Patents
Literature
4159 results about "Protection mechanism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
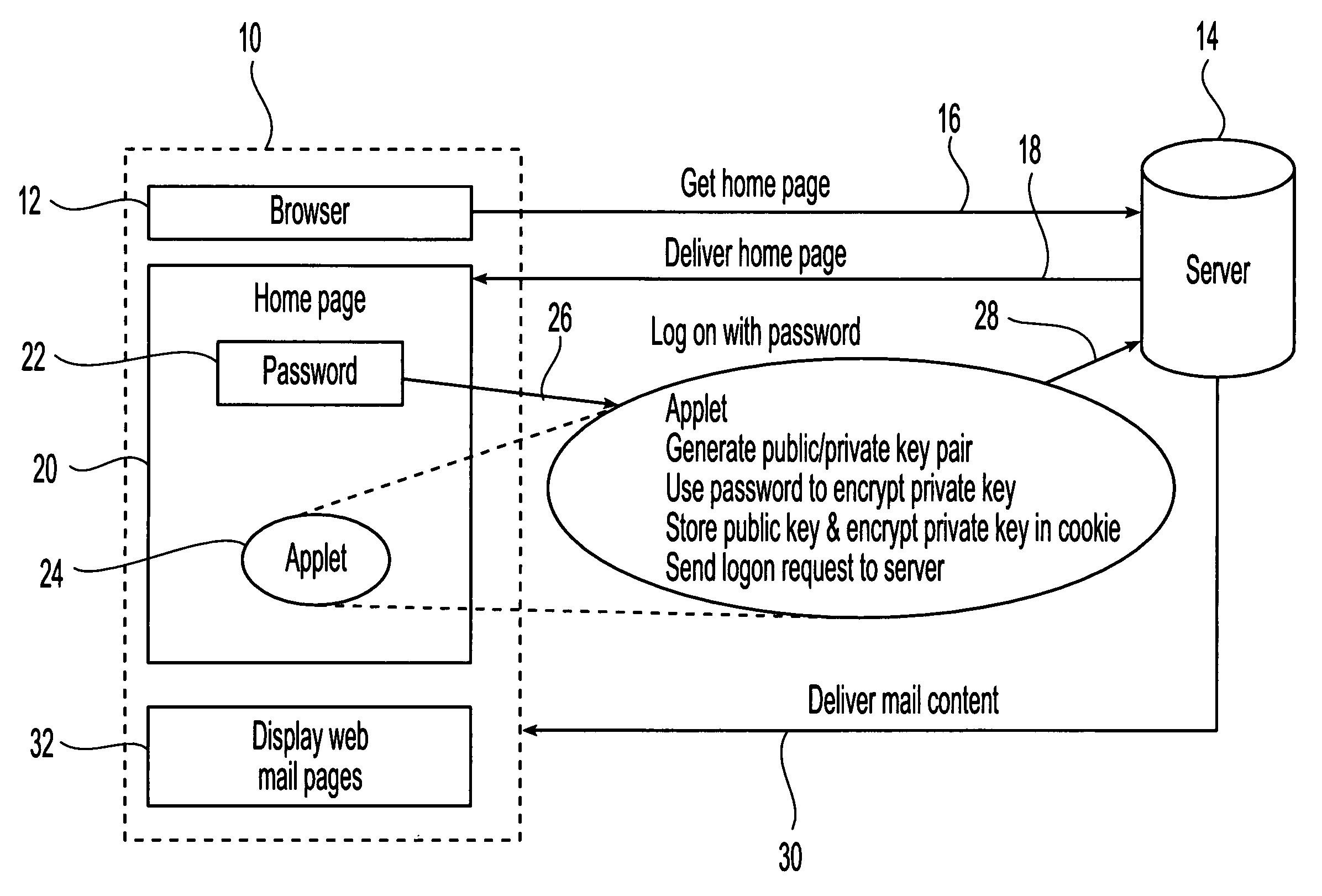
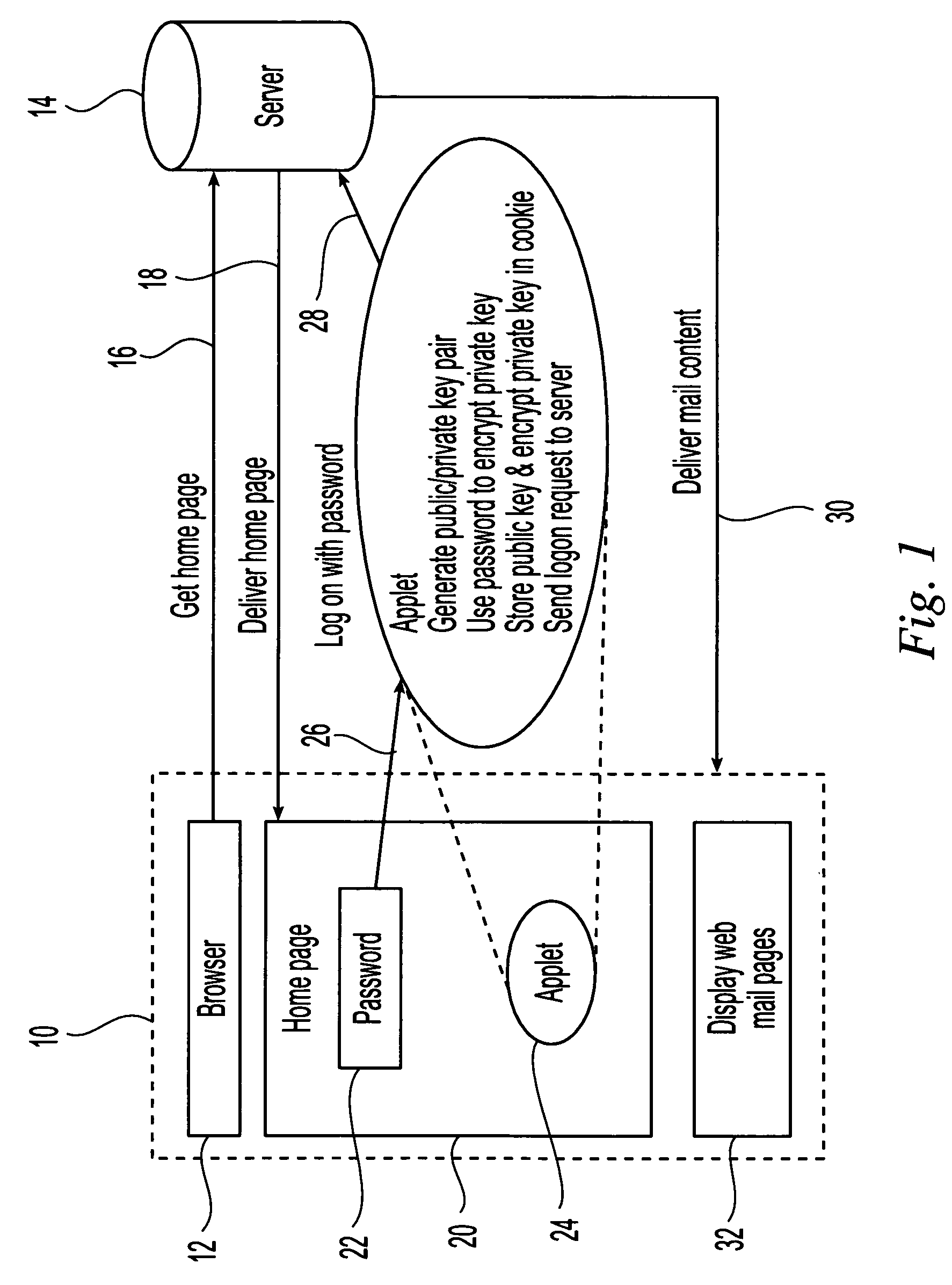
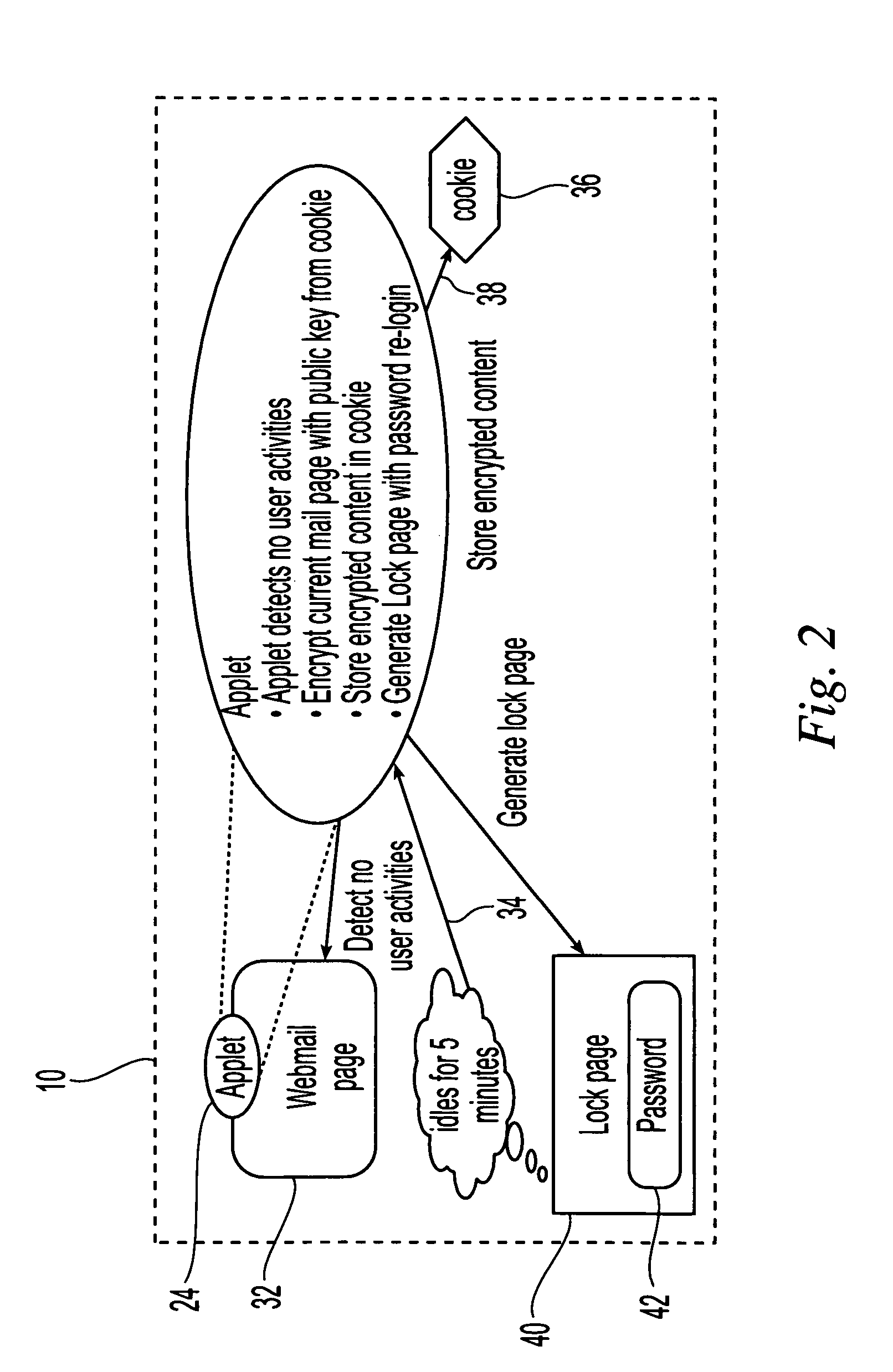
In computer science, protection mechanisms are built into a computer architecture to support the enforcement of security policies. A simple definition of a security policy is "to set who may use what information in a computer system".
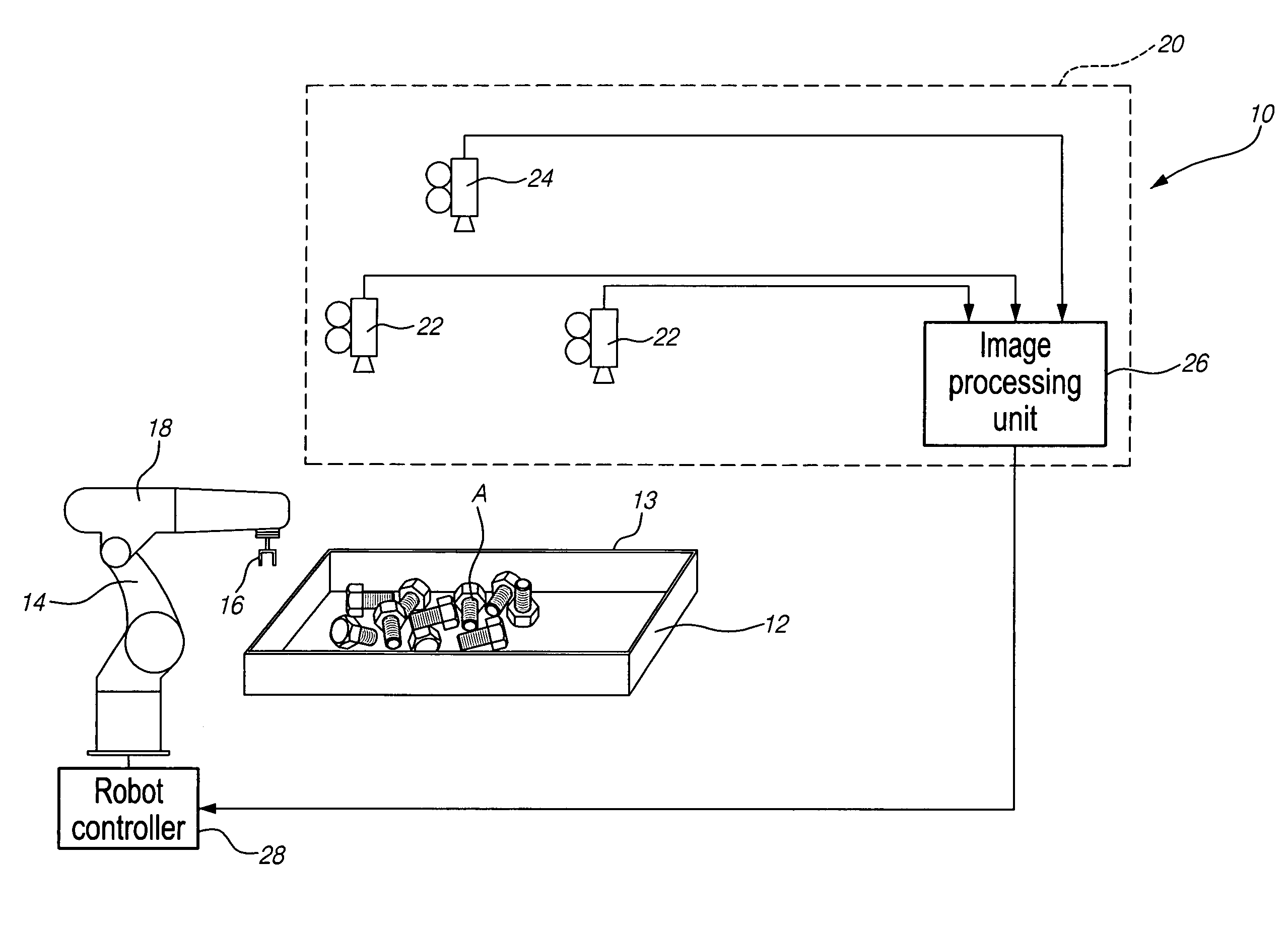
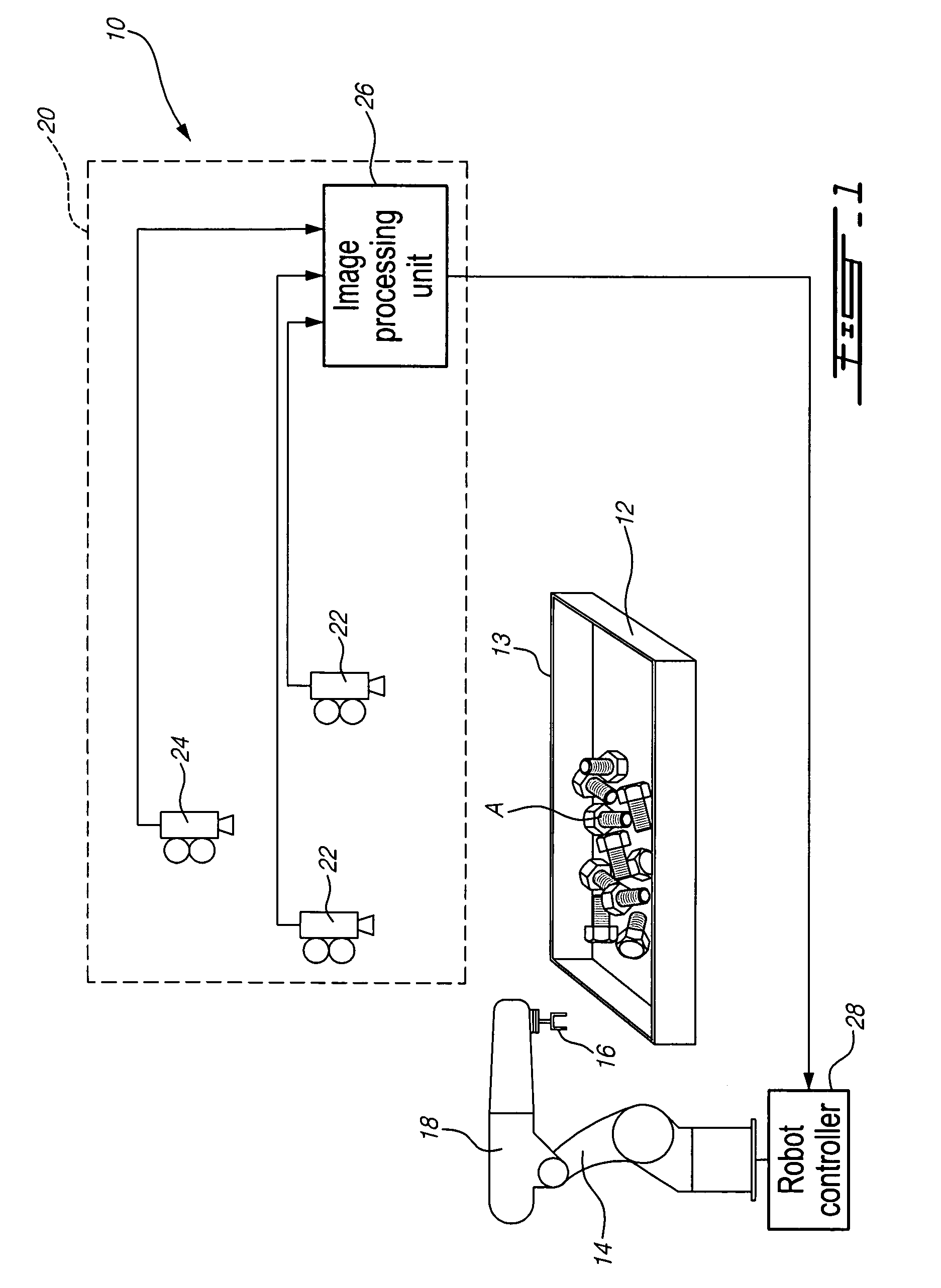
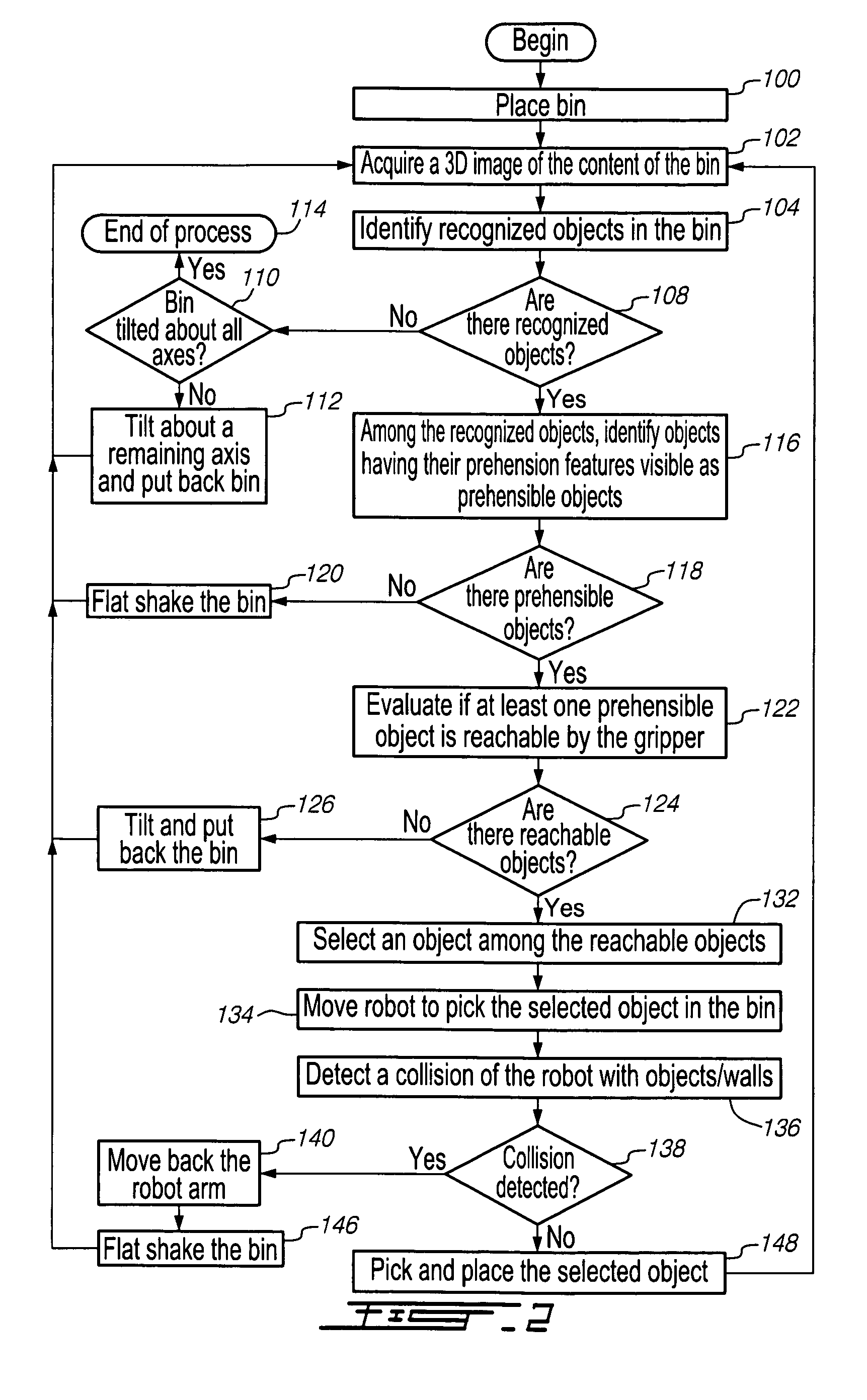
Bin-picking system for randomly positioned objects
ActiveUS7313464B1Programme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlComputer graphics (images)Protection mechanism
A method for picking up objects randomly arranged in a bin using a robot having a gripper for grasping the objects using prehension feature(s) on the object. The method includes a shaking scheme for rearranging the objects in the bin when no objects are recognized, when no objects are prehensible by the gripper or when the object to be picked up is not reachable by the gripper because, for example, its prehension feature is substantially facing a wall of the bin. The method also includes a criterion for determining that a bin is free of objects to be picked up and a criterion for selecting the object to be picked up first in the bin. The method also provides for a protection mechanism against damage of the objects and the robot when a recognition technique has failed in properly recognizing the object or the prehension feature on the object.
Owner:ORMON CORP
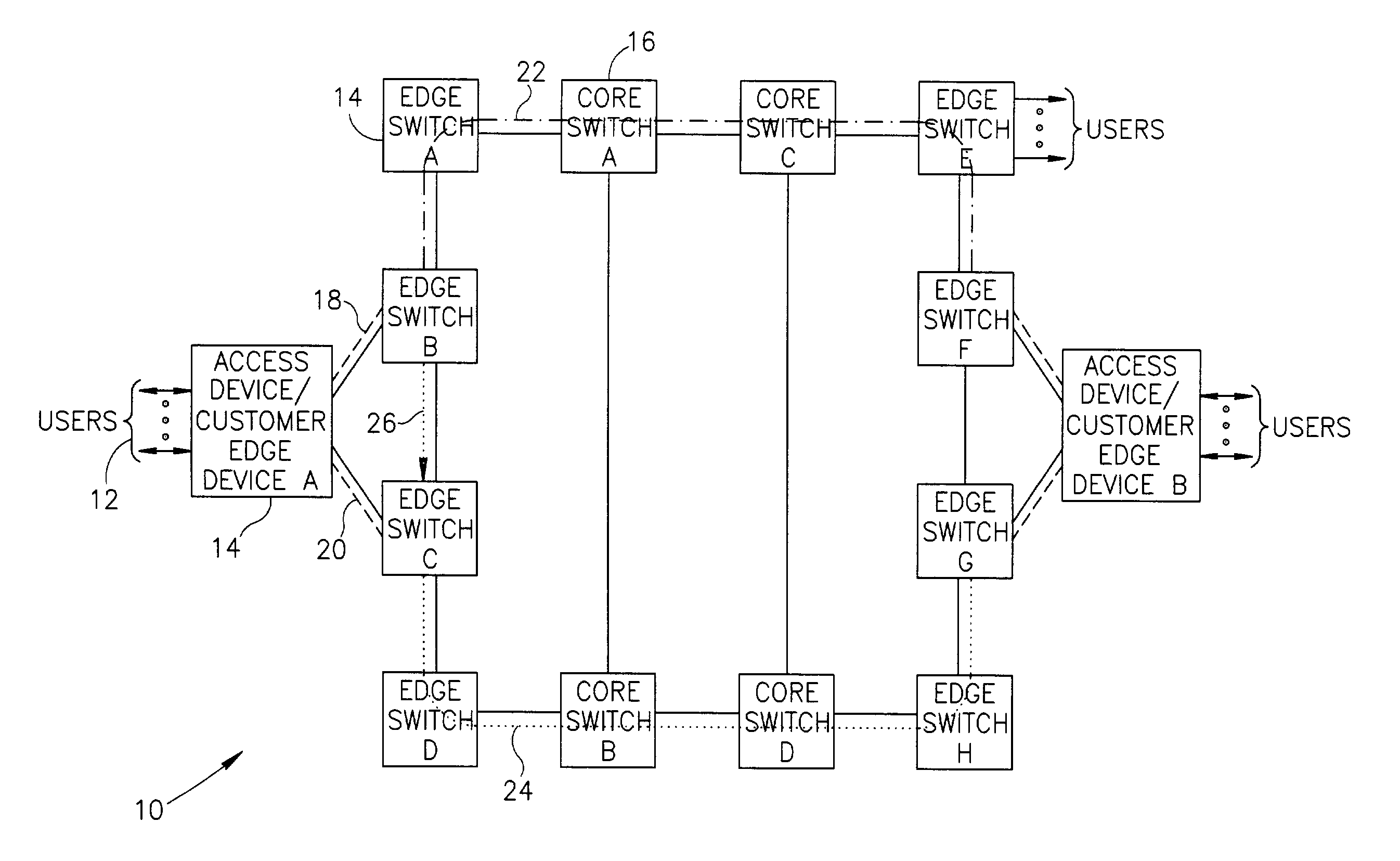
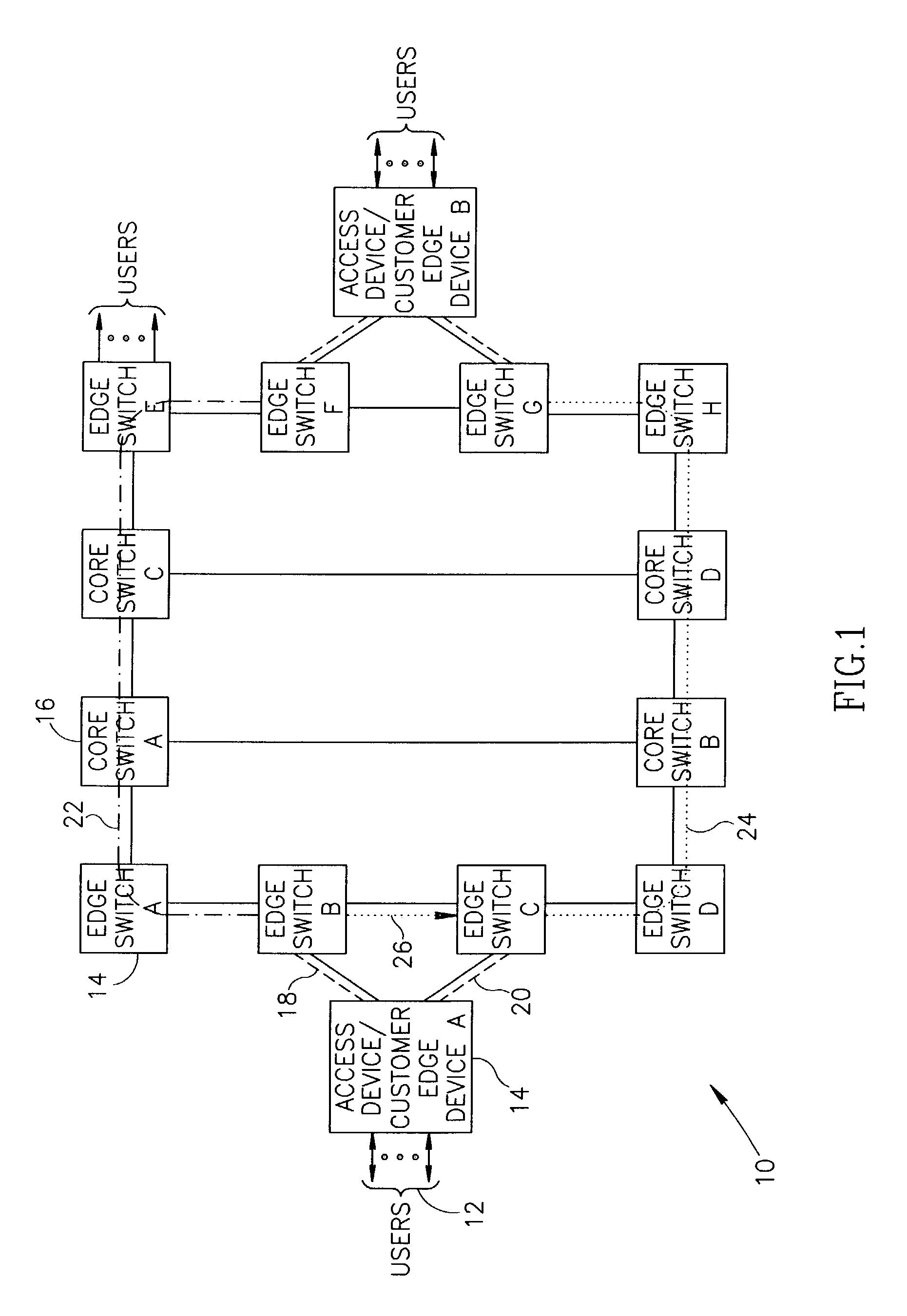
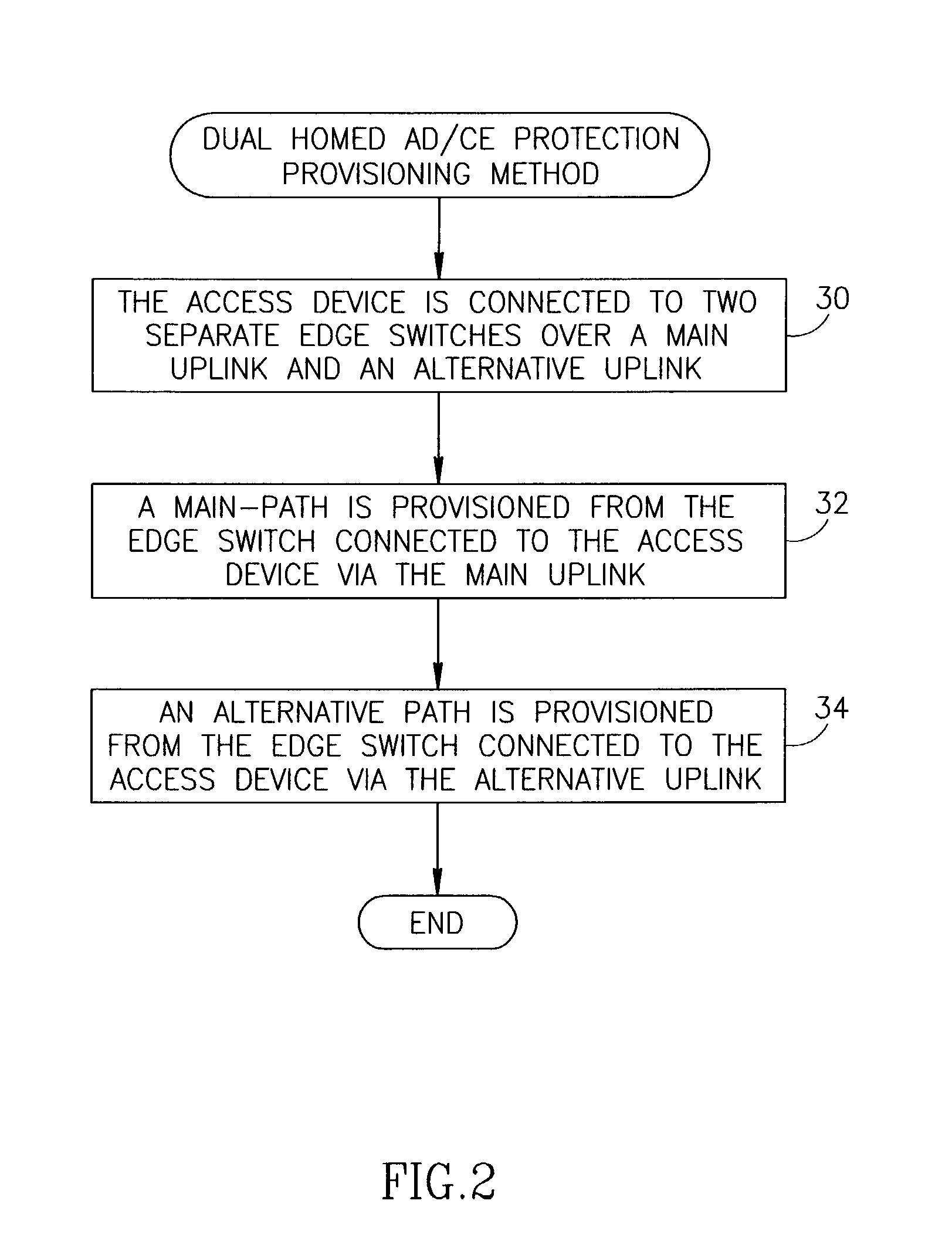
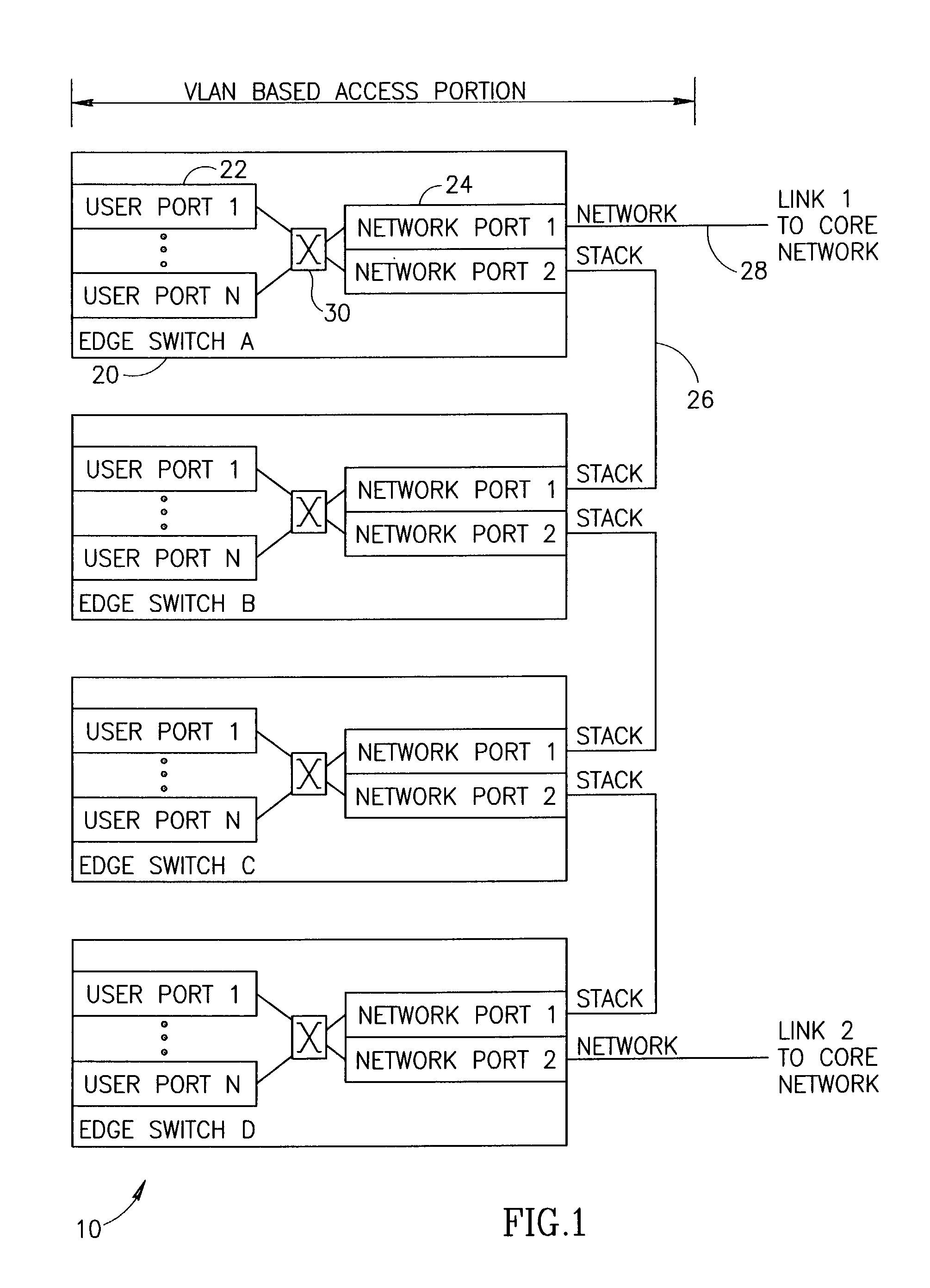
Connection protection mechanism for dual homed access, aggregation and customer edge devices
InactiveUS7345991B1Quick protectionImprove reliabilityEnergy efficient ICTError preventionOff the shelfProtection mechanism
A protection mechanism capable of providing both local and end-to-end connection protection for dual homed access / aggregation devices or customer-edge devices in a network. The protection mechanism provides end-to-end and fast local protection for off the shelf access devices that do not have any built in per-connection protection capabilities. The access device is connected via two separate physical uplinks to two edge switches of the network. For each connection to be protected, a main path is provisioned from one edge switch and an alternative path is provisioned from the other edge switch. The edge switches are adapted to comprise means for switching traffic from the main path to the alternative path in the event a failure along the main path is detected. Failures both in the stack portion, the core portion and in the access device uplinks are protected against.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS ETHERNET SOLUTIONS
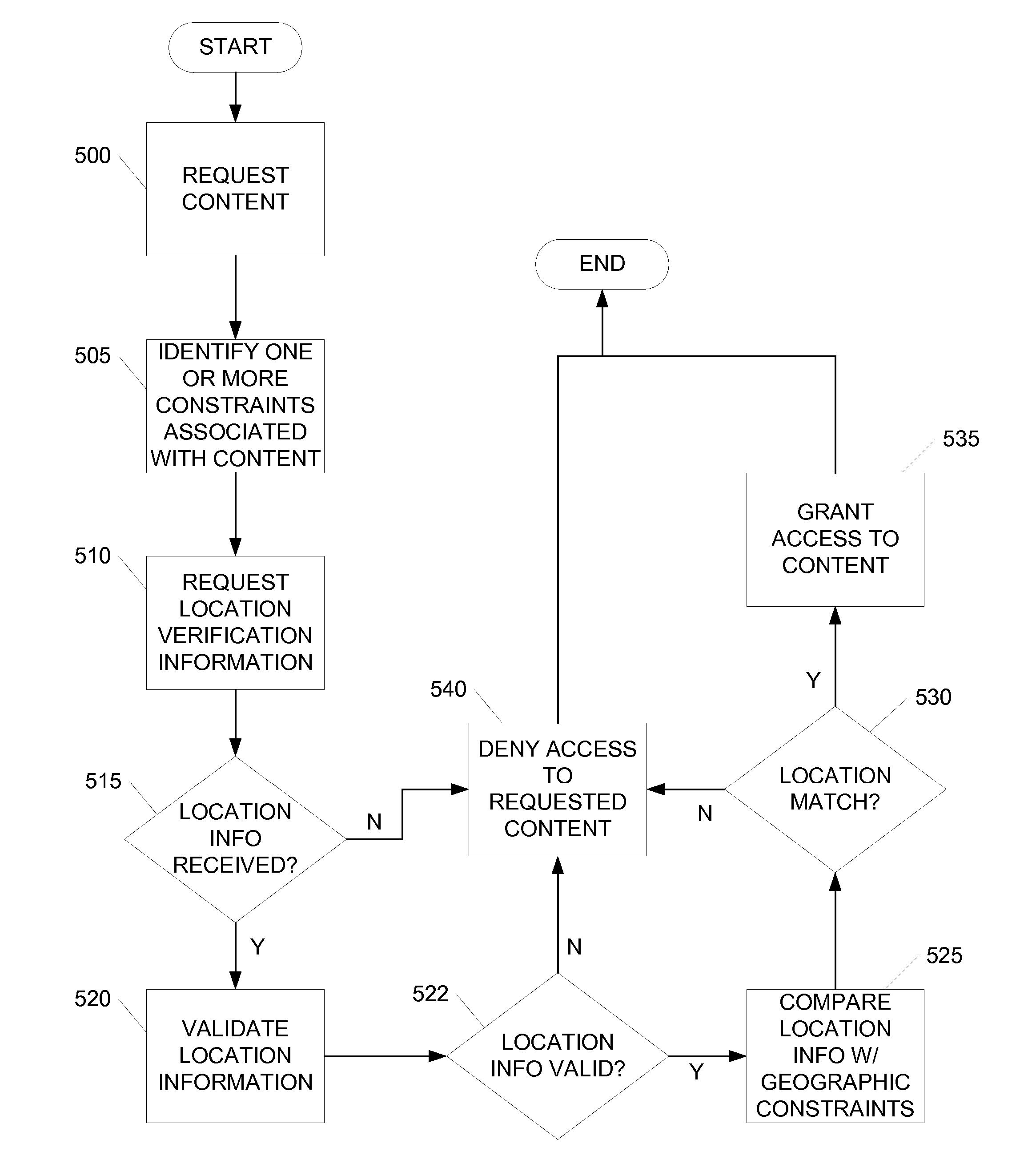
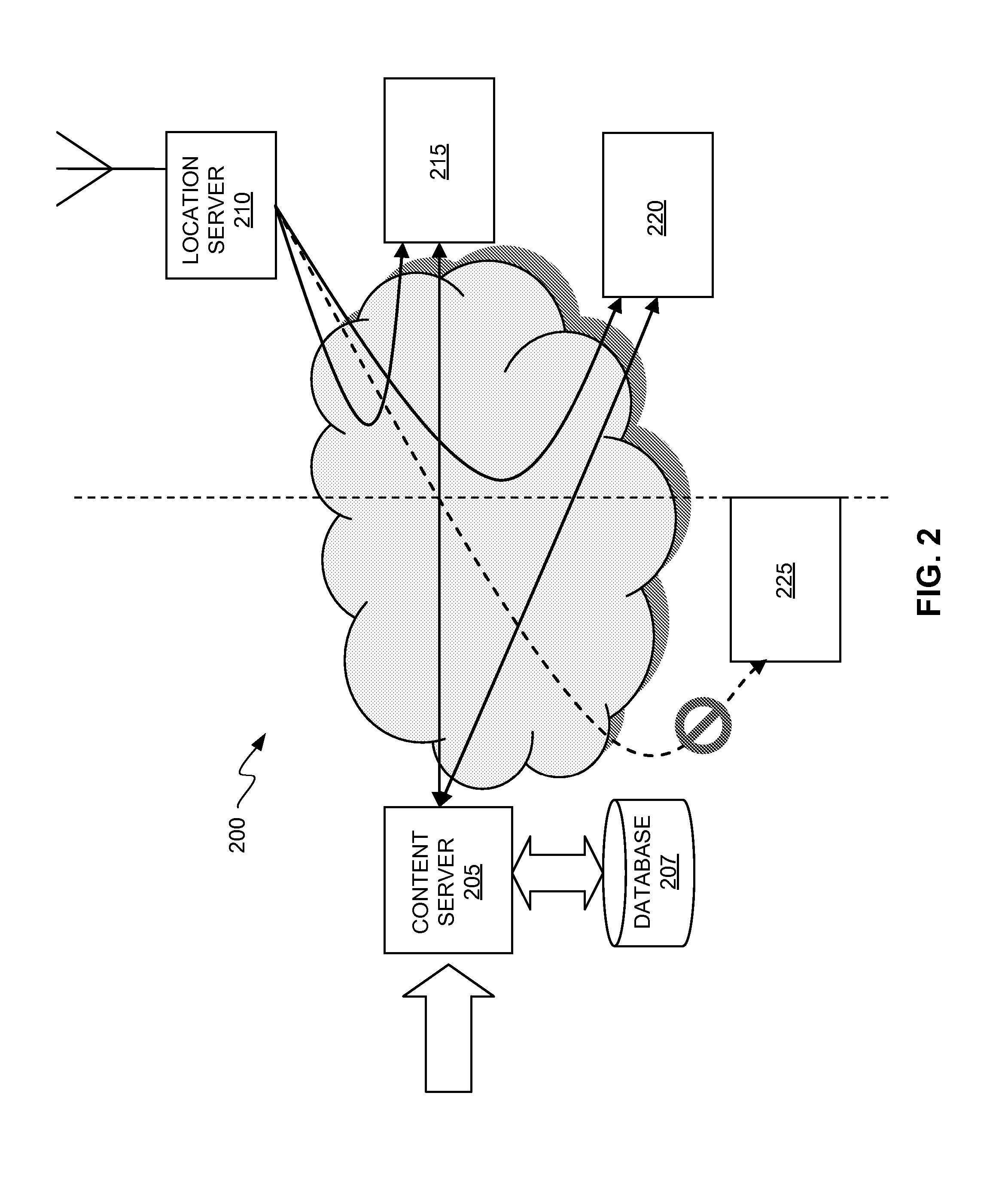
Enforcing Geographic Constraints in Content Distribution
ActiveUS20080022003A1Improve integrityInhibition of informationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsContent distributionProtection mechanism
Enforcement of geographic and location based constraints on content distribution is provided to allow distribution of content to remote devices while preventing unauthorized use and consumption of the content. Content requested by a device may be protected using a variety of content protection mechanisms that support geographic constraints. The requesting device may be required to validate and / or obtain the device's physical location prior to being granted access to the protected content. The requesting device may validate and / or obtain its physical location by requesting location information from a location server or another geographic aware device. The distribution of the location information from the location server may be limited to a predefined proximity. The proximity limit on the dissemination of the location information prevents remote devices from fraudulently using the location information. Location information may be encapsulated and may be formatted as a content file.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
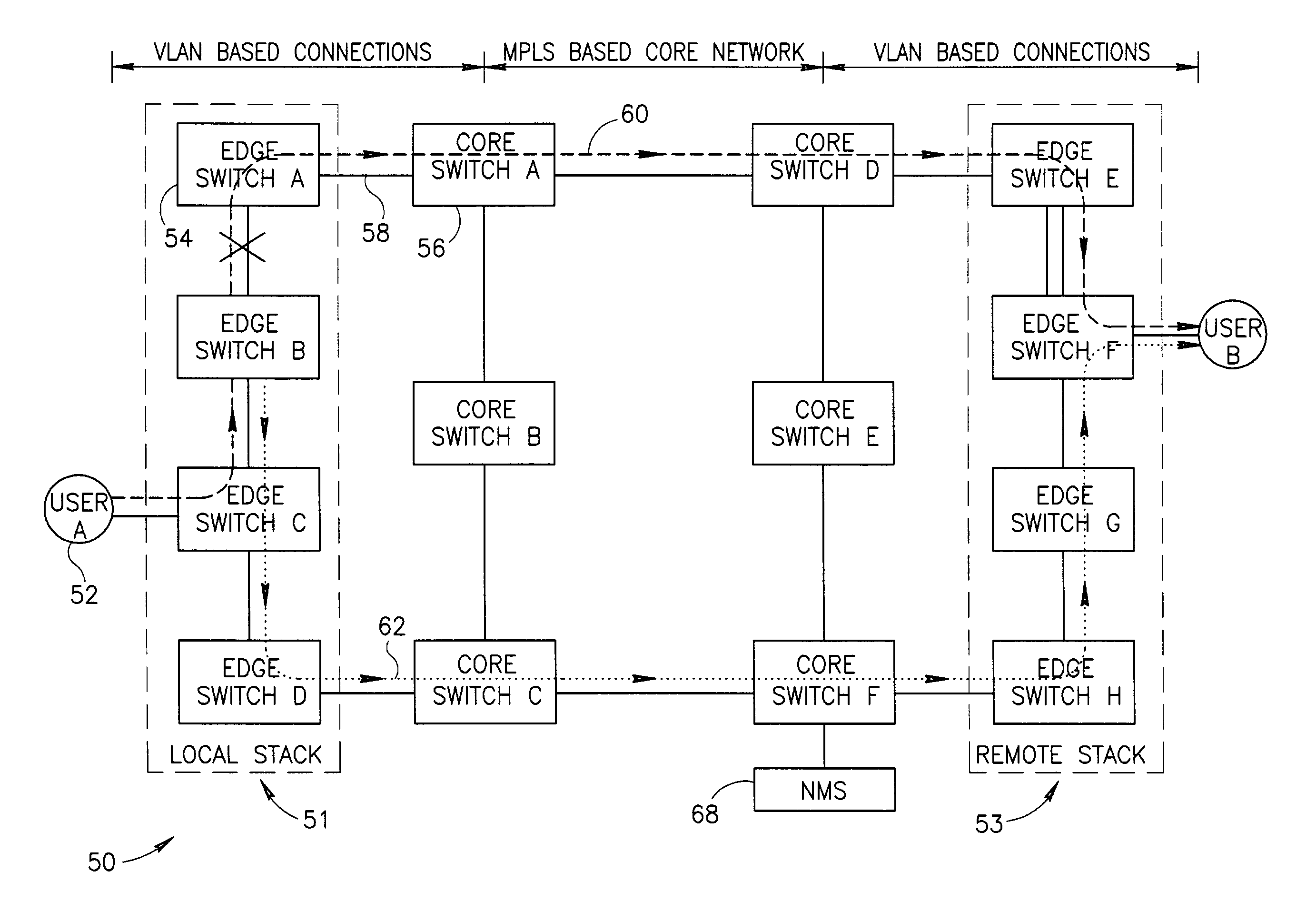
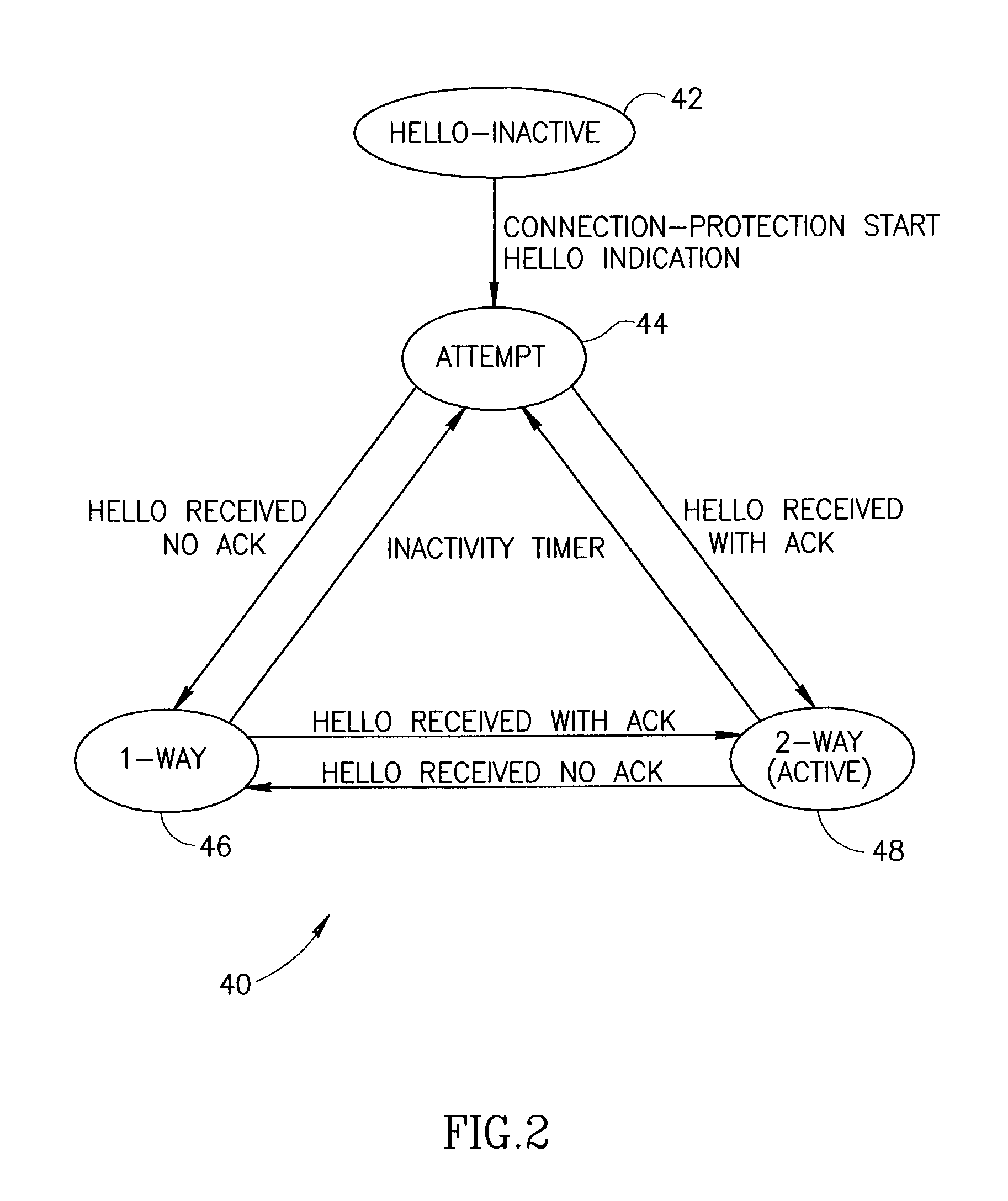
Fast connection protection in a virtual local area network based stack environment
A fast protection mechanism capable of maintaining end-to-end and fast local protection on the order of sub 50 ms for both VLAN only based connections and for connections that are based partially on VLAN technology and partially on MPLS technology. The present invention is suitable for use edge switches configured in a stack or ring topology. The NMS provisions both the main and alternative VLANs in each edge switch in the stack portions of the network. When a link failure occurs, the edge switches on either end of the failed link immediately switch all protected traffic going through that link to the alternative VLAN. The packets are then returned on the links over which they were received. Hello messages are used to signal the remote end that a link failure has occurred and that protected traffic must be switched to the main or alternative VLAN in accordance with the VLAN the Hello message was received on.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING III +1
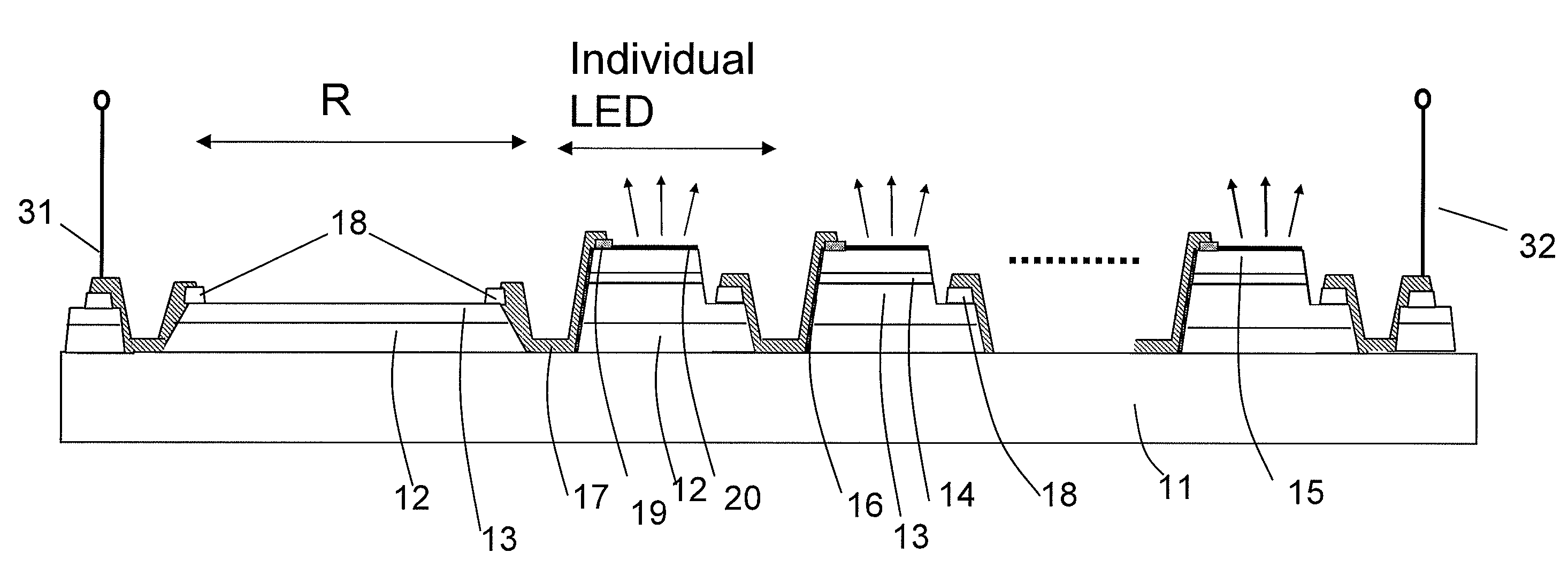
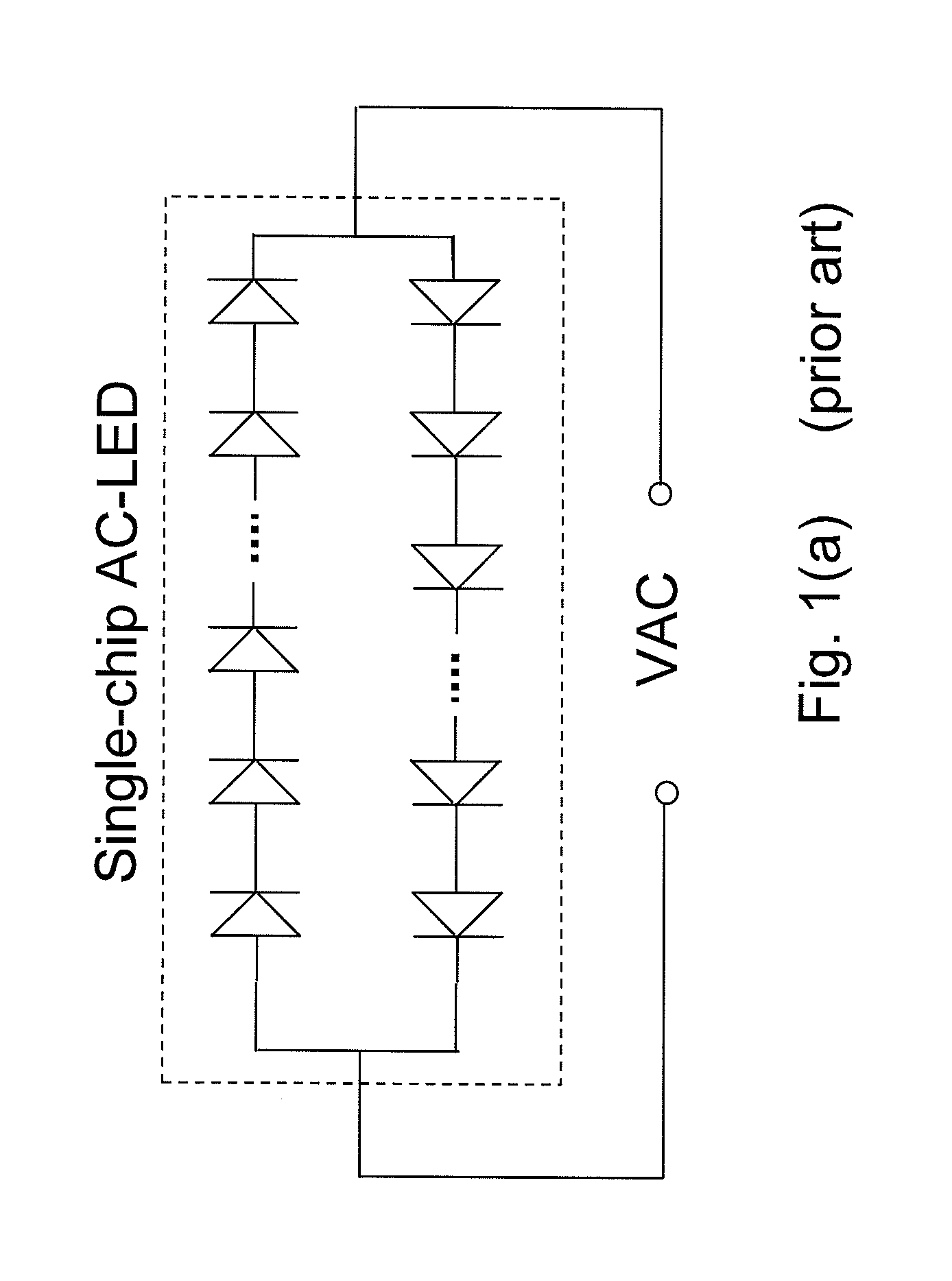
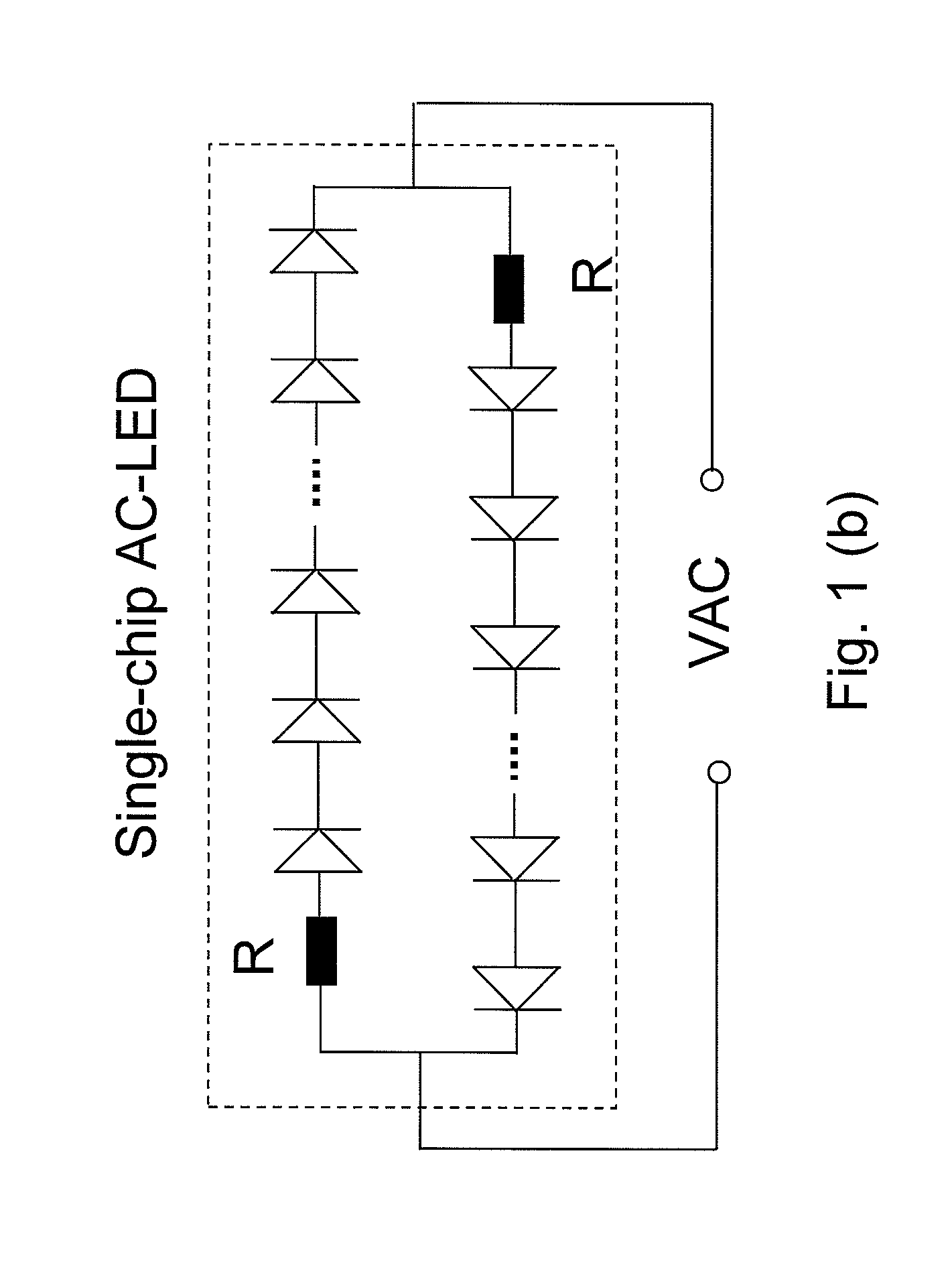
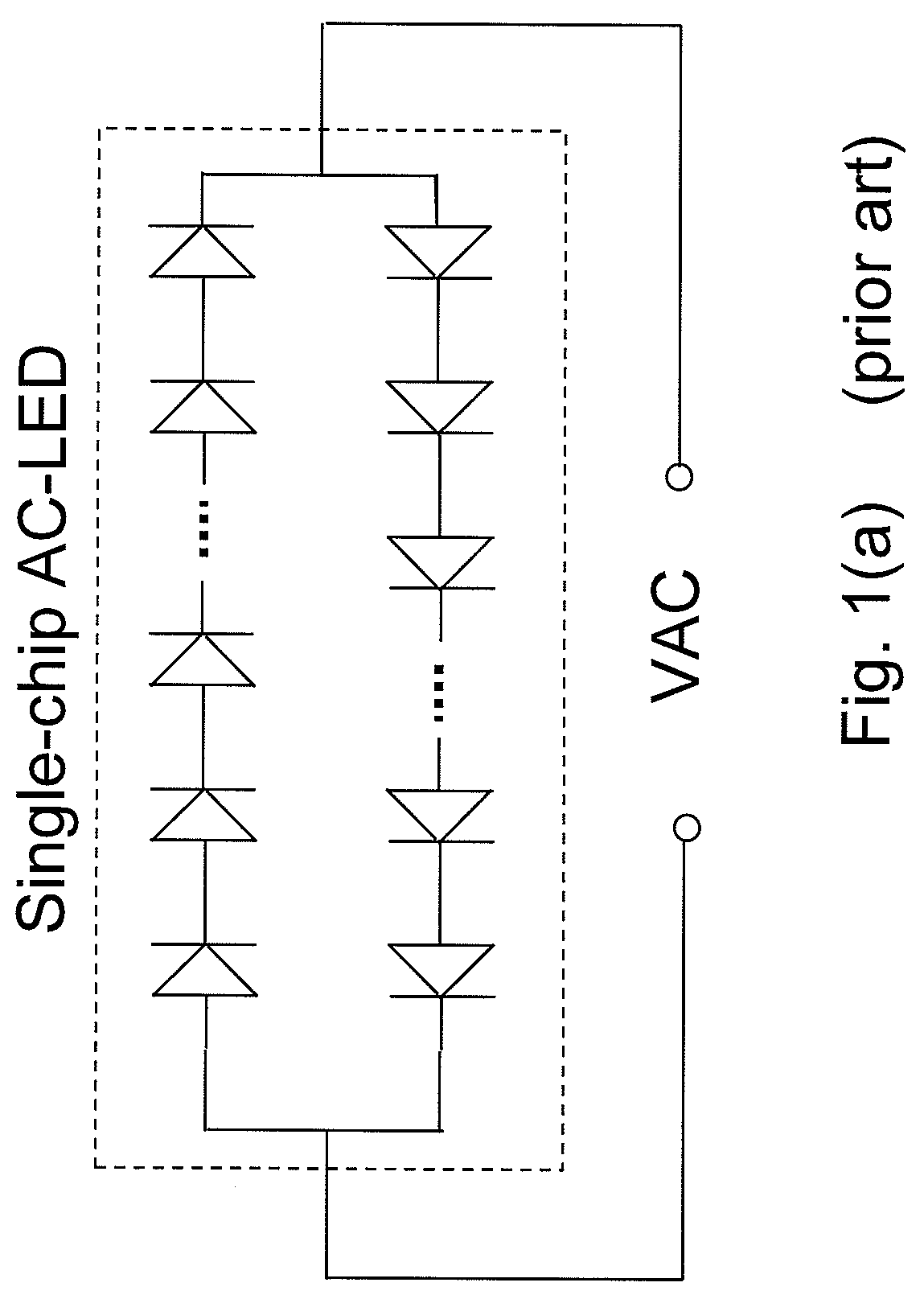
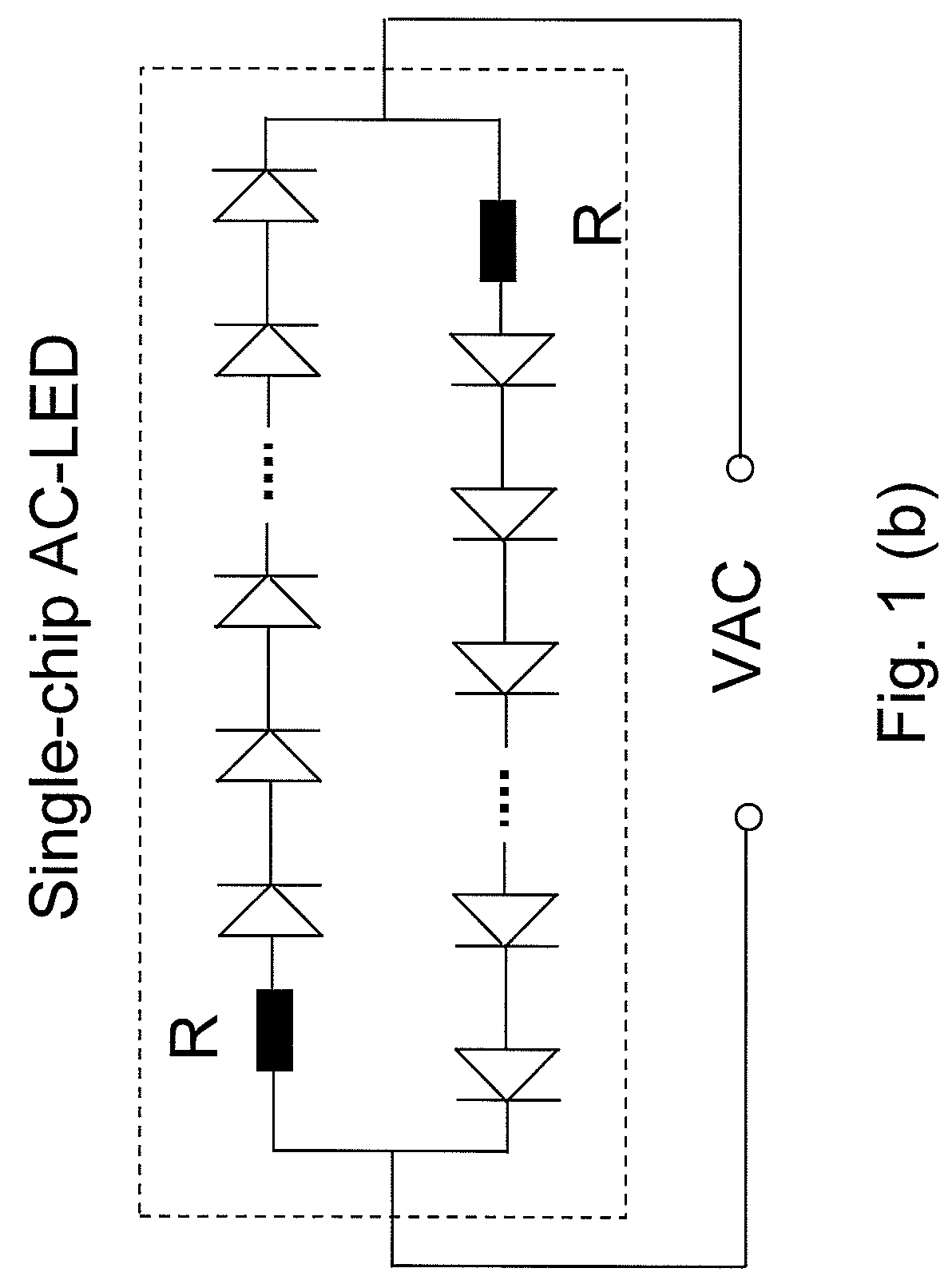
Ac/dc light emitting diodes with integrated protection mechanism
ActiveUS20080083929A1Inhibition effectElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesCurrent limitingProtection mechanism
A highly reliable, high voltage AC / DC LED device with integrated protection mechanism is disclosed. The protection element can be a current-limiting resistor, monolithically integrated on LED chip, or a discrete resistor assembled in the lamp package or submount. The protection elements may also include other parts integrated on a submount.
Owner:LED LIGHTING
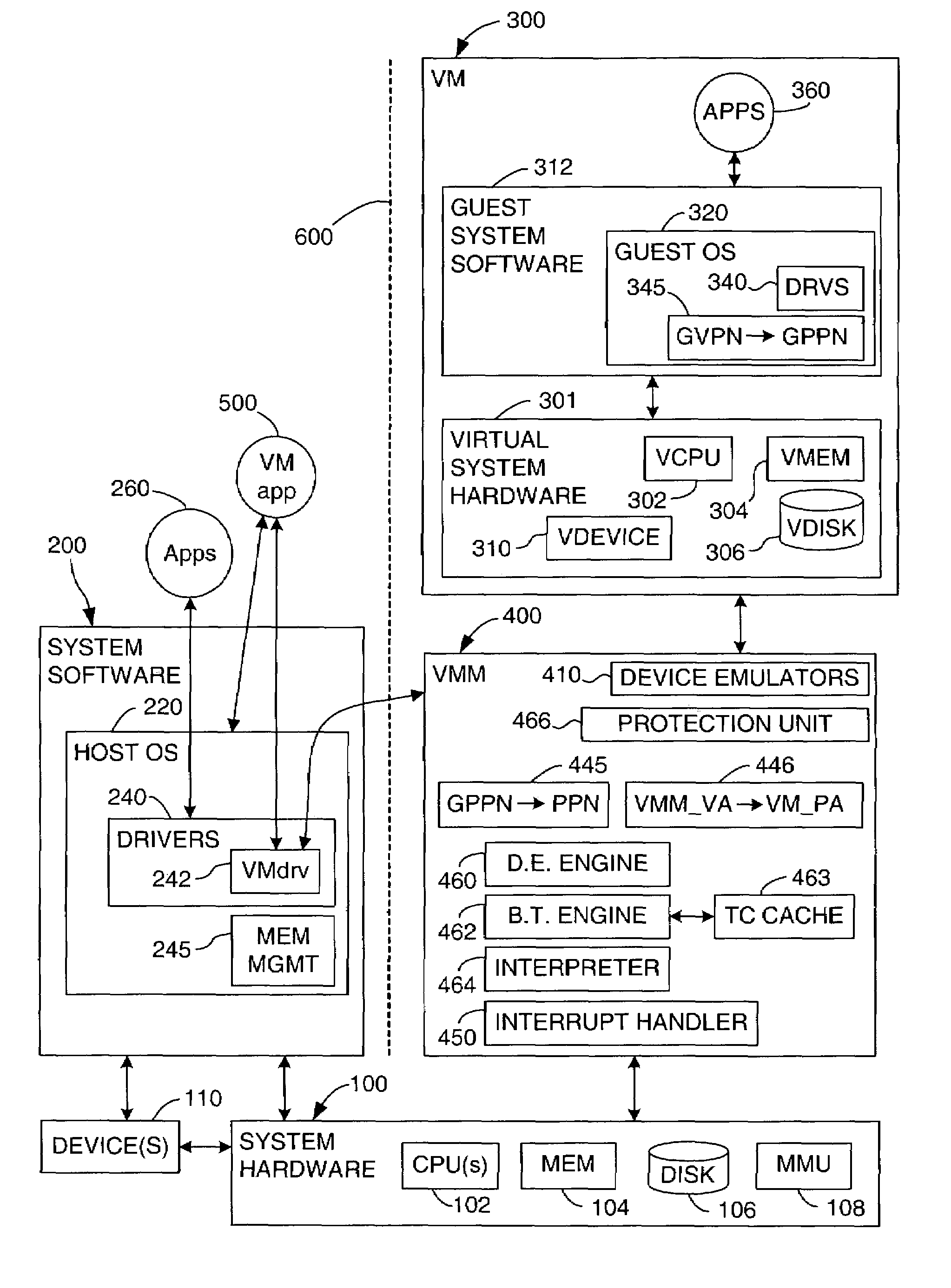
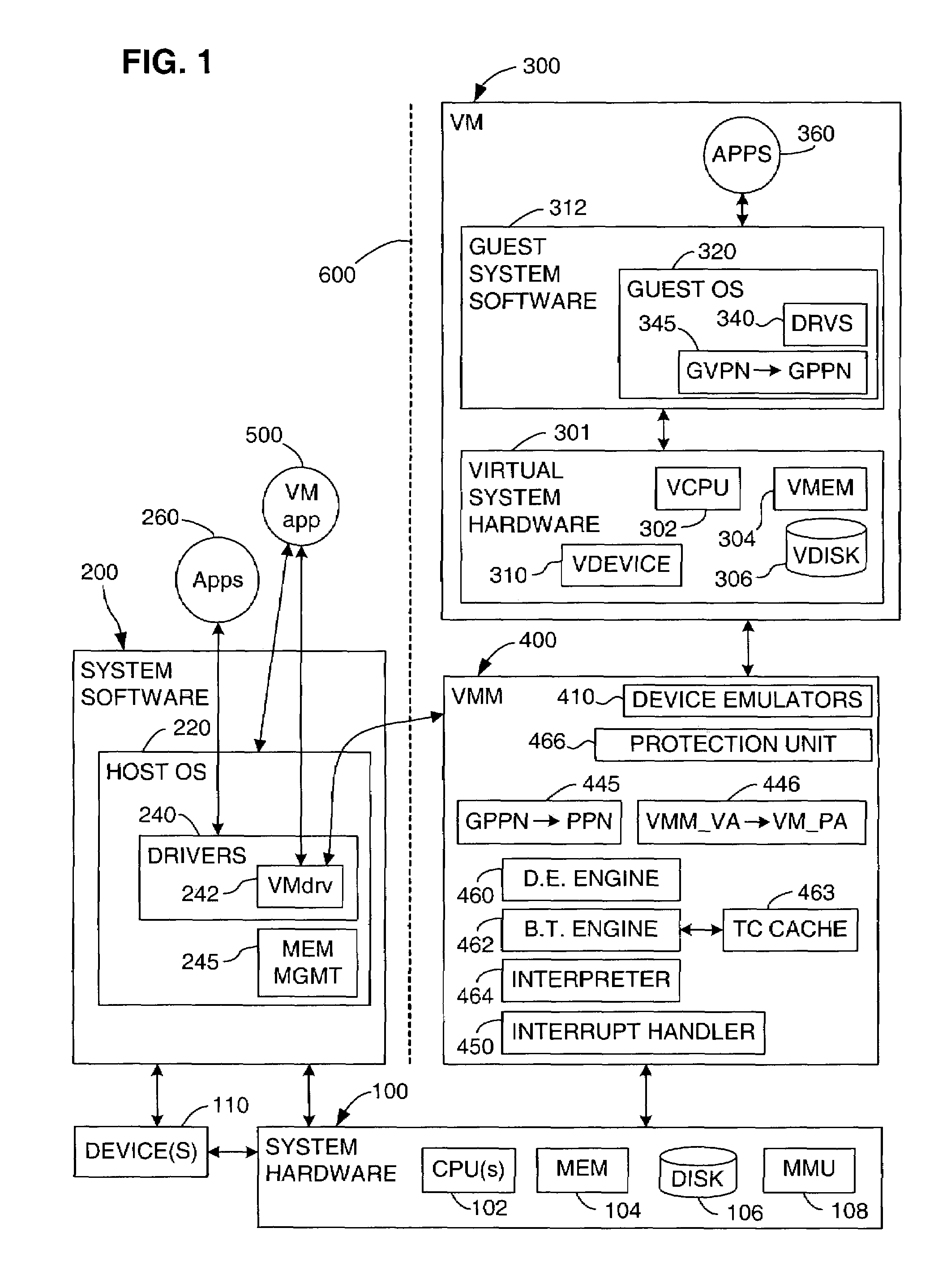
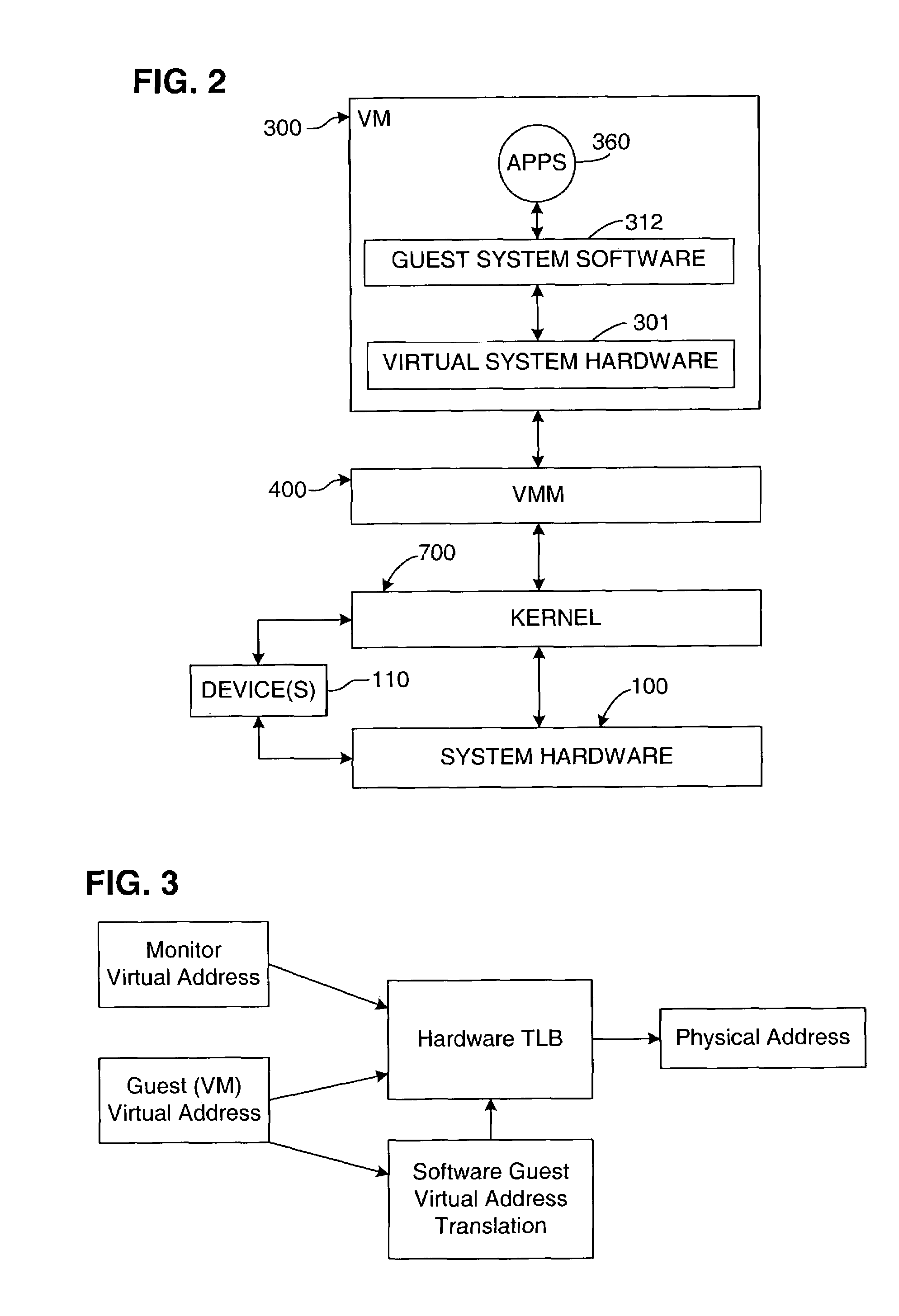
Virtualization system for computers having multiple protection mechanisms
ActiveUS7278030B1Prevention of memory accessUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringVirtualizationProtection mechanism
In a virtual computer system, the invention virtualizes a primary protection mechanism, which restricts memory accesses based on the type of access attempted and a current hardware privilege level, using a secondary protection mechanism, which is independent of the hardware privilege level. The invention may be used to virtualize the protection mechanisms of the Intel IA-64 architecture. In this embodiment, virtual access rights settings in a virtual TLB are translated into shadow access rights settings in a hardware TLB, while virtual protection key settings in a virtual PKR cache are translated into shadow protection key settings in a hardware PKR cache, based in part on the virtual access rights settings. The shadow protection key settings are dependent on the guest privilege level, but the shadow access rights settings are not.
Owner:VMWARE INC
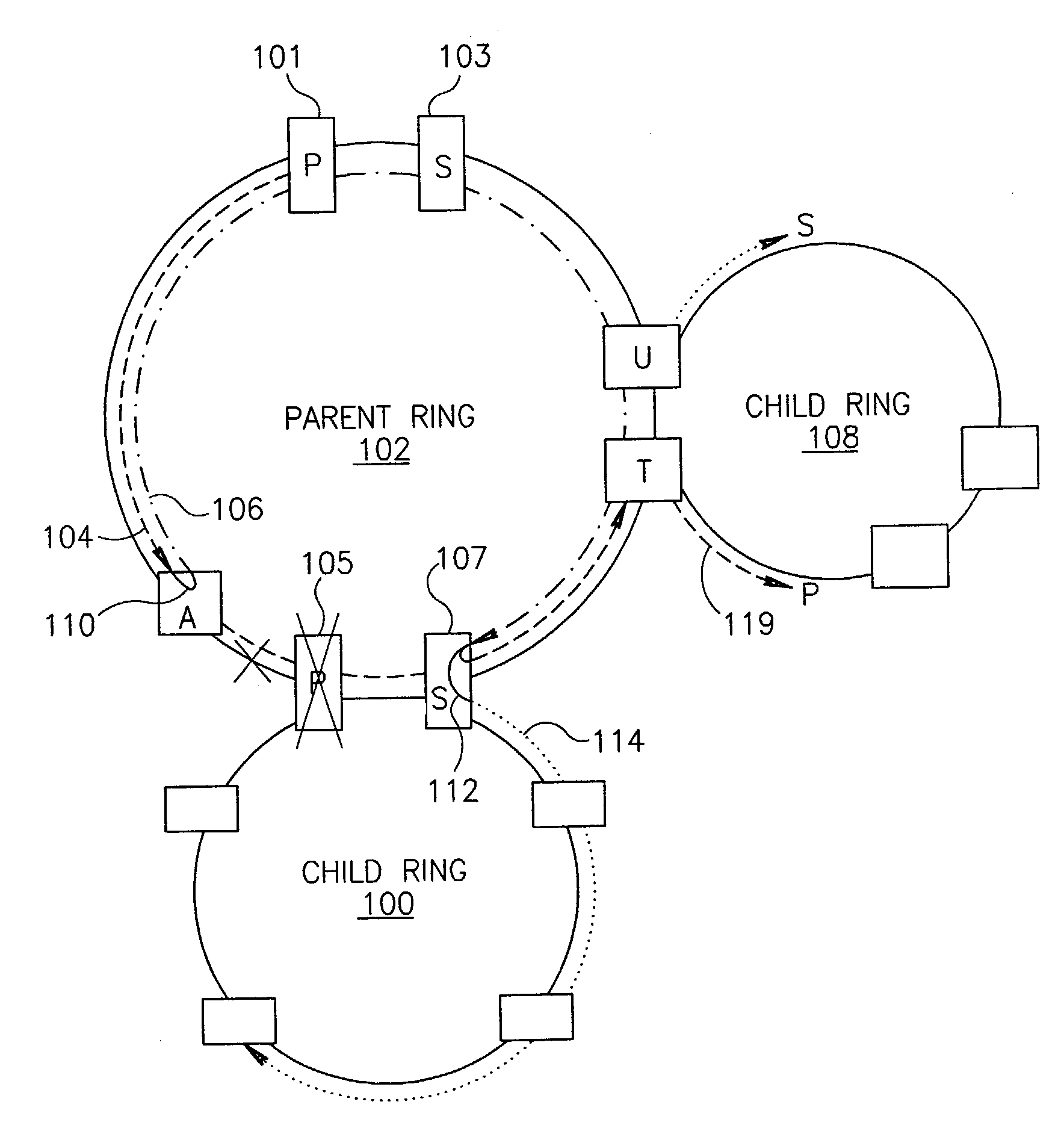
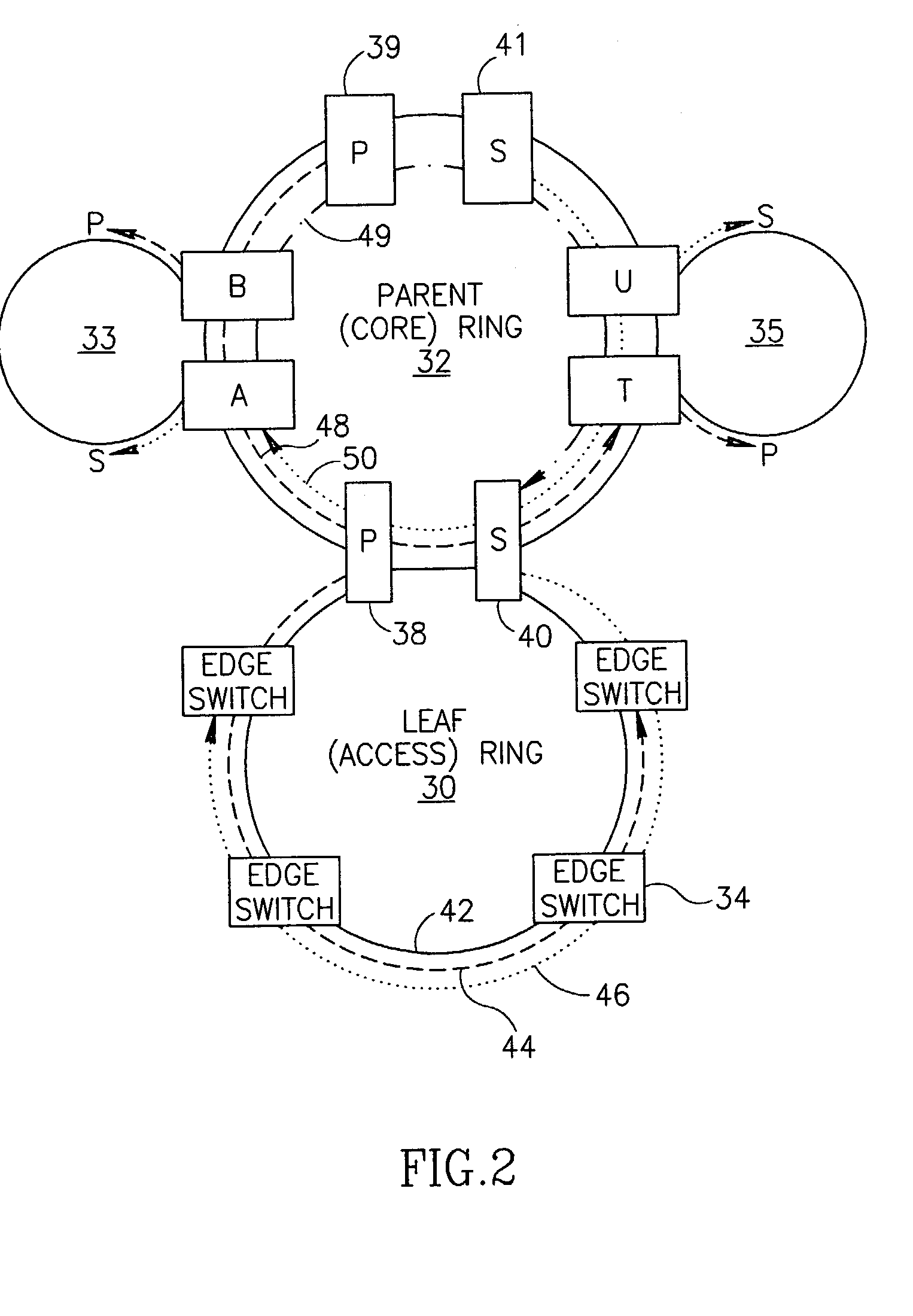
Scalable protection mechanism for hierarchical multicast service in ring based networks
ActiveUS7545735B1Reduce in quantityFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsTraffic capacityProtection mechanism
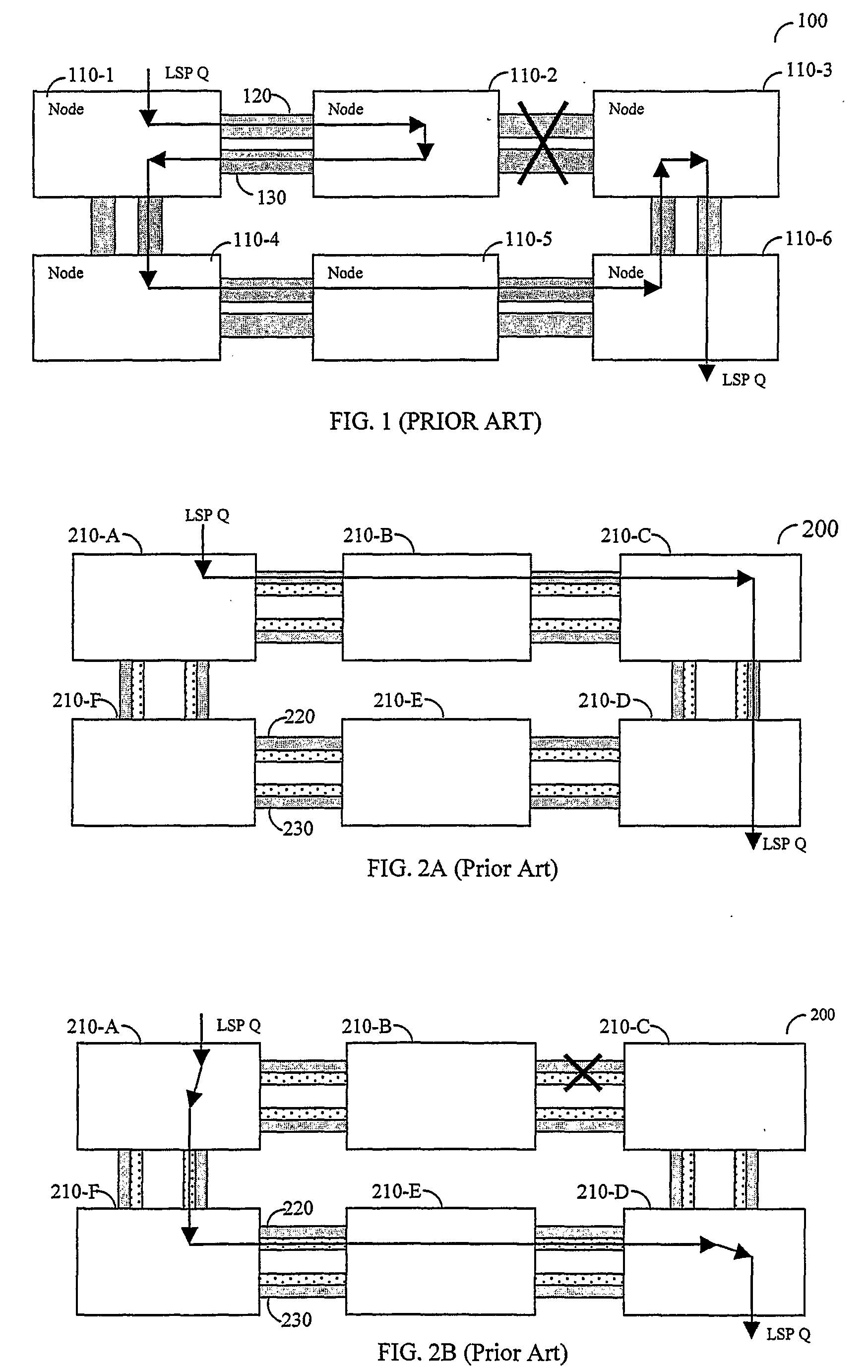
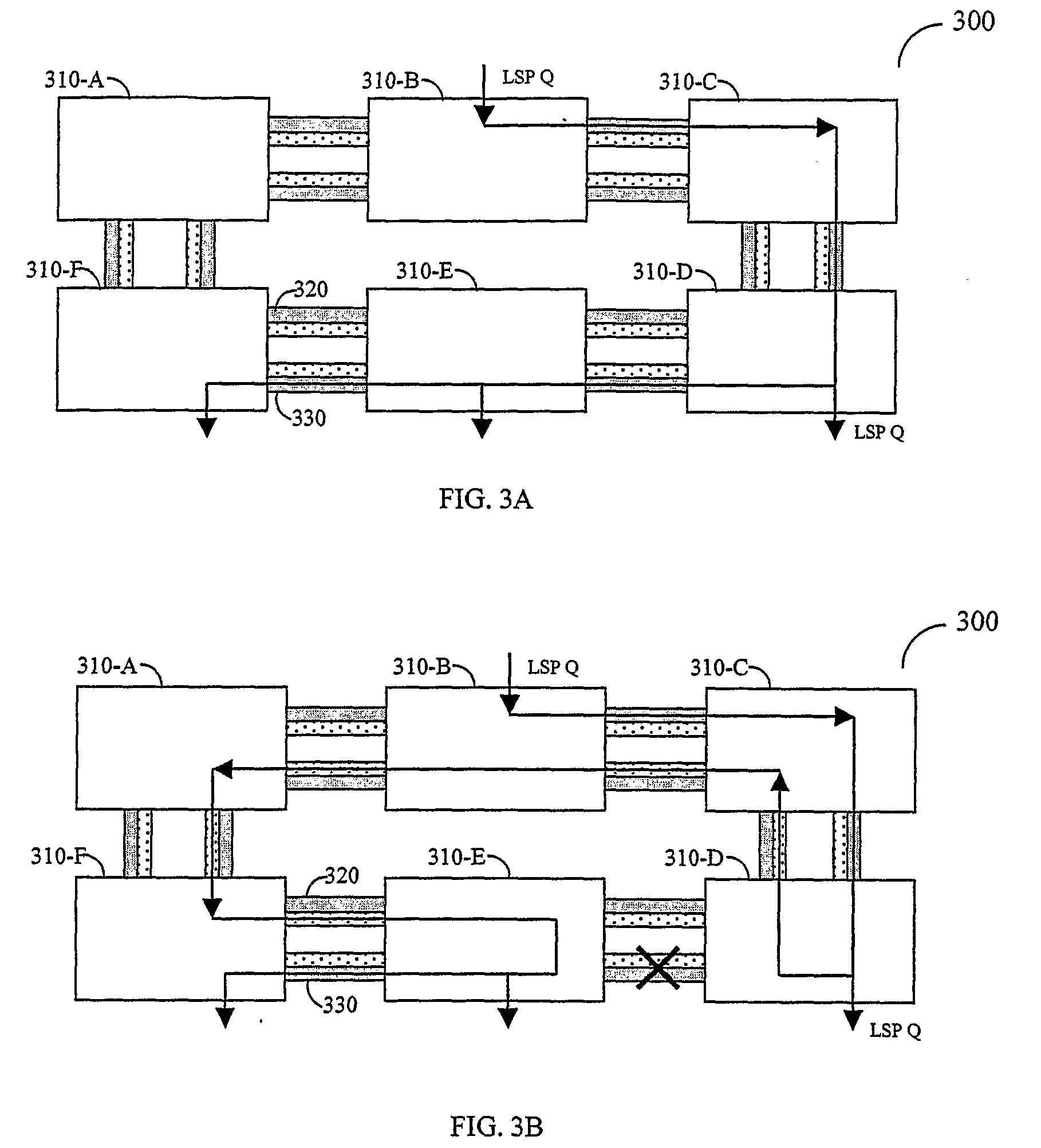
A novel fast and scalable protection mechanism for protecting hierarchical multicast service in ring based networks. The mechanism of the present invention is especially suitable for use in Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) ring based networks such as Metro Ethernet Networks (MENs). The mechanism provides fast protection for MPLS based point-to-multipoint (P2MP) Label Switched Paths (LSPs) in a scalable manner. Each multicast connection on each ring in the network is split into two sub-LSPs: a primary P2MP sub-LSP originating on a primary node and a secondary P2MP sub-LSP originating on a secondary node traveling opposite to the primary path. For each node to be protected, a point-to-point protection tunnel is provisioned from that node to a secondary node that forwards the packets to the secondary path on all child rings connected to that parent ring through the protected node and that are provisioned to receive the specific multicast connection. In the event of a failure, all the multicast traffic on that ring is directed through the protection tunnel to the secondary node. Upon exiting the protection tunnel, the packets are forwarded to the secondary LSP on the child rings for which this node is the secondary node and also continue along the primary LSP on the parent ring and along all child rings for which this node is the primary node.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS ETHERNET SOLUTIONS +1
Systems and methods for preventing unauthorized use of digital content
InactiveUS7237123B2Reduce eliminate broadly disseminated effectivenessNontrivial taskRandom number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationDigital contentProtection mechanism
Theft, distribution, and piracy of digital content (software, video, audio, e-books, any content of any kind that is digitally stored and distributed) is generally accomplished by copying it, if possible, or, if it is protected from being copied in any fashion, such piracy is based upon a number of reverse engineering techniques. Aside from the straightforward copying of unprotected content, all of these other methods require first an understanding of the protective mechanism(s) guarding the content, and finally an unauthorized modification of that protection in order to disable or subvert it. Methods that prevent a skilled individual from using reverse engineering tools and techniques to attain that level of understanding and / or prevent anyone from performing such modifications can offer significant advantages to content creators who wish to protect their products.
Owner:IPLA HLDG
Approach to provide self-protection function to web content at client side
ActiveUS7475152B2Increase flexibilityProvide securityComputer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsProtection mechanismApplication software
The present invention utilizes agents embedded in content delivered to clients across a network to provide client-side security for the data delivered to a client. These embedded agents provide application-specific protection for the delivered content in which they are embedded and eliminate the need for using plug-ins for security functions. Different agents, e.g. programs such as Java applets, are configured having a variety of different client or application specific protection mechanisms, and the agents are dynamically configured, e.g. selected, in accordance with the application, the client to be protected or other environment criteria. Once the agent has been appropriately configured, the agent is embedded in the content, and the content is delivered to the client. Once delivered, the embedded agent is uploaded to the client and executed, providing the configured security protection at the client side for the content in which it was embedded.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data processing apparatus
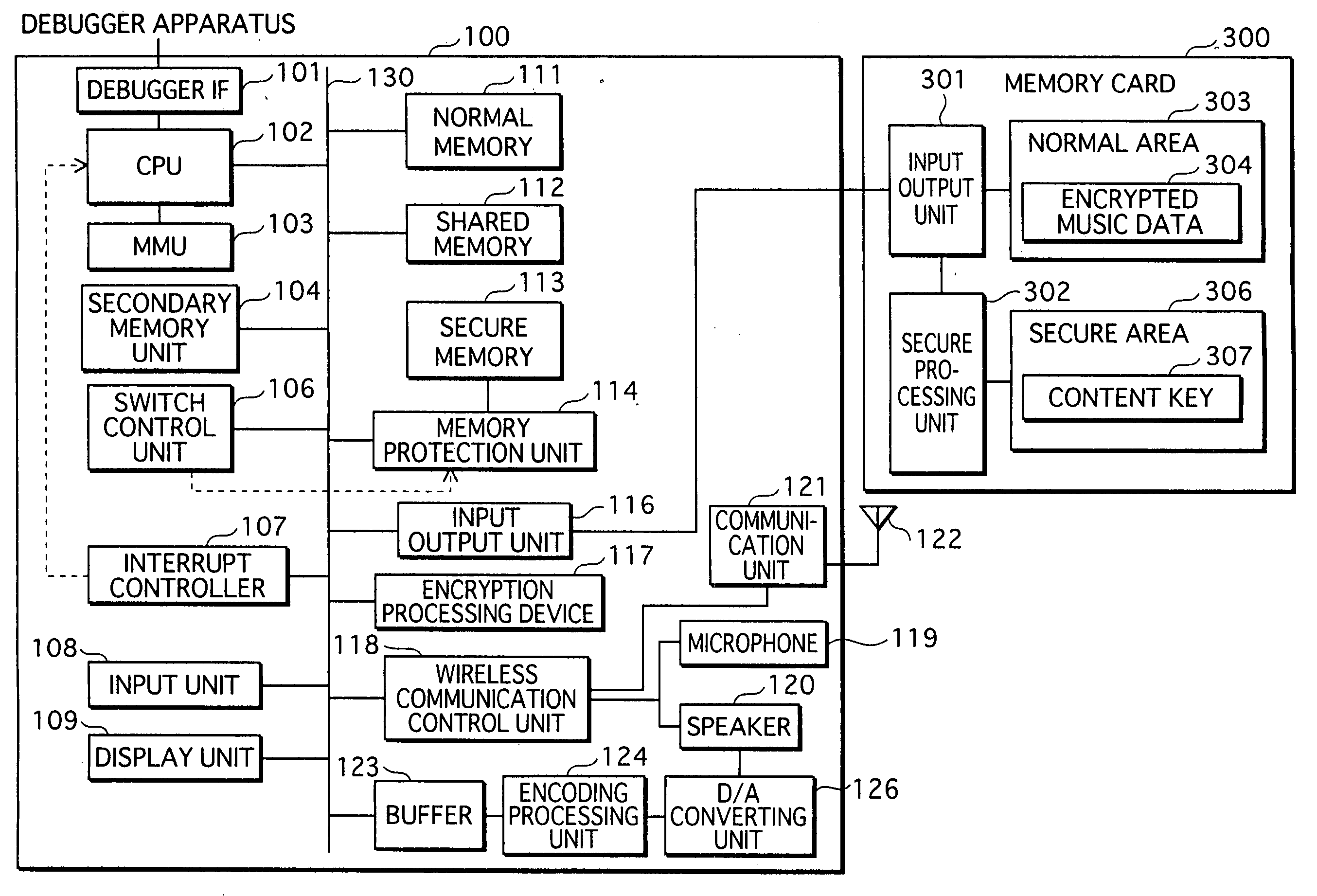
ActiveUS20070113079A1Reduce memorySmall sizeSpecific access rightsProgram initiation/switchingComputer hardwareProtection mechanism
In a data processing apparatus that switches between a secure mode and a normal mode during execution, the secure mode allowing access to secure resources to be protected, the normal mode not allowing access to the secure resources, when the secure resources increase in the secure mode, the load on a protection mechanism for protecting the resources becomes large. Thus, there is a demand for data processing apparatuses that are able to reduce secure resources. The present invention relates to a data processing apparatus that stores therein a secure program including one or more processing procedures which use secure resources and a call instruction for calling a normal program to be executed in a normal mode. While executing the secure program, the data processing apparatus calls the normal program with the call instruction and operates according to the called normal program.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Systems and methods for management of secure data in cloud-based network
ActiveUS8108912B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationCloud baseSocial Security number
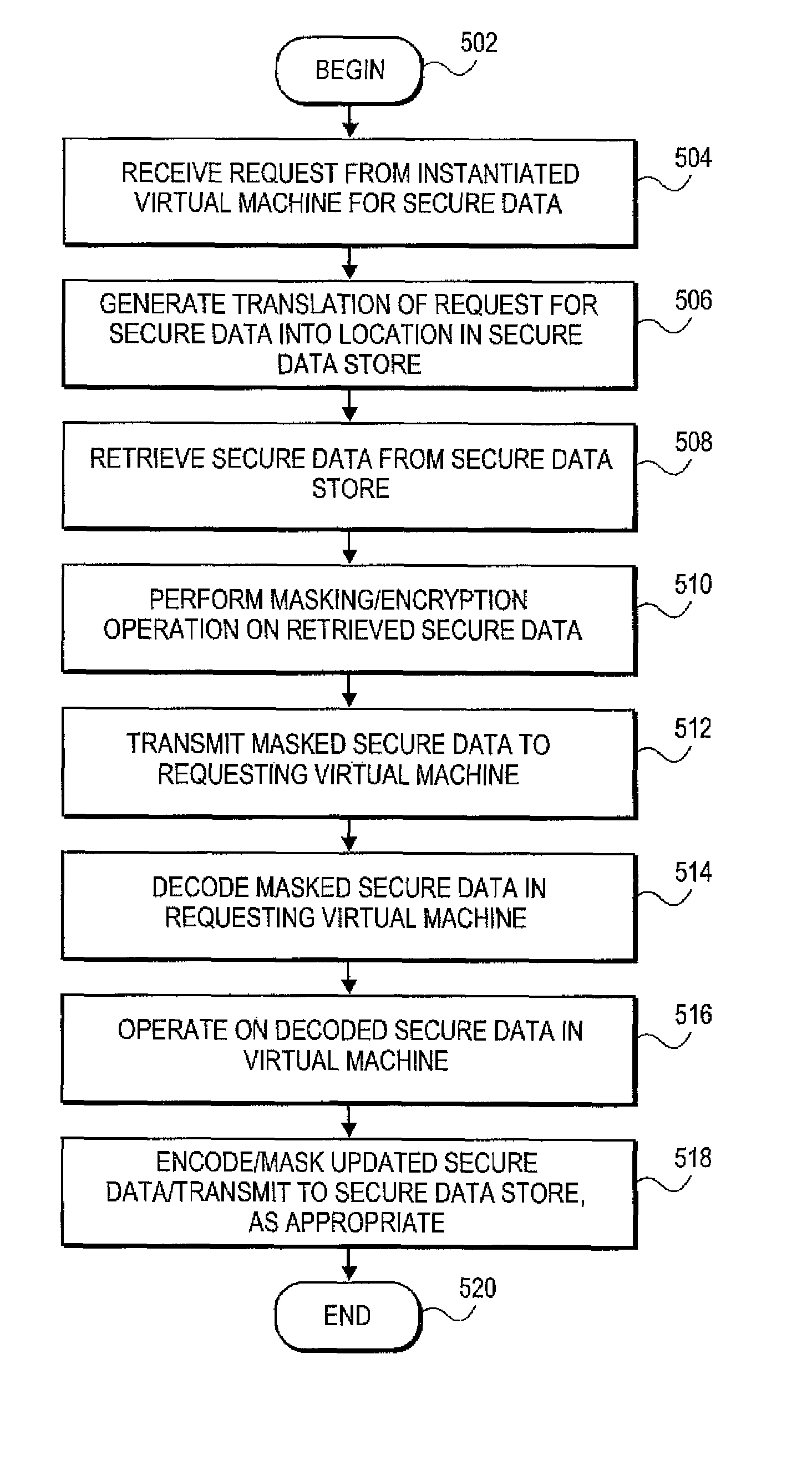
Embodiments relate to systems and methods for the management of secure data in a cloud-based network. A secure data store can store sensitive or confidential data, such as account numbers, social security numbers, medical or other information in an on-premise data facility. Regulatory and / or operational requirements may prohibit the migration or unprotected transmission of the secure data to the cloud. An operator can instantiate a set of virtual machines to access and process the secure data, for example to process online purchase transactions. To prevent unauthorized disclosure of the secure data, the secure data store can receive data access requests via a translation module that translates the secure data. The secure data store can retrieve and transmit the secure data using a protection mechanism such as a masking and / or encryption mechanism, avoiding the unprotected transport or exposure of that data to the cloud.
Owner:RED HAT
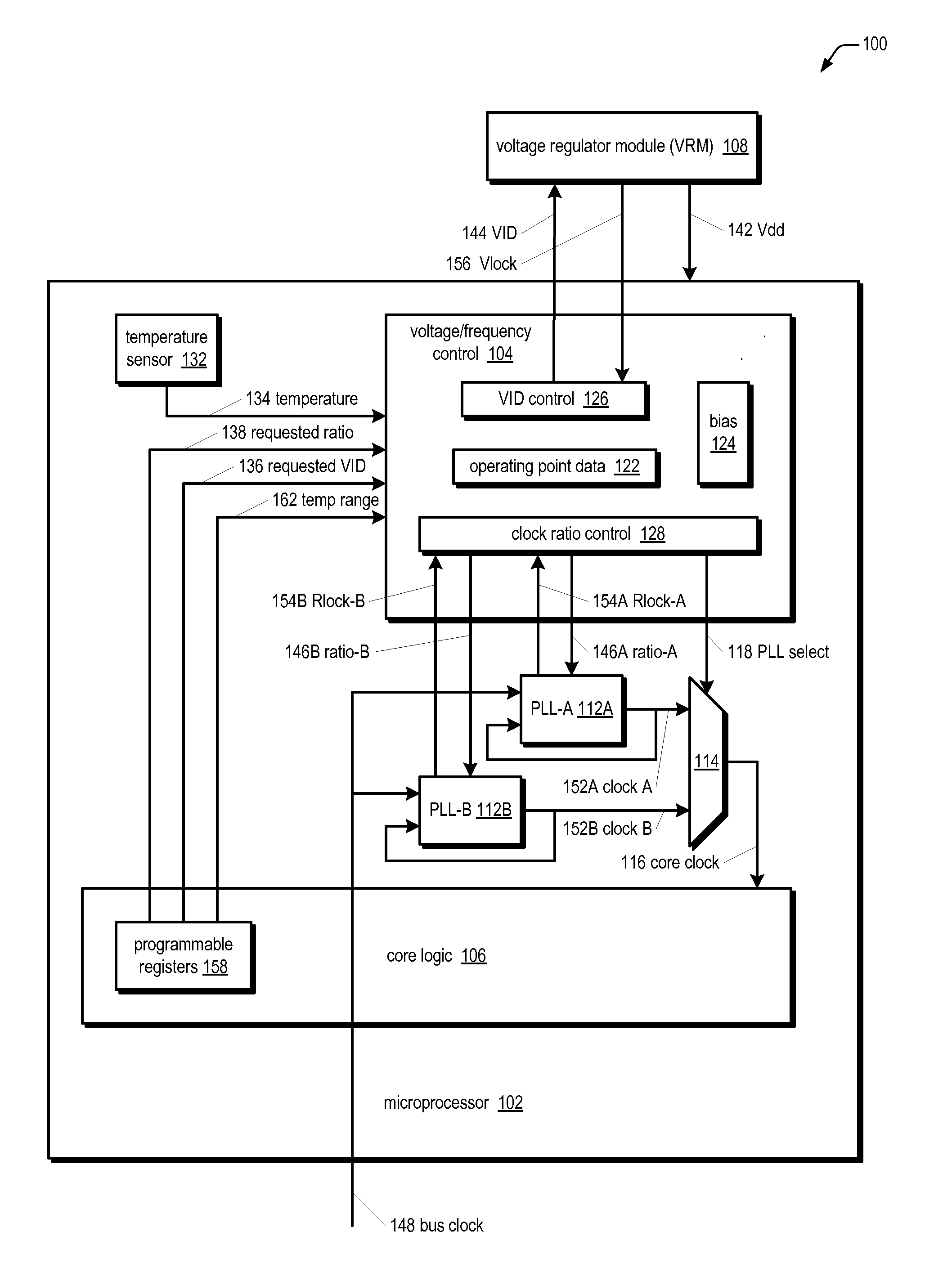
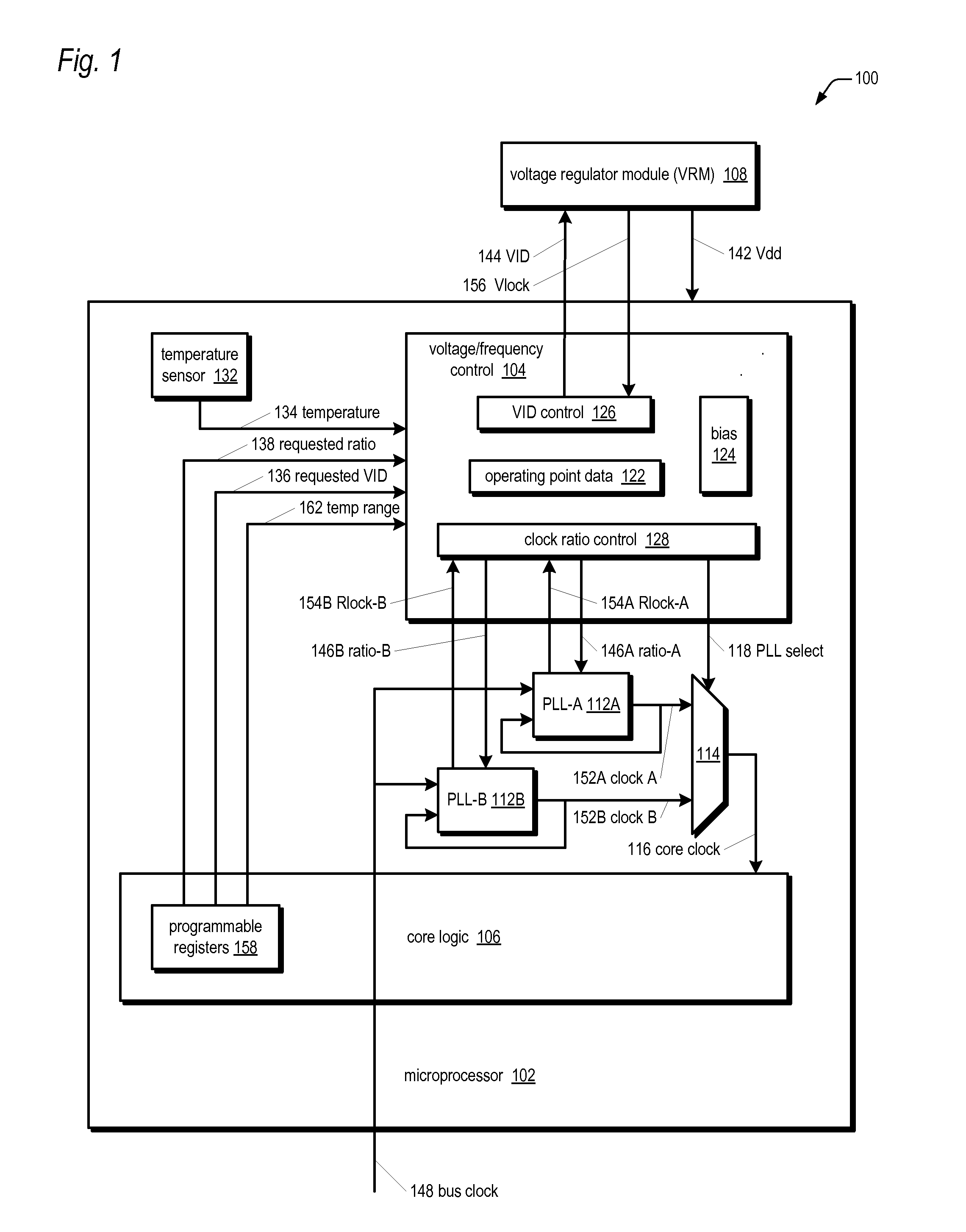
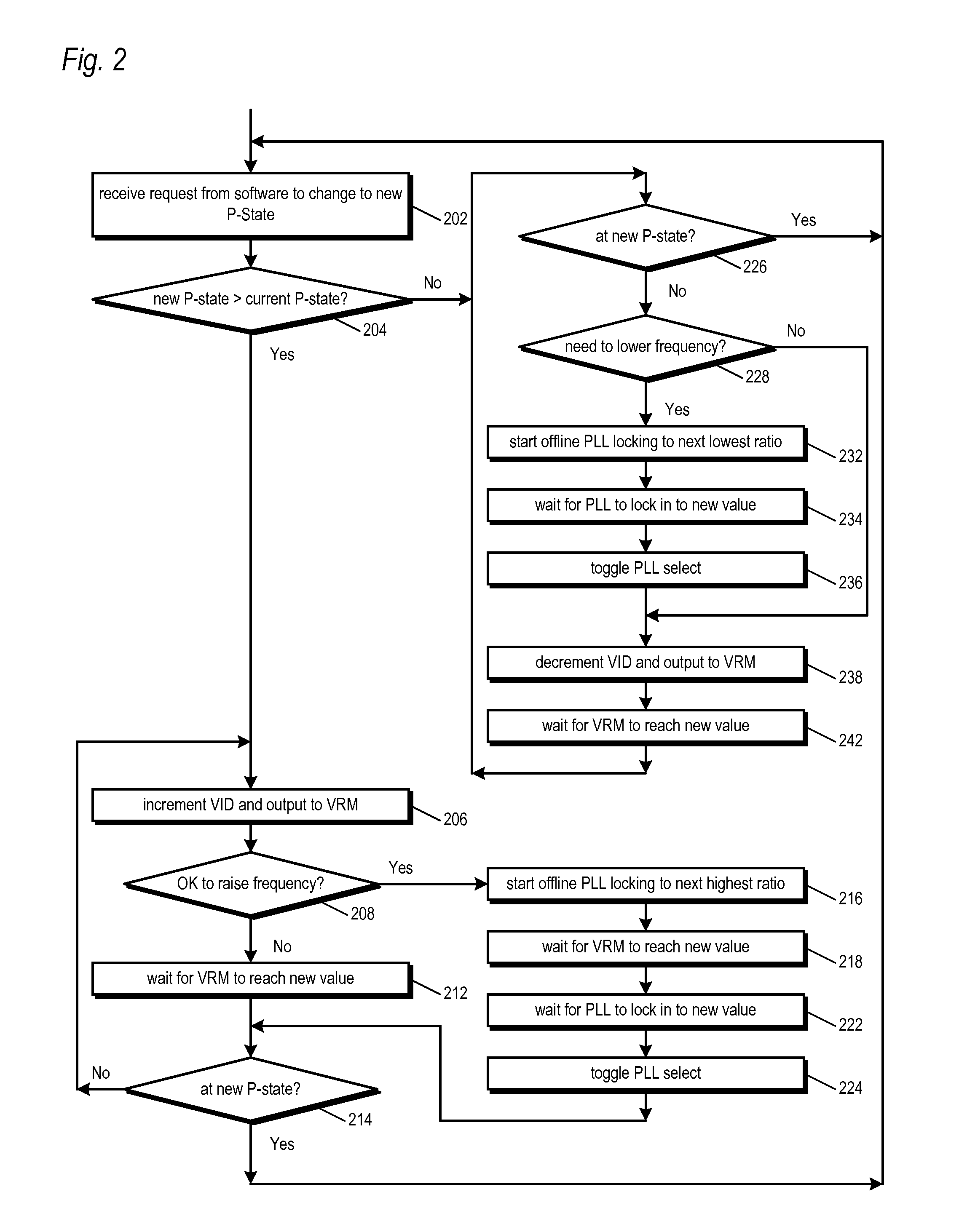
Microprocessor with improved thermal monitoring and protection mechanism
ActiveUS20080036613A1Improve performanceEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementThermal monitoringOperating point
A microprocessor including a temperature sensor that monitors a temperature of core logic of the microprocessor during operation thereof, and operating point information from which may be determined N operating points at which the microprocessor core may reliably operate at a first temperature. Each of the N operating points has a different combination of operating frequency and voltage. The N operating points comprise a highest operating point, a lowest operating point, and a plurality of operating points intermediate the highest and lowest operating points. The microprocessor also includes a control circuit that transitions operation of the core logic among the N operating points to attempt to keep the operating temperature of the core logic provided by the temperature sensor within a temperature range whose upper bound is the first temperature.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Dynamically reacting policies and protections for securing mobile financial transaction data in transit
ActiveUS20110178933A1Shorten the time to marketAcceptable levelFinanceMemory loss protectionEngineeringFinancial transaction
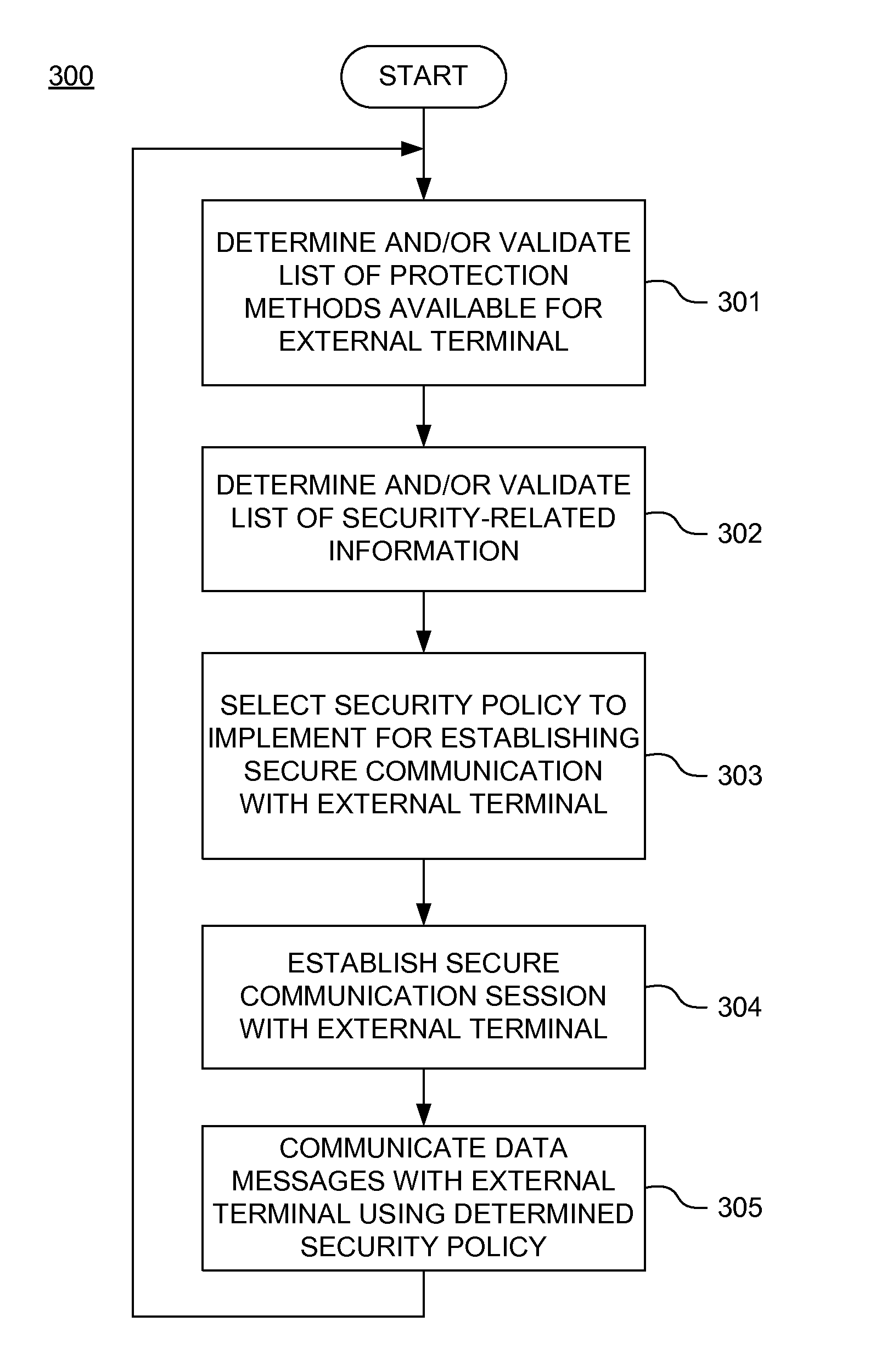
A secure mobile financial transaction is provided by receiving, over a communication network, a list of protection mechanisms available for implementation by an external terminal. Security-related data is received from one or more sensors and an attack signature is computed based on the security-related data. An appropriate security policy is selected from multiple security policies stored in a database based on the list of protection mechanisms and the attack signature. A secure communication session is established between the external terminal and an internal network component according to the selected security policy. A data message associated with a mobile financial transaction is communicated over the communication network during the communication session.
Owner:AMERICAN EXPRESS TRAVEL RELATED SERVICES CO INC
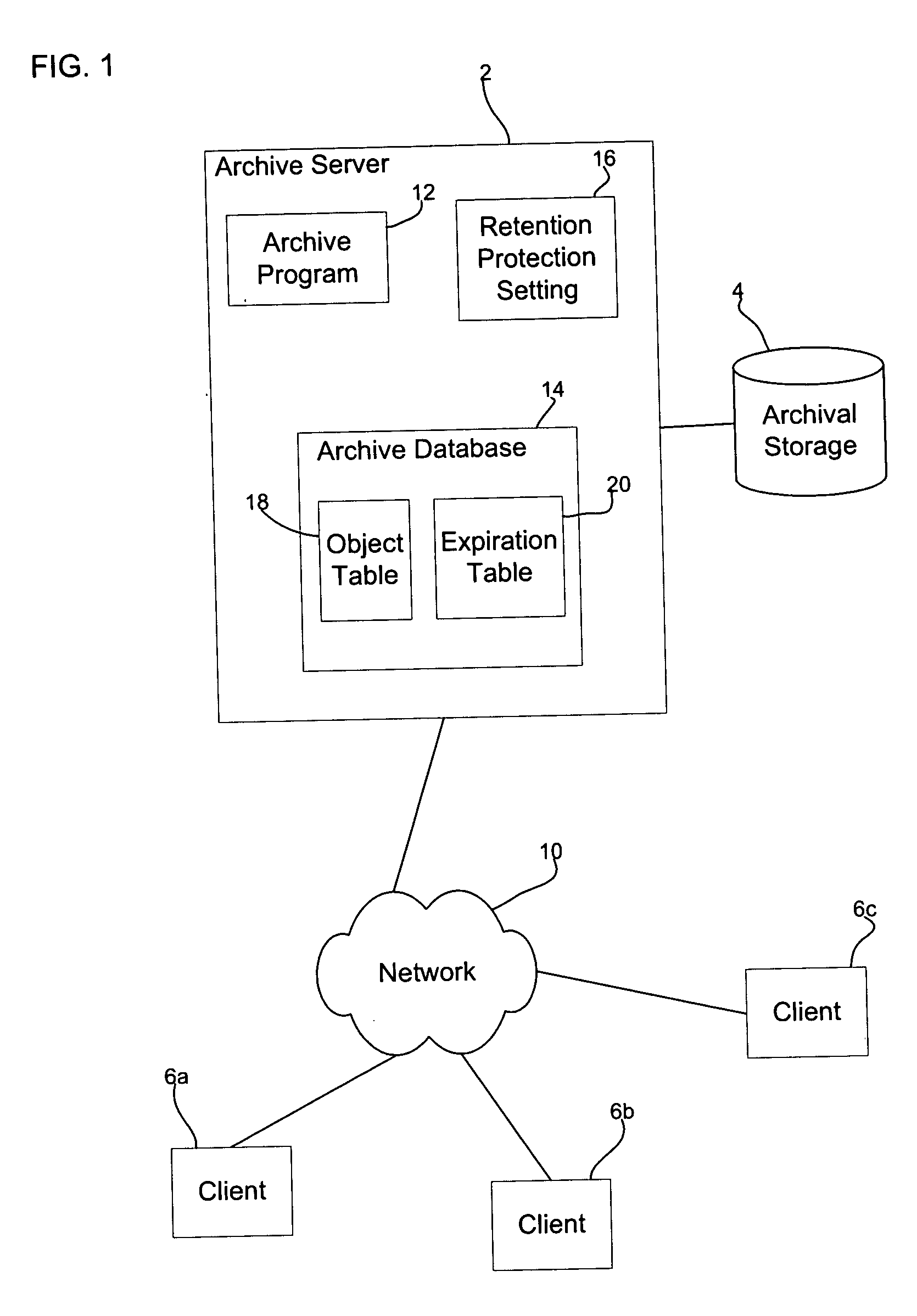
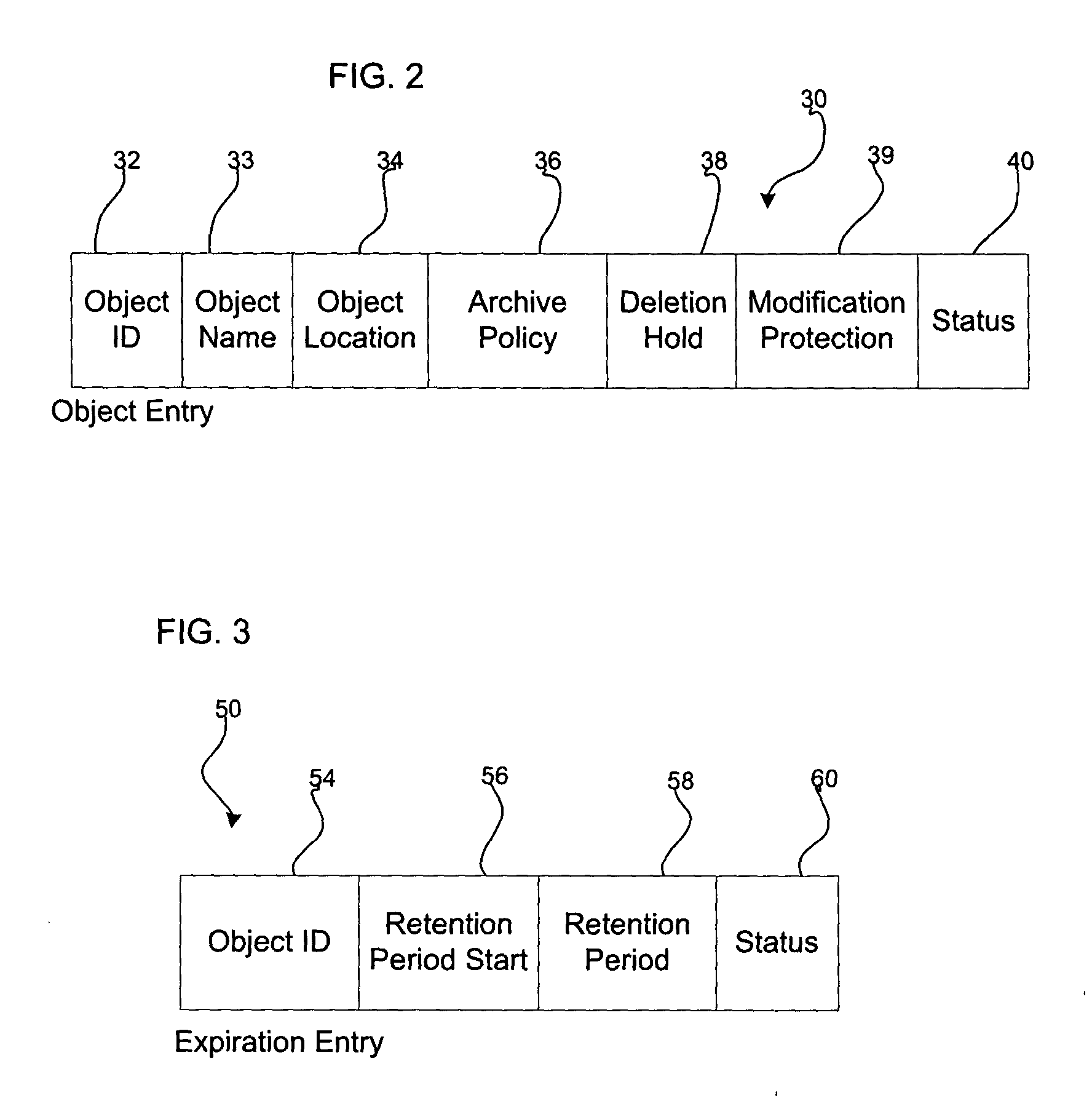
Method, system, and program for retention management and protection of stored objects
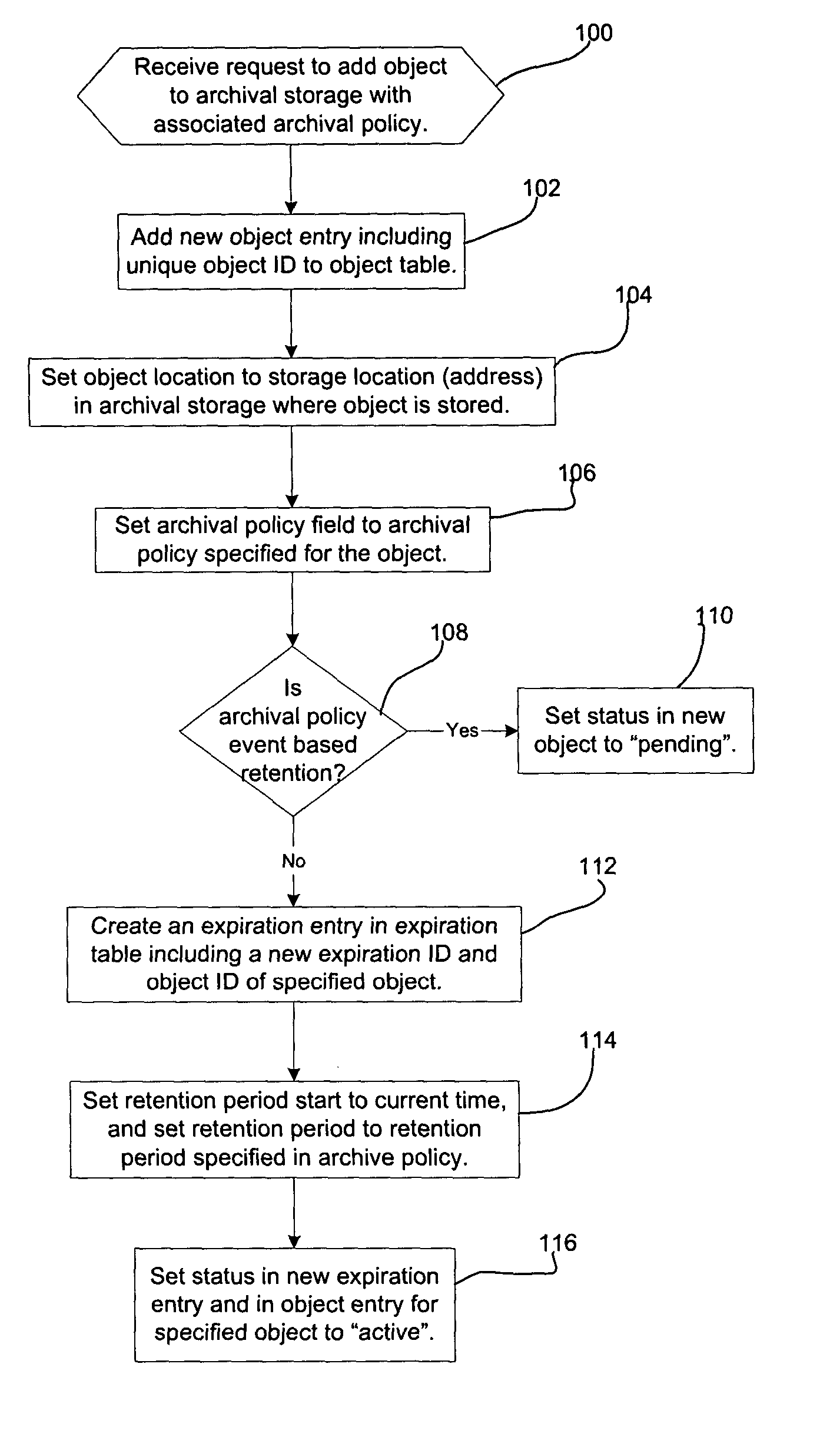
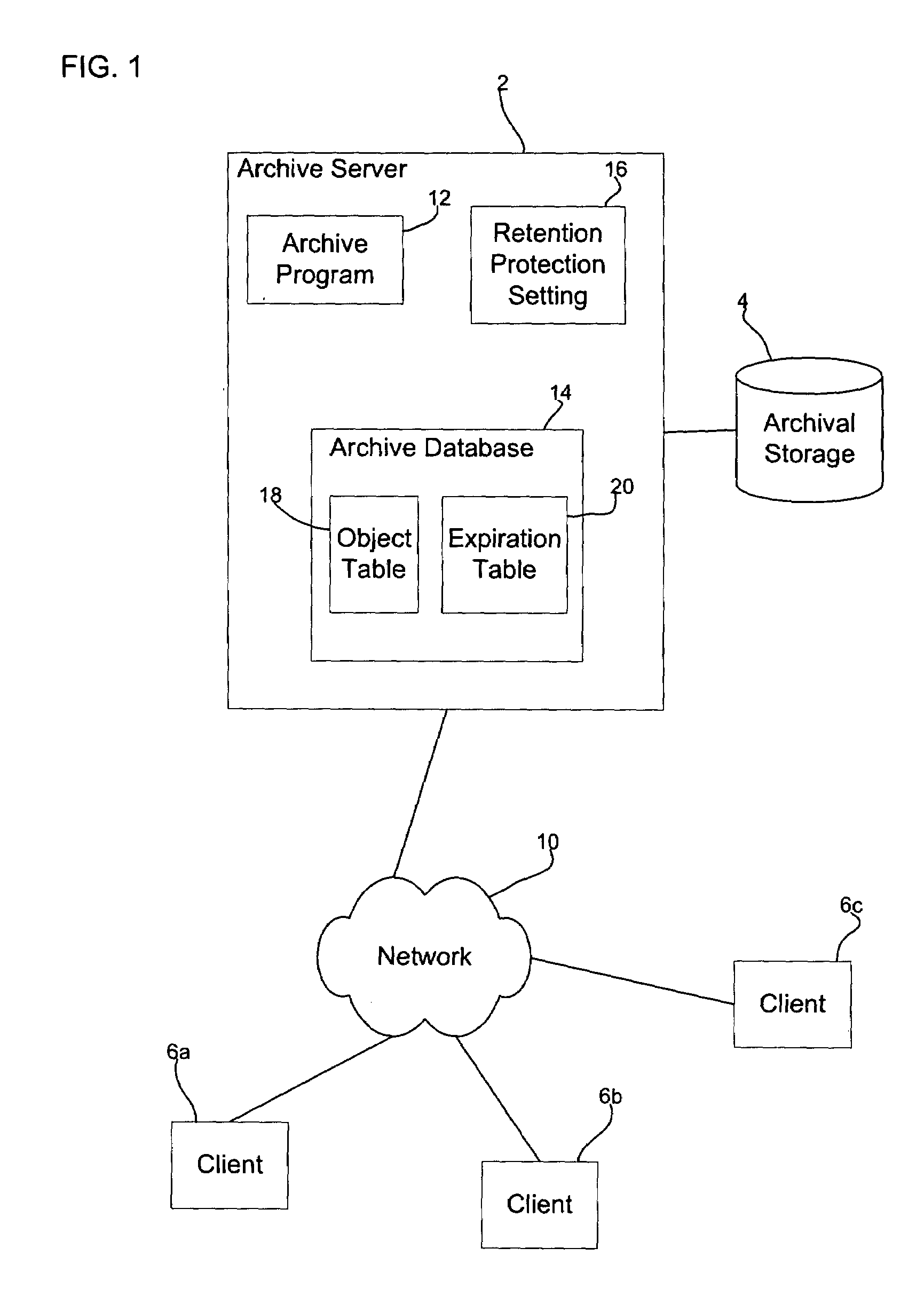
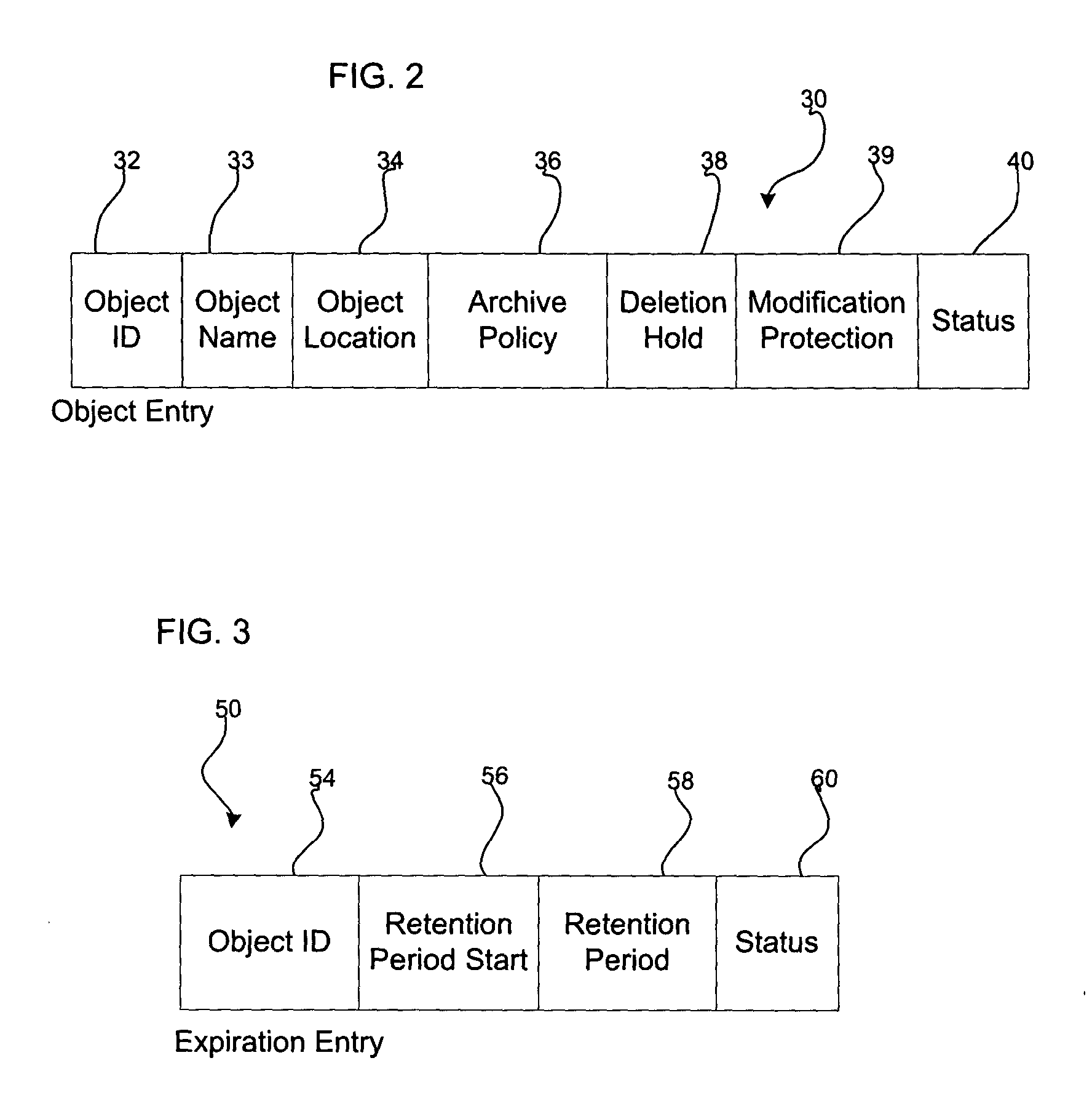
ActiveUS20050055518A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalProtection mechanism
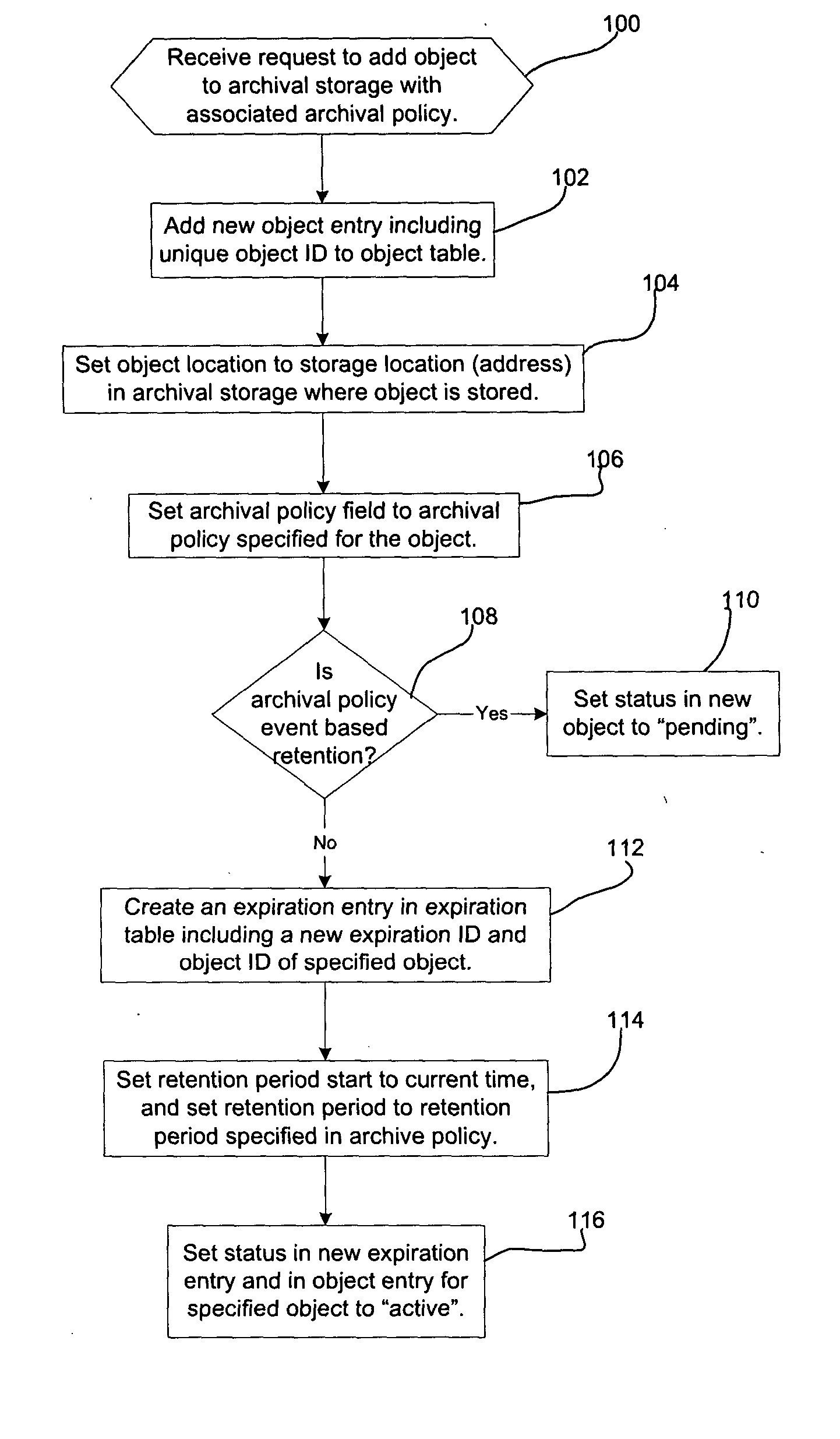
Provided are a method, system, and program for managing retention of stored objects. A modification request is received with respect to a stored object. A determination is made as to whether a retention protection mechanism is set and a storage policy associated with the stored object is processed to determine whether the stored object has expired according to the storage policy in response to determining that the retention protection mechanism is set. The modification request is allowed to proceed in response to determining that the stored object has expired.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Driving Data Backups With Data Source Tagging
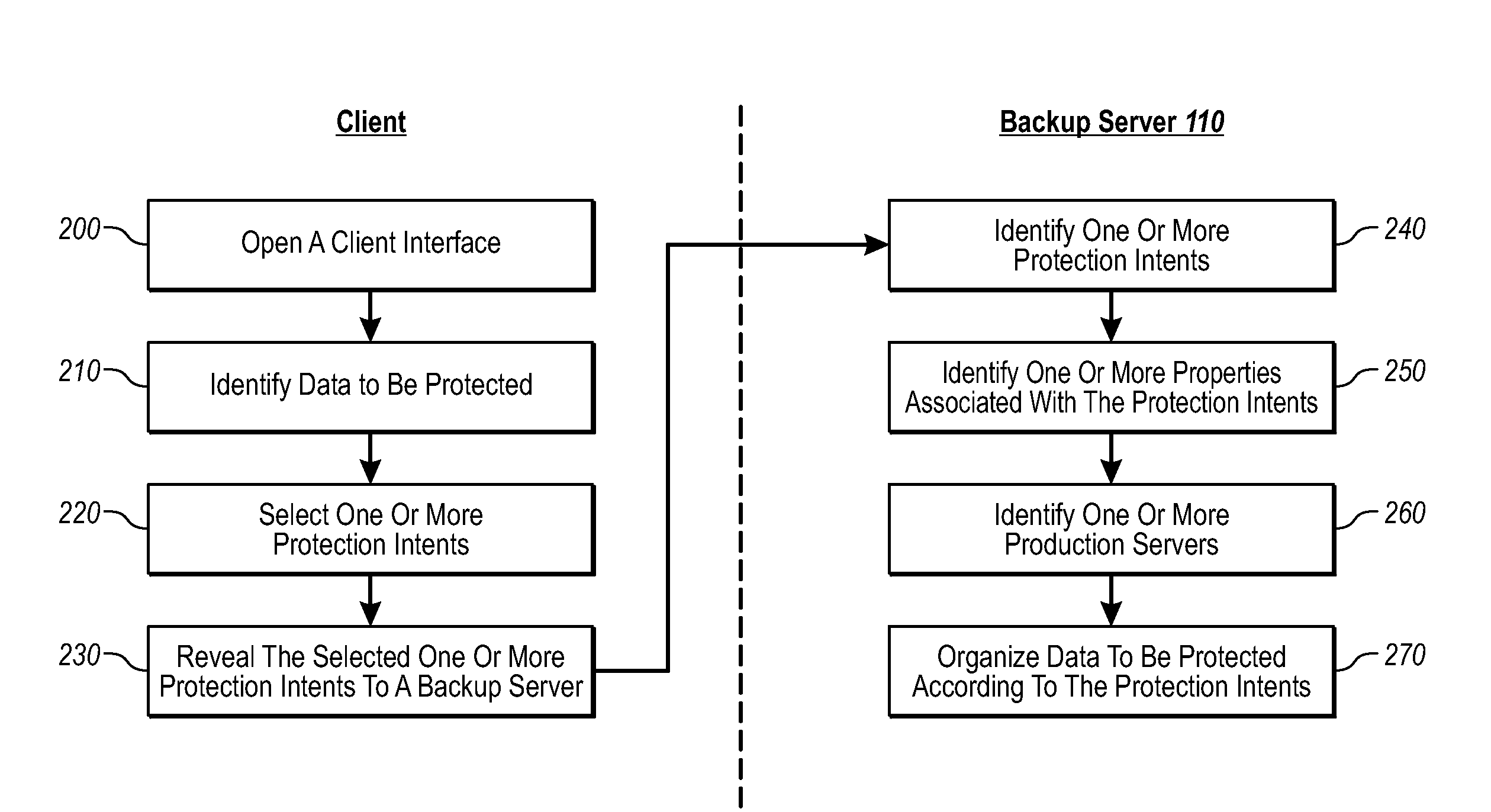
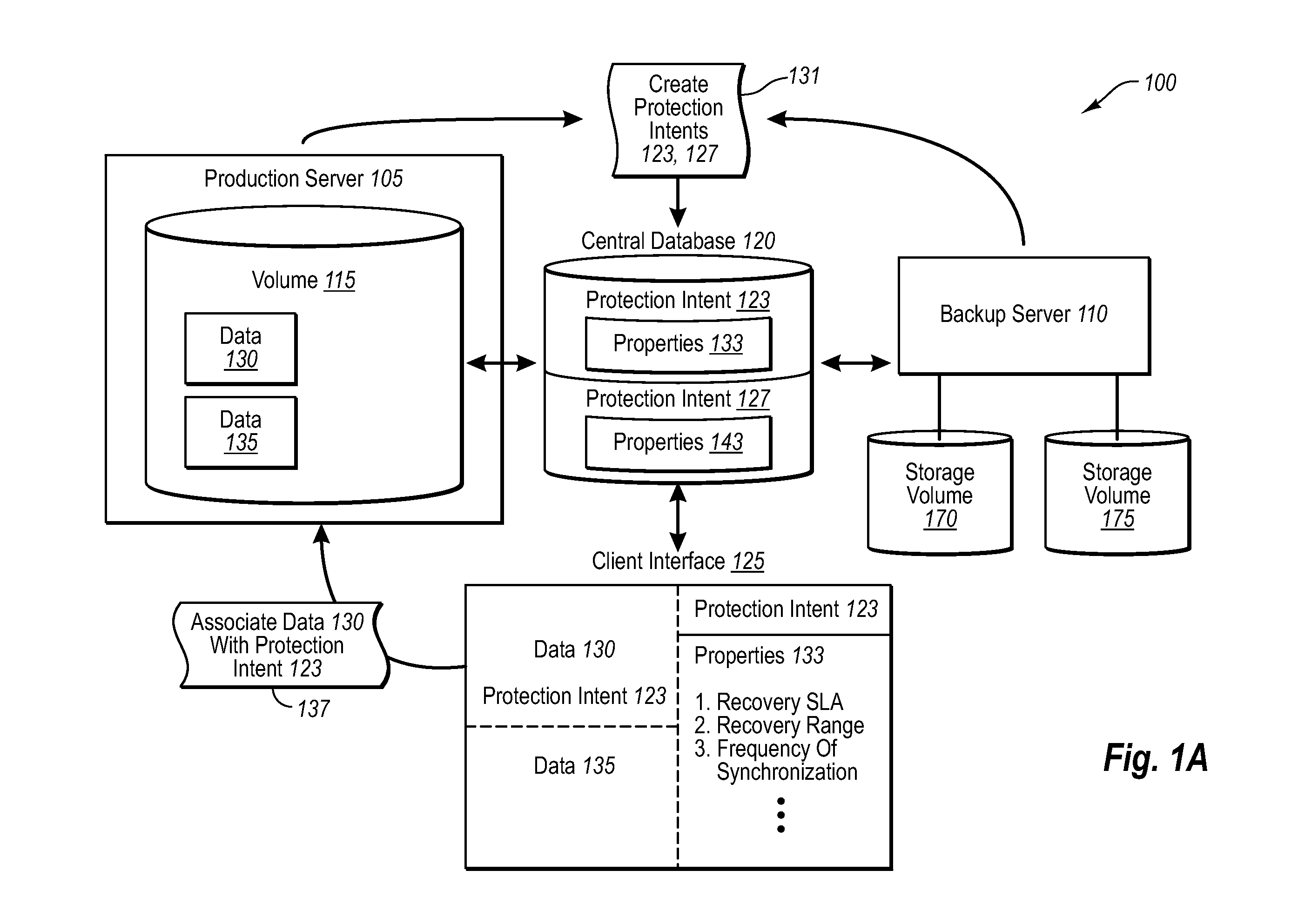
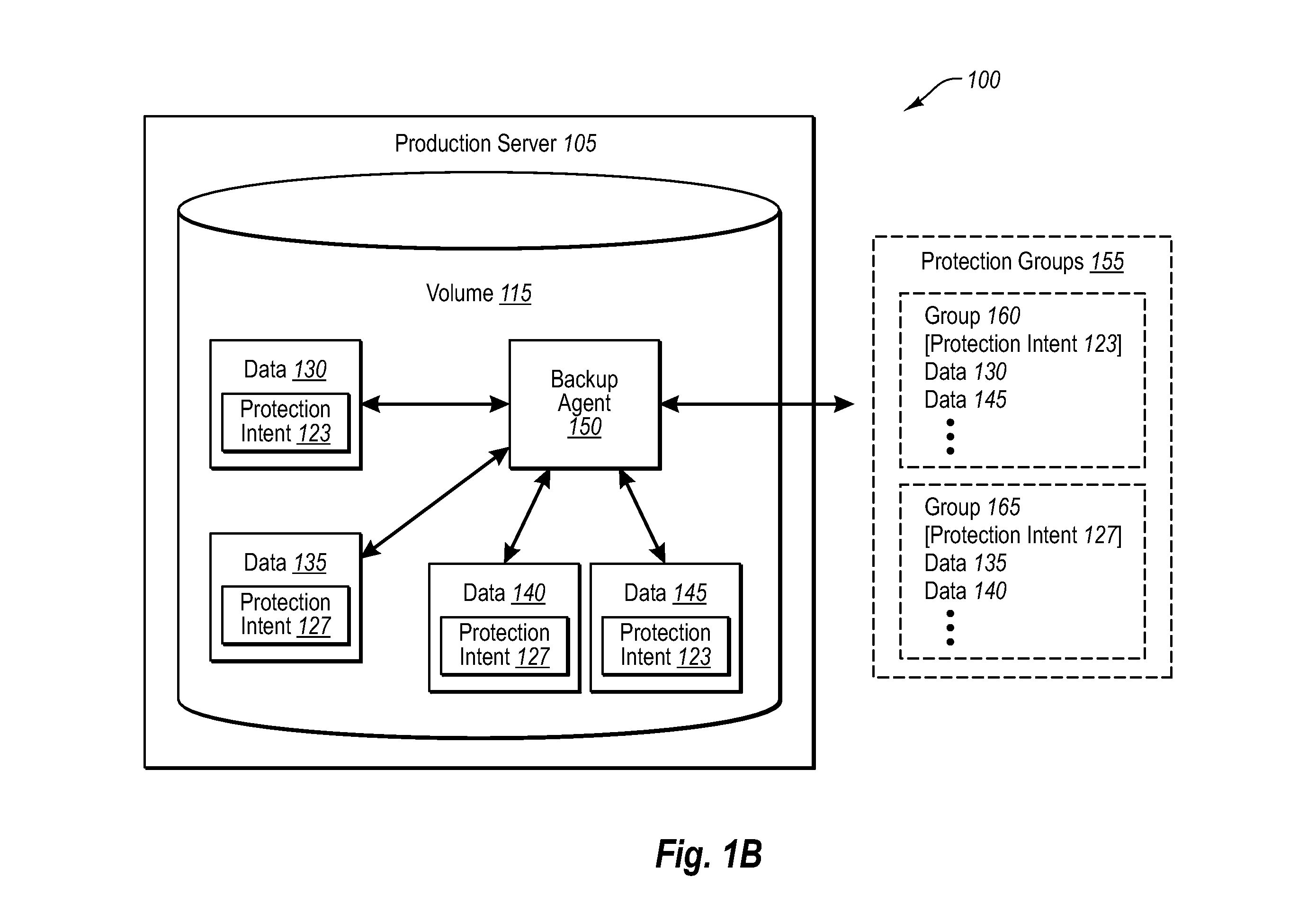
ActiveUS20070283017A1Fine granularityMemory loss protectionDigital computer detailsProtection mechanismData source
Implementations of the present invention allow clients (e.g., end-users, administrators, etc.) to associate data with one or more protection intents at the data / data source level. A backup server can then associate the data with a specific protection mechanism regardless of where the data / data source(s) are located, or regardless of how other like-data are being backed up. The backup server can then backup data that are associated with similar protection intents in a similar manner based on client specifications. The backup server can also monitor the various protection intents and associations to ensure that the protection intents are being met. For example, if the backup server identifies that data are not being backed up in accordance with their associated protection intent, the backup server can send one or more communications indicating the same, such that the protection mechanisms can be adjusted appropriately.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method, system, and program for retention management and protection of stored objects
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
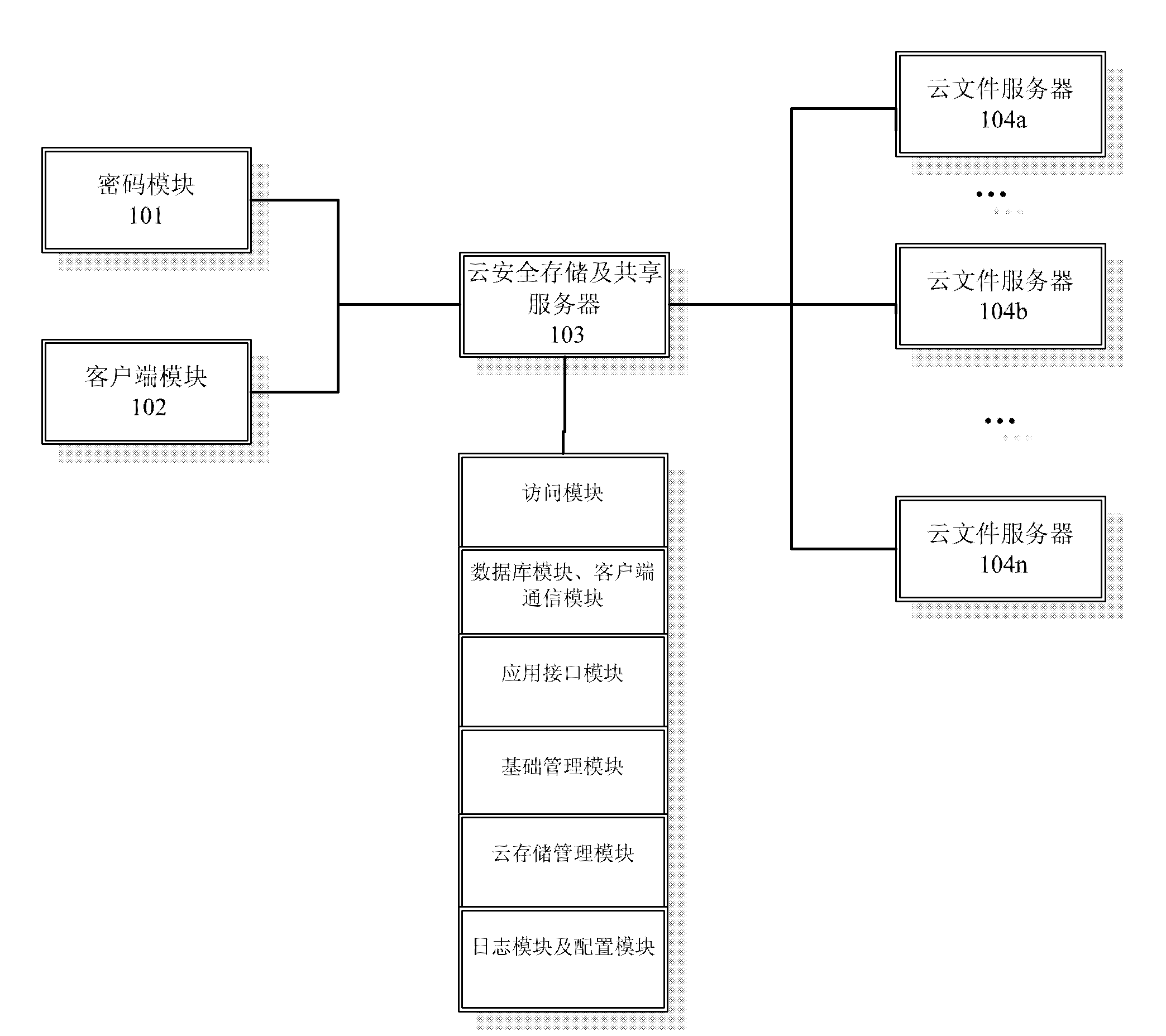
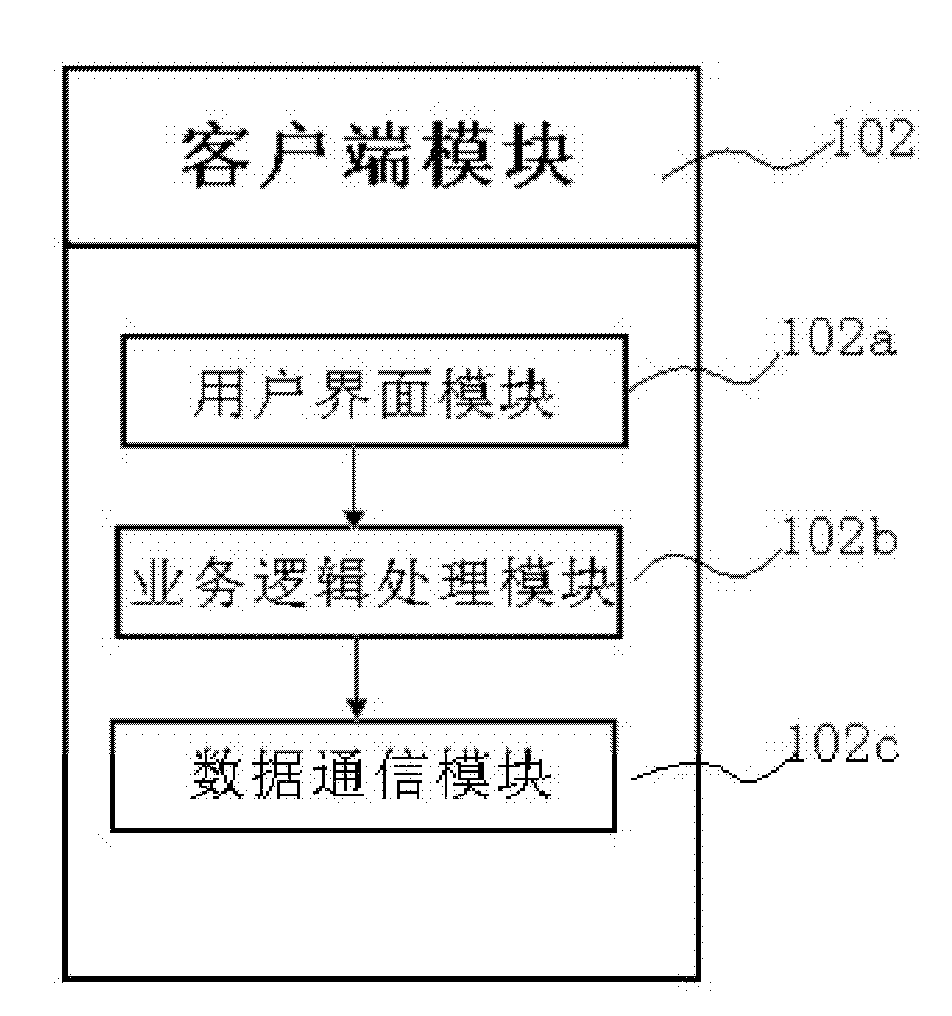
Cloud security storage and sharing service platform
The invention discloses a cloud security storage and sharing service platform comprising a cryptographic module, a client module, a cloud security storage and sharing server and a cloud file server. The cloud security storage and sharing server comprises an access module for the cloud file server, a database module, a client communication module, an application interface module, a basic management module, a cloud storage management module, a log module and a configuration module. The cryptographic module cooperates with the client module for realizing related operations of files, and performs communication with the cloud security storage and sharing server for realizing the operations of the files in the cloud file server. The cloud security storage and sharing service platform disclosed by the invention can realize three different protection mechanisms for the files in three different types and meet the requirements of cloud security storage and sharing service.
Owner:KOAL SOFTWARE CO LTD
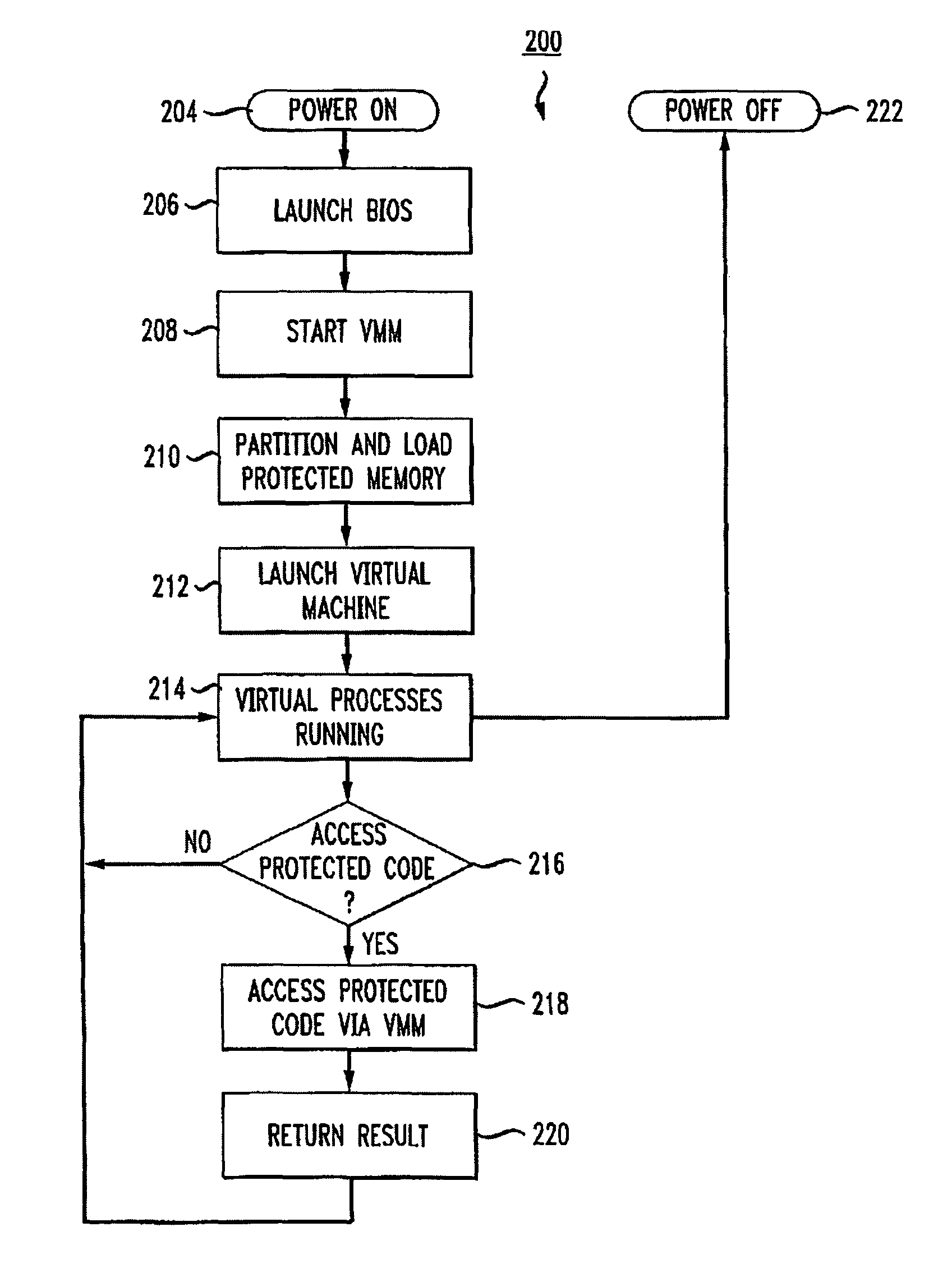
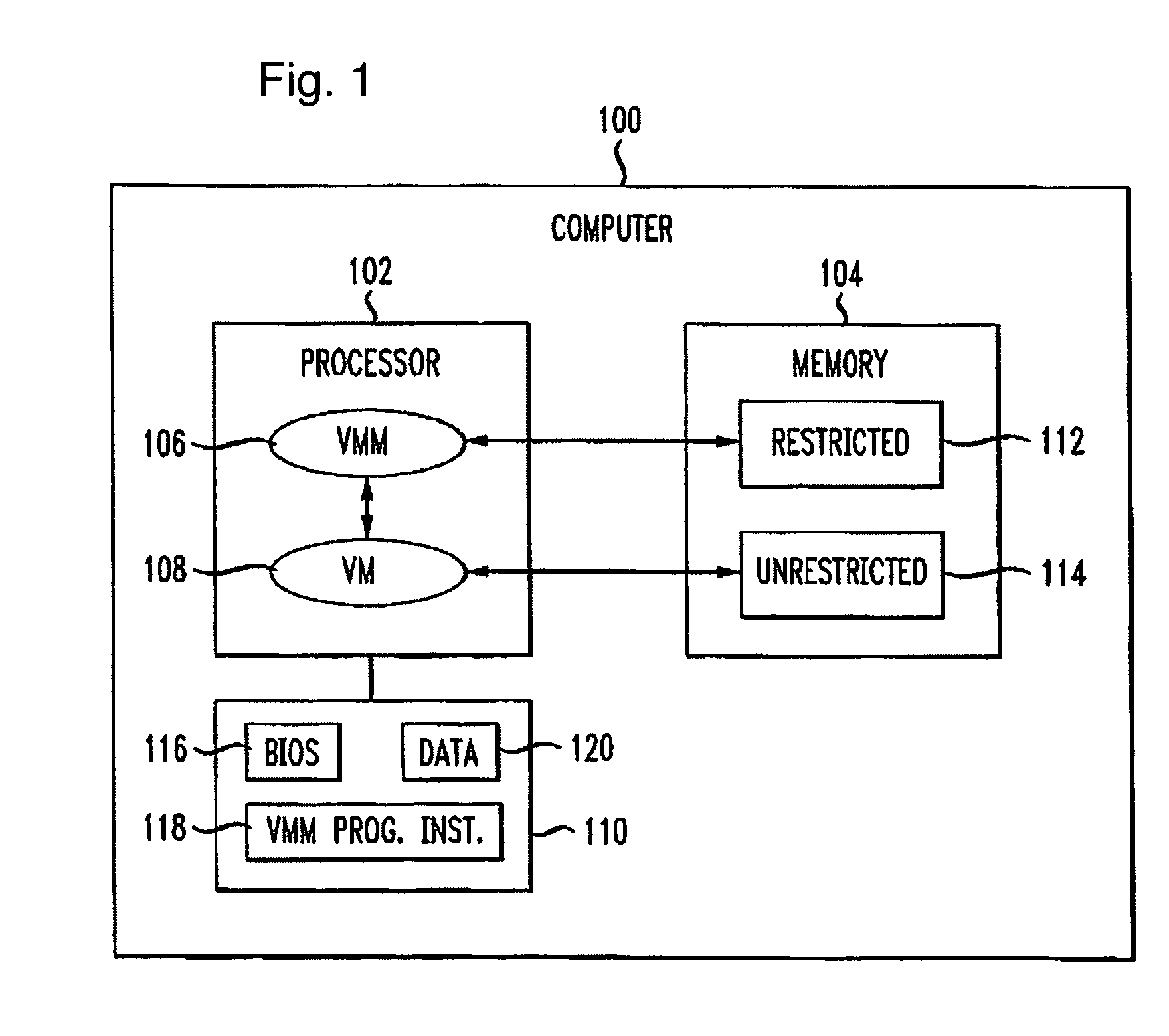
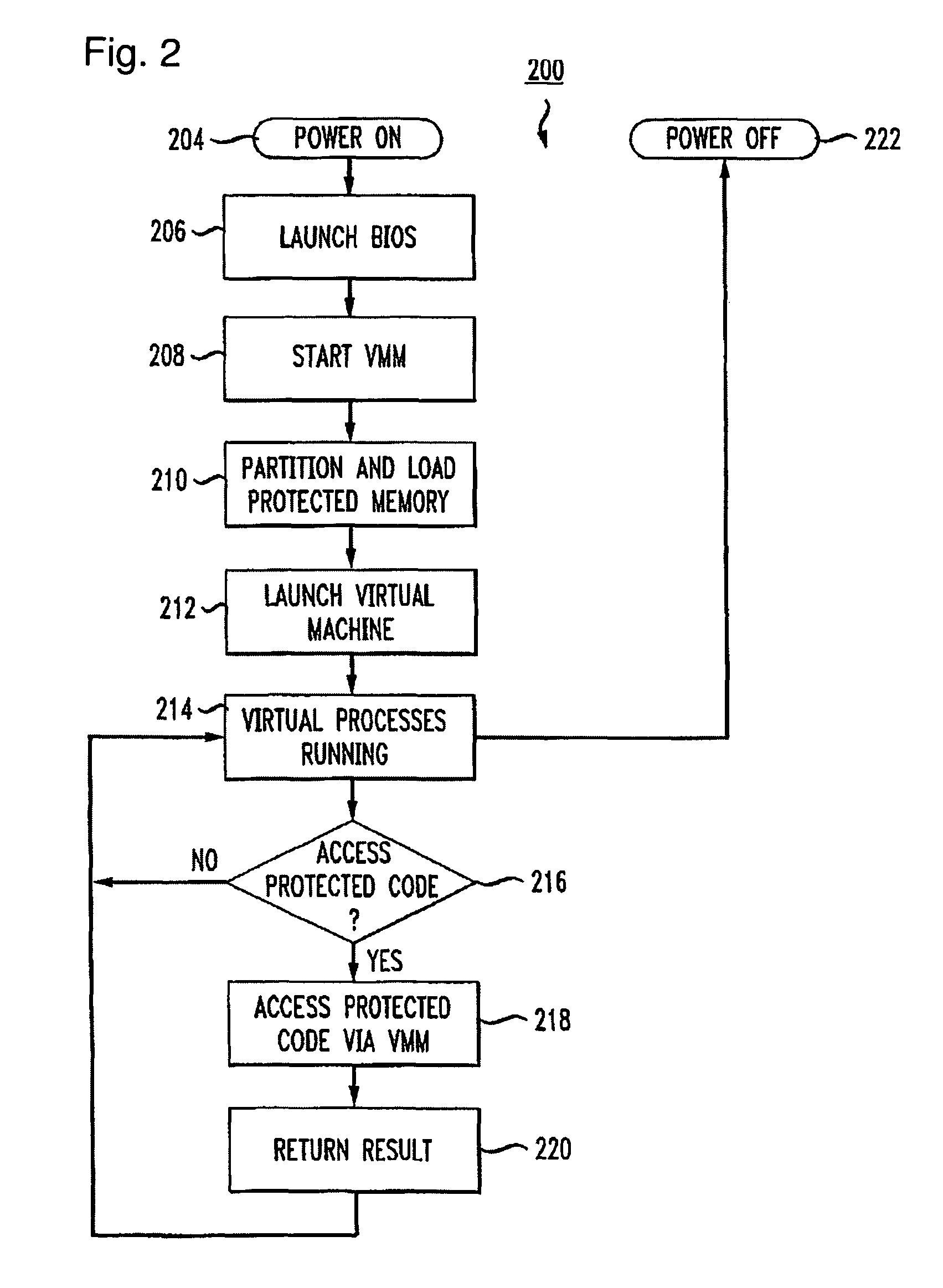
Virtualization-based security apparatuses, methods, and systems
InactiveUS8156298B1Avoid disadvantagesAvoid problemsMemory architecture accessing/allocationComputer security arrangementsOperational systemProtection mechanism
Apparatuses, devices, and methods for protecting content on a computer are disclosed that employ a novel hypervisor configured to segregate, or partition, hardware resources or portions thereof into protected and unprotected areas and devices. The partitioning, effectively hides protected hardware resources, such as the BIOS device, etc., from operating systems running on the computer. The hypervisor controls access resources into the protected area and limits the manner in which the operating systems on the computer can access the protected resources and content. The hypervisor can be configured to physically partition entire hardware resource or to employ virtualization technology to partition hardware resources, such as memory devices, into protected and unprotected areas that are virtually partitioned. The hypervisor of the present invention provides a new concept in employing anti-forensic techniques to bring about a protection mechanism that prevents unauthorized users including remote attackers who have obtained administrative access from accessing, reverse engineering, or otherwise exposing content protected. The content can generally be anything that can be maintained in a computer including data, algorithms, code, information and processes in general, etc., such as personal, sensitive, confidential and proprietary information and algorithms, and cryptographic keys.
Owner:NULLRING
Secure method and system for handling and distributing digital media
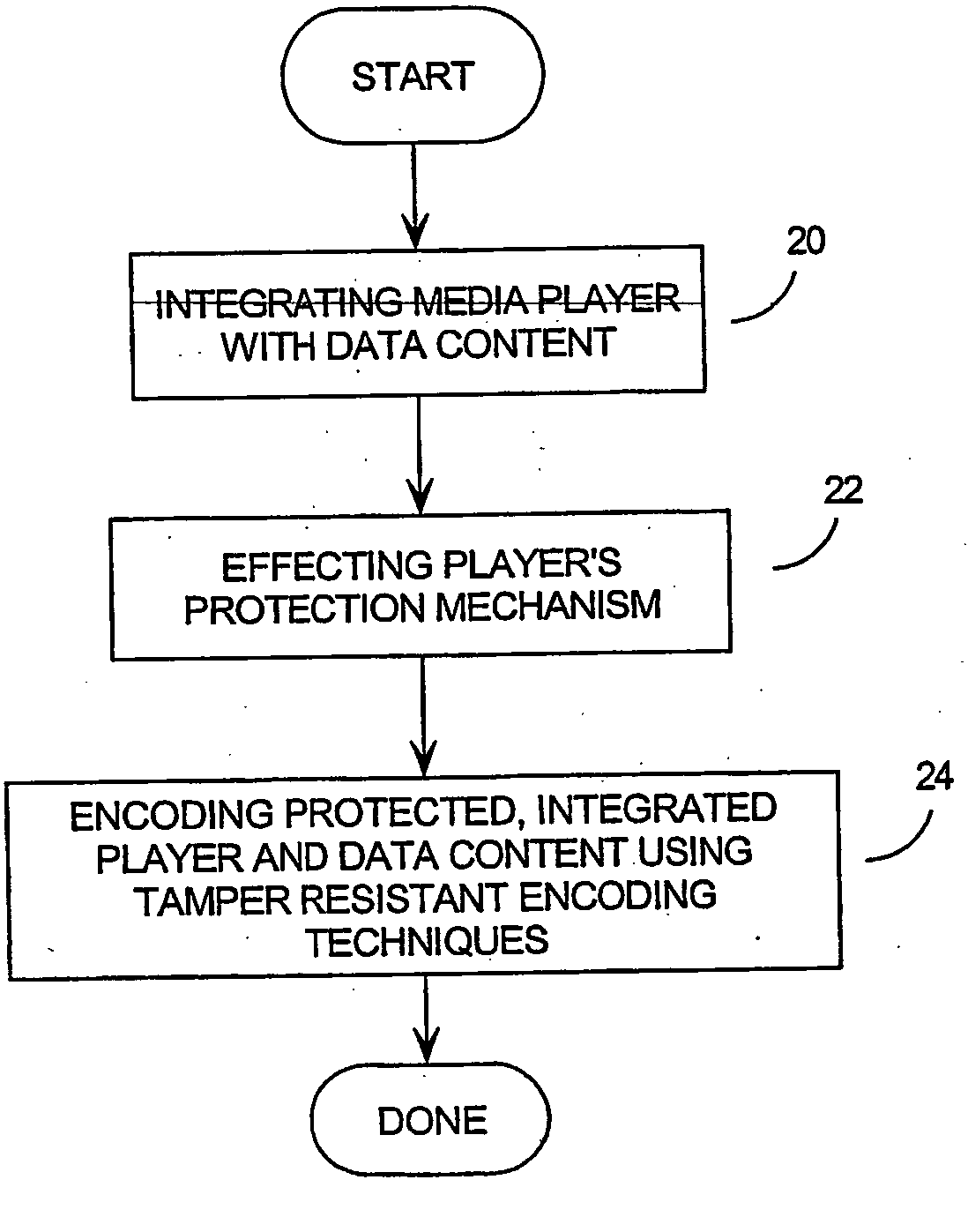
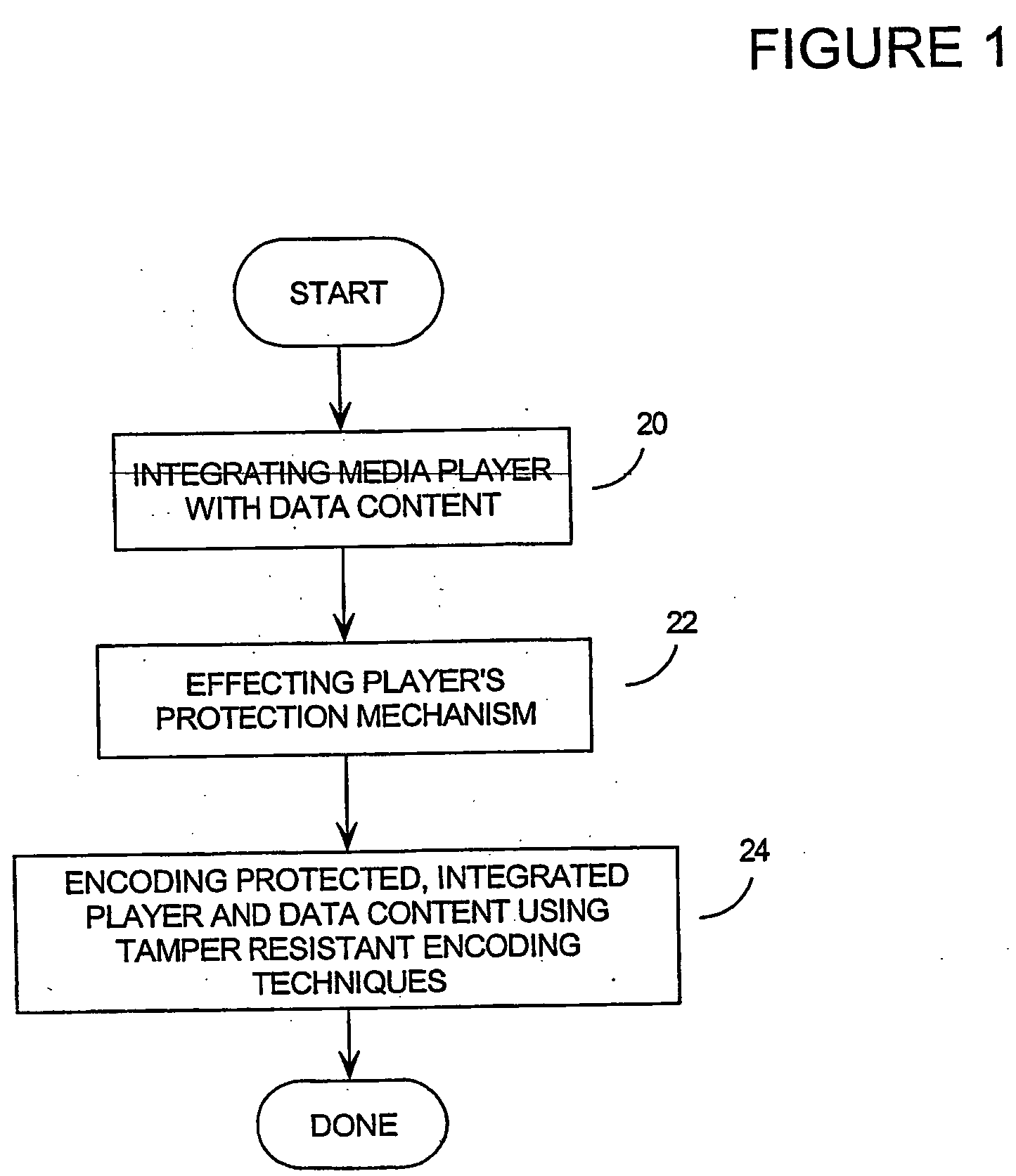
InactiveUS20050021989A1Effectively indelible digital markingReduce riskUser identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionData streamDigital content
A great deal of intellectual property is currenttly handled digitally, in the from of audible, visual, or audio-visual files or data streams. With today's powerful electronic equipment and communication networks such as the internet, this digital content can be reproduced flawlessly and distributed without control. While attemps have been made to protect such digital content, none of the existing protection techniques have been successful. The invention provides a system and method of protecting digital content by integrating the digital content with an executable software package such as a digital media player, executing some sort of protection mechanism (such as password, watermark or encryption protection), and then encoding the software into a tamper-resistant form. In this way, the digital content can be used by initiating the executable software it was encoded with, but the content itself cannot be accessed, nor can the protection mechanism be cracked.
Owner:IRDETO CANADA CORP
Directionless optical architecture and highly available network and photonic resilience methods
ActiveUS20090232492A1Lightweight deploymentIncrease elasticityMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsTransceiverRoute diversity
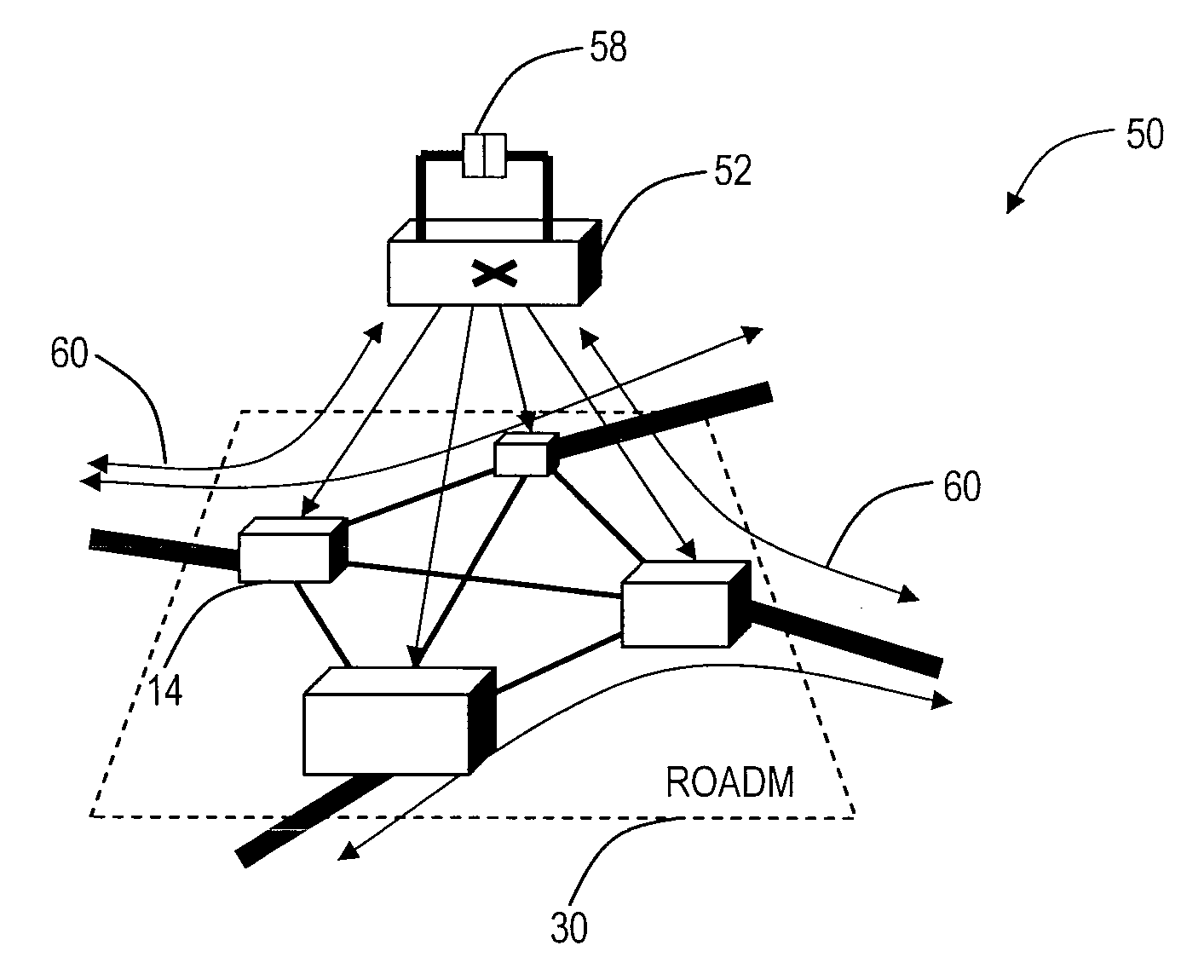
The present invention provides a directionless optical architecture for reconfigurable optical add / drop multiplexers (ROADMs) and wavelength selective switches (WSSs). The directionless architecture utilizes a directionless wavelength switch coupled between client devices and ROADMs / WSSs to eliminate the need to hard-wire client devices to a wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) network. Accordingly, client device connections can be automatically routed without manual intervention to provide a highly resilient network design which can recover route diversity during failure scenarios. Additionally, the present invention minimizes deployments of costly optical transceivers while providing superior resiliency. Further, the present invention couples the directionless optical architecture and associated optical protection mechanisms with existing mesh restoration schemes to provide additional resiliency.
Owner:CIENA
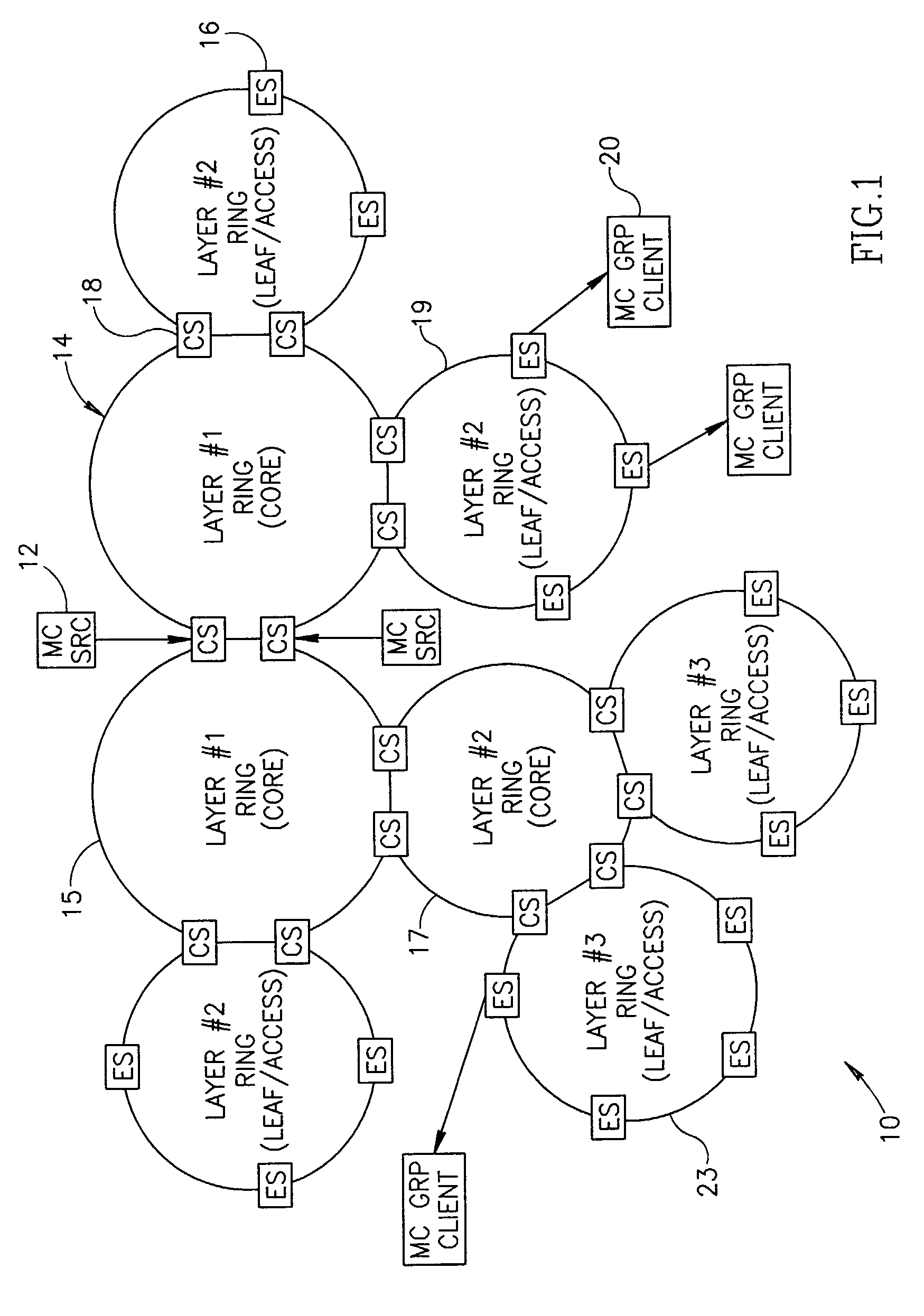
Efficient Protection Mechanisms For Protecting Multicast Traffic in a Ring Topology Network Utilizing Label Switching Protocols
Efficient protection mechanisms for ring-based label-switching networks, such as multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) networks. The protection mechanisms are designed to protect point-to-multipoint label switching paths (LSPs). In steering ring protection embodiments, the nodes of the ring network are provided with pre-configured tables that enable each node to operate in both working mode and protection mode. The information required for each node to switch between the two modes in included in its respective table during the pre-configuration of the ring network. In wrapping ring protection embodiments, the wrapping is performed by assigning a unique LSP label to each LSP and further configuring each intermediate node in the ring network to transparently pass data packets including the unique LSP label. Upon detecting a failure in a network node, the data packets including the unique LSP label are switched to a protection ring.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
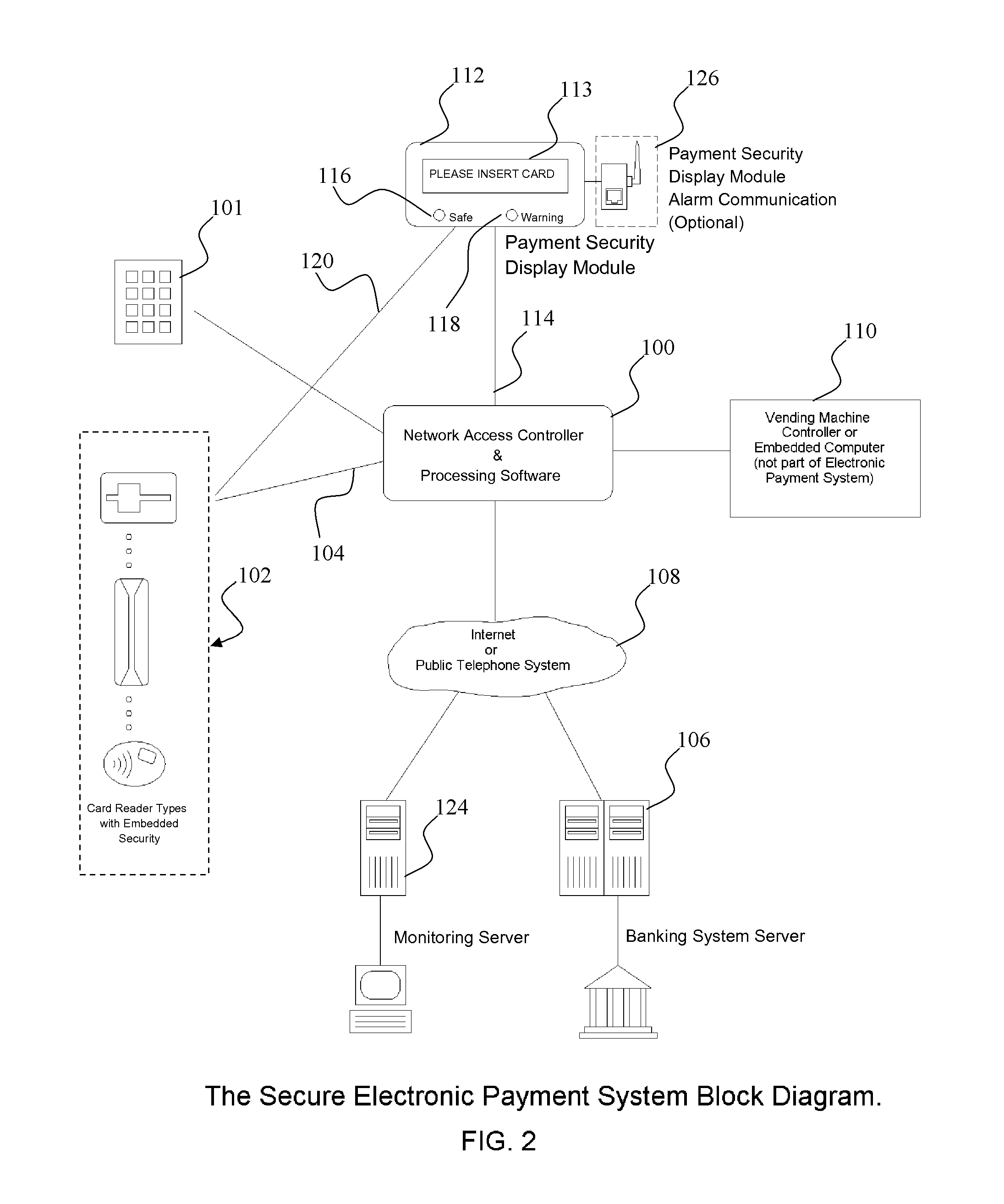
Secure electronic cash-less payment systems and methods
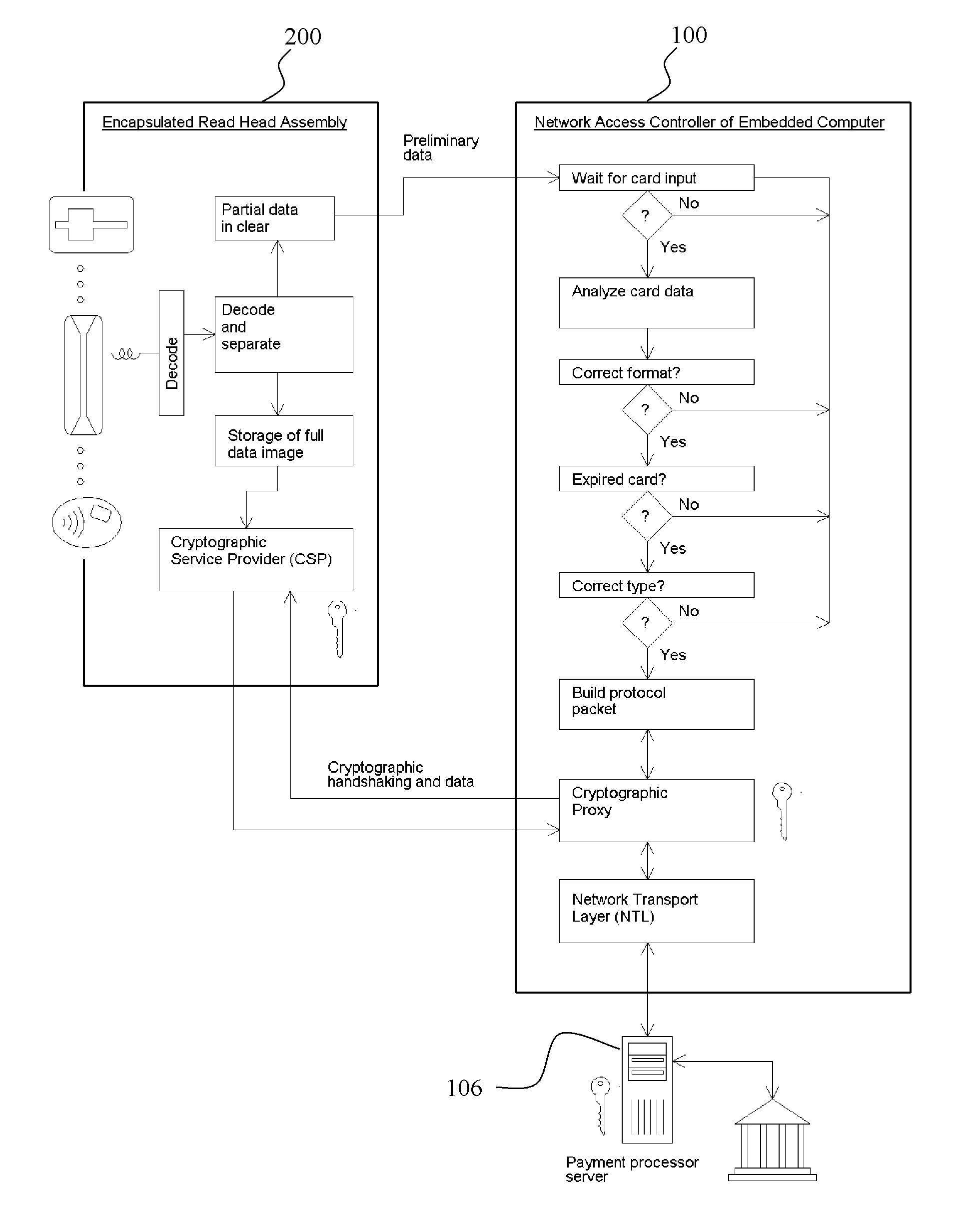
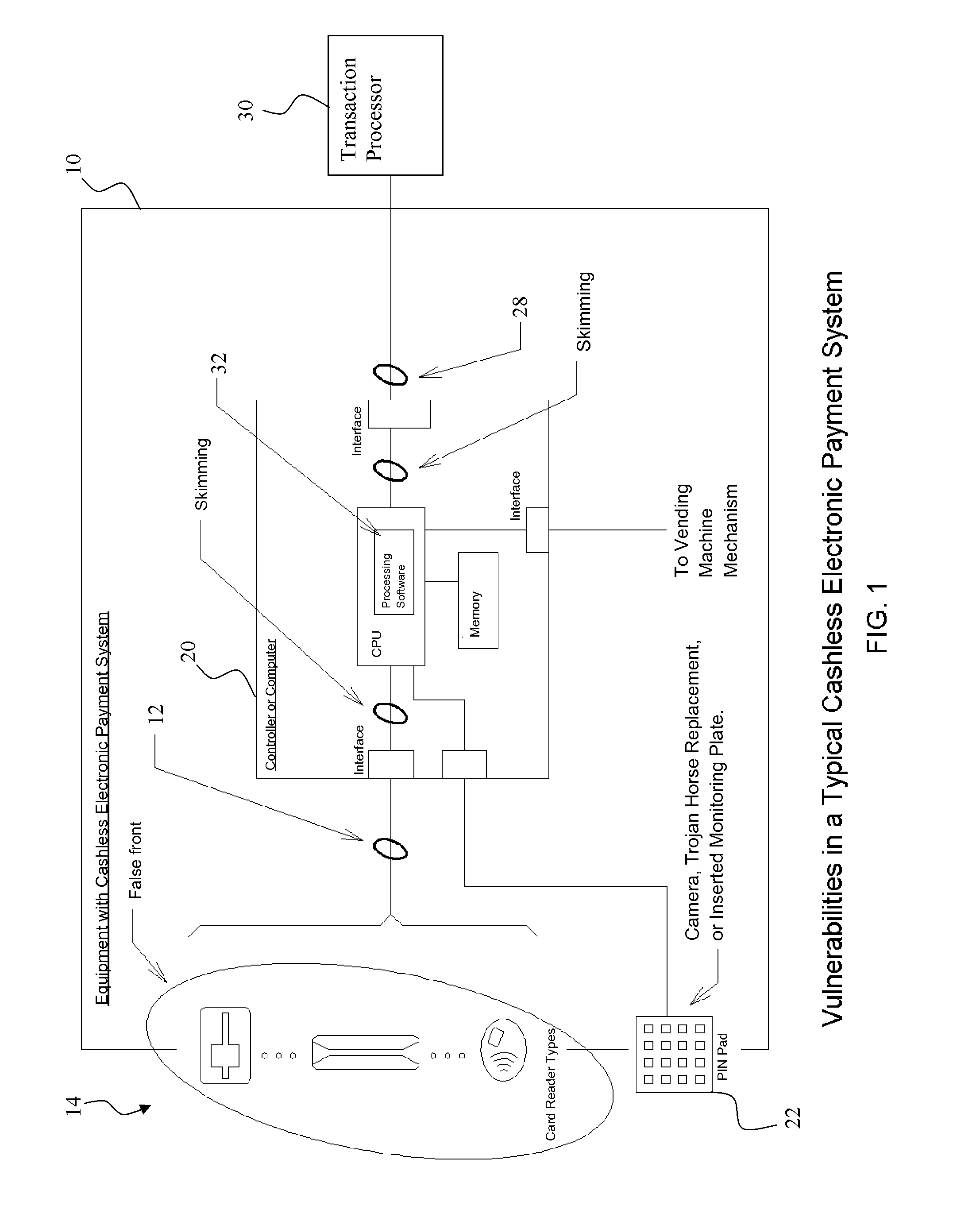
InactiveUS20110238581A1Improved fail-safe detectionImproved reporting mechanismAcutation objectsPayment circuitsEnd-to-end encryptionCredit card
Systems and methods to provide and maintain secure financial transaction conducted with a credit card or other cashless payment mechanism at a vending machine or other potentially unattended vending or point of sale device. Encapsulated card readers providing end-to-end encryption capabilities encrypt transaction data for secure transmission to a transaction host or server. Pre-authorization transaction data checking maintains account numbers in a secure encrypted format further enhancing security. Protection mechanisms that guard against, and provide warnings of equipment tampering, while also providing a visual indication to customers regarding the security of the system.
Owner:FORWARD PAY SYST
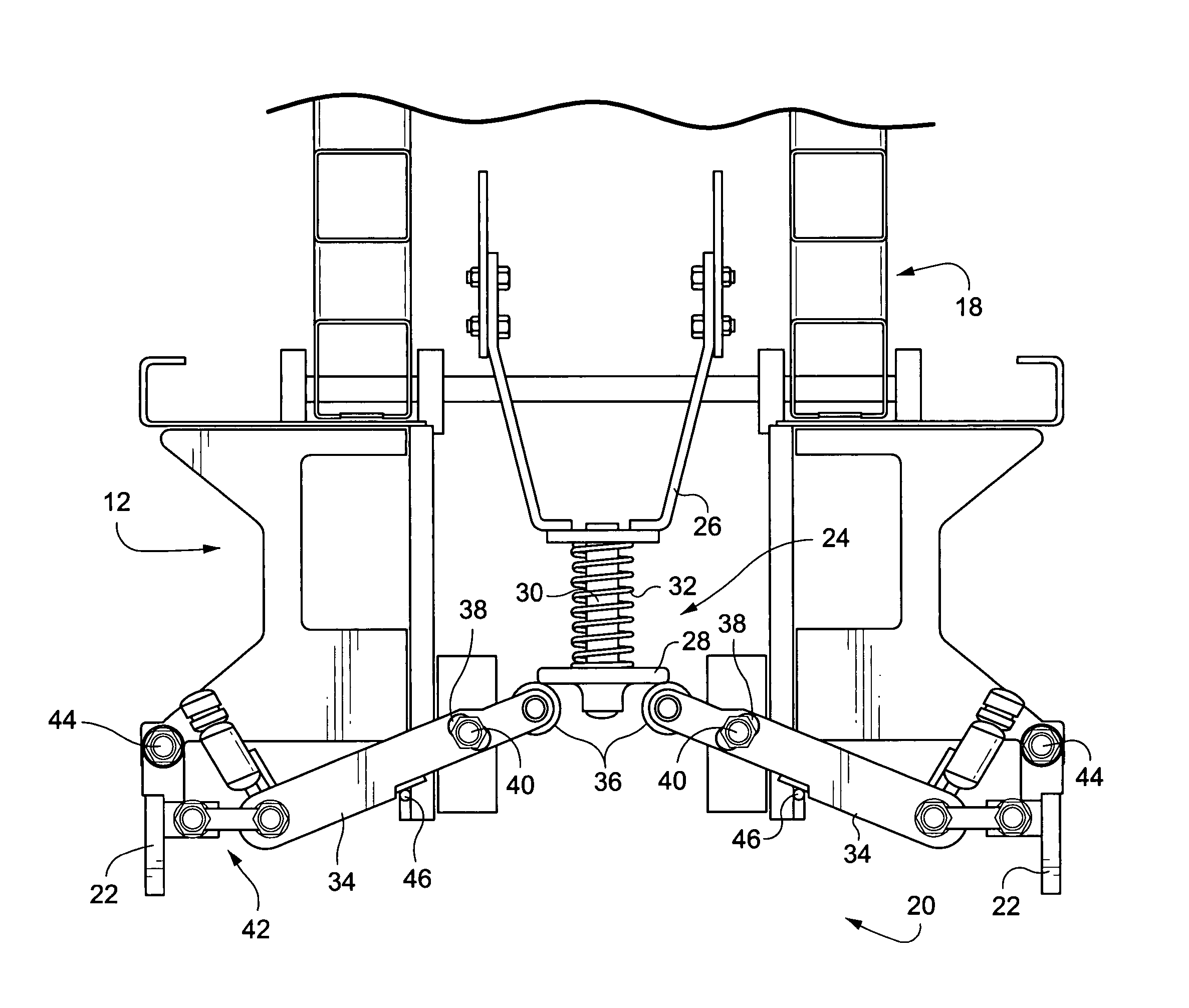
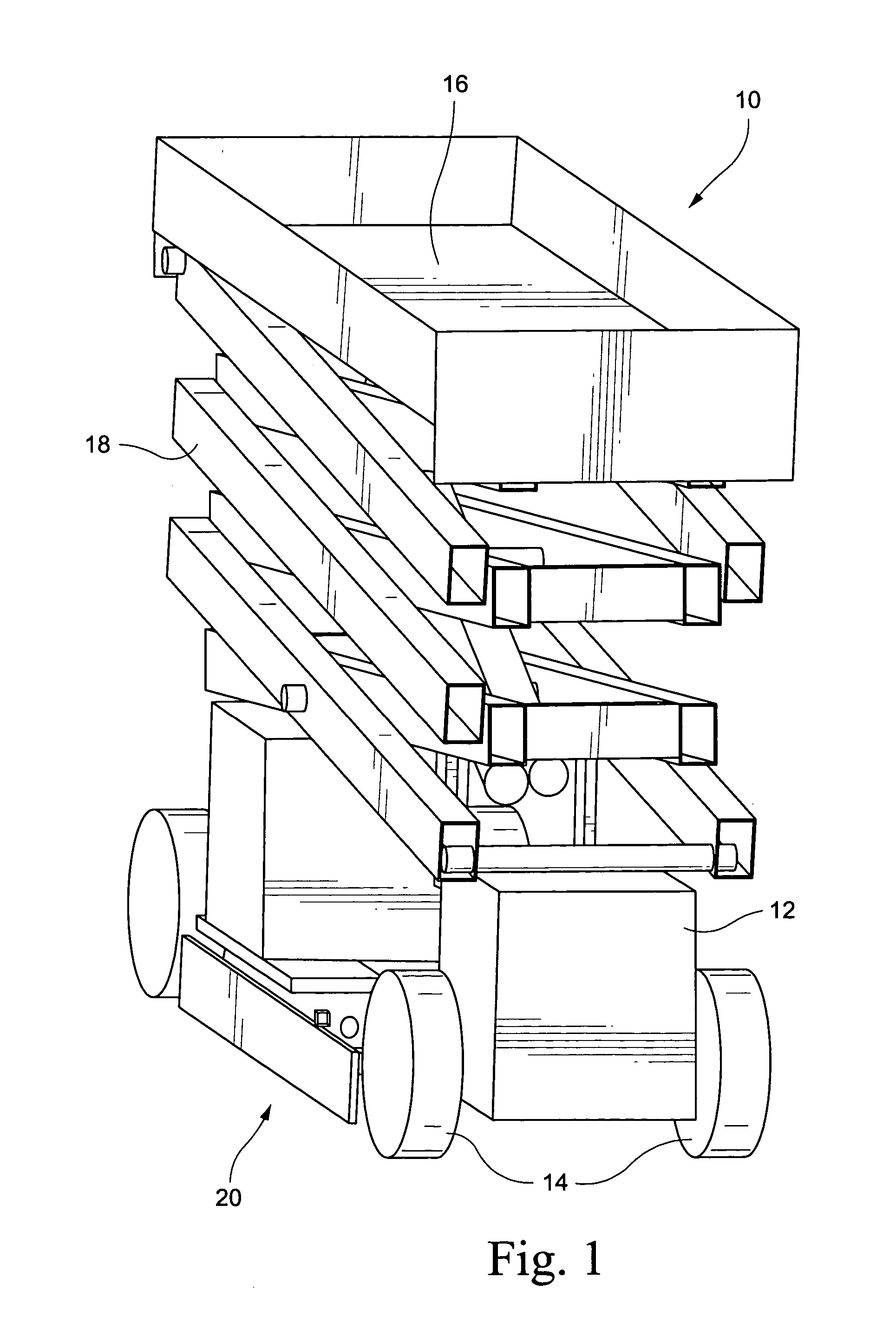
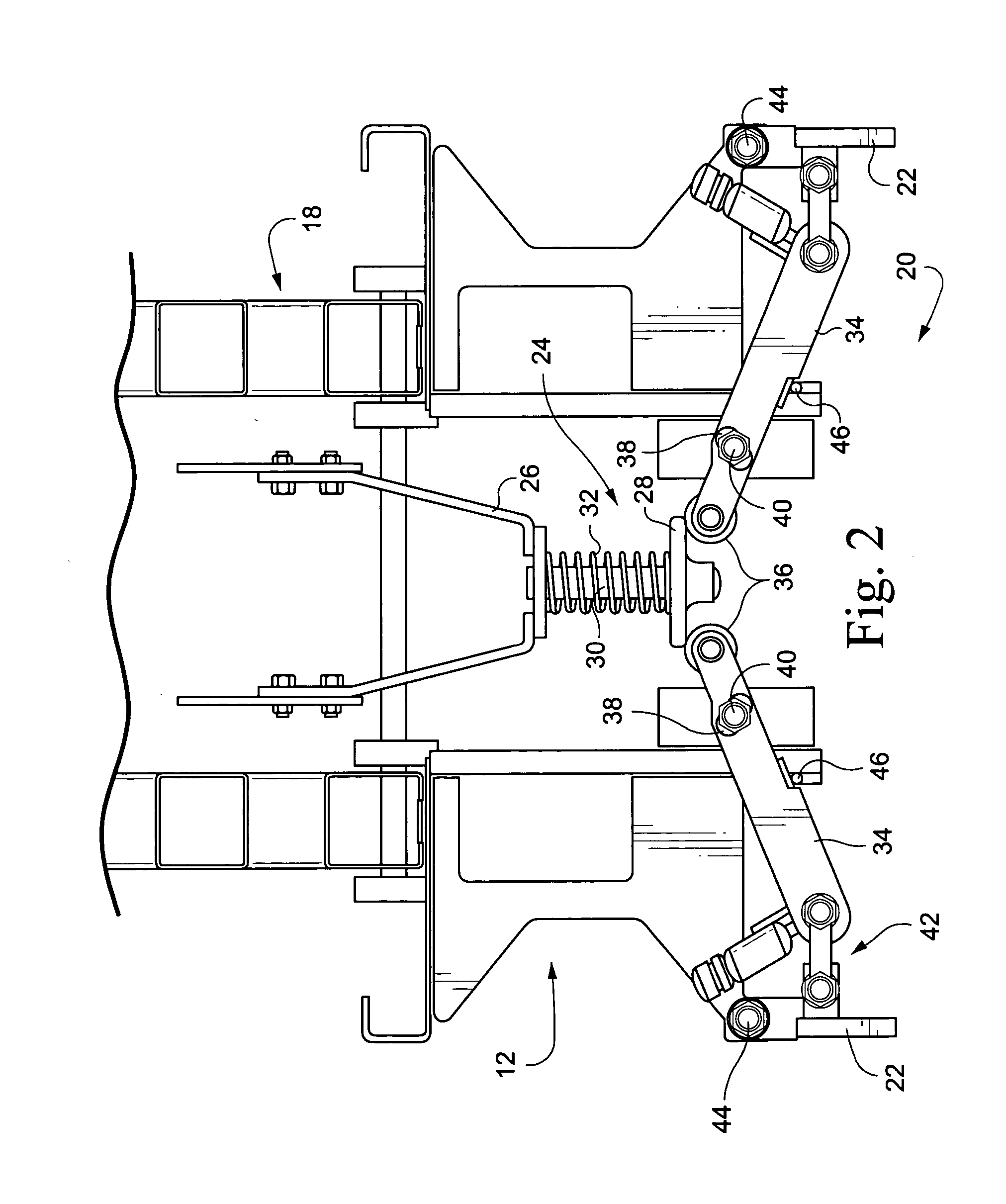
Pothole protection mechanism
ActiveUS20050224290A1Guaranteed uptimeSafety devices for lifting equipmentsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementProtection mechanismEngineering
A pothole protection mechanism provides additional support for the vehicle in the event a wheel is driven into a hole while the platform is elevated. The mechanism includes an extendible and retractable pothole protection bar. A five-bar mechanism serves to actuate the pothole protection bar based on a position of the vehicle lifting section. The construction of the mechanism serves to prevent a crushing hazard while deploying the bar and tolerates fixed objects on the ground while raising the bar.
Owner:JLG IND INC
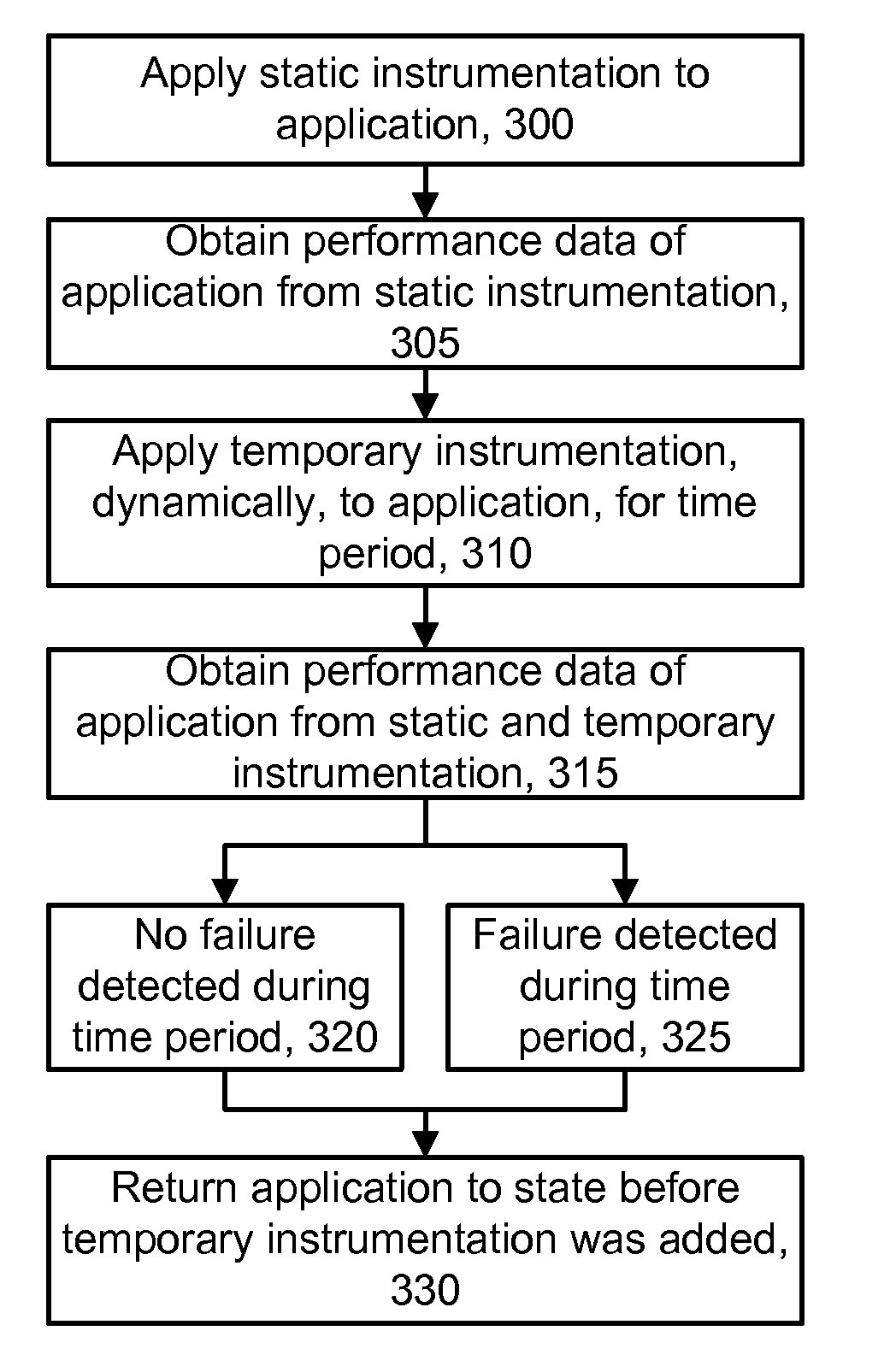
Failsafe mechanism for dynamic instrumentation of software using callbacks
InactiveUS20110283265A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware failureDynamic instrumentation
A failsafe mechanism for installing and removing temporary instrumentation during a runtime of an application. Initially, an application is configured with a baseline set of instrumented components such as methods. Additional instrumentation is then deployed in the application, such as to diagnose a performance problem. The failsafe mechanism ensures that the additional instrumentation is automatically removed, even when there is an interruption in a communication link to the application, a computing device failure, a software failure, or some other type of failure, which renders it impossible to manually roll back the instrumentation from a remote user interface. The failsafe mechanism can be provided using callbacks between the computing devices which detect when a connection is unexpectedly lost or closed. Termination of one callback can cascade to one or more other callbacks. The instrumentation rollback can involve reloading un-instrumented byte code of the application.
Owner:CA TECH INC
AC/DC light emitting diodes with integrated protection mechanism
ActiveUS7714348B2Electroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesCurrent limitingProtection mechanism
Owner:LED LIGHTING
Array substrate and preparing method thereof, display device and preparing method thereof
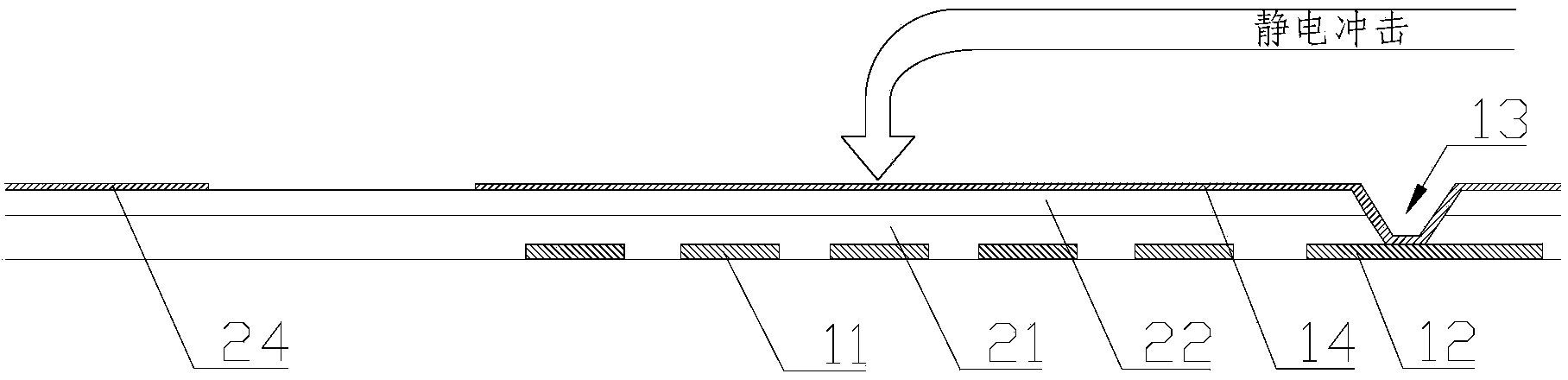
InactiveCN103513459AAvoid damageEffective electrostatic shock protection mechanismStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsProtection mechanismDisplay device
The invention relates to the technical field of display, in particular to an array substrate, a preparing method of the array substrate, a display device with the array substrate and a preparing method of the display device. The array substrate comprises a substrate body. The substrate body is provided with a plurality of pixel units and a drive circuit used for driving the pixel units. The edge of the substrate body is further provided with a ground lead and a first electrostatic protection layer connected with the ground lead. According to the array substrate, the preparing method of the array substrate, the display device with the array substrate and the preparing method of the display device, the ground lead and the first electrostatic protection layer are arranged, so that when a static shock occurs, electrostatic charges are discharged through the ground lead and the first electrostatic protection layer, an effective static shock protection mechanism is formed, damage, caused by electrostatic breakdown, to the drive circuit is avoided, and the reliability of the product is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD
Magnetic disk protection mechanism, computer system comprising protection mechanism, protection method for magnetic disk, and program for protection method
InactiveUS7042663B2Avoid lostPrevent returnDisposition/mounting of recording headsDriving/moving recording headsProtection mechanismComputerized system
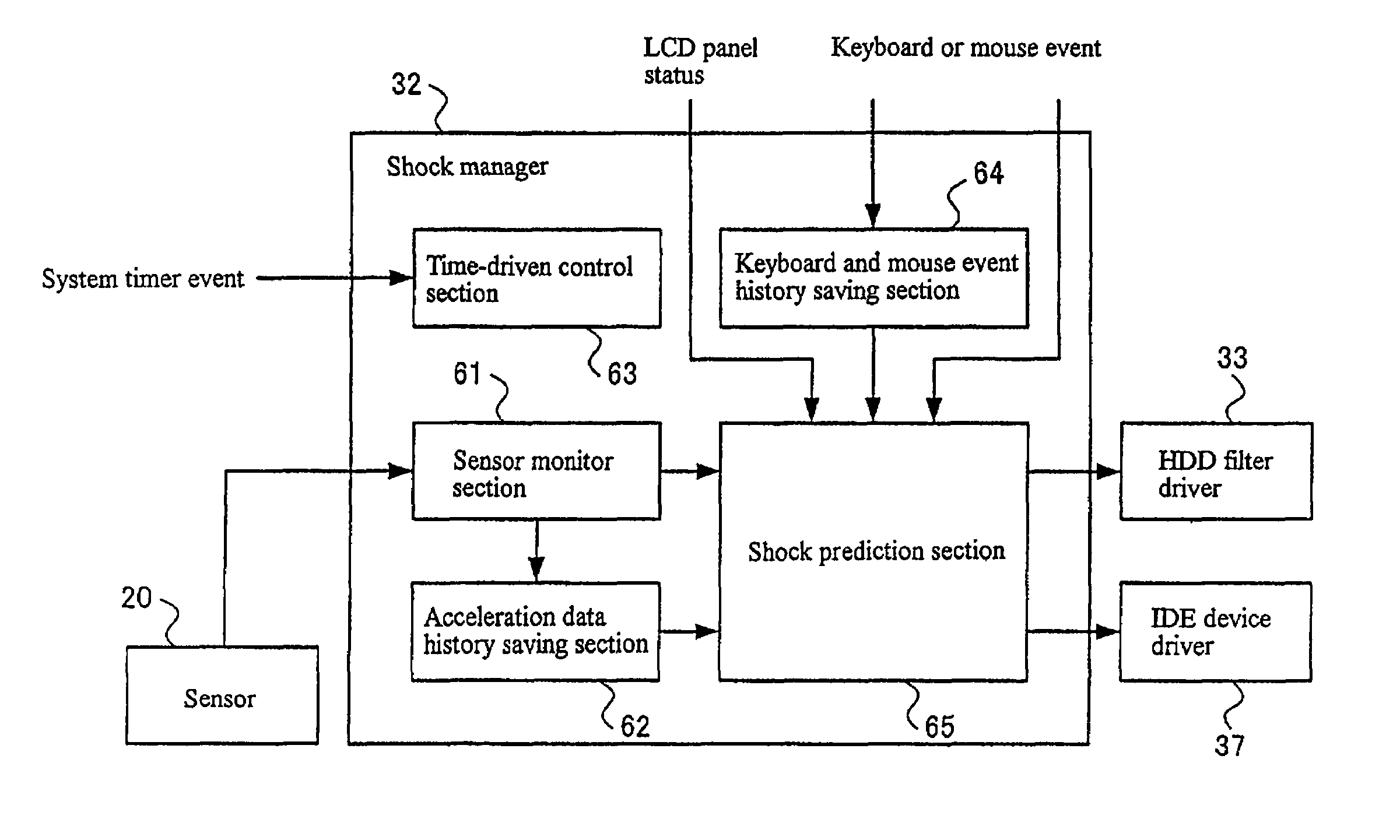
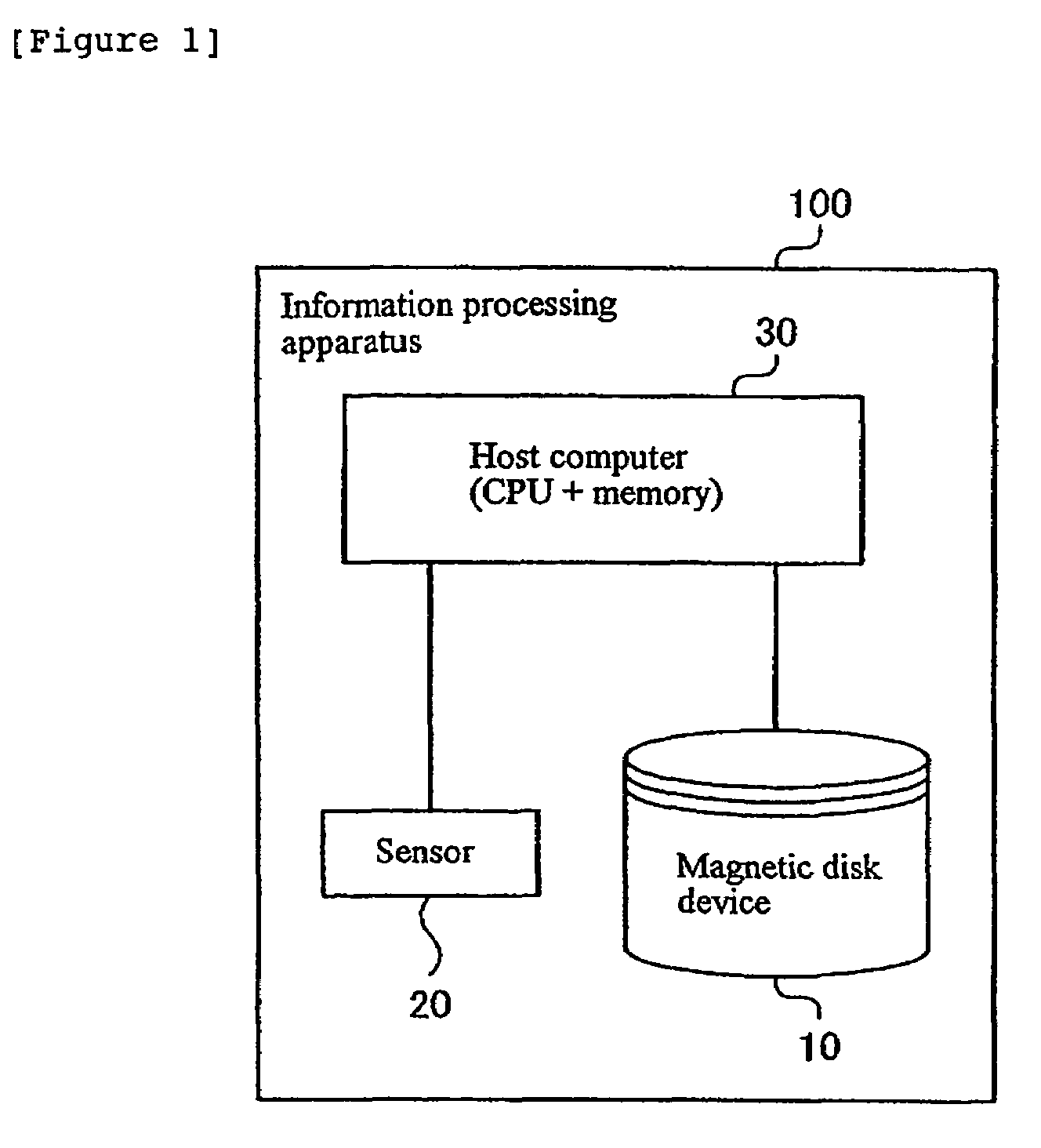
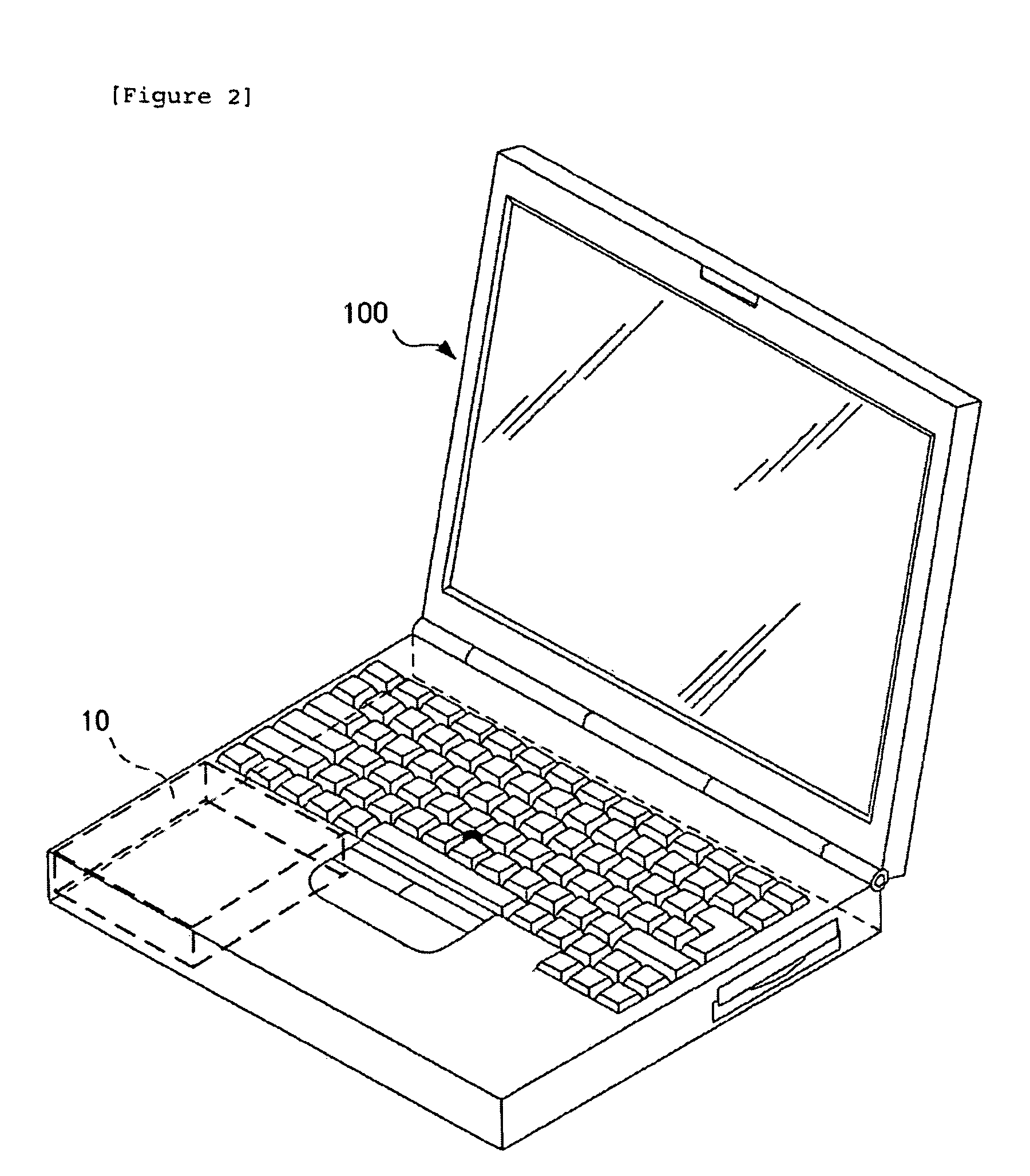
A magnetic disk device protection mechanism comprises a sensor that acquires information on changes in the environment of a magnetic disk device, a sensor driver, a shock manager that analyzes the information acquired by the sensor driver together with a history of the information to determine the status where the magnetic disk device is used to predict a shock, and an HDD filter driver that controls operations of the magnetic disk device including the escape of a magnetic head. The magnetic disk device can also comprise a diagnosis processing section that operates if a shock has occurred actually, to check whether or not the magnetic head could have completely escaped before the occurrence of this shock to carry out diagnosis as to whether or not a fault is occurring in the magnetic disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
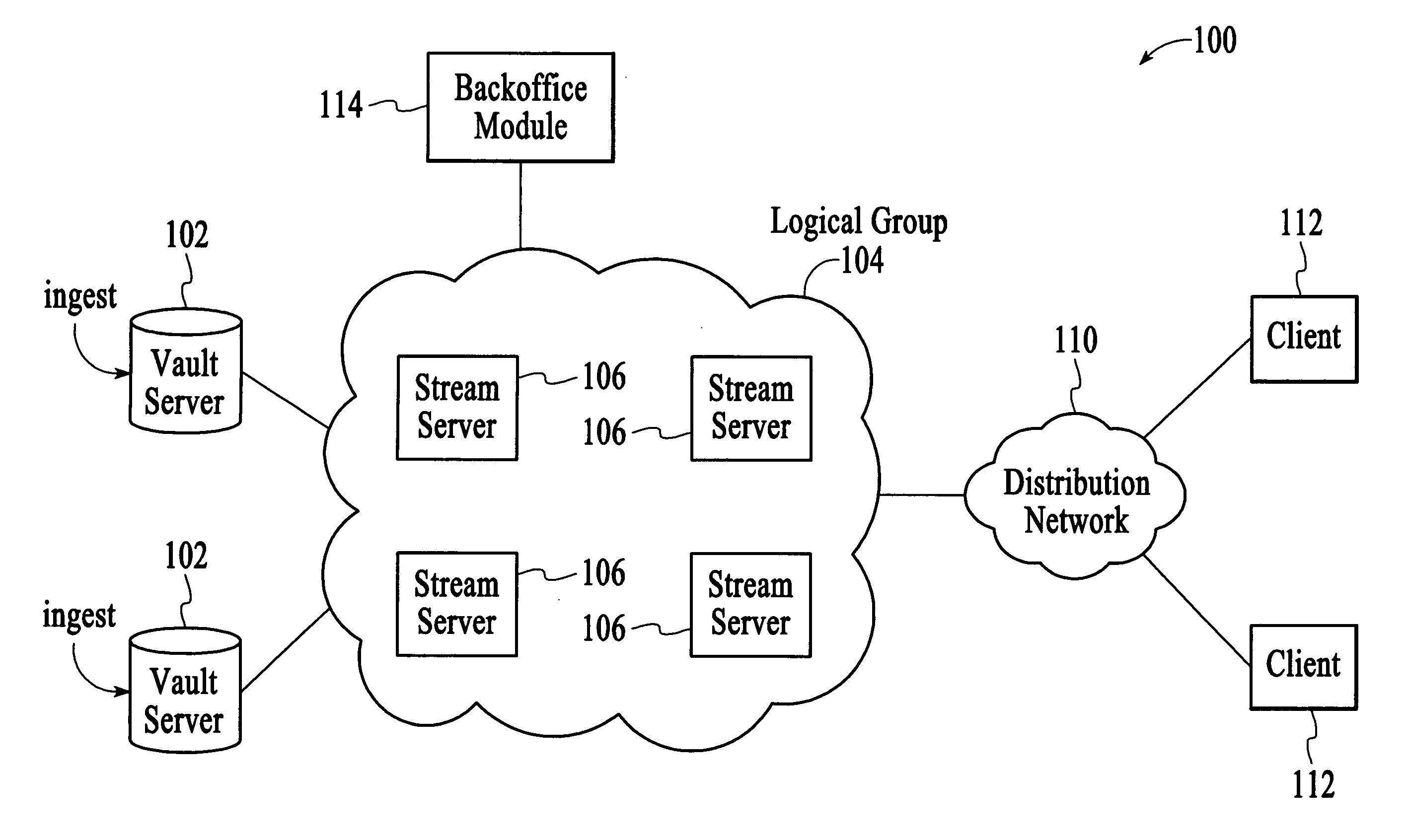
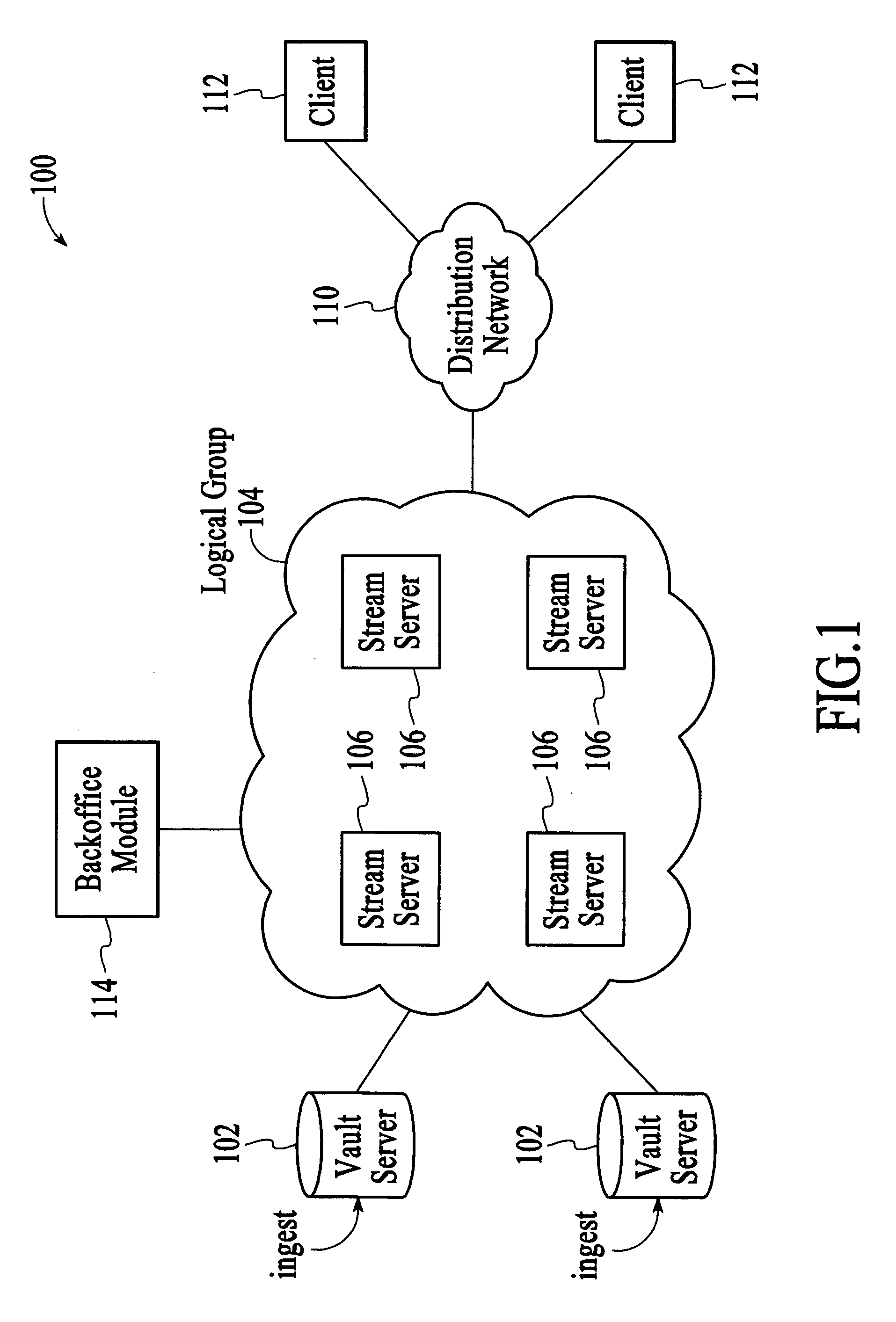
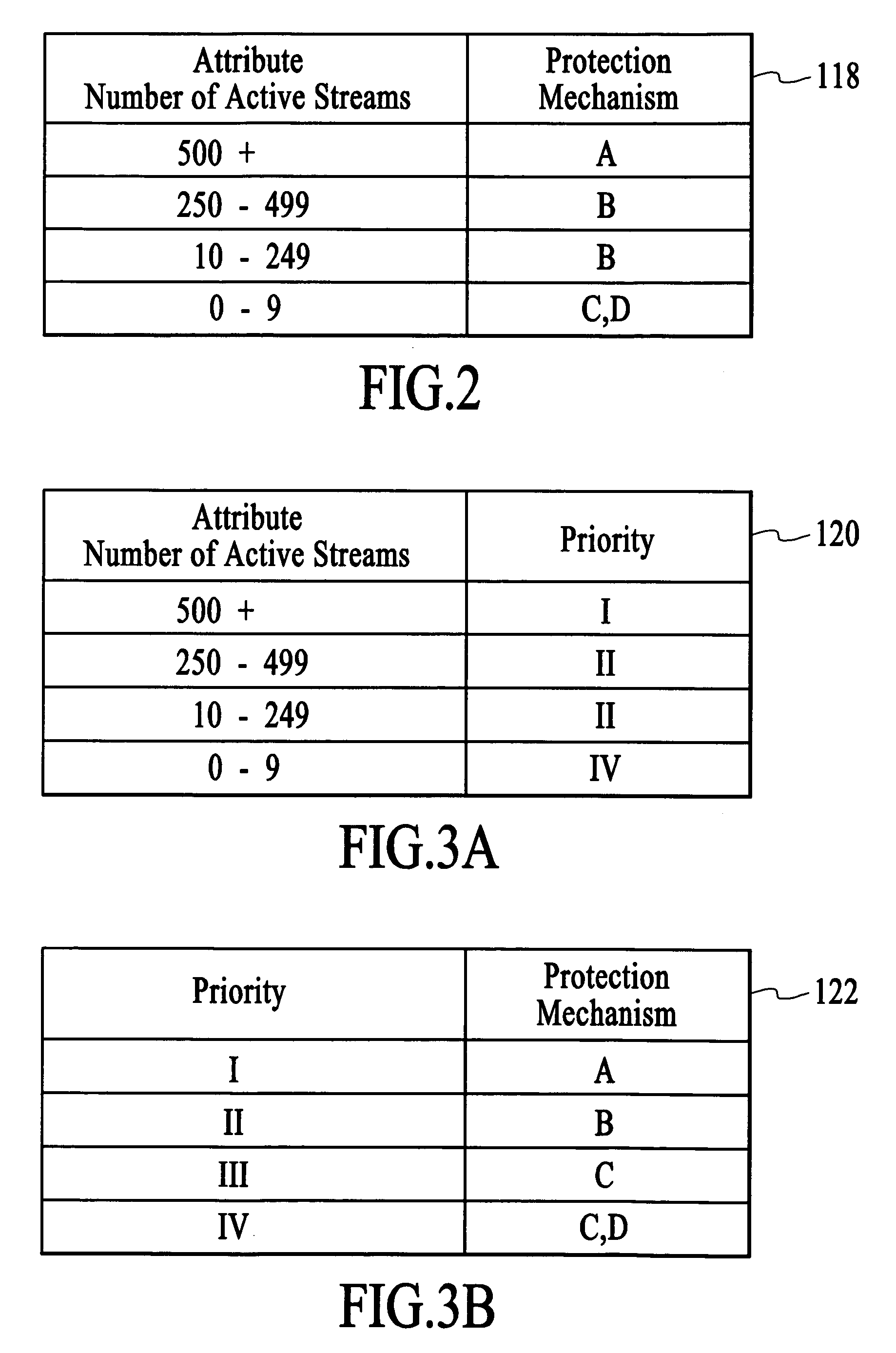
Stream control failover utilizing an attribute-dependent protection mechanism
ActiveUS20060248213A1Effective resourcesImprove scalabilityUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringDigital videoProtection mechanism
A technique for managing the streaming of digital video content to multiple clients involves identifying an attribute of a content element that is streamed to a client and selecting a protection mechanism for the content element as a function of the attribute, wherein the protection mechanism enables streaming of the content element to the clients in the event of a resource failure. In an example, the identified attribute is an indication of the popularity of the content element (e.g., as measured by the number of active streams), such that the protection mechanism is selected as a function of the popularity of the content element. In an embodiment, protection mechanisms that offer a higher level of protection are selected for the more popular content elements and protection mechanisms that offer a lower level of protection are selected for the less popular content elements.
Owner:SYNAMEDIA LTD
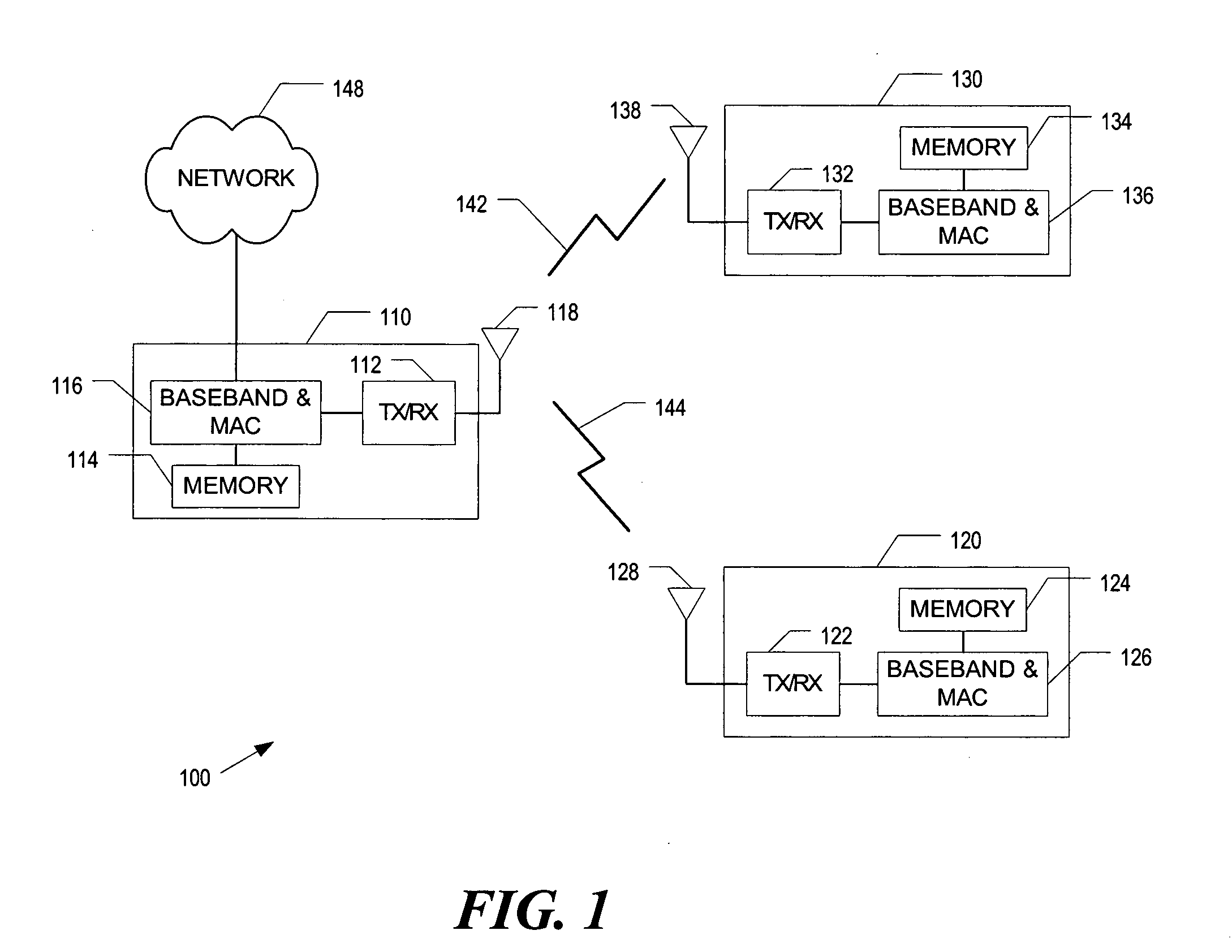
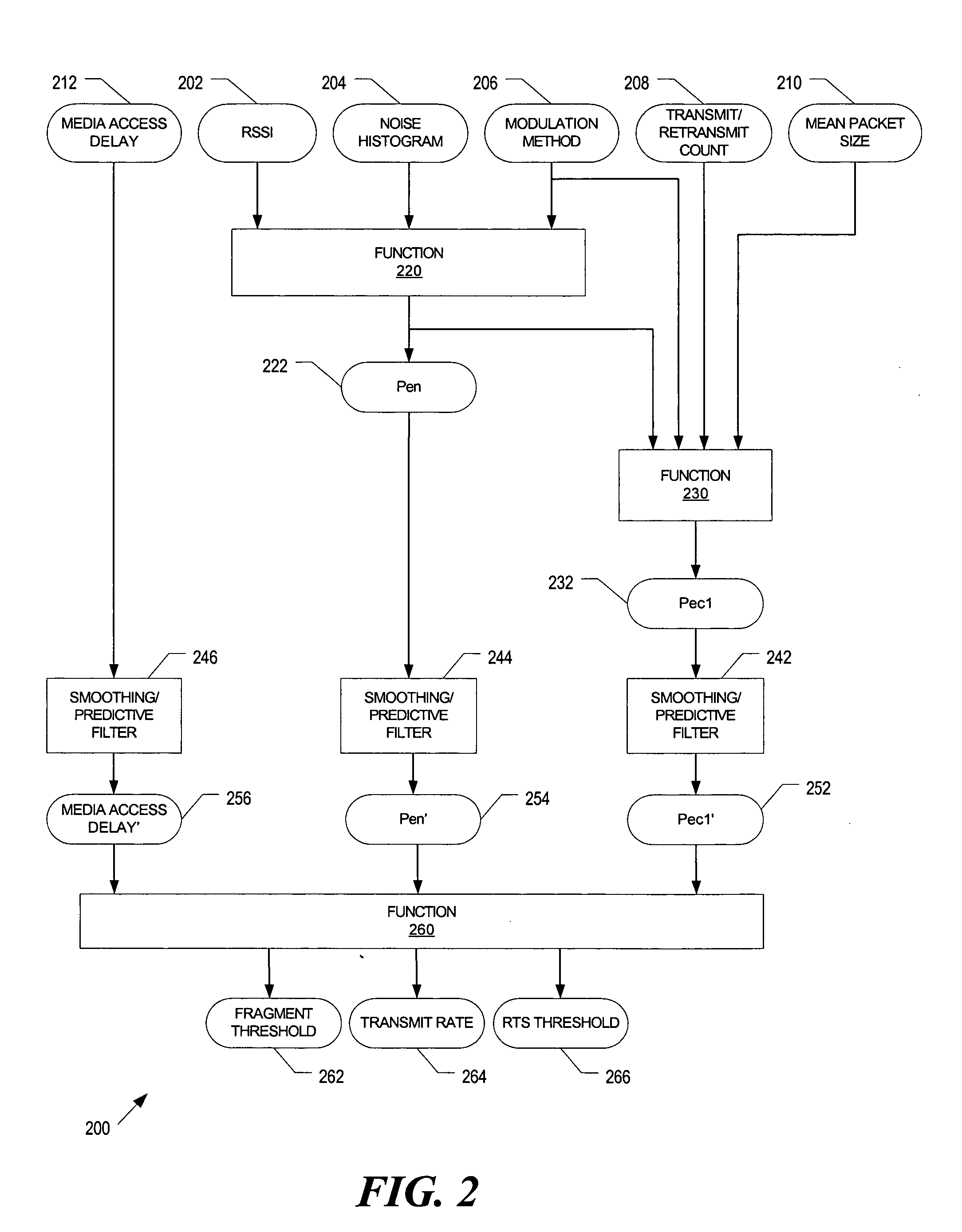
Method and apparatus to provide adaptive transmission parameters for wireless networks
InactiveUS20050268181A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsPacket collisionProtection mechanism
A method and apparatus that dynamically adjust transmission parameters based on channel conditions. Channel conditions include error rate due to packet collisions and an error rate due to noise. Transmission parameters include a fragmentation threshold, a transmit rate, and a transmission protection mechanism threshold.
Owner:INTEL CORP
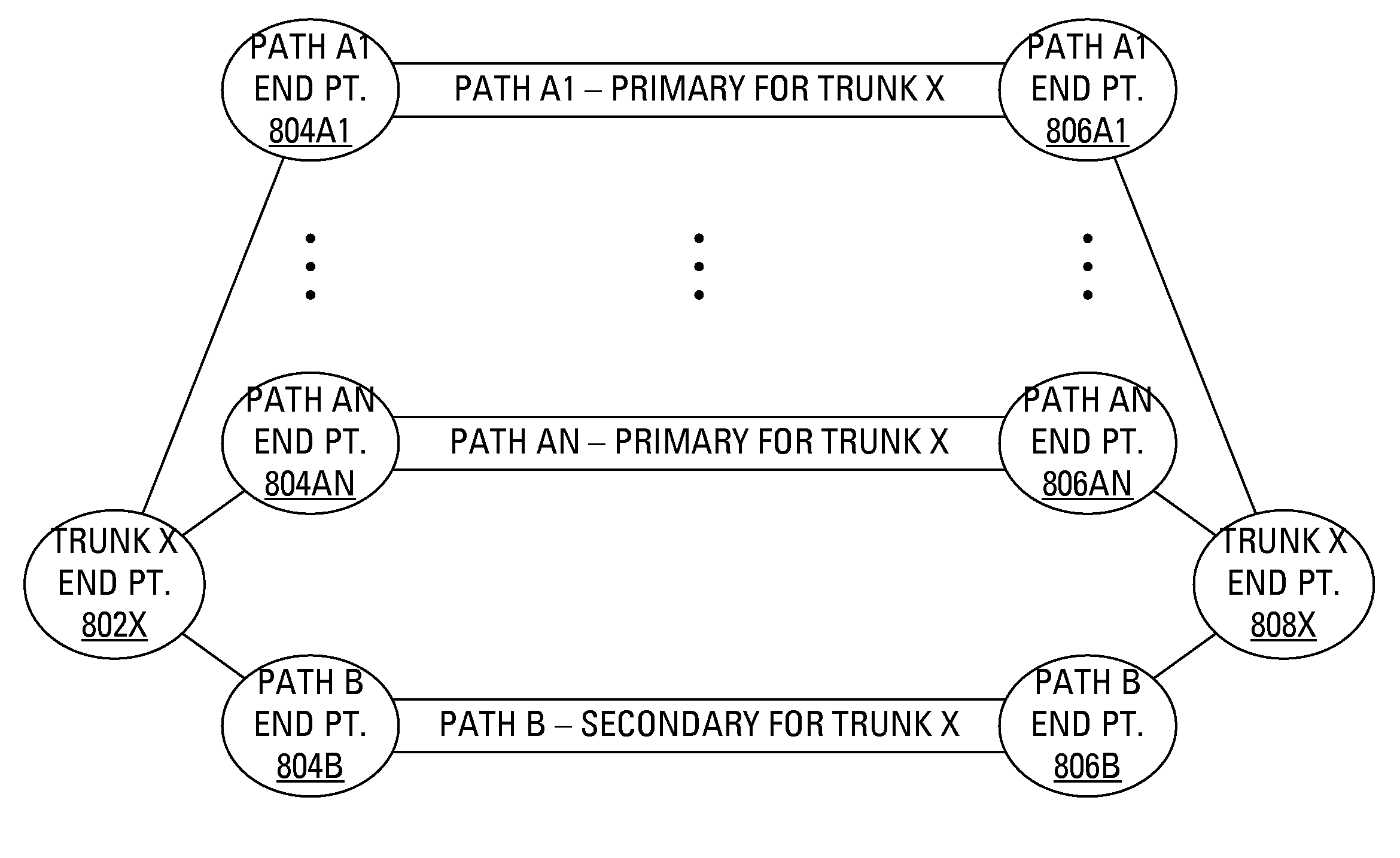
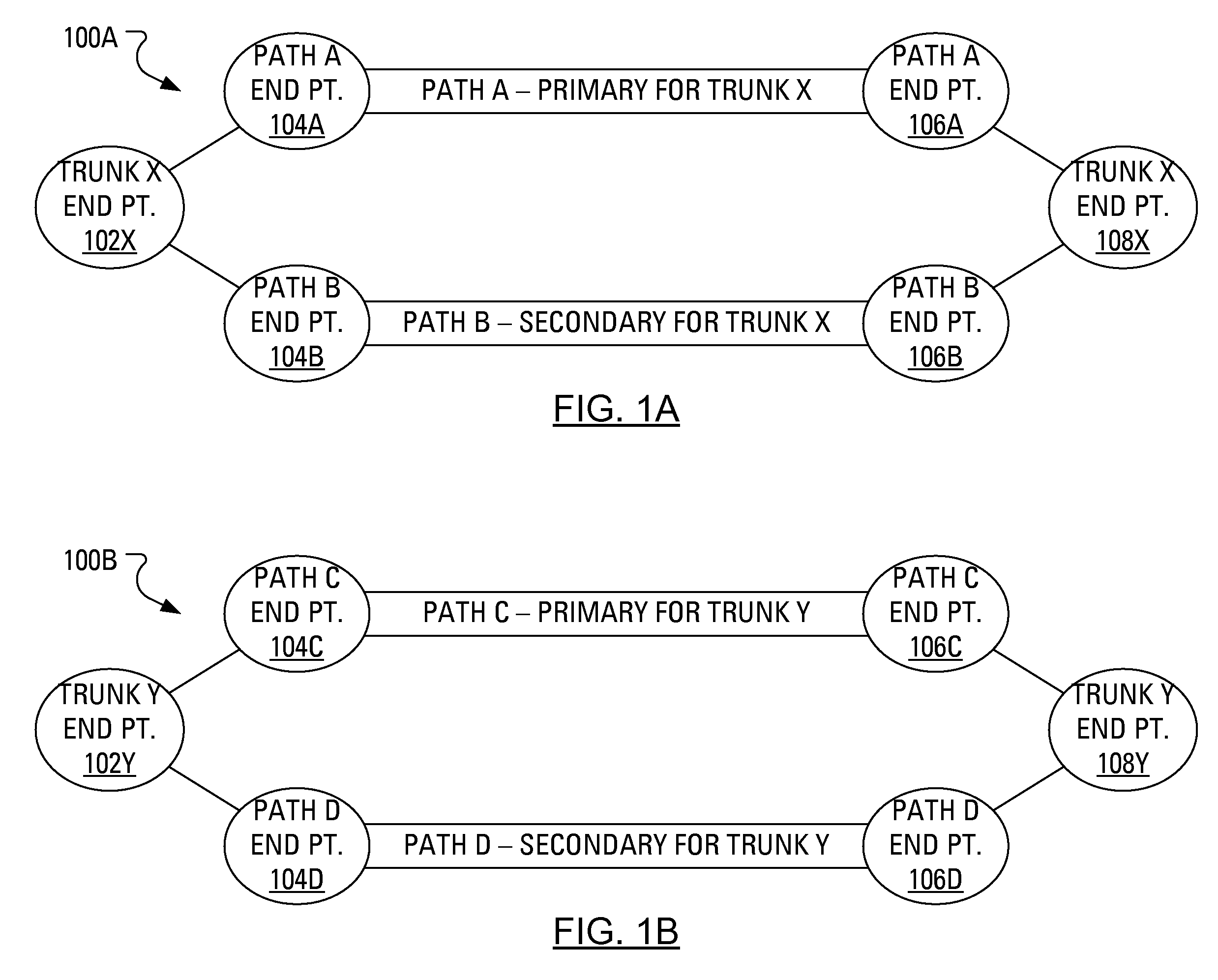
Facilitating automatic protection switching for provider backbone network
InactiveUS20080281987A1Optimization mechanismProtective mechanismMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksAutomatic protection switchingProtection mechanism
An existing protection mechanism is enhanced through the use of an automatic protection switching protocol data unit (APS PDU). In conjunction with transmitting Ethernet frames to a second bridge over a primary path, a first bridge transmits APS PDUs to the second bridge over a secondary path. The APS PDUs provide the second bridge with information about the protection switching mechanism being used and provide indications regarding the status of the primary path. In particular, protection switching may be facilitated by forming an APS PDU that is extended to include an indication of an identity for a trunk or a primary path before transmitting the APS PDU to the second bridge. Alternatively, after forming a regular APS PDU, protection switching may be facilitated by encapsulating the regular APS PDU with information identifying a trunk or a primary path before transmitting the APS PDU to the second bridge.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com