Patents
Literature
1249 results about "Routing algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
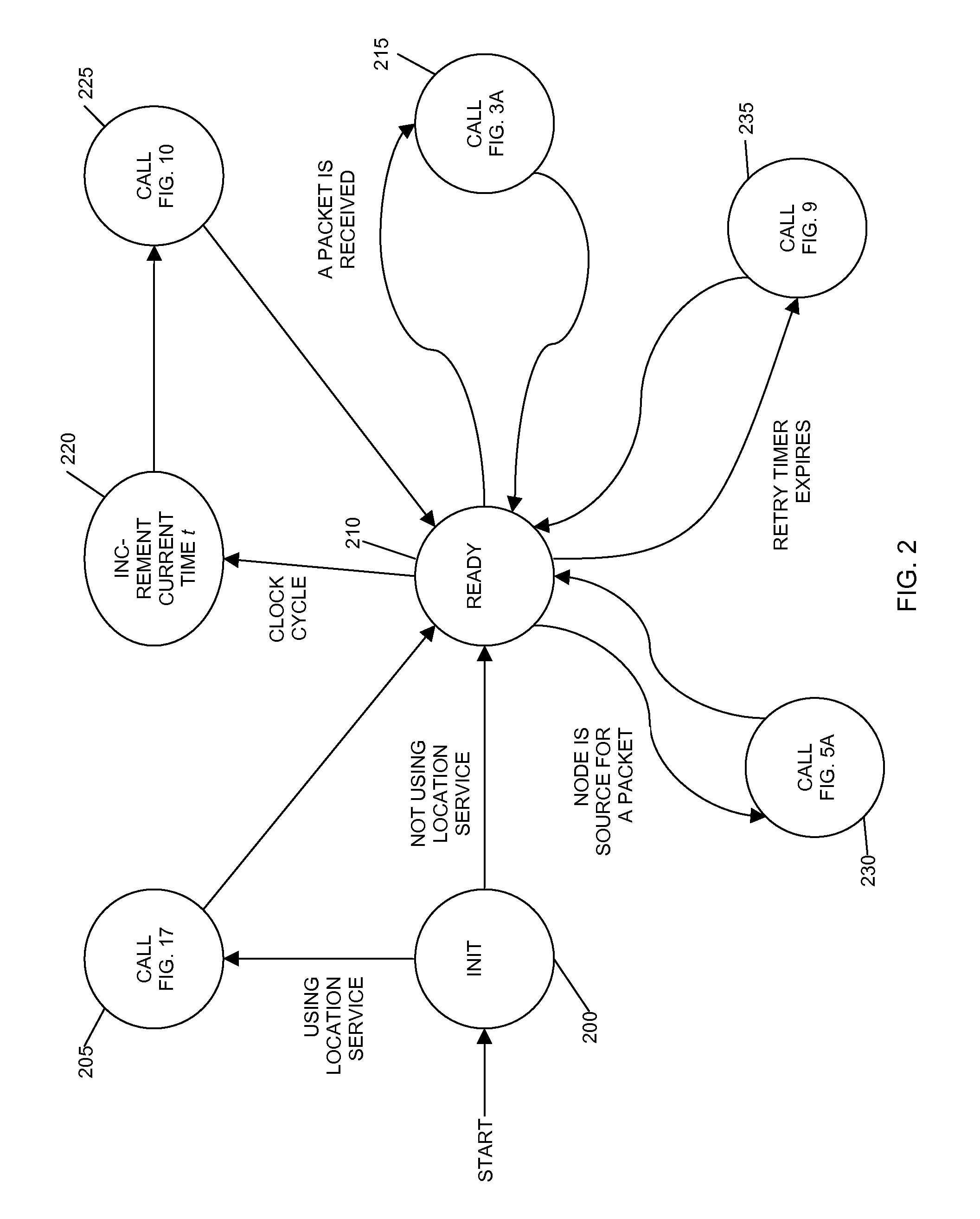
A Routing Algorithm is a method for determining the routing of packets in a node. For each node of a network, the algorithm determines a routing table, which in each destination, matches an output line. The algorithm should lead to a consistent routing, that is to say without loop.
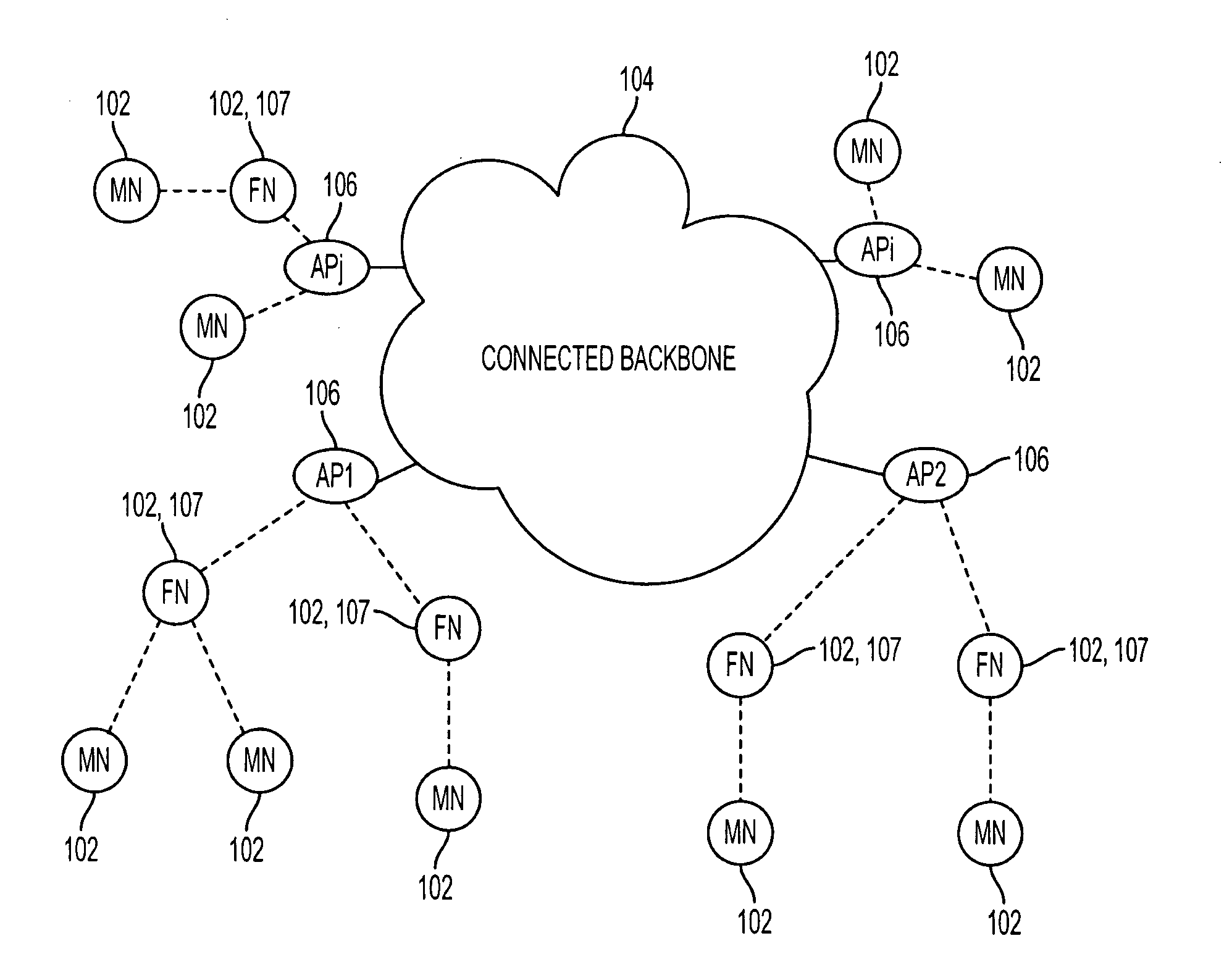
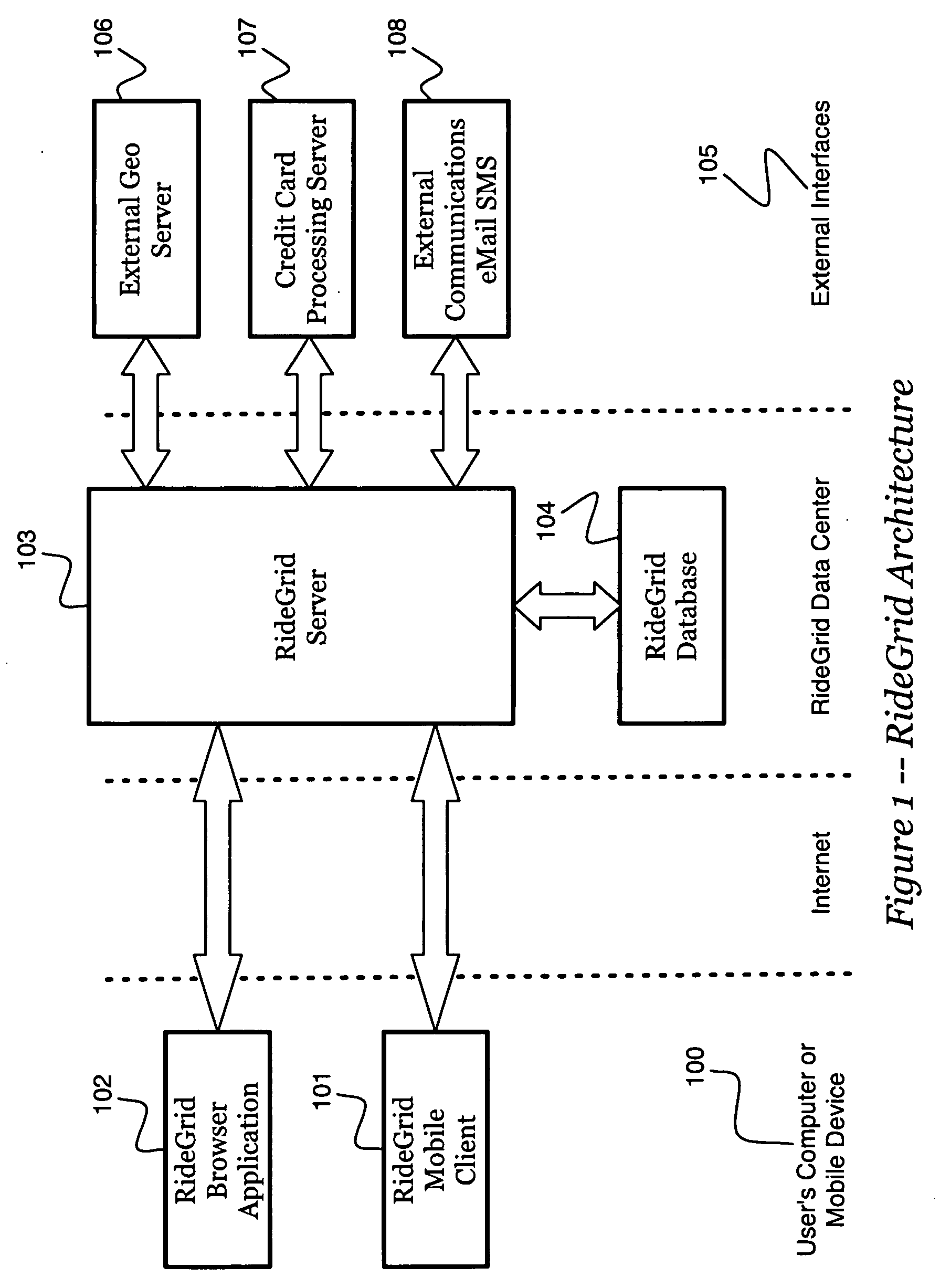
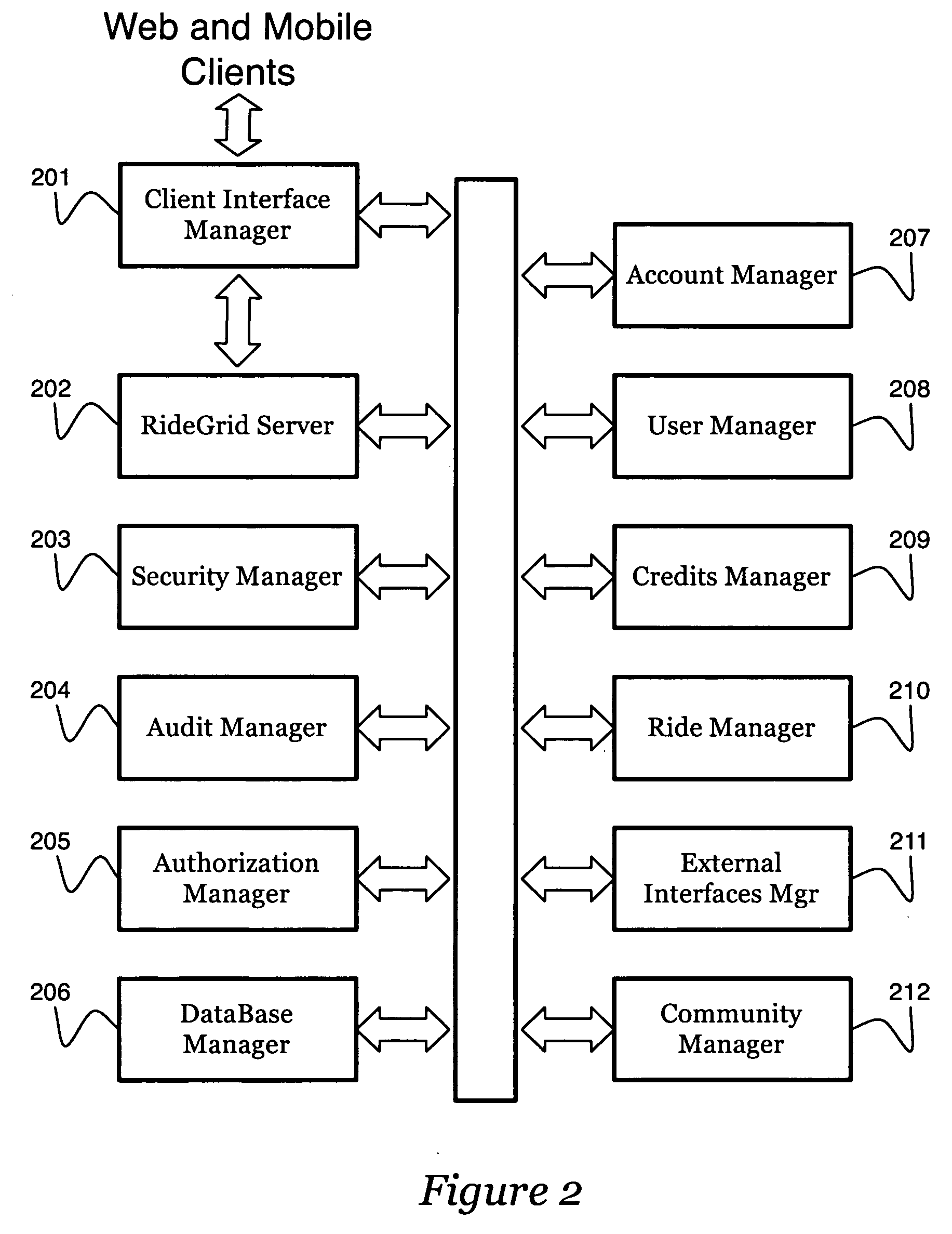
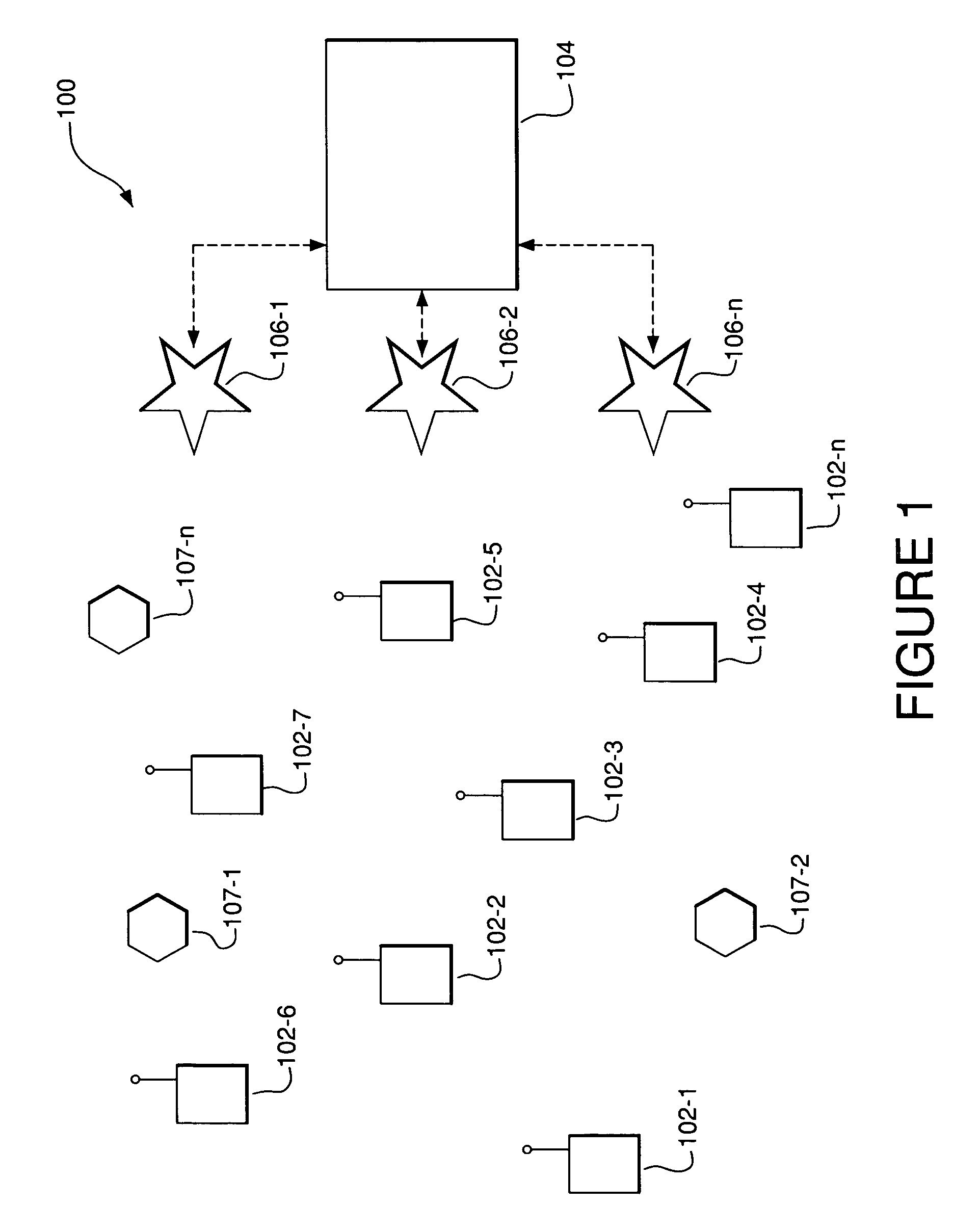
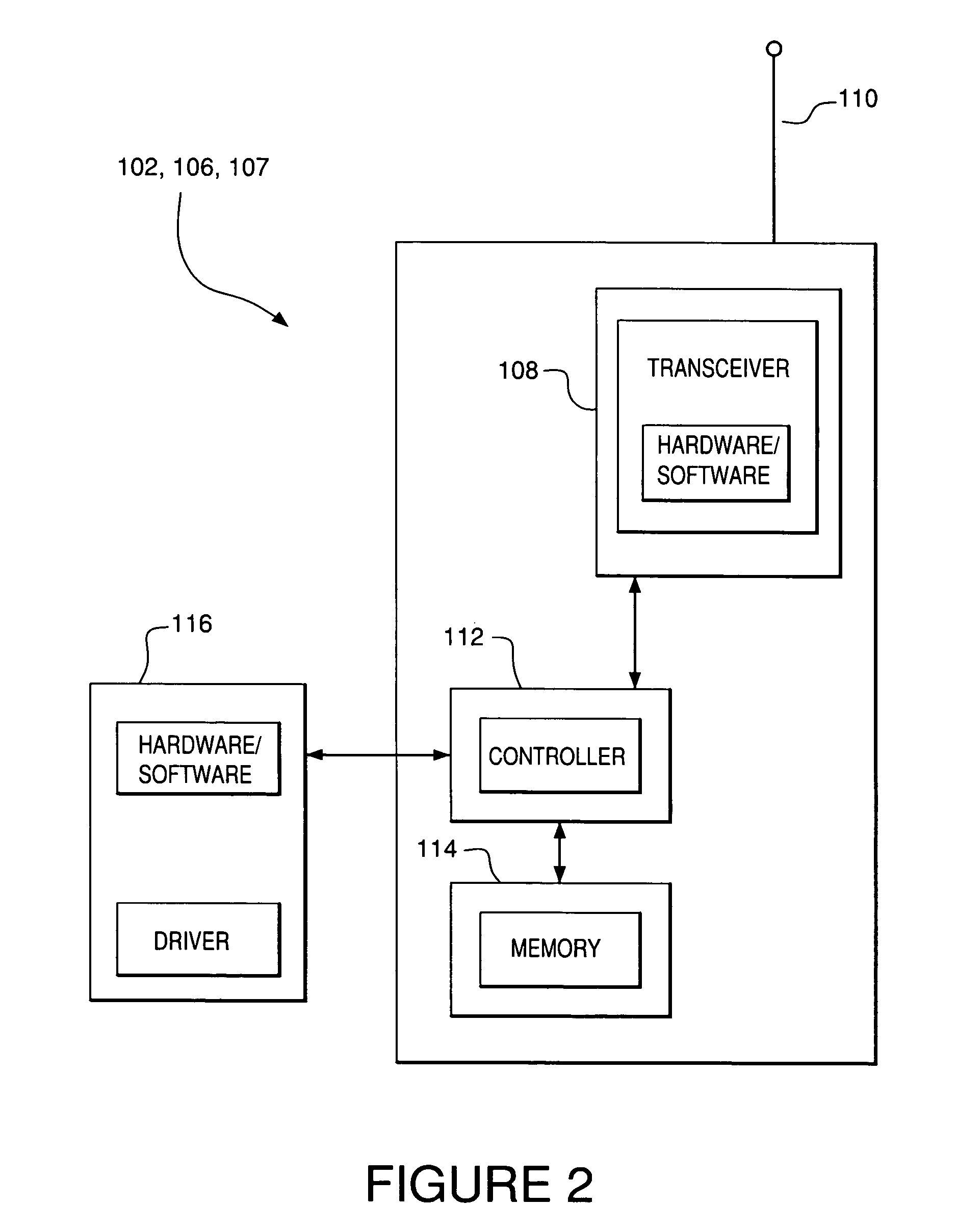
System and method to support multicast routing in large scale wireless mesh networks
ActiveUS20060098607A1Quick changeReduce overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsNetwork topologiesTree rootWireless mesh network
Provided is a system and method for a multicast routing algorithm to work in infrastructure based mesh networks. It chooses access points, fixed infrastructure gateway nodes connected to each other and / or the global internet via a wired / wireless backbone, as a group of local multicast group leaders to form a multicast group leader cloud. Each local multicast group leader is elected on-demand according to the local multicast group member's request. Each local multicast group leader forms a local multicast tree rooted at this leader connecting all multicast group members associated with the AP. The processes of electing and maintaining local multicast trees rooted at APs enable efficient coordination with underlying unicast routing to exploit the advantages of fixed infrastructure nodes. Therefore, routing overhead and multicast tree convergence time are reduced. The method can support large networks with fast topology change due to fast convergence and reduced routing overhead.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Systems and methods for enhancing private transportation
InactiveUS20080270019A1Good choiceEnhance and streamline and improve flexibility and efficiency and functionality of systemInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlPrivacy protectionRouting algorithm
Systems and methods are disclosed for enhancing the convenience, security, and efficiency of ridesharing through the incorporation of trusted communities, geotemporal routing algorithms, and by providing monetary incentives and privacy safeguards to encourage system growth.
Owner:HIGH REGARD SOFTWARE
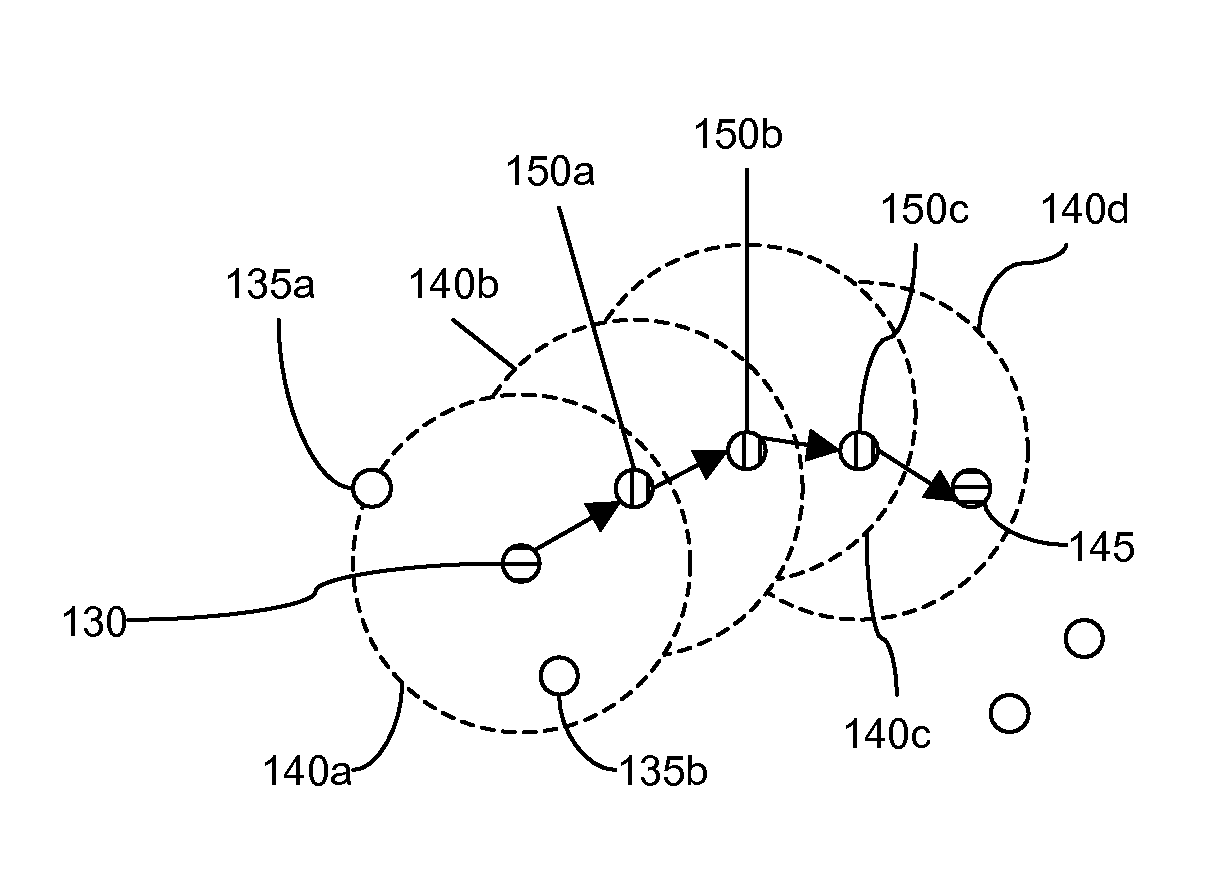
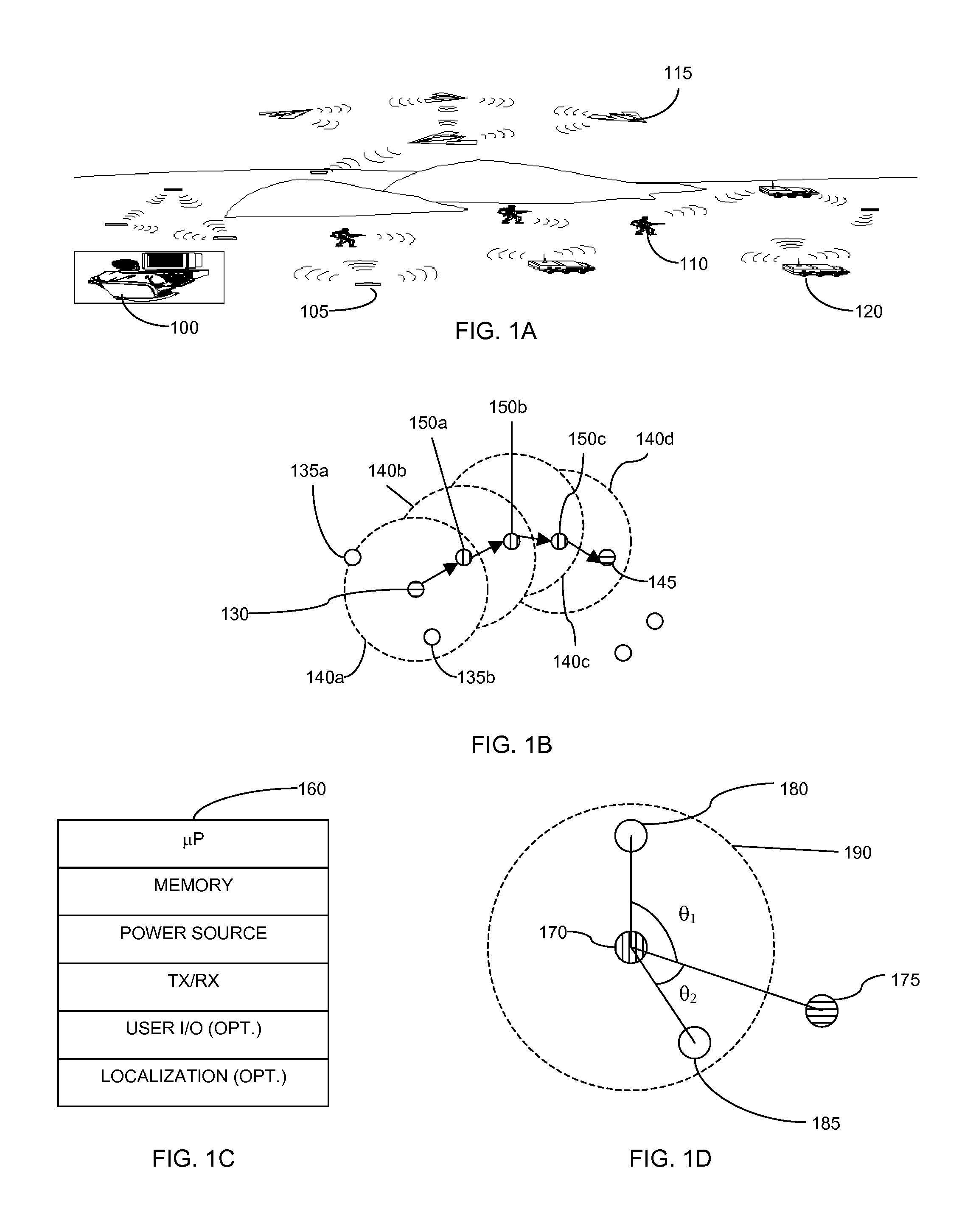
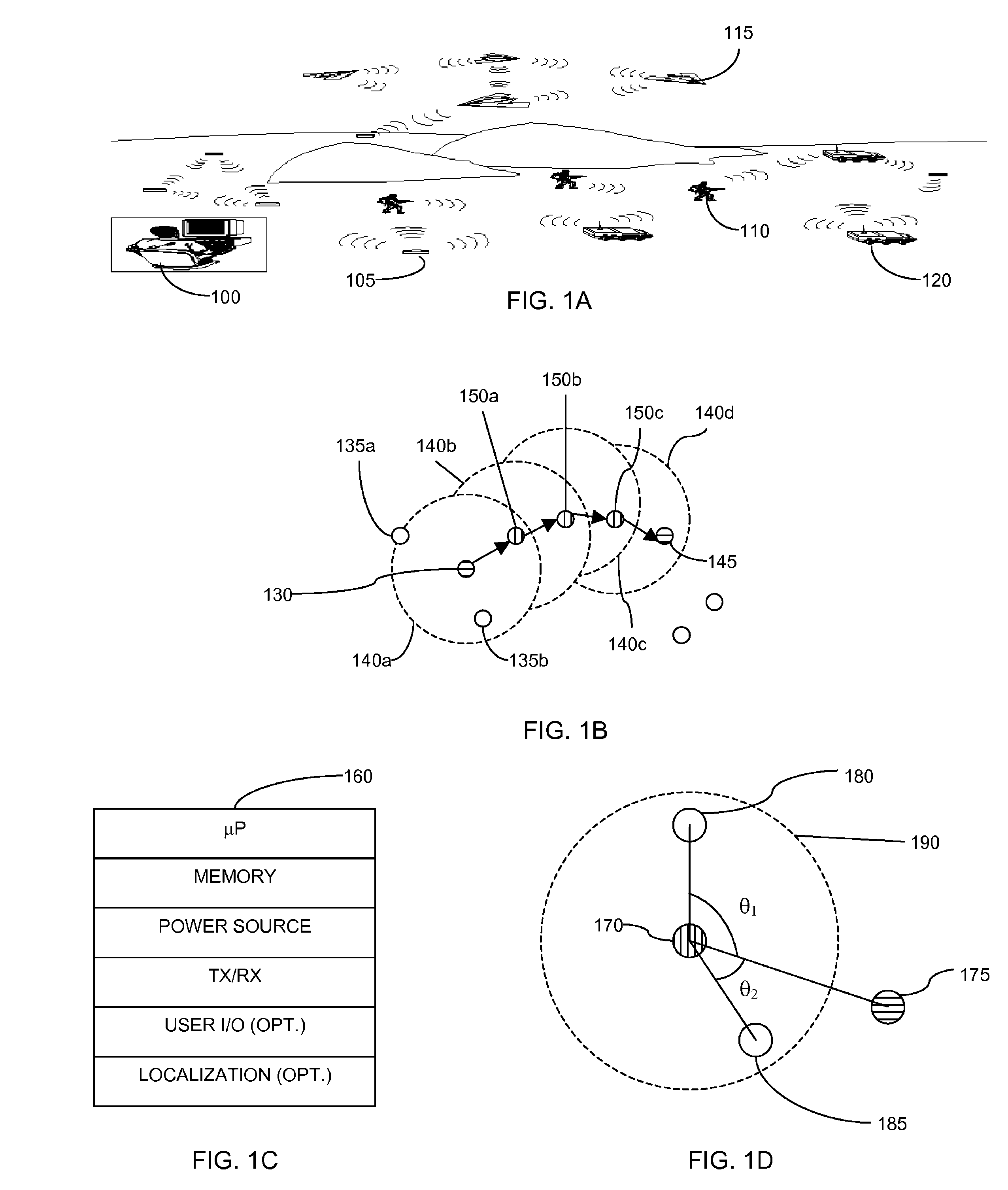
Swarm location service for mobile ad hoc network communications
InactiveUS7813326B1Efficient routingEasy to learnError preventionTransmission systemsRouting tableRouting algorithm
A Swarm Autonomous Routing Algorithm (SARA) is performed by simple communication node devices for node to node communications in a network, especially a Mobile Ad hoc NETwork (MANET). Each node maintains a table of pheromone values for known neighbor nodes. Pheromone values are dynamic for adapting to a dynamic arrangement of nodes, and are updated either passively or actively. Routing tables are not used. When a node receives a packet, it uses the pheromone table to simply determine whether or not to forward (rebroadcast) the packet to a neighbor node, and if possible, determines and indicates the best neighbor node for next forwarding the packet. Destination Zone Routing (DZR) and Swarm Location Service (SLS) are alternative enhancements of SARA that can be used for more efficient routing when nodes are location aware / knowledgeable. SLS may also be used to improve routing algorithms other than SARA.
Owner:BLUETRONIX
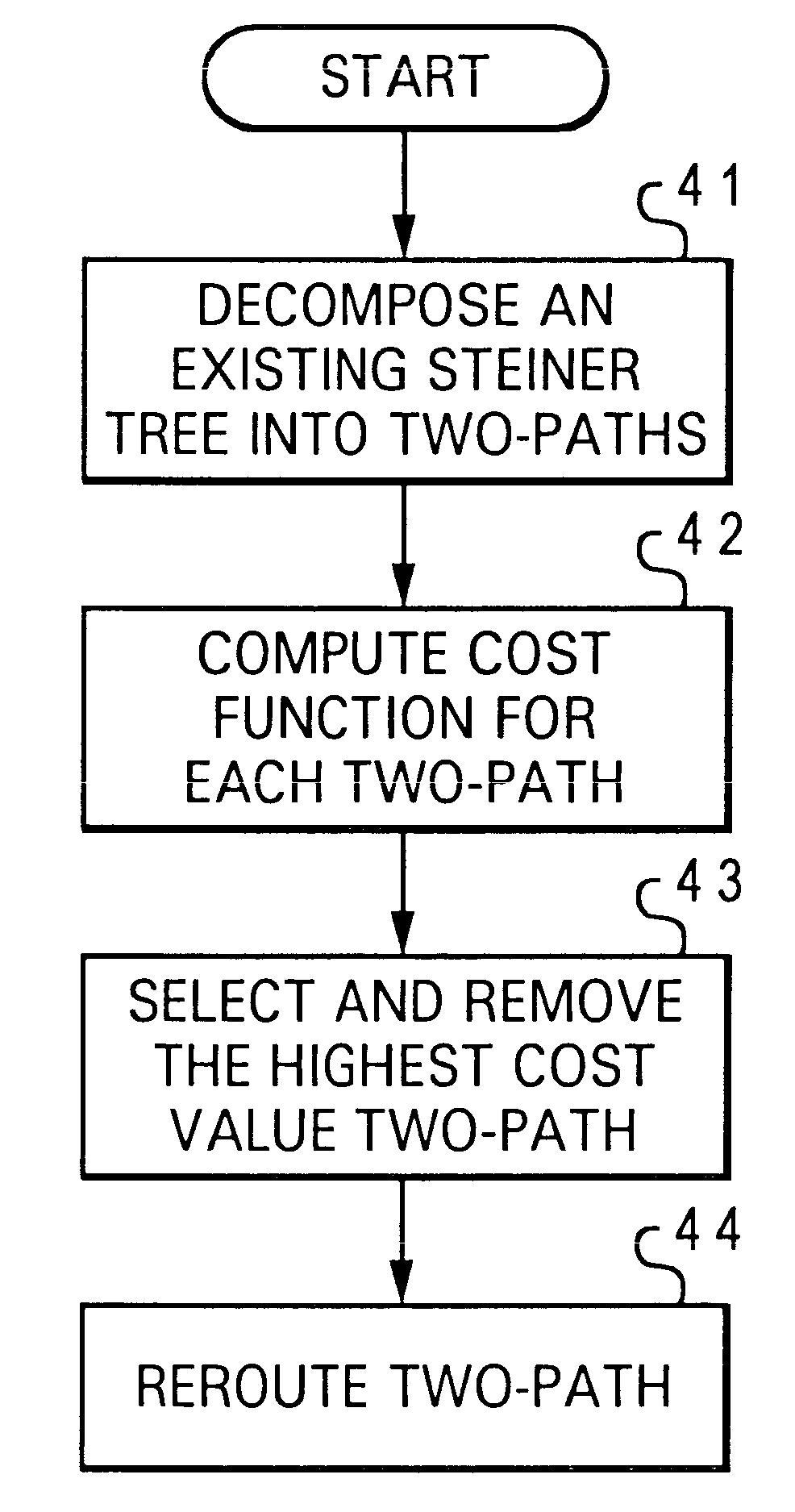
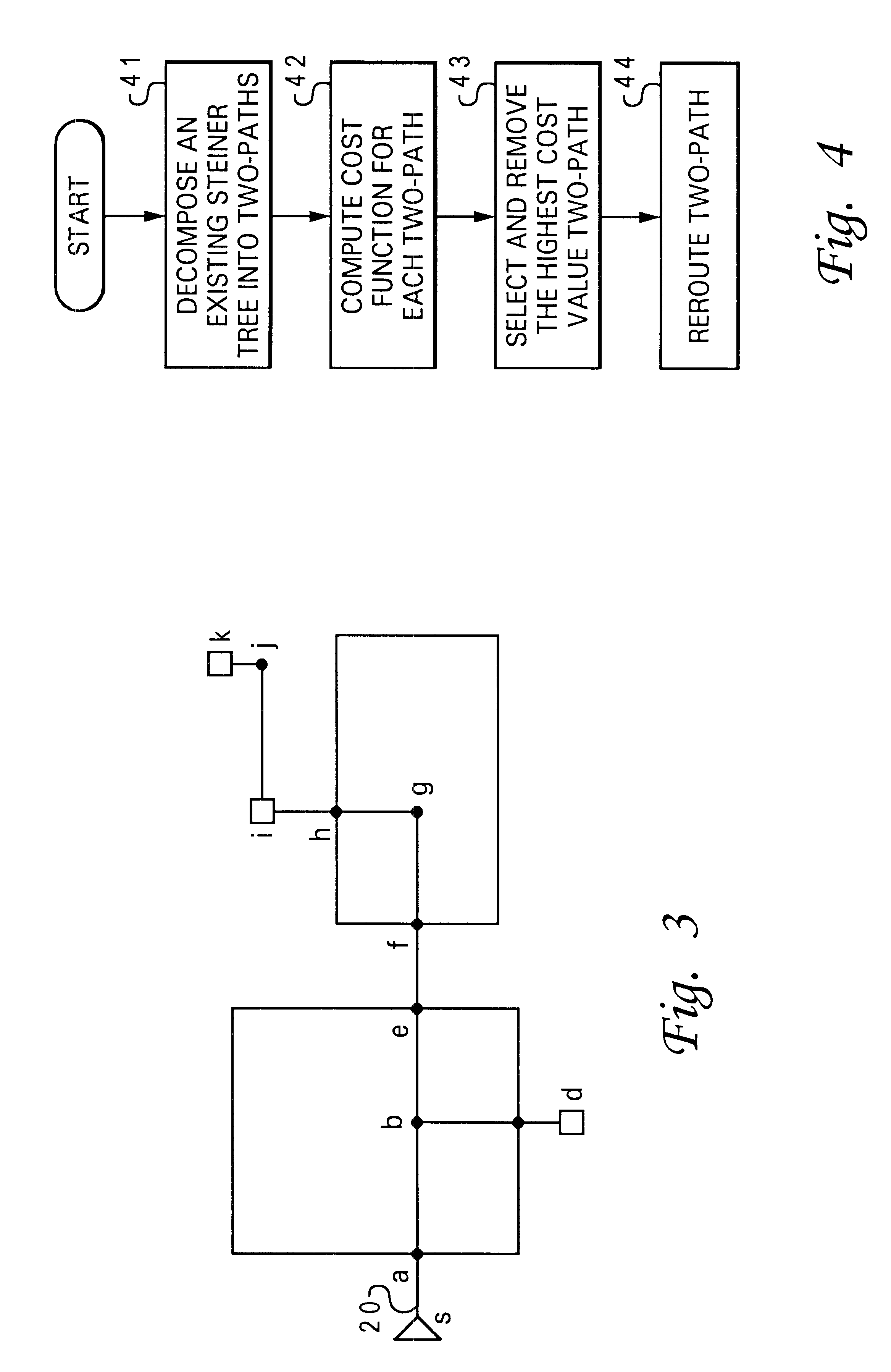
Method and system for re-routing interconnects within an integrated circuit design having blockages and bays
InactiveUS6401234B1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationRouting algorithmCircuit design
A method and system for re-routing interconnects within an integrated circuit design having blockages and bays is disclosed. A net within the integrated circuit design is initially decomposed into multiple two-paths. The net includes interconnects previously routed by utilizing a Steiner tree routing algorithm. Next, a cost associated with each of the two-paths is calculated. A two-path having a a high cost is subsequently selected and re-routed with a lower cost two-path.
Owner:IBM CORP
UAV decision and control system
ActiveUS20100163621A1Improve efficiencyAutonomous decision making processSpecial data processing applicationsGraph theoreticControl system
The present invention relates to a hierarchical system and method for task assignment (TA), coordination and communication of multiple Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV's) engaging multiple attack targets and conceives an ad-hoc routing algorithm for synchronization of target lists utilizing a distributed computing topology. Assuming limited communication bandwidth and range, coordination of UAV motion is achieved by implementing a simple behavioral flocking algorithm utilizing a tree topology for target list routing. The TA algorithm is based on a graph-theoretic approach, in which a node locates all the detectable targets, identifies them and computes its distance to each target. The node then produces an attack plan that minimizes the sum of distances of the UAV's in the subtree of a given node to the targets.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD +1
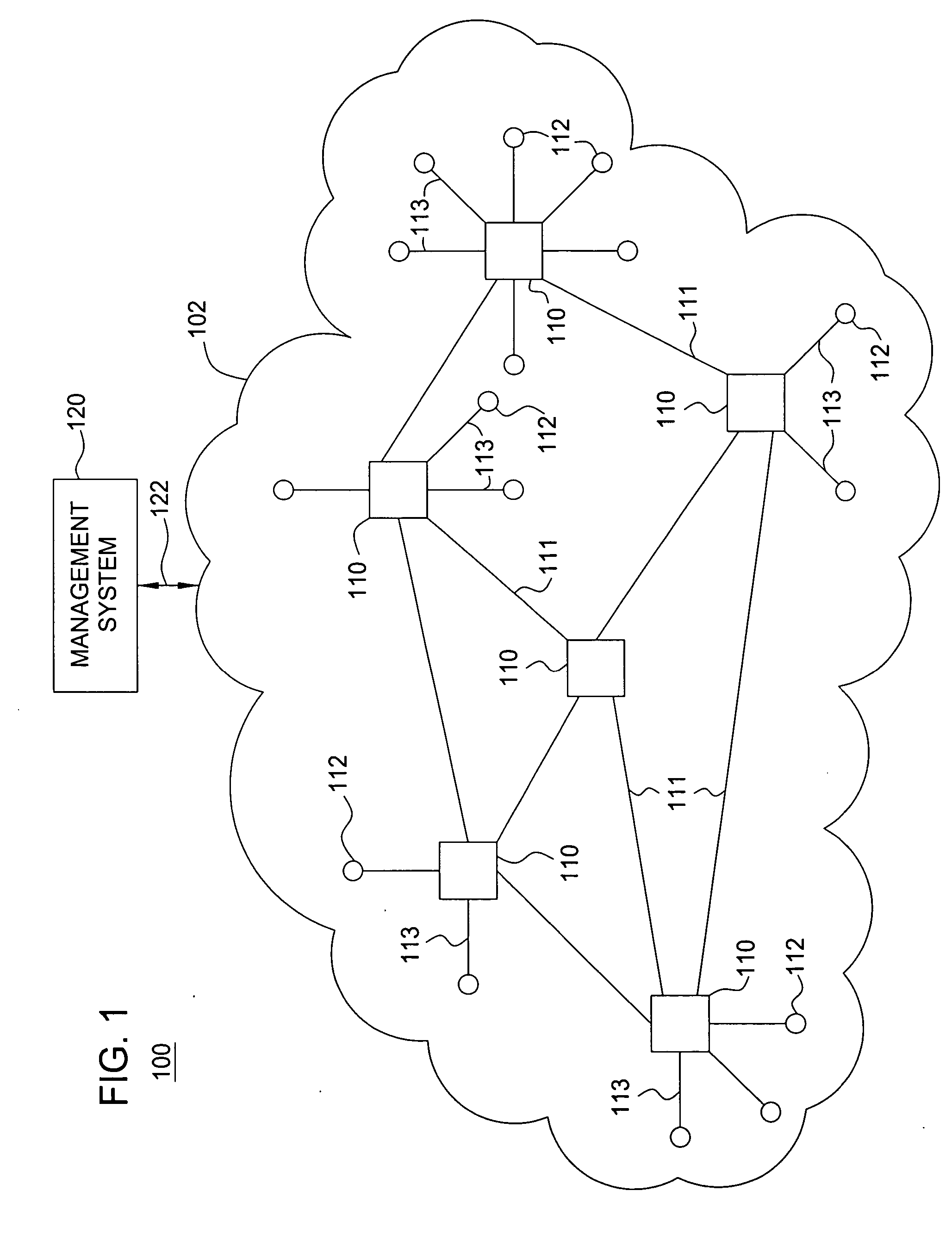
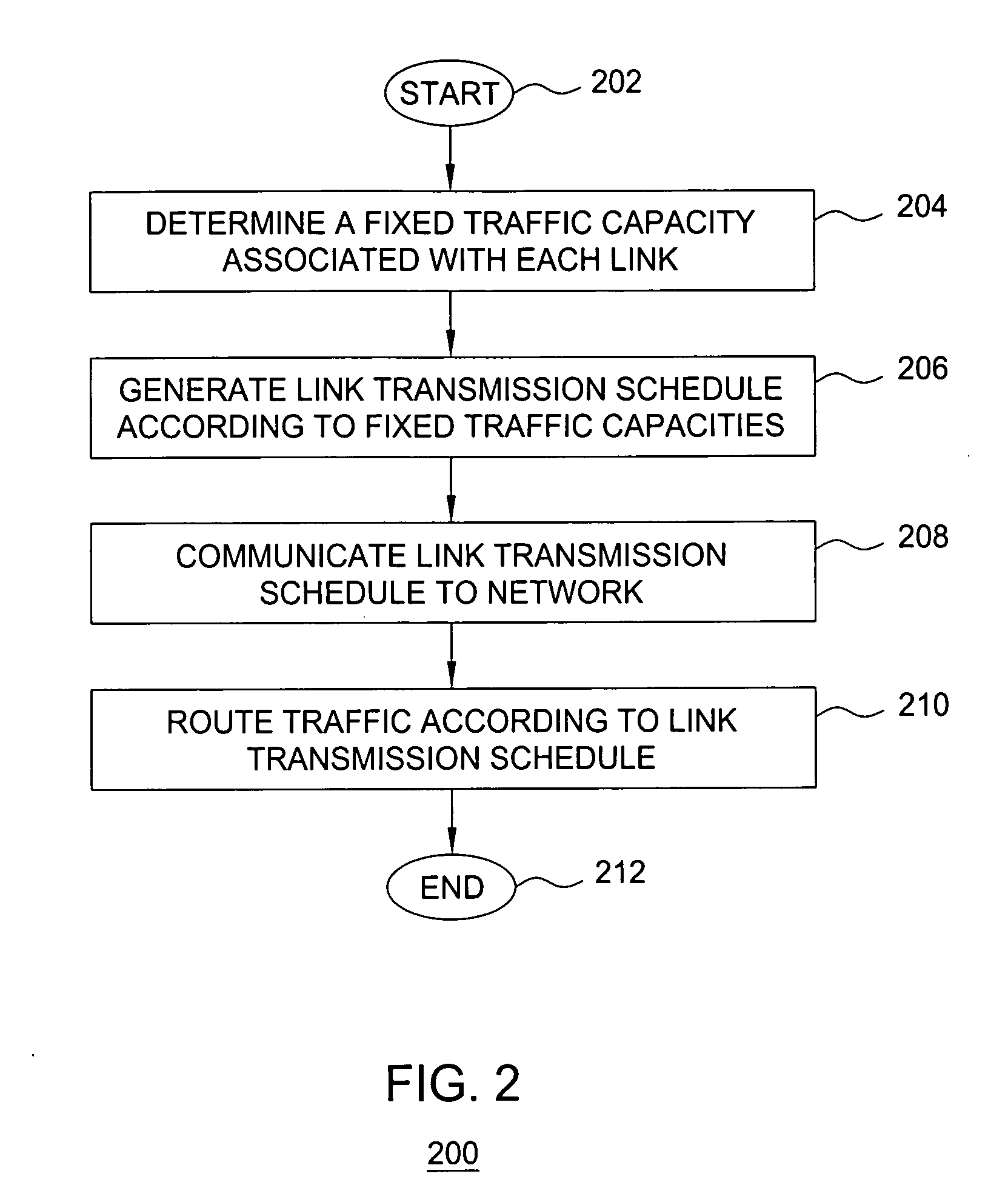
Method and apparatus for link transmission scheduling for handling traffic variation in wireless mesh networks
ActiveUS20070237081A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementTraffic capacityWireless mesh network
The invention includes a method and apparatus for generating a link transmission schedule for handling traffic variation in wireless networks without dynamic scheduling or routing. The method includes determining fixed traffic capacities associated with respective wireless links of a wireless network according to a routing algorithm, and generating, using the routing algorithm and the fixed traffic capacities, a link transmission schedule including at least one condition by which traffic is transmitted using each of the network links. The link transmission schedule is adapted to remain substantially fixed during dynamic traffic changes. The routing algorithm may be a two-phase routing algorithm in which traffic is distributed by each node in the wireless network to every node in the wireless network using traffic split ratios. For two-phase routing, fixed traffic capacities may be determined using ingress and egress traffic capacities and traffic split ratios associated with respective nodes in the wireless network.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
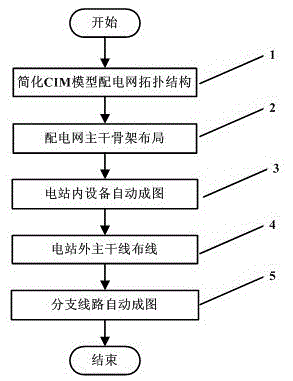
Automatic generation method used for single line diagram of distribution network and based on topological hierarchy
ActiveCN103150425ARealize automatic generationRealize a reasonable layoutSpecial data processing applicationsMassive gravityPower station
The invention discloses an automatic generation method used for a single line diagram of a distribution network and based on topological hierarchy. The method comprises the following steps: deleting related equipment in a topological structure of the distribution network, and simplifying the topological structure of the distribution network; acquiring key nodes of the topological structure of the distribution network, and generating a main framework of the topological structure of the distribution network; arranging the positions of the key nodes based on a gravitation-repulsion model, and obtaining a skeletal structure based on the gravitation-repulsion; describing the topological structure of the distribution network through an outgoing line-trunk line-T-shaped key node-branch line model of a power station; finishing the arrangement and the automatic mapping of the equipment in the power station on the basis of the topological structure of the equipment in the power station; and performing routing mapping without overlap or intersection on decibels of the trunk line and the branch line respectively. The automatic generation method achieves automatic generation of the single line diagram of the distribution network above a certain scale, and simultaneously, the generated single line diagram is clearer and more attractive through the routing algorithm without overlap or intersection.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Three Dimensional Routing
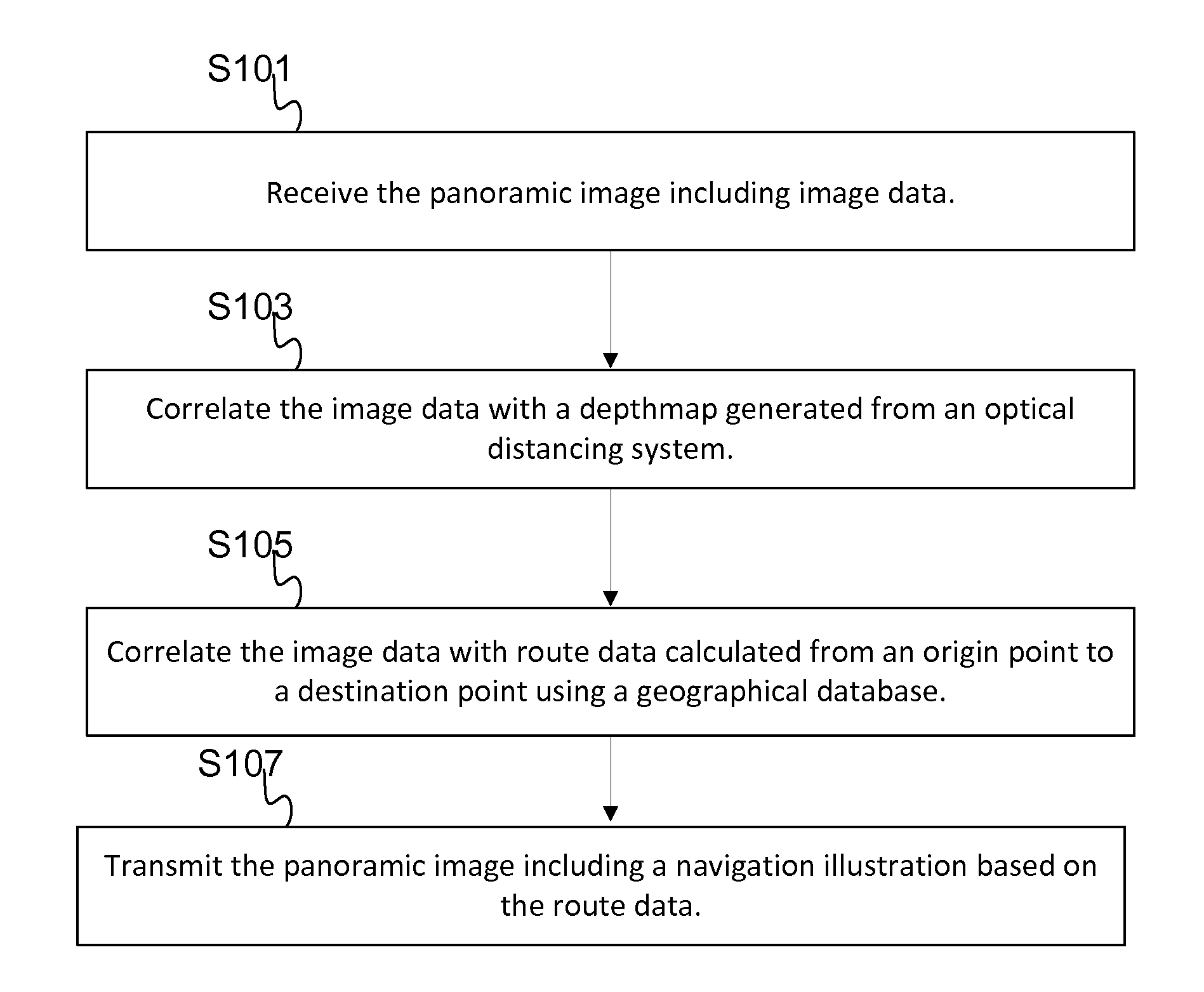
ActiveUS20130103303A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlComputer visionRouting algorithm
One or more systems, devices, and / or methods for three dimensional routing are disclosed. For example, one embodiment includes receiving image data selected based on a viewer perspective from a memory. The image data is correlated with a depthmap generated from an optical distancing system and correlated with route data calculated from an origin point to a destination point using a geographical database and a routing algorithm. The controller compares a first distance, from the viewer perspective to a point correlated with the route data, to a second distance, derived from the depth map at the point. If the comparison indicates that the first distance is closer to the viewer perspective than the second distance, the controller inserts at least one pixel of a navigation illustration into the image data. The image data including the navigation illustration is transmitted to or stored in a memory.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
Method to support multicast routing in multi-hop wireless networks
ActiveUS20060250999A1Network topologiesBroadcast transmission systemsExtensibilityWireless ad hoc network
A system and method for supporting multicast in highly dynamic wireless multi-hop networks, such as ad-hoc networks, with good scalability. The system and method provide a multicast routing algorithm to work in wireless ad-hoc networks without any fixed infrastructure nodes present. In doing so, the system and method provide a technique to build a multicast source specific tree on demand, while using a core source node to limit routing overhead. The system and method further provide a repair process to reduce the latency of discovery of topology change, employ a node sequence number mechanism to differentiate between upstream nodes and downstream nodes on the multicast tree in the repair process, and provide an active joining process to reduce the latency of discovery of membership change.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Method to support multicast routing in multi-hop wireless networks
A system and method for supporting multicast in highly dynamic wireless multi-hop networks, such as ad-hoc networks, with good scalability. The system and method provide a multicast routing algorithm to work in wireless ad-hoc networks without any fixed infrastructure nodes present. In doing so, the system and method provide a technique to build a multicast source specific tree on demand, while using a core source node to limit routing overhead. The system and method further provide a repair process to reduce the latency of discovery of topology change, employ a node sequence number mechanism to differentiate between upstream nodes and downstream nodes on the multicast tree in the repair process, and provide an active joining process to reduce the latency of discovery of membership change.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
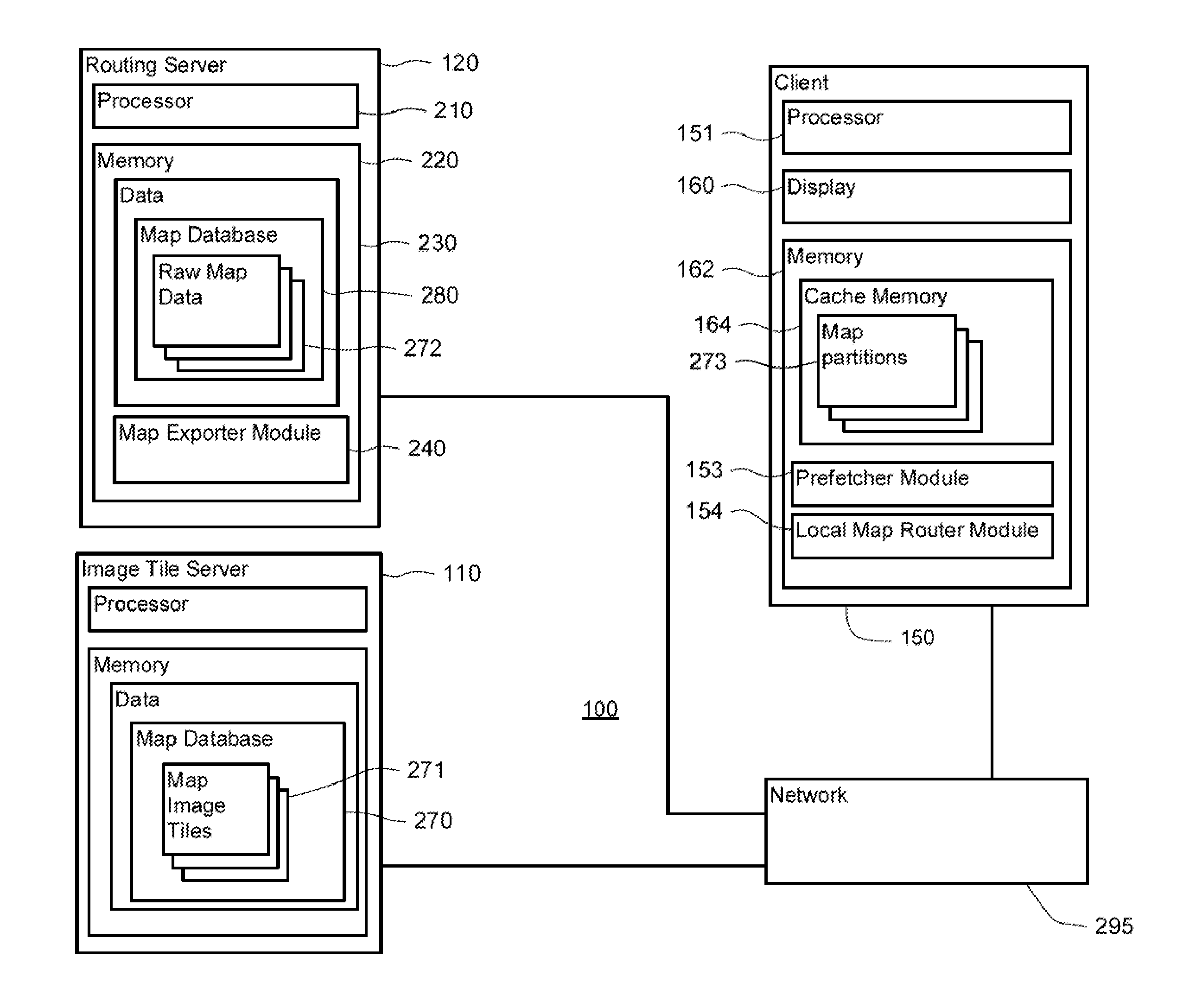
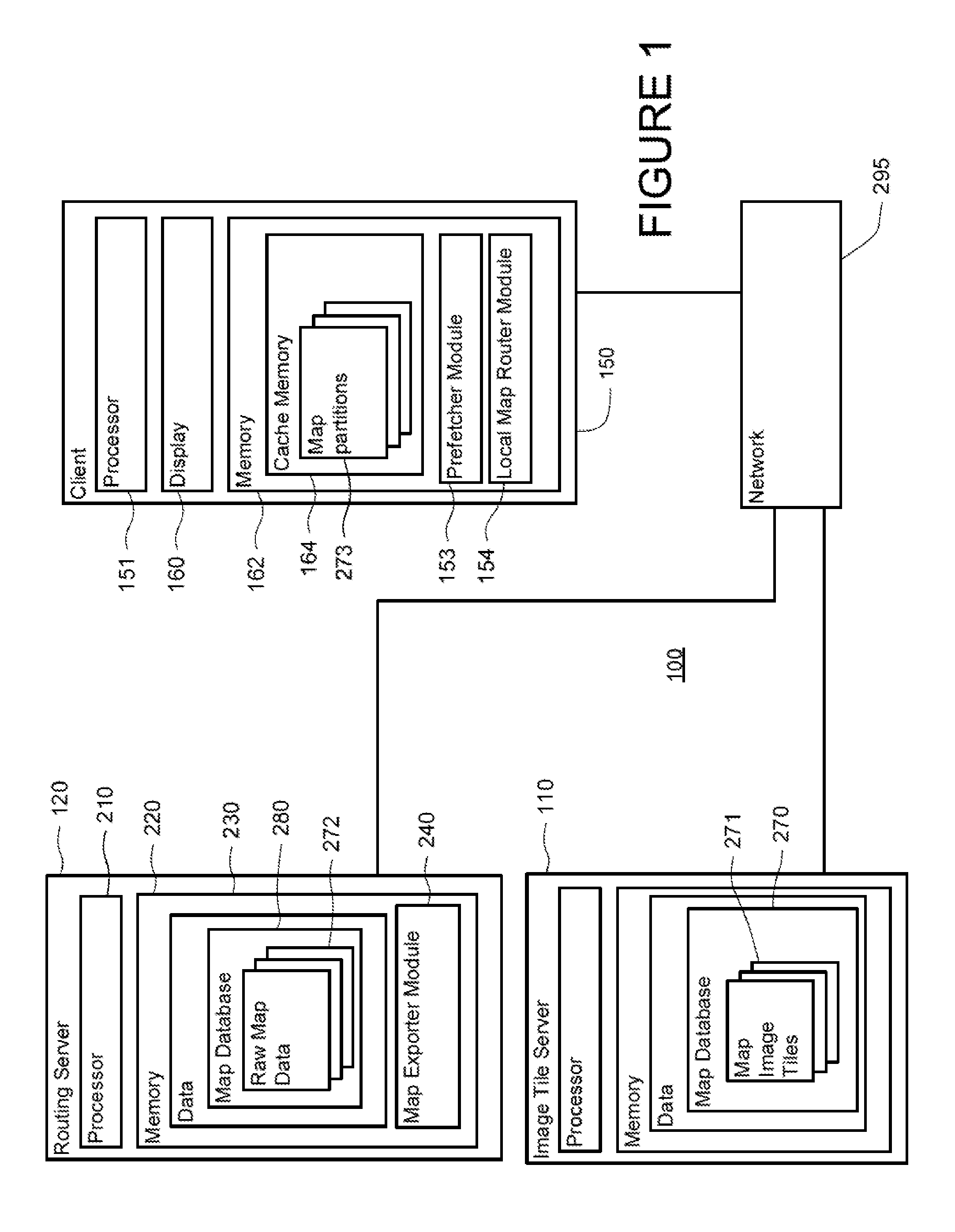
Method and apparatus of route guidance
ActiveUS20120143504A1Instruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsGuidance systemTurn-by-turn navigation
Systems and methods of route guidance on a user device are provided. In one aspect, a system and method transmit partitions of map data to a client device. Each map partition may contain road geometries, road names, road network topology, or any other information needed to provide turn-by-turn navigation or driving directions within the partition. Each map partition may be encoded with enough data to allow them to be stitched together to form a larger map. Map partitions may be fetched along each route to be used in the event of a network outage or other loss of network connectivity. For example, if a user deviates from the original route and a network outage occurs, the map data may be assembled and a routing algorithm may be applied to the map data in order to direct the user back to the original route.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and system for handover in cellular wireless using route programming and training processes
ActiveUS20070142050A1Improve handoverRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationImage resolutionRouting algorithm
A method and system for managing handover where a database that receives location information about a moving object includes information regarding which base station is used in a current radio link connection and which base stations were used from historic radio link connections. Using the base station radio link history of the object and an electronic map, a processor coupled to the memory of the database selects which physical path the moving object is using. Upon matching the object's path with a history of path routes on the list, the processor will apply an optimized handoff sequence to the moving object. The optimized route can be derived from an algorithm that processes previous historical data from moving objects traveling on the same route. Methods of providing the location of moving objects via location sensors may be used to provide the database with higher resolution information about a moving object's location on an electronic map and allow further enhancement of the handoff optimization. Generally, location data is used to quickly determine which route the moving object is using and more quickly assign an optimized handoff sequence. Historical data along known routes can include time and spatial information to be processed by the routing algorithm. The database may reside in a central location or within each moving object or a combination of both.
Owner:APPLE INC
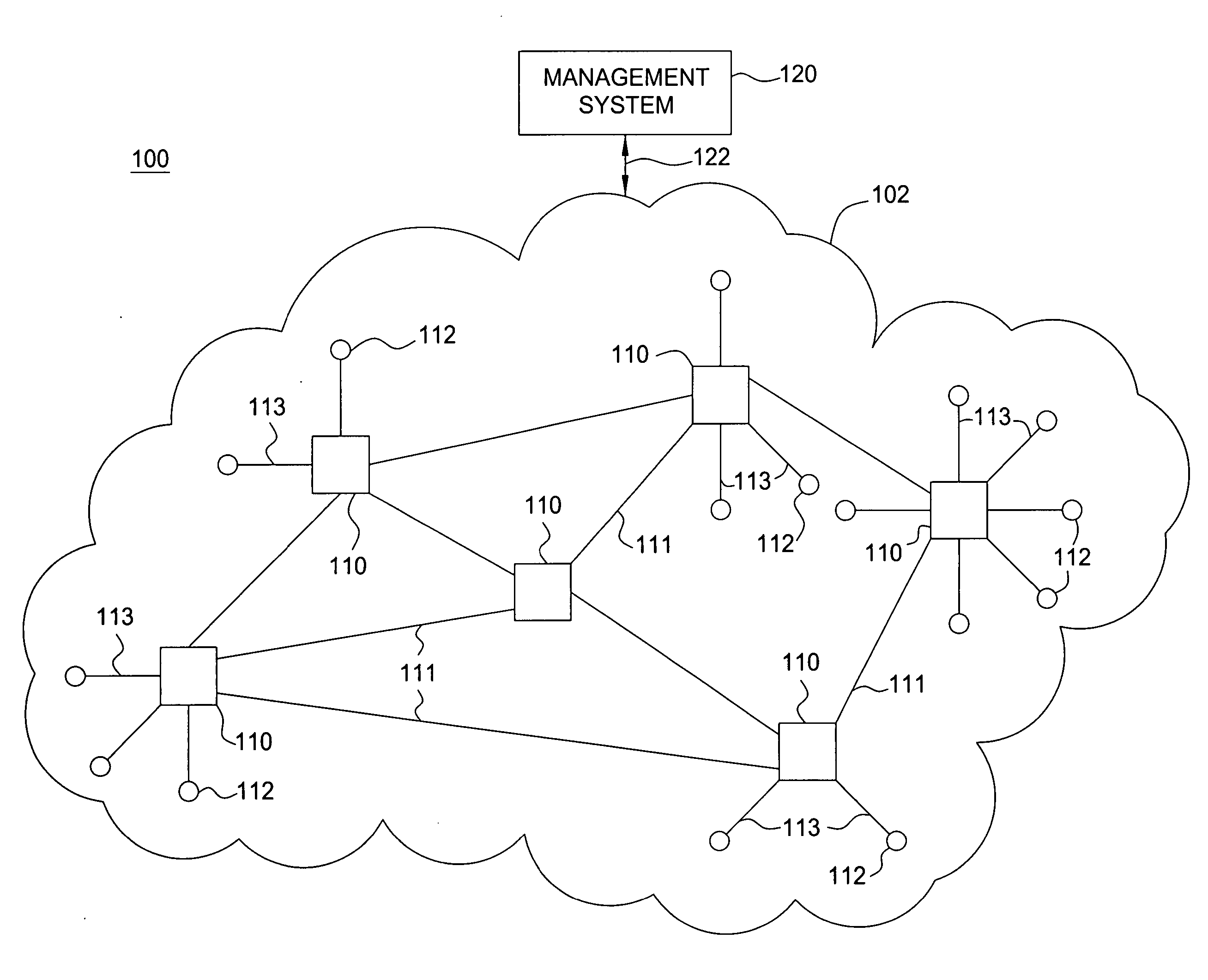
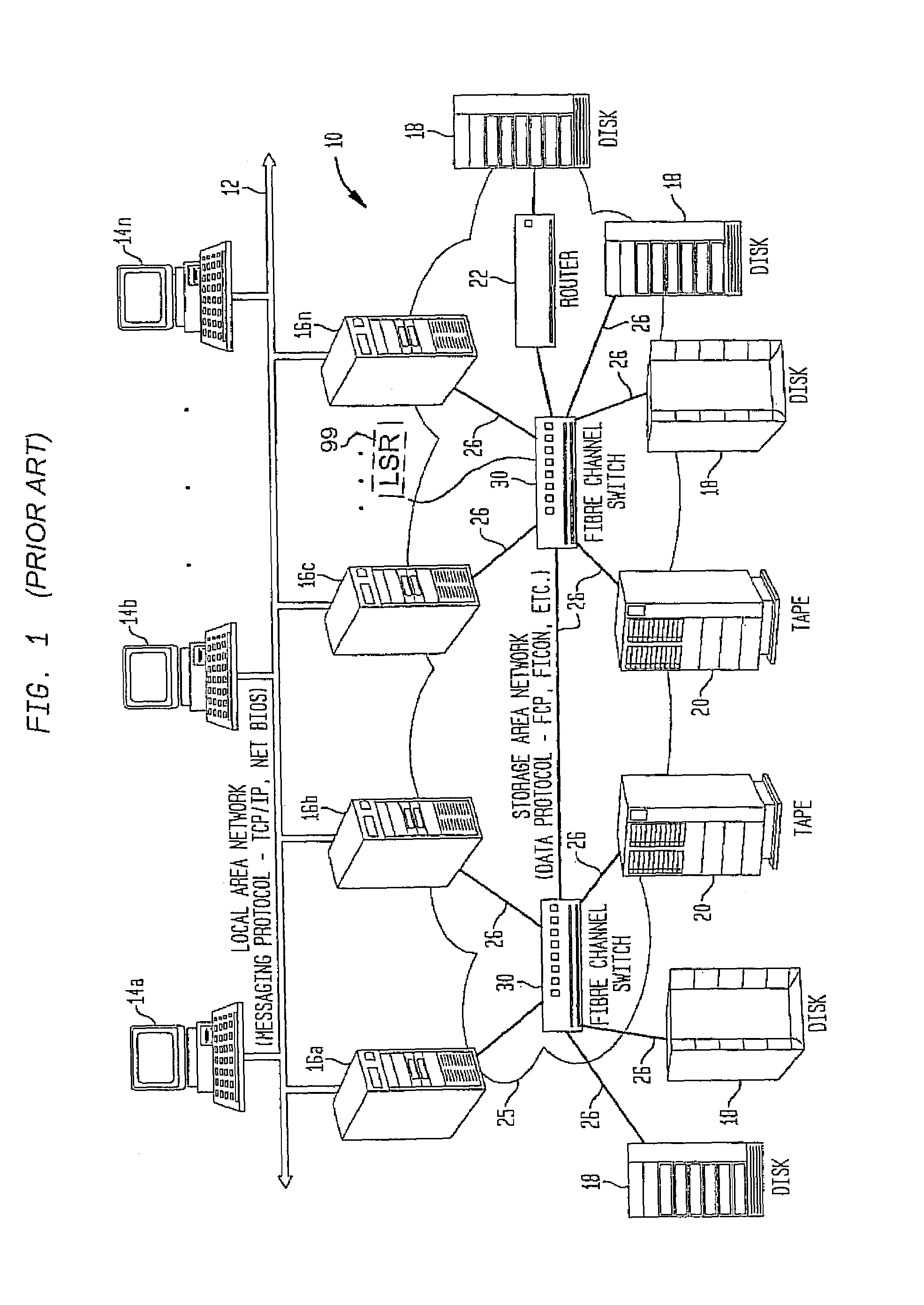
Detection of network topology changes affecting trail routing consistency
InactiveUS6564258B1Fast timeImprove scalabilityDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationNetwork controlPhysical layer
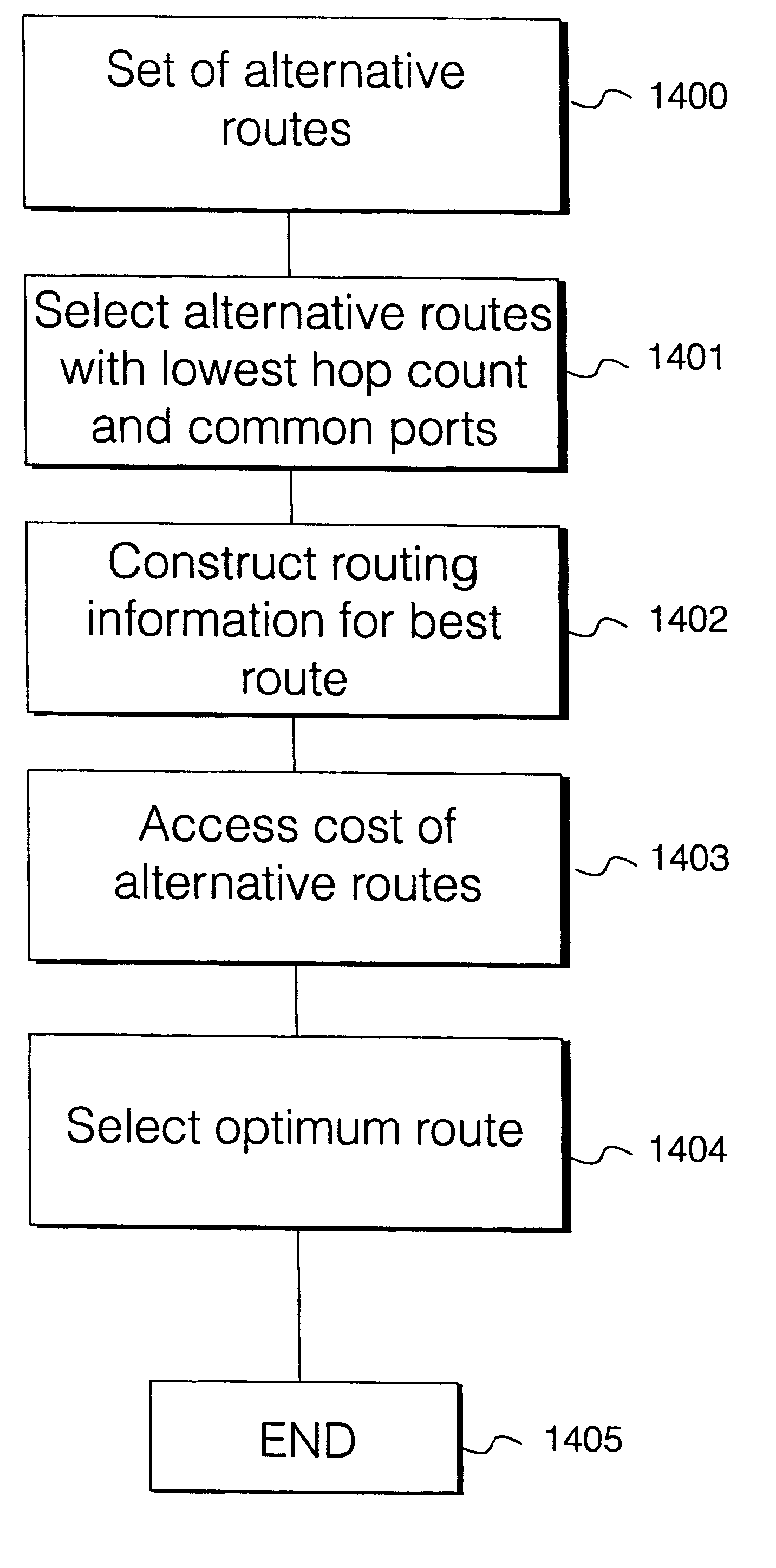
There is disclosed a method and apparatus for detection of client trails which may become unsupported due to reconfiguration of node elements within a network at a server layer, and a rerouting apparatus and method for proposing a set of alternative routes to support client trails during reconfiguration of a network at a physical layer. Data describing each trail, connection, node, link and other physical resource is maintained in a managed object database on a network controller. A trail detection algorithm investigates trail termination points corresponding to proposed deleted or created trails to see if those termination points support client trails at higher layers. If supported client trails are detected at higher layers, a routing algorithm is applied to find a set of alternative routes over which the client layer trails may be rerouted during network configuration at the physical or server layer.
Owner:CIENA
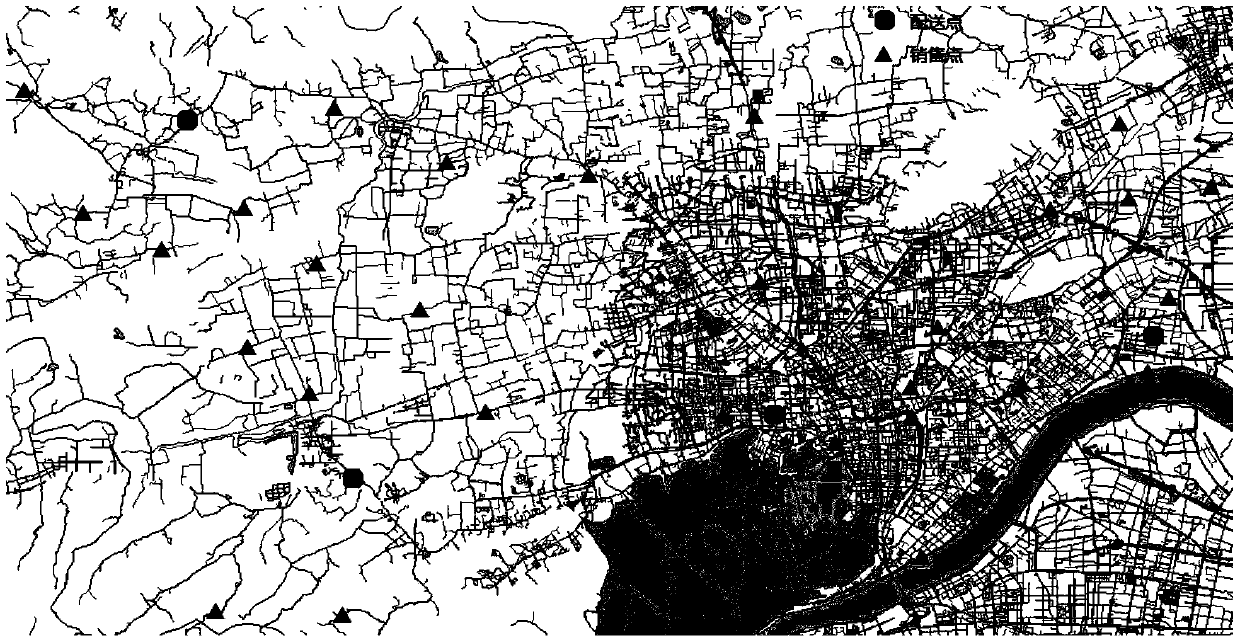
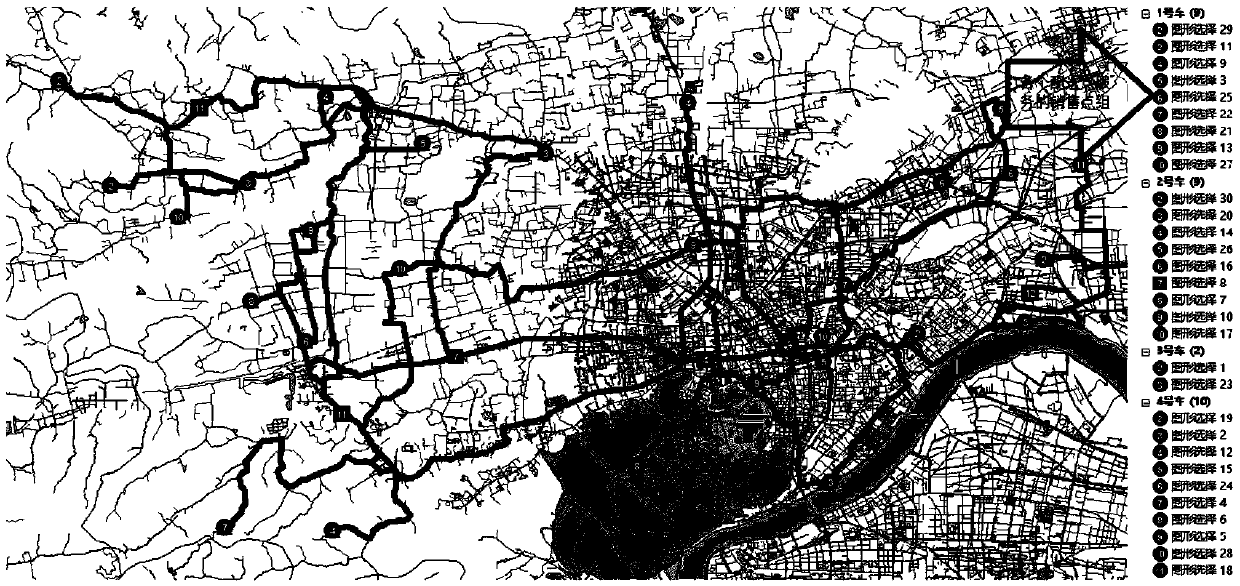
Logistics distribution control method with soft time windows
A logistics distribution control method with soft time windows includes the following steps: (A1) a network model is built, cost resistances are assigned to roads to which network data are concentrated, and taking road nodes into consideration, toll weights are assigned to road traffic light intersections and toll stations; (A2) an optimized vehicle routing model with soft time windows (VRPTW) is built, a target function is established with lowest transportation costs, and the transportation costs are respectively composed of fixed distribution vehicle cost, transportation cost, vehicle waiting cost and delay cost; (A3) a fuzzy clustering analysis algorithm is designed, and a method based on the integration of quantitative analysis and qualitative analysis is adopted for clustering; (A4) a heuristic optimized vehicle routing algorithm is designed, the optimized vehicle routing algorithm is adopted for distribution target nodes in each class, and thereby a distribution result can be obtained. The logistics distribution control method with soft time windows adopts the distances of actual delivery road network routes between distribution nodes as a calculation basis and also takes the actual traffic capacities of roads, large network node number and transportation time needed by distribution nodes into consideration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
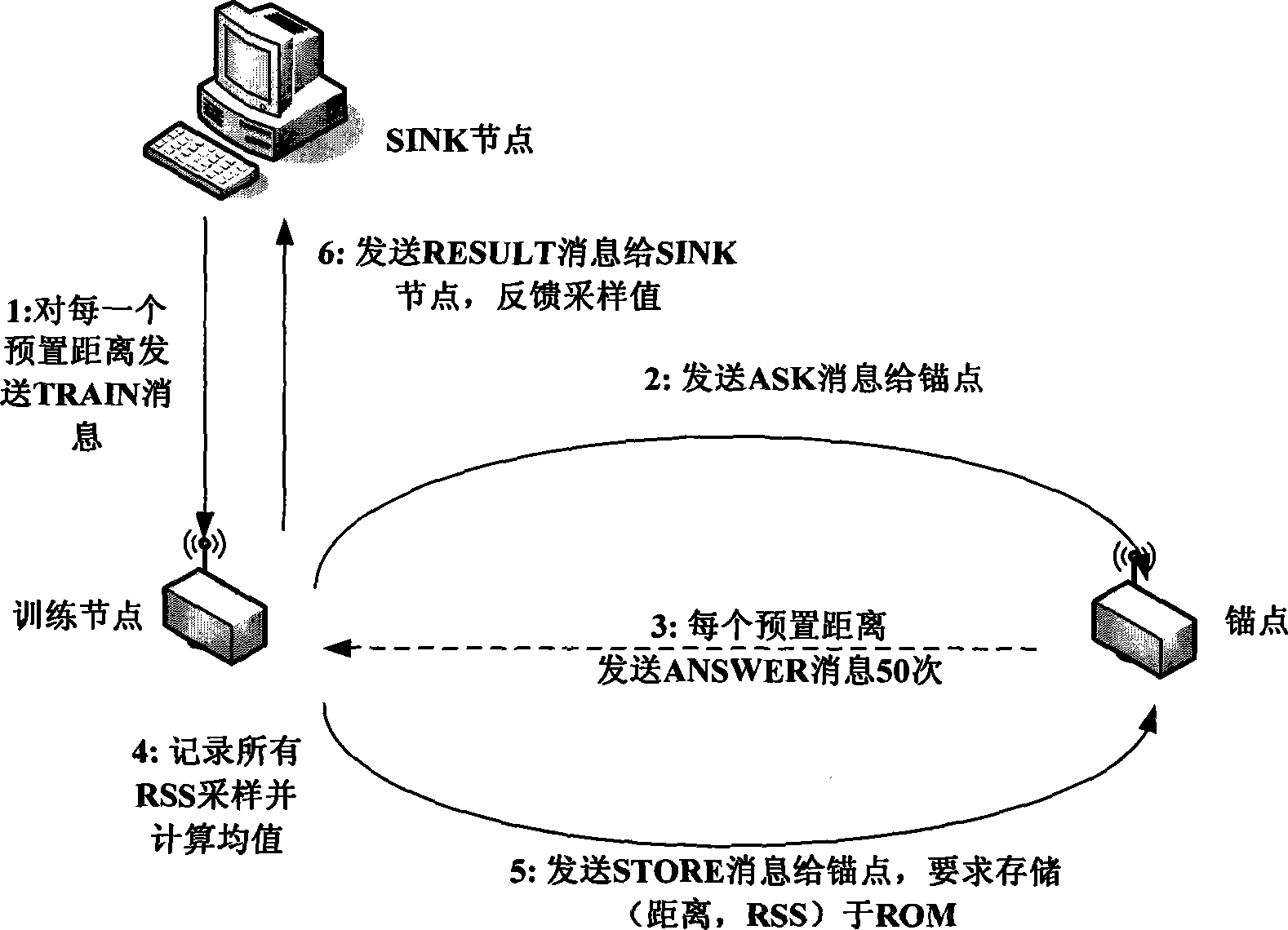
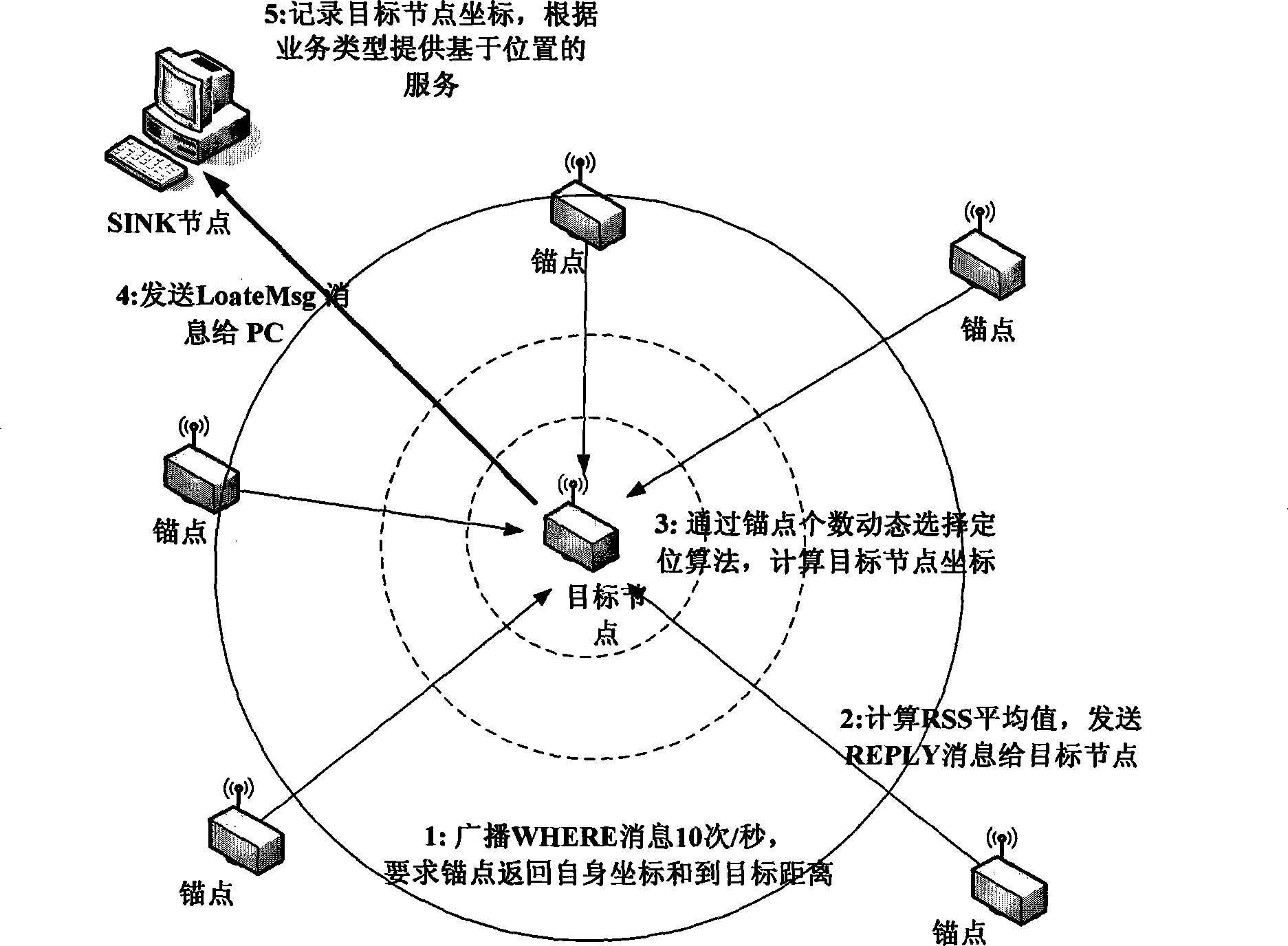
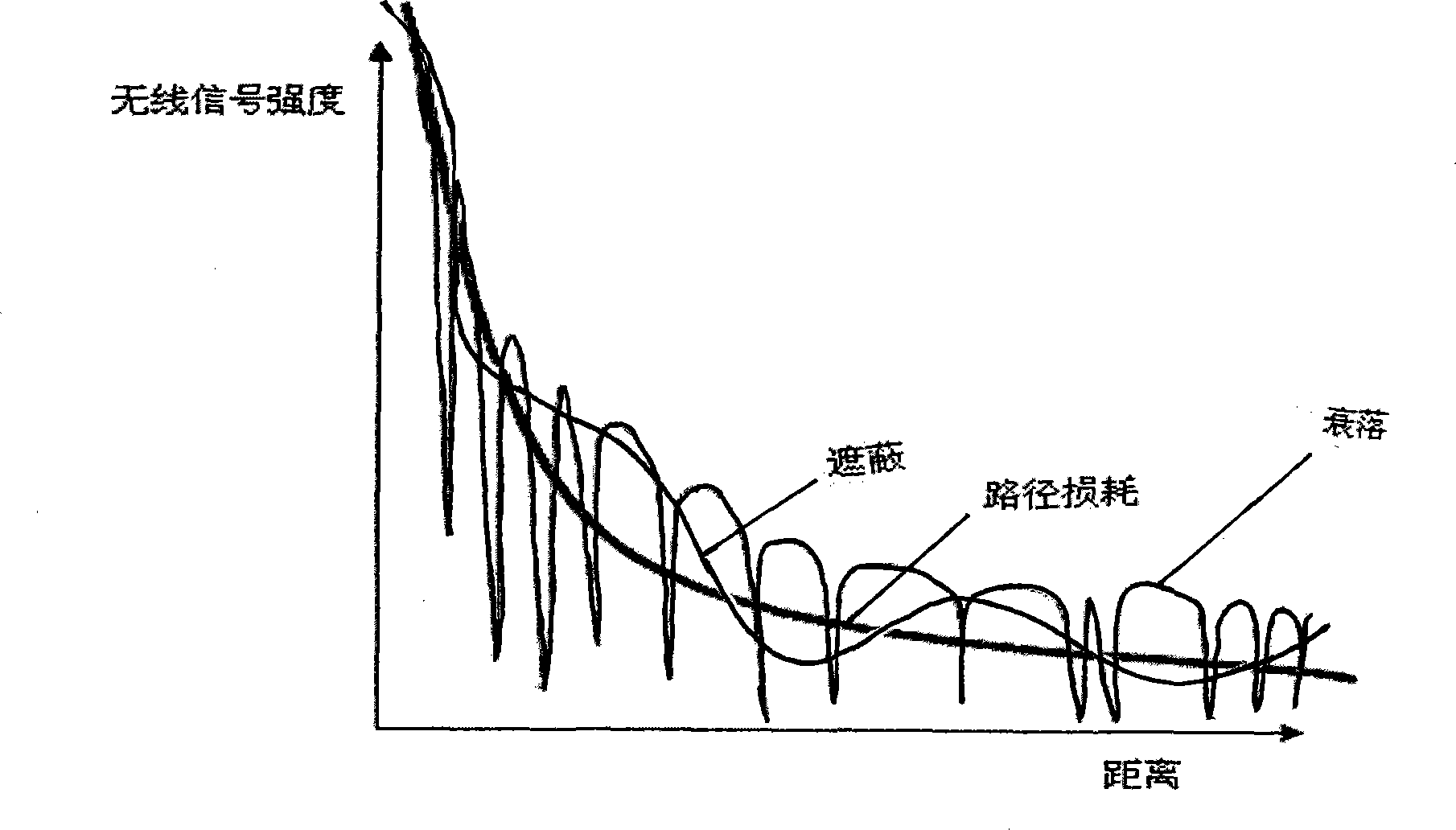
Node indoor locating method based on wireless signal strength in wireless sensor network
InactiveCN101247650AReduce communication consumptionSmall amount of calculationPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless mesh networkAnchor point
The present invention belongs to node self-localization field in large-scale wireless sensor network, and discloses a node indoor localization method based on wireless signal intensity, which main includes: getting relationship curve of signal intensity and distance, and putting forward concept of effective wireless signal intensity (Effective RSS, ERSS); obtaining coordinates of target node by selecting localization arithmetic (ERSS filter + maximum likelihood estimation, triangle localization, approximate location estimation) according with anchor point amount through distance between anchor point and target by training RSS curve; providing alerting service by using physics coordinate, providing navigation service according with route arithmetic and address chain by using sign coordinate (for example in hall). Precisely localization of indoor target can be realized in condition of low-cost, simple initial configuration, and a plurality of services based on location can also be provided.
Owner:JIAXING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS CENT CAS
Swarm autonomous routing algorithm for mobile ad hoc network communications
ActiveUS7957355B1Efficient routingEasy to learnData switching by path configurationRadio transmissionRouting tableRouting algorithm
A Swarm Autonomous Routing Algorithm (SARA) is performed by simple communication node devices for node to node communications in a network, especially a Mobile Ad hoc NETwork (MANET). Each node maintains a table of pheromone values for known neighbor nodes. Pheromone values are dynamic for adapting to a dynamic arrangement of nodes, and are updated either passively or actively. Routing tables are not used. When a node receives a packet, it uses the pheromone table to simply determine whether or not to forward (rebroadcast) the packet to a neighbor node, and if possible, determines and indicates the best neighbor node for next forwarding the packet. Destination Zone Routing (DZR) and Swarm Location Service (SLS) are alternative enhancements of SARA that can be used for more efficient routing when nodes are location aware / knowledgeable. SLS may also be used to improve routing algorithms other than SARA.
Owner:BLUETRONIX
Unmanned plane airline routing algorithm based on improved A* algorithm
InactiveCN104075717AImprove computing efficiencyMeet planning requirementsNavigational calculation instrumentsForecastingAlgorithmThree-dimensional space
The invention relates to an airline routing algorithm of an unmanned plane in a large-range complicated three-dimensional space. The algorithm comprises the following steps: first dividing a three-dimensional space on the basis of a 2.5-dimensional grid (each grid point includes longitude, altitude and elevation information); improving the A* cost function by comprehensively considering the influence factors such as airline height, detected probability, airline distance under the constraint conditions of radar, disaster weather and forbidden areas, and determining an initial airline on the basis of an algorithm search flow; serially processing the initial airline to obtain a final flying airline for meeting the performance constraint of the unmanned plane (such as minimal step length, turning radius, climbing rate, safety height). The algorithm is good in stability and astringency, high in efficiency, capable of meeting the wide-range low-altitude airline routing requirement and applicable to relevant fields such as military, national defense, emergency relief.
Owner:WUHAN JI JIA WEI YE TECH DEV CO LTD
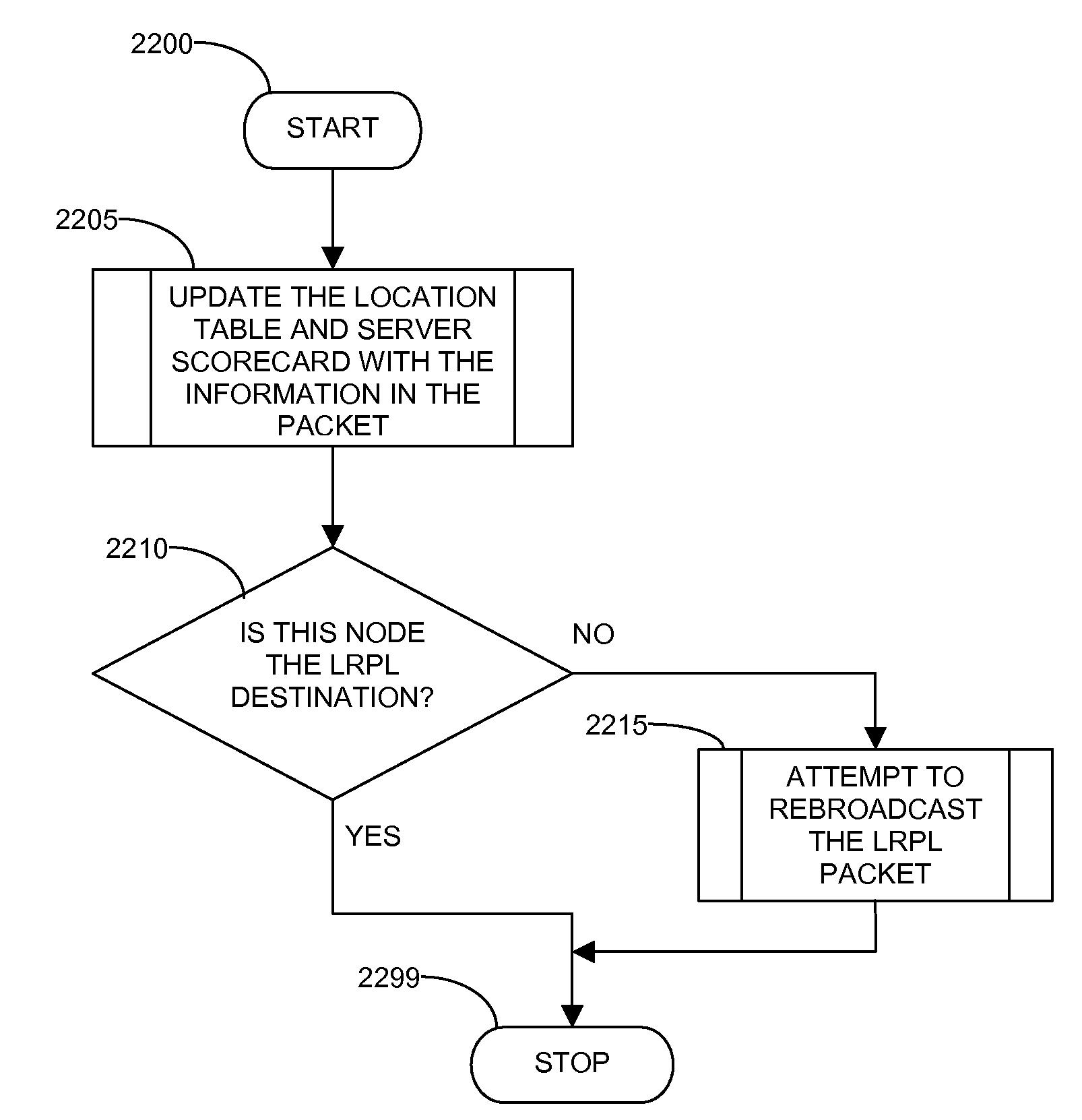
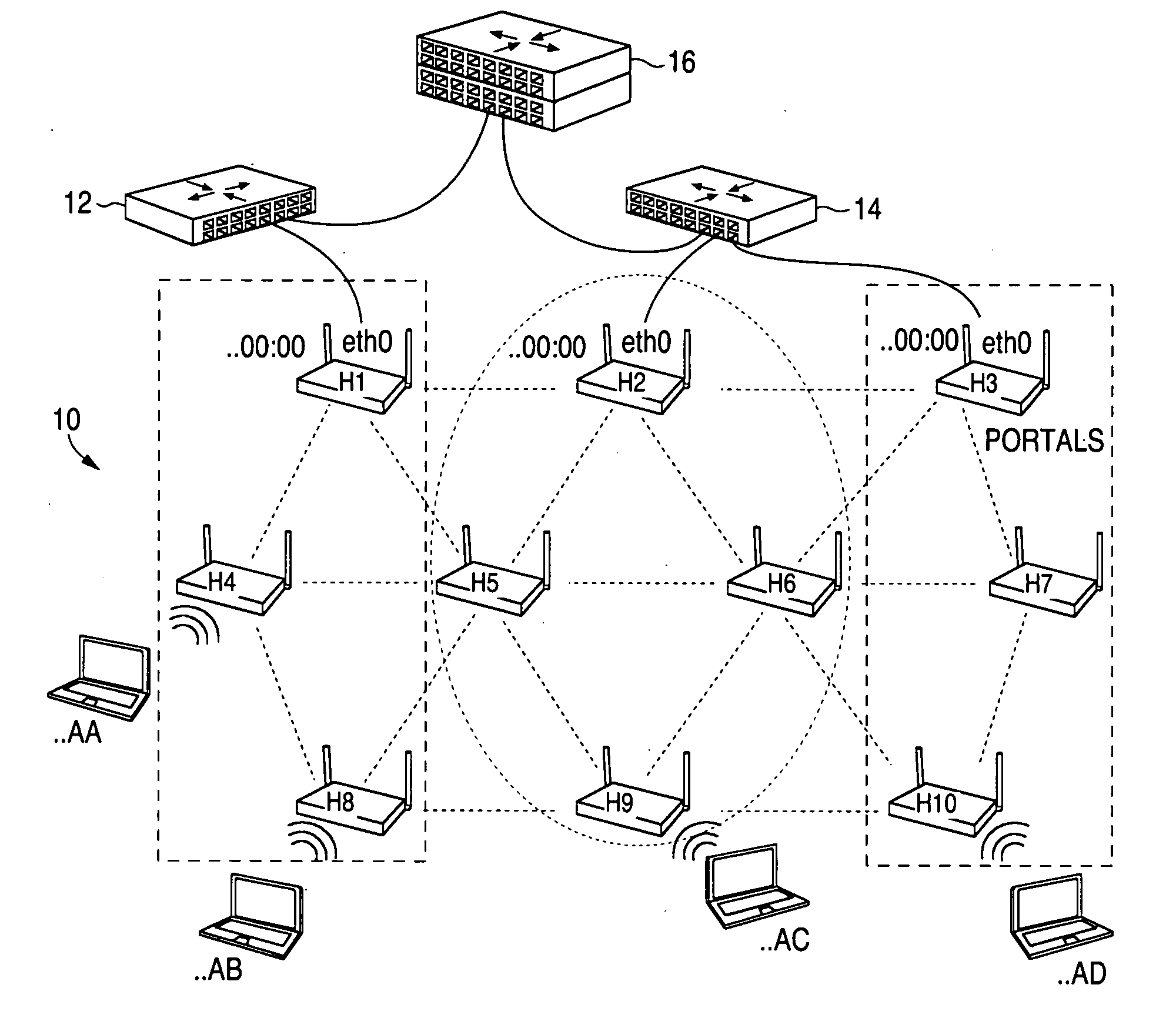
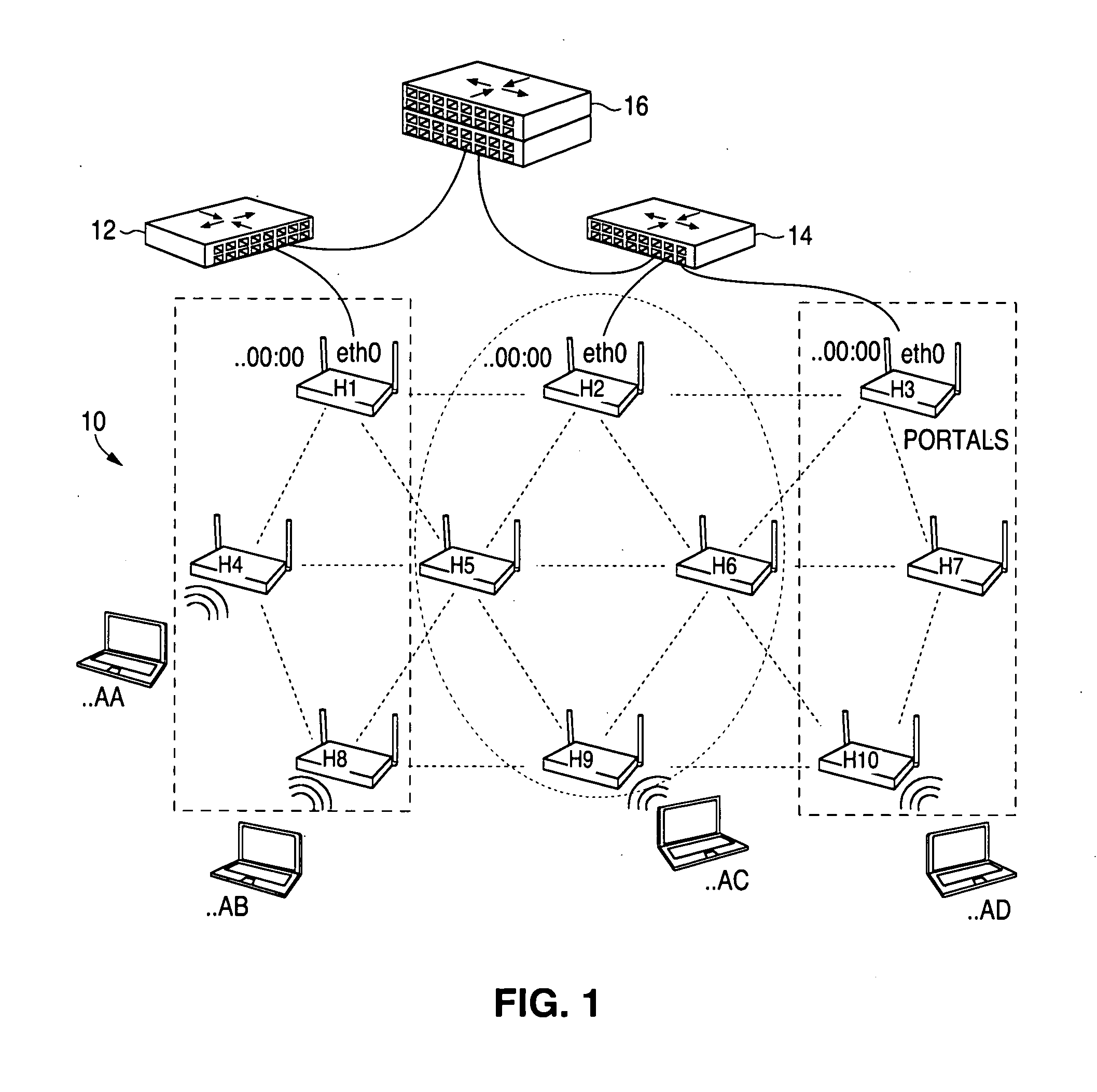
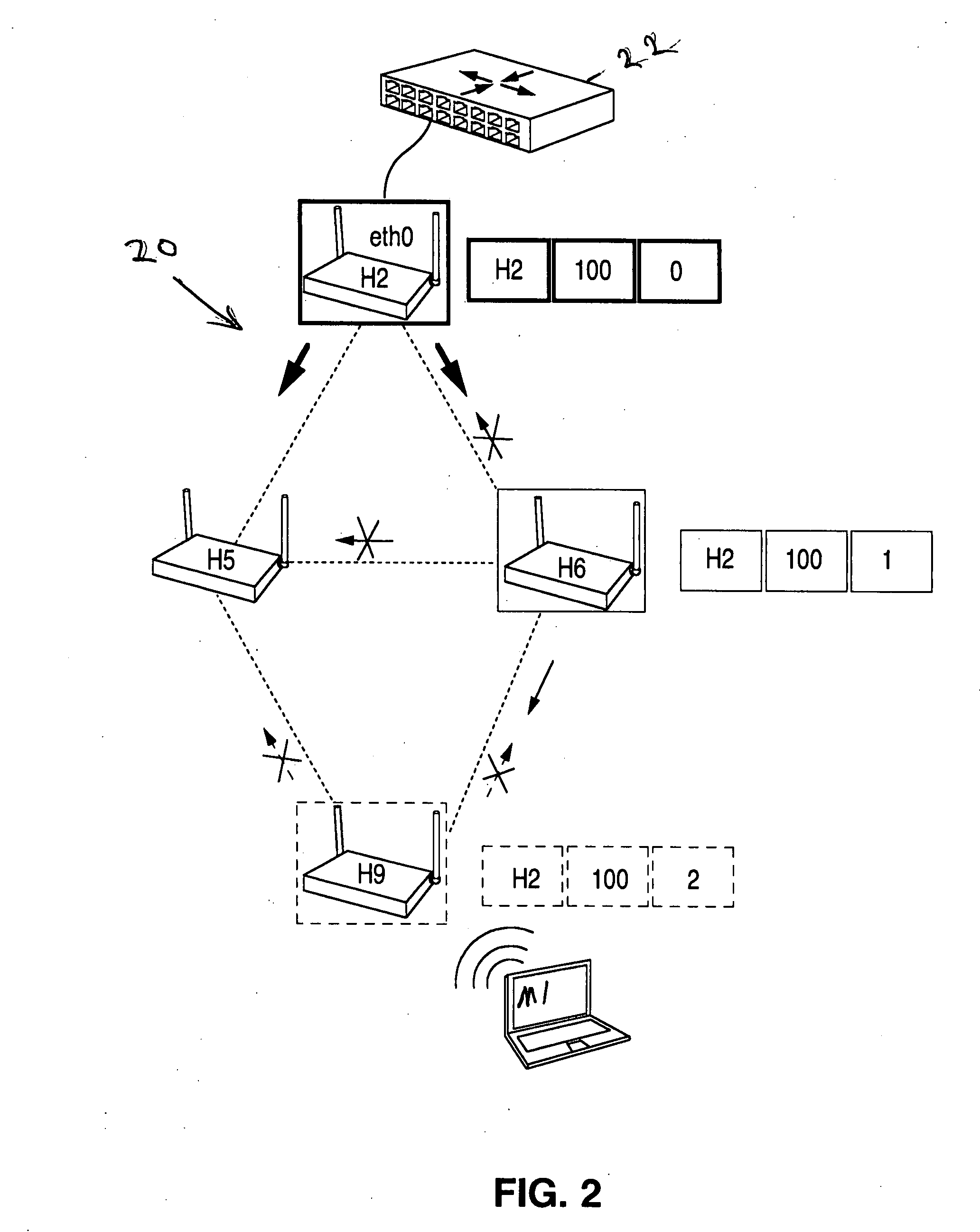
Routing method and system for a wireless network
ActiveUS20080267116A1Easy to extendPromote reductionNetwork topologiesBroadcast service distributionWireless mesh networkProcessor register
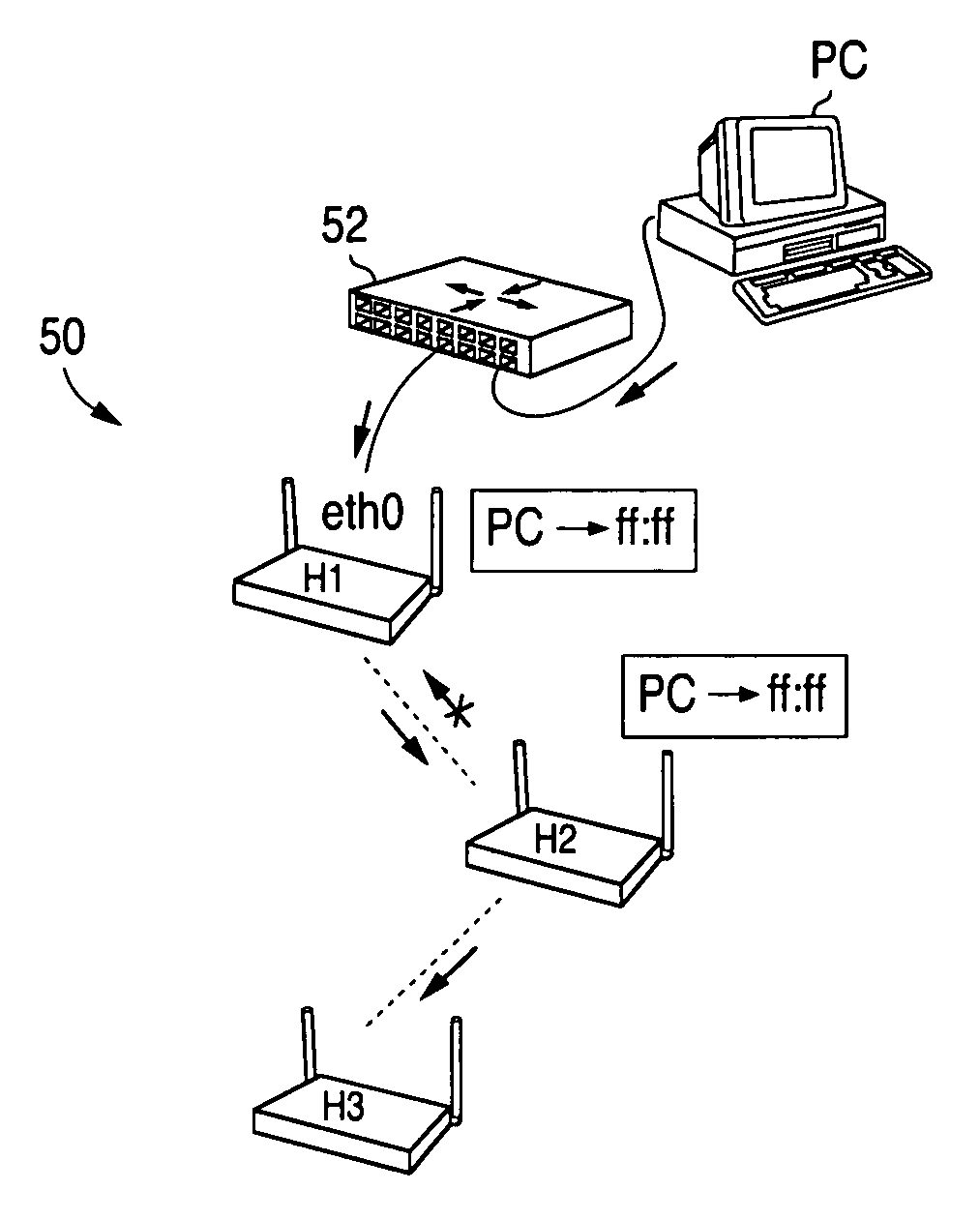
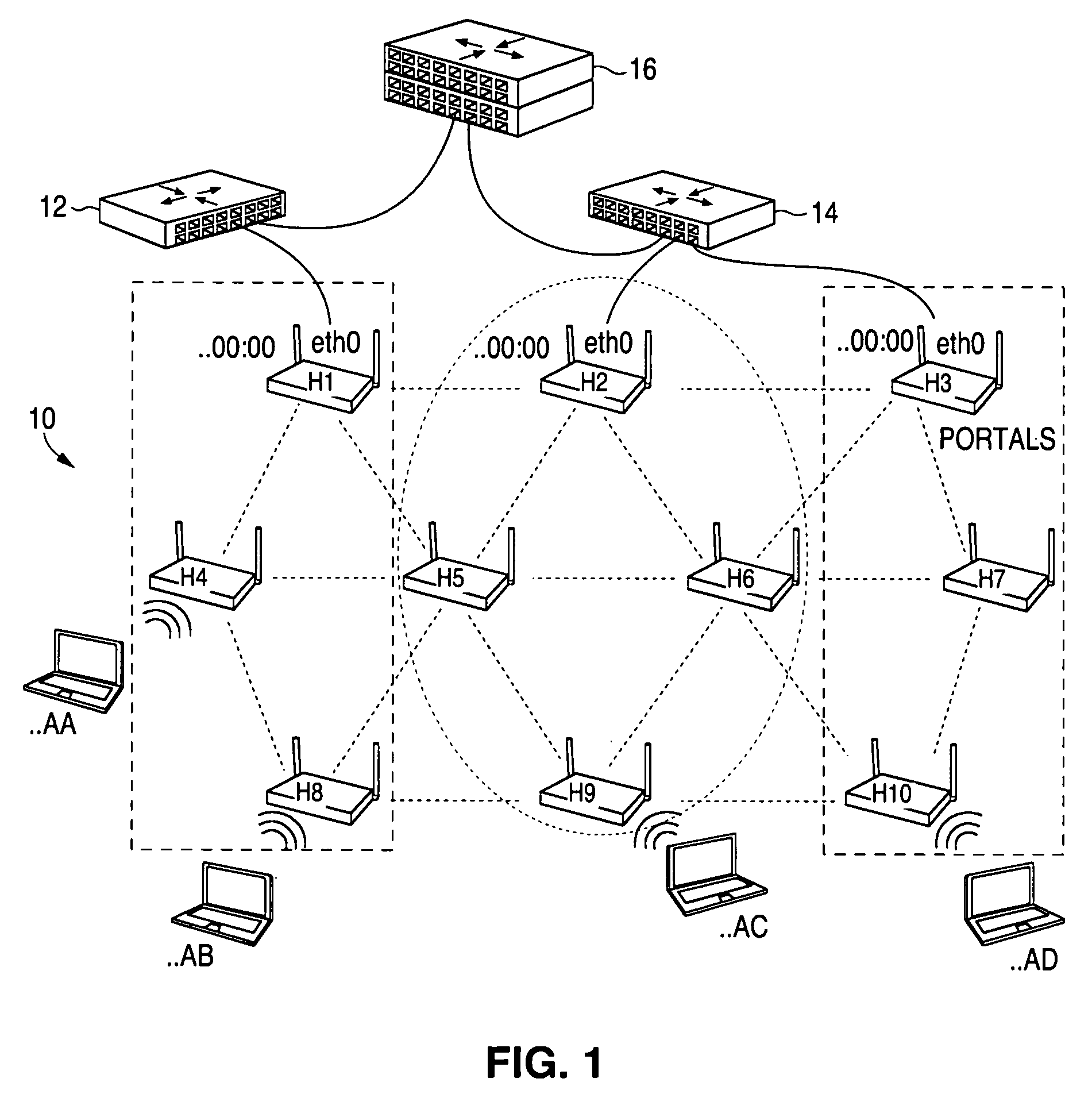
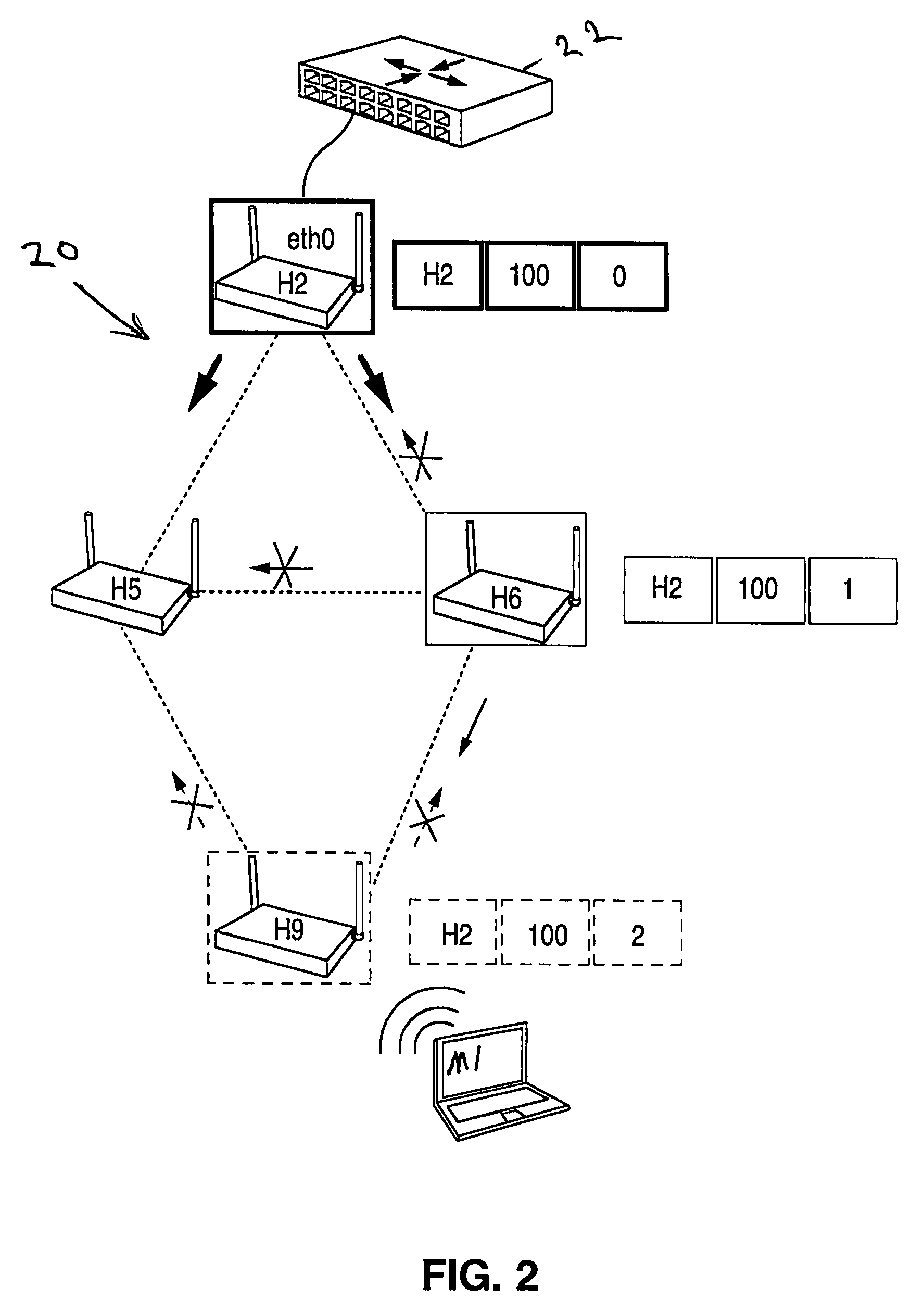
A method and system for selecting a route in a wireless network for the transmission of a data packet between wireless nodes in said network using a modified link-state routing algorithm wherein only a limited number of broadcast messages are generated to synchronize the link-state database throughout the wireless network. A subset of nodes called portal nodes within the network are elected to do the broadcasting for the entire network. Each portal node broadcasts an announcement of its identity to all of the wireless nodes. Each wireless node responds to these broadcasts to select one of the portal nodes as its root portal node. It then identifies a unicast route back to its root portal node, and sends a link-state register message to this portal node. These link-state register messages received by each portal node are aggregated by them and are broadcast to each of the wireless nodes for storage. When a data packet is thereafter received by a wireless node from a neighboring node, it detects if the data packet satisfies one of a plurality of predetermined conditions and rebroadcasts the data packet to neighboring wireless nodes if none of the conditions is satisfied.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
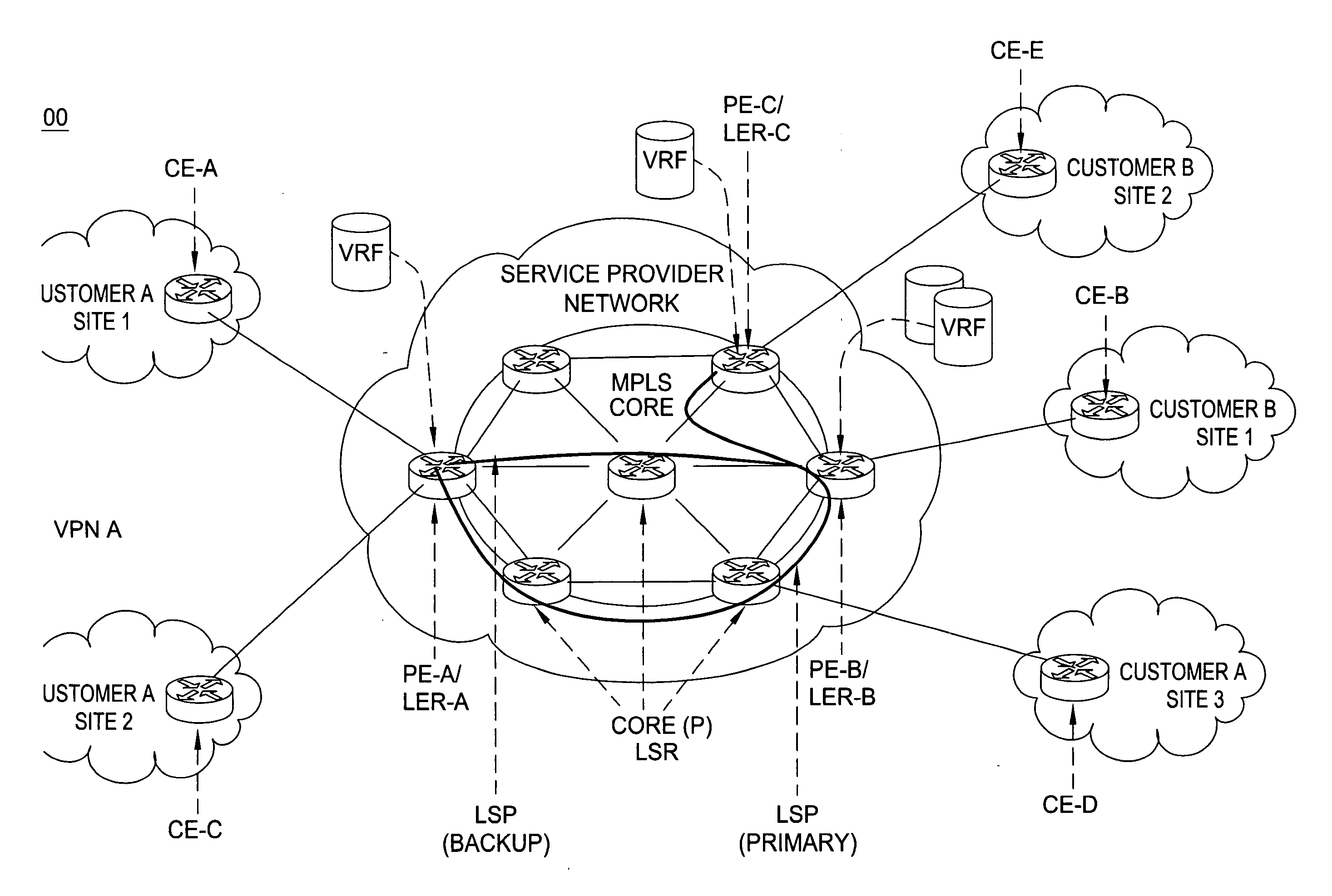
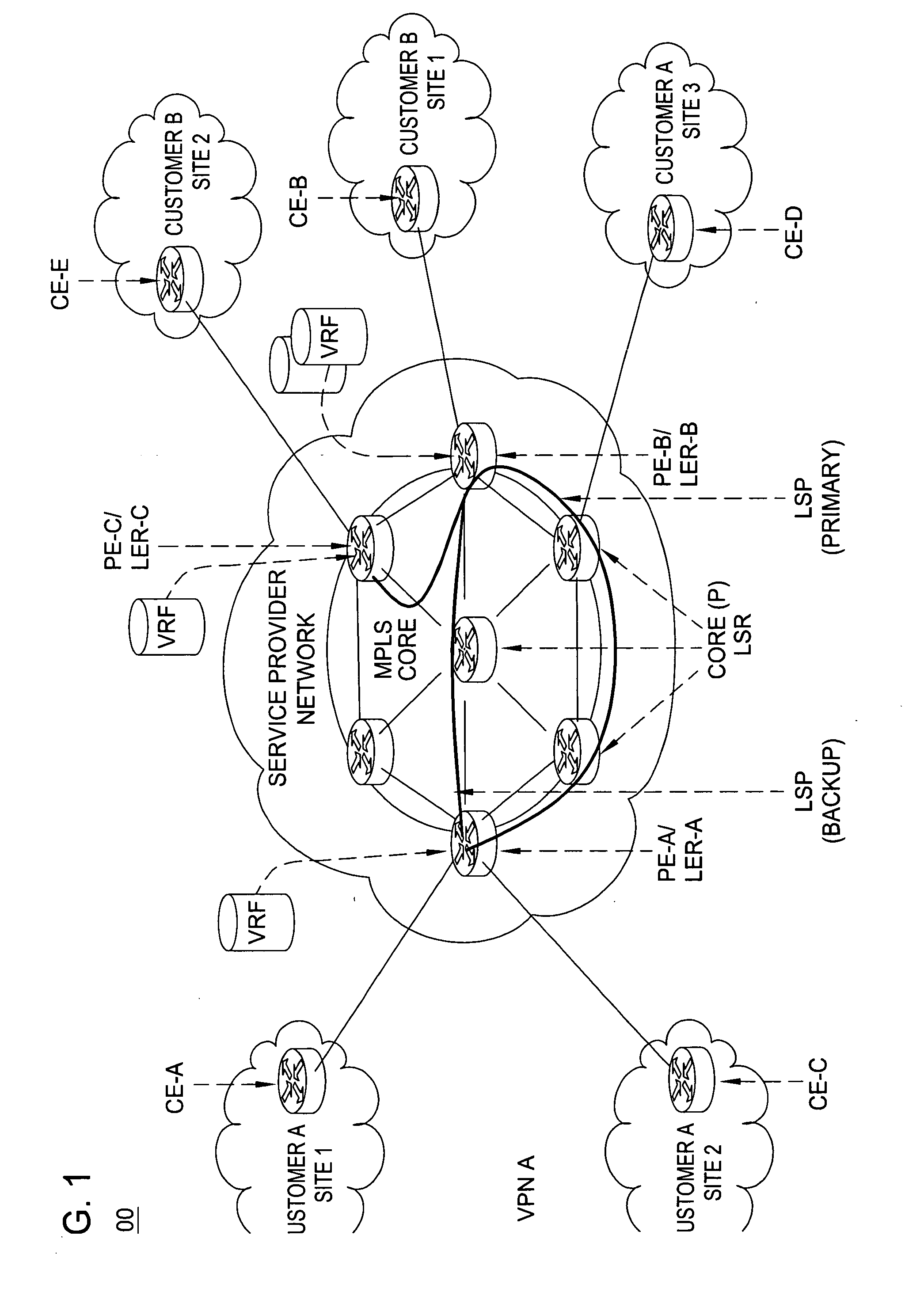
Method for optimal assignment of customer edge (CE) routers to virtual private network route forwarding (VRF) tables
A method for optimal assignment of customer edge (CE) routers to virtual private network route forwarding (VRF) tables uses a “peer model”, in which the CE routers communicate their routes to a Service Provider's edge routers (PE routers). The routes of a particular VPN are then exchanged among the PE routers that are attached to that VPN. This is accomplished in a manner which ensures that routes from different VPNs remain distinct and separate, even if two VPNs comprise an overlapping address space. The PE routers distribute, to the CE routers in a particular VPN, the routes from other CE routers in that VPN. The CE routers do not peer with each other and, as such, there is no “overlay” visible to a VPN's routing algorithm.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
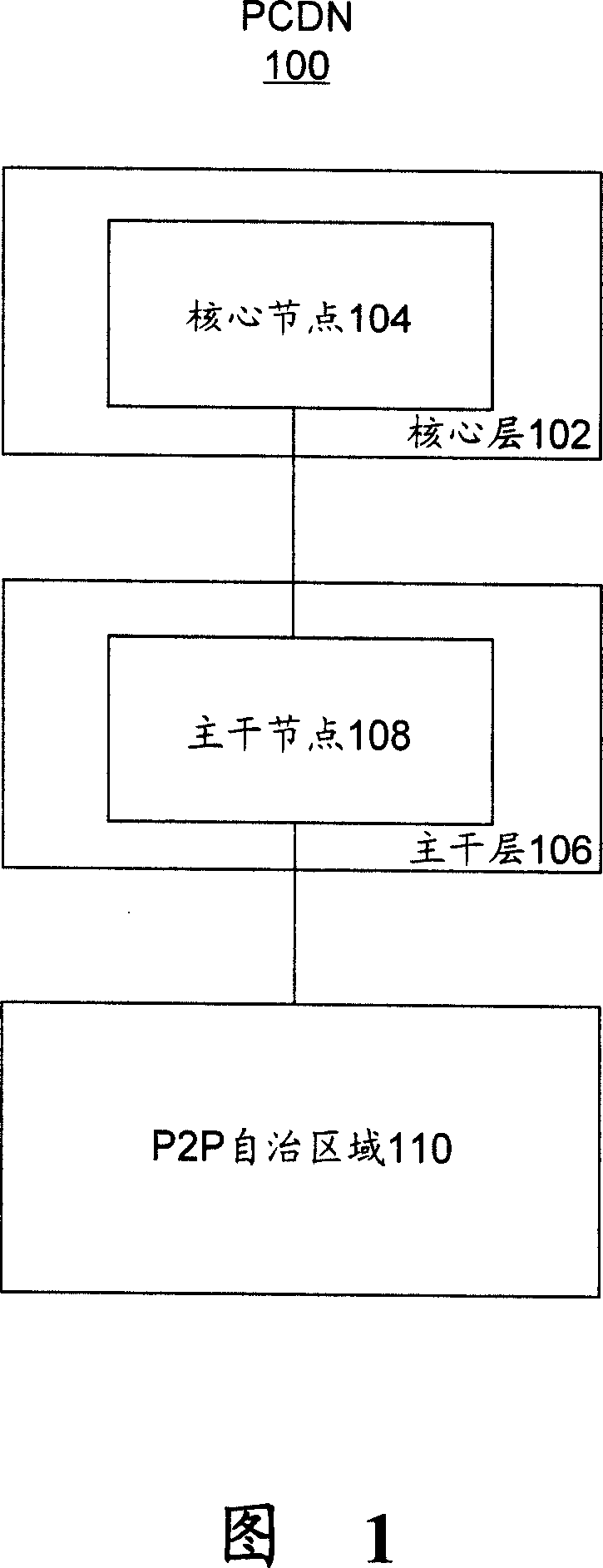
Routing system and method of content distribution network
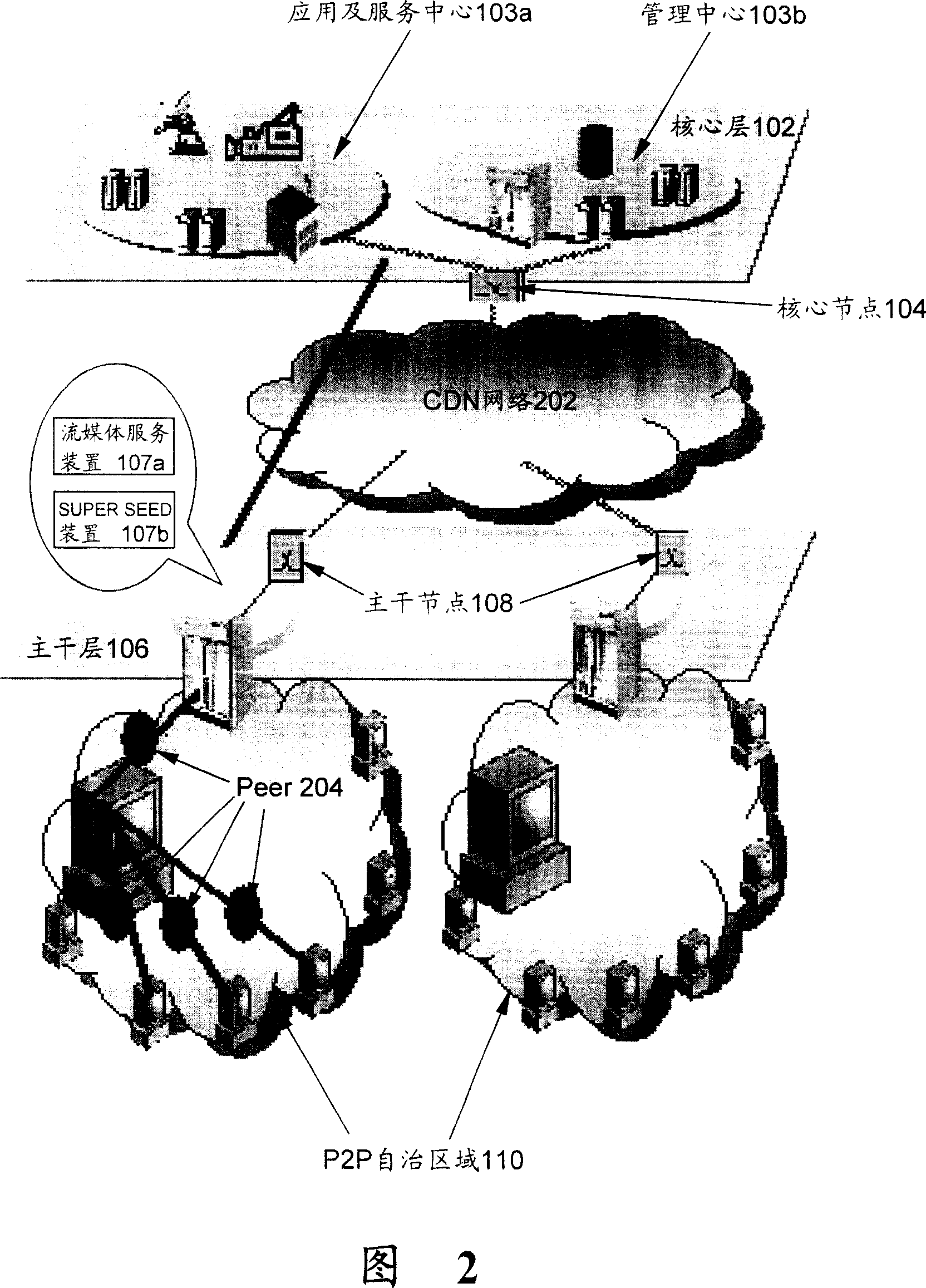
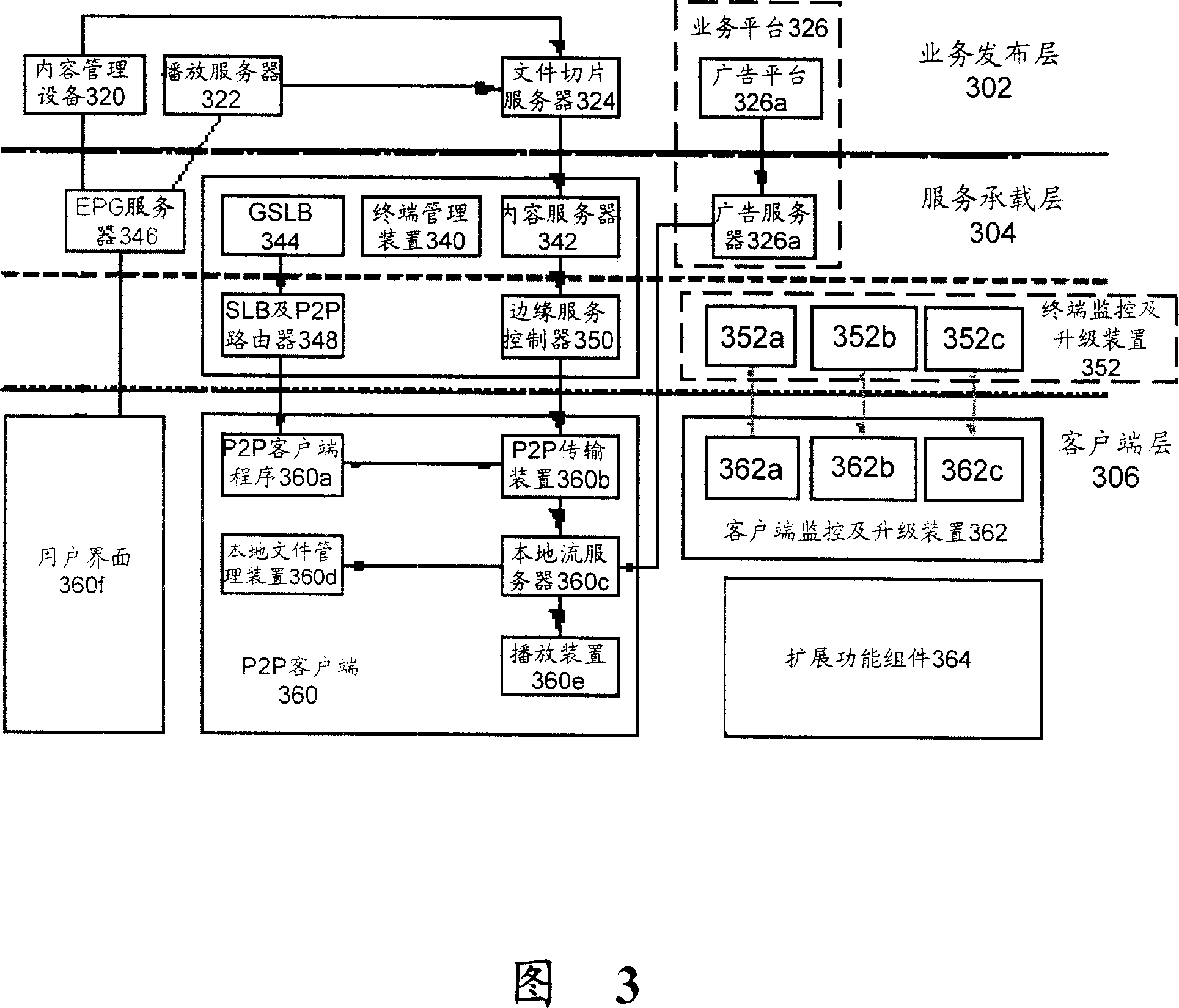
ActiveCN101146021AGuaranteed uptimeRun orderlyData switching by path configurationContent distributionClient-side
The invention discloses a route system for content distribution network. The content distribution network comprises a core layer for executing CDN protocol of a content distribution system, and the core layer includes a core node, a trunk layer for executing switching between CDN protocol and P2P protocol and including a trunk node, and a P2P autonomous region connected with the trunk layer and positioned at the edge of the P2P autonomous region. The trunk node at the edge serves as the server of the P2P autonomous region, and the core layer and the trunk layer share an implementation application distribution layer. The trunk layer achieves a service load layer, and the P2P autonomous region achieves a P2P client. The route system comprises a two-stage route device including a global server load balancing device GSLB and a local server load balancing device SLB, wherein the GSLB is positioned on the trunk node on a trunk network for achieving redirection of the service load layer; and the SLB is positioned on the trunk node at edge of the trunk network for achieving redirection in the P2P autonomous region based on P2P route algorithm and the distribution condition of P2P client Peer.
Owner:西安思华信息技术有限公司
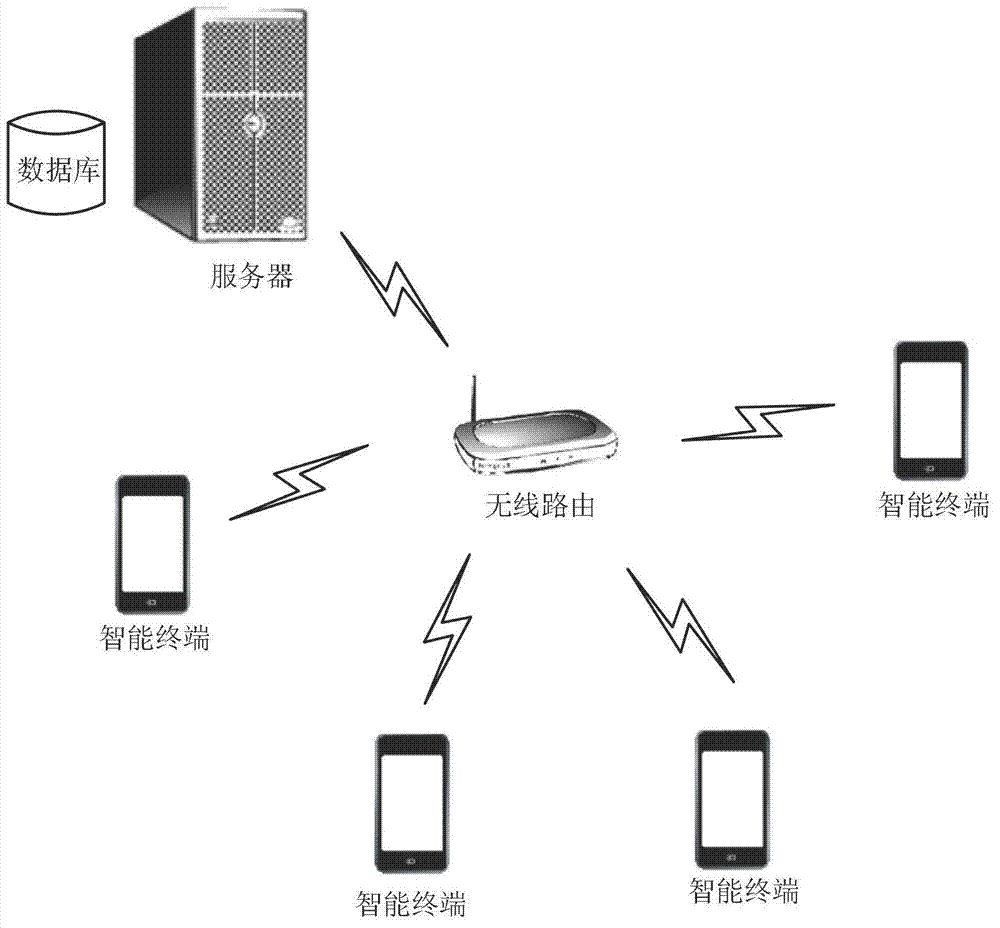
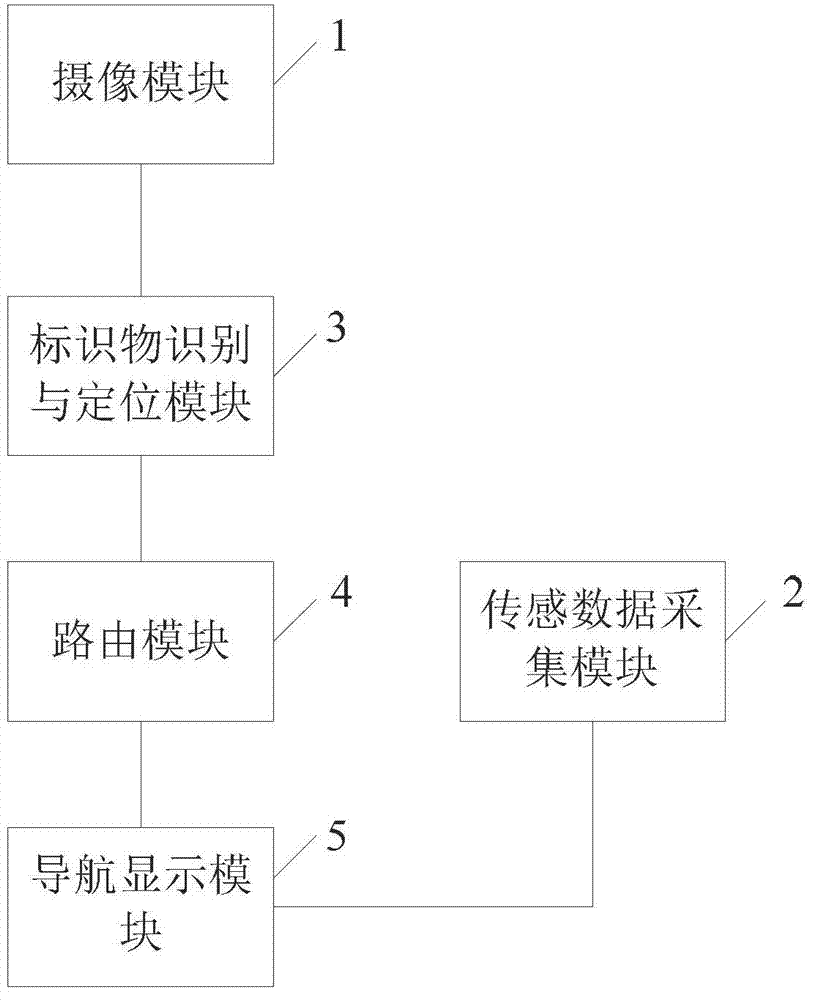
Indoor navigation method, systems and equipment
The invention discloses an indoor navigation method including: locating a user and a target location by the aid of the location technique based on marker recognition; finding out the shortest route from the user current location to a parking place according to the routing algorithm; and computing the direction and the displacement of a user by the aid of an internal sensor of an intelligent terminal during user movement, so that real-time tracking of the user location is completed. The invention further discloses an indoor navigation system, a navigation client-side system and the intelligent terminal. Based on marker recognition and by combining direction and acceleration sensor data for locating and navigation, the method and the systems are high in precision, low in cost and insusceptible to external signals.
Owner:CHENGDU IDEALSEE TECH
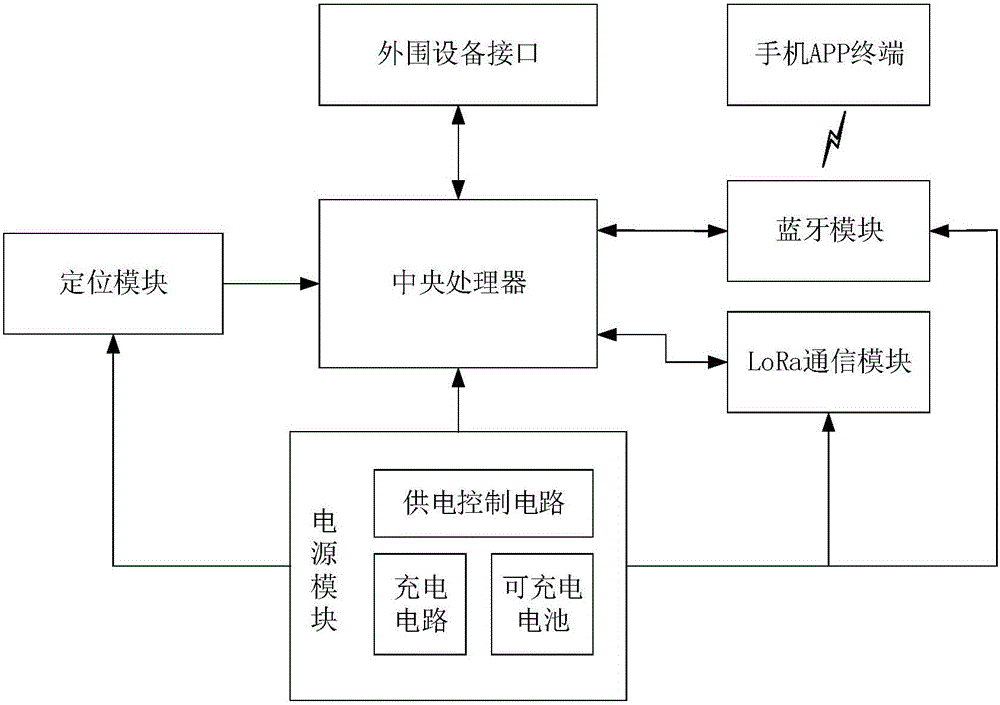
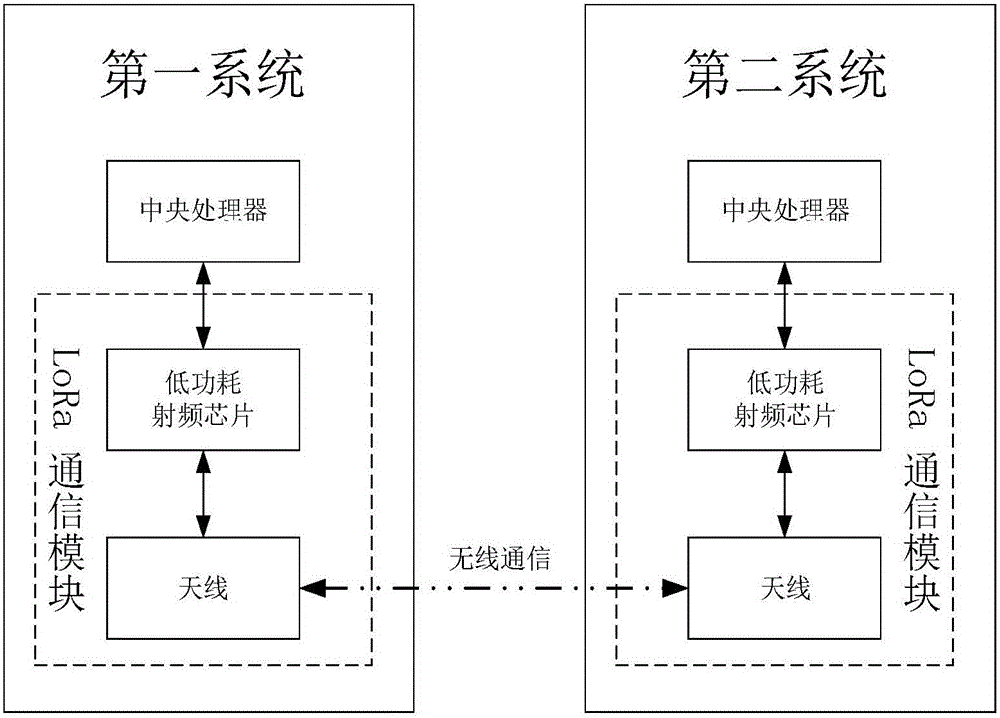
Outdoor wireless communication system based on LoRa ad-hoc network
ActiveCN105813099ASolve the problem of poor mobile network signalReduce power consumptionNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesCA protocolWireless mesh network
The invention provides an outdoor wireless communication system based on a LoRa ad-hoc network, which is used for solving technical problems of poor mobile network signals in severe environment, short transmission distance and absence of an interactive interface for information sharing of the existing outdoor wireless communication system. The outdoor wireless communication system based on the LoRa ad-hoc network comprises a central processing unit, a positioning module, a Bluetooth module, a peripheral interface, a power supply module, a LoRa communication module and a mobile phone APP terminal; the central processing unit is respectively connected with the positioning module, the Bluetooth module, the peripheral interface, the power supply module and the LoRa communication module; the LoRa communication module constructs a wireless Mesh network with the LoRa communication modules of other systems, and performs reliable data communication through a CSMA / CA protocol and an AODV routing algorithm; and the mobile phone APP terminal and the Bluetooth module perform data exchange through the Bluetooth. The outdoor wireless communication system based on the LoRa ad-hoc network performs communication without the mobile network, has long transmission distance, has the interactive interface for information sharing, and can be applied to the fields, such as the Internet of Vehicles and the Internet of Things.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
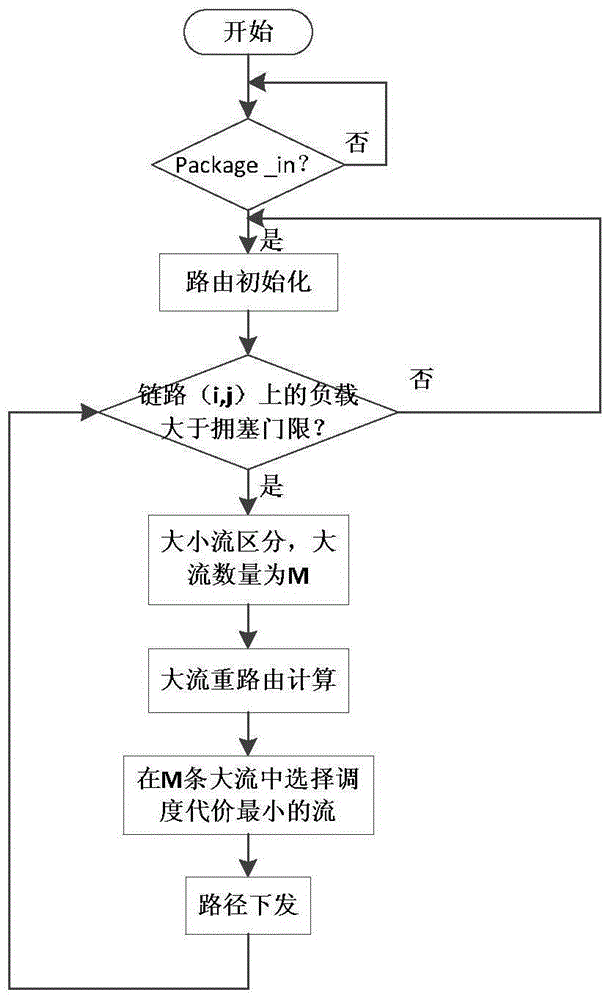
Software defined network (SDN) congestion control routing method based on minimization of path overhead and stream scheduling cost
ActiveCN105227481ASolve insufficient bandwidthIncrease profitData switching networksNetwork congestionRouting algorithm
The invention relates to a software defined network (SDN) congestion control routing algorithm based on minimization of a path overhead and a stream scheduling cost. A controller performs periodic monitoring on use ratios of all links connected with an interchanger controlled by the controller, wherein the formula of the use ratio is shown as in the description, when the use ratio is greater than or equal to a certain fixed value Etath, it is determined that the link is congested, and the congestion control routing algorithm is used. The algorithm comprises steps of determining all large streams on the links according to the stream rate of the congested link so as to reserve the large streams for scheduling; performing rerouting computation on all large streams on the links, computing the overhead of each path, and selecting a path of minimum overhead from a plurality of equivalent paths to be used as a scheduling path; and finally, computing the scheduling cost of each stream, and selecting the stream of the minimum cost to schedule. The algorithm not only can schedule the congested link effectively, but also makes the network link resource more efficient, improves the use ratio of the link and shortens the stream transmission time.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for setting multilayer satellite network system route
InactiveCN101299713AImprove effectivenessReduce transmission delayStar/tree networksRadio transmissionQuality of serviceNetworked system
The present invention relates to a method for setting multilayer satellite network system route, including steps of: 1. setting parameters for the network initialization; 2. fixing a time, solving satellite orbit parameters in the interval of time, calculating the location coordinates of the satellite and the length of the link between stars, and establishing a network topological structure; 3. calculating the load of link between stars of the multi-layer satellite network; 4. calculating the process and exchange time delay on stars according to the queuing theory; 5. searching source satellite and object satellite of each satellite layer; 6. selecting the satellite layer for transporting services according to the communication service instruction requirement and network states, and searching an optimum route according to routing algorithm. Relative to traditional stationary orbit satellite, the present invention has small transmission delay, and high validity. The system has advantages of more flexible routing, effective guaranty of service quality, multiple replaceable chain circuits, stronger survivability, a capacity of processing and exchanging on star, optical or microwave links between stars, and capability of providing wideband synthetic service for users in global scope.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Routing method and system for a wireless network
ActiveUS8948046B2Easy to handleEliminate the broadcast forwarding loopError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsBroadcastingRouting algorithm
A method and system for selecting a route in a wireless network for the transmission of a data packet between wireless nodes in said network using a modified link-state routing algorithm wherein only a limited number of broadcast messages are generated to synchronize the link-state database throughout the wireless network. A subset of nodes called portal nodes within the network are elected to do the broadcasting for the entire network. Each portal node broadcasts an announcement of its identity to all of the wireless nodes. Each wireless node responds to these broadcasts to select one of the portal nodes as its root portal node. It then identifies a unicast route back to its root portal node, and sends a link-state register message to this portal node. These link-state register messages received by each portal node are aggregated by them and are broadcast to each of the wireless nodes for storage. When a data packet is thereafter received by a wireless node from a neighboring node, it detects if the data packet satisfies one of a plurality of predetermined conditions and rebroadcasts the data packet to neighboring wireless nodes if none of the conditions is satisfied.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
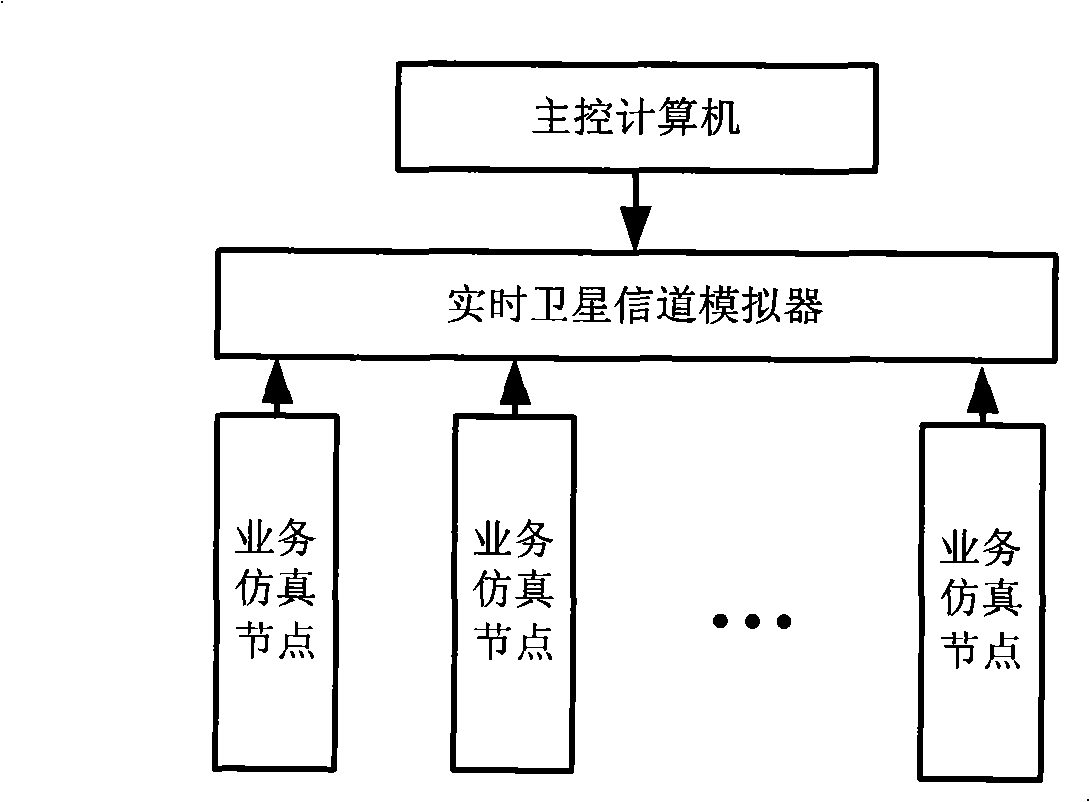
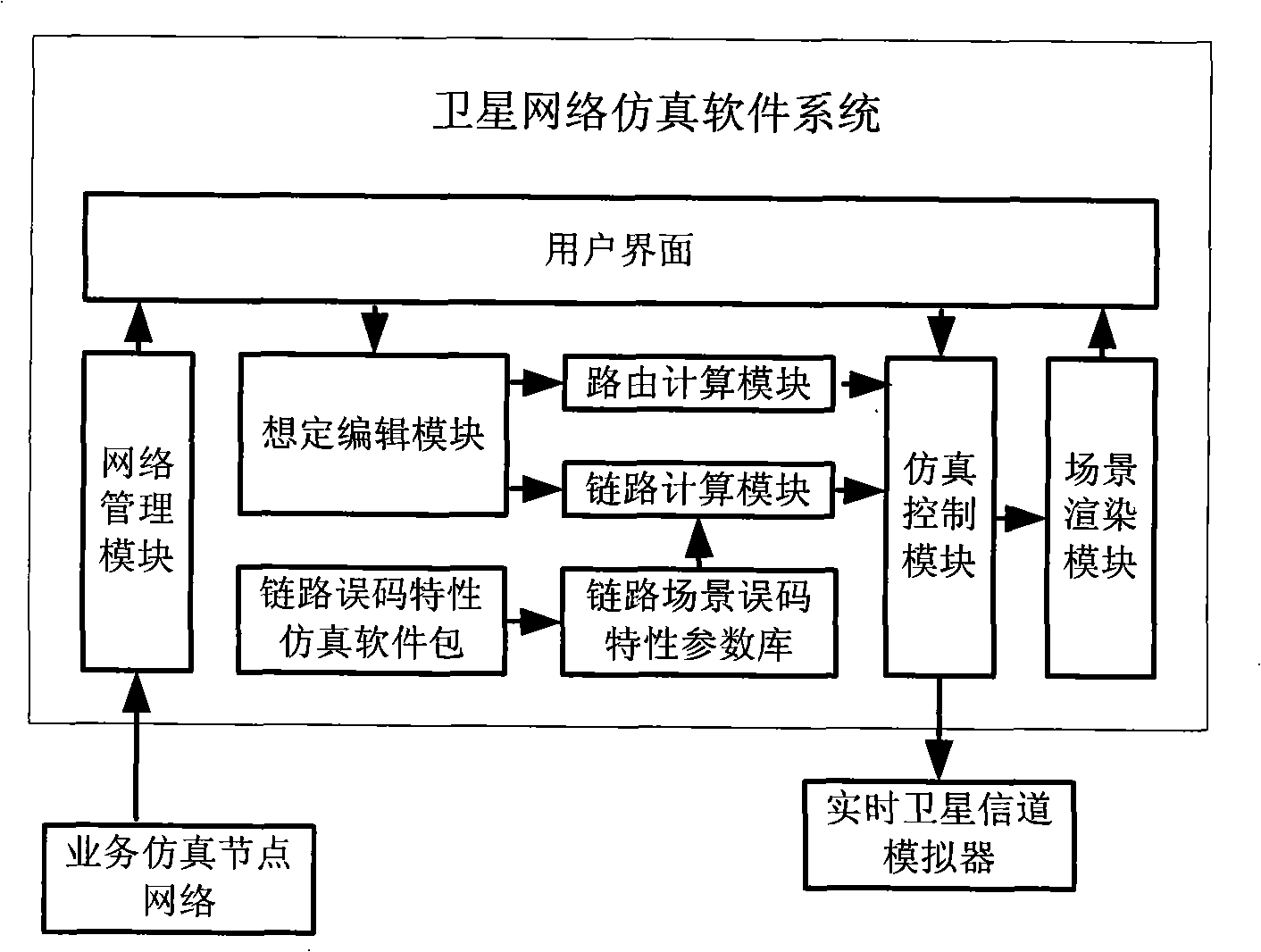
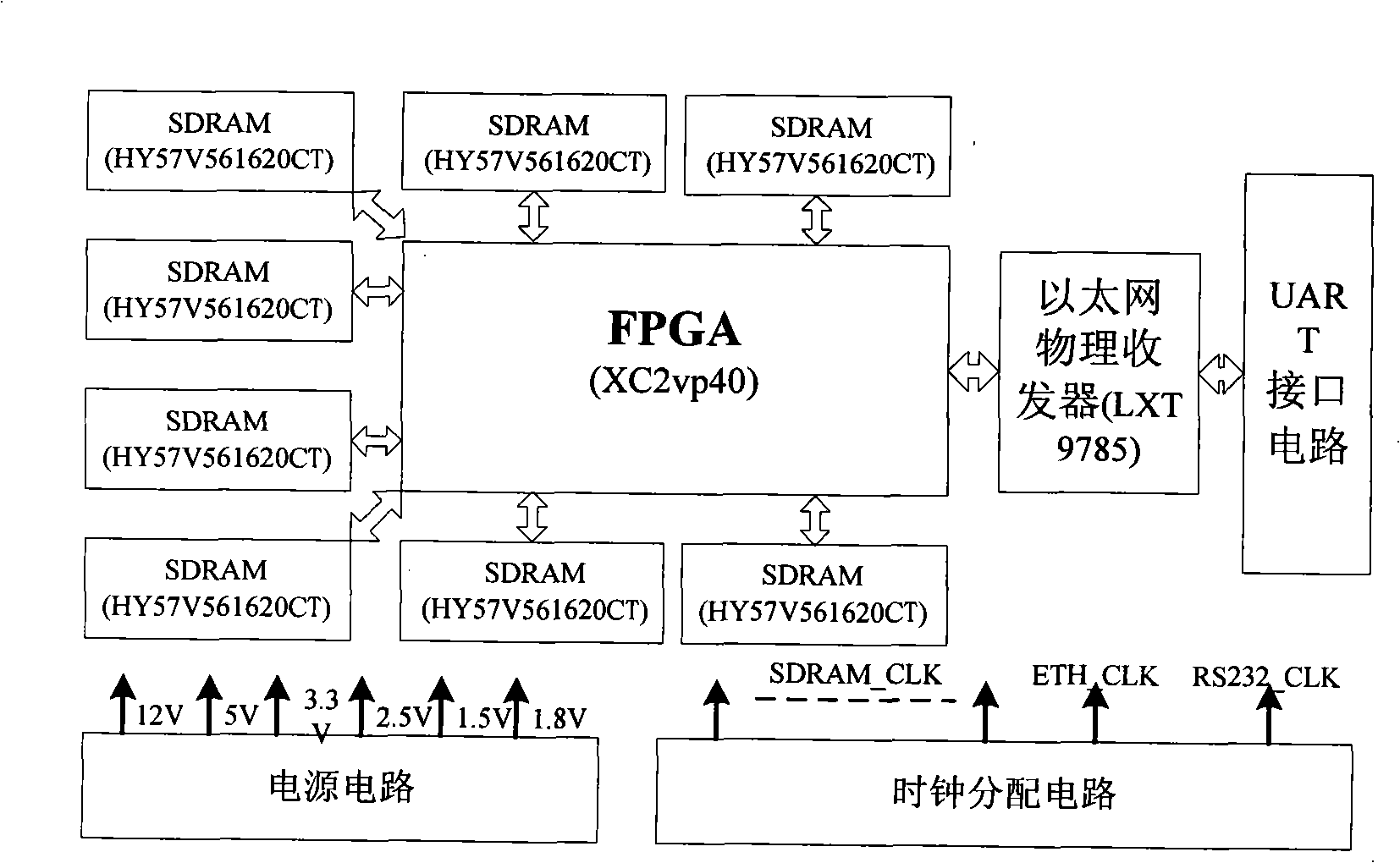
Satellite network simulation system
InactiveCN101404547AComprehensive solutionSolve the characteristicsRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringSoftware systemNetwork topology
The invention discloses a satellite network simulation system and belongs to the technical field of satellite communication simulation. The system comprises a main control computer, a real-time satellite channel simulator and a plurality of service simulation node computers; the main control computer is provided with a satellite network simulation software system which can achieve establishment of a satellite network simulation scene, can select a routing algorithm, set link parameters and achieve the information management of the simulation satellite network, and is connected with the real-time satellite channel simulator by an RS232 bus; the service simulation node is provided with a service simulation software which achieves simulation of a transmission process of the satellite network service, and is connected with the real-time satellite channel simulator by an Ethernet port. The satellite network simulation system can truly and comprehensively simulate topological changes of the satellite network, channel characteristics of an inter-satellite link and a satellite-to-earth link, and the transmission process of the satellite network service under the laboratory condition.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System, method and apparatus for dynamic path protection in networks
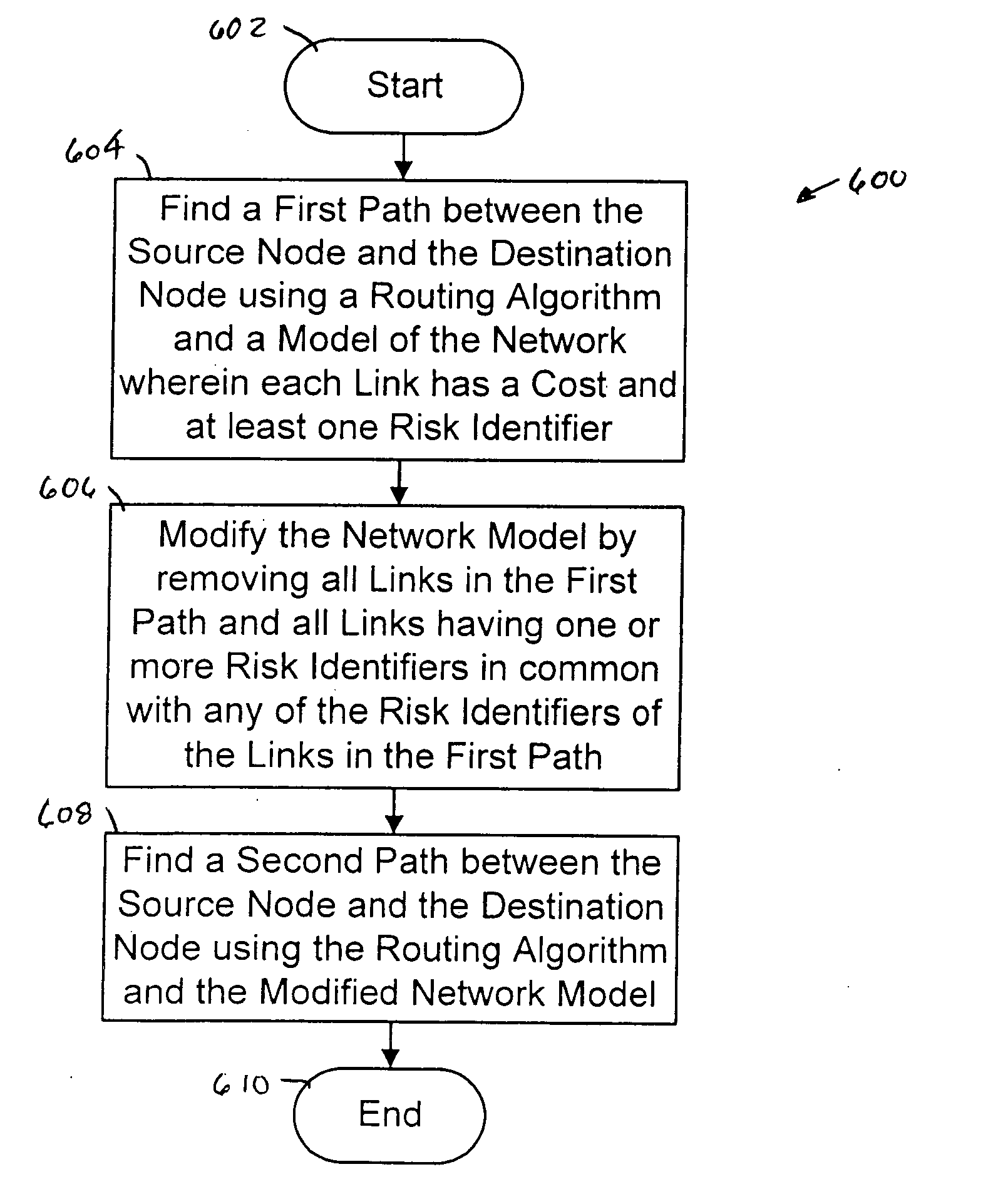
InactiveUS20050237950A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork modelPath protection
The present invention provides a system, method and apparatus for dynamic path protection in networks by finding two paths between a source node and a destination node in a network having multiple nodes and multiple links. A first path is found between the source node and the destination node using a routing algorithm and a model of the network. Each link has a cost and at least one risk identifier. The cost of the links having one or more risk identifiers that occur more than once in the network model are increased. The model is modified by removing all links in the first path and all links having one or more risk identifiers in common with any of the risk identifiers of the links in the first path. The second path is found between the source node and the destination node using the routing algorithm and the modified model.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
System and method for selecting fibre channel switched fabric frame paths
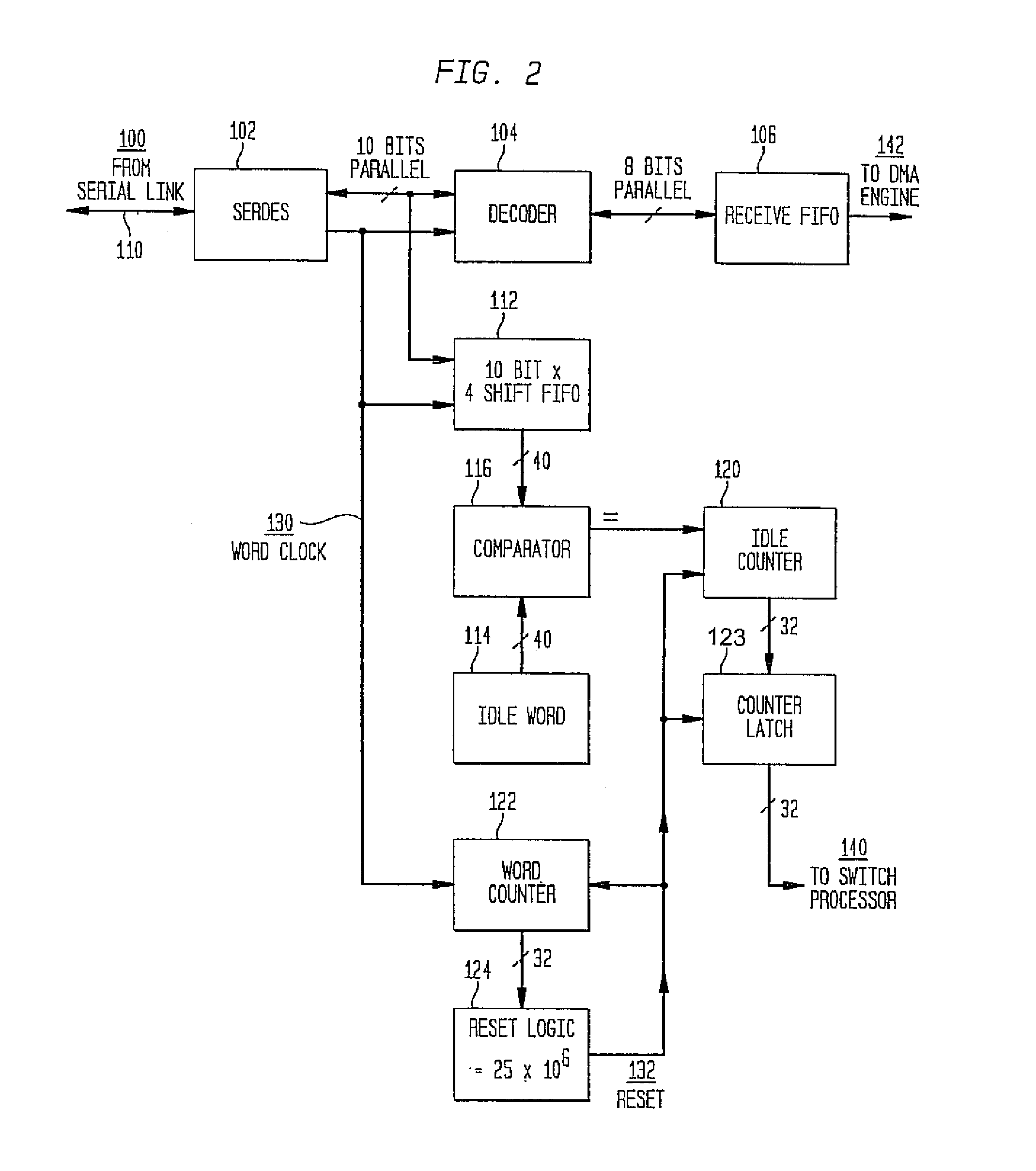
InactiveUS7327692B2Proper selectionFacilitate decision-makingError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsStorage area networkWord count
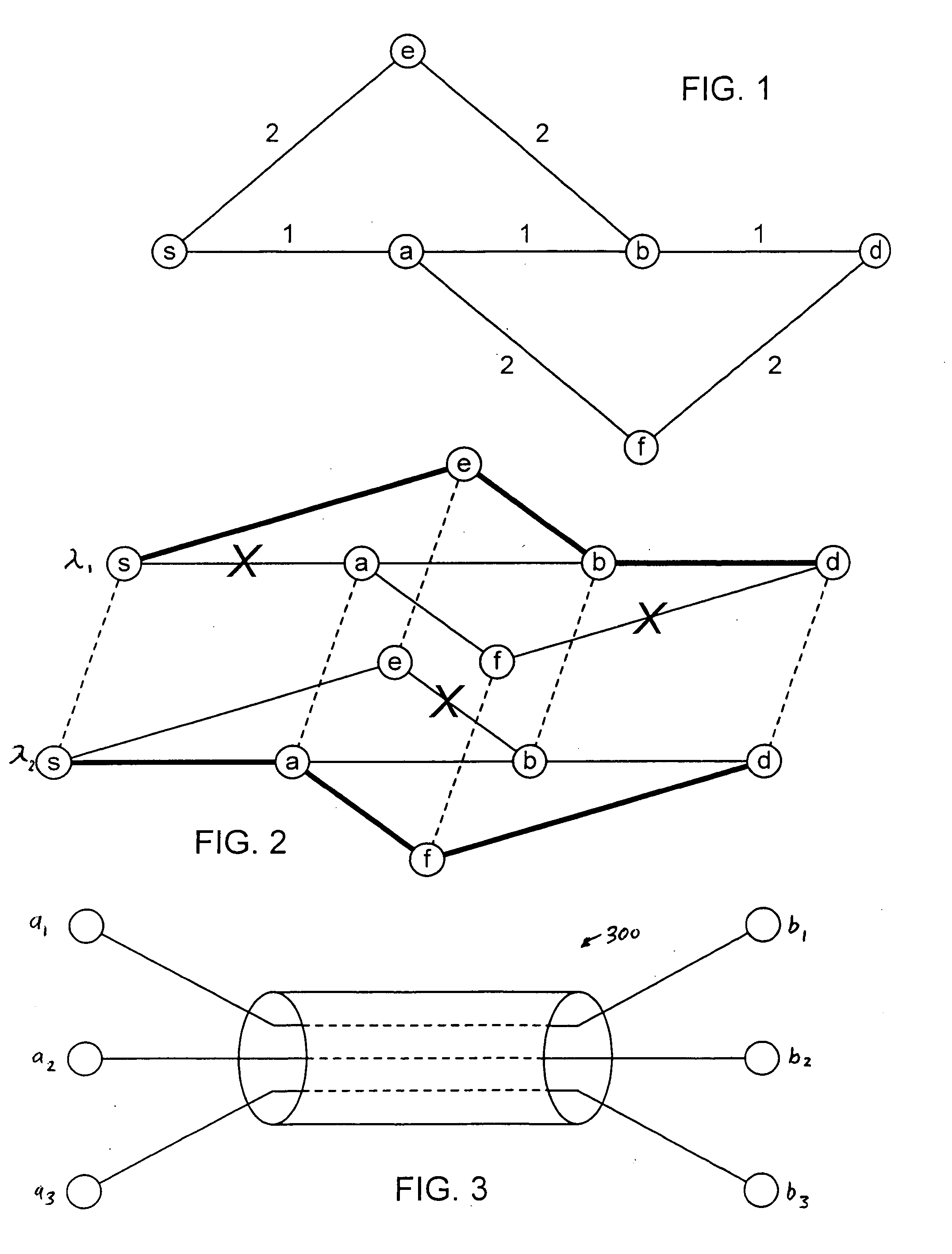
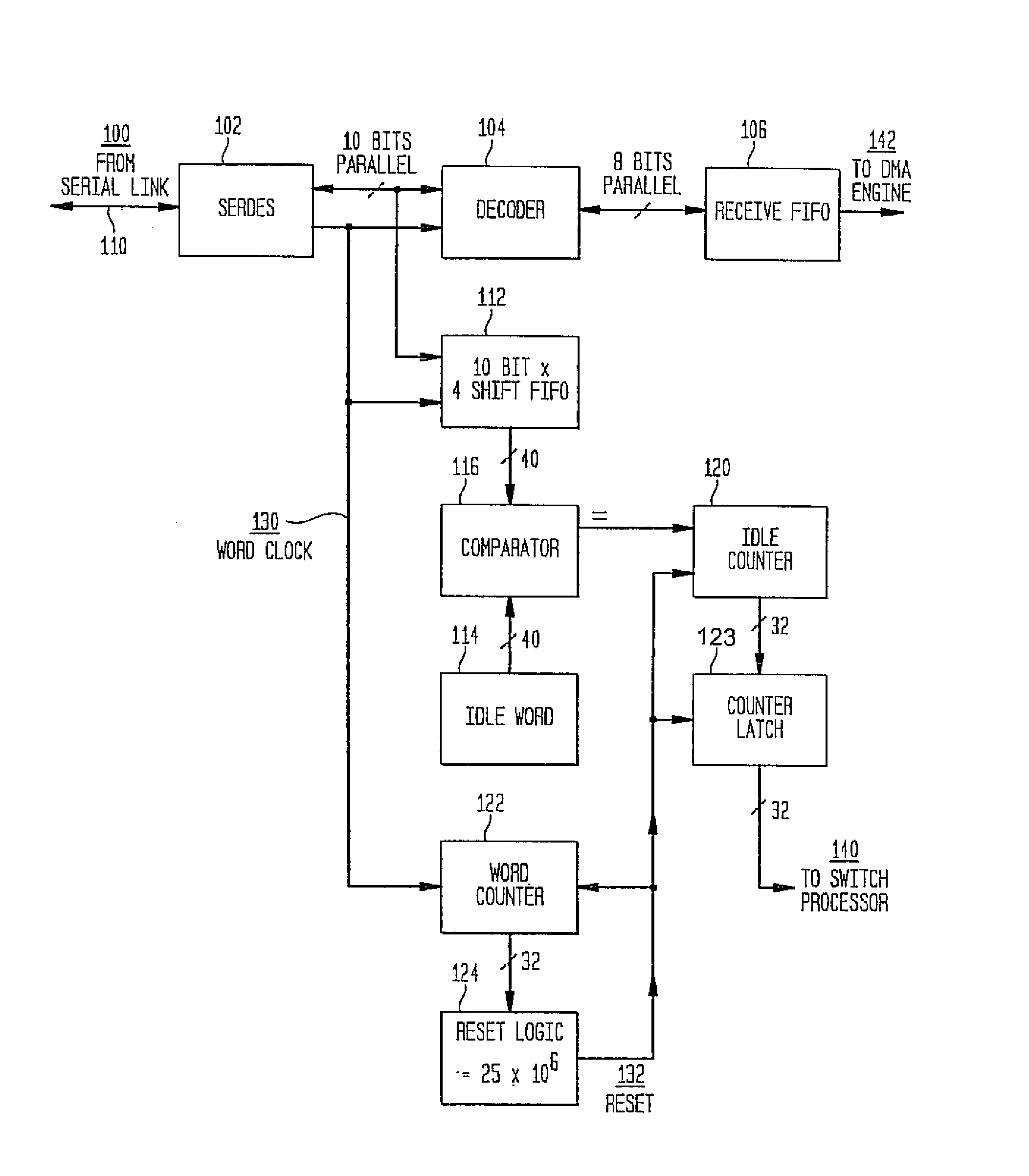
A system and method for measuring data transmission activity through a port of a switch device interconnecting nodes of a storage area network, the port transmitting data as words of predetermined length, one data word indicating idle port activity. The method includes steps of: counting a number of transmitted words received from the port in a first counter device; and, for each word counted, comparing that word with a predetermined word indicating no (idle) port transmission activity. In response to the comparing, a number of matches are counted in a second counter device. In this manner, a ratio of a number of counted matches with a total amount of words counted indicates available bandwidth for transmitting additional data over that link. Preferably, this available bandwidth information is included in a link state record that the switch communicates to other switch devices interconnecting that link. Processing devices at the switches determine a link cost factor, based on the available bandwidth of that link and, in addition, the link speed, the cost factor being used to optimize path selection over links in the network according to a path routing algorithm.
Owner:IBM CORP
Energy perception routing algorithm used for wireless sensing network
InactiveCN102149160ASolve the problem of "resource blind spot"Solve the "resource blind spot" problemNetwork topologiesHigh level techniquesRest energyWireless mesh network
The invention relates to an energy perception routing algorithm used for a wireless sensing network, which comprises the steps as follows: 1, a two-tier clustering mechanism based on a cellular network structure is realized for a wireless sensing network; 2, cluster heads are dynamically selected according to the rest energy of nodes and the central distance from the nodes to a cell to form a backbone network which processes and forwards data, wherein the nodes not serving as the cluster headers and not implementing data transmission enter a dormant state; and the nodes serving as the cluster headers manage the nodes in the clusters; and 3, a limited flooding mechanism is used for establishing routing taking a convergent node as a final target node; a routing table is established between the cluster headers according to the minimum path overhead between the clusters and the rest energy of the cluster headers; and optimal routing can be established for the nodes in the whole wireless sensing network only through one broadcasting by reasonably adjusting the parameters. The energy perception routing algorithm used for the wireless sensing network can improve the lifecycle of the whole wireless sensing network, thus satisfying the application of the wireless sensing networks sensitive to energy.
Owner:NINGBO POLYTECHNIC
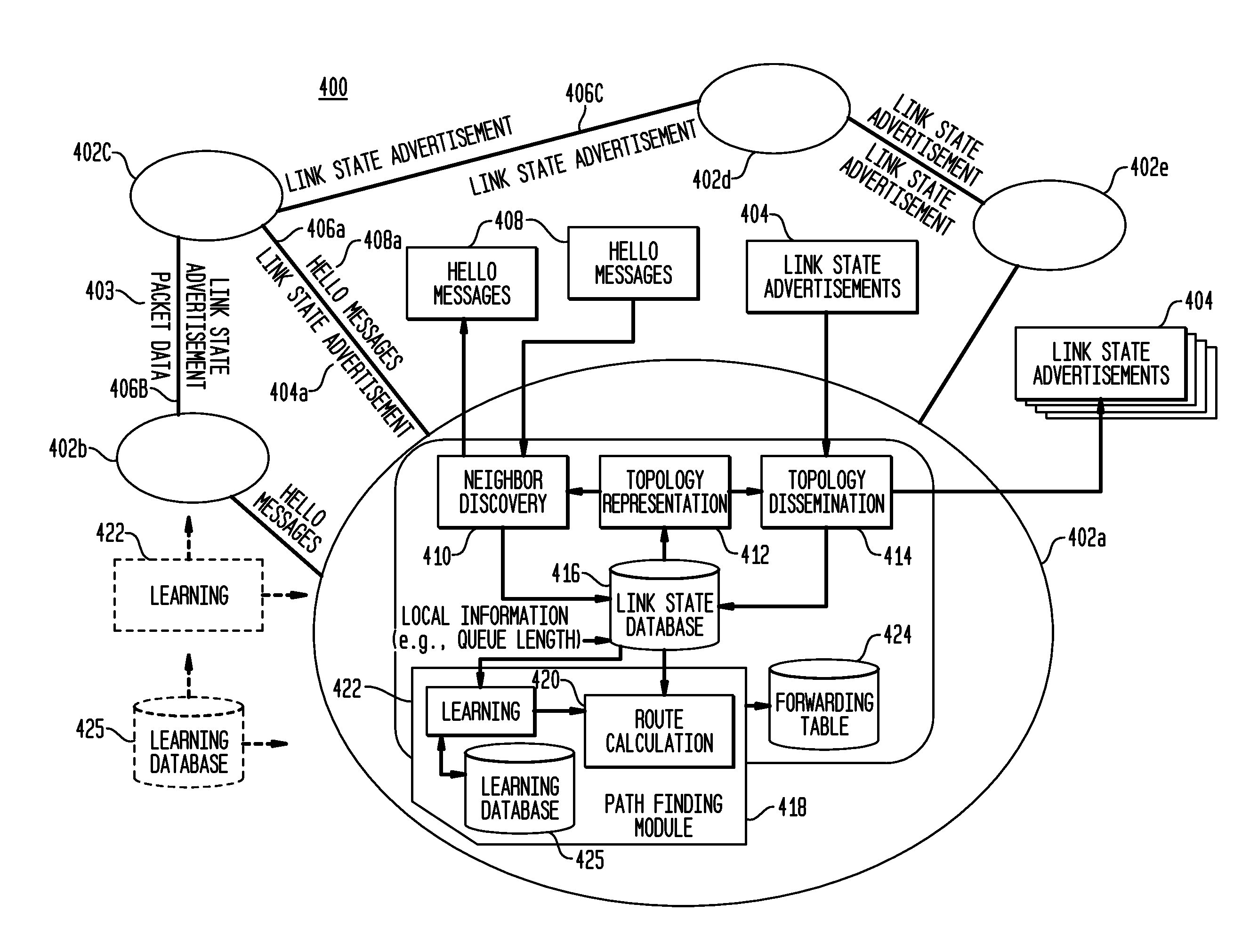
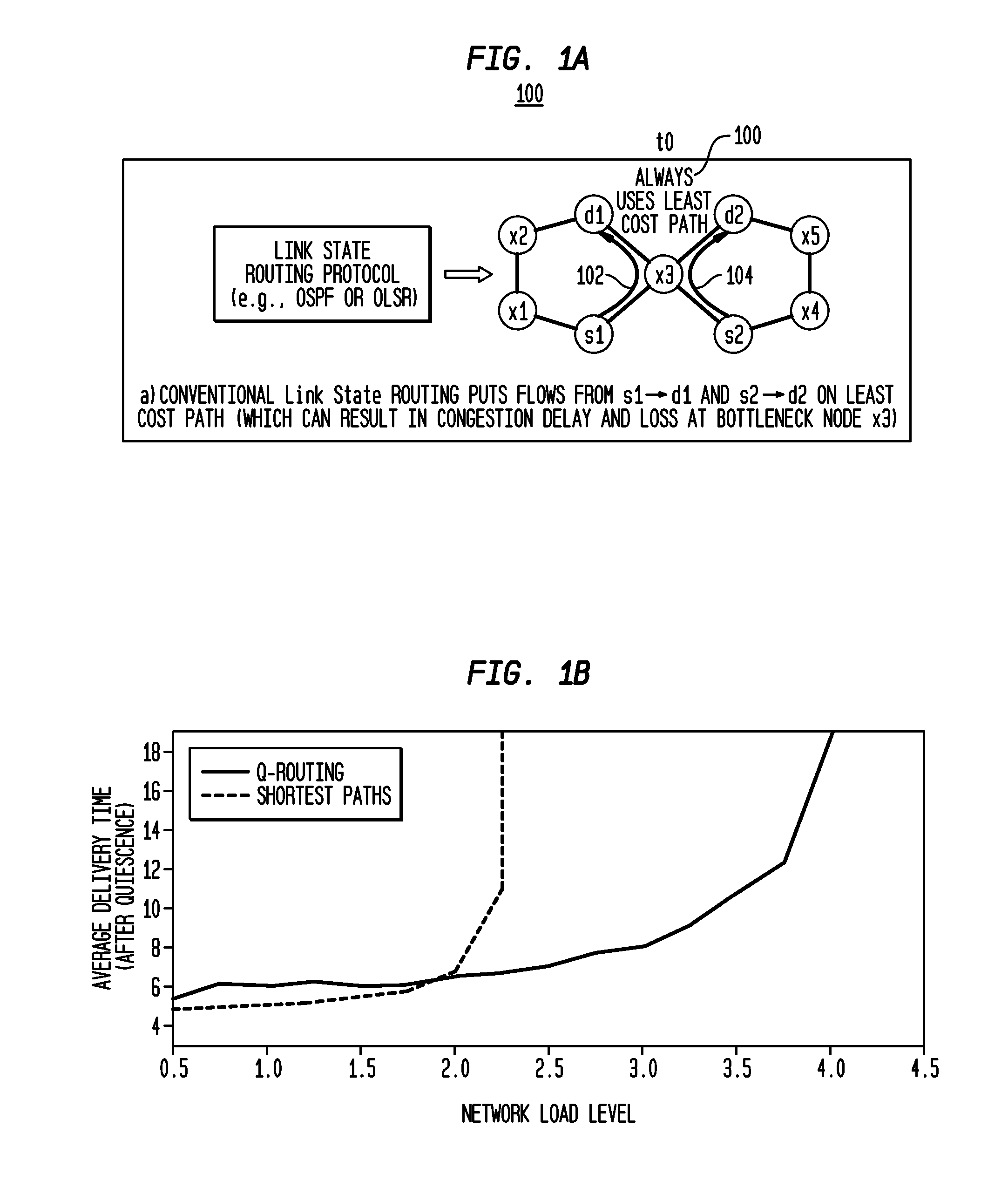
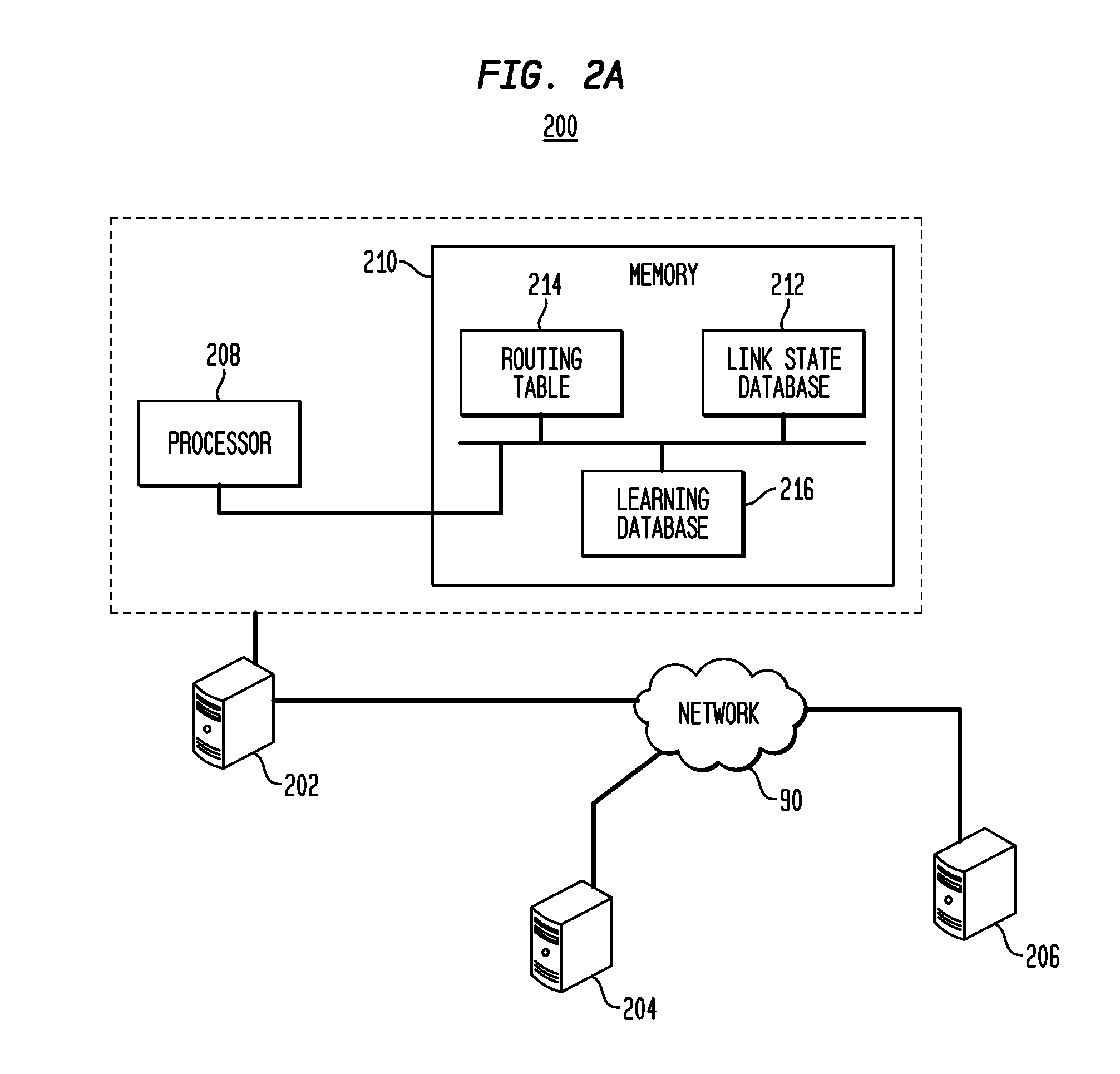
Hybrid Learning Component for Link State Routing Protocols
In a network that executes a link state routing protocol, a network node receives periodic disseminations of link state information from other network nodes. The link state information includes neighboring node identity and link cost metrics. The network node calculates the initial routing paths based on the received link state information by using a link state routing algorithm. It then adapts the calculated path based on both the current link state information and past link state information through a reinforcement learning process. The network node then selects a routing path to each destination node based on the adaptation and updates the routing table accordingly.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com