Patents
Literature
1314 results about "Admission control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Admission control is a validation process in communication systems where a check is performed before a connection is established to see if current resources are sufficient for the proposed connection.
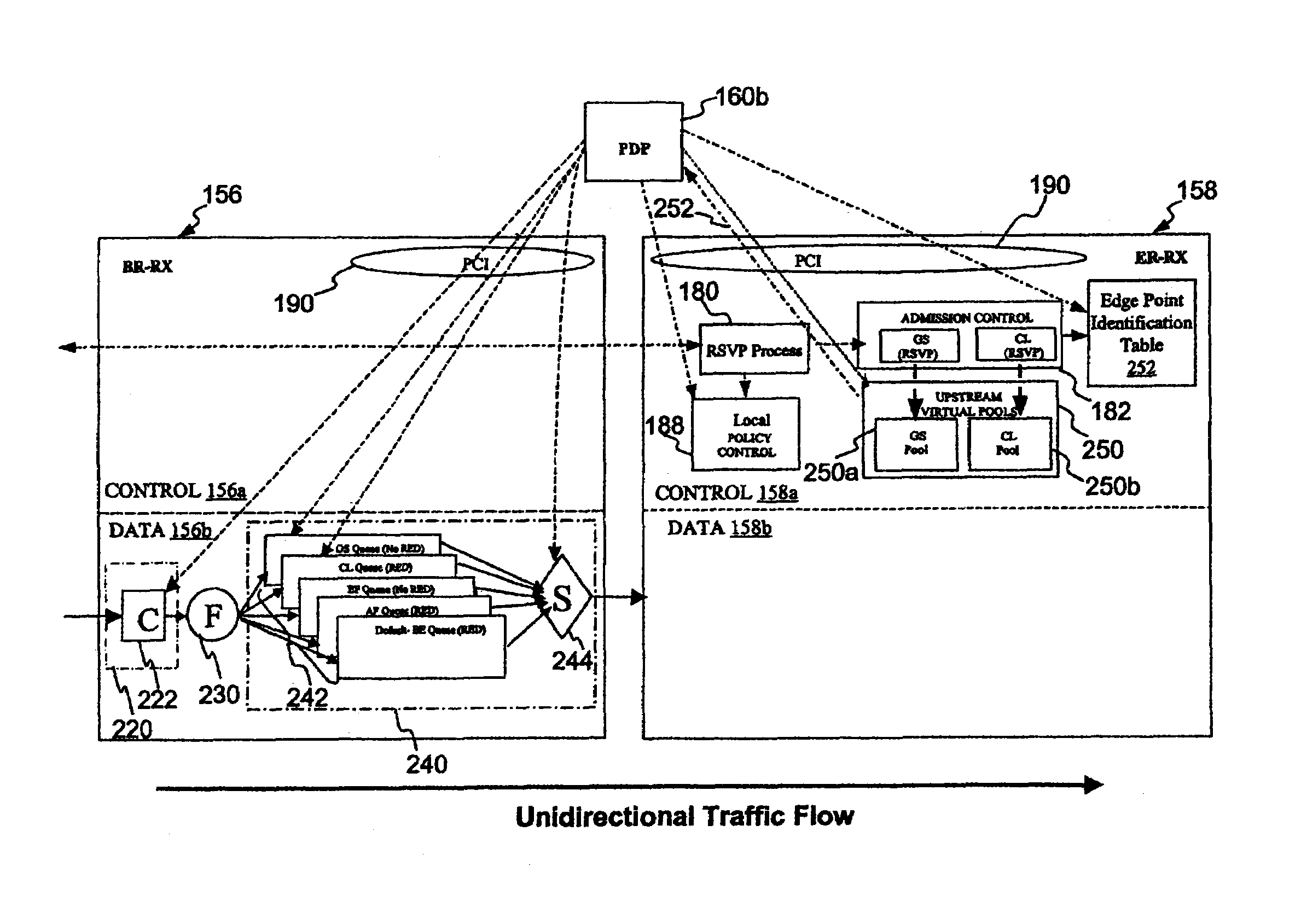
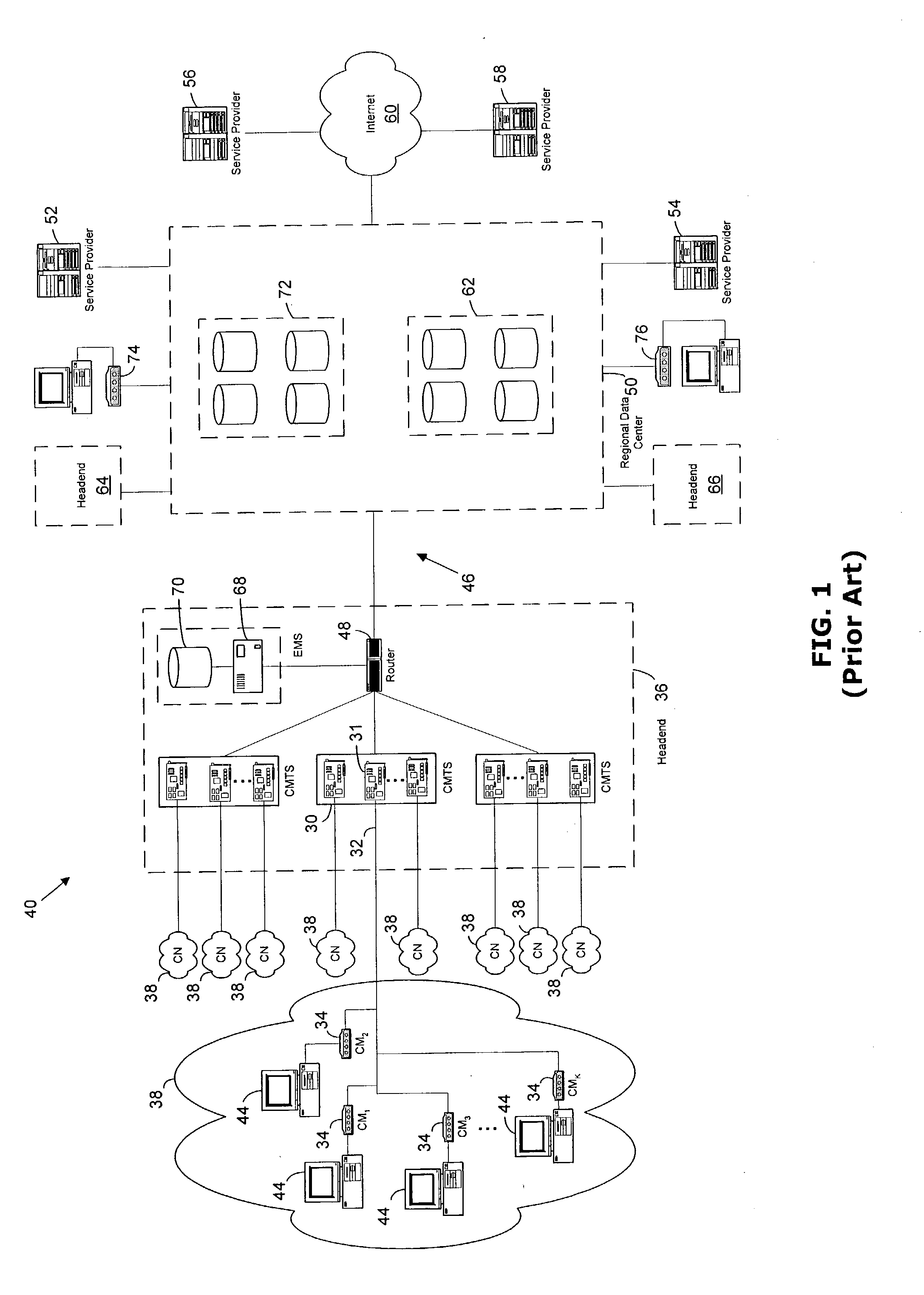
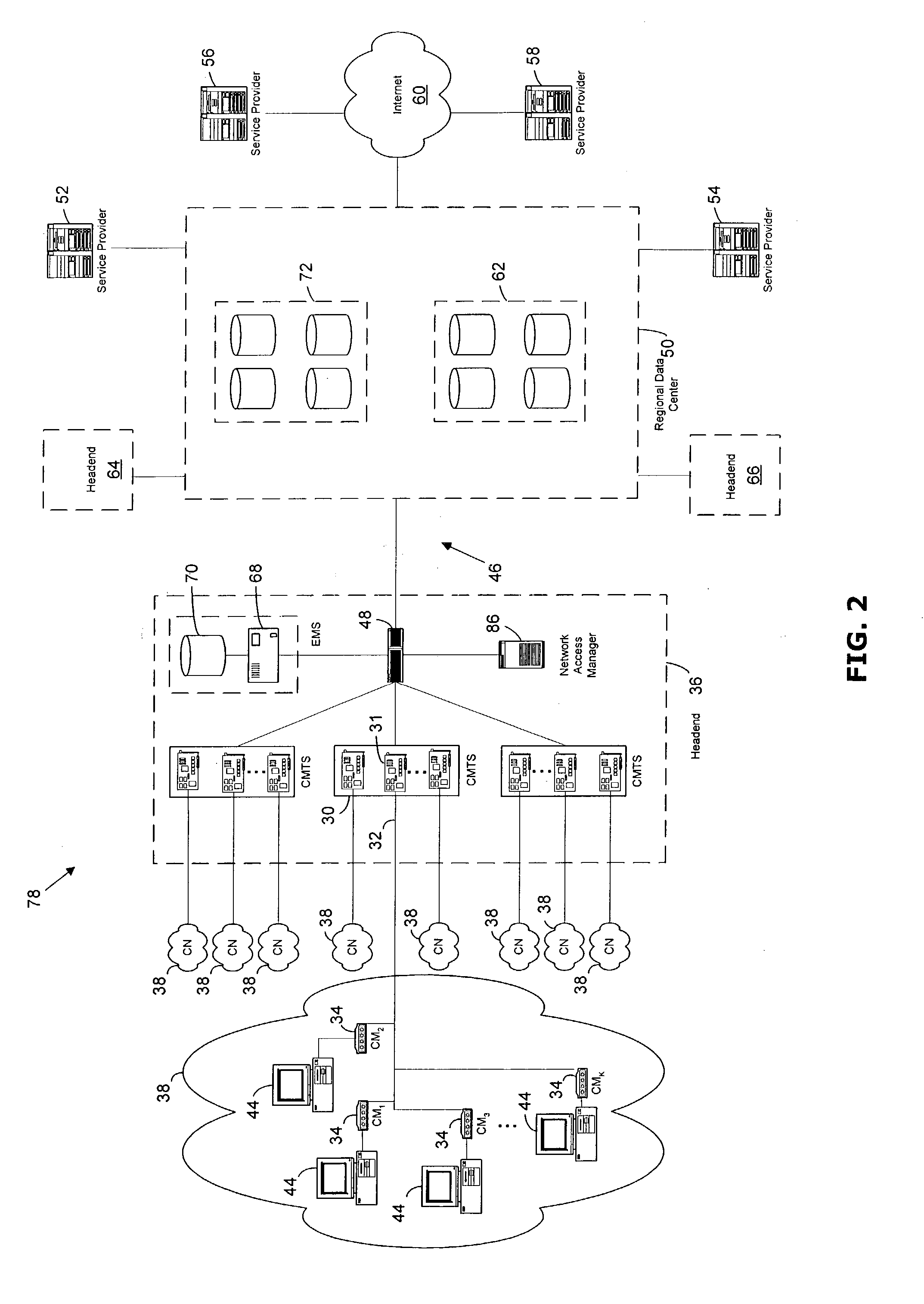
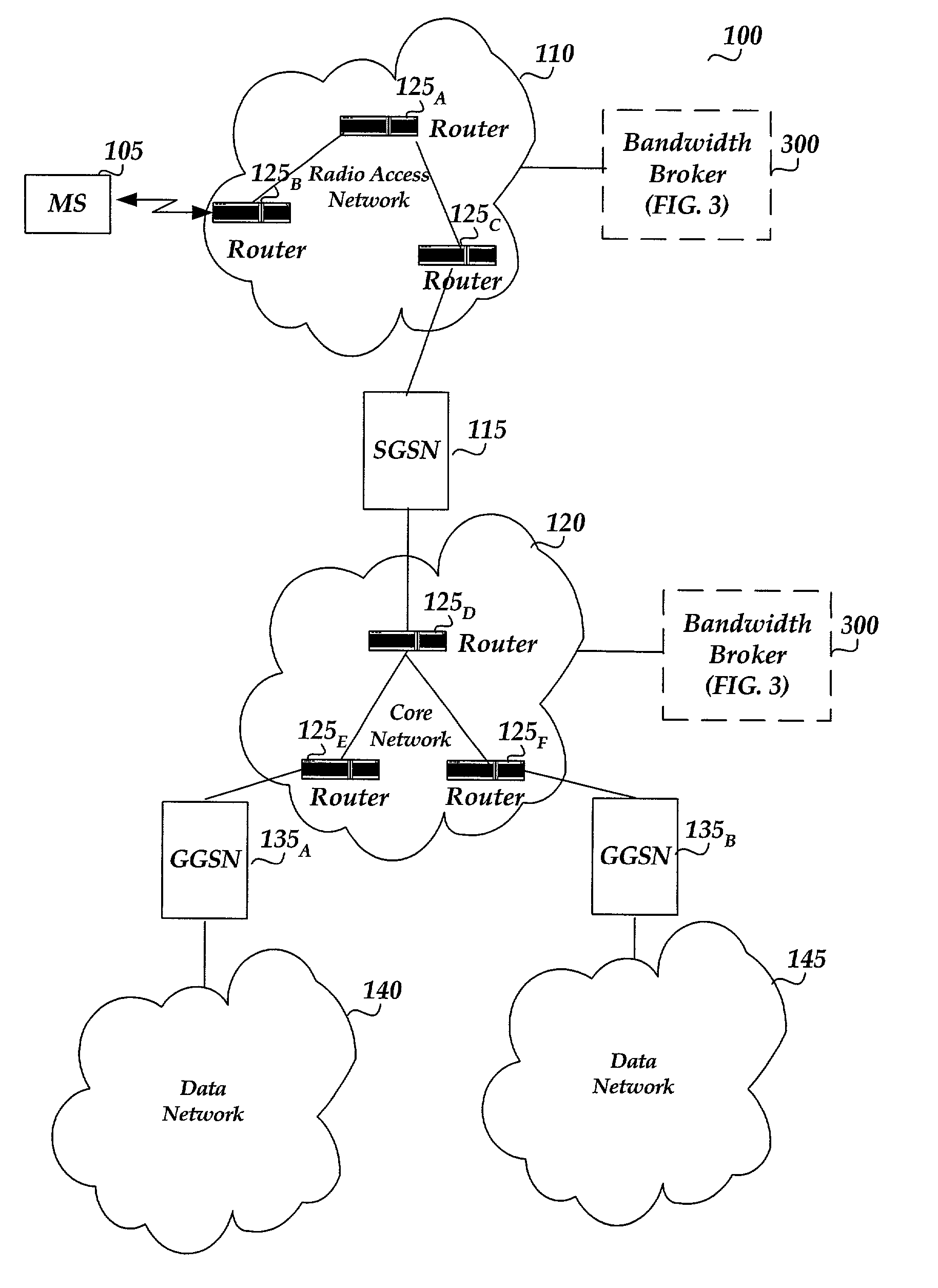
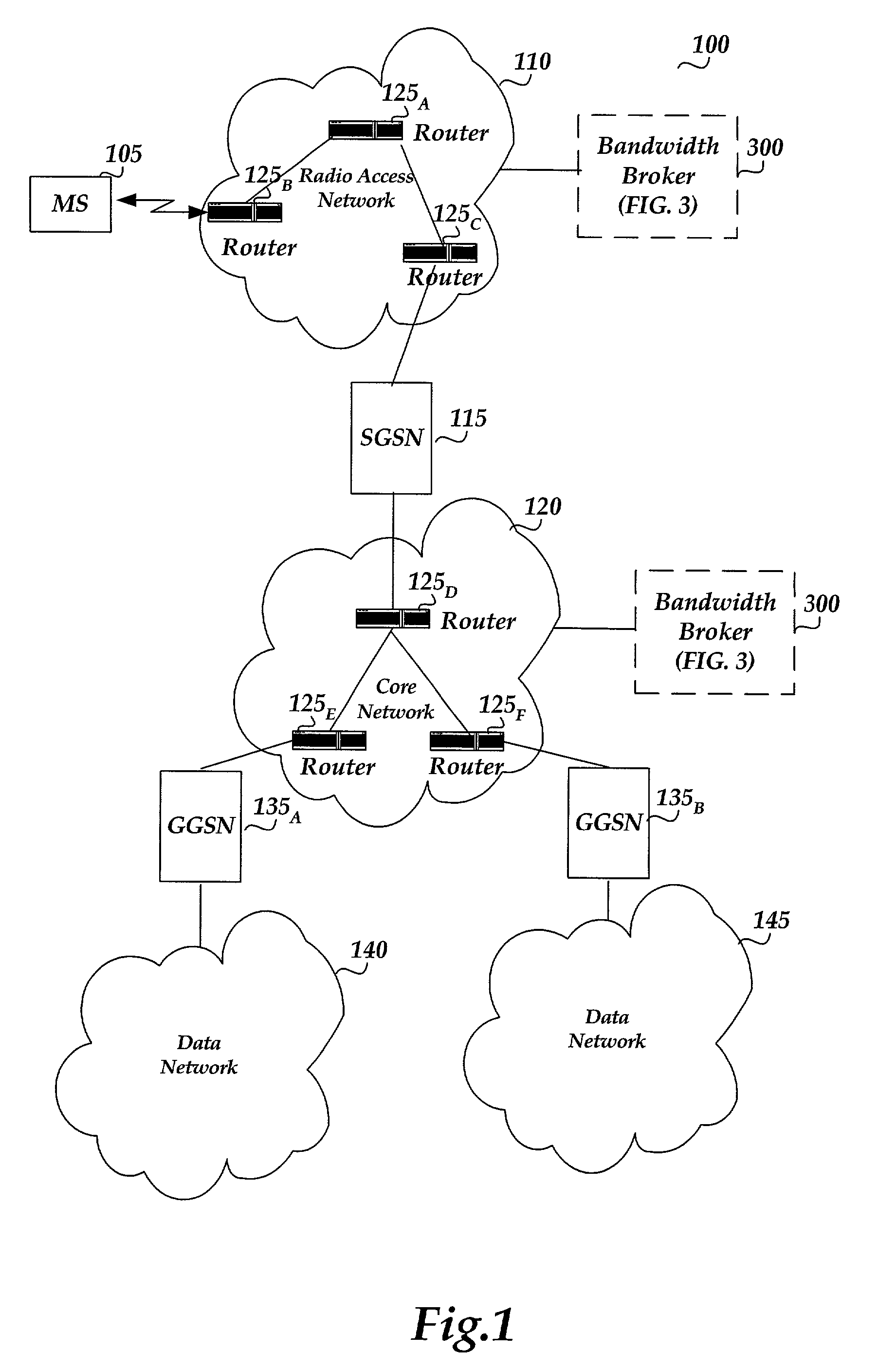
Pool-based resource management in a data network
ActiveUS7209439B2Metering/charging/biilling arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsNetworked systemResource management
In one embodiment, a network system of the present invention includes at least a first router and a second router coupled to an upstream link to permit data flow from the first router to the second router across the upstream link. The second router includes a control plane and a data plane having an input port coupled to the upstream link and an output port connectable to a downstream link. The control plane includes a virtual pool having a capacity corresponding to a resource capacity of the first router and an admission control function. In response to a request to reserve resources for a flow through the data plane from the input port to the output port, the admission control function performs admission control for the upstream link by reference to resource availability within the virtual pool. In one embodiment, the request is a request to reserve resources for an Integrated Services flow, and the capacity of the virtual pool corresponds to a resource capacity of a Integrated Services service class supported by the first router.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Apparatus and methods for incorporating bandwidth forecasting and dynamic bandwidth allocation into a broadband communication system
InactiveUS20060120282A1Energy efficient ICTError preventionDynamic bandwidth allocationComputer network
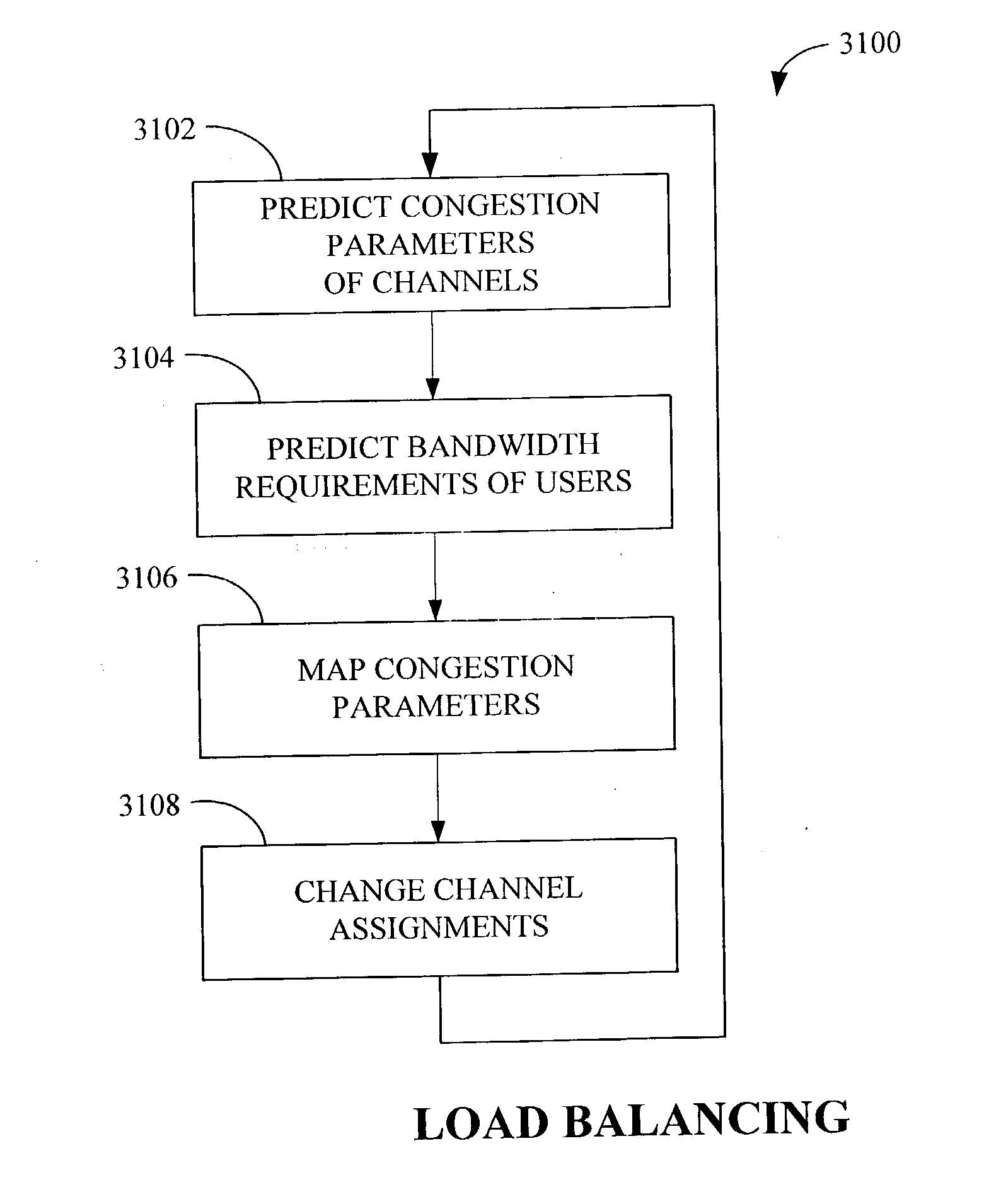
A method for providing network access to a shared access communications medium for a plurality of users includes the steps of conducting predictive admission control by arbitrating user requests for access to the shared medium based on predicted aggregate demands, conducting lookahead scheduling for use in making user channel assignments by forecasting schedule transmission opportunities one or more channels of the shared medium, and balancing load by making channel assignments such that a plurality users are each assigned a respective channel of the shared medium based upon a predicted need. Congestion parameters can predicted for each channel of the shared medium and mapped to a congestion measure using a mathematical function that takes into account packet loss rate, packet delay, packet delay jitter, and available capacity.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
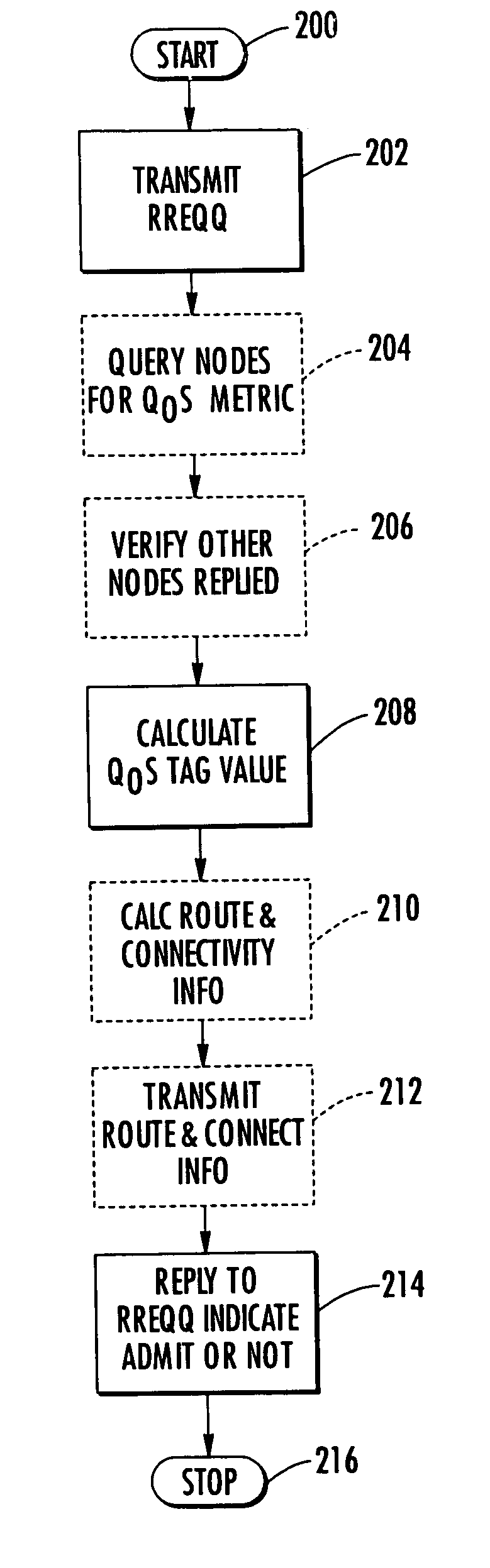
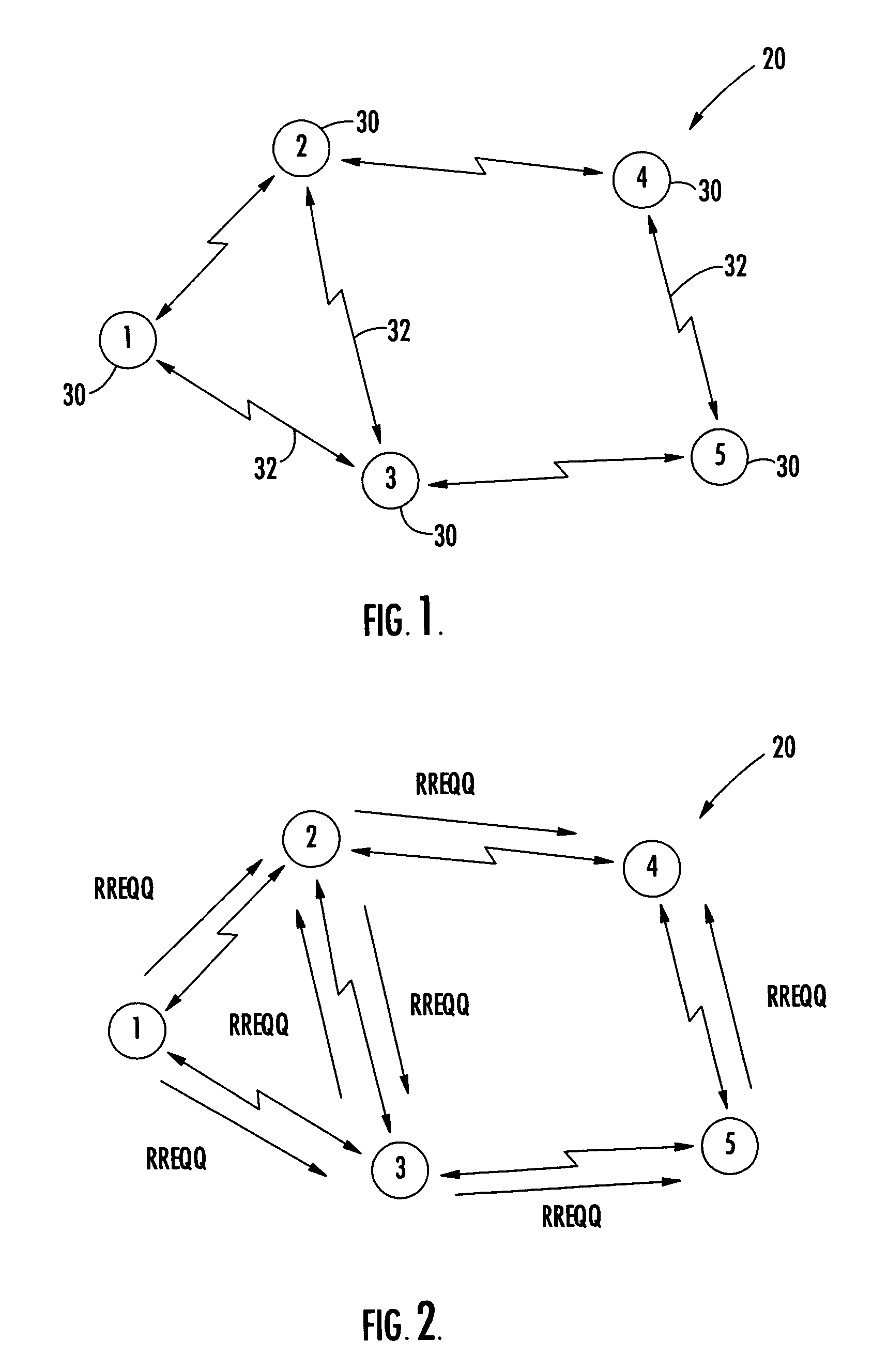
Traffic policing in a mobile ad hoc network
InactiveUS7068600B2Hinders its propagationError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic flowMobile ad hoc network
The method includes nodes transmitting quality-of-service (QoS) route requests to discover traffic routing based upon a QoS parameter, and the QoS route requests including a traffic flow identifier. Each node calculates a node QoS tag value to make traffic admission control decisions, and each node determines whether to admit traffic in response to QoS route requests based upon the calculated QoS tag value and the QoS parameter of QoS route requests. Also, each node replies to QoS route requests to indicate whether the node can support the QoS parameter of the route request and admit the traffic, and each node polices admitted traffic based upon the traffic flow identifier to ensure that admitted traffic does not exceed the QoS parameter of the QoS route request.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
Capacity enhancement for multi-code CDMA with integrated services through quality of service and admission control
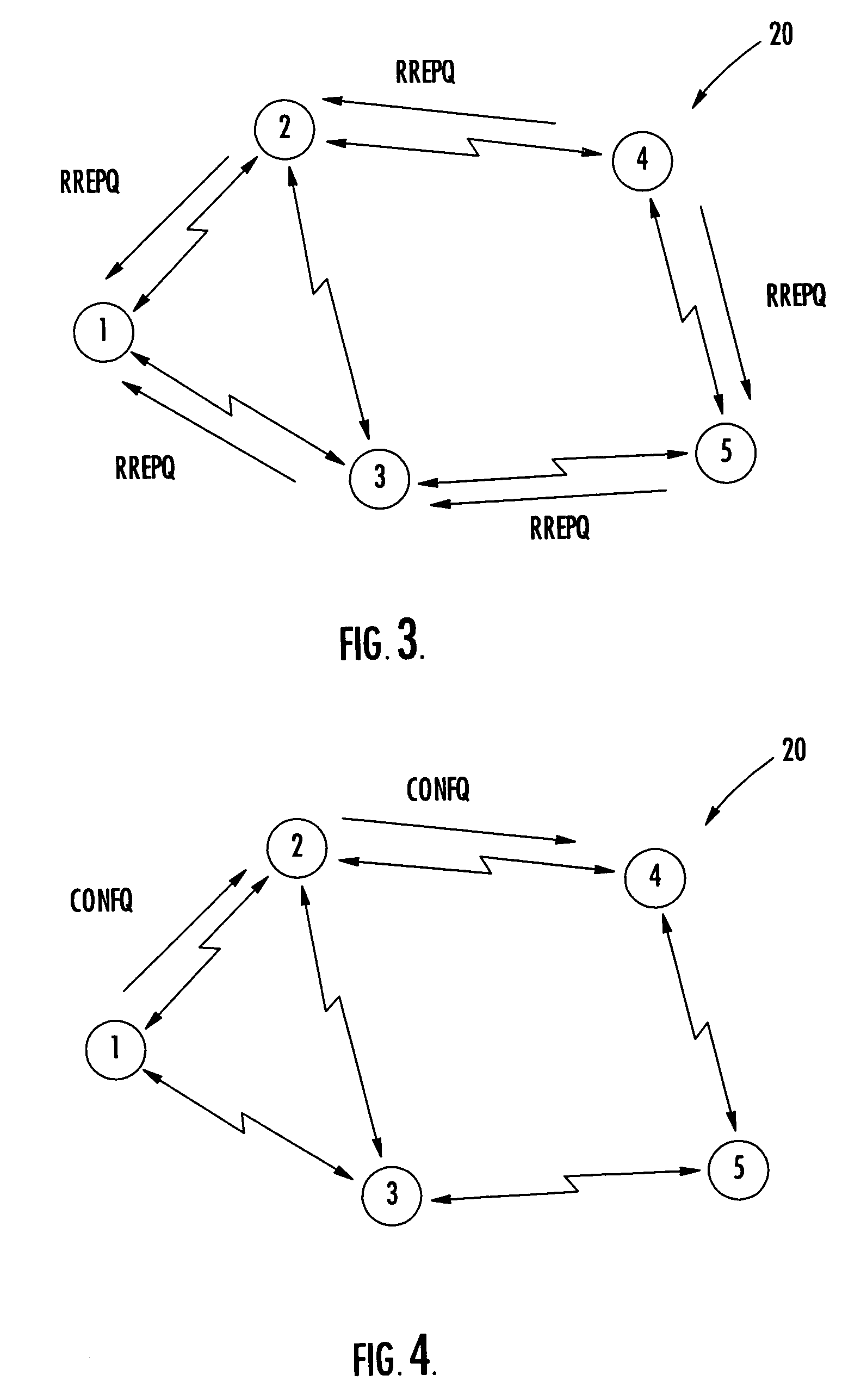
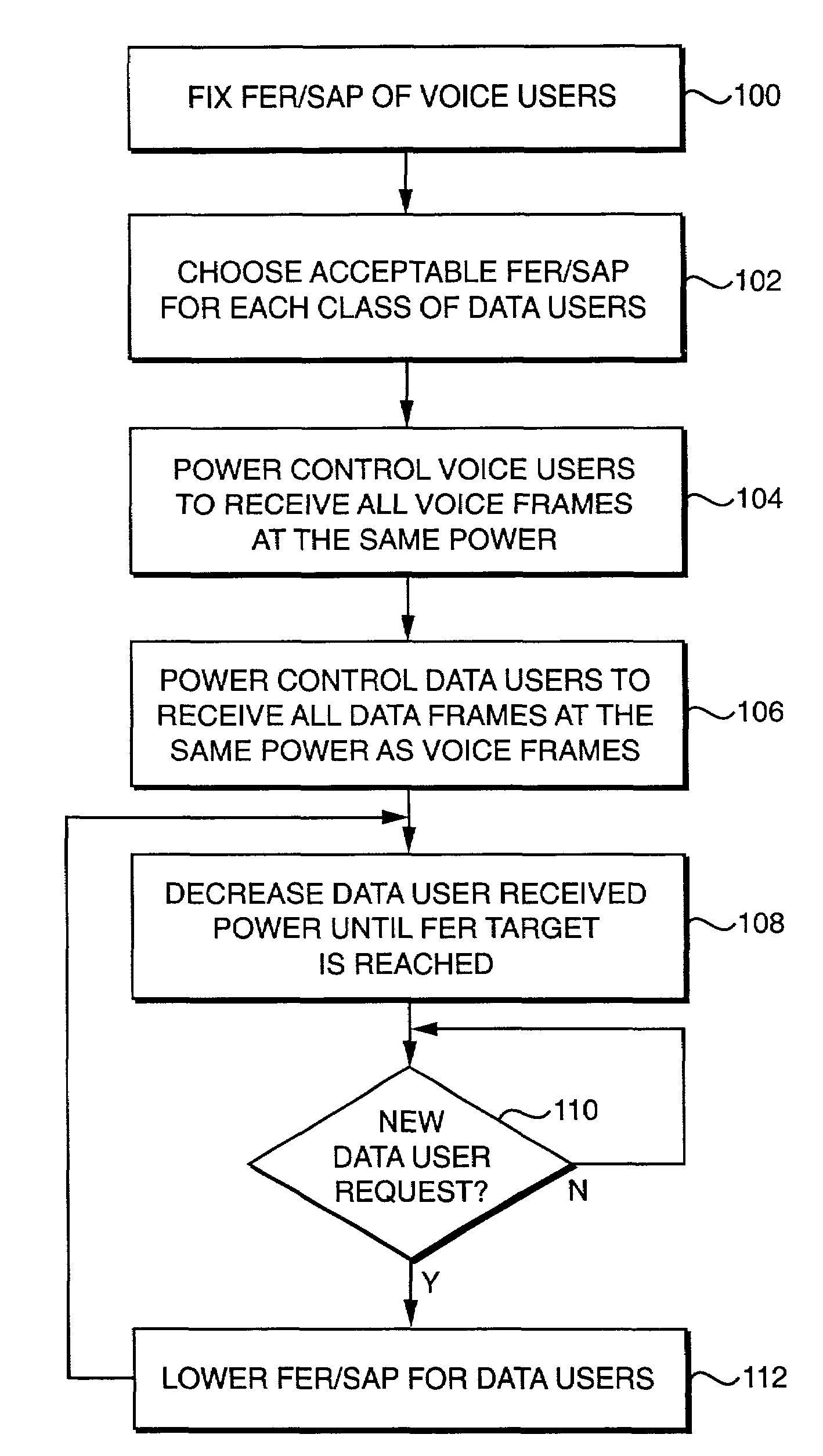
With the addition of high-speed data traffic to traditional CDMA cellular networks, there is a need to efficiently utilize system capacity so that the quality of service of existing voice and low-speed data users is maintained while new high-speed data users are added to the network. Methods and systems are presented that control allocation of power to users, quality of service requirements, and / or user activity levels to enhance capacity utilization. These methods and systems are based on a method for estimating the capacity of a CDMA carrier with both voice and data users using an interference-based analysis of the reverse link. In particular, the methods enhance capacity utilization in a multi-code CDMA network architecture, in which several codes are allocated to a single high-speed data user for parallel transmission.
Owner:VERIZON LAB
Method and apparatus to provide centralized call admission control and load balancing for a voice-over-IP network
InactiveUS6904017B1Improve service qualityBandwidth sharingInterconnection arrangementsError preventionExtensibilityBalancing network
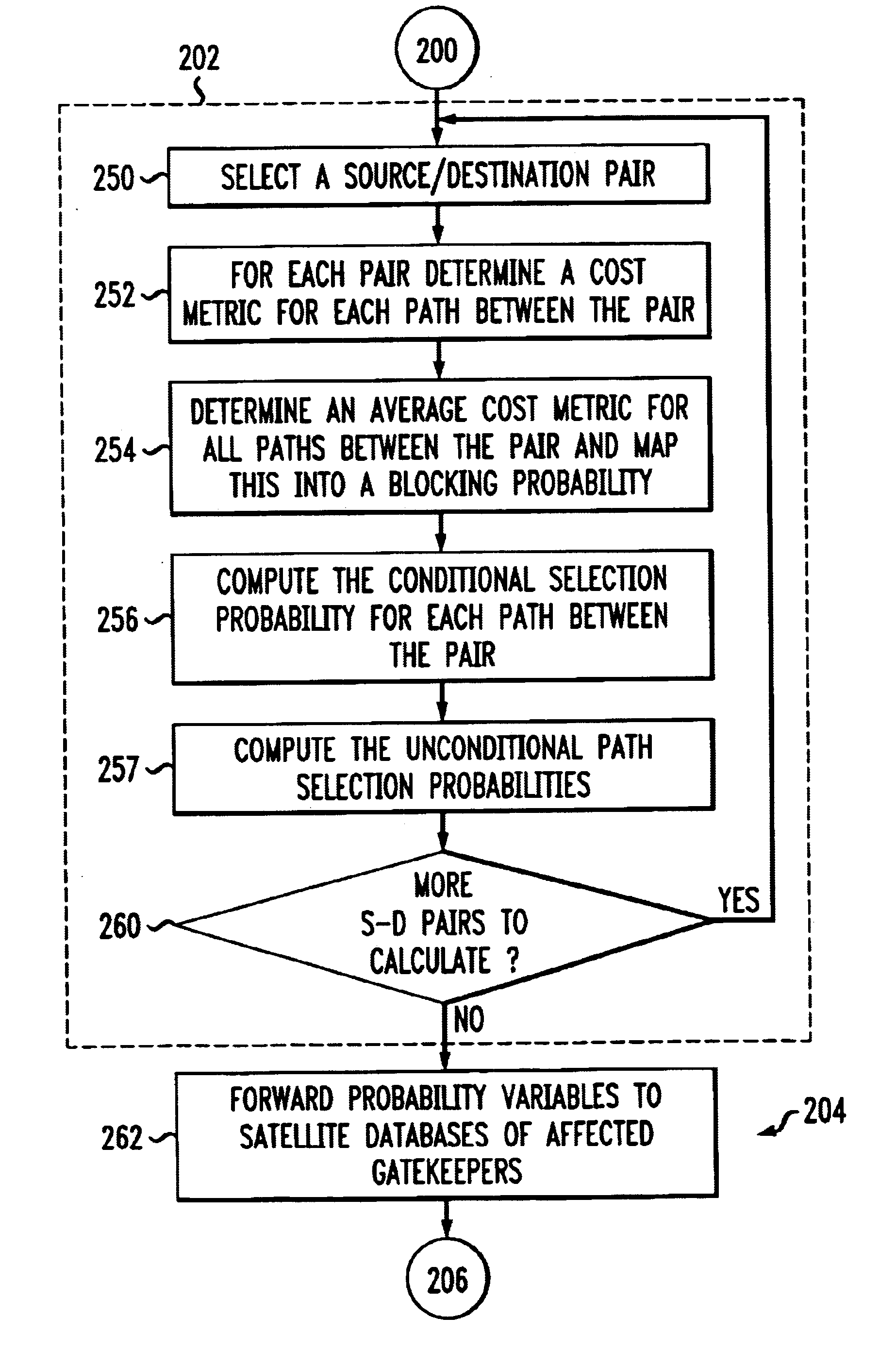
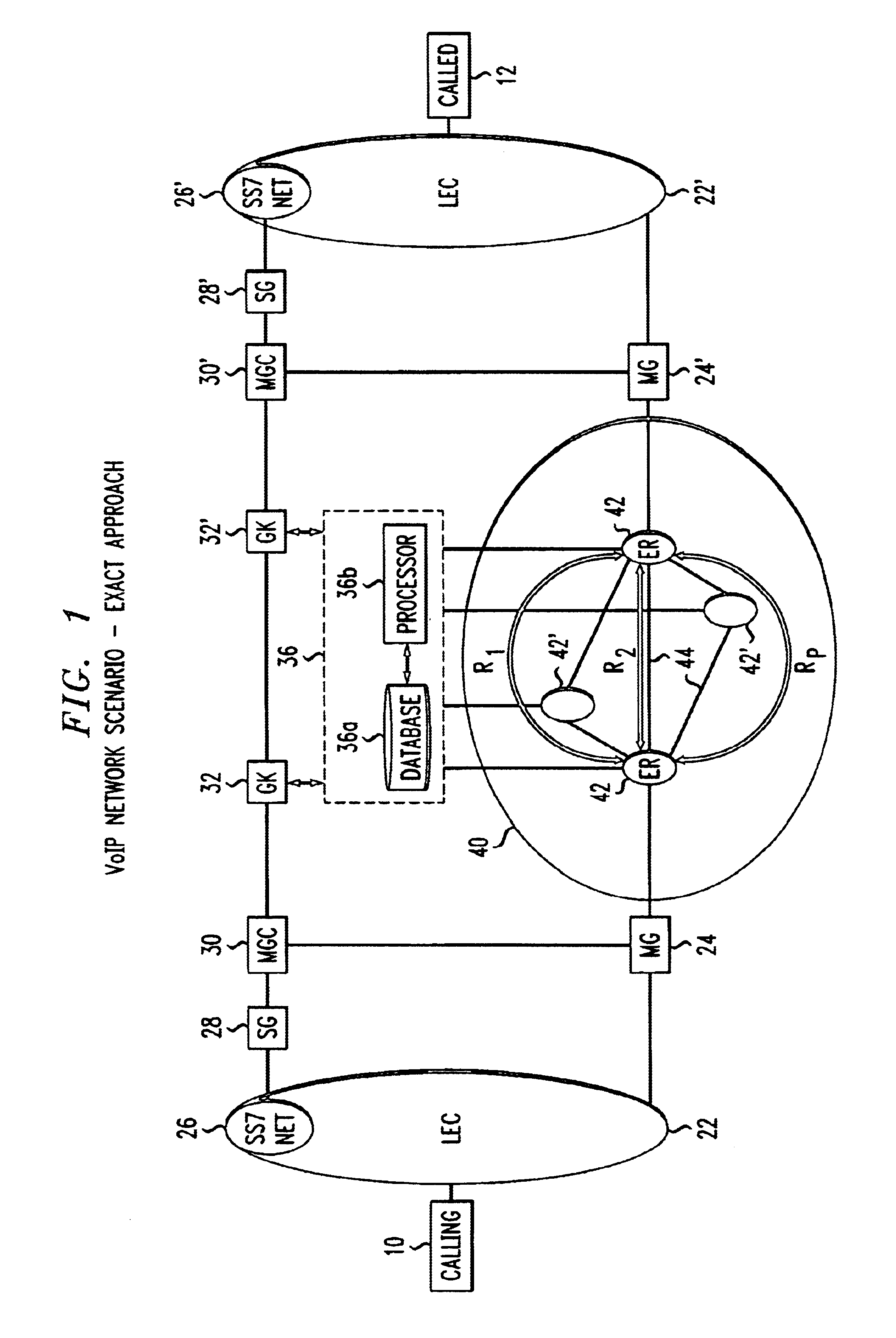
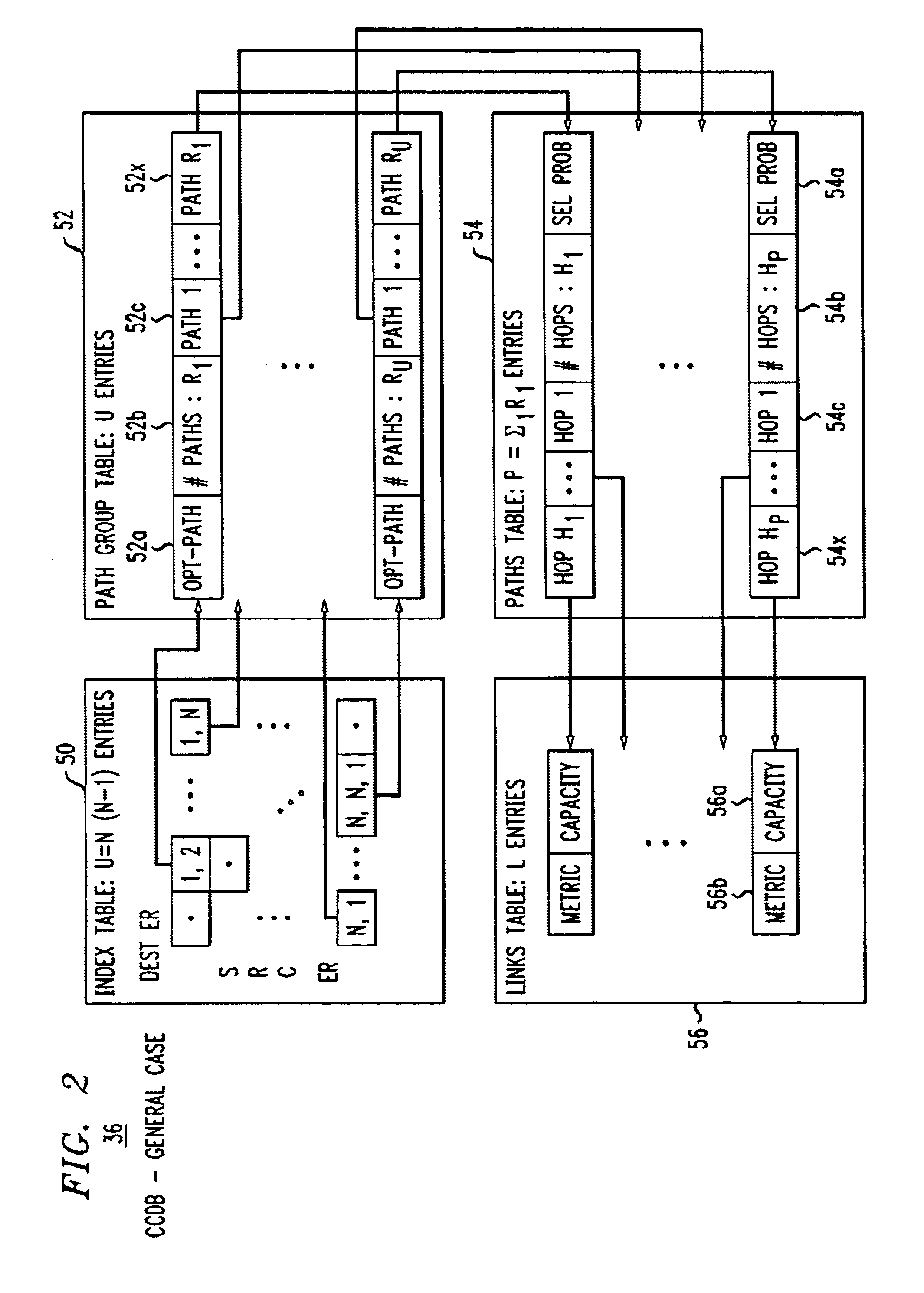
An admission control and load balancing system controls admission of packet streams or calls to a network and balances the packet traffic across the network, improving quality of service. The system includes a central database which stores information including cost data associated with individual paths and links across the network. A processor, in communication with the database, coordinates the admission control and load balancing decisions, and updates of the database cost data to reflect the dynamic network conditions, based on input from appropriate data sources. In one embodiment, referred to as the exact algorithm, the database is consulted by the admission control points or gatekeepers prior to admitting each arriving packet stream, and the database contents are updated call-by-call to reflect the allocation of resources to each admitted stream. In another embodiment, referred to as the inexact algorithm, control decision as well as database updates occur on a periodic rather than on a call-by-call basis to promote better scalability. In this embodiment, the processor periodically calculates admission decisions based on cost data in the central database. These admission decisions are then periodically forwarded to a satellite database associated with each gatekeeper, for storage and use in admission decisions until the next update epoch.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
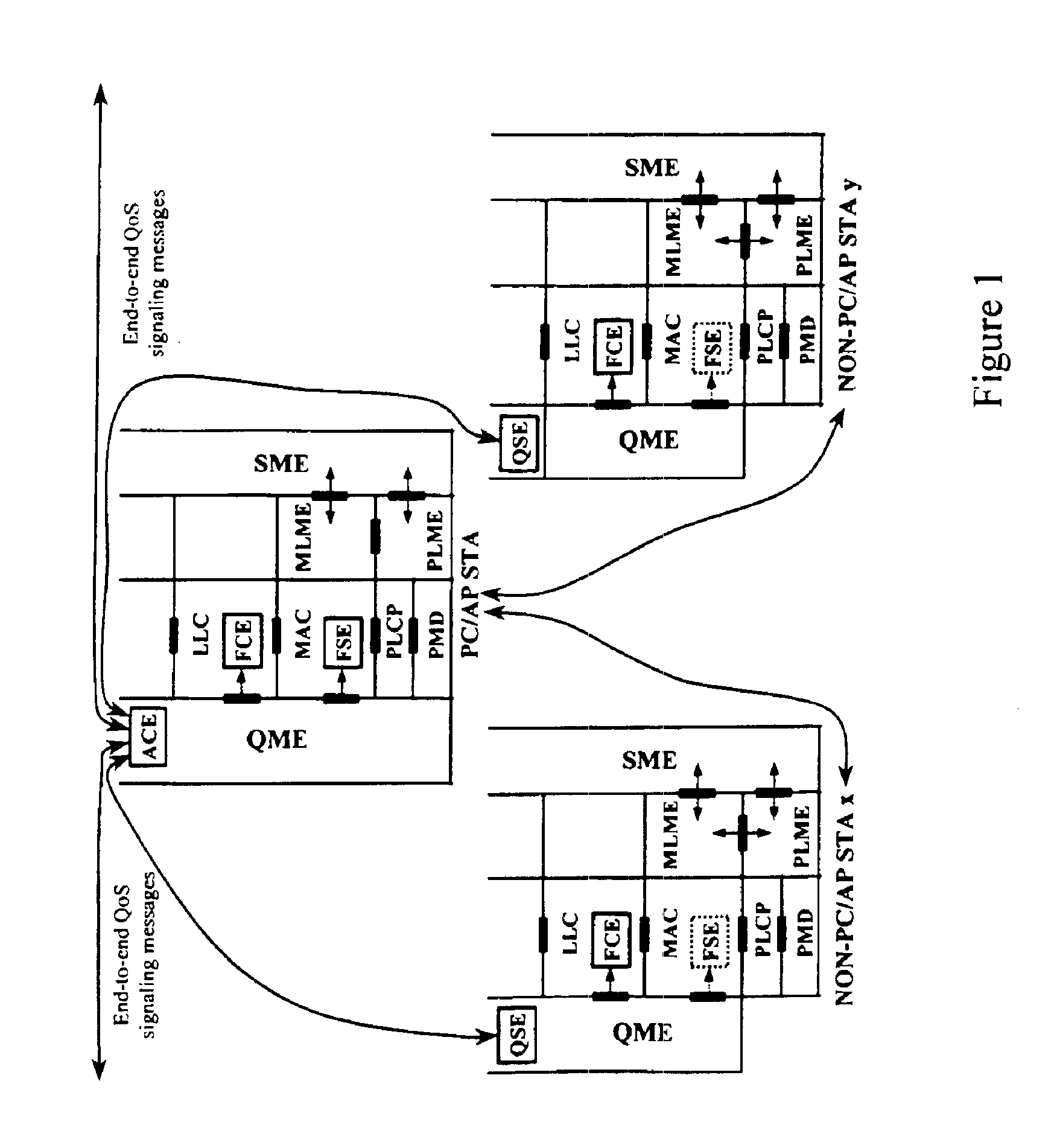
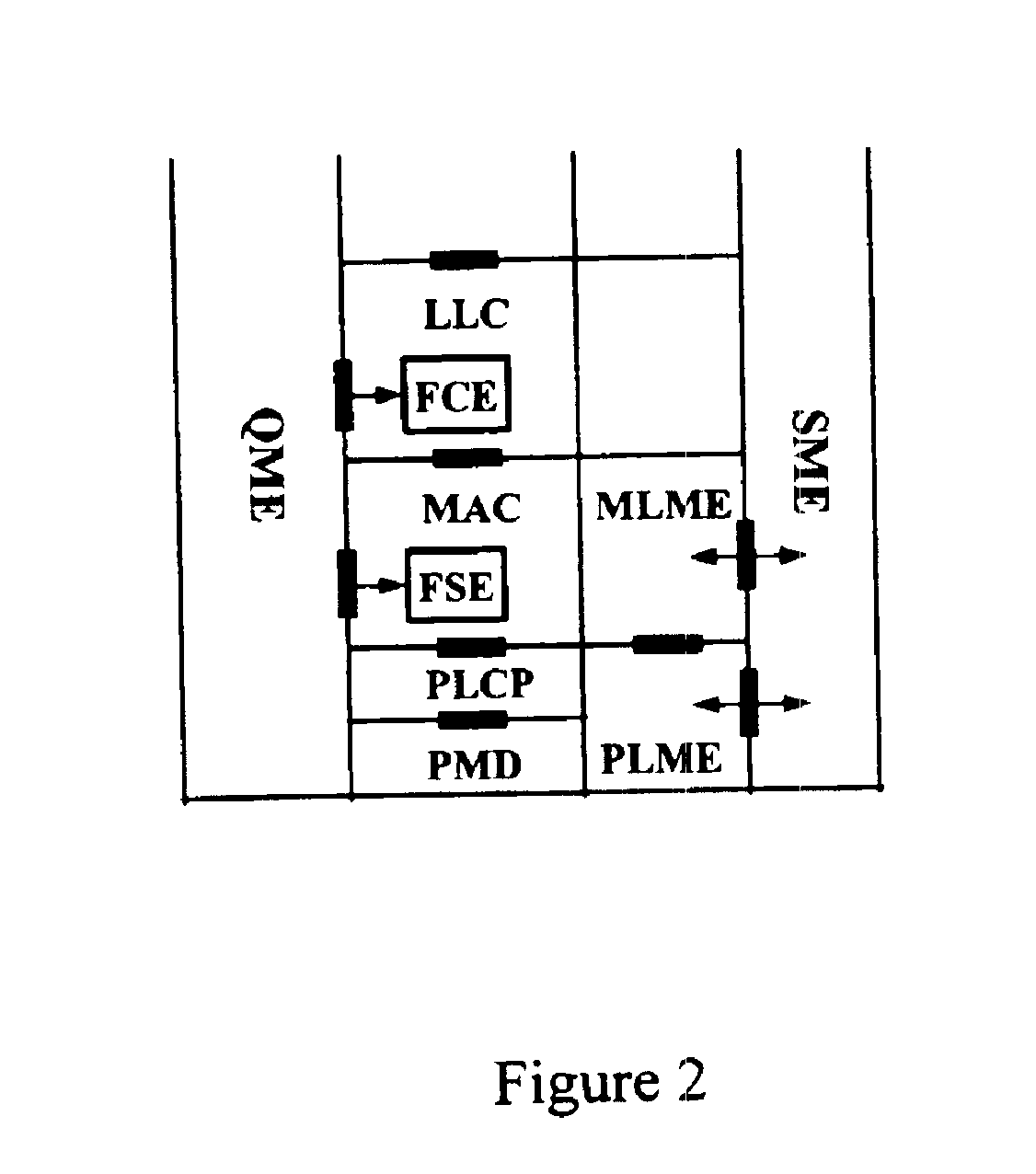
Architectural reference model for QoS-driven wireless LANs
InactiveUS6862270B1Enhanced channel accessImprove bandwidth utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesOpen Systems InterconnectionEnd to end qos
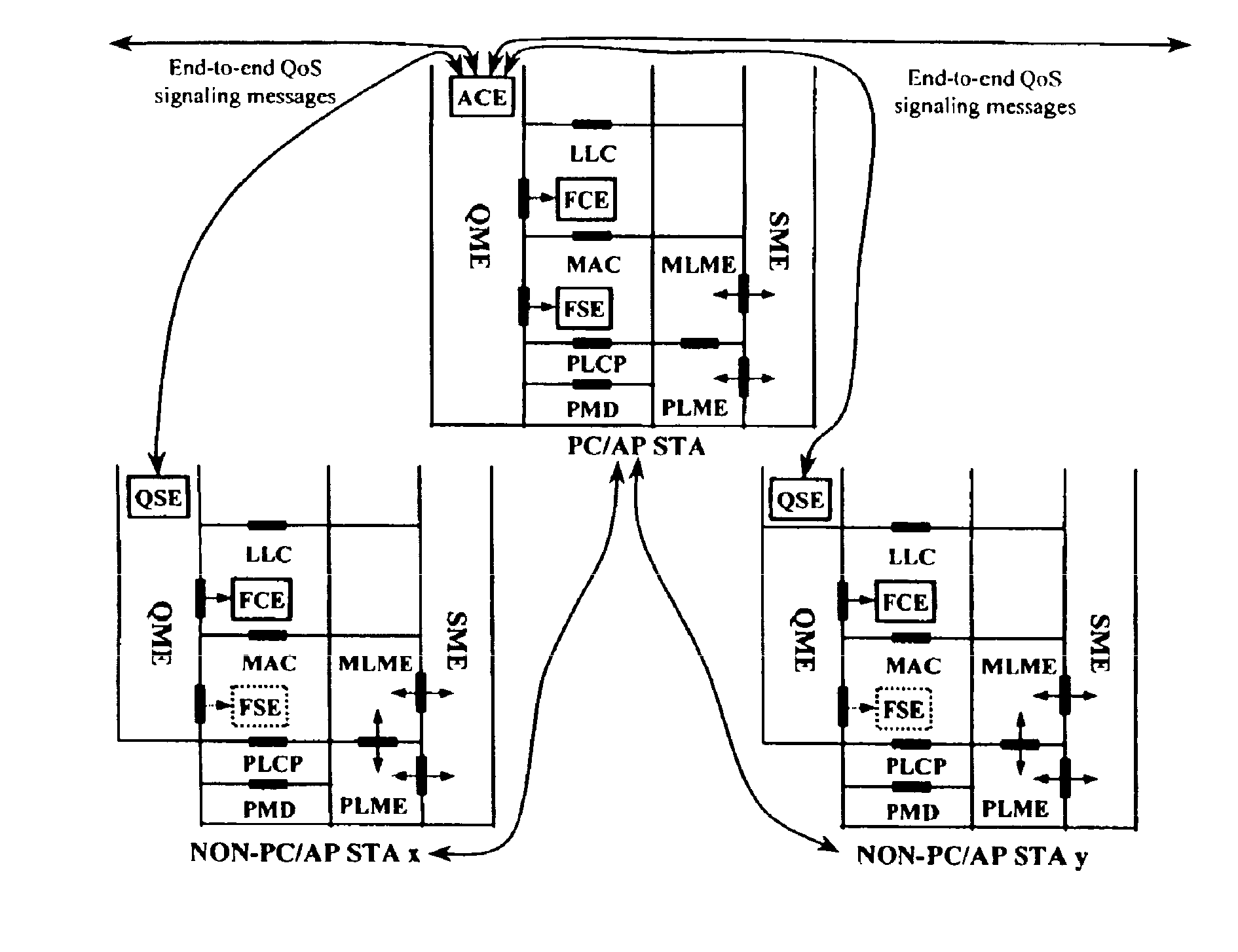
A quality of service (QoS) station is disclosed containing a point coordinator (PC) for a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless LAN. The PC station includes a QoS management entity (QME) and an admission control entity (ACE). The QME receives at least one end-to-end QoS message that characterizes a user application, such as a voice call, a video call, a data call and a multimedia call. The at least one end-to-end QoS message includes at least one QoS parameter set that is expressed at layer 3 and higher of an ISO / IEC basic reference model of Open Systems interconnection (OSI) (ISO / IEC 7498-1) and is to be passed down to layer 2 of the PC-station for enabling QoS traffic transport of the application. The ACE performs an admission control decision relating to the application based on the at least one end-to-end QoS message characterizing the application. The ACE reserves a resource based on a QoS parameter set contained in the end-to-end QoS message. The ACE can be part of the QME and can include a resource control module that performs at least one admission control decision based on resource permission, and a policy control module that performs at least one admission control decision based on policy permission.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
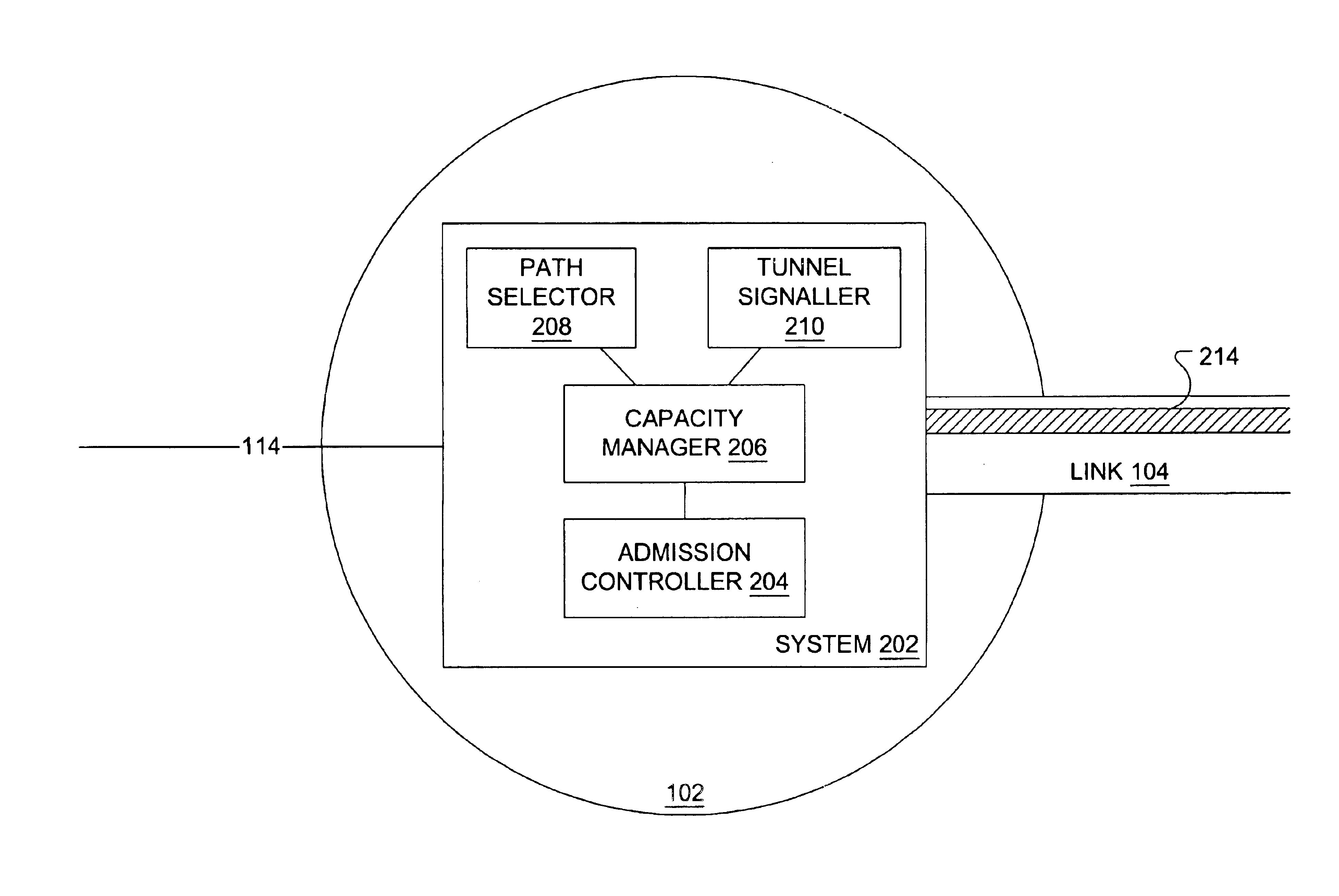
Automated and adaptive management of bandwidth capacity in telecommunications networks
InactiveUS6842463B1Fast and efficient bandwidth managementFast and efficient bandwidthError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunications linkAdaptive management
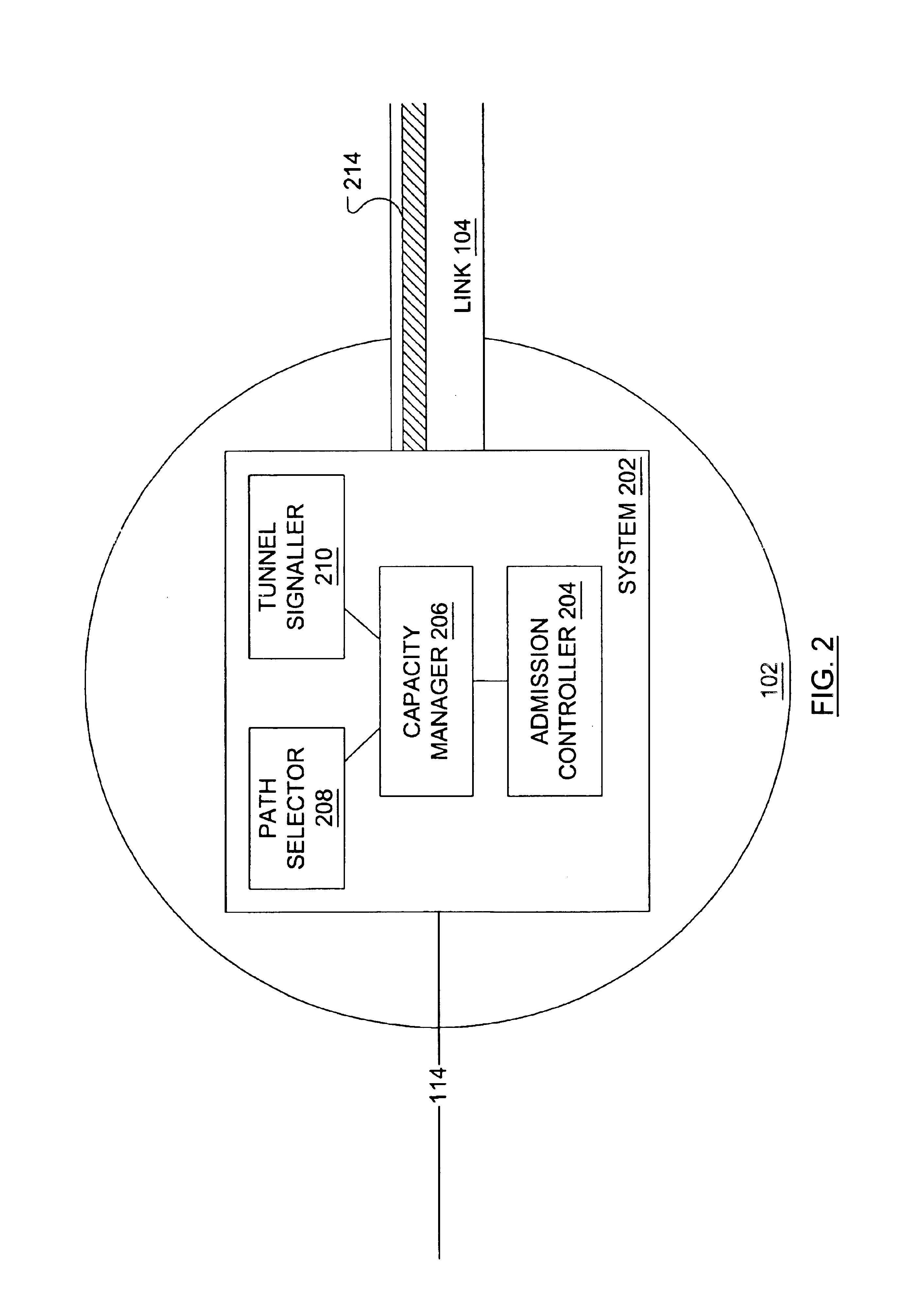
Management of the bandwidth capacity of tunnels through a network may be automated such that the network is adaptive to the stochastic nature of incoming traffic. An edge node in the network includes four main elements. Three of the elements, namely tunnel signaling, admission control and path selection, are derived from known technologies, generalized from their particular technologies and enhanced. With the addition of a fourth element, called capacity management, the four elements cooperate to accommodate the capacity needs of the traffic incoming to the network at the edge node. This accommodation is performed by estimating the traffic demand and dynamically adapting tunnels to the traffic demand.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Dynamic traffic conditioning
Multi-media networks will require that a data flow be given certain quality-of-service (QOS) for a network connection but pre-negotiation of this sort is foreign to the current data networking model. The real time traffic flow in the data network requires distinct limits on the tolerance to delay, and the variations in that delay. Interactive voice and video demand that the total delay does not exceed the threshold beyond which human interaction is unacceptably impaired. The present invention allows the network to discover the nature of the service for each traffic flow, classifies it dynamically, and exercises traffic conditioning by means of such techniques as admission control and scheduling when delivering the traffic downstream to support the service appropriately.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
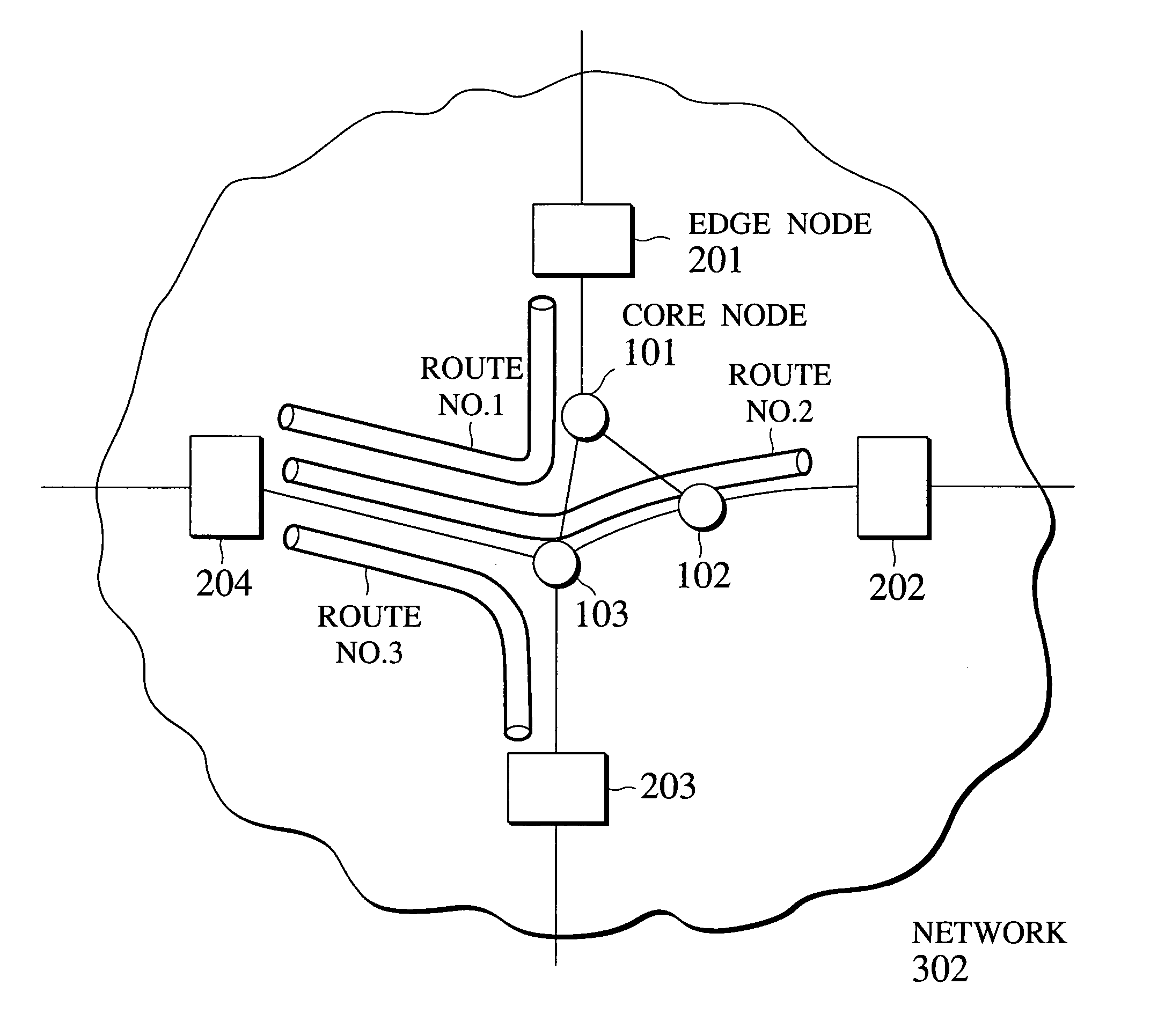
Communication resource management method and node control device using priority control and admission control
InactiveUS6999419B2Easy to conjectureSimple processError preventionTransmission systemsCommunication qualityEdge node
A communication resource management scheme capable of guaranteeing the communication quality with respect to the flow while not requiring the processing for each flow to nodes other than edge nodes is disclosed. The edge node stores an information for obtaining an available amount of communication resources that can be newly allocated in the network to one set of flows which share at least a route from that edge node to an egress node of the network. Then, the edge node carries out an admission control by newly receiving a request for allocation of communication resources for one flow belonging to that one set of flows, judging whether or not to accept the request according to a requested amount of communication resources and the available amount of communication resources as obtained from the information stored for that one set of flows, and allocating requested communication resources to that one flow when it is judged that the request is to be accepted, while the edge node and the core node carry out the priority control.
Owner:IBM CORP
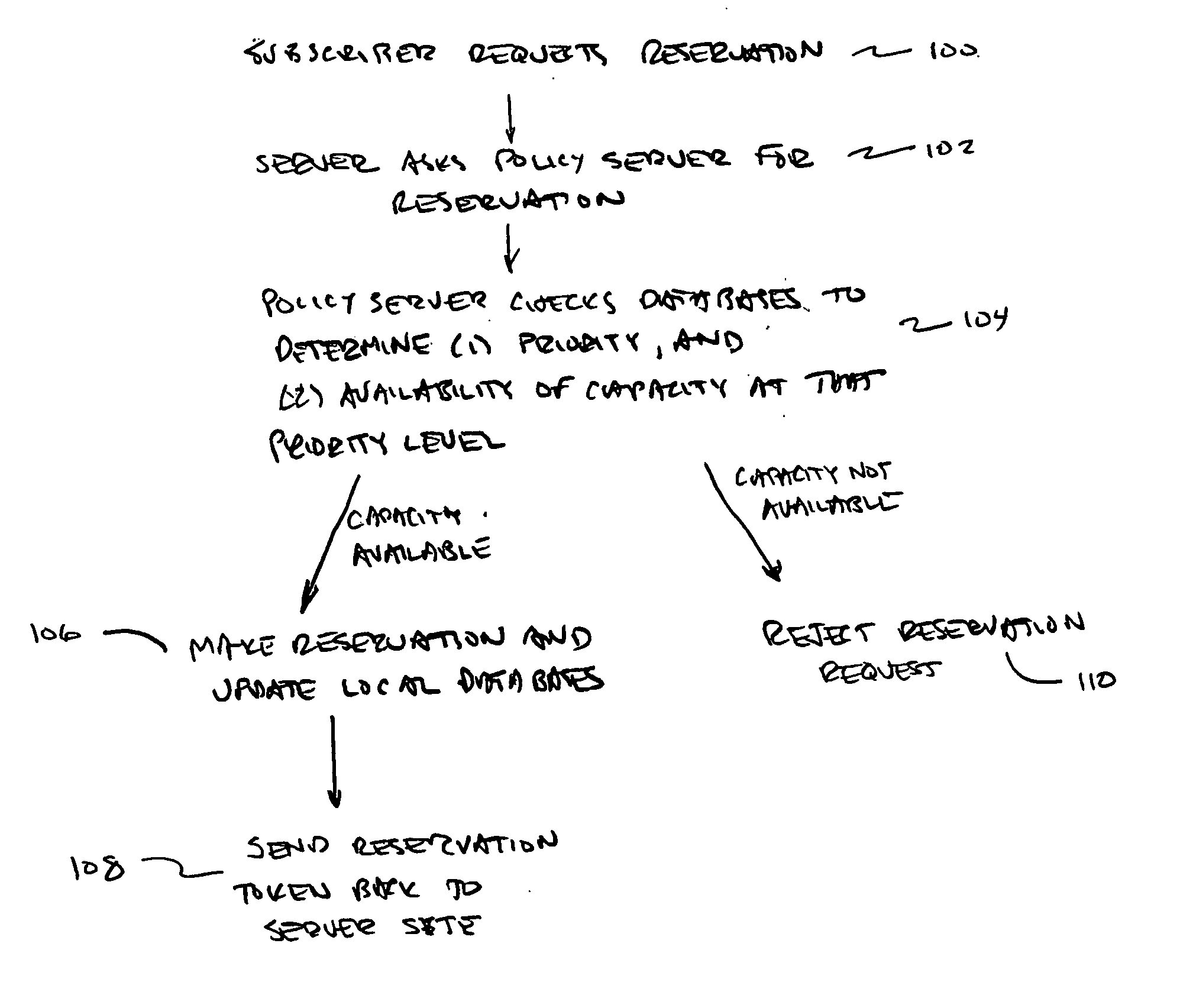
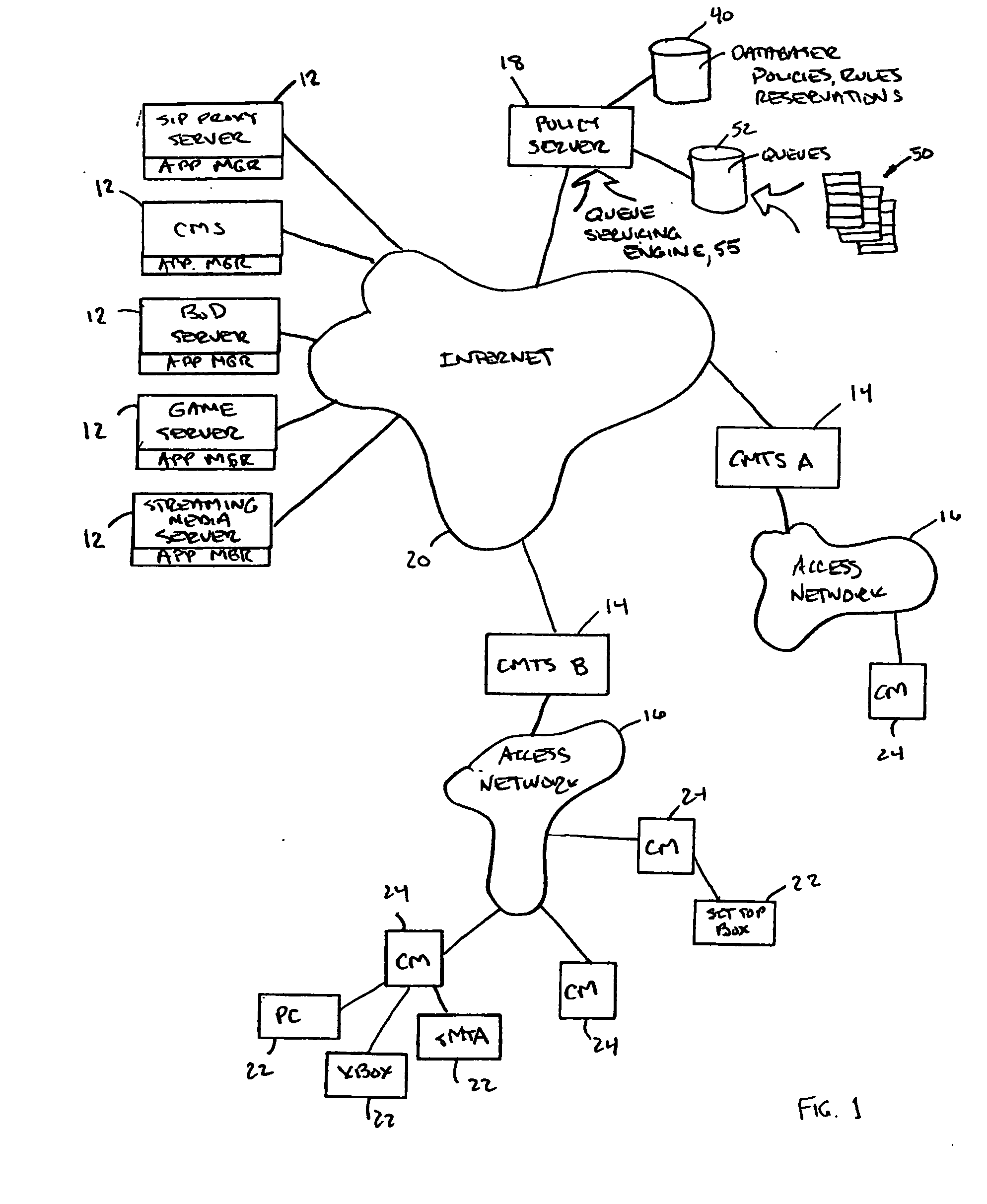
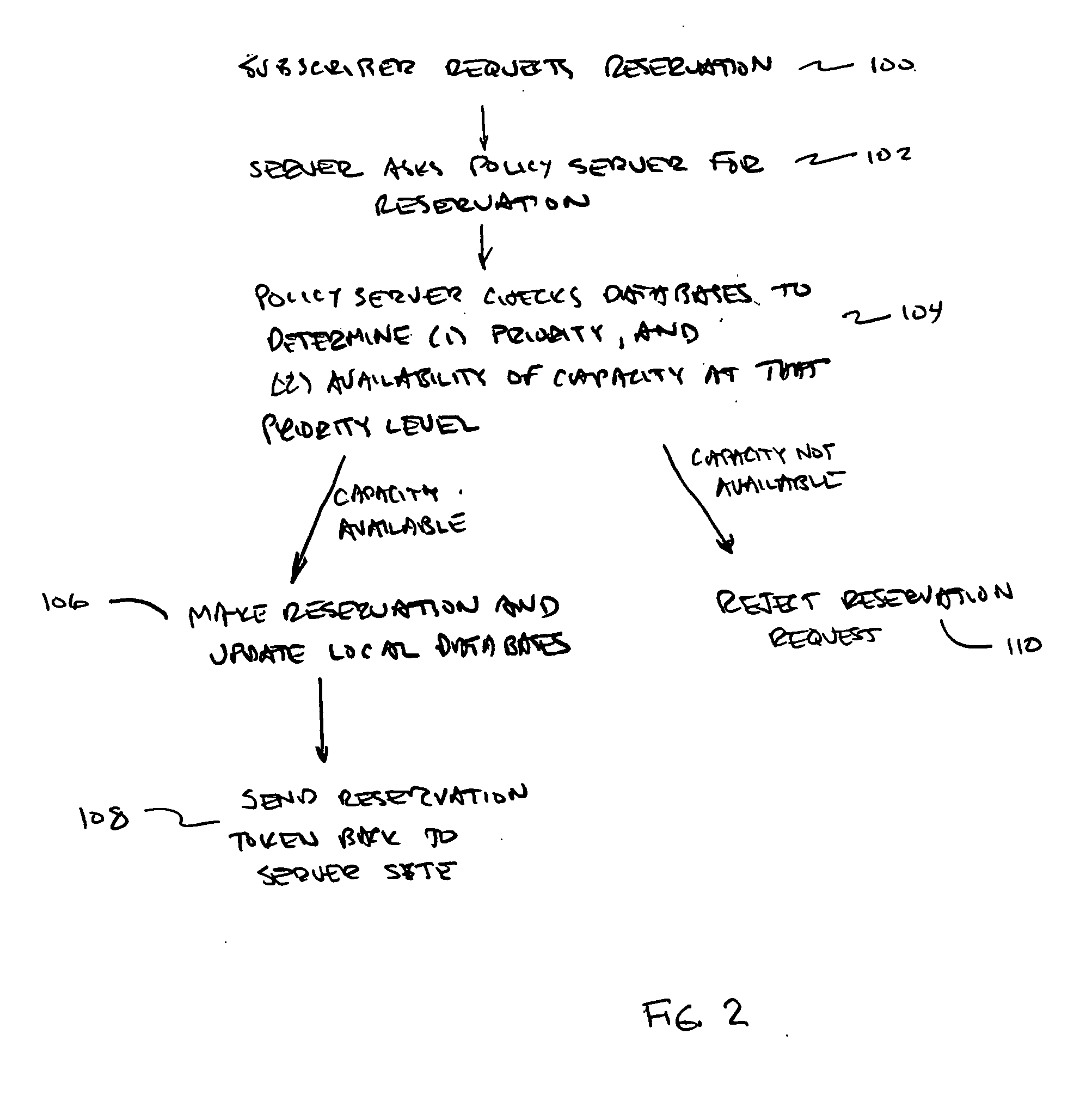
Policy-based admission control and bandwidth reservation for future sessions
ActiveUS20050228892A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksBandwidth reservationContent server
A method for delivering content over a network, the method involving: receiving a request to establish a session at a future time T1 over the network, the requested session for transferring content between a content server and a subscriber's equipment; reserving network capacity necessary to support the requested future session; acknowledging to the requestor that network resources have been reserved for said requestor for time T1; and when current time reaches time T1, causing the requested session to be set up for transferring content between the content server and the subscriber's equipment.
Owner:CAMIANT INC
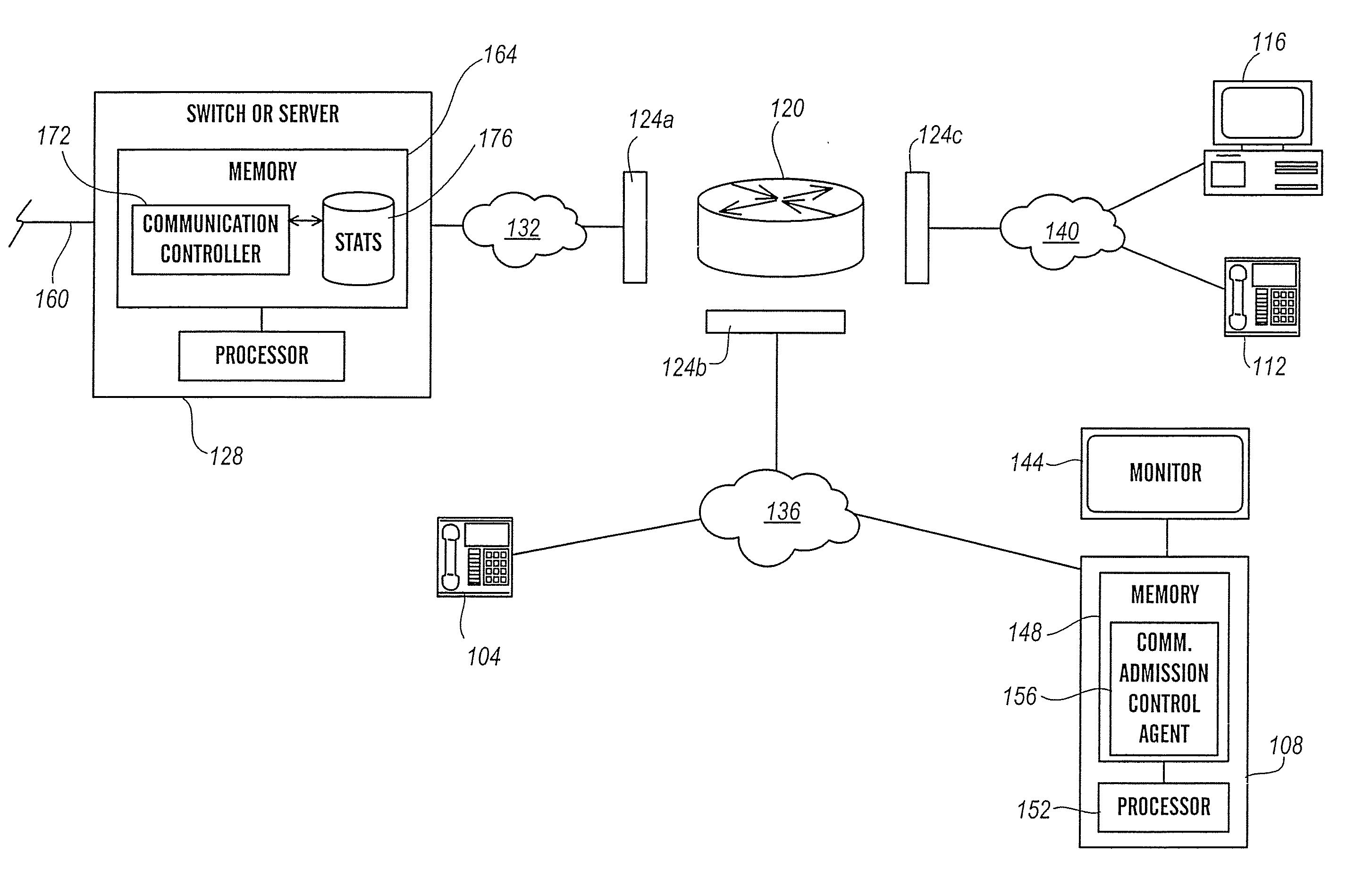
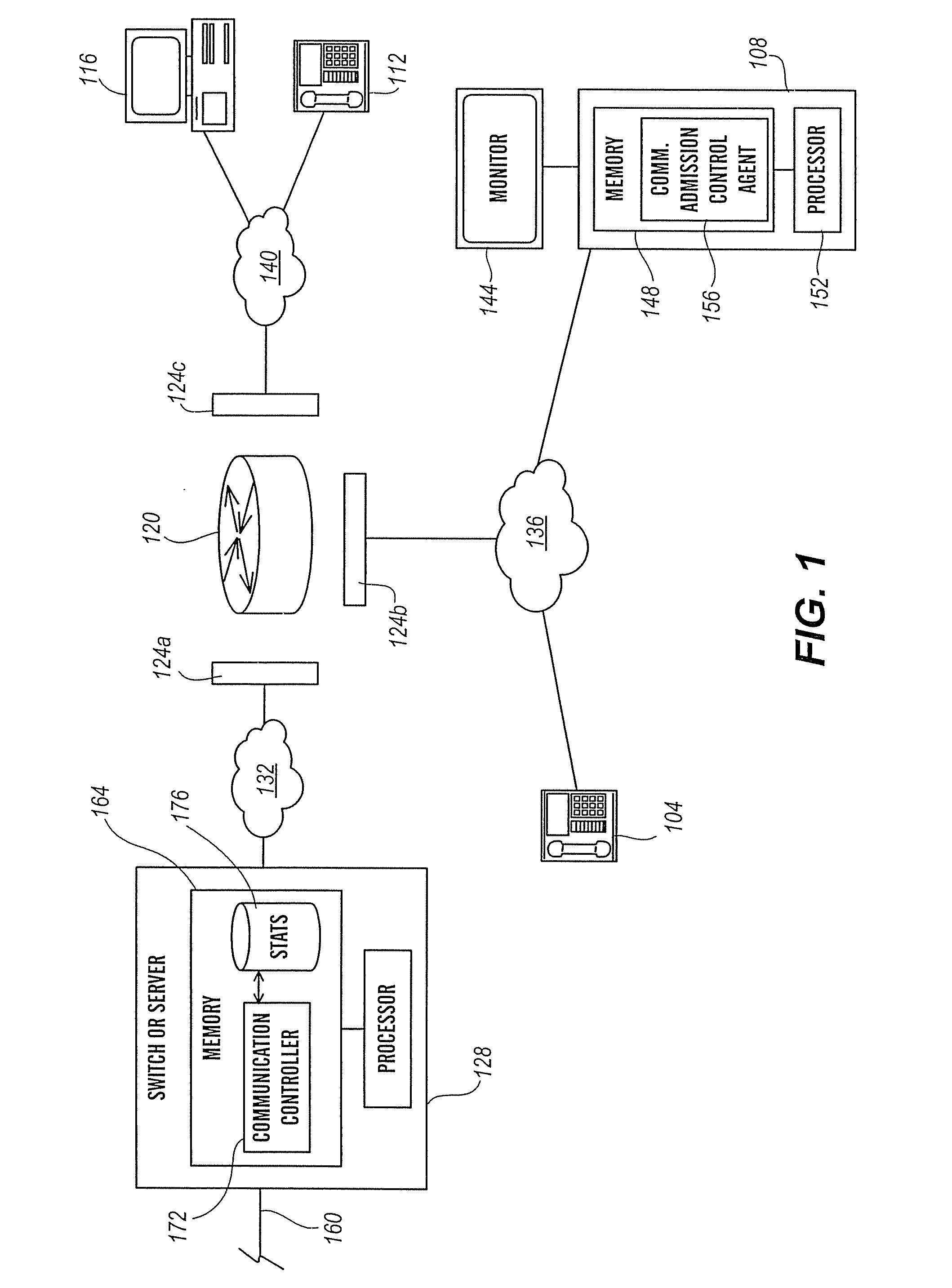
VOIP endpoint call admission
InactiveUS20070133403A1High likelihood of failureAvailable bandwidthError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsRelevant information
The present invention is directed generally to an intelligent endpoint or communication device that can collect available bandwidth-related information metrics and / or perform call admission control functions. The present invention is further directed to an architecture comprising a switch or media server in communication with a plurality of subscriber communication devices in which the subscriber communication devices act as network nodes to collect available bandwidth-related information.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Internet differentiated services service for transaction applications
InactiveUS6483805B1Avoid abuseError preventionTransmission systemsDifferentiated servicesTelecommunications network
A method of monitoring telecommunications network traffic comprising the steps of: receiving a packet stream comprising packets each identified as belonging to one of at least three classes; calculating a difference between the numbers of packets received identified as belonging to a first and a second of said classes; and deriving a measure of traffic load on the network responsive to said difference. The invention also relates to a method for admission control based on the above method of monitoring and a method for overcoming admission control avoidance. It also relates to apparatus embodying these methods.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Methods and apparatus for managing computing deployment in presence of variable workload
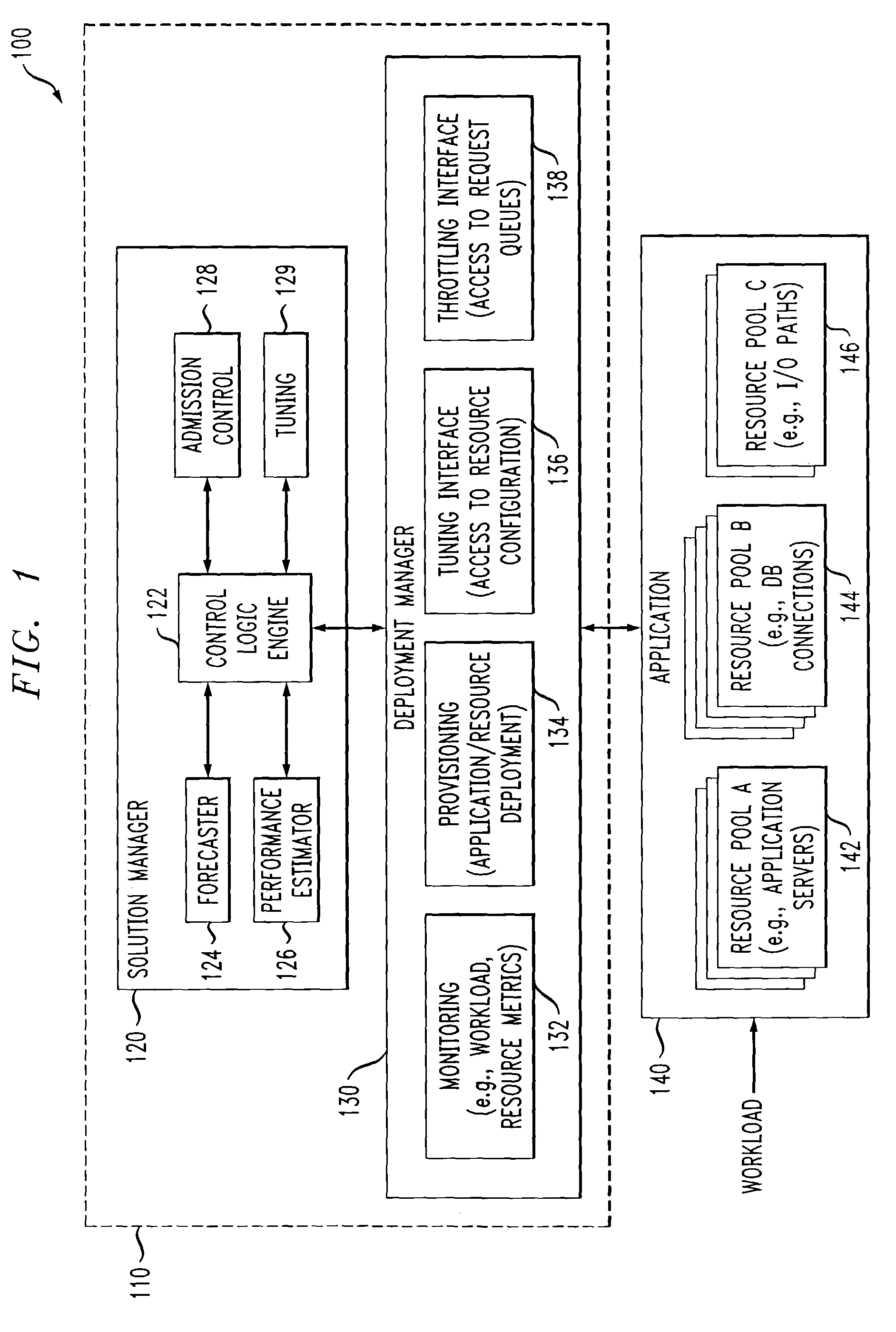
ActiveUS7350186B2Efficient and effectiveAccommodating unanticipated workloadResource allocationReliability/availability analysisWorkloadDistributed computing
Automated or autonomic techniques for managing deployment of one or more resources in a computing environment based on varying workload levels. The automated techniques may comprise predicting a future workload level based on data associated with the computing environment. Then, an estimation is performed to determine whether a current resource deployment is insufficient, sufficient, or overly sufficient to satisfy the future workload level. Then, one or more actions are caused to be taken when the current resource deployment is estimated to be insufficient or overly sufficient to satisfy the future workload level. Actions may comprise resource provisioning, resource tuning and / or admission control.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Call admission control in voip systems
InactiveUS20060251050A1Interconnection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementControl systemNetwork packet
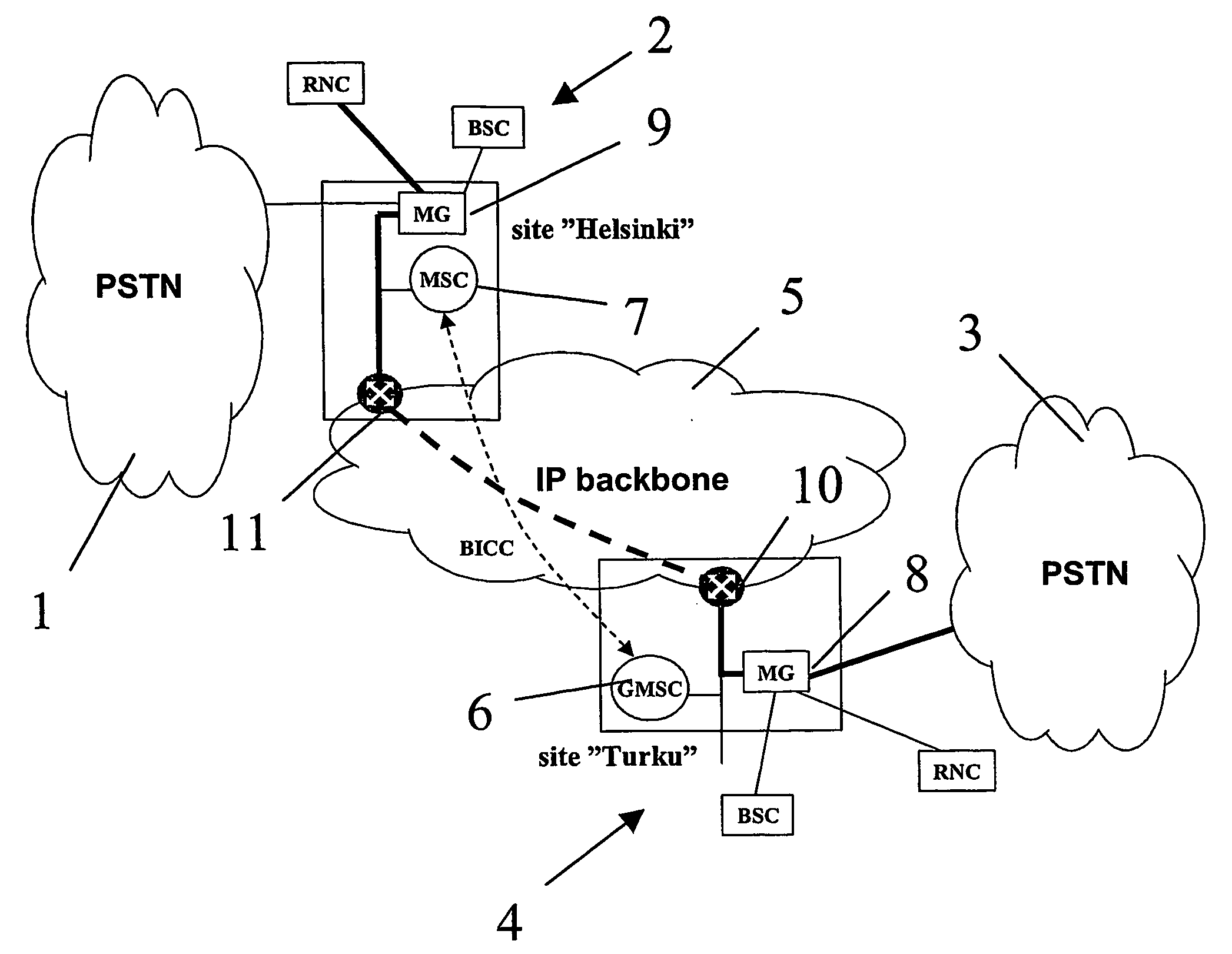
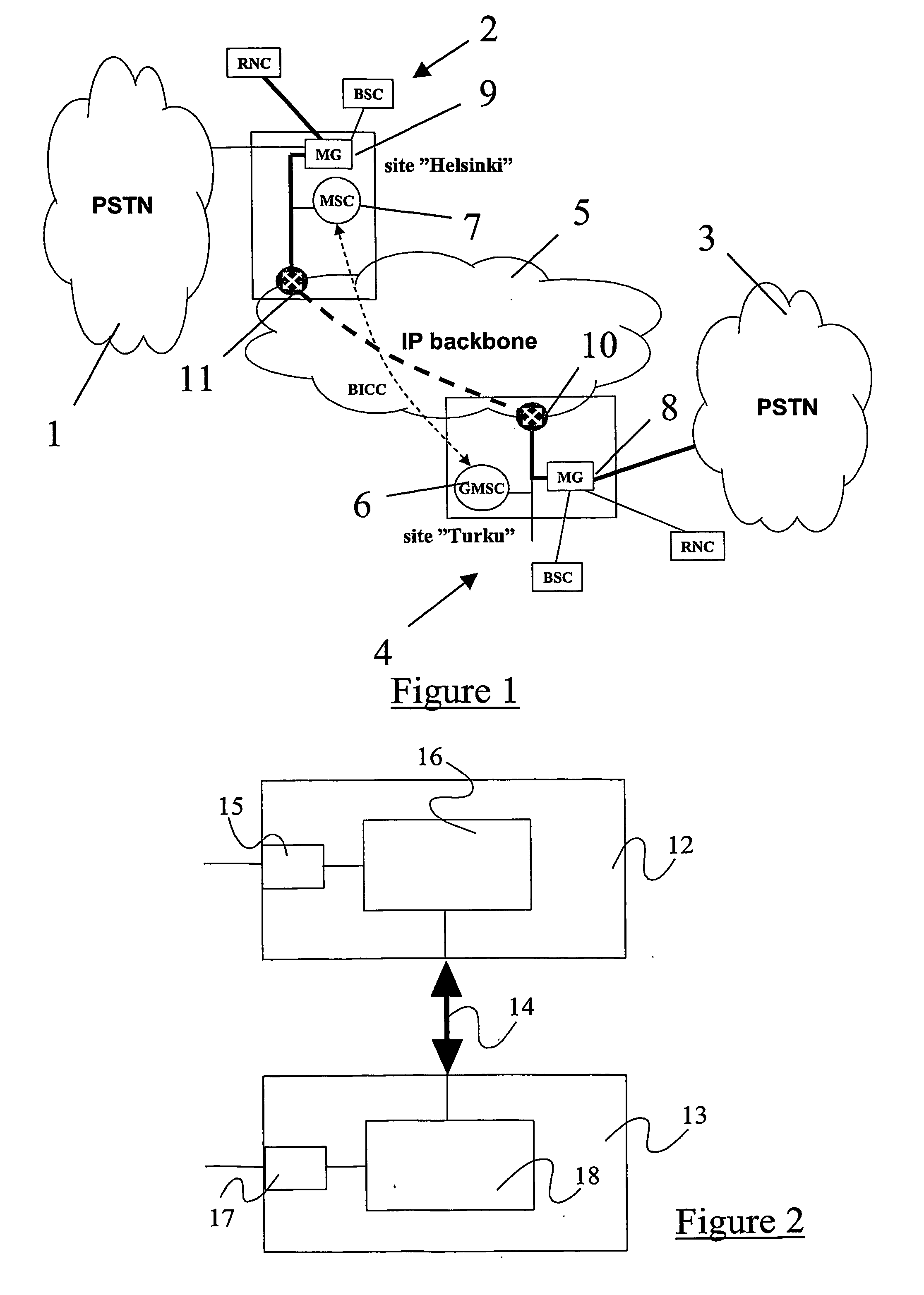
A method of controlling call admission within a system comprising a plurality of media gateways (8, 9) interconnected by a packet switched backbone (5). The method comprises, at least one media gateway (8, 9), monitoring the level of congestion suffered by incoming packets to that gateway from each other media gateway over said backbone. Following receipt of a request for a media gateway (8, 9) to terminate a bearer extending over said backbone (5) from a peer media gateway, making a decision on the admissibility of that request based upon the previously monitored level of congestion suffered by incoming packets from that peer media gateway.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
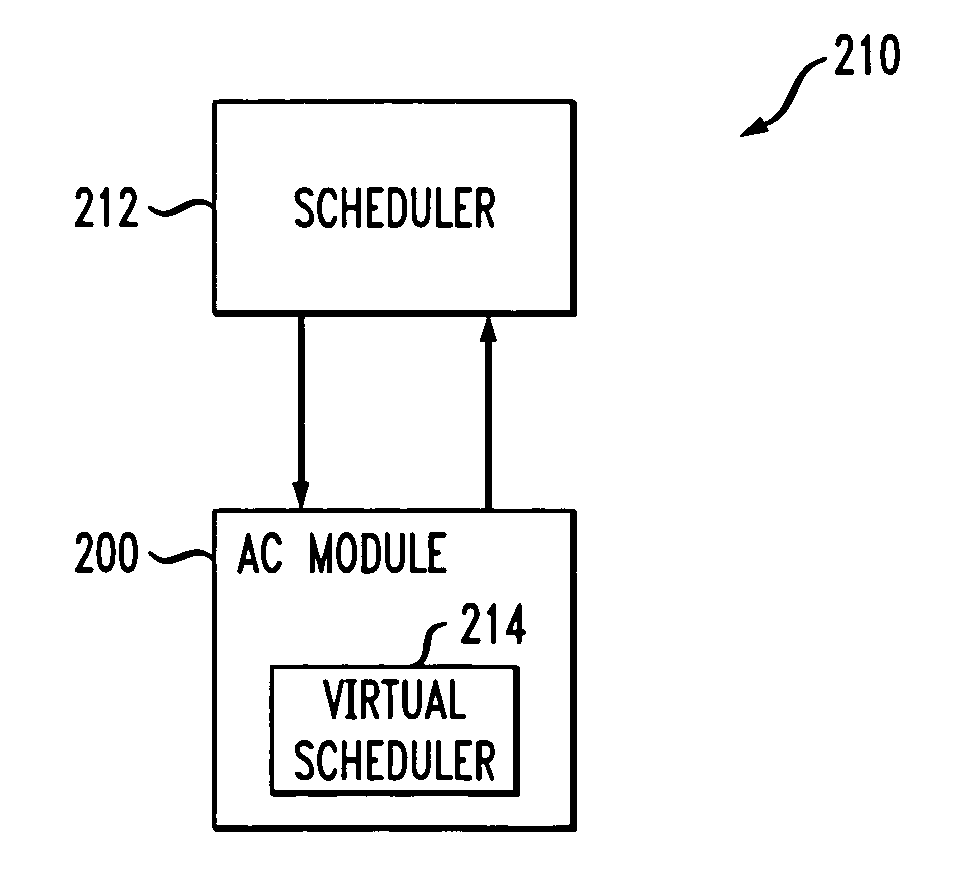
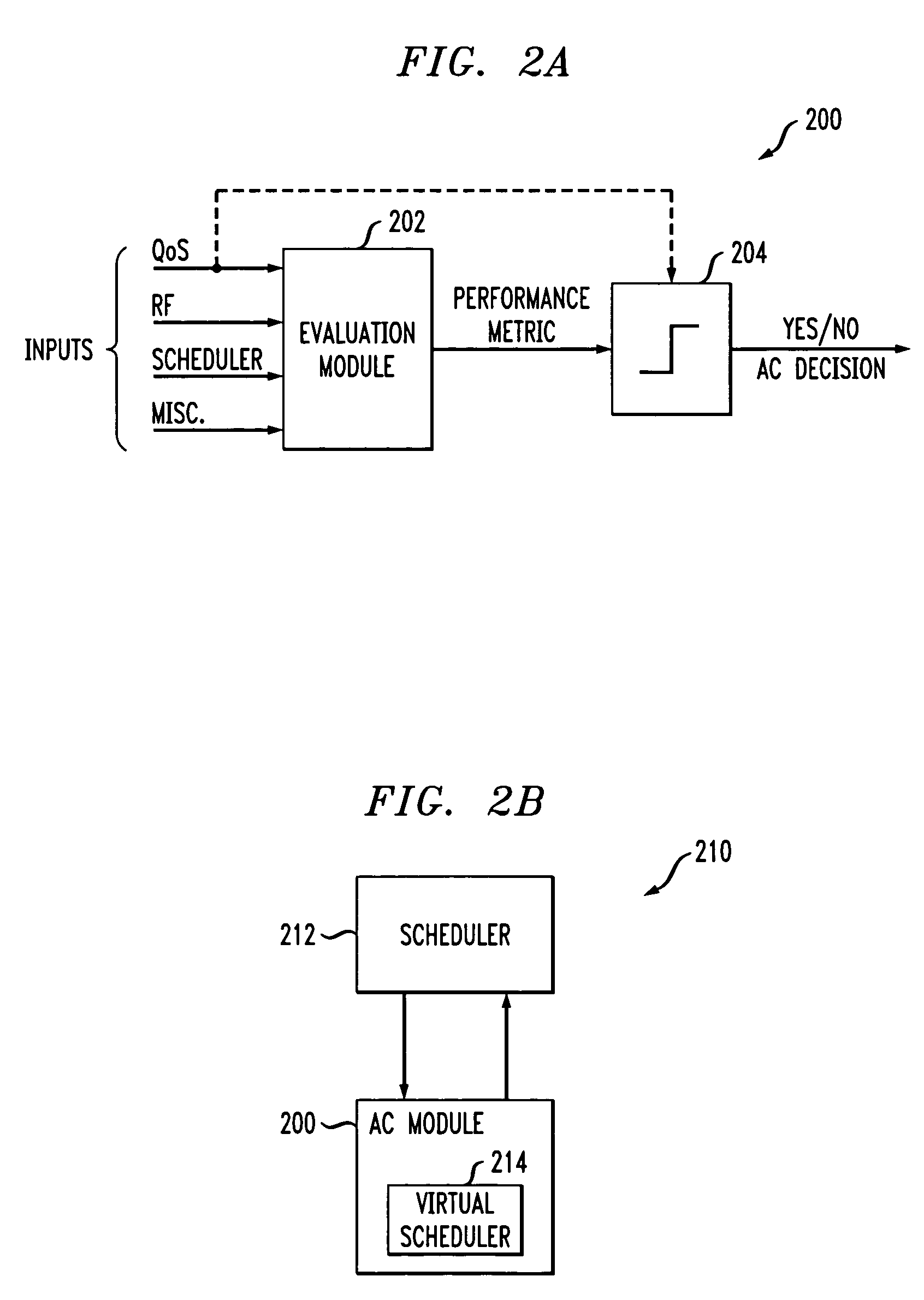
Method and apparatus for quality-of-service based admission control using a virtual scheduler
InactiveUS7660244B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemDistributed computing
In a wireless network or other communication system, admission of users to the system involves use of a first scheduler, which makes actual scheduling decisions for admitted users, and a second scheduler, which emulates the operation of the first scheduler. The first scheduler is configured to manage access to network resources for users already admitted to the system. The first scheduler is coupled to an admission control module which contains the second scheduler. The second scheduler, also referred to herein as a virtual scheduler, emulates operation of the first scheduler, under an operating scenario involving admission of at least one additional user to the system, in order to generate a performance metric. The performance metric is used to make an admission control decision regarding admission of the at least one additional user to the system.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
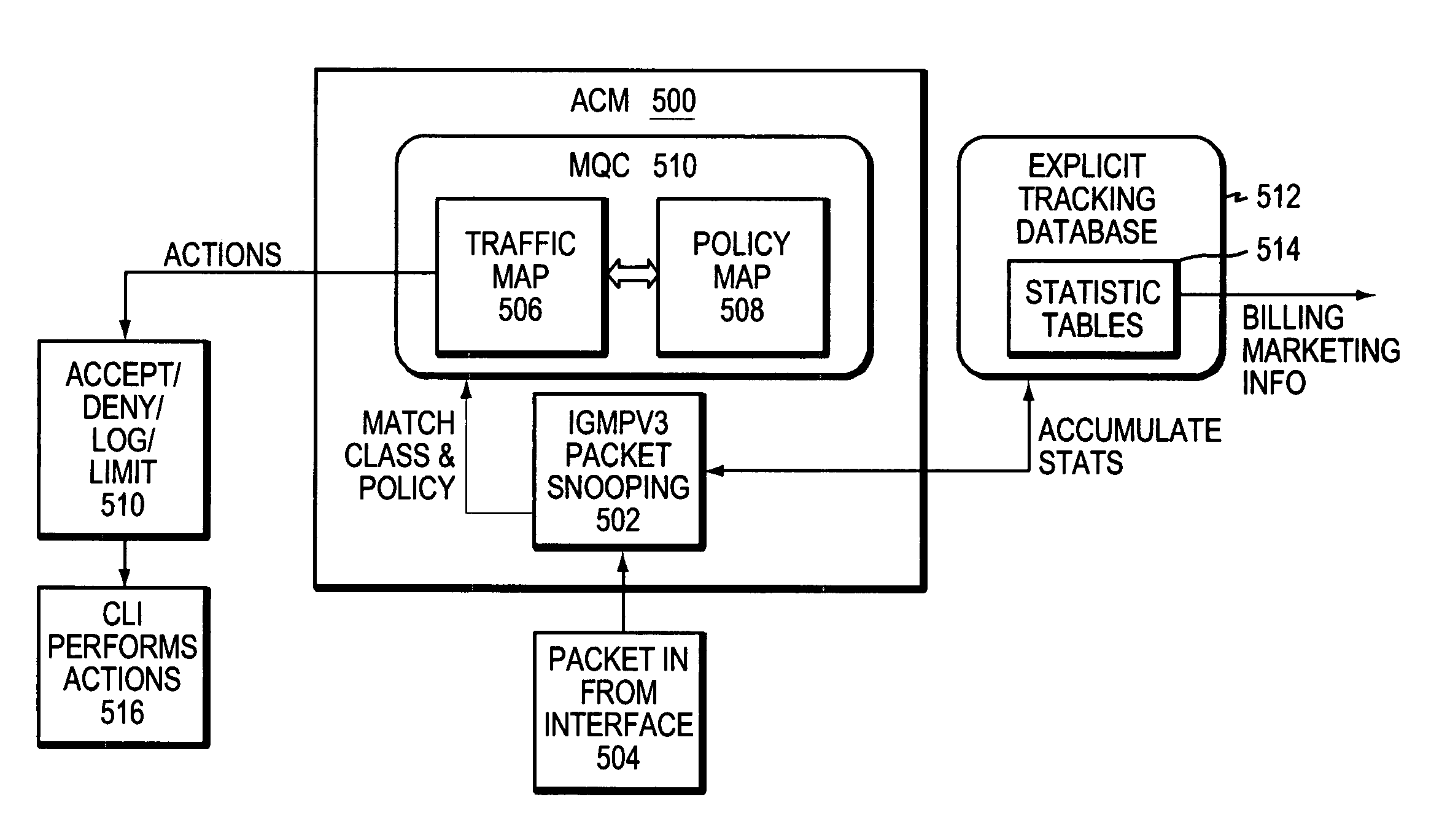
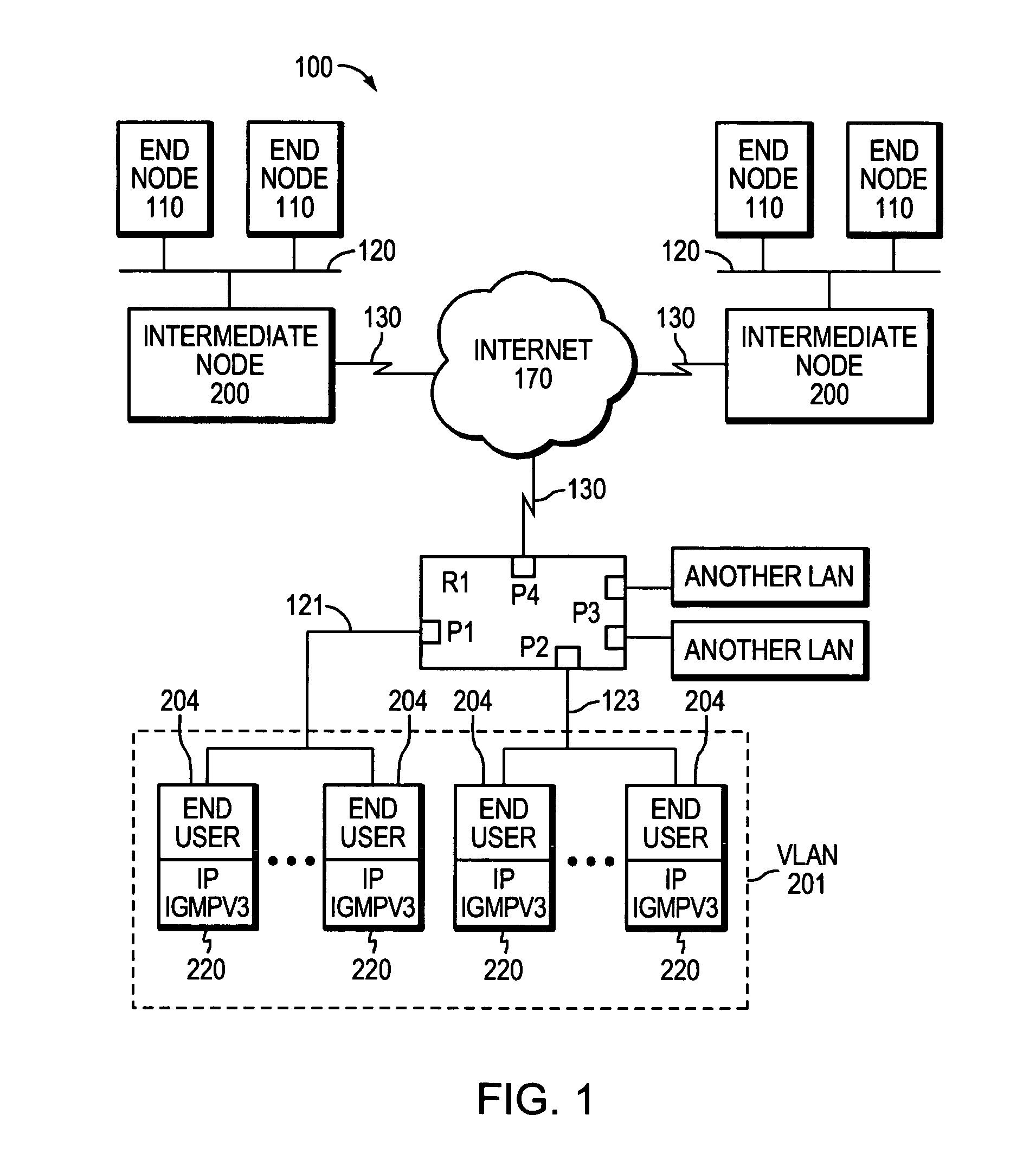
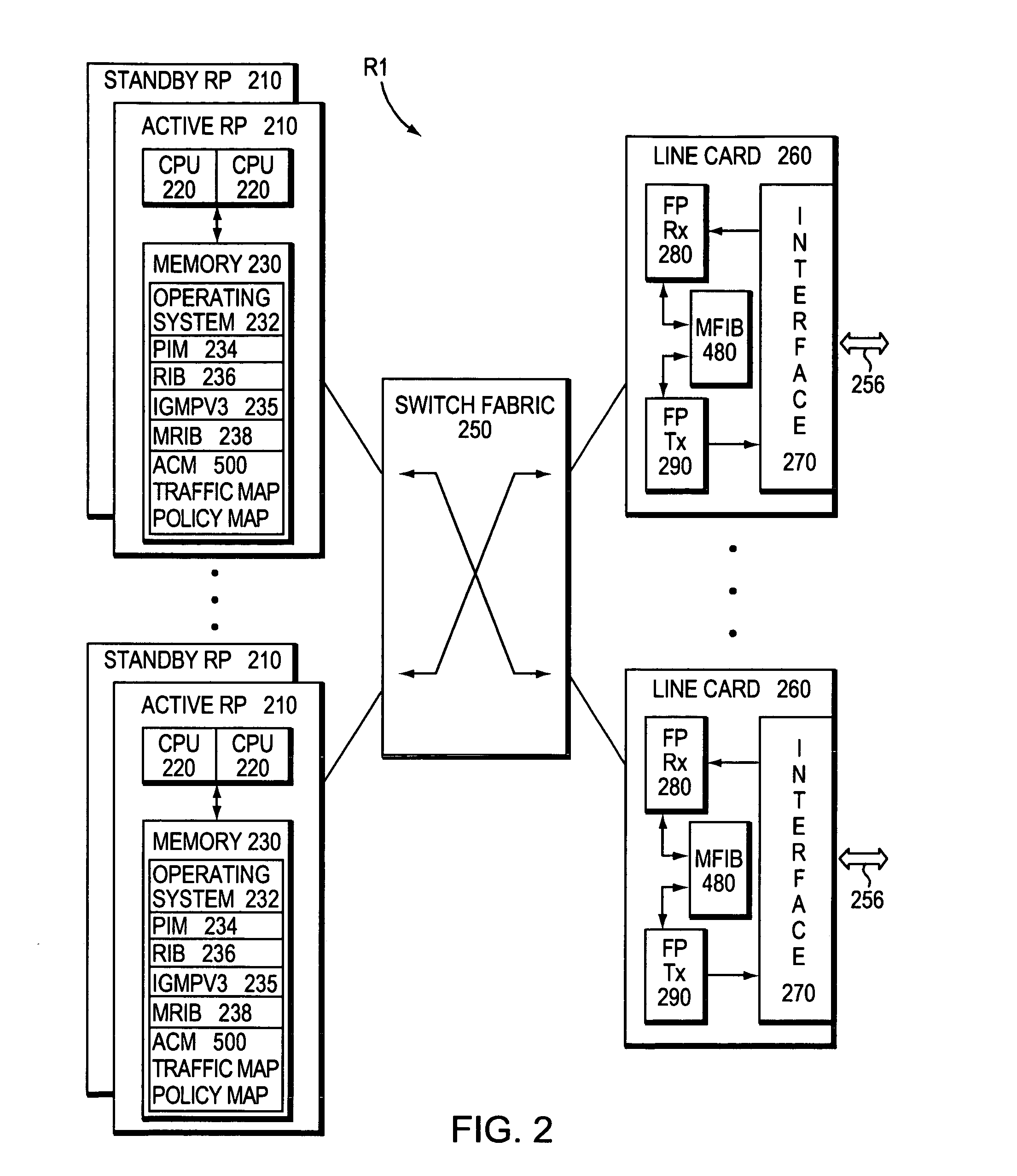
Admission control mechanism for multicast receivers
InactiveUS20060146857A1Avoid attackError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityNetwork packet
A method and system for controlling admission of an end user to a multicast channel over a network implementing a source filtering protocol. Incoming packet traffic received by an edge router is snooped and, when a request to join a multicast channel is received, the traffic is analyzed. Any service policy associated with the traffic class is found and applied to packet traffic from the requesting user. The actions include accepting membership in a group associated with a multicast channel and pushing the packets to the end user. If the action is to deny membership, then the multicast packets are prevented from reaching the end user. In addition information is logged and may be used for billing purposes or for accumulating marketing or other such information. Also, the actions may be to limit the number of routing states, by denying admittance to a groups once a limit number of requests to join, or other such parameter, is reached. Such limiting will substantially prevent DOS attacks on a multicast router.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
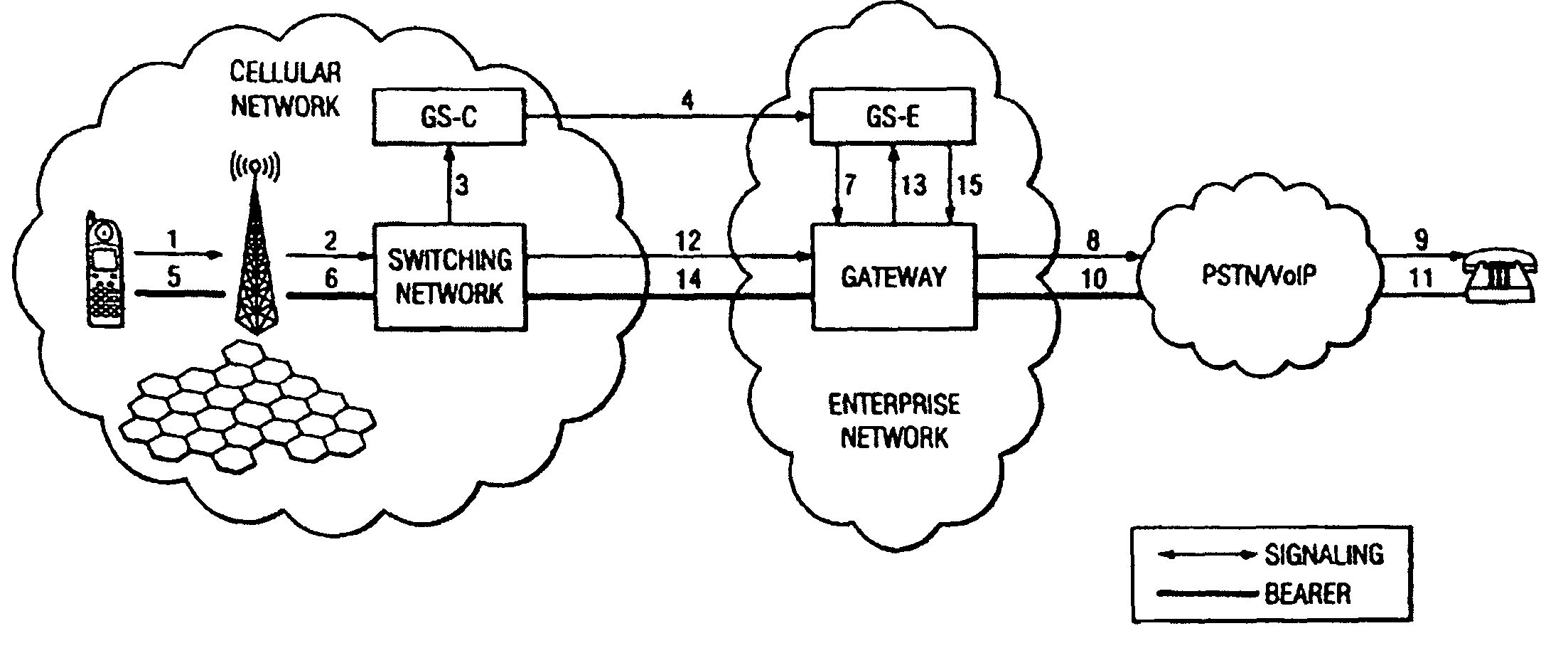
System and method for enabling VPN-less session setup for connecting mobile data devices to an enterprise data network
ActiveUS7873001B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesGPRS Tunnelling ProtocolMobile device
A mobile application gateway configured to interconnect mobile communication devices on a cellular network with an enterprise network is provided. The mobile application gateway includes a voice and data signaling gateway configured to provide routing functionalities, service functionalities and admission control. A gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) is configured to establish a secure data session between one or more of the mobile communication devices and the enterprise network by establishing a GPRS tunneling protocol (GTP) tunnel between a carrier-hosted serving GPRS support node (SGSN) and the GGSN.
Owner:TANGO NETWORKS
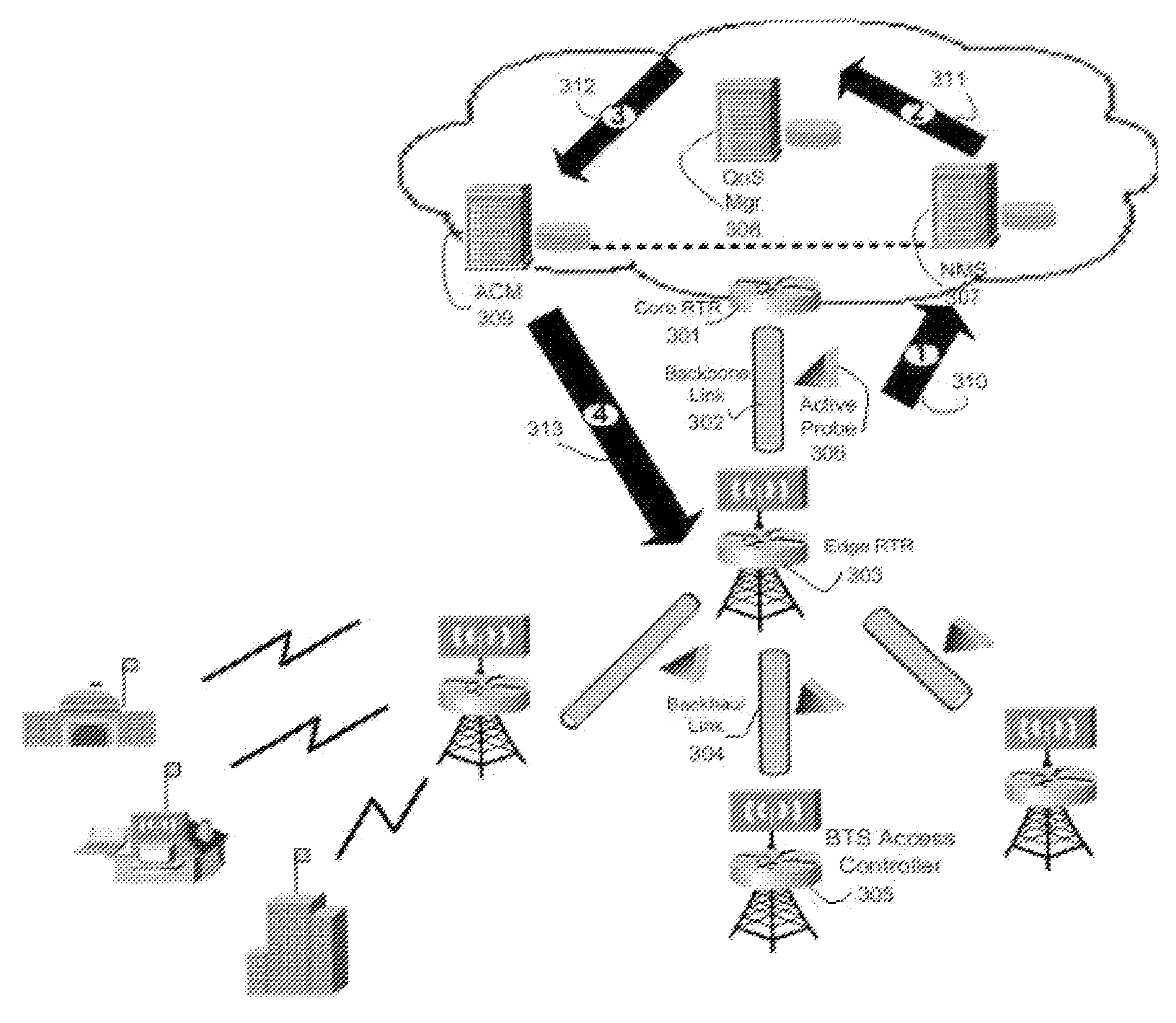
Methods And Systems For Dynamic Bandwidth Management For Quality Of Service In IP Core And Access Networks
InactiveUS20080130495A1Easy to useStringent qualityError preventionTransmission systemsPresent methodKey issues
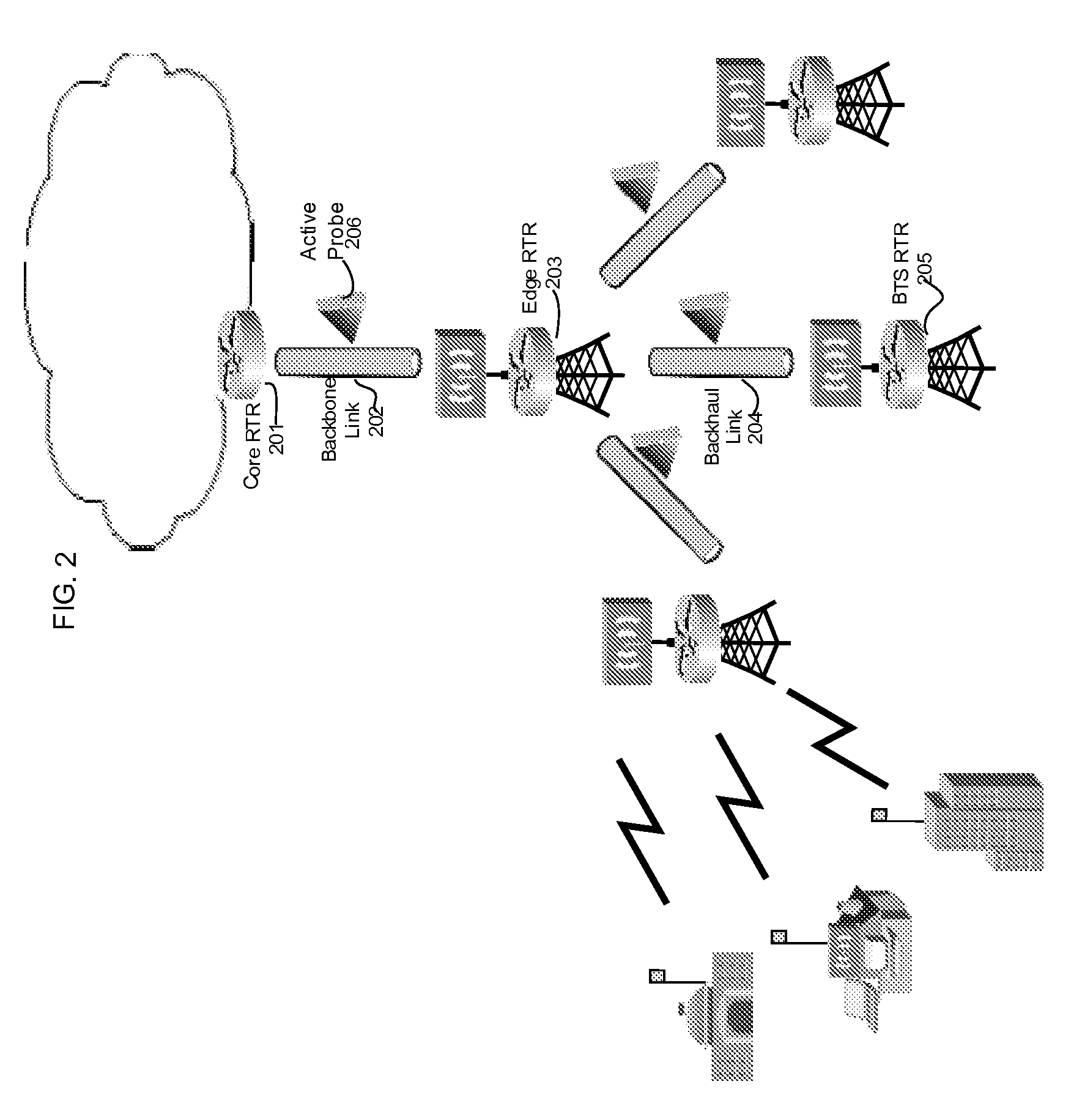
Proper allocation of network bandwidth is a crucial issue in rendering certain performance guarantees to meet the growing customer demands. Hence, allocation methodologies must explicitly be carried out for these guarantees to be given as efficiently as possible since the shared resources are limited. This invention presents methods and systems for Dynamic Bandwidth Management (DBM) and Quality of Service (QoS) in packet-based networks. DBM is an algorithm that dynamically adjusts the resource allocation in the IP Access Networks based upon measured QoS at the IP Core Network through an implementation of a Feedback Control Mechanism to manage available core transport bandwidth. Such a Feedback Control Mechanism is capable of maintaining a condition of non-congestion, a sufficient and necessary condition to meet end-to-end QoS requirements in a Next Generation Network (NGN). The emphasis is given on the system implementation of QoS policies for the fair distribution of network resources through a scalable architecture comprising key Resource and Admission Control Functional (RACF) entities, namely: a Network Management System (NMS), a QoS Manager, an Access Controller Manager (ACM), the Access Controllers, and the active probes.
Owner:LATITUDE BROADBAND
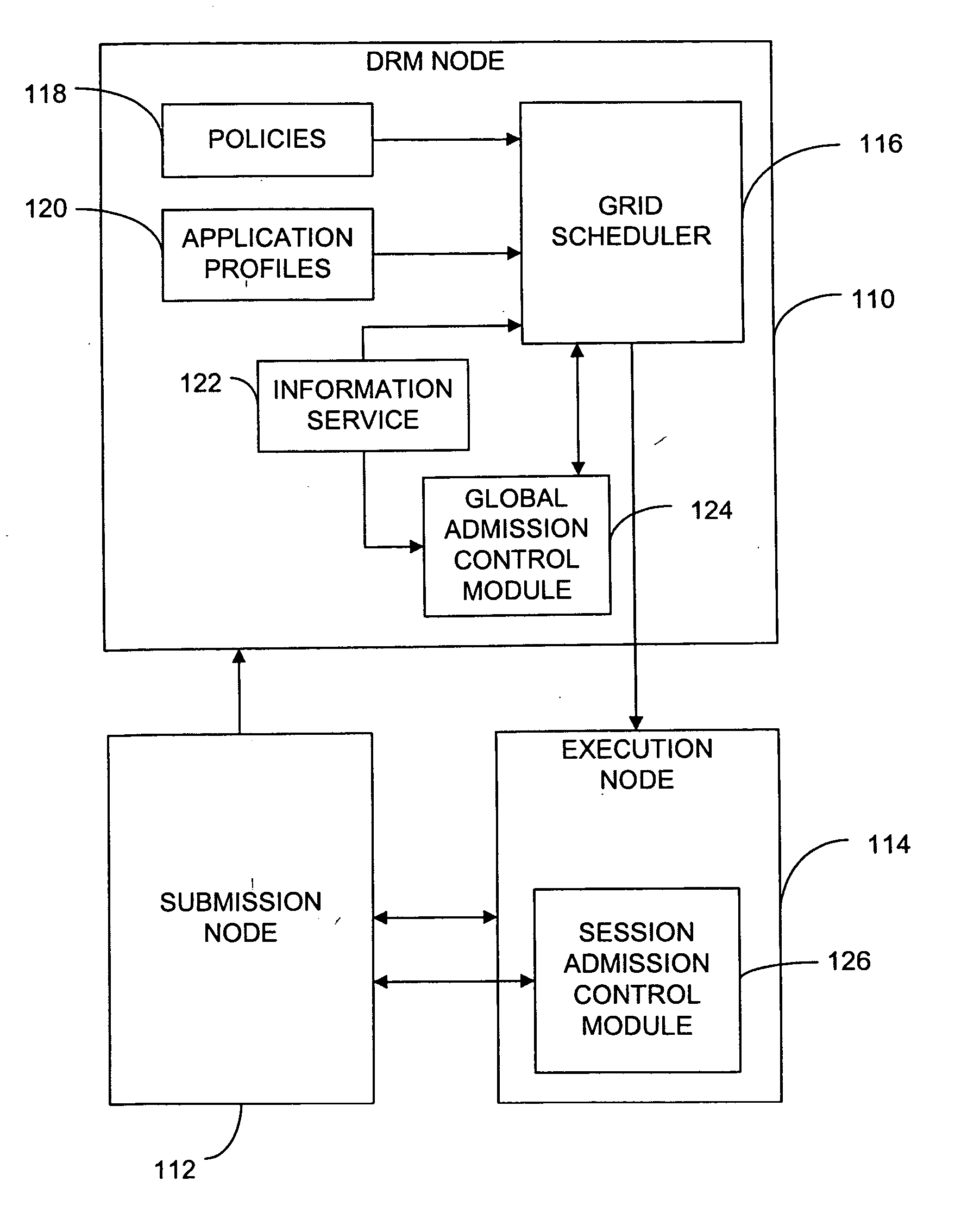
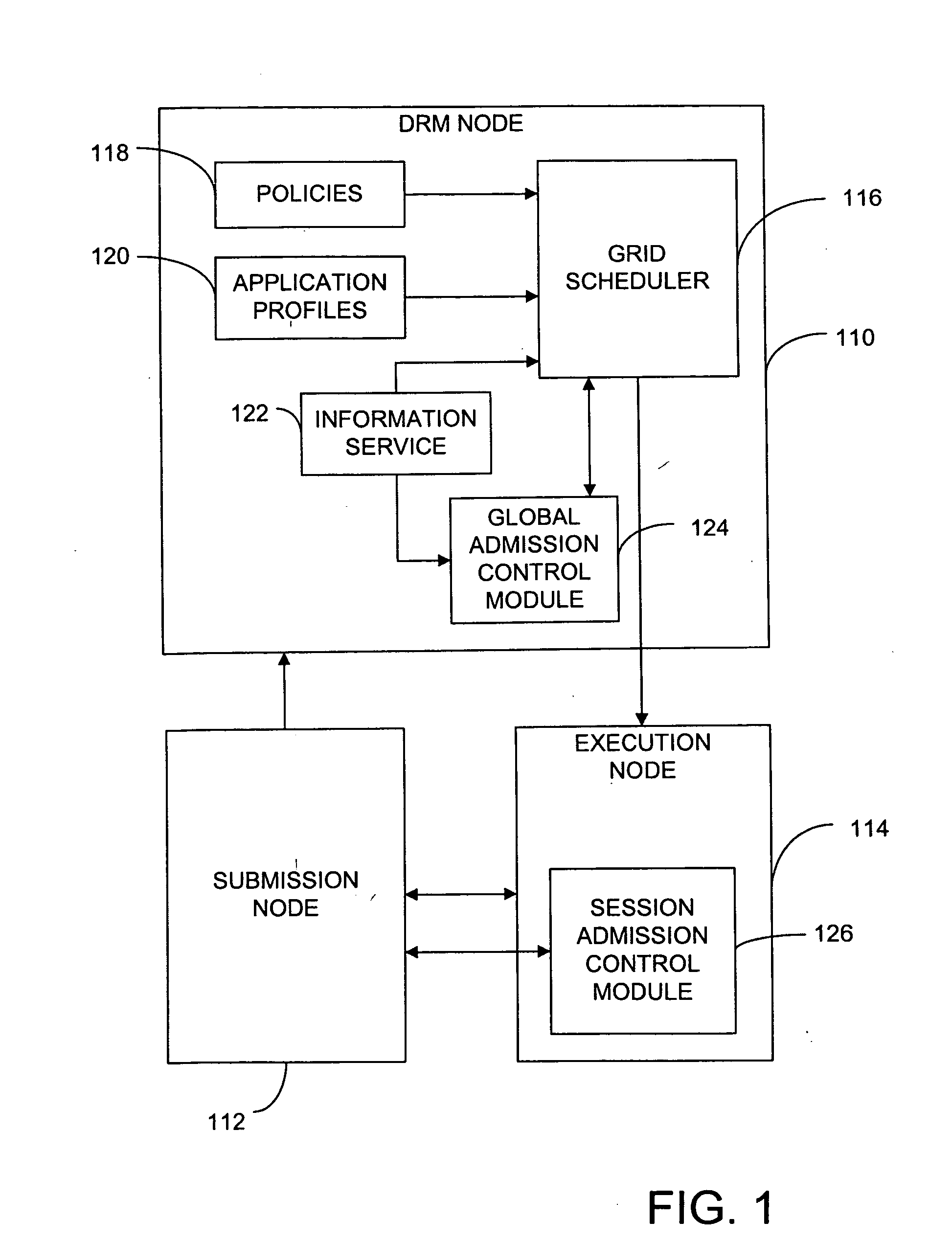
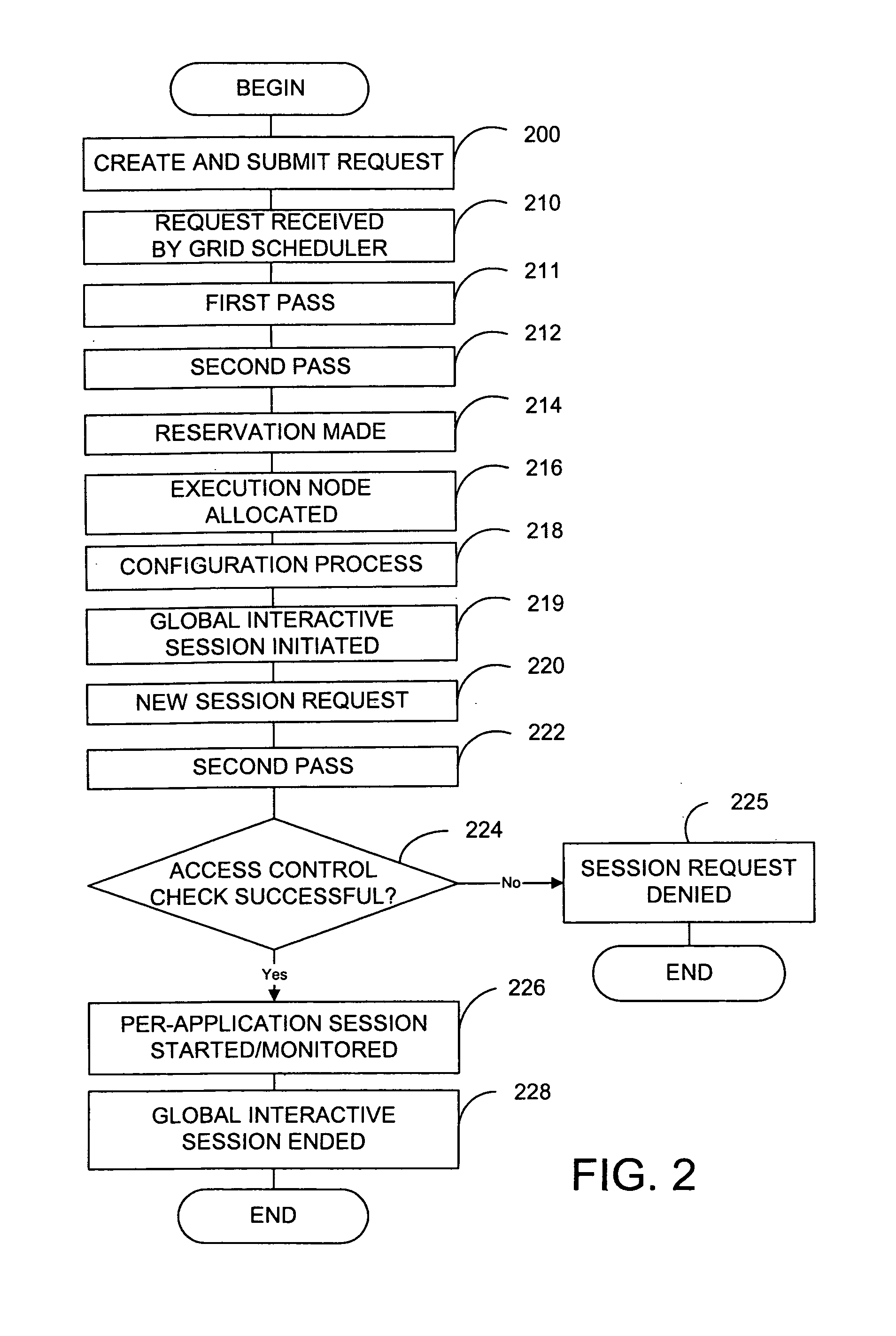
Method and system using admission control in interactive grid computing systems
In brief, the invention provides a method and system for admission control in a grid computing environment. When a user request for a global session is received from a submission node, applications to be launched through the global session are identified, and resource requirements are determined. A execution node is then allocated, and the global session is established between the execution node and the submission node. A user then requests an application session through the established global session, and the application session is established with the execution node.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
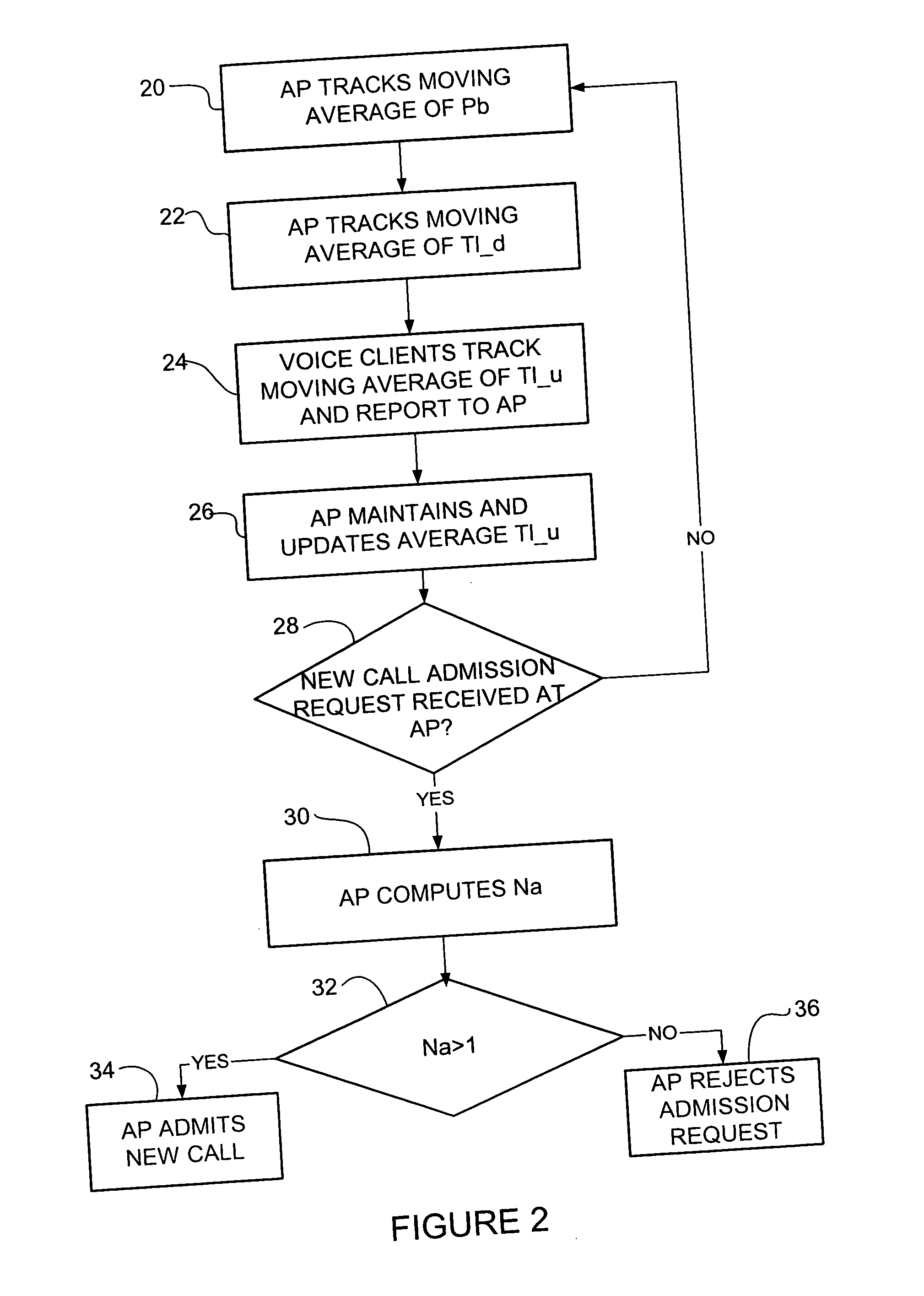
Method and system for evaluting number of additional admissible calls for use in call admission control
ActiveUS20060171314A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsBusy timeBandwidth requirement
A method for evaluating number of additional admissible calls for use in call admission control includes tracking a percentage of channel busy time and transmission time of downlink and uplink voice packets, receiving a call admission request, and calculating the number of admissible calls. The number of admissible calls is calculated based on a channel bandwidth requirement determined from the percentage of channel busy time and a voice packet queuing requirement determined from the transmission time of downlink and uplink voice packets. The call admission request is approved if the number of admissible calls is greater than one and rejected if the number of admissible calls is less than one.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Measurement and reporting for uplink enhanced dedicated channel (E-DCH)
InactiveUS20050249148A1Network traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmitted powerData rate
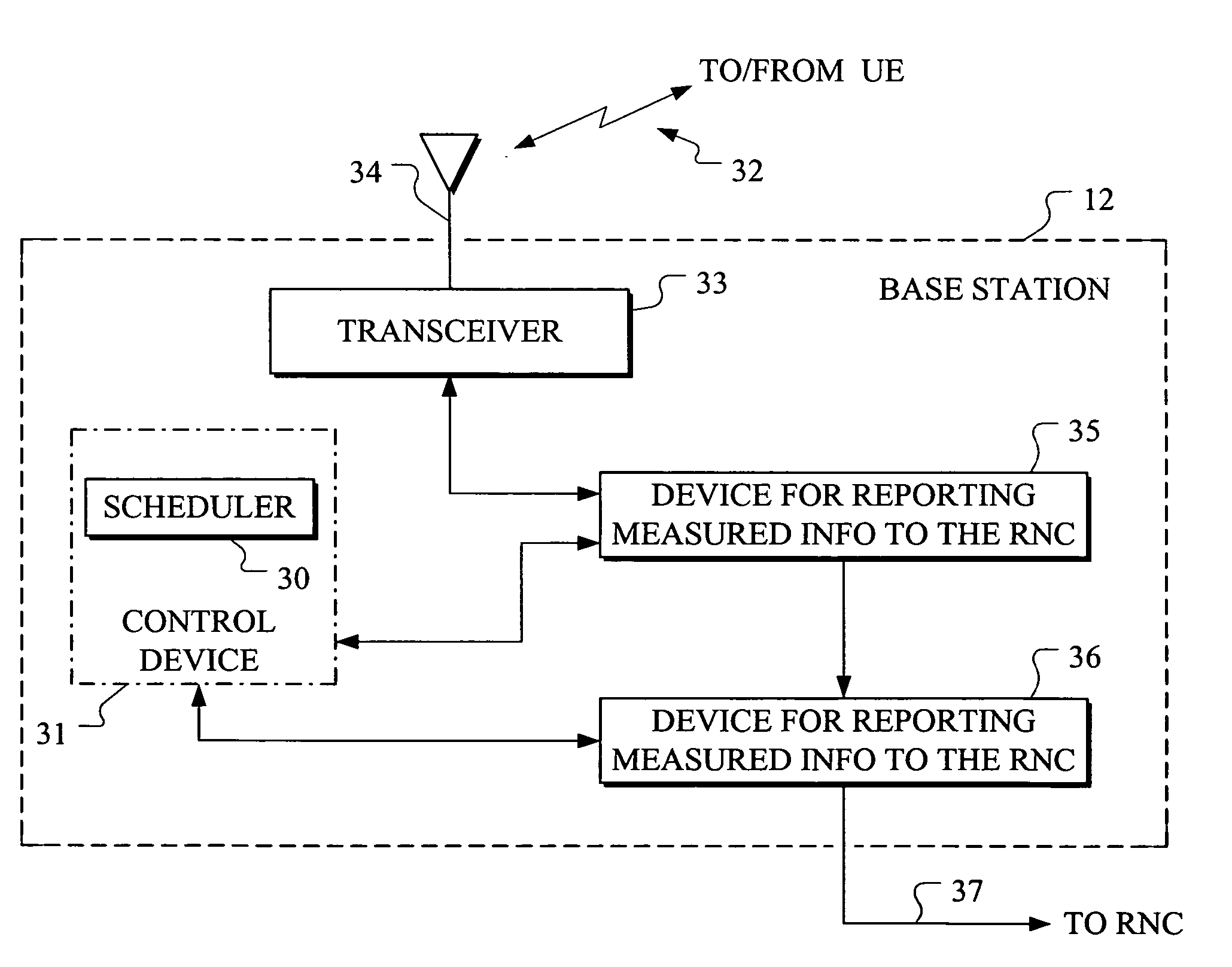
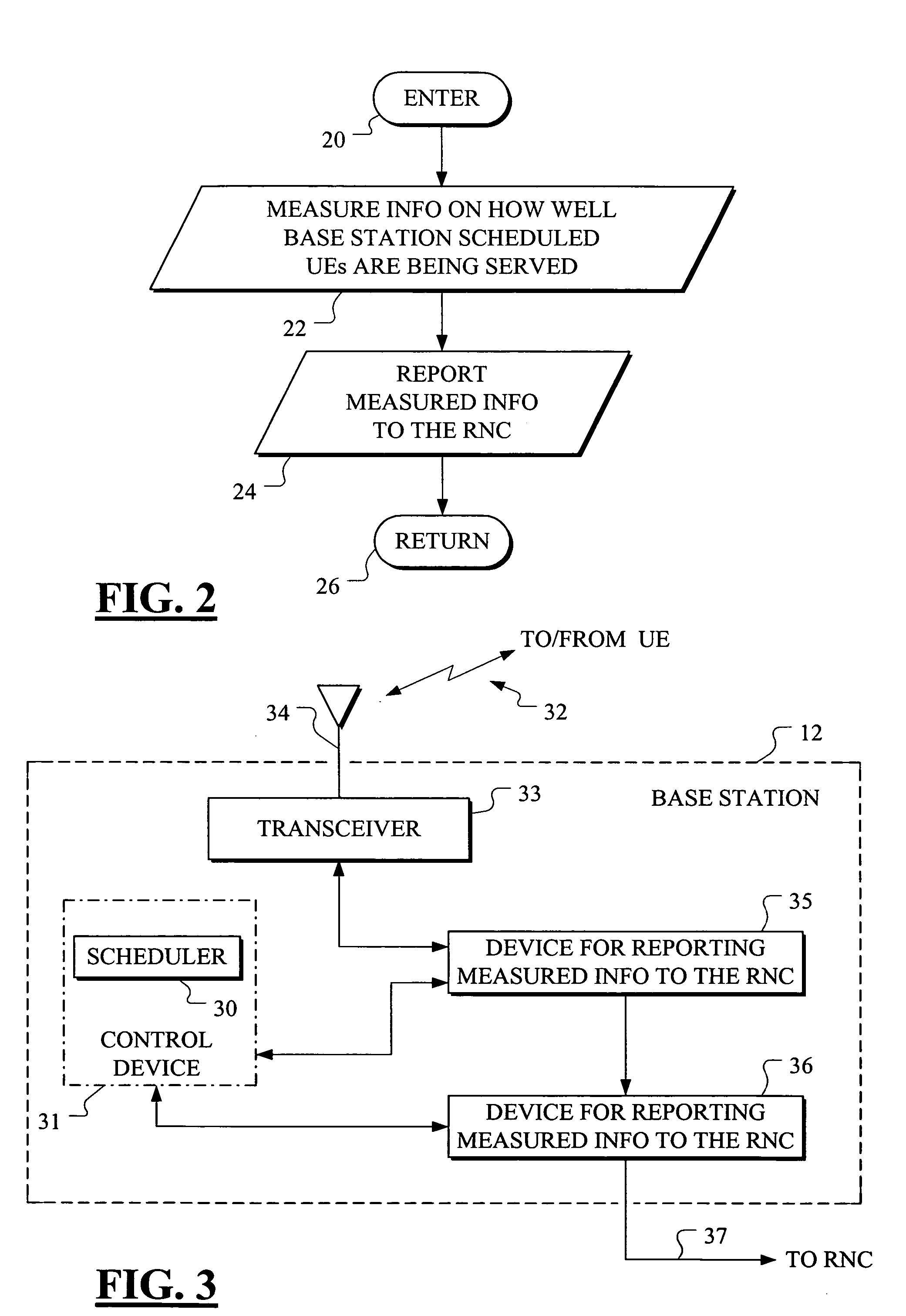
A base station (Node B) 12 provides information to a Radio Network Controller (RNC) 16 on how well User Equipment (UE) 14 subject to Node B scheduling is served for an Enhanced Dedicated Uplink Channel (E-DCH). This may be done for instance by the Node B measuring or estimating 22 the requested data rate per UE / cell, and communicating 24 the measured or estimated information to the RNC for enabling the RNC to perform Radio Resource Management (RRM). The RNC is thereby enabled to know the quality of the E-DCH transmission service per UE / cell. In addition to helping Admission Control and Load Control, it also enables the RNC to reconfigure the transport format combination set (TFCS) for E-DCH with more accurate timing. The UE and the Node B exchange information such as rate request / grant or UE Buffer and Transmit Power Status / Scheduling Assignment.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Multitask concurrent executive system and method for hybrid network service
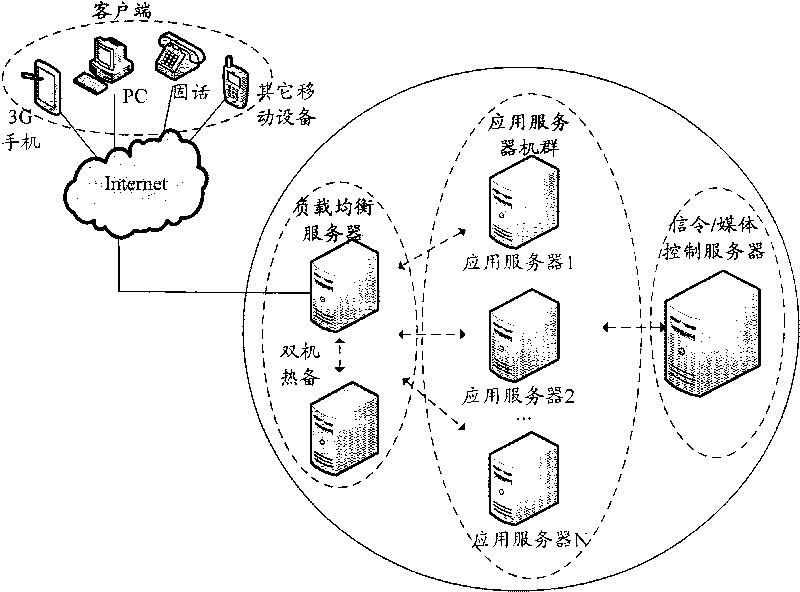
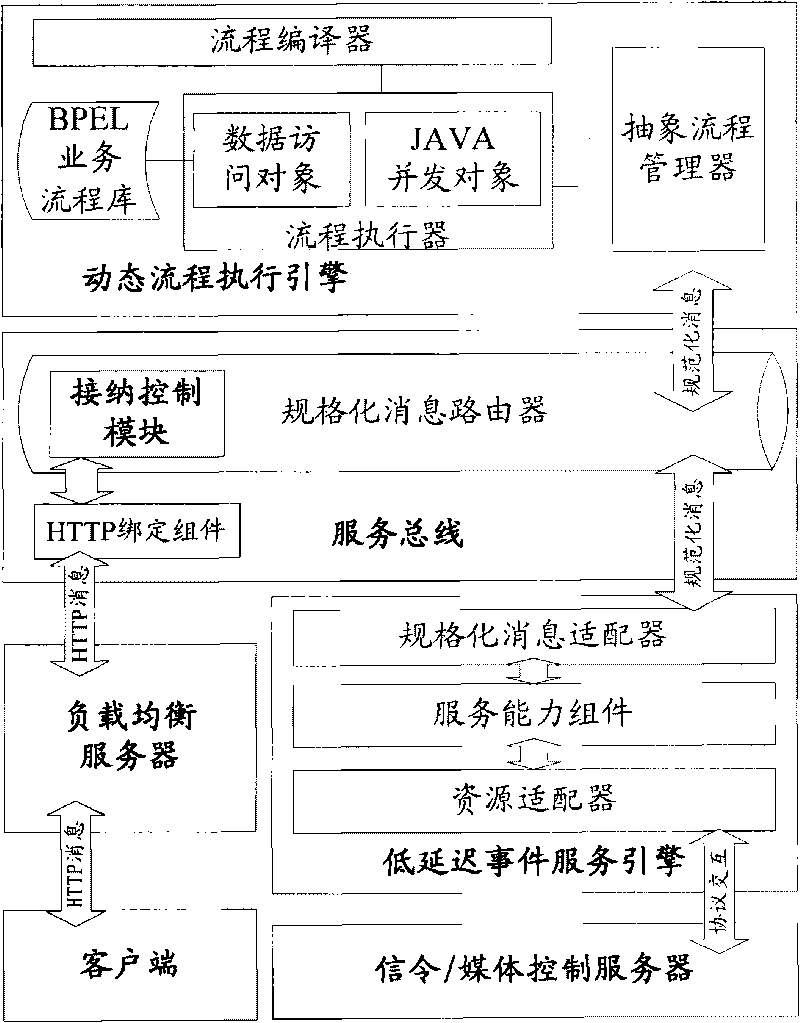
InactiveCN101741850AIntegrate business capabilitiesHybrid network services are flexible and diverseData switching networksService flowMedia controls
The invention relates to a multitask concurrent executive system and a method for hybrid network service. The system comprises a client side, a load-balancing server, a signalling / media control server and an application server cluster. The running method thereof is as follows: after the client side receives a service request, the load-balancing server selects an optimum application server and transmits the service request to a service bus thereof. After an admission control module of the application server carries out admission control on the request, the service bus transmits the request to a dynamic flow execution engine, the dynamic flow execution engine starts a service flow corresponding to the request to analyze and process, and the service bus calls a corresponding service capability component in a low deferred event service engine and interacts with the signalling / media control server through the resource adapter so as to call the service resource of the latter; and a processing result is returned to the client side according to a reverse process. The multitask concurrent executive system supports the supply of hybrid network service over a telecommunication network and the internet and the multitask concurrent on a heterogeneous network and terminals.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
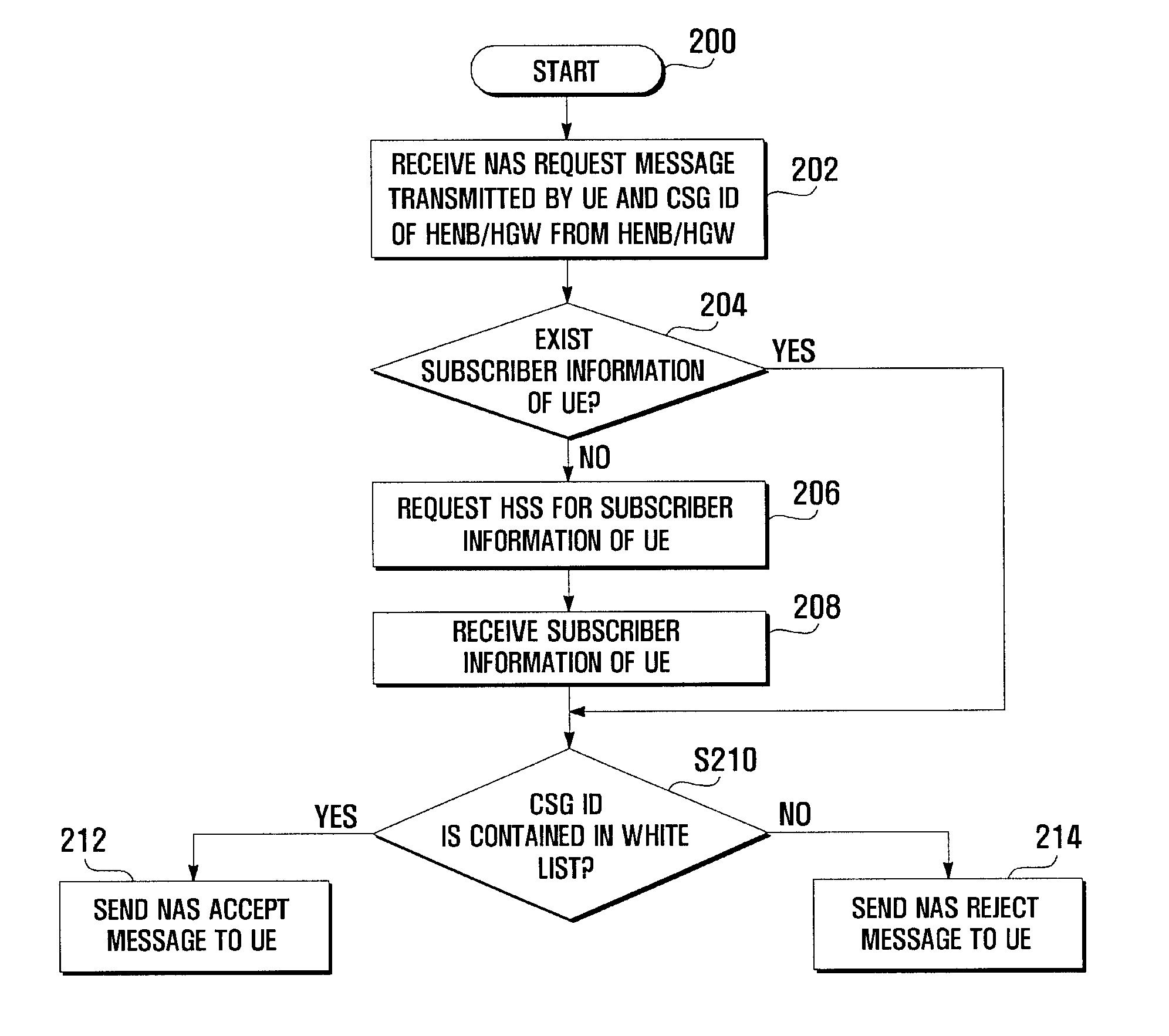
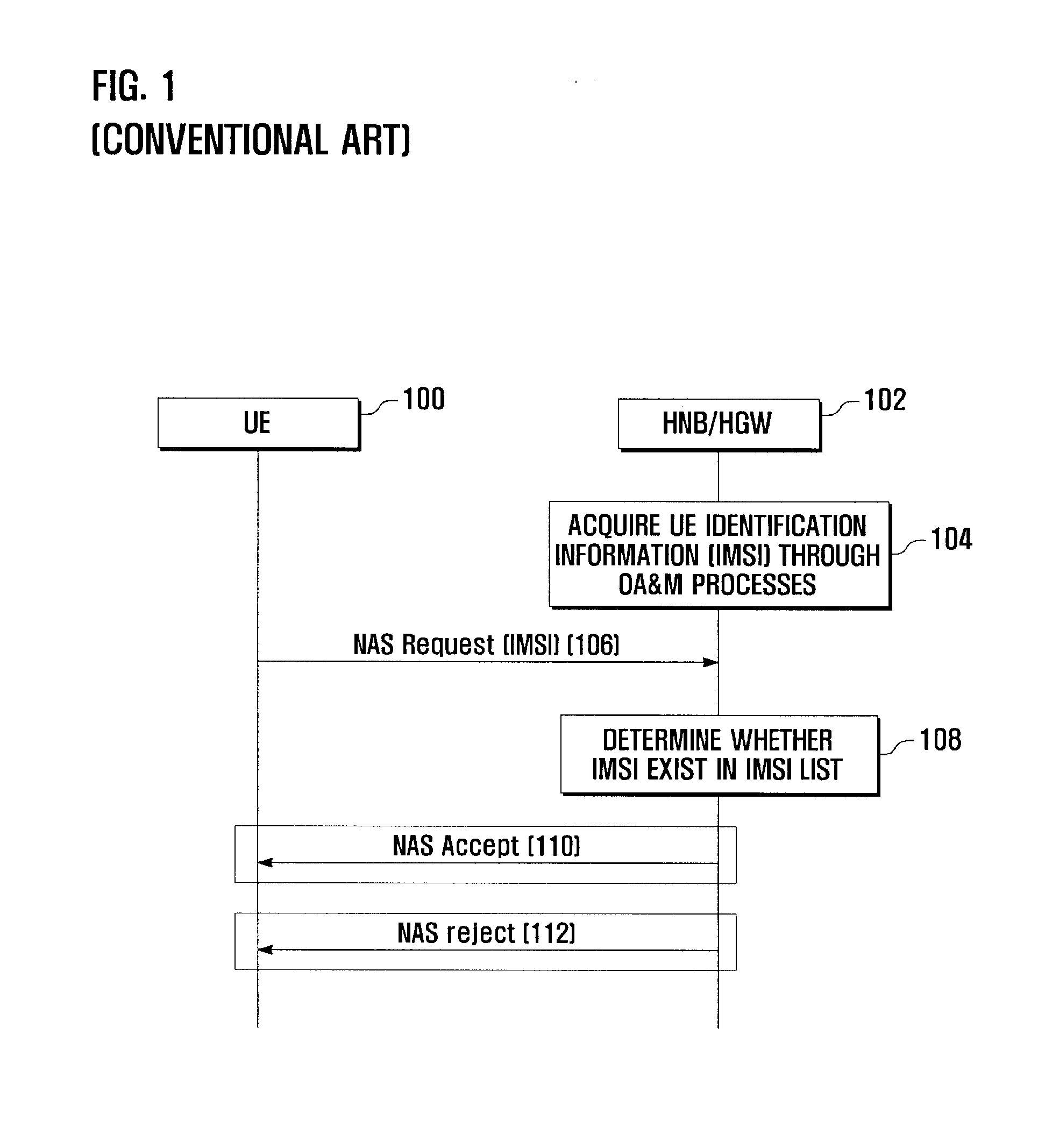
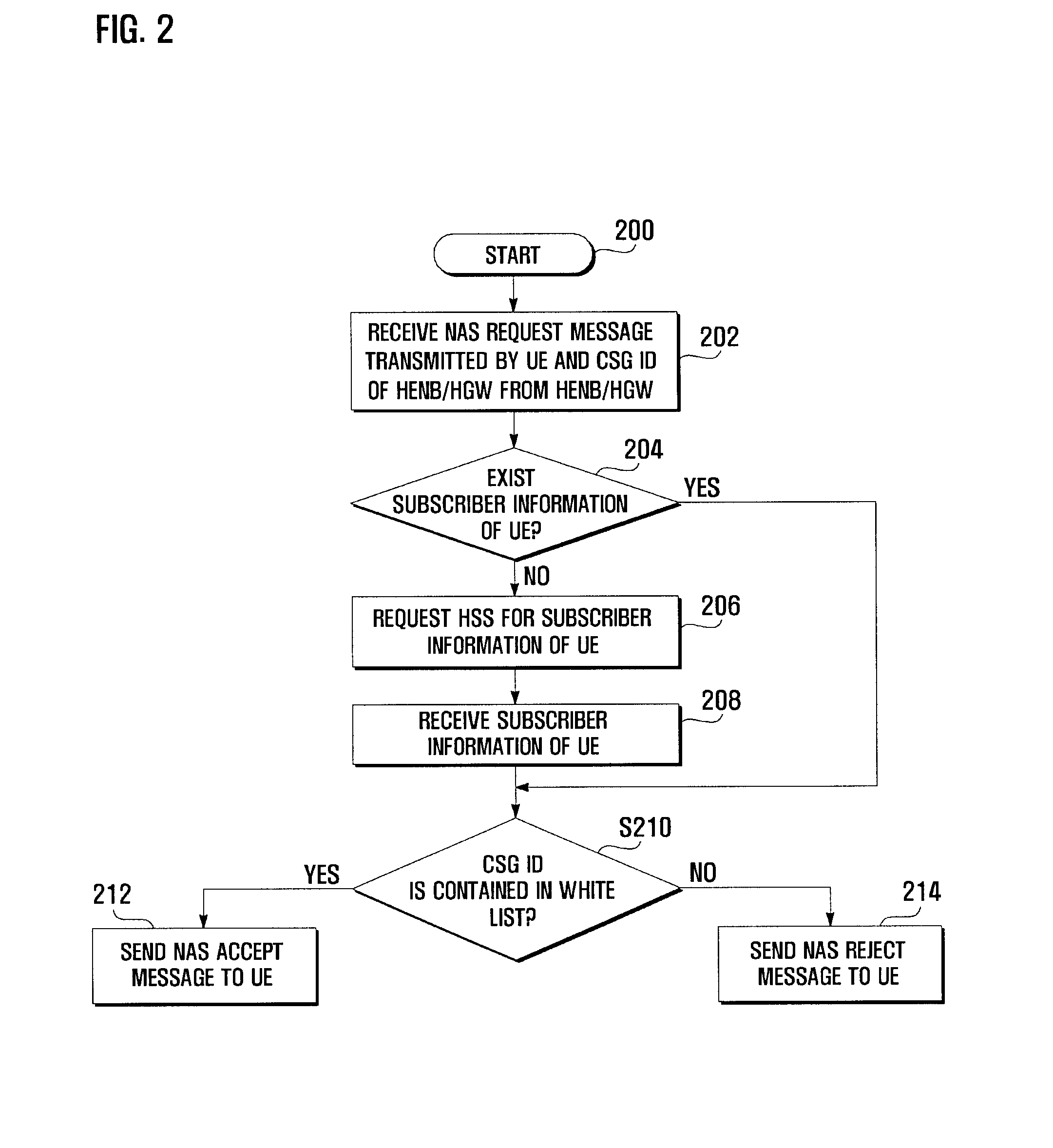
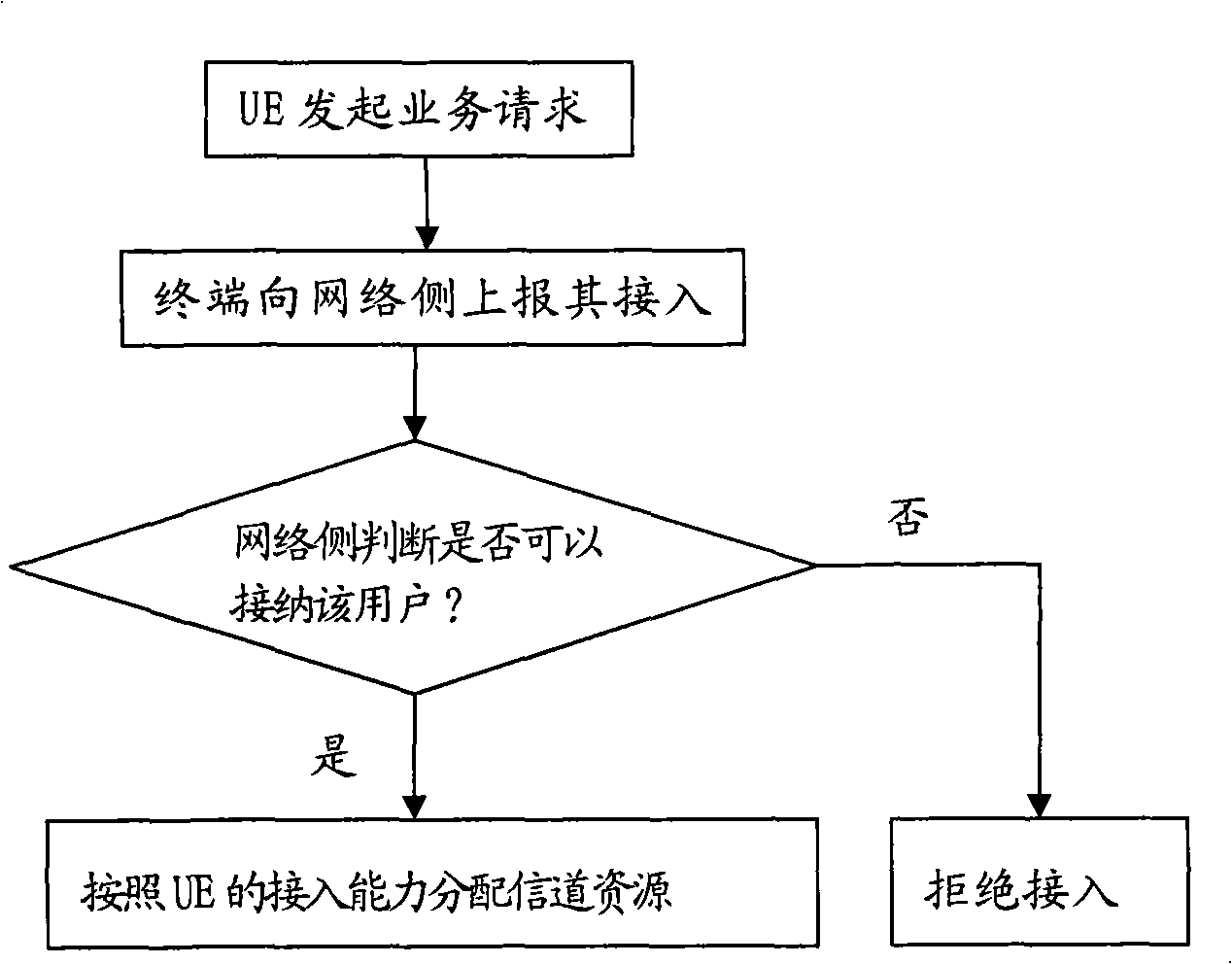
Access admission control method and system for mobile communication system
ActiveUS20100075635A1Effective controlUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionAssess restrictionMobile communication systemsWhitelist
An access admission control method and system for and SAE / LTE system is provided for determining whether to accept or reject an access of a User Equipment (UE) to a Home evolved Node B (HeNB) based on the subscriber information of the UE. In an access admission control method according to the present invention, a HeNB or HeNB Gateway (HGW) transmits, when an access request message is received from a UE, the access request message to a Mobility Management Entity (MME) together with a CSG ID of the HeNB, and the MME determines, whether to accept or reject the access of the UE to the HeNB based on whether the CSG ID is contained in a white list associated with the UE.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
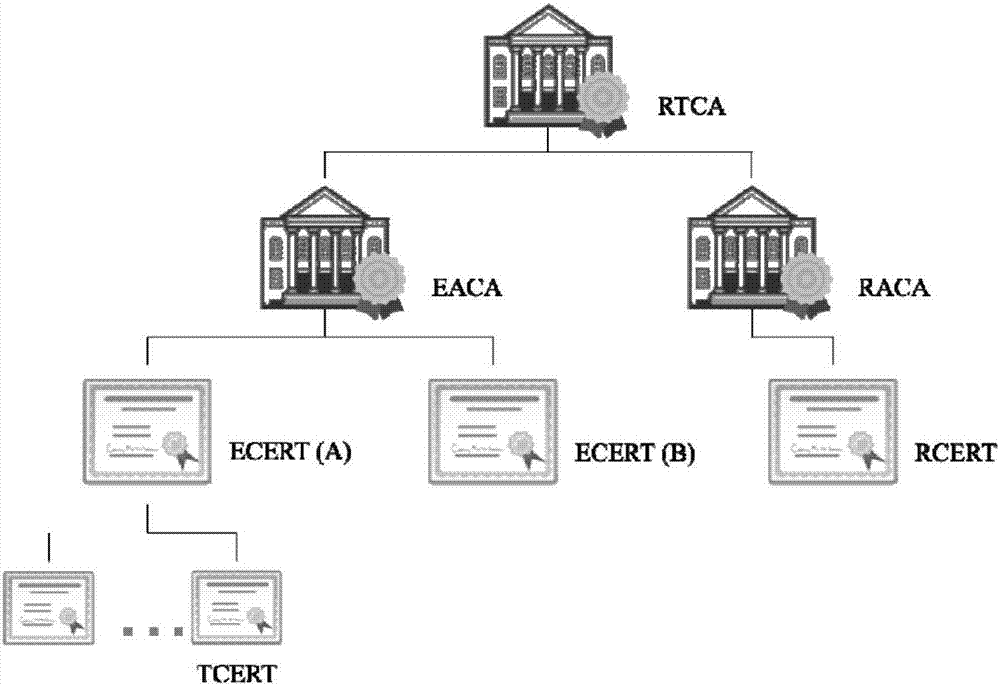
Consortium chain permission control method based on digital certificates and CA authentication system
ActiveCN107426157AProcess controlSecurityUser identity/authority verificationGranularityDigital Signature Algorithm
The invention discloses a consortium chain permission control method based on digital certificates and a CA authentication system. In a consortium chain, the enrollment control and automatic authorization of the consortium chain are realized through a layered digital certificate issuance system. The method of the invention pre-defines three kinds of permission mechanisms for respectively controlling enrollment permissions between consortium chain nodes, role permissions of the consortium chain nodes and access permissions of blockchain users. Three kinds of digital certificates including the enrollment certificate, role certificate and transaction certificate are used for respectively controlling the three permissions of node enrollment, role identification and client enrollment. An internationally accepted elliptic curve digital signature algorithm or a national crypto digital signature algorithm is used for achieving the generation of the digital certificates and secure message signature and validation, the defects of being large in permission granularity of a traditional blockchain or even having no enrollment functions and the like are overcome, the blockchain users are provided with anonymous transaction features, the security of blockchain transactions is improved, and the privacy needs of the users are met.
Owner:HANGZHOU QULIAN TECH CO LTD
Simple admission control for IP based networks
A simple admission control mechanism for IP based networks is provided. The decision on whether a new flow is accepted is based on the link load information on the paths from the source to destination. The new flow is accepted when the link load is less than a threshold. When at least one of the links on all of the available paths is larger than the acceptable threshold, access is denied to the flow. More than one threshold level may be used. Under the multiple threshold scenario, the traffic may be divided into different classes. The admission control mechanism helps to ensure a network that is not heavily congested.
Owner:VRINGO INFRASTRUCTURE +1
Method of admission control
InactiveUS20050050246A1Store-and-forward switching systemsInput/output processes for data processingDistributed computingAdmission control
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
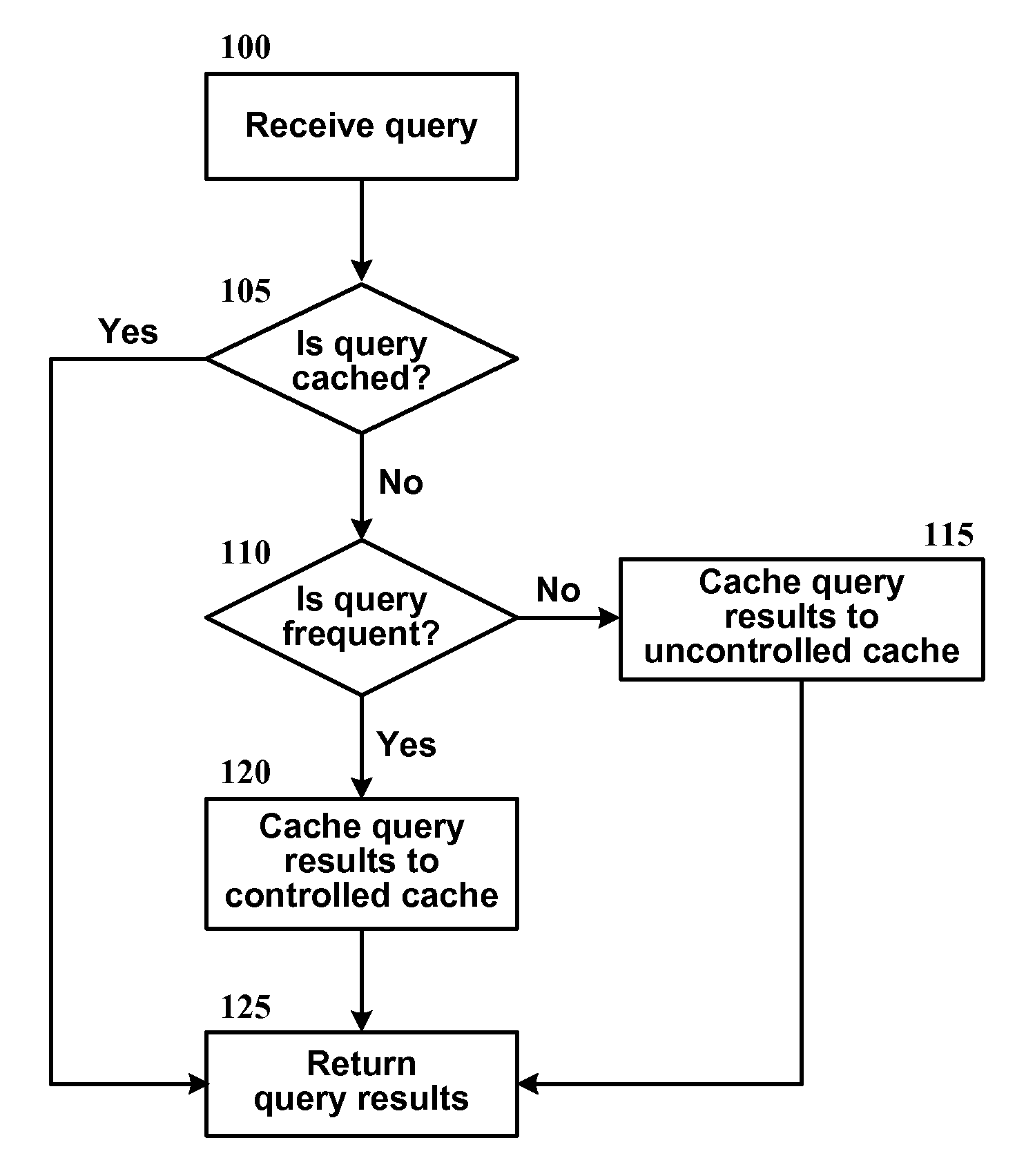
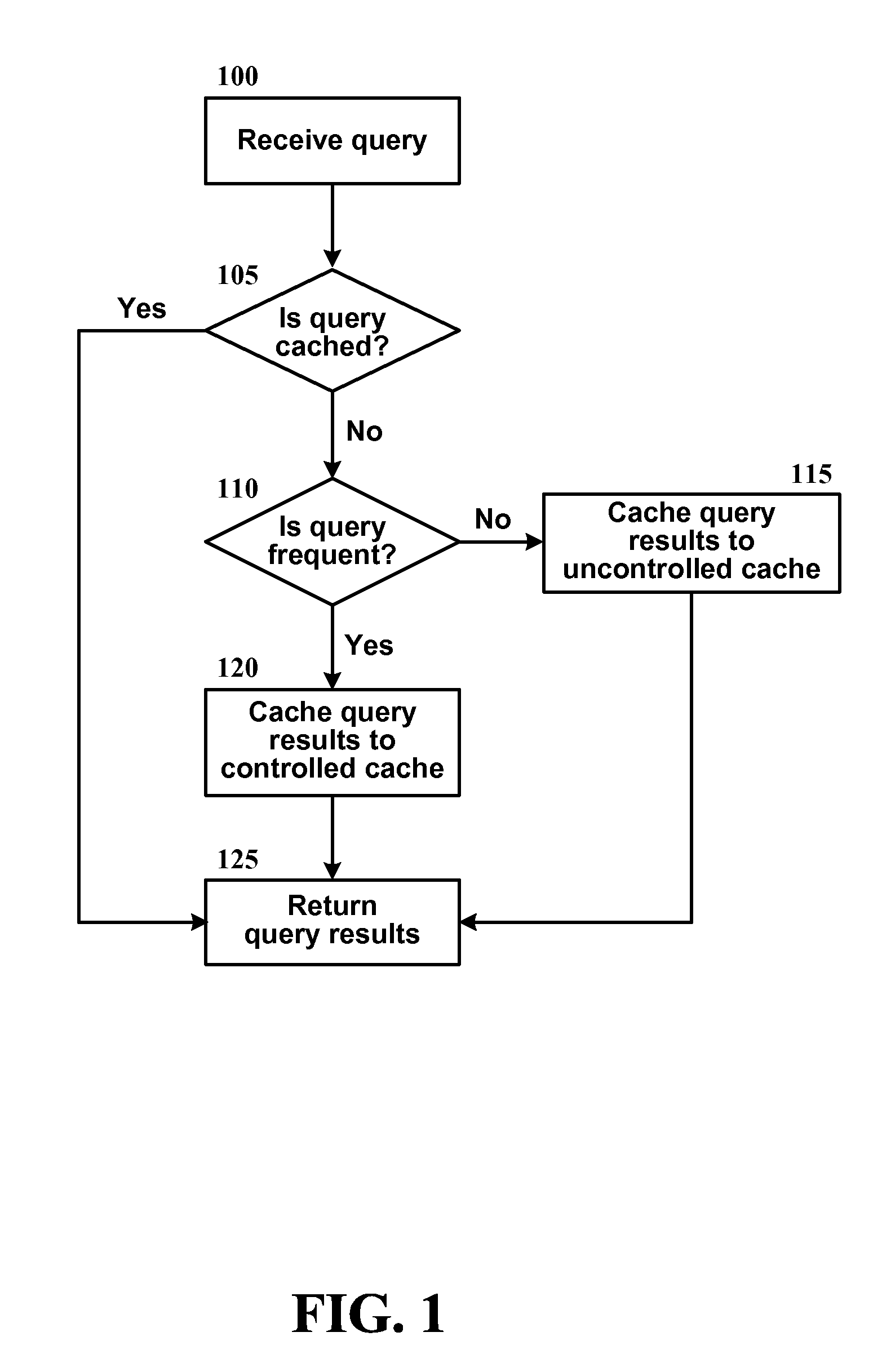
Method for Admission-controlled Caching
InactiveUS20090094200A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsSearch engine queryInformation retrieval
A method of caching the results of a search engine query divides a search engine cache into two parts, controlled and uncontrolled, and determines, through an admission policy, to which part the query results should be cached. In one implementation, the admission policy estimates whether a query is likely to be frequent or infrequent in the future by analyzing various features of the query.
Owner:OATH INC
Admissions control in a connectionless communications network
InactiveUS20030123388A1Easy to implementCost-effectiveInterconnection arrangementsError preventionConnectionless communicationTeleconference
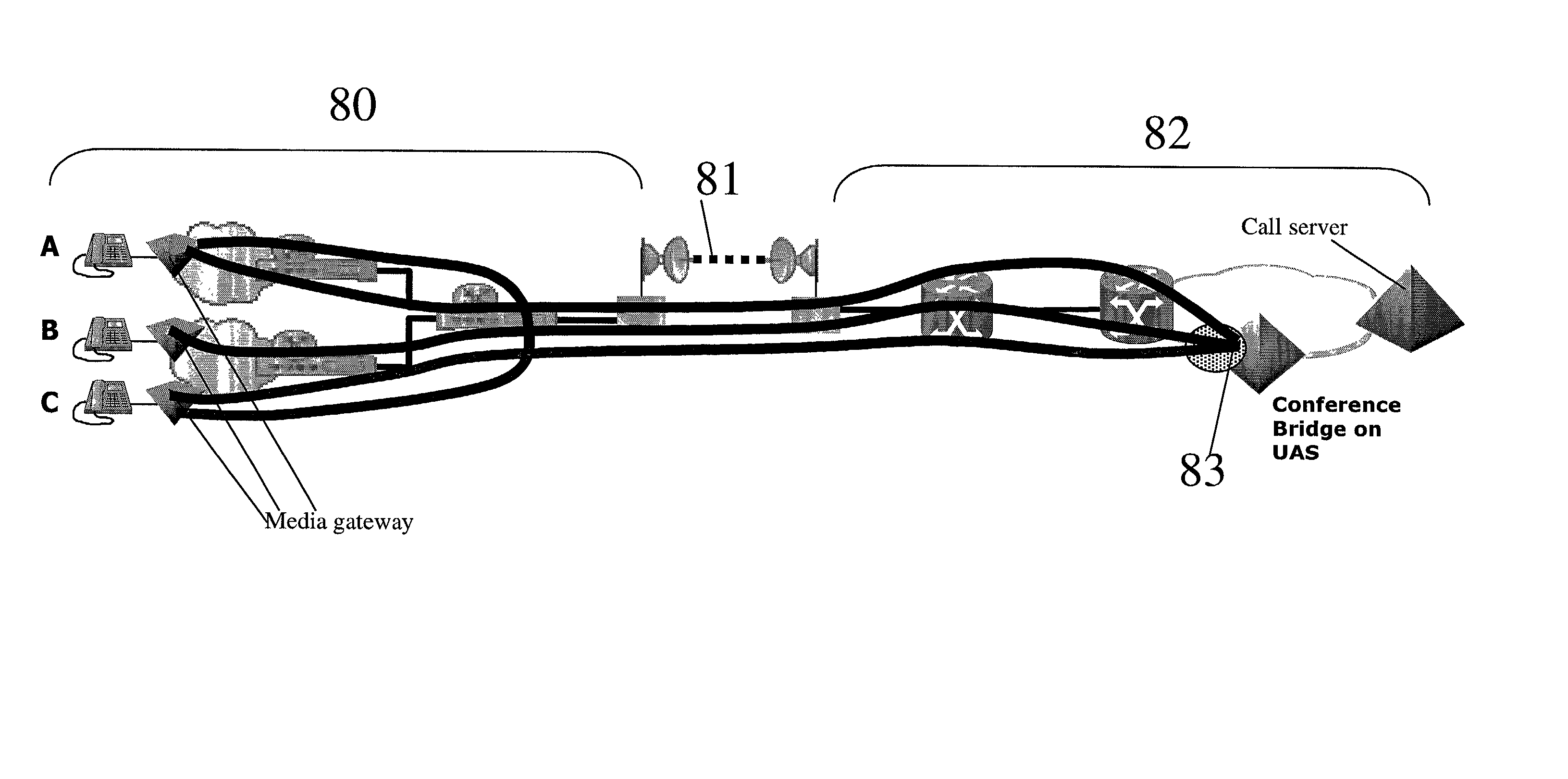
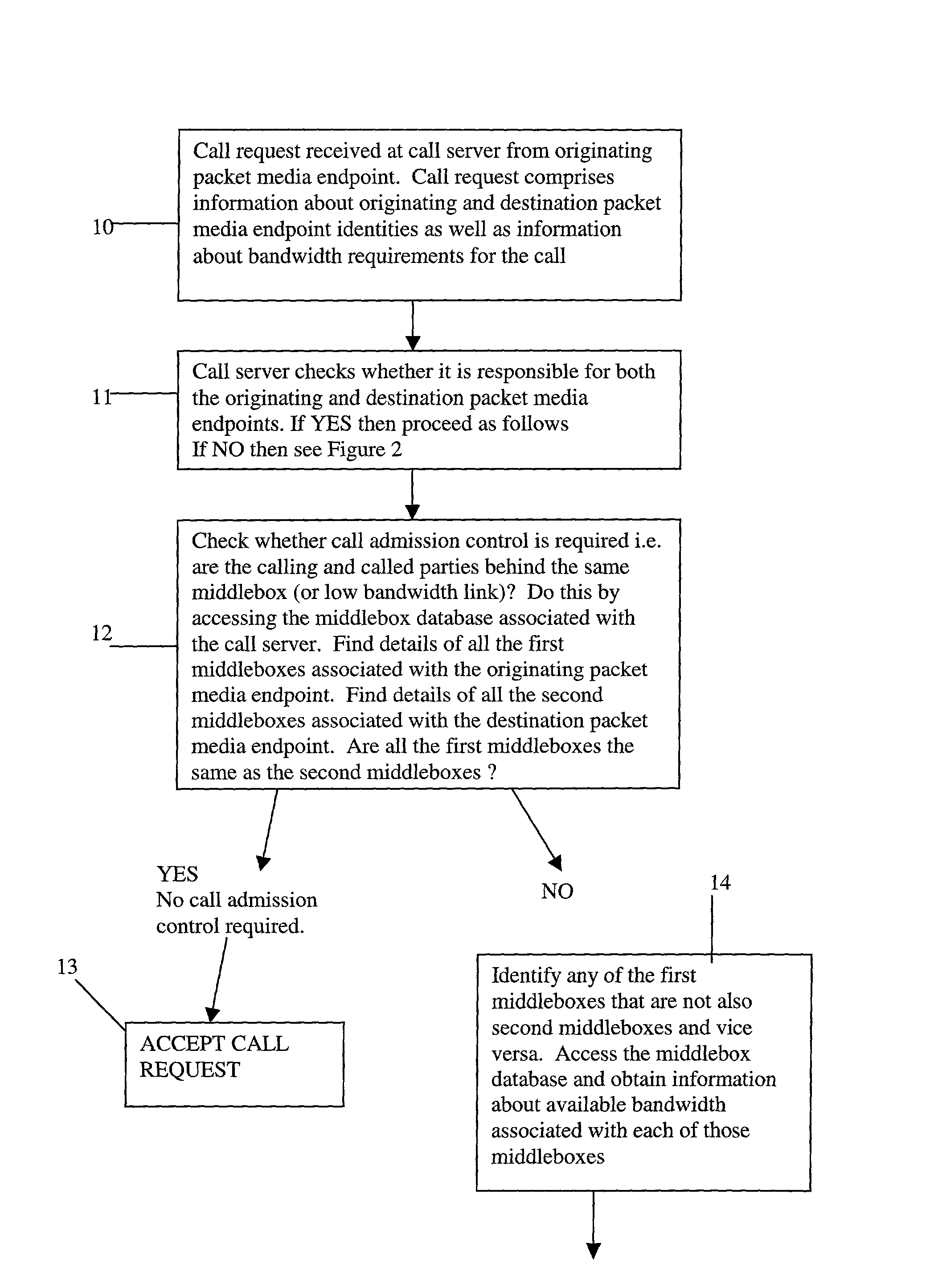
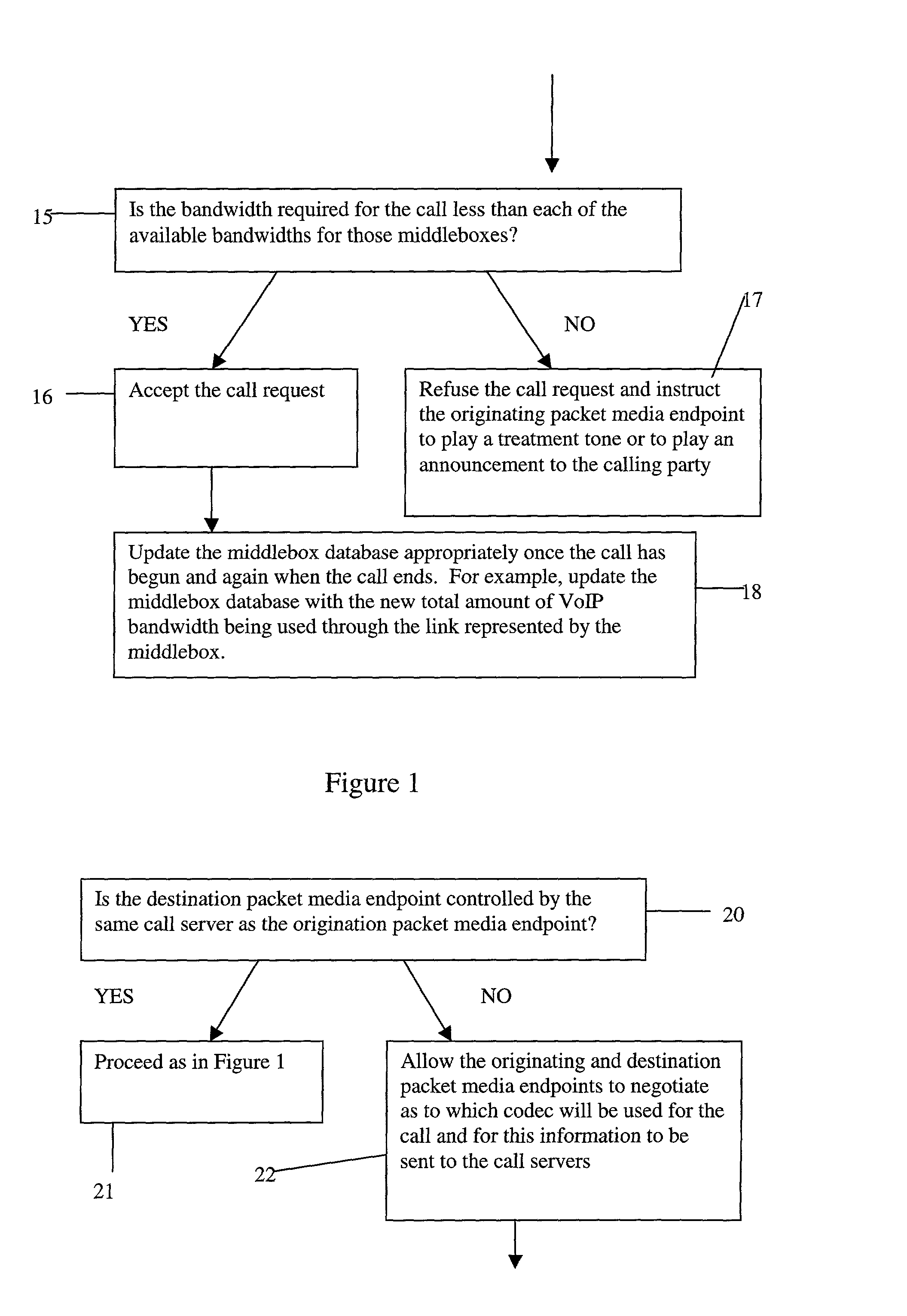
A method of providing call admission control which does not require using MIDCOM protocol methods, Packetcable protocols or COPS-RSVP approaches is described which is simple to implement, cost-effective and which is able to deal with particular situations such as conference calls. Each link in a communications network over which it is required to perform call admissions control is provided with a middlebox connected at each end of that link such that admissions control can be carried out at one end of the link. Call services are provided by Call Servers, each of which has access to a database containing pre-specified information about all middleboxes in that call server's realm. The database also has information about maximum bandwidths for the link associated with each middlebox. The call servers are used to keep a running tally of the amount of VolP call bandwidth associated with each middlebox on the edge of a low-bandwidth link, and to accept or refuse calls on the basis of the bandwidth information on a per-call basis.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Method for real-time traffic analysis on packet networks
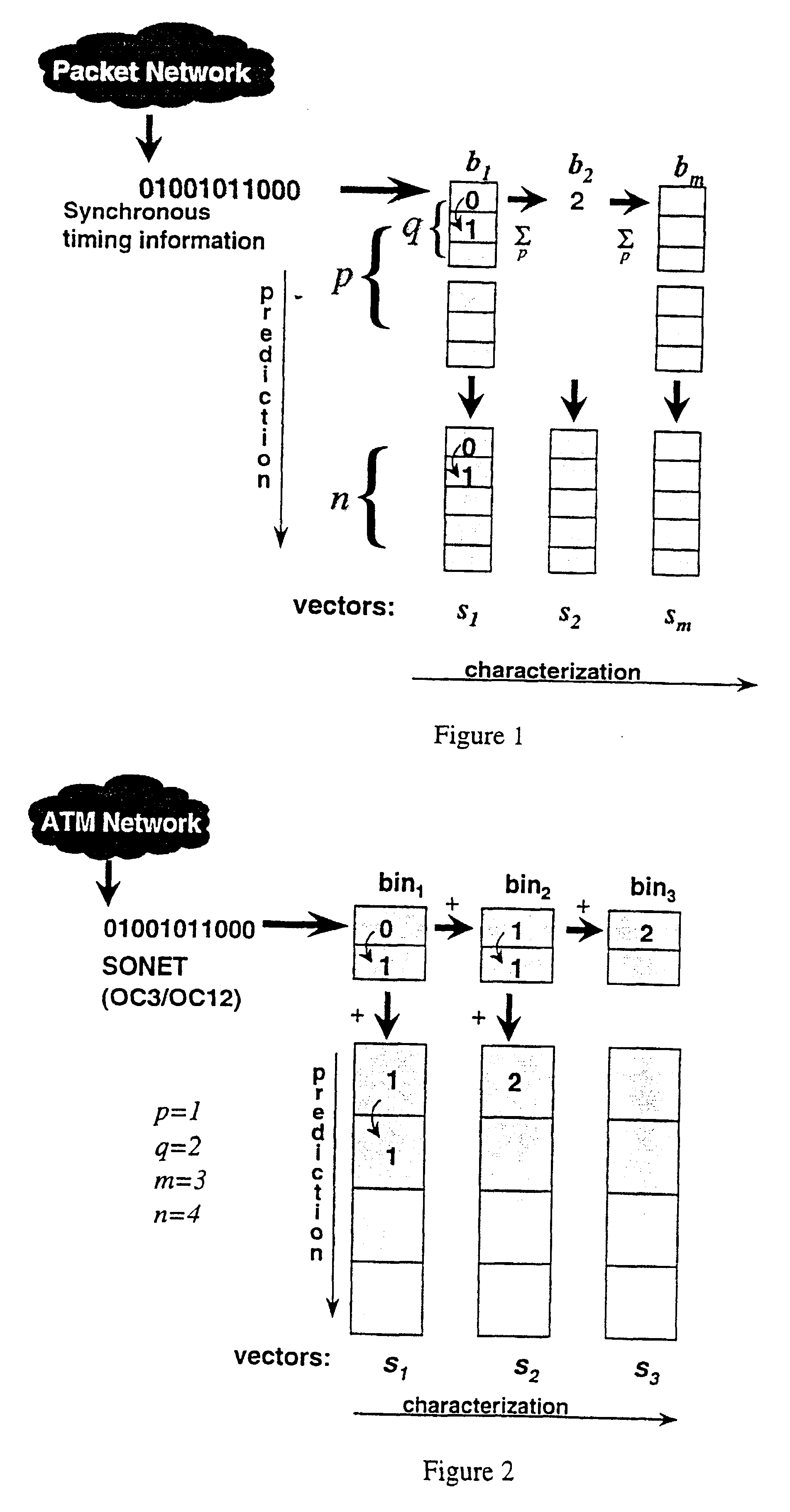
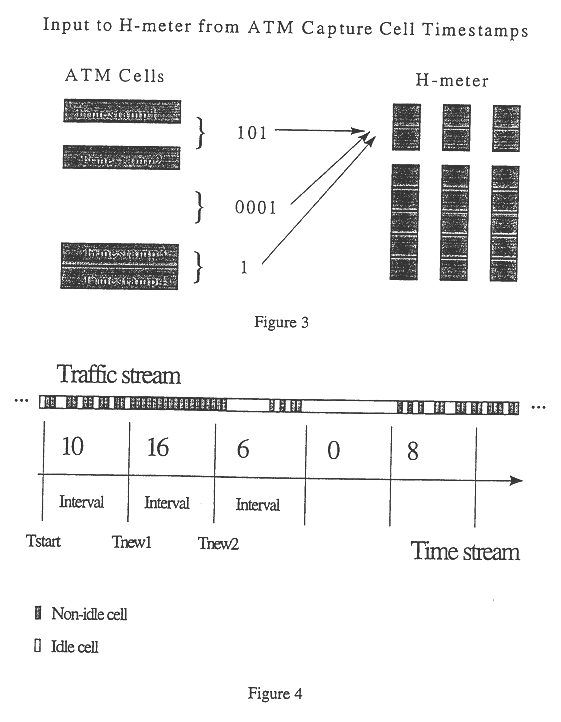
An architecture for capture and generation, and a set of methods for characterization, prediction, and classification of traffic in packet networks are disclosed. The architecture consists of a device that stores packet timing information and processes the data so that characterization, prediction, and classification algorithms can perform operations in real-time. A methodology is disclosed for real-time traffic analysis, characterization, prediction, and classification in packet networks. The methodology is based on the simultaneous aggregation of packet arrival times at different times scales. The traffic is represented at the synchronous carrier level by the arrival or non-arrival of a packet. The invention does not require knowledge about the information source, nor needs to decode the information contents of the packets. Only the arrival timing information is required. The invention provides a characterization of the traffic on packet networks suitable for a real-time implementation. The methodology can be applied in real-time traffic classification by training a neural network from calculated second order statistics of the traffic of several known sources. Performance descriptors for the network can also be obtained by calculating the deviation of the traffic distribution from calculated models. Traffic prediction can also be done by training a neural network from a vector of the results of a given processing against a vector of results of the subsequent processing unit; noticing that the latter vector contains information at a larger time scale than the previous. The invention also provides a method of estimating an effective bandwidth measure in real time which can be used for connection admission control and dynamic routing in packet networks. The invention provides appropriate traffic descriptors that can be applied in more efficient traffic control on packet networks.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
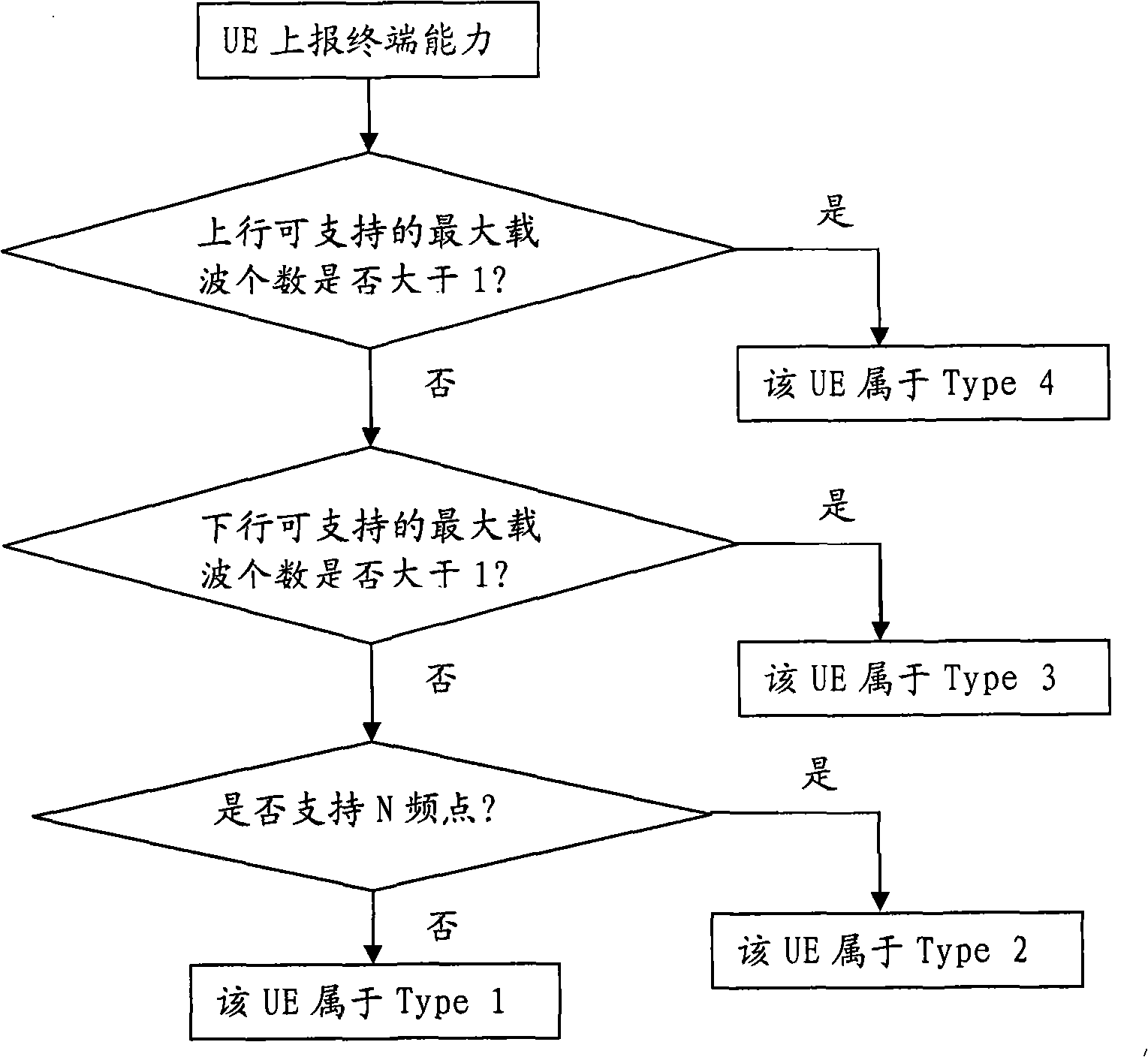
Resource allocation method and device of multi-carrier system
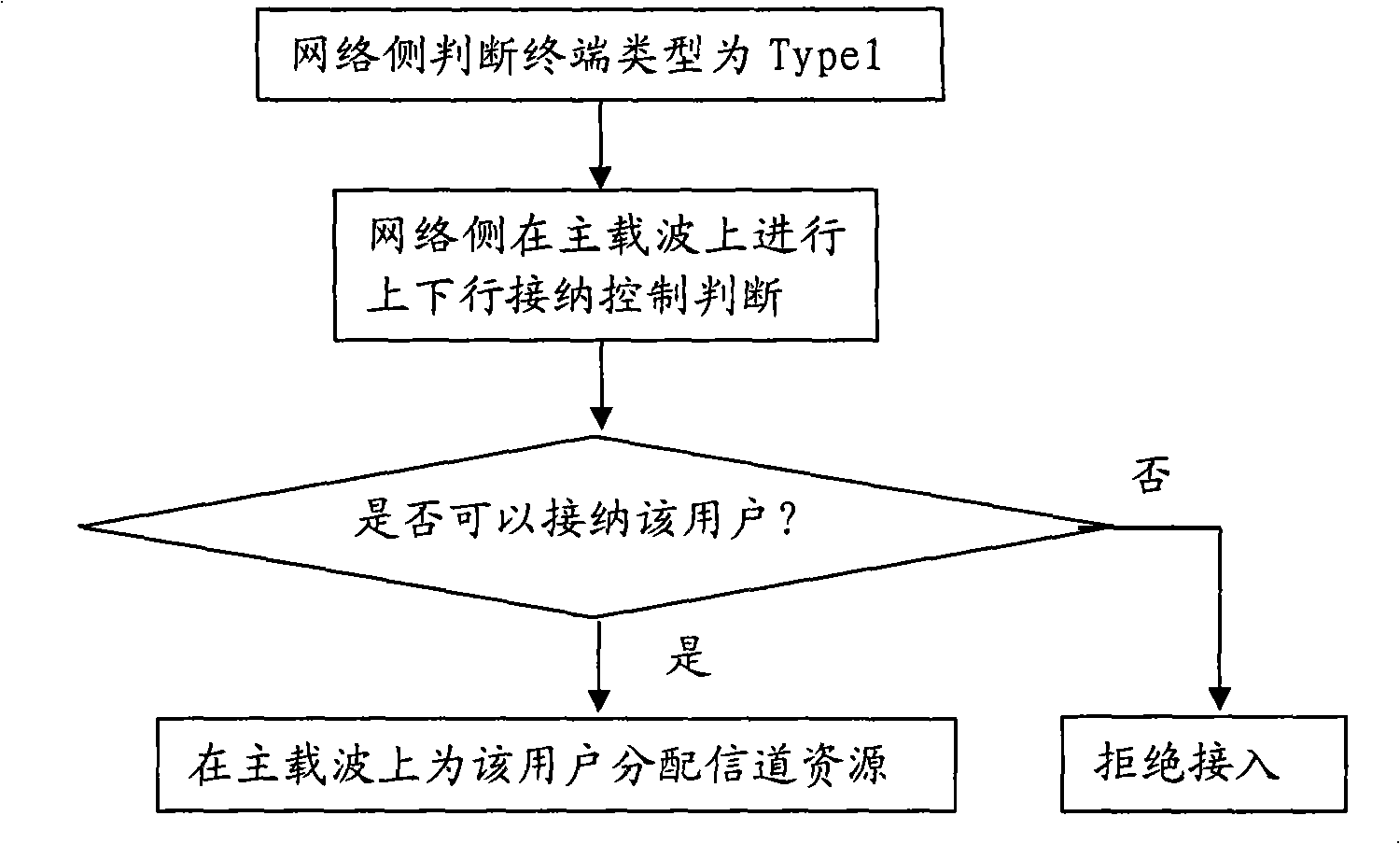
InactiveCN101345988ASolution success rateIncrease capacityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationTelecommunicationsCurrent technology
The invention provides a resource allocation method for multicarrier system, which comprises: network side carries out an admission control judge to users according to the resource condition in cell, and allocates wireless resources according to the reported access capacity for the successive admission user and informs the terminal to carry out chain establishment operation through channel configuration command. The technical scheme in the invention fully considers the compatibility to all types of terminals, solves the problem of the reduction of network access ratio and capacity exists in current technology caused by that user terminal does not support the wireless resource allocation scheme when the network side allocates resources to user terminals. The execution of the invention can reduce lost call rate efficiently, and improves the network quality and the revenue of operators.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TELECOMM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com