Patents
Literature
220 results about "Queuing delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunication and computer engineering, the queuing delay or queueing delay is the time a job waits in a queue until it can be executed. It is a key component of network delay. In a switched network, queuing delay is the time between the completion of signaling by the call originator and the arrival of a ringing signal at the call receiver. Queuing delay may be caused by delays at the originating switch, intermediate switches, or the call receiver servicing switch. In a data network, queuing delay is the sum of the delays between the request for service and the establishment of a circuit to the called data terminal equipment (DTE). In a packet-switched network, queuing delay is the sum of the delays encountered by a packet between the time of insertion into the network and the time of delivery to the address.
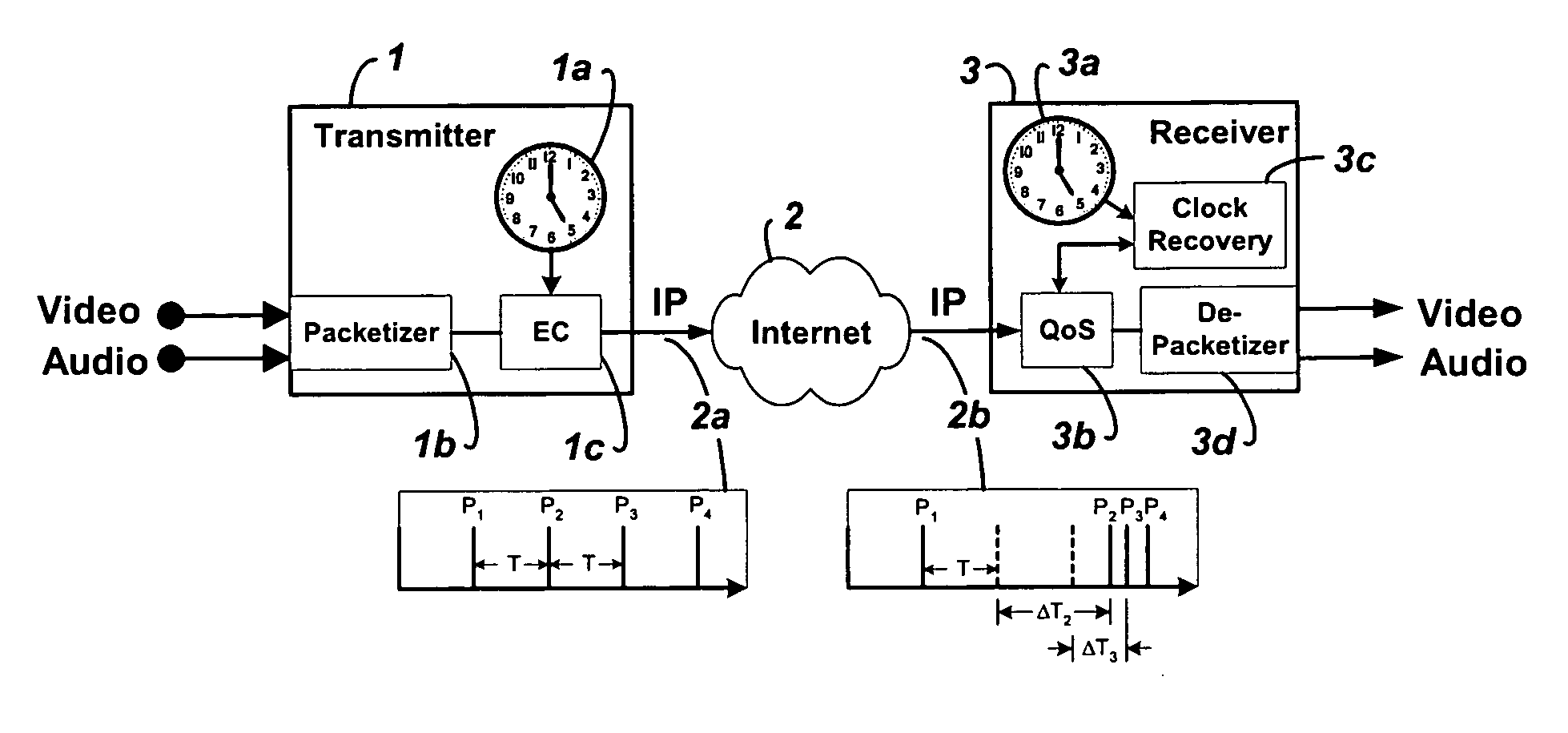
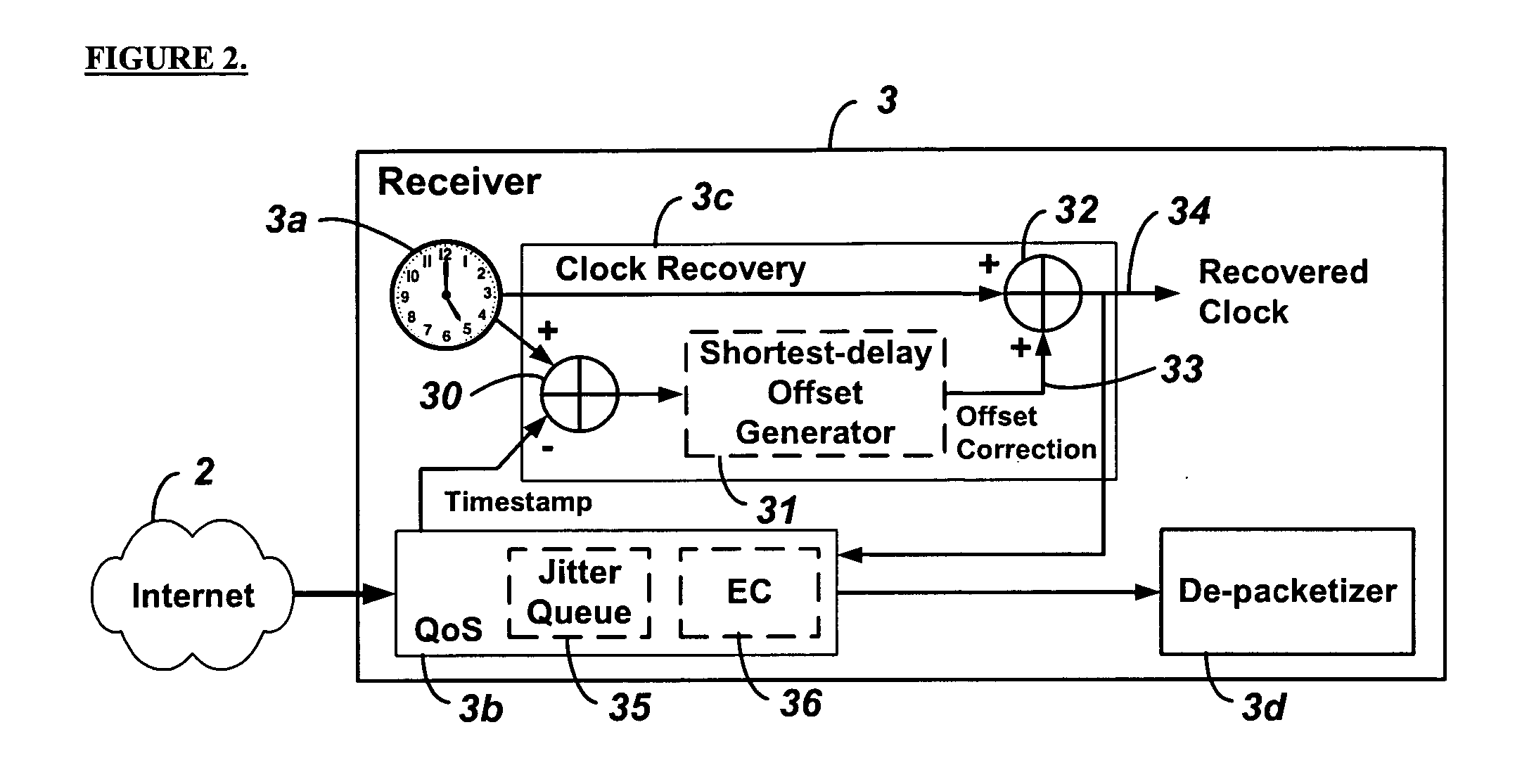
System and method for clock synchronization over packet-switched networks
ActiveUS20060013263A1Easy to replaceImprove abilitiesTime-division multiplexTransmissionQuality of serviceThe Internet
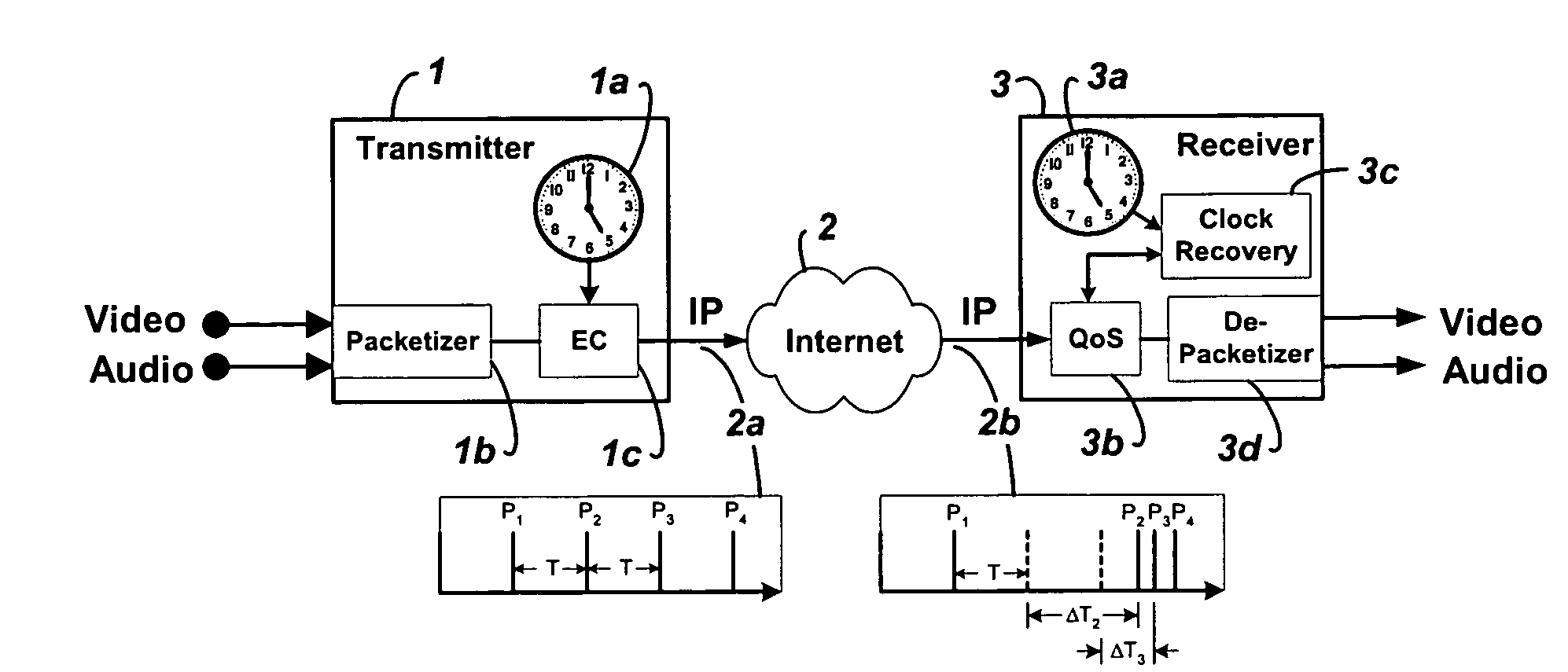
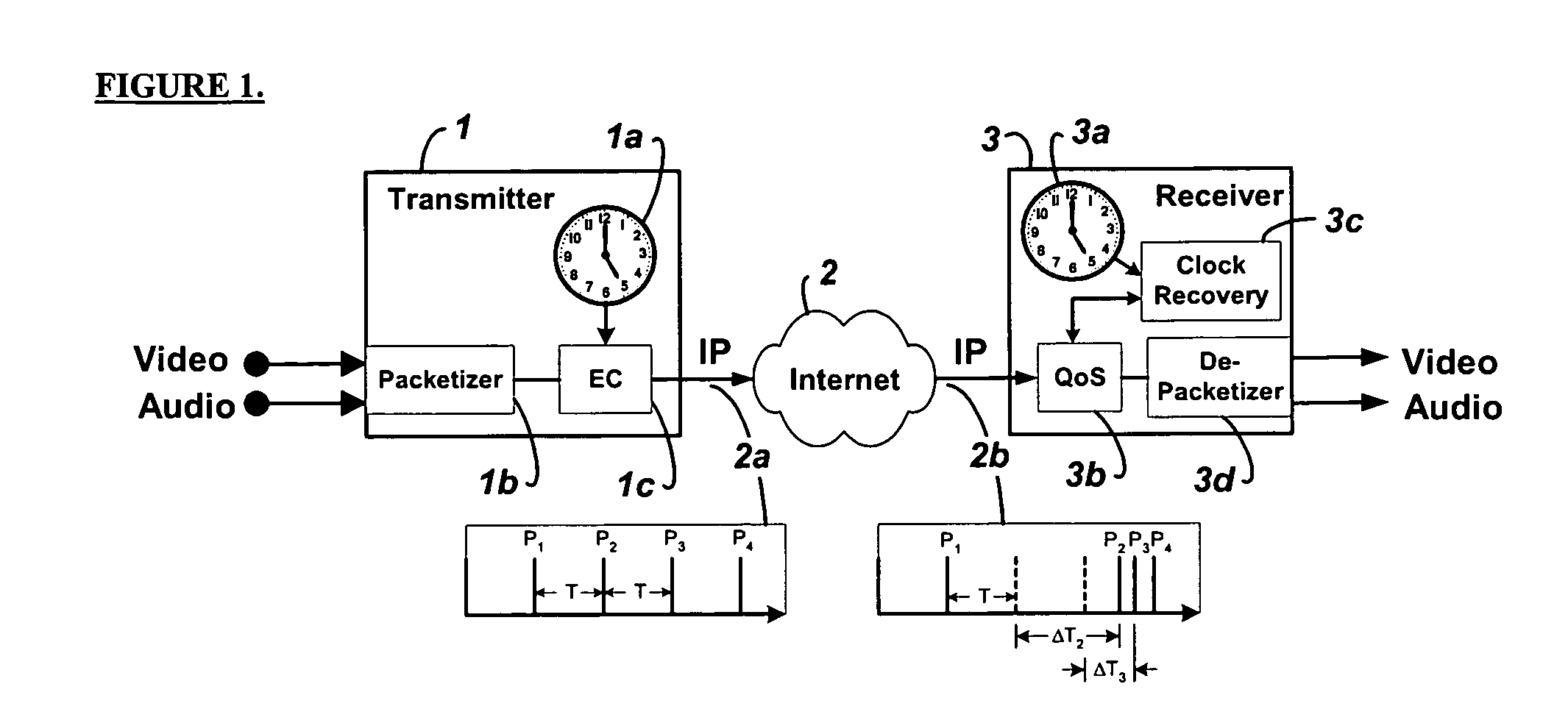
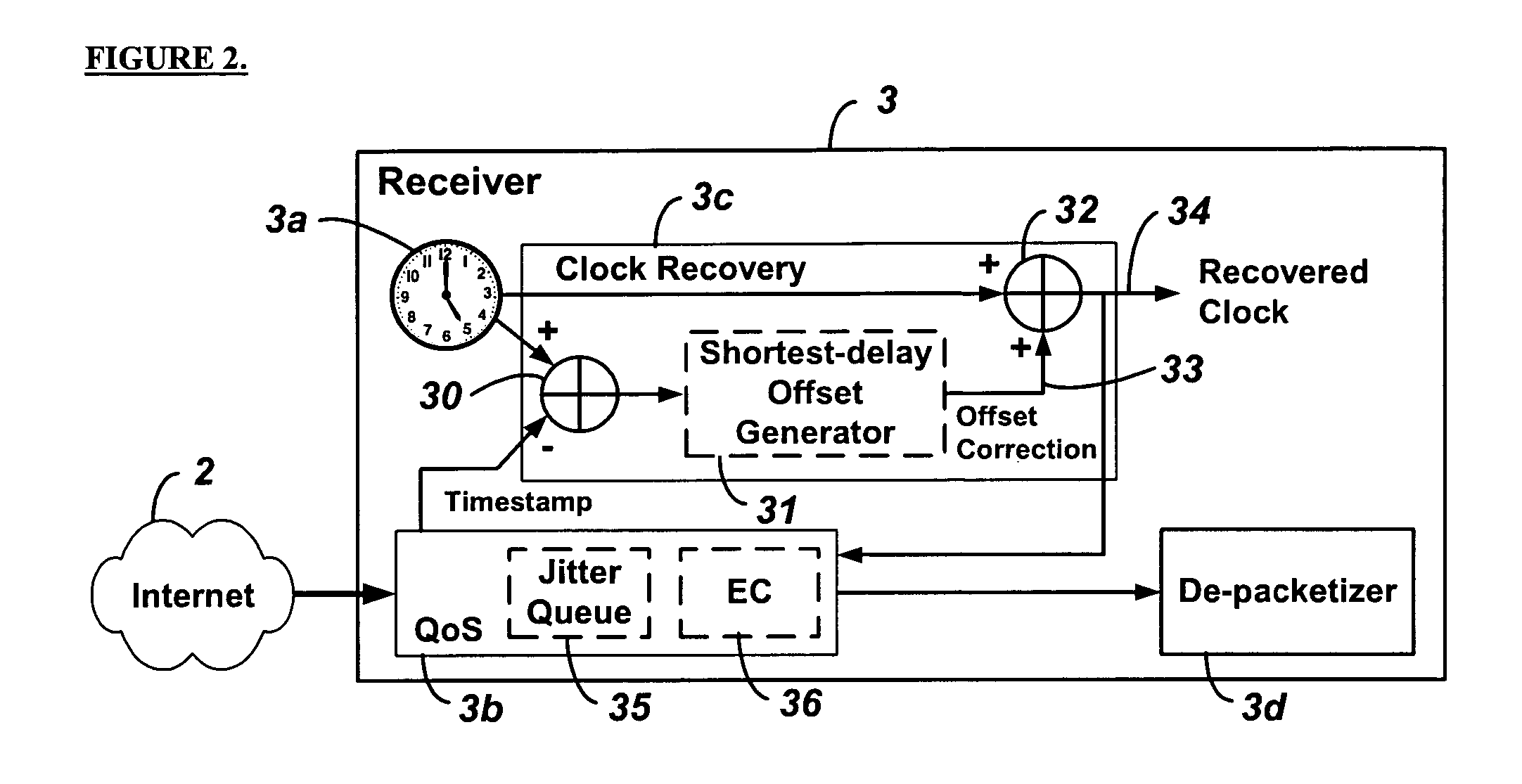
Embodiments of the invention enable the synchronization of clocks across packet switched networks, such as the Internet, sufficient to drive a jitter buffer and other quality-of-service related buffering. Packet time stamps referenced to a local clock create a phase offset signal. A shortest-delay offset generator uses a moving-window filter to select the samples of the phase offset signal having the shortest network propagation delay within the window. This shortest network propagation delay filter minimizes the effect of network jitter under the assumption that queuing delays account for most of the network jitter. The addition of this filtered phase offset signal to a free-running local clock creates a time reference that is synchronized to the remote clock at the source thus allowing for the transport of audio, video, and other time-sensitive real-time signals with minimal latency.
Owner:QVIDIUM TECH
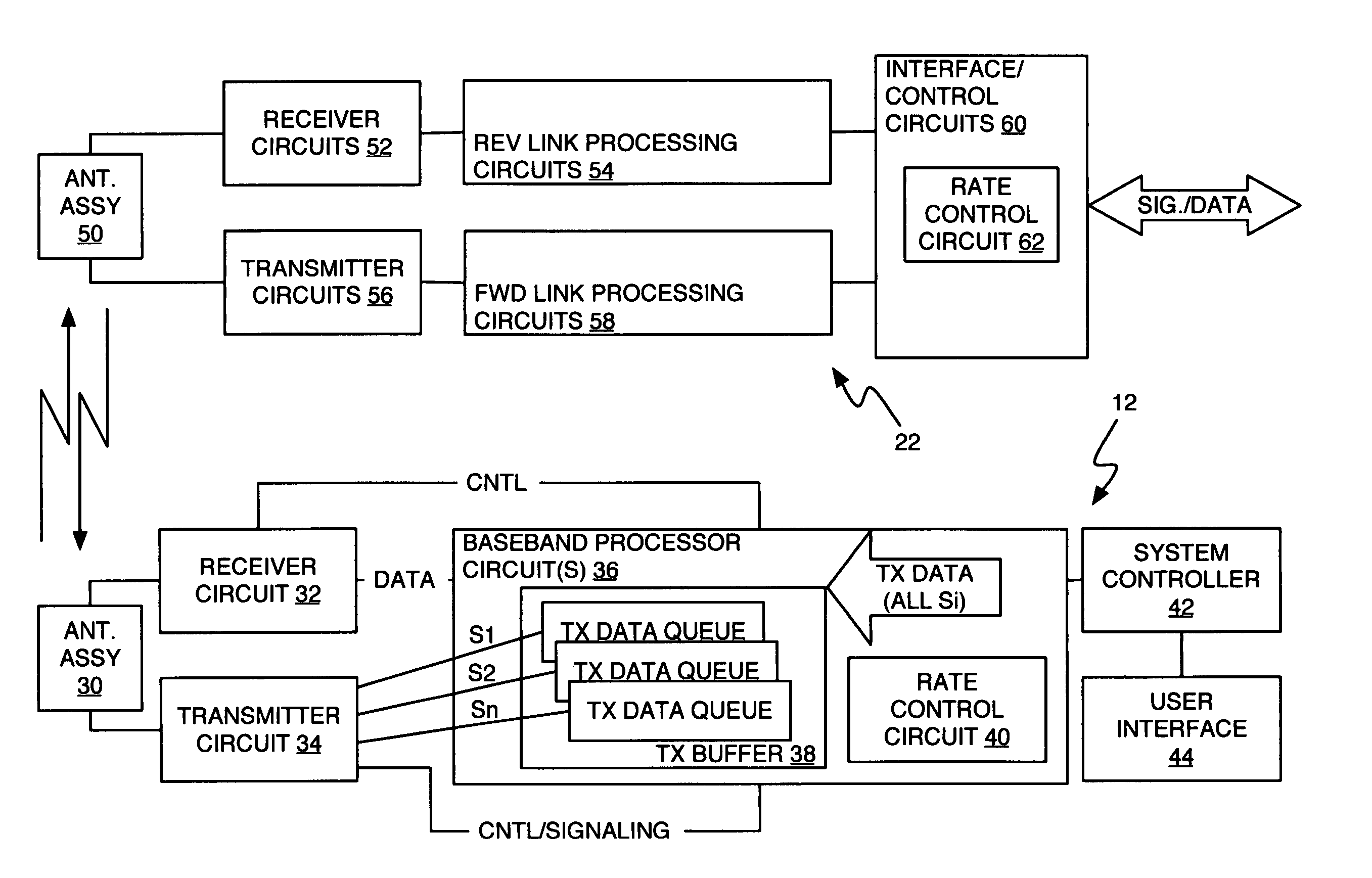
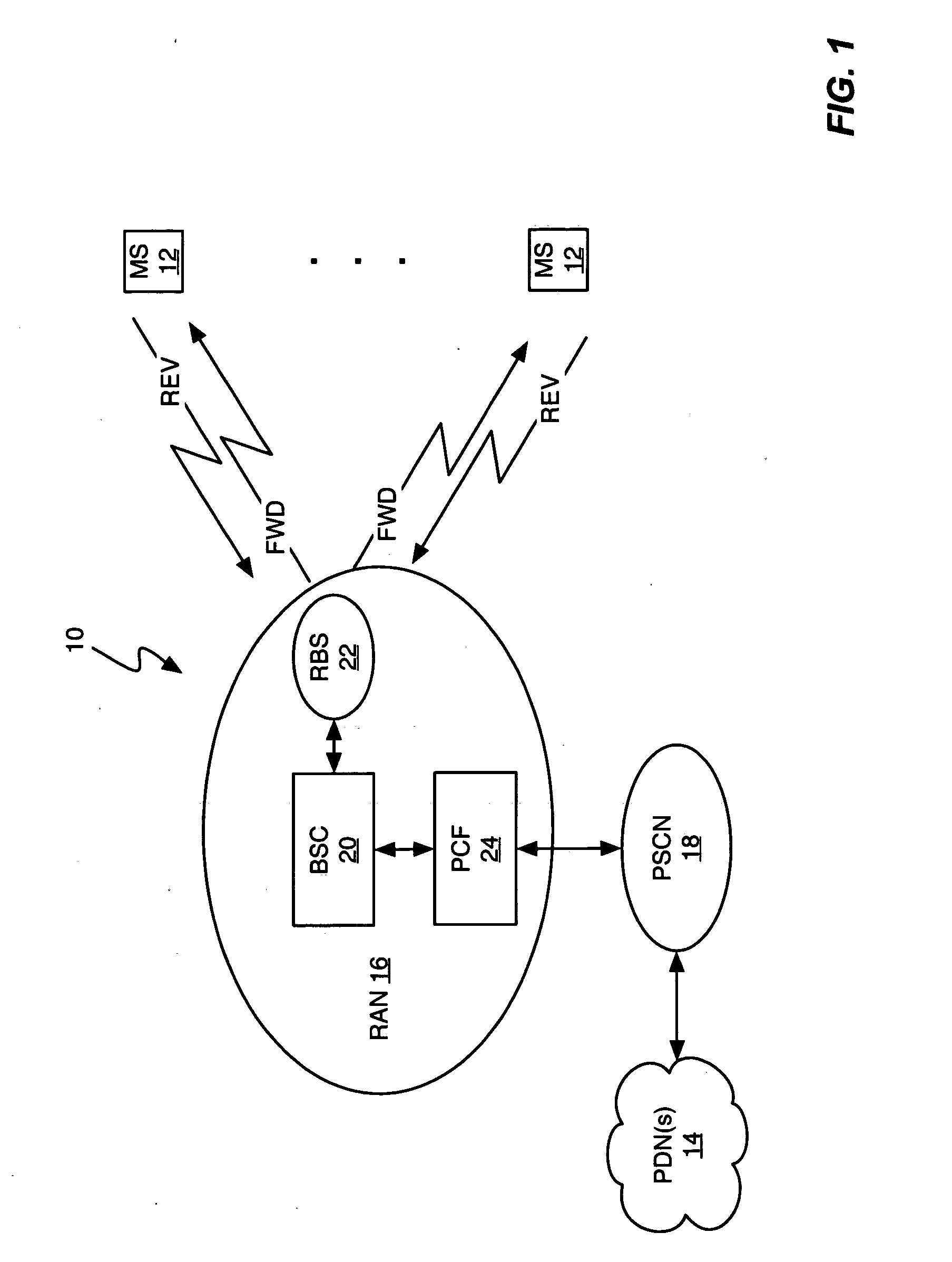
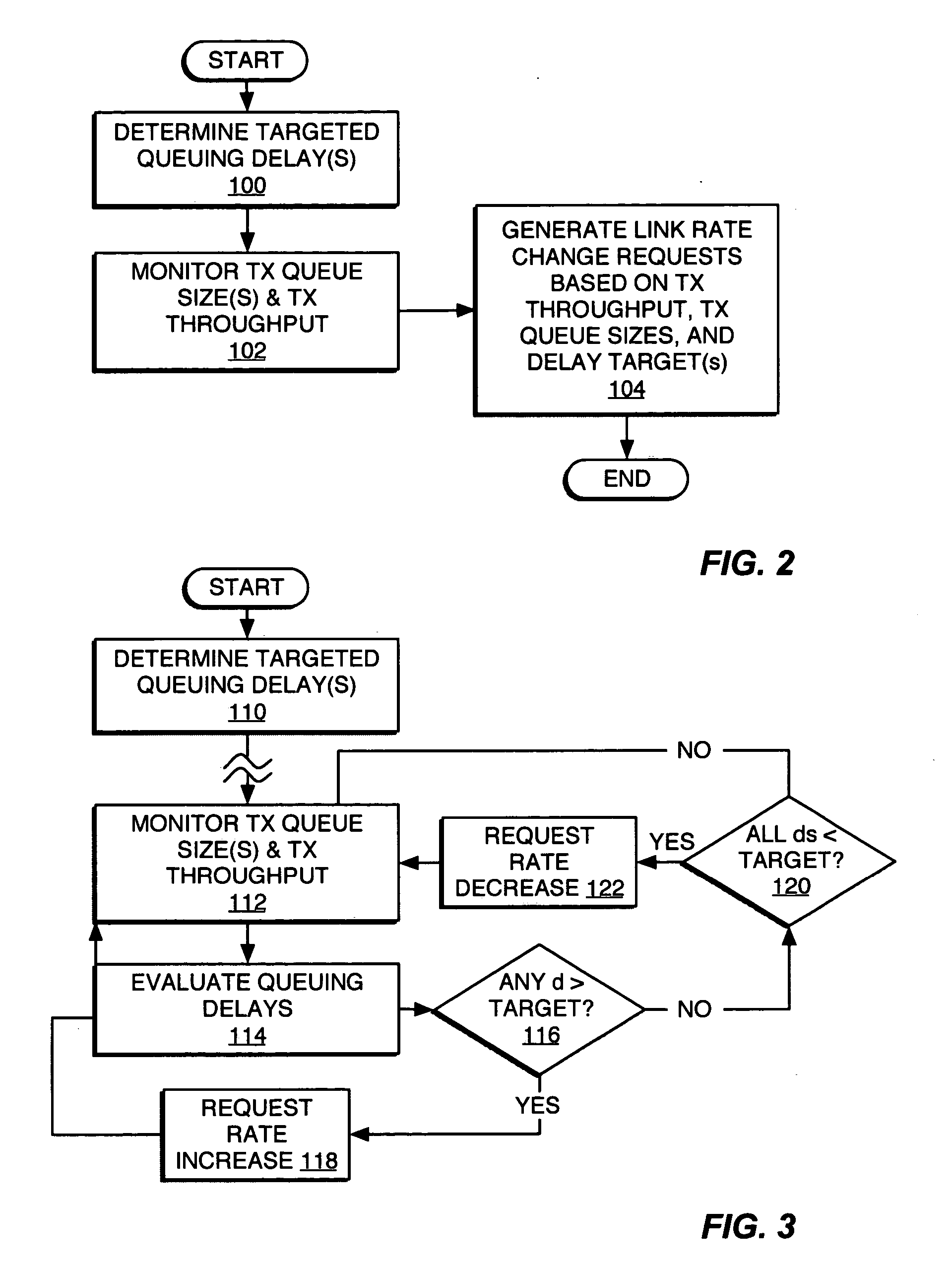
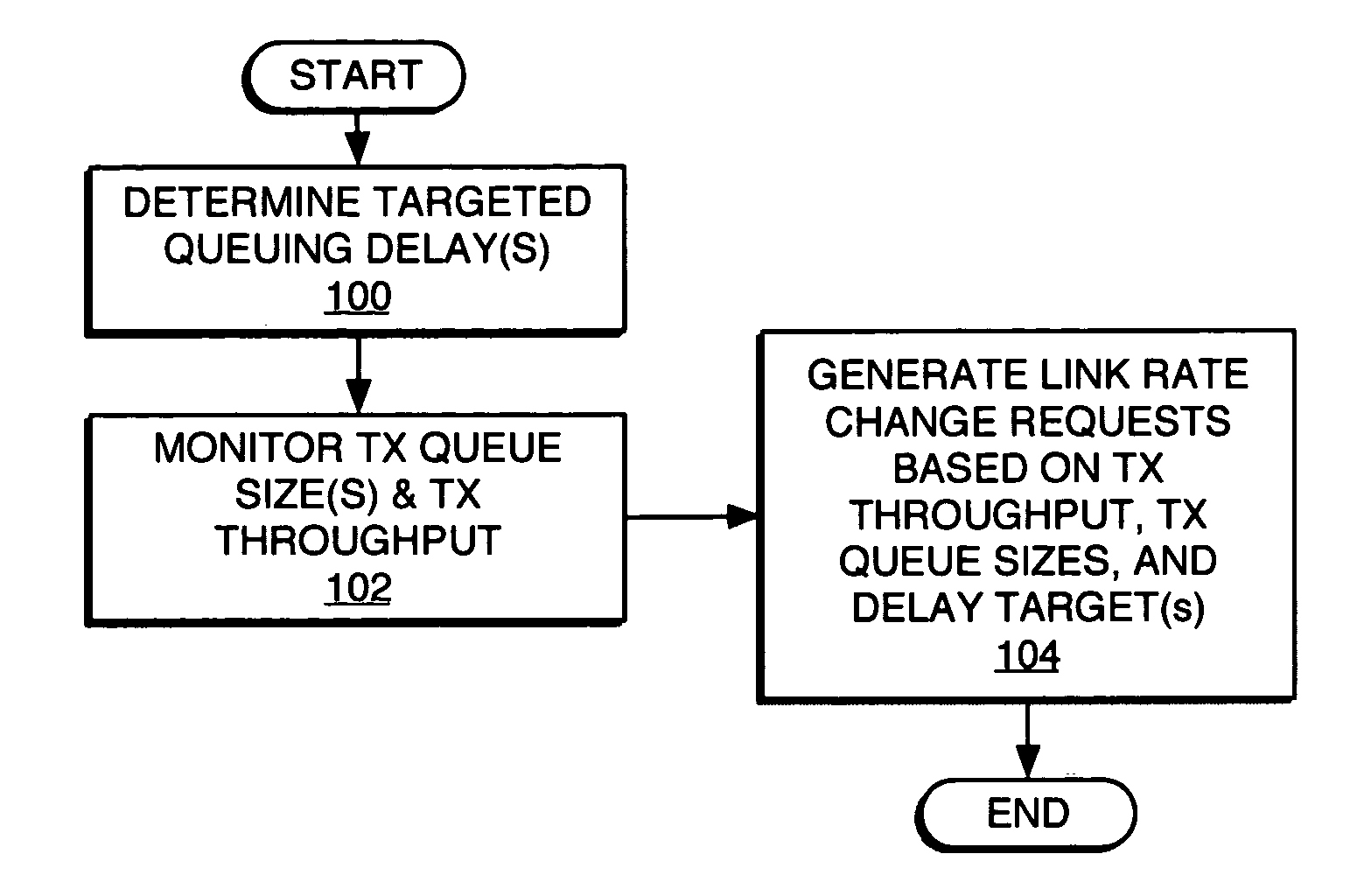
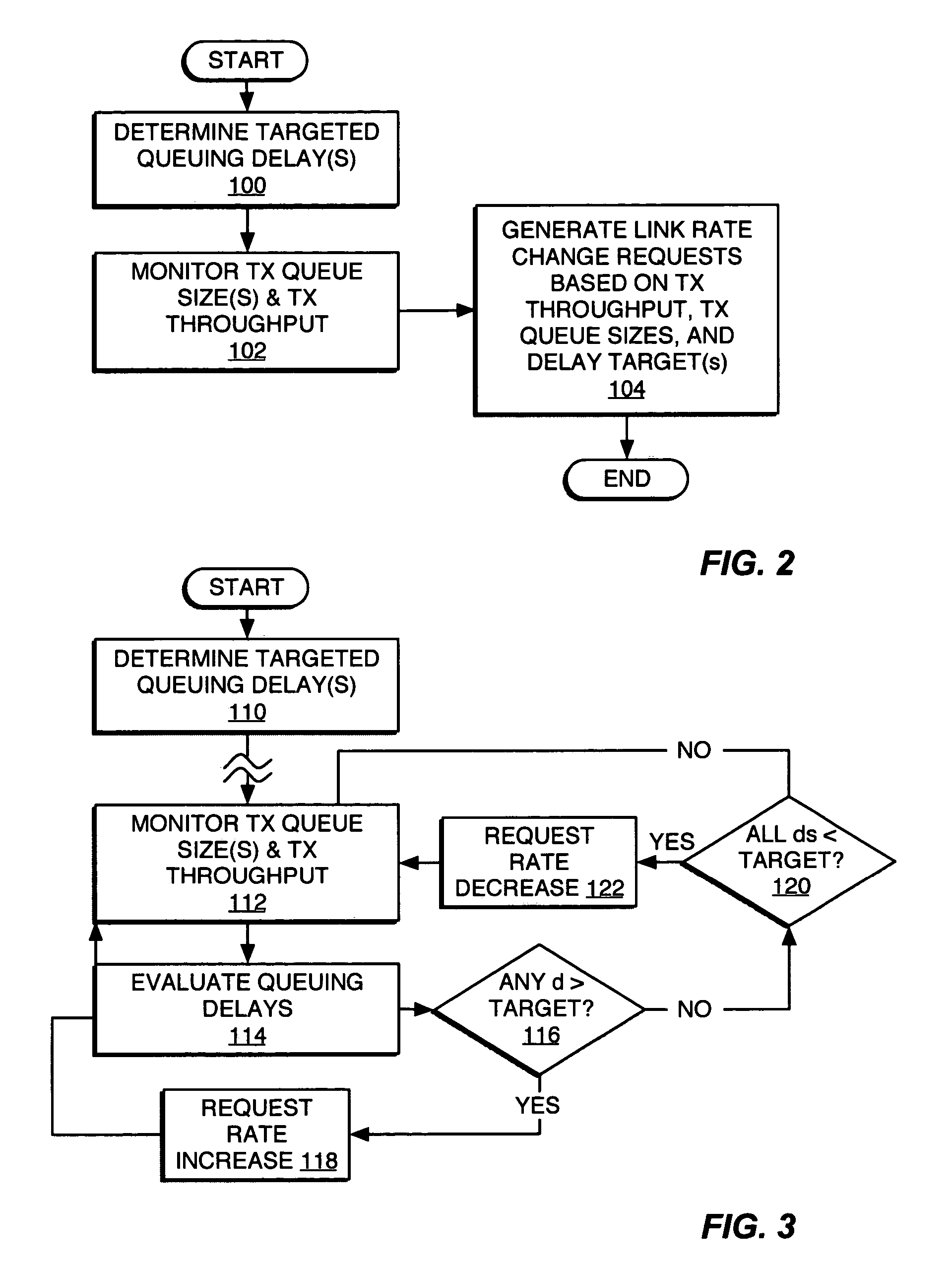
Queuing delay based rate control
InactiveUS20050111361A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceTelecommunications link
A method and apparatus for rate control adjusts or otherwise requests adjustment of a communication link data rate based on transmit queuing delays. For example, a mobile station may monitor expected transmit queuing delays relative to one or more delay targets or other Quality-of-Service constraints, and request reverse link rate increases or decreases accordingly. Similarly, the mobile station may be configured periodically to request reverse link rate changes based on determining the rate needed to meet targeted queuing delays for one or more service instances being supported by the mobile station in each of a succession of ongoing rate control intervals. Requested rates may be defined data rates or may be virtual rates that can be achieved by using combinations of defined data rates. Queuing-based rate control also can be applied to the base station's forward link, and, more broadly, to essentially any rate controlled communication link.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
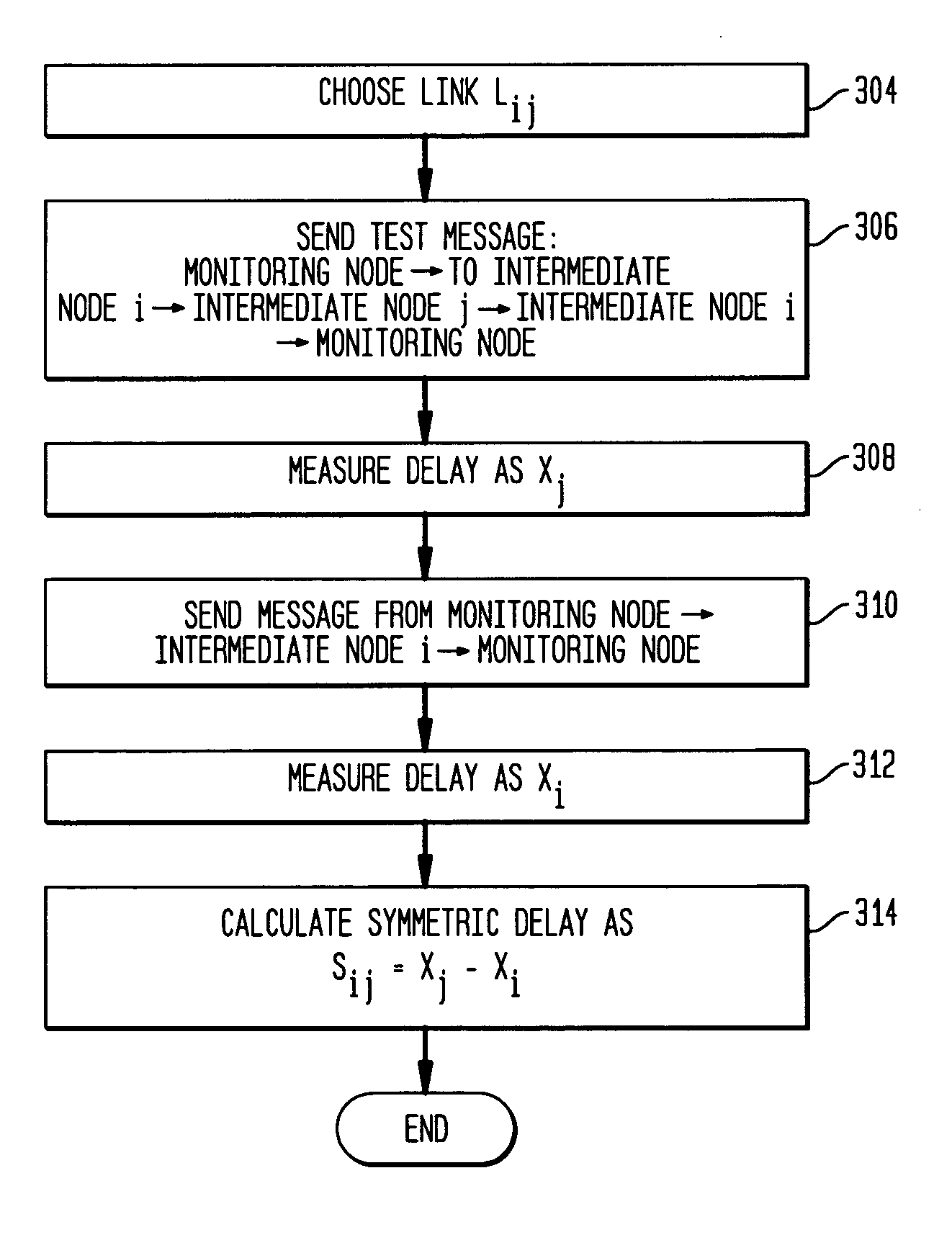
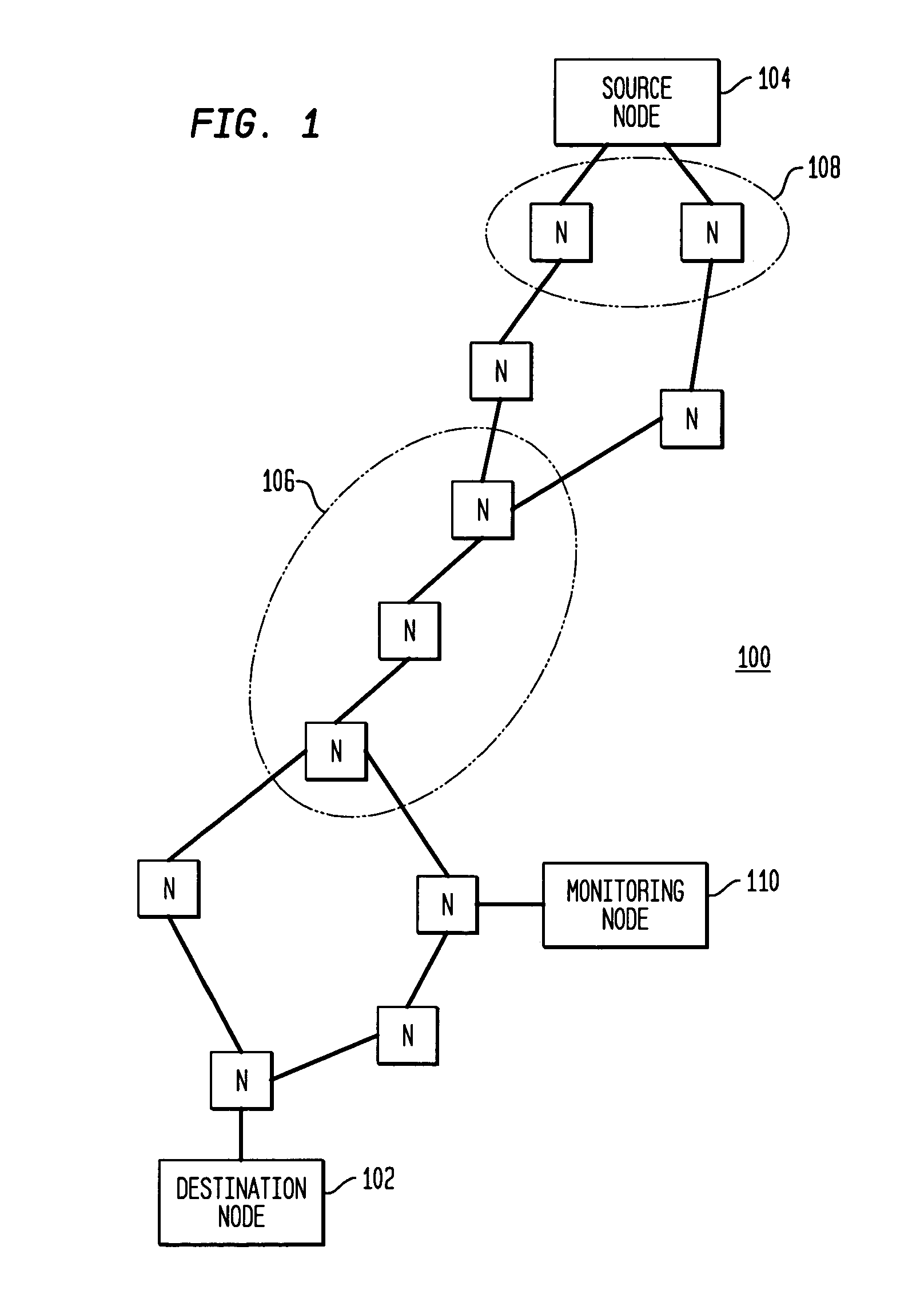
Remote estimation of round-trip delays in a data network
ActiveUS20060092850A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRouting tableNetwork topology
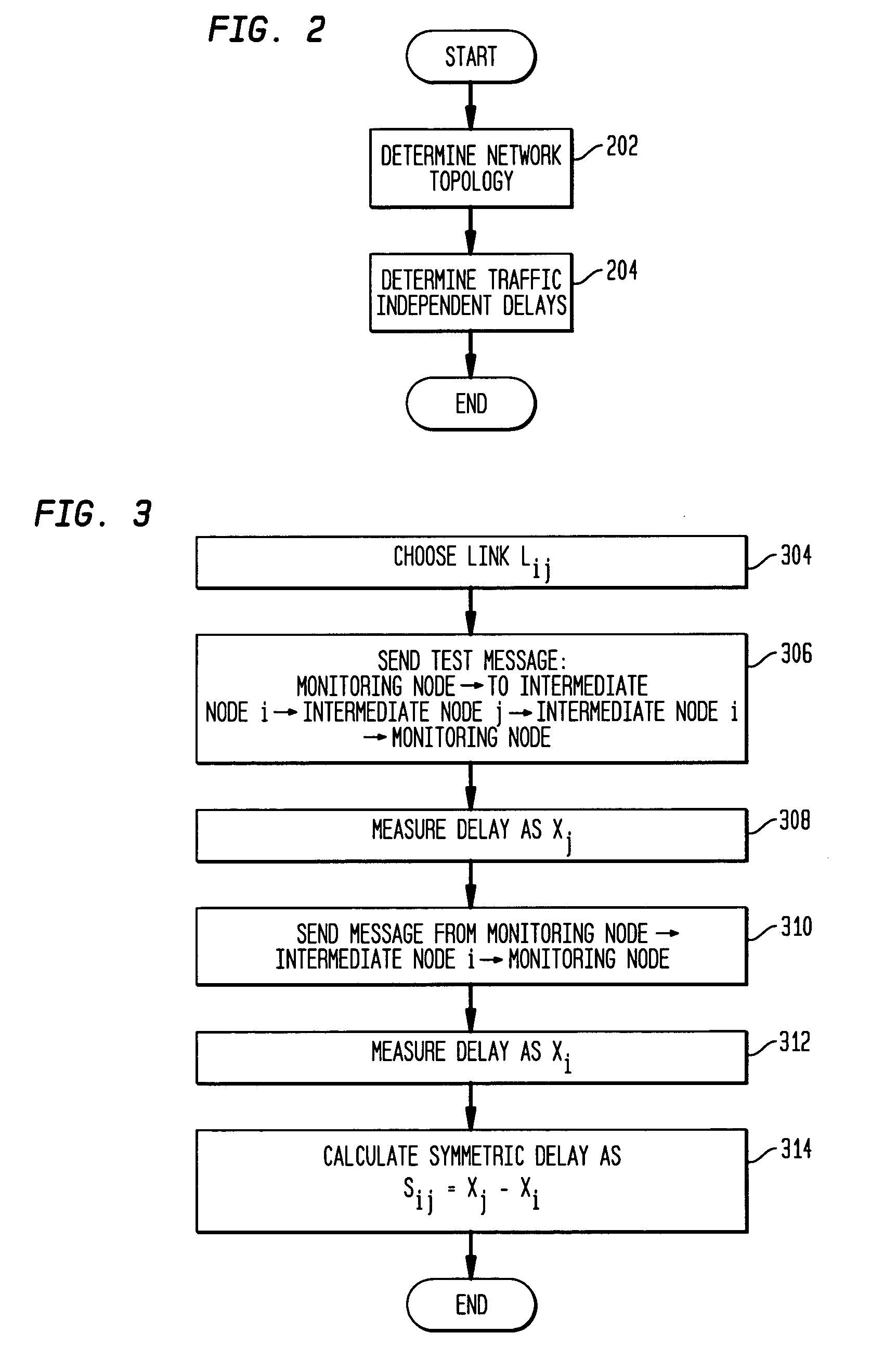
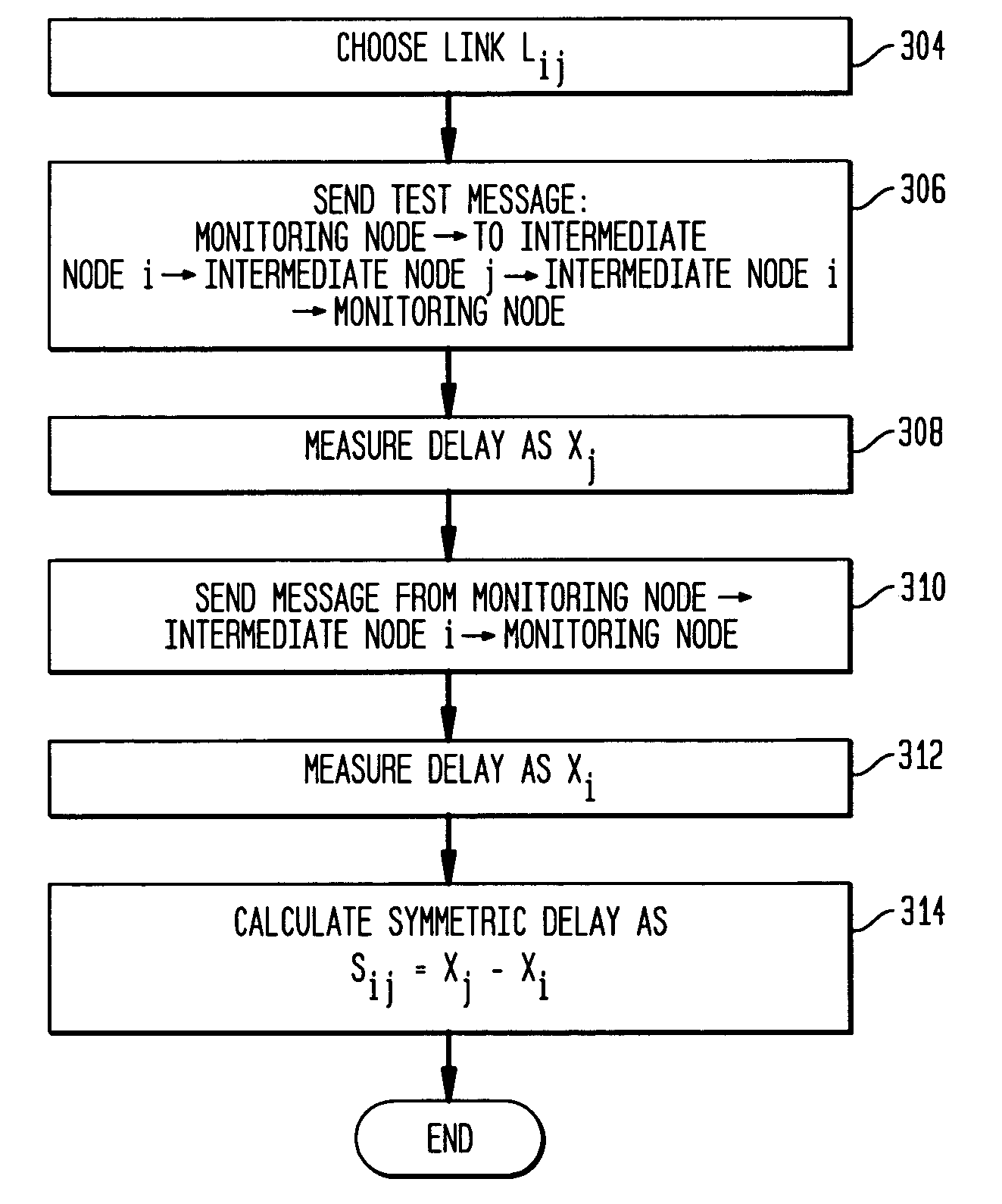
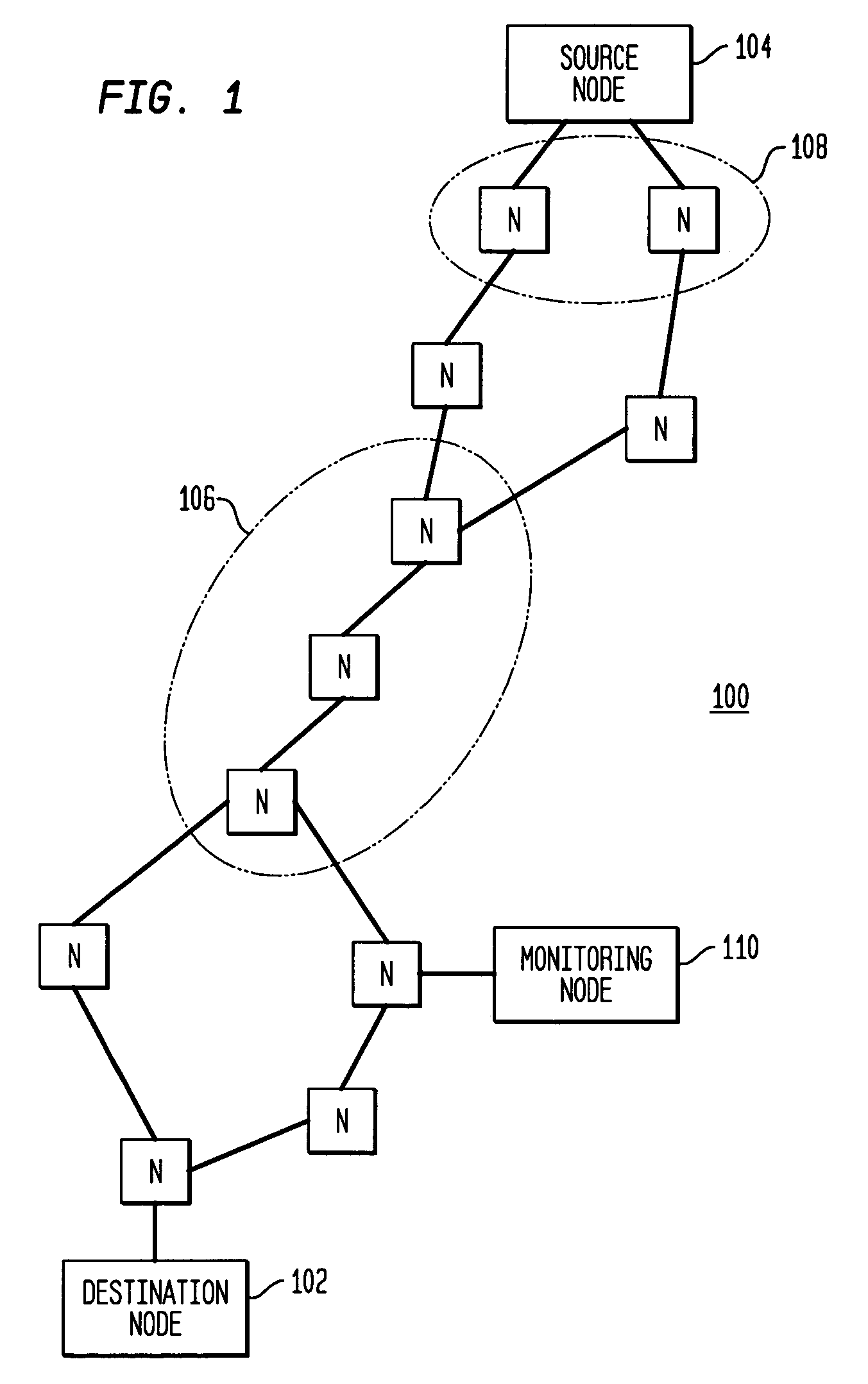
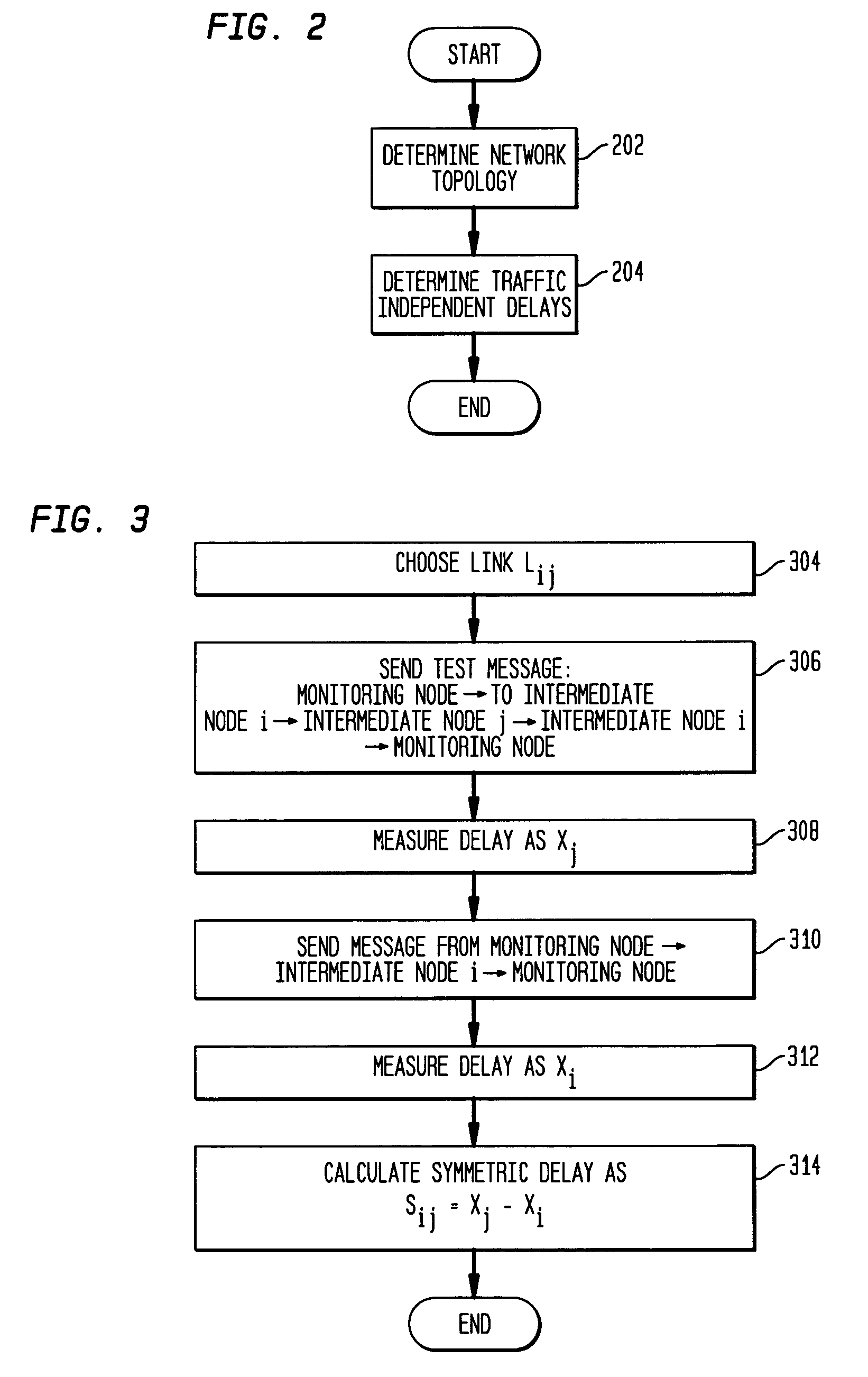
Disclosed is a technique for data network congestion diagnosis using remote estimation of round-trip delays. A monitoring node transmits test messages between network nodes and measures the transit times between when the test messages are transmitted from, and when they return to, the monitoring node. A path delay between network nodes is determined based on the measured time delays. The techniques for determining network path delay are also utilized in conjunction with a three phase test procedure for diagnosing network congestion problems. Due to various network topologies and routing tables, certain confirmatory checks may be required to determine whether the procedures of the first or second phase test procedures are appropriate for particular path segments. Further, queuing delays may be determined by subtracting traffic independent delays from the measured transit times of the test messages, and such queuing delays may be used to determine the path delays. Such traffic independent delays may be determined during periods of low network traffic.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Automated playlist chaser
ActiveUS20050102695A1Television system detailsRecord information storageProgram segmentTime function
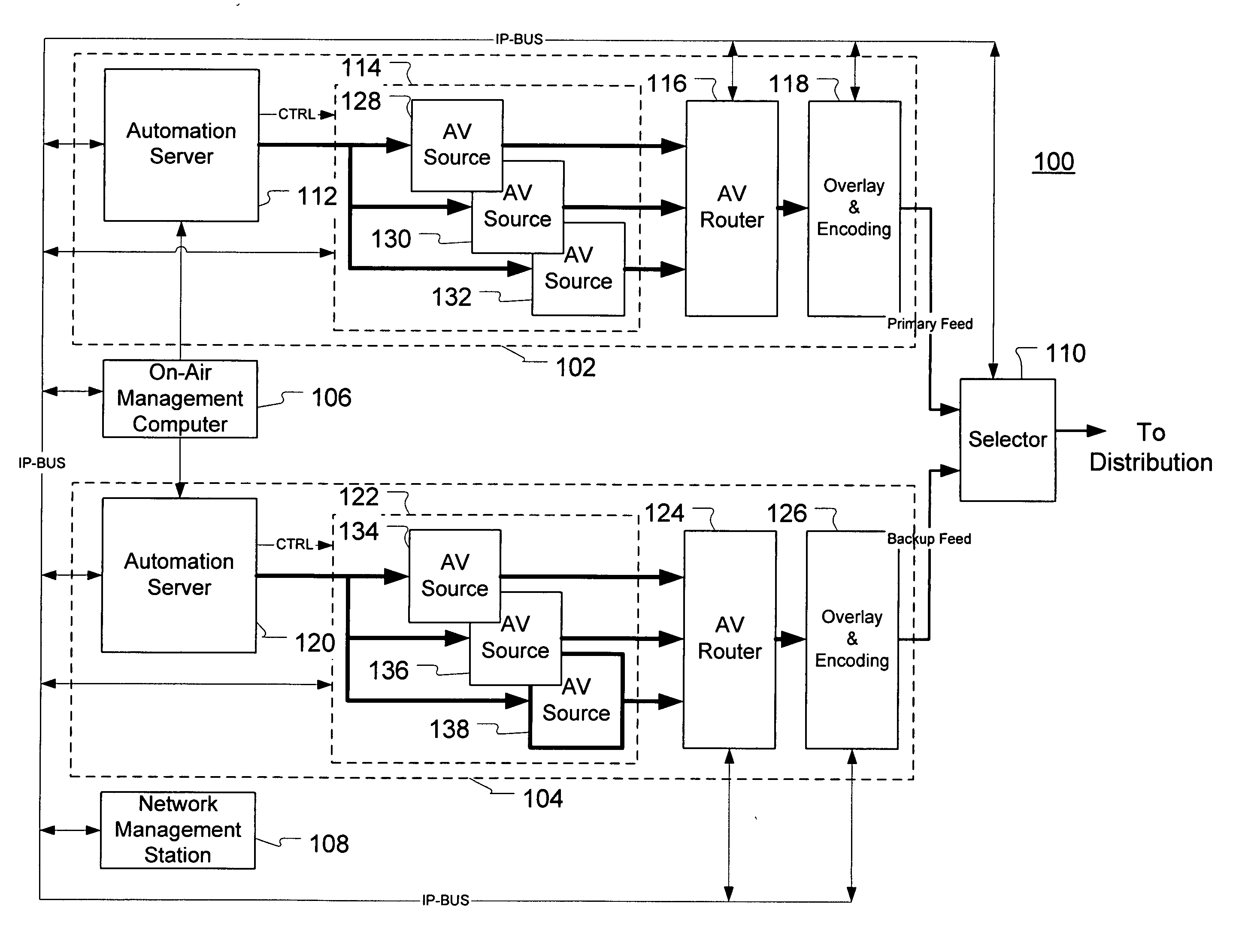
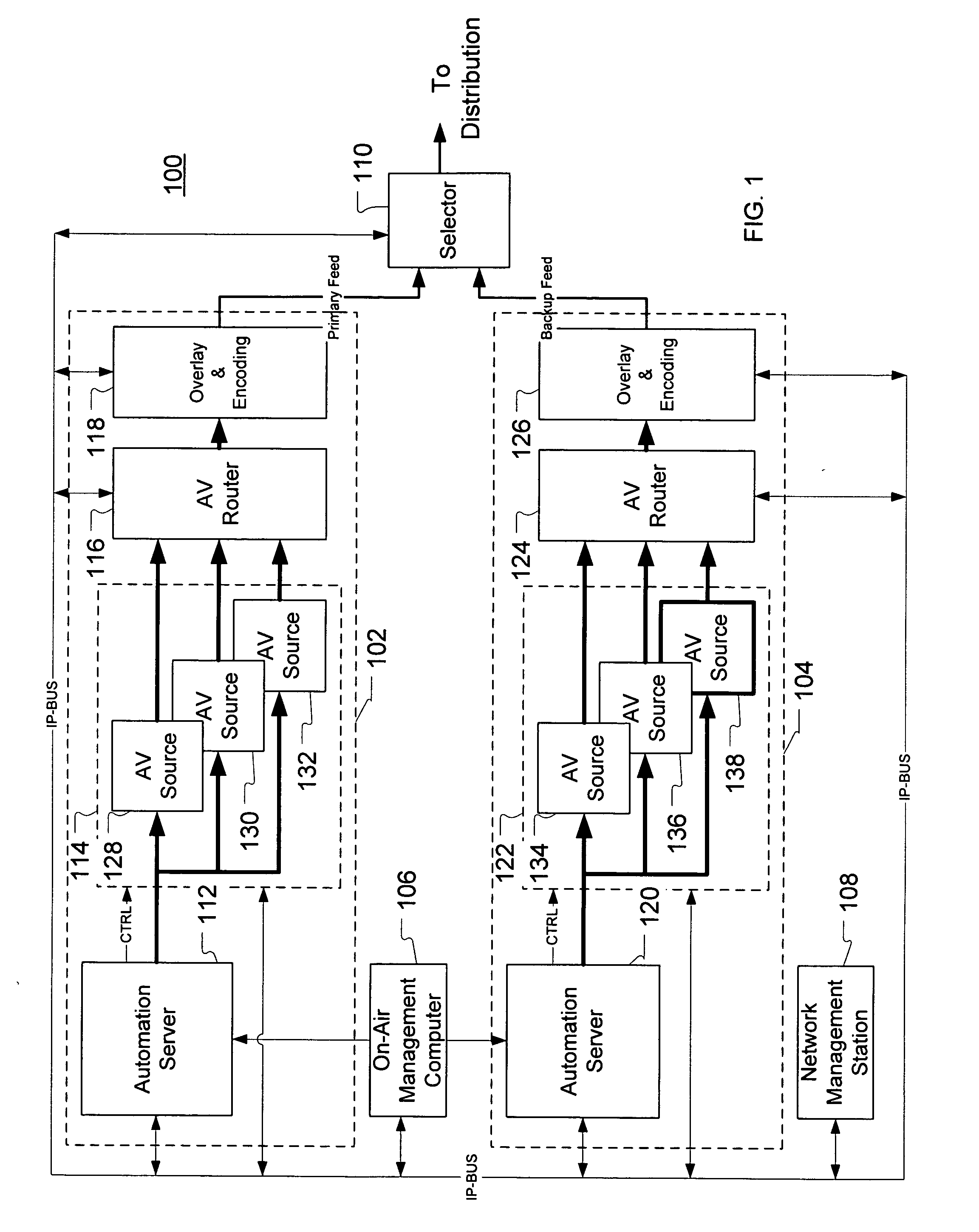
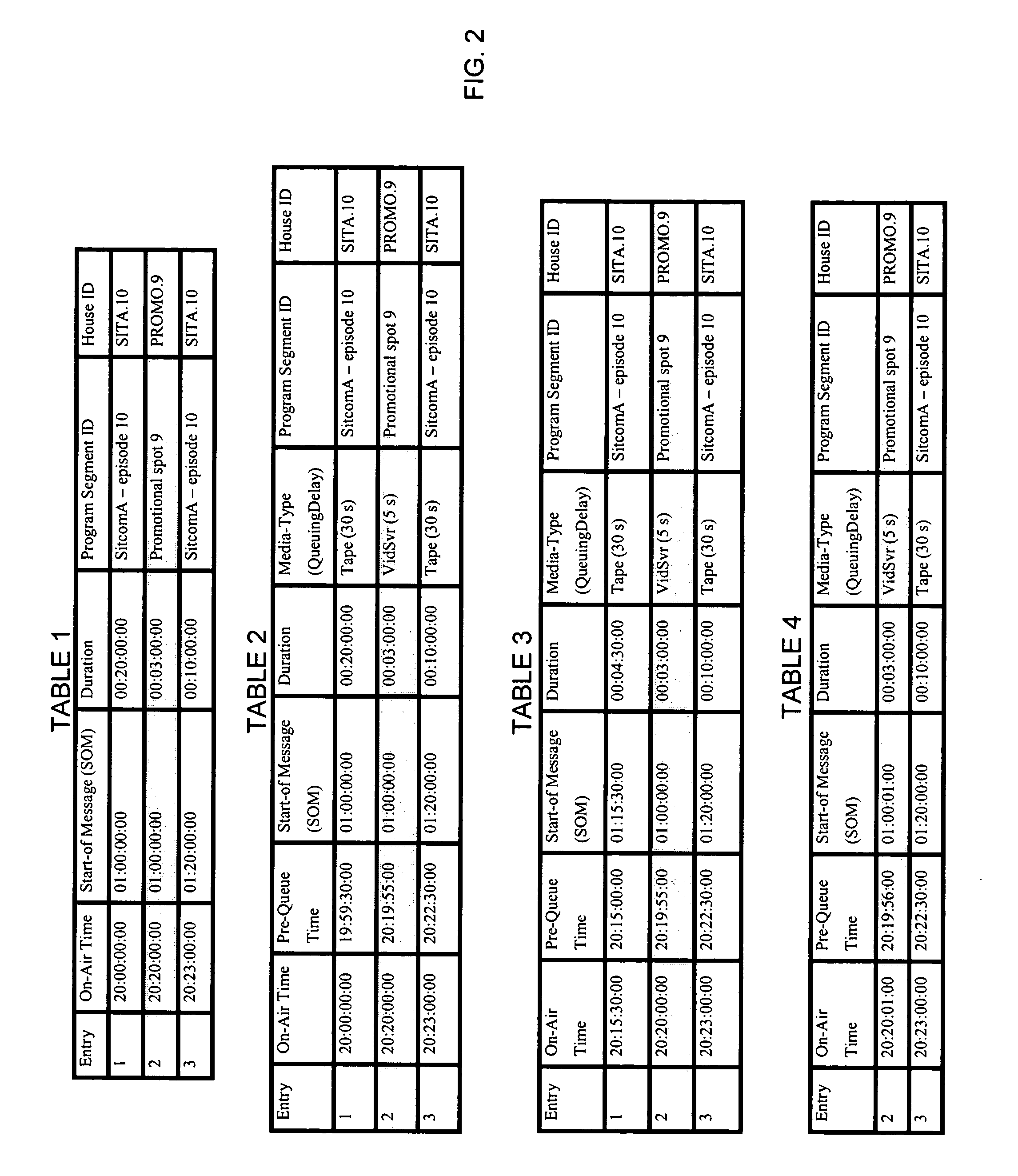
An automated playlist chaser (APC) improves the recovery time and robustness of playlists to component failures and / or human errors in a content sourcing and editing environment. Following detection and correction of an error in a content sourcing subsystem controlled by a playlist, the APC retrieves a last known good playlist from a playlist archive and automatically builds a new playlist for resynchronization of the subsystem. Building the new playlist involves iteratively solving for the first new program segment entry in the new playlist and the new “on-air time,”“start-of message,” and “duration” attributes for the entry as a function of a reference time (e.g., the present time of day), the original on-air time for the entry, the subsystem recovery time, the APC processing time, and the queuing delay of the audio-video source for the program segment.
Owner:HOME BOX OFFICE INC
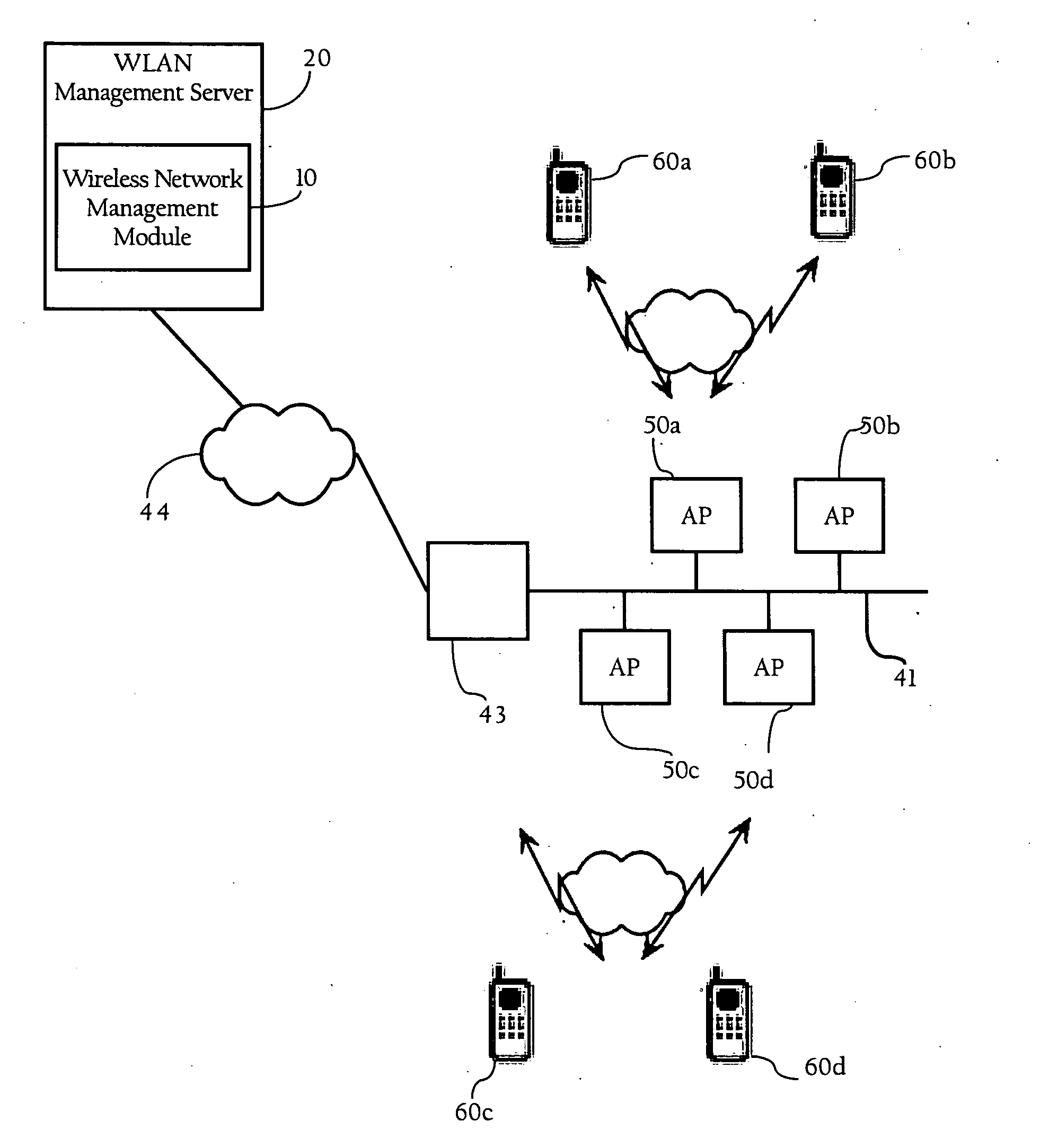
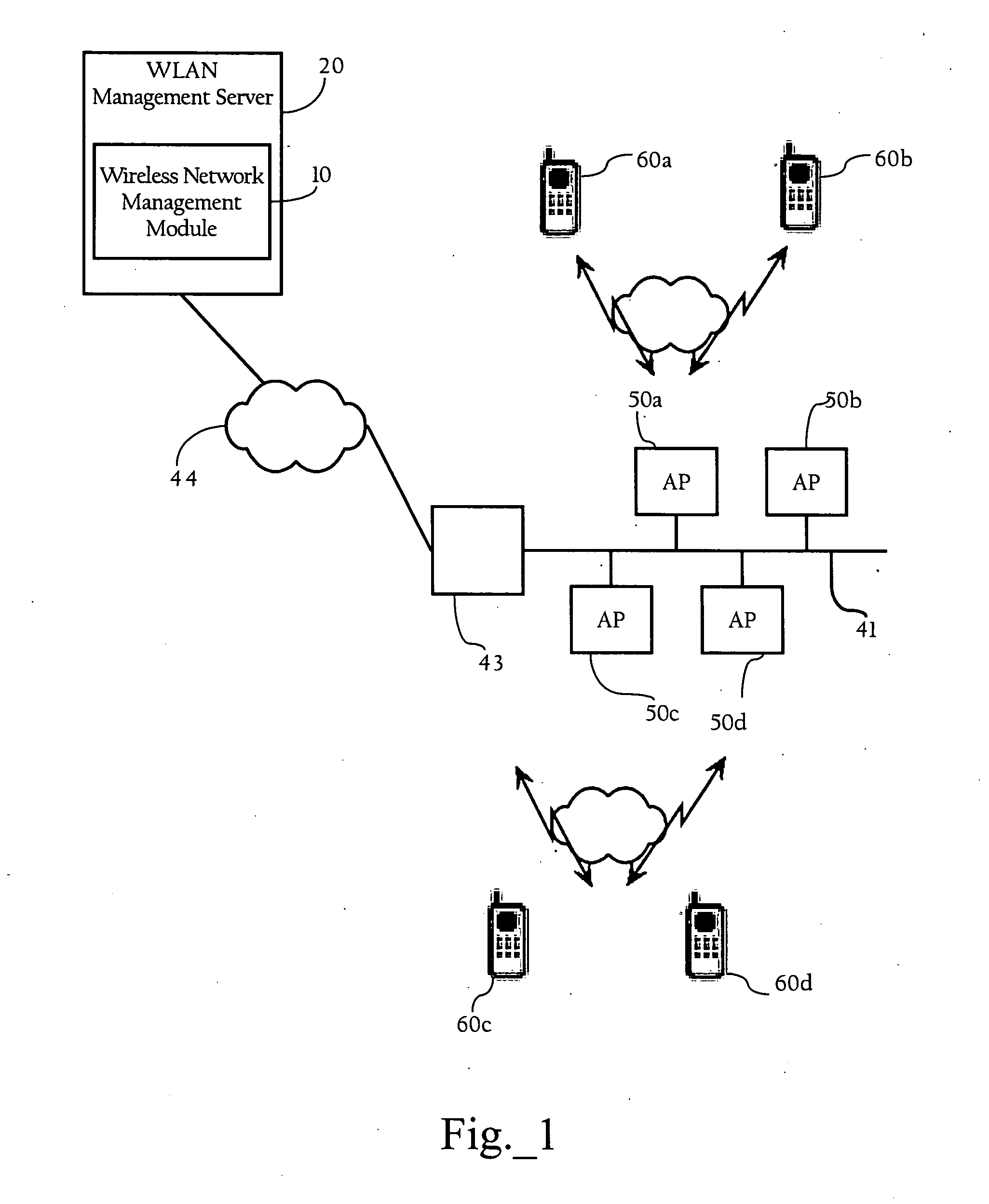
WLAN diagnostics using traffic stream metrics
Methods, apparatuses and systems directed to facilitating WLAN diagnostics and management using traffic stream metrics. In a data collection stage, according to one implementation of the present invention, localized uplink measurements are taken at a wireless client associated with a wireless access point. During periodic intervals (e.g., every 5 seconds), the wireless client, in one implementation, transmits uplink measurement information to the wireless access point. The wireless access point may also take downlink measurements, which may also include one or more of the following metrics: observed latency, queuing delay, packet loss rate, and packet count information. The wireless access point, in one implementation, may aggregate and report the uplink and downlink metric information to a network management system. In a diagnostic stage, according to one implementation, a wireless network management module performs diagnostics of the WLAN based on the uplink and / or downlink metrics received from the wireless access-point.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for network congestion control using queue control and one-way delay measurements
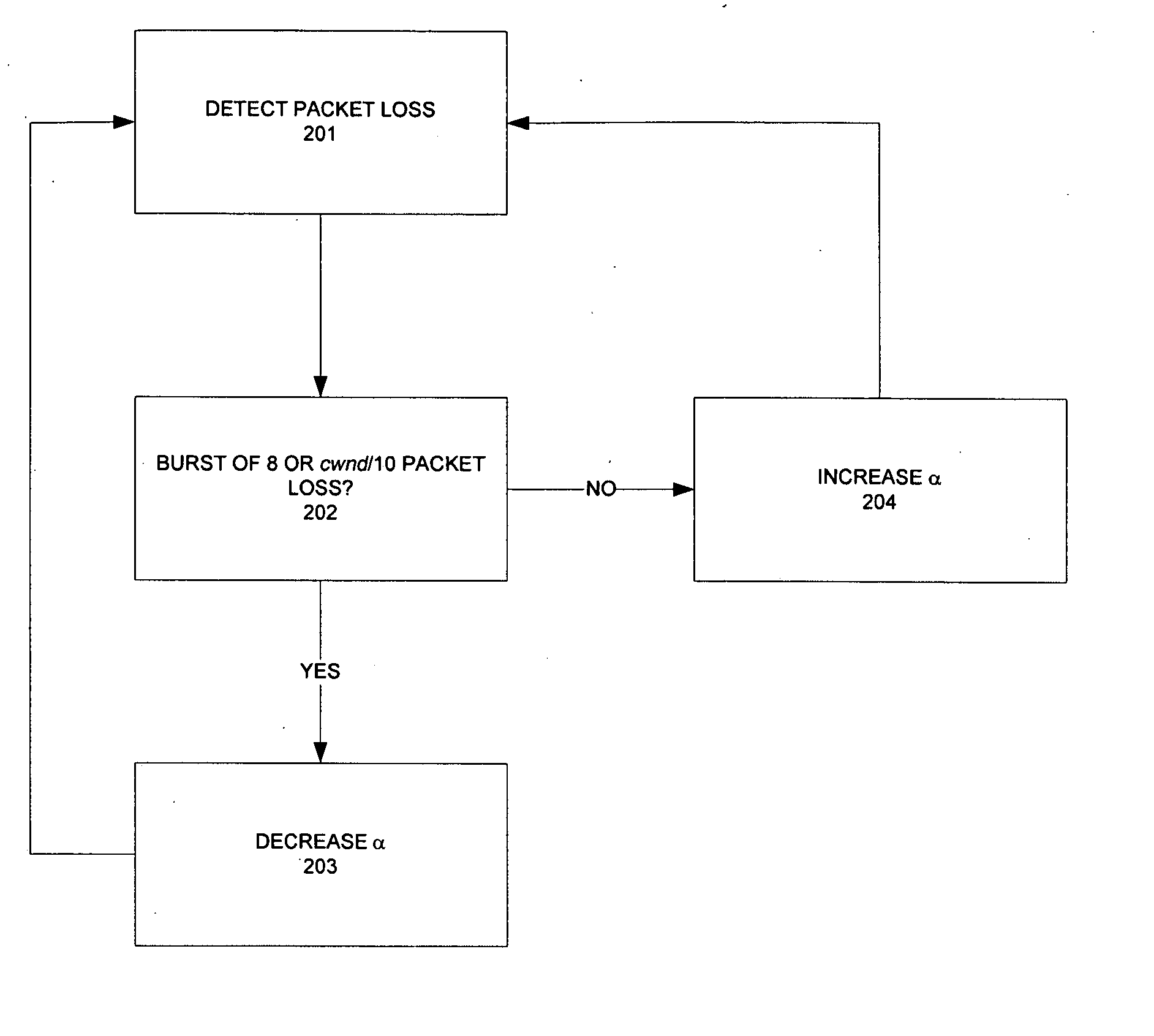
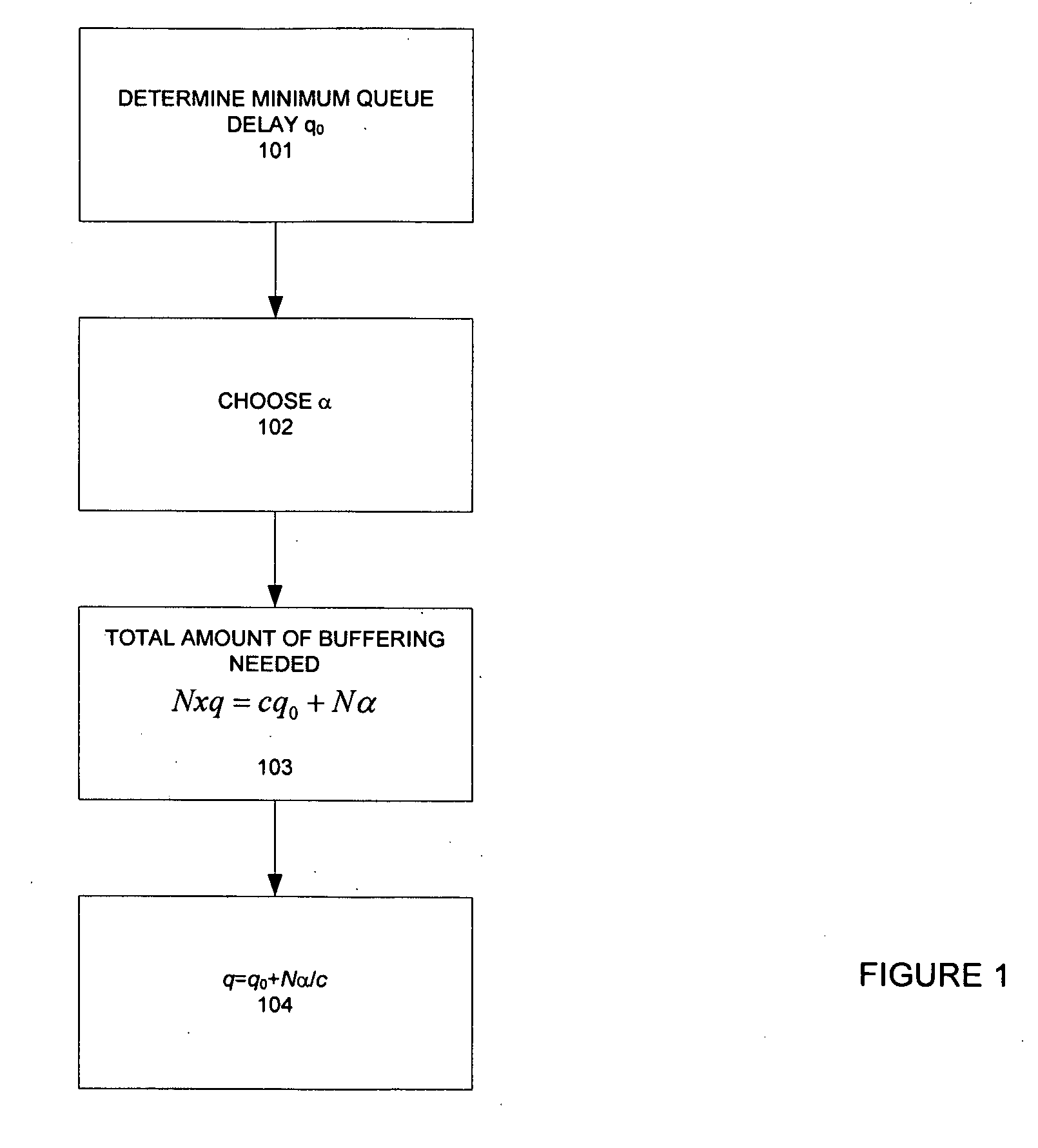
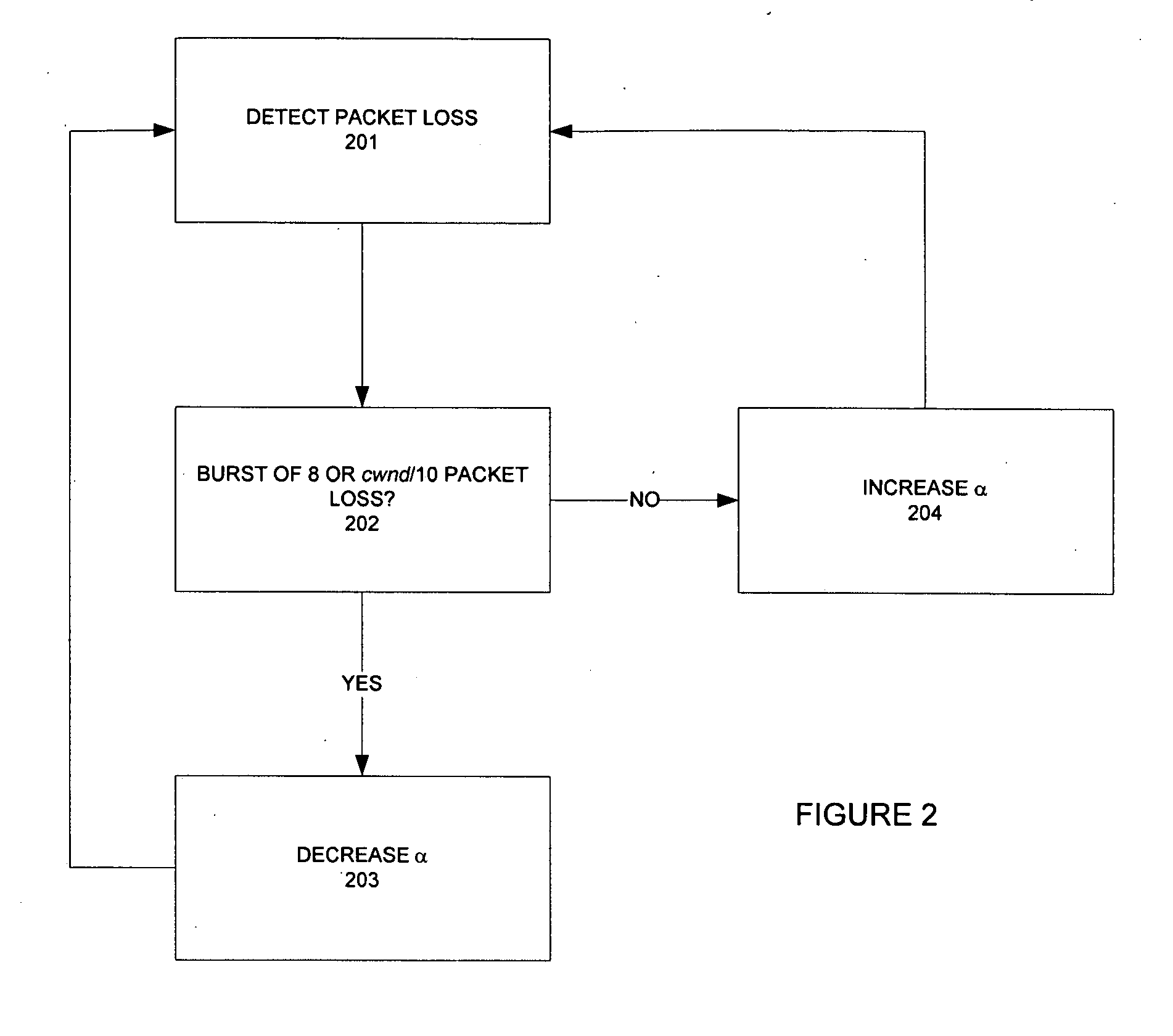
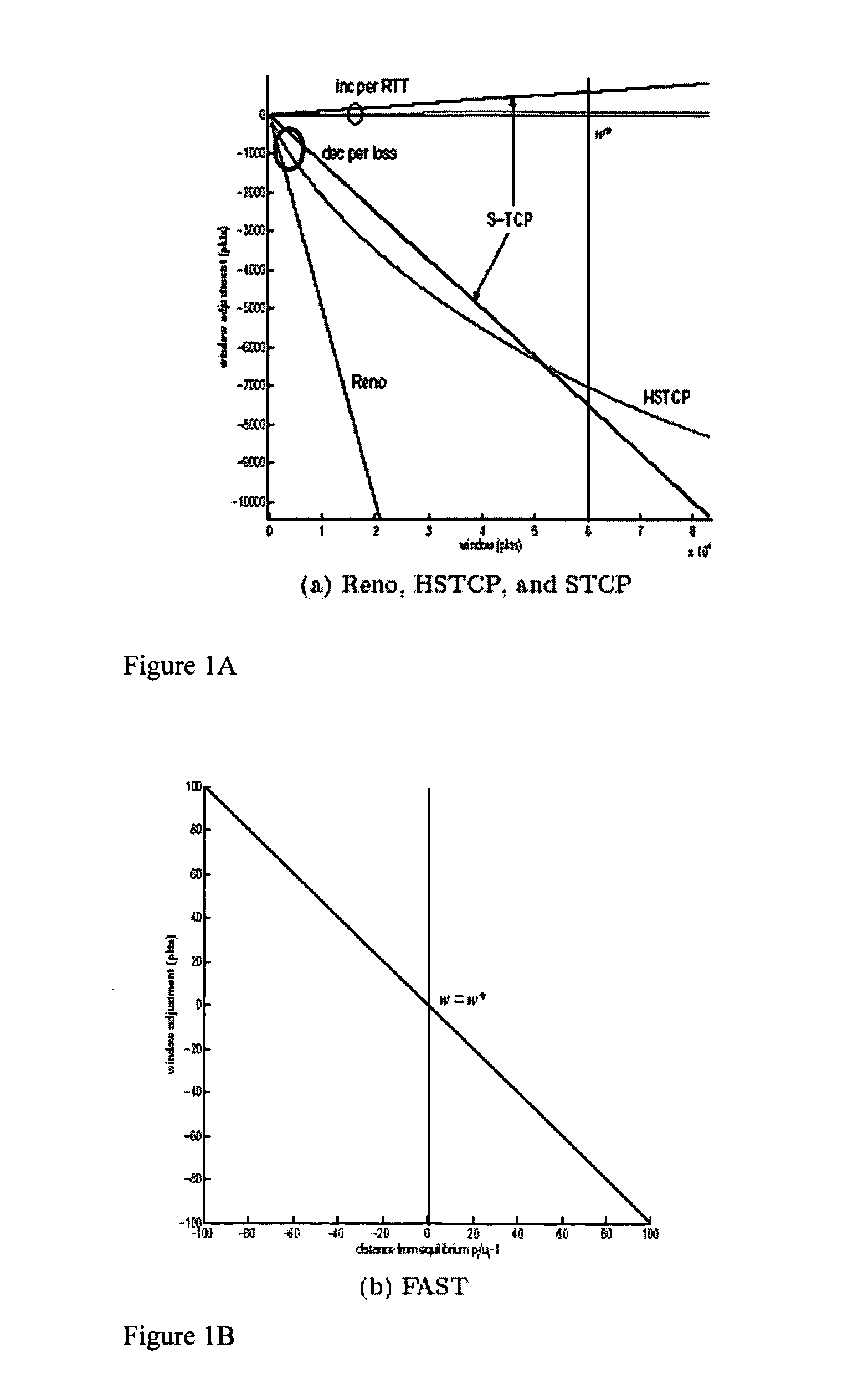
The invention provides a congestion control scheme that is a delay based scheme that includes a scalable queue size and one-way queueing delay measurement to reduce network congestion. Queue size is managed by queue control, a scalable utility function, dynamic alpha tuning, and / or randomized alpha tuning. One-way queueing delay is accomplished by measuring backward queueing delay management using various methods of estimating the receiver clock period. Embodiments include estimating the receiver clock period using single sample and multiple sample periods. The system includes a method for detecting route change.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for network congestion control
ActiveUS20050018617A1Maintain stabilityImprove overall utilizationError preventionTransmission systemsStable statePacket loss
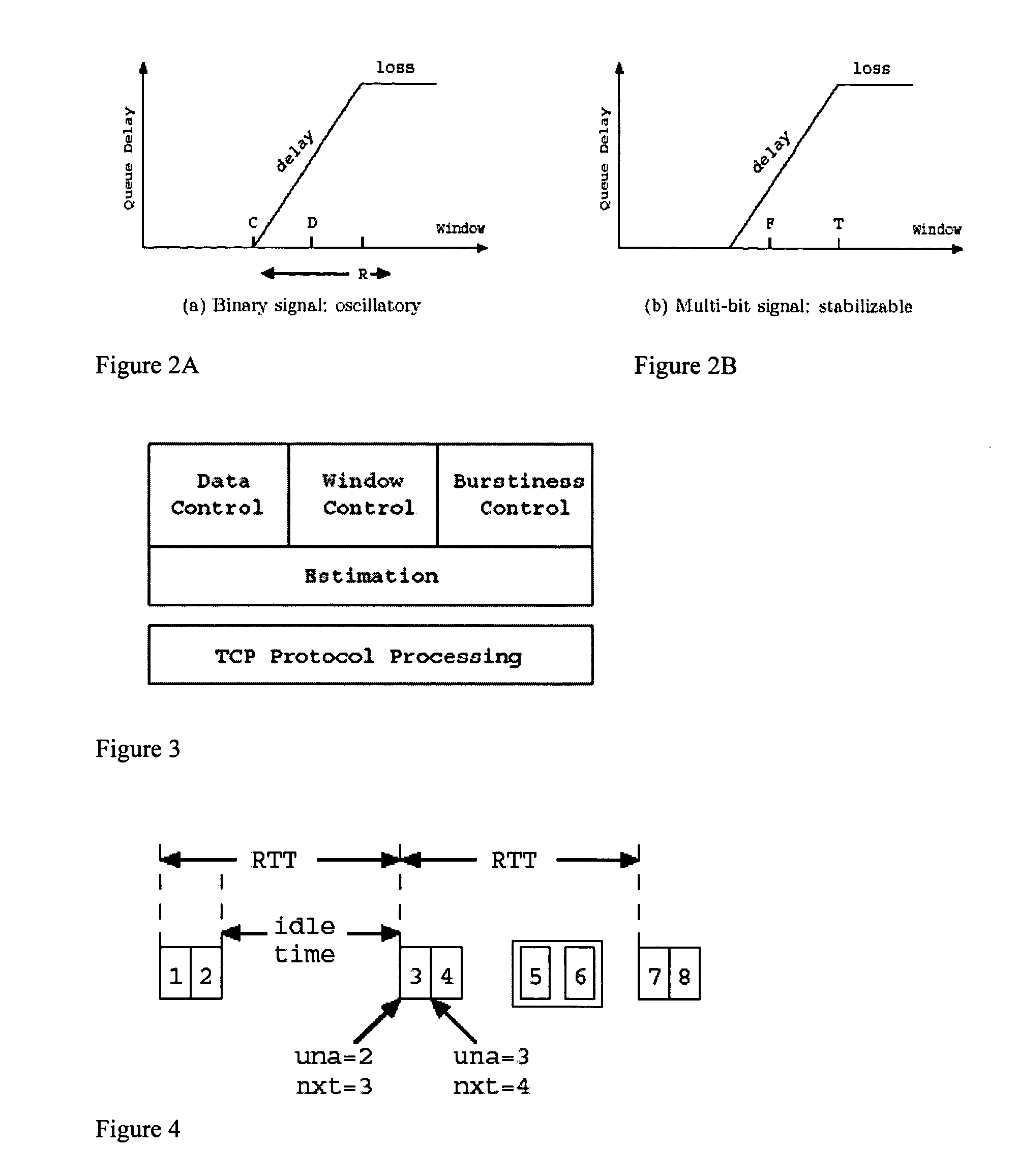
The present invention is a delay based model and in fact uses queueing delay as a congestion measure, providing advantages over prior art loss based systems. One advantage is that queueing delay can be more accurately estimated than loss probability. This is because packet losses in networks with large bandwidth-delay product are rare events under TCP Reno and its variants (probability on the order 10−7 or smaller), and because loss samples provide coarser information than queueing delay samples. Indeed, measurements of delay are noisy, just as those of loss probability. Thus, another advantage of the present invention is that each measurement of queueing delay provides multi-bit information while each measurement of packet loss (whether a packet is lost) provides only one bit of information for the filtering of noise. This makes it easier for an equation-based implementation to stabilize a network into a steady state with a target fairness and high utilization. In addition, the dynamics of queueing delay provides scaling with respect to network capacity. This helps maintain stability as a network scales up in capacity.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
System and method for clock synchronization over packet-switched networks
ActiveUS7551647B2Improve abilitiesEasy to replaceTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceThe Internet
Embodiments of the invention enable the synchronization of clocks across packet switched networks, such as the Internet, sufficient to drive a jitter buffer and other quality-of-service related buffering. Packet time stamps referenced to a local clock create a phase offset signal. A shortest-delay offset generator uses a moving-window filter to select the samples of the phase offset signal having the shortest network propagation delay within the window. This shortest network propagation delay filter minimizes the effect of network jitter under the assumption that queuing delays account for most of the network jitter. The addition of this filtered phase offset signal to a free-running local clock creates a time reference that is synchronized to the remote clock at the source thus allowing for the transport of audio, video, and other time-sensitive real-time signals with minimal latency.
Owner:QVIDIUM TECH
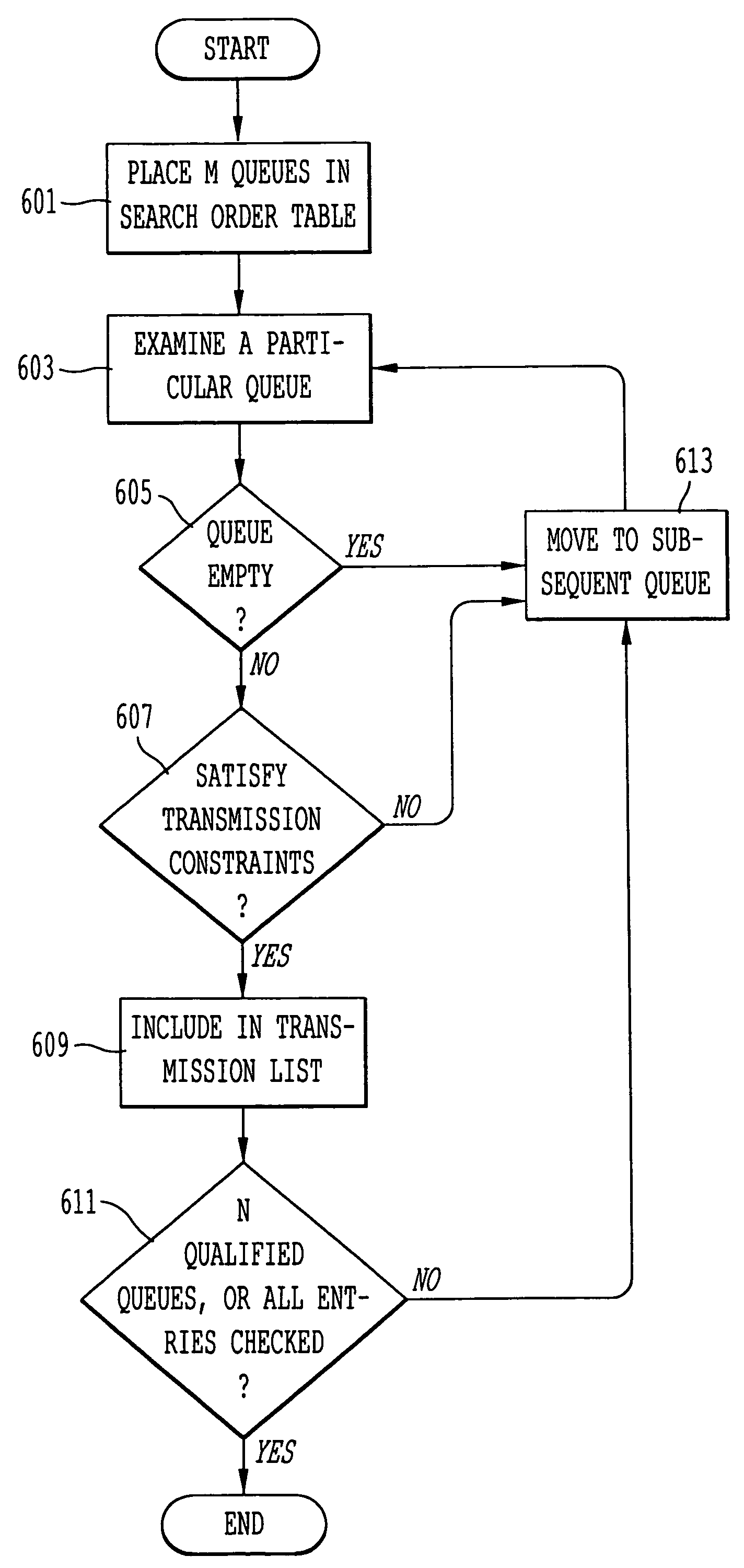
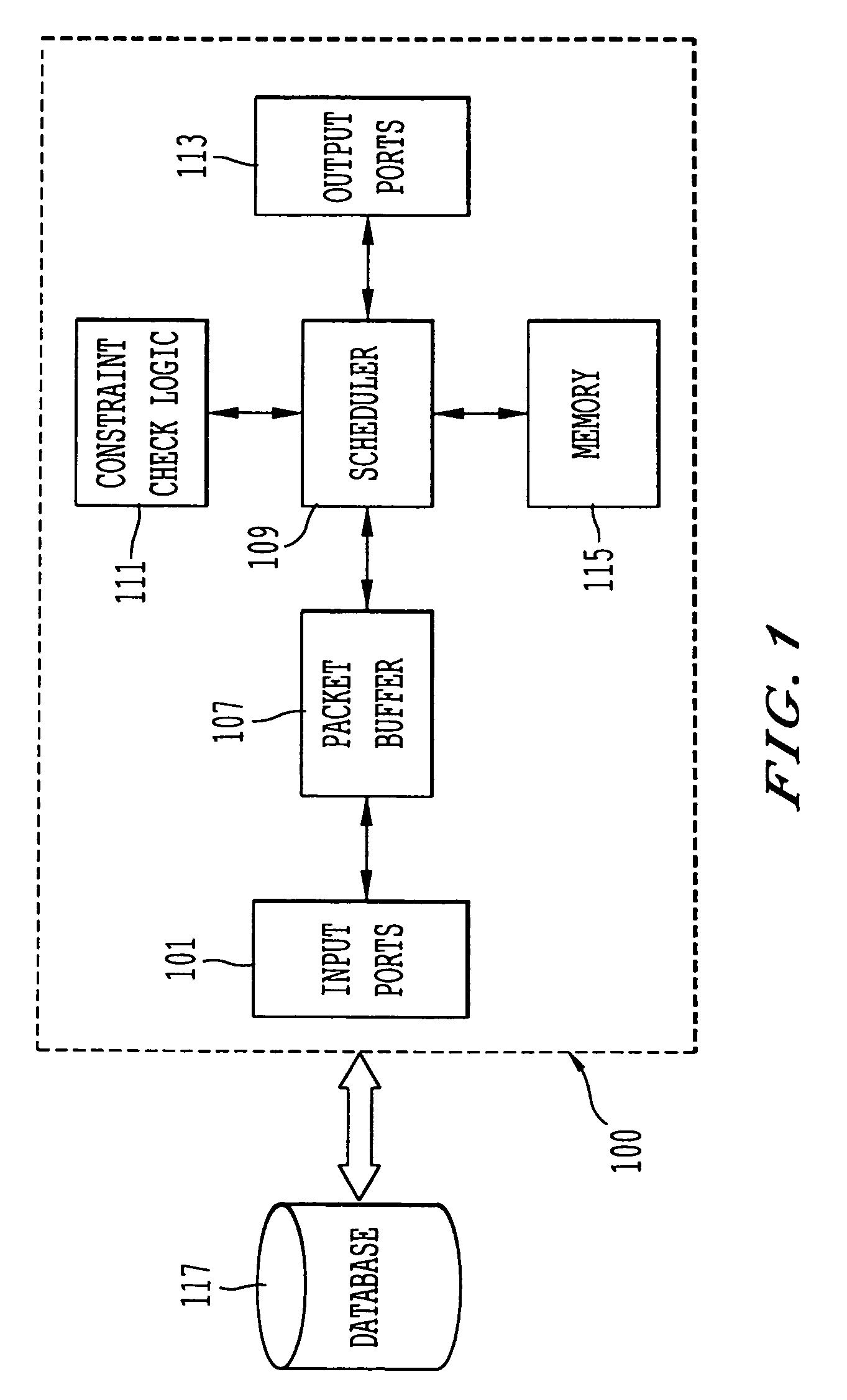
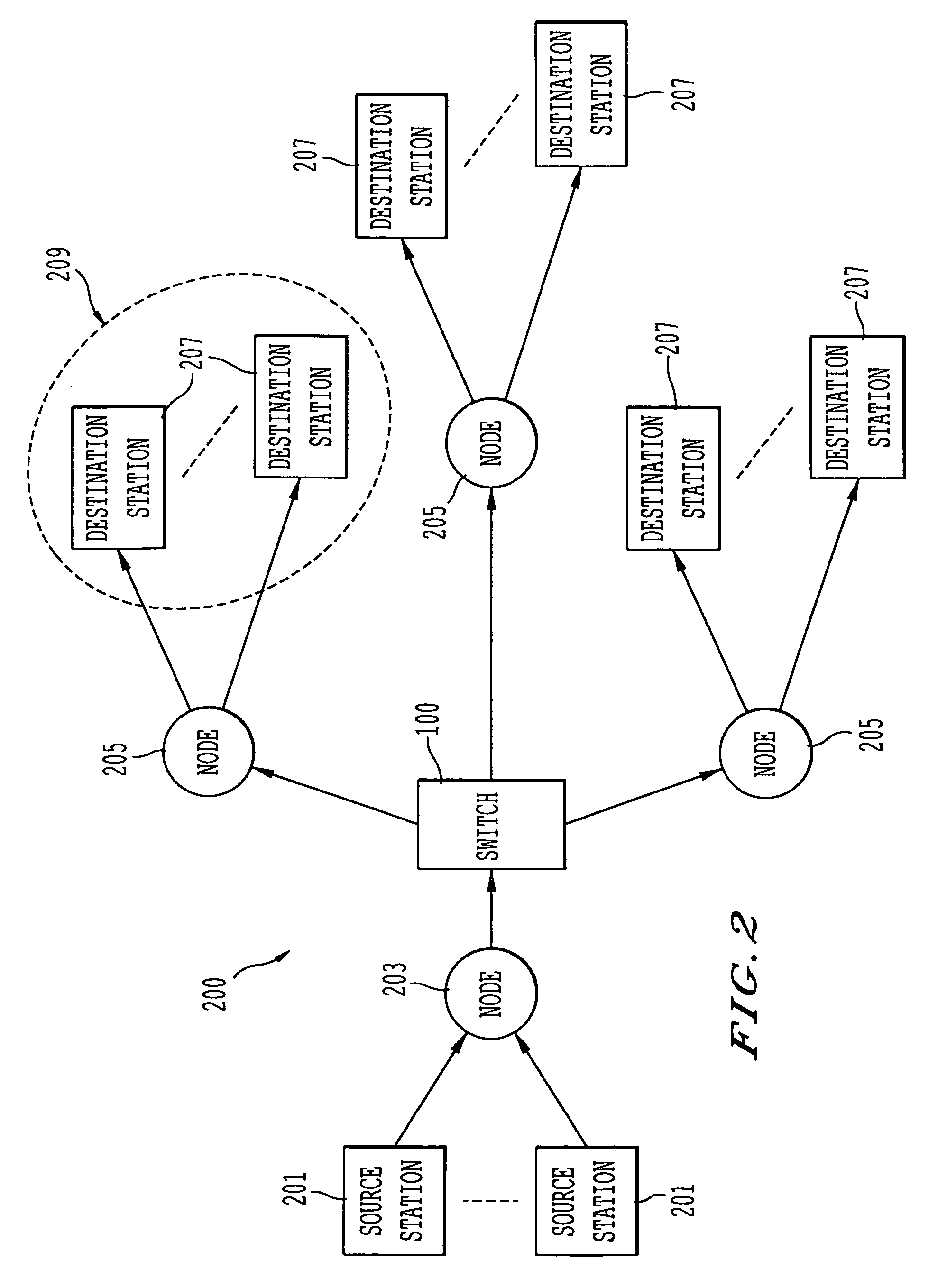
Approach to minimize worst-case queuing delay for a switching communication system with transmission constraints
InactiveUS7370116B2Minimize delayMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksCommunications systemReal-time computing
An approach for minimizing queuing delay of packets is disclosed. M number of queues are configured to store packets. A memory stores a search order table that has table entries corresponding to the M queues. Specifically, the table entries store values that correspond to relative positions of the M queues and that are selected based upon a transmission constraint of the communication system. A scheduler is coupled to the memory and is configured to schedule transmission of the packets stored in the M queues based upon the search order table. According to one embodiment of the present invention, this queuing mechanism is applied in a satellite communication system with transmission constraints to the downlink cells.
Owner:U S BANK NAT ASSOC
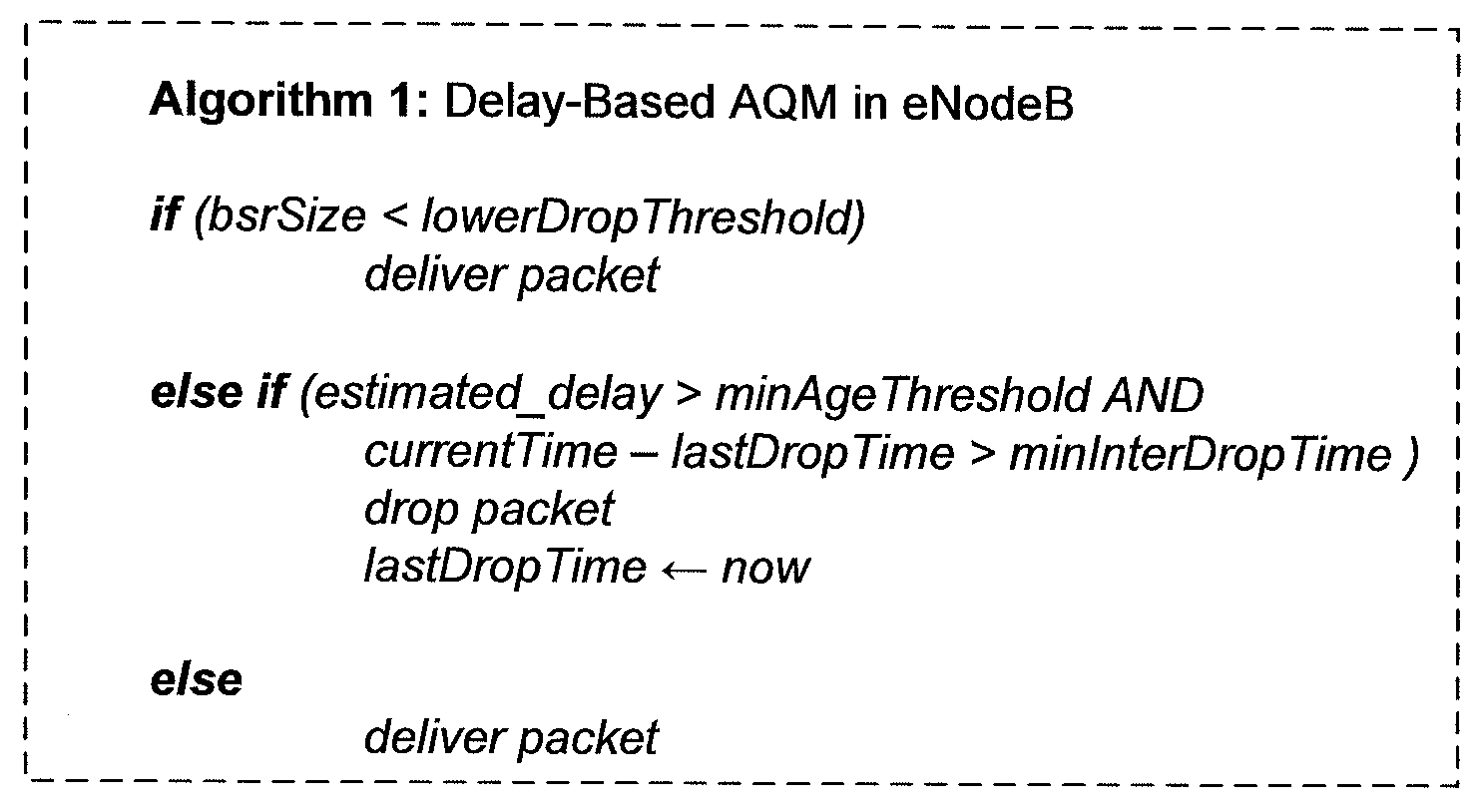
Active Queue Management for Wireless Communication Network Uplink
InactiveUS20120039169A1Process controlQueue size be smallError preventionTransmission systemsUplink transmissionComputer terminal
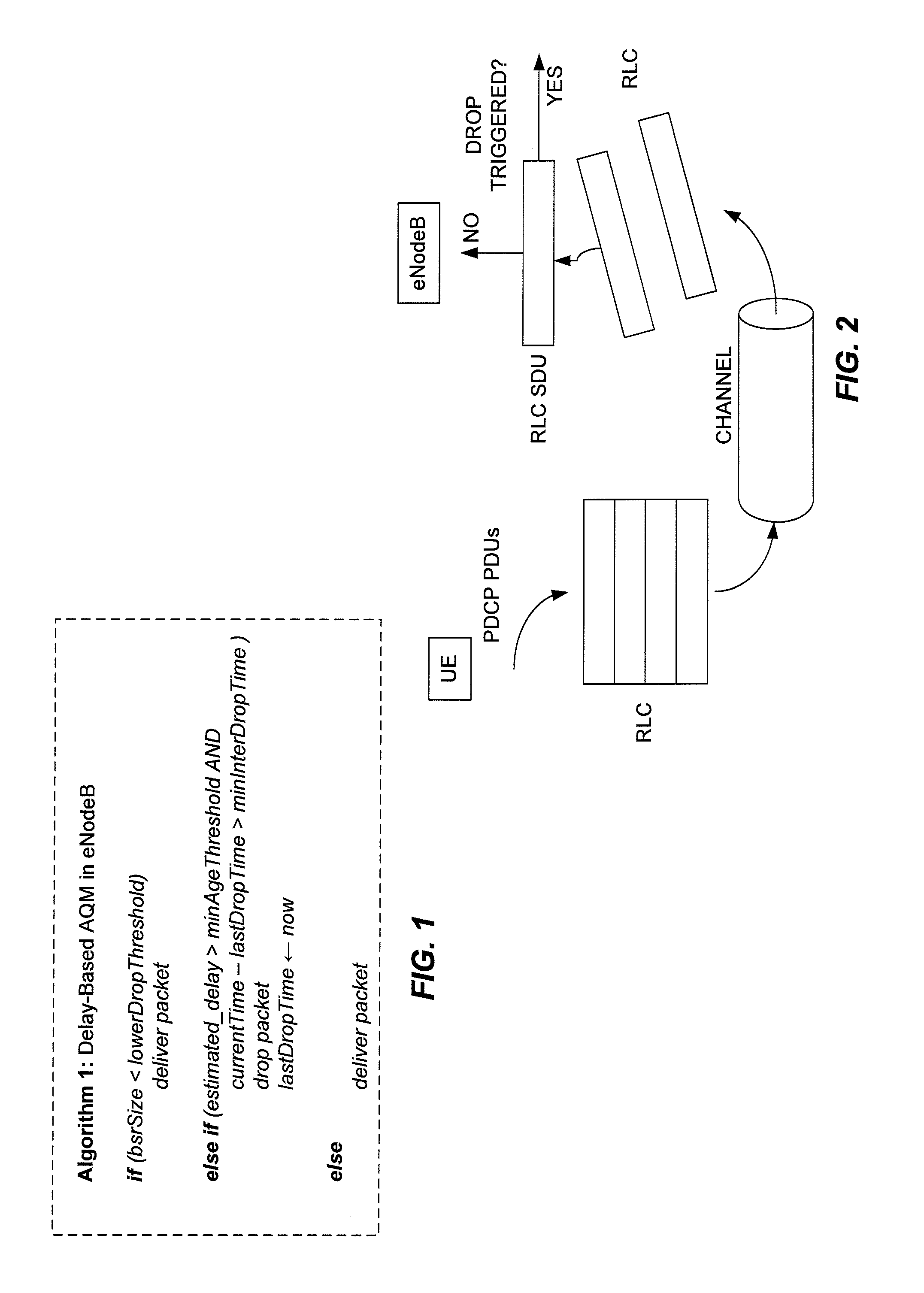
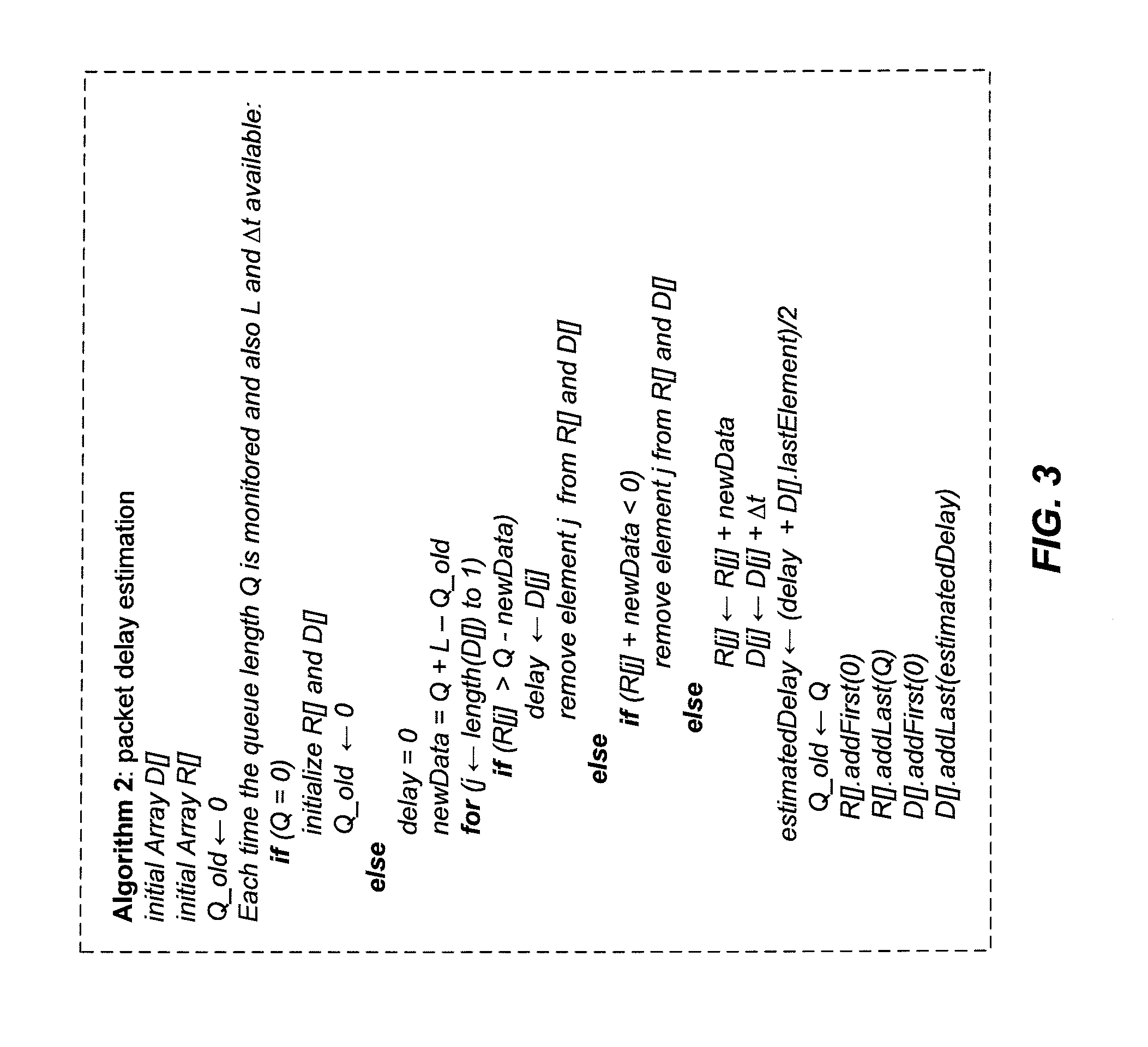
According to the teachings presented herein, a base station implements active queue management (AQM) for uplink transmissions from user equipment (UE), such as a mobile terminal. The base station, e.g., an eNodeB in a Long Term Evolution (LTE) network, uses buffer status reports, for example, to estimate packet delays for packets in the UE's uplink transmit buffer. In one embodiment, a (base station) method of AQM for the uplink includes estimating at least one of a transmit buffer size and a transmit buffer queuing delay for a UE, and selectively dropping or congestion-marking packets received at the base station from the UE. The selective dropping or marking is based on the estimated transmit buffer size and / or the estimated transmit buffer queuing delay.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
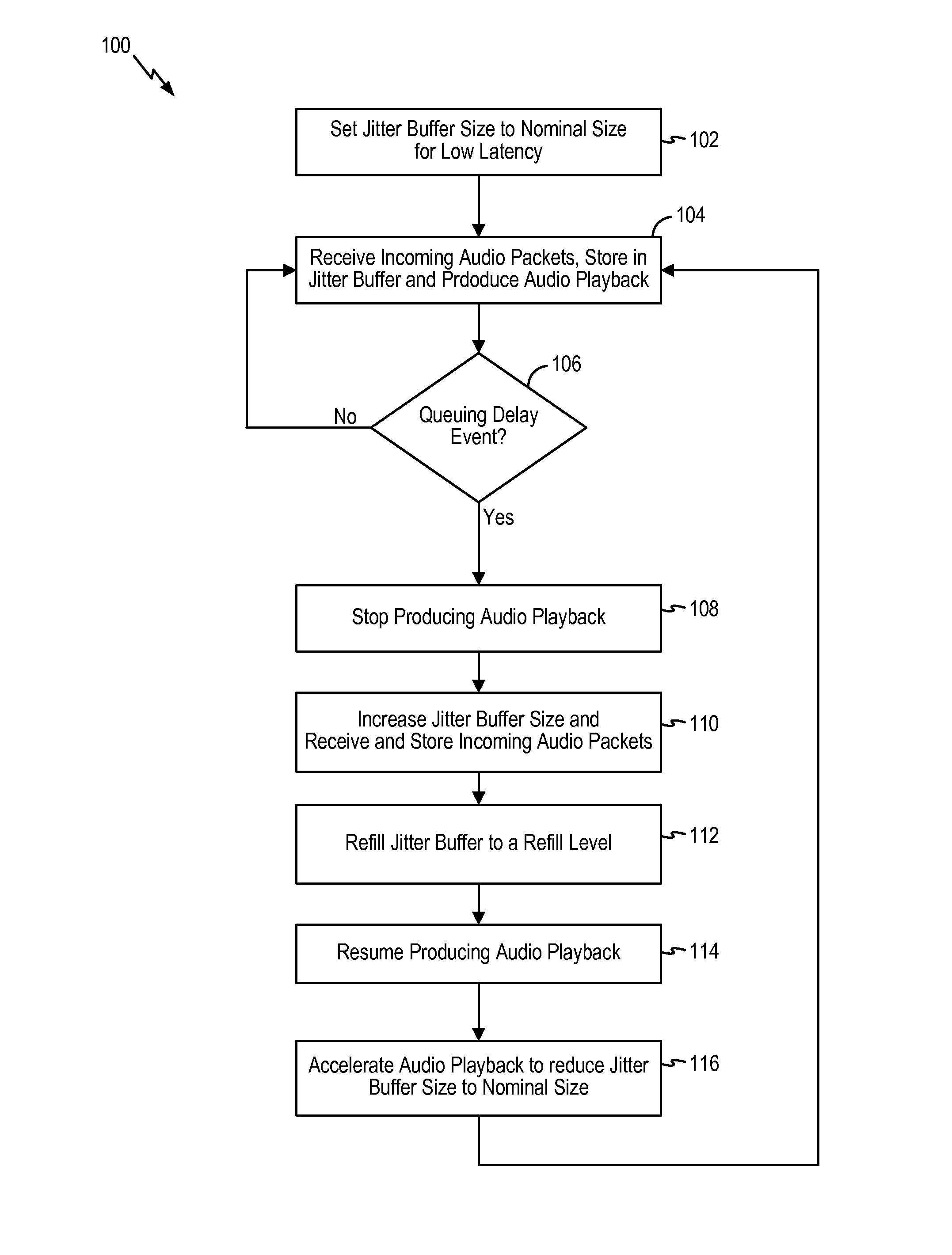
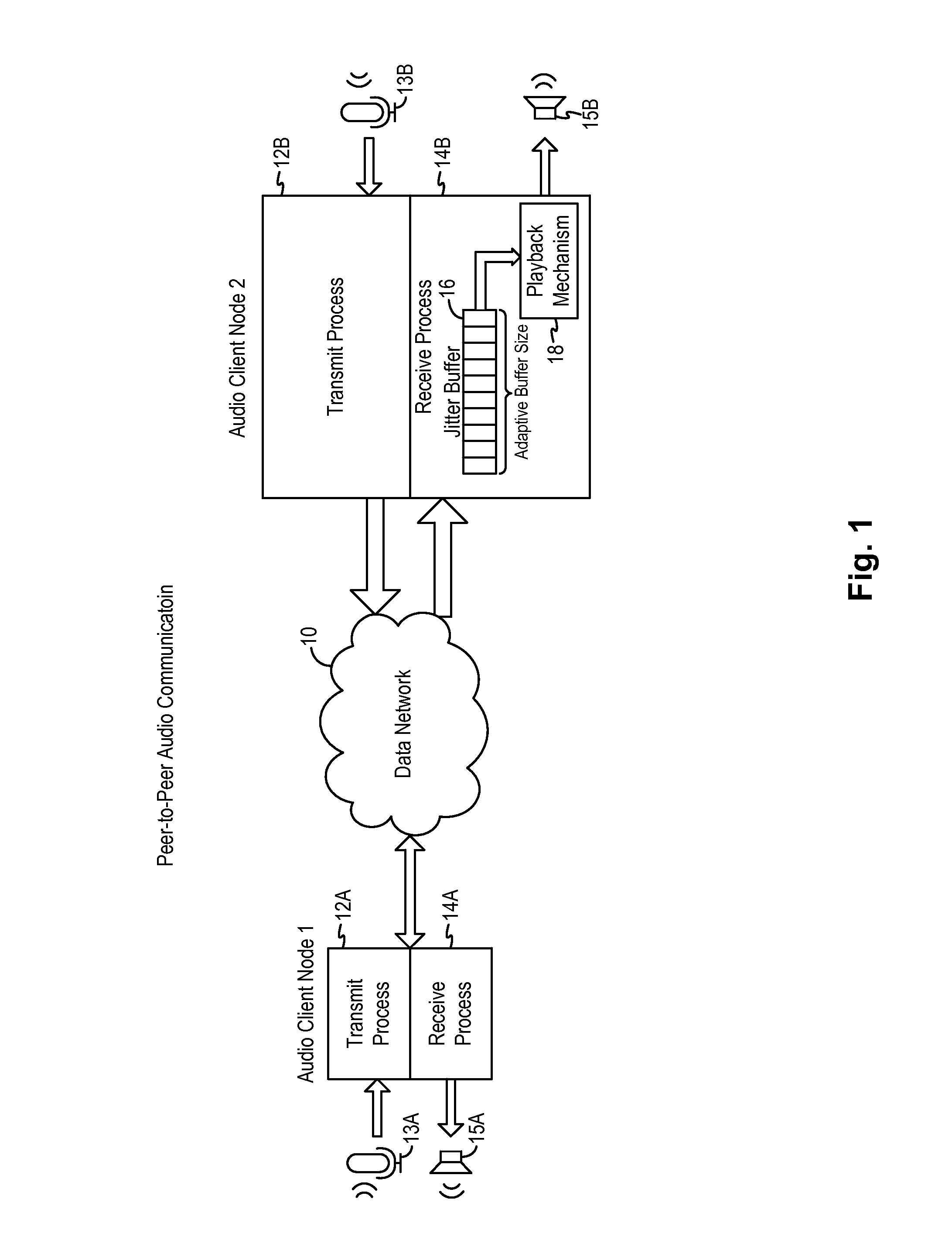
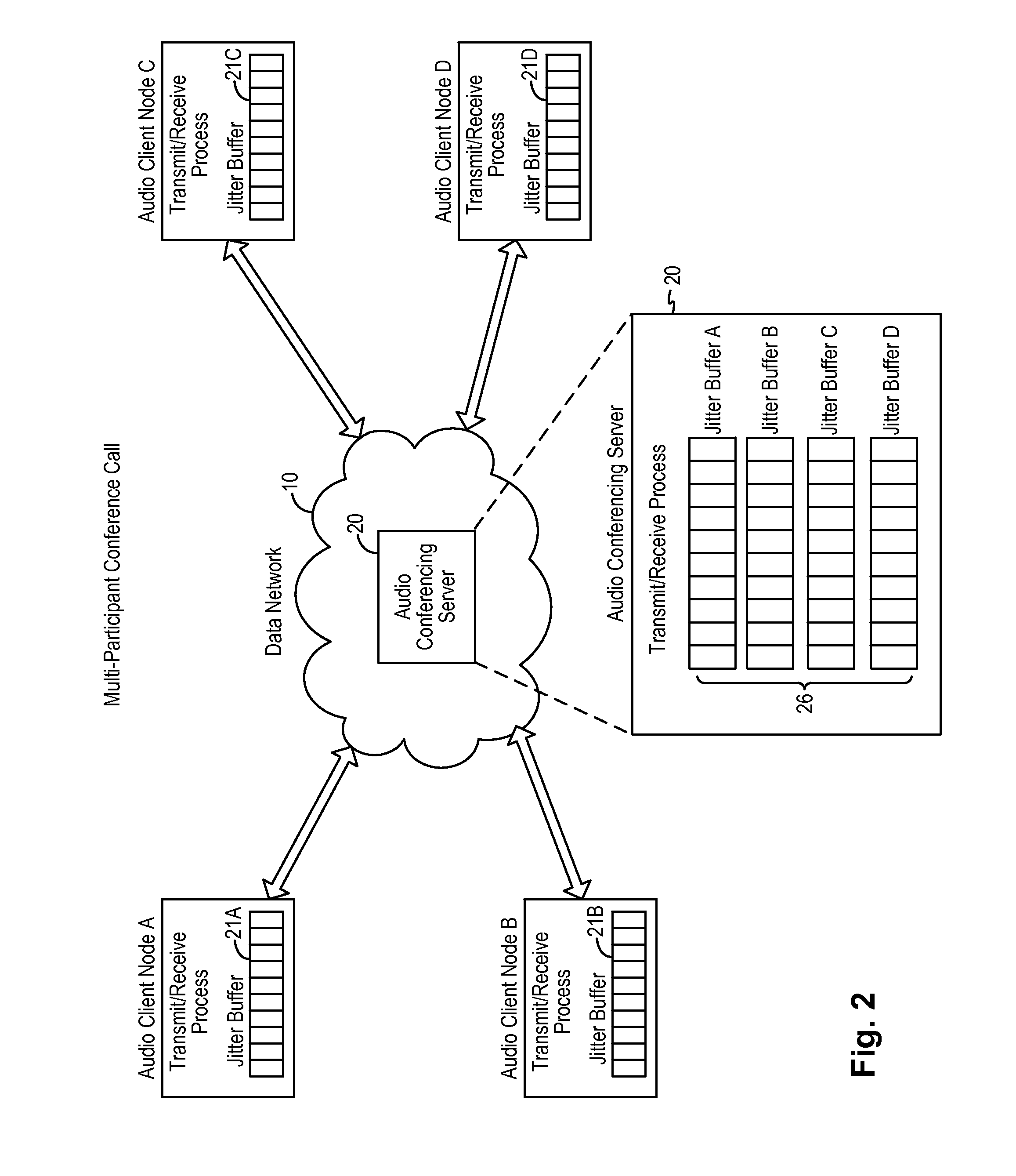
Adaptive audio stream with latency compensation
ActiveUS20160105473A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationUser devicePacket loss
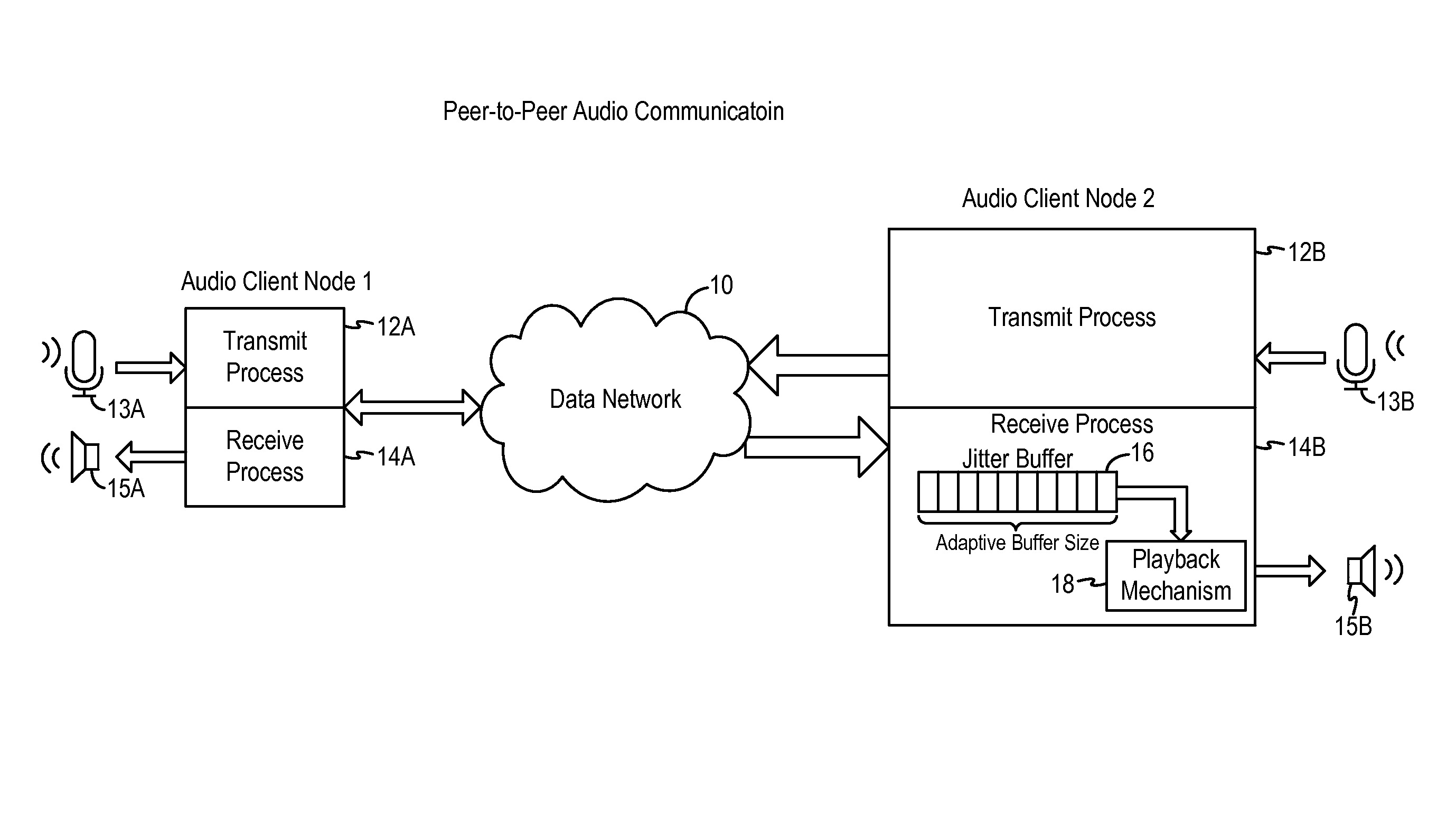
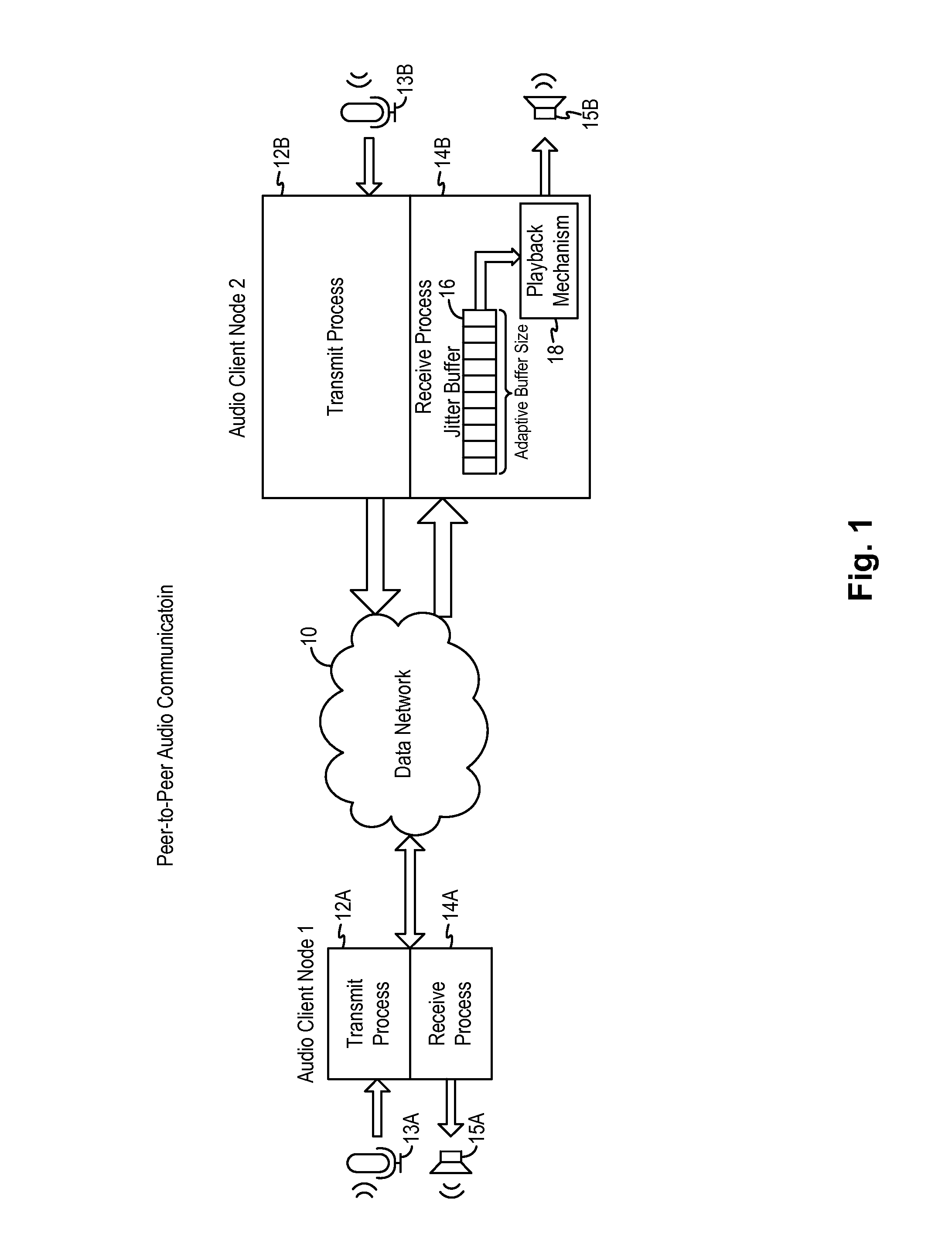
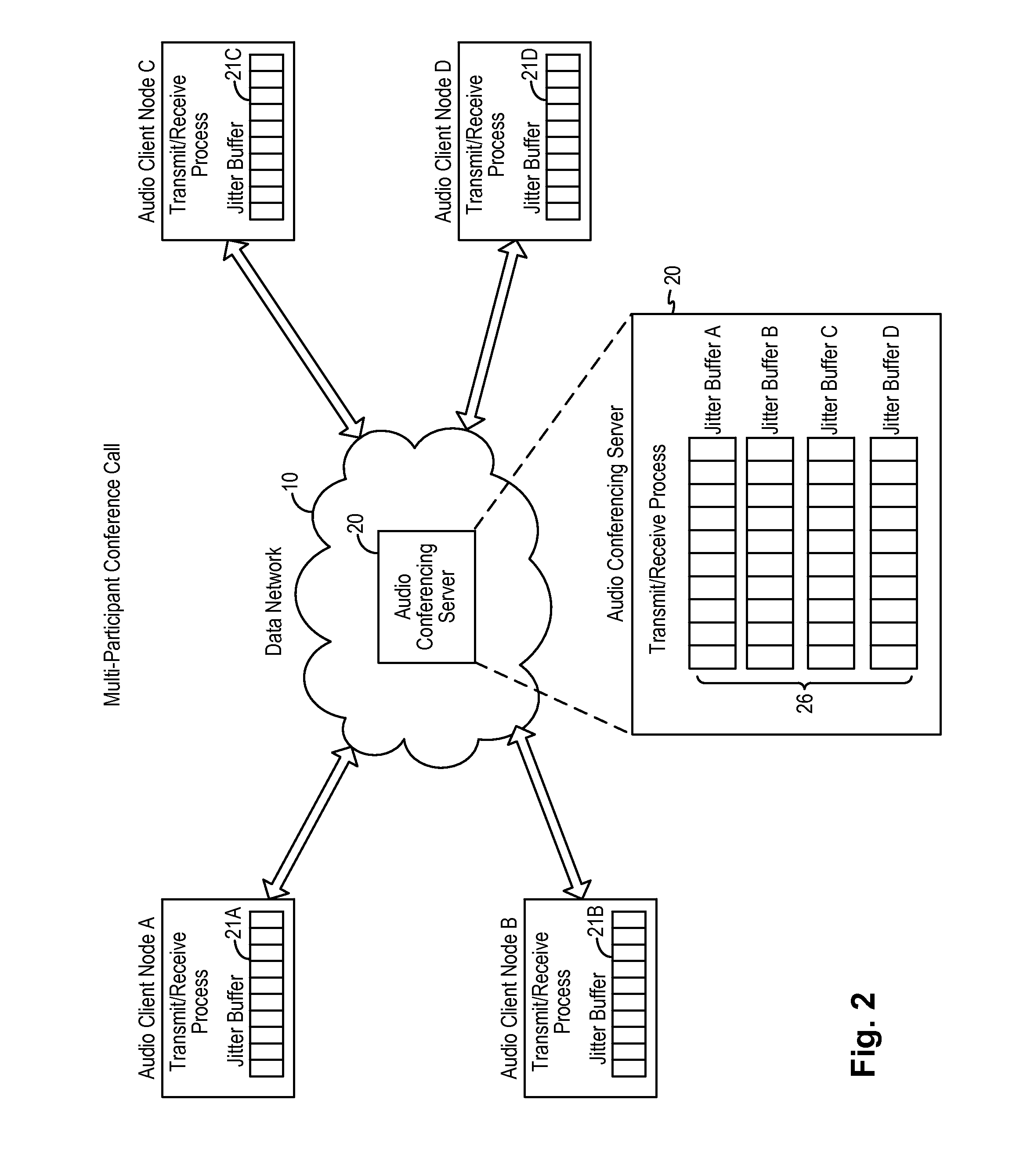
A latency compensating adaptive jitter buffer method is implemented in an audio client running on a user device or in an audio server to adaptively adjust the size of a jitter buffer to optimize latency while minimizing packet loss during audio signal transmission. In some embodiments, the jitter buffer is kept to a nominal size for low latency. In response to a queuing delay event being detected, audio production is temporarily stopped and the size of the jitter buffer is temporarily increased to receive all incoming audio packets up to a certain refill level. The method then resumes audio production using accelerated playback to reduce the jitter buffer size back to the nominal size.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Remote estimation of round-trip delays in a data network
Disclosed is a technique for data network congestion diagnosis using remote estimation of round-trip delays. A monitoring node transmits test messages between network nodes and measures the transit times between when the test messages are transmitted from, and when they return to, the monitoring node. A path delay between network nodes is determined based on the measured time delays. The techniques for determining network path delay are also utilized in conjunction with a three phase test procedure for diagnosing network congestion problems. Due to various network topologies and routing tables, certain confirmatory checks may be required to determine whether the procedures of the first or second phase test procedures are appropriate for particular path segments. Further, queuing delays may be determined by subtracting traffic independent delays from the measured transit times of the test messages, and such queuing delays may be used to determine the path delays. Such traffic independent delays may be determined during periods of low network traffic.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
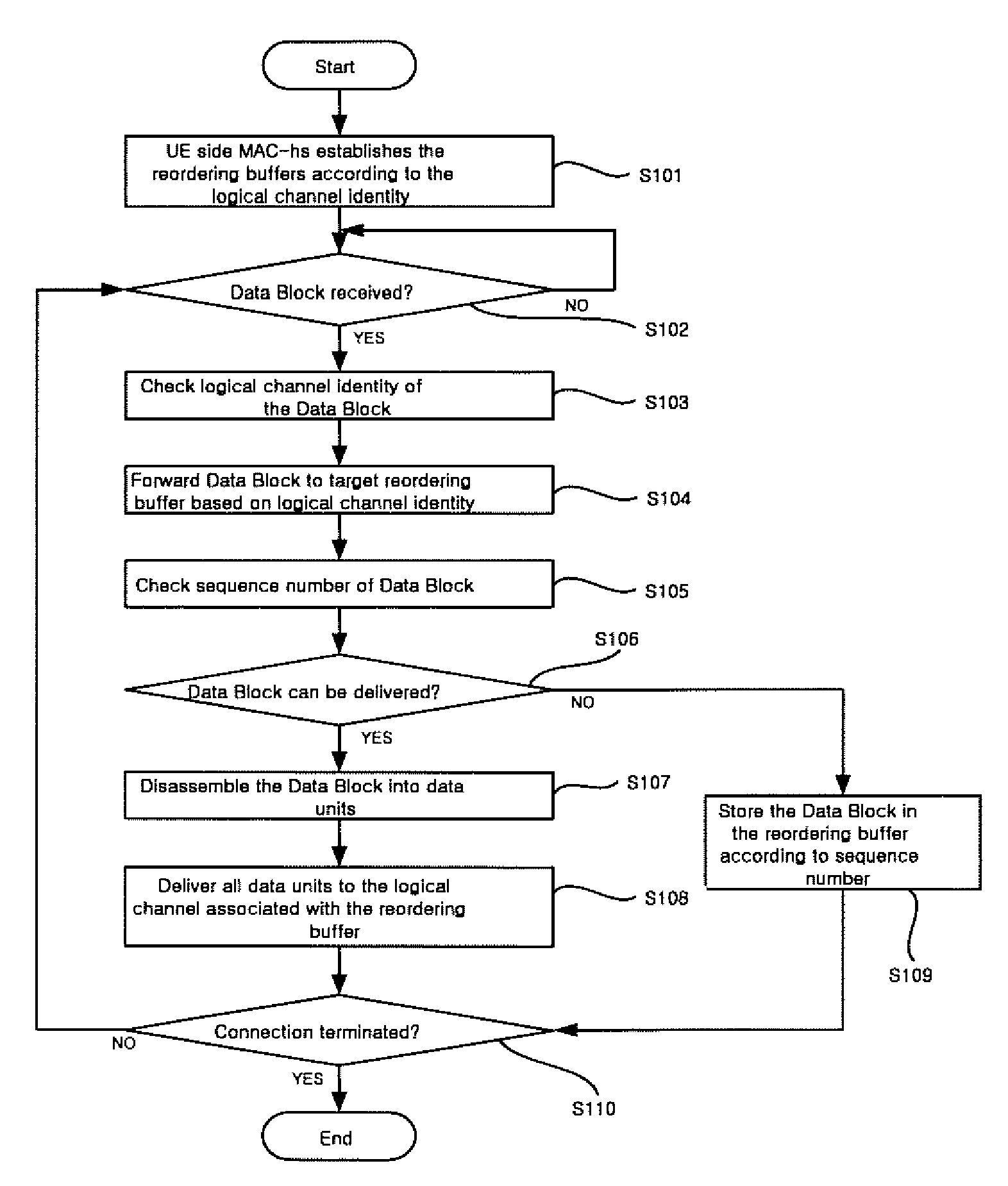
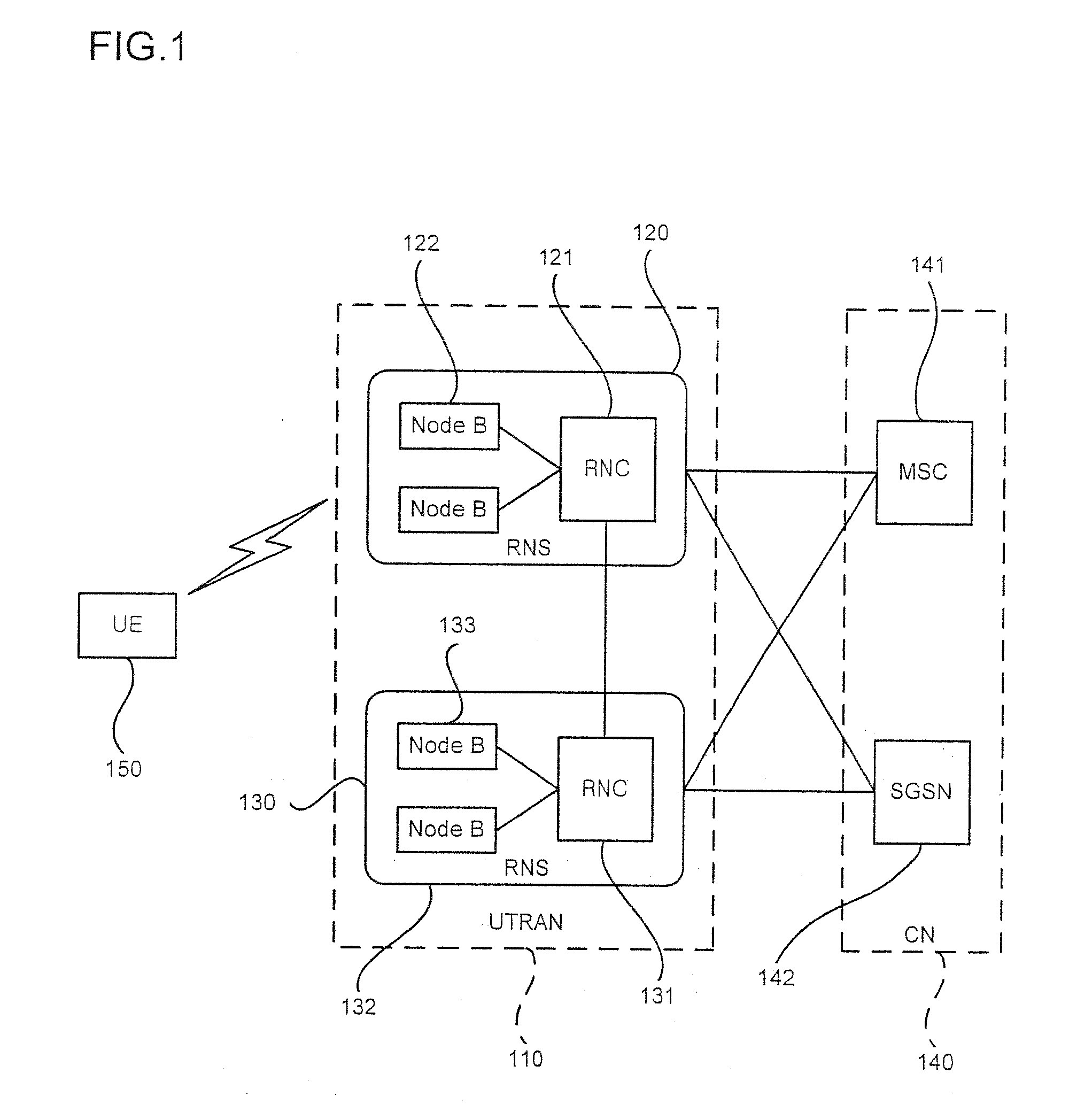
Data transmission method for HSDPA
ActiveUS7403541B2Delay minimizationFacilitate transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexMultiplexingData transmission
In the data transmission method of an HSDPA system according to the present invention, a transmitter transmits Data Blocks each composed of one or more data units originated from a same logical channel, and a receiver receives the Data Block through a HS-DSCH and distributes the Data Block to a predetermined reordering buffer. Since each Data Block is composed of the MAC-d PDUs originated from the same logical channel, it is possible to monitor the in-sequence delivery of the data units, resulting in reduction of undesirable queuing delay caused by logical channel multiplexing.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
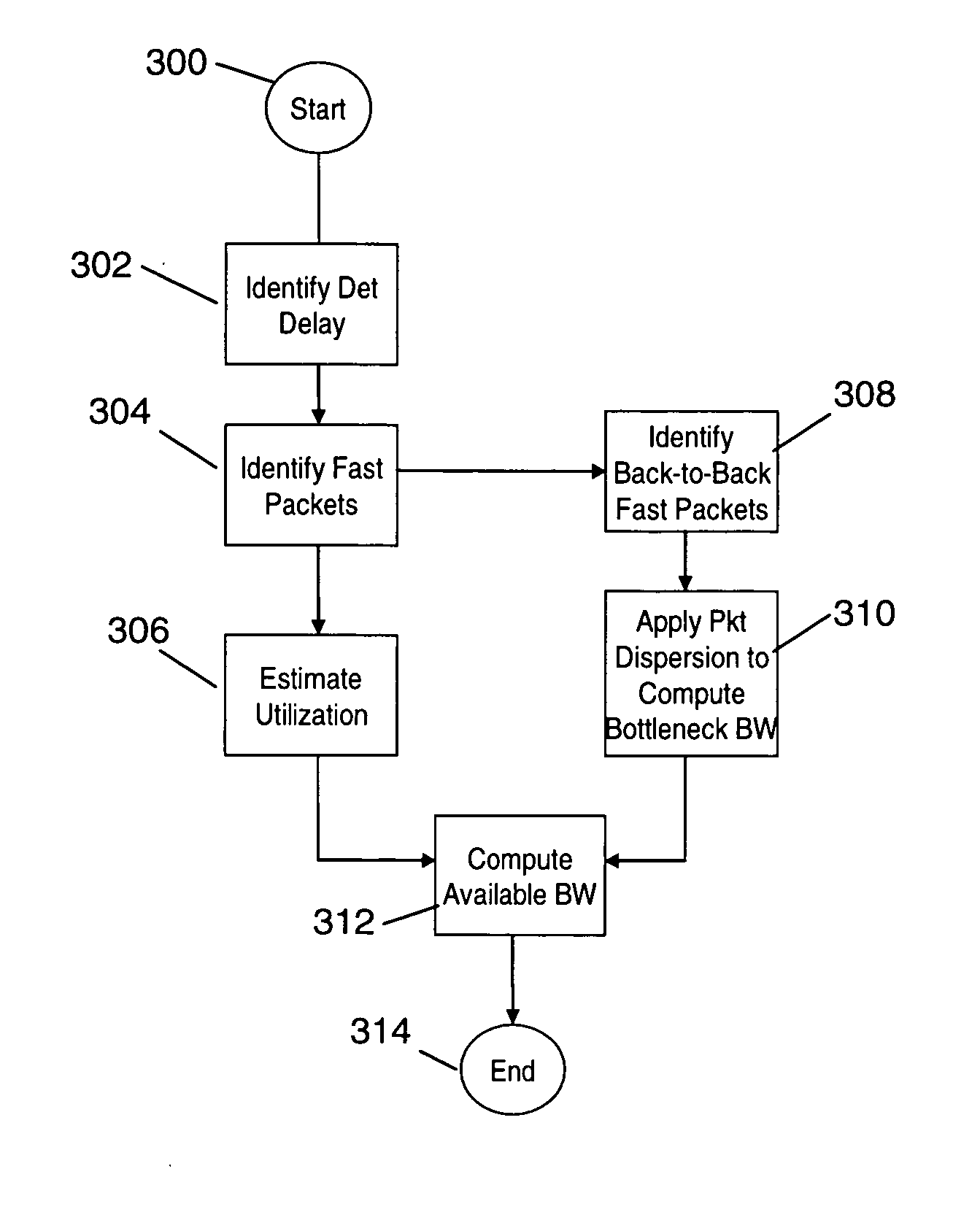
Estimating available bandwith and enhancing narrow link bandwith estimations in telecommunications networks using existing user traffic
ActiveUS20070242616A1Reduce uncertaintyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPropagation delayTelecommunications network
Without using additional probing packets, estimates of the narrow link bandwidth and available bandwidth of a network path are computed based on existing traffic. The network can be of different types such as a wireless battlefield network context or a wired or wireless commercial network environment. “Fast packets”, i.e. those packets which do not experience any queuing delay in the network, are identified. Fast packets are identified to resolve end-to-end packet delay into its constituent components (deterministic, transmission and queuing delays), estimate path utilization and eliminate the uncertainty (false alarms) that causes the prior art method to lose its effectiveness. An estimation algorithm computes end-to-end transmission delay and end-to-end deterministic delay of fast packets traveling along a path in a network. Examples of deterministic delay include satellite propagation delays and clock effects. Then, based on the results of the fast packet identifying algorithm, two logic branches are followed. A first branch calculates utilization and a second branch calculates narrow link bandwidth. The narrow link bandwidth is determined from the packet pair dispersion. The available bandwidth is obtained from the narrow link bandwidth and the utilization. Estimation of available bandwidth for an end-to-end network path allows traffic sources to judiciously regulate the volume of application traffic injected into the network.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
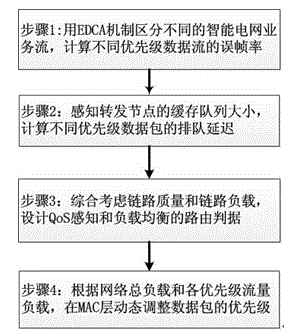
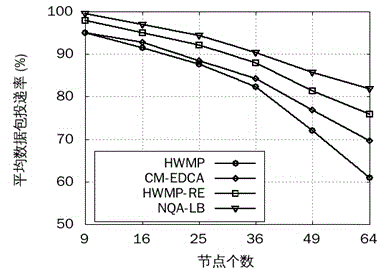
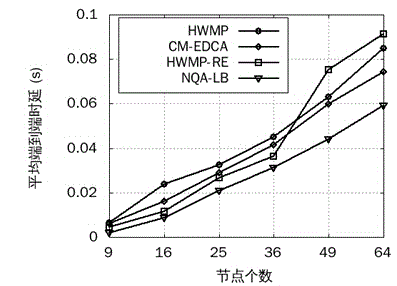
Wireless Mesh intelligent power grid routing mechanism with QoS perceiving and loading balancing
ActiveCN104661260AReduce end-to-end latencyImprove delivery rateNetwork traffic/resource managementHigh level techniquesService flowPacket collision
The invention provides a wireless Mesh intelligent power grid routing mechanism NQA-LB with QoS perceiving and loading balancing. The mechanism comprises four steps: firstly differentiating intelligent power grid service flows with different QoS requirements through an EDCA mechanism, and calculating the frame error rate of different service flows according to the data packet collision rate of the EDCA mechanism; secondly, calculating data packet queuing delay with different priorities of the queue length of forwarding node cache and the successful transmission probability of data packets; then designing the routing metric of QoS perceiving and loading balancing by comprehensively considering the data frame error rate and queuing delay of different service flows, and selecting an optimal path with less load for the service flow with different QoS demands; finally dynamically adjusting the data packet priority on an MAC layer according to network total loading and loading conditions of all priority service flows. The mechanism can more accurately perceive the link quality of the MAC layer, guarantees the QoS demands of different service flows of a power grid, further increases the data packet delivery rate and average throughput capacity, and reduces the end-to-end delay of all service flows.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Queuing delay based rate control
InactiveUS7706403B2Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexQuality of serviceTelecommunications link
A method and apparatus for rate control adjusts or otherwise requests adjustment of a communication link data rate based on transmit queuing delays. For example, a mobile station may monitor expected transmit queuing delays relative to one or more delay targets or other Quality-of-Service constraints, and request reverse link rate increases or decreases accordingly. Similarly, the mobile station may be configured periodically to request reverse link rate changes based on determining the rate needed to meet targeted queuing delays for one or more service instances being supported by the mobile station in each of a succession of ongoing rate control intervals. Requested rates may be defined data rates or may be virtual rates that can be achieved by using combinations of defined data rates. Queuing-based rate control also can be applied to the base station's forward link, and, more broadly, to essentially any rate controlled communication link.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
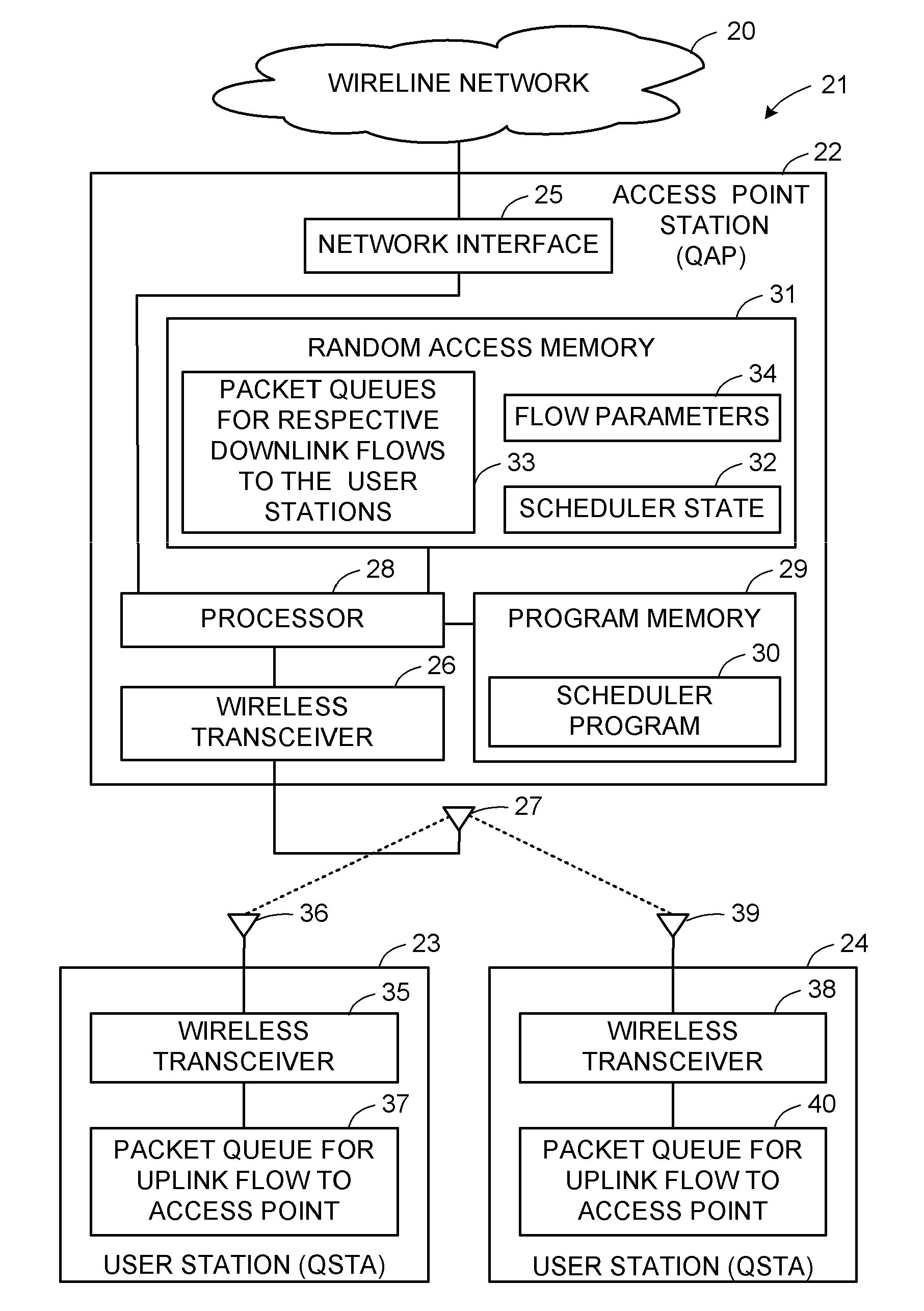
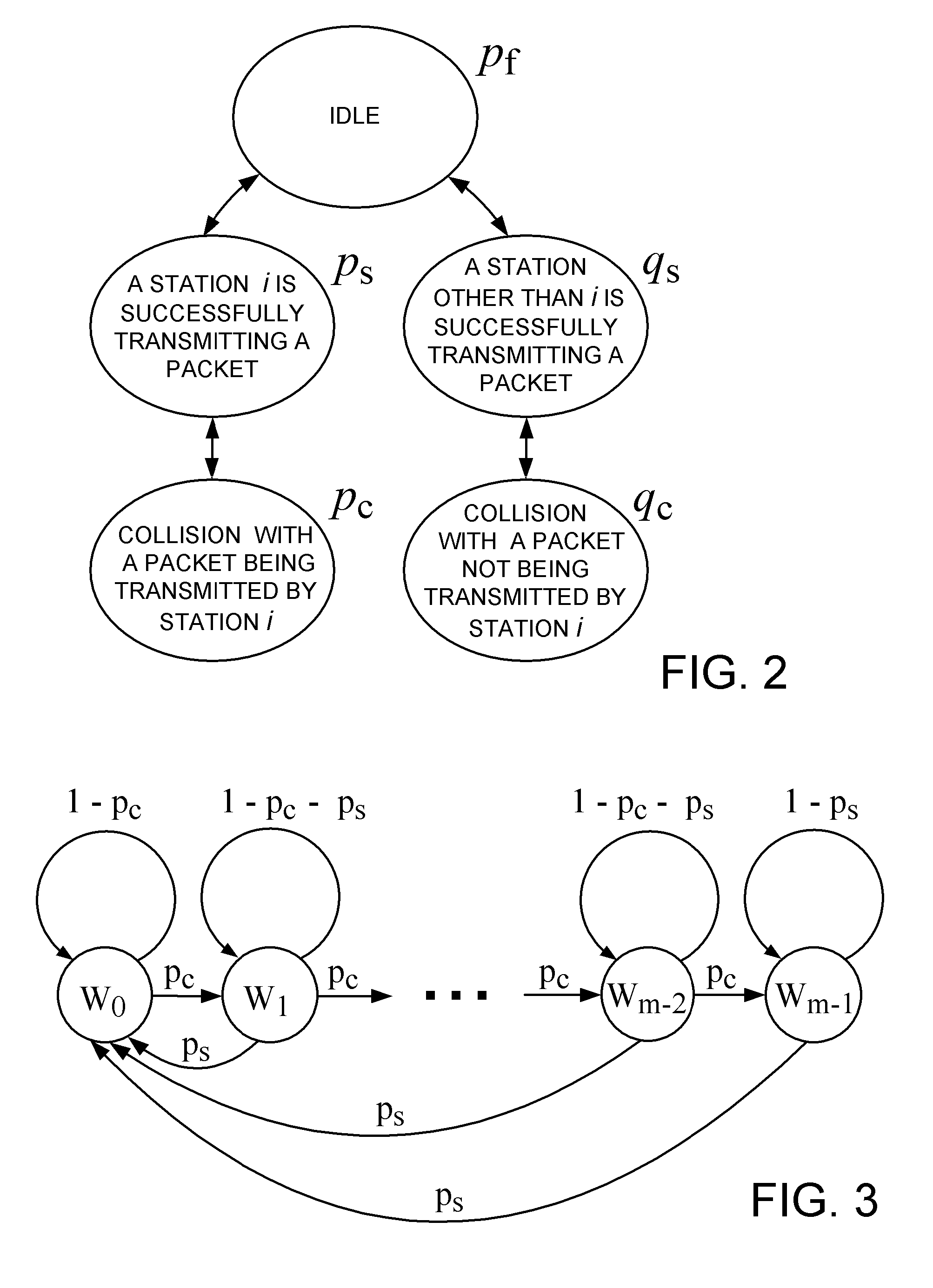
An admission control for contention-based access to a wireless communication medium
ActiveUS20070070902A1Difficult problemIncreasing WLAN data throughput and qualityError preventionTransmission systemsSuccessful transmissionWireless transmission
An access point station responds to a request from a user station for contention-based access of a new traffic flow to a wireless transmission medium by applying a model of the wireless local area network to estimate delay that data packets will experience when delivered through the wireless network, in order to admit the new flow upon determining that admission will not violate quality of service requirements of neither the new flow nor of already admitted flows. For example, the access point station applies the model by determining an average packet inter-arrival rate, solving a system of nonlinear equations to determine probabilities of successful transmission, applying network stability conditions, computing an upper bound on queuing delay for the packets, computing a service delay budget for the packets, and computing an expected fraction of missed packets from the service delay budget.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Method for optimal path selection for data traffic undergoing high processing or queuing delay
ActiveUS20200220805A1Facilitate communicationReduce in quantityData switching by path configurationData packPathPing
Described embodiments provide systems and methods for path selection proportional to a penalty delay in processing packets. A server-side intermediary may identify a delay penalty for processing packets of a server destined for a client. The server-side intermediary may be in communication via links of different latencies with a client-side intermediary. The server-side intermediary may select a second link with a latency that deviates from the lowest latency of a first link by the delay penalty. The server-side intermediary may transmit, to the client-side intermediary, duplicates of the packets via the selected second link with information indicating to hold the duplicates at the client-side intermediary. The server-side intermediary may receive an indication to drop or send the duplicates to the client. The server-side intermediary may transmit the indication to the client-side intermediary to drop or send the duplicates according to the indication.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Adaptive audio stream with latency compensation
A latency compensating adaptive jitter buffer method is implemented in an audio client running on a user device or in an audio server to adaptively adjust the size of a jitter buffer to optimize latency while minimizing packet loss during audio signal transmission. In some embodiments, the jitter buffer is kept to a nominal size for low latency. In response to a queuing delay event being detected, audio production is temporarily stopped and the size of the jitter buffer is temporarily increased to receive all incoming audio packets up to a certain refill level. The method then resumes audio production using accelerated playback to reduce the jitter buffer size back to the nominal size.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Ramp control method for multiple lanes of expressway based on density
ActiveCN106710245AEasy accessImprove stabilityControlling traffic signalsData acquisitionDensity based
The invention discloses a ramp control method for multiple lanes of an expressway based on density, which belongs to the technical field of traffic information. Firstly, ramp traffic and mainline traffic are considered, and the density parameters of ramp traffic and mainline traffic are simultaneously integrated in a control target. Thus, the mainline traffic flow is the largest, and the problems of long queue on the ramp and big queuing delay are solved. Secondly, density instead of occupancy and traffic is directly selected as a control parameter, so that convenient data acquisition and unique description of traffic are realized. Thirdly, the difference between multiple lanes in traffic flow characteristic and the lane-changing behaviors of vehicles are fully considered, the traffic state is accurately judged from a more micro perspective, and therefore, the effect of ramp control is improved.
Owner:四川易方智慧科技有限公司
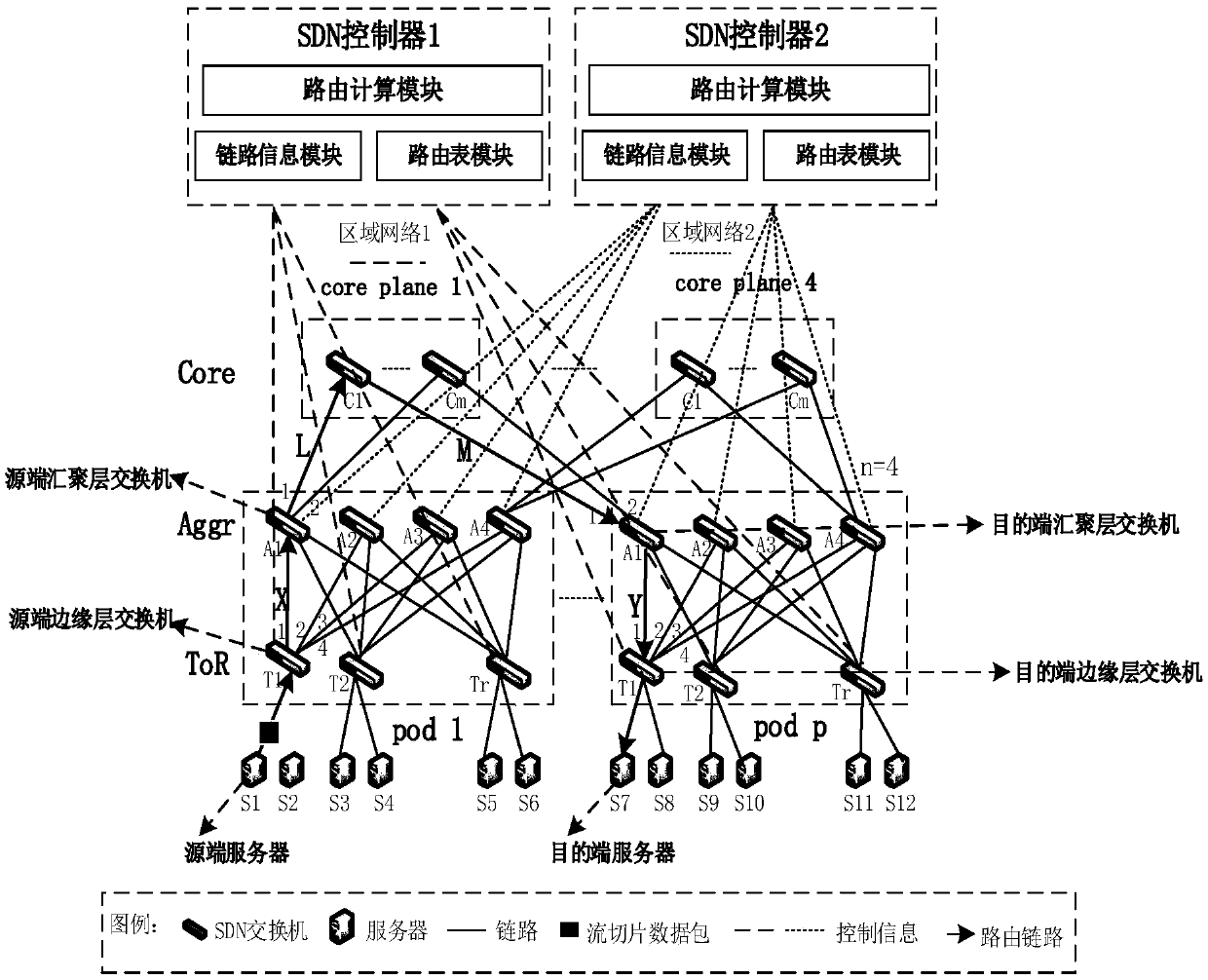
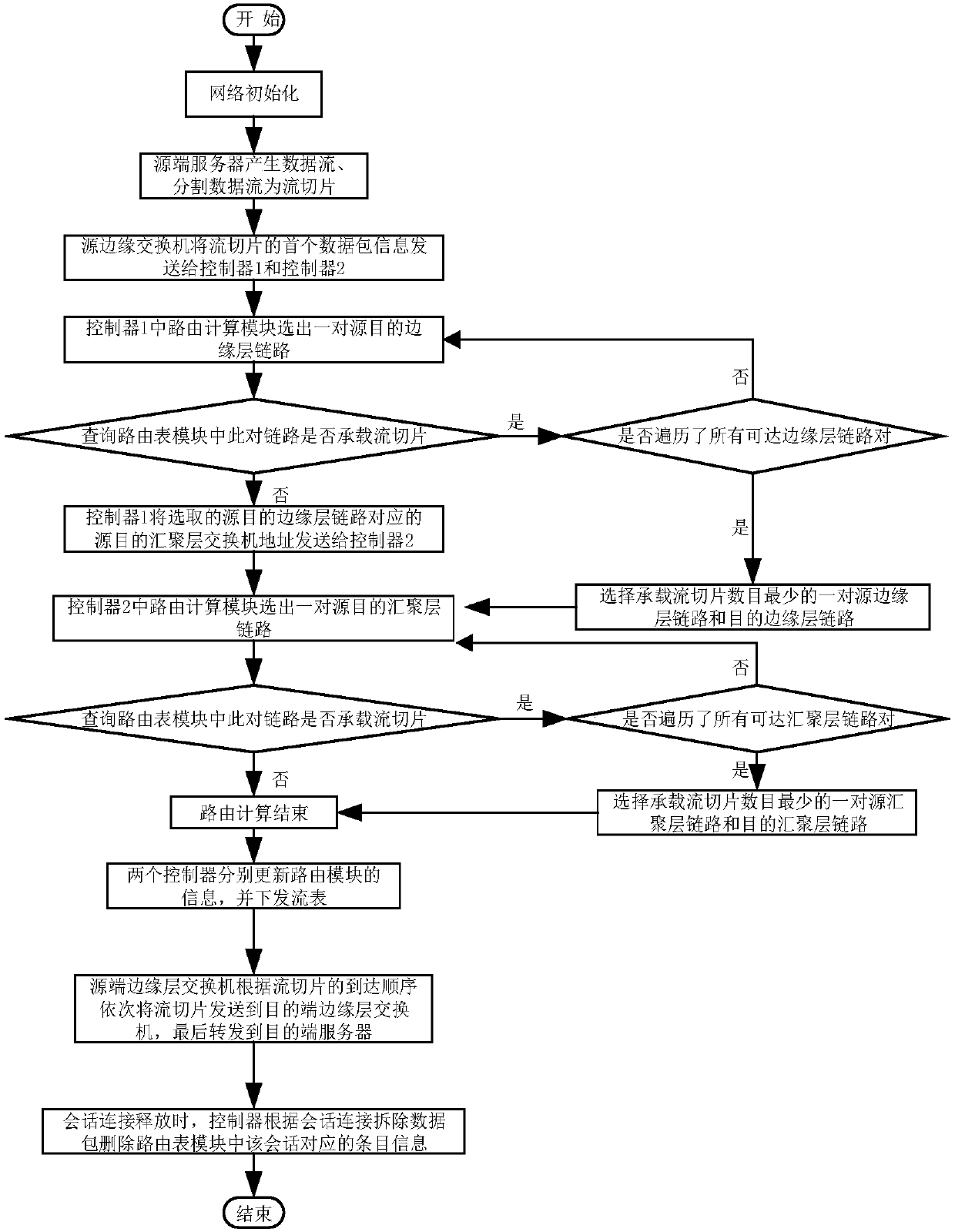
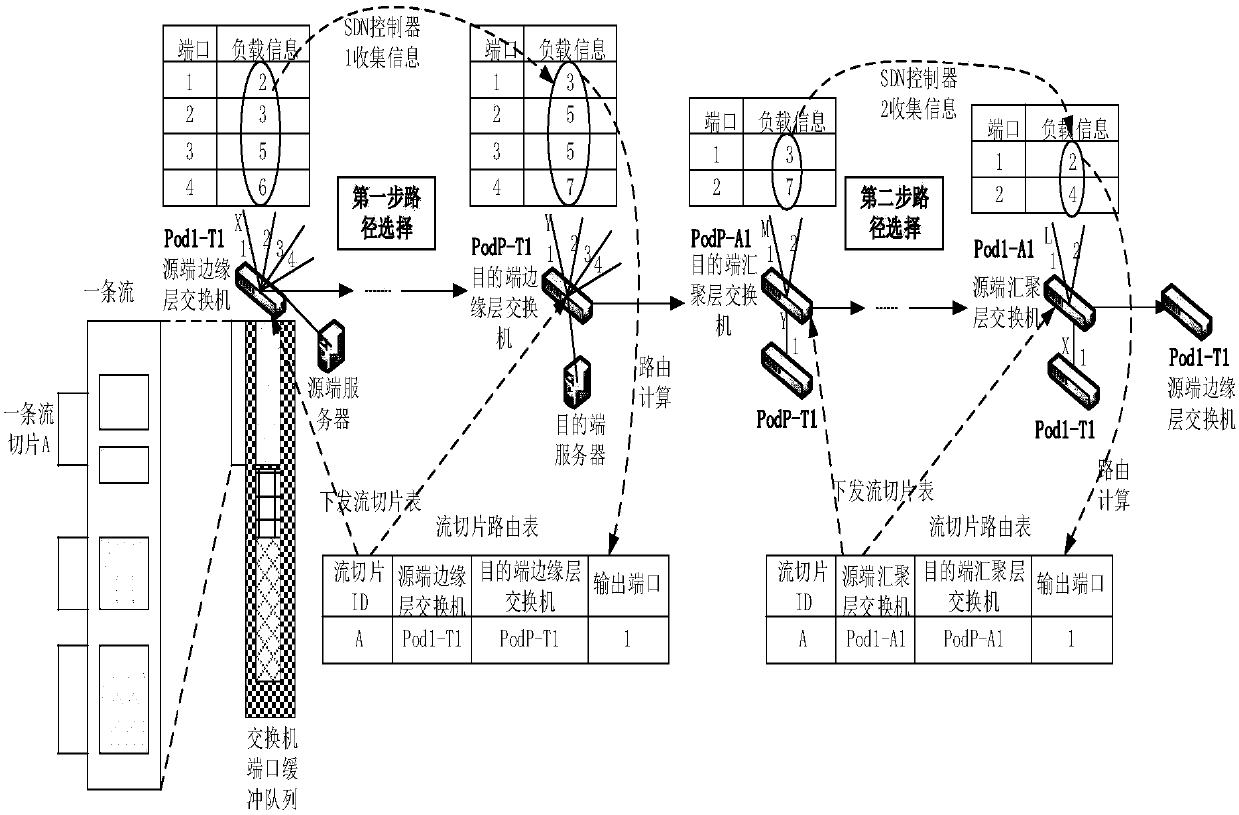
SDN based distributed control load balancing system and method
ActiveCN107819695AOvercoming the Distributed Scaling ProblemOvercome overheadData switching networksData streamRouting table
The invention discloses an SDN based distributed control load balancing system and method, aiming at mainly solving the problems of distributed extension, network overheads, uneven load and link congestion in existing small-scale single data center networks. The system disclosed by the invention comprises a three-layer Clos underlying network and two SDN controllers, wherein the SDN controller isadditionally provided with link information, a routing table and a routing calculation module, and the above modules act together to calculate a path for a data stream. The load balancing method includes the following steps: adopting two-step path selection, partitioning the data stream into stream slices in a buffer area of an end host, separately monitoring and collecting local link informationof two local area networks by using the two controllers, and taking a queuing delay of each port of a switch as the link information to optimize the selection of routing links. According to the schemeof the invention, the distributed multi-controller and two-step path selection are adopted in the three-layer Clos network, and a significant network balancing effect can be achieved; and the schemecan be used for load balancing control of large-scale single data center networks.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
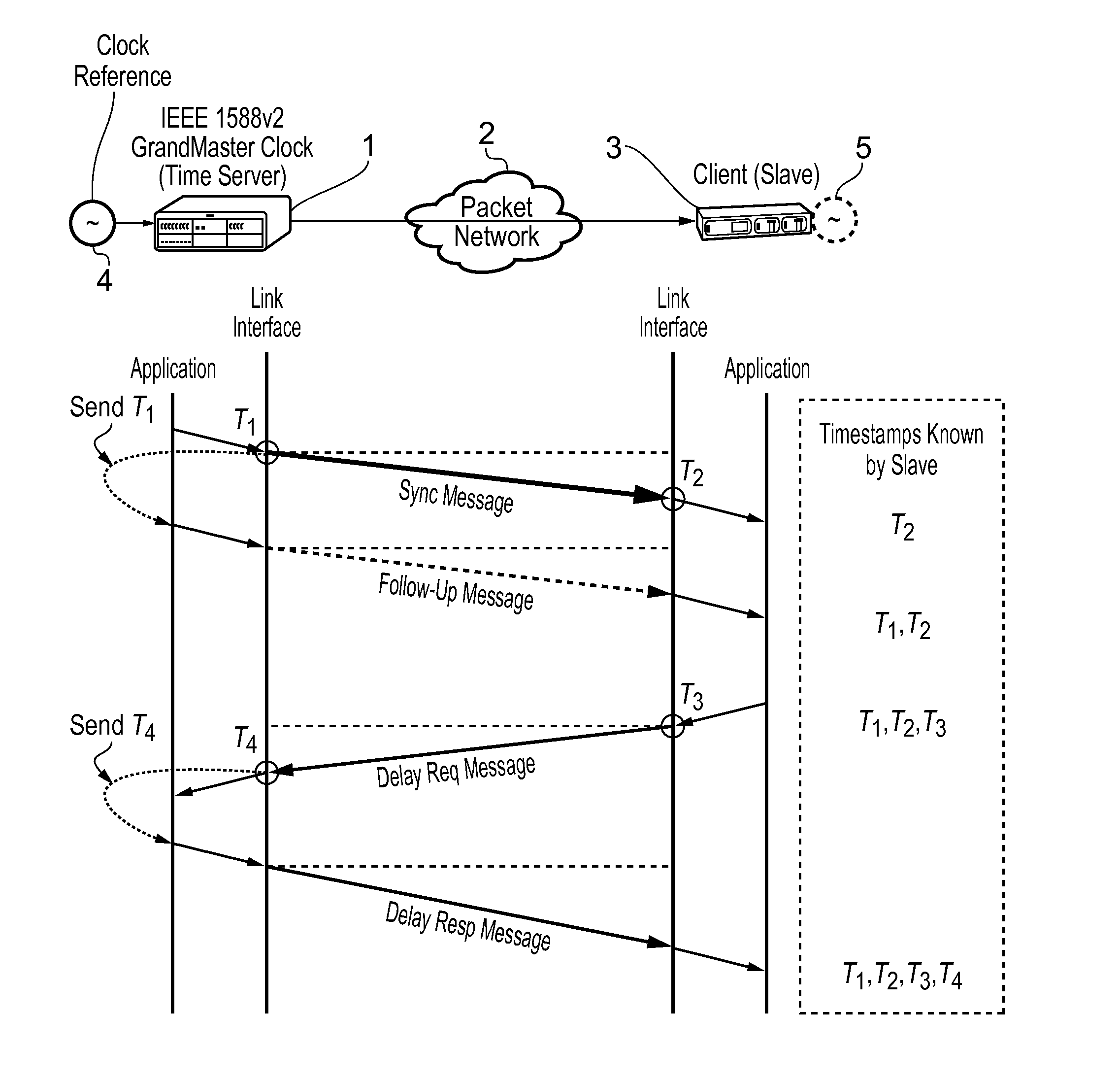
Method and devices for compensating for path asymmetry
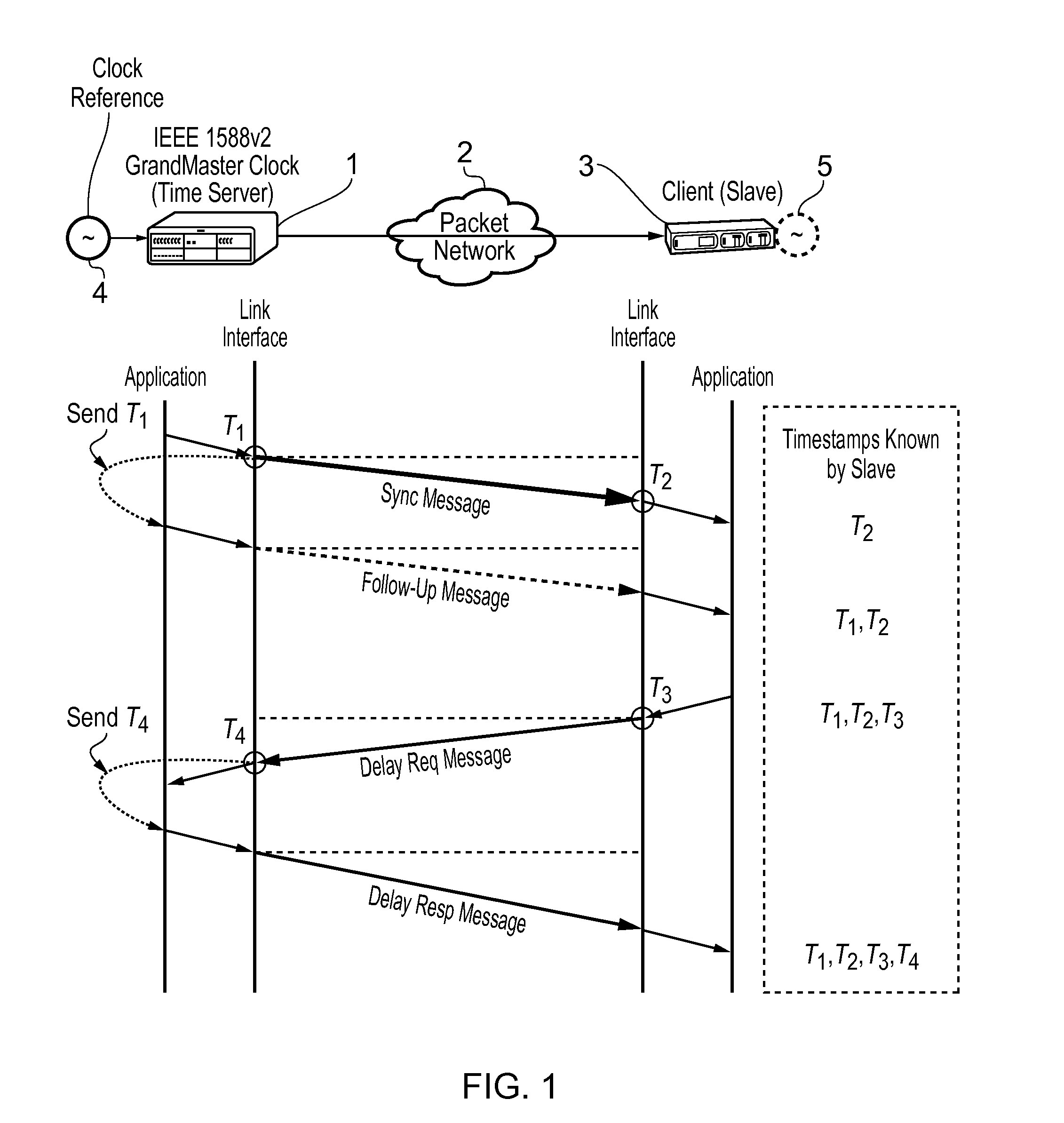
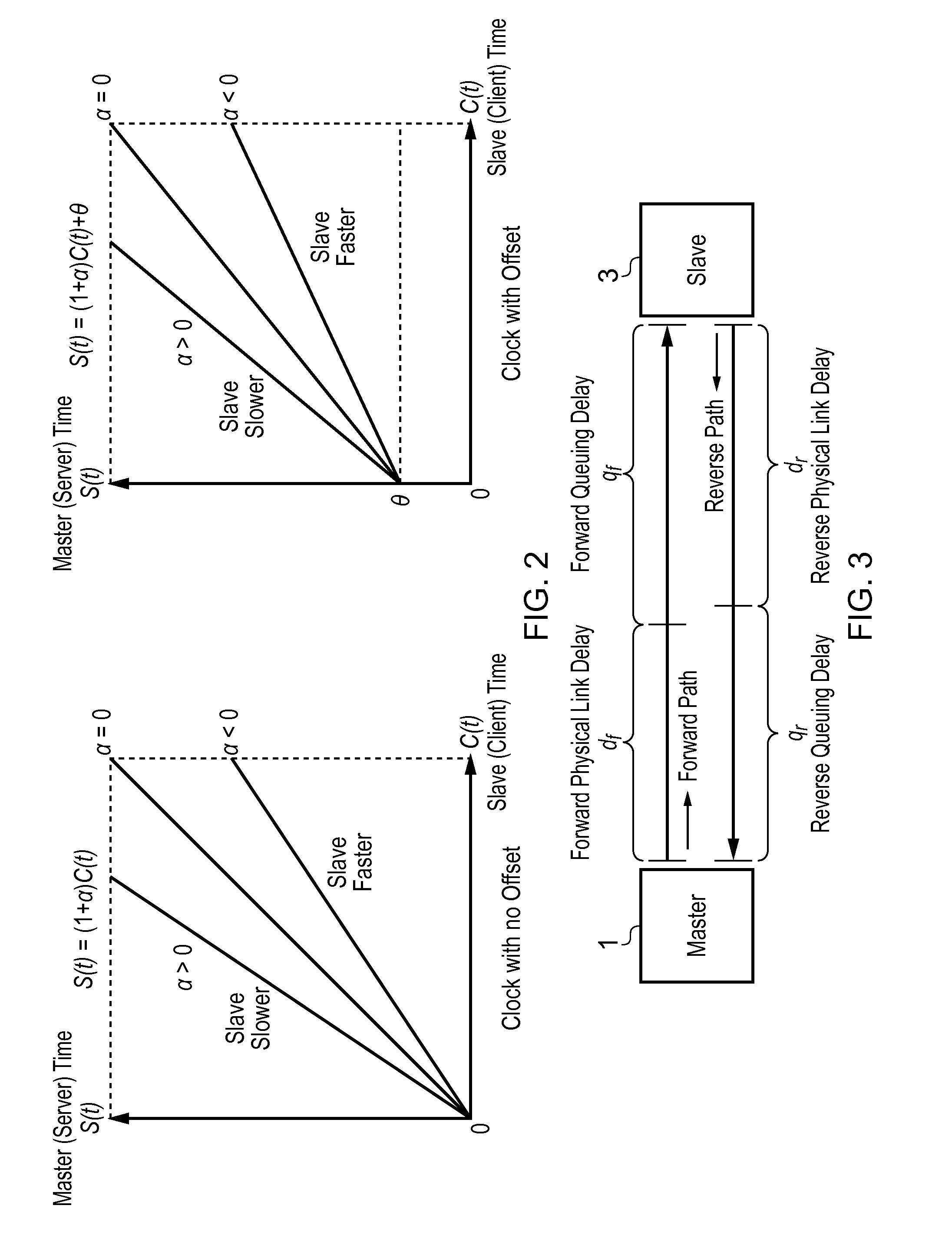
This invention relates to methods and devices for compensating for path asymmetry, particularly with reference to time and frequency synchronization. The invention has particular application where time and frequency synchronization over packet networks using, for example, the IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is being carried out. Typically communication path delays between a time server (master) and a client (slave) are estimated using the assumption that the forward delay on the path is the same as the reverse delay. As a result, differences between these delays (delay asymmetries) can cause errors in the estimation of the offset of the slave clock from that of the master. Embodiments of the invention provide techniques and devices for compensating for path delay asymmetries that arise when timing protocol messages experience dissimilar queuing delays in the forward and reverse paths.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC +2
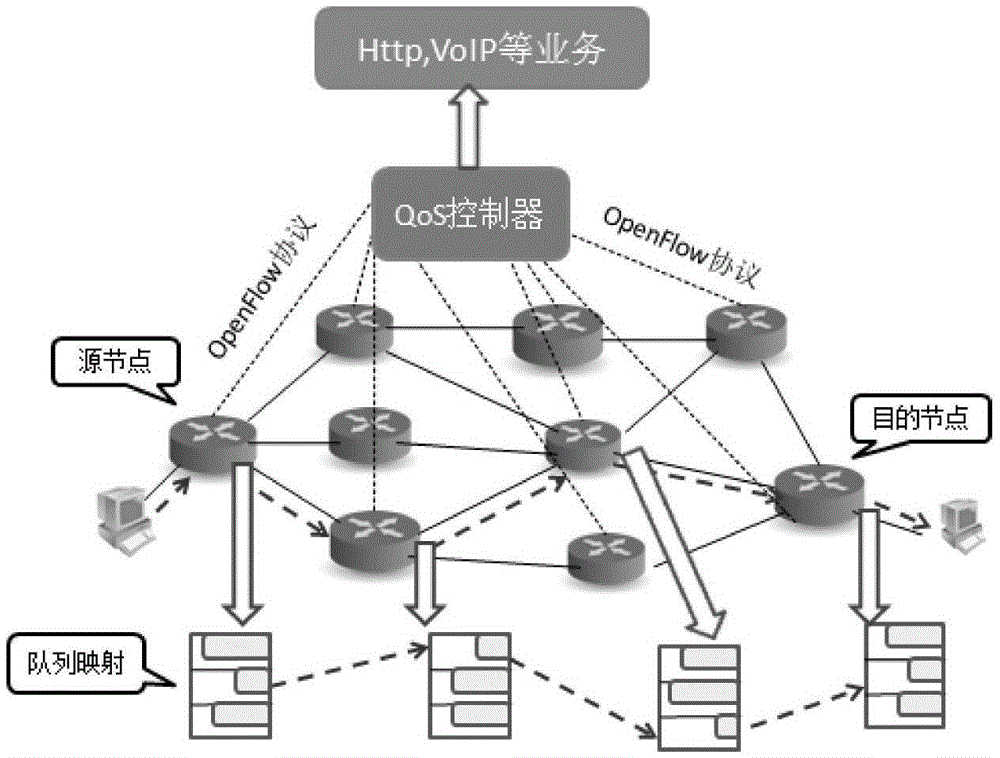
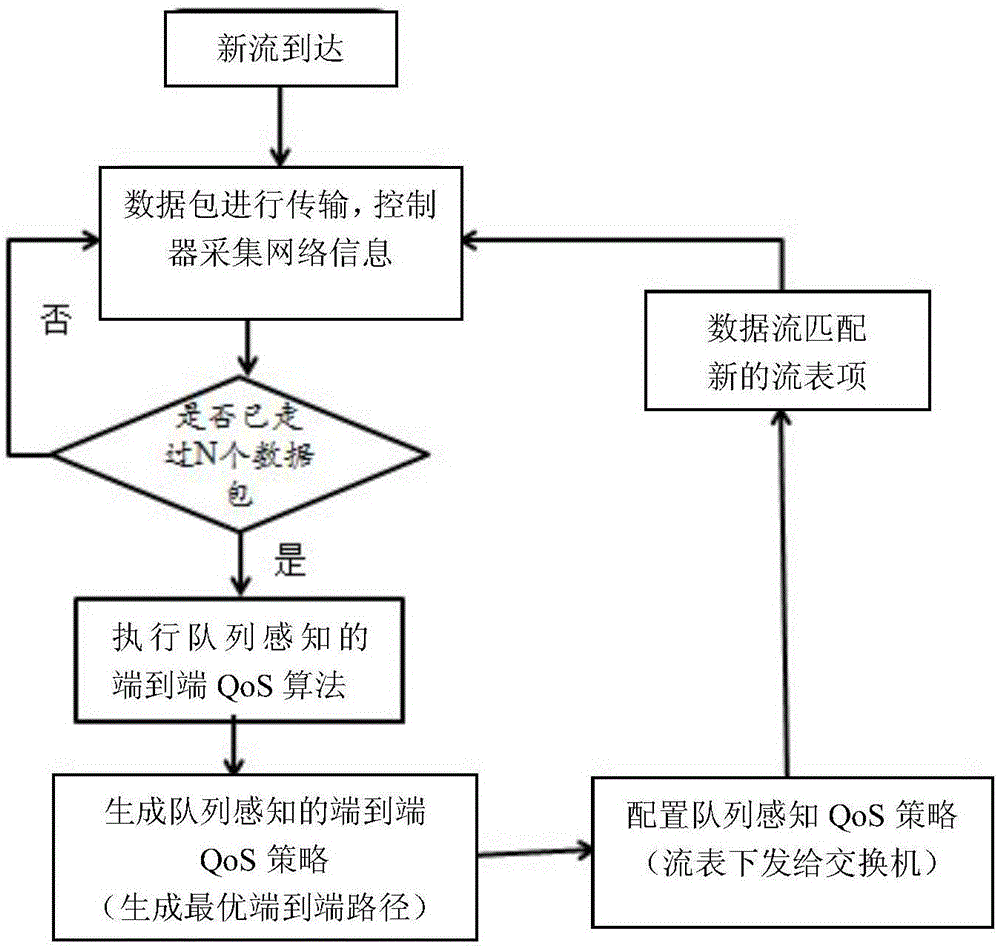
Method for guaranteeing end-to-end QoS in SDN network
The invention discloses a method for guaranteeing the end-to-end QoS in an SDN network, comprising the following steps: (1) for each new data flow arriving at an SDN network, an SDN network controller periodically collects network status information; (2) the SDN network controller calculates the cost of each of all alternative paths for transmitting the new data flow according to the collected network status information, and determines an optimal transmission path; and (3) the SDN network controller packages the information of the optimal transmission path into a flow entry and issues the flow entry to a switch node of the SDN network, and the switch node forwards a received data packet according to the flow entry. According to the invention, an OpenFlow switch queue mechanism is designed, and the queue status of the switch is monitored in real time through the controller. When a new data flow arrives, a minimum-cost path is selected to transmit the data flow according to the transmission delay of the link on the path and the queuing delay of the switch node queue as well as the congestion situation of the current link.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
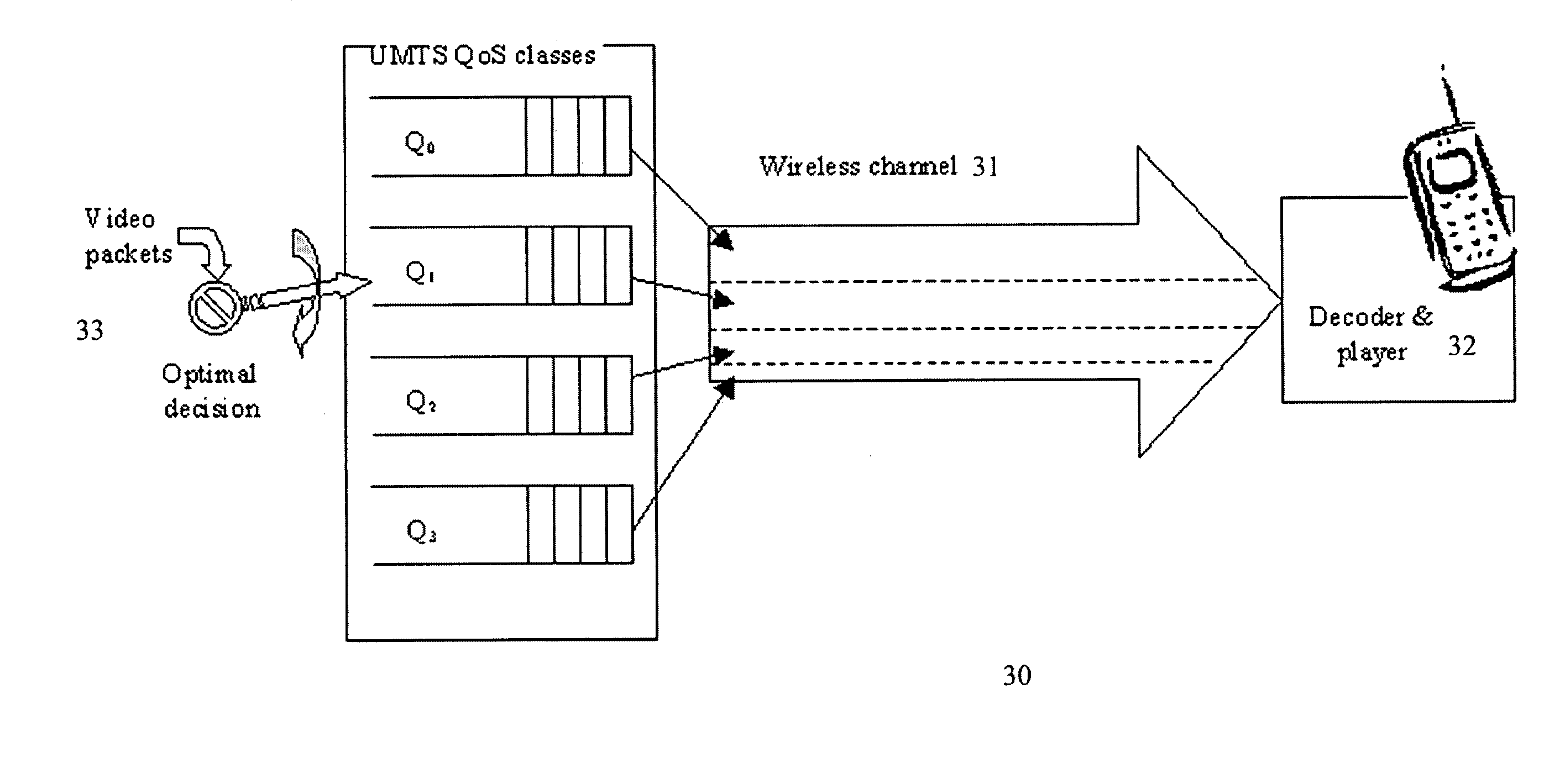
Video packets over a wireless link under varying delay and bandwidth conditions
ActiveUS7161957B2Optimal bandwidth allocationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceWireless transmission
An apparatus in a wireless network includes a video encoder for encoding uncompressed video information into packets with variable length of compressed frames, and a decision processor for selecting a partial bandwidth and queuing delay on a wireless channel for each of the packets based on an intended reception quality. Preferably, the queuing delay and partial bandwidth are one of a plurality of distinct queuing delay and partial bandwidth representative of wireless transmission quality of service classes.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
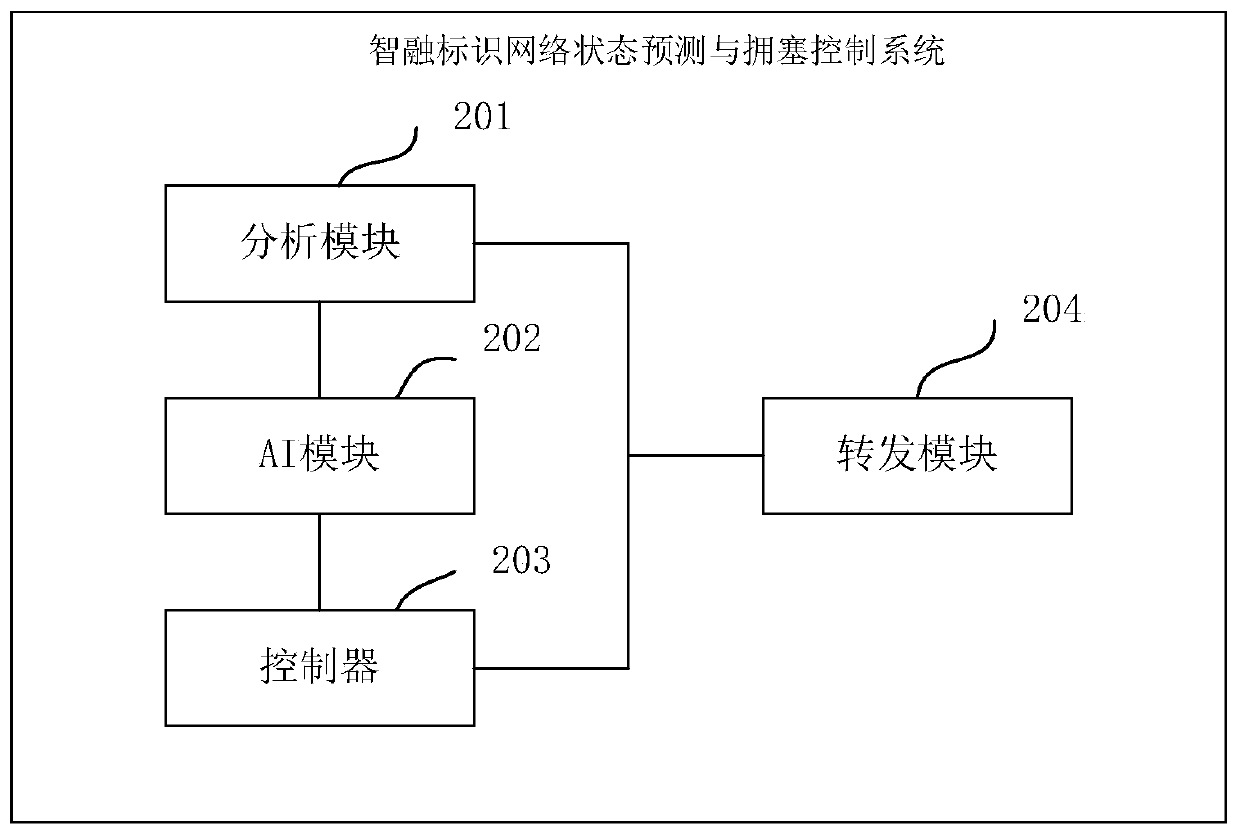
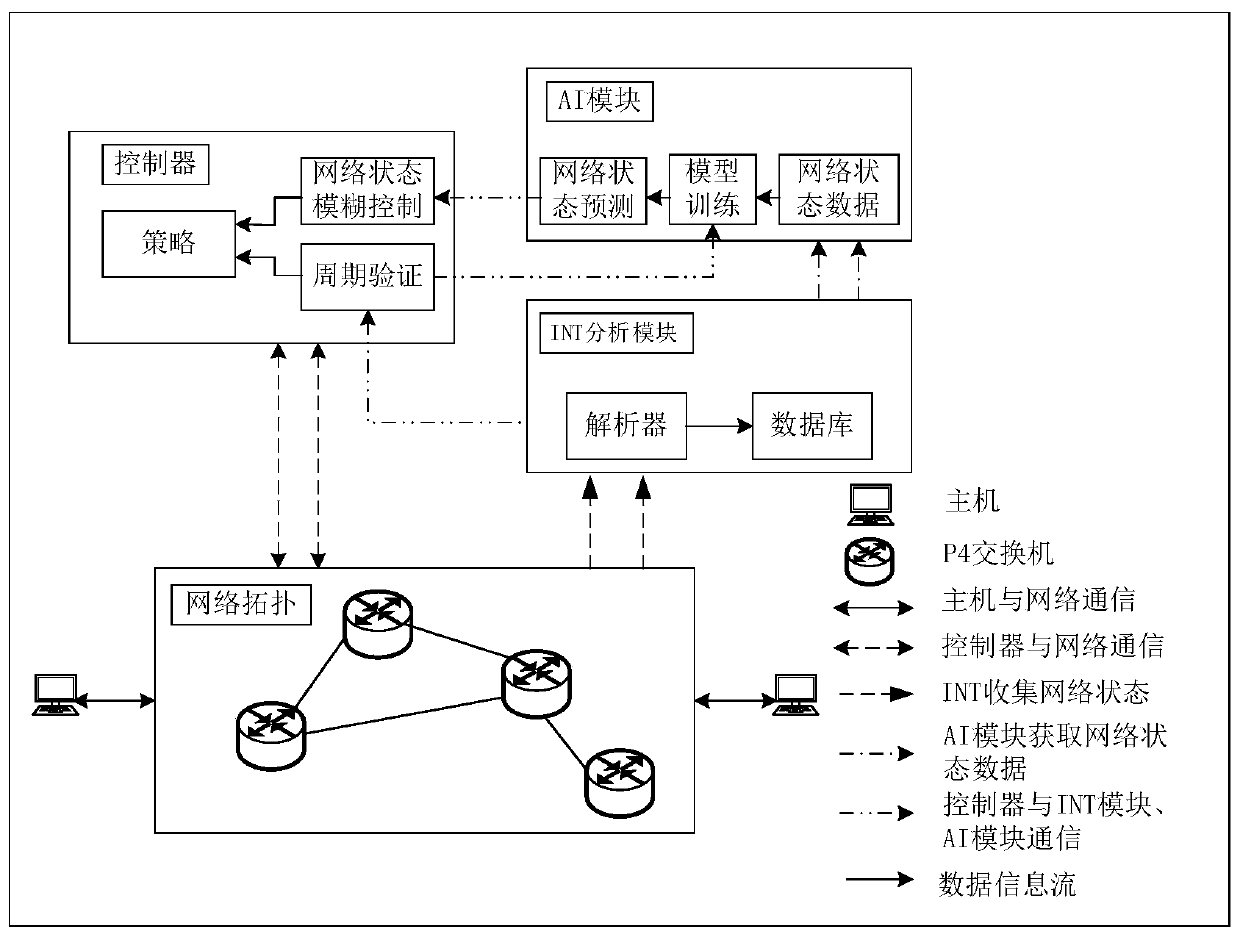
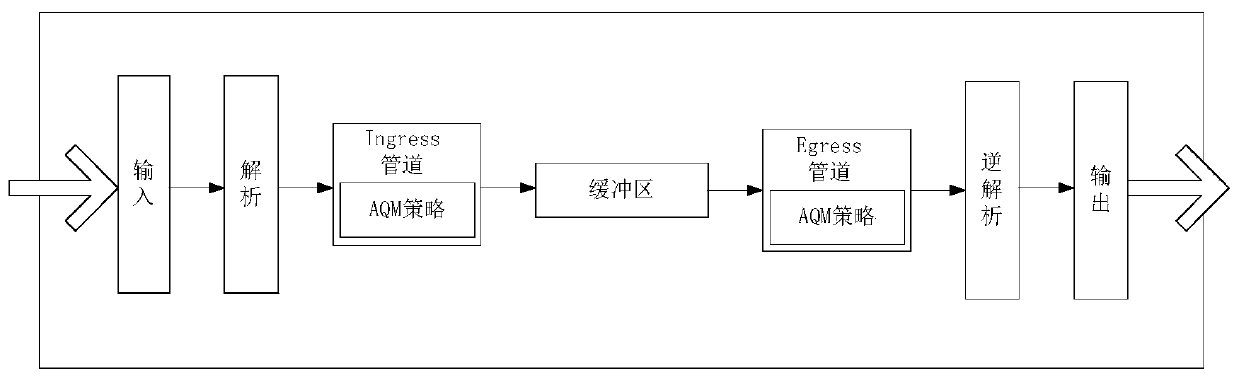
Intelligent fusion identification network state prediction and congestion control system
ActiveCN111526096ASmall queuing delayTo achieve the effect of congestion controlCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData packState prediction
The invention provides an intelligent fusion identification network state prediction and congestion control system. The invention discloses a method and a system for realizing network state predictionand data packet queue congestion control on a programmable data plane by combining a machine learning model method based on P4. The method comprises the following steps: collecting network state feature information in real time through an in-band network telemetry (INT) technology; and achieving network state characteristic value prediction by adopting an 'LSTM-fuzzy clustering' model method combining a long short term memory (LSTM) neural network model and a fuzzy clustering algorithm, and achieving the prediction of the network state characteristic value by adopting a fuzzy clustering algorithm. According to the obtained network state characteristic value, fuzzy clustering is carried out to obtain four network states; a normal state, a congestion early warning state, a continuous congestion state and a congestion alleviation state; corresponding strategies are formulated for different network states, the controller issues corresponding flow tables and formulates switch actions in different network states, and a comprehensive and dynamic queue feedback mechanism is provided to ensure that data packet queuing delay is as small as possible and achieve the effect of congestion control.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Multipath load balance implementing method and data forwarding apparatus
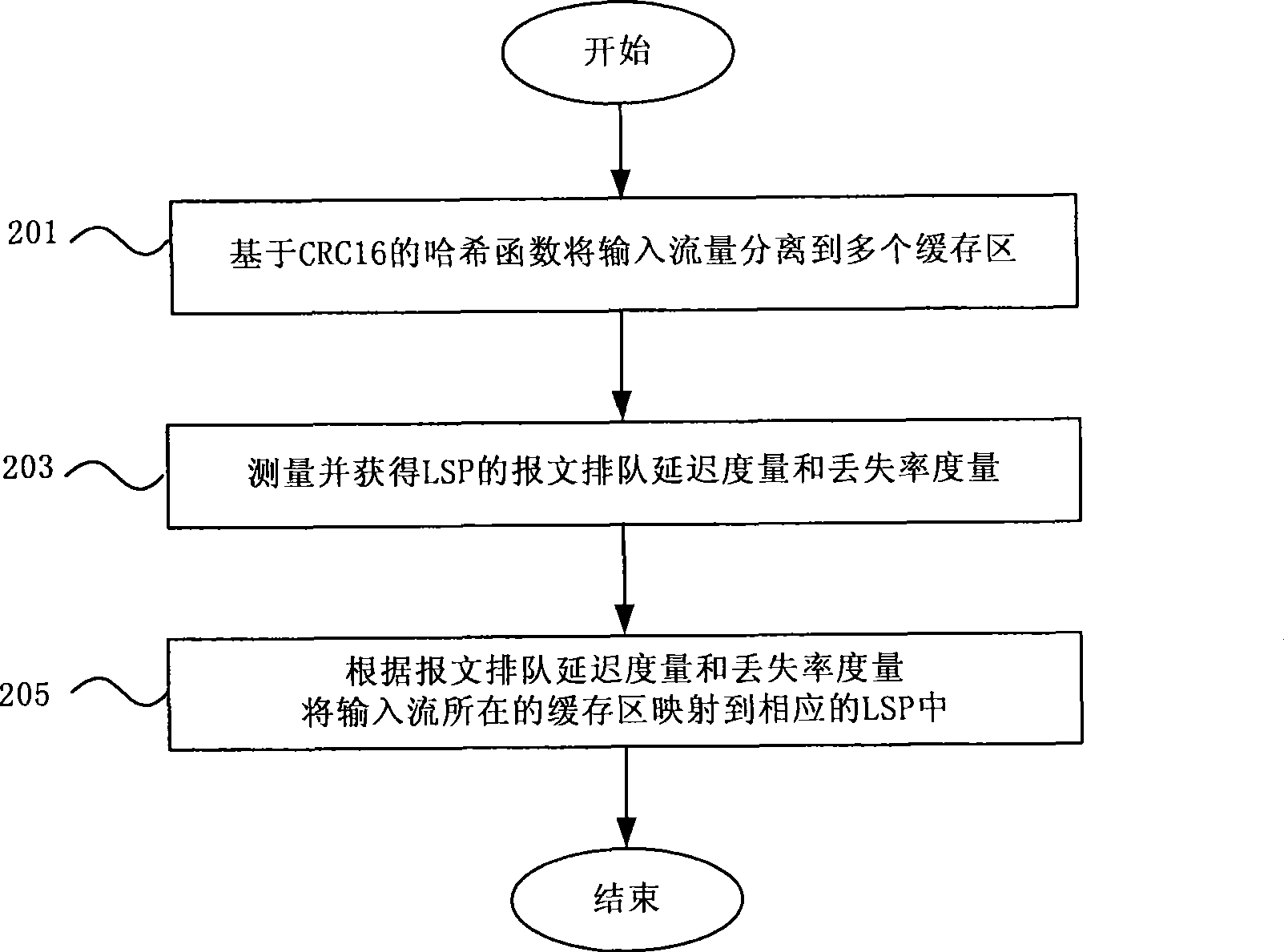
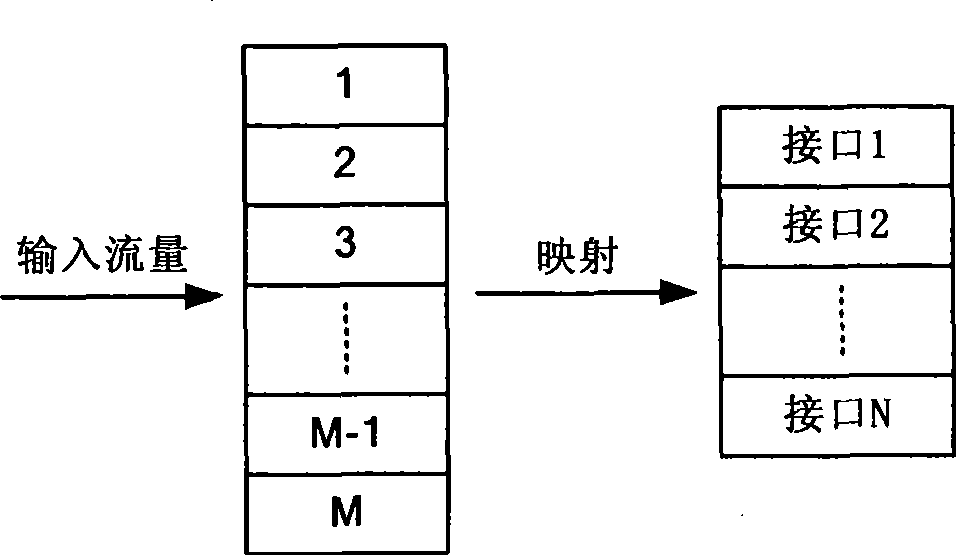
ActiveCN101499957AMultipath load balancingLoad reflectionData switching networksExtensibilityLoss rate
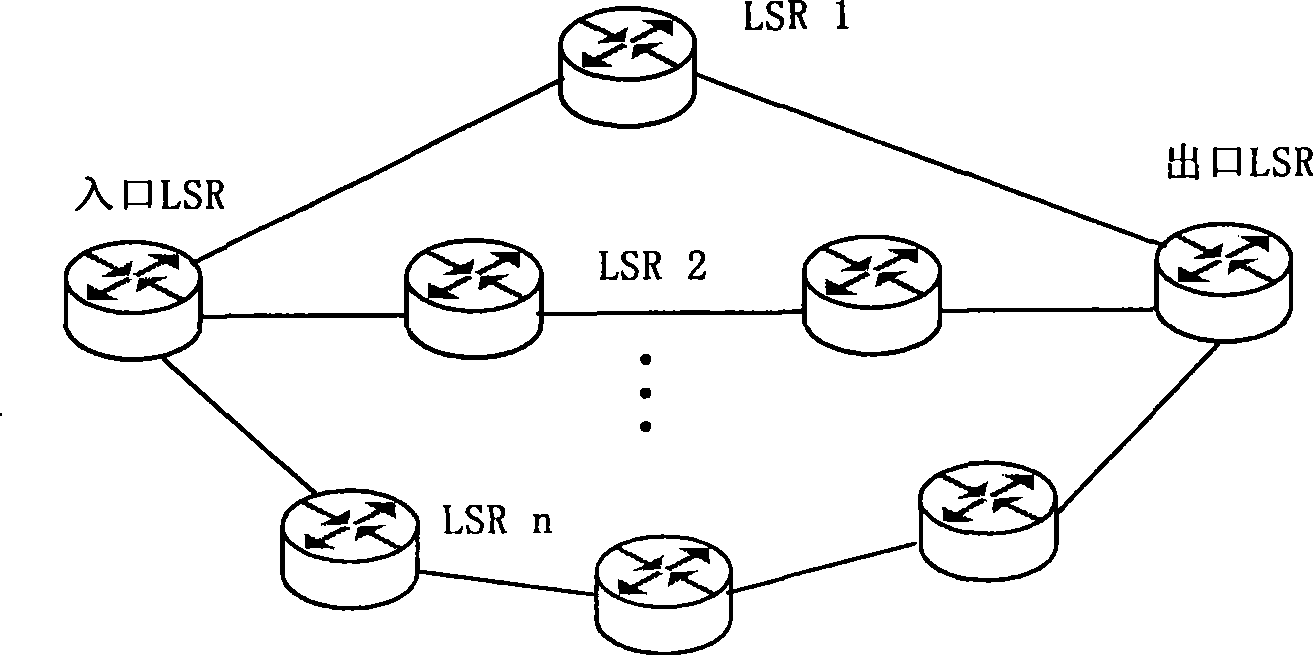
The invention discloses a method for realizing multipath load balance in an MPLS network and a data transmitting device. The method comprises the following steps: input flow is separated into a plurality of flow buffers; the least message queuing delay metrics and the loss rate metrics of each label switched path are measured; and according to the least message queuing delay metrics and the loss rate metrics of the label switched path, the flow in the buffer is mapped into the label switch path. The flow separation is simple and high-efficient, and the message queuing delay metrics and the loss rate metrics can reflect the load on each LSP better, thus realizing the multipath load balance. The method has good stability and expandability and is easy to realize in an operation network.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Measuring method, measuring apparatus and forwarding device for route congestion state in IP network
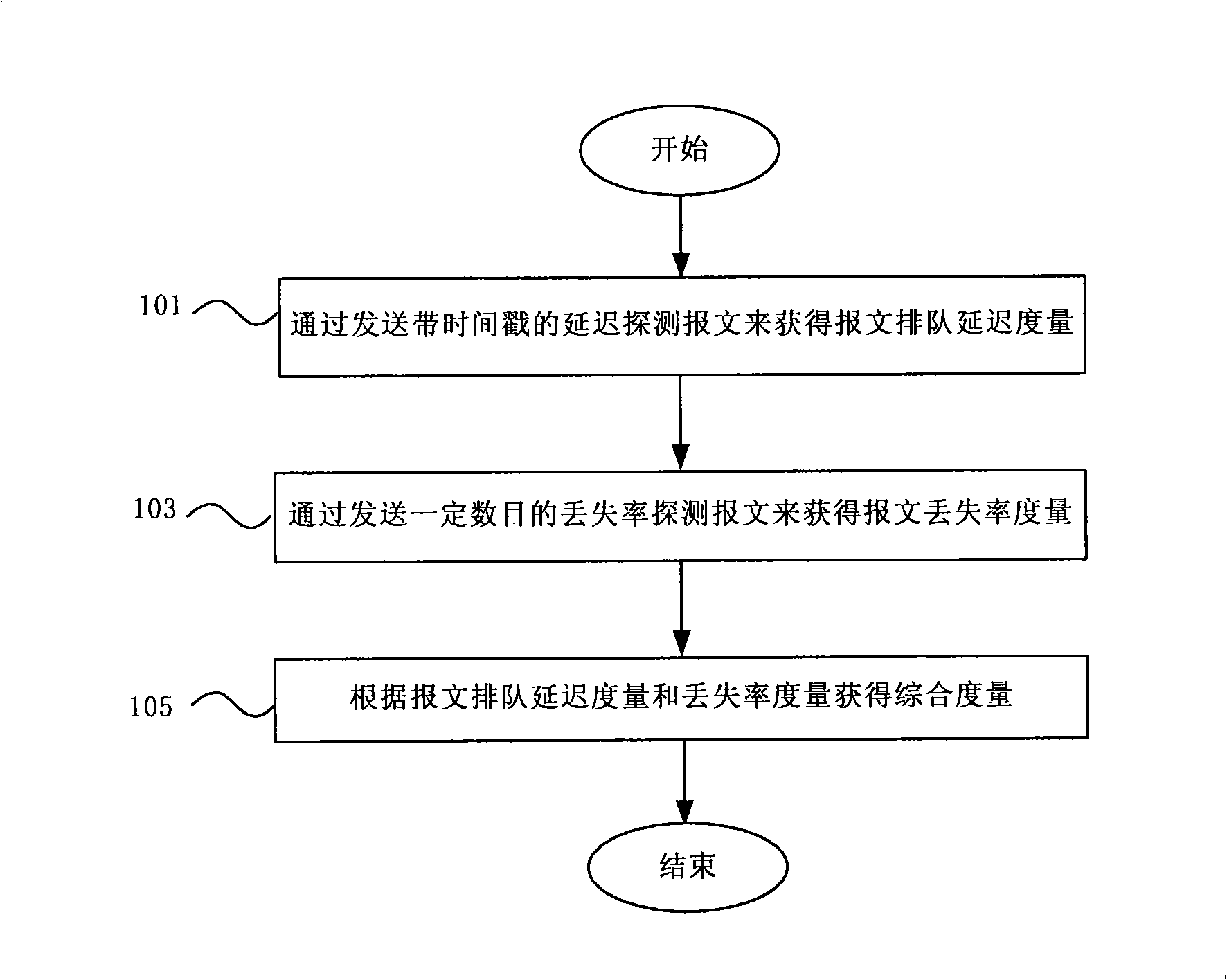
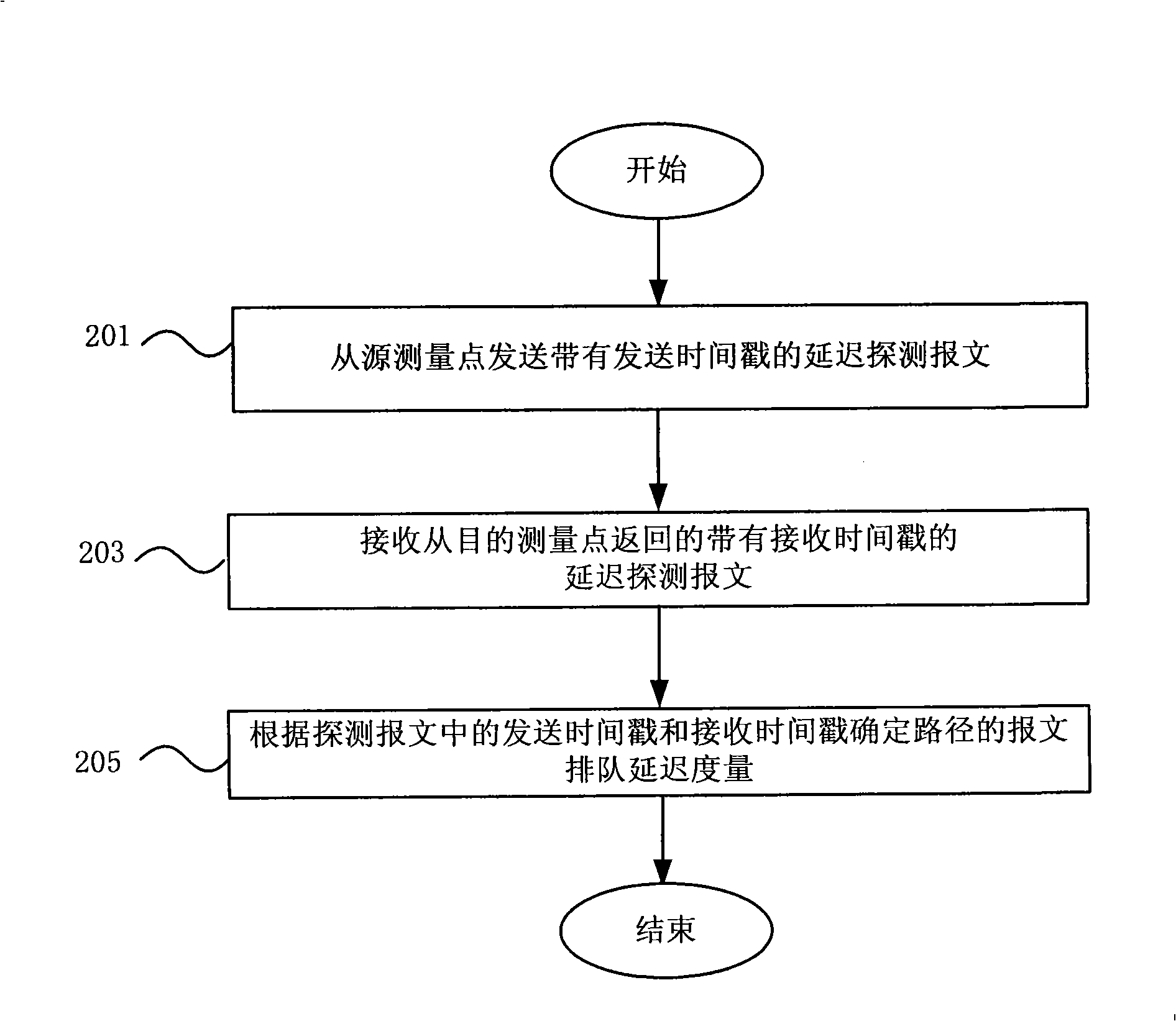
ActiveCN101272290AReflect the load levelAccurately reflect load levelsData switching networksLoss rateRouting congestion
The invention discloses a measurement method for path congestion status in an IP network, a measuring device and a data retransmitting device thereof. The measurement method comprises the steps: measuring the measurement of message queuing delay of the path in the network; measuring the measurement of message loss rate of the path in the network; acquiring a comprehensive measurement of the congestion status of the path according to the measurement of message queuing delay and the measurement of message loss rate. The measurement method of the invention acquires the comprehensive measurement through measuring the measurement of message queuing delay and the measurement of message loss rate, thus can reflect path load level in real network more exactly.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
TDMA based long propagation delay wireless link time slot distribution method
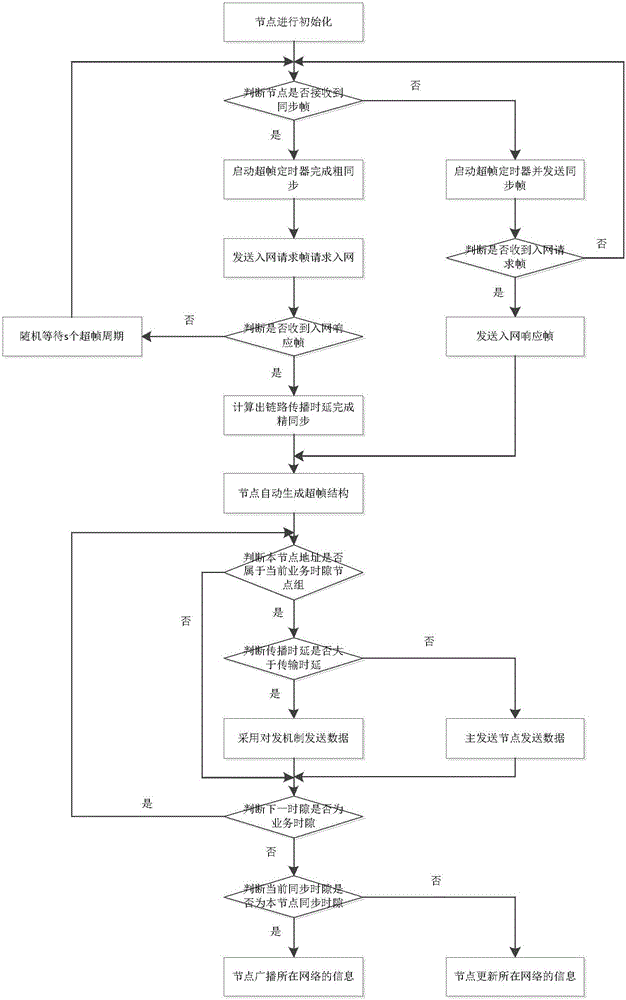
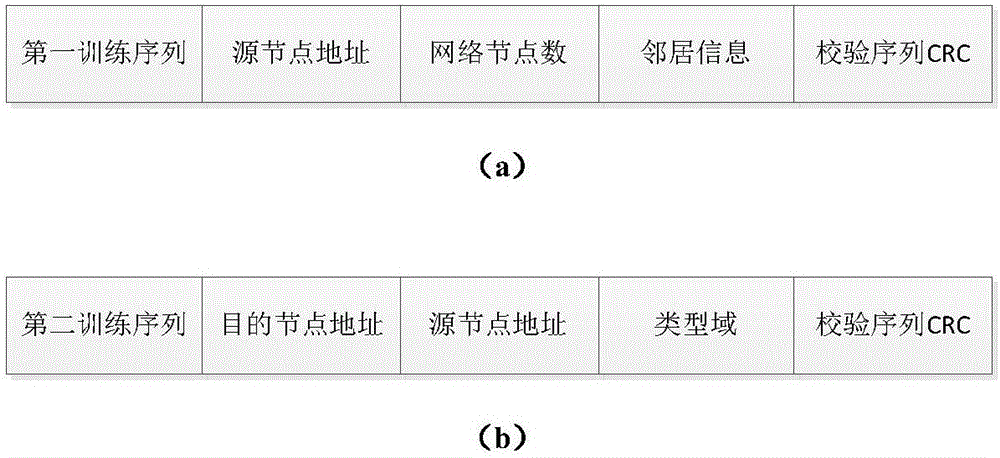
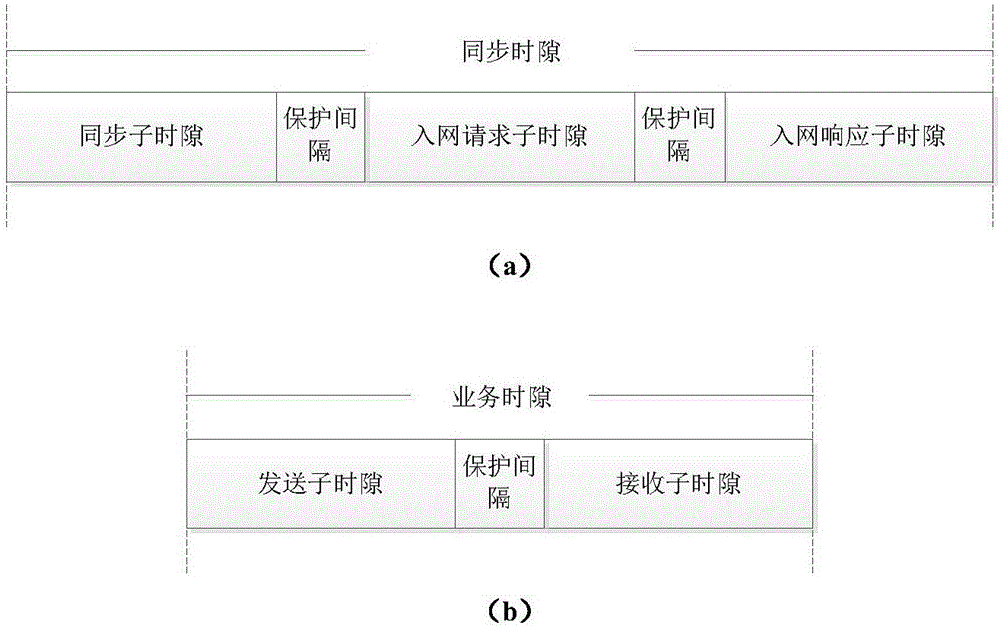
ActiveCN106658735AHigh speedImprove efficiencyTime-division multiplexWireless communicationWireless ad hoc networkSynchronous frame
The invention discloses a TDMA based long propagation delay wireless link time slot distribution method which is mainly used for solving the problem of low throughput rate and low channel utilization rate of an existing long propagation delay wireless ad hoc network. The implementation scheme comprises the steps of 1, initializing a node; 2, judging whether the node receives a synchronous frame, if so, carrying out network access synchronization by the node, and otherwise, building a network by regarding the local clock as a reference by the node; 3, after synchronization is finished, generating a super-frame structure automatically by the node, and dividing the local time into multiple time slots with different functions; and 4, judging whether the current time slot is a service time slot by the node, if so, sending and receiving data, and otherwise, updating network information. as the TDMA is adopted as a channel access mode, the node can access the channel without any conflict; and through an interactive sending mechanism and a data frame queue scheduling mechanism, the network throughput rate and the channel utilization rate are increased, the queuing delay of the data frames is reduced; and the TDMA based long propagation delay wireless link time slot distribution method can be used for a time division multiple access ad hoc network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
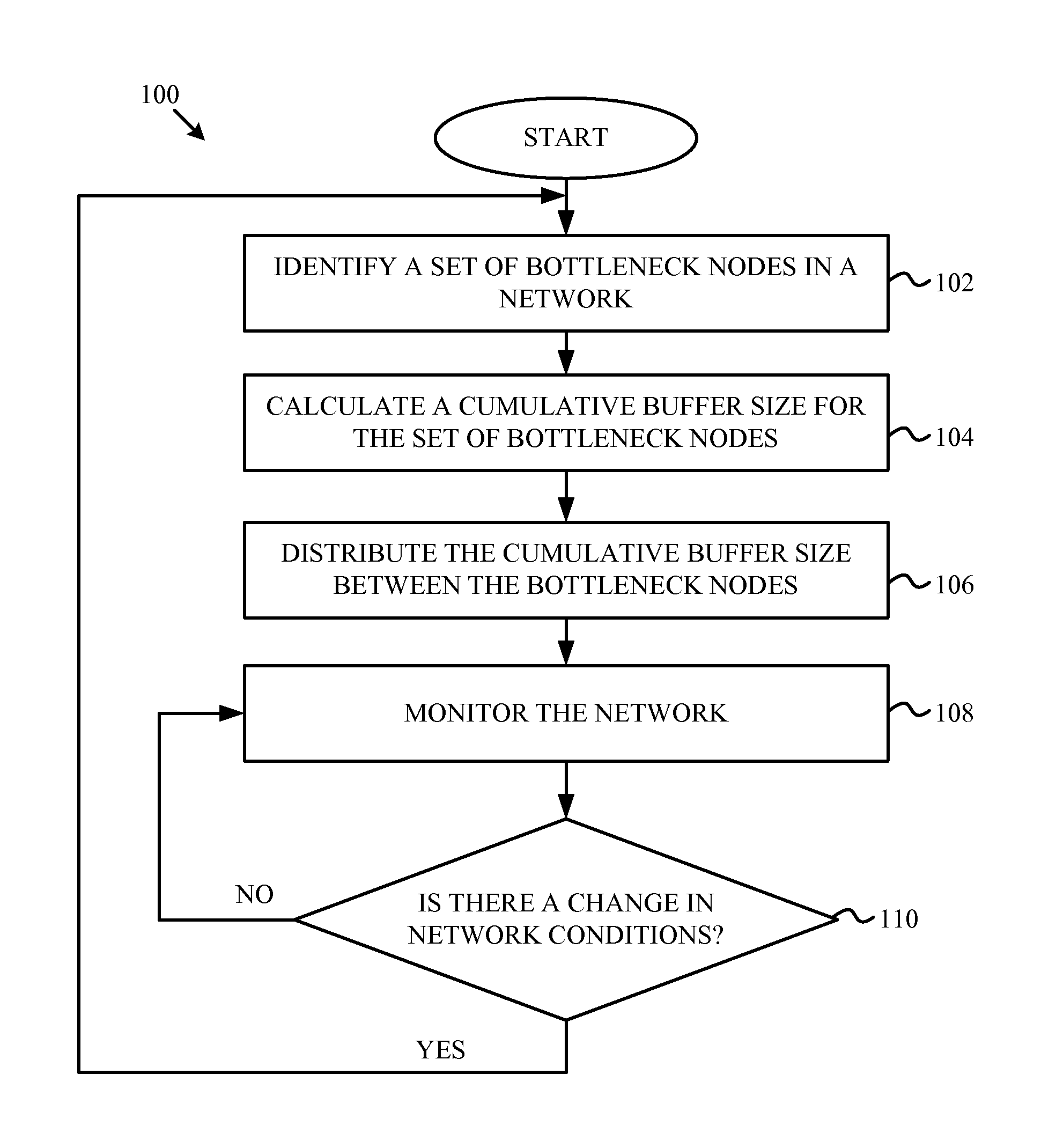
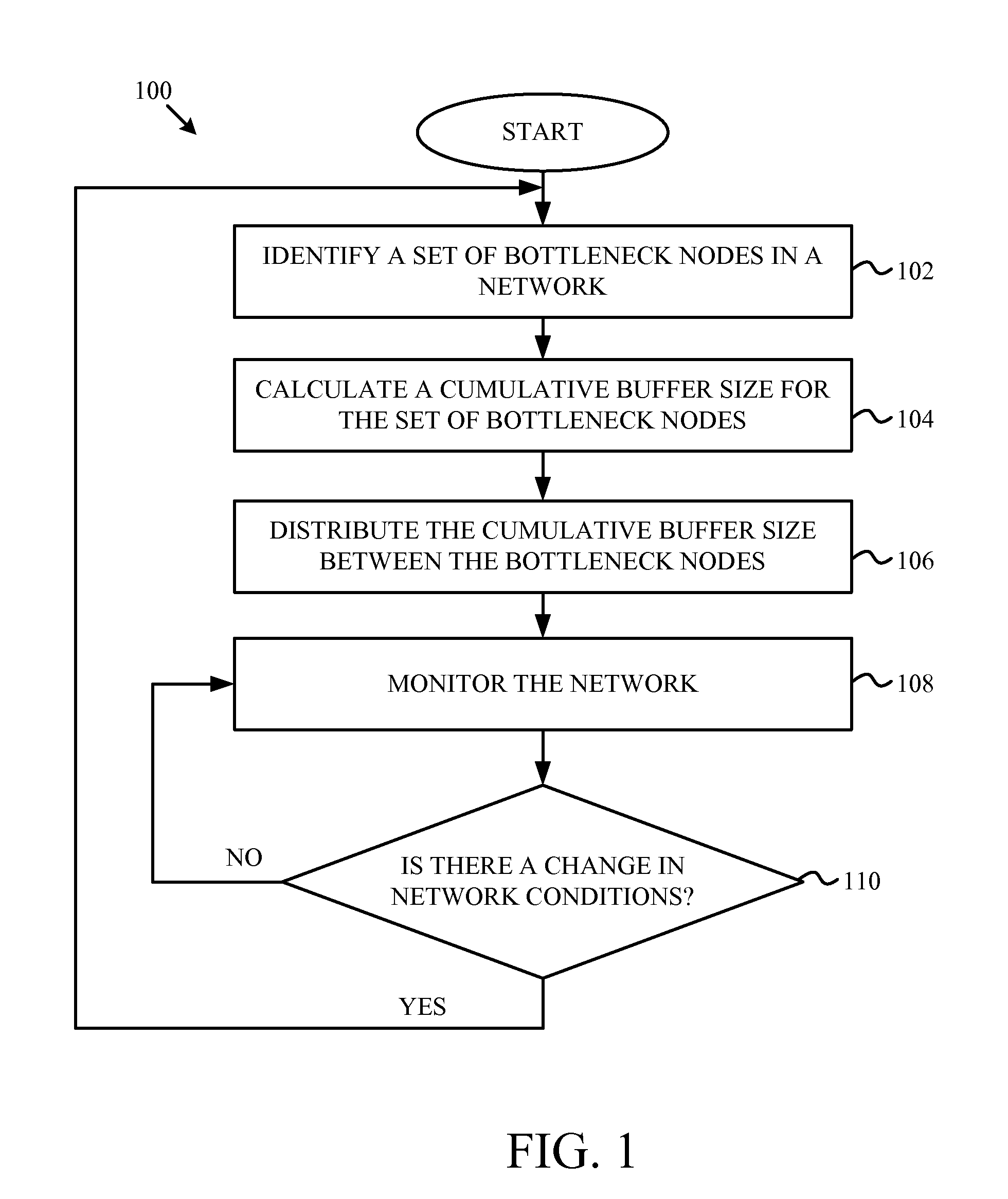
Buffer Sizing for Multi-Hop Networks
ActiveUS20120236726A1Error preventionTransmission systemsTelecommunications linkWireless mesh network
A cumulative buffer may be defined for an interference domain in a wireless mesh network and distributed among nodes in the network to maintain or improve capacity utilization of network resources in the interference domain without increasing packet queuing delay times. When an interference domain having communications links sharing resources in a network is identified, a cumulative buffer size is calculated. The cumulative buffer may be distributed among buffers in each node of the interference domain according to a simple division or according to a cost function taking into account a distance of the communications link from the source and destination. The network may be monitored and the cumulative buffer size recalculated and redistributed when the network conditions change.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Data transmission method for hsdpa
ActiveUS20080253375A1Delay minimizationFacilitate transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexComputer hardwareMultiplexing
In the data transmission method of an HSDPA system according to the present invention, a transmitter transmits Data Blocks each composed of one or more data units originated from a same logical channel, and a receiver receives the Data Block through a HS-DSCH and distributes the Data Block to a predetermined reordering buffer. Since each Data Block is composed of the MAC-d PDUs originated from the same logical channel, it is possible to monitor the in-sequence delivery of the data units, resulting in reduction of undesirable queuing delay caused by logical channel multiplexing.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com