Patents
Literature
123 results about "End to end qos" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
End-to-end Quality of Service (QoS) is included with the FlexNoC interconnect product and is designed to ensure all on-chip data flows can concurrently meet latency and bandwidth requirements while sharing the finite bandwidth of DDR memory.
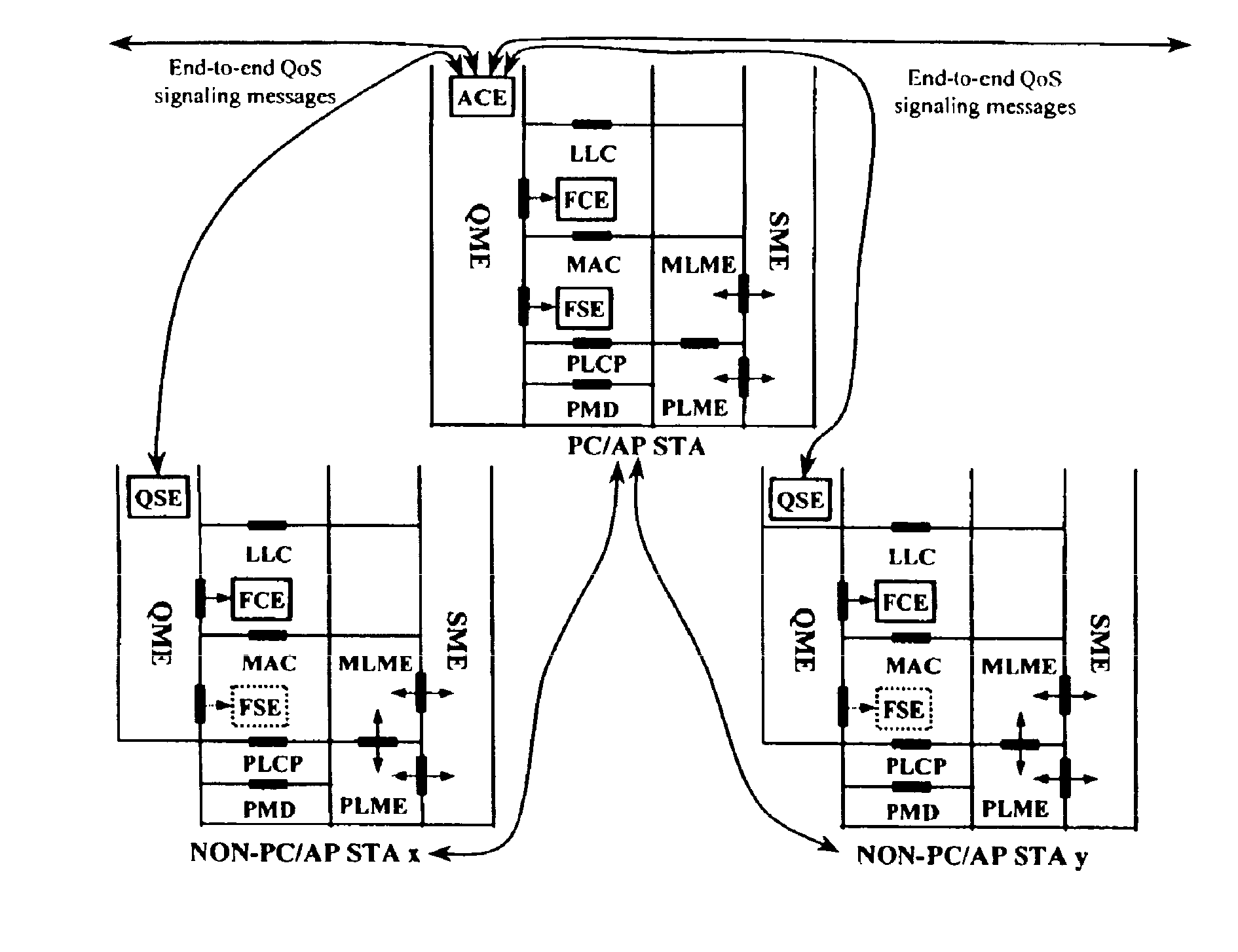
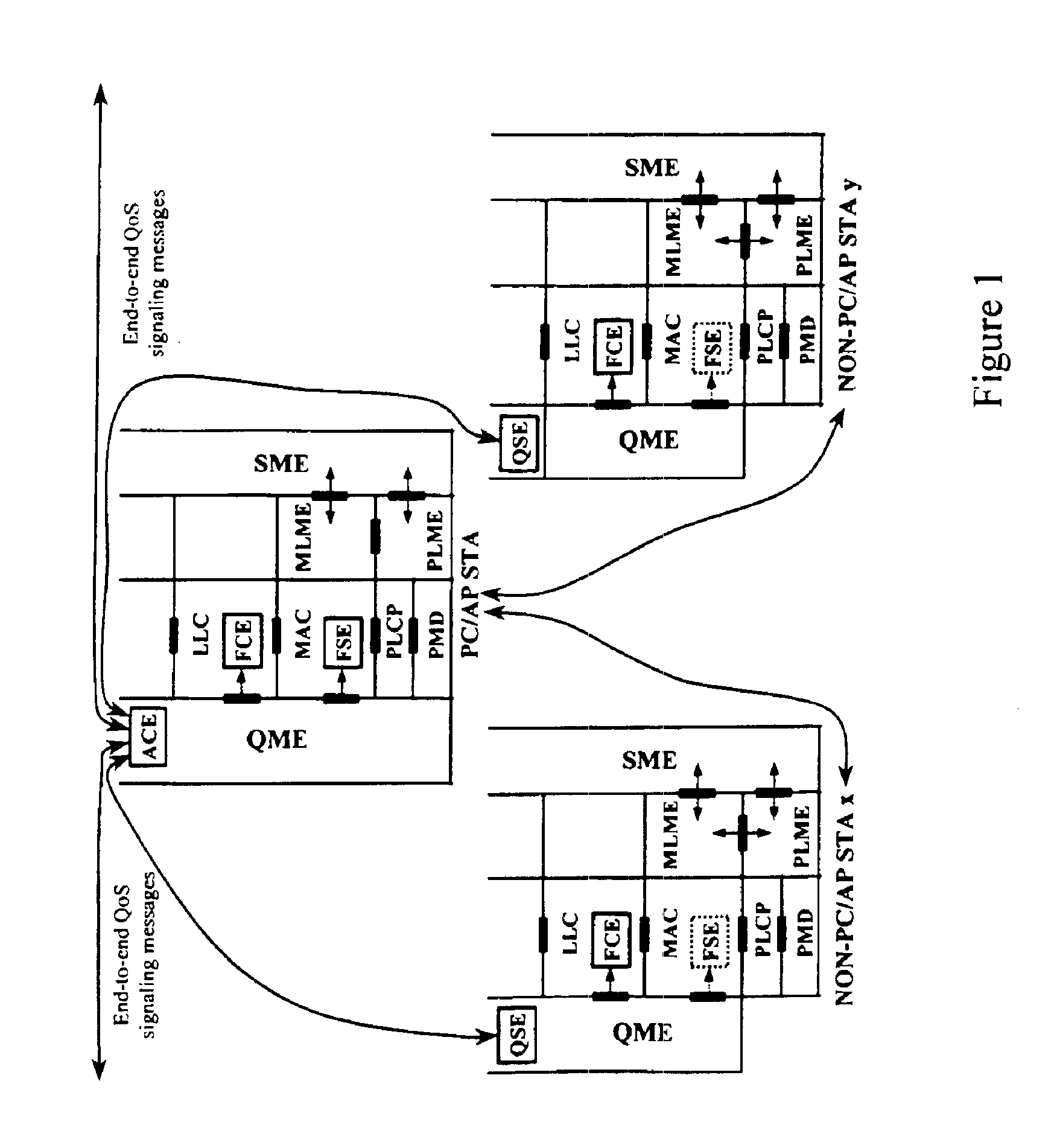
Architectural reference model for QoS-driven wireless LANs
InactiveUS6862270B1Enhanced channel accessImprove bandwidth utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesOpen Systems InterconnectionEnd to end qos
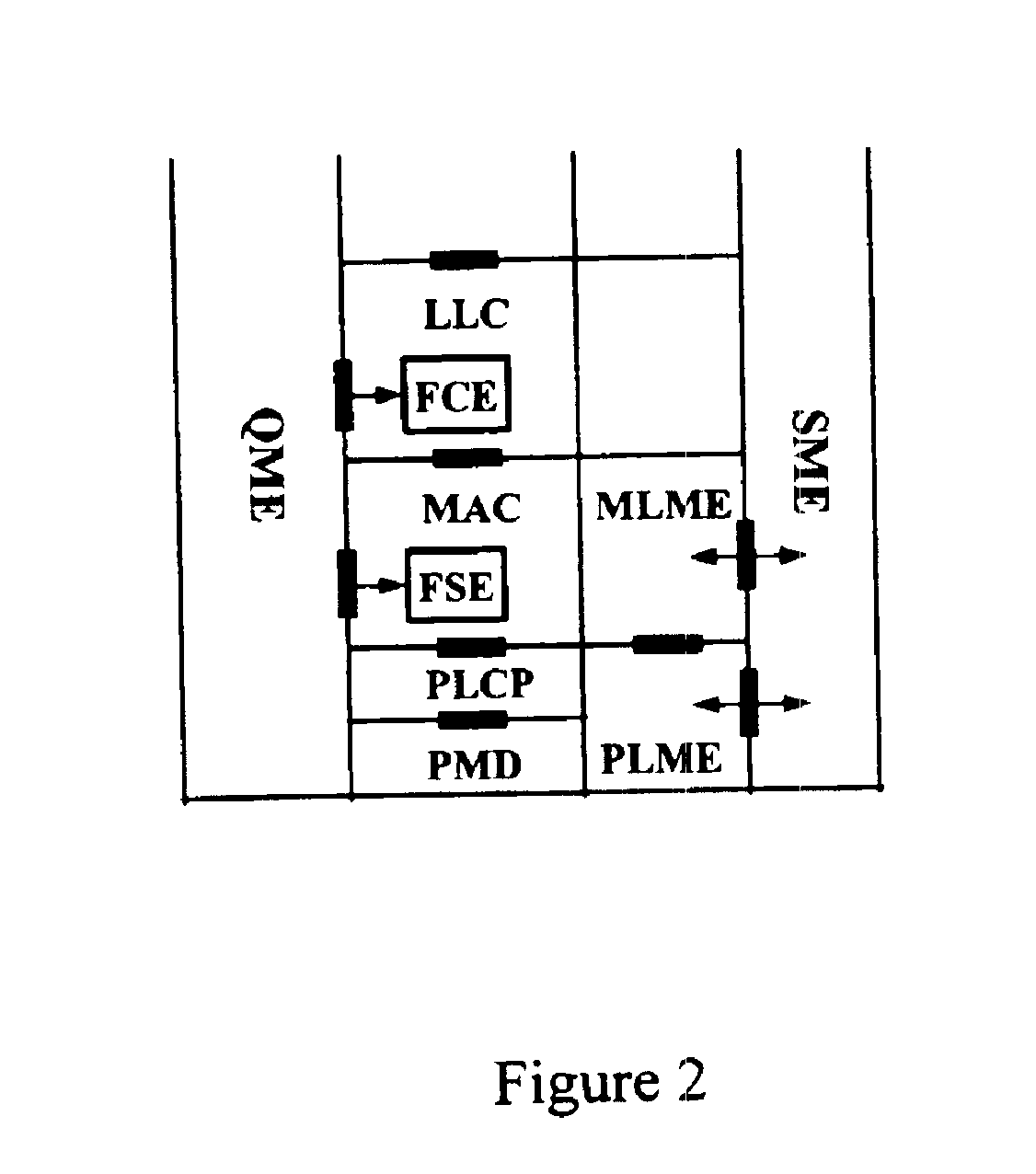
A quality of service (QoS) station is disclosed containing a point coordinator (PC) for a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless LAN. The PC station includes a QoS management entity (QME) and an admission control entity (ACE). The QME receives at least one end-to-end QoS message that characterizes a user application, such as a voice call, a video call, a data call and a multimedia call. The at least one end-to-end QoS message includes at least one QoS parameter set that is expressed at layer 3 and higher of an ISO / IEC basic reference model of Open Systems interconnection (OSI) (ISO / IEC 7498-1) and is to be passed down to layer 2 of the PC-station for enabling QoS traffic transport of the application. The ACE performs an admission control decision relating to the application based on the at least one end-to-end QoS message characterizing the application. The ACE reserves a resource based on a QoS parameter set contained in the end-to-end QoS message. The ACE can be part of the QME and can include a resource control module that performs at least one admission control decision based on resource permission, and a policy control module that performs at least one admission control decision based on policy permission.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Communication system and communication method
InactiveUS20060218302A1Not unnecessarily trafficError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemQos management
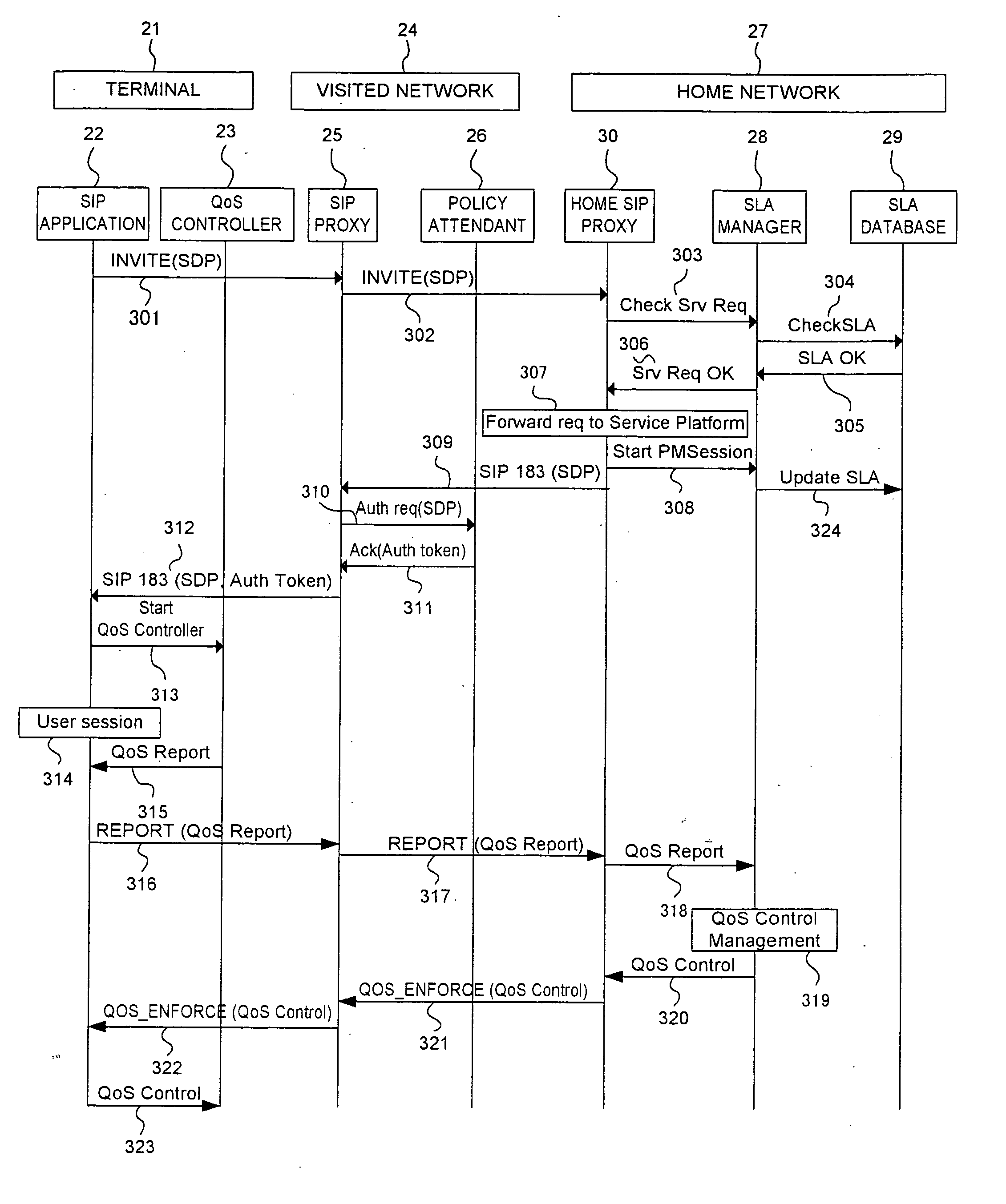
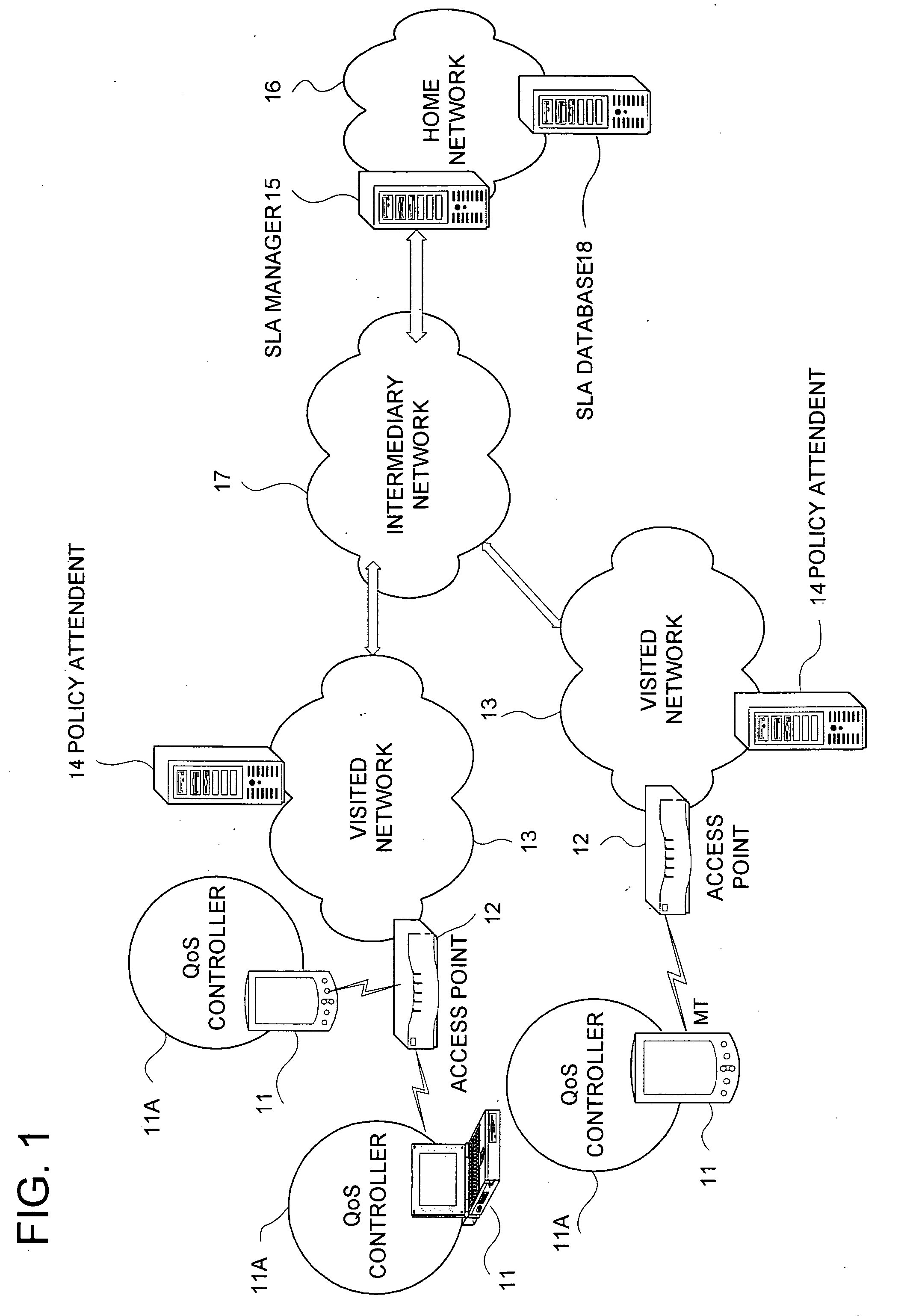
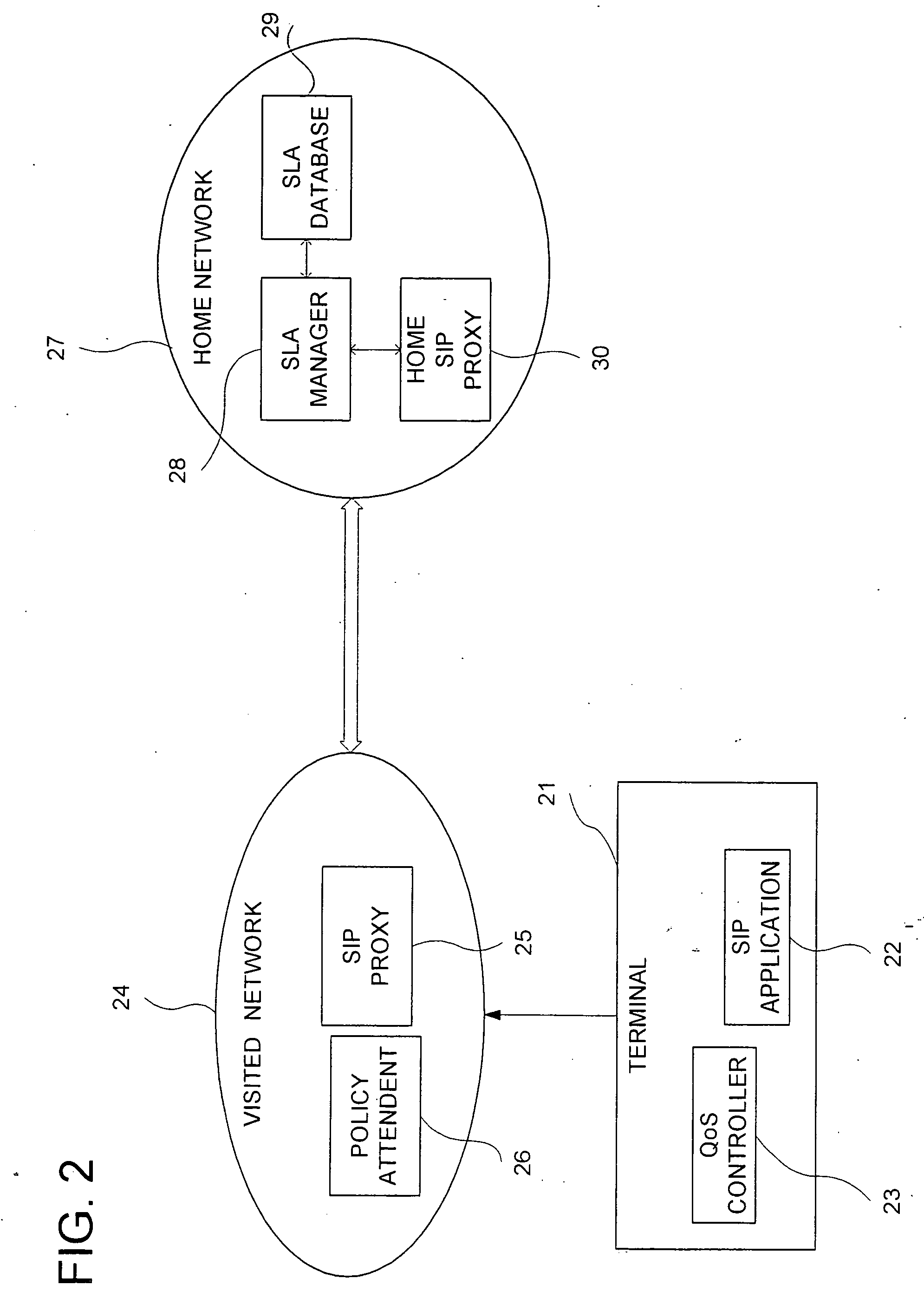
A technique for the end terminal provided with services to handle QoS process is disclosed. According to this technique, a terminal based QoS management scheme is implemented to achieve end-to-end QoS wherein the end terminal 21 is responsible for handling of the QoS related functions. In order for QoS management to be handled at terminal, the terminal needs to know the network conditions and external state of entities in order to know what action to be taken. For example, the terminal performs monitoring and usage collection. These performance data are then reported to a central server (SLA manager 28). The central server collects these data from all terminals within its administration domain. The central server also has access to information on the QoS to be given to individual terminals, such as service level. Based on the information, the central server decides what action to be taken by individual terminal and enforces these actions into the affected terminals.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
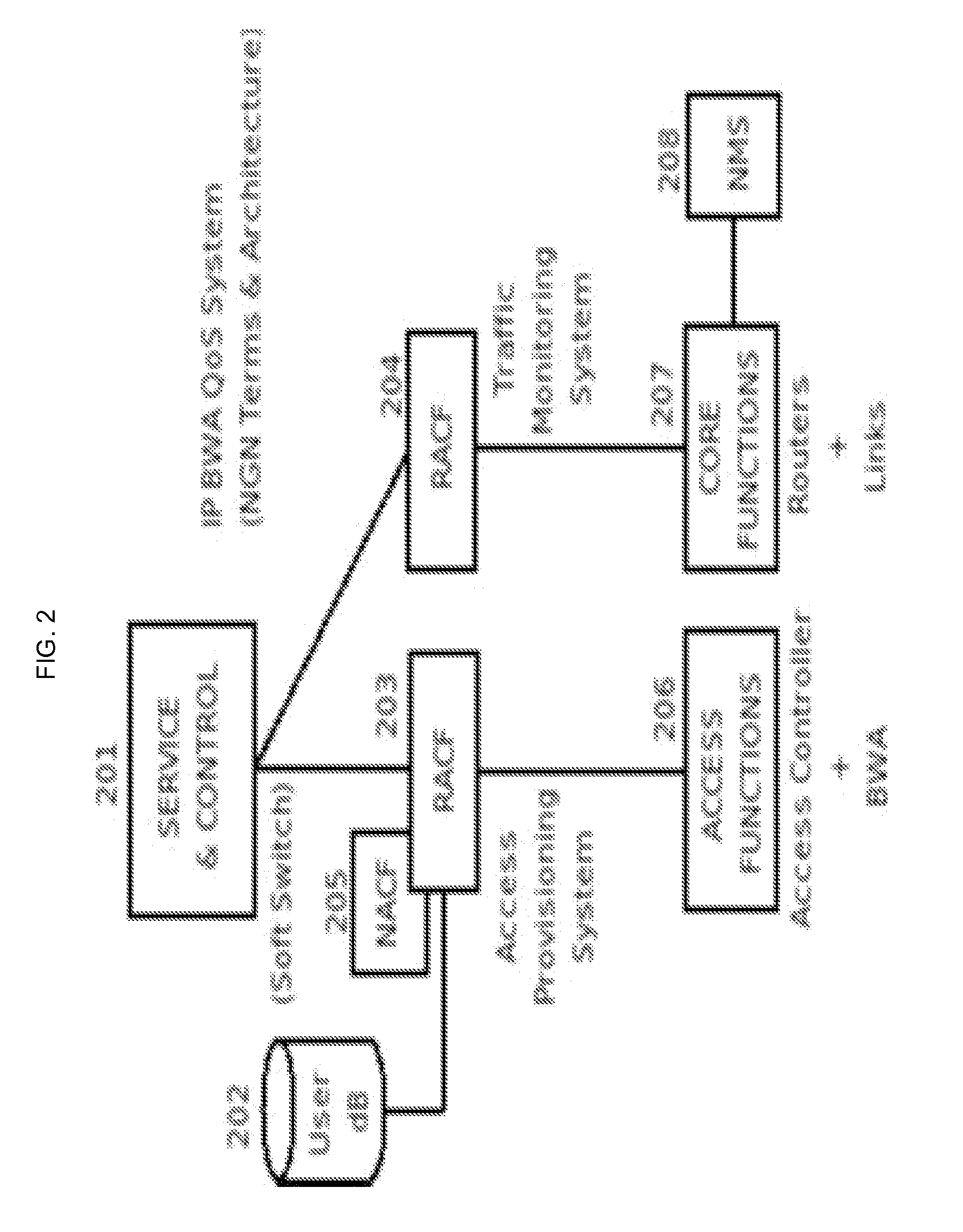
Methods And Systems For Dynamic Bandwidth Management For Quality Of Service In IP Core And Access Networks
InactiveUS20080130495A1Easy to useStringent qualityError preventionTransmission systemsPresent methodKey issues
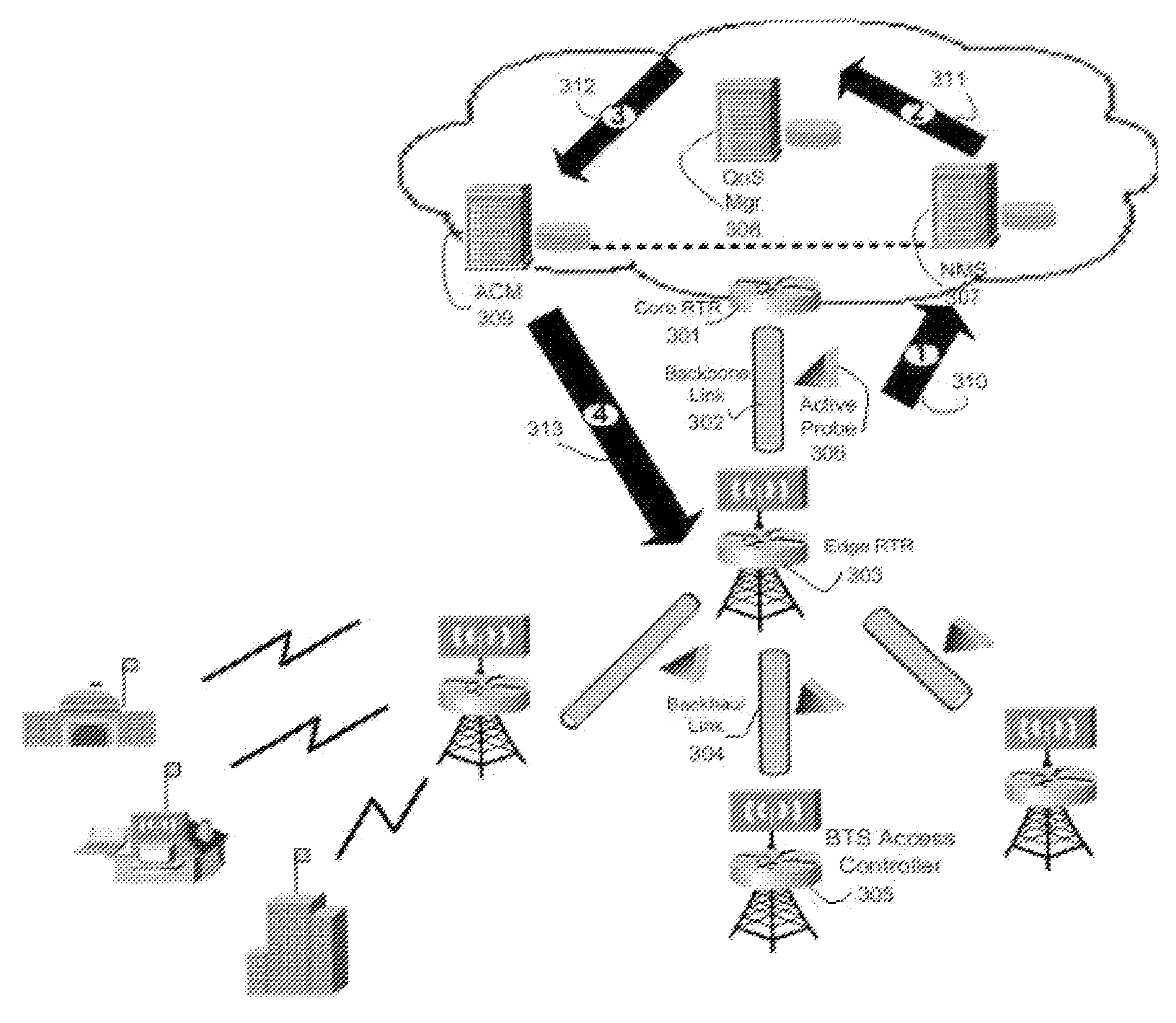
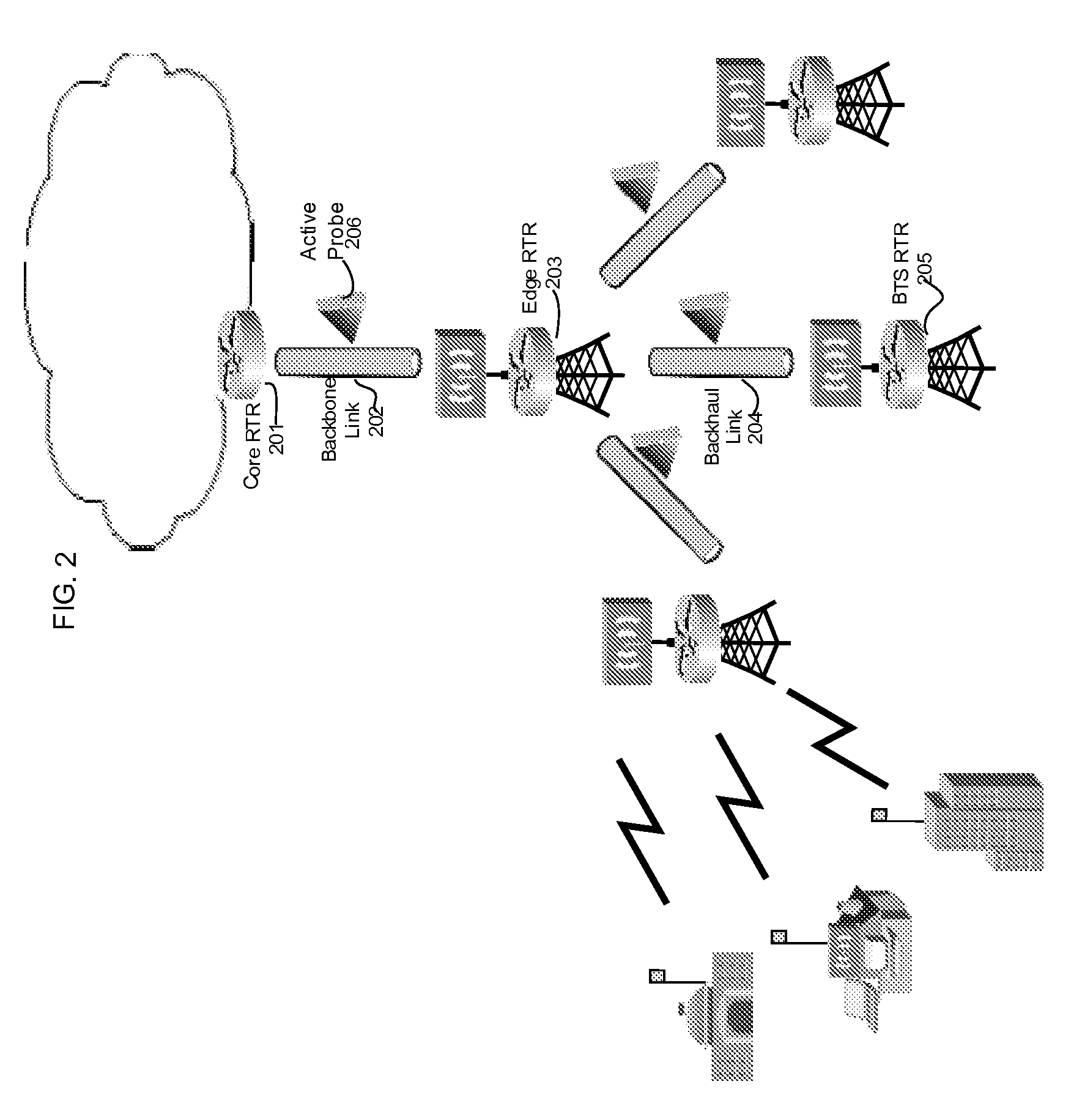
Proper allocation of network bandwidth is a crucial issue in rendering certain performance guarantees to meet the growing customer demands. Hence, allocation methodologies must explicitly be carried out for these guarantees to be given as efficiently as possible since the shared resources are limited. This invention presents methods and systems for Dynamic Bandwidth Management (DBM) and Quality of Service (QoS) in packet-based networks. DBM is an algorithm that dynamically adjusts the resource allocation in the IP Access Networks based upon measured QoS at the IP Core Network through an implementation of a Feedback Control Mechanism to manage available core transport bandwidth. Such a Feedback Control Mechanism is capable of maintaining a condition of non-congestion, a sufficient and necessary condition to meet end-to-end QoS requirements in a Next Generation Network (NGN). The emphasis is given on the system implementation of QoS policies for the fair distribution of network resources through a scalable architecture comprising key Resource and Admission Control Functional (RACF) entities, namely: a Network Management System (NMS), a QoS Manager, an Access Controller Manager (ACM), the Access Controllers, and the active probes.
Owner:LATITUDE BROADBAND
NETWORK ARCHITECTURE FOR DYNAMICALLY SETTING END-TO-END QUALITY OF SERVICE (QoS) IN A BROADBAND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
InactiveUS20080273520A1Efficient settingsNetwork traffic/resource managementTelephonic communicationQuality of servicePolicy decision
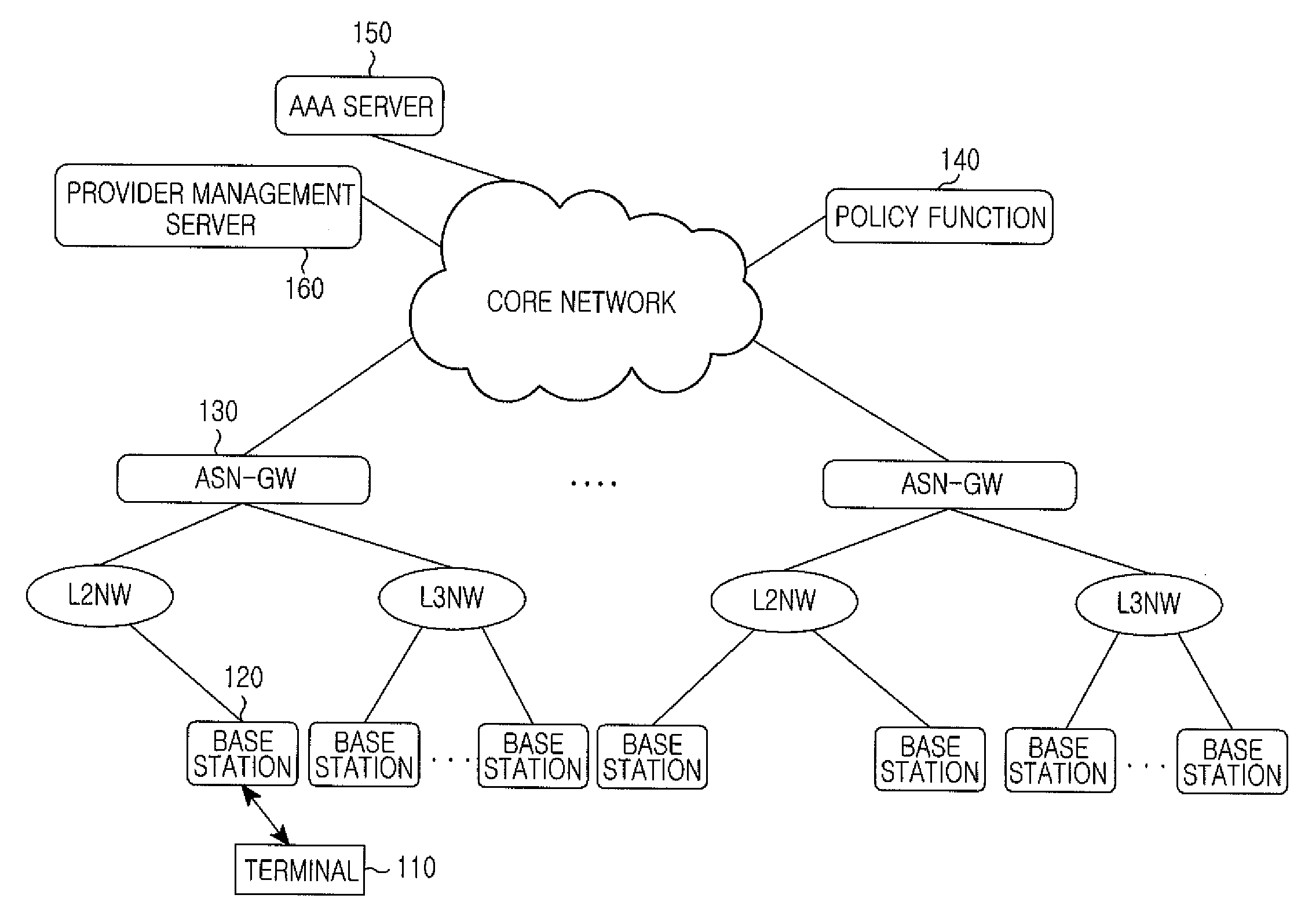
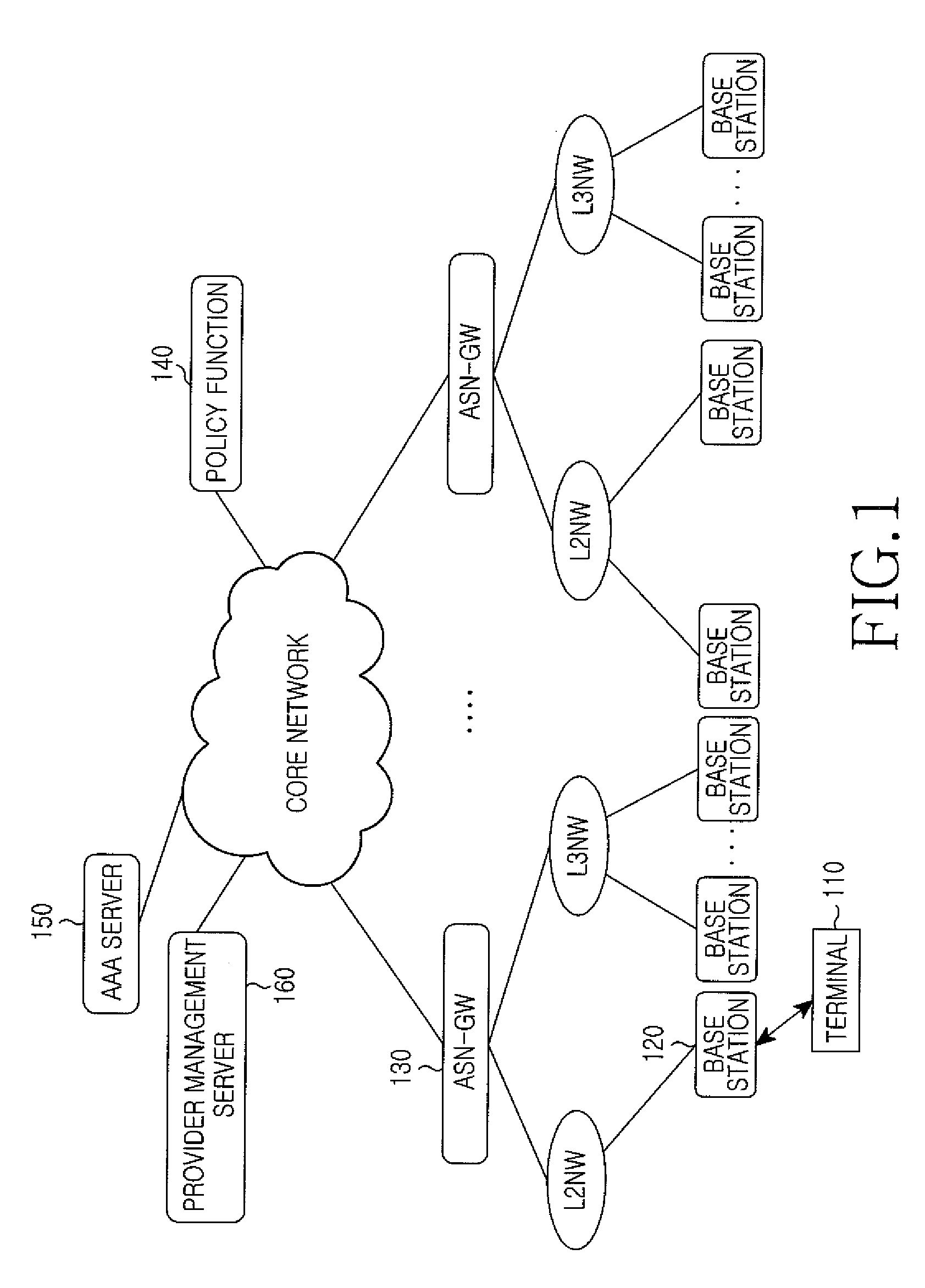
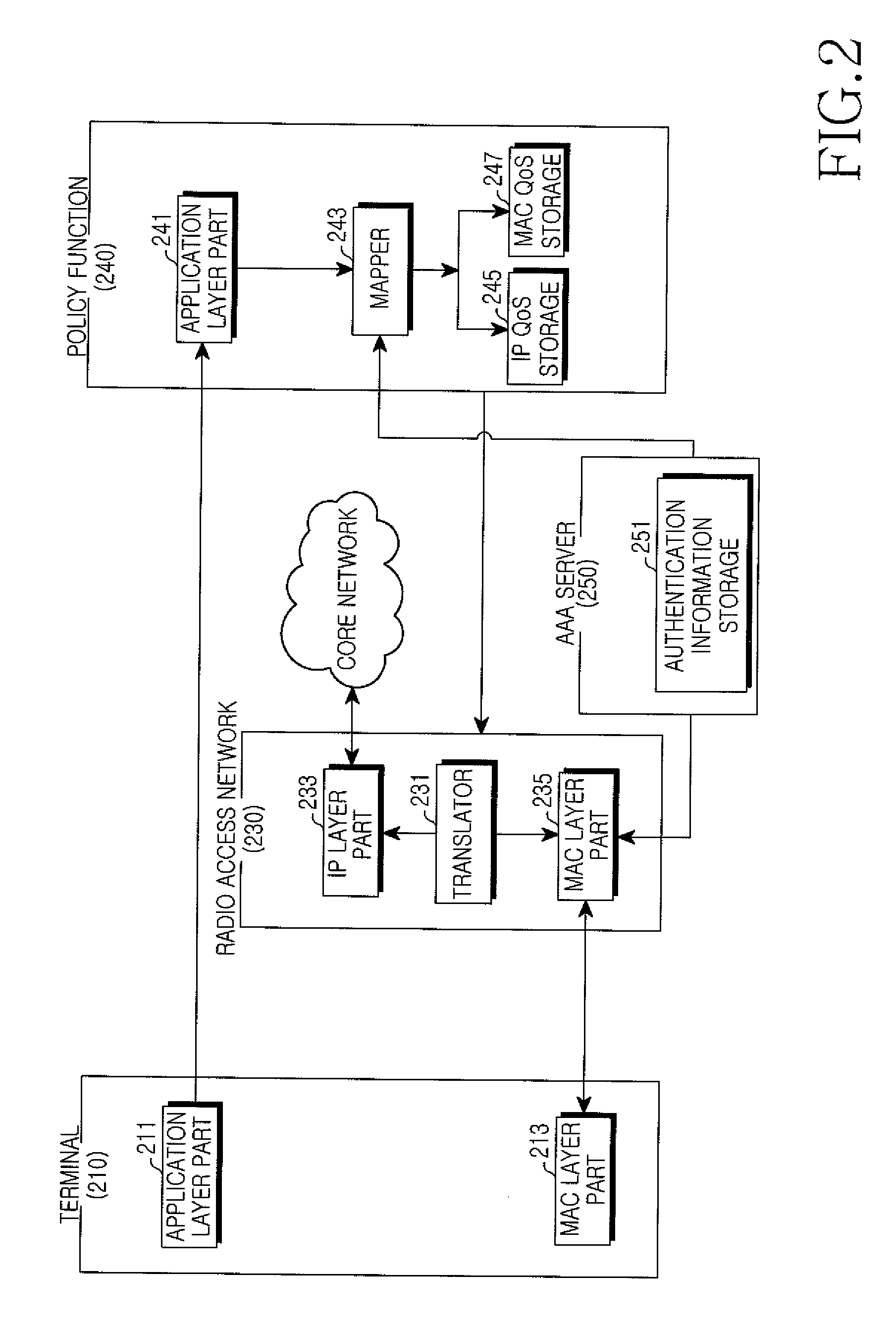
A communication network architecture including a broadband radio access network is provided. The architecture includes a terminal for transmitting an application layer service request message to request a service, a Policy Charging Rule Function (PCRF) for generating Quality of Service (QoS) parameters of an Internet Protocol (IP) layer using QoS parameters of an application layer contained in the application layer service request message, a first Policy Decision Function (PDF) for generating one or more QoS parameters of the IP layer in addition to the IP layer QoS parameters generated at the PCRF and a second PDF for generating a QoS parameter set of a radio access network using the IP layer QoS parameters generated at the PCRF and the one or more IP layer QoS parameters generated at the first PDF. The communication network guarantees an end-to-end QoS.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Model for enforcing different phases of the end-to-end negotiation protocol (E2ENP) aiming QoS support for multi-stream and multimedia applications
ActiveUS7602723B2Dynamic characteristicCoupling device connectionsError preventionMulti streamExtensible markup
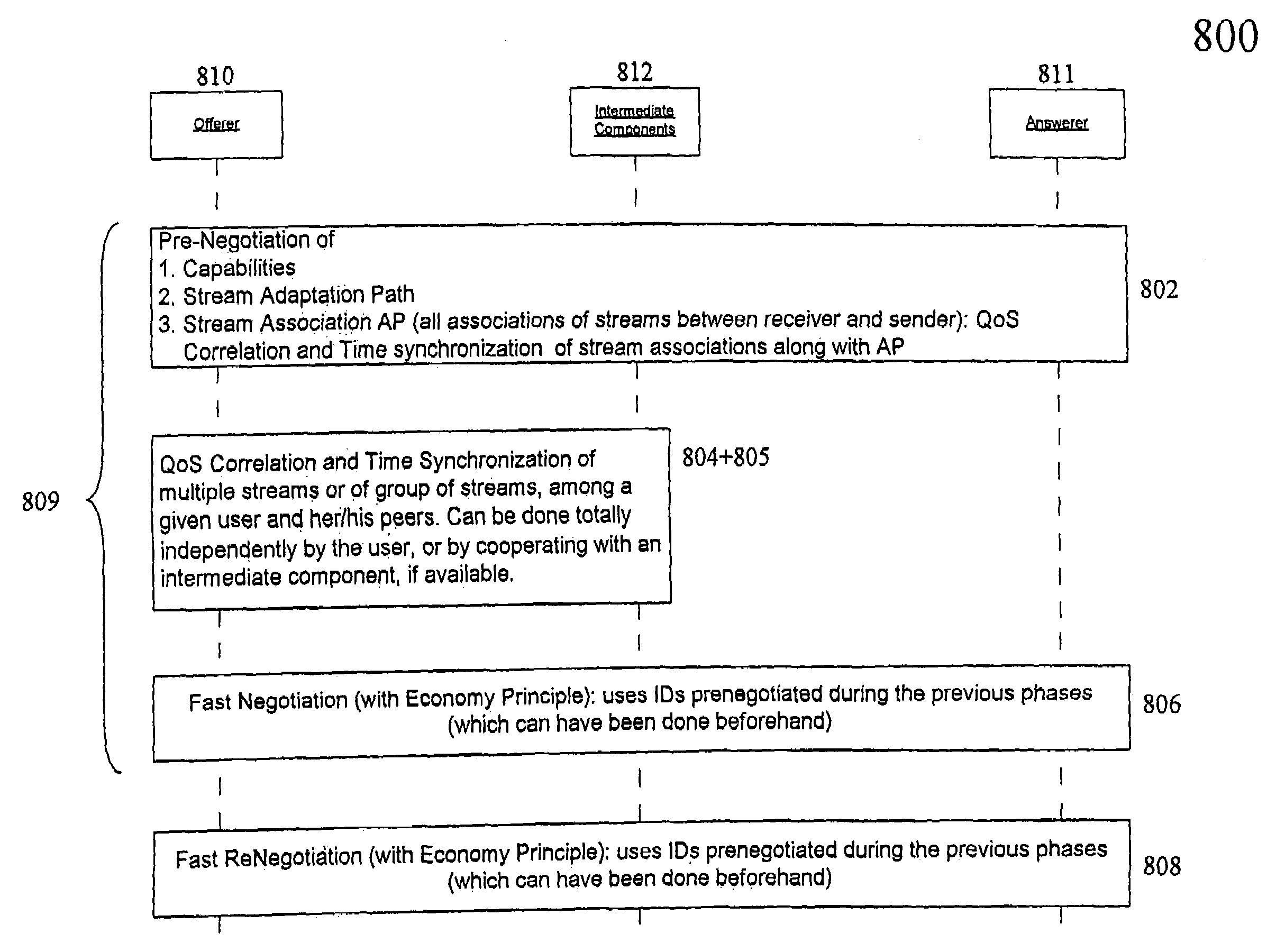
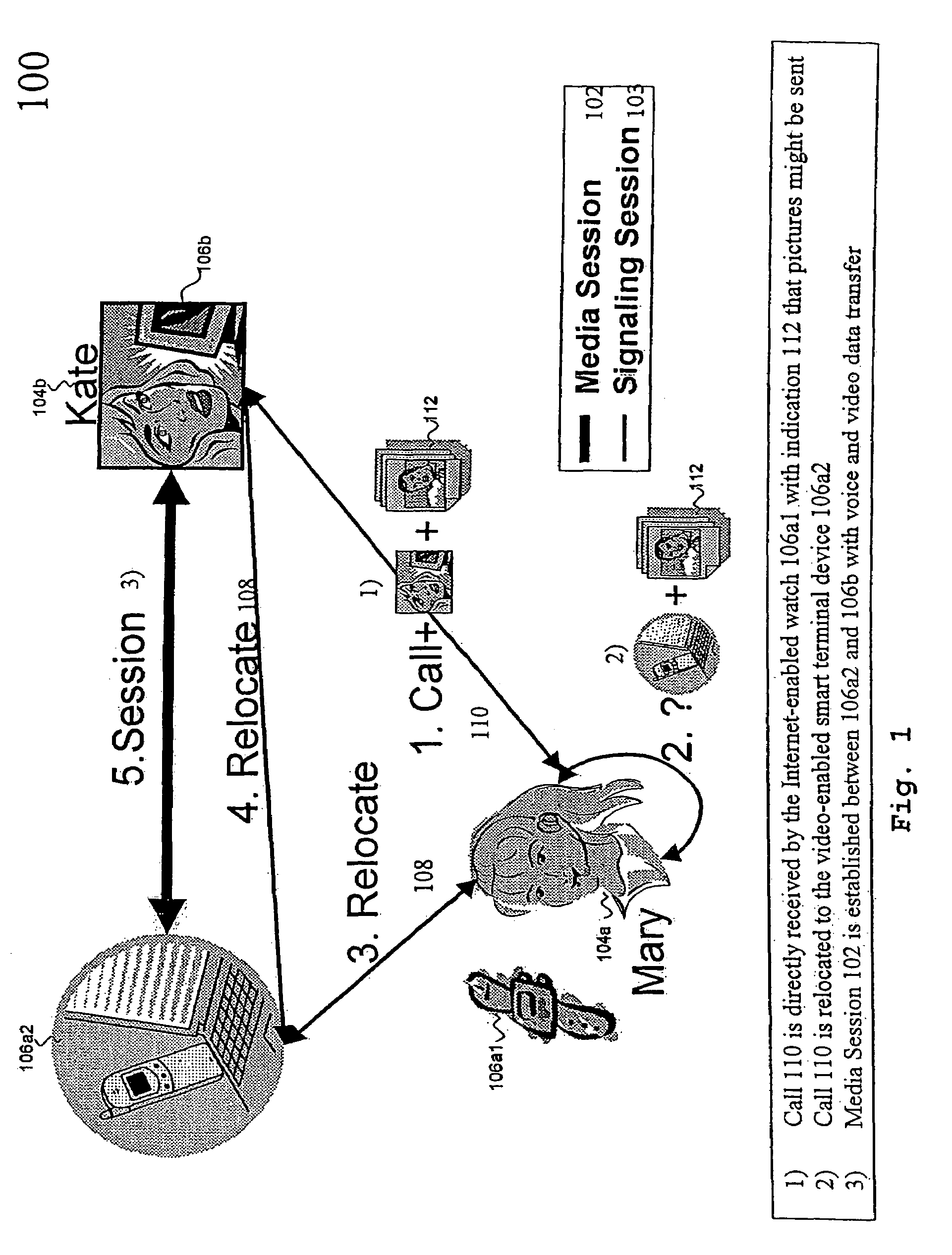
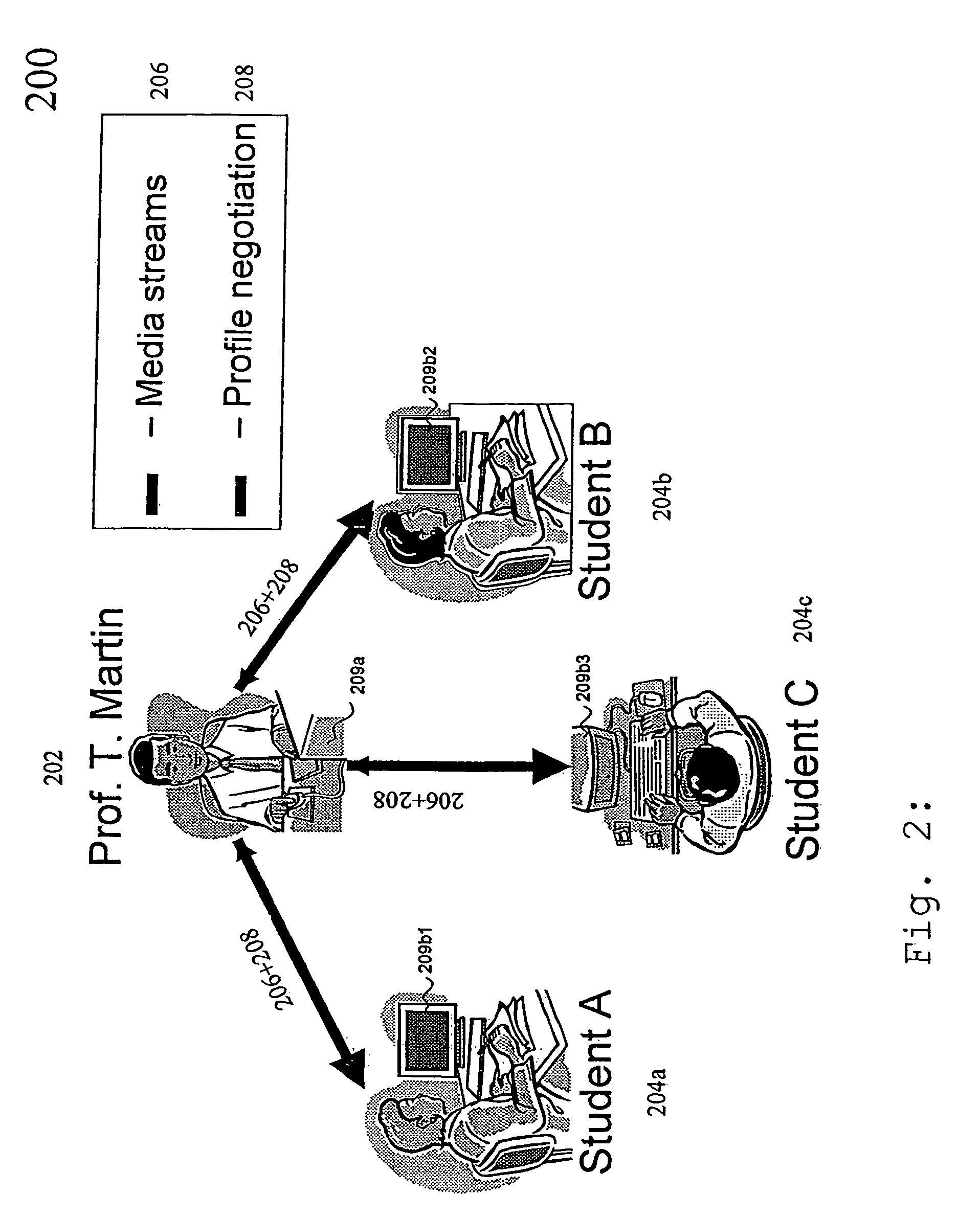
The underlying invention generally relates to the field of mobile computing in a networking environment with distributed multimedia applications and technologies. More specifically, it is directed to the concept of the End-to-End Negotiation Protocol (E2ENP) phases, which enable a pre-negotiation (802, 804, 805), fast negotiation (806) and a fast, dynamic renegotiation (808) of the end-to-end quality and capabilities for telecommunication sessions (102), for multiple configurations of two or a multiplicity of end peers and / or intermediate components in a consistent, reliable, and incremental way by enabling the mobile users' applications to efficiently and timely react to QoS violations. In this context, the invention proposes a model for defining user profiles and terminal capability information in such a way that hierarchical QoS contract specifications (1108), e.g. compelling correlations (804) across different sets of QoS contracts (1108) for related media streams (206), can be enforced and used for deriving negotiable information. As a reference implementation of this concept, this invention proposes a novel usage of the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP, 910) standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in conjunction with extensions of the Session Description Protocol Next Generation (SDPng, 912) specification based on the Extensible Markup Language (XML) in order to implement concepts of the End-to-End QoS Negotiation Protocol (E2ENP, 908).
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH +1
Fast Signalling Procedure For Streaming Services Quality Of Service Management In Wireless Networks
InactiveUS20070213038A1Improve standardsAvoiding media playback stallingNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceMobile Web
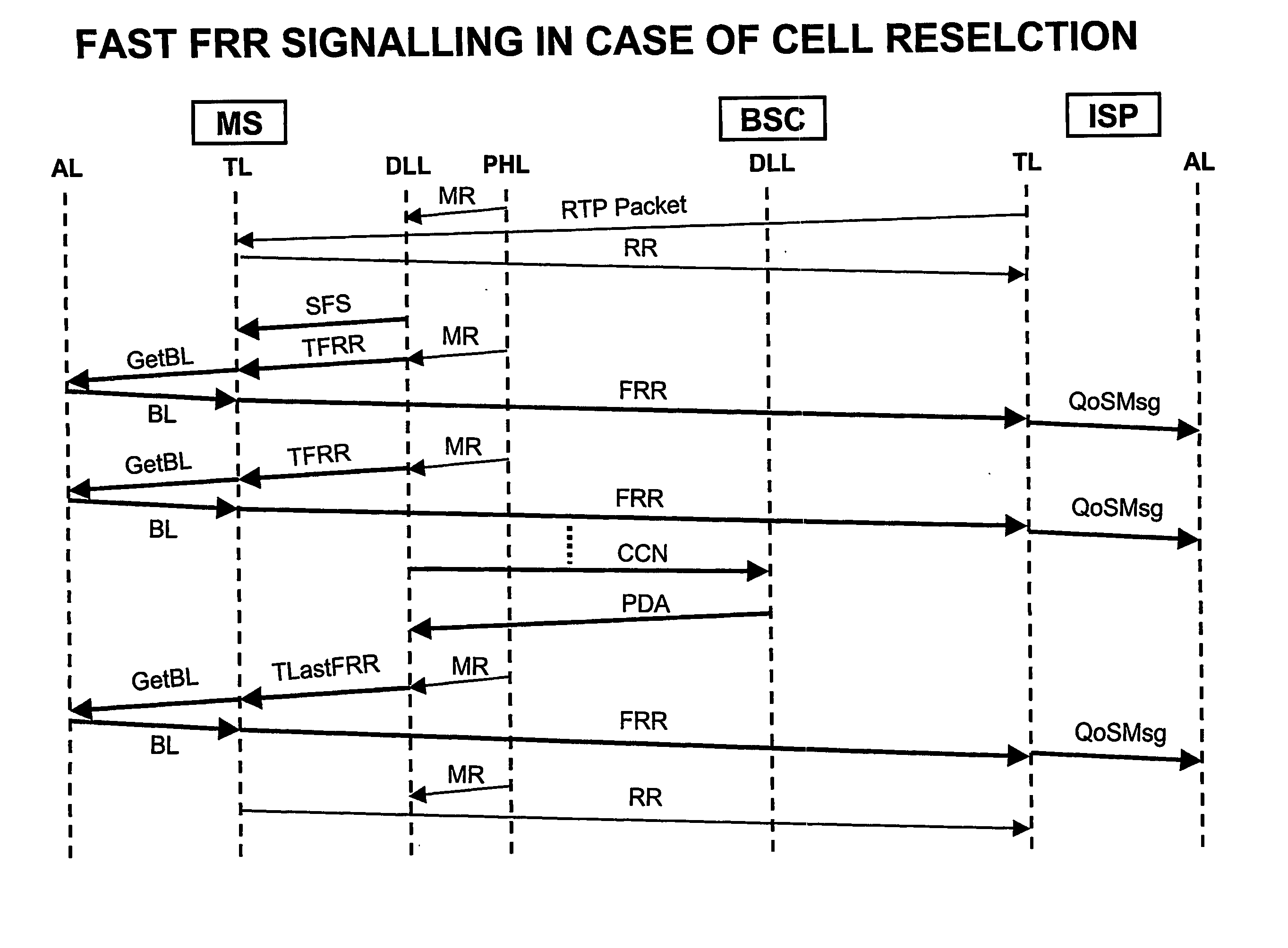
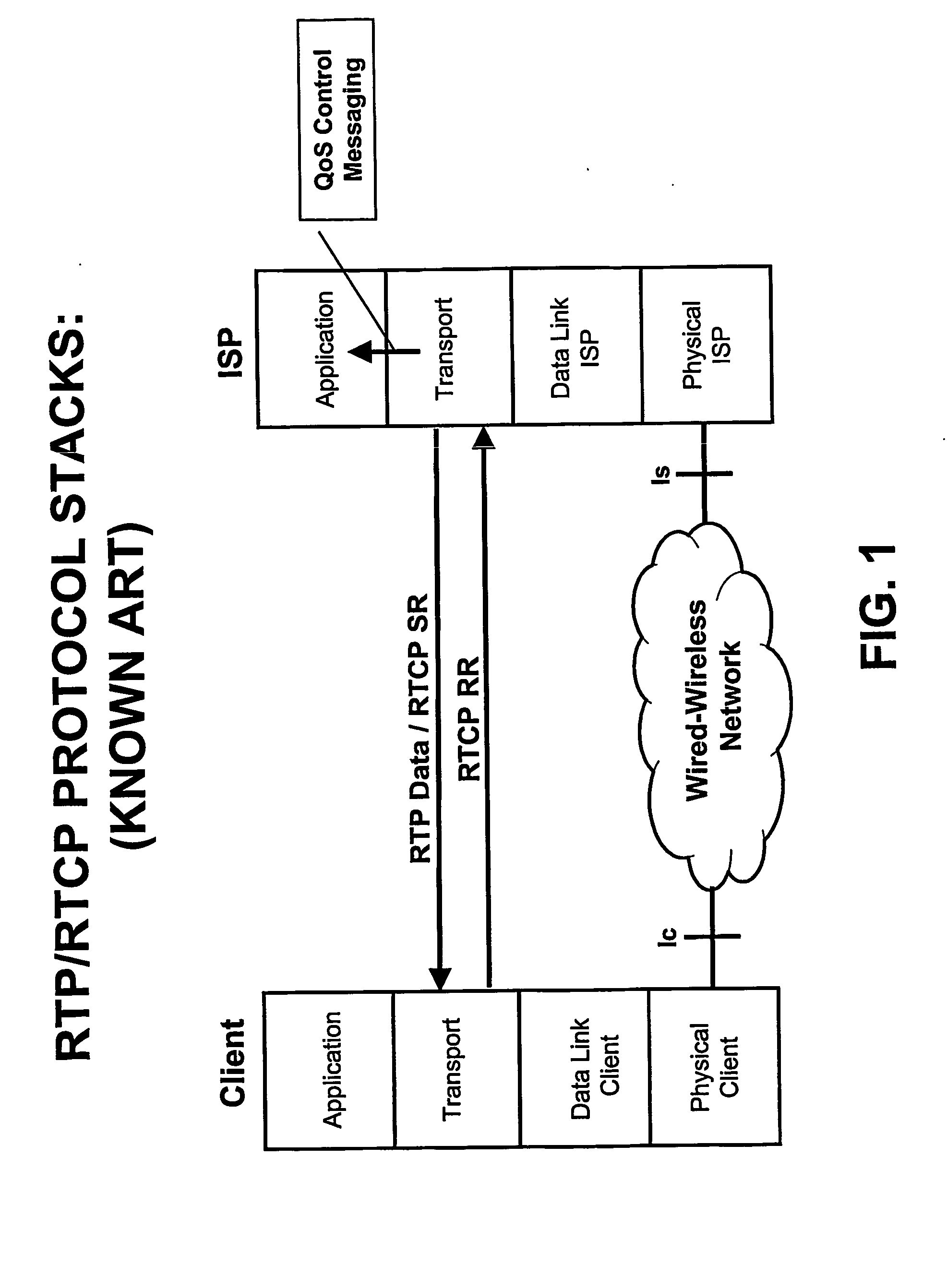
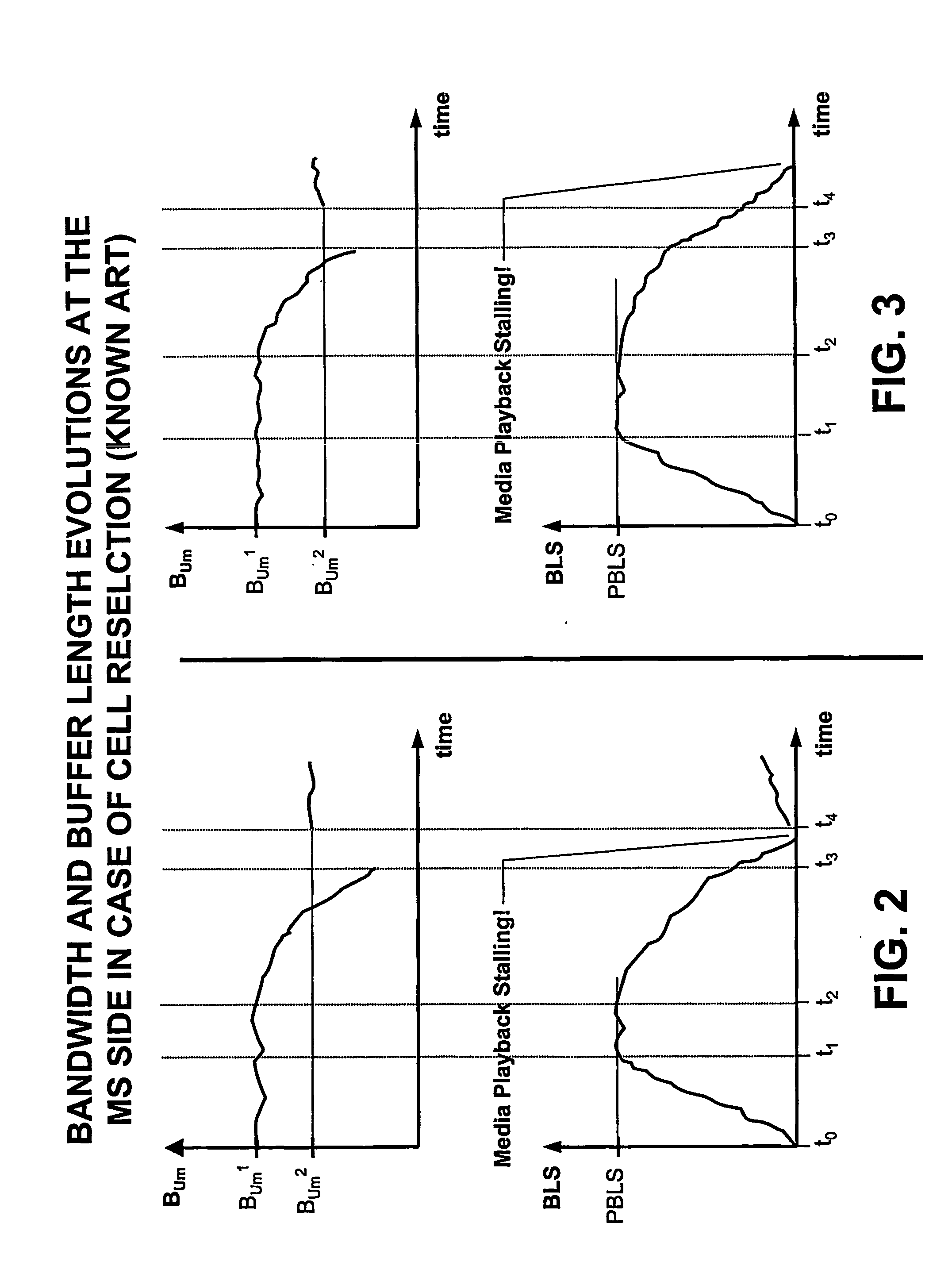
An end to end fast signalling procedure is disclosed in order to improve standard RTP / RTCP transport protocols for the support of streaming services within any kind of wireless and / or mobile networks, in particular for the introduction within GSM-GPRS. The streaming flow is expected to be sent from an Internet Service Provider (ISP) to Mobile Stations (MS). During fast signalling procedure, RTCP feedback messages are sent at a rate higher then the one expected in standard RTCP protocol. Fast signalling messages are made by upgraded Receiver Reports (FRR) intended to make the end to end QoS control mechanism able to react quickly to sudden changes in the available bandwidth that can occur at the radio interface.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS SPA
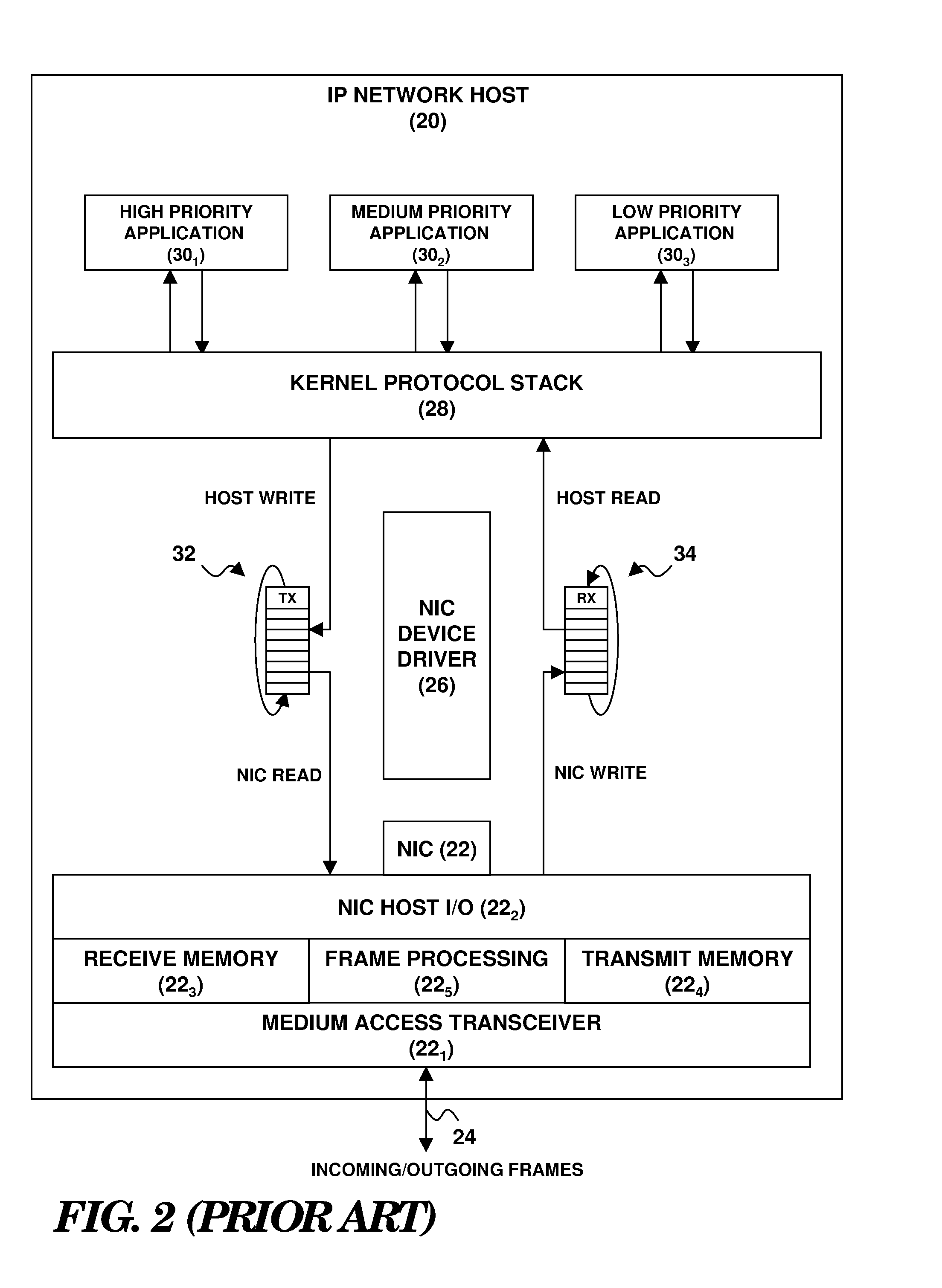
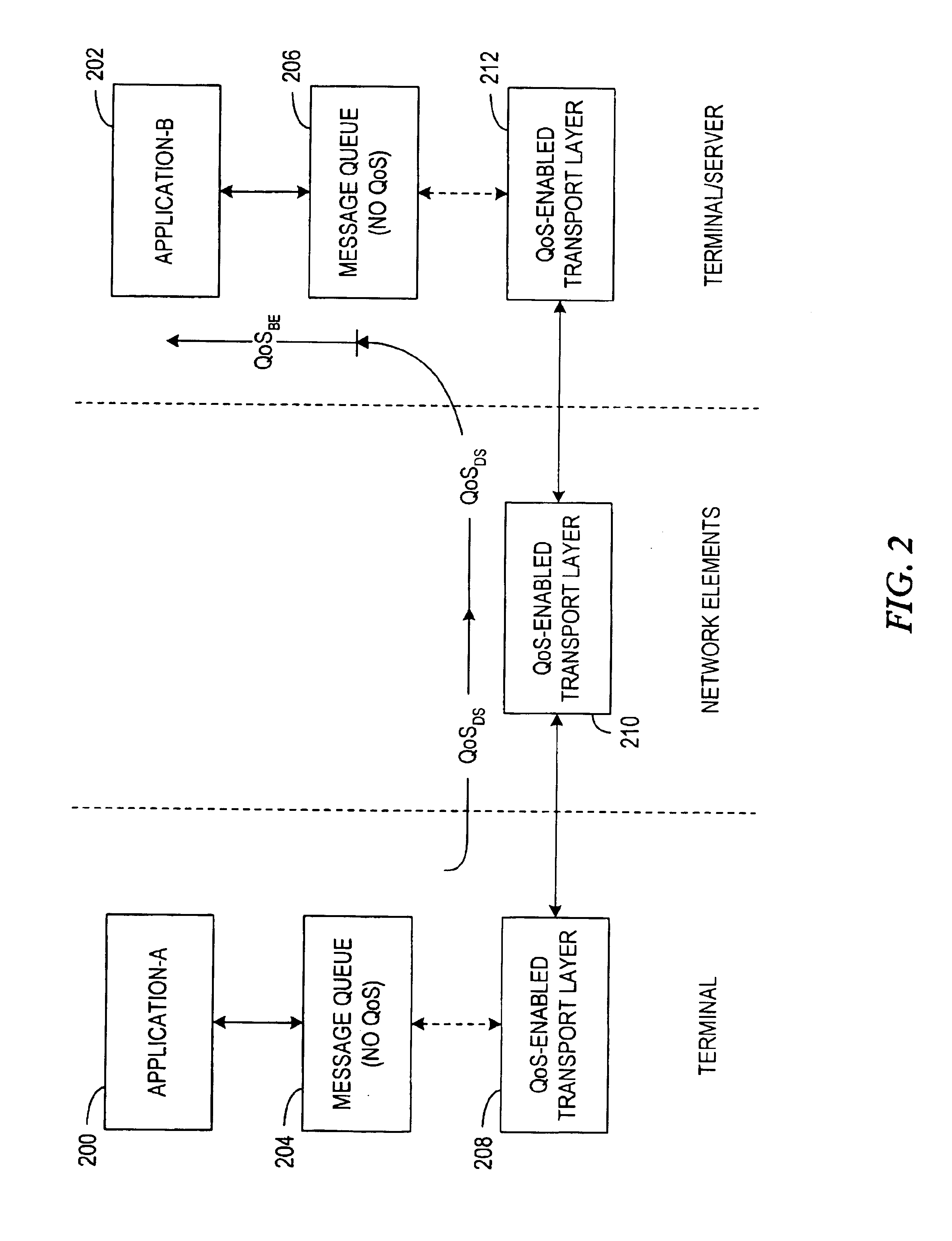
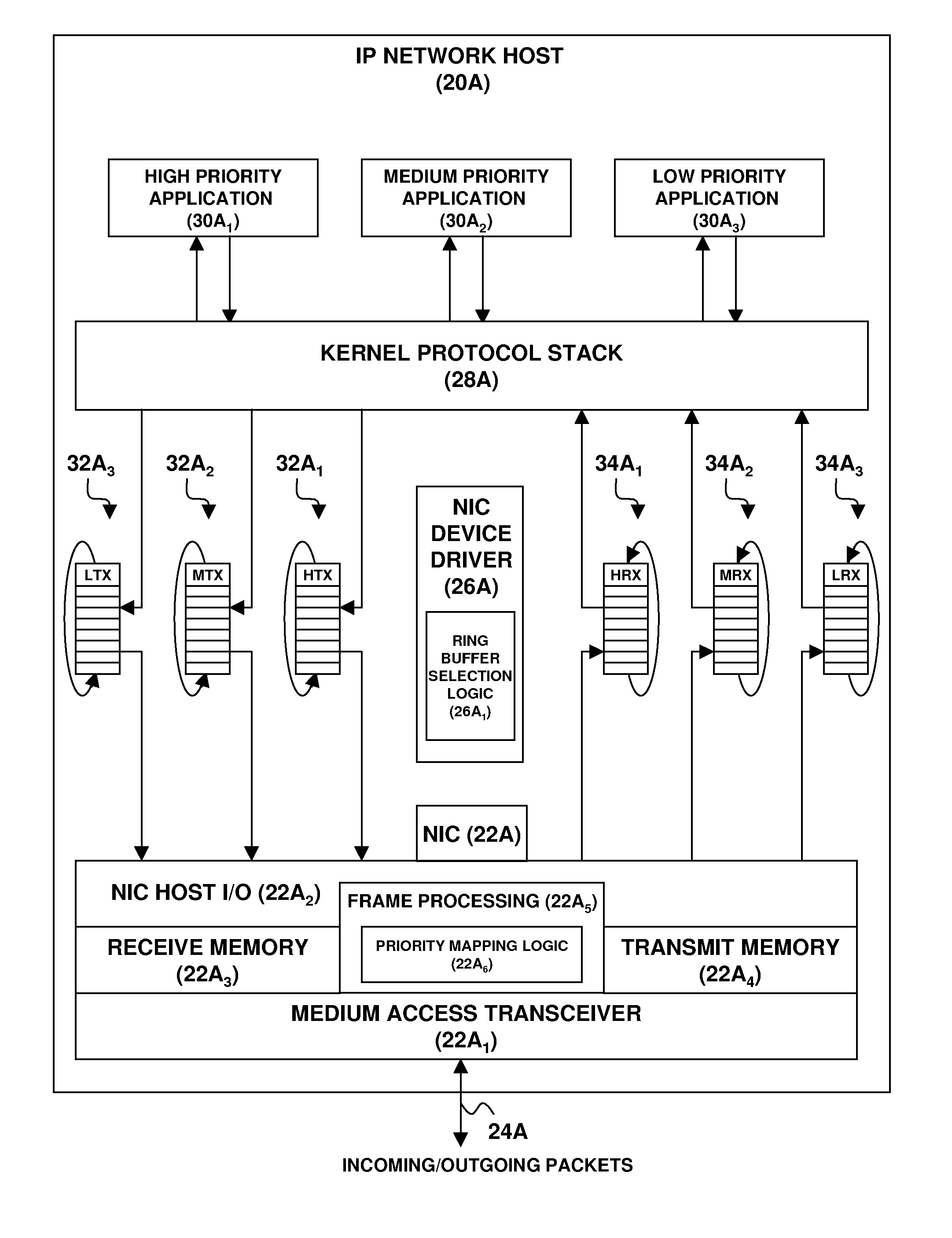
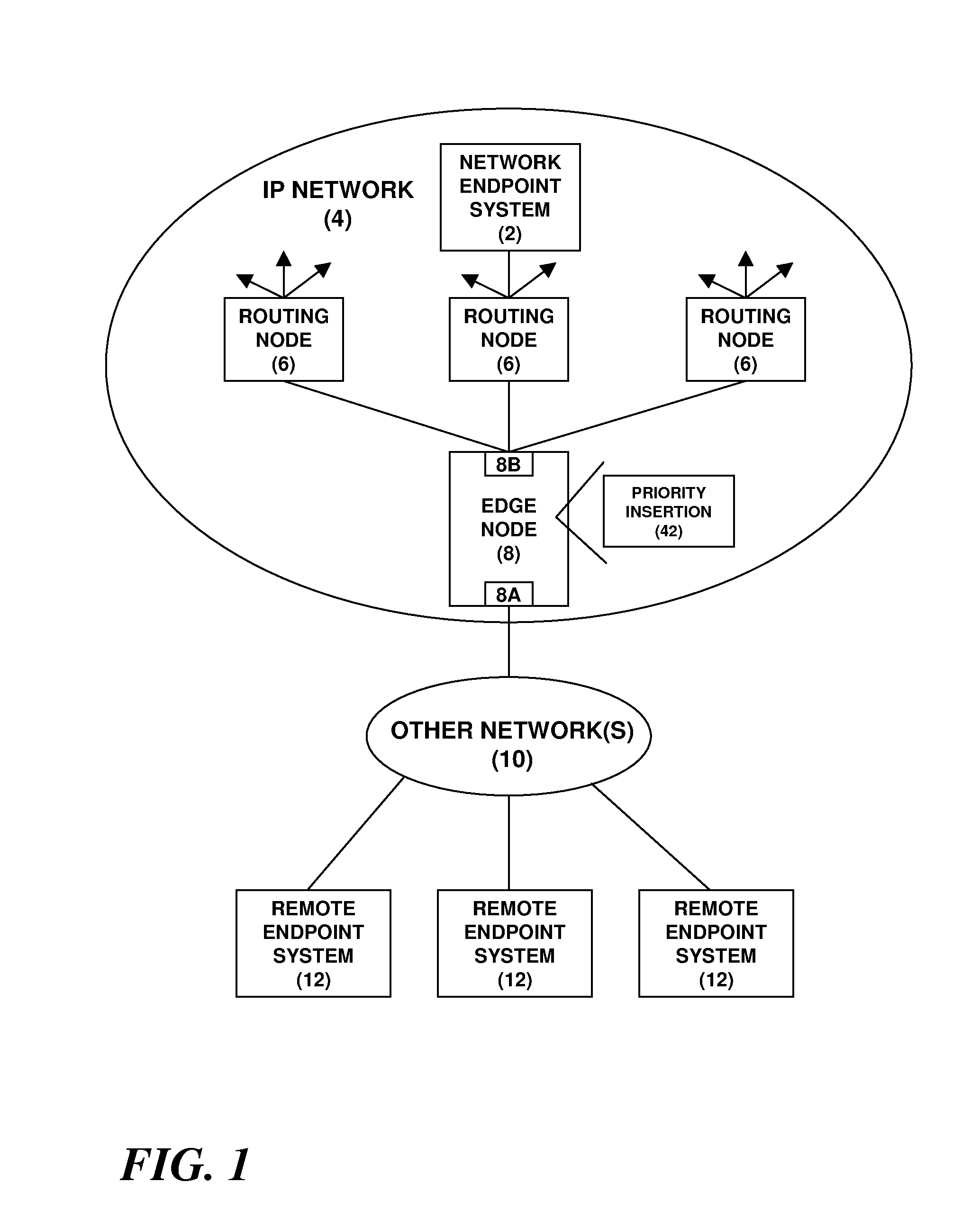
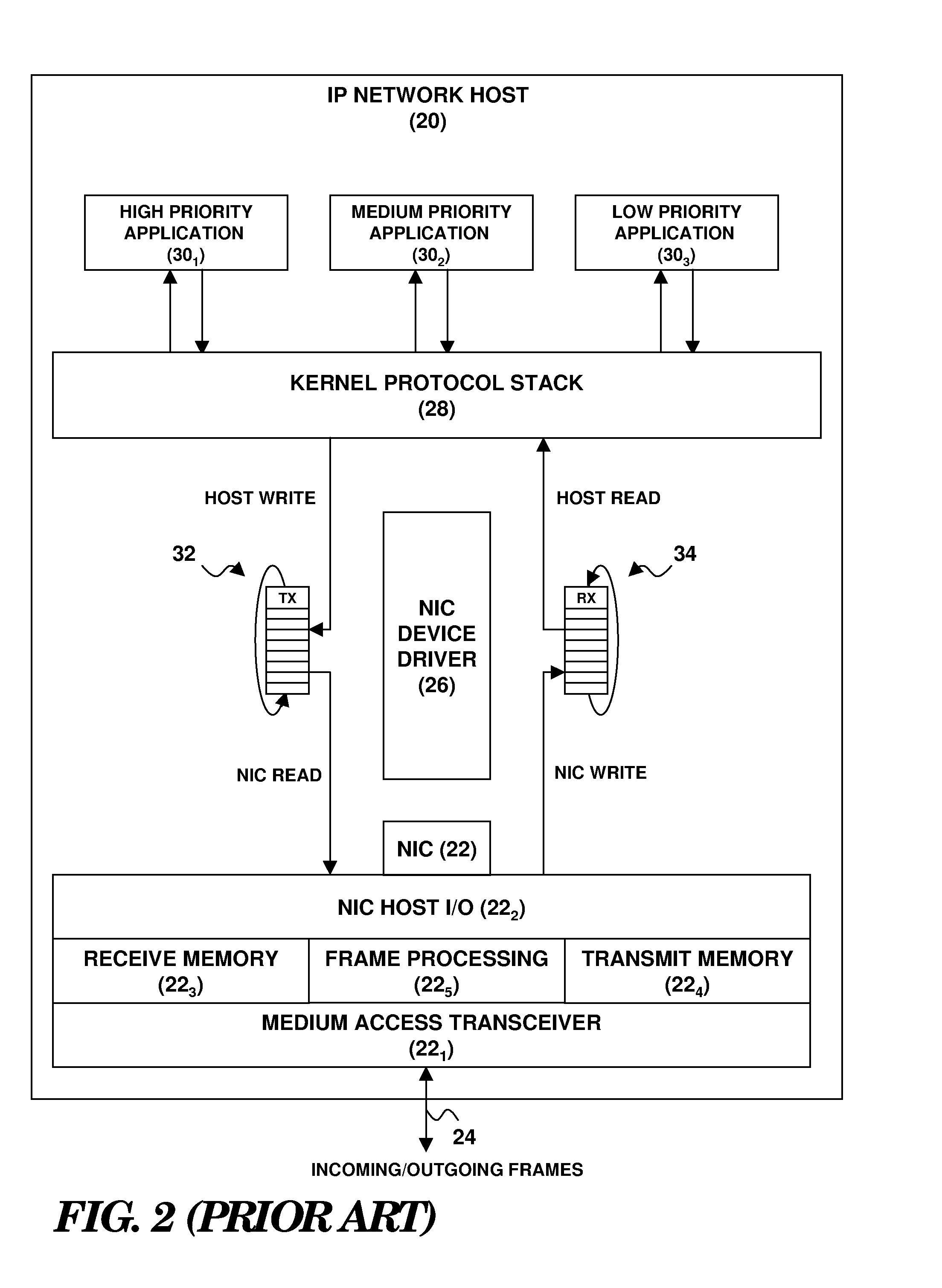
Enhancement of end-to-end network QOS
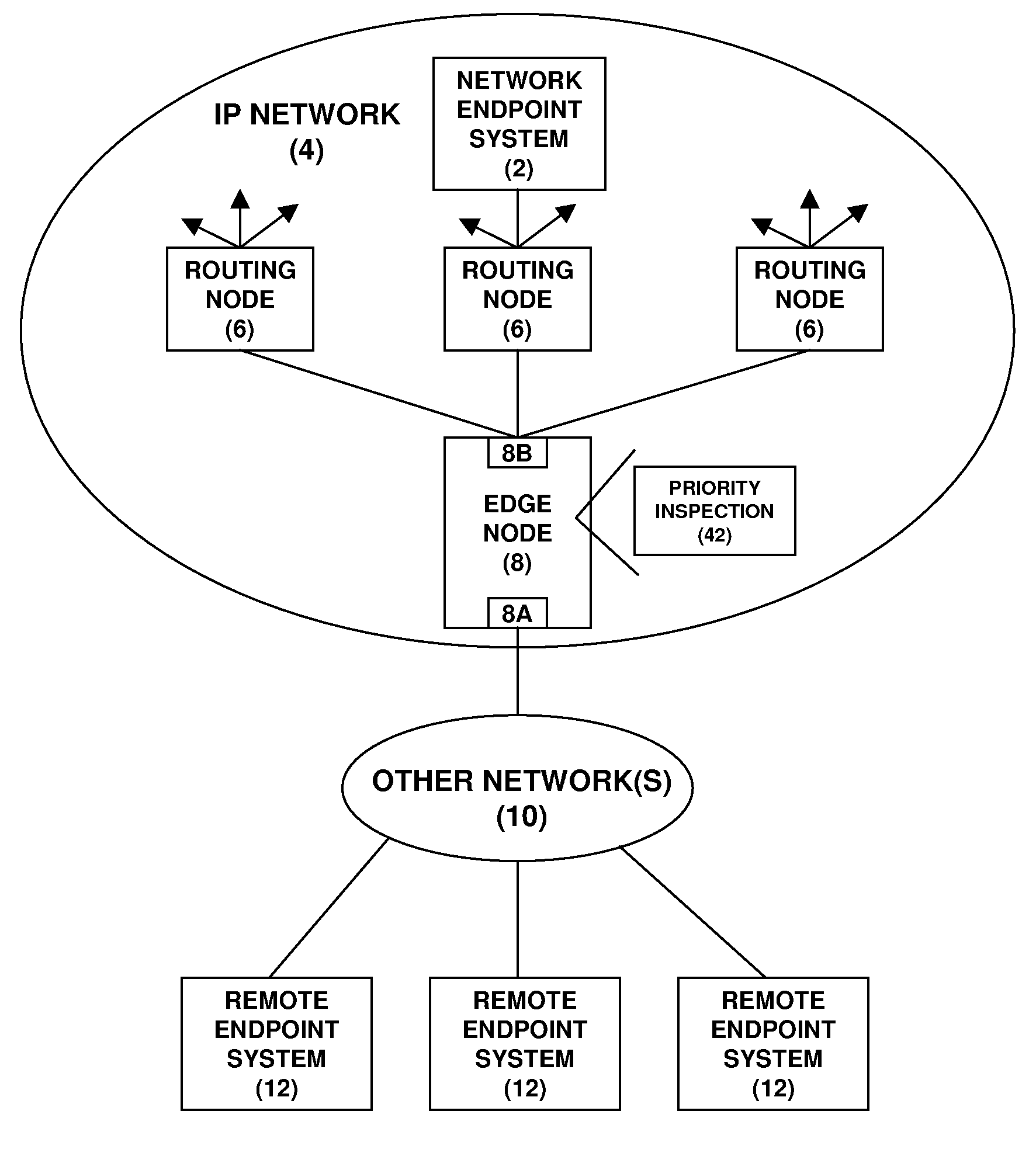
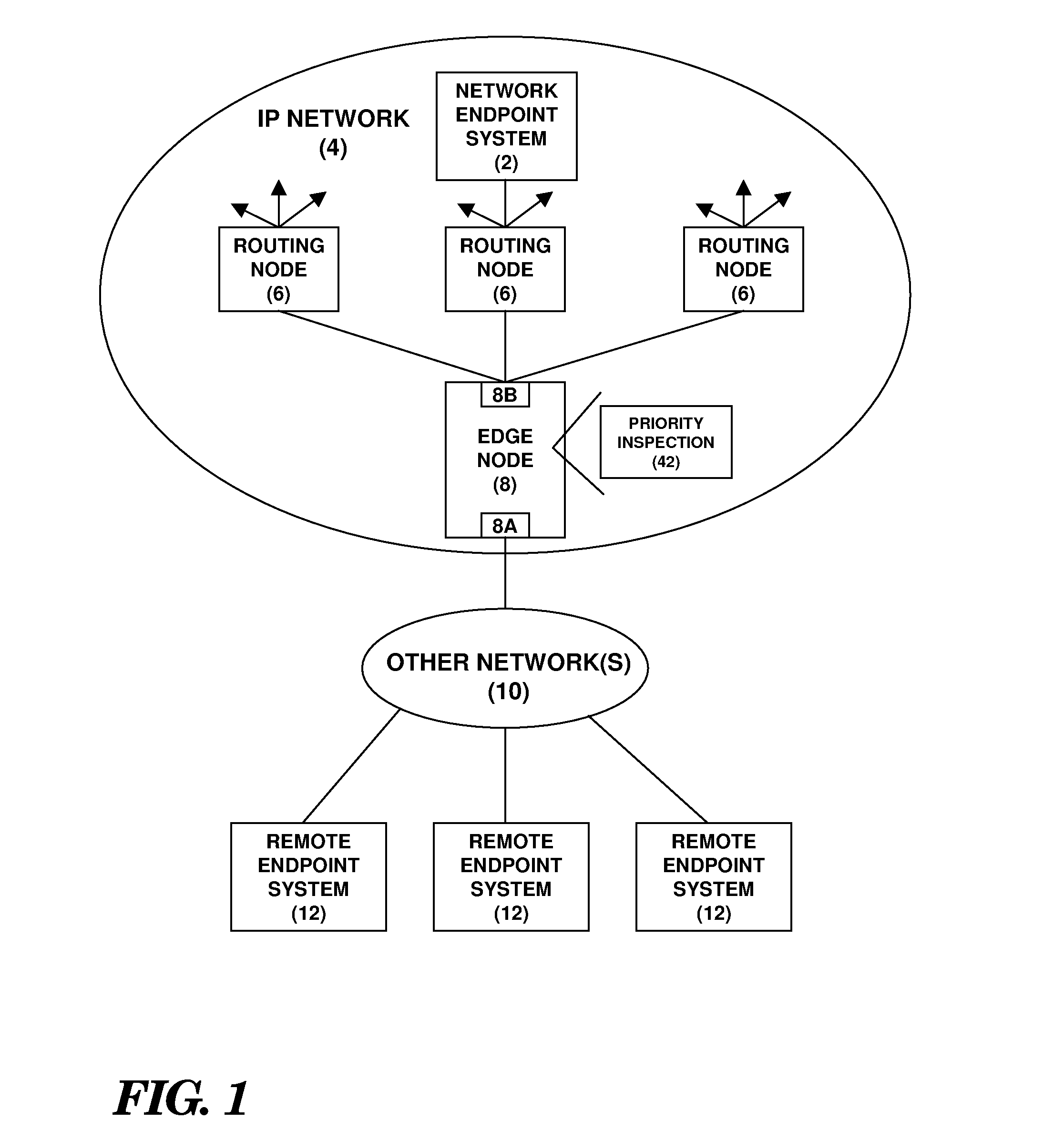
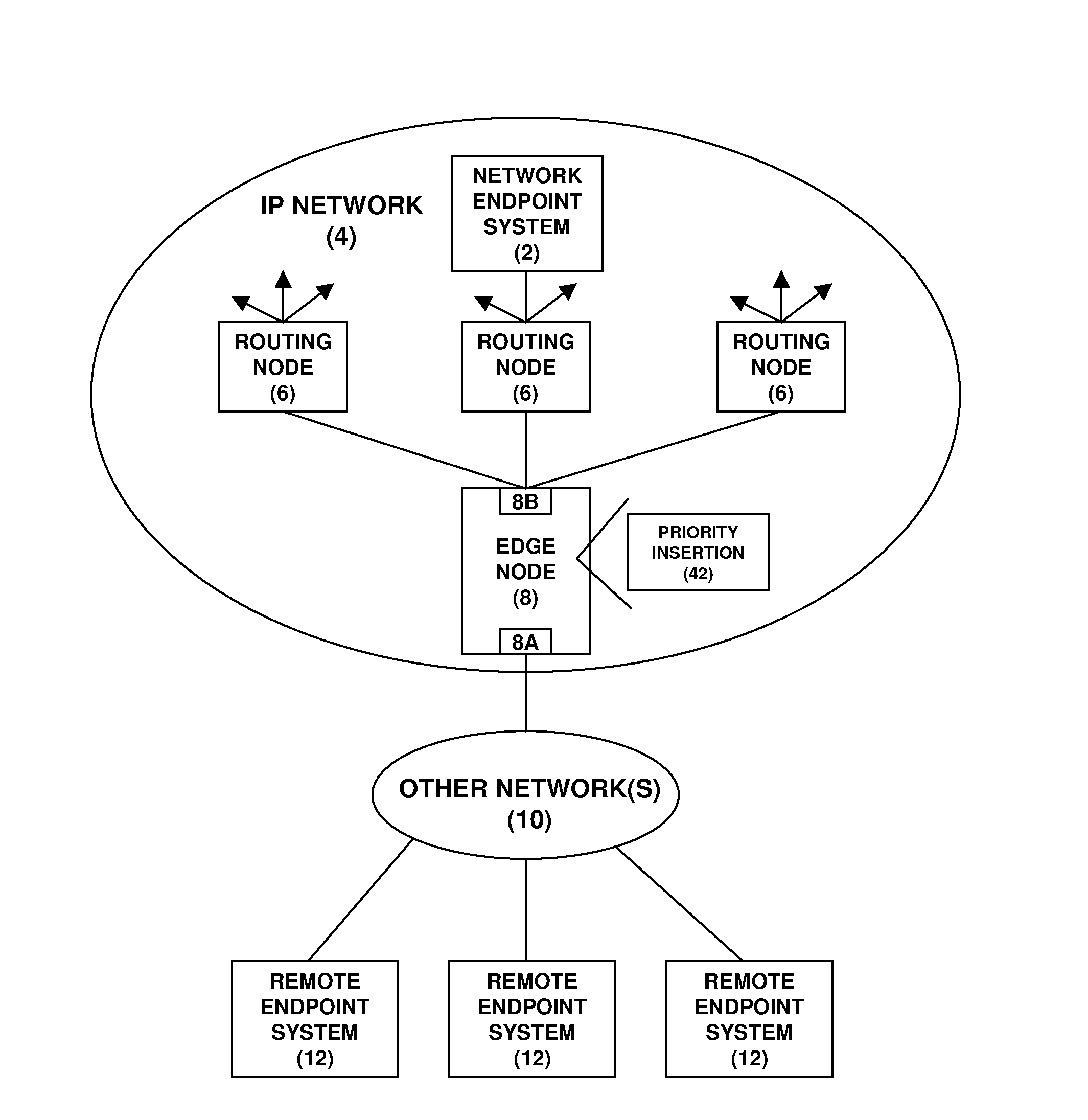
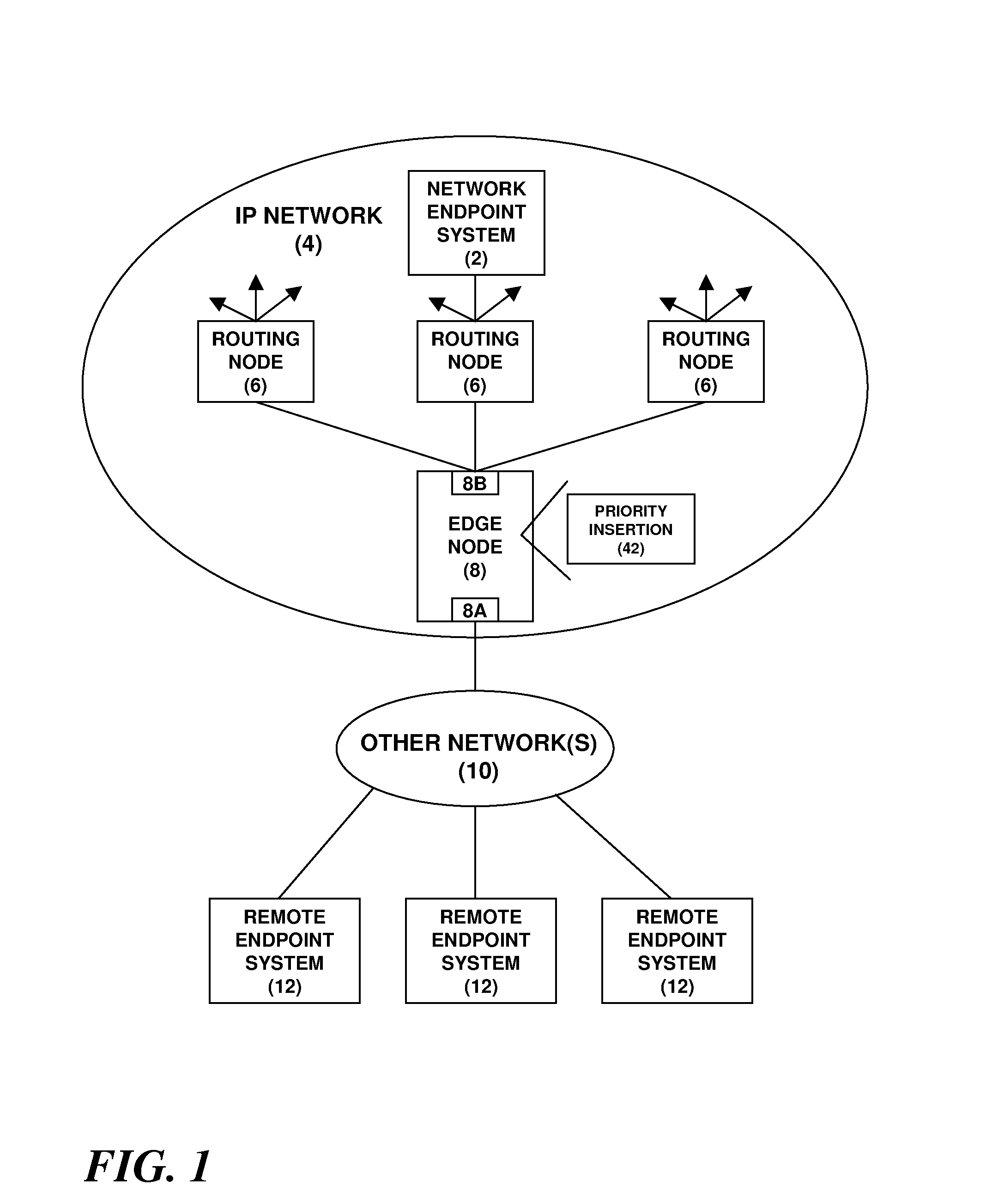
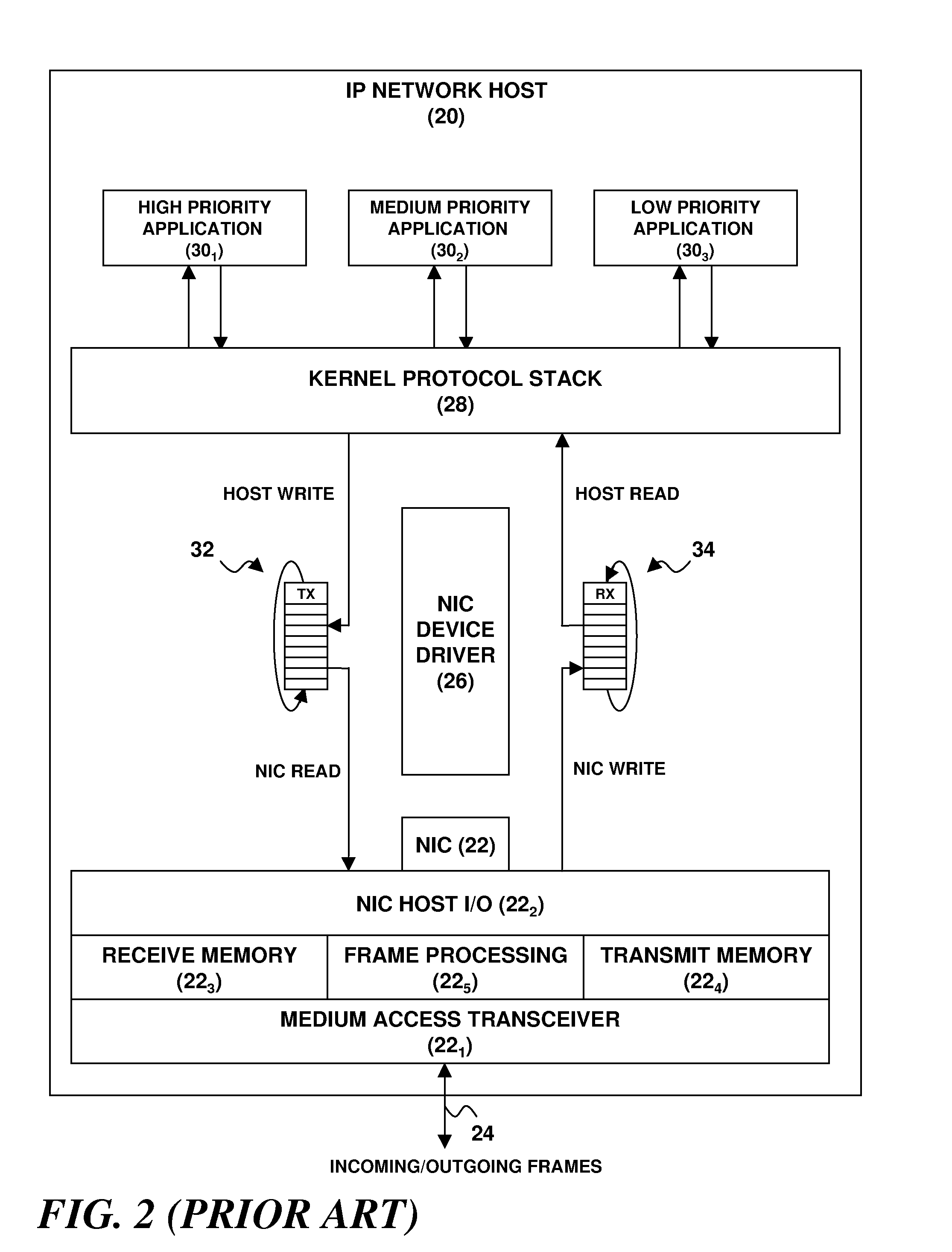
A network endpoint system and related method and computer program product for use in a network to support enhanced end-to-end QoS in the network. The network endpoint system is adapted to receive network data of varying priority on behalf of a data consumer operating at the application layer of a network protocol stack implemented by the network endpoint system. The network endpoint system includes a network interface controller adapted to receive network frames containing the network data, plural network data handling channels each having an associated priority, and priority processing logic adapted to transfer the network data from the network interface controller to the plural data handling channels on a prioritized basis according to the network data priority. Also disclosed are a network interface controller and a network node to support enhanced end-to-end QoS in a network.
Owner:IBM CORP
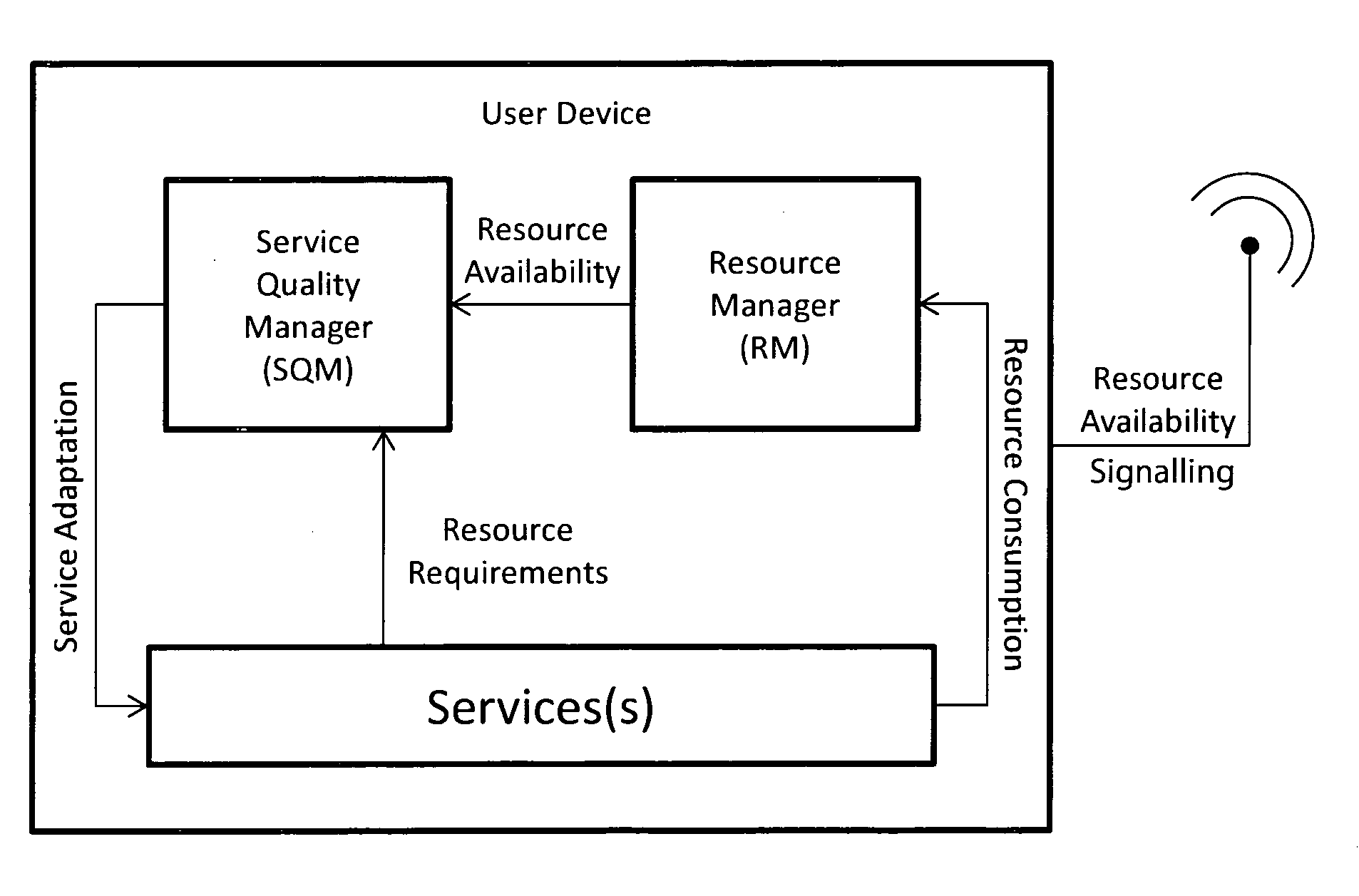
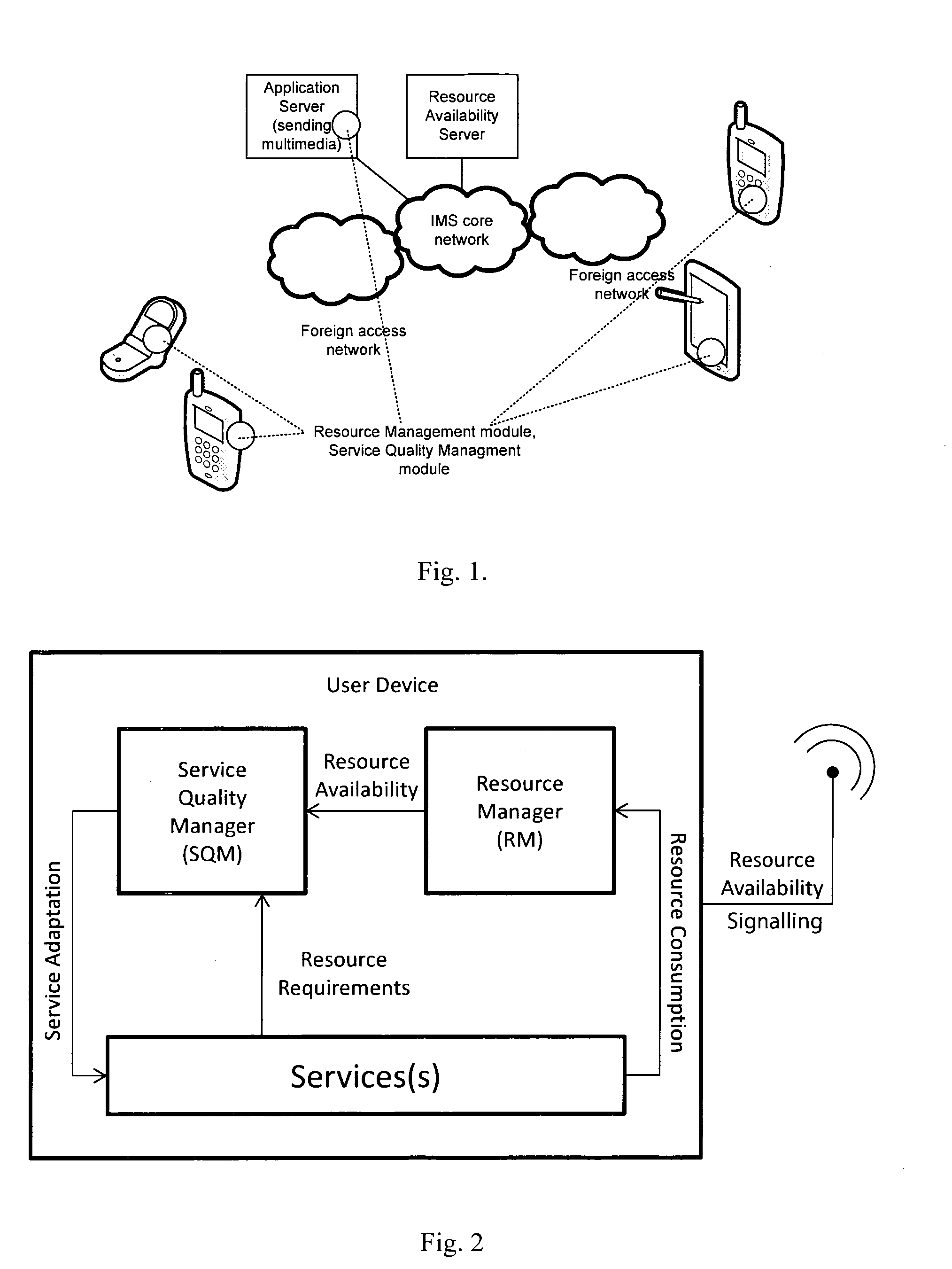
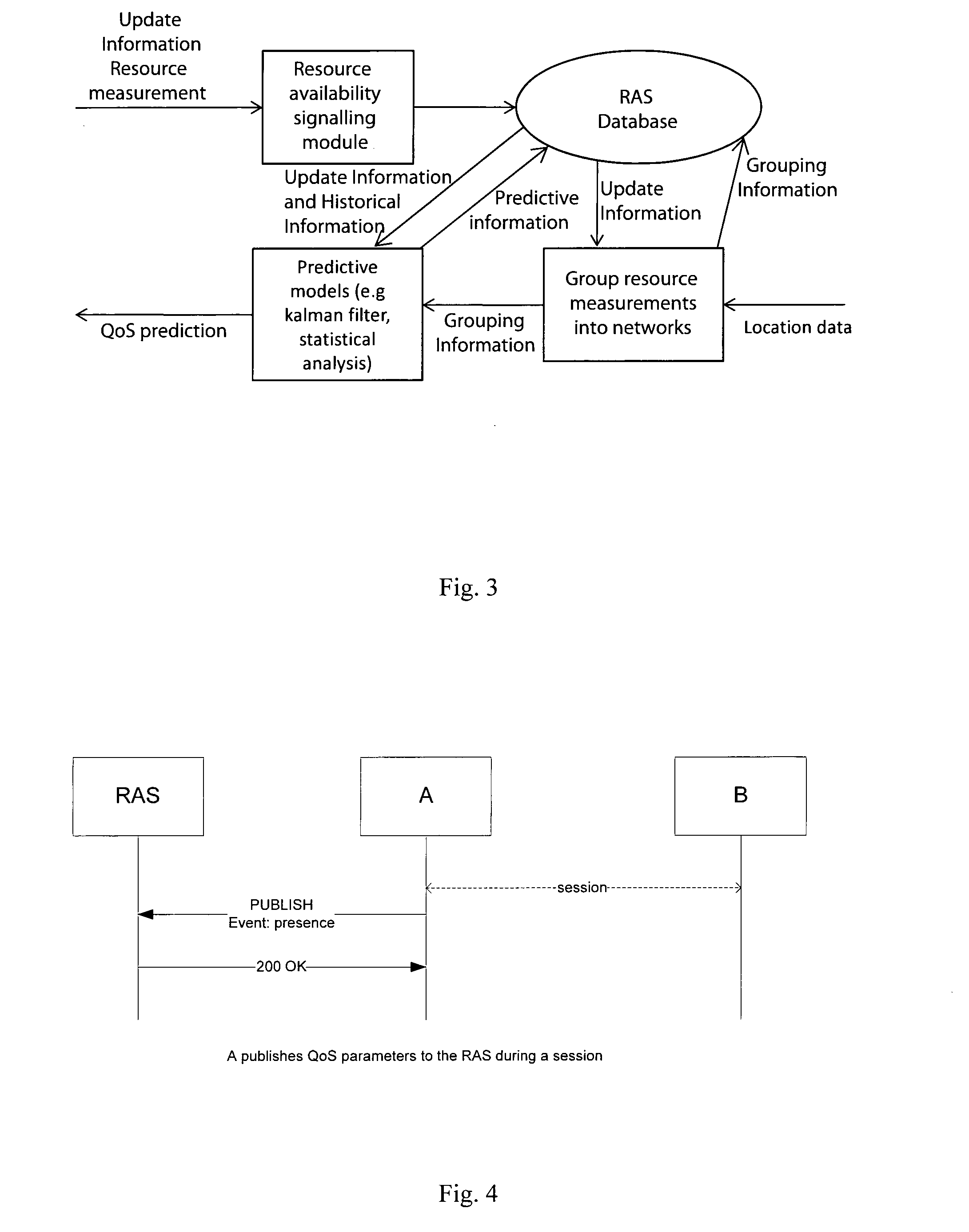
Network resource management
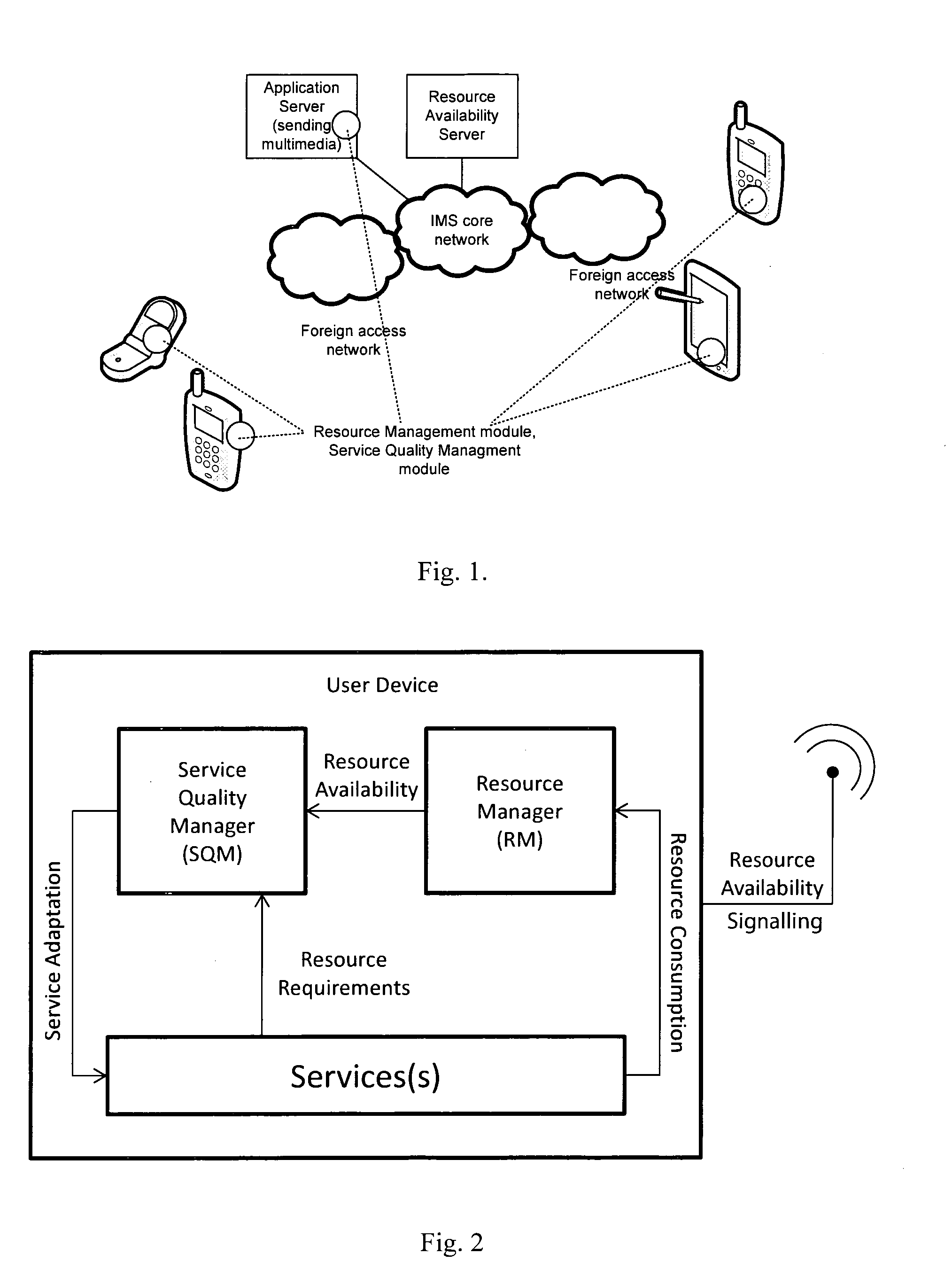
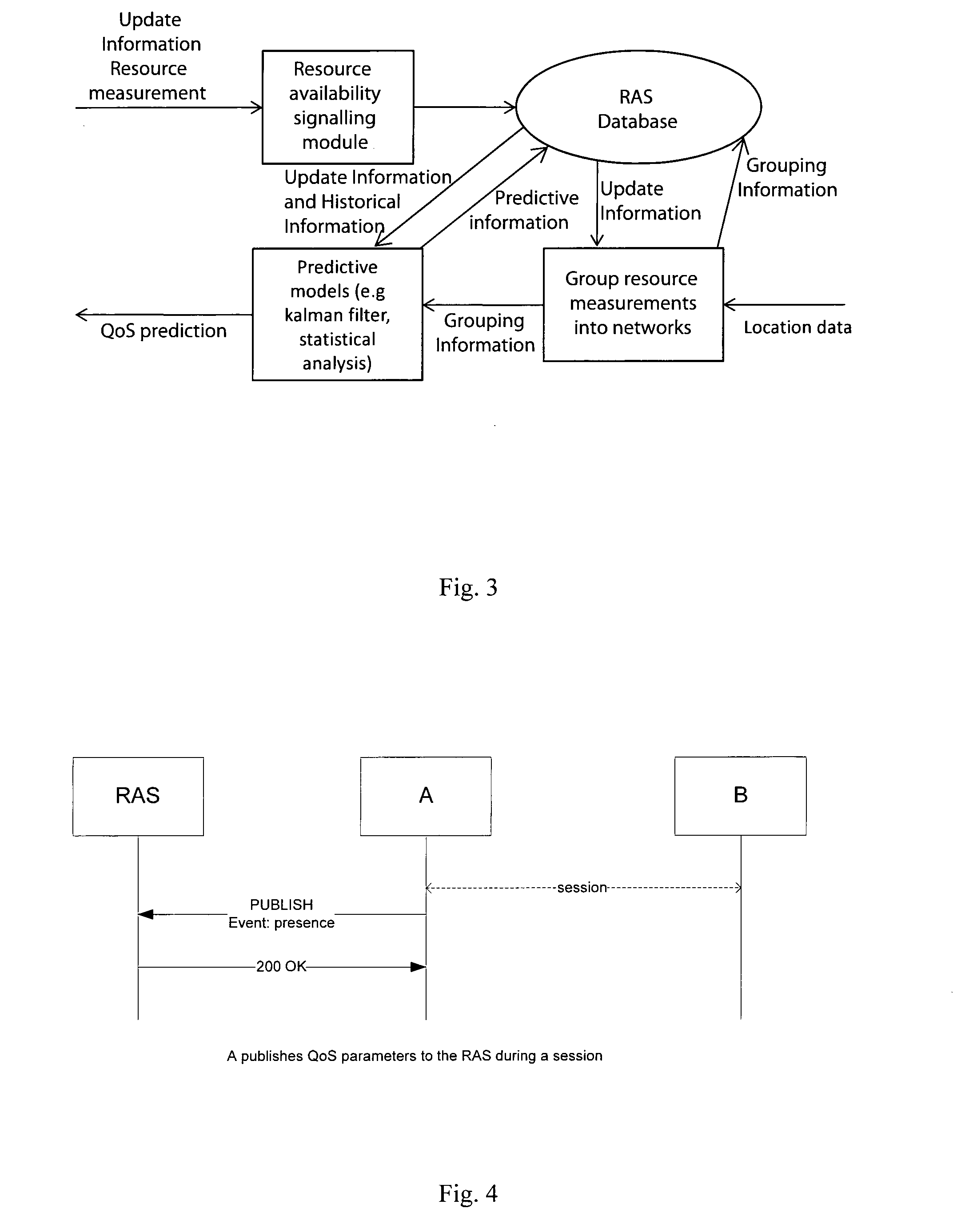
ActiveUS20100299433A1Quality improvementImprove service qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork resource managementPacket loss
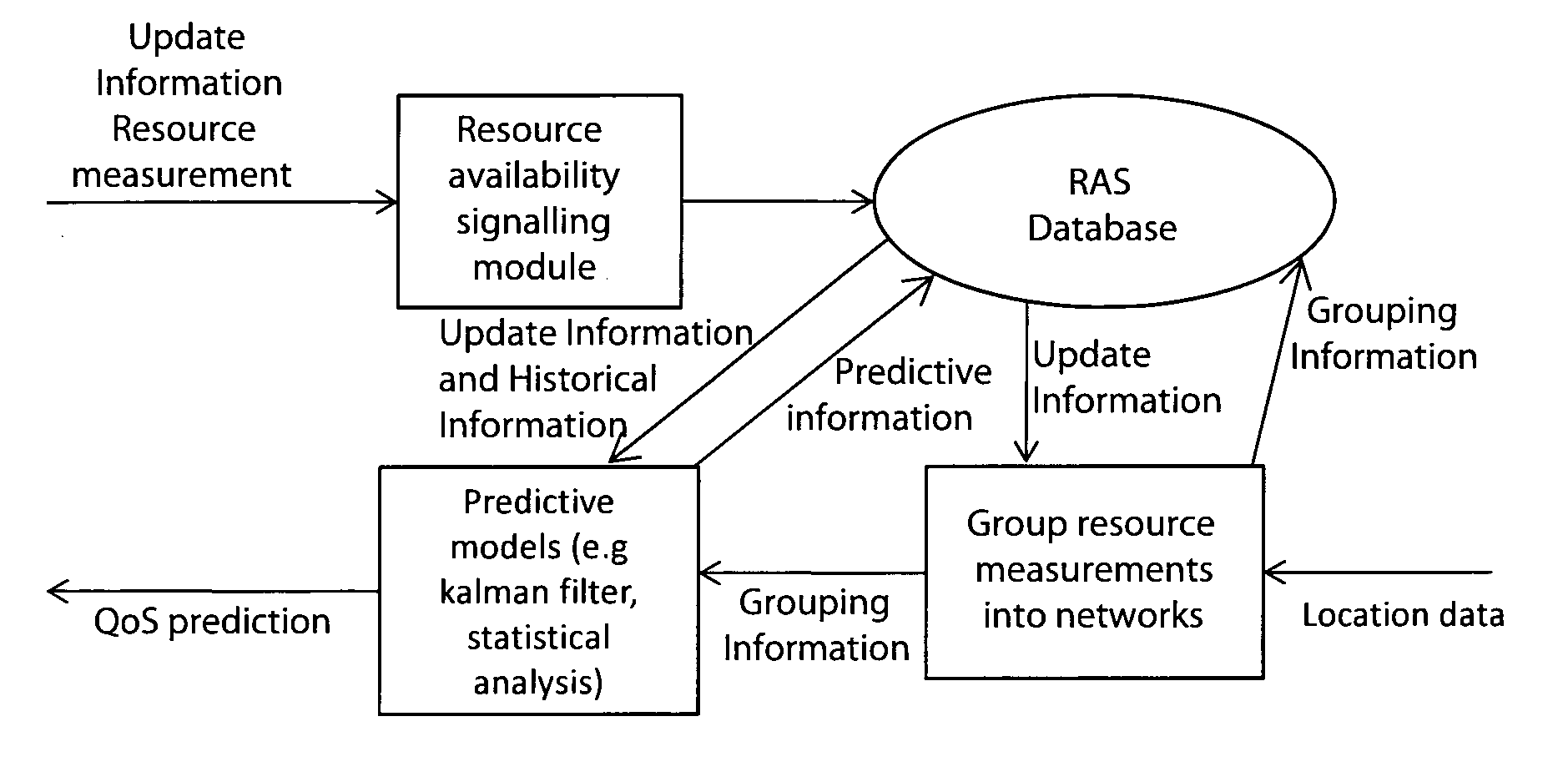
The invention provides real time dynamic resource management to improve end-to-end QoS by mobile devices regularly updating a resource availability server (RAS) with resource update information. Examples of resource update information are device battery status, available memory, session bandwidth, delay, packet loss, and jitter, network element storage capacity, network element processing power. This information is made available by the RAS. In addition, the RAS generates and maintains predictive models and makes available predictive data from these models. Network elements and devices retrieve this information in the form of notifications from the RAS or by way of querying the RAS. The network elements and devices, based on these predictions, act to negotiate sessions to optimise QoS. In one embodiment the RAS is updated by only mobile devices subscribed to the operator which hosts the RAS. The update information is addressed to the RAS as a stand-alone entity. However, it is envisaged that the server may be hosted by multiple operators and may receive updates from devices subscribed to different operators. Also, it is envisaged that not only mobile devices but also network elements such as MMSCs may send update information.
Owner:MARKPORT LTD
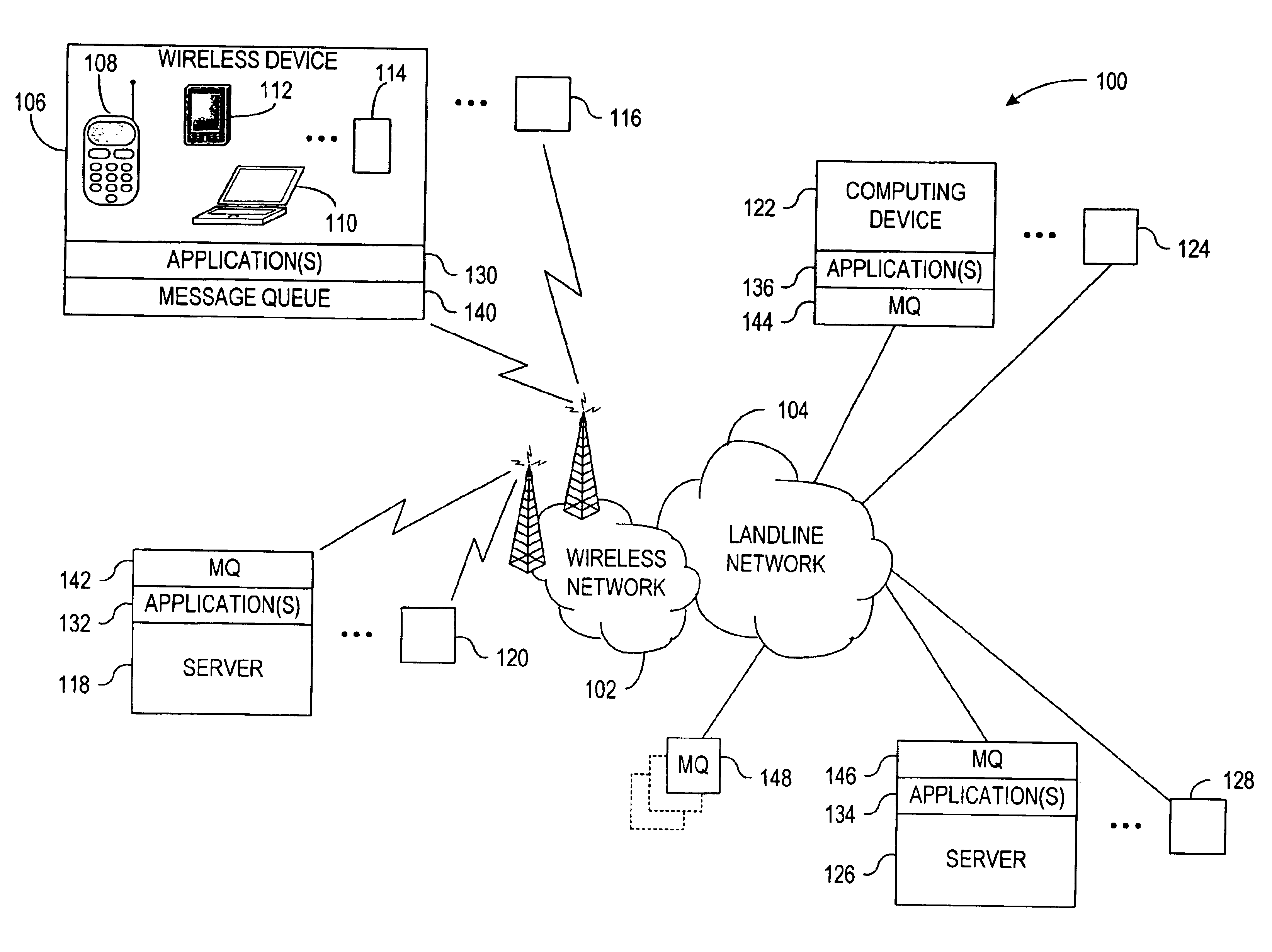
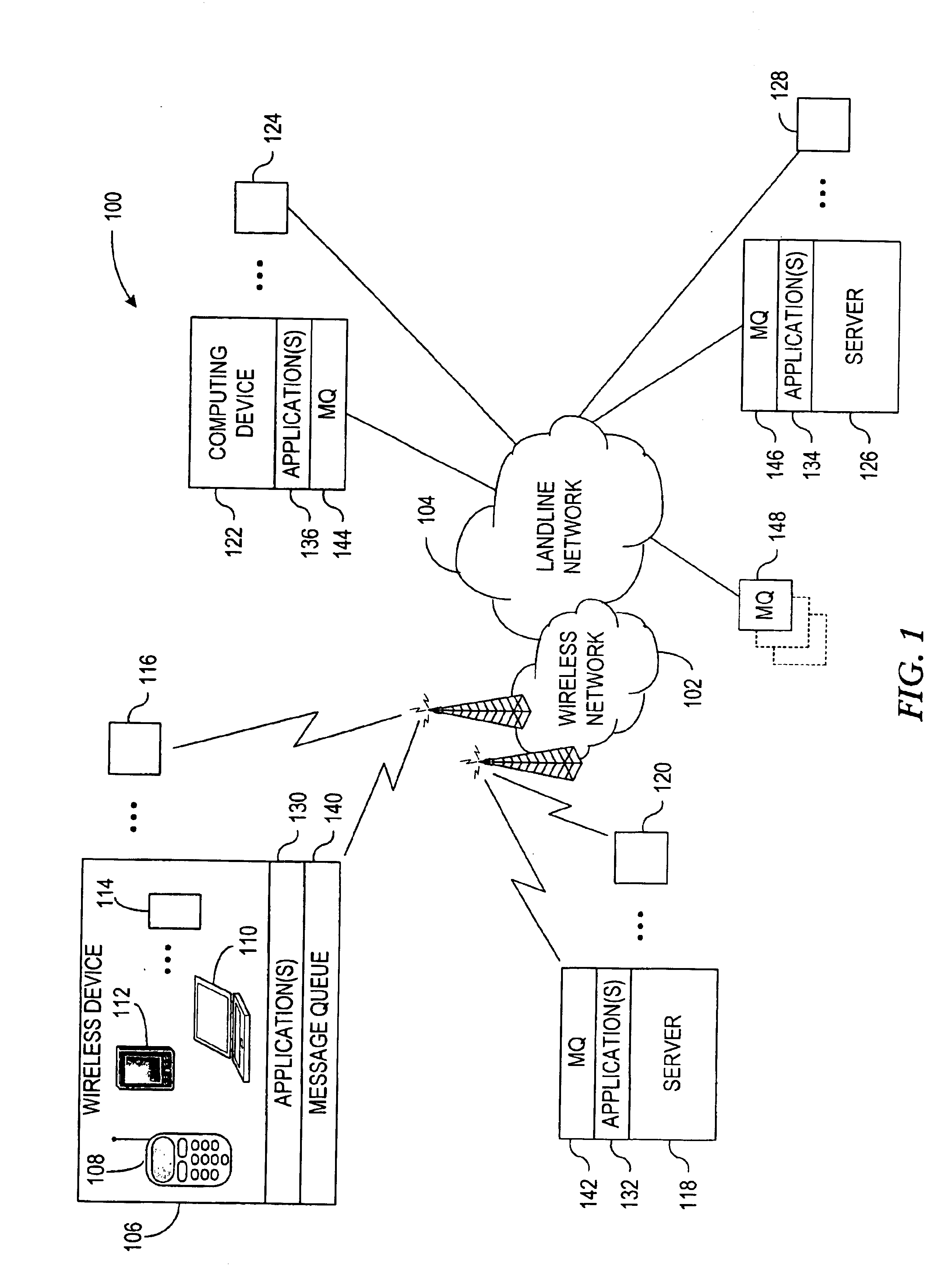
System and method for facilitating end-to-end quality of service in message transmissions employing message queues
InactiveUS6940813B2Improve service qualityError preventionTransmission systemsMessage queueQuality of service
A system and method for buffering messages between at least two applications over a network implementing a Quality of Service (QoS) framework. Messages are transmitted from a source application to an intermediary message queue for message buffering. A message queue QoS is imparted at the message queue to the flow of the messages traversing the message queue, and the end-to-end QoS can then be provided for the flow of messages over the network.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
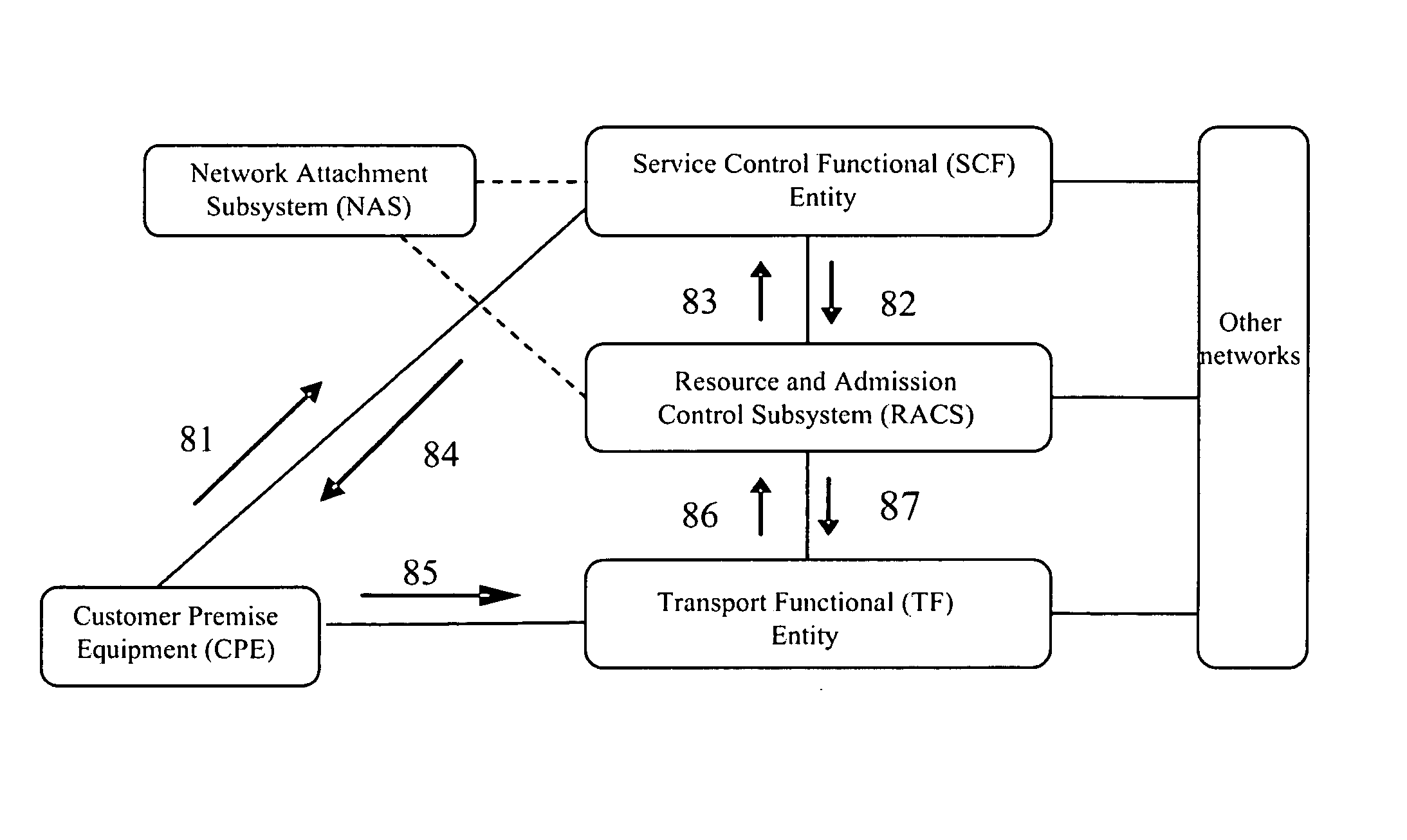
System And Method Of Dynamic Qos Negotiation In Next Generation Network
ActiveUS20070201366A1Improve resource utilizationEffectively ensureError preventionTransmission systemsService controlTransport network
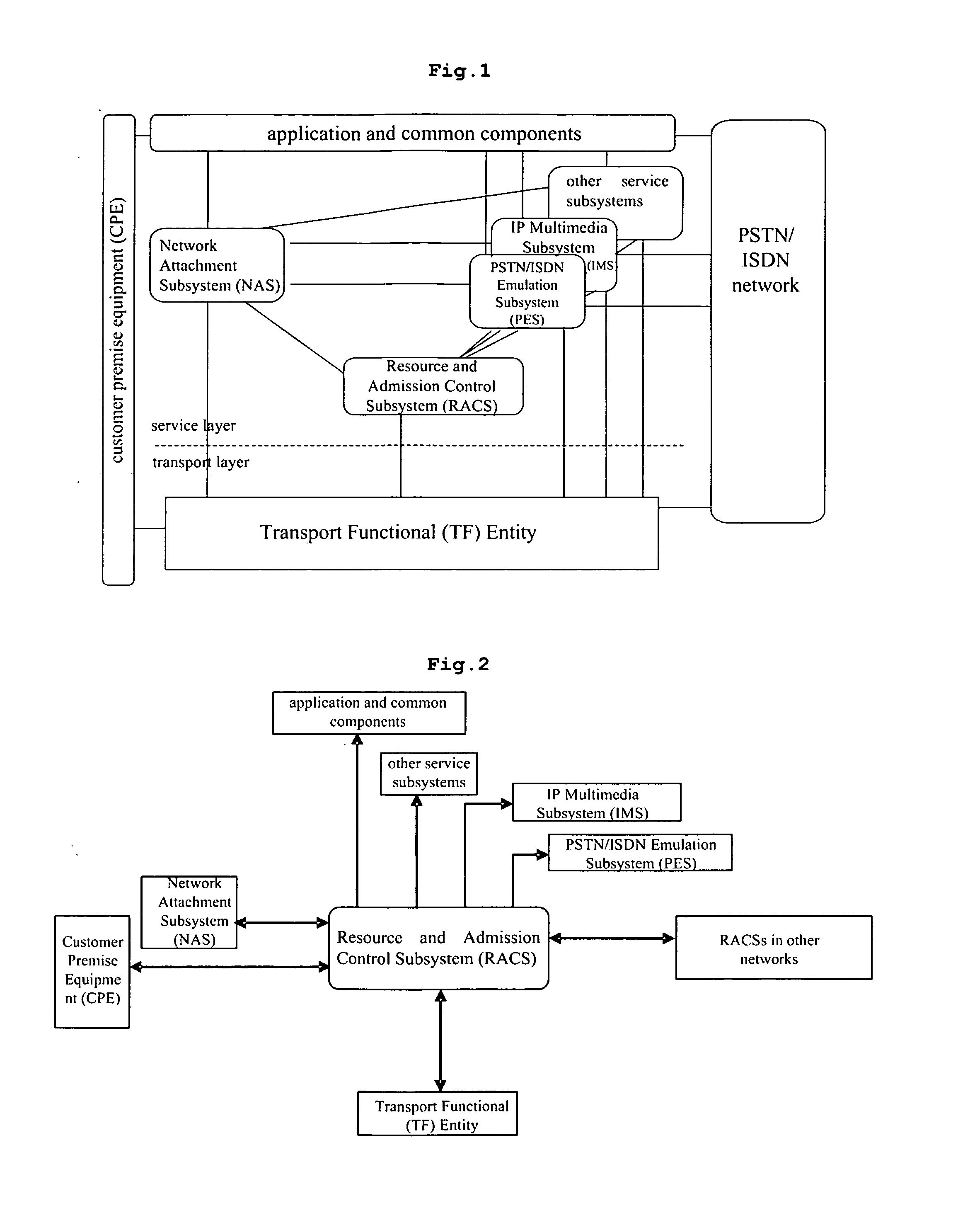
The present invention discloses a system and a method of dynamic QoS negotiation in NGN. The Resource and Admission Control Subsystem (RACS) provides intercommunication interfaces with Transport functional (TF) entity, Service Control Functional (SCF) entities, and Network Attachment Subsystem (NASS), and thereby, when a user terminal in NGN is to develop a service with QoS requirement, the RACS can obtain the QoS requirement parameters of a service, determine the admission control decision parameters in accordance with the QoS requirement parameters, and the RACS send the determined admission control decision parameters to the TF entity for execution, such that the QoS assurance for the service is realized. The present invention allows an end-to-end QoS negotiation in NGN in accordance with the availability of current transport network resources, and thereby can effectively improve the transport resource utilities. Therefore, the present invention can effectively ensure QoS of service transported in NGN.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
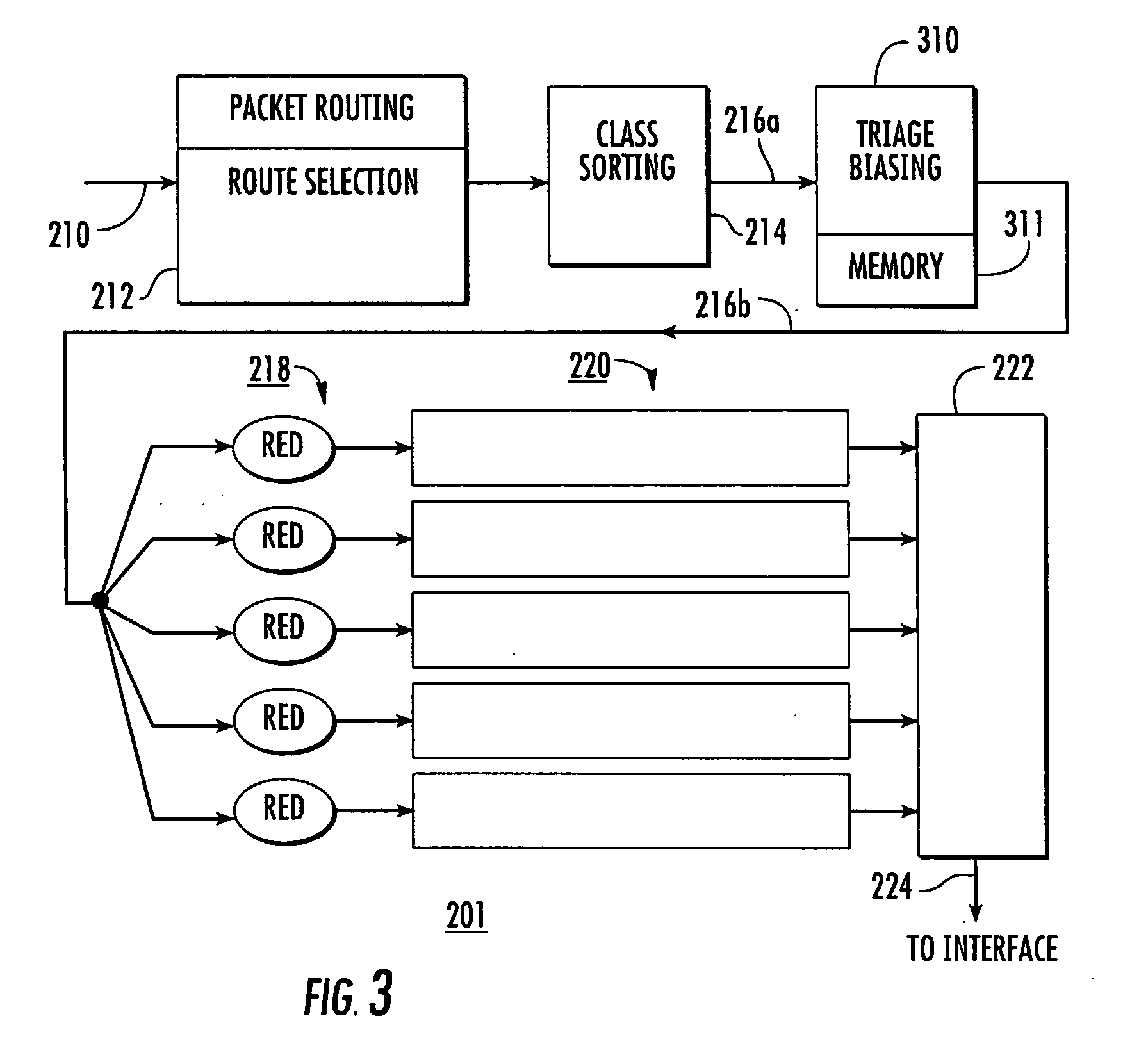
Biasing of network node prioritization to improve per-hop behavior based on performance necessary for a packet to meet end-to-end QoS goals
InactiveUS20070002740A1High travel costLoad on networkError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork packetNetwork topology
Each local node of a network adjusts the priority of messages passing through the node based on locally available information. If network topology is available, priority can be given to those messages which have the most hops to go. If source identity or time is / are known, the priority of a message can be upgraded for those messages which have already taken a long time or have already experienced a large number of hops. If destination address and network topology are additionally known, end-to-end QoS can tend to be equalized for all paths.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
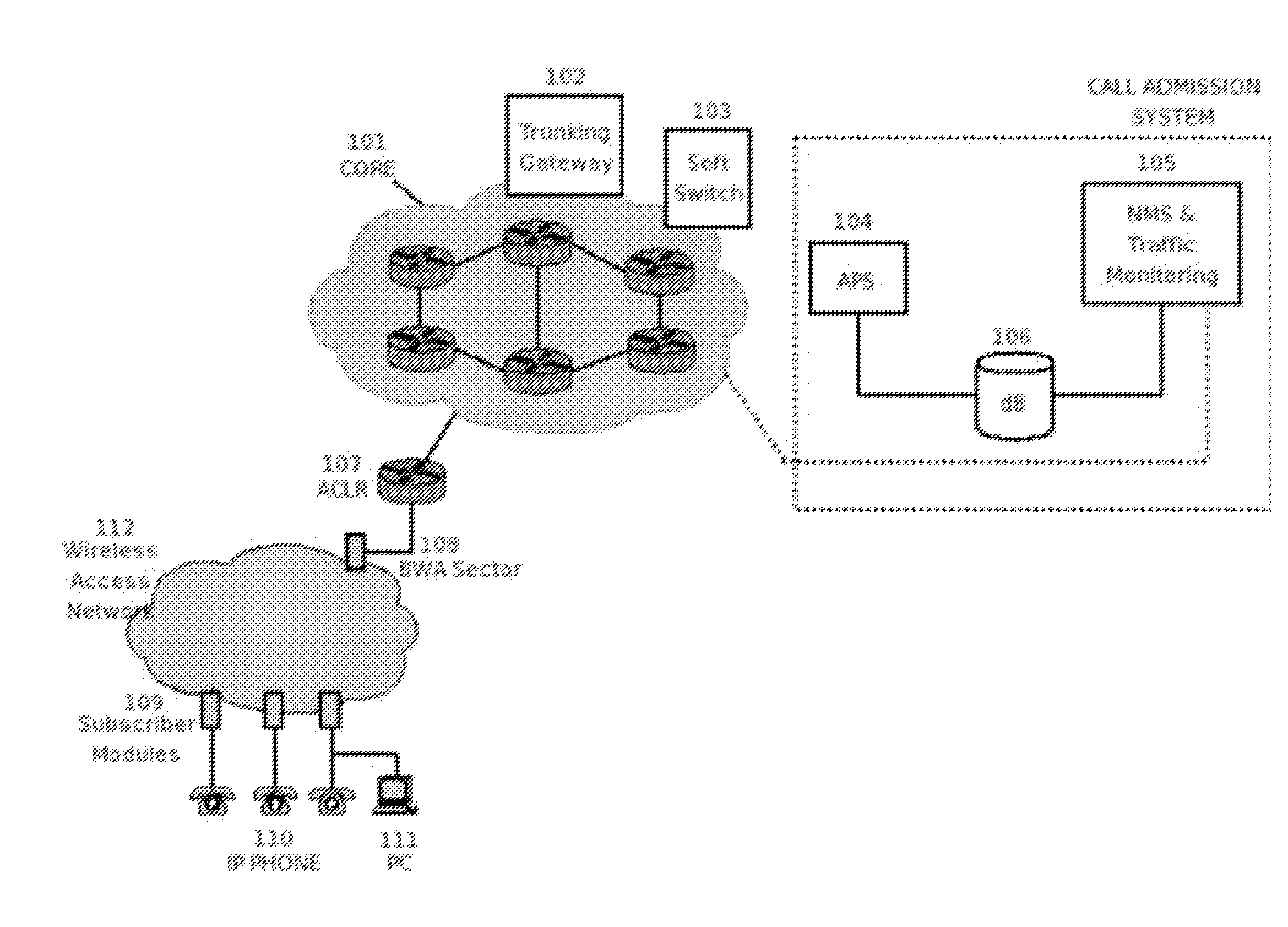
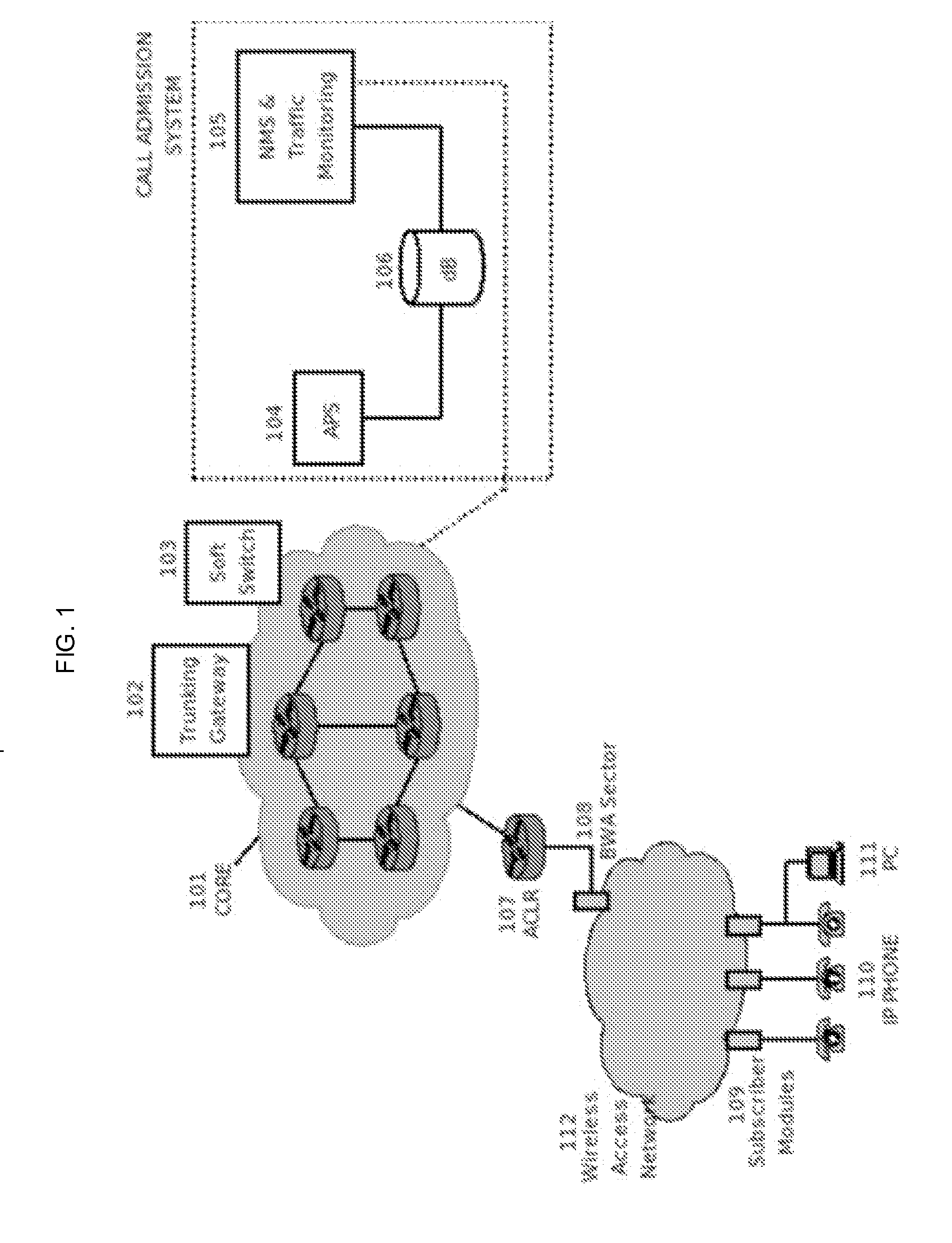
Methods and Systems for Call Admission Control and Providing Quality of Service in Broadband Wireless Access Packet-Based Networks
InactiveUS20070286202A1Avoid congestionNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationVoice over IPPaper document
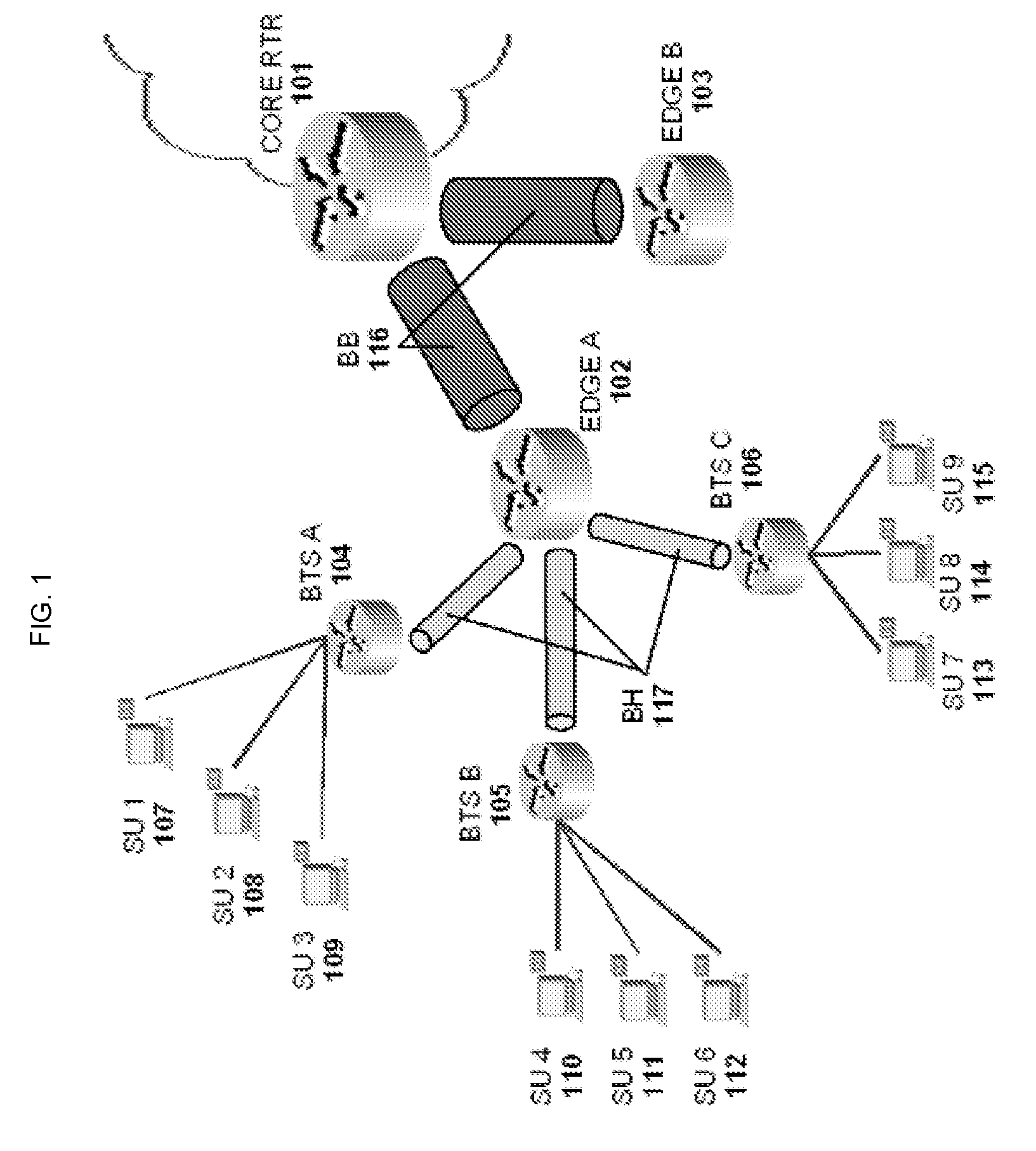
Methods and systems for call admission control and providing Quality of Service (QoS) in packet-based networks, with emphasis on those utilizing Wireless Broadband Access, are disclosed. This invention presents a mechanism for implementing call admission in packet-based networks. Quality of Service is also provided by implementing key network functions. Although the access network call admission criteria are illustrated over broadband wireless access, the call admission mechanism principle is access technology-agnostic. Broadband wireless is given emphasis because of its bandwidth-sharing property and relative inefficiency in handling small Voice over IP packets. The invention contemplates on a call admission mechanism for providing reliable packet stream service in IP networks and at the same time passing burstable IP data traffic. Whenever convenient, NGN terms are used in the document—which also stresses the fact that the invention provides a mechanism for implementing NGN end-to-end QoS.
Owner:LATITUDE BROADBAND GLOBAL
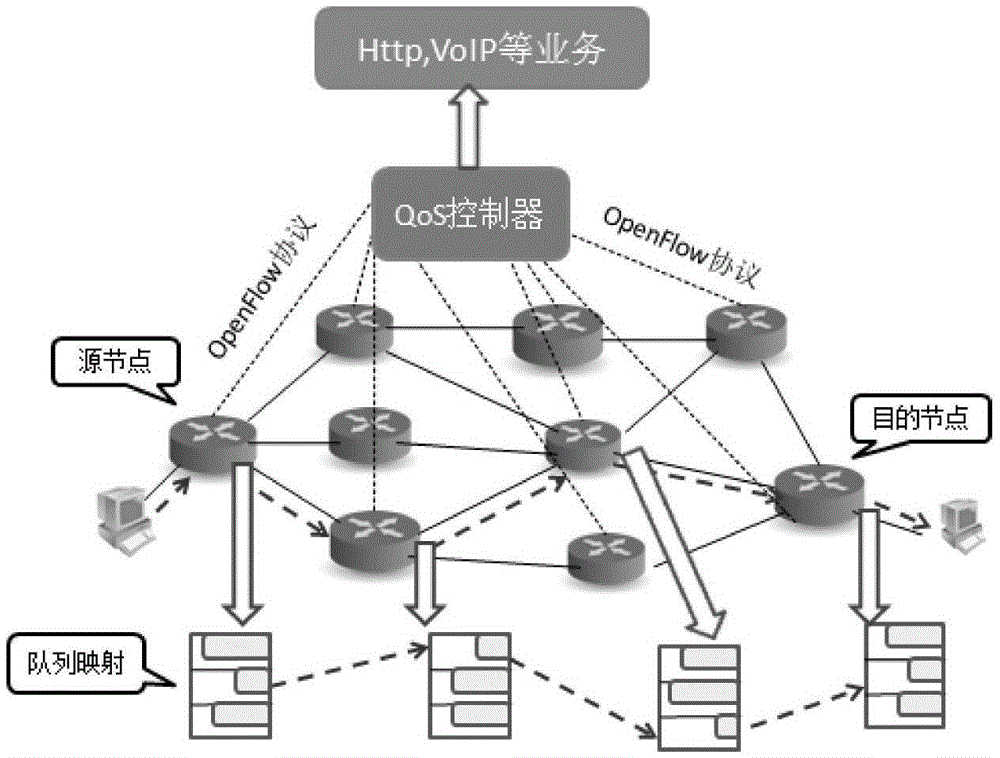
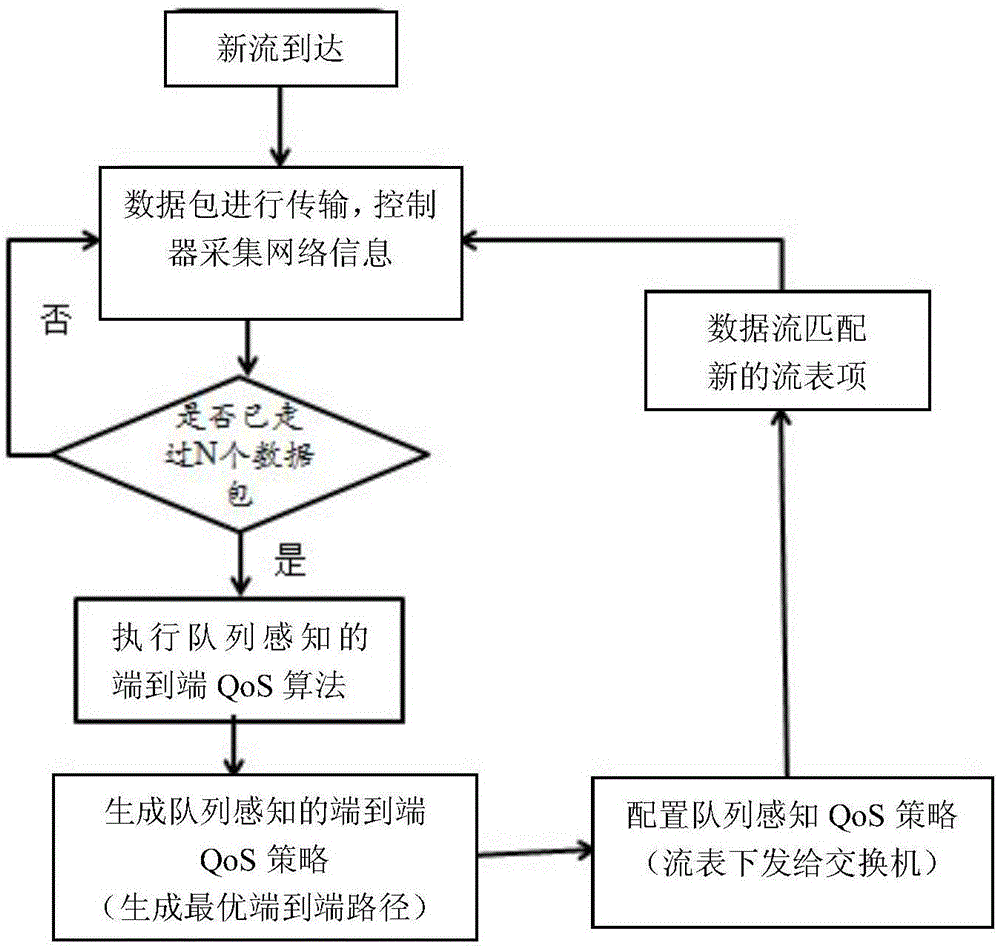
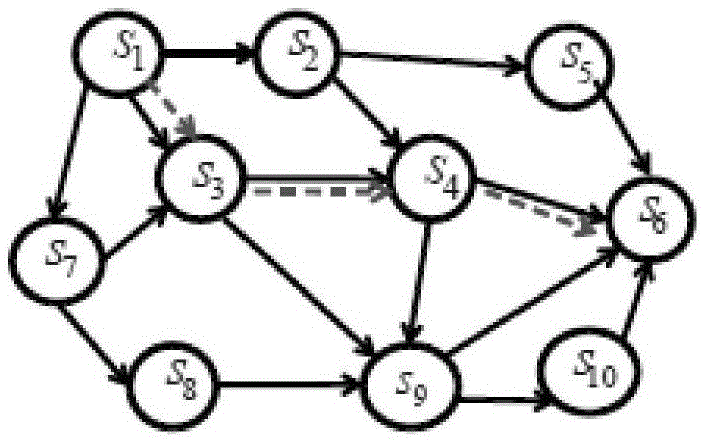
Method for guaranteeing end-to-end QoS in SDN network
The invention discloses a method for guaranteeing the end-to-end QoS in an SDN network, comprising the following steps: (1) for each new data flow arriving at an SDN network, an SDN network controller periodically collects network status information; (2) the SDN network controller calculates the cost of each of all alternative paths for transmitting the new data flow according to the collected network status information, and determines an optimal transmission path; and (3) the SDN network controller packages the information of the optimal transmission path into a flow entry and issues the flow entry to a switch node of the SDN network, and the switch node forwards a received data packet according to the flow entry. According to the invention, an OpenFlow switch queue mechanism is designed, and the queue status of the switch is monitored in real time through the controller. When a new data flow arrives, a minimum-cost path is selected to transmit the data flow according to the transmission delay of the link on the path and the queuing delay of the switch node queue as well as the congestion situation of the current link.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for estimating performance metrics in a packet-switched communication network
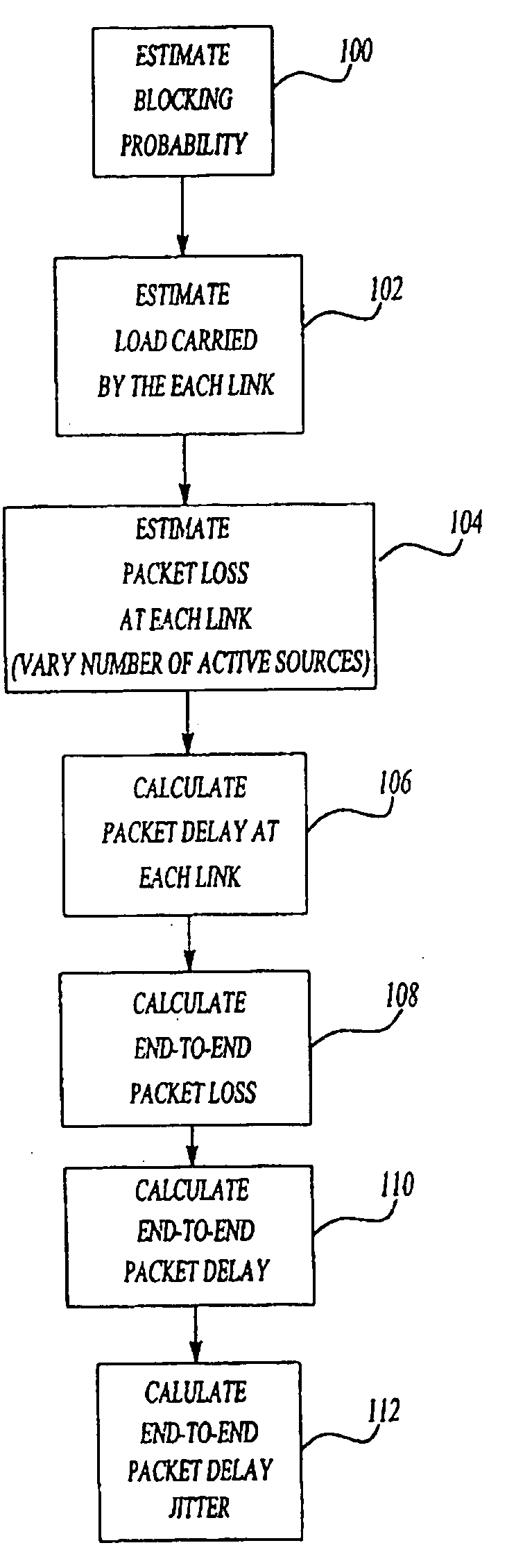
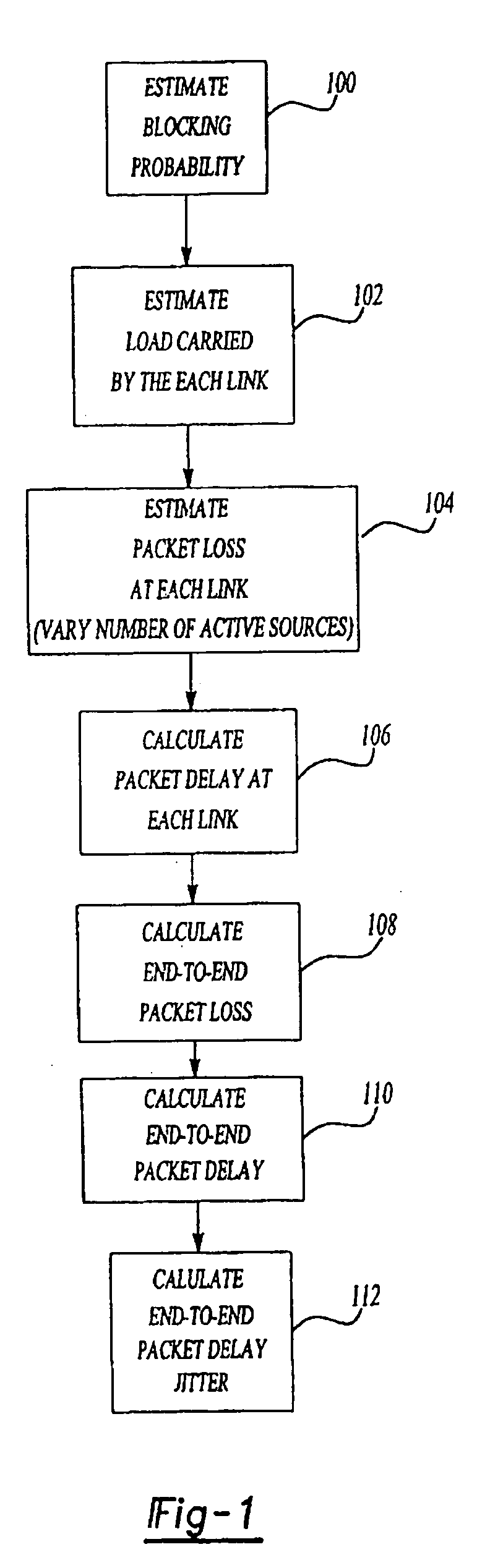
InactiveUS6912216B1Enhances network planningOptimize networkError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of servicePacket loss
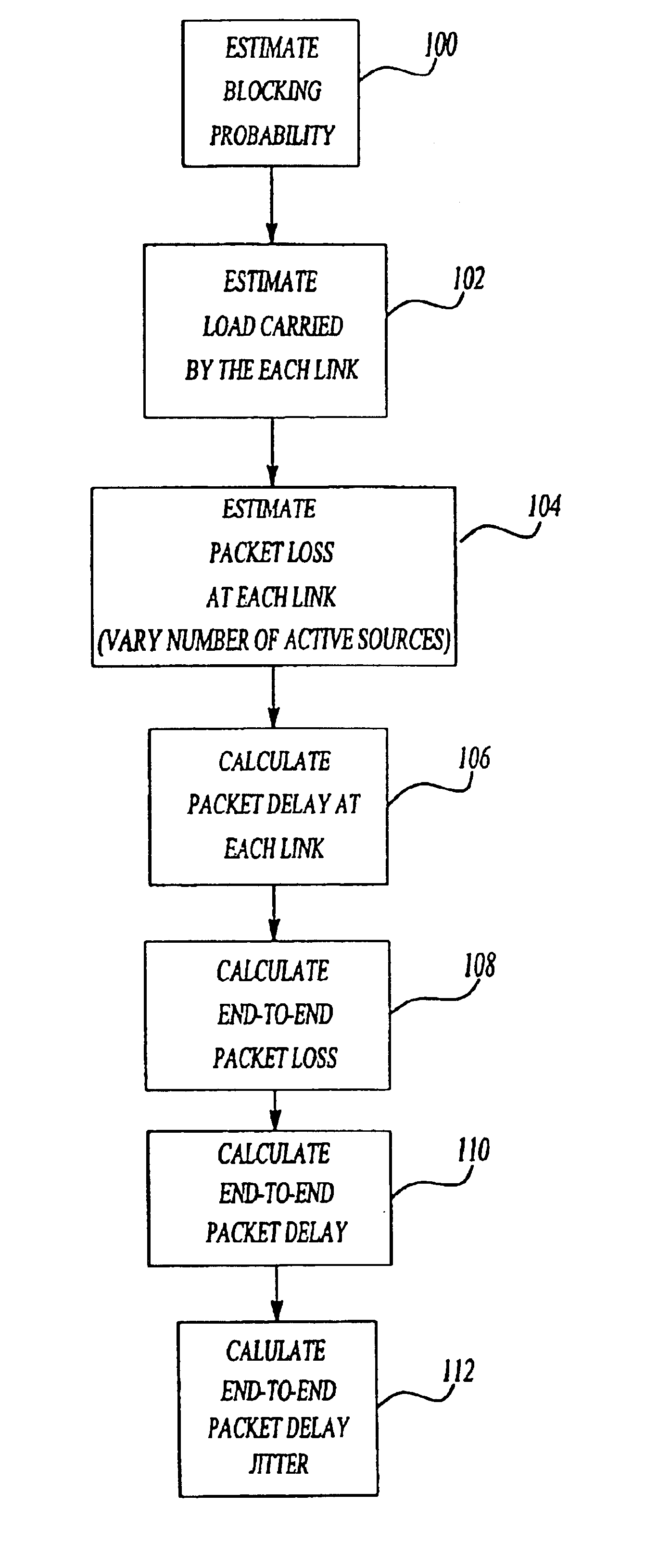
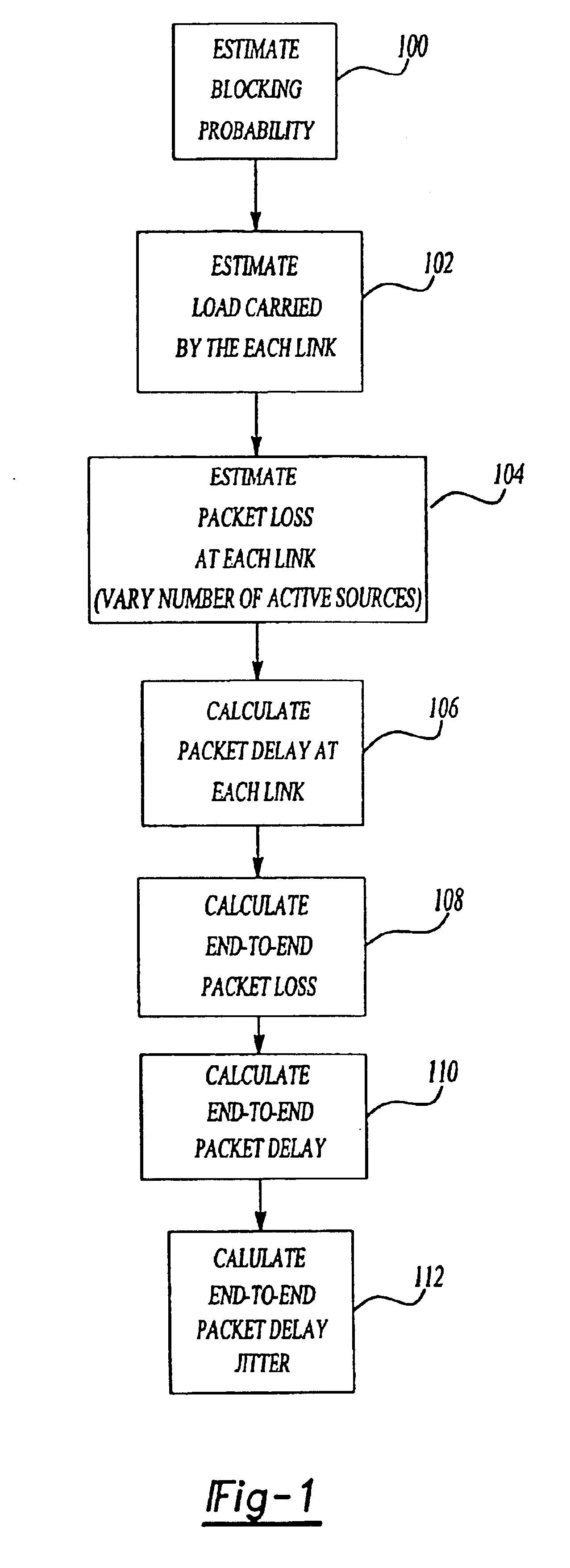
A method for estimating end-to-end quality of service (QOS), such as packet loss, delay, and delay jitter, in a packet-switched communications network includes steps for calculating packet loss and packet delay each router output link in a network path and using the packet loss and packet delay calculations for each individual router output link to estimate end-to-end QOS. The method includes calculating the loss probability for all possible numbers of active sources to take into account changes in the number of active sources as active sources connect to and disconnect from the network. As a result, the inventive method allows the number of active sources to vary in its estimation of end-to-end packet loss, delay, and delay jitter for enhanced Internet Protocol network planning.
Owner:VERIZON LAB
Methods and system for achieving QoS (quality of service) reflection mechanism
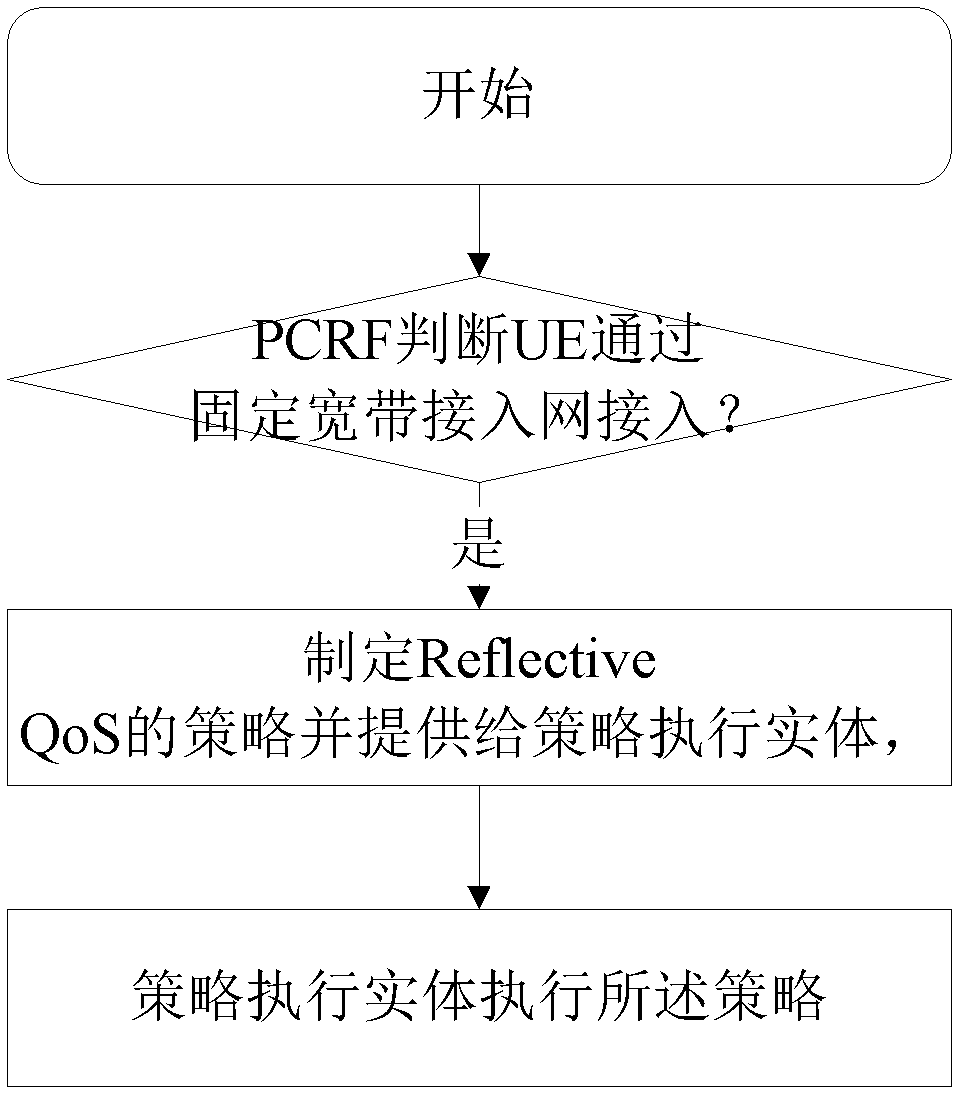
InactiveCN103209410AControl misconductNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementQuality of serviceCharge control
The invention discloses methods and a system for achieving a QoS reflection mechanism. One method comprises that a policy and charging rule function (PCRF) entity devises and provides a QoS refection policy for a policy execution entity after judging that user equipment (UE) is accessed through a fixed broadband access network, and the policy execution entity executes the policy to the UE, wherein the QoS reflection policy comprises a policy and charging control (PCC) rule or a QoS rule. The other method comprises that the PCRF entity determines whether the US executes the decision of the QoS reflection mechanism and whether the QoS reflection policy is devised and provided for the policy execution entity according to the obtained network, and the policy execution entity executes the policy to the UE. According to the methods and the system for achieving the QoS reflection mechanism, the end-to-end QoS of the service of the UE which executes the QoS reflection can be guaranteed, and misconducts of the UE which is forbidden to execute the QoS reflection by the network can be controlled.
Owner:ZTE CORP
3G media stream cross-layer rate control method based on channel measurement
ActiveCN103648058AMeet end-to-end QoS requirementsImprove bandwidth utilizationError prevention/detection by using return channelSelective content distributionTime delaysAir interface
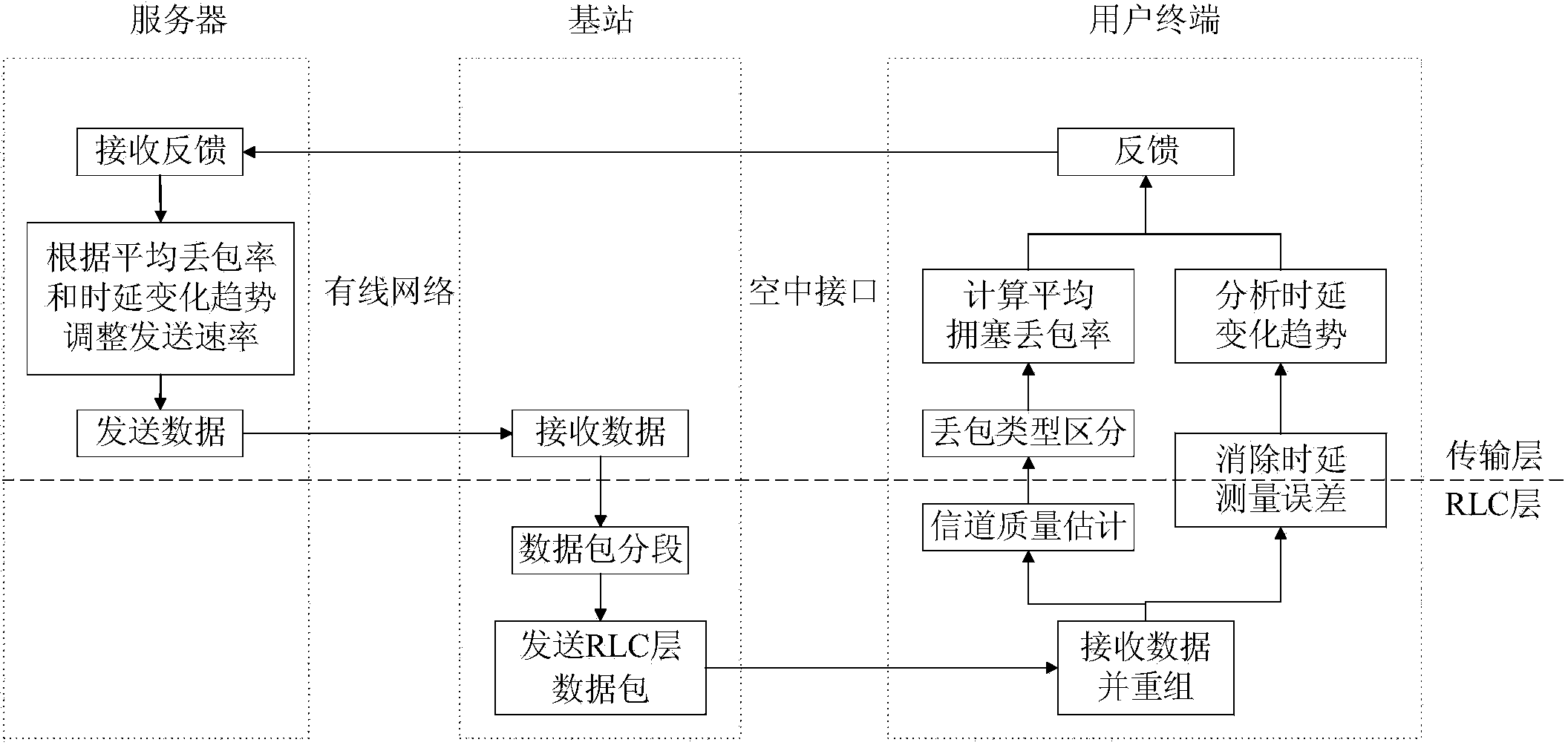
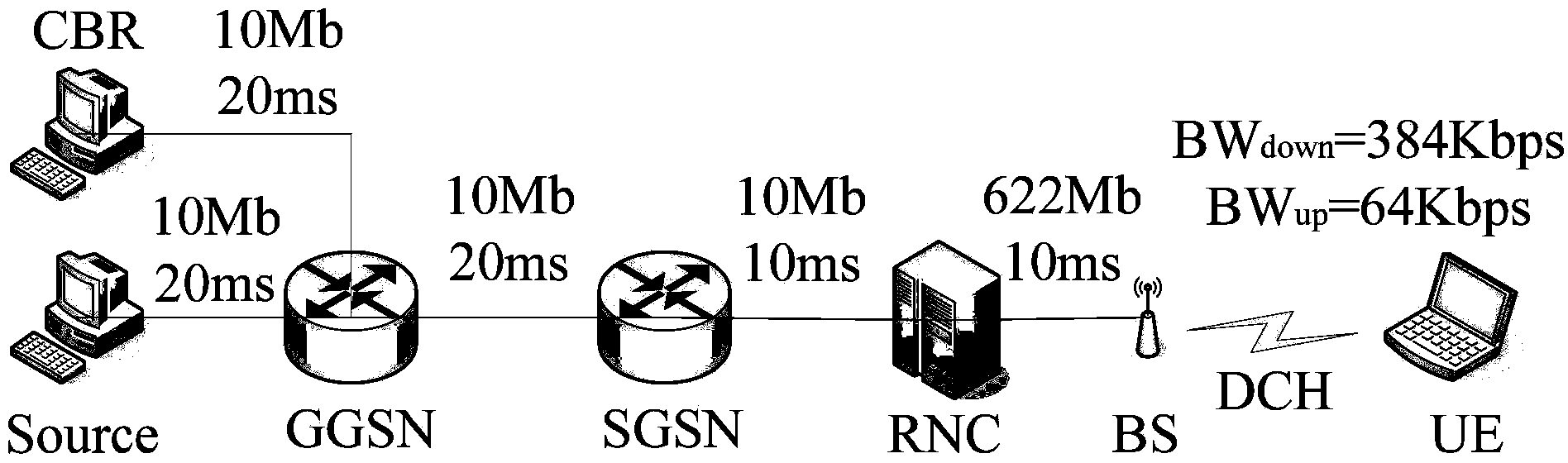
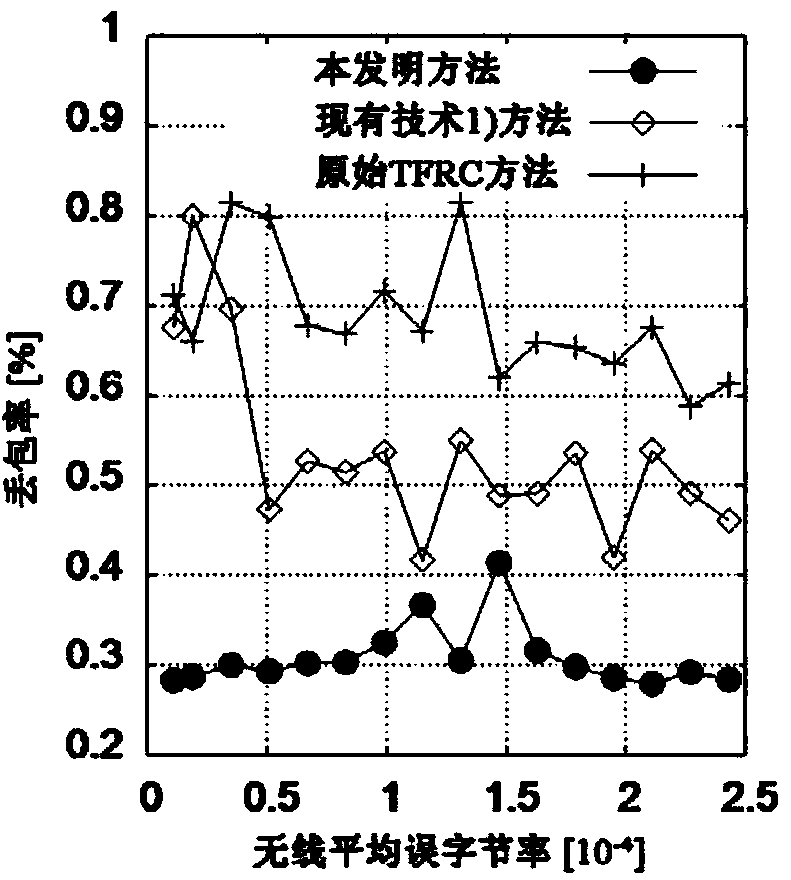
The invention discloses a 3G media stream cross-layer rate control method based on channel measurement. According to the method, wireless channel quality is estimated through ARQ message of an RLC layer for transmission characteristics of a 3G / UMTS air interface so as to distinguish packet loss types, and a server will be used to judge the network congestion situation and adjust the sending rate according to the channel quality which is fed back and the time delay change trend by means of the time delay measurement error brought to the transmission layer caused by the RLC layer eliminating ARQ mechanism, the packet loss rate and the throughput performance have substantial characteristics and significant improvements compared with the prior art, so the method can be used to ensure that end-to-end QoS requirements of media services can be fully satisfied by the rate control.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Enhancement of end-to-end network QoS
InactiveUS7936772B2Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsEnd to end qosNetworking protocol
A network endpoint system and related method and computer program product for use in a network to support enhanced end-to-end QoS in the network. The network endpoint system is adapted to receive network data of varying priority on behalf of a data consumer operating at the application layer of a network protocol stack implemented by the network endpoint system. The network endpoint system includes a network interface controller adapted to receive network frames containing the network data, plural network data handling channels each having an associated priority, and priority processing logic adapted to transfer the network data from the network interface controller to the plural data handling channels on a prioritized basis according to the network data priority. Also disclosed are a network interface controller and a network node to support enhanced end-to-end QoS in a network.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Congestion control and QoS in NoC by regulating the injection traffic
Systems and methods described herein are directed to solutions for NoC interconnects that provide congestion avoidance and end-to-end uniform and weighted-fair allocation of resource bandwidths among various contenders in a mesh or torus interconnect. The example implementations are fully distributed and involve using explicit congestion notification messages or local congestion identification for congestion detection. Based on the congestion level detected, the injection rates of traffic at various agents are regulated that avoids congestion and also provides end-to-end QoS. Alternative example implementations may also utilize end-to-end credit based flow control between communicating agents for resource and bandwidth allocation of the destination between the contending sources. The resource allocation is performed so that both the weighted and strict bandwidth allocation QoS policies are satisfied.
Owner:INTEL CORP
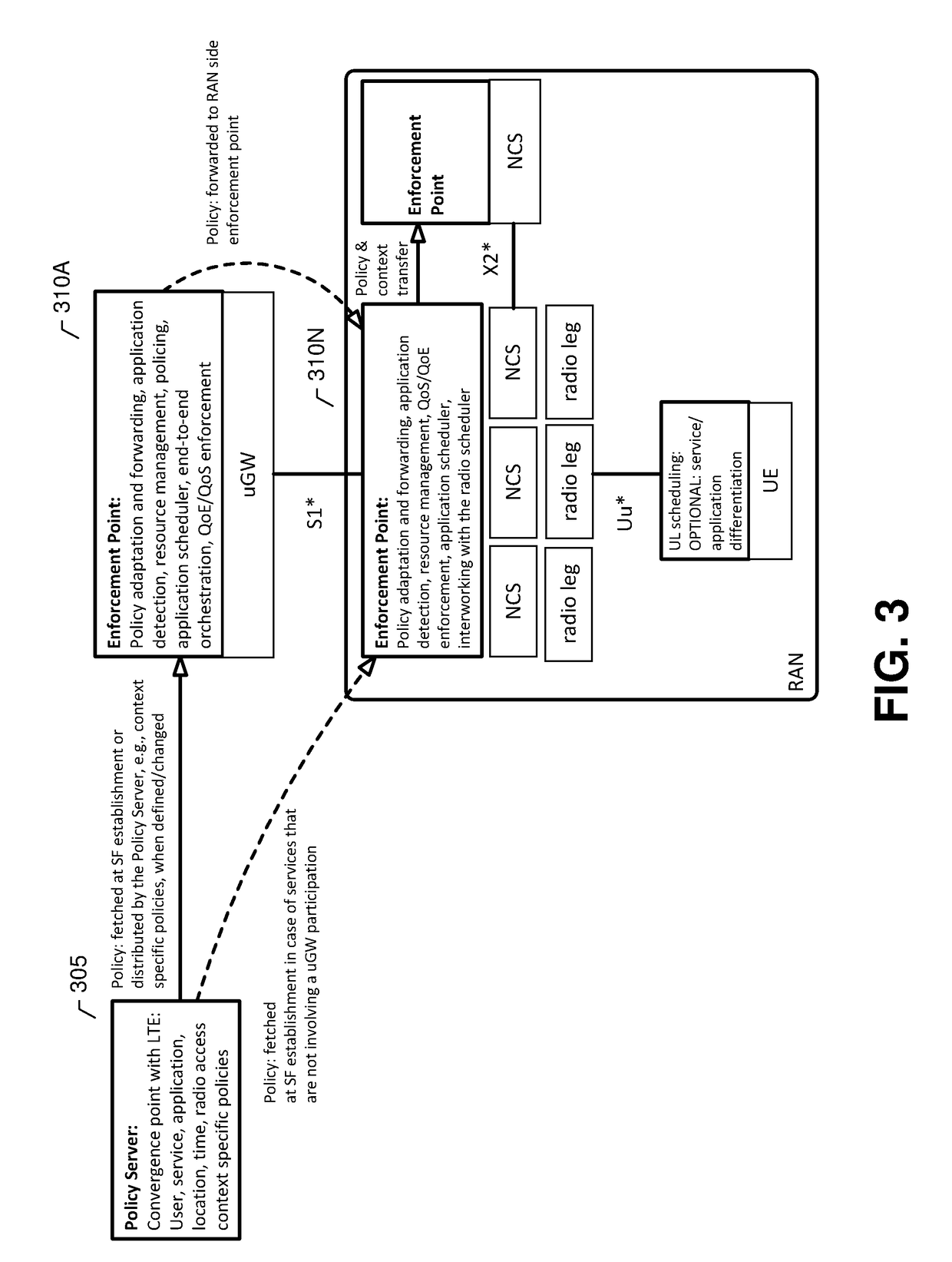
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR END-TO-END QoS/QoE MANAGEMENT IN 5G SYSTEMS
ActiveUS20170289047A1Increase experienceImprove experienceNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksTraffic capacityComputer network
Various methods are provided for providing dynamic and adaptive QoS and QoE management of U-Plane traffic while implementing user and application specific differentiation and maximizing system resource utilization by, for example, providing utilizing a system comprised of a policy server and one or more enforcement points. In one example system, the policy server may be a logical entity configured for storing a plurality of QoS / QoE policies, each of the plurality of policies identifying at least one of a user, service vertical, application, or context, and associated QoE targets. The policy server may be further configured to provide one or more of the plurality of QoS / QoE policies to the one or more enforcement points. In some embodiments, the QoS / QoE policies may be configured to provide QoE targets, for example, at a high abstraction level and / or at an application session level.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
SDN-based QoS-supported communication tunnel establishment method and system
InactiveCN104954226AImprove general performancePracticalNetworks interconnectionHigh level techniquesDistributed computingPriority queue
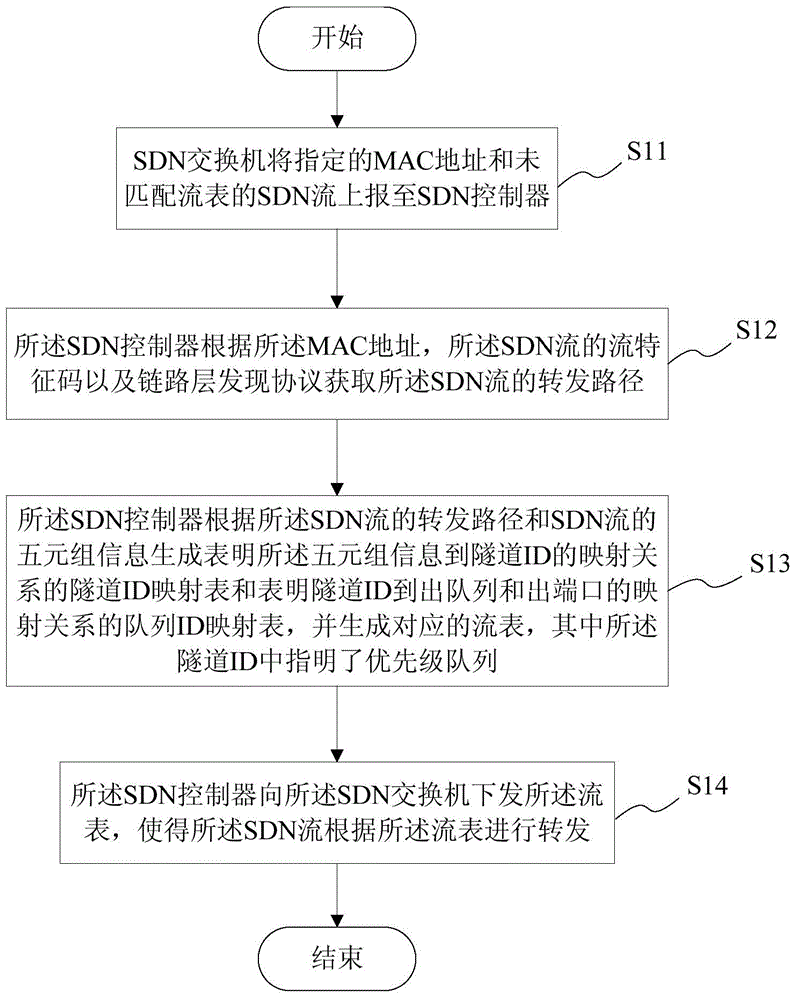
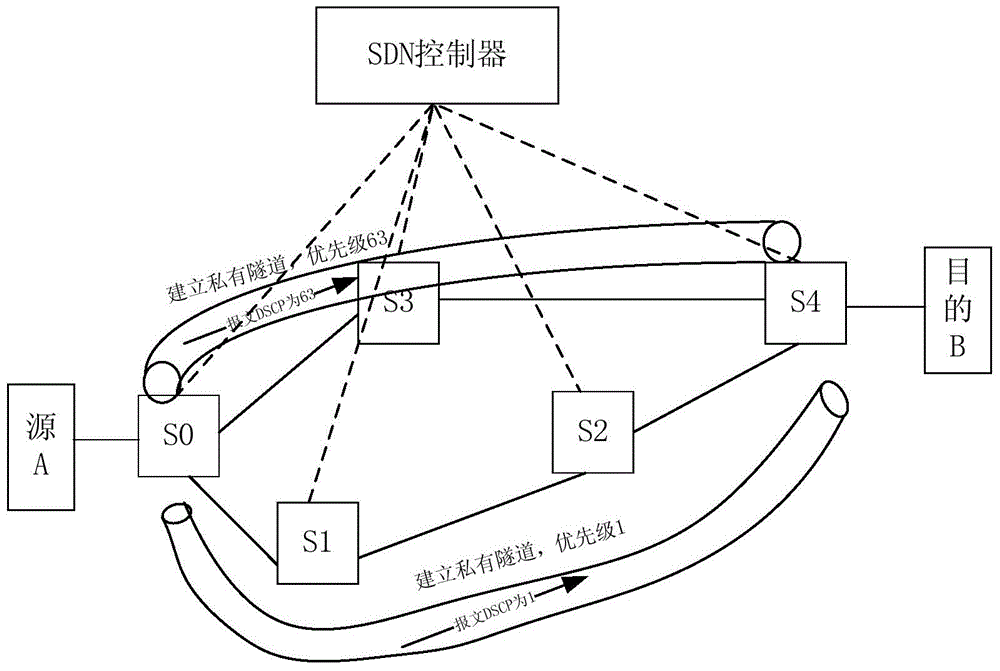
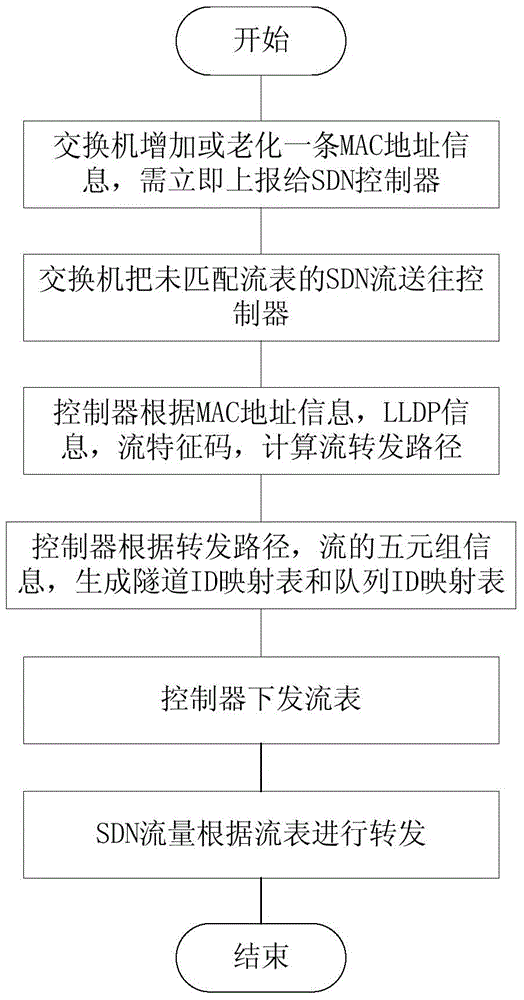
The invention provides an SDN-based QoS-supported communication tunnel establishment method and system, which are applied to a communication network comprising an SDN exchanger and an SDN controller. The method comprises the following steps: reporting the assigned MAC address and SDN streams of an unmatched stream table to the SDN controller by the SDN exchanger; obtaining the forwarding path of the SDN streams by the SDN controller; generating a tunnel ID mapping table and a queue ID mapping table according to the forwarding path of the SDN streams and five-component group information of the SDN stream by the SDN controller and generating a corresponding stream table, wherein a priority queue is pointed out in the tunnel ID; issuing the stream table to the SDN exchanger by the SDN controller; obtaining an output queue and an output port by the SDN exchanger. According to the invention, on the basis of the SDN framework, establishment of a communication tunnel is completed by the SDN controller in a unified manner, the communication tunnel is established according to DSCP fields of the IP header of the SDN stream, the priority queue is pointed out and end-to-end QoS service is provided.
Owner:PHICOMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
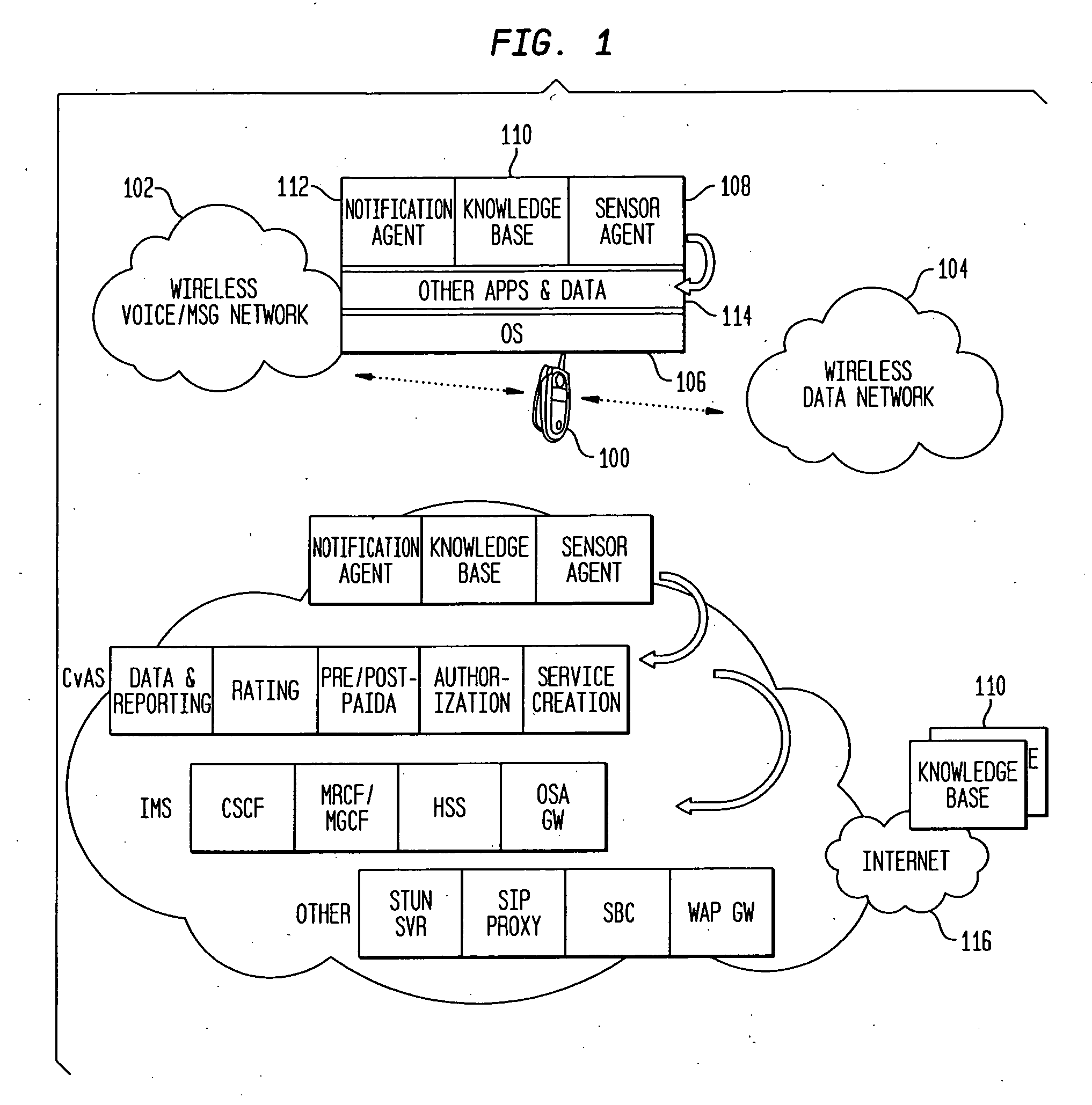
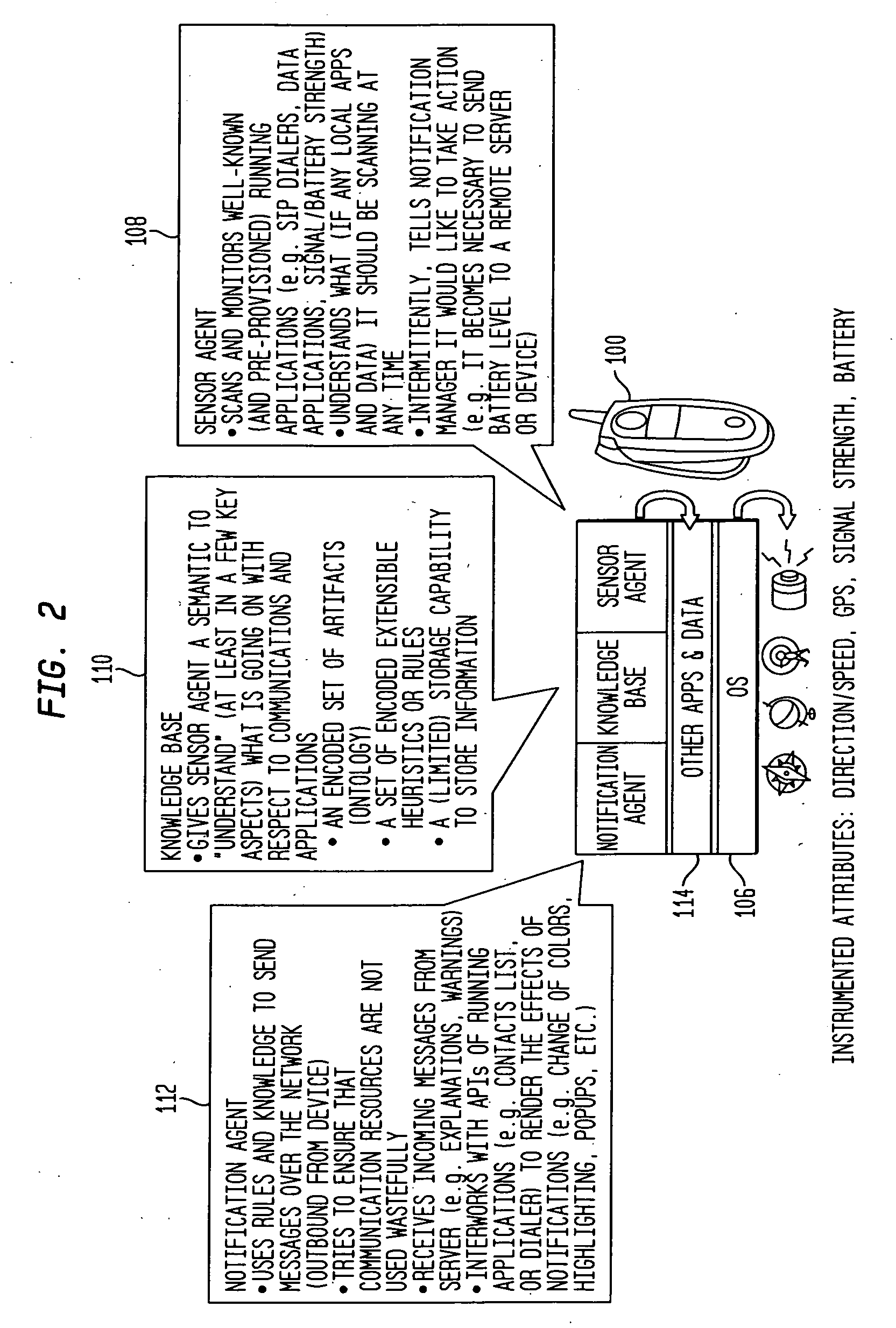
Method and System for Improving Wireless Customer Experience by Anticipating and Explaining Communication Quality Problems Through Notifications
InactiveUS20090081994A1Improve customer experiencePower managementDevices with GPS signal receiverCommunication qualityWireless mobile devices
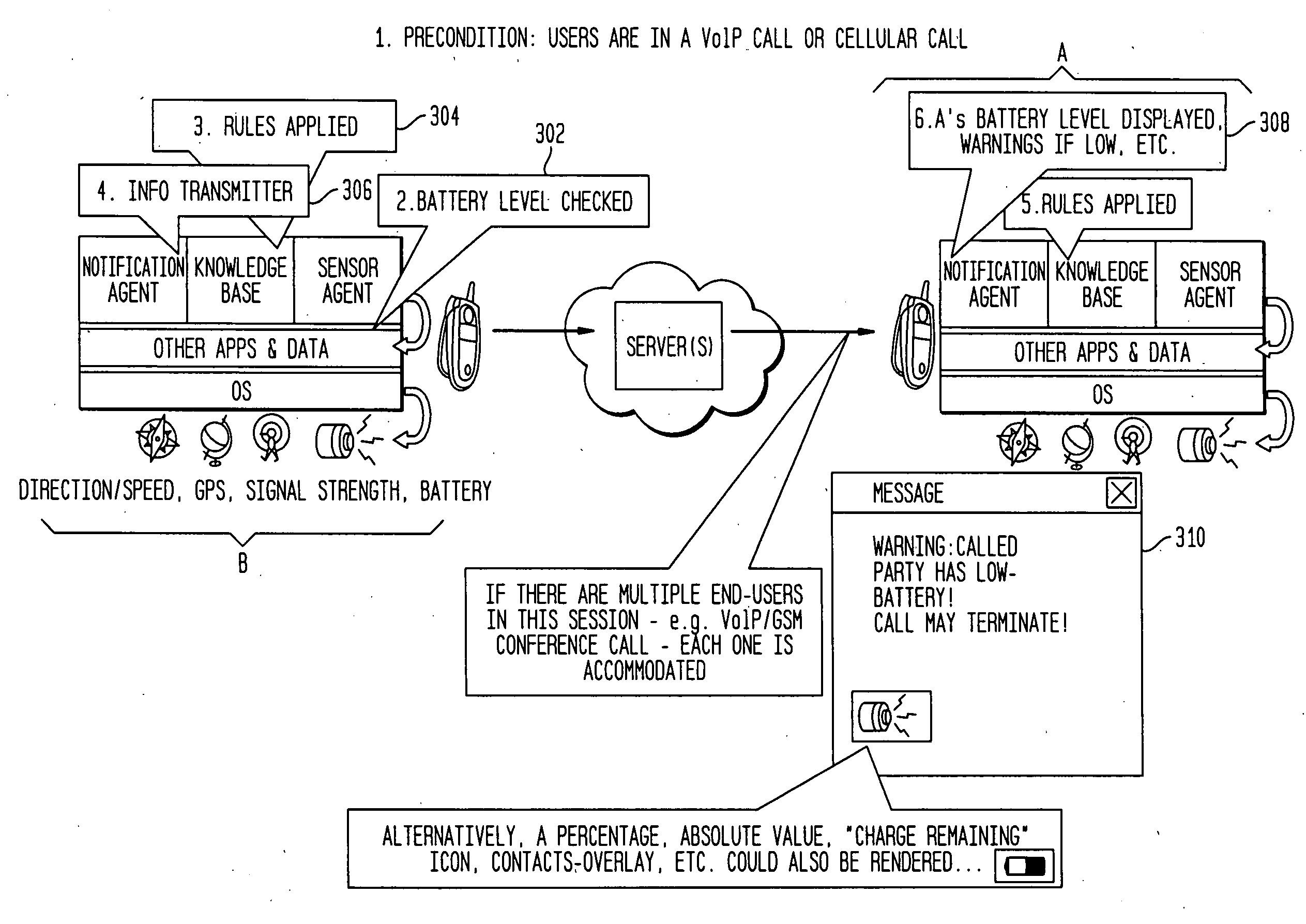
In wireless mobile device system a distributed set of software and / or hardware components provide continual warnings, monitoring, and explanations of device and system communication issues to mobile devices / users. The warnings and explanations are relevant to past, current, and future communications events that cause end-to-end quality problems such as disruptions including “dropped call”.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Apparatus and method for providing terminal-to-terminal service quality guaranty in service network
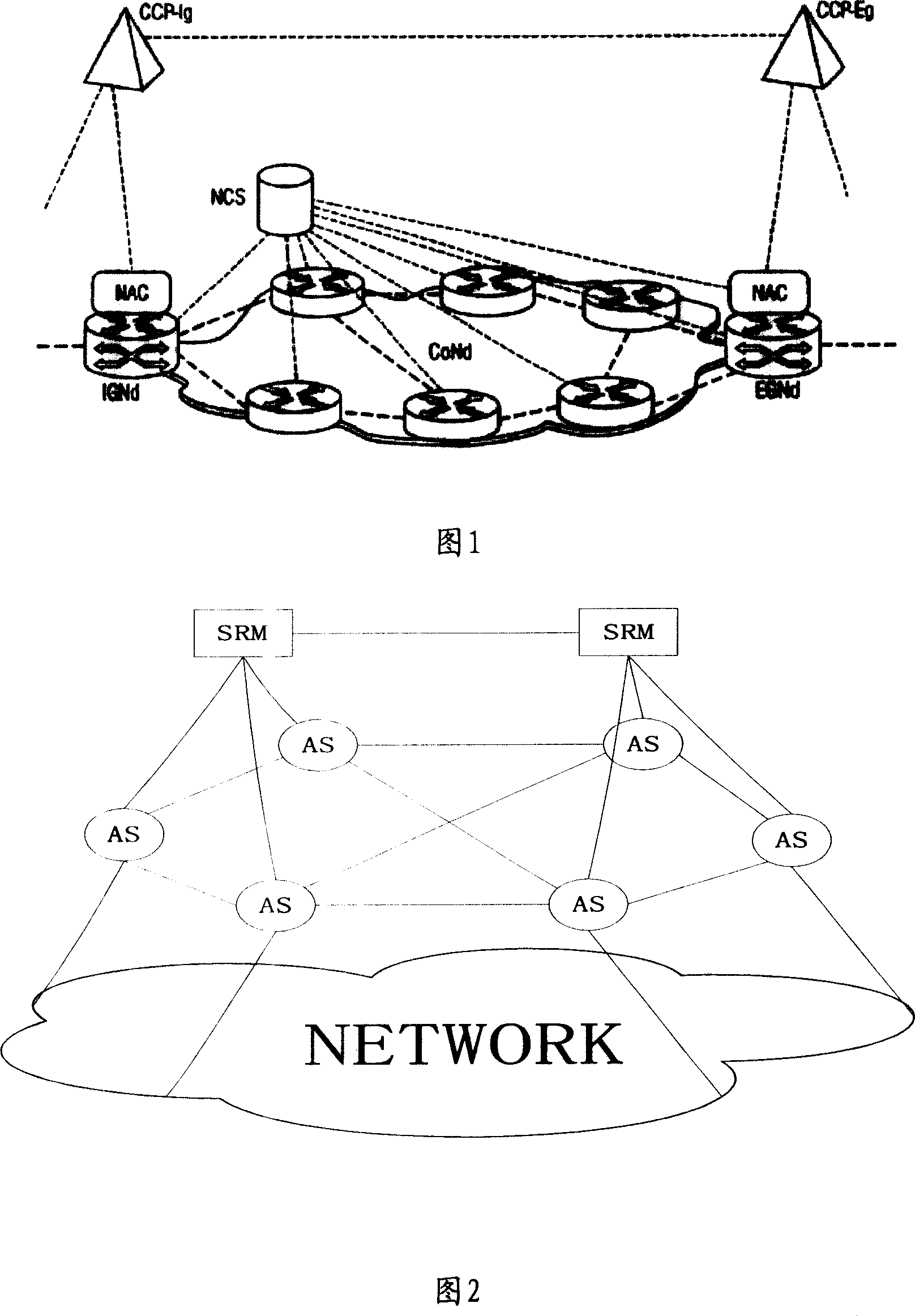
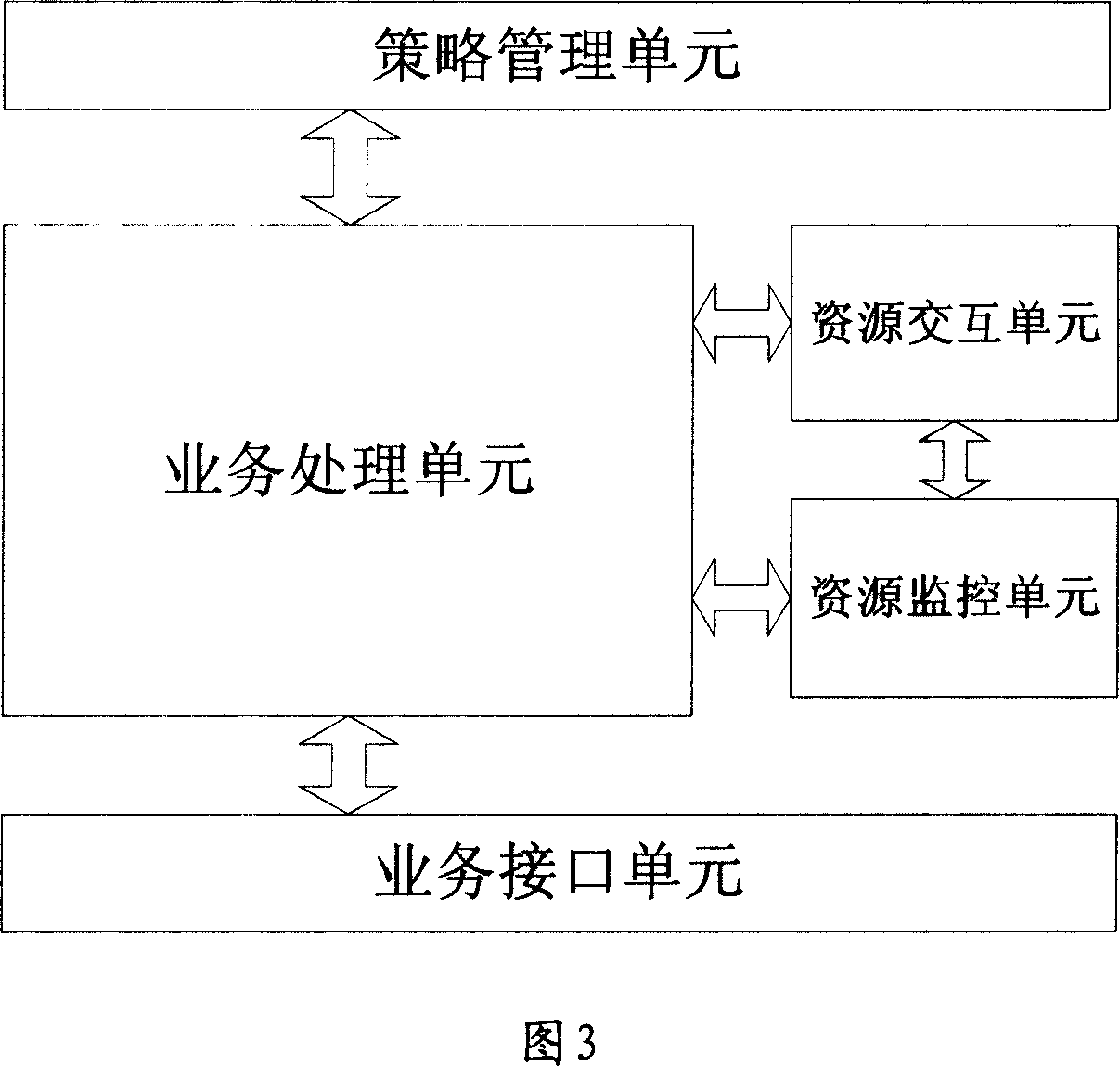
InactiveCN101083517AEasy to useGuaranteed experienceError prevention/detection by using return channelStore-and-forward switching systemsQuality of serviceApplication server
The invention provides a device and method for providing end-to-end quality of service (QoS) assurance in service network, and the device is implemented by SRM and mainly comprises: service processing unit, resource management unit and service interface unit. And the method comprises: SRM receives user service request and processes the user service according to the monitored resource utilization condition of application server and QoS requirements of user service, and returns the processing results to the service request sender side. And the invention can assure end-to-end QoS in service network, and raises utilization efficiency of application server in service network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
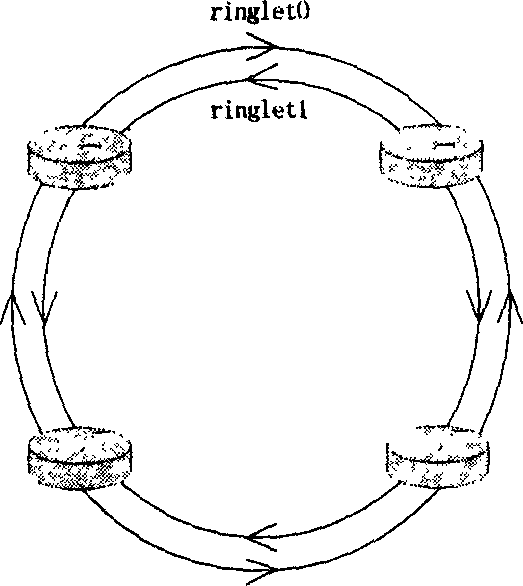
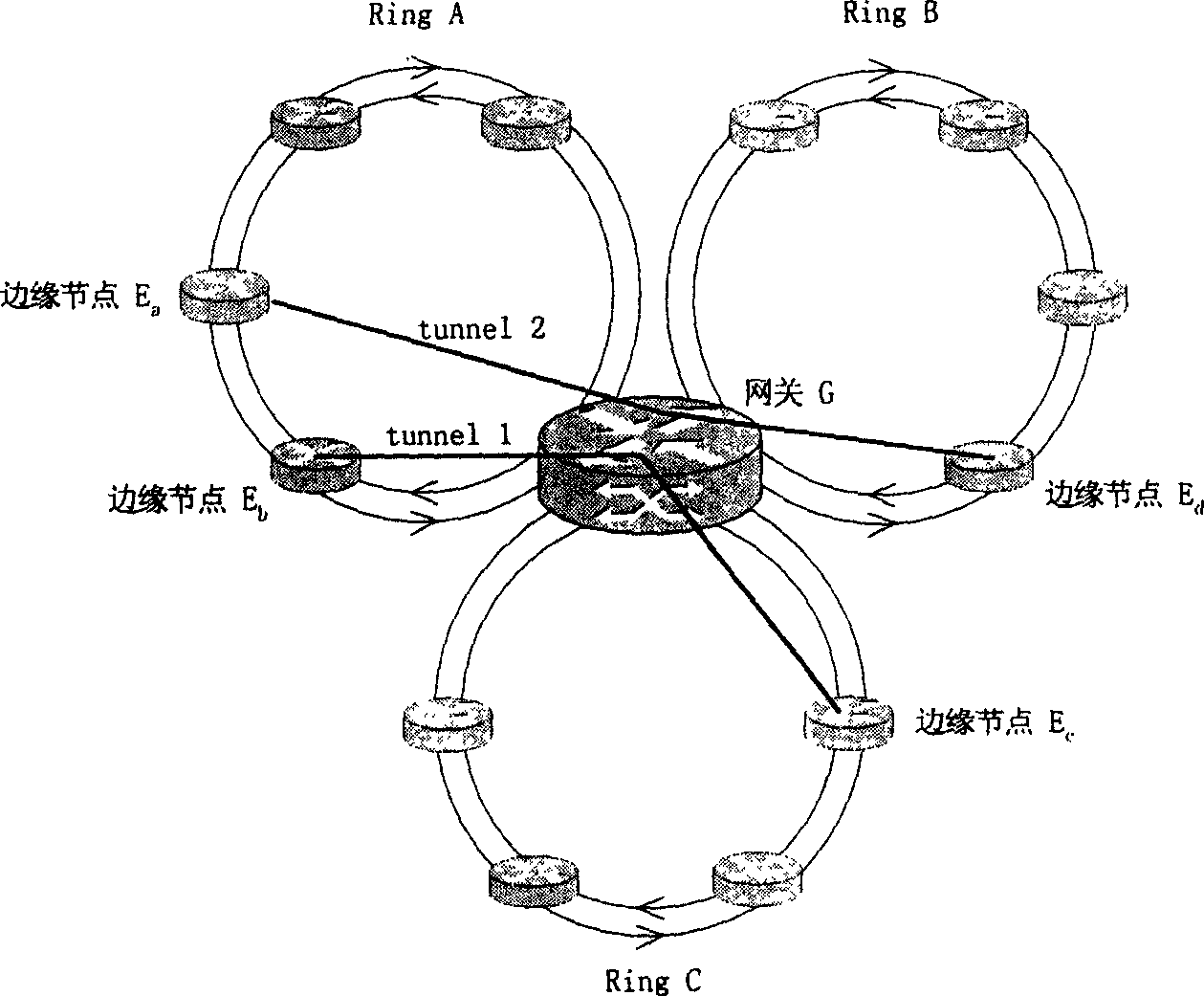
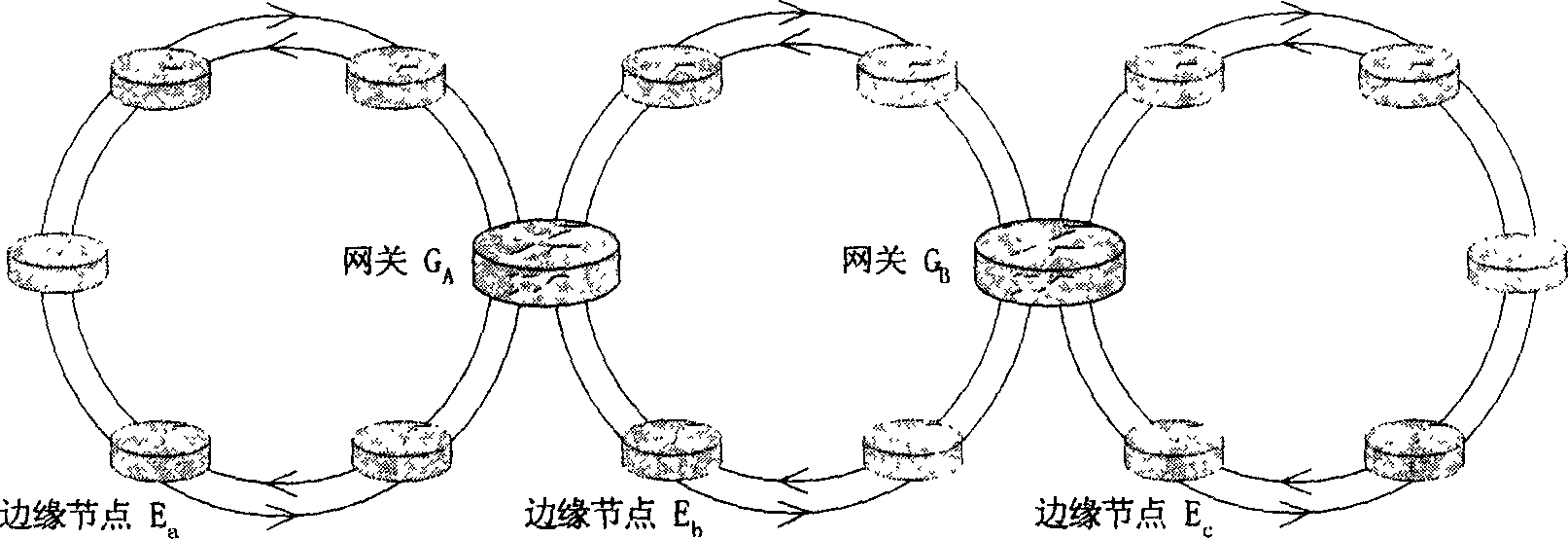
Method for implementing message forwarding along RPR ring and RPR network
A message transmission method in plurality of RPR loop and network thereof, which contains each RPR directly connected with at least one gateway, each gateway directly connected with two or more than two RPR loop, each RPR containing one gateway and several edge nodes or only containing gateway, each edge node and gateway containing respectively MAC address, establishing whole network label exchange route through control plane, each gateway only storing local information, each cross-loop transmitted message containing one MAC address information field of destination station, one source station address information field and one MPLS label information field of said loop gateway to carry route information, defining the package format for realizing right RPR grouping route selection using tunnel label and cross-loop function, insuring whole end-to-end QoS, said gateway having MPLS label exchange router function, capable of interconnected with MPLS network, can be widely used data transmission network communication field.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
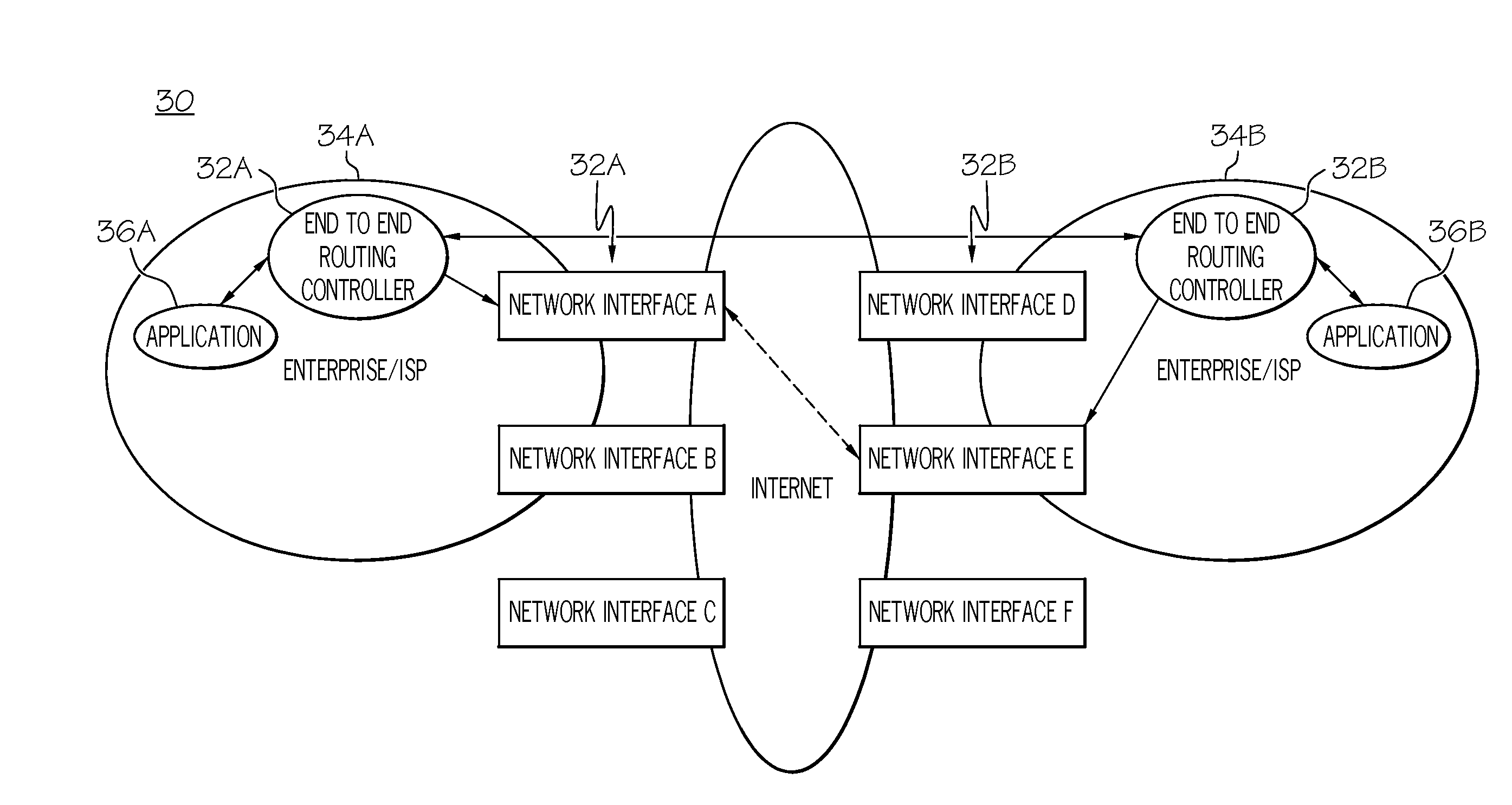
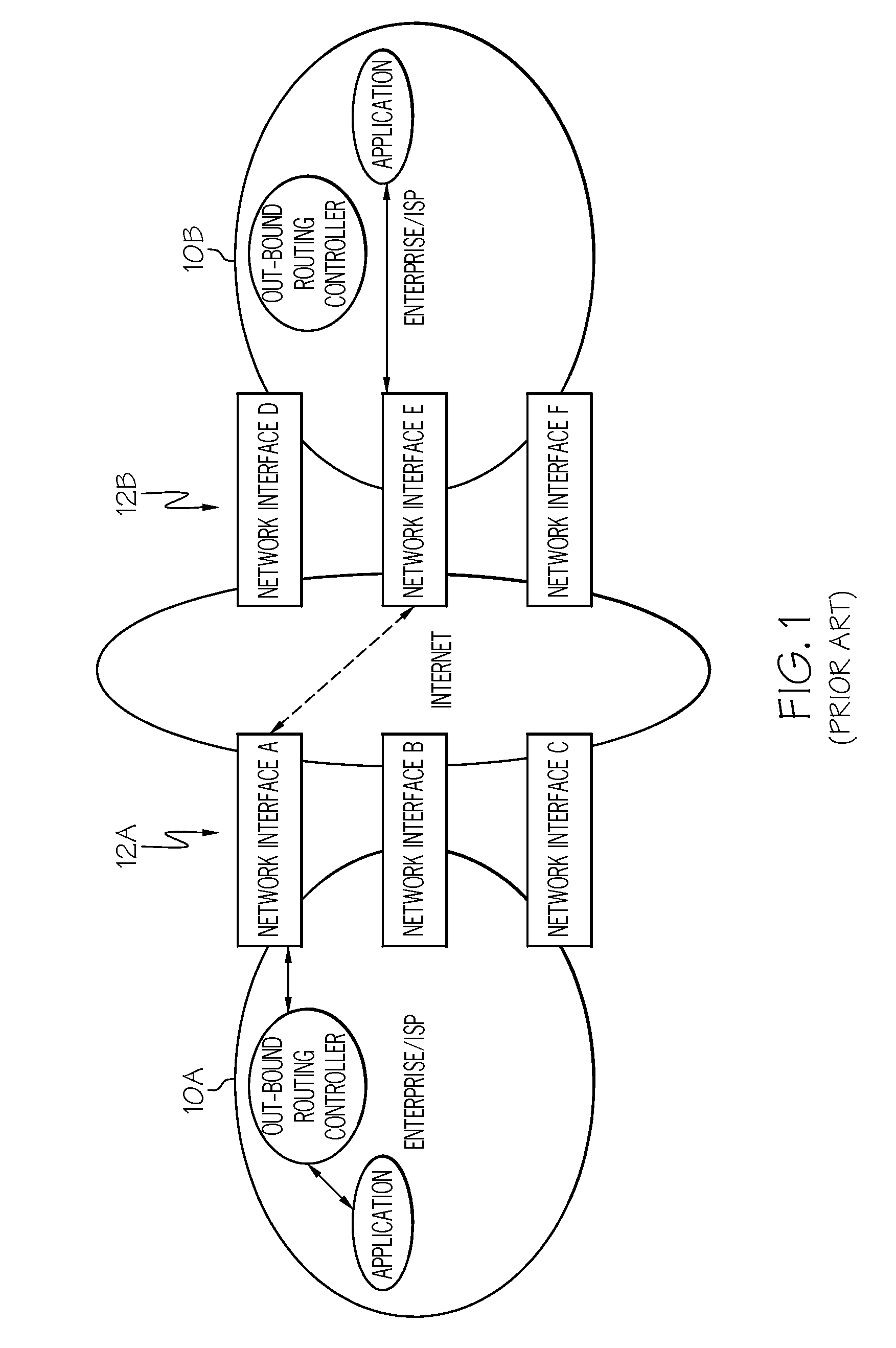
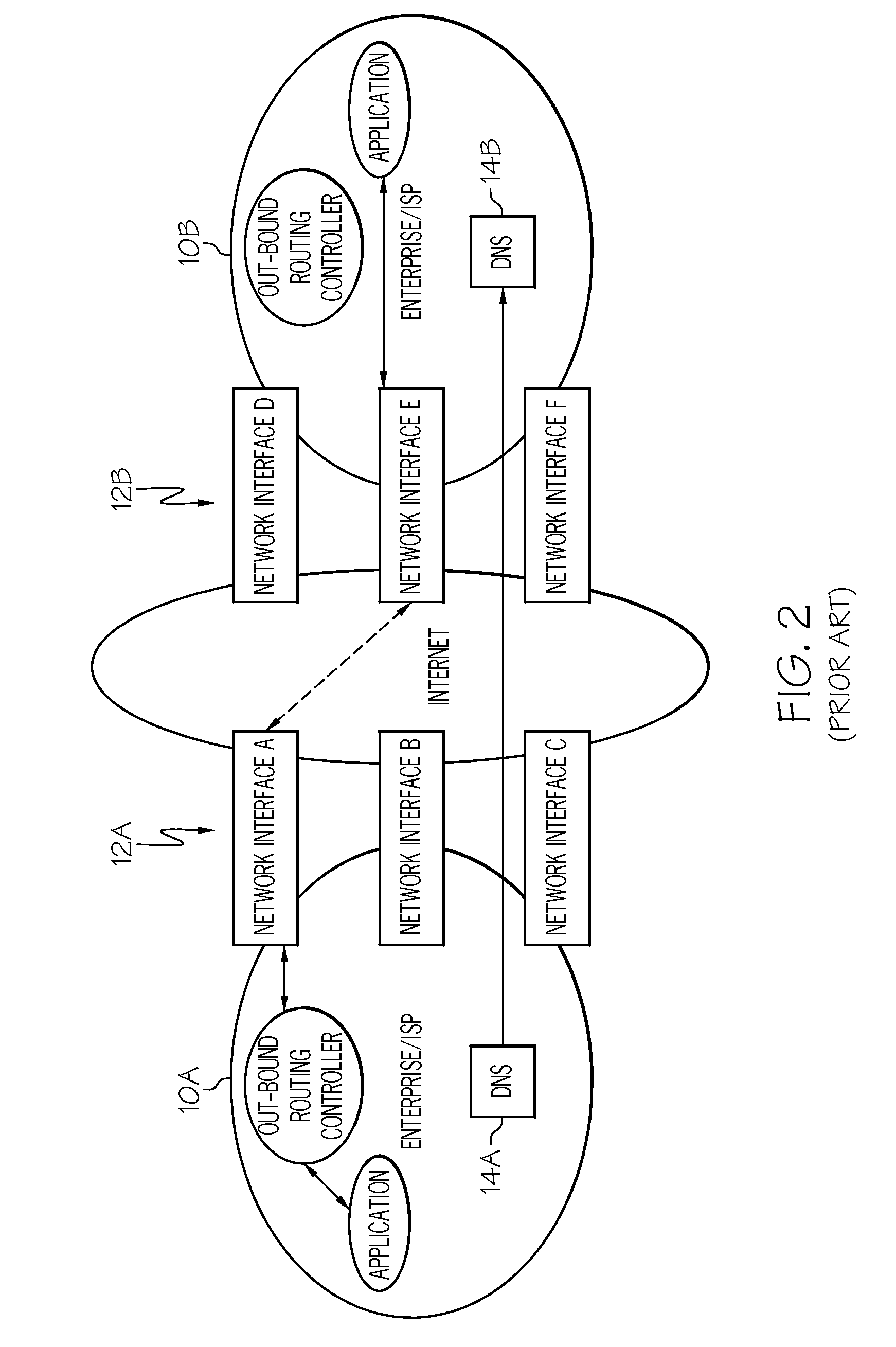
Method, system, and program product for enhancing network communications between endpoints
InactiveUS20080165683A1Facilitate communicationError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityNetwork link
The present invention provides a method, system and program product for enhancing communications between endpoints. Specifically, the present invention provides mechanisms (e.g., routing controllers either at a network or application layer) that negotiate and specify which network interface to use at each endpoint (both sending and receiving) in multi-homing interface environments. This approach allows the application traffic to be routed through these two specified network interfaces for the better end-to-end QoS. This network interfaces used can also be dynamic changed (e.g., in real-time) to adapt to changing conditions of the network links.
Owner:IBM CORP
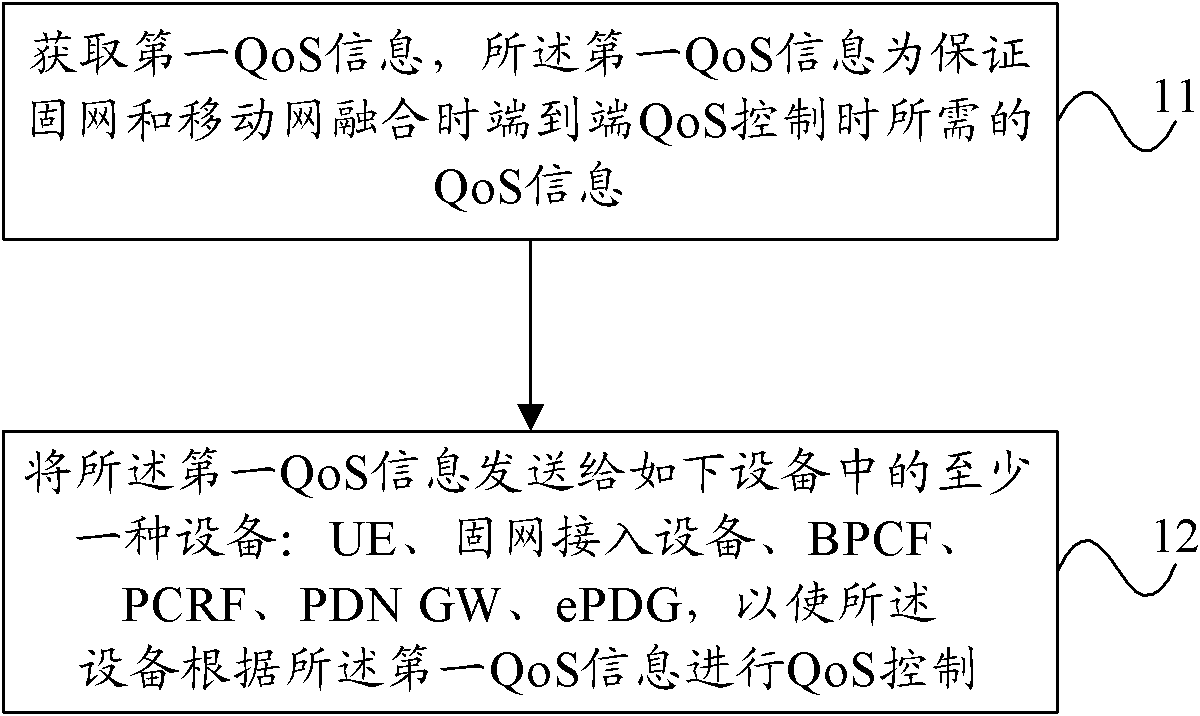
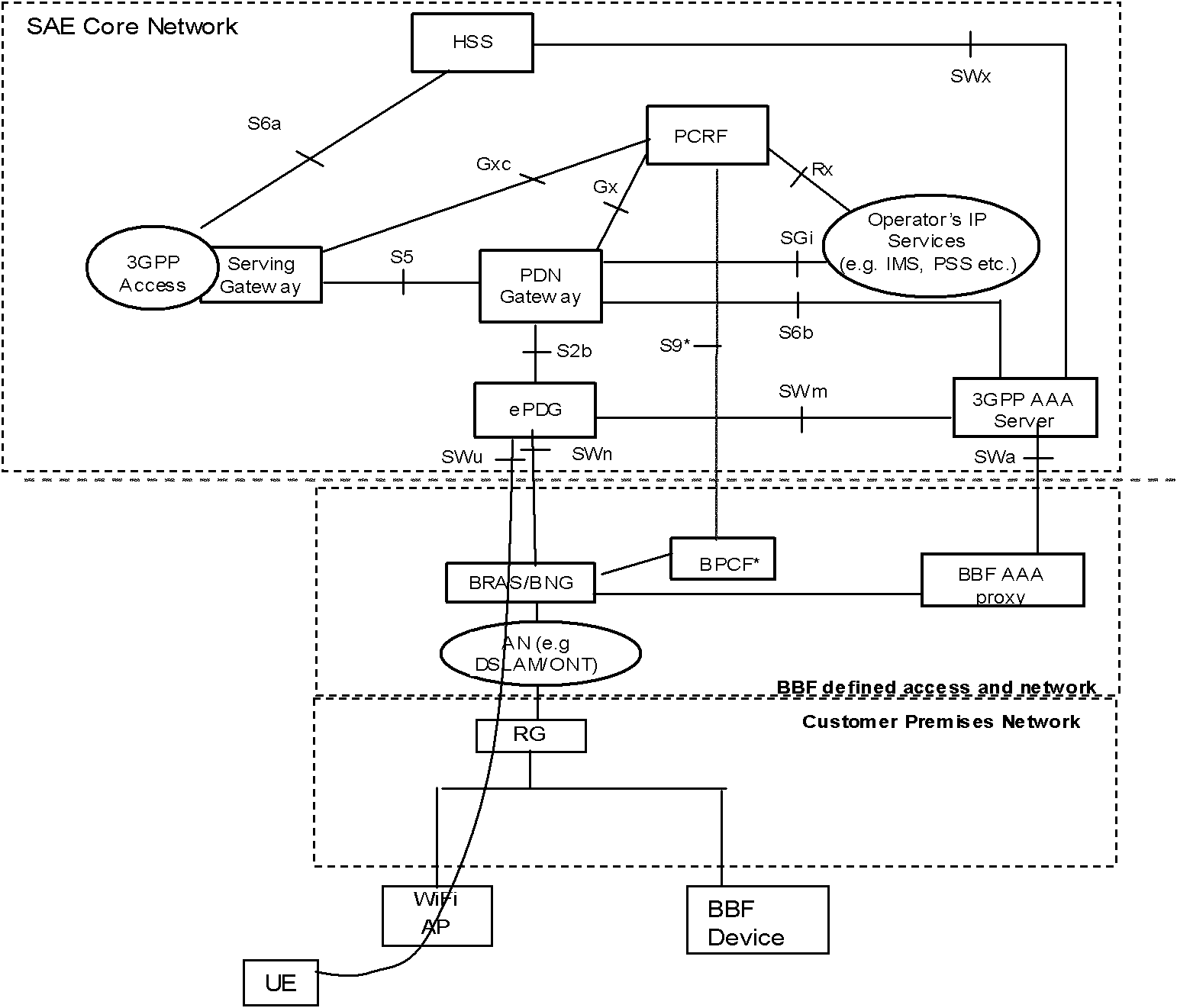
QoS control method and equipment thereof
ActiveCN102469531AAssurance controlImprove fusion effectNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementQuality of serviceBroadband
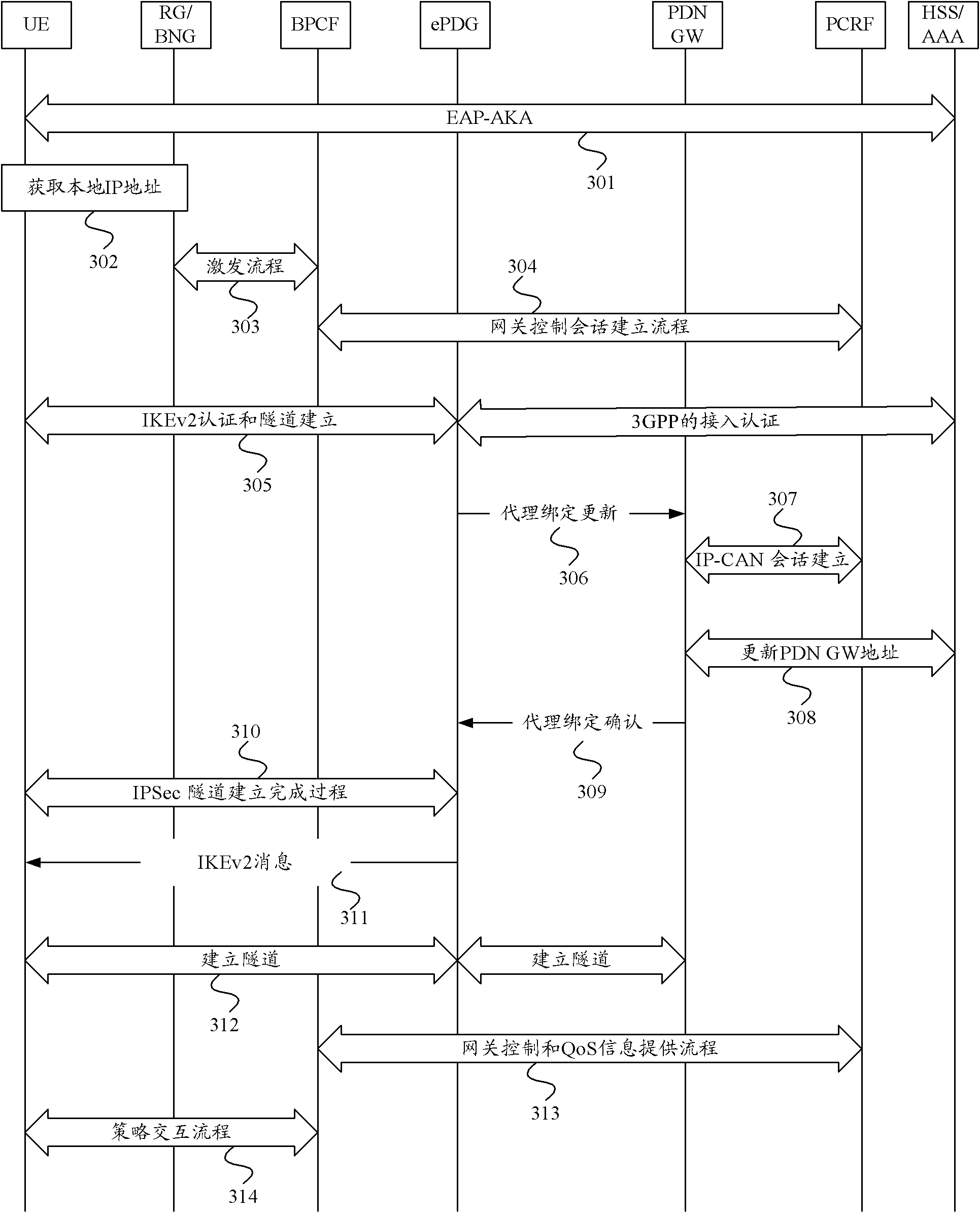
The invention provides a control method for a quality of service (QoS) and equipment thereof. The method comprises the following steps that: QoS information is obtained, wherein the QoS information is one that is used for ensuring end-to-end QoS control during convergence of a fixed network and a mobile network; and the QoS information is sent to at least one equipment of the following equipment: user equipment (UE), fixed network access equipment, a broadband policy control framework (BPCF), a policy and charging rule function (PCRF), a packet data network gateway (PDN GW), and an evolution packet data gateway (ePDG), so that the corresponded equipment carries out QoS control on the QoS information. According to the embodiment of the information, end-to-end QoS control can be ensured during convergence of a fixed network and a mobile network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
System and method for realizing the resource distribution in the communication network
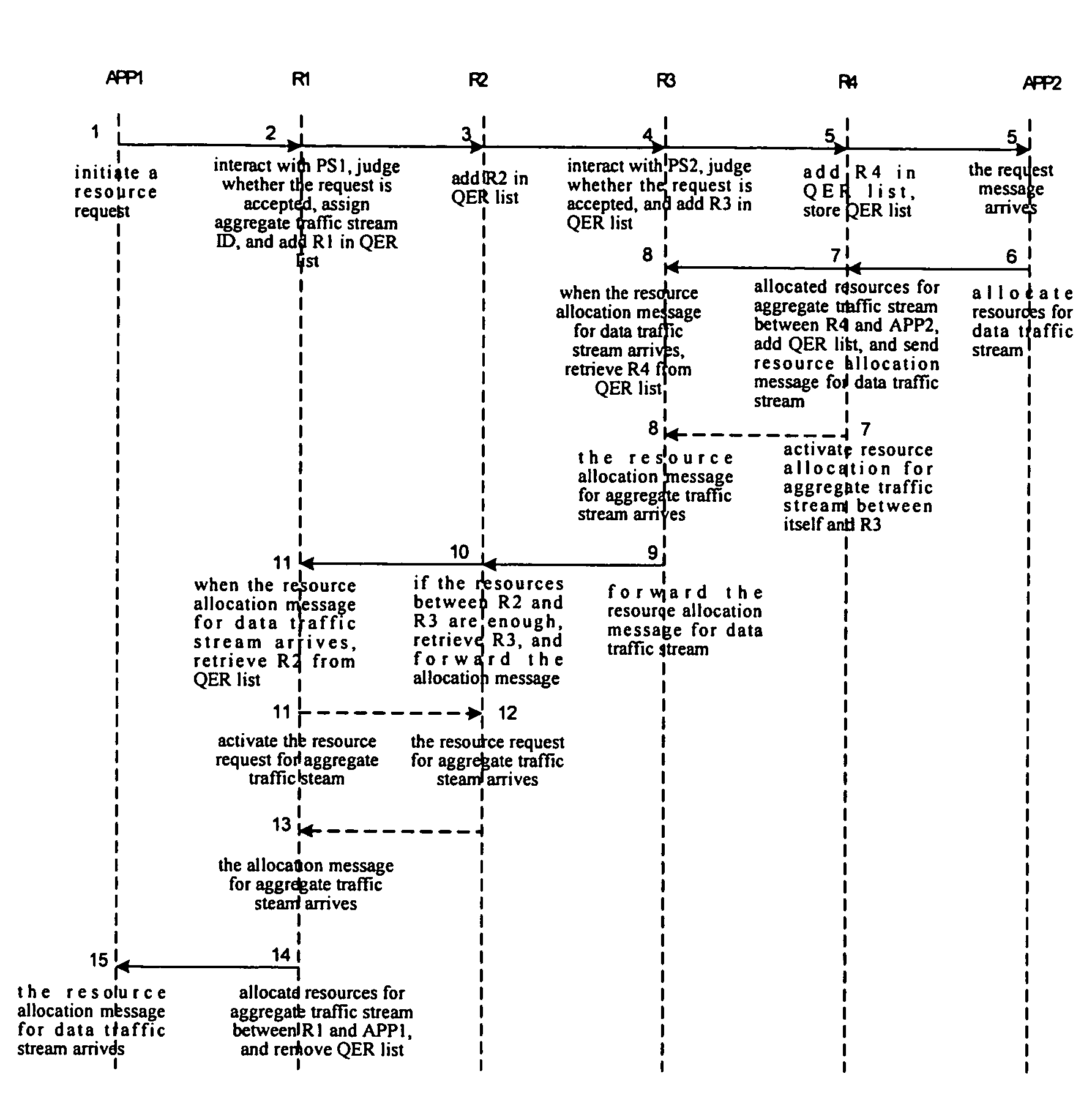
ActiveUS7636781B2Efficient solutionShort set-up timeError preventionTransmission systemsNetwork communicationSignaling protocol
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method, device and system for achieving wireless local area network (WLAN) terminal end-to-end quality of service (QoS) control
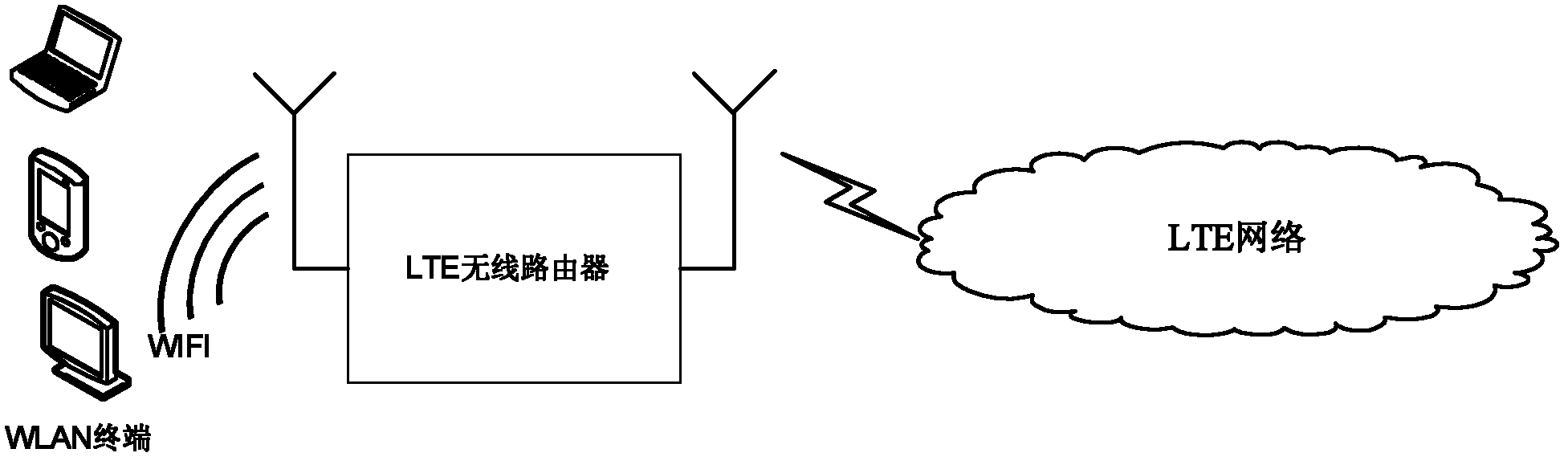
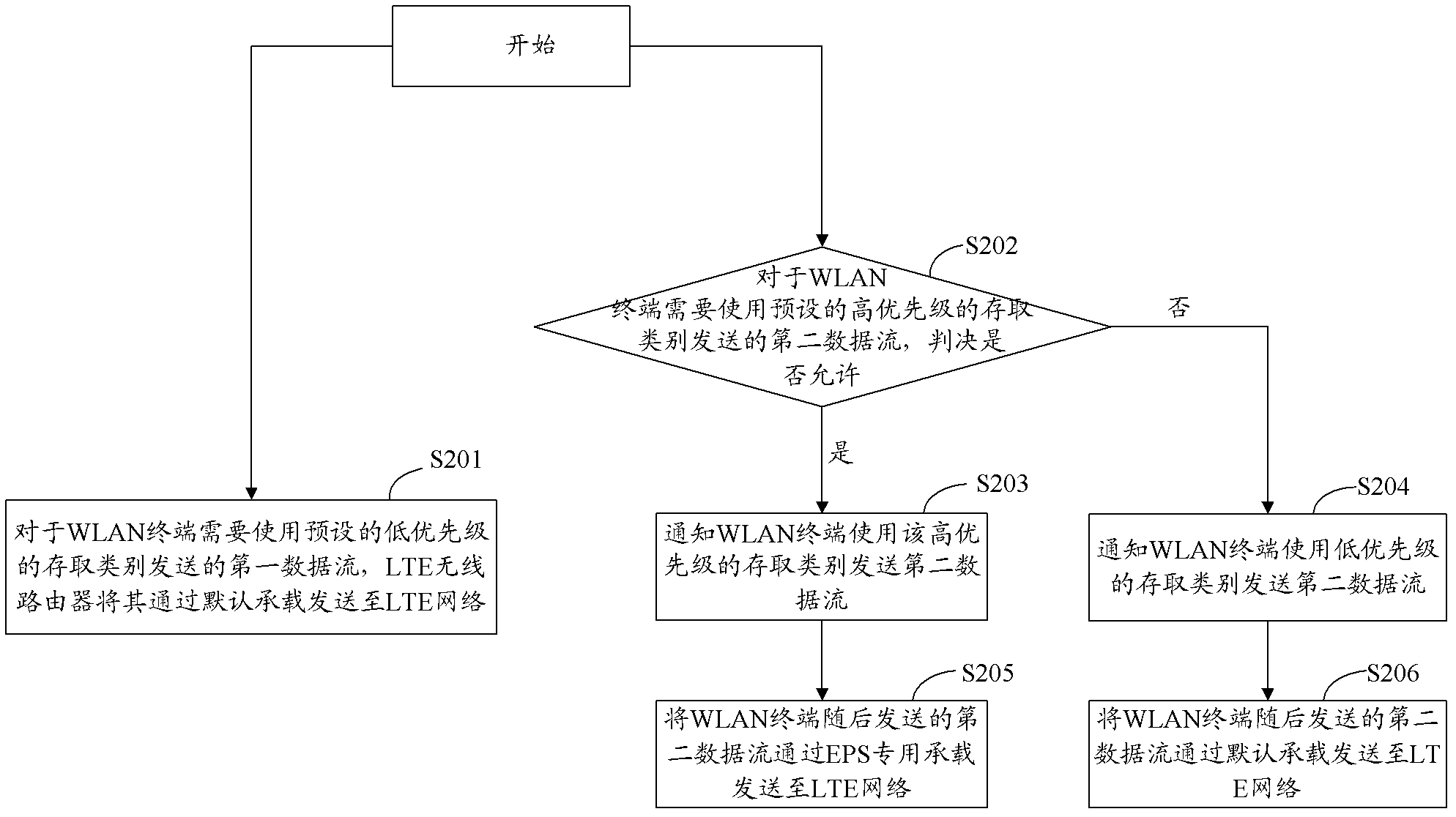
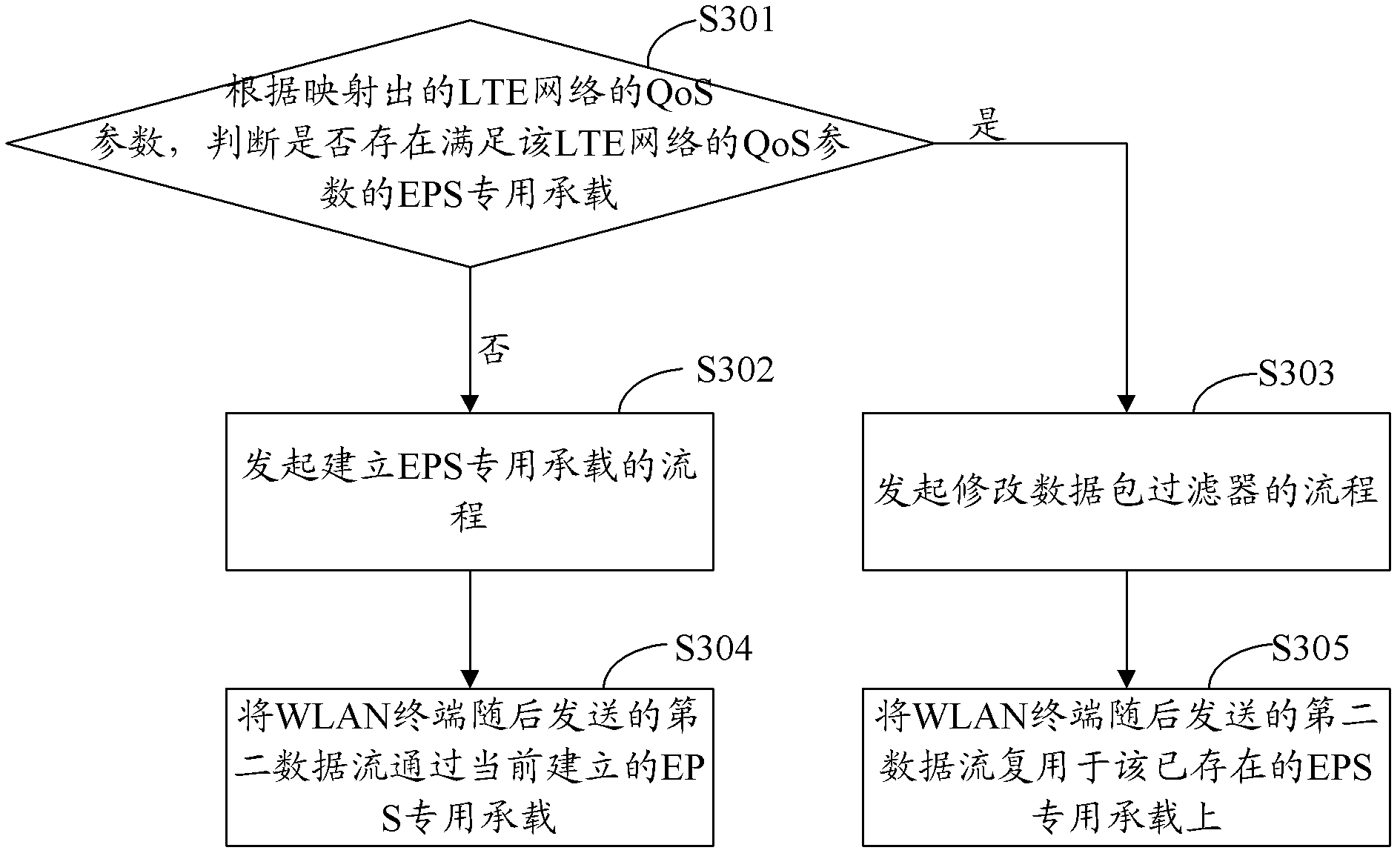
The invention provides a method, a device and a system for achieving wireless local area network (WLAN) terminal end-to-end quality of service (QoS) control. Permission access control is not carried out to data flow, needed to be sent by an access class of a low priority, of a WLAN terminal, the WLAN terminal is born on a default bearer, permission access control is carried out to data flow, needed to be sent by an access class of a high priority, of the WLAN terminal, whether the WLAN terminal is permitted to use the access class of the requested high priority to send or not is judged according to actual conditions of a WLAN and a long term evolution (LTE) network, if the WLAN terminal is permitted to use the access class of the requested high priority to send, the WLAN terminal is born on a bearer special for an evolved packet system (EPS), and if the WLAN terminal is not permitted to use the access class of the requested high priority to send, the WLAN terminal is born on the default bearer. According to the device and the system for achieving the WLAN terminal end-to-end QoS control, part of a decision making function of QoS is shifted down to an LTE wireless router, effective WLAN terminal permitting access control and QoS decision-making can be carried out according to resource conditions of the WLAN and the LTE network, and the problem that WLAN terminal end-to-end cannot be well ensured in the prior art is avoided.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP SHAIHAI
Network resource management
ActiveUS8452866B2Quality improvementImprove service qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementDigital computer detailsNetwork resource managementPacket loss
The invention provides real time dynamic resource management to improve end-to-end QoS by mobile devices regularly updating a resource availability server (RAS) with resource update information. Examples of resource update information are device battery status, available memory, session bandwidth, delay, packet loss, and jitter, network element storage capacity, network element processing power. This information is made available by the RAS. In addition, the RAS generates and maintains predictive models and makes available predictive data from these models. Network elements and devices retrieve this information in the form of notifications from the RAS or by way of querying the RAS. The network elements and devices, based on these predictions, act to negotiate sessions to optimise QoS. In one embodiment the RAS is updated by only mobile devices subscribed to the operator which hosts the RAS. The update information is addressed to the RAS as a stand-alone entity. However, it is envisaged that the server may be hosted by multiple operators and may receive updates from devices subscribed to different operators. Also, it is envisaged that not only mobile devices but also network elements such as MMSCs may send update information.
Owner:MARKPORT LTD
Method and system for estimating performance metrics in a packet-switched communication network
InactiveUS20050220088A1Optimize networkAccurate operationError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of servicePacket loss
Owner:VERIZON LAB
Enhancement of end-to-end network QOS
A network endpoint system and related method and computer program product for use in a network to support enhanced end-to-end QoS in the network. The network endpoint system is adapted to receive network data of varying priority on behalf of a data consumer operating at the application layer of a network protocol stack implemented by the network endpoint system. The network endpoint system includes a network interface controller adapted to receive network frames containing the network data, plural network data handling channels each having an associated priority, and priority processing logic adapted to transfer the network data from the network interface controller to the plural data handling channels on a prioritized basis according to the network data priority. Also disclosed are a network interface controller and a network node to support enhanced end-to-end QoS in a network.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com