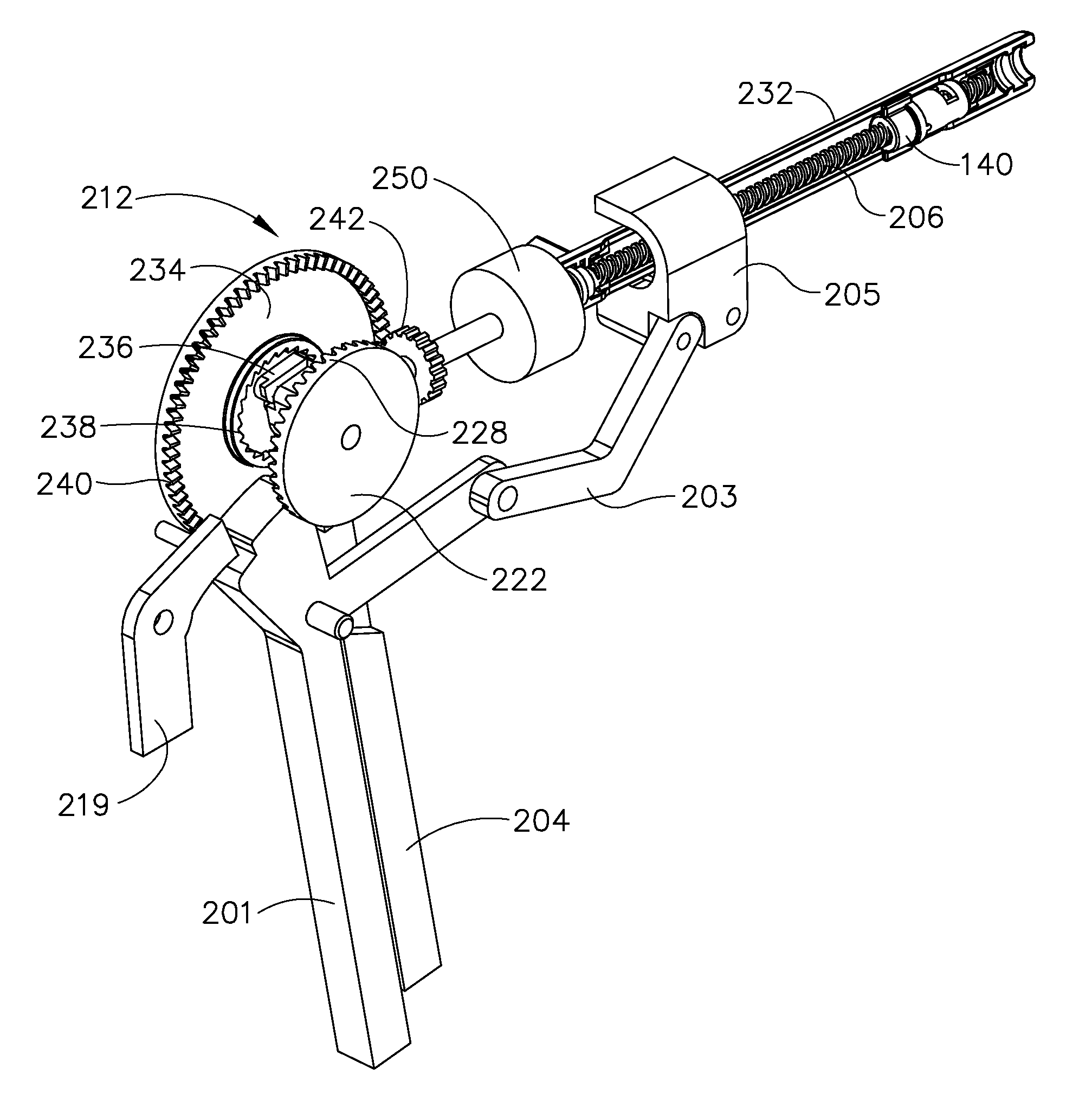
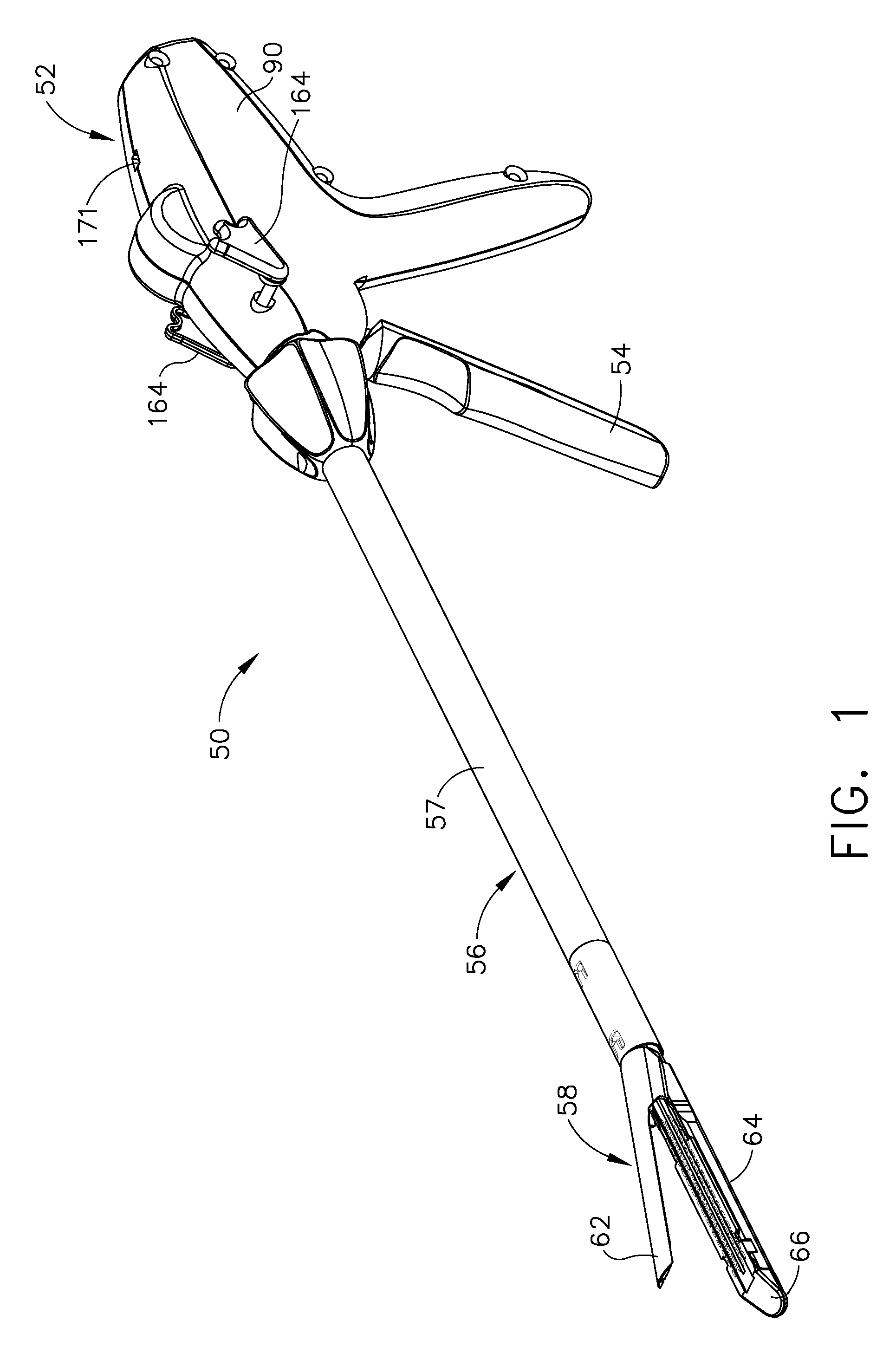
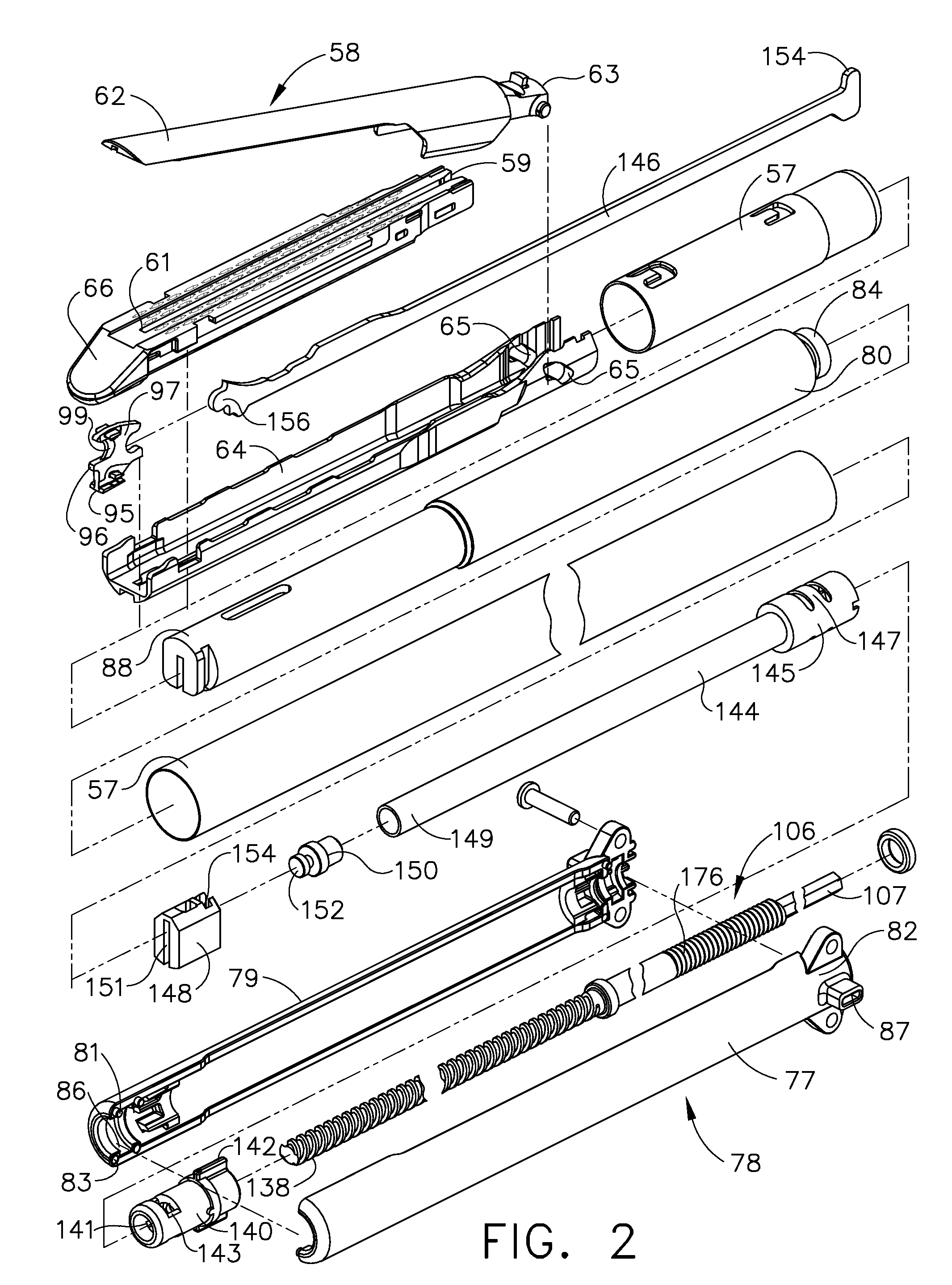
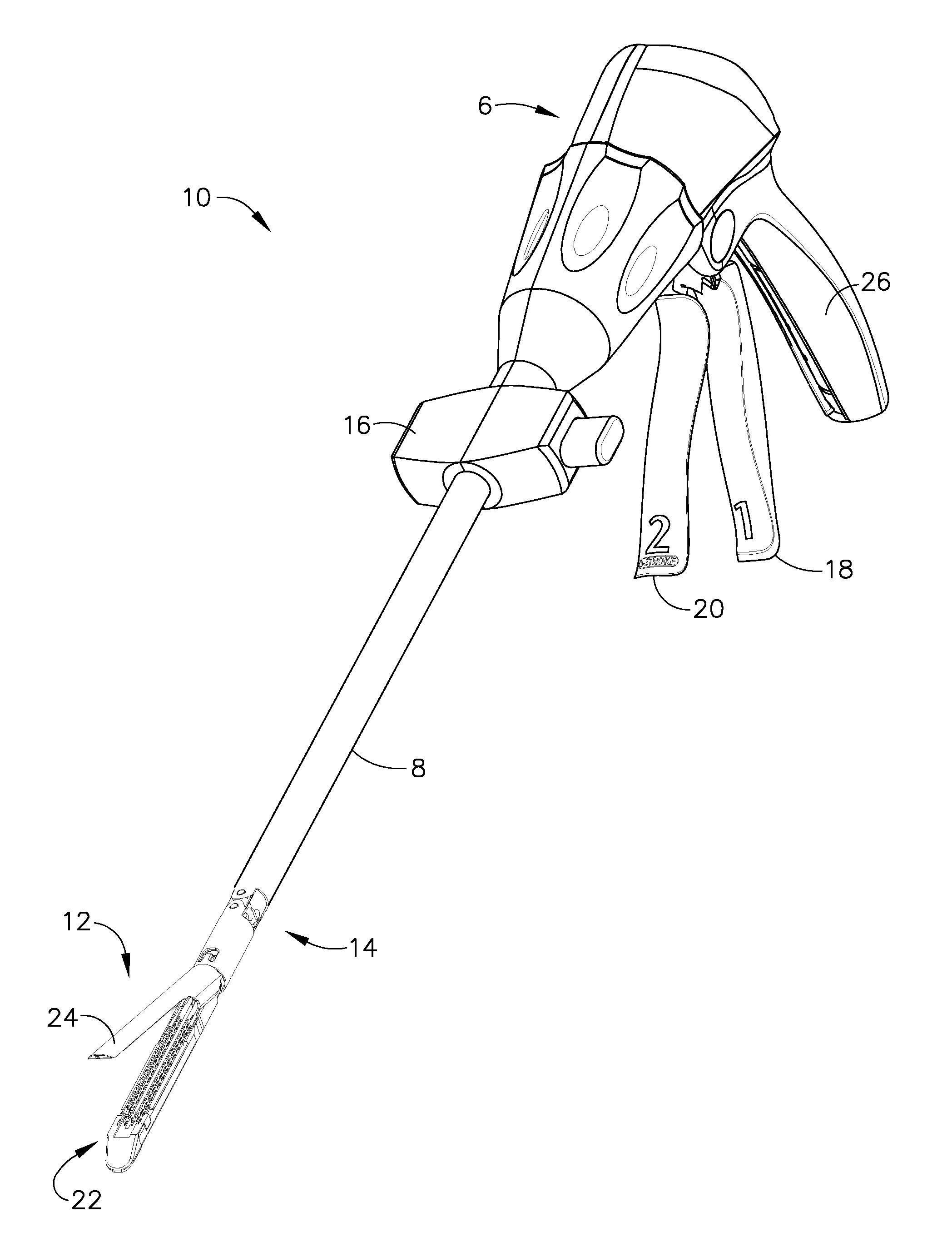
Patents
Literature
46540 results about "General surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
General surgery is a surgical specialty that focuses on abdominal contents including esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, appendix and bile ducts, and often the thyroid gland (depending on local referral patterns). They also deal with diseases involving the skin, breast, soft tissue, trauma, peripheral vascular surgery and hernias and perform endoscopic procedures such as gastroscopy and colonoscopy.
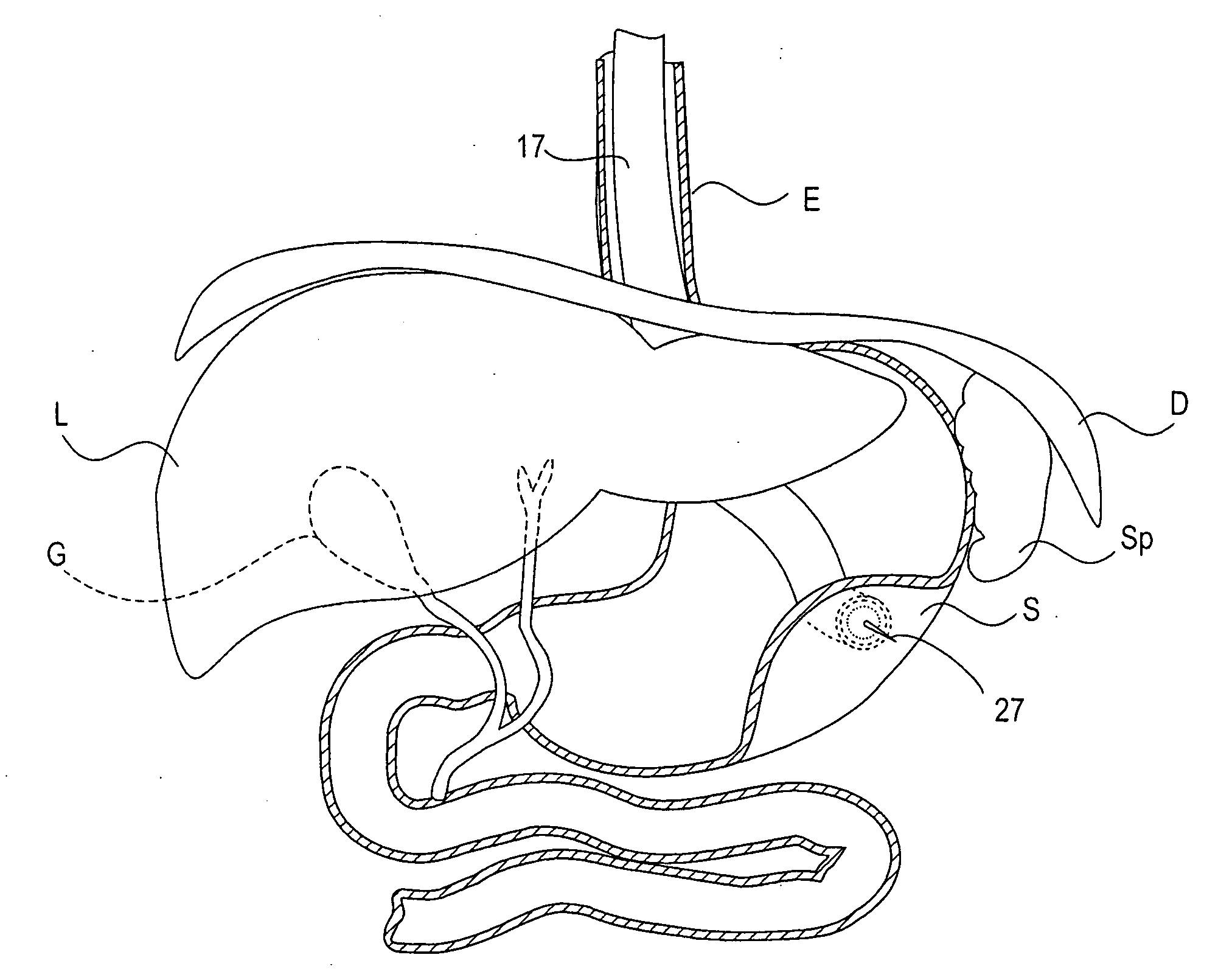
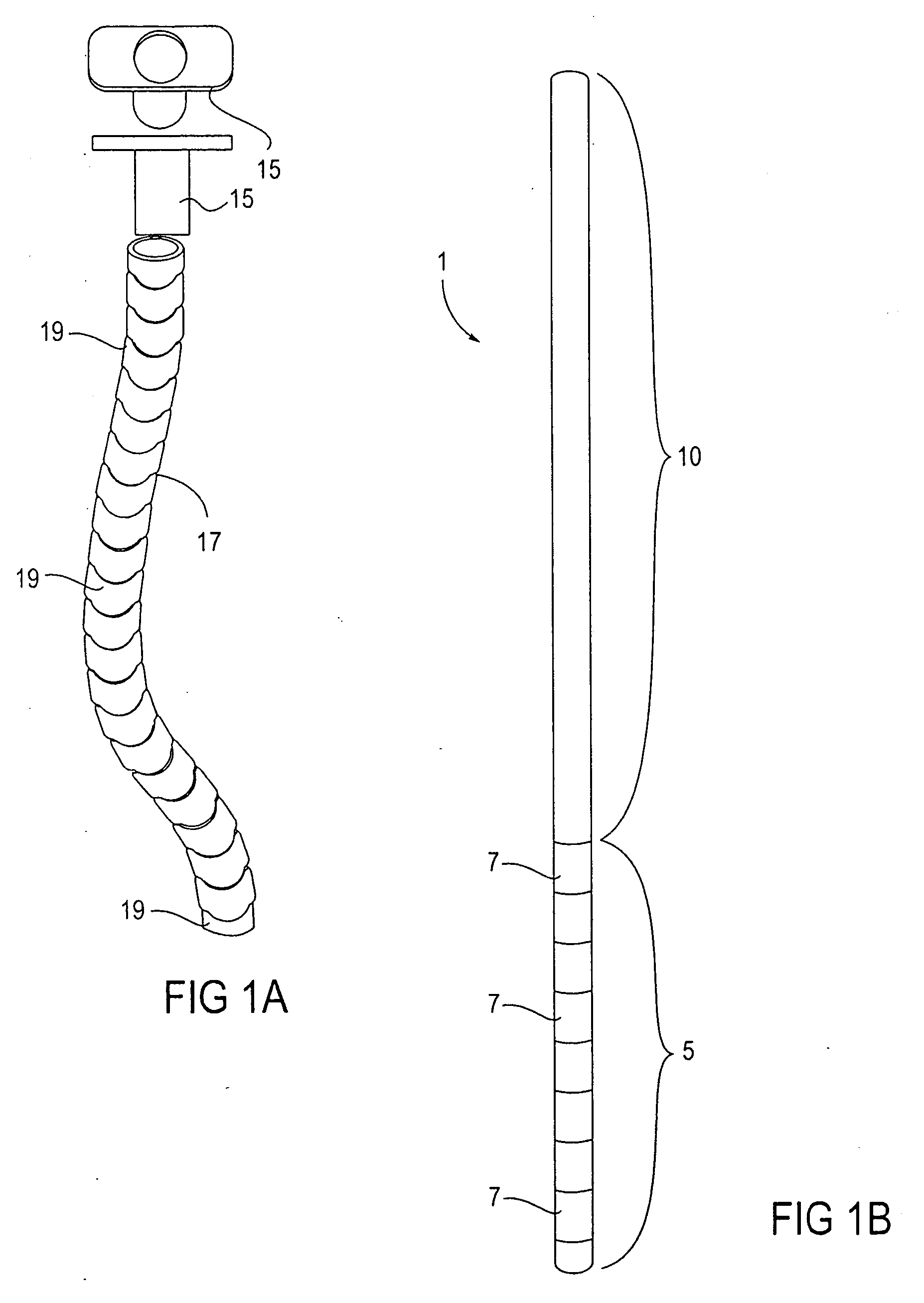
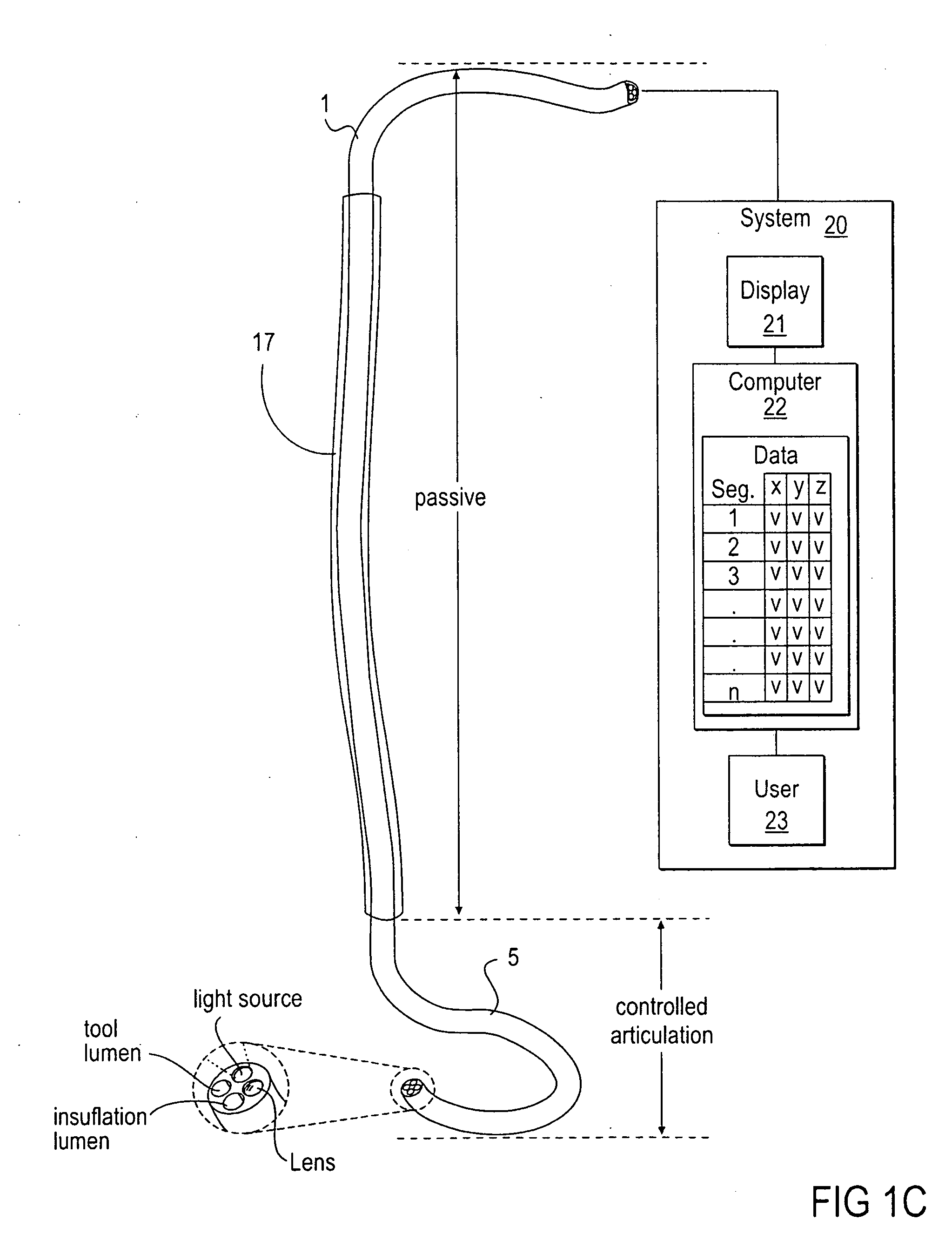
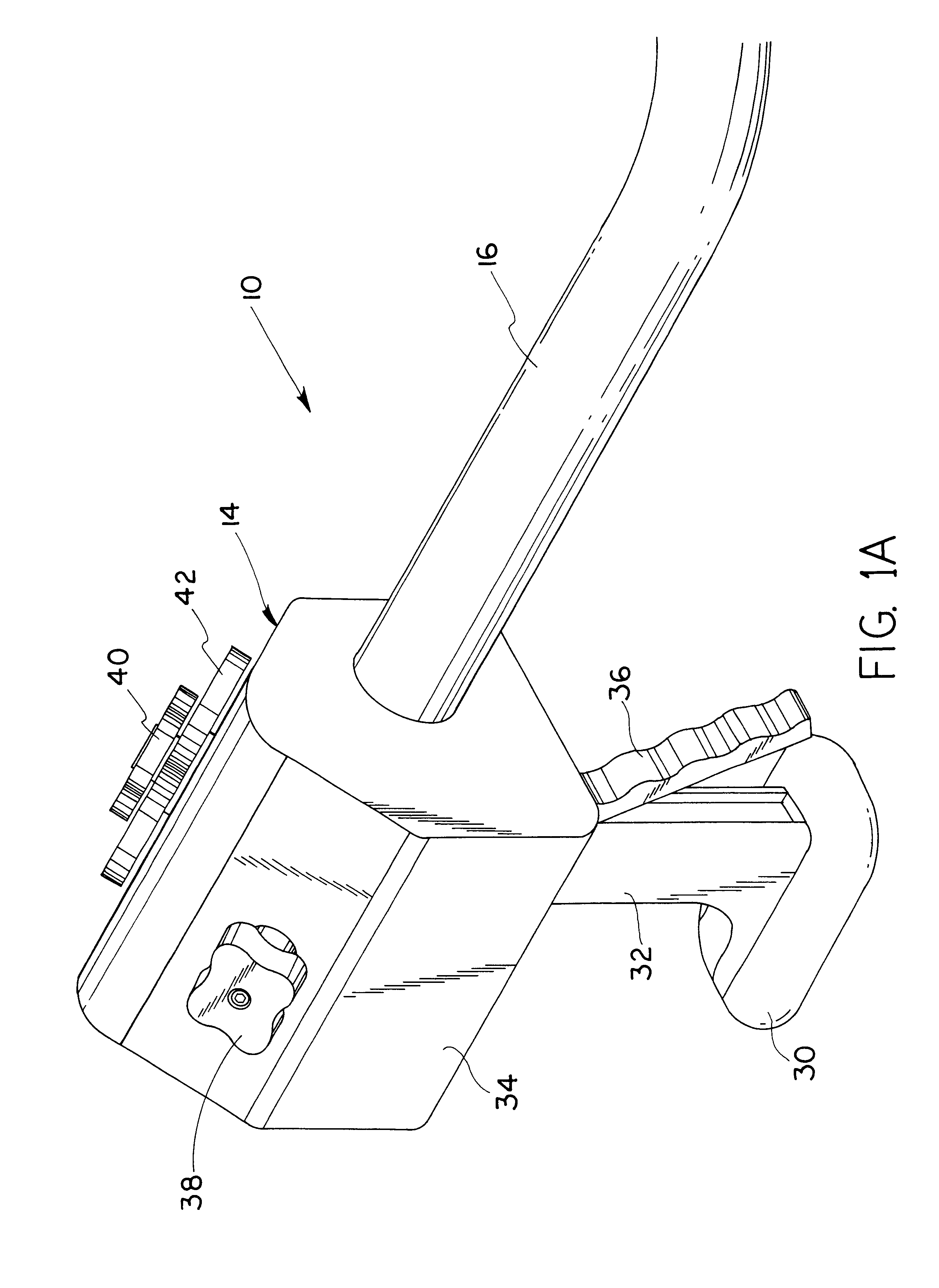
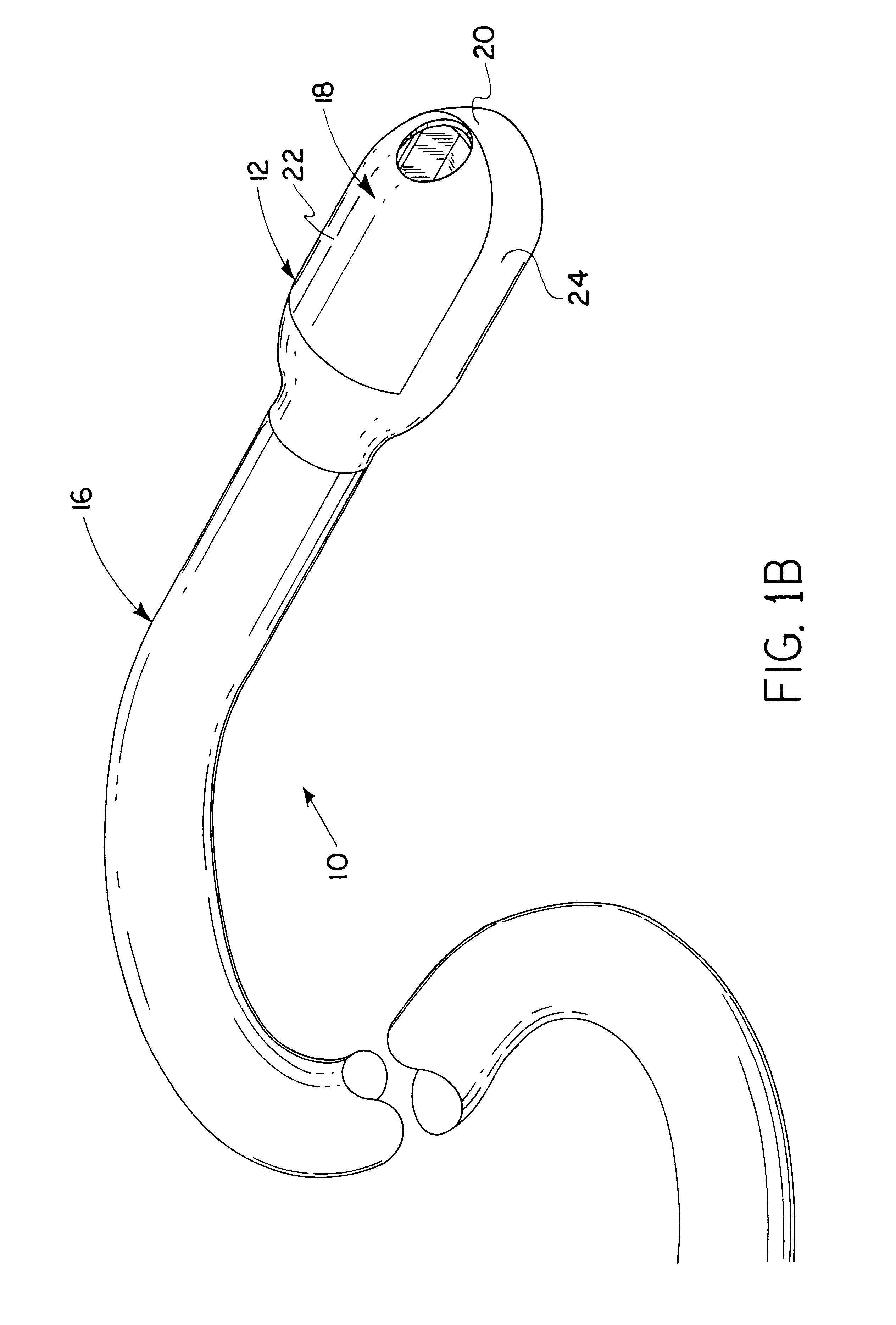
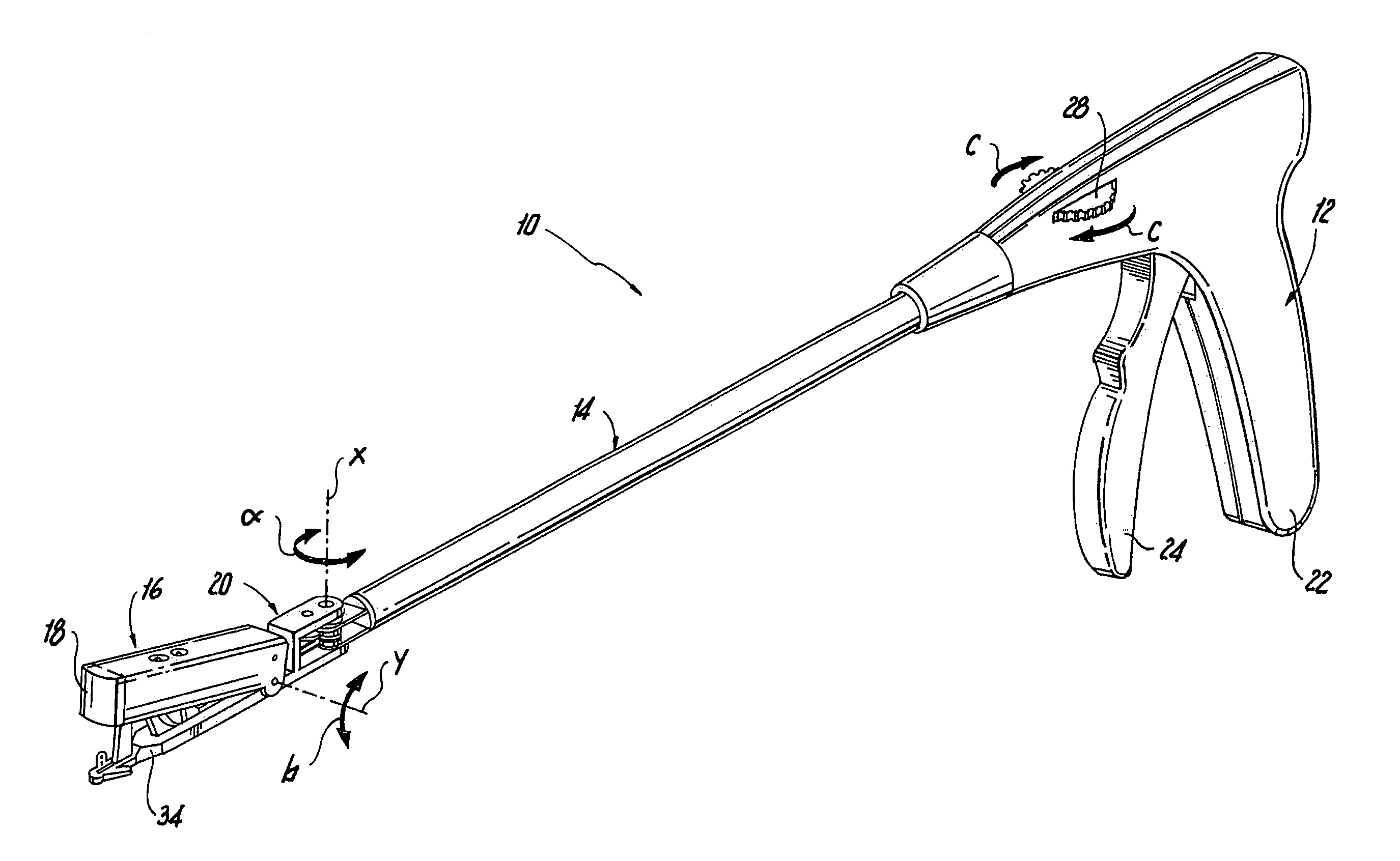
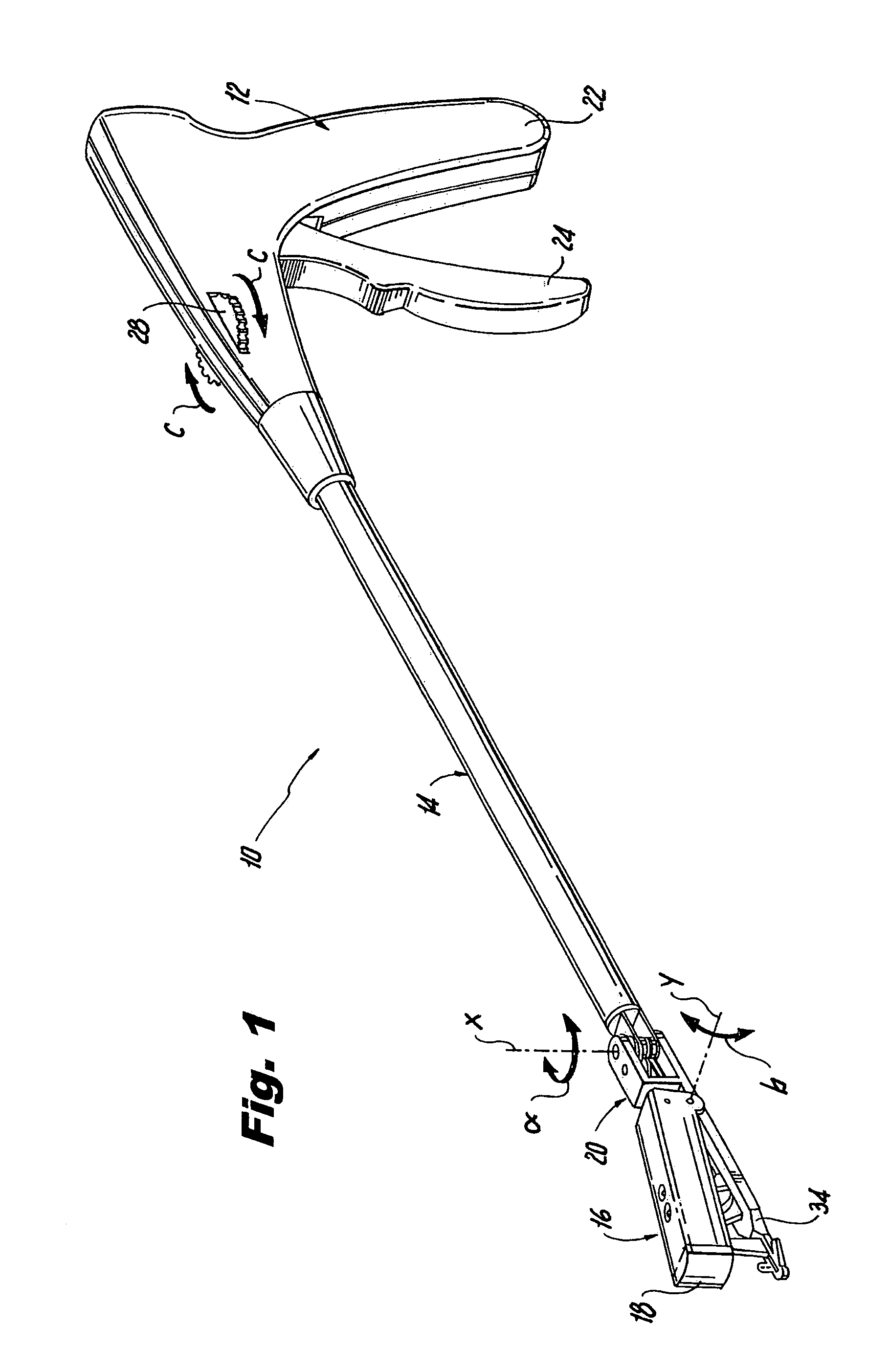
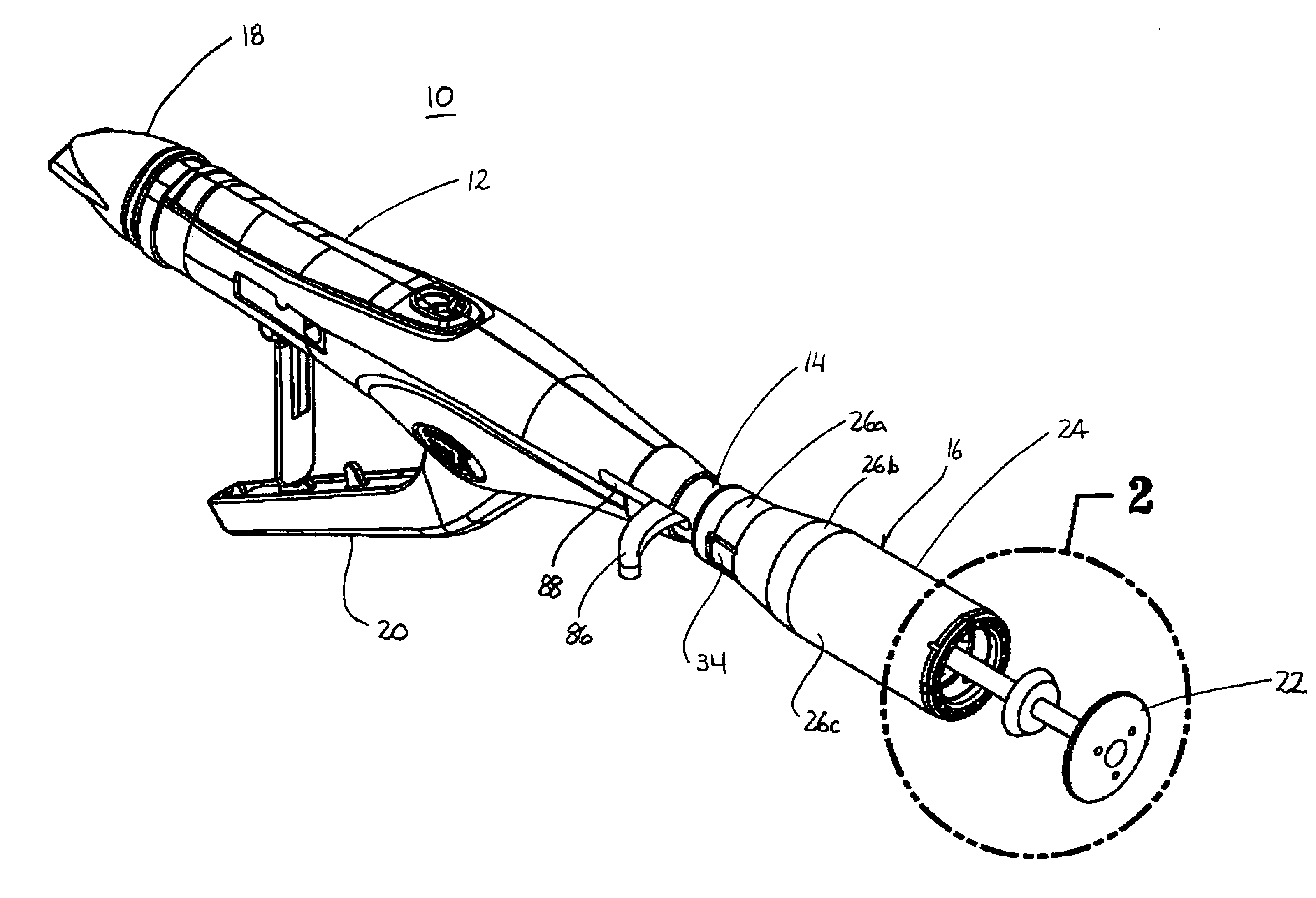
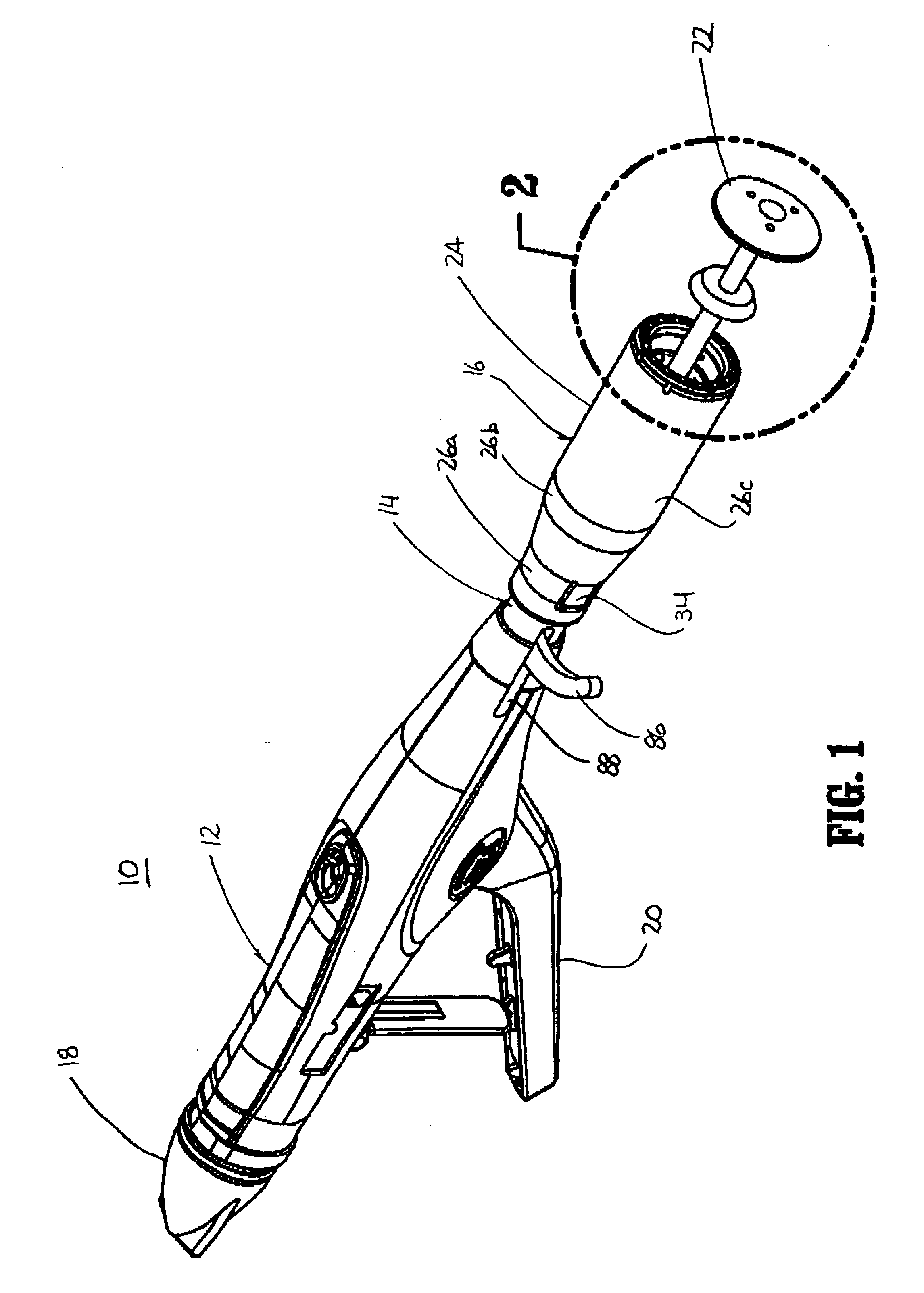
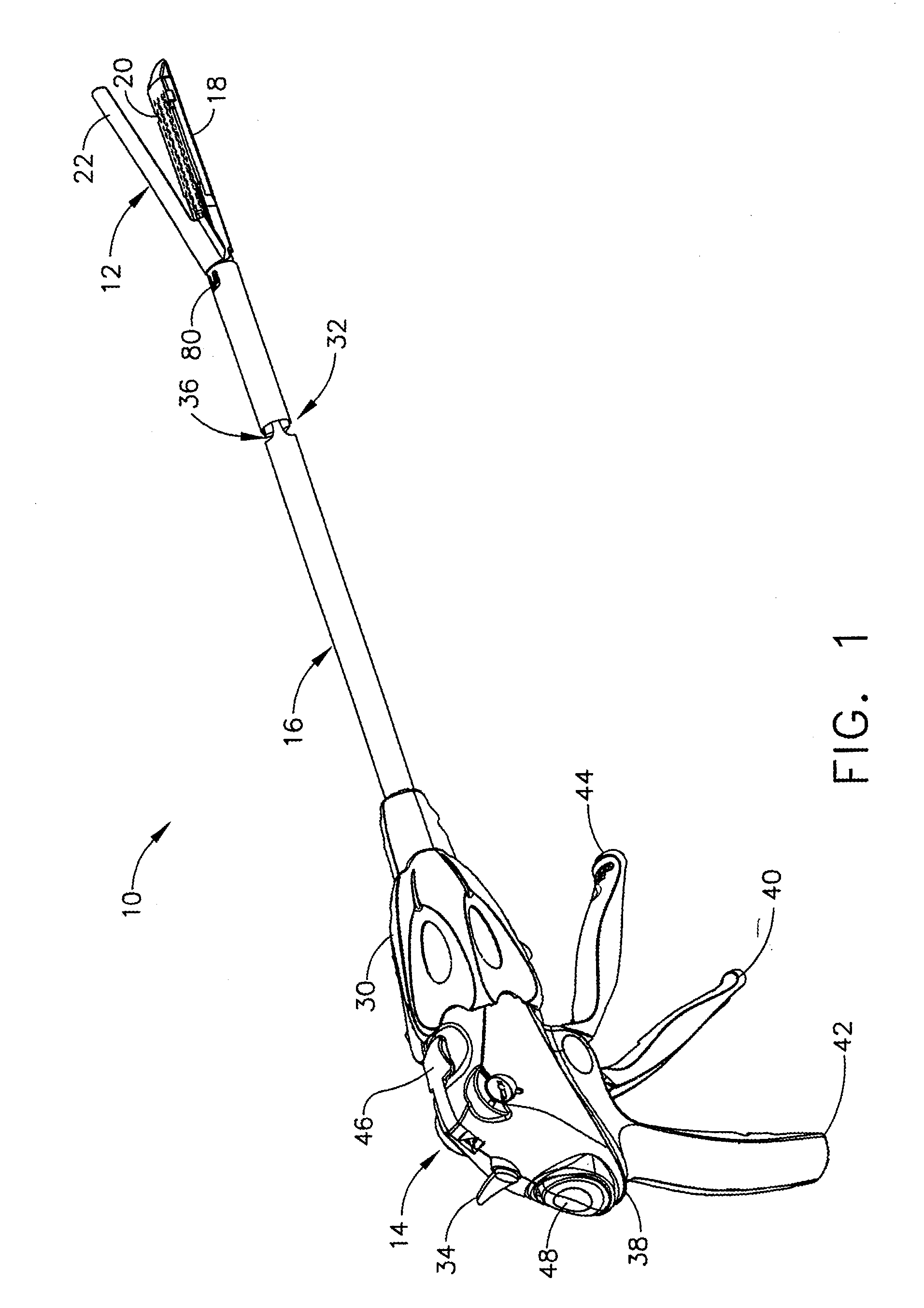
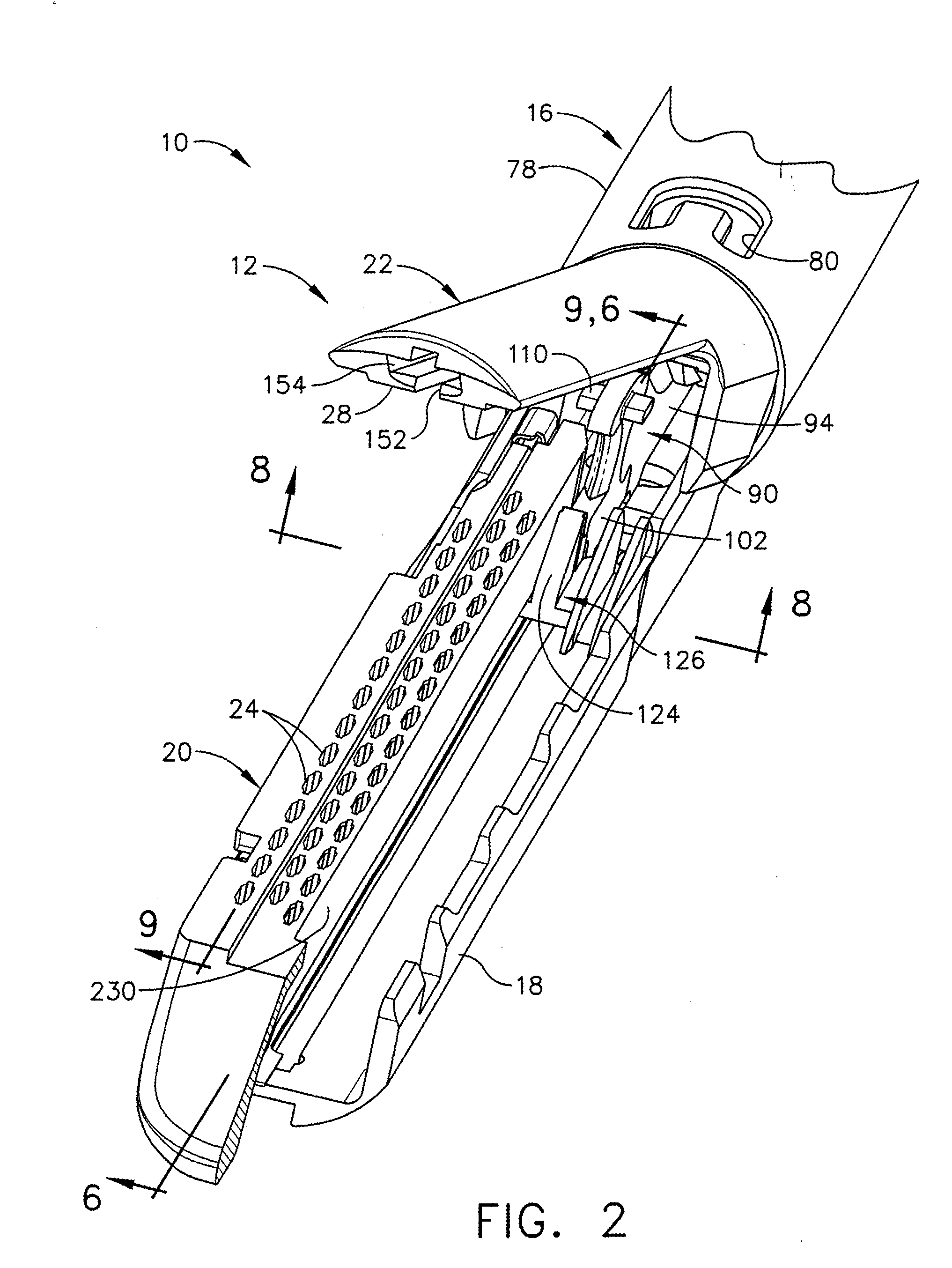
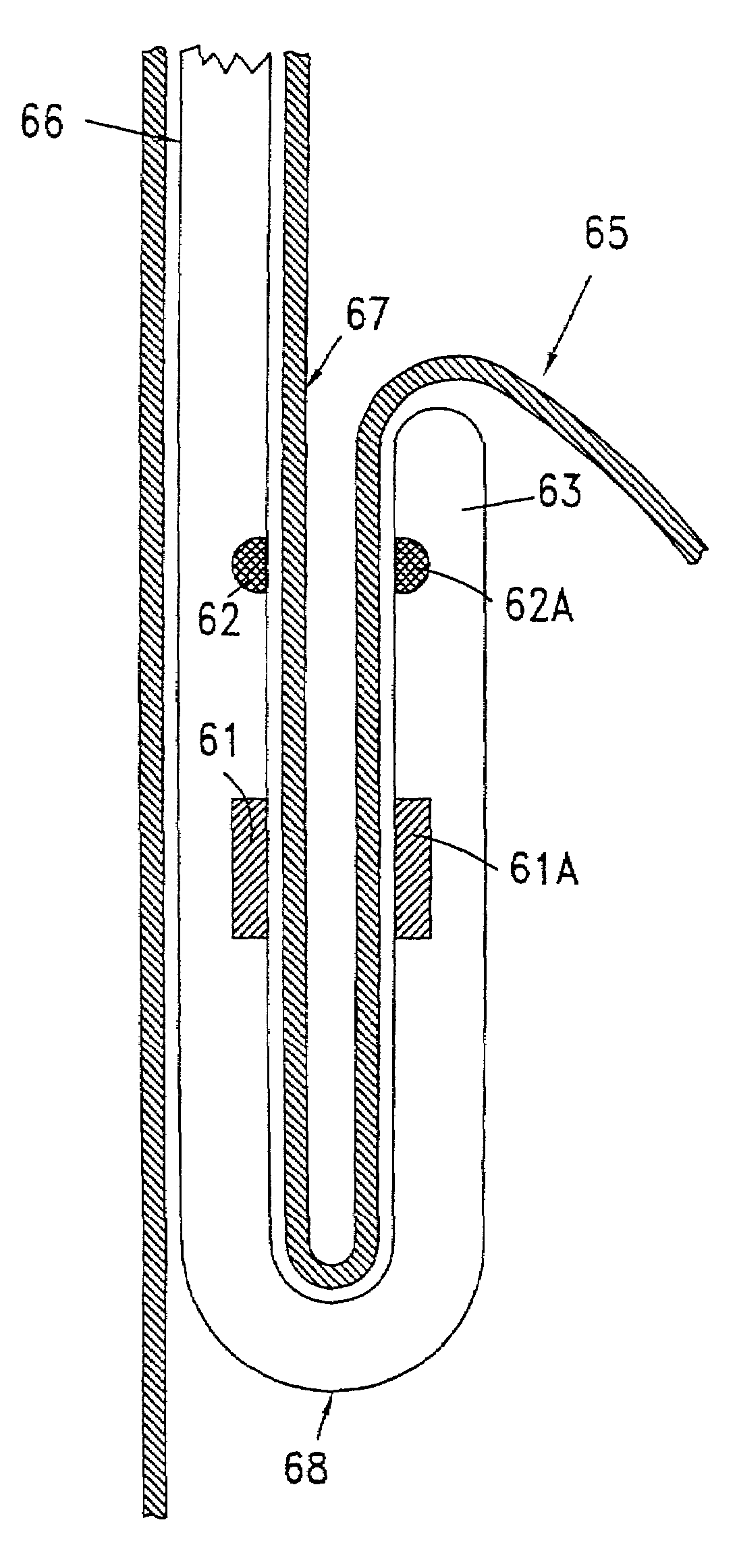
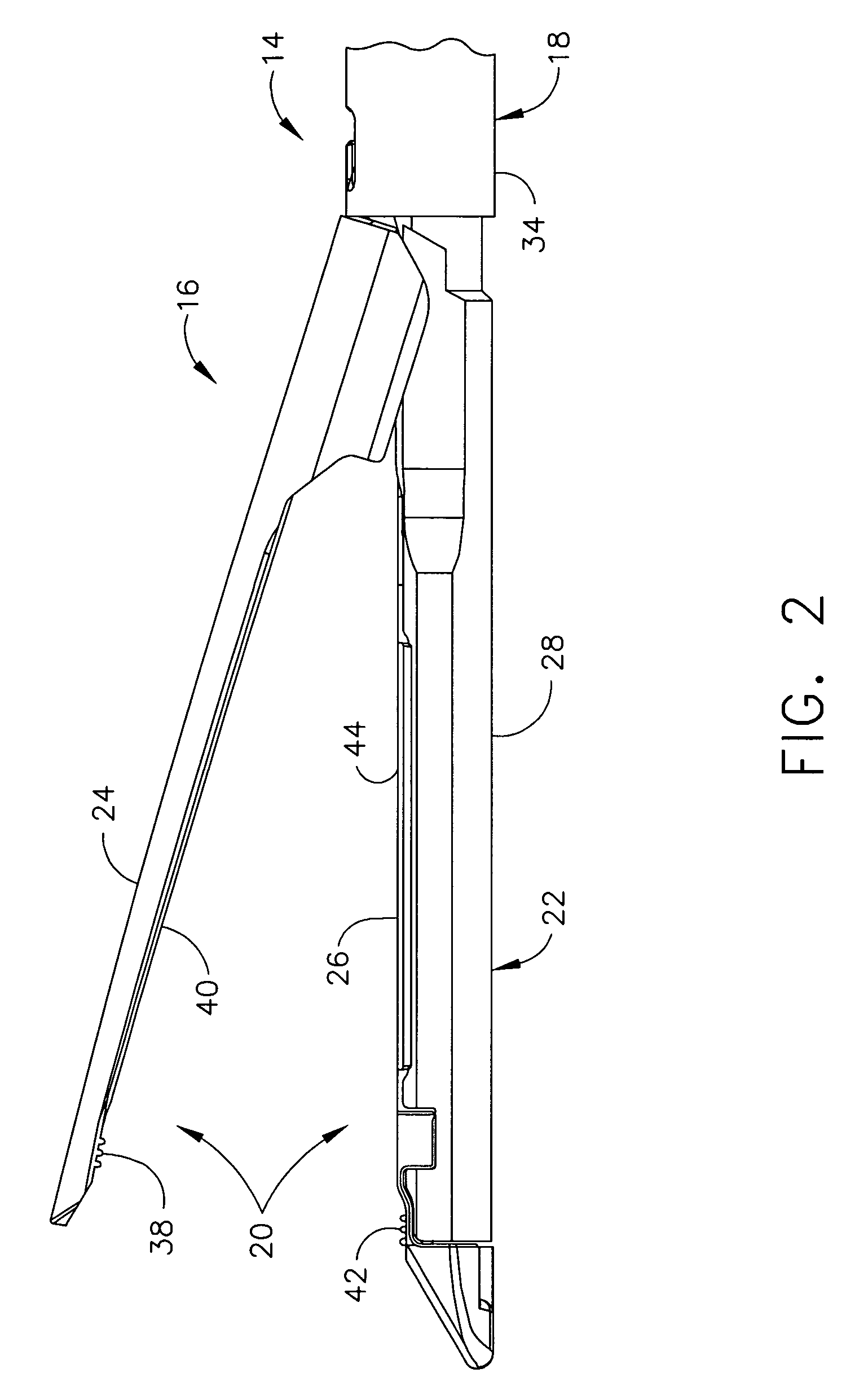
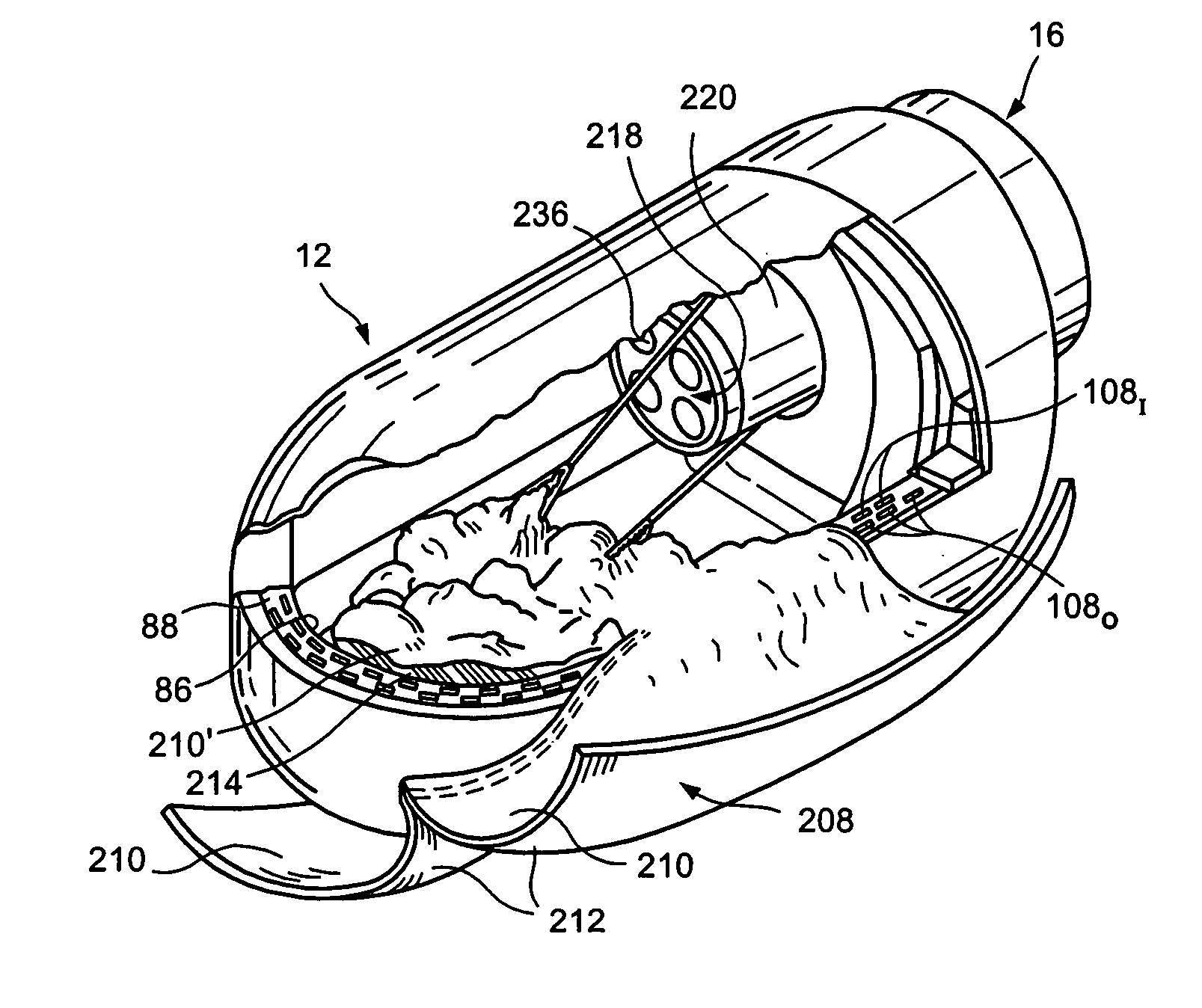
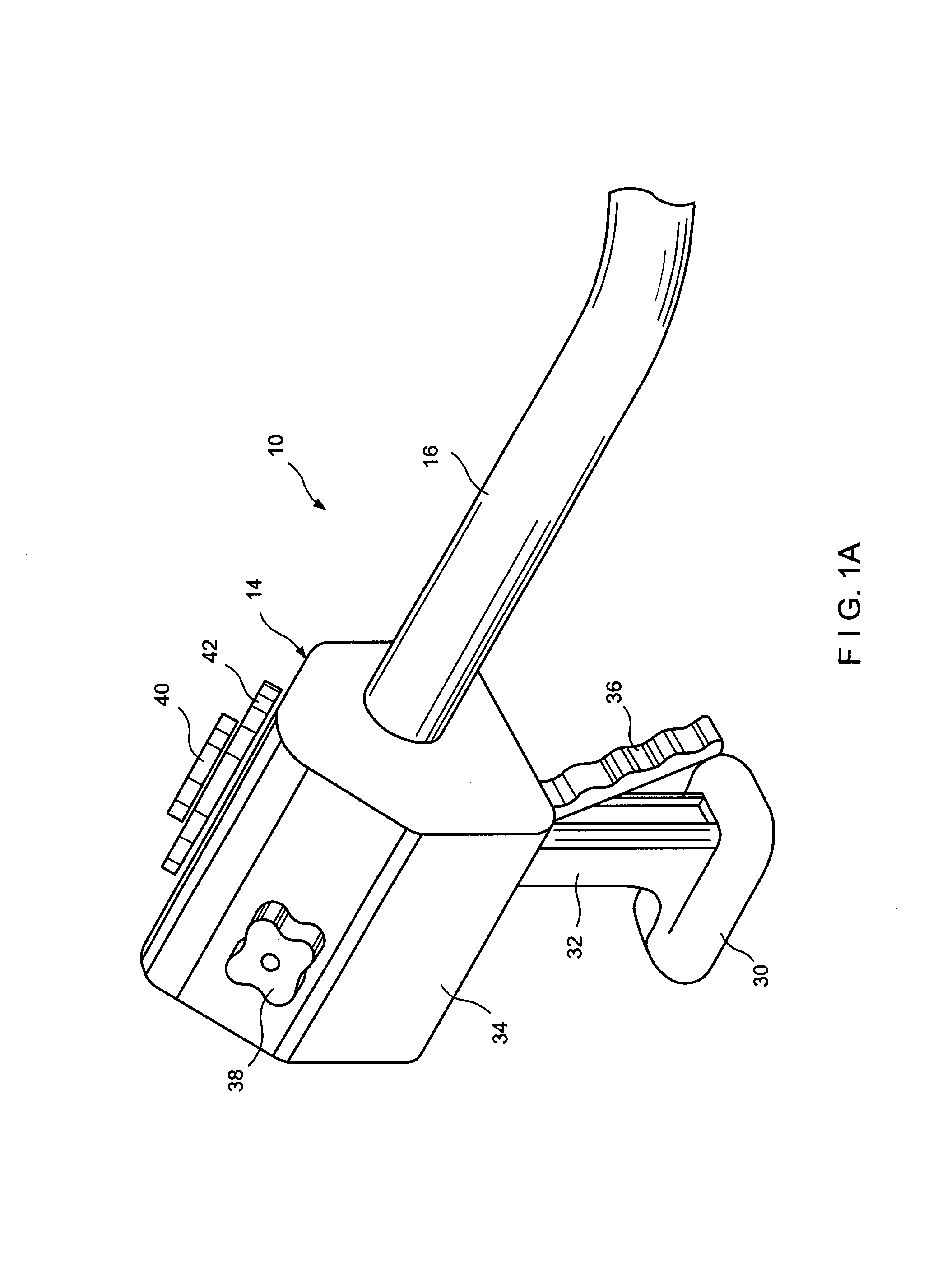
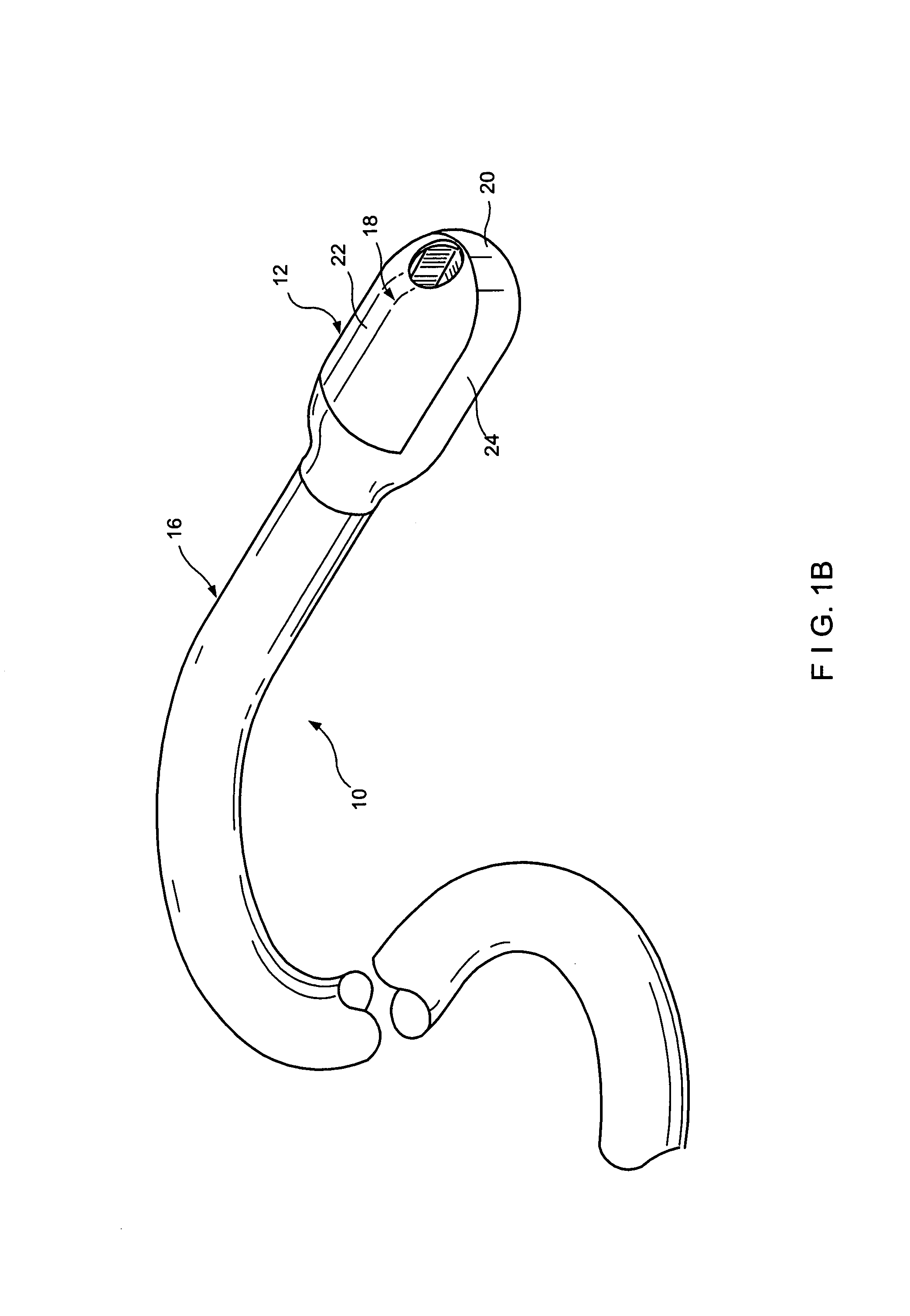
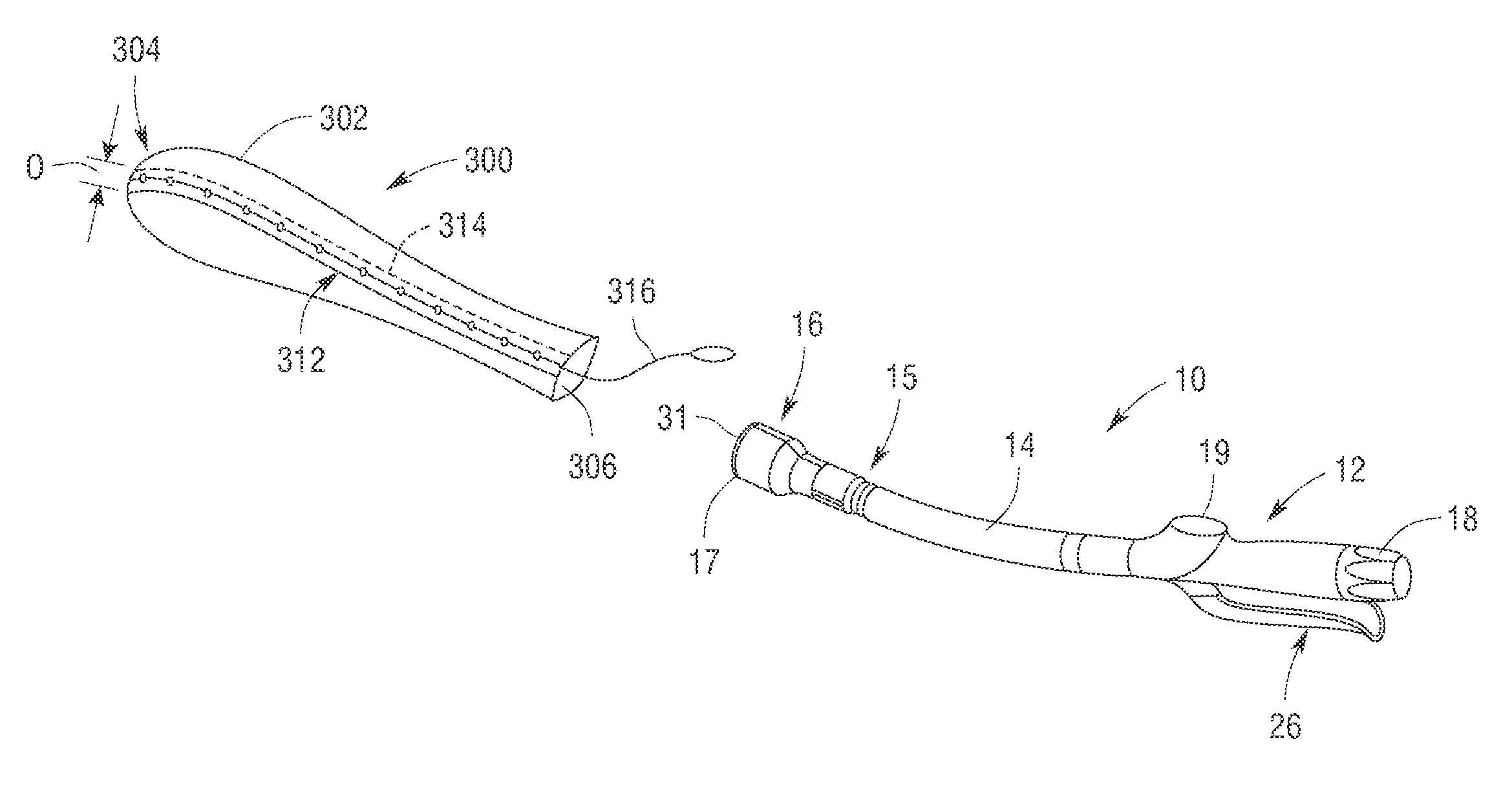
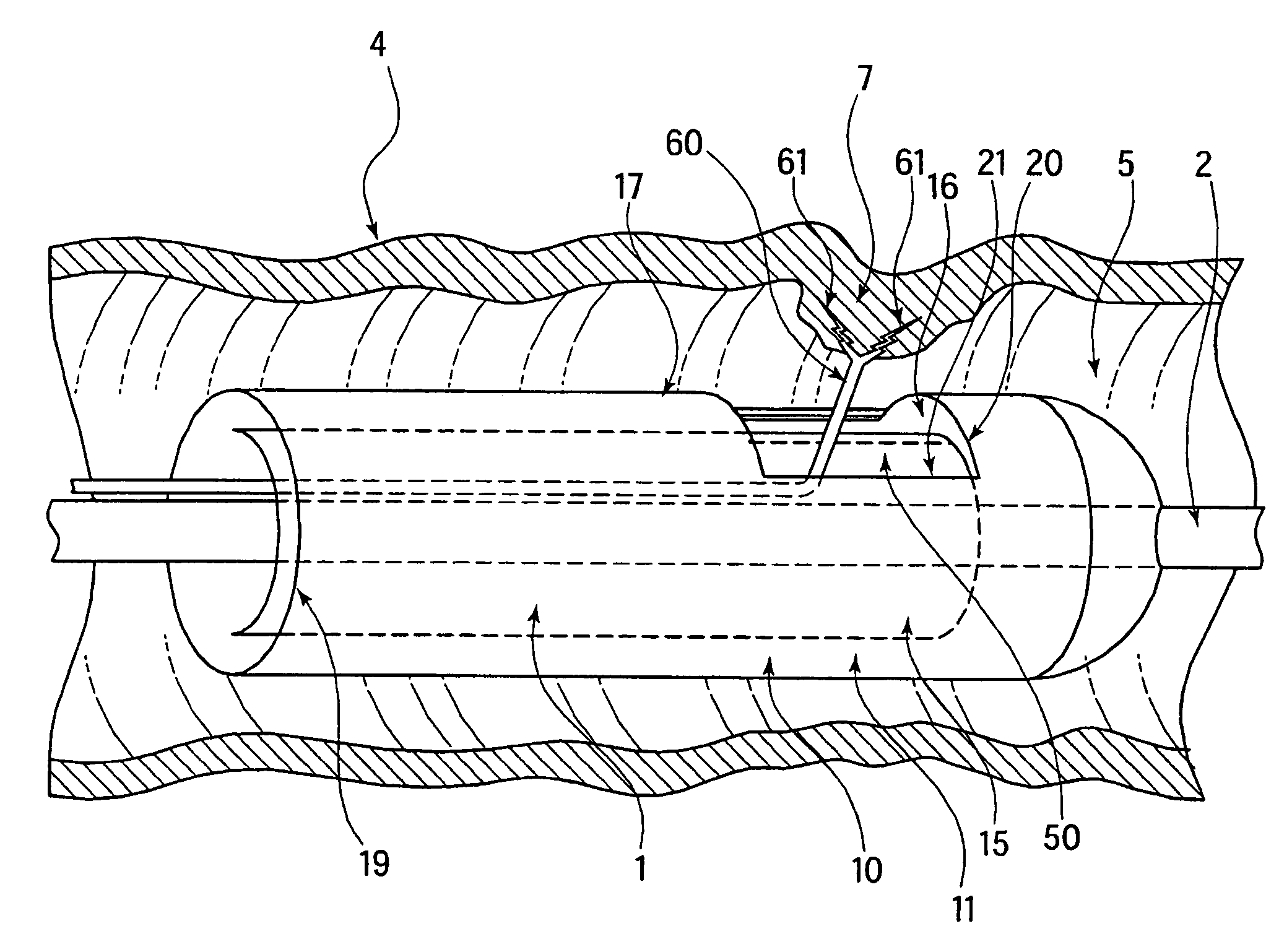
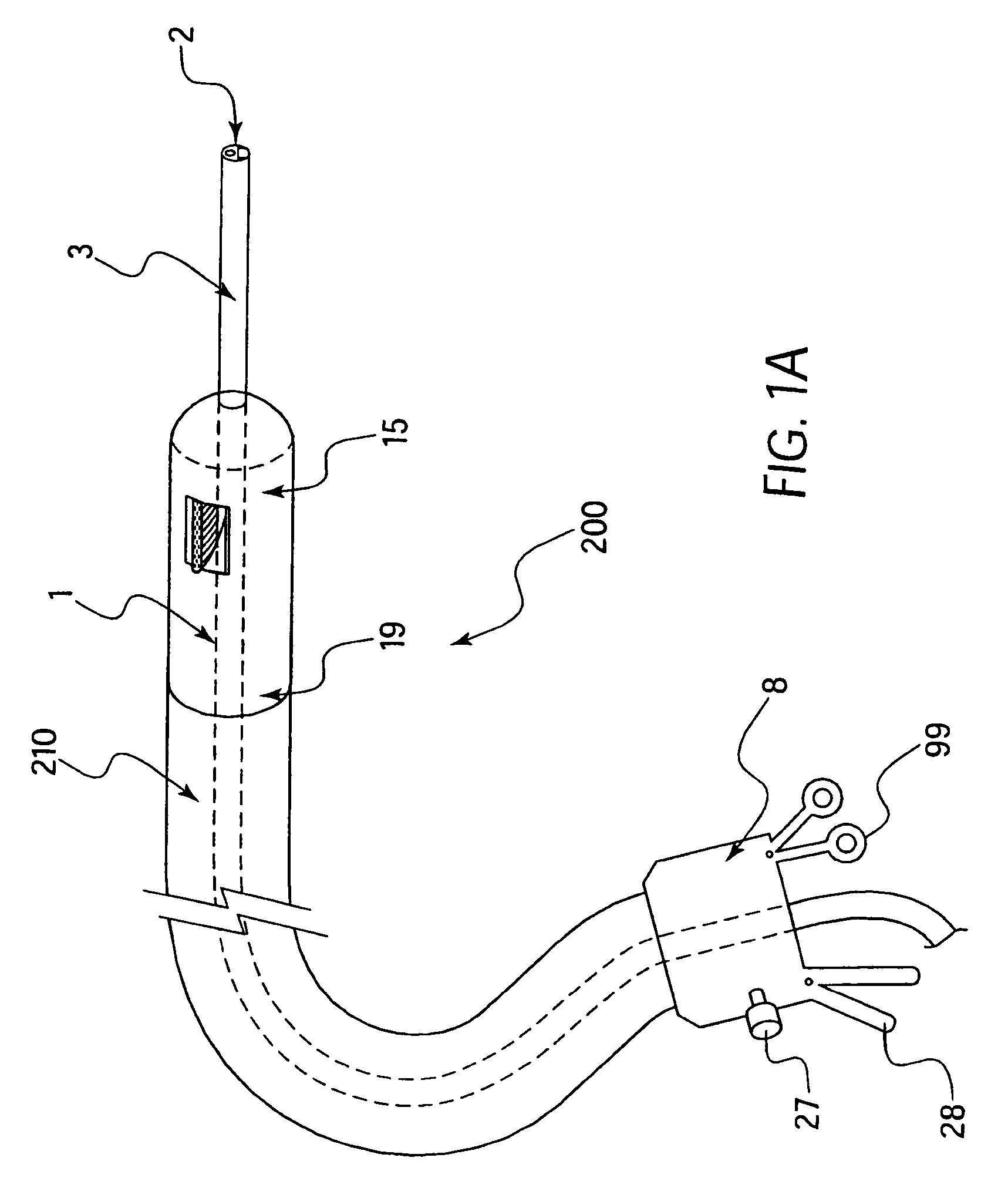
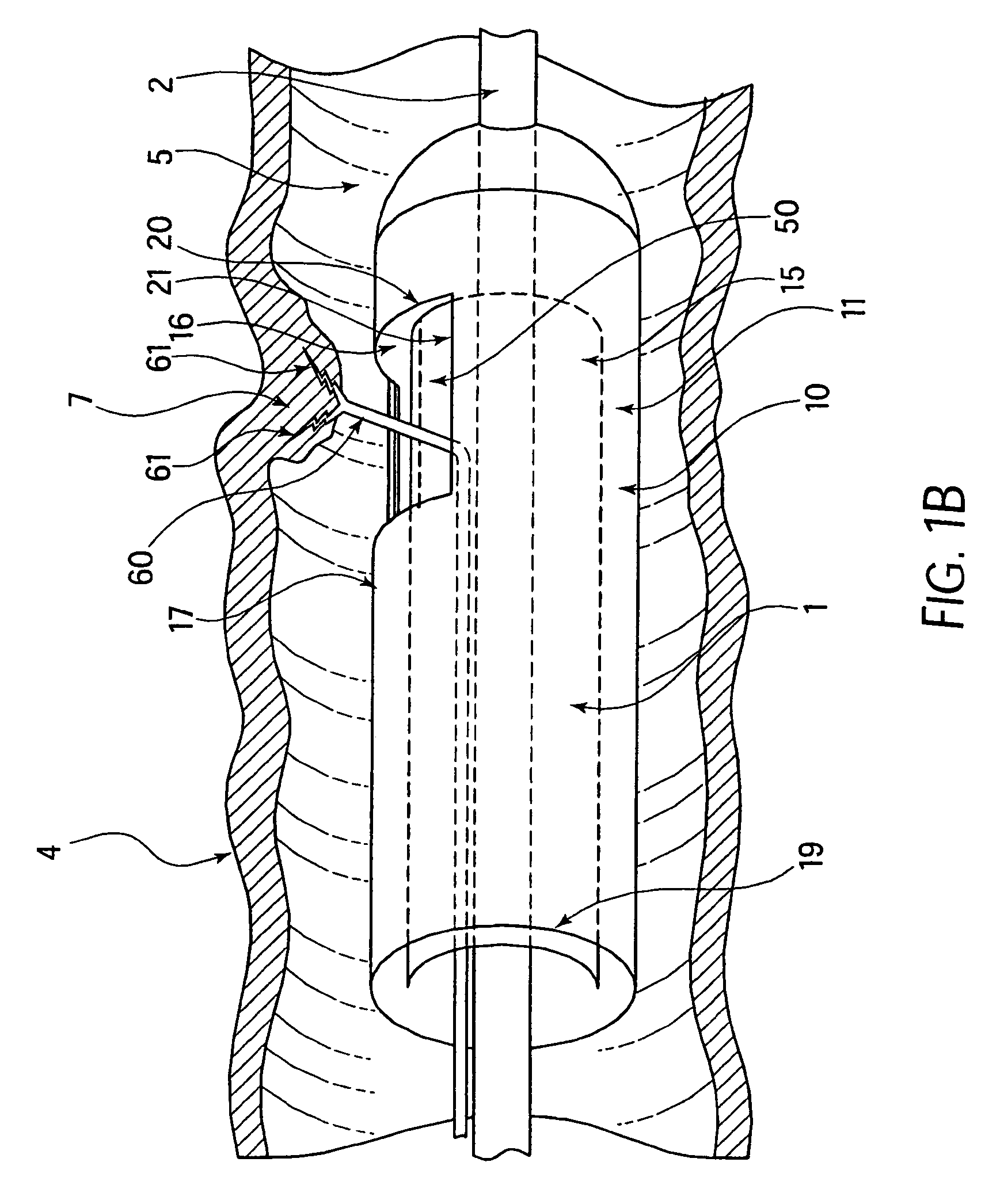
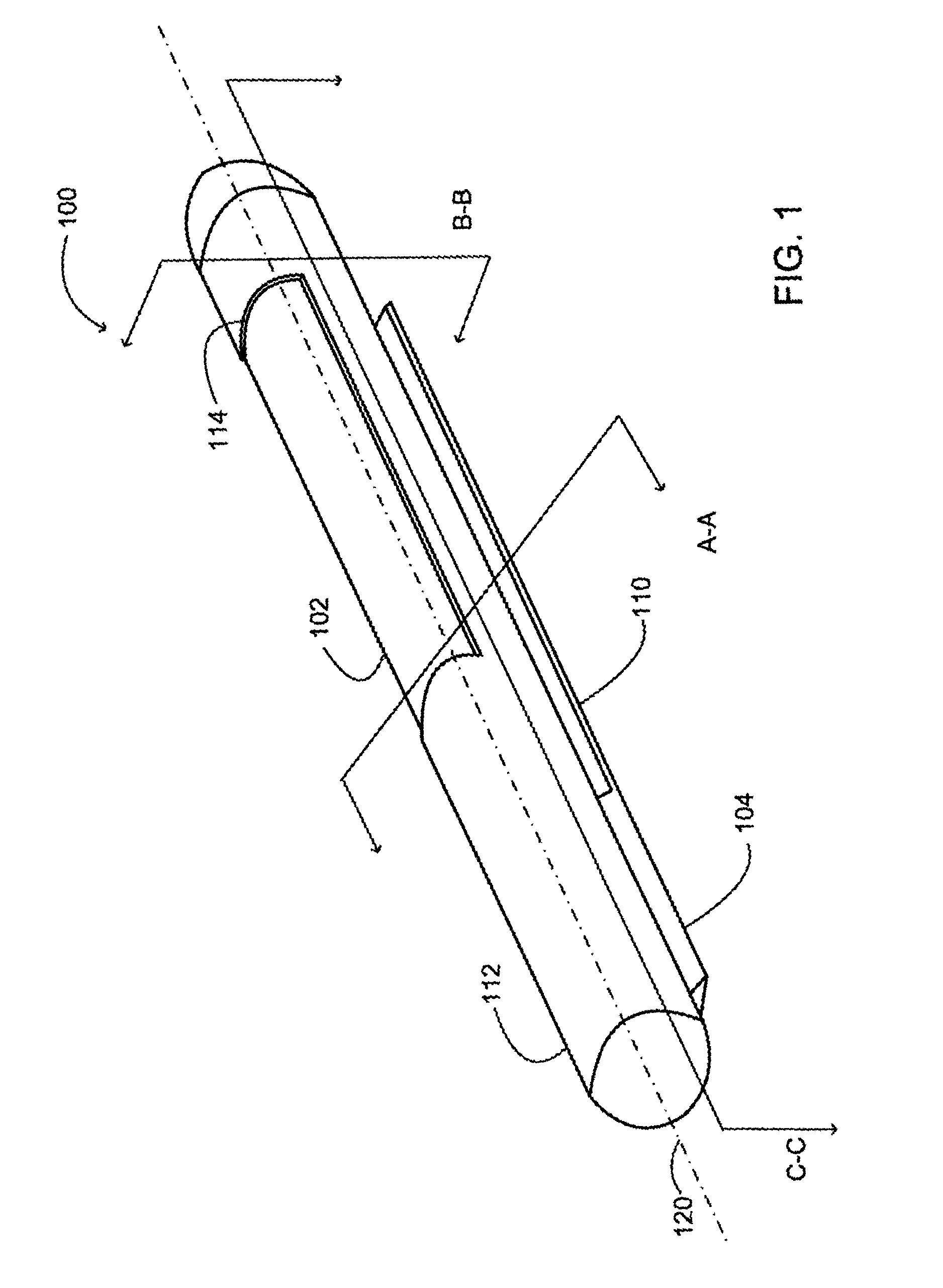
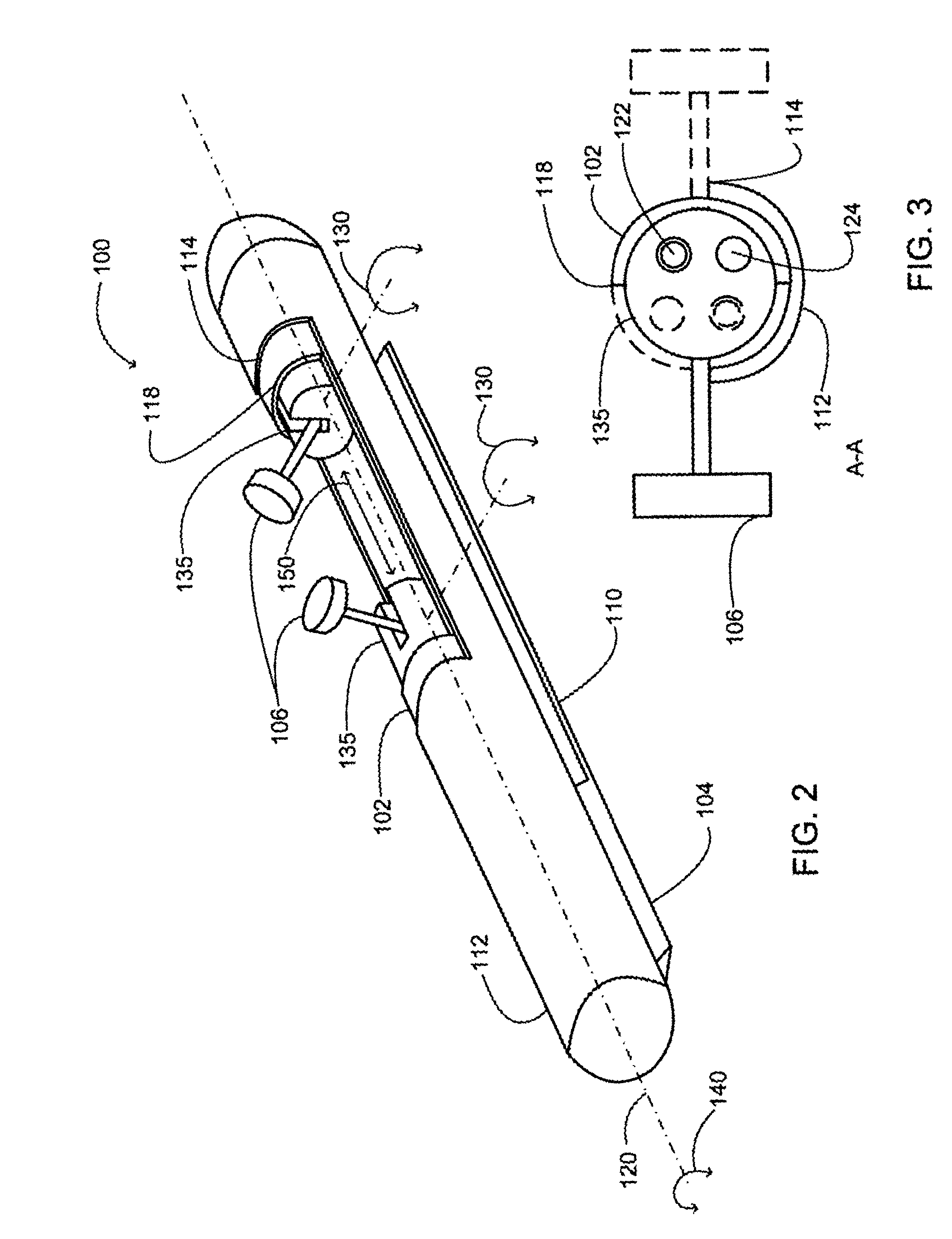
Methods and apparatus for performing transluminal and other procedures
InactiveUS20070135803A1Prevent overflowPrevent leakageSuture equipmentsEar treatmentSurgeryInstrumentation
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
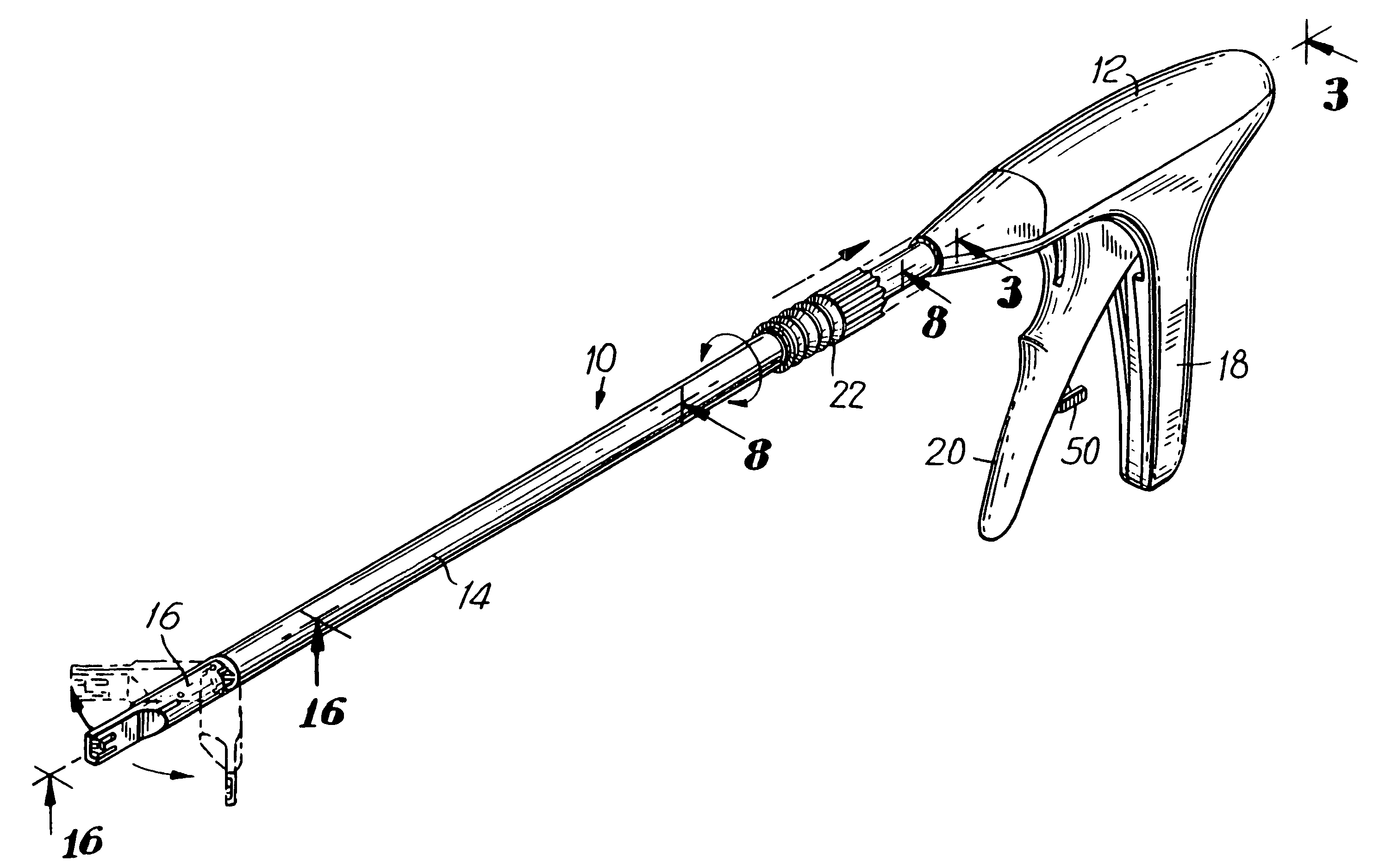
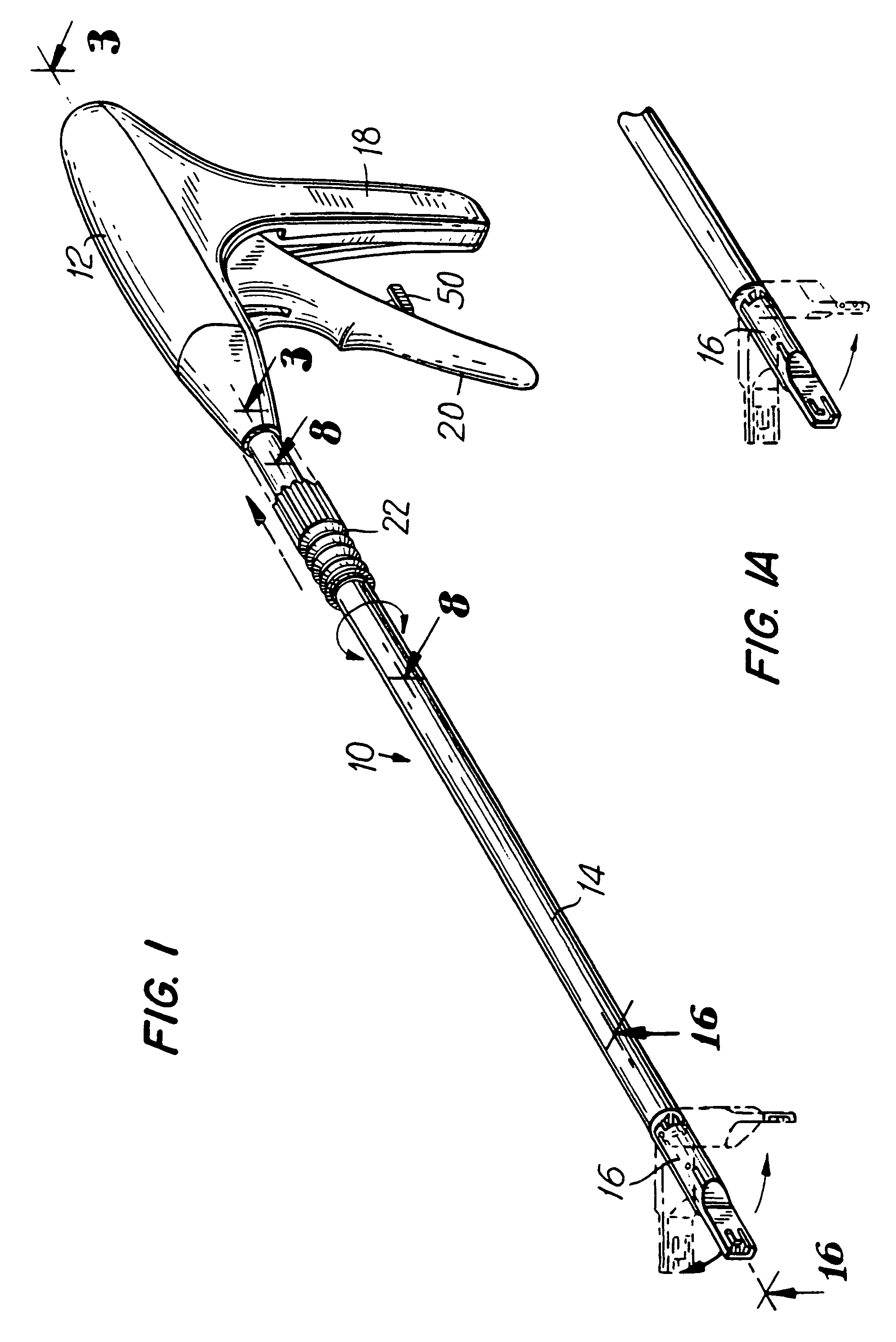
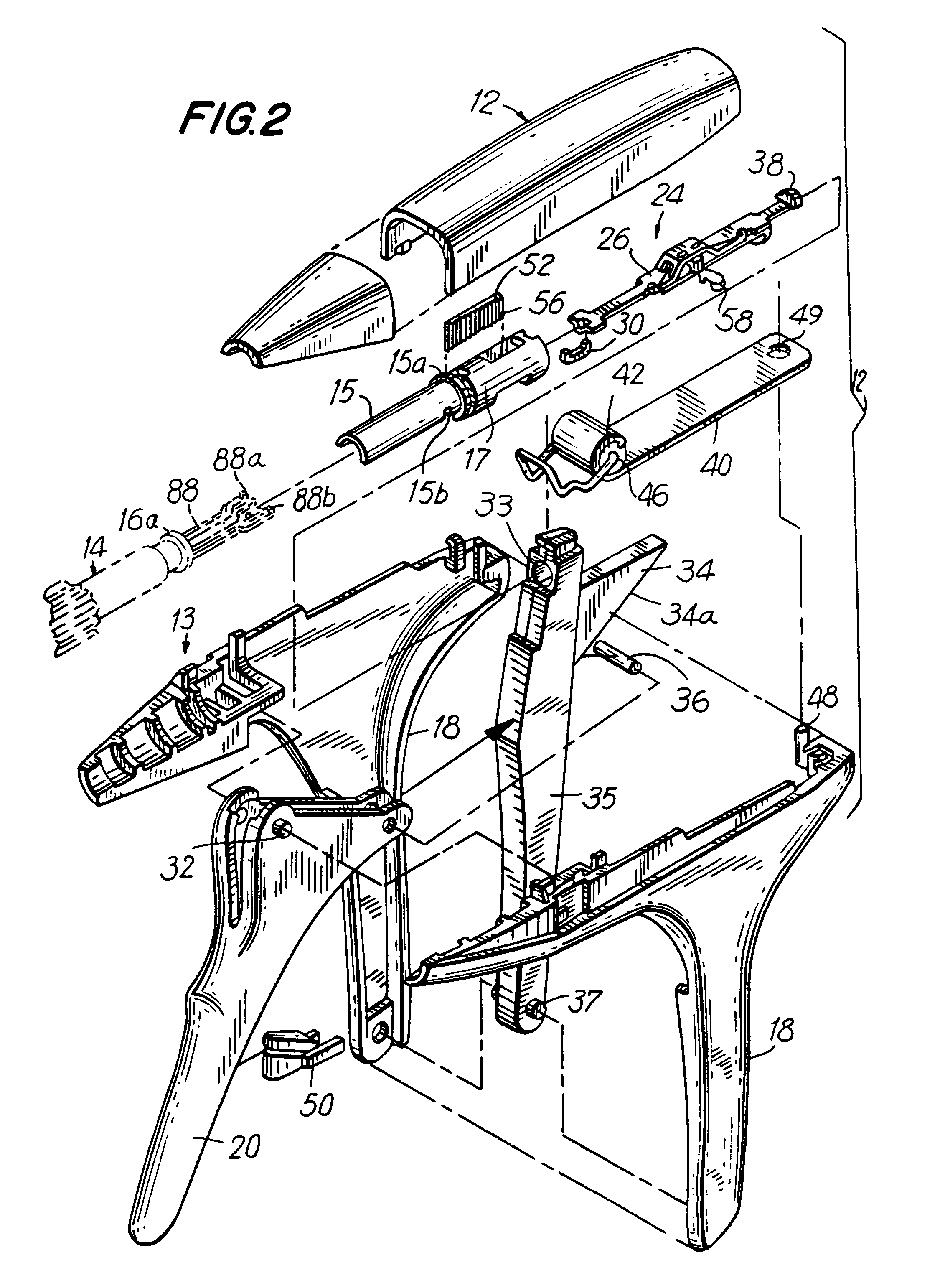
Surgical apparatus and method
InactiveUS6264086B1Minimizing chanceGood removal effectSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleSurgical incision
Owner:MCGUCKIN JR JAMES F
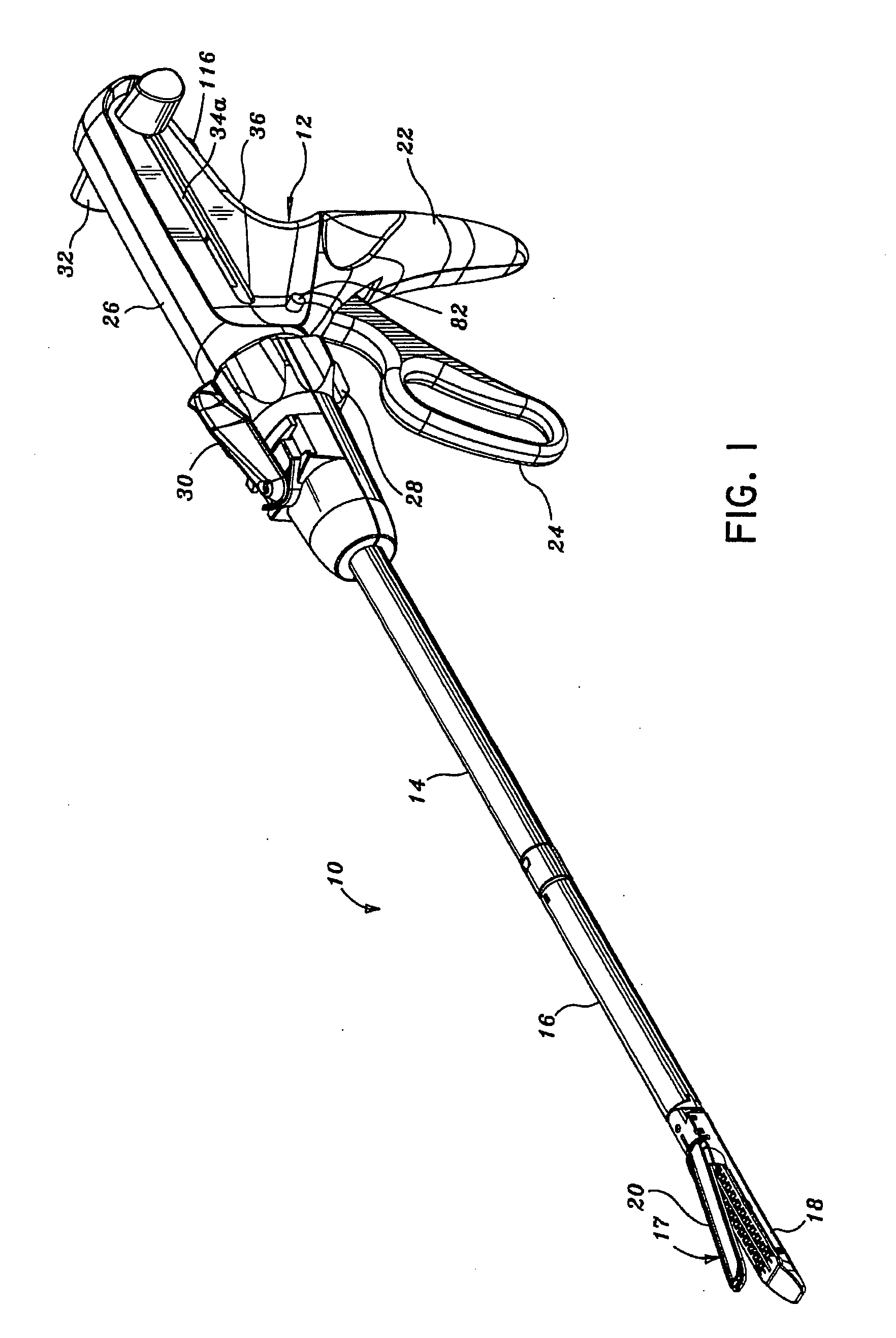
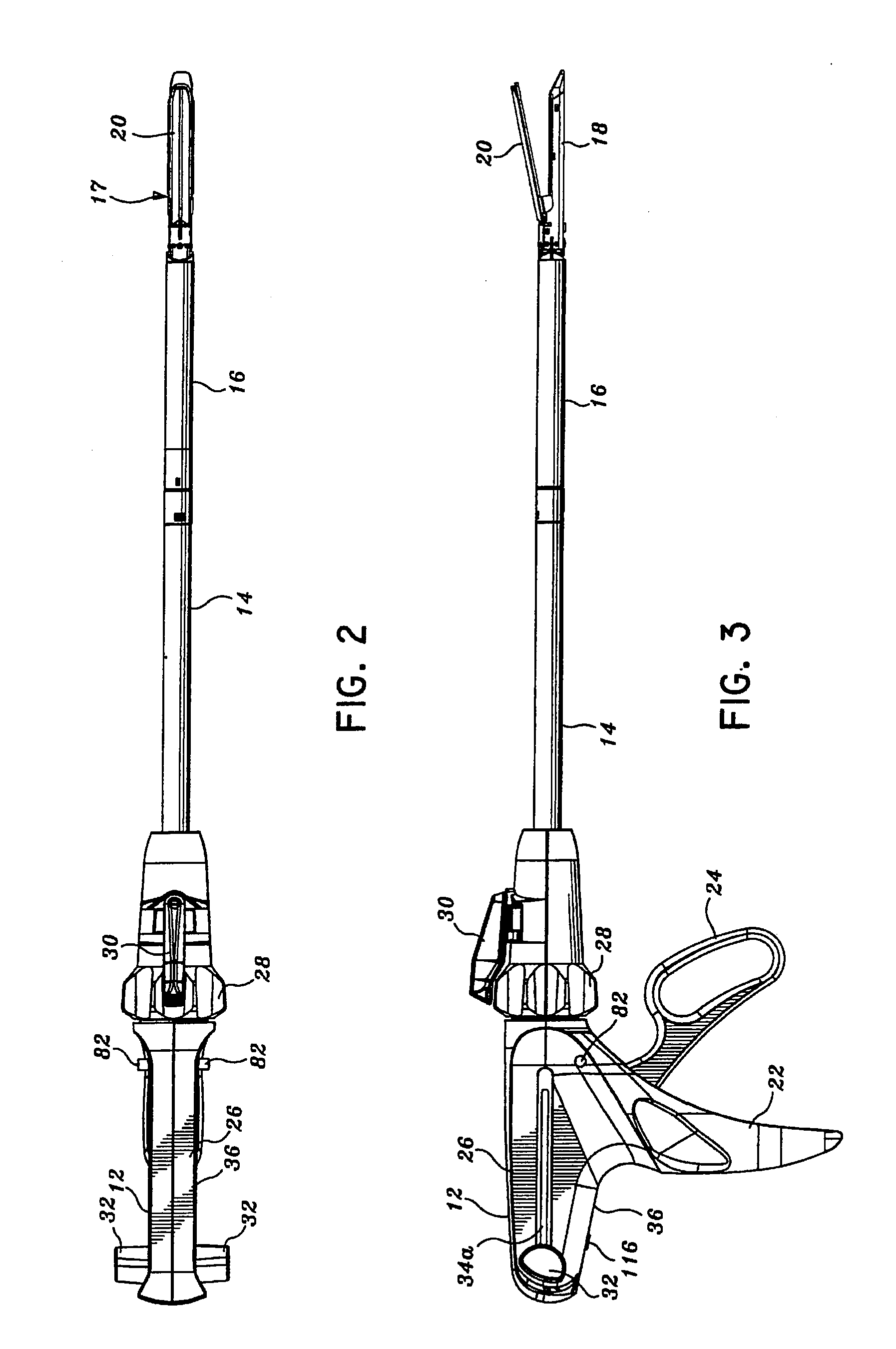
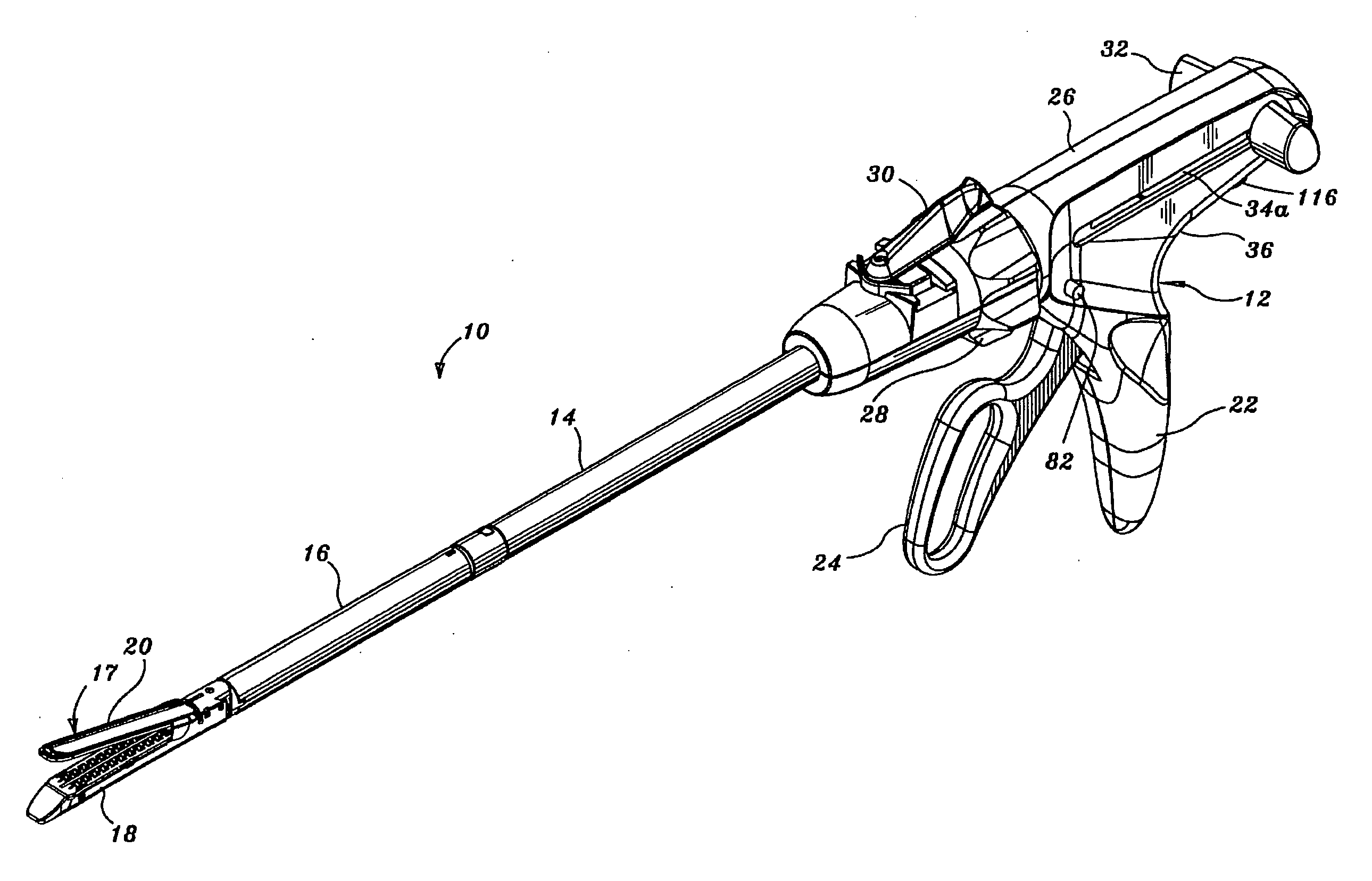
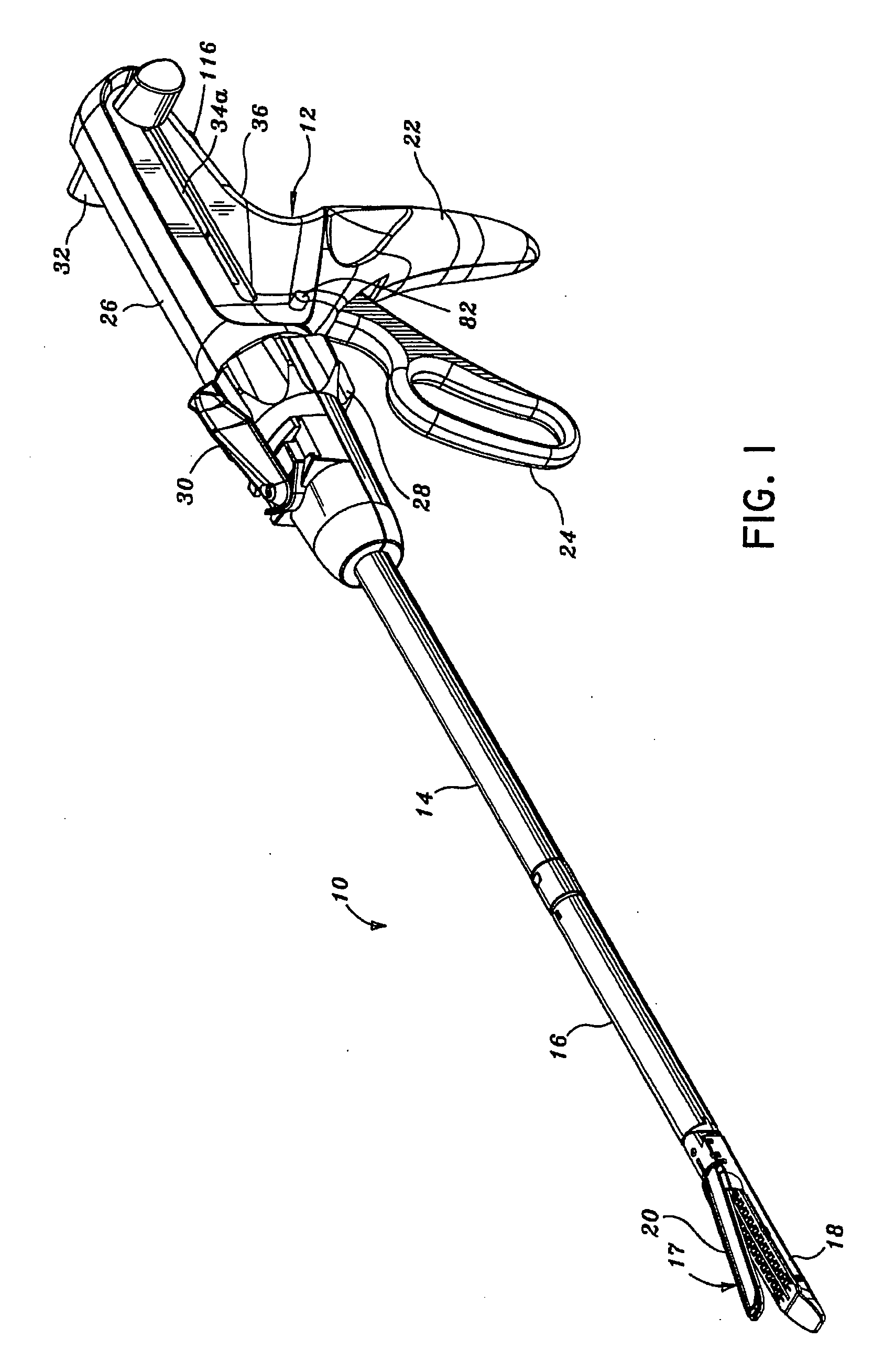
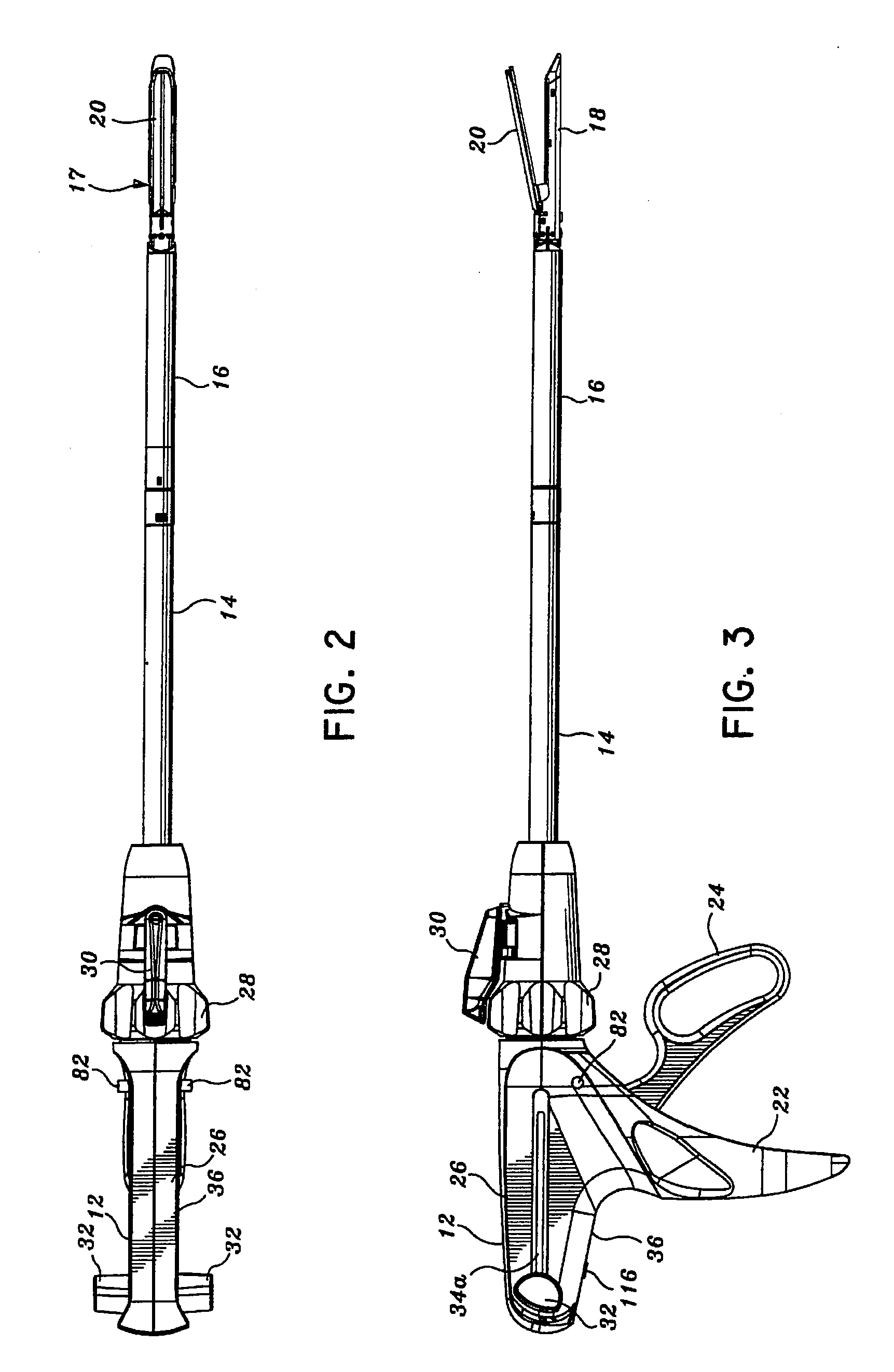
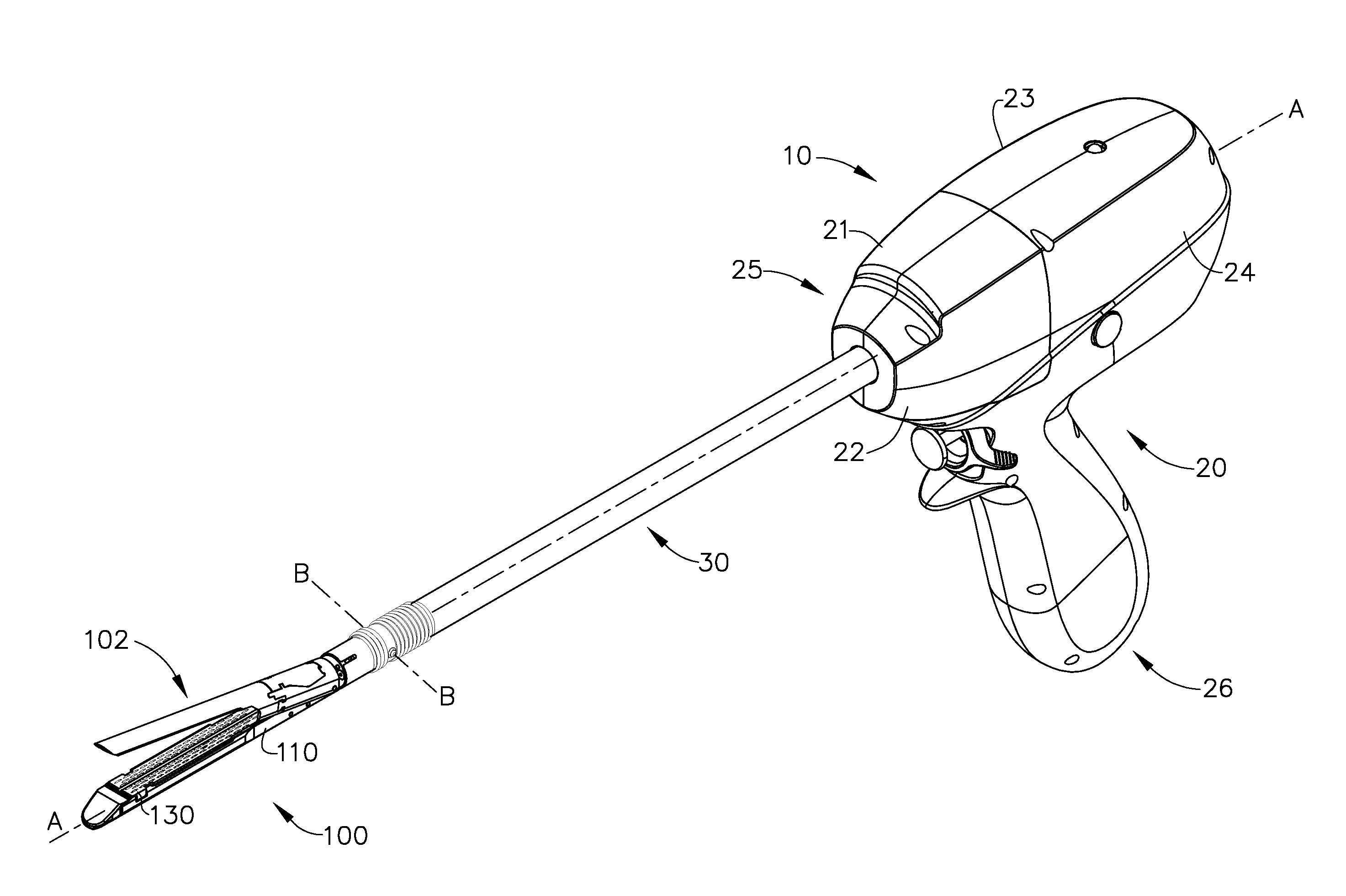
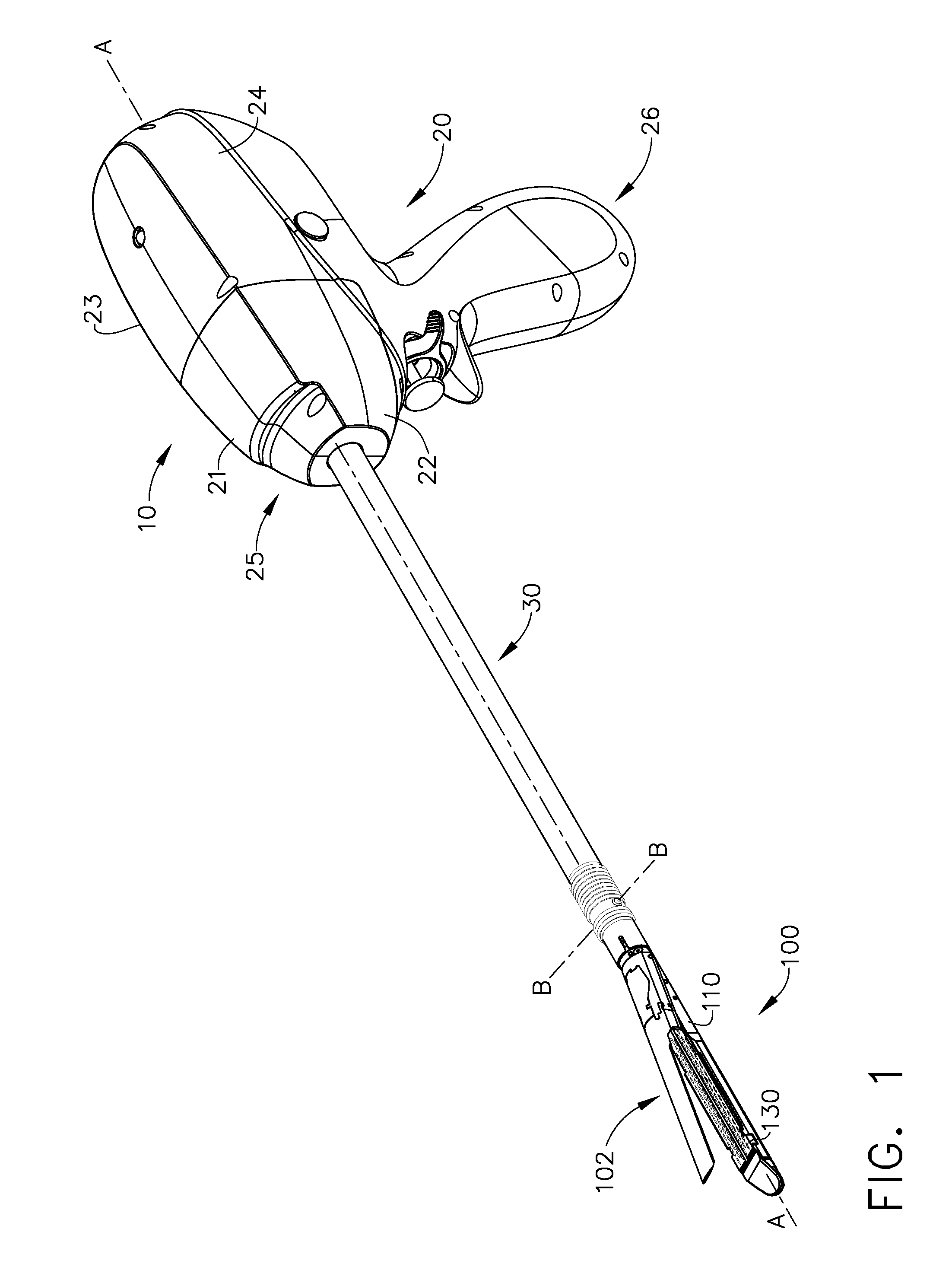
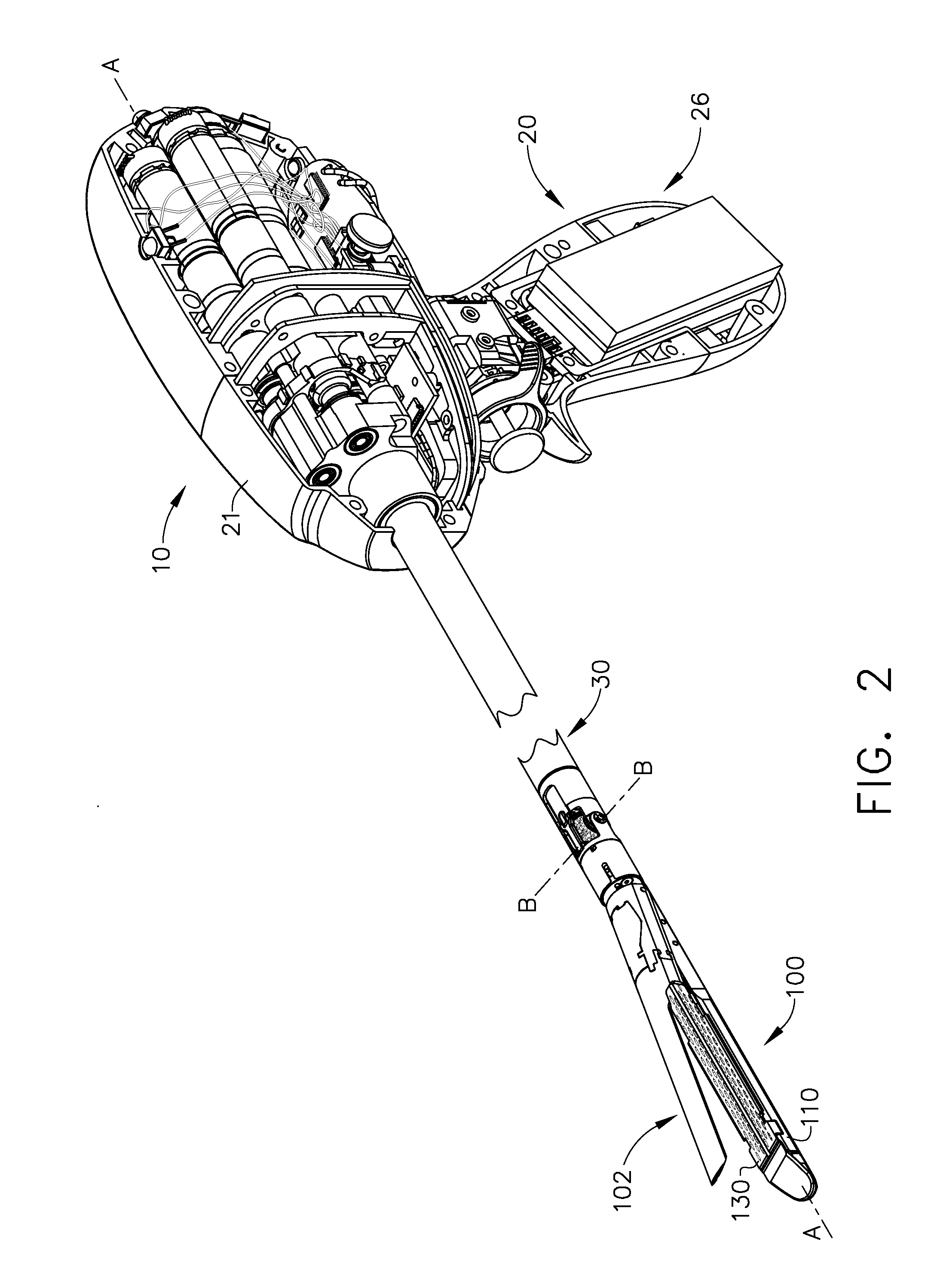
Surgical instrument for progressively stapling and incising tissue
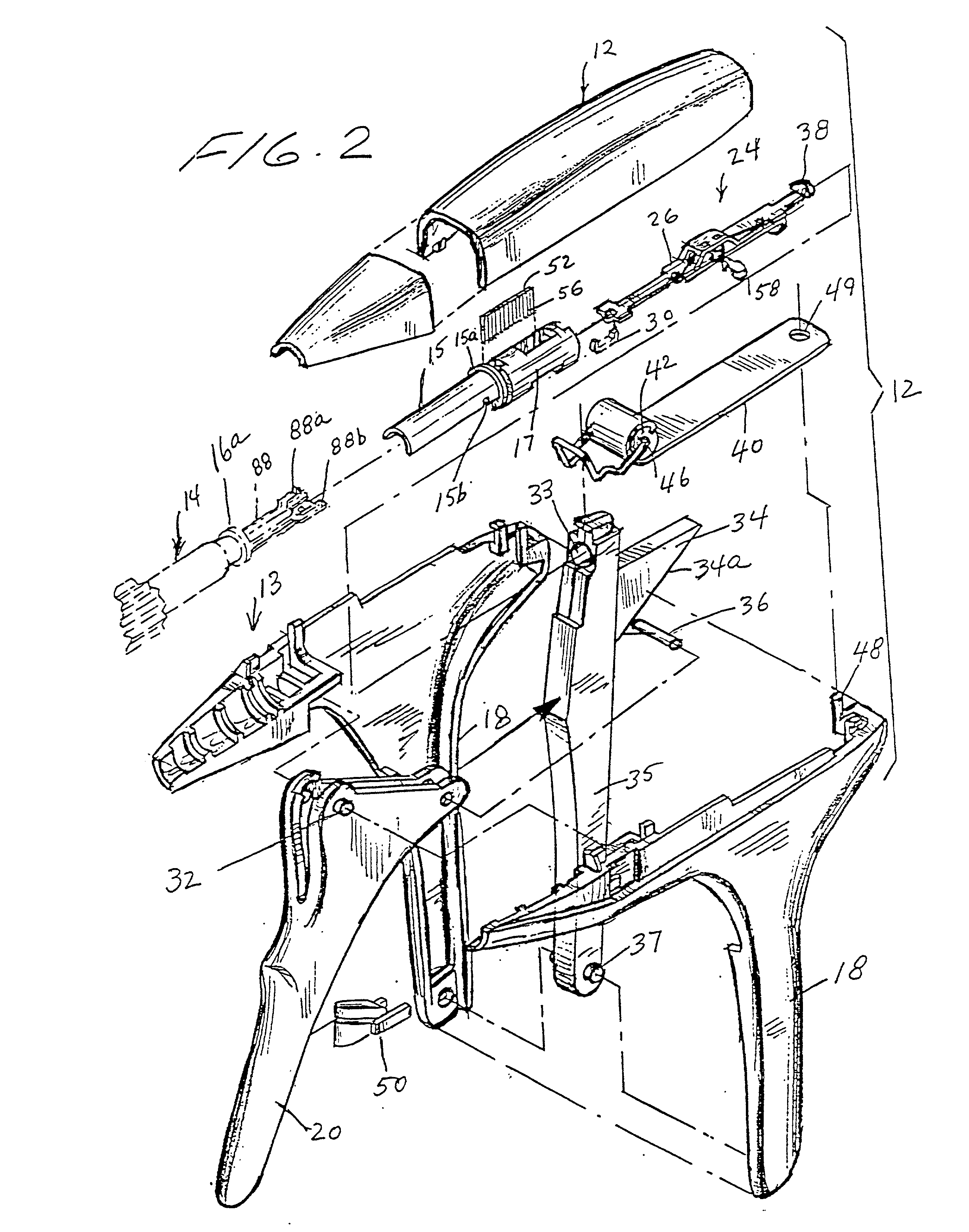
An instrument including a clamping jaw with an anvil defining an elongated slot and staple forming cups on opposing sides of the elongated slot. A housing rotatably mounts on the anvil and a pusher rotatably mounts within the housing. A handle actuates the clamping jaw from the open to the intermediate position by rotating the housing towards the clamping jaw. To move from the intermediate position to the closed position, the pusher rotates towards the anvil. A staple cartridge, disposed in the housing, includes a staple track for retaining two rows of staples on opposing sides of the elongated slot. Two staple drivers align with the distal most staples. The drivers slidably mount in the staple cartridge and couple to the pusher such that each staple driver forces a staple into the forming cups and, in turn, staples the body tissue as the pusher rotates from the intermediate to closed position. A knife rotatably mounts on the staple cartridge and couples to the pusher such that the knife passes into the elongated slot and, in turn, cuts the body tissue as the pusher rotates from the intermediate to closed position.
Owner:GREEN DAVID T
Surgical instrument incorporating a fluid transfer controlled articulation mechanism
ActiveUS7559450B2Give flexibilityOverall design flexibilitySuture equipmentsStapling toolsFluid controlEndoscope
A surgical instrument particularly suited to endoscopic use articulates an end effector by including a fluid transfer articulation mechanism that is proximally controlled. A fluid control, which is attached to a proximal portion, transfers fluid through the elongate shaft through a first fluid passage to a first fluid actuator that responds by articulating an articulation joint. Two opposing fluid actuators may respond to differential fluid transfer to effect articulation. Thereby, design flexibility is achieved by avoiding the design constraints of transferring a mechanical motion through the tight confines of the elongate shaft sufficient to effect articulation.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Surgical instrument having a directional switching mechanism
A surgical instrument including a switching mechanism which allows a surgeon to selectively advance or retract a staple driver and / or cutting member within a staple cartridge. In various embodiments, the surgical instrument can include a handle, a trigger operatively coupled to the handle, a firing drive, and an end effector. The firing drive can include a first ratchet assembly configured to advance a cutting member in the end effector and a second ratchet assembly configured to retract the cutting member. The trigger can include first and second pawls pivotably mounted thereon which are configured to be selectively engaged with the first and second ratchet assemblies, respectively. In at least one embodiment, the trigger can be configured to slide between a first position in which the first pawl is engaged with the first ratchet assembly and a second position in which the second pawl is engaged with the second ratchet assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
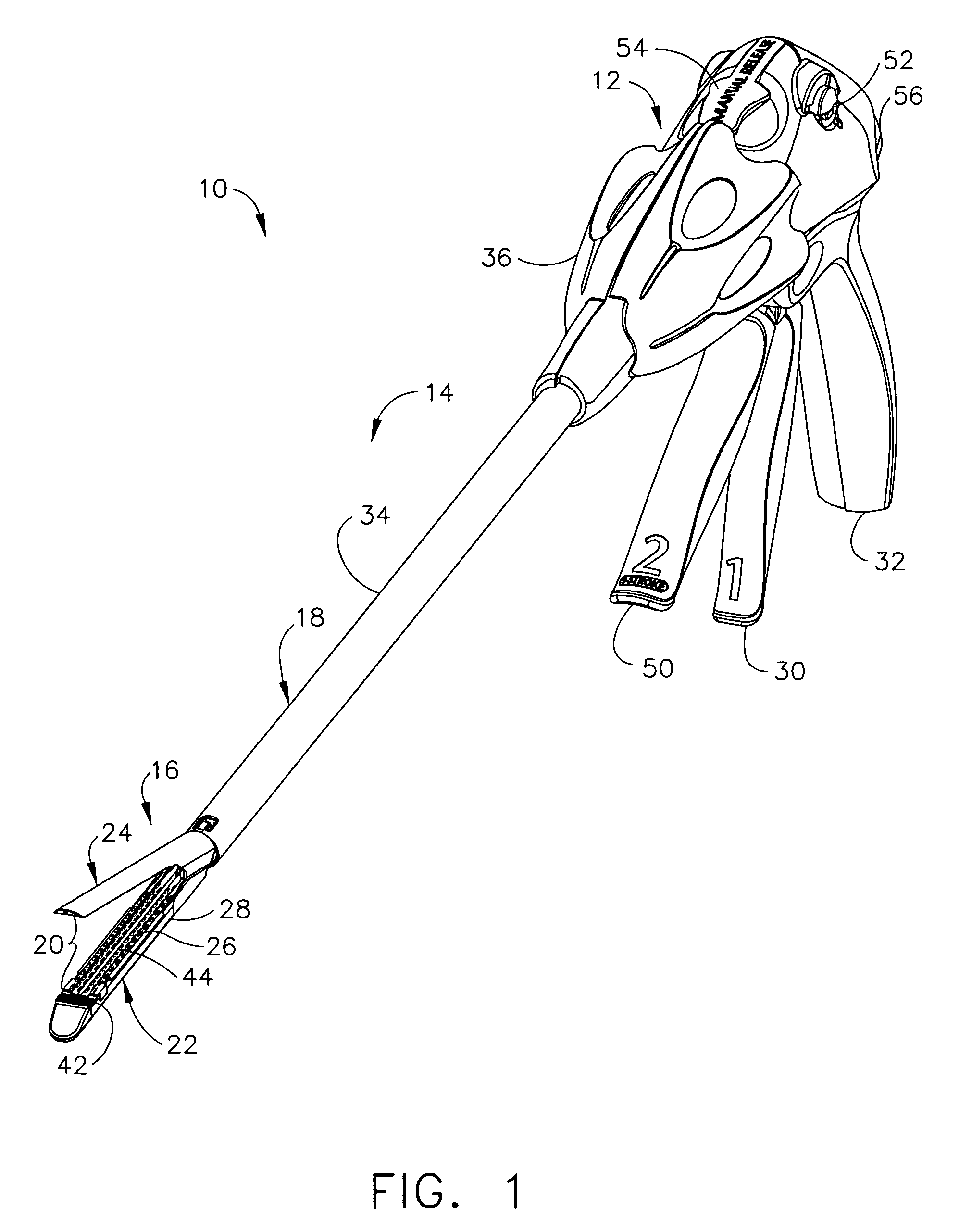
Powered surgical cutting and stapling apparatus with manually retractable firing system
In one general aspect, various embodiments of the present invention can include a motorized surgical cutting and fastening instrument having a drive shaft, a motor selectively engageable with the drive shaft, and a manual return mechanism configured to operably disengage the motor from the drive shaft and retract the drive shaft. In at least one embodiment, a surgeon, or other operator of the surgical instrument, can utilize the manual return mechanism to retract the drive shaft after it has been advanced, especially when the motor, or a power source supplying the motor, has failed or is otherwise unable to provide a force sufficient to retract the drive shaft.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Surgical device having a rotatable jaw portion
ActiveUS7918230B2Prevent movementSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical operationSurgical department
A surgical device is provided that includes a jaw portion, having a first jaw in opposed correspondence with a second jaw, the second jaw including a surgical member. The surgical device may include a shaft portion coupled to a proximal end of the jaw portion and at least one motor configured to rotate the jaw portion relative to the shaft portion, to move the jaw portion relative to the shaft portion, move the first jaw relative to the second jaw and move the surgical member within the second jaw. The surgical member may be prevented from moving within the second jaw unless the first jaw is in a closed position relative to the second jaw. Advantageously, the surgical member may include one or both a cutting element or a stapling element, disposed within one of the jaws.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
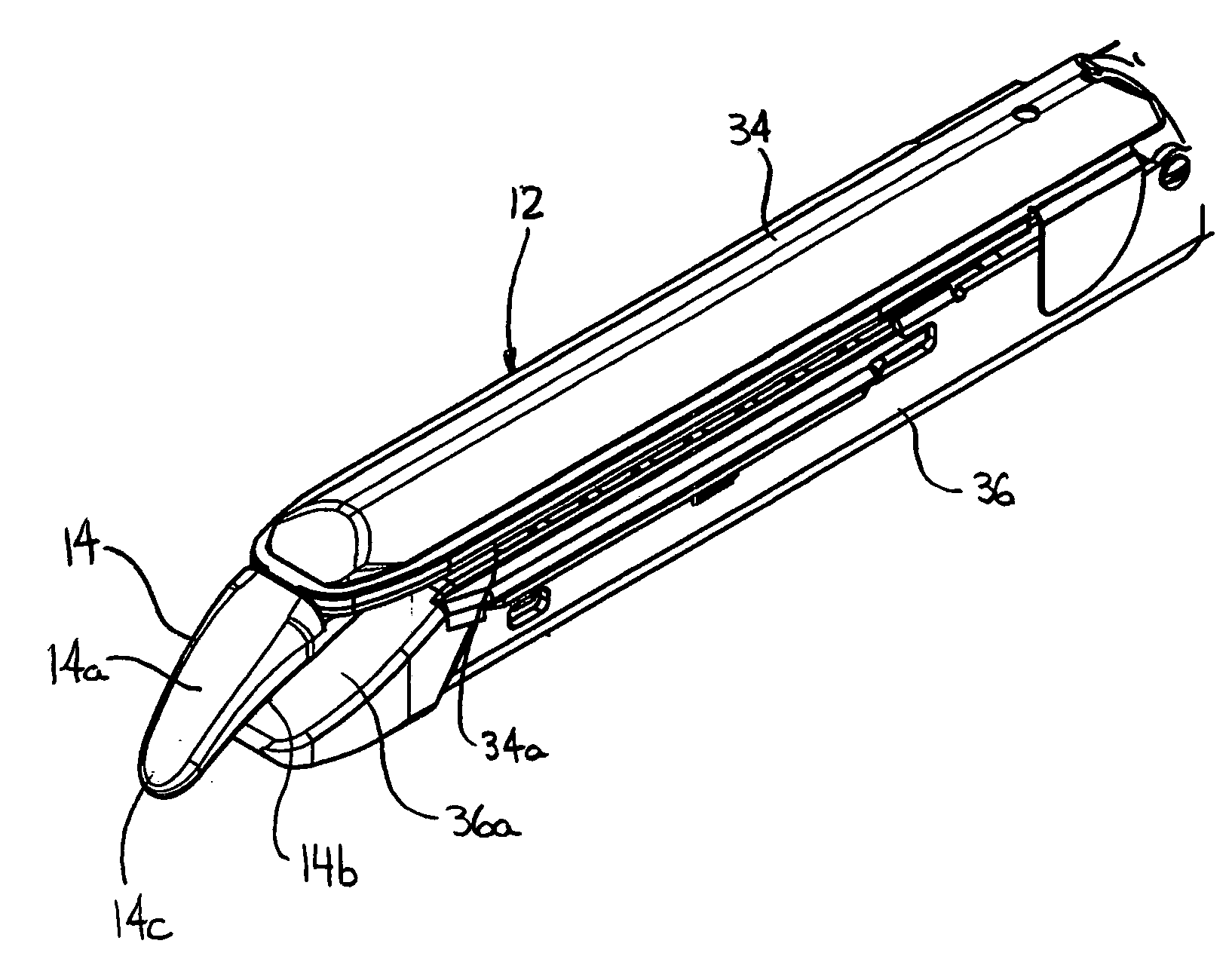
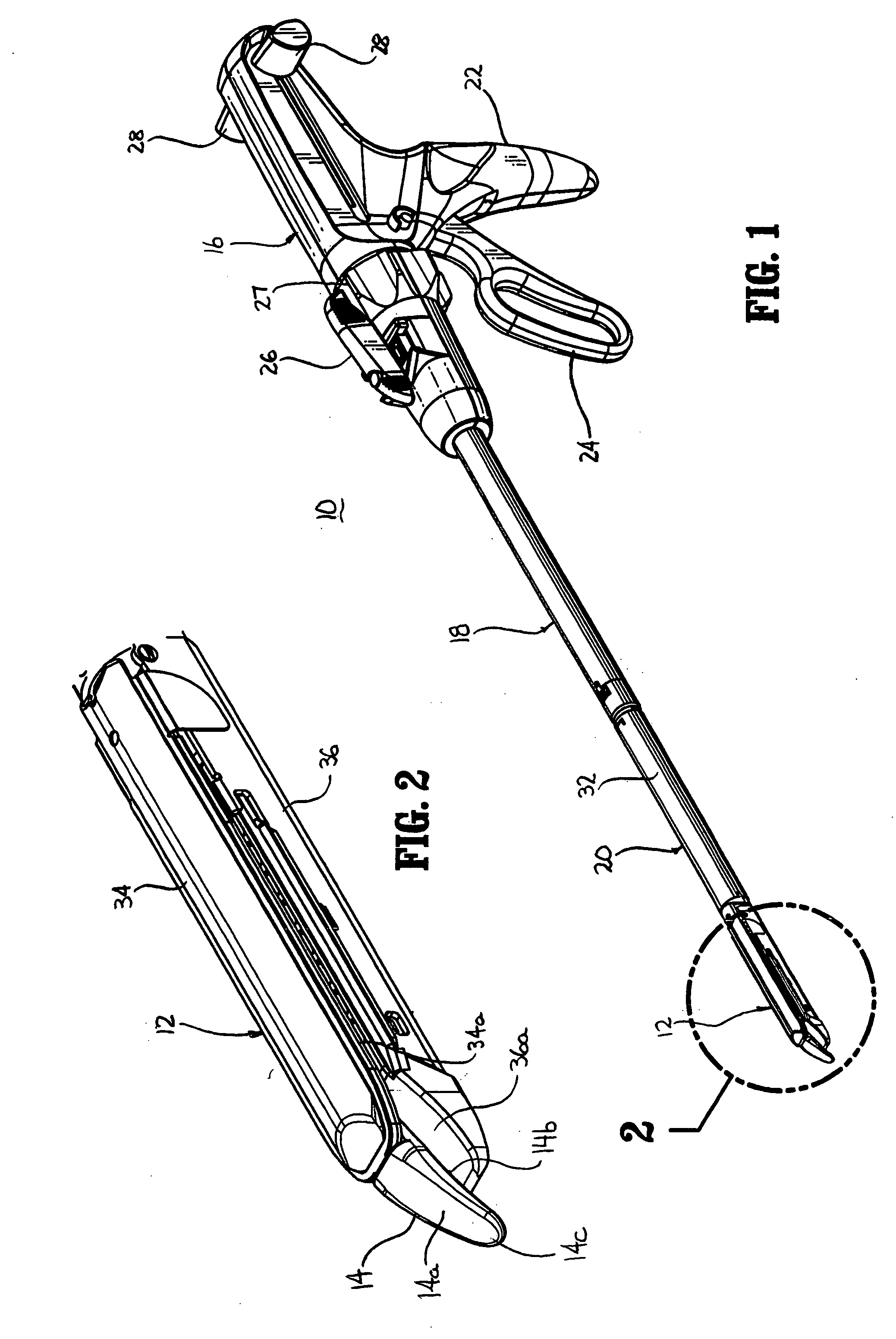
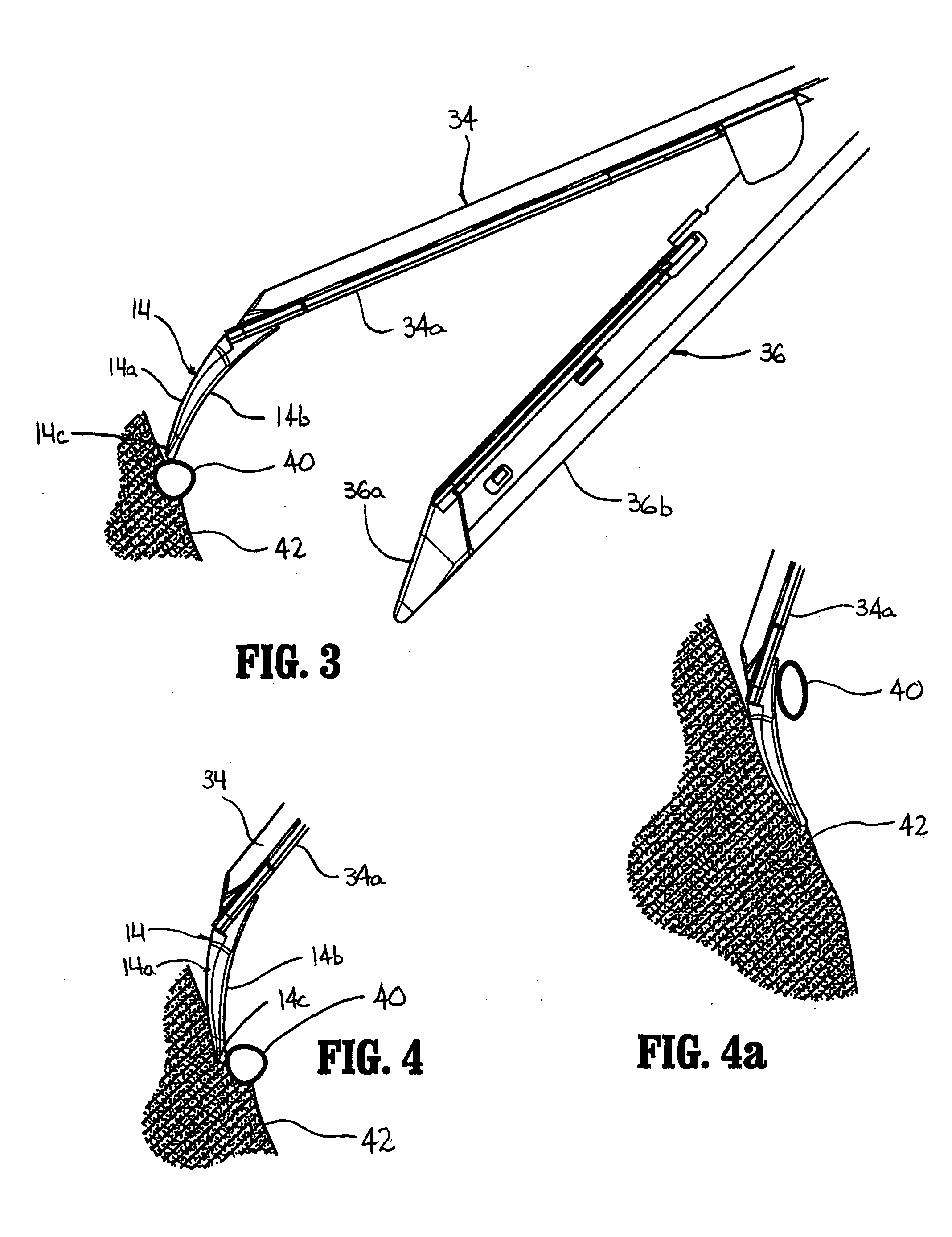
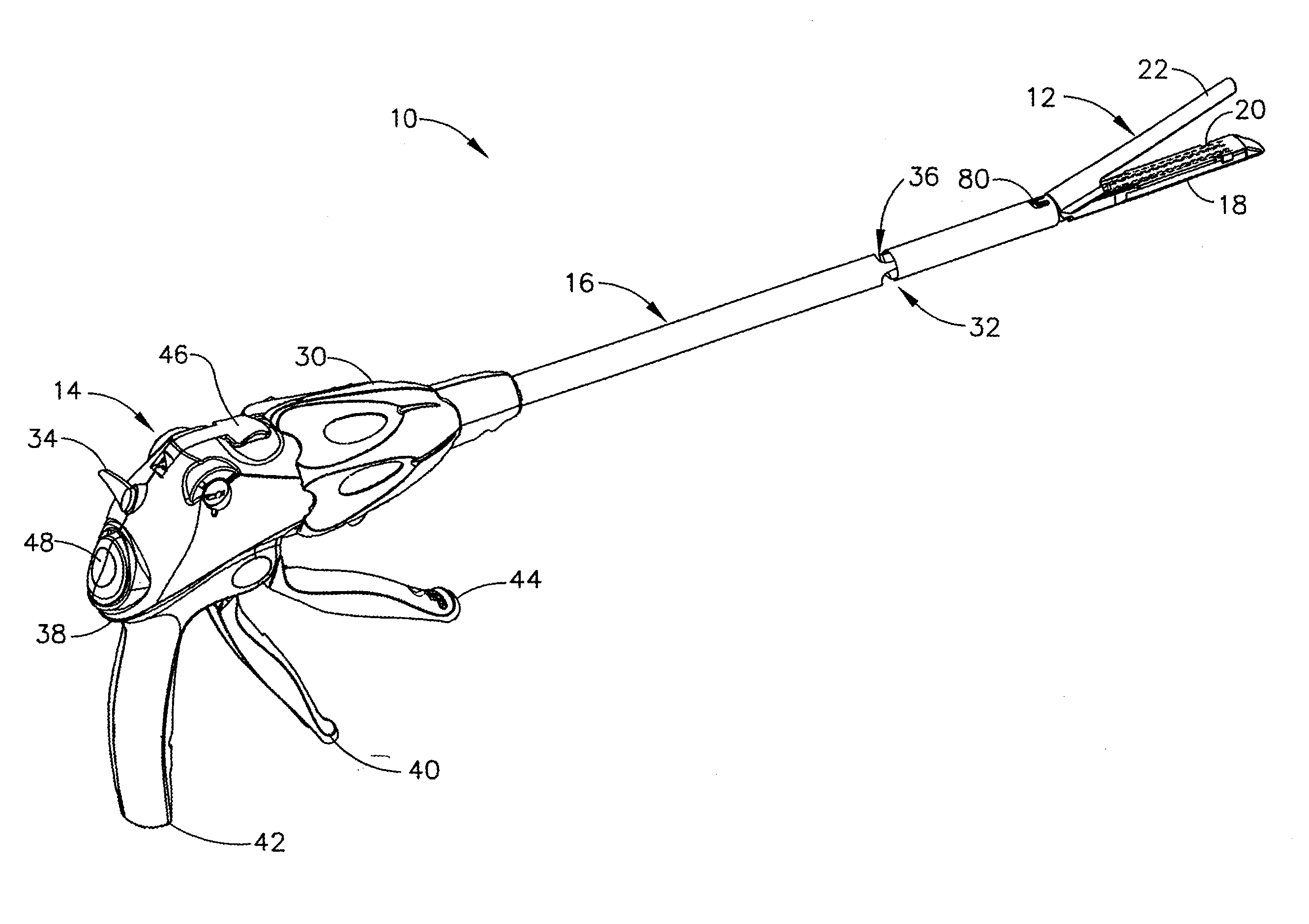
Surgical device
A surgical device that includes a first jaw having a distal end and a second jaw having a distal end. The second jaw is disposed in opposed correspondence with the first jaw. The first jaw is pivotably coupled to the second jaw. The surgical device also includes a biasing element, such as a spring, that biases the distal end of the first jaw towards the distal end of the second jaw. The device may also include a first driver disposed in the second jaw and coupled to the first jaw. The first driver is configured to cause separation of the first jaw and the second jaw when the first driver is actuated for opening the jaws and to close the first jaw and the second jaw when the first driver is actuated for closing the jaws. The device may also include at least one of a cutting element and a stapling element disposed within the second jaw, preferably a blade rotatably mounted on a wedge. A second driver is configured to move the cutting element and / or the stapling element proximally from a distal end toward the proximal end of the second jaw to at least one of cut and staple a section of tissue disposed between the first and second jaws. By biasing the distal ends of the first and second jaws towards each other, the surgical device may prevent a section of tissue which is disposed between the first and second jaws from escaping out from between the distal ends of the first and second jaws.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
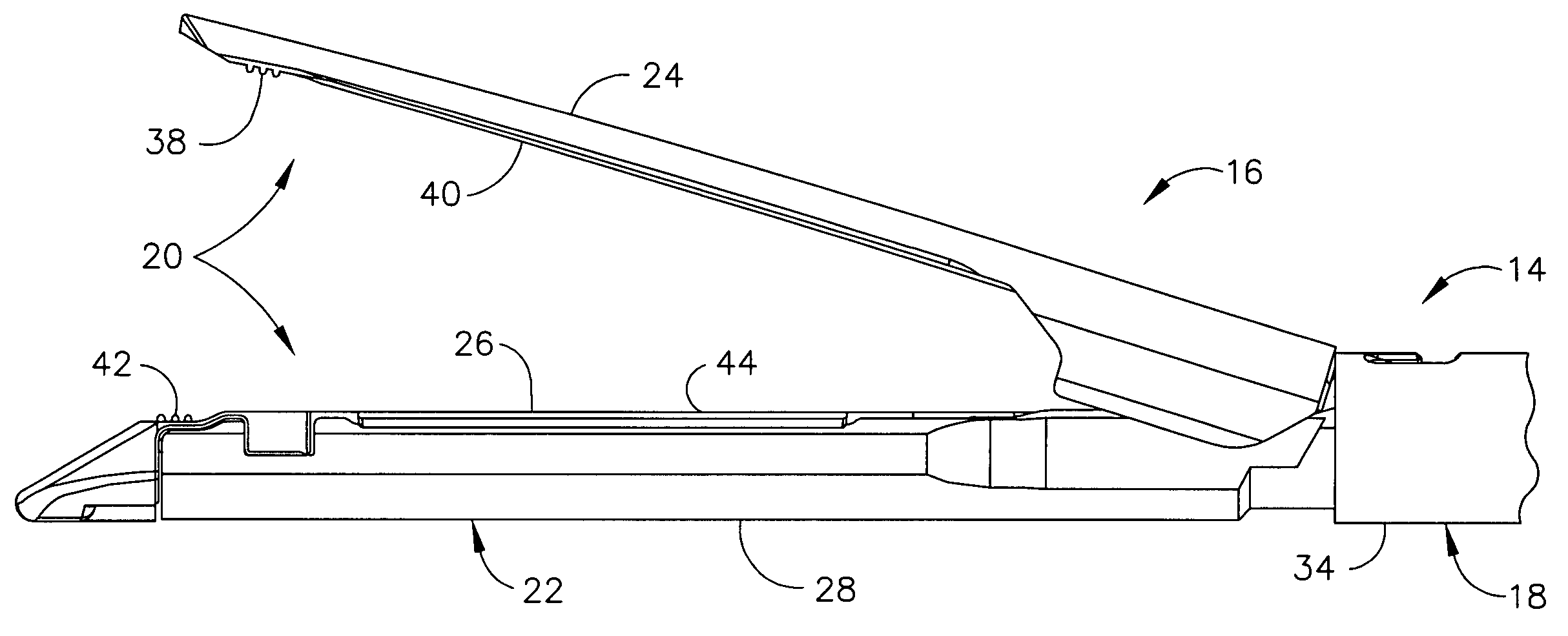
End effector coupling arrangements for a surgical cutting and stapling instrument
InactiveUS20090206131A1Affected deploymentImprove the forceSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleDetent
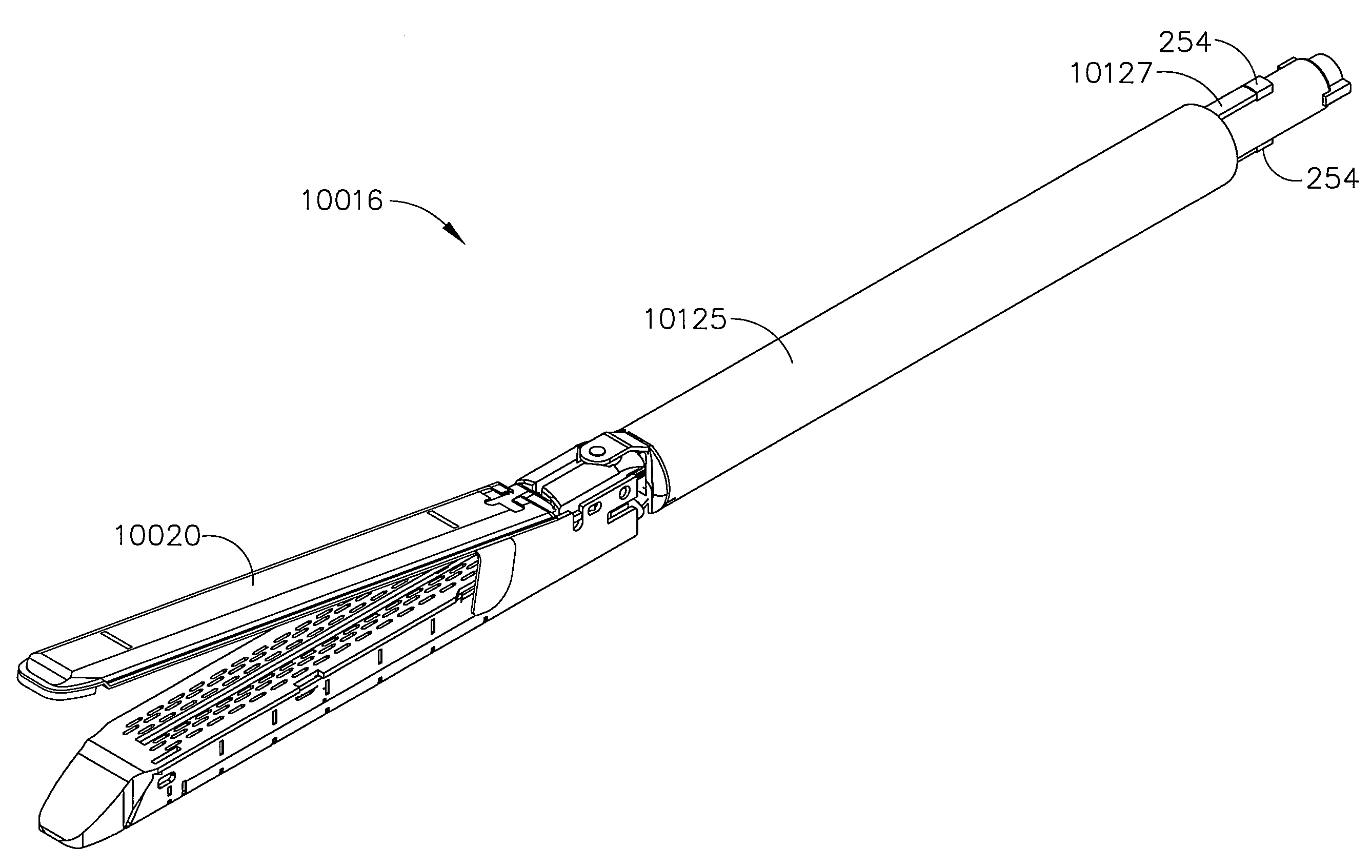
In various embodiments, a surgical stapling instrument can include a handle, a shaft extending from the handle, wherein the shaft defines an axis, and a disposable loading unit which is assembled to the shaft in a direction which is transverse to the shaft axis. Such a connection between the disposable loading unit and the shaft can prevent, or at least inhibit, the disposable loading unit from being unintentionally displaced proximally and / or distally relative to the shaft of the surgical instrument. The surgical stapling instrument and / or disposable loading unit can further include a threaded collar and / or detent assembly configured to hold the disposable loading unit in place. In various embodiments, a disposable loading unit can include a lockout feature which can prevent, or at least inhibit, an expended disposable loading unit from being reassembled to the elongated body of the surgical instrument.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
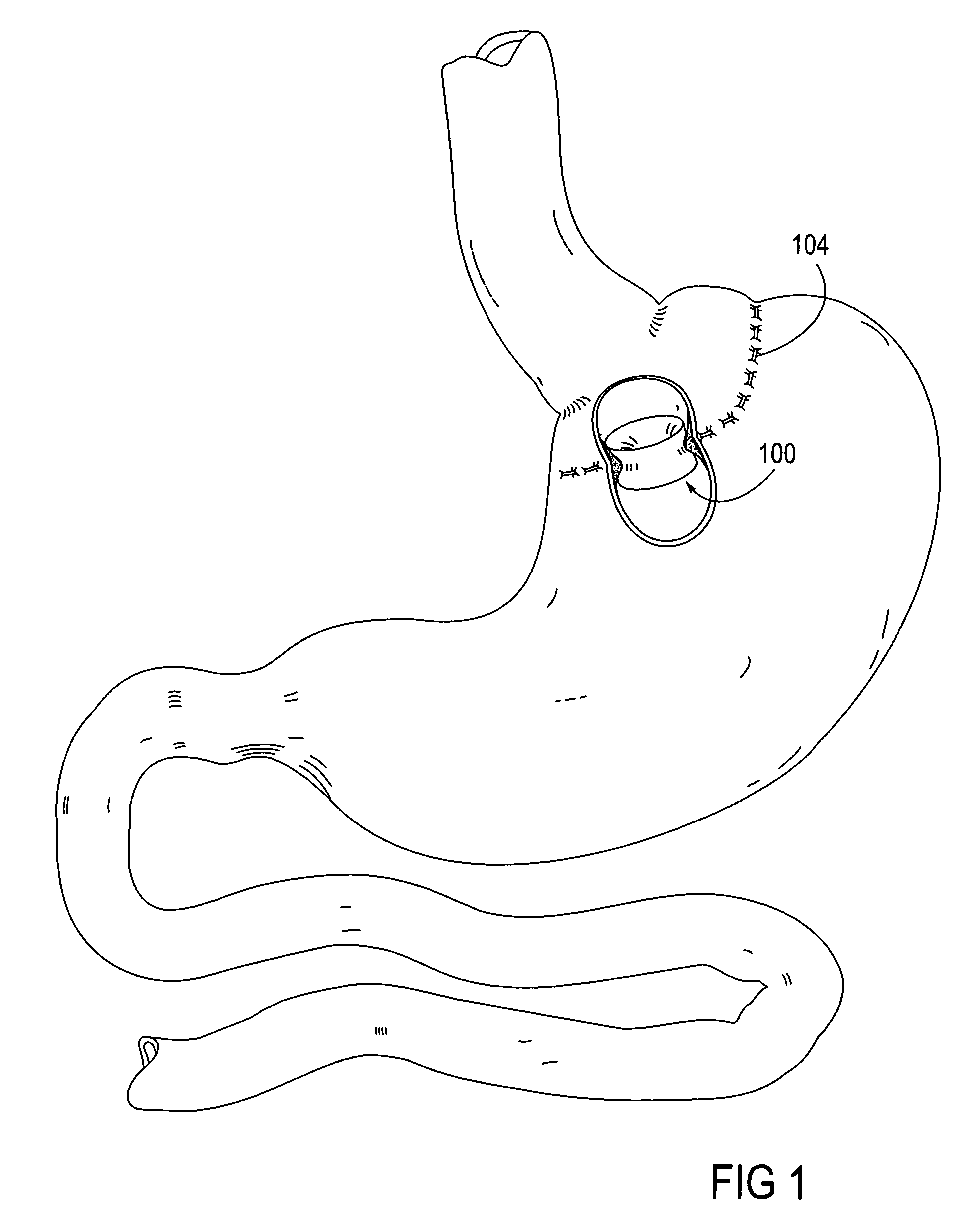
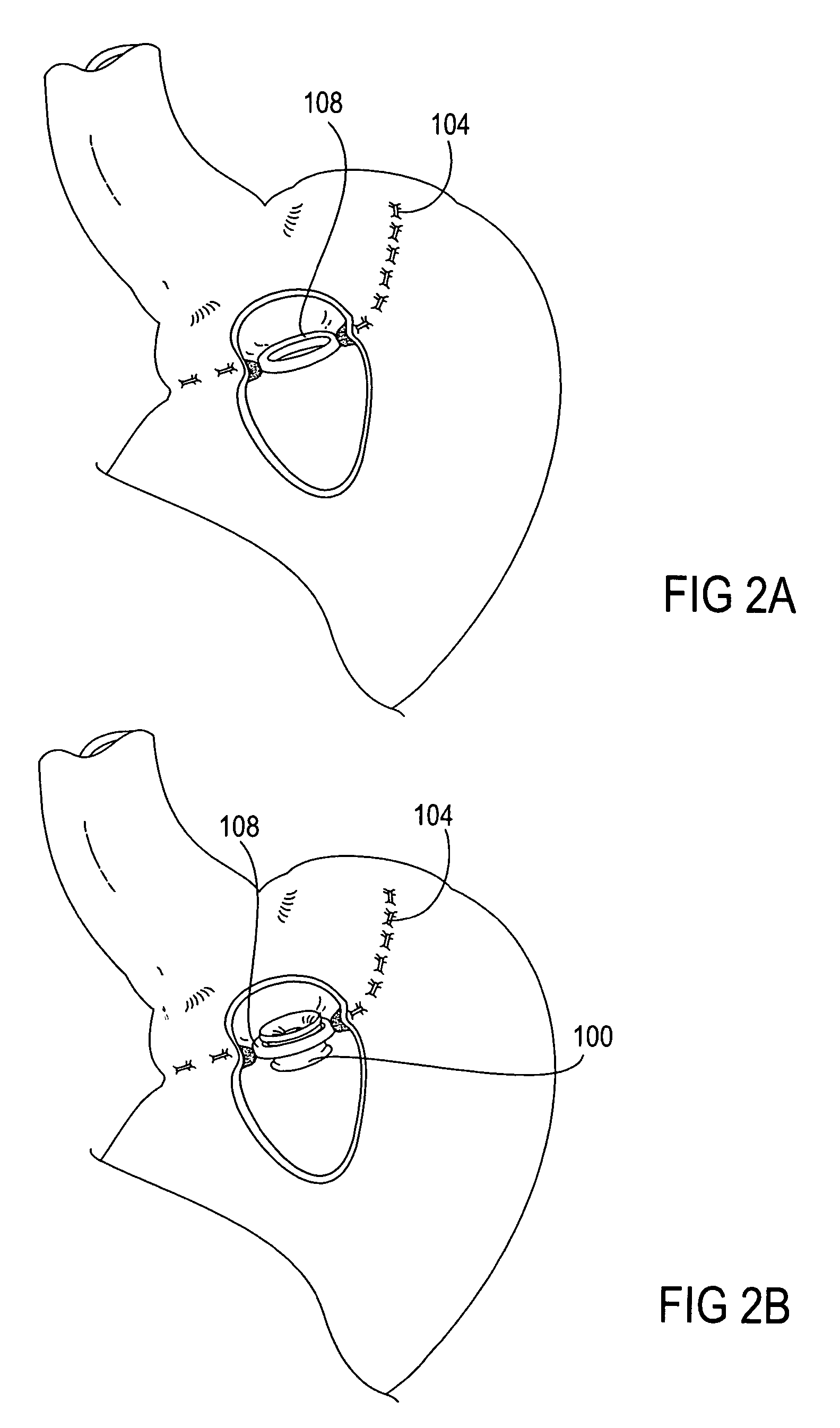
Apparatus and methods for treatment of morbid obesity
Apparatus and methods are described for treatment of morbid obesity using minimally invasive techniques. The apparatus includes a system of components that may be used separately or in combination for effectively reducing stomach volume, bypassing a portion of the stomach and / or small intestines, reducing nutrient absorption in the stomach and / or small intestines and / or depositing minimally or undigested food farther than normal into the intestines, thereby stimulating intestinal responses. The components described include an artificial stoma device, a gastric sleeve device, an intestinal sleeve device and a combined gastrointestinal sleeve device.
Owner:VALENTX
Surgical stapling device with tissue tensioner
A circular stapling device particularly suited for surgical treatment of internal hemorrhoids is provided. The stapling device includes a distal head portion having an anvil and a shell assembly. A tissue tensioner device including a tissue engagement member is movably positioned between the anvil and the shell assembly and is operable via a tensioner trigger to position tissue within a bore defined within the shell assembly.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Palm-size surgical stapler for single hand operation
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
Surgical stapling device with dissecting tip
InactiveUS20050216055A1Prevent snaggingAvoid pullingSuture equipmentsStapling toolsActuatorSurgical department
A dissecting tip is provided for use with a surgical stapler or instrument. In one embodiment, the dissecting tip is secured to the end effector of the surgical instrument, e.g., to the cartridge assembly. The dissecting tip extends distally from the end effector and is configured to dissect or separate target tissue from certain tissue, e.g., adherent, connective, joined or other tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
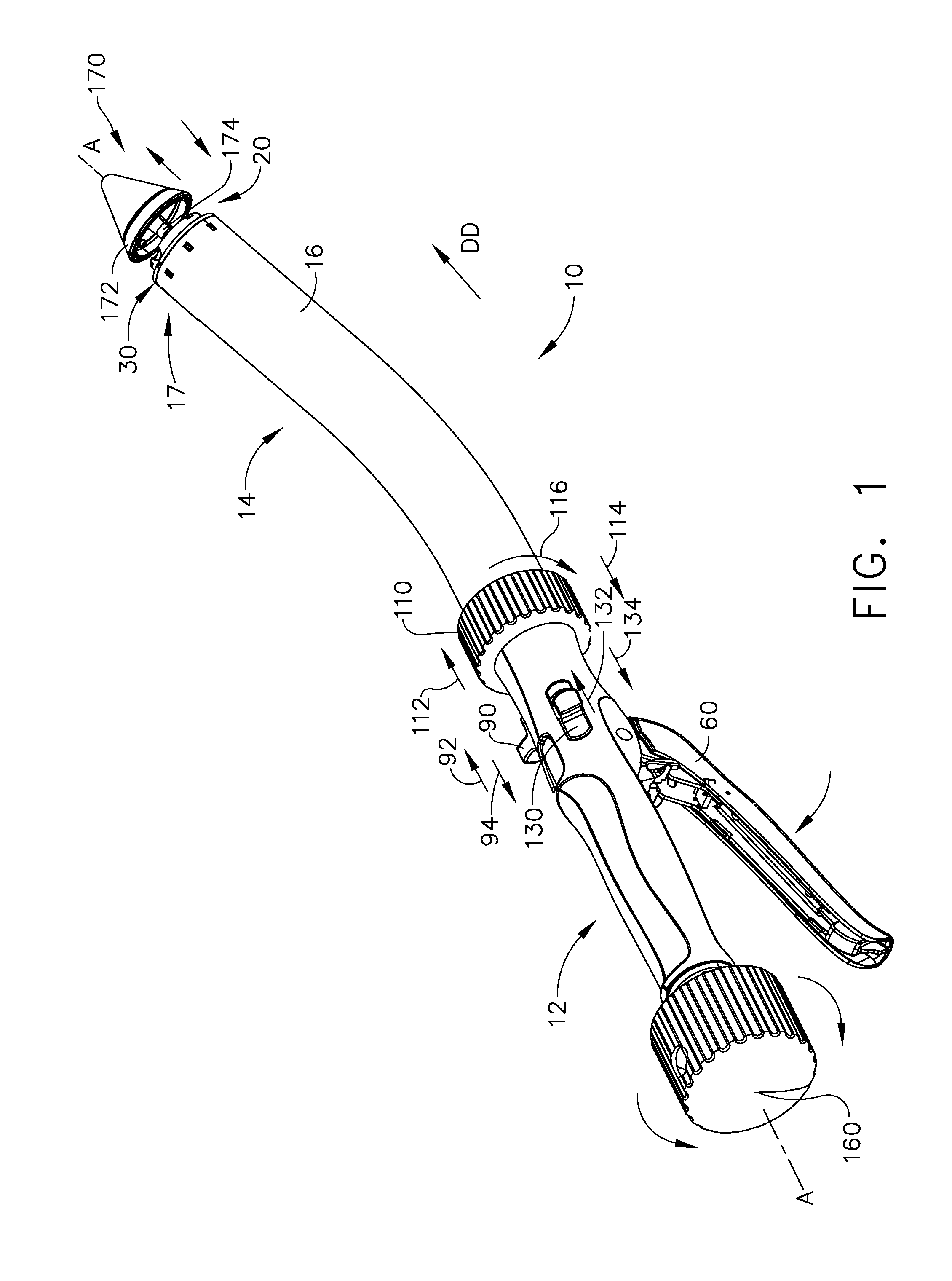
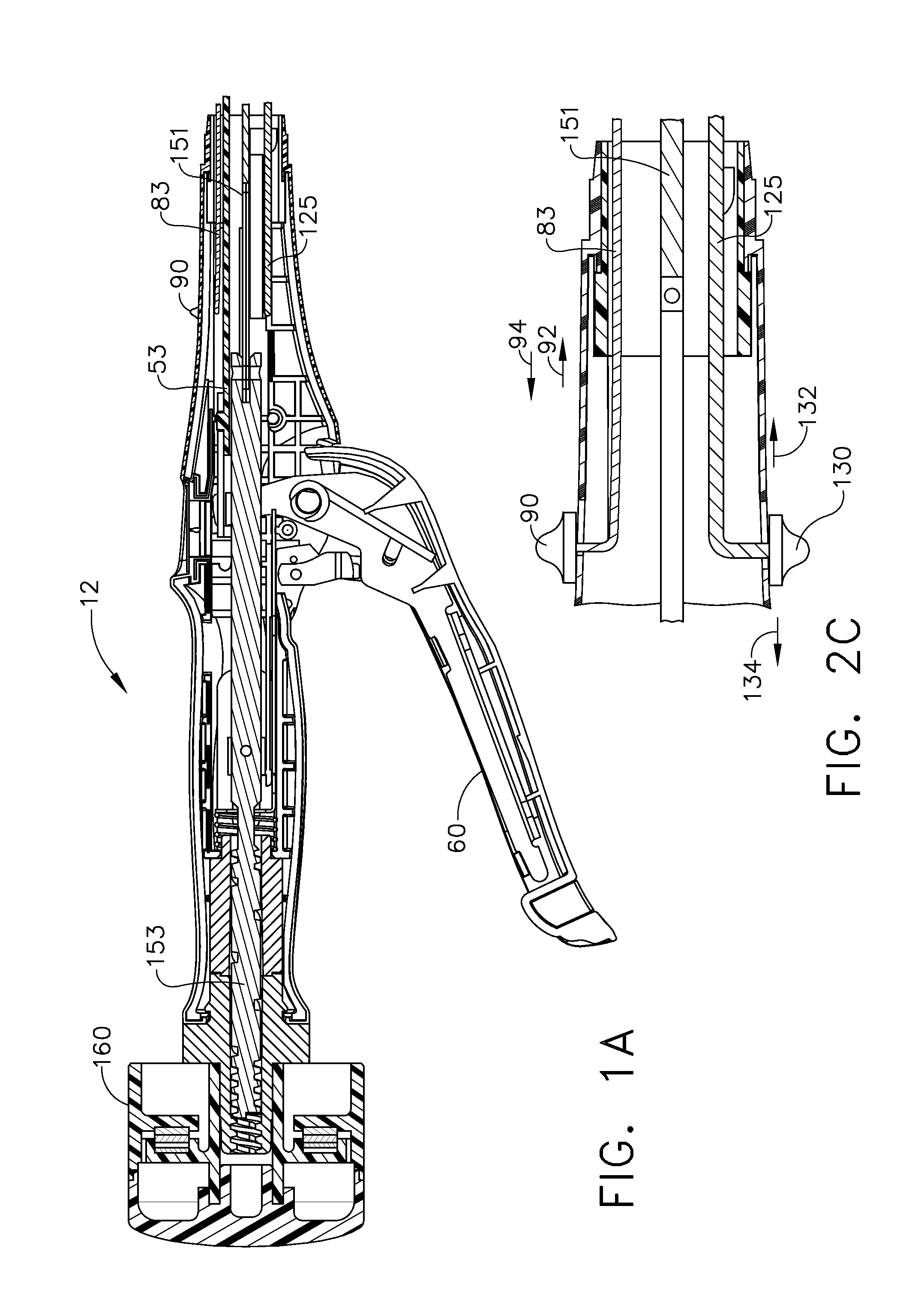
Articulating surgical stapling instrument incorporating a two-piece e-beam firing mechanism
InactiveUS20110147433A1Solve the lack of spaceEasy to useSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleEngineering
A surgical severing and stapling instrument, suitable for laparoscopic and endoscopic clinical procedures, clamps tissue within an end effector of an elongate channel pivotally opposed by an anvil. An E-beam firing bar moves distally through the clamped end effector to sever tissue and to drive staples on each side of the cut. The E-beam firing bar affirmatively spaces the anvil from the elongate channel to assure properly formed closed staples, especially when an amount of tissue is clamped that is inadequate to space the end effector. In particular, an upper pin of the firing bar longitudinally moves through an anvil slot and a channel slot is captured between a lower cap and a middle pin of the firing bar to assure a minimum spacing. Forming the E-beam from a thickened distal portion and a thinned proximal strip enhances manufacturability and facilitates use in such articulating surgical instruments.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
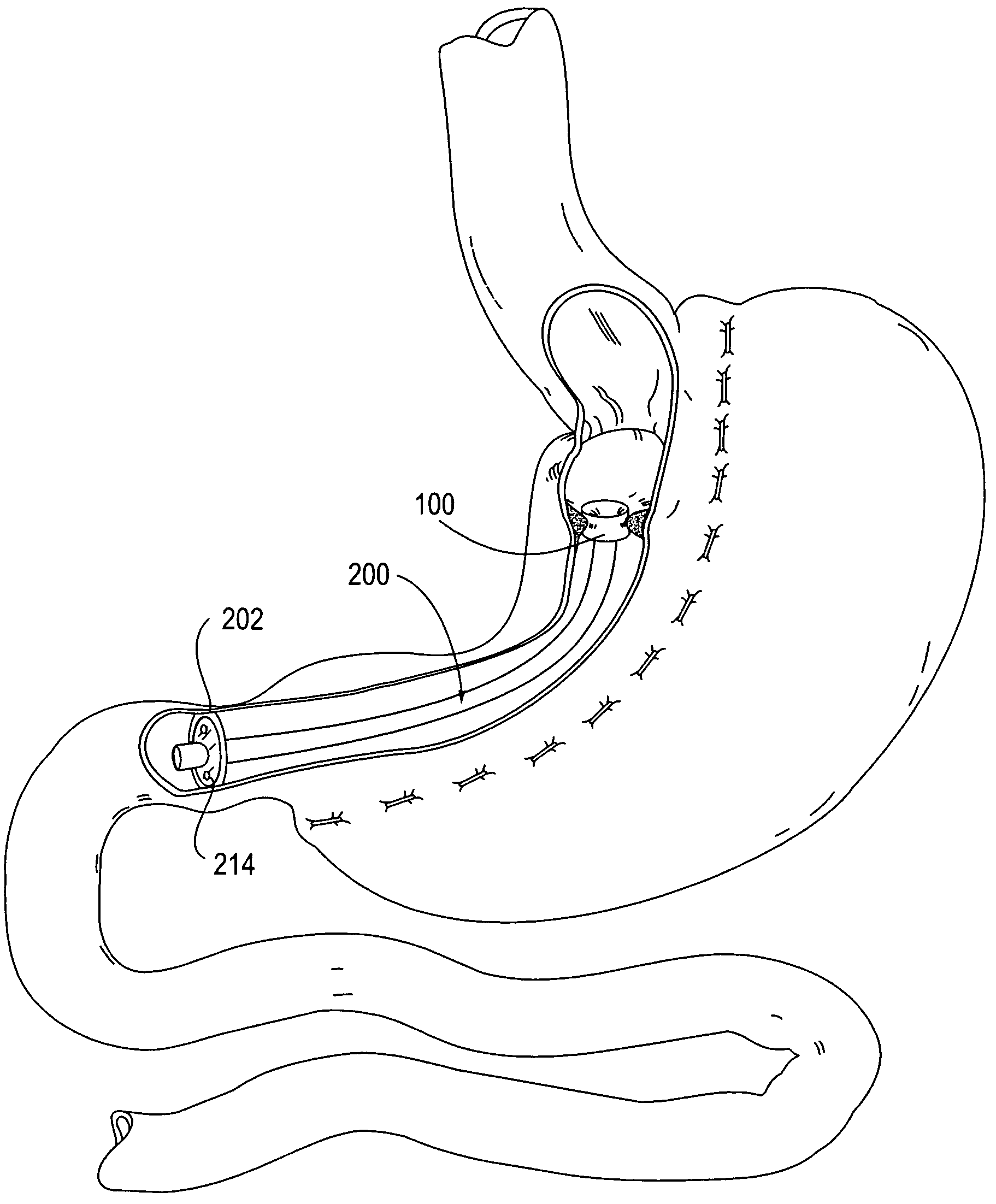
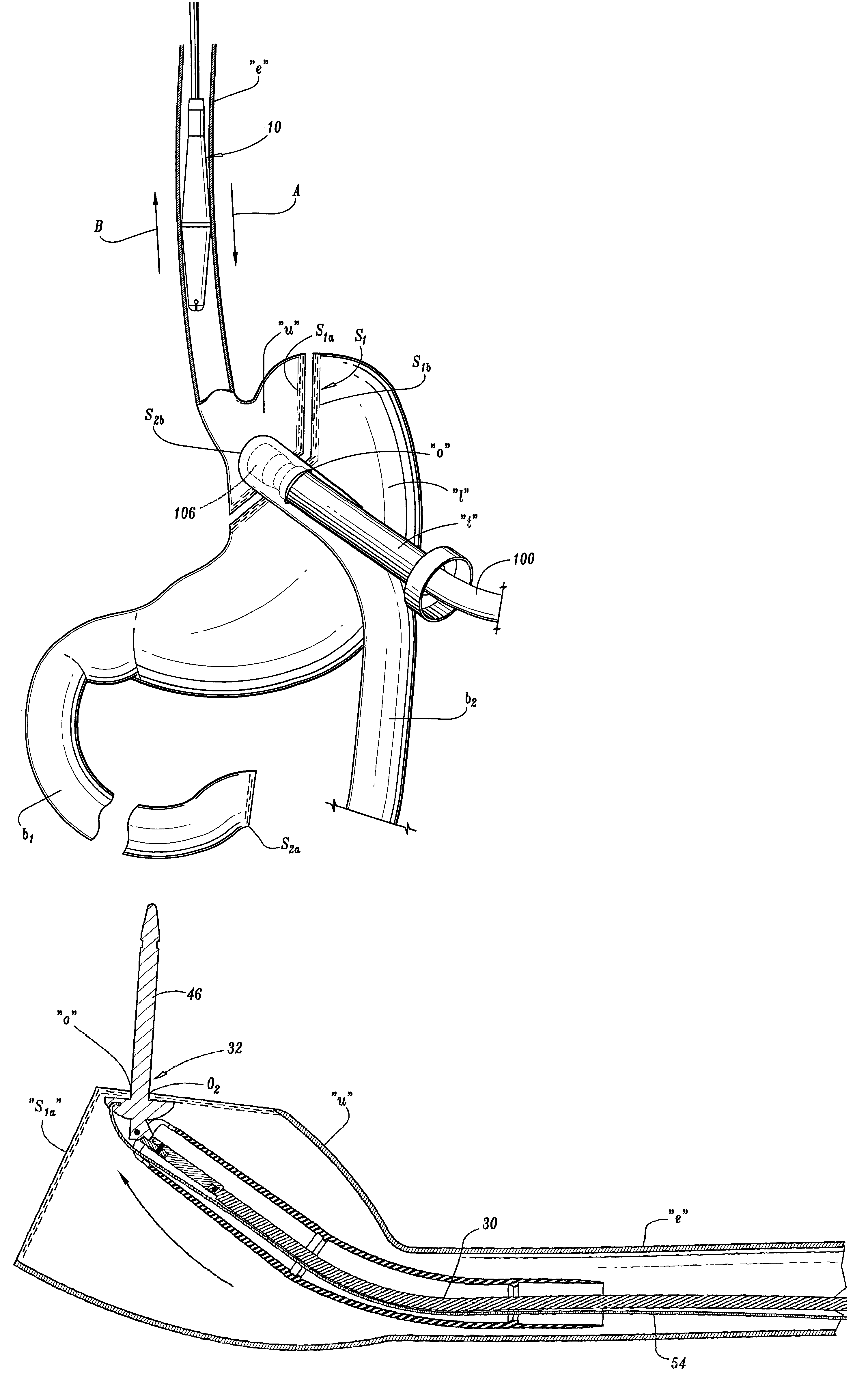
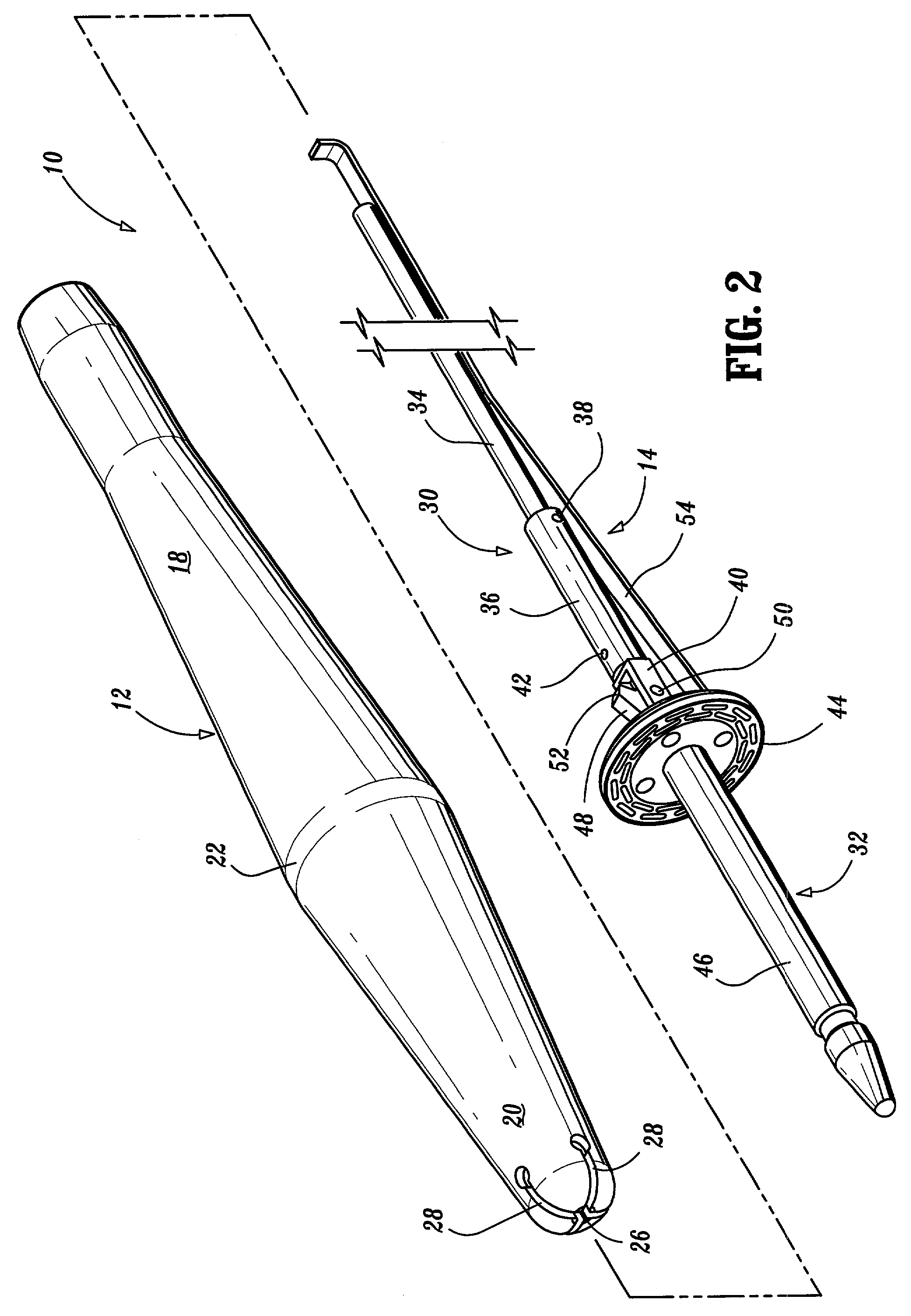
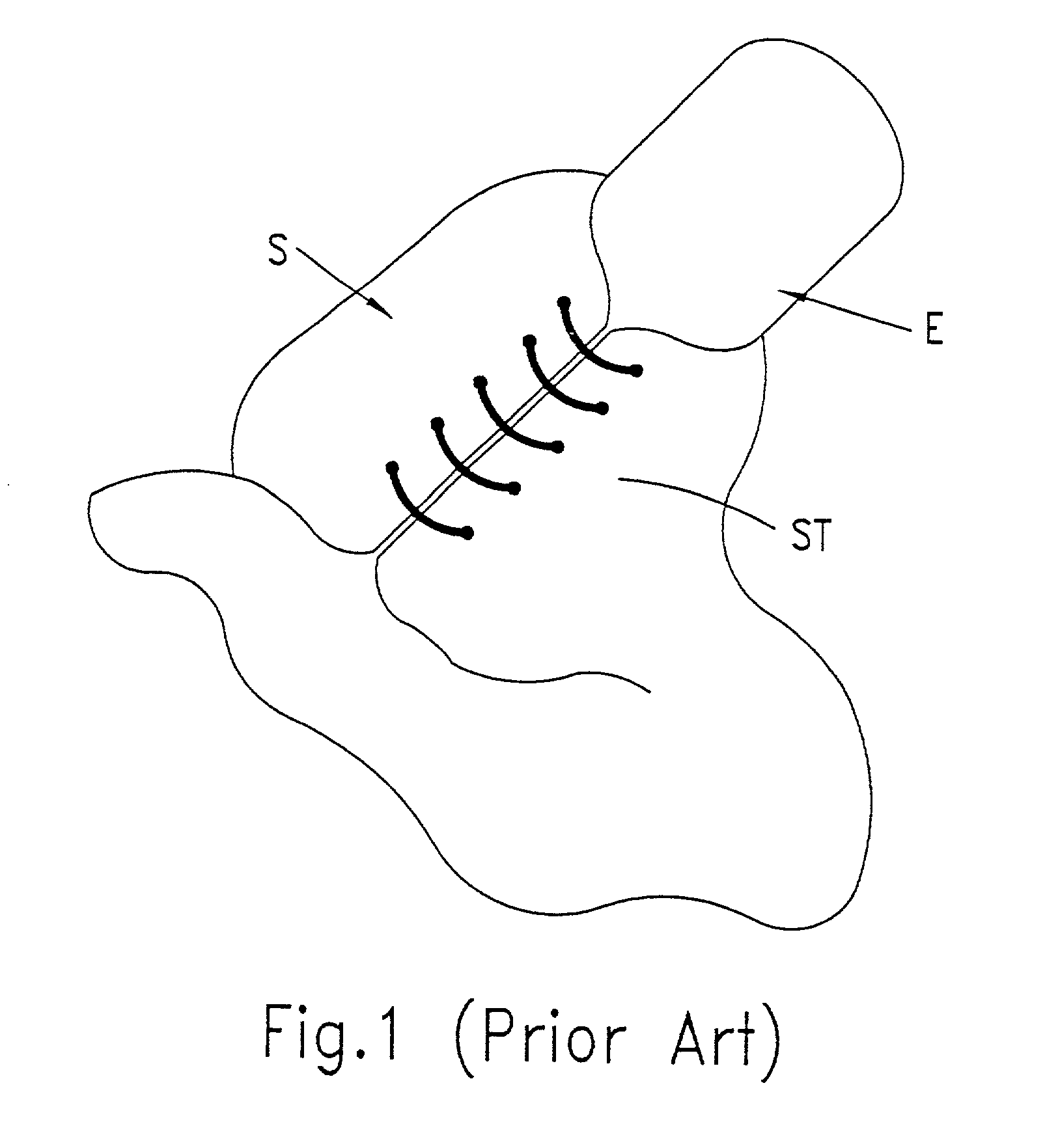
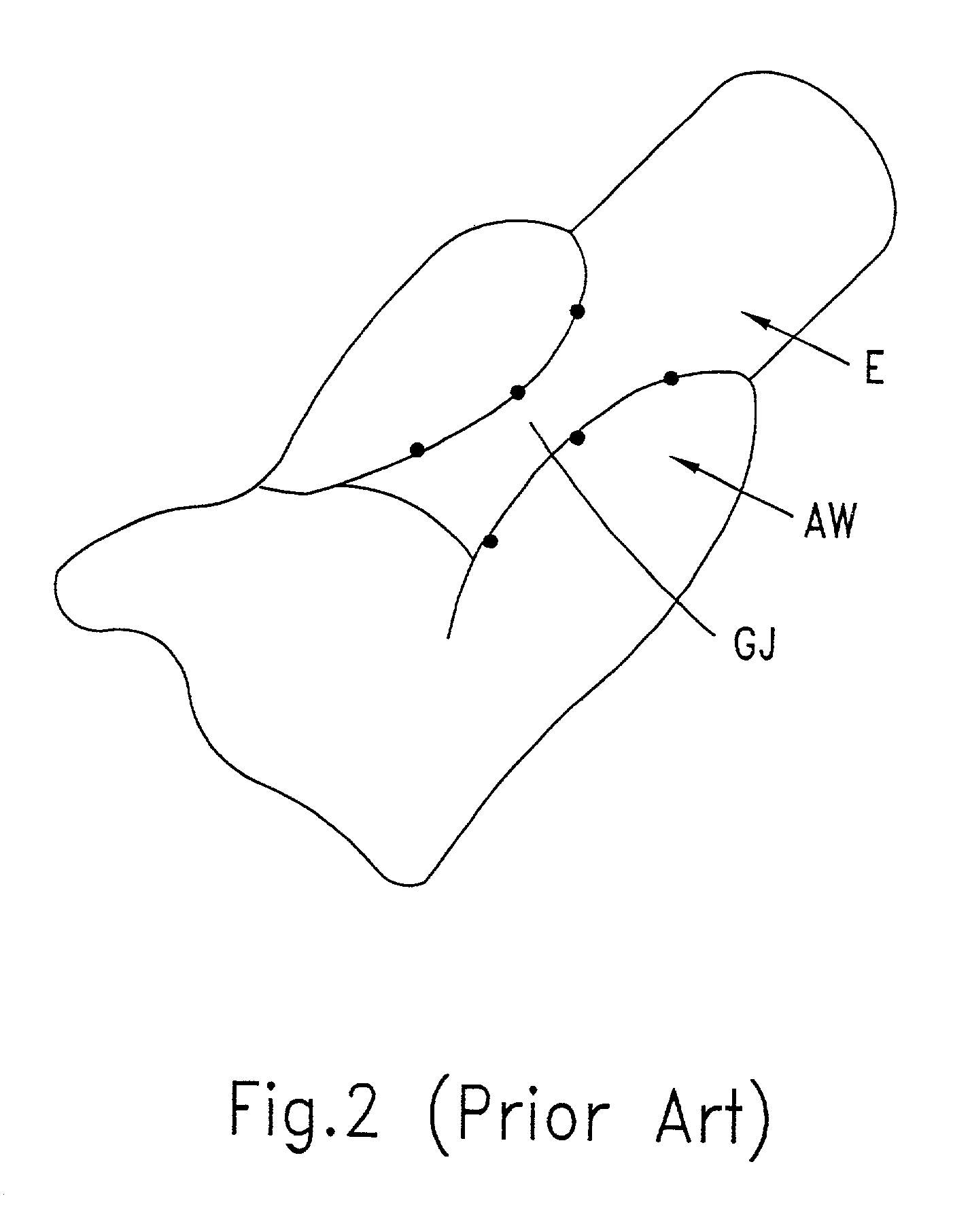
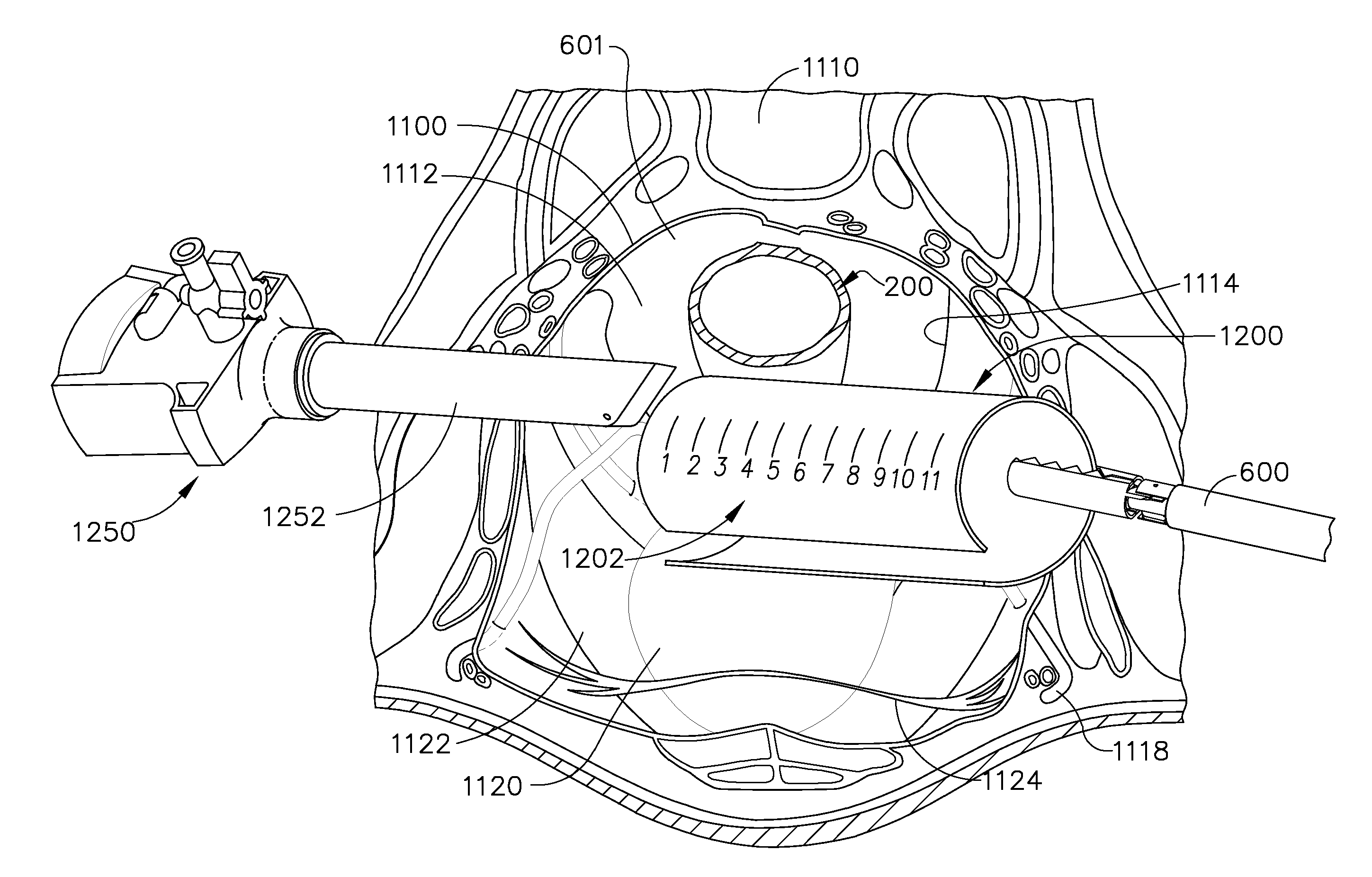
Apparatus and method for performing a bypass procedure in a digestive system
Surgical instrumentation and methods for performing a bypass procedure in a digestive system incorporate laparoscopic techniques to minimize surgical trauma to the patient. The instrumentation includes an outer guide member dimensioned for insertion and passage through an esophagus of a patient and defining an opening therein extending at least along a portion of the length of the outer guide member, an elongate anvil delivery member at least partially disposed within the opening of the outer guide member and being adapted for longitudinal movement within the outer guide member between an initial position and an actuated position and an anvil operatively engageable with the delivery member. The anvil includes an anvil rod defining a longitudinal axis and an anvil head connected to the anvil rod. The anvil head is at least partially disposed within the opening of the outer guide member when in the initial position of the delivery member and is fully exposed from the distal end of the outer guide member upon movement of the delivery member to the actuated position.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
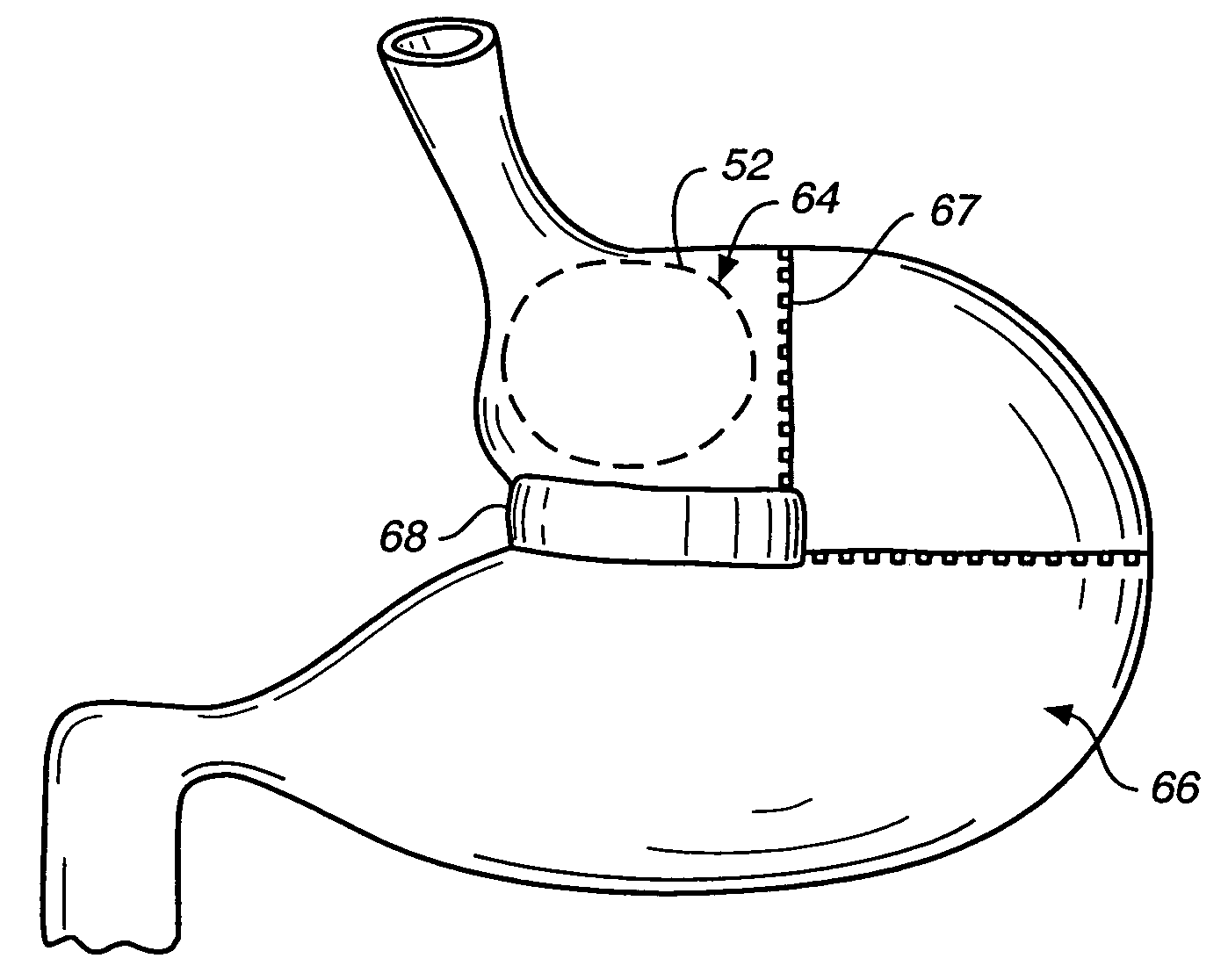
Methods and devices for maintaining a space occupying device in a relatively fixed location within a stomach
Methods and devices for maintaining a space-occupying device in a fixed relationship relative to a patient's stomach by manipulation of the stomach. In one variation, two or more regions of the stomach wall are brought into appromixation with one another and secured together in a manner that secures a space-occupying device within the stomach of the patient. In another variation, two or more regions of the stomach wall are wrapped around a space-occupying device to maintain the position of the space-occupying device relative to the stomach wall. In another variation, a system having a space-occupying member and a locking member capable holding the space-occupying member against the inner wall of the stomach are provided. In a further variation, a pouch is created within the stomach that receives and retains a space-occupying device.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
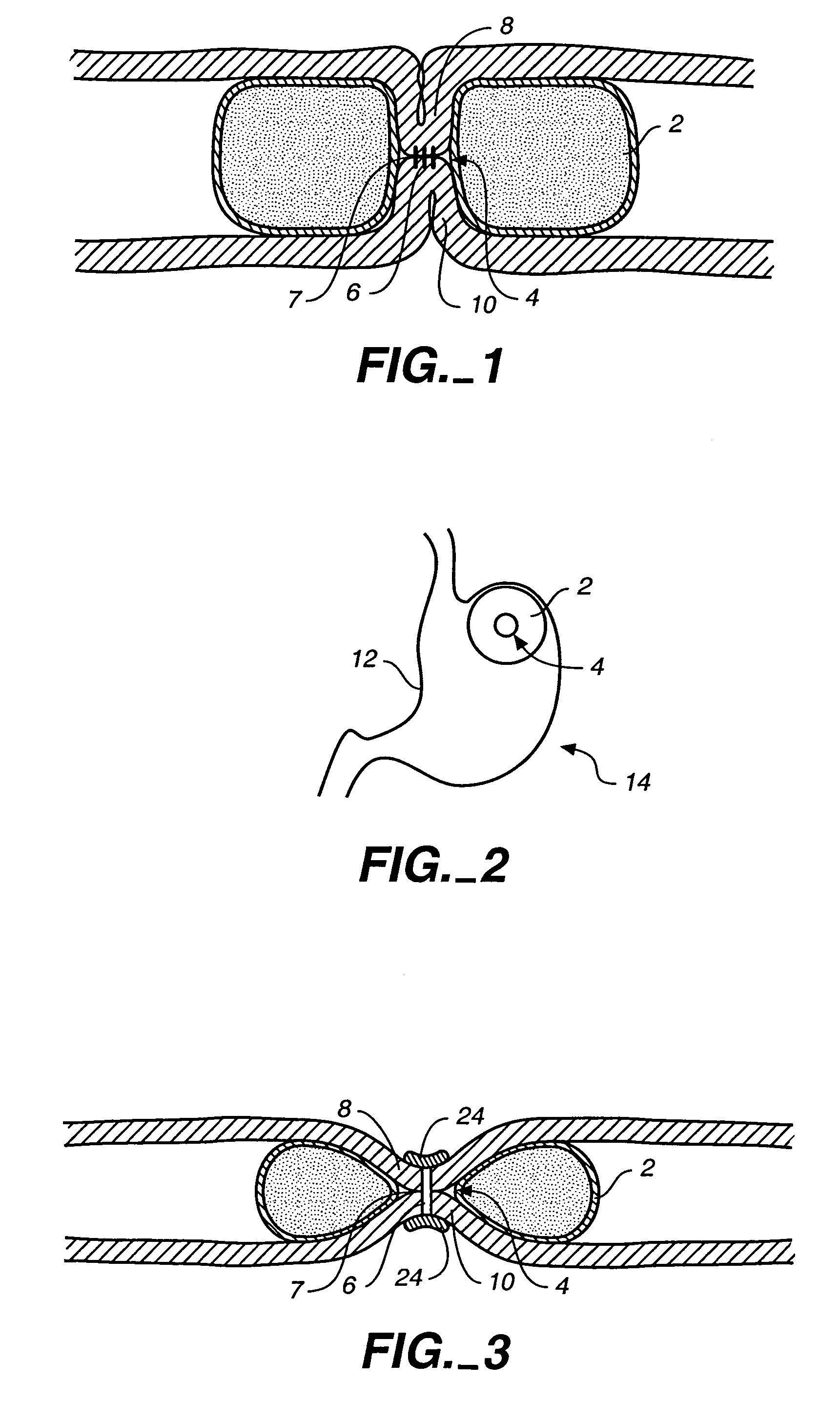
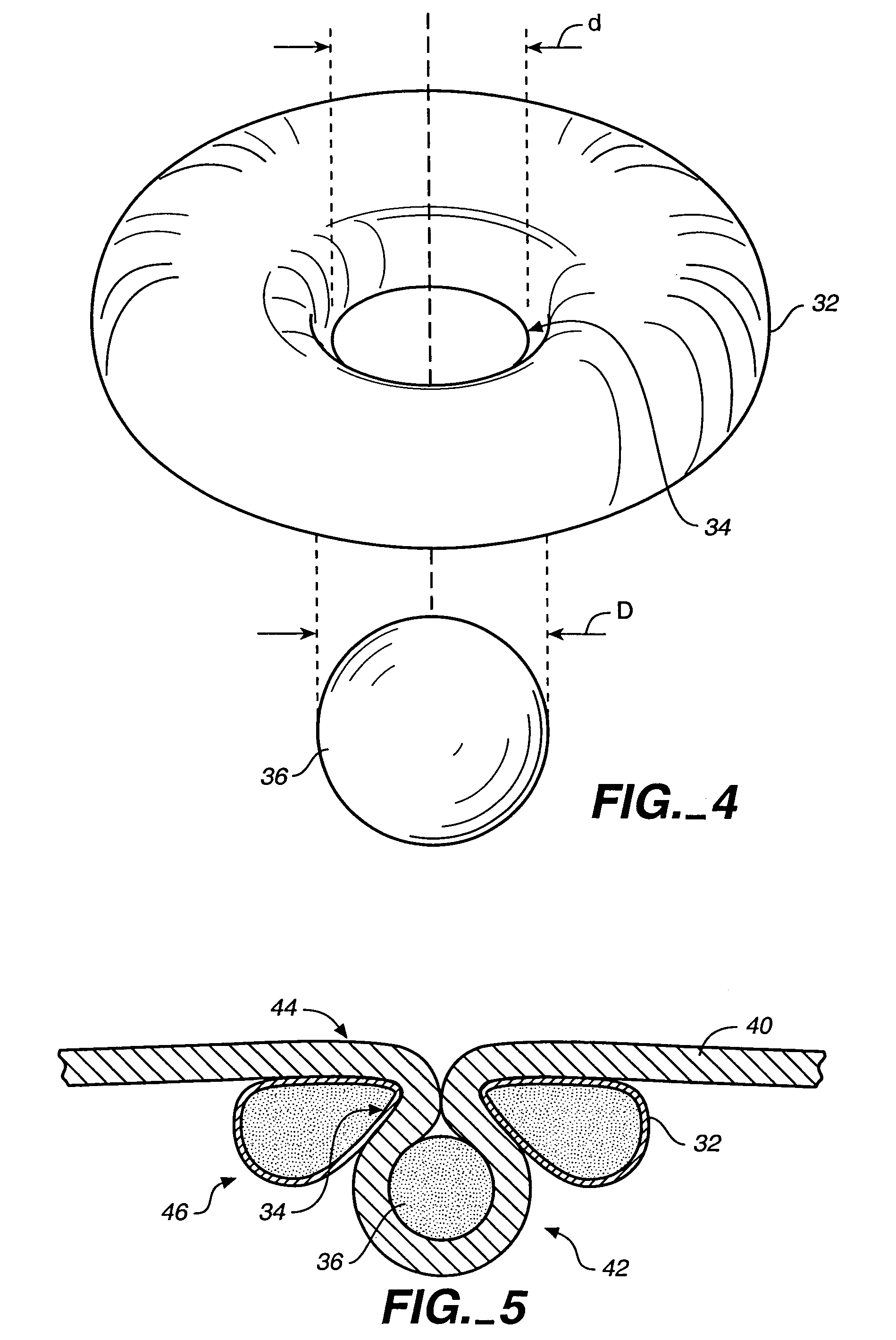
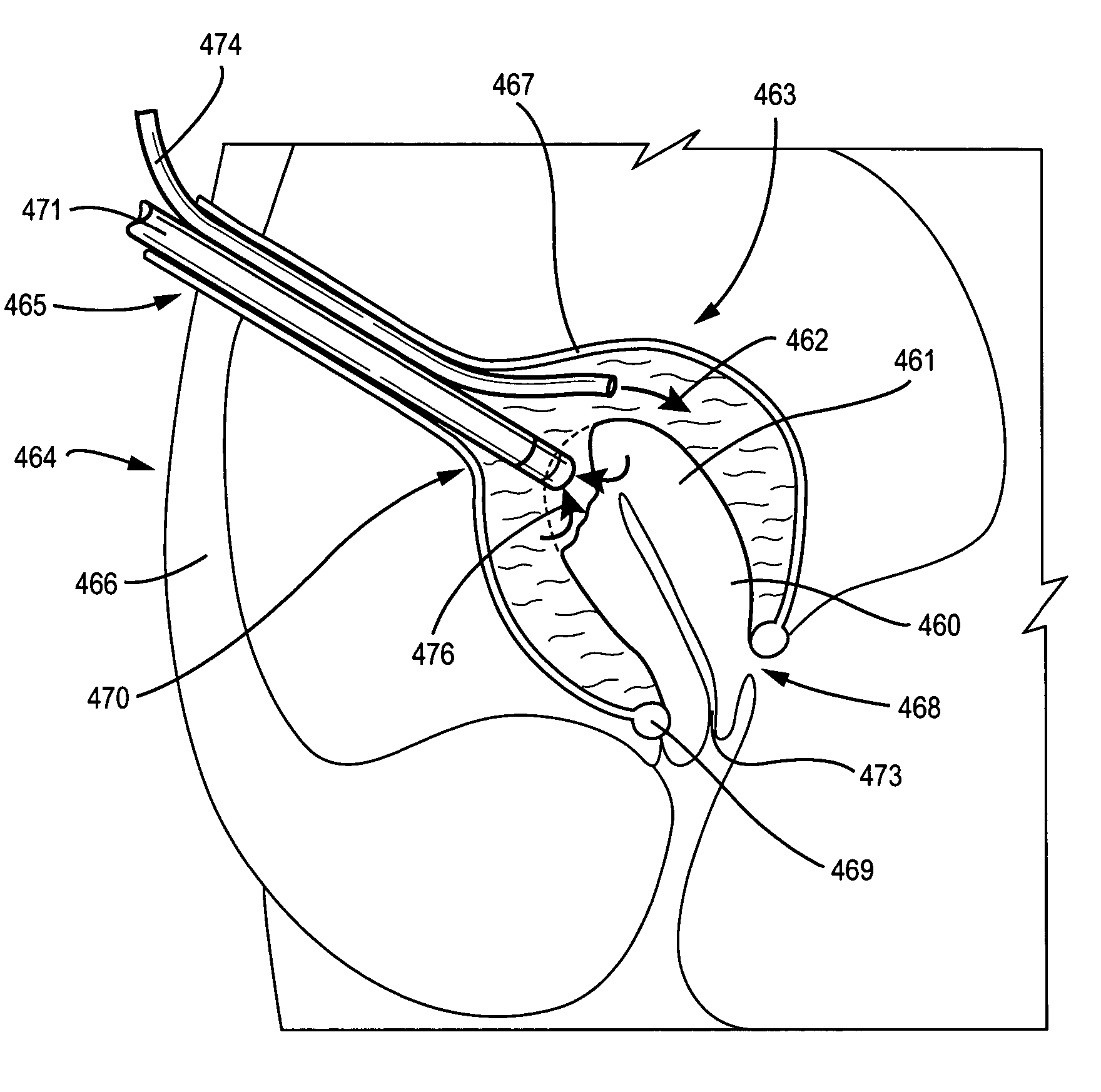
Fundoplication apparatus and method
An endoscopic device for the partial fundoplication for the treatment of GERD, comprises: a) a distal bending portion and a flexible portion suitable to be positioned in extended shape within the esophagus of a subject; b) a positioning assembly comprising two separate elements, one of which is located on said distal bending portion, and the other on said flexible portion; c) a stapling assembly comprising a staple ejecting device, wherein said staple ejecting device is located on either said bending portion or on said flexible portion, said staple ejecting devices being in working positioned relationship when said two separate elements of said positioning assembly are aligned; and d) circuitry for determining when said two separate elements of said positioning assembly are aligned.
Owner:MEDIGUS LTD
Disposable loading units for a surgical cutting and stapling instrument
InactiveUS20090206137A1Affected deploymentImprove the forceSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical instrumentSurgical department
In various embodiments, a disposable loading unit for a surgical stapling instrument can include an anvil, a staple cartridge, a staple cartridge channel for operably supporting the staple cartridge, and a connector for removably attaching the disposable loading unit to the surgical instrument. In at least one embodiment, a first staple cartridge can be replaced with another staple cartridge after the first staple cartridge has been at least partially expended. In various embodiments, a staple cartridge can include a staple driver for deploying staples from the staple cartridge and a cutting member for incising tissue, wherein a new staple driver and a new cutting member can be provided with each new staple cartridge. The anvil can be removably attachable to the disposable loading unit such that a new anvil can be utilized with a new staple cartridge.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC +1
Surgical stapling instrument having end effector gripping surfaces
ActiveUS7451904B2Improve efficiencyIncrease flexibilitySuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical staplePERITONEOSCOPE
A surgical instrument for being endoscopically or laparoscopically inserted through a cannula of a trocar into an insufflated body cavity or lumen (“surgical site”) for simultaneous stapling and severing of tissue including gripping surfaces on inner surfaces of an upper and lower jaw that enhance use as a grasping instrument to preposition tissue prior to performing a stapling and severing procedure. An illustrative version advantageously includes a separate closure trigger and closure mechanism that facilitates use as a grasper without the possibility for inadvertent firing (i.e., stapling and severing).
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Apparatus for applying surgical fastners to body tissue
InactiveUS7624903B2Increase awarenessAvoid deformationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleSupporting system
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Surgical apparatus and method
InactiveUS7235089B1Reduce morbidityReduce mortalitySuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleSurgical incision
Surgical method and apparatus for resectioning tissue, preferably lumenal tissue, with a remaining portion of an organ being anastomized with staples or other fastening devices, preferably endolumenally. The apparatus may be inserted via a naturally occurring body orifice or a surgical incision and then advanced using either endoscopic or radiological imaging guidance to an area where surgery is to be performed. Under endoscopic or diagnostic imaging guidance the apparatus is positioned so tissue to be resected is manipulated into an inner cavity of the apparatus. The apparatus then cuts the diseased tissue after stapling and retains the diseased tissue within the apparatus. The rent resulting in a border of healthy tissue is anastomosed with surgical staples.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP
Circular stapler introducer with multi-lumen sheath
Owner:CILAG GMBH INTERNATIONAL +1
Bipolar cauterizing instrument
A bipolar surgical instrument that includes opposing grips that can engage the tissue. A current is delivered from an electrosurgical power source to electrodes disposed on the grips to cauterize the tissue. The electrode configurations provide efficient cauterization of the tissue. In some embodiments, the positive and negative electrodes will be offset from each other to prevent shorting and to provide a thin line of coagulation heating to the gripped tissue. In some embodiments the electrodes are removably coupled to the grips through nonconductive sleeves. In some embodiments, the first electrode is disposed in a groove and the second electrode is disposed on a boss.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Electrosurgical instrument that directs energy delivery and protects adjacent tissue
ActiveUS8128624B2Reduce heat spreadWeaken energySurgical instrument detailsSurgical forcepsTransmittanceBiomedical engineering
An electrode sealing assembly is designed for use with an electrosurgical instrument for sealing tissue and includes first and second jaw members each having an insulative housing and being movable from a first position in spaced relation relative to one another to at least one second position for grasping tissue therebetween. Each of the jaw members includes an electrically conductive sealing member disposed within the respective insulative housing. At least one of the insulative housings includes at least one tissue engaging surface configured to extend beyond the electrically conductive sealing member of one of the jaw members. The tissue engaging surface of the insulative housing cooperates with the opposing insulative housing of the opposing jaw member to both pinch and spread tissue when the jaw members are moved to the second position to decrease extraneous energy transmittance to tissue surrounding the jaw members.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Apparatus and methods for protecting adjacent structures during the insertion of a surgical instrument into a tubular organ
A device for protecting tissues and structures adjacent to a tubular organ during performance of a surgical procedure on a portion of the tubular organ. Various embodiments may comprise a member that may be deployed through a surgical instrument in a first configuration and expanded to a second configuration such that when in the second configuration, the protective member may extend substantially around an outer circumference of the portion of the tubular organ.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Sensor straightened end effector during removal through trocar
In various forms, a sensor-straightened end effector is disclosed. The sensor-straightened end effector may comprise an end effector coupled to a shaft at an articulation point. The end effector may be articulable at an angle with respect to the shaft. A sensor may be disposed on the sensor-straightened end effector, such as on the shaft or on the end effector. The sensor is configured to detect a gross proximal movement. When detecting a gross proximal movement, the sensor may generate a signal to control a motor to begin a straightening process to straighten the end effector with respect to the shaft.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INTERNATIONAL
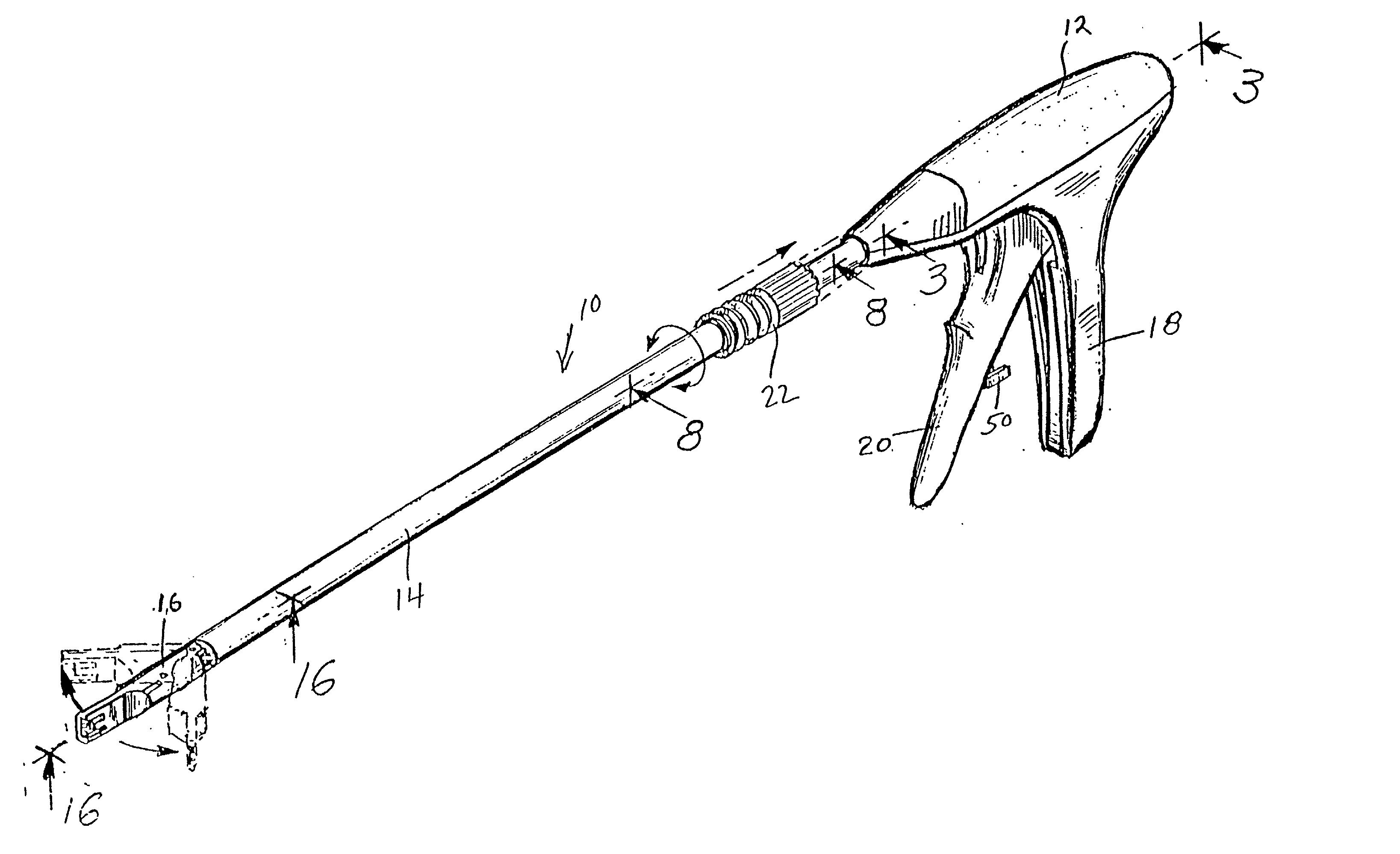
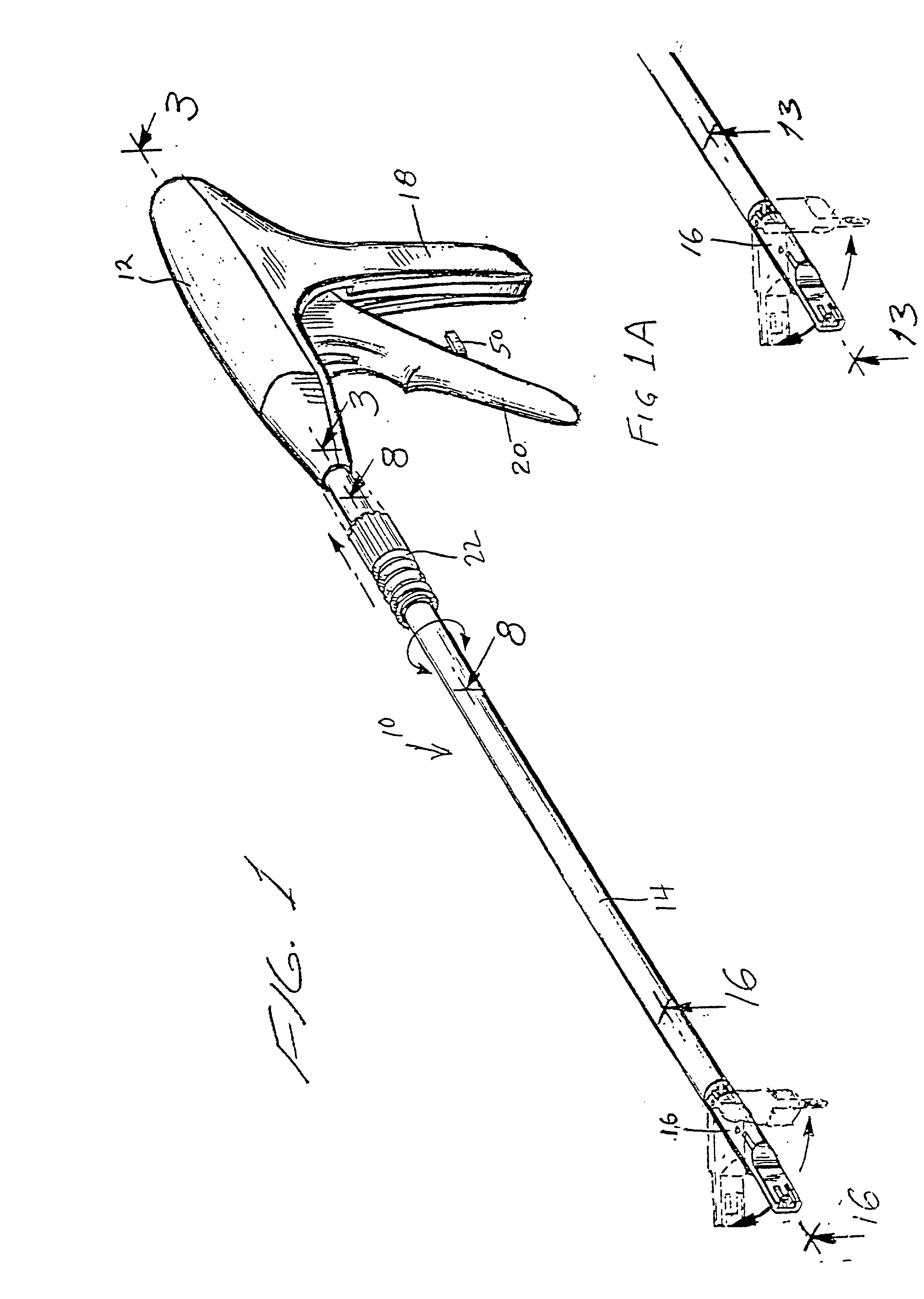
Apparatus and method for applying surgical staples to attach an object to body tissue
InactiveUS20020117534A1Avoid deformationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSupporting systemSurgical staple
An apparatus is disclosed for endoscopic application of surgical staples adapted to attach surgical mesh to body tissue in laparoscopic hernia surgery. The apparatus includes a frame, and a generally elongated endoscopic section connected to the frame and extending distally therefrom. A staple storage cartridge is removably supported on a pivotal support system at the distal end portion of the endoscopic section with each staple being configured and adapted to attach the mesh to the body tissue. An elongated pusher system formed of several assembled components and extending from the frame to the endoscopic section is provided for individually advancing at least one staple at a time distally for positioning adjacent the surgical mesh and the body tissue. The pusher system also includes a trigger system to actuate the pusher. The trigger system is provided with perceptible tactile sensing means to indicate when the legs of the staple being advanced are exposed so as to be visible to the user for positioning and orientation purposes. Anvil means provides for individually closing each staple to encompass at least a portion of the surgical mesh and to penetrate the body tissue in a manner to attach the portion of the mesh to the body tissue. Projecting distally of the cartridge support system is a pair of legs which are dimensioned and configured to engage the staple during closure to prevent unwanted roll or deformation outside of the plane of the staple.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Electrosurgical instrument
InactiveUS7278994B2Lower impedanceReduced effectivenessCannulasDiagnosticsGynecologyPeritoneal cavity
A system and method are disclosed for removing a uterus using a fluid enclosure inserted in the peritoneal cavity of a patient so as to enclose the uterus. The fluid enclosure includes a distal open end surrounded by an adjustable loop, that can be tightened, a first proximal opening for inserting an electrosurgical instrument into the fluid enclosure, and a second proximal opening for inserting an endoscope. The loop is either a resilient band extending around the edge of the distal open end or a drawstring type of arrangement that can be tightened and released. The fluid enclosure is partially inserted into the peritoneal cavity of a patient in a deflated condition and then manipulated within the peritoneal cavity over the body and fundus of the uterus to the level of the uterocervical junction. The loop is tightened around the uterocervical junction, after which the enclosure is inflated using a conductive fluid. The loop forms a pressure seal against the uterocervical junction to contain the conductive fluid used to fill the fluid enclosure. Endoscopically inserted into the fluid enclosure is an electrosurgical instrument that is manipulated to vaporize and morcellate the fundus and body of the uterus. The fundus and body tissue that is vaporized and morcellated is then removed from the fluid enclosure through the shaft of the instrument, which includes a hollow interior that is connected to a suction pump The fundus and body are removed after the uterus has been disconnected from the tissue surrounding uterus.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
Stapling and cutting in resectioning for full thickness resection devices
A stapling unit for use with an endoscopic stapling system adapted to be advanced along an endoscope to a predetermined location within a body lumen to staple the portion of tissue, as part of an occlusal or full thickness resectioning procedure. The stapling unit comprises a first casing having a distal end, a proximal end and a stapling device mounted thereto adjacent to a first window extending through a periphery of the first casing. The invention includes methods for the stapling, severing and removal of tissue by using the device.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
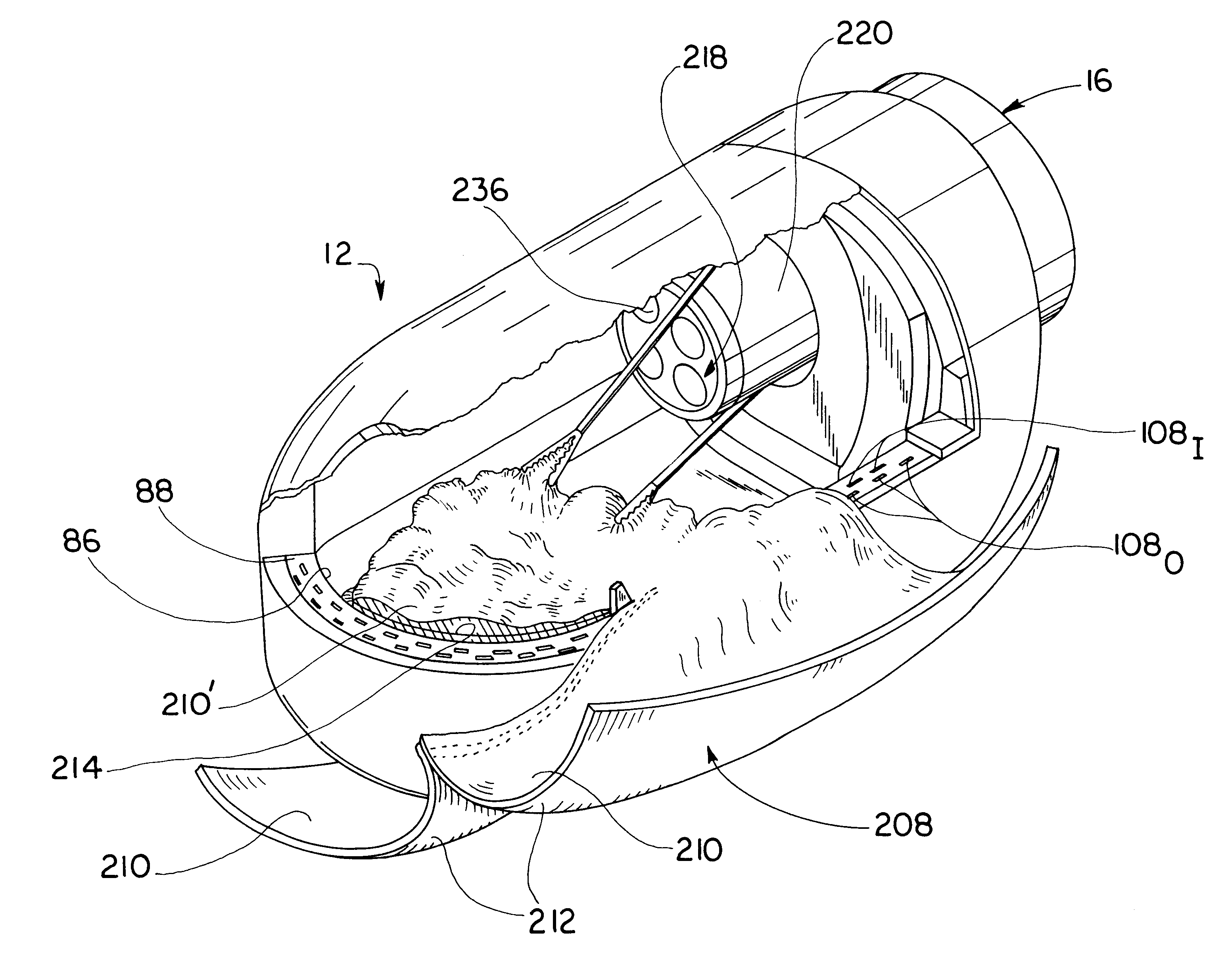
Insertable device and system for minimal access procedure
ActiveUS7066879B2Limited mobilityWide field of viewEndoscopesLaproscopesAbdominal cavityProcedure Indication
The present invention provides a system and single or multi-functional element device that can be inserted and temporarily placed or implanted into a structure having a lumen or hollow space, such as a subject's abdominal cavity to provide therewith access to the site of interest in connection with minimally invasive surgical procedures. The insertable device may be configured such that the functional elements have various degrees of freedom of movement with respect to orienting the functional elements or elements to provide access to the site from multiple and different orientations / perspectives as the procedure dictates, e.g., to provide multiple selectable views of the site, and may provide a stereoscopic view of the site of interest.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com