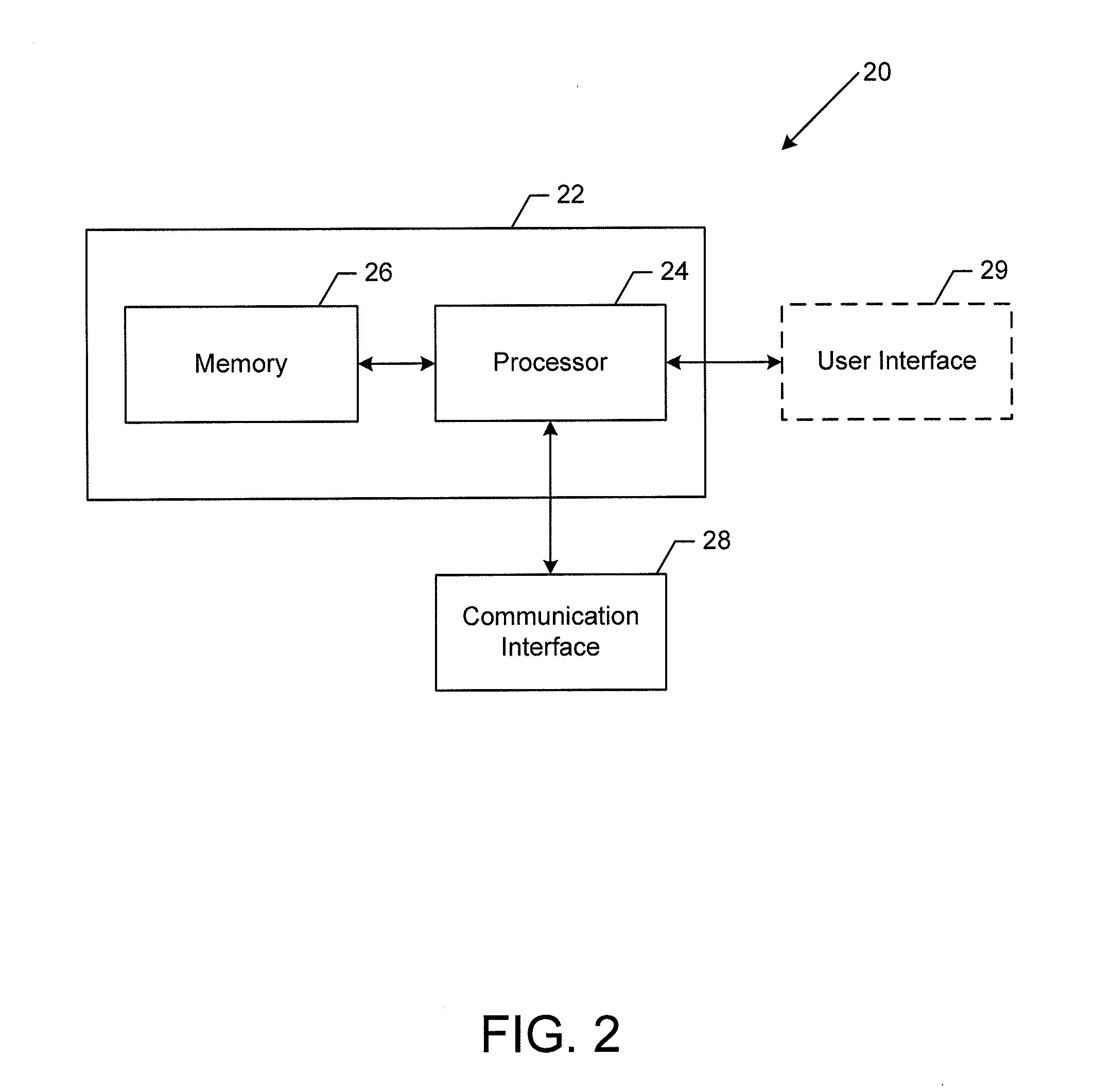
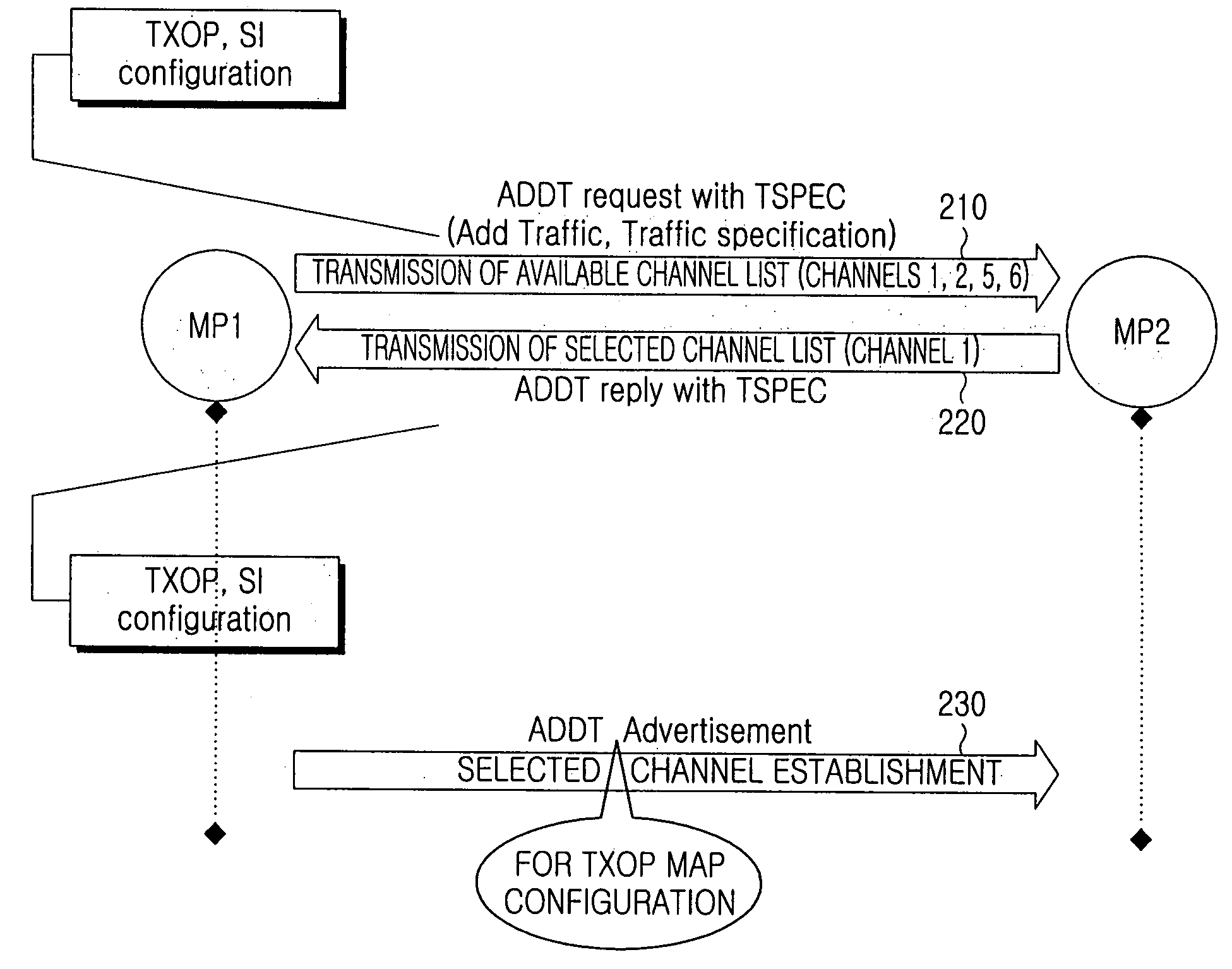
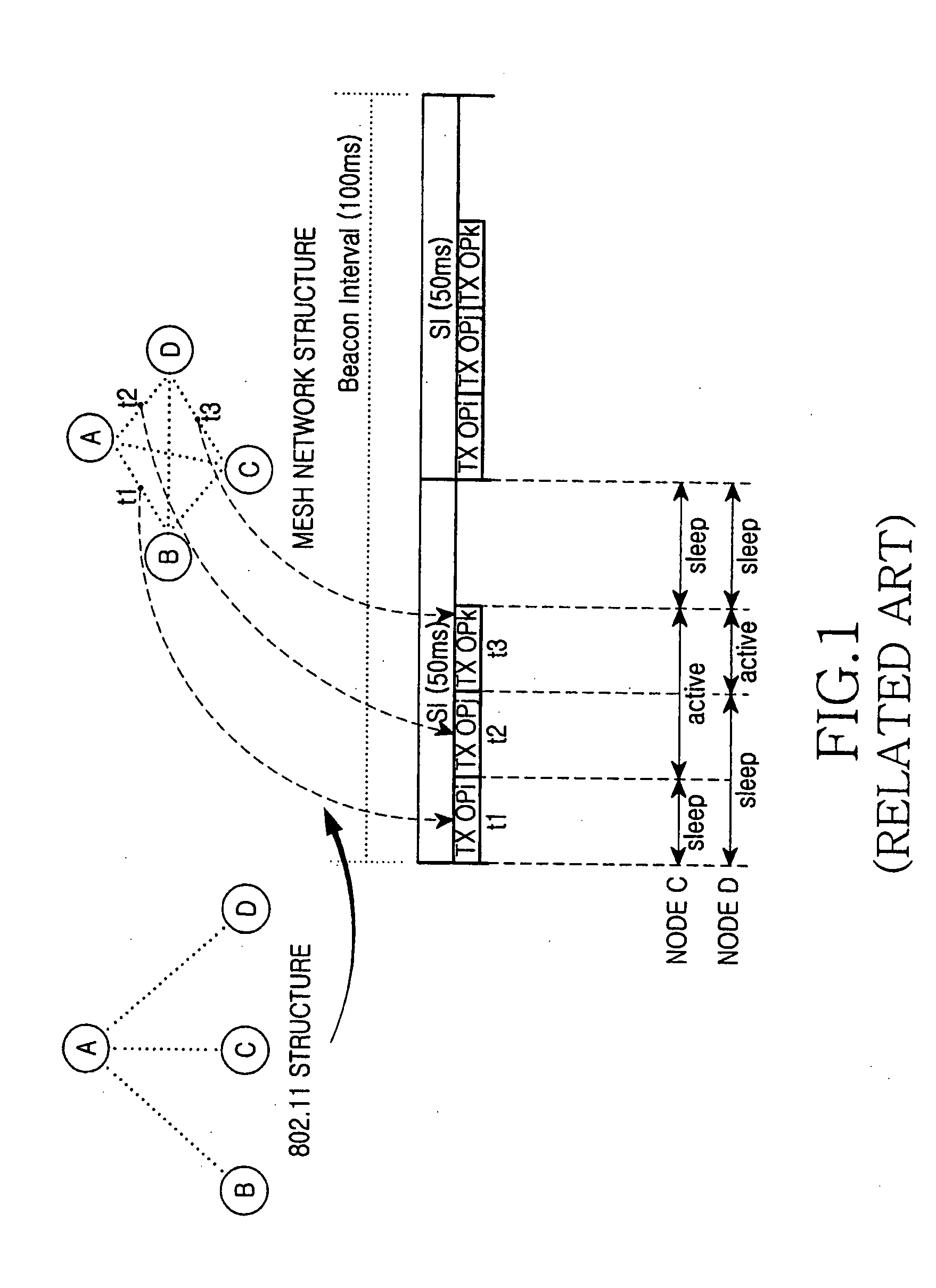
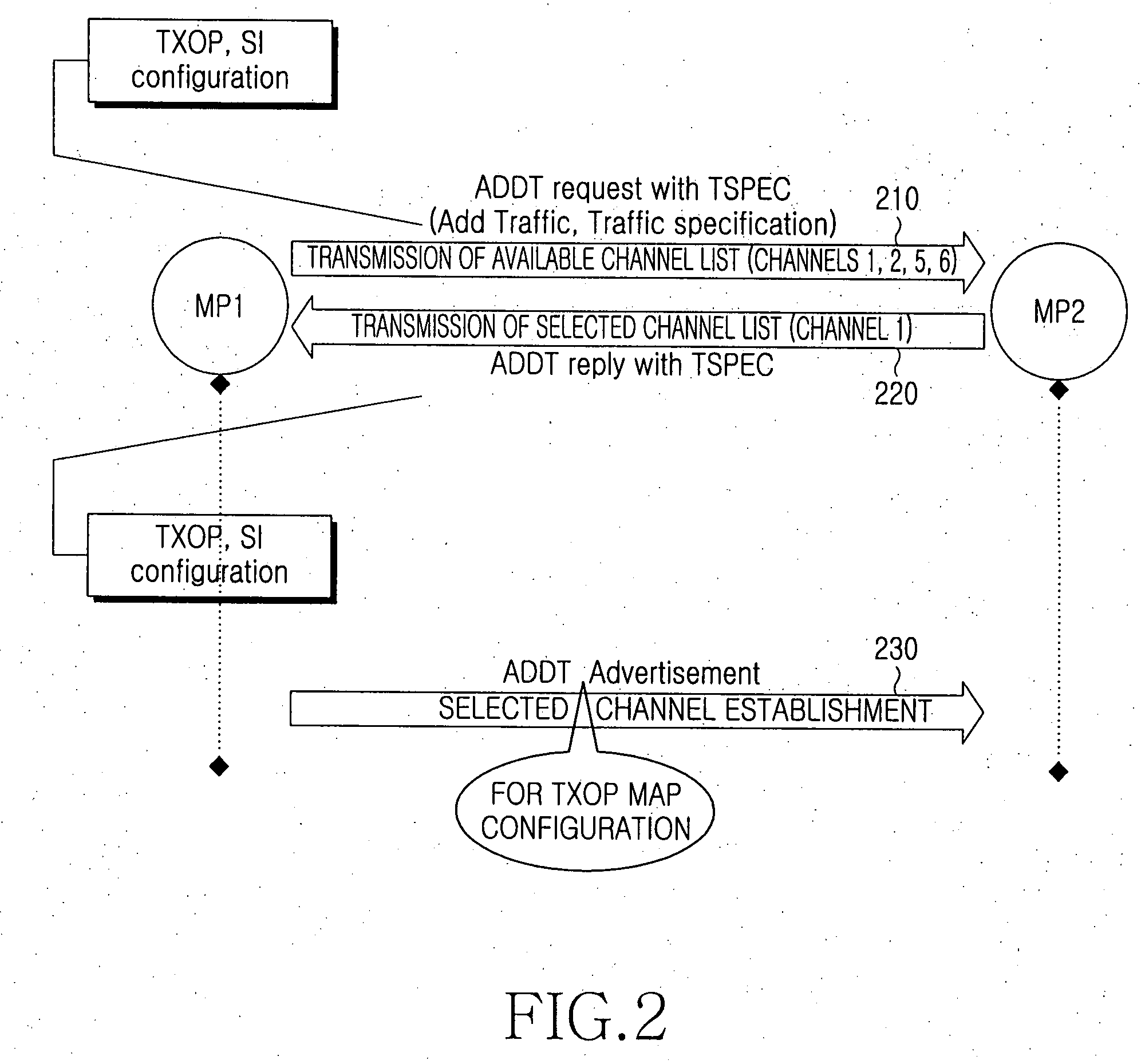
Patents
Literature
630 results about "Transmission opportunity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
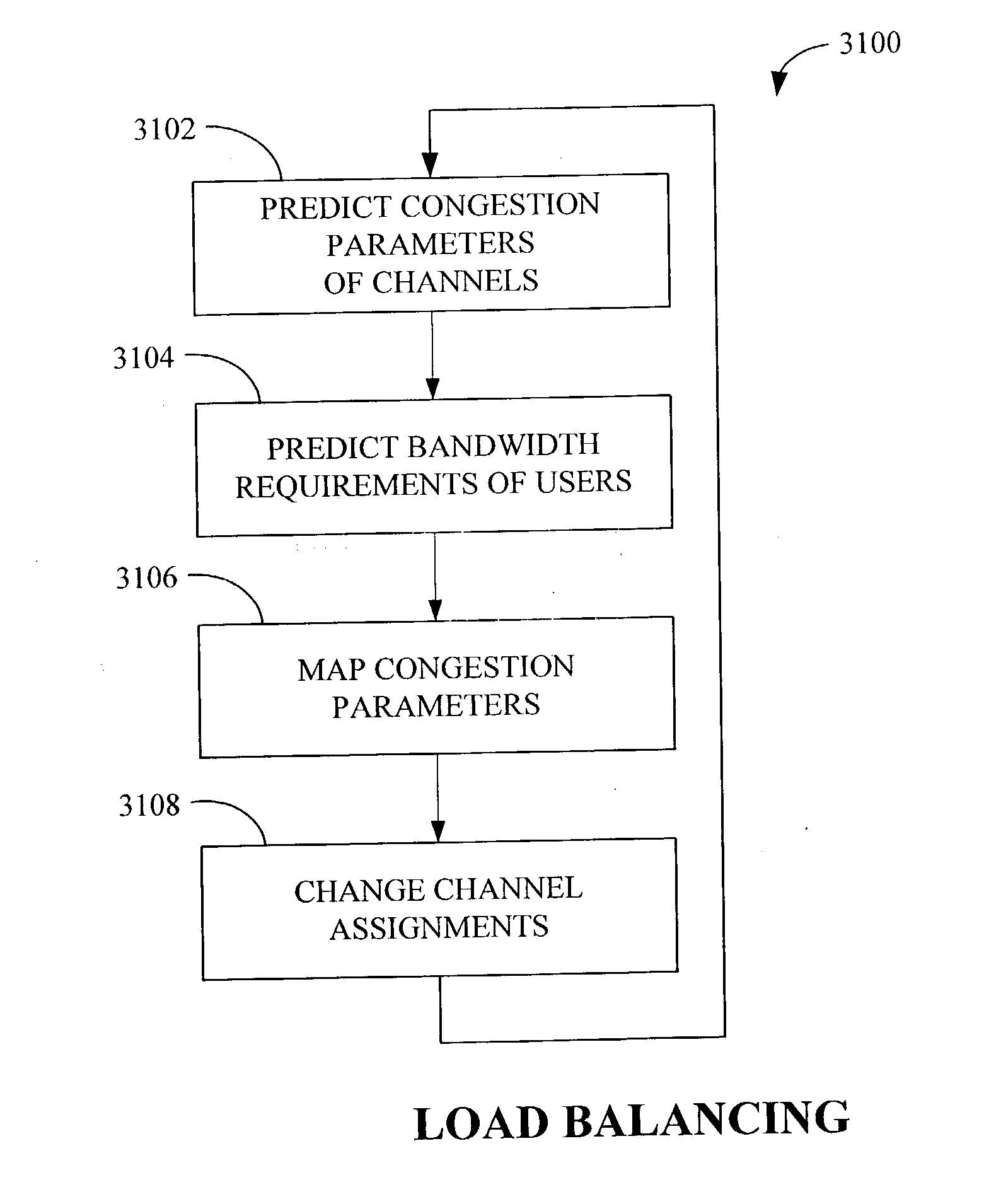
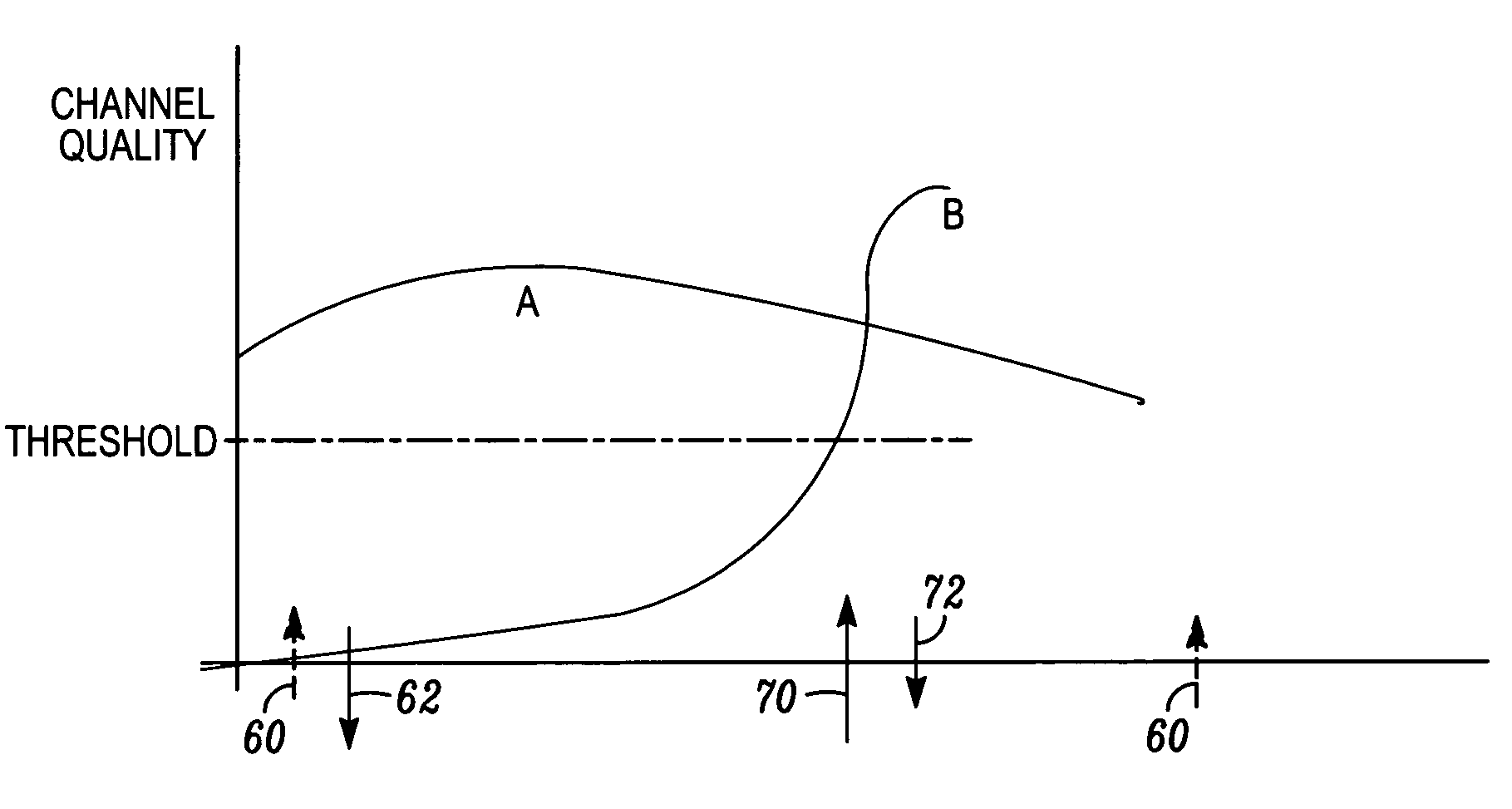
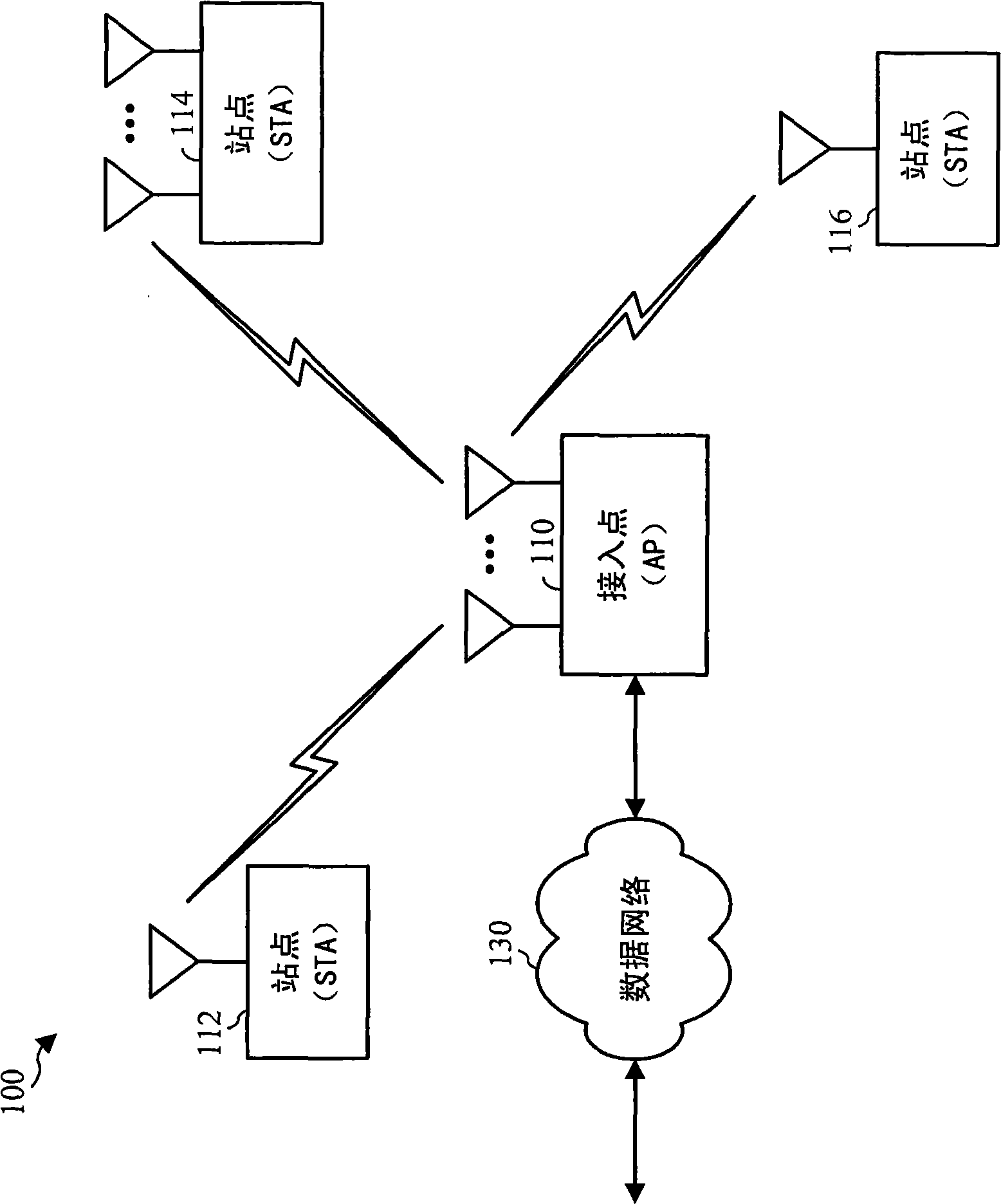
Apparatus and methods for incorporating bandwidth forecasting and dynamic bandwidth allocation into a broadband communication system
InactiveUS20060120282A1Energy efficient ICTError preventionDynamic bandwidth allocationComputer network
A method for providing network access to a shared access communications medium for a plurality of users includes the steps of conducting predictive admission control by arbitrating user requests for access to the shared medium based on predicted aggregate demands, conducting lookahead scheduling for use in making user channel assignments by forecasting schedule transmission opportunities one or more channels of the shared medium, and balancing load by making channel assignments such that a plurality users are each assigned a respective channel of the shared medium based upon a predicted need. Congestion parameters can predicted for each channel of the shared medium and mapped to a congestion measure using a mathematical function that takes into account packet loss rate, packet delay, packet delay jitter, and available capacity.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Buffer occupancy used in uplink scheduling for a communication device
InactiveUS6993342B2Site diversityData switching by path configurationUplink schedulingDistributed computing
A method for using buffer occupancy in uplink scheduling for a communication device includes a first step of sending buffer occupancy information and a time stamp indicating a last transmission opportunity provided to the communication device to an active set base stations. A next step includes utilizing the buffer occupancy information and time stamp to adjust a scheduling fairness setting for the communication device. A next step includes receiving scheduling information from a scheduler in accordance with the scheduling fairness setting. A next step includes transmitting on an uplink channel in accordance with the scheduling information.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for transmitting data frame in WLAN system
ActiveUS20120218983A1Improve throughputEfficiently channel bandwidthNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesWireless lanTransmitter
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Quality of service for WLAN and bluetooth combinations
ActiveUS20100284380A1Easy to useNetwork topologiesMultiple digital computer combinationsQuality of serviceBluetooth piconets
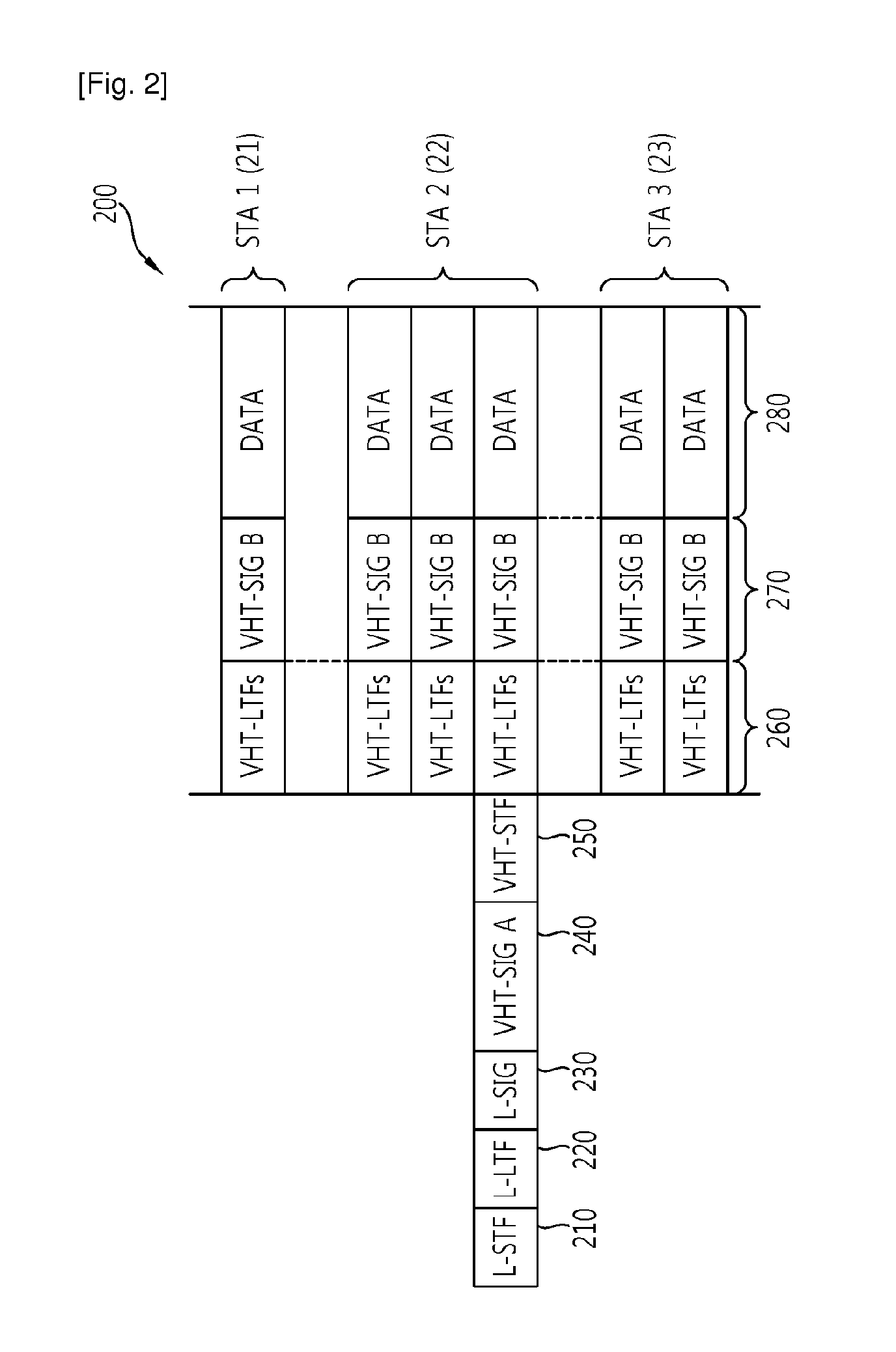
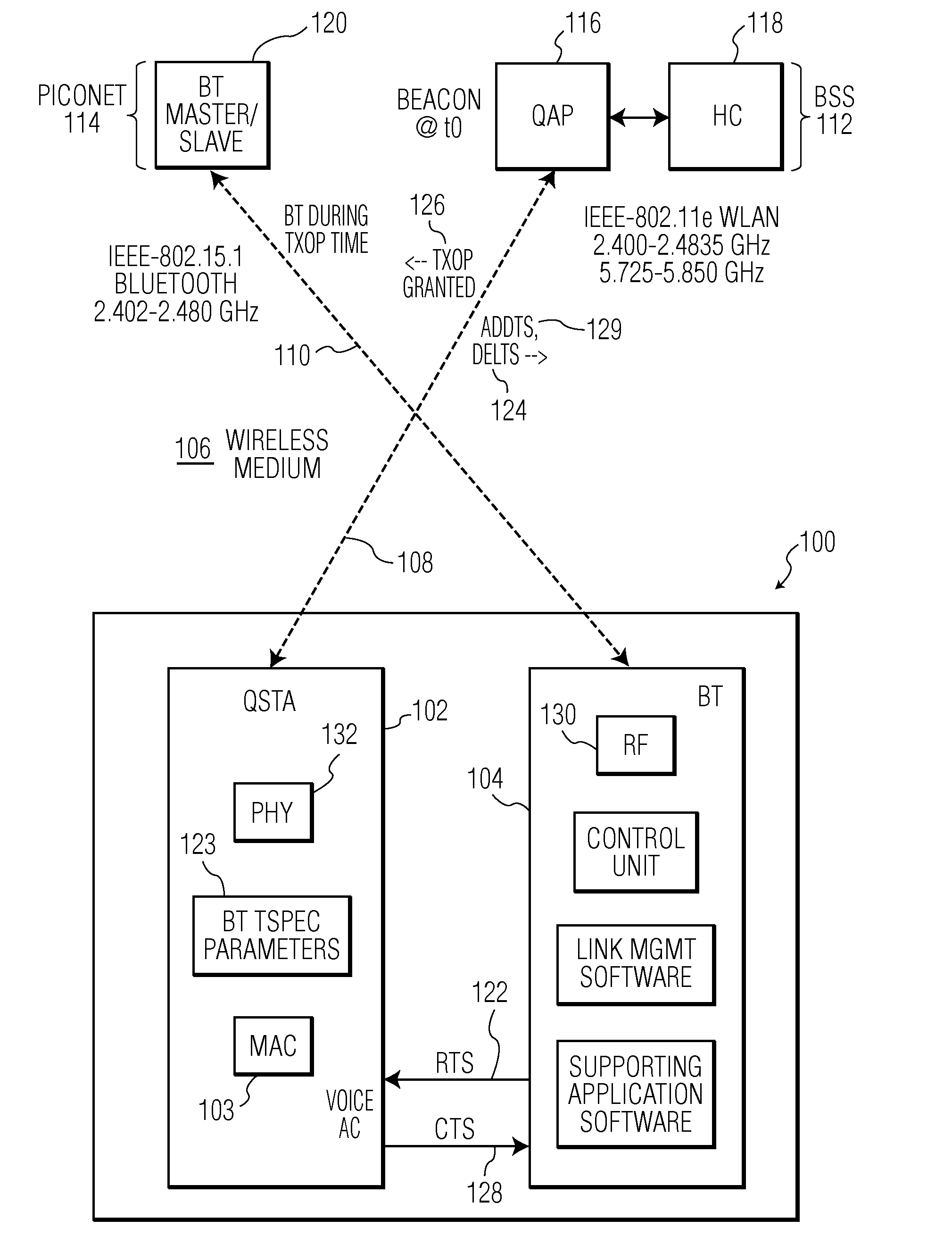
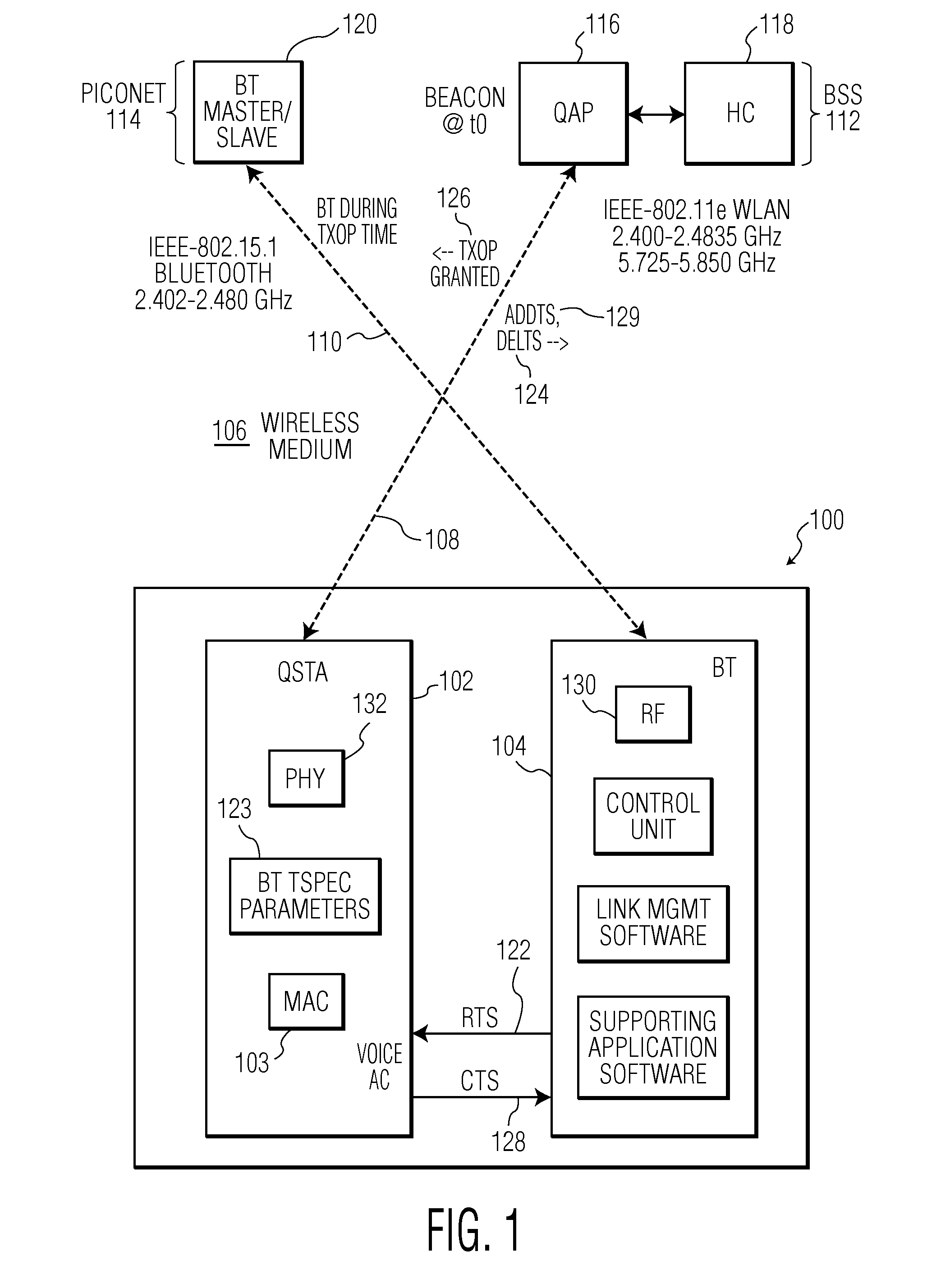
A hybrid device (100) includes both a IEEE-802.11e type WLAN client station (QAP) (102) and a BLUETOOTH piconet unit (104) interconnected such that the BLUETOOTH transmissions are scheduled to occur according to a transmission opportunity (TXOP) (126) that was granted by a quality of service (QoS) access point (QAP) (116) in a basic service set (BSS) (112). Requests for BLUETOOTH traffic are handled by the associated QSTA (102) which generates an add traffic service (ADDTS) (124) to the QAP.
Owner:NXP BV
Simultaneous transmissions during a transmission opportunity
InactiveUS20110222408A1Increase capacityError preventionTransmission systemsTransfer modeComputer science
Method, apparatus, and computer program product embodiments are disclosed to enhance capacity of a wireless communication network through spatial reuse of the shared communication medium, using an autonomous parallel operation without central coordination and header frames. Example embodiments of the invention include a signaling method that defines and sets up a Simultaneous Transmissions mode between two pairs of devices to reuse a transmission opportunity (TXOP). In example embodiments of the invention, an arrangement may be made between device pairs (each pair comprising a transmitter device and a receiver device) to allow selected pairs to communicate at a same time. The example signaling method defines example signaling for setting up simultaneous transmitter / receiver pairs in a network and operating the transmitter / receiver pairs in simultaneous transmission. If a device in a setup pair detects some other transmission than that is not allowed by one of its device pair arrangements, the device ceases its transmission.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Enhanced channel access mechanisms for QoS-driven wireless lans
InactiveUS7068633B1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionQuality of serviceWireless lan
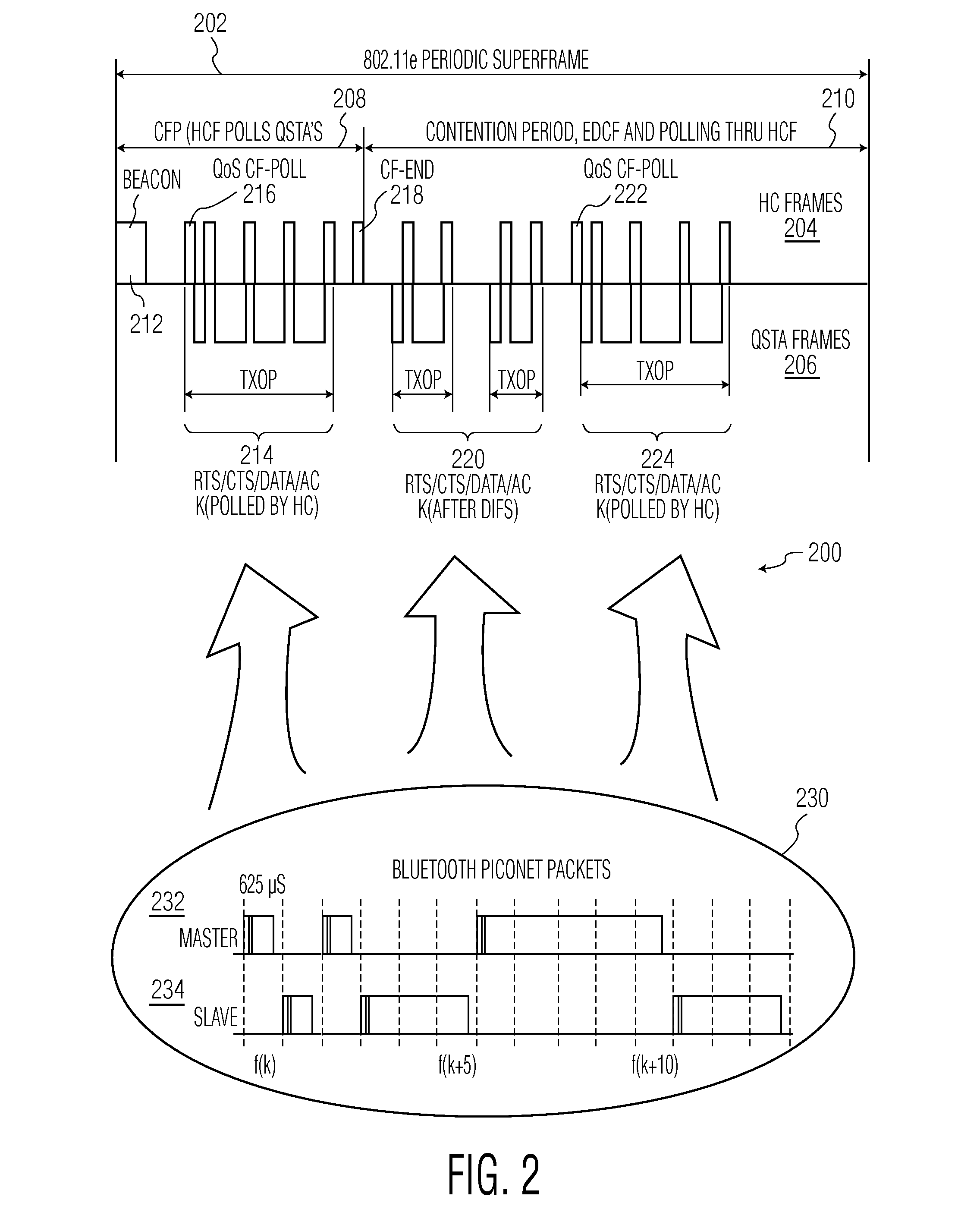
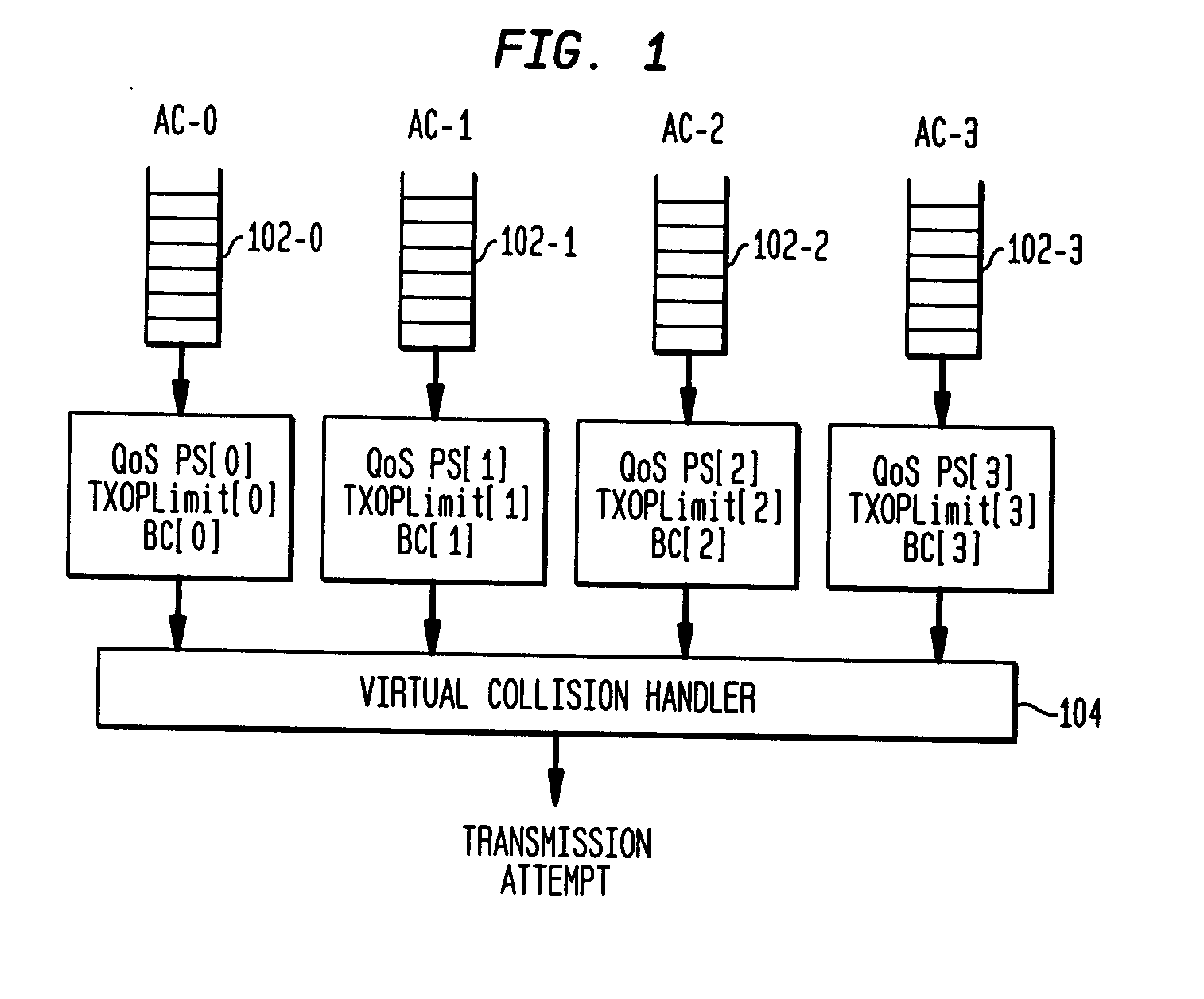
A method and a system is disclosed for providing quality of service (QoS)-driven channel access within a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless network. A contention control (CC) frame is sent from a point coordinator (PC) station of the BSS. The CC frame contains information relating to a number of available centralized contention opportunities (CCOs) for receiving a reservation request (RR) in a centralized contention interval (CCI) following the CC frame. The CC frame also contains information relating to the identification of stations from which an RR was successfully received by the PC station in a preceding CCI. The CC frame is sent by the PC station during a contention-free period (CFP) of a superframe. The superframe includes a contention-free period (CFP) and a contention period (CP). The CC frame is received at a non-PC station in the BSS. An RR is then sent in a selected one of the available CCOs in the CCI in response to the received CC frame. The RR is sent from the non-PC station when the non-PC station has a burst of data frames to send, and the RR indicating an amount of bandwidth requested by the non-PC station sending the RR for transmitting the burst. The RR frame is received at the PC-station in one of the CCOs of the CCI. A multipoll frame is then sent from the PC station containing information relating to at least two transmission opportunities (TOs) assigned to at least one non-PC station in the BSS for data transmission. The information contained in the multipoll frame can include information relating to a length of each TO.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
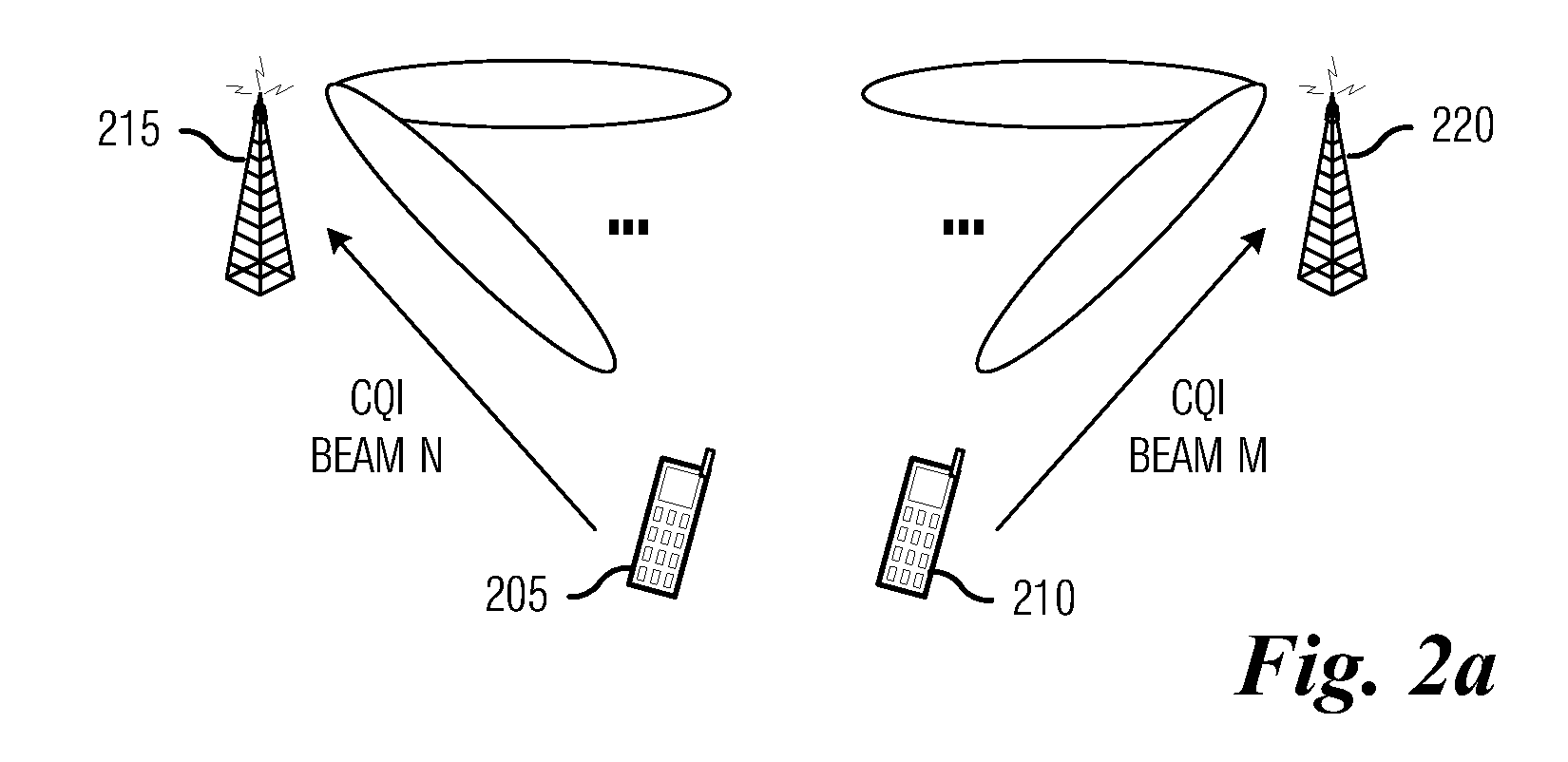
System and Method for Coordinating Electronic Devices in a Wireless Communications System
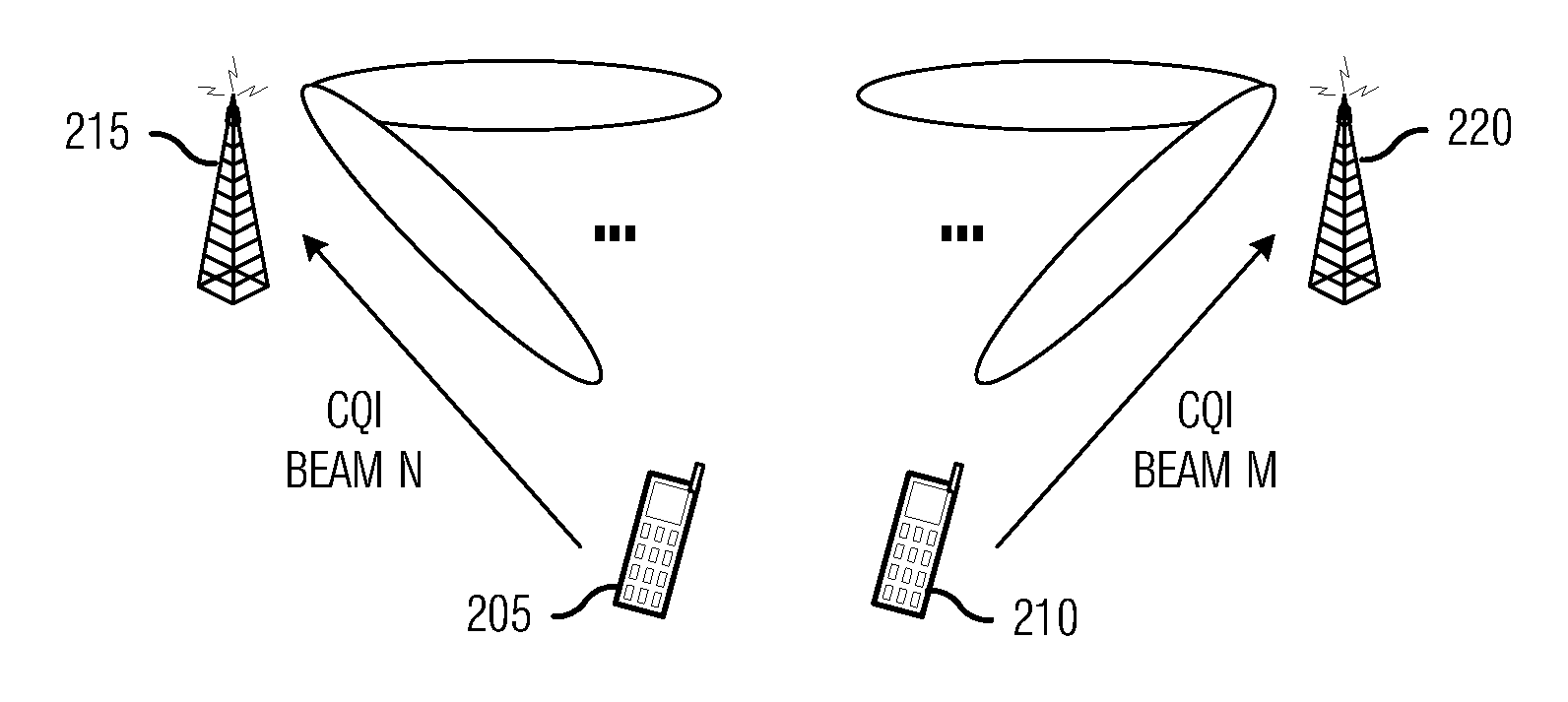
ActiveUS20100273499A1Little controlSmall impactWireless commuication servicesNetwork planningCommunications systemMobile device
A system and method for coordinating electronic devices in a wireless communications system are provided. A method for transmitting information by a controller includes computing a beam cycle based on transmissions from a plurality of mobile devices, receiving resource-specific channel quality indicators from the plurality of mobile devices, scheduling a transmission opportunity for a mobile device in the plurality of mobile devices, and transmitting information to the mobile device based on the scheduled transmission opportunity. The mobile devices are being served by the controller, and the scheduling is based on the beam cycle and the channel quality indicators.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
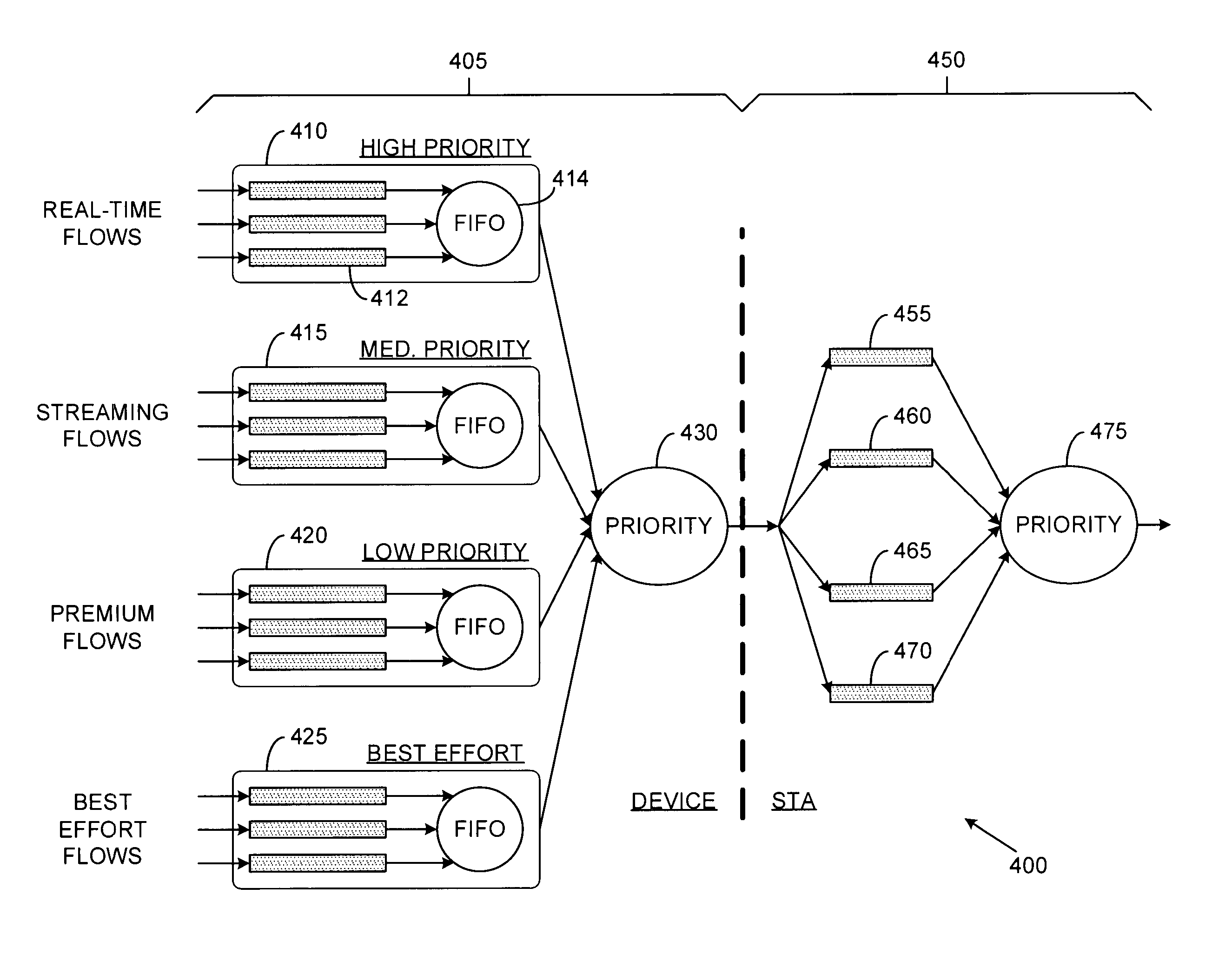
Hierarchical scheduling for communications systems
InactiveUS20050047425A1Addressing slow performanceEasy to modifyNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationCommunications systemDistributed computing
System and method for scheduling messages in a digital communications system with reduced system resource requirements. A preferred embodiment comprises a plurality of traffic queues (such as traffic queue 410) used to enqueue message of differing traffic types and a first scheduler (such as priority scheduler 430). The first scheduler to select messages from the traffic queues and provide them to a plurality of priority queues (such as priority queue 455) used to enqueue messages of differing priorities. A second scheduler (such as priority scheduler 475) then selects messages for transmission based on message priority, transmission opportunity, and time to transmit.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
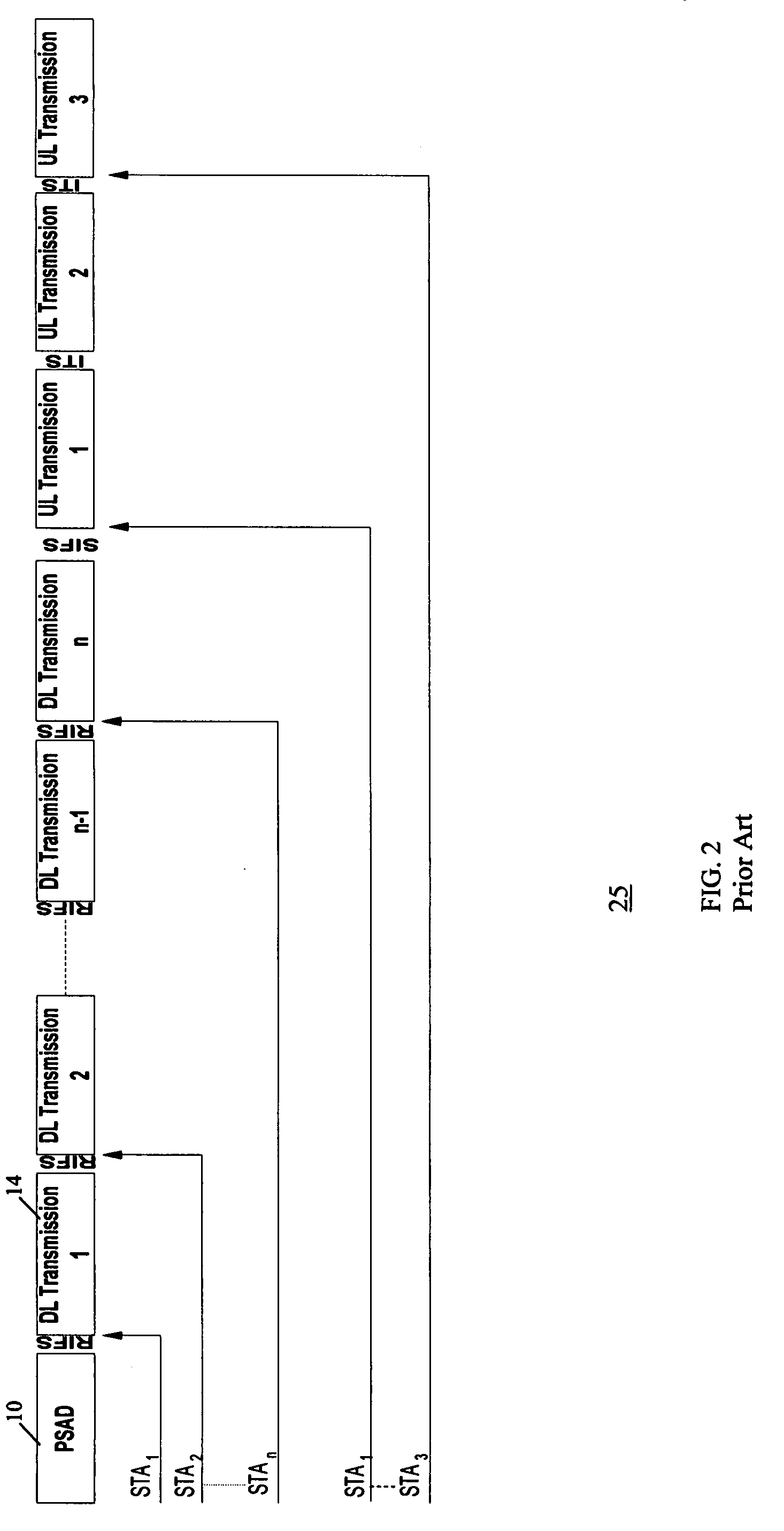
Method and system for power saving scheduling in wireless local area networks
InactiveUS20080232287A1Improve efficiencyMore powerEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemUplink transmission
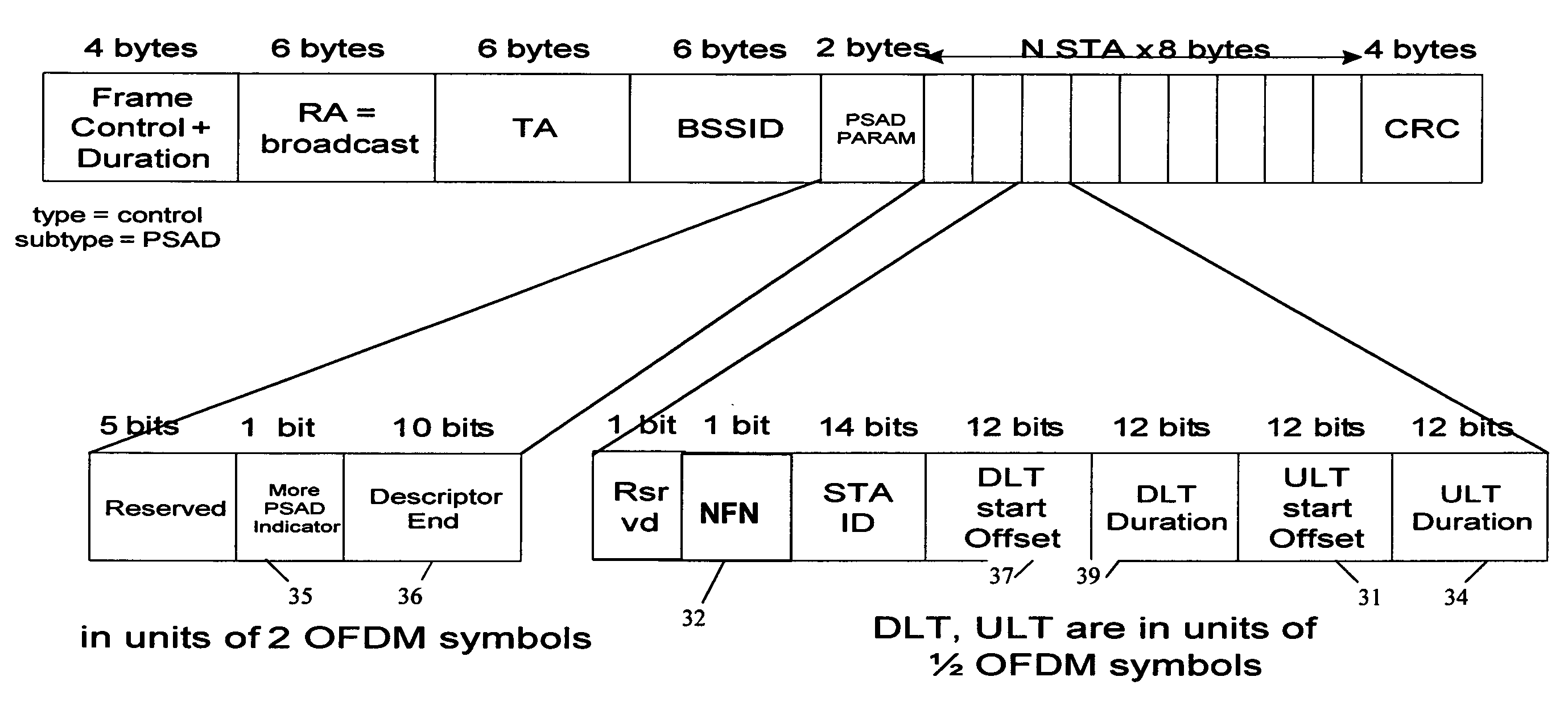
A power saving (PS) scheduling process is provided for scheduling uplink and downlink frame transmissions between a PS transmitter and at least one PS receiver using PSAD sequences in a wireless communication system. The power saving scheduling process involves determining a power saving schedule of transmission opportunities for communication between a PS transmitter and at least one PS receiver over a shared channel, wherein the schedule includes corresponding durations for uplink transmissions of frames from each PS receiver to the PS transmitter. A Power Saving Aggregation Descriptor (PSAD) frame containing said schedule is constructed. A PSAD sequence is initiated by transmitting the PSAD from the PS transmitter to each PS receiver.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
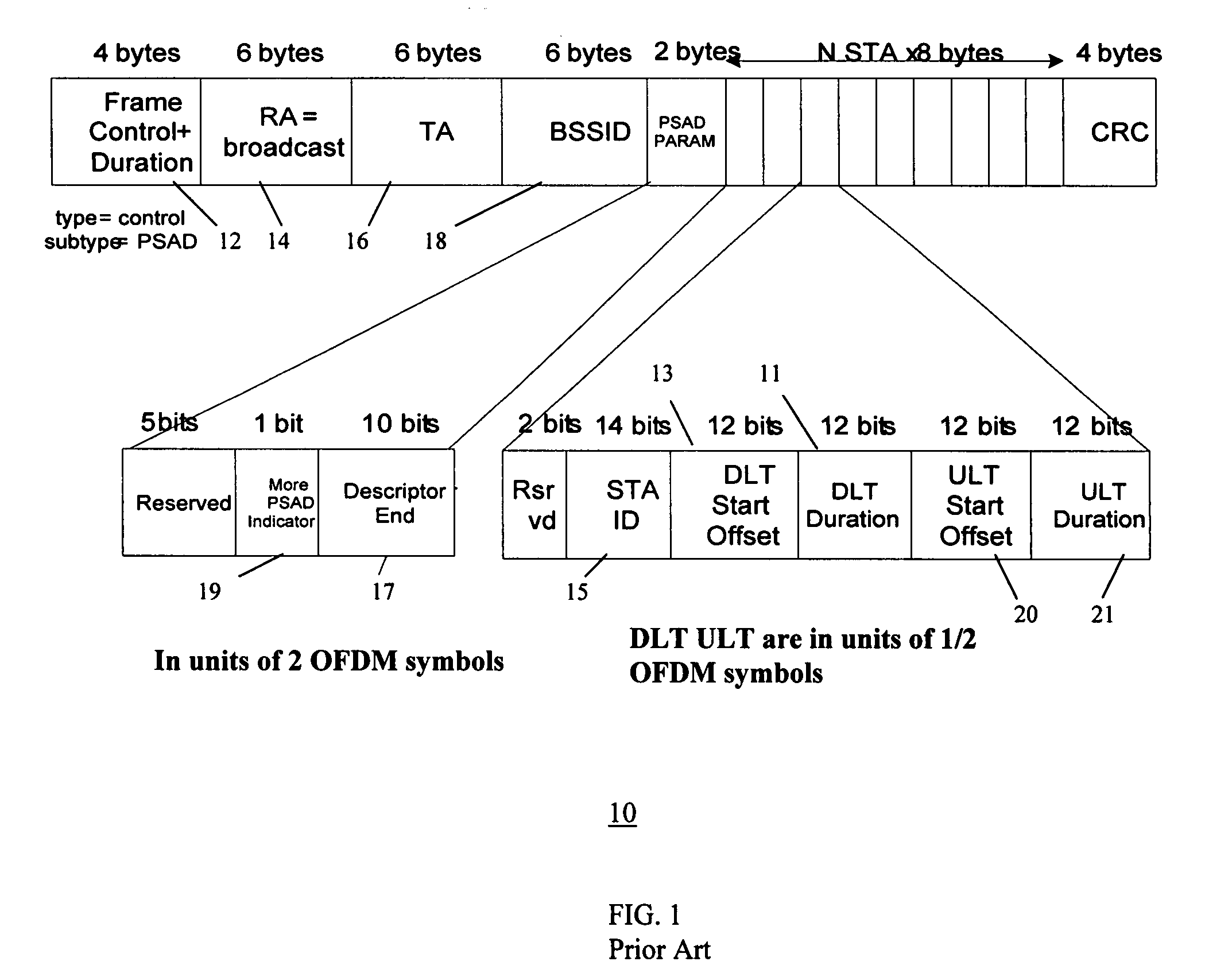
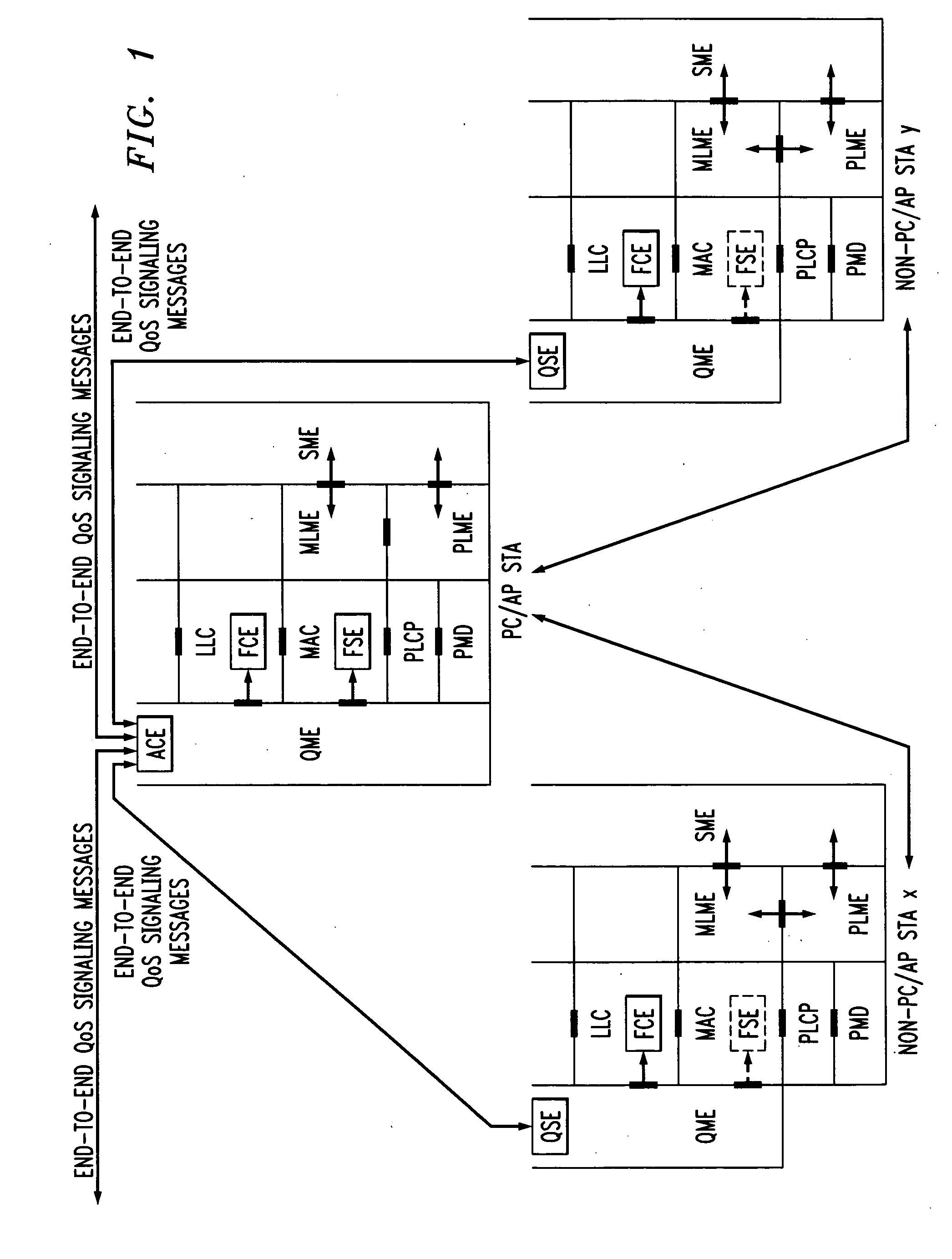
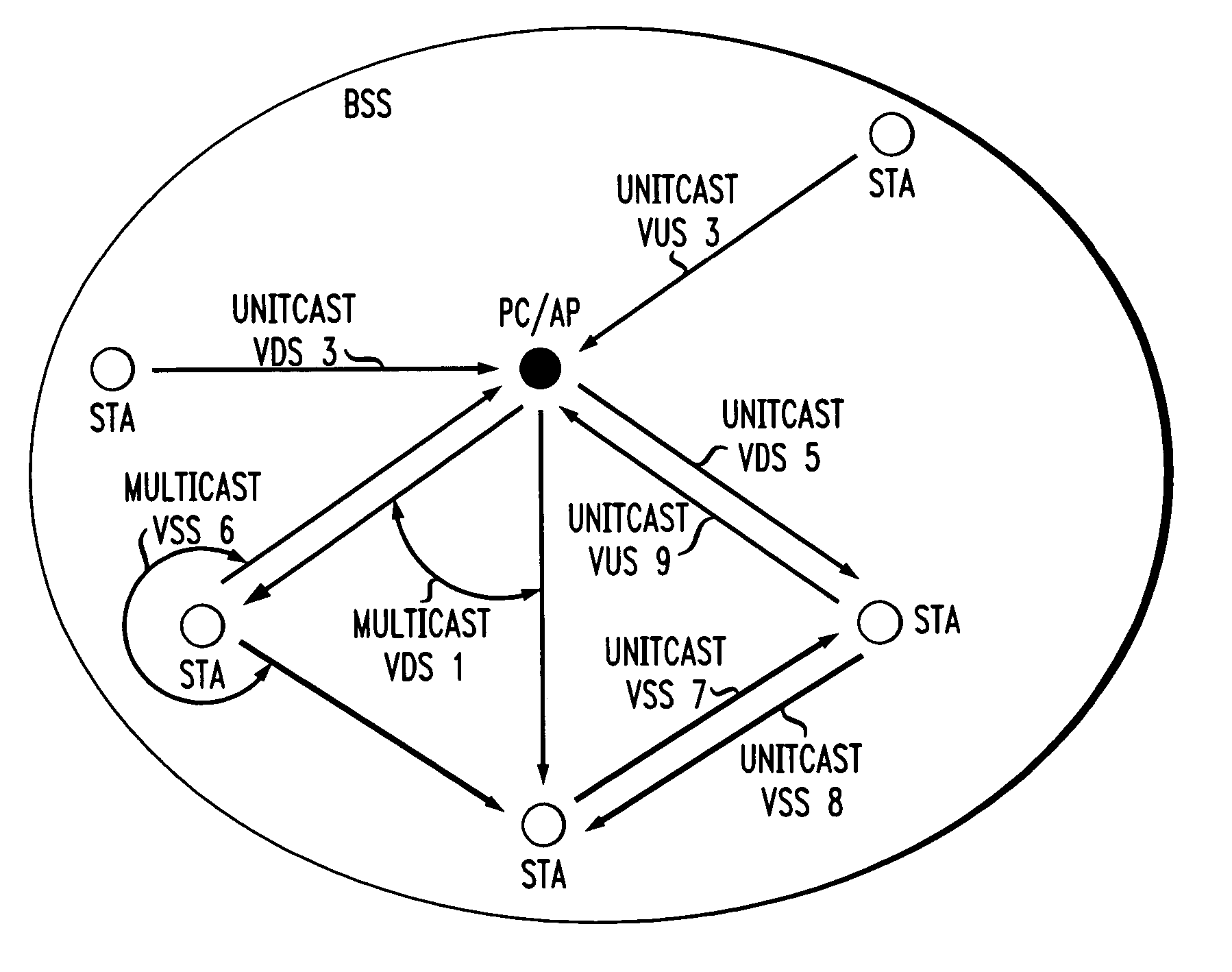
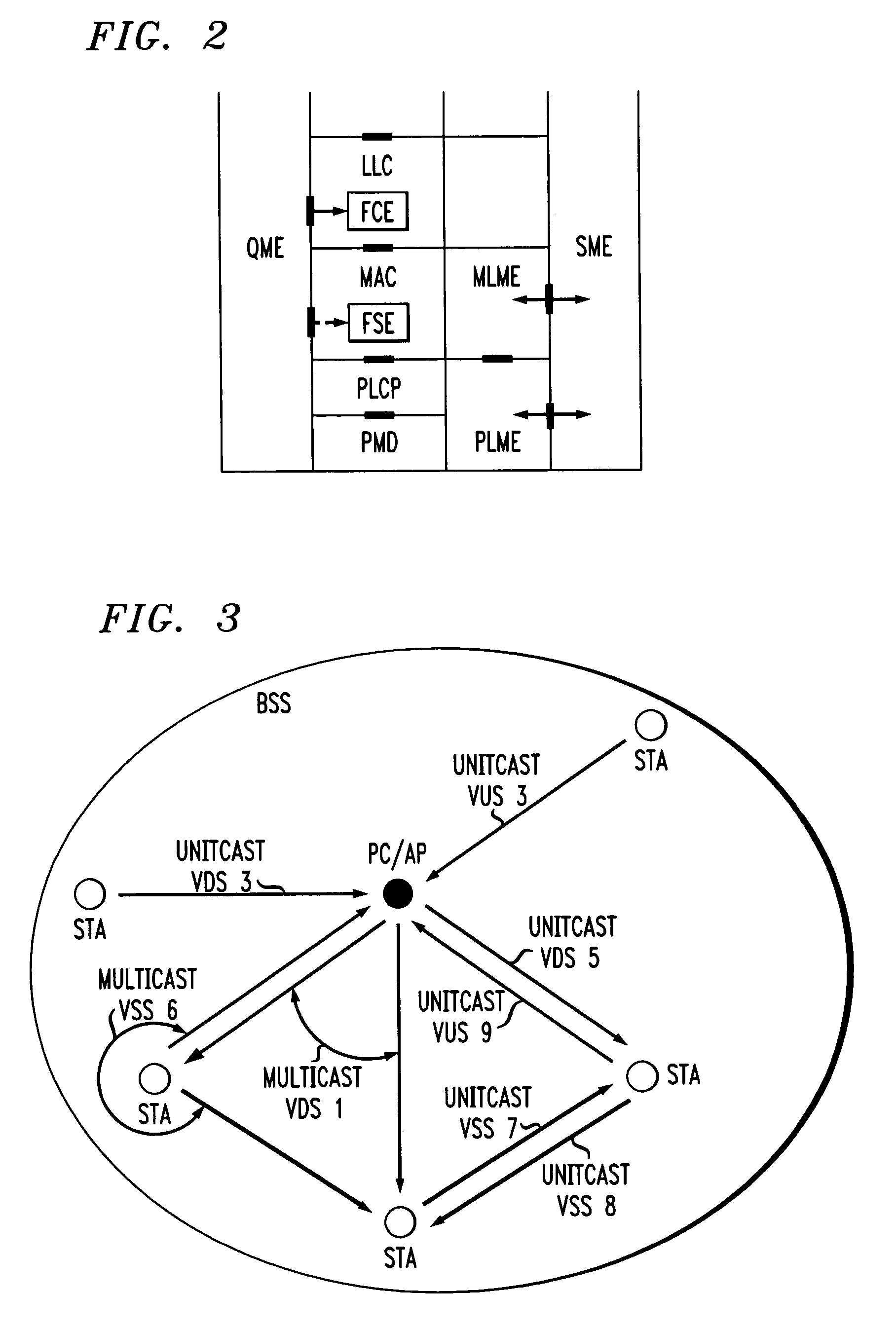
In-band QoS signaling refernce model for QoS-driven wireless lans
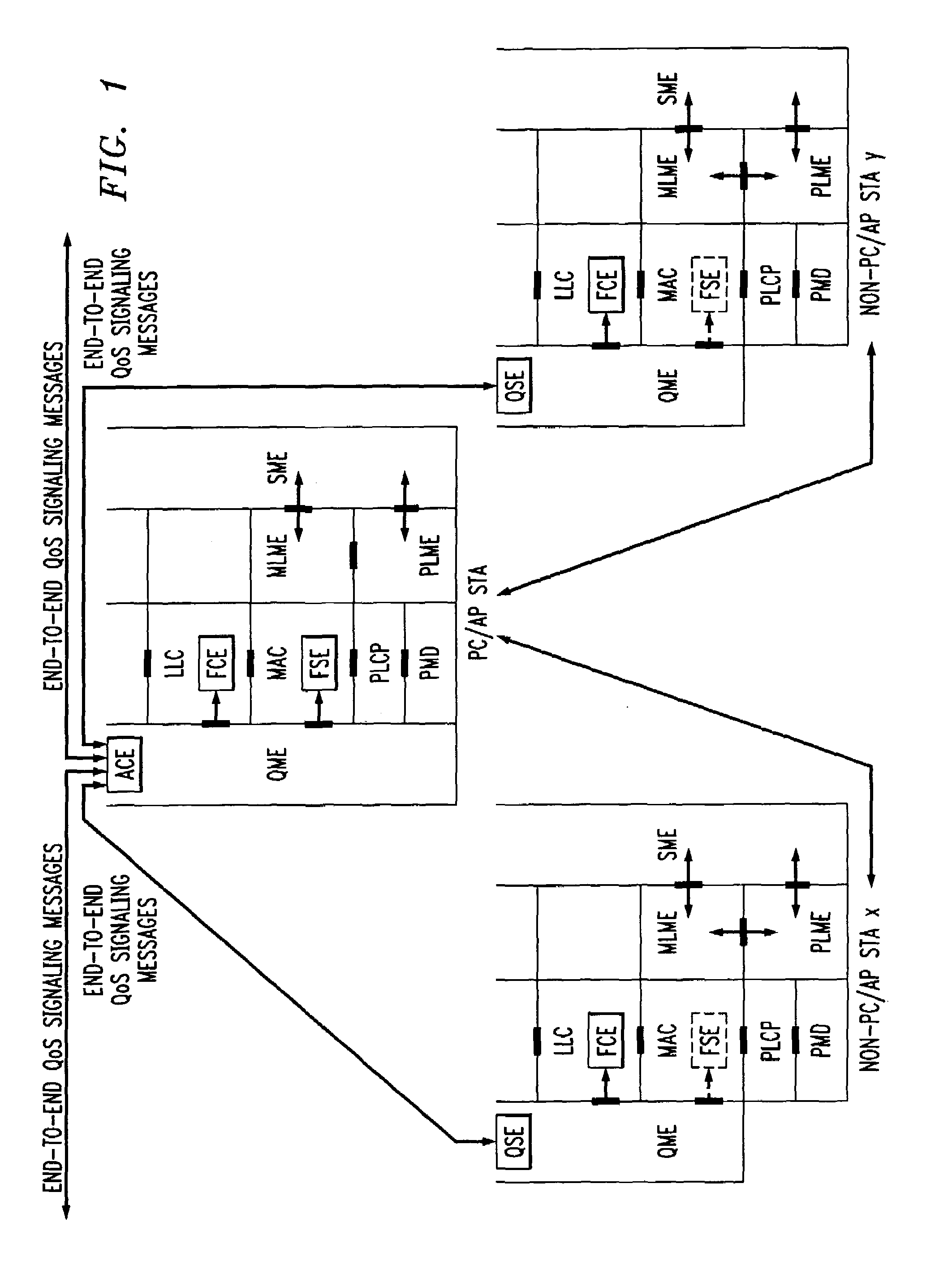
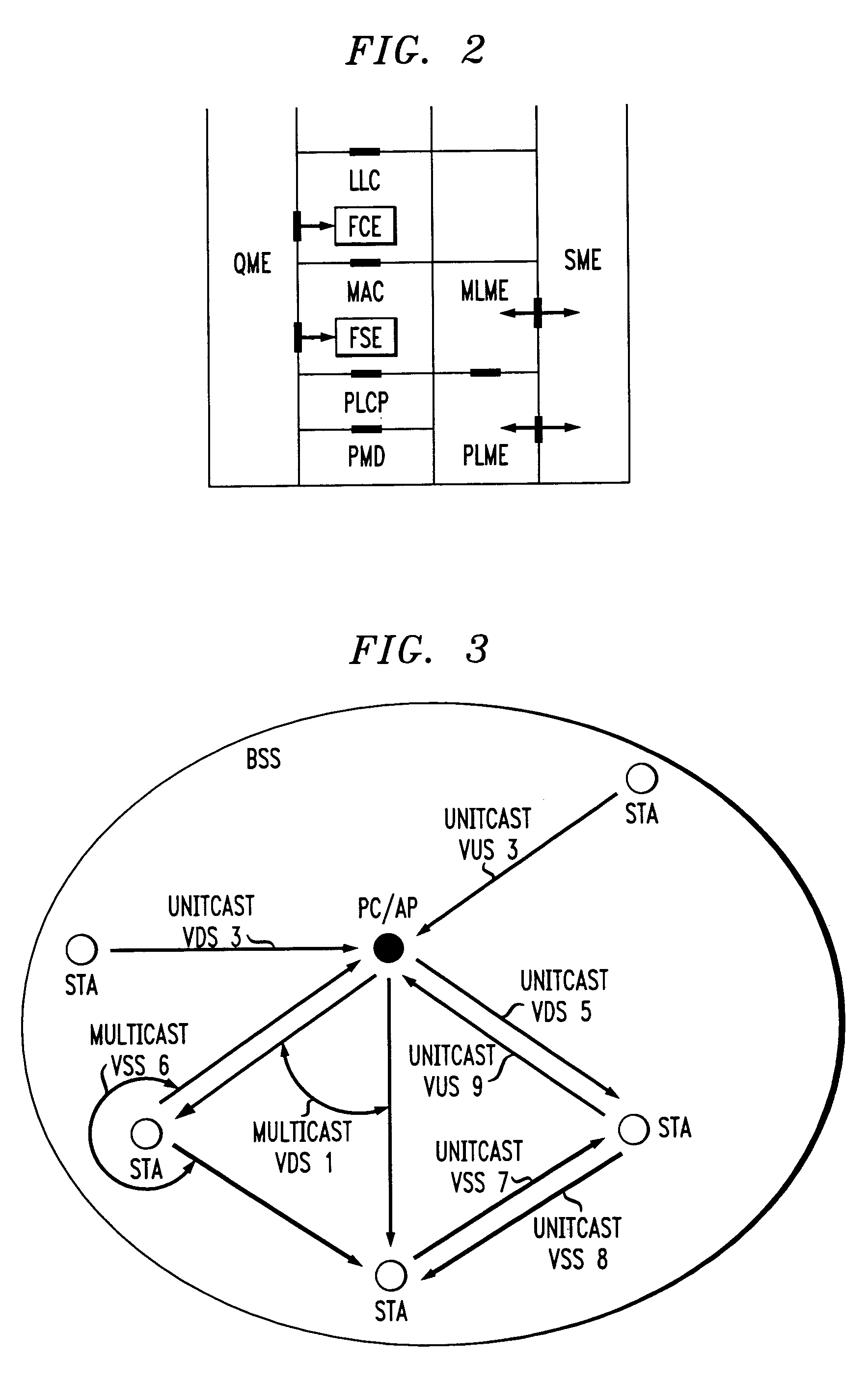
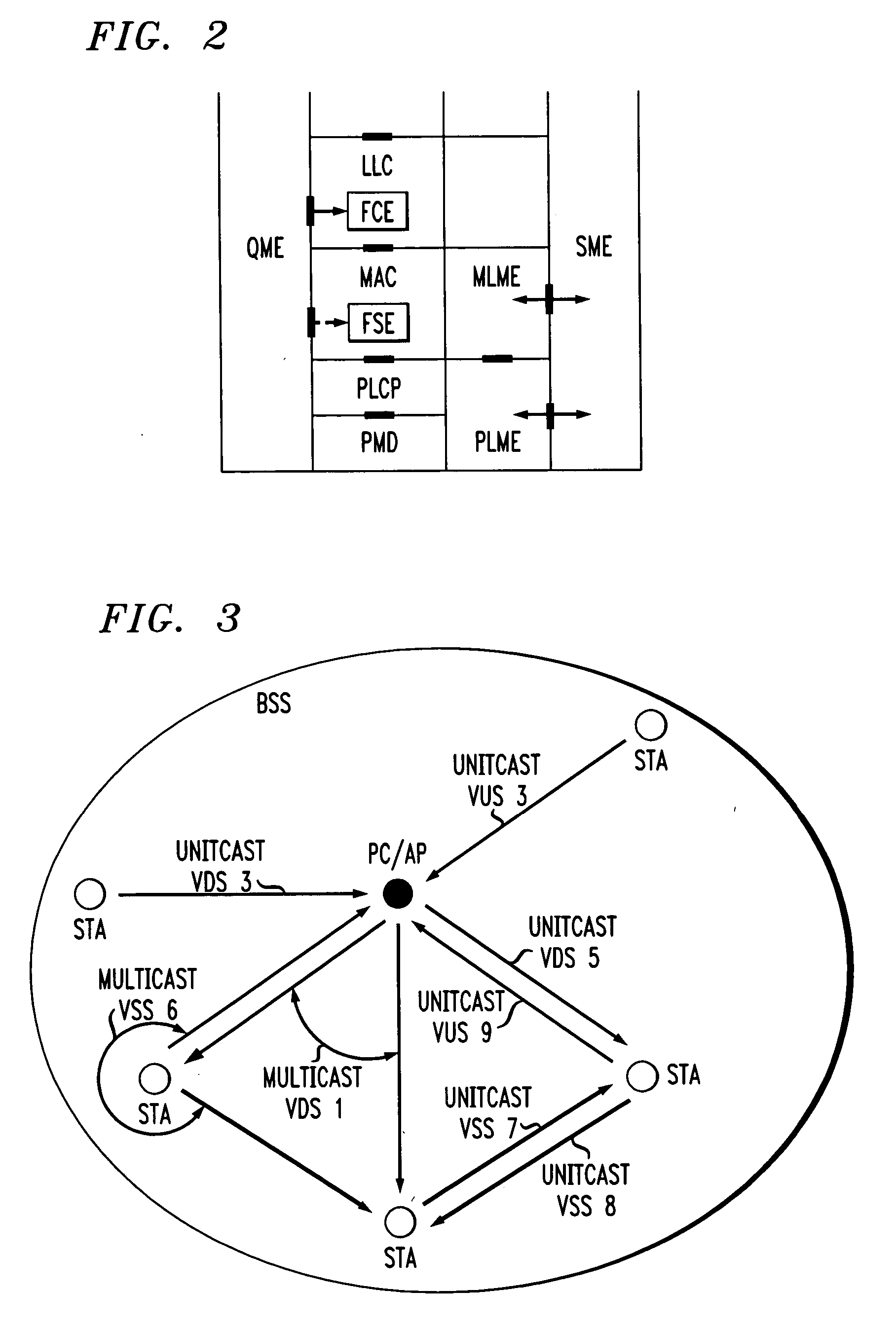
InactiveUS20050041670A1Function increaseError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceFrame based
A station, such as a point coordinator (PC) or a non-PC station, in a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN) is disclosed. The station includes a frame classification entity (FCE), a frame scheduling entity (FSE) and a QoS management entity (QME). The FCE is logically located in a logical link control (LLC) layer of the station and has a classification table containing at least one classifier entry. Each classifier entry contains a virtual stream identifier (VSID) and a frame classifier associated with a user session. The FCE receives a data frame associated with the user session, which can be one of a voice session, a video session, a data session and a multimedia session. The data frame contains in-band quality of service (QoS) signaling information for the user session. The FCE classifies the received data frame to a selected VSID contained in a classifier entry in the classification table based on a match between an in-band frame classification information contained in the received frame and the frame classifier contained in the classifier entry. The FSE is logically located in a medium access control (MAC) sublayer of the station and has a frame scheduling table containing at least one entry. Each entry in the frame scheduling table contains a VSID and a QoS parameter set associated with a user session identified by the VSID. The FSE is responsive to the classified data frame by scheduling a transmission opportunity (TO) for the classified data frame based on the at least one QoS parameter value associated with the VSID and characterizing the user session. The QME interfaces with the FCE and The FSE.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
TXOP duration adaptation for dual radio devices
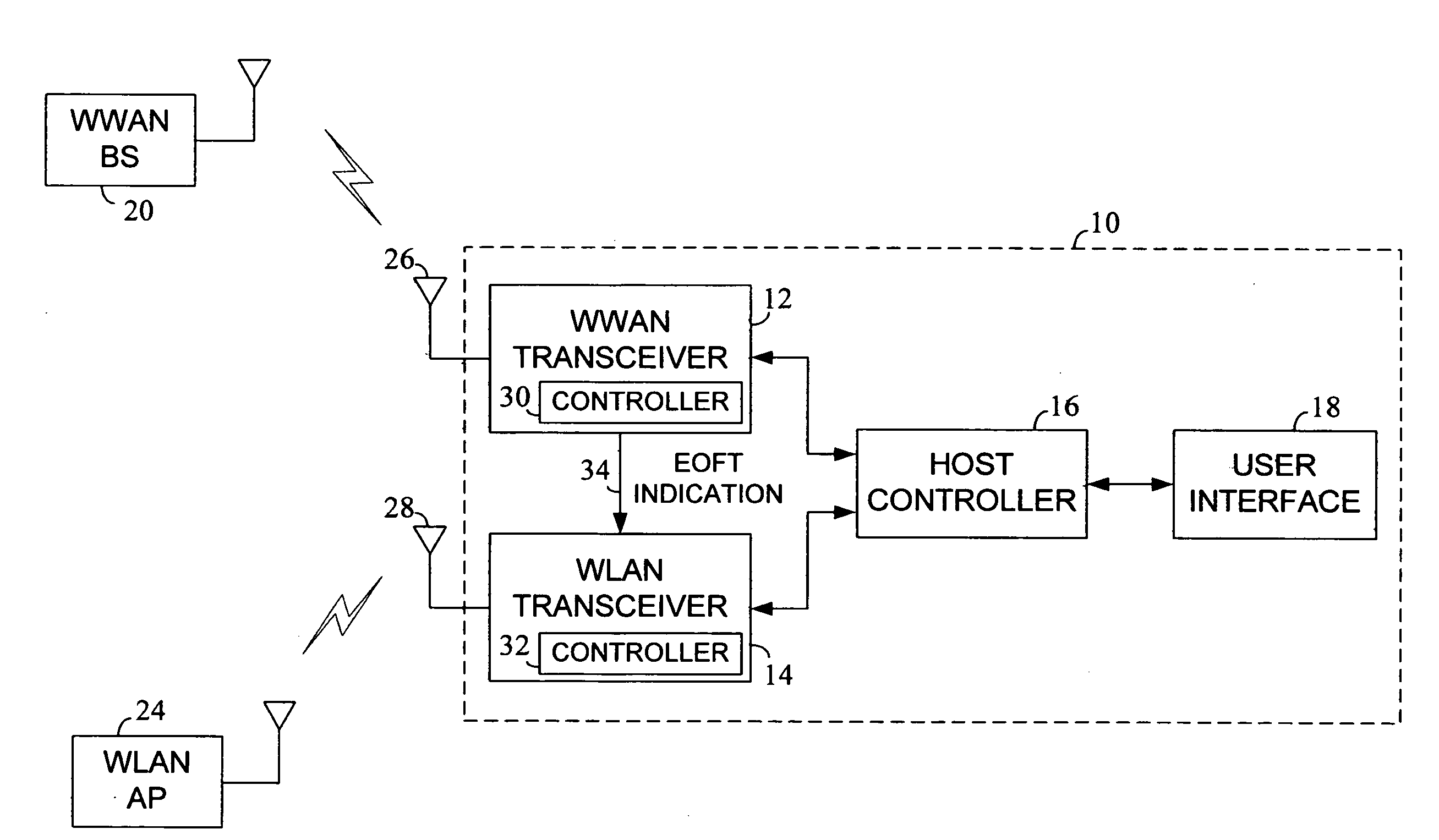
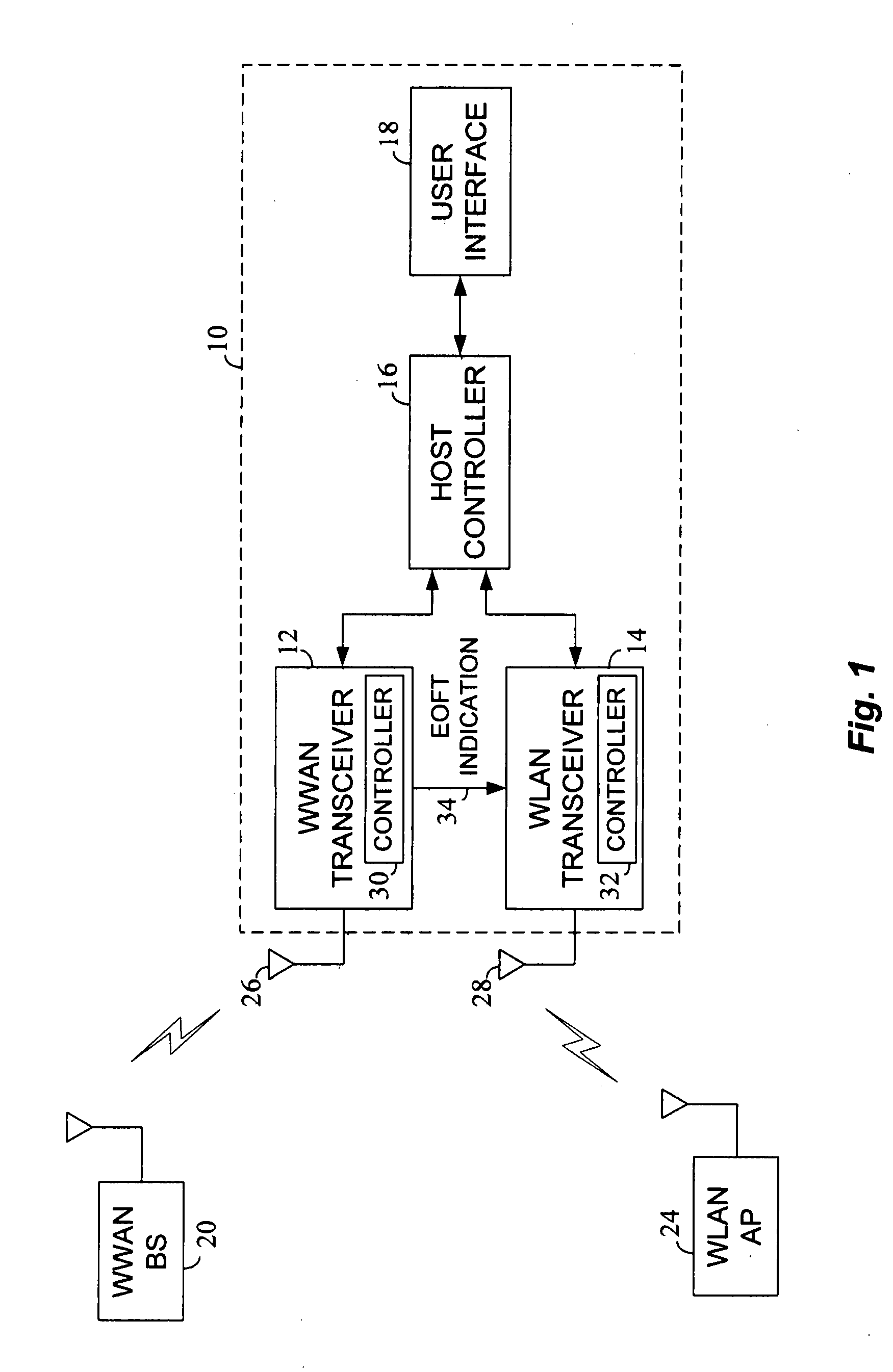
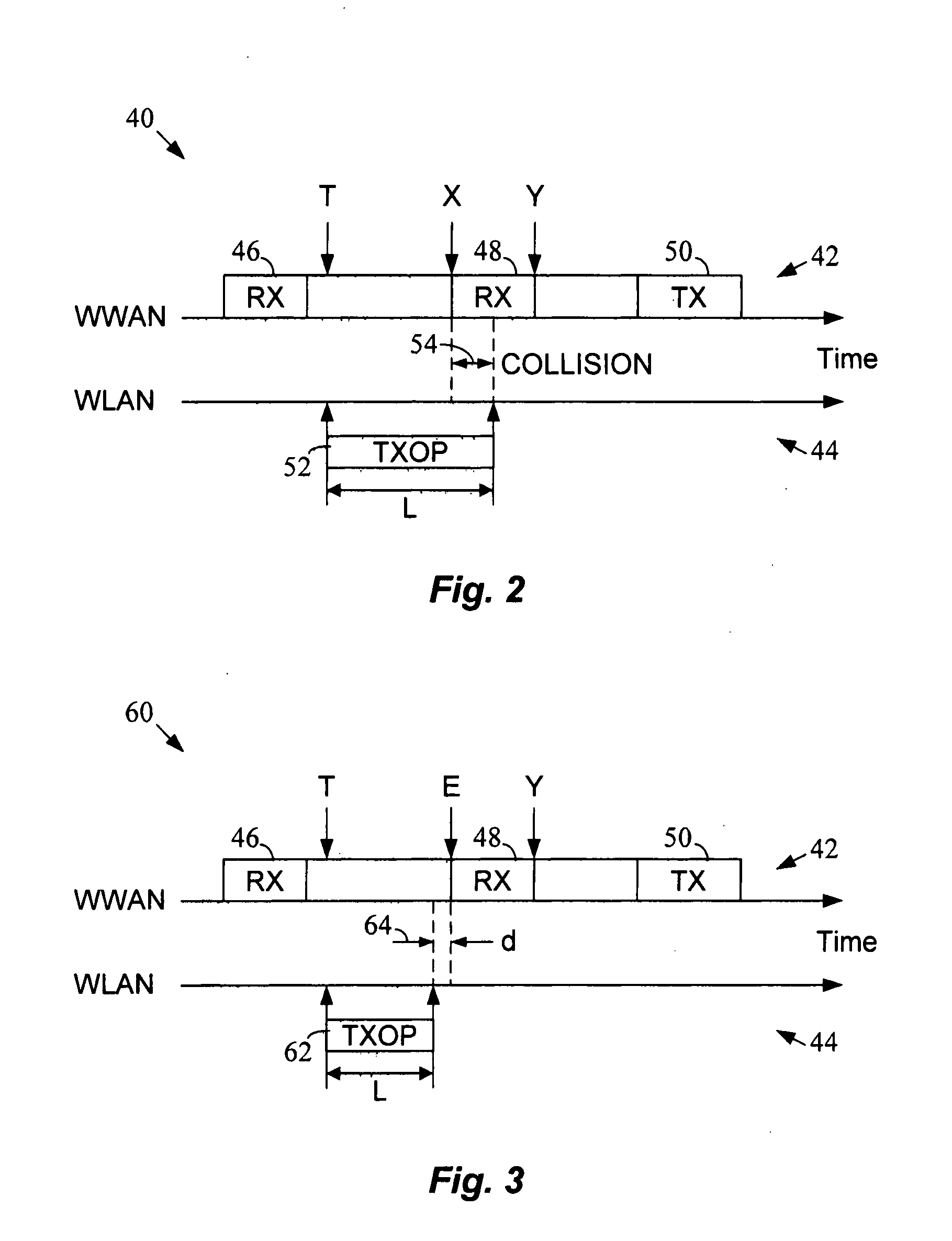
Transmission opportunity (TXOP) duration is adapted for a wireless local area network (WLAN) transceiver in a dual radio wireless device based on an end of free time indication associated with a wireless wide area network (WWAN) transceiver within the same device. In this manner, the occurrence of collisions between WLAN communication activity and WLAN communication activity within the dual radio device may be reduced or eliminated.
Owner:INTEL CORP
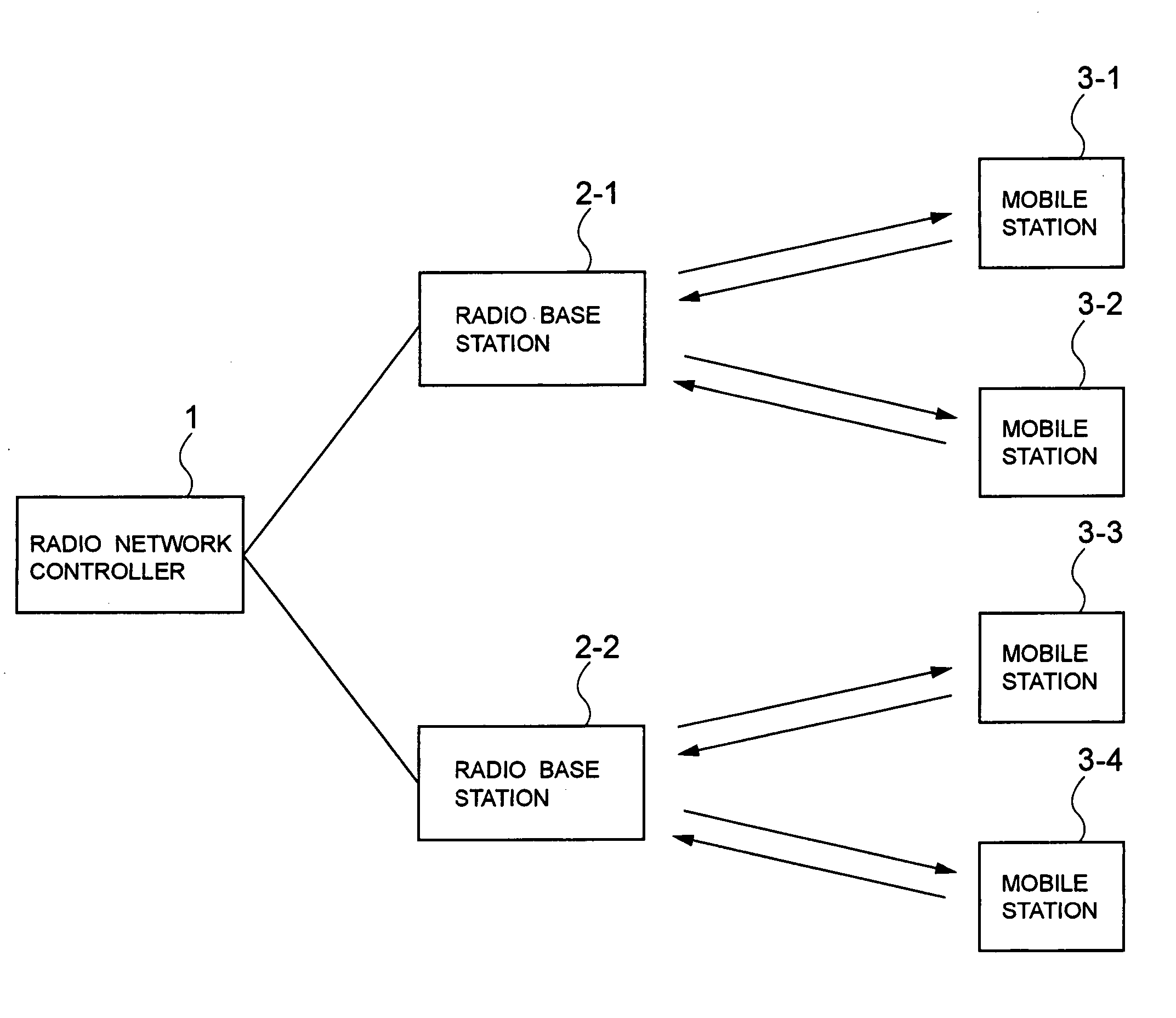
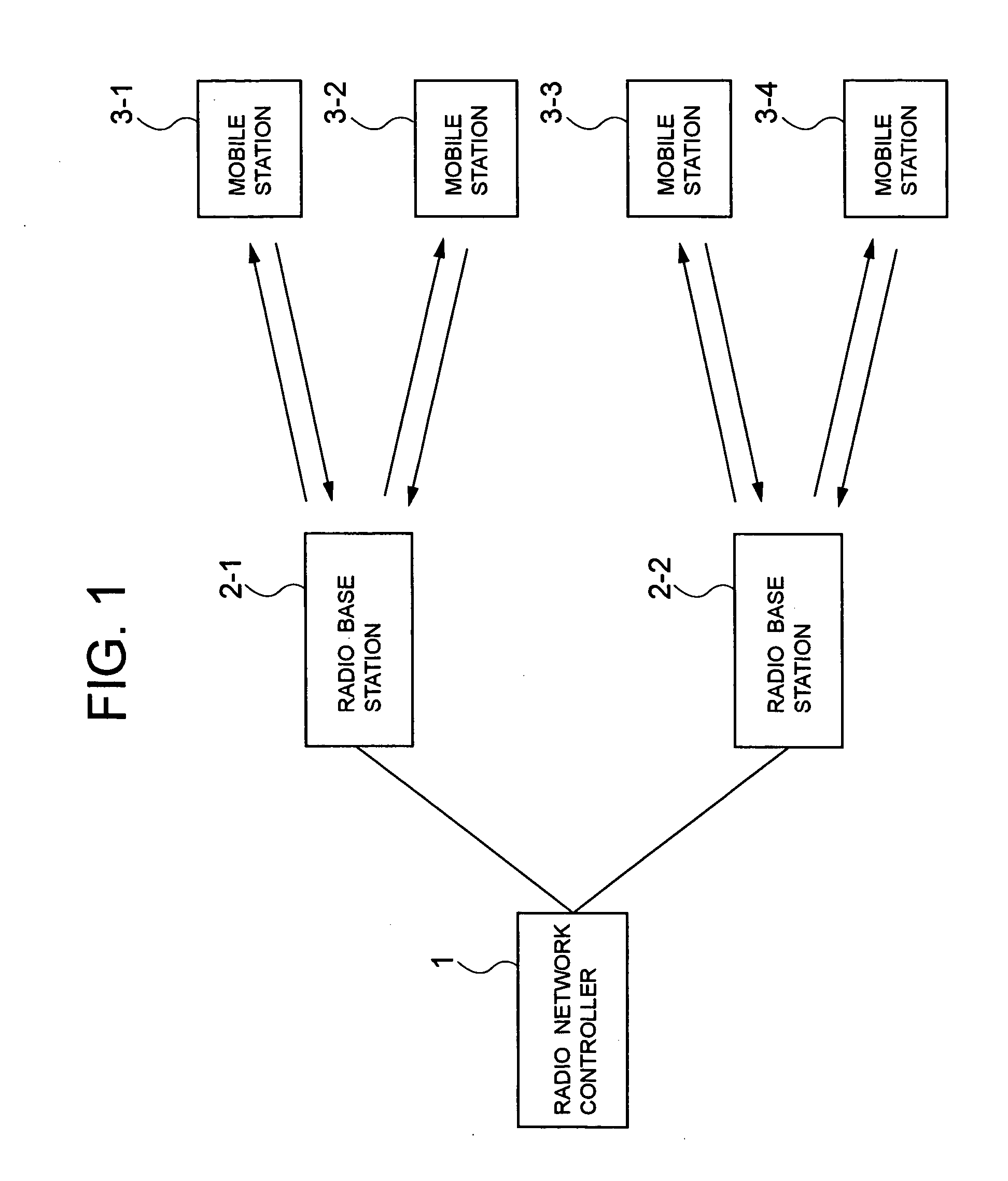
Radio communication system
ActiveUS20060221879A1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationCommunications systemRadio Base Station
A radio base station apparatus used in a radio communication system in which an initiator holds a transmission opportunity (TXOP) period in a frame exchange sequence and a responder responds to the initiator in the frame exchange sequence is disclosed. The apparatus includes a setting device which sets a ratio between a first period necessary for transmitting a first frame from the initiator to the responder and a second period necessary for transmitting a second frame from the responder to the initiator. The apparatus also includes a calculation device which calculates the first period to be used by the initiator and the second period to be used by the responder, on the basis of the transmission opportunity period and of the ratio which is set.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
System and Method for Discontinuous Transmissions and Measurements
ActiveUS20150289208A1Increase the number ofImprove performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelPower managementCommunications systemPhysical layer
A method for operating a first communications controller adapted for operation in a first communications band in a communications system with a plurality of communications bands includes signaling a first higher layer message to a user device in the first communications carrier, the first higher layer message including information regarding an activation of operations in a second communications carrier, coordinating with a second communications controller adapted for operations in the second communications carrier, an opportunistic transmission opportunity in the second communication carrier, generating a first physical layer message comprising an aperiodic trigger configured to prompt a channel measurement in accordance with a reference signal transmitted in the second communications carrier, the first physical layer message serving as an indication of the opportunistic transmission opportunity, and signaling the first physical layer message to the user device in the first communications carrier.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Management of frame bursting
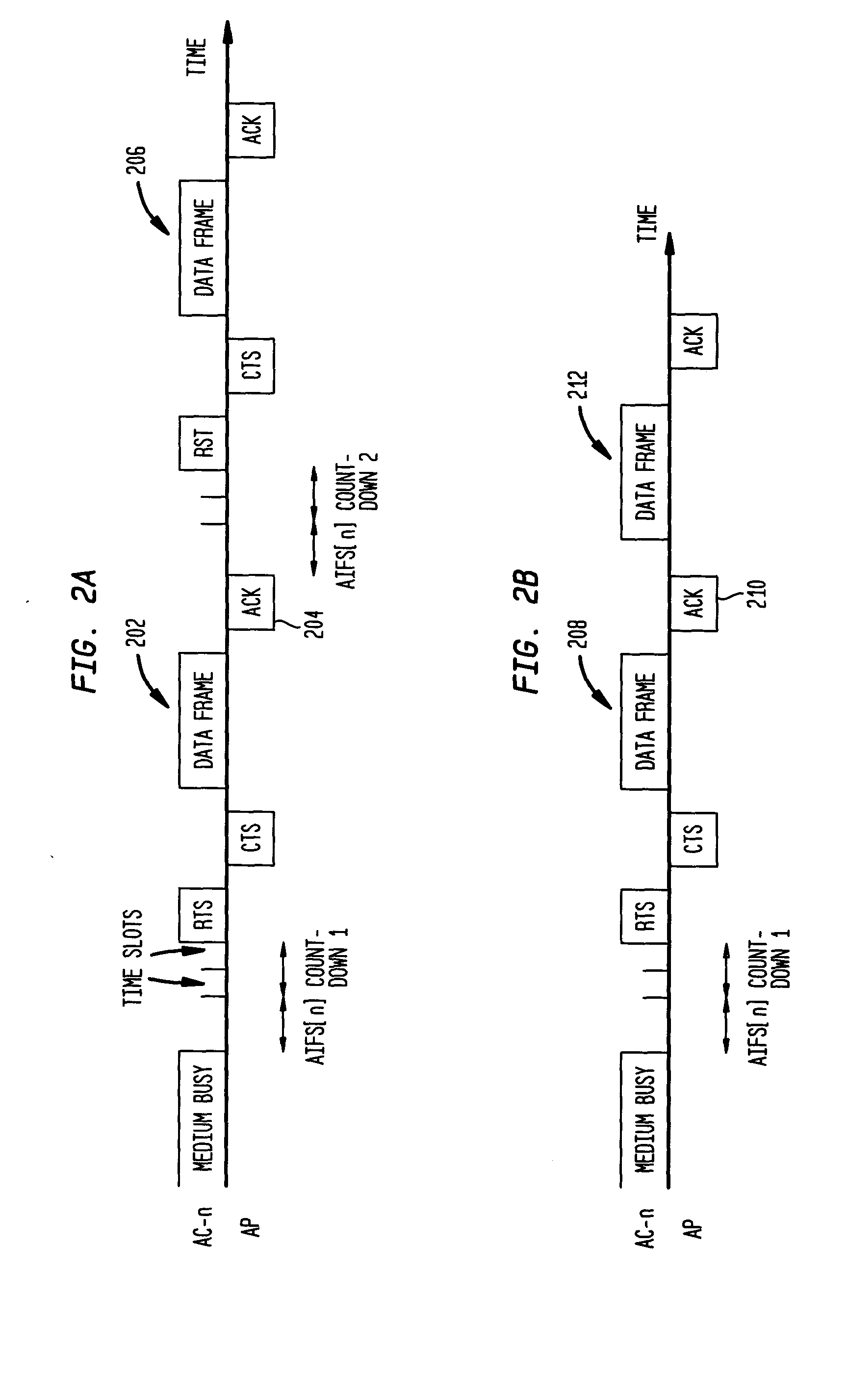
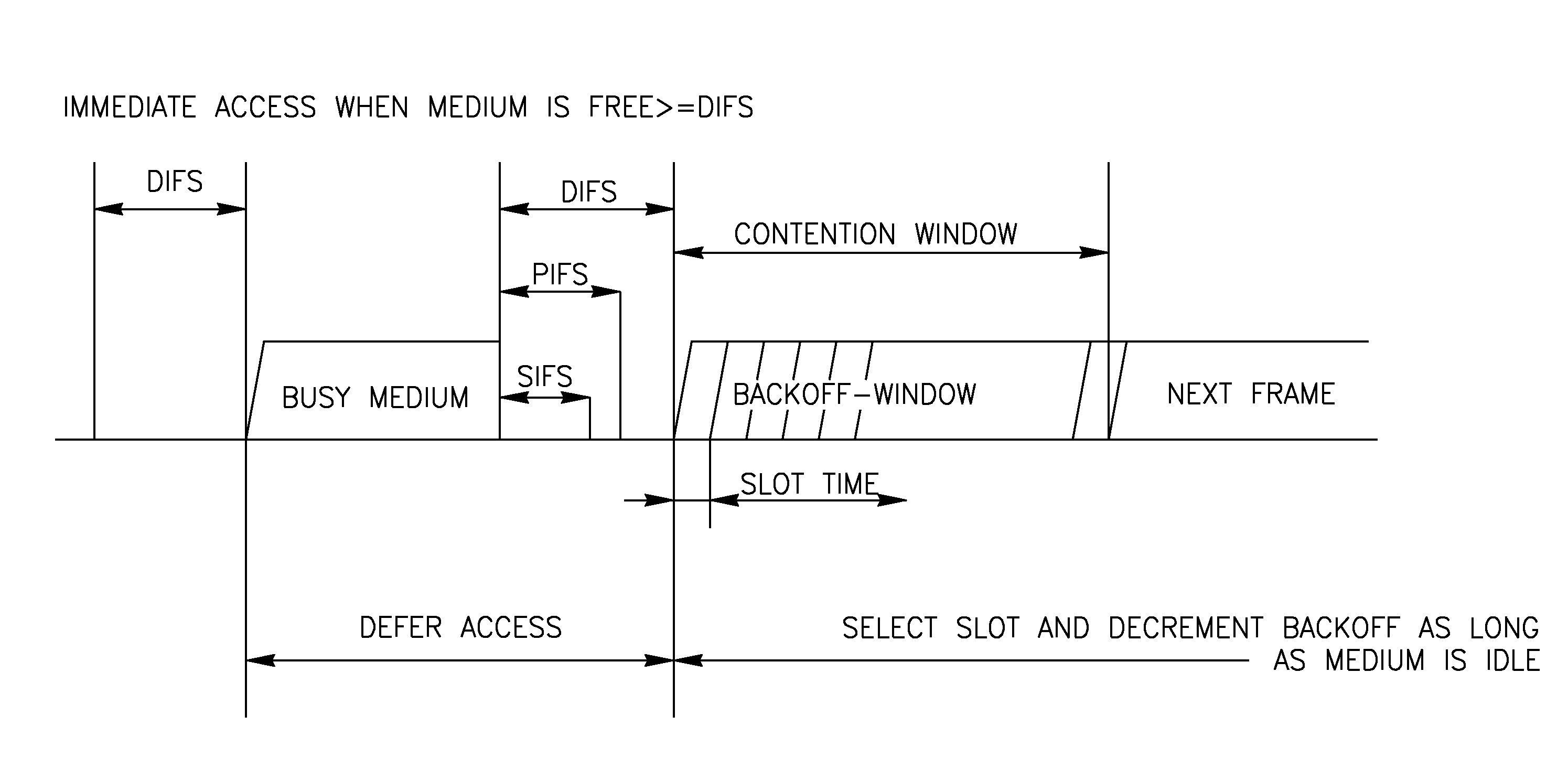
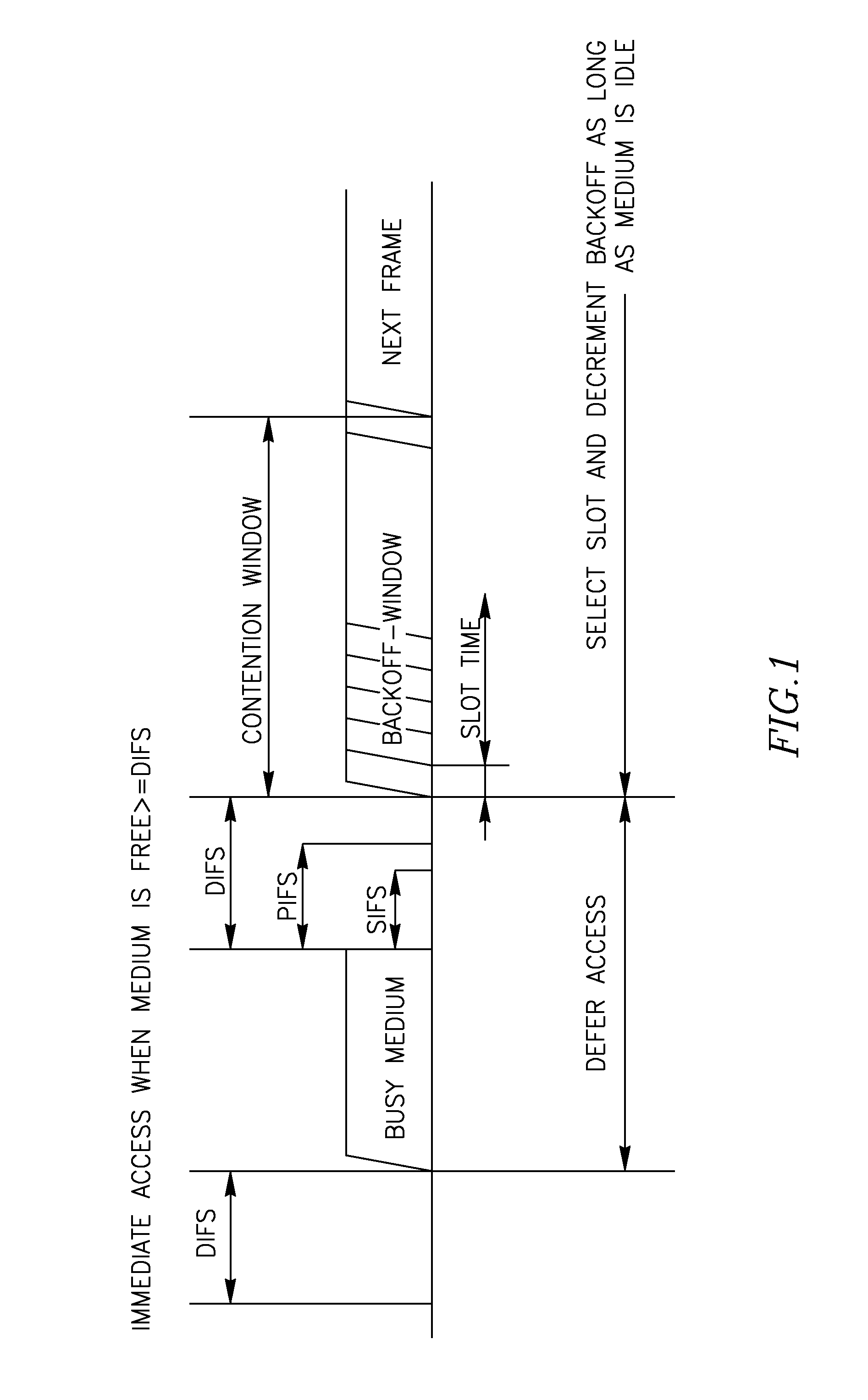
ActiveUS20050036448A1High trafficReduce overheadError preventionTransmission systemsData transmissionTransmission opportunity
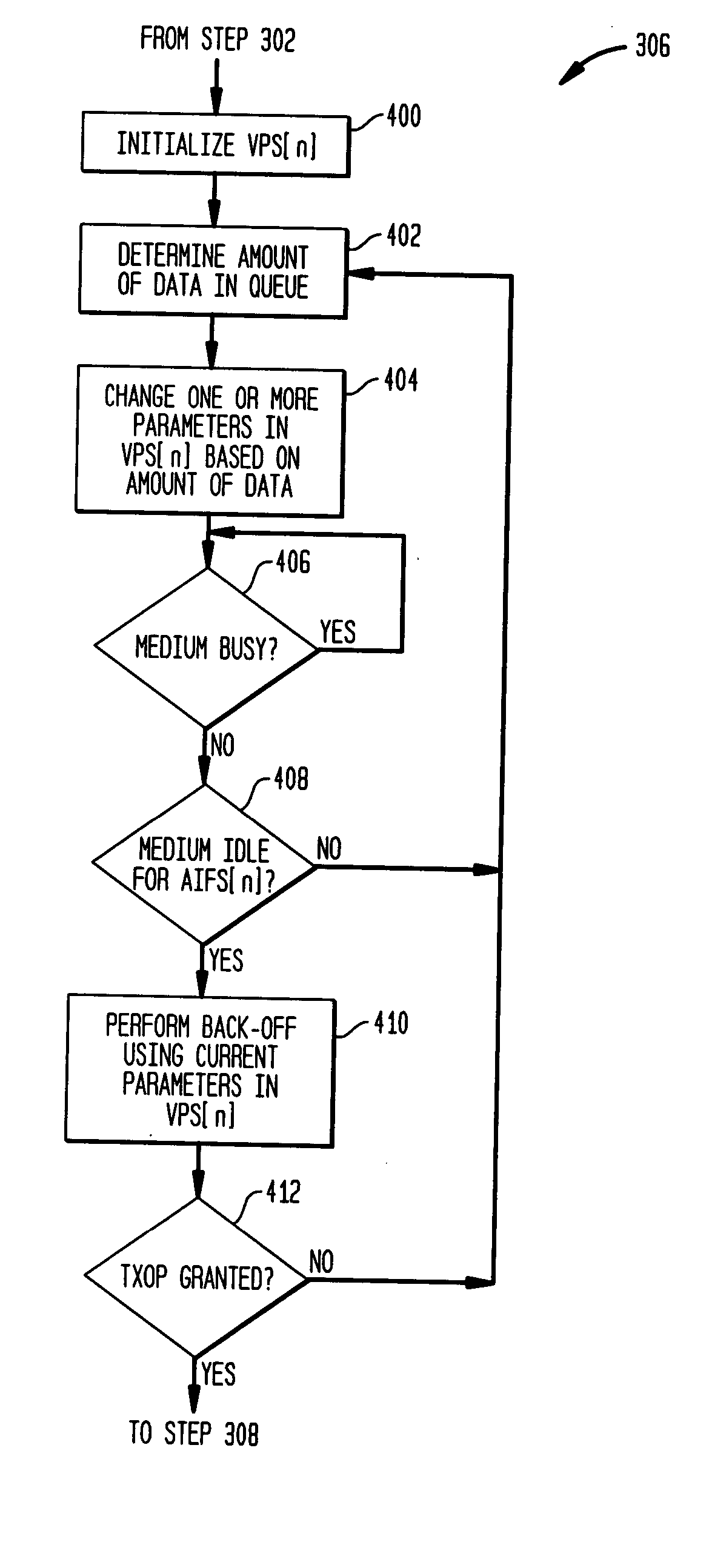
A method of data transmission employing frame bursting to improve traffic in a WLAN system. According to a representative embodiment of the invention, a variable parameter set, VPS[n], is provided to a channel access function in the process of obtaining a transmission opportunity (TXOP) for a corresponding access category, AC-n, at a wireless station of the WLAN system. The variation of one or more values in VPS[n] is based on the amount of buffered traffic and is preferably performed such that, when a TXOP is granted, AC-n has buffered an amount of traffic suitable for transmission using frame bursting in such a manner that the service and back-off overheads for AC-n are substantially reduced. Due to the overhead reduction, more channel time becomes available to traffic from other access categories and / or wireless stations. For example, bursting video traffic in accordance with the invention may significantly improve best-effort traffic. In addition, less channel time may be lost to collisions.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Transmission time interval (TTI) bundling operation within communication systems
ActiveUS20140040694A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemTransmission opportunity
TTI bundling is included for Msg3 transmissions in LTE communications. A reserved group of preambles or reserved set of random access preamble transmission opportunities are used to indicate user equipment (UE) need of uplink (UL) transmission of a TTI-bundled Msg3. The UE transmits the same redundancy version for transmissions within a TTI bundle as the eNB expects even if any of the transmissions are dropped due to collisions with an Msg3 transmission. In addition, co-existence of TTI bundling and UL semi-persistent scheduling (SPS) for TDD DL / UL configurations is provided using SPS intervals which are multiples of various fixed time periods.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
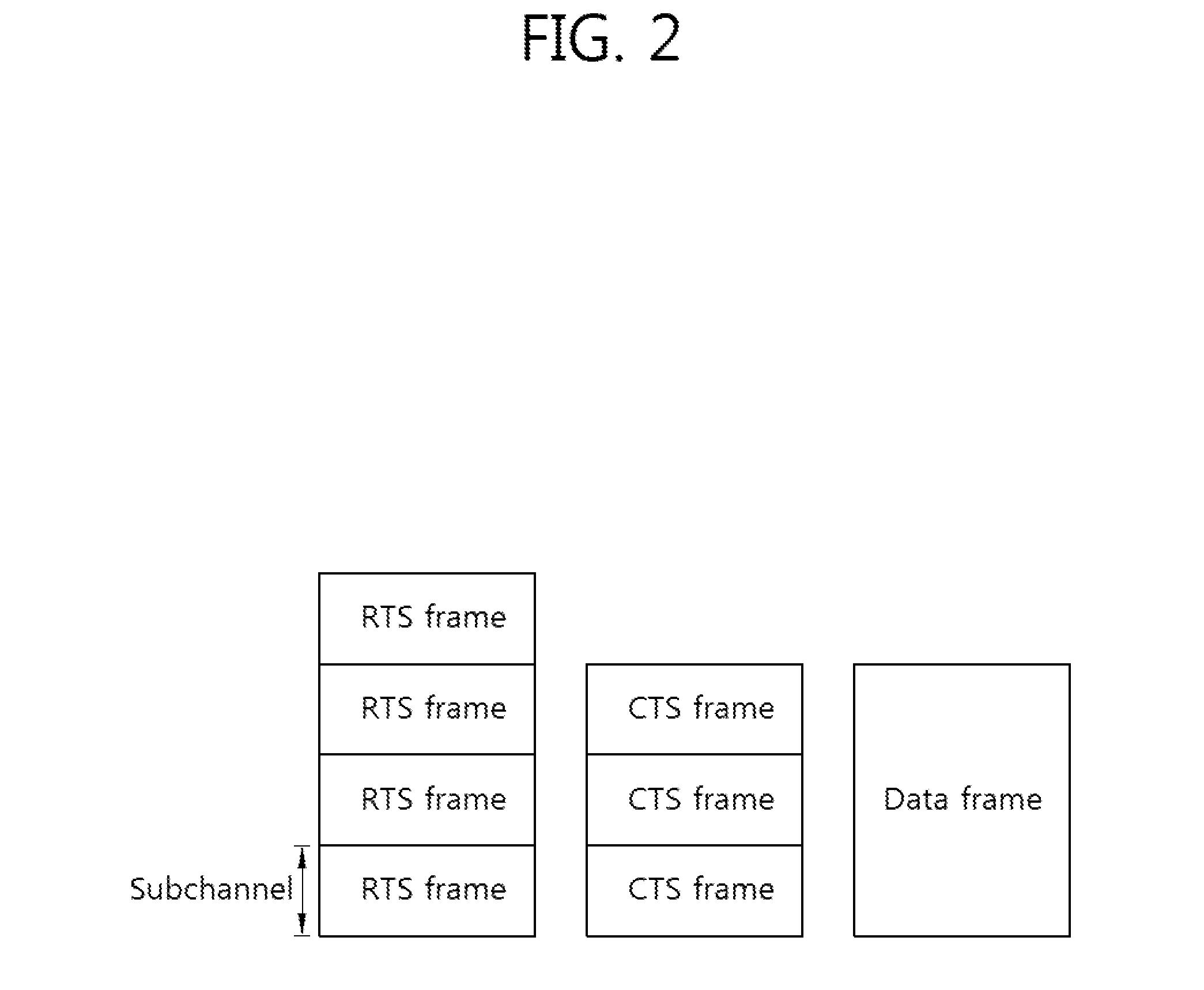
Method for granting a transmission opportunity in a wireless LAN system that uses a combined channel constituted by a plurality of subchannels, and station supporting the method
ActiveUS20110310834A1Easy to useImprove efficiencyNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionTelecommunicationsWireless lan
A method for granting a contention-free transmission opportunity in a wireless LAN system using a combined channel comprised of a plurality of subchannels, and a station supporting the method are provided. The method for granting transmission opportunity includes: transmitting a transmission opportunity granting frame granting a transmission opportunity of a plurality of target stations; and receiving a frame from each of the plurality of target stations which have acquired a transmission opportunity upon receiving the transmission opportunity granting frame. The station supports granting of a transmission opportunity by the foregoing method.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for uplink multi-user transmission in a high efficiency wireless LAN
Methods and apparatus for transmission opportunity limits, backoff procedures, uplink random access related to uplink multi-user transmission in a High Efficiency WLAN (HEW) are described. An embodiment is a method for performing a frame exchange sequence including an uplink multi-user (UL MU) transmission by an access point (AP) in a wireless local area, the method including acquiring a transmission opportunity (TXOP) for initiating the frame exchange sequence; determining if a time required for the frame exchange sequence not including a control response frame exceeds a TXOP limit; and transmitting a trigger frame to one or more stations (STAs) when the time required for the frame exchange sequence not including the control response frame does not exceed the TXOP limit.
Owner:ATLAS GLOBAL TECH LLC
Wireless power transmission system and method controlled via digital messages
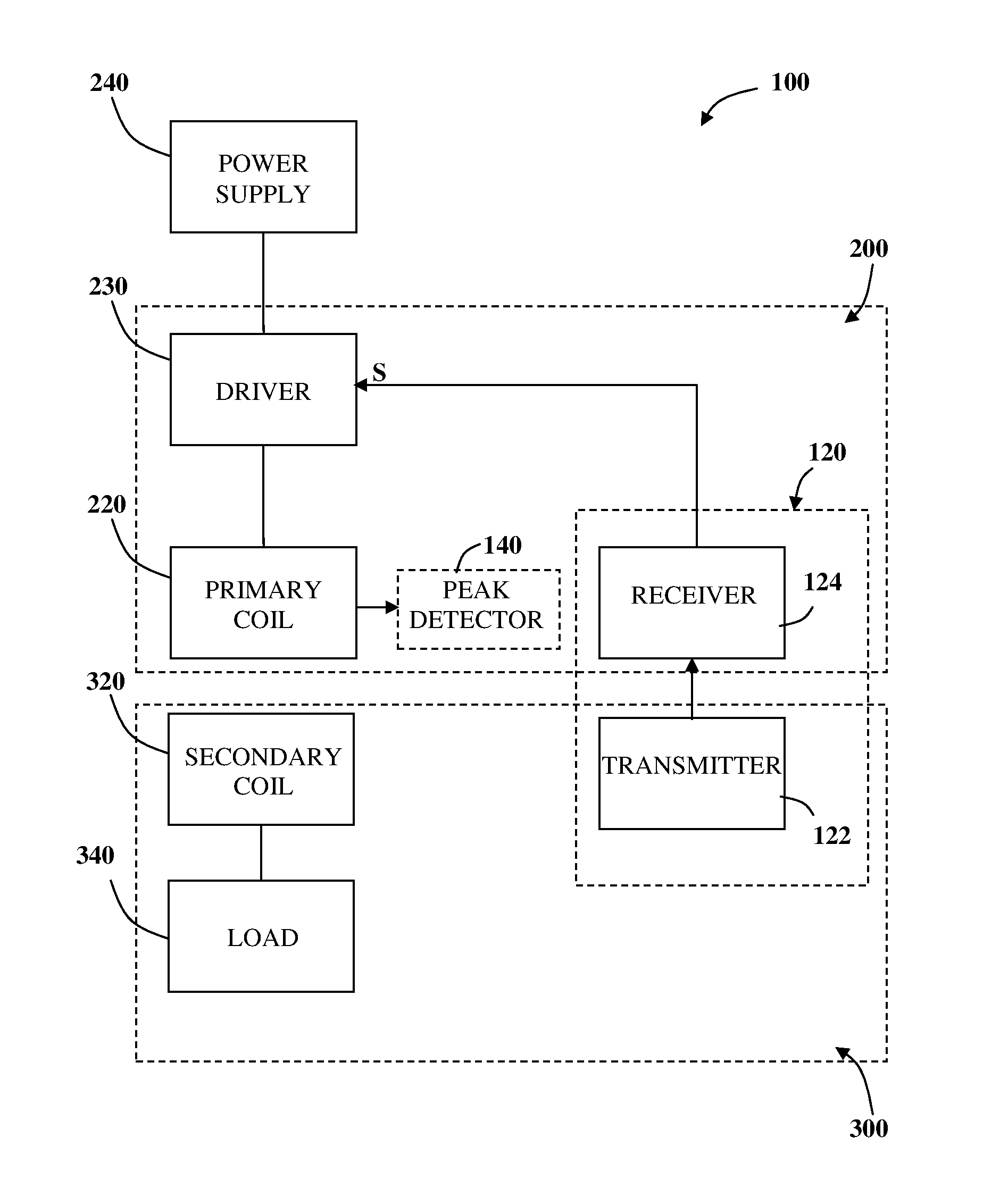
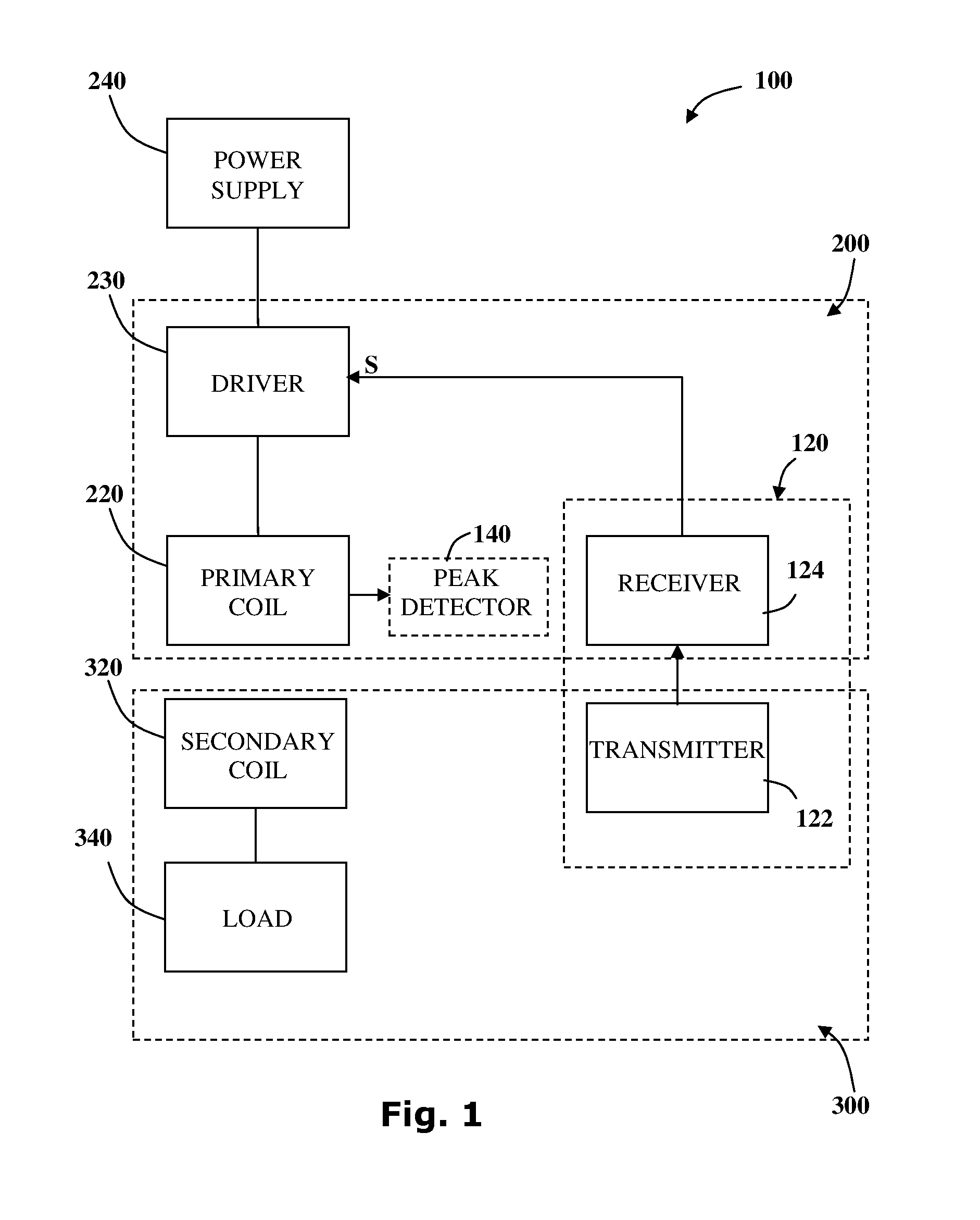
InactiveUS20160329751A1Improve transmission performanceGood detection functionCircuit authenticationElectric powerTransmitter coilElectric power transmission
The disclosure relates to systems and methods for controlling a wireless power transfer system based upon Inductive Charging Technology using frequency based signaling communication protocol, operable to function in modes of Standby, Digital Ping, Identification, Power Transfer and End of Charge (EOC). The power transfer system comprising at least one wireless power outlet associated with a wireless power transmitter coil and at least one electrical device associated with a wireless power receiver coil, where the wireless power receiver coil is in multi-directional communication with the wireless power transmission of a message transmitter coil. The amount of power transferred is controlled by feedback communication between the receiver and the transmitter configured to increase or NO decrease power. More specifically, the present disclosure supports wireless power transfer incorporating transmission opportunity extended signaling supporting uni-directional and bi-directional communication enabling data transfer over extended range, higher power levels of power transfer and improved foreign object detection functionality.
Owner:POWERMAT TECHNOLOGIES
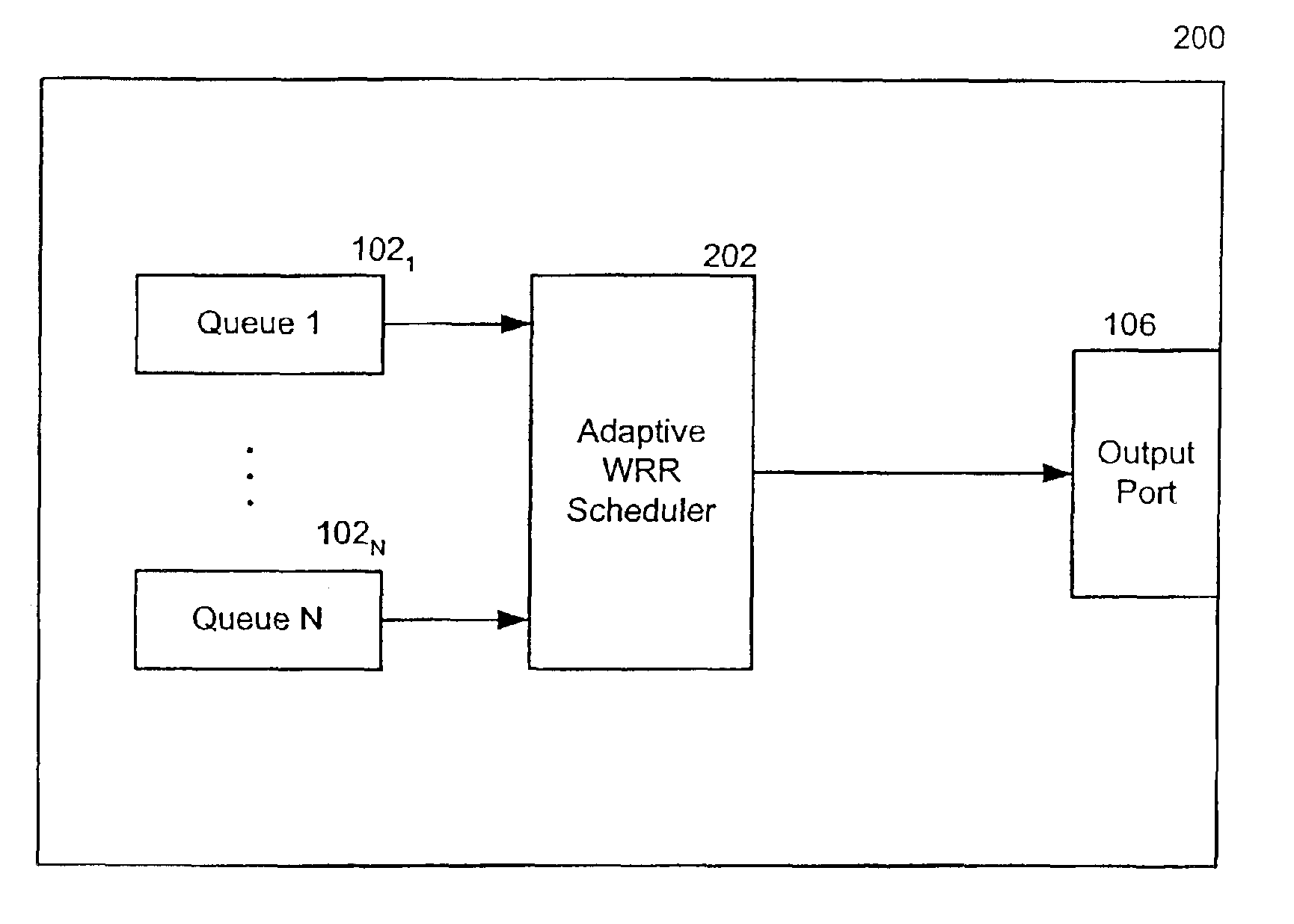
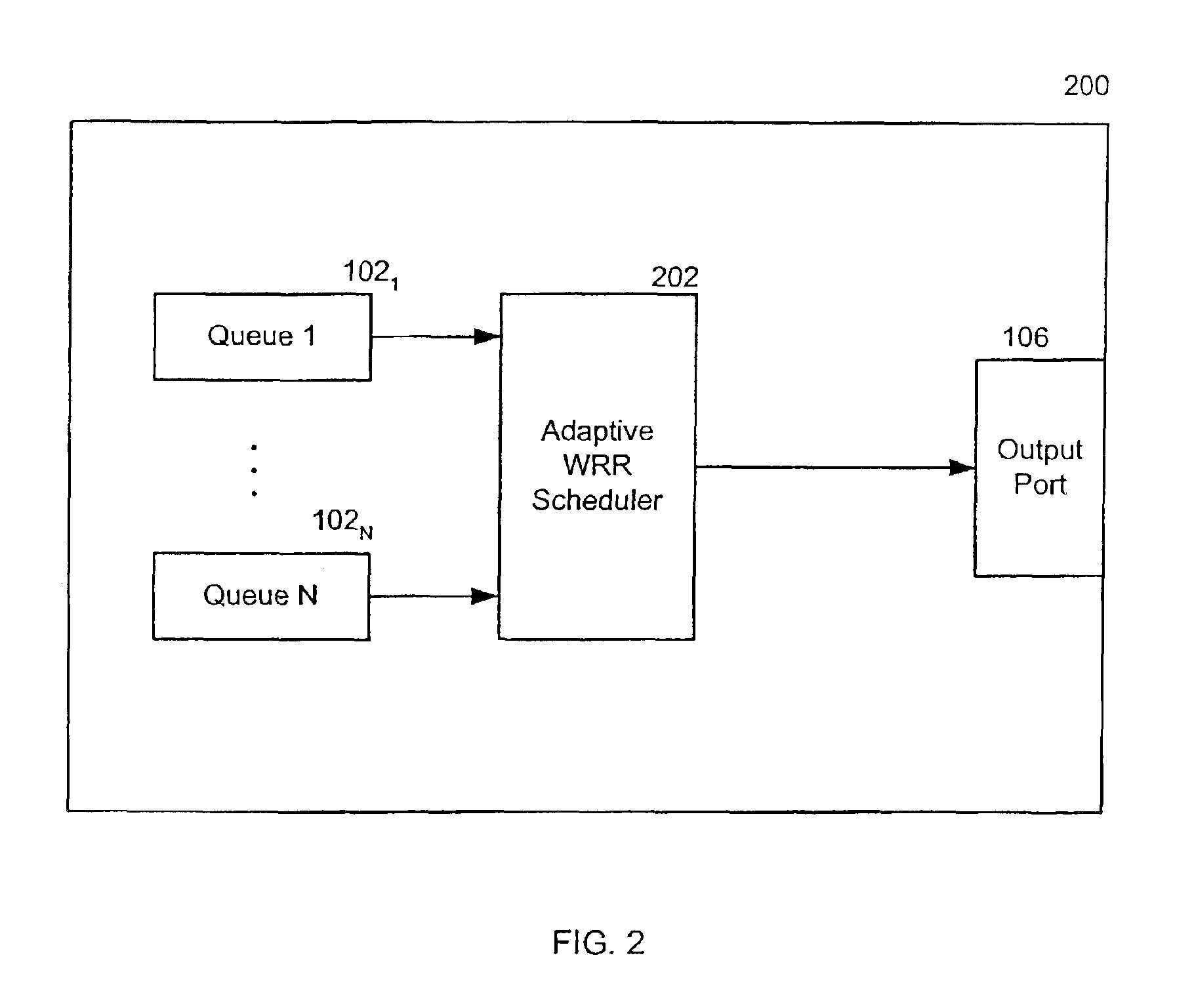
Servicing output queues dynamically according to bandwidth allocation in a frame environment
InactiveUS6891835B2Reduce in quantityAttenuation bandwidthData switching by path configurationDynamic bandwidth allocationAdaptive weighting
An adaptive weighted round robin scheduling apparatus and method schedules variable-length frame transmissions from a plurality of output queues having different transmission priorities by first allocating, for each queue, a number of bandwidth segments for a bandwidth cycle and a number of transmission opportunities for a round robin cycle, and then processing the queues consecutively in a round-robin fashion, beginning with a highest priority queue, until none of the queues has any bandwidth remaining. More specifically, during each iteration of a round robin cycle, a queue is permitted to transmit a frame if the queue has at least one remaining transmission opportunity, the queue has a frame ready for transmission, and the queue has at least one remaining bandwidth segment, and furthermore the number of transmission opportunities for the queue is decremented by at least one. Upon transmitting a frame, the number of bandwidth segments for the queue is decreased by the number of bandwidth segments in the frame. If a queue has no frame ready for transmission, then the queue may be either penalized, in which case the number of bandwidth segments for the queue is reduced, or forced to forfeit its bandwidth segments, in which case any remaining bandwidth segments are reallocated to other queues and the number of bandwidth segments and the number of transmission opportunities for the queue are set to zero.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
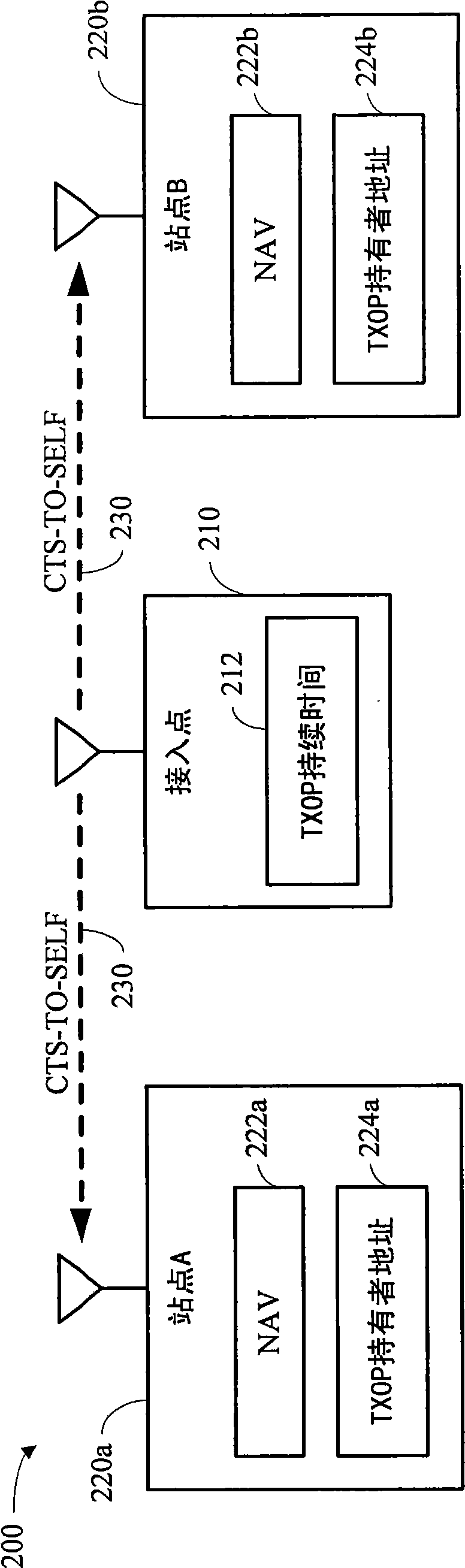
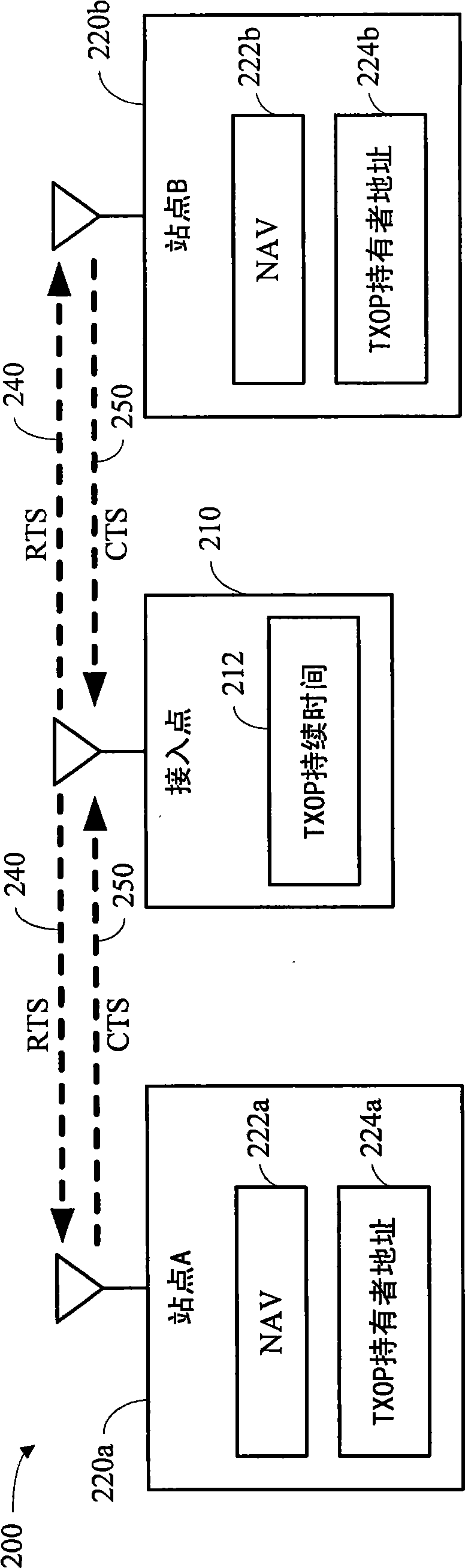
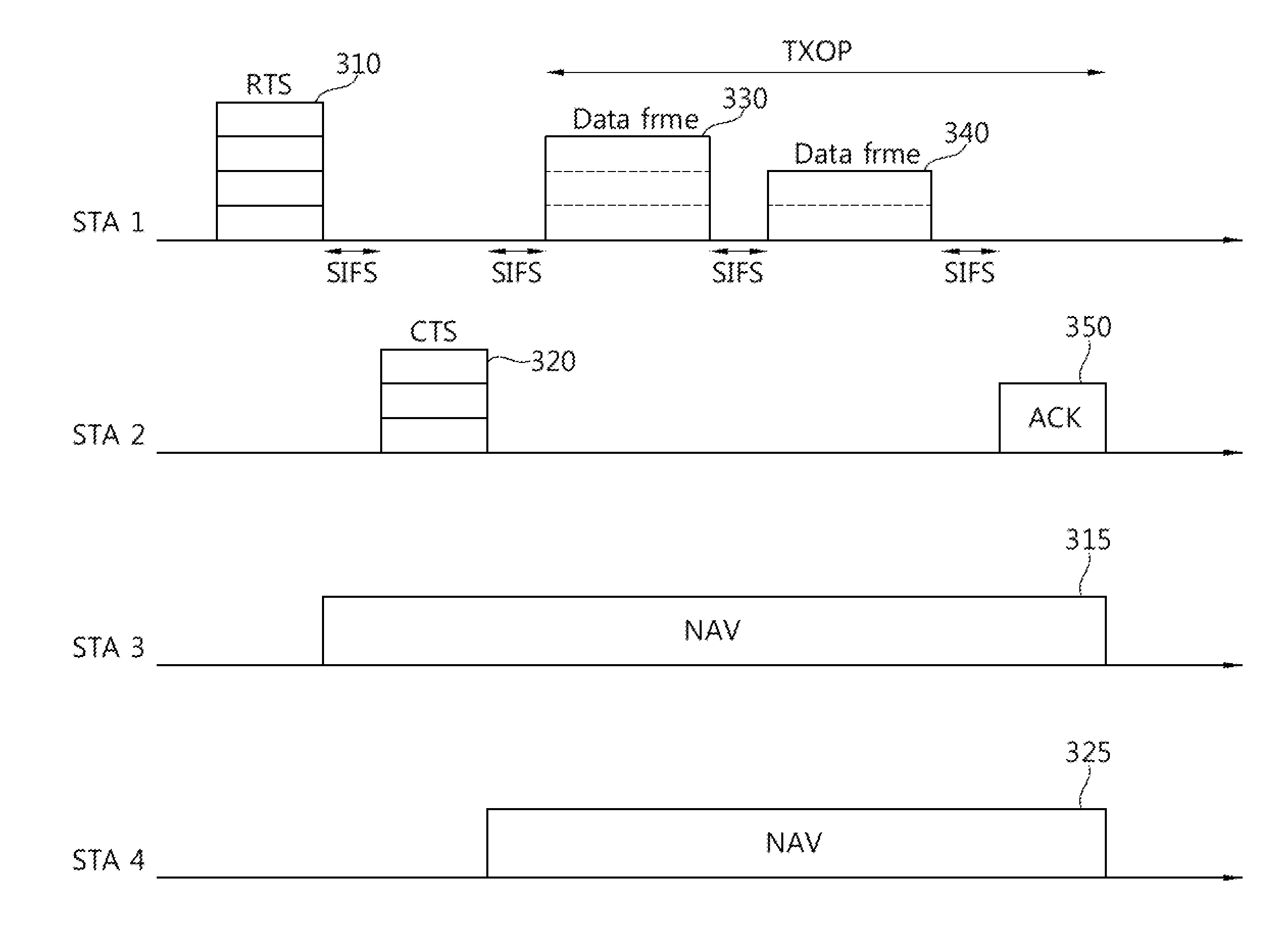
Transmissions to multiple stations in wireless communication systems
The present invention discloses systems and methodologies that facilitate coordinating and conducting transmissions to multiple stations in a wireless communication system during a single transmission opportunity. A holder of a transmission opportunity can communicate a request-to-send message or a self-addressed clear-to-send message to one or more stations to establish the transmission opportunity. Subsequently, data transmissions with respective stations can be initiated by transmitting request-to-send messages to the respective stations. At each receiving station, the source address of a received request-to-send message is compared to the address of the holder of the transmission opportunity. If the addresses match for a given request-to-send message, the receiving station transmits aclear-to-send message to the holder of the transmission opportunity in response to the request-to-send message.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
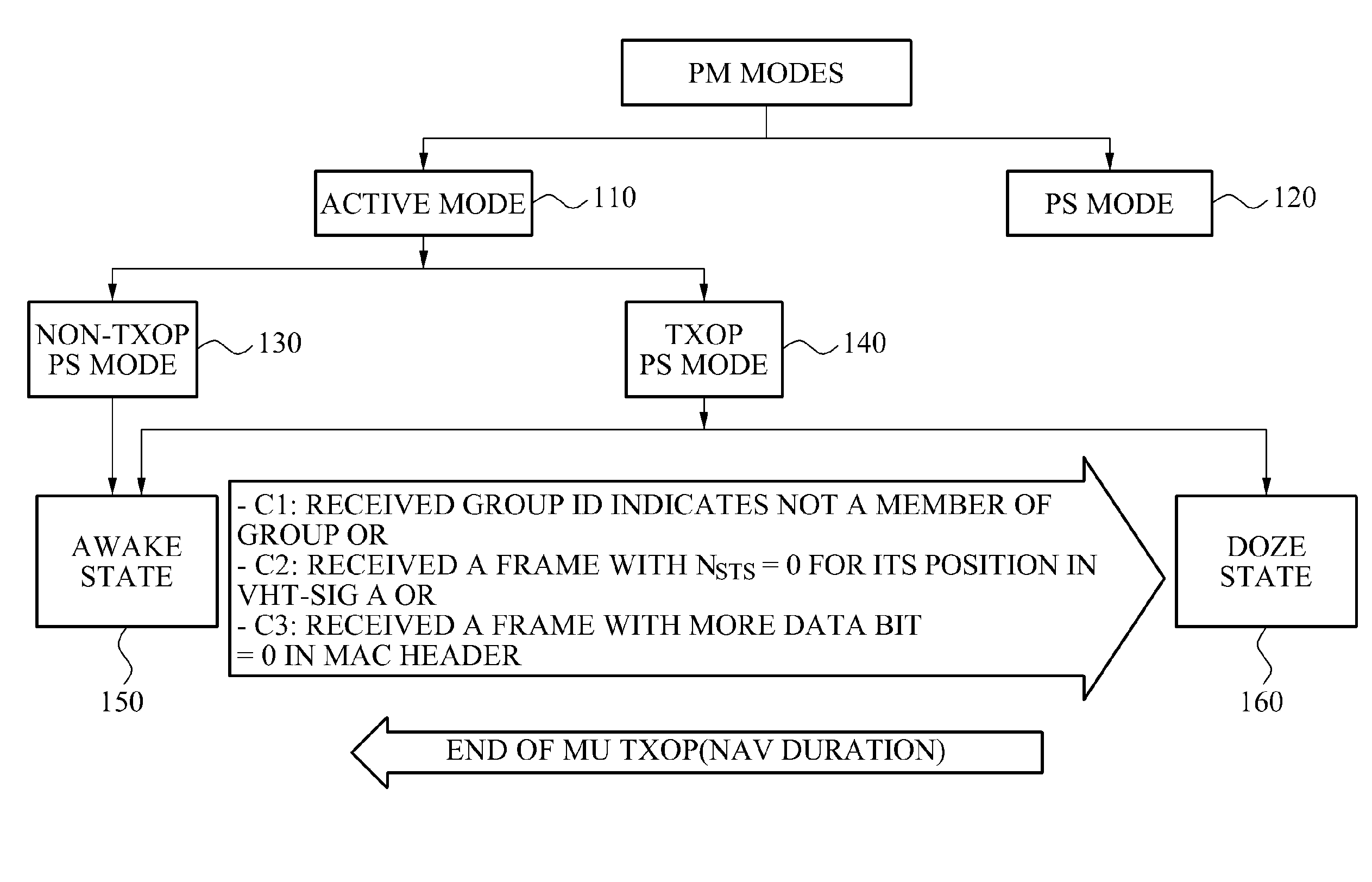
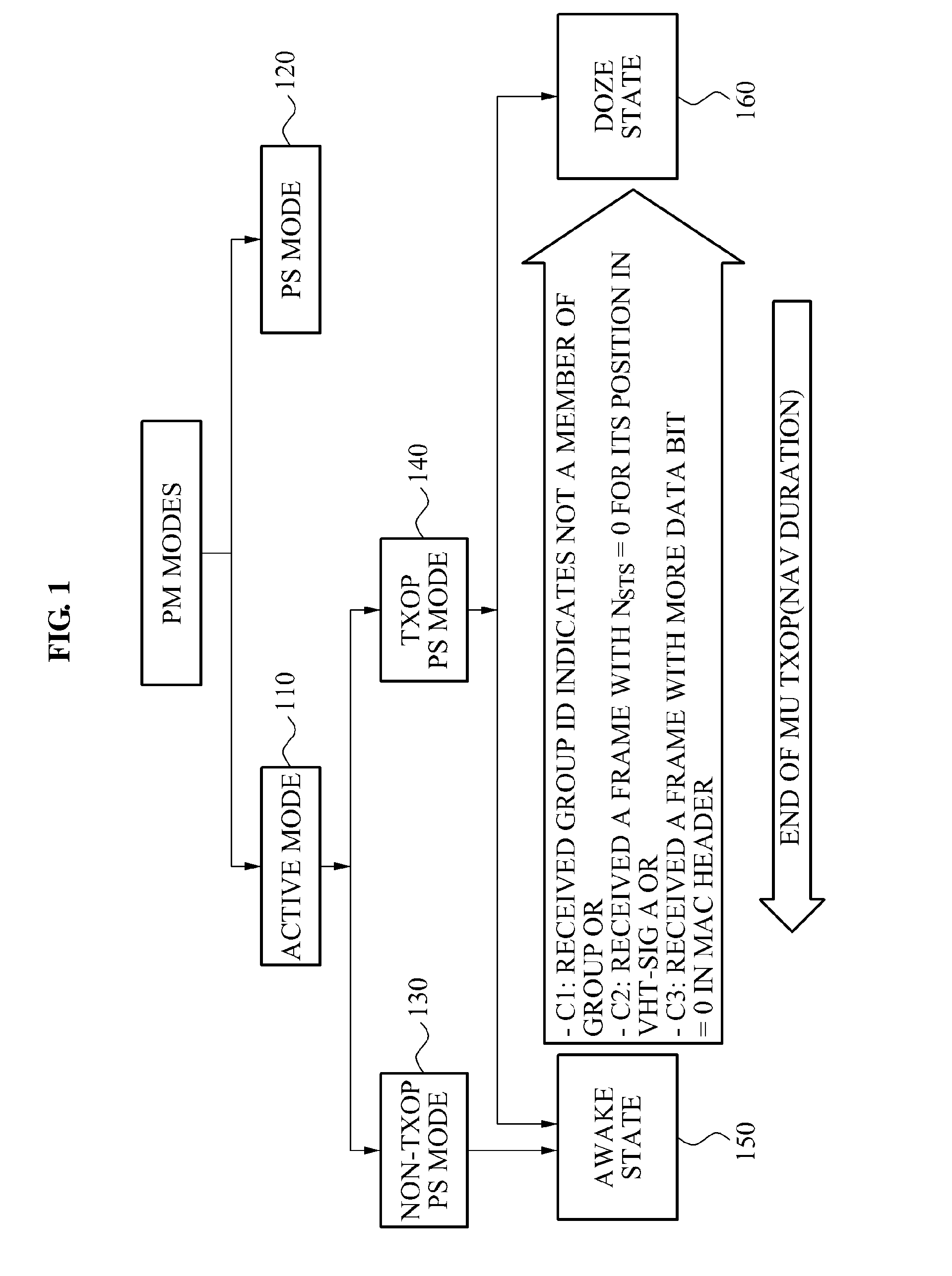
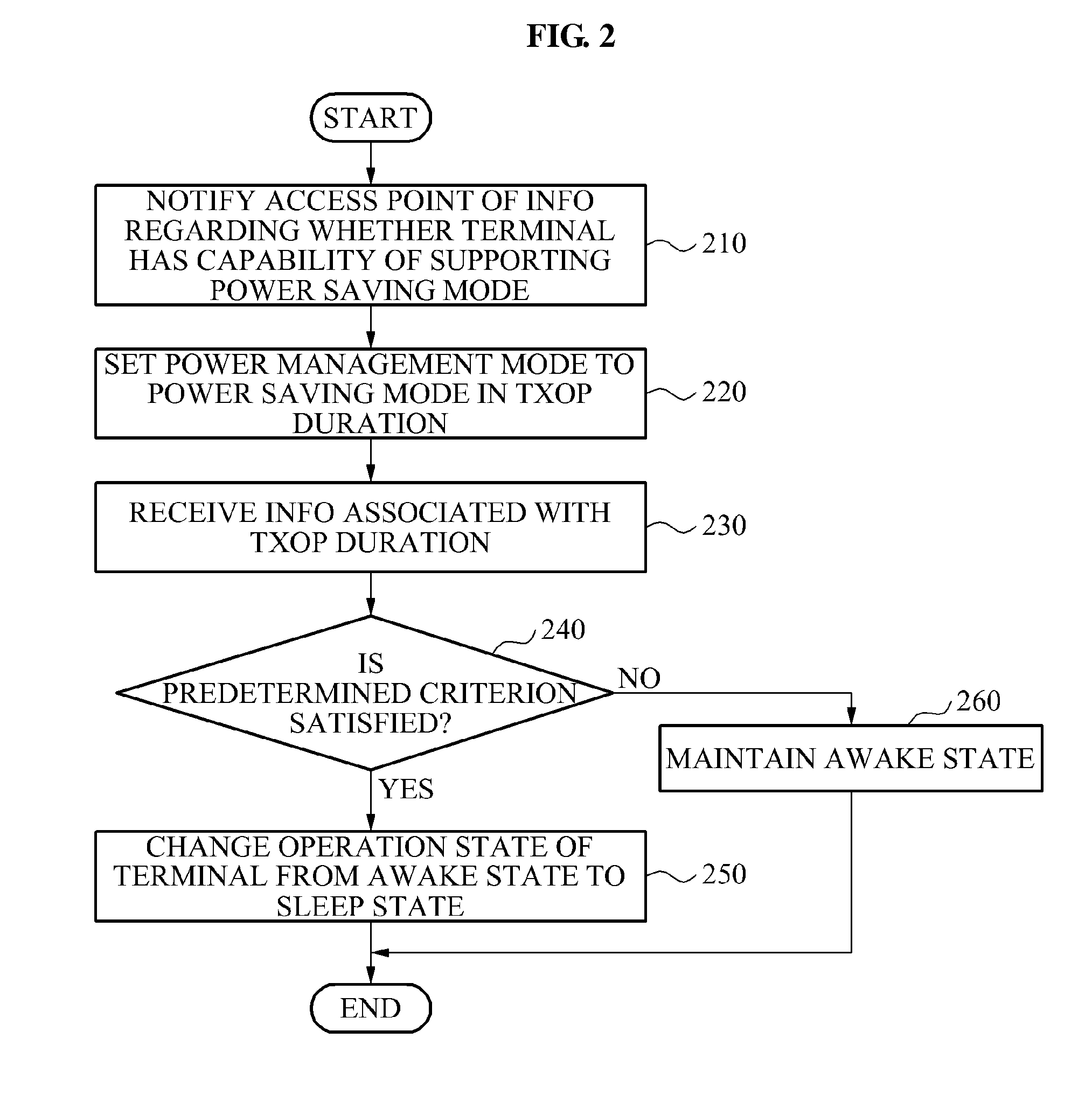
Communication method of a terminal and an access point for power saving
Provided is a communication technology of an access point and a terminal that may decrease power consumption by changing an operation state of the terminal from an awake state to a sleep state when a data stream to be transmitted to the terminal is absent or has completed in a transmission opportunity (TXOP) duration.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Combining transmissions of different protocols in a wireless communications
InactiveUS20090040974A1Interference minimizationPreserve the QoS (quality of service)Time-division multiplexWireless commuication servicesTime domainContention-based protocol
A method and devices for allowing communications between a central station and subscriber terminals along a frequency channel in a wireless network comprising a central station and a plurality of subscriber terminals, out of which at least one uses a scheduled based protocol. The method comprises: providing a plurality of time domain frames each comprising at least one first time interval for implementing schedule based protocol, and at least one second time interval for implementing a contention based protocol; scheduling a plurality of unconditioned transmissions in a plurality of present and / or future frames during the first time interval of corresponding time domain frames to / from the subscriber terminal(s) operating under the schedule based protocol; scheduling a plurality of conditioned transmission opportunities in a plurality of present and / or future frames during the second time interval of corresponding time domain frames to / from the terminals operating under the schedule based protocol; determining, prior to sending a conditioned transmission, whether the value of received power level is below a pre-defined threshold value and transmitting communications during the second time interval upon determining that this value does not exceed a pre-defined threshold.
Owner:ALVARION
Sounding reference signal transmitting method and device, sounding reference signal receiving method and device, UE and base station
InactiveCN107294686AEasy transferSolve the problem of low transmission opportunitiesSignal allocationConnection managementSounding reference signalCarrier signal
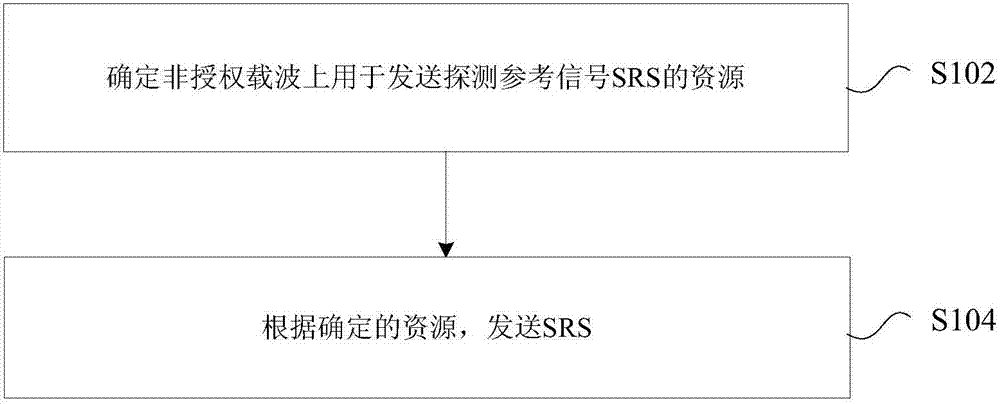
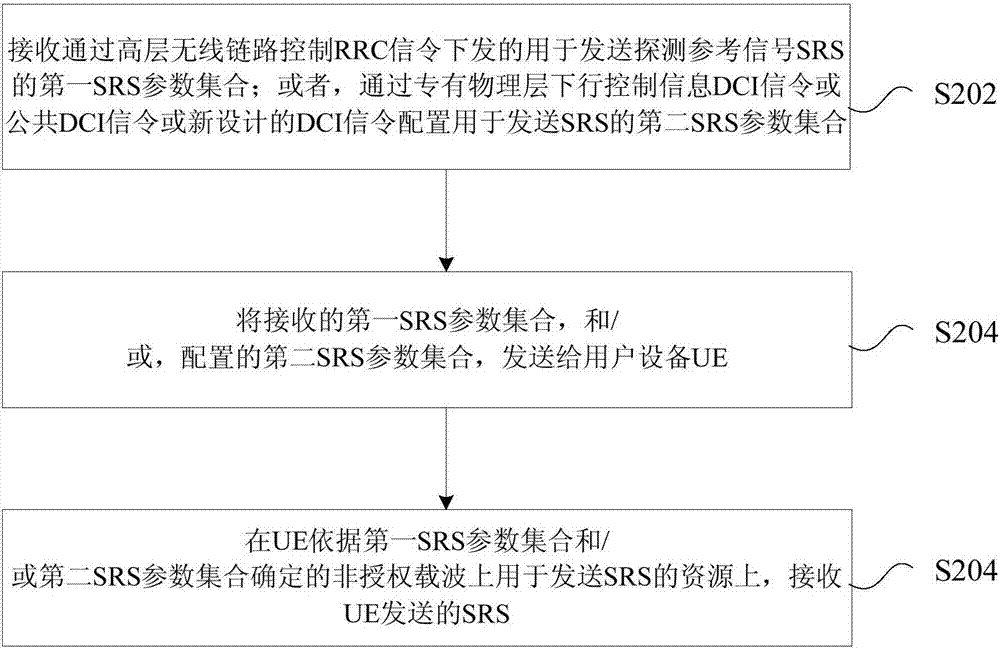
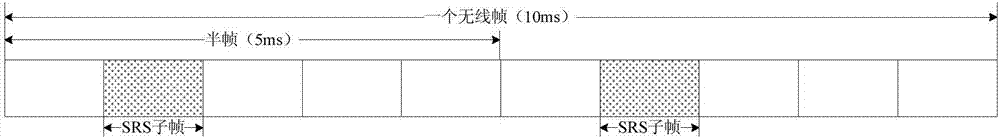
The invention discloses a sounding reference signal transmitting method and device, a sounding reference signal receiving method and device, UE and a base station. The sounding reference signal transmitting method comprises the steps of determining a resource used for transmitting sounding reference signals (SRS) on an unlicensed carrier; and transmitting the SRS according to the determined resource. According to the invention, a problem of little transmission opportunity for transmitting the SRS on the unlicensed carrier in related technologies is solved, and thus the effect of improving the opportunity for transmitting the SRS on the unlicensed carrier is achieved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Wireless communication system and wireless communication method
ActiveUS20150172012A1High frequencyImprove system throughputError prevention/detection by using return channelSpectral gaps assessmentTime division multiple accessCommunications system
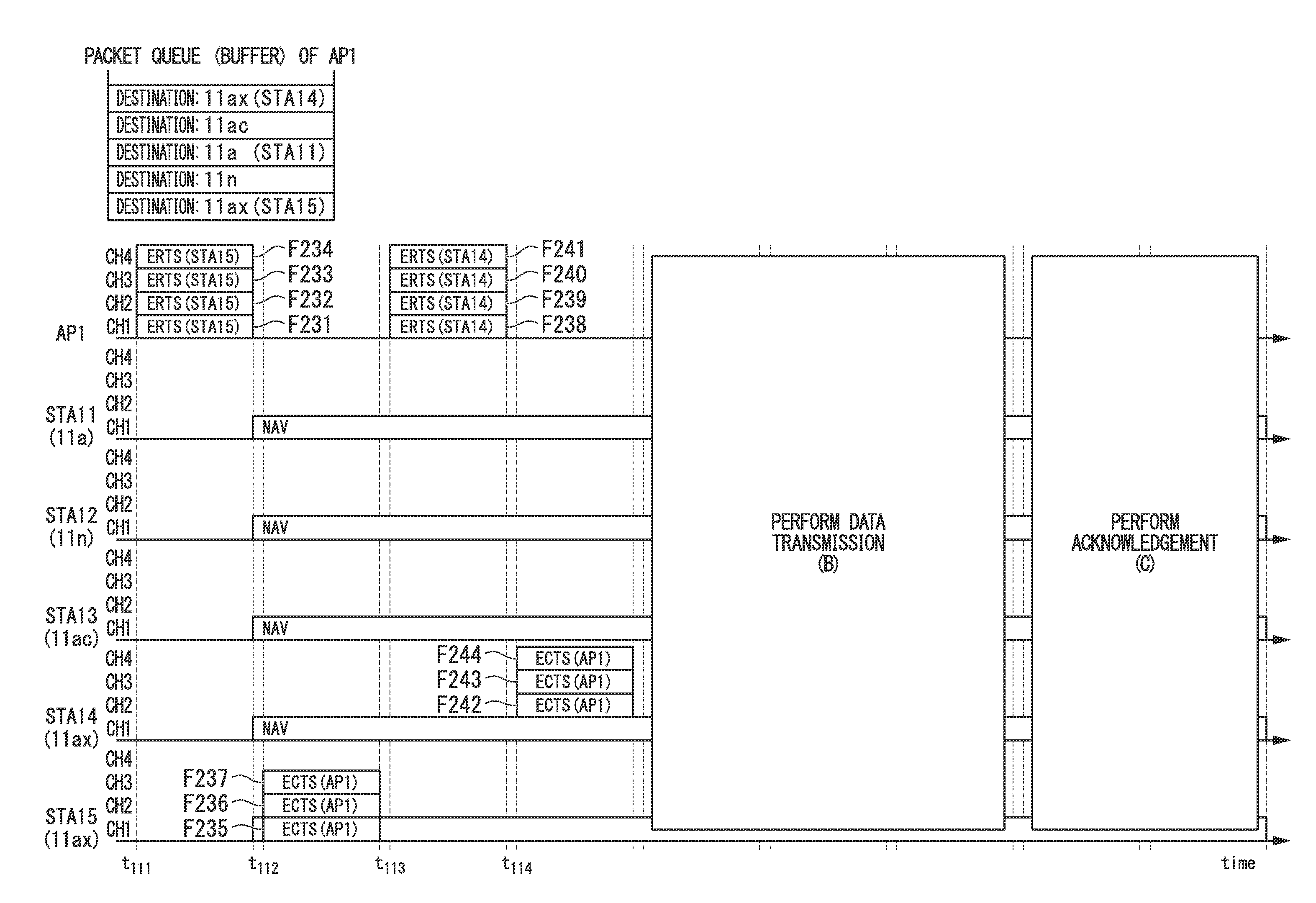
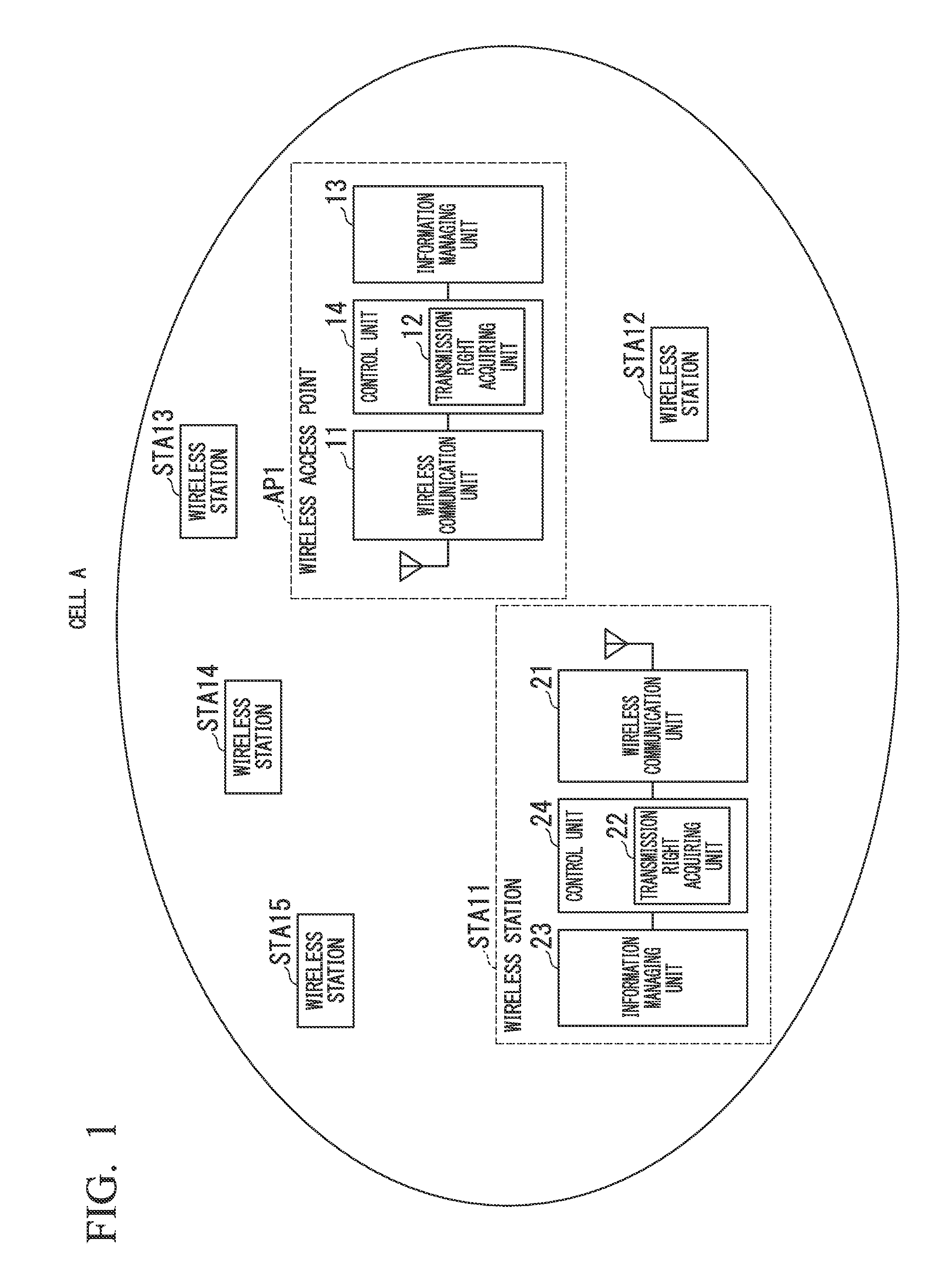
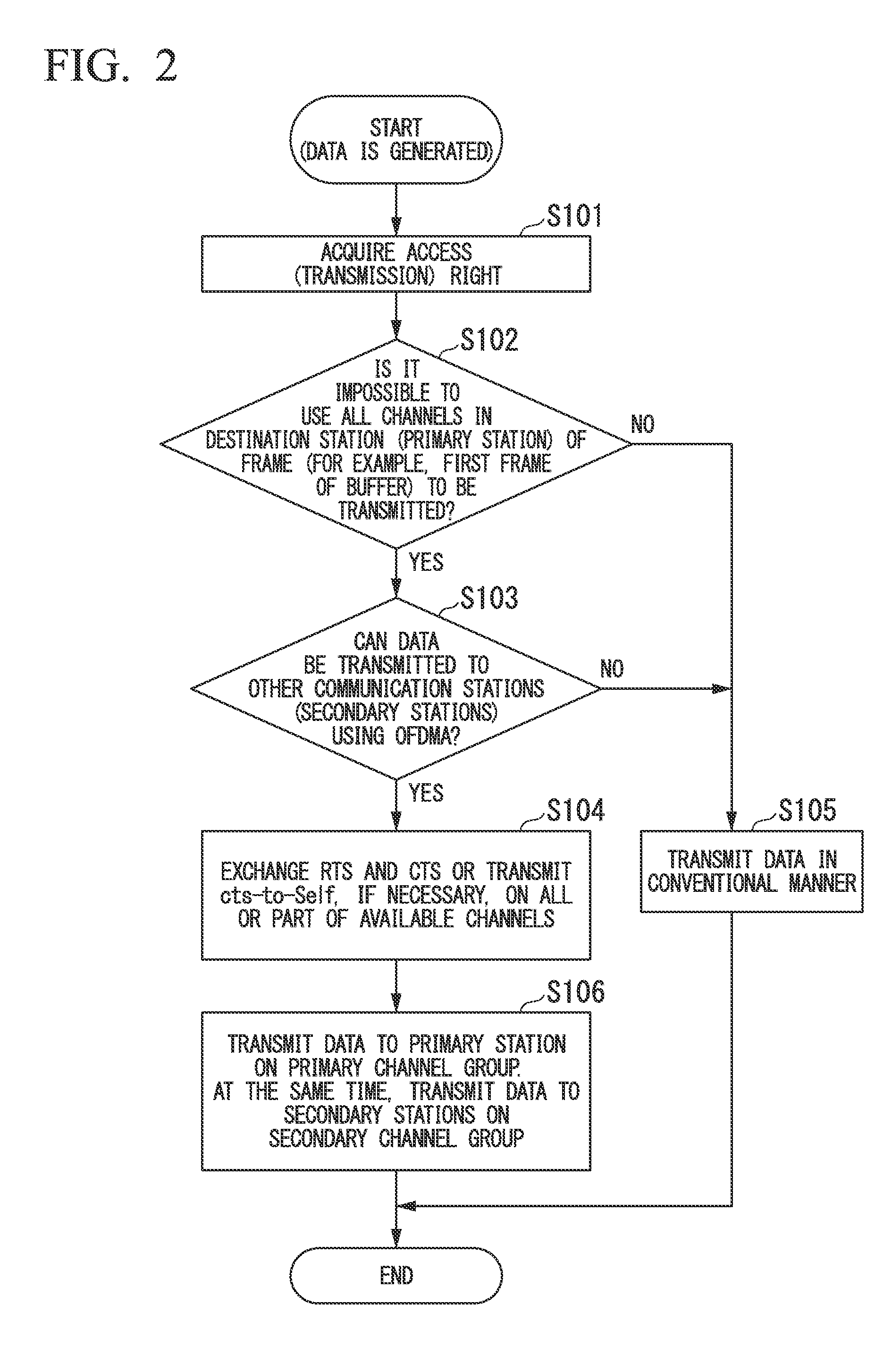
In order to provide a wireless communication system capable of improving the throughput of wireless communication by effectively using frequency resources, in a wireless communication system in which a first wireless access point which communicates with one or more wireless stations within a first cell by orthogonal frequency-division multiple access and a second wireless access point which is capable of performing carrier sensing with the first wireless access point and communicates with one or more wireless stations within a second cell by the orthogonal frequency-division multiple access operate in cooperation with each other, the first wireless access point includes a transmission opportunity acquiring unit which acquires a transmission opportunity when data to be transmitted is generated; and a transmitting unit of permission for use which transmits permission for use of channels which are not scheduled to use within the first cell, to the second wireless access point in a period in which the transmission opportunity is acquired, and the second wireless access point includes a communication unit which communicates with the wireless station within the second cell via the channel in which the permission for use is acquired from the first wireless access point.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method of transmitting RLC data
A method of transmitting data is performed by detecting a triggering of a first event, further detecting a triggering of a second event until a third event occurs, and performing a first action if the triggering of the second event is not detected, wherein the first action is based on the detected first event. The first event may be the expiry of a poll retransmit timer, the second event may be a detecting whether a ACK or NACK is not received, the third event may be a next transmission opportunity, and the first action may be setting a polling bit of a data PDU to be transmitted.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
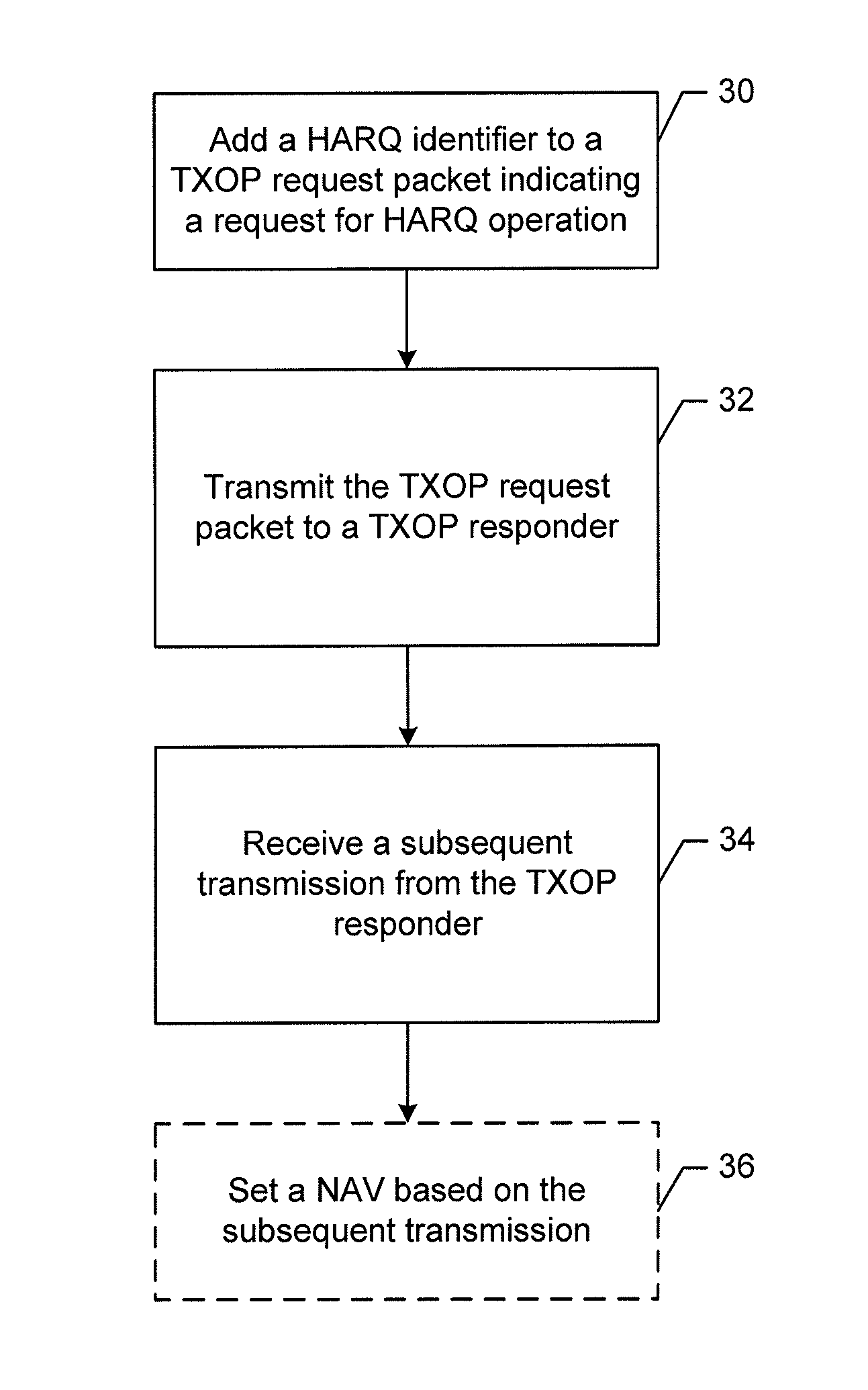
Method and apparatus for providing a transmission opportunity
ActiveUS20150236822A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunication deviceHybrid automatic repeat request
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided for use in a communication device. The method may add a transmission type identifier to a transmission opportunity (TXOP) request packet, wherein the transmission type identifier includes one or more bits indicating a request for either Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request (HARQ) operation or for non-HARQ operation. The method may further causes the communication device to transmit the TXOP request packet to a TXOP responder and receives a subsequent transmission from the TXOP responder indicating acceptance, modified acceptance, or rejection of the request. A corresponding apparatus and computer program product are also provided.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Power saving method and apparatus using multiple channels in a mesh network
ActiveUS20080037570A1Save powerMaximize useEnergy efficient ICTPower managementEngineeringMesh networking
A power saving method and apparatus are provided for saving power by reducing the number of changes between active mode and sleep mode using multiple channels. A process for negotiating which of multiple channels will be assigned a transmission opportunity (TXOP) is performed. A TXOP MAP is configured by exchanging a packet through a common channel during a predetermined time at every monitoring time according to a negotiated channel. The TXOP is allocated to each channel according to the TXOP MAP. As a change between the active mode and the sleep mode is reduced, power can be saved, resources of the mesh network can be efficiently used, and interference between nodes can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
In-band QoS signaling reference model for QoS-driven wireless LANs
InactiveUS7298724B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceReference model
A station, such as a point coordinator (PC) or a non-PC station, in a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN) is disclosed. The station includes a frame classification entity (FCE), a frame scheduling entity (FSE) and a QoS management entity (QME). The FCE is logically located in a logical link control (LLC) layer of the station and has a classification table containing at least one classifier entry. Each classifier entry contains a virtual stream identifier (VSID) and a frame classifier associated with a user session. The FCE receives a data frame associated with the user session, which can be one of a voice session, a video session, a data session and a multimedia session. The data frame contains in-band quality of service (QoS) signaling information for the user session. The FCE classifies the received data frame to a selected VSID contained in a classifier entry in the classification table based on a match between an in-band frame classification information contained in the received frame and the frame classifier contained in the classifier entry. The FSE is logically located in a medium access control (MAC) sublayer of the station and has a frame scheduling table containing at least one entry. Each entry in the frame scheduling table contains a VSID and a QoS parameter set associated with a user session identified by the VSID. The FSE is responsive to the classified data frame by scheduling a transmission opportunity (TO) for the classified data frame based on the at least one QoS parameter value associated with the VSID and characterizing the user session. The QME interfaces with the FCE and The FSE.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
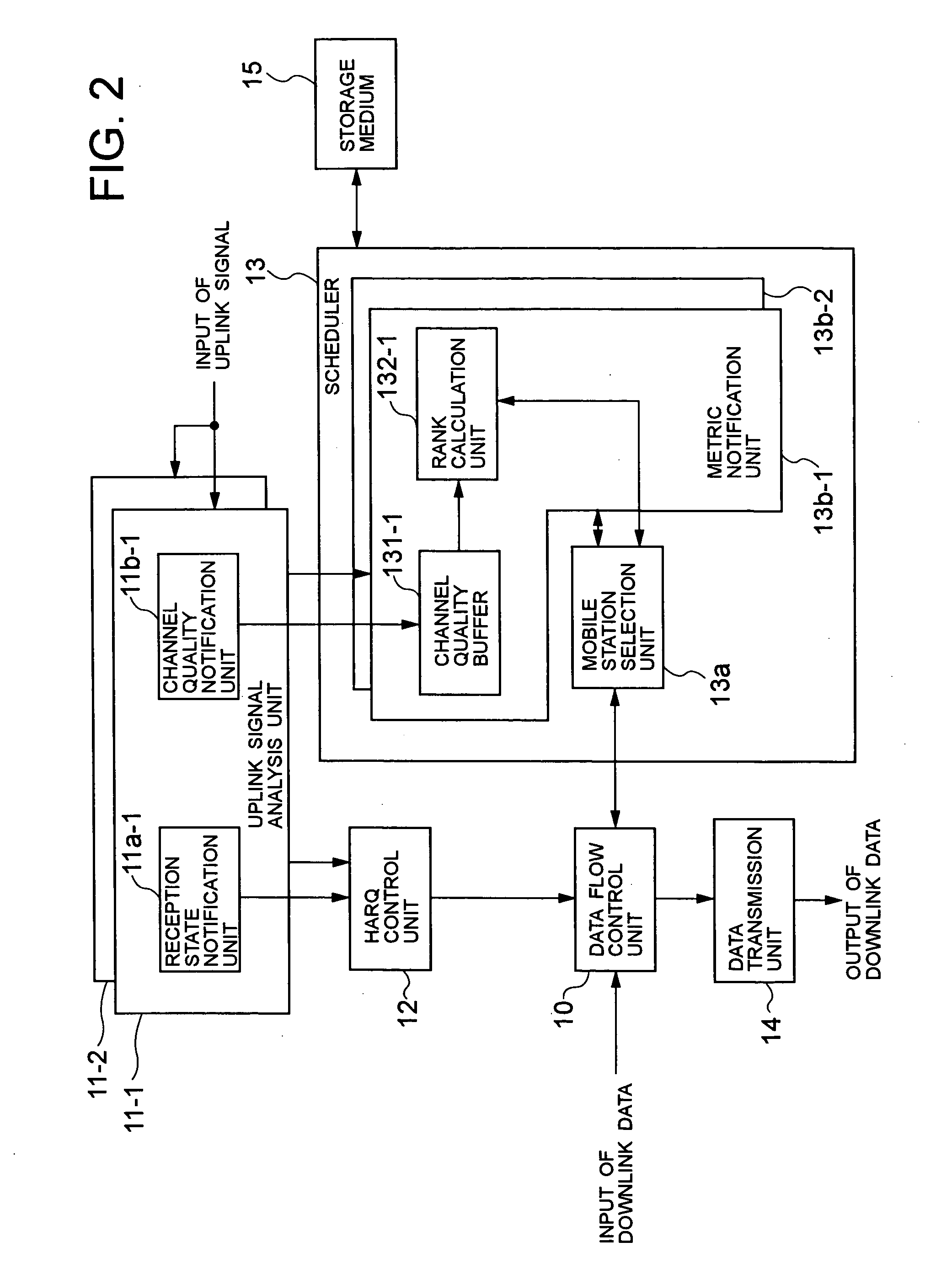
Mobile communications system, radio base station, scheduling apparatus, scheduling method employed in the same, and program therefor
ActiveUS20050054359A1Increase transmission opportunitiesQuality improvementNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementData streamCommunications system
The present invention provides a radio base station which can equally assign a transmission opportunity based on the radio channel quality. A mobile station selection unit issues a request for a metric notification to a metric notification unit corresponding to a mobile station notified by a data flow control unit, and receives metrics. The metric notification unit periodically receives radio channel quality information from a channel quality notification unit of an uplink signal analysis unit, obtains through a rank calculation unit the rank at the time when the channel quality is preferably arranged in a channel quality buffer according to the radio channel quality information, and notifies the mobile station selection unit of the result as metrics. The mobile station selection unit selects a mobile station having the smallest metrics notified by the metric notification unit, assigns radio resources to the mobile station, and notifies the data flow control unit of the assignment.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method of multiple frame transmission in wireless communication system and transmitter
InactiveUS20120099664A1Network traffic/resource managementModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemMultiple frame
A method for multiple frame transmission in a wireless communication system and a transmitter are provided. The transmitter transmits a request to send (RTS) frame to a receiver. The RTS frame has a first bandwidth. The transmitter receives a clear to send (CTS) frame as a response of the RTS frame from the receiver to establish a transmission opportunity (TXOP) indicating an interval of time when the transmitter has the right to transmit at least one data frame. The CTS frame has a second bandwidth. The transmitter transmits a plurality of data frames sequentially to the receiver during the TXOP.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com