Patents
Literature
284 results about "Customer edge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
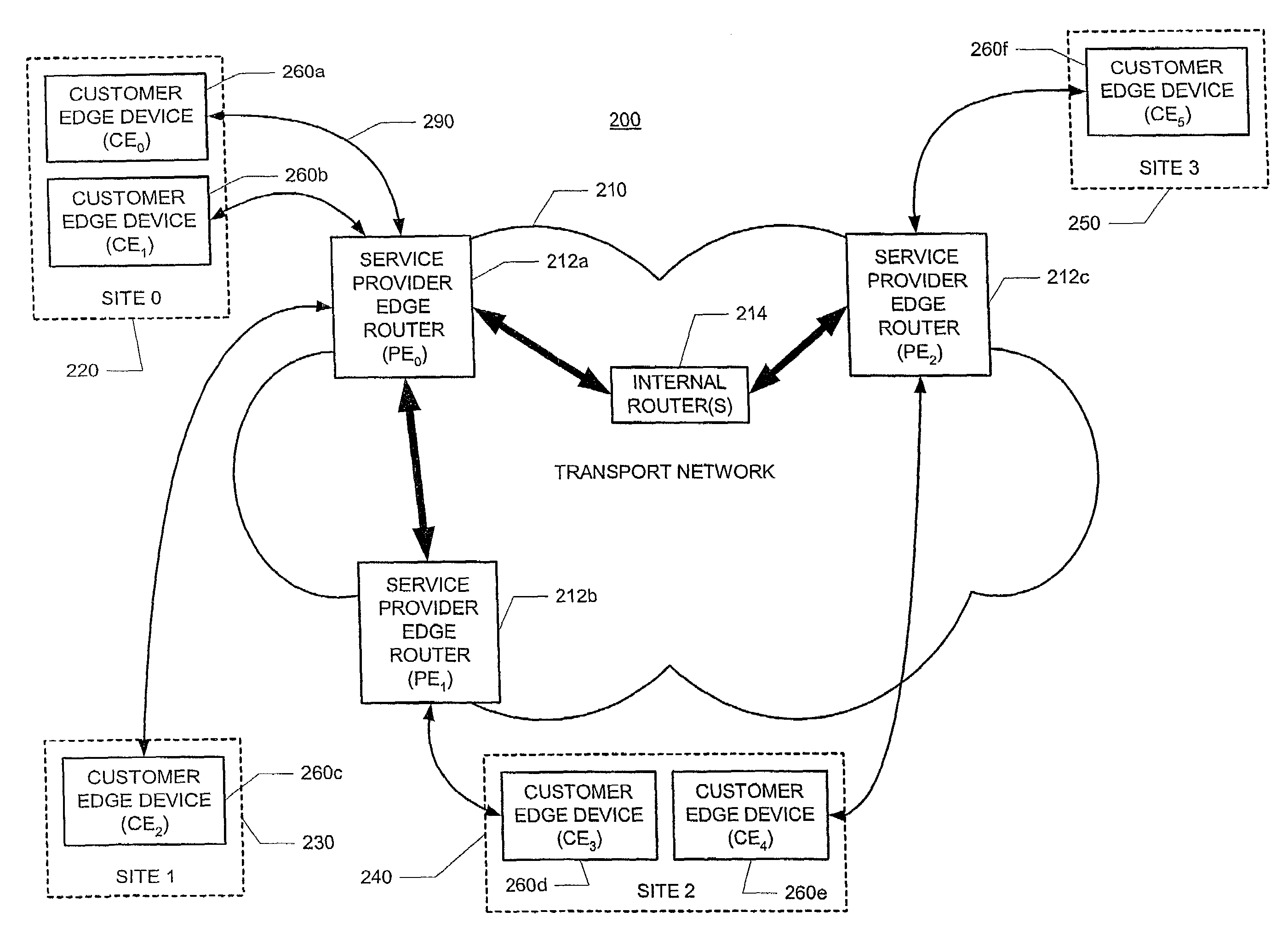
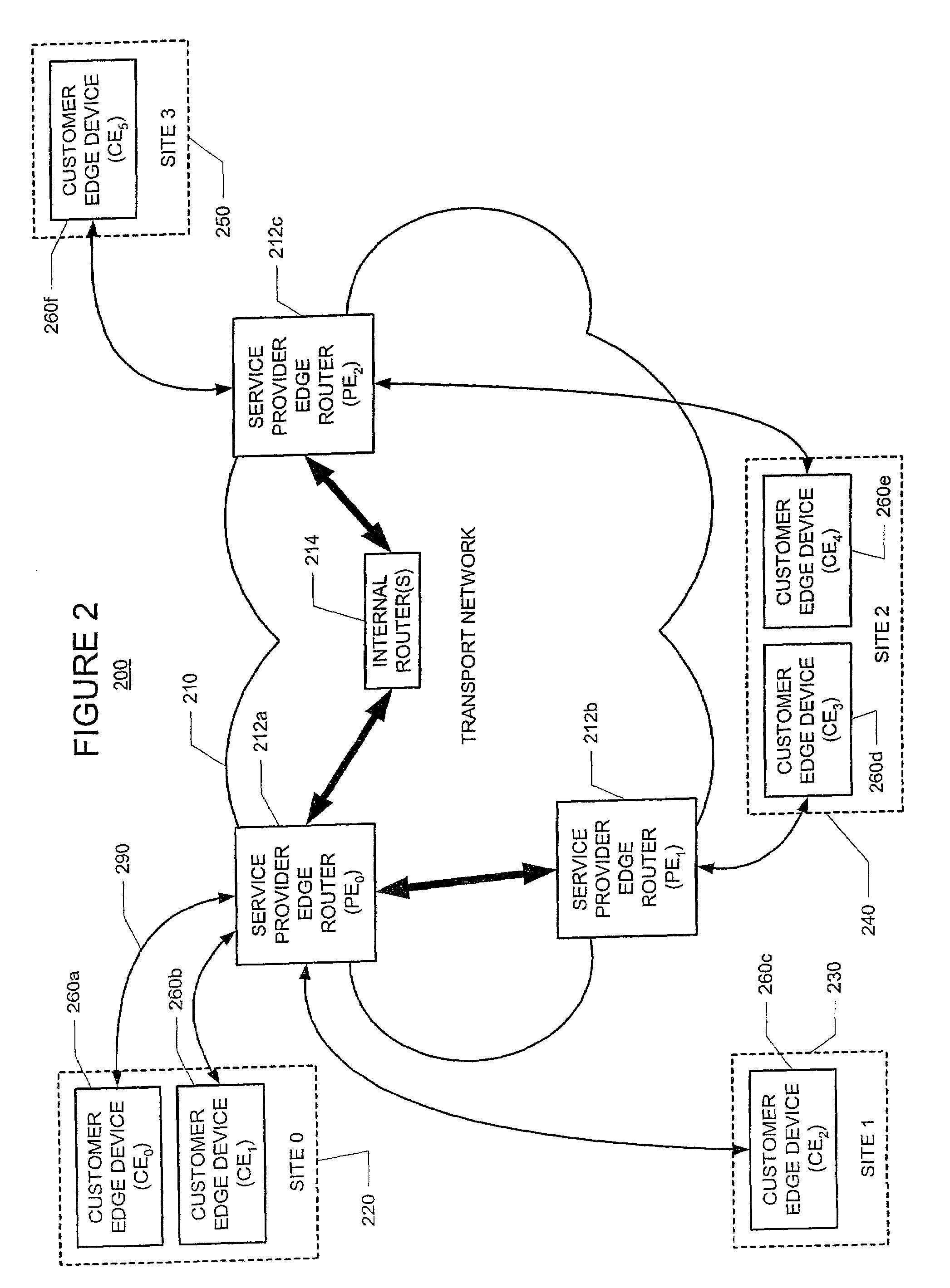
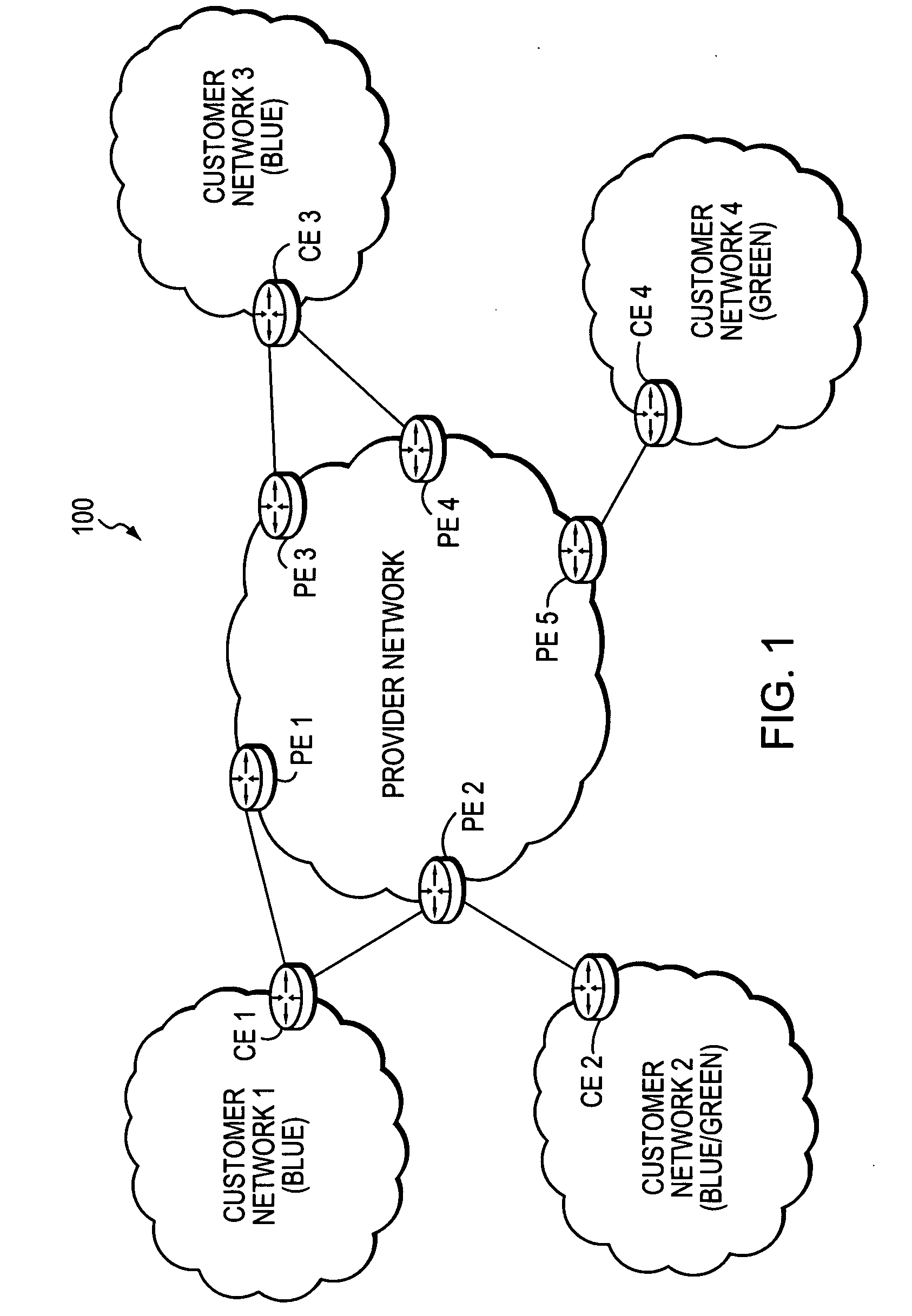
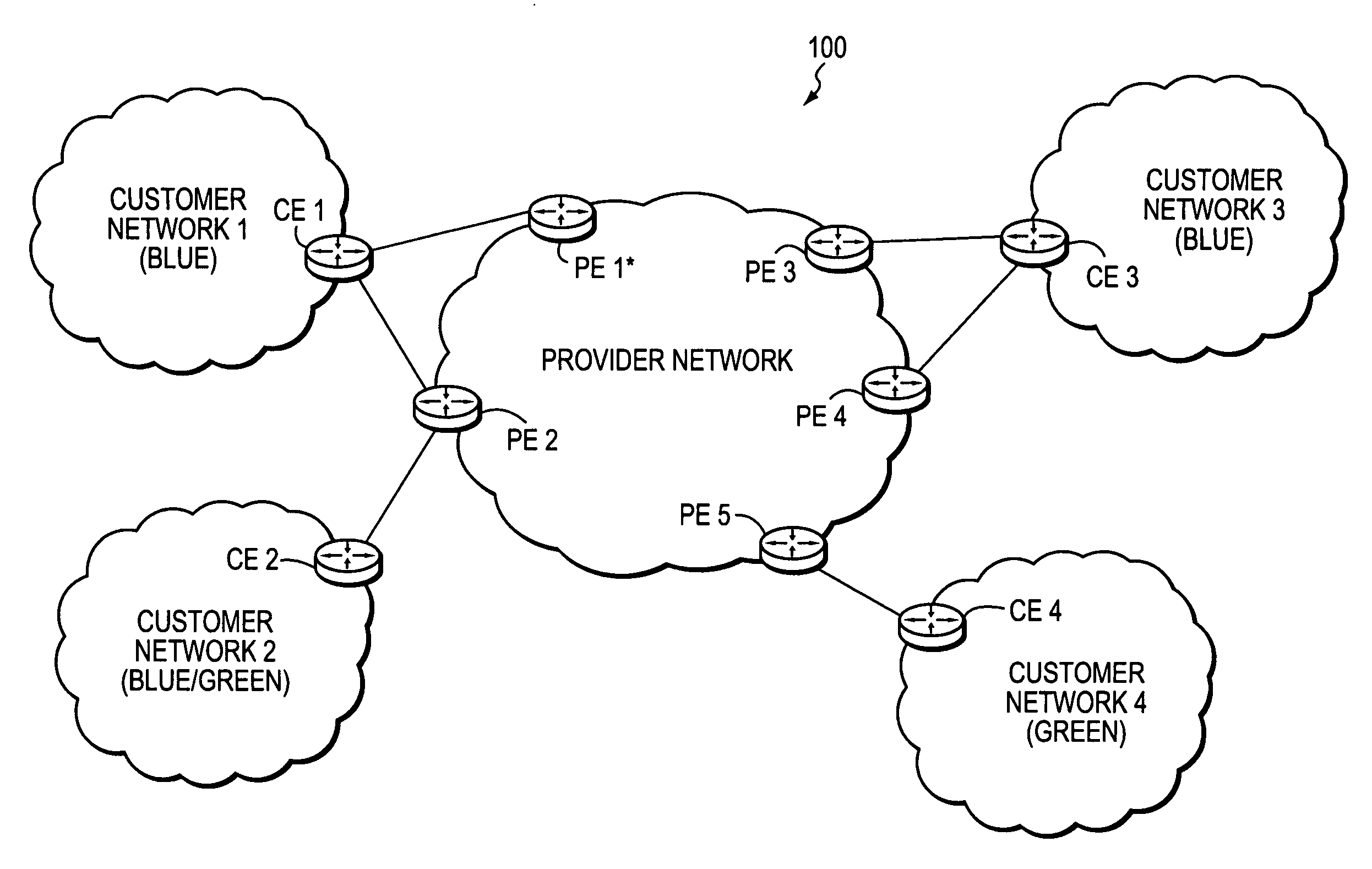
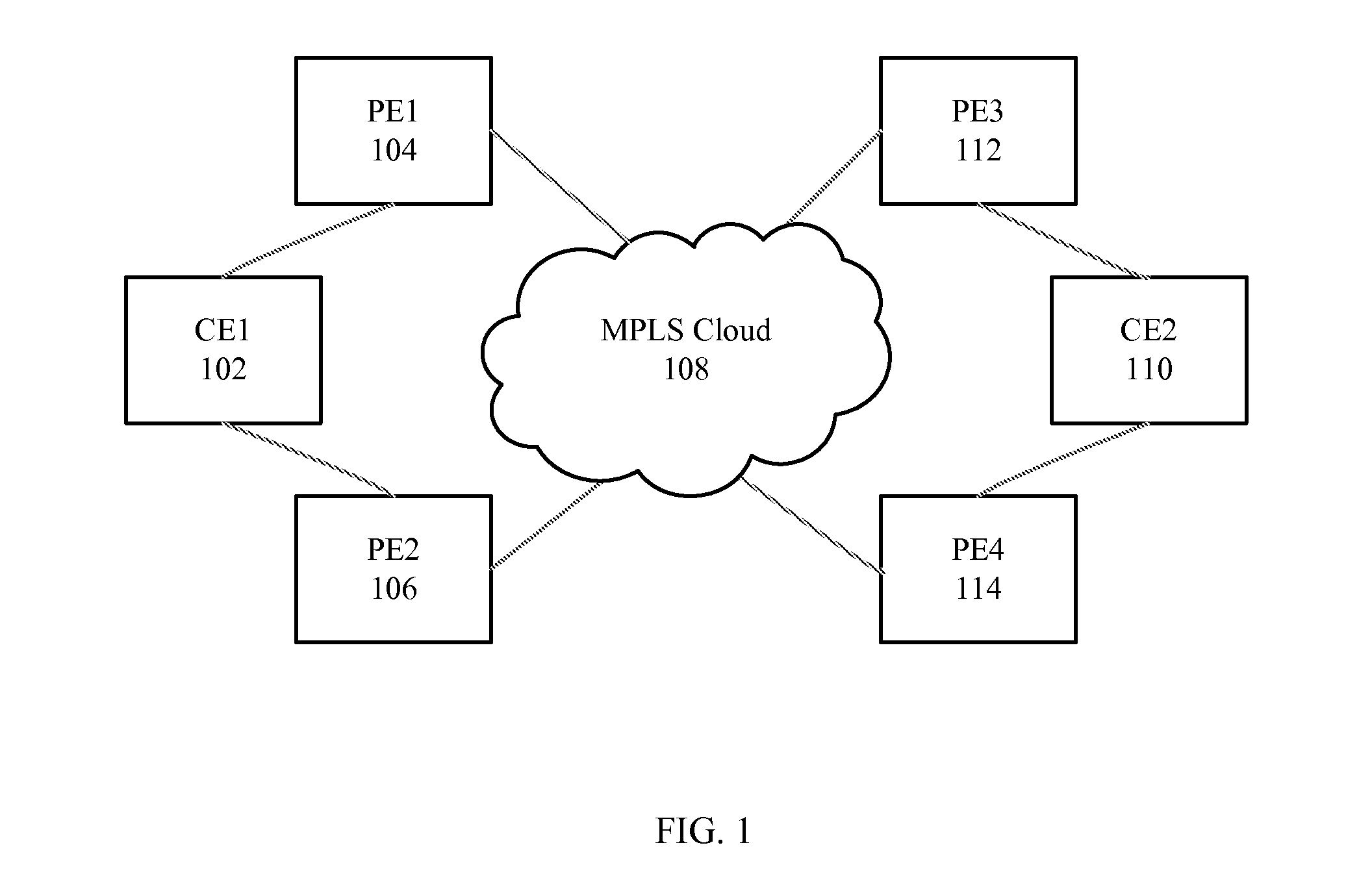
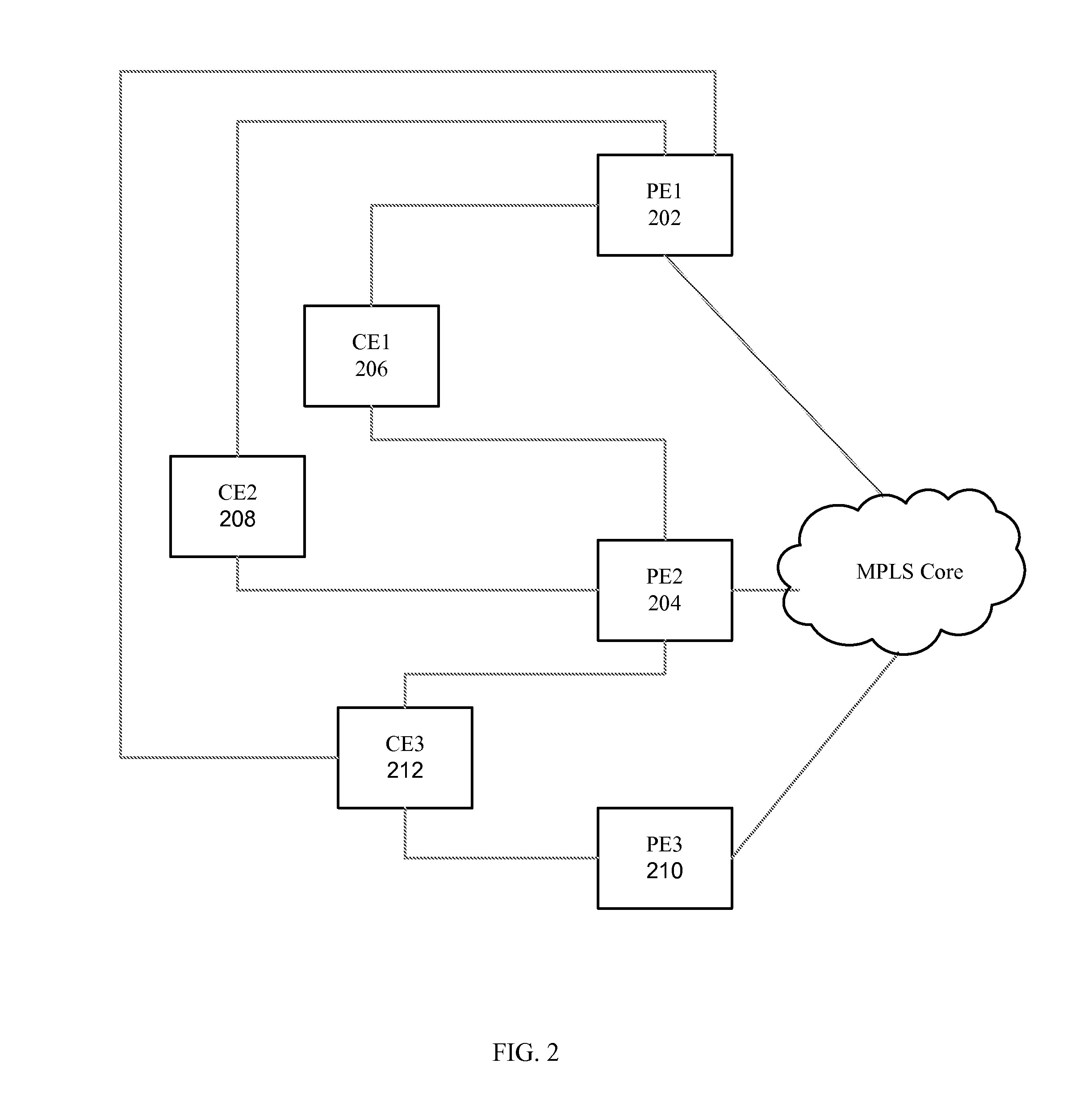
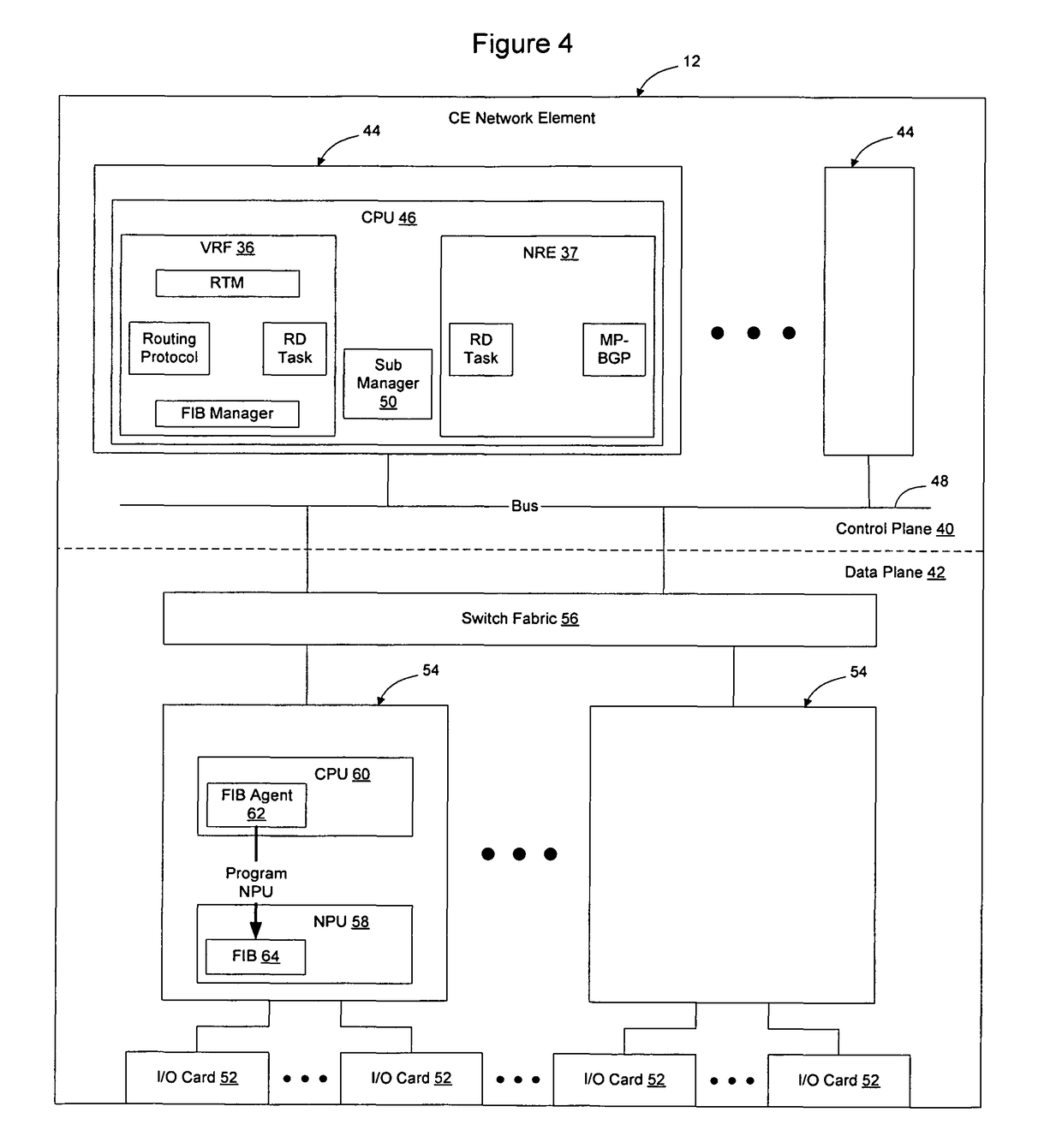
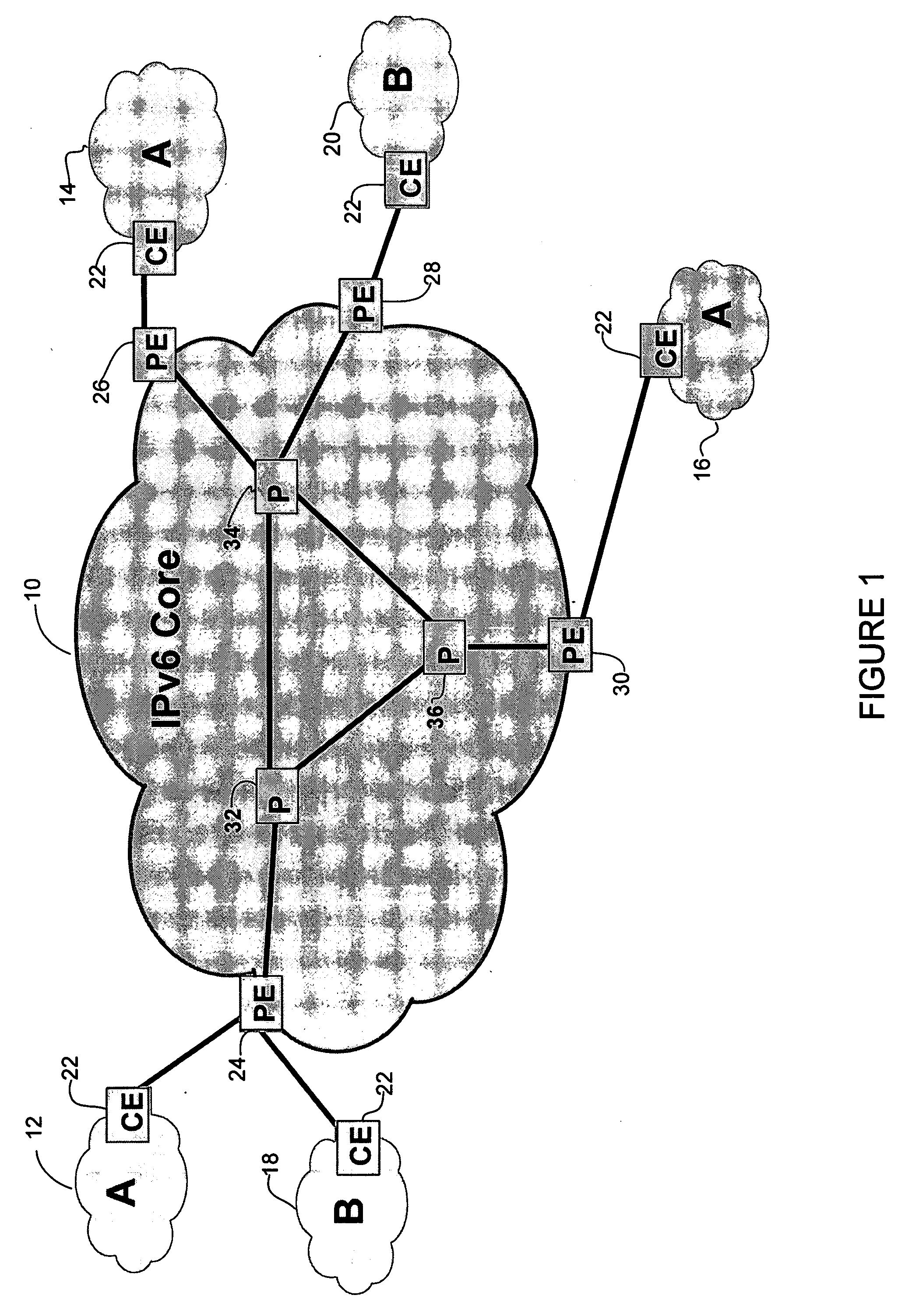
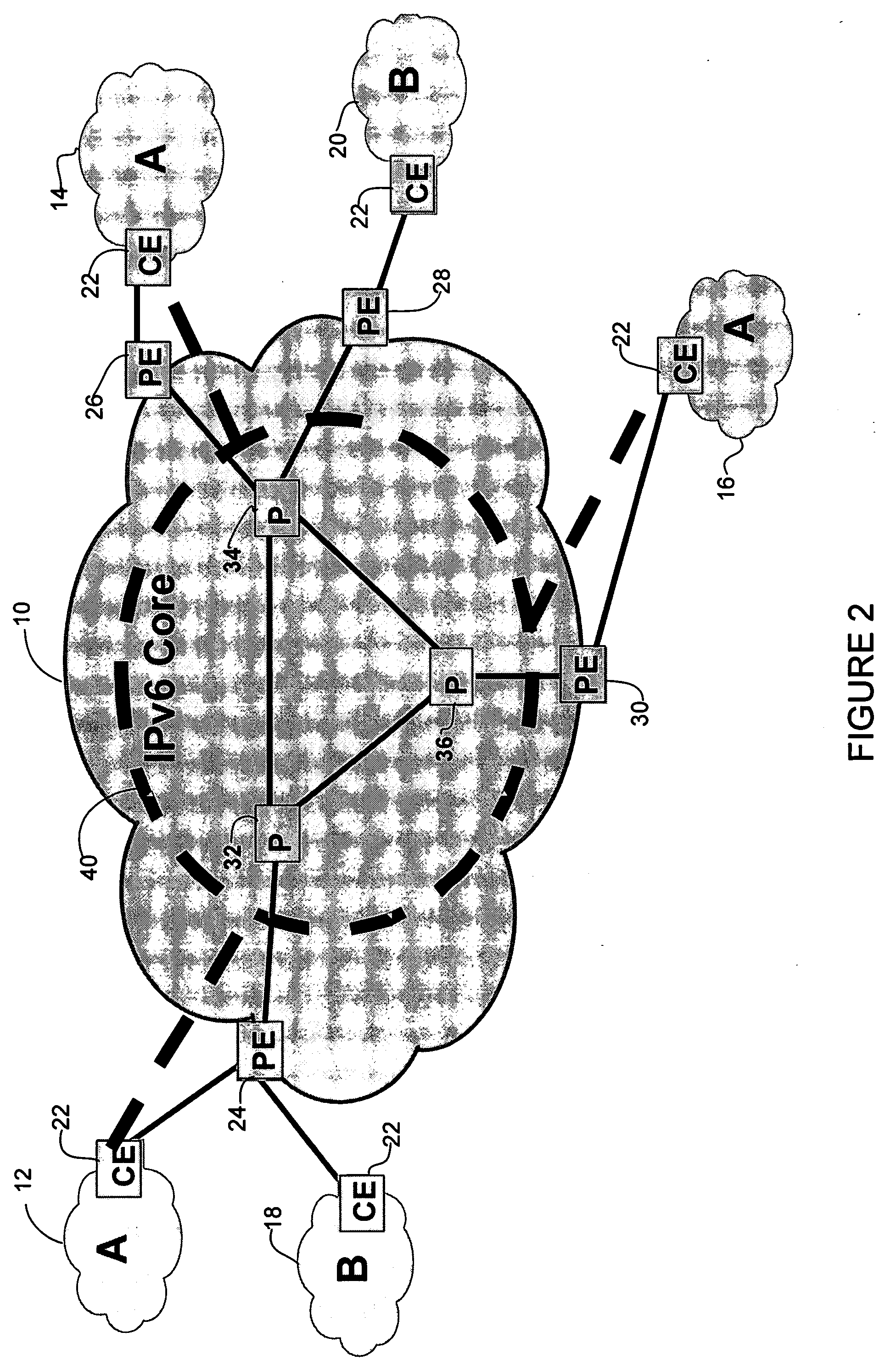
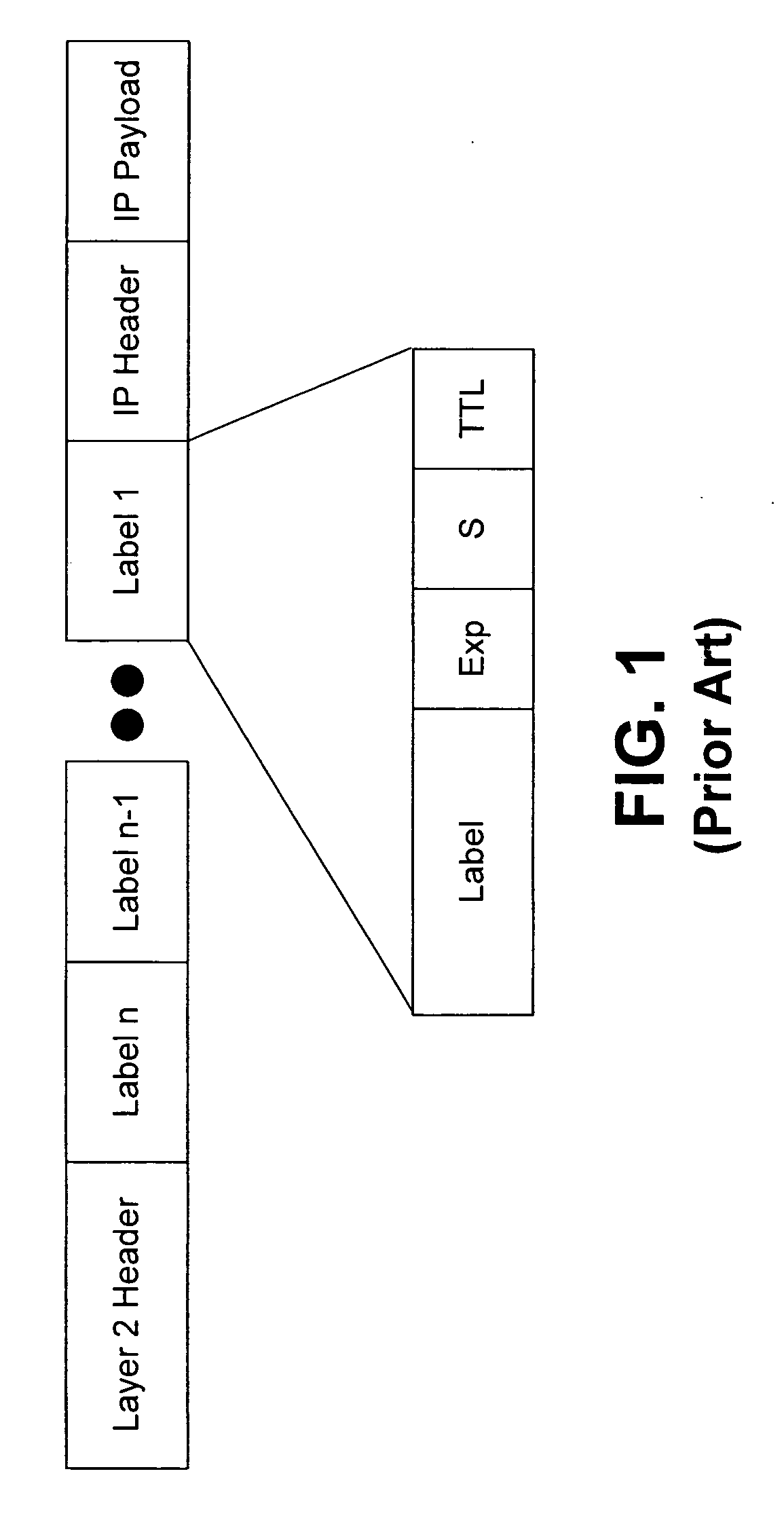
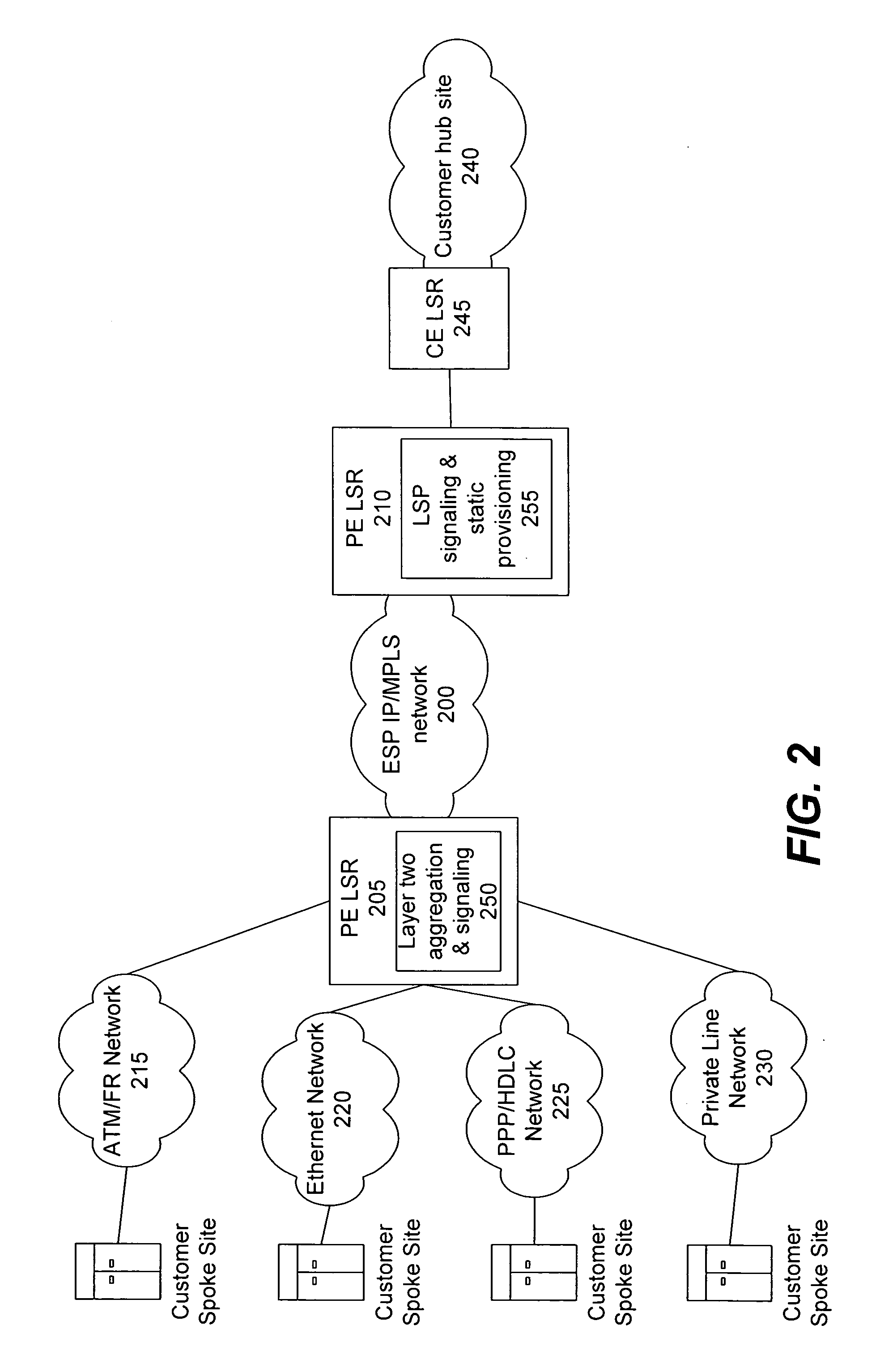
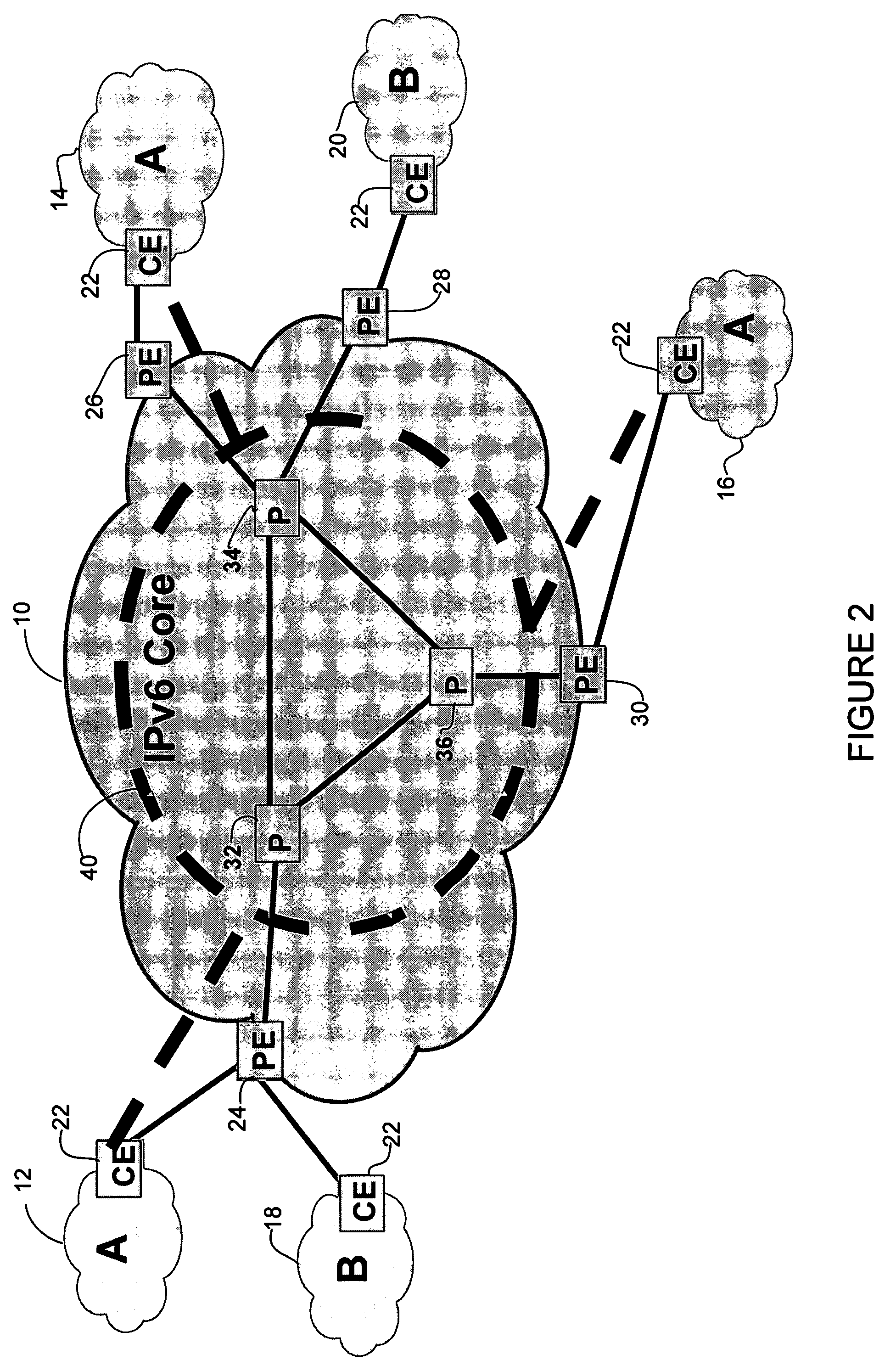
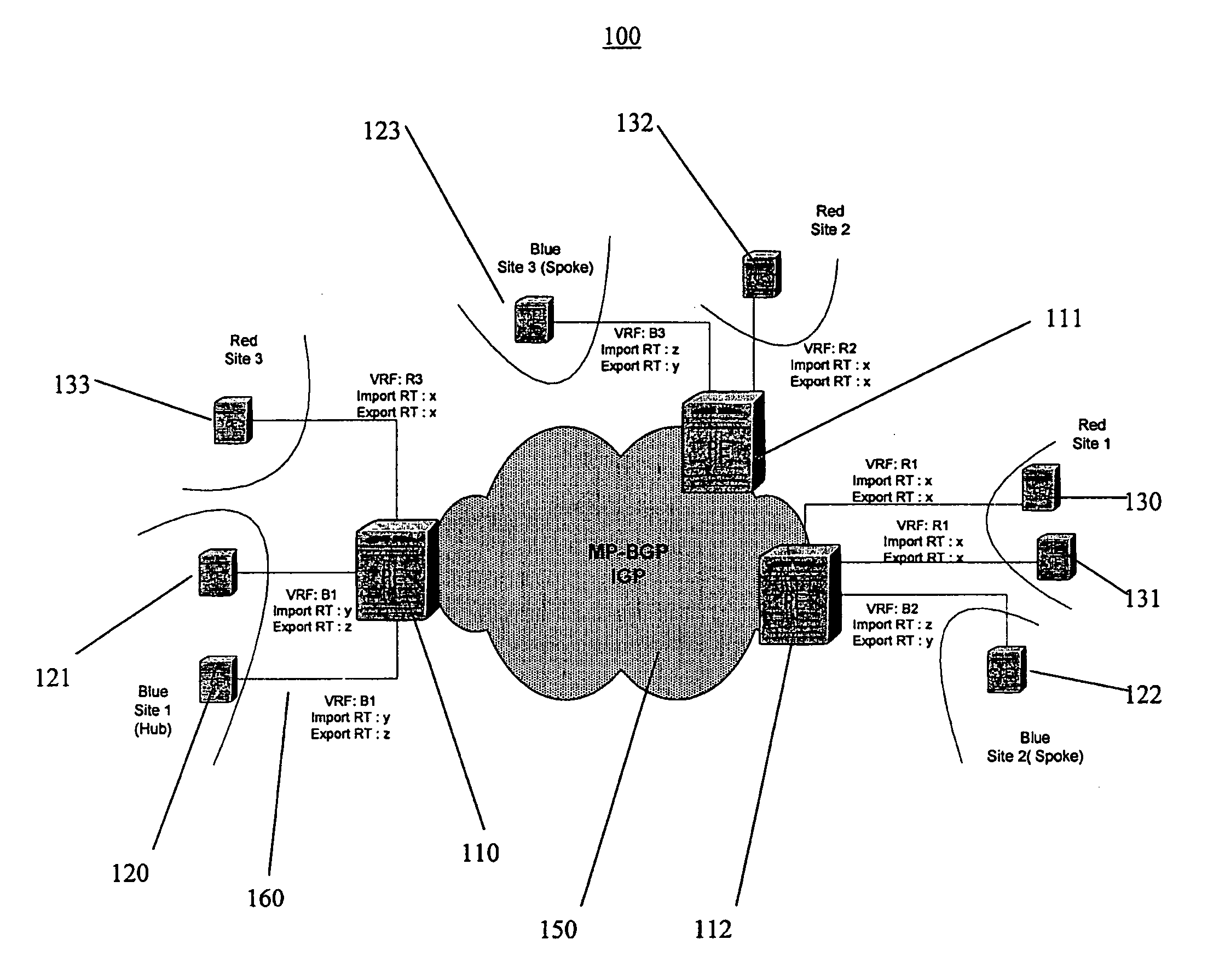
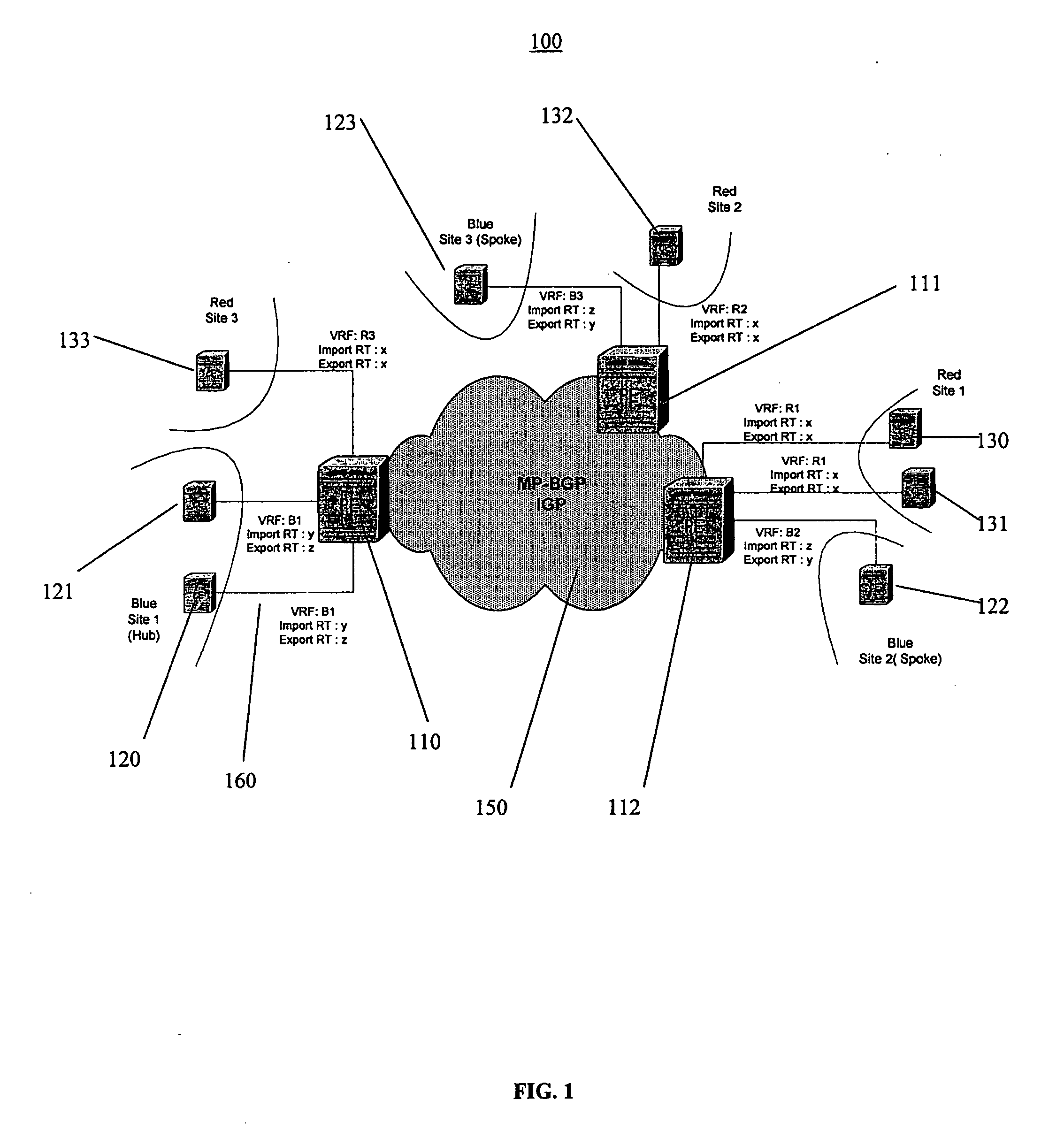
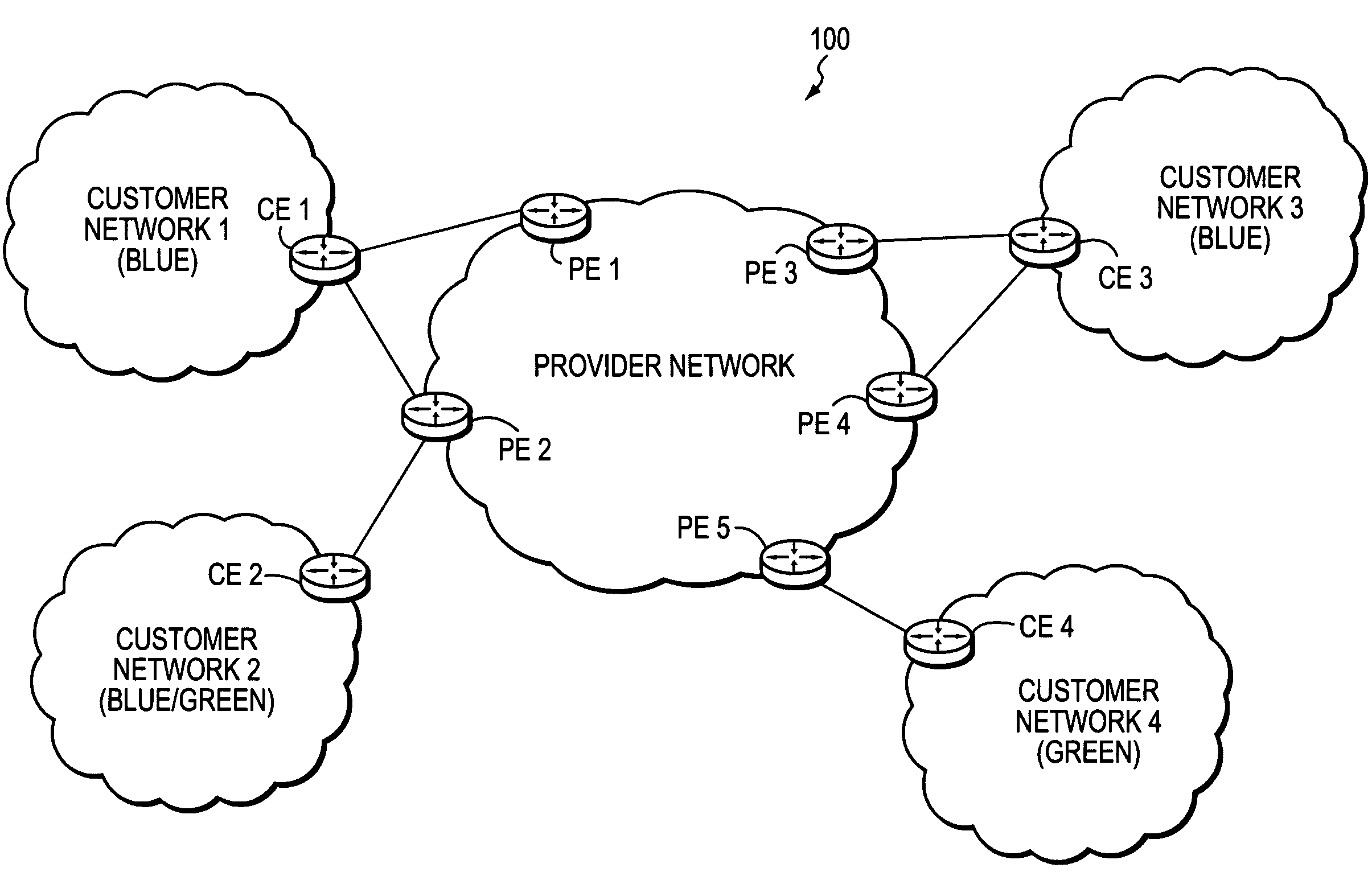
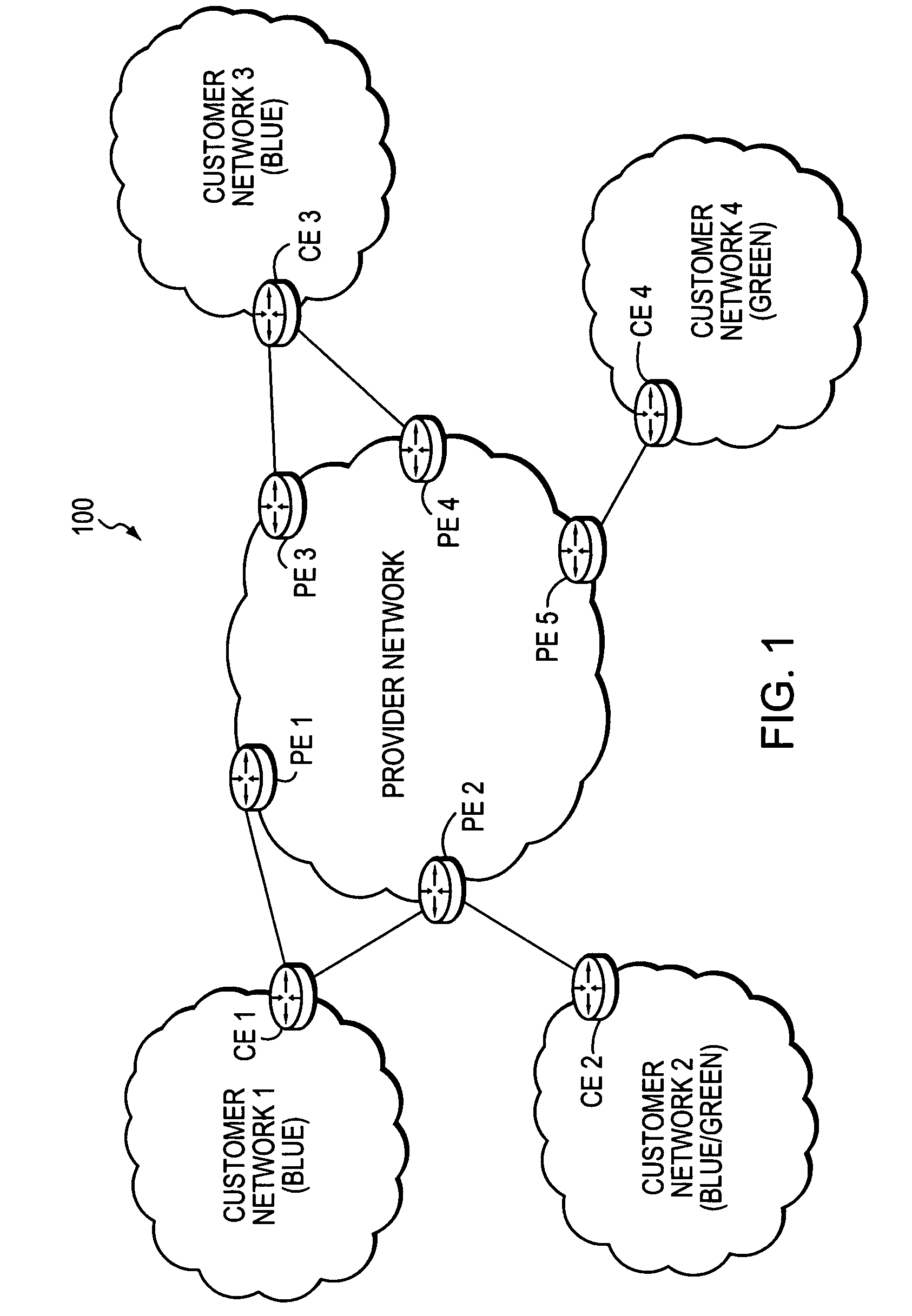
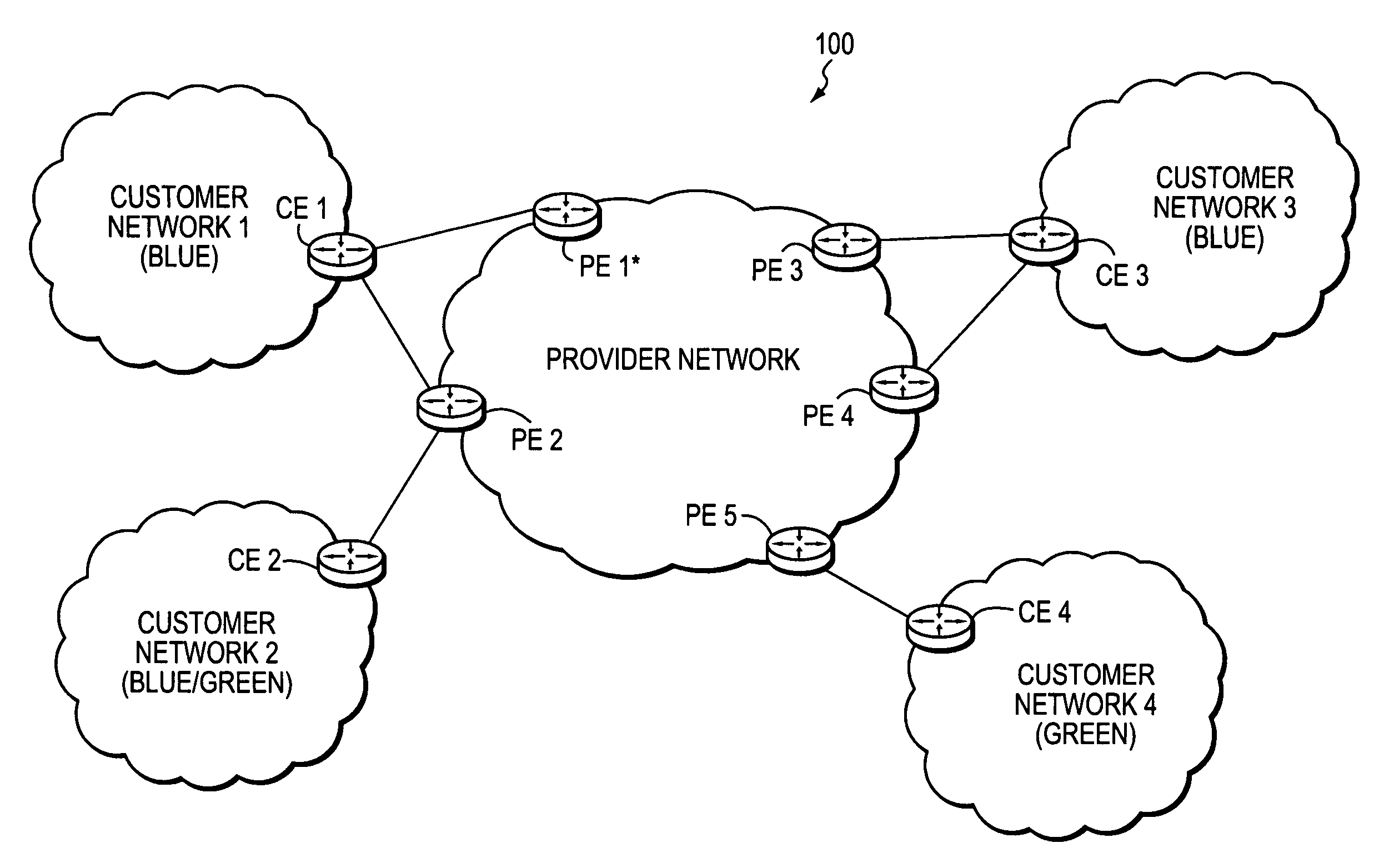
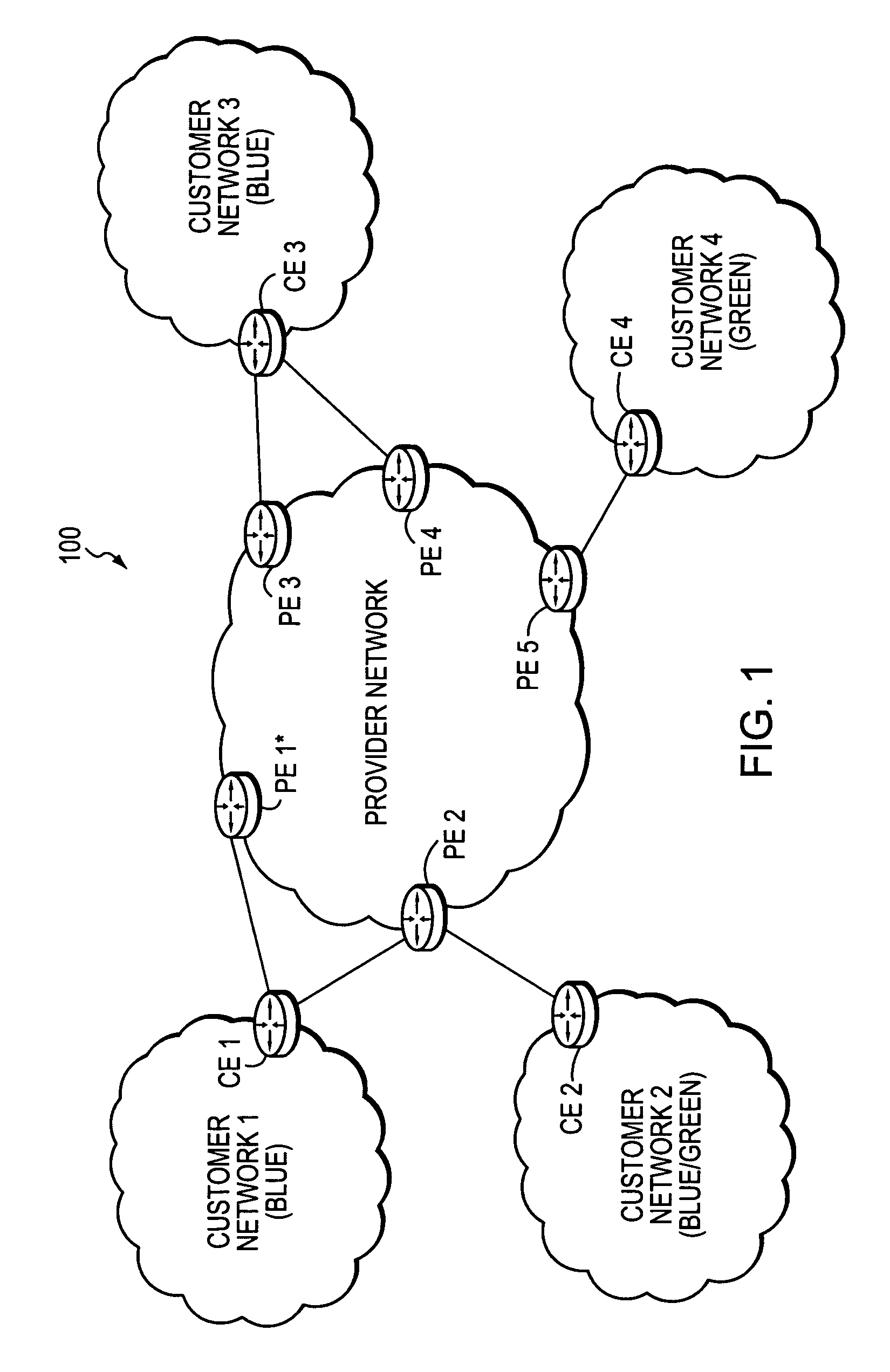
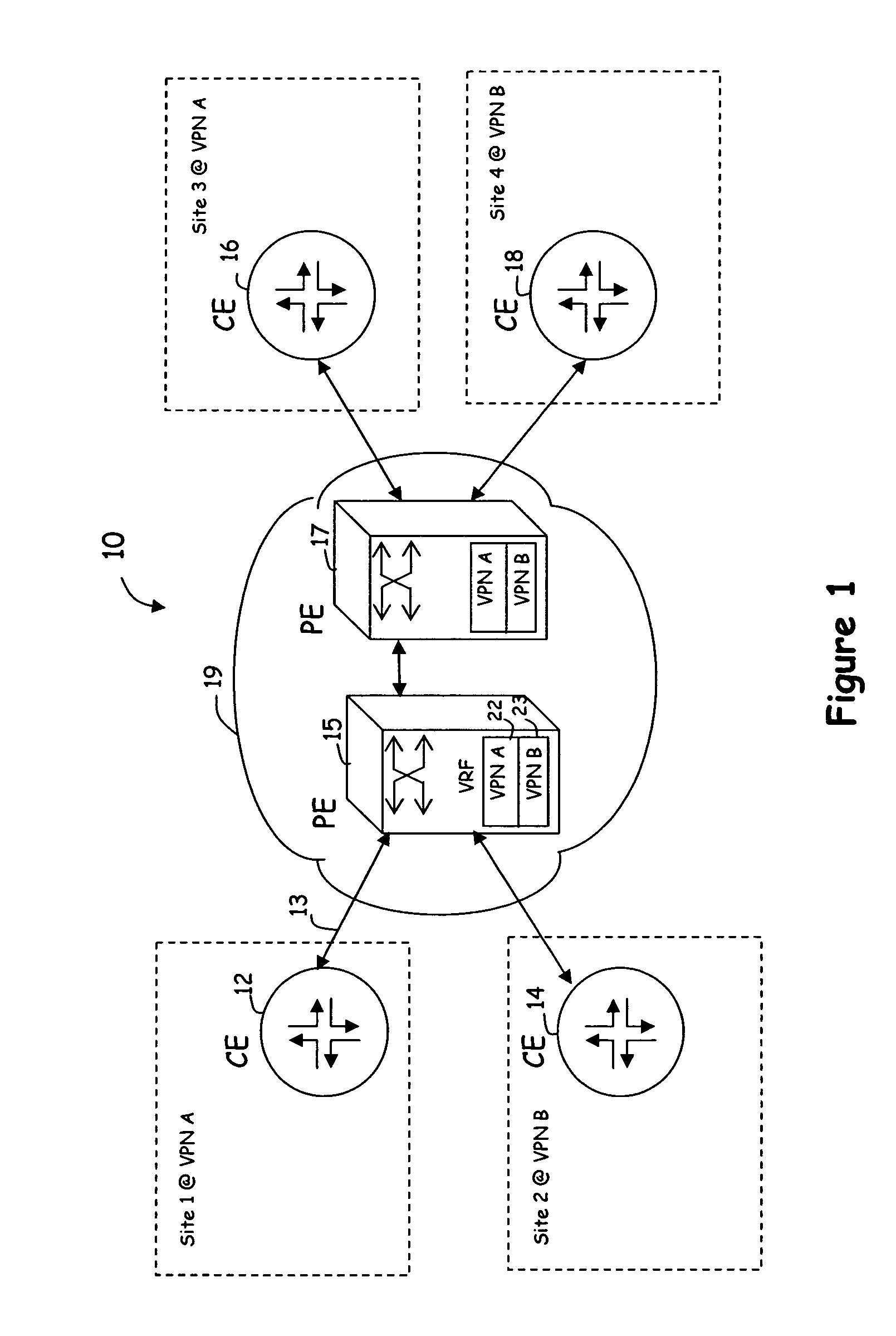
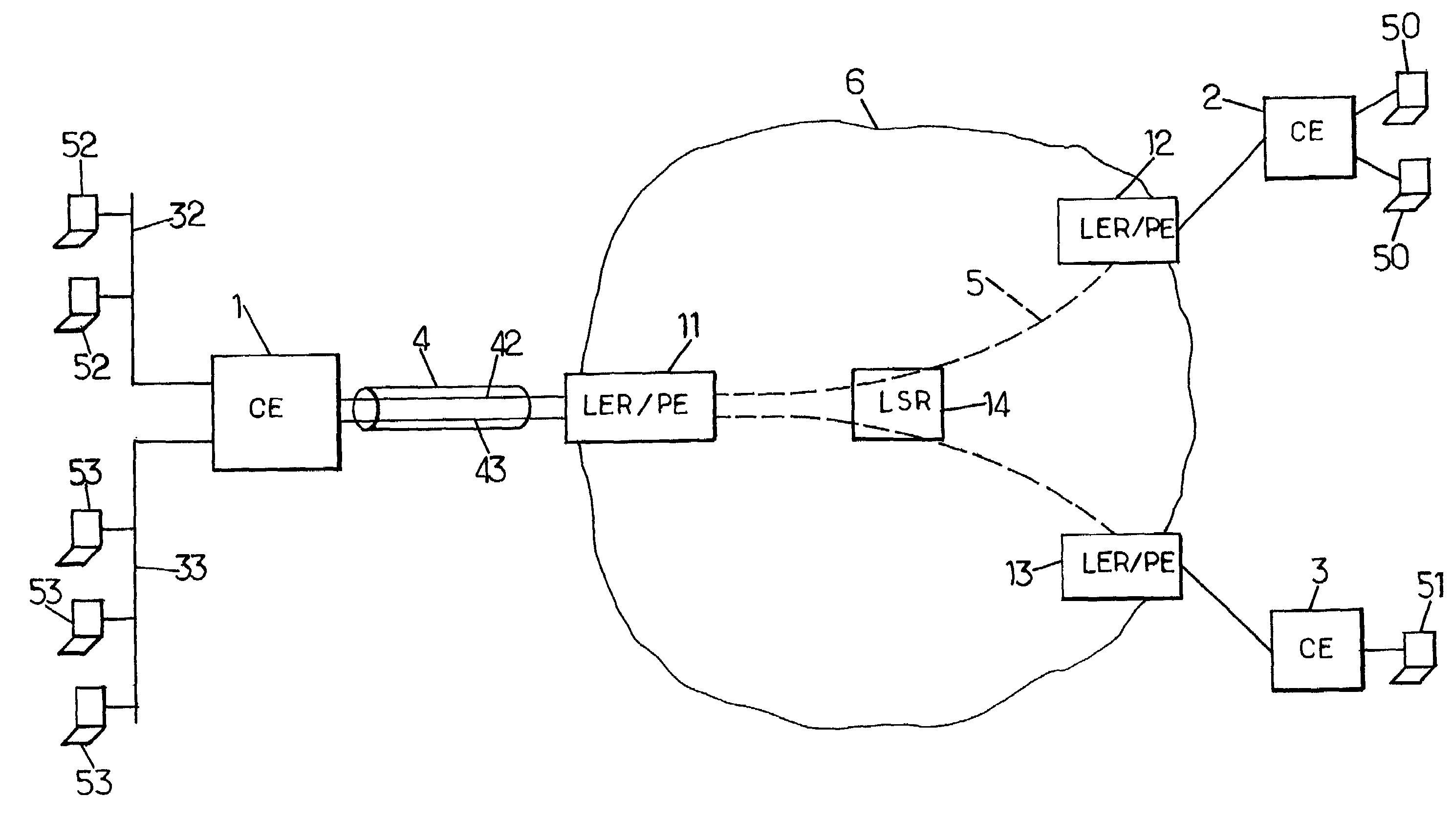
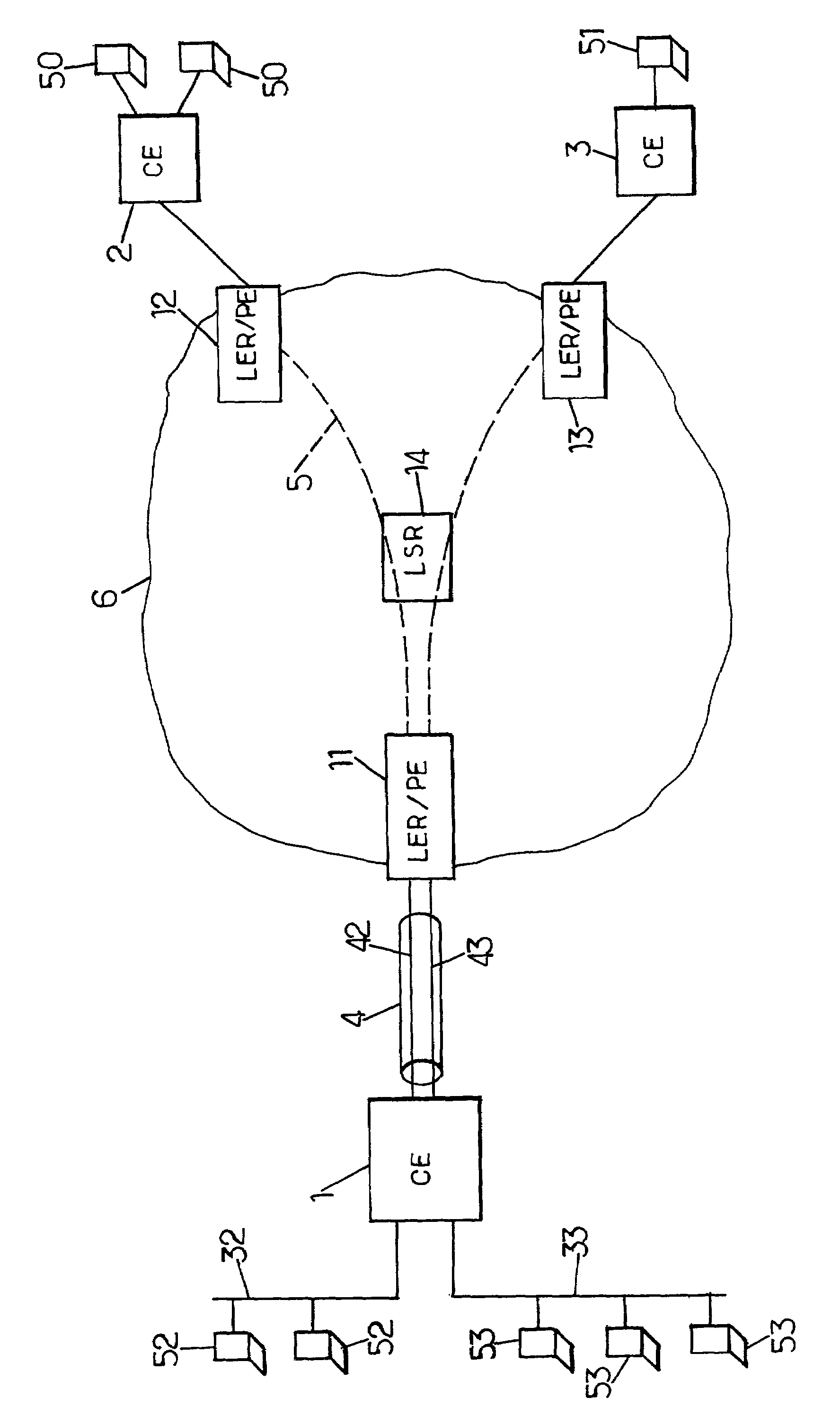
The customer edge (CE) is the router at the customer premises that is connected to the provider edge of a service provider IP/MPLS network. CE peers with the Provider Edge (PE) and exchanges routes with the corresponding VRF inside the PE. The routing protocol used could be static or dynamic (an interior gateway protocol like OSPF or an exterior gateway protocol like BGP).
Method and apparatus for performing data flow ingress/egress admission control in a provider network
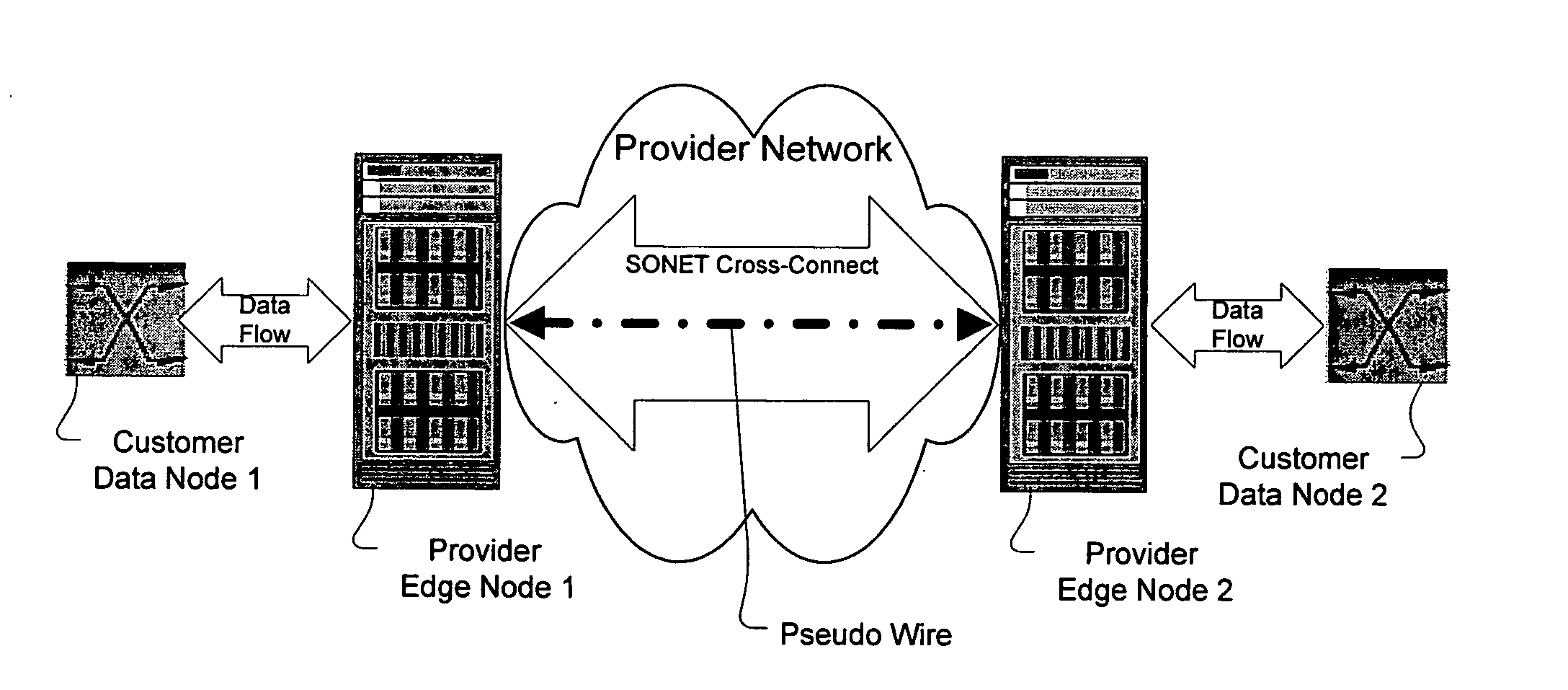
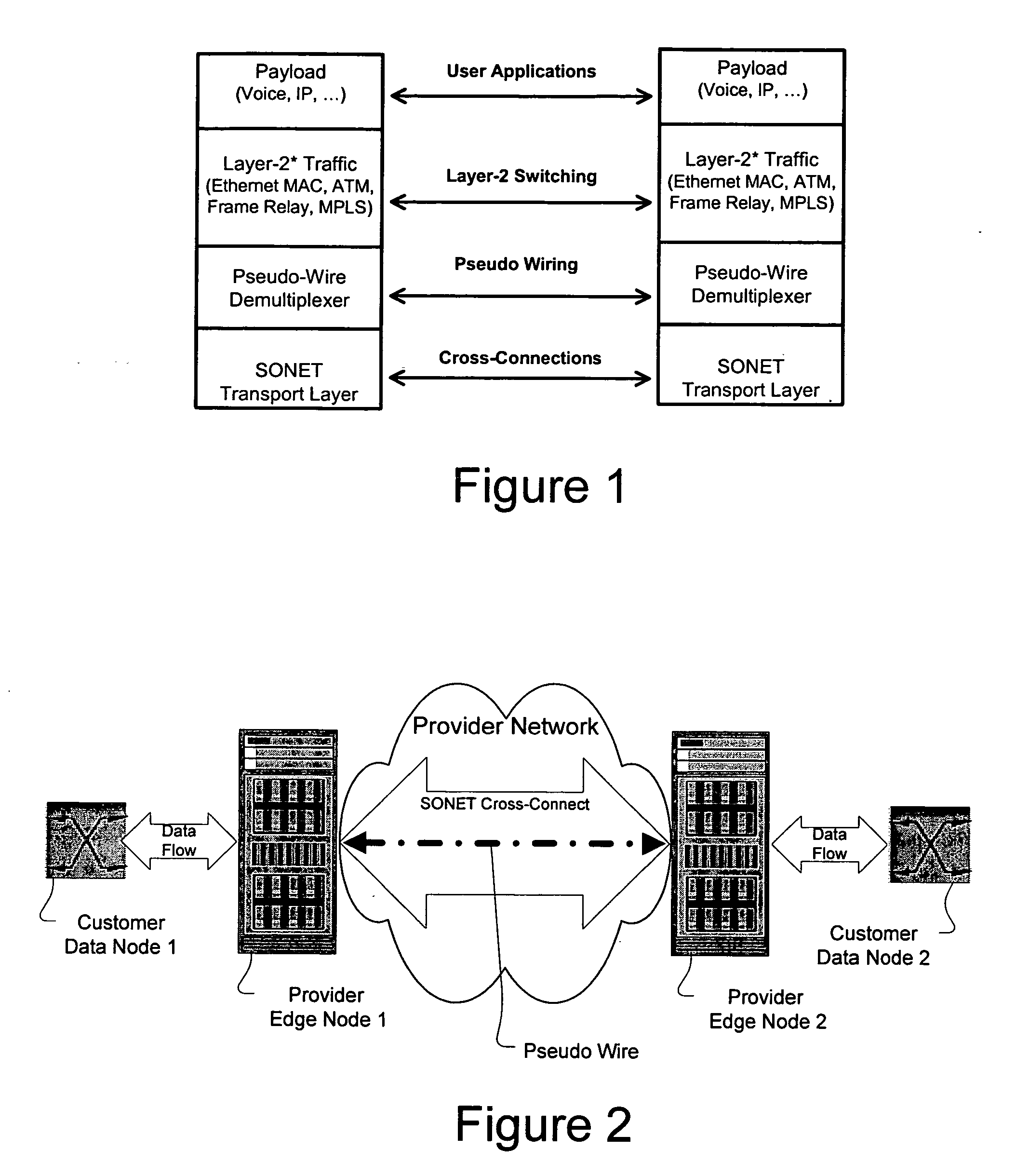
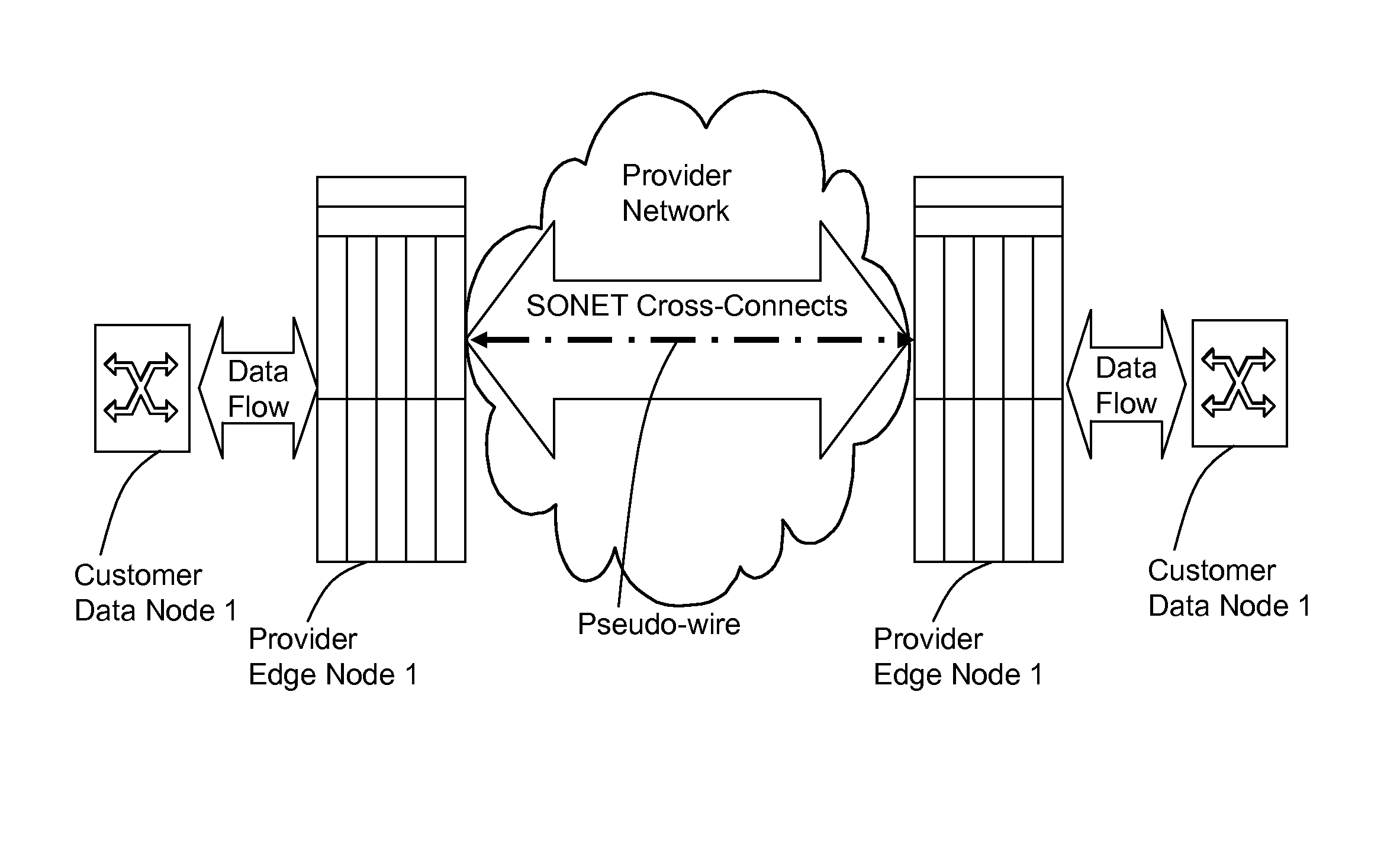
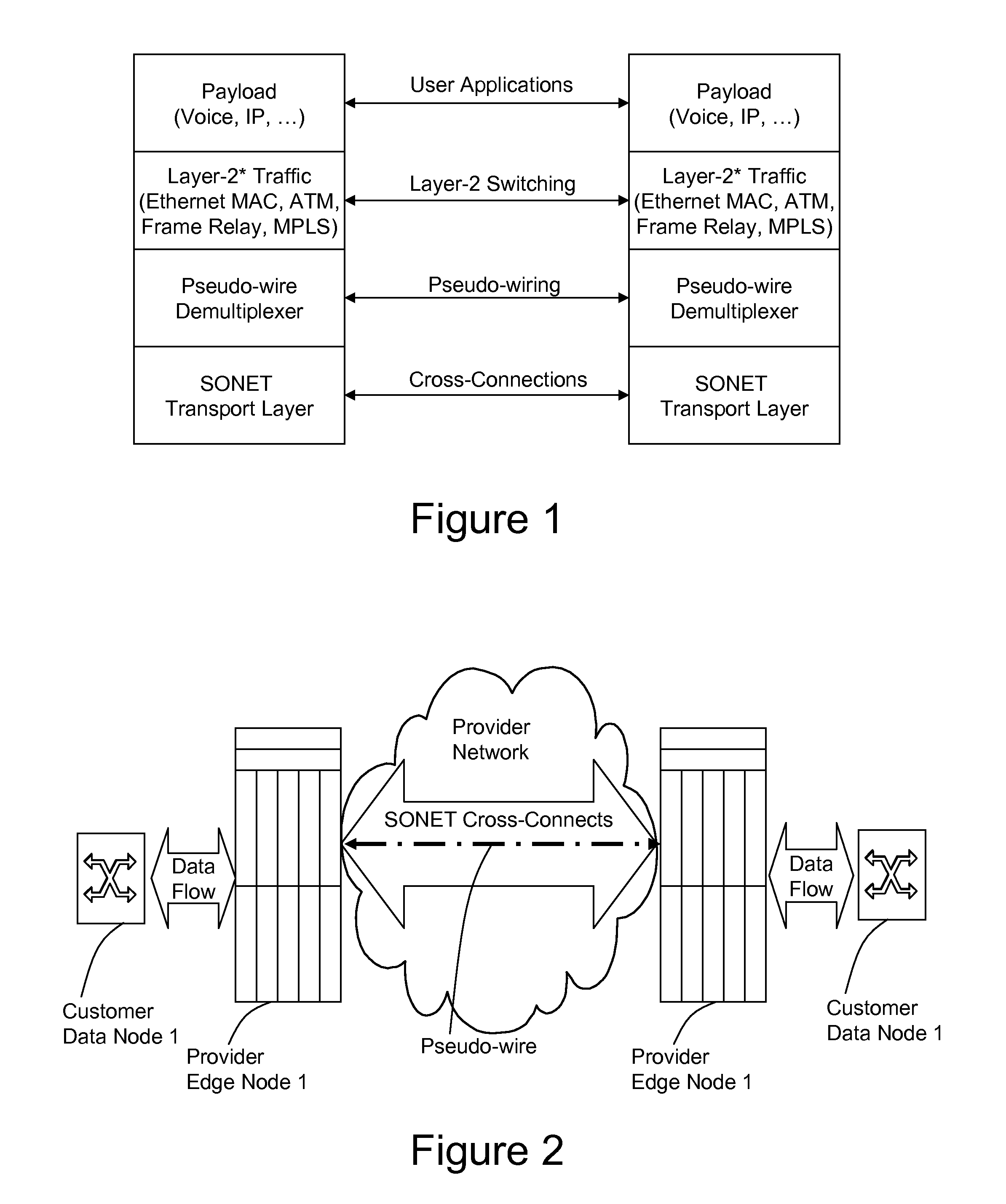
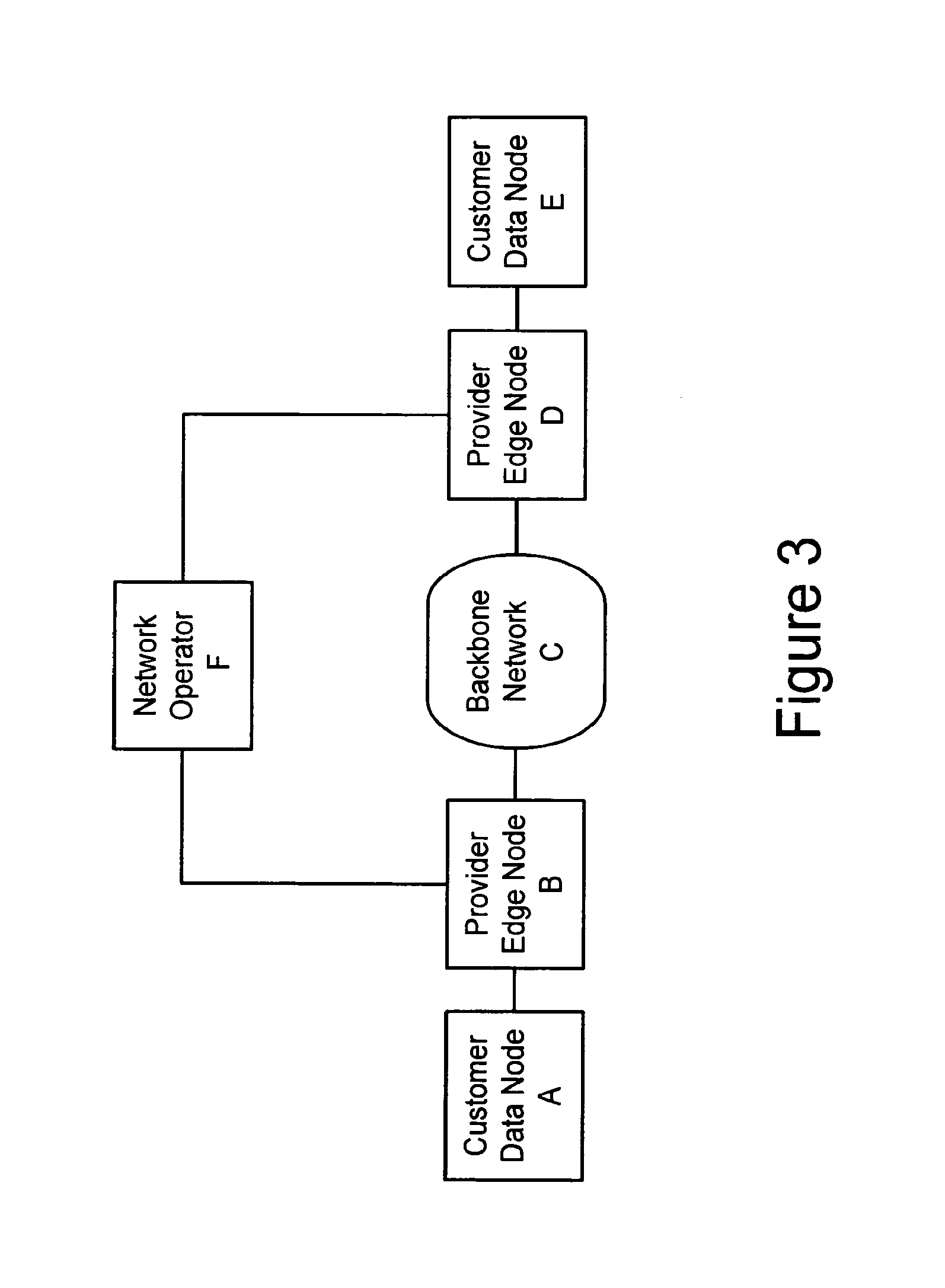
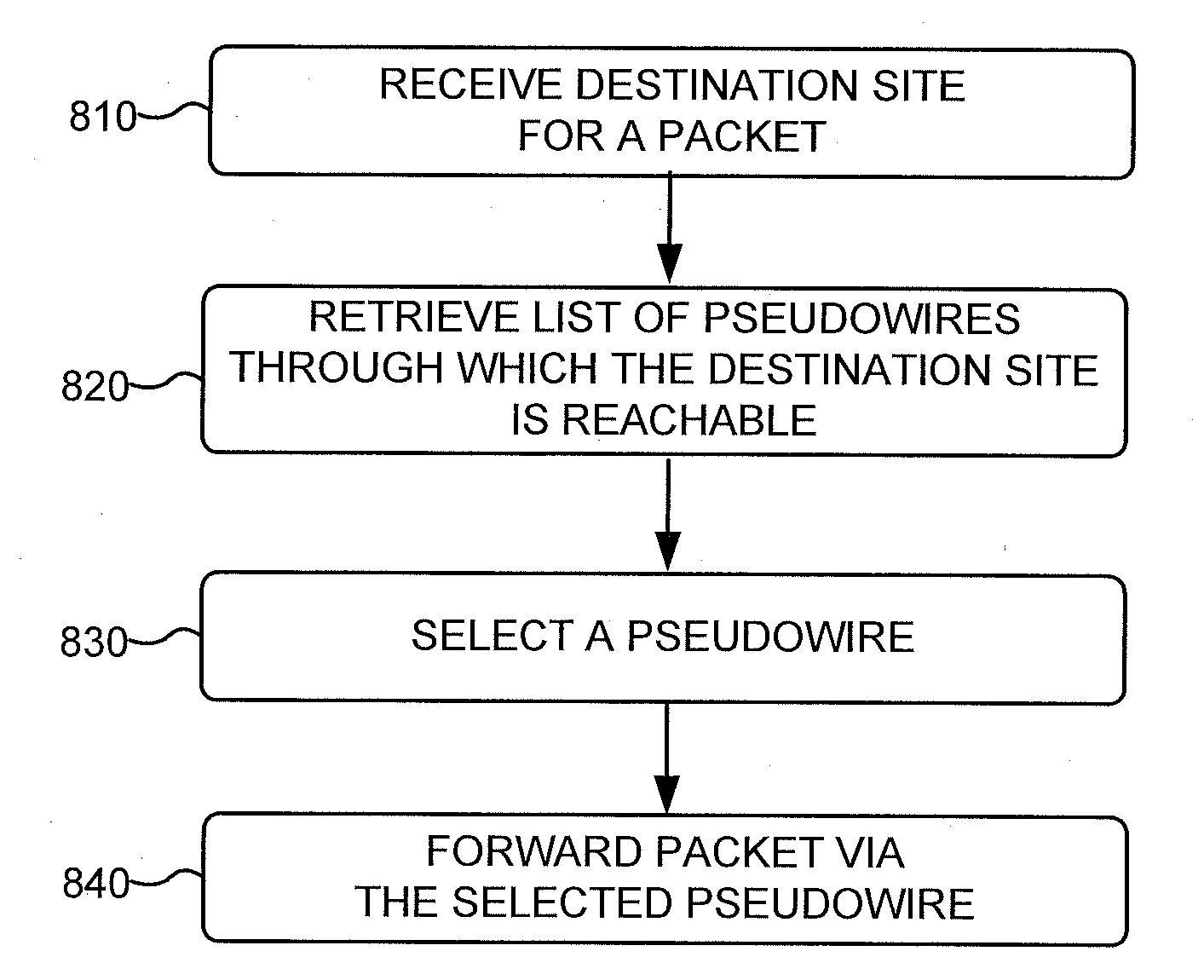
A method, apparatus and network for transporting layer-2 frames, such as Ethernet MAC, ATM AAL5, and Frame Relay, over MPLS, SONET / SDH, or OTN optical transport networks as well as electrical transport networks is disclosed. The method establishes "pseudo-wires" between, for example, routers, Layer-2 packet switches, or SONET / SDH switches. Inter-related ingress and egress resource tables may be used by provider edge nodes to negotiate consistently managed data tunnels across a provider network on behalf of data flowing from / to a diverse base of customer edge nodes. Detailed network resource information particular to each of the data flows is exchanged between provider edge nodes during the creation of pseudo-wires. Admission control algorithms are applied at the ingress and egress points in order to manage the data flows into a provider network and exiting from a provider network to customer equipment. By applying pseudo-wire shuffling and preemption techniques, the providers can make better use of their network resources by admitting more pseudo-wires.
Owner:CIENA
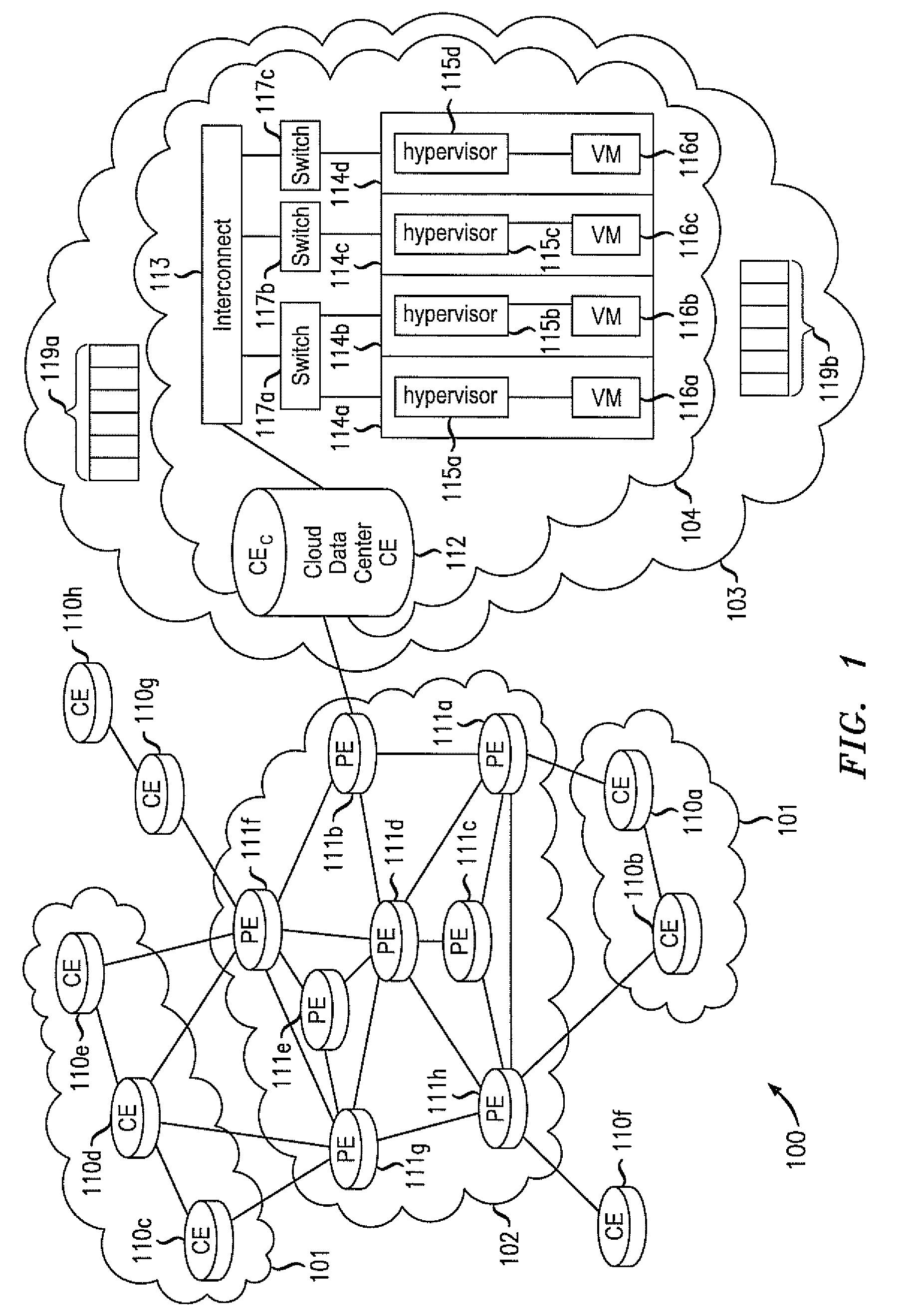
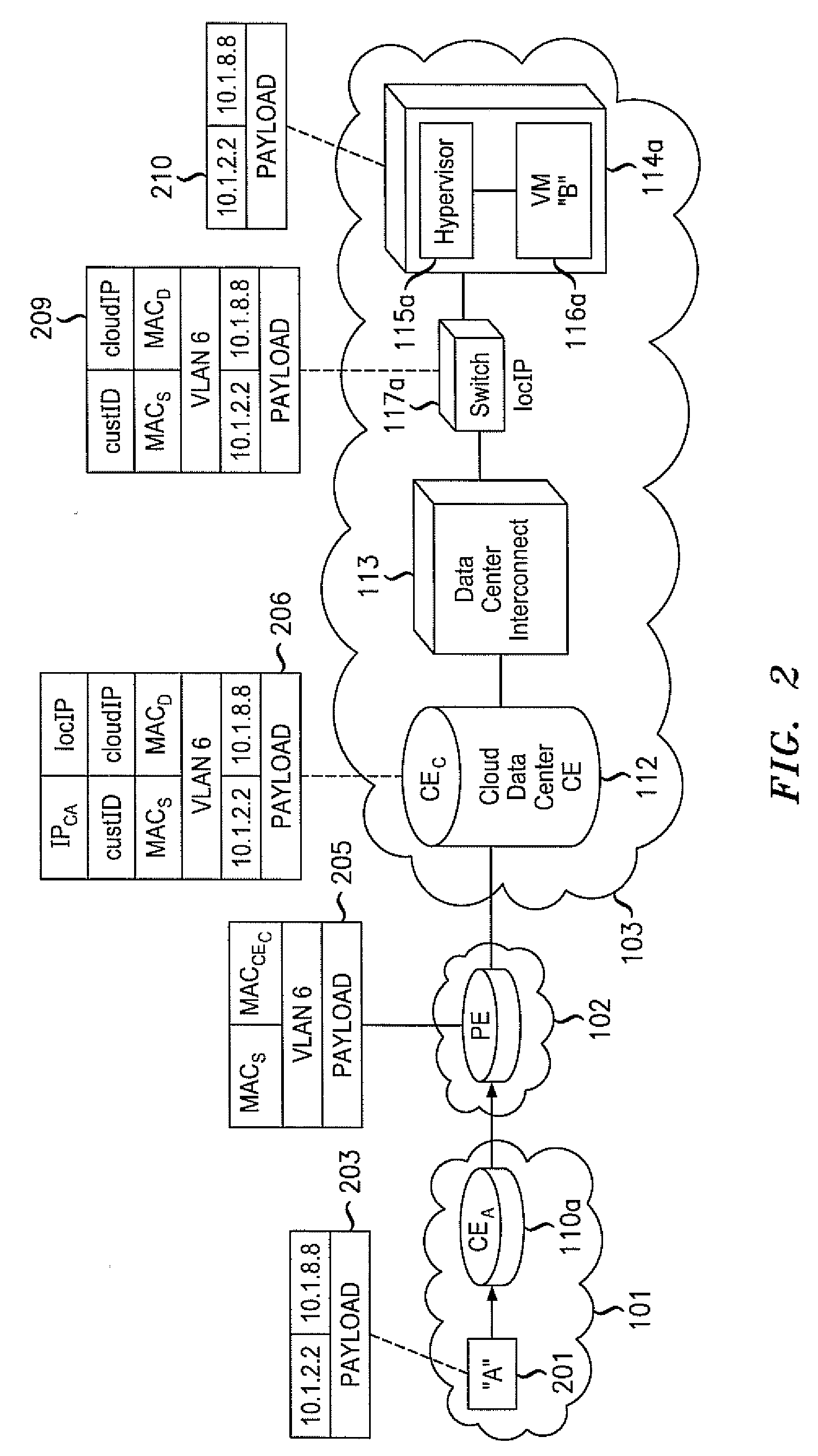
Layer 2 seamless site extension of enterprises in cloud computing
ActiveUS20110075667A1Ensure safetyHighly-dynamic scalability of cloud resourcesMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionNetwork packetIp address
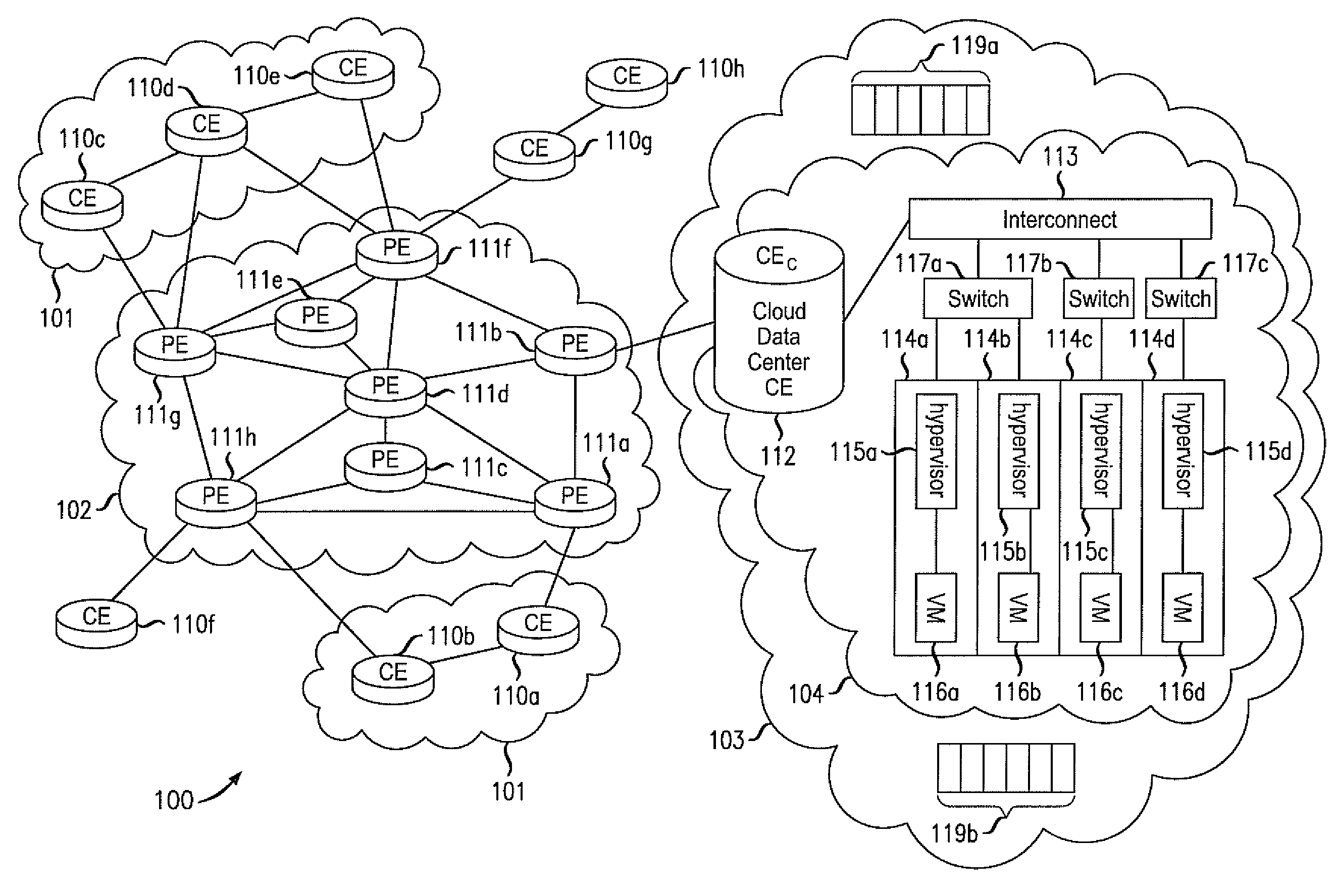
Various embodiments relate to a Cloud Data Center, a system comprising the Cloud Data Center, and a related method. The Cloud Data Center may include a logical customer edge router to send packets between addresses in a private enterprise network and addresses in a logical network within a cloud network using Layer 2 protocol and MAC addressing. The logical network may have resources, known as virtual machines, allocated to the private enterprise network and may share a common IP address space with the private enterprise network. A directory at the Cloud Data Center may correlate the enterprise IP addresses of virtual machines with a MAC address, cloud IP address, and a location IP address within the logical network. The Cloud Data Center may double encapsulate packets with MAC, cloudIP, and locIP headers, when sending a packet to a destination in the logical network.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
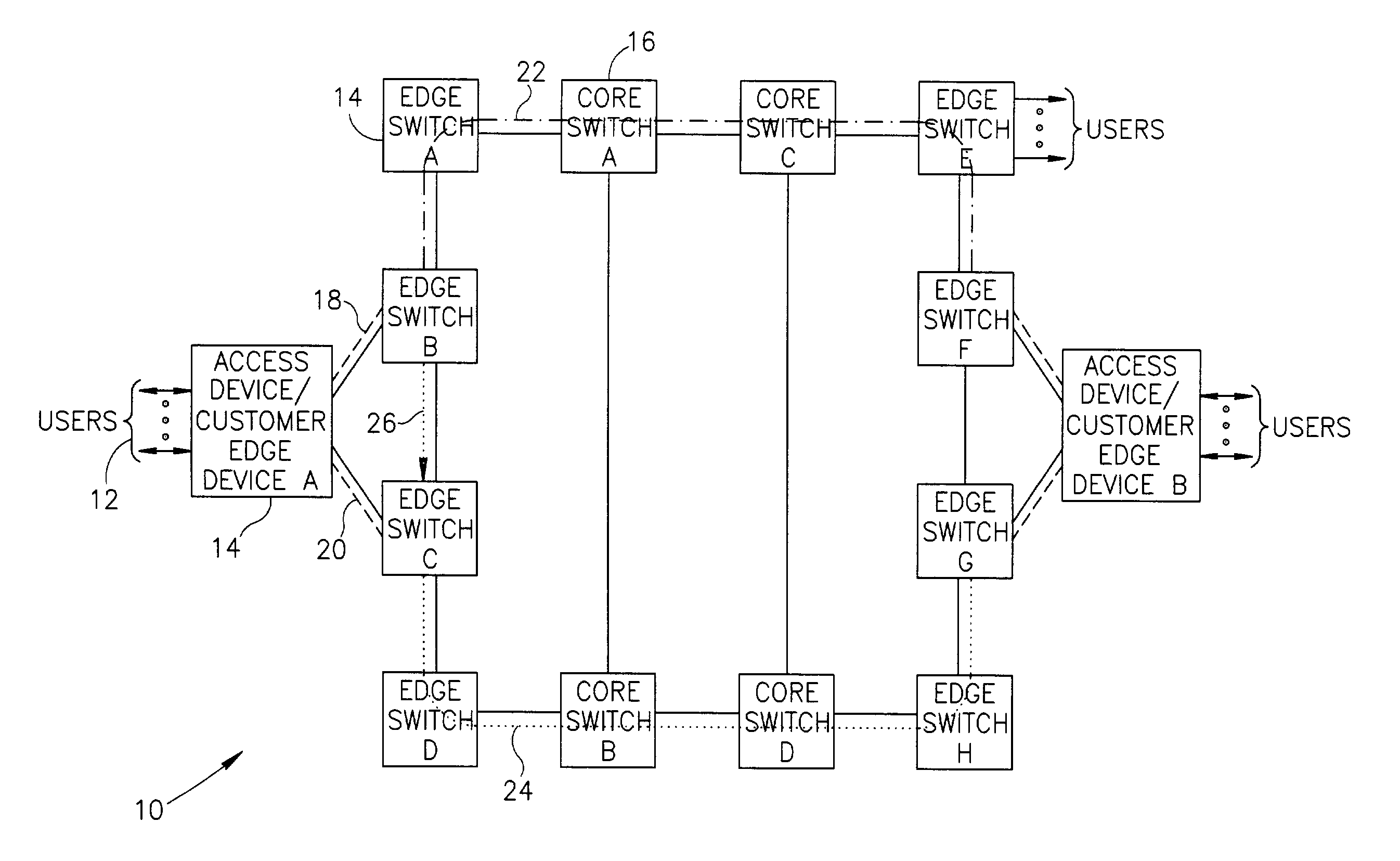
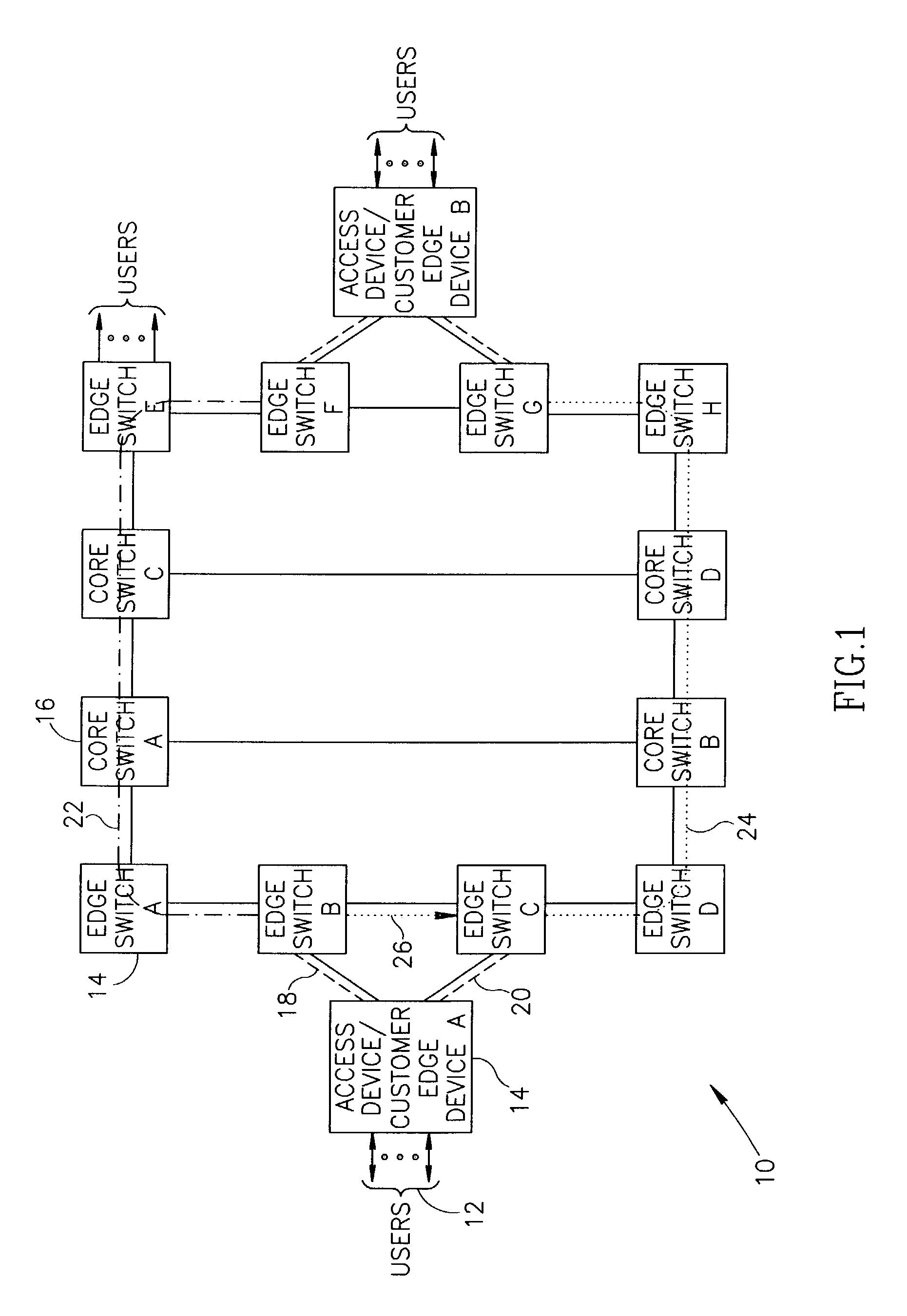
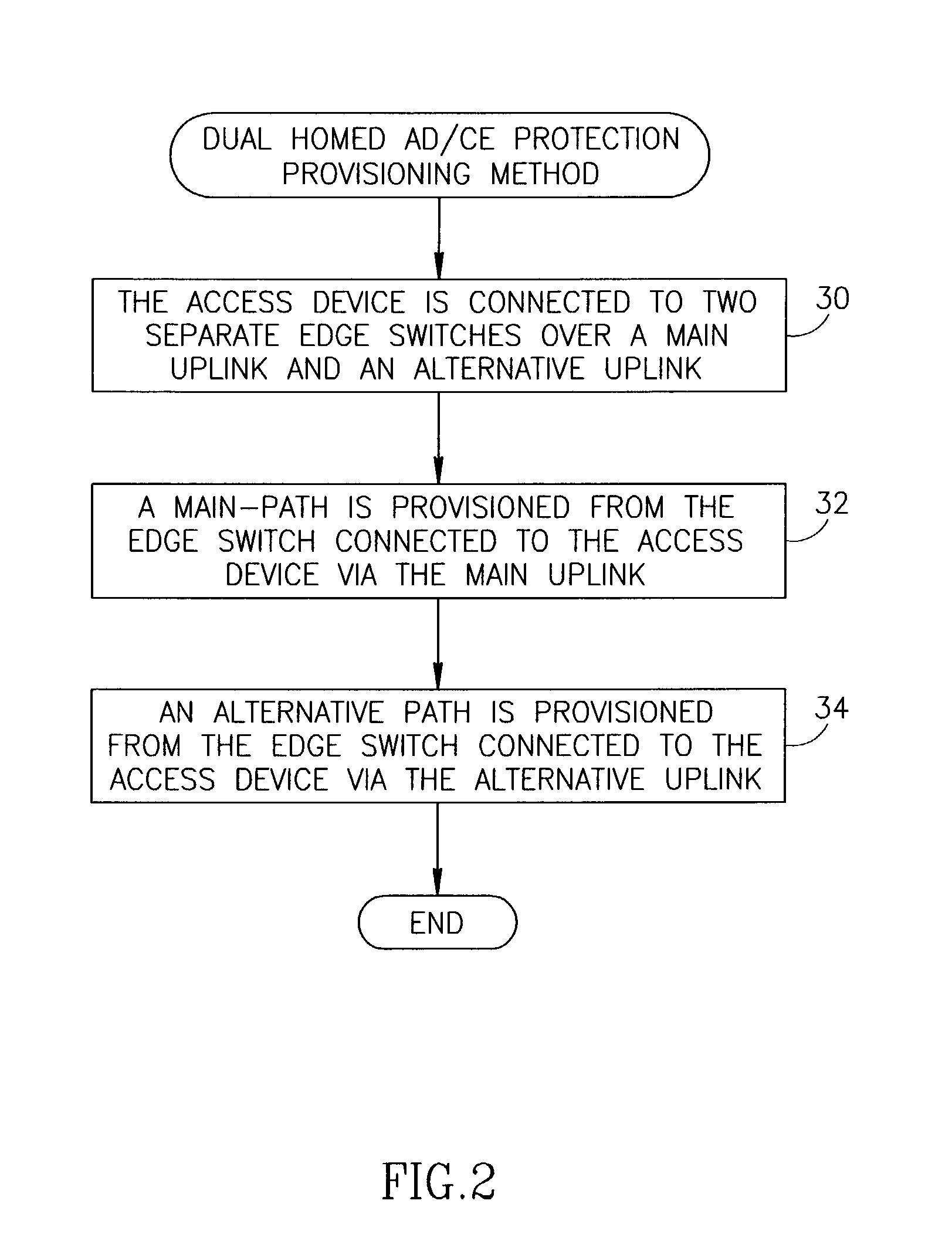
Connection protection mechanism for dual homed access, aggregation and customer edge devices
InactiveUS7345991B1Quick protectionImprove reliabilityEnergy efficient ICTError preventionOff the shelfProtection mechanism
A protection mechanism capable of providing both local and end-to-end connection protection for dual homed access / aggregation devices or customer-edge devices in a network. The protection mechanism provides end-to-end and fast local protection for off the shelf access devices that do not have any built in per-connection protection capabilities. The access device is connected via two separate physical uplinks to two edge switches of the network. For each connection to be protected, a main path is provisioned from one edge switch and an alternative path is provisioned from the other edge switch. The edge switches are adapted to comprise means for switching traffic from the main path to the alternative path in the event a failure along the main path is detected. Failures both in the stack portion, the core portion and in the access device uplinks are protected against.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS ETHERNET SOLUTIONS
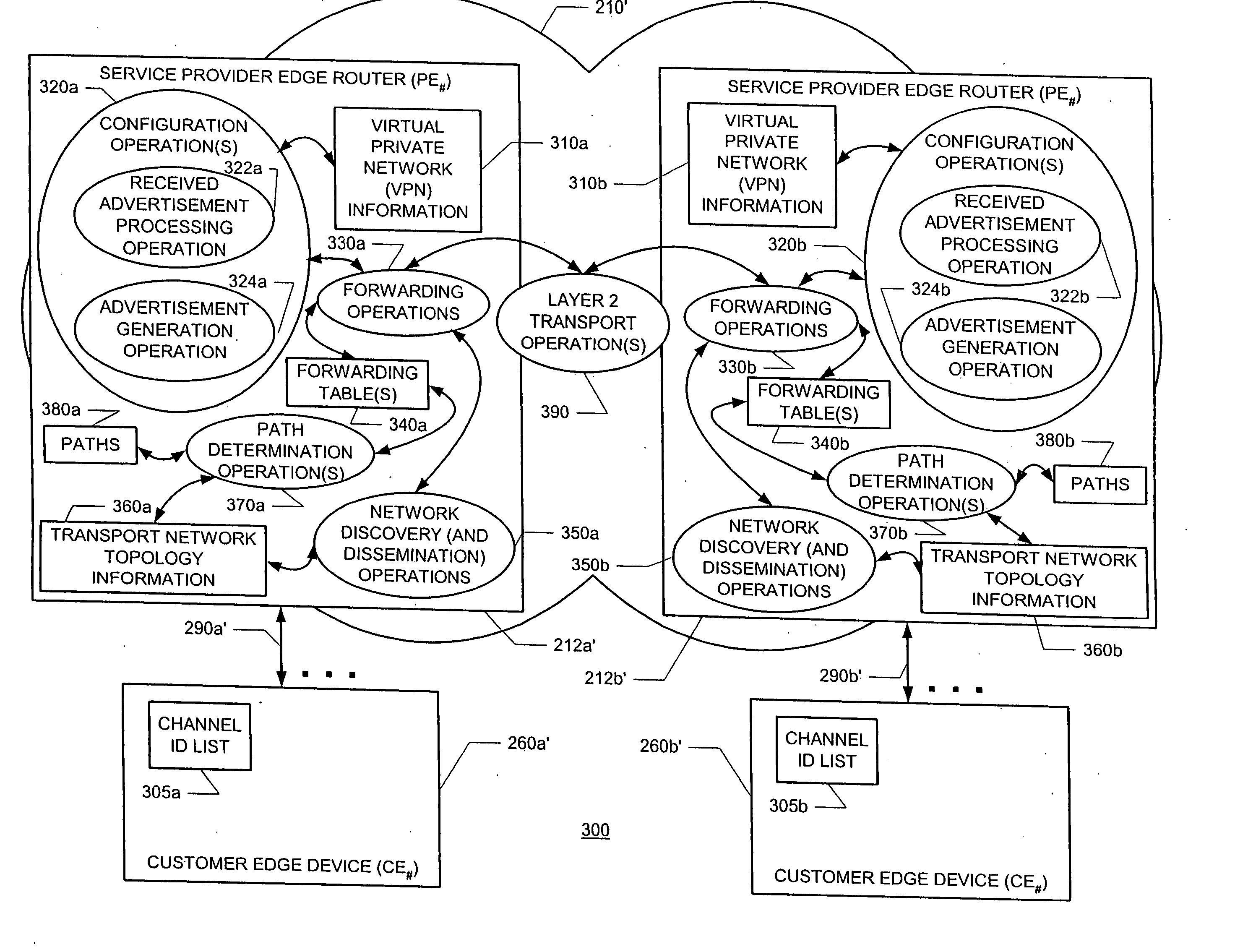
Transport networks supporting virtual private networks, and configuring such networks
InactiveUS7136374B1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsPrivate networkTransport network
A layer 2 transport network, and components thereof, supporting virtual network functionality among customer edge devices. Virtual private network configuration can be accomplished with merely local intervention by preprovisioning extra channel (or circuit) identifiers at each customer edge device and by advertising label base and range information corresponding to a list of channel (or circuit) identifiers.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
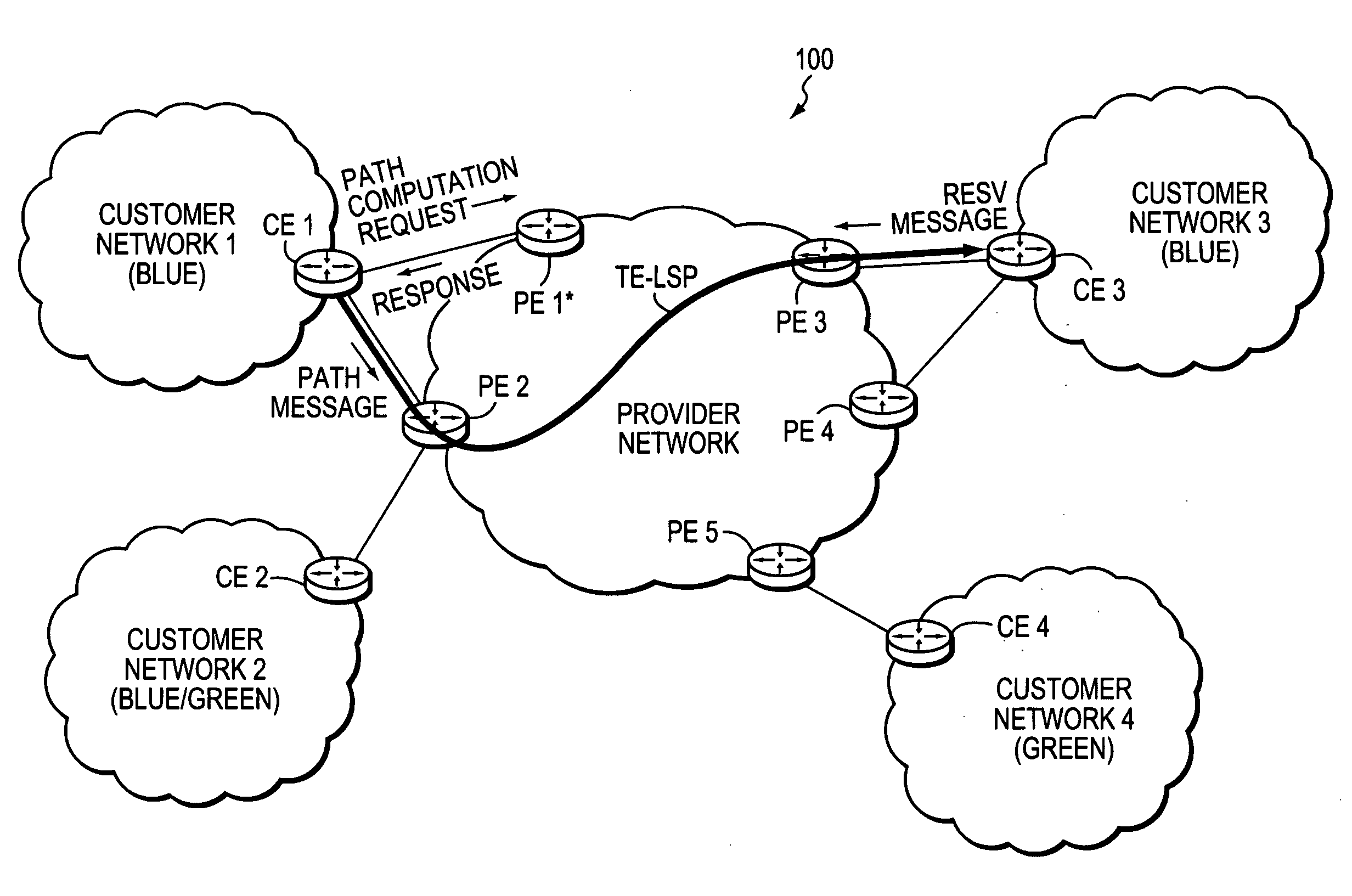
Technique for enabling traffic engineering on CE-CE paths across a provider network
ActiveUS20070133406A1Create efficientlyReduce needError preventionTransmission systemsPrivate networkDistributed computing
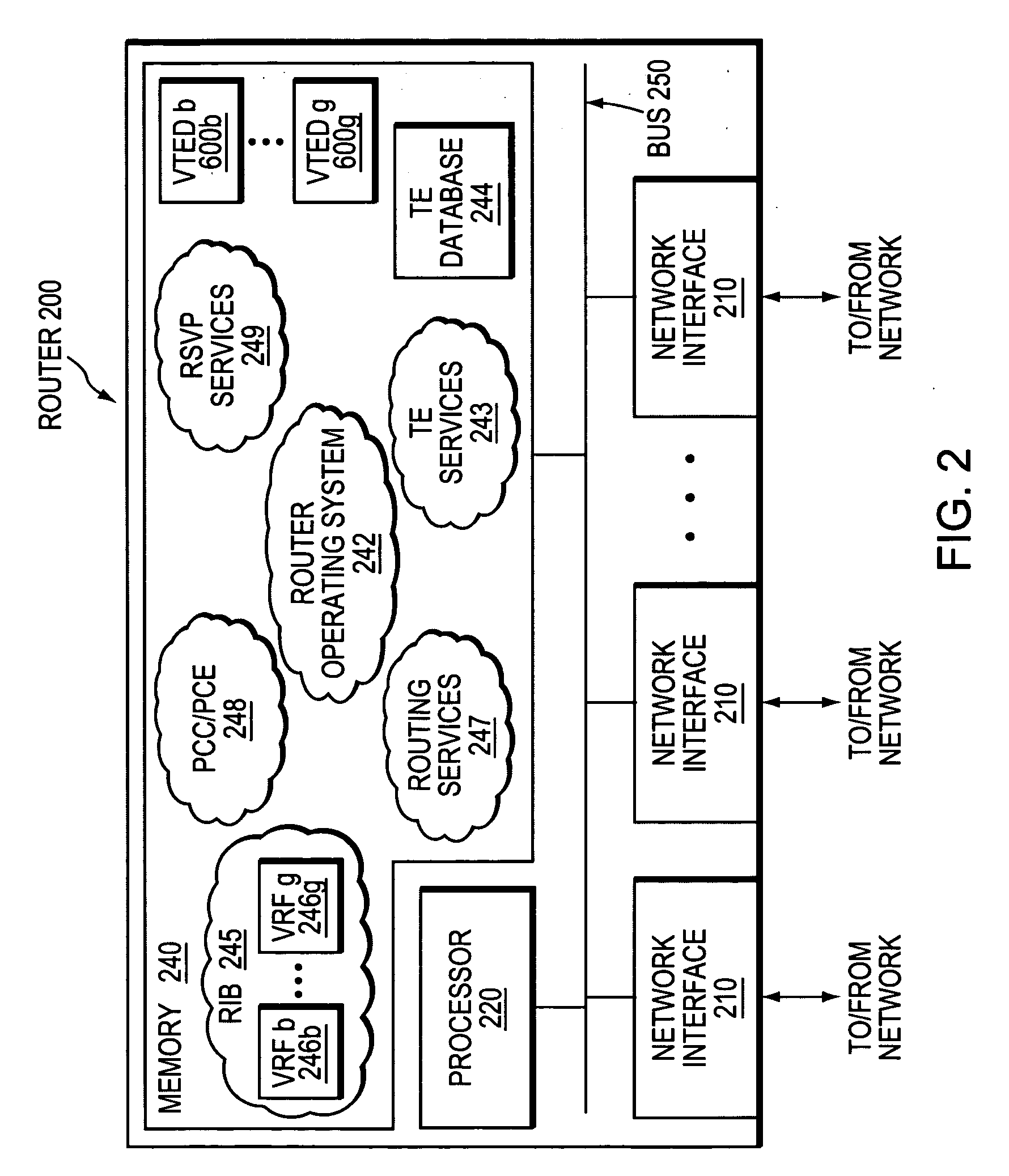
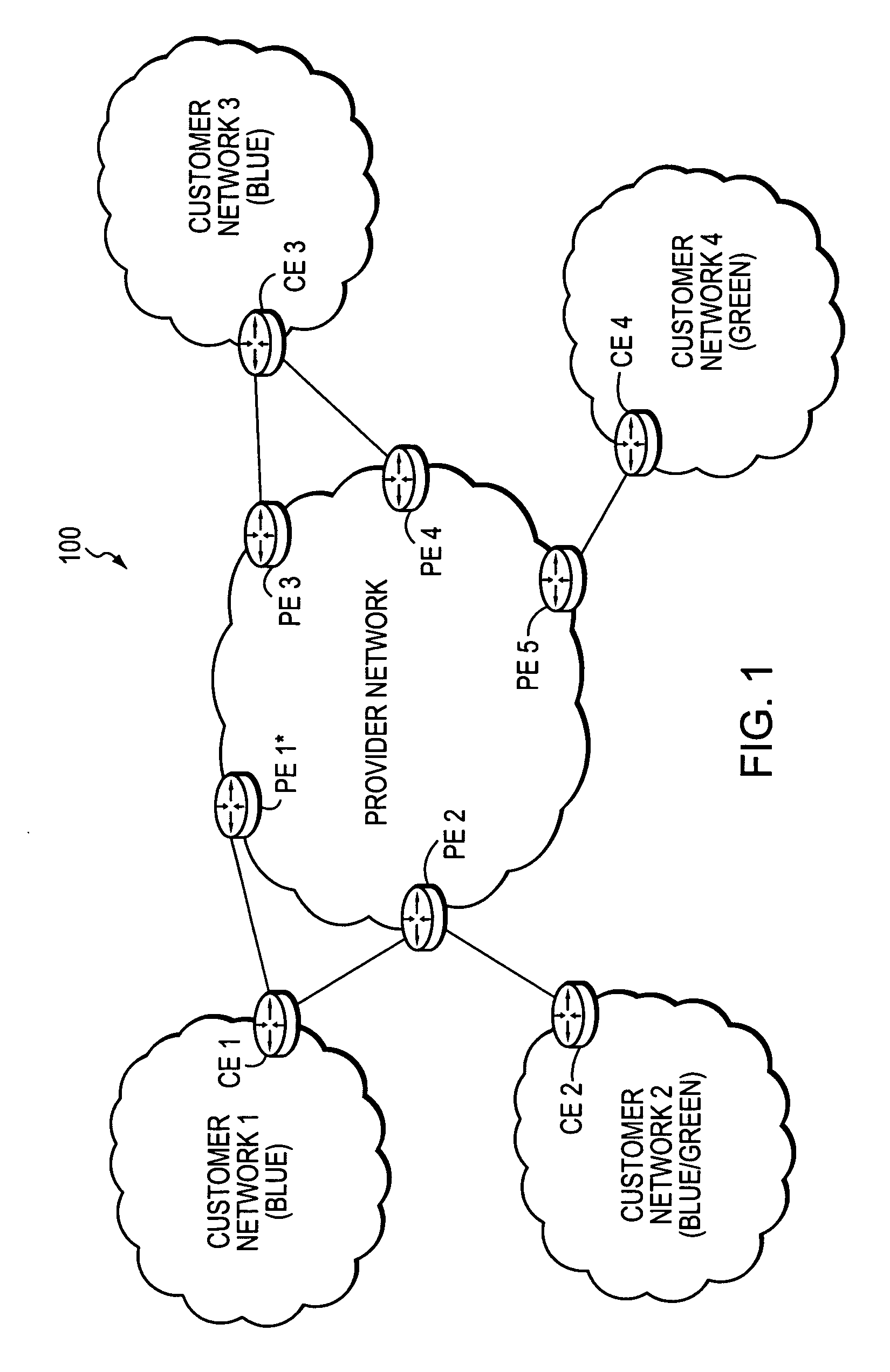
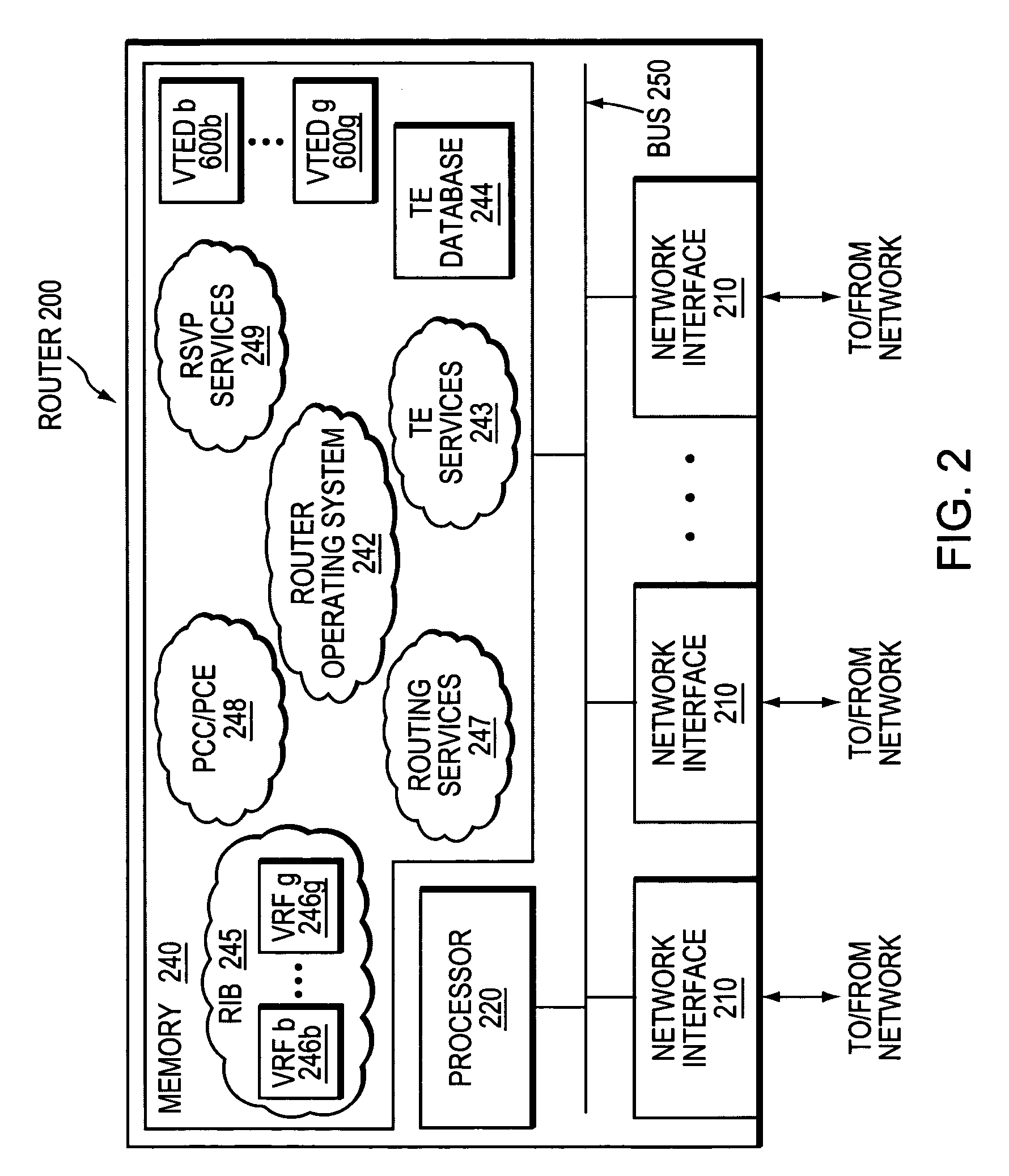
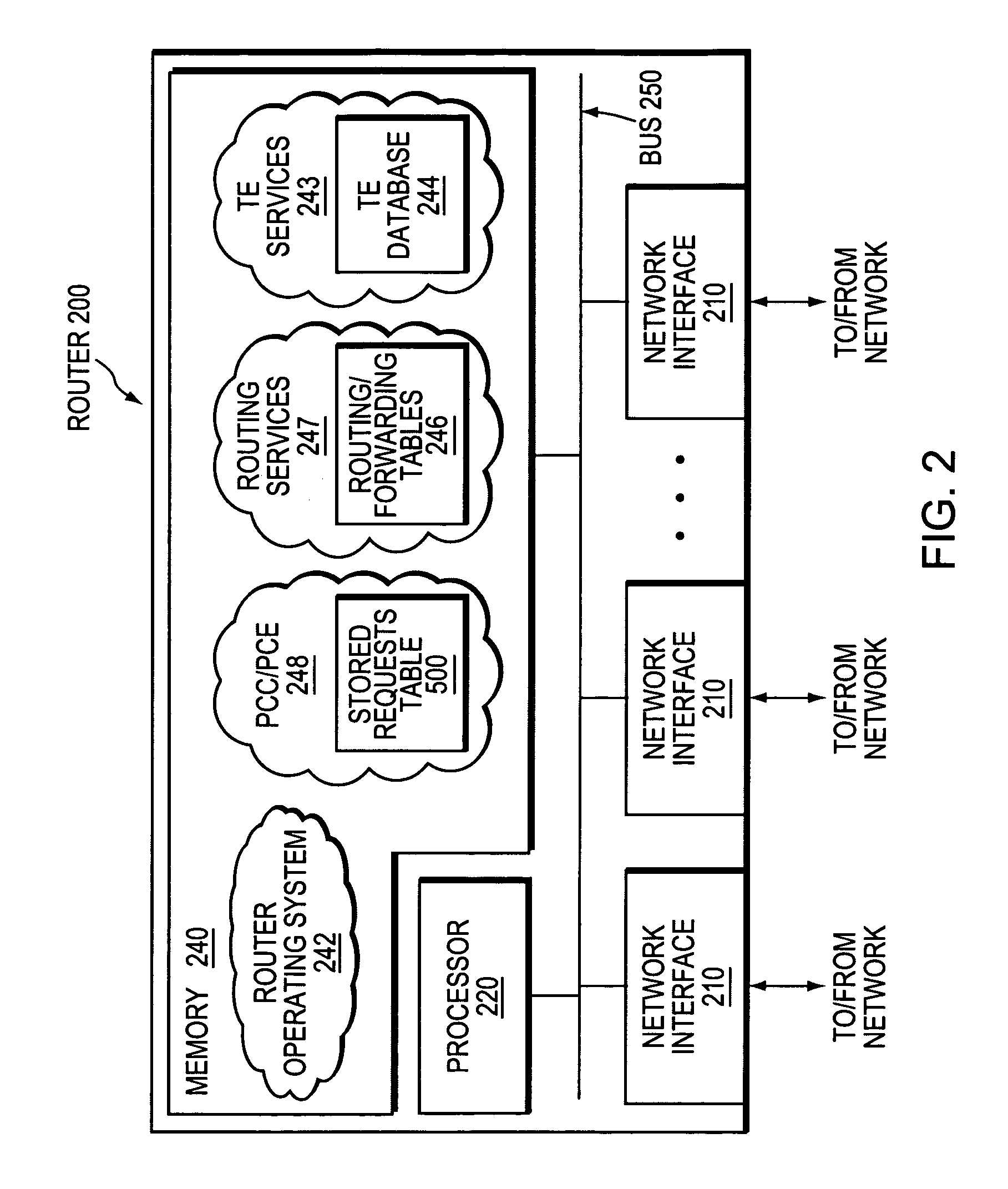
A technique enables Traffic Engineering (TE) on paths between customer edge devices (CEs) across a provider network (“CE-CE paths”) in a computer network. According to the novel technique, TE is configured on a link from a sending provider edge device (PE) to a first CE (“PE-CE link”), e.g., a CE of one or more virtual private networks (VPNs). The sending PE conveys TE information of the PE-CE link to one or more receiving PEs in the provider network. Upon receiving the TE information, each receiving PE expands a TE database (TED) for information regarding the provider network (i.e., a “core TED”) to include TE-configured PE-CE links, e.g., by updating one or more corresponding VPN TEDs (VTEDs) for each VPN maintained by the receiving PE. Once the receiving PEs have the TE information for configured PE-CE links from the provider network, one or more TE techniques may be applied to paths from a second CE of the receiving PE to the first CE (a CE-CE path) to thereby facilitate, e.g., establishment of TE-LSPs along CE-CE paths.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Technique for efficiently routing IP traffic on CE-CE paths across a provider network
InactiveUS20070217419A1Efficient routingImprove overall utilizationError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityPath computation element
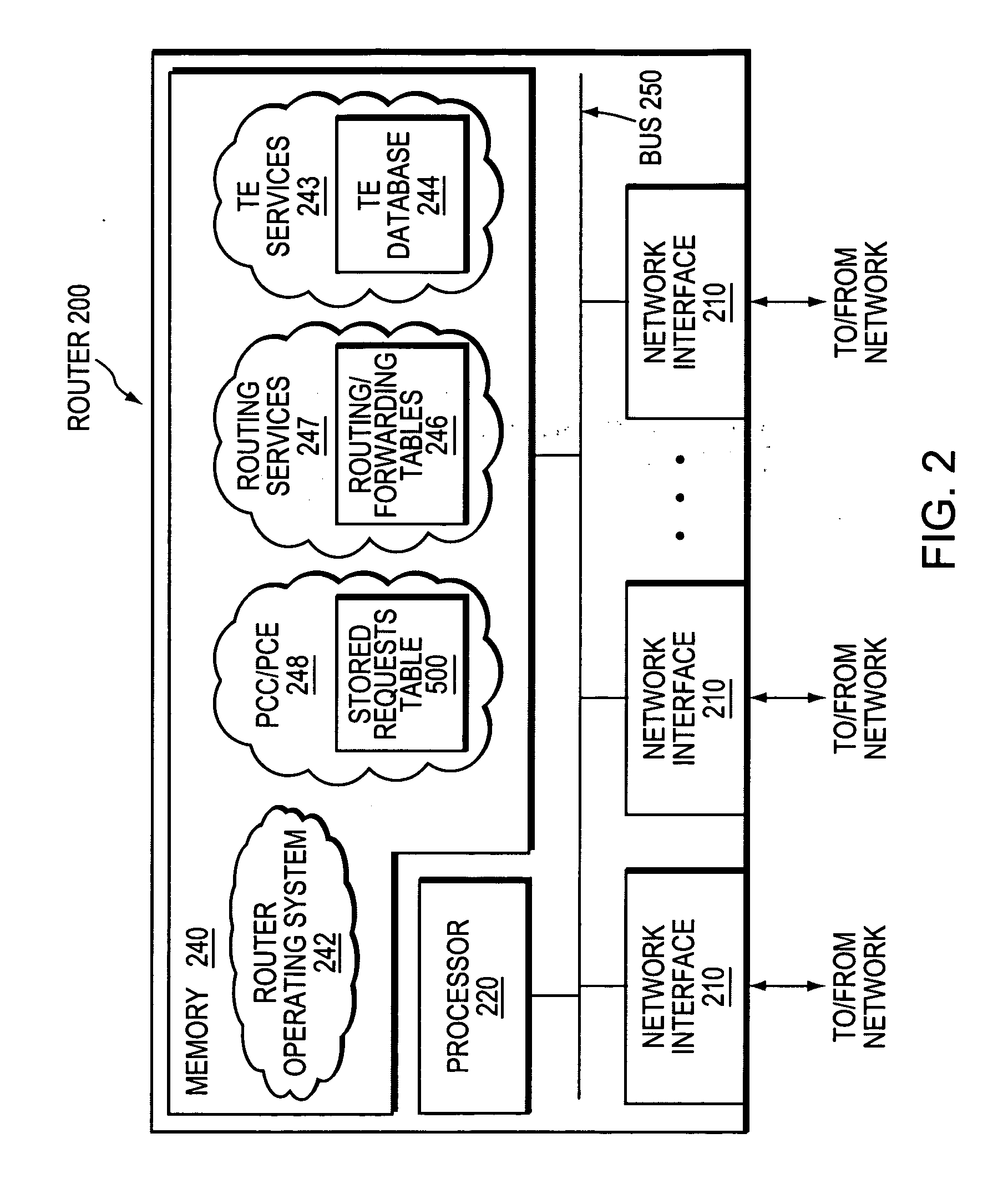
A technique efficiently routes Internet Protocol (IP) traffic on paths between customer edge devices (CEs) across a provider network (“CE-CE paths”) in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a path computation element (PCE), e.g., a provider edge device (PE), may learn dynamic link attribute information of remote links from the provider network to one or more remote CEs (e.g., “PE-CE links” or “CE-PE links”). A multi-homed requesting CE requests from the PCE a set of CE-CE path metrics (e.g., costs) to one or more remote destination address prefixes, e.g., via each multihomed CE-PE link from the requesting CE. In response to the request, the PCE computes the set of available CE-CE paths and current metrics to the remote destination address prefixes and returns the corresponding CE-CE path metrics to the requesting CE. The requesting CE modifies its IP forwarding entries accordingly in order to perform IP traffic routing corresponding to the CE-CE path metrics (e.g., asymmetrical load balancing) across its multi-homed CE-PE links.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for performing data flow ingress/egress admission control in a provider network
A method, apparatus and network for transporting layer-2 frames, such as Ethernet MAC, ATM AAL5, and Frame Relay, over MPLS, SONET / SDH, or OTN optical transport networks as well as electrical transport networks is disclosed. The method establishes “pseudo-wires” between, for example, routers, Layer-2 packet switches, or SONET / SDH switches. Inter-related ingress and egress resource tables may be used by provider edge nodes to negotiate consistently managed data tunnels across a provider network on behalf of data flowing from / to a diverse base of customer edge nodes. Detailed network resource information particular to each of the data flows is exchanged between provider edge nodes during the creation of pseudo-wires. Admission control algorithms are applied at the ingress and egress points in order to manage the data flows into a provider network and exiting from a provider network to customer equipment. By applying pseudo-wire shuffling and preemption techniques, the providers can make better use of their network resources by admitting more pseudo-wires.
Owner:CIENA
Systems and methods for equal-cost multi-path virtual private LAN service
A provider edge device, associated with a virtual private local area network service (VPLS) system, includes a memory to store instructions to implement a pseudowire mechanism to receive a first data frame from a source customer edge (CE) device associated with the VPLS system, incorporate the first data frame into a first VPLS packet, determine whether the source CE device is a single-homed CE device or a multi-homed CE device, and incorporate, into the first VPLS packet, a first pseudowire label, if the source CE device is a single-homed CE device, and incorporate, into the first VPLS packet, a second pseudowire label, different from the first pseudowire label, if the source CE device is a multi-homed CE device; and a processor to execute the instructions.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method for Fast Converging End-to End Services and Provider Edge Equipment Thereof
ActiveUS20080240121A1Improve service reliabilityIncreasing end-to-end service convergence speedData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsComputer networkCustomer edge
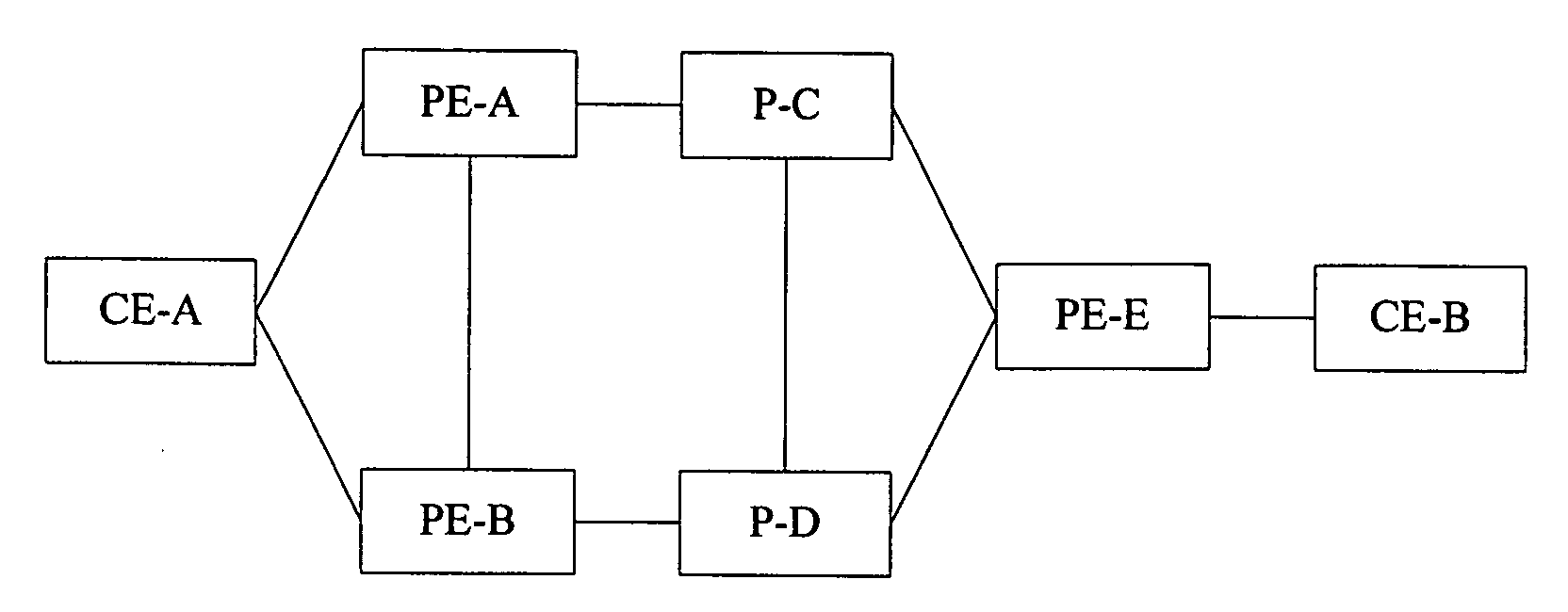
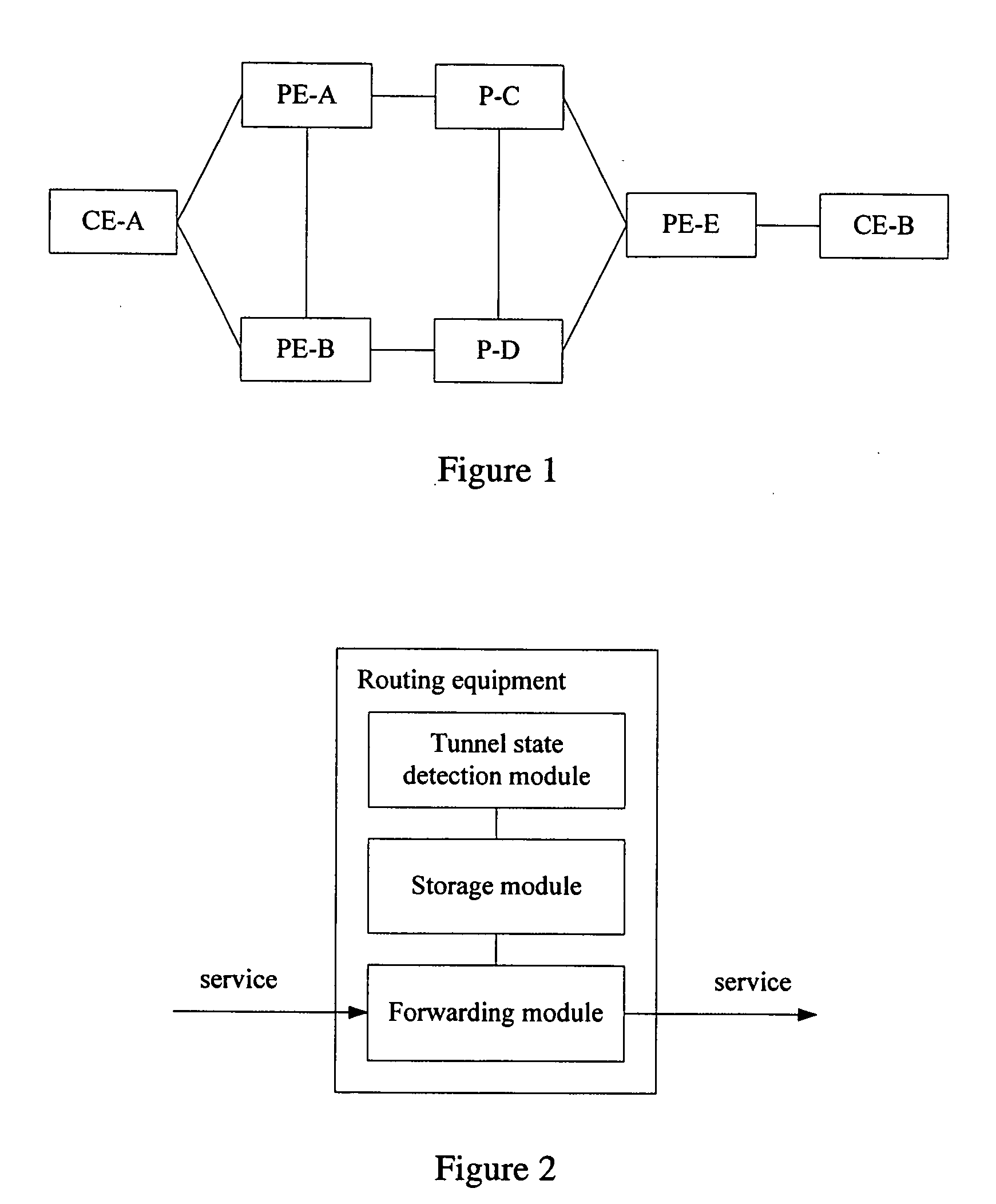
A method for fast converging an end-to-end service and a Provider Edge (PE) includes: setting routing information of at least two tunnels in a double-ascription PE of a remote Customer Edge (CE), wherein, the two tunnels are from the double-ascription PE of the remote CE to the PE connected with the remote CE; detecting tunnel states to obtain state information of the tunnels; the double-ascription PE obtaining available routing information and routing information of the at least two tunnels, and forwarding the service according to the available routing information. The double-ascription PE of the remote CE can directly forward the service according to the pre-configured routing information of other tunnels when the current tunnel is unavailable, such as a terminal node of the current tunnel is abnormal, thereby avoids the procedure of re-selecting the route, and increases the end-to-end service convergence speed and improves the service reliability.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
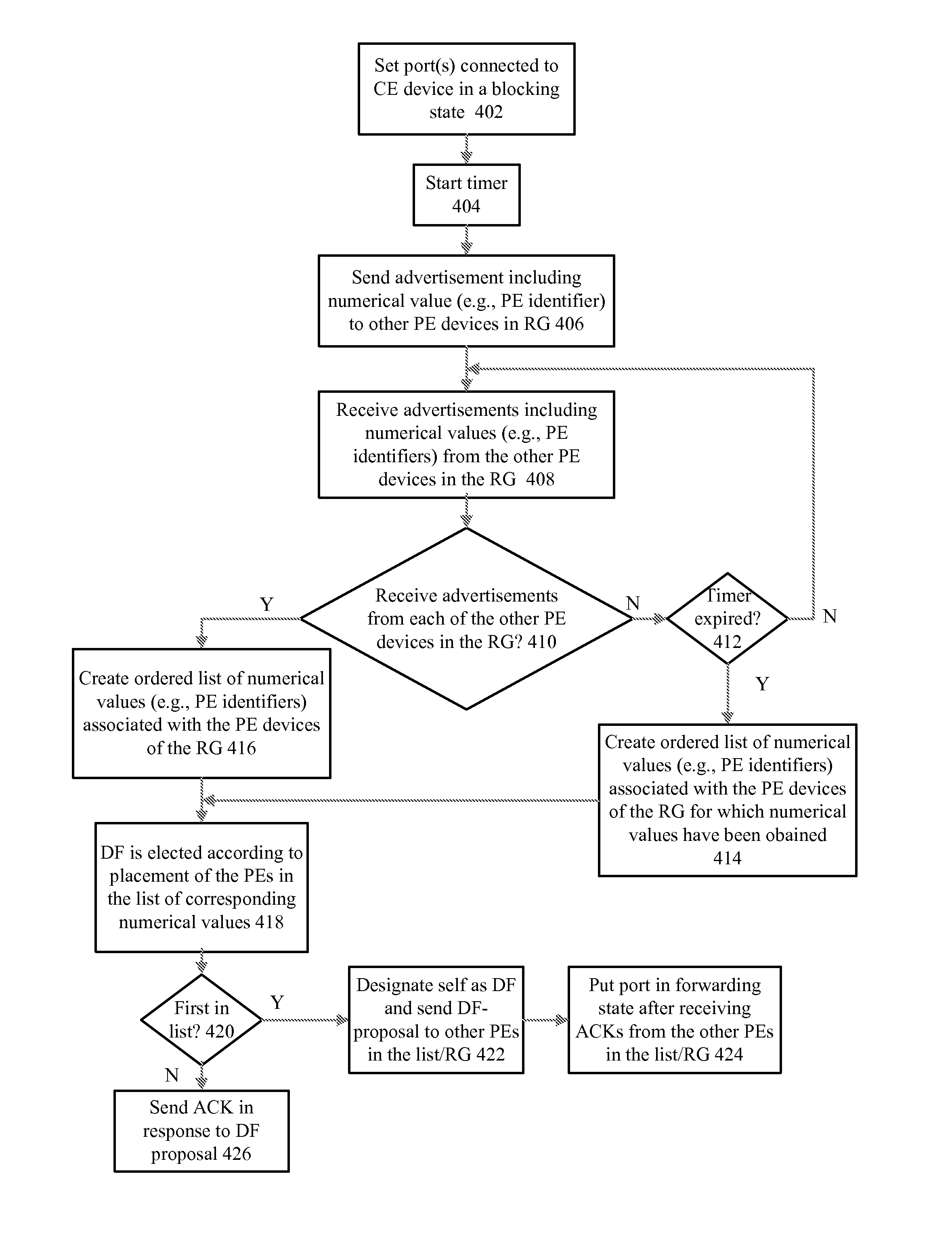
Designated forwarder election for vpls with bgp-based mac learning
In one embodiment, a network device may participate in an election process to elect one of two or more Provider Edge devices of a Redundancy Group to be a Designated Forwarder for the Redundancy Group, where the Redundancy Group is in a Service Provider network, and where the Redundancy Group serves a Customer Edge device of a customer network. The network device may forward multi-destination traffic to the Customer Edge device according to whether the network device is elected to be the Designated Forwarder for the Redundancy Group. Multi-destination traffic may include multicast traffic, broadcast traffic, or destination unknown unicast traffic.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
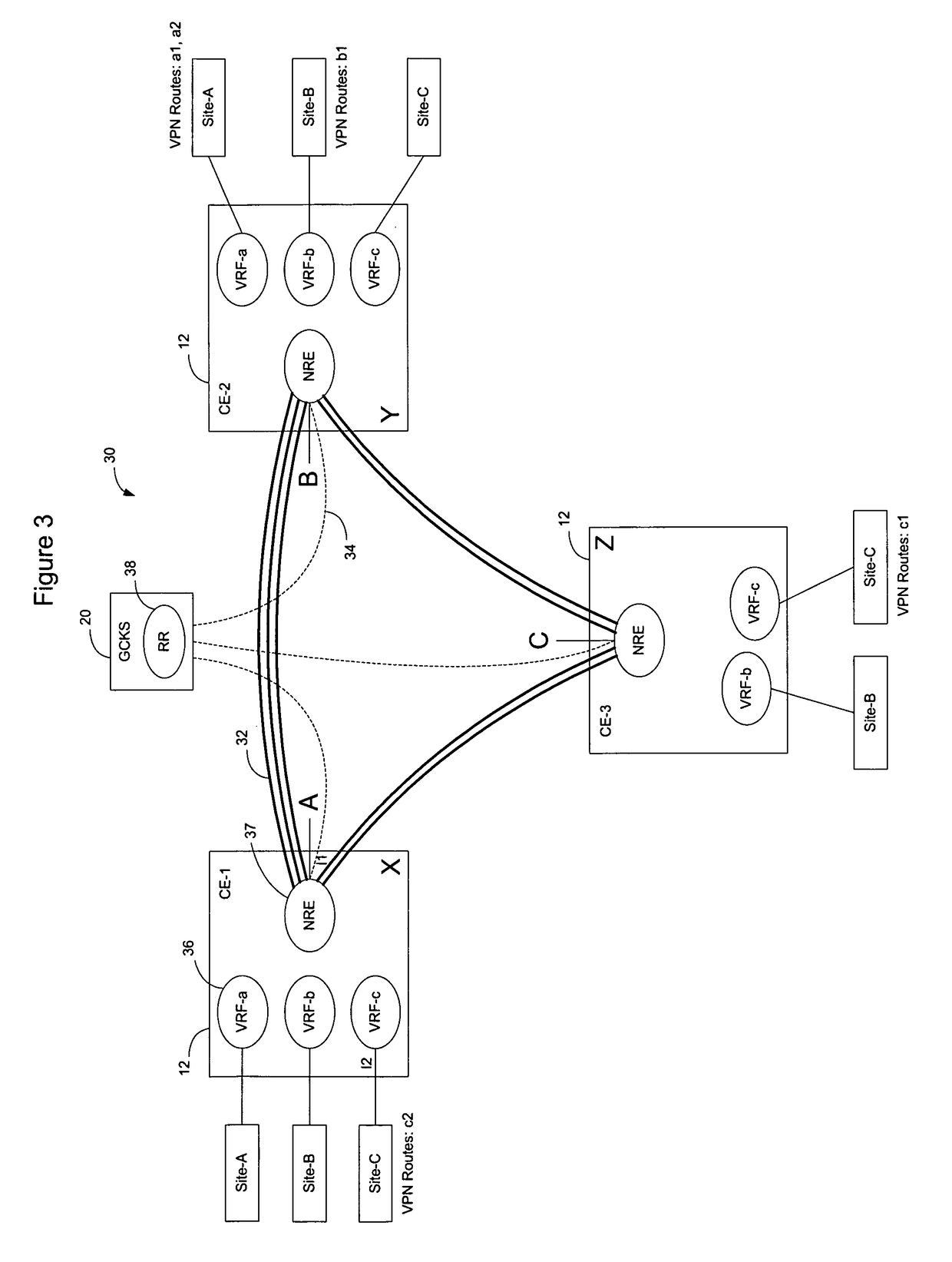
Method for optimal assignment of customer edge (CE) routers to virtual private network route forwarding (VRF) tables
A method for optimal assignment of customer edge (CE) routers to virtual private network route forwarding (VRF) tables uses a “peer model”, in which the CE routers communicate their routes to a Service Provider's edge routers (PE routers). The routes of a particular VPN are then exchanged among the PE routers that are attached to that VPN. This is accomplished in a manner which ensures that routes from different VPNs remain distinct and separate, even if two VPNs comprise an overlapping address space. The PE routers distribute, to the CE routers in a particular VPN, the routes from other CE routers in that VPN. The CE routers do not peer with each other and, as such, there is no “overlay” visible to a VPN's routing algorithm.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Method and apparatus for learning endpoint addresses of IPSec VPN tunnels
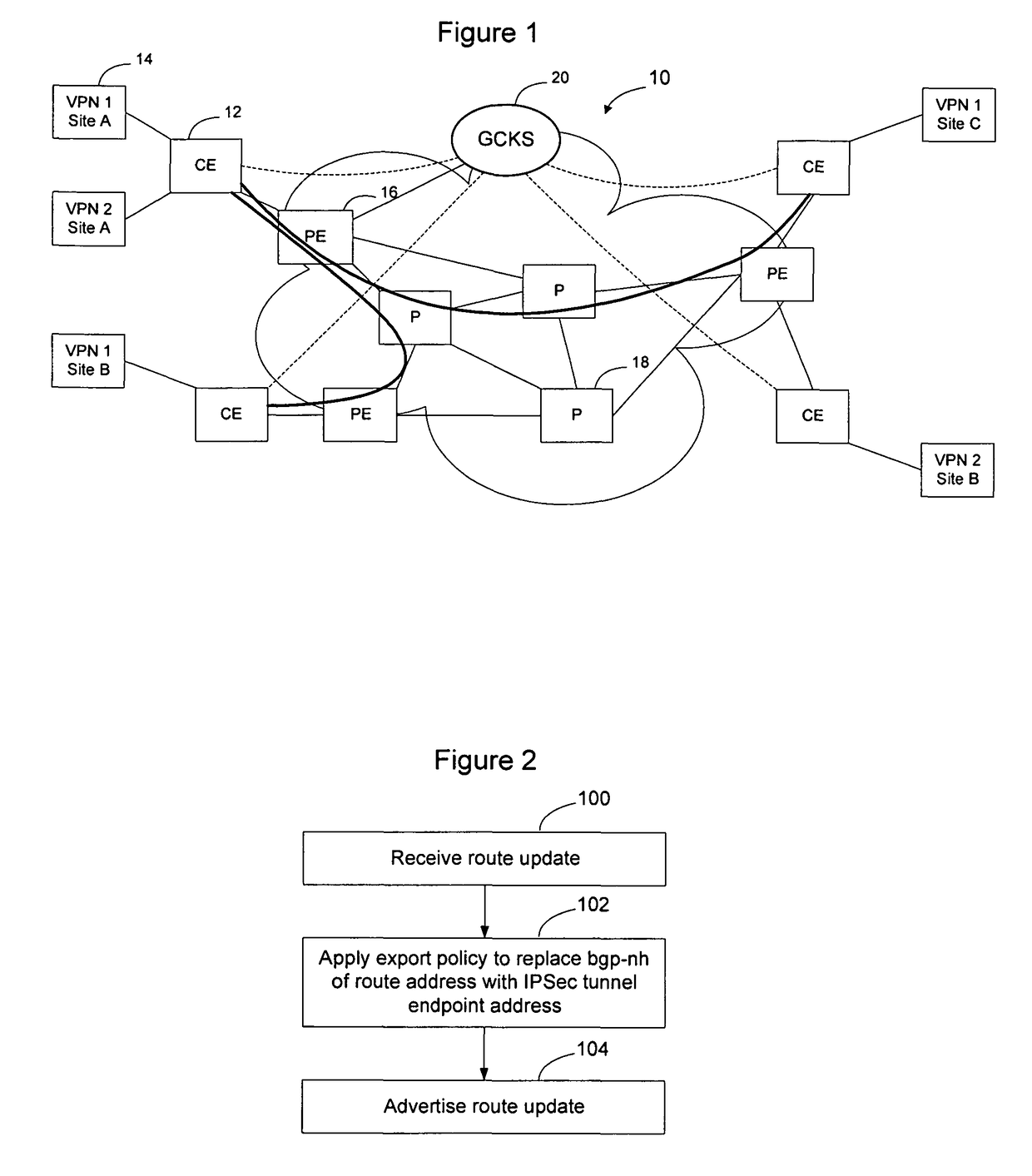
Customer Edge (CE) network elements can automatically learn IPSec tunnel endpoints for other CEs connected to sites in a Virtual Private Network (VPN) so that manual configuration of IPSec tunnel endpoints is not required and so that a centralized database of IPSec tunnel endpoints is not required to be separately maintained. According to an embodiment of the invention, a BGP export route policy is set on all CEs, so that when they announce their VPN routes in the standard format, the application of this export route policy changes the announcement to replace the BGP peering point address that would ordinarily be advertised with the IPSec tunnel endpoint address. When any given site receives a VPN route update formatted in this manner, it processes the VPN route update and learns from the update the IPSec tunnel endpoint as well as the associated VPN routes.
Owner:AVAYA INC
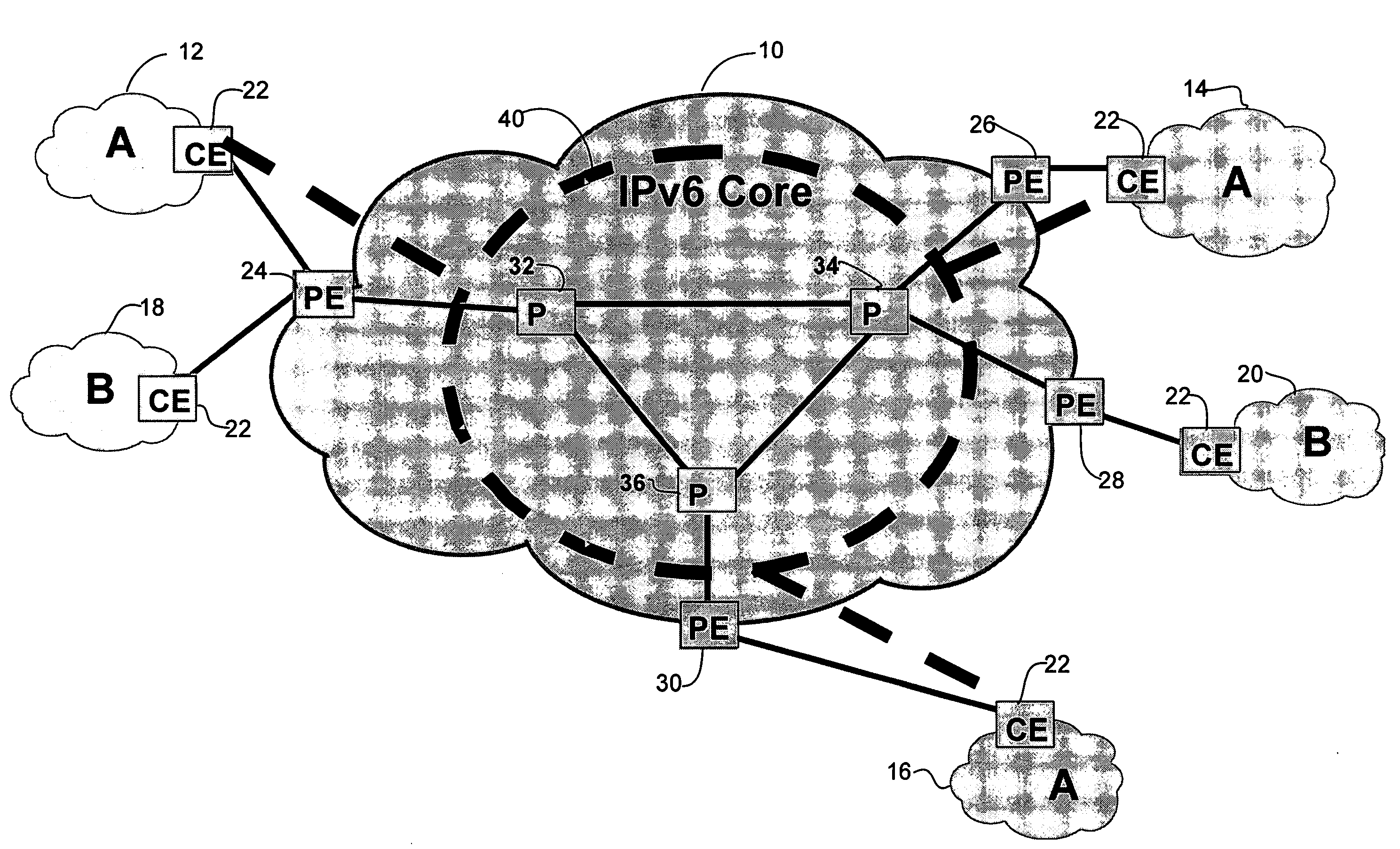
VPN services using address translation over an IPv6 network
A method and system for translation of virtual private network (VPN) addresses over a provider network are disclosed. The method includes creating a multipoint tunnel extending between customer edge routers in a VPN network and over the provider network. The multipoint tunnel is identified with a multicast address and multicast packets are sent over the tunnel to identify tunnel endpoints at customer edge routers within the VPN. The method further includes converting, at one of the customer edge routers, a VPN join message to a provider join message and sending it over the provider network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
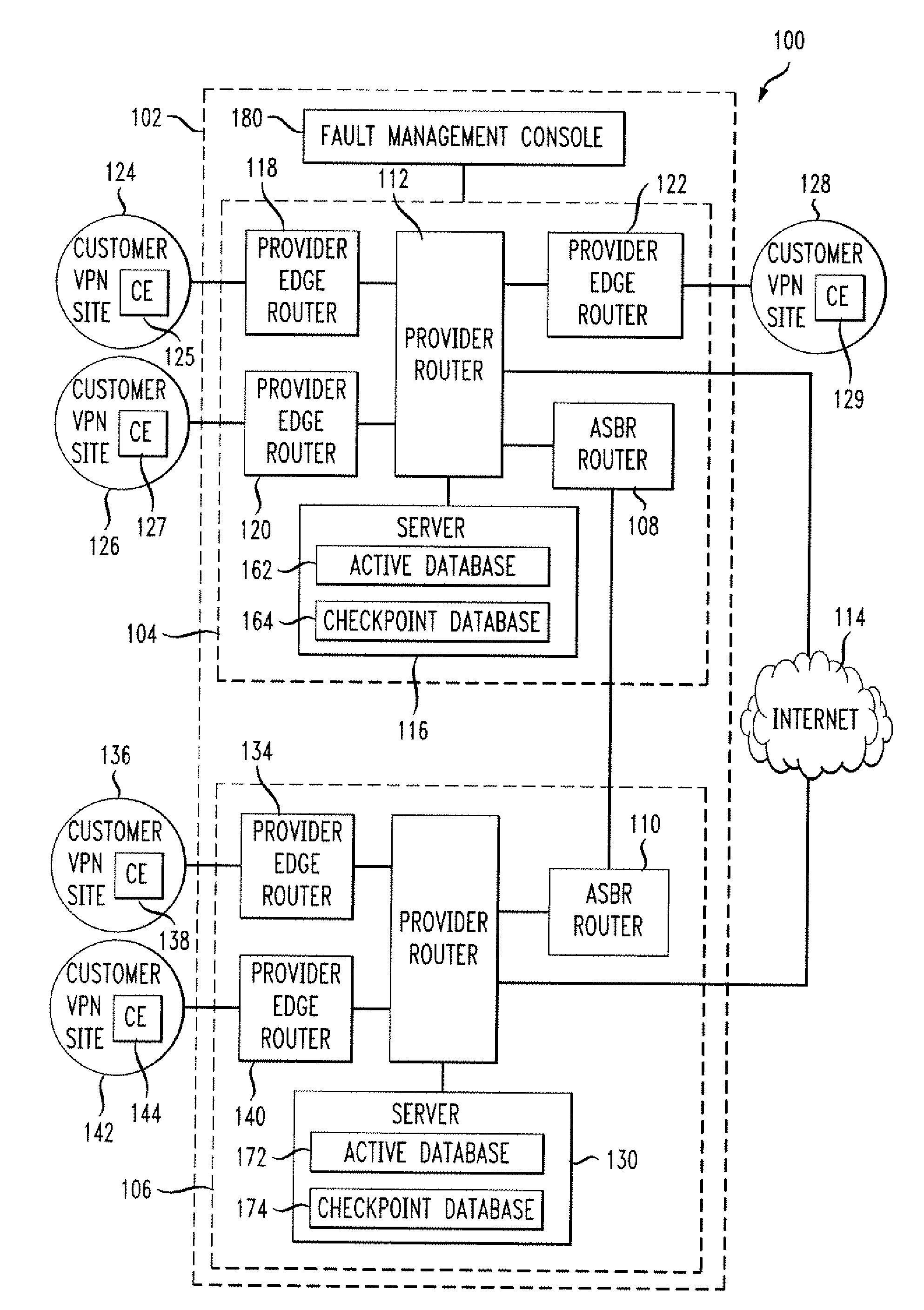
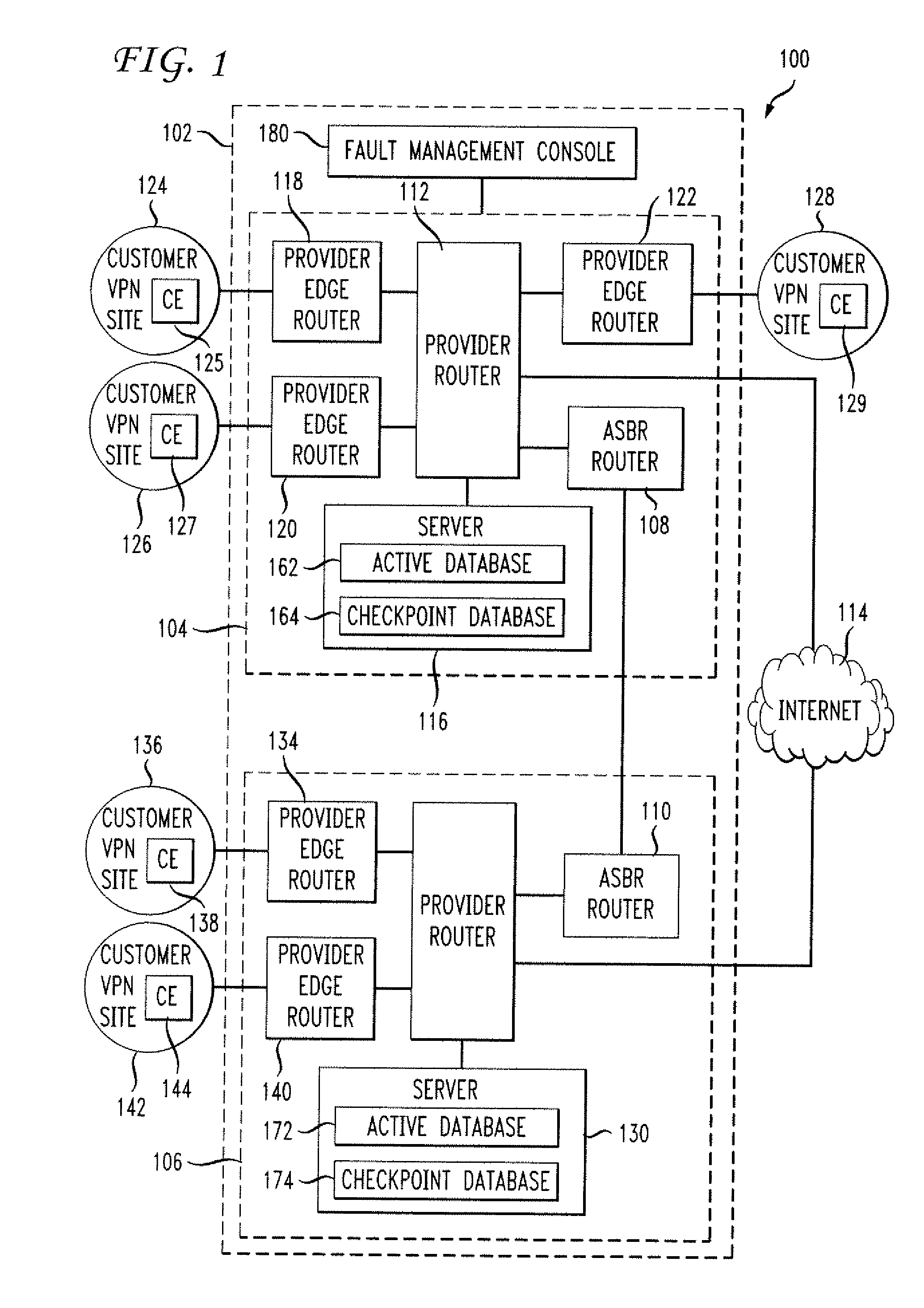
Faults and status in virtual private networks
ActiveUS20060002409A1Quick identificationError preventionTransmission systemsPrivate networkColor scheme
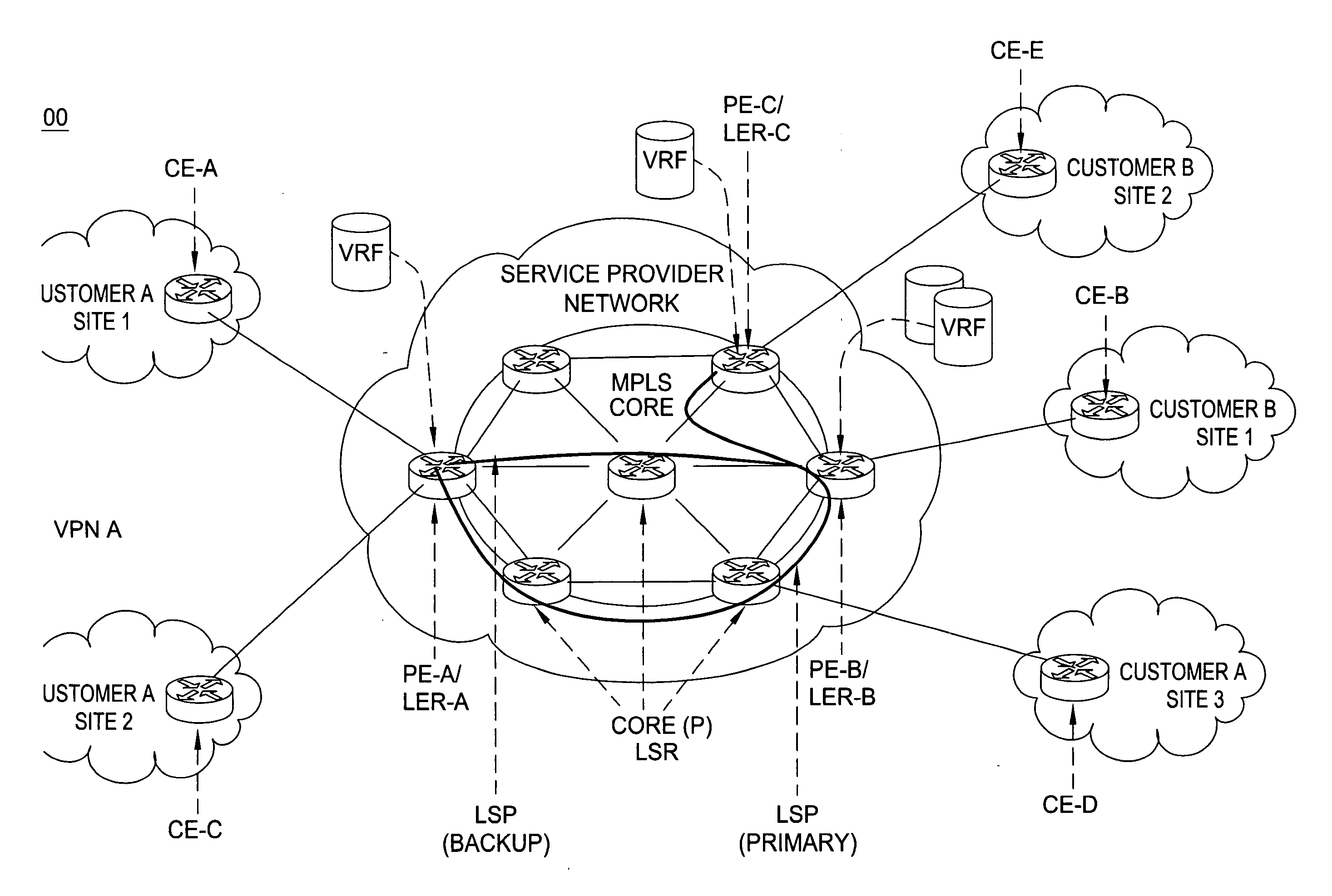
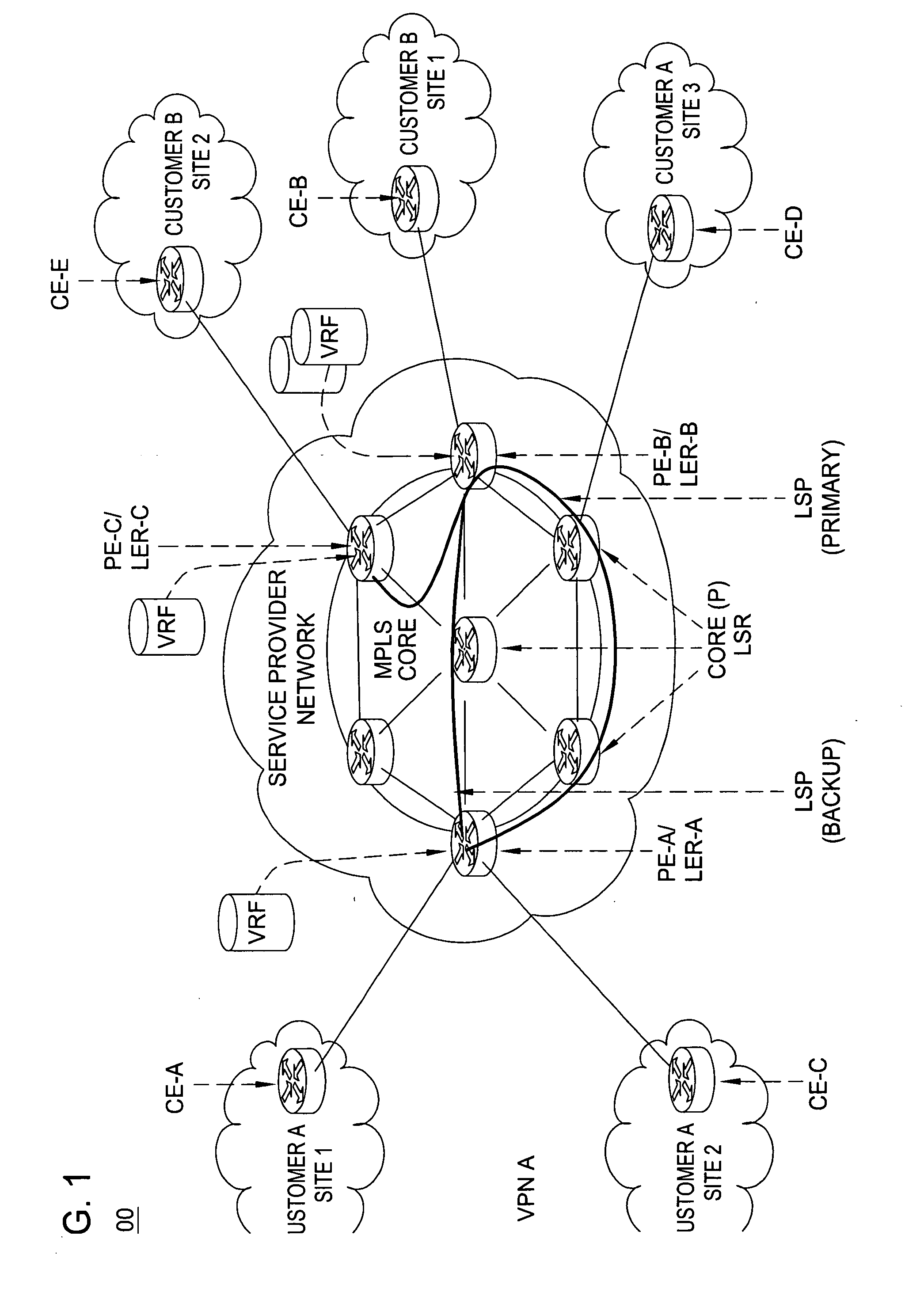
In an embodiment, a network service provider (NSP) operates a provider network to provide VPN services to its customers. A VPN links various customer sites allowing customers to send data between these sites over the NSP network. Each site network includes a customer edge router (CE) while the provider network includes a plurality of provider edge routers (PEs) to communicate with the CEs. The PEs include virtual routing address (VRFs), and the PEs and CEs include interfaces (IFs). A database stores information related to the relationships between the network components (e.g., VPNs, PEs, CEs, VRFs, IFs, etc.), and a management software package (MSP) has access to the database. When a fault occurs, the MSP, based on collected information and information in the database, determines the impacted network components. Other features include classifying the seriousness of the network's faults and representing different faults by a color scheme.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
Address resolution in IP interworking layer 2 point-to-point connections
InactiveUS20040202199A1Time-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionAddress Resolution ProtocolFrame Relay
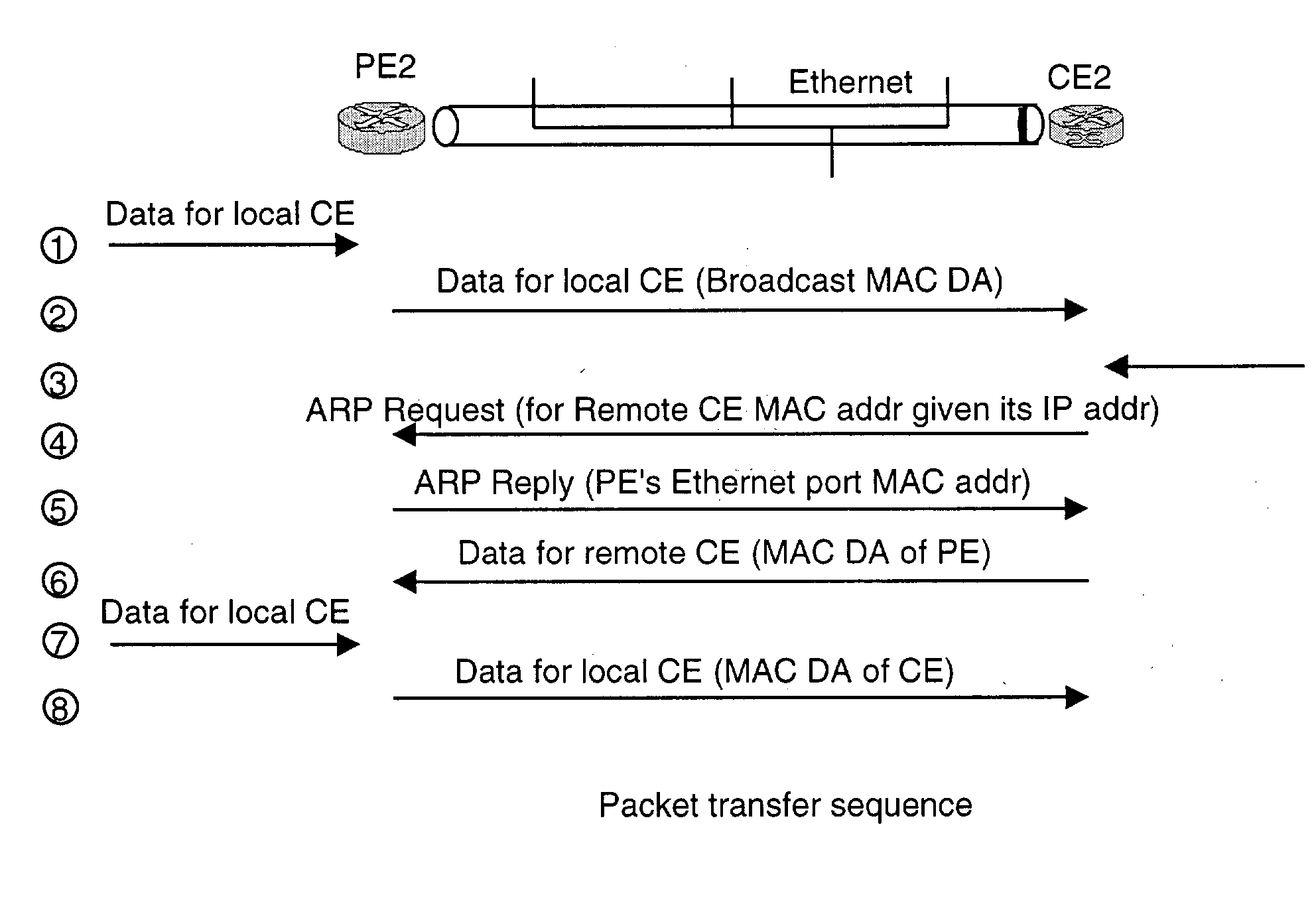
A heterogeneous point-to-point links involves different technologies at it two ends, e.g., Ethernet at one end and ATM or Frame Relay at the other end. If two IP systems are connected via a heterogeneous point-to-point link, each may be using different address learning techniques. It is up to the Provider Edge devices to make these different techniques inter-work. A novel provider edge device and procedures that the edge device it to perform for forwarding packets properly are described. According to the invention, the provider edge device uses a broadcast address to forward the packet in one direction toward a customer edge device. In another direction, the provider edge device responds to an ARP request from the customer edge device with its own MAC address so that it can receive a packet from the customer edge device.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Mechanism for e-vpn interoperability with vpls
In one embodiment, a network device in a set of network devices obtains a pseudowire label for a Provider Edge (PE) device, where the pseudowire label corresponds to a Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) on the PE device. In addition, the network device obtains a set of one or more MAC addresses reachable via the PE device, wherein the set of network devices support Ethernet Virtual Private Network (E-VPN) and are in the same redundancy group such that the set of network devices are coupled to the same customer edge device. The network device stores the pseudowire label in association with the set of one or more MAC addresses. The network device uses the pseudowire label to encapsulate traffic associated with the VLAN that is received from the customer edge device and destined to the set of MAC addresses reachable via the PE device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
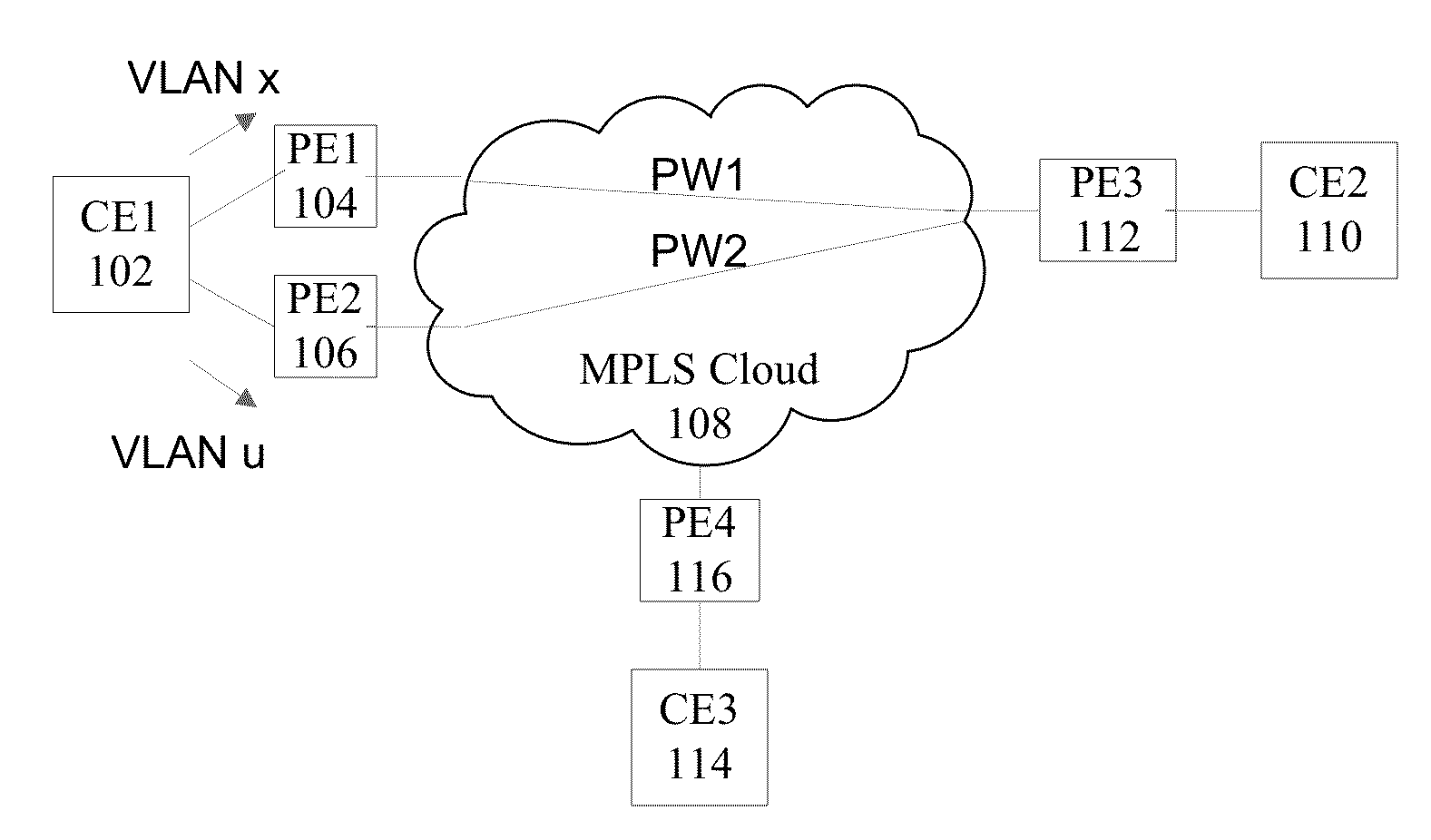
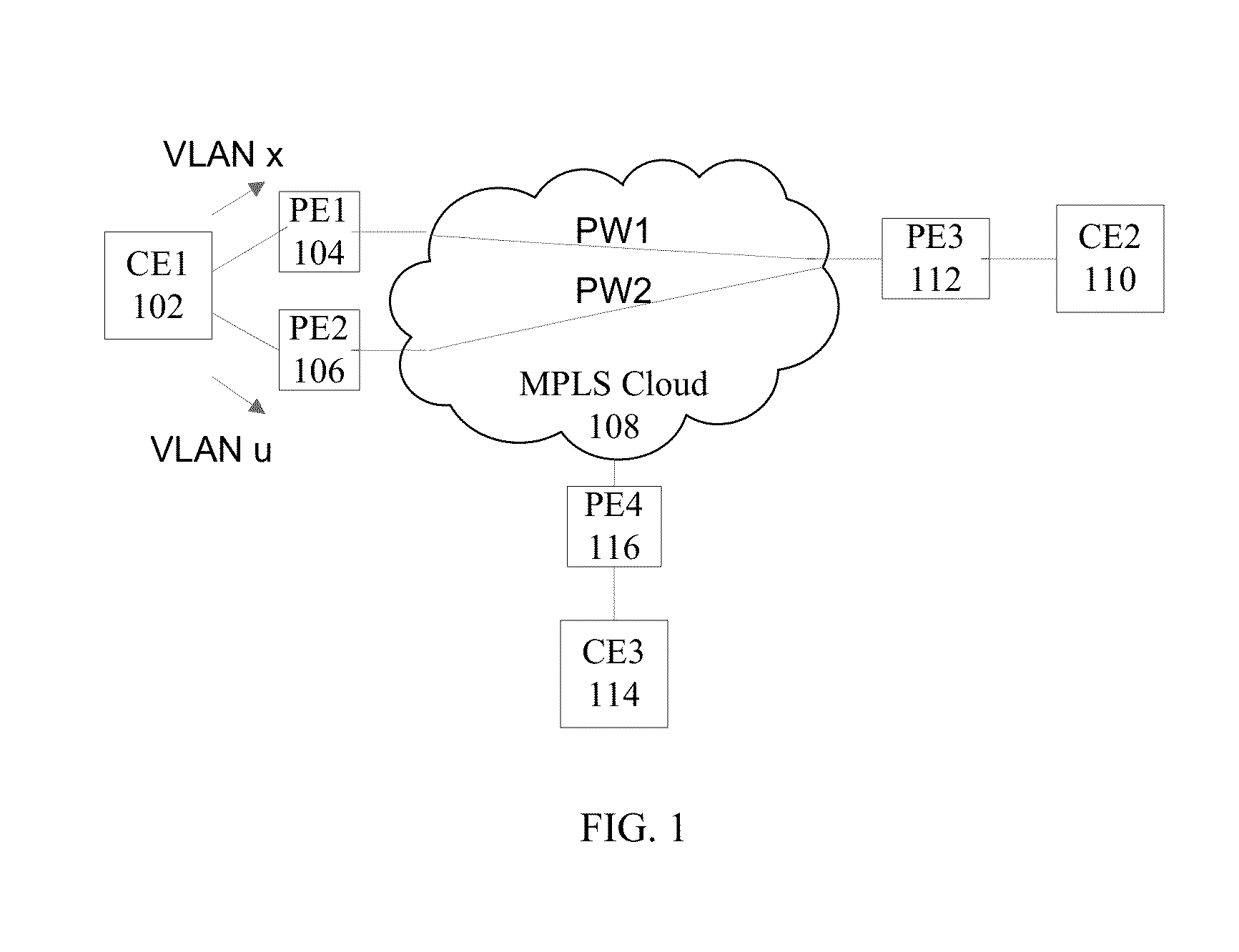
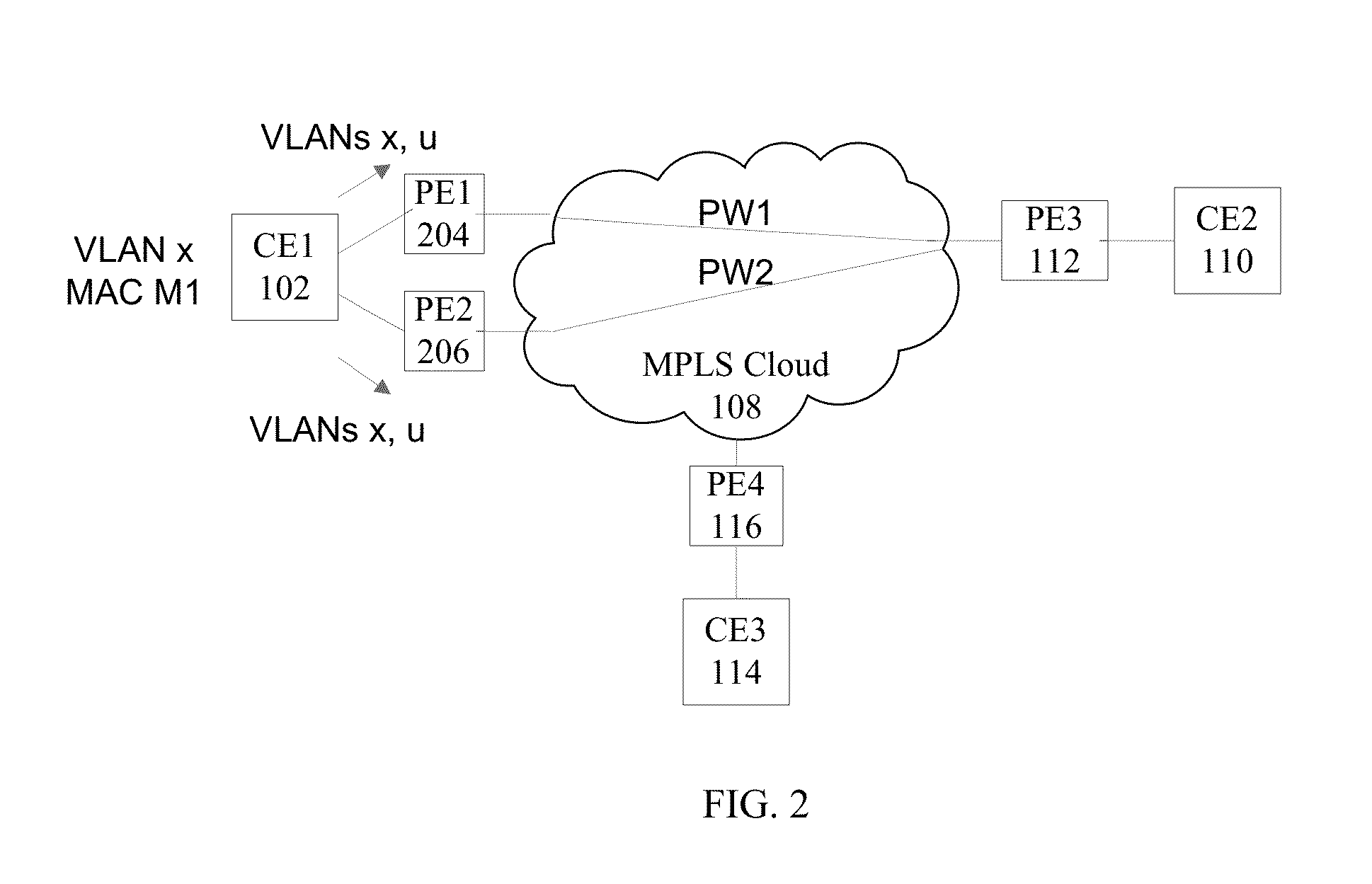
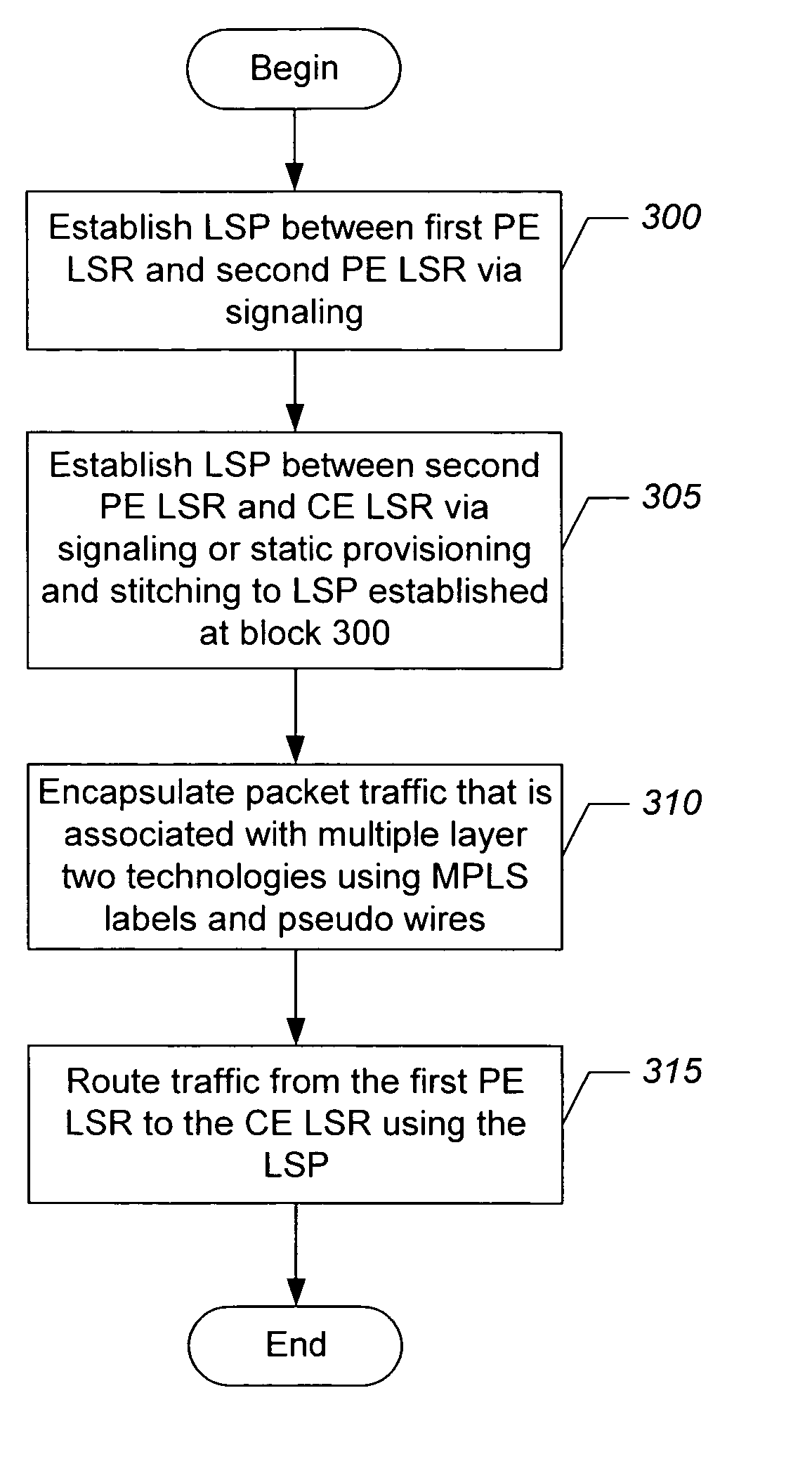
Methods, systems, and computer program products for encapsulating packet traffic associated with multiple layer two technologies
InactiveUS20050141504A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData packLabel switch router
A multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) network is operated by establishing a label switched path (LSP) that connects a first provider edge (PE) label switched router (LSR) a second PE LSR, and a customer edge (CE) LSR. The packet traffic that is associated with a plurality of different layer two technologies is encapsulated with an MPLS label. The encapsulated traffic is securely routed from the first PE LSR through the second PE LSR to the CE LSR using the LSP.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
VPN services using address translation over an IPv6 network
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
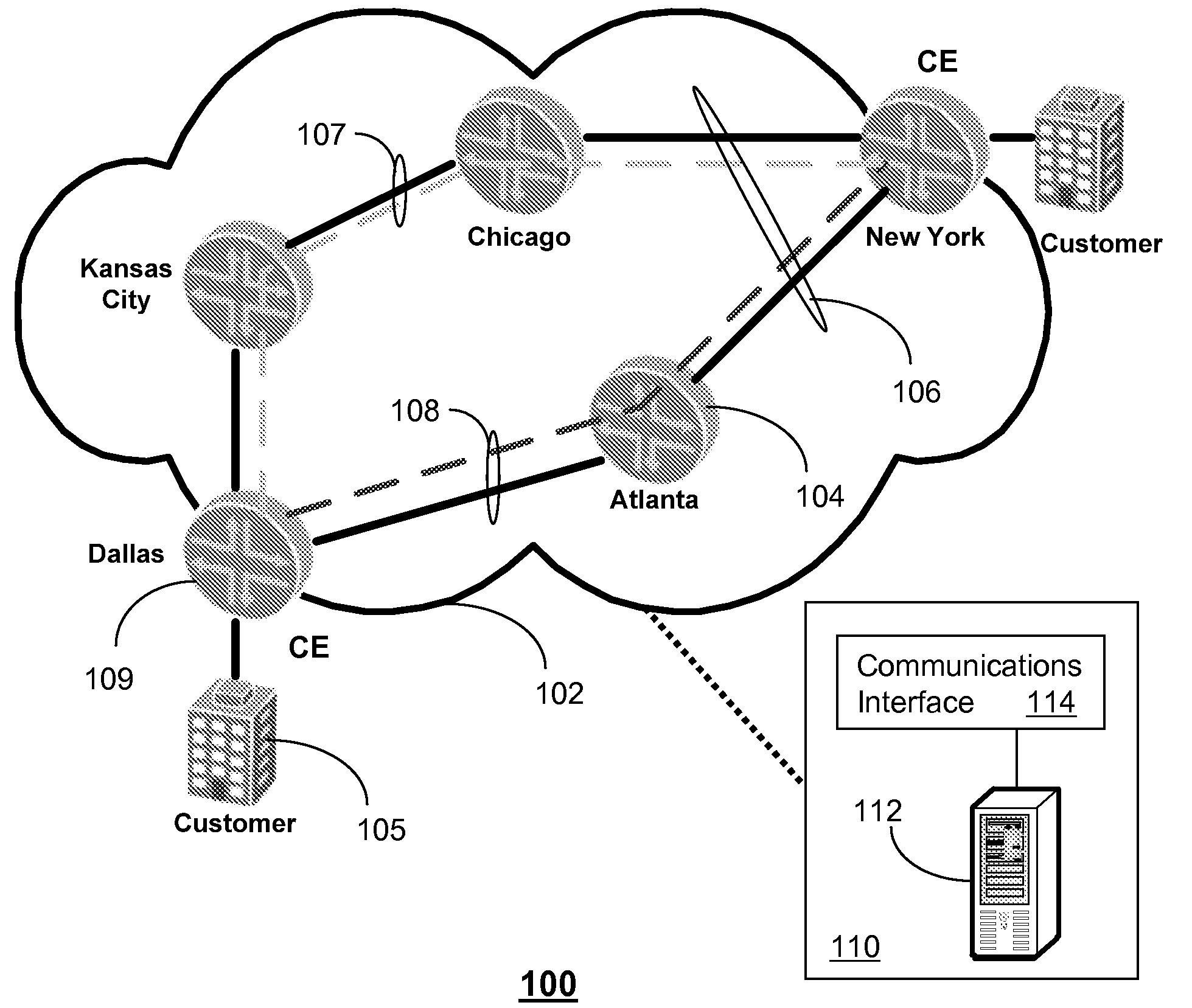
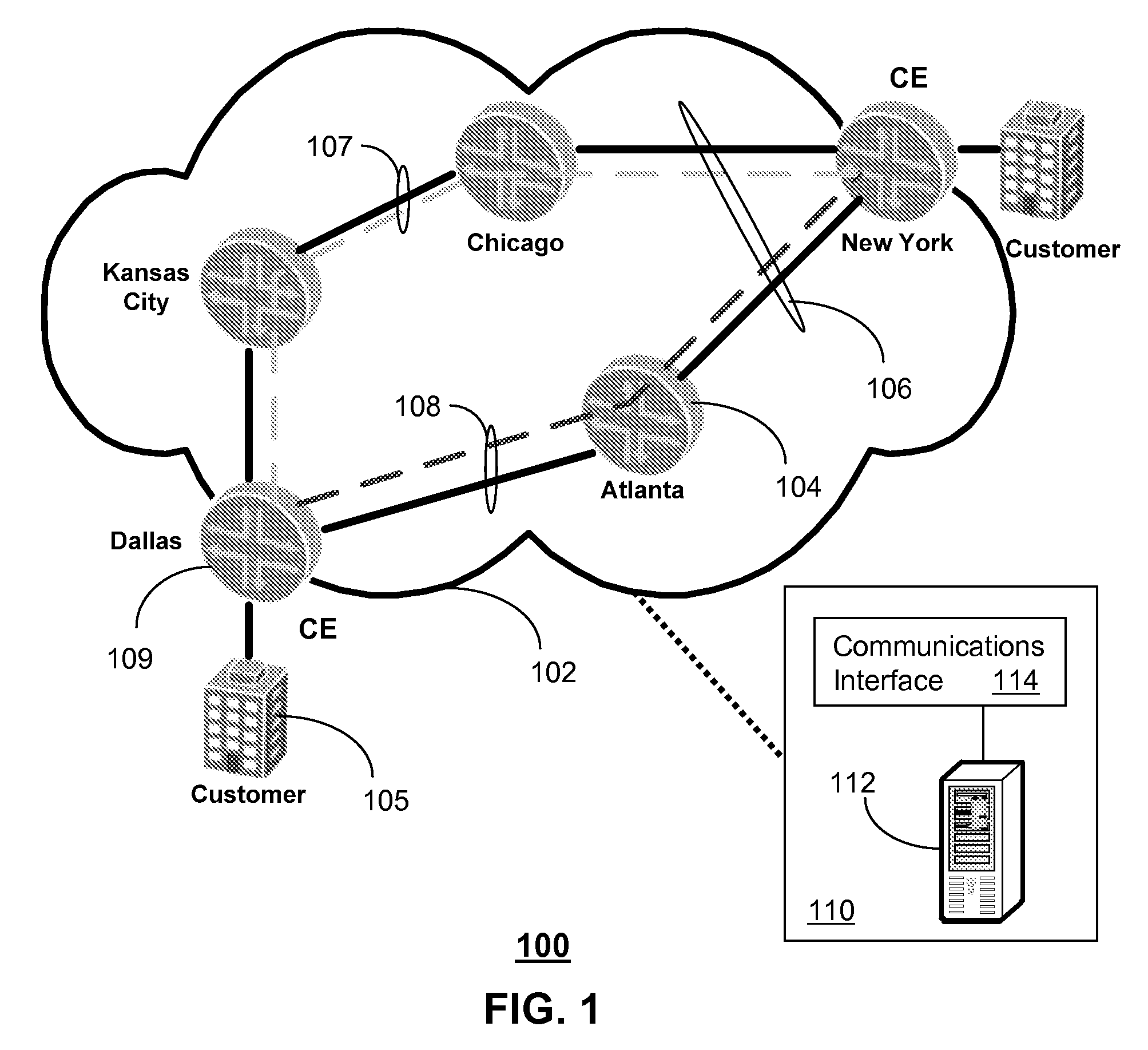
Method and apparatus for reliable communications in a packet network
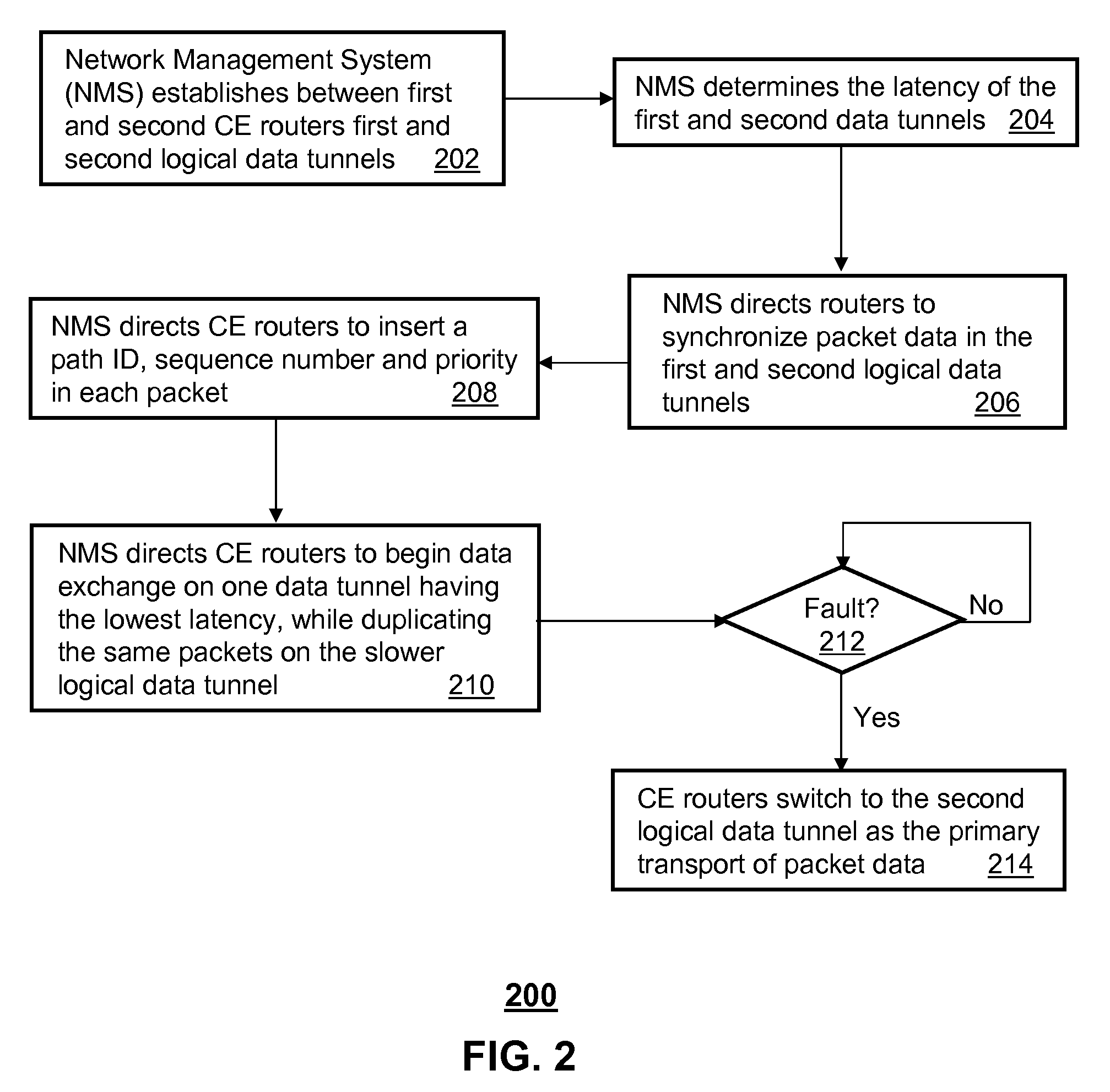
A system and method are disclosed for reliable communications in a packet network. A system that incorporates teachings of the present disclosure may include, for example, a network management system (NMS) having a controller programmed to establish between first and second customer edge (CE) routers in a full mesh packet network first and second logical data tunnels conforming to an isolation protocol, synchronize packet data in the first and second logical data tunnels, enable packet data exchanges between the first and second CE routers over the first logical data tunnel, direct the first and second CE routers to duplicate the packet data exchanged between them over the second logical data tunnel, and direct the first and second CE routers to synchronously switch to the second logical data tunnel upon detecting a fault in the first logical data tunnel.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
Method and system for virtual private network connectivity verification
InactiveUS20070226630A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksPrivate networkNetwork management
A method for testing connectivity of virtual private networks, the virtual private networks including customer edge routers and provider edge routers, the provider edge routers belonging to a network managed by a service provider, the method comprising: displaying a list of the virtual private networks on a display screen of a network management system for the network; receiving a signal from a user to select a virtual private network from the list of the virtual private networks, the virtual private network having a topology, an import route target, and an export route target associated therewith; generating a list of operations to test connectivity of the virtual private network from the topology, the import route target, and the export route target; displaying the list of operations to the user on the display screen; receiving a signal from the user to select an operation from the list of operations, the operation having a source provider edge router and a destination provider edge network associated therewith; and, transmitting a message from the network management system to the source provider edge router to perform the operation.
Owner:RPX CORP
Technique for enabling traffic engineering on CE-CE paths across a provider network
ActiveUS7710872B2Create efficientlyReduce needError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPrivate networkTraffic volume
A technique enables Traffic Engineering (TE) on paths between customer edge devices (CEs) across a provider network (“CE-CE paths”) in a computer network. According to the novel technique, TE is configured on a link from a sending provider edge device (PE) to a first CE (“PE-CE link”), e.g., a CE of one or more virtual private networks (VPNs). The sending PE conveys TE information of the PE-CE link to one or more receiving PEs in the provider network. Upon receiving the TE information, each receiving PE expands a TE database (TED) for information regarding the provider network (i.e., a “core TED”) to include TE-configured PE-CE links, e.g., by updating one or more corresponding VPN TEDs (VTEDs) for each VPN maintained by the receiving PE. Once the receiving PEs have the TE information for configured PE-CE links from the provider network, one or more TE techniques may be applied to paths from a second CE of the receiving PE to the first CE (a CE-CE path) to thereby facilitate, e.g., establishment of TE-LSPs along CE-CE paths.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Technique for efficiently routing IP traffic on CE-CE paths across a provider network
InactiveUS7522603B2Efficiently routedEfficient routingError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPath computation element
A technique efficiently routes Internet Protocol (IP) traffic on paths between customer edge devices (CEs) across a provider network (“CE-CE paths”) in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a path computation element (PCE), e.g., a provider edge device (PE), may learn dynamic link attribute information of remote links from the provider network to one or more remote CEs (e.g., “PE-CE links” or “CE-PE links”). A multi-homed requesting CE requests from the PCE a set of CE-CE path metrics (e.g., costs) to one or more remote destination address prefixes, e.g., via each multi-homed CE-PE link from the requesting CE. In response to the request, the PCE computes the set of available CE-CE paths and current metrics to the remote destination address prefixes and returns the corresponding CE-CE path metrics to the requesting CE. The requesting CE modifies its IP forwarding entries accordingly in order to perform IP traffic routing corresponding to the CE-CE path metrics (e.g., asymmetrical load balancing) across its multi-homed CE-PE links.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
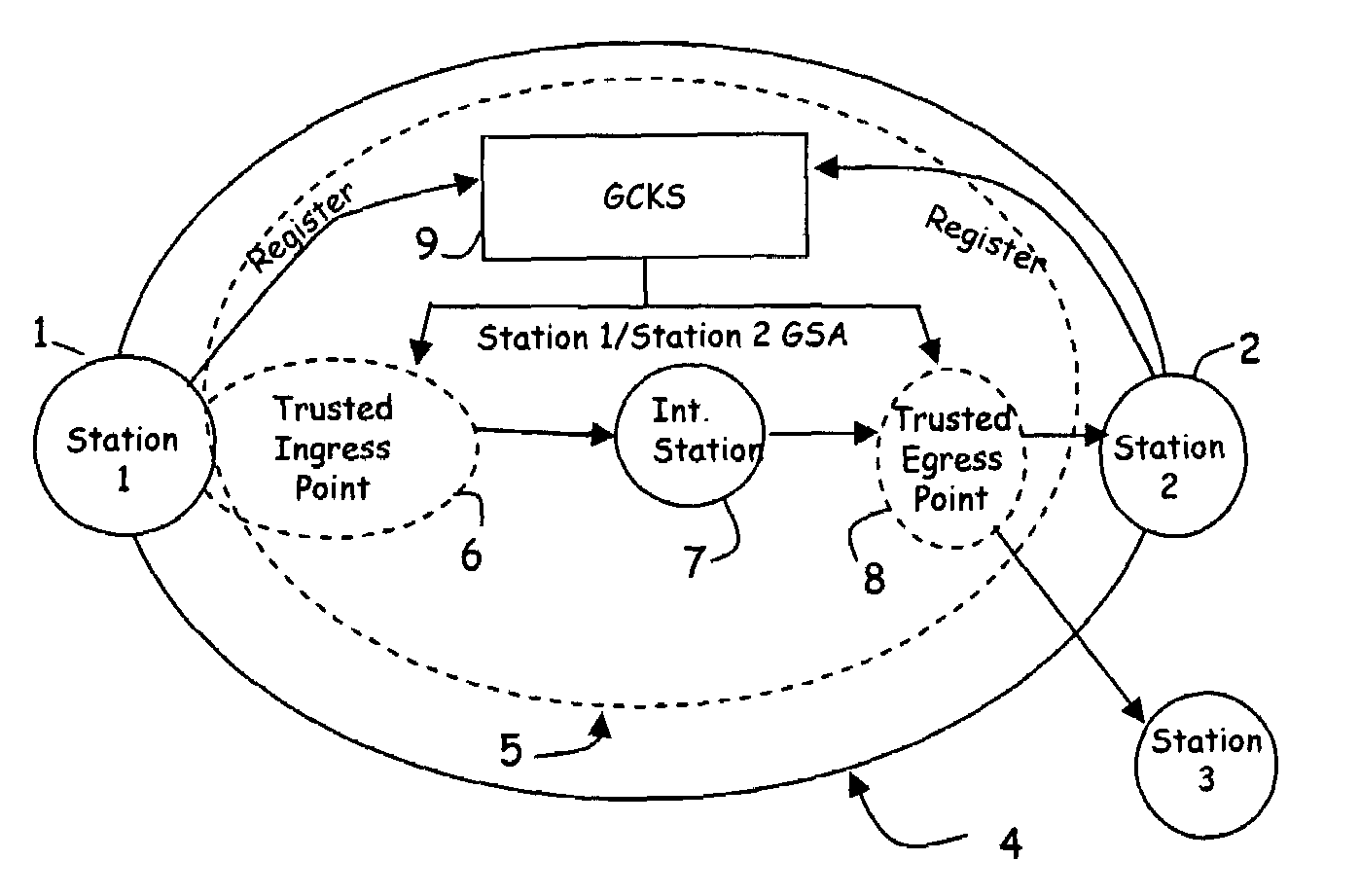
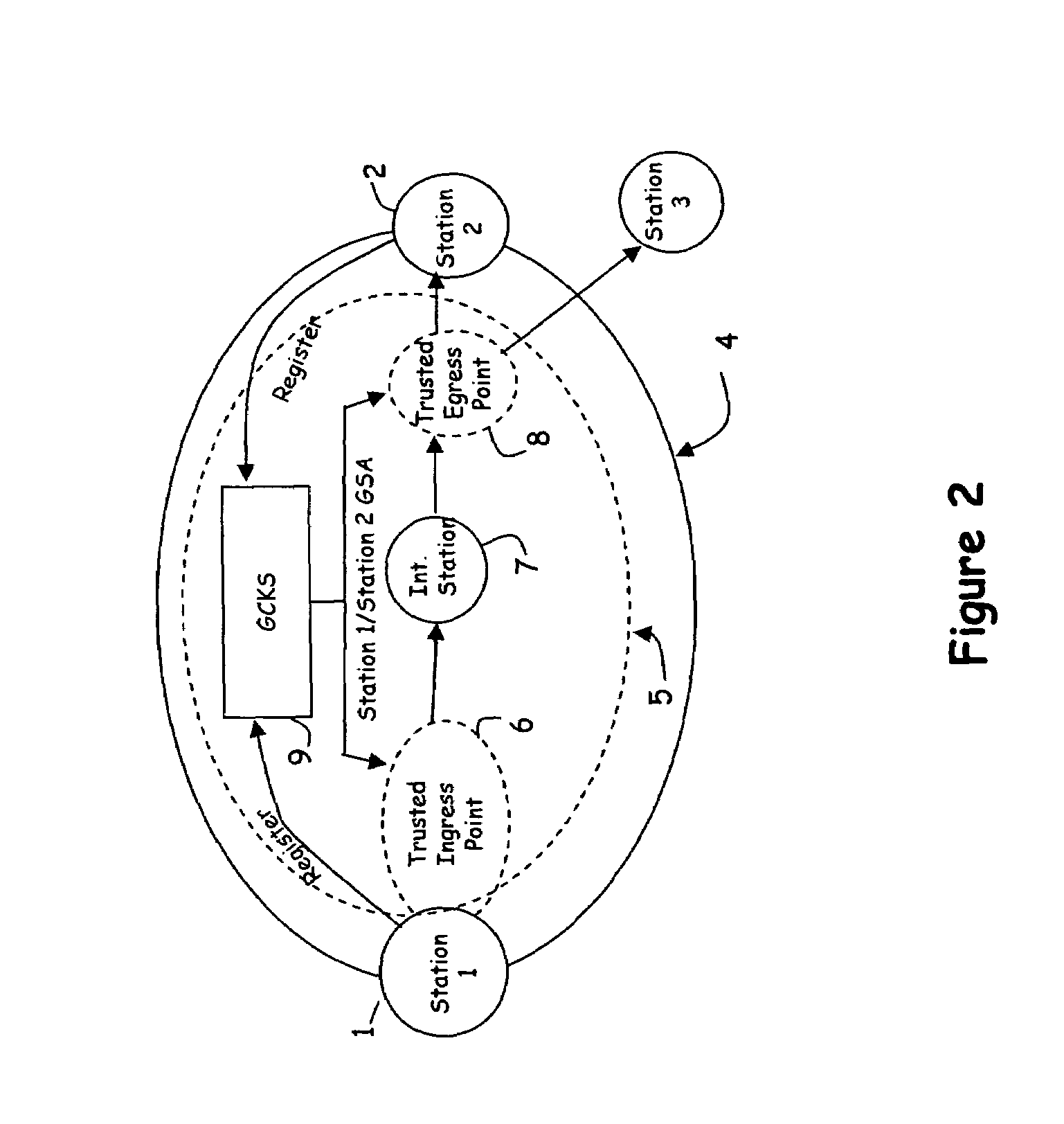
Scalable, distributed method and apparatus for transforming packets to enable secure communication between two stations
InactiveUS7526658B1Secure transmissionMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsSecure communicationSecurity association
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Address resolution method for a virtual private network, and customer edge device for implementing the method
ActiveUS7221675B2Save address resourcesSave resourcesTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionAddress Resolution ProtocolVirtual LAN
A virtual private network (VPN) service is provided through a shared network infrastructure, with customer edge (CE) devices each having a provider edge (PE) interface having a single layer 3 address in the VPN. An address resolution request message is transmitted by a first CE device on plural layer 2 virtual circuits of its PE interface. The address resolution request message including the layer 3 address allocated to a second CE device of the VPN. In response to reception of such request message at the second CE device, an address resolution response message is returned to the first CE device. In response to reception of this response message, the first CE device maps the layer 3 address allocated to the second CE device to a virtual LAN identifier of the layer 2 virtual circuit on which the response message is received.
Owner:CIENA
Interconnection method of transparent interconnection network of lots of links in different places and operator edge device
InactiveCN102075446ARealize remote interconnectionNetworks interconnectionPrivate networkMultistage interconnection networks
The invention discloses an interconnection method of a transparent interconnection network of lots of links in different places and an operator edge device, wherein a first site and a second site belong to the same VPN (Virtual Private Network), implement interconnection in different places through an MPLS (Multiple Protocol Label Switching) L3VPN (Layer-3 Virtual Private Network), and respectively achieve the access to the MPLS L3VPN through a first PE (Provider Edge) and a second PE, a first CE (Customer Edge) and a second CE are respectively located at the first site and the second site, and a first RB and a second RB are respectively an optional RB under the first CE and the second CE; the method comprises the steps that: the first PE and the first CE interacts a TRILL (Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links) IS-IS message to learn local TRILL route of the first RB, and transmit the local TRILL route of the first RB to the second PE after adding a VPN identifier; the second PE transmits the local TRILL route of the first RB to the second RB via the second CE; the second PE receives a TRILL data message of which the destination is the first RB, and transmits the message to the first PE according to the local TRILL route of the first RB, and the first PE transmits the message to the first RB according to the local TRILL route of the first RB. The interconnection method of the transparent interconnection network of lots of links in different places implements the interconnection of the TRILL network in different places.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
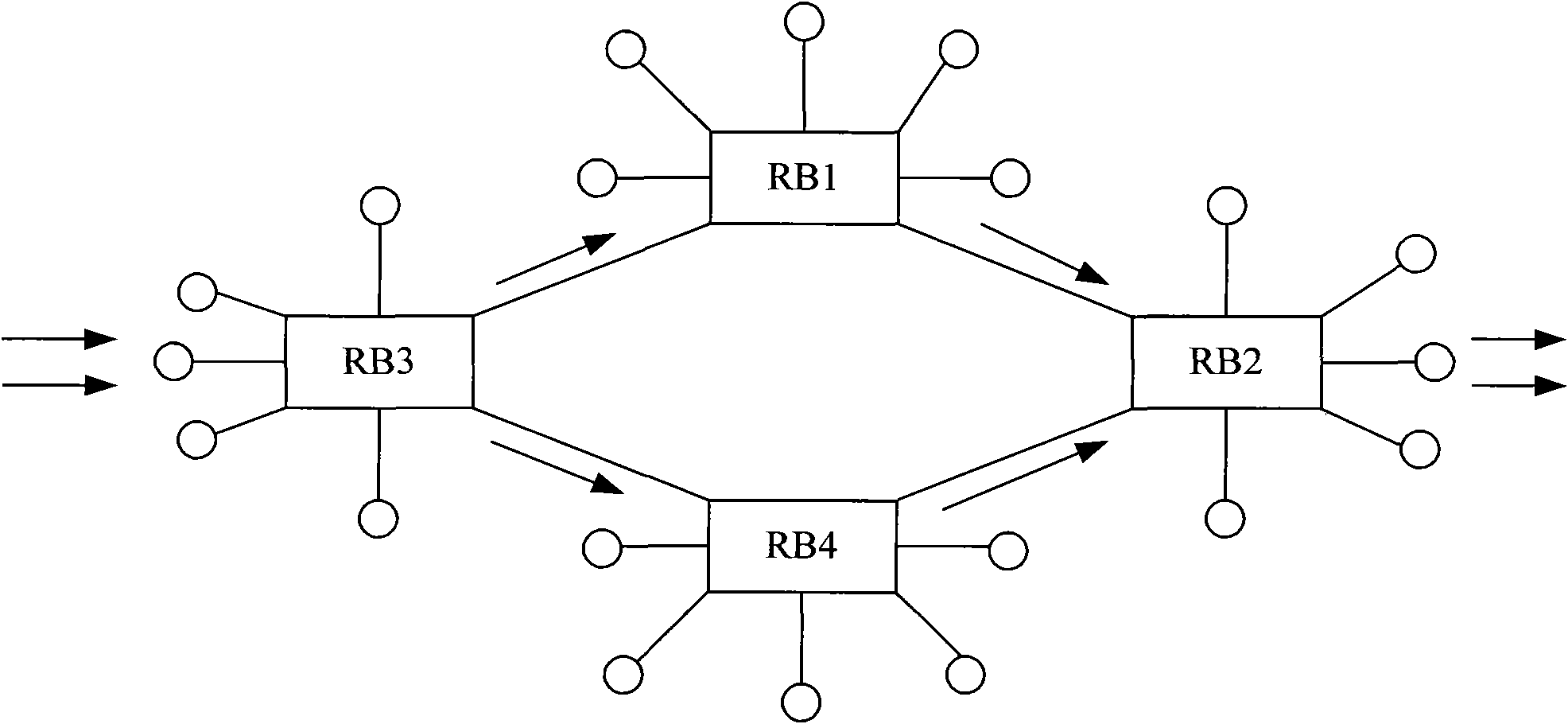
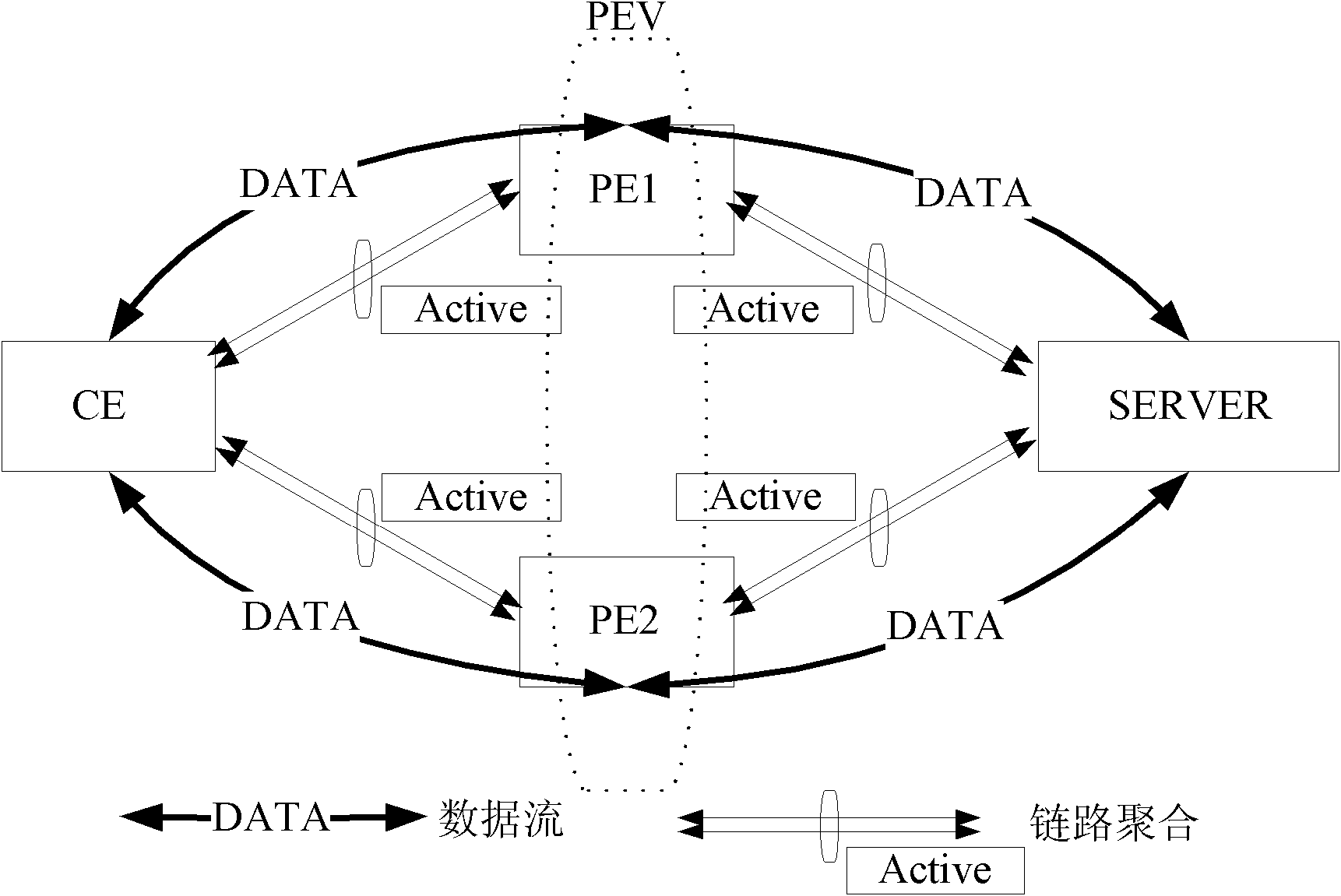
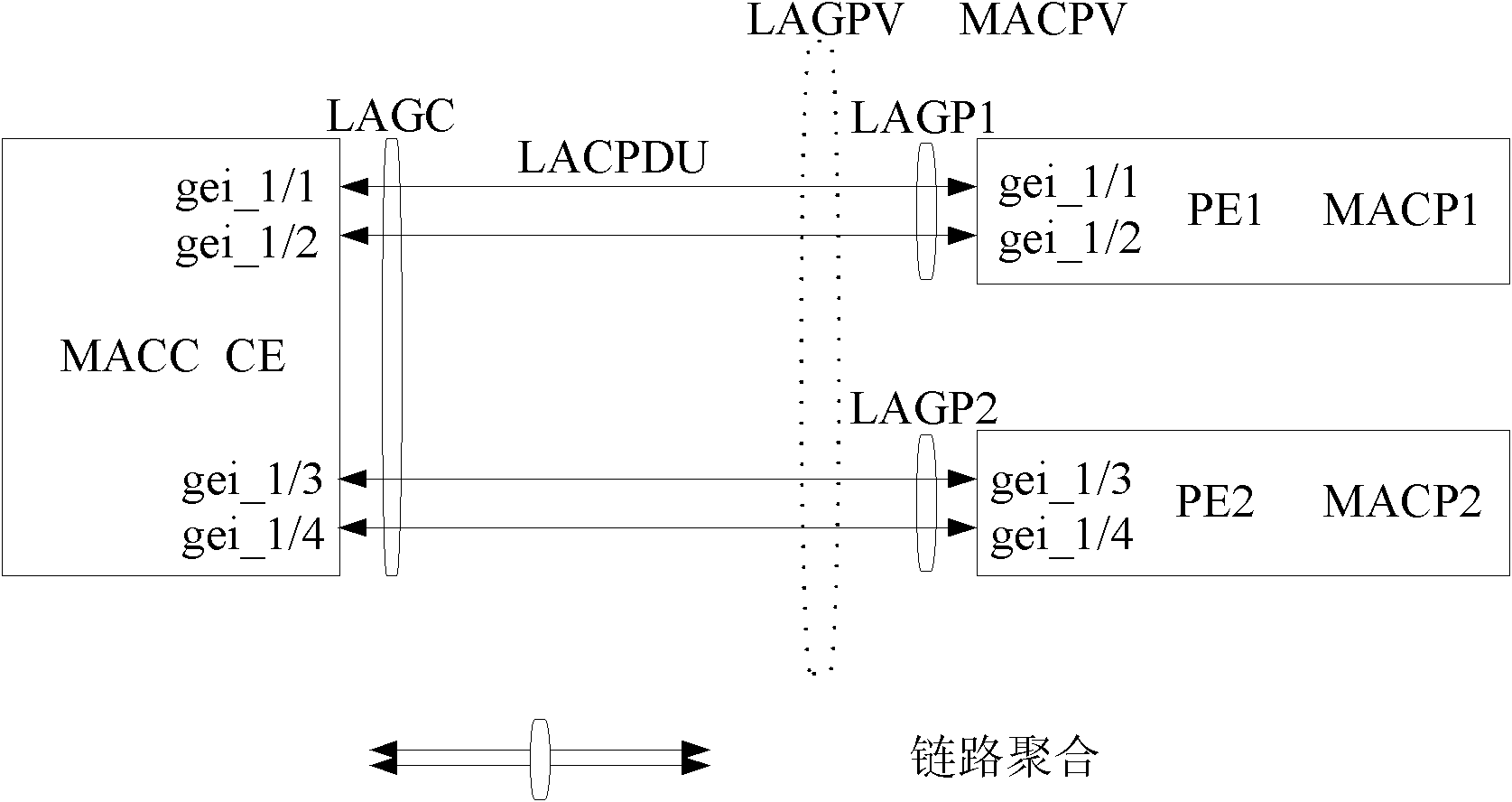
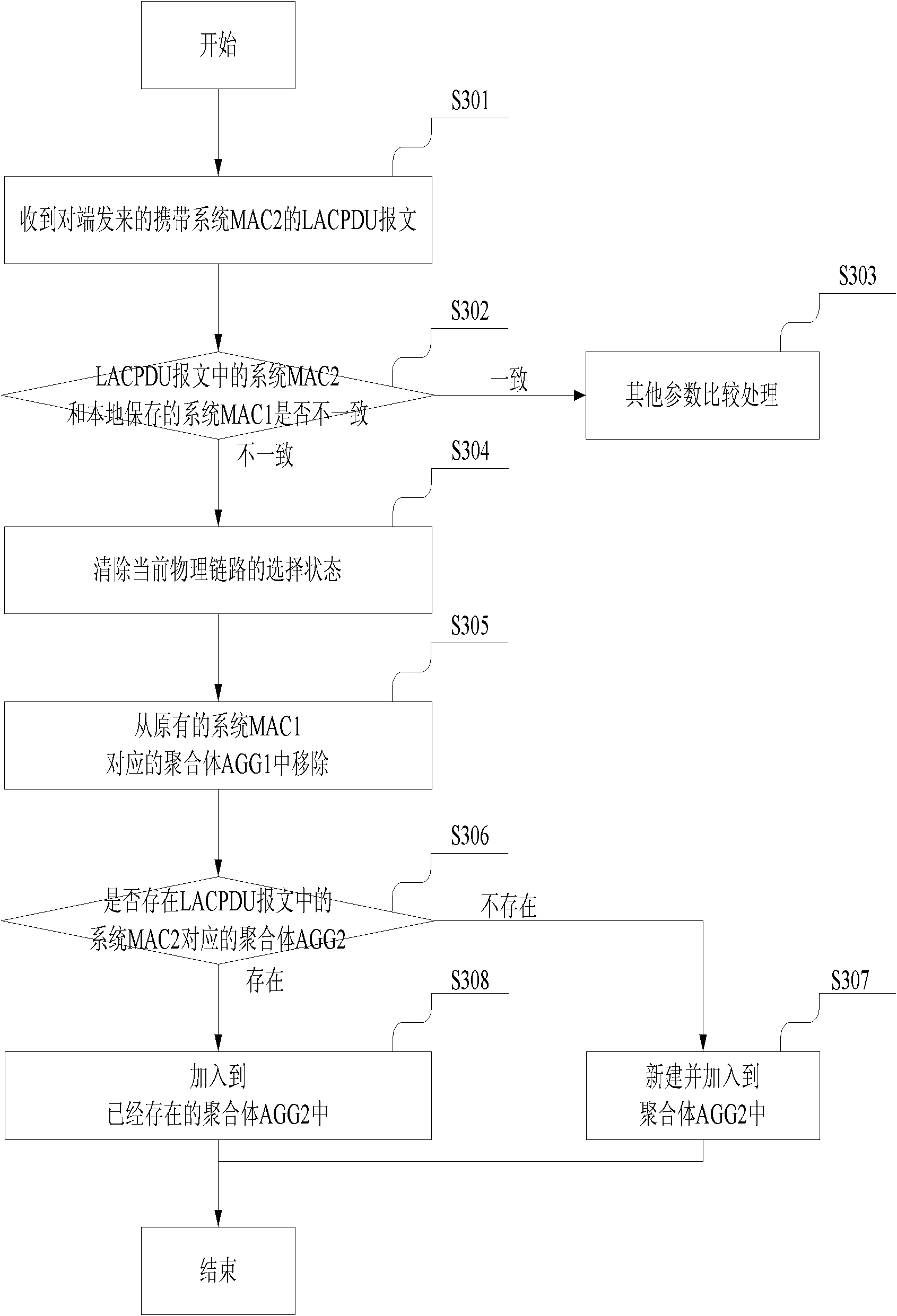
Device-level redundancy protection method and system based on LACP
The invention relates to a device-level redundancy protection method and system based on LACP (link aggregation control protocol); the method comprises the following steps: aggregation groups LAGP1 and LAGP2 on a first device and a second device are configured with the same parameters and transmit LACPDU messages of the parameters with same configuration to an aggregation group LAGC on the customer edge; the LAGC adds physical links connected with the LAGP1 and the LAGP2 to the same aggregator by interaction of the LACPDU message; the LAGP1 and the LAGP2 respectively add the physical link connected with the LAGC to the individual aggregator to form a virtual aggregator AGGV; and the customer edge processes the message interaction with a server by an AGGC and an AGGV. The invention implements that multiple PEs can be aggregated with CEs successfully at the same moment, thereby improving the utilization rate of the device and the service continuity when switching.
Owner:ZTE CORP
A method, apparatus and system for forwarding message
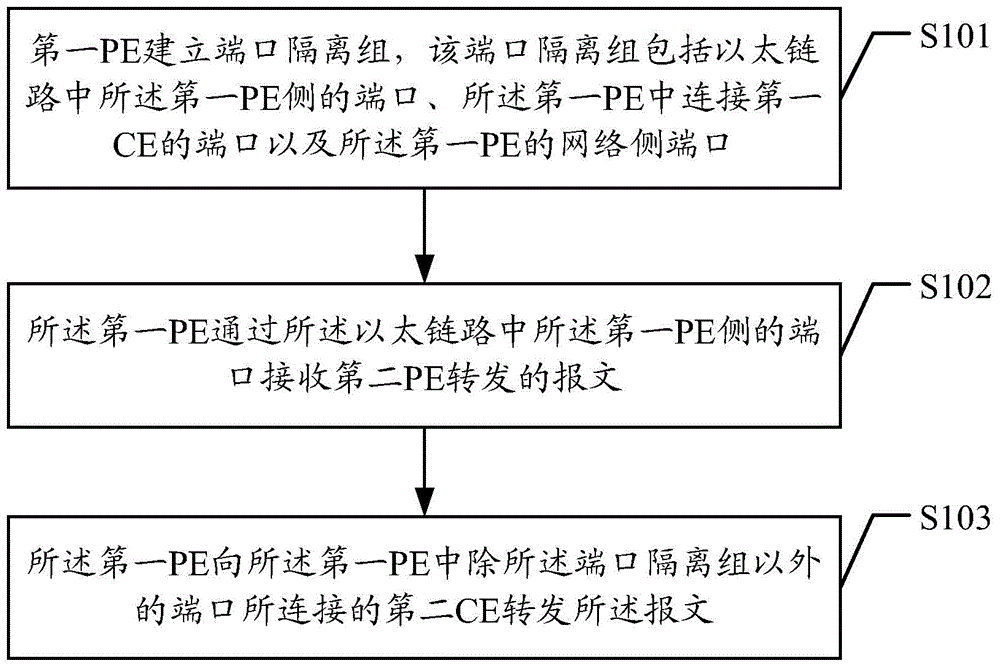
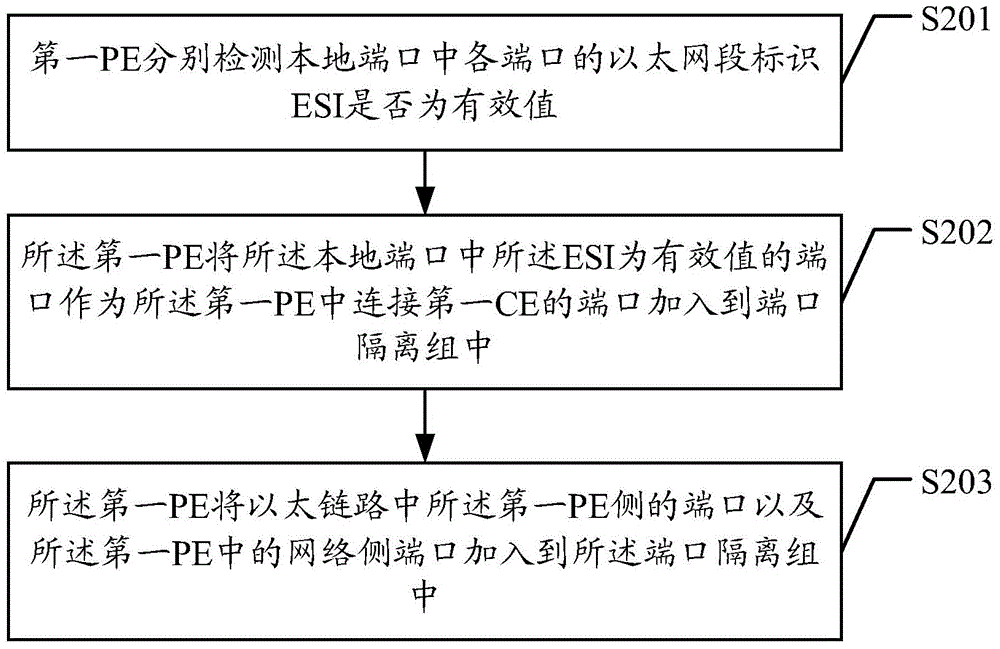
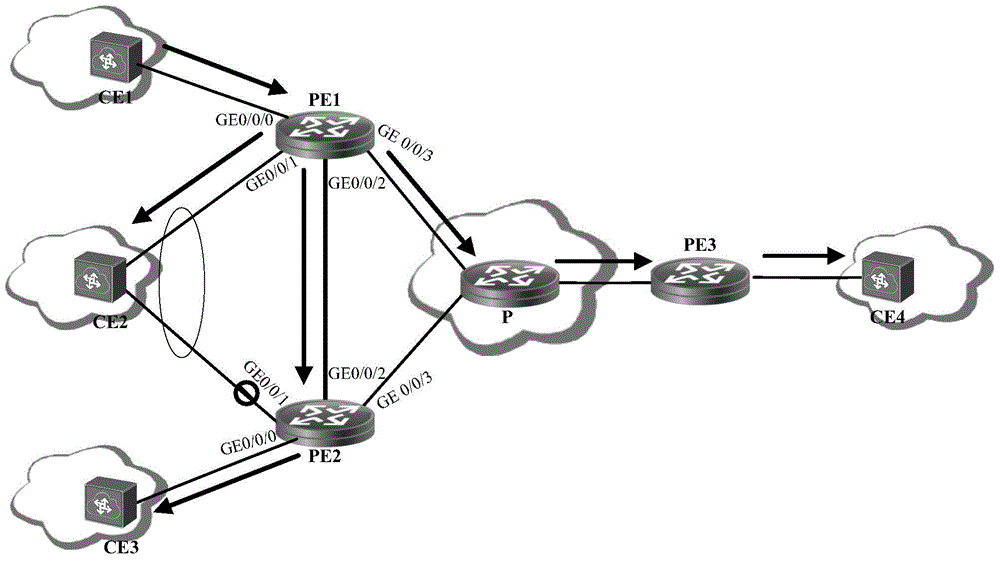
ActiveCN104135420ATroubleshoot postbacksPrevent postbackNetworks interconnectionPrivate networkMessage forwarding
Embodiments of the present invention disclose a method, apparatus and system for forwarding a message, which are adapted for the scenario that a customer edge apparatus CE is connected to an Ether Virtual Private Network (EVPN) by way of dual homing through a first provider edge apparatus PE and a second PE. An Ether link is established between the first PE and the second PE. The method includes: establishing, by the first PE, a port isolation group; receiving, by the first PE, the message forwarded by the second PE through the port at the side of the first PE in the Ether link; and forwarding, by the first PE, the message to CEs connected to ports except the port isolation group in the first PE. Using the present invention, the technical problem, i.e., traffic passing back at the customer side during message forwarding in the EVPN network in the prior art, can be effectively solved without changing the current hardware chip design.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Transport networks supporting virtual private networks, and configuring such networks
A layer 2 transport network, and components thereof, supporting virtual network functionality among customer edge devices. Virtual private network configuration can be accomplished with merely local intervention by preprovisioning extra channel (or circuit) identifiers at each customer edge device and by advertising label base and range information corresponding to a list of channel (or circuit) identifiers.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
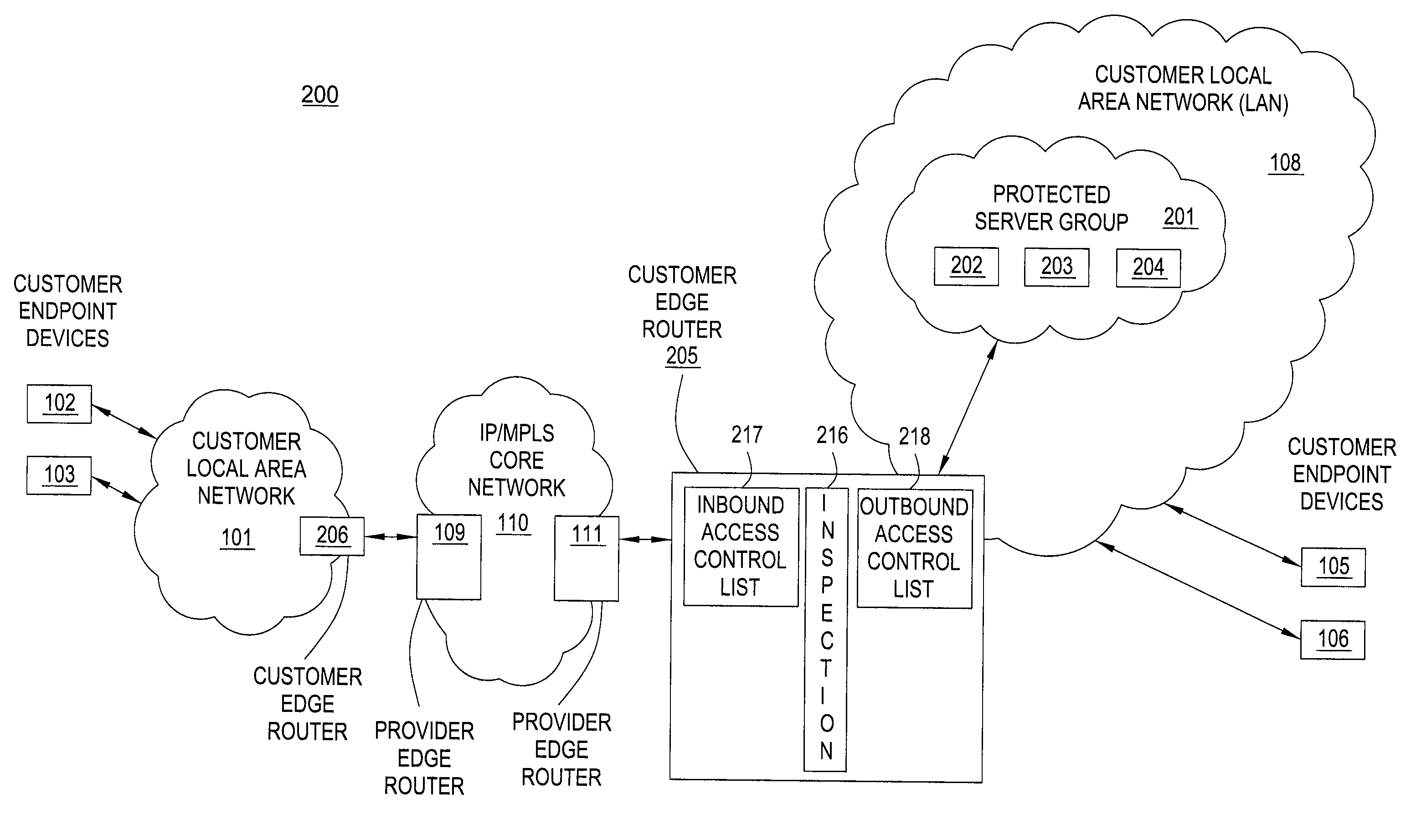
Method and apparatus for providing security in an intranet network
InactiveUS20100037309A1Provide securityComputer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork packetAccess control list
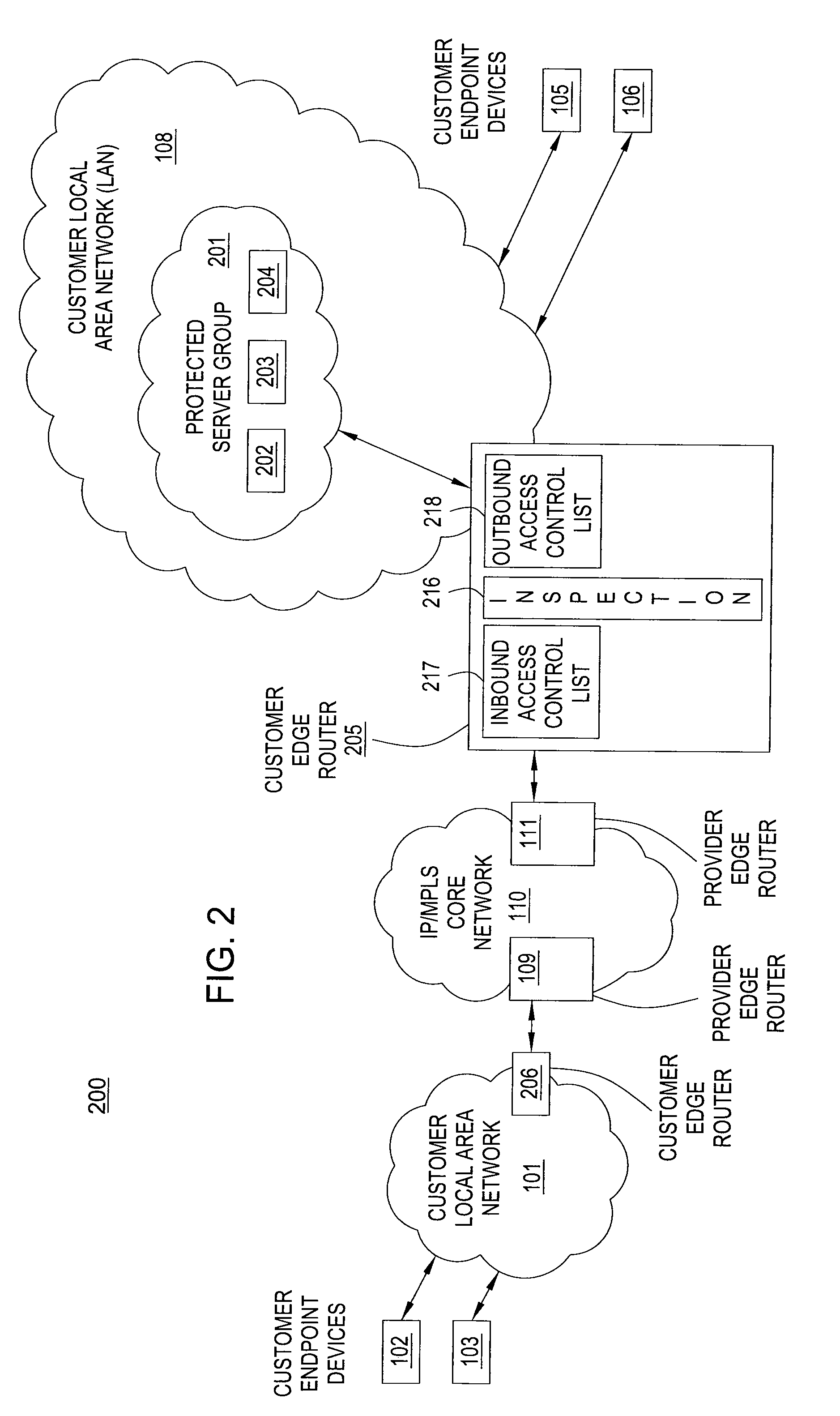
A method and an apparatus for providing security in an intranet network are disclosed. For example, the method receives a packet at a customer edge router, and applies an inbound access control list by the customer edge router to the packet if the packet is destined to a server in a protected server group, wherein said protected server group identifies one or more servers within the intranet network to be protected. The method applies an outbound access control list by the customer edge router to the packet if the packet is from a server in the protected server group.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
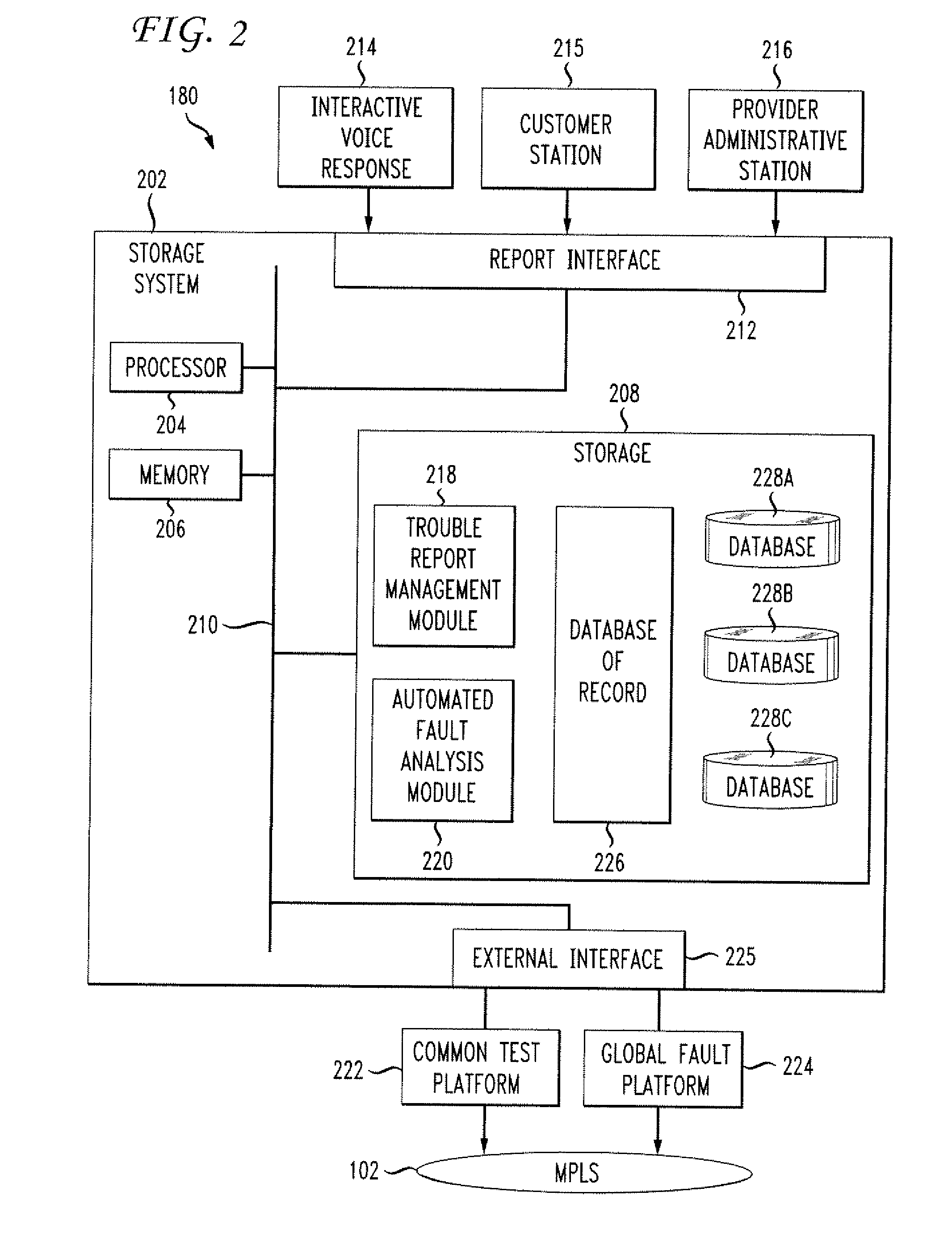
Methods and Apparatus for Fault Identification in Border Gateway Protocol Networks
InactiveUS20090161556A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityBorder Gateway Protocol
Systems and techniques for fault analysis in a data communication system. A fault analysis console in a provider network serving one or more customer networks responds to a reported loss of connectivity in the customer network by analyzing traffic statistics for a router serving the customer network. If traffic statistics indicate network functionality, border gateway protocol status is evaluated for logical channels being served by the router. Test communications are performed for customer edge router addresses for the logical channels and border gateway protocol status is evaluated for each customer edge router address. Test communications are then performed from a local provider edge router to each remote customer edge router being served.
Owner:LYFT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com