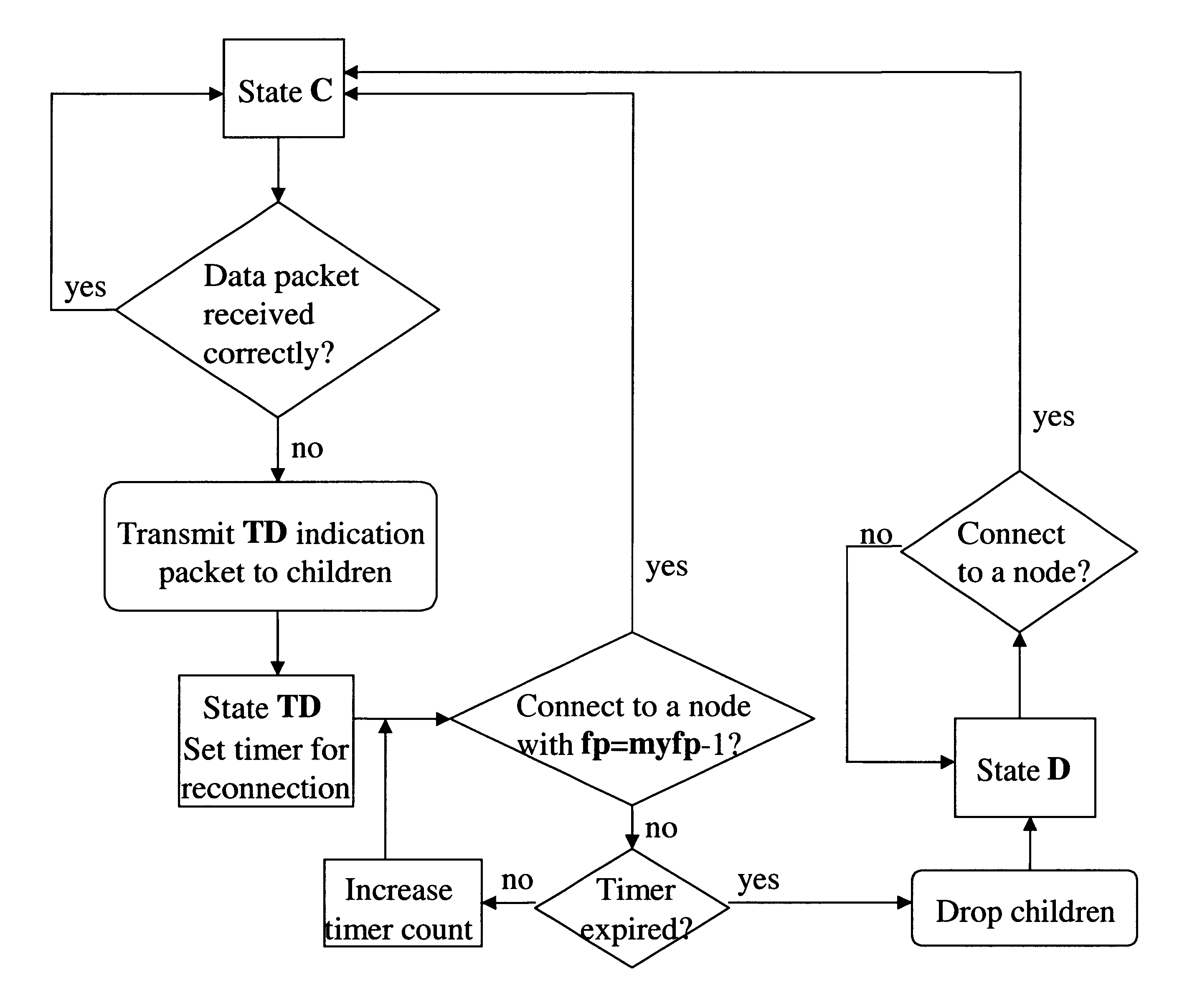
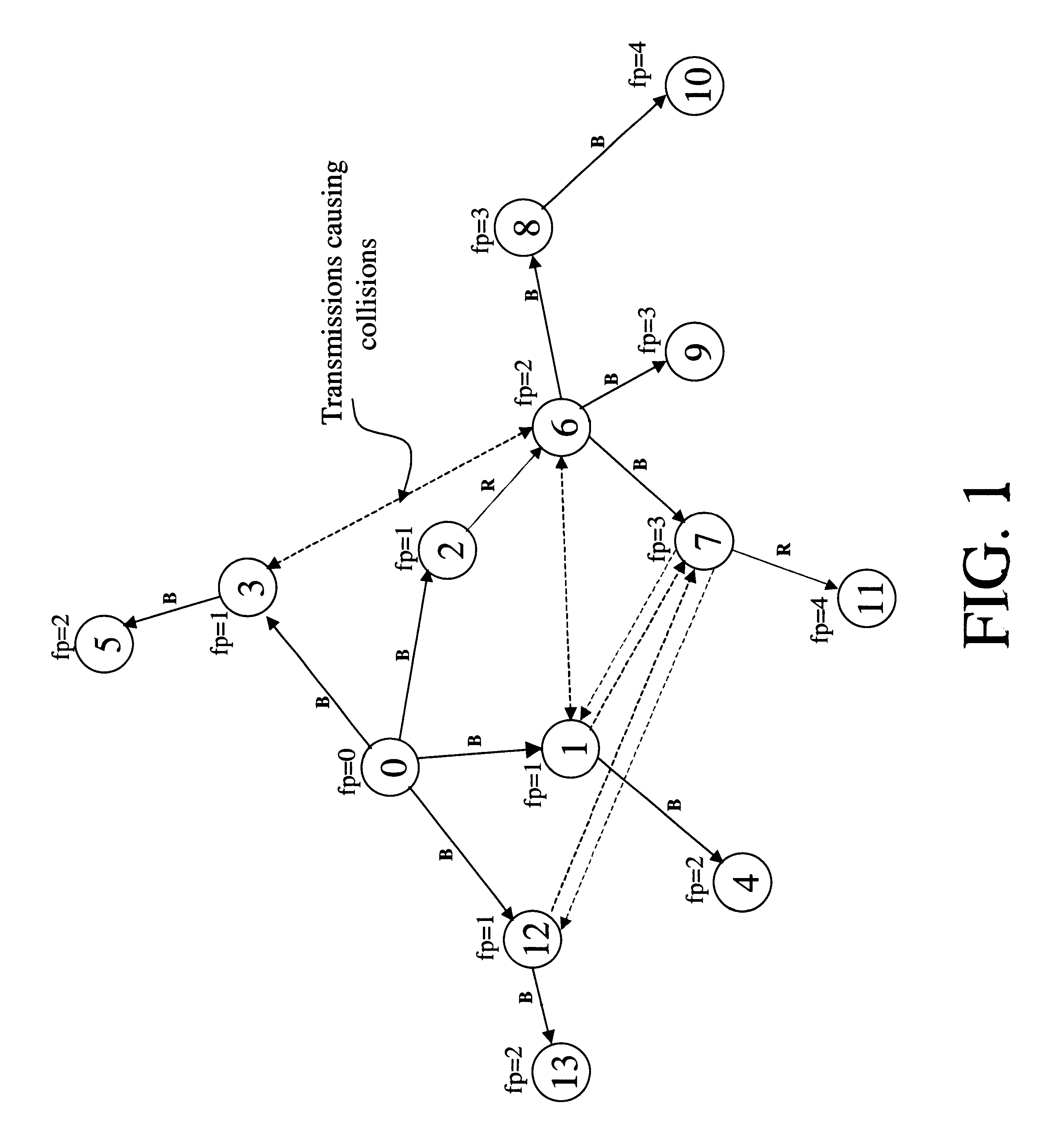
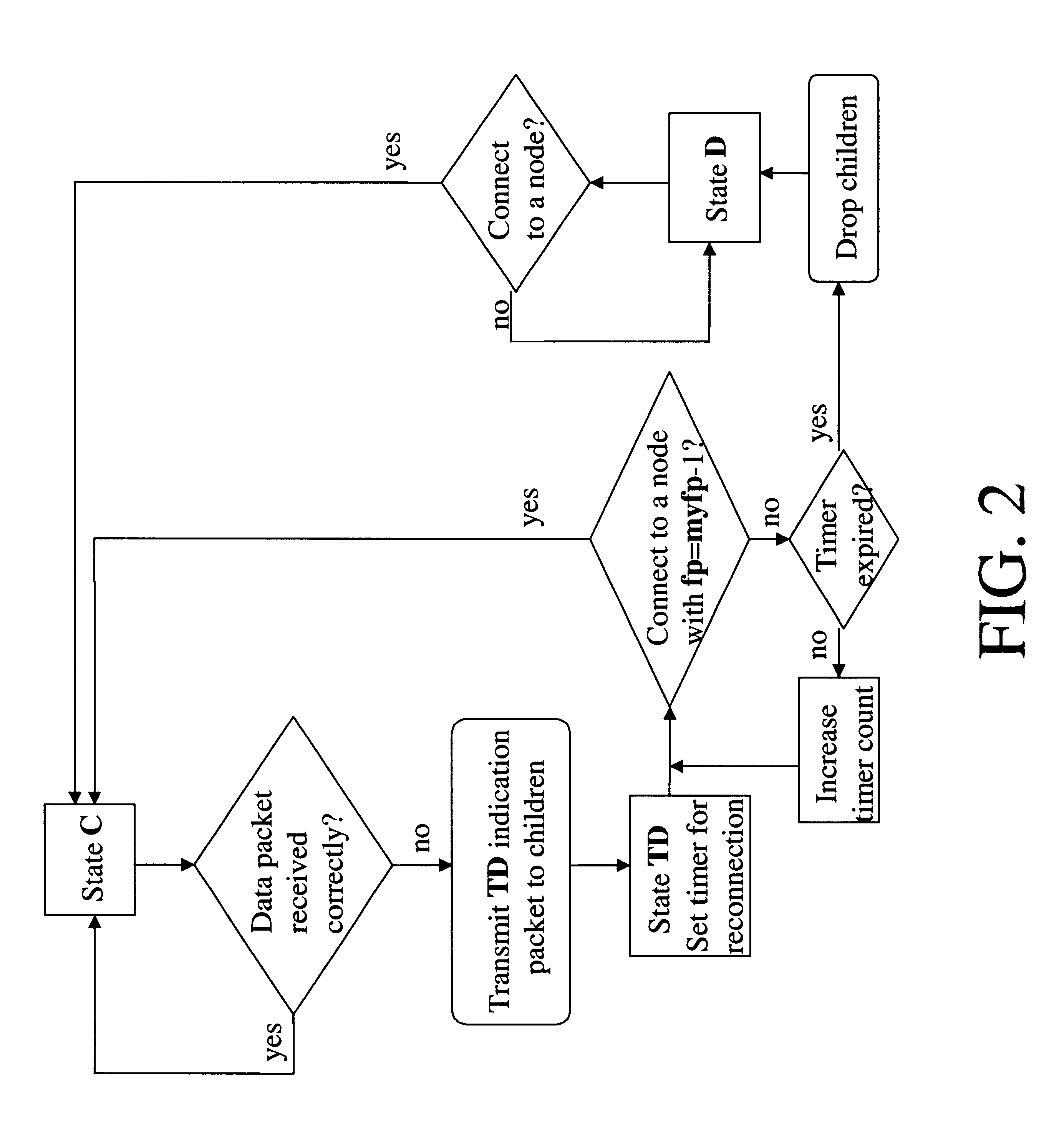
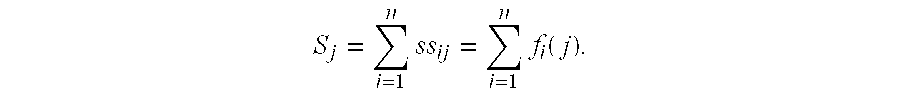Patents
Literature
1153 results about "Wireless ad hoc network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
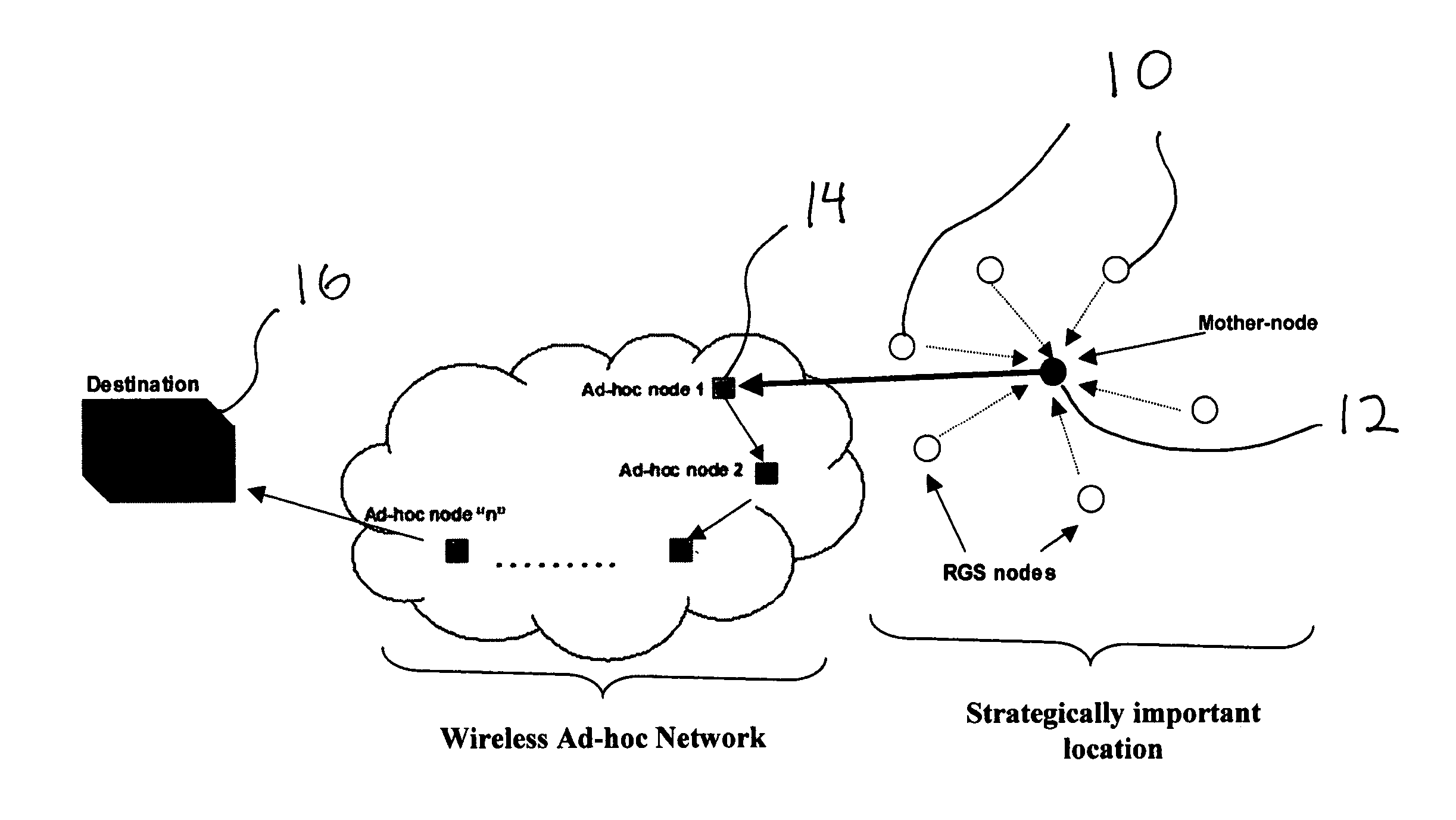
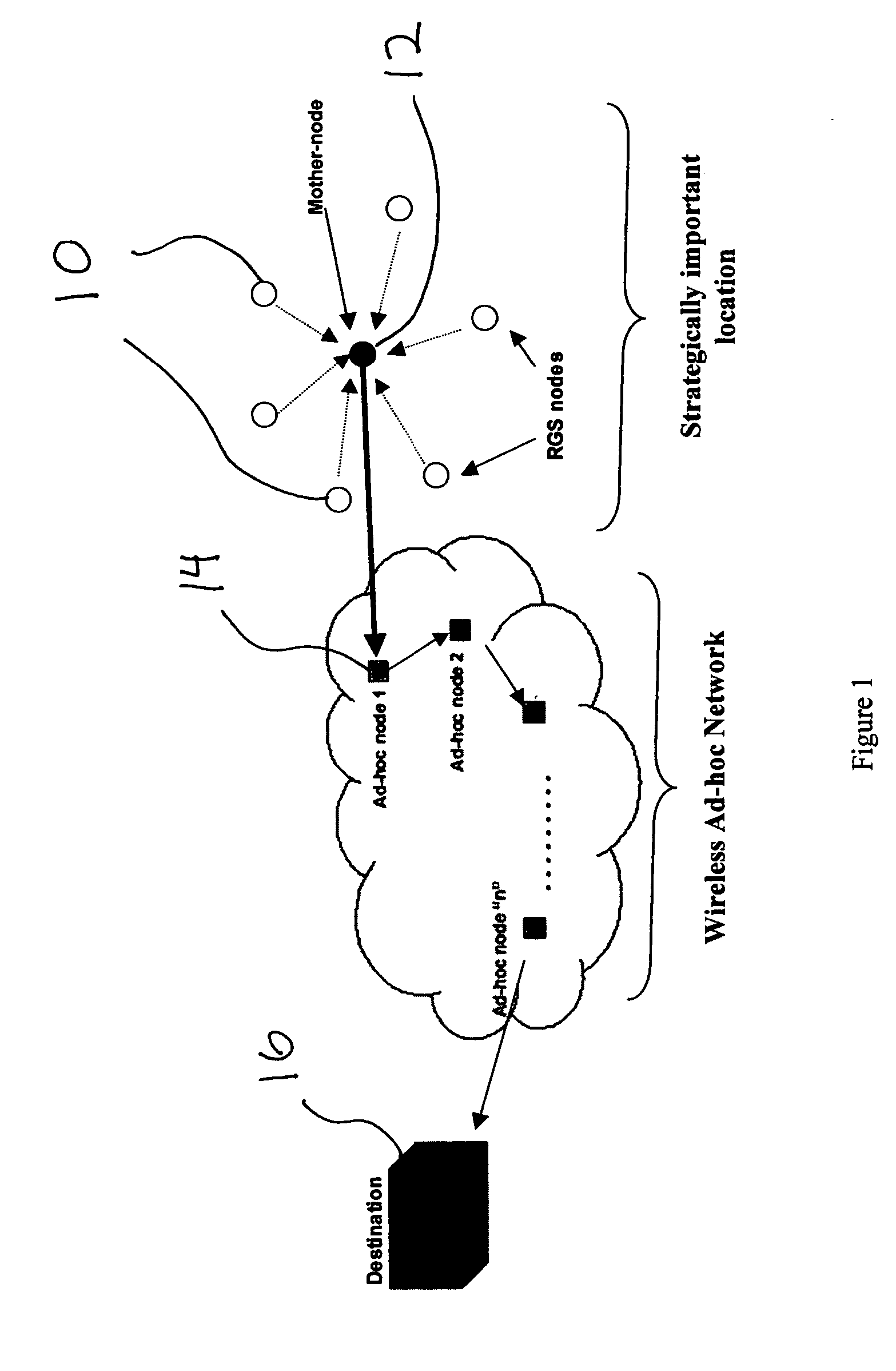
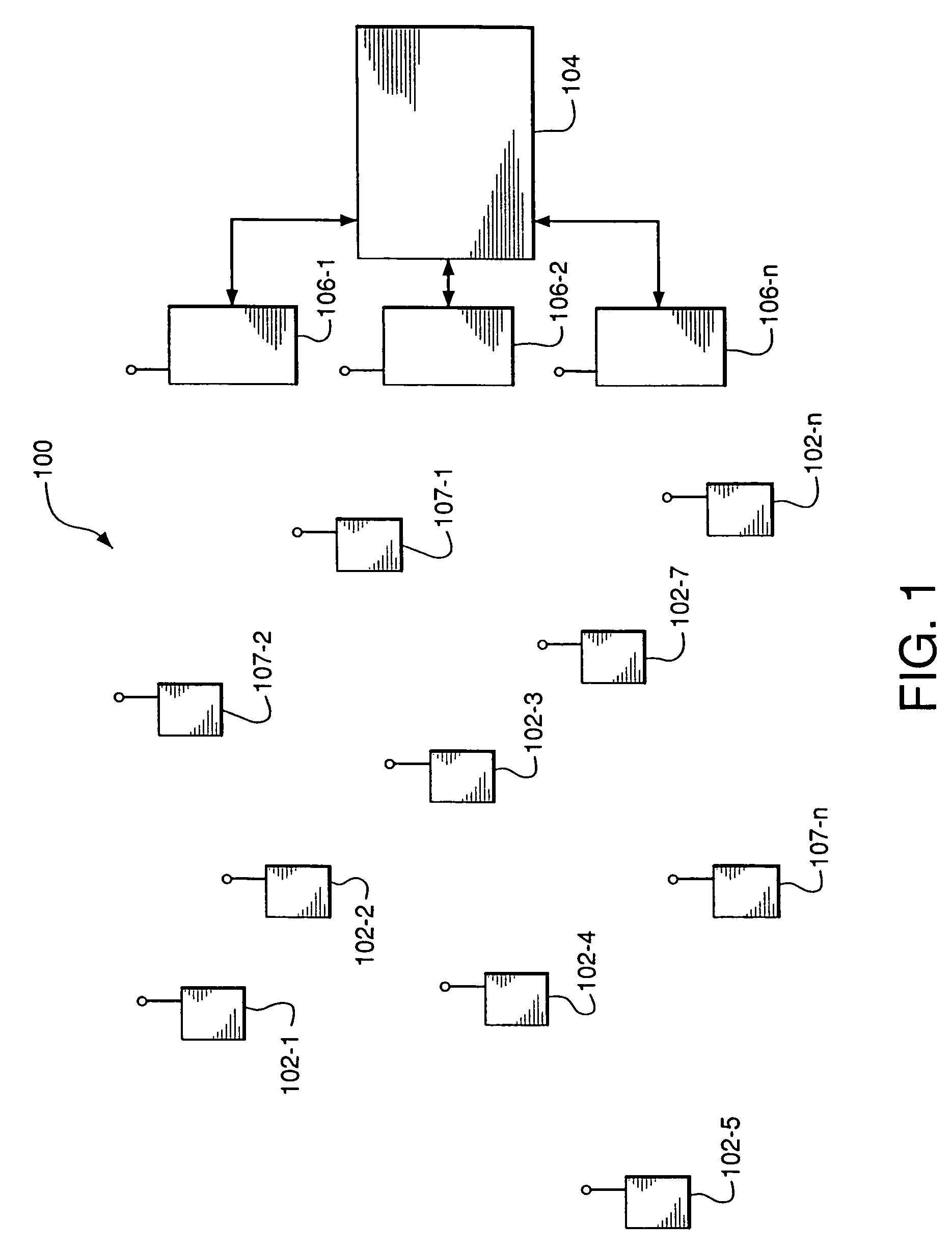
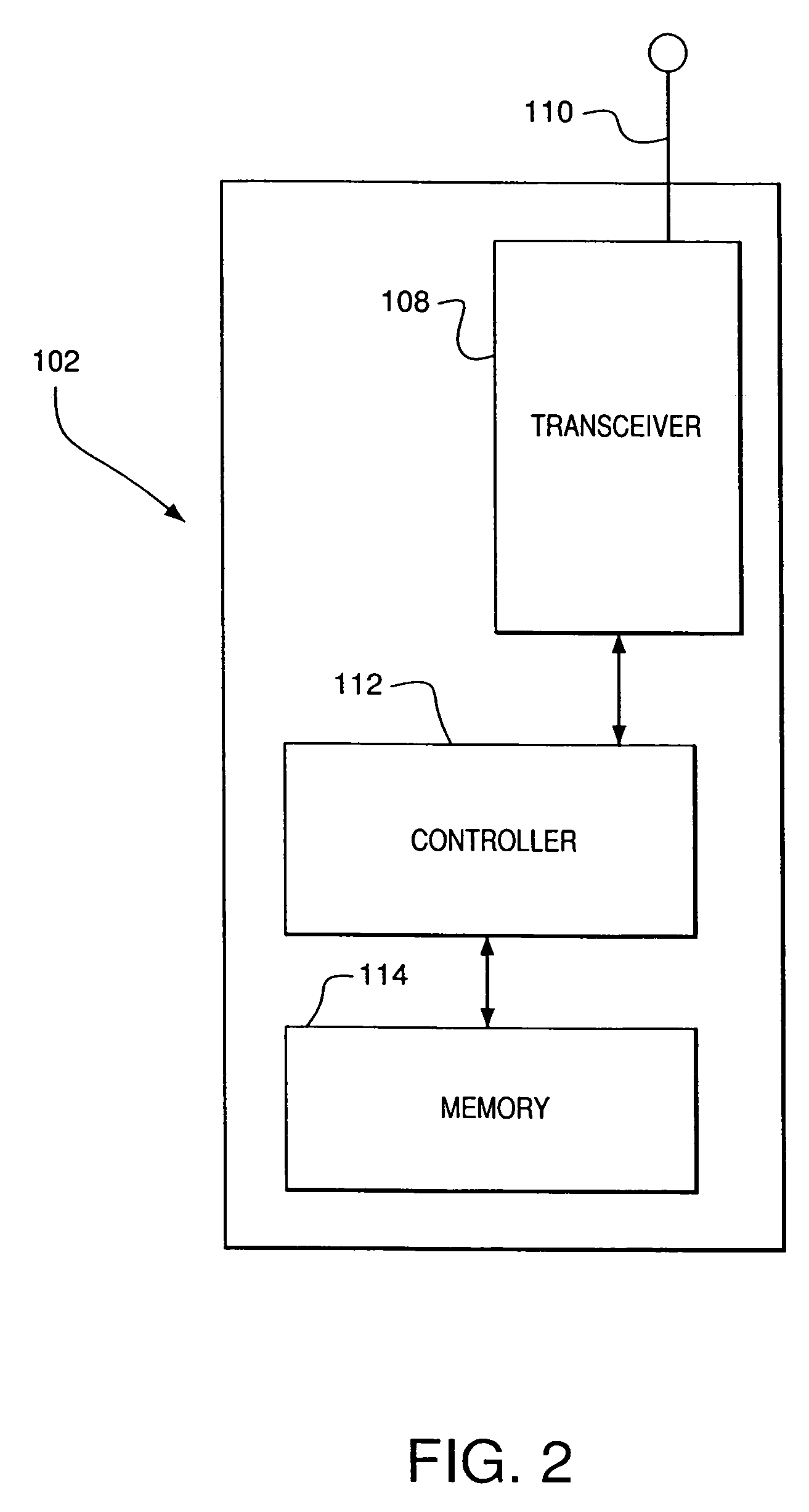
A wireless ad hoc network (WANET) or Mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is a decentralised type of wireless network. The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a pre-existing infrastructure, such as routers in wired networks or access points in managed (infrastructure) wireless networks. Instead, each node participates in routing by forwarding data for other nodes, so the determination of which nodes forward data is made dynamically on the basis of network connectivity and the routing algorithm in use.
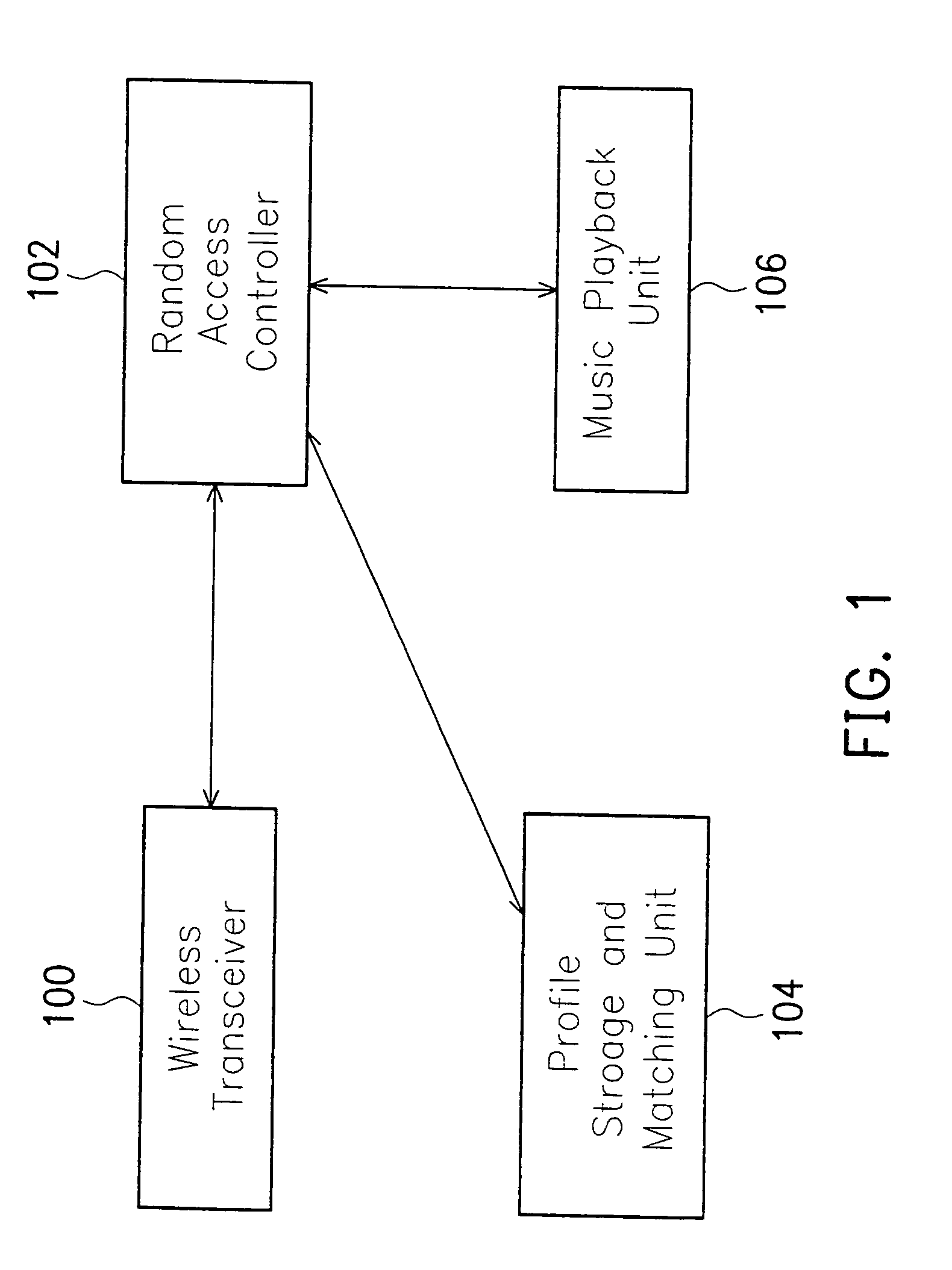
Apparatus and method for coordinated music playback in wireless ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS7236739B2Precise positioningNetwork topologiesBroadcast transmission systemsWireless ad hoc networkSelf-organizing network
The present invention details a novel application of wireless networking and digital music technologies to achieve coordinated and synchronized music playback among peer listeners connected by wireless ad-hoc networks. Two or more listeners in local proximity allowed by short-range wireless transmission can participate and listen to the same song at the same time. Moreover, the present invention allows listeners in the transmission range to discover each other through profile matching. A high matching score may indicate similar preference or taste to a certain music style thereby easily locating mutual interests, which would not have been possible.
Owner:DEDICATED LICENSING LLC
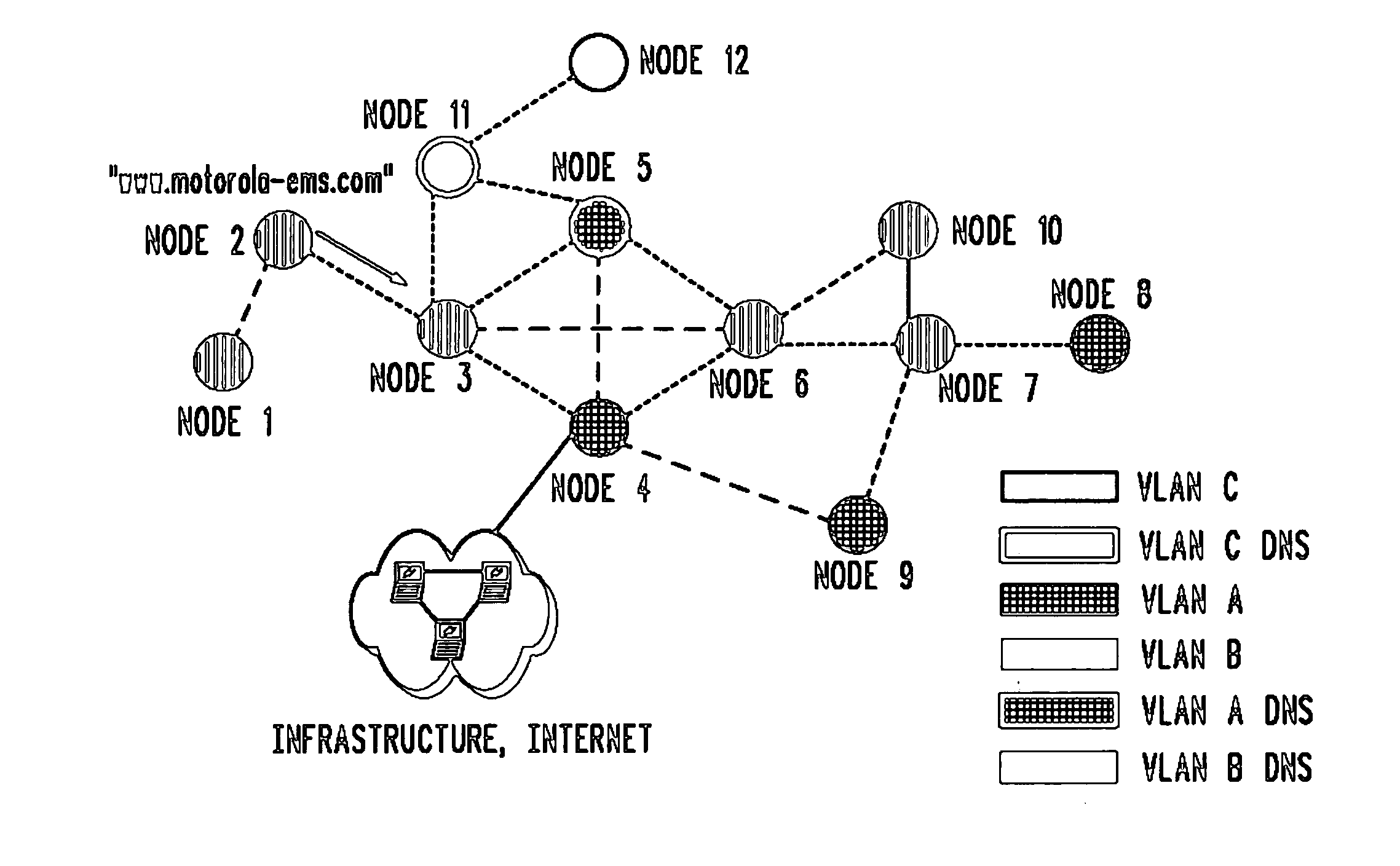
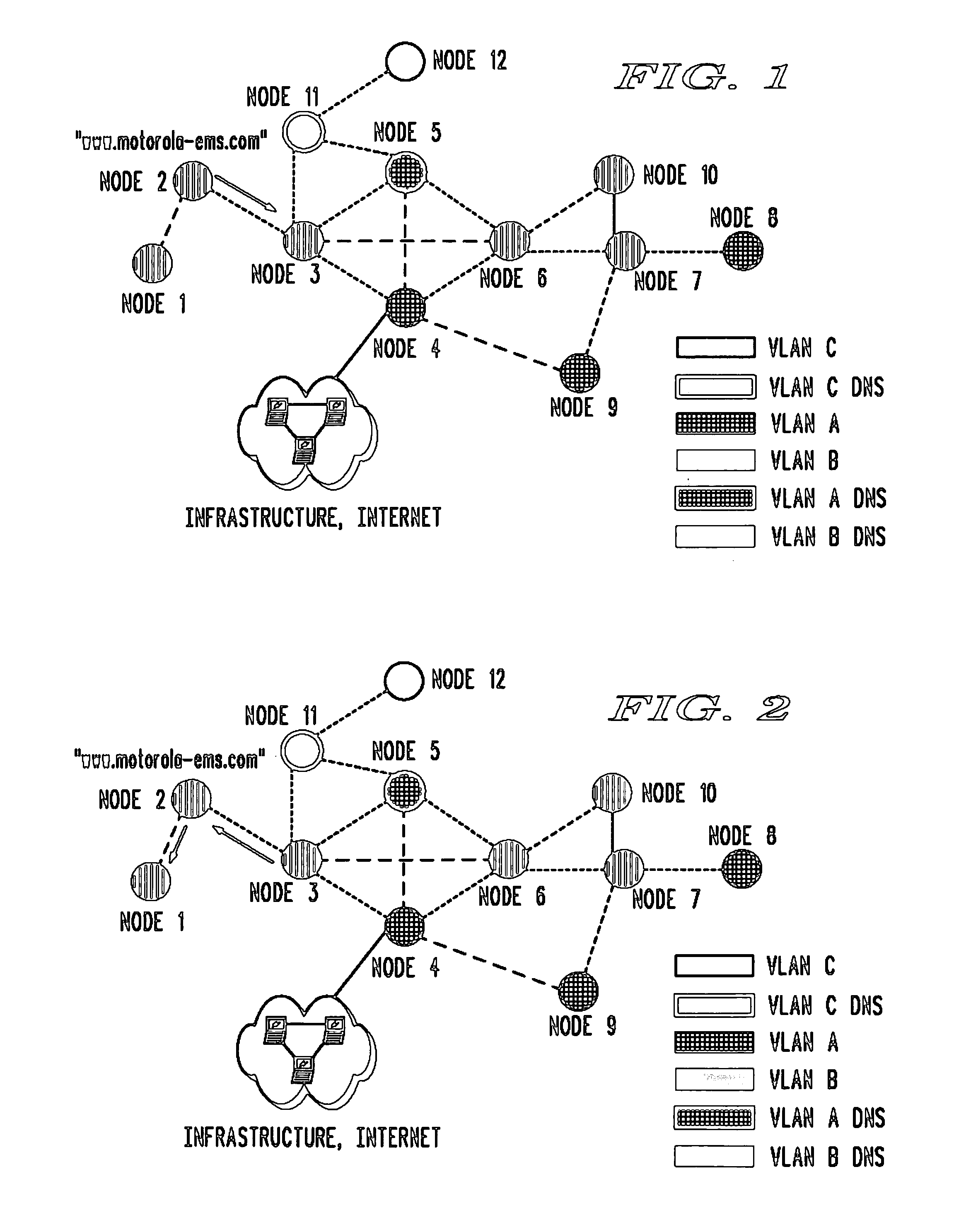
Method for domain name service (DNS) in a wireless ad hoc network
In a wireless ad hoc network comprising a plurality of nodes, a primary node receives a domain name service (DNS) query from a node. The primary node determines whether the query can be resolved based on cached information. If the DNS query can be resolved based on cached information, the primary node sends a response to the node. If the DNS query cannot be resolved based on cached information, the primary node sends the DNS query outside the ad hoc network for resolution.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
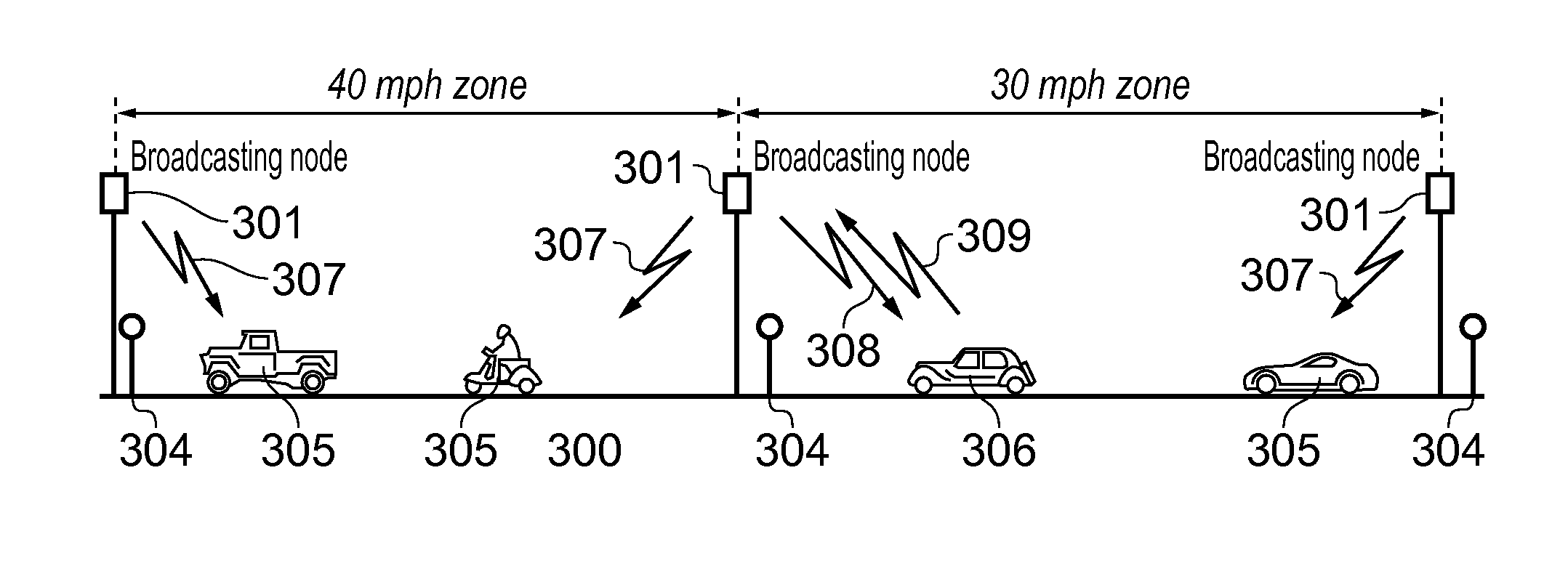
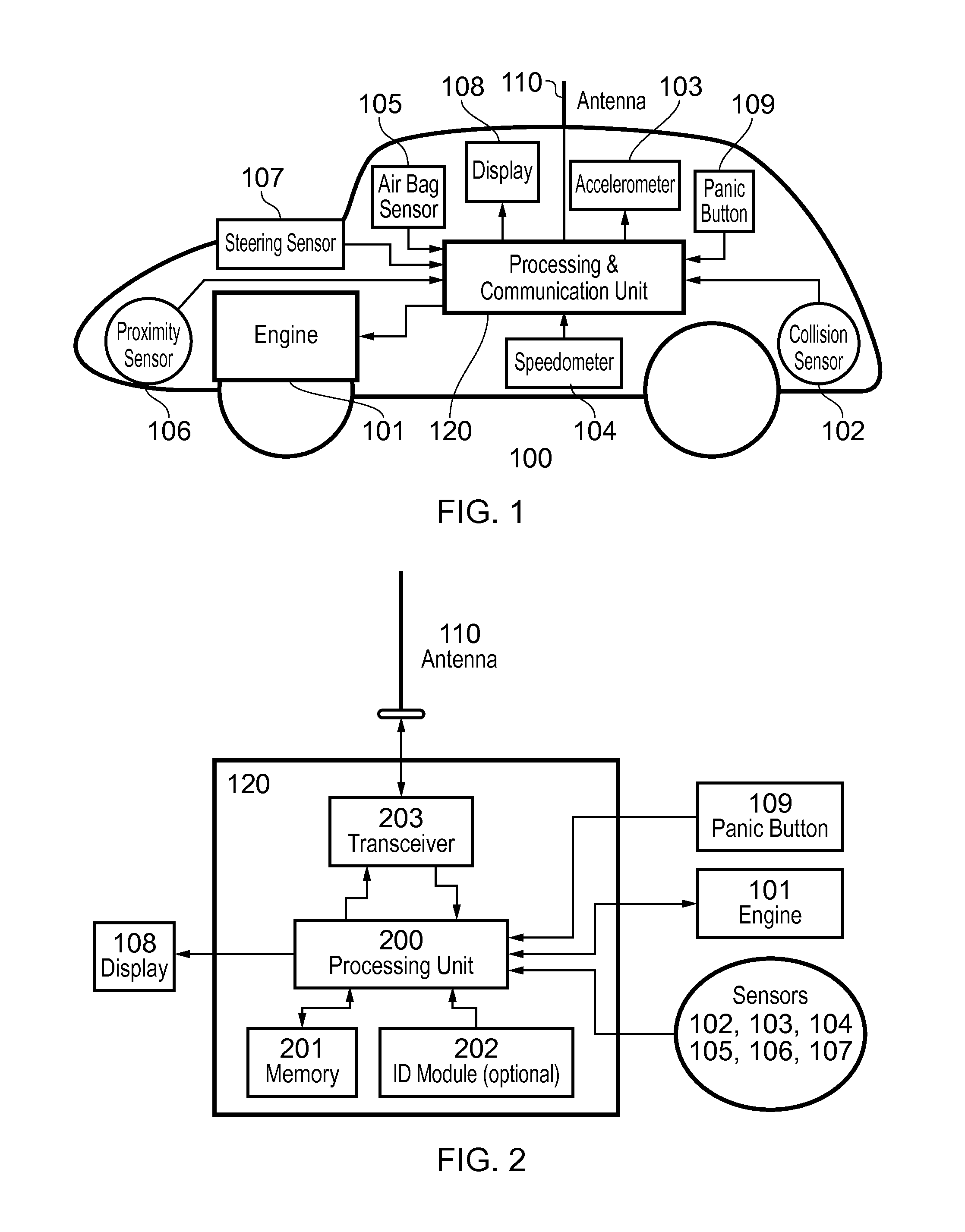
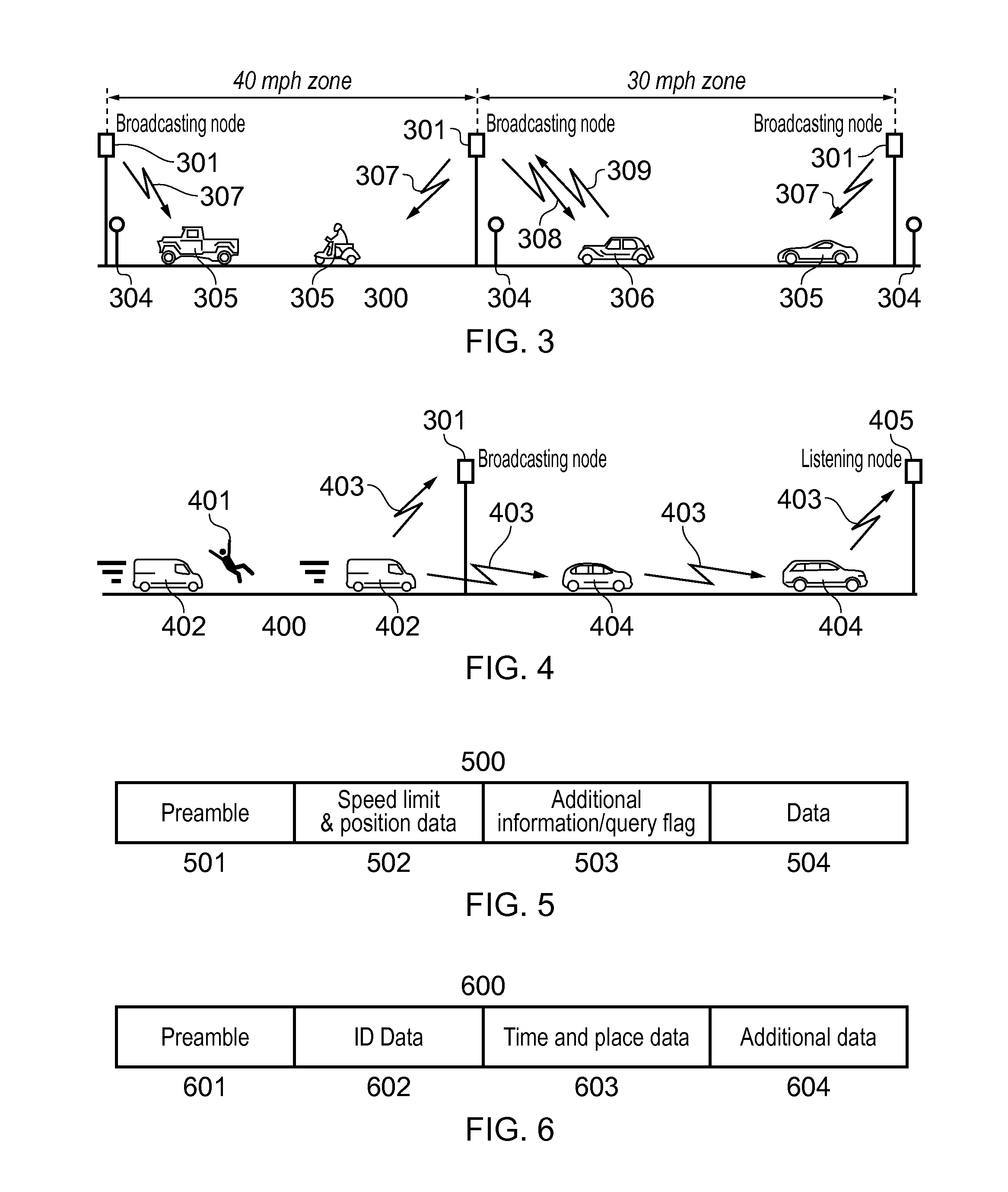
Vehicular safety system
ActiveUS20150310742A1Curb number of fatalityImprove road safetyArrangements for variable traffic instructionsAlarmsInformation dispersalEvent type
A vehicular safety system employing an adaptive epidemic information dissemination protocol running on a wireless ad-hoc network composed by neighboring vehicles and roadside stations. The protocol is based on storage and re-transmission of messages by vehicle on-board units; both storage time and re-transmission period are adaptively adjusted to make information spread through the network reasonably certain. An on-board vehicle system monitors a speed and acceleration to detect collisions or any other dangerous situations that might compromise the safety; when such an event is detected a time-stamped message identifies the vehicle and approximate location and event type. A panic button can trigger an emergency message in an immediate threat situation. Roadside stations add their location to the messages they relay; they also receive messages transmitted from passing vehicles, relaying them to law-enforcement agencies. Roadside stations can also broadcast messages aimed at locating and safely disabling stolen vehicles.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
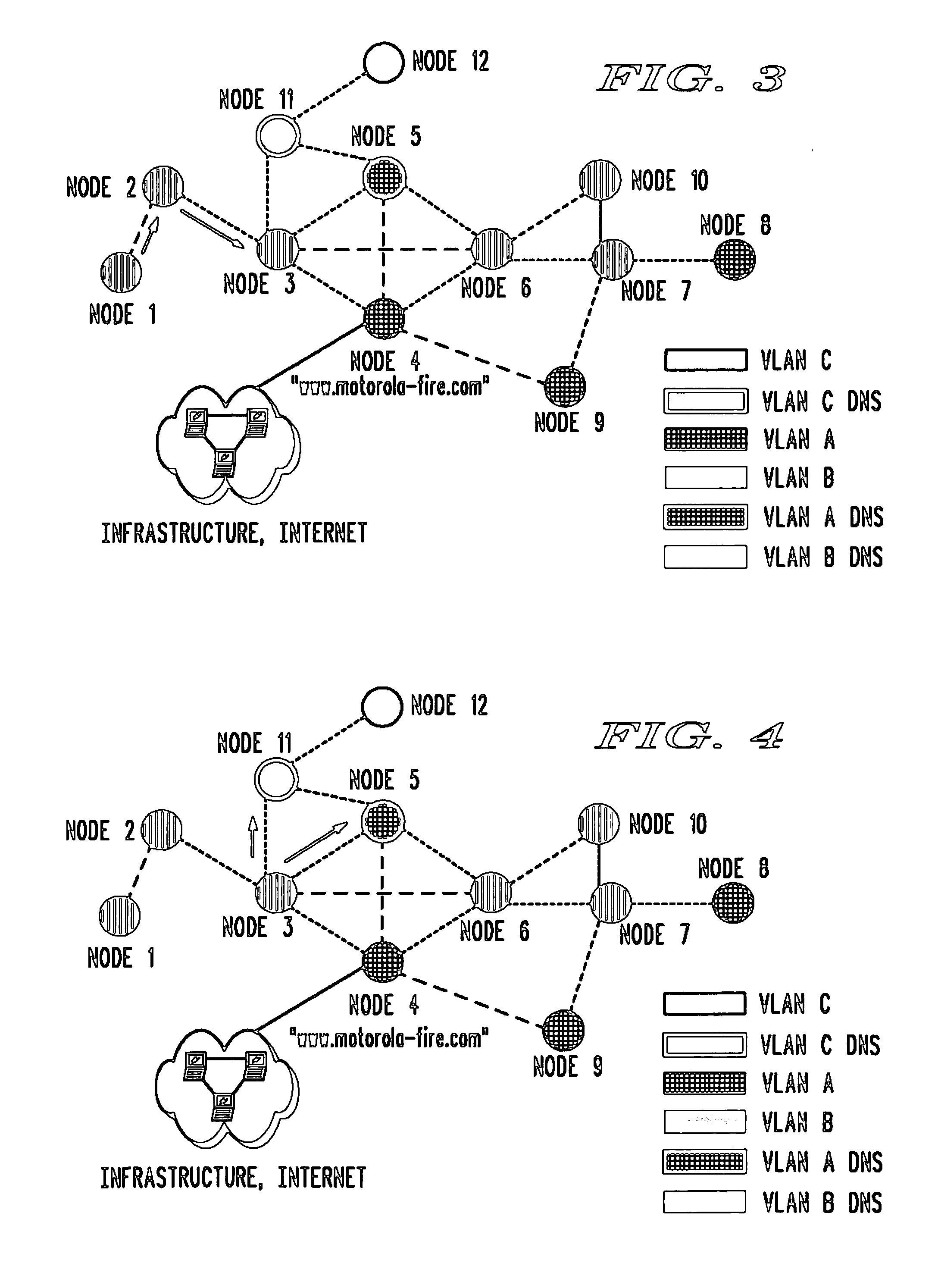
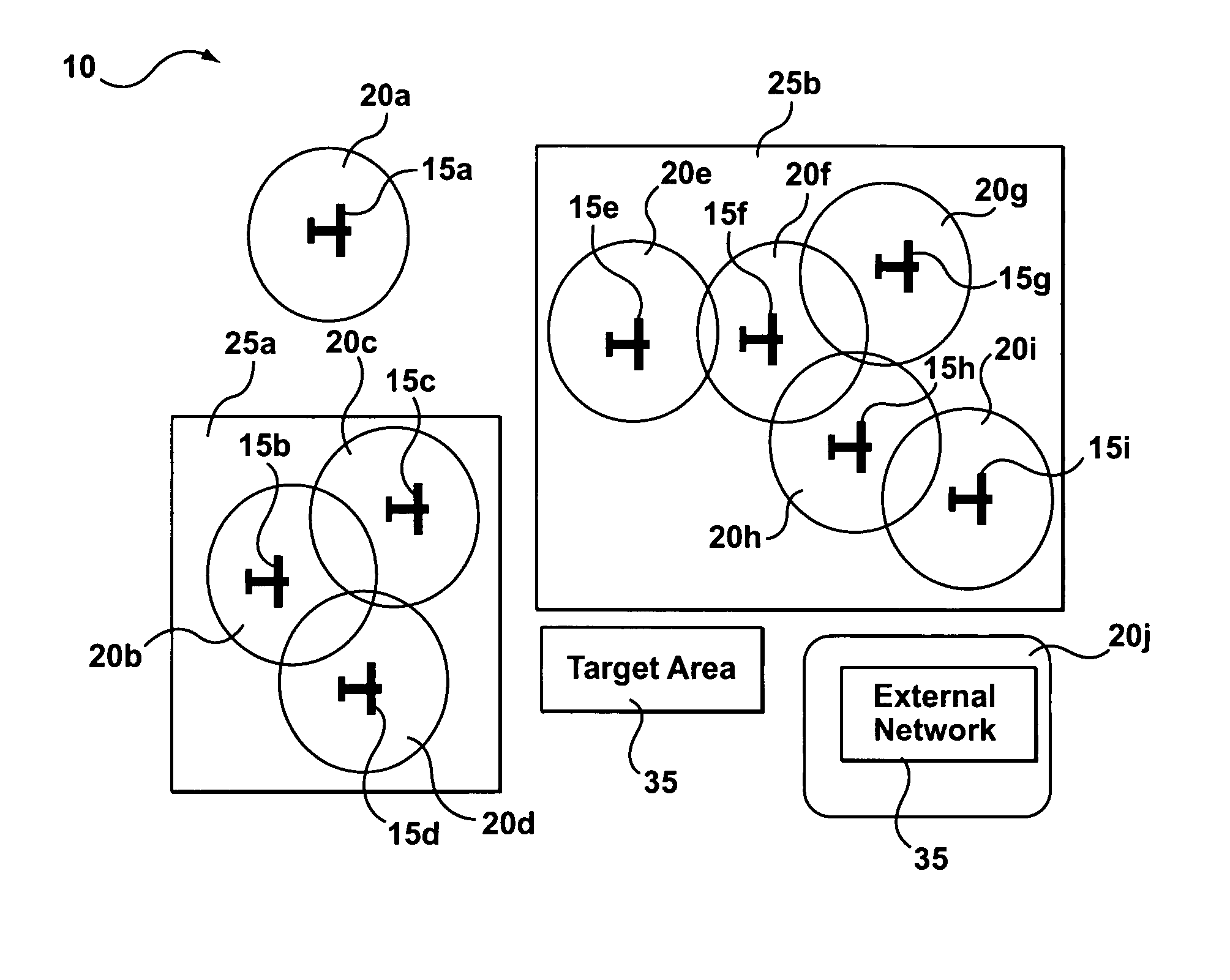
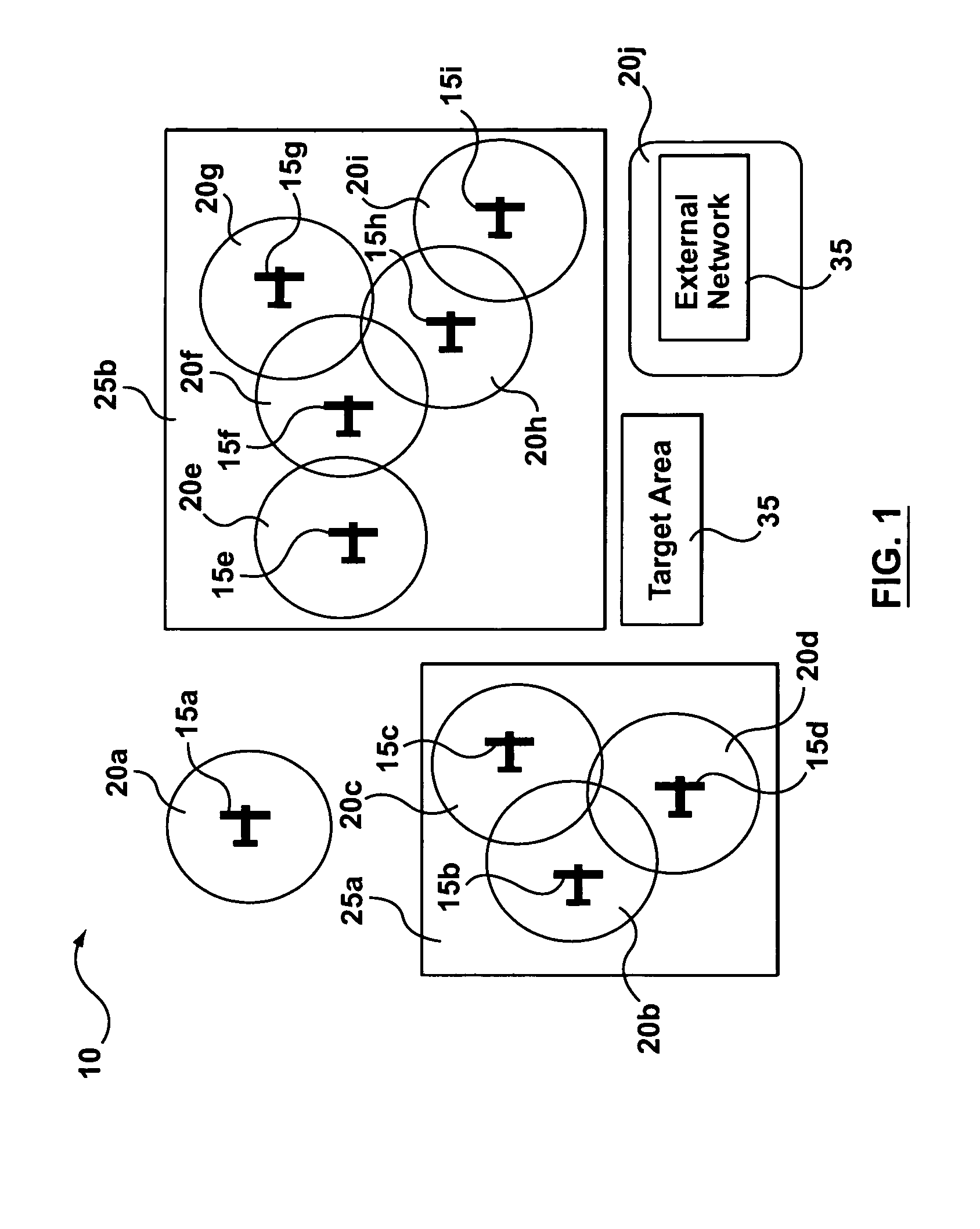
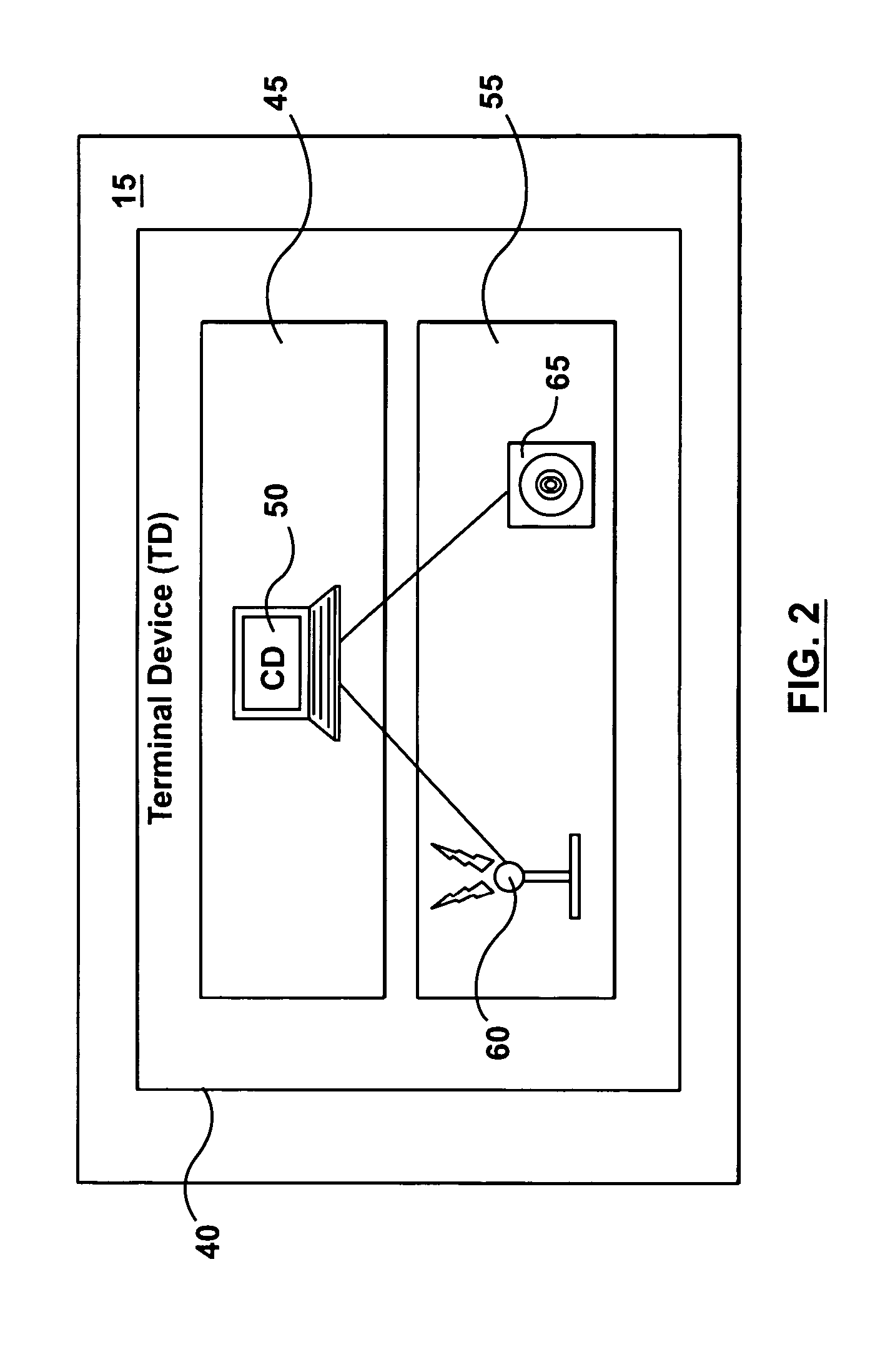
System and method for a mobile AD HOC network suitable for aircraft
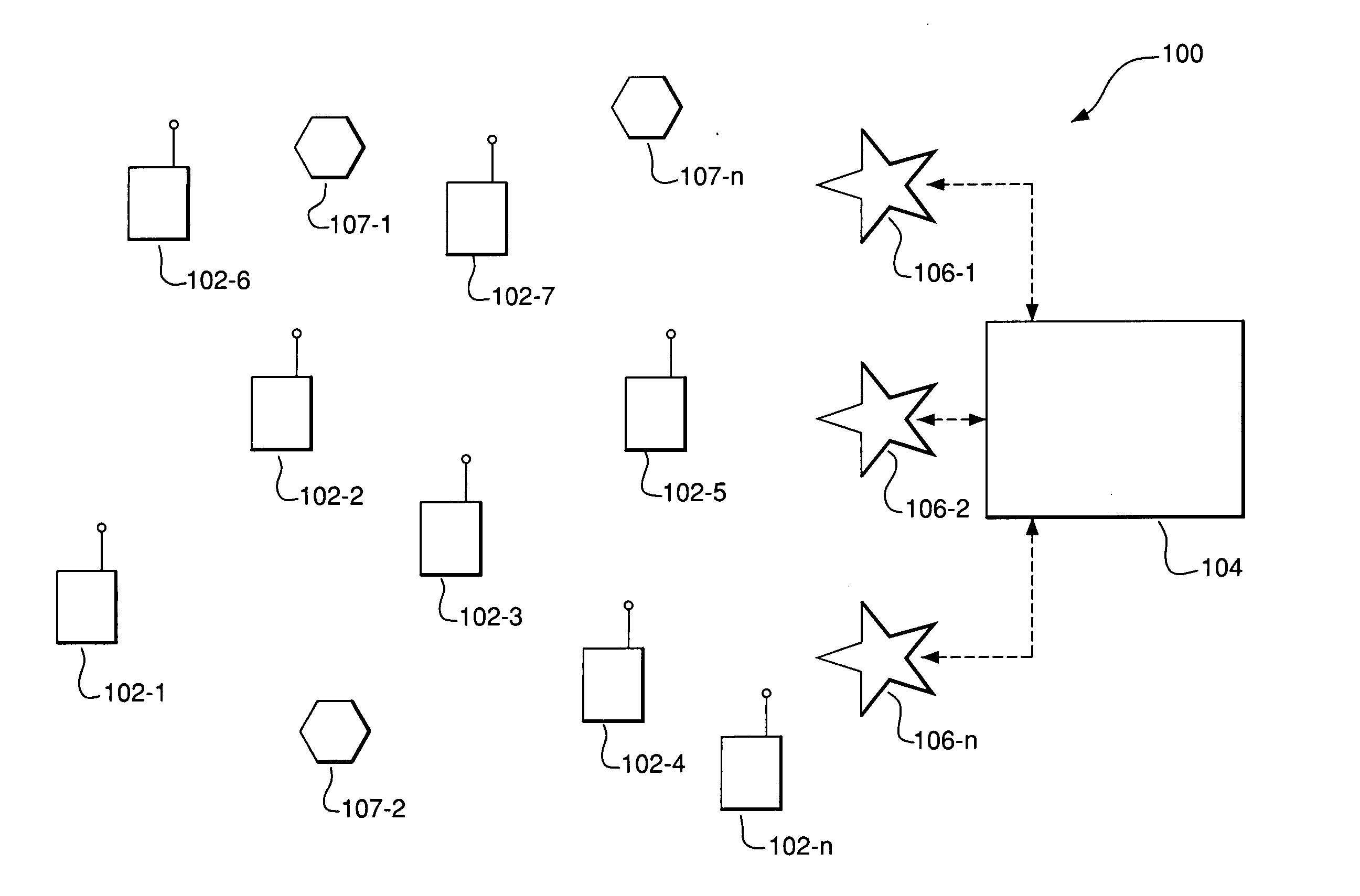
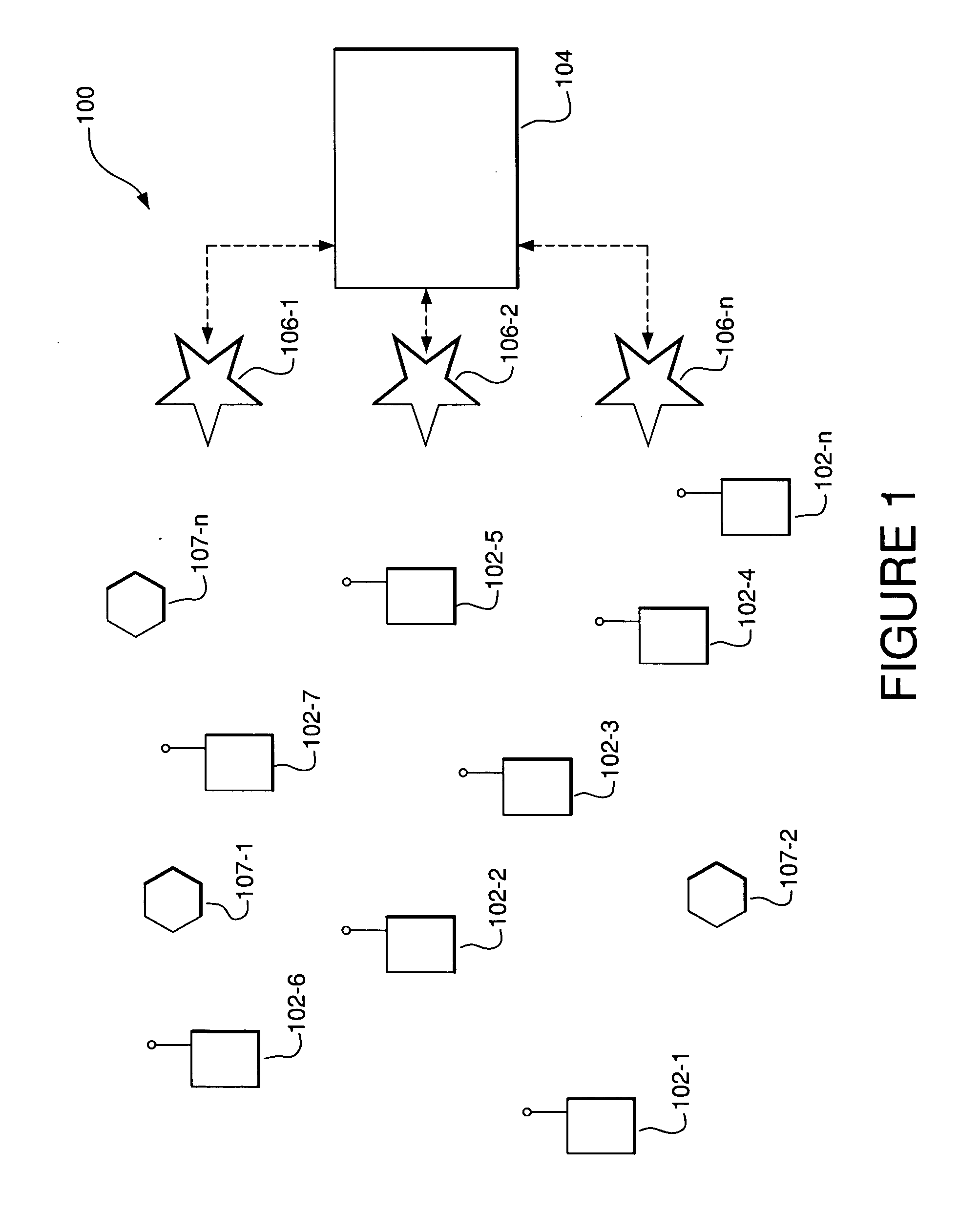
The present invention provides a wireless ad hoc network suitable for sharing data on a peer-to-peer basis between nodes, some of which may be aircraft, having a terminal device comprising a wireless communications transceiver, a sensor, and a computing device. Multiple hops between nodes maximize range of the network. In addition, architectures for terminal devices allow for use of a wide variety of wireless communications transceivers and sensors, without affecting applications that use the network. Such invention may include, among others, a fire fighting application allowing different aircraft to co-ordinate firefighting activities by using shared fire and positional data for aircraft.
Owner:9G WIRELESS
Hierarchical mobile ad-hoc network and methods for performing reactive routing therein using dynamic source routing (DSR)
InactiveUS6870846B2Use to determineError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWireless ad hoc networkSelf-organizing network
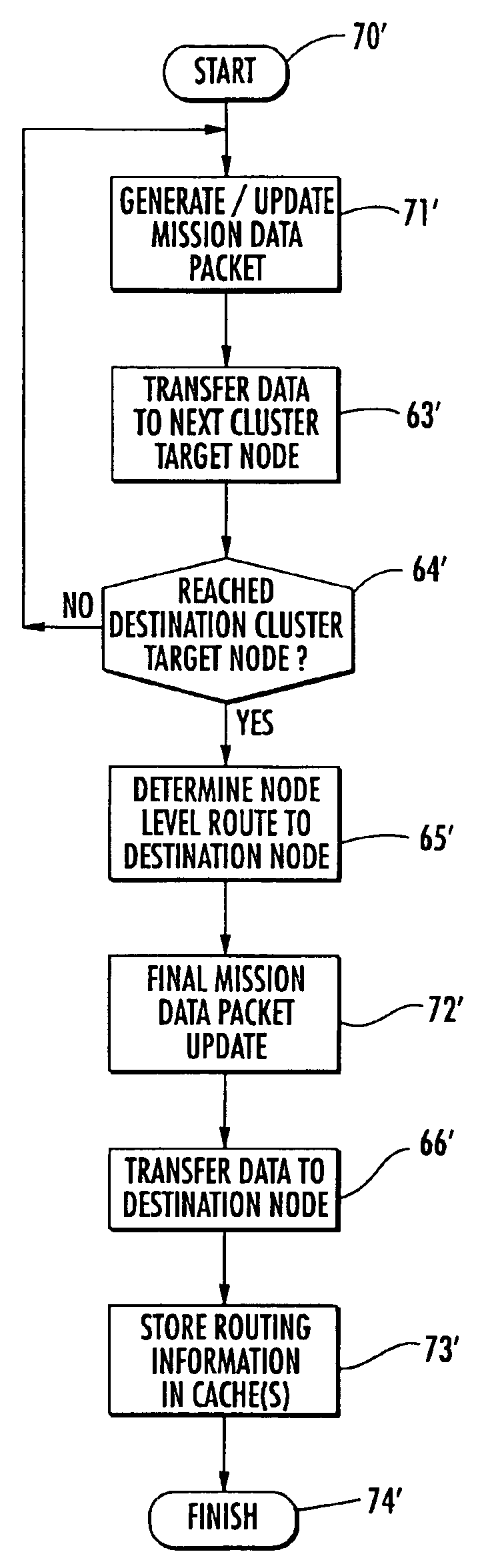
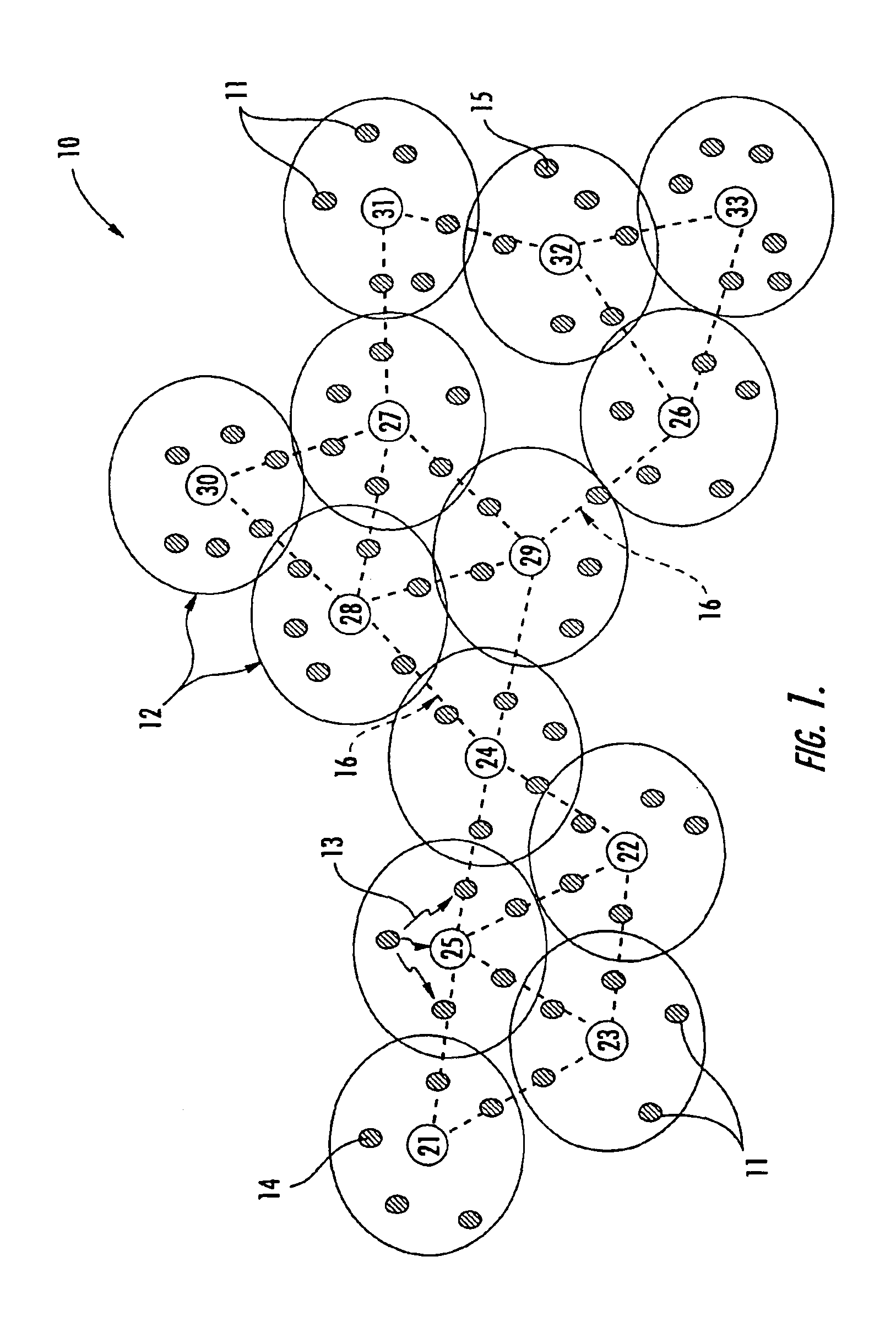
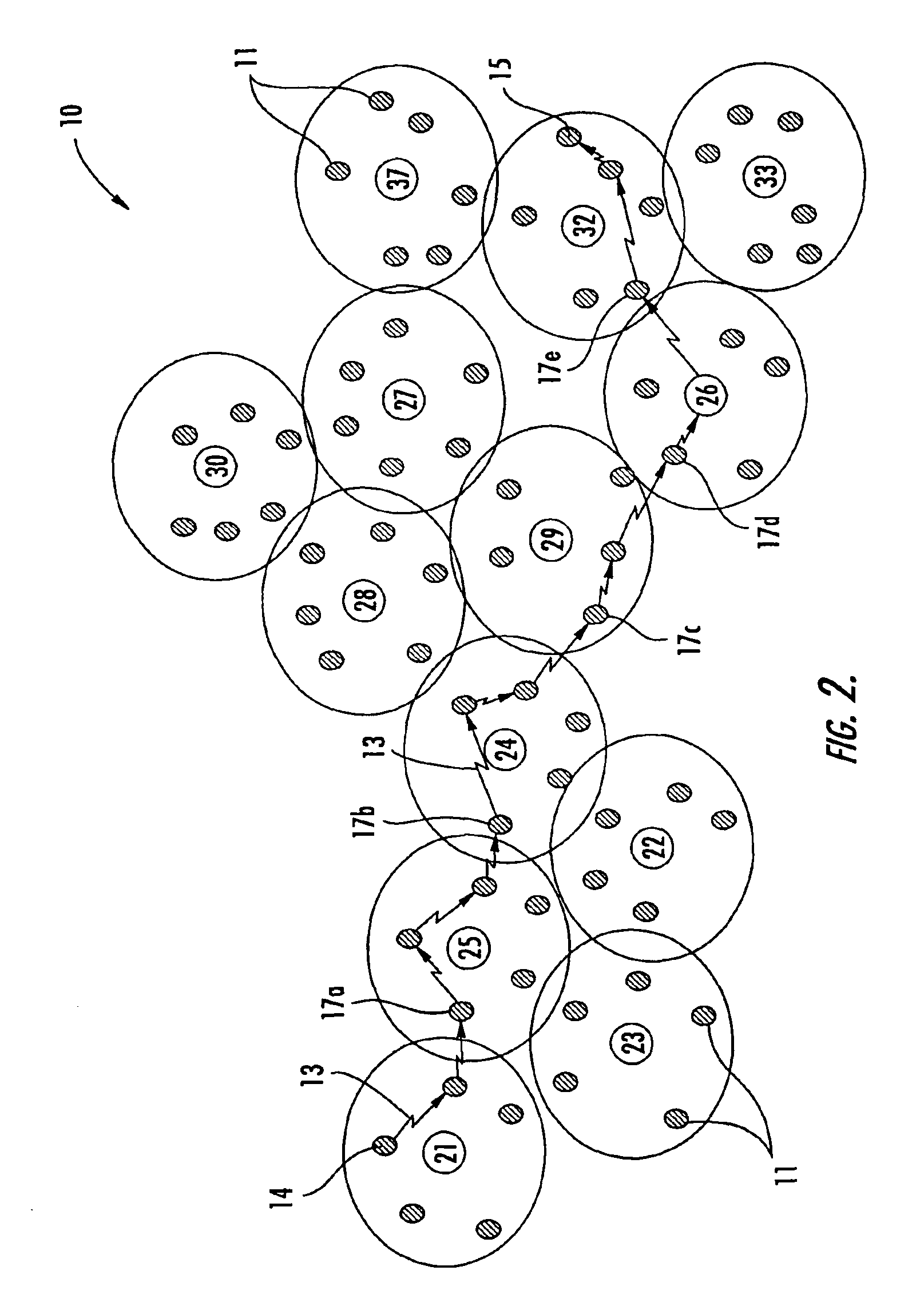
A method is provided for sending data in a wireless ad-hoc network including a plurality of nodes grouped into clusters of nodes and a plurality of wireless links connecting the plurality of nodes, where each cluster node has a designated cluster leader node. The method may include sending a cluster-level route request from a source node of a source cluster to a cluster leader node of the source cluster, and determining a cluster-level route between the source cluster and a destination cluster including a destination node responsive to the cluster-level route request and using a plurality of the cluster leader nodes. Furthermore, at least one cluster target node may be designated in a cluster along the cluster-level route, and a node-level route determined from the source node to the destination node including the at least one cluster target node. In addition, the method may also include generating a mission data packet for transferring the data.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
Traffic management in distributed wireless networks
InactiveUS20120224484A1Error preventionTransmission systemsService-level agreementInterference ratio
Wireless networks and devices are ubiquitous today. For service providers to offer customers QoS and Service Level Agreements (SLAs) means in part providing resilient connectivity of wireless devices with good signal strength, good Signal to Noise and Interference Ratio (SNIR), and adequate useable bandwidth. Doing so requires that devices transmitting and receiving packets use over-the-air bandwidth efficiently and manage over-the-air congestion. According to embodiments of the invention QoS measurements and controls are incorporated only in the network (i.e. APs or controllers) and therefore QoS and SLAs can be achieved with all deployed client stations versus standards based approaches that require additional capabilities in network nodes, client stations and in most cases modifications to the applications. SLAs can be provided exploiting embodiments of the invention for traffic prioritization, capacity improvements through load distribution, and adjacent channel interference mitigation discretely or in combination with standards based mechanisms.
Owner:3INOVA NETWORKS
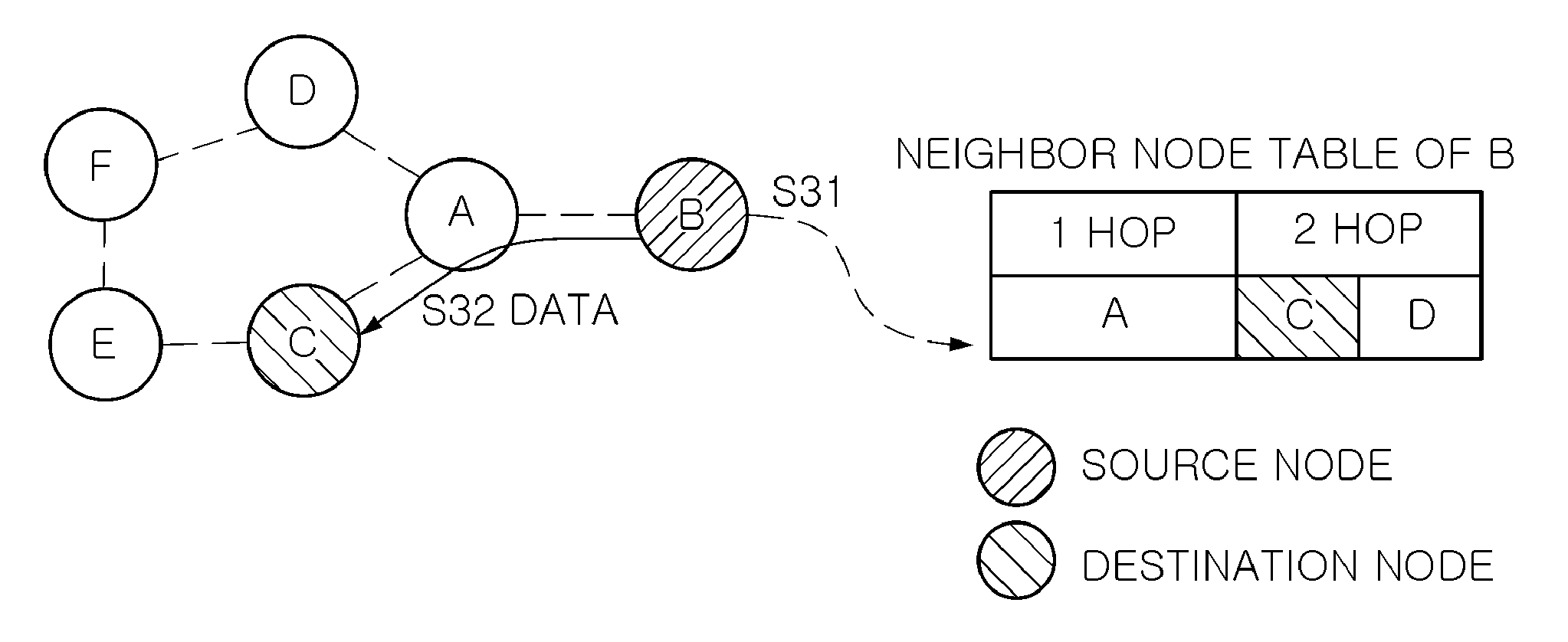
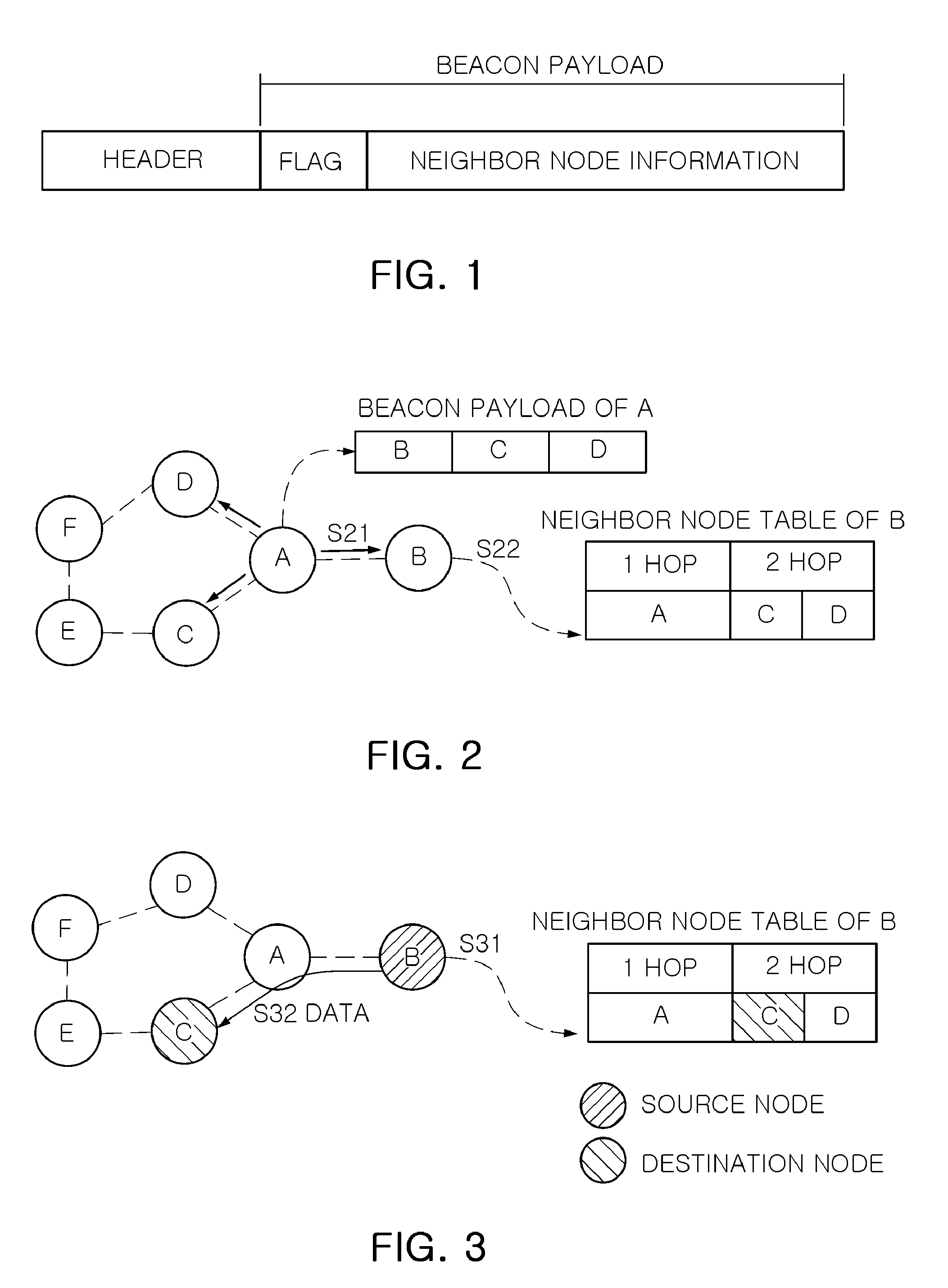
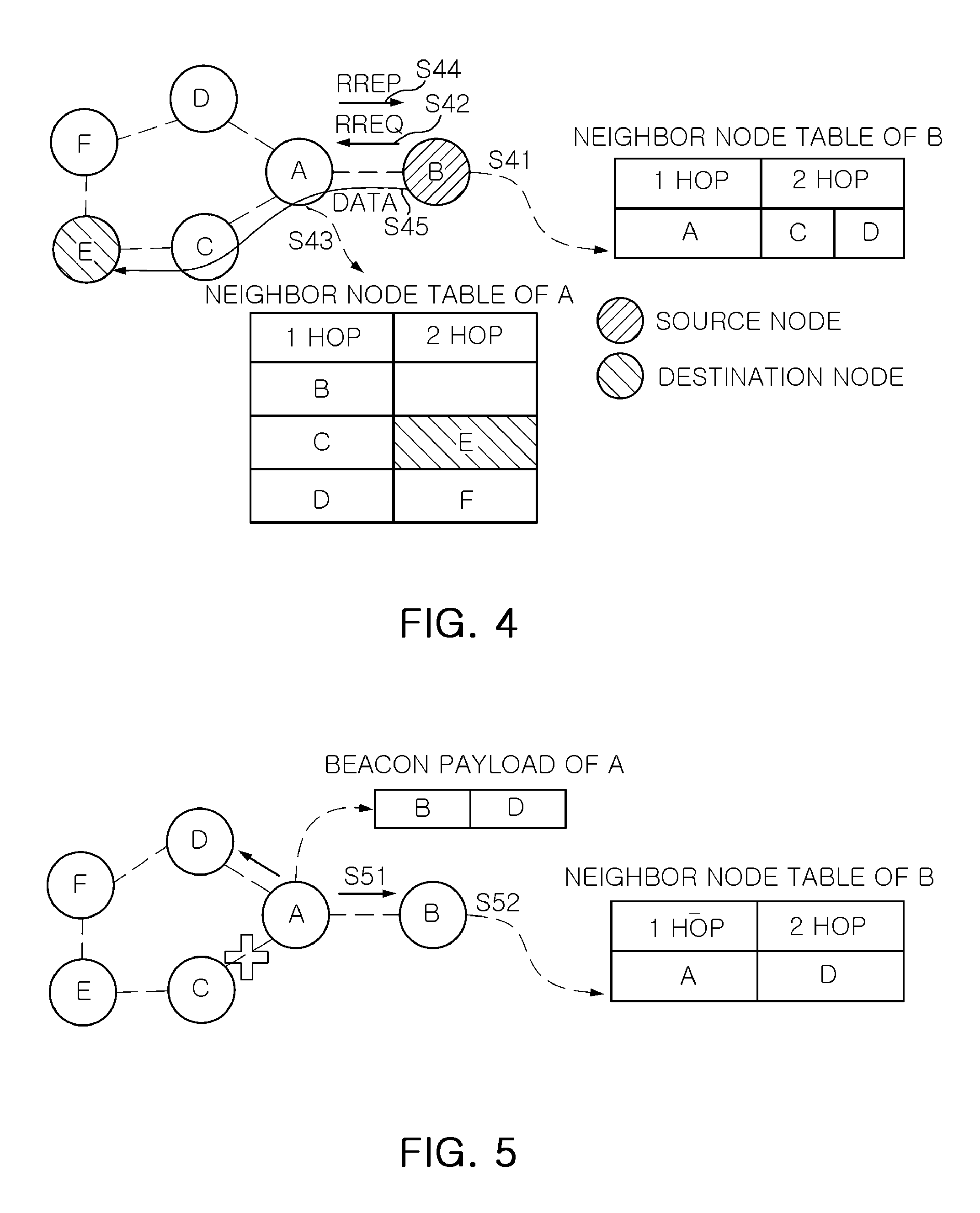
Mesh routing method and mesh routing apparatus in beacon enabled wireless ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS20110149858A1MinimizationNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationMesh routingWireless ad hoc network
There is provided a mesh routing method in beacon-enabled wireless AD-HOC networks that includes: broadcasting, by nodes constituting a wireless AD-HOC network, a beacon message loading neighbor node information on a beacon payload; managing, by a node receiving the broadcasted beacon message, its own neighbor node table by extracting the neighbor node information loaded on the beacon payload; and performing, by a source node attempting to transmit data or commands, mesh routing on the basis of its own neighbor node table.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
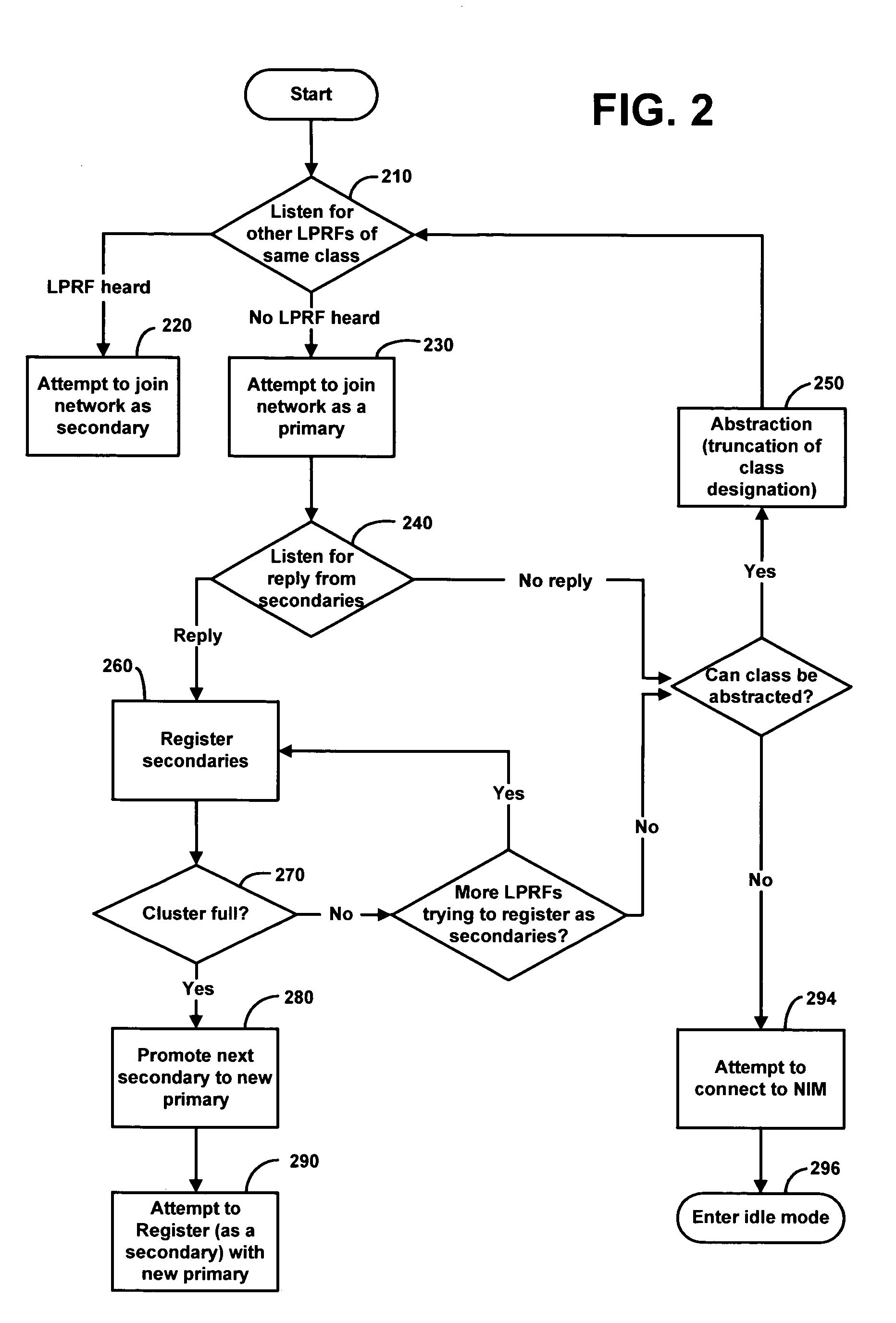
Forming communication cluster of wireless AD HOC network based on common designation
InactiveUS7209468B2High sensitivityIncrease rangeEnergy efficient ICTPosition fixationWireless transceiverTransceiver
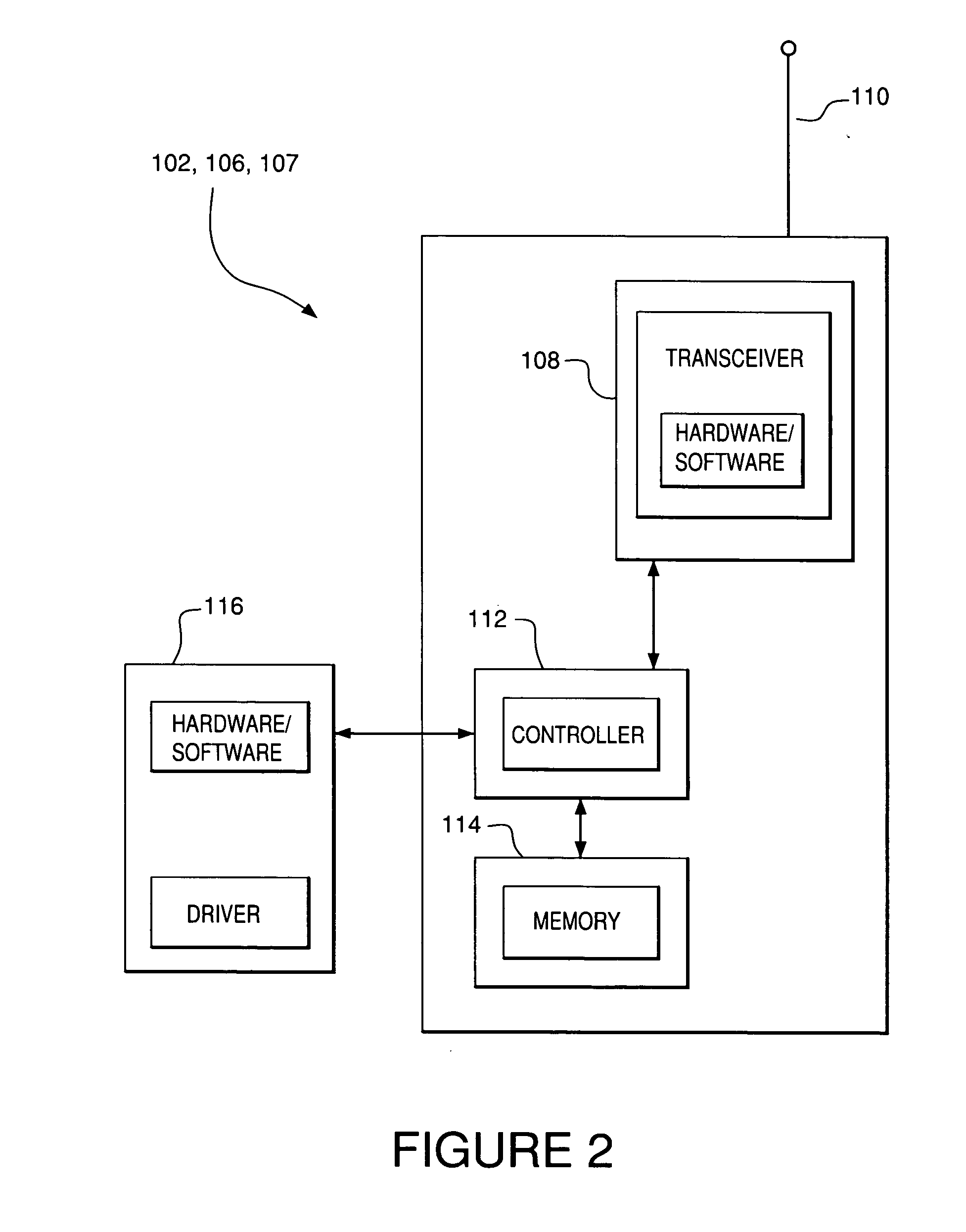
A method of forming an ad hoc hierarchical communication network among a plurality of wireless transceiver includes assigning to each of the transceivers one or more common designations. A network organization routine of the transceivers operates to establish hierarchical networks based on the transceivers' common designations, resulting in a logical network organization that provides efficiencies for acquiring information from particular transceivers that share a common designation. Each transceiver's common designation is used by a digital processor of the transceiver to selectively receive data packets that are intended for receipt by transceivers sharing the particular common designation. Such a “common designation” network reduces power consumption and signal interference, which increases battery life in the transceivers. The transceivers may include a query handling routine in communication with a memory of the transceiver for serving as a dynamic distributed hierarchical database system of information such as, for example, sensor-derived information and time-sensitive information.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
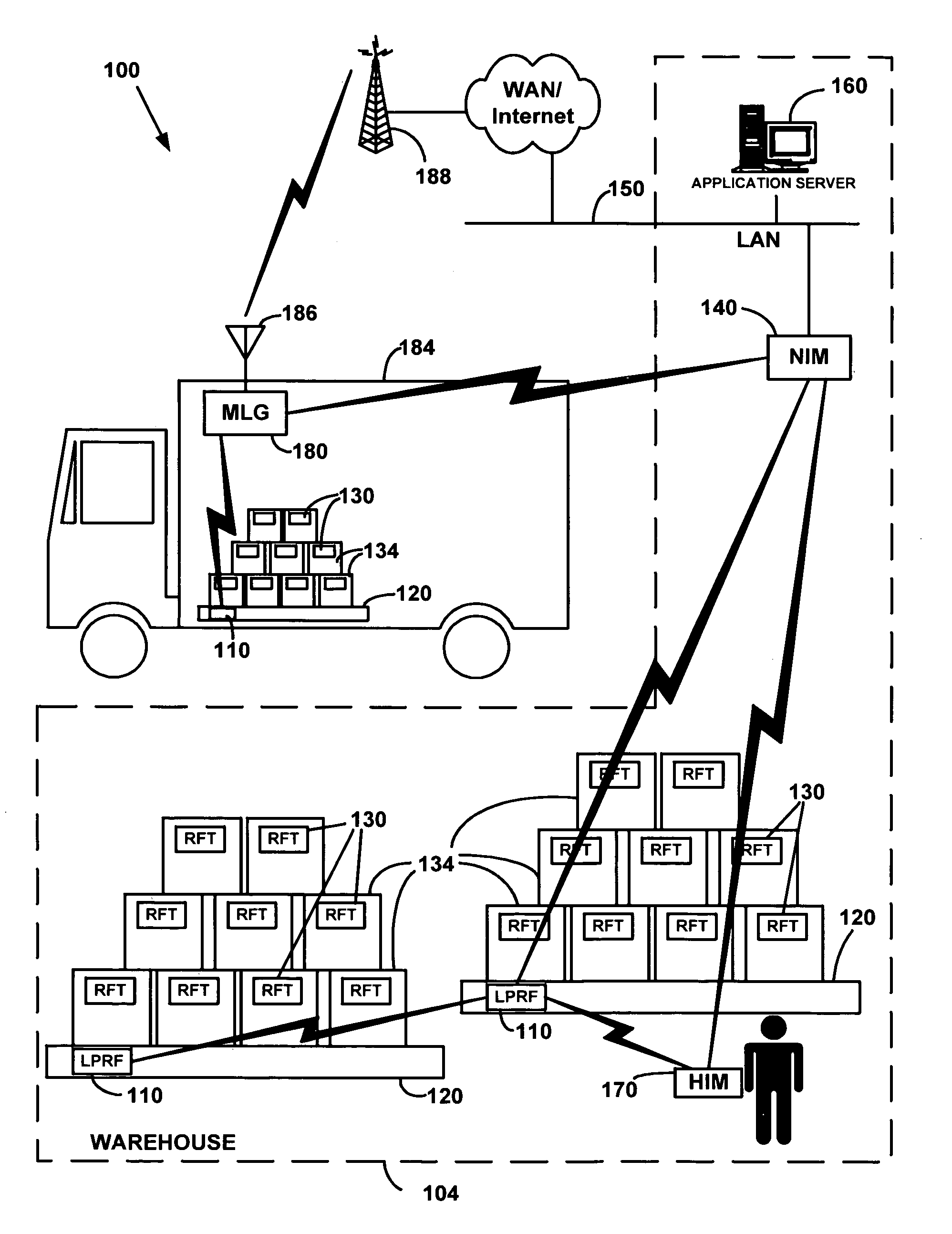
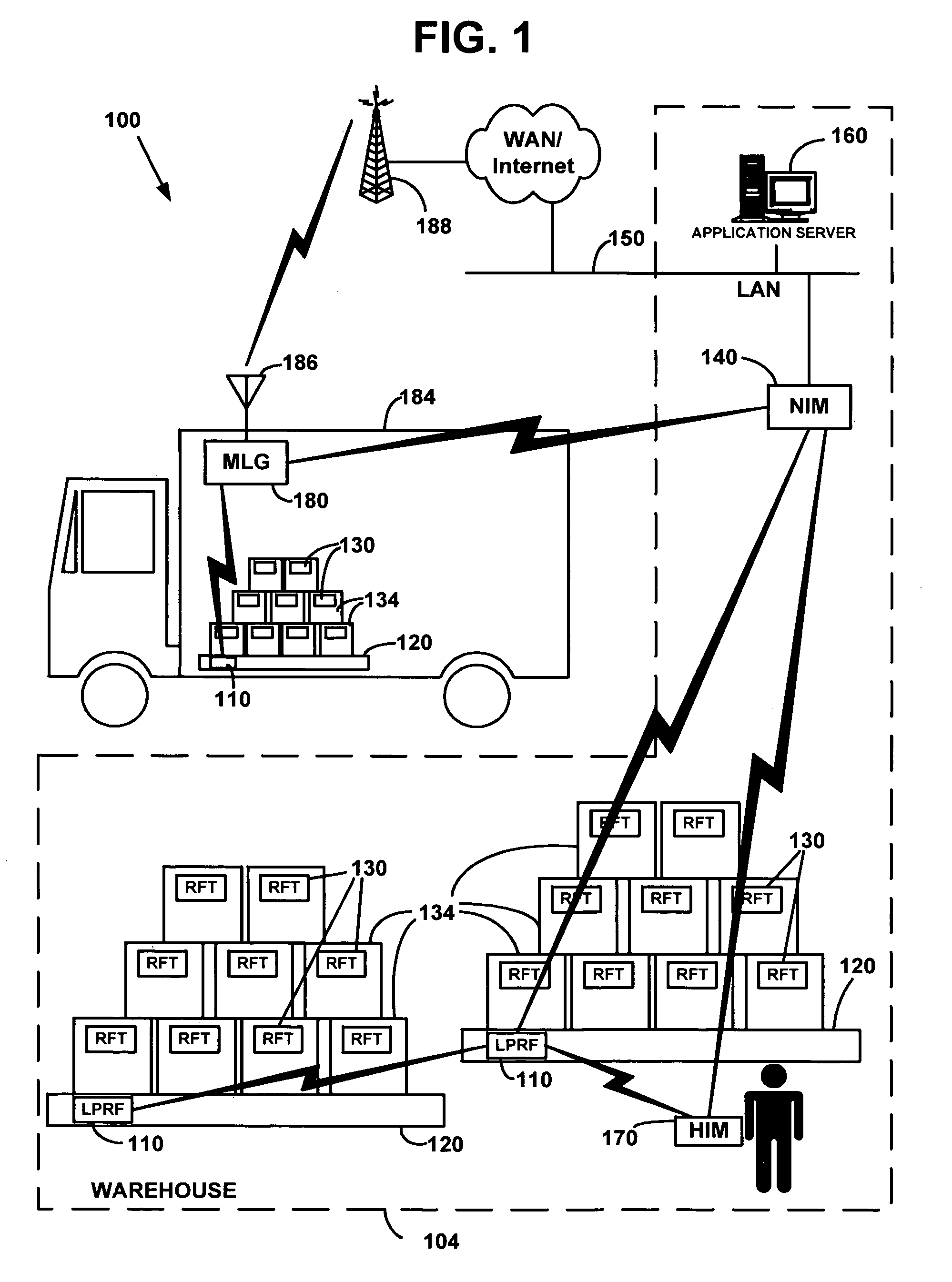
Wireless ad-hoc RFID tracking system
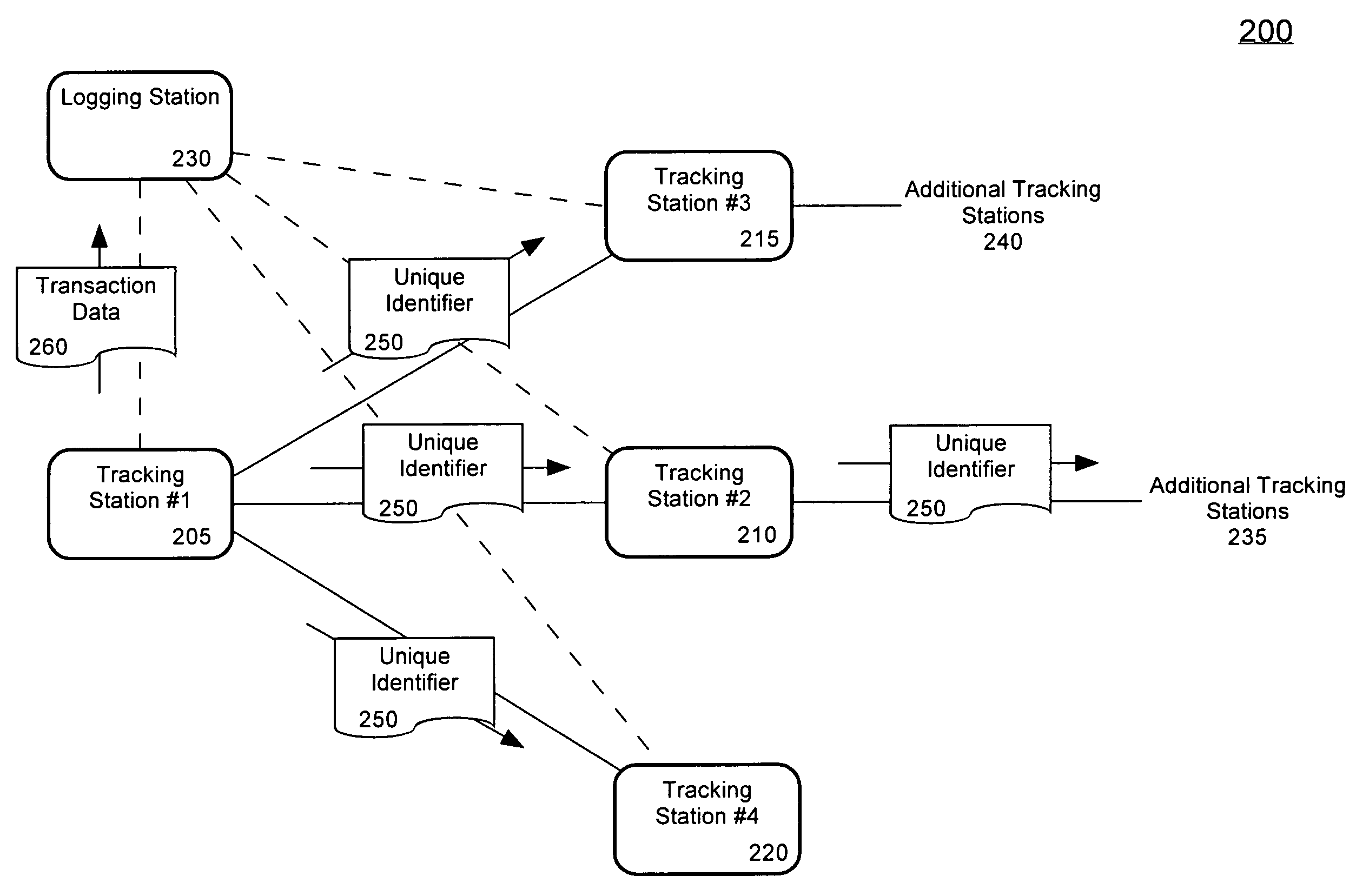
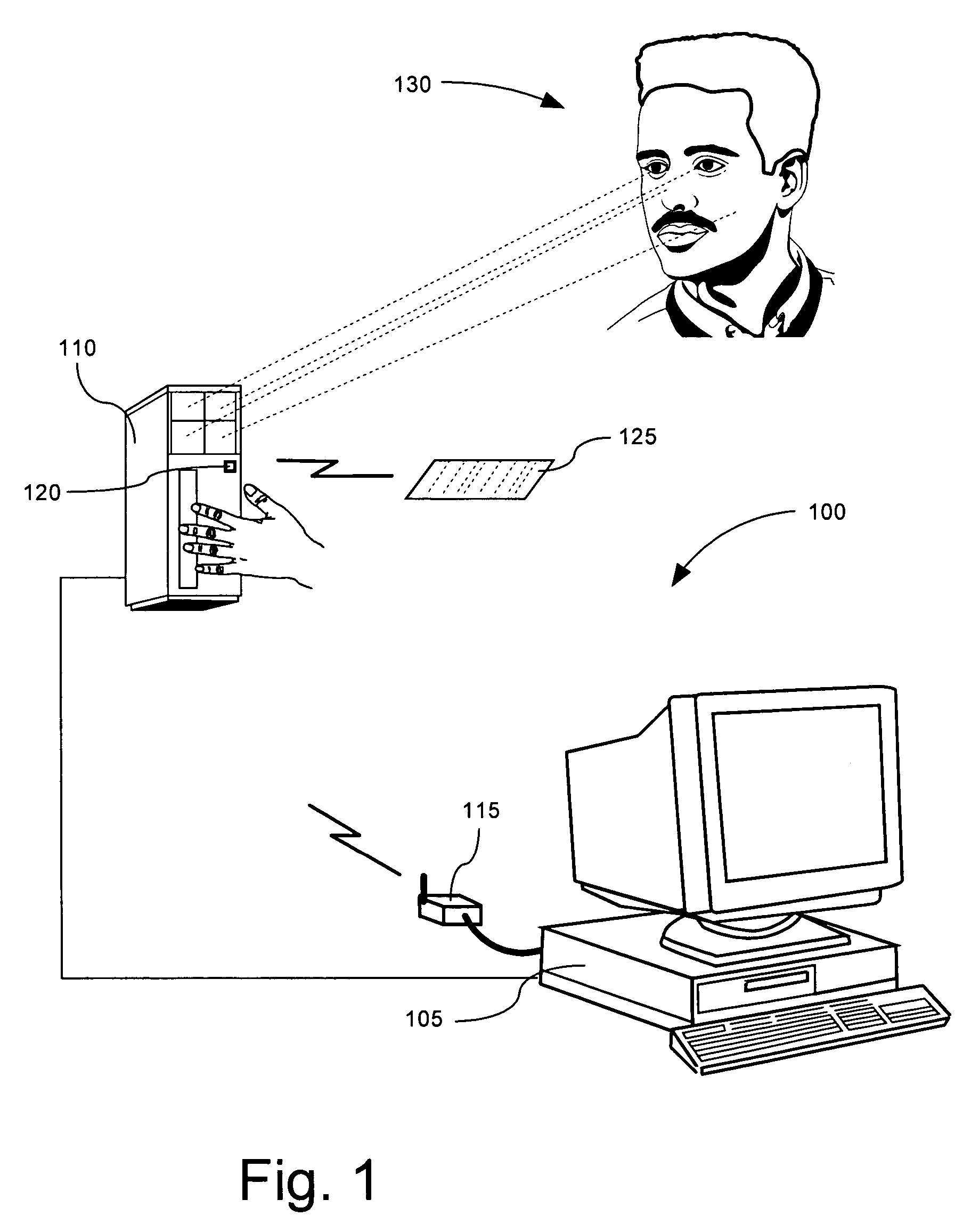
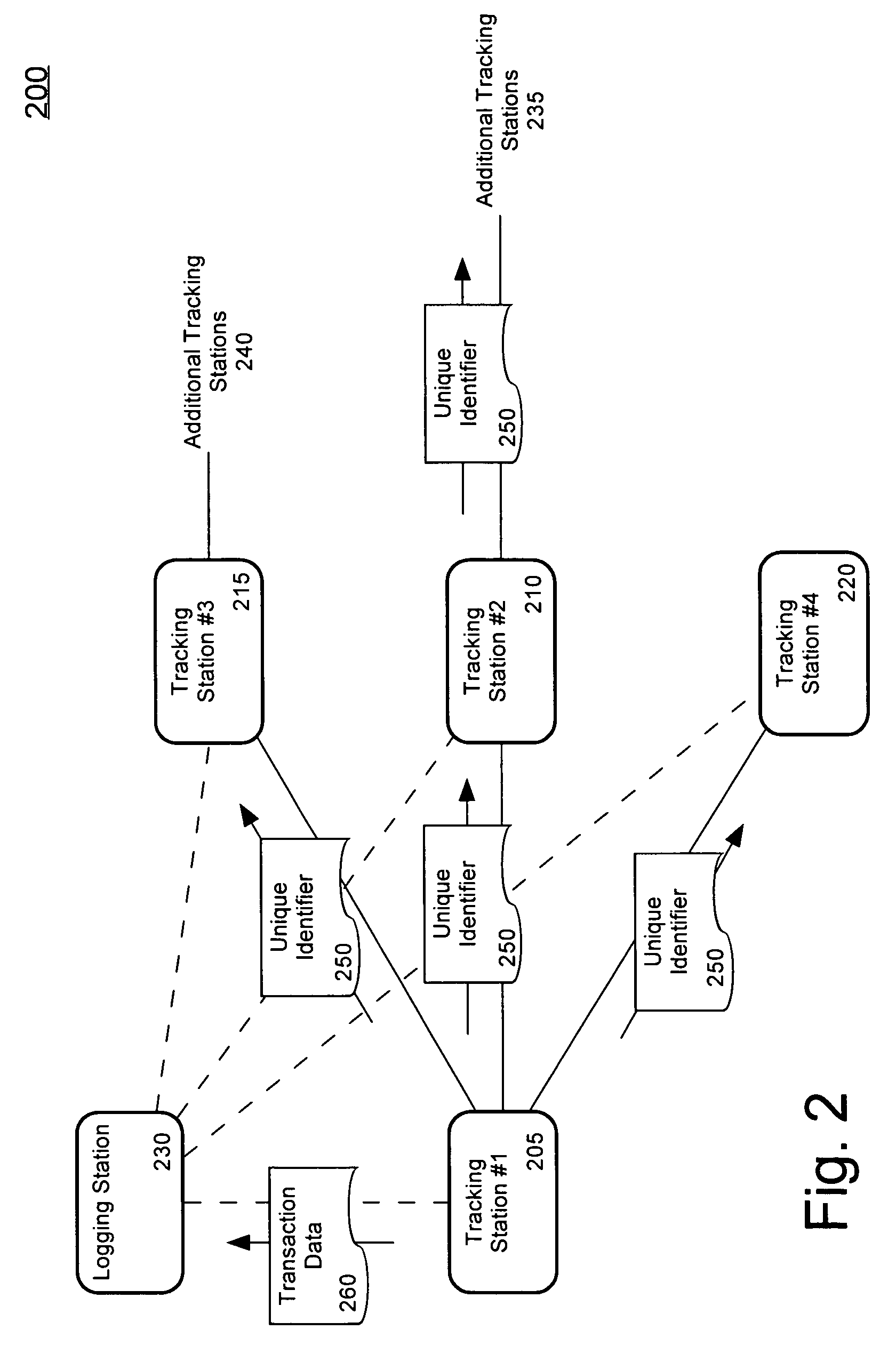
ActiveUS7126470B2Electric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageUnique identifierWireless ad hoc network
A method of tracking an entity (130) through a plurality of tracking stations (205, 210, 215, 220) in a wireless ad-hoc network. A unique identifier (250) can be assigned to the entity at a first (205) of the plurality of tracking stations and wirelessly transmitted to at least a second tracking station (210). The number of the tracking stations can be dynamically varied on an ad-hoc basis responsive to variations in a tracking environment. The unique identifier can be selectively communicated to at least a second tracking station based on a predicted transit scenario of the entity. The identifier can be stored on a datastore, such as a radio frequency identification tag (125) attached to the entity. A biometric scan of the entity can be performed. For example, a facial scan, an iris scan, a fingerprinting, or palm printing can be performed to assign a unique identifier.
Owner:OLLNOVA TECH LTD
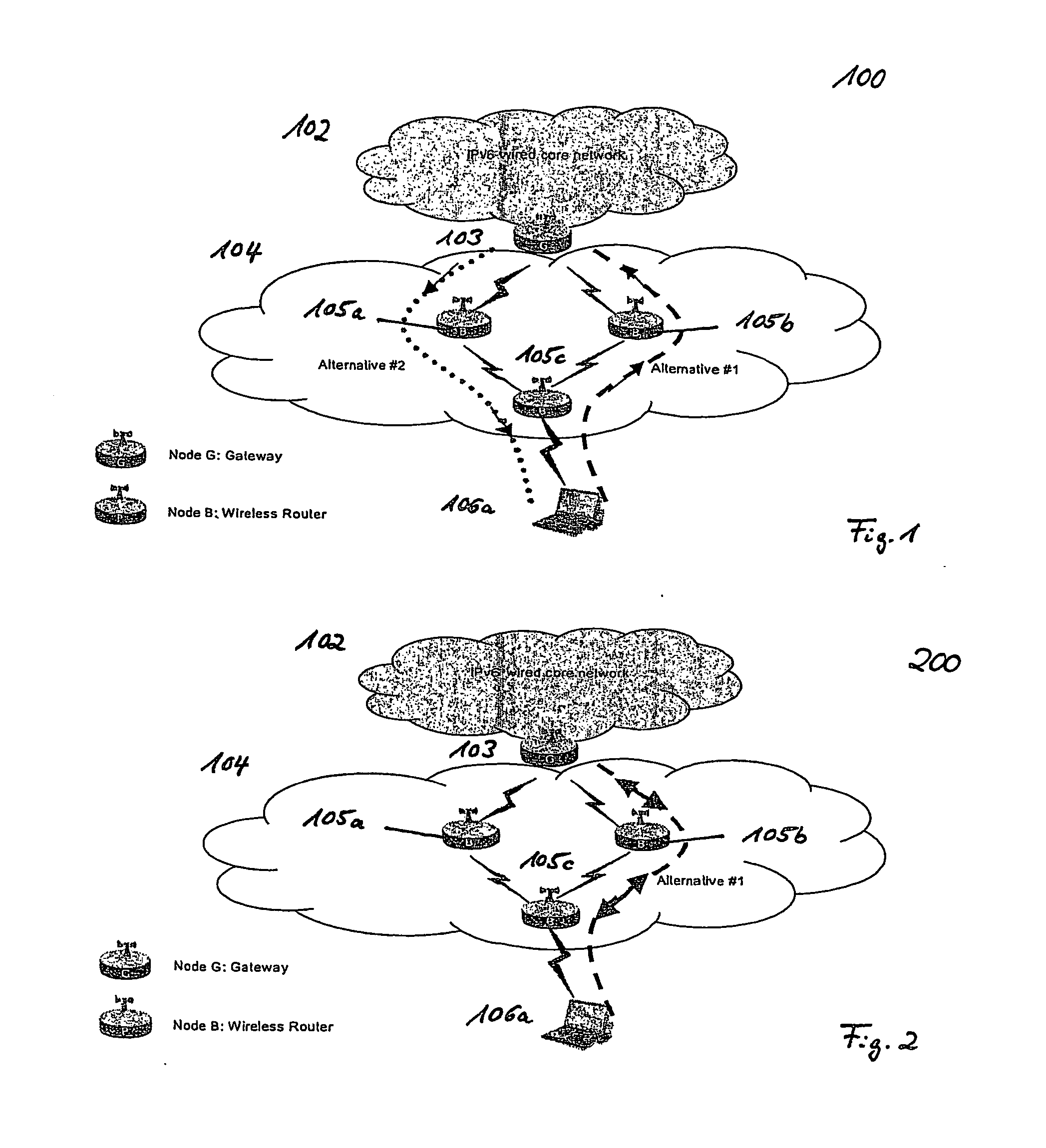
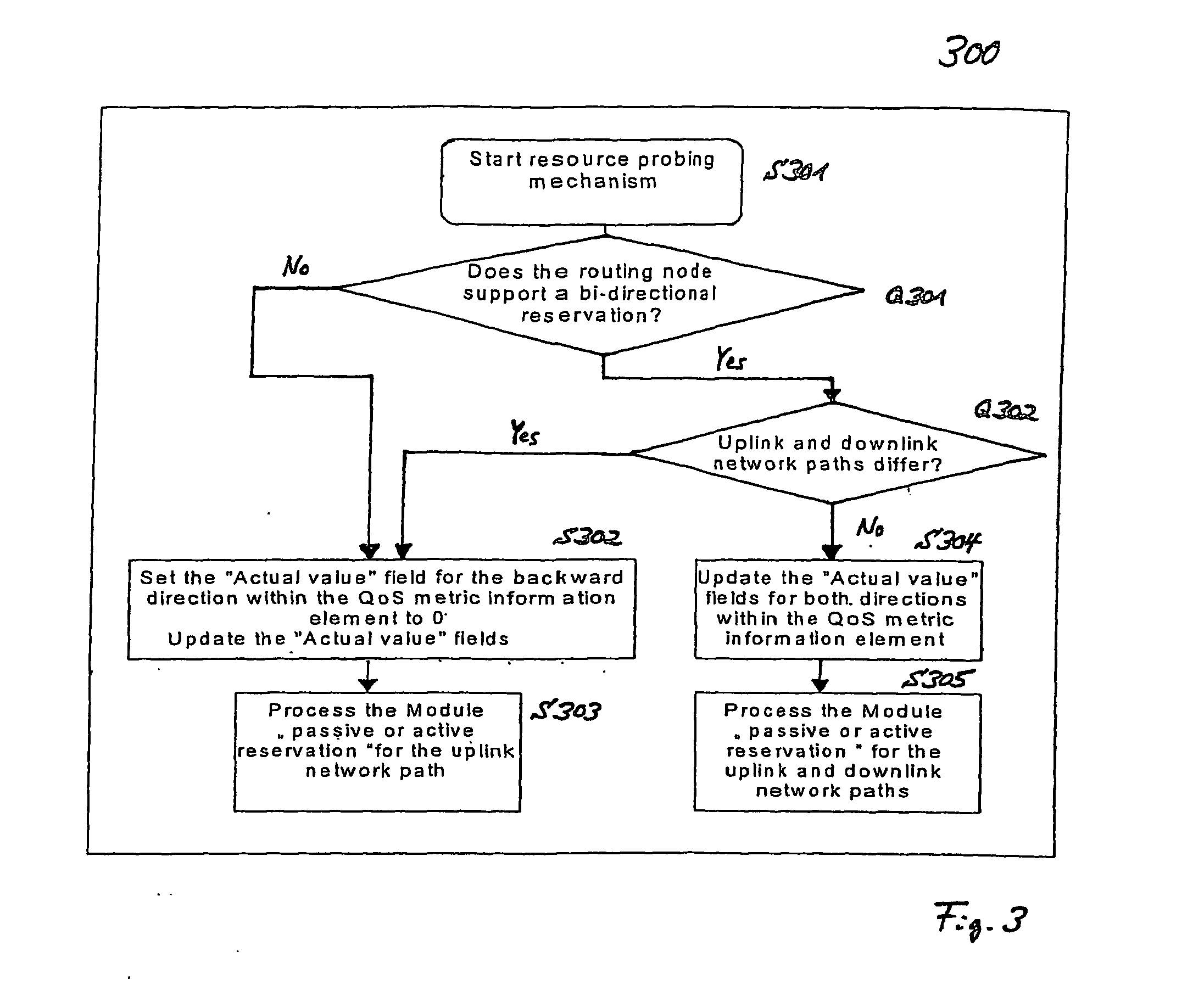
Bidirectional Qos Reservation Within an in-Band Signaling Mechanism
InactiveUS20070217406A1Optimize networkImprove network utilizationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesReal time servicesWireless ad hoc network
A mechanism for a bidirectional reservation procedure within an in-band signaling mechanism gives symmetric real-time services running on mobile devices, which are used to support different access technologies in dynamic, mobile, wireless IP networks where the quality of the node connectivity can sometimes be unpredictably time-varying, the possibility to mutually reserve, monitor and adapt resources and service parameters for upstream and downstream direction along a communication path. The mechanism optimizes reservation mechanisms, especially for adaptive real-time services in wireless and wireless ad-hoc networks, by making use of a dynamic bidirectional reservation in-band signaling approach.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG +1
Threshold and identity-based key management and authentication for wireless ad hoc networks
InactiveUS20060023887A1Reduce usageReduce resource requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationConfidentialityWireless ad hoc network
As various applications of wireless ad hoc network have been proposed, security has become one of the big research challenges and is receiving increasing attention. The present invention provides for a distributed key management and authentication approach by deploying the recently developed concepts of identity-based cryptography and threshold secret sharing. Without any assumption of pre-fixed trust relationship between nodes, the ad hoc network works in a self-organizing way to provide the key generation and key management service, which effectively solves the problem of single point of failure in the traditional public key infrastructure (PKI)-supported system. The identity-based cryptography mechanism provided not only to provide end-to-end authenticity and confidentiality, but also saves network bandwidth and computational power of wireless nodes.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Method and apparatus for multicasting real time traffic in wireless ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS6721290B1Speed up decision making processSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of servicePacket loss
A real-time multicast scheduler method and apparatus is presented, to facilitate multicasting of real-time constant bit rate data in wireless ad-hoc networks. Constant bit rate traffic cannot tolerate delay jitter. However, a small amount of packet losses may be tolerable. In order to ensure the provisioning of a desired level of quality of service, bandwidth is reserved on the multicast structure. A goal of the real-time multicast scheduler is to avoid packet collisions and to facilitate color re-use, where "color" is defined as a channel selected as a combination of time-division multiple access, frequency-division multiple access, and code-division multiple access schemes. The real-time multicast scheduler provides a self-healing network which corrects for disconnections caused by node movement and nodes moving out of range of each other, while accounting for colors already assigned for data transmission in order to prevent packet collisions.
Owner:HRL LAB
Methods and electronic devices for wireless ad-hoc network communications using receiver determined channels and transmitted reference signals
InactiveUS20040110508A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path divisionCommunications systemWireless ad hoc network
Electronic devices for communicating in wireless ad-hoc networks and multiple access systems (such as mobile radio telephone communications systems) are disclosed. For example, a disclosed transmitter can transmit data to a first receiver in an ad-hoc wireless network (or multiple access system) over a first channel and can, further, transmit data to a second receiver in the ad-hoc wireless network (or multiple access system) over a second channel that is separate from the first channel, where the first and second channels are determined by the respective receivers which will receive the first and second transmitted data. Accordingly, communications between transmitters and different receivers in the ad-hoc wireless network (or multiple access system) can be carried on simultaneously. Related receivers as well as methods, computer program products, and systems for communicating are also disclosed.
Owner:ERICSSON TECH LICENSING
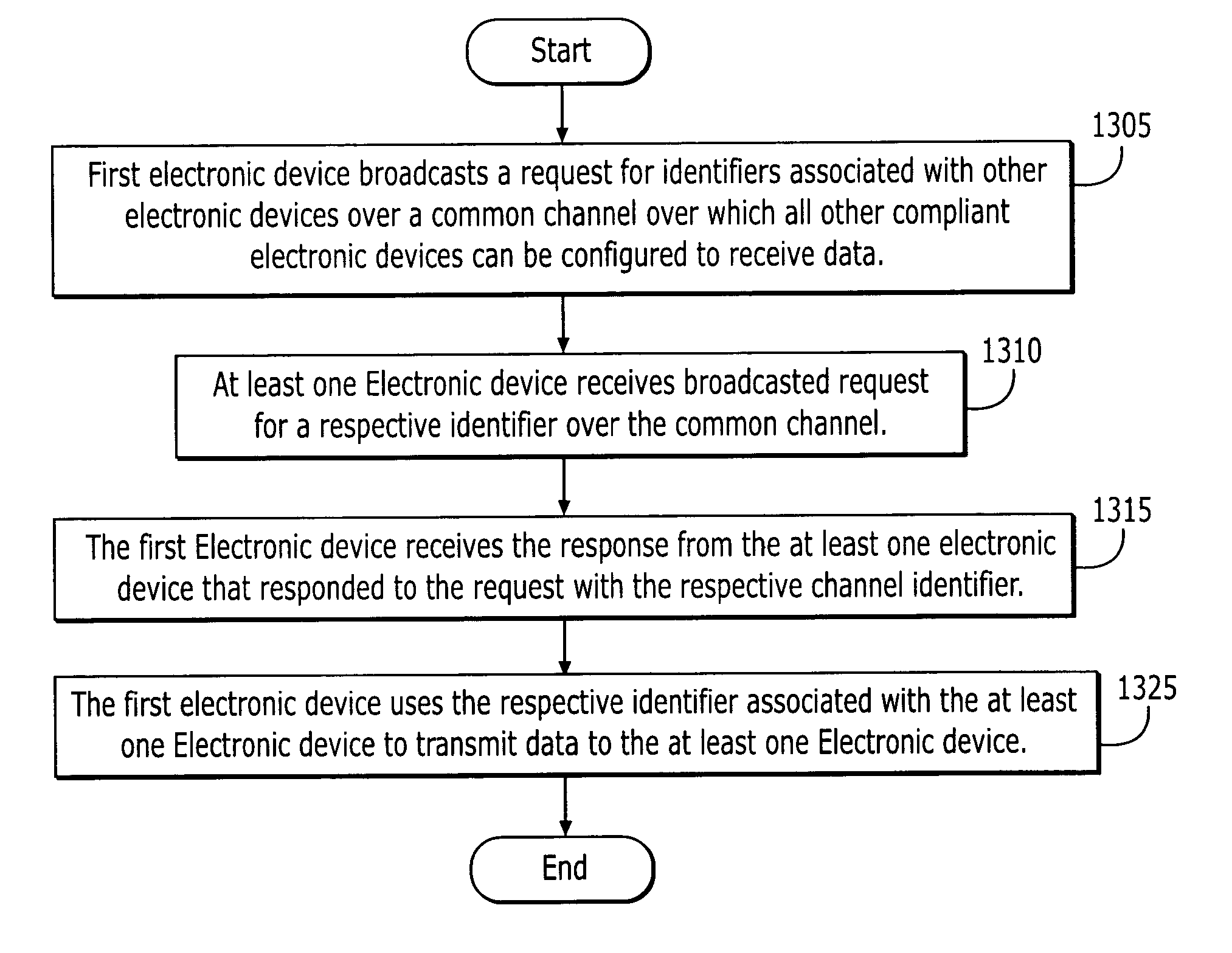
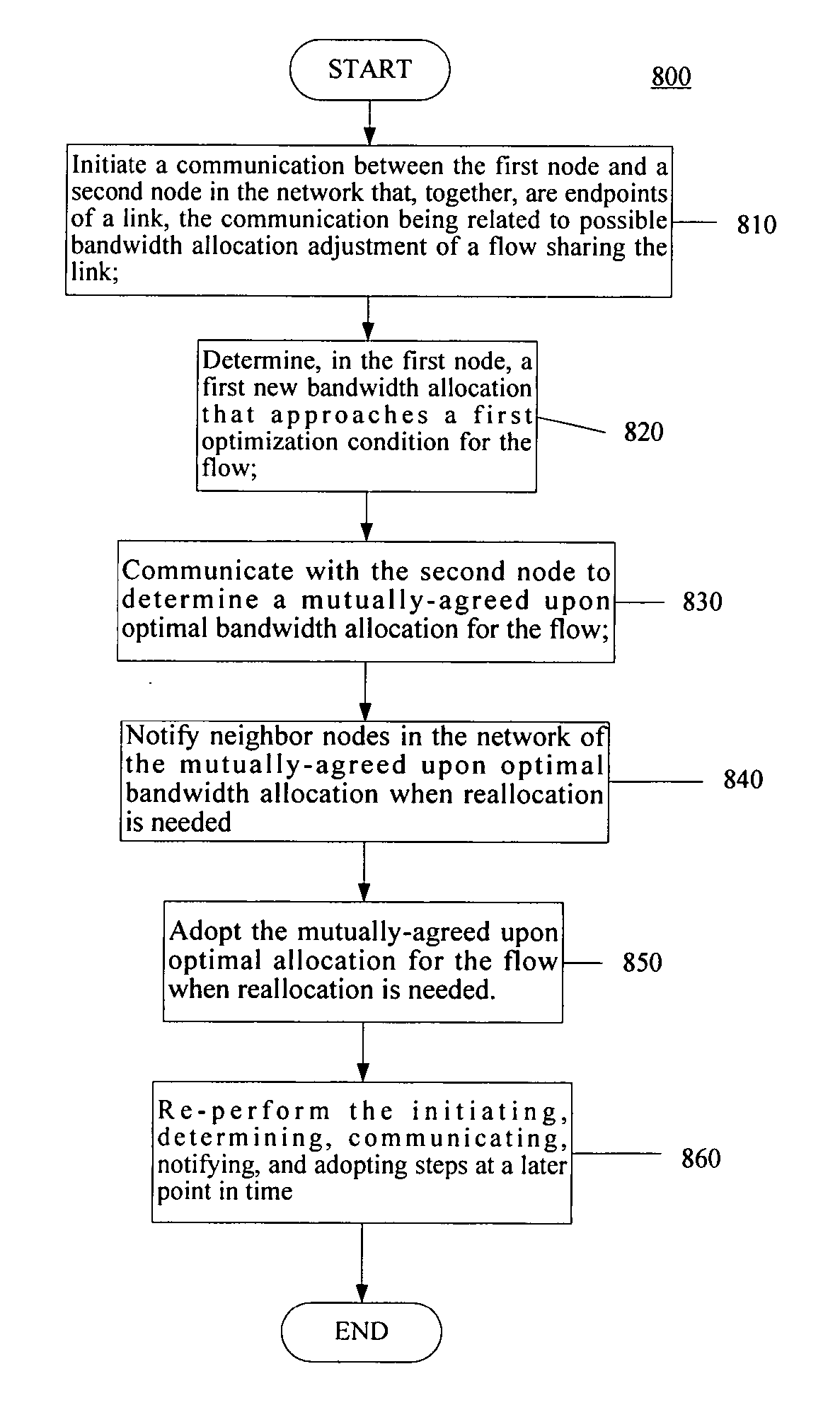
Distributed bandwidth allocation and transmission coordination method for quality of service provision in wireless AD HOC networks
InactiveUS20040156312A1Near-field transmissionError preventionDynamic bandwidth allocationWireless ad hoc network
Methods, devices, systems, and computer programs are provided that allow for optimally allocating bandwidth in an ad hoc, wireless network configured to support at least one guaranteed feasible flow allocation. According to some of these methods, devices, systems, Quality of Service guarantees may be provided across the network. Also, in many instances, the methods are iterative and allow for convergence to an optimized bandwidth allocation.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
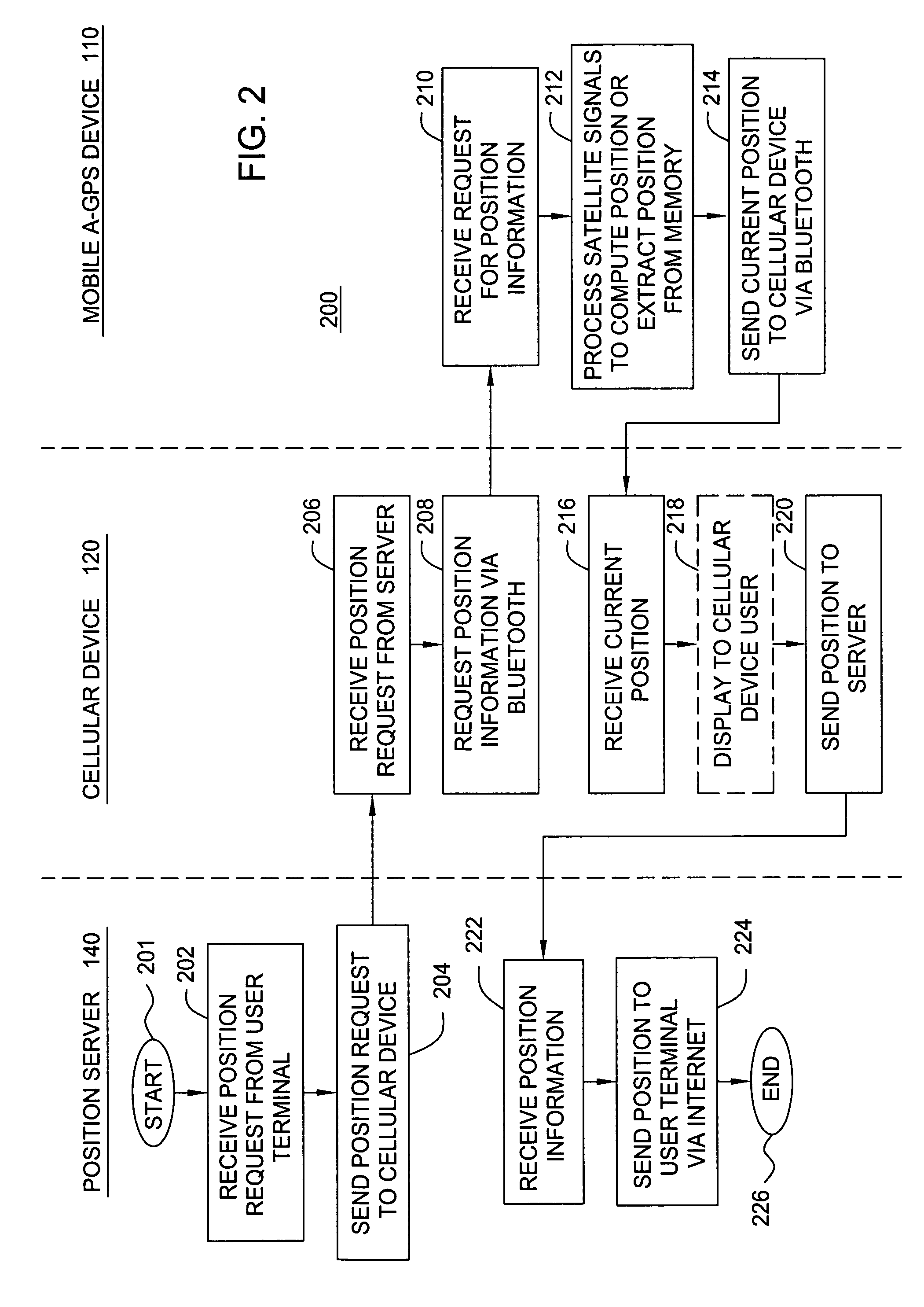
Method and apparatus for locating position of a mobile device in an assisted satellite positioning system
InactiveUS20060046749A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionGps receiverWireless ad hoc network
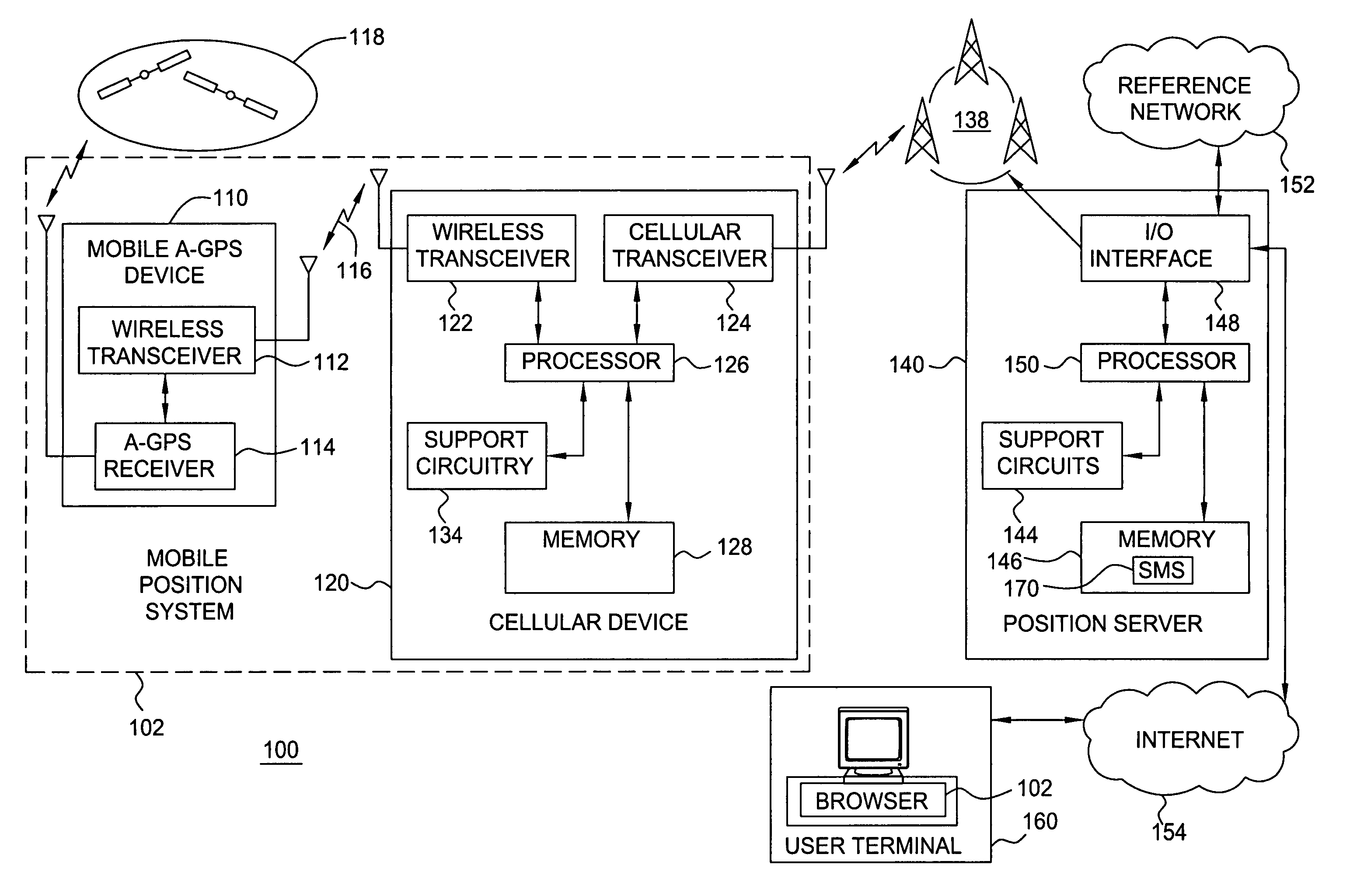
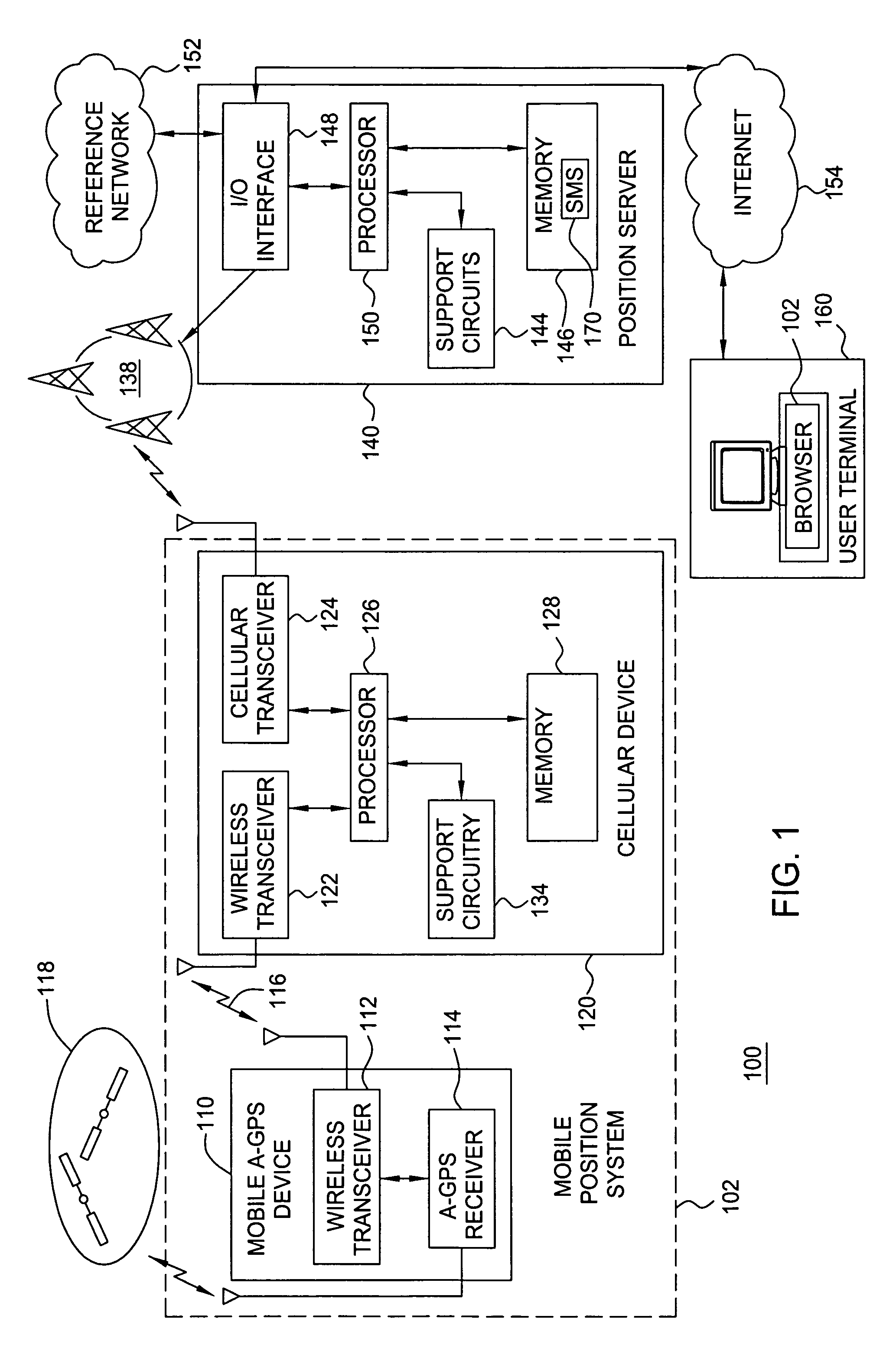
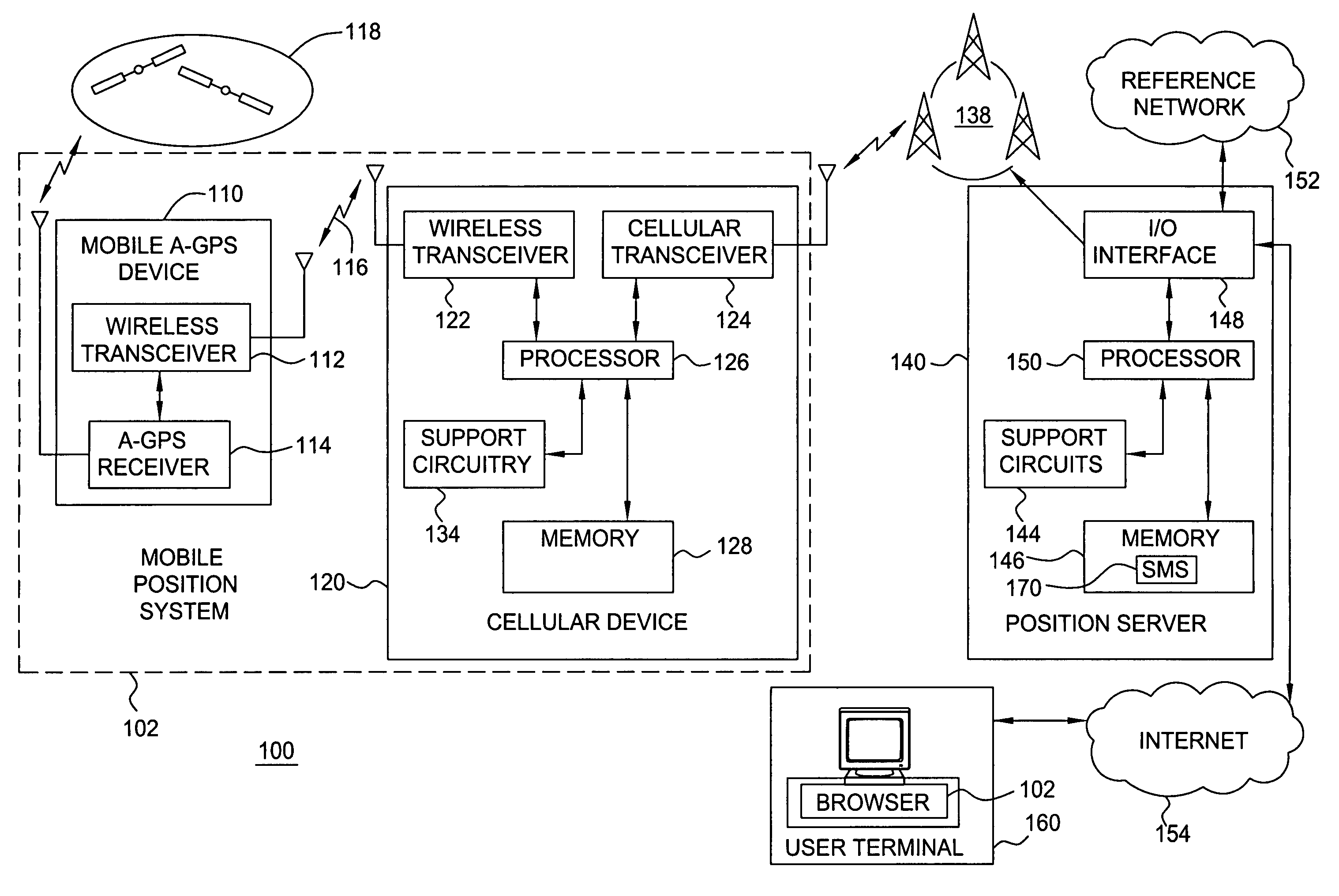
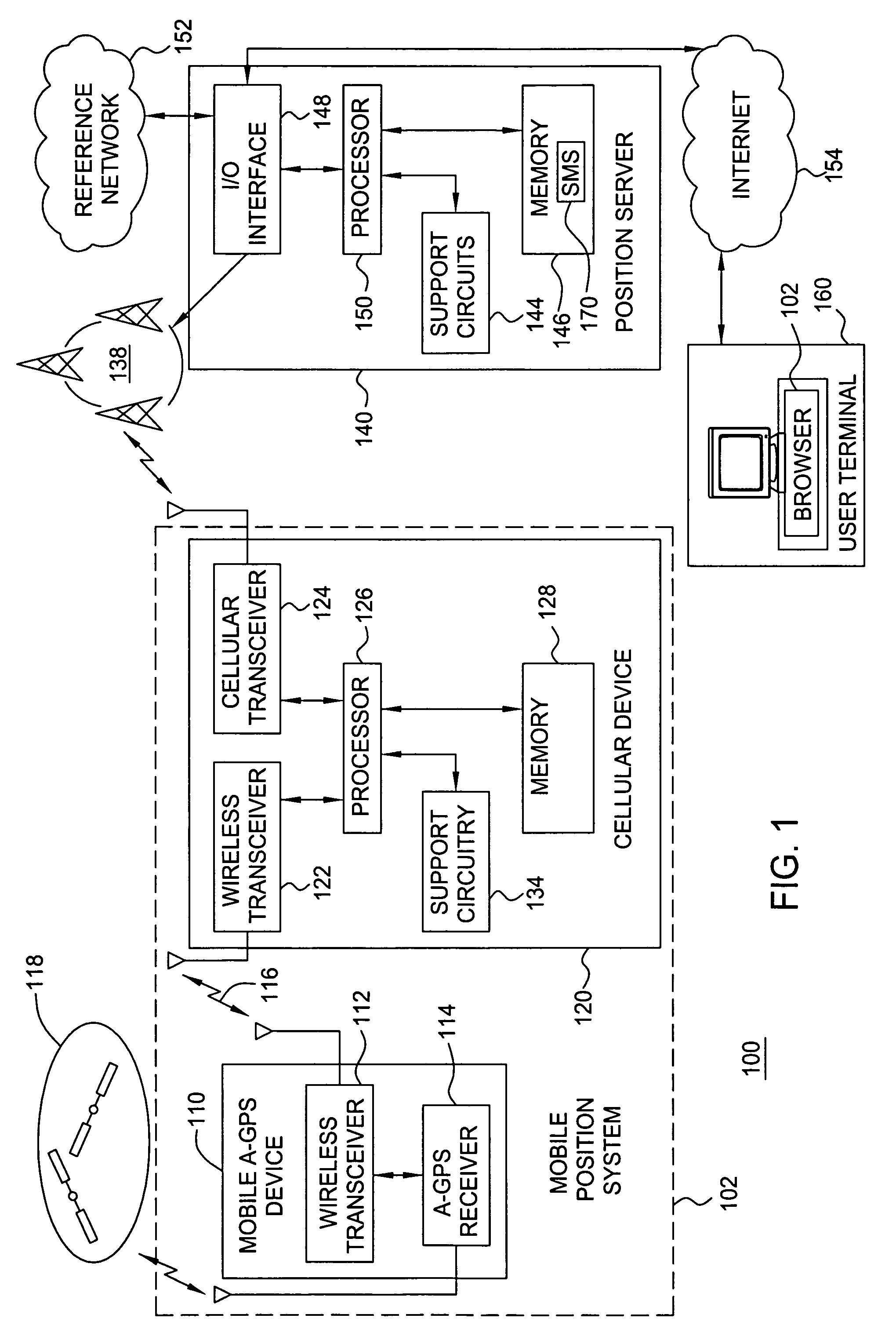
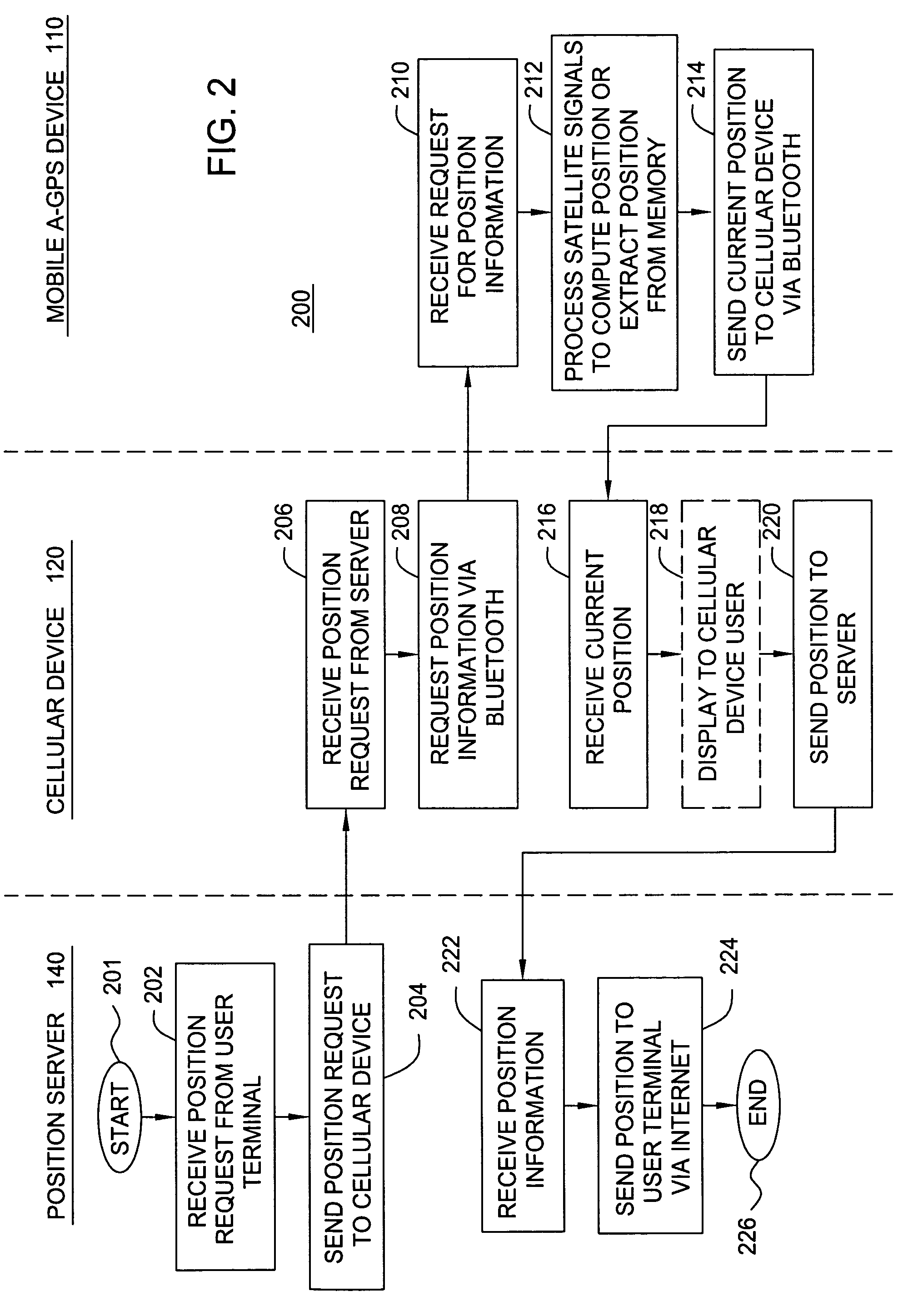
Method and apparatus for locating position of a mobile device in an assisted satellite positioning system is described. In one example, satellite measurement data is obtained from a plurality of satellites at a mobile device. Position of the mobile device is computed using the satellite measurement data. The position is sent to a cellular device via a wireless ad hoc network. In one example, the wireless ad hoc network comprises a BLUETOOTH communication link. In one example, the mobile device is configured to receive assistance data from a position server through the wireless ad hoc network. For example, the mobile device may comprise a housing configured to plug into a cigarette lighter connector of an automobile and the cellular device may comprise a cellular telephone without location-determination capabilities (i.e., the cellular telephone does not include an integrated GPS receiver).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for locating devices
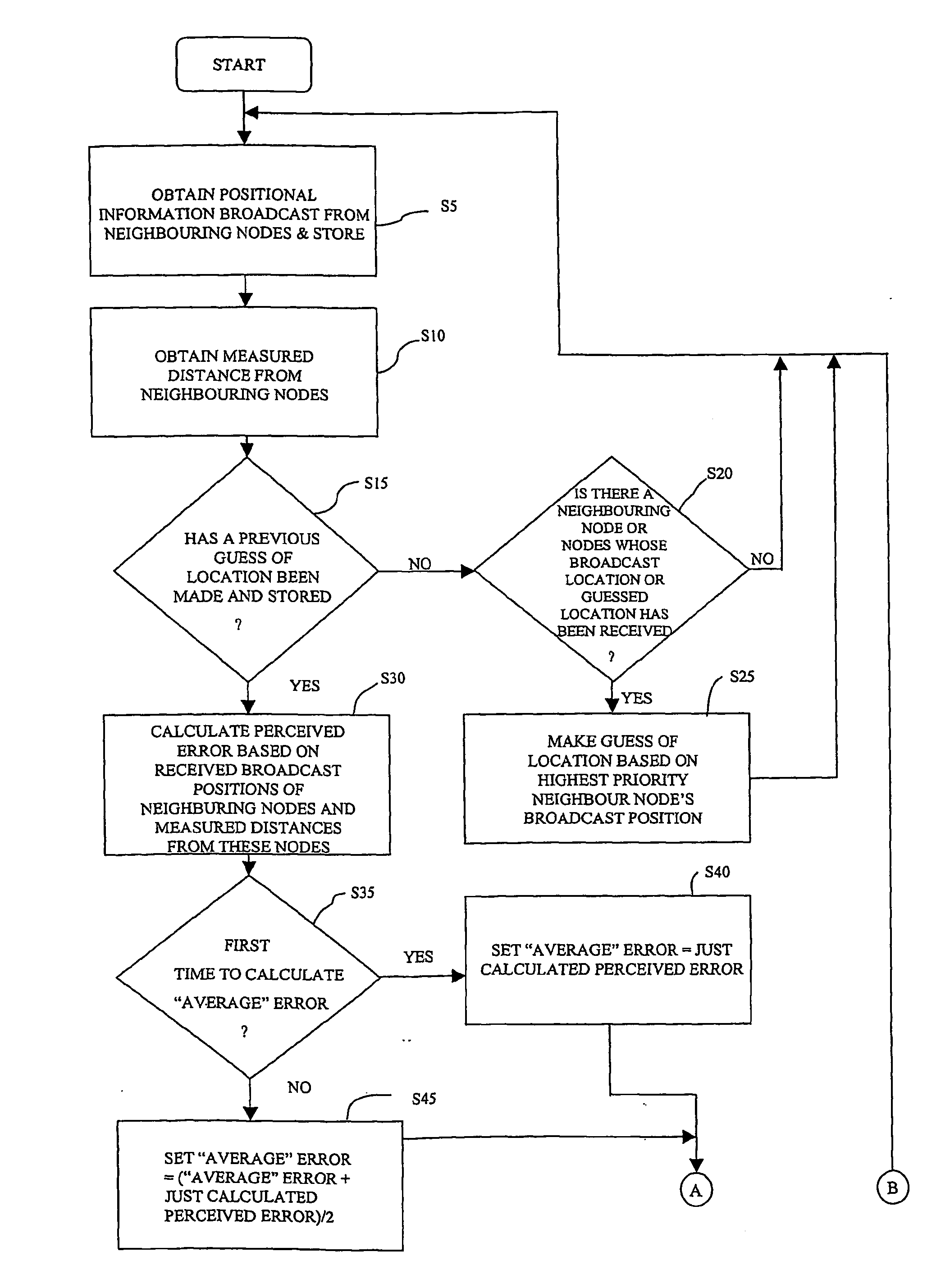
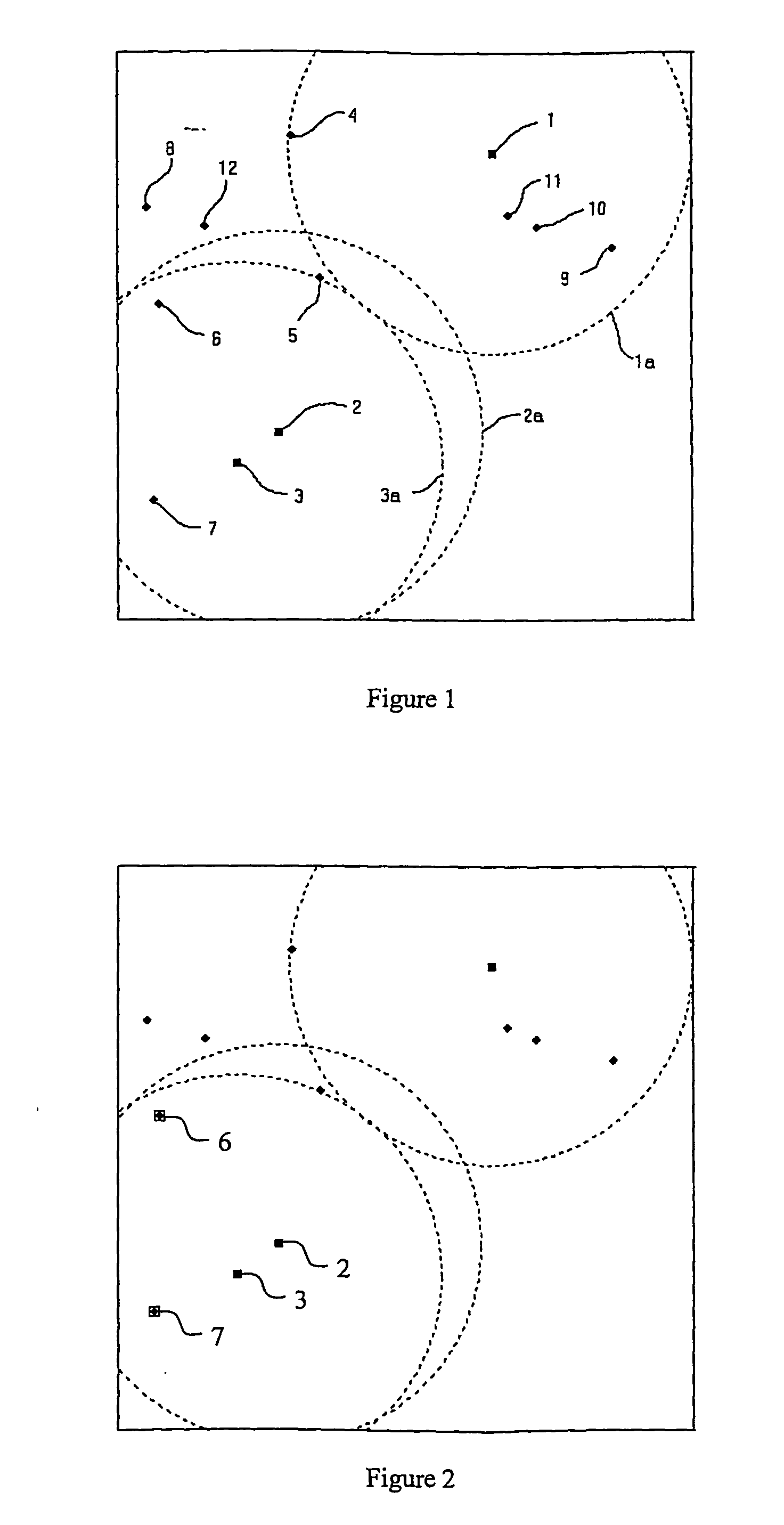
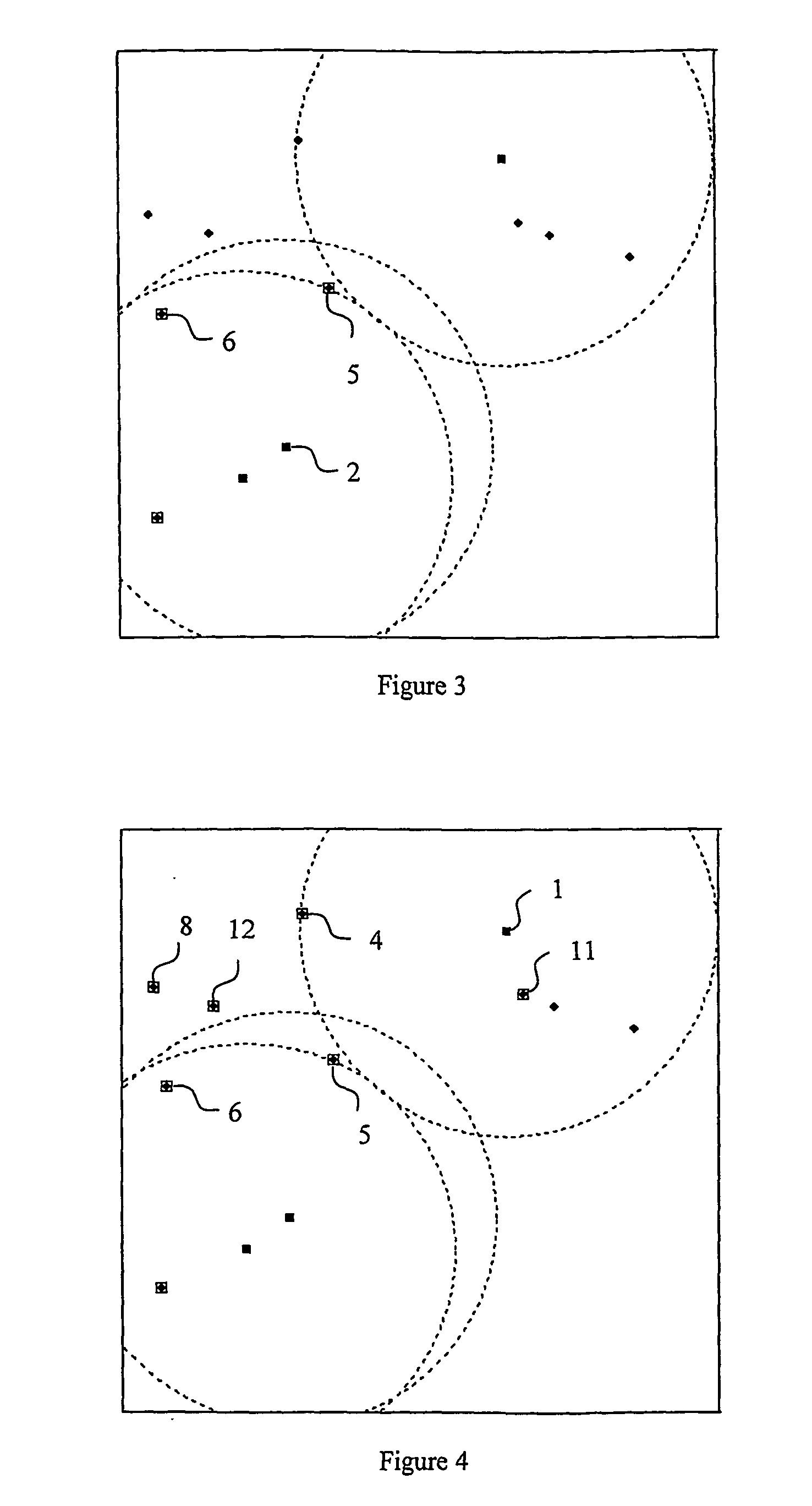
InactiveUS20050233748A1Low costEffective positioningPosition fixationData switching by path configurationWireless ad hoc networkError function
A method of obtaining positional information about individual wireless devices a1-a16, r1-r125 within a wireless ad-hoc network including a plurality of position determining devices r1-r125 which include means for estimating the distance between themselves and other similar devices which are within range. The method includes the steps of: calculating the hypothetical distance between a respective node's estimated position and the estimated position of each of its neighbouring devices whose broadcast estimated position has been received and whose distance from the respective node has been measured comparing the calculated hypothetical distance with the measured distance; modifying the respective node's estimated position so as to reduce an error function dependent upon the difference between the hypothetical and measured distances and periodically resetting the respective node's estimated location to a new position in a manner which does not seek to reduce the error function within a single iteration so as to avoid the location from getting stuck in a local minimum value of the error function.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Method to support multicast routing in multi-hop wireless networks
ActiveUS20060250999A1Network topologiesBroadcast transmission systemsExtensibilityWireless ad hoc network
A system and method for supporting multicast in highly dynamic wireless multi-hop networks, such as ad-hoc networks, with good scalability. The system and method provide a multicast routing algorithm to work in wireless ad-hoc networks without any fixed infrastructure nodes present. In doing so, the system and method provide a technique to build a multicast source specific tree on demand, while using a core source node to limit routing overhead. The system and method further provide a repair process to reduce the latency of discovery of topology change, employ a node sequence number mechanism to differentiate between upstream nodes and downstream nodes on the multicast tree in the repair process, and provide an active joining process to reduce the latency of discovery of membership change.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Name service in a multihop wireless ad hoc network
InactiveUS20100002635A1Efficient use ofNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTraffic capacityCommunications system
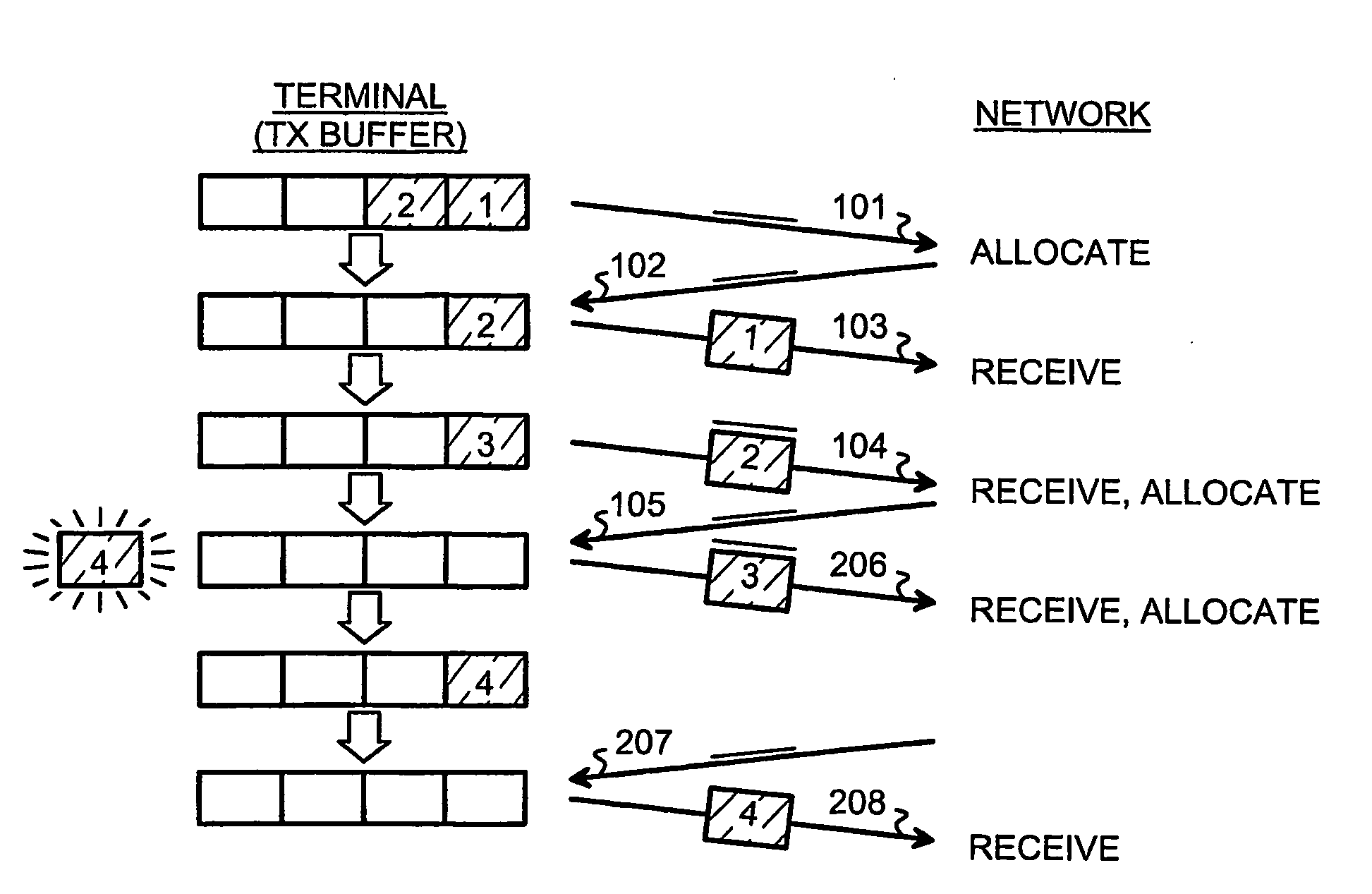
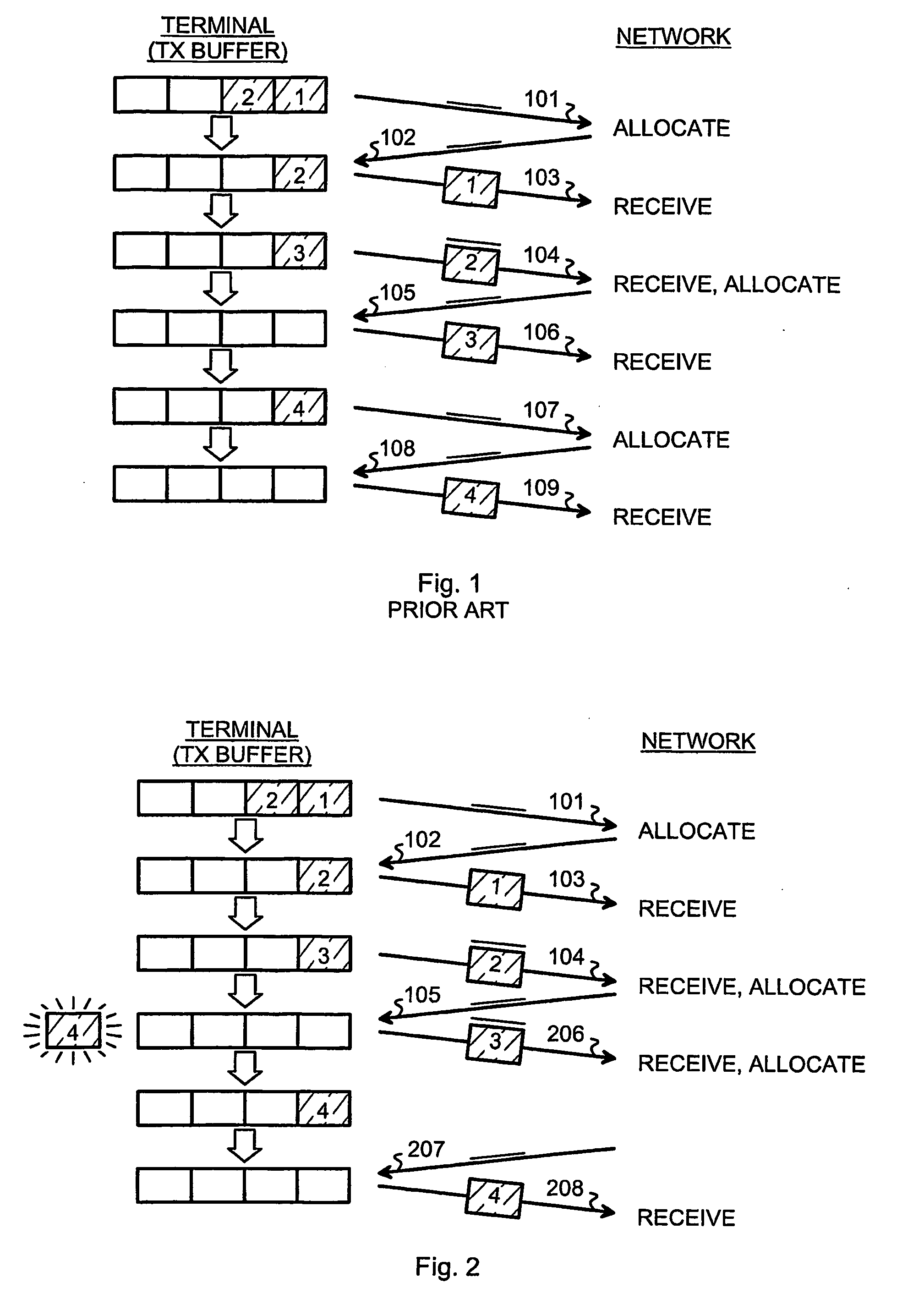
Piggy-backed requests for resources are handled in a packet-switched communications system. A terminal arrangement sends an access request to a network element in order to request permission to use communications resources for transmitting a data packet found in a transmission buffer of the terminal arrangement. Knowledge is established about a predicted data packet which is to appear in the transmission buffer of the terminal arrangement in the near future. The terminal arrangement transmits to the network element an access request for predicted traffic, requesting permission to use communications resources for transmitting said predicted data packet once it appears. This access request for predicted traffic is piggy-backed onto another transmission.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method to support multicast routing in multi-hop wireless networks
A system and method for supporting multicast in highly dynamic wireless multi-hop networks, such as ad-hoc networks, with good scalability. The system and method provide a multicast routing algorithm to work in wireless ad-hoc networks without any fixed infrastructure nodes present. In doing so, the system and method provide a technique to build a multicast source specific tree on demand, while using a core source node to limit routing overhead. The system and method further provide a repair process to reduce the latency of discovery of topology change, employ a node sequence number mechanism to differentiate between upstream nodes and downstream nodes on the multicast tree in the repair process, and provide an active joining process to reduce the latency of discovery of membership change.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
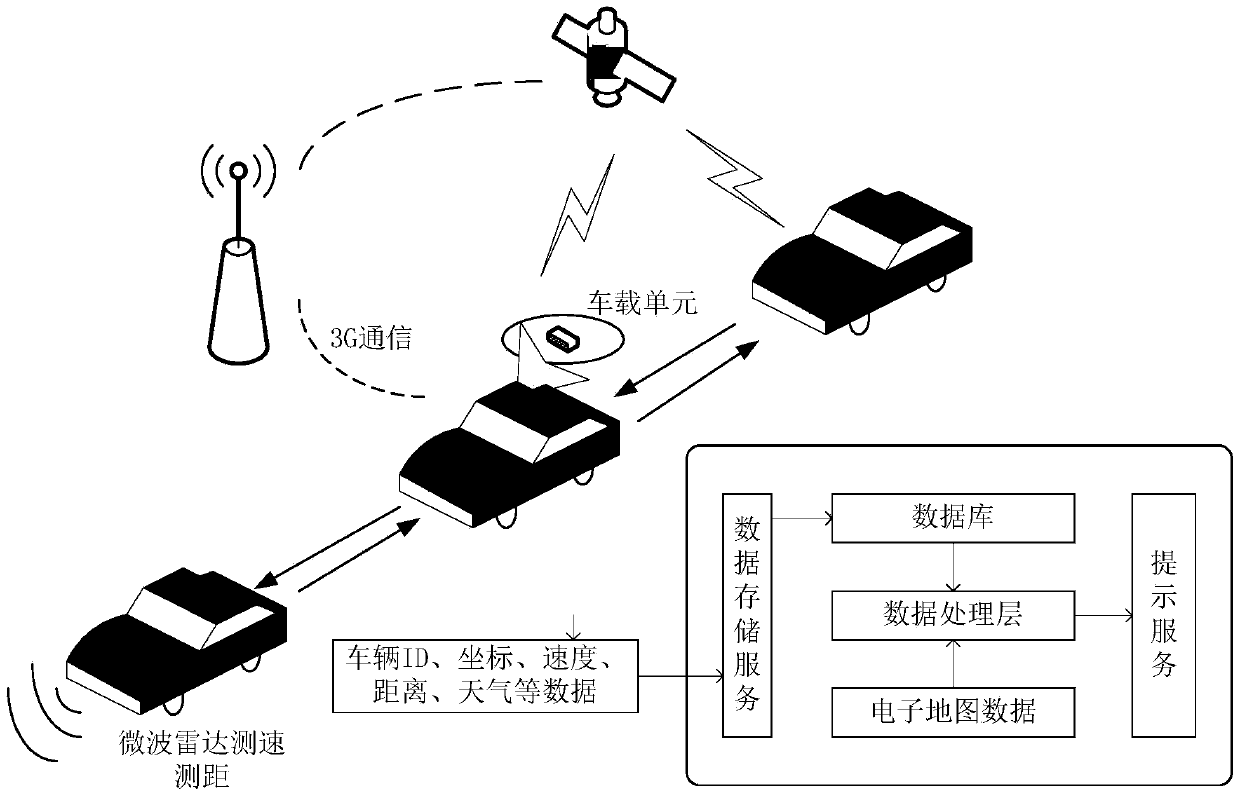
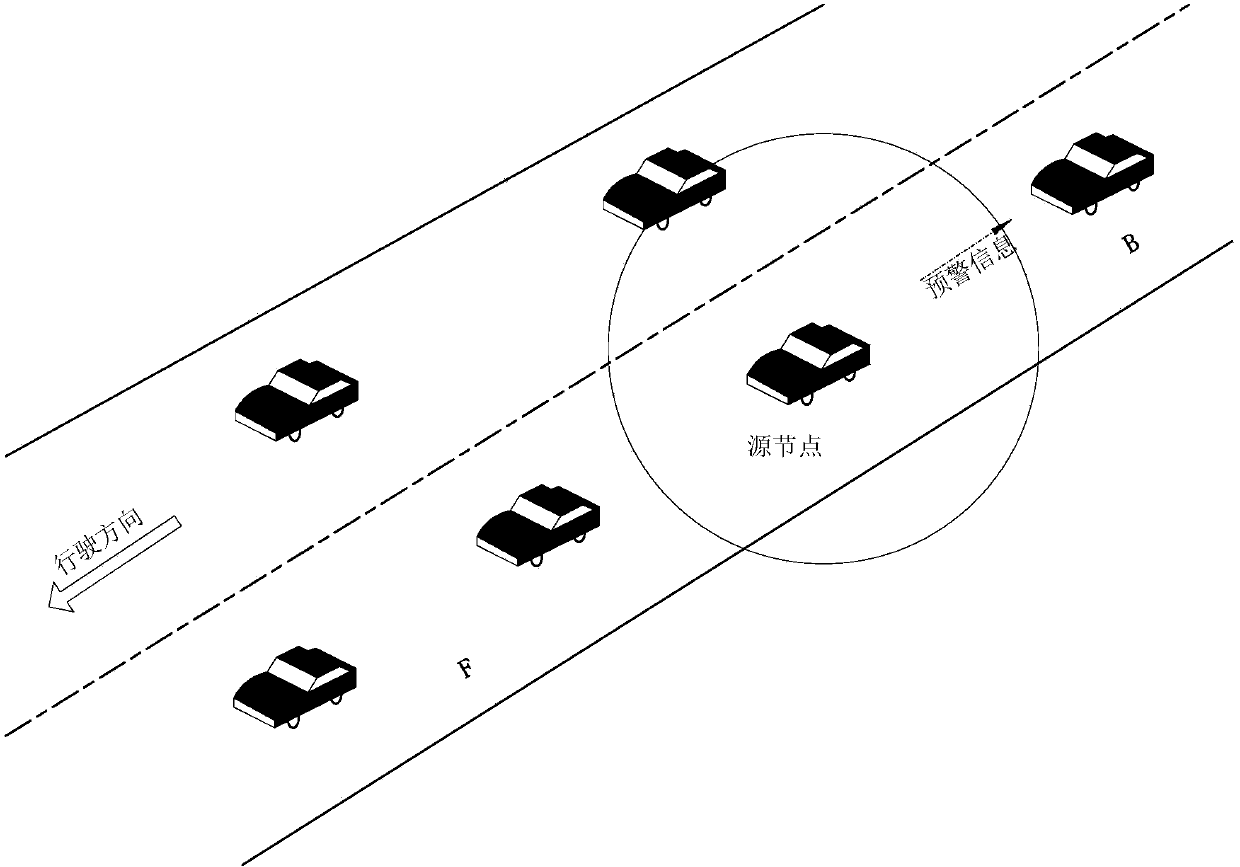
VANET-based early-warning system and early-warning method for driving safety in expressway
The invention discloses VANET-based early-warning system and early-warning method for driving safety in an expressway, and relates to an early-warning system and an early-warning method for driving safety in an expressway, for realizing real-time and effective safety early-warning on running vehicles. The invention designs a Vehicle ad-hoc network-based early-warning vehicle-mounted system for driving safety in an expressway. By virtue of the system, the different levels of early-warning prompts of the current driving safety of vehicles can be given according to the weather / road conditions (visibility, road slippery degree and the like), the current running state (real-time position and real-time speed) of a vehicle and the running states of 'neighbour' vehicles in a certain space range around the vehicle. On the basis of VANET, the system enables the vehicles to carry put wireless ad-hoc networking in a certain space range and share in-network vehicle running state information, and automatically generates safety early-warning information for every vehicle in the network, thus improving the driving safety of the vehicles on a road. The system and the method disclosed by the invention are applicable to a driving process in an expressway.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
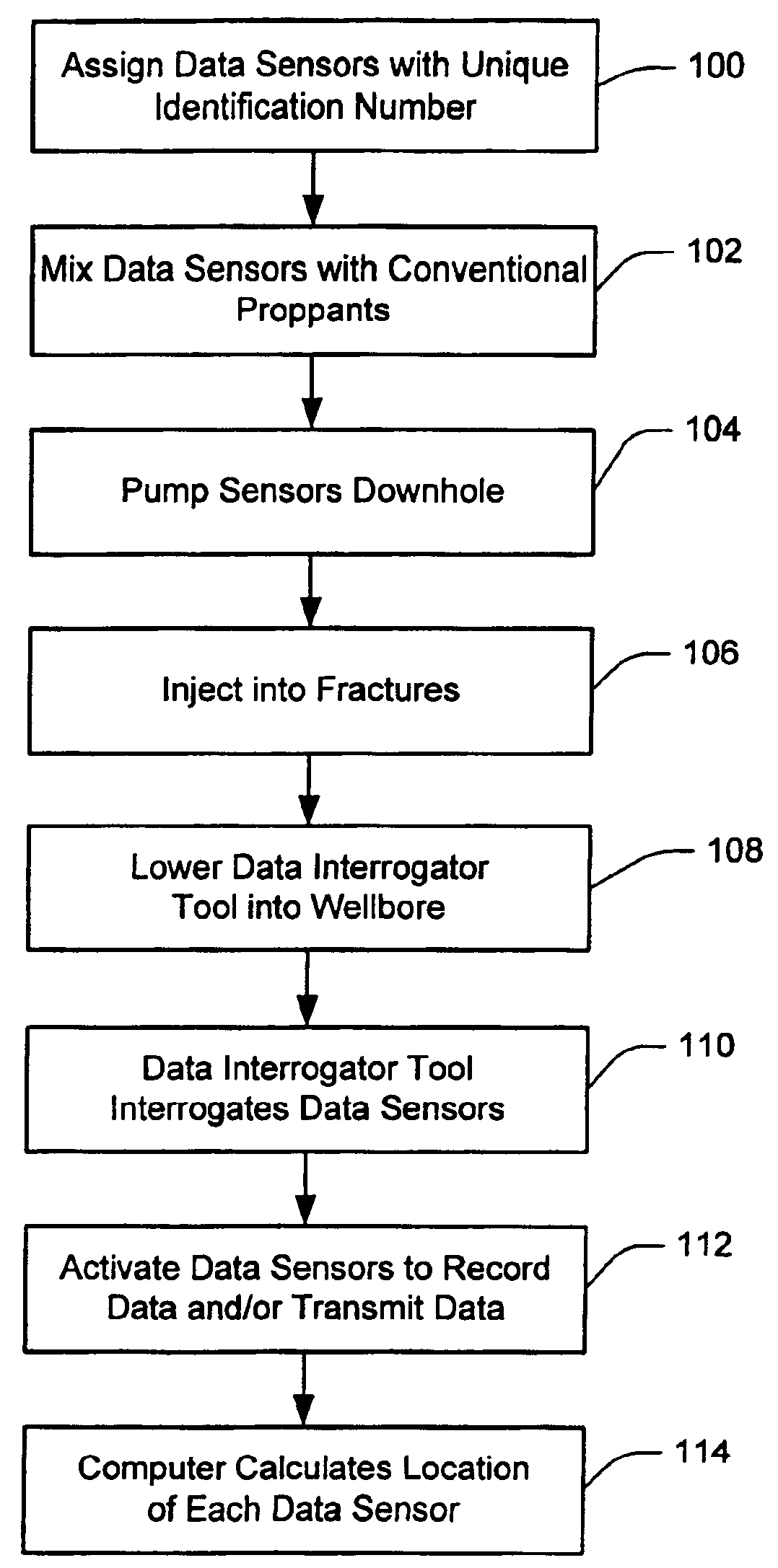
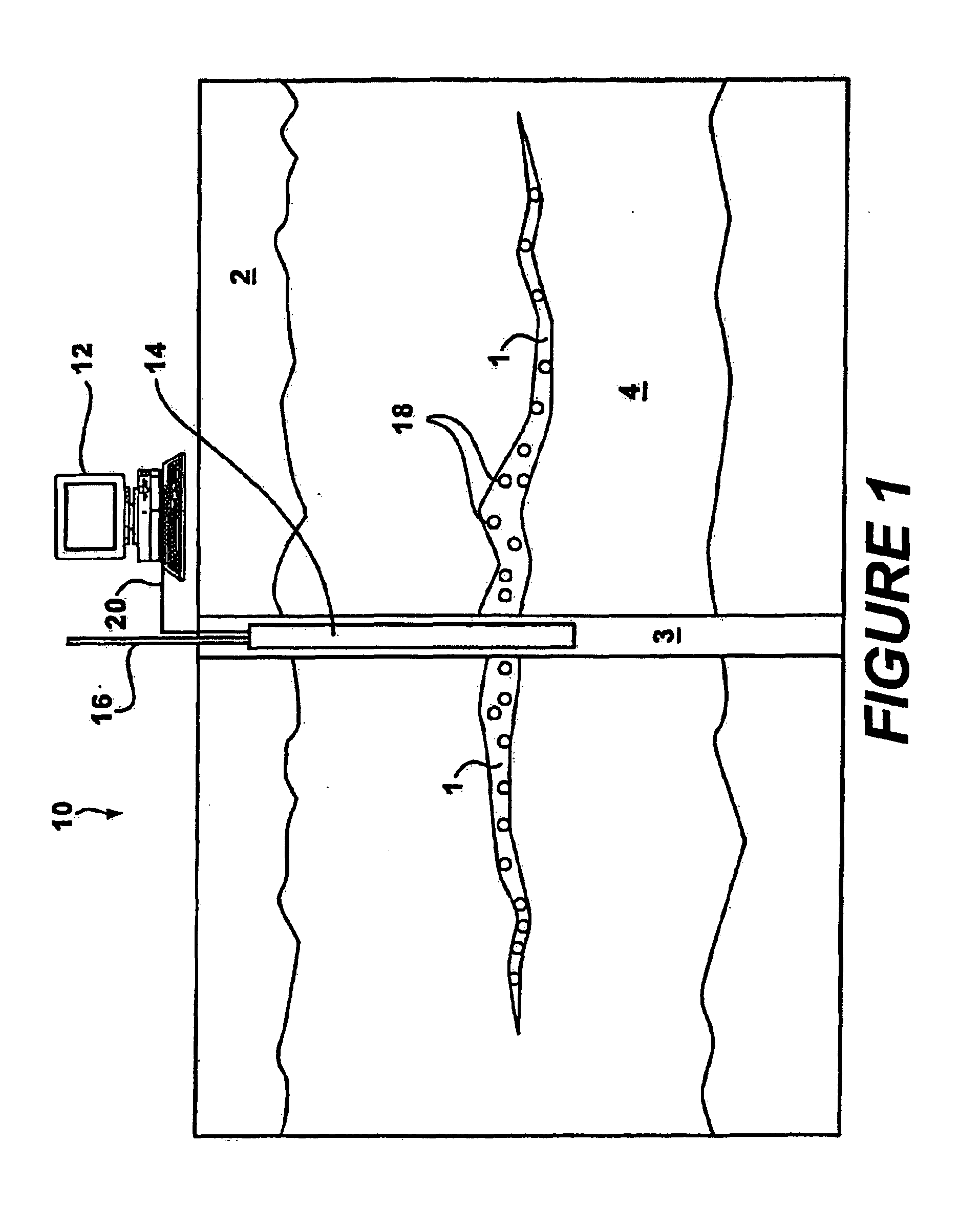
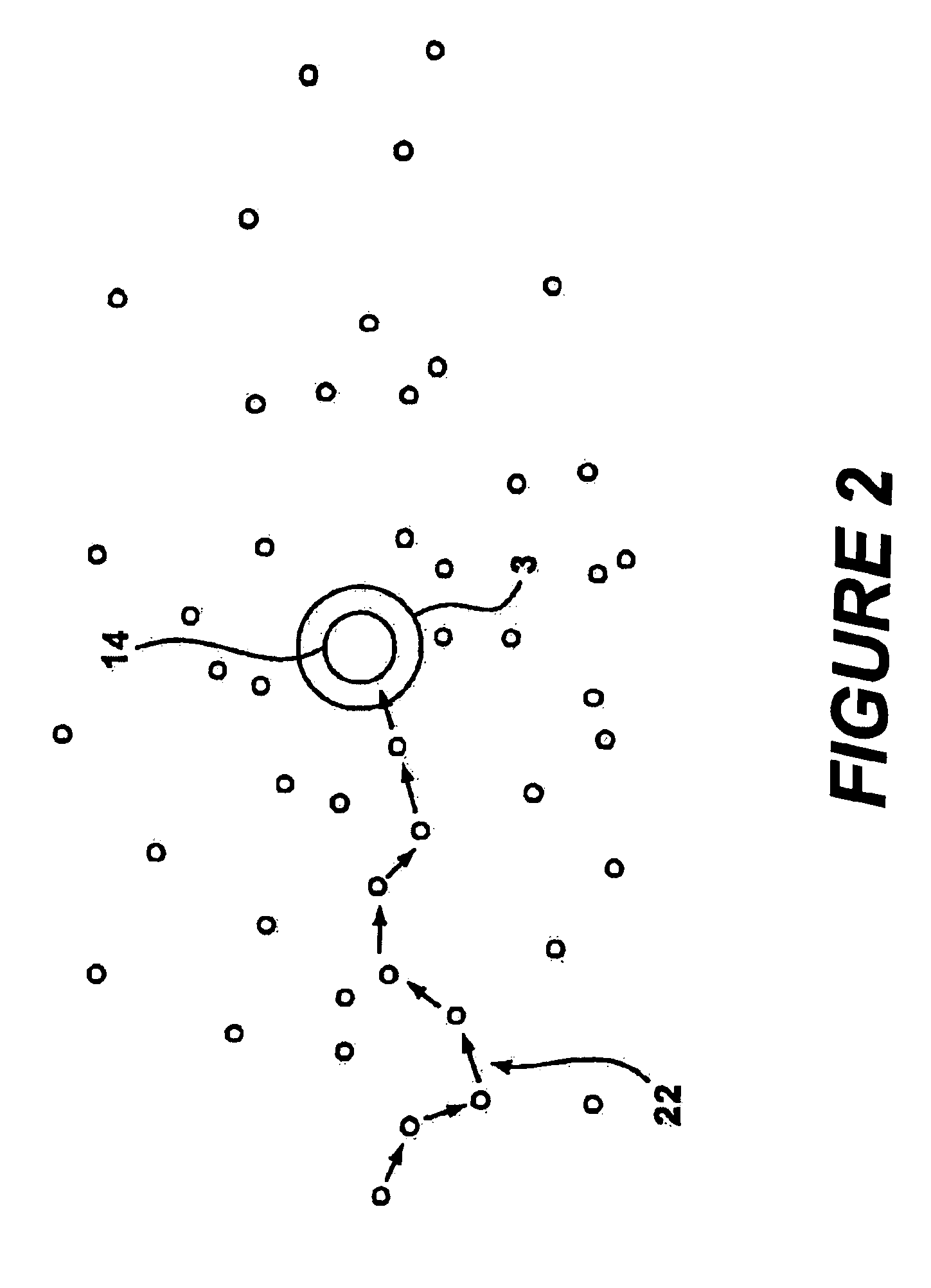
Method and system for determining parameters inside a subterranean formation using data sensors and a wireless ad hoc network
InactiveUS6898529B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsWireless dataWireless ad hoc network
The present invention is directed to a method and system for determining parameters inside a subterranean formation. In accordance with the present invention, a plurality of wireless data sensors are injected into the pores or fractures of a subterranean formation. The data sensors includes sensors that record parameters such as temperature, pressure and certain time stamps. Either autonoumously or upon command from a data interrogator tool located down hole, the plurality of data sensors form a wireless ad hoc network and telemeter the recorded data back to the data interrogator tool, which in turn communicates the data to a microprocessor located at the surface. Based on these data, the spatial distribution of the sensors and formation parameters such as temperature and pressure at each data sensor inside the subterranean formation can be obtained.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Intelligent bag
InactiveCN105430767APrecise Indoor PositioningDynamic correction positioningCyclesPursesSelf maintenanceAutomatic control
The invention discloses an intelligent bag. The intelligent bag comprises a portable bag, a power source, an intelligent sensor, a network layer, a microprocessor, a man-machine interaction apparatus and an application layer. The intelligent bag is reasonably and effectively integrated with a series of technologies such as navigation positioning, block chains, electronic sensing, data networks, artificial intelligence, distributed calculation, automatic control, machine identification, mobile computation, man-machine interaction and the like and is embedded into a portable terminal so as to improve trip experience of people. An intelligent bag user, as a manager, a supervisor and a user of a peer-to-peer network system in a wireless Ad-hoc network, can perform self-disposition, self-maintenance, self-learning and self-production so that a decentralized self-growing trip database can be constructed. Hopefully, the intelligent bag can be a terminal member of the internet of things of an intelligent city traffic system.
Owner:罗轶
Method and apparatus for locating position of a mobile device in an assisted satellite positioning system
Method and apparatus for locating position of a mobile device in an assisted satellite positioning system is described. In one example, satellite measurement data is obtained from a plurality of satellites at a mobile device. Position of the mobile device is computed using the satellite measurement data. The position is sent to a cellular device via a wireless ad hoc network. In one example, the wireless ad hoc network comprises a BLUETOOTH communication link. In one example, the mobile device is configured to receive assistance data from a position server through the wireless ad hoc network. For example, the mobile device may comprise a housing configured to plug into a cigarette lighter connector of an automobile and the cellular device may comprise a cellular telephone without location-determination capabilities (i.e., the cellular telephone does not include an integrated GPS receiver).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
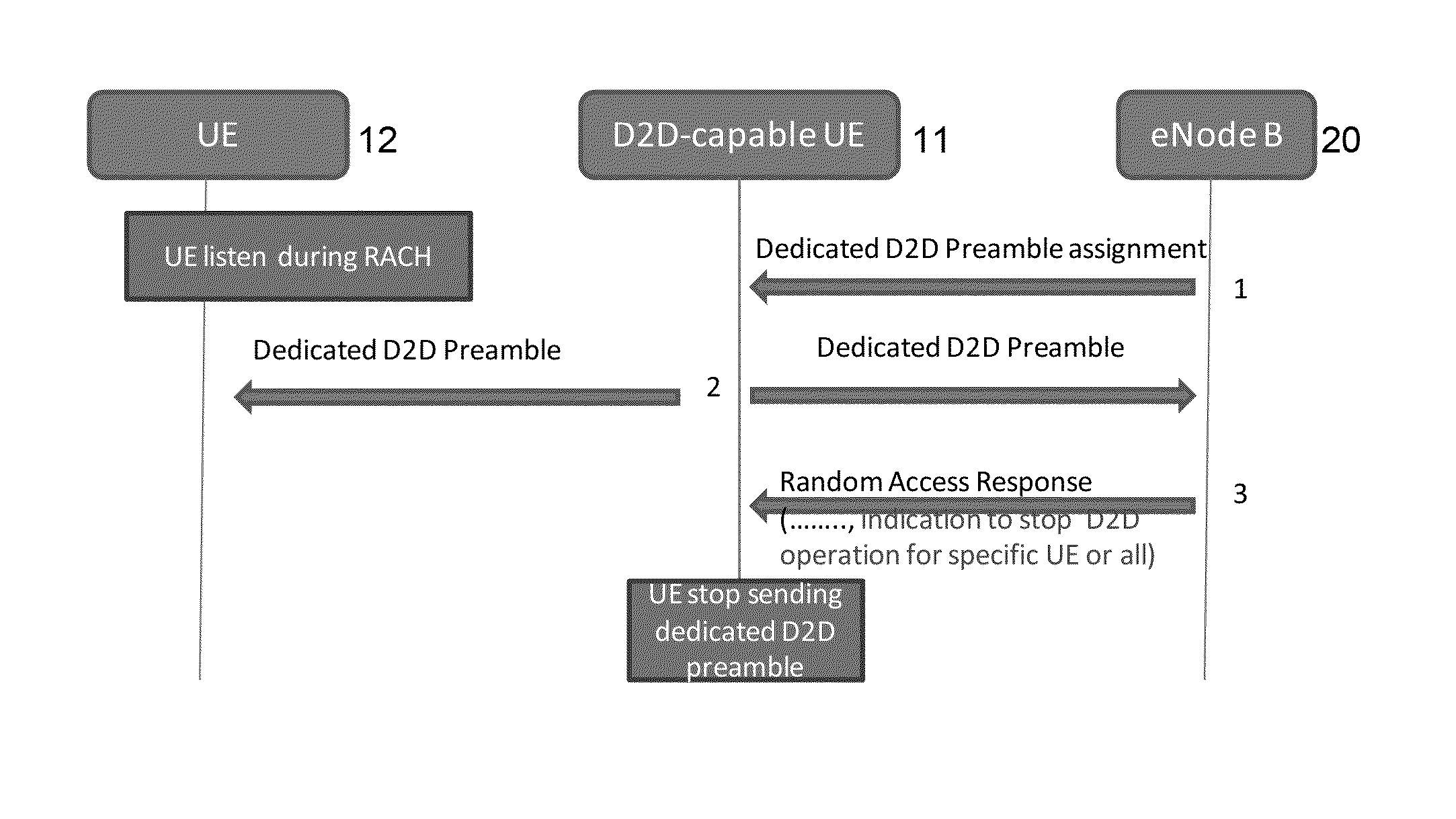
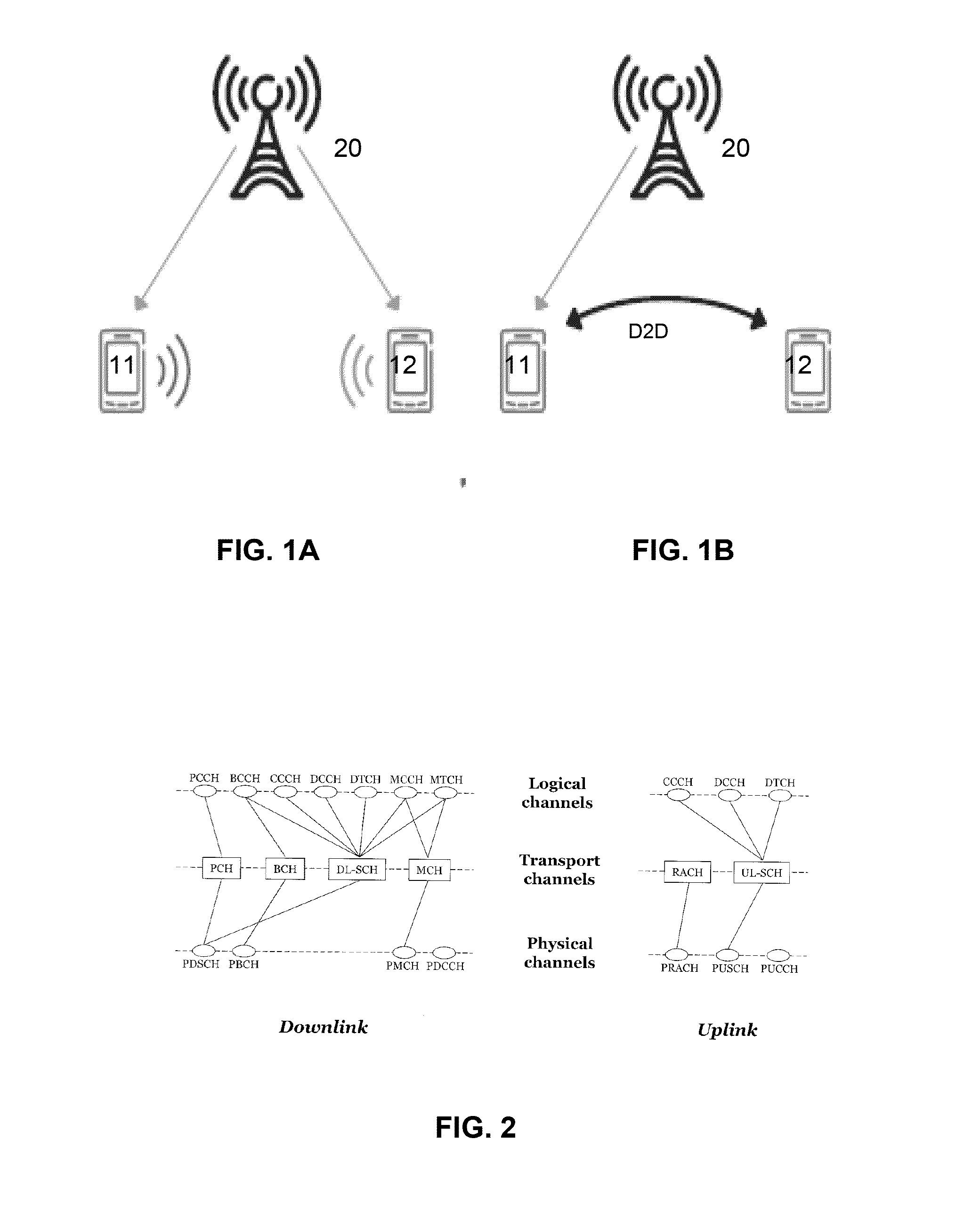
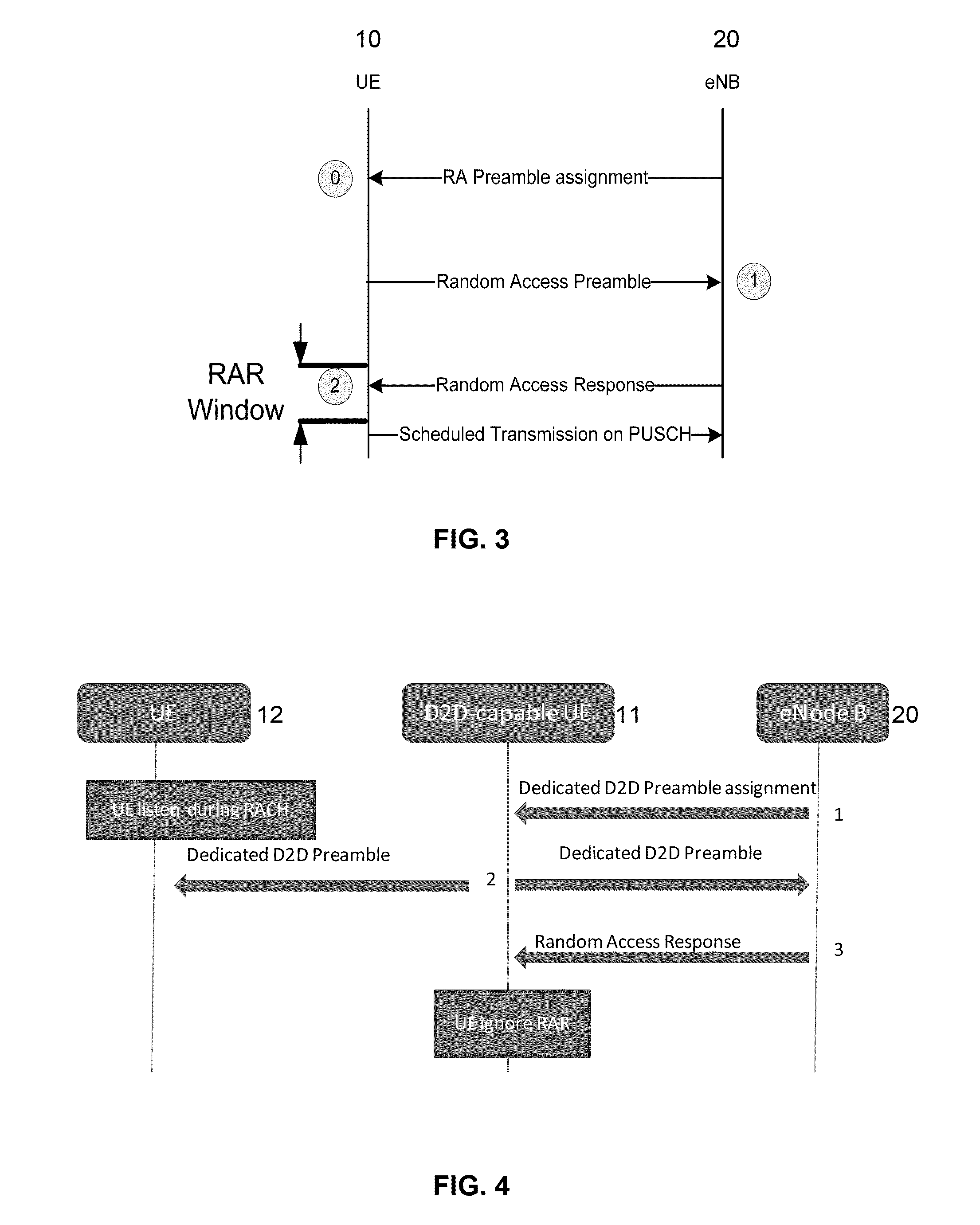
D2d communication in wireless networks
InactiveUS20140307611A1Broadcast transmission systemsConnection managementWireless mesh networkWireless ad hoc network
In a wireless communication network, a Device-to-Device (D2D) link is set up using a modified Random Access (RACH) procedure. The conventional RACH procedure is modified to enable a D2D-capable UE (11) to indicate its capability to other UEs (12), to receive additional information from a base station (20), and to enable the handshake procedure used to establish a D2D link. Broadcast system information may additionally be modified to enable D2D links between UEs (11, 12) in the same or different coverage areas, taking into consideration the RRC UE states (RRC_Connected or RRC_Idle). The proposed modifications to the broadcast system information include: an indication of D2D link opportunities with other UEs under a different coverage area to that of the D2D capable UE; and RACH parameters in the coverage area of the D2D capable UE, to indicate the listening period for the D2D link.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Ultra-wideband radar sensors and networks
InactiveUS20080007445A1Long monitoring capabilityContinuous and reliable operationLoop antennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionUltra wideband radarWireless ad hoc network
Ultra wideband radar motion sensors strategically placed in an area of interest communicate with a wireless ad hoc network to provide remote area surveillance. Swept range impulse radar and a heart and respiration monitor combined with the motion sensor further improves discrimination.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
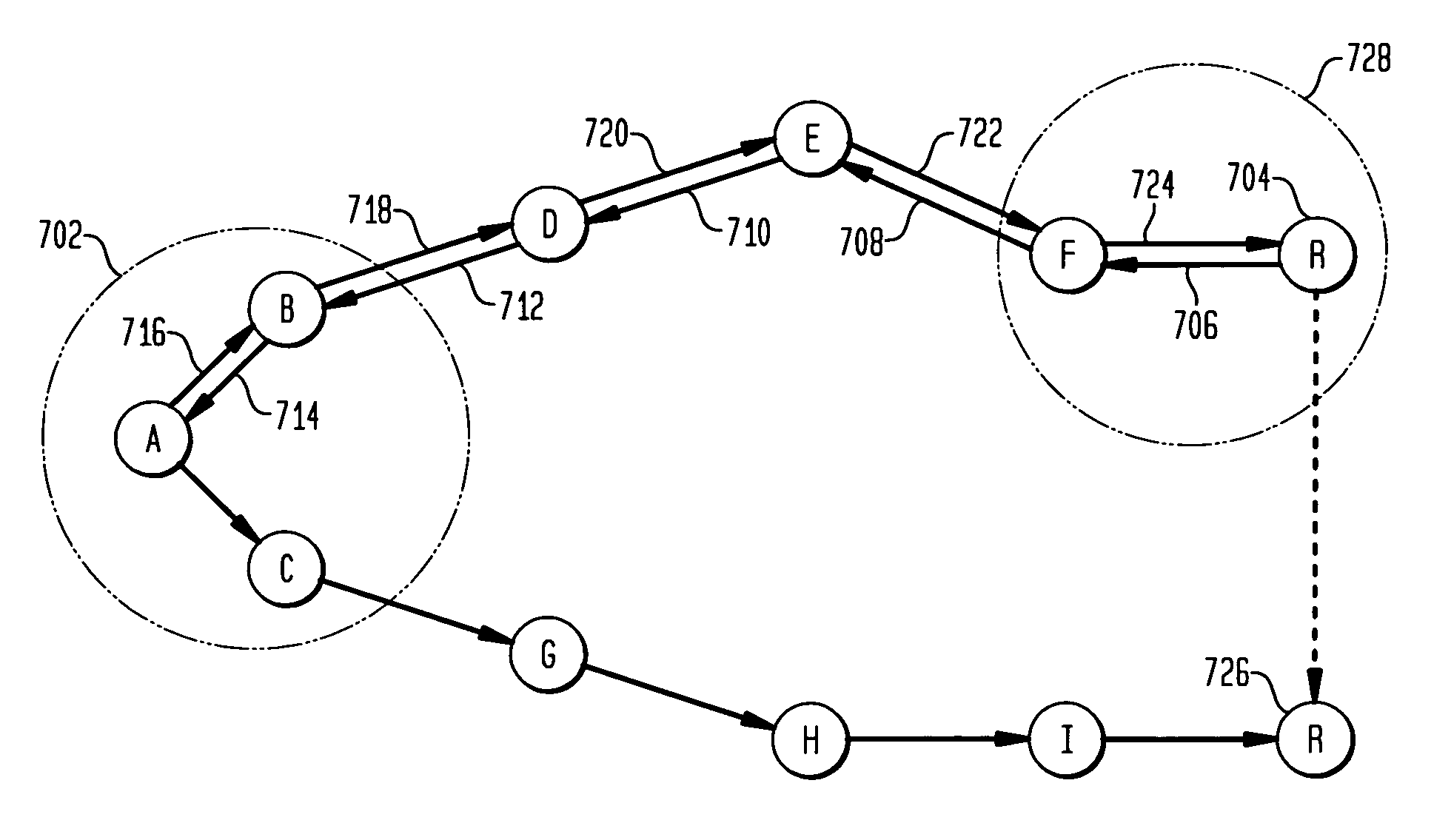
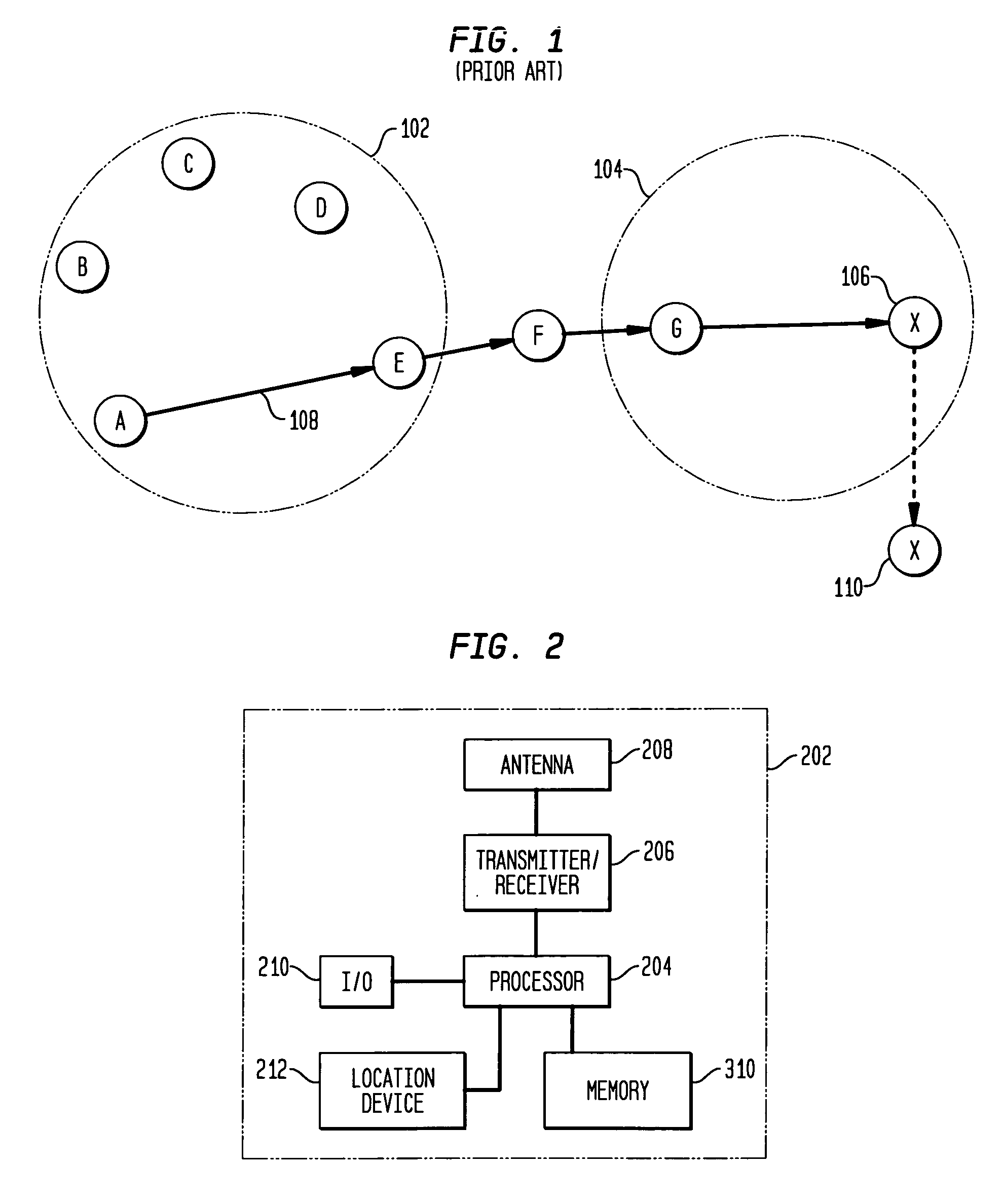
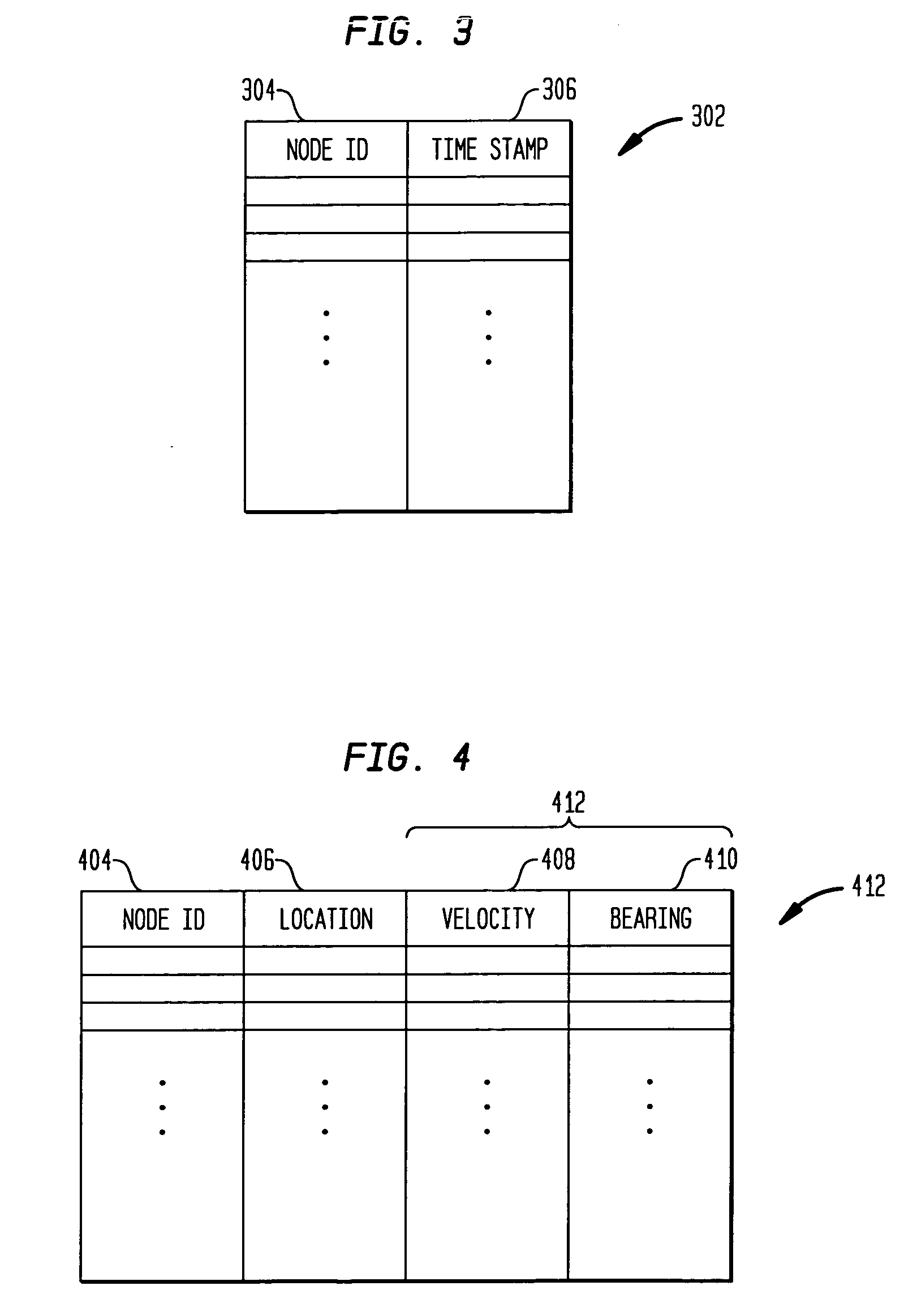
Proactive location based routing in a wireless ad-hoc network
ActiveUS20060062175A1Accurate dataPrecise routingNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesPropagation delayWireless ad hoc network
Disclosed is an improved proactive location based routing protocol for ad-hoc wireless networks. When a source node has a data packet to send to a destination node, the source node calculates an estimated future location of the destination node prior to forwarding a data packet to the destination node. The estimated future location may be based on the last known location, velocity and bearing of the destination node, as well as upon the estimated propagation delay (i.e., the estimated time it will take the data packet to reach the destination node after being transmitted by the source node). The source node routes the data packet by identifying which one of a plurality of its neighbor nodes is closest to the estimated future location of the destination node, and routes the data packet the identified neighbor node as an intermediate node along the route from the source node to the destination node. Further, the frequency of flooding broadcasts is based on the velocity of the network nodes. As the velocity of a network node increases, the rate at which the node broadcasts its location and mobility data also increases. The broadcast frequency of a network node may be dynamically adjusted as its velocity changes.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
Method and Apparatus for Medium Access Control for a Decentralized Network with Adapted Beamforming and Power Control
InactiveUS20070002734A1Improve throughputReduce transmit powerError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmitted powerPhysical layer
A method and apparatus for medium access control in a wireless ad hoc network is disclosed that takes advantage of physical layer properties to jointly and collectively optimize in a distributed fashion transmission parameters such as beam-patterns and transmit powers of all active links in the network. To resolve signal transmission contention, each potential link is associated with a persistence parameter and the persistence parameter is adapted locally, with no central control, to provide medium access for transmissions. Where a node contending for a transmission slot is unable to optimize its transmission parameters due to an invalidity condition or infeasibility condition, the persistence parameter is updated, preferably so as to reduce the probability of such conditions.
Owner:NEC CORP
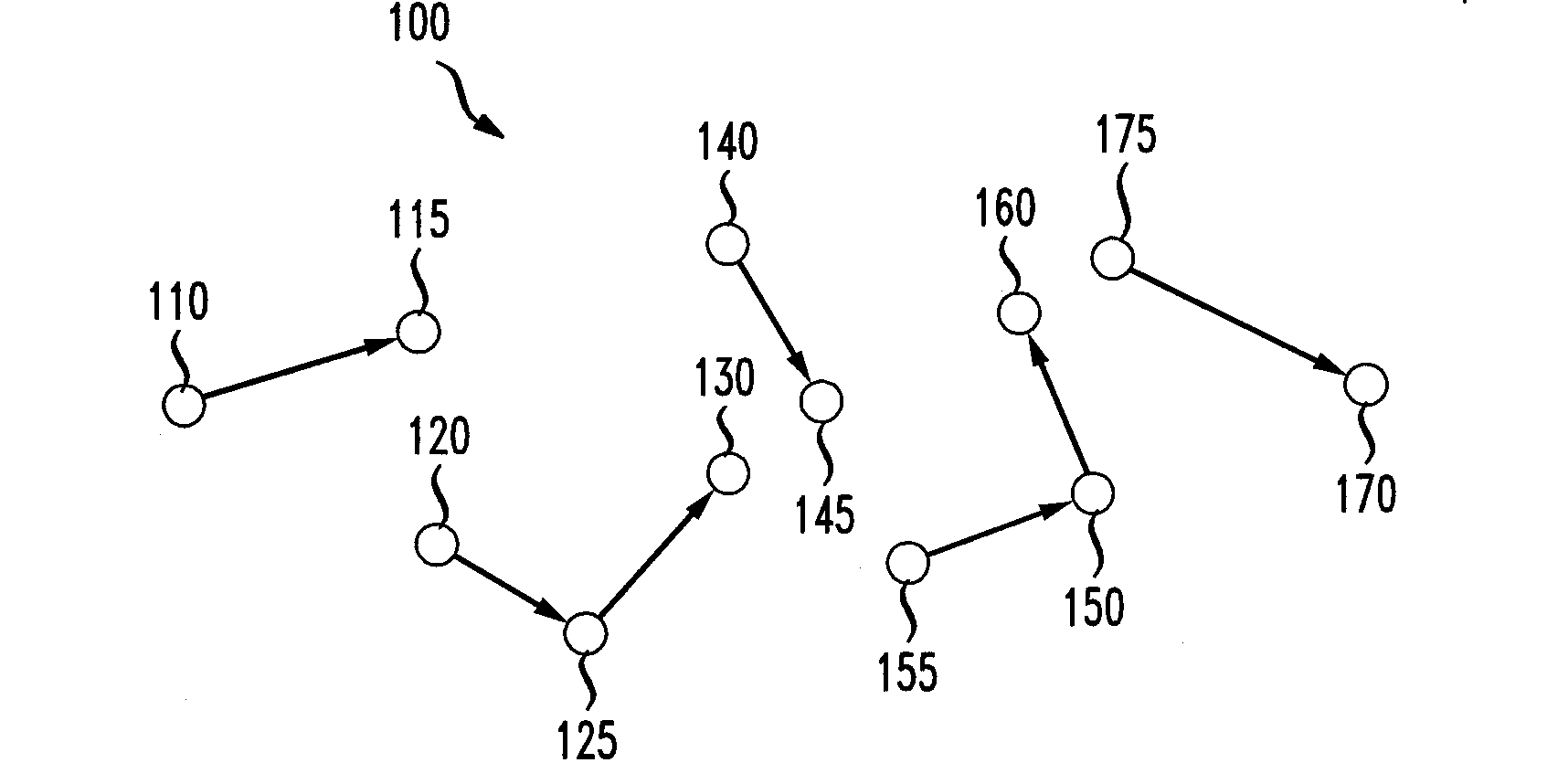
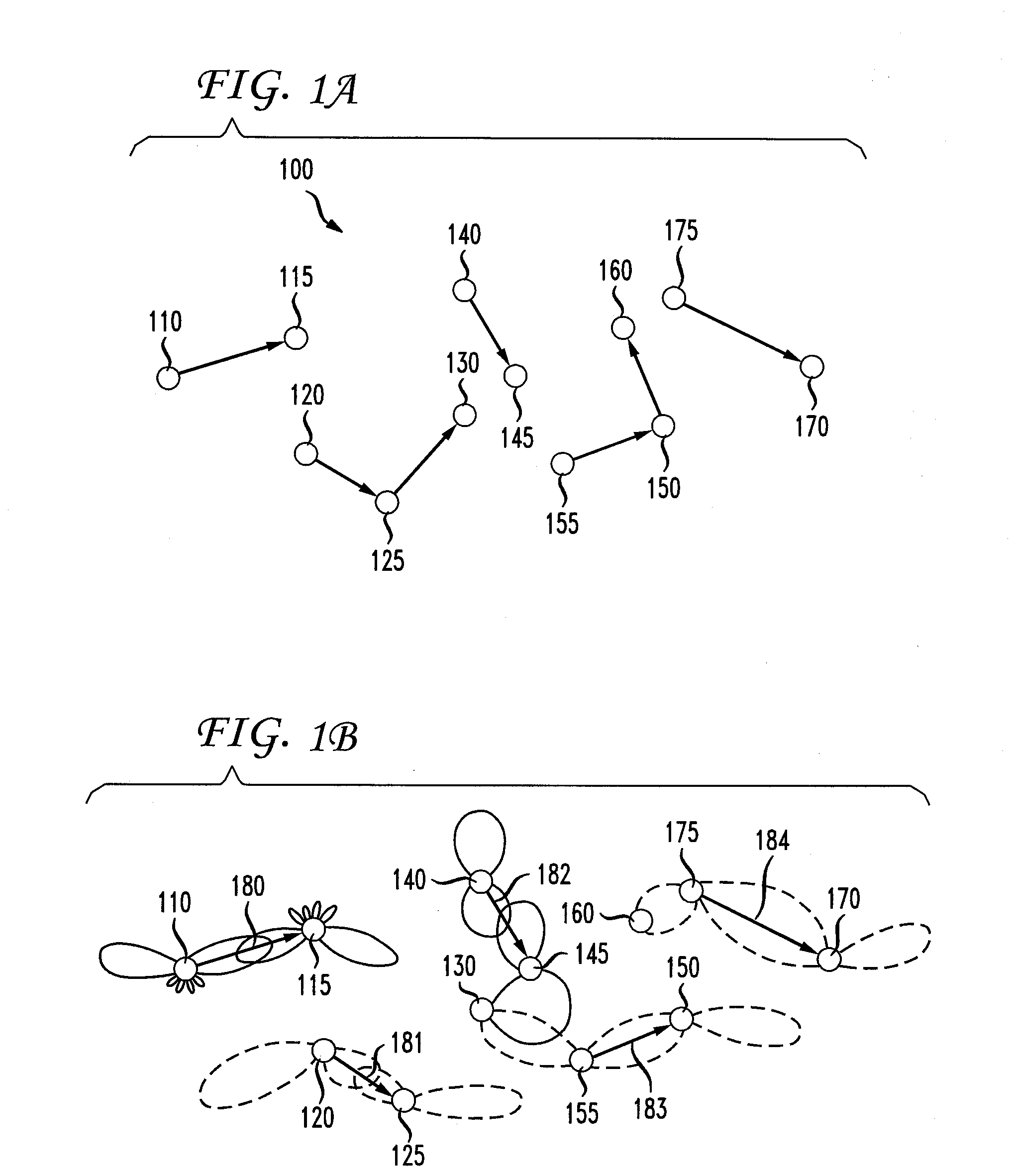
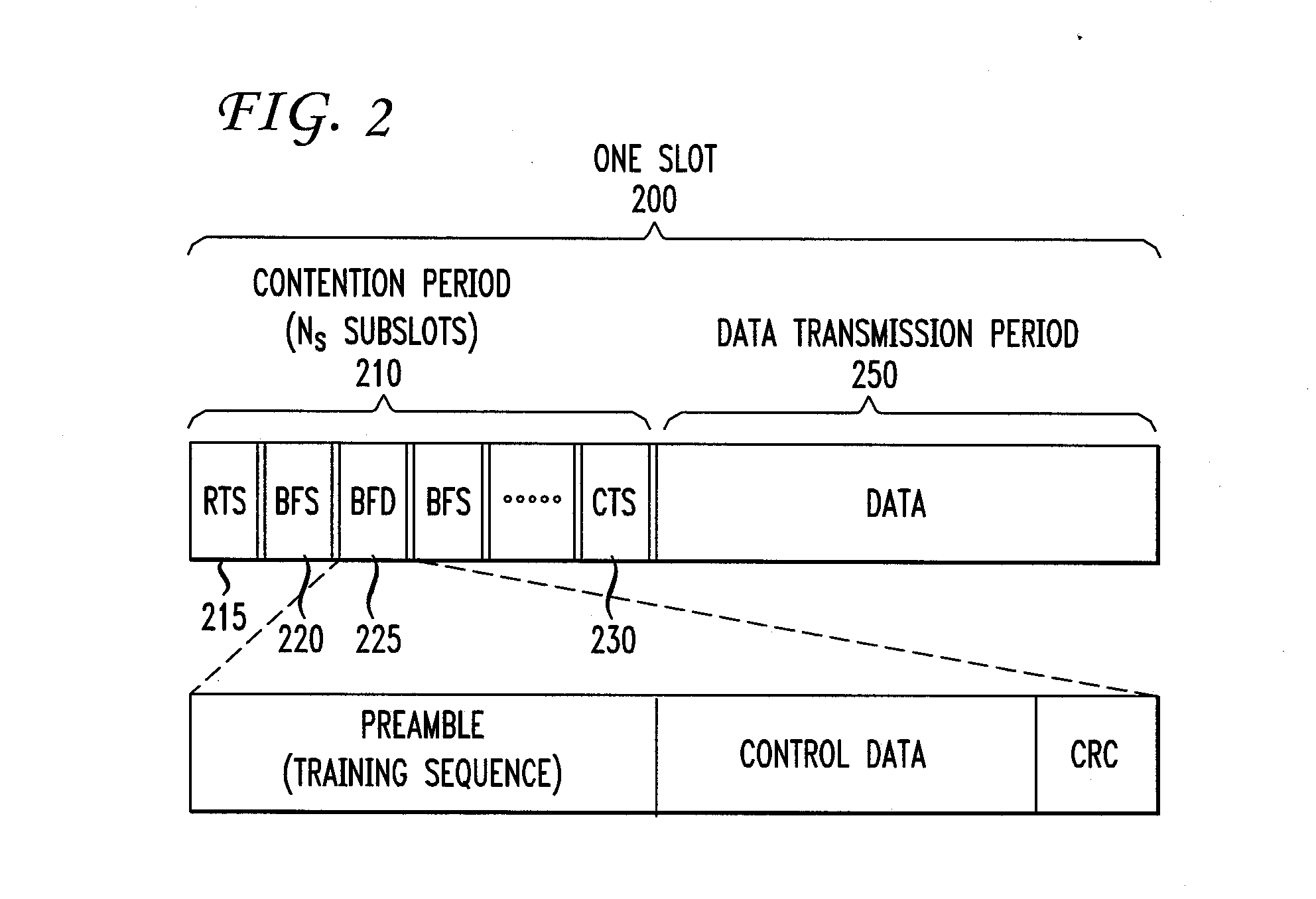
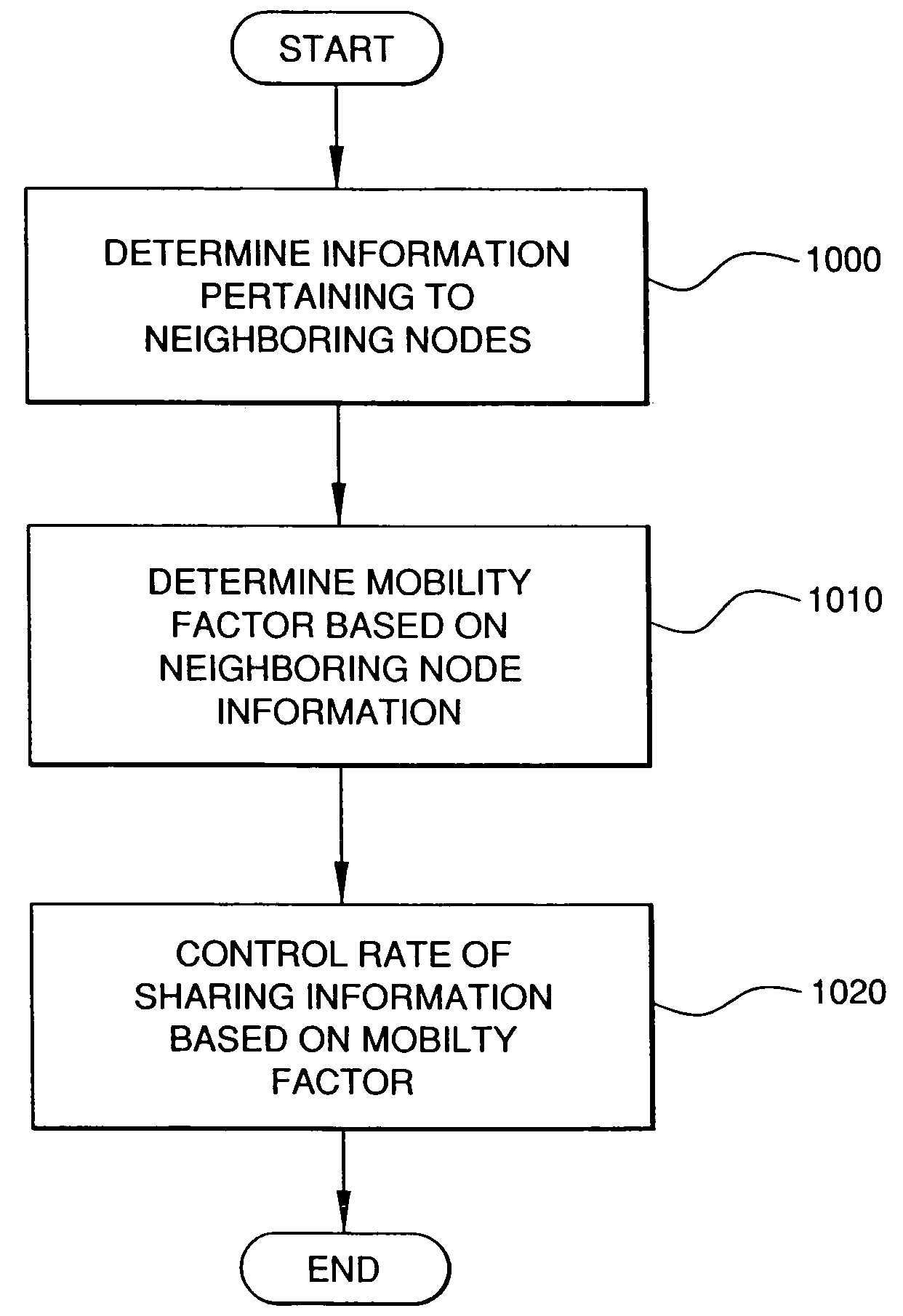
System and method for determining the measure of mobility of a subscriber device in an ad-hoc wireless network with fixed wireless routers and wide area network (WAN) access points
ActiveUS7181214B1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationWireless routerWireless mesh network
A system and method for determining the mobility of a node in a network, such as a wireless ad-hoc network that requires the node to share its information with other mobile and stationary nodes, such as fixed wireless routers and intelligent access points, so that the rate at which the node shares this information and receives location information, such as Geo-location updates, could be based on the rate of mobility of the node. The node includes a transceiver which is adapted to communicate or attempt to communicate with at least one of the stationary other nodes in the network, and a controller which is adapted to determine a mobility factor of the node based on the communication or attempted communication with the at least one stationary other node. The controller is further adapted to control a rate at which the transceiver sends information pertaining to the node to at least one of the other nodes in the network based on the mobility factor. The mobility factor represents a rate of mobility of the node, and the rate at which the controller controls the transceiver to send the information is proportional to the rate of mobility.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
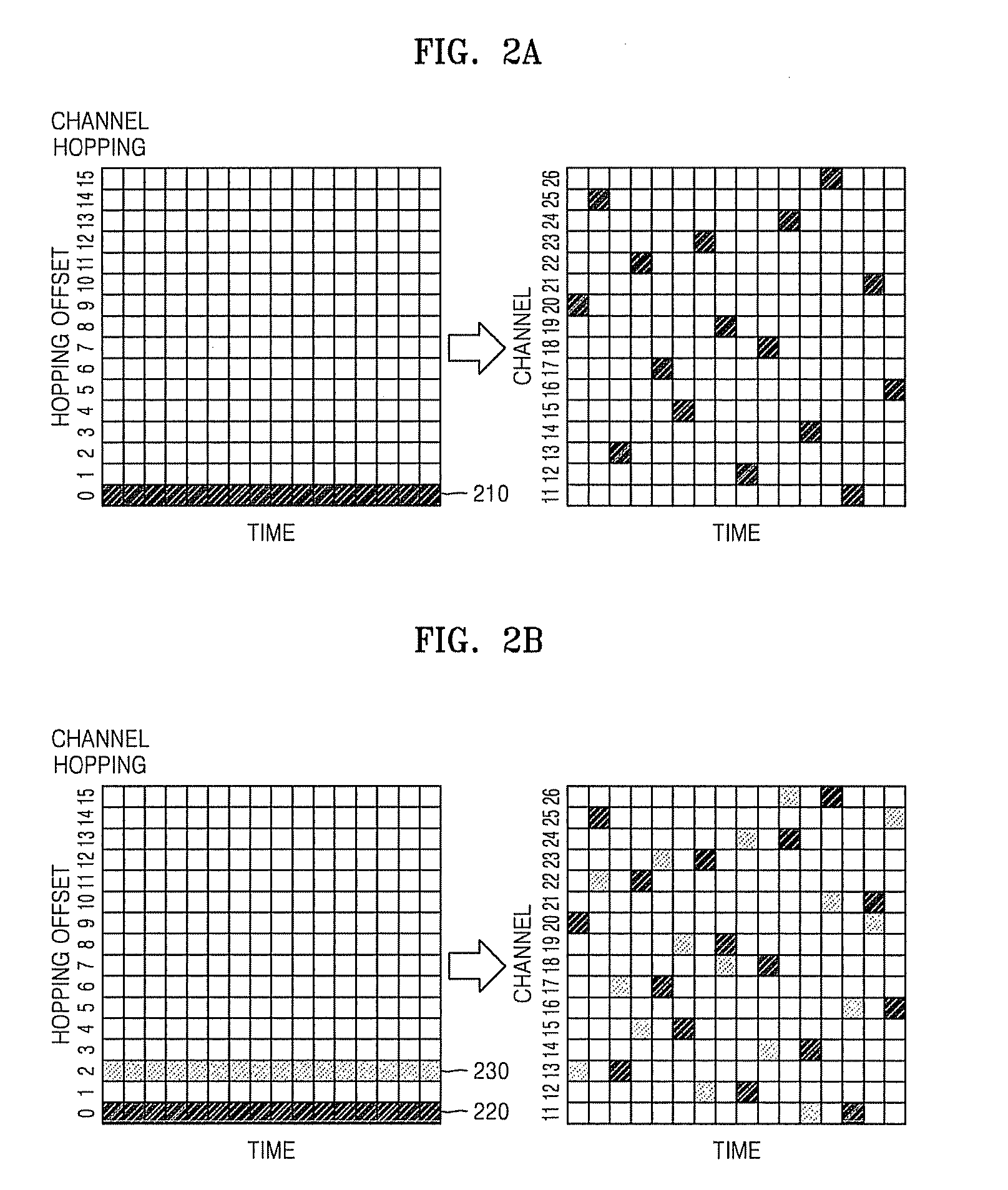
Distributed channel hopping method in wireless ad-hoc network
InactiveUS20100296493A1Avoid collisionTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionWireless ad hoc networkSelf-organizing network
A distributed channel hopping communication method in a low power wireless ad-hoc network. A beacon transmission and reception scheduling method using a distributed channel hopping method in a wireless ad-hoc network, the method includes: transmitting beacons using channel hopping, before establishing the wireless ad-hoc network including a plurality of nodes having a BP including at least one time slot, and receiving beacons of a plurality of neighboring nodes of each of the plurality of nodes; collecting information about the wireless ad-hoc network and information about the plurality of neighboring nodes from the received beacons; scheduling the receiving of the beacons that are transmitted from the plurality of neighboring nodes in the BP, using TDMA in each of the at least one time slot based on the information about the plurality of neighboring nodes; and scheduling transmitting of a beacon in each of the at least one time slot.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
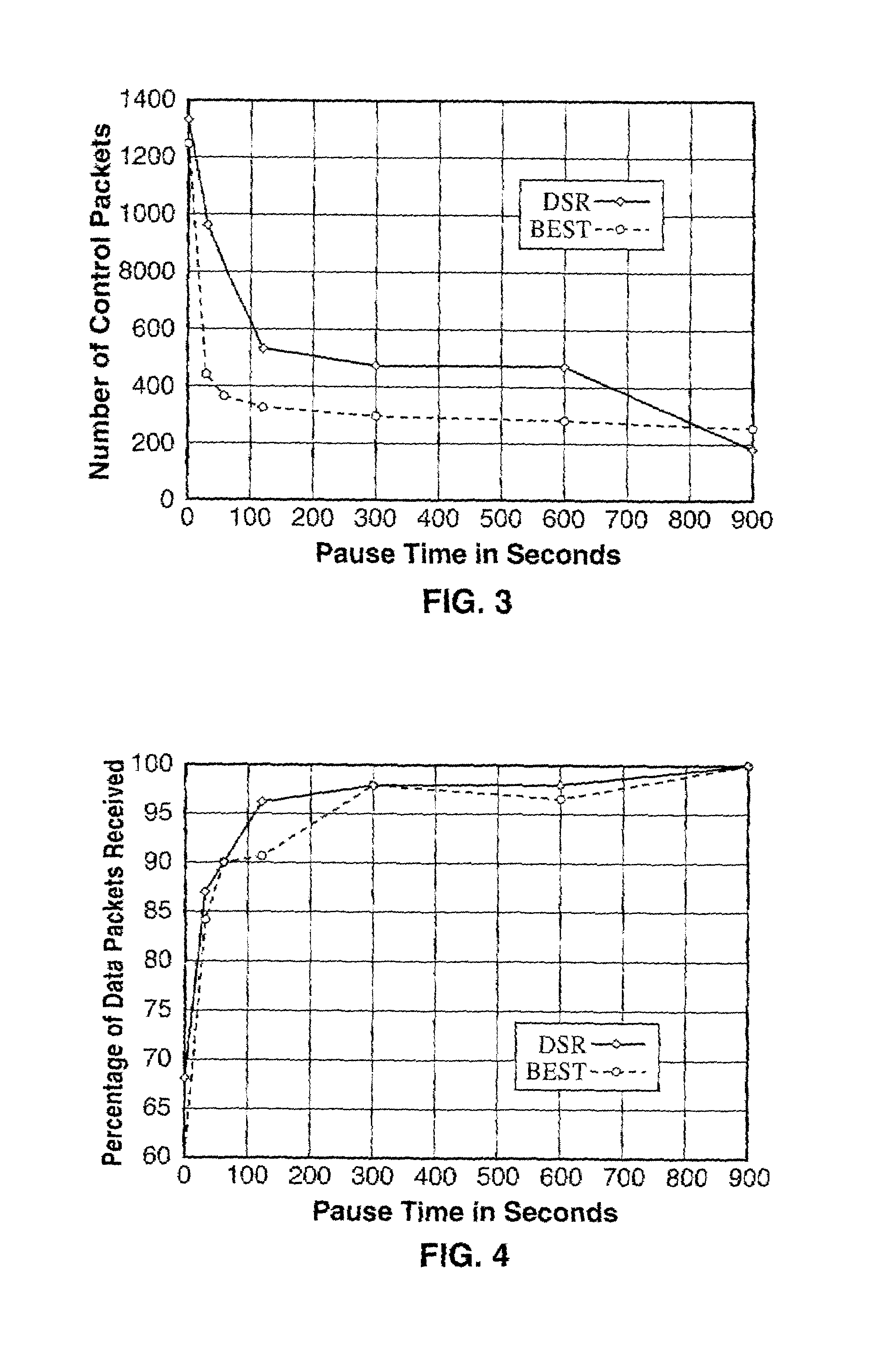
Bandwidth efficient source tracing (BEST) routing protocol for wireless networks
ActiveUS7002949B2Reduce control overheadIncrease available bandwidthPower managementNetwork topologiesPathPingDistance-vector routing protocol
A bandwidth efficient routing protocol for wireless ad-hoc networks. This protocol can be used in ad-hoc networks because it considerably reduces control overhead, thus increasing available bandwidth and conserving power at mobile stations. It also gives very good results in terms of the throughput seen by the user. The protocol is a table-driven distance-vector routing protocol that uses the same constraints used in on-demand routing protocols, i.e., paths are used as long as they are valid and updates are only sent when a path becomes invalid. The paths used by neighbors are maintained and this allows the design of a distance-vector protocol with non-optimum routing and event-driven updates, resulting in reduced control overhead.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com