Patents
Literature
893 results about "Performed Procedure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A completed activity whose immediate and primary intention is the alteration of the physical or mental condition of the subject, study subject or experimental unit. EXAMPLE(S): Procedures may involve the disruption of some body surface (e.g. an incision in a surgical procedure) conservative procedures such as reduction of a luxated joint, including physiotherapy such as chiropractic treatment, massage, balneotherapy, acupuncture, shiatsu, counseling, etc.
Methods and devices for performing procedures within the ear, nose, throat and paranasal sinuses
Devices, systems and methods for performing image guided interventional and surgical procedures, including various procedures to treat sinusitis and other disorders of the paranasal sinuses, ears, nose or throat.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
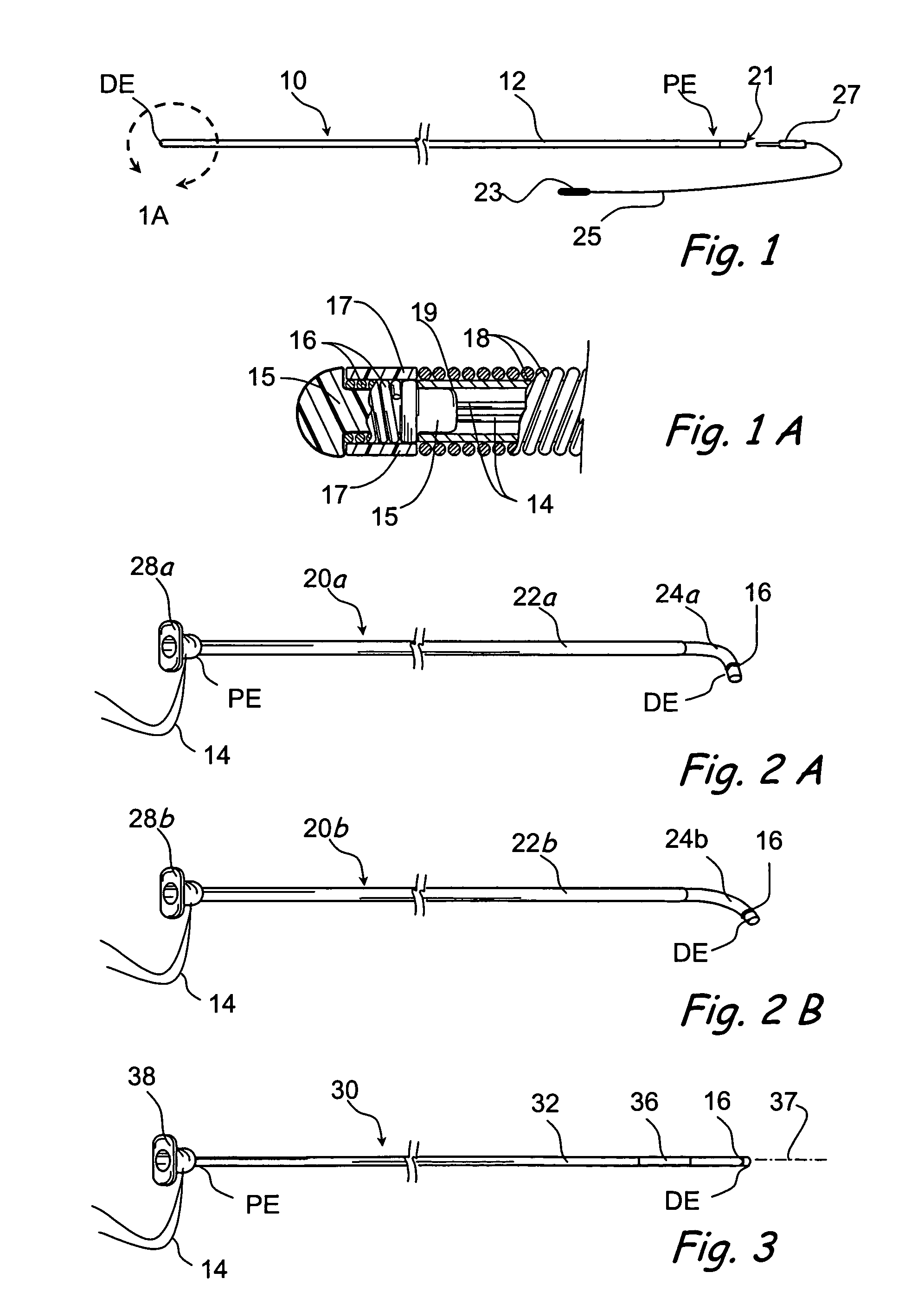
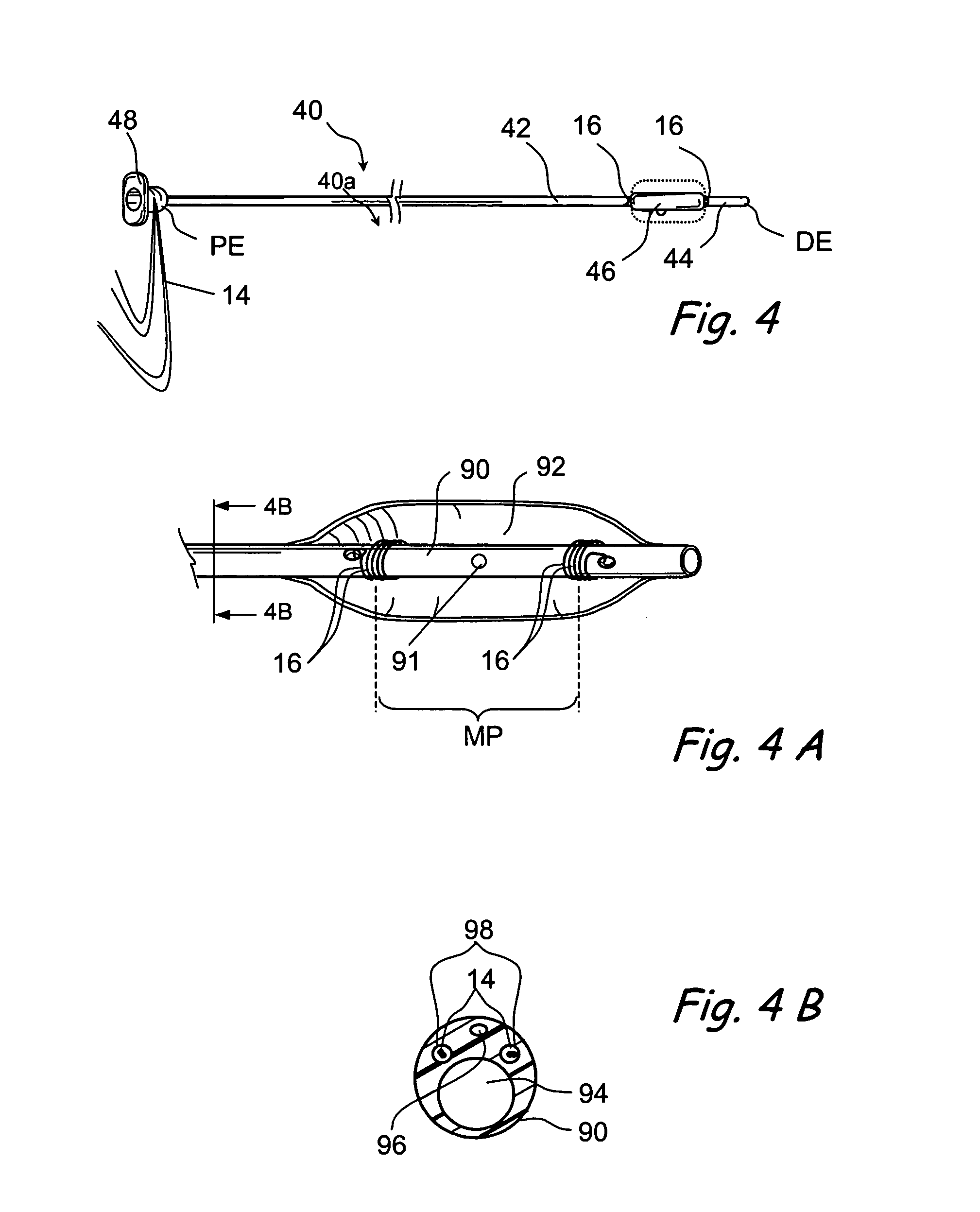
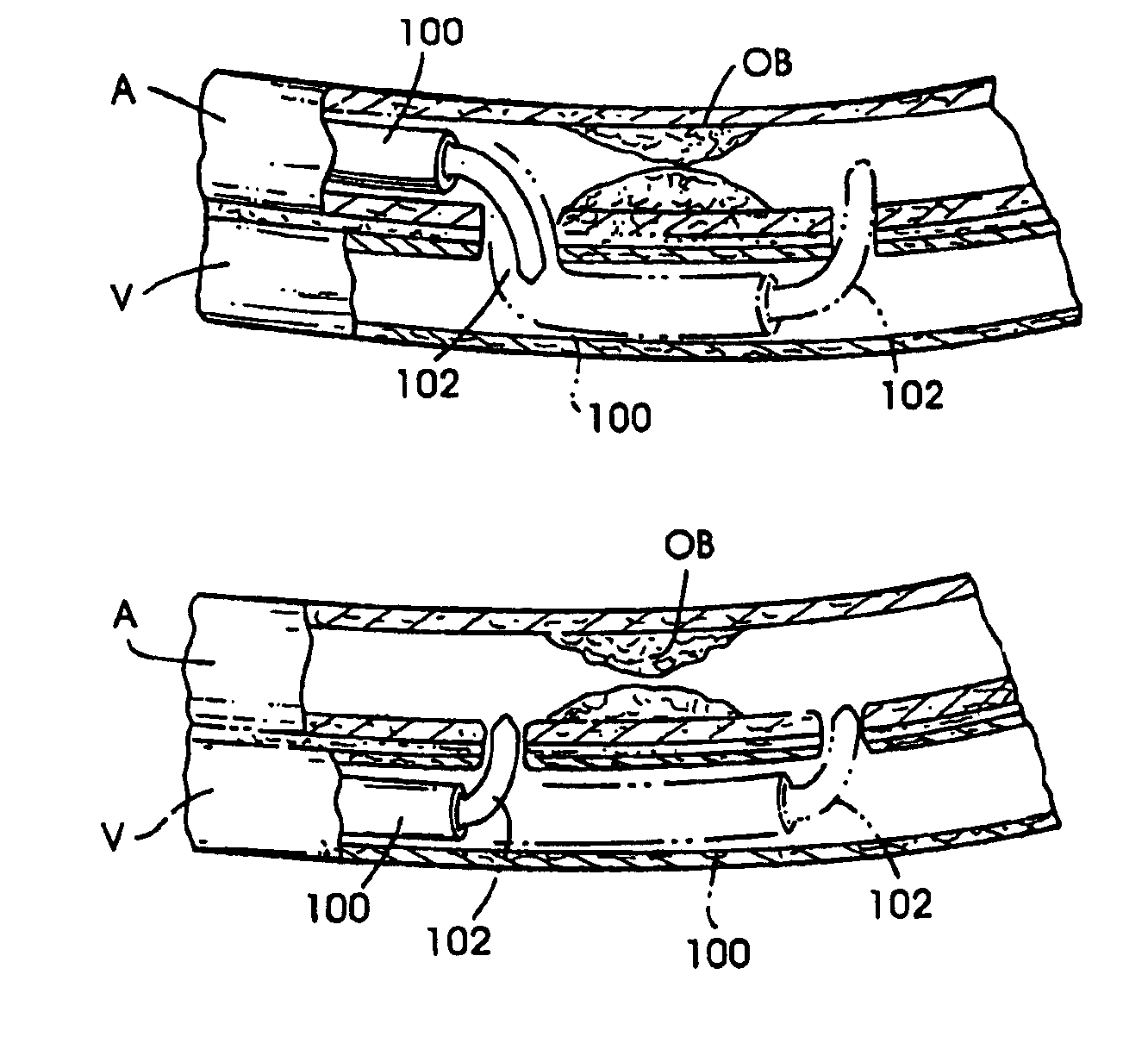
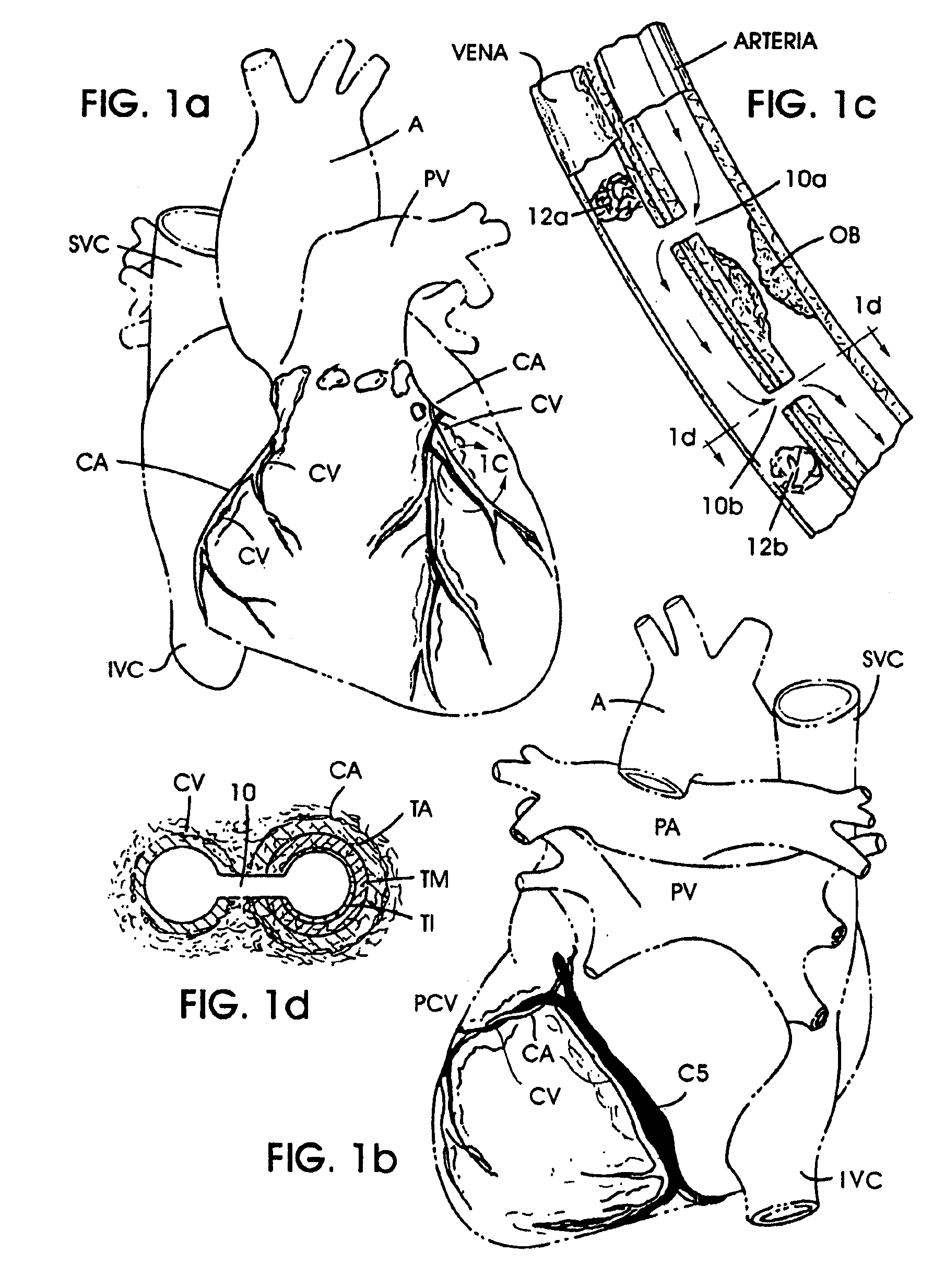
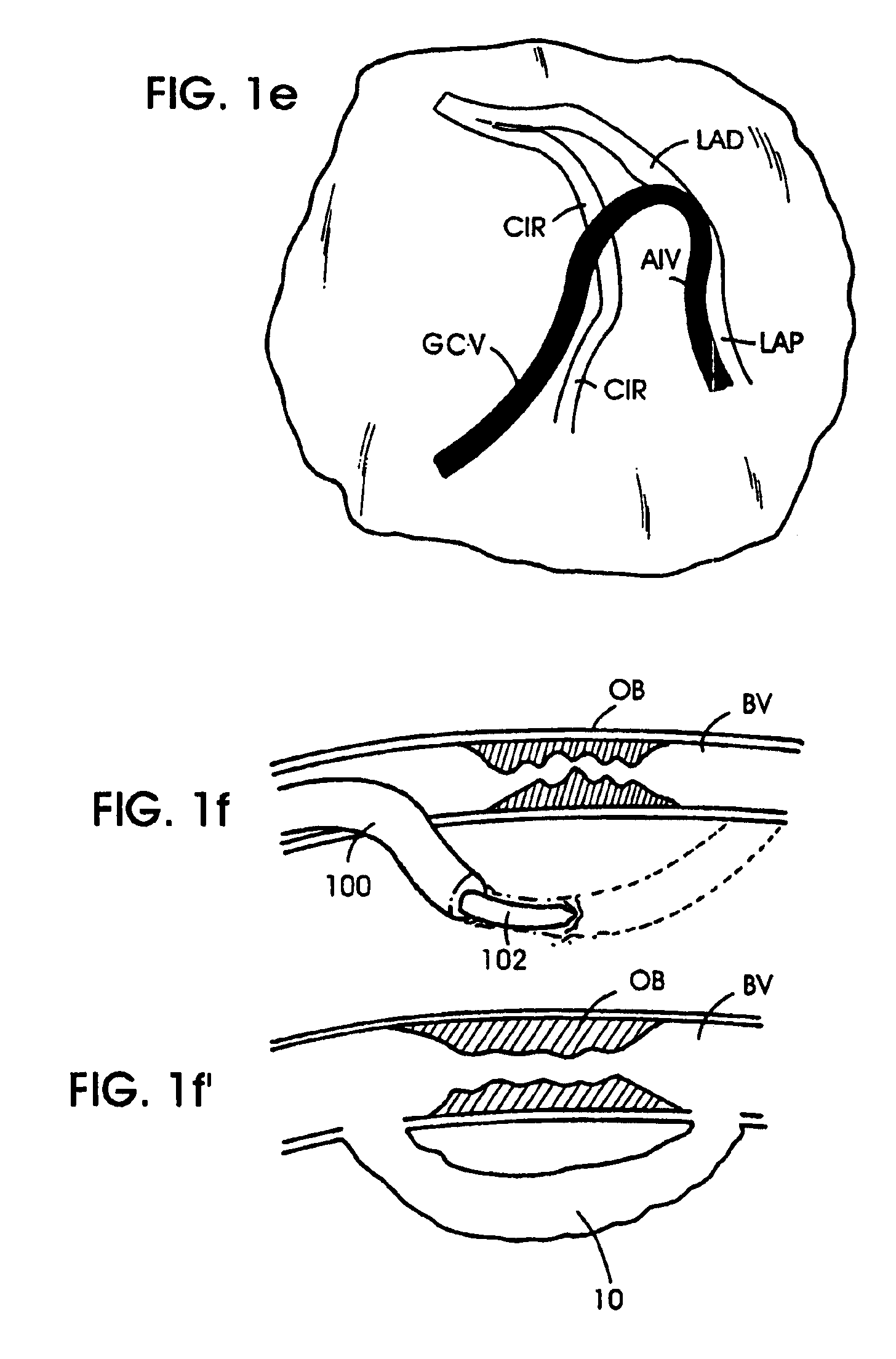
Method of Forming a Lesion in Heart Tissue
InactiveUS7100614B2Facilitate responsive and precise positionabilitySuture equipmentsElectrotherapyDefect repairPatch type
Owner:HEARTPORT
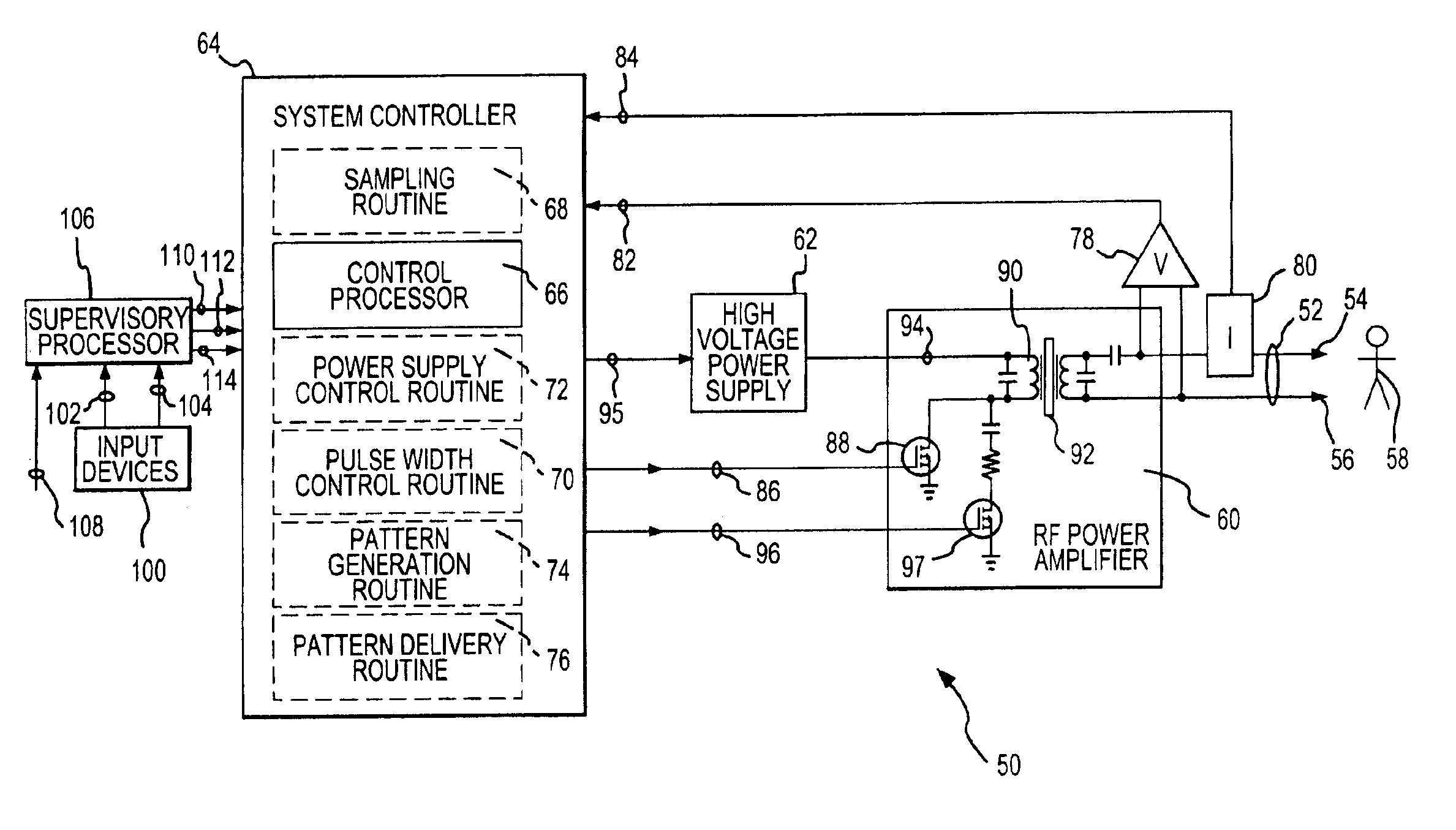
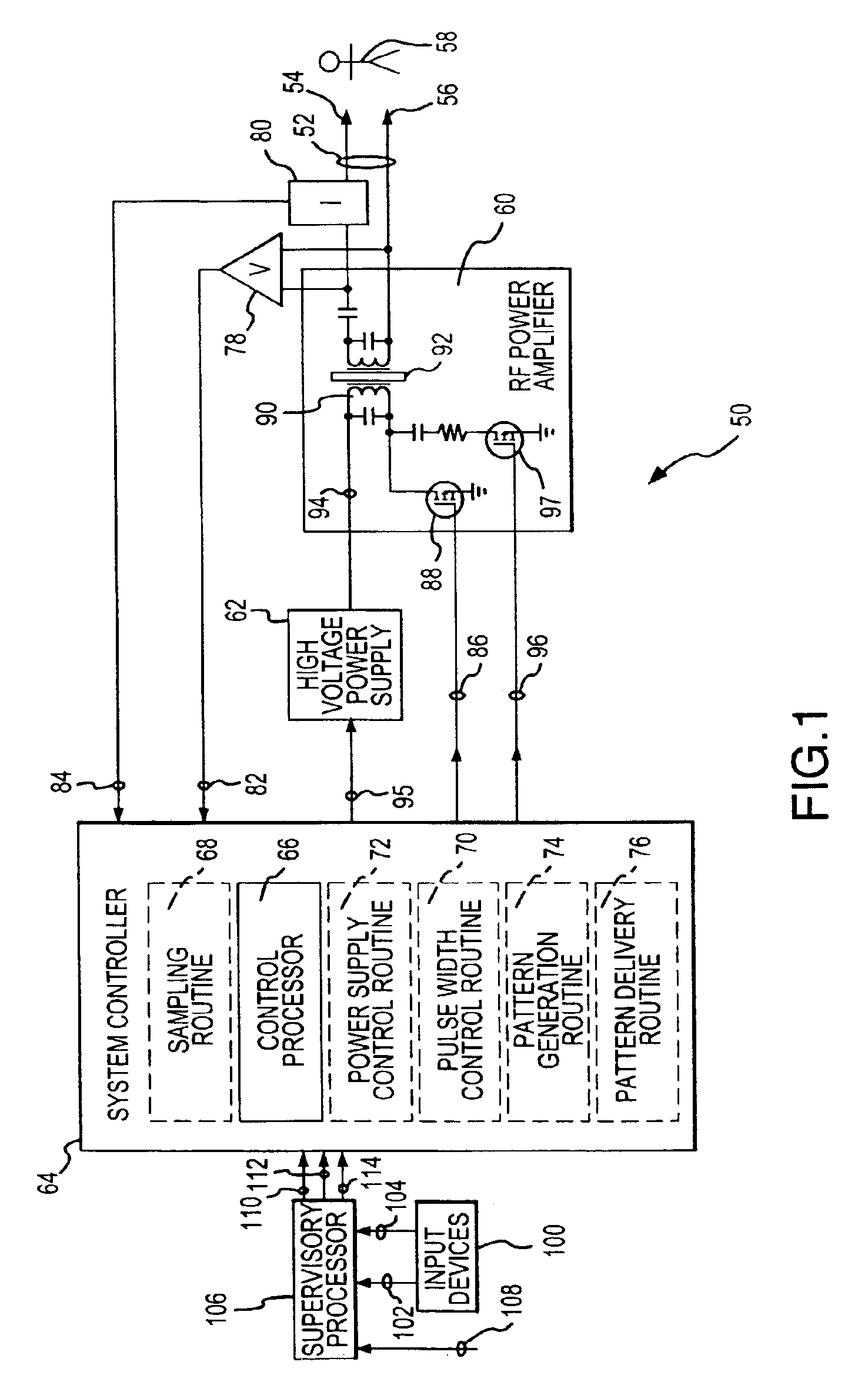
Electrosurgical generator and method with multiple semi-autonomously executable functions
InactiveUS6942660B2Compromising performanceCompromising safetySurgical instruments for heatingPattern generationOperation mode
Semi-autonomously executed routines accomplish the primary functions of electrosurgical energy delivery on a responsive basis for power control purposes and to adapt the delivered output waveform to perform new and better surgical procedures. The routines include and output voltage and output current sampling routine, a control routine for establishing the width of drive pulses used to create the output waveform, a pattern generation routine for establishing the pattern of drive pulses to be delivered in one mode cycle established by a selected mode of operation, a pattern delivery routine for repeatedly delivering sequences of the mode cycle pattern of drive pulses, and a power supply control routine for varying the voltage of the drive pulses in coordination with varying the width of the drive pulses.
Owner:CONMED CORP
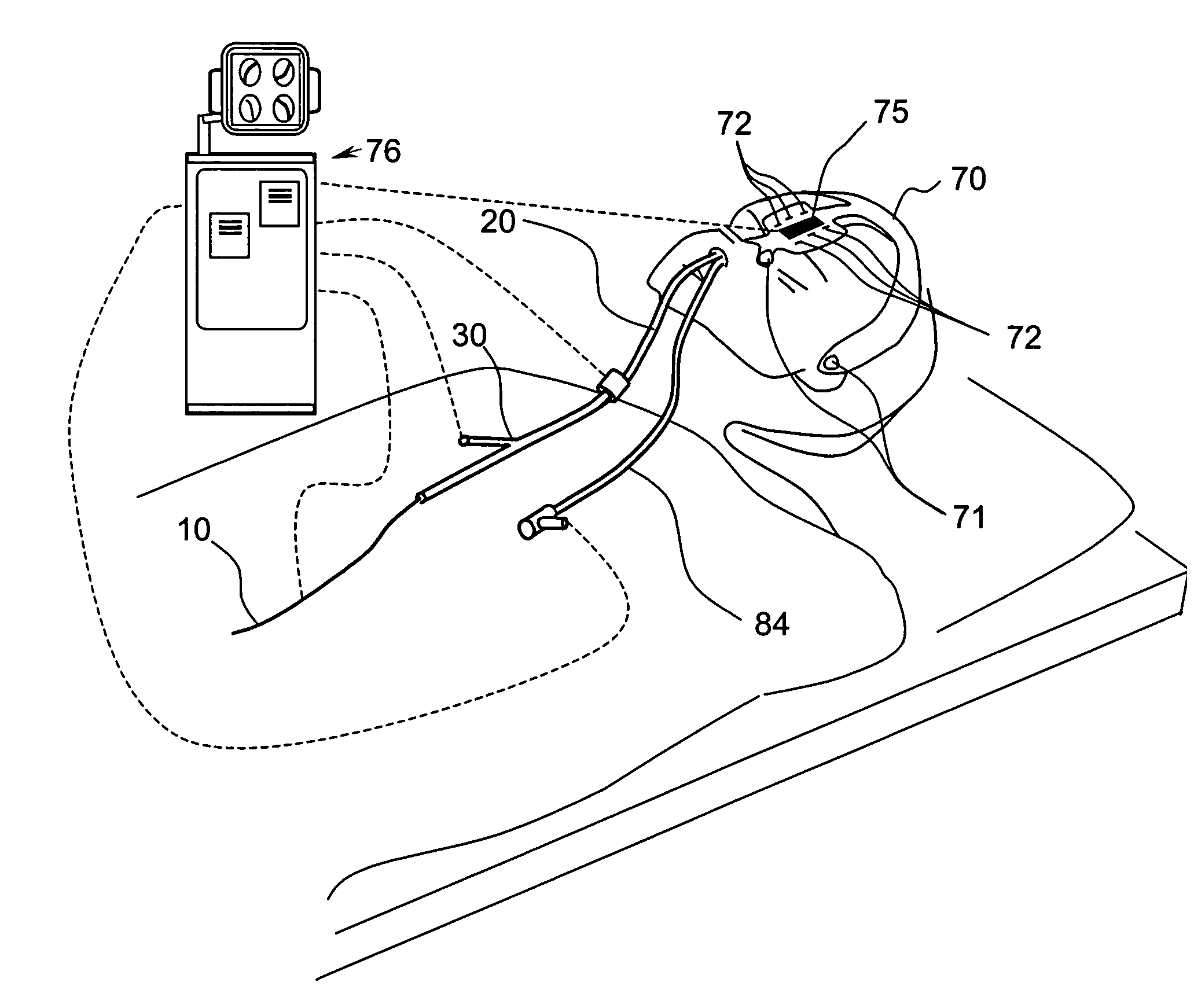
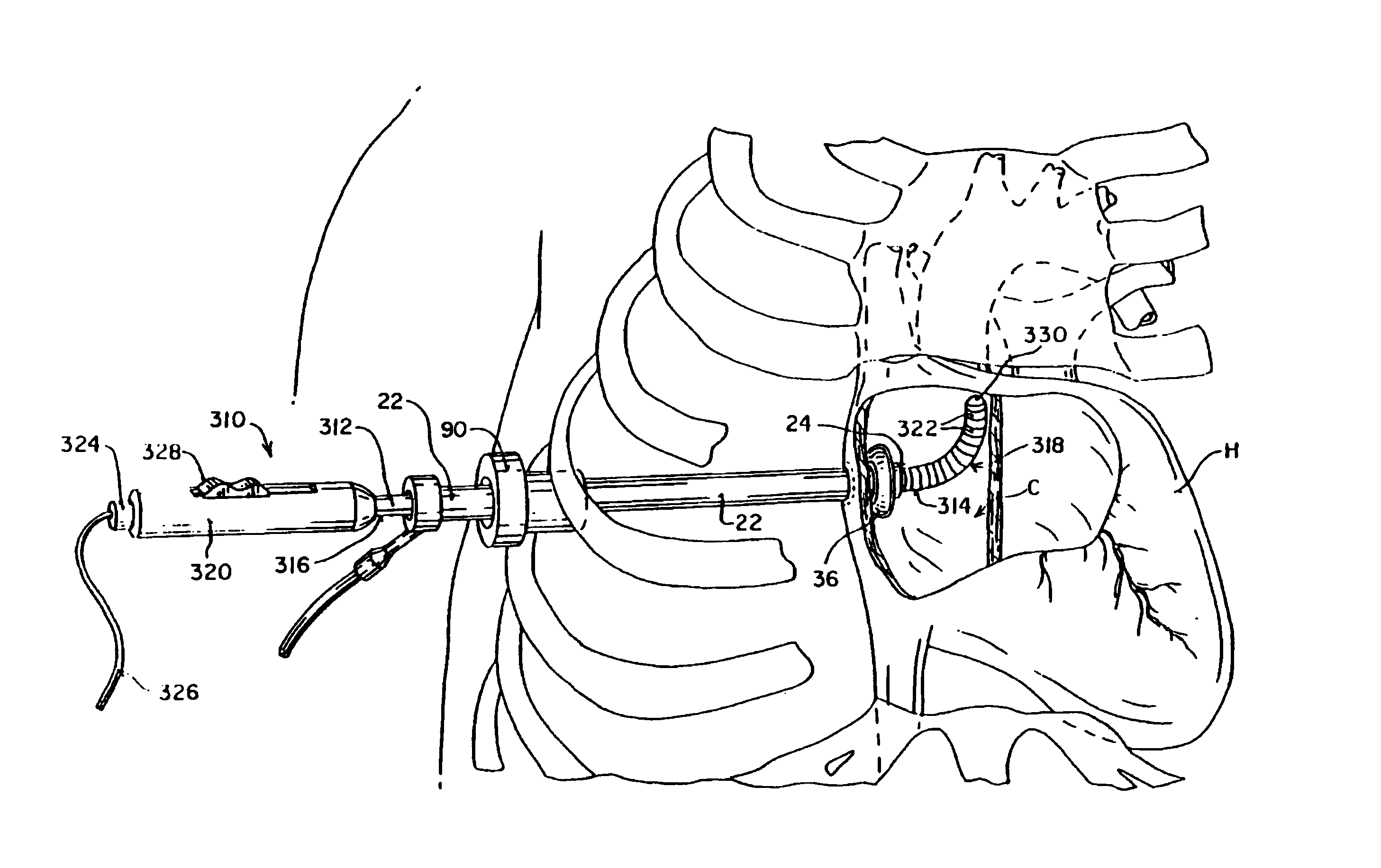
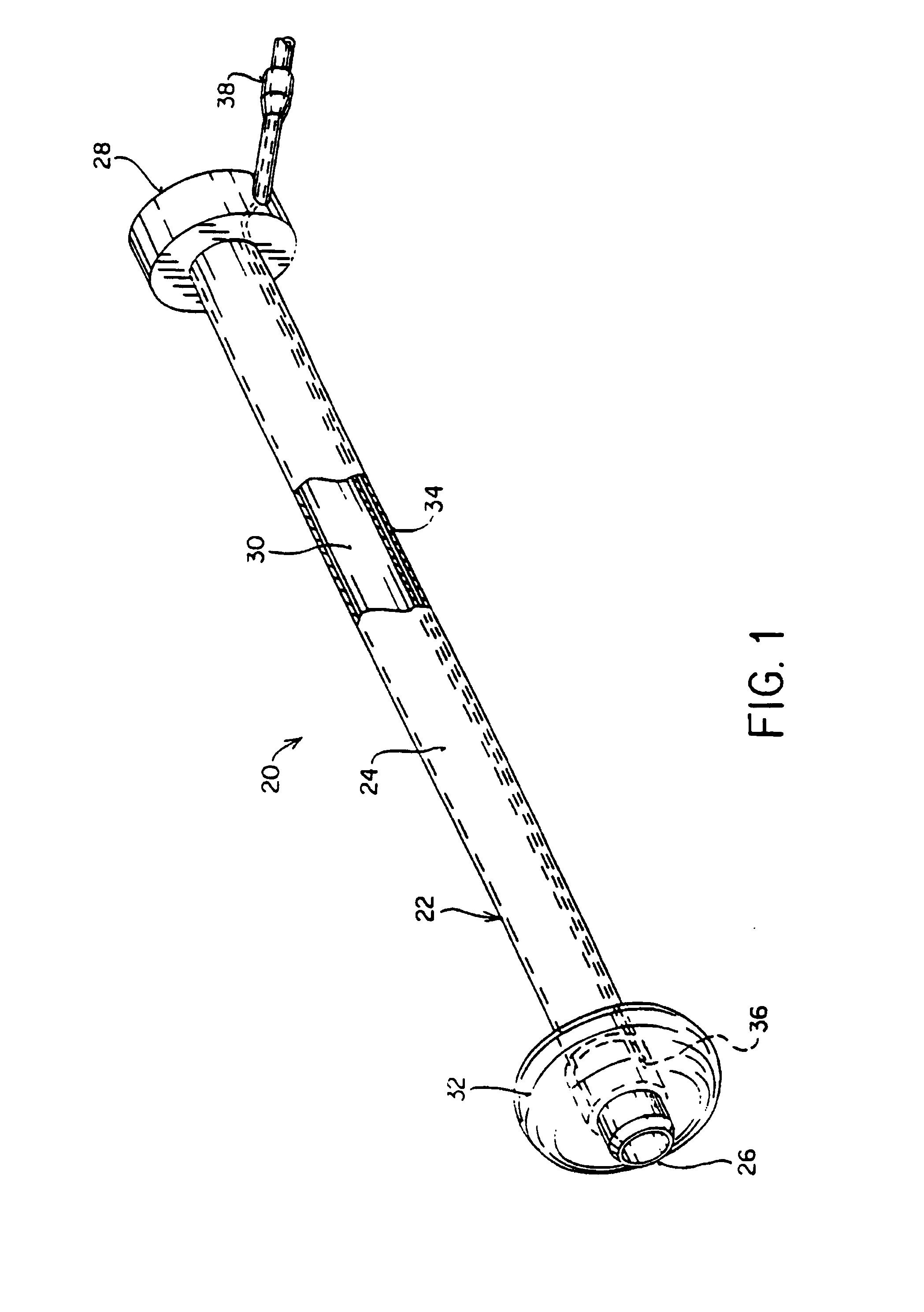
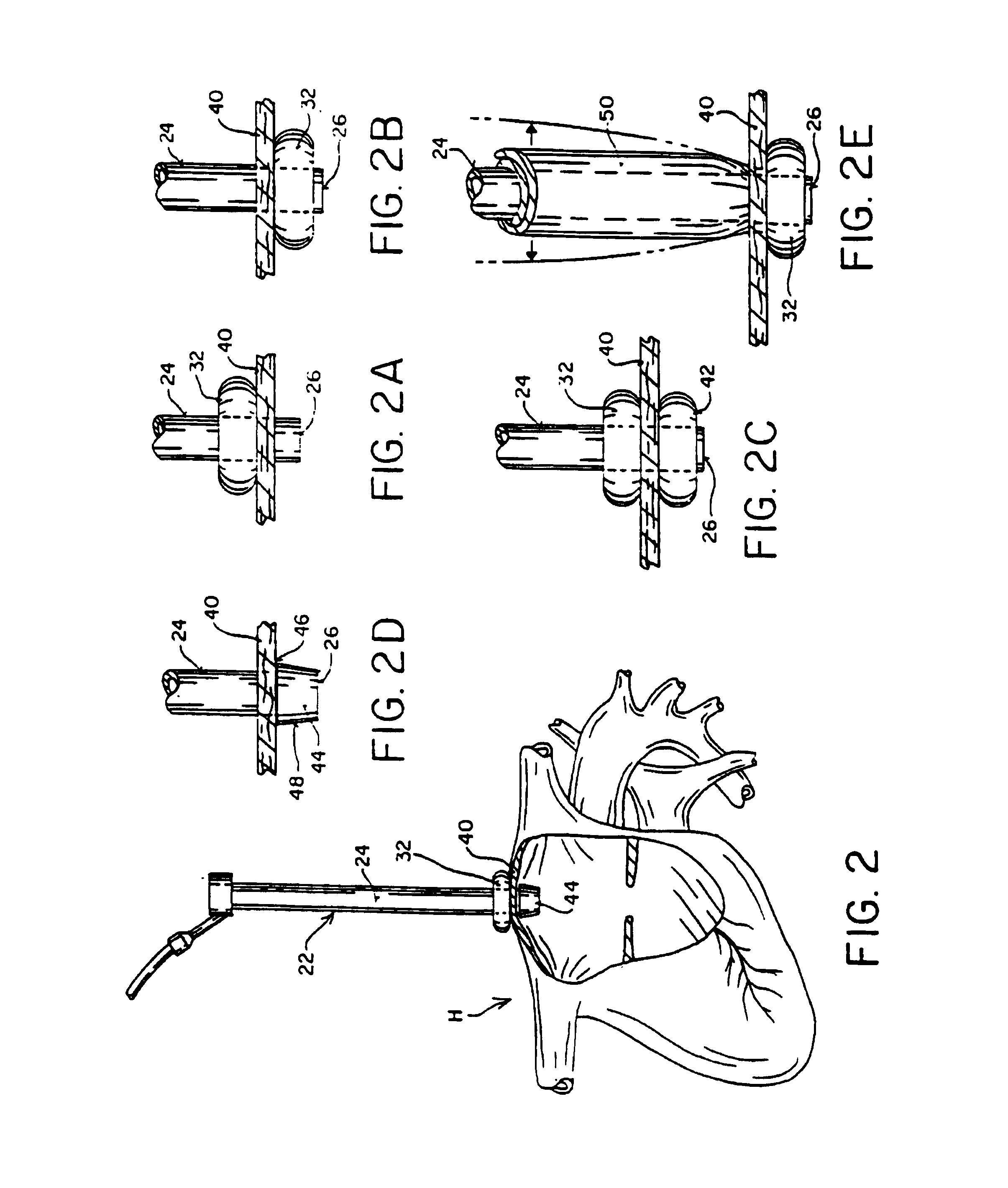
Method and apparatus for thoracoscopic intracardiac procedures
InactiveUS6955175B2Facilitate responsive and precise positionabilitySuture equipmentsElectrotherapyDefect repairThoracic cavity
Devices, systems, and methods are provided for accessing the interior of the heart and performing procedures therein while the heart is beating. In one embodiment, a tubular access device having an inner lumen is provided for positioning through a penetration in a muscular wall of the heart, the access device having a means for sealing within the penetration to inhibit leakage of blood through the penetration. The sealing means may comprise a balloon or flange on the access device, or a suture placed in the heart wall to gather the heart tissue against the access device. An obturator is removably positionable in the inner lumen of the access device, the obturator having a cutting means at its distal end for penetrating the muscular wall of the heart. The access device is preferably positioned through an intercostal space and through the muscular wall of the heart. Elongated instruments may be introduced through the tubular access device into an interior chamber of the heart to perform procedures such as septal defect repair and electrophysiological mapping and ablation. A method of septal defect repair includes positioning a tubular access device percutaneously through an intercostal space and through a penetration in a muscular wall of the heart, passing one or more instruments through an inner lumen of the tubular access device into an interior chamber of the heart, and using the instruments to close the septal defect. Devices and methods for closing the septal defect with either sutures or with patch-type devices are disclosed.
Owner:STEVENS JOHN H +4
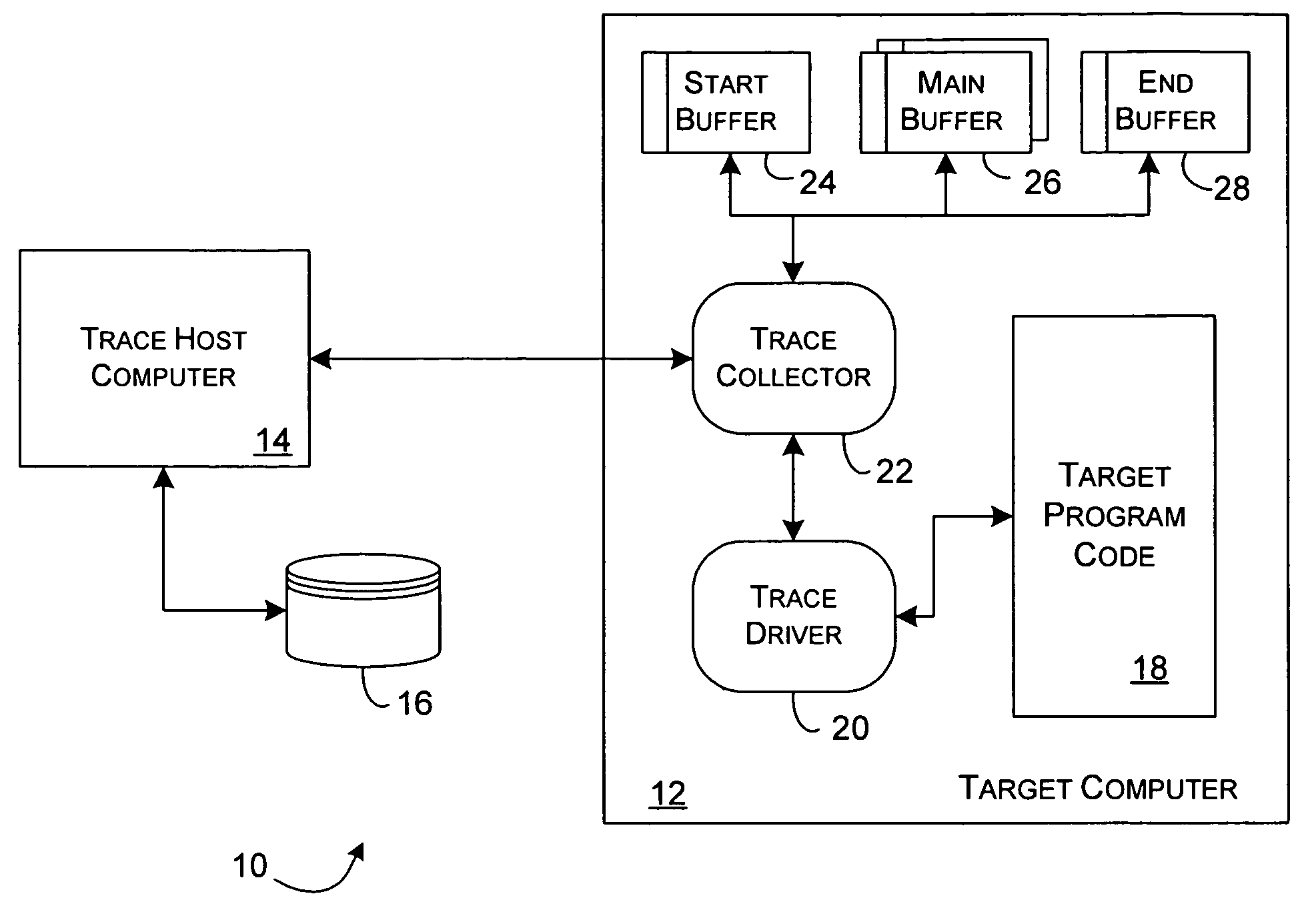
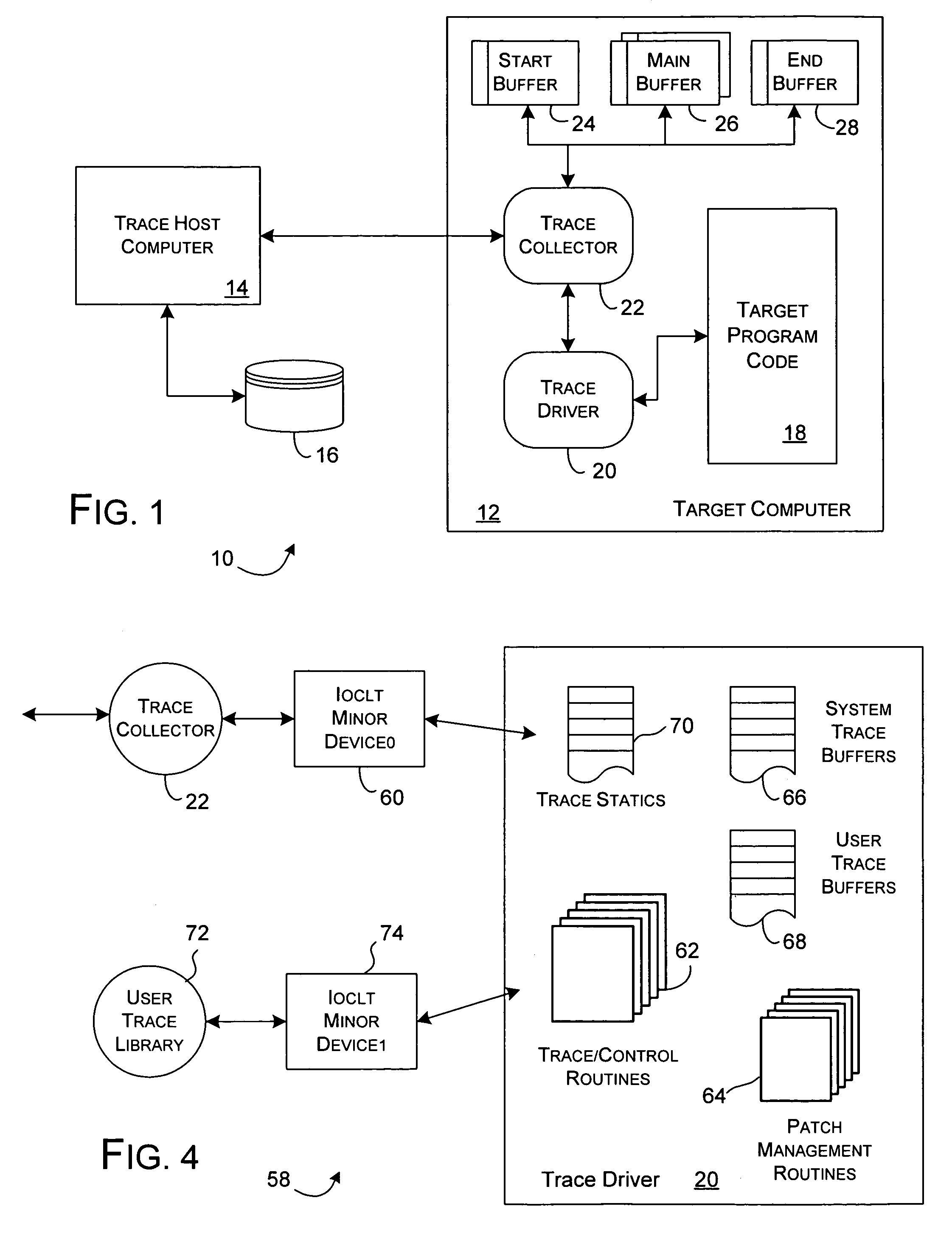
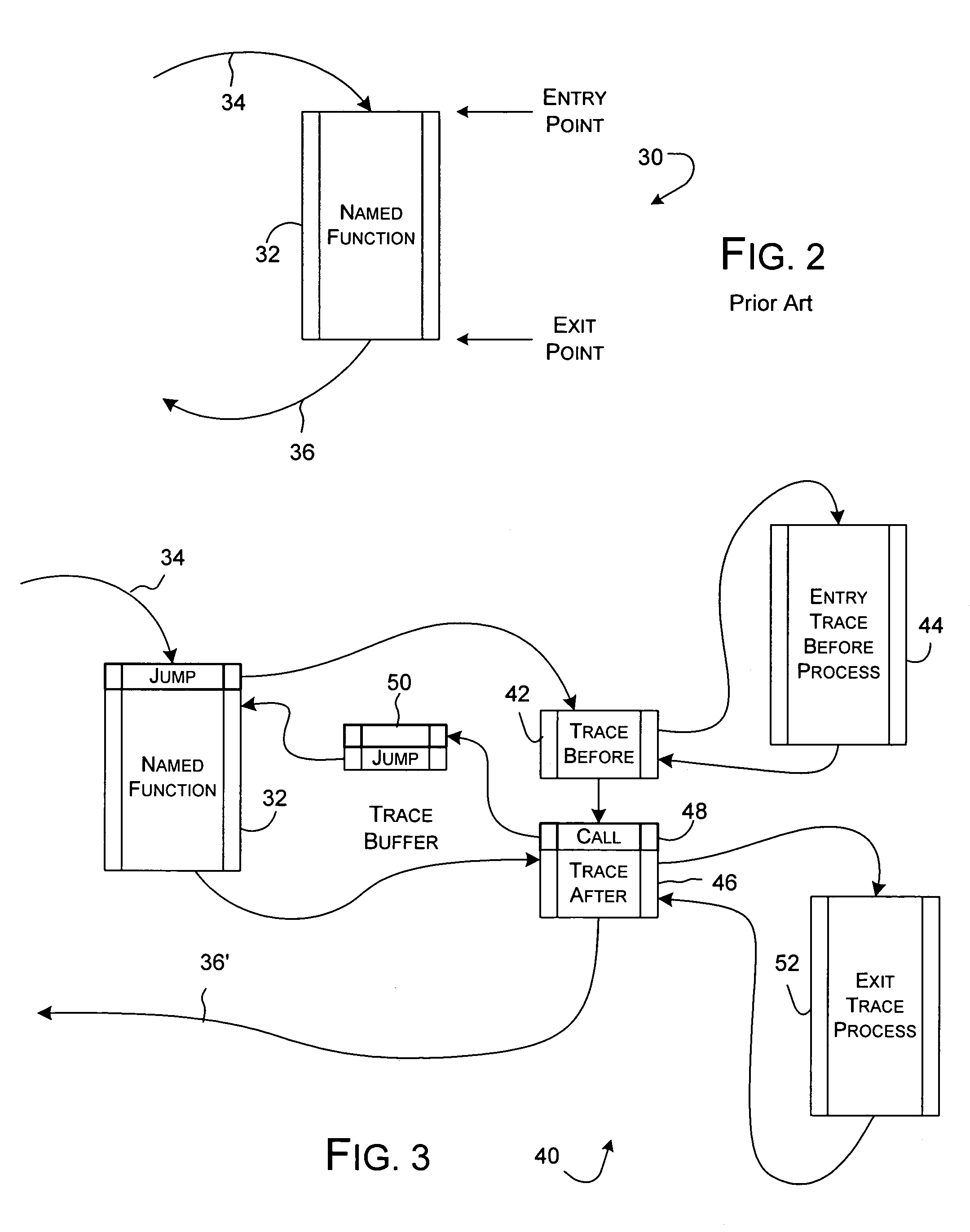
Dynamic instrumentation event trace system and methods
InactiveUS7047521B2Performance impact is minimalMaximize discriminating detectionHardware monitoringSoftware testing/debuggingDynamic instrumentationParallel computing
Program code loaded for execution by a computer can be dynamically instrumented to collect event data by inserting an instruction at a trace point within the program code as loaded in a memory space of a computer, where the trace point corresponds to the beginning of a predefined function of the program selected for event tracing. The instruction provides for the direction of the execution of said computer to a function proxy routine, which includes a call to an instance of the predefined function. Event data is collected in connection with the calling of the instance of the predefined function.
Owner:LYNX SOFTWARE TECH
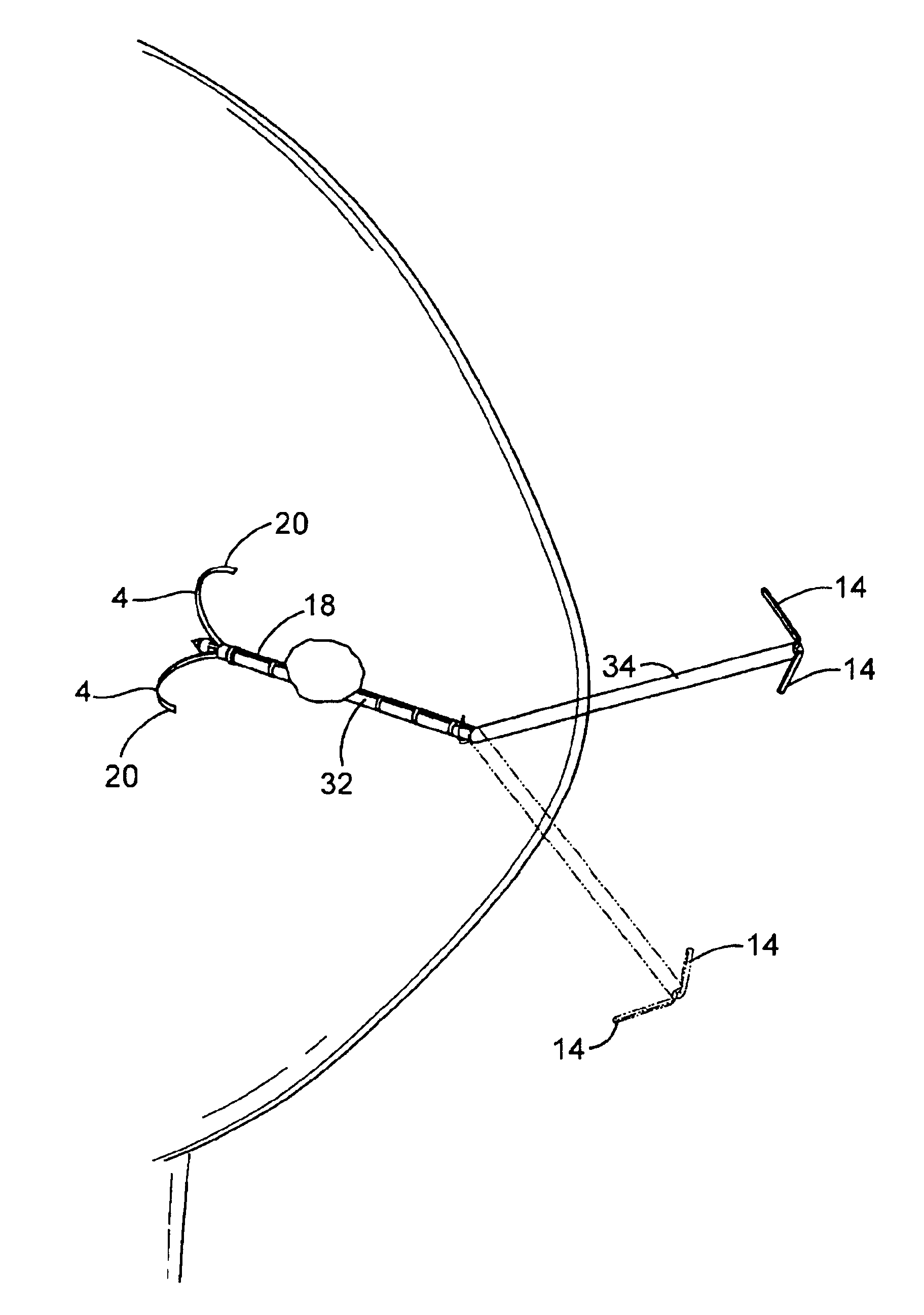
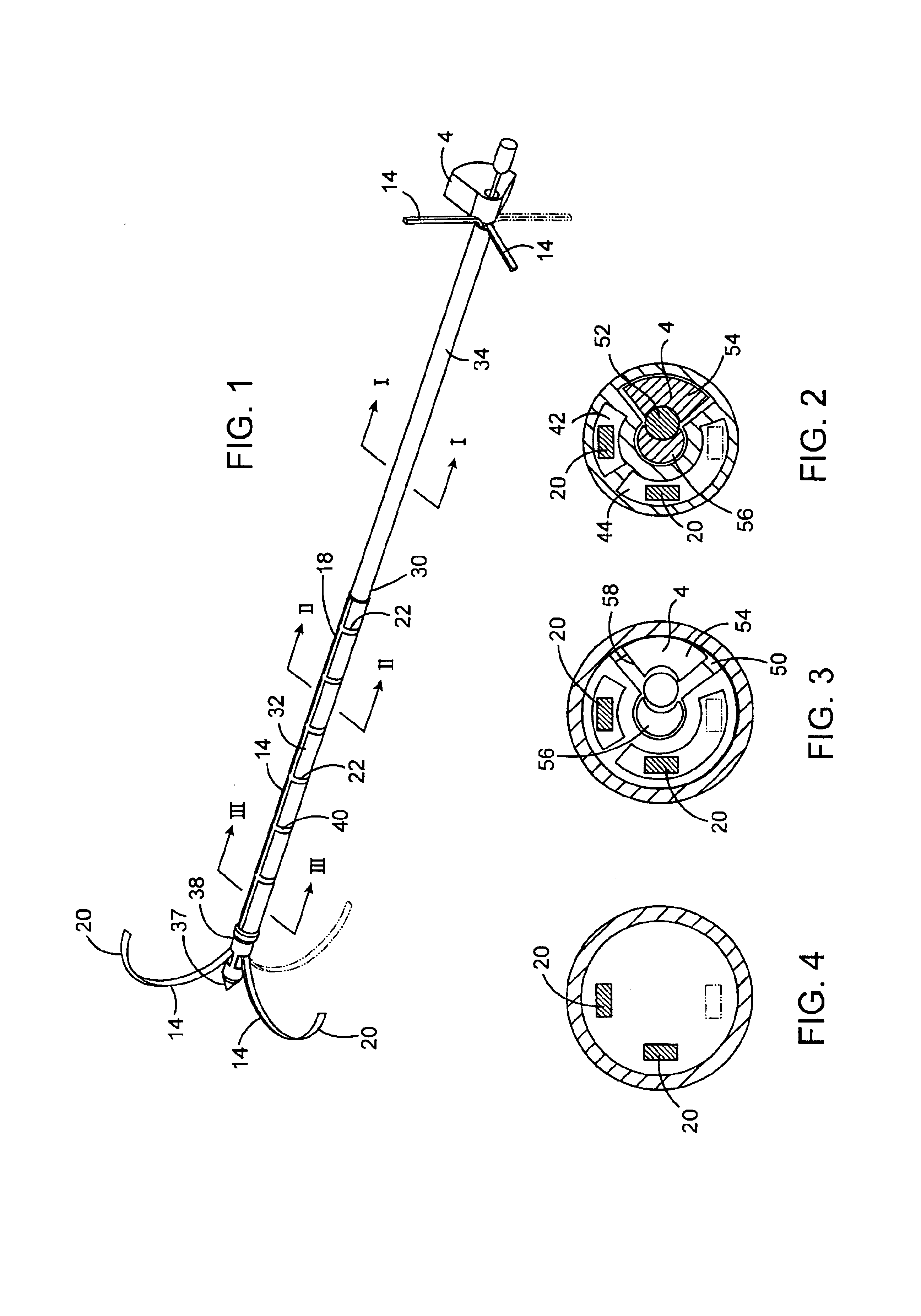
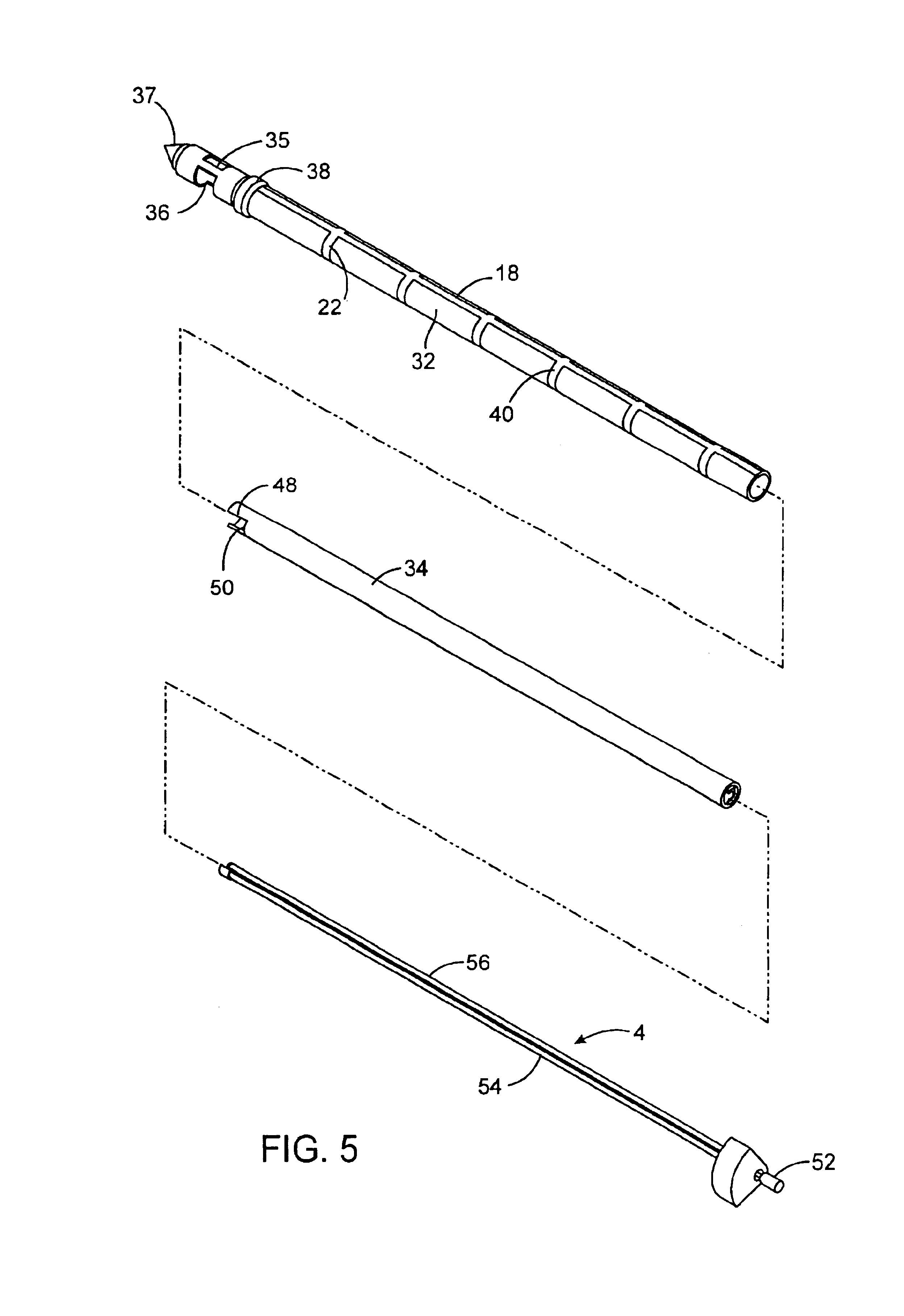
Osteotomy system
InactiveUS20080195099A1Sufficient widthSuture equipmentsSurgical furniturePerformed ProcedureValgus deformity
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
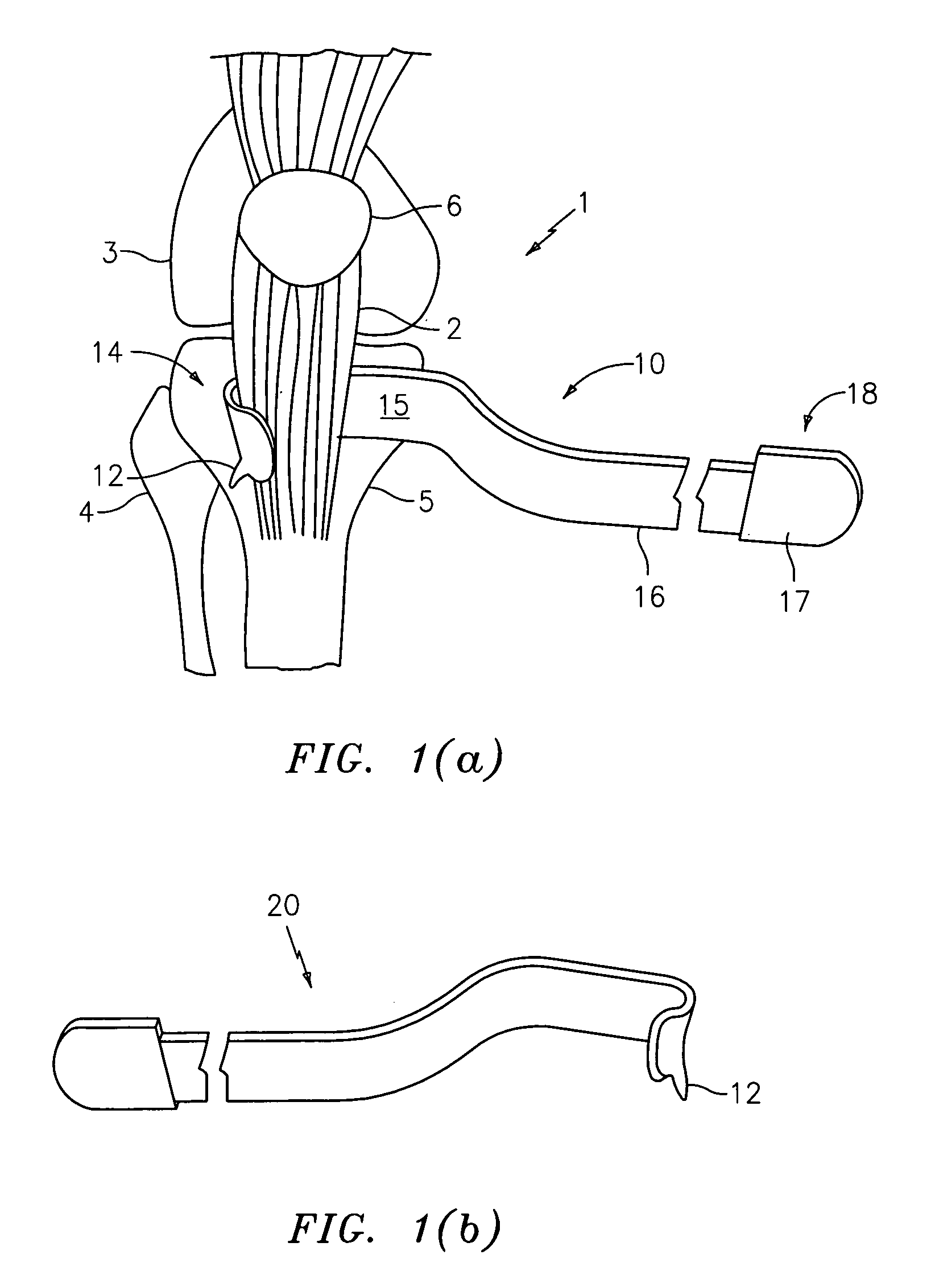
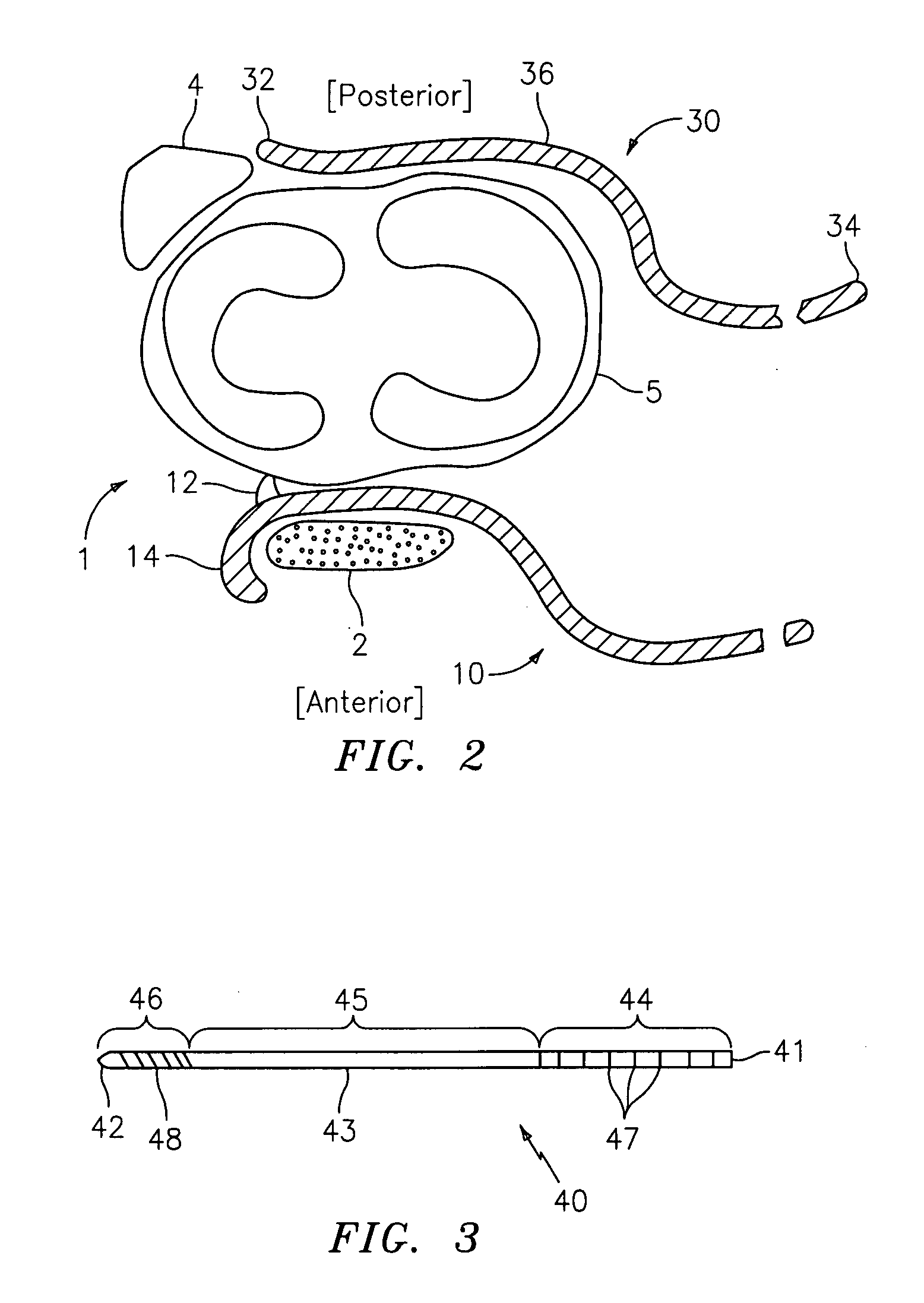
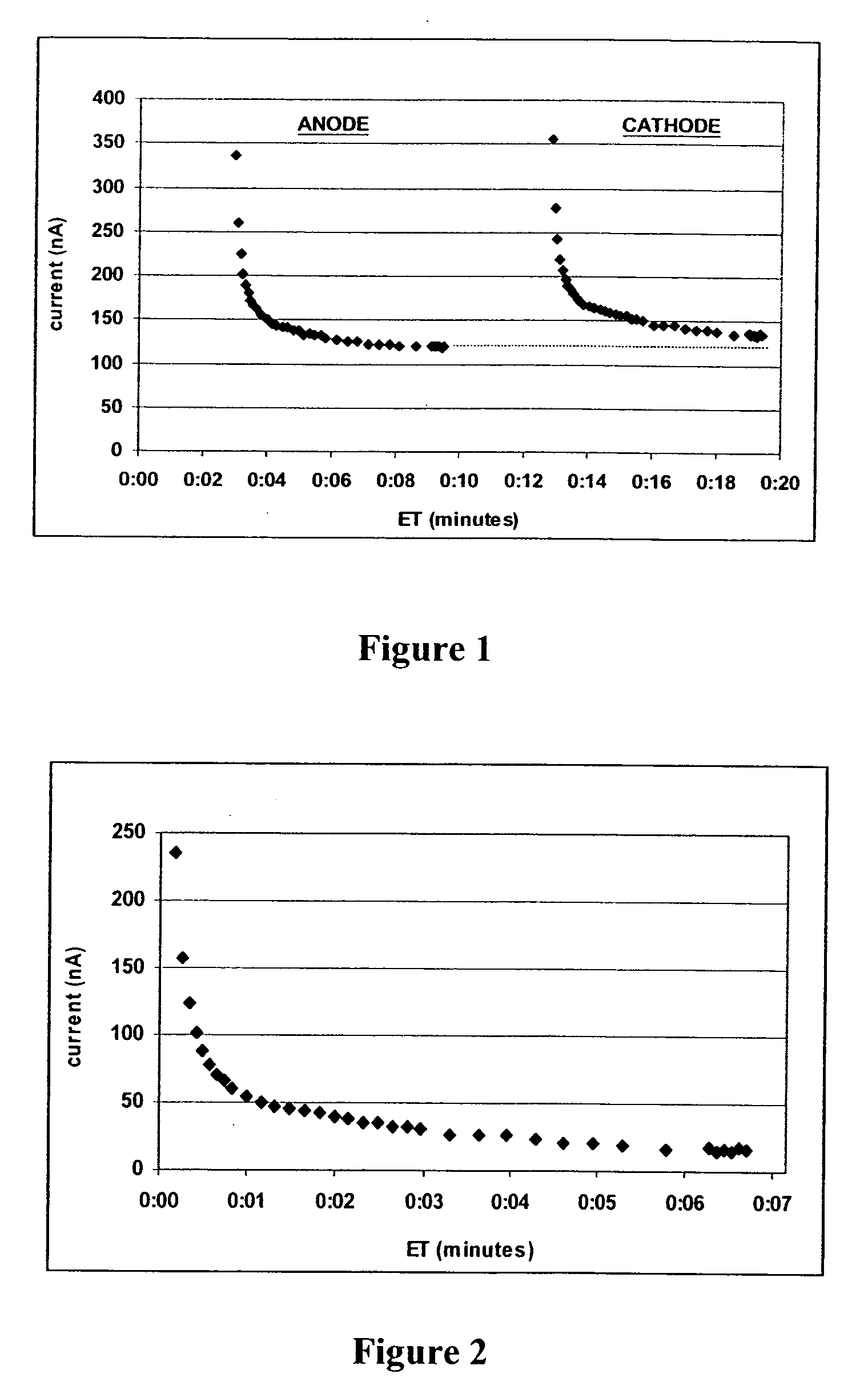
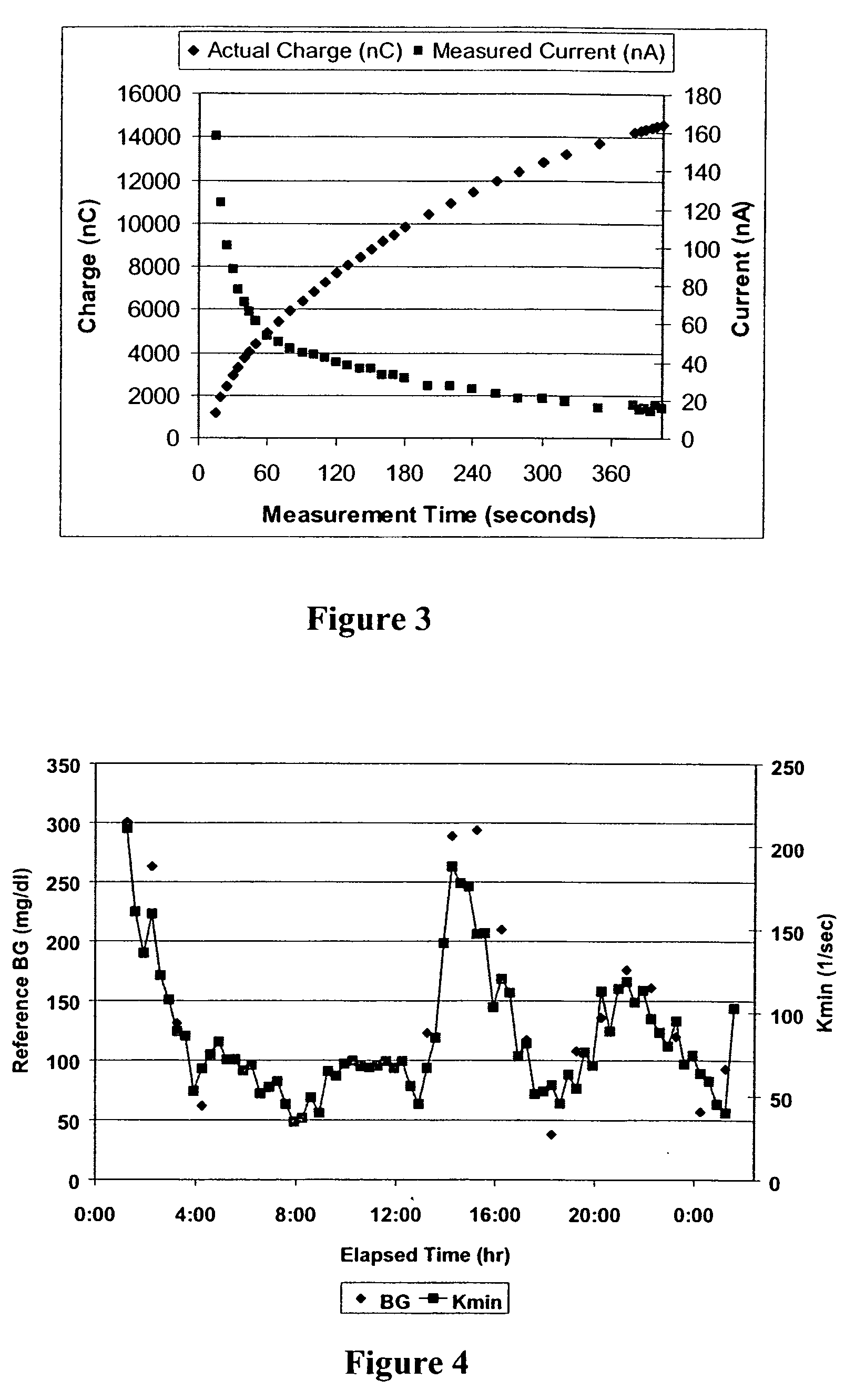
Micropressors, devices and methods for use in analyte monitoring systems
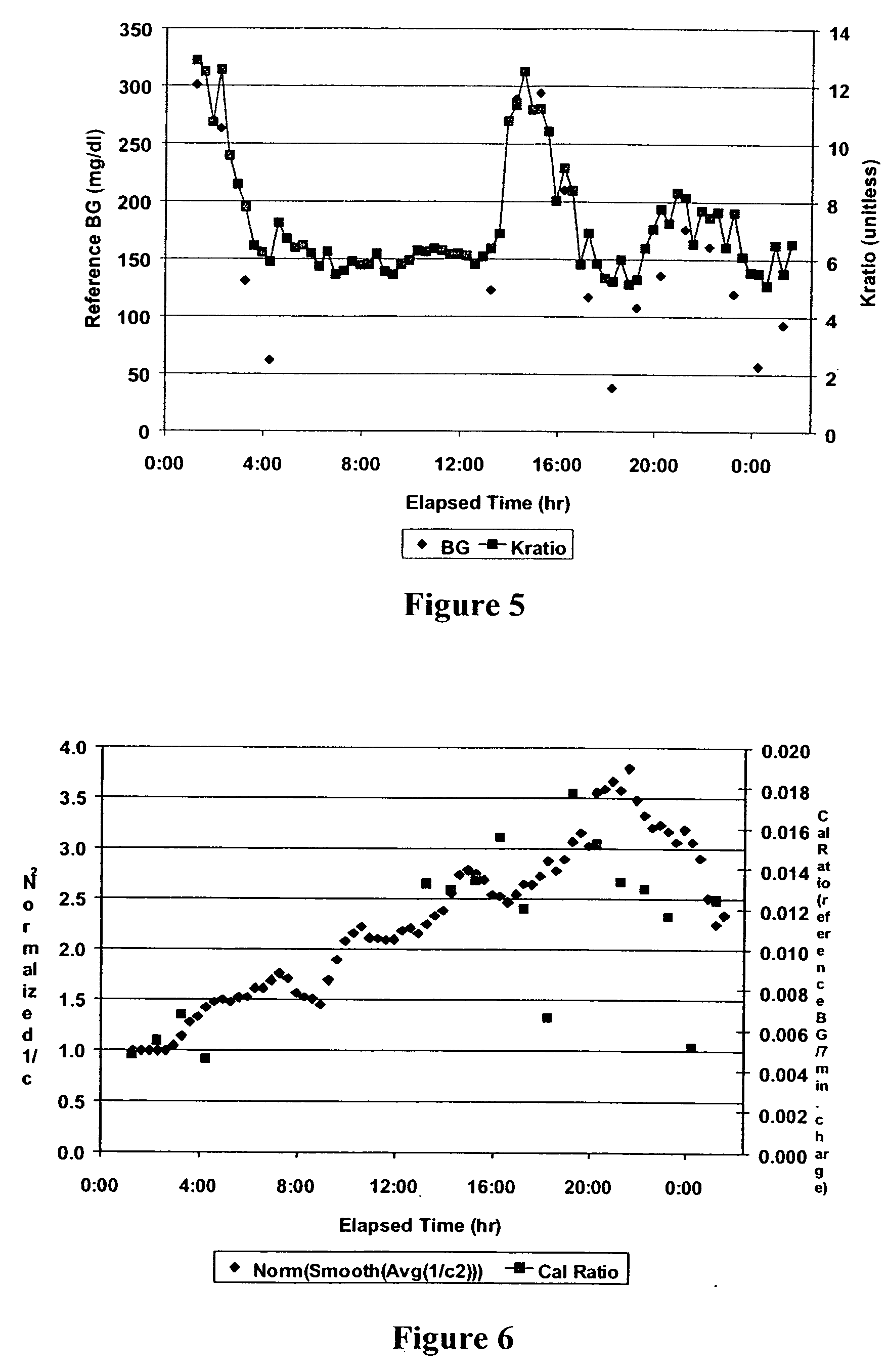
ActiveUS20060063218A1Reduce lag timeImprove usabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementSensorsAnalyteMonitoring system
The present invention comprises one or more microprocessors programmed to execute methods for improving the performance of an analyte monitoring device including prediction of glucose levels in a subject by utilizing a predicted slower-time constant (1 / k2). In another aspect of the invention, pre-exponential terms (1 / c2) can be used to provide a correction for signal decay (e.g., a Gain Factor). In other aspects, the present invention relates to one or more microprocessors comprising programming to control execution of (i) methods for conditional screening of data points to reduce skipped measurements, (ii) methods for qualifying interpolated / extrapolated analyte measurement values, (iii) various integration methods to obtain maximum integrals of analyte-related signals, as well as analyte monitoring devices comprising such microprocessors. Further, the present invention relates to algorithms for improved optimization of parameters for use in prediction models that require optimization of adjustable parameters.
Owner:ANIMAS TECH +1
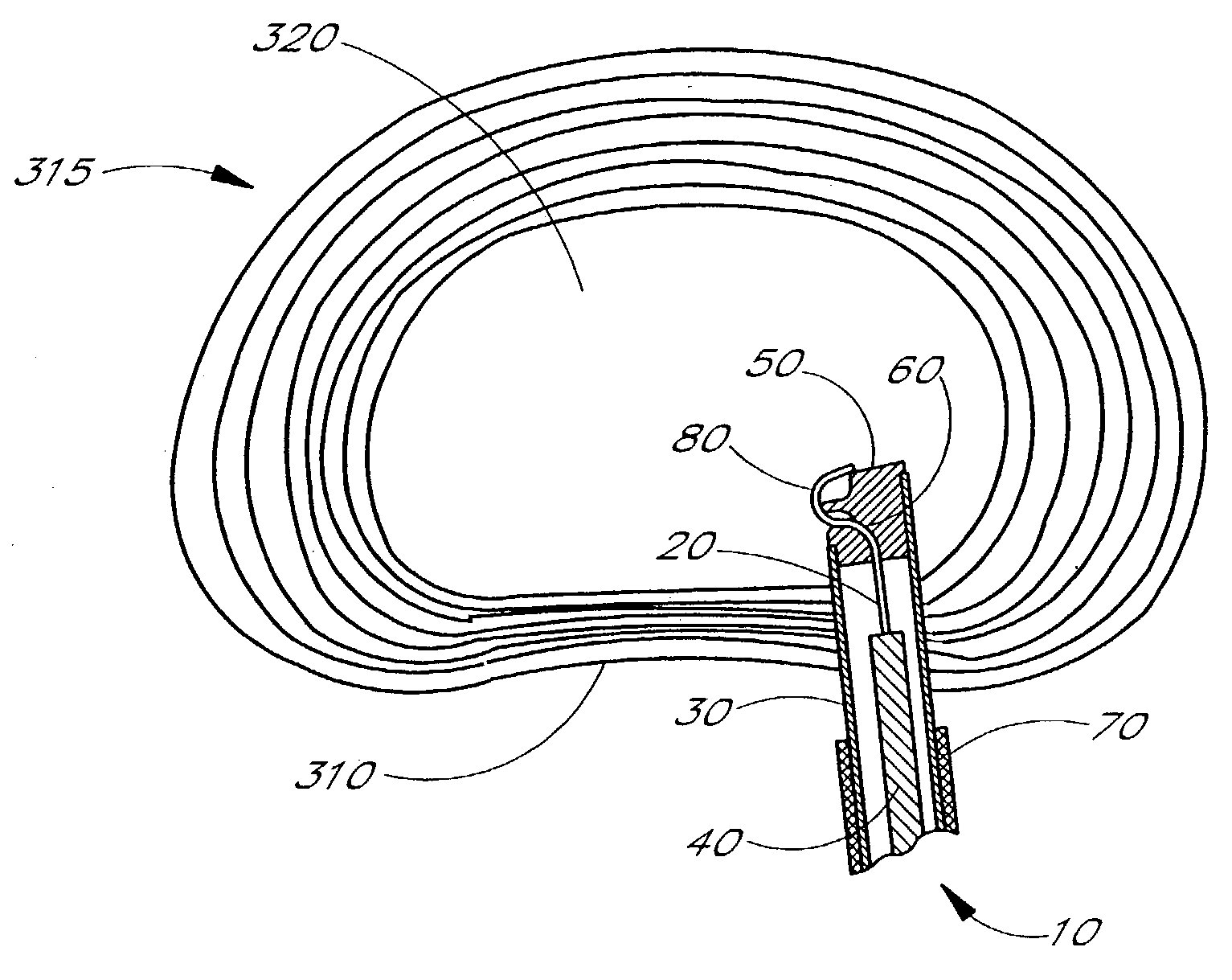
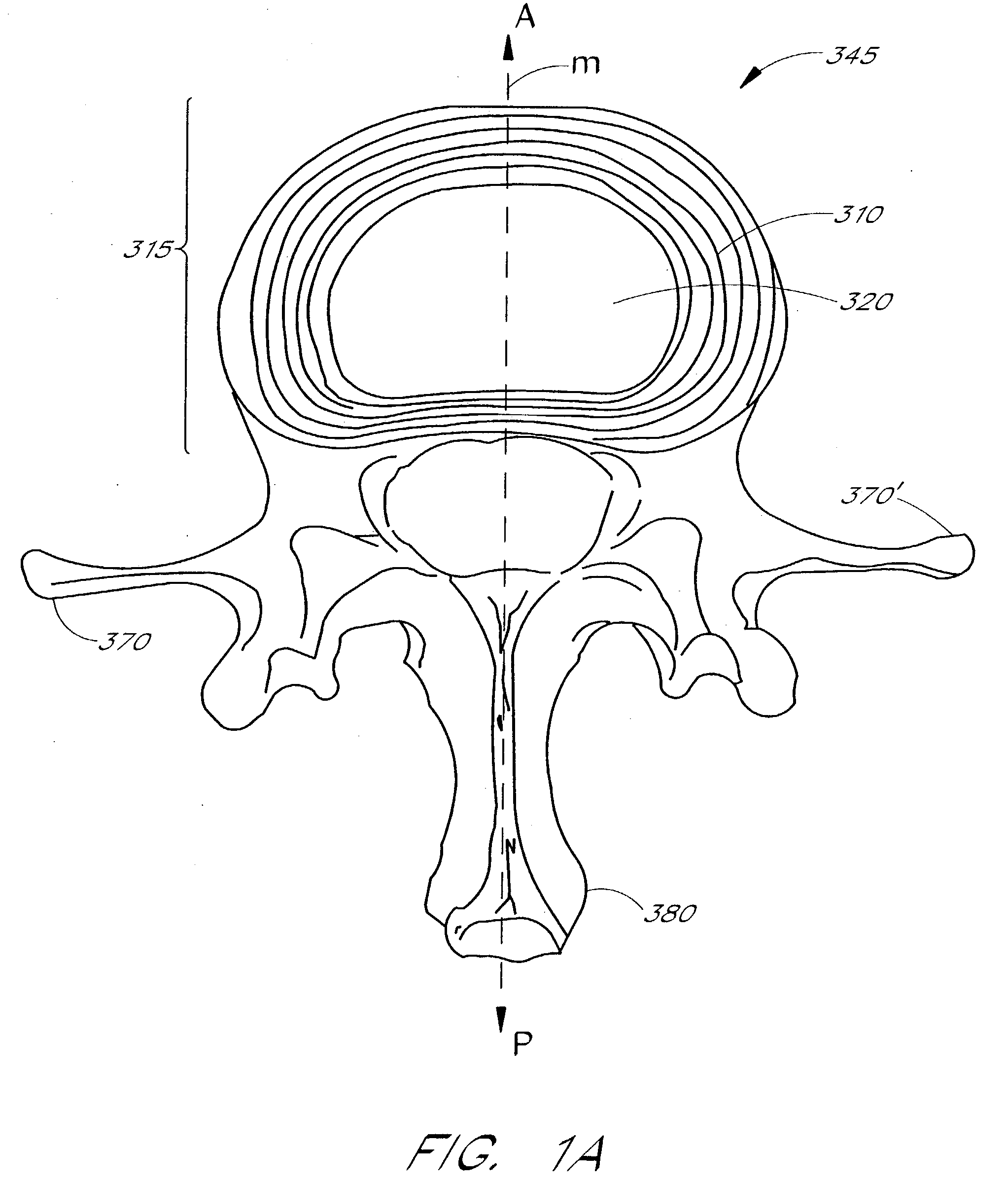
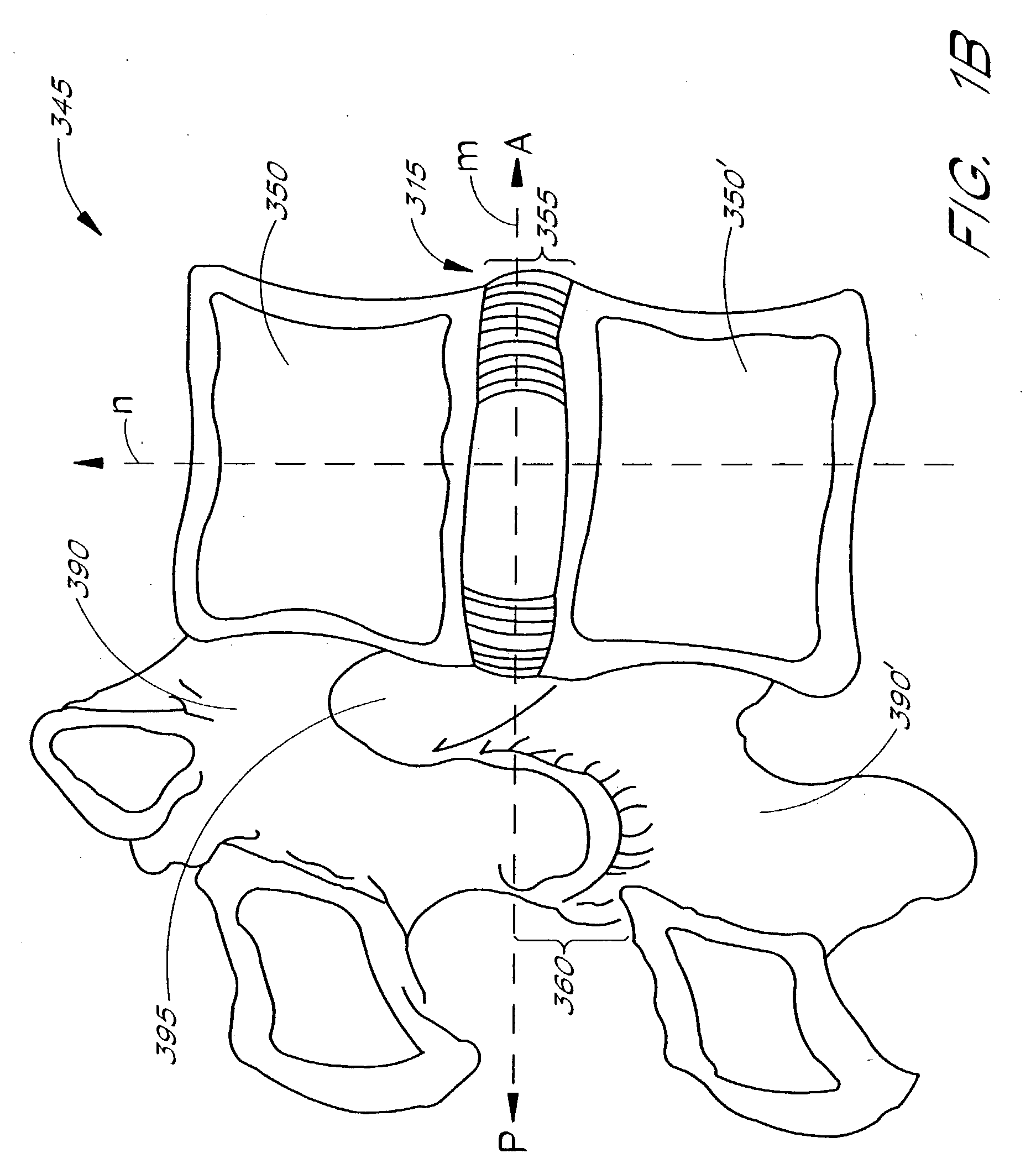
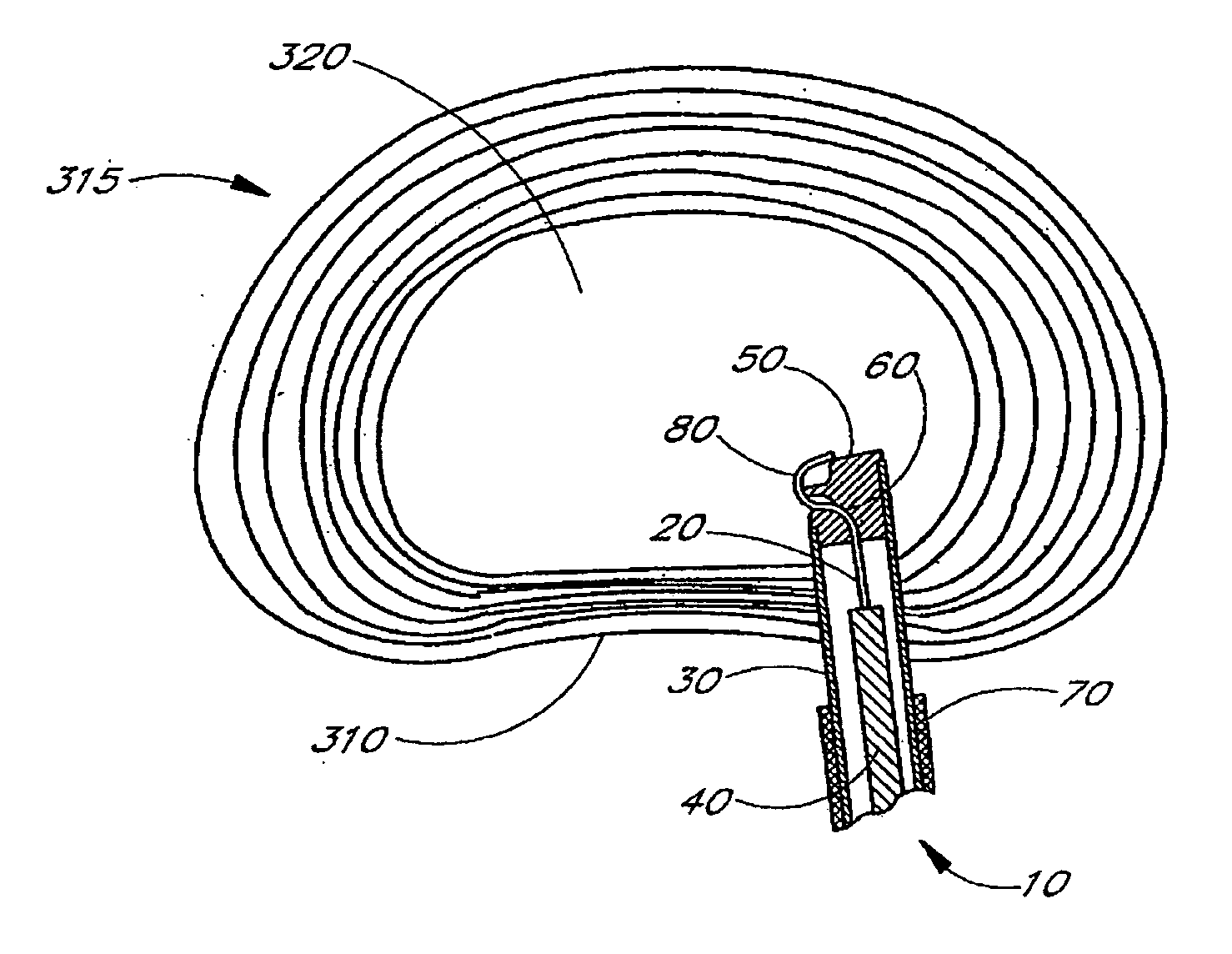
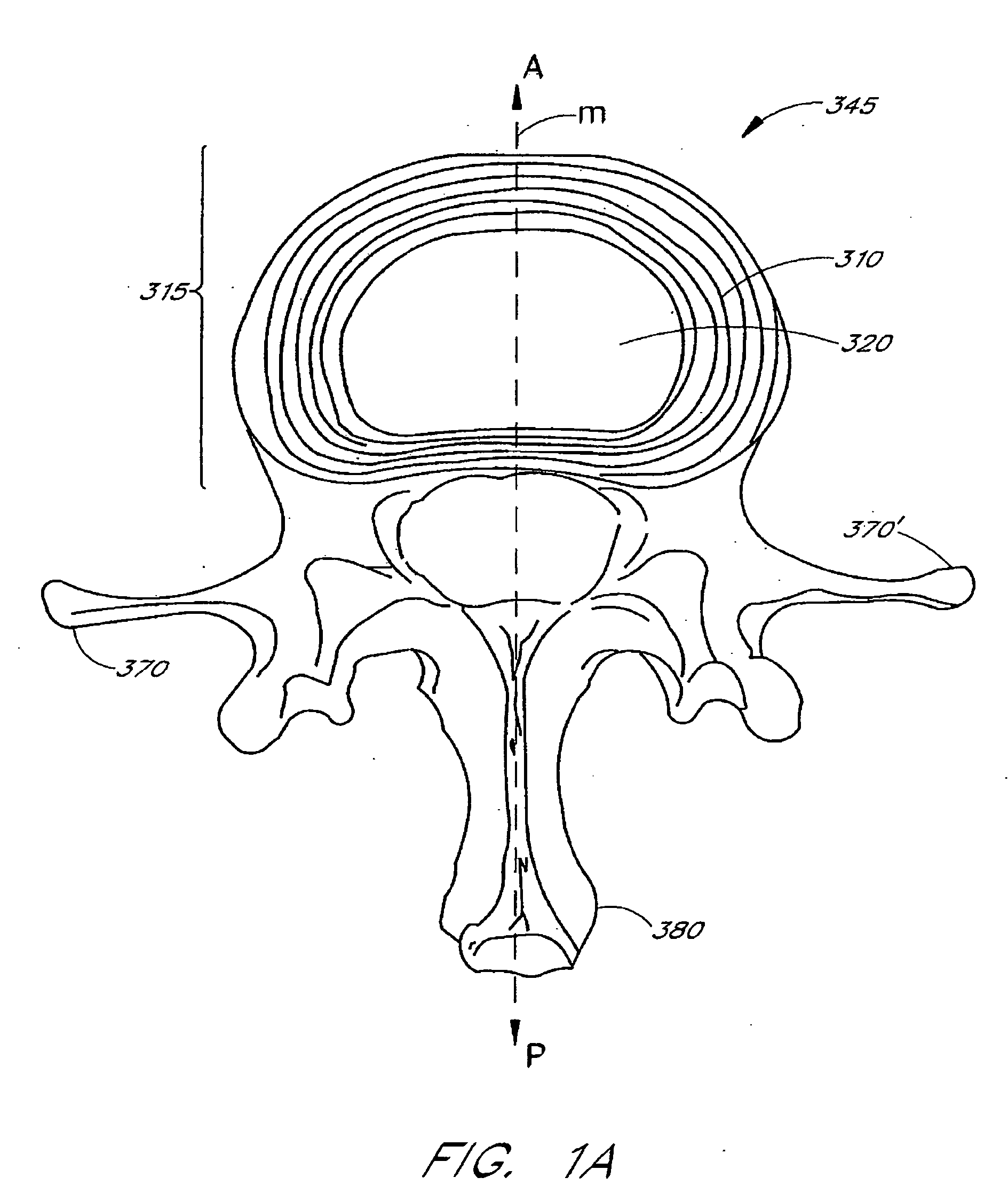
Apparatus delivery in an intervertebral disc
ActiveUS20050004578A1Convenient and reliable and accurateConvenient guidanceInternal osteosythesisCannulasDiagnostic agentIntervertebral disc
The present invention relates generally to intervertebral disc devices and methods and instrumentation for intervertebral disc procedures. Methods include performing procedures such as implant delivery, tissue manipulation, tissue diagnostics, and therapeutic and diagnostic agent delivery at selected locations within intervertebral discs.
Owner:INTRINSIC THERAPEUTICS
Methods and apparatus for bypassing arterial obstructions and/or performing other transvascular procedures
InactiveUS7059330B1Increasing tissue perfusionInhibition formationCannulasHeart valvesBlood vesselArterial obstruction
Methods, devices, and systems for a) revascularization and / or b) performing other medical procedures at vascular or non-vascular intracorporeal locations within a mammalian body. The methods generally comprise the formation of at least one extravascular passageway from a blood vessel to a vascular or non-vascular target location. In the revascularization methods the extravascular passageway is utilized for blood flow. In the medical procedure methods the extravascular passageway is utilized as a conduit for accessing or performing procedures at the vascular or non-vascular target location. Also disclosed are catheter devices and systems which are useable to form the extravascular passageways of the invention, as well as apparatus for modifying, maintaining and / or closing such extravascular passageways.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
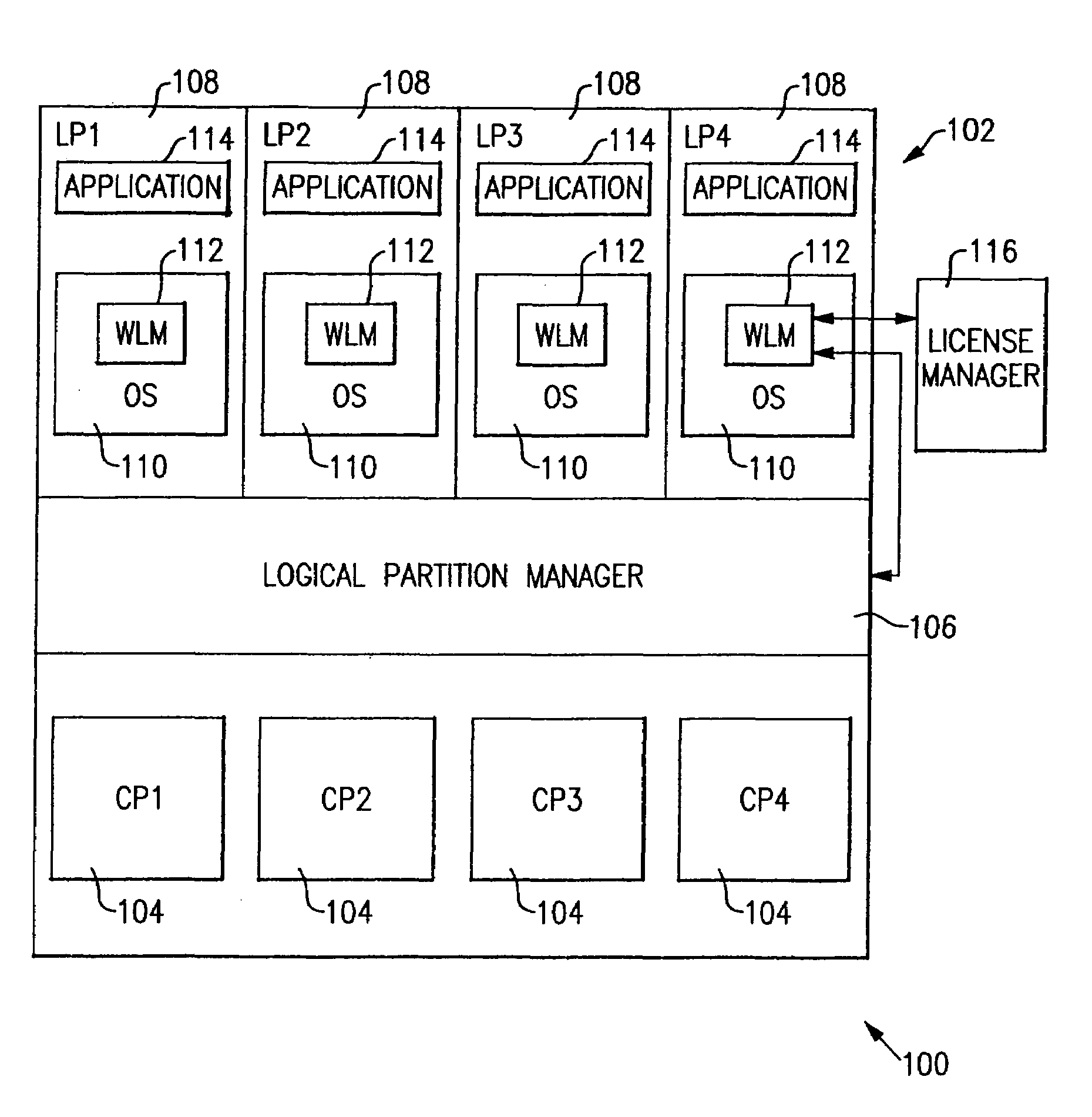
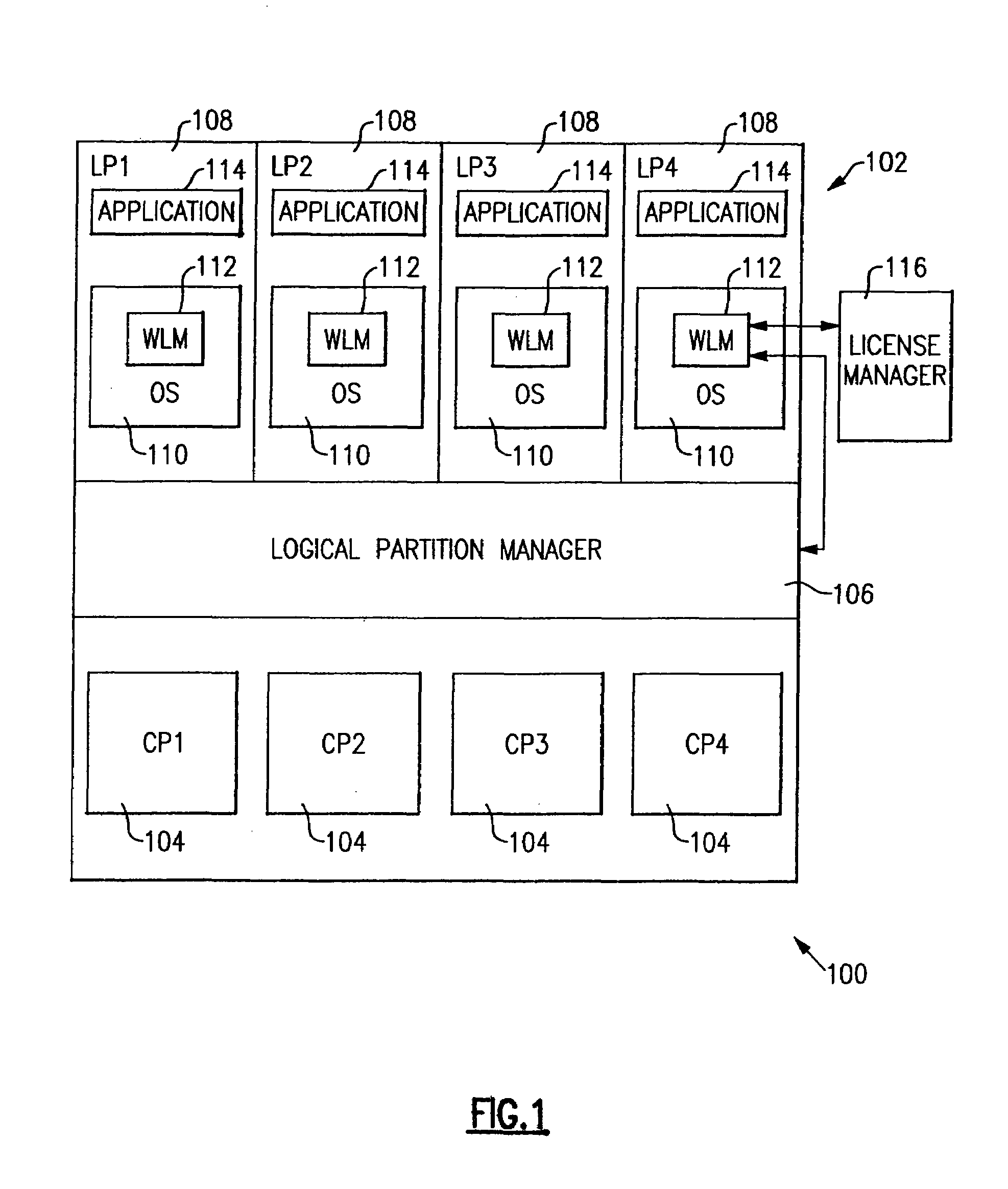
Method and apparatus for enforcing capacity limitations in a logically partitioned system
InactiveUS7096469B1Minimal costIncrease workloadResource allocationDigital computer detailsSoftware licenseHandling system
A method and apparatus for enforcing capacity limitations such as those imposed by software license agreements in an information handling system in which a physical machine is divided into a plurality of logical partitions, each of which is allocated a defined portion of processor resources by a logical partition manager. A software license manager specifies a maximum allowed consumption of processor resources by a program executing in one of the logical partitions. A workload manager also executing in the partition measures the actual consumption of processor resources by the logical partition over a specified averaging interval and compares it with the maximum allowed consumption. If the actual consumption exceeds the maximum allowed consumption, the workload manager calculates a capping pattern and interacts with the logical partition manager to cap the actual consumption of processor resources by the partition in accordance with the calculated capping pattern. To provide additional capping flexibility, partitions are assigned phantom weights that the logical partition manager adds to the total partition weight to determine whether the partition has exceeded its allowed share of processor resources for capping purposes. The logical partition thus becomes a “container” for the licensed program with an enforced processing capacity less than that of the entire machine.
Owner:IBM CORP
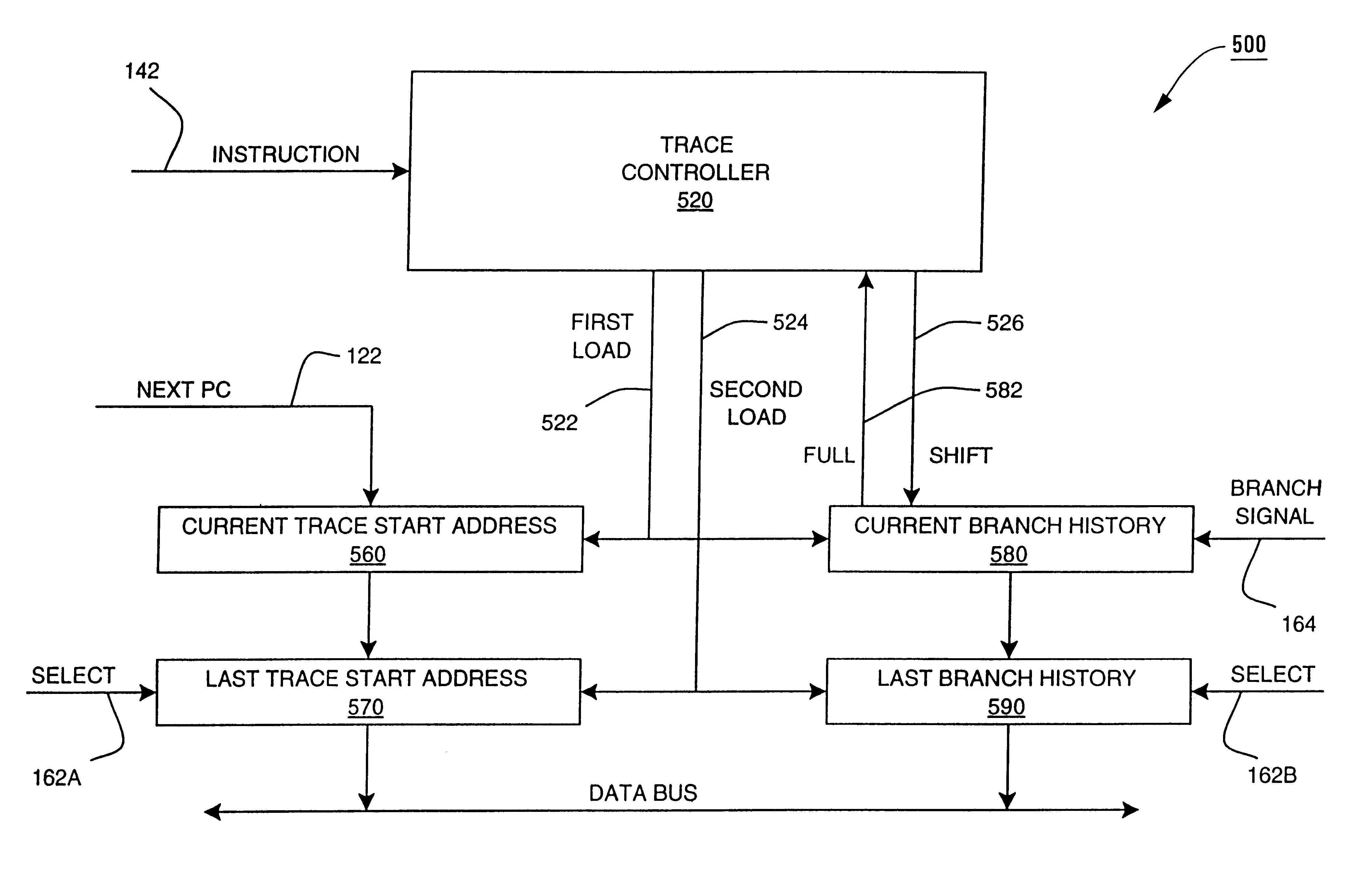
Method and apparatus for profiling of non-instrumented programs and dynamic processing of profile data
InactiveUS6233678B1Digital computer detailsNext instruction address formationProcessor registerParallel computing
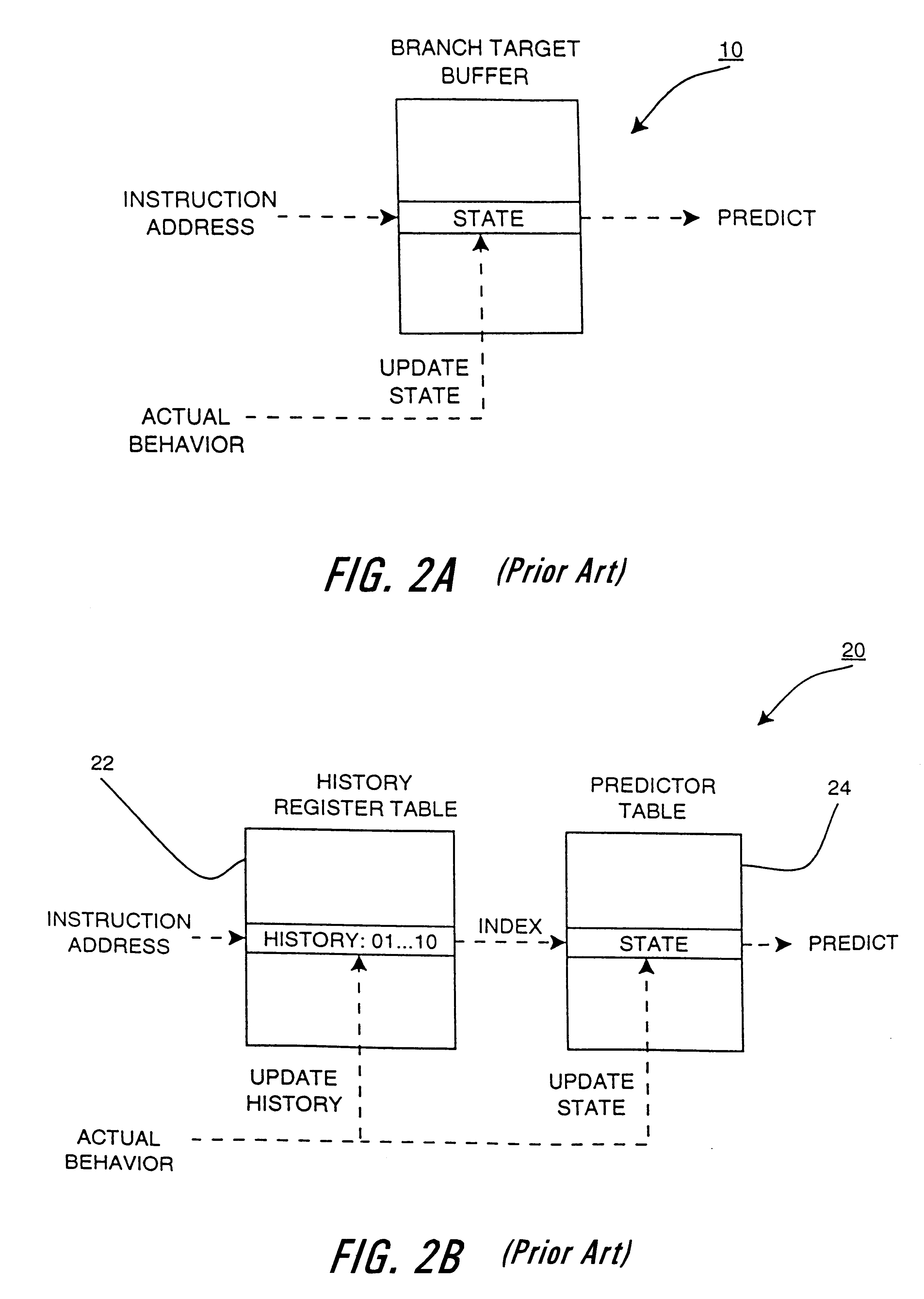
An apparatus and method are shown for collecting a branch history value of a program executing in a processor. A current start address register latches a program count value in response to a trace termination condition, such as an indirect branch instruction. A current branch history register is cleared in response to the trace termination condition and shifts in a branch outcome value of the processor in response to a conditional direct branch instruction. A last trace start address latches the content of the current trace start address and a last branch history register latches the content of the current branch history register when a trace termination condition occurs.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO
Method, system, and program for diagnosing a computer in a network system
InactiveUS6697969B1Avoid serious problemsEasy diagnosisDetecting faulty hardware by remote testDigital computer detailsThe InternetDiagnostic system
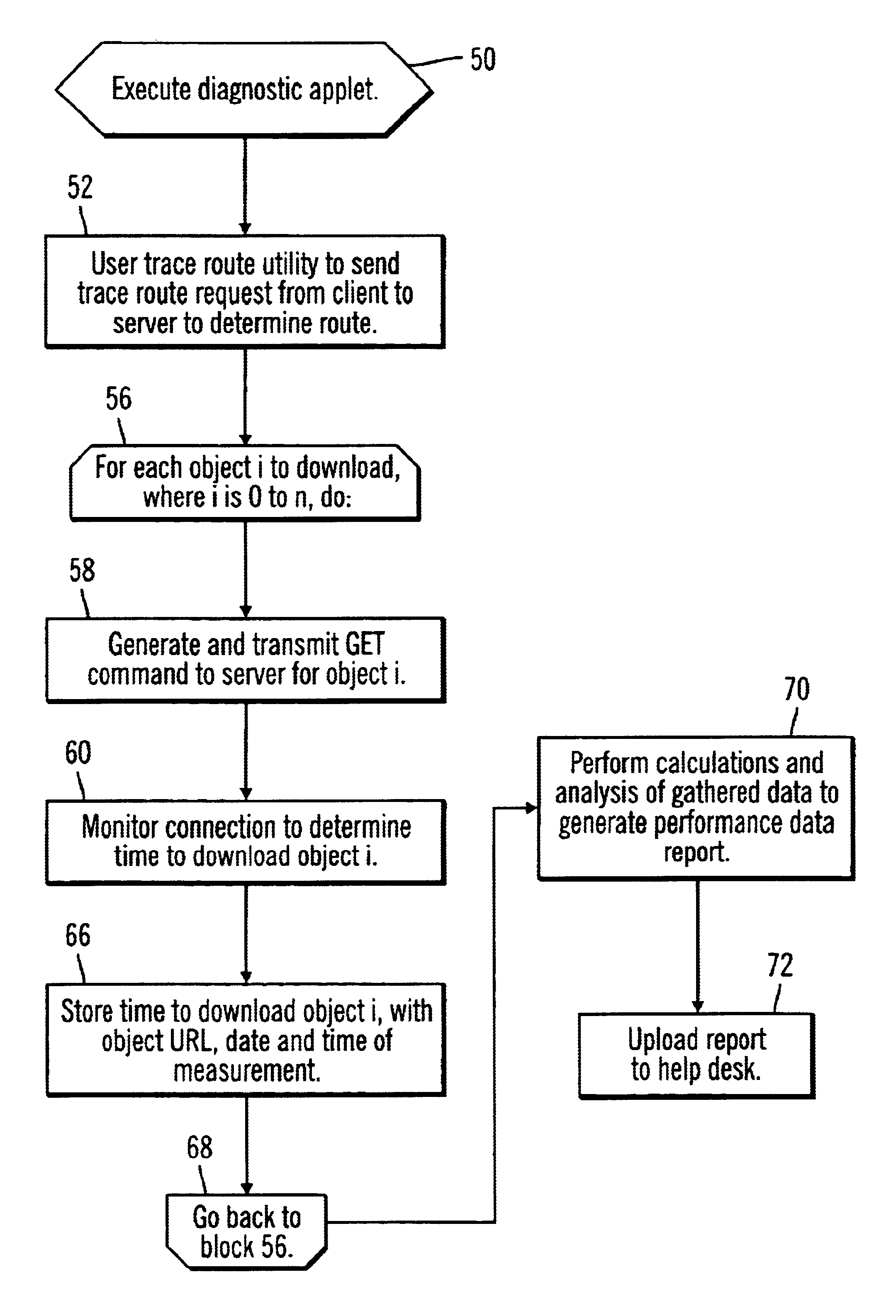
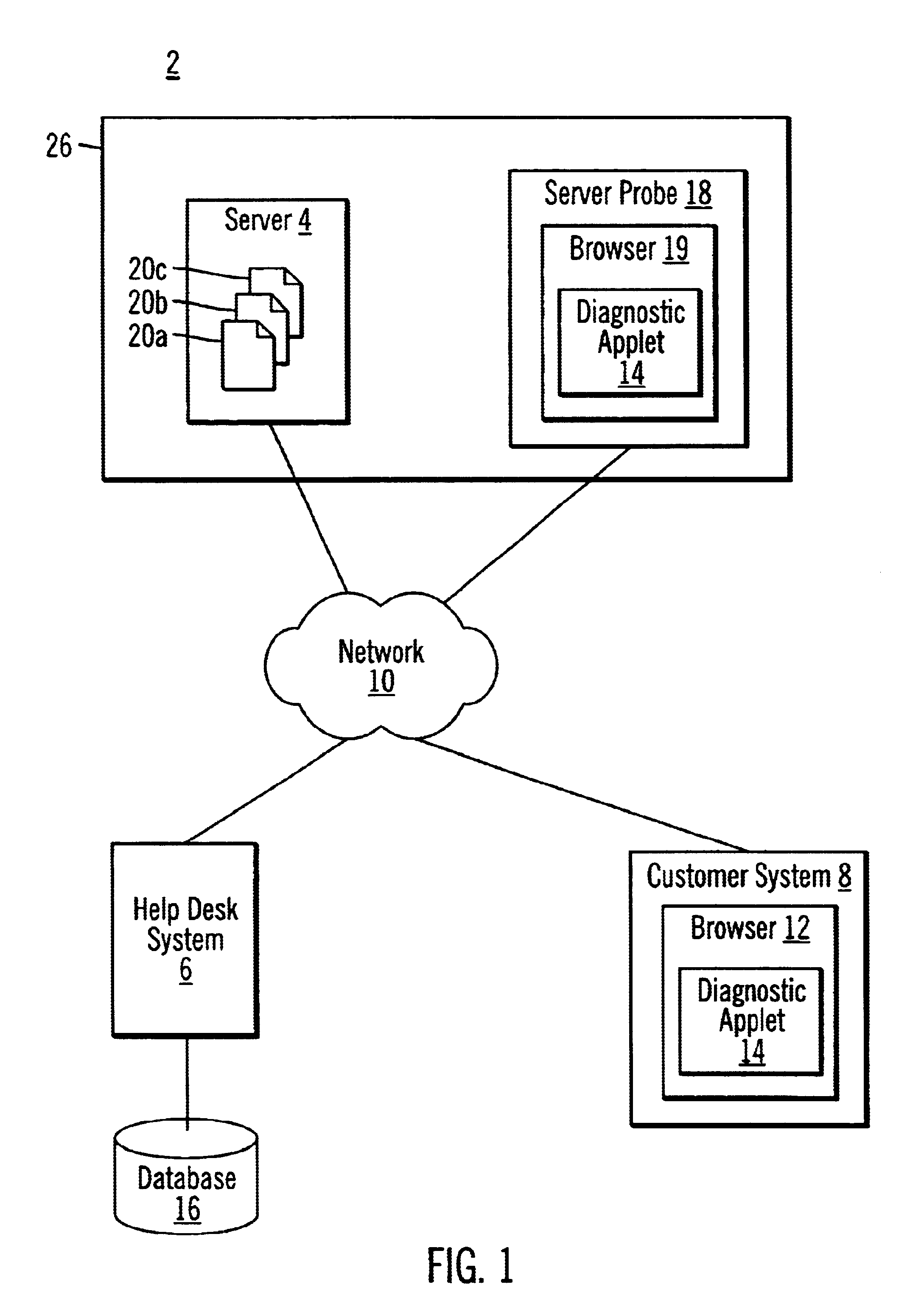
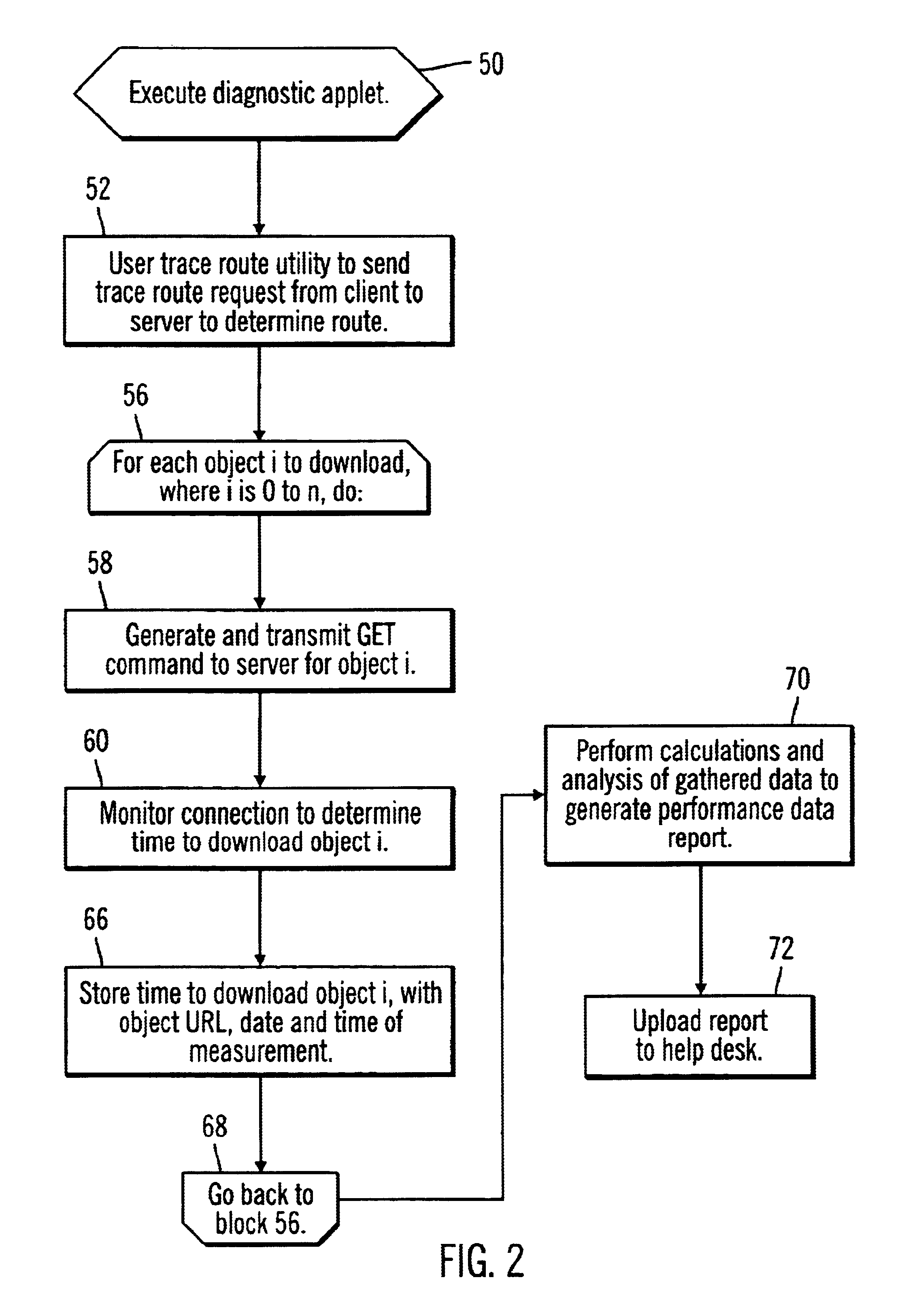
Disclosed is a method, system, and program for diagnosing a computer over a network, such as the Internet. A program, such as an applet, is provided that executes on the computer. The program causes the computer to download at least one object from a server over the network. Performance data is determined with respect to downloading the object from the server to the computer over the network in order to diagnose performance problems with the computer. The determined performance data is then transmitted to a diagnostic system over the network.
Owner:IBM CORP
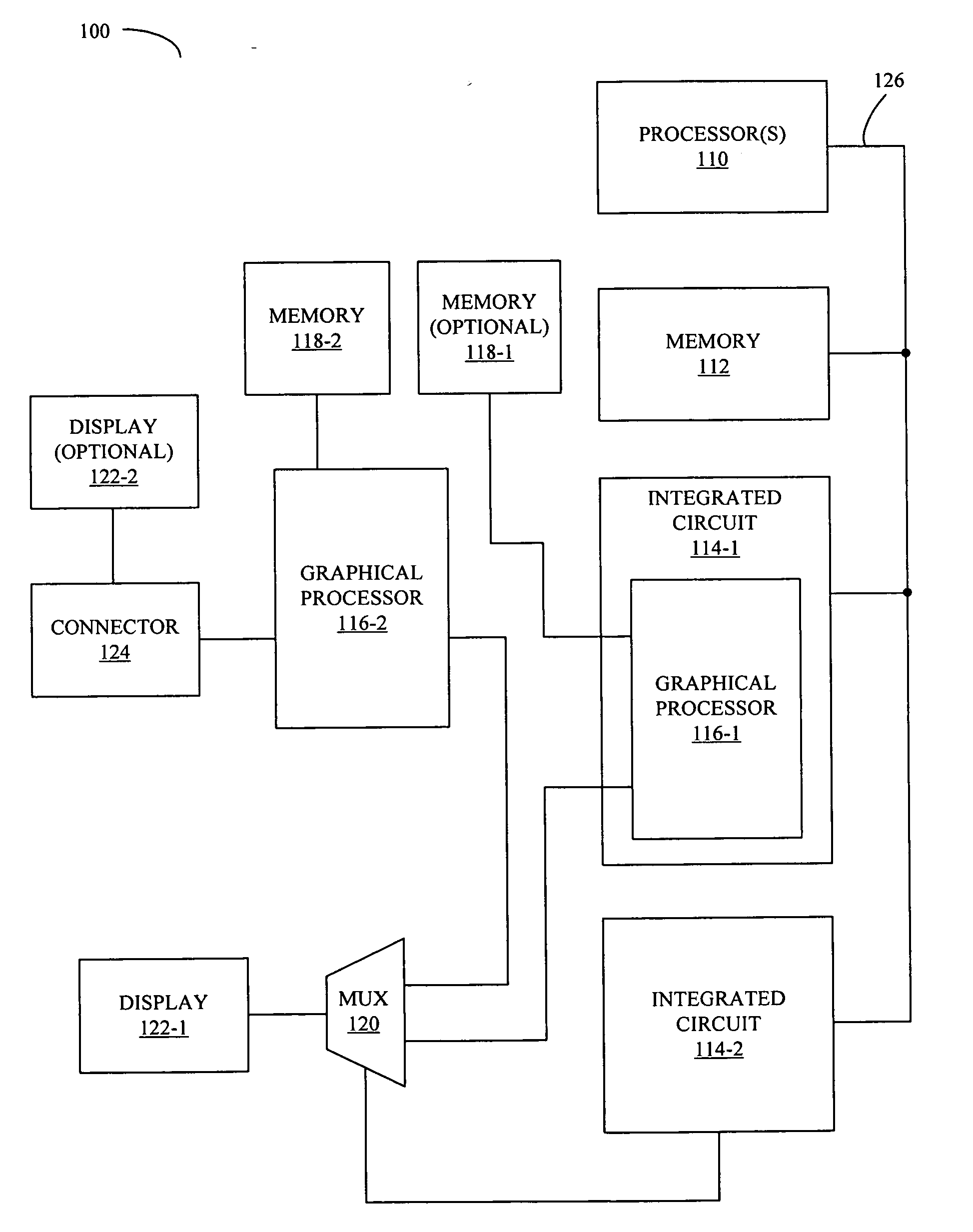
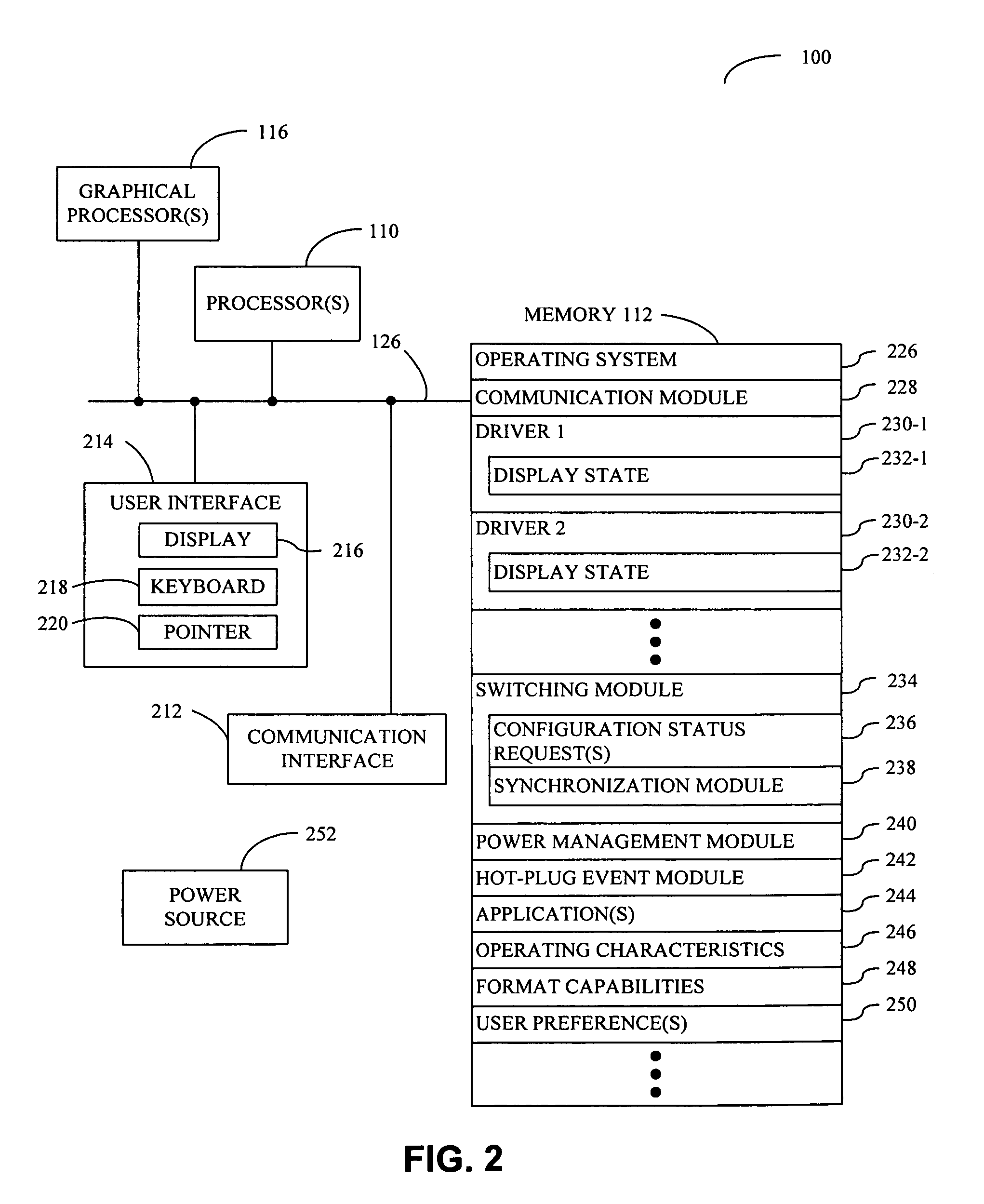
Multiplexed graphics architecture for graphics power management
ActiveUS20080034238A1Volume/mass flow measurementMultiple digital computer combinationsGraphicsOperational system
A computer system includes a processor, a memory, first and second graphical processors that have different operating characteristics, a switching mechanism coupled to the graphical processors, and a display coupled to the switching mechanism. The switching mechanism is configured to couple a given graphical processor to the display, and is initially configured to couple the first graphical processor to the display. Furthermore, a program module, which is stored in the memory and configured to be executed by the processor, is configured to change a configuration of the switching mechanism thereby decoupling the first graphical processor from the display and coupling the second graphical processor to the display. Note that the changing of the configuration and switching module operations are configured to occur while an operating system is running and are based on the operating condition of the computer system.
Owner:APPLE INC
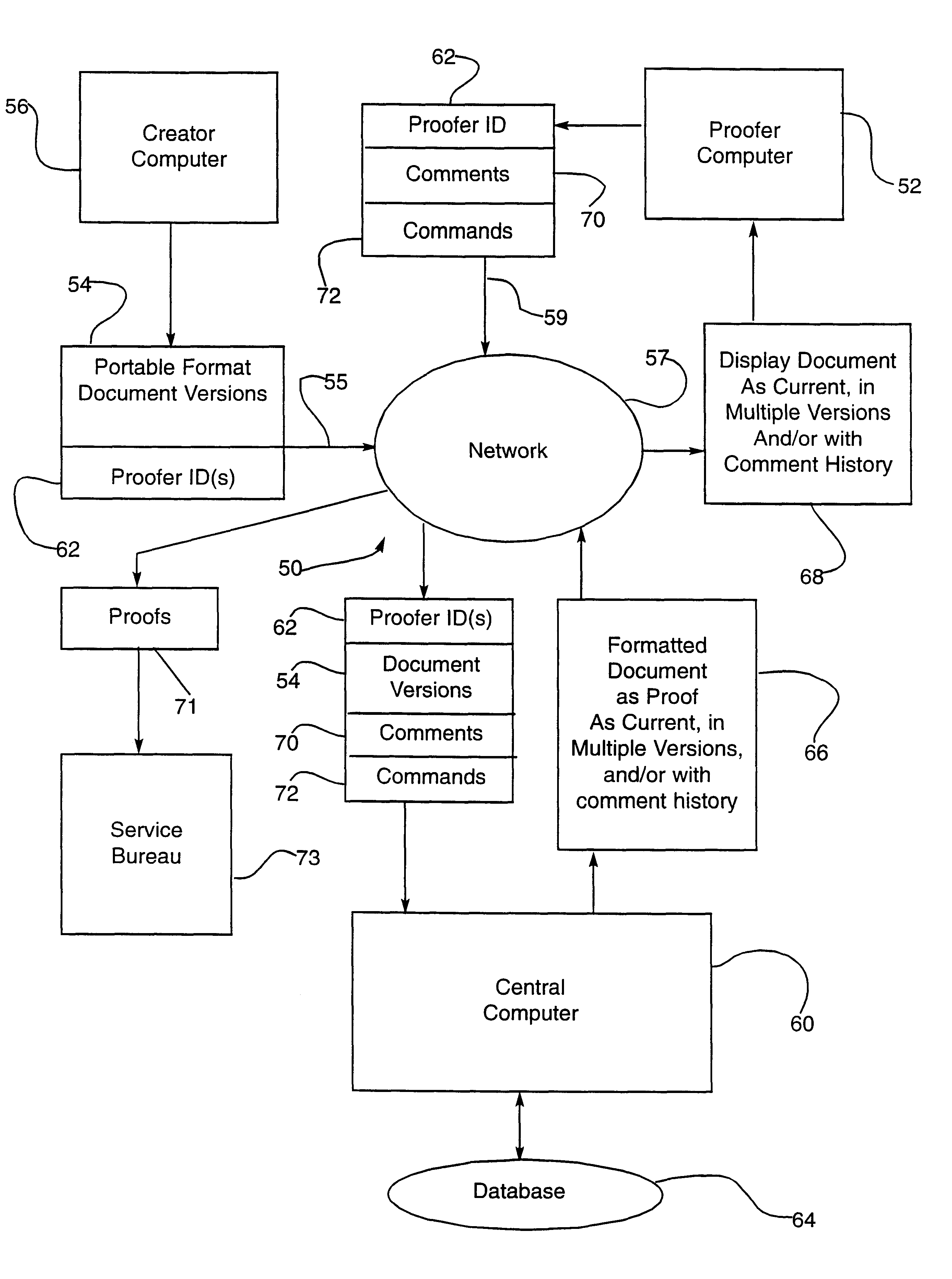
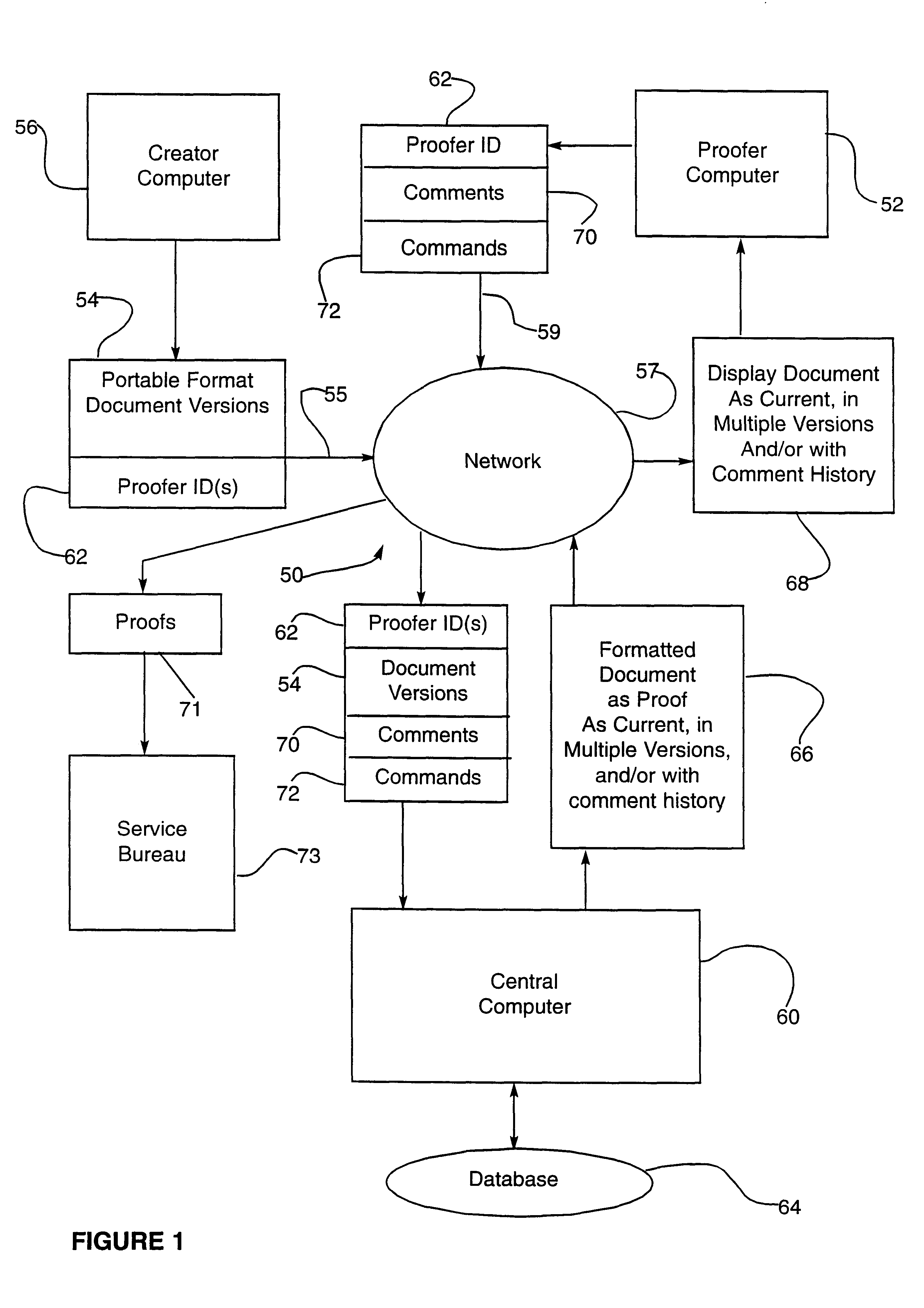
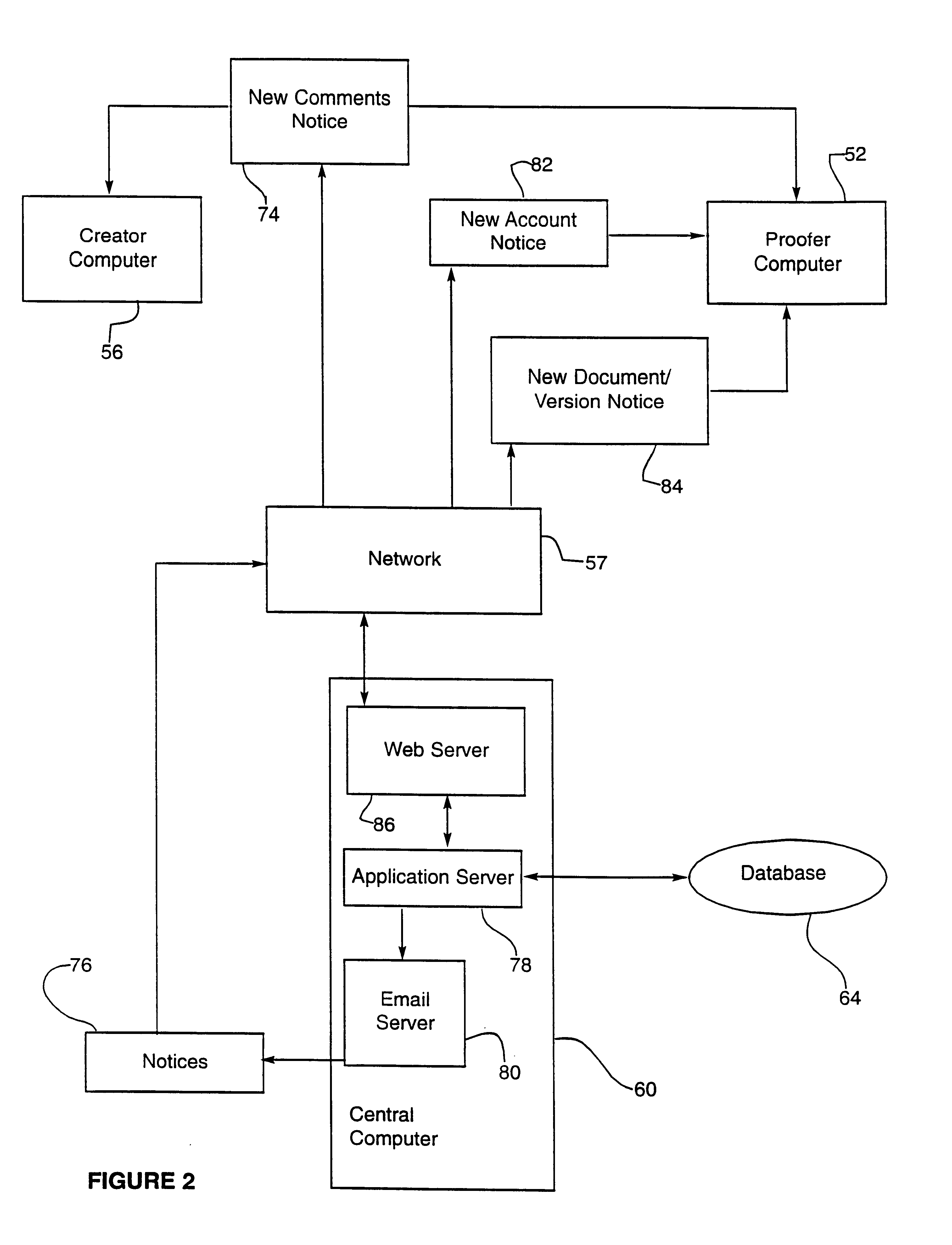
Electronic document proofing system
InactiveUS6918082B1Digital computer detailsNatural language data processingElectronic documentDocument format
A system is provided for proofing electronic documents delivered over a network. The system comprises a plurality of electronic documents in portable document file format, a computer connectable to the network for receiving the plurality of portable format documents together with at least one associated proofer identifier, a program executing on the computer for assigning a version number to each of the plurality of received portable format documents, and a database accessible by the computer for storing the documents and associated version numbers. The computer for receiving a request, from a proofer presenting the proofer identifier, to review a portable format electronic document, and the program for retrieving and formatting the requested document for display.
Owner:LONE STAR DOCUMENT MANAGEMENT
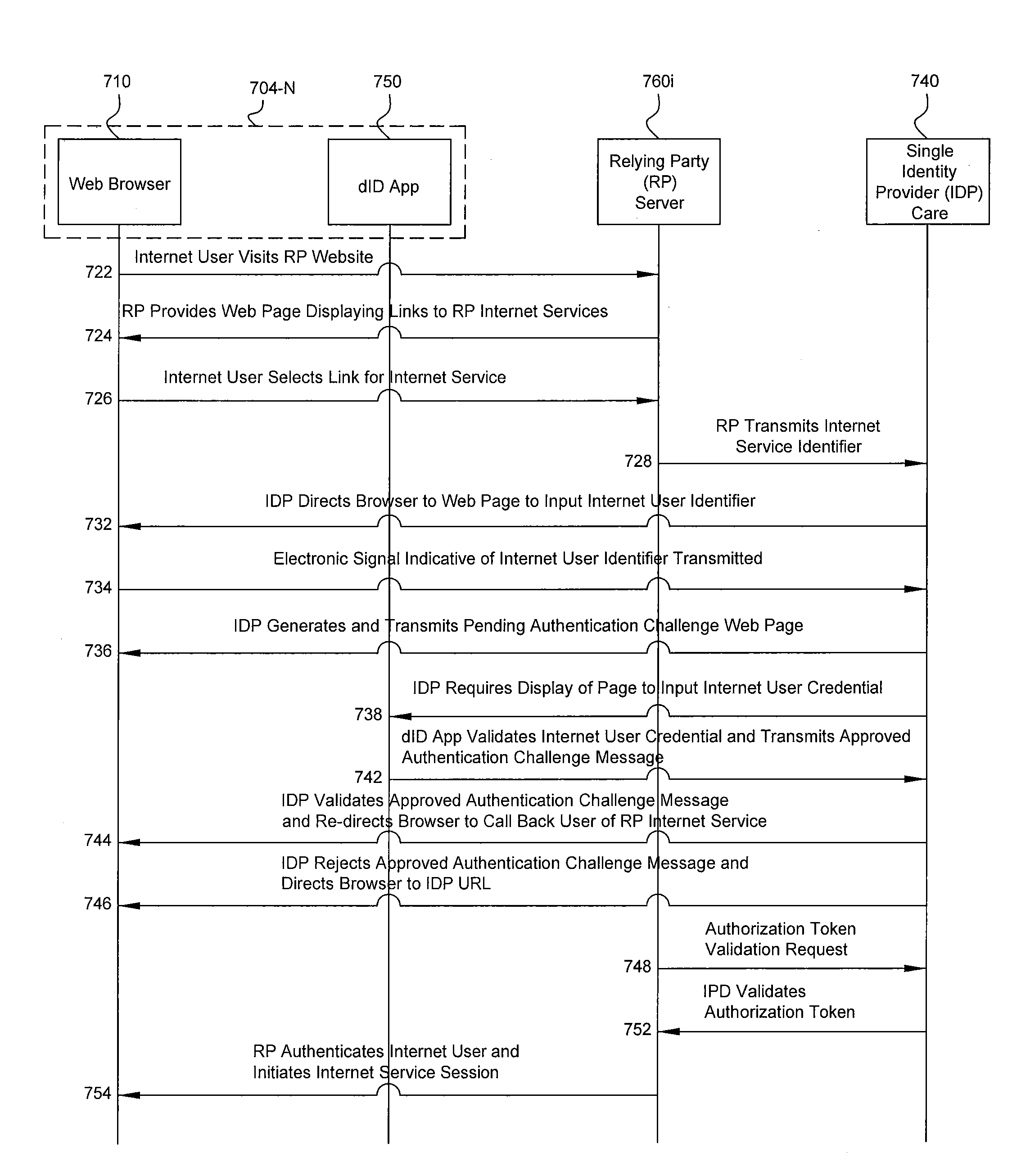
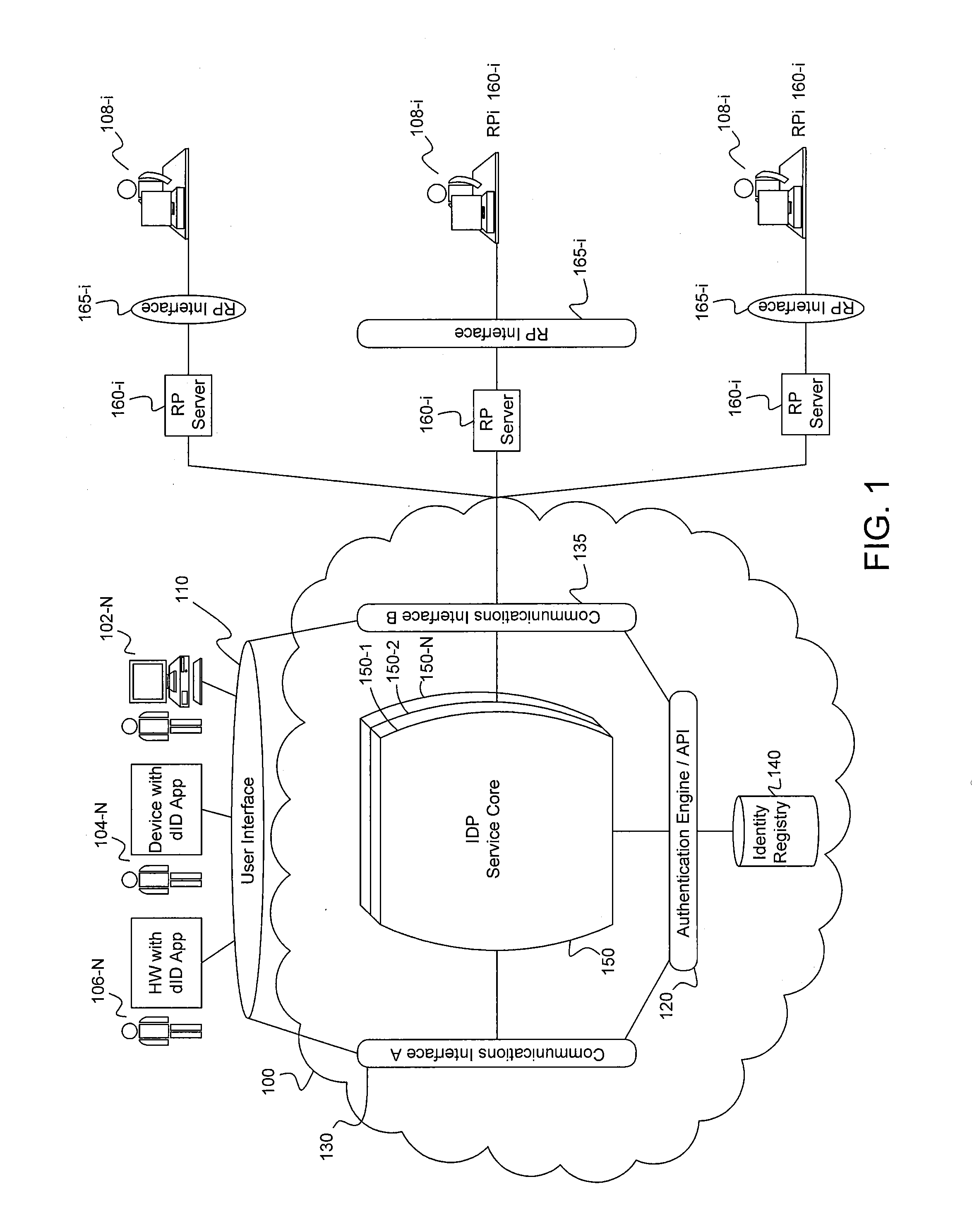
Computer-implemented systems and methods of device based, internet-centric, authentication
ActiveUS20160134599A1User identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationInternet usersIdentity provider
Systems and computer-implemented methods for authorizing respective access by each of a plurality of Internet users to a respective one or more Internet services provided by each of a plurality of Internet service providers. A system includes a processor, and non-transient computer readable storage media, at a single identity provider. The storage media is encoded with program code executable by the processor for requiring an identity provider application residing on each of a plurality of devices to create a respective authentication token that is specific to a respective identifier and user credential of a respective Internet user, a respective device identifier, and the respective identity provider application, and for authorizing respective access by the plurality of Internet users to a respective requested one of the Internet services provided by each Internet service provider using the respective created authentication tokens and respective identifiers for each of the respective requested Internet services.
Owner:PRIVAKEY INC
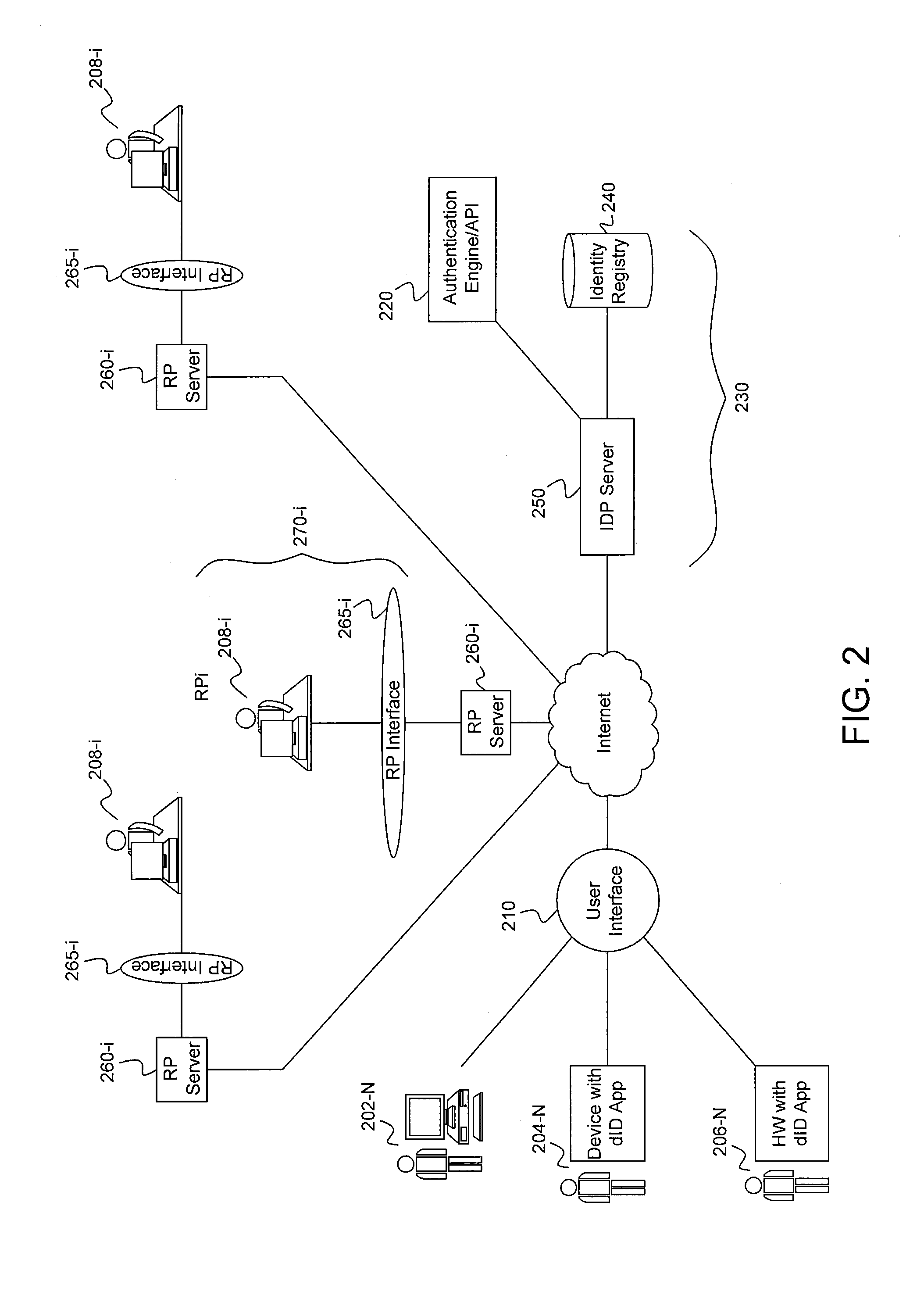
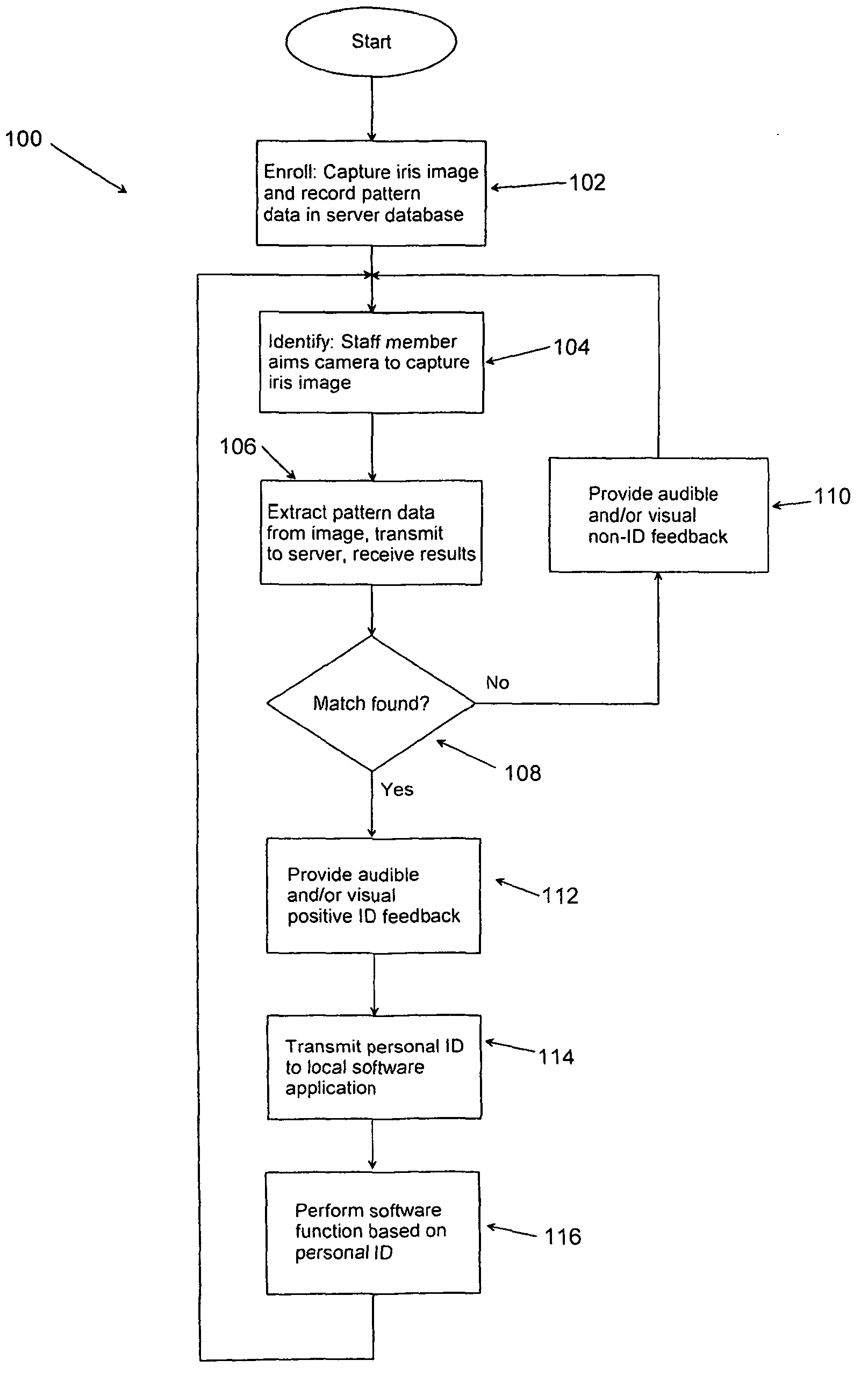
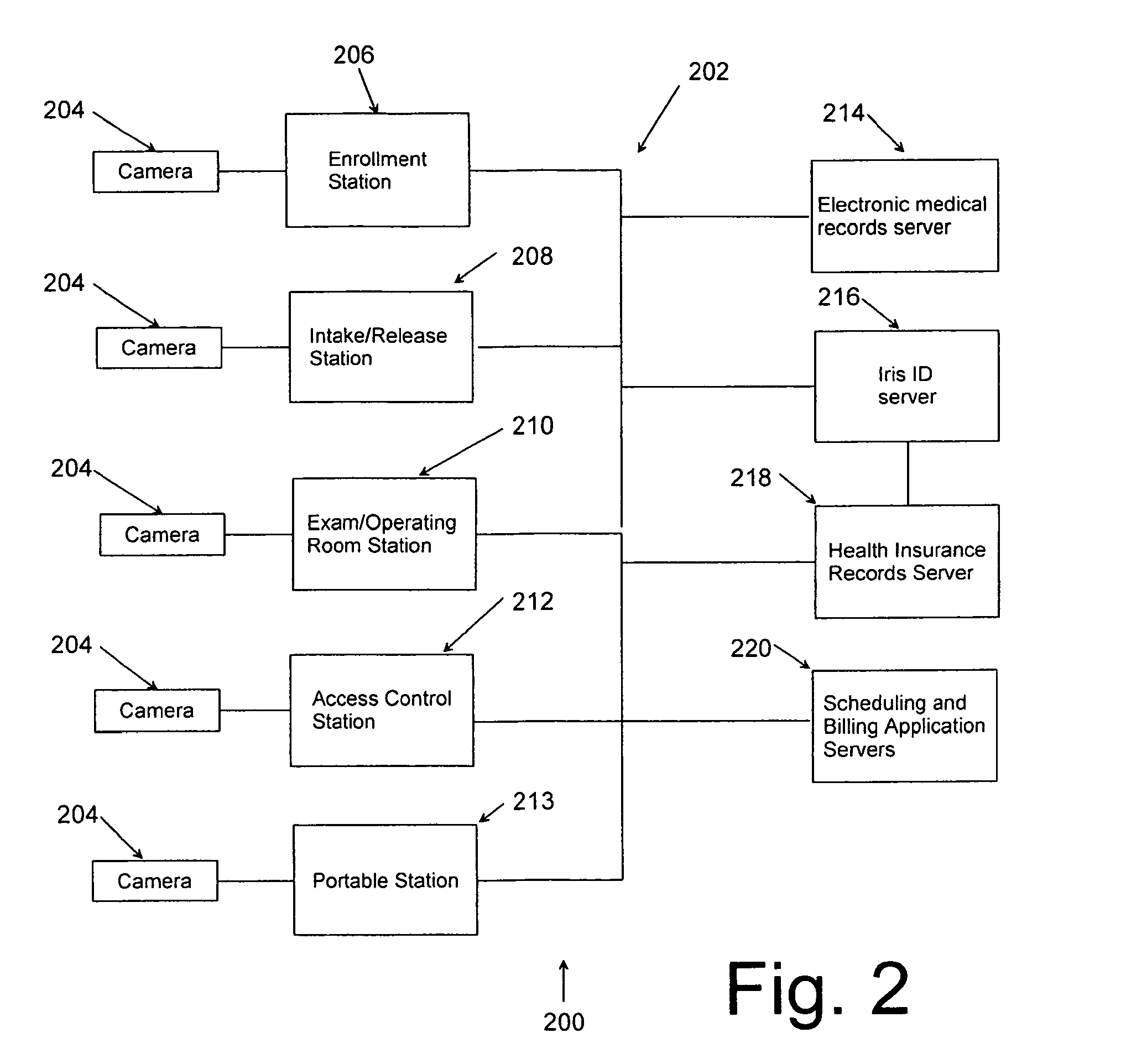
Systems and methods for biometric identification
InactiveUS20100183199A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsMedical recordDatabase server
An automated method of performing various processes and procedures includes central and / or distributed iris identification database servers that can be accessed by various stations. Each station may be equipped with a handheld staff-operated iris camera and software that can query the server to determine whether an iris image captured by the iris camera matches a person enrolled in the system. The station takes selective action depending on the identification of the person. In disclosed medical applications, the station may validate insurance coverage, locate and display a medical record, identify a procedure to be performed, verify medication to be administered, permit entry of additional information, history, diagnoses, vital signs, etc. into the patient's record, and for staff members may permit access to a secure area, permit access to computer functions, provide access to narcotics and other pharmaceuticals, enable activation of secured and potentially dangerous equipment, and other functions.
Owner:EYE CONTROLS
Object-oriented, parallel language, method of programming and multi-processor computer
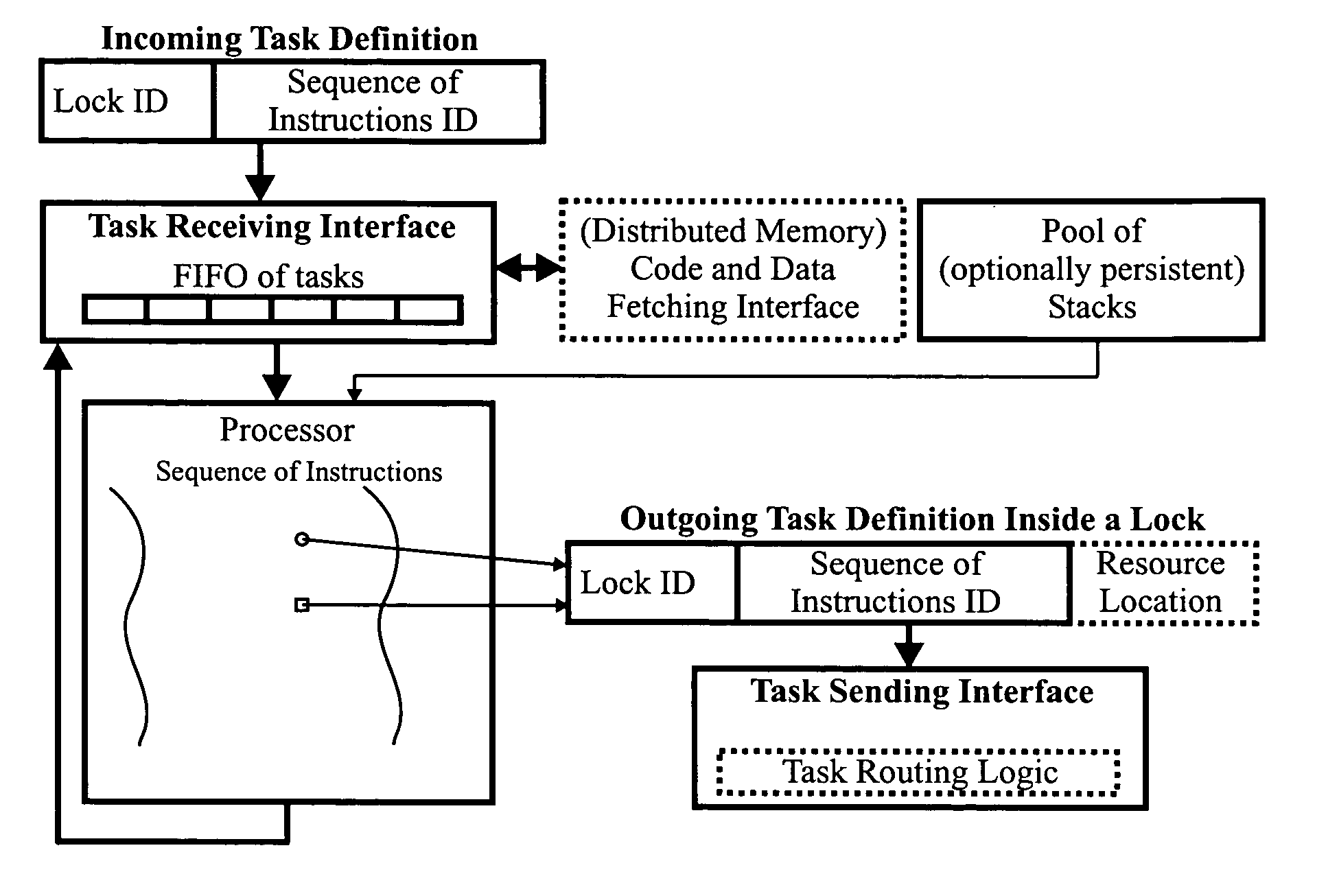
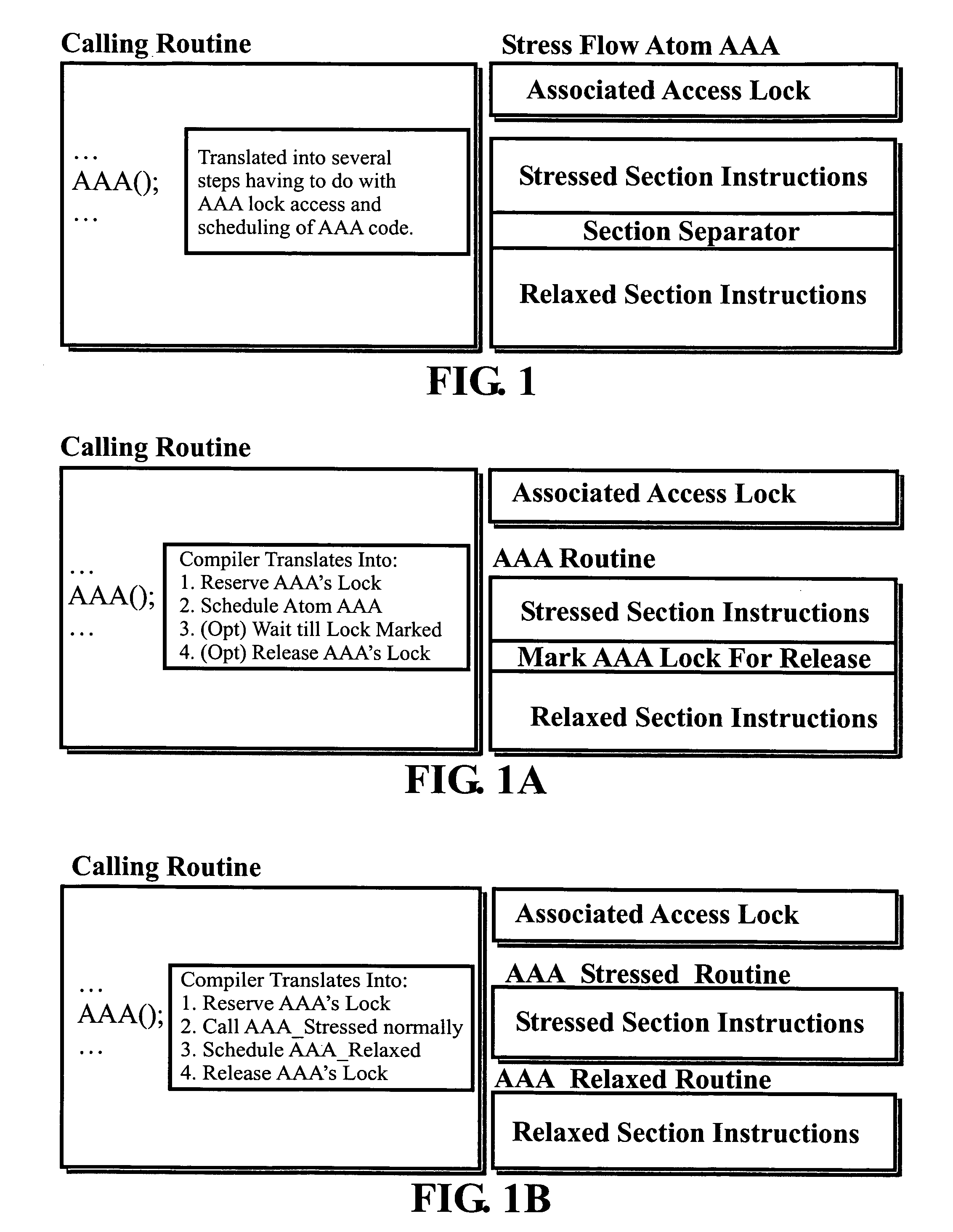
This invention relates to architecture and synchronization of multi-processor computing hardware. It establishes a new method of programming, process synchronization, and of computer construction, named stress-flow by the inventor, allowing benefits of both opposing legacy concepts of programming (namely of both data-flow and control flow) within one cohesive, powerful, object-oriented scheme. This invention also relates to construction of object-oriented, parallel computer languages, script and visual, together with compiler construction and method to write programs to be executed in fully parallel (or multi-processor) architectures, virtually parallel, and single-processor multitasking computer systems.
Owner:JANCZEWSKA NATALIA URSZULA +2
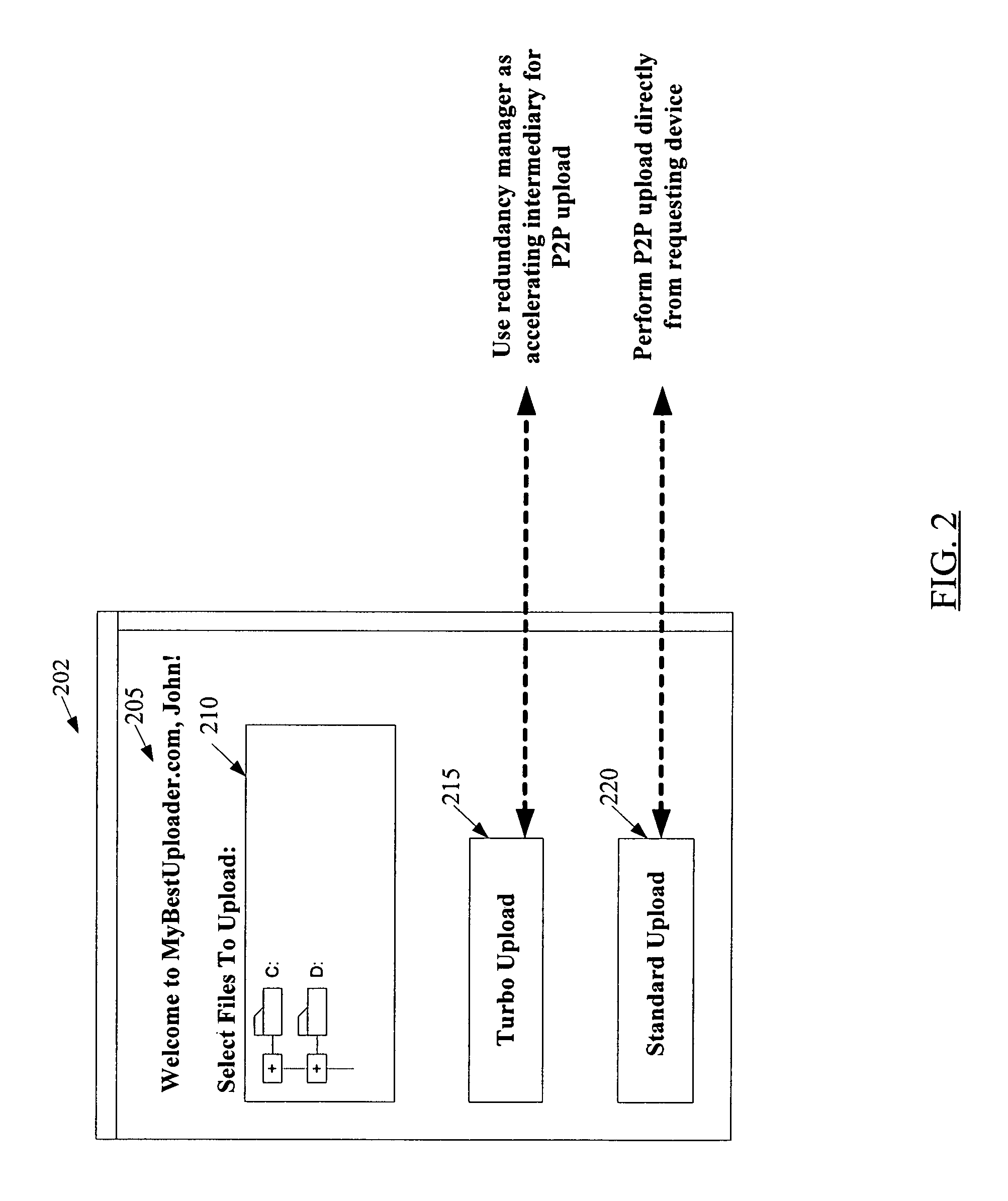
Redundancy management service for peer-to-peer networks
InactiveUS7783600B1Reduce client-side overheadDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsProgram instructionDistributed computing
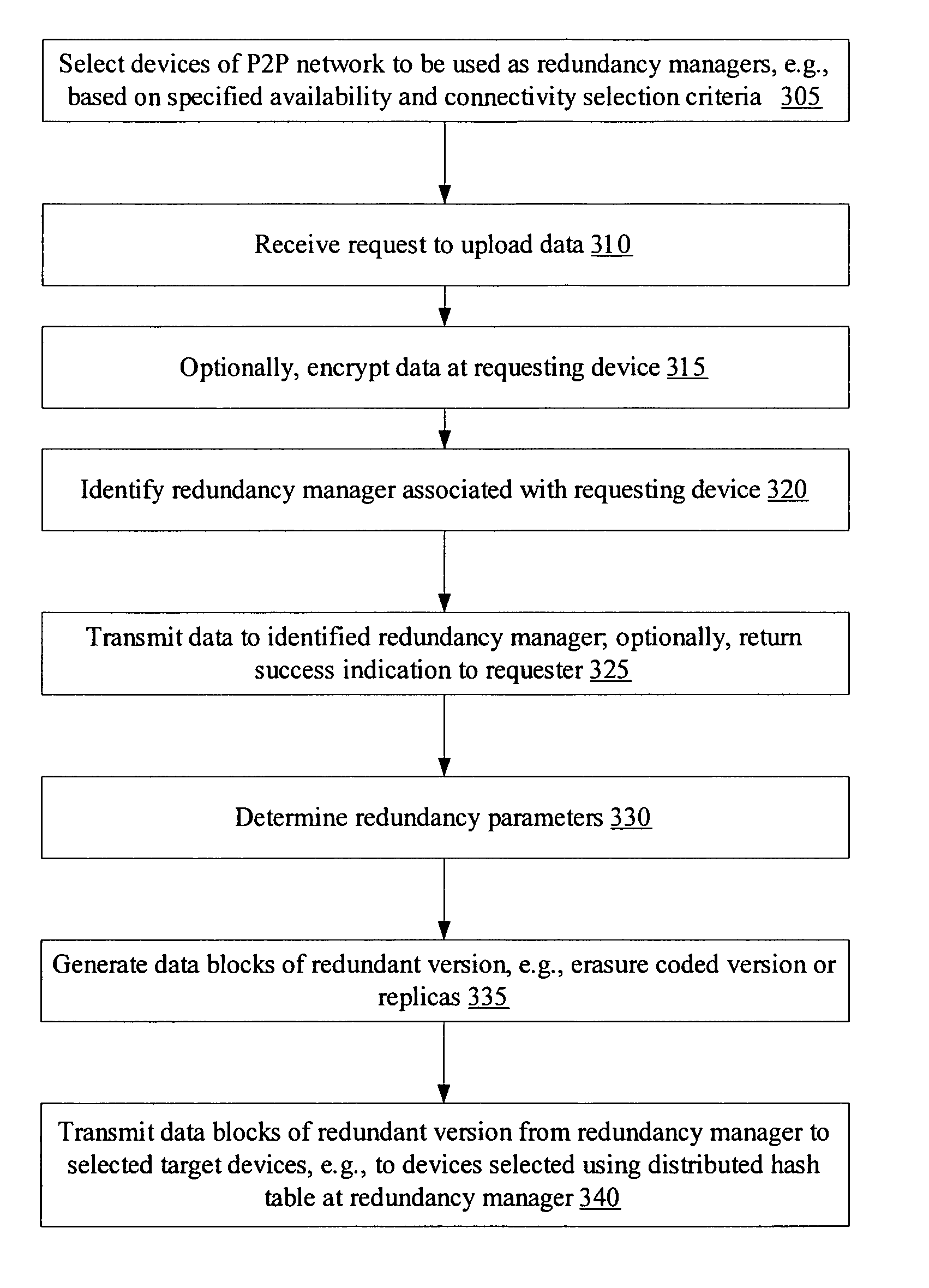
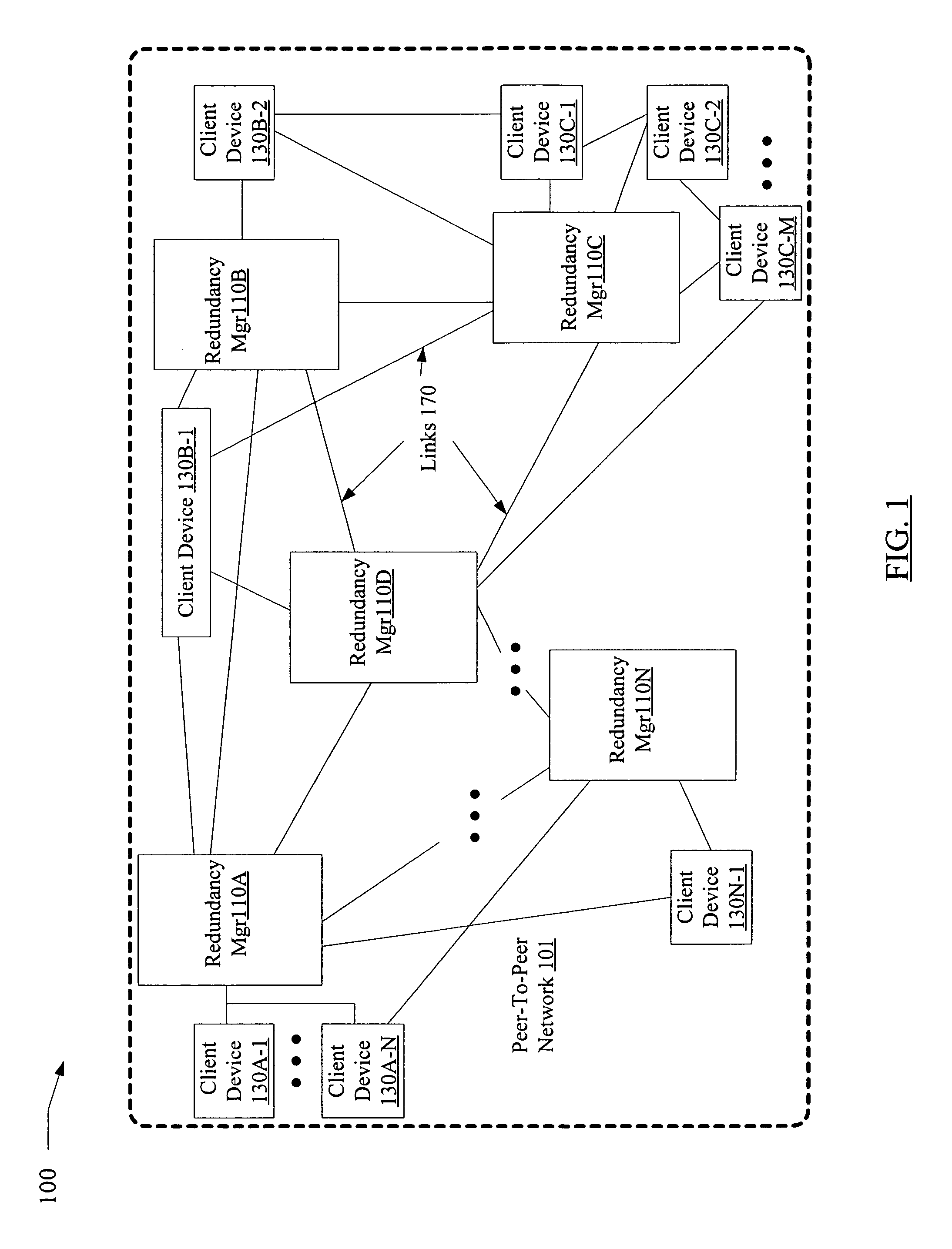
A system for a redundancy management service for peer-to-peer (P2P) networks includes one or more processors and memory coupled to the processors. The memory stores program instructions executable by the processors to receive a request at a device to upload a data object from the device into a P2P network. In response to receiving the request, the instructions are executable to identify a redundancy manager associated with the device and to transmit the data object to the redundancy manager. In addition, the instructions are executable to upload, from the redundancy manager to one or more target devices of the P2P network, a plurality of data blocks derived from the data object, such that the data object may be recovered from a subset of the plurality of data blocks.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Devices and methods for performing procedures on a breast
InactiveUS6936014B2Less obtrusiveLess susceptible to inadvertent bumpingSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsMedicineAngular orientation
Owner:ENCAPSULE MEDICAL
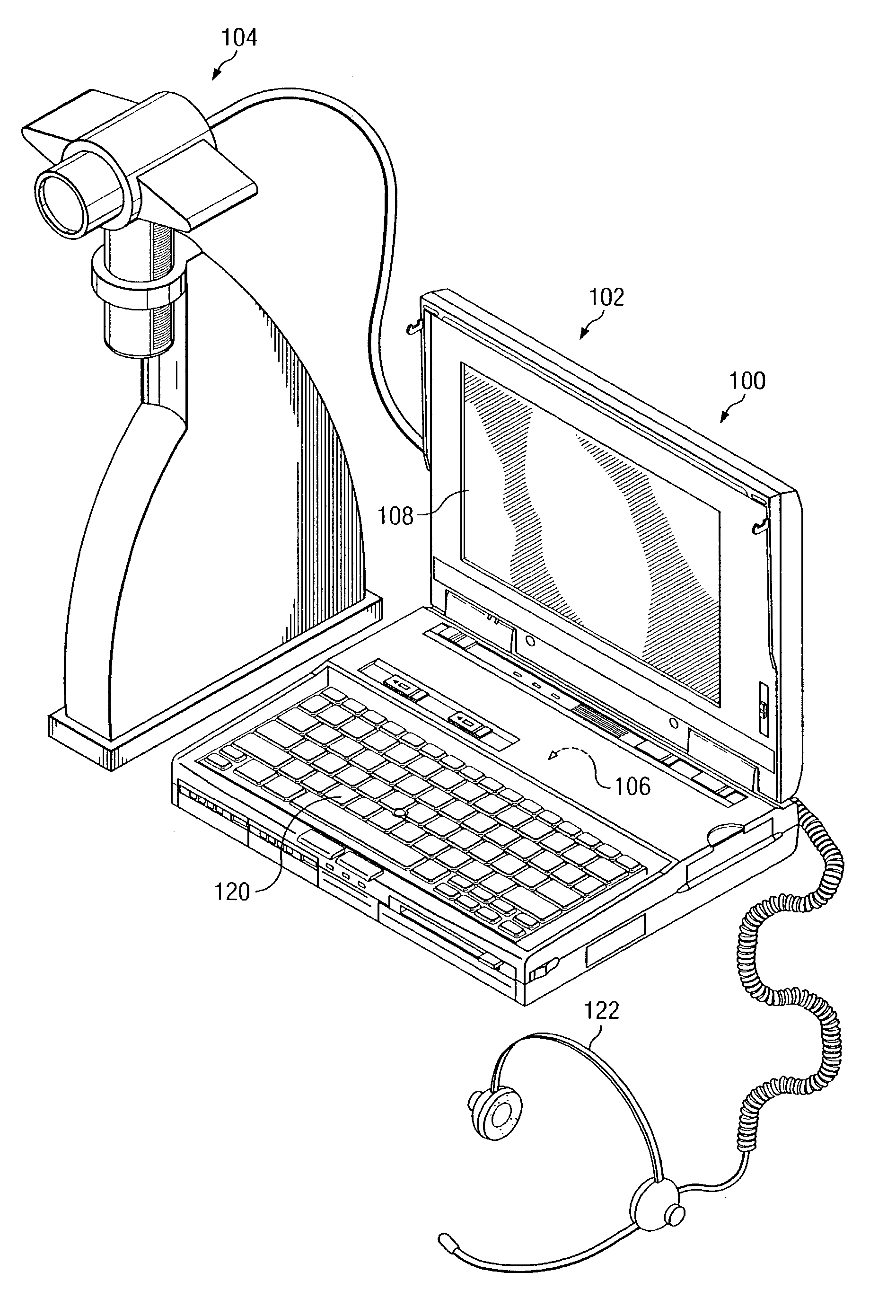
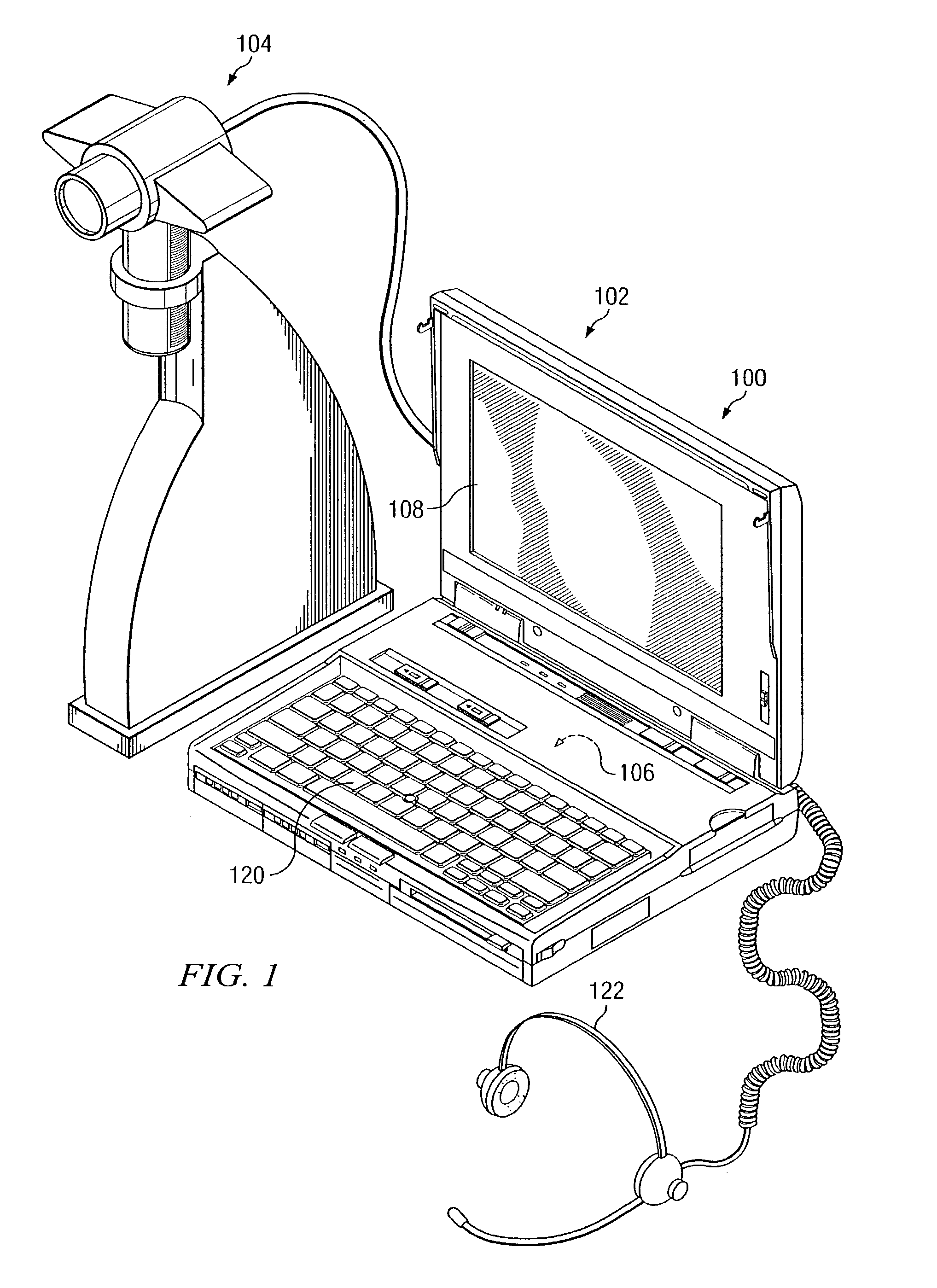
Apparatus and method for computerized multi-media medical and pharmaceutical data organization and transmission
InactiveUS7956894B2Television system detailsData processing applicationsDisplay deviceUser interface
An apparatus for multi-media data organization and transmission is provided. The apparatus has a computer having a microprocessor, a memory storage, a display for providing information to a user, and an input device. An image-recording device is electrically-coupled to the computer for capturing images for storage in the memory storage of the computer. A database, which has a structure defined in the memory storage, receives and stores a plurality of information relating to an event. A program, being executable by the computer, provides a graphical user interface on the display. The program has an imaging module with document and image capture filing and scanning functions. The graphical user interface receives an input from the input device and from the image-recording device. In a further aspect of the invention, the program has a communications module for transmission of the plurality of information relating to the event to a remote location.
Owner:AKERS WILLIAM REX
Direct drive methods
Described herein are various method of using a direct drive system to perform procedures at a distance. One exemplary method include tying a knot or suturing at a distance with a first and second end effector. The direct drive system can enable sufficient end effector dexterity, including the ability to control various degrees of freedom of end effector movement, and allow a user to perform complicated task at a distance. In one aspect the direct drive system includes flexible tools that permit access to surgical site via a natural orifice.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
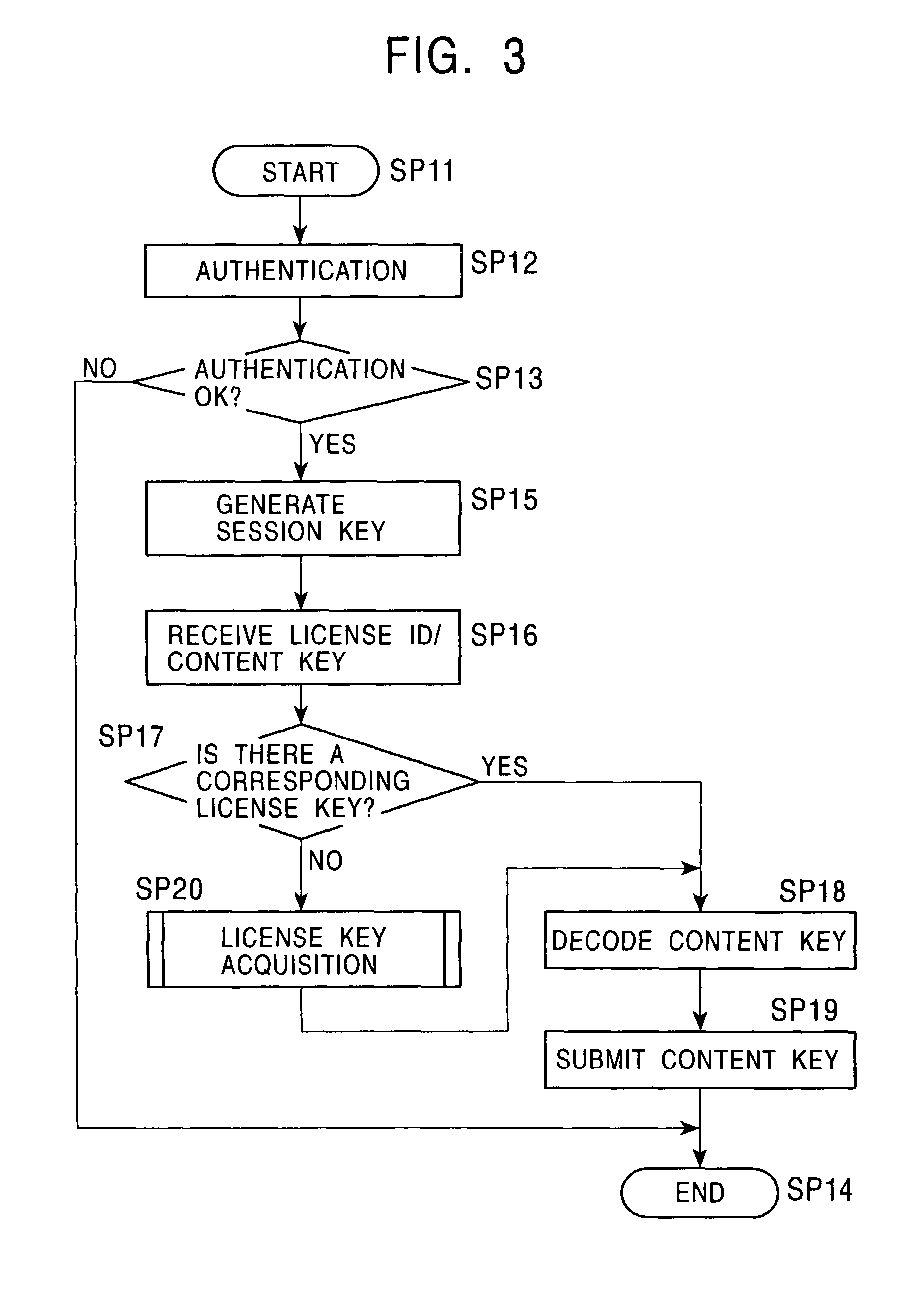
Method and apparatus for providing information for decrypting content, and program executed on information processor
InactiveUS7809944B2Solve the lack of reliabilitySimple structureUser identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsComputer hardwareUser authentication
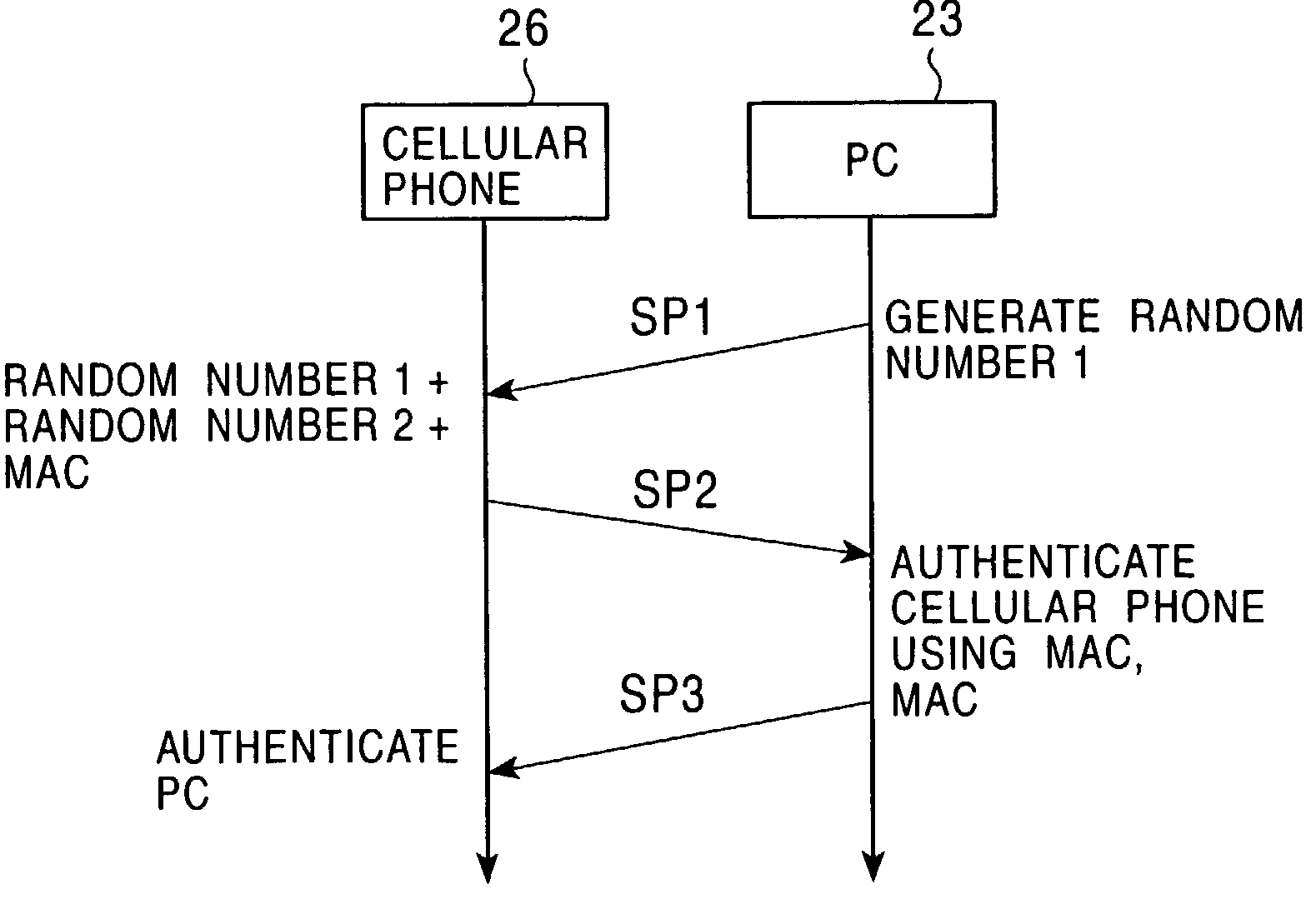
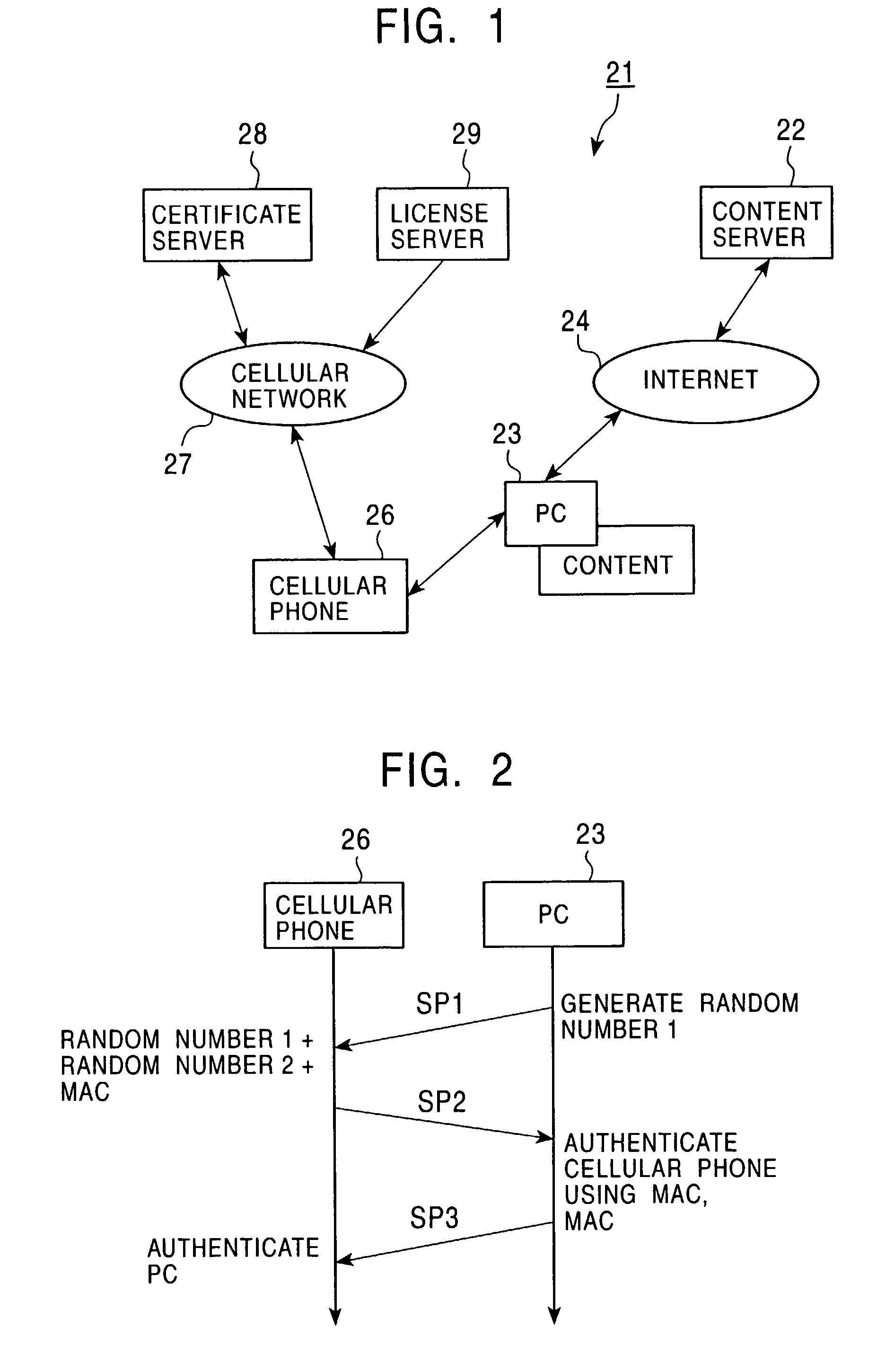
The authentication capability of a portable terminal connected to a playback device is used to perform user authentication, thereby providing content with a sufficient reliability while only requiring a simple mechanism.
Owner:SONY CORP
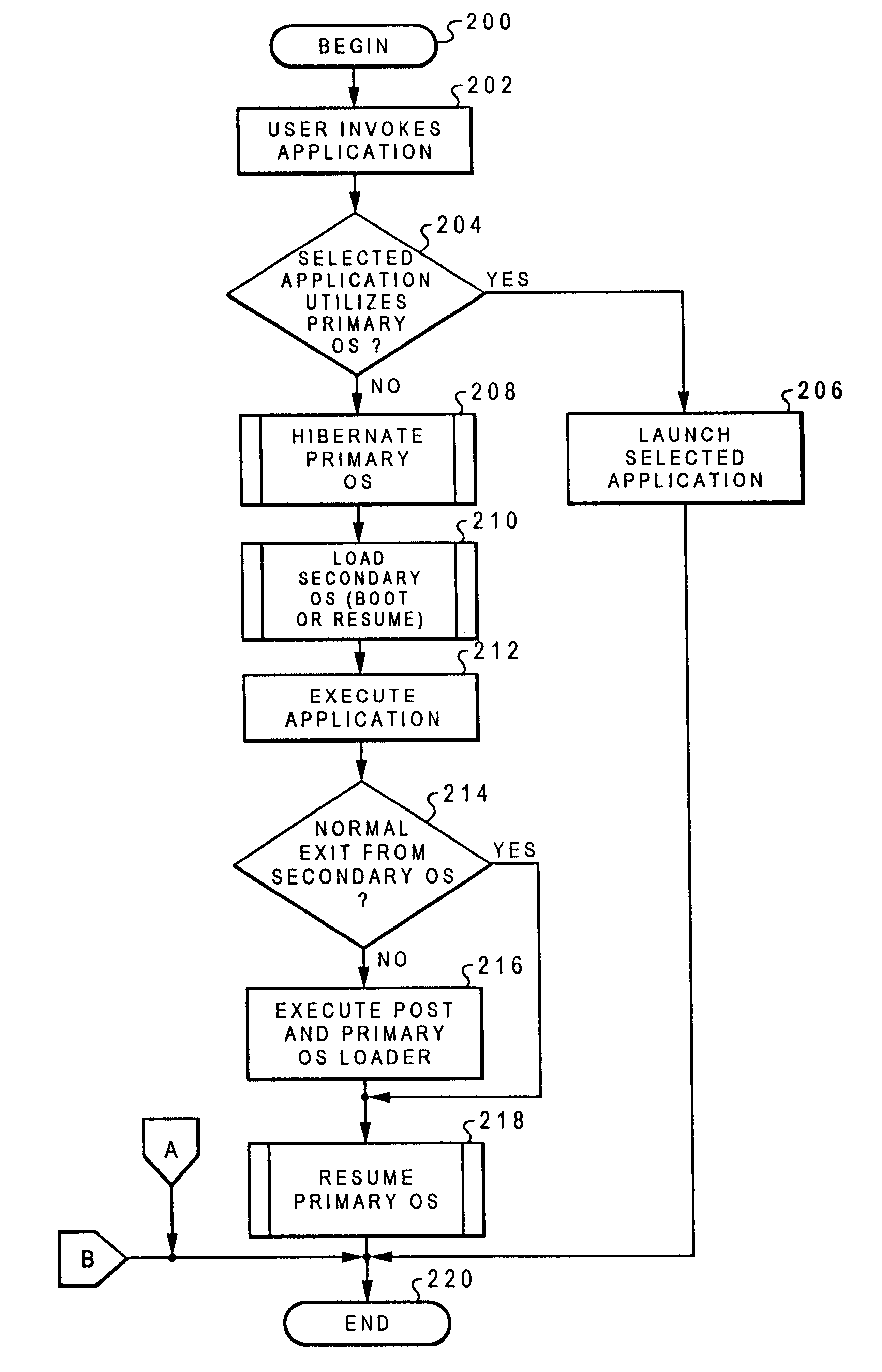
Method and system for executing a program under one of a plurality of mutually exclusive operating environments
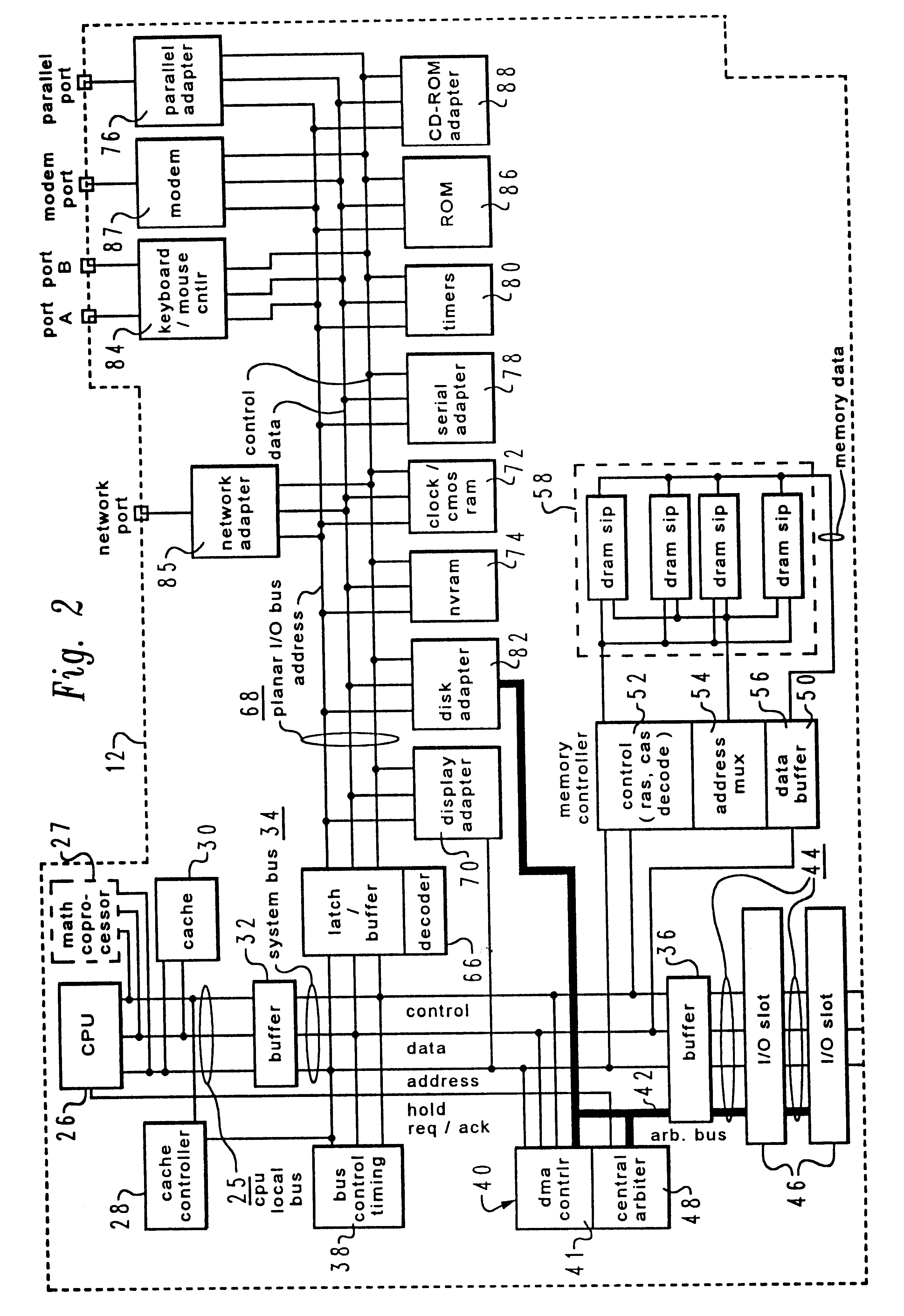
InactiveUS6678712B1Program initiation/switchingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMass storageData processing system
A method and system within a data processing system for executing a program under one of a number of mutually exclusive operating systems are disclosed. The data processing system includes a nonvolatile mass storage device, a volatile memory, and a processor. According to the present invention, a program which executes under a second operating system is invoked while the processor is executing a first operating system. In response to invocation of the program, the data processing system is forced to a quiescent state. A state of the first operating system is then determined from contents of the volatile memory and stored within either the volatile memory or the nonvolatile mass storage device. In response to storage of the state of the first operating system, at least a portion of the second operating system is automatically loaded into the volatile memory. Thereafter, the program is executed under the second operating system, wherein interchange between mutually incompatible operating systems within a single data processing system is efficiently accomplished. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the method of the present invention is embodied within a computer program product for causing a data processing system to perform the foregoing steps.
Owner:IBM CORP
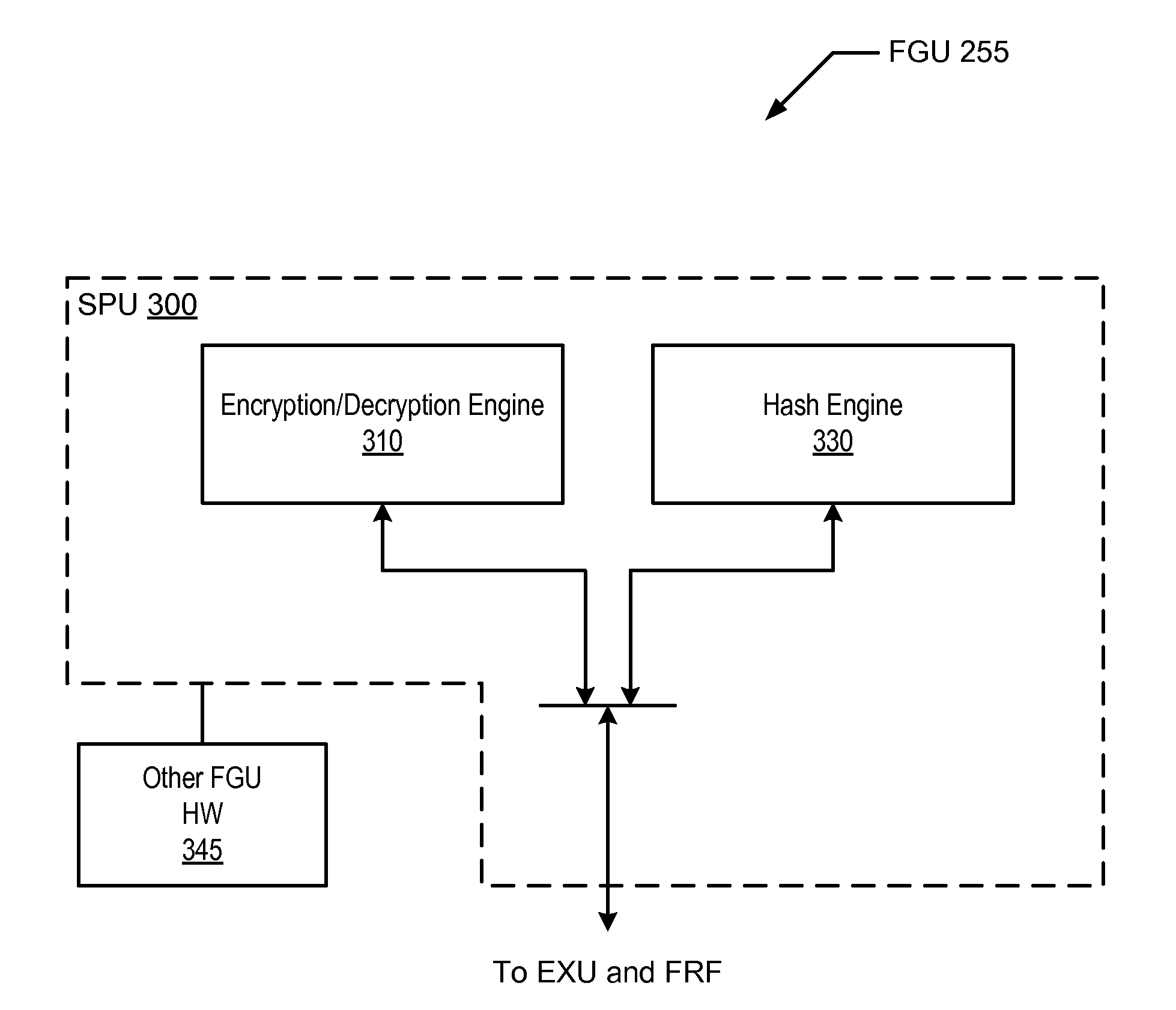
Processor and method for implementing instruction support for hash algorithms
ActiveUS20100250966A1Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareProcessor register
A processor including instruction support for implementing hash algorithms may issue, for execution, programmer-selectable hash instructions from a defined instruction set architecture (ISA). The processor may include a cryptographic unit that may receive instructions for execution. The instructions include hash instructions defined within the ISA. In addition, the hash instructions may be executable by the cryptographic unit to implement a hash that is compliant with one or more respective hash algorithm specifications. In response to receiving a particular hash instruction defined within the ISA, the cryptographic unit may retrieve a set of input data blocks from a predetermined set of architectural registers of the processor, and generate a hash value of the set of input data blocks according to a hash algorithm that corresponds to the particular hash instruction.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
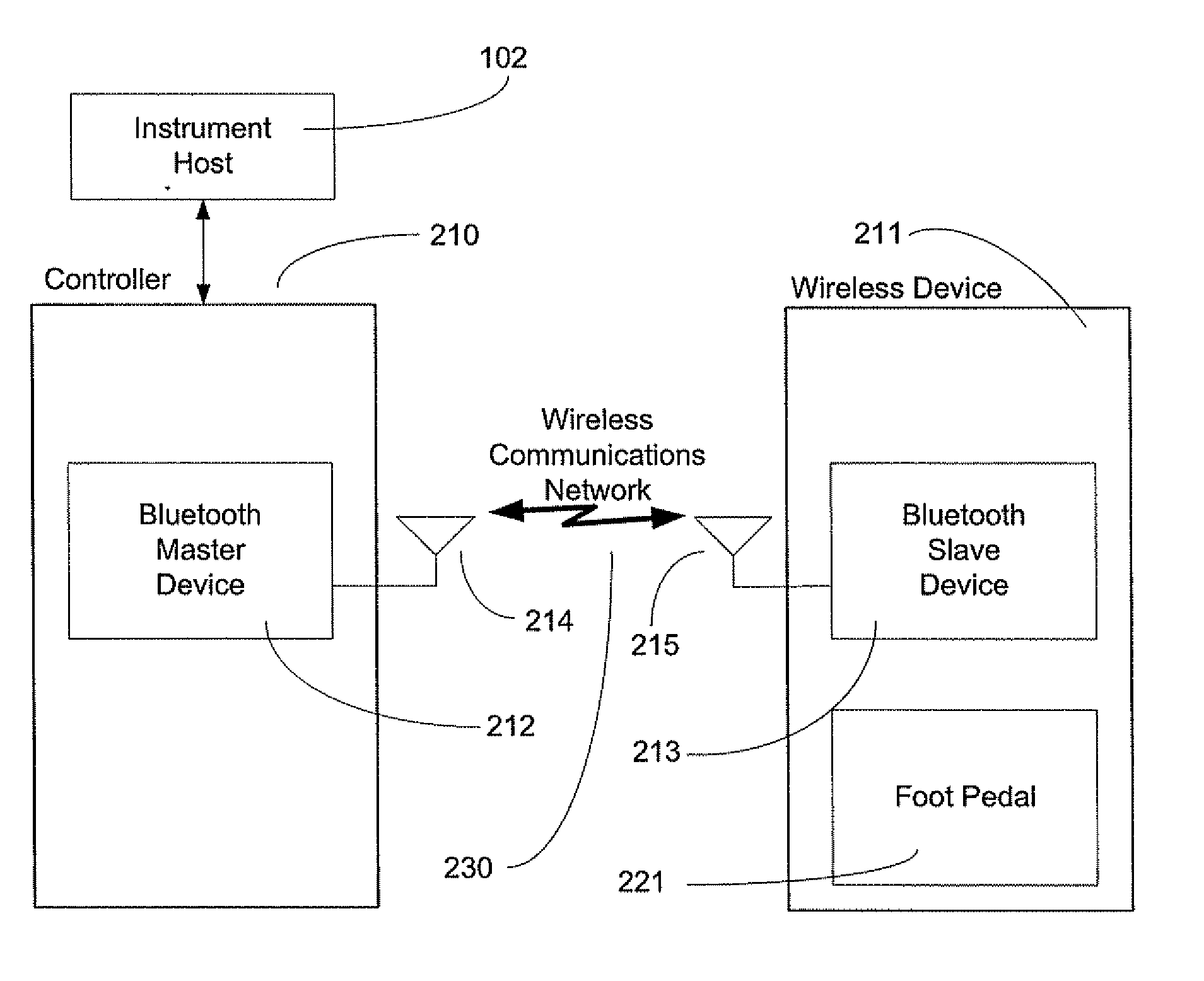
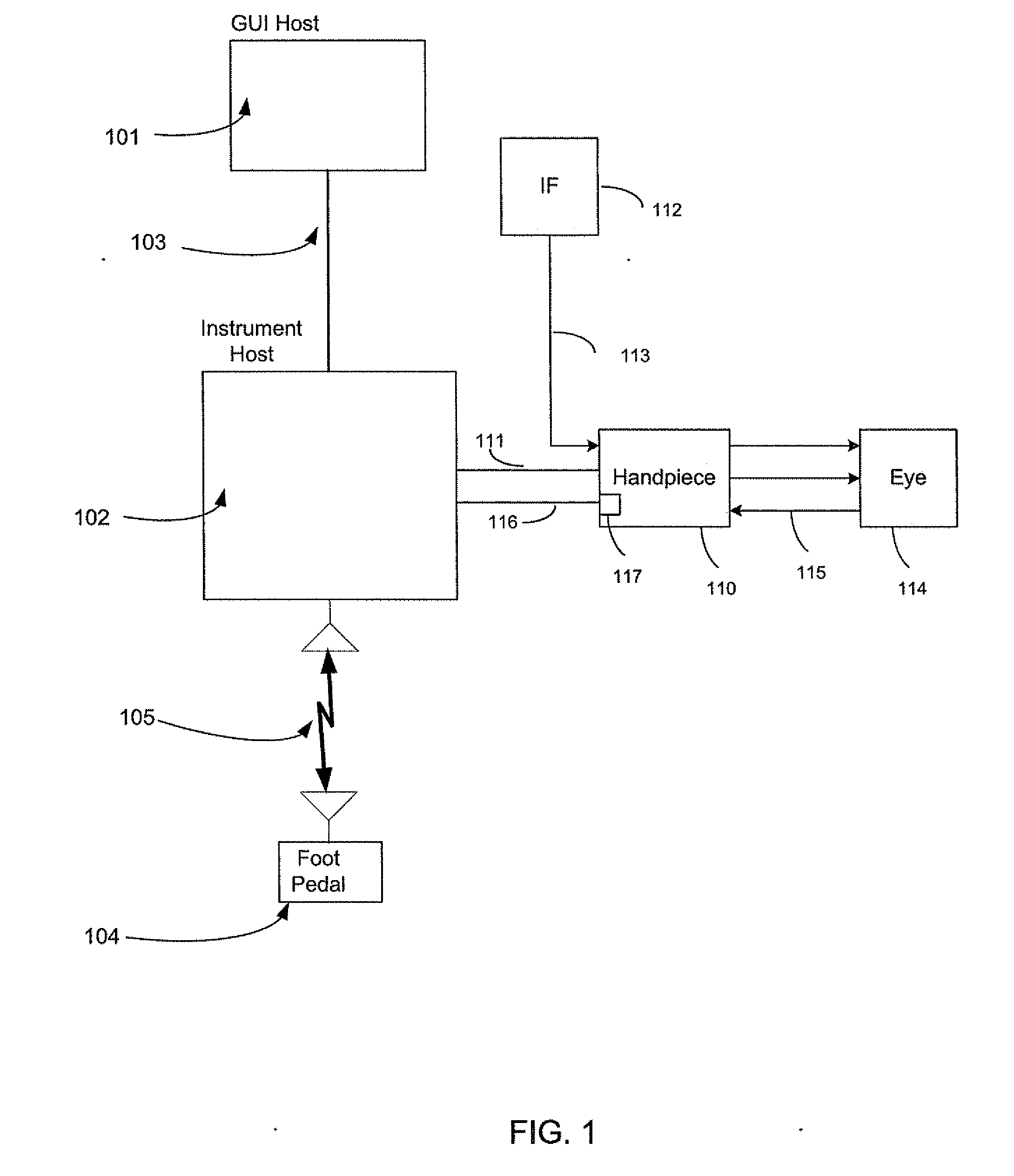
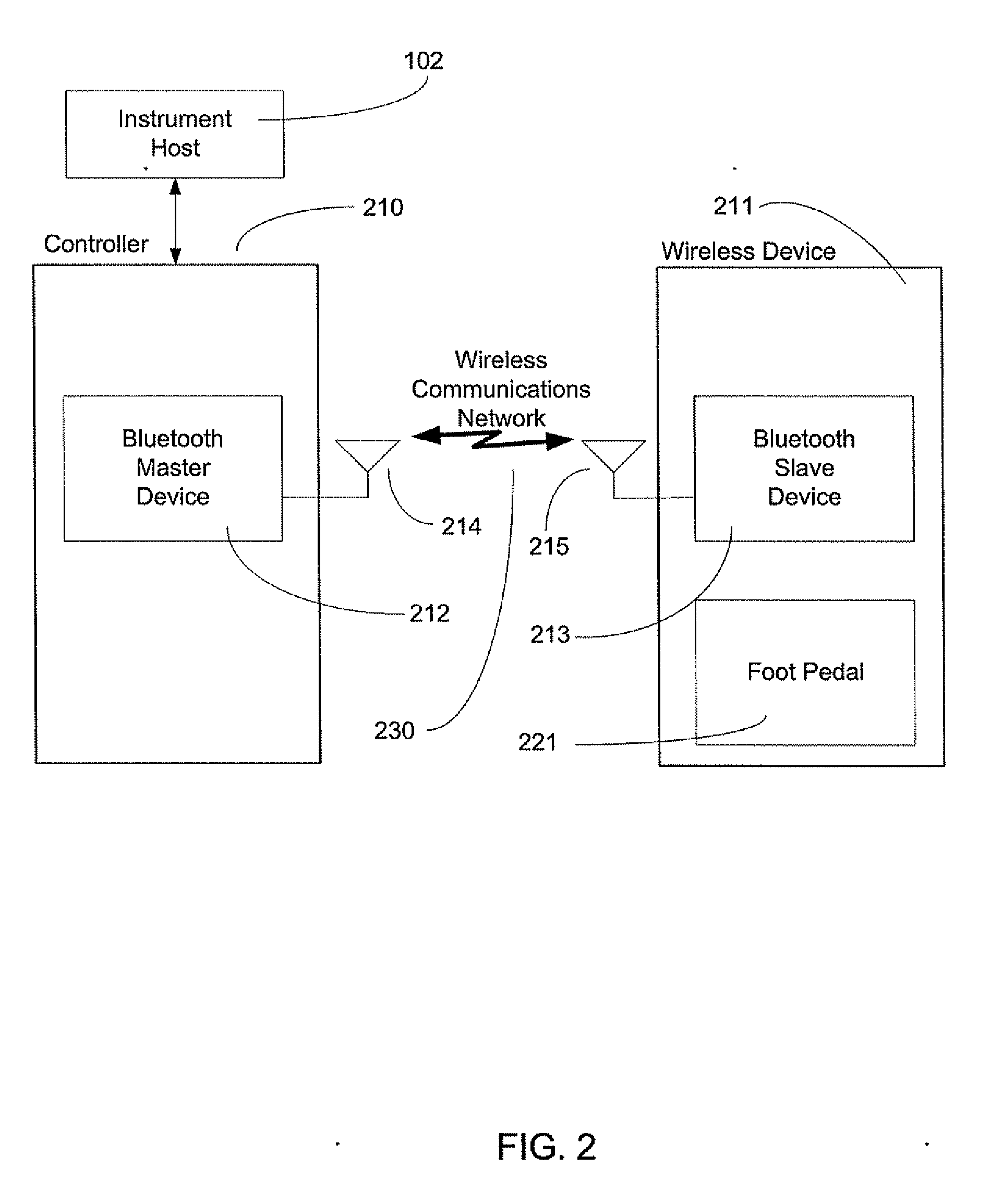
Exclusive pairing technique for bluetooth compliant devices
A method and system of establishing communications between at least two independent software modules in a safety critical system, such as a medical system, is provided. The design comprises providing an exclusive Bluetooth connection between at least two wireless devices. A master wireless device is configured with Bluetooth master device functionality and a slave wireless device is configured with Bluetooth slave device functionality. The wireless devices are employed in performing procedures in a safety critical environment. The method further comprises acquiring a stored unique address from the slave wireless device over the Bluetooth connection, comparing the stored unique address to a master wireless device unique address available at the master wireless device, and exclusively pairing the master wireless device and the slave wireless device when the unique address acquired from the slave wireless device is found to identically match the master wireless device unique address.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
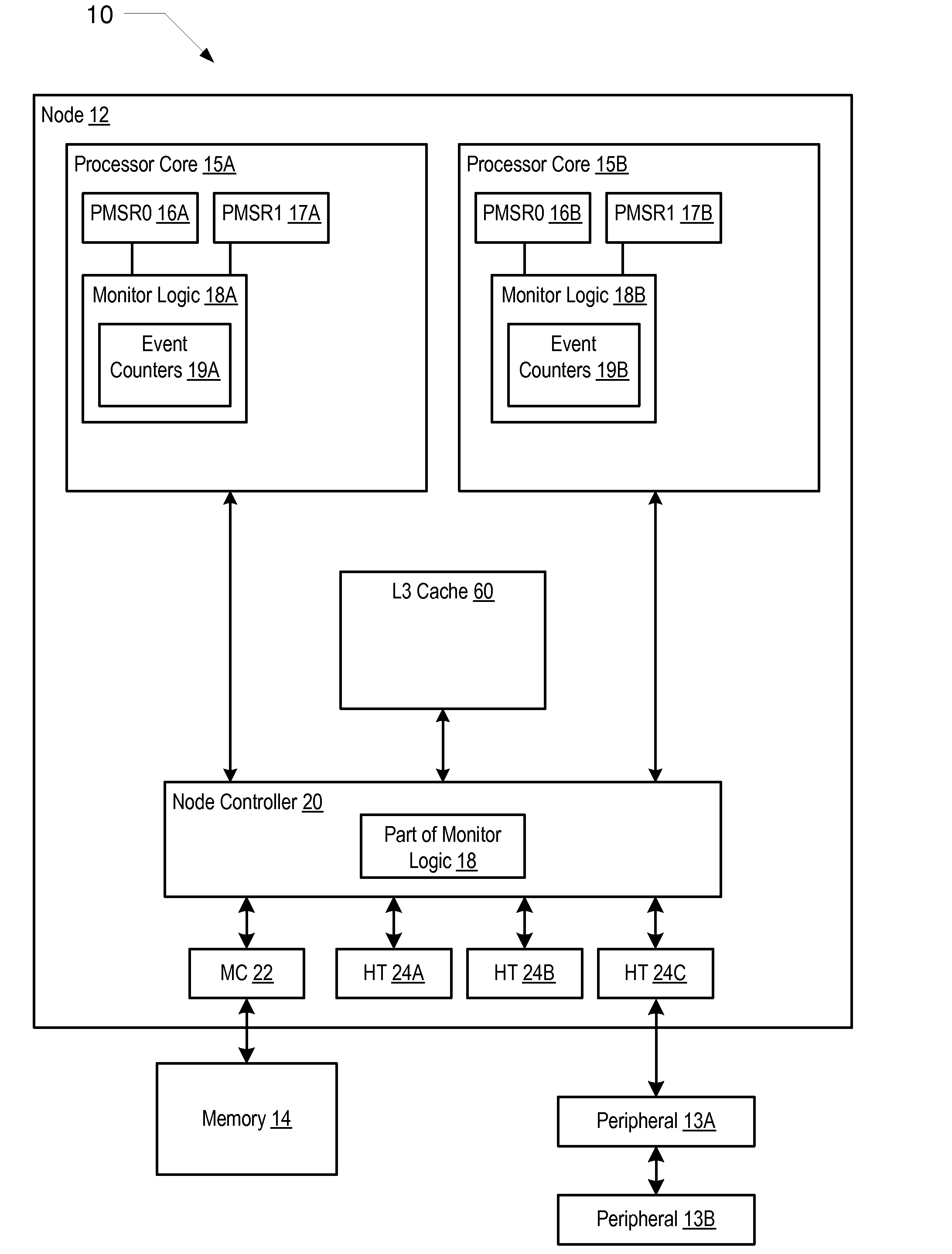
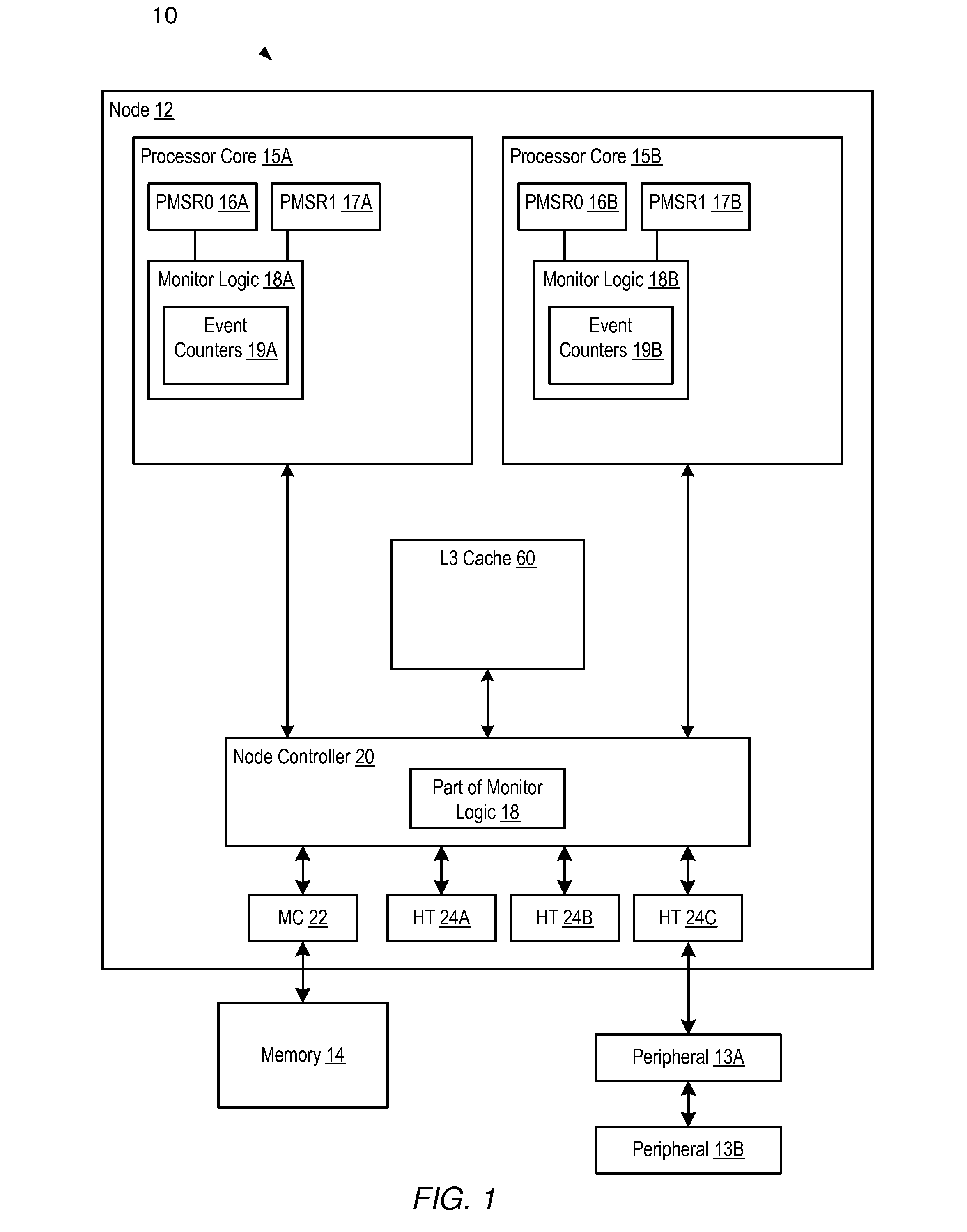
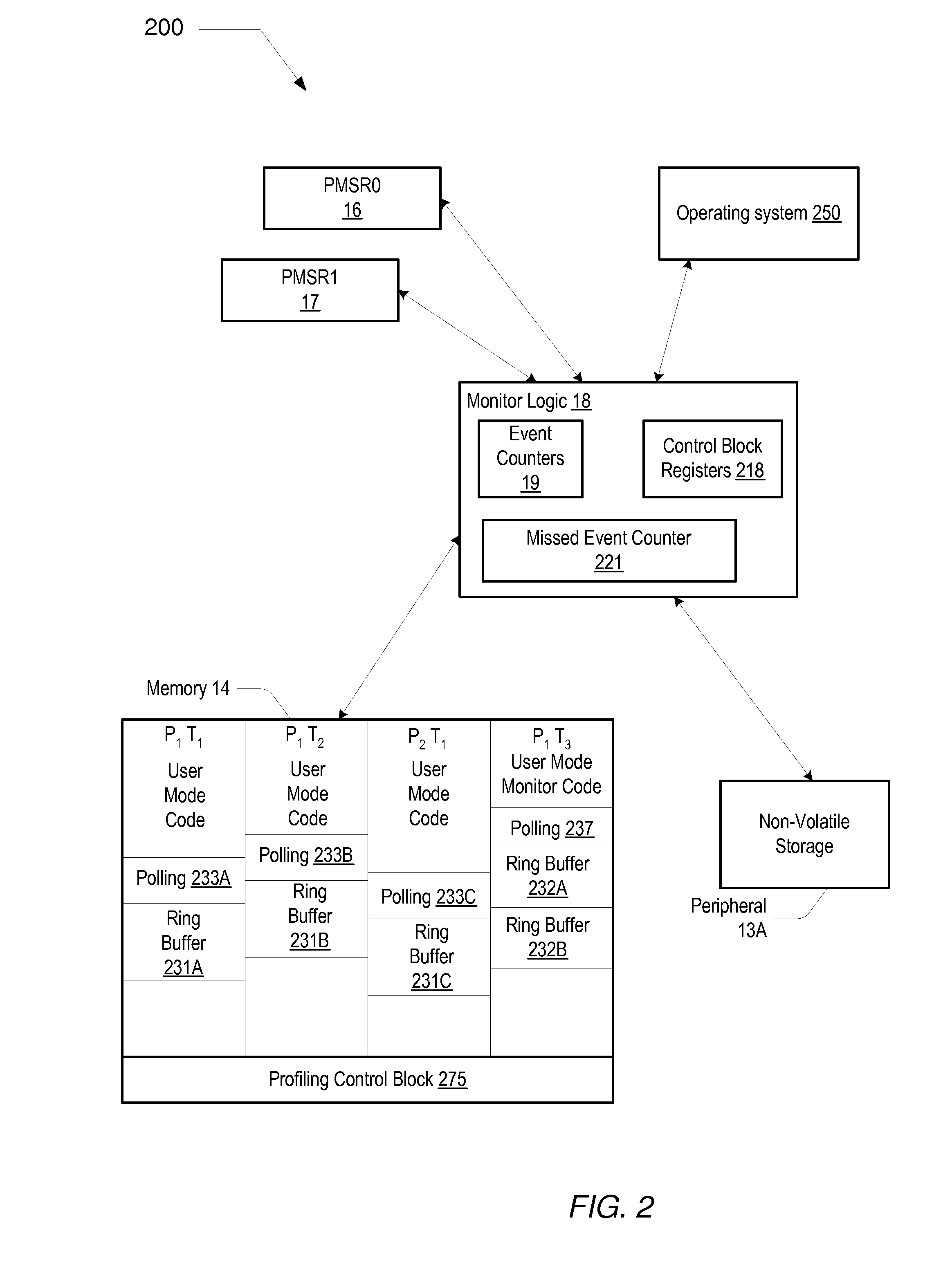
Mechanism for profiling program software running on a processor
InactiveUS20090157359A1Nuclear monitoringDigital computer detailsProgram instructionPerformed Procedure
A processor having one or more processor cores includes execution logic that may execute instructions including one or more processes. Each process may include one or more execution threads. The processor also includes a profiling mechanism that includes monitor logic and a monitor process. The monitor logic may monitor the one or more processes and provide access to performance data associated with the one or more processes without interrupting a flow of control of the one or more processes being monitored. The monitor process may gather the performance data. In addition, the monitor process may include program instructions executable by the one more processor cores while operating in user mode.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
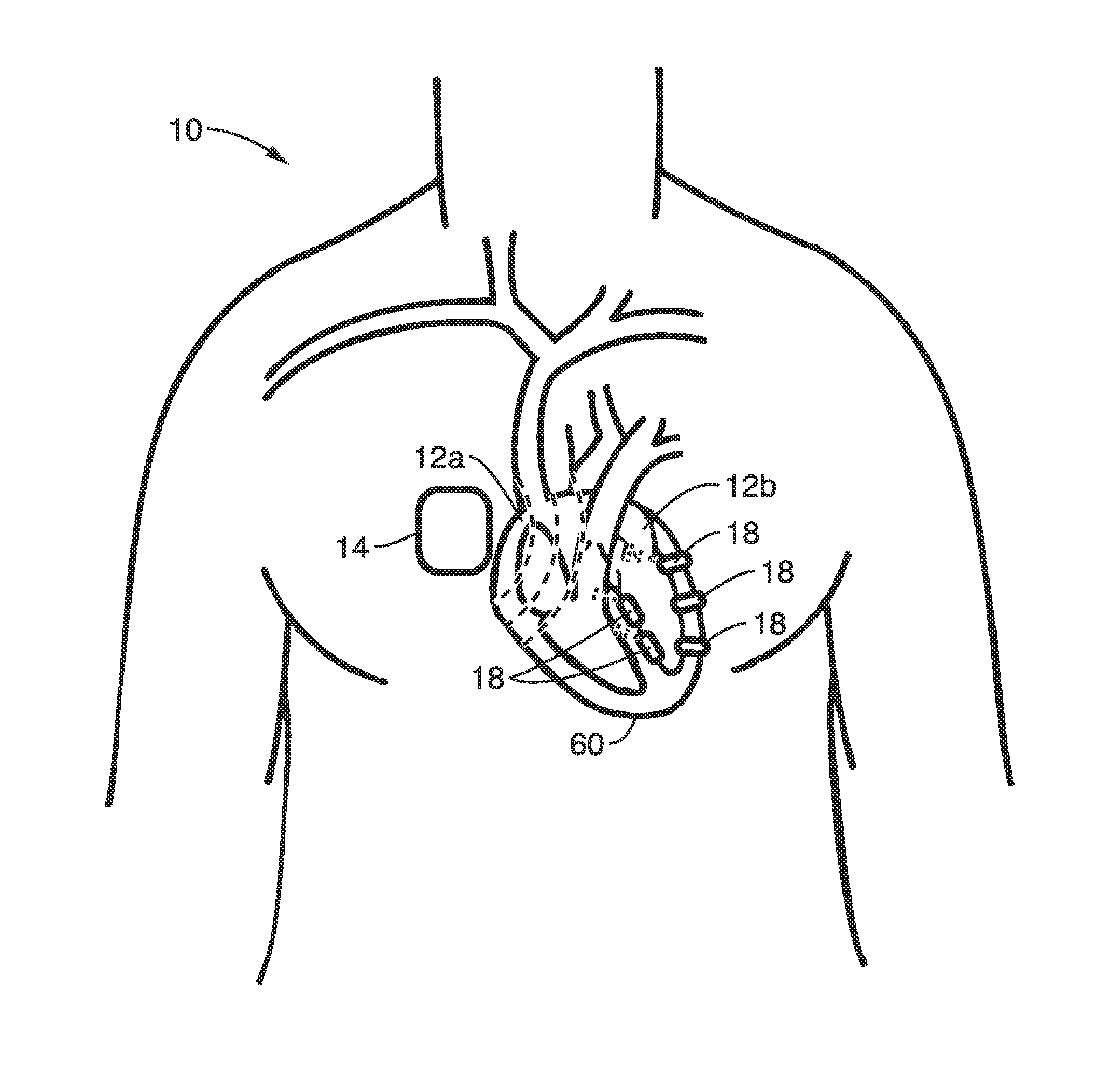
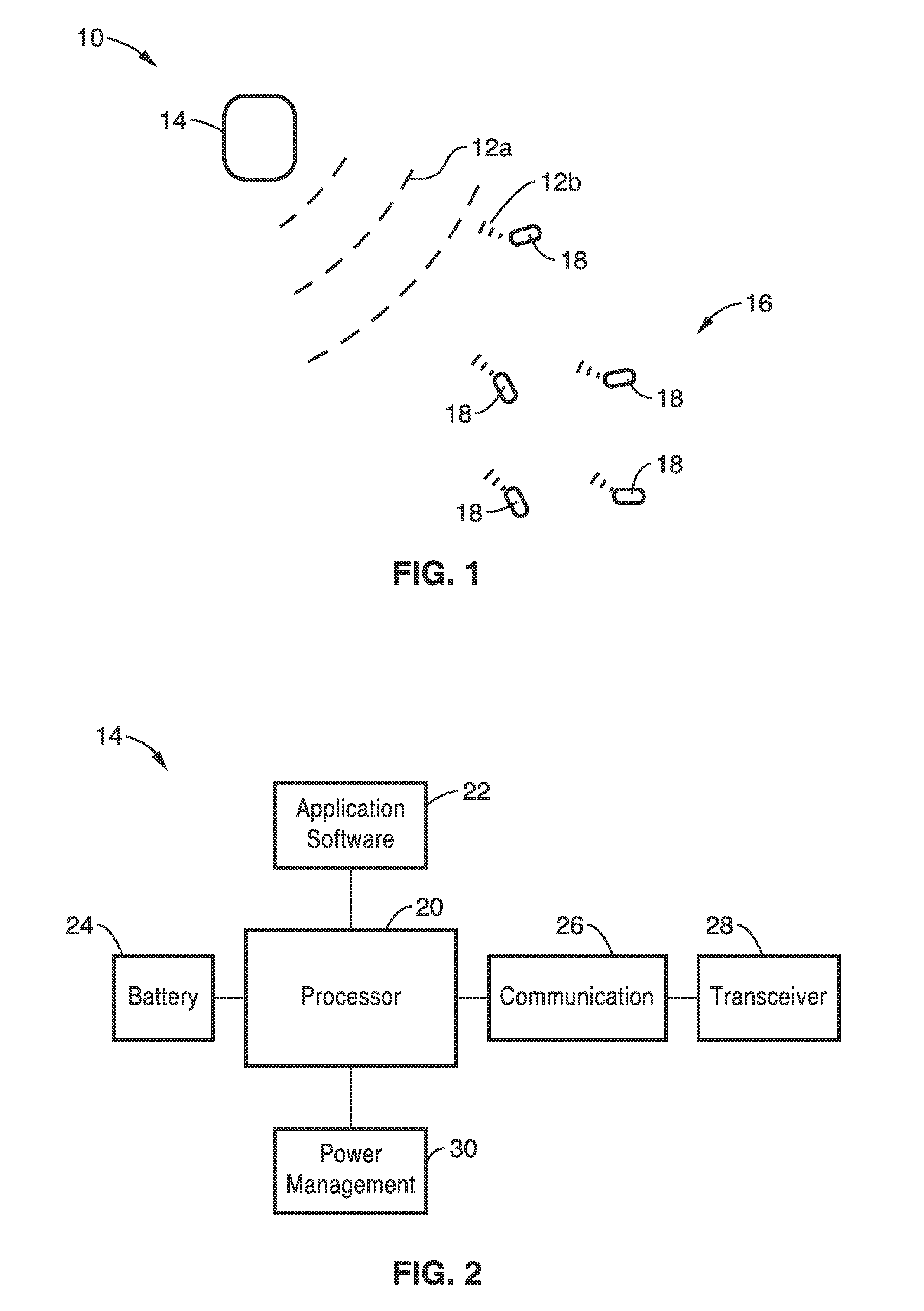
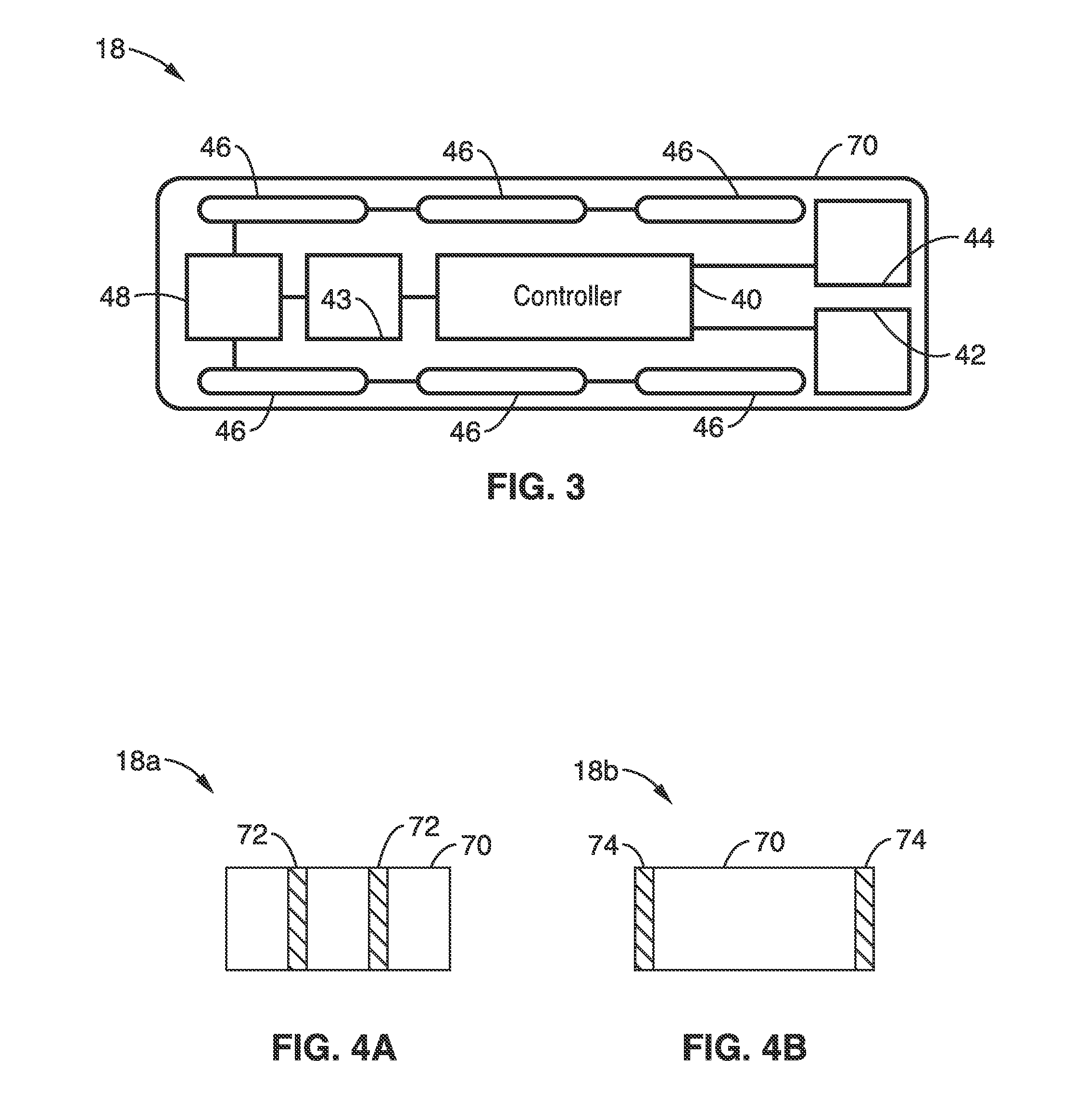
Intelligent self-organizing electrode stimulation delivery system
InactiveUS8977358B2Effective treatmentLower energy requirementsHeart stimulatorsZero phaseBiological activation
An electrode stimulation delivery system is described having a unit and a network of wireless remote electrodes configured for implantation within a plurality of spaced apart locations in the tissue, e.g. myocardium, of a patient. The control unit is configured to be positioned at or subcutaneous to the patient's skin, and includes a processor, an antenna configured for delivering RF energy in proximity to the plurality of wireless remote electrodes, and programming executable on the processor for wirelessly communicating to the network of wireless remote electrodes via the delivered RF energy to individually control pacing of the plurality of wireless remote electrodes. Each of the plurality of wireless remote electrodes comprises a metamaterial-based biomimetic harvesting antenna comprising a Van Atta array zero-phase transmission lines to receive the RF energy to power activation of the plurality of wireless remote electrodes.
Owner:NORTH DAKOTA STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
User authentication method and apparatus based on audio and video data
ActiveUS20140237576A1Reduce riskAvoid many riskDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsUser authenticationMobile device
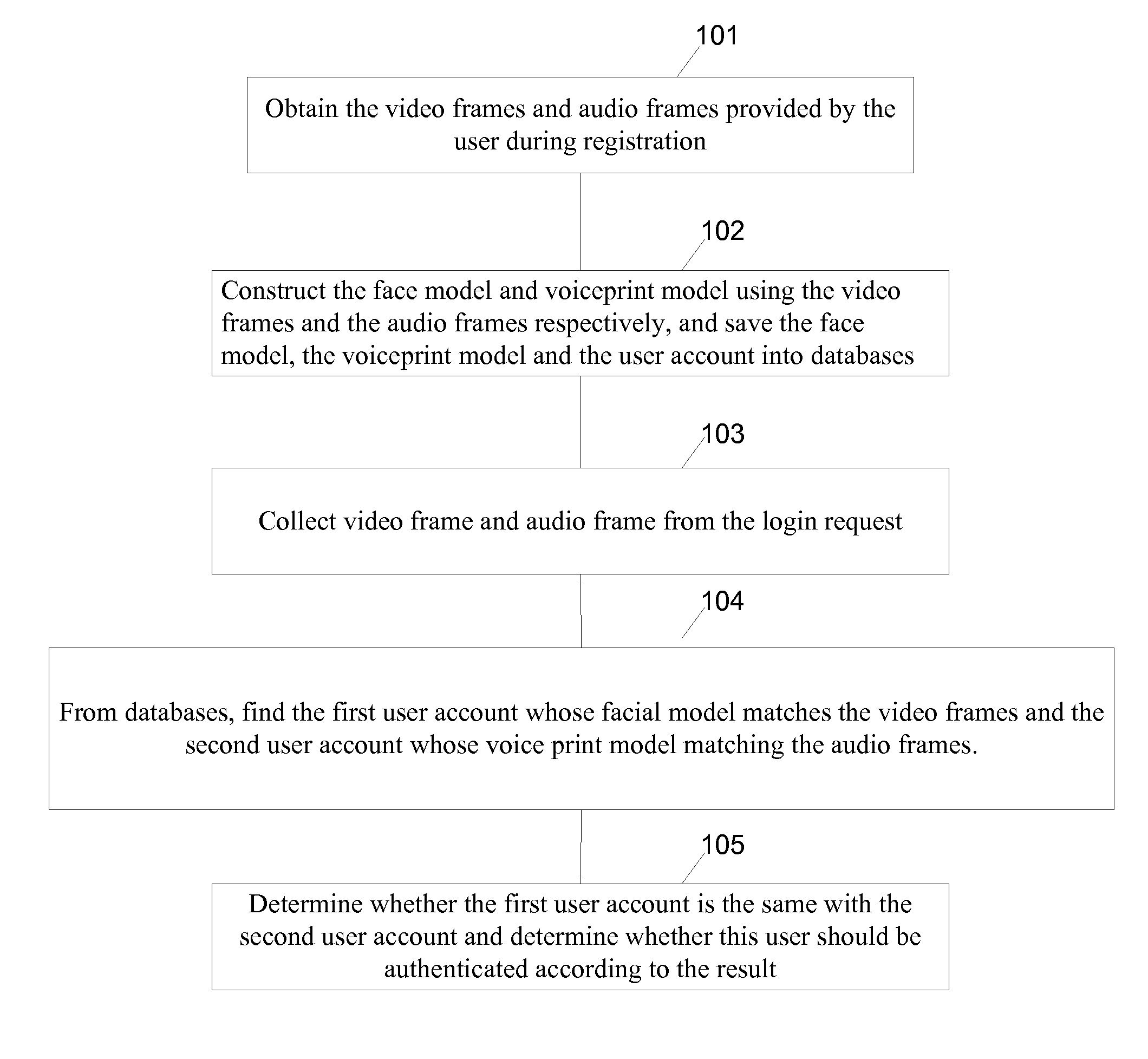
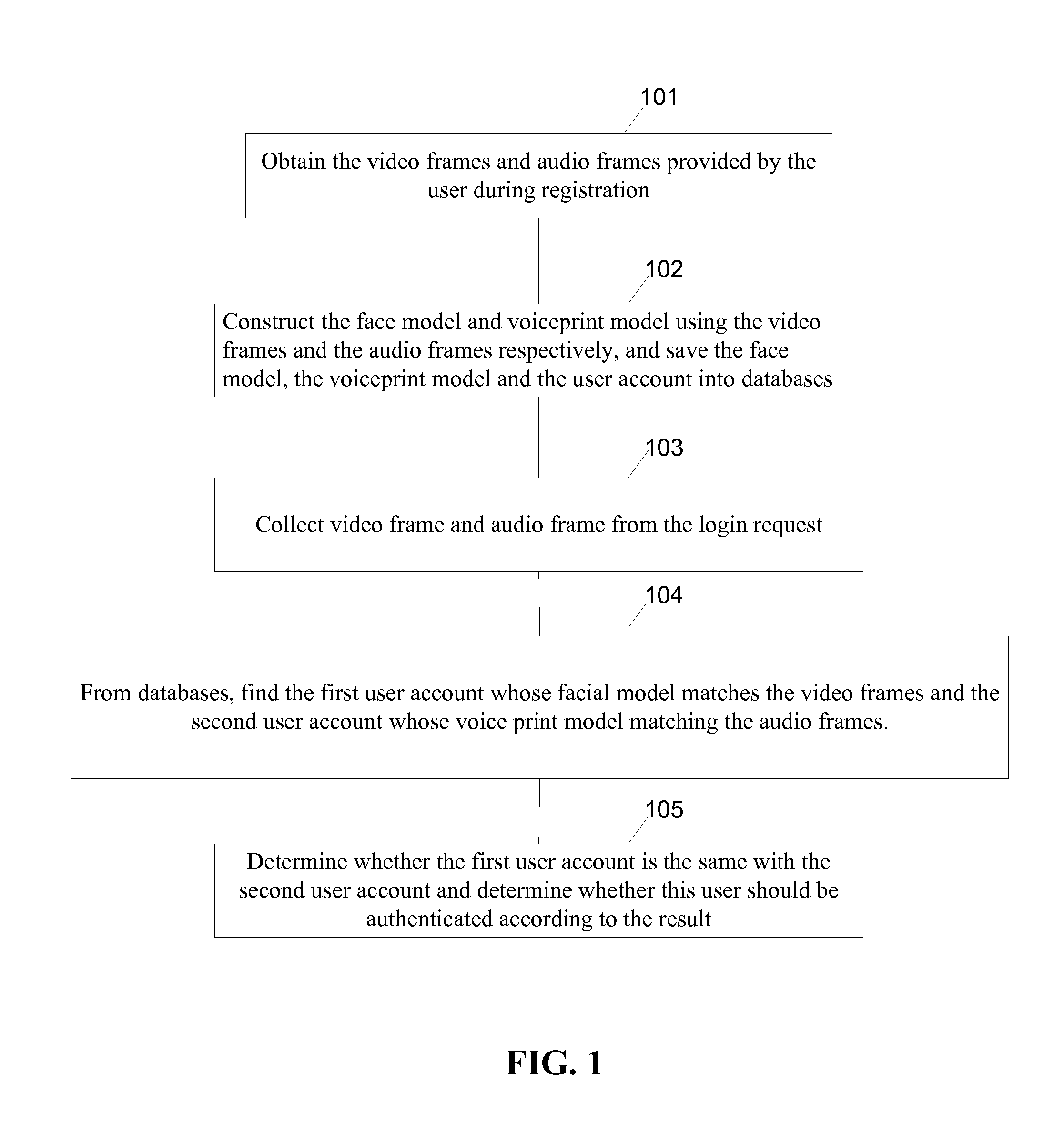
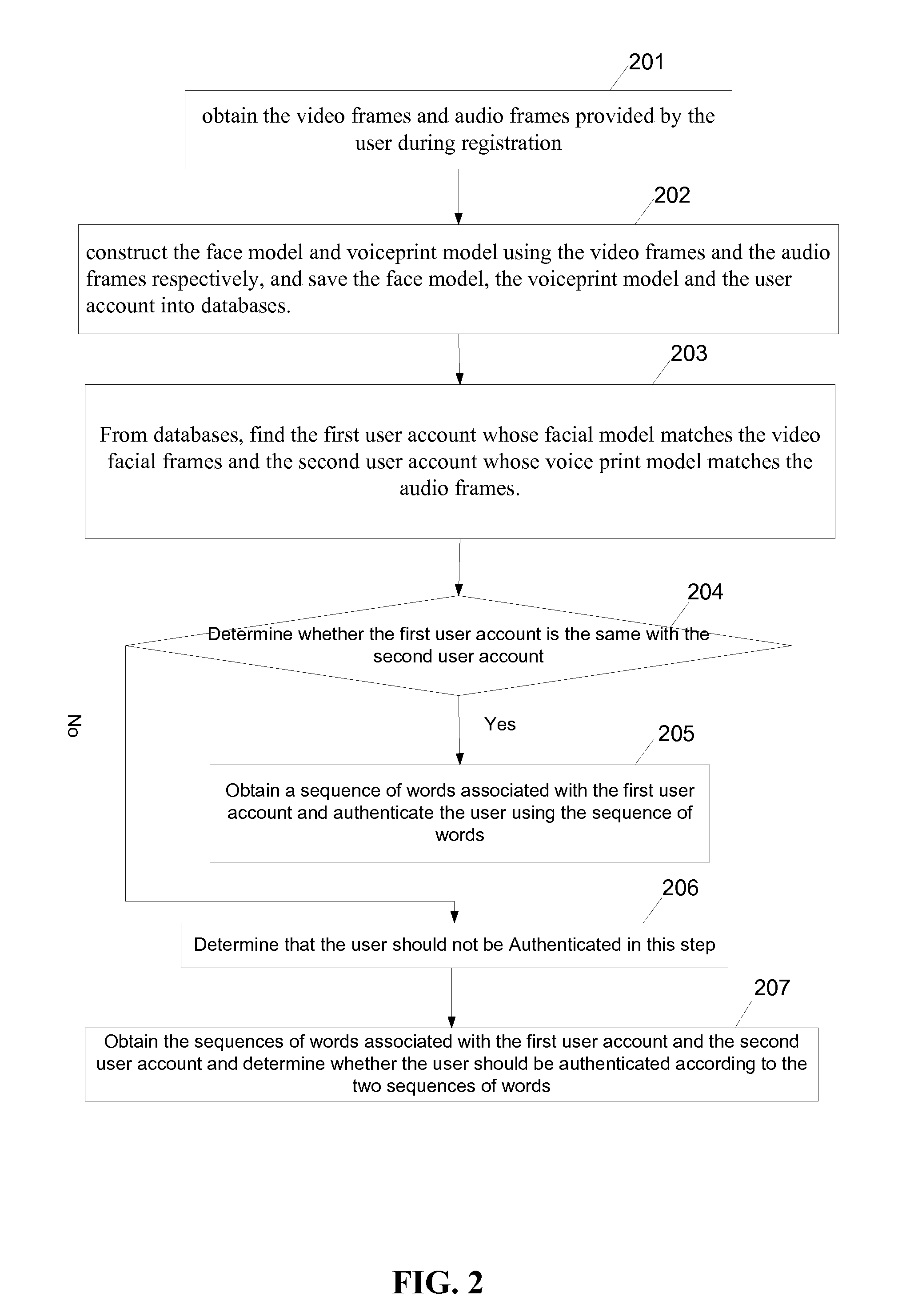
A computer-implemented method is performed at a server having one or more processors and memory storing programs executed by the one or more processors for authenticating a user from video and audio data. The method includes: receiving a login request from a mobile device, the login request including video data and audio data; extracting a group of facial features from the video data; extracting a group of audio features from the audio data and recognizing a sequence of words in the audio data; identifying a first user account whose respective facial features match the group of facial features and a second user account whose respective audio features match the group of audio features. If the first user account is the same as the second user account, retrieve the sequence of words associated with the user account and compare the sequences of words for authentication purpose.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
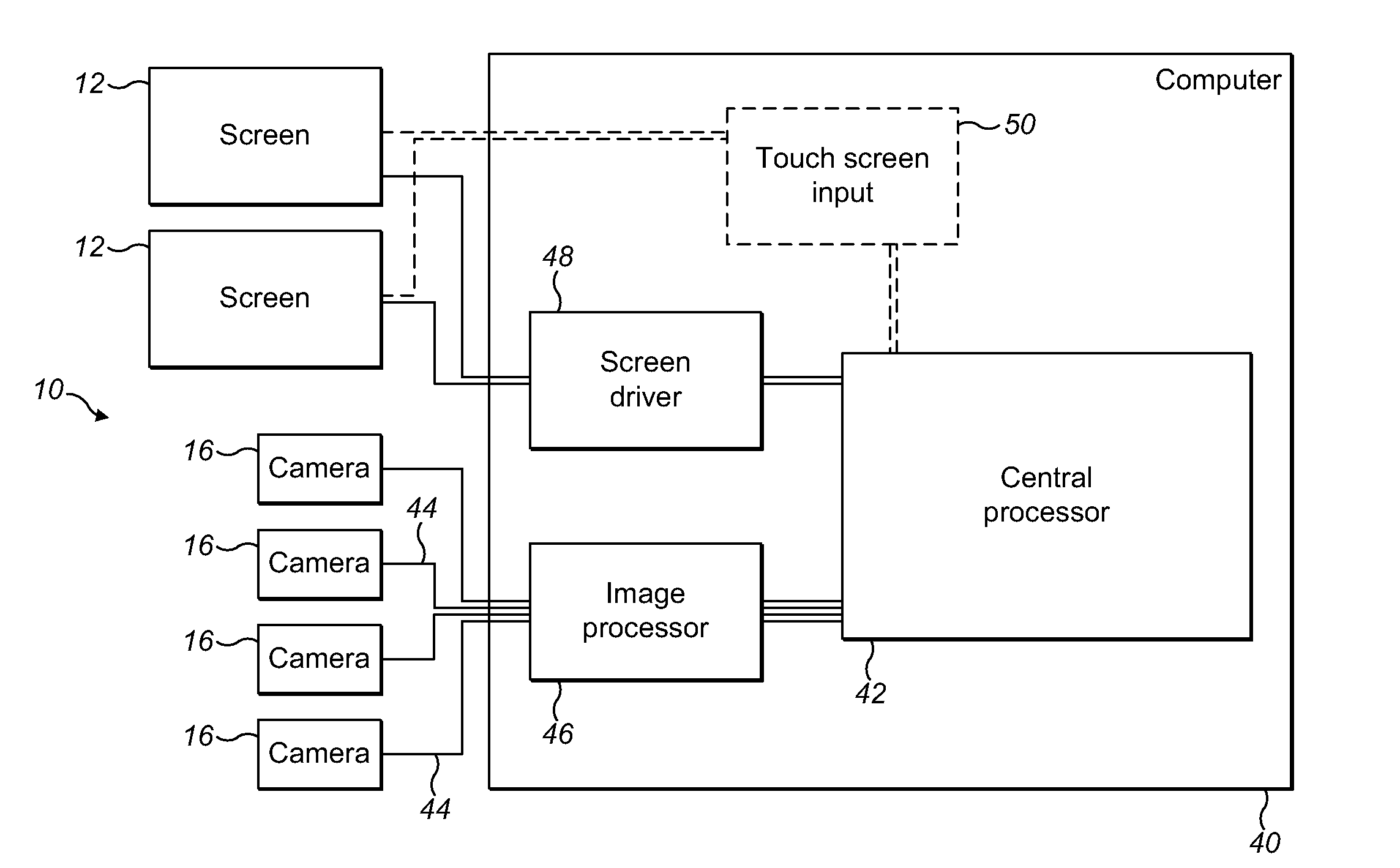
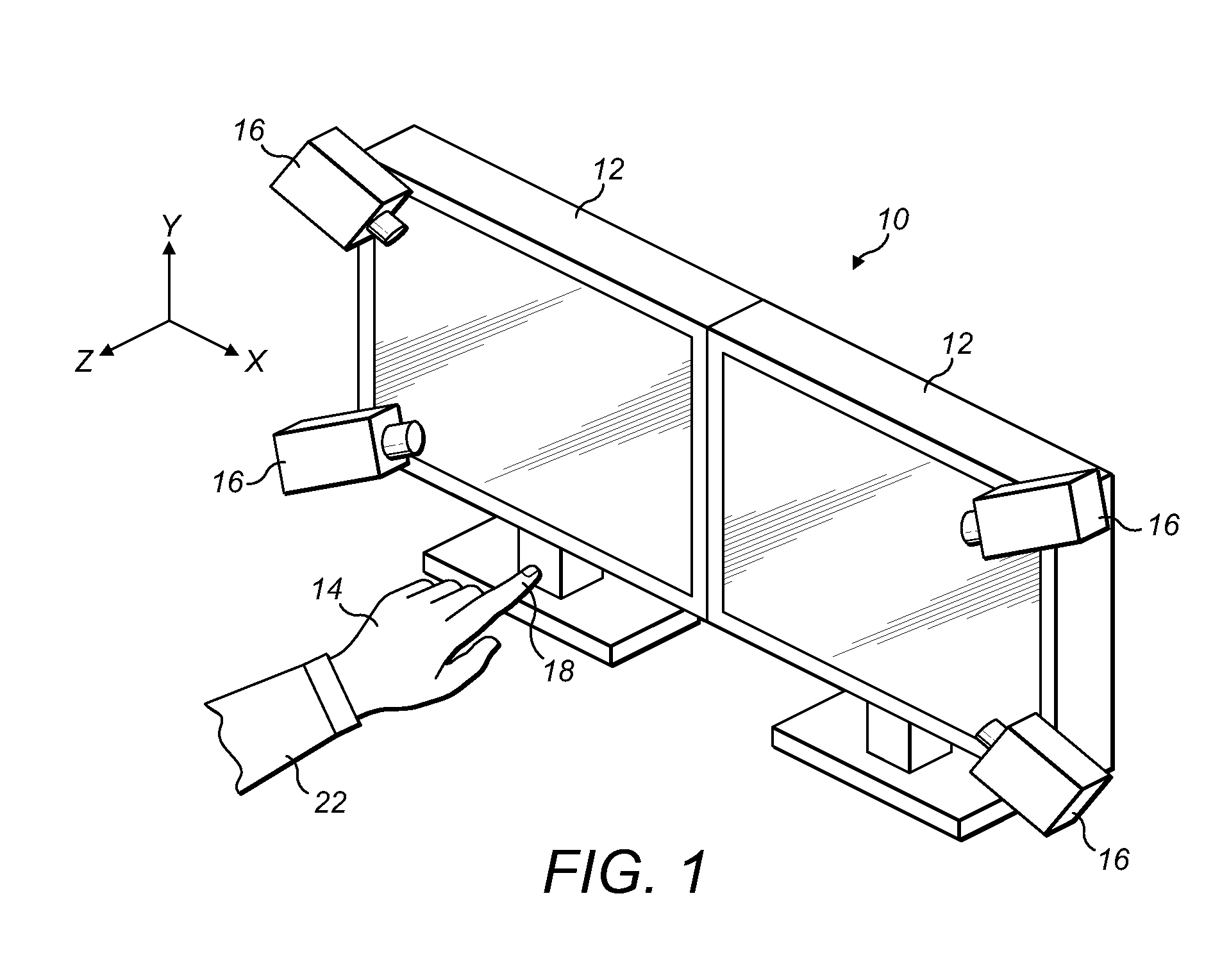
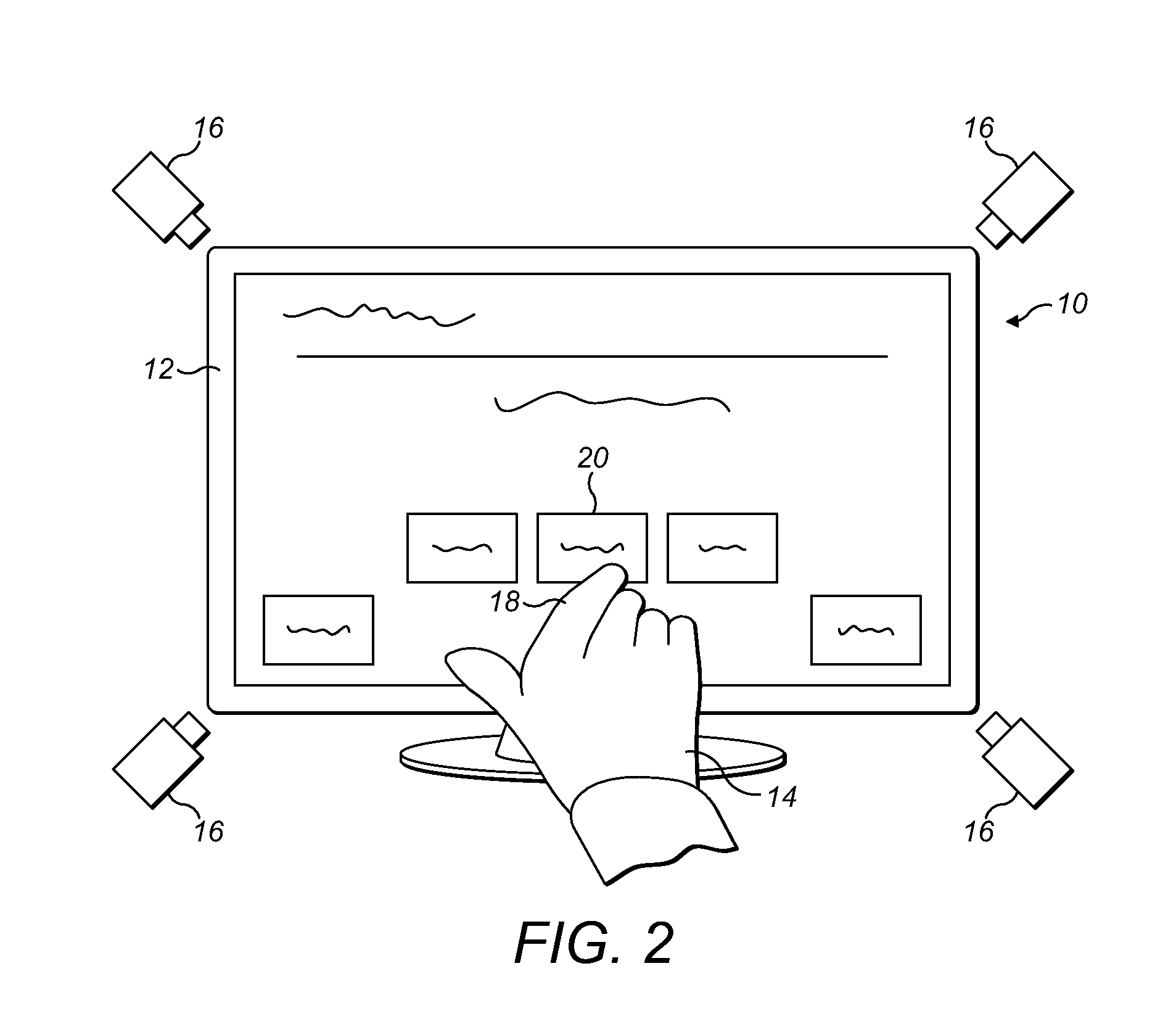
Gesture-Based Human Machine Interface
ActiveUS20110304650A1Geometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsHuman–machine interfaceHuman–computer interaction
A gesture-based human machine interface, for example, a user interface for controlling a program executing on a computer, and related method are provided. Gestures of the user are monitored and a response is provided that is based upon the detected gestures. An object is used to point to information displayed on a screen. The information displayed on the screen is modified in response to a determination of the position on the screen to which the object is pointing and in response to the distance of the object from the screen.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
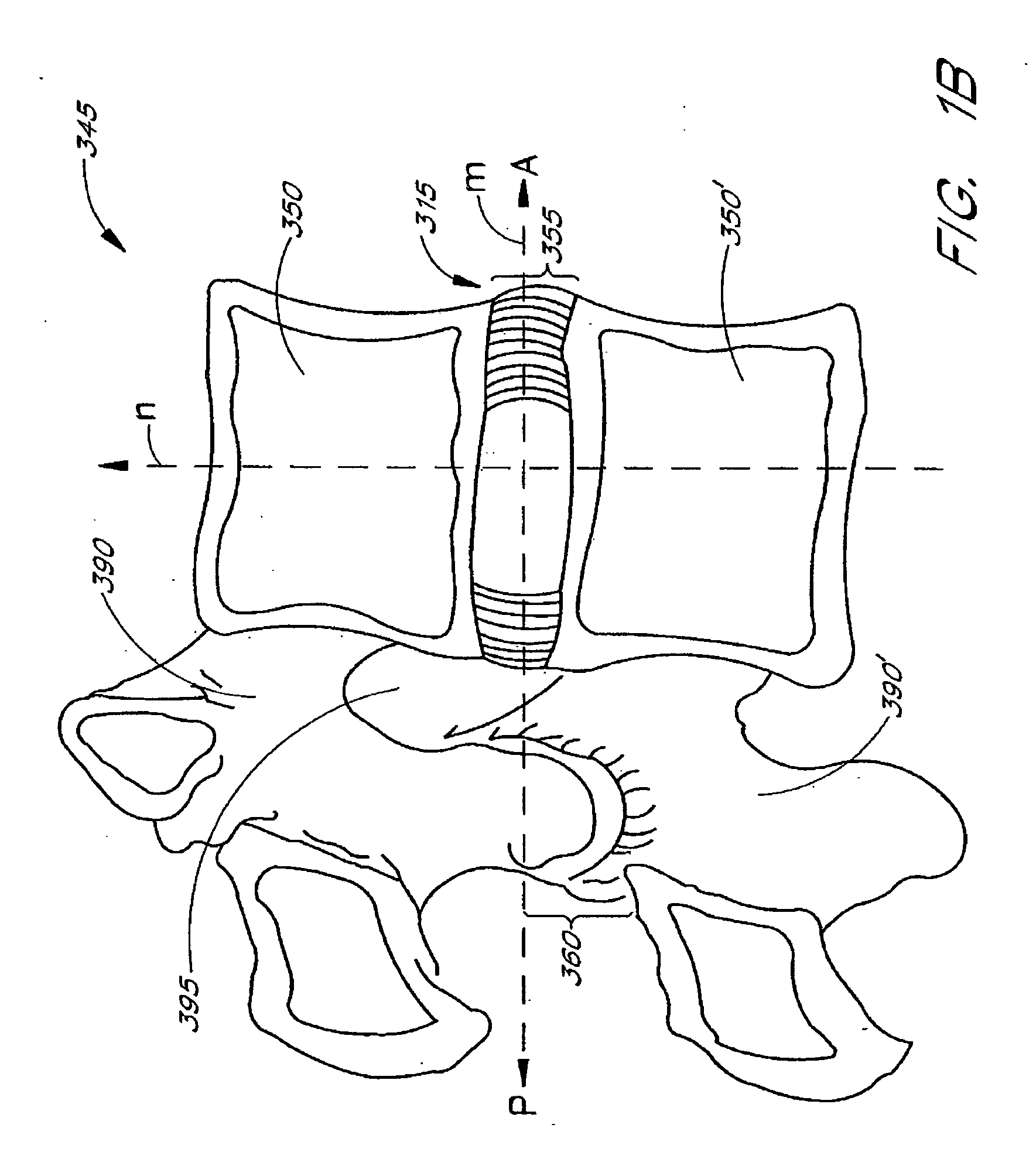
Method of performing a procedure within a disc
InactiveUS20060217811A1Avoid accessConvenient guidanceInternal osteosythesisCannulasDiagnostic agentIntervertebral disc
The present invention relates generally to intervertebral disc devices and methods and instrumentation for intervertebral disc procedures. Methods include performing procedures such as implant delivery, tissue manipulation, tissue diagnostics, and therapeutic and diagnostic agent delivery at selected locations within intervertebral discs.
Owner:INTRINSIC THERAPEUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com