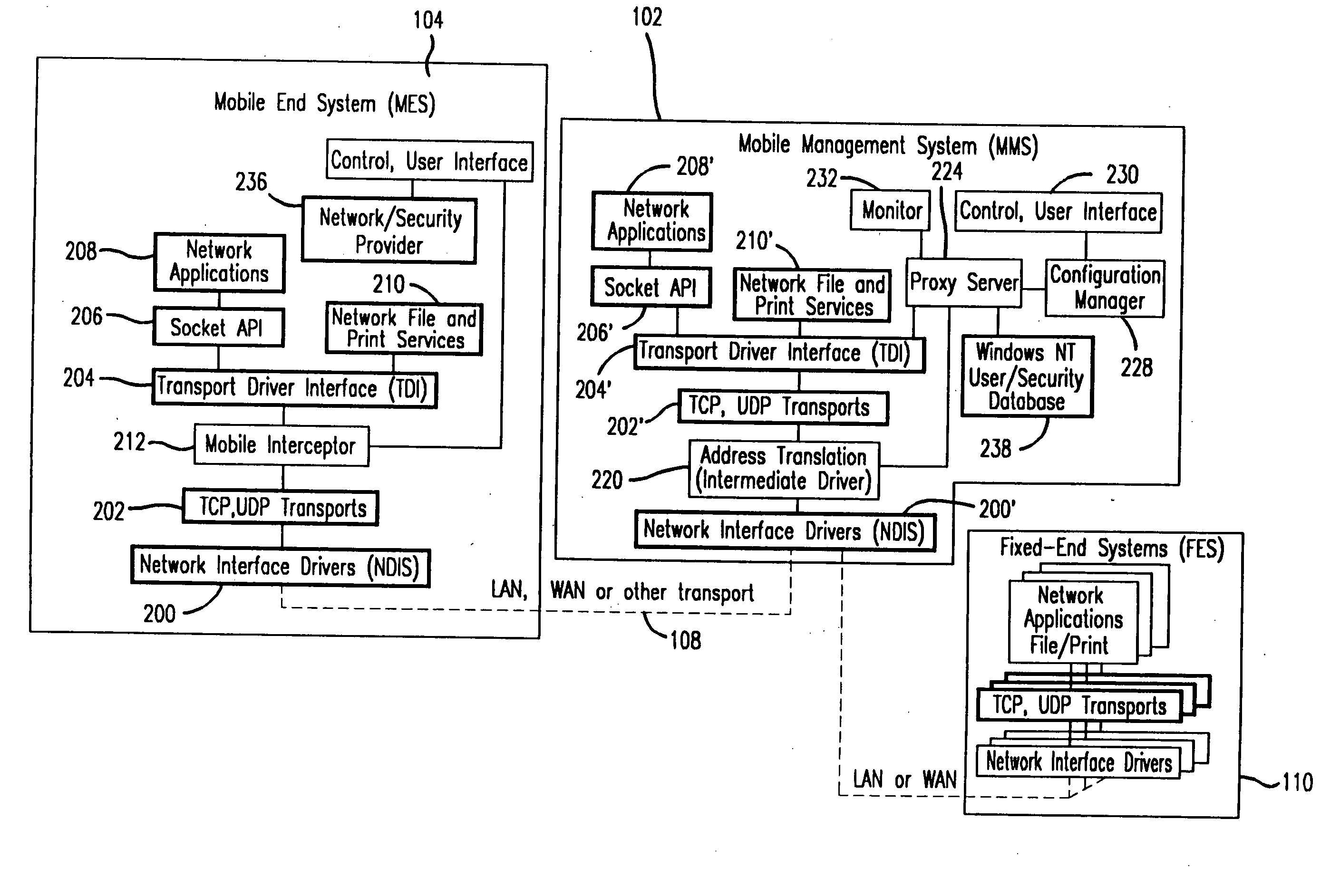
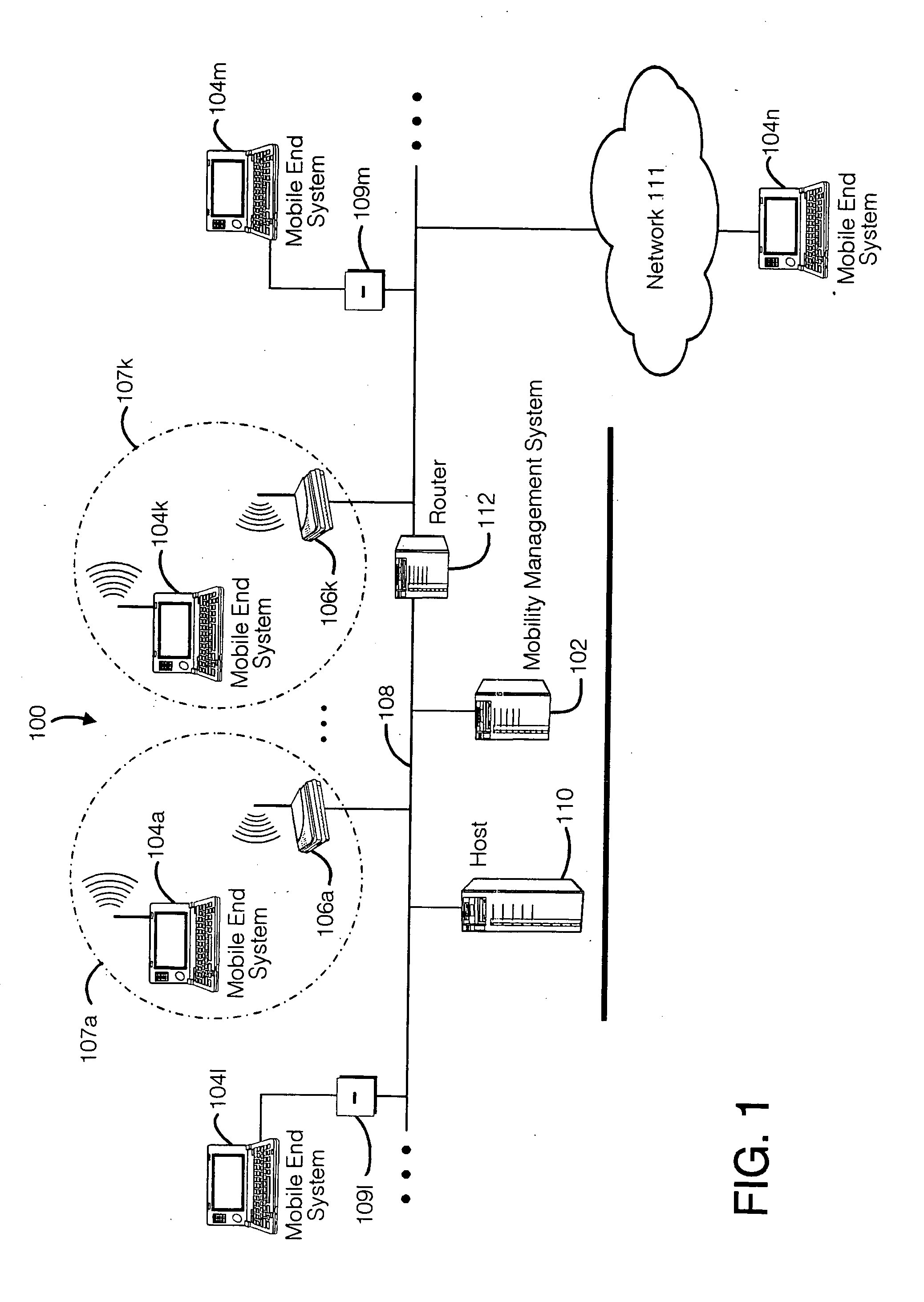
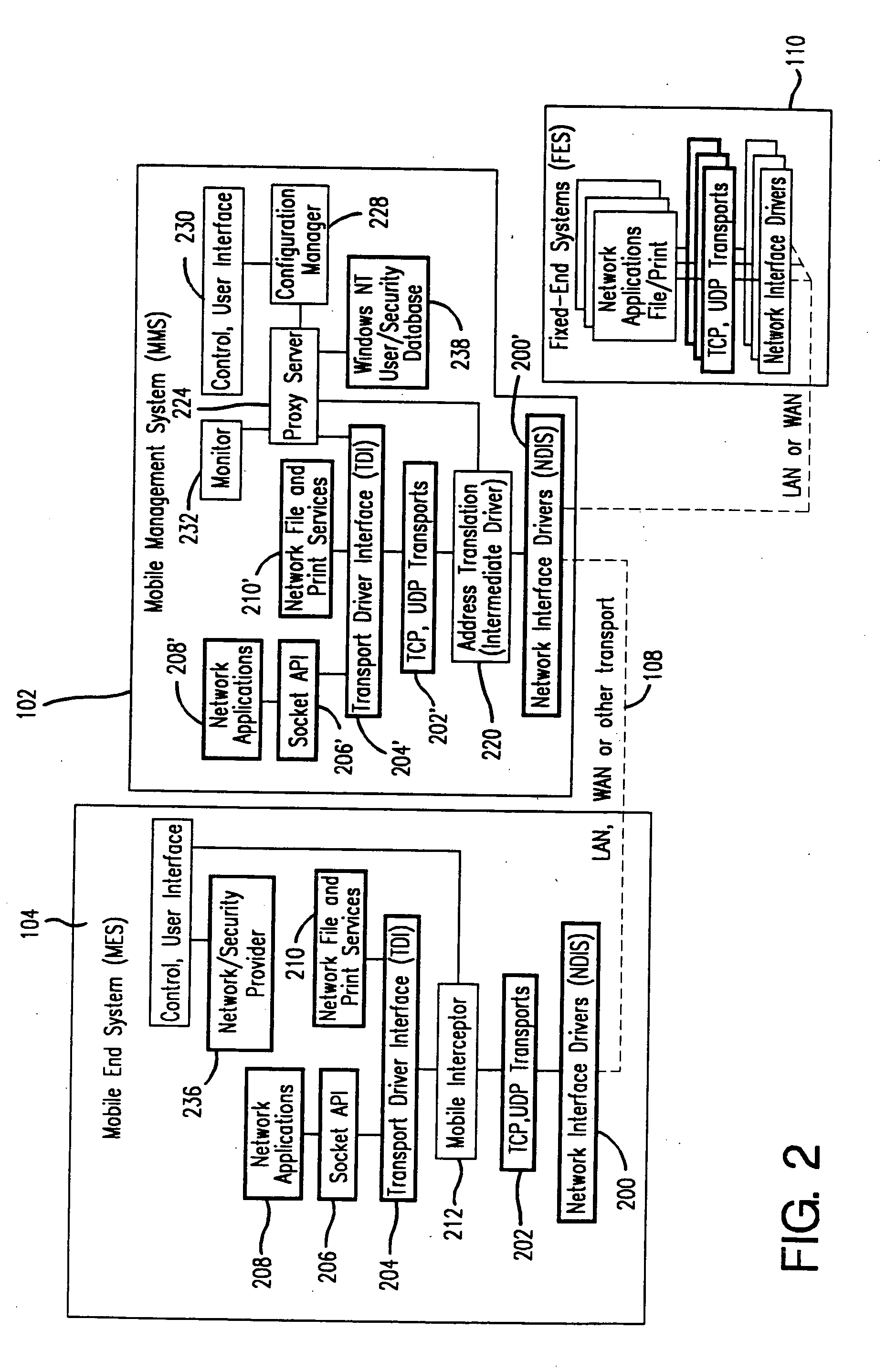
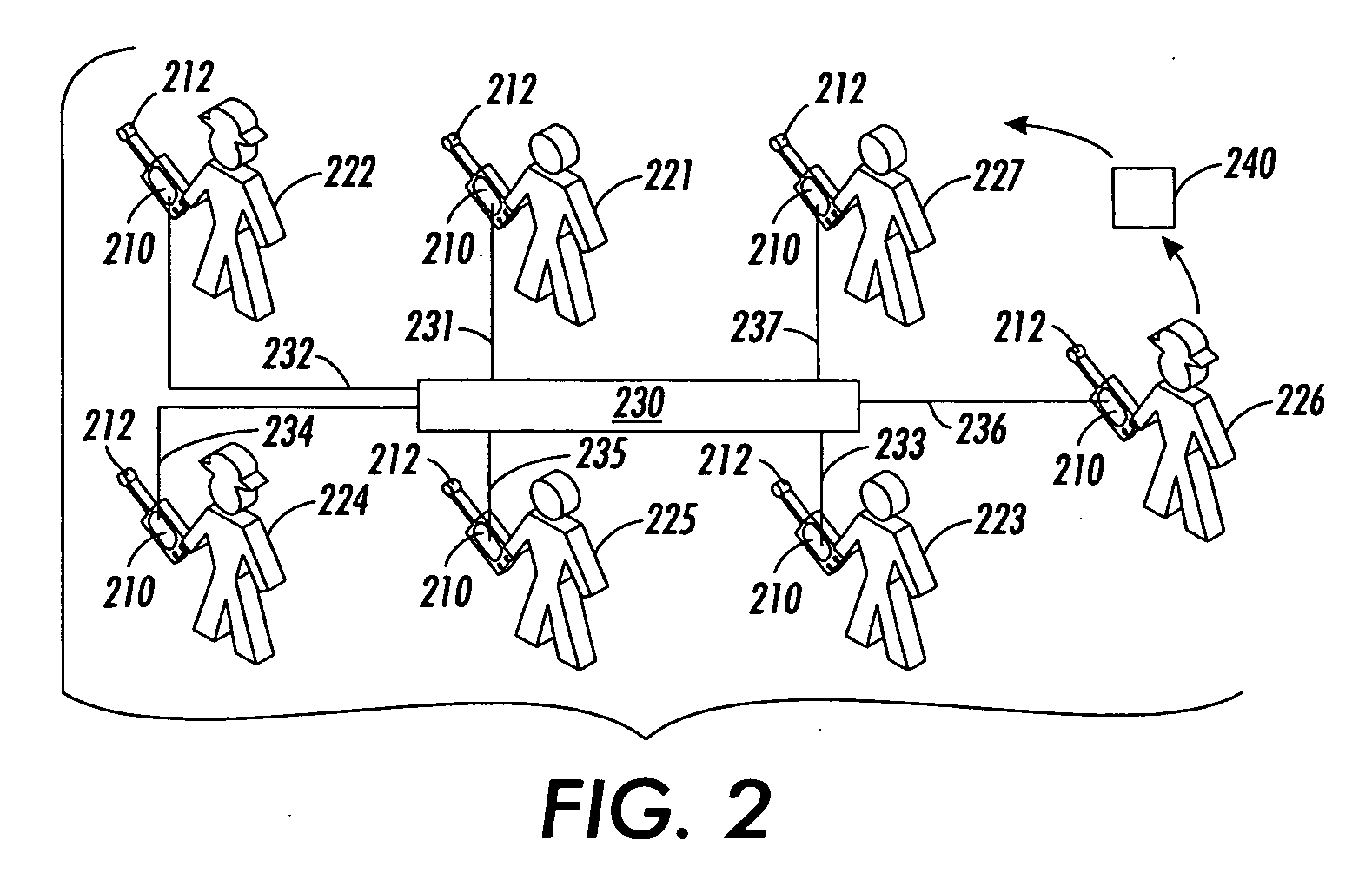
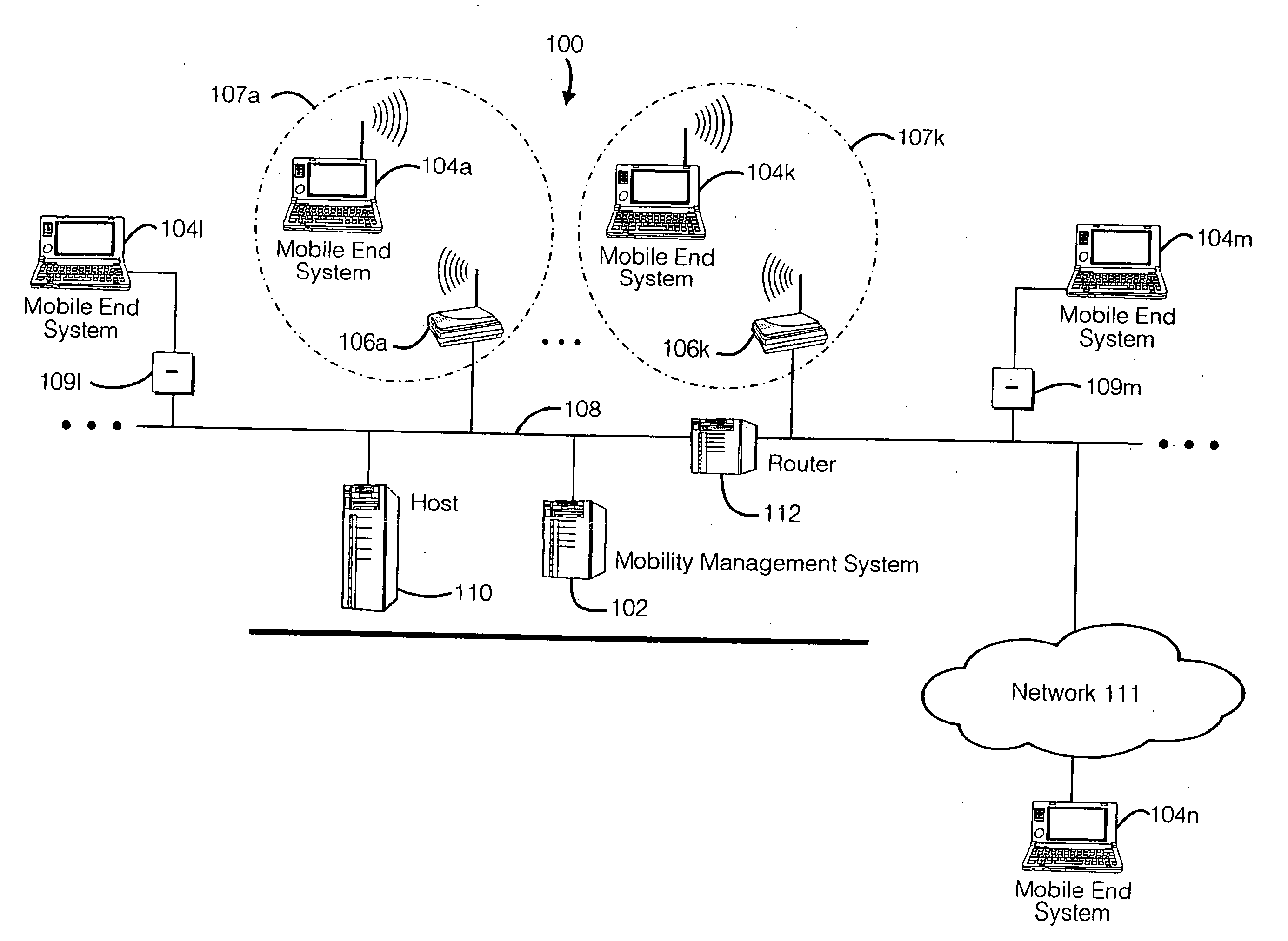
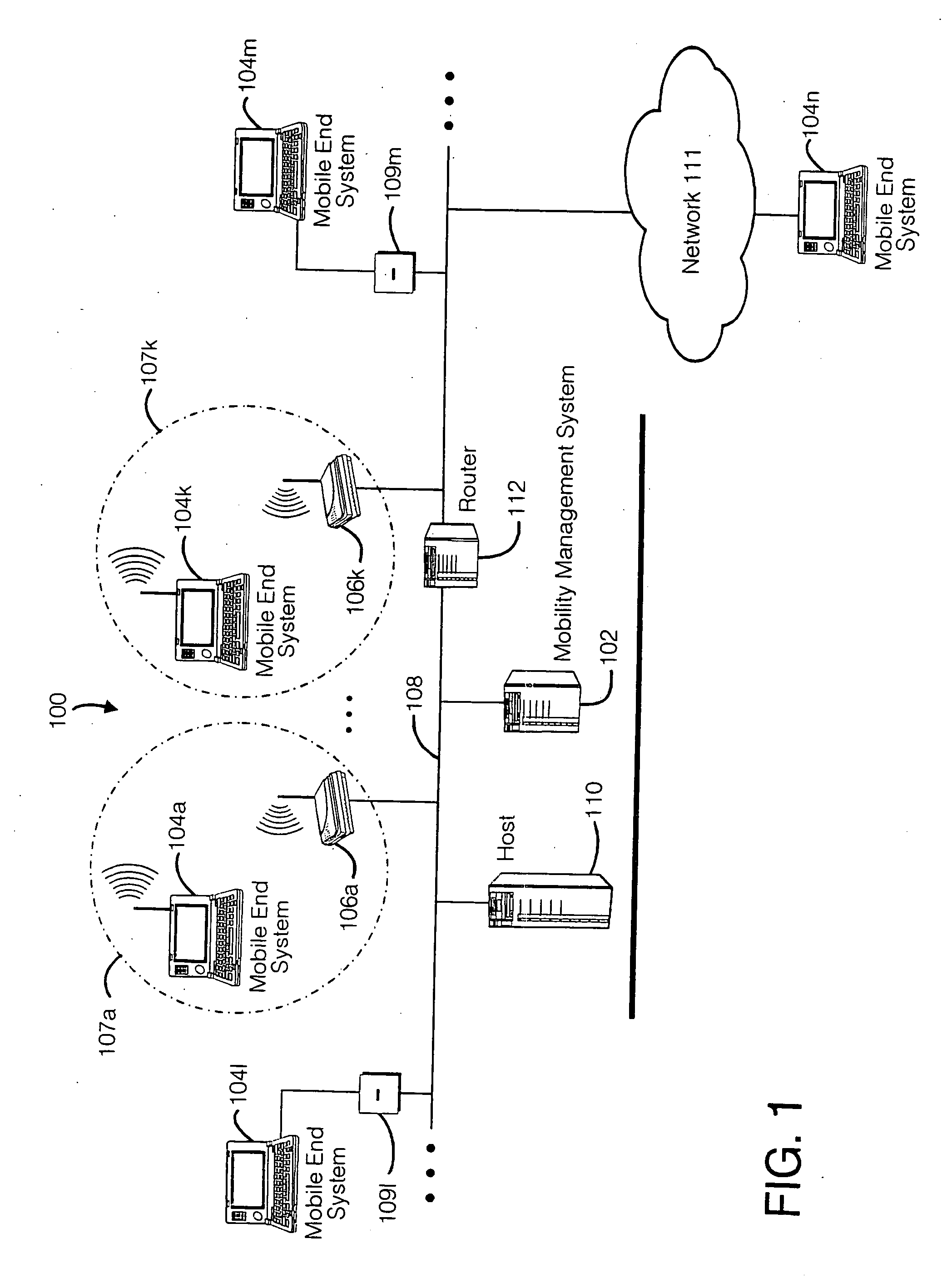
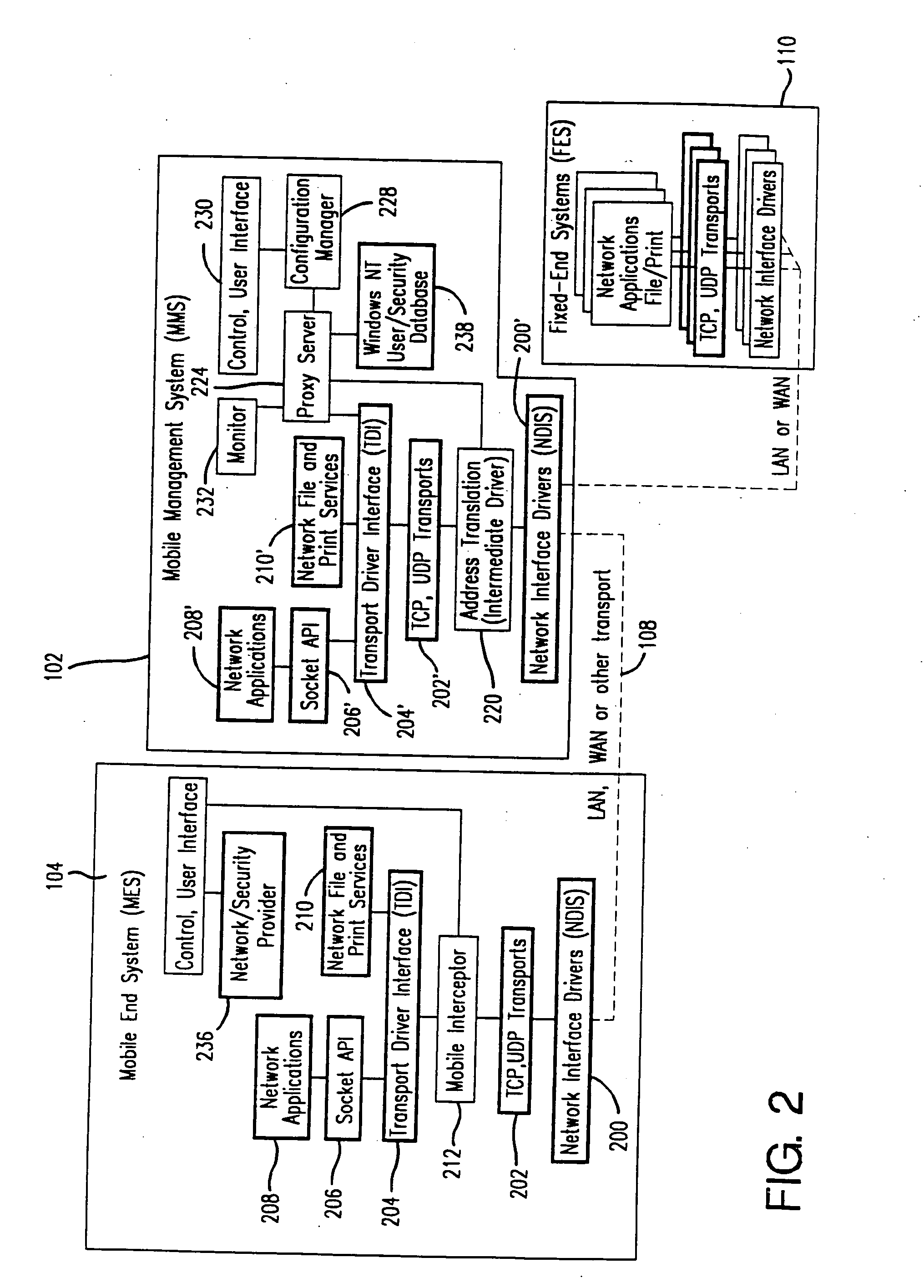
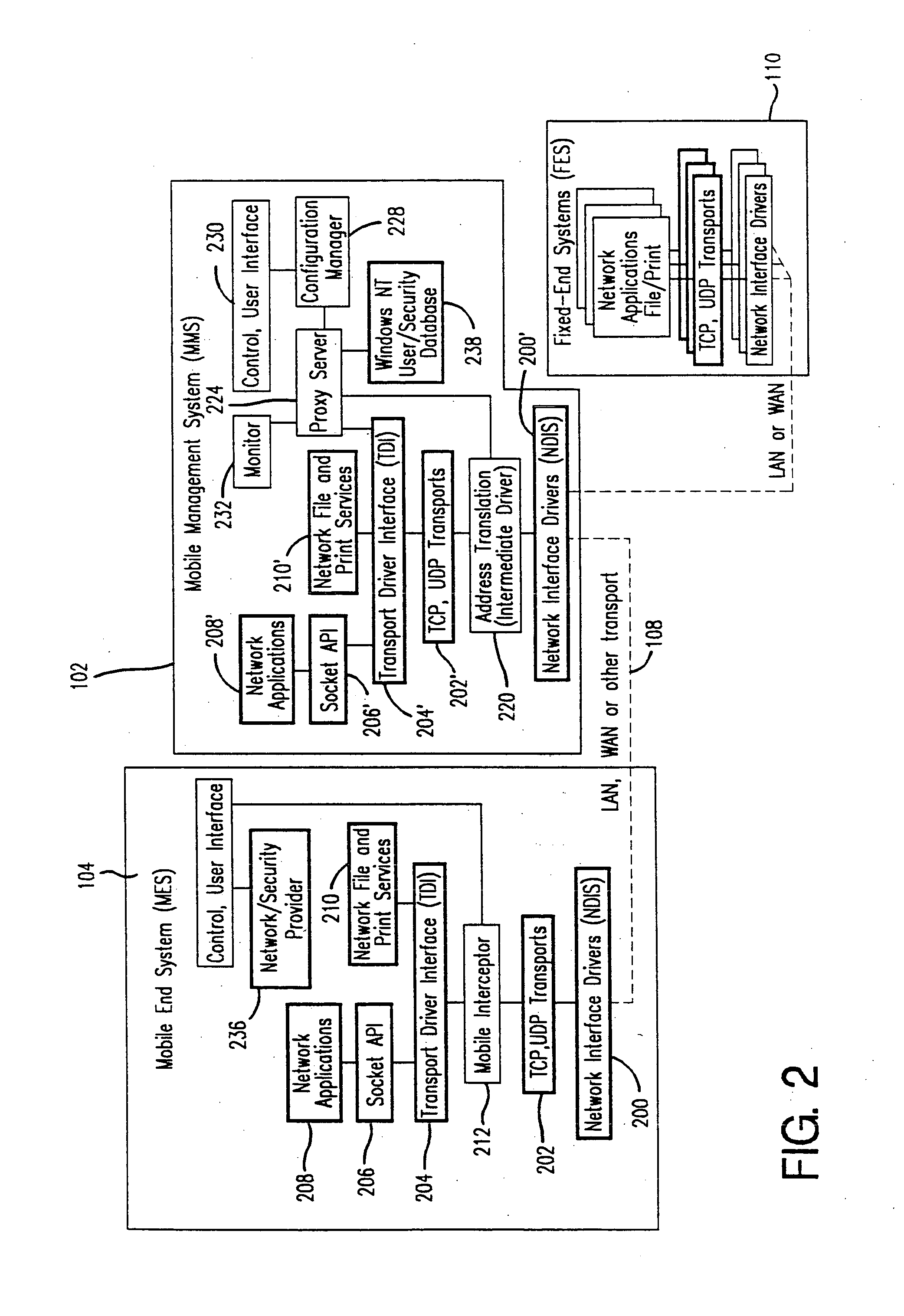
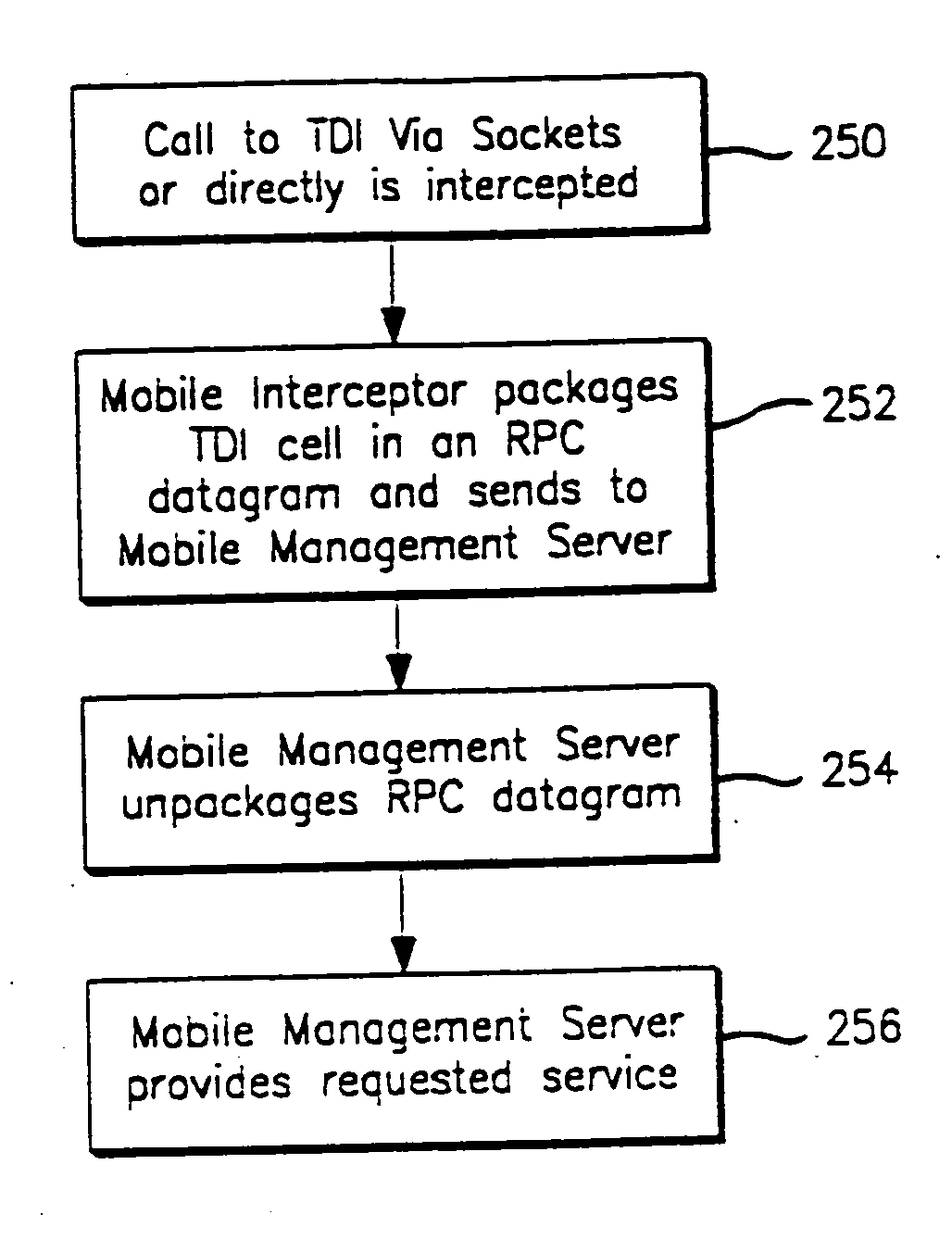
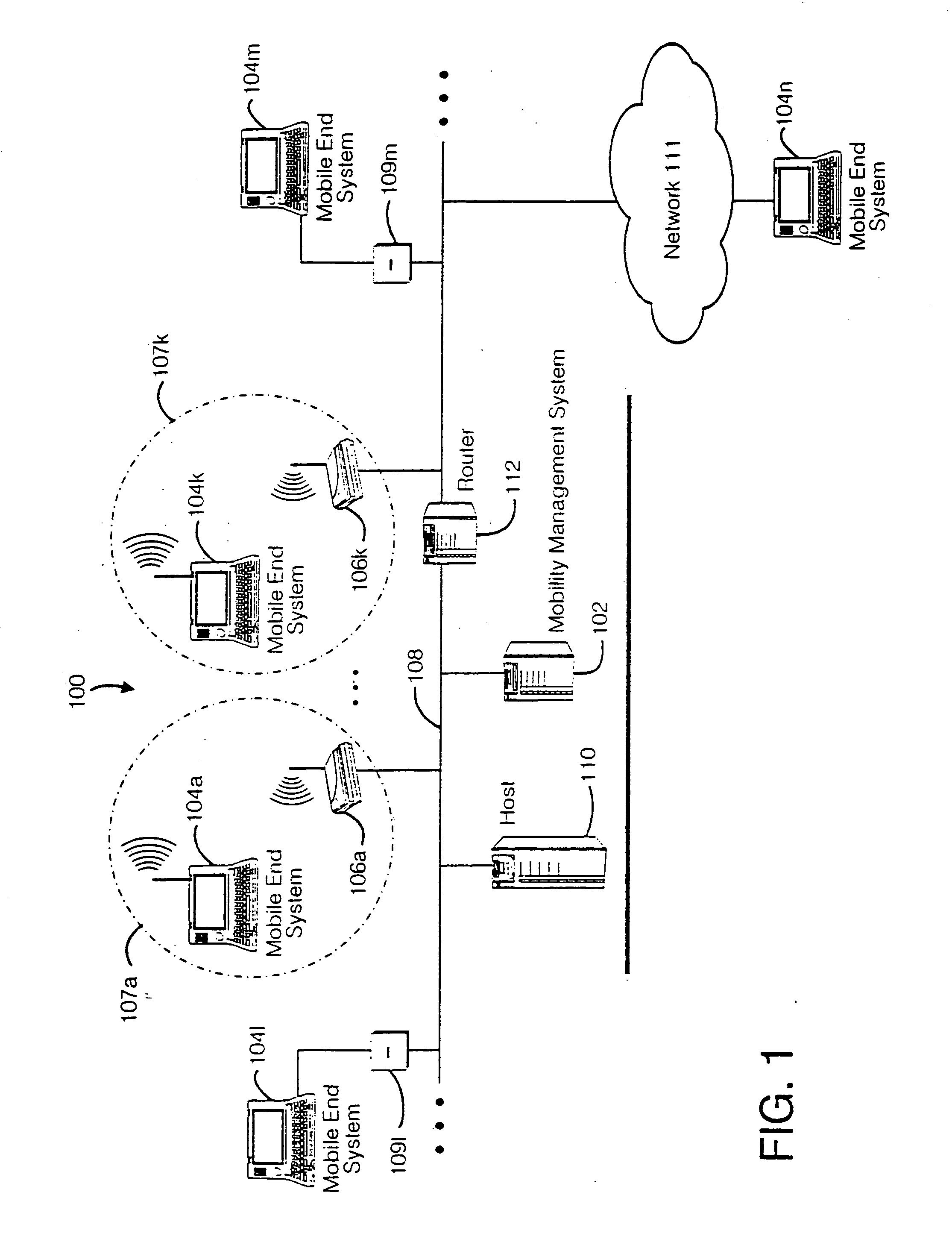
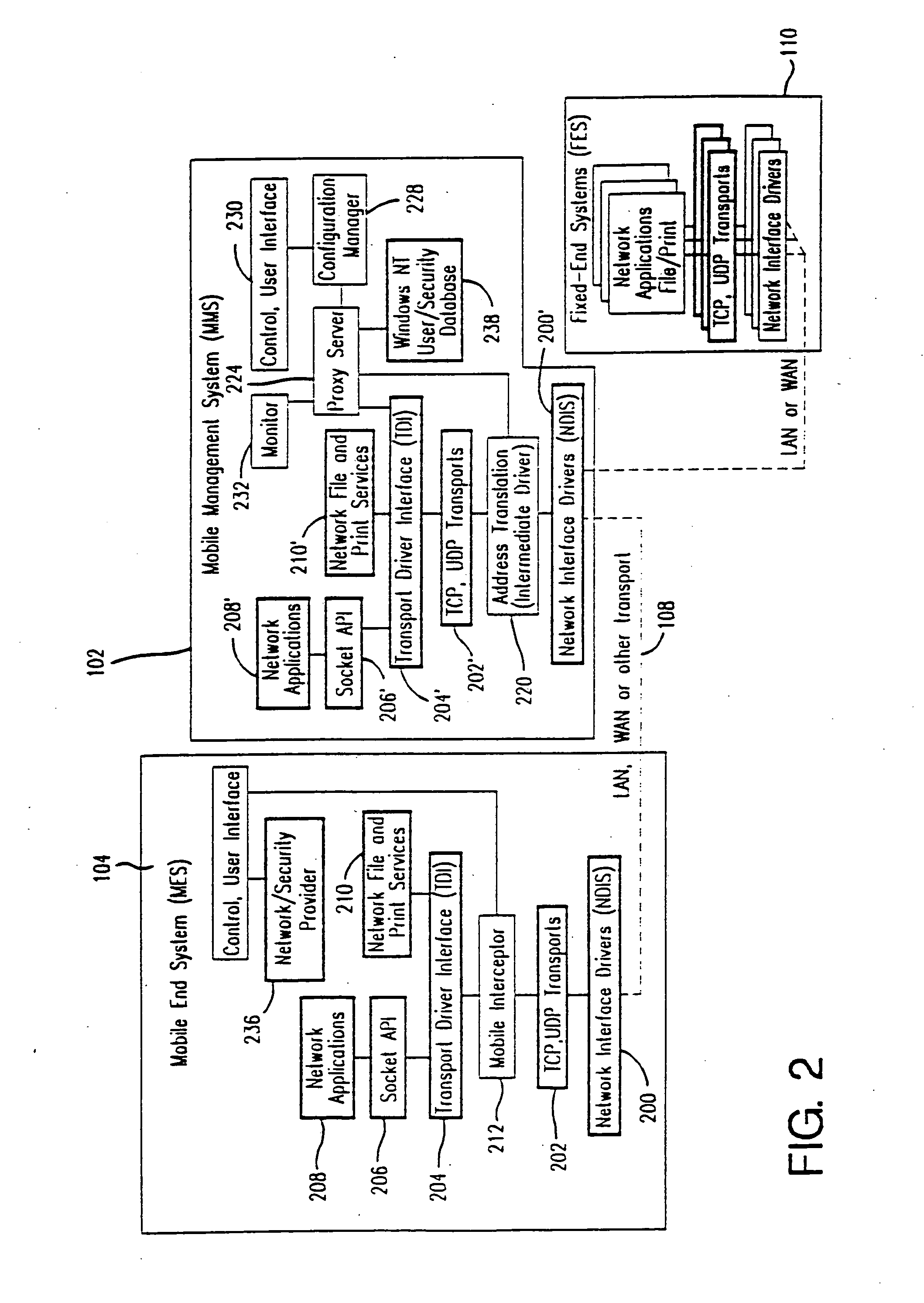
Method and apparatus for providing mobile and other intermittent connectivity in a computing environment
InactiveUS7136645B2Low costEasy accessError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork connectionMobile end
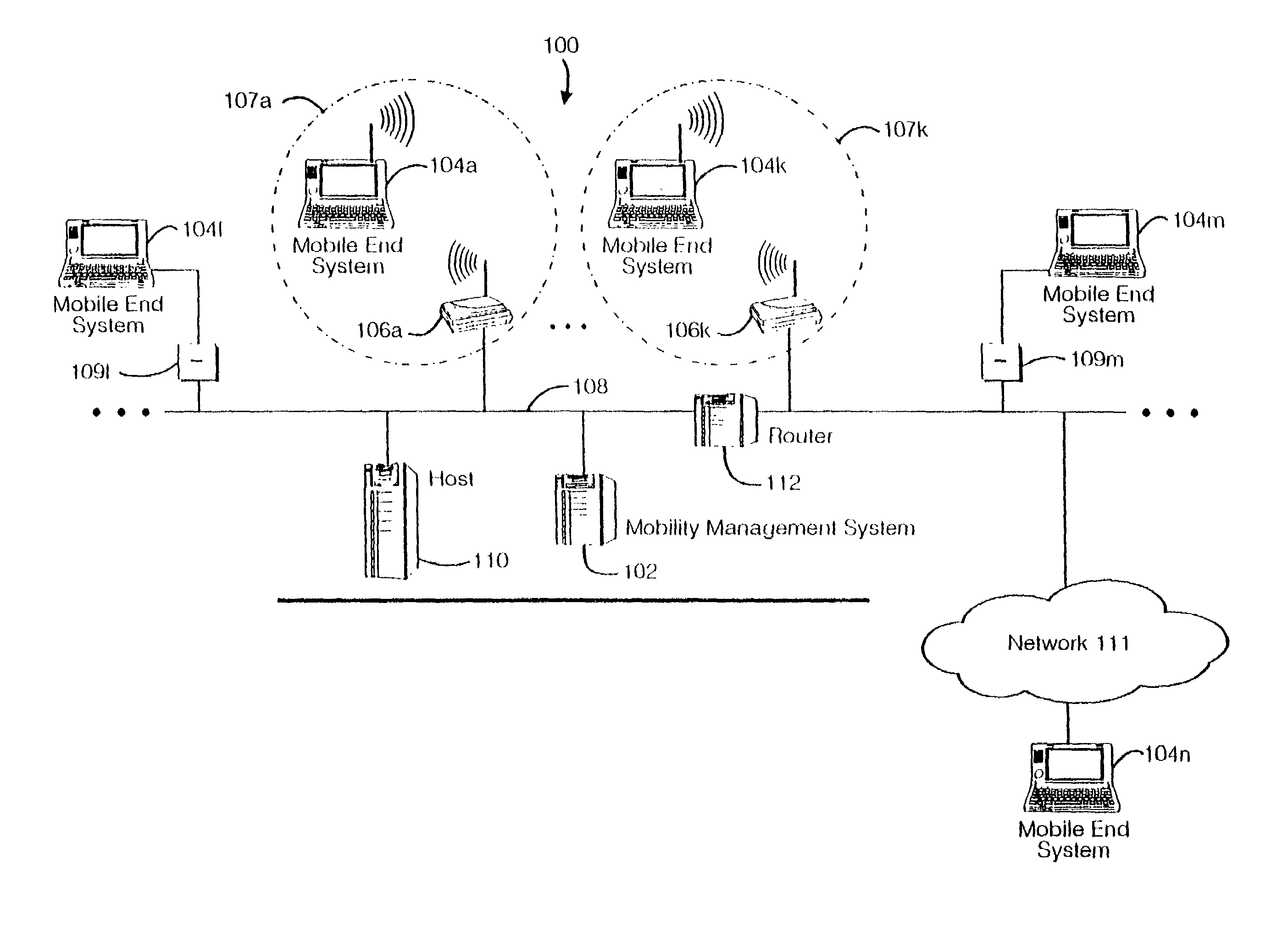
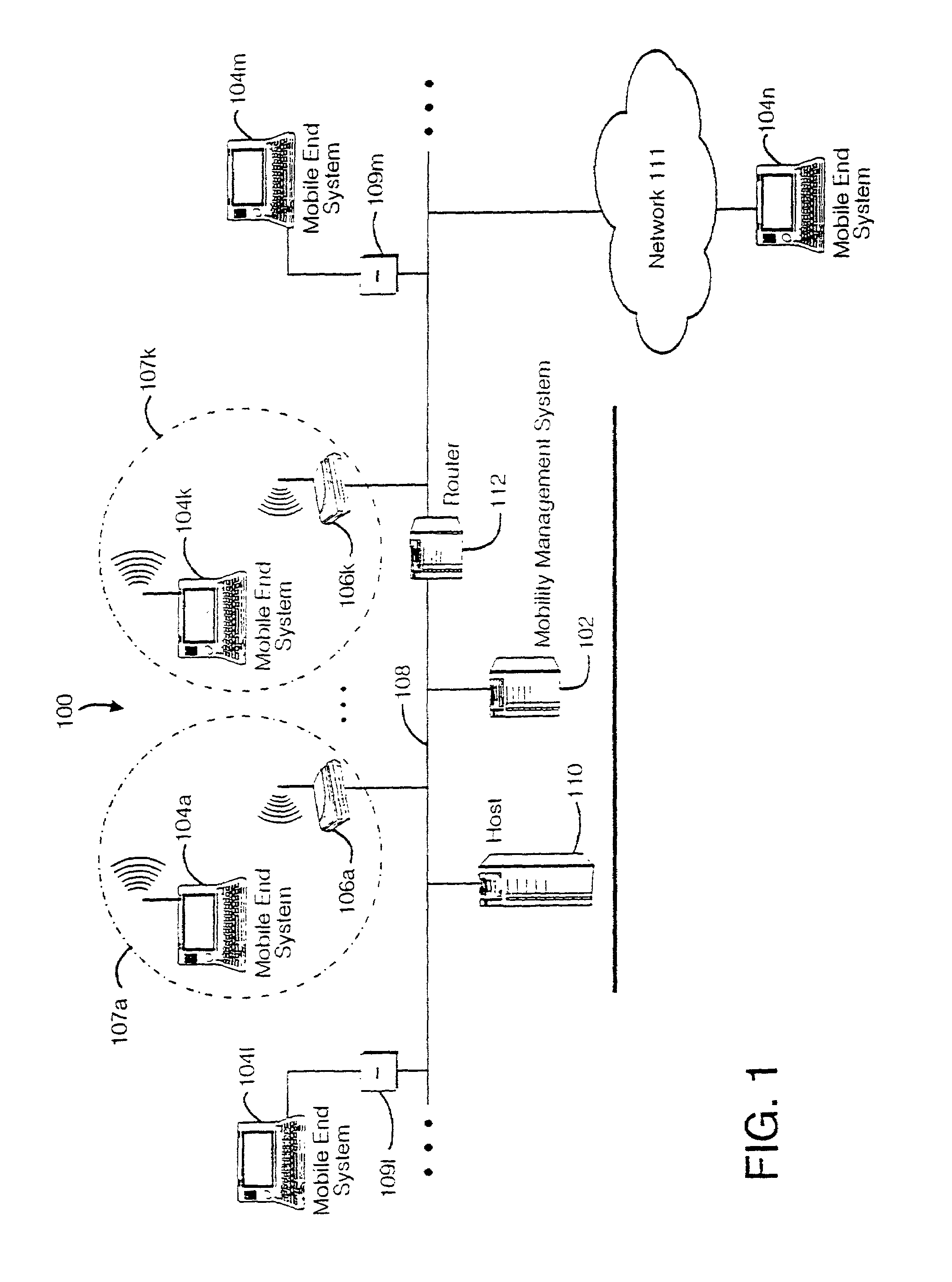
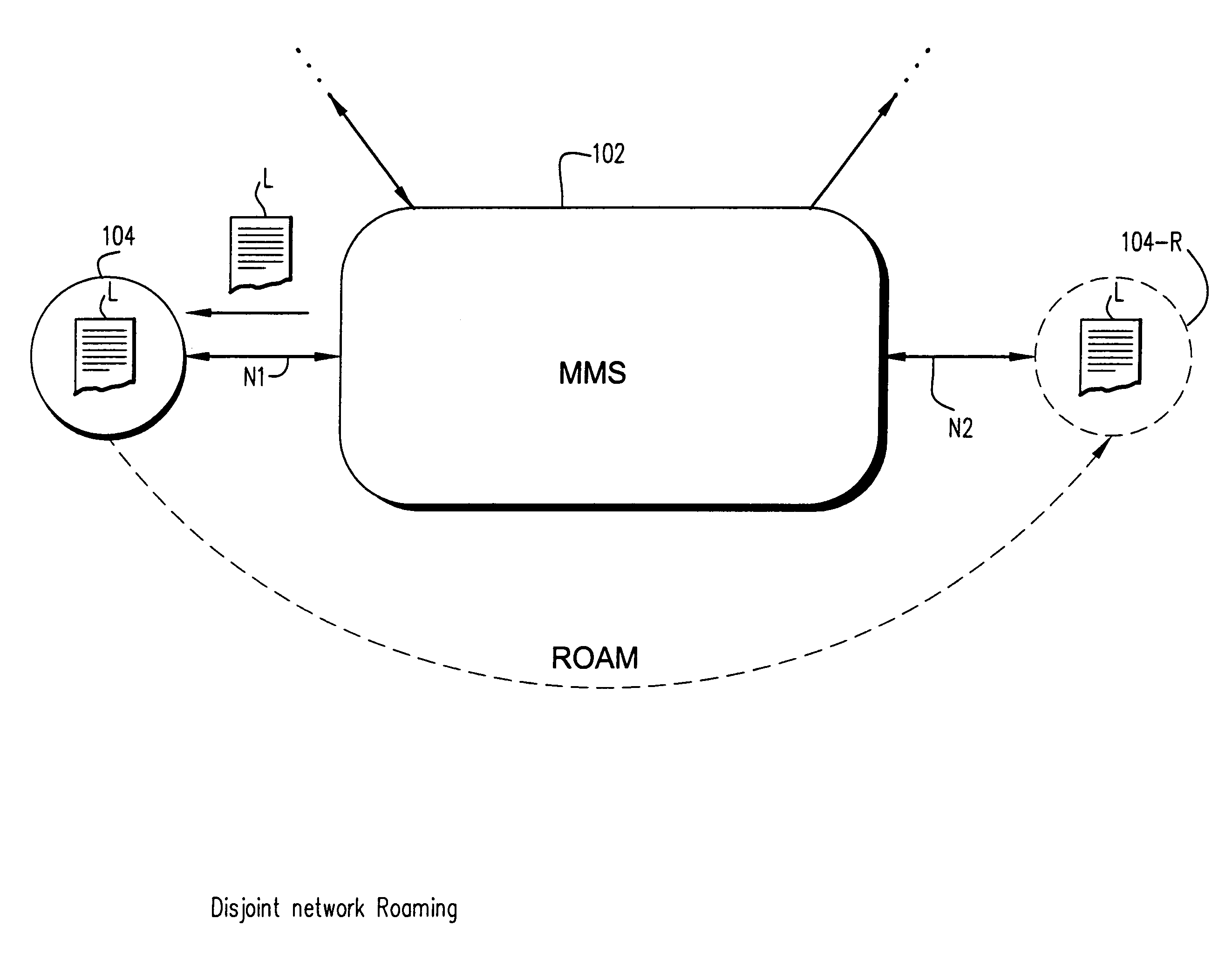
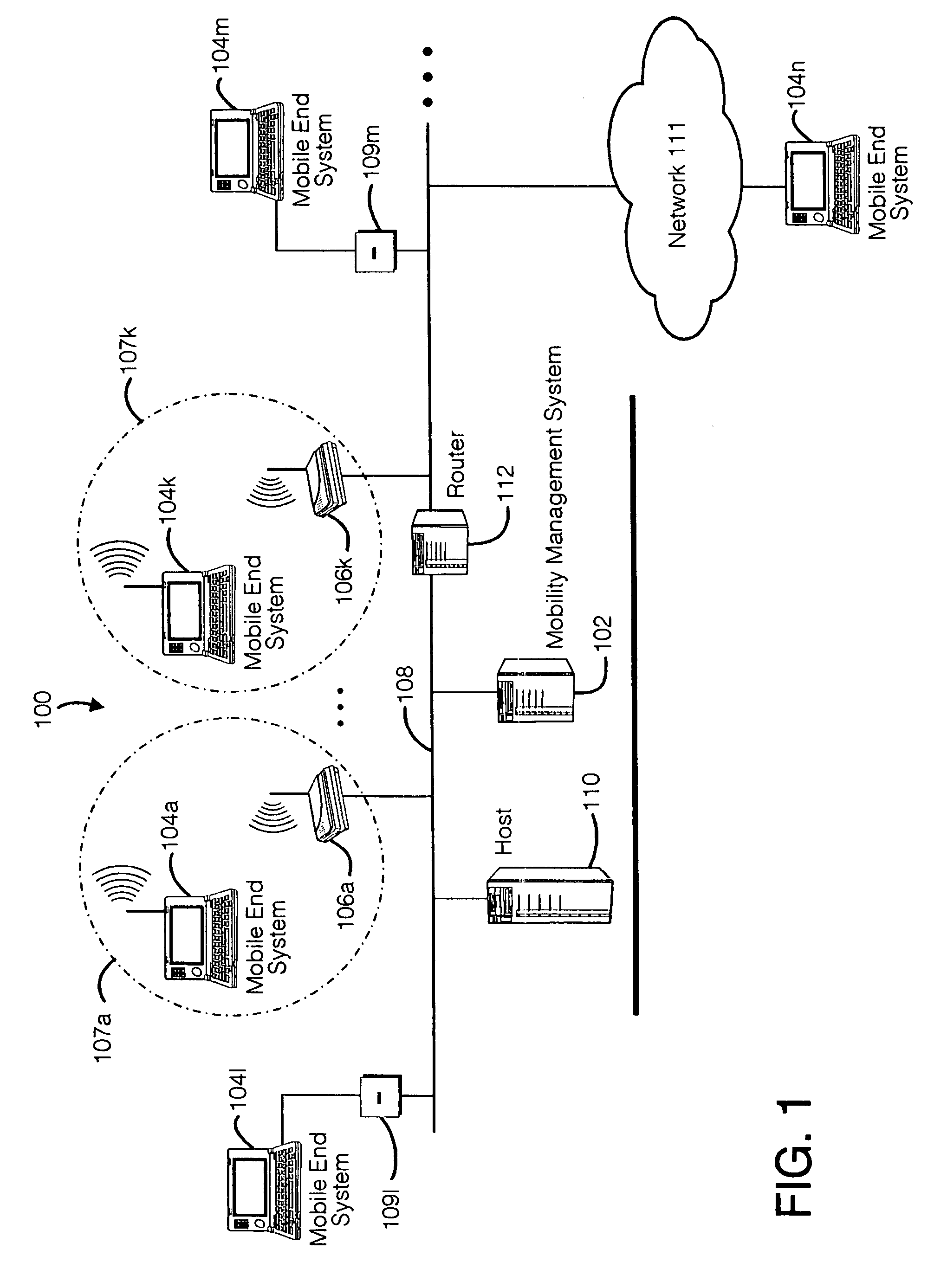
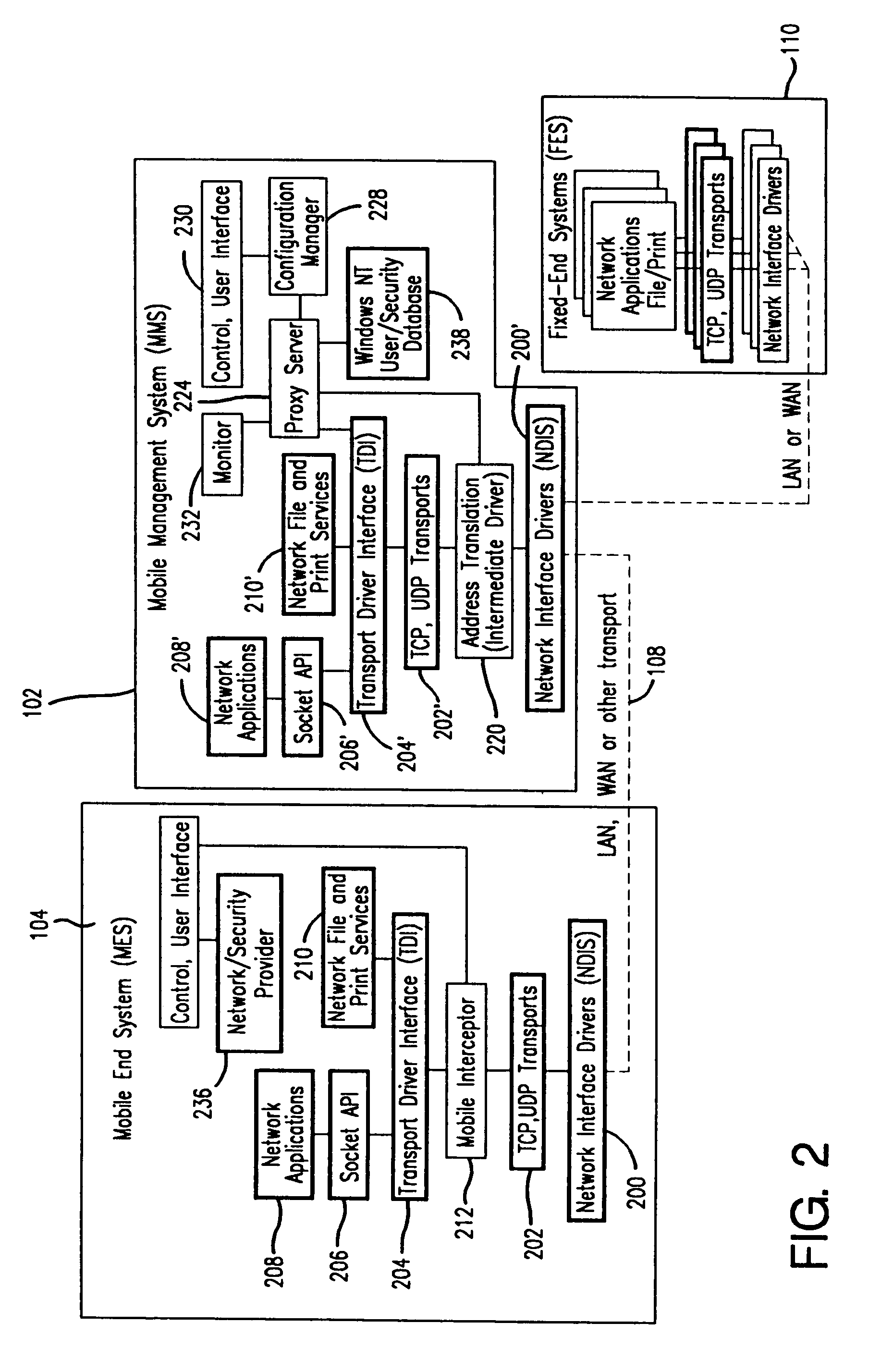
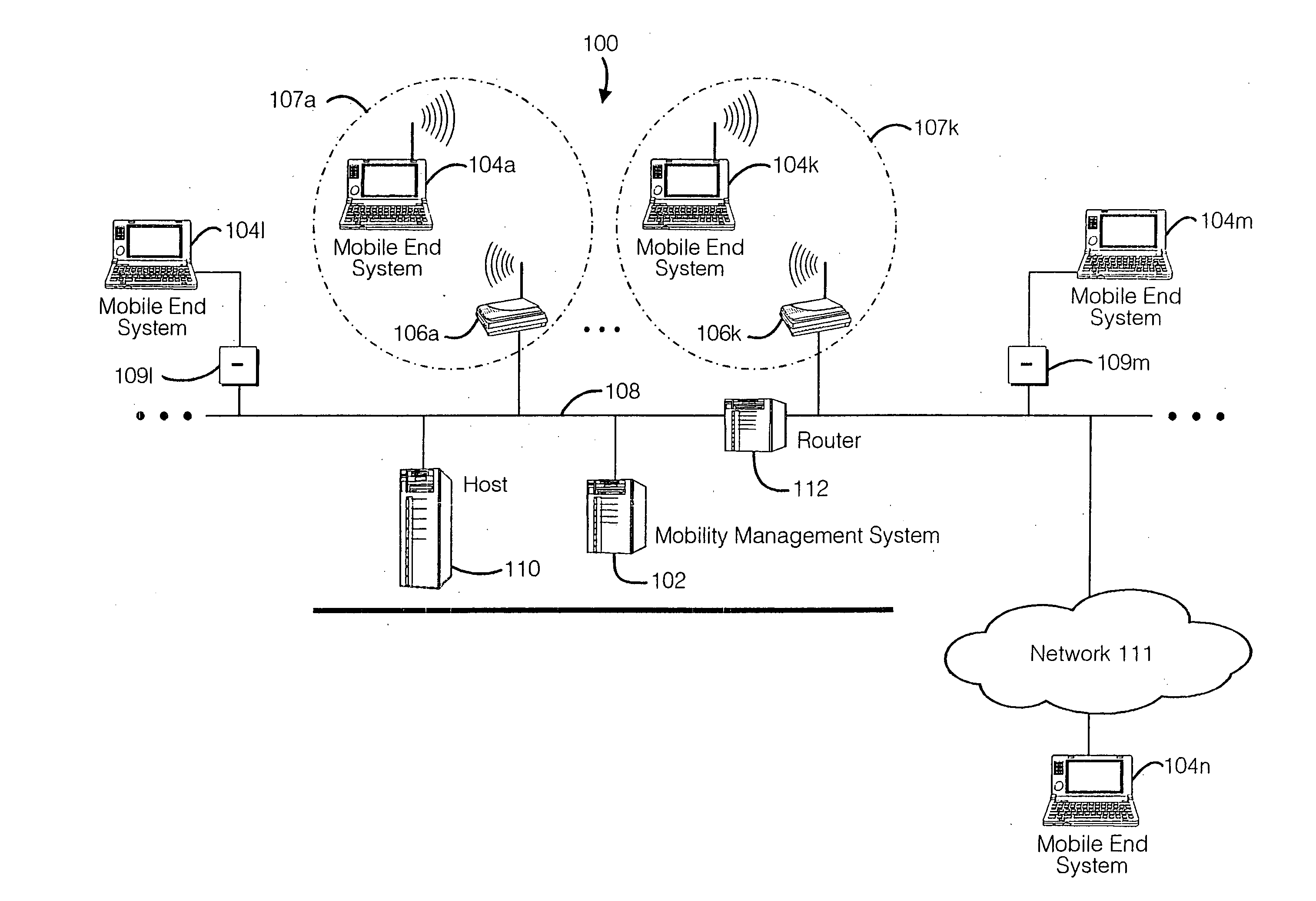
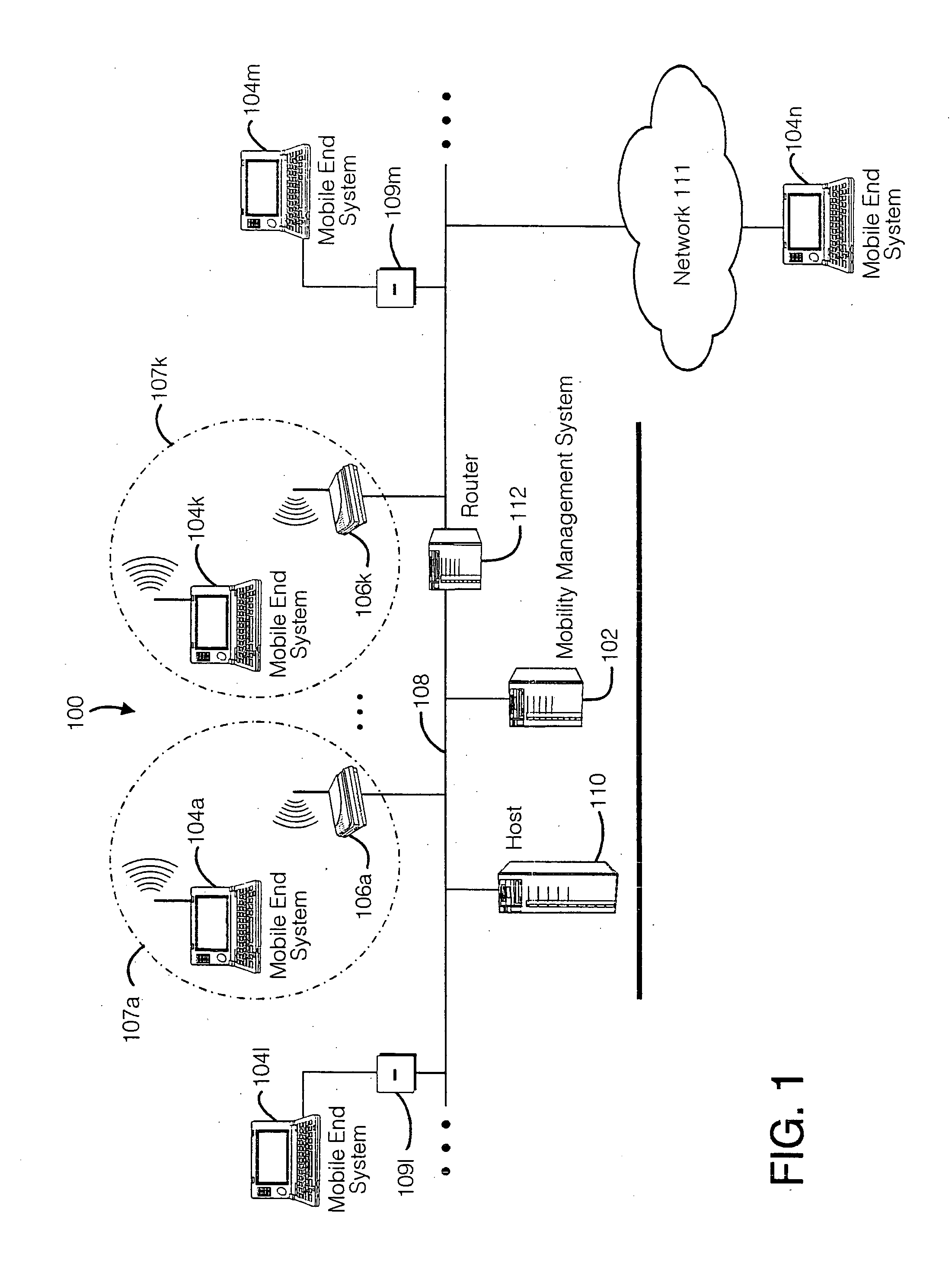
A seamless solution transparently addresses the characteristics of nomadic systems, and enables existing network applications to run reliably in mobile environments. A Mobility Management Server coupled to the mobile network maintains the state of each of any number of Mobile End Systems and handles the complex session management required to maintain persistent connections to the network and to other peer processes. If a Mobile End System becomes unreachable, suspends, or changes network address (e.g., due to roaming from one network interconnect to another), the Mobility Management Server maintains the connection to the associated peer task—allowing the Mobile End System to maintain a continuous connection even though it may temporarily lose contact with its network medium. An interface-based listener uses network point of attachment information supplied by a network interface to determine roaming conditions and to efficiently reestablish connection upon roaming. The Mobility Management Server can distribute lists to Mobile End Systems specifying how to contact it over disjoint networks.
Owner:MOBILE SONIC INC
Method and apparatus for providing mobile and other intermittent connectivity in a computing environment
InactiveUS6981047B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelData switching by path configurationMobile endNetwork address
A seamless solution transparently addresses the characteristics of nomadic systems, and enables existing network applications to run reliably in mobile environments. The solution extends the enterprise network, letting network managers provide mobile users with easy access to the same applications as stationary users without sacrificing reliability or centralized management. The solution combines advantages of existing wire-line network standards with emerging mobile standards to create a solution that works with existing network applications. A Mobility Management Server coupled to the mobile network maintains the state of each of any number of Mobile End Systems and handles the complex session management required to maintain persistent connections to the network and to other peer processes. If a Mobile End System becomes unreachable, suspends, or changes network address (e.g., due to roaming from one network interconnect to another), the Mobility Management Server maintains the connection to the associated peer task—allowing the Mobile End System to maintain a continuous connection even though it may temporarily lose contact with its network medium. In one example, Mobility Management Server communicates with Mobile End Systems using Remote Procedure Call and Internet Mobility Protocols.
Owner:MOBILE SONIC INC
Method and apparatus for providing mobile and other intermittent connectivity in a computing environment
InactiveUS7293107B1Easy accessSacrificing reliability or centralized managementNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionMobile end
A seamless solution transparently addresses the characteristics of nomadic systems, and enables existing network applications to run reliably in mobile environments. A Mobility Management Server coupled to the mobile network maintains the state of each of any number of Mobile End Systems and handles the complex session management required to maintain persistent connections to the network and to other peer processes. If a Mobile End System becomes unreachable, suspends, or changes network address (e.g., due to roaming from one network interconnect to another), the Mobility Management Server maintains the connection to the associated peer task—allowing the Mobile End System to maintain a continuous connection even though it may temporarily lose contact with its network medium. An interface-based listener uses network point of attachment information supplied by a network interface to determine roaming conditions and to efficiently reestablish connection upon roaming. The Mobility Management Server can distribute lists to Mobile End Systems specifying how to contact it over disjoint networks.
Owner:MOBILE SONIC INC
Adaptive pattern recognition based control system and method
A network media appliance, comprising at least one packet data network interface, adapted for communicating data packets with a data network according to an Internet Protocol; a media data interface, and a processor, having an associated memory for storing executable code, said code defining at least a remote virtual interface function, and a data transfer function for controlling transfer of data through said media data interface.
Owner:BLANDING HOVENWEEP
Systems and methods for authenticating communications in a network medium
InactiveUS20030149874A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey exchangeExchange protocol
Pre-authentication information of devices is used to securely authenticate arbitrary peer-to-peer ad-hoc interactions. In one embodiment, public key cryptography is used in the main wireless link with location-limited channels being initially used to pre-authenticate devices. Use of public keys in the pre-authenticate data allows for the broadening of types of media suitable for use as location-limited channels to include, for example, audio and infrared. Also, it allows a range of key exchange protocols which can be authenticated in this manner to include most public-key-protocols. As a result, a large range of devices, protocols can be used in various applications. Further, an eavesdropper is forced to mount an active attack on the location-limited channel itself in order to access an ad-hoc exchange. However, this results in the discovery of the eavesdropper.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
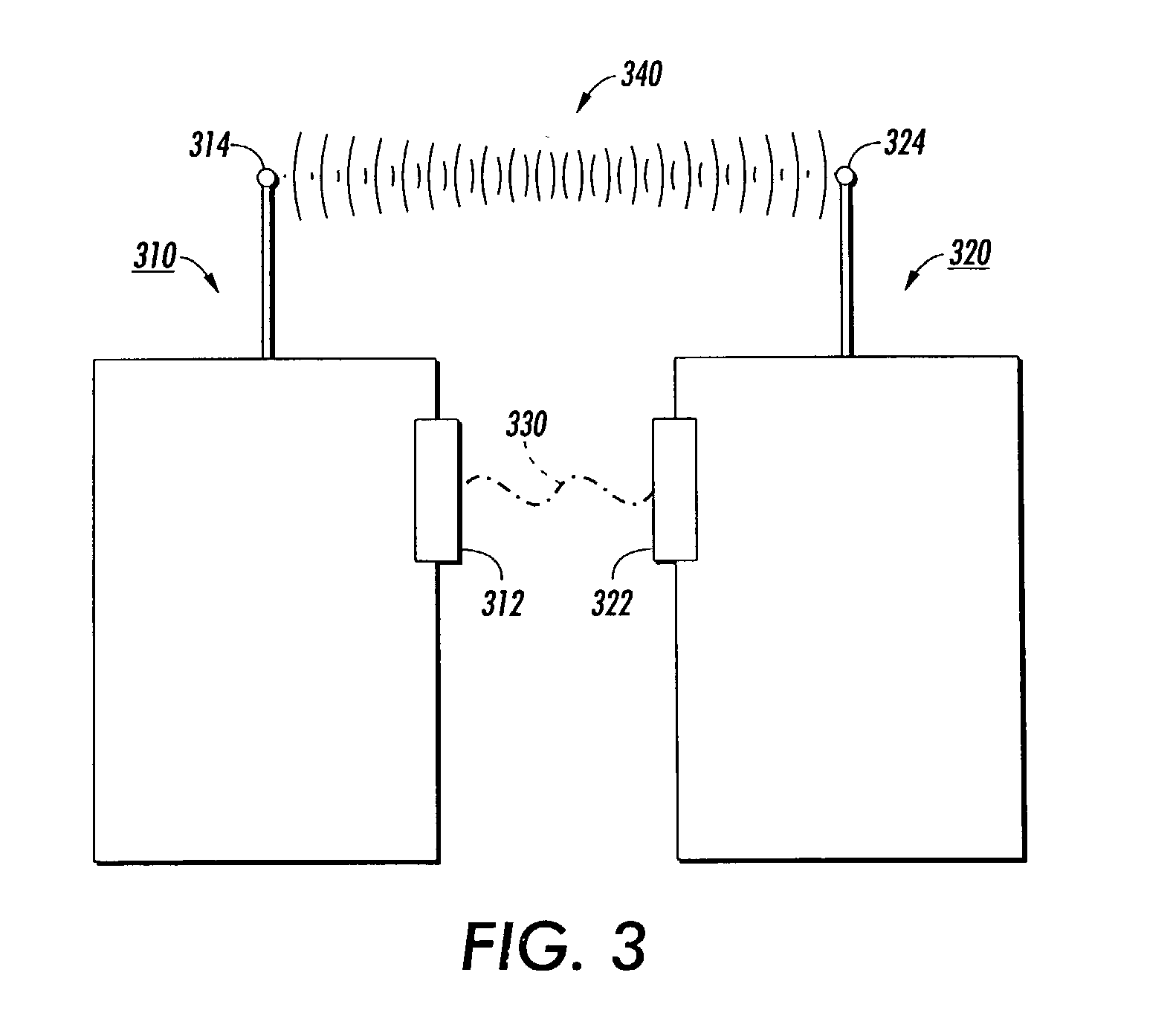
System and Method for Synchronizing Media Presentation at Multiple Recipients
InactiveUS20070110074A1Reduce the impactAvoid user-perceivable echoSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationNetwork communicationNetwork media
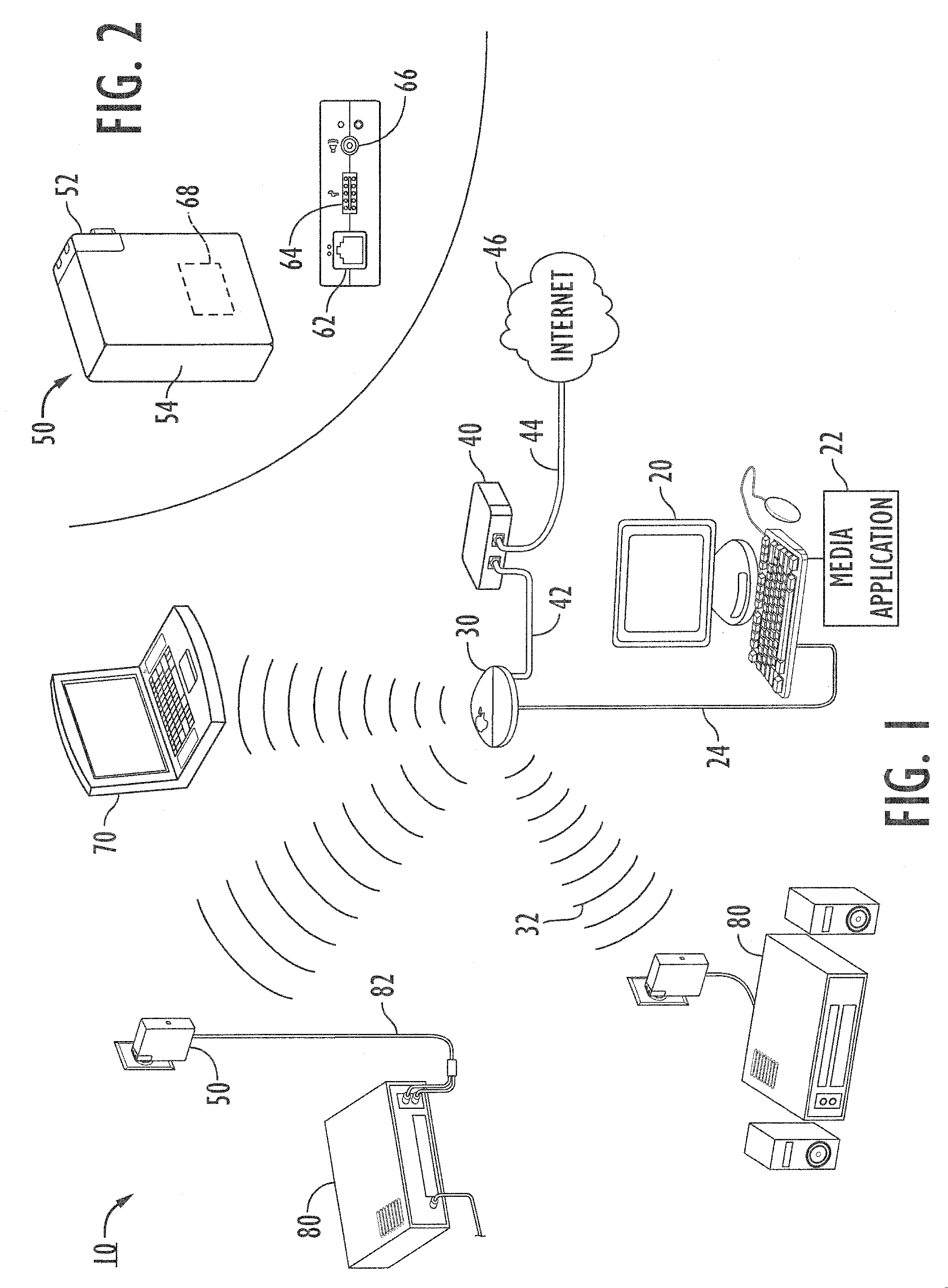
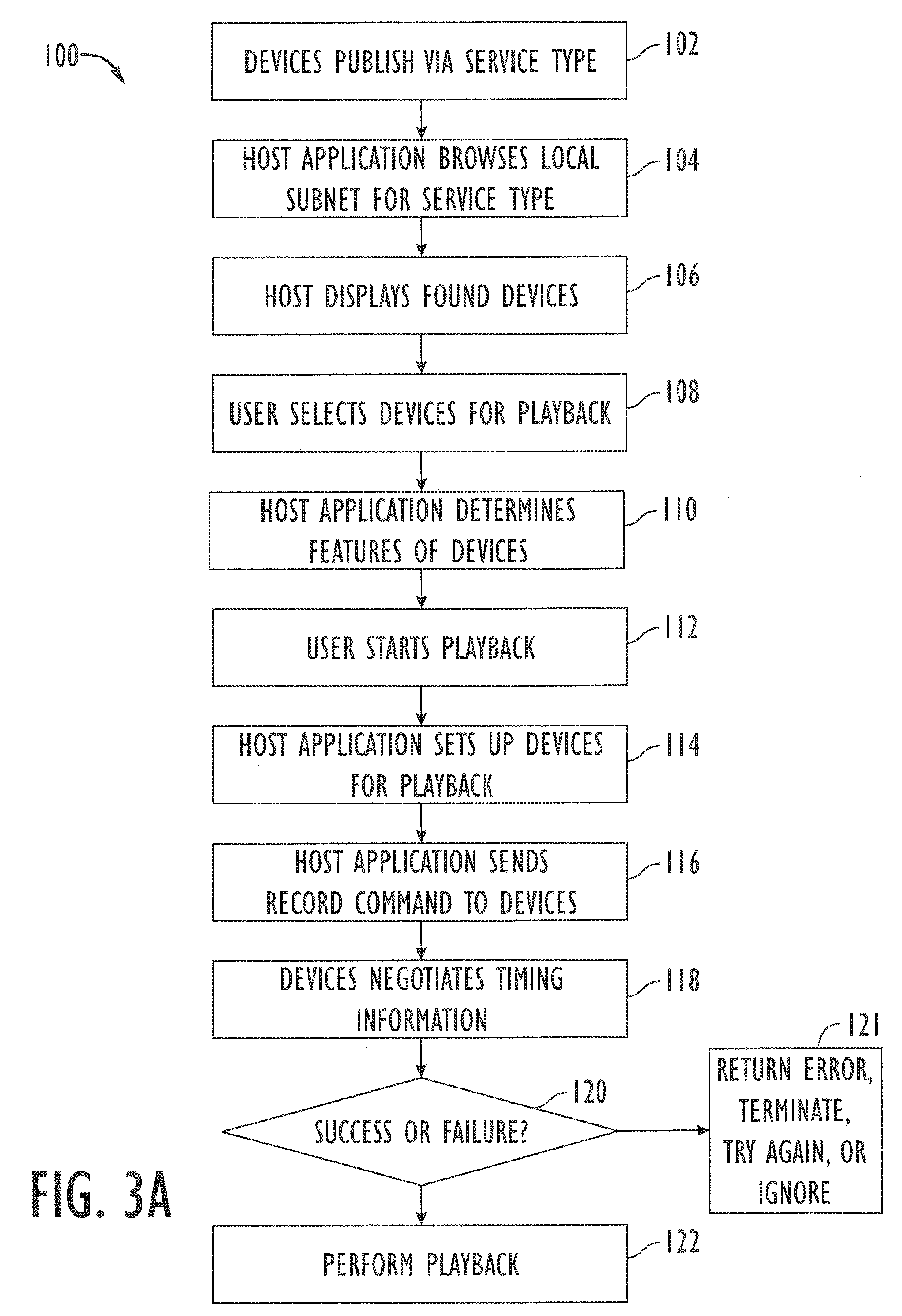
A network media delivery system includes client devices and a host device. Each client device has a network interface, an engine for processing media data, and a media interface. The host device, which can be a computer, establishes network communication links with the client devices, which can be networked media stations, and sends media data to the client devices. The media data can be sent wirelessly as packets of media data transmitted at intervals to each client device. In one embodiment, the host device controls processing of media data such that processed media is delivered in a synchronized manner at each of the client devices. In another embodiment, the host device controls processing of media data such that processed media is delivered in a synchronized manner at the host device and at least one client device.
Owner:APPLE INC
Network media appliance system and method
A network router, comprising at least one network interface, and a processor, supporting an embedded web server to provide a remote virtual user interface, for controlling said at least one network interface, analyzing data passing through said at least one network interface and making decisions in dependence thereon, and communicating control information using a markup language through said at least one network interface.
Owner:BLANDING HOVENWEEP
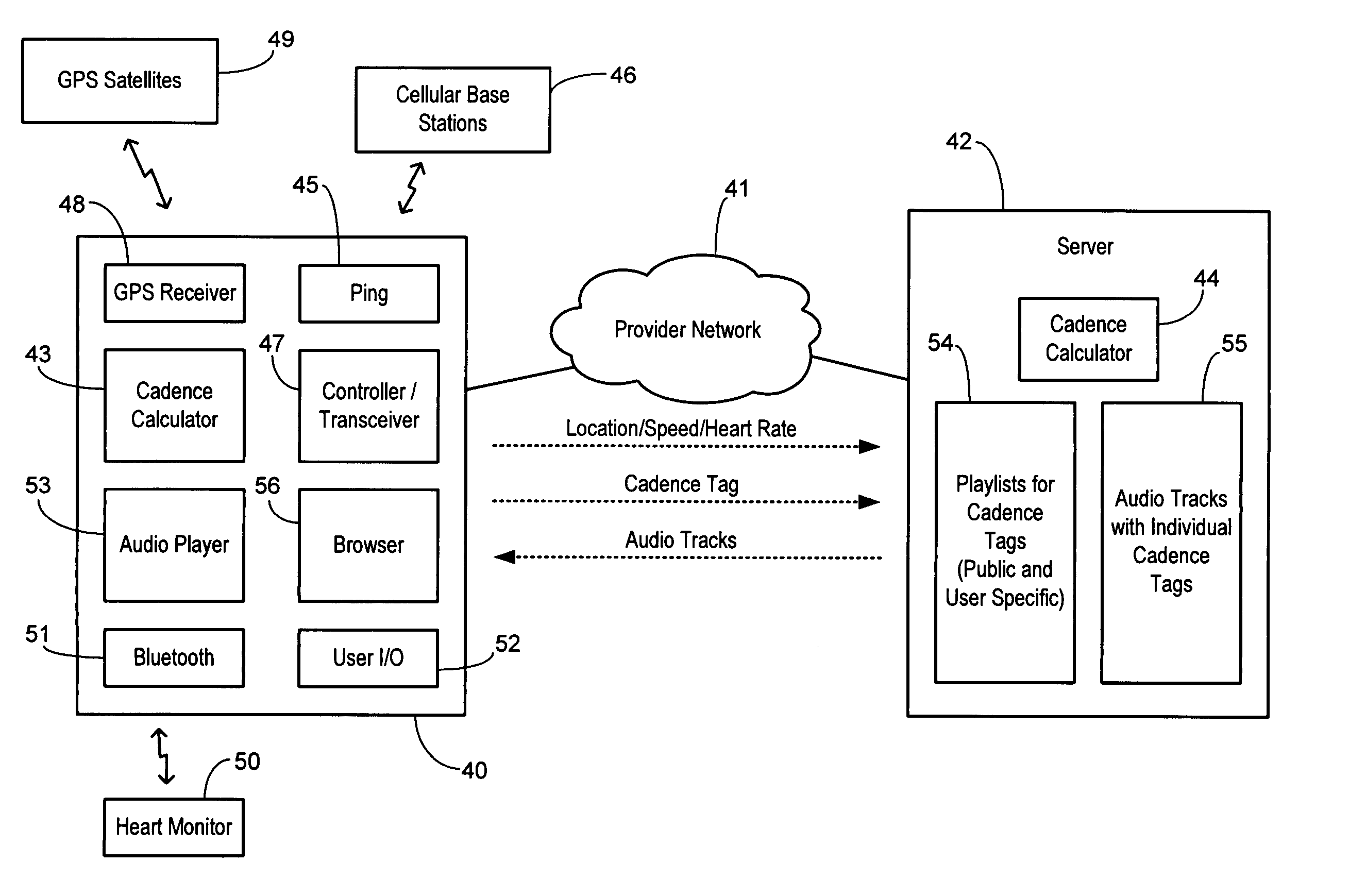
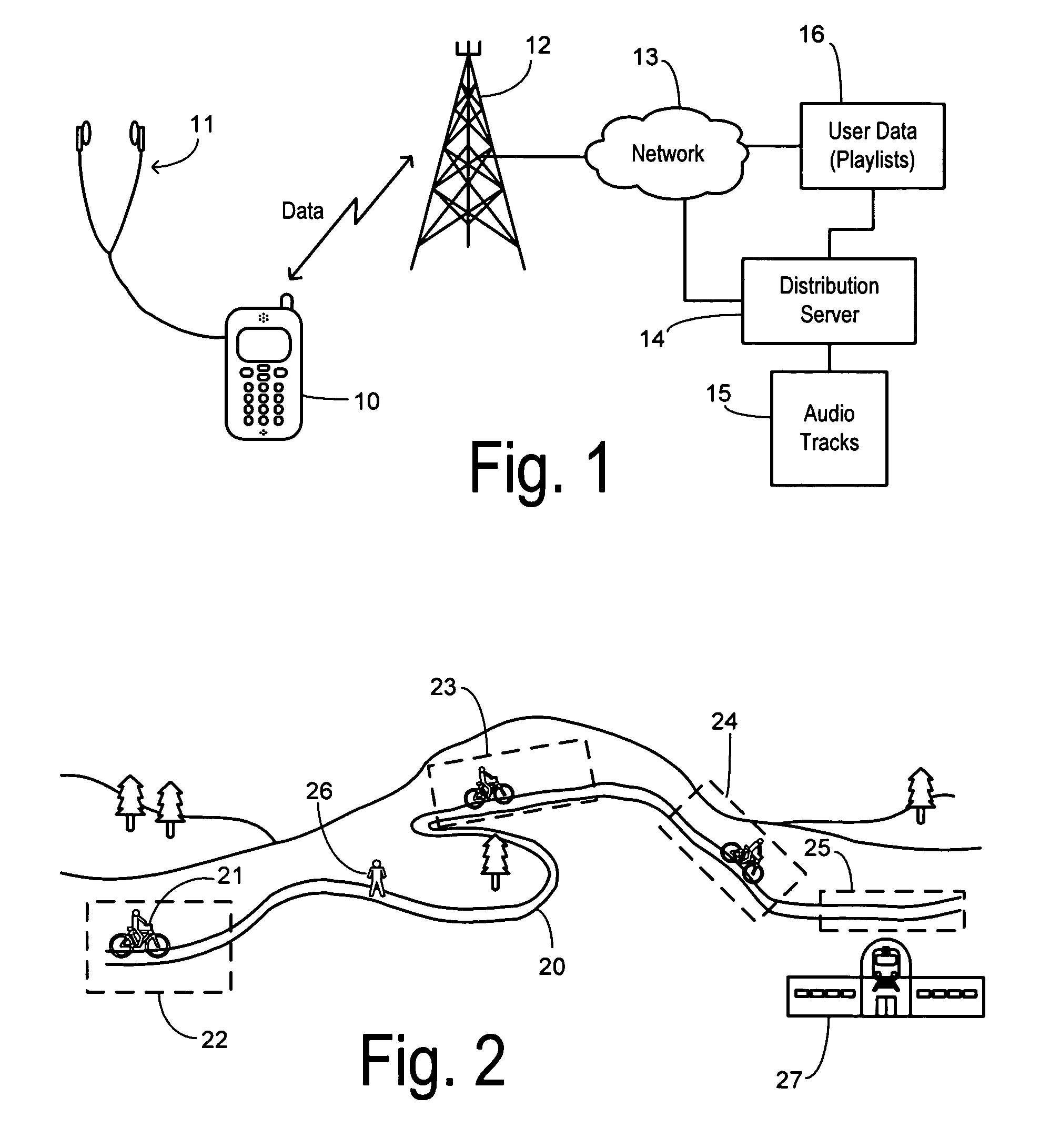
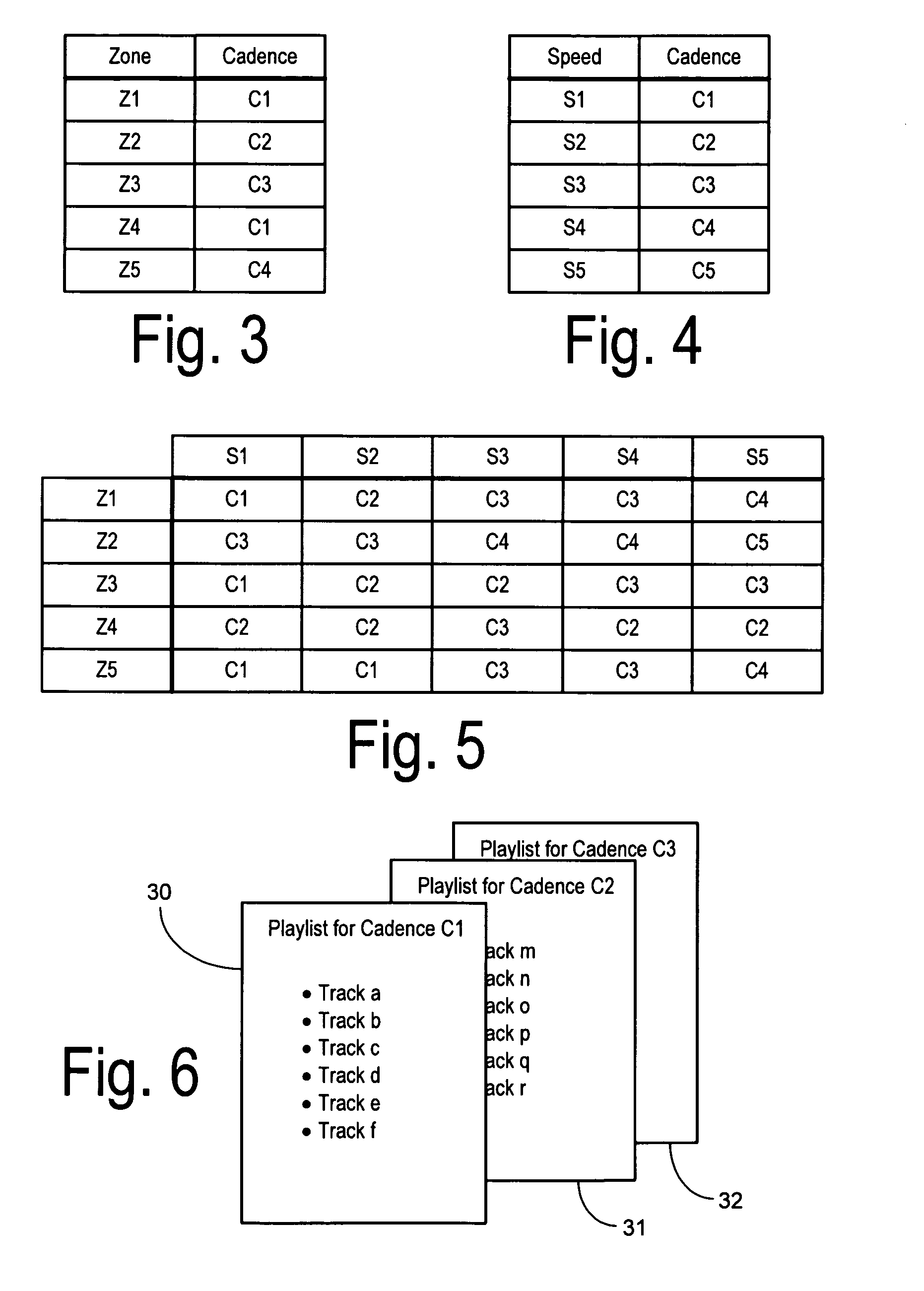
Network media service with track delivery adapted to a user cadence
InactiveUS8254829B1Digital data information retrievalSpecial service for subscribersNetwork mediaRhythm
A wireless network service delivers audio tracks to a user via a mobile wireless terminal. A server maintains a plurality of audio tracks, wherein each audio track is stored in conjunction with a respective cadence tag. A cadence evaluator identifies a substantially instantaneous user status and selects a cadence tag corresponding to the user status. The server streams a selected audio track having a cadence tag matching the selected cadence tag, and the mobile wireless terminal plays it back to the user. The cadence can be selected to match a desired pace of an athletic workout, a desired heart rate, or the particular geographic surroundings, for example.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
System and methods for use of voice mail and email in a mixed media environment
ActiveUS7812986B2Facilitate methodDigital data processing detailsAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingGeotargetingMedia server
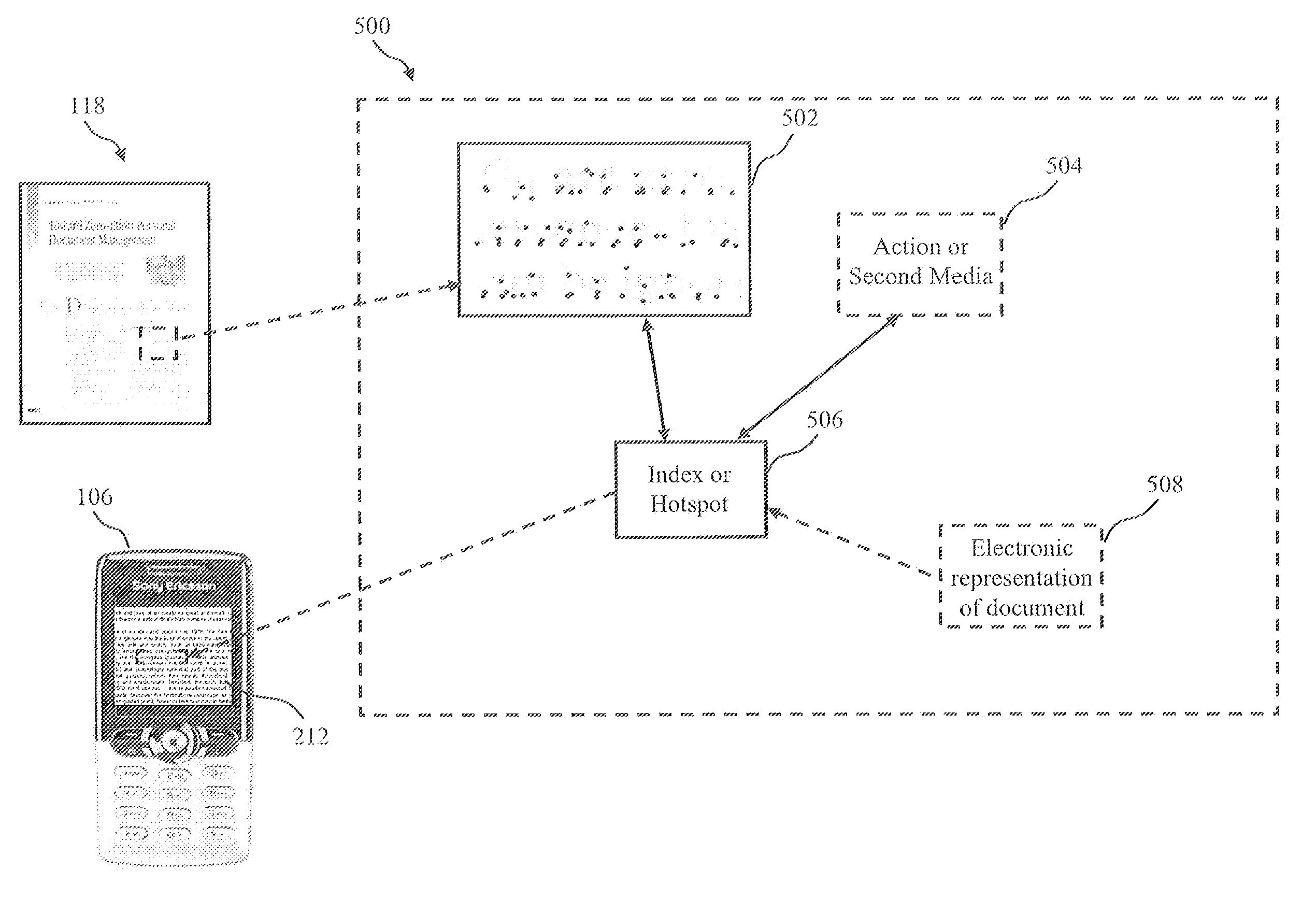
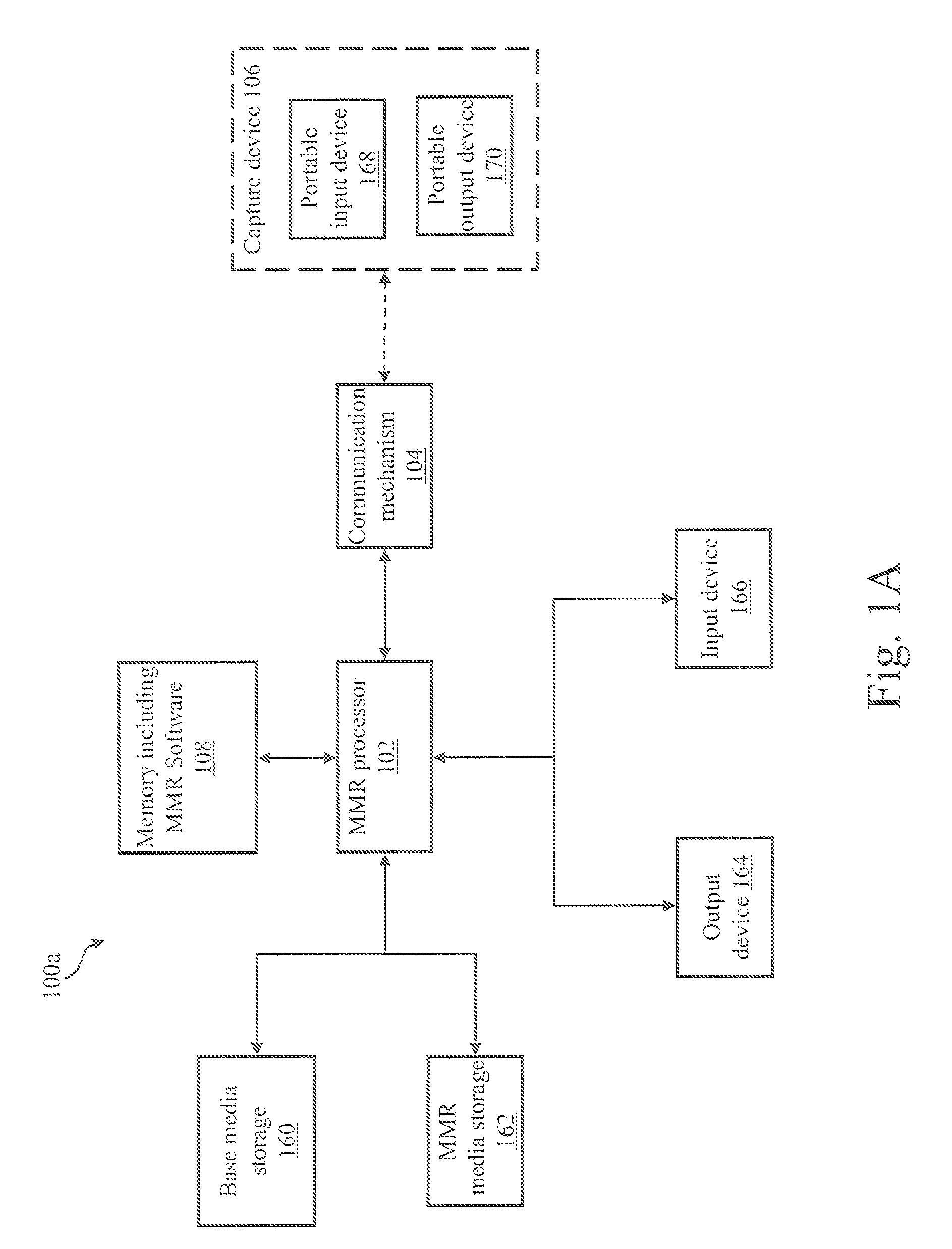
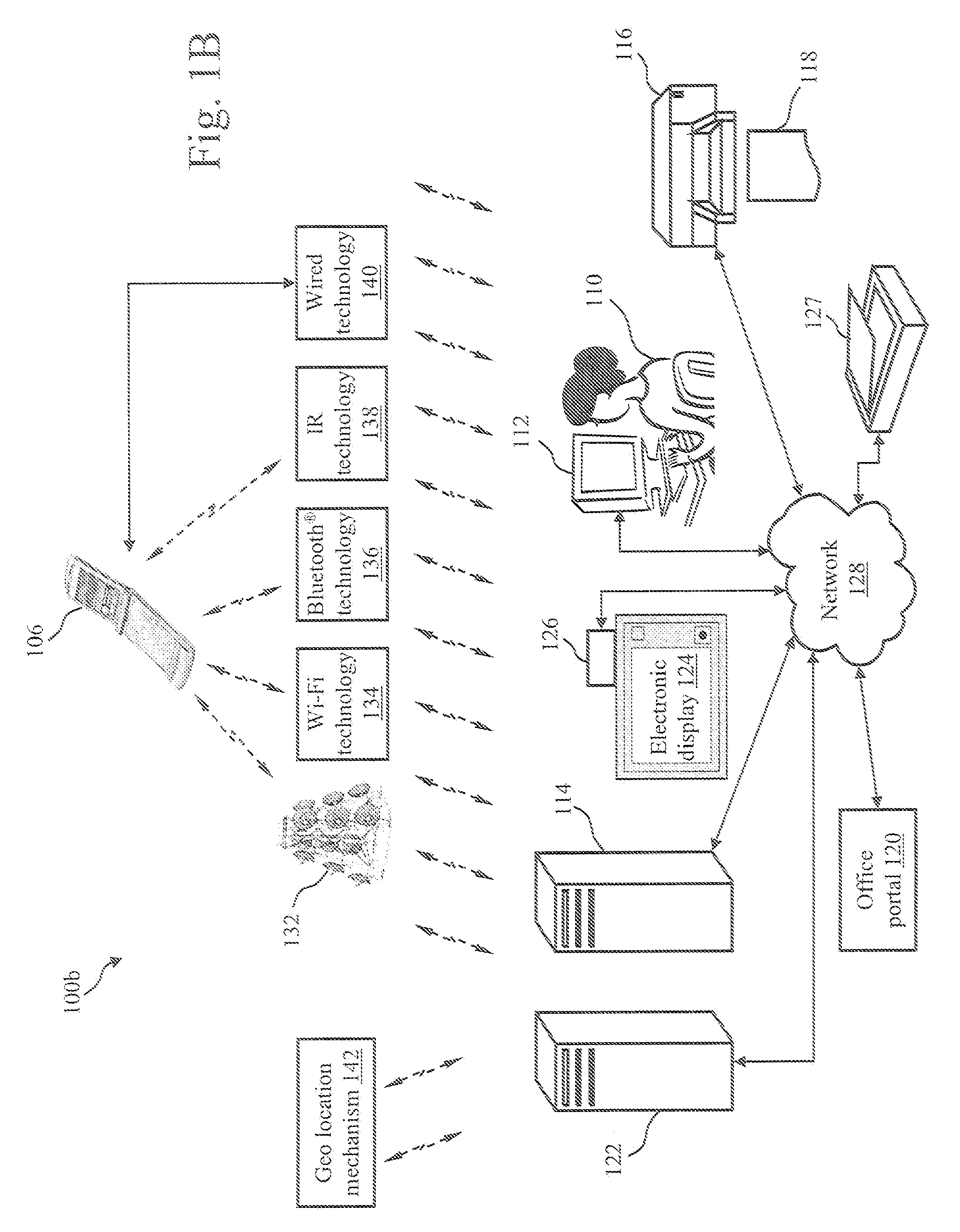
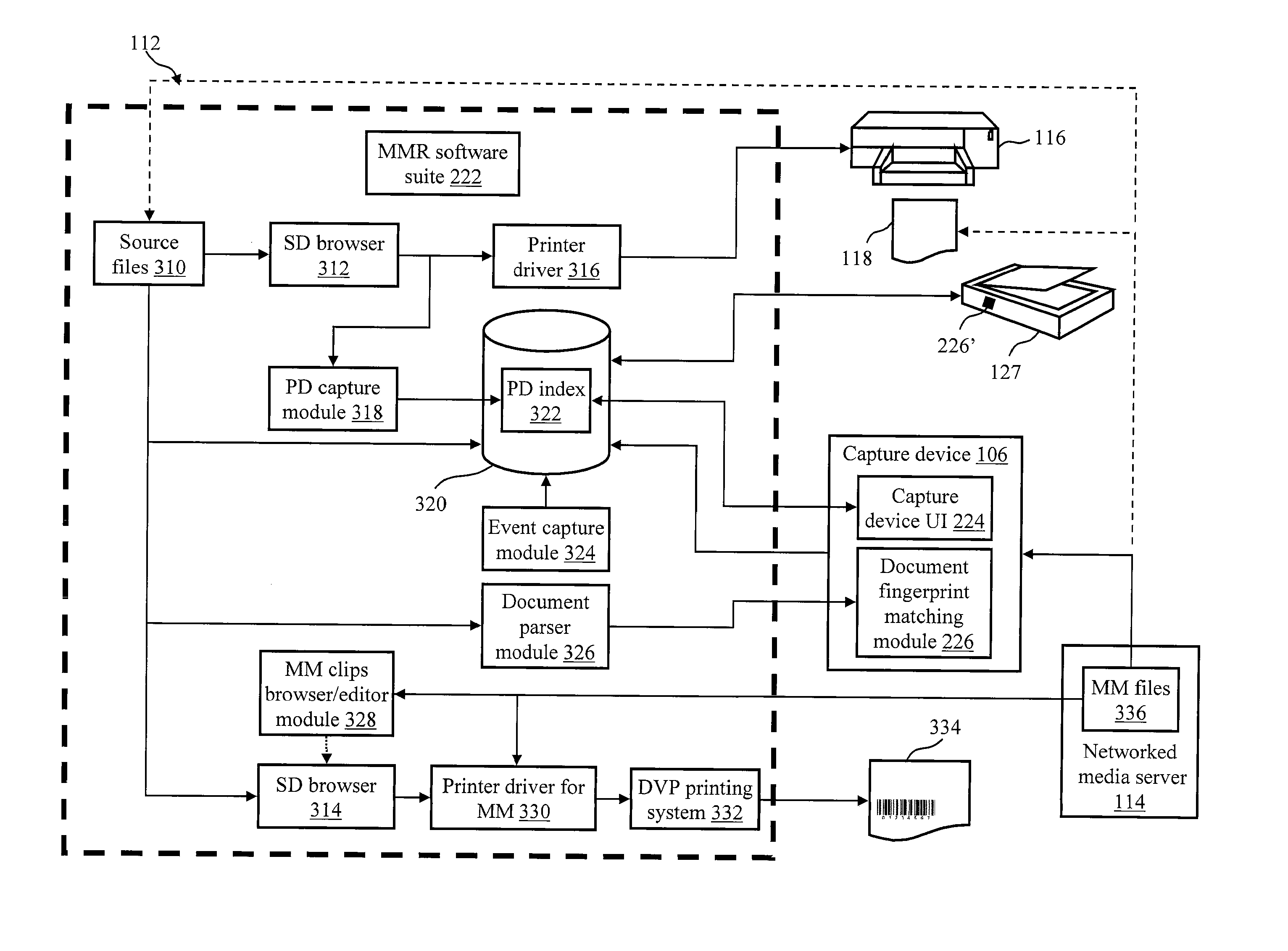
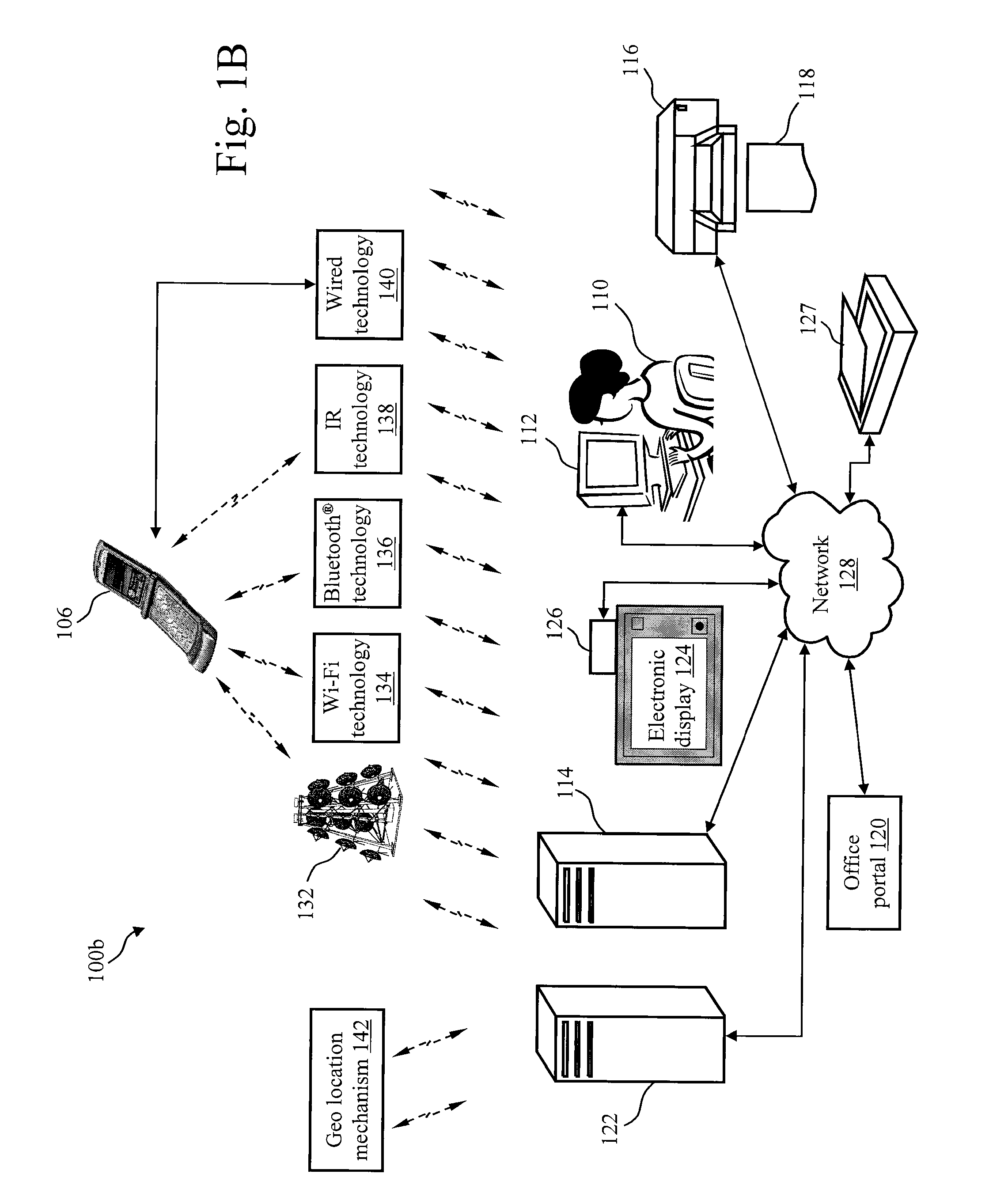
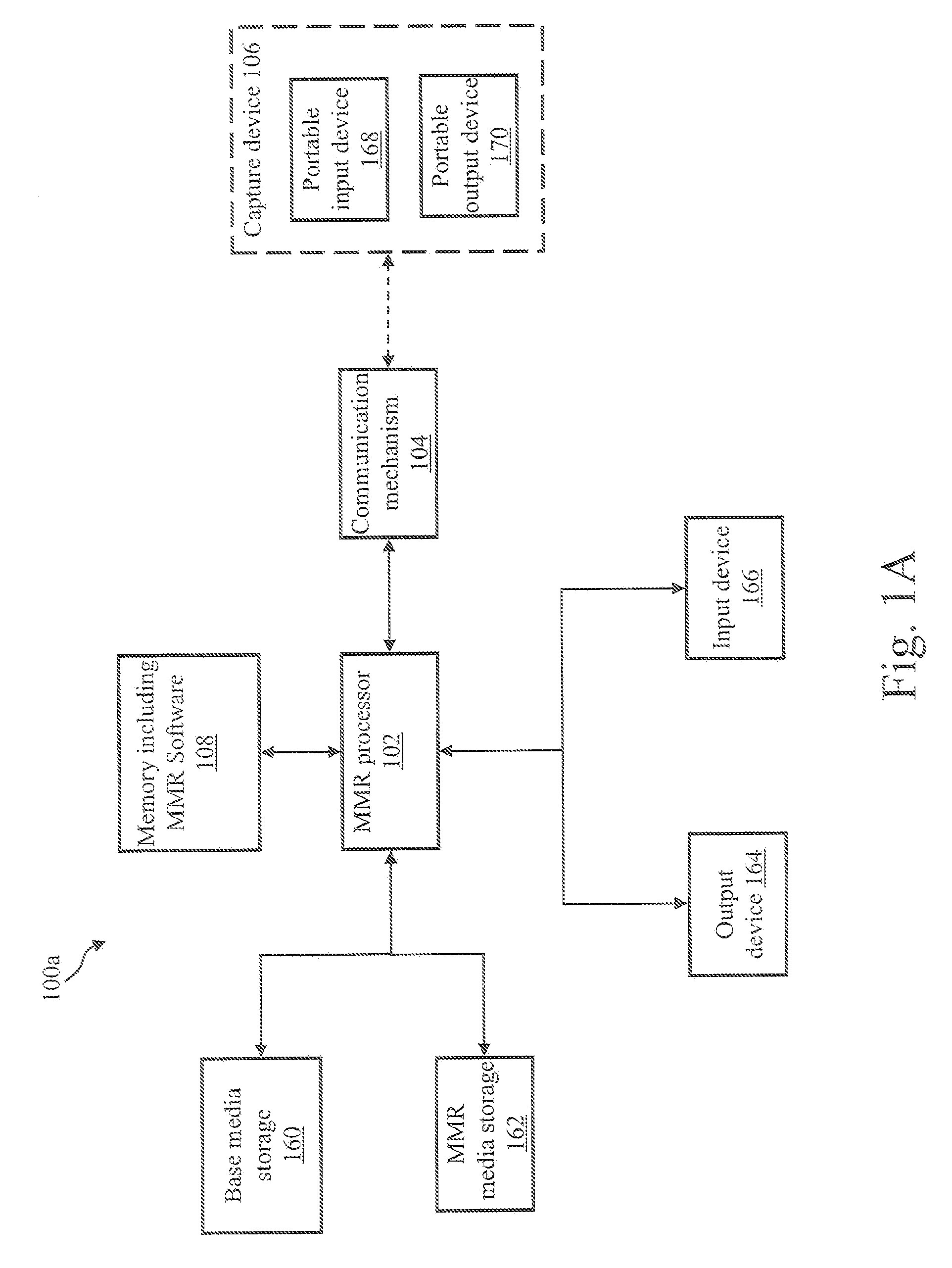
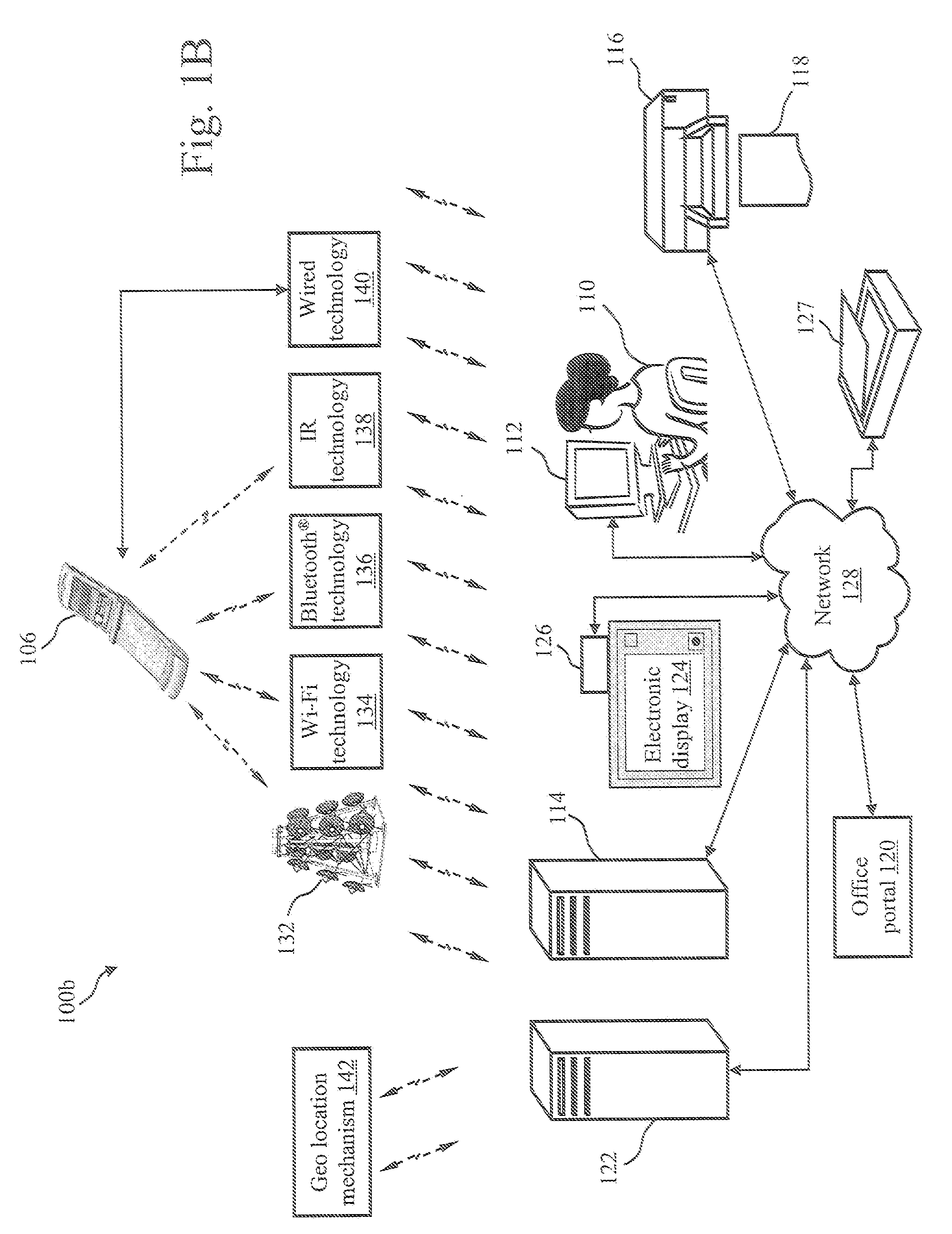
A mixed media reality (MMR) system includes an MMR user, a MMR computer, a user printer that produces a printed document, a networked media server, an office portal, a service provider server, an electronic display that is electrically connected to a set-top box, a document scanner, a network, a capture device, a cellular infrastructure, wireless fidelity (Wi-Fi) technology, Bluetooth® technology, infrared (IR) technology, wired technology, and a geo location mechanism. The MMR system provides mechanisms for forming a mixed media document that includes media of at least two types, such as printed paper as a first medium and a digital photograph, digital movie, digital audio file, or web link as a second medium. Furthermore, the MMR system facilitates business methods that take advantage of the combination of a portable electronic device, voice mail or email, and a paper document.
Owner:RICOH KK
System and methods for creation and use of a mixed media environment
ActiveUS20060285772A1Easy to optimizeFacilitate methodText processingInternal/peripheral component protectionCamera phoneComputer printing
A Mixed Media Reality (MMR) system and associated techniques are disclosed. The MMR system provides mechanisms for forming a mixed media document that includes media of at least two types (e.g., printed paper as a first medium and digital content and / or web link as a second medium). In one particular embodiment, the MMR system includes an MMR user, a MMR computer, a user printer that produces a printed document, a networked media server, an office portal, a service provider server, an electronic display that is electrically connected to a set-top box, a document scanner, a network, a capture device, a cellular infrastructure, wireless fidelity (Wi-Fi) technology, Bluetooth® technology, infrared (IR) technology, wired technology, and a geo location mechanism. The MMR system of the present invention provides mechanisms for forming a mixed media document that includes media of at least two types, such as printed paper as a first medium and a digital photograph, digital movie, digital audio file, or web link as a second medium. Furthermore, the MMR system of the present invention facilitates business methods that take advantage of the combination of a portable electronic device, such as a cellular camera phone, and a paper document.
Owner:RICOH KK
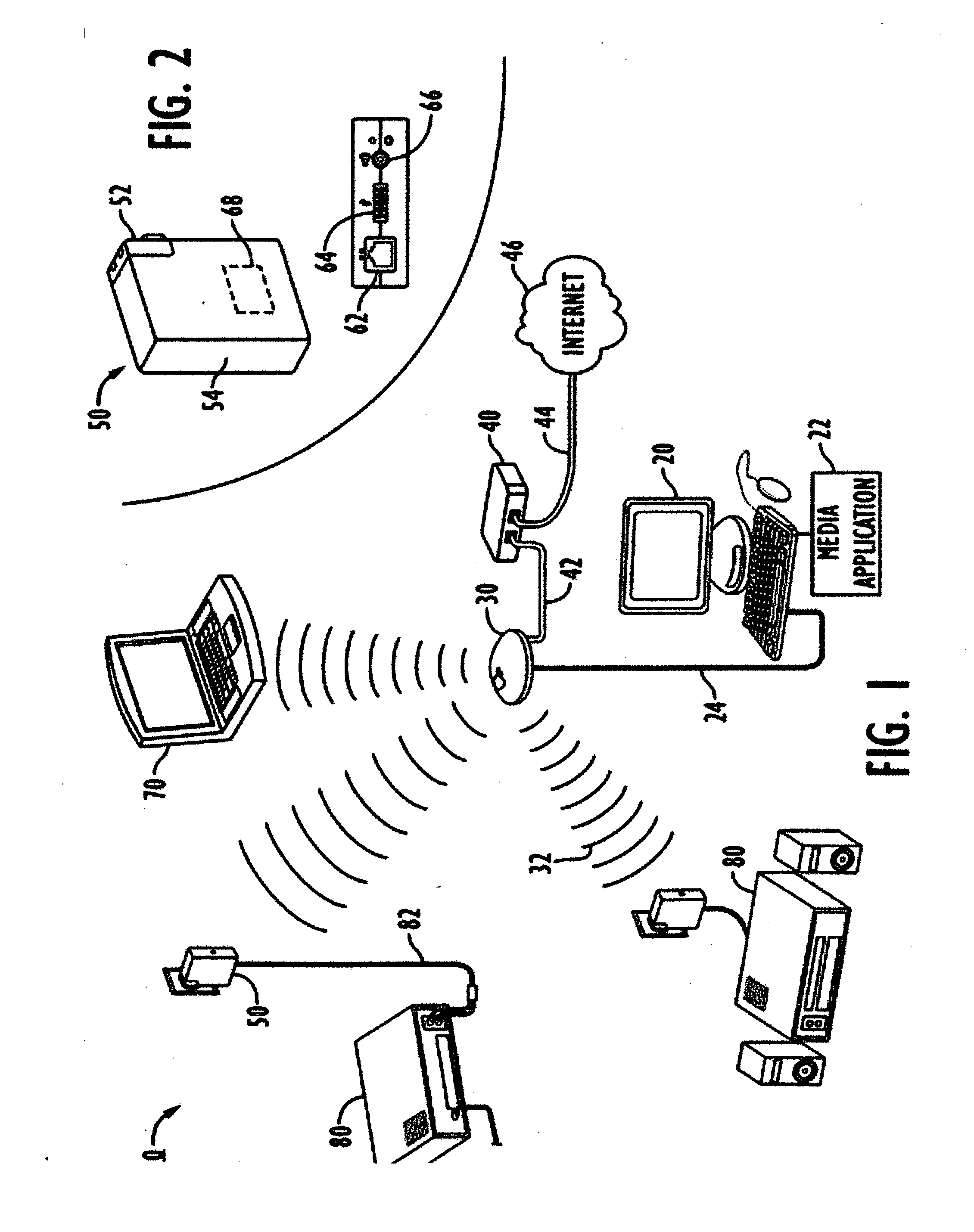
Method and apparatus for providing mobile and other intermittent connectivity in a computing environment
InactiveUS20060009213A1Take advantage ofEasy accessRepeater circuitsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile endNetwork address
A seamless solution transparently addresses the characteristics of nomadic systems, and enables existing network applications to run reliably in mobile environments. A Mobility Management Server coupled to the mobile network maintains the state of each of any number of Mobile End Systems and handles the complex session management required to maintain persistent connections to the network and to other peer processes. If a Mobile End System becomes unreachable, suspends, or changes network address (e.g., due to roaming from one network interconnect to another), the Mobility Management Server maintains the connection to the associated peer task—allowing the Mobile End System to maintain a continuous connection even though it may temporarily lose contact with its network medium. An interface-based listener uses network point of attachment information supplied by a network interface to determine roaming conditions and to efficiently reestablish connection upon roaming. The Mobility Management Server can distribute lists to Mobile End Systems specifying how to contact it over disjoint networks.
Owner:MOBILE SONIC INC
System and method for synchronizing media presentation at multiple recipients
ActiveUS20070250761A1Reduce impactAvoid user-perceivable echoSpecial service provision for substationDigital computer detailsTelecommunications linkNetwork communication
A network media delivery system includes client devices and a host device. Each client device has a network interface, an engine for processing media data, and a media interface. The host device, which can be a computer, establishes network communication links with the client devices, which can be networked media stations, and sends media data to the client devices. The media data can be sent wirelessly as packets of media data transmitted at intervals to each client device. In one embodiment, the host device controls processing of media data such that processed media is delivered in a synchronized manner at each of the client devices. In another embodiment, the host device controls processing of media data such that processed media is delivered in a synchronized manner at the host device and at least one client device.
Owner:APPLE INC
Systems and methods for authenticating communications in a network medium
InactiveUS20050100166A1Efficiently exchanging authentication credentialSimple and efficientDigital data processing detailsMilling cuttersProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessNetwork media
A location-limited channel is implemented using physical exchanges of physical tokens. The physical tokens are implemented using writeable or re-writeable storage media. Location-limited channels, when used to implement pre-authentication protocols, provide demonstrative identification and authenticity. A group originator loads pre-authentication information and a network location from a communication device onto the location-limited physical token channel. The location-limited physical token channel is passed to another participant, who copies the originator's pre-authentication information and location onto that participant's communication device. That participant then adds that participant's own pre-authentication information and network location onto the location-limited physical token channel. This is repeated until the last participant passes the location-limited physical token channel back to the group originator. The originator thus has pre-authentication information and network locations for all other participants. The originator establishes secure communications with each participant based on the originator' and that participant's shared information.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Mobile networking system and method
ActiveUS20060123079A1Take advantage ofEasy accessMultiple digital computer combinationsWireless network protocolsMobile endNetwork address
A seamless solution transparently addresses the characteristics of nomadic systems, and enables existing network applications to run reliably in mobile environments. A Mobility Management Server coupled to the mobile network maintains the state of each of any number of Mobile End Systems and handles the complex session management required to maintain persistent connections to the network and to other peer processes. If a Mobile End System becomes unreachable, suspends, or changes network address (e.g., due to roaming from one network interconnect to another), the Mobility Management Server maintains the connection to the associated peer task—allowing the Mobile End System to maintain a continuous connection even though it may temporarily lose contact with its network medium. An interface-based listener uses network point of attachment information supplied by a network interface to determine roaming conditions and to efficiently reestablish connection upon roaming. The Mobility Management Server can distribute lists to Mobile End Systems specifying how to contact it over disjoint networks. Architectures are provided for bridging between IPv4 and IPv6 Internet Protocols.
Owner:MOBILE SONIC INC
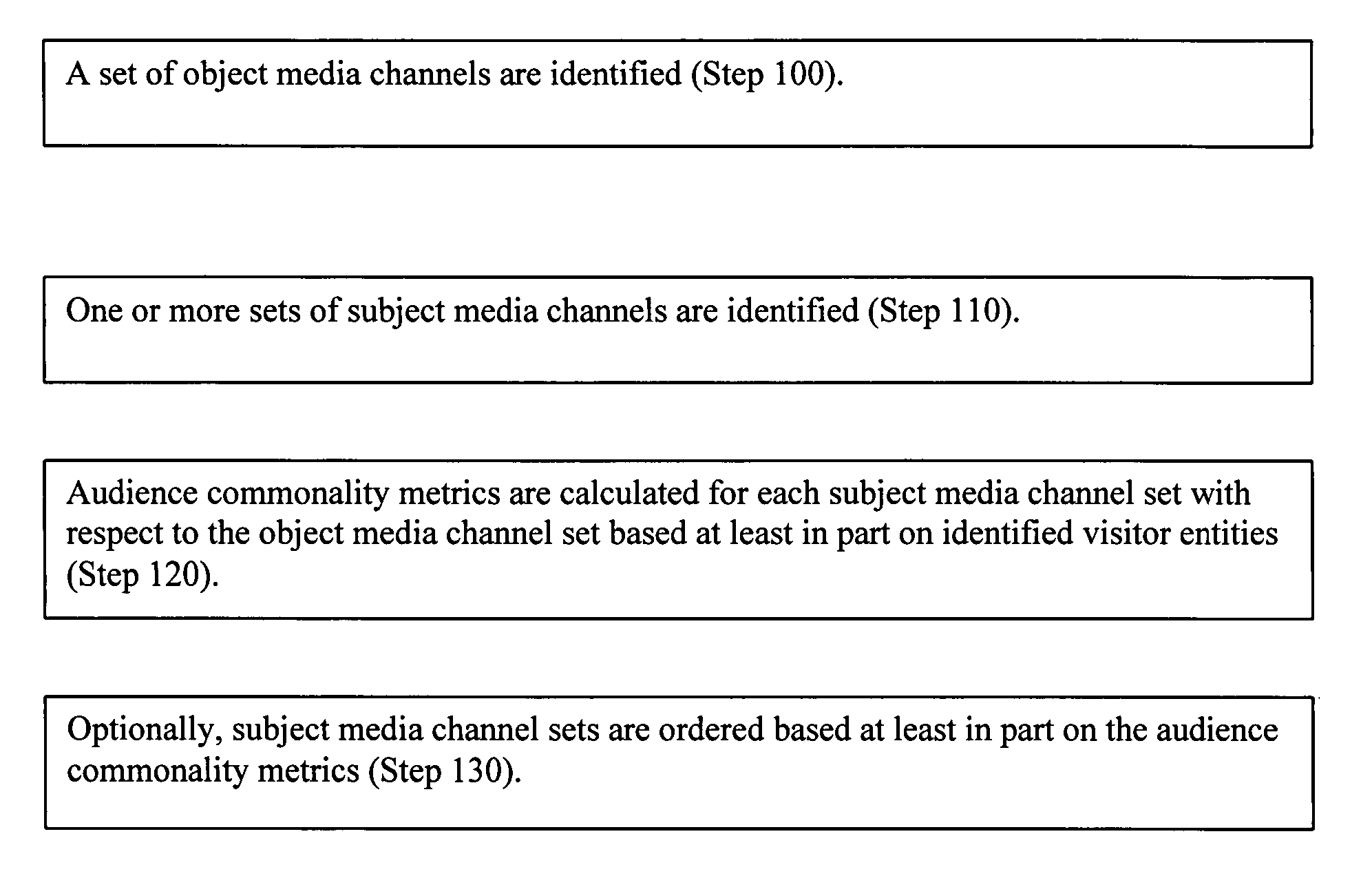
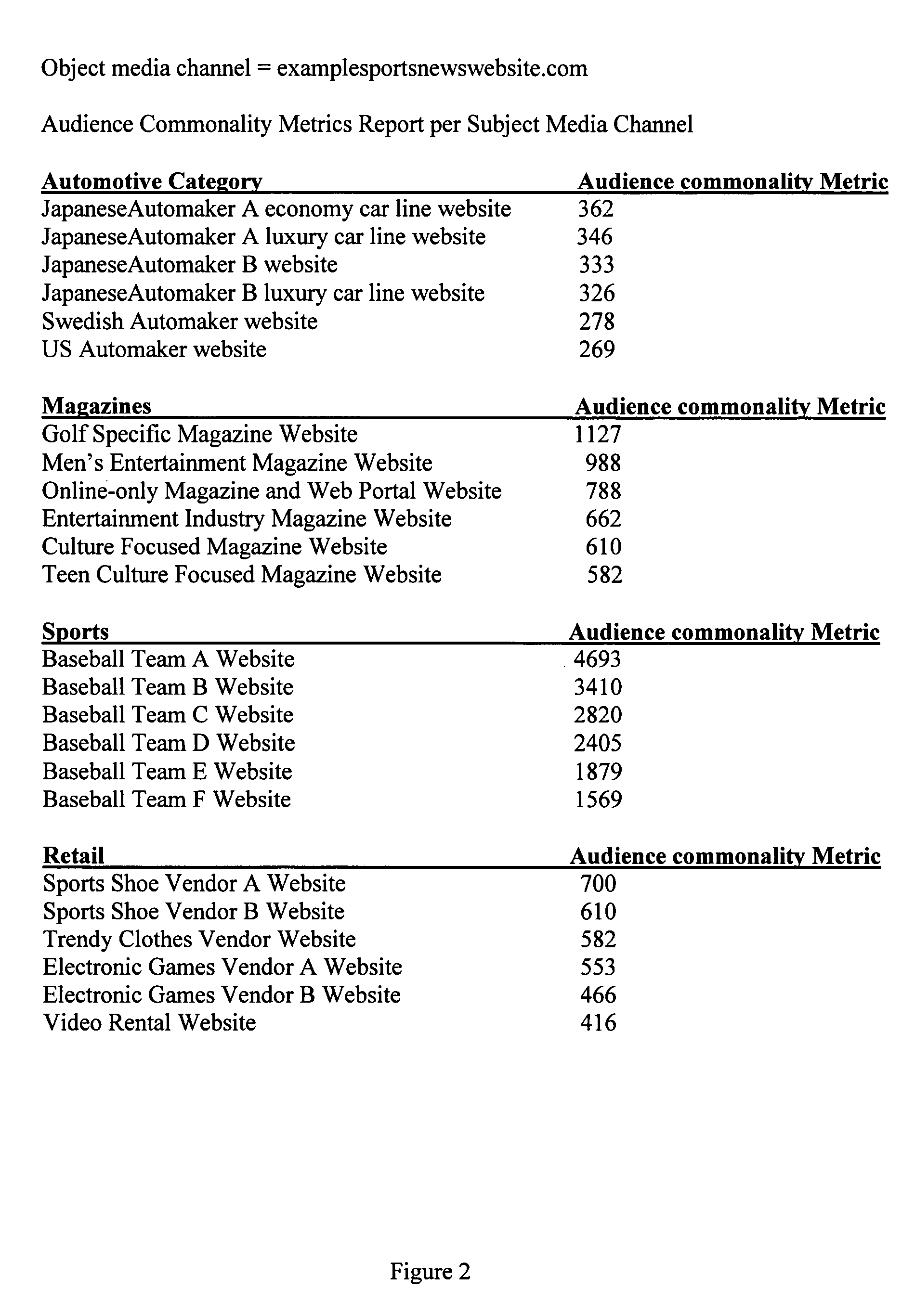
Audience commonality and measurement
InactiveUS20080086741A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast information monitoringNetwork activityClient agent
Audience commonality metrics for characterizing the relationship between networked media channels based on audience overlap of identified visitor entities and their related media consumption histories. Audience commonality metrics may be scalars or multi-dimensional metrics and may take into account and / or be used in conjunction with data related to on- or off-network media channels, on- or off-network activities, sociographics and / or demographics. The current invention may be used in the design of networked advertising campaigns, identification of new or unusual market segments and / or valuation of media buys. A system according to the current invention comprises access to a configuration, an input for receiving audience commonality data, an audience commonality metrics engine and an output for providing calculated audience commonality metrics. Data related to identified visitor entities may be received, determined and / or inferred from resources such as a cookie, log file, sniffer, firewall, proxy server, client agent, tracking pixel and / or tool
Owner:QUANTCAST CORP
Method and apparatus for providing mobile and other intermittent connectivity in a computing environment
ActiveUS20050223115A1Reduce network trafficMaximum performanceError preventionConnection managementMobile endNetwork address
A seamless solution transparently addresses the characteristics of nomadic systems, and enables existing network applications to run reliably in mobile environments. The solution extends the enterprise network, letting network managers provide mobile users with easy access to the same applications as stationary users without sacrificing reliability or centralized management. The solution combines advantages of existing wire-line network standards with emerging mobile standards to create a solution that works with existing network applications. A Mobility Management Server coupled to the mobile network maintains the state of each of any number of Mobile End Systems and handles the complex session management required to maintain persistent connections to the network and to other peer processes. If a Mobile End System becomes unreachable, suspends, or changes network address (e.g., due to roaming from one network interconnect to another), the Mobility Management Server maintains the connection to the associated peer task—allowing the Mobile End System to maintain a continuous connection even though it may temporarily lose contact with its network medium. In one example, Mobility Management Server communicates with Mobile End Systems using Remote Procedure Call and Internet Mobility Protocols.
Owner:MOBILE SONIC INC
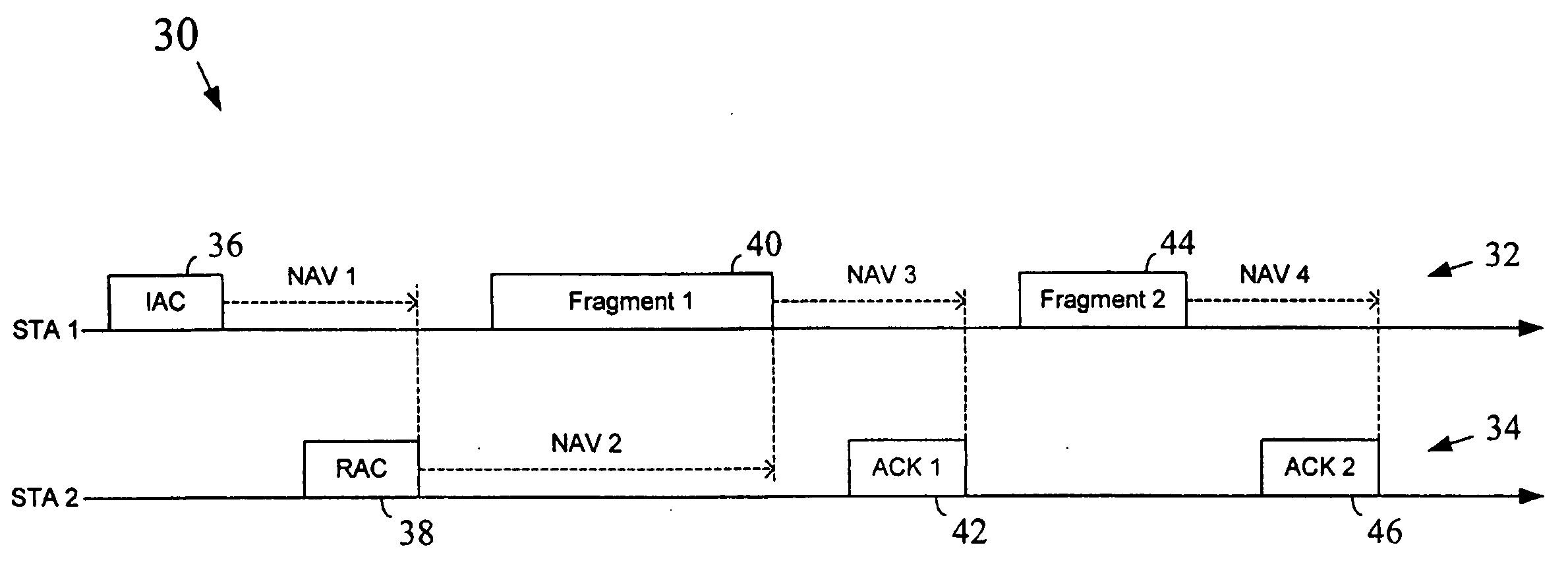
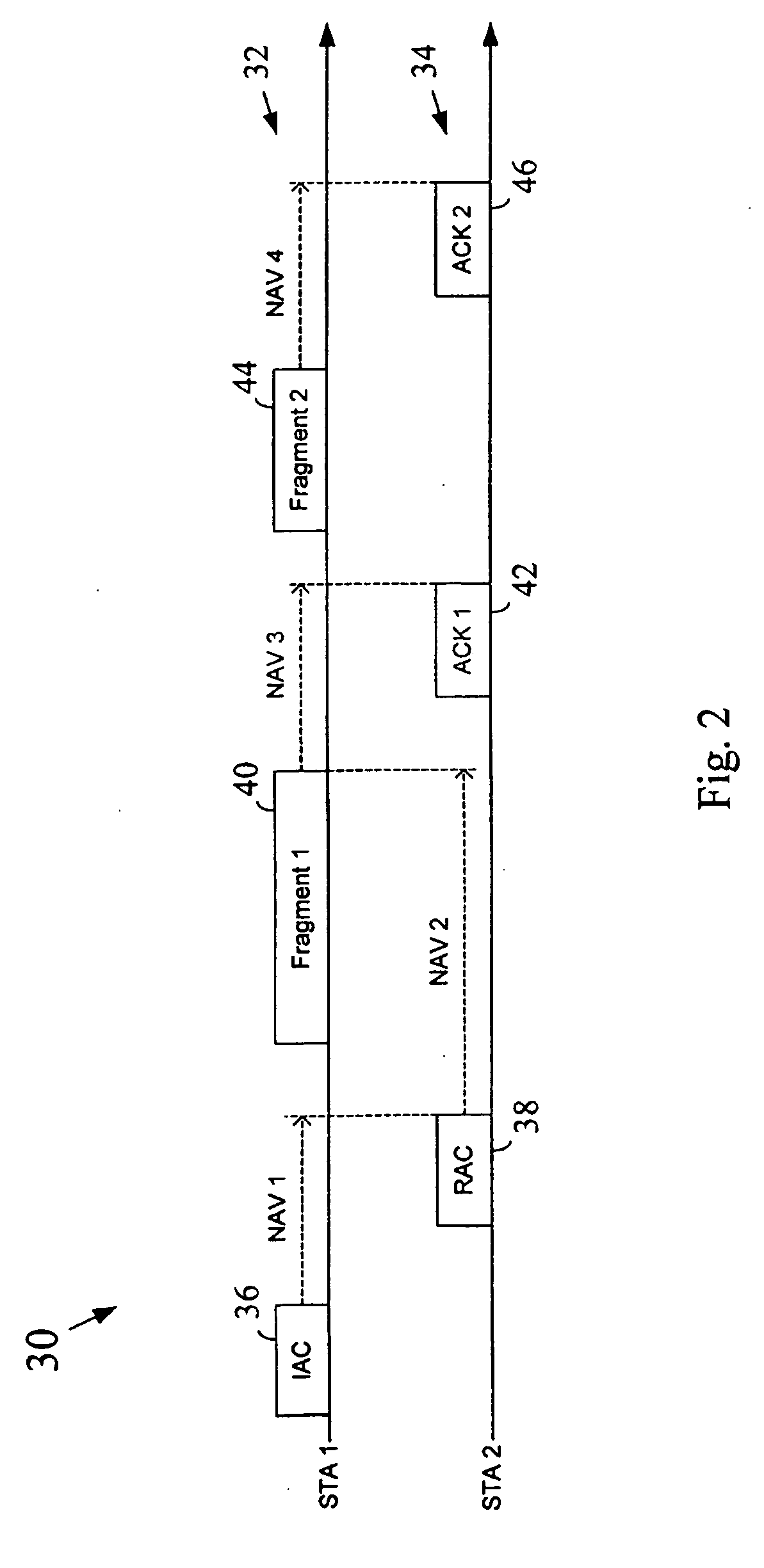
Method and apparatus to perform network medium reservation in a wireless network
InactiveUS20060187964A1Network traffic/resource managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork mediaSelf adaptive
Techniques and structures are provided to support a short-NAV type wireless medium reservation scheme in a network that utilizes adaptive modulation techniques.
Owner:INTEL CORP
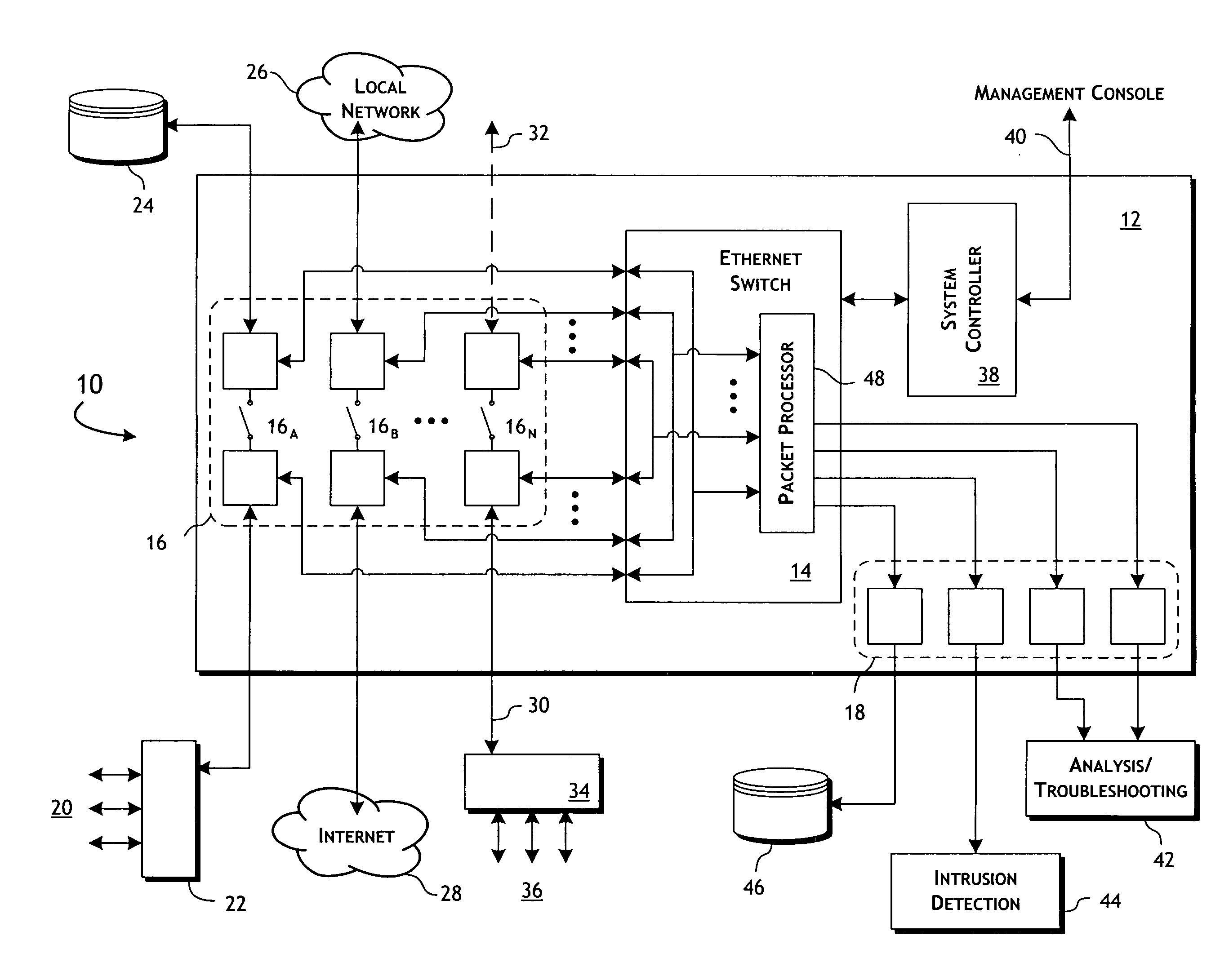
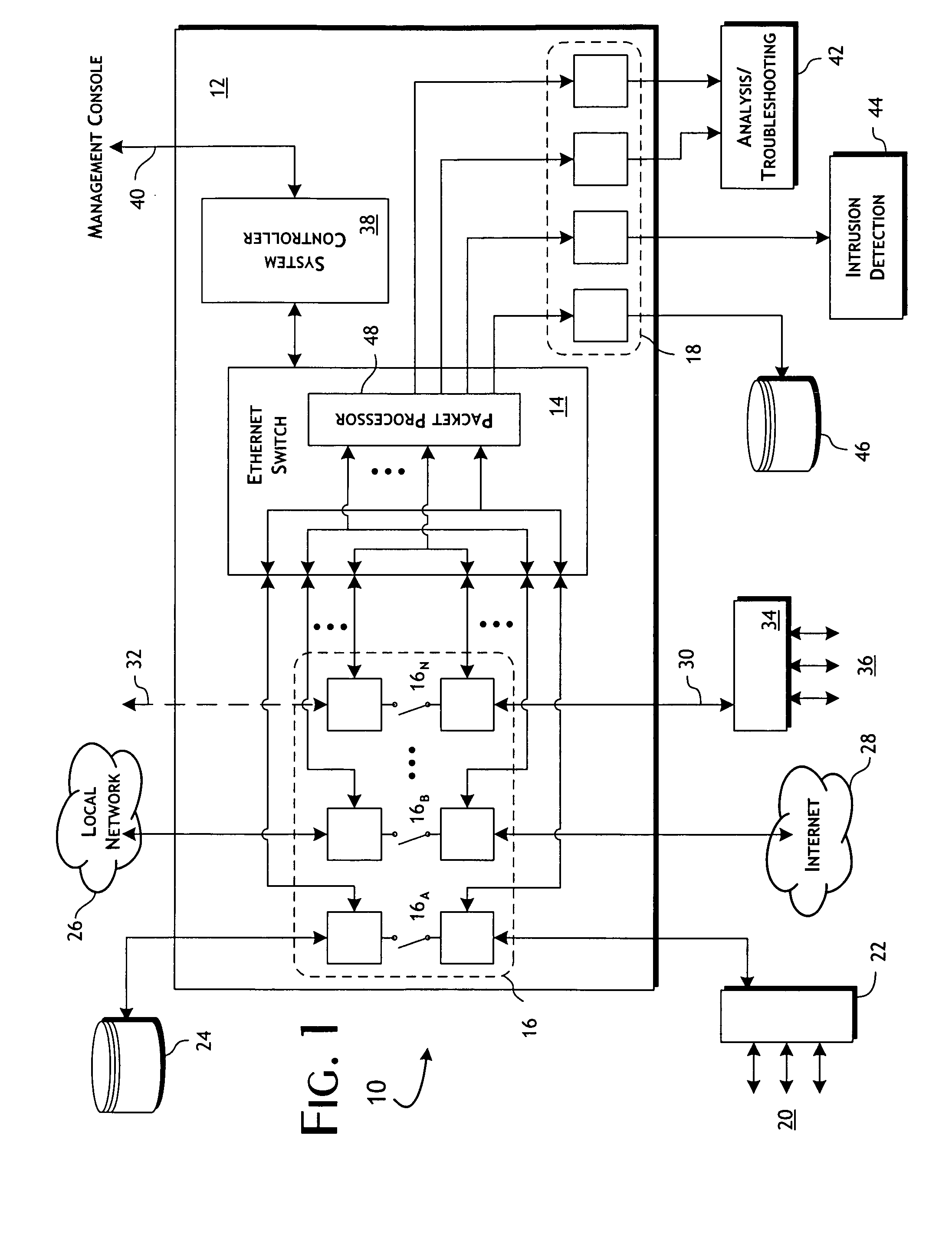
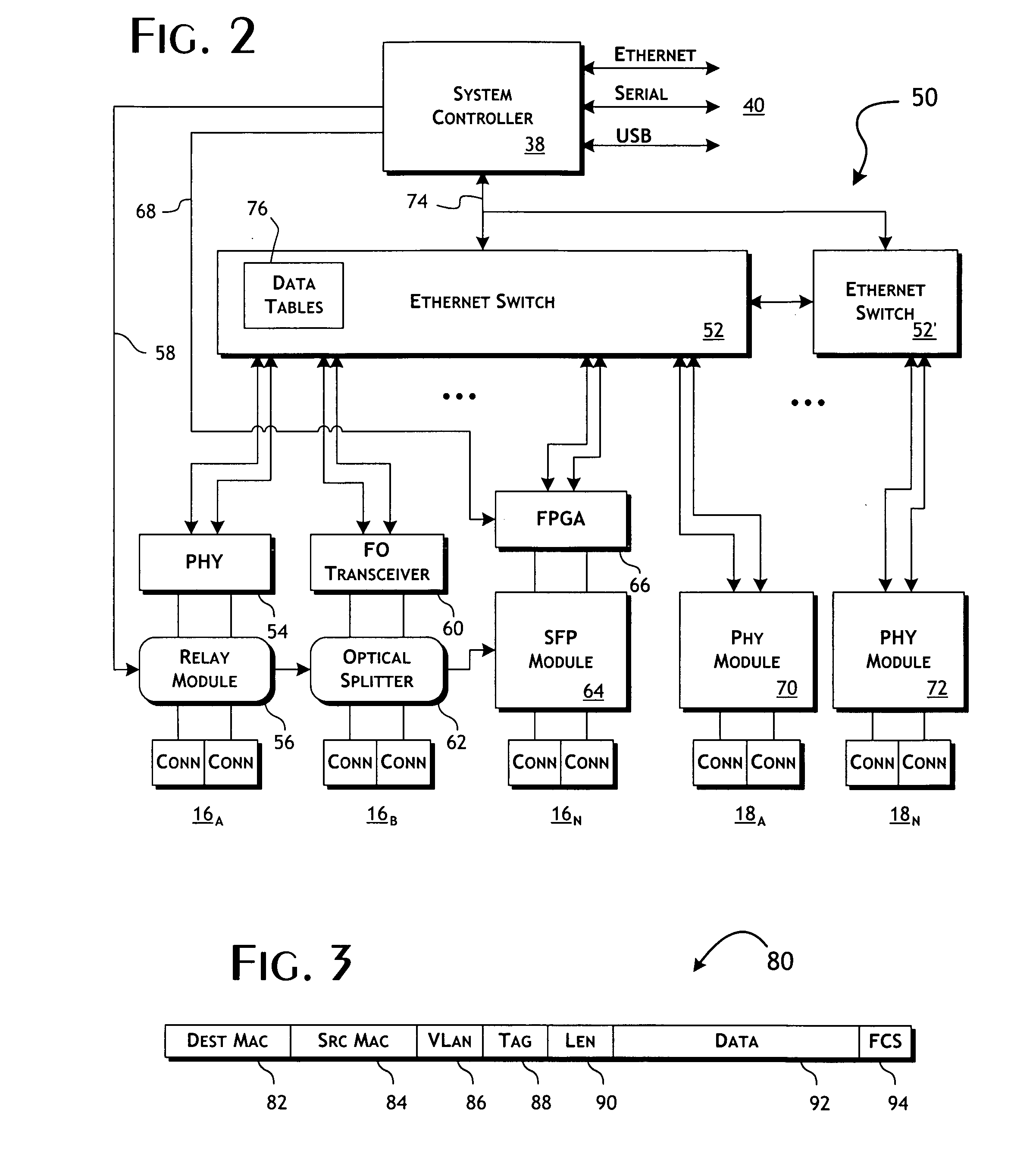
Ethernet switch-based network monitoring system and methods
ActiveUS20090303883A1Preserve integrityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData streamMulti port
A network data monitoring device provides for the flexible, programmable port-to-multi-port steering of data packet traffic between network port pairs, with tap data streams being directed to any of a plurality of monitor ports. The network data monitoring device is constructed utilizing one or more switching integrated circuits programmed to disable layer-2 routing and impose port-to-multiport data packet steering. Physical layer protocol encoding / decoding circuits enable connectivity to physical network media connectors though a system of fail-safe relays. A system controller, preferably implemented by a microprocessor, is connected to all switching integrated circuits and relays for configuration, status and control. Hardware-based logic selectively in complement to the switching integrated circuits provides for the programmable filtering, modification and programmable steering of data packets through the device.
Owner:NETSCOUT SYSTEMS
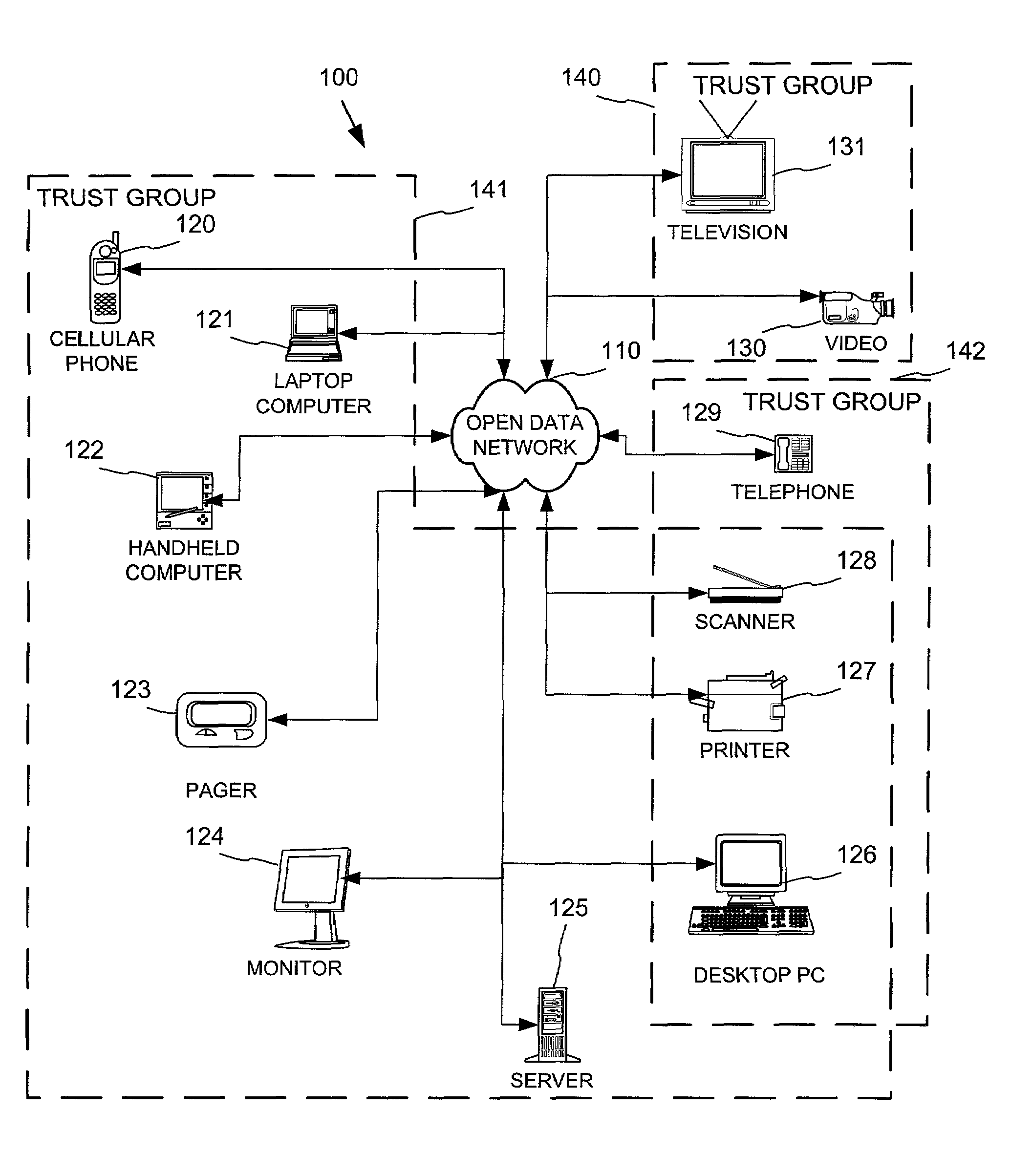
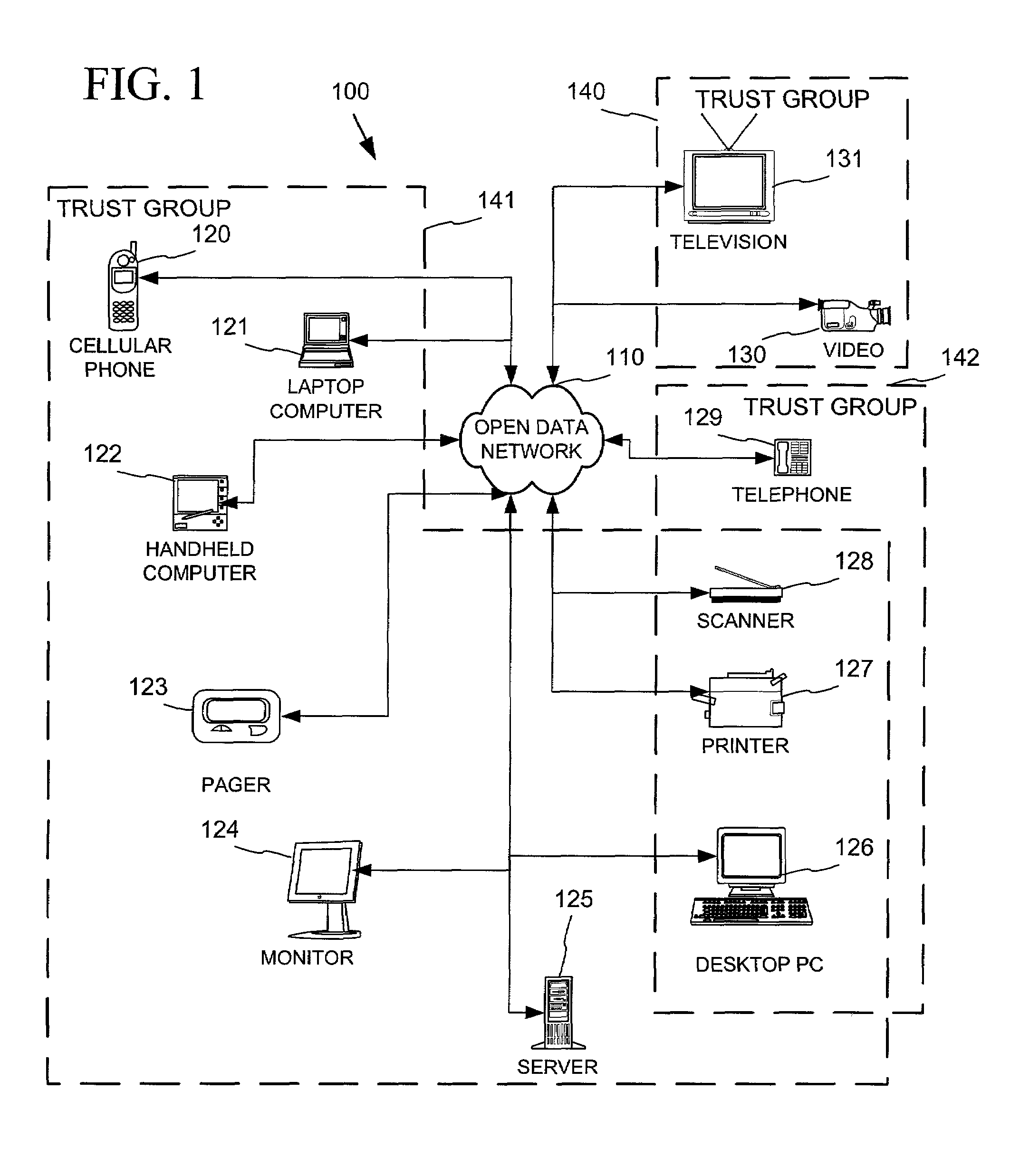
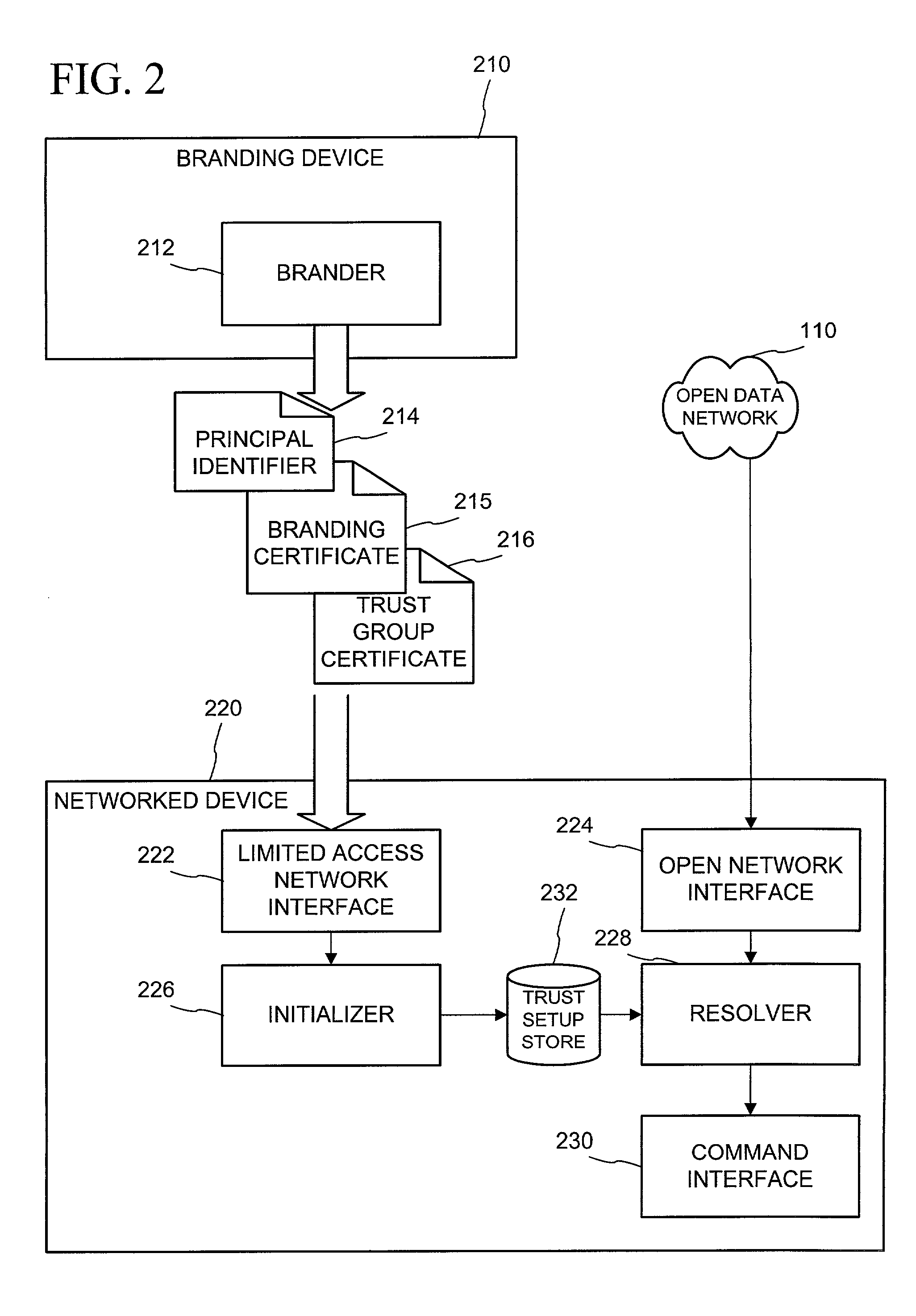
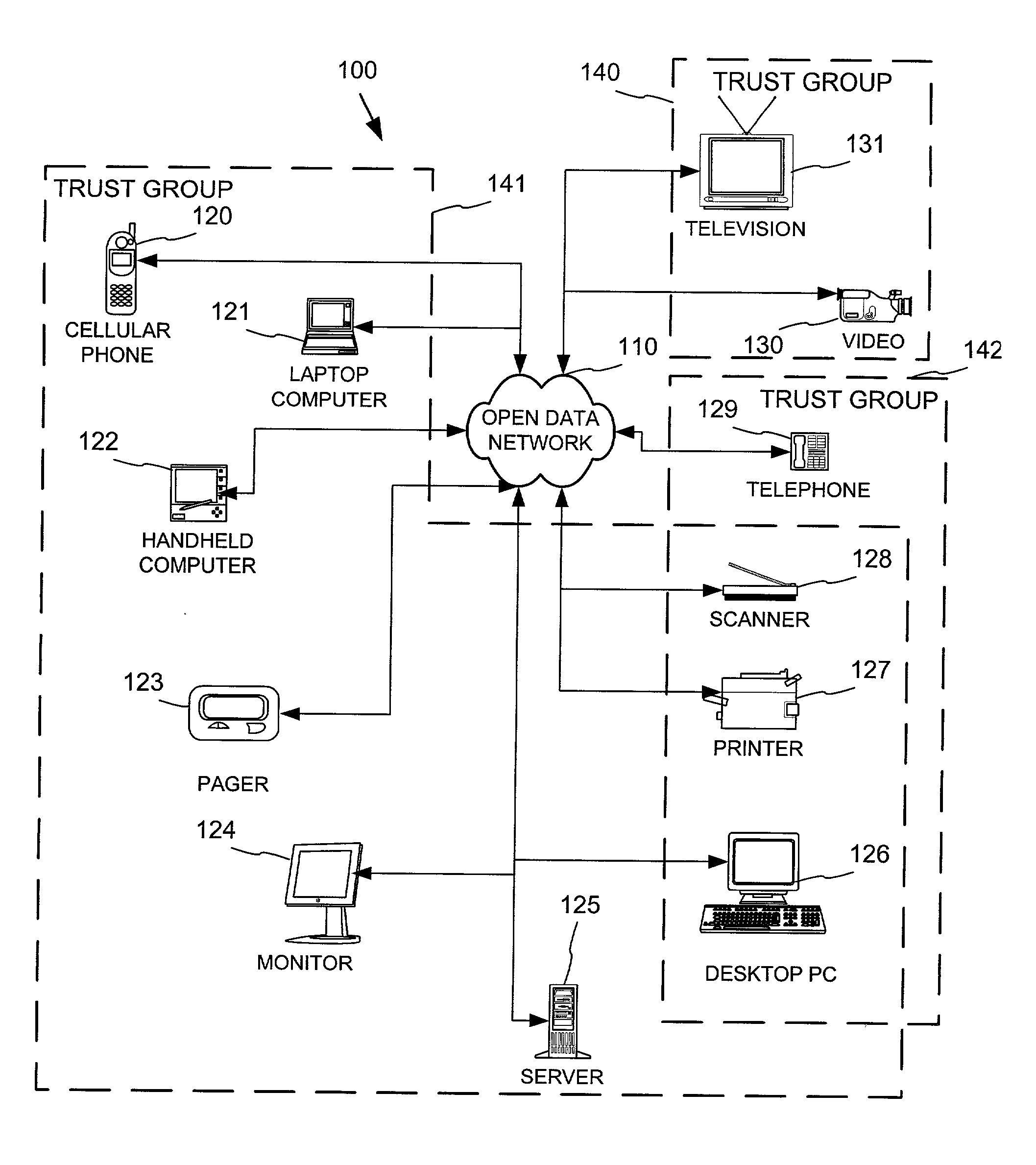
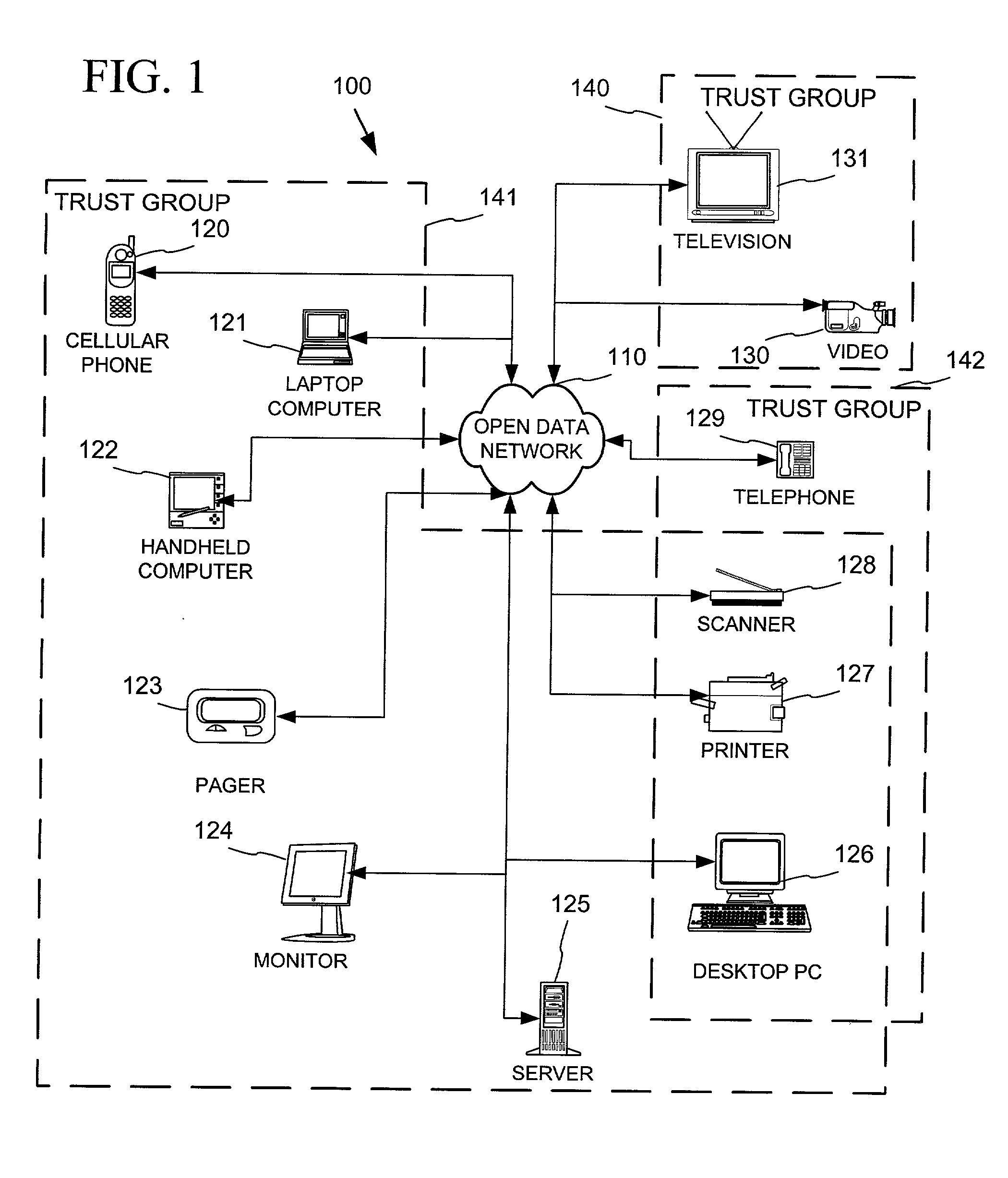
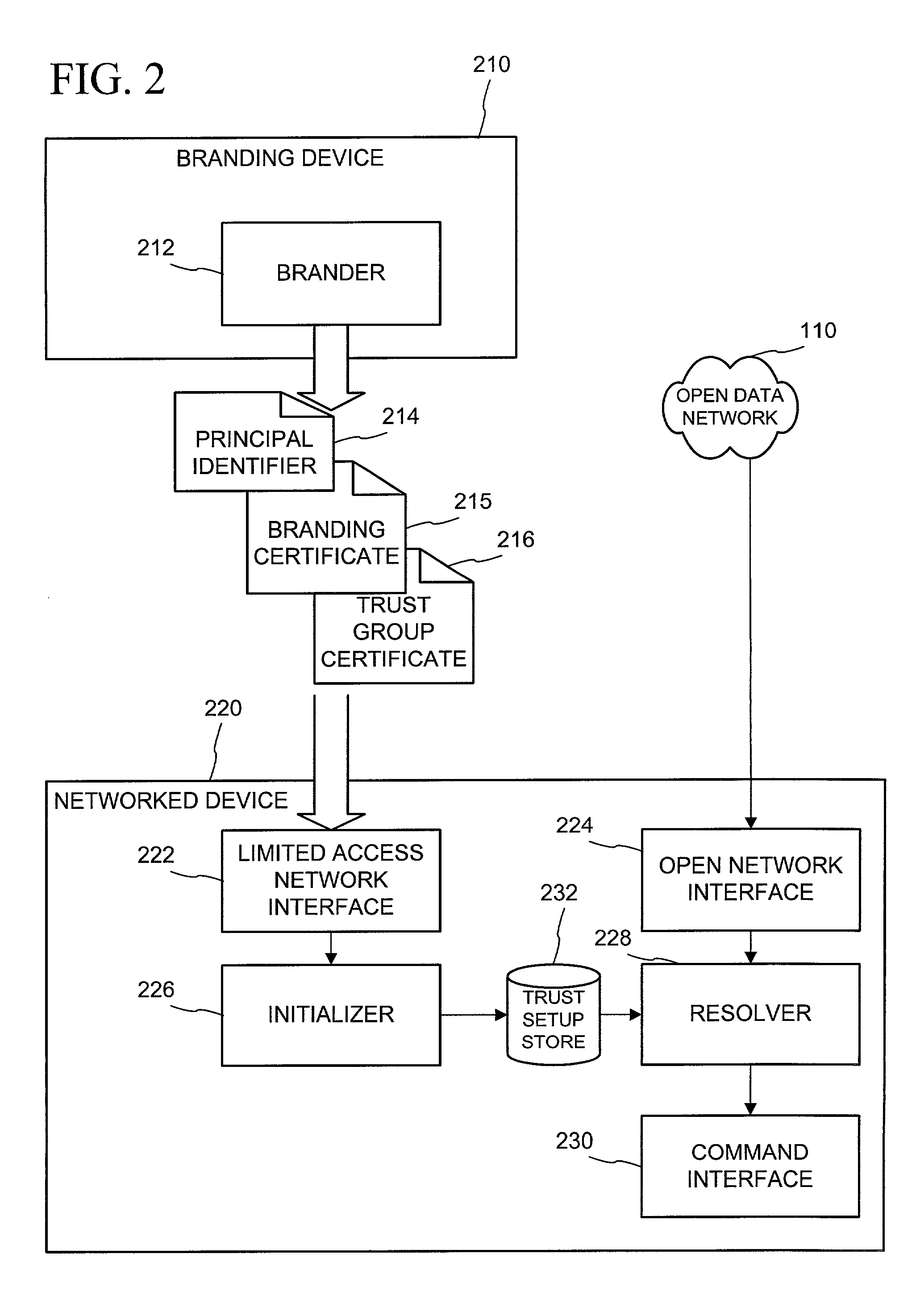
Networked device branding for secure interaction in trust webs on open networks
InactiveUS7500104B2CostSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesDigital data processing detailsLimited accessNetwork media
A branding process provides a networked computing device with initial set up information, including a name, a public / private key pair, and a set of certificates the device will need to inter-operate with other devices in the trust group. A branding device conveys the initial set-up information to the networked computing device via a limited access network interface, or alternatively via a broadcast network media with the device enclosed in a wave guide and / or Faraday cage. The networked computing device can then use the set up information to verify that other devices on the network that seek to interact with the device are also members of the trust group, with which networked computing device can interact.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
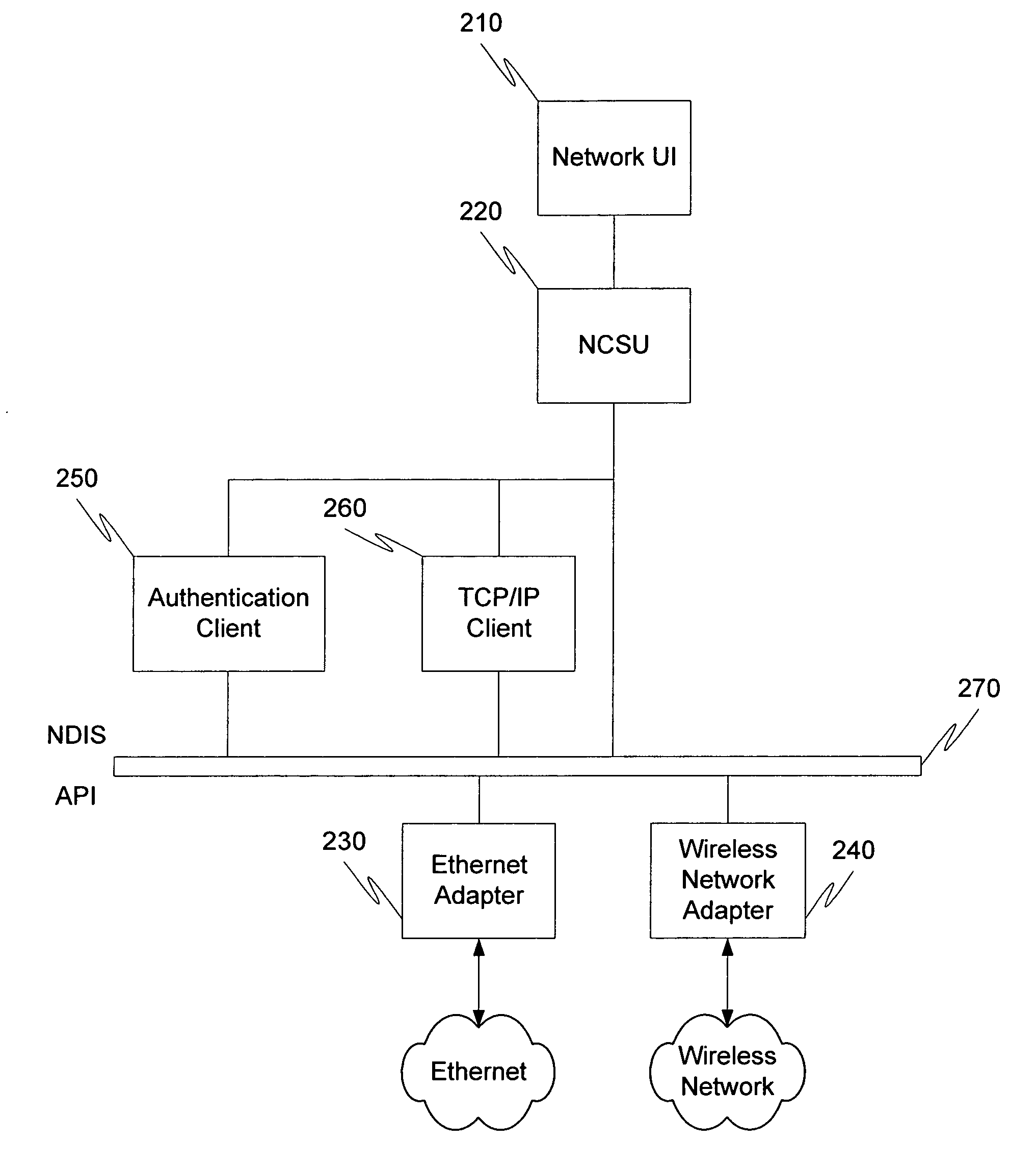
System, method and user interface for network status reporting
ActiveUS20060026289A1Connection managementMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionIp address
A method and user interface for informing a user of the status of a network connection are provided. Conventionally, the “connected” icon in the system tray only informs the user that the computer is linked to a network medium, such as an Ethernet or wireless access point. This icon does not indicate whether a routable IP address has been obtained. In this invention, an icon is used to inform the user that the network connection is disabled, connecting, connected (routable IP address obtained), or in a warning state. The warning state indicates that a non-routable IP address (e.g. autonet address) has been obtained, which will likely be unsatisfactory to the user. However, when connected to an 802.11 ad-hoc network, or when IP status checking is disabled, a non-routable IP address is deemed acceptable, and thus the “connected” icon is displayed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
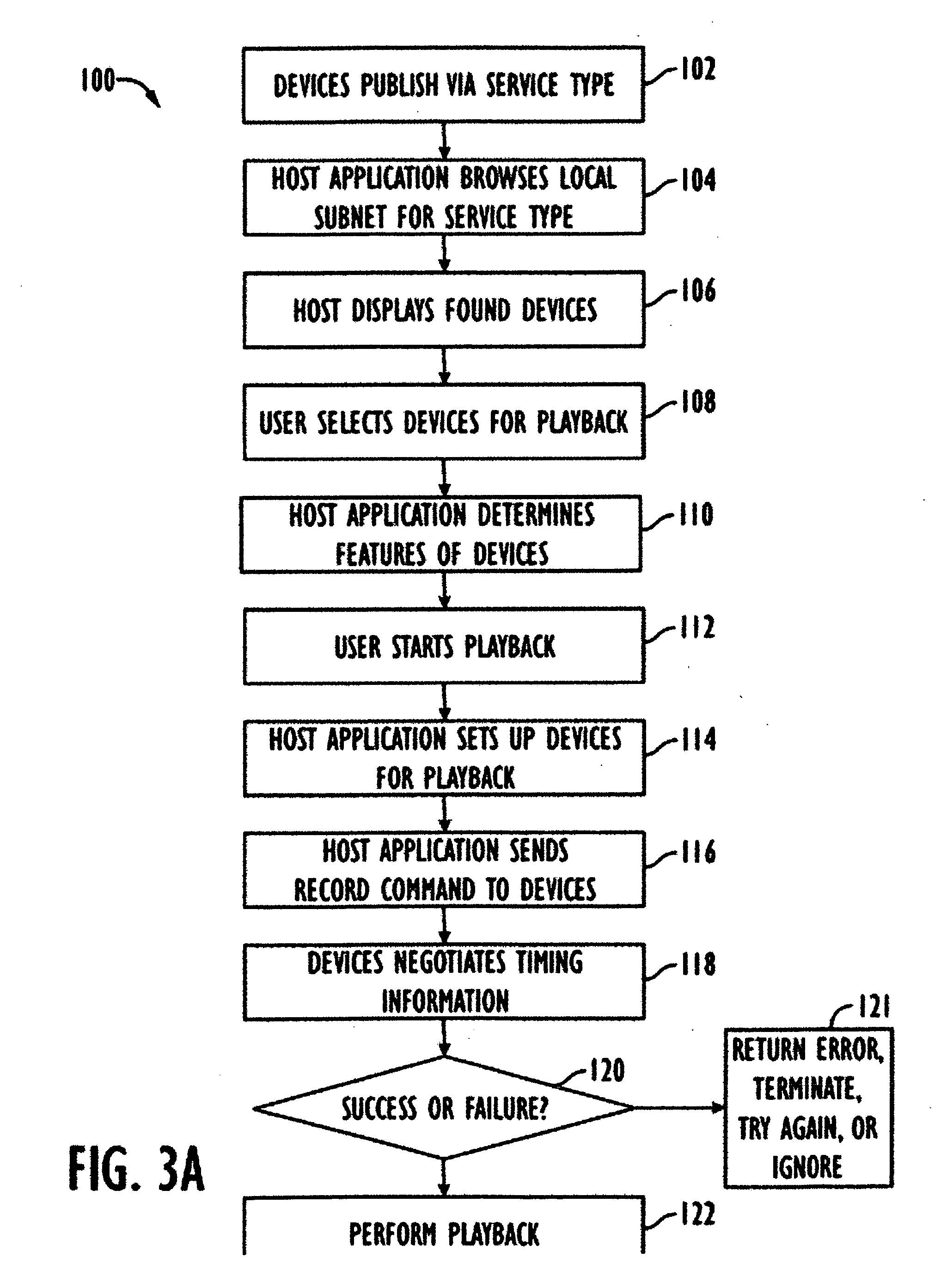
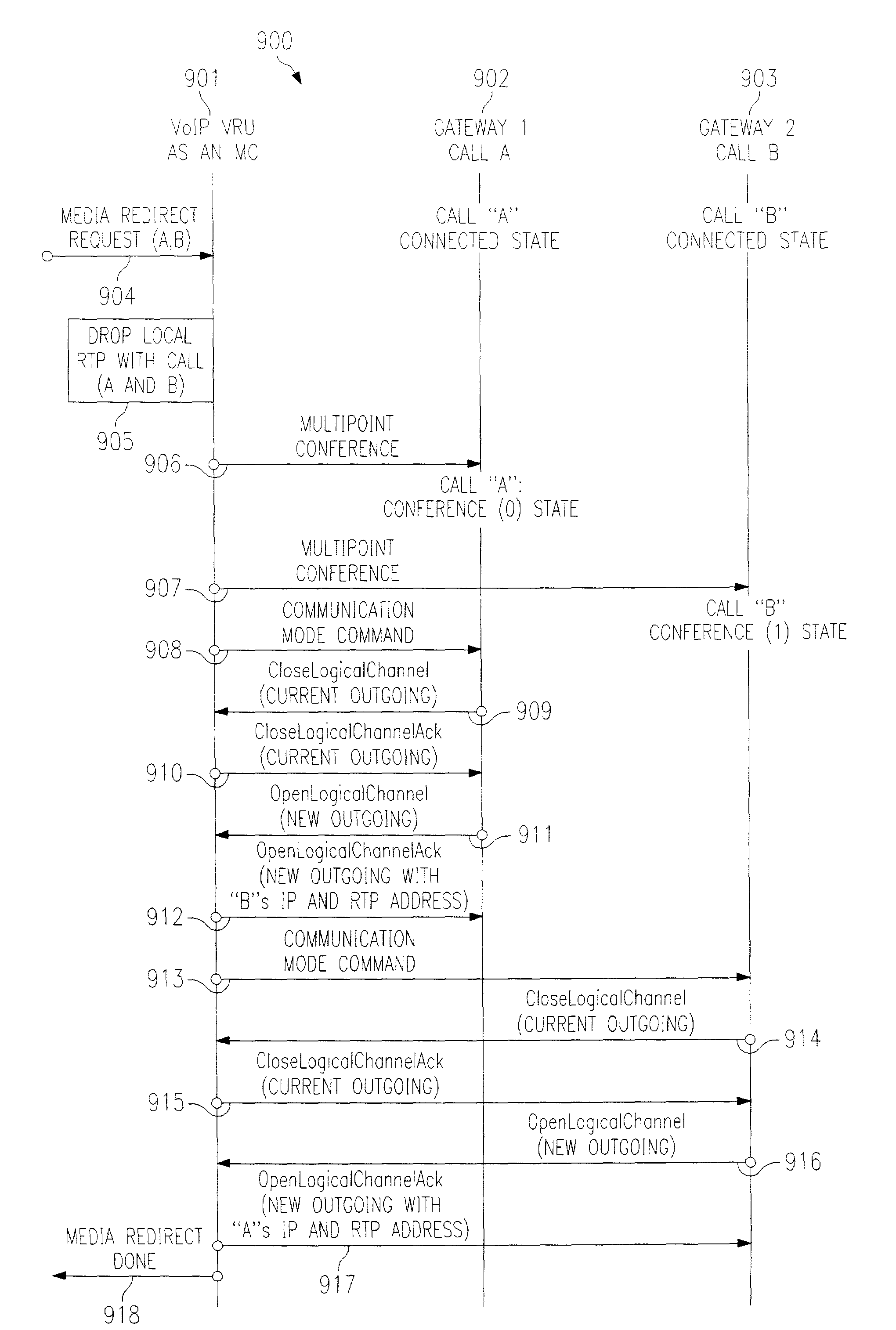
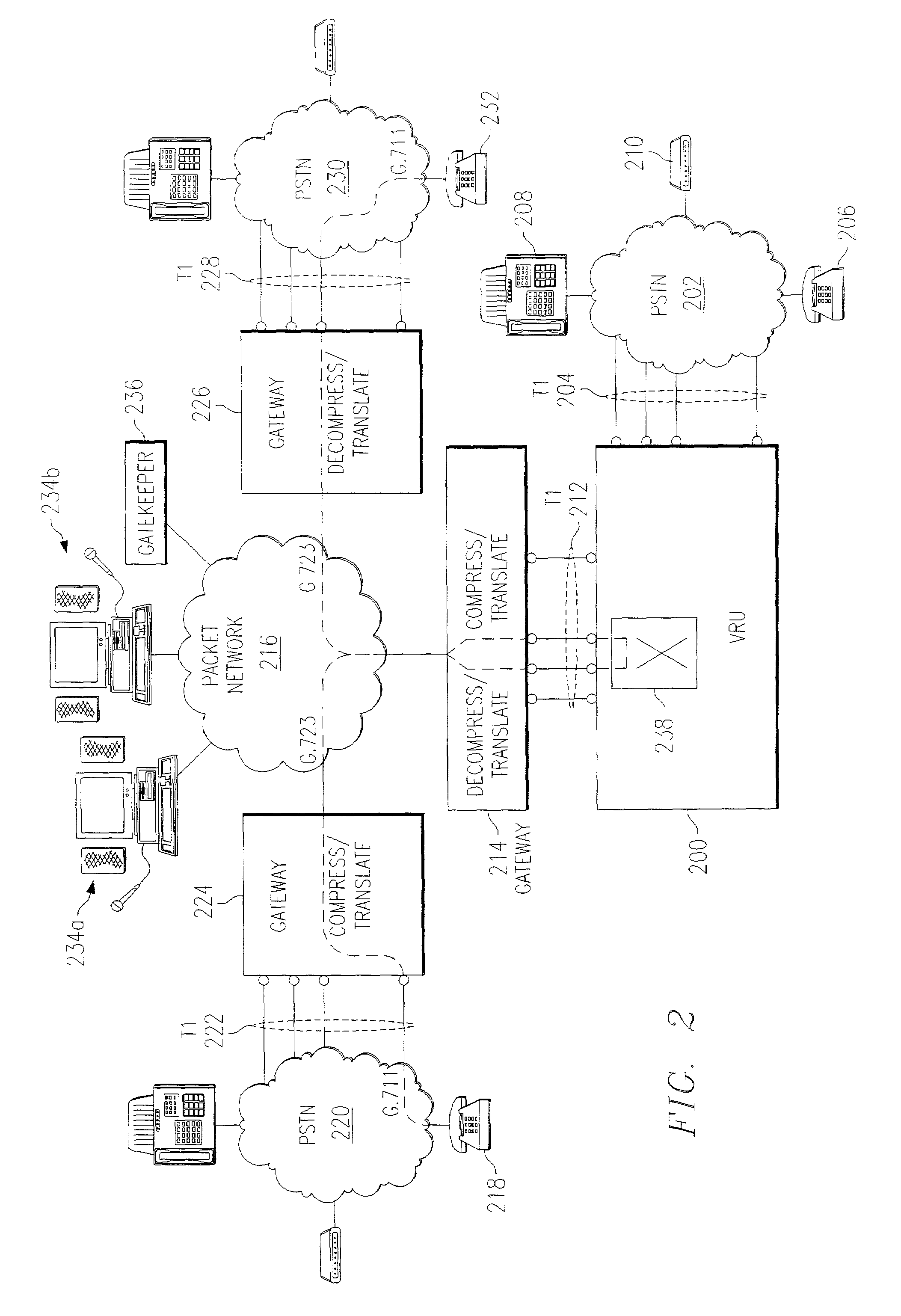
Cooperative media applications using packet network media redirection
InactiveUS7035252B2Good serviceAvoid conversionMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersNetworking protocolPacket generator
Owner:INTERVOICE PARTNERSHIP
Network media gateway
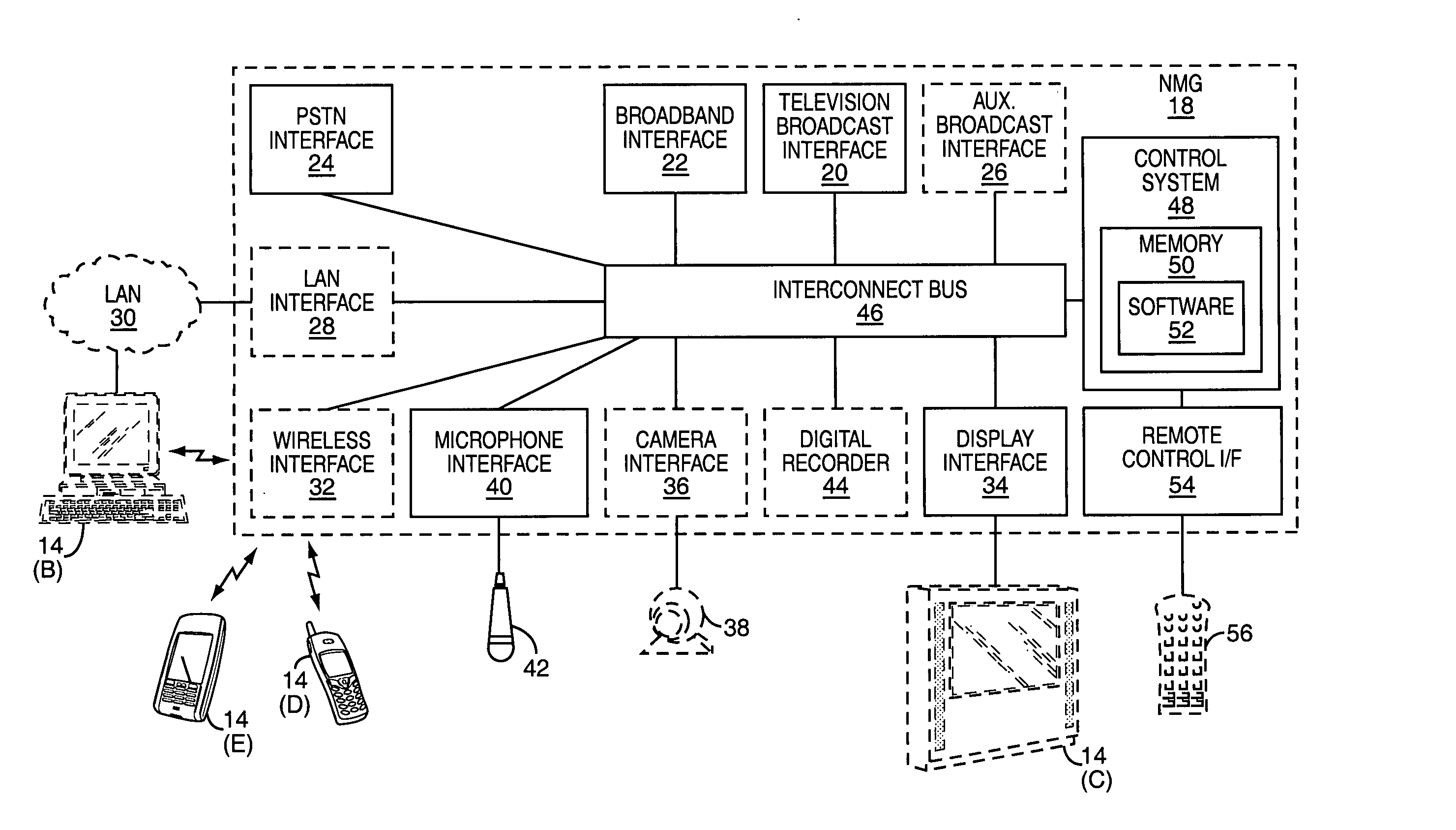
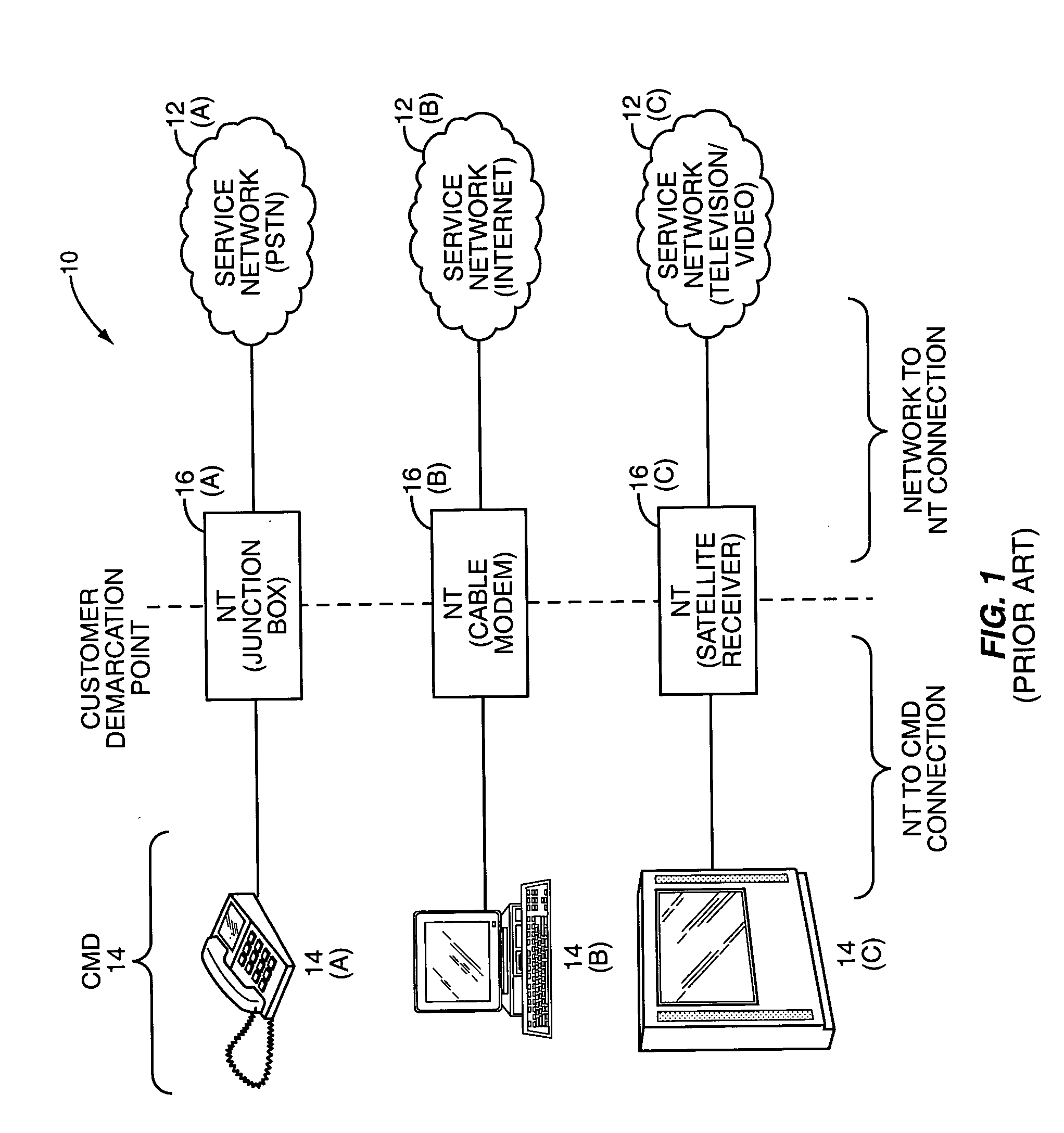
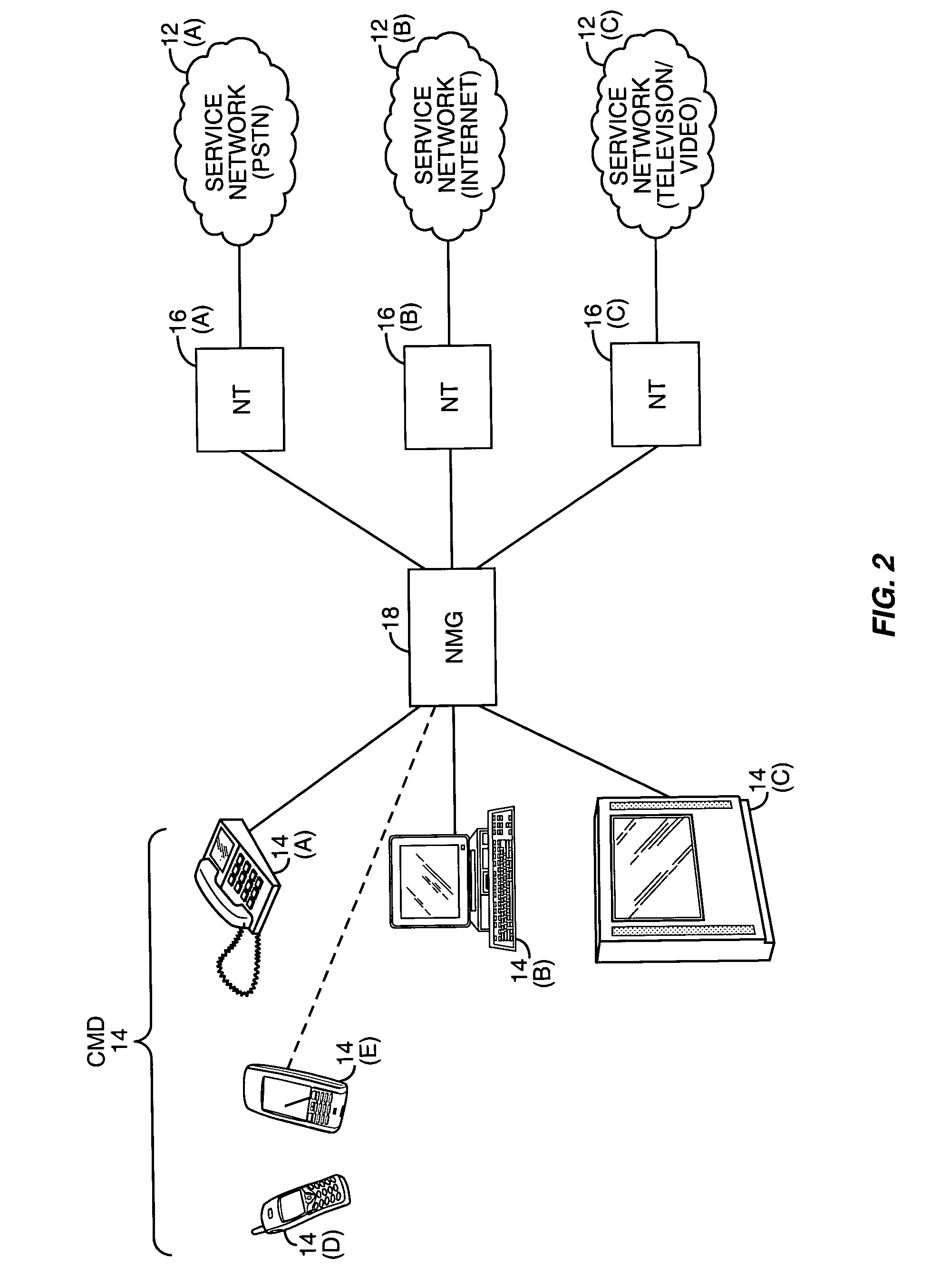
InactiveUS20060075108A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionService provisionNetwork media
The present invention provides a network media gateway (NMG) that provides a centralized interface between different types of consumer electronics devices and service providers through one or more disparate networks. The network media gateway may enable a single consumer electronics device to interact with different service providers over different types of networks in order to receive one or more services. The network media gateway may also allow multiple consumer electronics devices, which typically interact with different service providers, to interact with multiple service providers over disparate types of networks. The network media gateway may also allow the consumer electronics devices to interact with one another.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
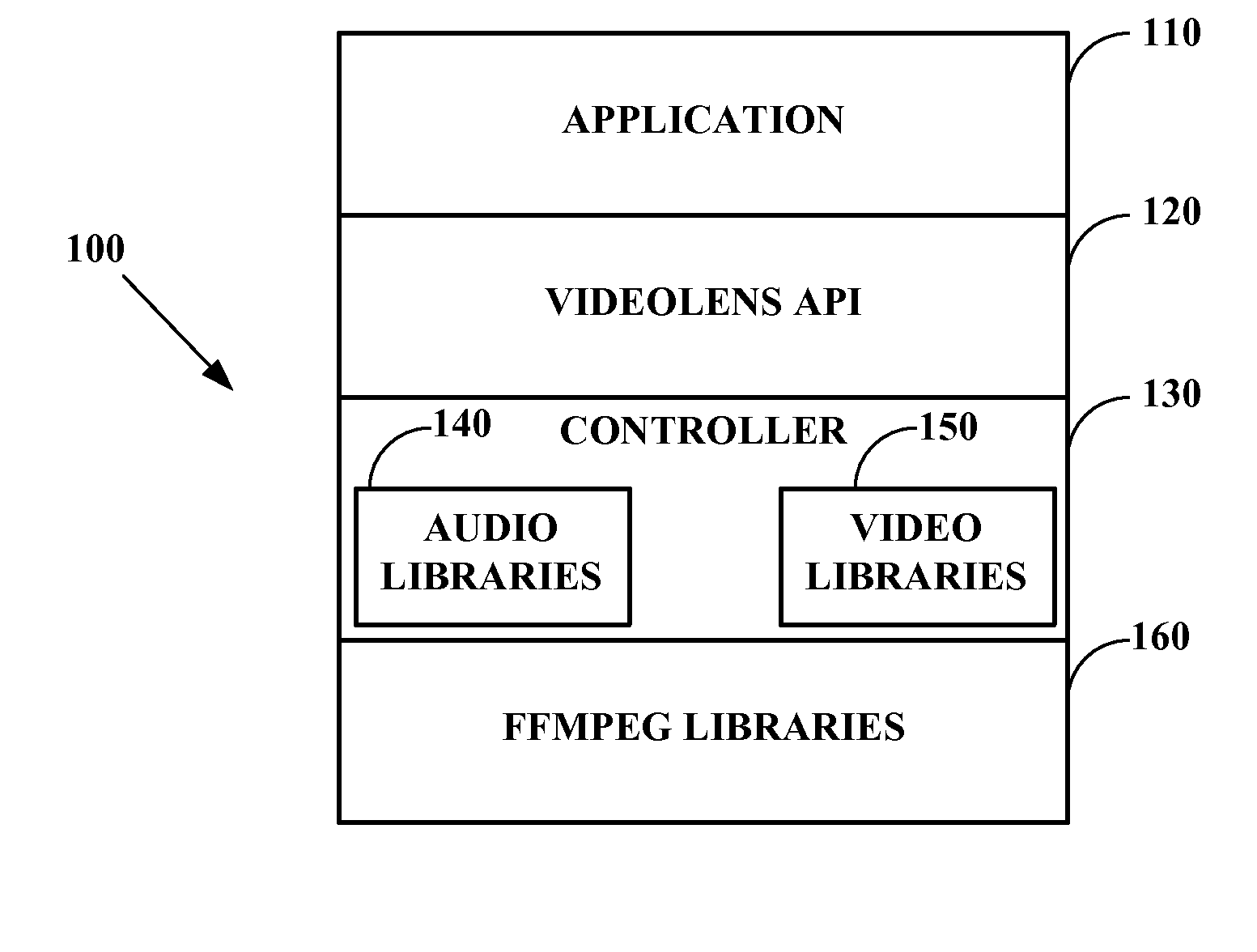
Extended videolens media engine for audio recognition
InactiveUS20130006625A1Improve recognition accuracySpeech recognitionSelective content distributionClosed captioningNetwork media
A system, method, and computer program product for automatically analyzing multimedia data audio content are disclosed. Embodiments receive multimedia data, detect portions having specified audio features, and output a corresponding subset of the multimedia data and generated metadata. Audio content features including voices, non-voice sounds, and closed captioning, from downloaded or streaming movies or video clips are identified as a human probably would do, but in essentially real time. Particular speakers and the most meaningful content sounds and words and corresponding time-stamps are recognized via database comparison, and may be presented in order of match probability. Embodiments responsively pre-fetch related data, recognize locations, and provide related advertisements. The content features may be also sent to search engines so that further related content may be identified. User feedback and verification may improve the embodiments over time.
Owner:SONY CORP
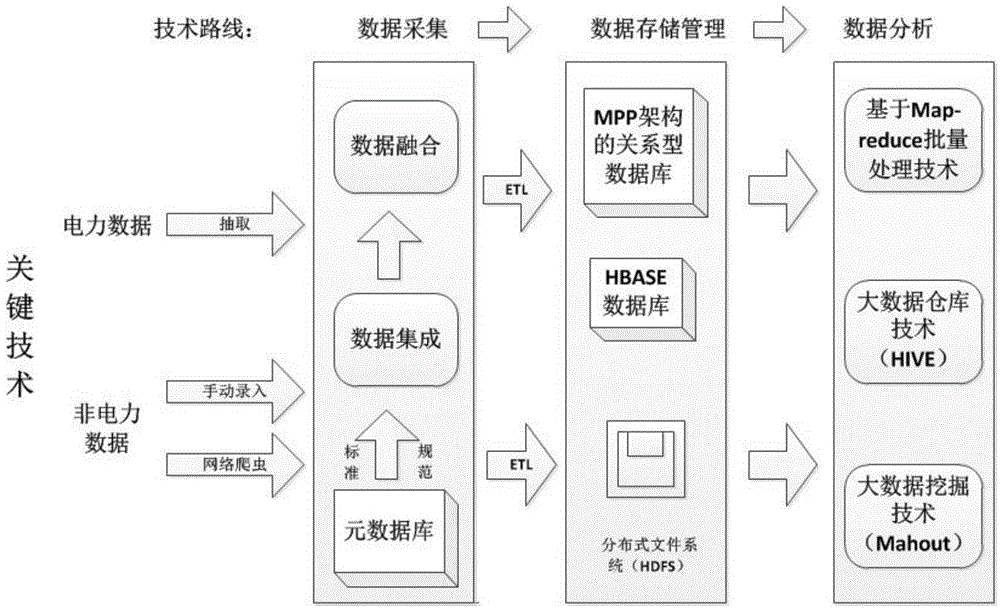
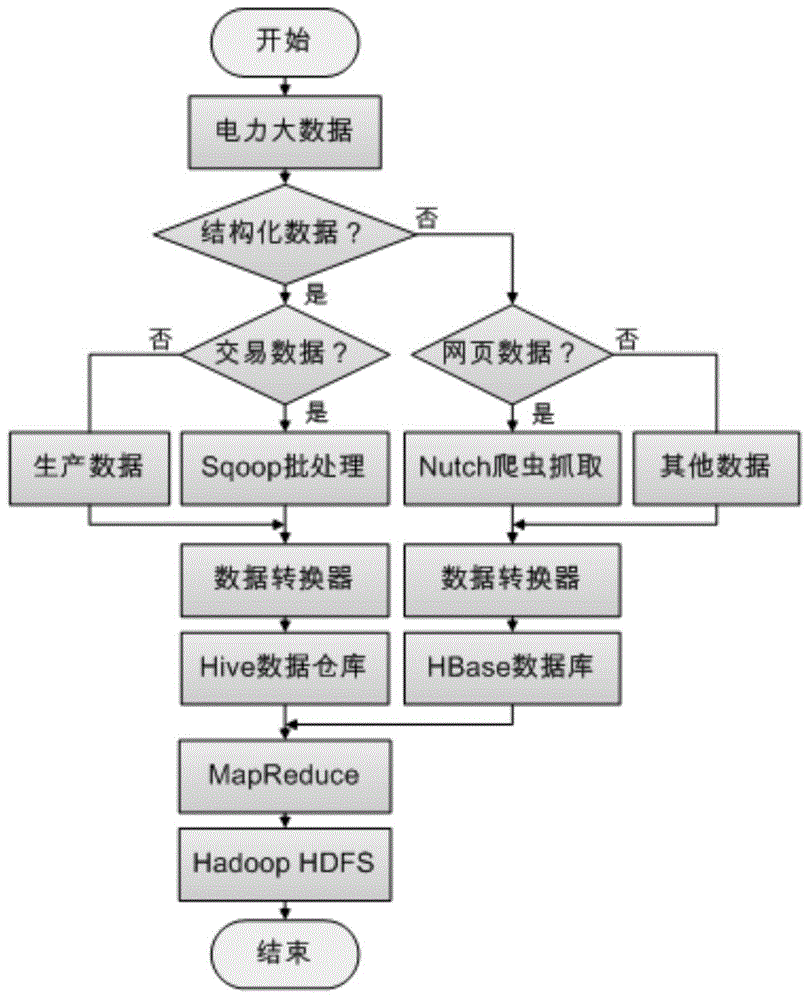
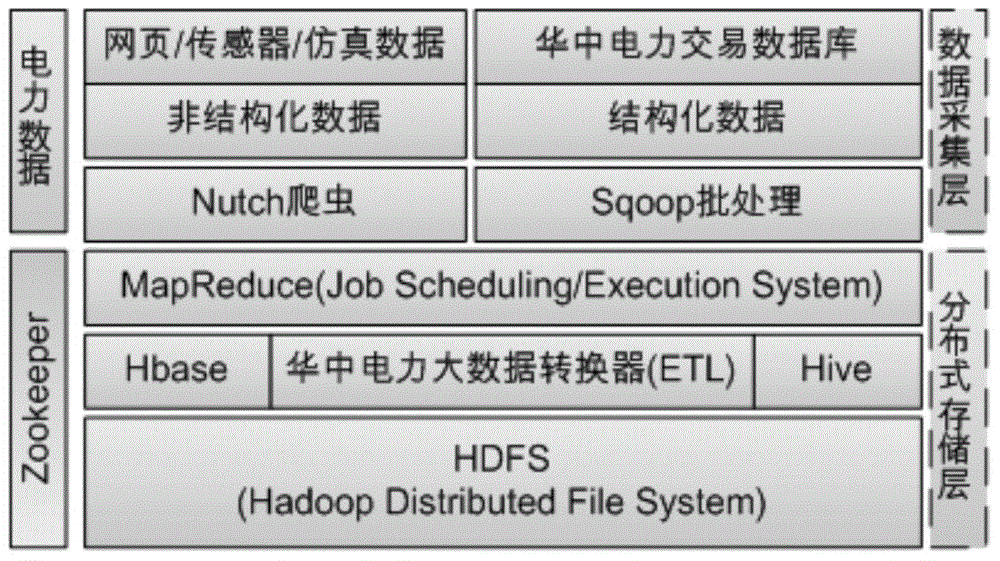
Method for acquiring and storing big data of power information
ActiveCN104820670AFunction is easy to expandGood analysis functionData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsData acquisitionNetwork media
The present invention, belonging to the field of acquisition and storage of big data of power information, relates to a method for acquiring and storing the big data of power information, and solves the problems in the acquisition and storage process of the big data of power information. The method comprises three steps: data acquisition, data storage and management, and data analysis. The method achieves the beneficial effects that the present invention provides the method for acquiring and storing the power information big data; and the problems of low response speed of a service system and long consumed time for waiting of a user, which are generated due to a large cardinal number of power users and a large quantity of information, can be well solved. Meanwhile, for massive information generated by a trading system on the basis of power data, the method can better complete data extension and analysis functions than a traditional database. Moreover, according to the method, massive Internet media data can be acquired, stored and processed so as to better learn about the trade trend; and during the operation process, the storage method has an efficient inquiring function so that retrieval can be rapidly completed when the data volume is increased sharply.
Owner:CENT CHINA GRID +2
Method and apparatus for providing mobile and other intermittent connectivity in a computing environment
InactiveUS20070038759A1Sacrificing reliability or centralized managementEasy accessError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementMobile endNetwork address
A seamless solution transparently addresses the characteristics of nomadic systems, and enables existing network applications to run reliably in mobile environments. A Mobility Management Server coupled to the mobile network maintains the state of each of any number of Mobile End Systems and handles the complex session management required to maintain persistent connections to the network and to other peer processes. If a Mobile End System becomes unreachable, suspends, or changes network address (e.g., due to roaming from one network interconnect to another), the Mobility Management Server maintains the connection to the associated peer task—allowing the Mobile End System to maintain a continuous connection even though it may temporarily lose contact with its network medium. An interface-based listener uses network point of attachment information supplied by a network interface to determine roaming conditions and to efficiently reestablish connection upon roaming. The Mobility Management Server can distribute lists to Mobile End Systems specifying how to contact it over disjoint networks.
Owner:MOBILE SONIC INC
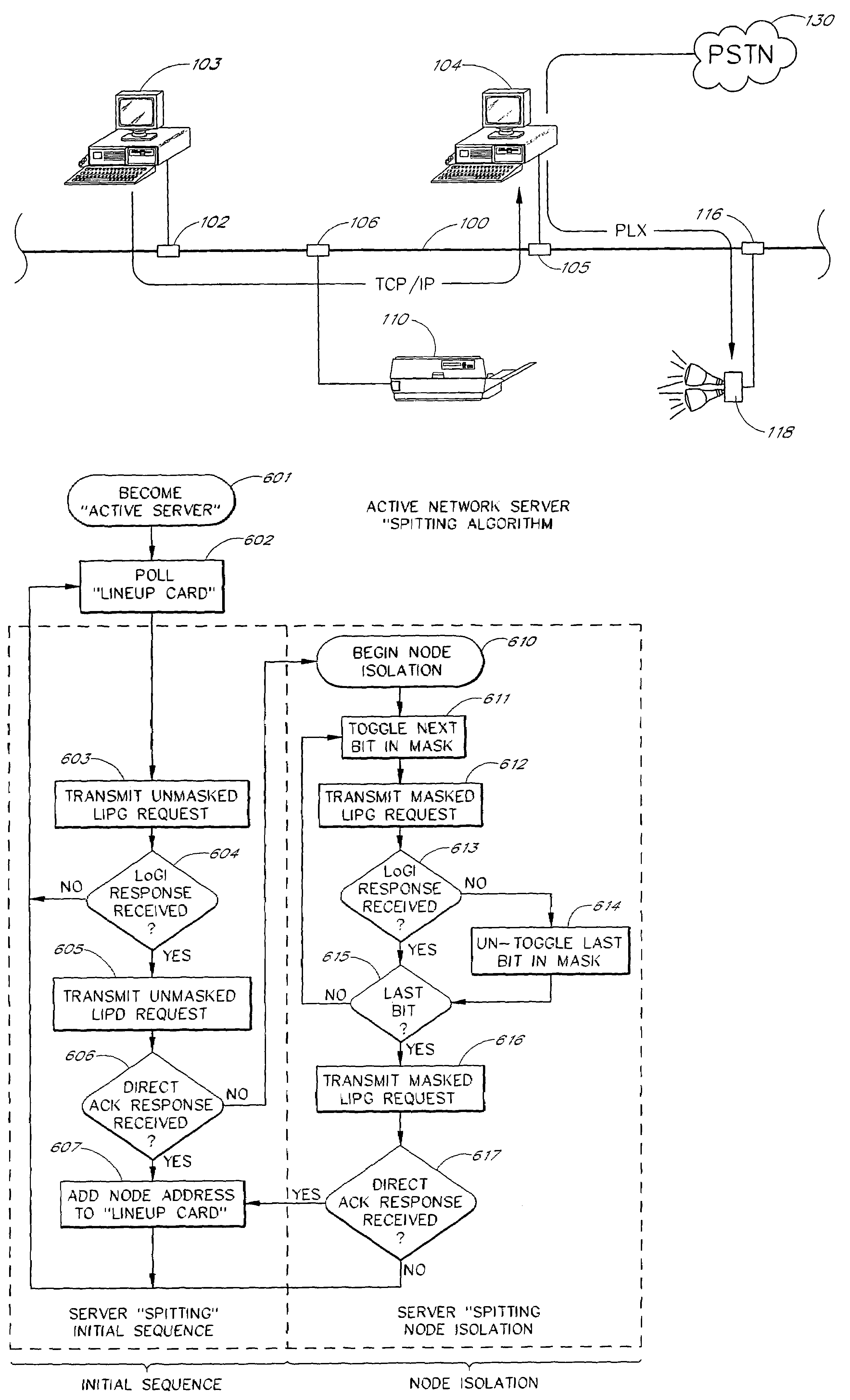
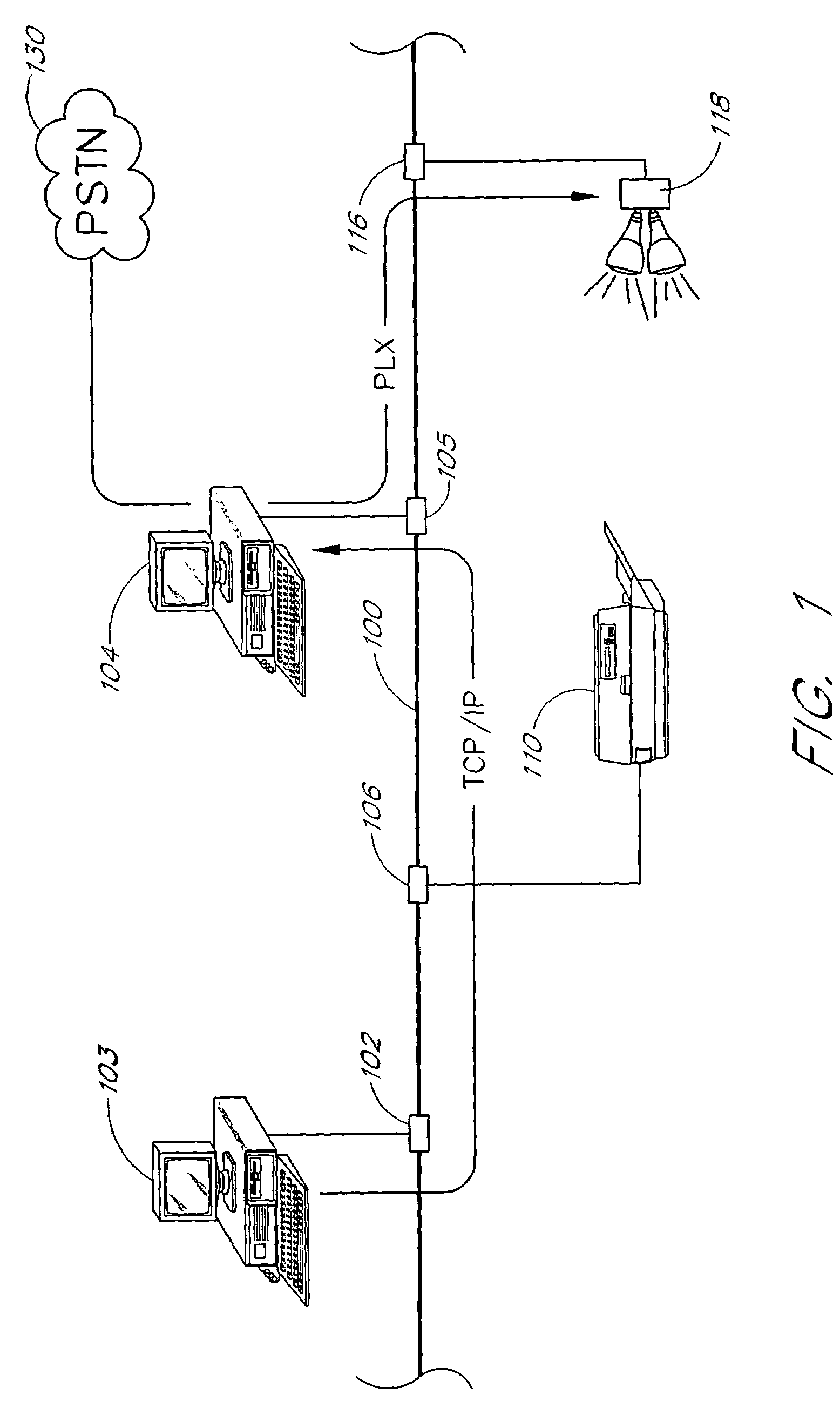
Multi-channel power line exchange protocol
InactiveUS7310670B1Easy to usePreserve bandwidthError prevention/detection by using return channelDigital data processing detailsStream dataExchange protocol
A scalable networking protocol that allows multiple nodes to communicate via a multi-channel network medium is described. The networking protocol allows any node on the network to assign itself as the active network server. The active network server polls client nodes based on a lineup card. The lineup card includes a high priority queue for low-latency devices, and a low priority queue for devices that can tolerate higher latencies. Network information is sent on the channels as fragments. The protocol provides bad-channel detection and retransmission of fragments in a fragment-by-fragment basis. Support for streaming data or asynchronous data is provided by allocating time slots on the network and allowing two intelligent nodes to talk directly to each other during count-limited token sessions, as arbitrated by the active network server. The network node serving as the active network server can be changed on a dynamic basis, and is typically determined by the first node initiating a transmit request on a sleeping network. Client nodes are addressed by dynamic-polling using an address isolation scheme.
Owner:INARI +2
Networked device branding for secure interaction in trust webs on open networks
InactiveUS20030056114A1CostInexpensive and reliableDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationLimited accessNetwork media
A branding process provides a networked computing device with initial set up information, including a name, a public / private key pair, and a set of certificates the device will need to inter-operate with other devices in the trust group. A branding device conveys the initial set-up information to the networked computing device via a limited access network interface, or alternatively via a broadcast network media with the device enclosed in a wave guide and / or Faraday cage. The networked computing device can then use the set up information to verify that other devices on the network that seek to interact with the device are also members of the trust group, with which networked computing device can interact.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Mixed media reality brokerage network and methods of use
InactiveUS20070050419A1Easy to optimizeFacilitate methodDigital data information retrievalCommerceCamera phoneComputer printing
A Mixed Media Reality (MMR) system associated techniques are disclosed. The MMR system provides mechanisms for forming a mixed media document that includes media of at least two types (e.g., printed paper as a first medium and digital content and / or web link as a second medium). In one particular embodiment, the MMR system includes an MMR user, a MMR computer, a user printer that produces a printed document, a networked media server, a service provider server and a capture device. The MMR system of the present invention provides mechanisms for forming a mixed media document that includes media of at least two types, such as printed paper as a first medium and a digital photograph, digital movie, digital audio file, or web link as a second medium. The MMR system includes a MMR brokerage network having a customer, an MMR broker, an MMR service bureau and an MMR clearinghouse. The MMR brokerage network allows these entities to interact to provide a unified point of business access for the customer who wants to add MMR functionality to a document. More specifically, the MMR technology may be used to provide advertising associated with documents and MMR hotspots. Furthermore, the MMR system of the present invention facilitates business methods that take advantage of the combination of a portable electronic device, such as a cellular camera phone, and a paper document. The present invention also includes a number of novel methods including: a method for operation of a MMR brokerage network, a method for layout independent MMR recognition, a strip fragment candidate generation process, and a page candidate accumulation process.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com