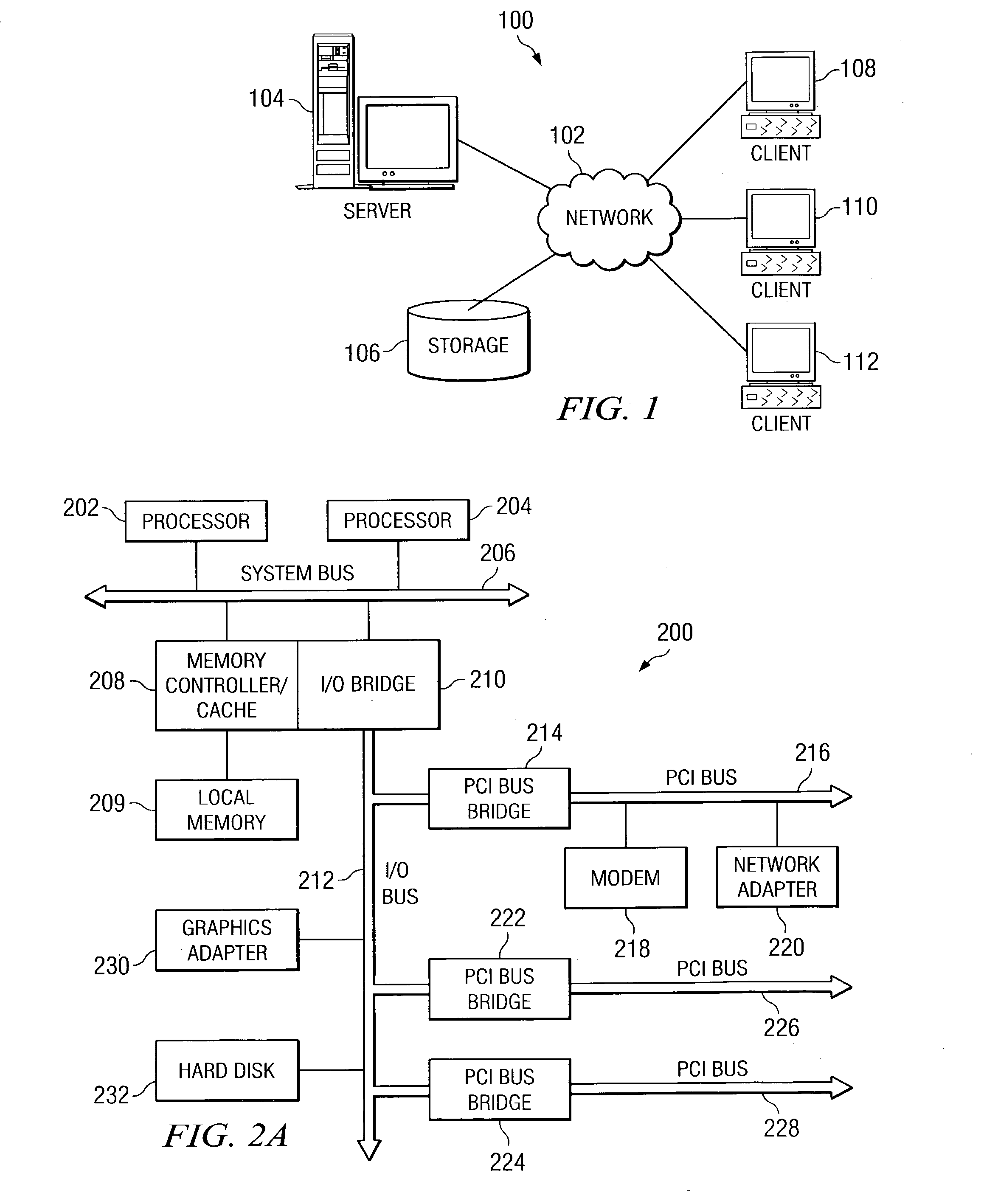
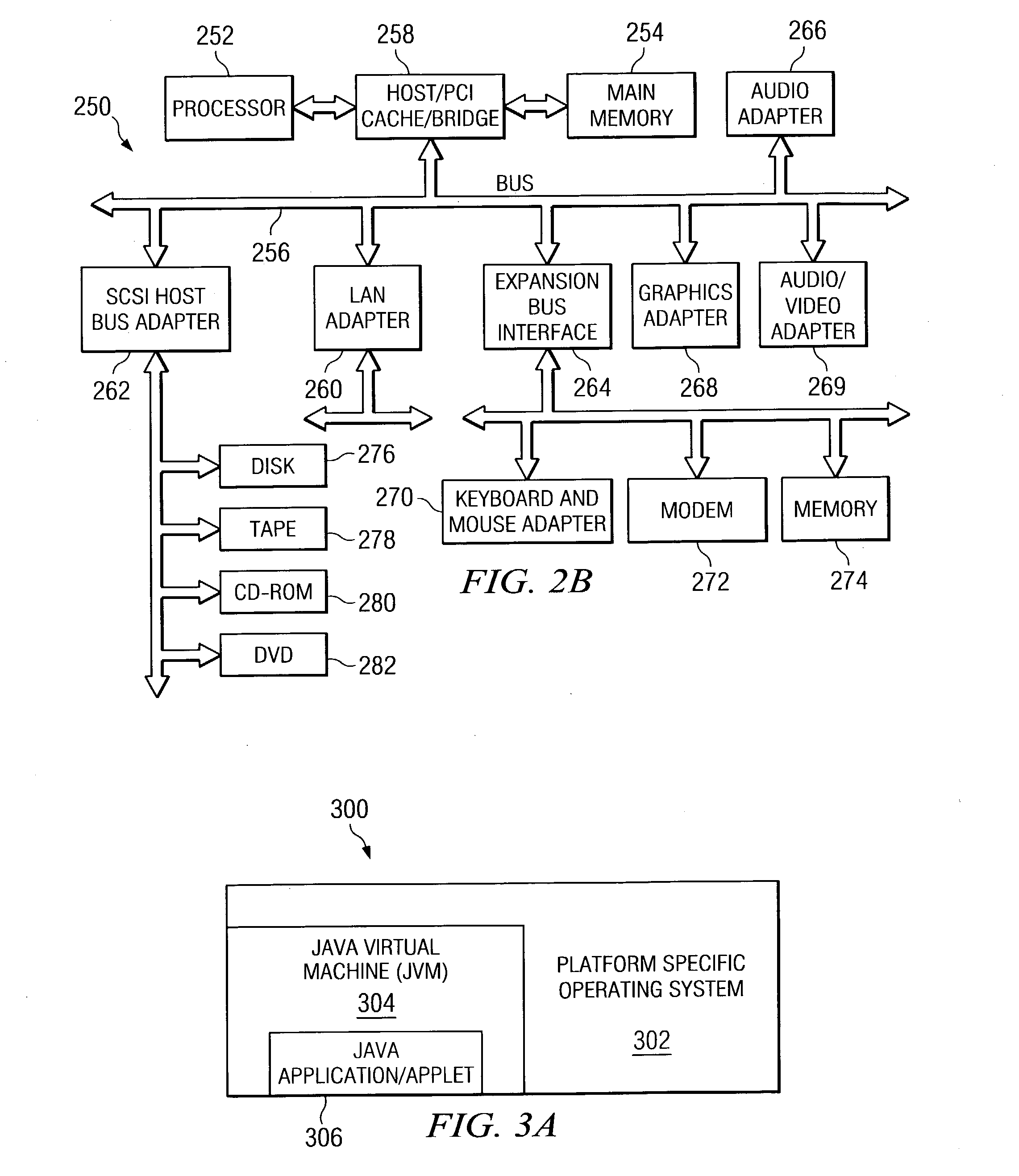
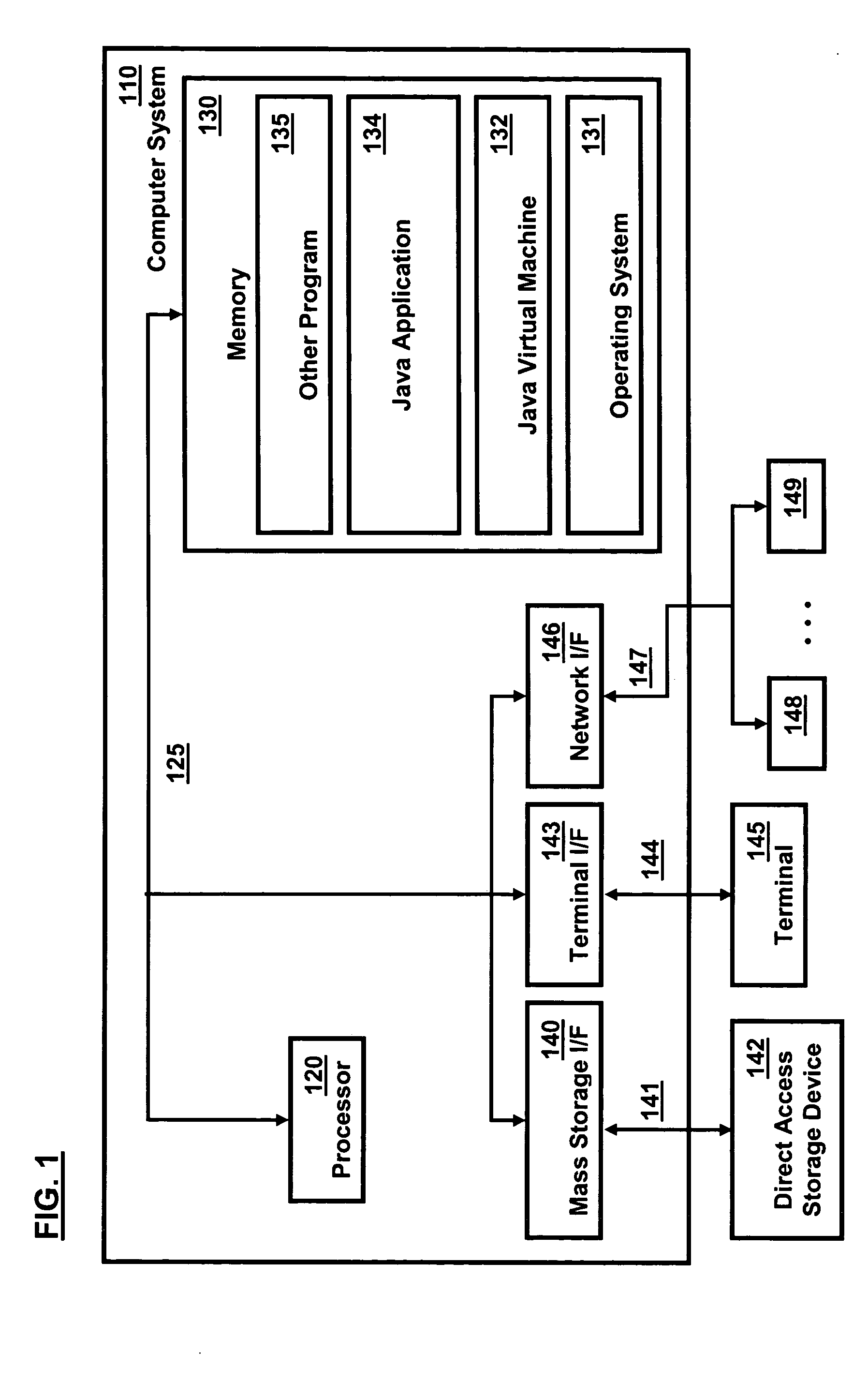
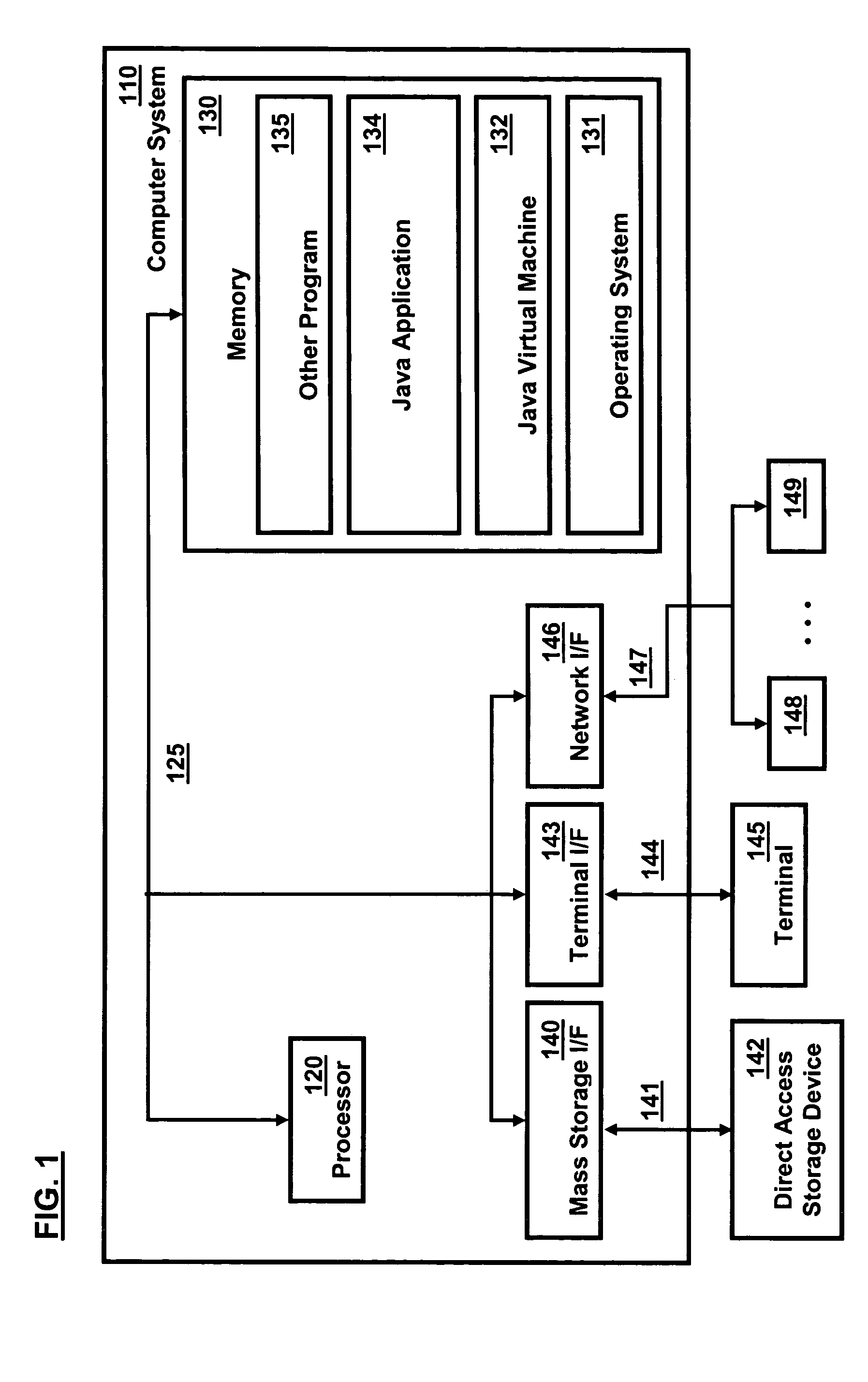
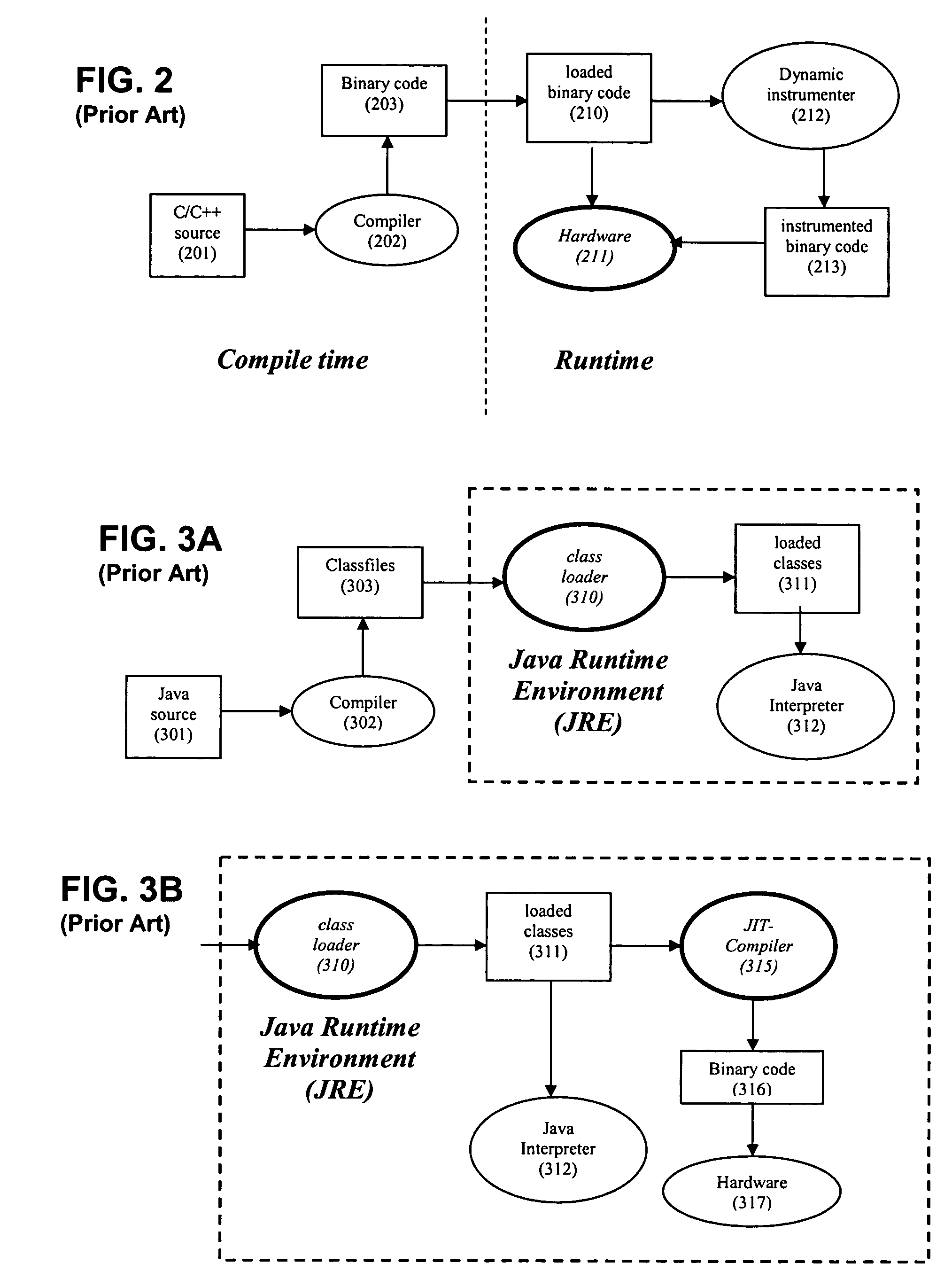
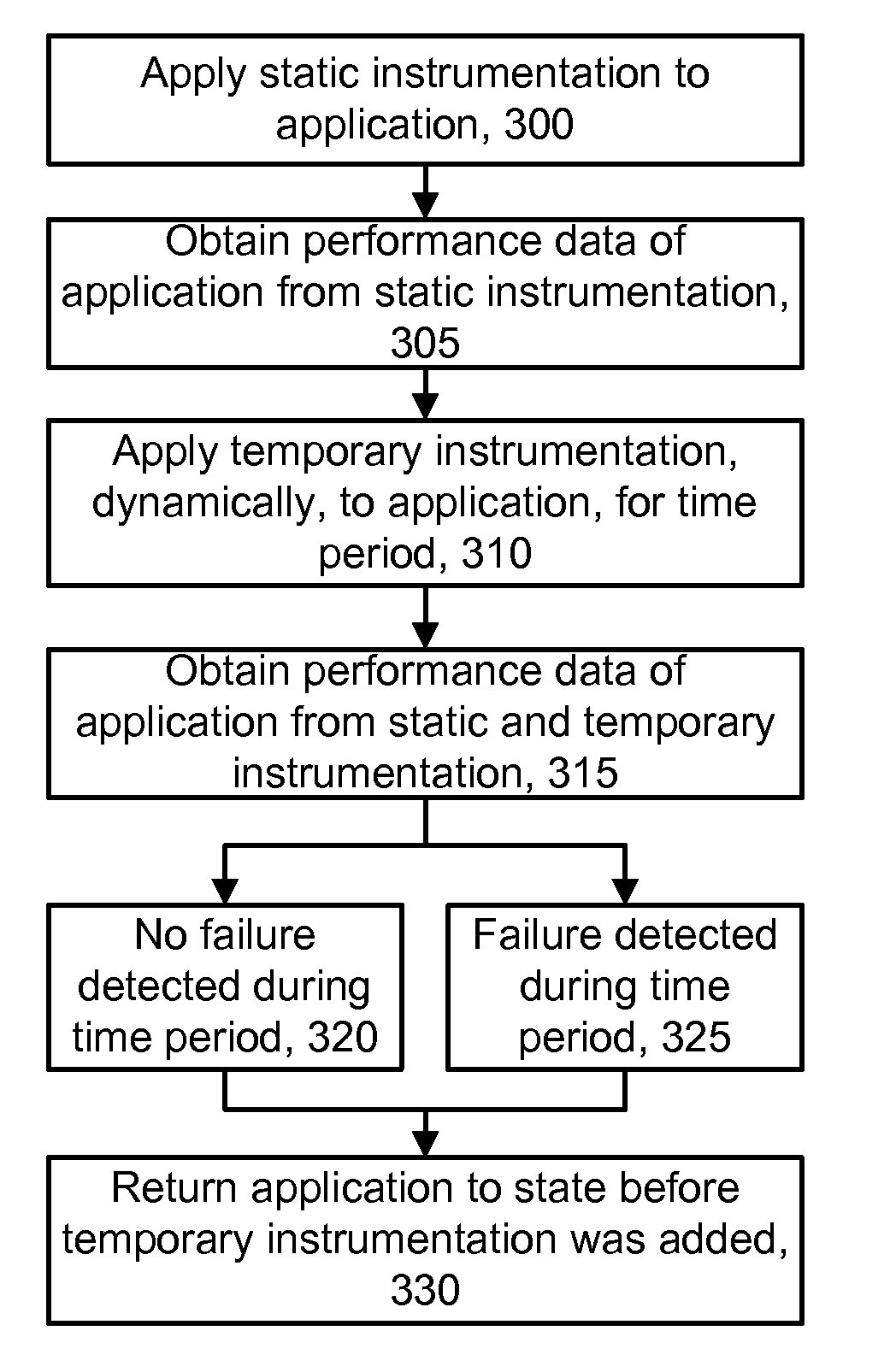
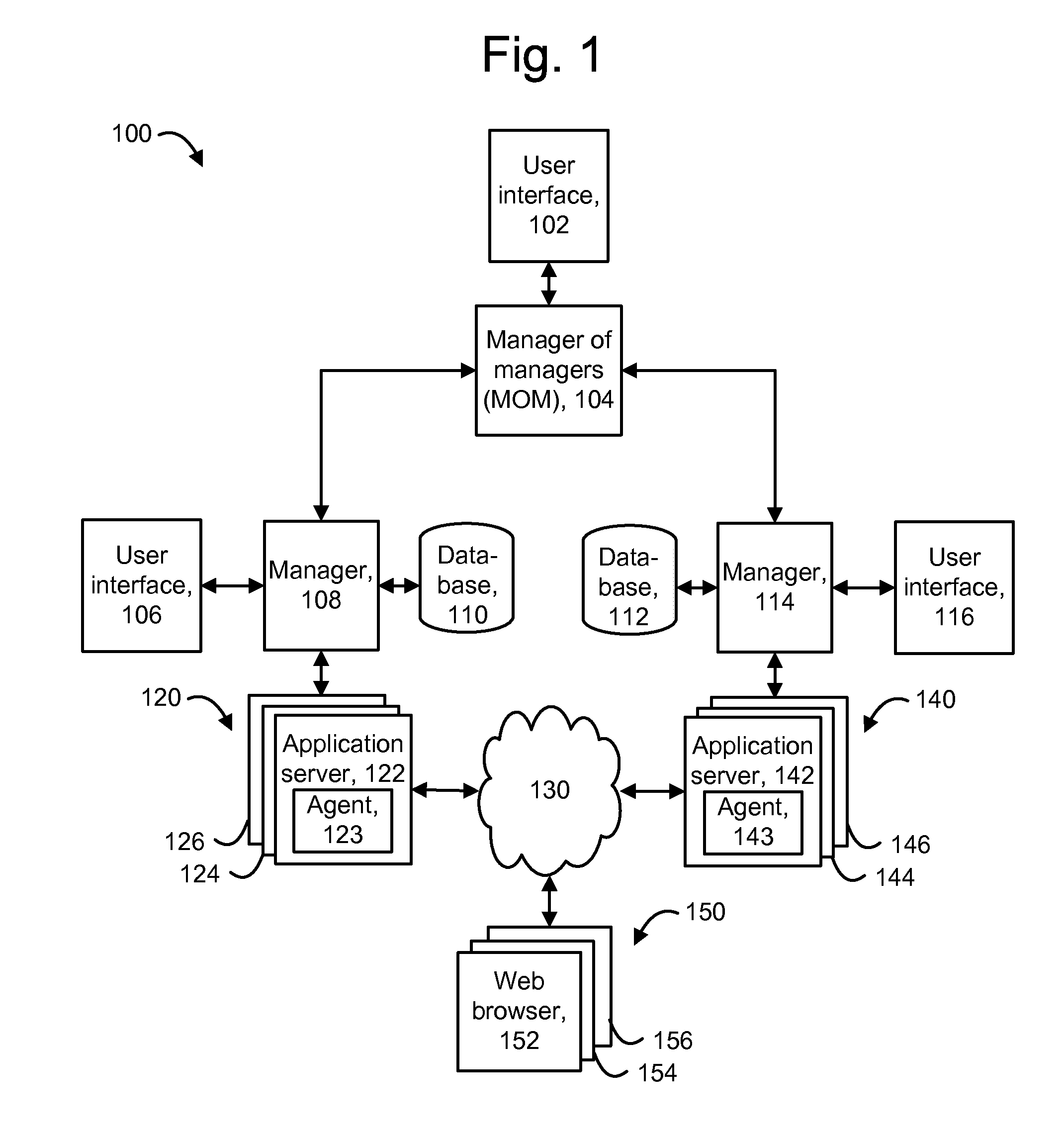
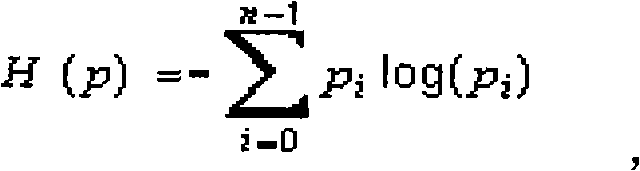Patents
Literature
57 results about "Dynamic instrumentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
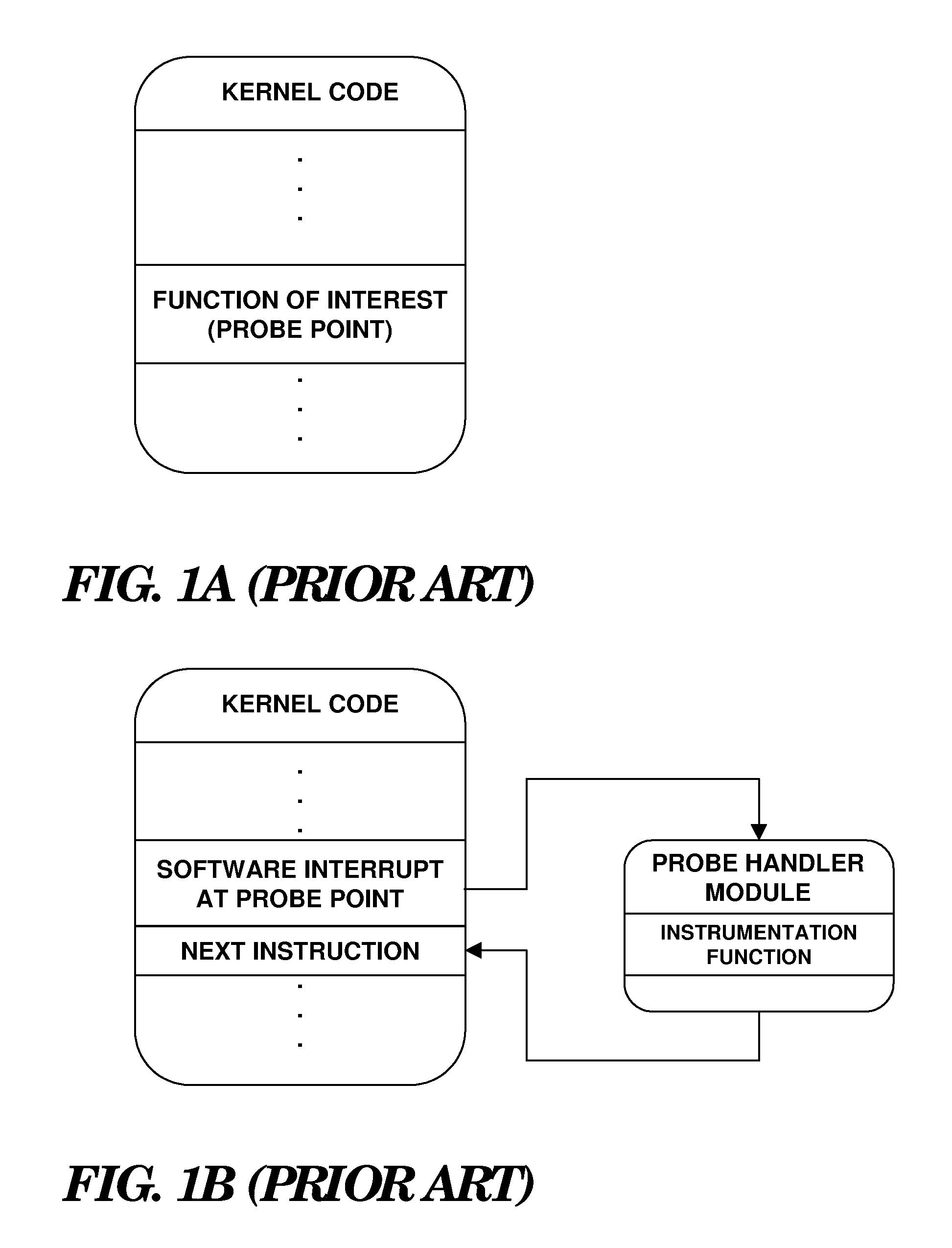
The instrumentation used in dynamic stabilization is designed to control the amount of motion between adjacent vertebrae, but it does not completely eliminate this movement. One of the major problems with spinal fusion is that even when all goes well and the spinal segments fuse, problems can arise down the road.
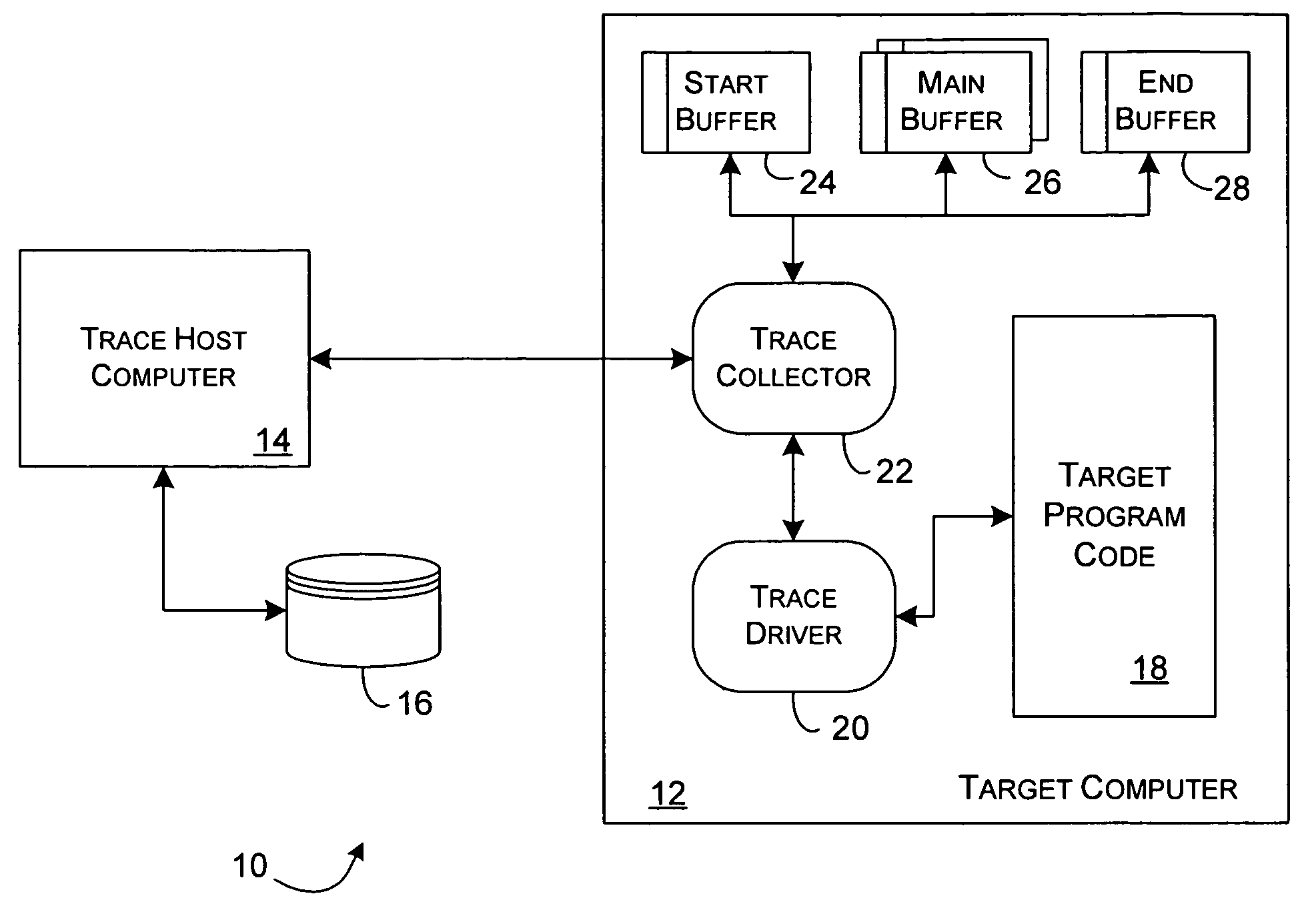
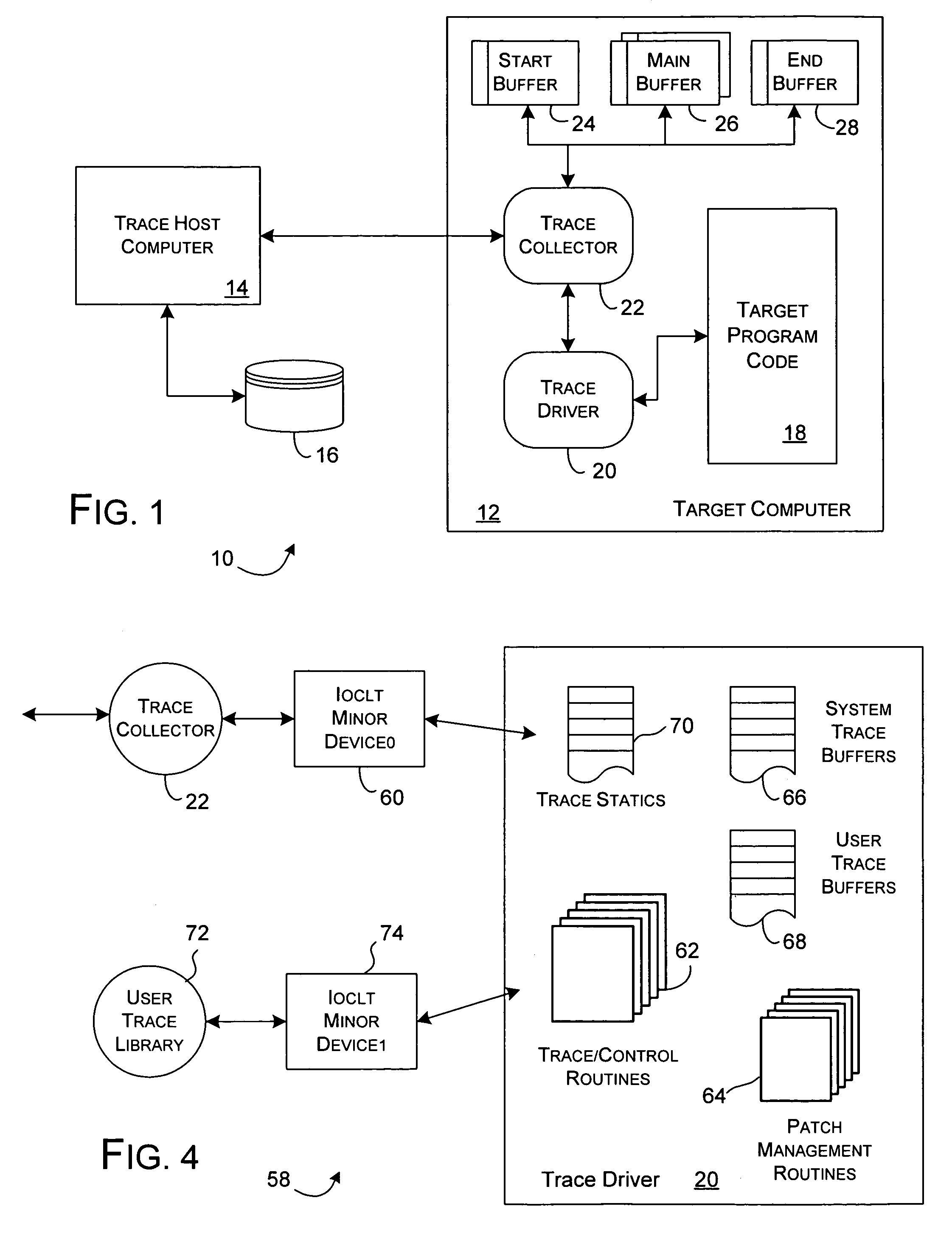
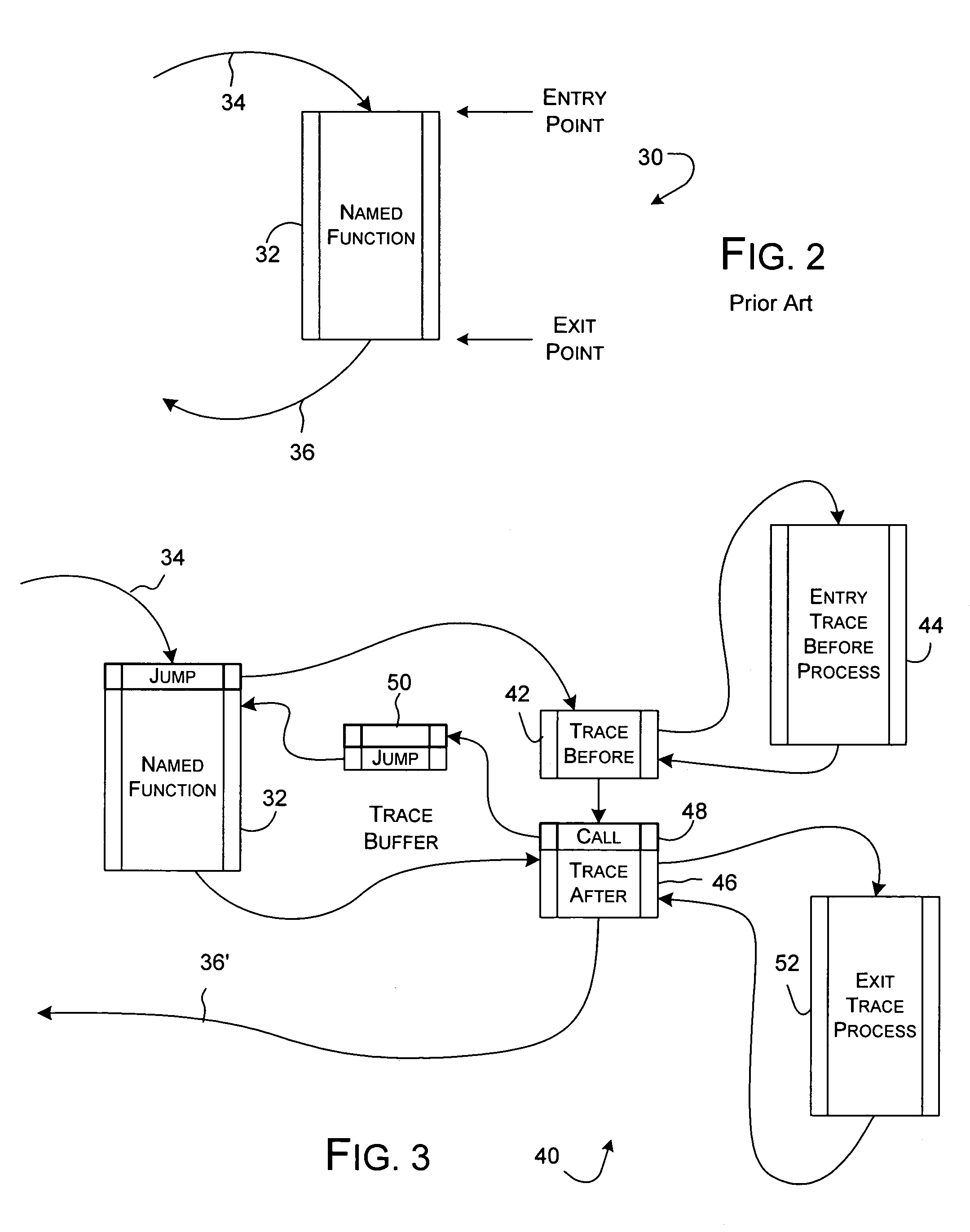
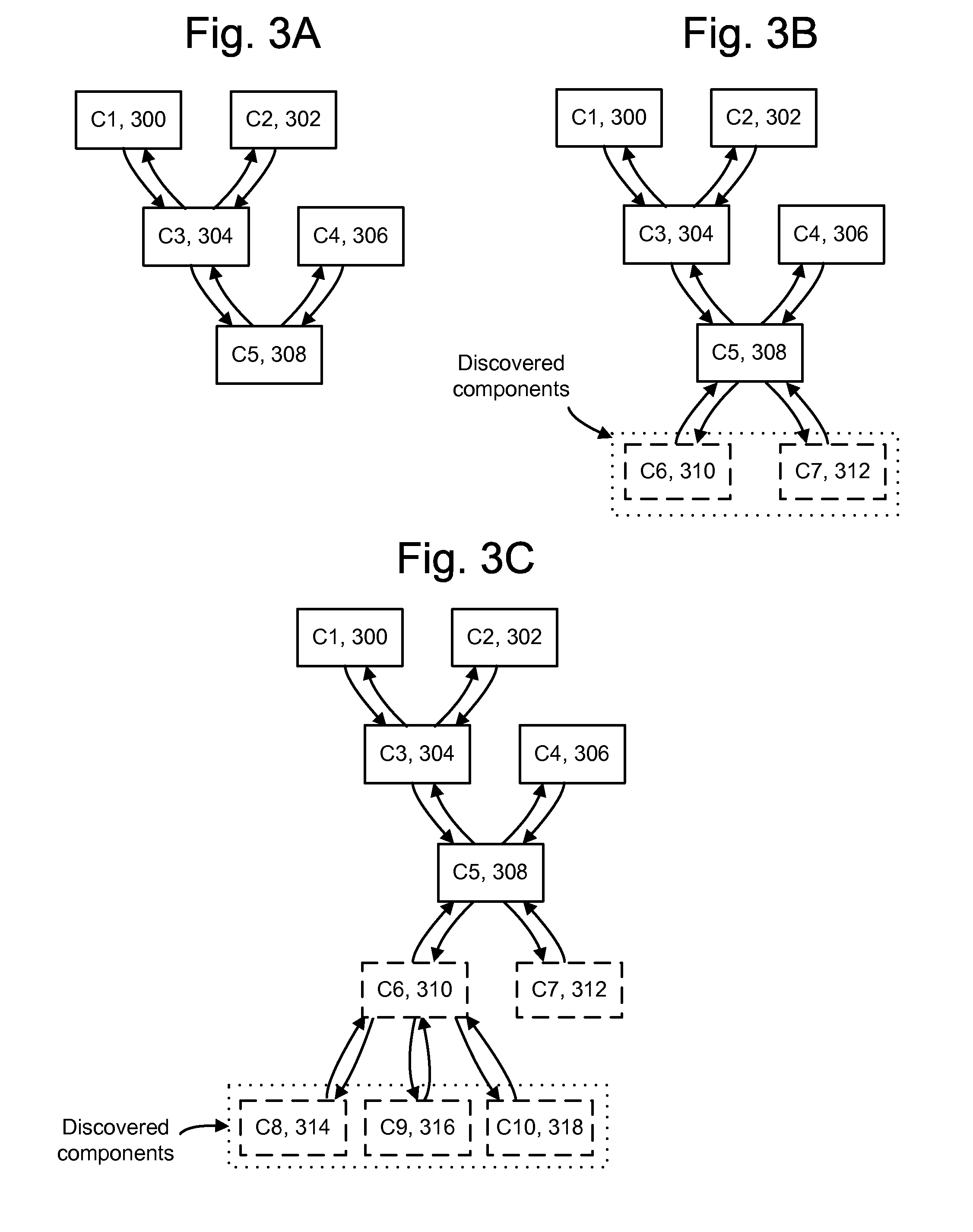
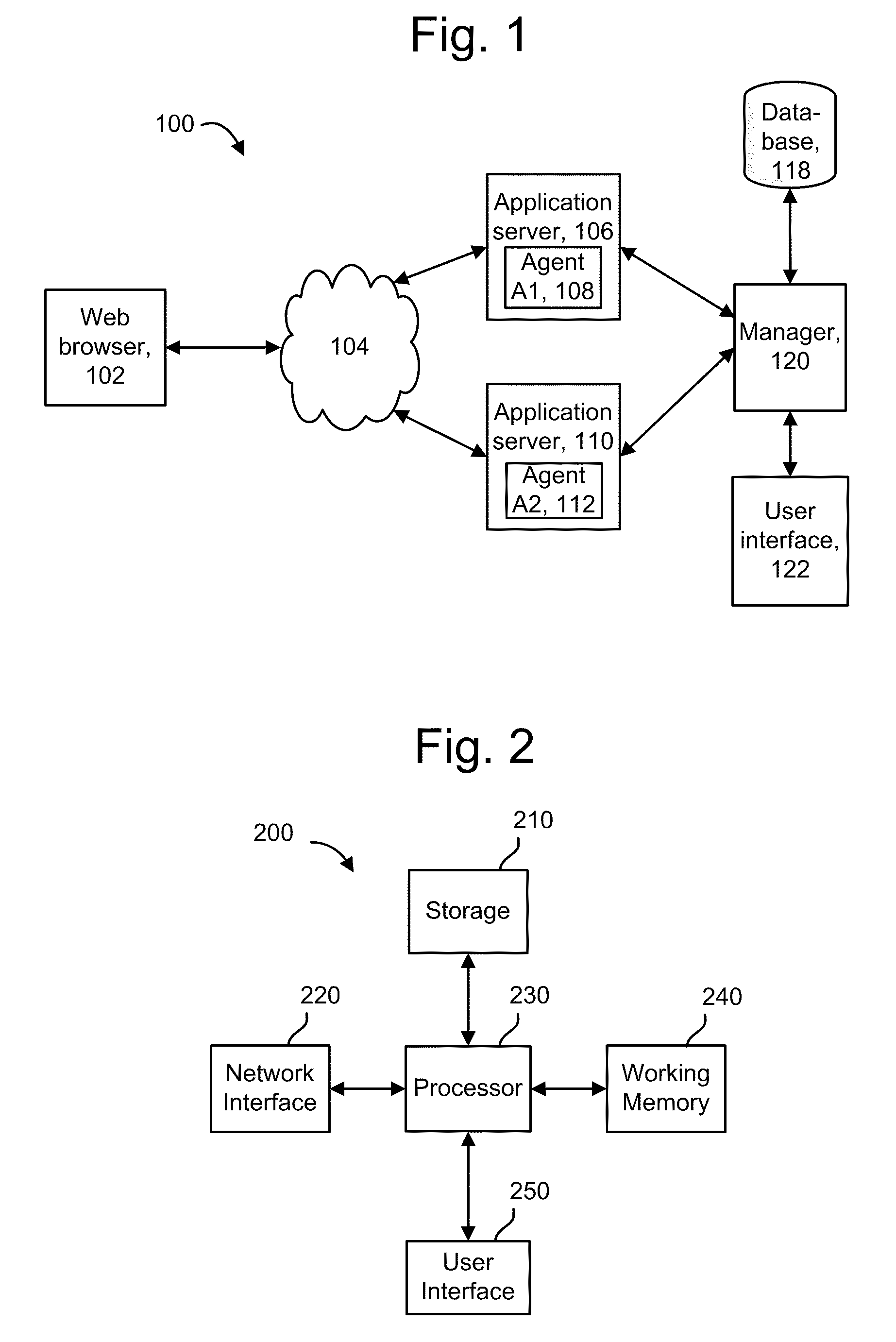
Dynamic instrumentation event trace system and methods
InactiveUS7047521B2Performance impact is minimalMaximize discriminating detectionHardware monitoringSoftware testing/debuggingDynamic instrumentationParallel computing
Program code loaded for execution by a computer can be dynamically instrumented to collect event data by inserting an instruction at a trace point within the program code as loaded in a memory space of a computer, where the trace point corresponds to the beginning of a predefined function of the program selected for event tracing. The instruction provides for the direction of the execution of said computer to a function proxy routine, which includes a call to an instance of the predefined function. Event data is collected in connection with the calling of the instance of the predefined function.
Owner:LYNX SOFTWARE TECH
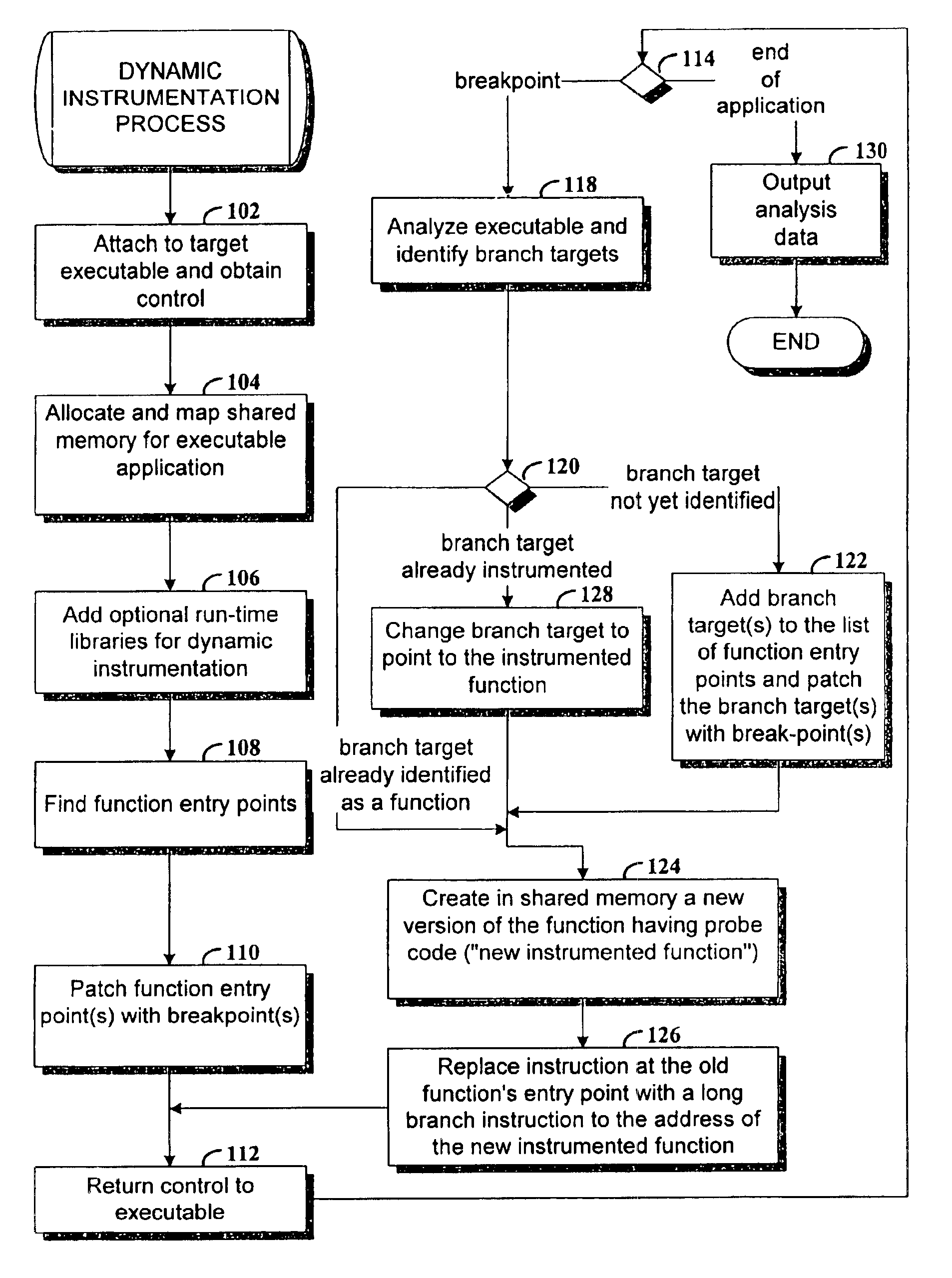
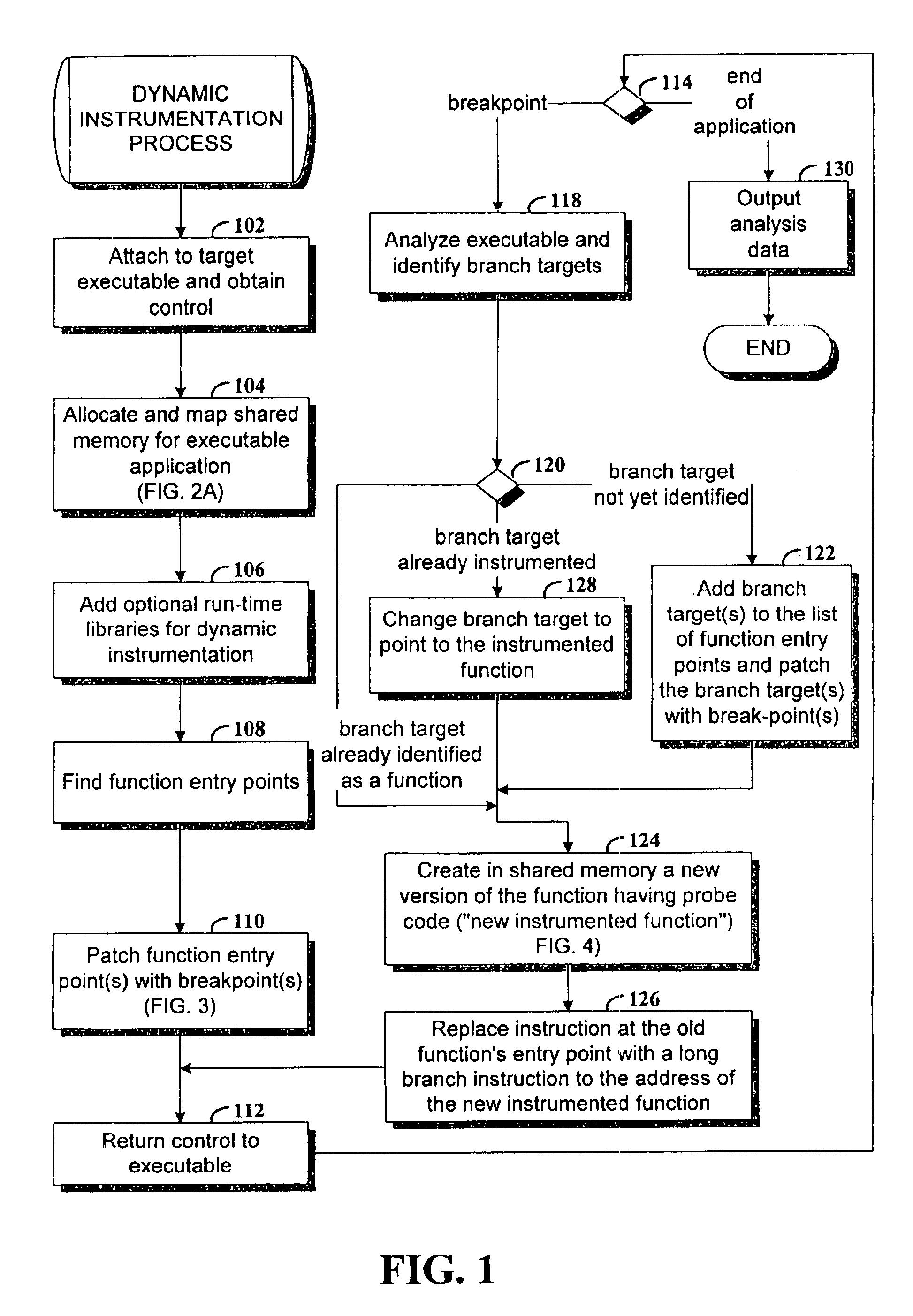
Dynamic instrumentation of an executable program by means of causing a breakpoint at the entry point of a function and providing instrumentation code
InactiveUS6918110B2Software testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsDynamic instrumentationEntry point
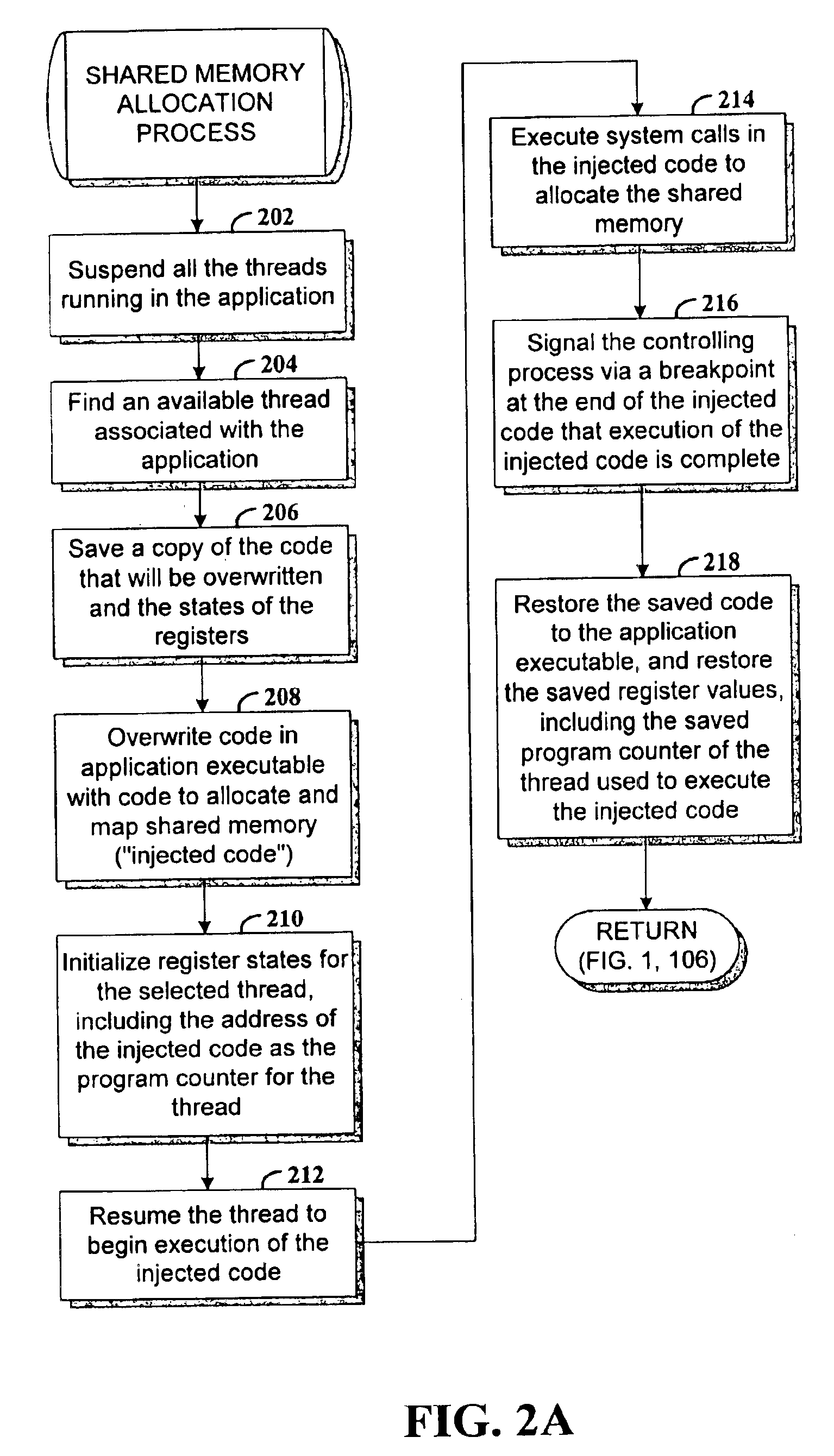
Method and apparatus for dynamic instrumentation of an executable application program. The application program includes a plurality of functions, each function having an entry point and an endpoint. When the application is executed, a shared memory segment is created for an instrumentation program and the application program. Upon initial invocation of the original functions in the application program, corresponding substitute functions are created in the shared memory segment, the substitute versions including instrumentation code. Thereafter, the substitute functions are executed in lieu of the original functions in the application program.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Conditional dynamic instrumentation of software in a specified transaction context
ActiveUS20110283263A1Error detection/correctionSoftware maintainance/managementDynamic instrumentationTransaction data
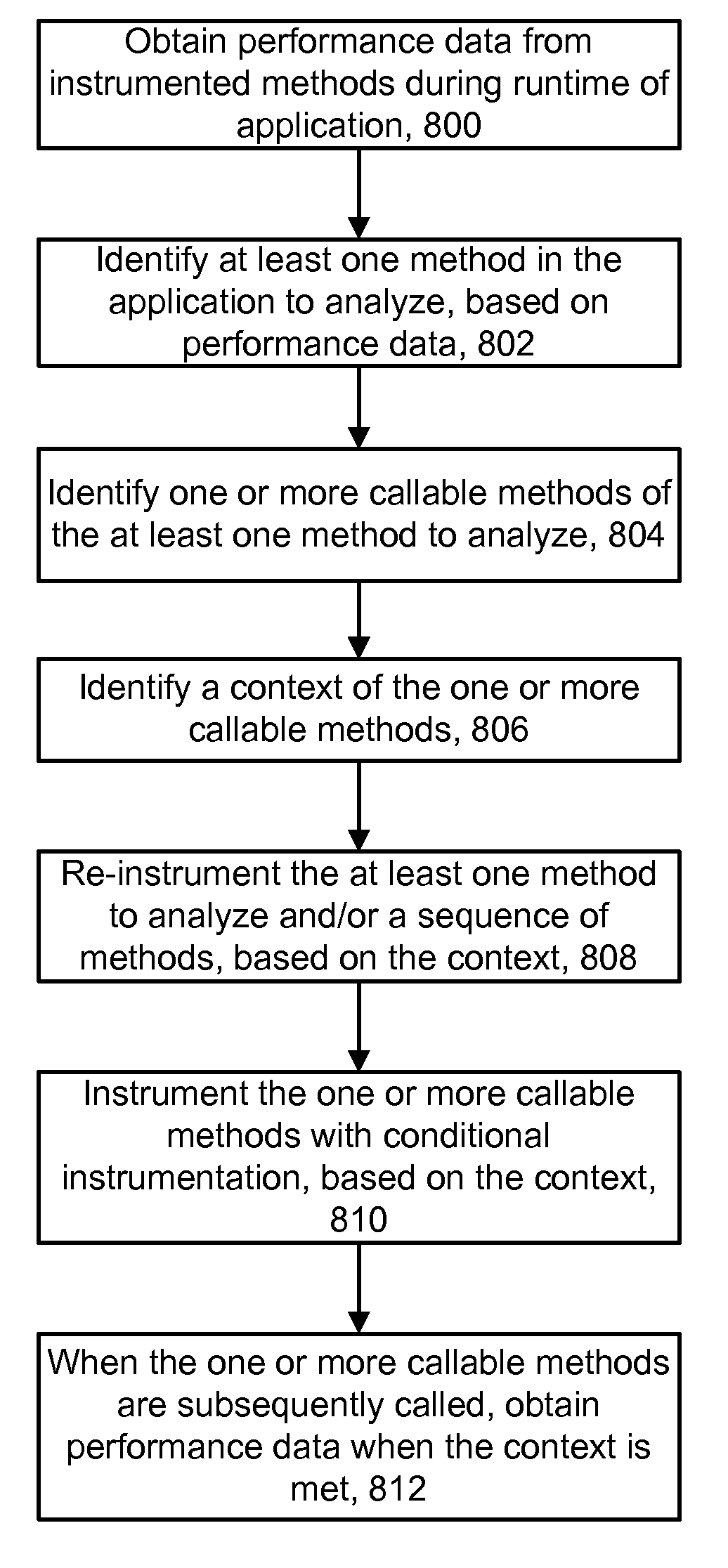
Techniques for analyzing software in which un-instrumented components can be discovered and conditionally instrumented during a runtime of the software. Initially, software such as an application can be configured with a baseline set of instrumented components such as methods. As the application runs, performance data gathered from the instrumentation may indicate that the performance of some methods is below expectations. To analyze this, any methods which are callable from a method at issue are discovered, such as by inspecting the byte code of loaded classes in a JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM). To limit and focus the diagnosis, the instrumentation which is added to the discovered components can be conditional, so that the instrumentation is executed only in a specified context. The context can involve, e.g., a specified sequence of components in which a discovered component is called, and / or transaction data in which a discovered component is called.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Application program interface for dynamic instrumentation of a heterogeneous program in a distributed environment
InactiveUS7263689B1Easy to modifyData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDistributed Computing EnvironmentDynamic instrumentation
Described is an application program interface (API) that enables dynamic modification to applications executing in a heterogeneous distributed computing environment. The application program interface includes a navigation function, a query function, a thread management function, and a modifier function. The navigation function returns program information for a local or remote computer (i.e., specified computing device). The query function returns information about a program on the specified computing device. The thread management function controls execution of other programs on the specified computing device. The modifier function modifies a system memory on the specified computing device that stores the heterogeneous program. The API works in conjunction with a hierarchical intermediate representation of the heterogeneous program such that pre-defined program tools can modify the intermediate representation and write these modifications to the specified computing device while the heterogeneous program remains operational.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Apparatus and method for dynamic instrumenting of code to minimize system perturbation
InactiveUS20070006168A1Minimize the numberError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsCall stackDynamic instrumentation
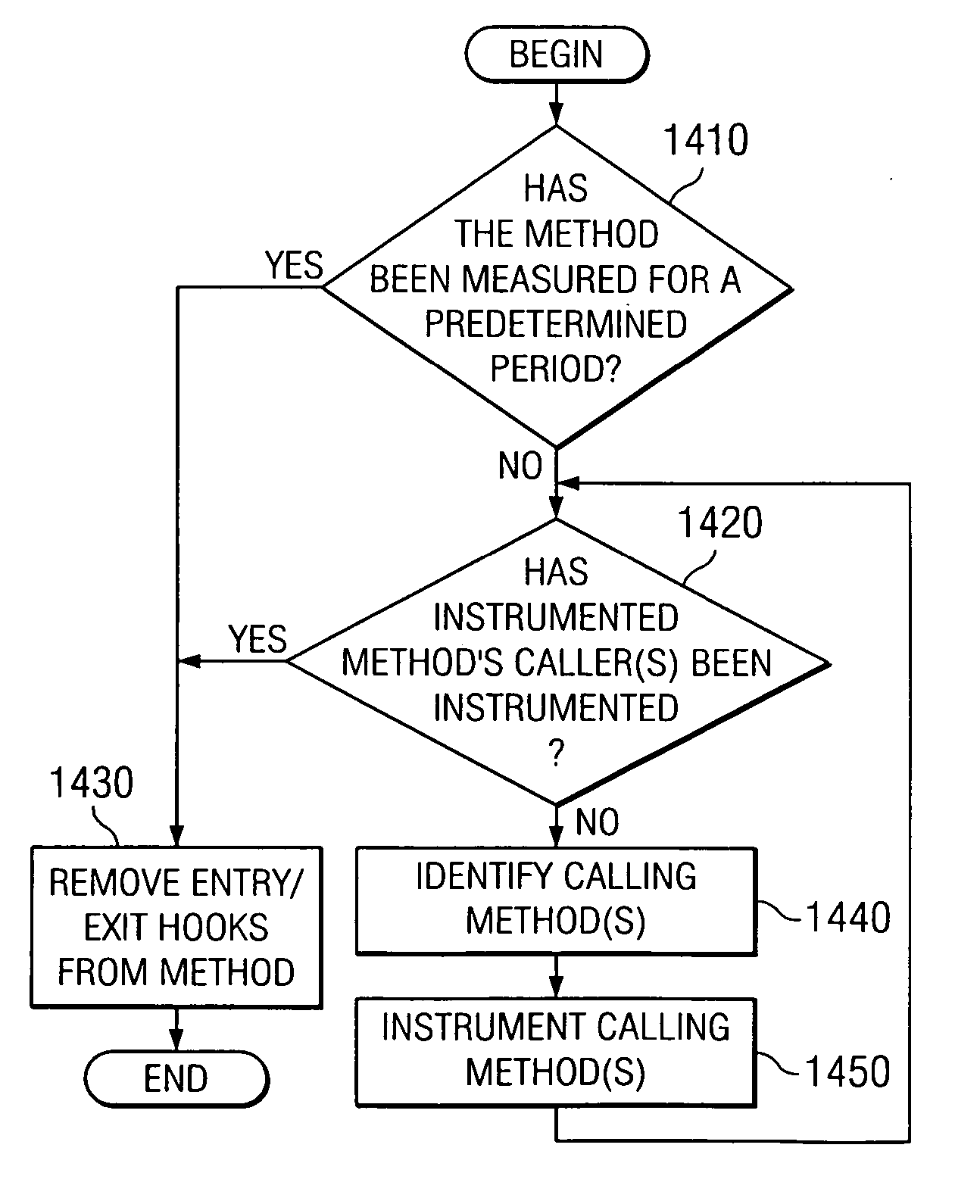
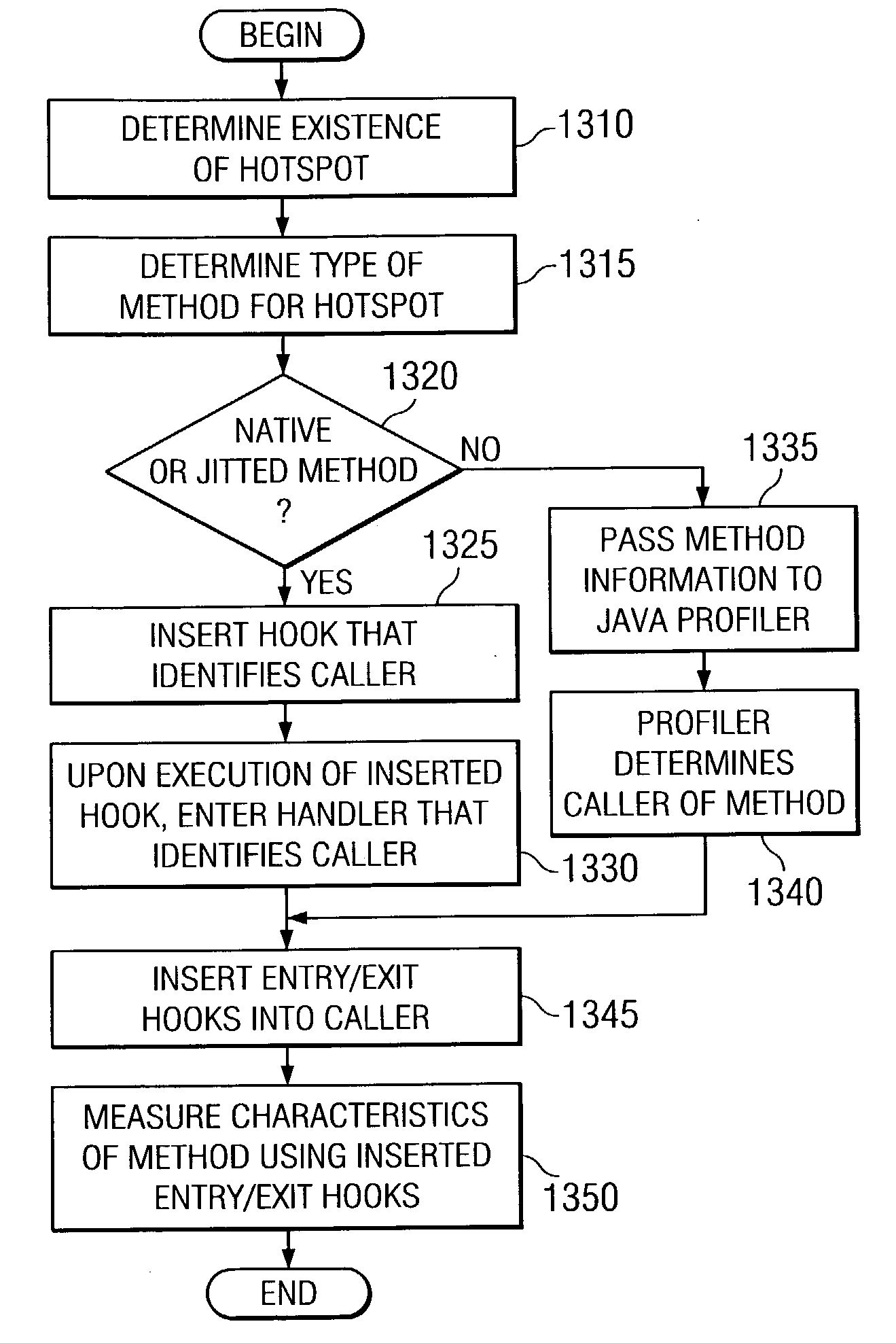
An apparatus and method are provided for the dynamic instrumentation of code to minimize system perturbation during tracing of the execution of the code. With the apparatus and method, “hot spots” in the execution of the code are dynamically determined during tracing of the execution of the code. These “hot spots” are dynamically instrumented, i.e. an event hook is inserted, to cause control to be passed to a handler that determines a caller of the “hot spot” method. The method that called the “hot spot” method, or “caller” method, is identified from a call stack and is dynamically instrumented for an appropriate metric so that the next time the calling method is executed, the dynamically inserted hooks are executed. The execution of the hooks in the caller method is continued for a predetermined period, e.g., number of invocations, to get an understanding of the caller method's characteristics. A list of callers of instrumented methods is maintained and used to determine one or more calling methods of the instrumented caller method. One or more of these calling methods may be instrumented and the hooks inserted in the instrumented caller method (called by the one or more calling methods), are removed. In this way, the call graph of the hot spots of a program execution is “walked up” and characterized over time.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for dynamic instrumenting of code to minimize system perturbation
InactiveUS7114150B2Minimize the numberError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsTime scheduleCall stack
An apparatus and method are provided for the dynamic instrumentation of code to minimize system perturbation during tracing of the execution of the code. With the apparatus and method, “hot spots” in the execution of the code are dynamically determined during tracing of the execution of the code. These “hot spots” are dynamically instrumented, i.e. an event hook is inserted, to cause control to be passed to a handler that determines a caller of the “hot spot” method. The method that called the “hot spot” method, or “caller” method, is identified from a call stack and is dynamically instrumented for an appropriate metric so that the next time the calling method is executed, the dynamically inserted hooks are executed. The execution of the hooks in the caller method is continued for a predetermined period, e.g., number of invocations, to get an understanding of the caller method's characteristics. A list of callers of instrumented methods is maintained and used to determine one or more calling methods of the instrumented caller method. One or more of these calling methods may be instrumented and the hooks inserted in the instrumented caller method (called by the one or more calling methods), are removed. In this way, the call graph of the hot spots of a program execution is “walked up” and characterized over time.
Owner:IBM CORP
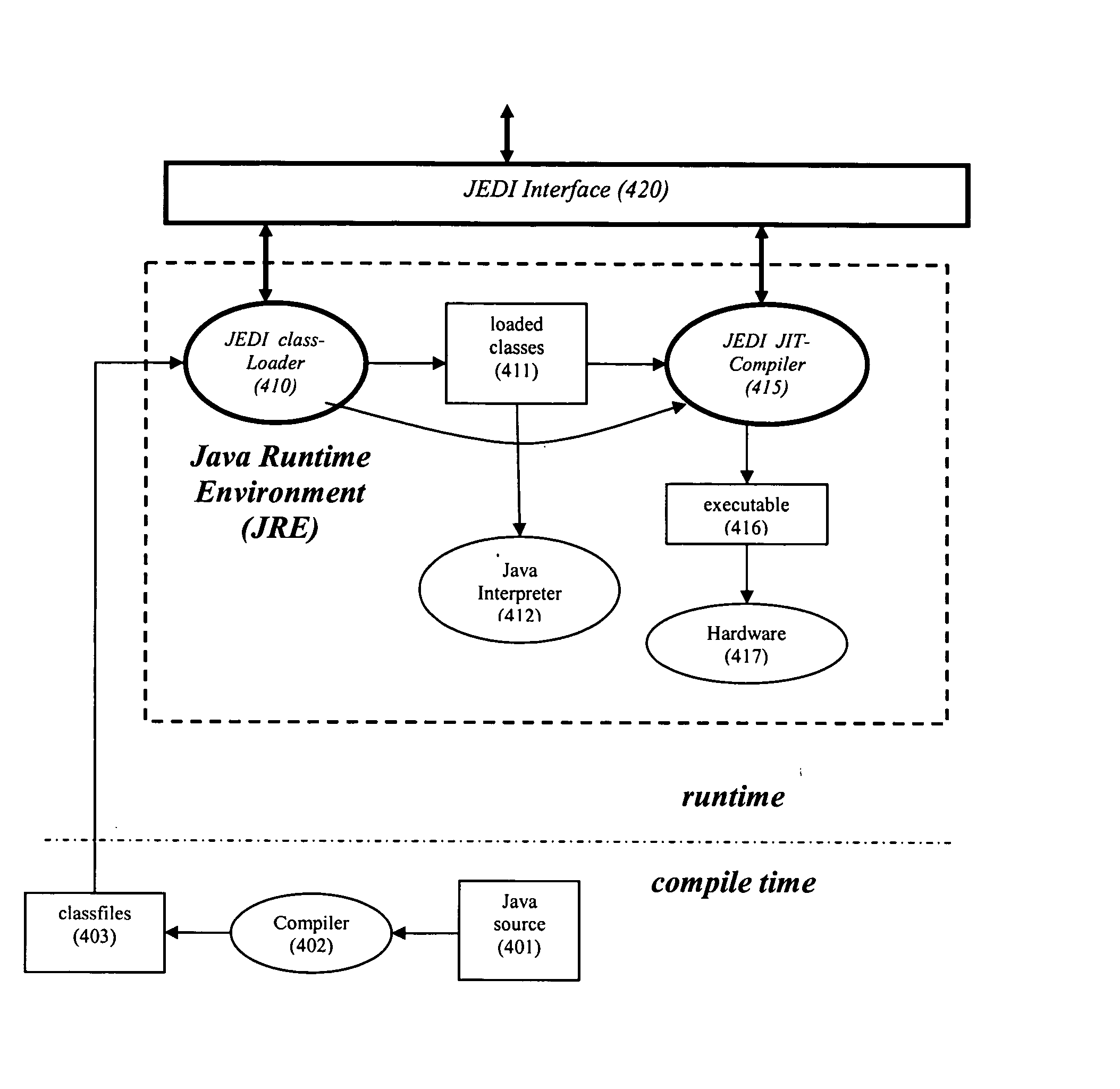
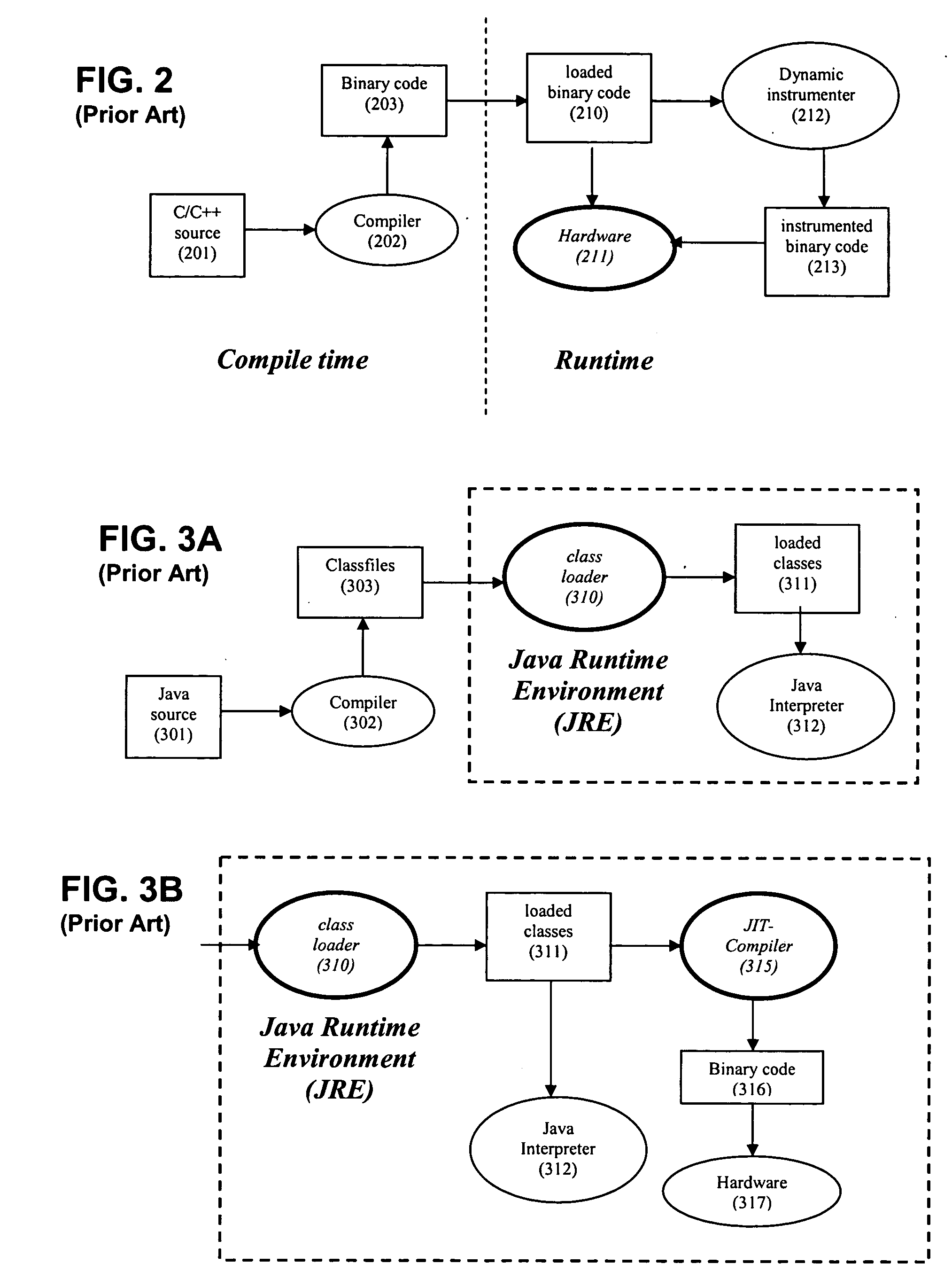
Dynamic instrumentation for a mixed mode virtual machine
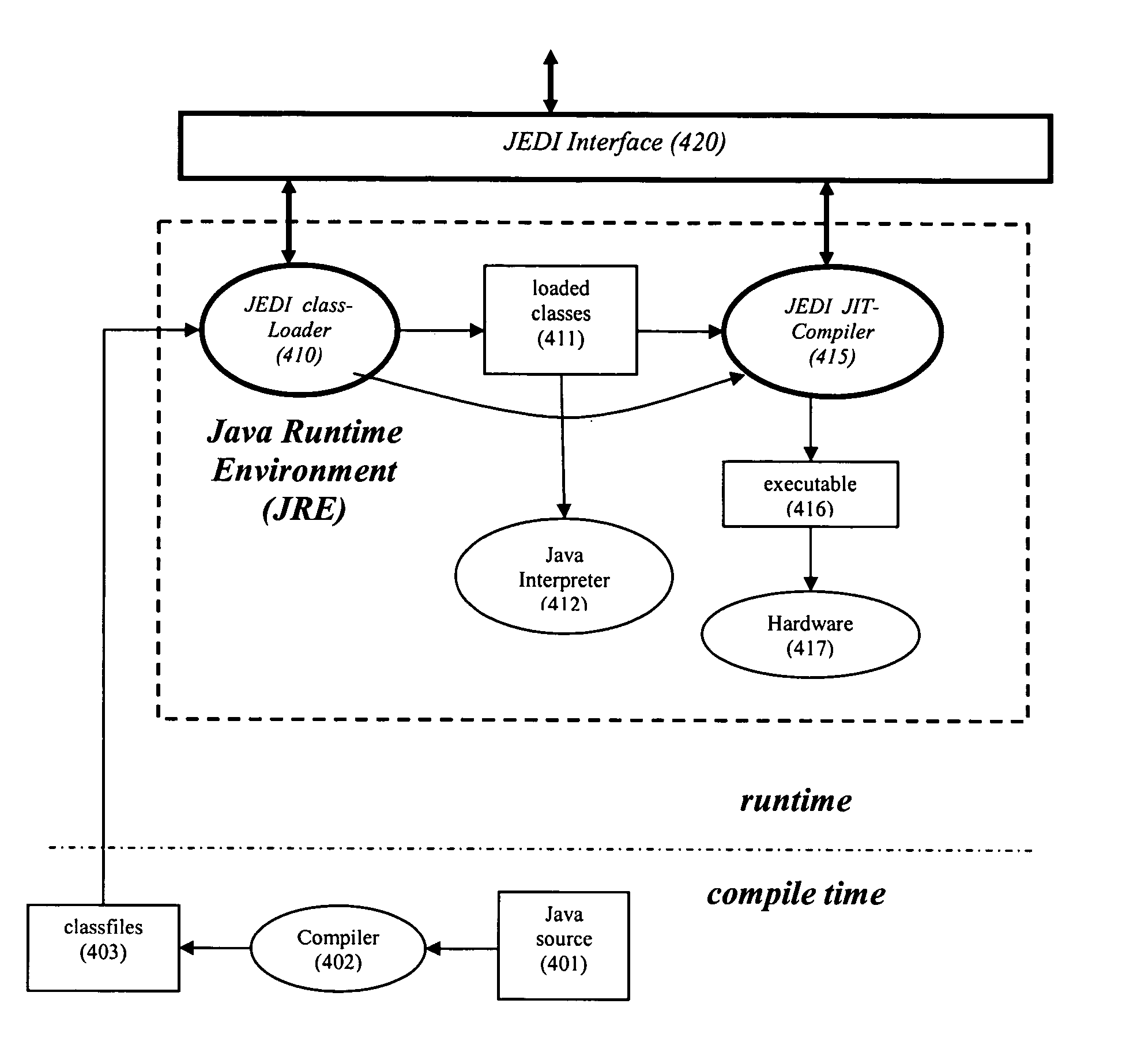
The present invention provides a method, apparatus, and computer instructions for dynamic intermediate code transformation in a mixed mode compiler. In an exemplary embodiment, an object code compiler of a virtual-machine, such as the just-in-time (JIT) compiler (415) of a Java virtual machine (JVM), takes loaded classes and compiles these into object code (416). A JIT-enabled dynamic instrumentation (JEDI) interface (420) provides information to an application (e.g., a tool with a GUI), and passes requests for transformation to the JIT (415) and class-loader (410). If loaded, JEDI controls the JIT compiler (415) to compile and transform the class into object code. Thus, dynamically transformed object code is produced without transformation or re-loading of the loaded classes.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Conditional dynamic instrumentation of software in a specified transaction context
ActiveUS8473925B2Error detection/correctionSoftware maintainance/managementDynamic instrumentationTransaction data
Techniques for analyzing software in which un-instrumented components can be discovered and conditionally instrumented during a runtime of the software. Initially, software such as an application can be configured with a baseline set of instrumented components such as methods. As the application runs, performance data gathered from the instrumentation may indicate that the performance of some methods is below expectations. To analyze this, any methods which are callable from a method at issue are discovered, such as by inspecting the byte code of loaded classes in a JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM). To limit and focus the diagnosis, the instrumentation which is added to the discovered components can be conditional, so that the instrumentation is executed only in a specified context. The context can involve, e.g., a specified sequence of components in which a discovered component is called, and / or transaction data in which a discovered component is called.
Owner:CA TECH INC
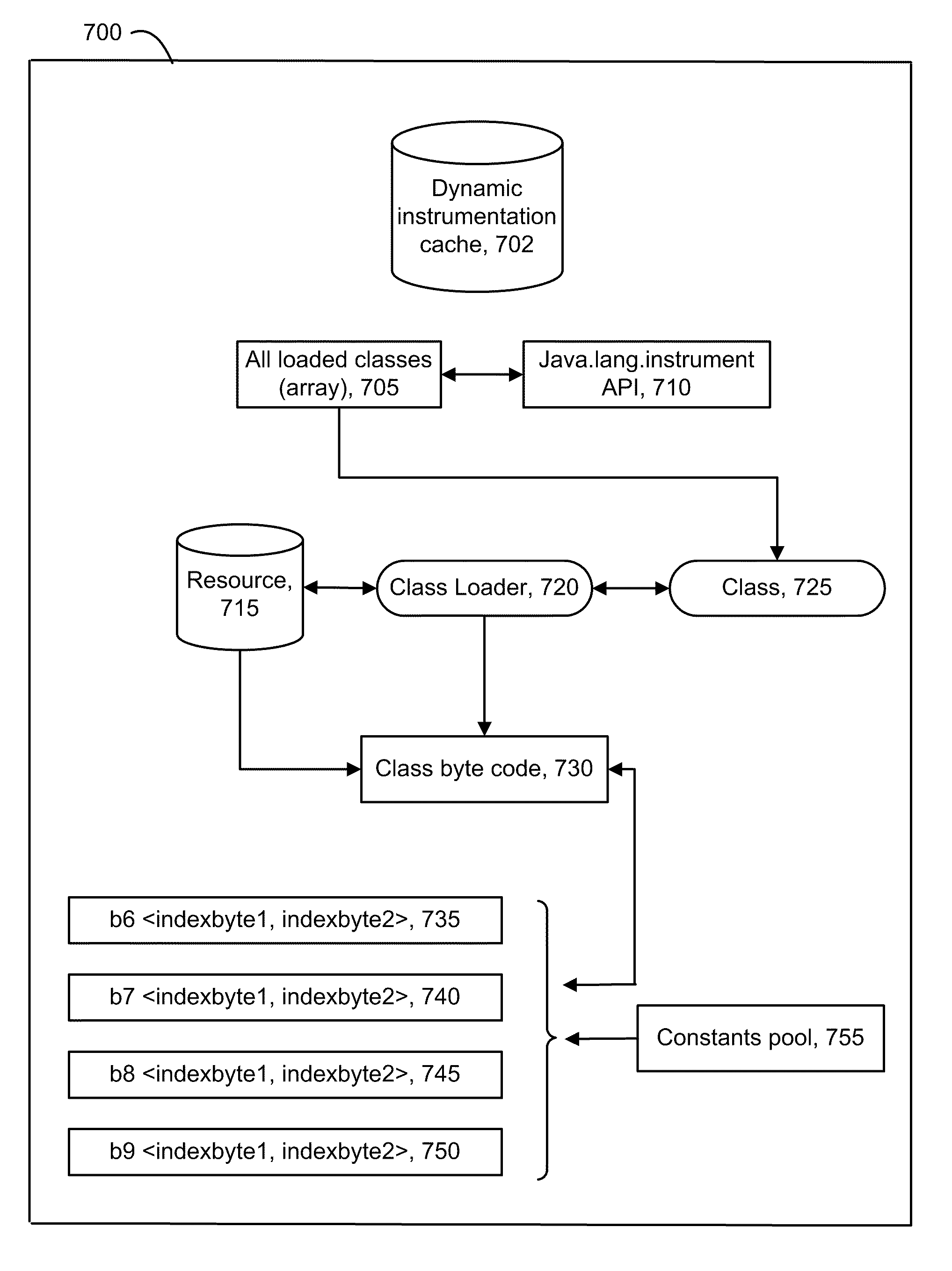
Detection of method calls to streamline diagnosis of custom code through dynamic instrumentation
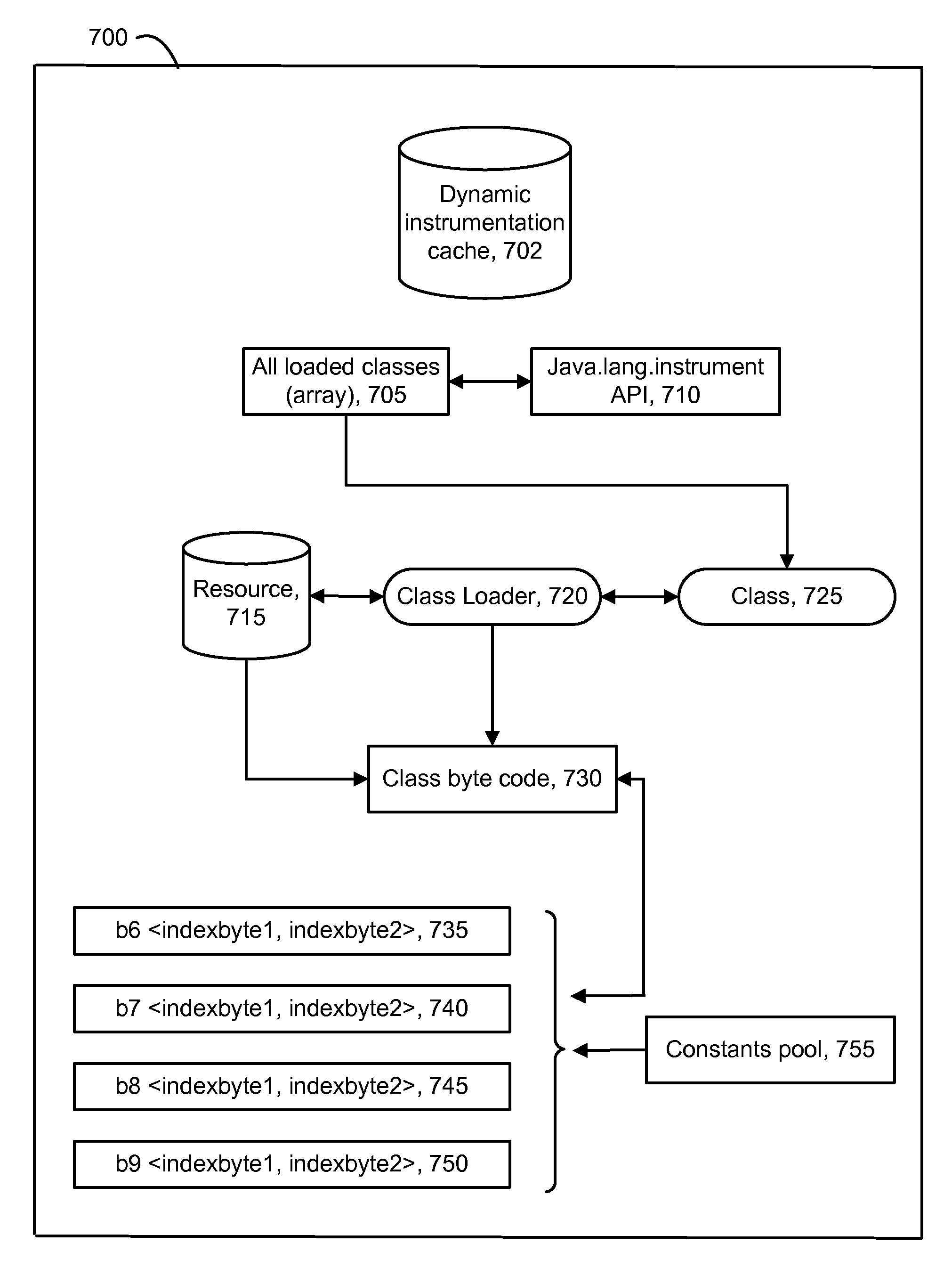
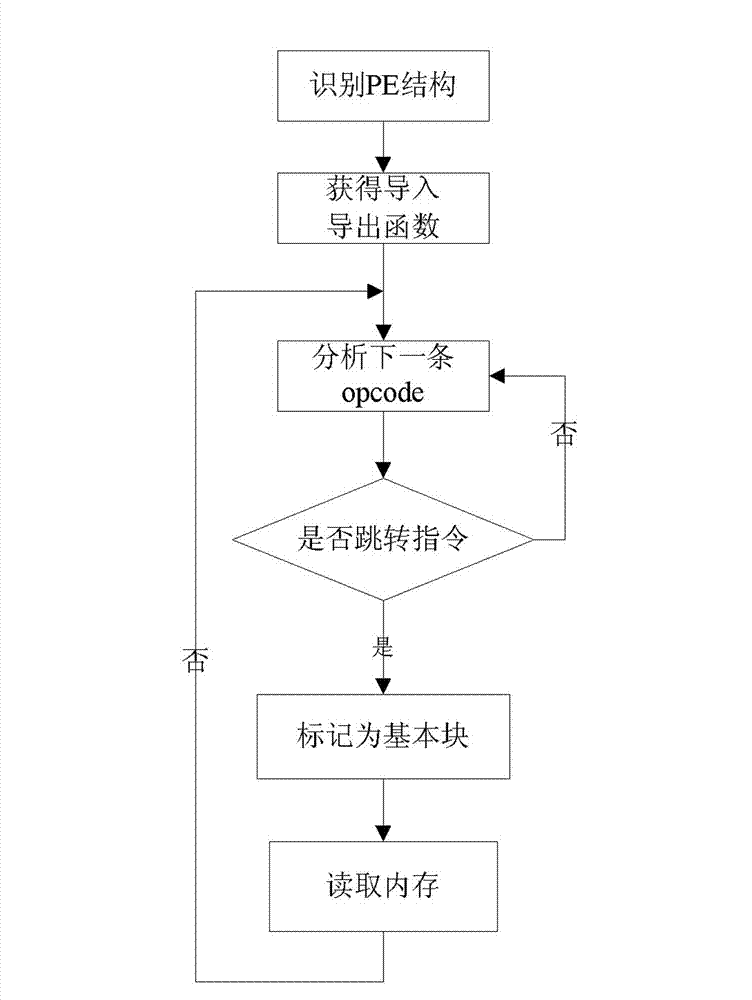
A technique for analyzing software in which un-instrumented components can be discovered and dynamically instrumented during a runtime of the software. Initially, an application configured with a baseline set of instrumented components such as methods. As the application runs, performance data is gathered from the instrumentation, and it may be learned that the performance of some methods is an issue. To analyze the problem, any methods which are callable from a method at issue are discovered by inspecting the byte code of loaded classes in a JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM). Byte code of the class is parsed to identify opcodes which invoke byte code to call other methods. An index to an entry in a constants pool table is identified based on an opcode. A decision can then be made to instrument and / or report the discovered methods.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Dynamic instrumentation for a mixed mode virtual machine
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Failsafe mechanism for dynamic instrumentation of software using callbacks
InactiveUS20110283265A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware failureDynamic instrumentation
A failsafe mechanism for installing and removing temporary instrumentation during a runtime of an application. Initially, an application is configured with a baseline set of instrumented components such as methods. Additional instrumentation is then deployed in the application, such as to diagnose a performance problem. The failsafe mechanism ensures that the additional instrumentation is automatically removed, even when there is an interruption in a communication link to the application, a computing device failure, a software failure, or some other type of failure, which renders it impossible to manually roll back the instrumentation from a remote user interface. The failsafe mechanism can be provided using callbacks between the computing devices which detect when a connection is unexpectedly lost or closed. Termination of one callback can cascade to one or more other callbacks. The instrumentation rollback can involve reloading un-instrumented byte code of the application.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Dynamic taint analysis device and application thereof to document format reverse analysis
InactiveCN103440201AReduce I/O operationsShorten the timeSoftware testing/debuggingData streamReverse analysis
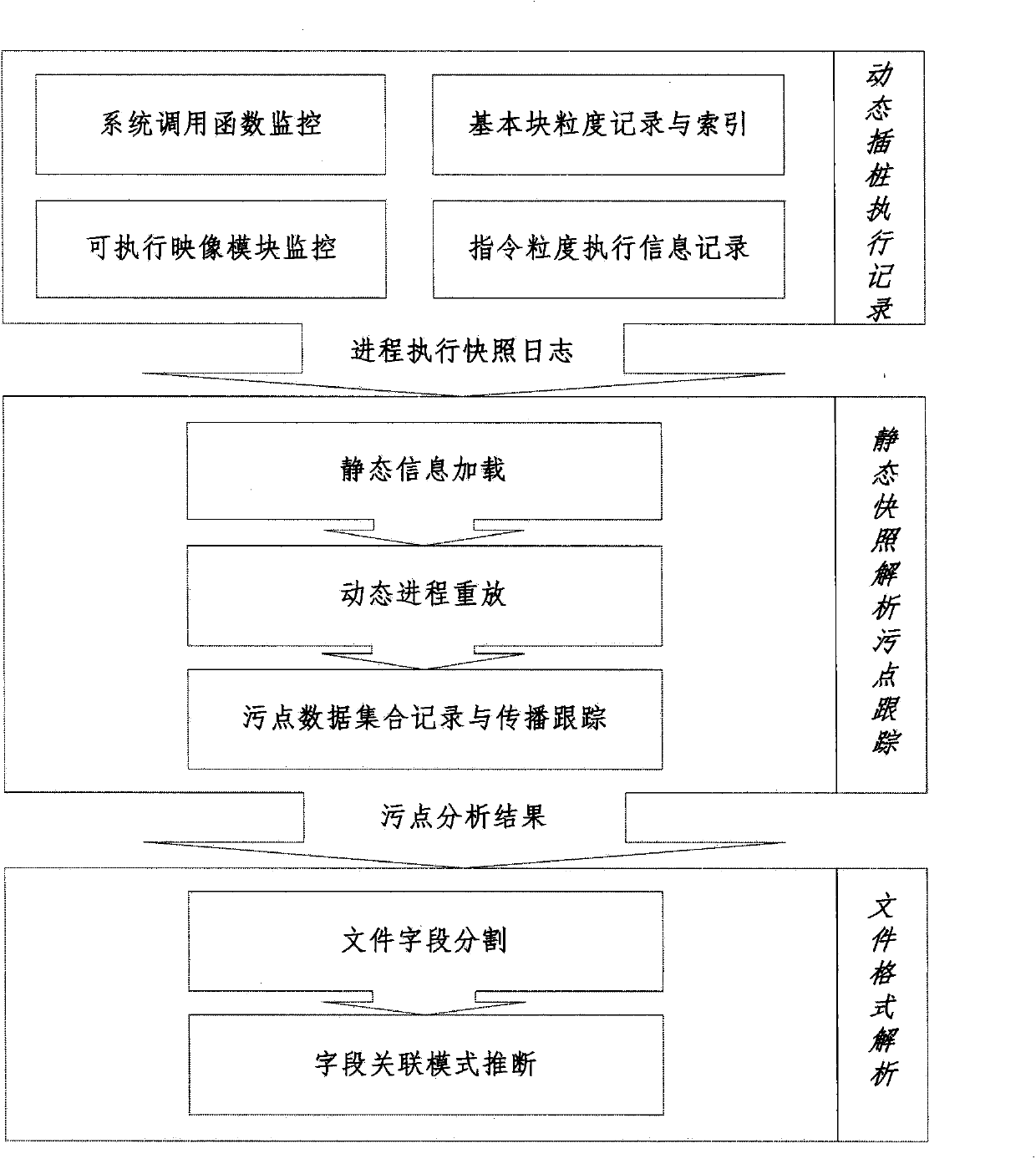
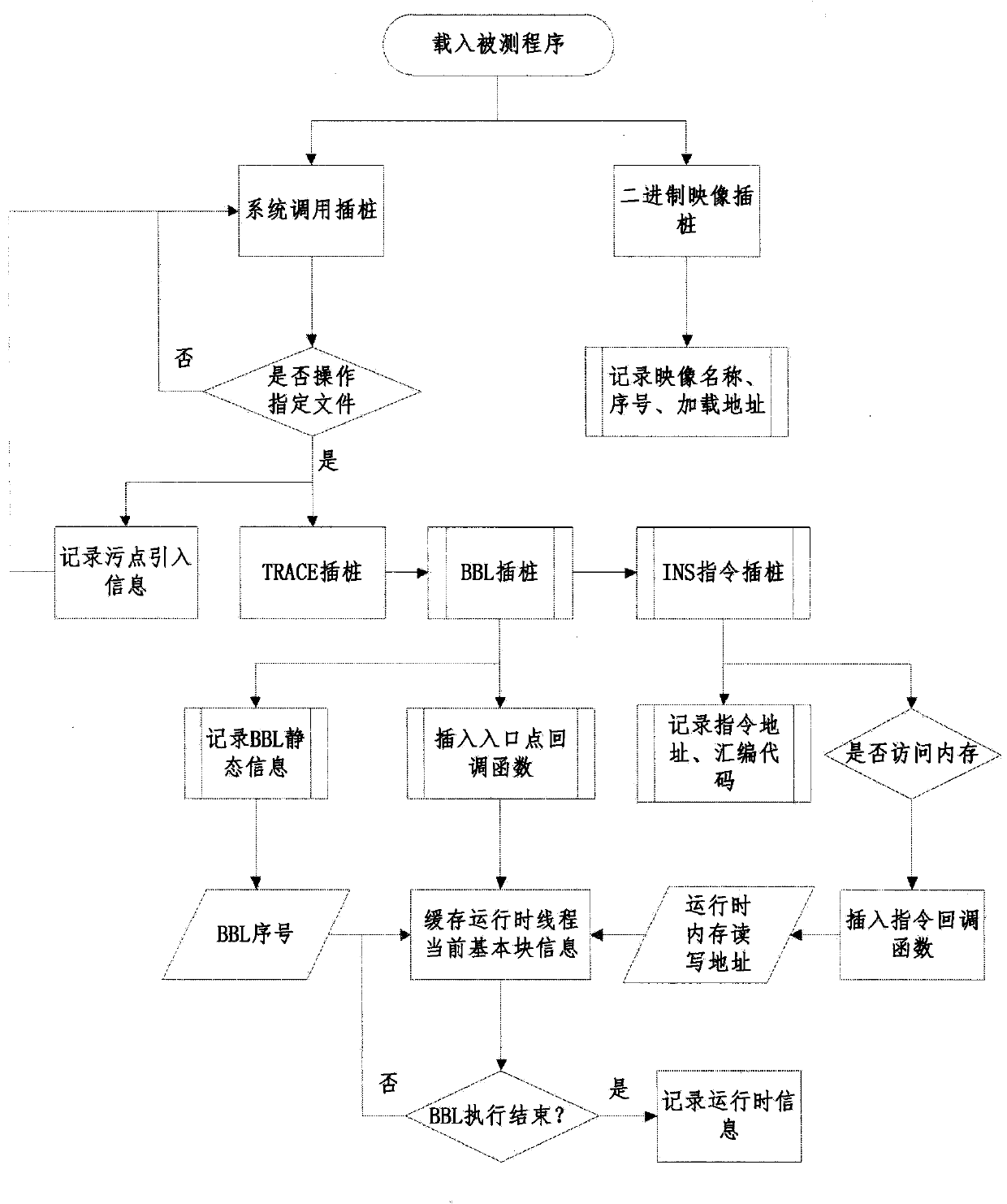
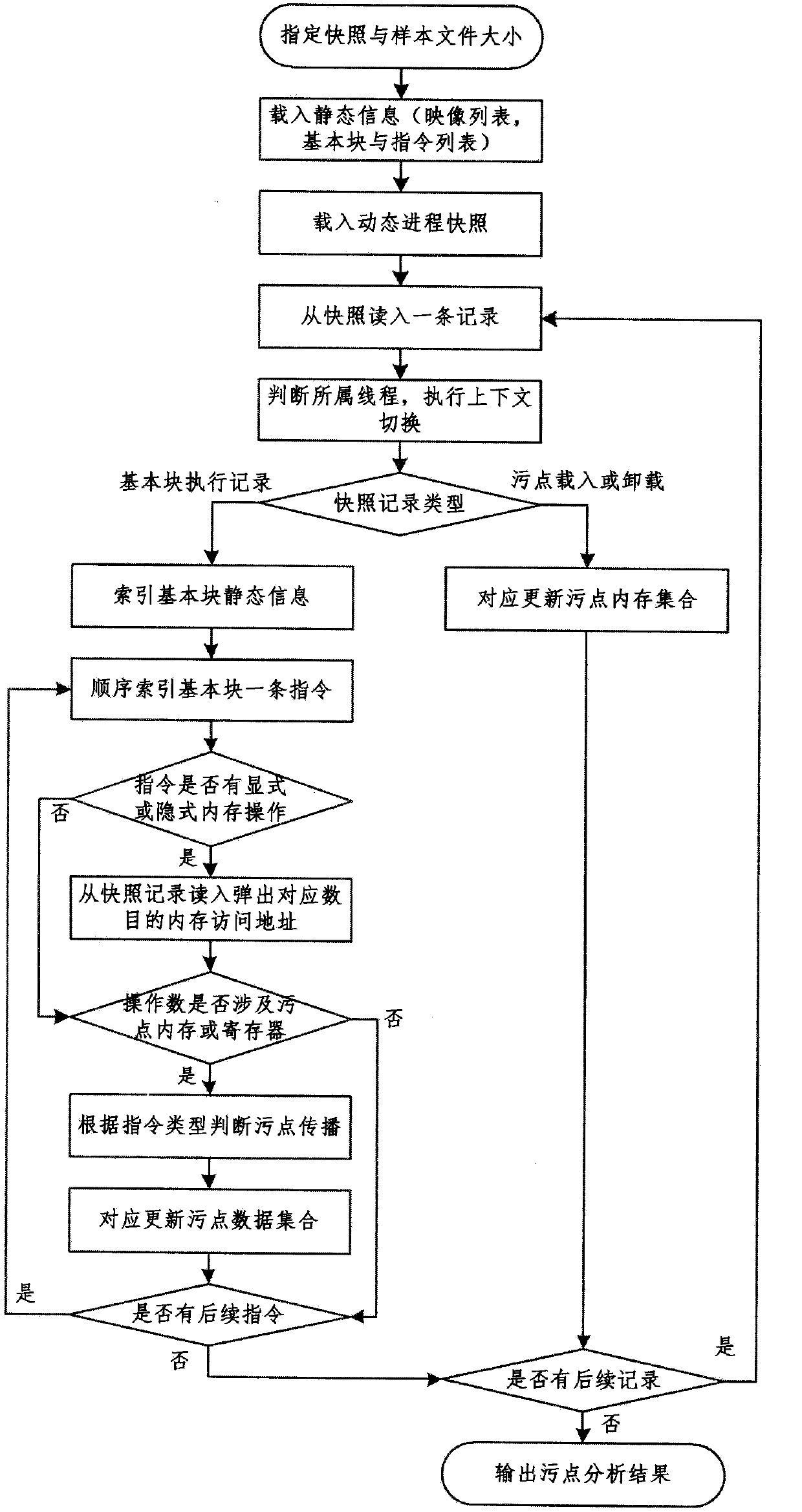
The invention relates to a dynamic taint analysis device and application of the dynamic taint analysis device to document format reverse analysis, wherein the dynamic taint analysis device comprises a dynamic instrumentation executive logging module and a static snapshoot analysis taint tracking module, wherein the dynamic instrumentation executive logging module is used for calling and executing a tested program by using a binary program instrumentation platform, monitoring opening, analyzing and closing behaviors of a data document including original taint data in a process of executing the tested program, and acquiring snapshoot logs of all command processes, context information and memory access information in the process of executing the tested program according to the process of executing the tested program; the static snapshoot analysis taint tracking module is used for analyzing the snapshoot logs and simulating replay execution of a progress according to information obtained by analysis and recording processing and spread information of original taint data in the data document to obtain a taint data stream path. According to the dynamic taint analysis device, I / O (Input / Output), time and space overhead of dynamic taint analysis in a dynamic execution process can be reduced, an extended instruction set can be supported, and the continuity and incidence relation of original taint data can be obtained.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Software fault analysis method based on multi-sample difference comparison
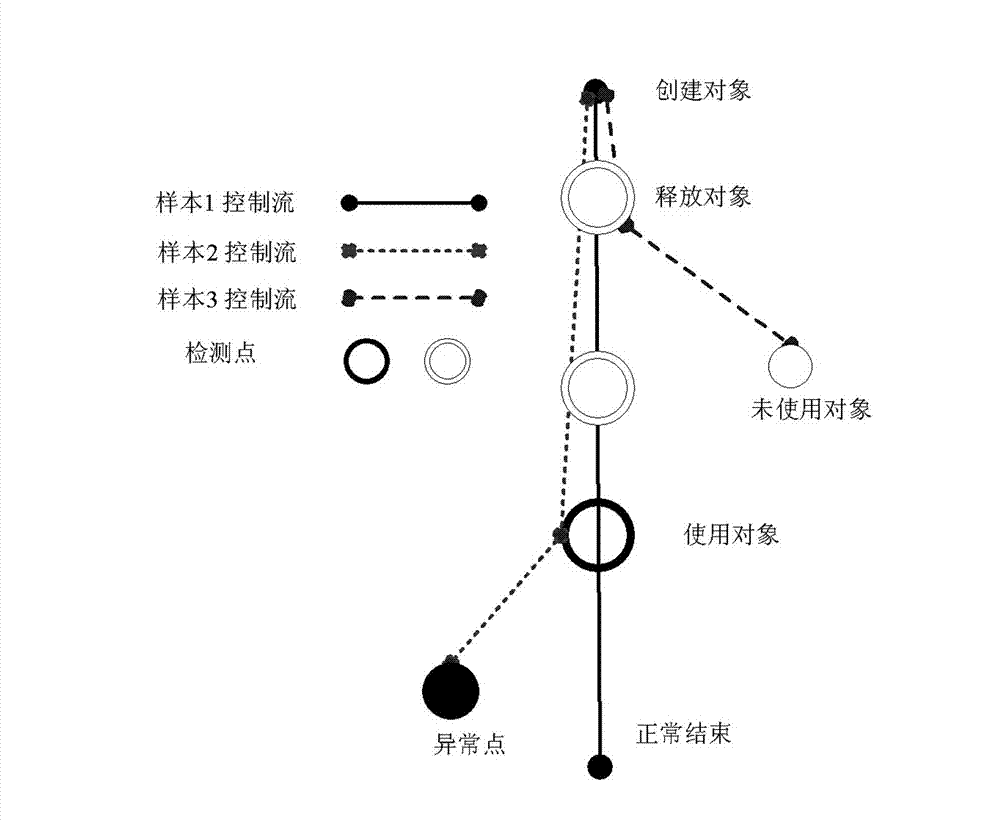
InactiveCN102789419AFailure Analysis Work Efficiency ImprovementUnable to locateSoftware testing/debuggingControl flowDynamic instrumentation
The invention relates to a software analysis method belonging to the technical field of computers, and particularly relates to a software fault analysis method based on multi-sample difference comparison. The method comprises the steps as follows: (1) executing disassemble and dynamic instrumentation of an analyzed program; (2) tracking and recording an execution instruction flow of a program to be analyzed and constructing control flow graphs of the program, which take a basic block as the minimum unit; and (3) selecting a data processing access point as a comparison basic point, constructing a multi-sample difference tree model, executing comparison of control flow graphs of multiple samples which are divided into several groups, wherein each group consists of two samples, finding out a key instruction flow branch point, and acquiring a key path from a false data input point to each difference point. The software fault analysis method, provided by the invention, effectively solves the problem that a dual-sample difference comparison method cannot achieve positioning of complex faults, thereby remarkably improving analysis efficiency of software faults.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
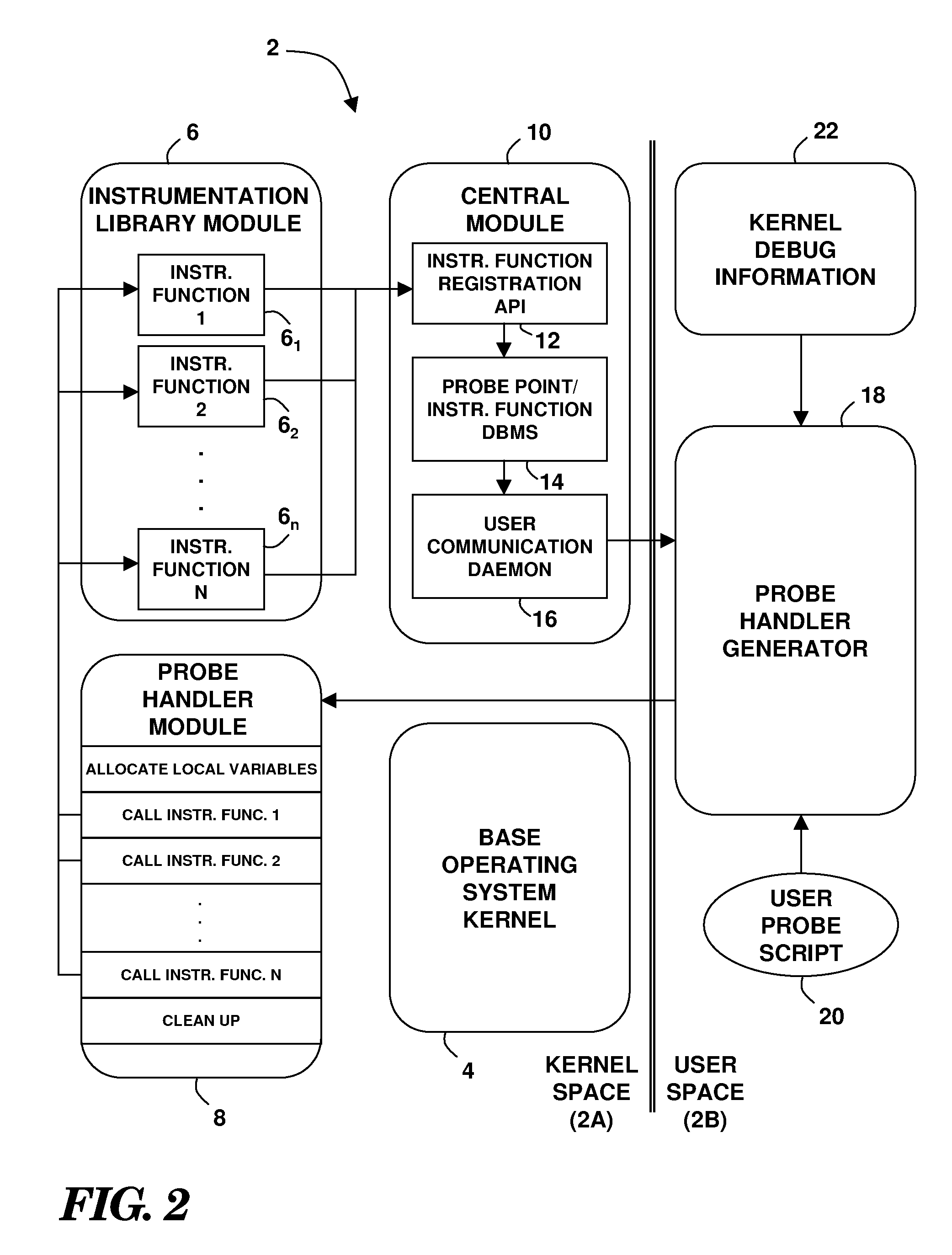
Maintainable Dynamic Instrumentation Technique For Changing Versions Of Software
InactiveUS20080052696A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsInstrument functionSoftware system
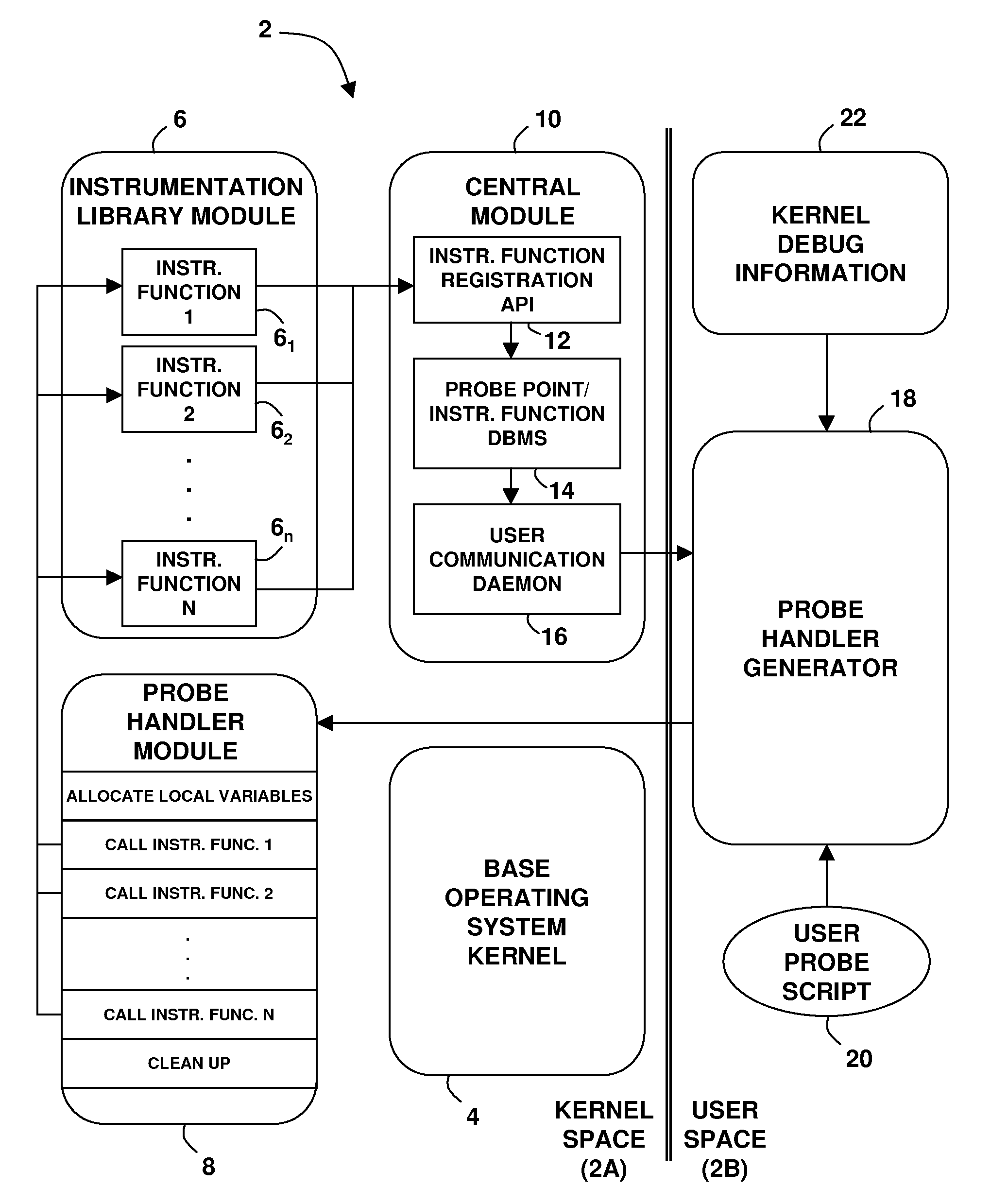
A technique for the dynamic instrumentation of a running software system. One or more callable instrumentation functions are accessible in a first memory space associated with the software system. The one or more callable instrumentation functions are adapted to probe an operation of the software system and return data regarding the probed operation. Probed operation environment information needed by the one or more instrumentation functions is provided to a second memory space associated with the software system. First memory space addresses associated with the probed operation environment information are determined from a resource that is accessible in the second memory space. A probe handler is generated that includes calls to the one or more instrumentation functions with references to the first memory space addresses. The probe handler is callable as part of the probed operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
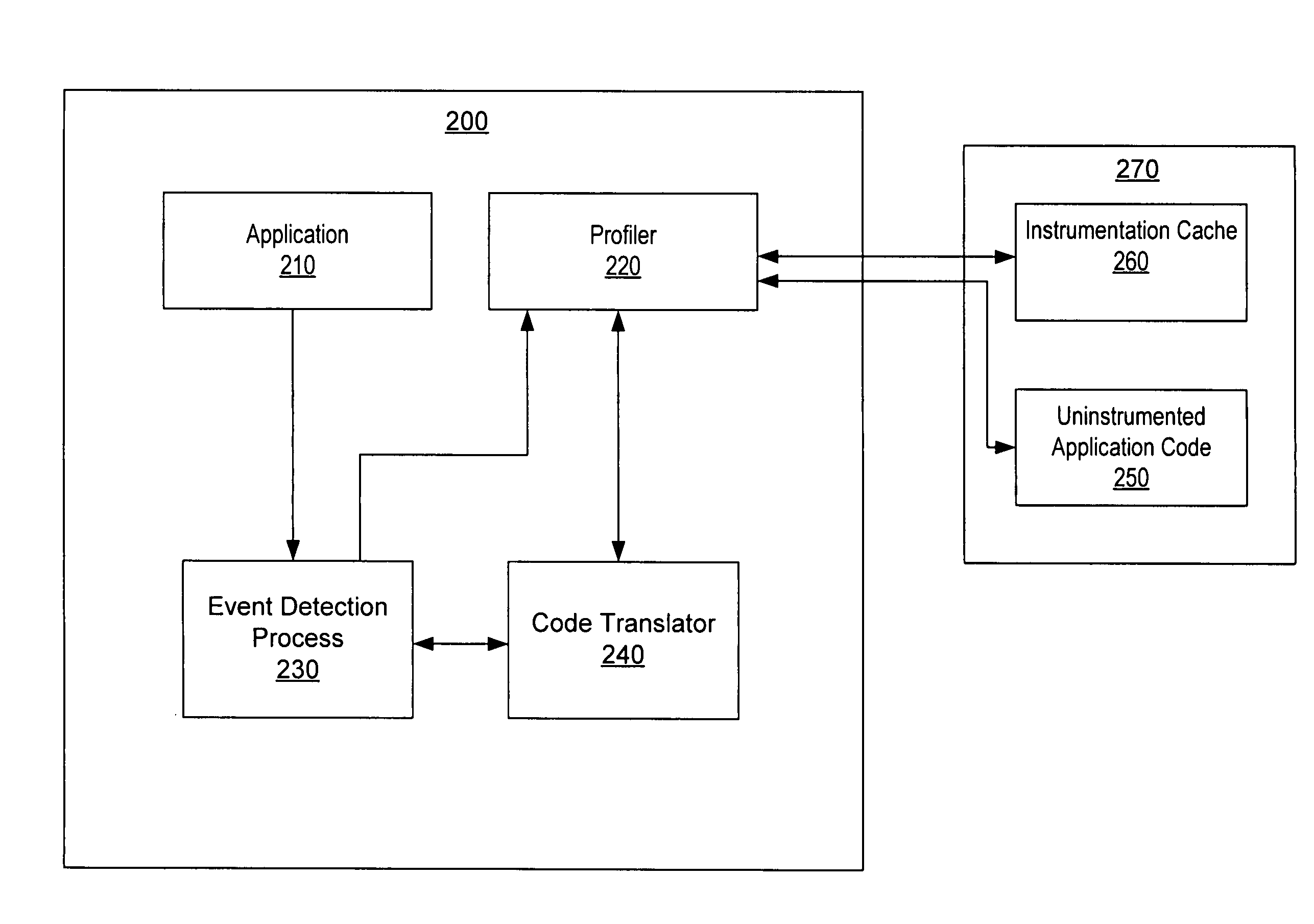
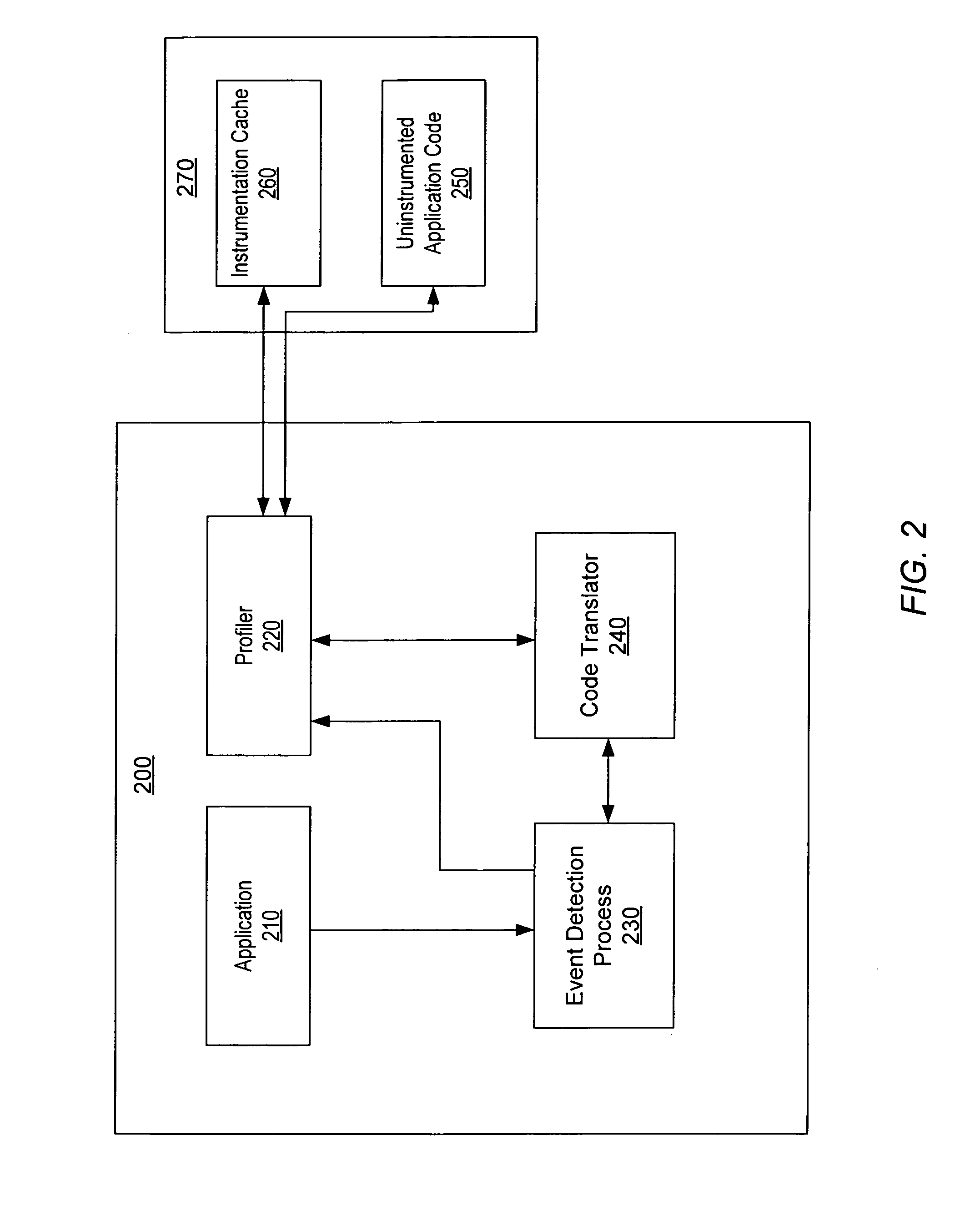
Pre-computed dynamic instrumentation
InactiveUS7805717B1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsProgram instructionDynamic instrumentation
A system and method for instrumenting program instructions. A processing system includes a compiler and a profiler. The compiler is configured to notify the profiler of a compilation event corresponding to first program instructions. In response to detecting the event, the profiler is configured to intercept compilation of the first program instructions, determine whether an instrumented version of the first program instructions is currently available, instruct the compiler to compile the instrumented version of the first program instructions if available, and retrieve and instrument the first program instructions if not available. The profiler may maintain an instrumentation cache for storing instrumented versions of program instructions. The instrumentation cache may further include metadata which identifies portions of program code which have been instrumented and their location. The profiler may generally instrument program instructions once during the resident life of a corresponding application.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
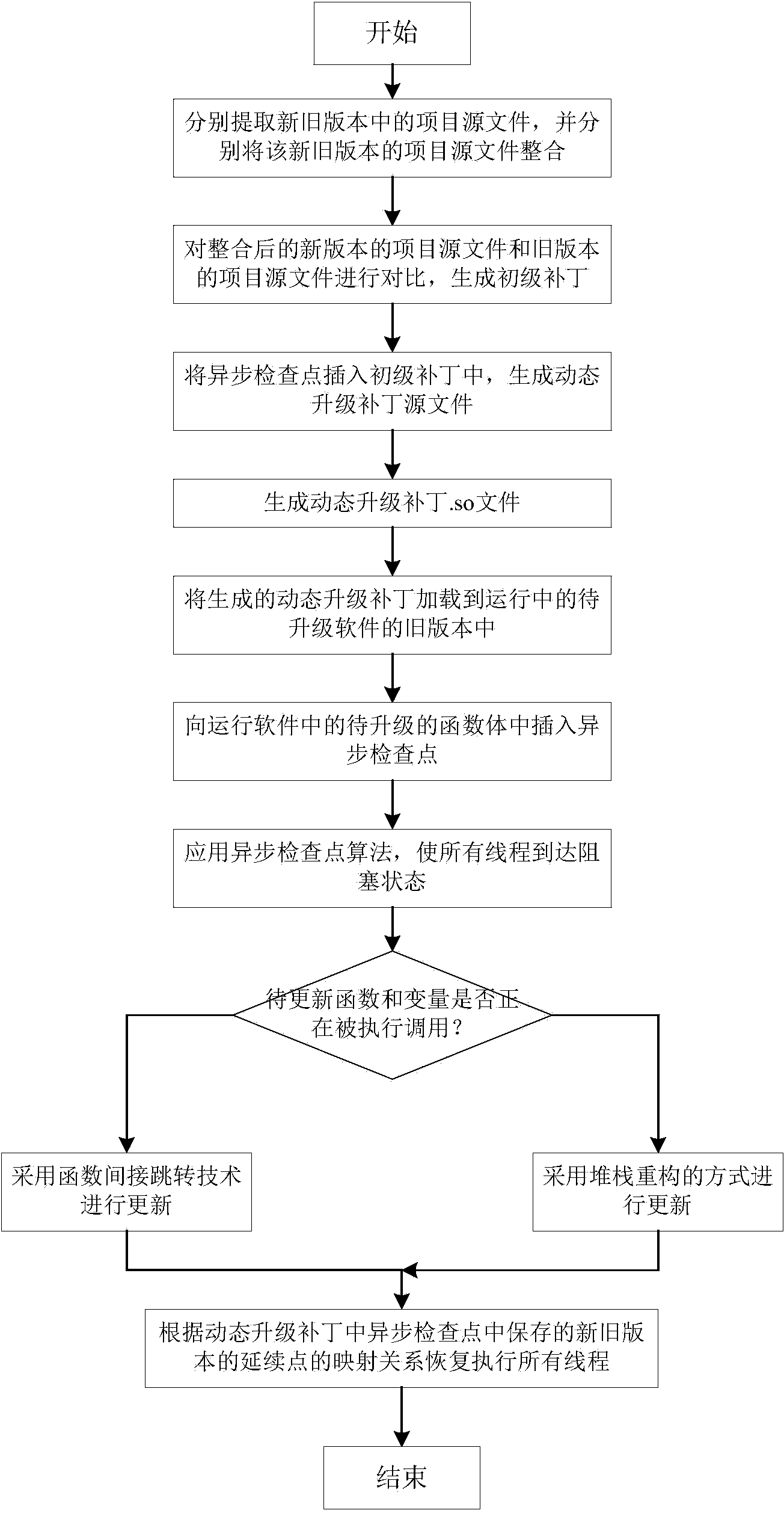
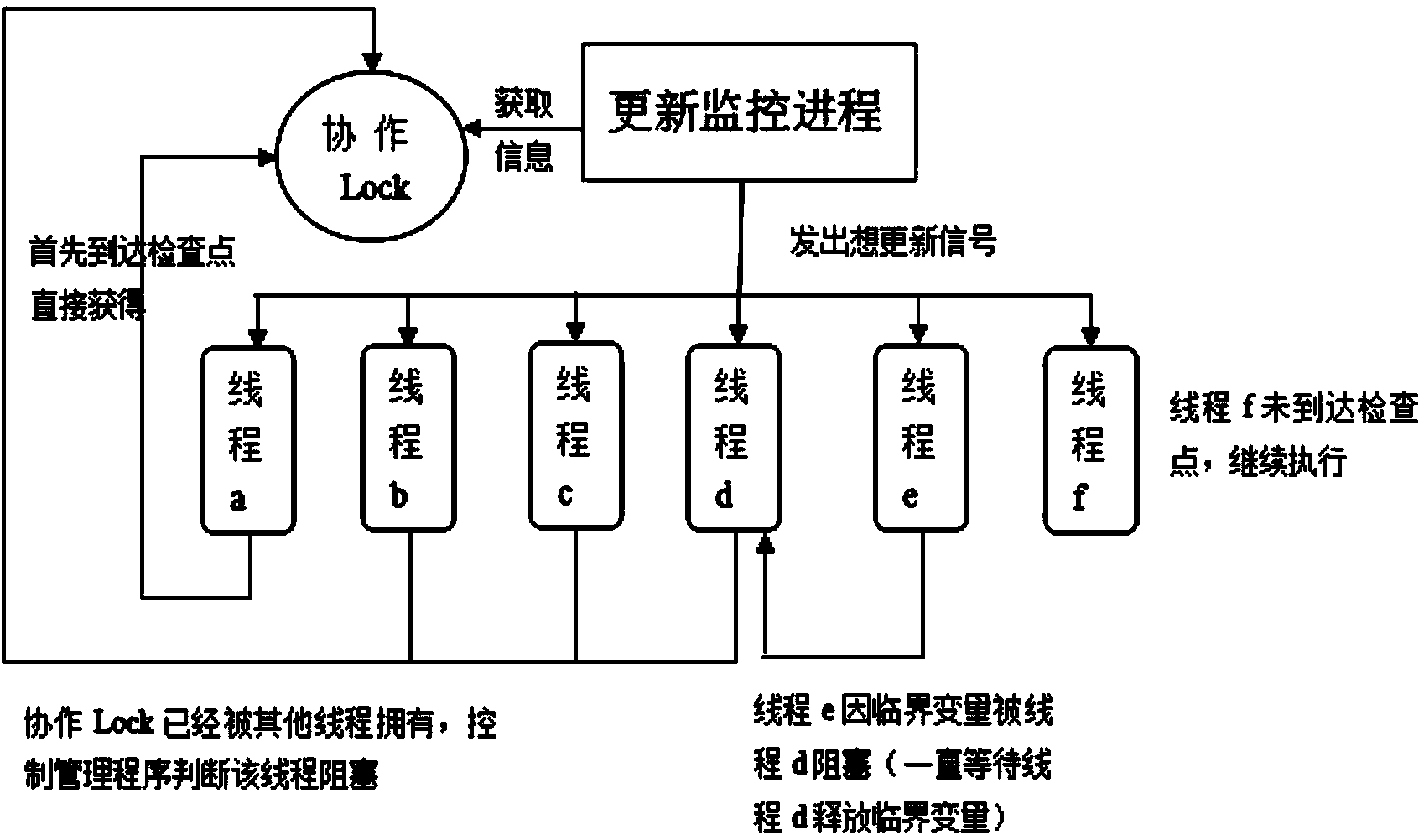
Multi-thread software dynamic upgrading method based on asynchronous check points
ActiveCN104111848ARemove constraintsIncrease flexibilityProgram loading/initiatingCheck pointDynamic instrumentation
The invention discloses a multi-thread software dynamic upgrading method based on asynchronous check points. The method includes the steps that based on a dynamic instrumentation mode, key codes are arranged in a source program in operation in an instrumentation mode at a binary level, not a source code level, so that upgrading does not need to depend on a specific compiler; based on an asynchronous check point algorithm, it can be guaranteed that all threads are in a blocked state before dynamic upgrading, so that all the threads are updated in a one-off mode, and expenditure caused by new and old version maintenance is avoided; a mode of binary system rewriting is adopted for function indirect skipping, and functions to be updated are upgraded, wherein the functions are not executed; a stack reconstruction mode can be used for upgrading functions to be updated in execution, so that in the dynamic upgrading process, unexpected waiting time which is caused by loop body and main function updating and others are eliminated. The loss, which is caused by downtime due to version maintenance, of applications and services (such as an electronic payment system) high in reliability requirement is reduced to the minimum, and cost caused by additional arrangement of redundancy hardware is reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
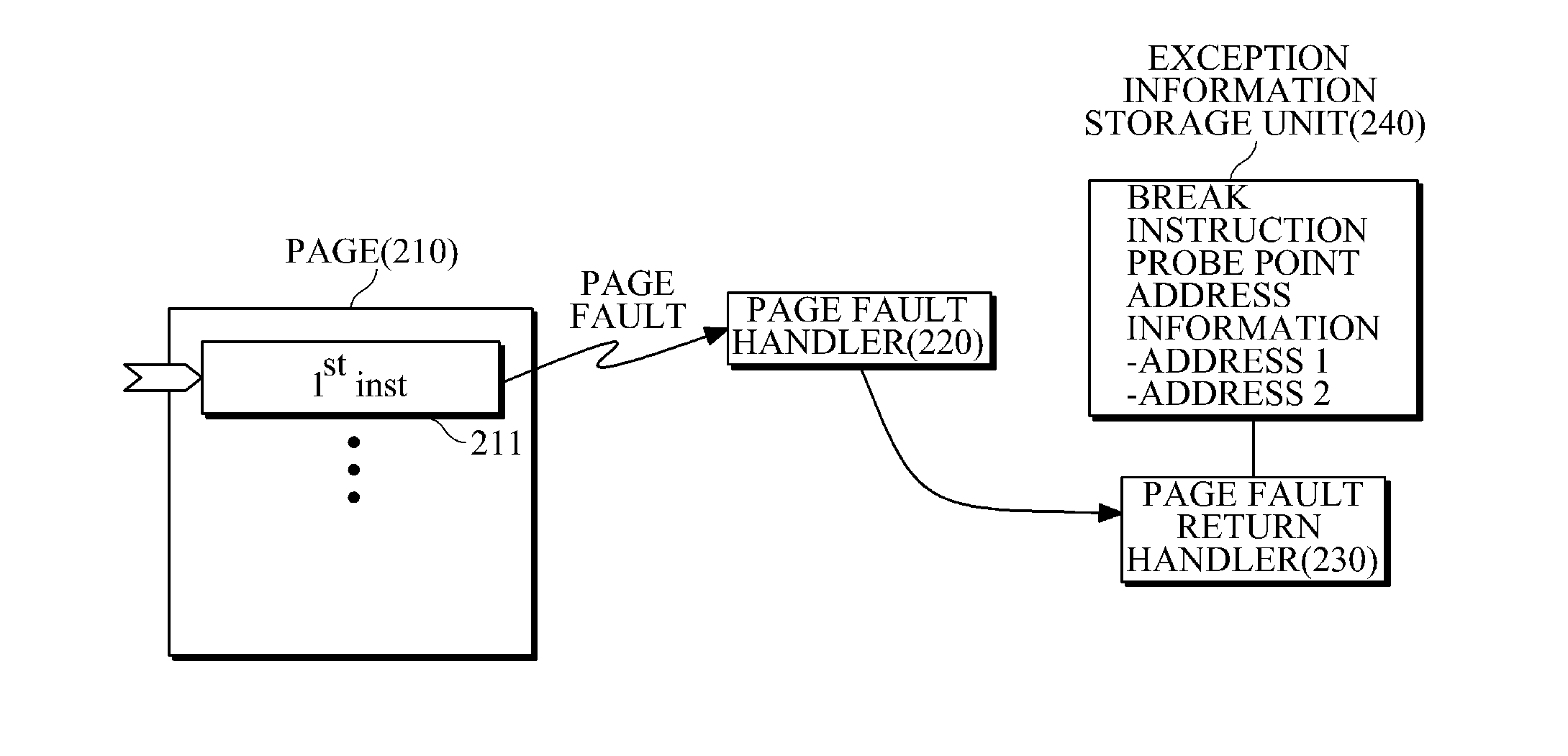
Method and apparatus for dynamically instrumenting a program
InactiveUS20100251220A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsDynamic instrumentationParallel computing
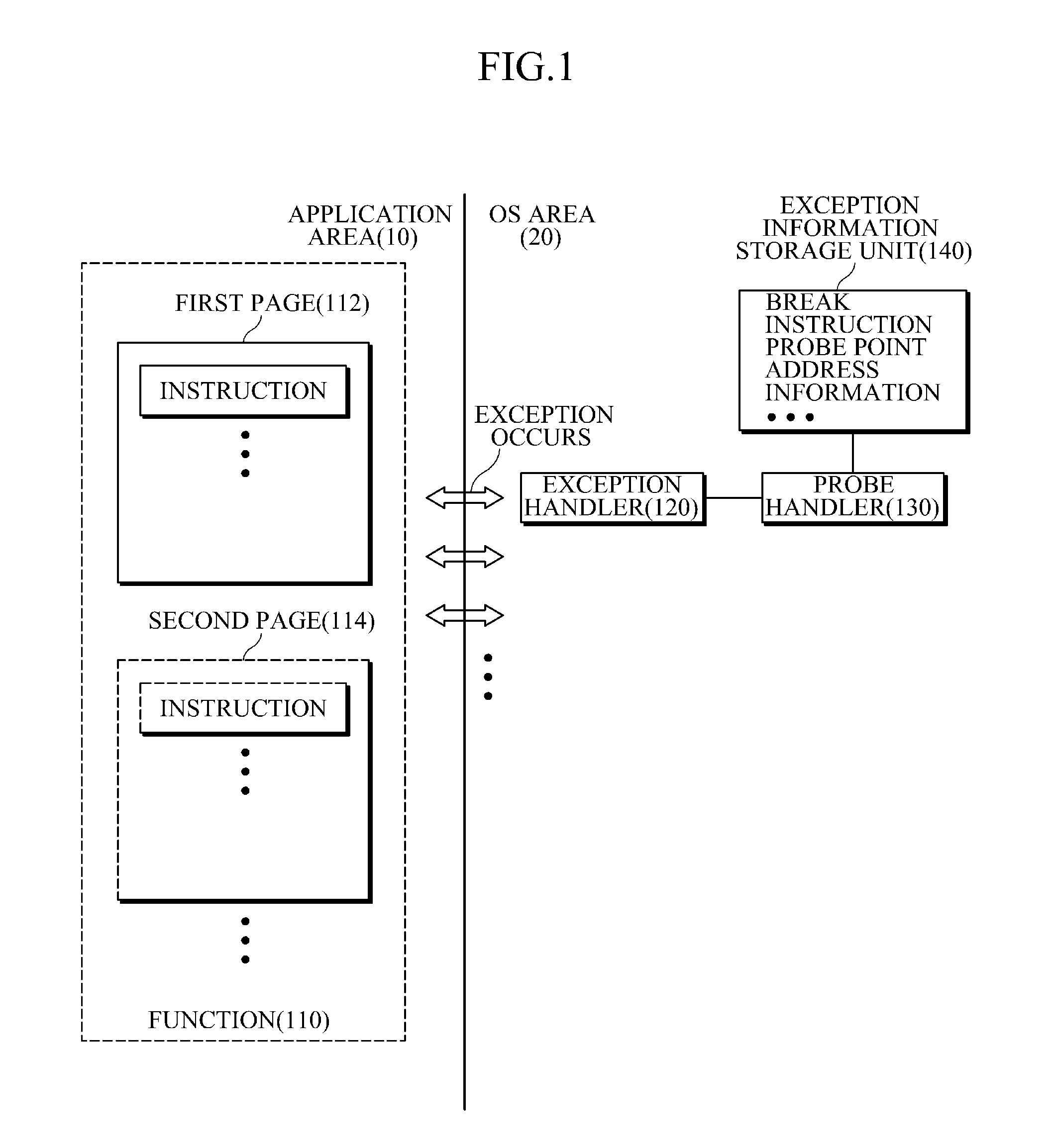
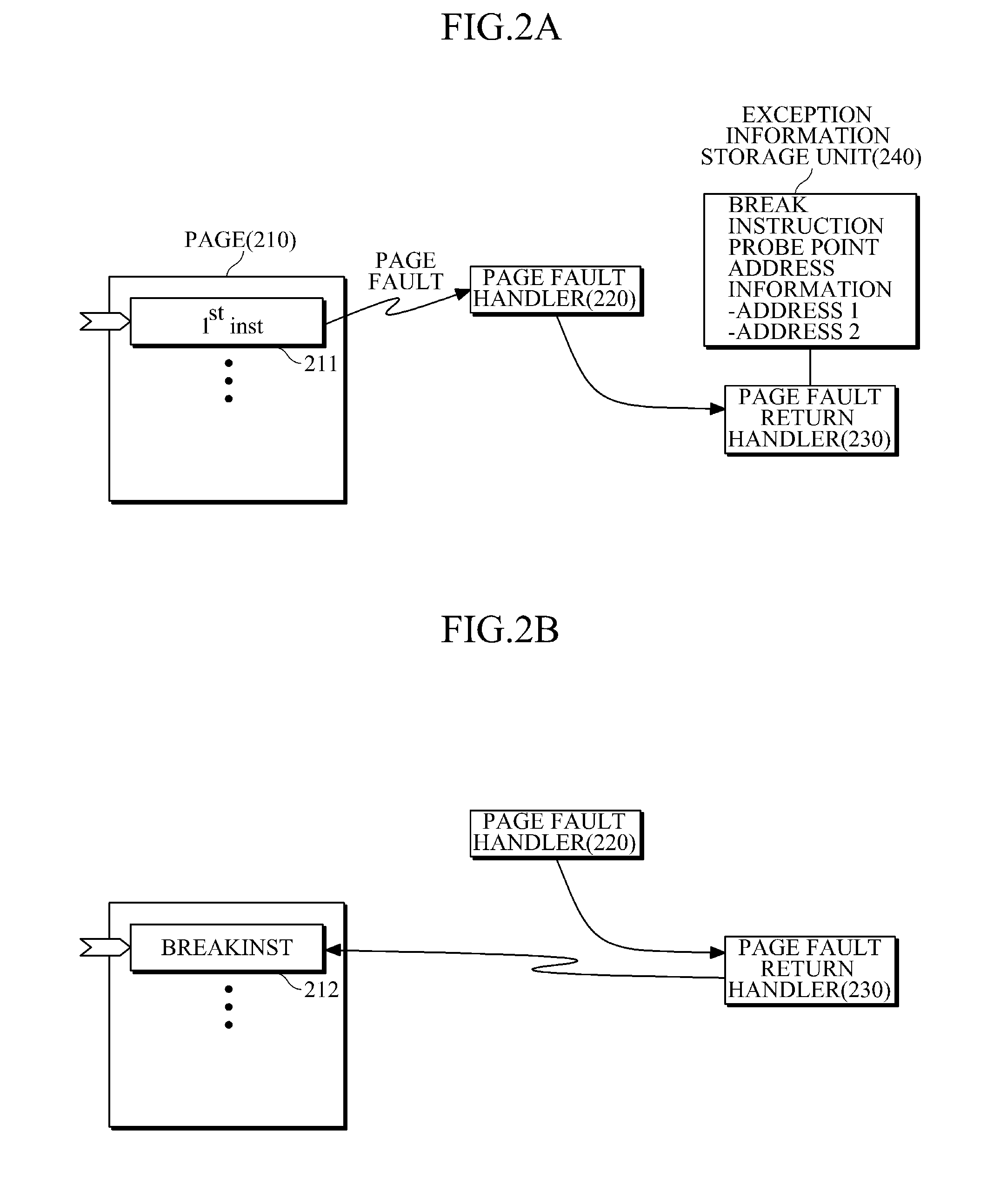
A dynamic instrumentation method and apparatus which may trace, debug, and profile the execution of a running program without affecting the operation of the program, are provided. According to the method, a break instruction is inserted and executed at start of execution of a first instruction and immediately after execution of the last instruction of a function constituting the program. Environment values of the function before and after execution may be identified. The program may be dynamically instrumented without being affected by any tracing or debugging operations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
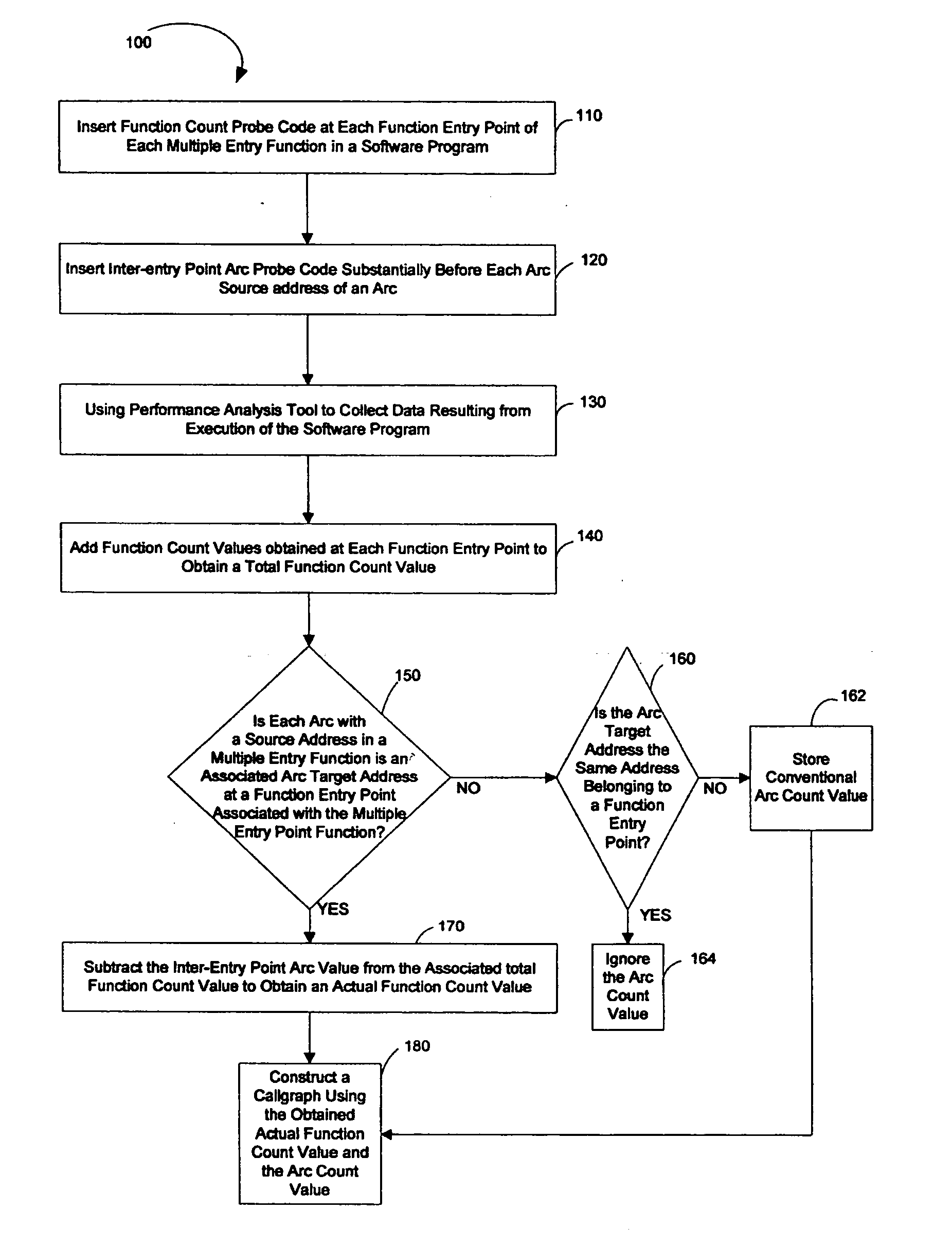
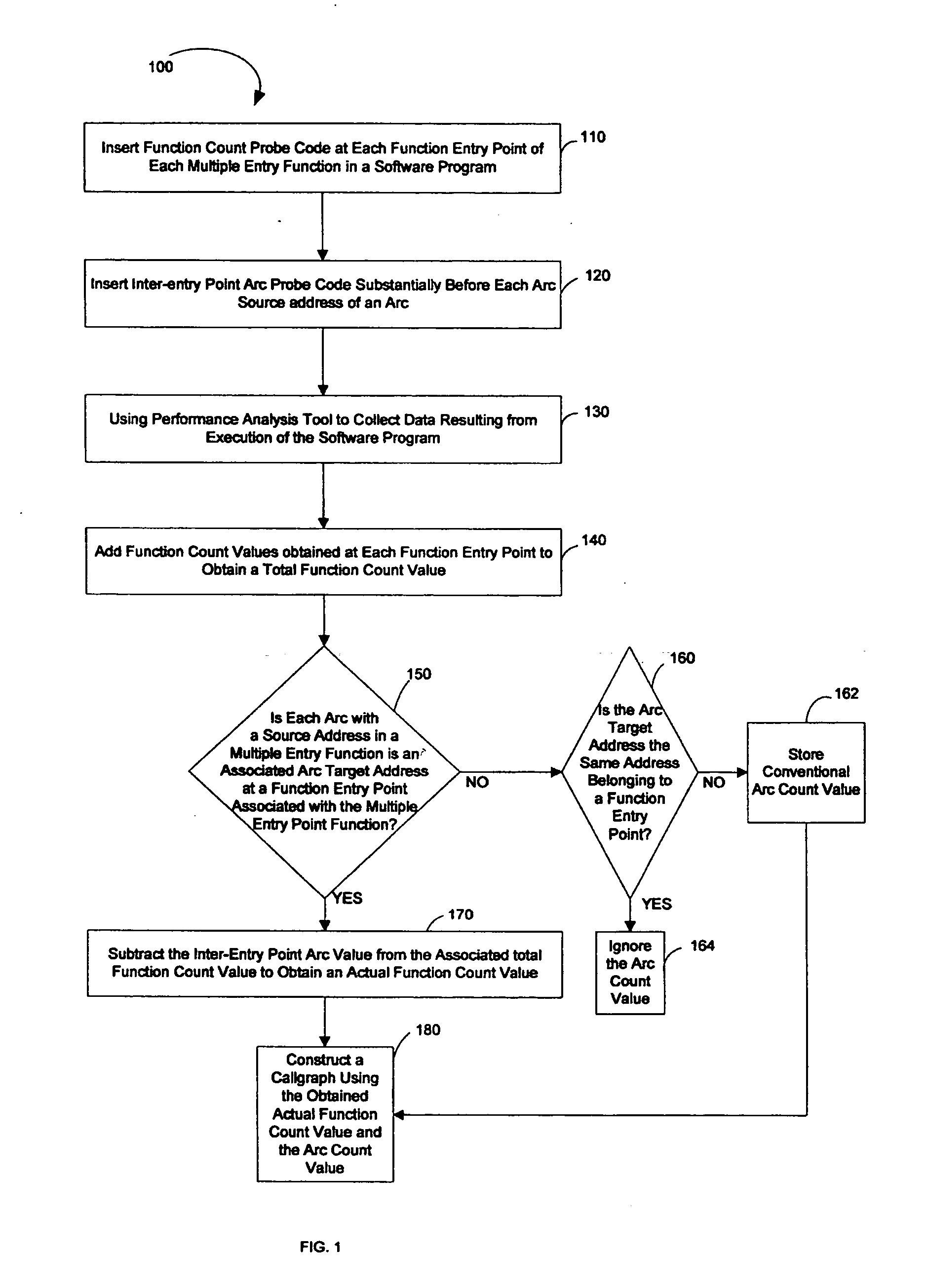
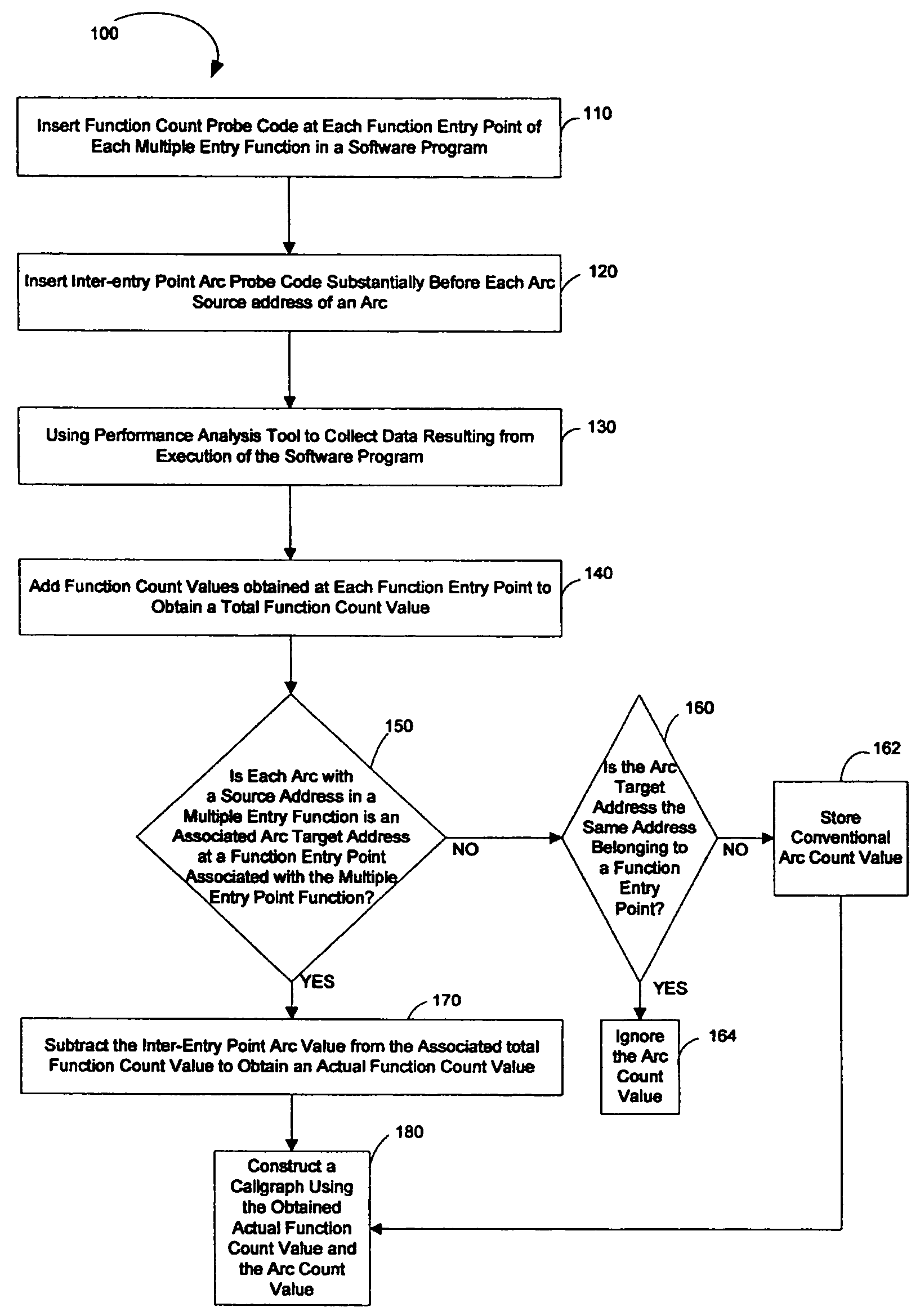
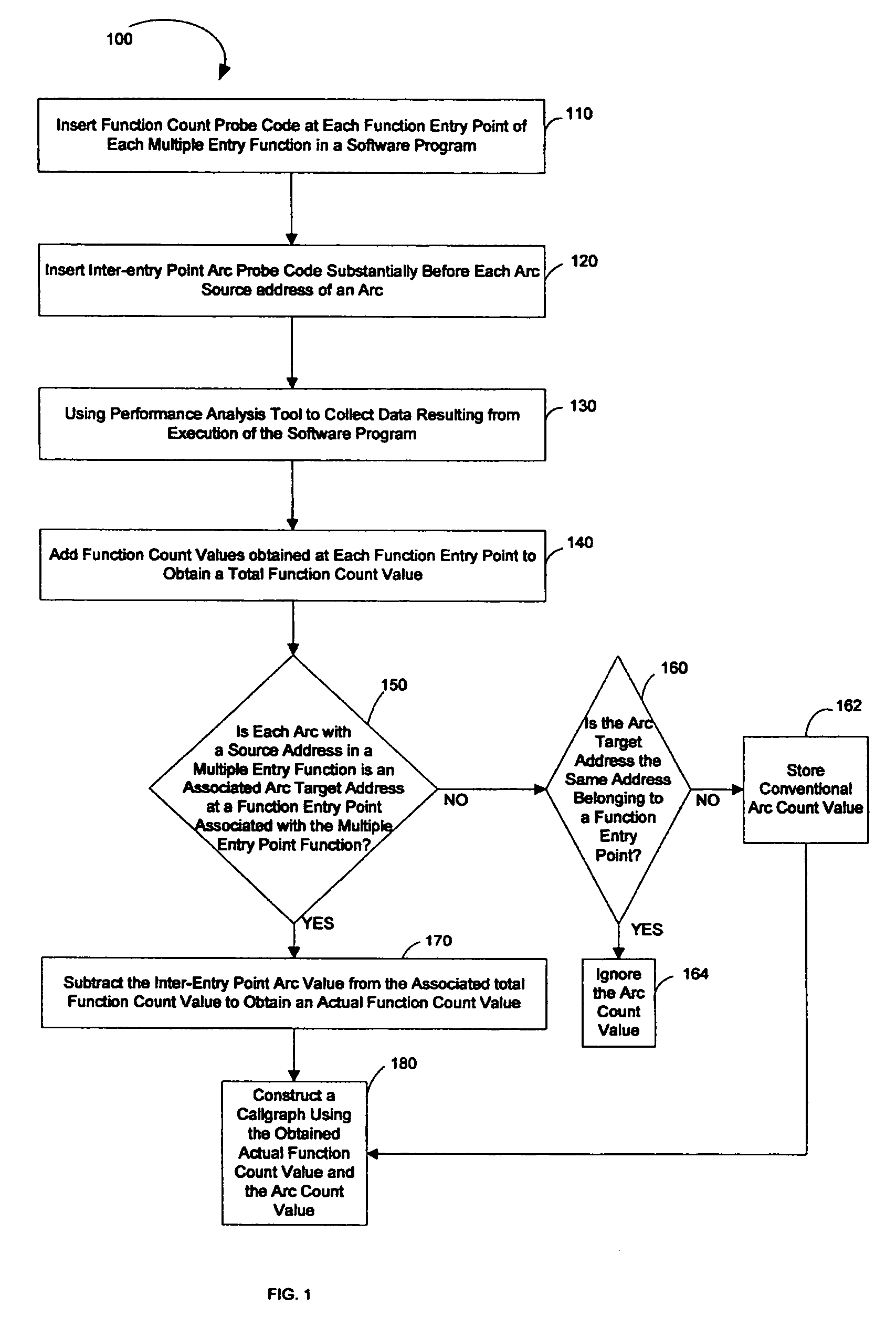
System and method to build a callgraph for functions with multiple entry points
ActiveUS20060236309A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsEntry pointDynamic instrumentation
A technique for building a callgraph for a software program that includes multiple function entry points using dynamic instrumentation. In one example embodiment, this is achieved by inserting function count probe code at each function entry point of each multiple entry function having multiple function entry points in the software program. Inter-entry point arc probe code is then inserted substantially before each arc source address of an arc. A performance analysis tool is then used to collect data resulting from execution of the software program including the function count probe code and the inter-entry point arc probe code and to obtain an actual function count value for each multiple entry function. A callgraph is then built using the obtained actual function count values.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Malicious code detecting system and method based on dynamic instrumentation
ActiveCN104715195AEasy to detectRealize judgmentPlatform integrity maintainanceDynamic instrumentationSoftware engineering
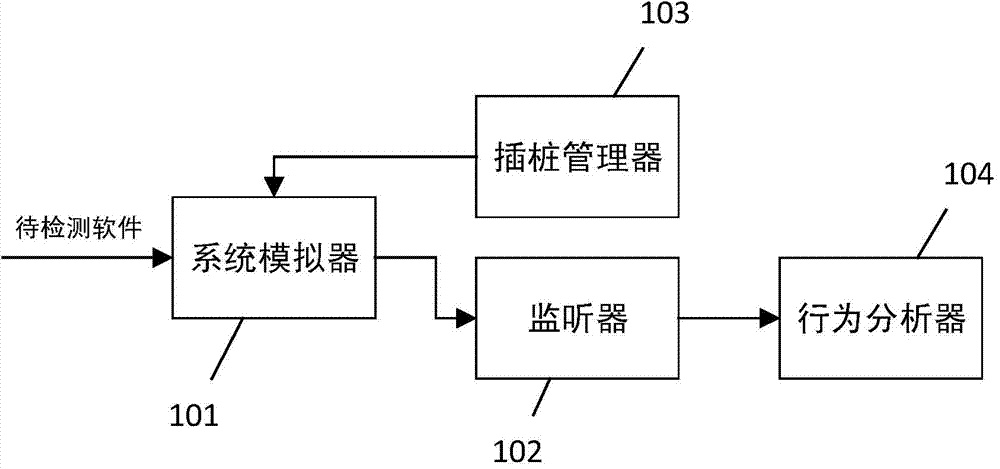
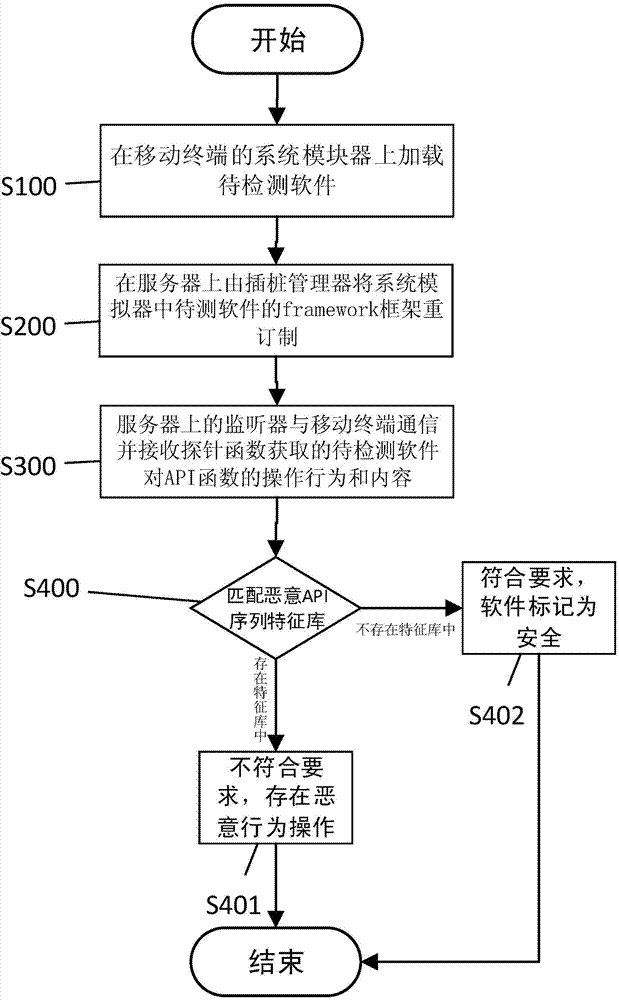
The invention discloses a malicious code detecting system and method based on dynamic instrumentation. The method comprises the steps that a software to be detected is uploaded on a system simulator of a mobile terminal; a framework of the software to be detected of the system simulator is ordered again by an instrumentation manger of a server, an instrumentation strategy file is implanted into the system simulator, and one or more probe functions monitor an API function of the framework according to the instrumentation strategy file; a sound monitor of the server communicates with the mobile terminal and receives the operation behaviors and content of the software to be detected which are conducted to the API function and obtained by the probe functions; the detected content is compared with a malicious API sequence feature library, if the detected content exists in the malicious API sequence feature library, the software is marked to have malicious behavior operation, and if the detected extent does not exist in the malicious API sequence feature library, the software is marked to be safe, so that the safety of the software to be detected is determined. By means of the system and method, it is achieved that the software to be detected is installed and operated in the system simulator of the mobile terminal, and malicious codes are detected through instrumentation, so that it is avoided that safety hazards or hidden dangers are caused to the mobile terminal.
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD INFORMATION CENT
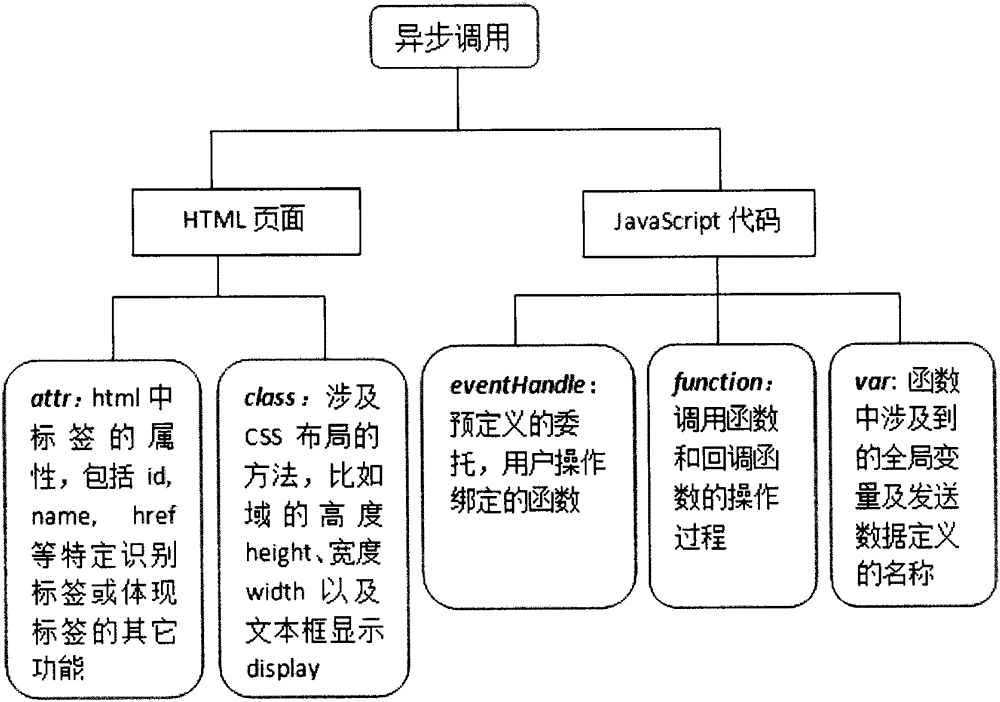
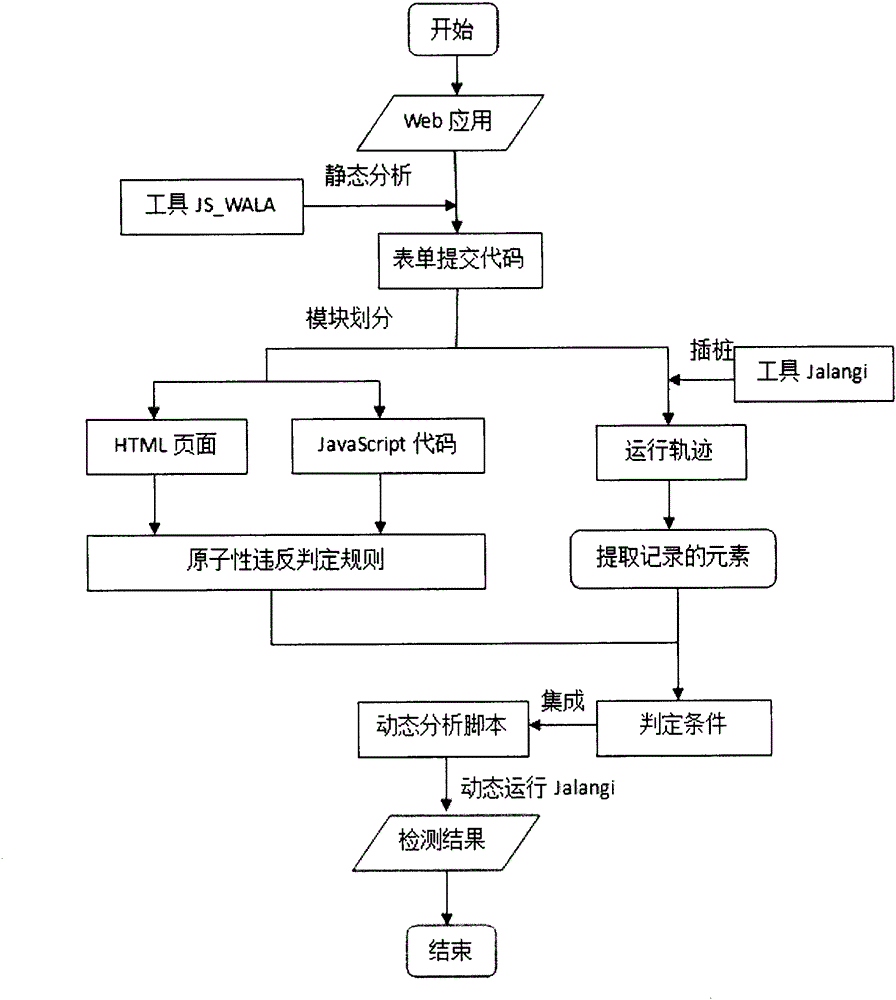
Static analysis and dynamic operation based detection of atomic violation of JS (JavaScript) code in Web application
InactiveCN105095092AComprehensive detectionAccurate detectionSoftware testing/debuggingStatic timing analysisWeb application
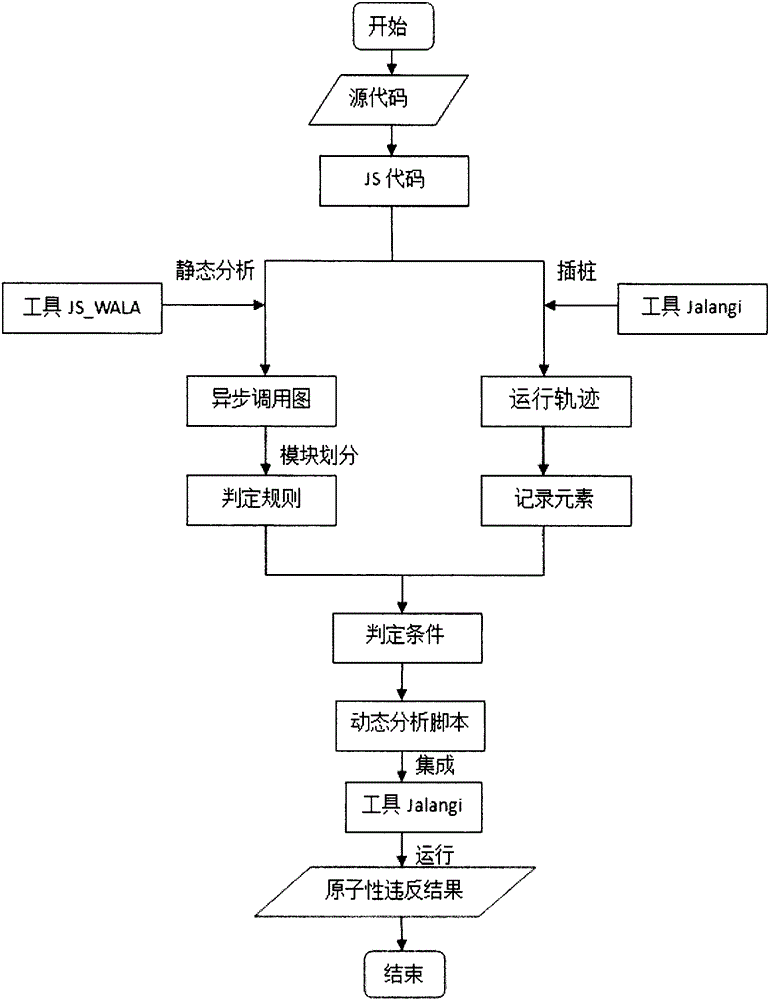
The invention provides a static analysis and dynamic operation based detection method of atomic violation. The method comprises the following steps: a function and a method related to asynchronous call in JS are acquired through static analysis of a JS code, and code coverage is guaranteed; a dynamic instrumentation record mechanism of a cross-language platform is adopted, a probe point is arranged in an asynchronous call function, not only can elements in JS program be obtained, but also elements in an HTML (hypertext markup language) mode can be recorded, and the accuracy of detection of potential atomic violation is improved; decision rules of atomic violation are designed according to the elements related in the whole process from a request to response of the a Web application, so that effective detection of atomic violation can be performed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Detection of method calls to streamline diagnosis of custom code through dynamic instrumentation
A technique for analyzing software in which un-instrumented components can be discovered and dynamically instrumented during a runtime of the software. Initially, an application configured with a baseline set of instrumented components such as methods. As the application runs, performance data is gathered from the instrumentation, and it may be learned that the performance of some methods is an issue. To analyze the problem, any methods which are callable from a method at issue are discovered by inspecting the byte code of loaded classes in a JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM). Byte code of the class is parsed to identify opcodes which invoke byte code to call other methods. An index to an entry in a constants pool table is identified based on an opcode. A decision can then be made to instrument and / or report the discovered methods.
Owner:CA TECH INC
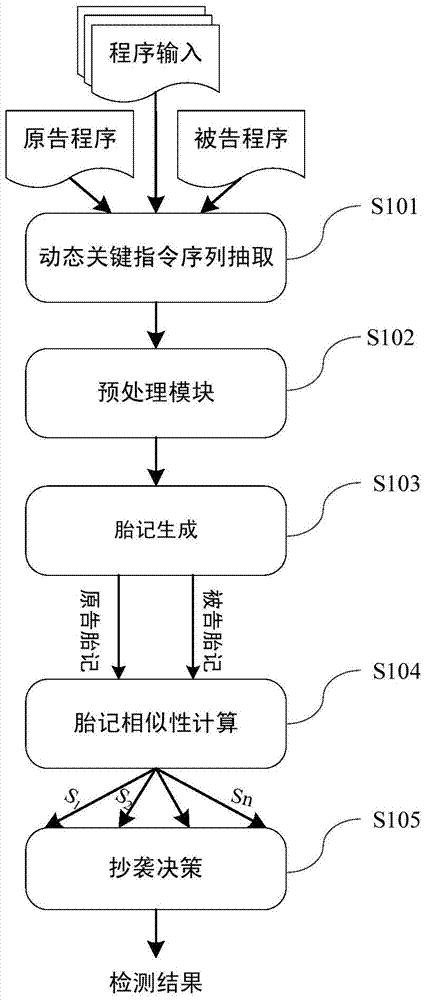
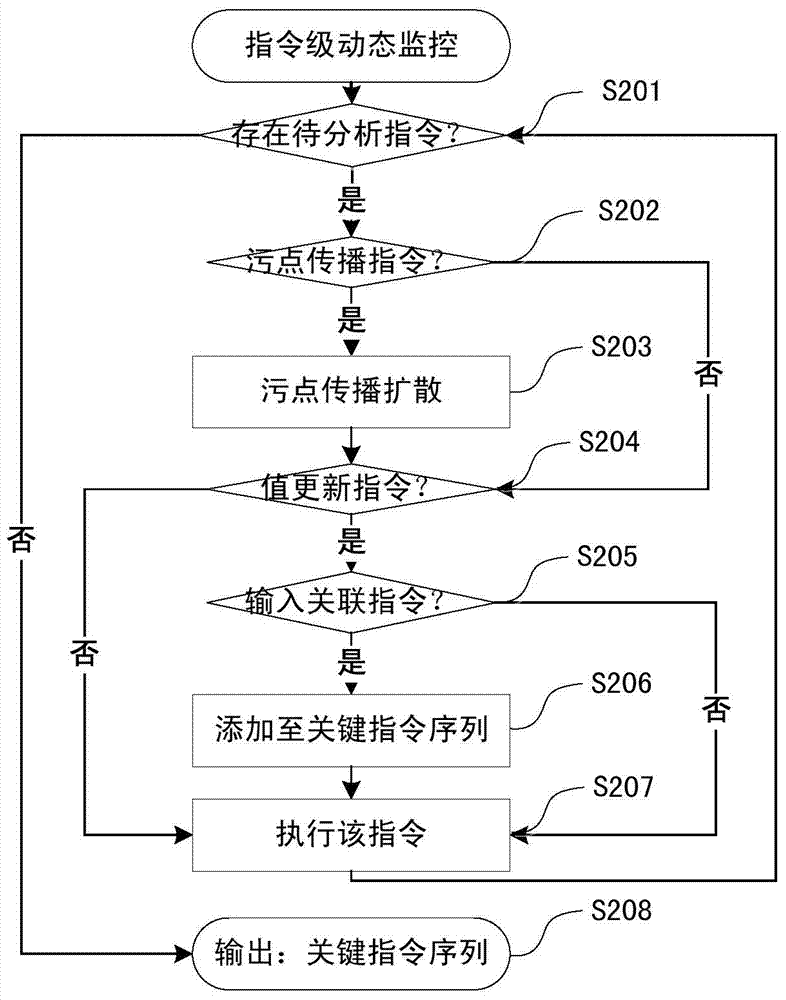
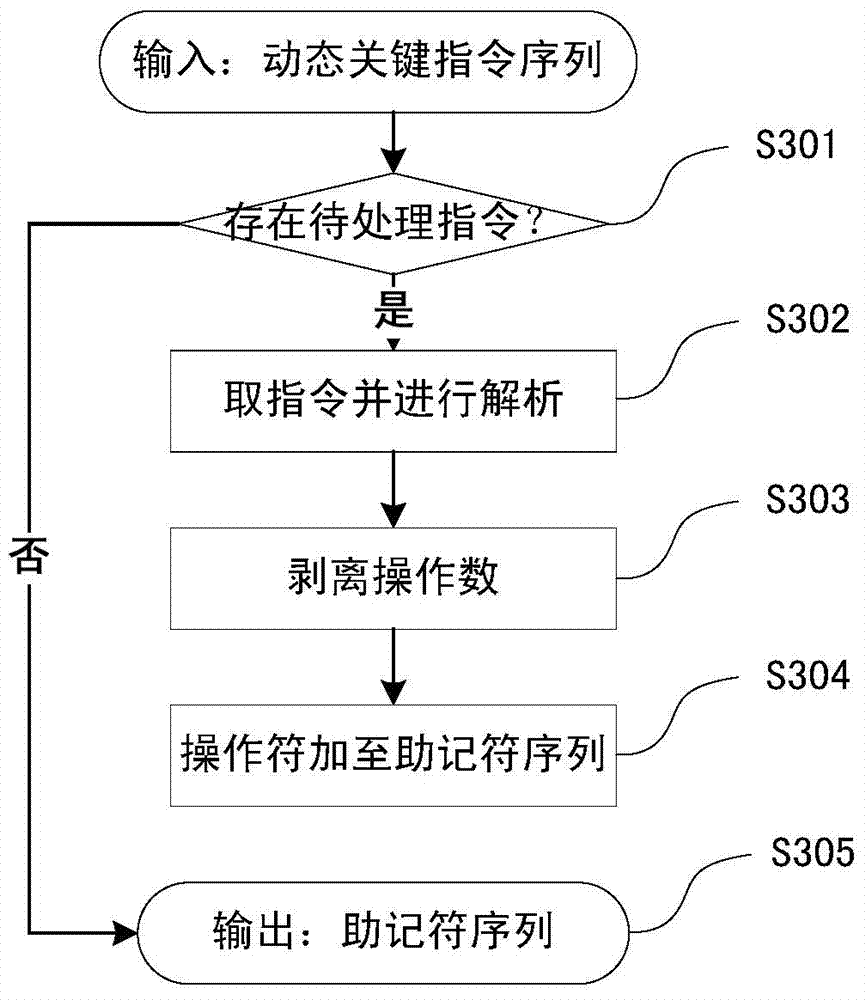
Dynamic key command sequence birthmark-based software plagiarism detecting method
ActiveCN103577323ANo limitationsStrong resistanceSoftware testing/debuggingObfuscationDynamic instrumentation
The invention provides a dynamic key command sequence birthmark-based software plagiarism detecting method, which comprises the steps of (1) monitoring a program to be analyzed based on a dynamic instrumentation and identifying and recording a key command by combining with dynamic stain analysis in real time; (2), preprocessing the recorded key command sequence, stripping an operation number and extracting a mnemonic sequence; (3) on the basis, respectively generating a dynamic key command sequence birthmark for two software to be detected; (4) calculating the similarity of the birthmarks; (5) making the design of plagiarism or not by the average value of the similarity of the birthmarks and a given threshold value. The dynamic key command sequence birthmark-based software plagiarism detecting method directly aims at the binary codes without the need of existence of source codes and has more practical significance; the detection means does not depend on a specific platform or programming language, has wider application range and has better resistance to the code obfuscation technology with reversed semantics, so the detection capability of deep plagiarism is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
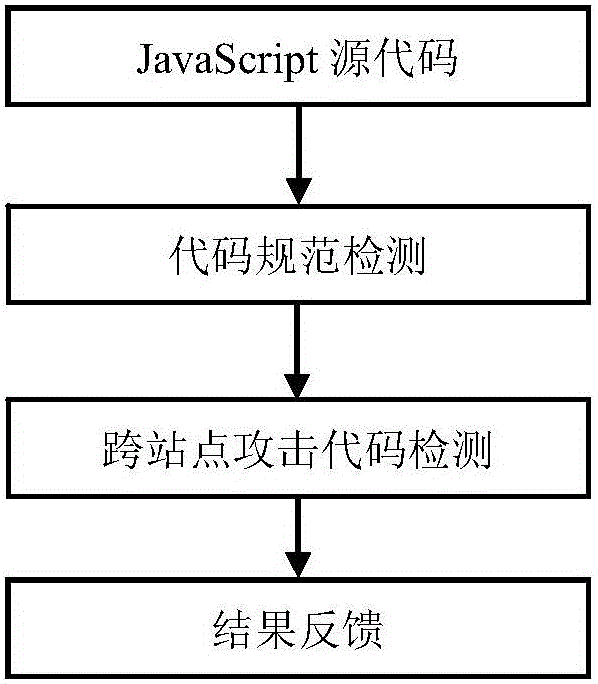
Rule-based JavaScript security testing method
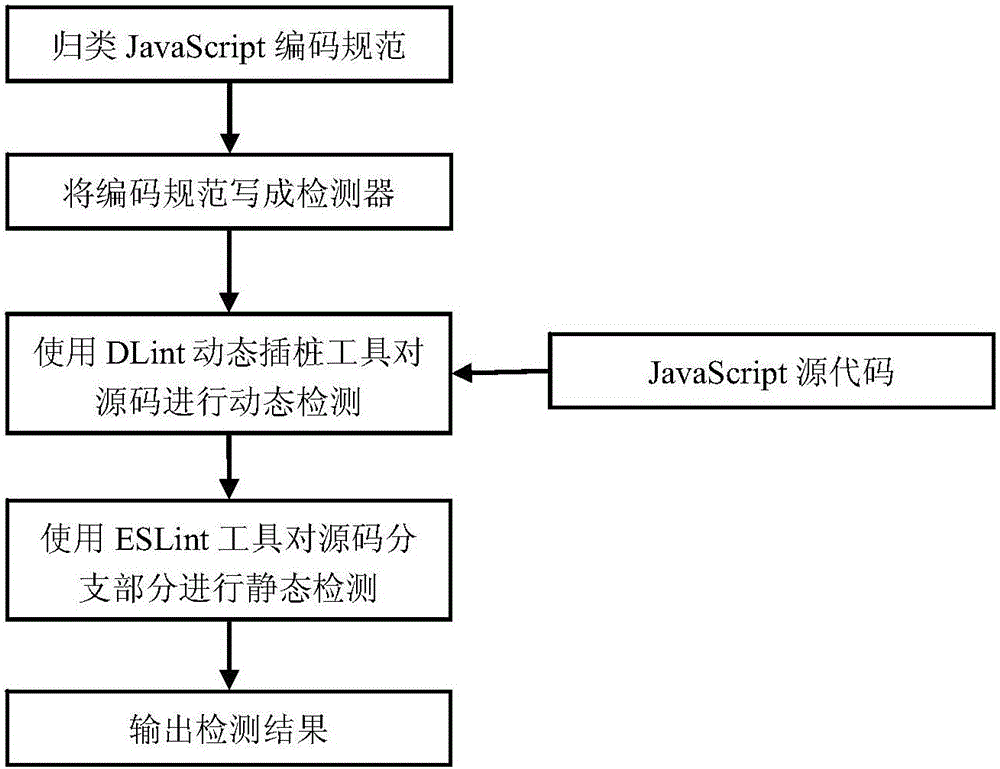
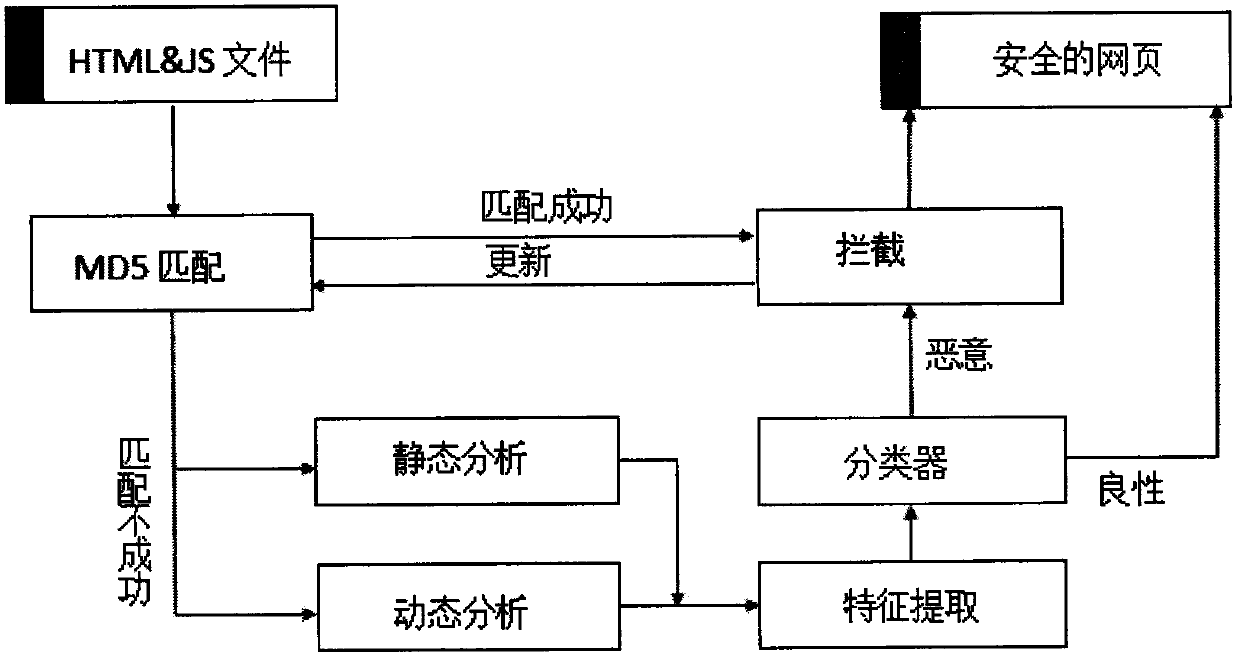
ActiveCN106055980AReduce missed detection rateImprove efficiency in detecting security issuesPlatform integrity maintainanceWeb siteDynamic instrumentation
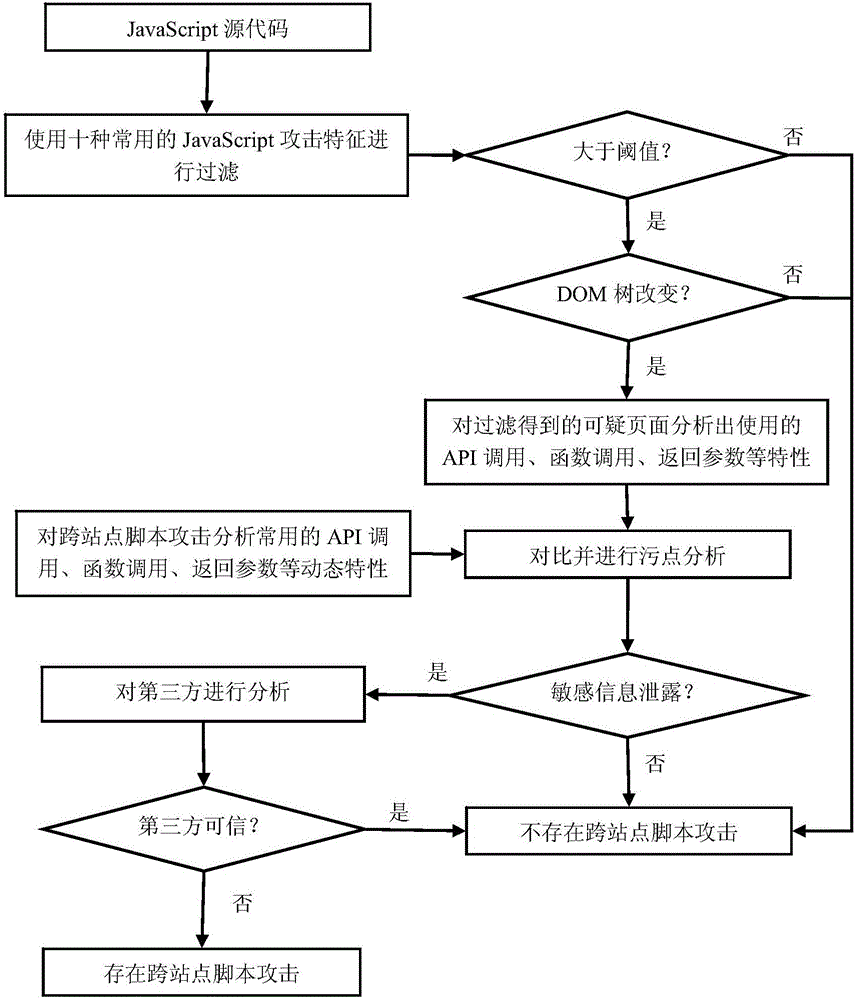
The invention discloses a rule-based JavaScript security testing method. A program analysis method in which static analysis and dynamic analysis are combined is utilized for testing the security problem of a JavaScript code in a website and performing feedback, thereby finding out the security problems which comprise JavaScript coding standardization un-qualification and over-site script attack malicious codes. The method comprises the steps of dynamically finding out a JavaScript coding standardization un-qualification problem by means of a DLint tool, then testing the branched parts of a source code by means of an open-source static code standardization testing tool ESLint; then filtering a page which may contain over-site script attack malicious codes in the source code according to JavaScript page characteristics and a preset threshold according to a static analysis method; and then performing dynamic Instrumentation on the filtered page for performing strain analysis by means of a Jalangi frame, thereby determining whether the filtered page contains an over-site script attack. The rule-based JavaScript security testing method effectively improves testing efficiency for code standardization and malicious codes based on miss rate reduction.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
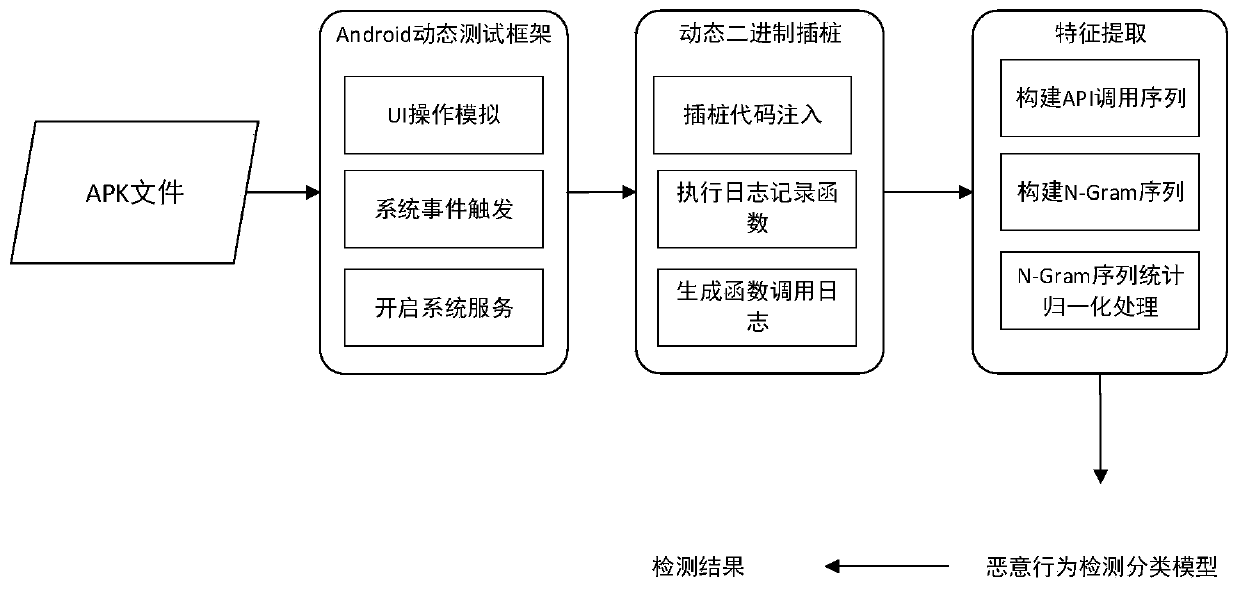
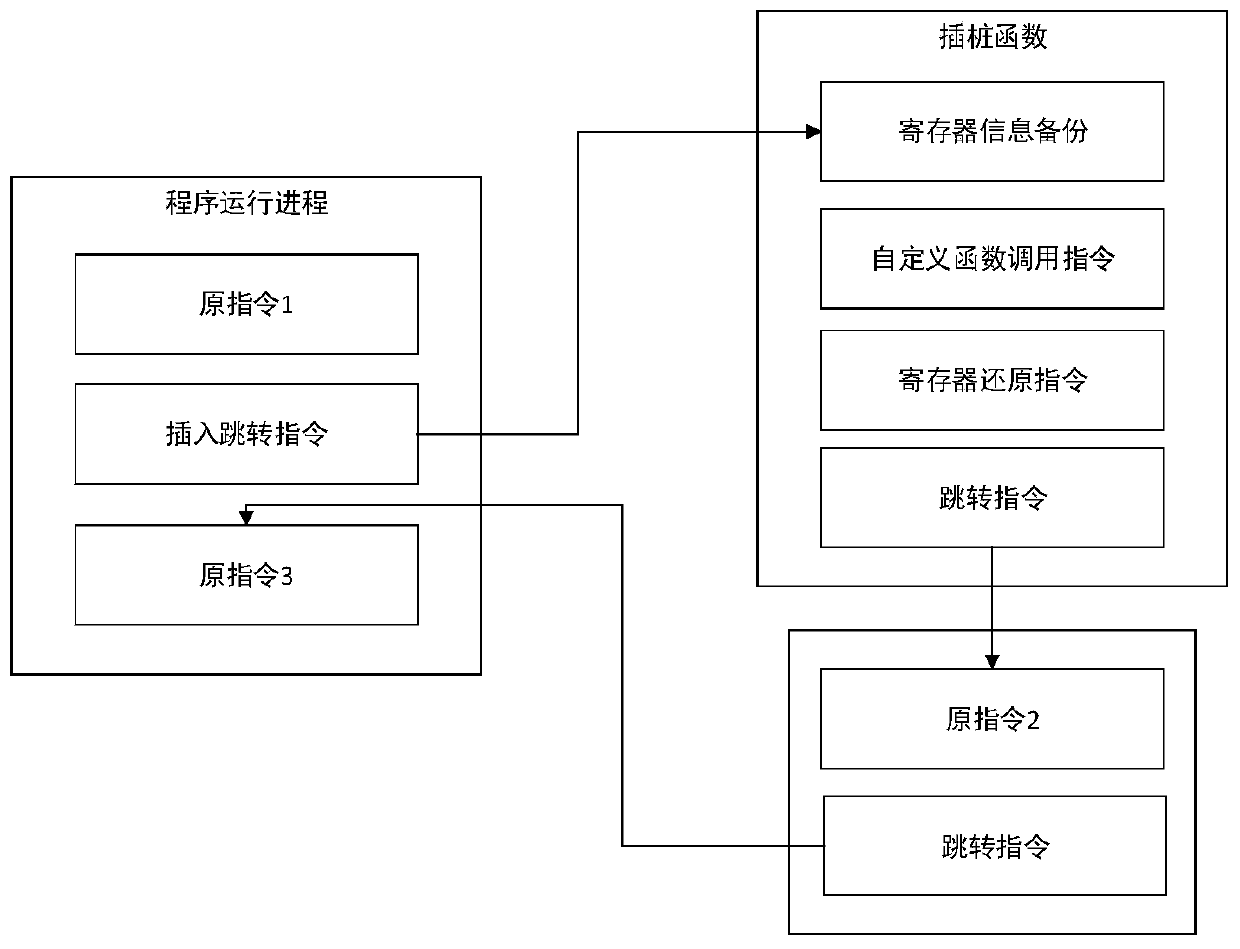
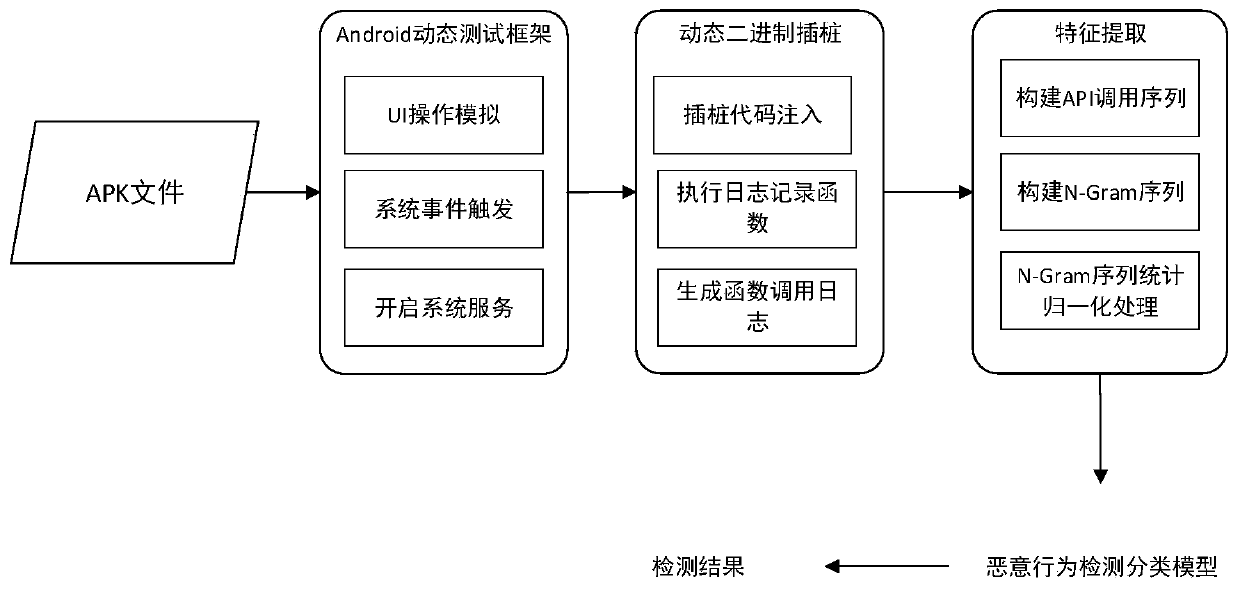
Android malicious behavior dynamic detection method based on binary dynamic instrumentation
InactiveCN109992968AImprove detection efficiencyImprove accuracyPlatform integrity maintainanceSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationGranularityDynamic instrumentation
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
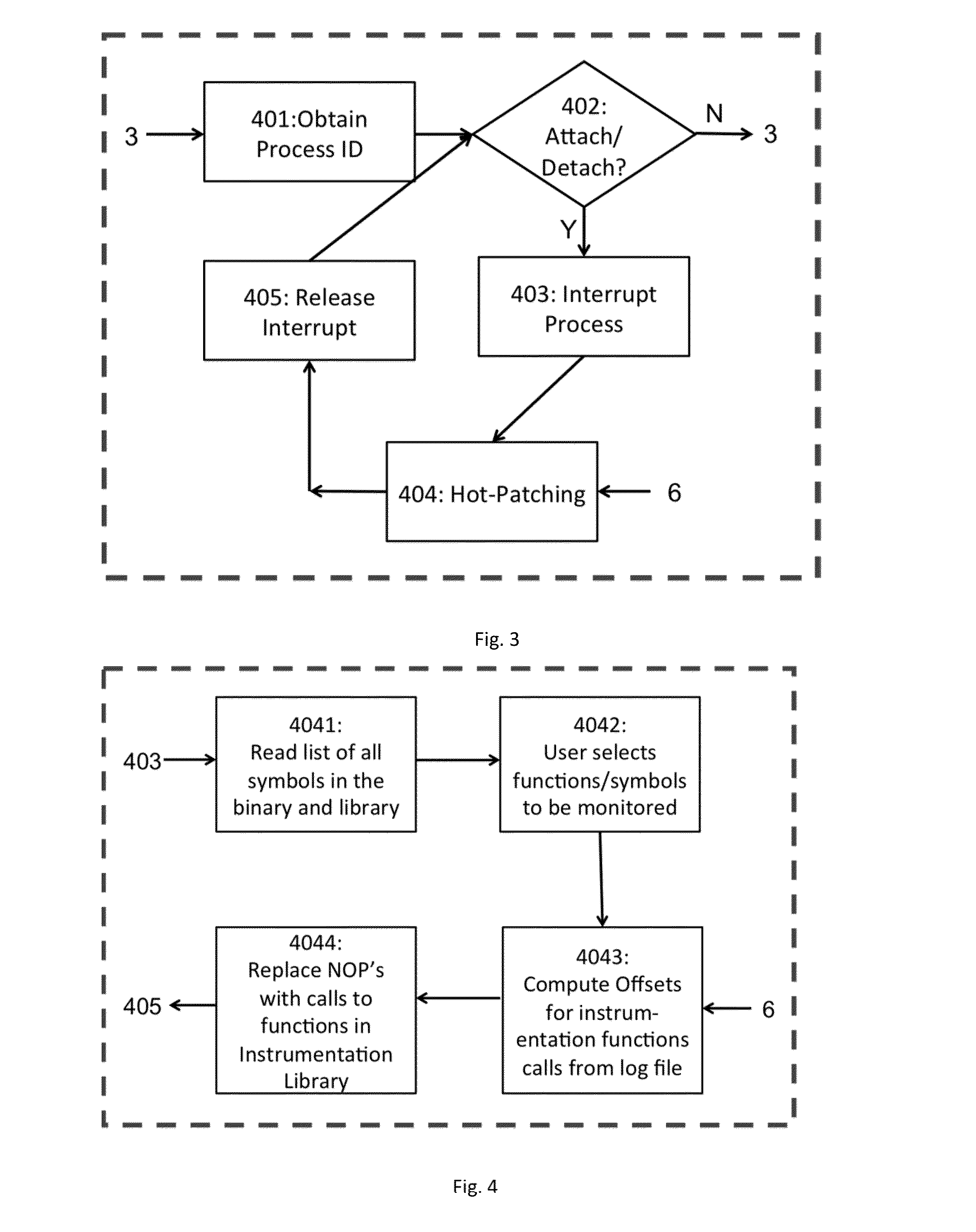
Method and System for Computer Assisted Hot-Tracing Mechanism
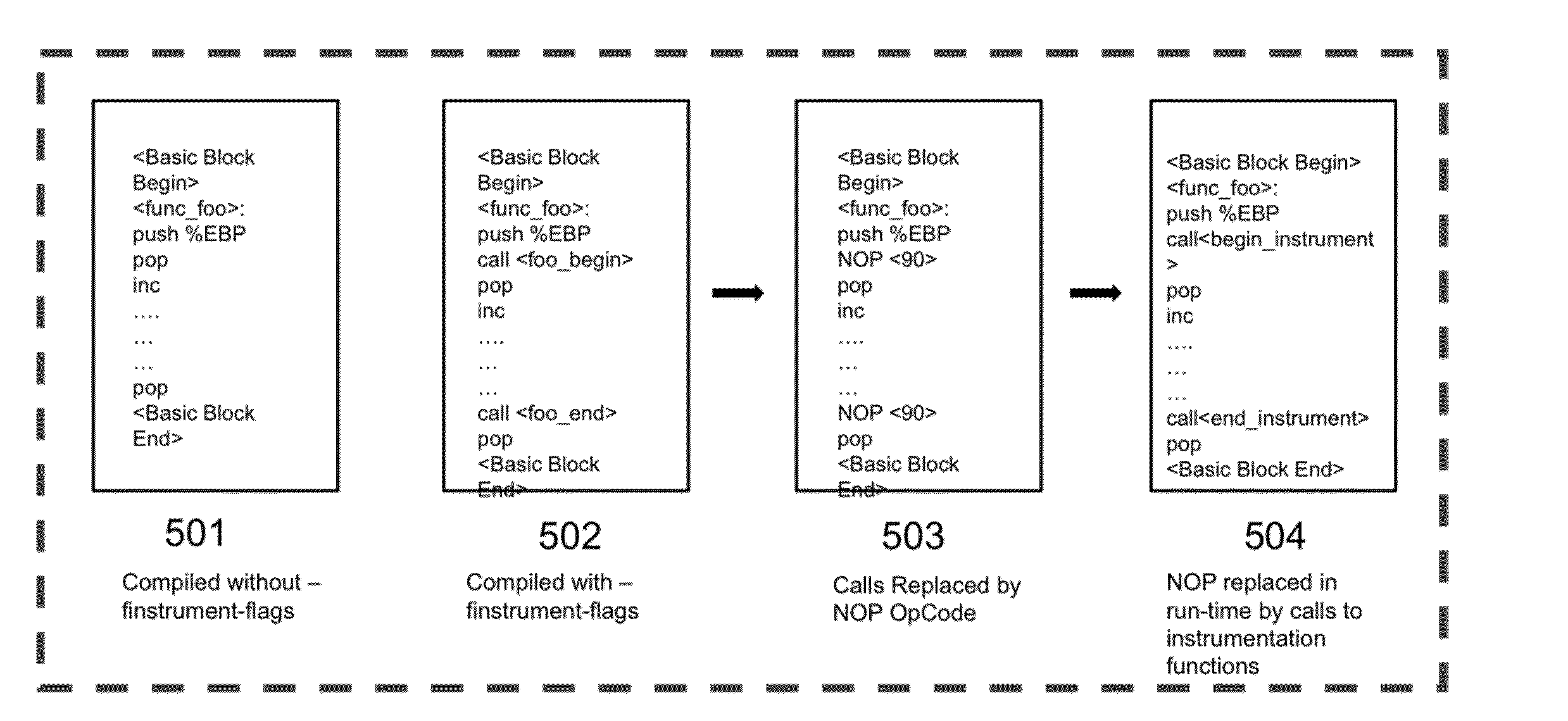
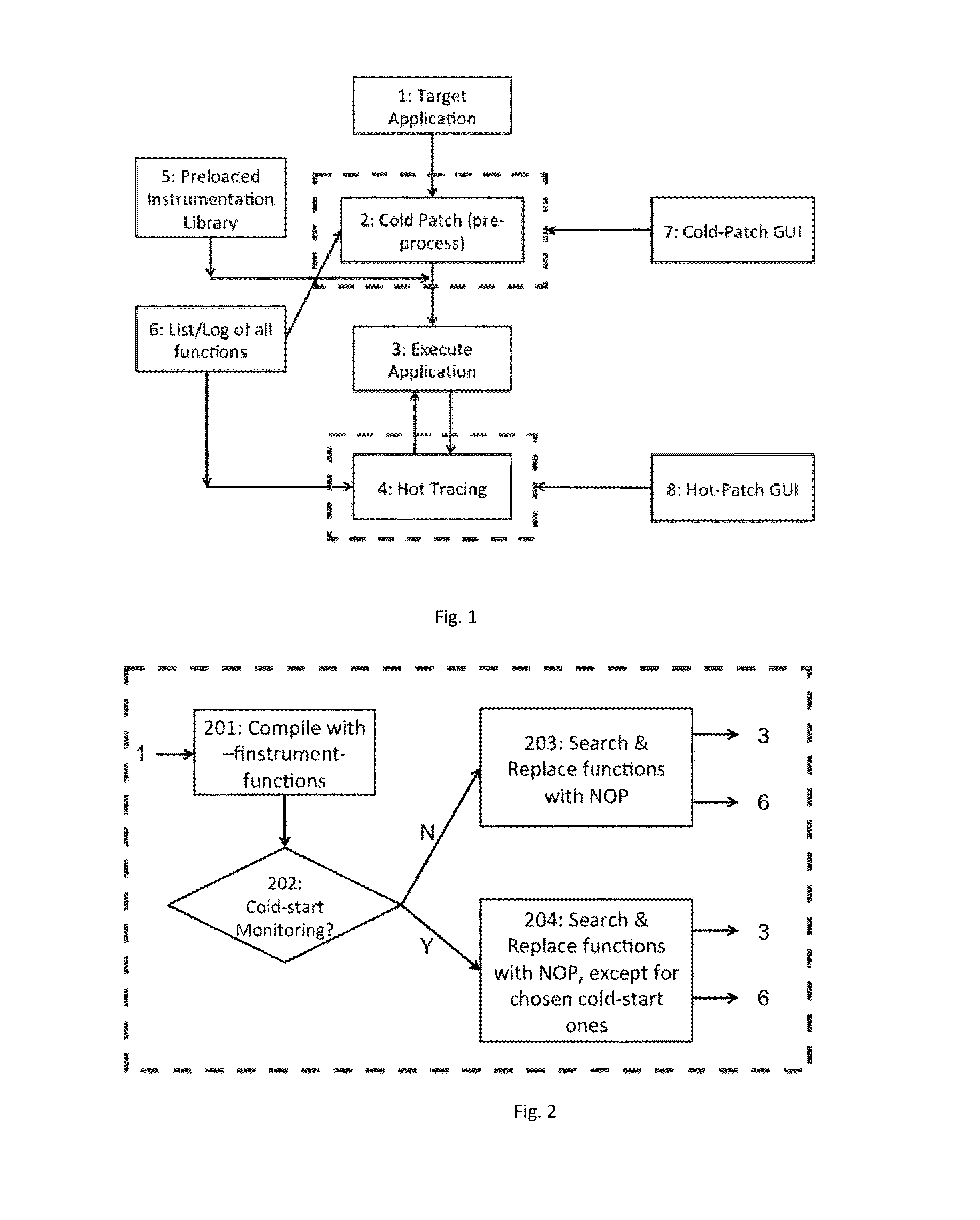
ActiveUS20140229921A1Software testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsInstrument functionDynamic instrumentation
This invention provides a new mechanism for “Hot-Tracing” using a novel placeholder mechanism and binary rewriting techniques, which leverages existing compiler flags in order to enable light-weight and highly flexible dynamic instrumentation. Broadly, I-Probe can be divided in 2 distinct workflows—1. Pre-processing (ColdPatch), and 2. Hot Tracing. The first phase is a pre-processing mechanism to prepare the binary for phase 2. The second phase is the actual hot-tracing mechanism, which allows users to dynamically instrument functions (more specifically symbols) of their choice.
Owner:NEC CORP
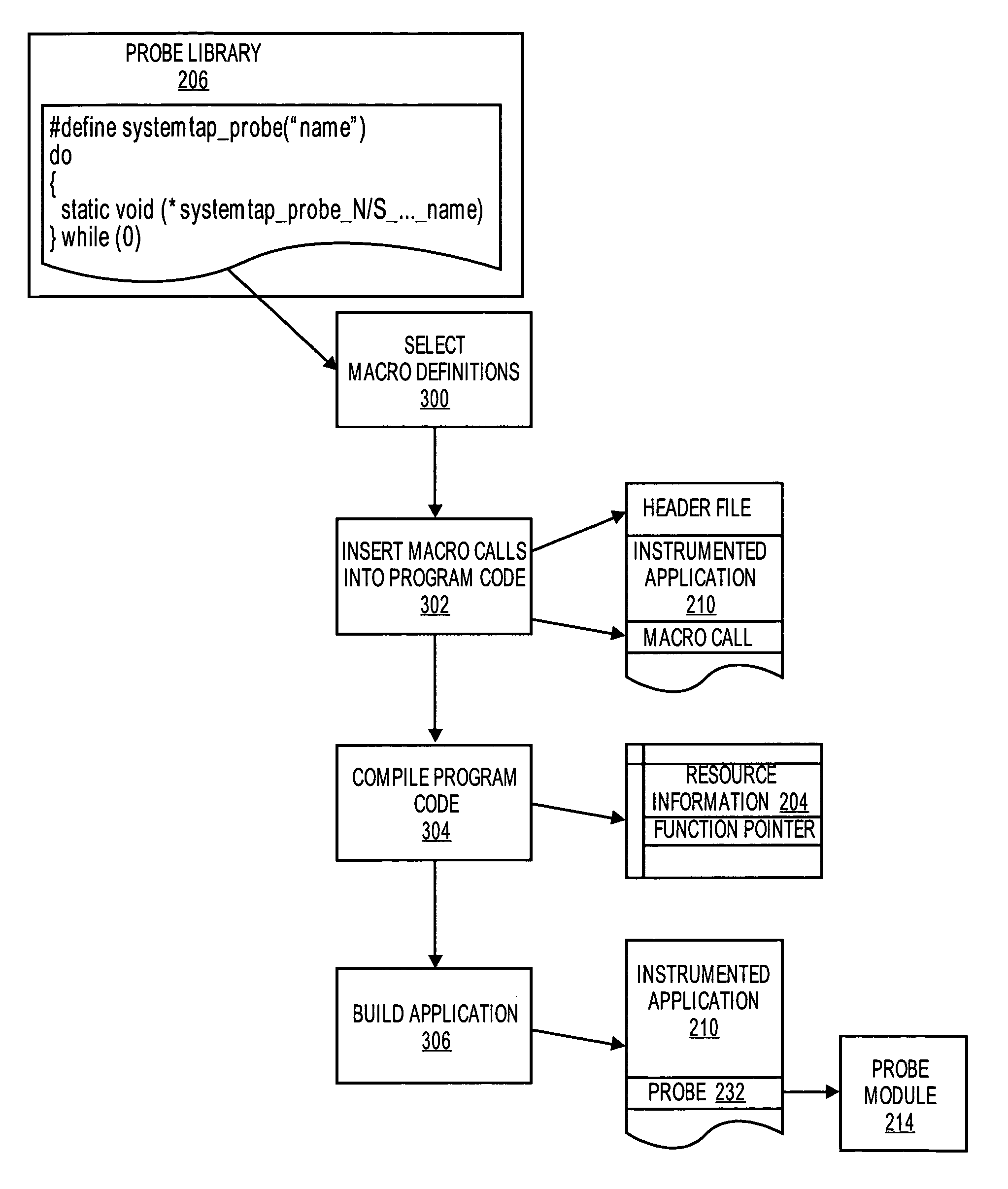
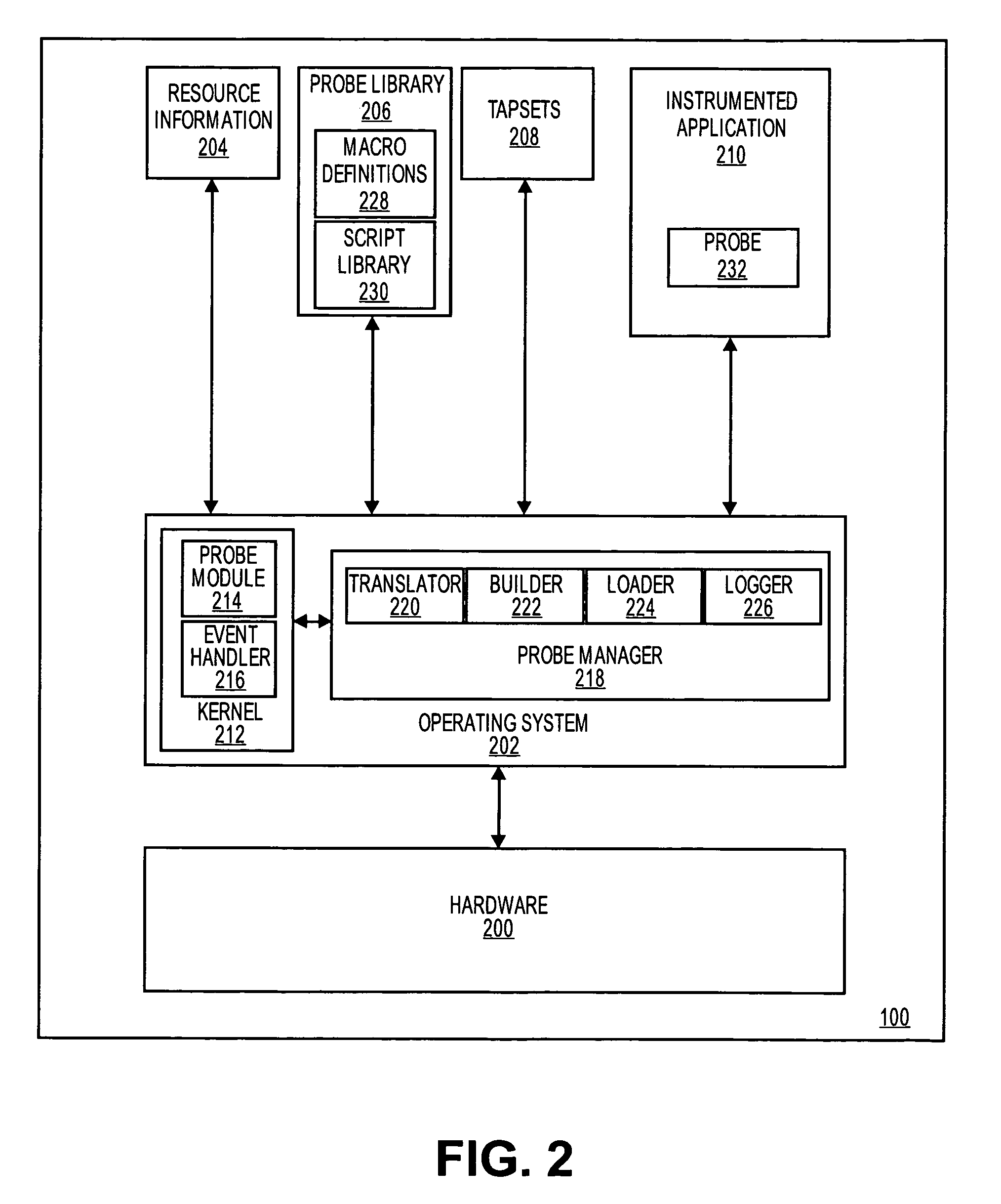
Static instrumentation macros for fast declaration free dynamic probes
ActiveUS8739135B2Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsDynamic instrumentationComputerized system
Owner:RED HAT
Webpage malicious JavaScript code recognition and anti-obfuscation method based on hybrid analysis
PendingCN110502897AReduce operating overheadEfficient detectionPlatform integrity maintainanceObfuscationTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a webpage malicious JavaScript code recognition and anti-obfuscation method based on hybrid analysis. The webpage malicious JavaScript code recognition and anti-obfuscation method comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting related webpage source codes, and extracting malicious JS files in the source codes and malicious JS codes embedded in HTML documents; then, constructing an abstract syntax tree in the syntax analysis stage, and expressing nodes as conventional JS objects for program analysis and feature extraction; then, carrying out instrumentation on the JS code, carrying out overwriting on basic operation, needing to be monitored, during running, of the JS code, dynamically monitoring the state and information during JS execution, and extracting an execution track and dynamic characteristic information during running; then, rewriting the dynamic and static features into feature vectors, and training a malicious JS code recognition model based on arandom forest algorithm model; and then, based on a dynamic instrumentation method, monitoring and recording memory overwriting related operations, and carrying out effective anti-obfuscation on obfuscated malicious JS codes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method and system for automatically generating dynamic breakpoints
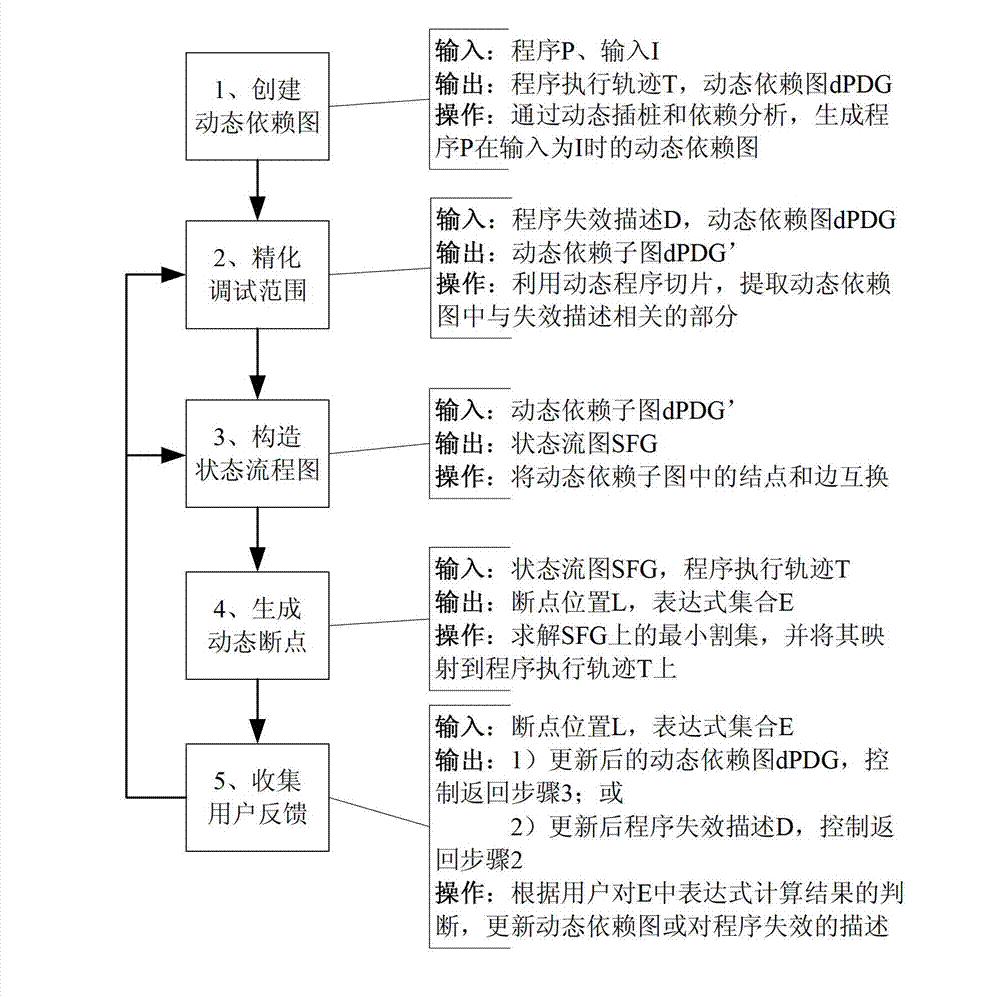
ActiveCN102968369AReduce the burden onLess interactive informationSoftware testing/debuggingProgramming languageDynamic instrumentation
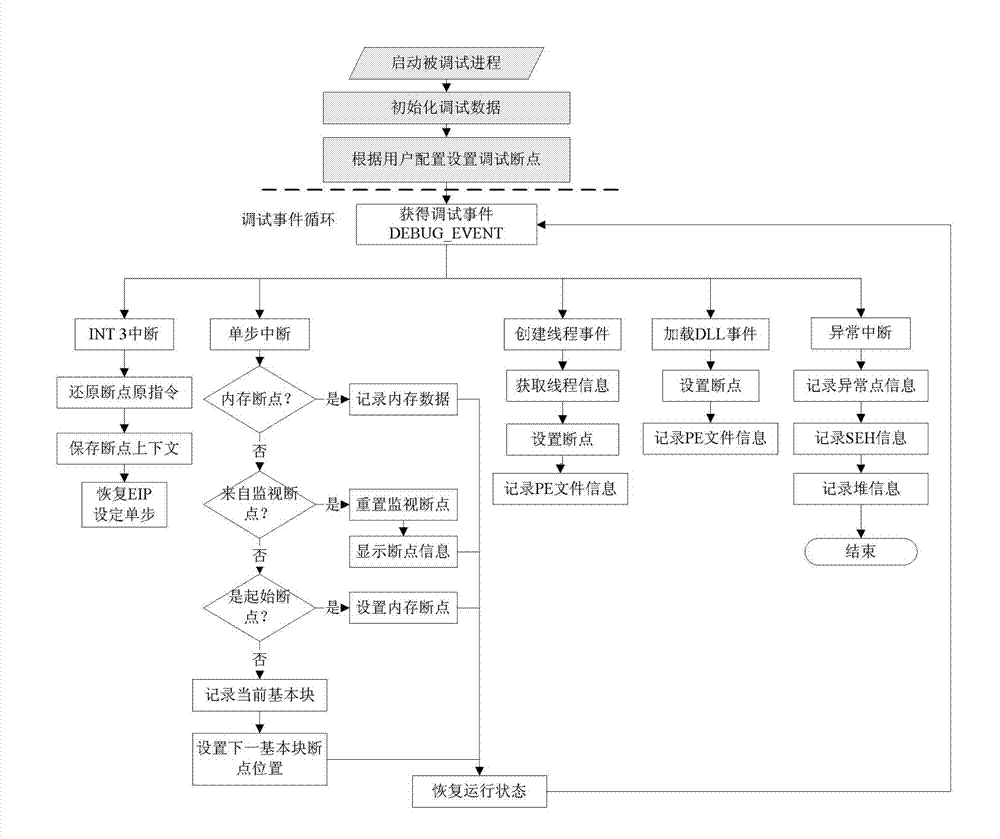
The invention discloses a method and system for automatically generating dynamic breakpoints, wherein the system comprises a dynamic dependence graph creation module, a debugging range refinement module, a state-flow graph creation module, a dynamic breakpoint generation module and a debugging feedback collection module, wherein the dynamic dependency graph creation module is used for not only collecting execution examples of program statements, but also collecting execution sequences and dependency relationship between the examples by utilizing a dynamic instrumentation technique during the program execution process, so as to create a dynamic program dependence graph on the bases; the debugging range refinement module is used for extracting parts of the dynamic program dependence graph relevant with program failure descriptions by utilizing a program dynamic-slicing technique; the state-flow graph creation module is used for interchanging connection points and sides in the dynamic dependence graph output by the debugging range refinement module and transforming a debugging range into a state-flow graph; the dynamic breakpoint generation module is used for generating dynamic breakpoints and aggregations of expressions required being inspected at the breakpoints; and the debugging feedback collection module is used for collecting the results of judgments made by a user about the provided breakpoints and the aggregations of the expressions required being inspected at the breakpoints.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
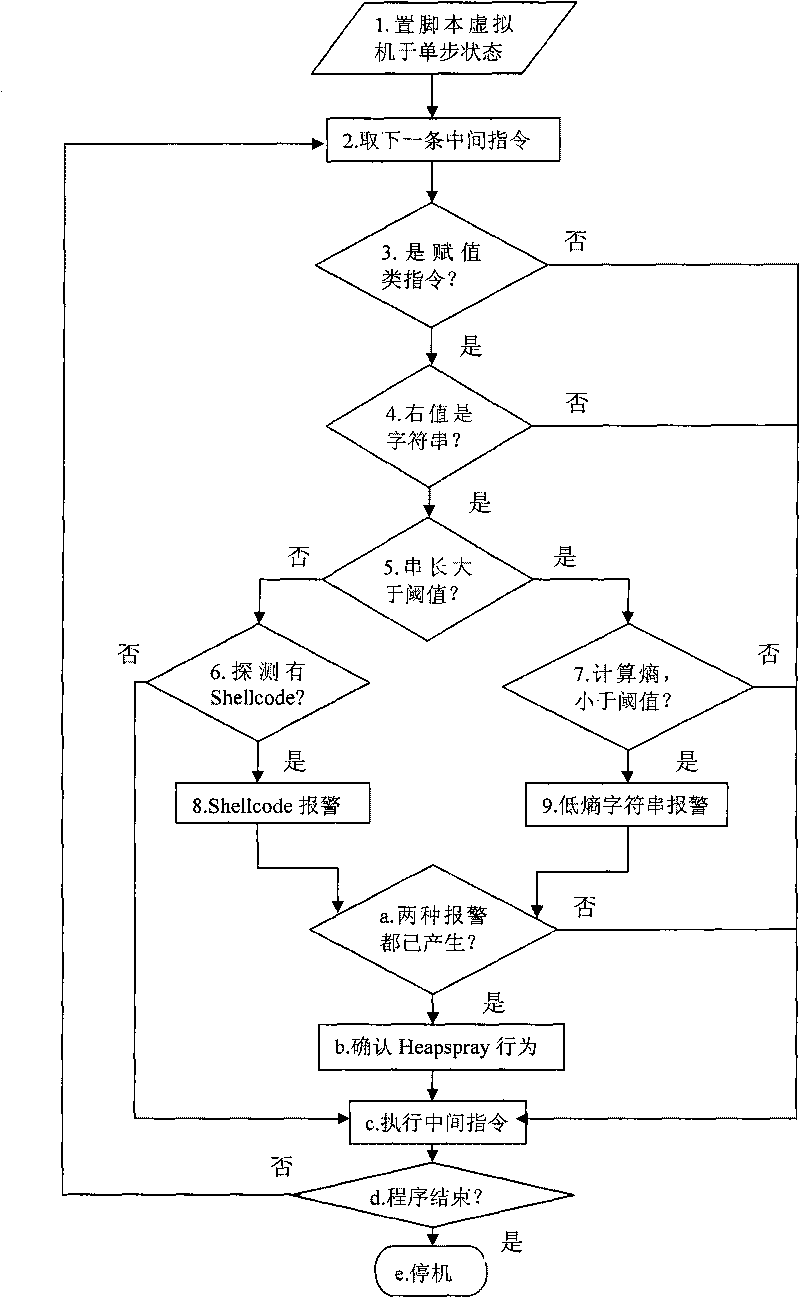
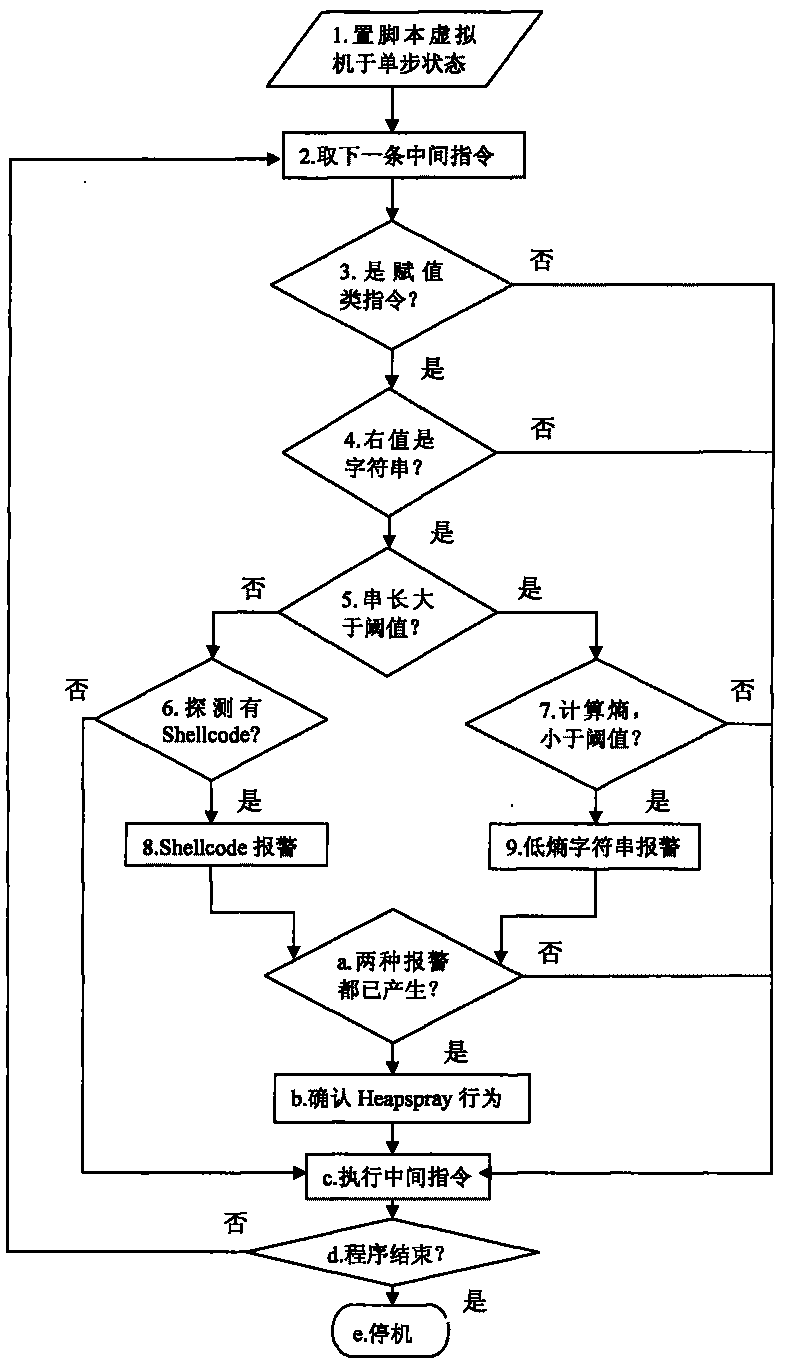
Heapspray detection method based on intermediate command dynamic instrumentation
InactiveCN101719204AAccurately determine the semanticsAccurately determine behaviorPlatform integrity maintainanceAlgorithmDynamic instrumentation
The invention discloses a Heapspray detection method based on intermediate command dynamic instrumentation, belonging to the technical field of computer security. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) setting a virtual machine used for explaining and implementing webpage dynamic script into a single-step operating state; (2) judging whether an intermediate command to be implemented currently is an assignment type intermediate command or not; (3) if so, then judging whether a rvalue parameter type in command parameters is a alphabetic string type or not; if the rvalue parameter is the alphabetic string type and a value thereof is less than a set threshold value P, then checking whether shellcode exists or not; if the rvalue parameter is larger than the set threshold value P, then calculating an information entropy value thereof; and (4) taking a next intermediate command and repeating the step (2) and the step (3); if a rvalue parameter of an assignment type intermediate command has the shellcode and an entropy value of a rvalue parameter of the other assignment type intermediate command is less than the set threshold value, then judging the script to have a Heapspray action. The invention can reduce system overhead and improve the accuracy rate of detection.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
System and method to build a callgraph for functions with multiple entry points
ActiveUS7661095B2Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsDynamic instrumentationEntry point
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com