Patents
Literature
886 results about "Priority queue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
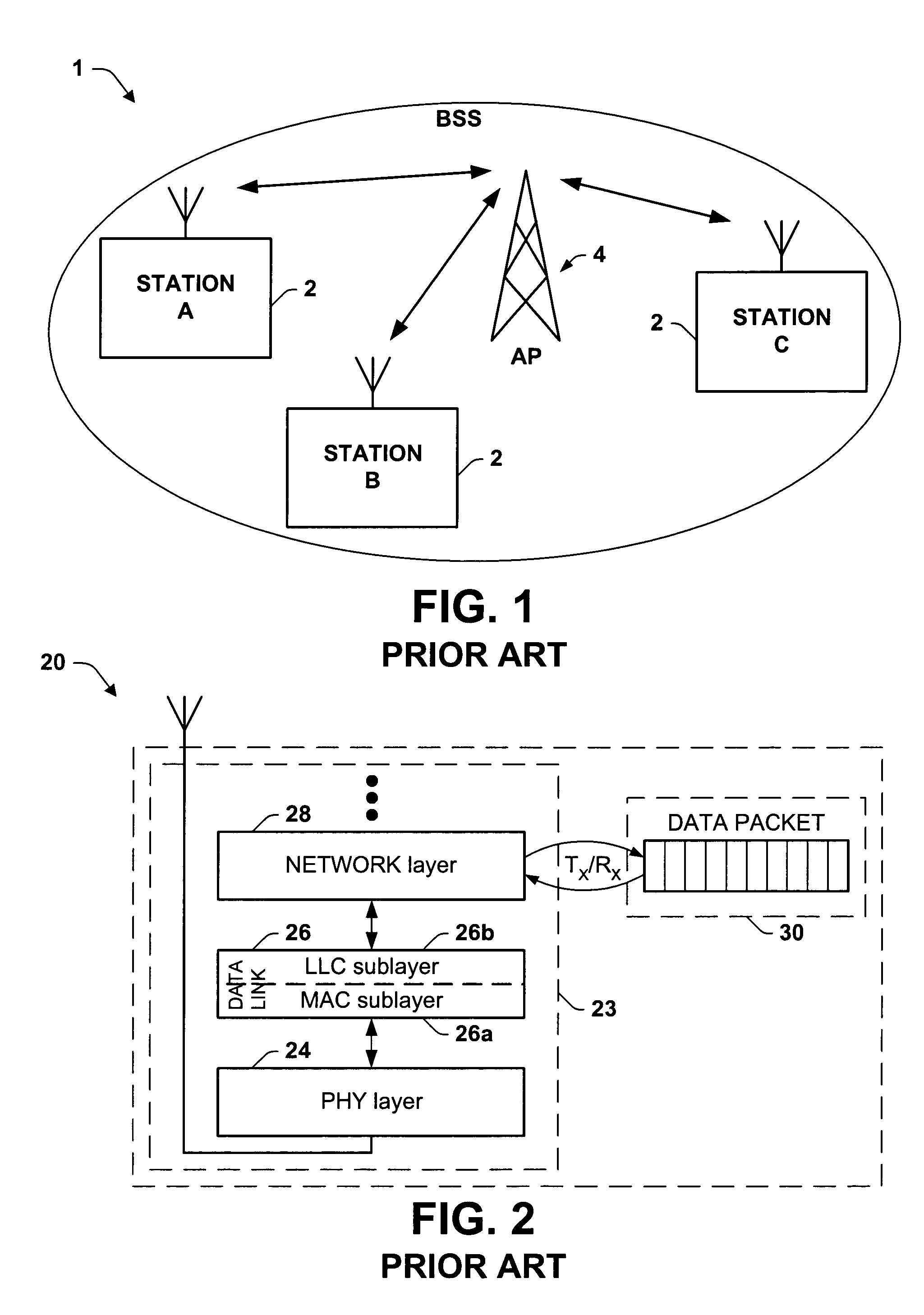
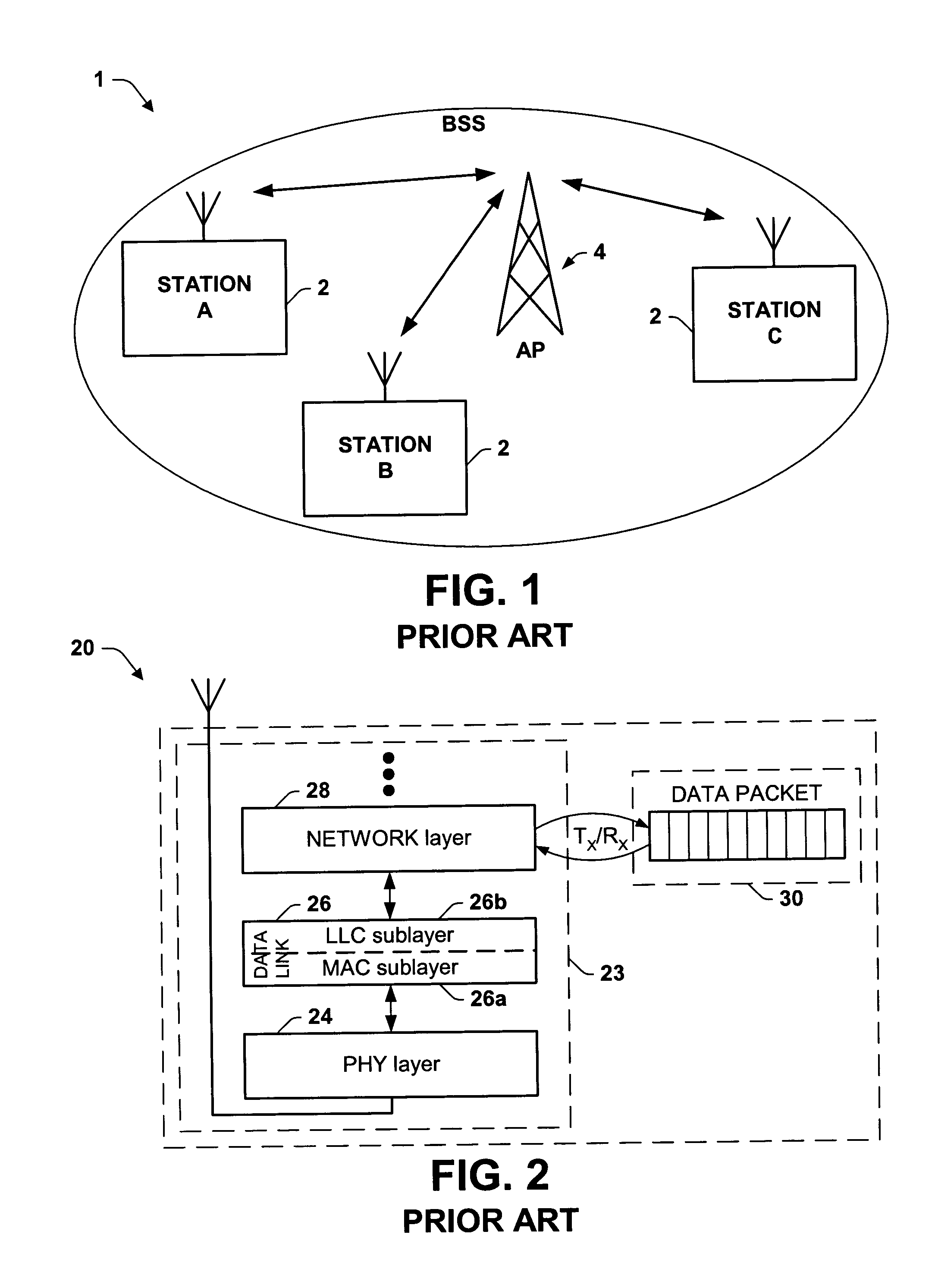
In computer science, a priority queue is an abstract data type which is like a regular queue or stack data structure, but where additionally each element has a "priority" associated with it. In a priority queue, an element with high priority is served before an element with low priority. In some implementations, if two elements have the same priority, they are served according to the order in which they were enqueued, while in other implementations, ordering of elements with the same priority is undefined.
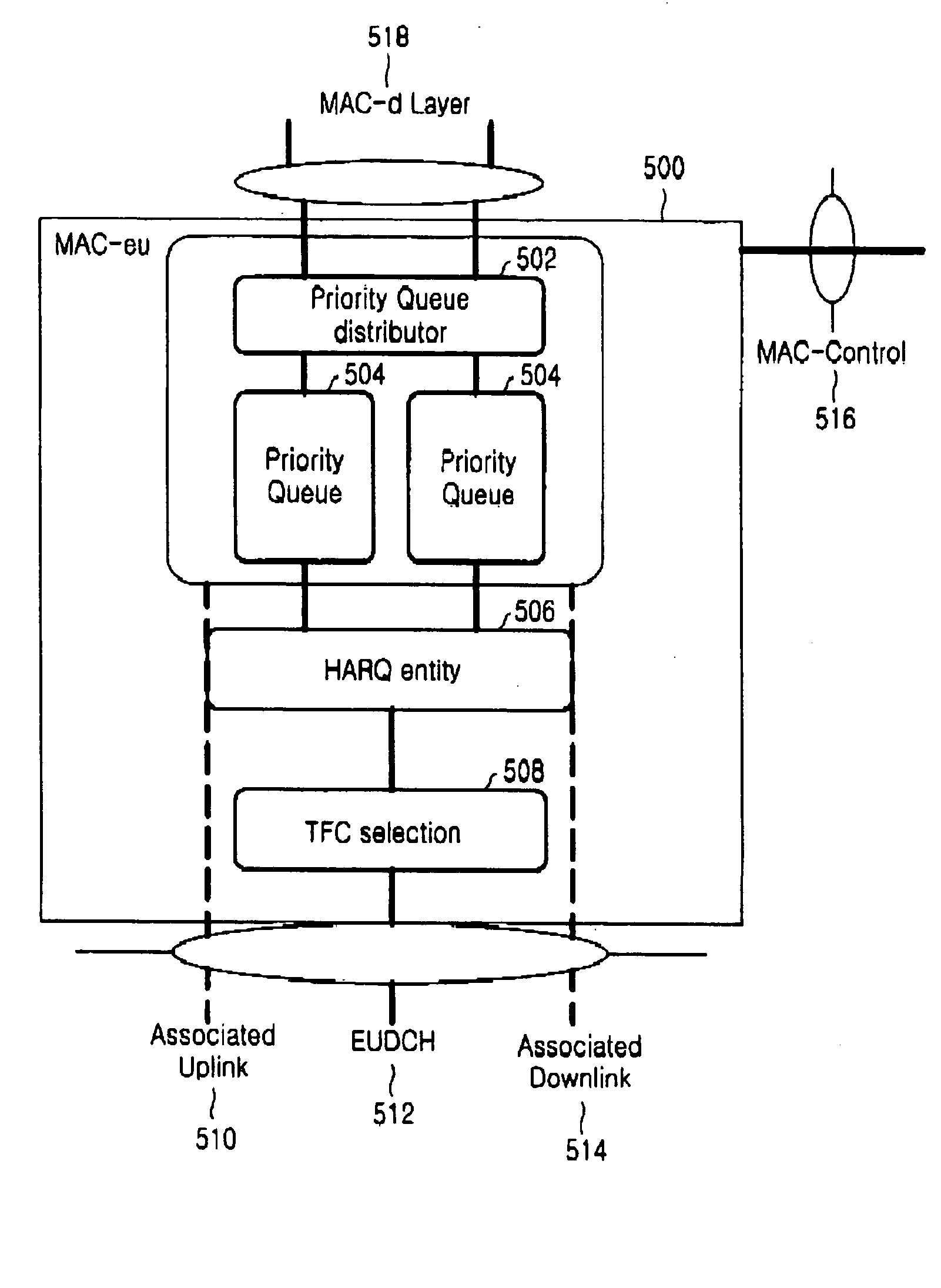
Method and apparatus for scheduling assignment of uplink packet transmission in mobile telecommunication system
ActiveUS20050047416A1Easy to useNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesMobile communication systemsData storing
A method and an apparatus for reporting a buffer status of a buffer storing packet data to be transmitted by a user equipment for a scheduling assignment of an uplink packet data service in a mobile communication system supporting the uplink packet data service are disclosed. A user equipment stores packet data having a priority corresponding to a plurality of priority queues having inherent priorities and relating to at least one service, and transmits buffer status information containing queue identifiers of the priority queues and buffer payload information representing an amount of the packet data stored in the priority queues. Herein, the user equipment inserts the buffer status information into a header part of a protocol data unit for the uplink packet data service, inserts the packet data into a payload part of the protocol data unit, and then transmits the protocol data unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
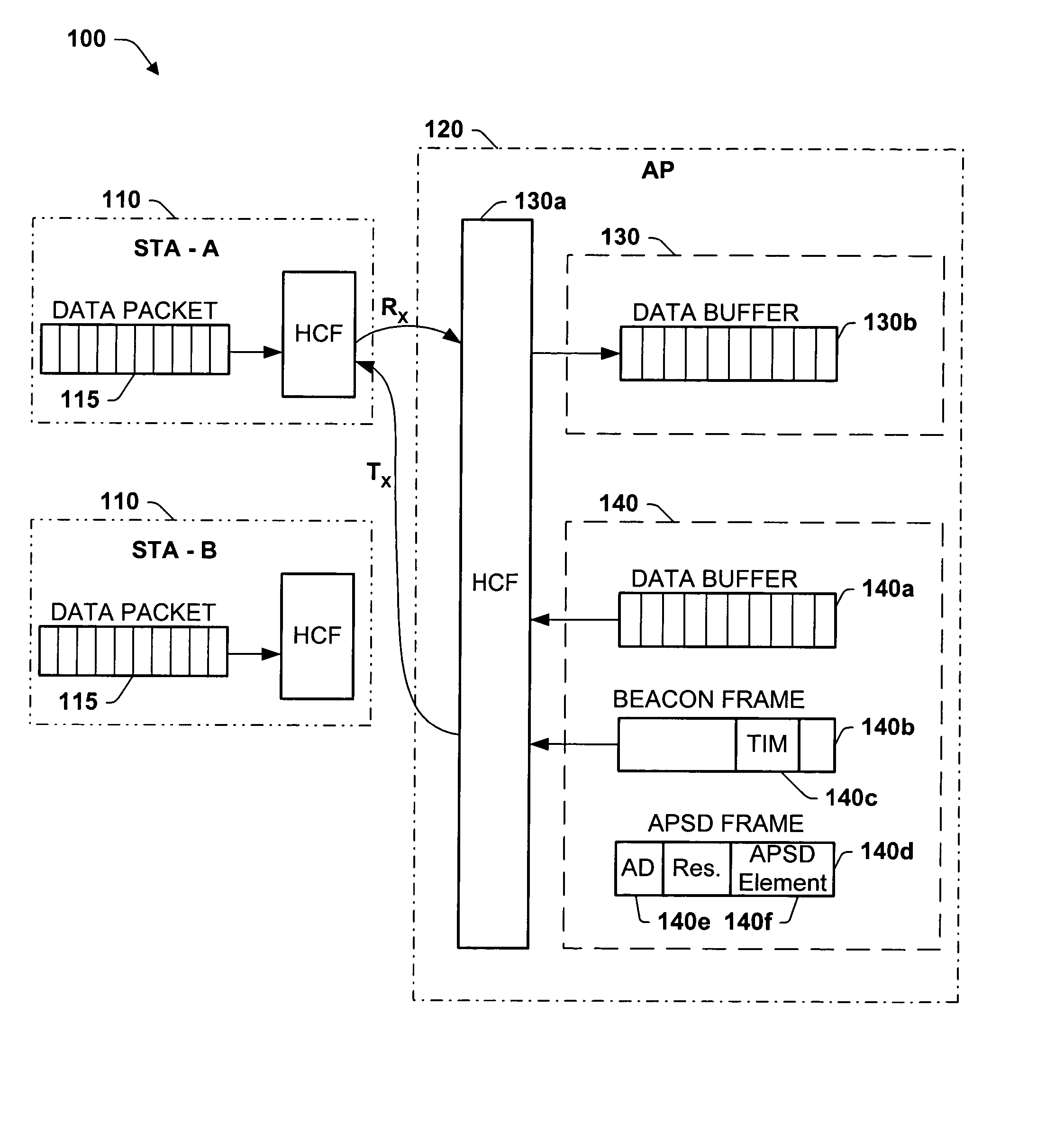
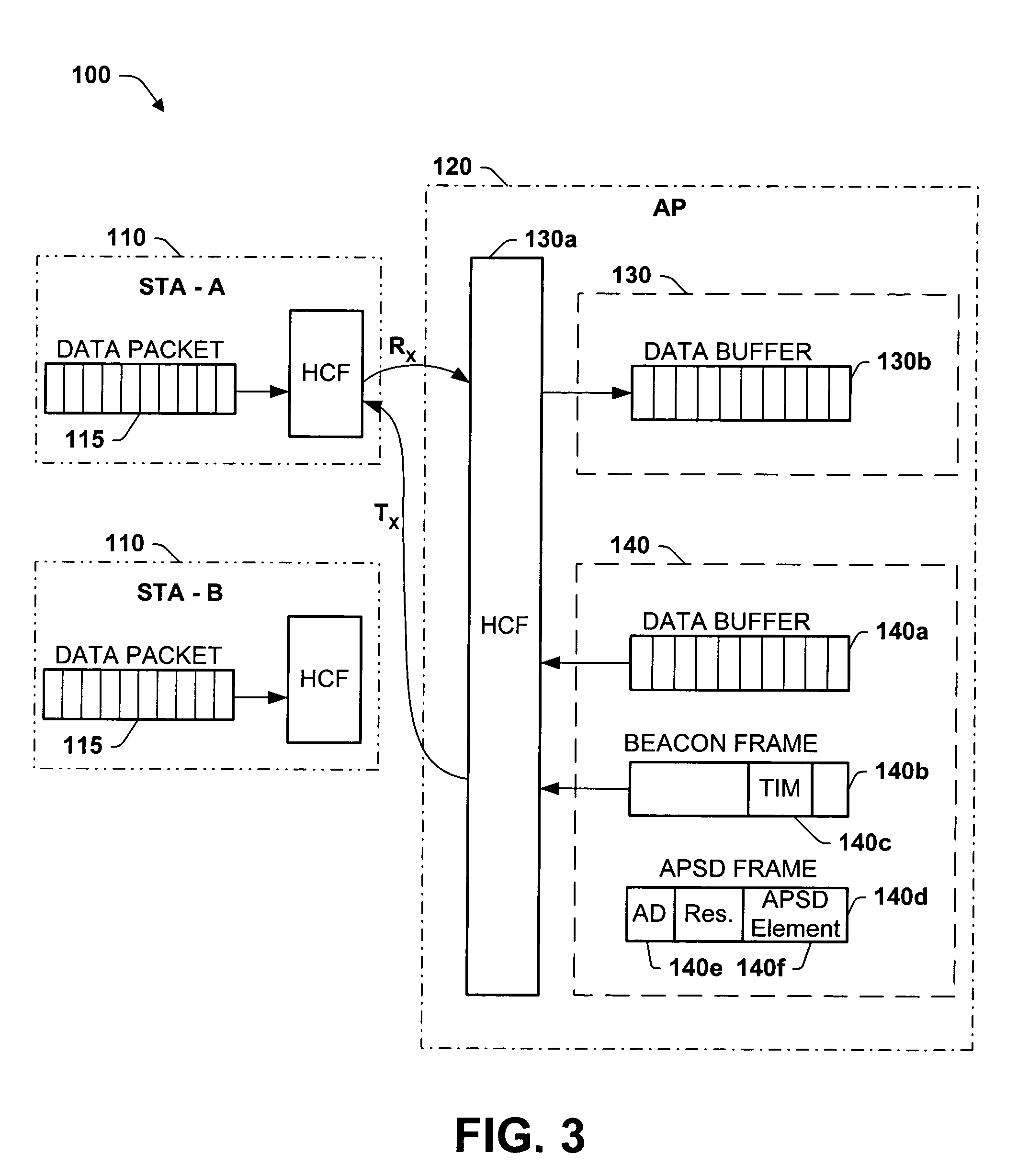
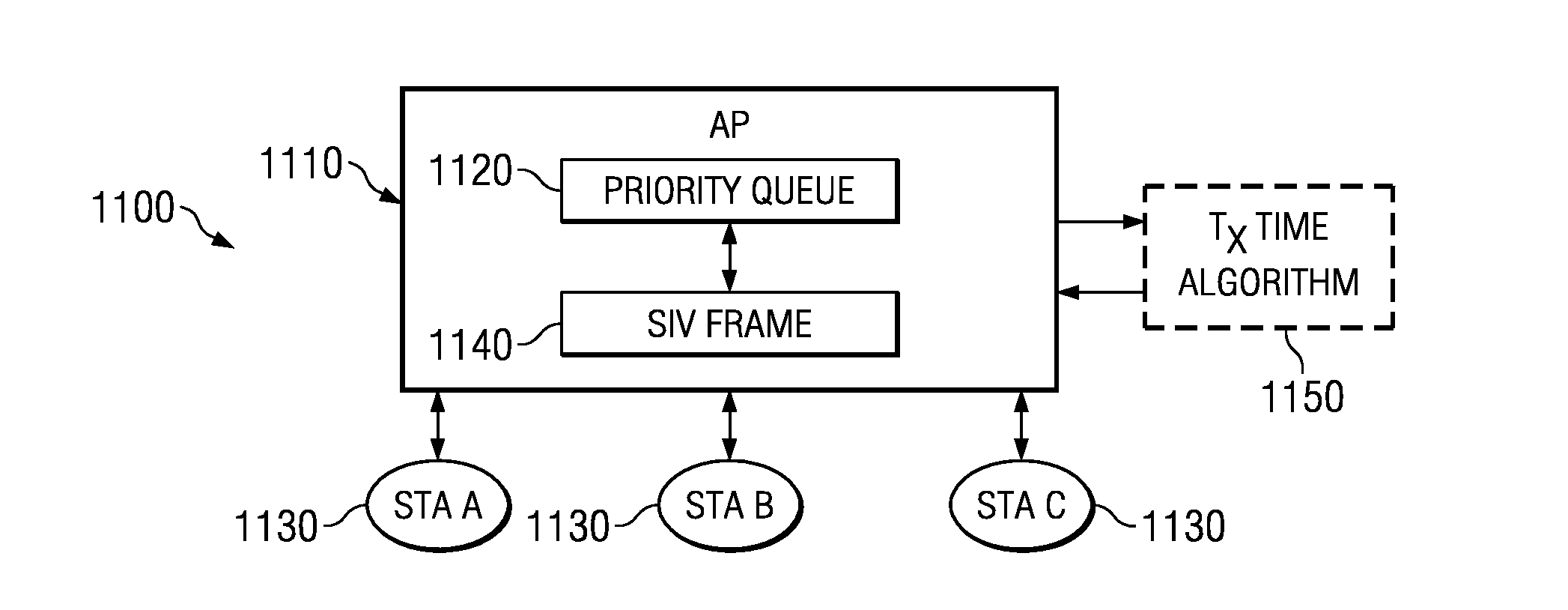
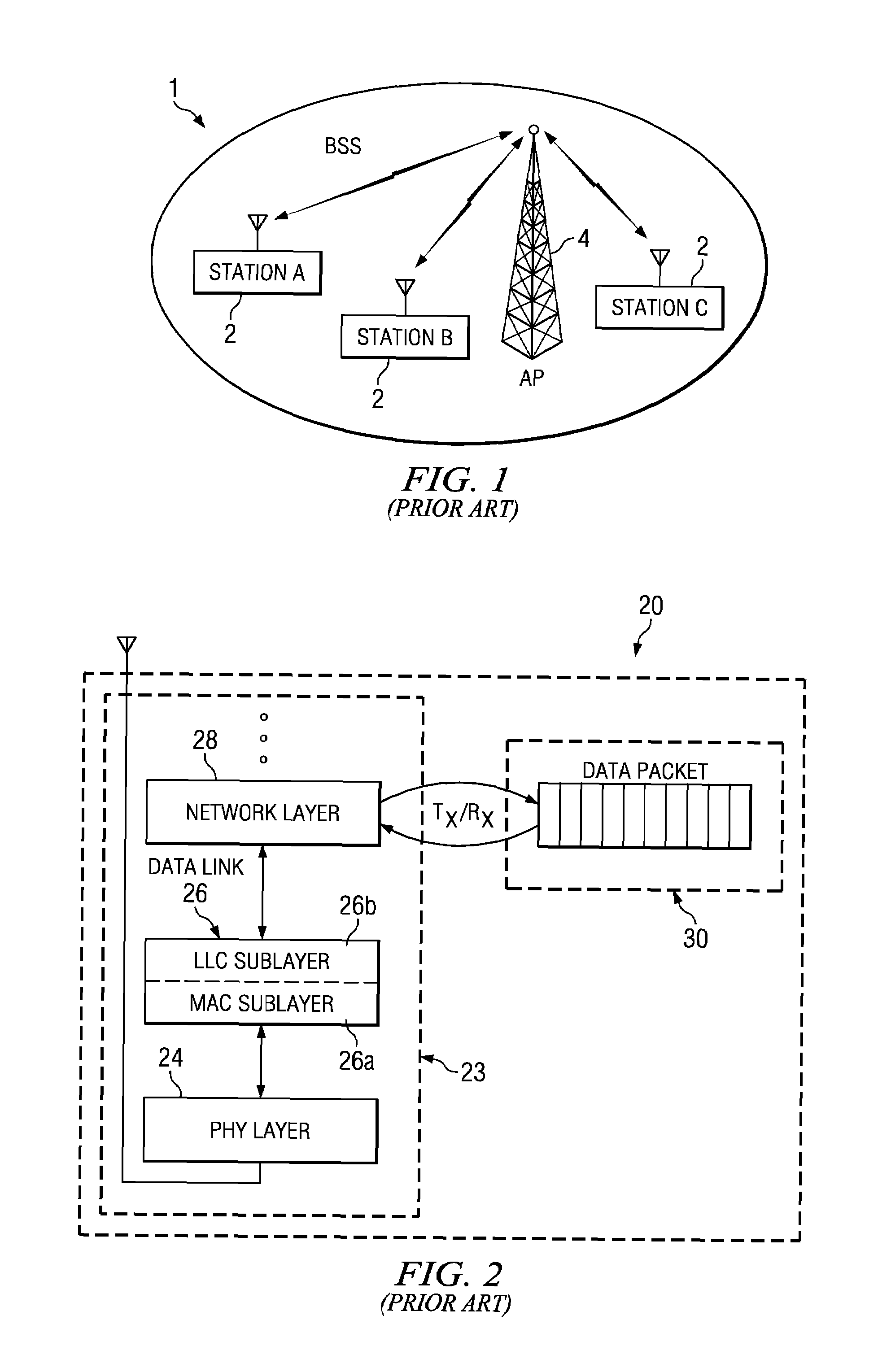
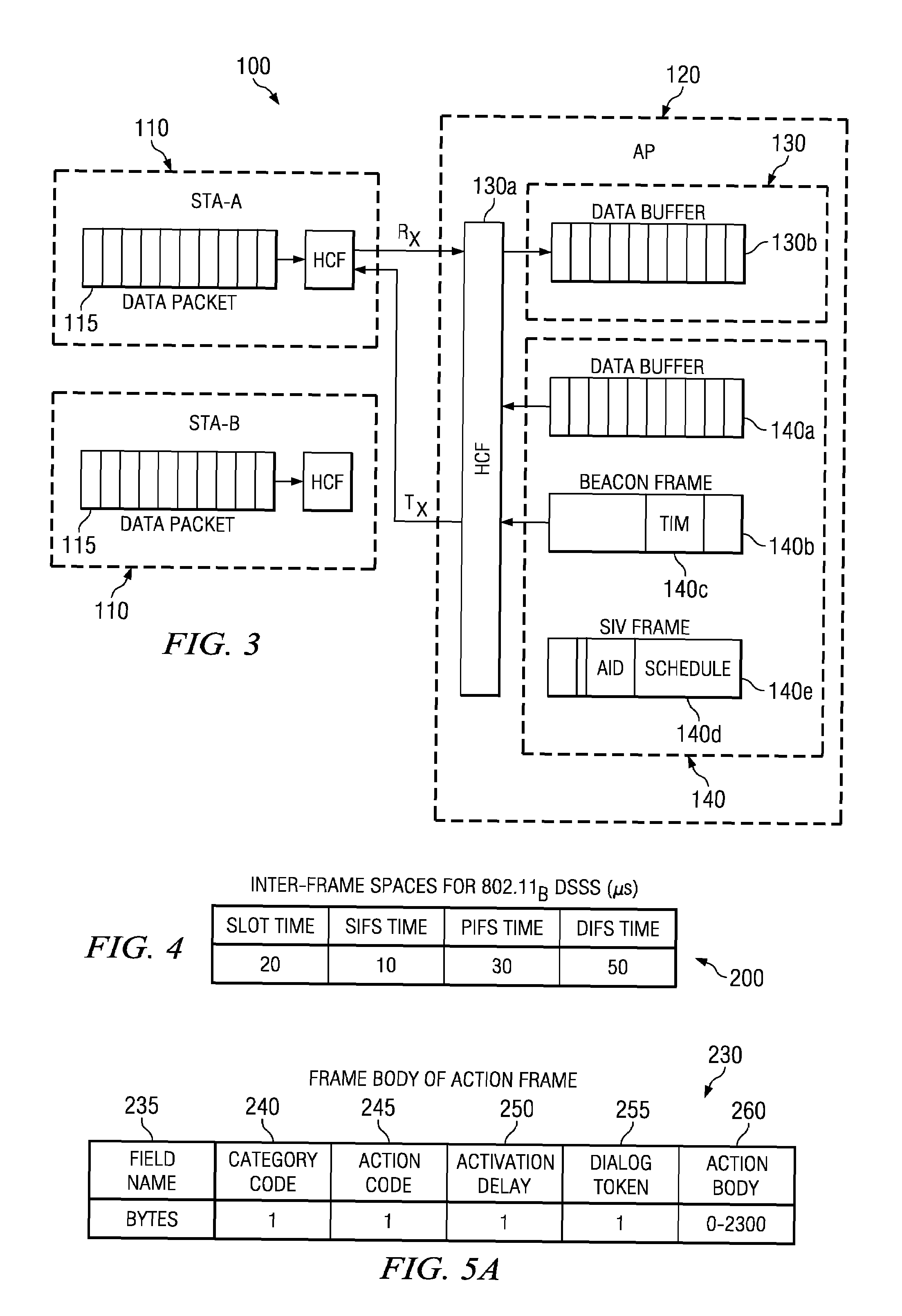
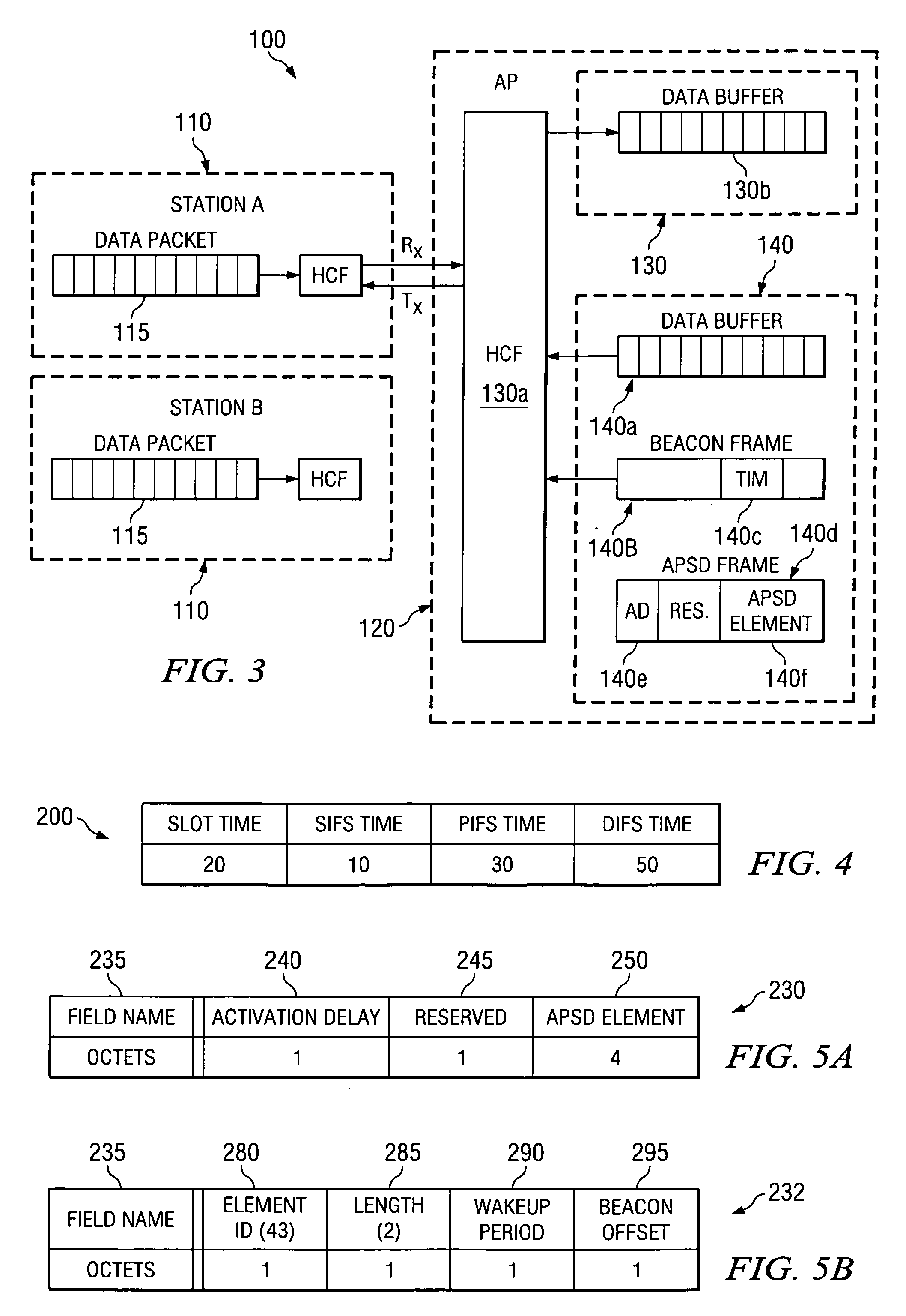
Optimal power saving scheduler for 802.11e APSD
A new system and method is described, utilizing a scheduler based on a transmission power consumption calculation and prioritizing algorithm. The system utilizes the (APSD) protocol specified in the 802.11e draft for saving power in wireless local area networks. The system comprises an access point having a priority queue, one or more stations, an APSD frame comprising an association ID for identifying one of the stations and a scheduled wake-up time for the identified station. An algorithm is employed for calculating the total transmission power consumption of downlink data for the stations. The AP originates and transmits to the one or more stations the APSD frame of the scheduled activation delay time. The current data to be transmitted to each station is accessed by the algorithm to determine the total transmission power consumption to each station. A priority queue in the AP is ordered from the lowest to the highest receiving power consumption, assigning the highest priority to the lowest power consumption transmission to minimize total power consumption to the PS stations in the AP queue.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
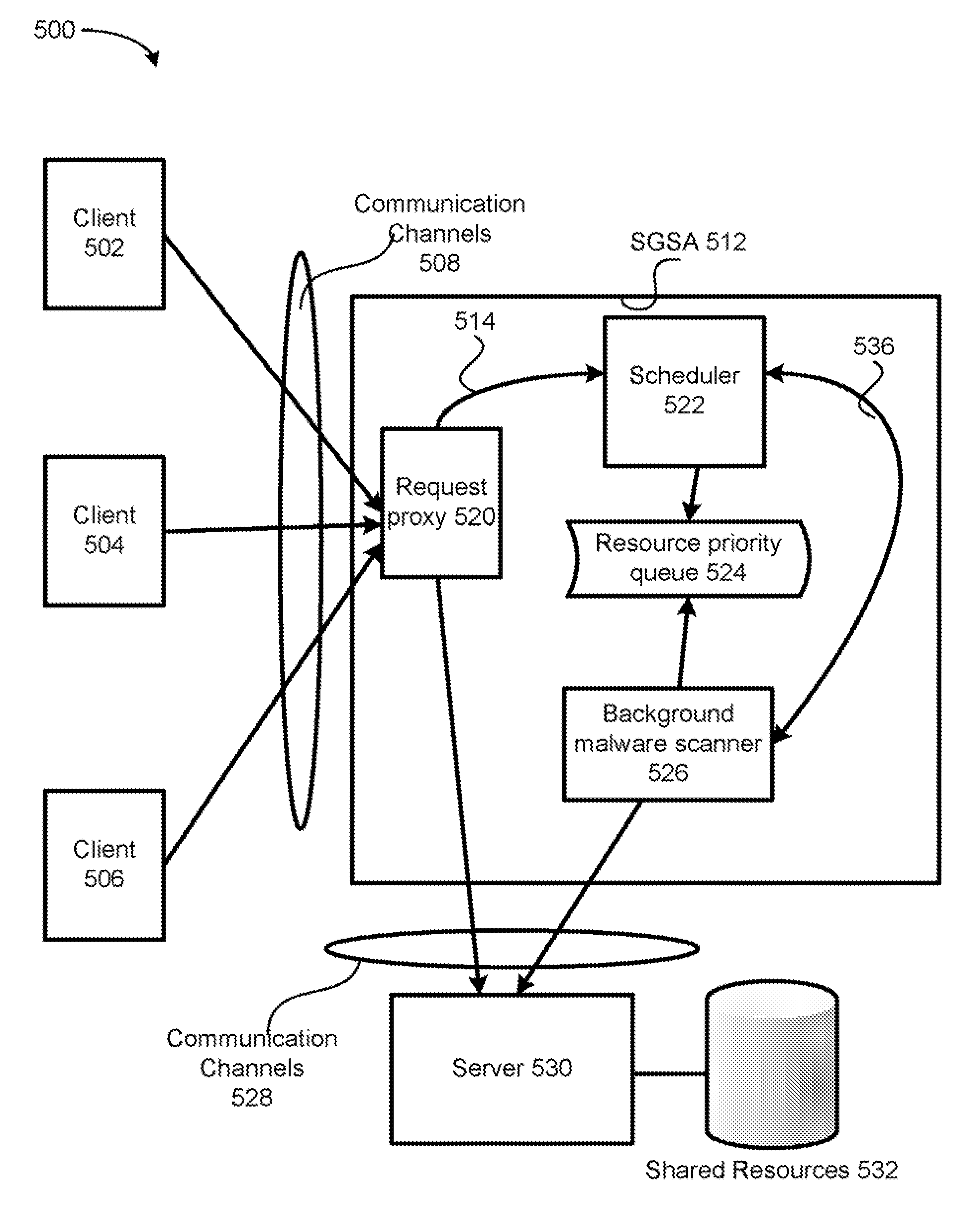
Scheduled gateway scanning arrangement and methods thereof
InactiveUS7836502B1Raise priorityMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionResource basedComputer science
A method for performing content analysis of a plurality of resources is provided. The method includes performing background content scanning on the plurality of resources based on a resource priority queue. The method also includes storing already scanned resources of the plurality of resources in a scan result database. The method further includes receiving a first access request asynchronously with the scanning and the storing. The method yet also includes, if the first access request pertains to a given resource not contemporaneously designated as a satisfactory scan result according to the scan result database, granting the given resource a higher priority in the resource priority queue than resources remaining to be scanned in the plurality of resources, thereby enabling the given resource to be scanned ahead of the resources remaining to be scanned.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
System and Method of Prioritizing Items in a Queue
A system and method of prioritizing items in a queue is provided. The system and method includes the creation of a document queue comprising a plurality of items and the assignment of a queue position to each of the plurality of items based upon one or more determining factors, such as the date of receipt of each item. A fee can be calculated for moving an item to a different priority queue position and a right-of-first refusal can be provided for one or more items that would have their respective queue positions changed as a result of payment of the fee.
Owner:LEVIATHAN ENTERTAINMENT
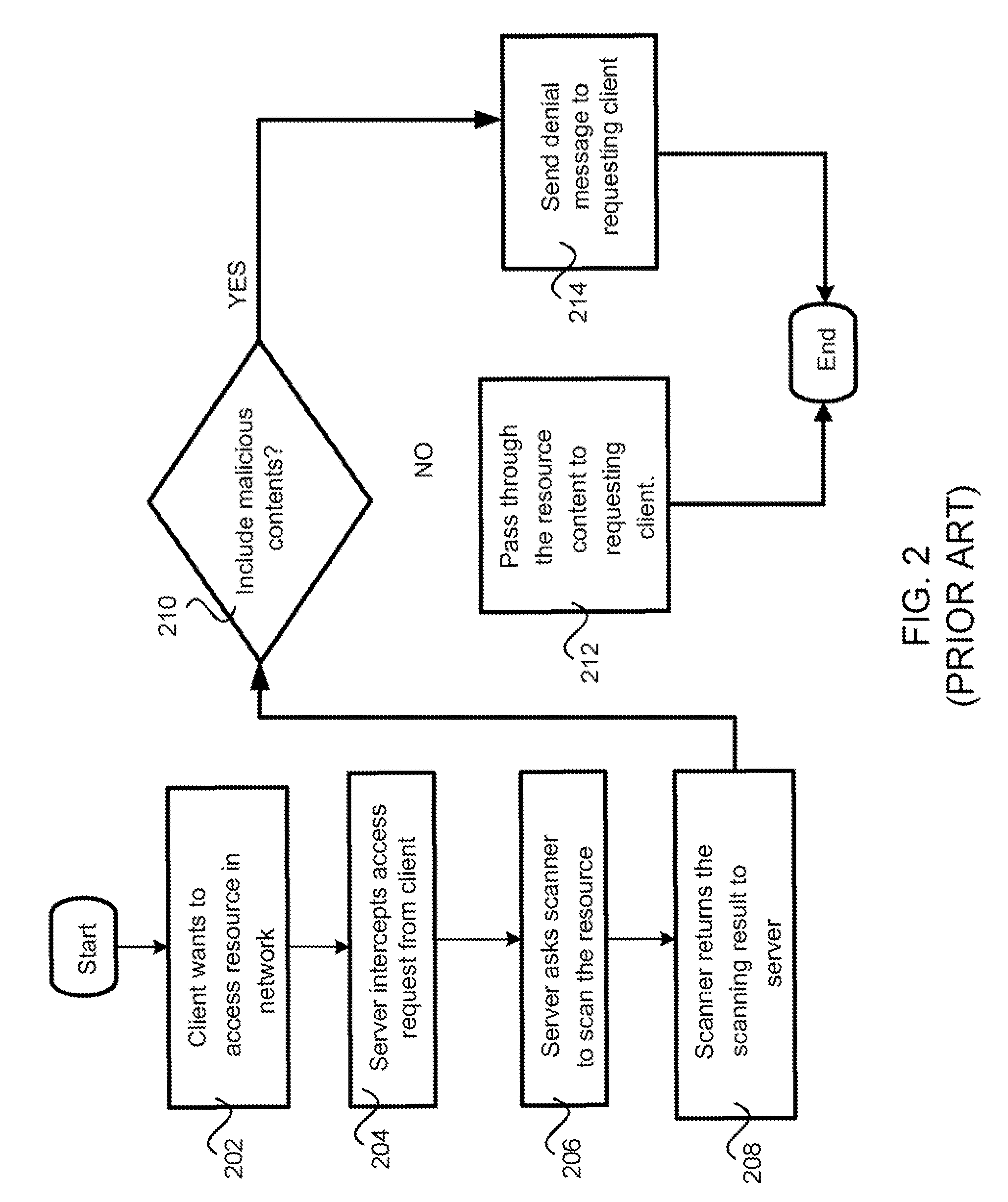
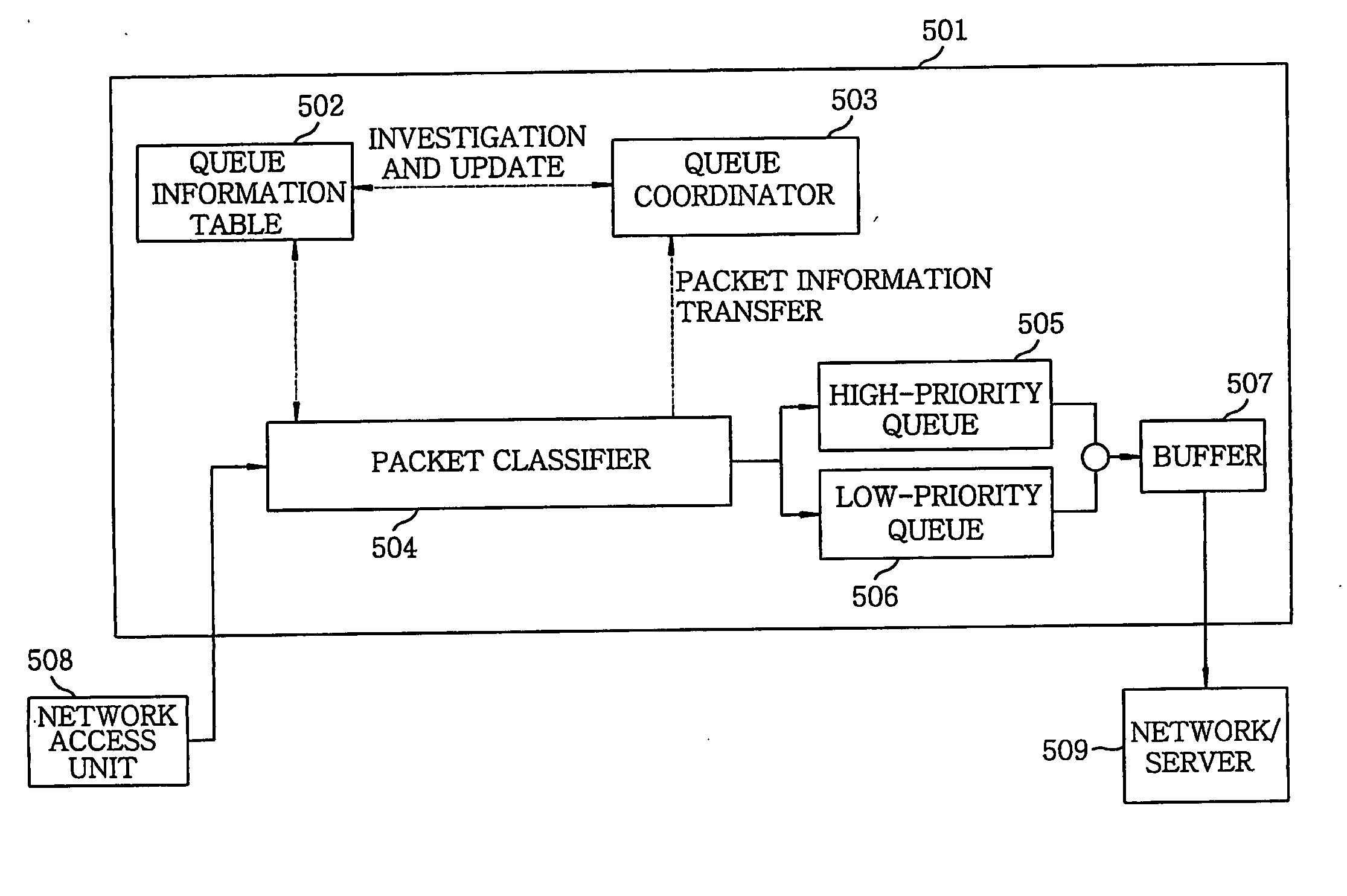
Method and apparatus for protecting legitimate traffic from dos and ddos attacks
InactiveUS20060041667A1Protection attackError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistributed computingLower priority
An apparatus for protecting legitimate traffic from DoS and DDoS attacks has a high-priority (505) and a low-priority (506) queue. Besides, a queue information table (402) has STT (Source-based Traffic Trunk) service queue information of a specific packet. A queue coordinator (502) updates the queue information table (502) based on a load of a provided STT and a load of the high-priority queue (505). A packet classifier (504) receives a packet from the network access unit (508), investigates an STT service queue of the packet from the queue information table (502), selectively transfers the packet to the high-priority (505) or the low-priority (506) queue and provides information on the packet to the queue coordinator (503). A buffer (507) buffers outputs of the high-priority (505) and the low-priority (506) queue and provides outputs to the network (509) to be protected.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Transfer ready frame reordering
InactiveUS20030056000A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksLatency (engineering)Distributed computing
A system and method for reordering received frames to ensure that transfer ready (XFER_RDY) frames among the received frames are handled at higher priority, and thus with lower latency, than other frames. In one embodiment, an output that is connected to one or more devices may be allocated an additional queue specifically for XFER_RDY frames. Frames on this queue are given a higher priority than frames on the normal queue. XFER_RDY frames are added to the high priority queue, and other frames to the lower priority queue. XFER_RDY frames on the higher priority queue are forwarded before frames on the lower priority queue. In another embodiment, a single queue may be used to implement XFER_RDY reordering. In this embodiment, XFER_RDY frames to be inserted in front of other types of frames in the queue.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
Optimal power saving scheduler for schedule information vector
ActiveUS20050003794A1Minimize timeSave powerEnergy efficient ICTError preventionSorting algorithmData transmission time
A new system and method is described, utilizing a scheduler based on a transmission time calculation and prioritizing algorithm. The system utilizes a Schedule Information Vector (SIV) protocol for saving power in wireless local area networks. The system comprises an access point having a priority queue, one or more stations, an SIV frame comprising an association ID for identifying one of the stations and a scheduled wake-up time for the identified station. An algorithm is employed for calculating the transmission time of downlink data for the stations. The access point originates and transmits to the one or more stations the SIV frame of the scheduled wake-up times. The current data to be transmitted to each station is accessed by the algorithm to determine the total transmission time to each station. A priority queue in the access point is ordered from the shortest to the longest transmission, assigning the highest priority to the shortest power save transmission to minimize the total power consumption of the network.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
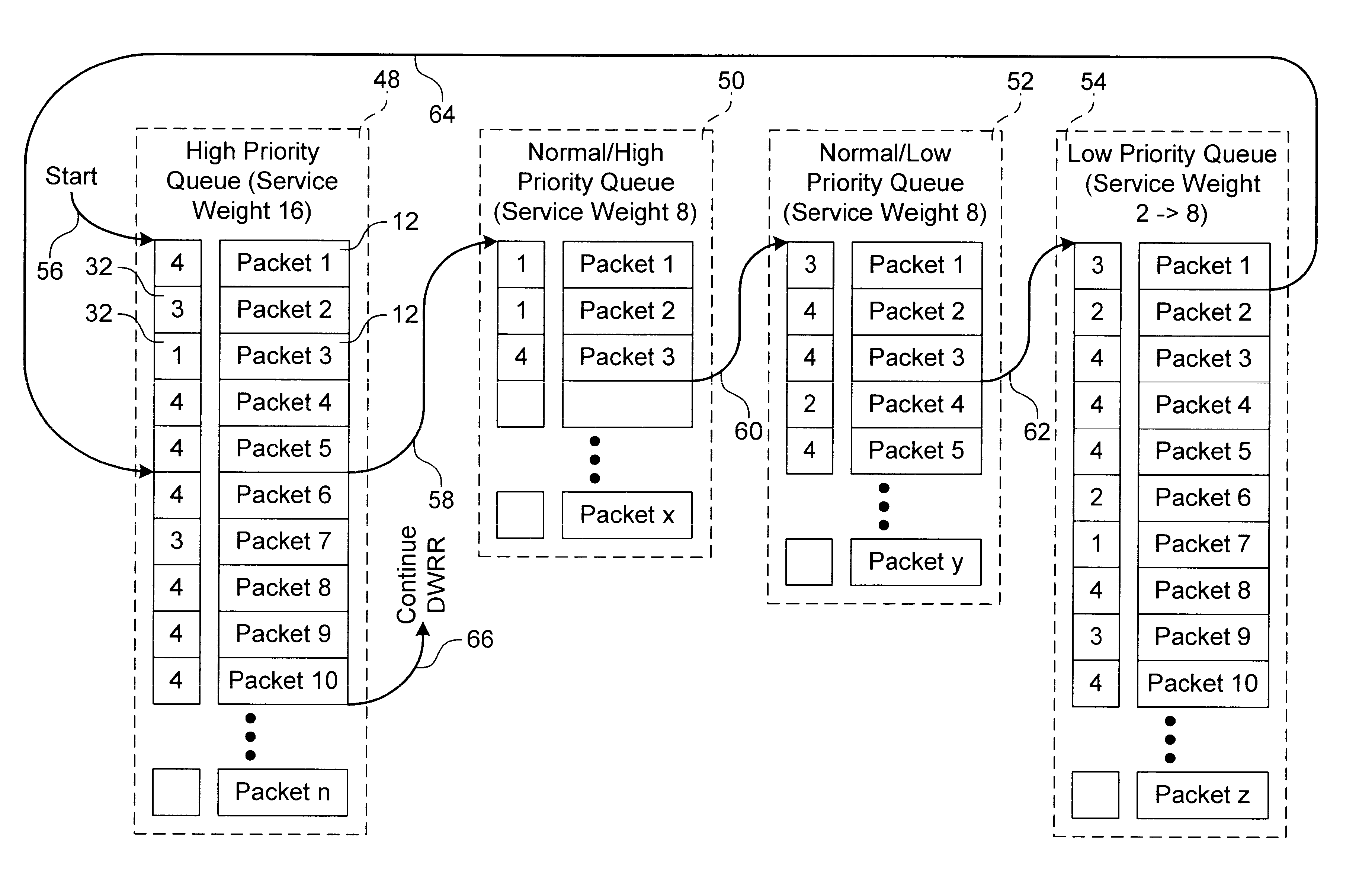
Dynamic weighted round robin queuing
InactiveUS6438135B1Improve performanceData switching by path configurationNetwork packetDistributed computing
A method for transmitting a plurality of data packets through a network. Each data packet is assigned to one of a plurality of priority queues and each priority queue has a service weight. A priority weight is assigned to each of the data packets and each priority weight has a value. Data packets are delivered from one of the priority queues until a service satisfied condition is met. The service satisfied condition is met when a combination of the values of the priority weights for each of the delivered data packets is equal to or is greater than the service weight assigned to the priority queue. A queuing switch for implementing this method is also discussed. The queuing switch includes an incoming data packet processor and a plurality of priority queues.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
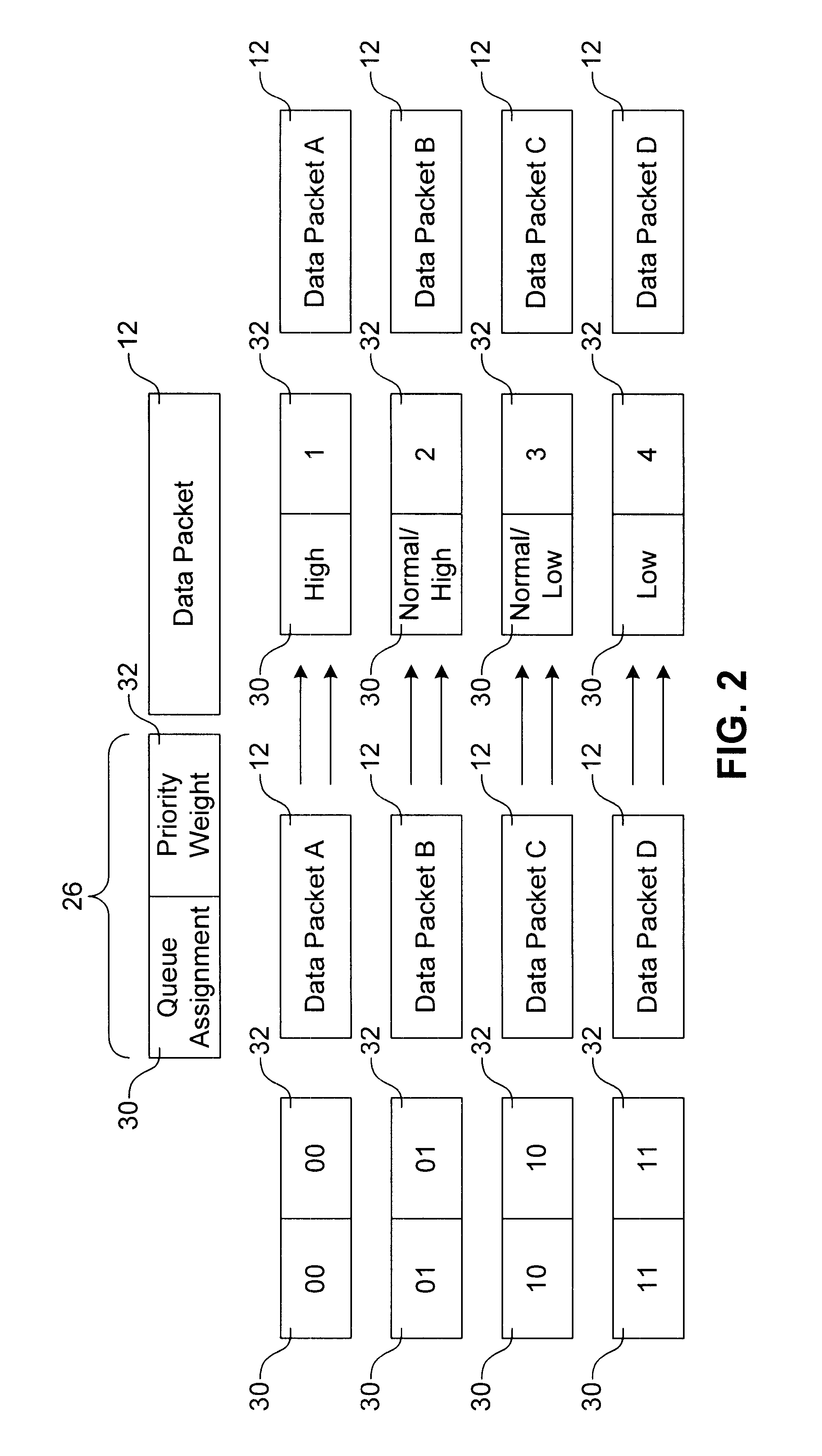
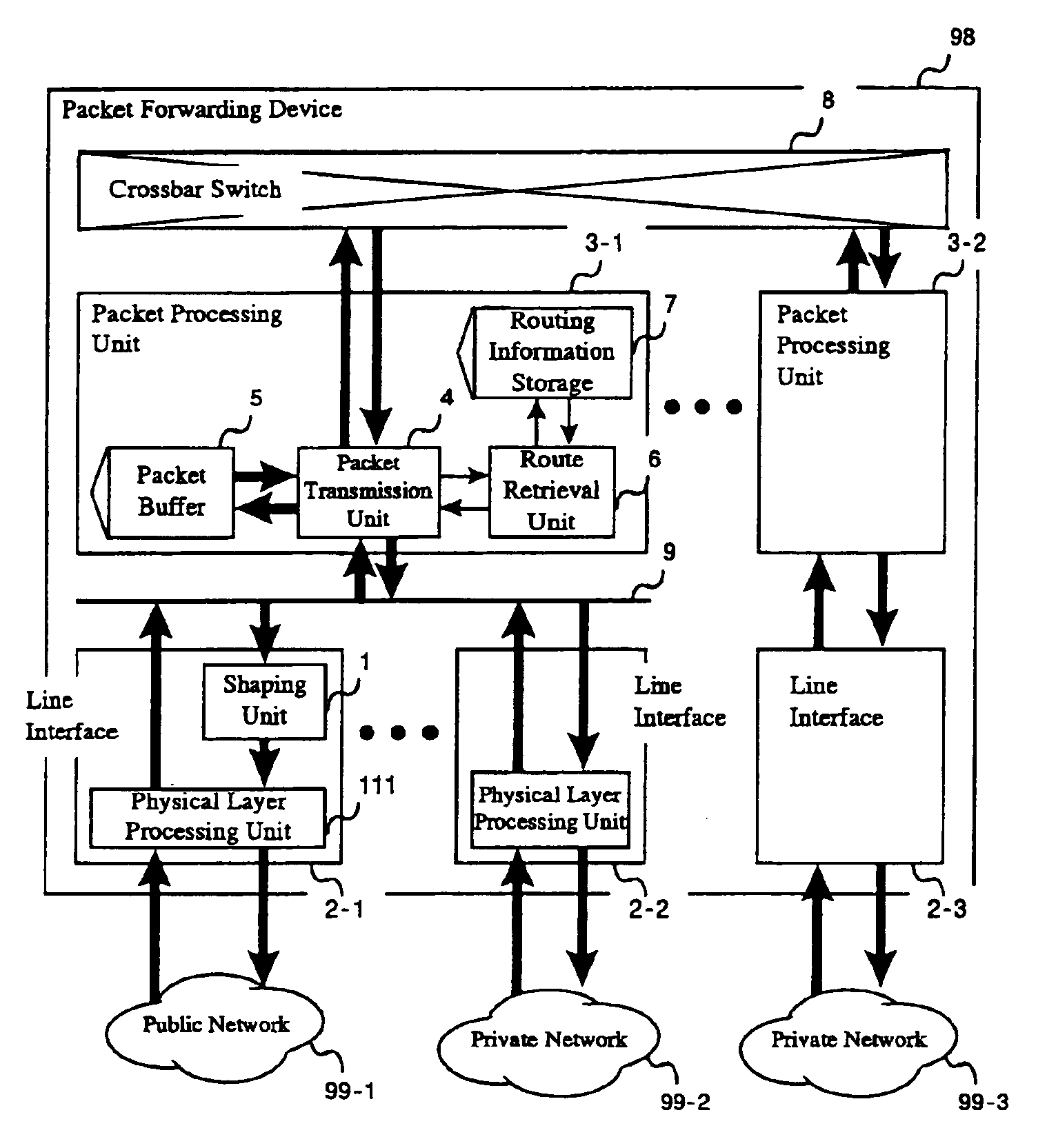
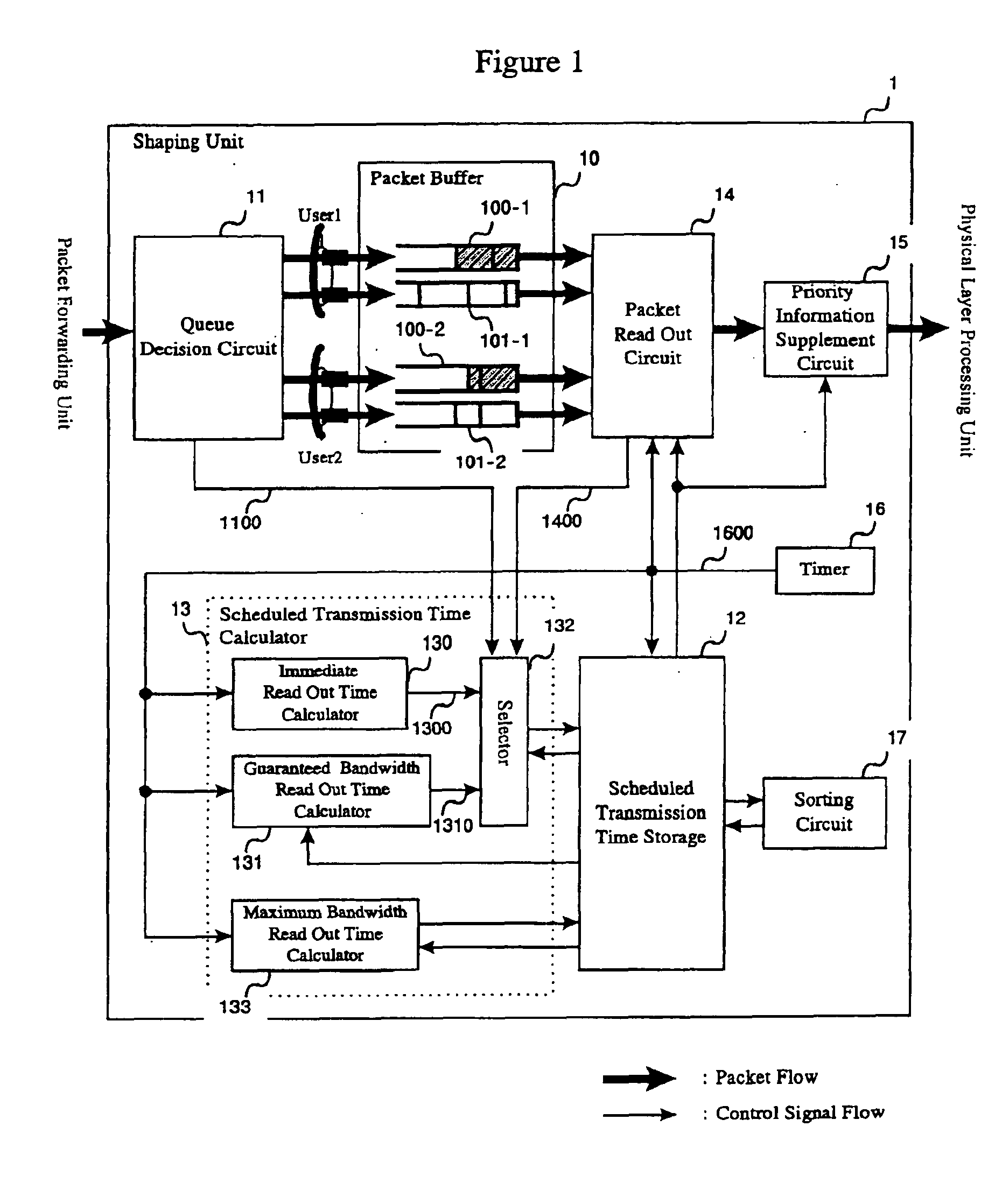
Packet forwarding device and packet priority setting method
InactiveUS6912225B1Easy to useRaise priorityError preventionTransmission systemsPriority settingLower priority
A packet forwarding device with a shaping unit, which is provided with queues for storing high priority packets and queues for storing low priority packets. The shaping unit transmits a packet read out from the non priority queue by giving a high priority when no transmit-wait packet exist in the priority queue even though the time to transmit a packet from the priority queue is reached.
Owner:ALAXALA NETWORKS
Hierarchical scheduling for communications systems
InactiveUS20050047425A1Addressing slow performanceEasy to modifyNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationCommunications systemDistributed computing
System and method for scheduling messages in a digital communications system with reduced system resource requirements. A preferred embodiment comprises a plurality of traffic queues (such as traffic queue 410) used to enqueue message of differing traffic types and a first scheduler (such as priority scheduler 430). The first scheduler to select messages from the traffic queues and provide them to a plurality of priority queues (such as priority queue 455) used to enqueue messages of differing priorities. A second scheduler (such as priority scheduler 475) then selects messages for transmission based on message priority, transmission opportunity, and time to transmit.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
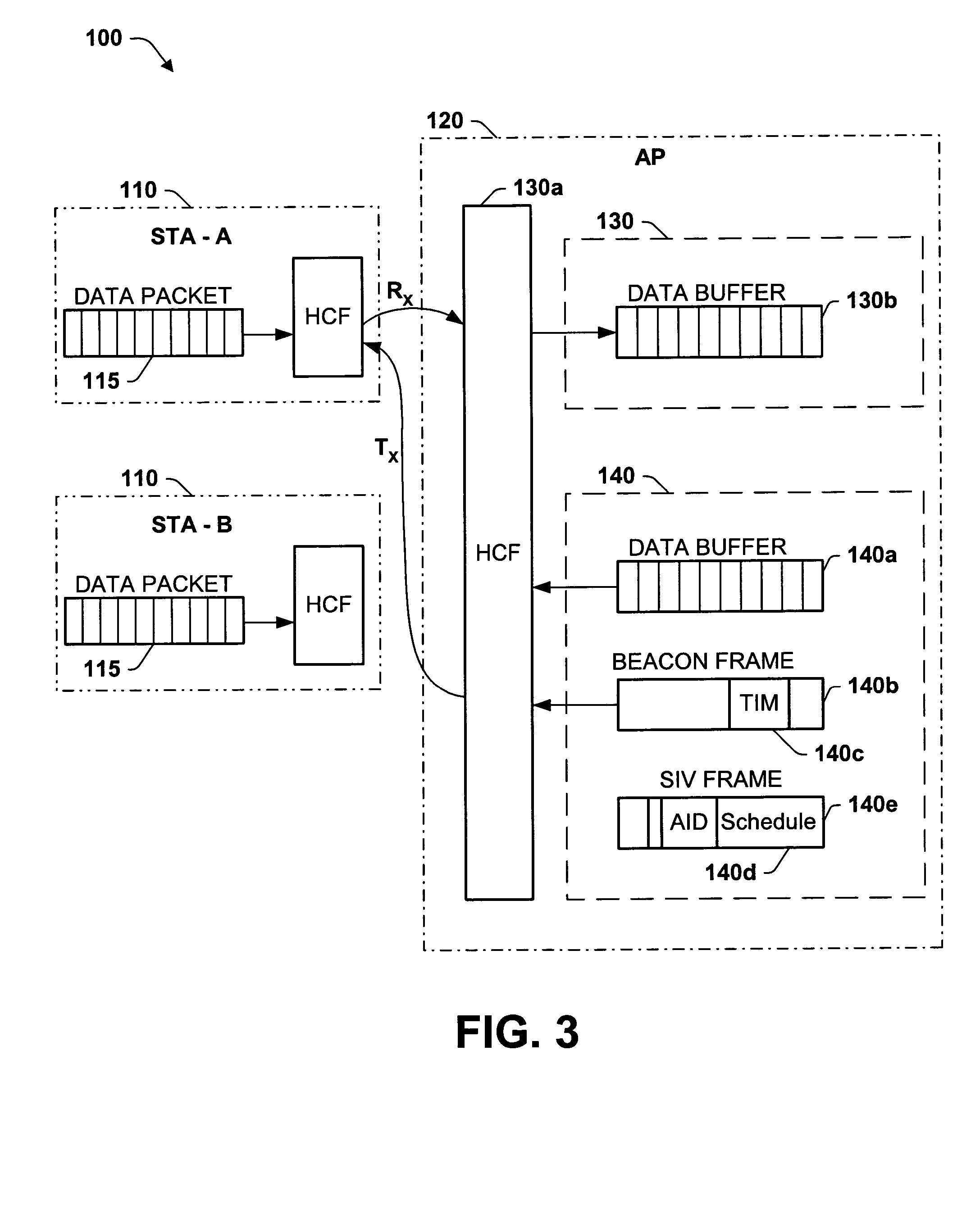
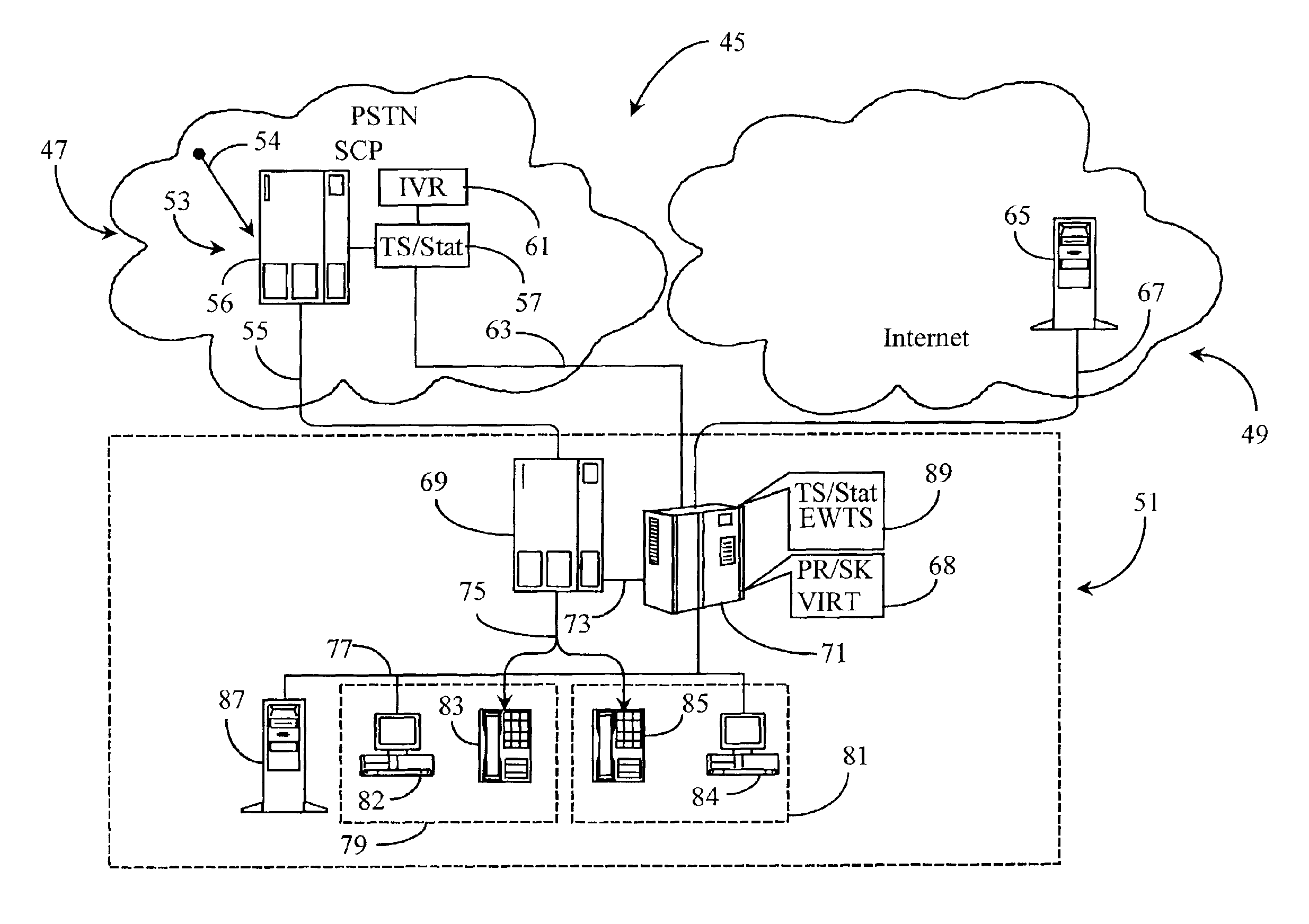
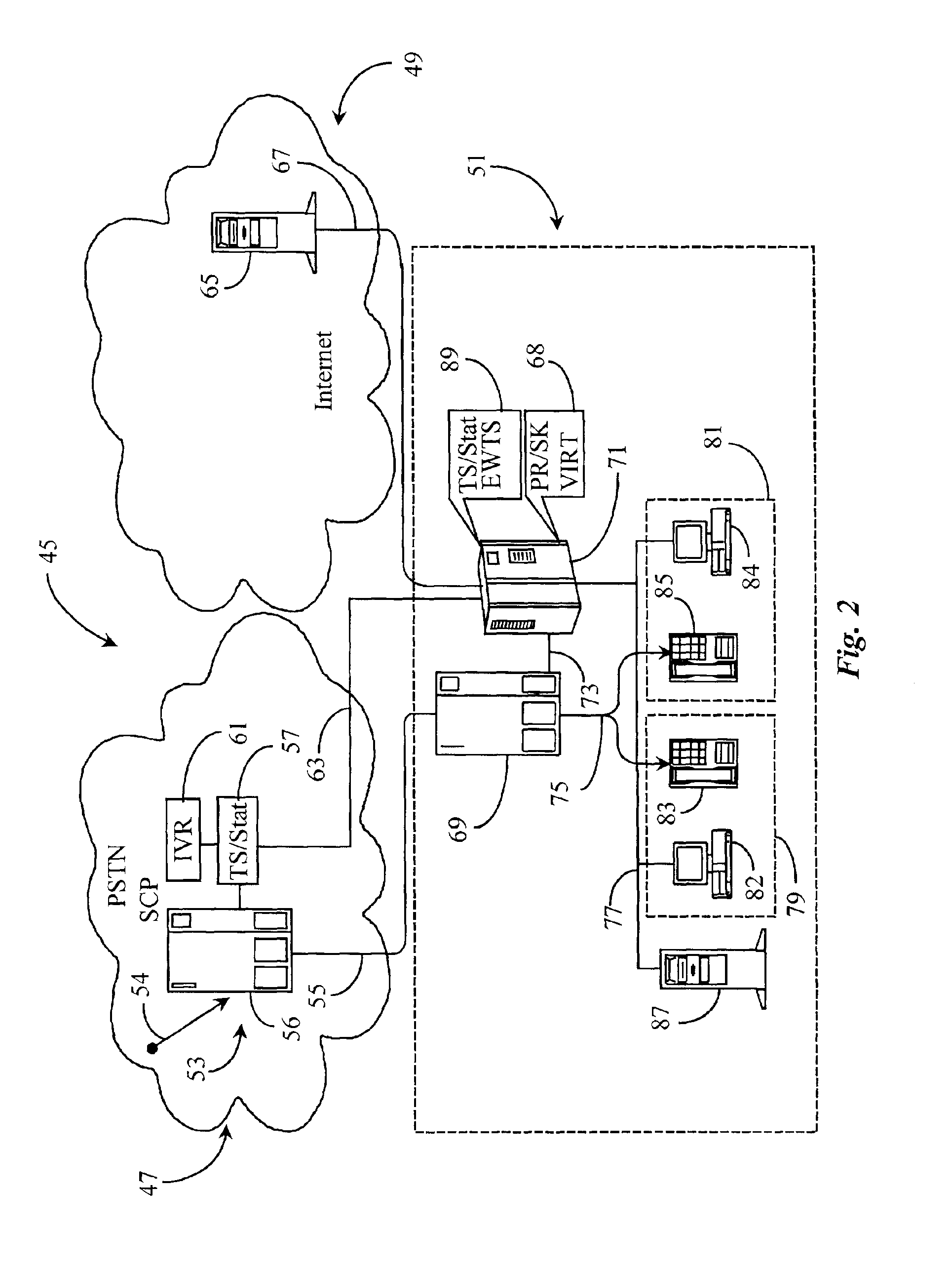
System and method for prioritizing data transmission and transmitting scheduled wake-up times to network stations based on downlink transmission duration
ActiveUS7457973B2Saving powerSave trafficEnergy efficient ICTError preventionData transmissionDownlink transmission
A new system and method is described, utilizing a scheduler based on a transmission time calculation and prioritizing algorithm. The system utilizes a Schedule Information Vector (SIV) protocol for saving power in wireless local area networks. The system comprises an access point having a priority queue, one or more stations, an SIV frame comprising an association ID for identifying one of the stations and a scheduled wake-up time for the identified station. An algorithm is employed for calculating the transmission time of downlink data for the stations. The access point originates and transmits to the one or more stations the SIV frame of the scheduled wake-up times. The current data to be transmitted to each station is accessed by the algorithm to determine the total transmission time to each station. A priority queue in the access point is ordered from the shortest to the longest transmission, assigning the highest priority to the shortest power save transmission to minimize the total power consumption of the network.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
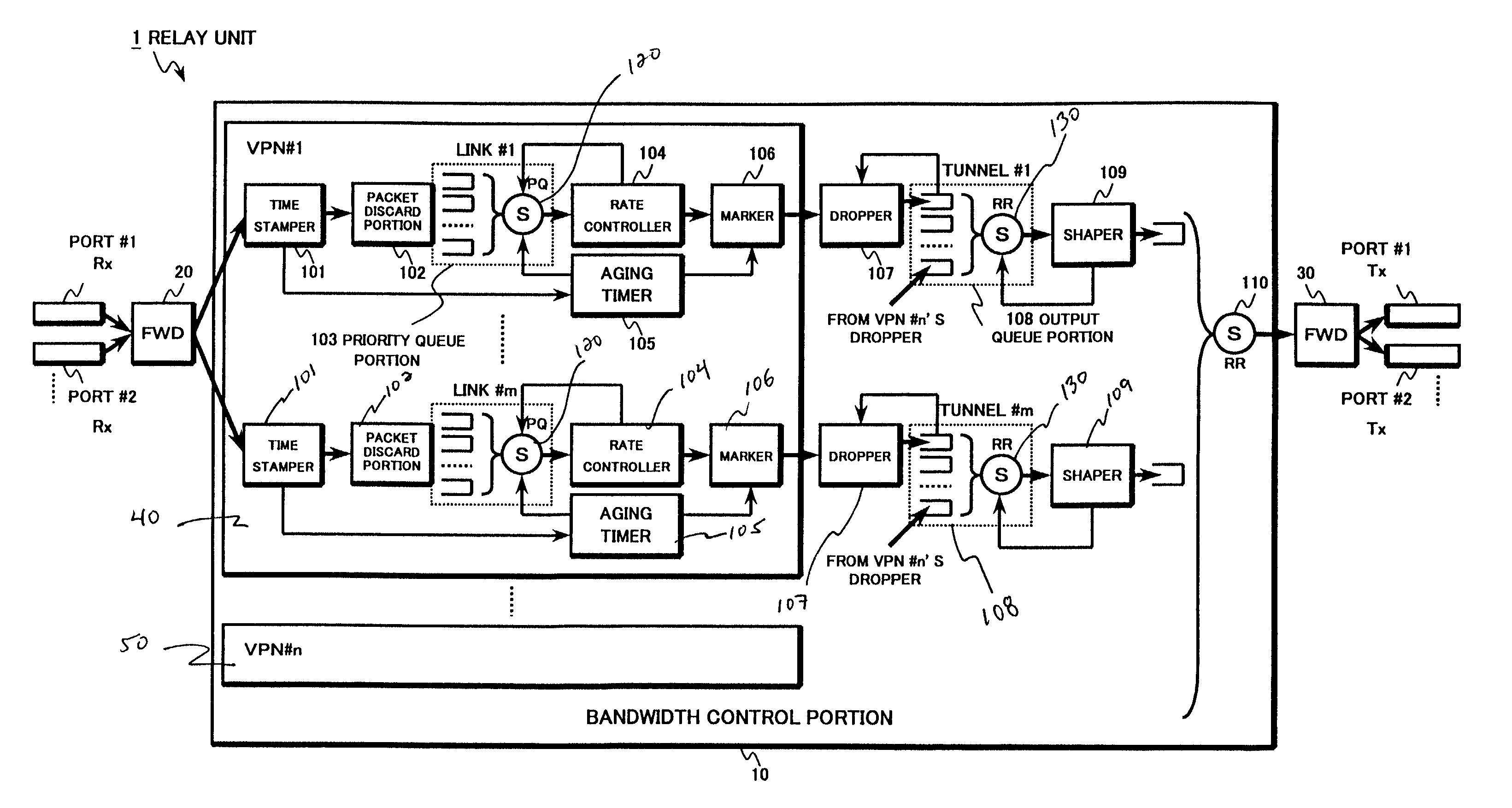
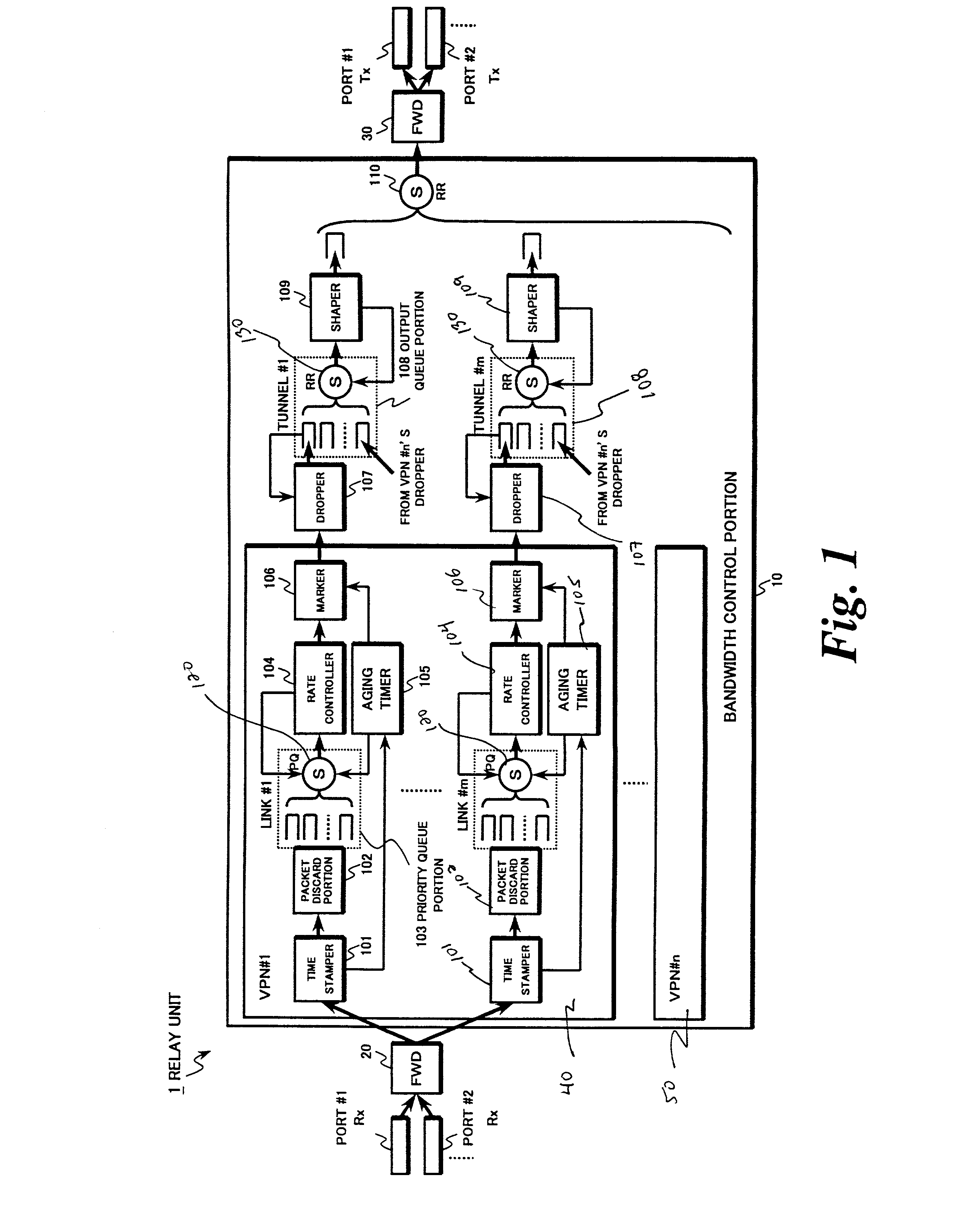
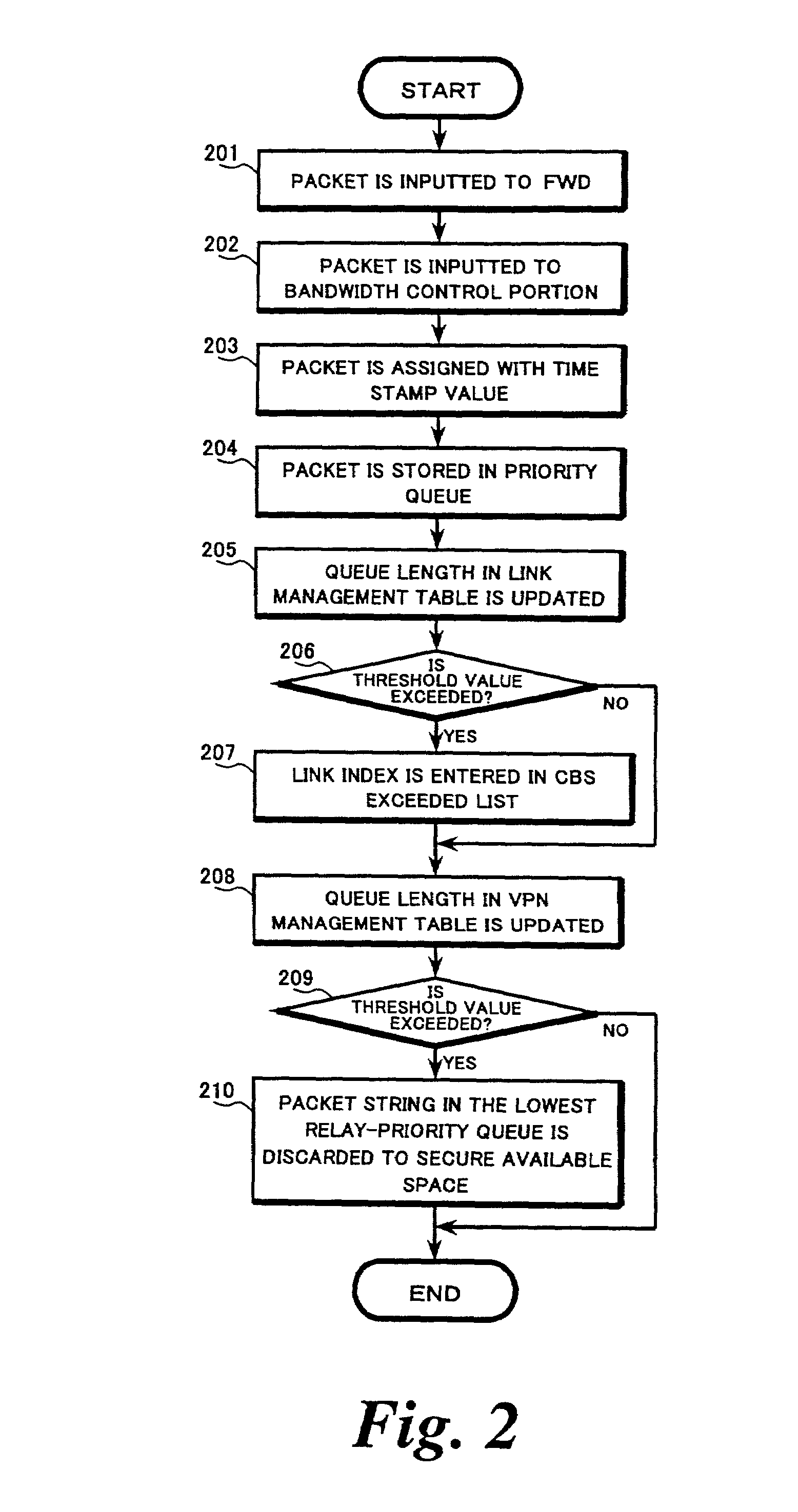
Inter-network relay system and method
An inter-network relay unit is provided that is capable of simultaneously achieving guaranteed minimum bandwidth and priority control (including relay priority, discard priority, delay priority, etc.). A rate controller outputs relatively high priority packets from priority queues as guaranteed traffic based on guaranteed bandwidth for each link. Relatively low priority packets left in the priority queues are marked for preferential discard and output as best-effort traffic by an aging timer. When an output port is congested, an output queue portion discards only the marked packets. Thus, traffic having a plurality of relay priorities can use the guaranteed minimum bandwidth effectively and the guaranteed minimum bandwidth can be secured, irrespective of change in traffic volume for each relay priority level.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
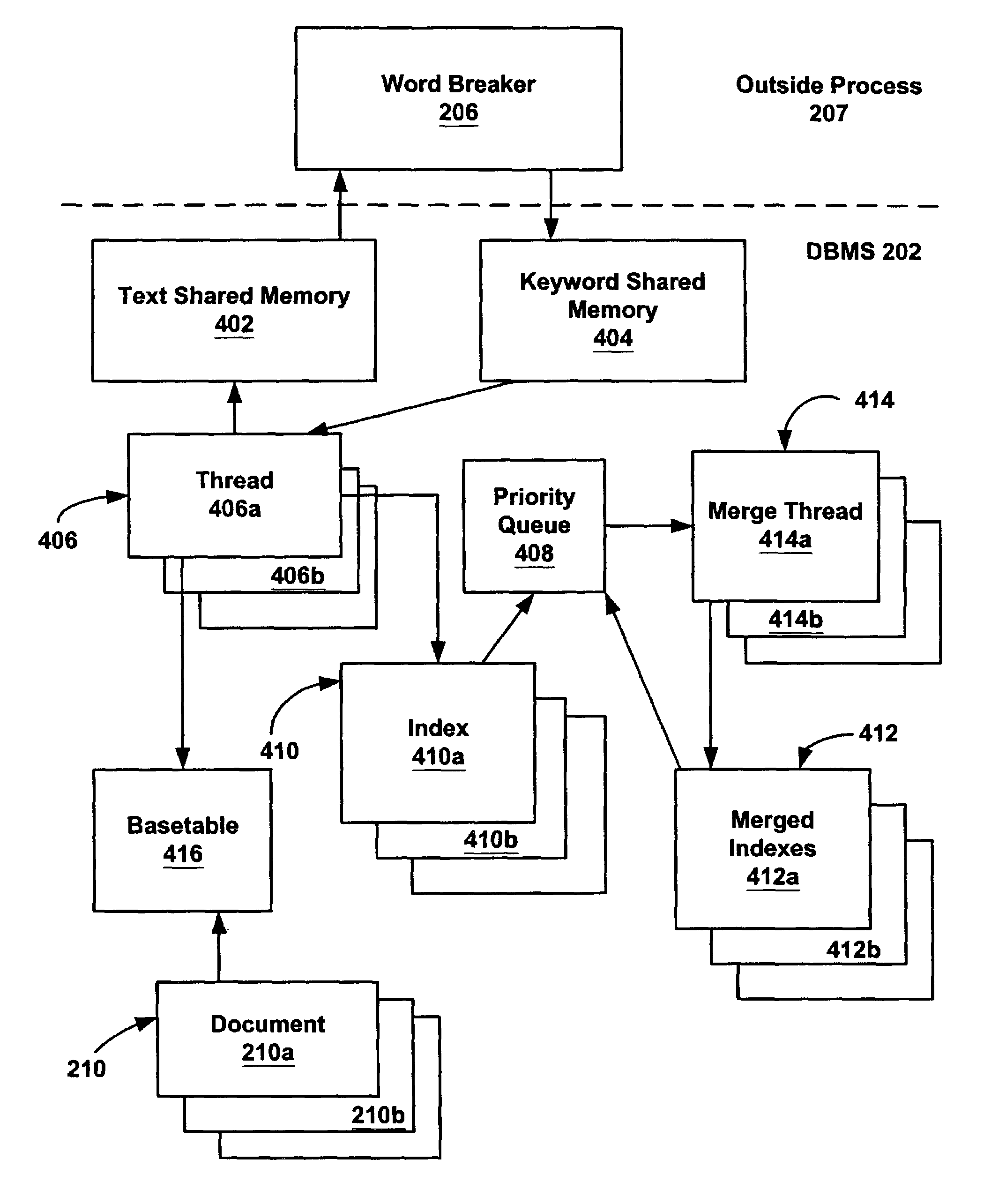
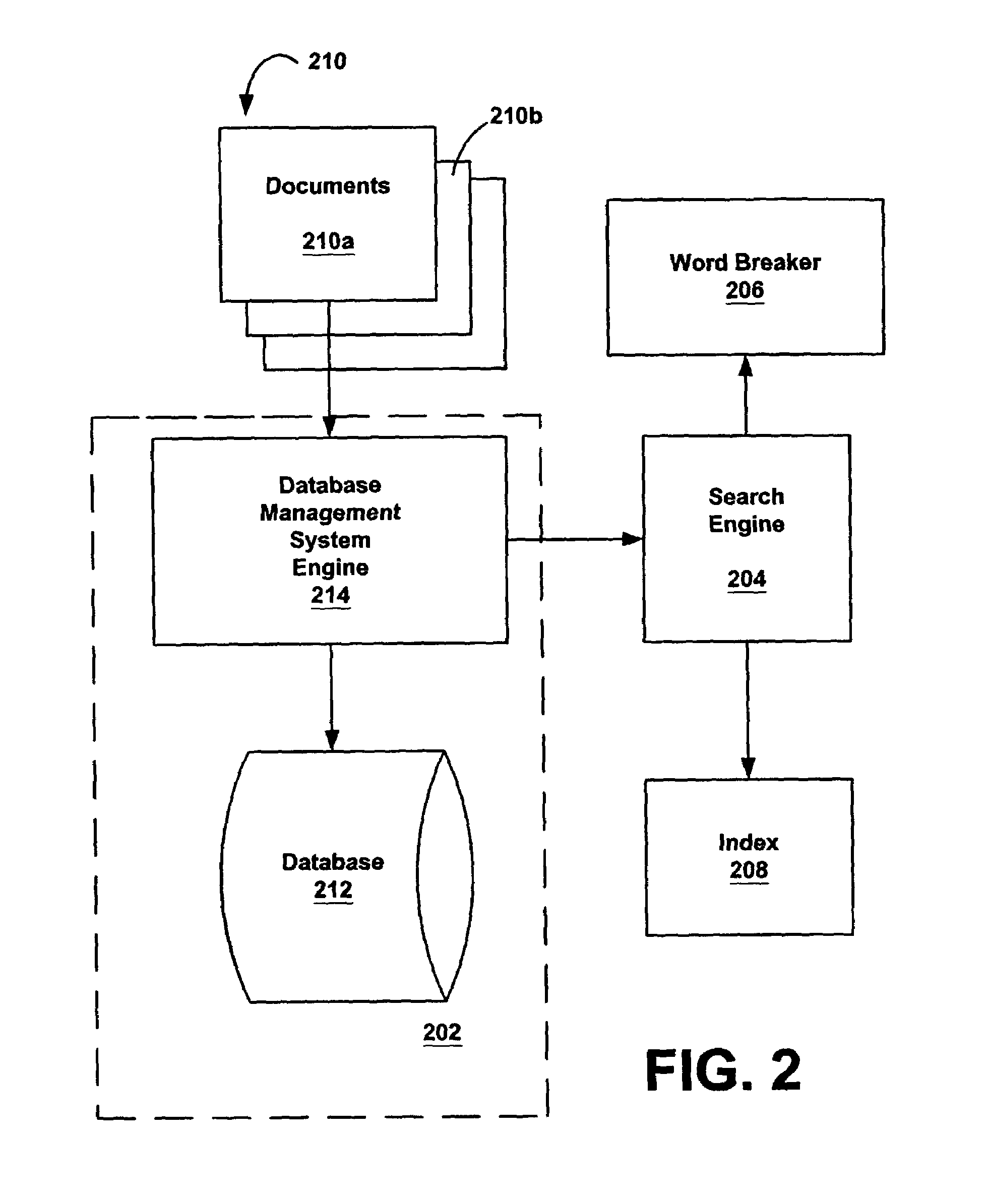
Prioritized merging for full-text index on relational store
A full-text search index system and method is generated by creating instances of a database index from an in-memory inverted list of keywords associated with a text identifier and the occurrences of the keyword in the text. Instances of the index are placed in a priority queue. A merge scheduling process determines when a merge should be initiated, selects instances of the index to be merged and selects a type of merge to perform.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multi-channel power line exchange protocol
InactiveUS7310670B1Easy to usePreserve bandwidthError prevention/detection by using return channelDigital data processing detailsStream dataExchange protocol
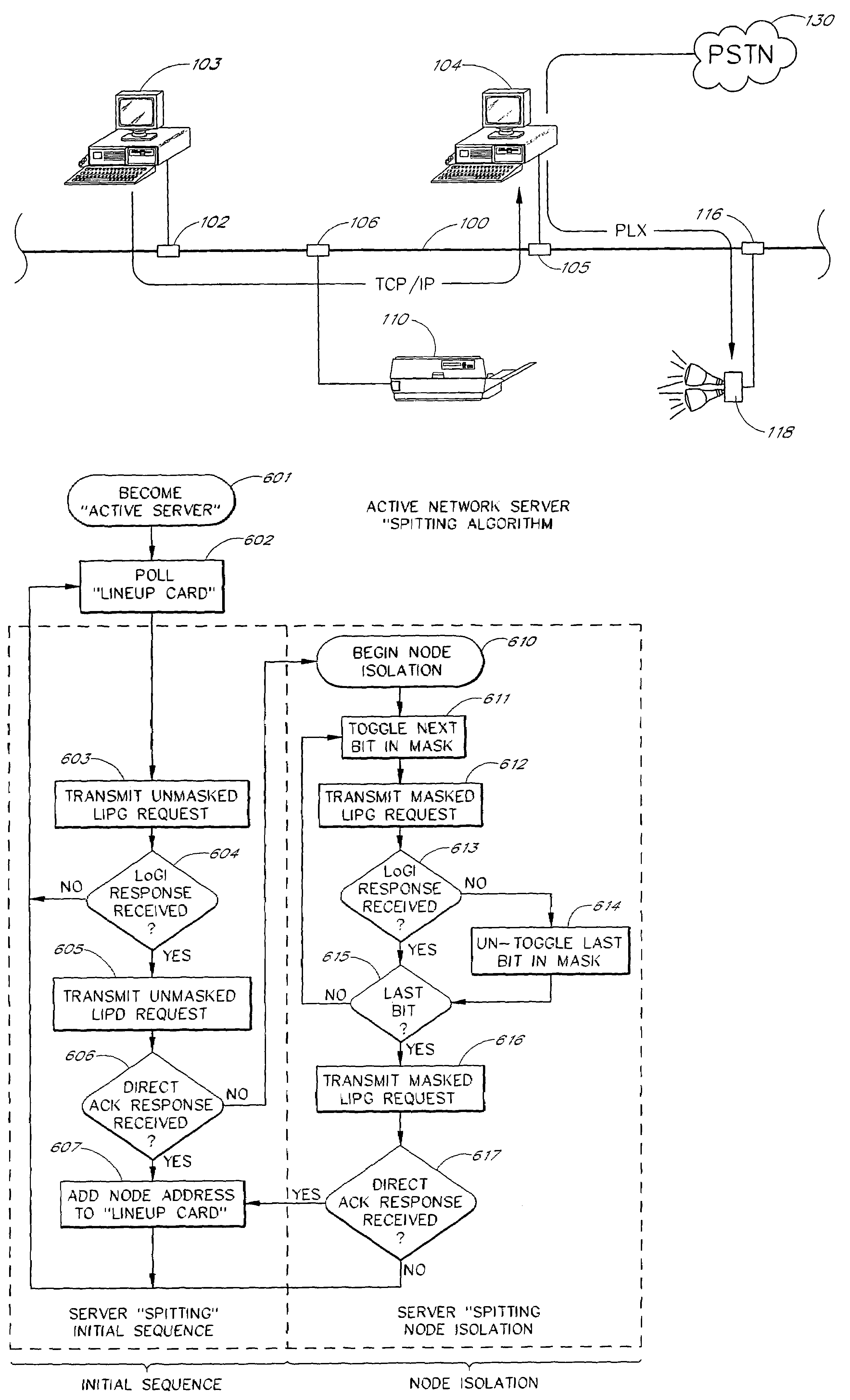
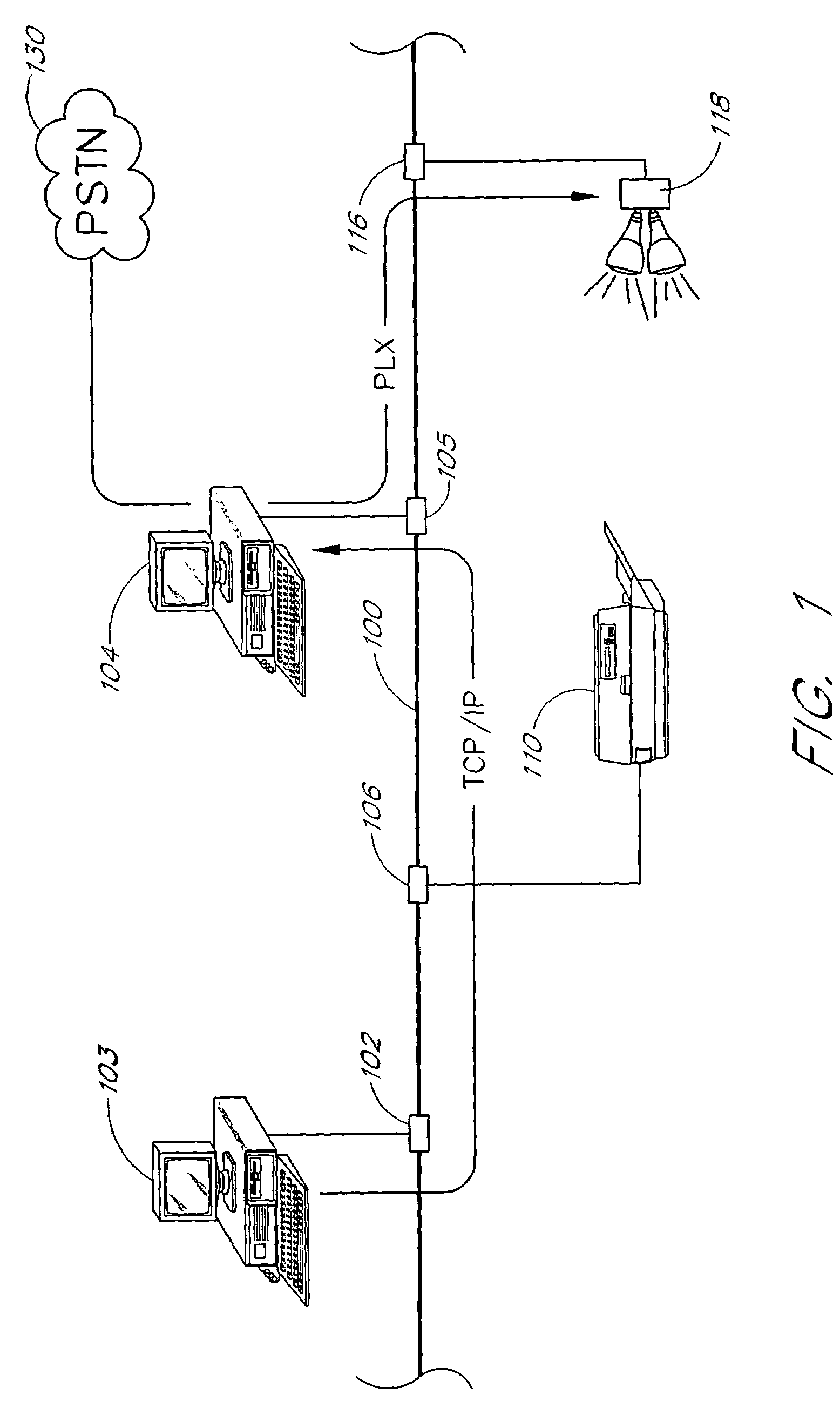
A scalable networking protocol that allows multiple nodes to communicate via a multi-channel network medium is described. The networking protocol allows any node on the network to assign itself as the active network server. The active network server polls client nodes based on a lineup card. The lineup card includes a high priority queue for low-latency devices, and a low priority queue for devices that can tolerate higher latencies. Network information is sent on the channels as fragments. The protocol provides bad-channel detection and retransmission of fragments in a fragment-by-fragment basis. Support for streaming data or asynchronous data is provided by allocating time slots on the network and allowing two intelligent nodes to talk directly to each other during count-limited token sessions, as arbitrated by the active network server. The network node serving as the active network server can be changed on a dynamic basis, and is typically determined by the first node initiating a transmit request on a sleeping network. Client nodes are addressed by dynamic-polling using an address isolation scheme.
Owner:INARI +2
Relaying apparatus
InactiveUS20020061027A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationEngineeringQueue manager
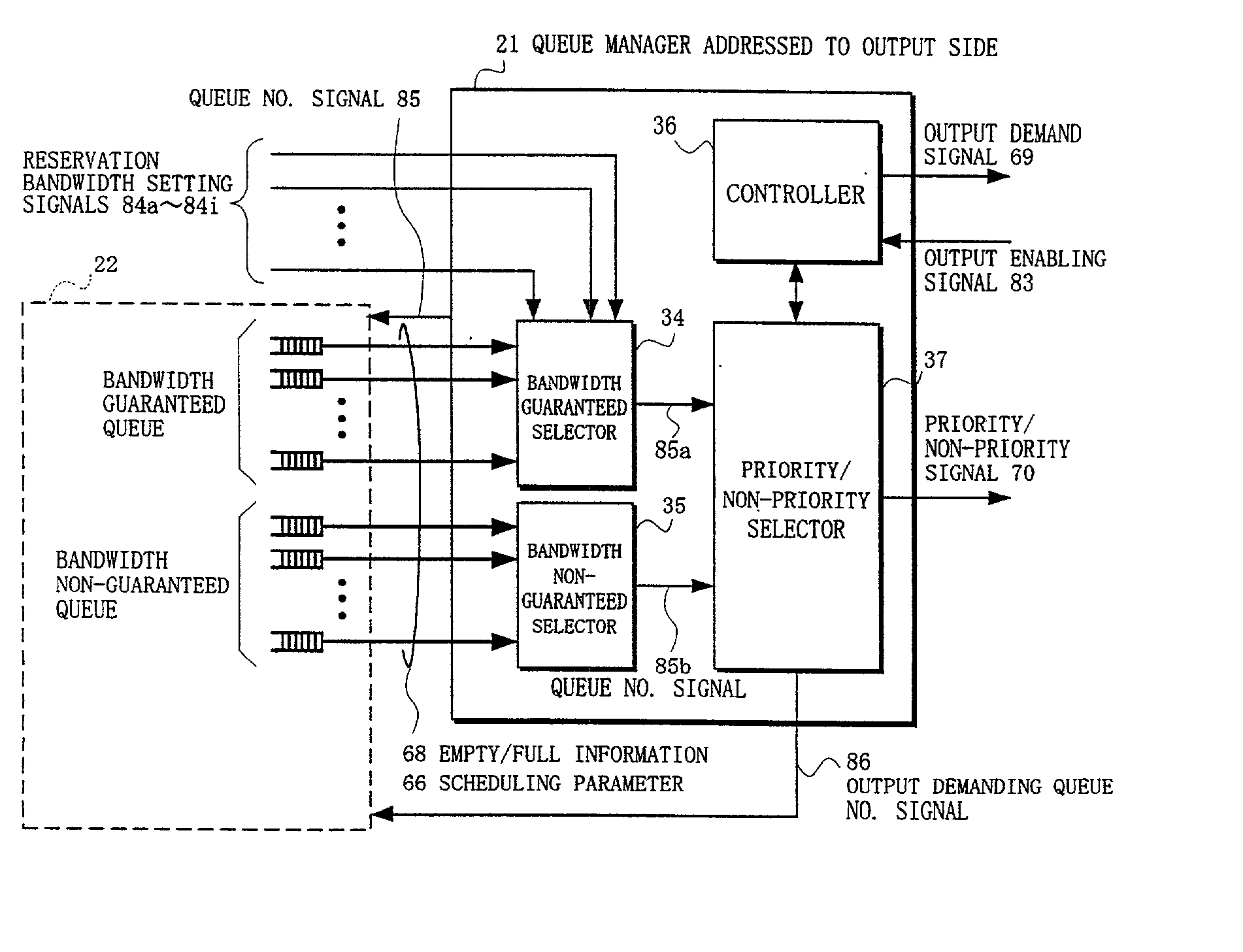
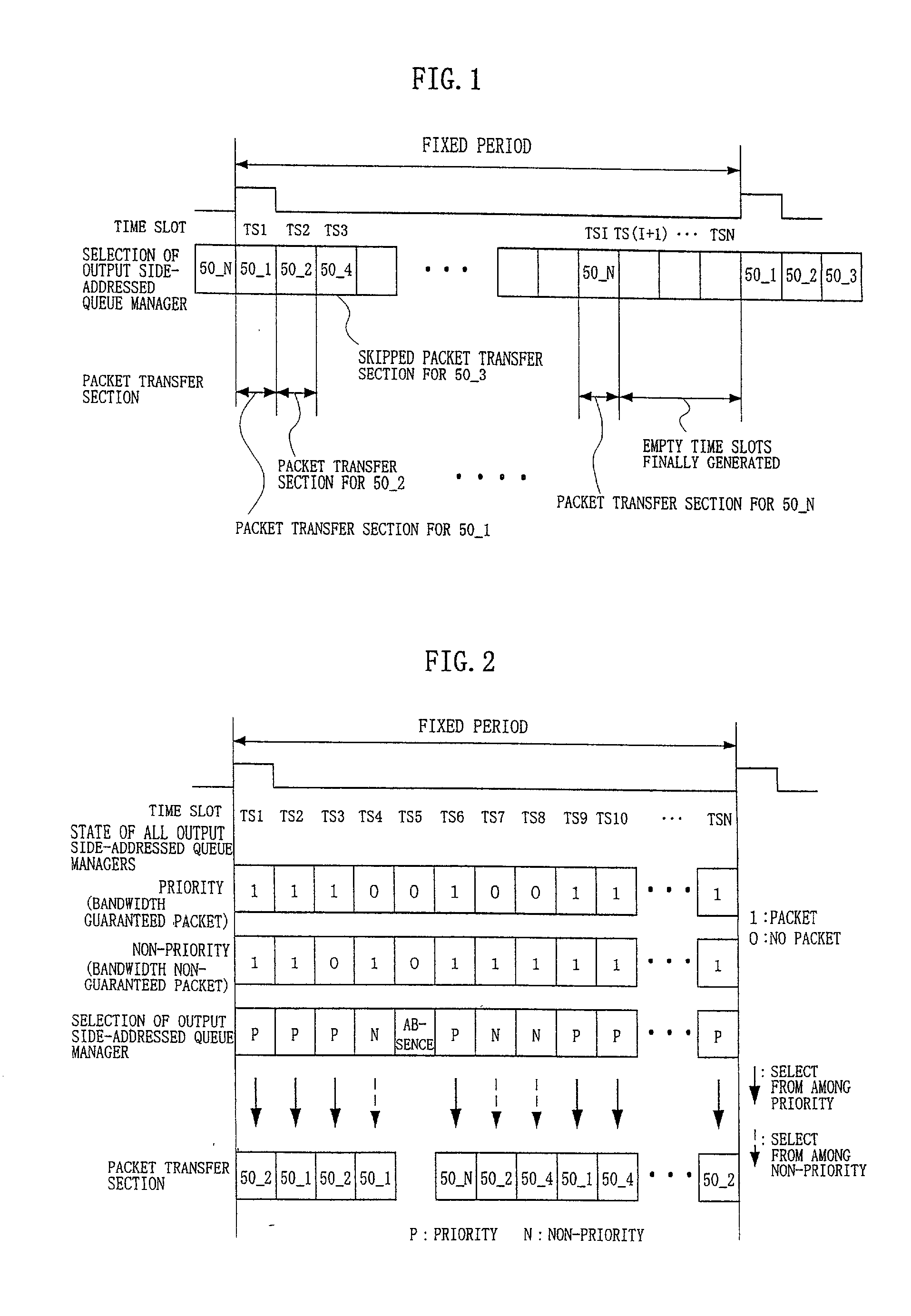
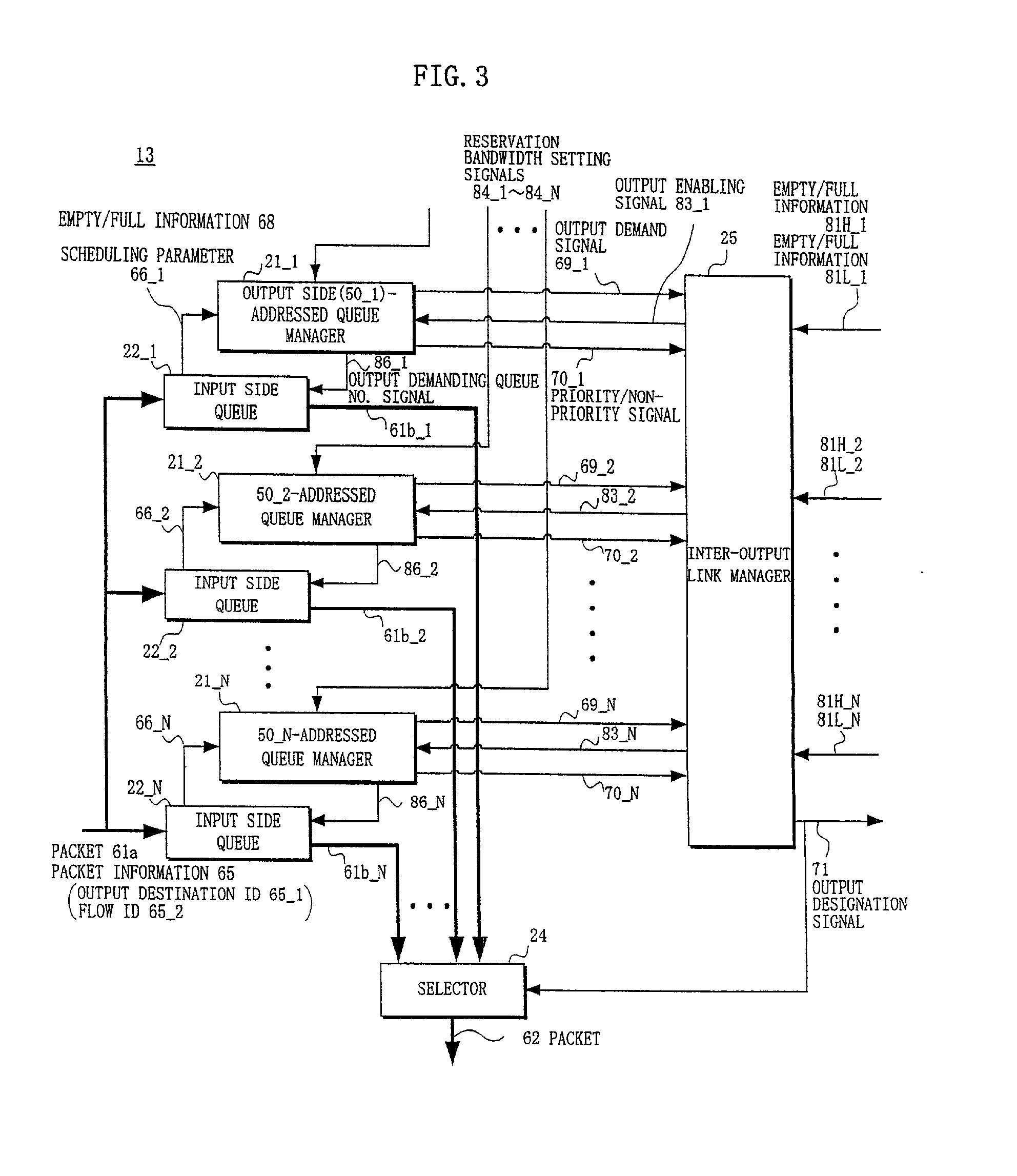
In a relaying apparatus comprising input side accommodating portions including input side queues, a plurality of output side accommodating portions including output side queues, and a switch fabric for mutually connecting the input side queues and the output side queues in a mesh form, in a time slot of a fixed period, the output side-addressed queue managers corresponding to the output side accommodating portions select a bandwidth guaranteed packet so as to guarantee a bandwidth, and output priority / non-priority signals for indicating which of the bandwidth guaranteed packet and a bandwidth non-guaranteed packet has been selected, and output demand signals of the packet. An inter-output link manager selects the packet having an empty area in the priority queue or non-priority queue of the output side accommodating portion as a destination corresponding to the packet which is demanded to be outputted.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
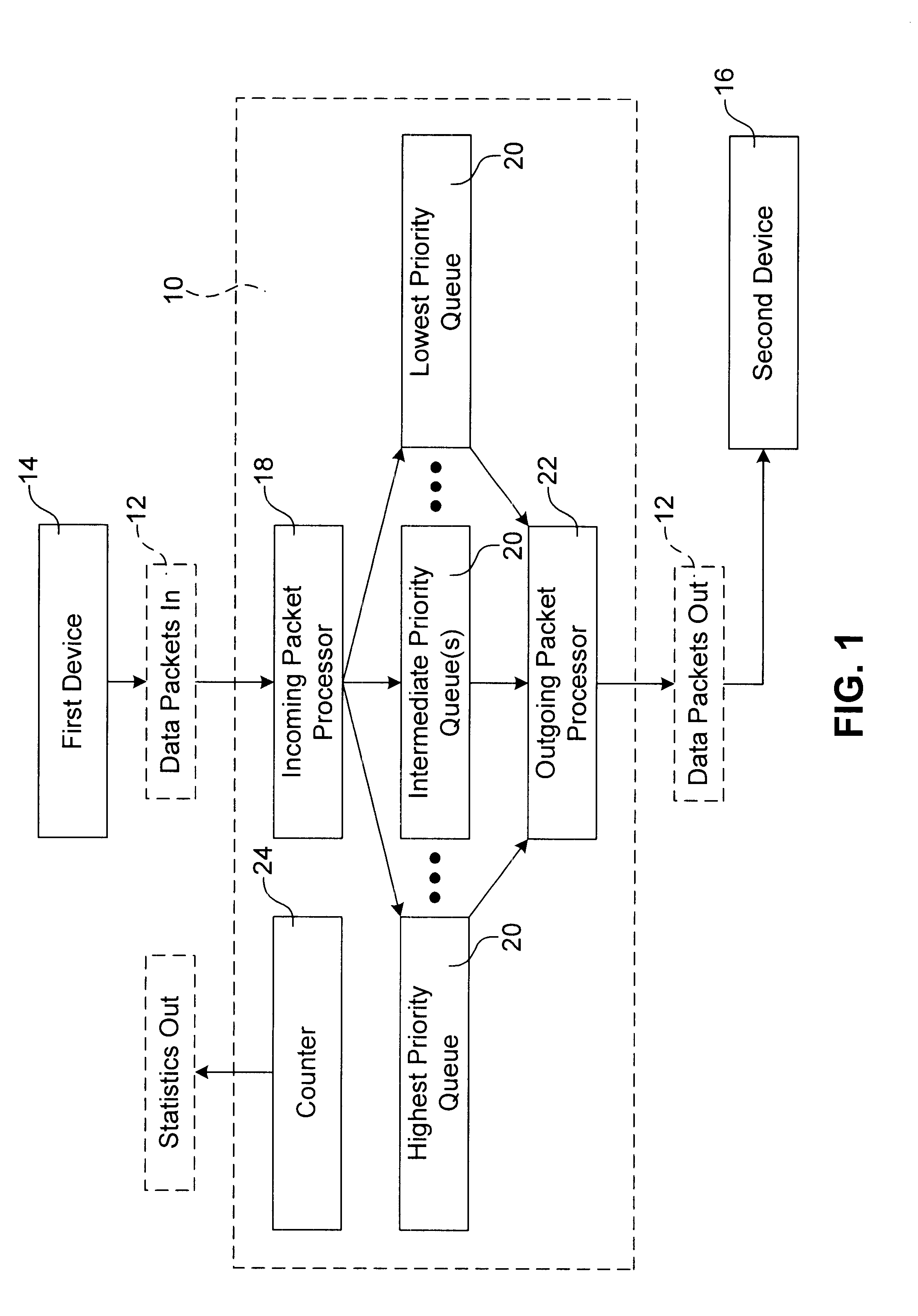
Managing priority queues and escalation in wireless communication systems
InactiveUS20040092278A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesStreaming dataLower priority
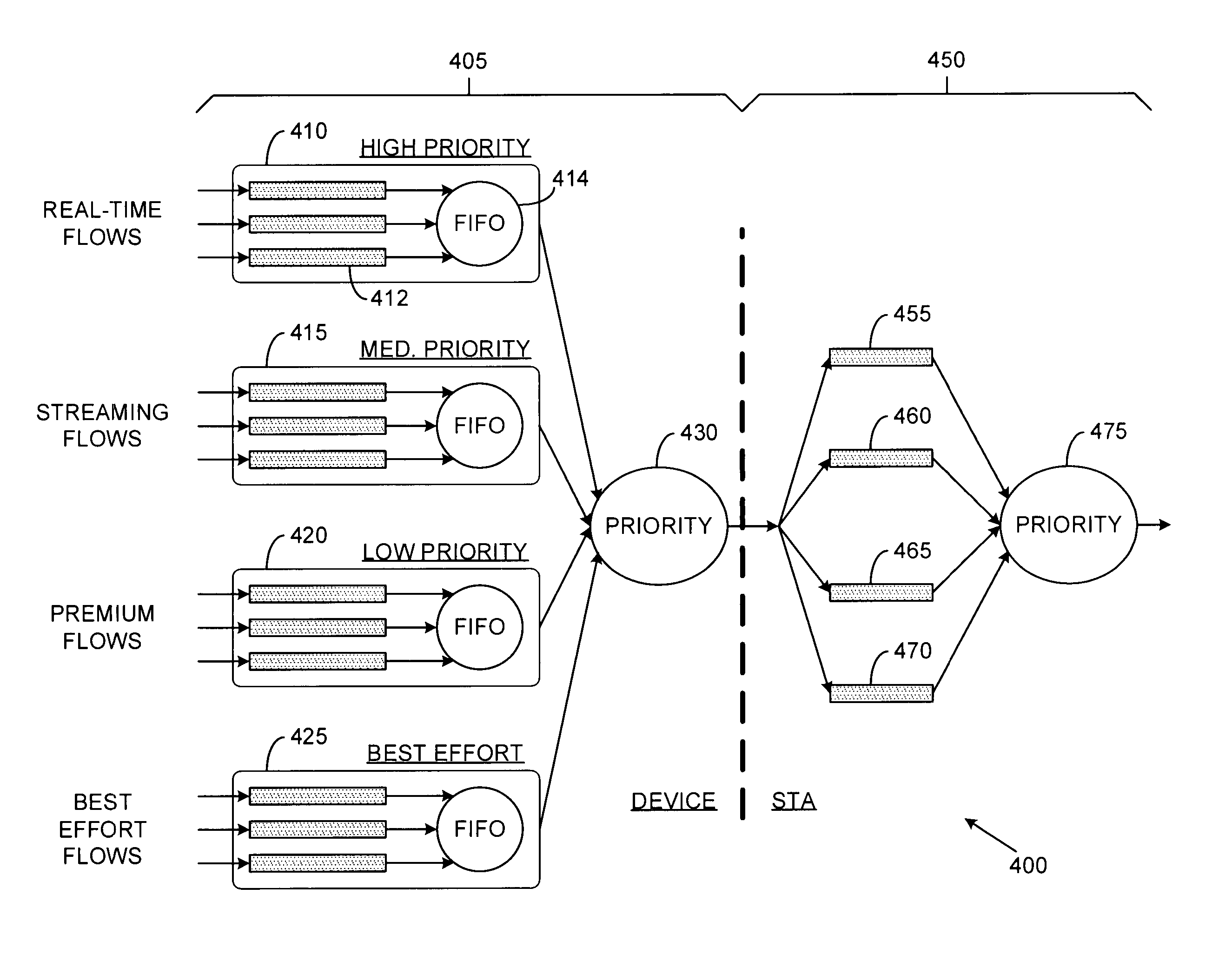
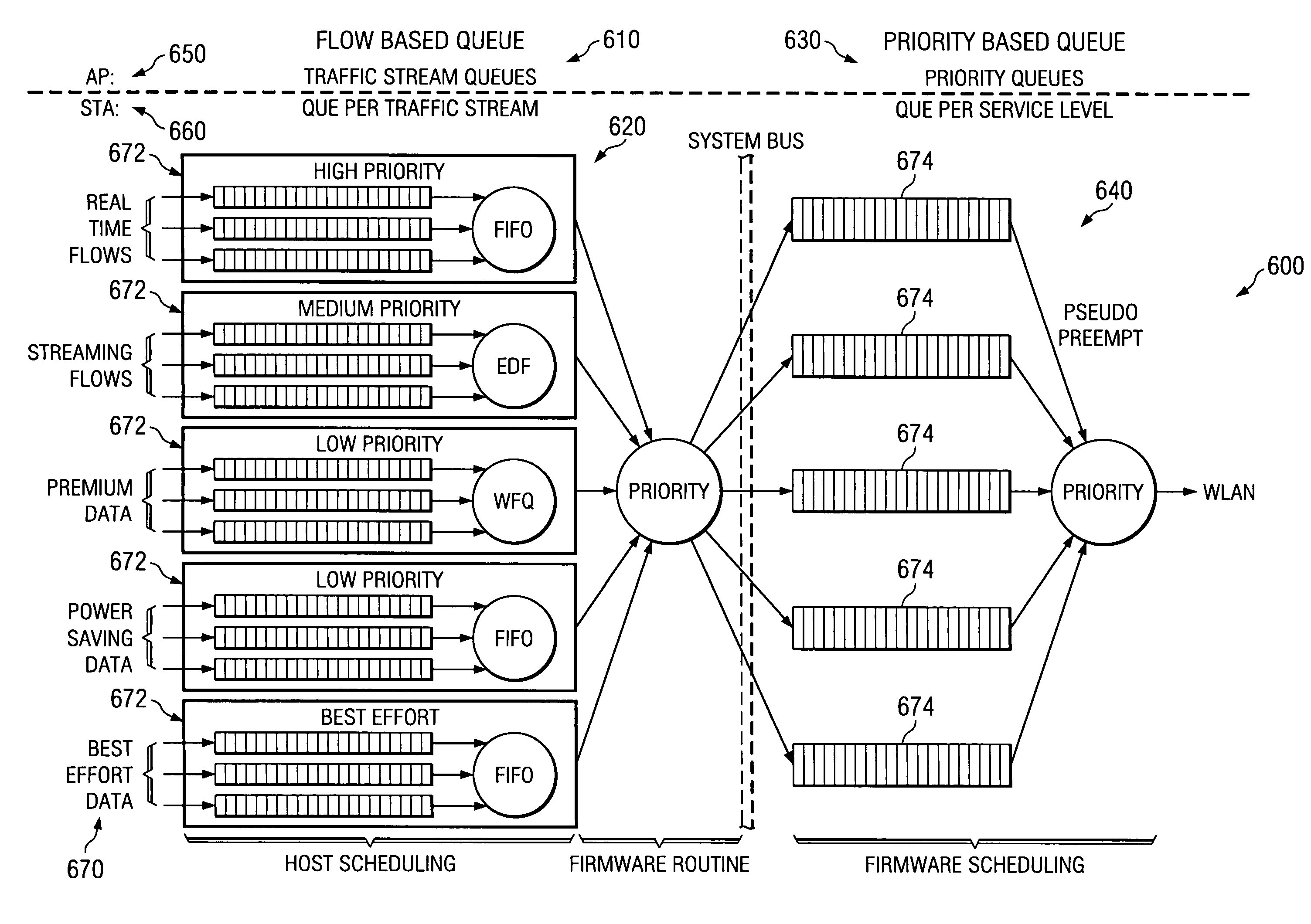
A method and system for servicing data traffic in wireless local area networks (such as IEEE 802.11 networks) in multiple queues having different levels of priority. These queues include at least a low priority queue for 'best effort' traffic, a medium priority queue for streaming data such as video pictures, and a high priority queue for voice traffic, and are serviced in order of decreasing priority. To prevent the 'best effort' traffic in the low priority queue from being 'starved', a bit is set to indicate when such a condition is likely to occur, and the low priority queue is served first when that bit has been set. Alternatively, low and medium priority traffic is handled on a weighted round-robin basis, and high priority traffic is given strict priority over both. Transmit and receive queues are handled on a rotating priority basis.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for scheduling satellite data product production tasks in parallel based on multithread
ActiveCN101739293ASolve scheduling problemsIncrease the number of tasksResource allocationSatellite dataIdle time
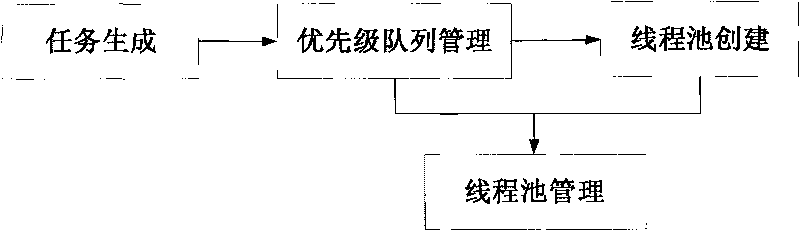
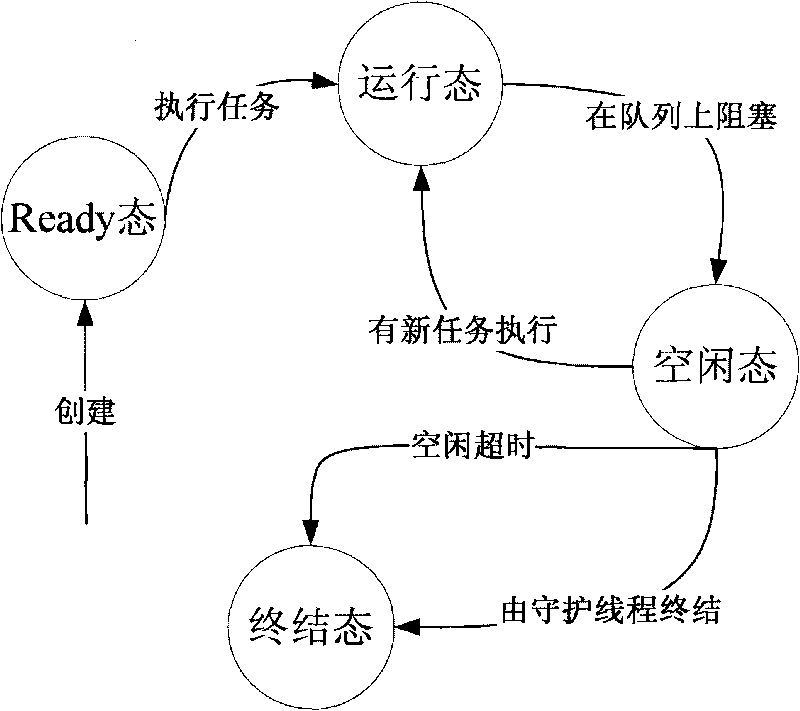
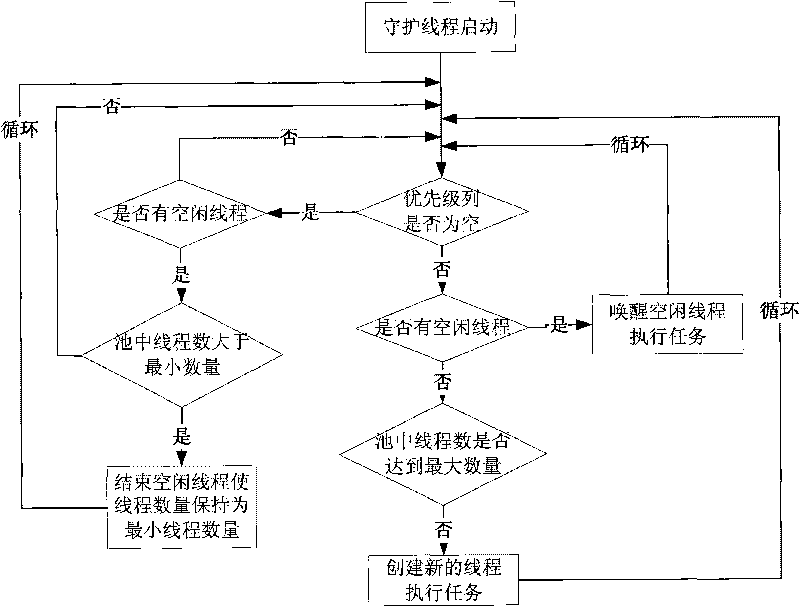
The invention discloses a method for scheduling satellite data product production tasks in parallel based on multithread. The method comprises the following steps: setting priorities for tasks to be scheduled for executing and realizing a uniformed interface; adding the tasks into a priority queue according to an order of the priorities from high to low; setting the maximum number and the minimal number of the tasks of a thread pool, and the longest idle time of a thread; and starting a daemon thread in the thread pool and a plurality of task threads to execute the tasks, wherein the daemon thread regulates the number of the task threads dynamically according to the situation of task amount. The method can utilize system resource rationally, aims at the data product production of a satellite ground application system, and solves the difficult points of complicated product production processes, long task executing time, large task amount, high real time and parallelism degree for scheduling the tasks and the like.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for scheduling tasks
InactiveUS7372857B1Increase flexibilityEasy to findData switching by path configurationMulti parameterDistributed computing
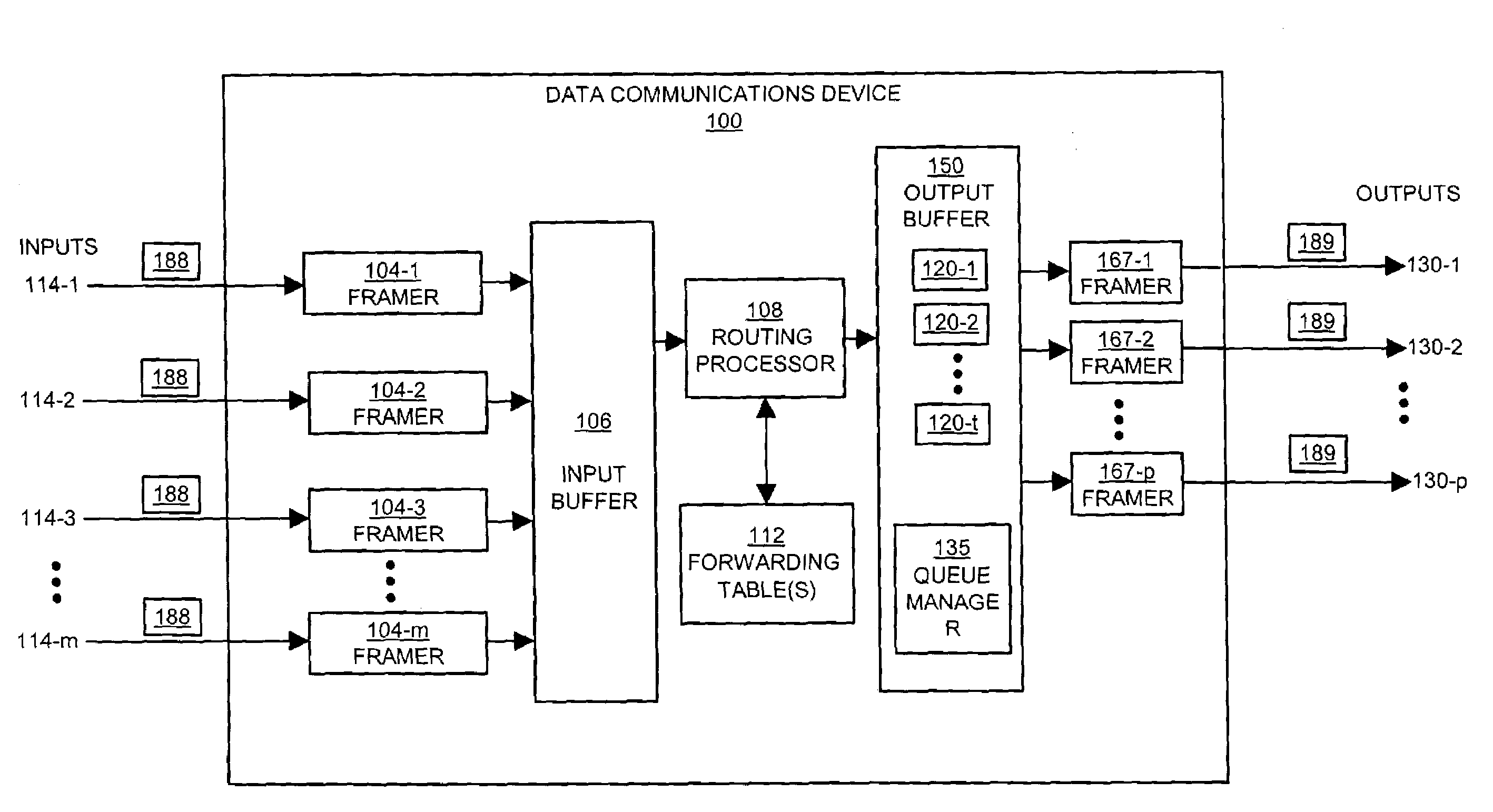
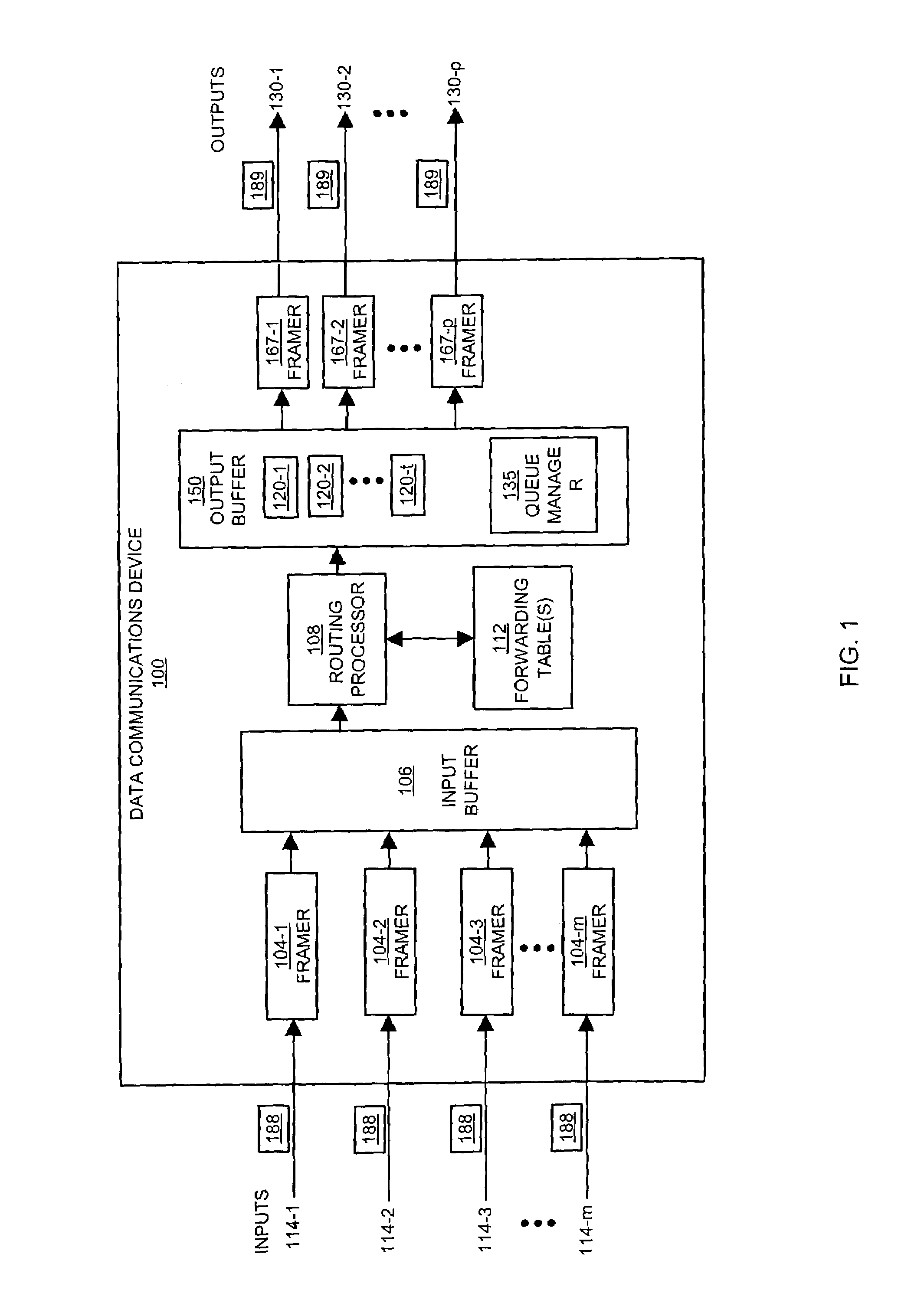
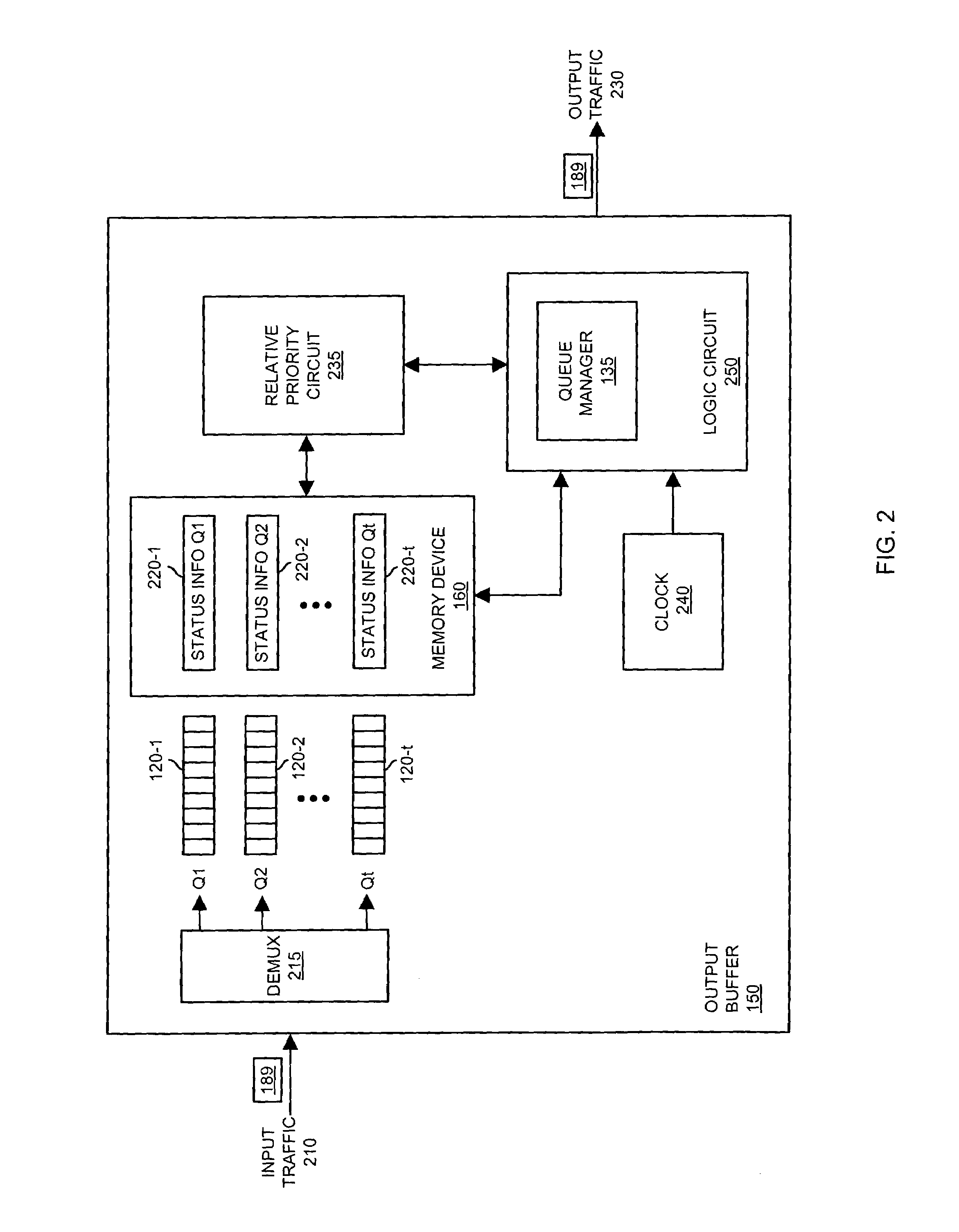
Queues are scheduled for outputting data using a hierarchical tree. Each level of the hierarchical tree includes multiple entries for storing status information associated with the queues. For example, a given entry of the tree stores multi-parameter status information associated with a corresponding queue to be serviced. To determine which of the queues is next in line for servicing, a logic circuit compares the multi-parameter status information stored in two or more entries of the tree. The next scheduled queue or highest priority queue in the tree is then serviced by outputting at least some of its data.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Optimal power saving scheduler for 802.11e APSD
ActiveUS7245946B2Save trafficSave powerEnergy efficient ICTPower managementSorting algorithmDelayed time
A new system and method is described, utilizing a scheduler based on a transmission power consumption calculation and prioritizing algorithm. The system utilizes the (APSD) protocol specified in the 802.11e draft for saving power in wireless local area networks. The system comprises an access point having a priority queue, one or more stations, an APSD frame comprising an association ID for identifying one of the stations and a scheduled wake-up time for the identified station. An algorithm is employed for calculating the total transmission power consumption of downlink data for the stations. The AP originates and transmits to the one or more stations the APSD frame of the scheduled activation delay time. The current data to be transmitted to each station is accessed by the algorithm to determine the total transmission power consumption to each station. A priority queue in the AP is ordered from the lowest to the highest receiving power consumption, assigning the highest priority to the lowest power consumption transmission to minimize total power consumption to the PS stations in the AP queue.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multidimensional resource scheduling system and method for cloud environment data center
InactiveCN102932279AAccurate abstractionIncrease weightData switching networksResource poolVirtualization
The invention provides a multidimensional resource scheduling system and method for a cloud environment data center, belonging to the field of cloud computing. The system provided by the invention comprises a user application request submitting module, a resource status acquiring module, a resource scheduling module, an application request priority queuing module and a virtualized physical resource pool. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: firstly detecting the status information of multidimensional resources in the virtualized physical resource pool and a current application request set in the user application request submitting module, which are acquired by the resource status acquiring module; then defining an application request priority queue which is suitable for the status balanced consumption of the current multidimensional resources in the virtualized physical resource pool by using a multiple-attribute-decision-making application priority scheduling algorithm; and finally submitting the application request which has the highest priority and meets resource constraints to the cloud environment data center for execution.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
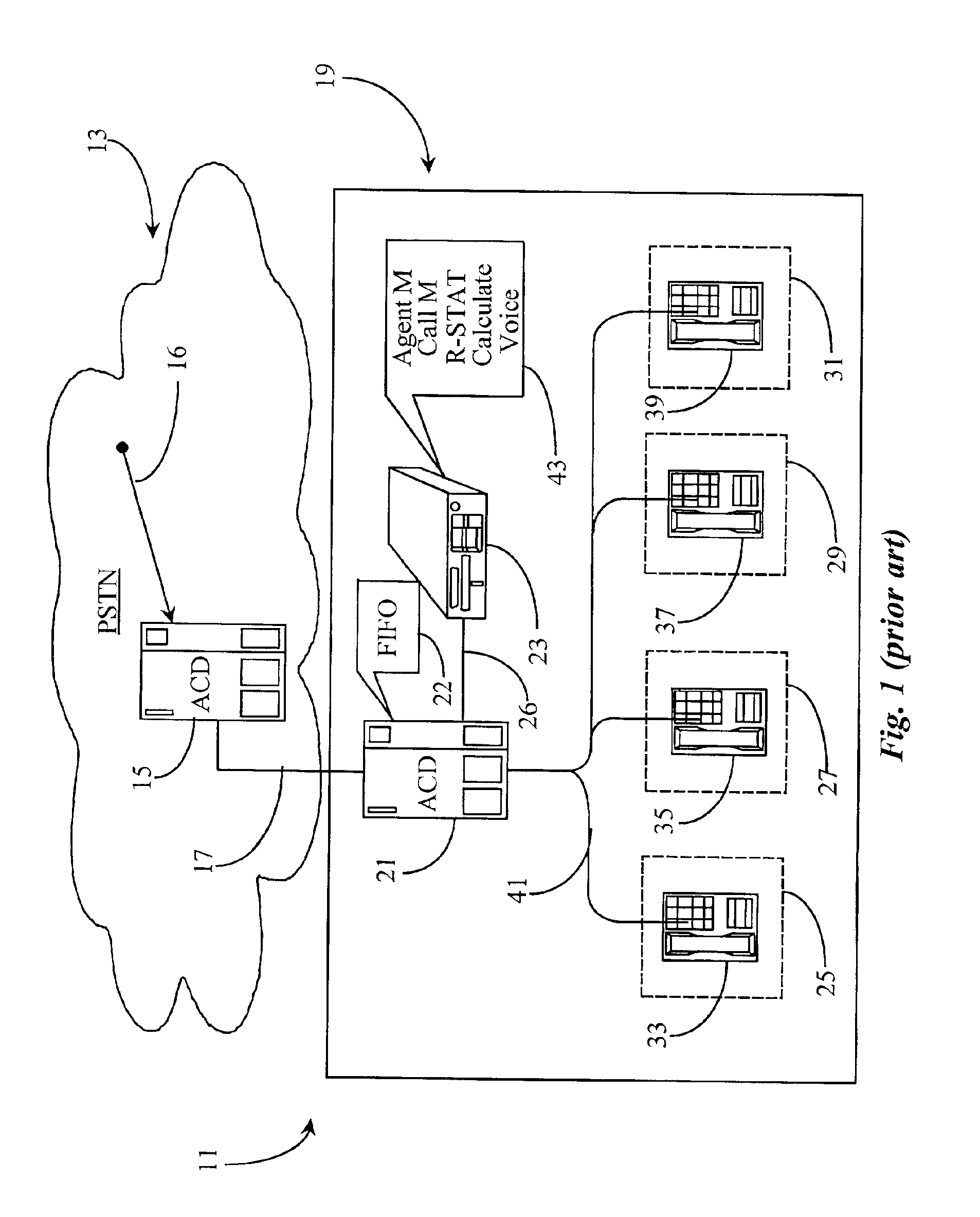
Method for estimating telephony system-queue waiting time in an agent level routing environment
InactiveUS6898190B2Special service provision for substationError preventionComputer telephony integrationNetwork level
A system for estimating call waiting time for a call in a queue takes into account multiple queues wherein agents are shared between queues, abandoned call history, and virtual and priority queues. The system in a preferred embodiment is a computer-telephony integration (CTI) software application adapted to execute on a CTI processor, which may be coupled to switching equipment at network level in a connection-oriented, switched telephony (COST) network or to a switch at call-center level, or both.
Owner:GENESYS TELECOMM LAB INC AS GRANTOR +3
Providing quality of service for disks I/O sub-system with simultaneous deadlines and priority
InactiveUS6871011B1Improving input/output performanceTelevision system detailsInput/output to record carriersQuality of serviceTime limit
The disk scheduling algorithms try to service a request with lower priority and strict deadline only if serving this request is not going to violate the deadline constraints of a higher priority request. One of the algorithms uses a single queue to hold all the requests regardless of their priority. The single queue is reorganized after the arrival of a new request according to the order requests would be serviced. A second algorithm uses multiple queues. Each queue holds only requests with the same priority, and the requests in each priority queue are sorted according to their deadlines. The decision of servicing a request is made at scheduling time.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
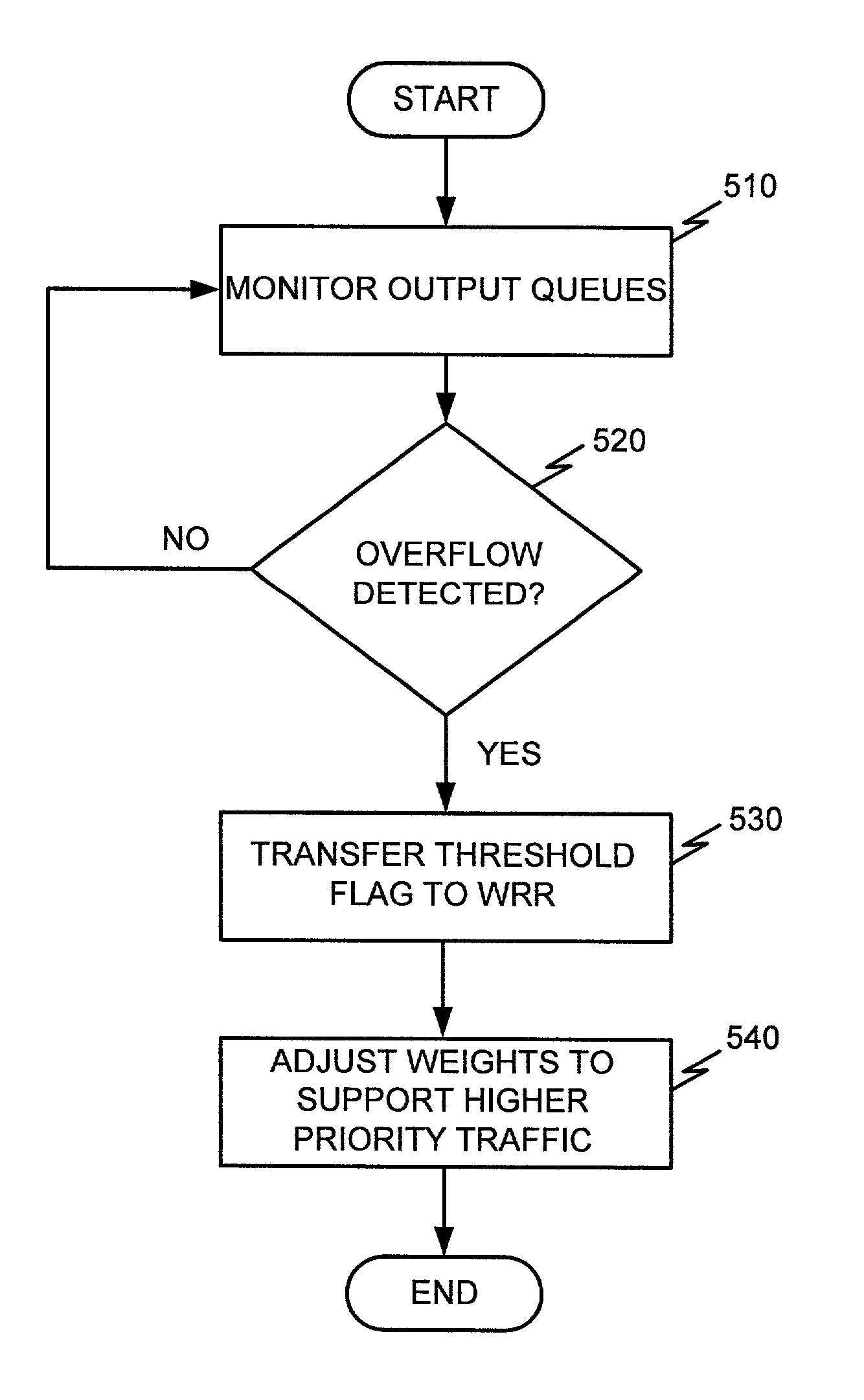
System and method for dynamically updating weights of weighted round robin in output queues
ActiveUS7110359B1Reduce congestionError preventionTransmission systemsWeighted round robinPriority queue
A network device includes a group of queues, each having a weighted round robin mechanism. The priority queues on a port detect an overflow condition and transfer a flag to the weighted round robin device in response to detecting the overflow condition. The weighted round robin mechanism adjusts the weight associated with one or more of the priority queues in response to receiving the flag and transfers data from the queues based on the adjusted weights.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
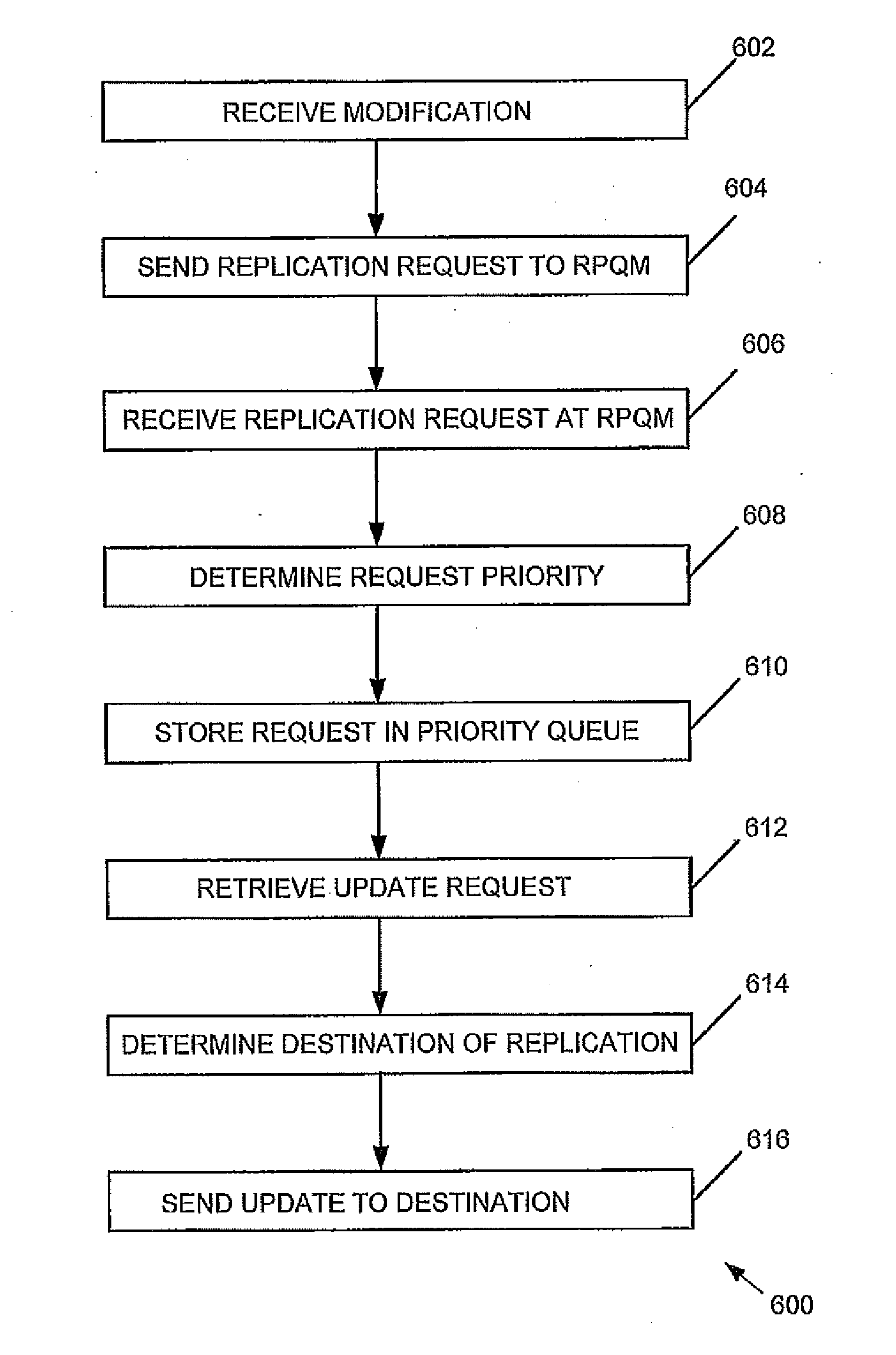
LDAP Replication Priority Queuing Mechanism
A replication priority queuing system prioritizes replication requests in accordance with a predetermined scheme. An exemplary system includes a Replication Priority Queue Manager that receives update requests and assigns a priority based upon business rules and stores the requests in associated storage means. A Replication Decision Engine retrieves the requests from storage and determines a destination for the update based upon predetermined replication rules, and sends the update to the destination.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
Distributed priority queue that maintains item locality
ActiveUS20080276241A1Raise priorityMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsDistributed computingPriority queue
A method of administering a distributed priority queue structure that includes removing a highest priority item from a current root node of a tree structure to create a temporary root node, determining for each subtree connected to the temporary root node a subtree priority comprising the priority of the highest priority data item in the each subtree, determining as the highest priority subtree connected to the temporary root node the subtree connected to the temporary root node having the highest subtree priority, determining whether any of the one or more data items stored at the temporary root node has a higher priority than the highest subtree priority and directing an arrow to the subtree having the highest priority or to the temporary root itself if the priority of the data items stored at temporary root is higher than the priorities of the connected subtrees.
Owner:AVAYA INC
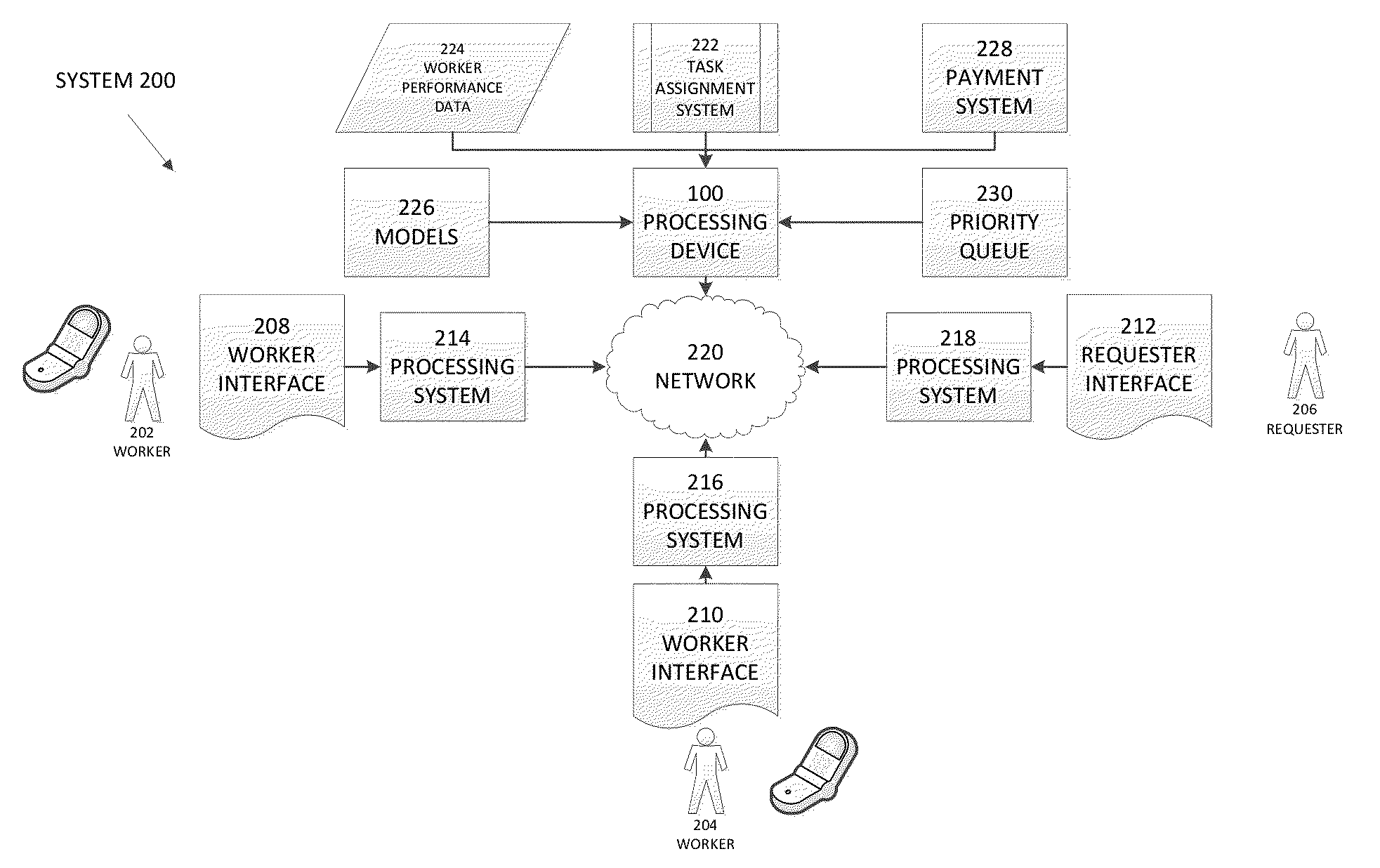
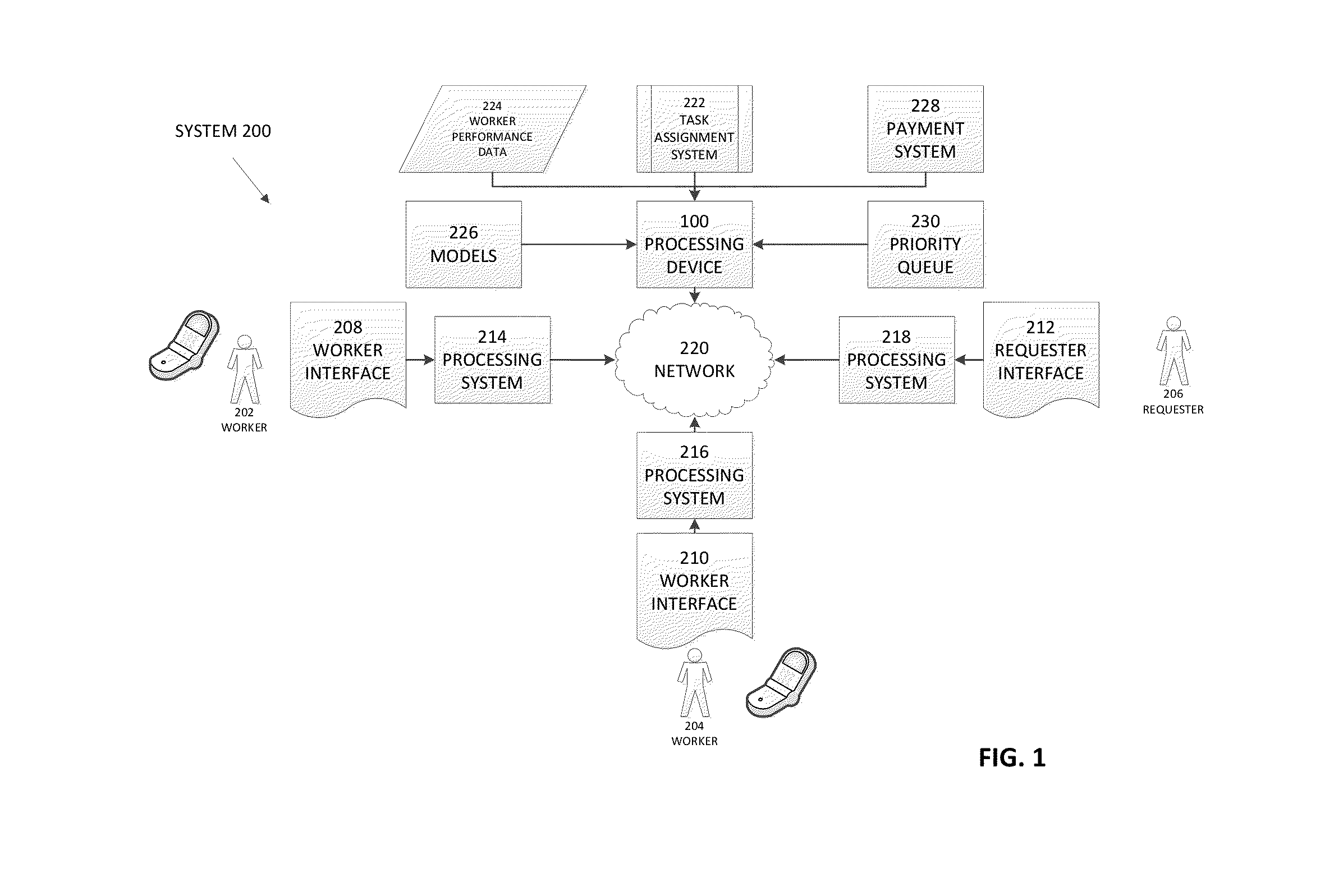
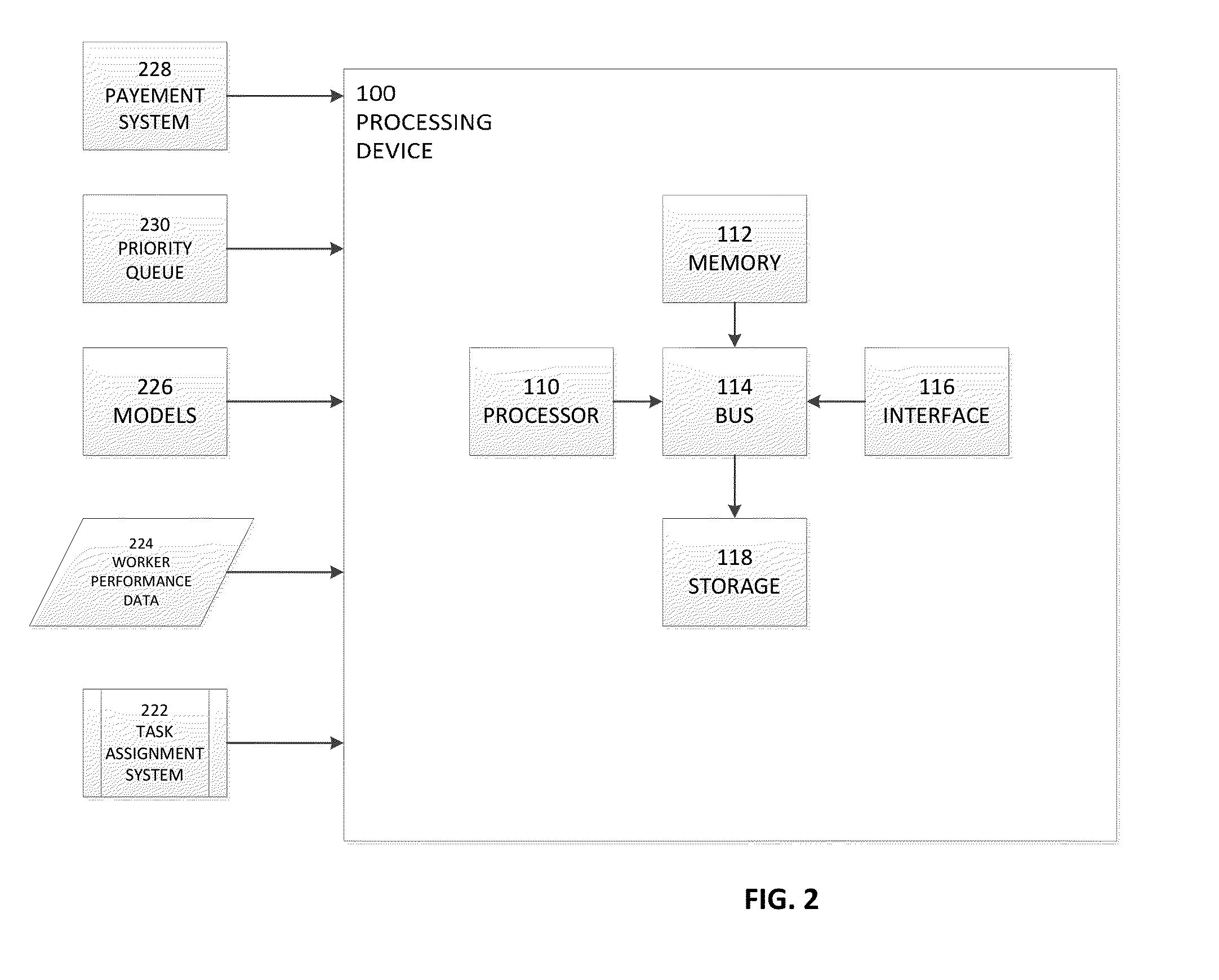
Methods and apparatus for online sourcing
A system, method, and article of manufacture for online crowd-sourcing and for communicating with a requester and with several of workers, the system includes a central controller that communicates with each requester via an interface, to receive the task(s) to be performed and to provide a response for that task(s), and with each worker via an interface, to deliver task assignments and to receive responses, the central controller further including a task assignment system that is structured and arranged to insert tasks to be performed into a priority queue multiple times and to push a next task in the priority queue to a selected worker based on information about the selected worker; and a data storage device for storing information about workers that includes a worker identification, a worker skill level, a worker accuracy rating, a list of historical tasks performed by the worker, and a list of historical tasks that the worker has not performed.
Owner:MOBILEWORKS
Traffic scheduling system for wireless communications
InactiveUS20110116373A1Optimize and guarantee performanceOptimize and guarantee and low latencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityTime segment
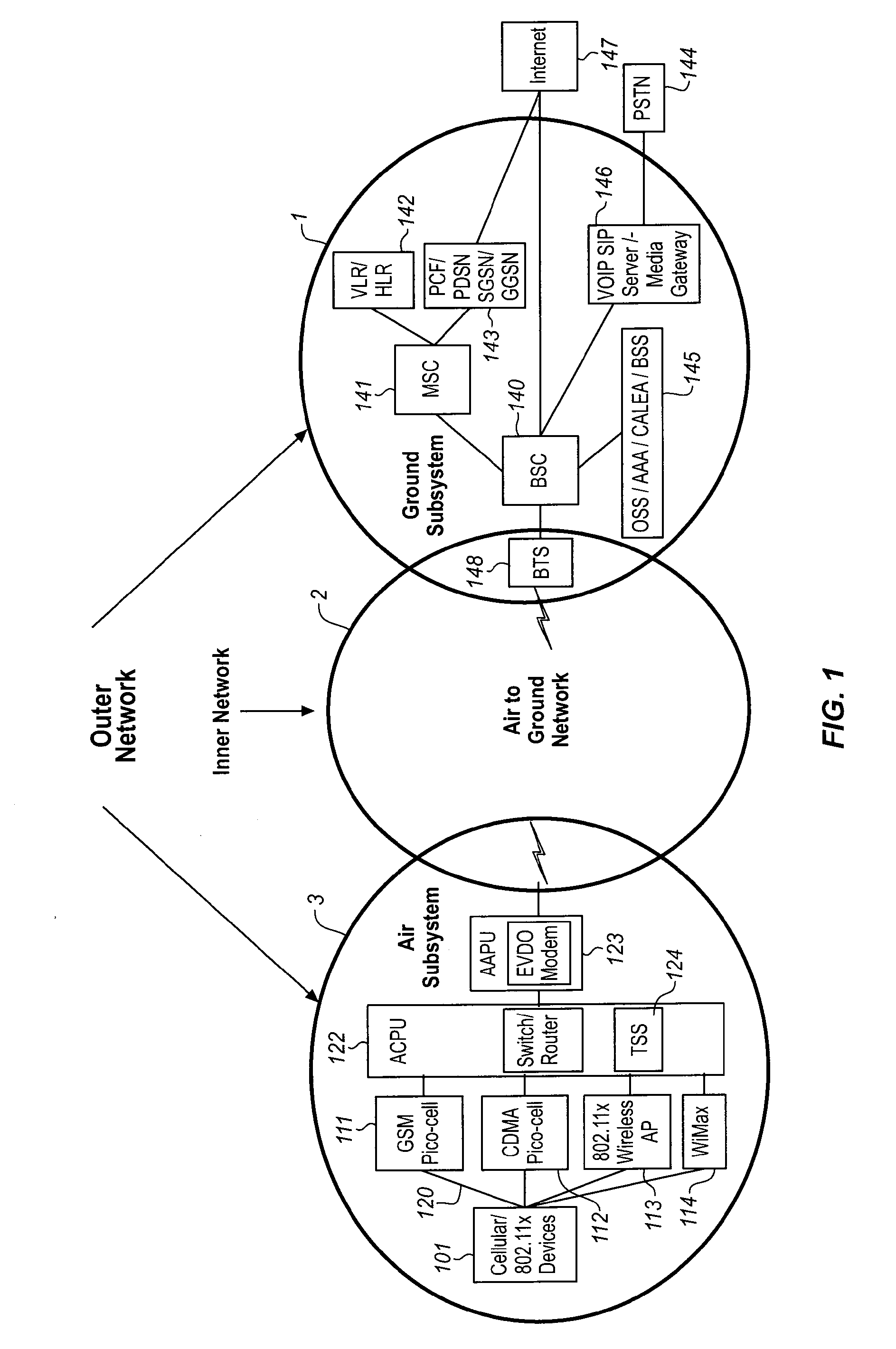
The Traffic Scheduling System executes a multi-step process first to identify the bandwidth intensive traffic. The identification of the bandwidth intensive traffic is effected at the stream level by measuring the byte volume of the stream over a predetermined period of time and using this data to classify the stream into one of a plurality of usage categories. The classification of bandwidth intensive traffic is network neutral in that all data is classified at the stream level (source IP, destination IP, source port, destination port). Otherwise, the data is not inspected. Once streams have been classified by the Traffic Scheduling System, the Bandwidth Intensive and Near Real Time traffic can be controlled by a simple Traffic Shaping process executed by the Traffic Scheduling System, using a traffic management parameter such as via the Round-Trip Time of the next higher priority queue, in the set of queues.
Owner:GOGO BUSINESS AVIATION LLC
Systems and methods for traffic shaping
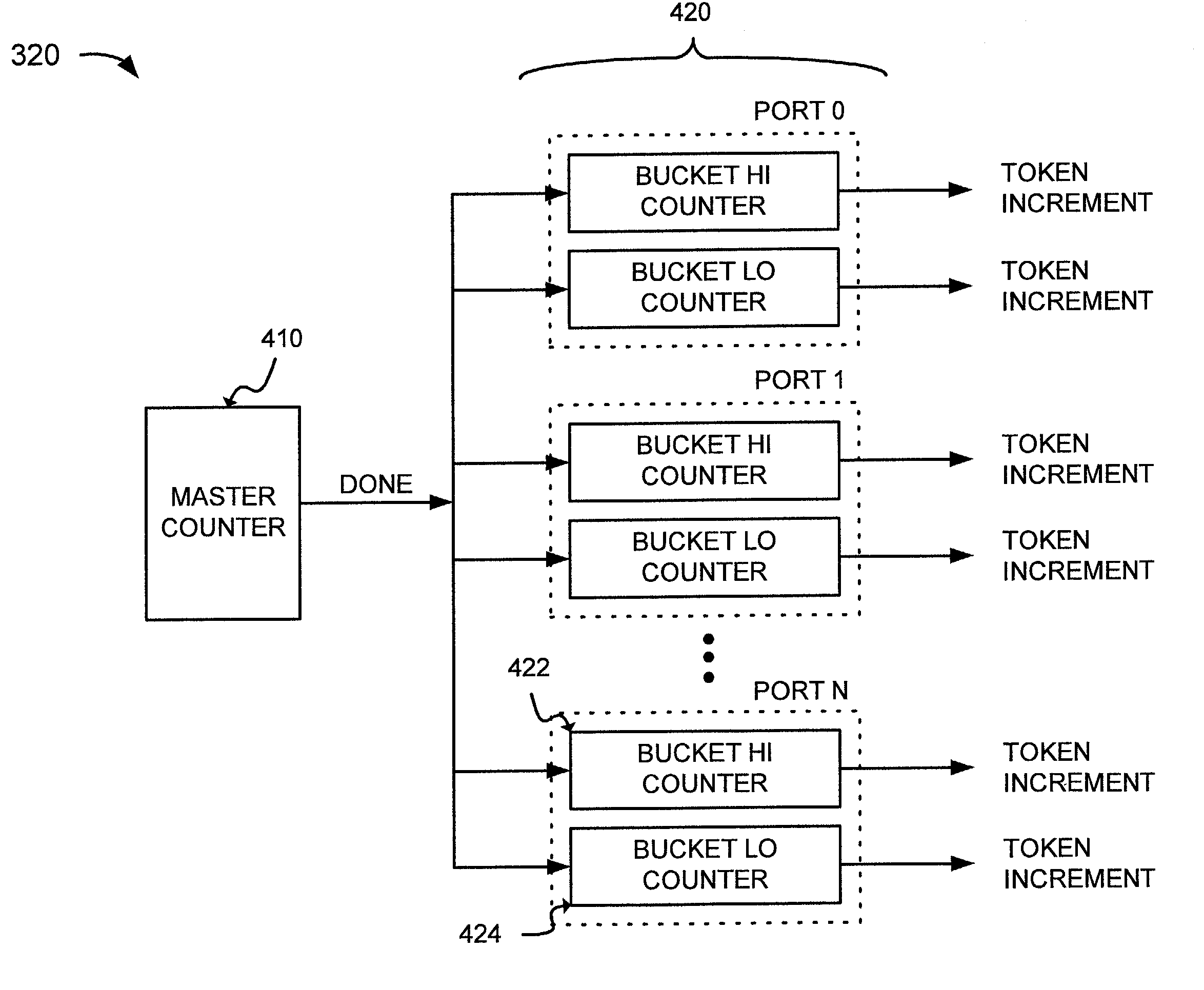
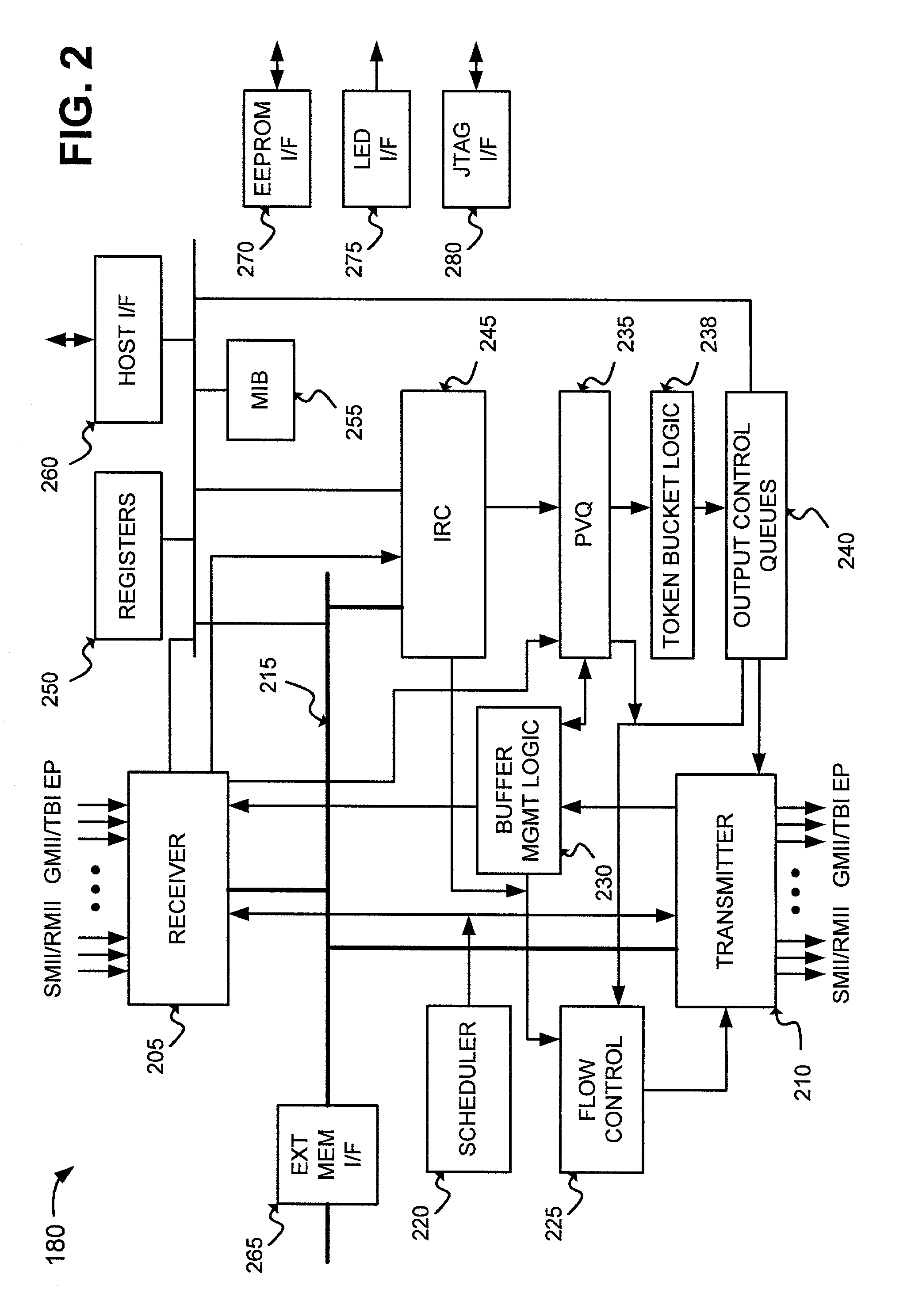
InactiveUS6925055B1To offer comfortError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsByteControl logic
A system shapes traffic in a multiport network device. The system includes multiple token buckets and token bucket logic. The token buckets correspond to multiple priority queues of the multiple output ports of the network device and store one or more tokens. Each of the tokens corresponds to a byte of one or more received packets to be transmitted by the network device. The token bucket control logic generates the tokens for the token buckets. The token bucket control logic includes a master counter and multiple bucket counters. The master counter counts to a first count value and generates a done signal when the count reaches the first count value. The bucket counters, corresponding to the token buckets, receive the done signal, count to a second count value, and generate a token increment signal for storing a token in the corresponding token buckets when the count reaches the second count value.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Systems and methods for scheduling, processing, and monitoring tasks
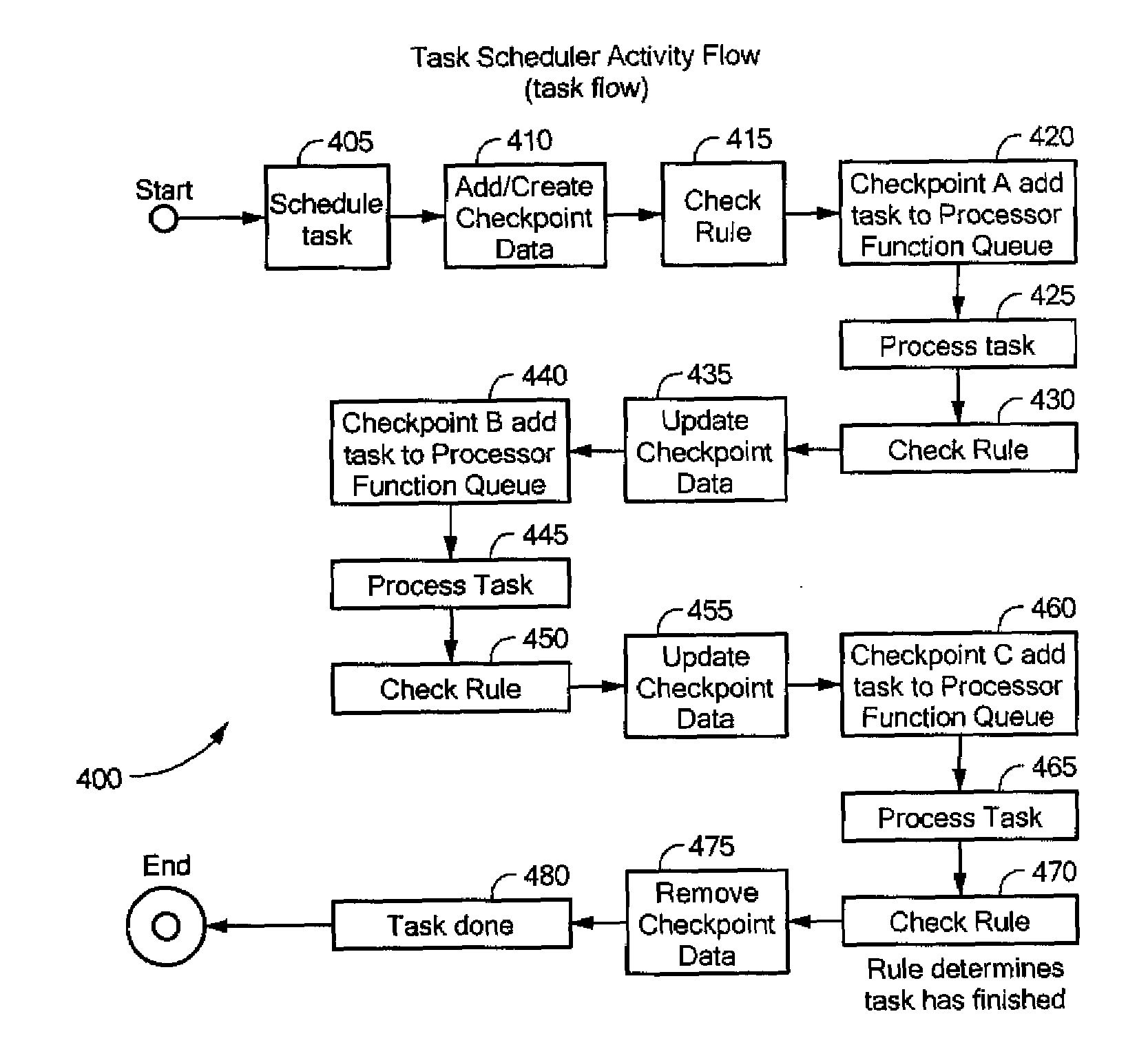
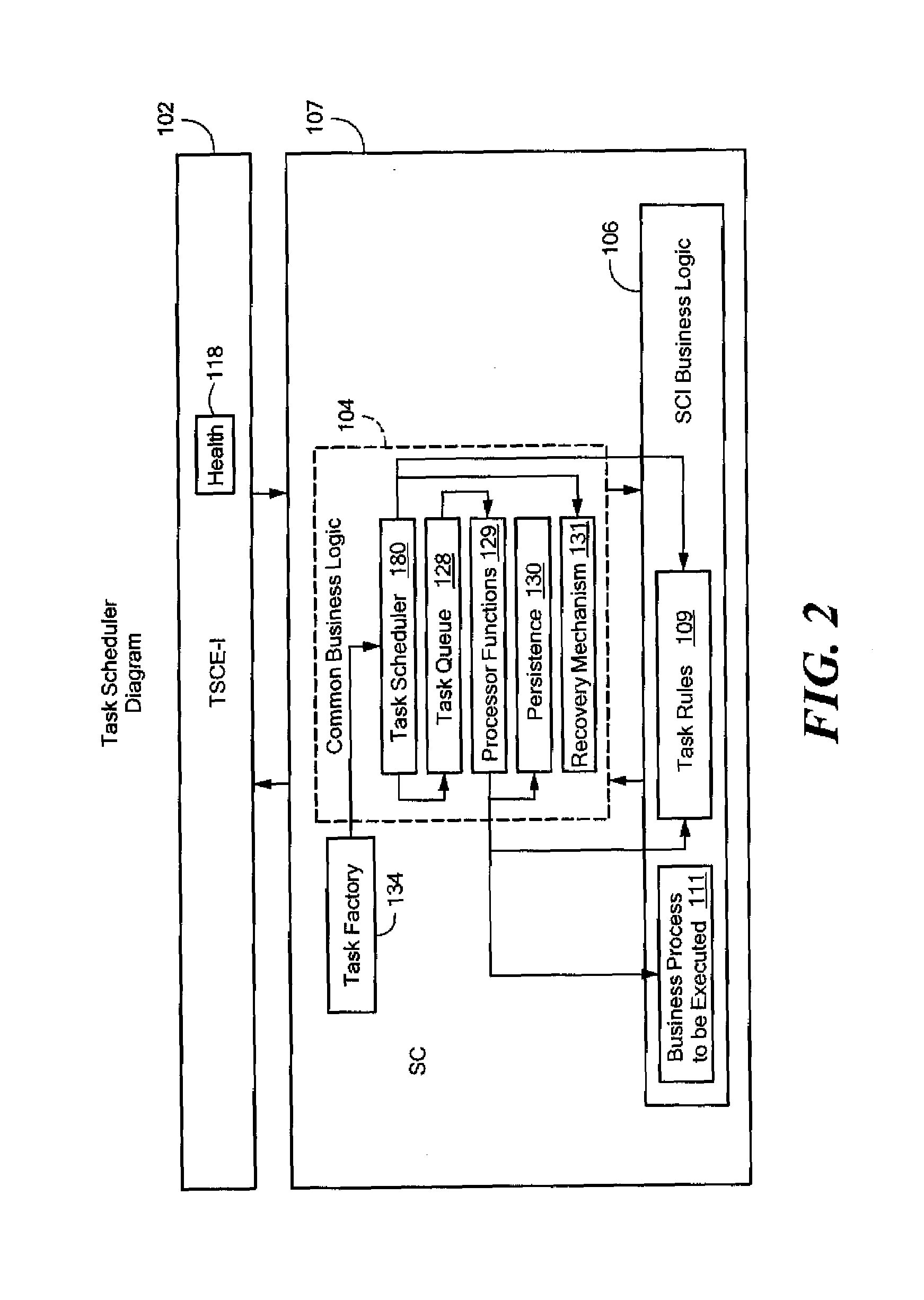
ActiveUS20080120620A1Save stateMaintain integrityError detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsOperating systemPriority queue
A computer-implemented method for performing a process is provided. The method comprises: (a) receiving a request to perform a process, the process comprising a plurality of tasks and at least a scheduler rule; (b) receiving a plurality of checkpoints associated with the process, each checkpoint comprising checkpoint state data and at least a respective checkpoint rule governing execution of the process; (c) determining a first task of the plurality of tasks to be scheduled into a priority queue, in accordance with the scheduler rule; (d) determining the first checkpoint of the plurality of checkpoints that is to be the first checkpoint used in processing the first task, in accordance with the scheduler rule; (e) creating the checkpoint state data for the first checkpoint; (f) saving the checkpoint state data for the first checkpoint; (g) processing the first task in accordance with the checkpoint rule associated with the first checkpoint; (h) determining the next task in the plurality of tasks to perform, based on the checkpoint rule associated with the first checkpoint; (i) updating the saved checkpoint data for the first checkpoint with the data and state associated with the first task; and (j) repeating steps (c) through (i) for each subsequent task and checkpoint, in accordance with the respective scheduler and checkpoint rules, until a predetermined condition has been reached.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
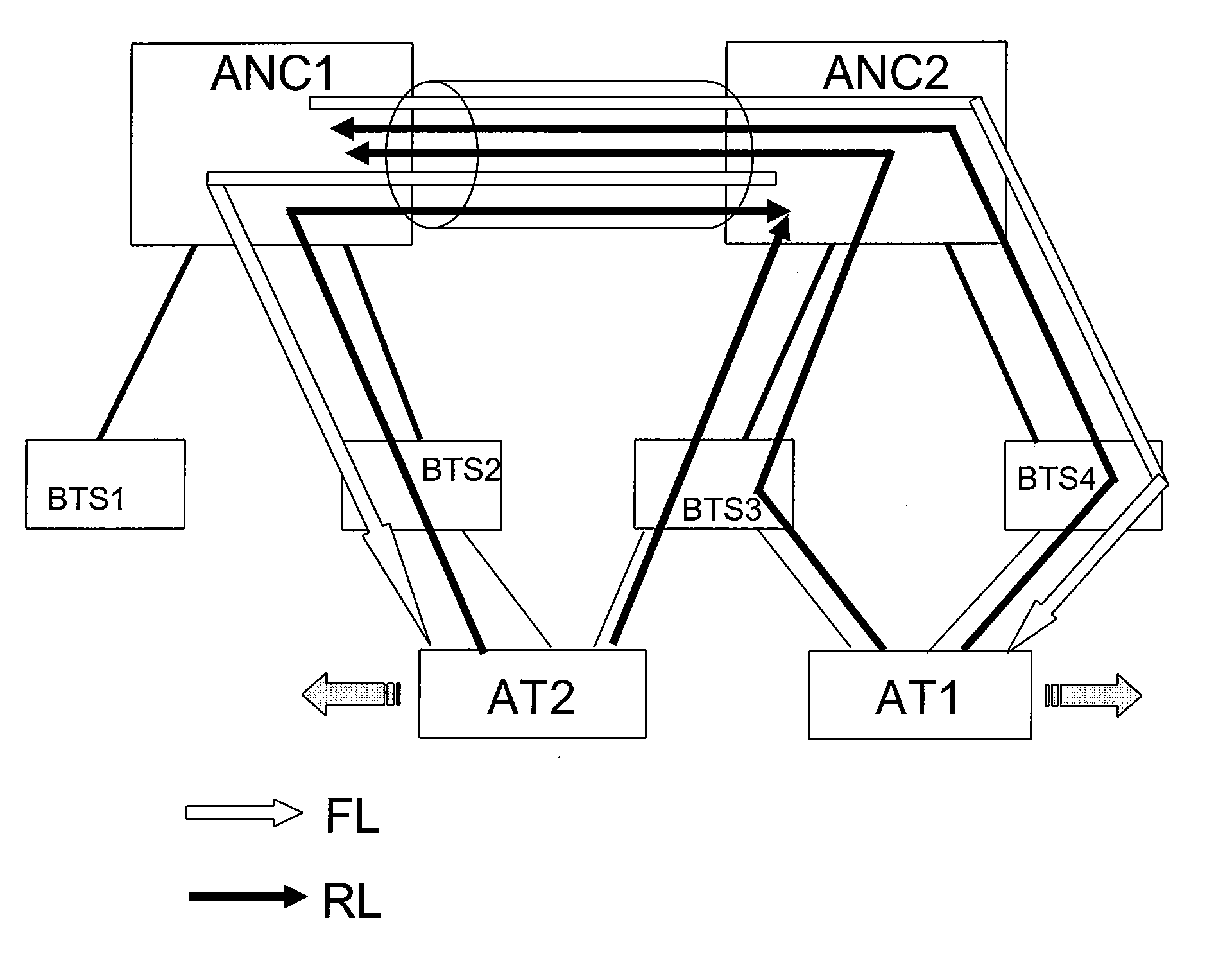
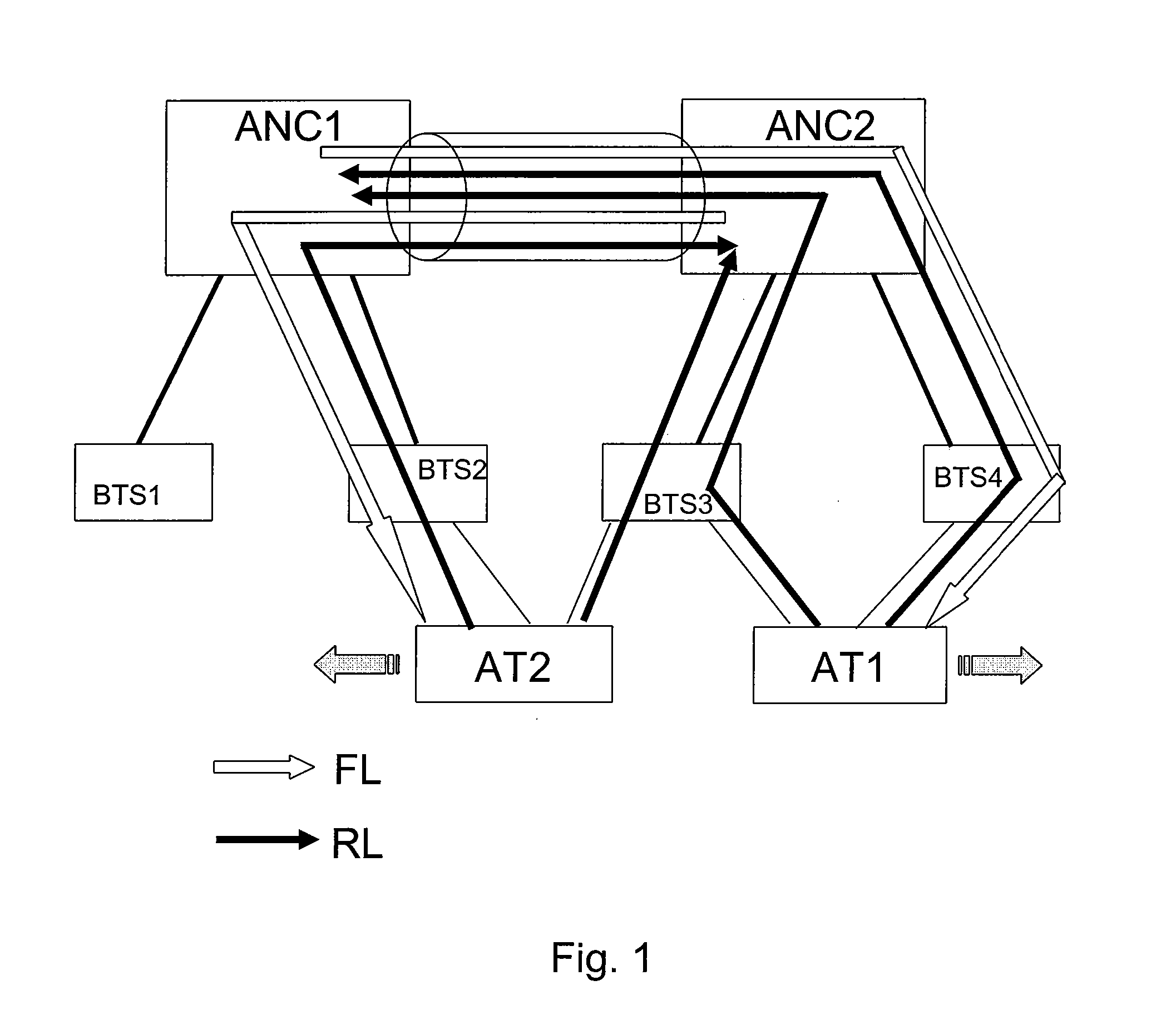
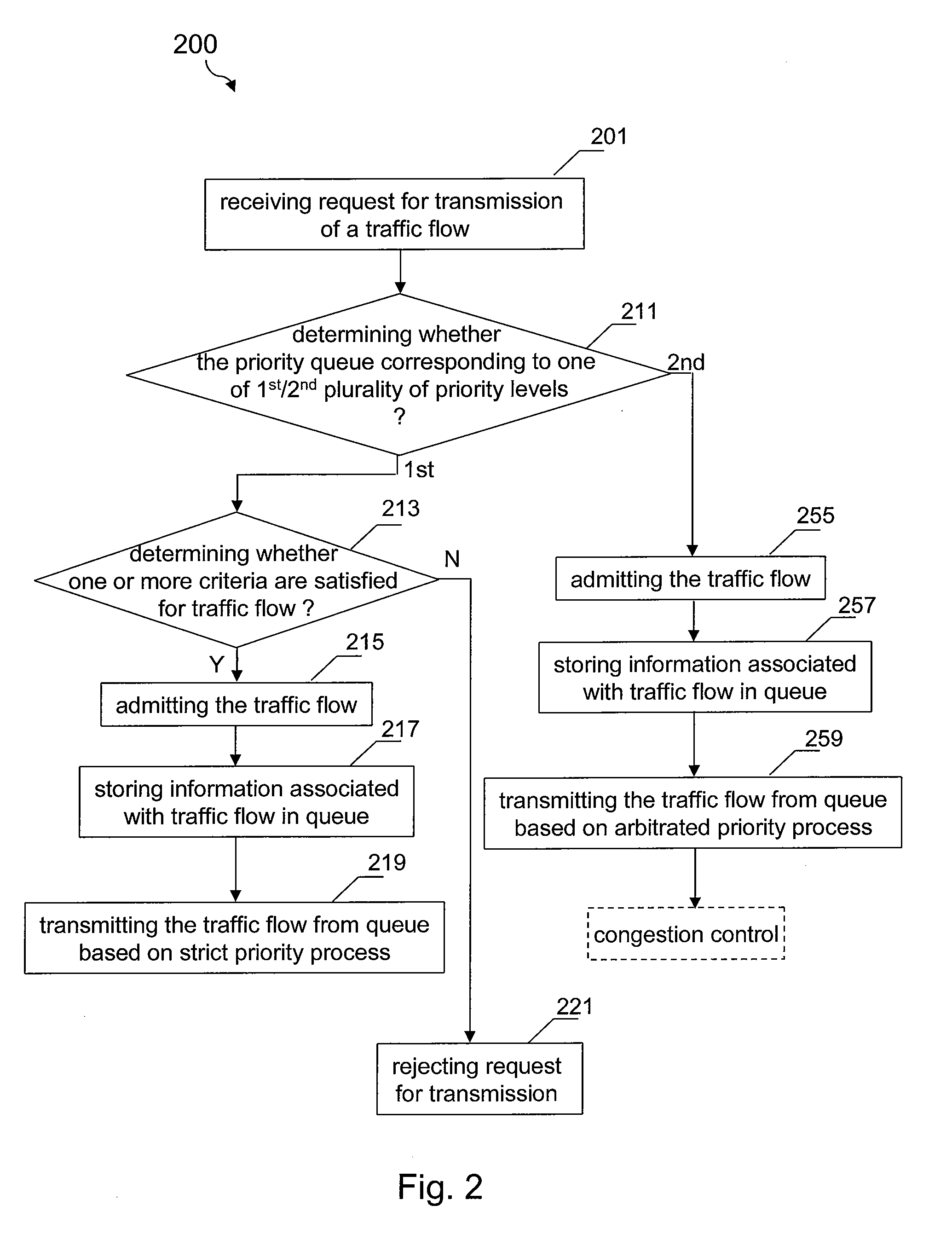
Method and system for admission and congestion control of network communication traffic
InactiveUS20080075003A1Control congestionError preventionTransmission systemsAccess networkPriority call
A method for controlling communications traffic on an inter-access-network link includes receiving a request for transmission of a traffic flow and determining a priority queue associated with the traffic flow. If the priority queue corresponds to the one of a first plurality of priority levels, the method further includes determining whether one or more predetermined criteria for the traffic flow are satisfied. If yes, the method additionally admitting the traffic flow, storing information associated with the traffic flow in the queue, and transmitting information associated with the traffic flow from the queue based on at least a strict priority process. If the queue corresponds to the one of a second plurality of priority levels, the method further admitting the traffic flow, storing information associated with the traffic flow in the queue, and transmitting information associated with the traffic flow from the queue based on at least an arbitrated priority process.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com