Patents
Literature
68 results about "Latency jitter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Jitter and Latency are two terms that often get bandied about together, but are actually two distinctly different things. In a nutshell, latency is a term used to outline the amount of time it takes for a packet to transfer to its destination. In contrast, jitter is the delay that varies over time when the signal wanes or jitters.
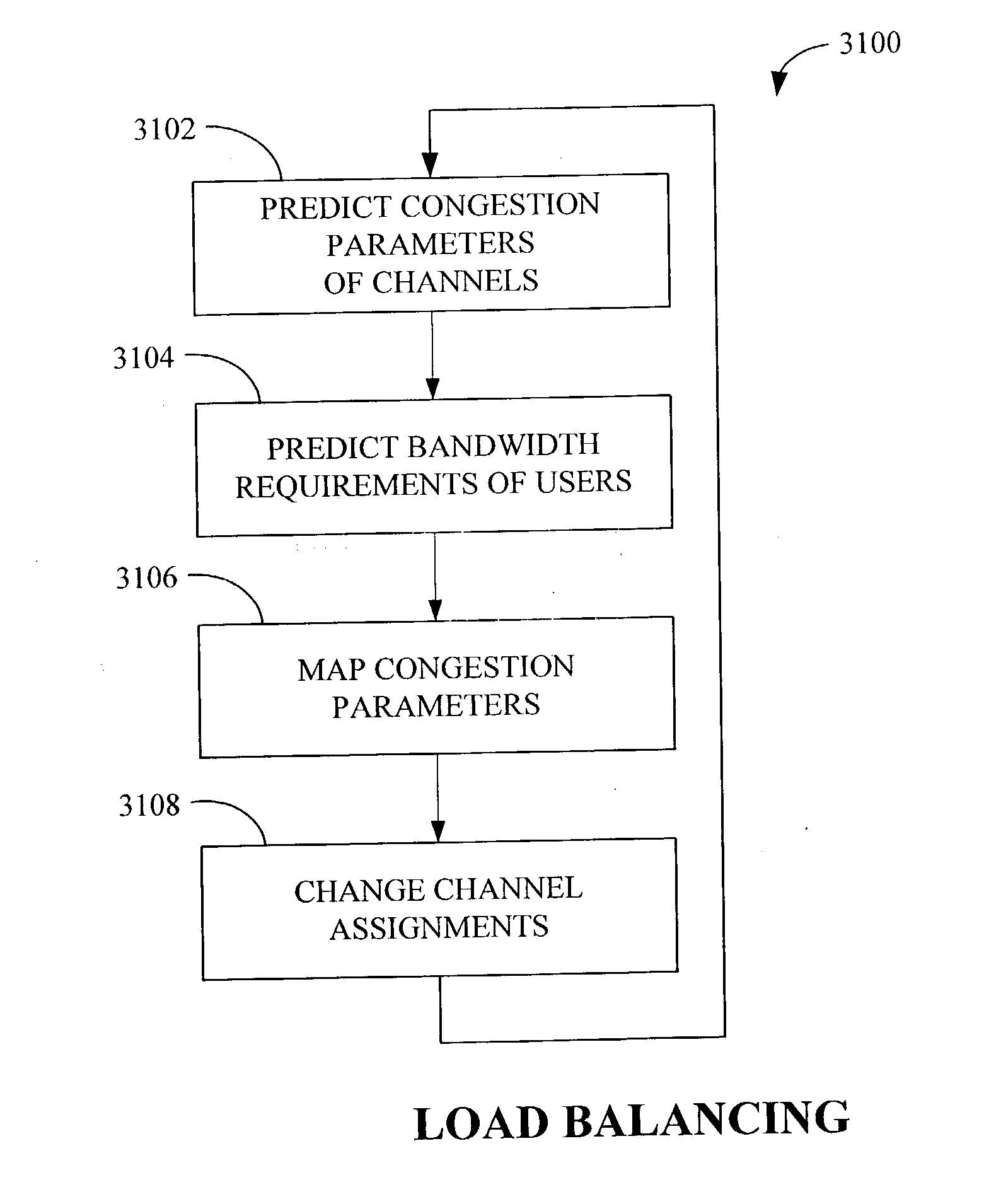
Apparatus and methods for incorporating bandwidth forecasting and dynamic bandwidth allocation into a broadband communication system
InactiveUS20060120282A1Energy efficient ICTError preventionDynamic bandwidth allocationComputer network
A method for providing network access to a shared access communications medium for a plurality of users includes the steps of conducting predictive admission control by arbitrating user requests for access to the shared medium based on predicted aggregate demands, conducting lookahead scheduling for use in making user channel assignments by forecasting schedule transmission opportunities one or more channels of the shared medium, and balancing load by making channel assignments such that a plurality users are each assigned a respective channel of the shared medium based upon a predicted need. Congestion parameters can predicted for each channel of the shared medium and mapped to a congestion measure using a mathematical function that takes into account packet loss rate, packet delay, packet delay jitter, and available capacity.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for monitoring latency, jitter, packet throughput and packet loss ratio between two points on a network
InactiveUS7961637B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCorrect operation testingPacket lossWaiting time
Owner:SPIRENT COMM
Method and apparatus for multicasting real time traffic in wireless ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS6721290B1Speed up decision making processSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of servicePacket loss
A real-time multicast scheduler method and apparatus is presented, to facilitate multicasting of real-time constant bit rate data in wireless ad-hoc networks. Constant bit rate traffic cannot tolerate delay jitter. However, a small amount of packet losses may be tolerable. In order to ensure the provisioning of a desired level of quality of service, bandwidth is reserved on the multicast structure. A goal of the real-time multicast scheduler is to avoid packet collisions and to facilitate color re-use, where "color" is defined as a channel selected as a combination of time-division multiple access, frequency-division multiple access, and code-division multiple access schemes. The real-time multicast scheduler provides a self-healing network which corrects for disconnections caused by node movement and nodes moving out of range of each other, while accounting for colors already assigned for data transmission in order to prevent packet collisions.
Owner:HRL LAB
Adaptive communication protocol for wireless networks
InactiveUS7184413B2Network topologiesTime-division multiplexWireless mesh networkNetwork Communication Protocols
A communication protocol that provides link-level and media access control (MAC) level functions for wireless (e.g., ad-hoc) networks and is robust to mobility or other dynamics, and for scaling to dense networks. In a mobile or otherwise dynamic network, any control-packet collisions will be only temporary and fair. In a dense network, the network performance degrades gracefully, ensuring that only a certain percentage of the common channel is consumed with control packets. The integrated protocol allows packets (e.g., data scheduling control packets) to be scheduled in a collision-free and predictable manner (known to all neighbors), multicast packets can be reliably scheduled, as well as streams of delay- or delay-jitter-sensitive traffic. Further, using an optional network code, the scheduling of control packets can appear to observers to be randomized.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
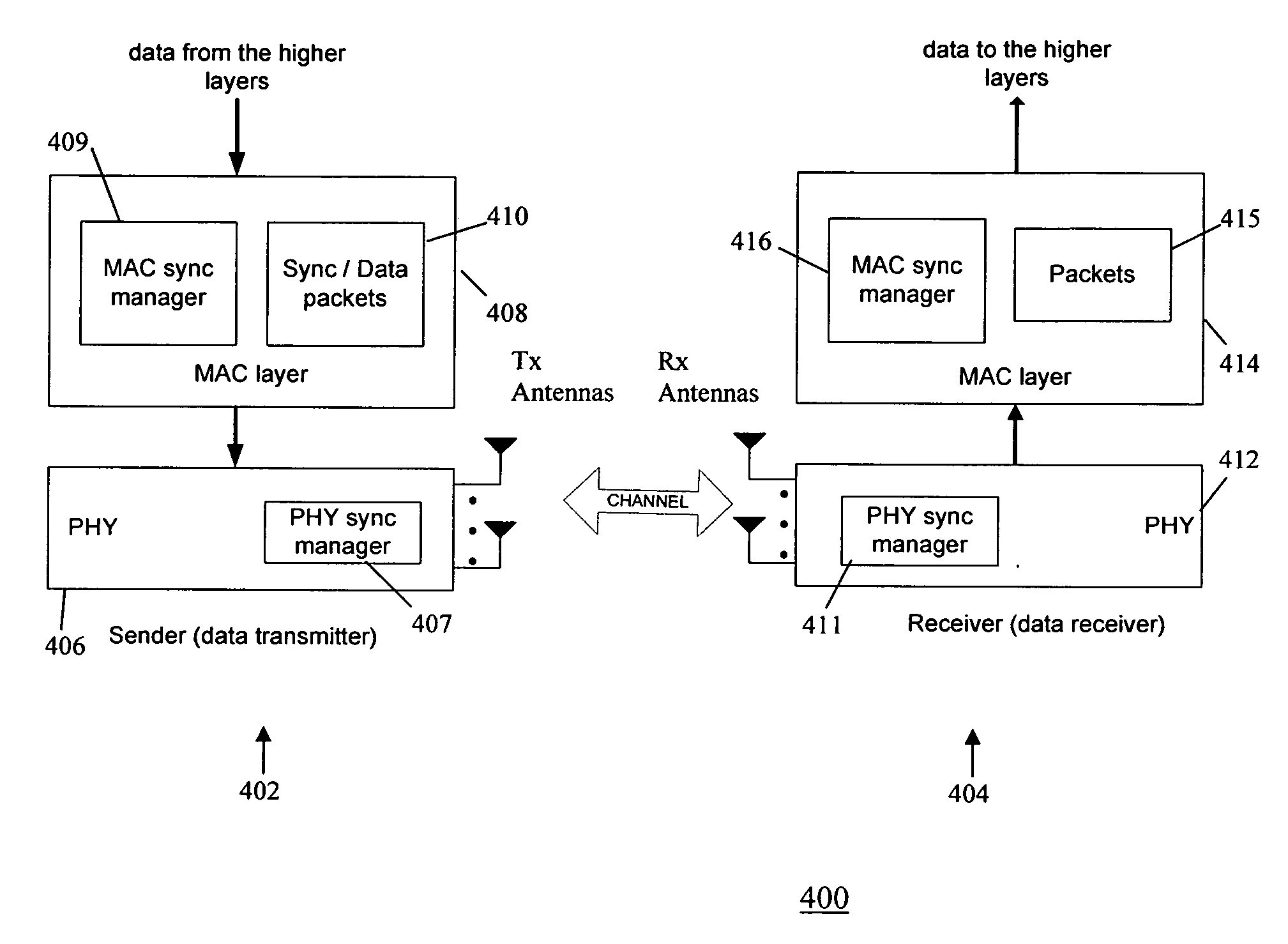
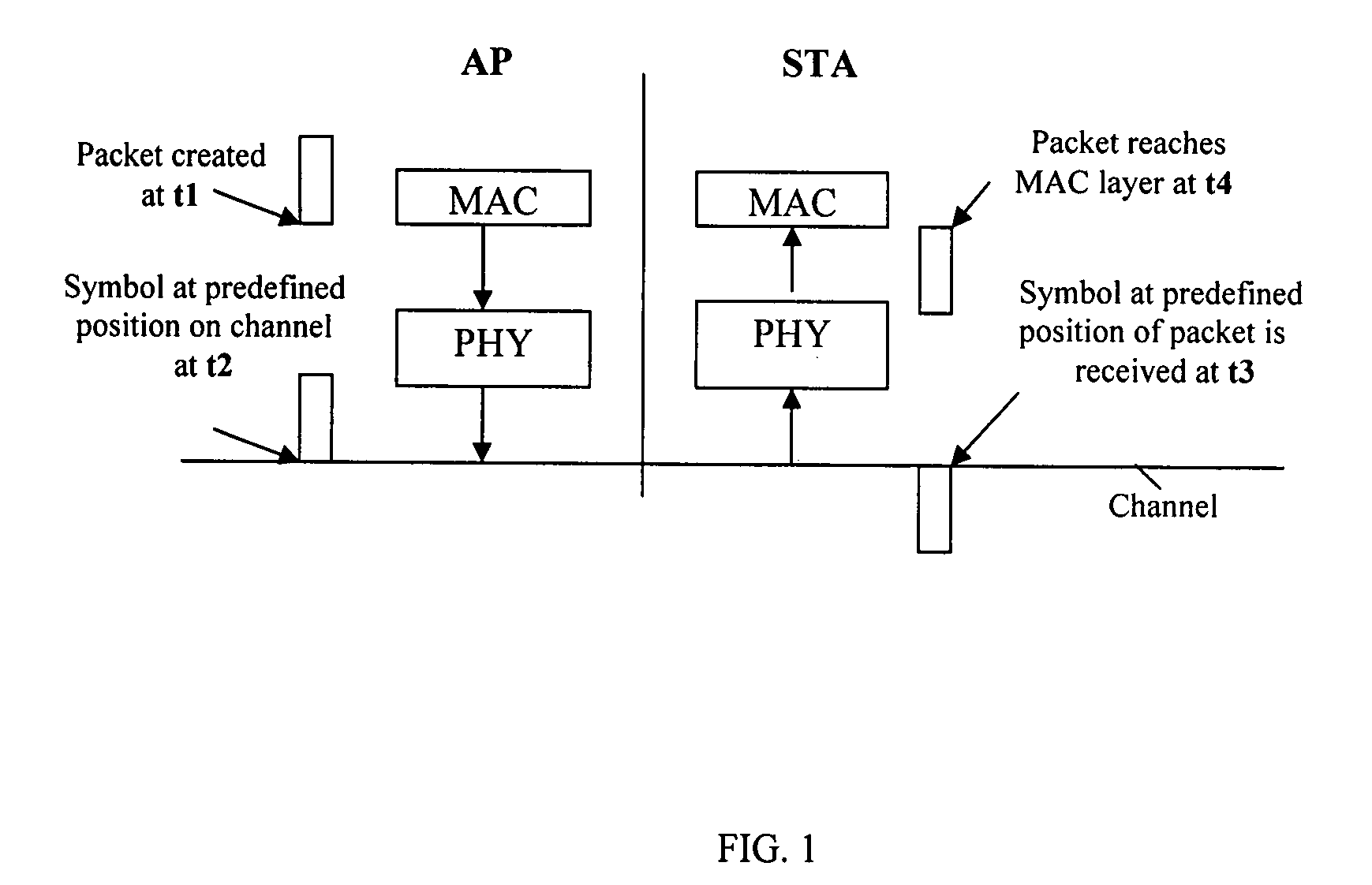
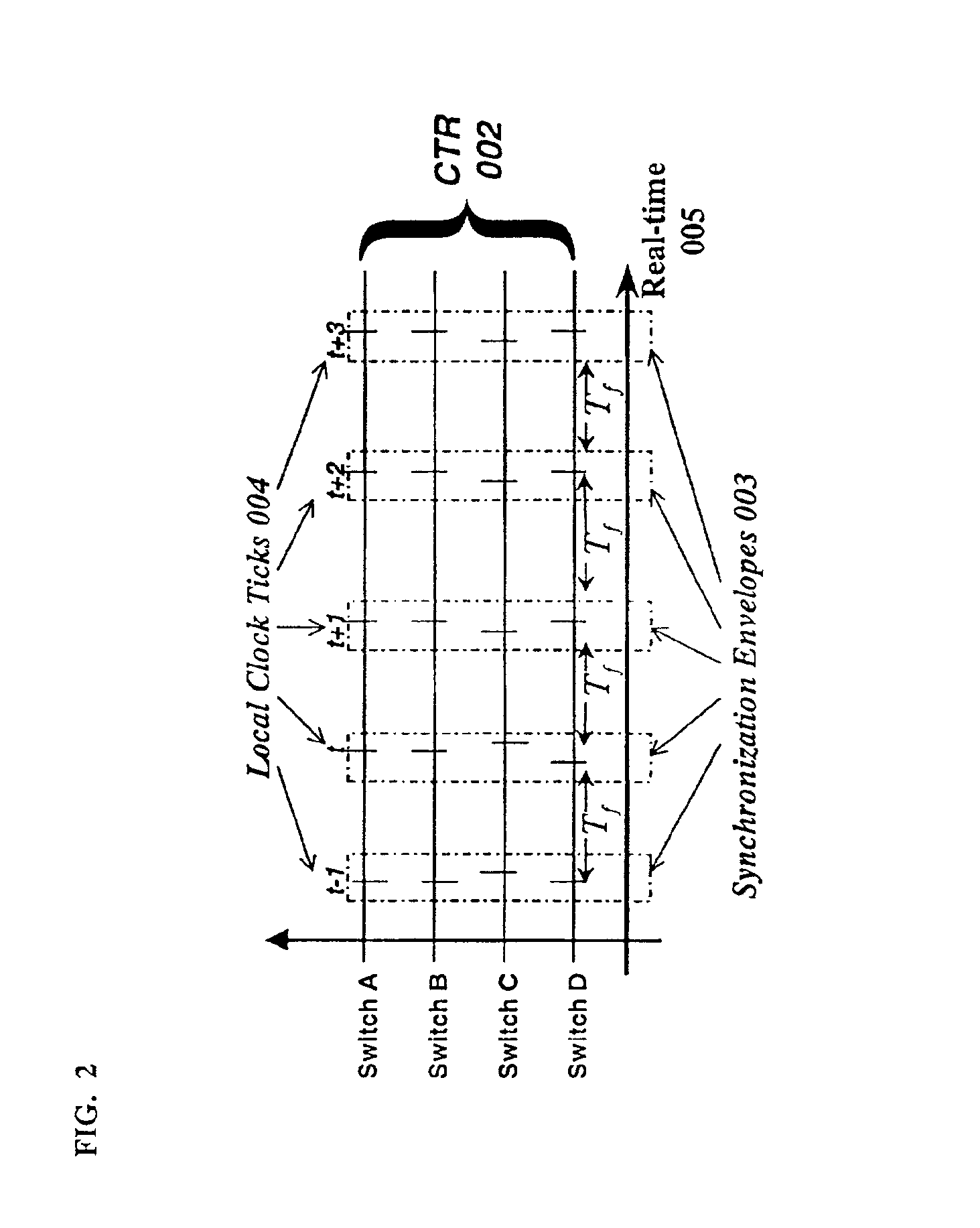
Method and system for accurate clock synchronization for communication networks
InactiveUS20080273521A1Improve accuracyMinimize synchronization delay jitterSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexDistributed computingClock synchronization
A high accuracy clock synchronization mechanism between a sender and a receiver in a communication network achieves time synchronization using broadcast beacons, directly at the PHY / MAC layer of the sender and the receiver, to minimize synchronization delay jitter. This provides a more efficient synchronization method than either NTP or SNTP, because multiple handshaking information exchange is avoided. Further, using beacons avoids the overhead of introducing additional synchronization packets in higher layer synchronization.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
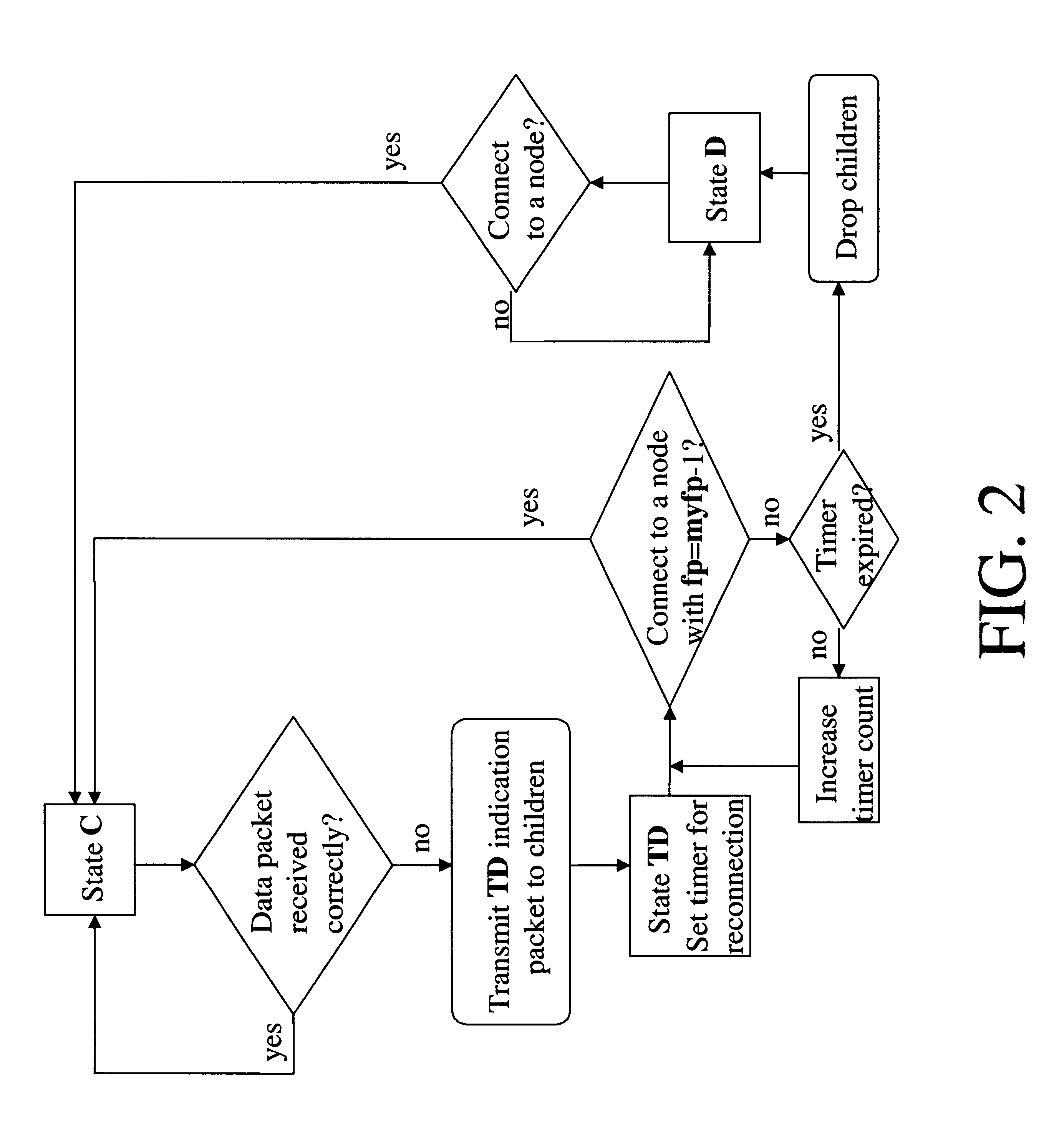
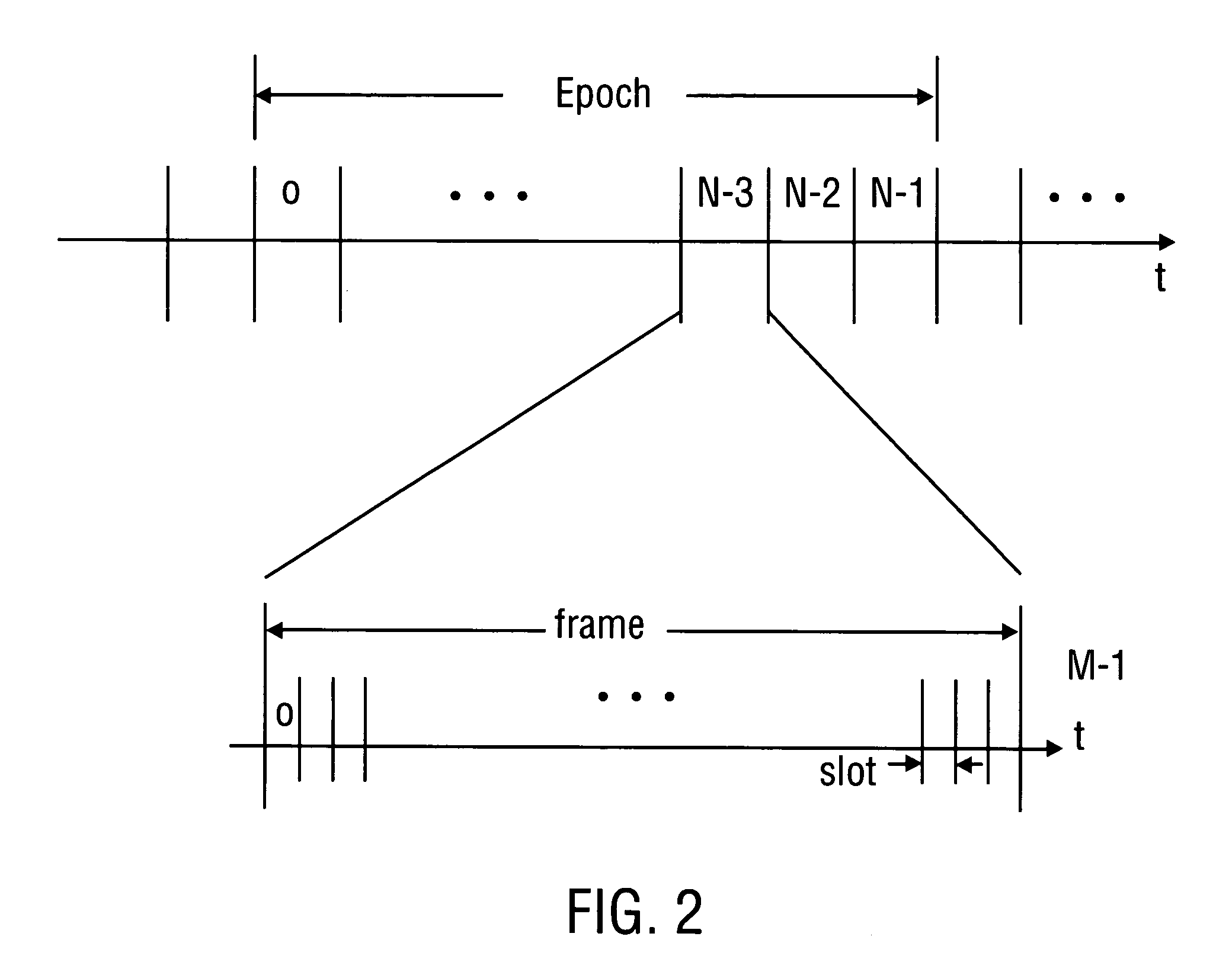
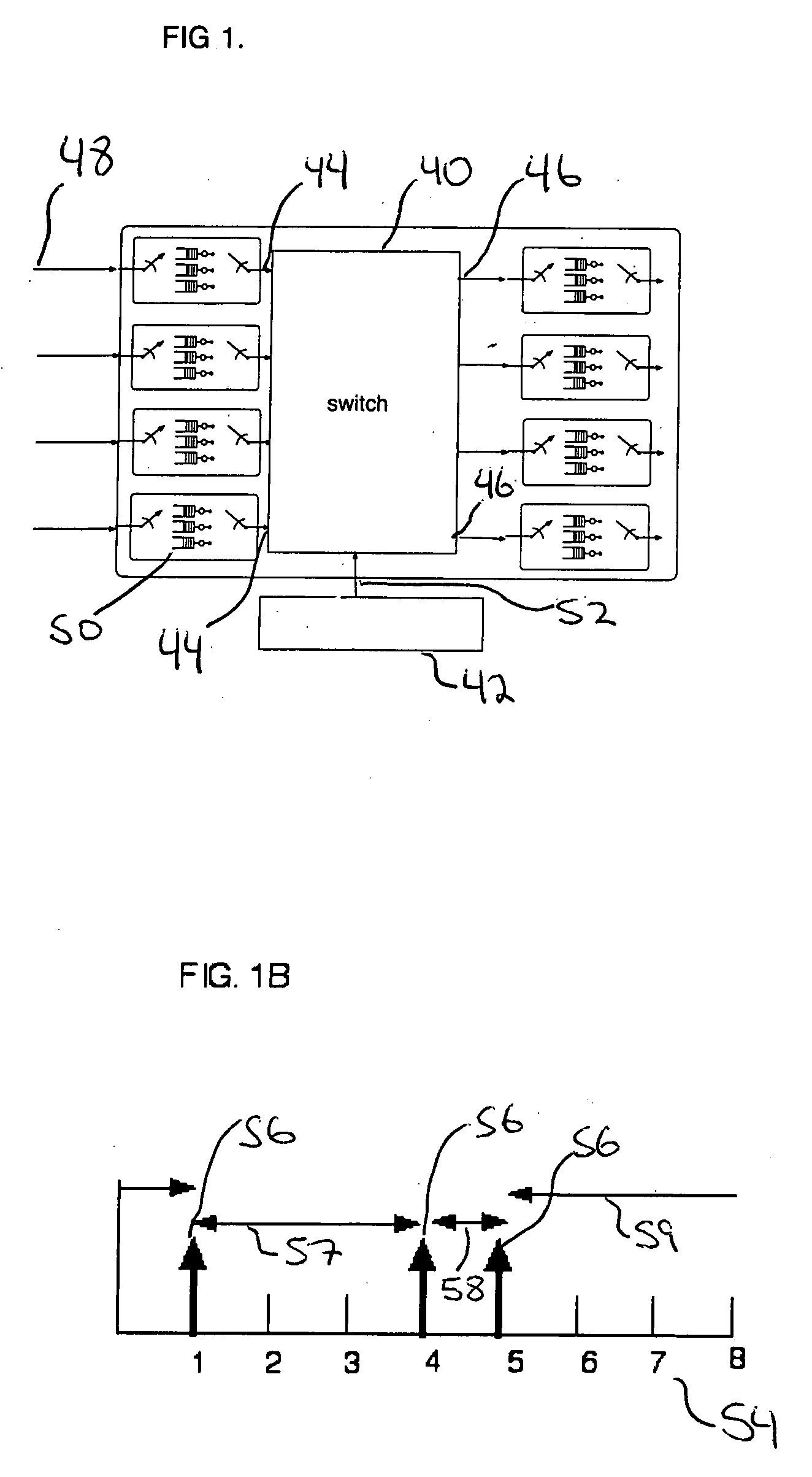
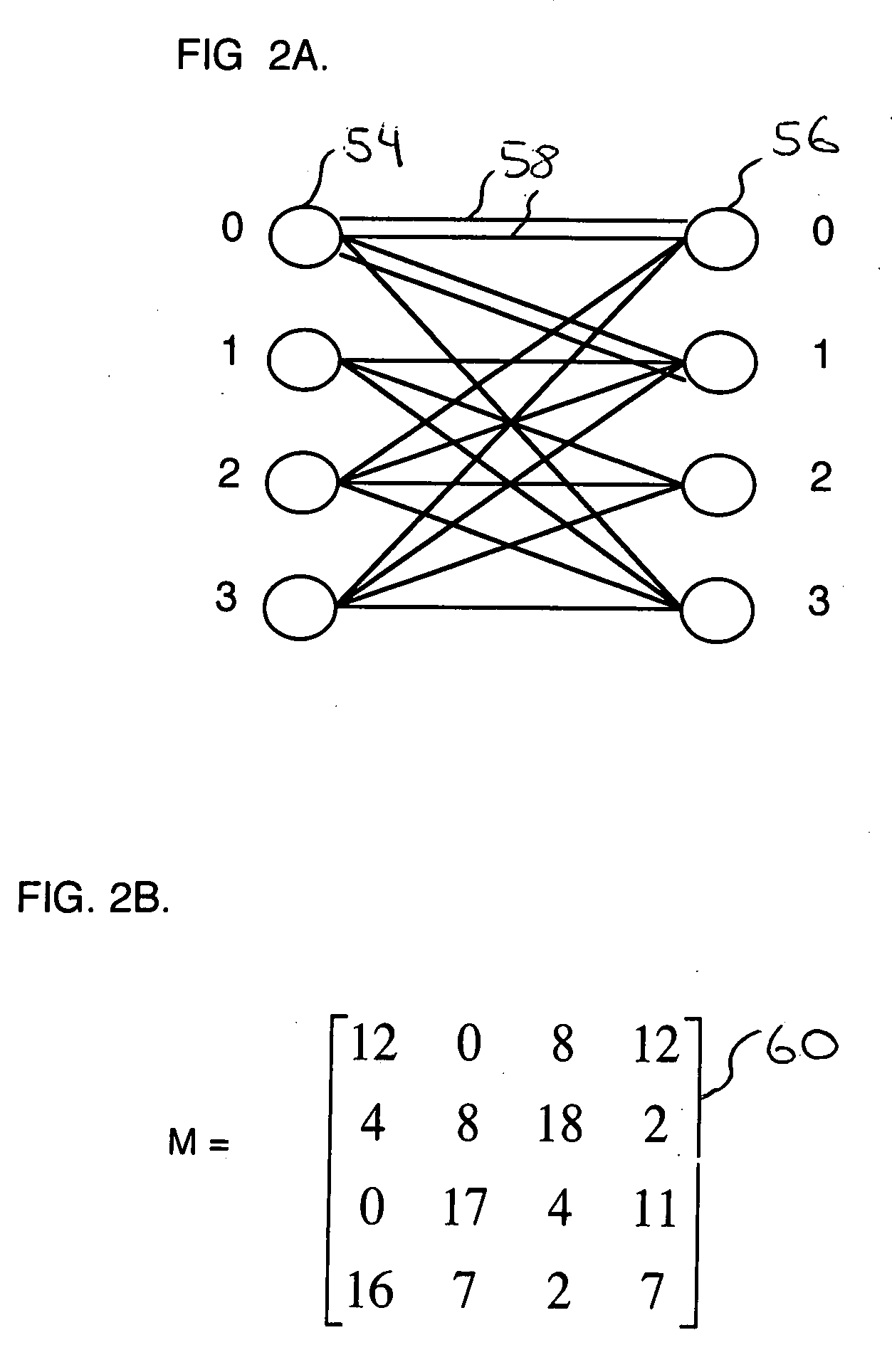
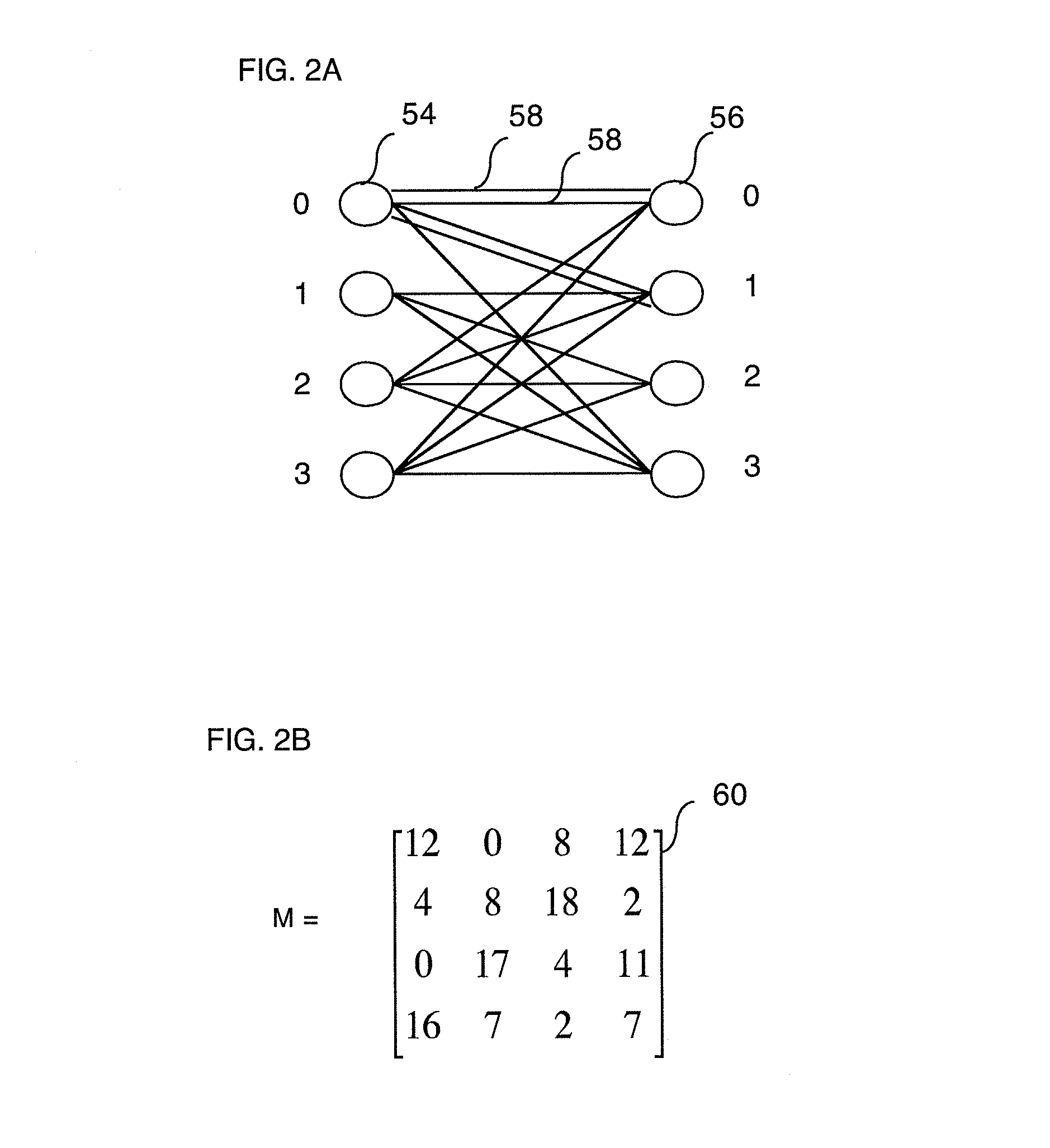
Method and apparatus to schedule packets through a crossbar switch with delay guarantees
ActiveUS20070280261A1Minimize delay jitterMeet bandwidth requirementsMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationCrossbar switchDifferentiated services
A method for scheduling cell transmissions through a switch with rate and delay guarantees and with low jitter is proposed. The method applies to a classic input-buffered N×N crossbar switch without speedup. The time axis is divided into frames each containing F time-slots. An N×N traffic rate matrix specifies a quantized guaranteed traffic rate from each input port to each output port. The traffic rate matrix is transformed into a permutation with NF elements which is decomposed into F permutations of N elements using a recursive and fair decomposition method. Each permutation is used to configure the crossbar switch for one time-slot within a frame of size F time-slots, and all F permutations result in a Frame Schedule. In the frame schedule, the expected Inter-Departure Time (IDT) between cells in a flow equals the Ideal IDT and the delay jitter is bounded and small. For fixed frame size F, an individual flow can often be scheduled in O(logN) steps, while a complete reconfiguration requires O(NlogN) steps when implemented in a serial processor. An RSVP or Differentiated Services-like algorithm can be used to reserve bandwidth and buffer space in an IP-router, an ATM switch or MPLS switch during a connection setup phase, and the proposed method can be used to schedule traffic in each router or switch. Best-effort traffic can be scheduled using any existing dynamic scheduling algorithm to fill the remaining unused switch capacity within each Frame. The scheduling algorithm also supports multicast traffic.
Owner:SZYMANSKI TED HENRYK
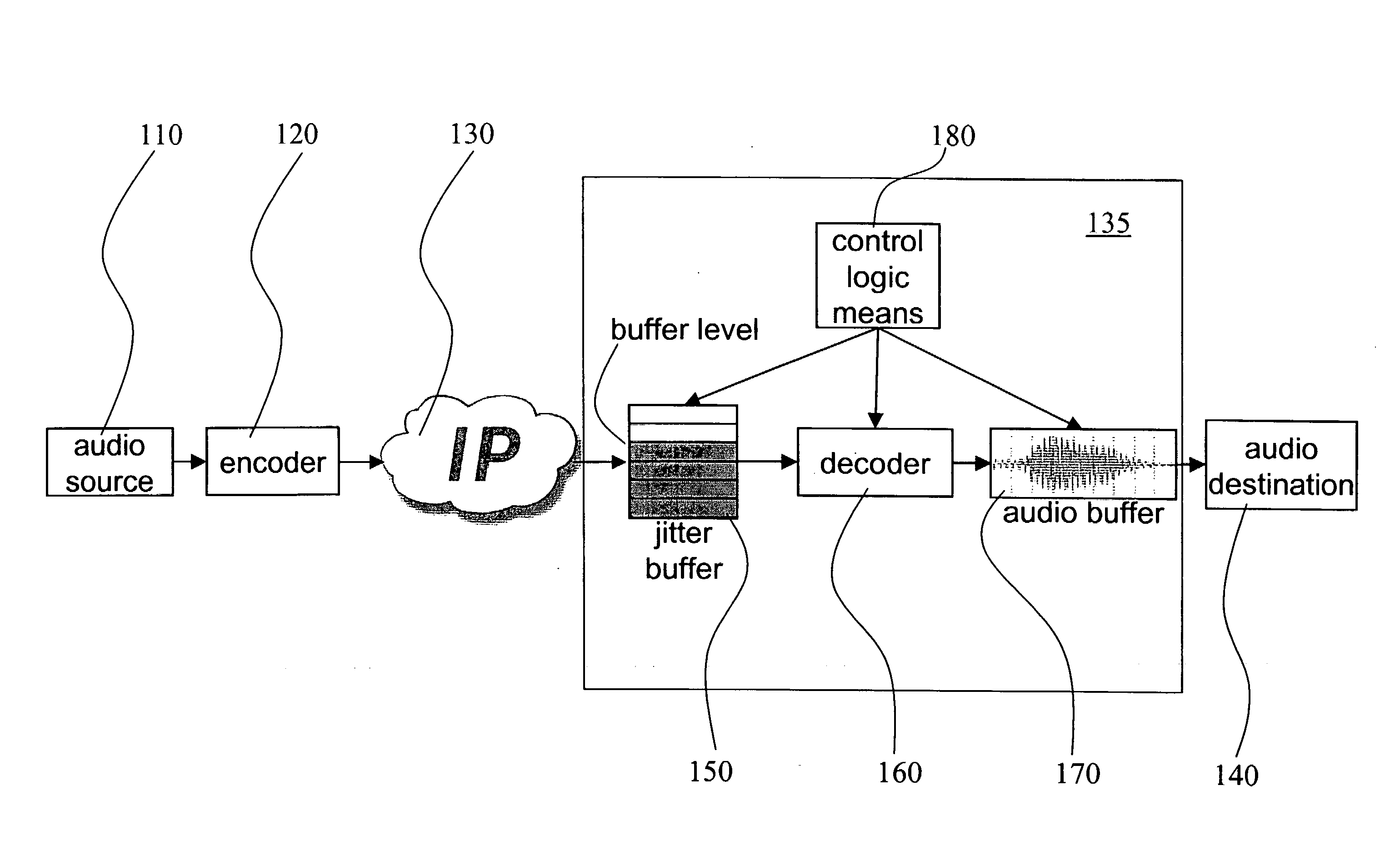
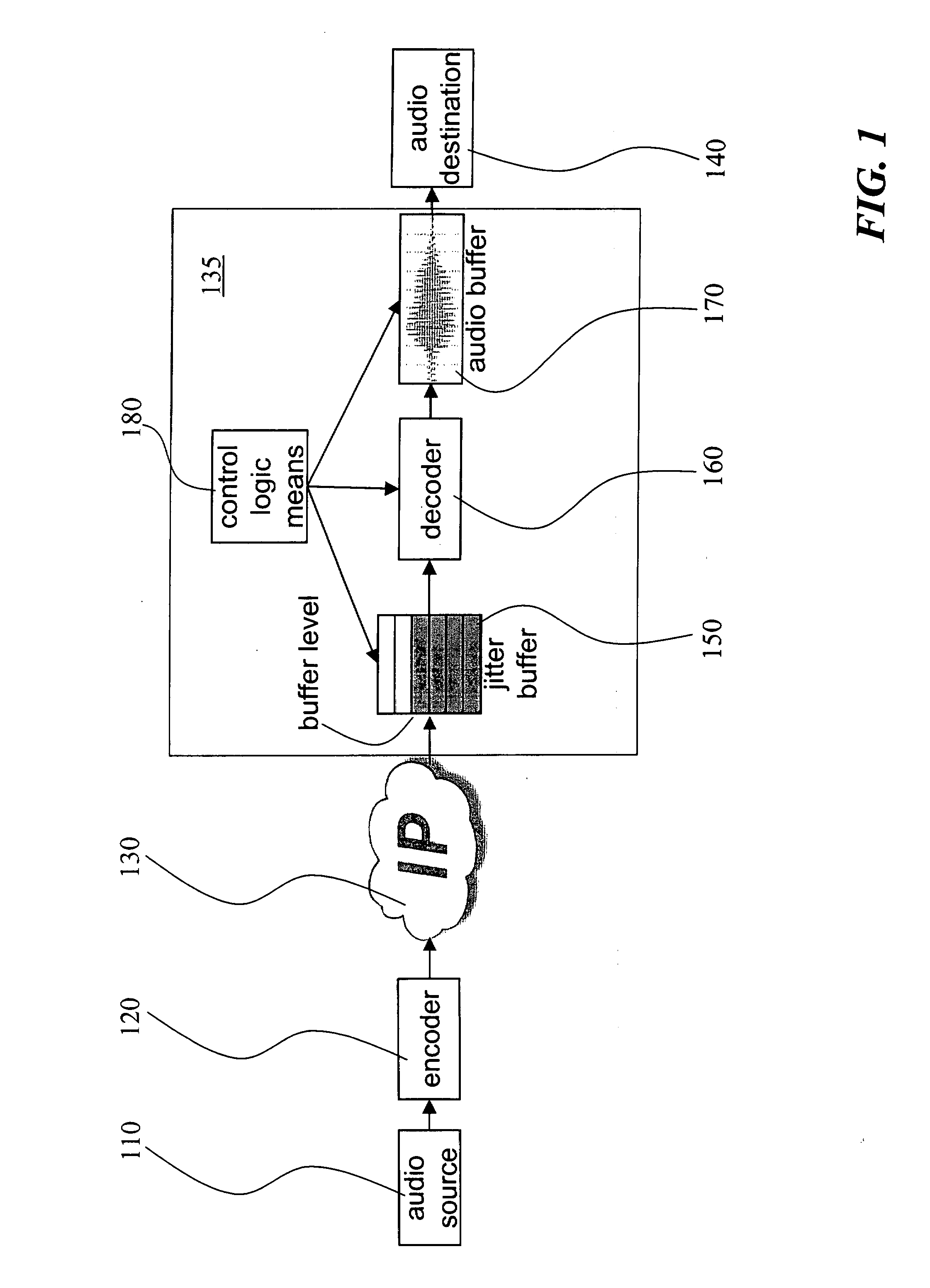
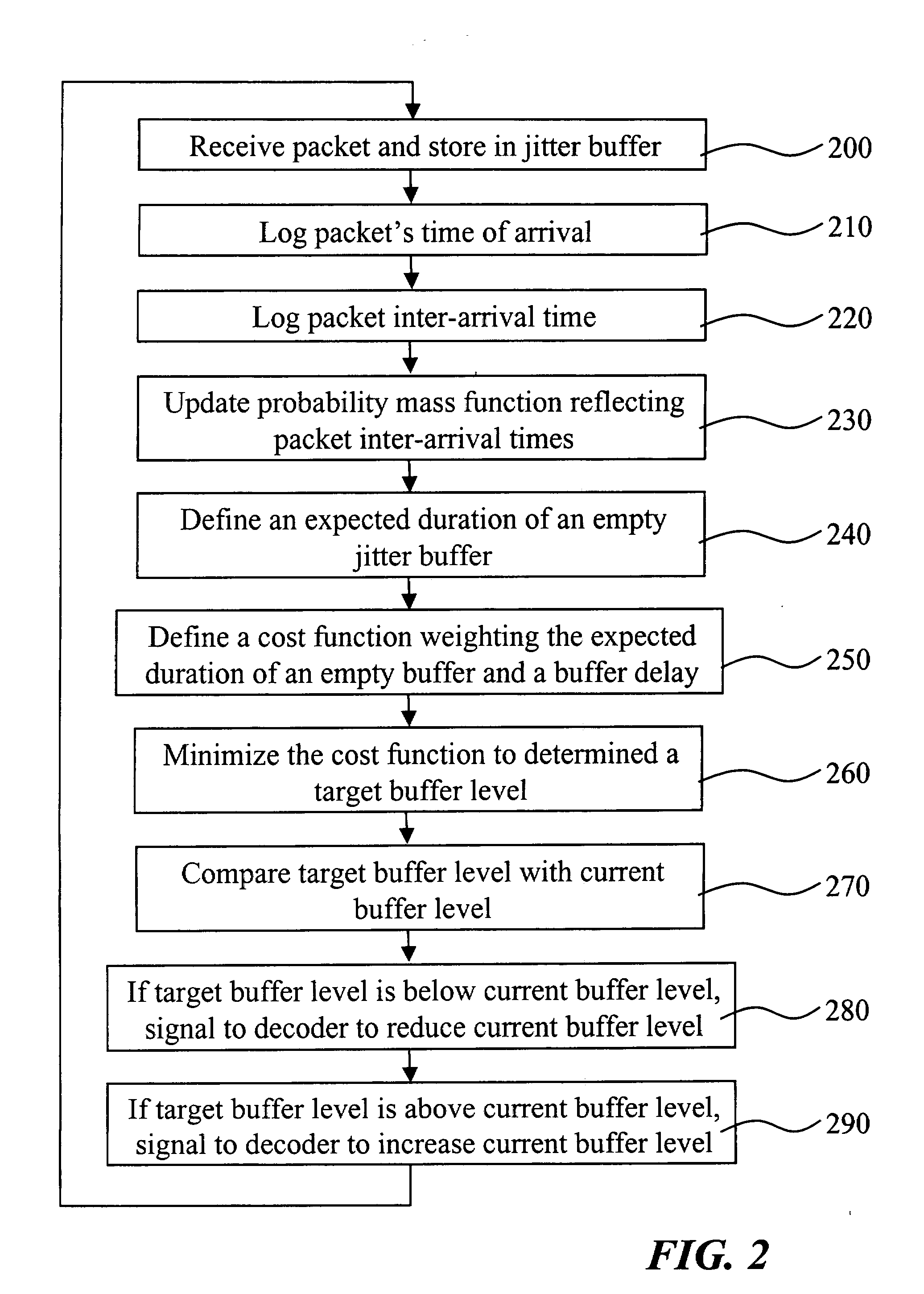
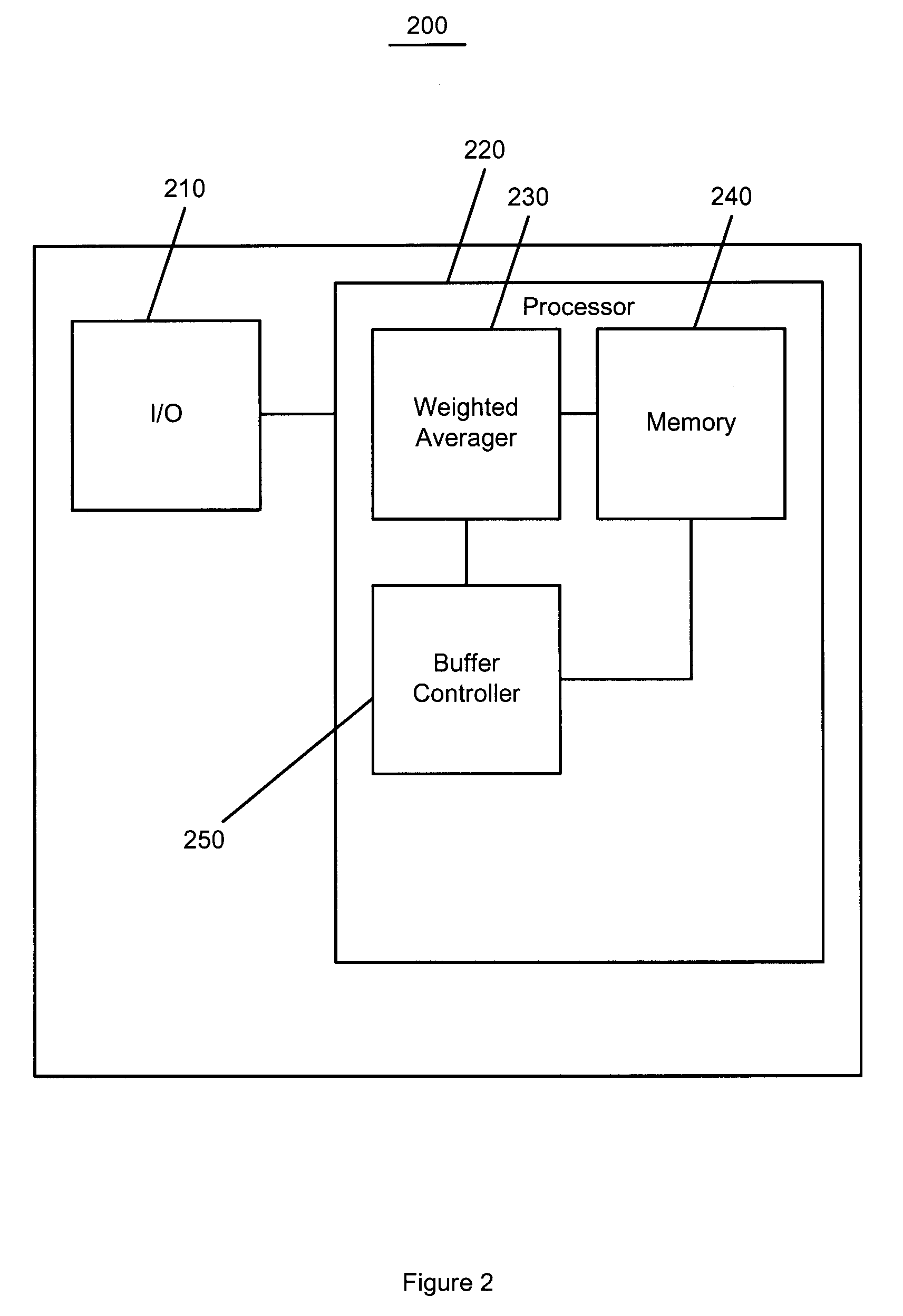
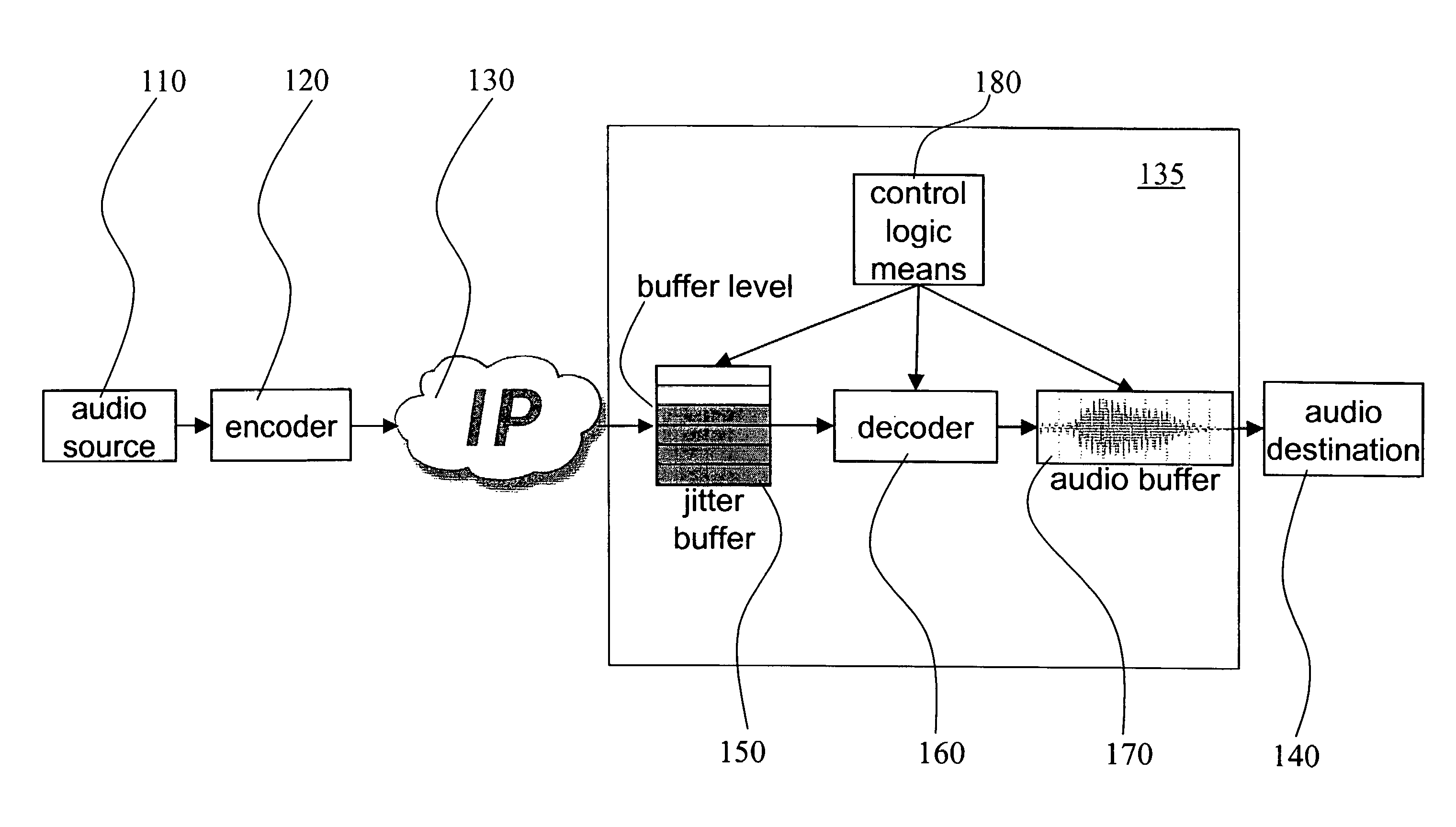
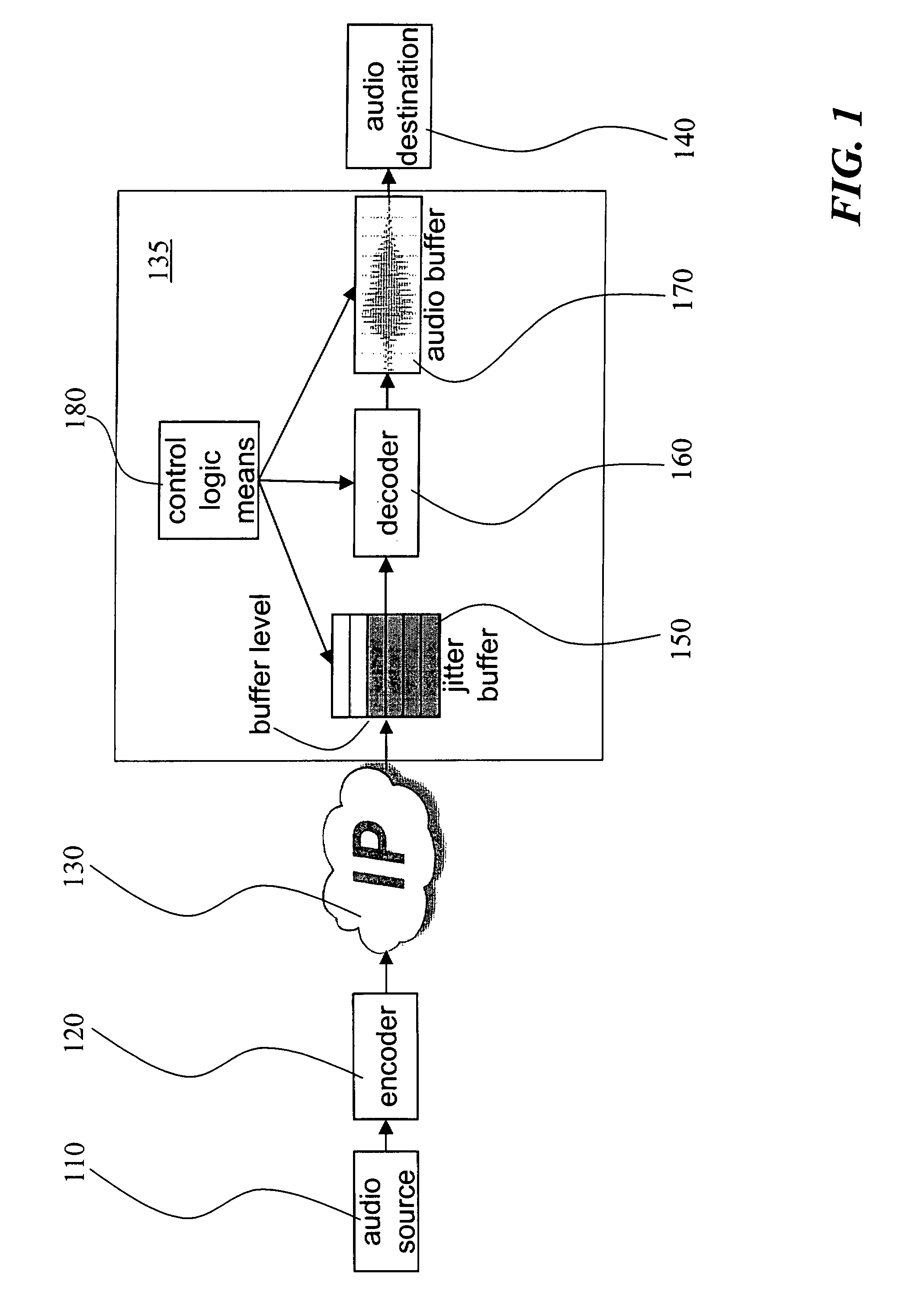
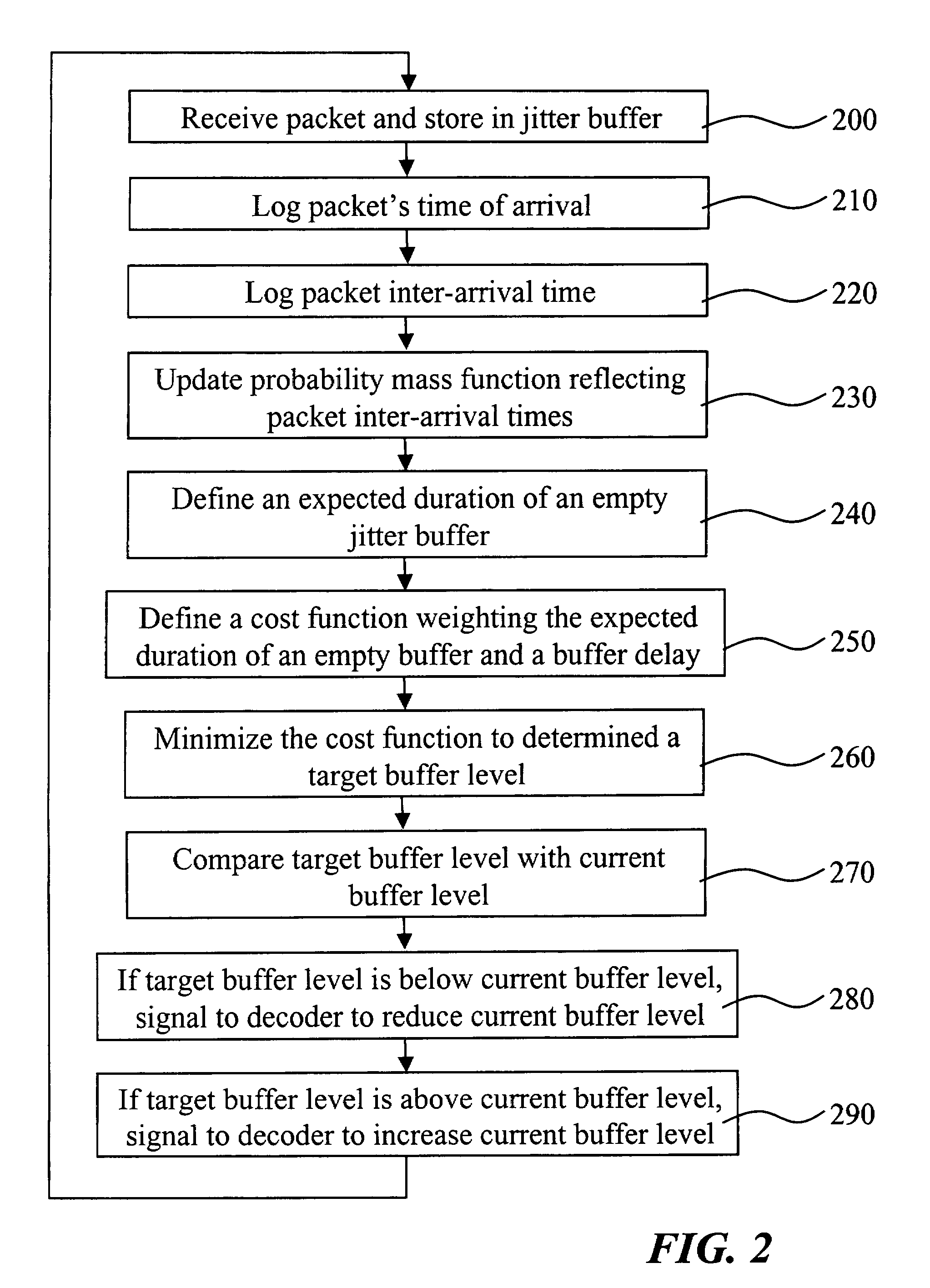
Method and receiver for determining a jitter buffer level
ActiveUS20090003369A1Suitable buffer levelMinimize cost functionTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPacket lossNetwork conditions
The invention relates to a method and a receiver having control logic means for determining a target packet level of a jitter buffer adapted to receive packets with digitized signal samples, which packets are subject to delay jitter, from a packet data network. According to the invention, the jitter buffer is made adaptive to current network conditions, i.e., the nature and magnitude of the jitter observed by the receiver, by collecting statistical measures that describe these conditions. The target buffer level is determined with regard to the effect of packet losses in terms of duration of the discontinued playback of the true signal. This effect is derived from statistical measures of the network conditions as perceived by the receiving side and as reflected by a probability mass function which is continuously updated with packet inter-arrival times. The target buffer level is the result of minimization of a cost function which weights the internal buffer delay and an expected length of buffer underflow.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
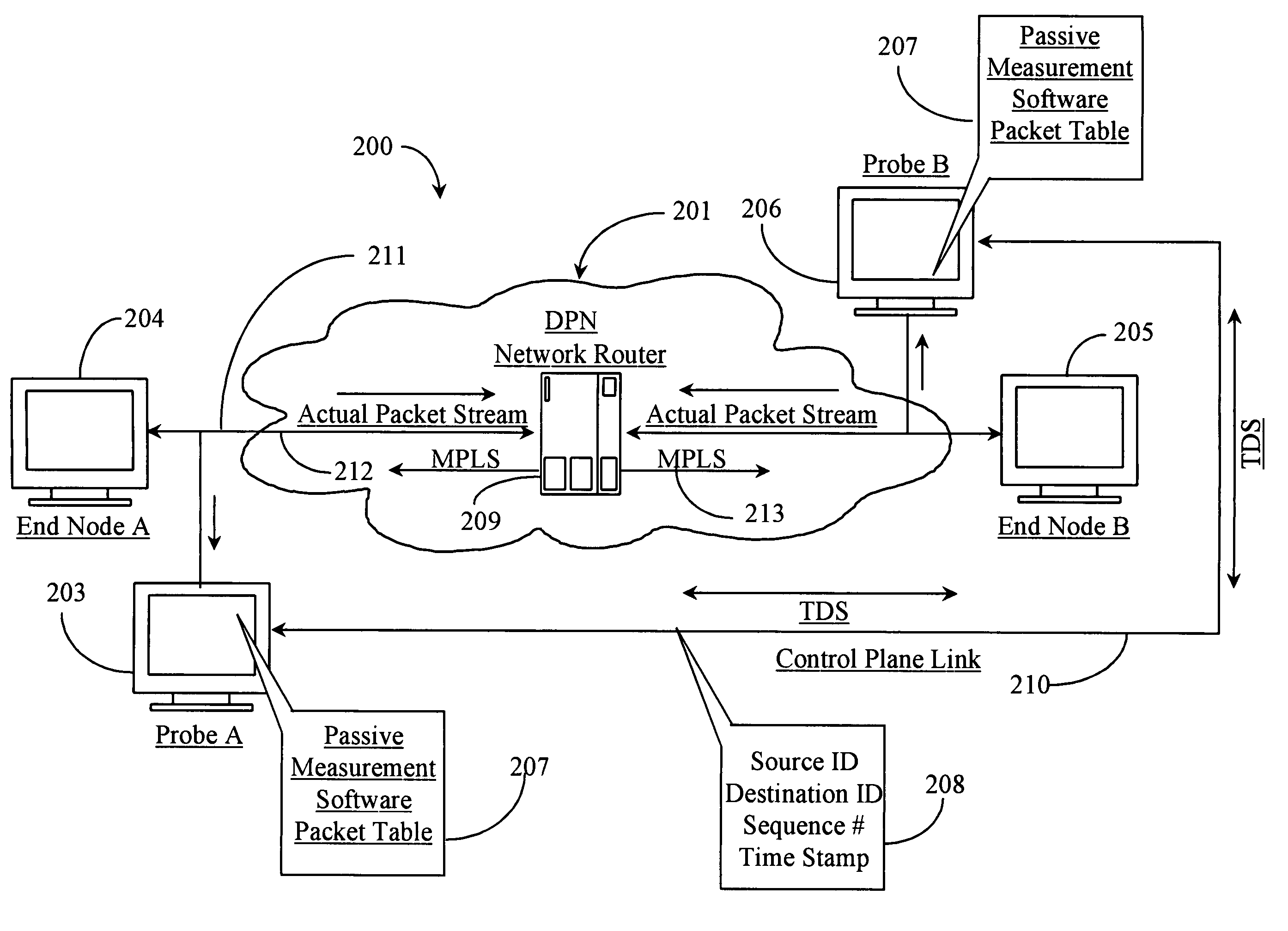
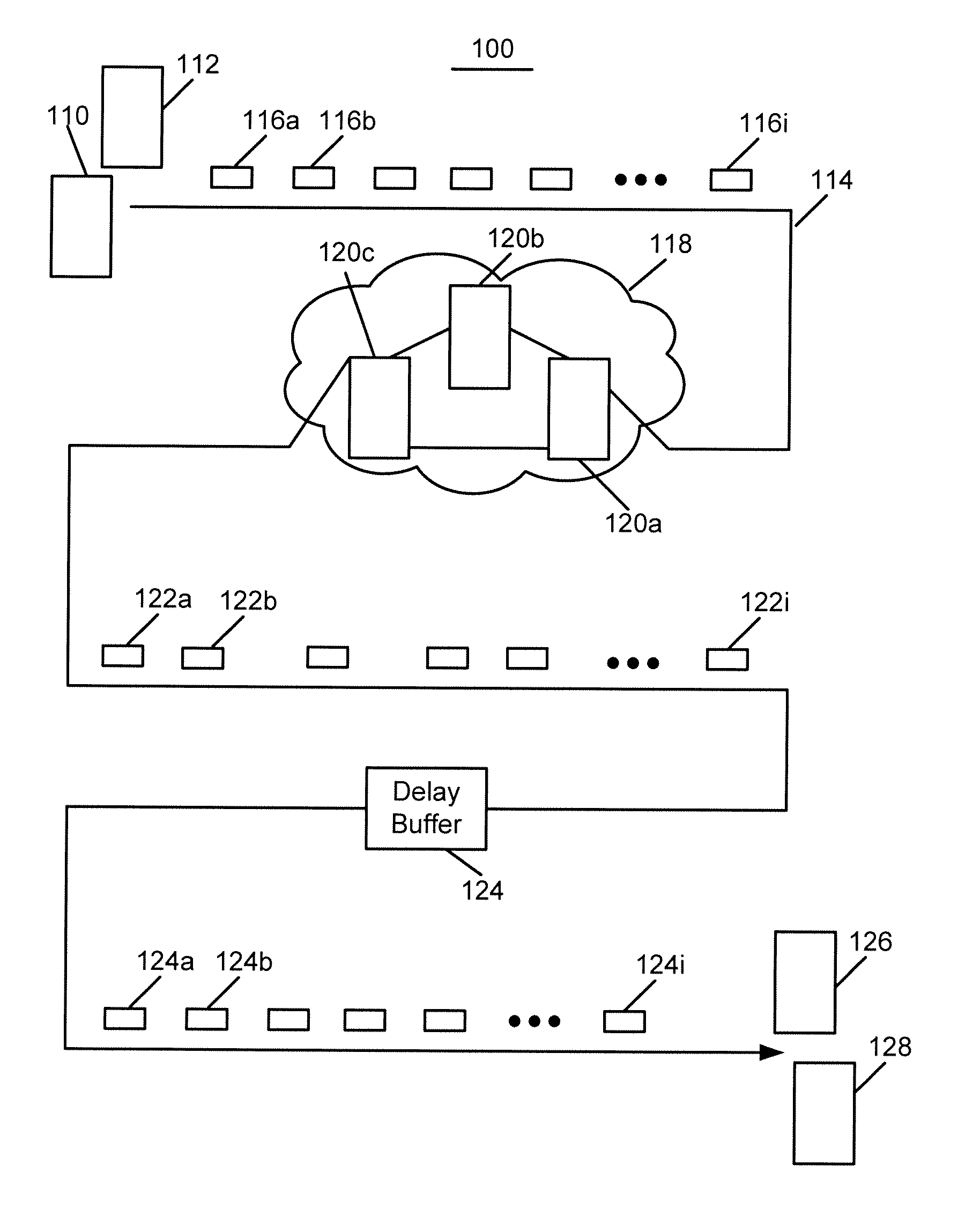
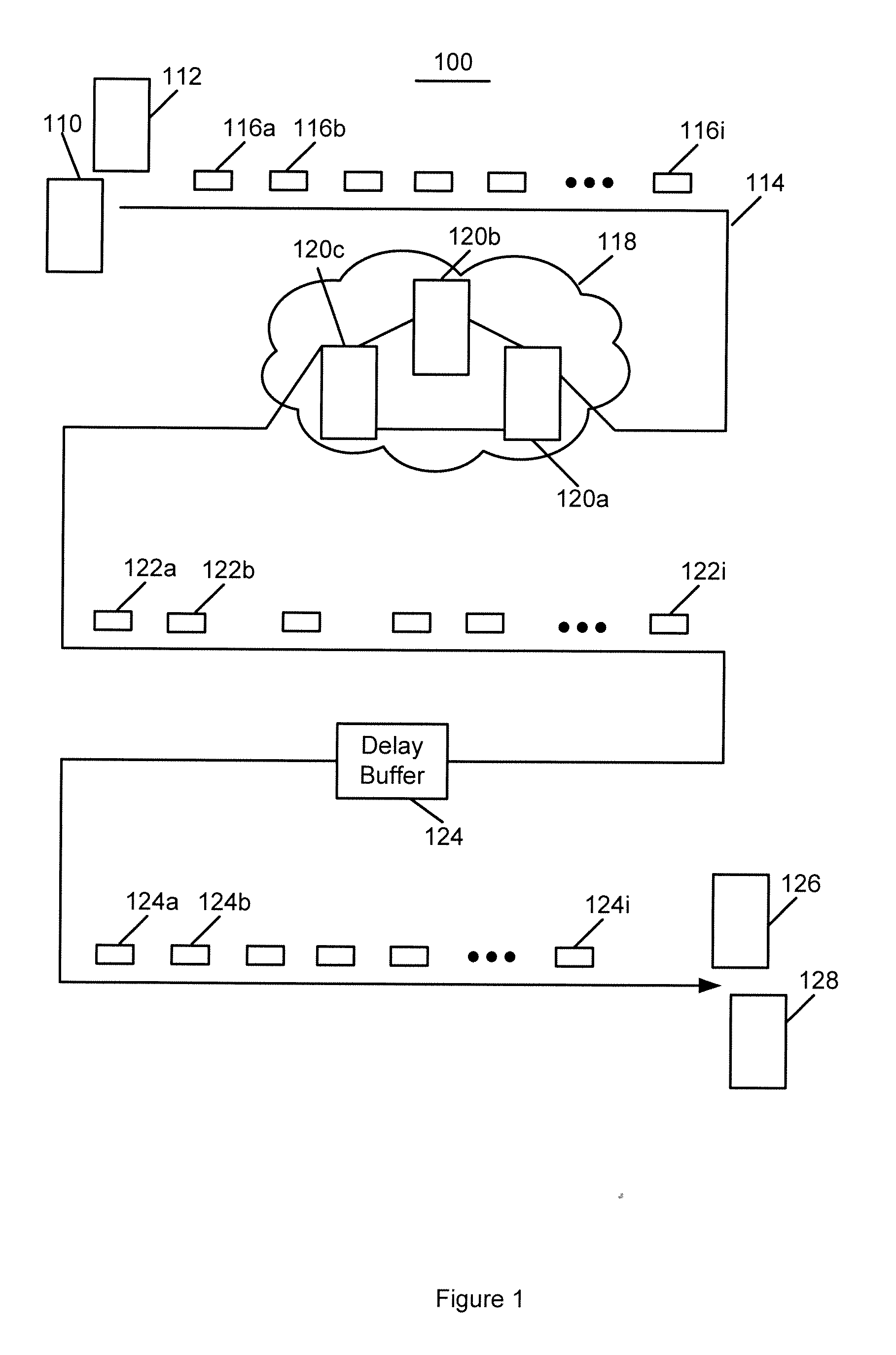
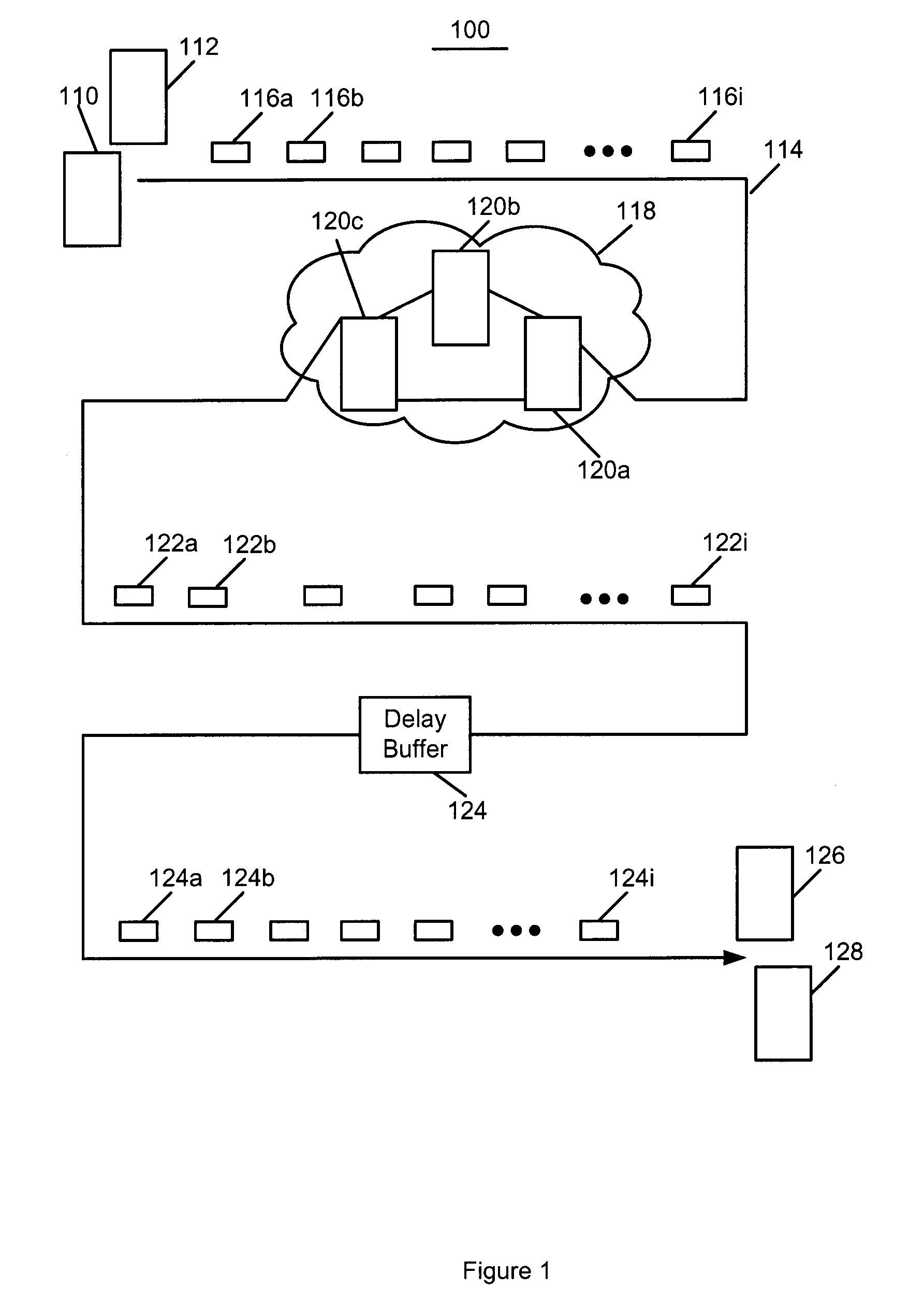
Real time mesh measurement systen stream latency and jitter measurements
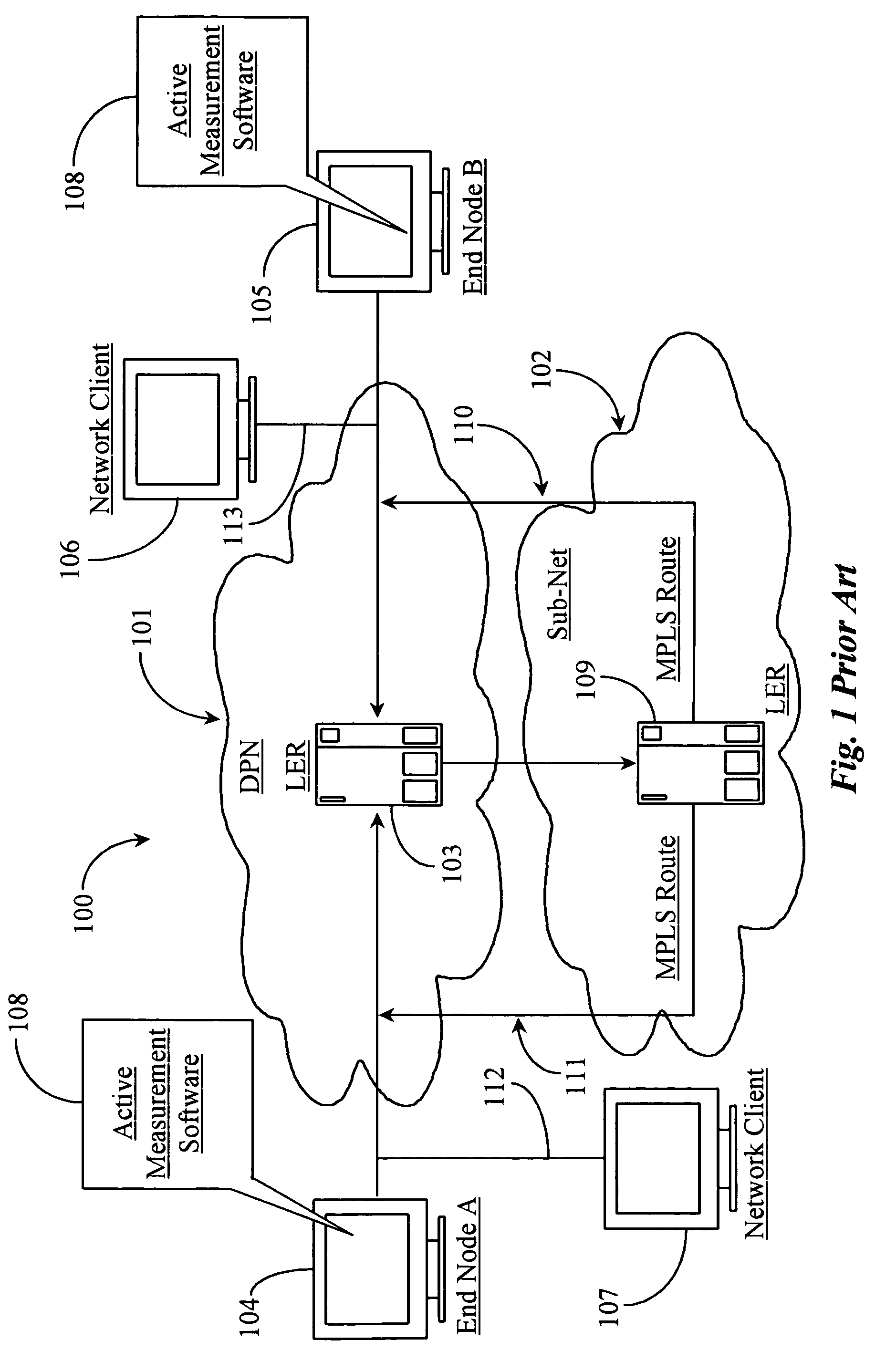
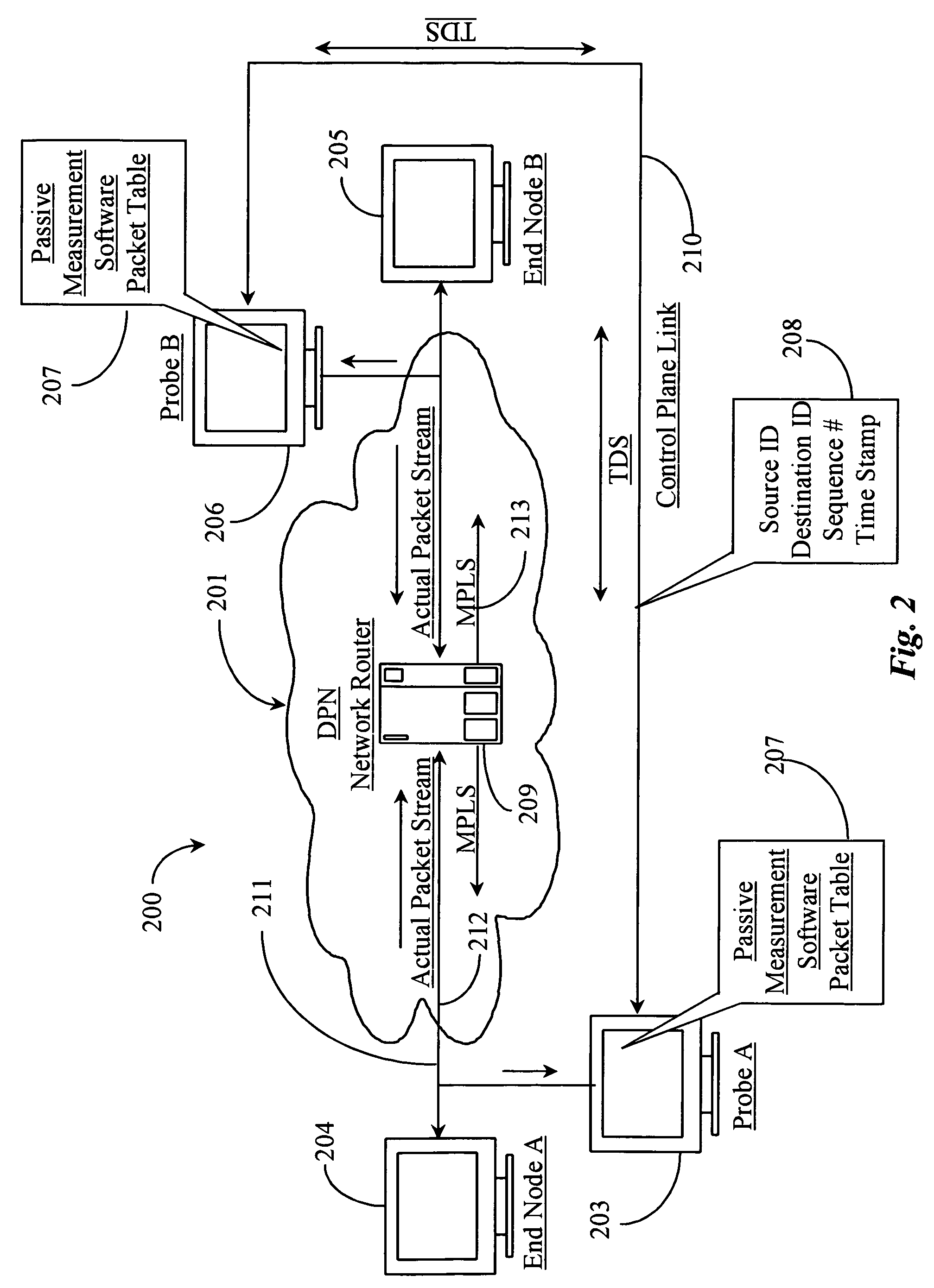
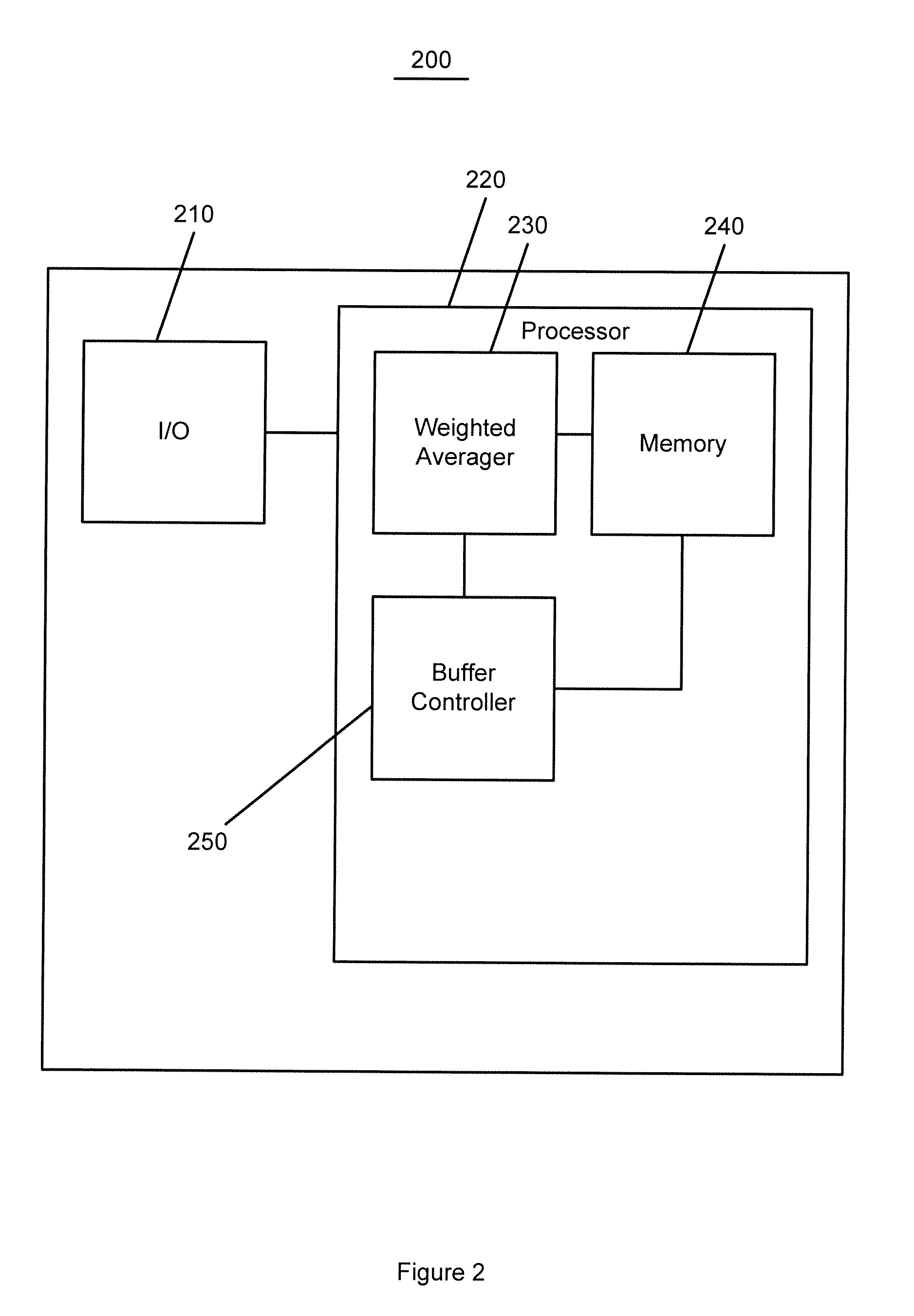
A method is described for measuring system latency and latency jitter on a near real-time basis regarding packets of information moving from sources to destination. The method for measuring system latency and latency jitter includes time-stamping packets of information as they pass through a plurality of locations between the source and destination of these packets, with the time-stamping being performed by real-time clocks set to a universal standard. The time-stamped packets are analyzed to determine latency and latency jitter. The measurements of system latency and latency jitter can be performed based upon packet types so as to obtain accurate information concerning different types of business bandwidths associated with an observed network.
Owner:INFRASTRUCTURE INNOVATIONS
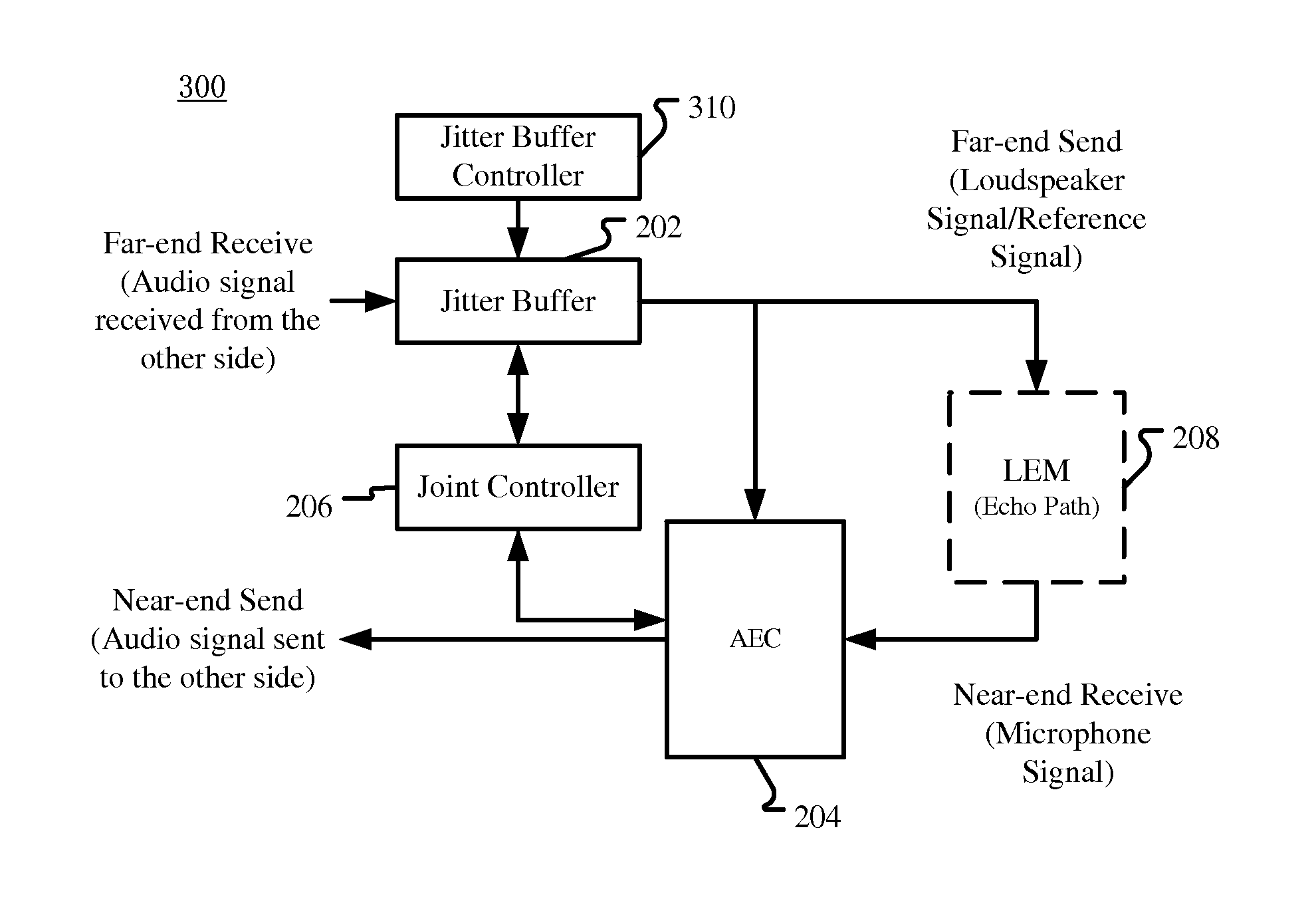
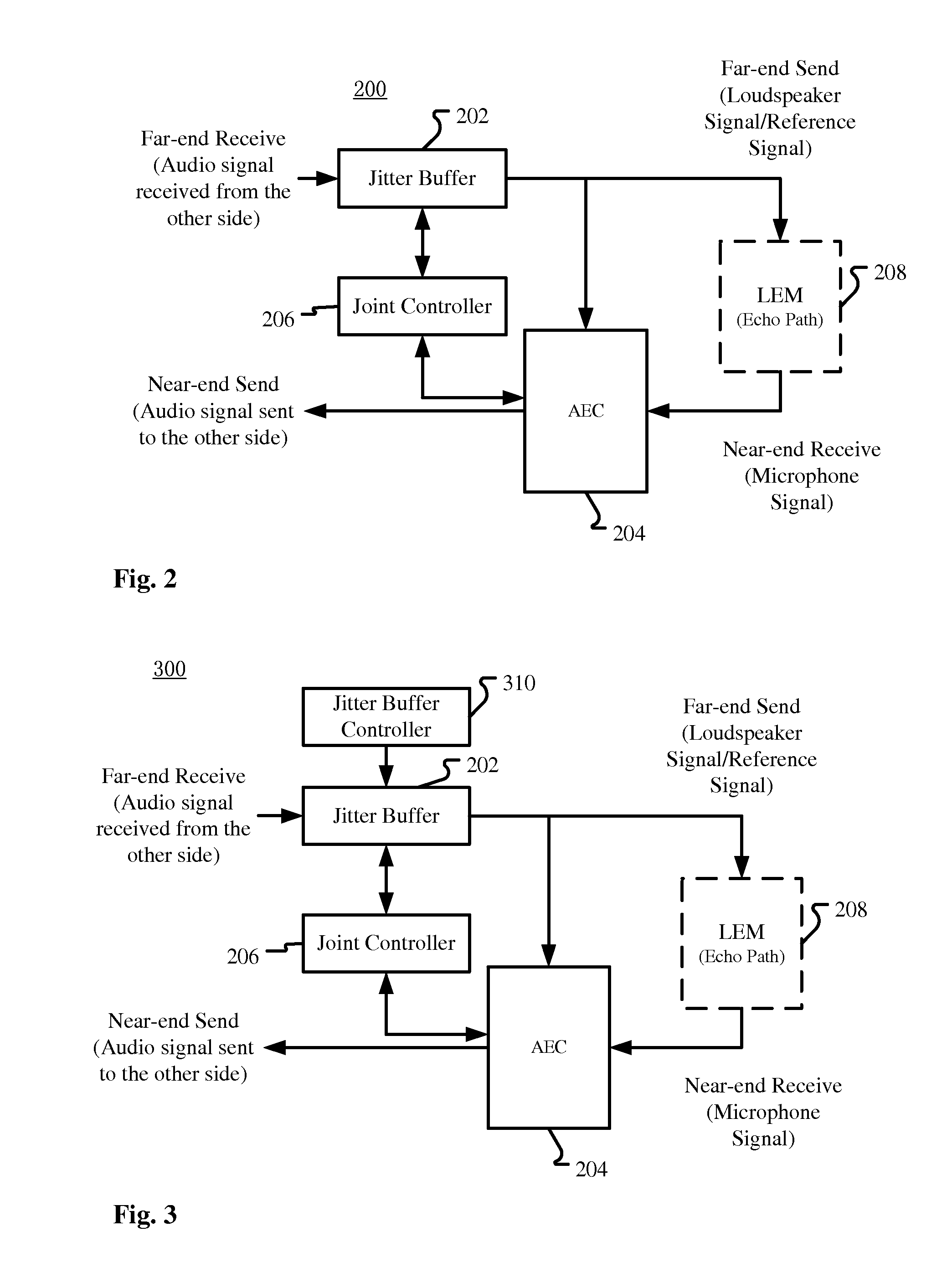
Method for Controlling Acoustic Echo Cancellation and Audio Processing Apparatus
ActiveUS20150332704A1Reducing delay jitterReduce latency jitterInterconnection arrangementsSpeech analysisMicrophone signalAudio frequency
A method for controlling acoustic echo cancellation and an audio processing apparatus are described. In one embodiment, the audio processing apparatus includes an acoustic echo canceller for suppressing acoustic echo in a microphone signal, a jitter buffer for reducing delay jitter of a received signal, and a joint controller for controlling the acoustic echo canceller by referring to at least one future frame in the jitter buffer.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus to schedule packets through a crossbar switch with delay guarantees
ActiveUS8089959B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationDifferentiated servicesCrossbar switch
A method for scheduling cell transmissions through a switch with rate and delay guarantees and with low jitter is proposed. The method applies to a classic input-buffered N×N crossbar switch without speedup. The time axis is divided into frames each containing F time-slots. An N×N traffic rate matrix specifies a quantized guaranteed traffic rate from each input port to each output port. The traffic rate matrix is transformed into a permutation with NF elements which is decomposed into F permutations of N elements using a recursive and fair decomposition method. Each permutation is used to configure the crossbar switch for one time-slot within a frame of size F time-slots, and all F permutations result in a Frame Schedule. In the frame schedule, the expected Inter-Departure Time (IDT) between cells in a flow equals the Ideal IDT and the delay jitter is bounded and small. For fixed frame size F, an individual flow can often be scheduled in O(log N) steps, while a complete reconfiguration requires O(N log N) steps when implemented in a serial processor. An RSVP or Differentiated Services-like algorithm can be used to reserve bandwidth and buffer space in an IP-router, an ATM switch or MPLS switch during a connection setup phase, and the proposed method can be used to schedule traffic in each router or switch. Best-effort traffic can be scheduled using any existing dynamic scheduling algorithm to fill the remaining unused switch capacity within each Frame. The scheduling algorithm also supports multicast traffic.
Owner:SZYMANSKI TED HENRYK
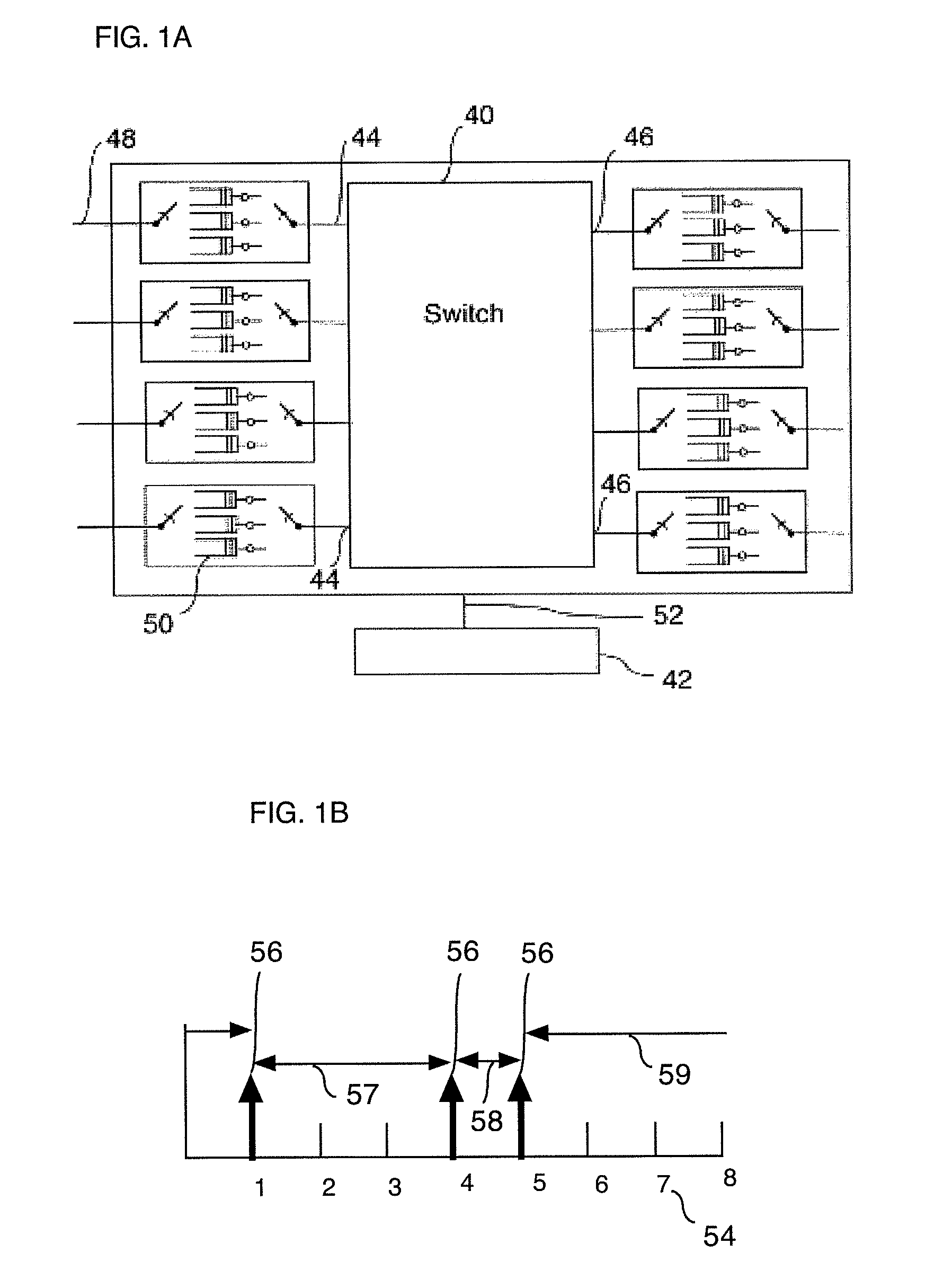
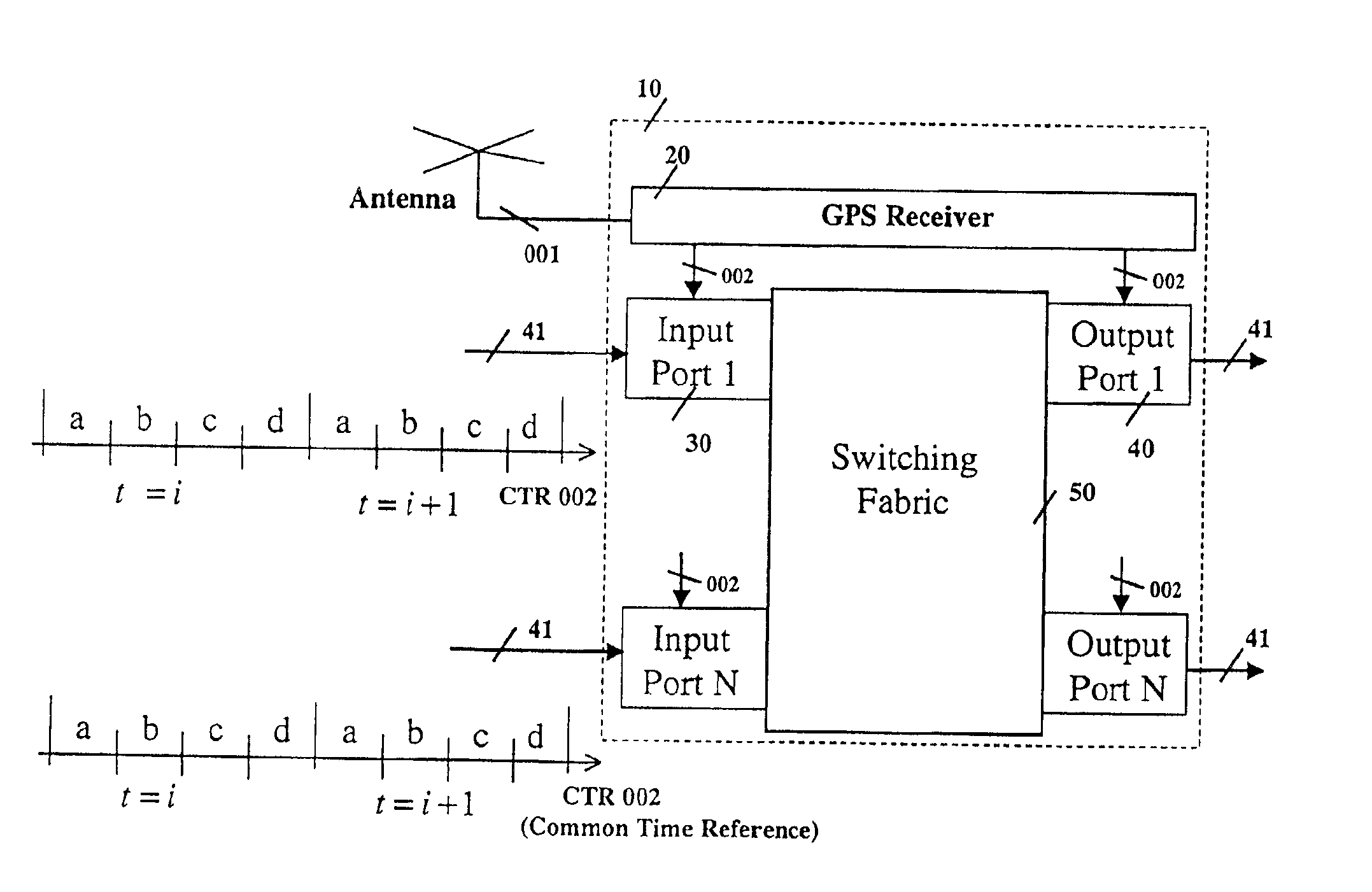
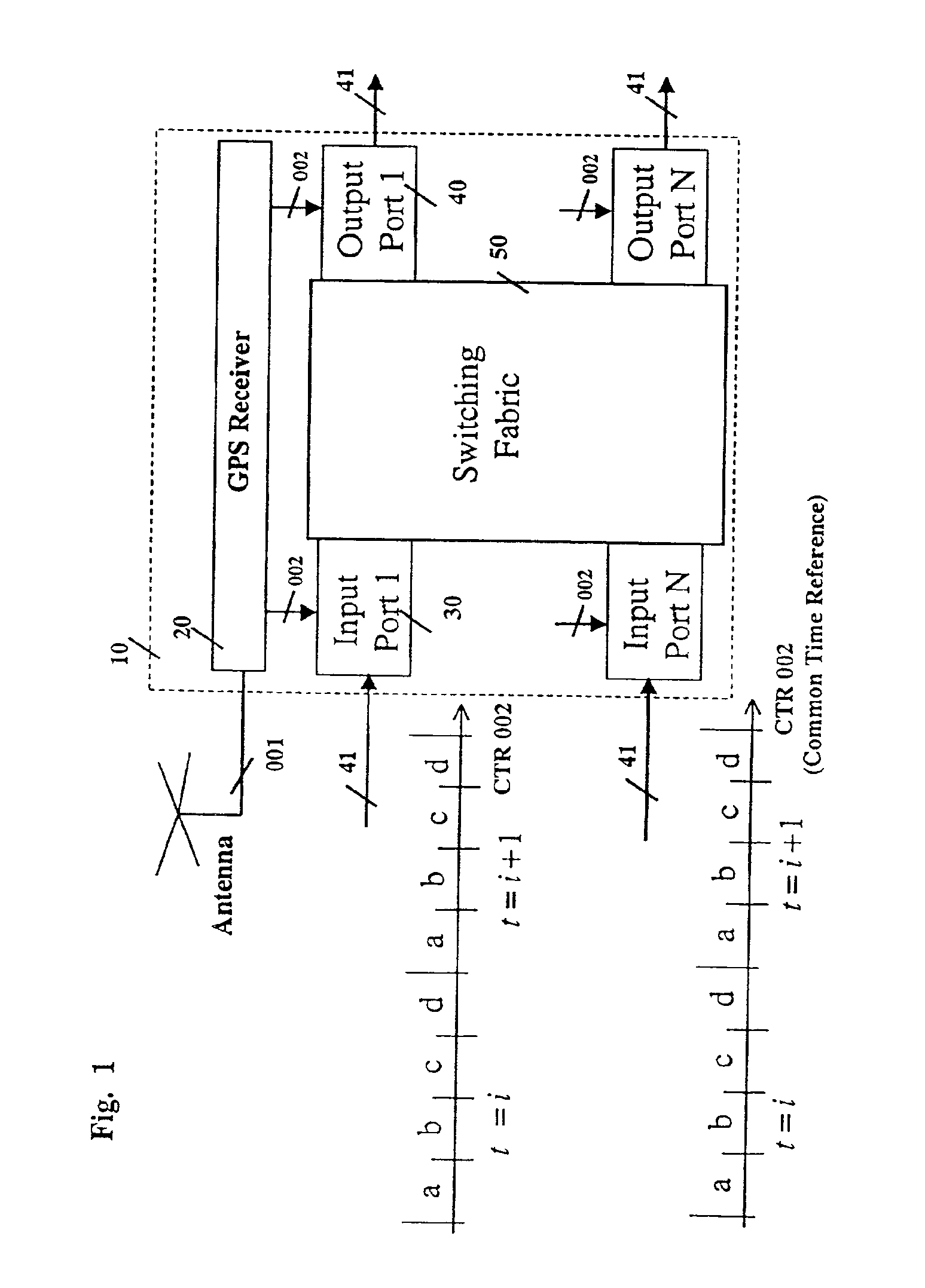
Distributed switching system and method with time-based routing
InactiveUS6885664B2Lower latencyGuaranteed performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTime informationExchange network
This invention describes a method for transmitting and forwarding packets over a switching network using time information. The network switches maintain a common time reference, which is obtained either from an external source (such as GPS—Global Positioning System) or is generated and distributed internally. The time intervals are arranged in simple periodicity and complex periodicity (like seconds and minutes of a clock). A data packet that arrives to an input port is switched to an output port based on its order or time position in the time interval in which it arrives at the switch. The time interval duration can be longer than the time duration required for transmitting a data packet, in which case the exact position of a data packet in its forwarding time interval is predetermined.This invention provides congestion-free data packet switching for data packets for which capacity in their corresponding forwarding links and time intervals is reserved in advance. Furthermore, such data packets reach their destination, which can be one or more (i.e., multicast) in predefined time intervals, which guarantees that the delay jitter is smaller than or equal to one time interval.
Owner:SYNCHRODYNE
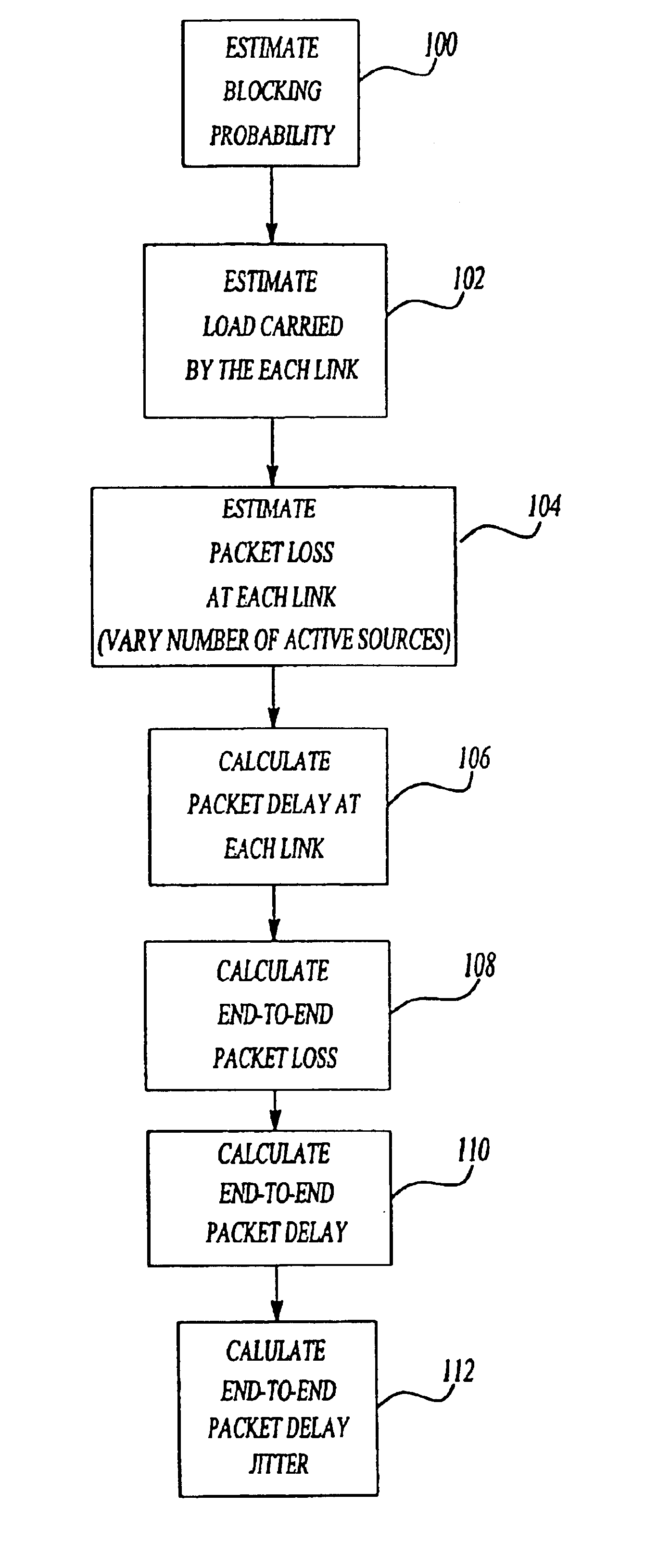
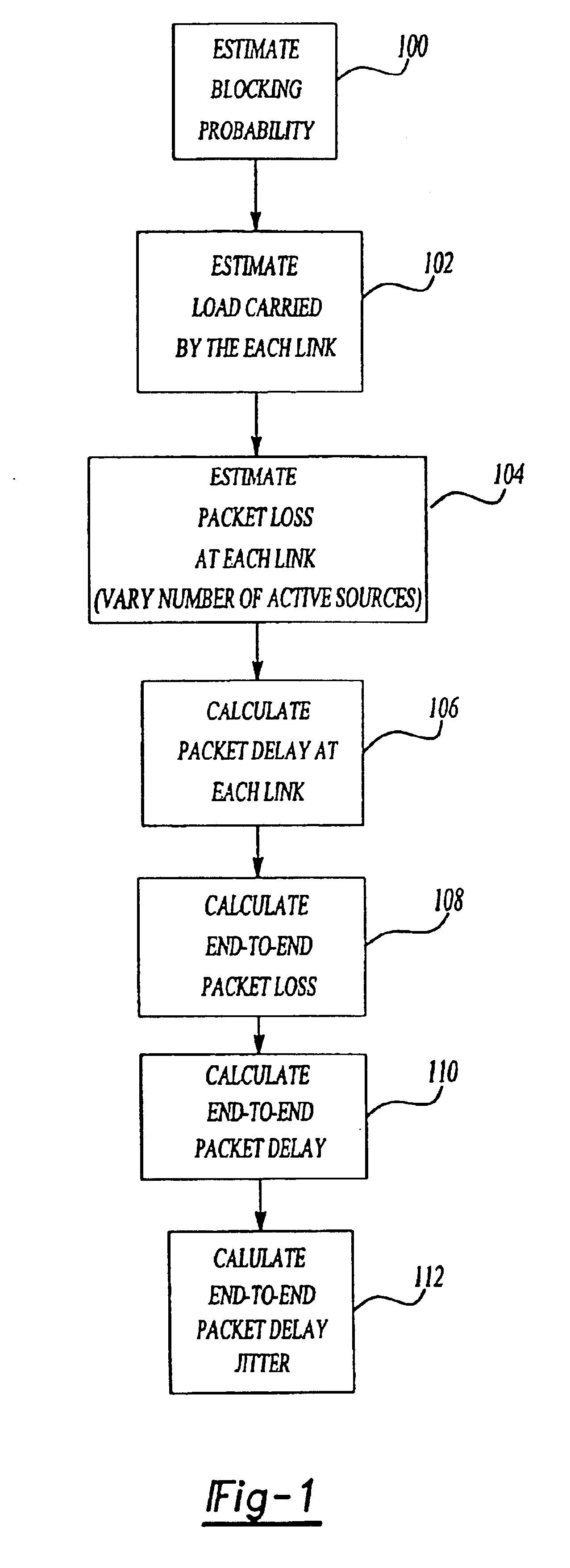
Method and system for estimating performance metrics in a packet-switched communication network
InactiveUS6912216B1Enhances network planningOptimize networkError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of servicePacket loss
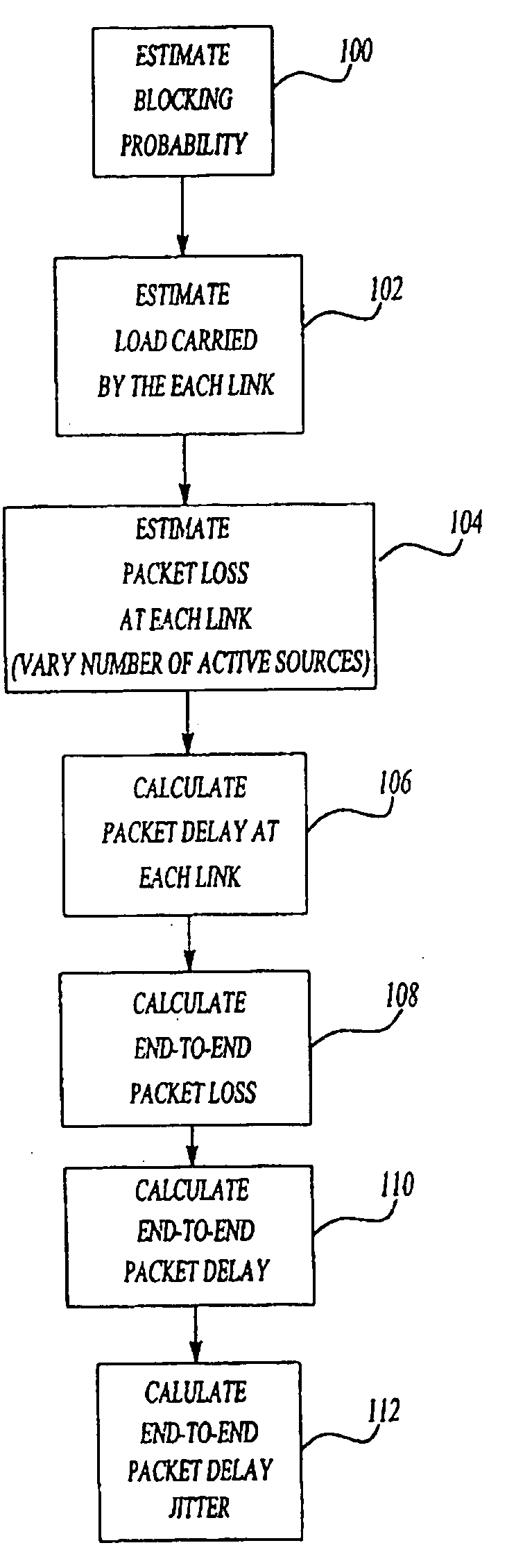
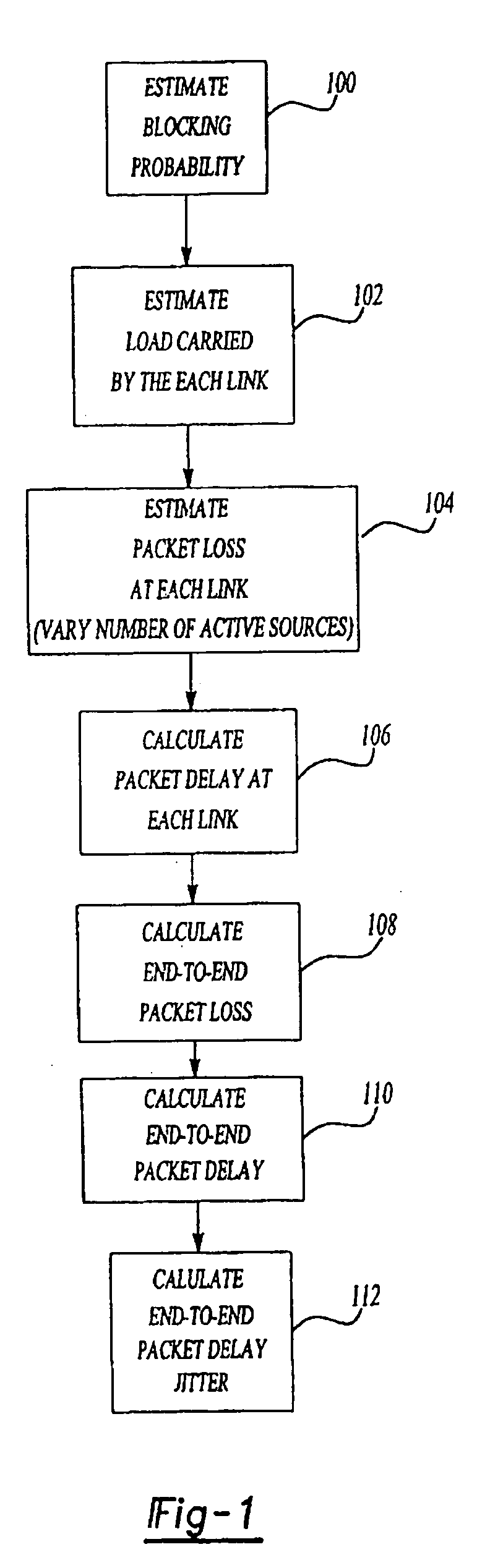
A method for estimating end-to-end quality of service (QOS), such as packet loss, delay, and delay jitter, in a packet-switched communications network includes steps for calculating packet loss and packet delay each router output link in a network path and using the packet loss and packet delay calculations for each individual router output link to estimate end-to-end QOS. The method includes calculating the loss probability for all possible numbers of active sources to take into account changes in the number of active sources as active sources connect to and disconnect from the network. As a result, the inventive method allows the number of active sources to vary in its estimation of end-to-end packet loss, delay, and delay jitter for enhanced Internet Protocol network planning.
Owner:VERIZON LAB
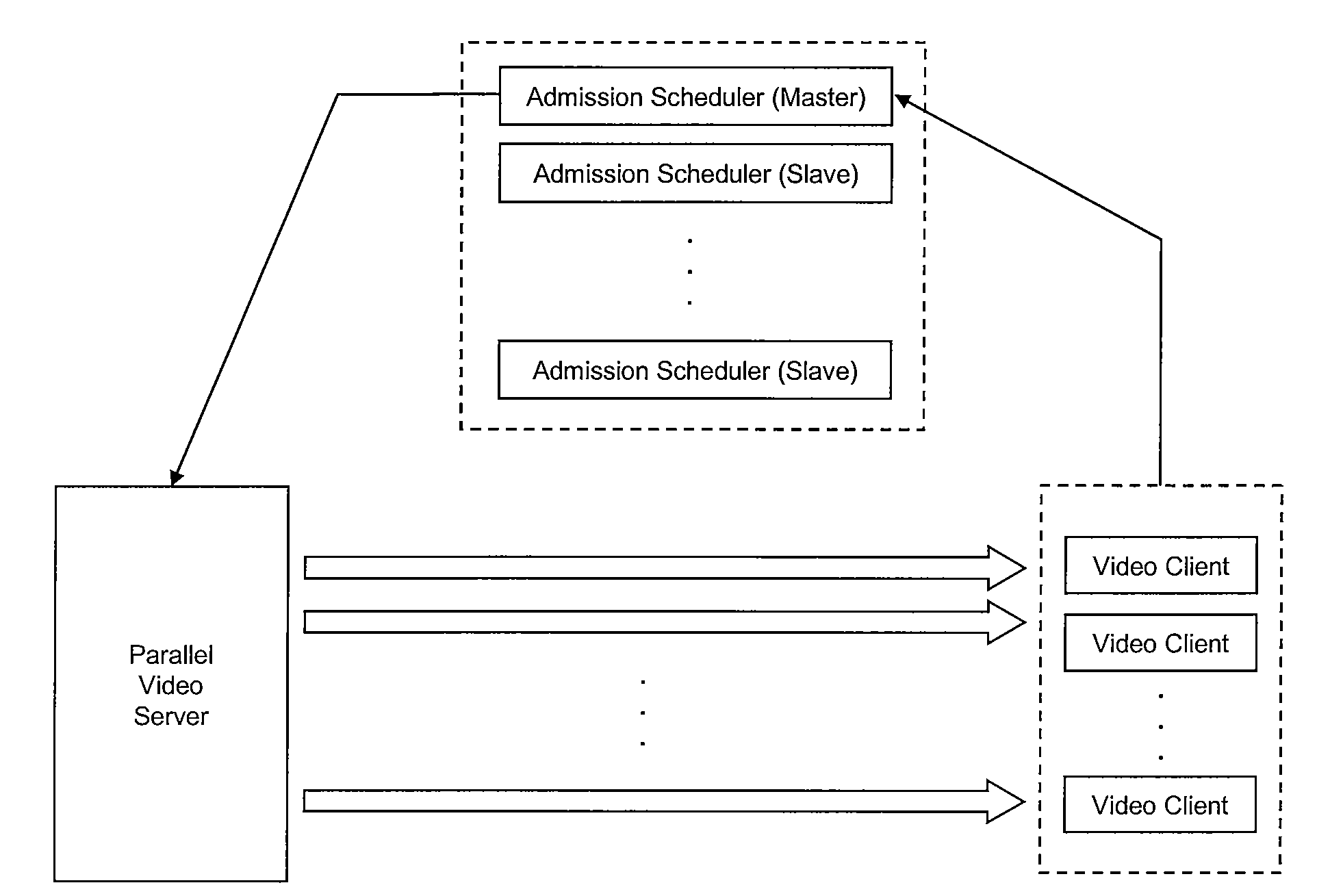
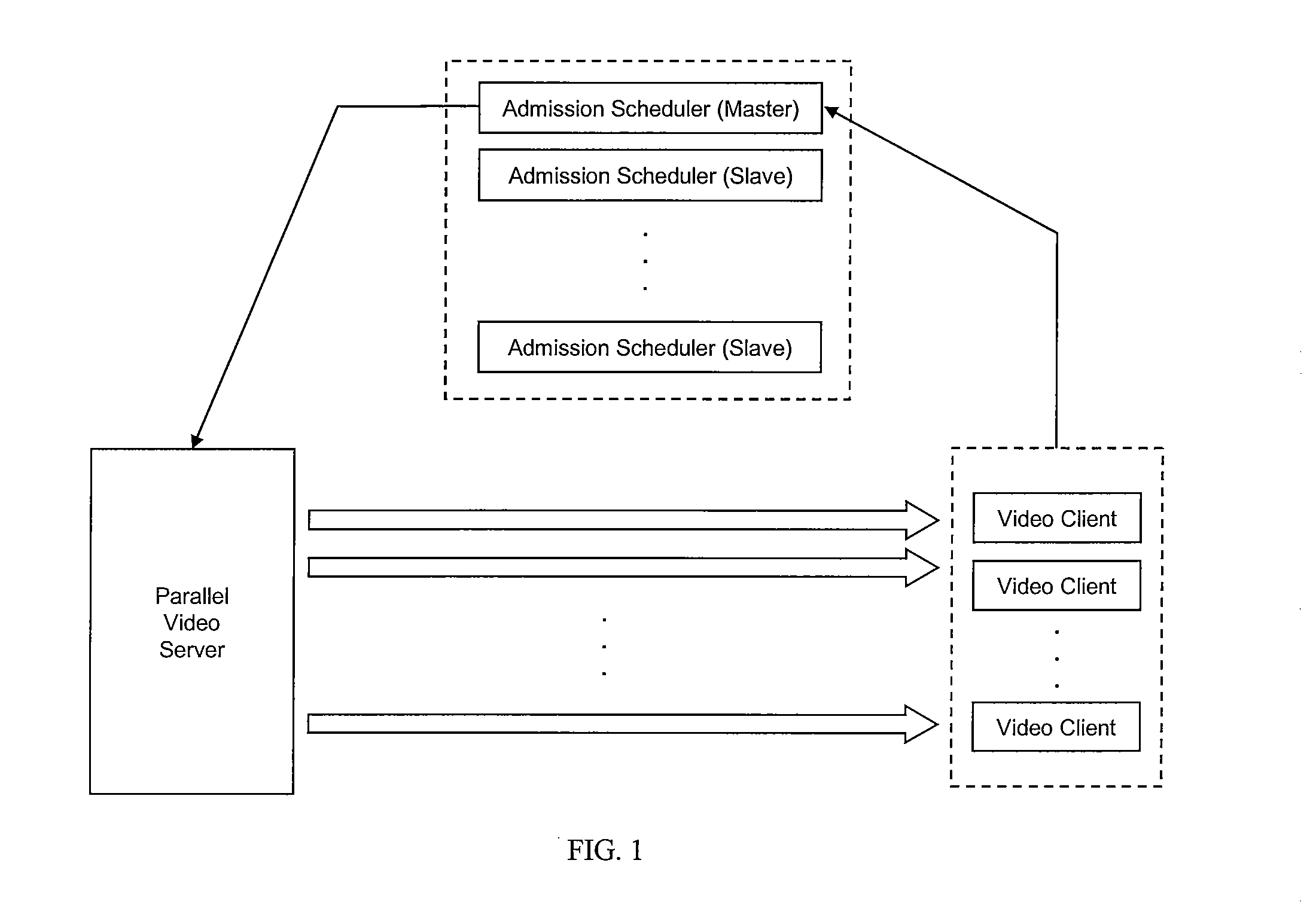
Load balancing and admission scheduling in pull-based parallel video servers
ActiveUS20090077246A1Improves video data throughputImprove data throughputMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsData packPacket loss
A pull-based parallel video server system and method of implementation useful in an on-demand video system includes a plurality of slave admission schedulers operating in parallel with a master admission scheduler to back up the master admission scheduler that controls access to an array of pull-based video servers according to a protocol that accounts for jitter and loss of packets, as well as network delays. A transport protocol is provided that improves video data throughput under such conditions. To determine the architecture and functional requirements of the redundant admission schedulers, an analytical tool in the form of a performance model has been developed that incorporates network delays, delay jitters and packet losses on the communication links between the clients, schedulers and servers.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method and system for accurate clock synchronization for communication networks
InactiveUS8023976B2Avoid overheadHigh synchronizationSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexDistributed computingClock synchronization
A high accuracy clock synchronization mechanism between a sender and a receiver in a communication network achieves time synchronization using broadcast beacons, directly at the PHY / MAC layer of the sender and the receiver, to minimize synchronization delay jitter. This provides a more efficient synchronization method than either NTP or SNTP, because multiple handshaking information exchange is avoided. Further, using beacons avoids the overhead of introducing additional synchronization packets in higher layer synchronization.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
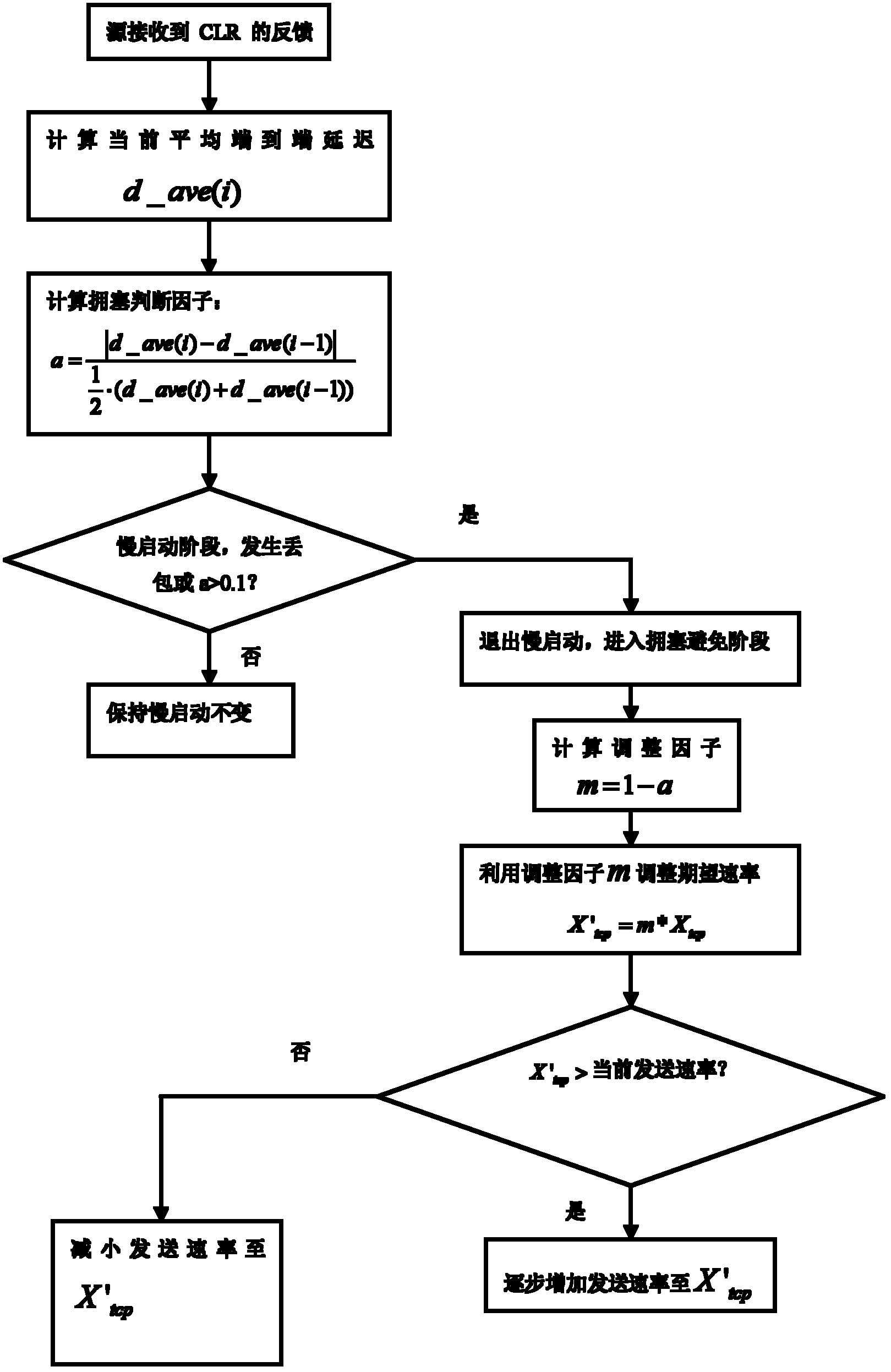
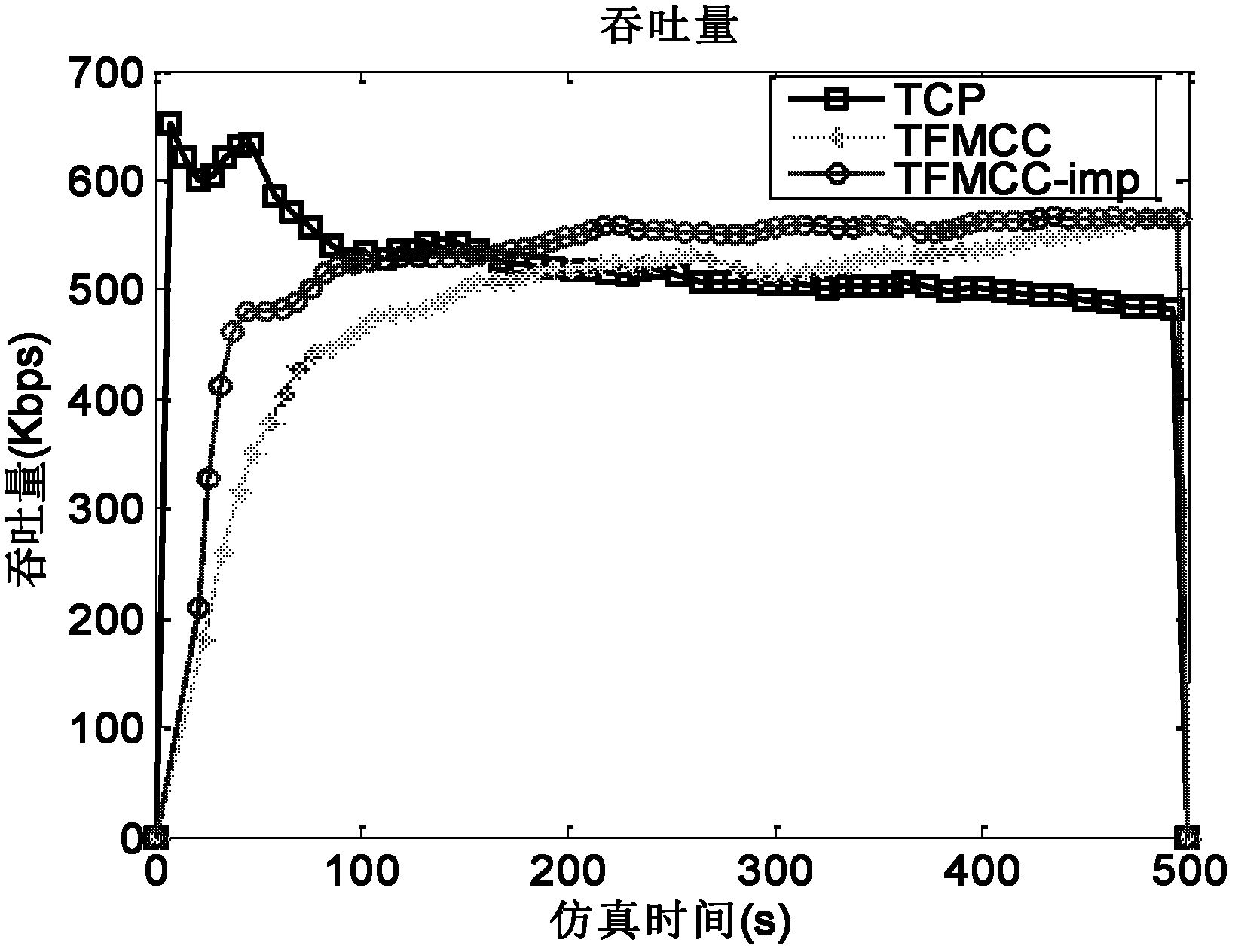
Improved-transmission control protocol-friendly multicast congestion control (TFMCC)-protocol-based communication method
The invention discloses an improved-transmission control protocol-friendly multicast congestion control (TFMCC)-protocol-based communication method, which is implemented by the following steps of: every time when a source receives a feedback data packet from a current limiting receiver (CLR), computing end-to-end one-way delay jitter between the source and the CLR according to effective timestamp information in the feedback data packet, and computing a congestion judgment factor by utilizing the delay jitter to judge congestion; and computing a correction factor by utilizing the congestion judgment factor to regulate expected throughput and further regulate a transmission rate. In the method, the transmission rate is regulated by calculating the end-to-end delay jitter between the source and the CLR as a congestion signal, and the end-to-end delay jitter of a TFMCC protocol is effectively controlled, thereby effectively reducing the jitter of the protocol, average end-to-end delay, average end-to-end delay jitter, an average packet loss rate and the like, improving the stability and overall performance of the TFMCC protocol, and making the protocol better serve a multicast protocol and more suitable for the transmission of multimedia services.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
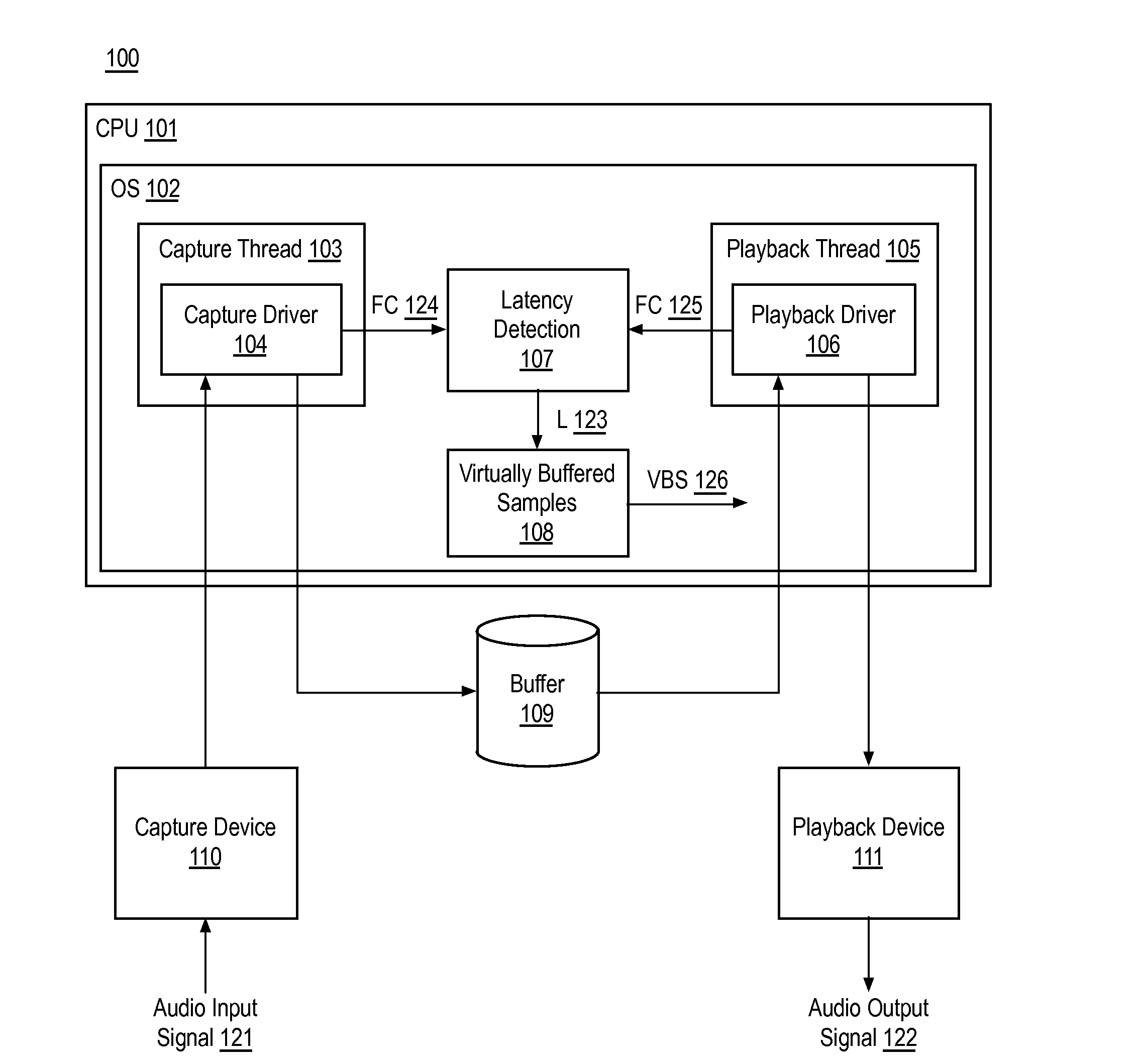
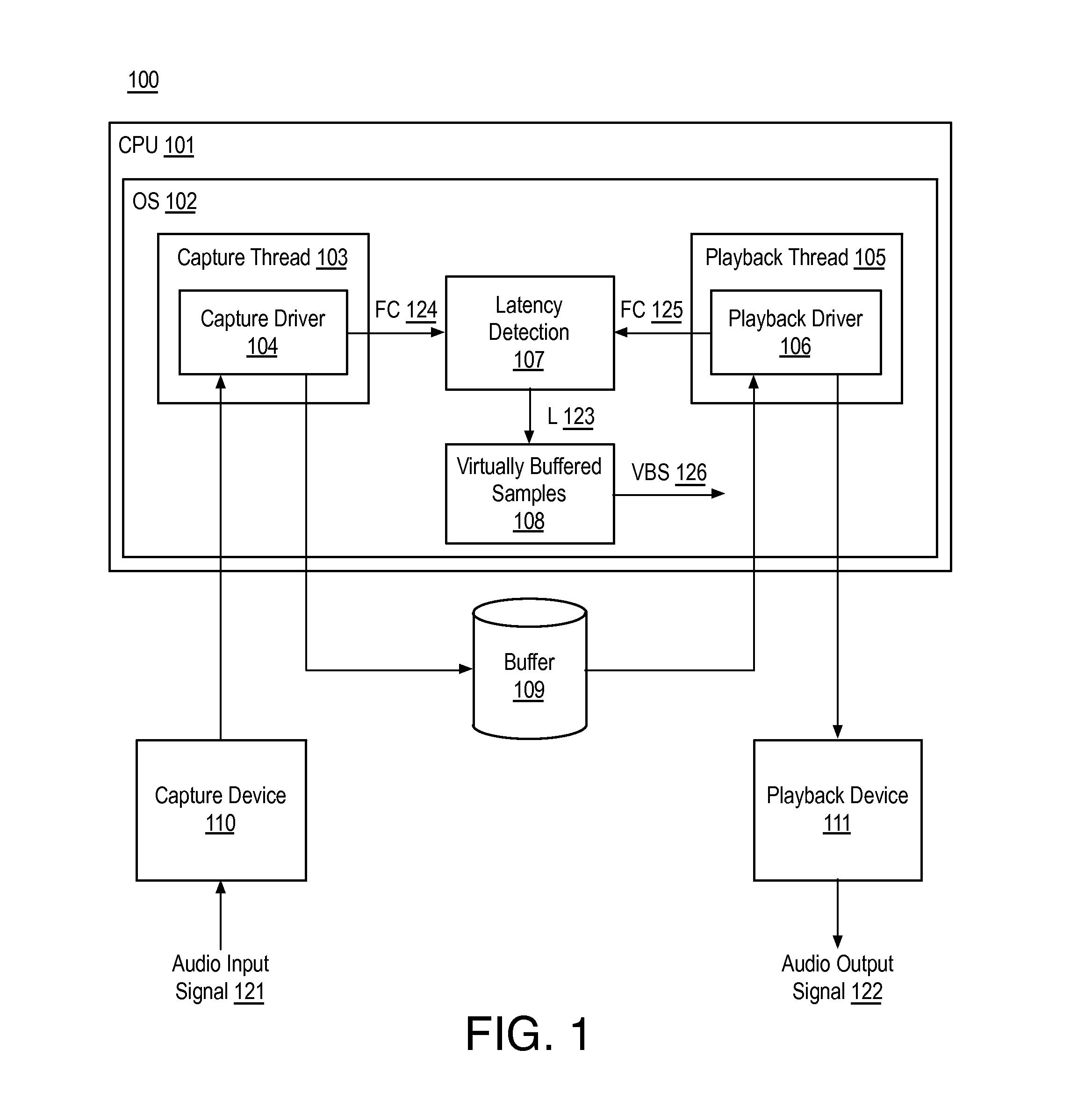
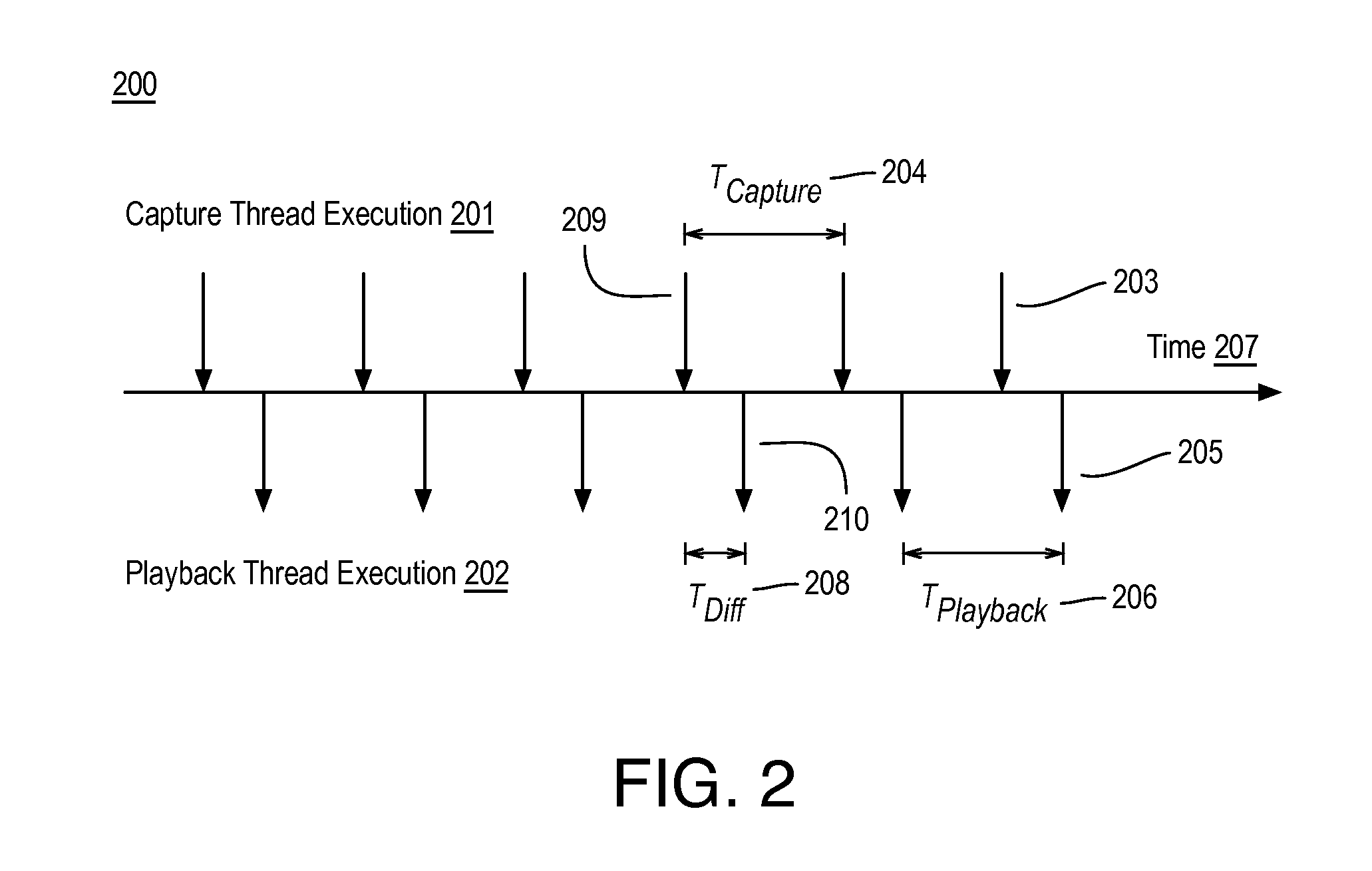
Signal synchronization and latency jitter compensation for audio transmission systems
Techniques related to input and output signal synchronization and latency jitter compensation for audio systems are discussed. Such techniques may include determining a number of virtually buffered samples based on a detected latency between an audio capture thread and an audio playback thread and synchronizing an audio input signal and an audio output signal based on the number of virtually buffered samples.
Owner:INTEL CORP
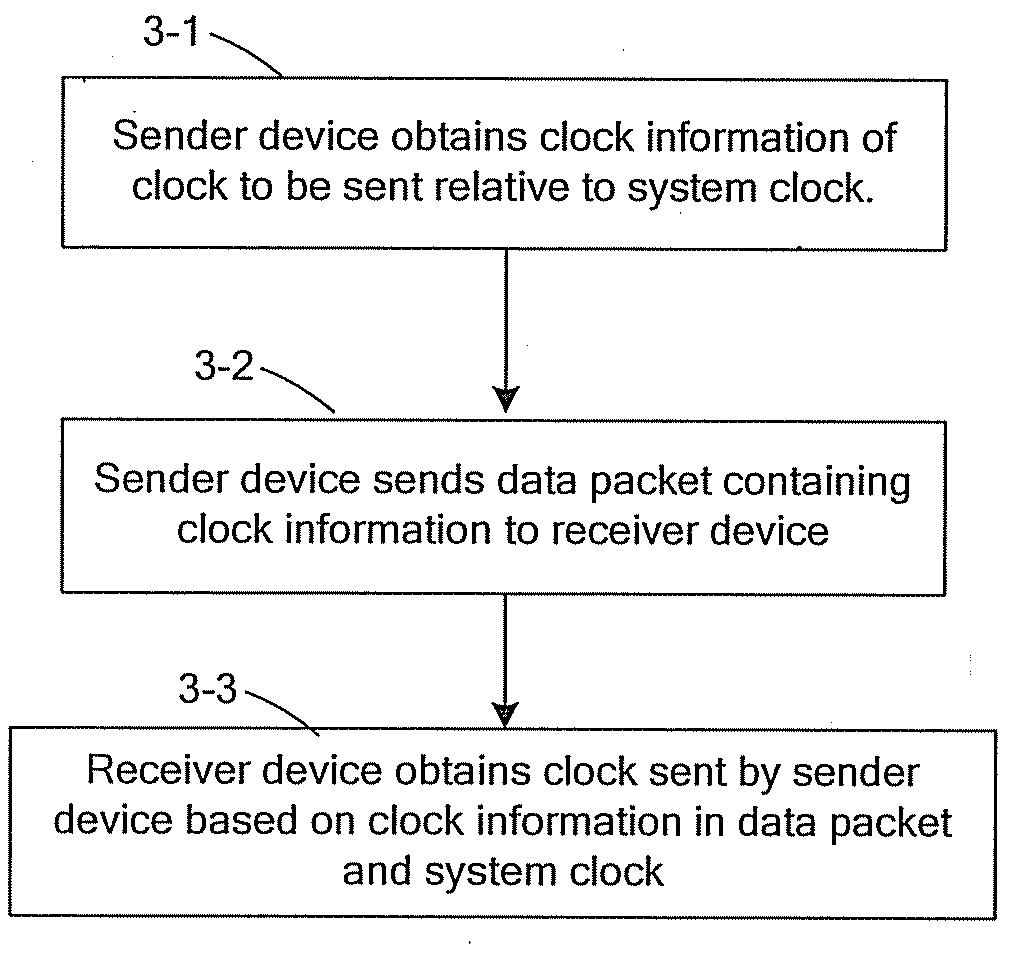
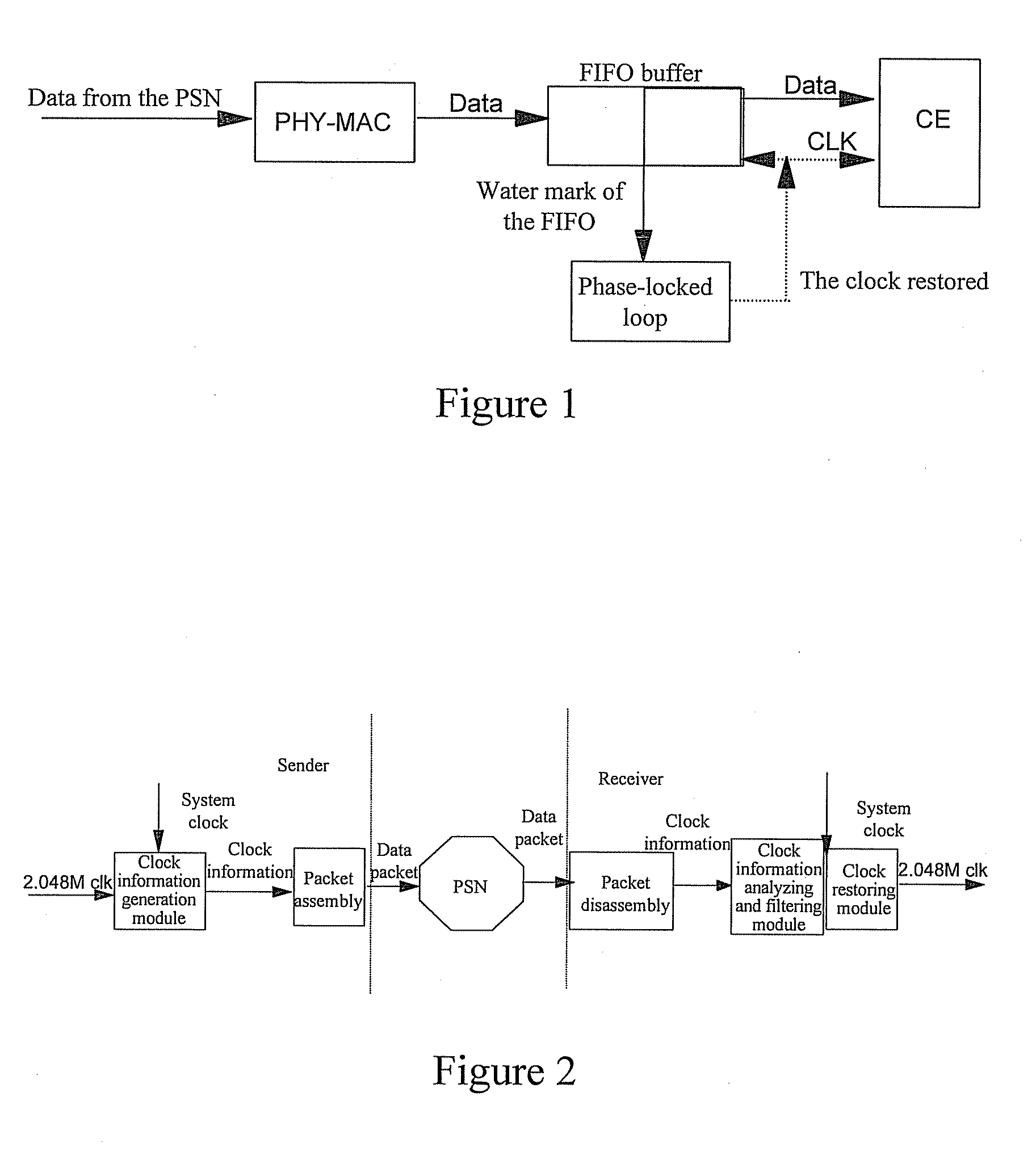
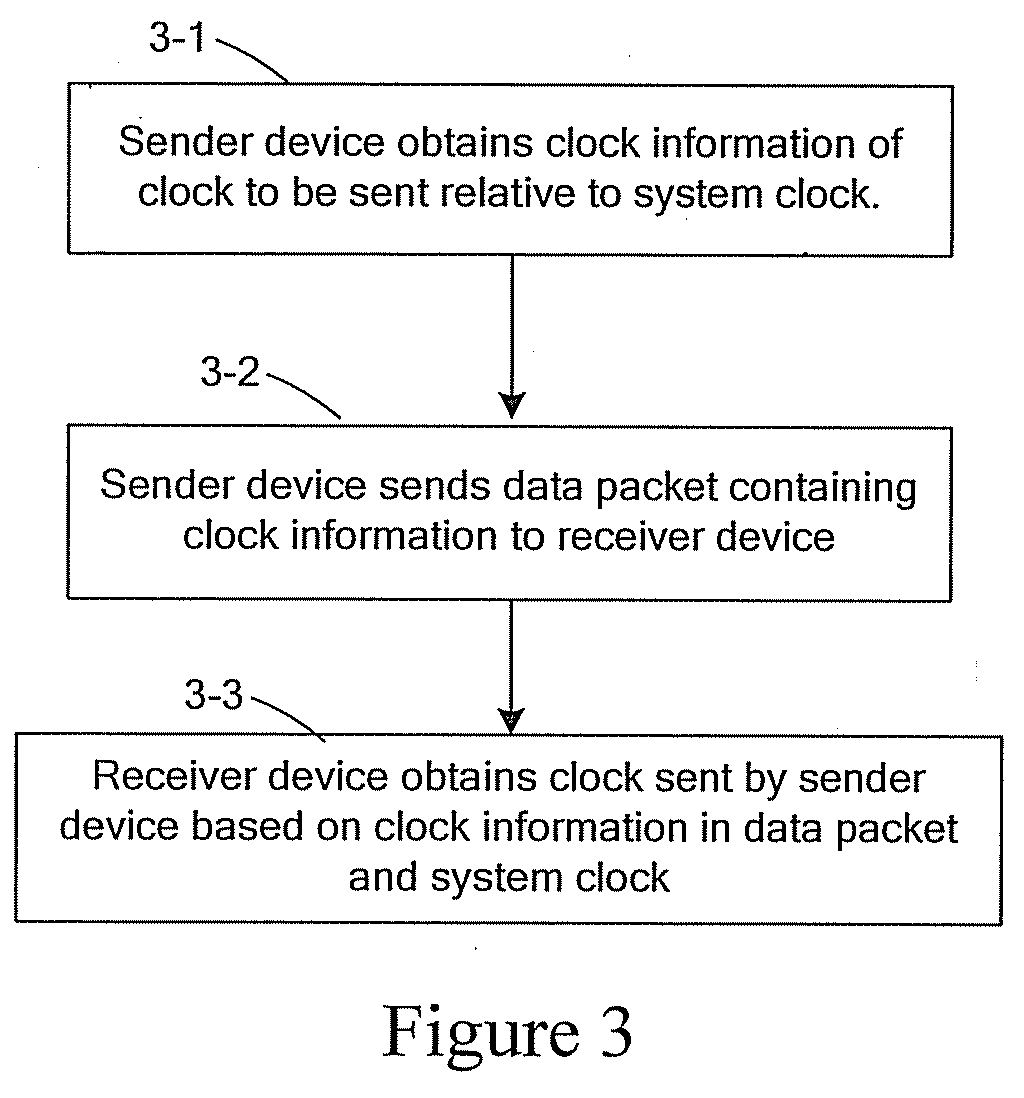
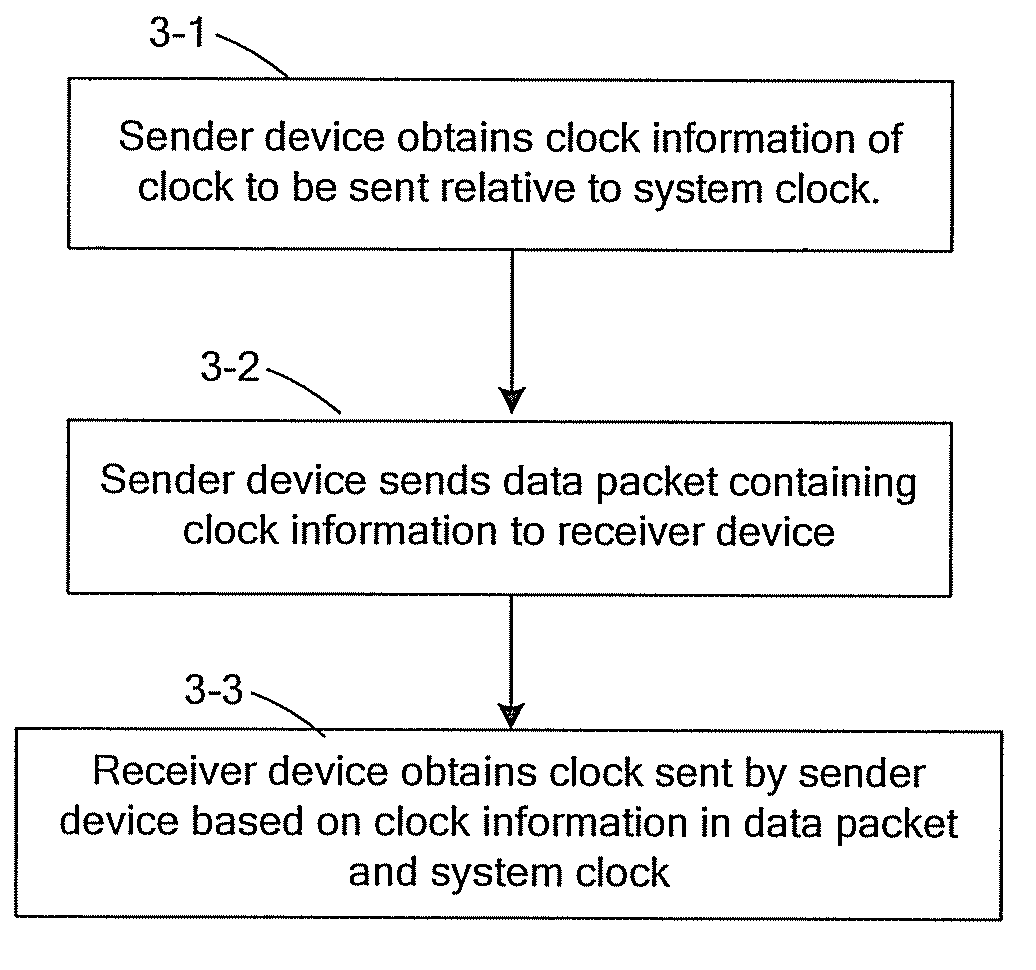
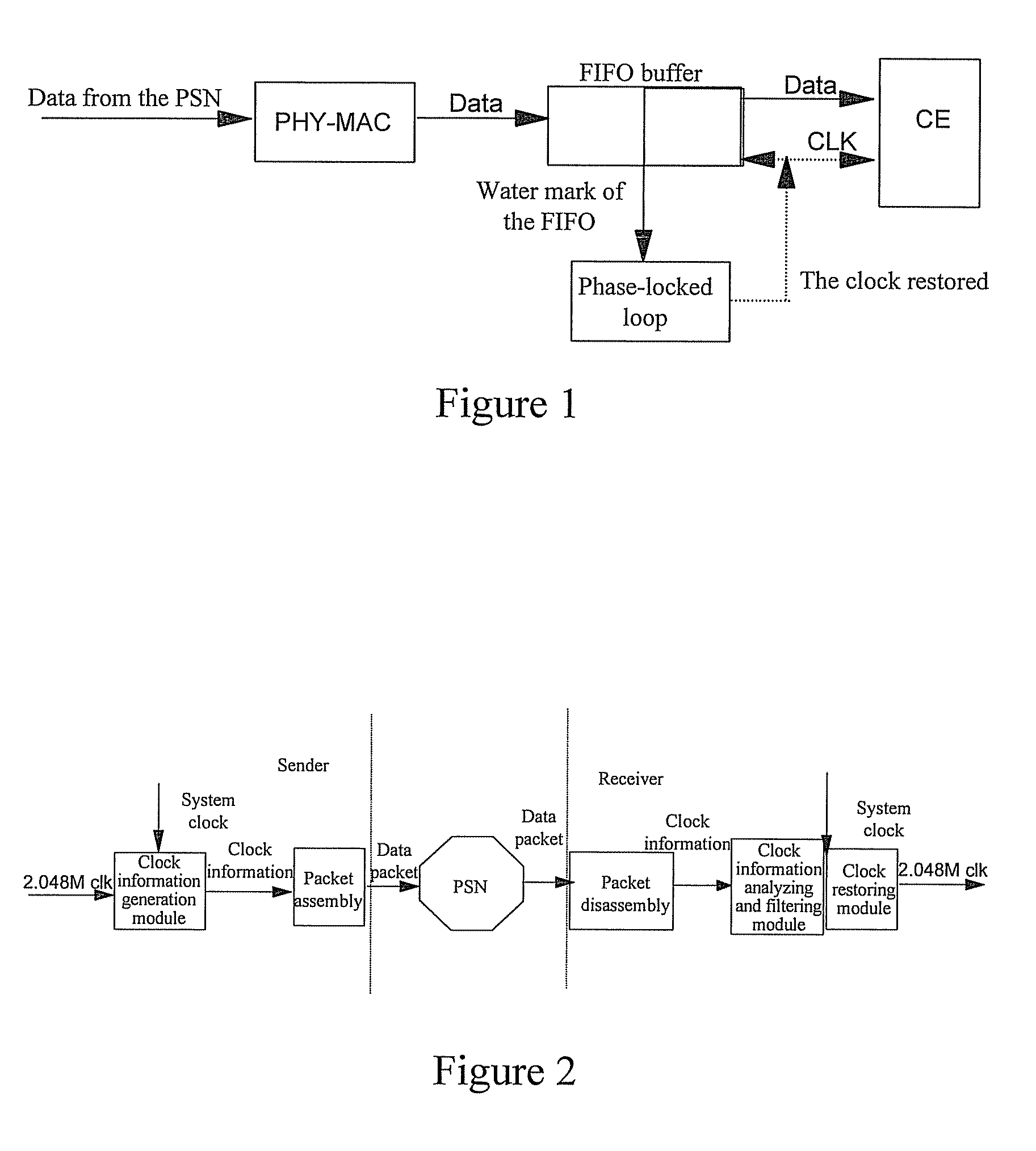
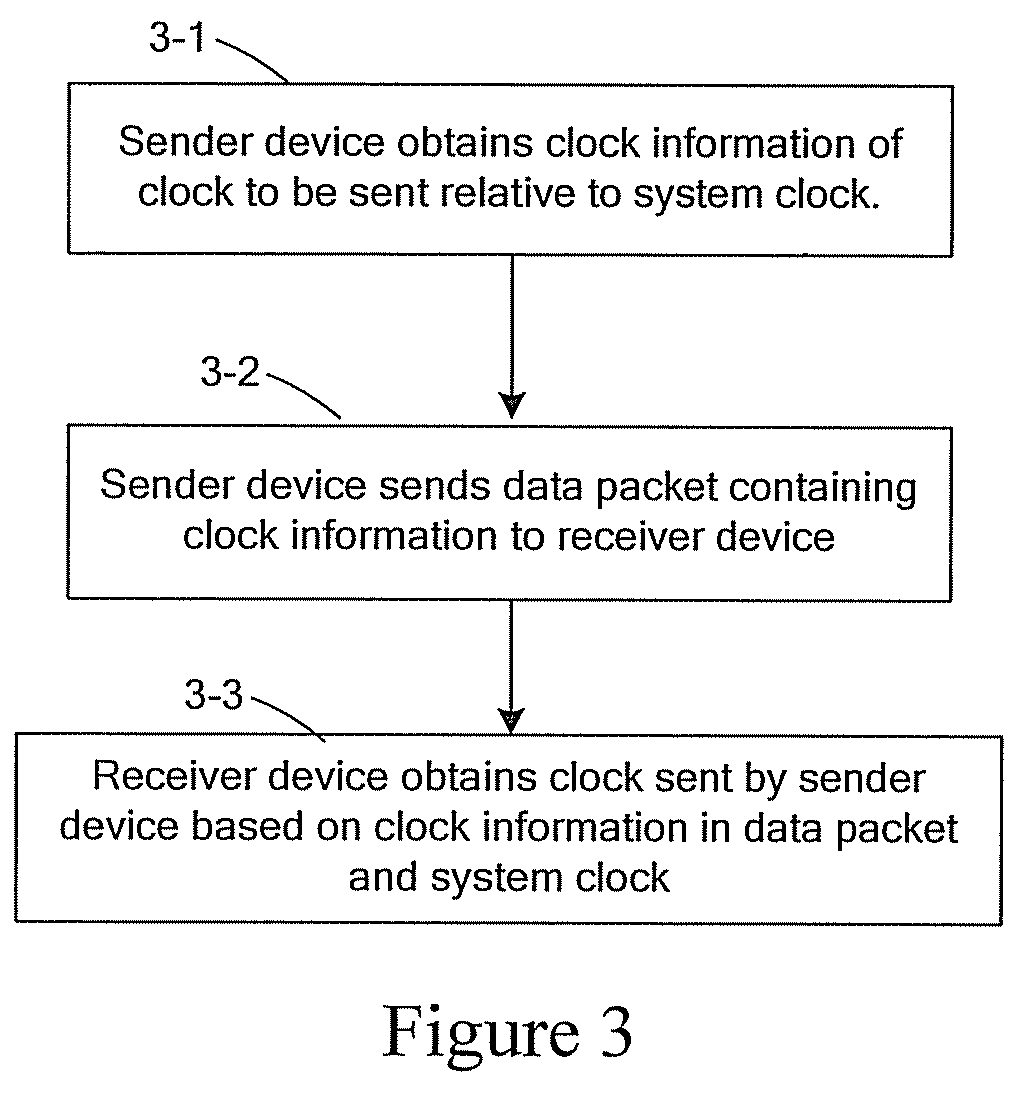
Method, system and device for clock transmission between sender and receiver
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method, system and device for clock transmission between a sender and a receiver. The sender generates clock information of a clock to be sent relative to a system clock and sends a data packet containing the clock information to the receiver over a Packet-Switched Network (PSN). The receiver obtains the clock information in the data packet received and obtains the clock sent by the sender according to the clock information and the system clock. According to the embodiments of the present invention, after the clock of the sender is transmitted over the PSN, the receiver may obtain the clock of the sender without being affected by such damage as a network delay jitter and a packet loss.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
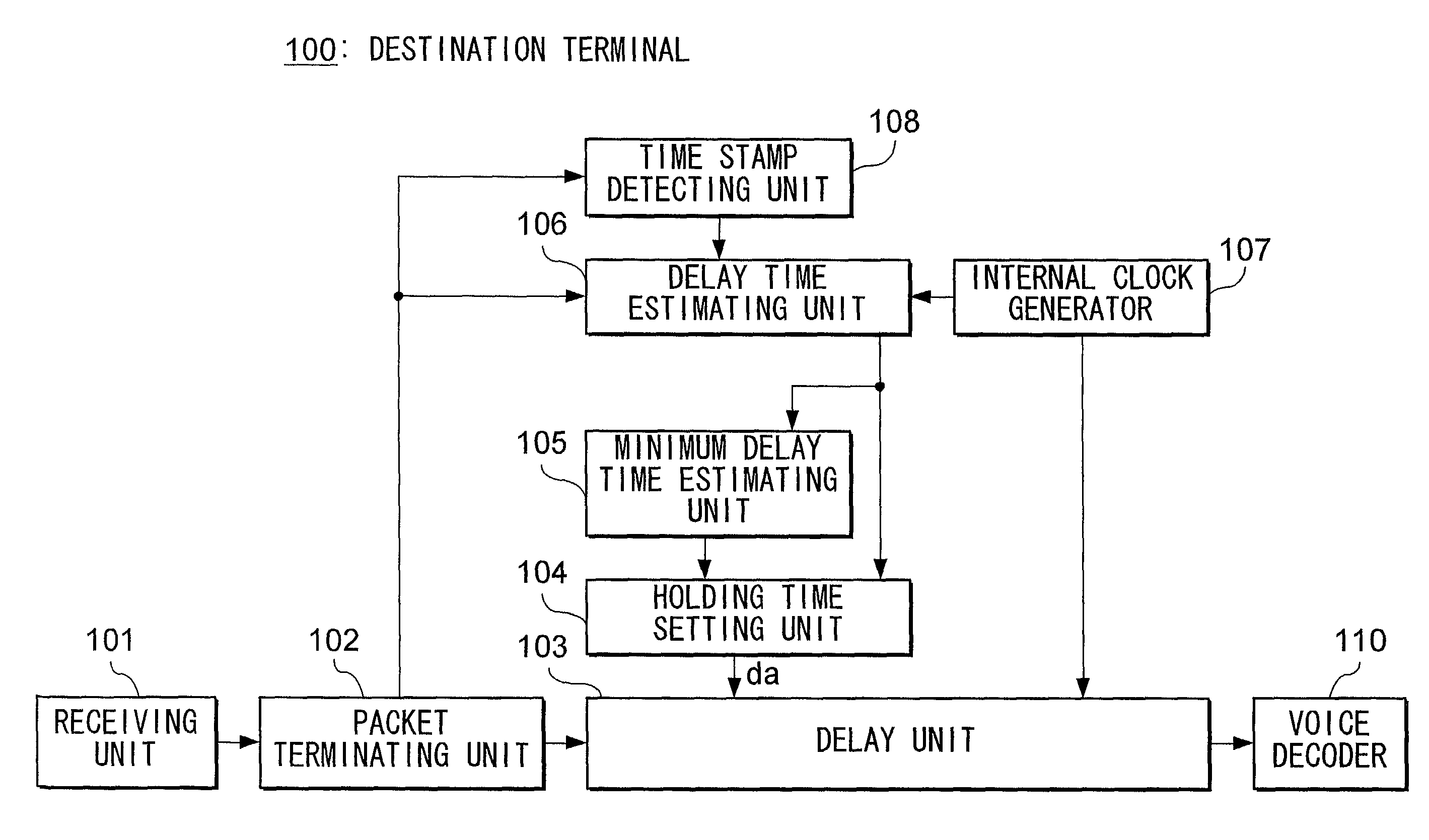
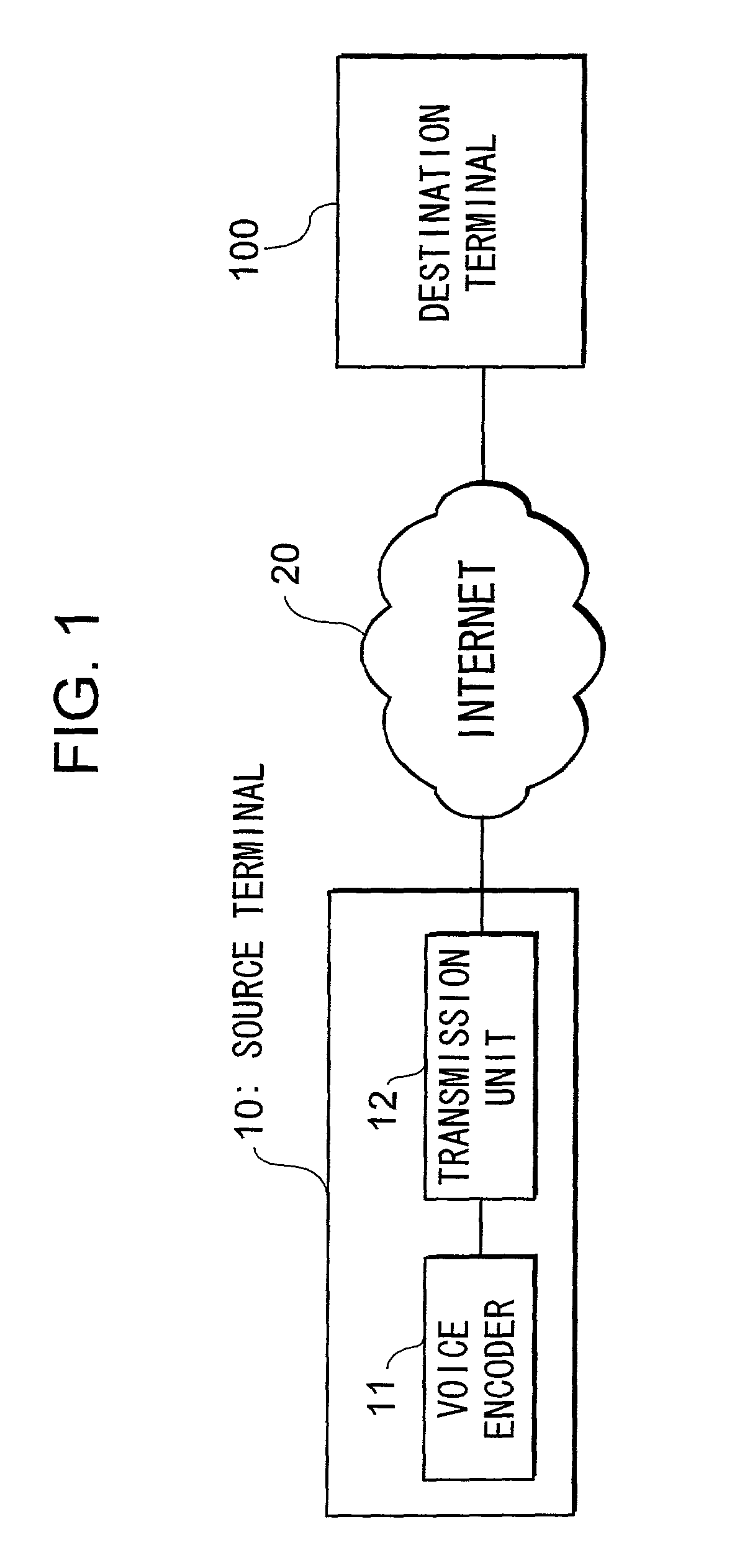
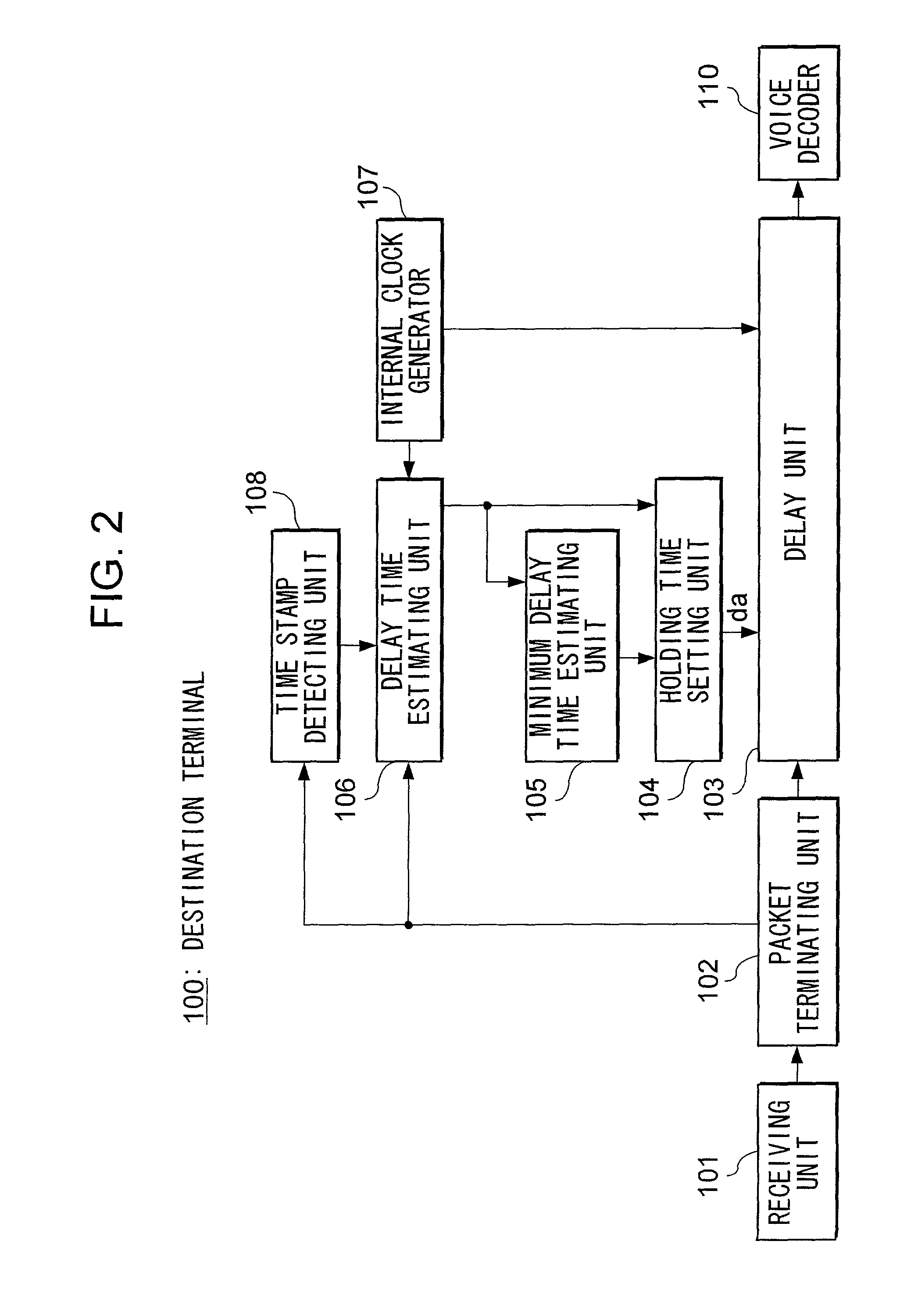
Device and method for reducing delay jitter in data transmission
InactiveUS6985501B2Reduce latencyDelay jitterError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTotal delayData transmission
A delay unit 103 adds holding time that has been set by a holding time setting unit 104 to a received data. The holding time is computed based on delay time of received data and the minimum delay time of data received up to a certain point for the purpose of reducing a total delay time. The delay time is estimated in a delay time estimating unit 106 from the difference between a reception time of a packet counted based on an internal clock generator 107 and a time designated by a time stamp in the received packet.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
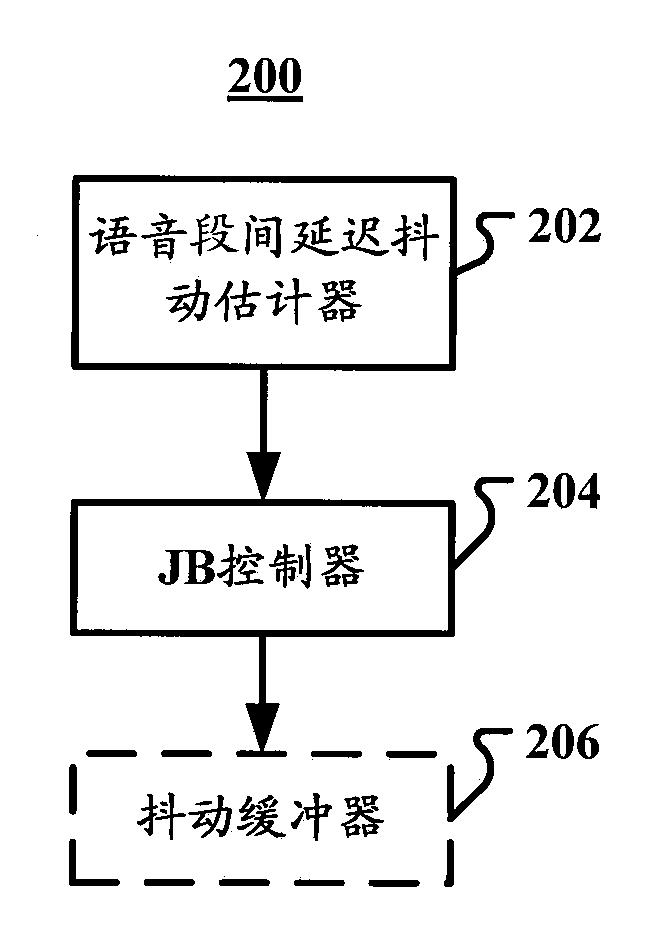
Device and method used for controlling jitter buffer
Described are a device and method used for controlling a jitter buffer. In one execution mode, the device used for controlling the jitter buffer includes an inter-voice-segment delay jitter estimator which is used for estimating an offset value of a delay of a first frame in a current voice segment relative to a delay of a last anchor frame in a prior voice segment; and a jitter butter controller which is used for adjusting the length of the jitter buffer on the basis of a long-term length of each frame of the jitter buffer and the offset value.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and system for estimating performance metrics in a packet-switched communication network
InactiveUS20050220088A1Optimize networkAccurate operationError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of servicePacket loss
Owner:VERIZON LAB
Clock synchronization method and device, computer storage medium and electronic equipment
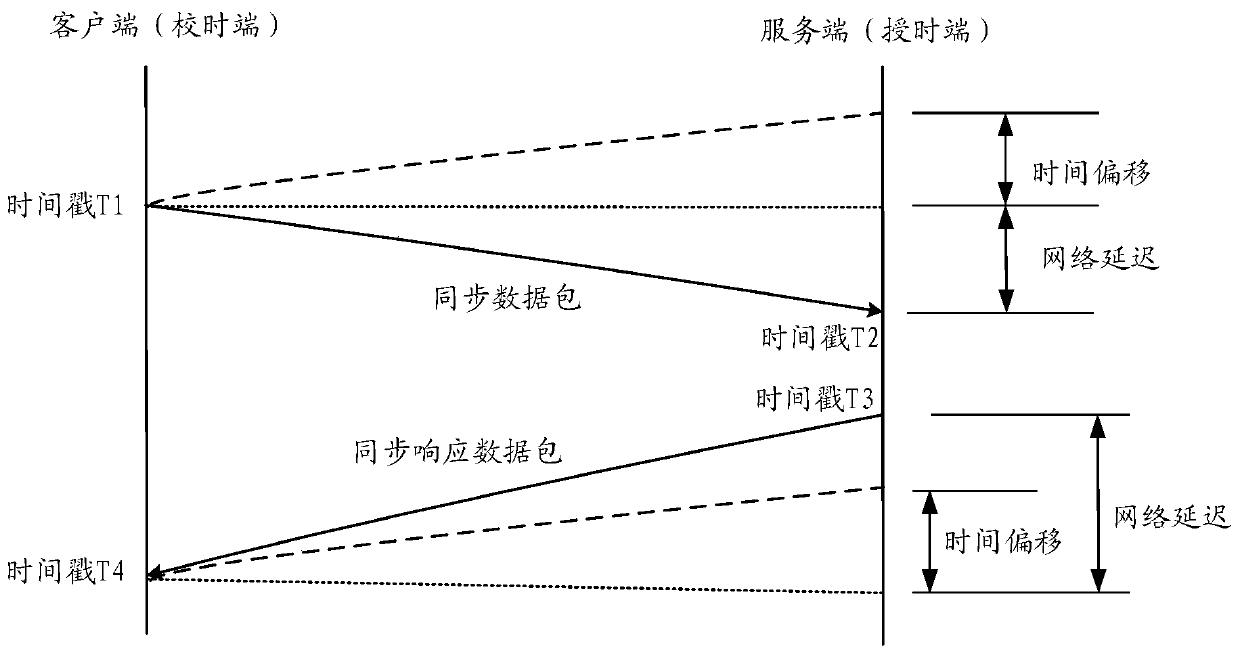
The invention discloses a clock synchronization method and device, a computer storage medium and electronic equipment, and the method comprises the steps: achieving the determination of time deviationthrough the receiving and transmitting of a time stamp of a conventional message, and judging whether to carry out the time synchronization or not according to the time deviation through network delay. Furthermore, the excessive delay jitter is judged through the network delay, so that the influence of the excessive delay jitter on the time correction of the time service end is avoided.
Owner:北京和利时系统集成有限公司
System and method for adaptive removal of delay jitter effect and low end-to-end delay
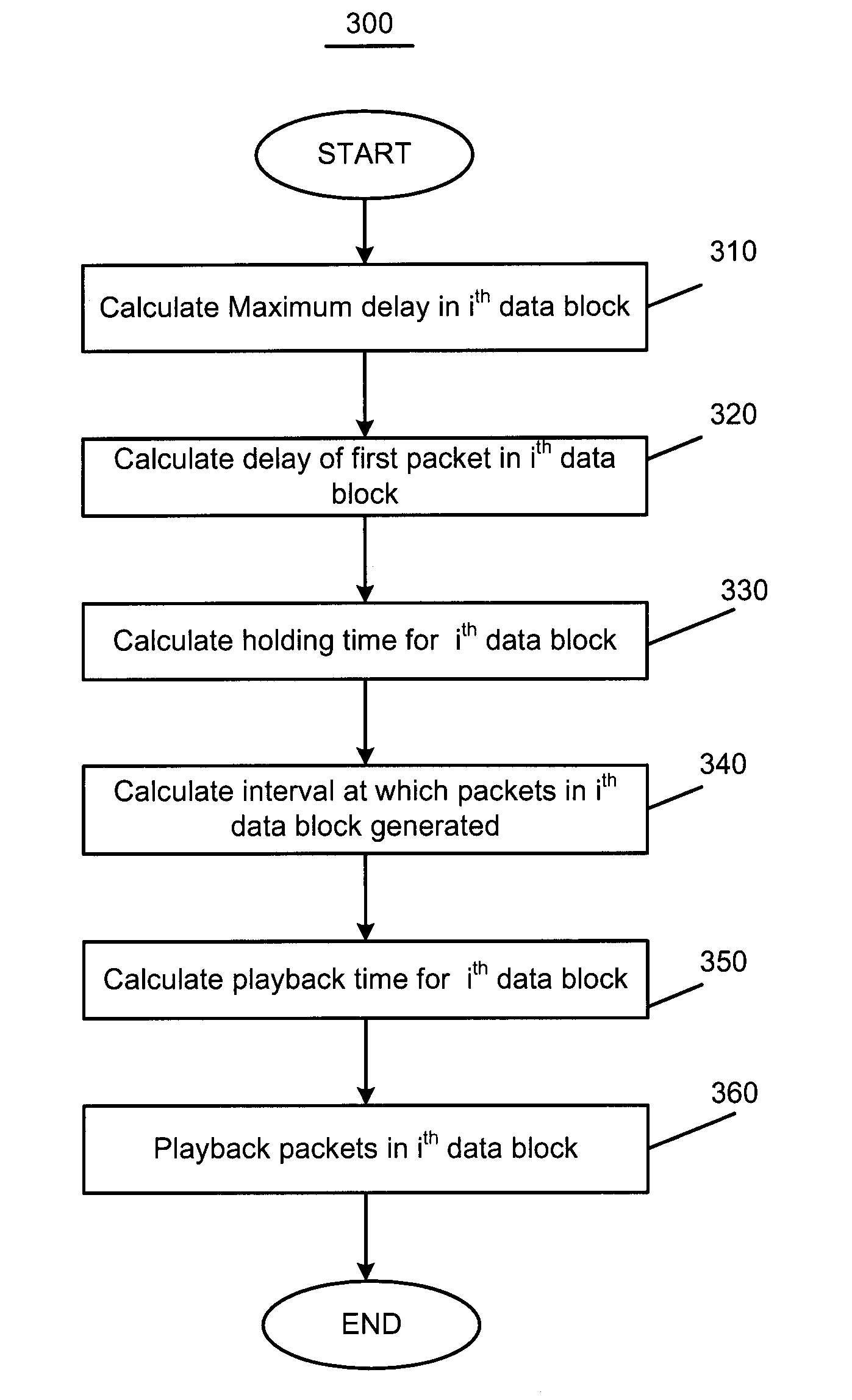
ActiveUS20110158094A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer moduleSelf adaptive
Systems, modules, methods and computer readable mediums for adaptive removal of delay jitter and low end-to-end delay are provided. The method may include the following operations at a delay buffer: calculating a holding time for a plurality of packets input into a network; buffering each of the plurality of packets for the duration of the holding time; and arranging the buffered packets in a sequence indicative of an order in which the buffered packets were input into the network. The holding time may be based on a difference between a current maximum delay of the plurality of packets in a current time window and a delay of a first packet of the plurality of packets in the current time window. The method may also include playing back the buffered packets at a selected playback time. Playing back the buffered packets may be performed at a reception mechanism.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Real time mesh measurement system stream latency and jitter measurements
A method is described for measuring system latency and latency jitter on a near real-time basis regarding packets of information moving from sources to destination. The method for measuring system latency and latency jitter includes time-stamping packets of information as they pass through a plurality of locations between the source and destination of these packets, with the time-stamping being performed by real-time clocks set to a universal standard. The time-stamped packets are analyzed to determine latency and latency jitter. The measurements of system latency and latency jitter can be performed based upon packet types so as to obtain accurate information concerning different types of business bandwidths associated with an observed network.
Owner:INFRASTRUCTURE INNOVATIONS
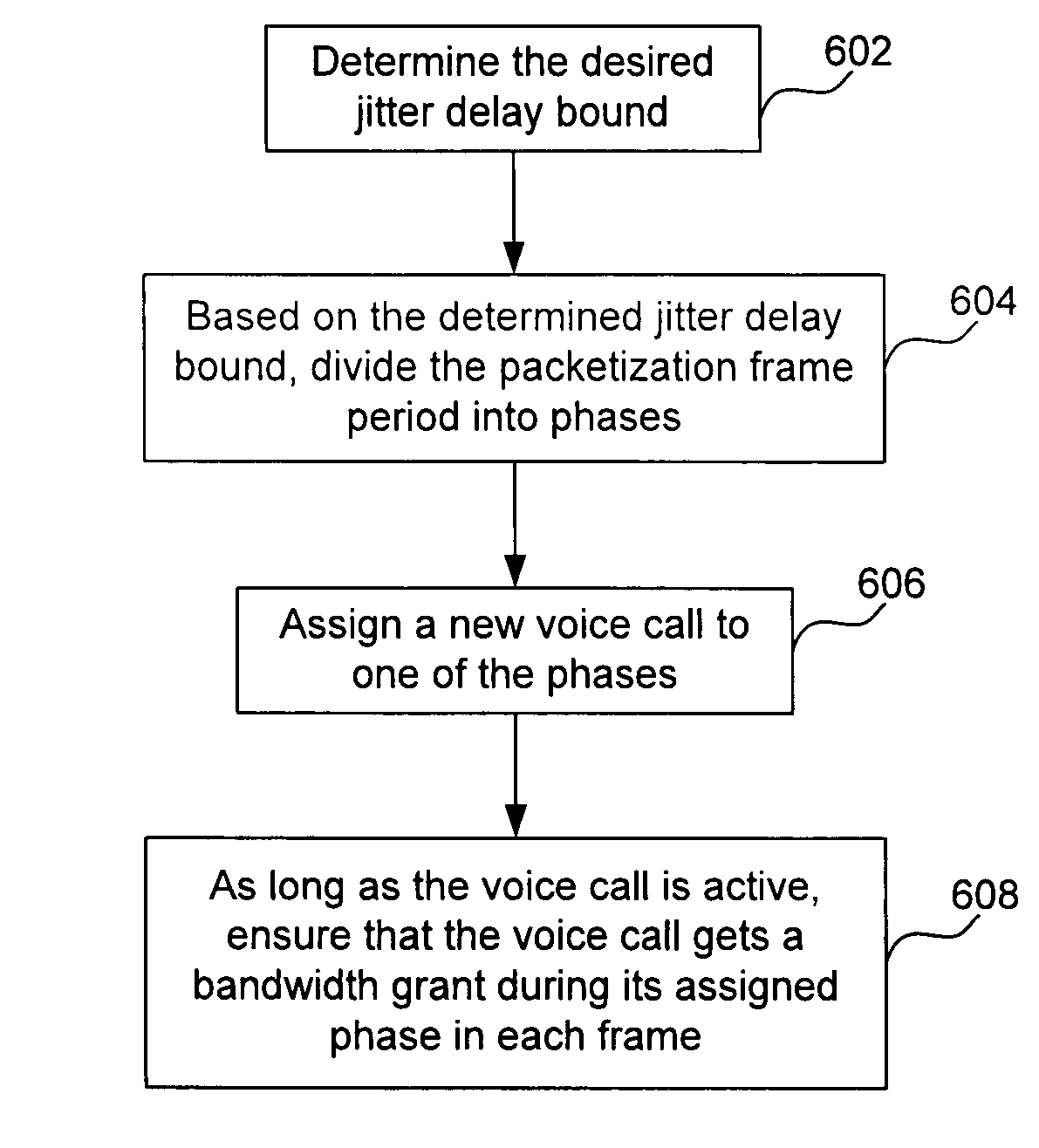
System and method for a guaranteed delay jitter bound when scheduling bandwidth grants for voice calls via cable network
InactiveUS7106744B2Improve efficiencyImprove system efficiencyError preventionTransmission systemsSpeech soundCommunications media
A system and method for guaranteeing a delay jitter bound when scheduling bandwidth grants for voice calls via a communication medium is provided. The method includes the steps of: determining the delay jitter bound; based on the determined delay jitter bound, dividing a packetization frame period into phases; assigning a voice call to one of the phases; and scheduling a bandwidth grant to the voice call during the assigned phase, thereby guaranteeing the delay jitter bound. The system includes a scheduler, where the scheduler determines the delay jitter bound, divides a packetization frame period into phases based on the determined delay jitter bound, assigns a voice call to one of the phases, and schedules a bandwidth grant to the voice call during the assigned phase, thereby guaranteeing the delay jitter bound. A dejitter buffer implements a way to provide zero jitter service, even though the packet transmission on the cable network has jitter, by delaying the packet and thus converting jitter into delay.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method for adaptive removal of delay jitter effect and low end-to-end delay
Systems, modules, methods and computer readable mediums for adaptive removal of delay jitter and low end-to-end delay are provided. The method may include the following operations at a delay buffer: calculating a holding time for a plurality of packets input into a network; buffering each of the plurality of packets for the duration of the holding time; and arranging the buffered packets in a sequence indicative of an order in which the buffered packets were input into the network. The holding time may be based on a difference between a current maximum delay of the plurality of packets in a current time window and a delay of a first packet of the plurality of packets in the current time window. The method may also include playing back the buffered packets at a selected playback time. Playing back the buffered packets may be performed at a reception mechanism.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Sampling value synchronization interpolation algorithm with data delay jitter or loss compatible
The invention relates to a sampling value synchronization interpolation algorithm with data delay jitter or loss compatible. The sampling value synchronization interpolation algorithm is applied to a protecting, measuring and controlling system which comprises a sampling unit, a merging unit and a function unit. The sampling value synchronization interpolation algorithm can be applied to two scenes: (1) when the merging unit receives a sampling value sent from the sampling unit and the sampling value is initially integrated, the merging unit conducts primary interpolation replenishing and primary interpolation calculating on the sampling value, and the sampling value after being initially integrated is established; (2) when the function unit receives the sampling value sent from the merging unit after initial integration and the sampling value is integrated once again, the function unit conducts secondary interpolation replenishing and secondary interpolation calculating on the sampling value, and the sampling value after being integrated once again is established. According to the sampling value synchronization interpolation algorithm, the fact that the sampling unit and the merging unit, and the merging unit and the function unit choose sampling points according to needs in the protecting, measuring and controlling system can be achieved, when data delay jitter or loss occurs, supplement and calibration can be used, and high efficiency and flexibility are achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU POWER SUPPLY OF JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER +3
Method and receiver for determining a jitter buffer level
ActiveUS7733893B2Suitable buffer levelMinimize cost functionTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPacket lossNetwork conditions
The invention relates to a method and a receiver having control logic means for determining a target packet level of a jitter buffer adapted to receive packets with digitized signal samples, which packets are subject to delay jitter, from a packet data network. According to the invention, the jitter buffer is made adaptive to current network conditions, i.e., the nature and magnitude of the jitter observed by the receiver, by collecting statistical measures that describe these conditions. The target buffer level is determined with regard to the effect of packet losses in terms of duration of the discontinued playback of the true signal. This effect is derived from statistical measures of the network conditions as perceived by the receiving side and as reflected by a probability mass function which is continuously updated with packet inter-arrival times. The target buffer level is the result of minimization of a cost function which weights the internal buffer delay and an expected length of buffer underflow.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method, system and device for clock transmission between sender and receiver
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method, system and device for clock transmission between a sender and a receiver. The sender generates clock information of a clock to be sent relative to a system clock and sends a data packet containing the clock information to the receiver over a Packet-Switched Network (PSN). The receiver obtains the clock information in the data packet received and obtains the clock sent by the sender according to the clock information and the system clock. According to the embodiments of the present invention, after the clock of the sender is transmitted over the PSN, the receiver may obtain the clock of the sender without being affected by such damage as a network delay jitter and a packet loss.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
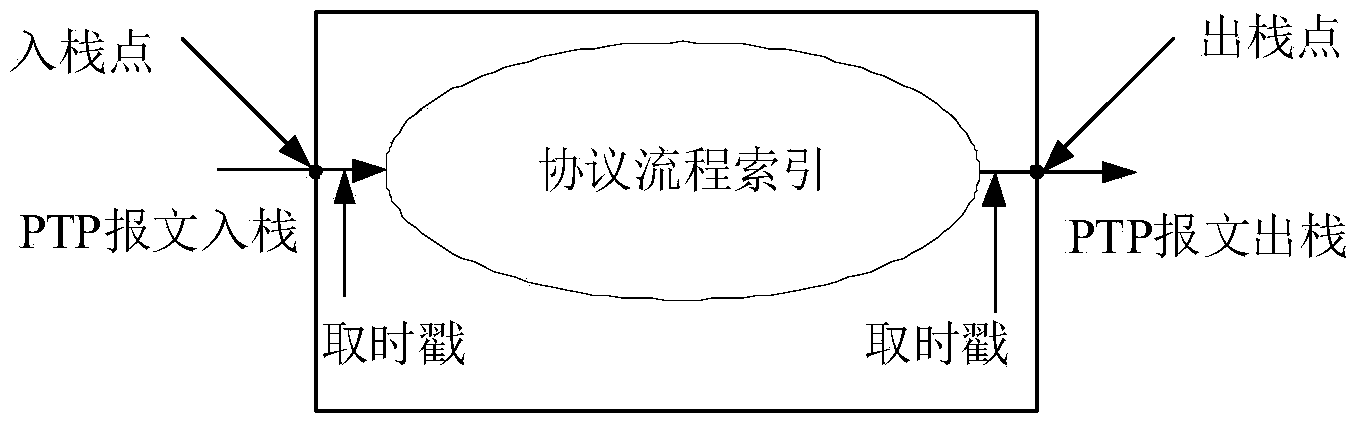
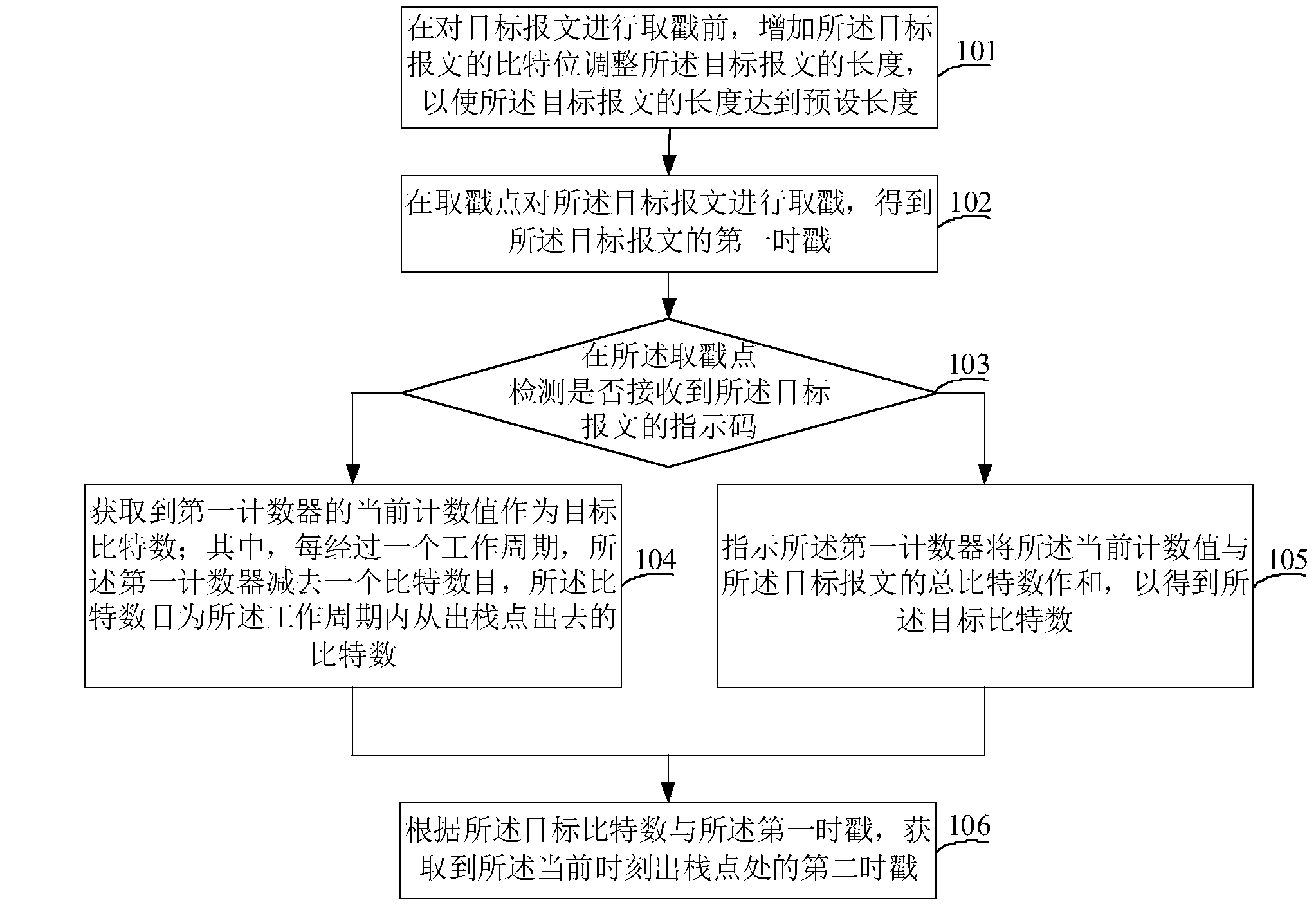
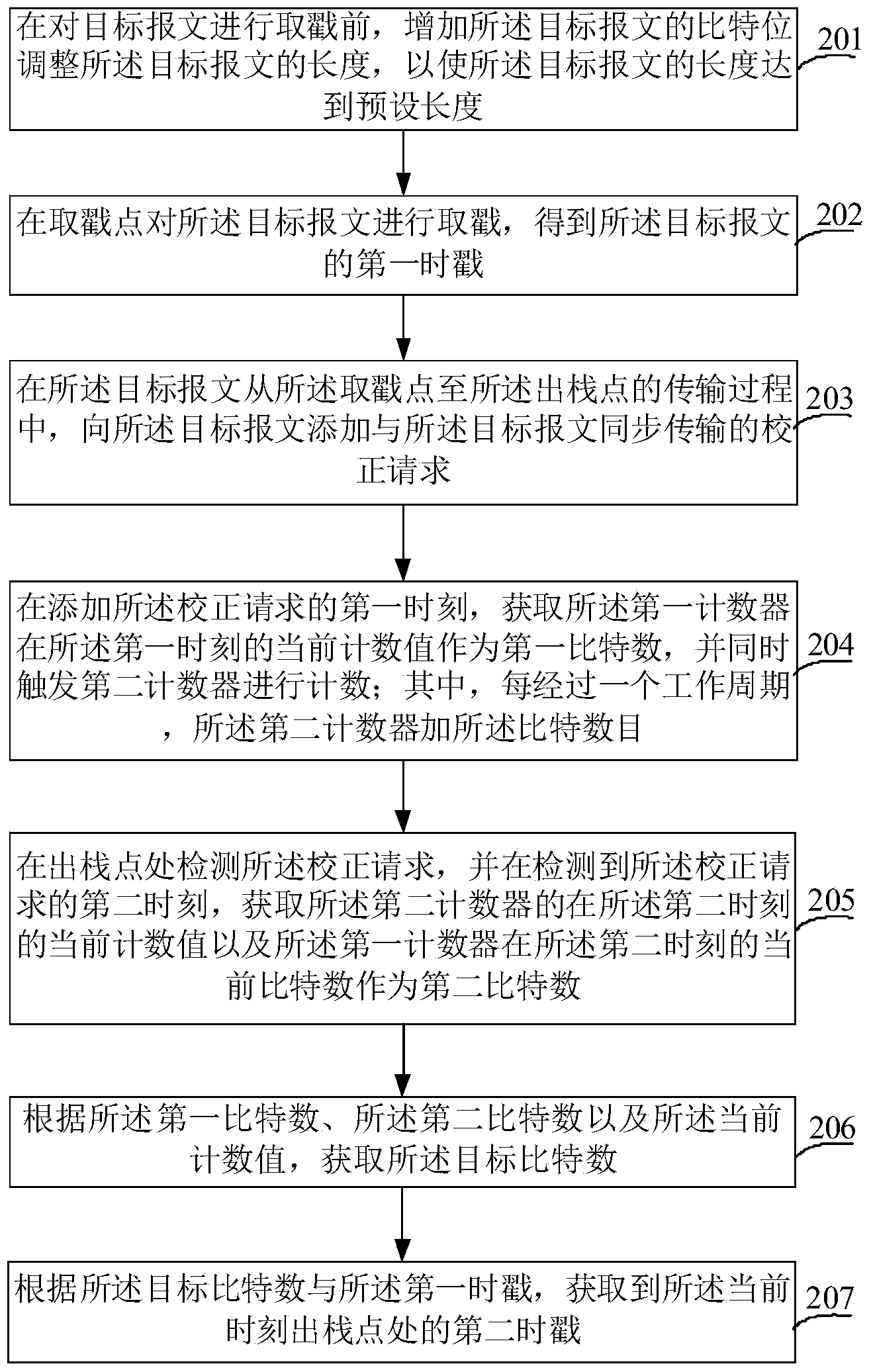
Method and apparatus for delay jitter elimination during message transmission process
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and apparatus for delay jitter elimination during a message transmission process. The method comprises the following steps that: before stamp taking is carried out on a target message, the bit of the target message is increased and the length of the target message is adjusted , so that the length of the target message reaches a preset one; stamp taking is carried out on the target message at a stamp taking point so as to obtain a first timestamp of the target message; whether an indication code of the target message is received is detected at the stamp taking point; if no indication code is detected, a current counting value of a first counter is obtained and is used as a target bit number, wherein a bit number is subtracted from the first counter after one work cycle each time and is also one going out of a stack outgoing point in the work cycle; and according to the target bit number and the first timestamp, a second timestamp at the stack outgoing point at current moment is obtained. According to the invention, the length of the target message is adjusted before stamp taking and the to-be-transmitted bit number in a protocol stack is measured by the counter, thereby realizing delay jitter correction and eliminating the delay jitter during the transmission.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
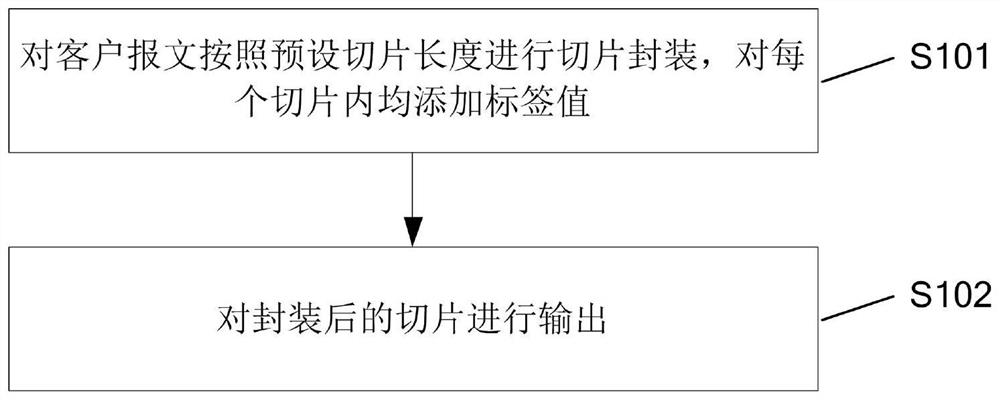
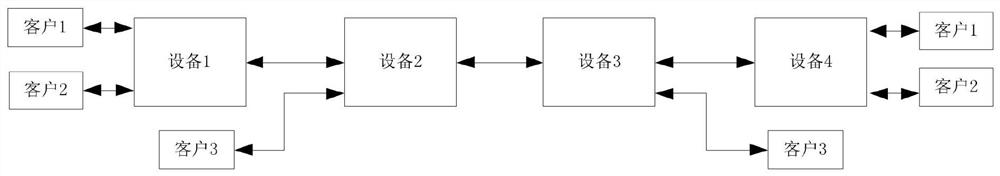
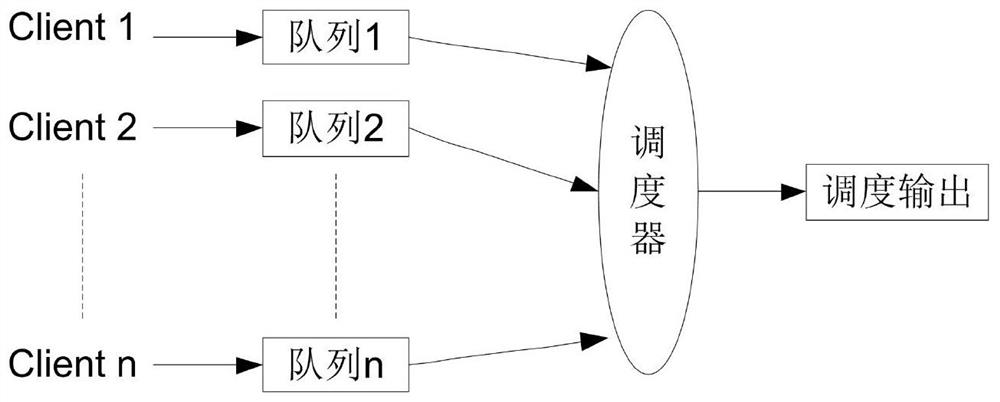
Message processing method and related device
PendingCN112217733AAchieving Deterministic Latency OutputAvoid delay jitter problemsAdaptation strategy characterisationData switching networksEngineeringMessage processing
The invention discloses a message processing method and a related device, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the slicing and packaging of a client message according to a preset slicing length, enabling the lengths of all slices to be equal, enabling the lengths of slices waiting for scheduling in all queues to be the same, and enabling the scheduling time of each slice to be equal; therefore, the phenomenon of preempting scheduling resources between the slices is avoided, congestion is also avoided, deterministic delay output of the message is realized, and the problem of delay jitter caused by uncertain message processing delay time due to different lengths of the message is avoided.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com