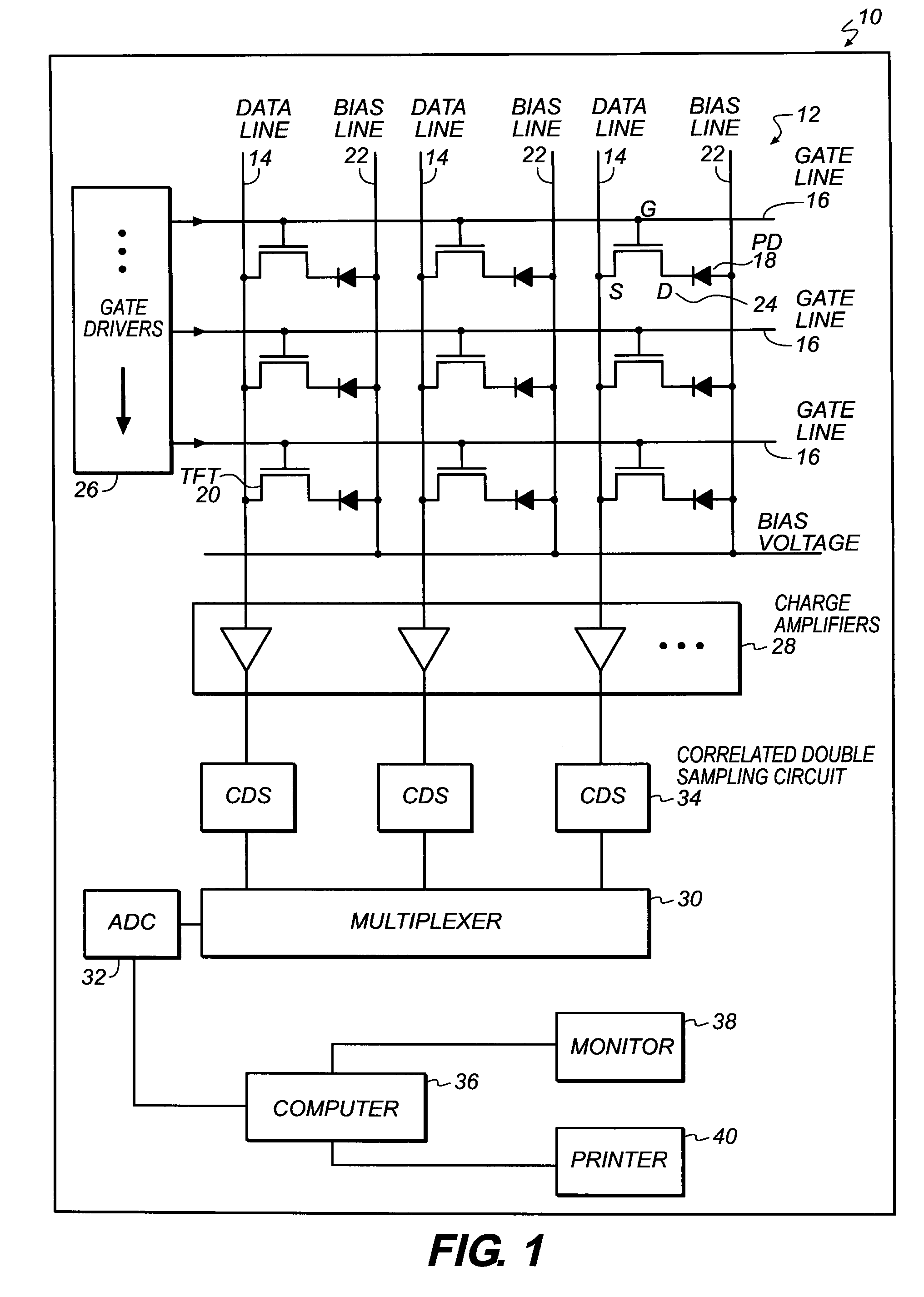
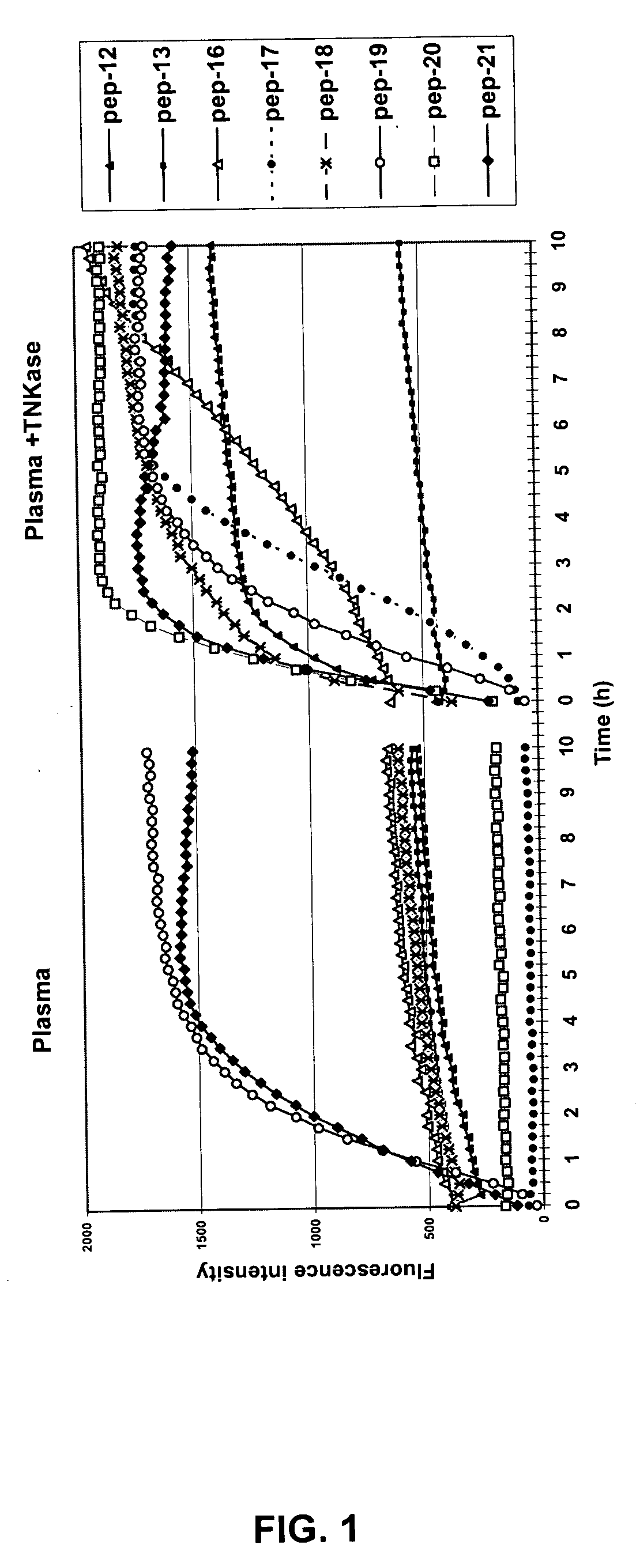
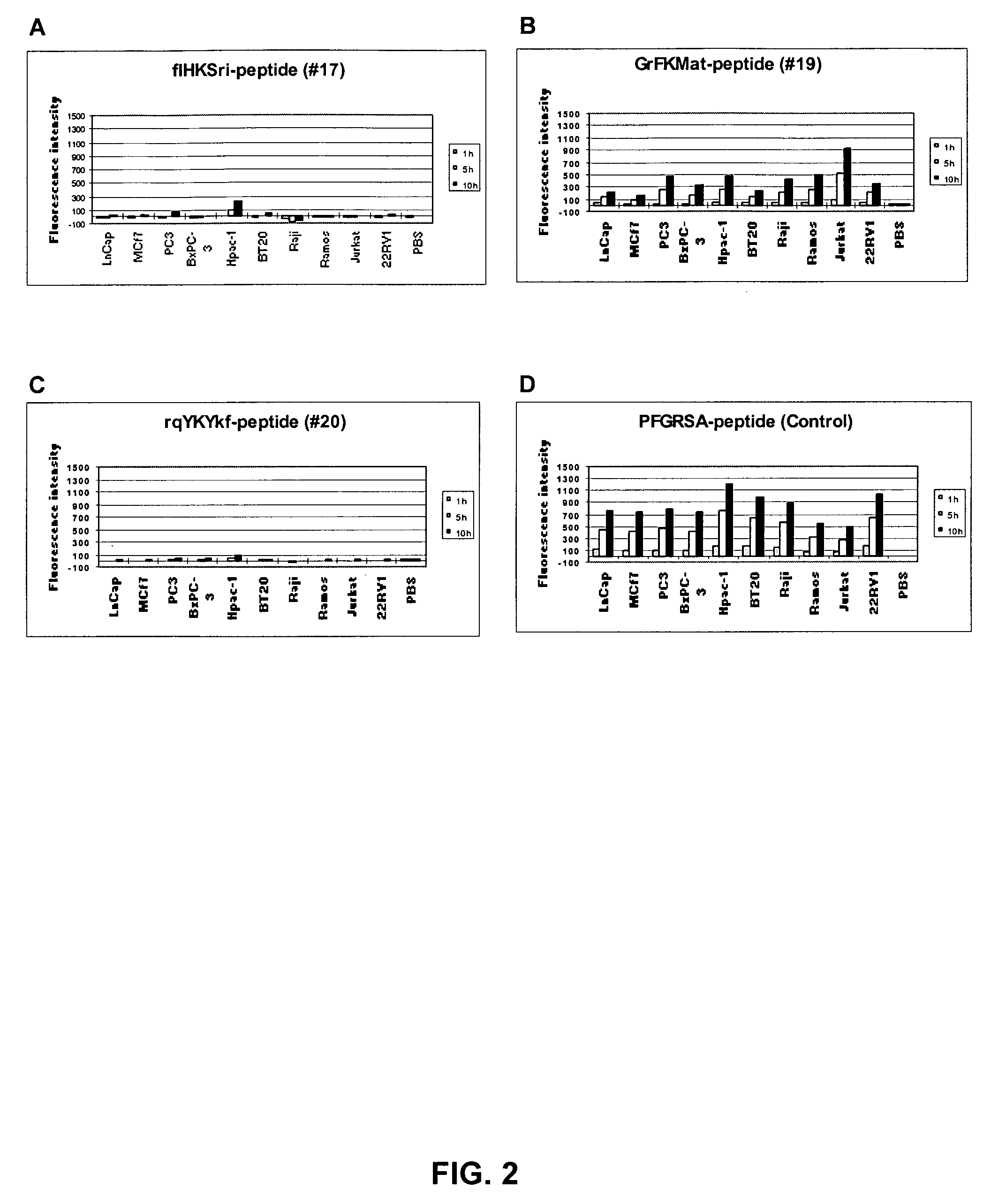
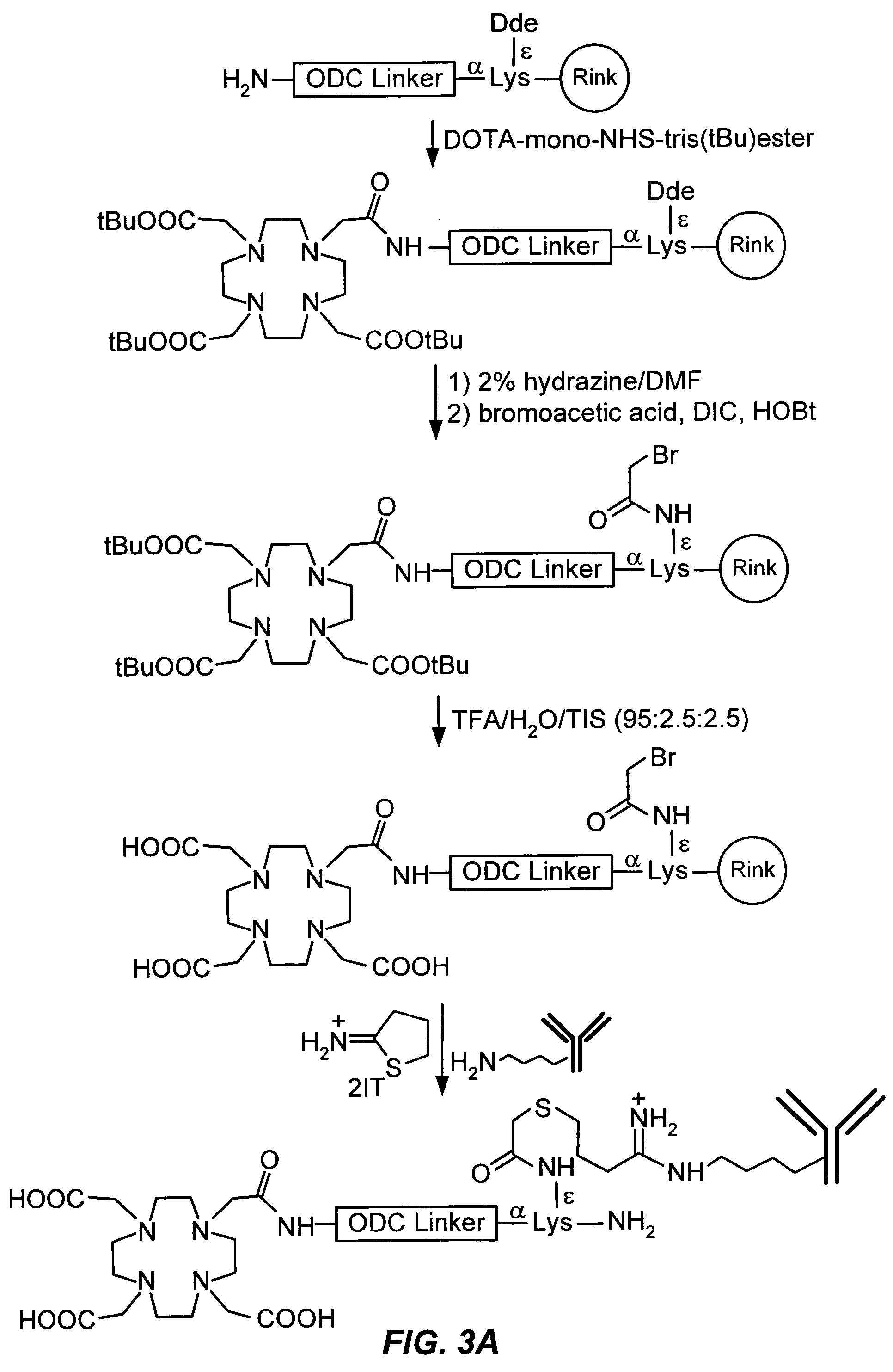
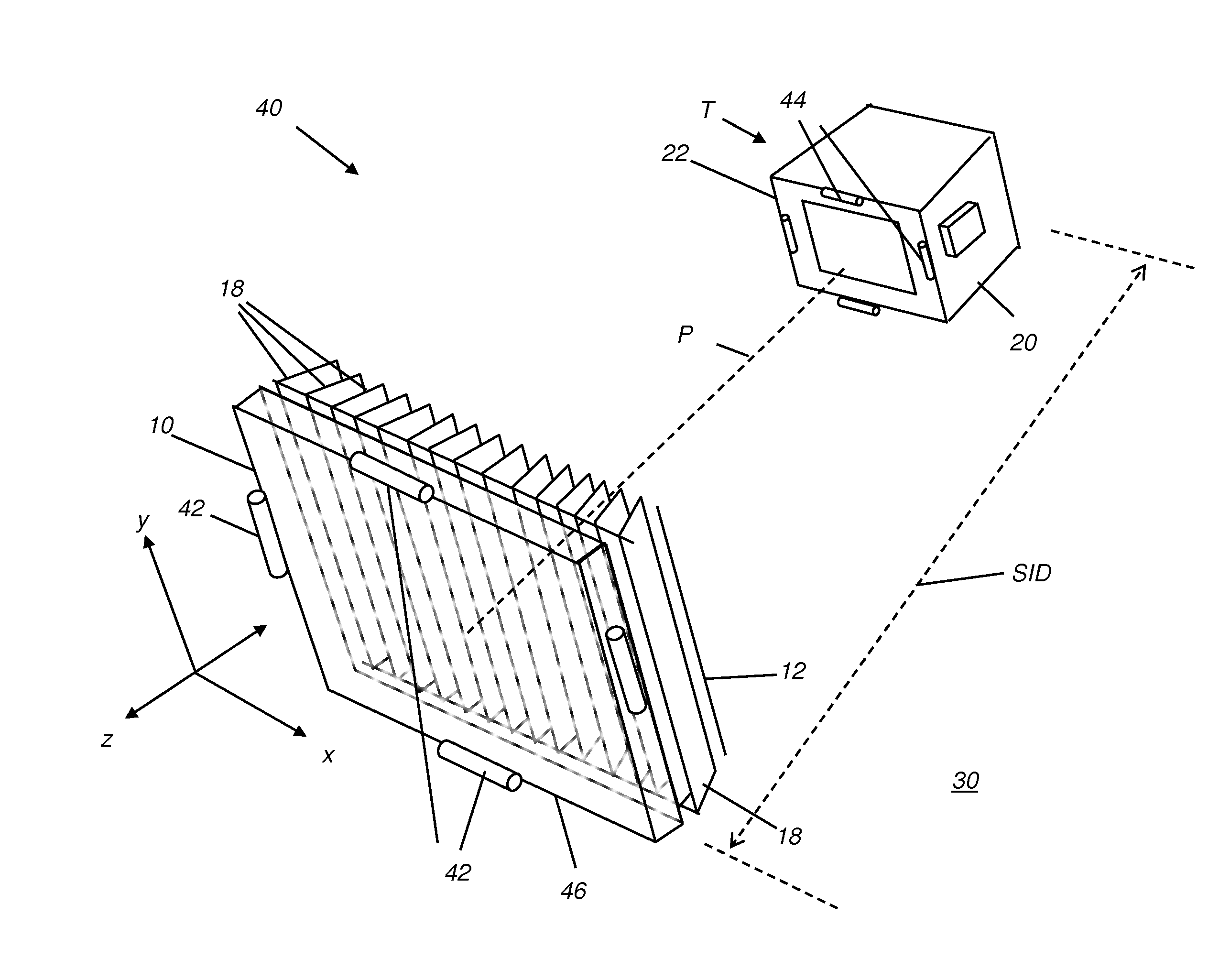
Patents
Literature
657 results about "Radiology/imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
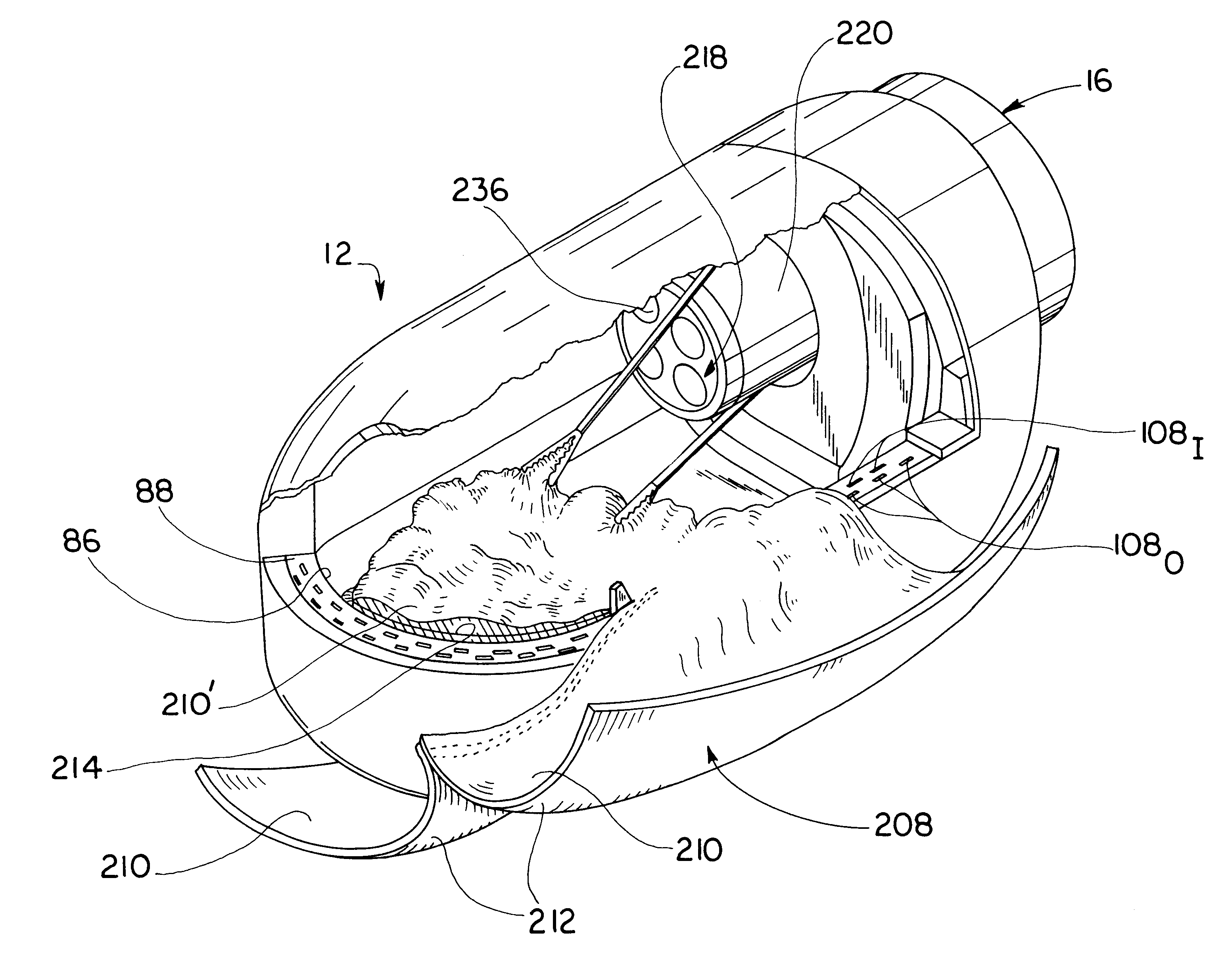
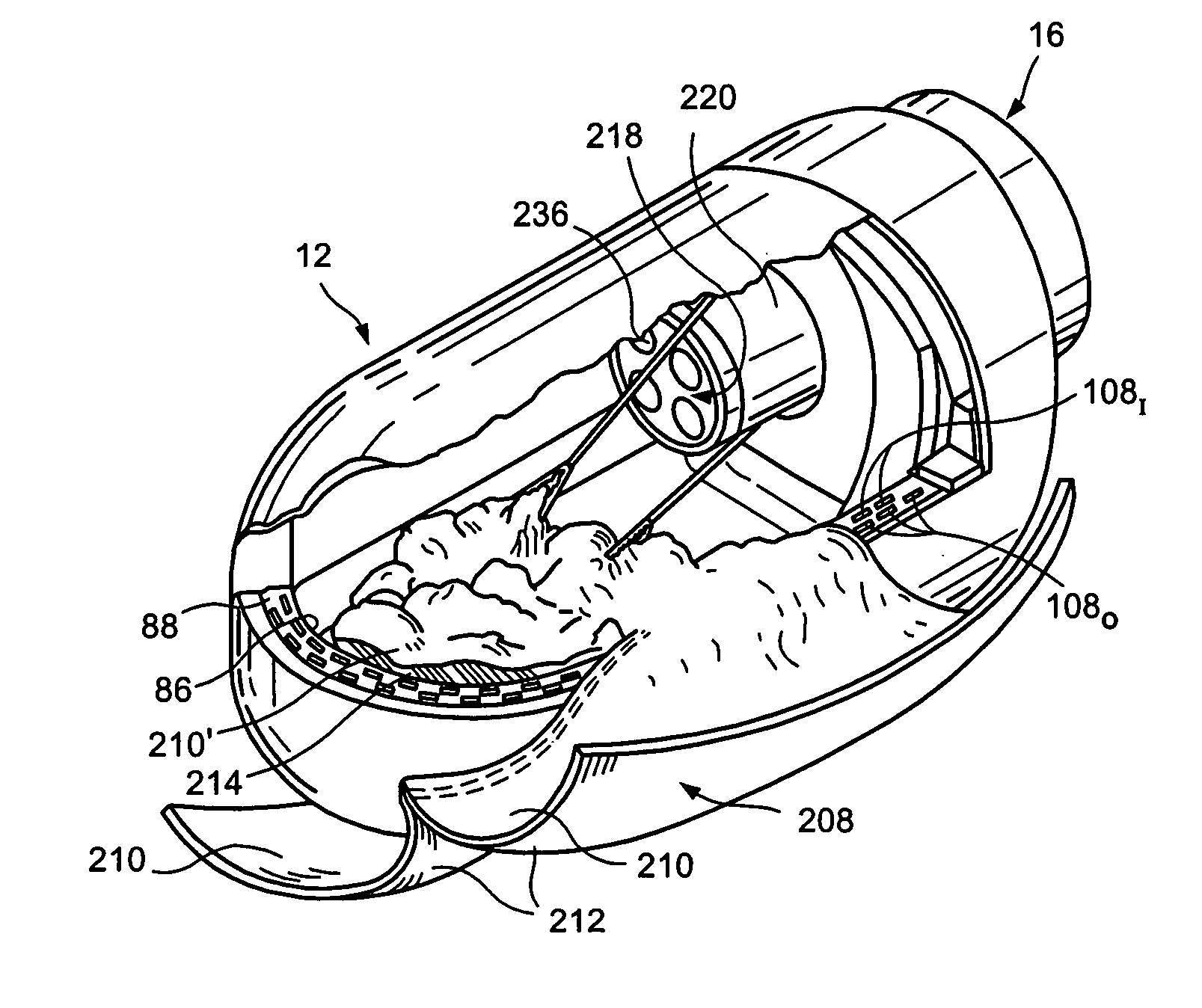
Surgical apparatus and method
InactiveUS6264086B1Minimizing chanceGood removal effectSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleSurgical incision
Owner:MCGUCKIN JR JAMES F
Surgical apparatus and method
InactiveUS7235089B1Reduce morbidityReduce mortalitySuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleSurgical incision
Surgical method and apparatus for resectioning tissue, preferably lumenal tissue, with a remaining portion of an organ being anastomized with staples or other fastening devices, preferably endolumenally. The apparatus may be inserted via a naturally occurring body orifice or a surgical incision and then advanced using either endoscopic or radiological imaging guidance to an area where surgery is to be performed. Under endoscopic or diagnostic imaging guidance the apparatus is positioned so tissue to be resected is manipulated into an inner cavity of the apparatus. The apparatus then cuts the diseased tissue after stapling and retains the diseased tissue within the apparatus. The rent resulting in a border of healthy tissue is anastomosed with surgical staples.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP
Spot-size effect reduction
InactiveUS7418078B2Reduce adverse effectsImprove image qualityRadiation/particle handlingTomographyX-rayRadiography
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Methods, Devices, Systems, Circuits and Associated Computer Executable Code for Detecting and Predicting the Position, Orientation and Trajectory of Surgical Tools
The present invention includes methods, devices, systems, circuits and associated computer executable code for detecting and predicting the position and trajectory of surgical tools. According to some embodiments of the present invention, images of a surgical tool within or in proximity to a patient may be captured by a radiographic imaging system. The images may be processed by associated processing circuitry to determine and predict position, orientation and trajectory of the tool based on 3D models of the tool, geometric calculations and mathematical models describing the movement and deformation of surgical tools within a patient body.
Owner:ORTHOPEDIC NAVIGATION
Method to detect a retained surgical object
An imaging method, executed at least in part by a computer, tracks the disposition of surgical supplies used in an operation and identifies a radiographic imaging technique for detecting a retained surgical foreign object according to the tracking. One or more radiographic images are acquired in the operating room. The acquired image content is analyzed to identify one or more candidate foreign objects. At least a portion of the acquired image content is displayed with the one or more candidate foreign objects in the acquired image content highlighted.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
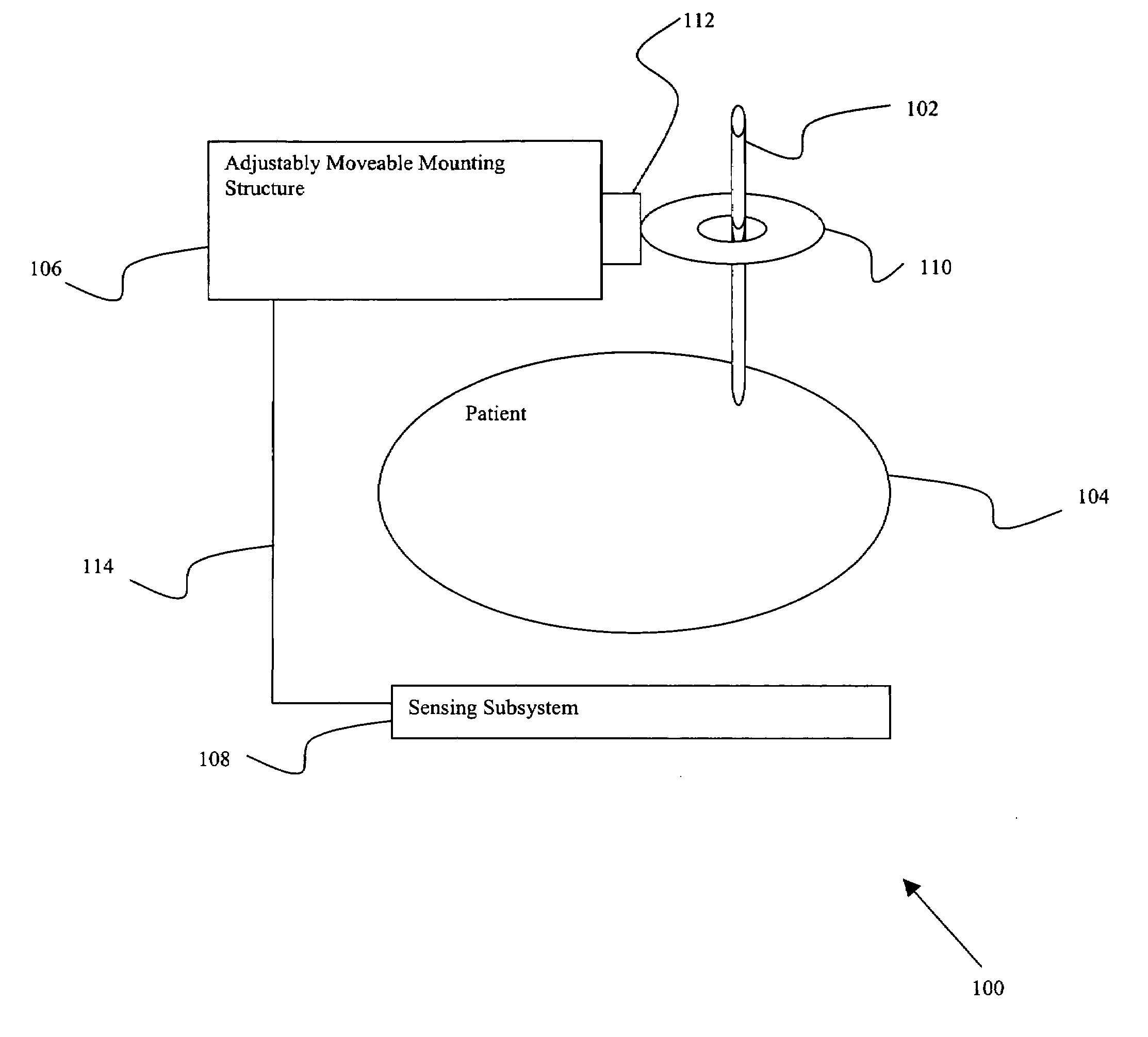
Surgical tool guide
InactiveUS20080004523A1Precise positioningDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFluoroscopic imagingEngineering
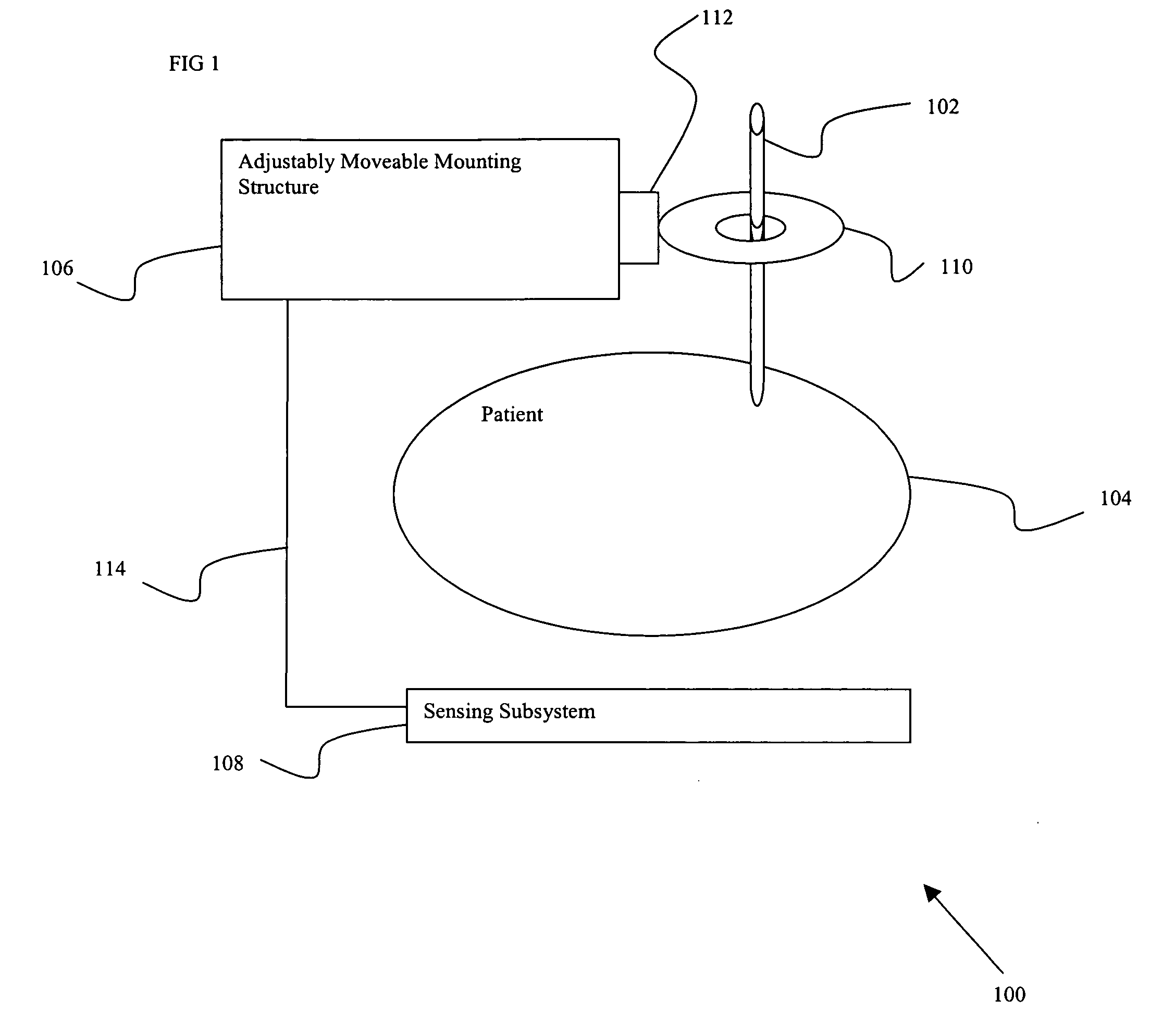
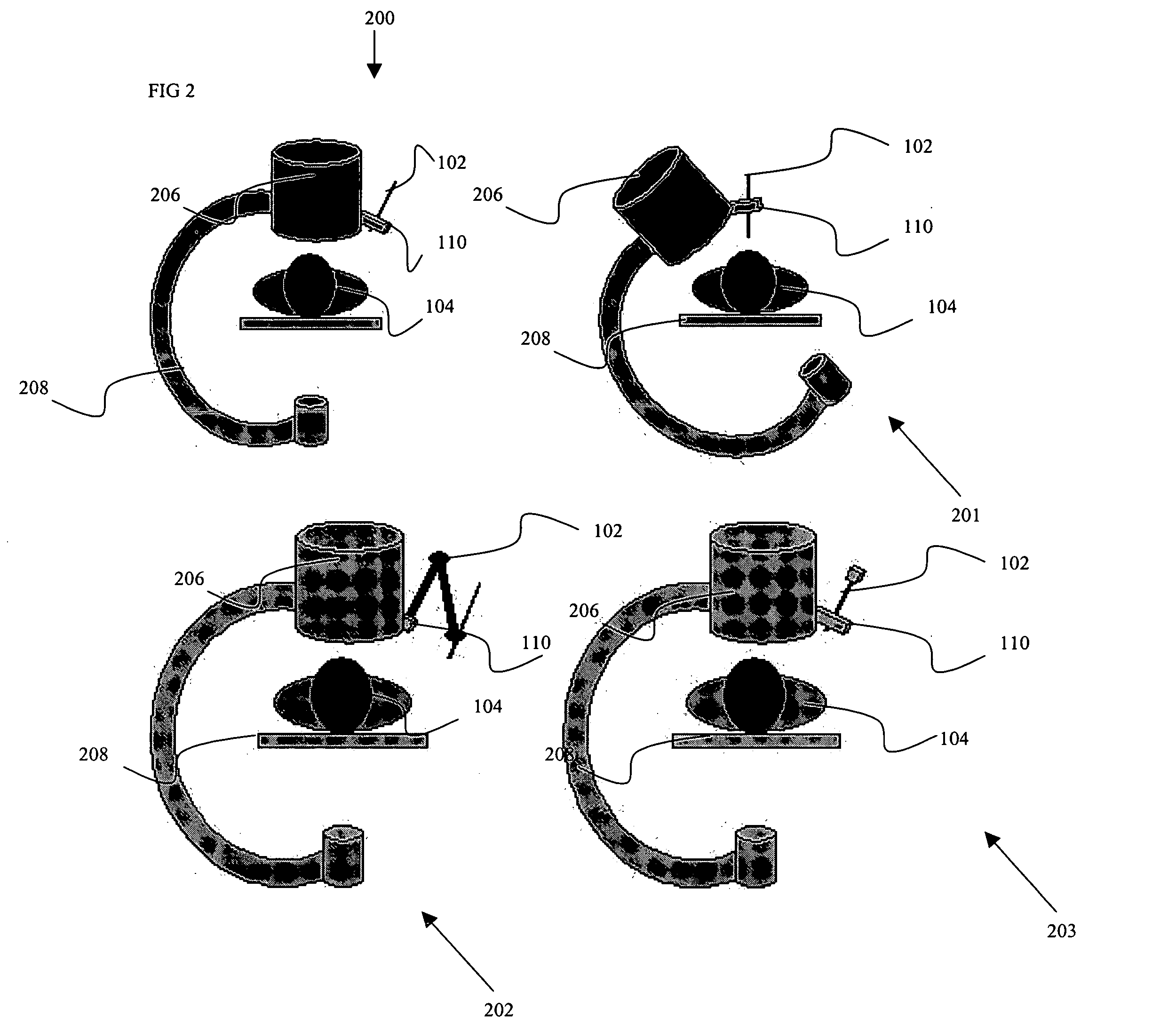
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide n system for orienting a surgical tool with respect to a patient including: a tool guide for facilitating orientation of the surgical tool with respect to the patient, the tool guide including a mounting portion and a tool receiving portion, wherein the tool guide is capable of being integrated with at least a portion of a radiological imaging subsystem including an adjustably moveable mounting structure. In an embodiment, the tool receiving portion is capable of receiving an end-effector. In an embodiment the at least a portion of the radiological imaging subsystem comprises a C-arm. In an embodiment the radiological imaging subsystem comprises a fluoroscopic imaging subsystem. In an embodiment, the end-effector comprises at least one of: an aperture, a cutting device, a drilling device, a clamp, a sleeve, a mounting surface, a ring, a rail, a threaded shaft, a clasp, a bayonet mount, an imaging device, an ultrasound probe, a surgical tool, a catheter, a pin, a screw, a plate, a drill, an awl, and a probe. In an embodiment, the tool guide further comprises an end-effector. In an embodiment, a position of the surgical tool is capable of being adjusted by automatically moving the adjustably movable mounting structure. In an embodiment, the system further comprises at least one position sensing subsystem for ascertaining a position of the surgical tool with respect to the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
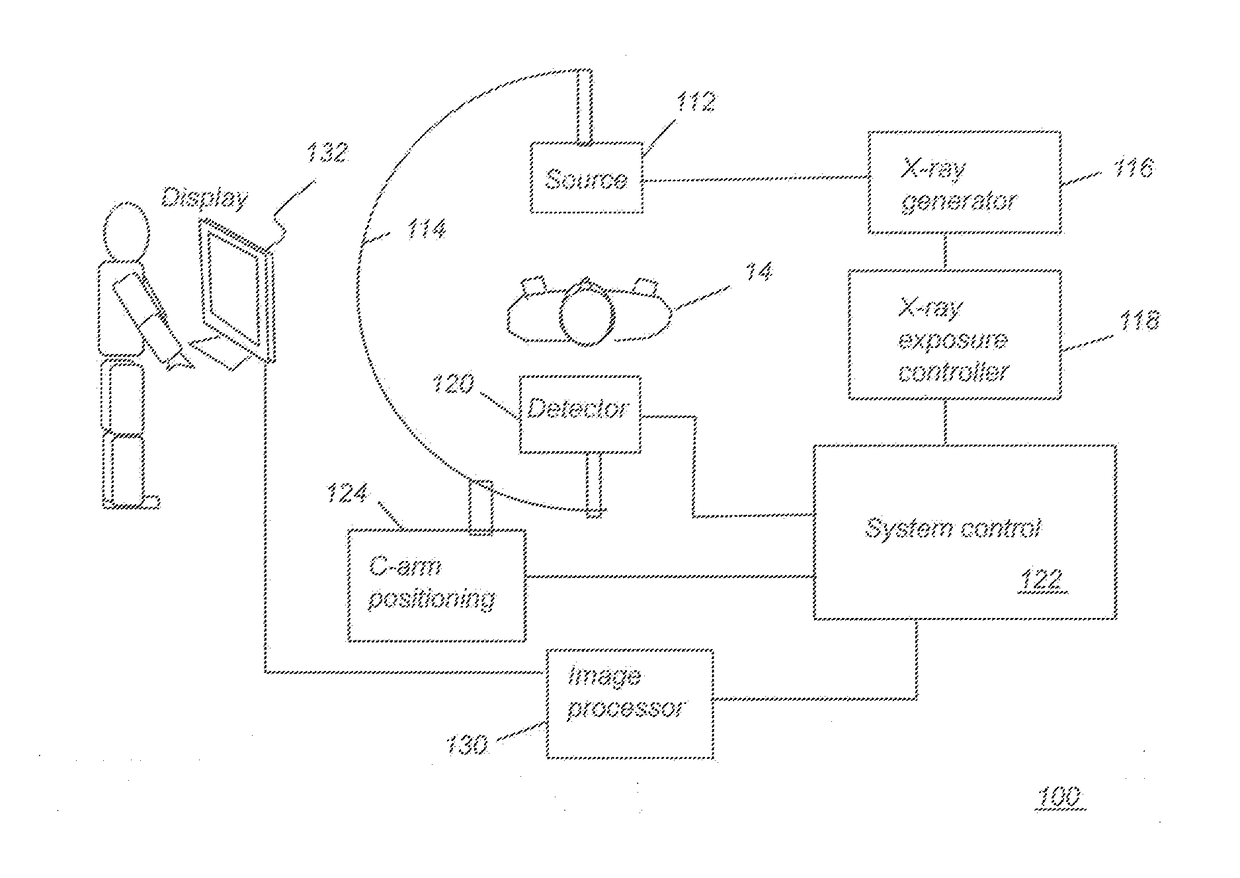
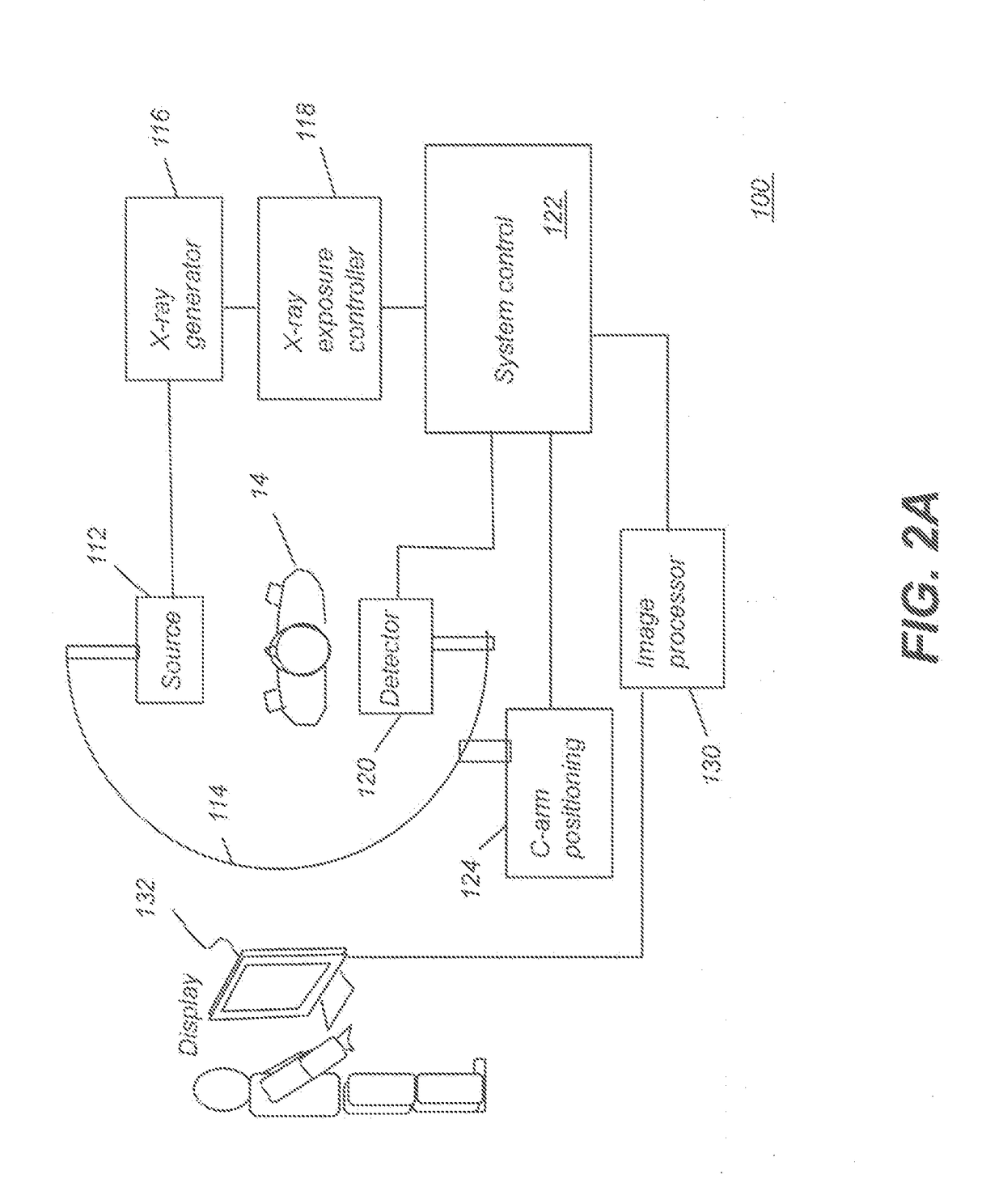
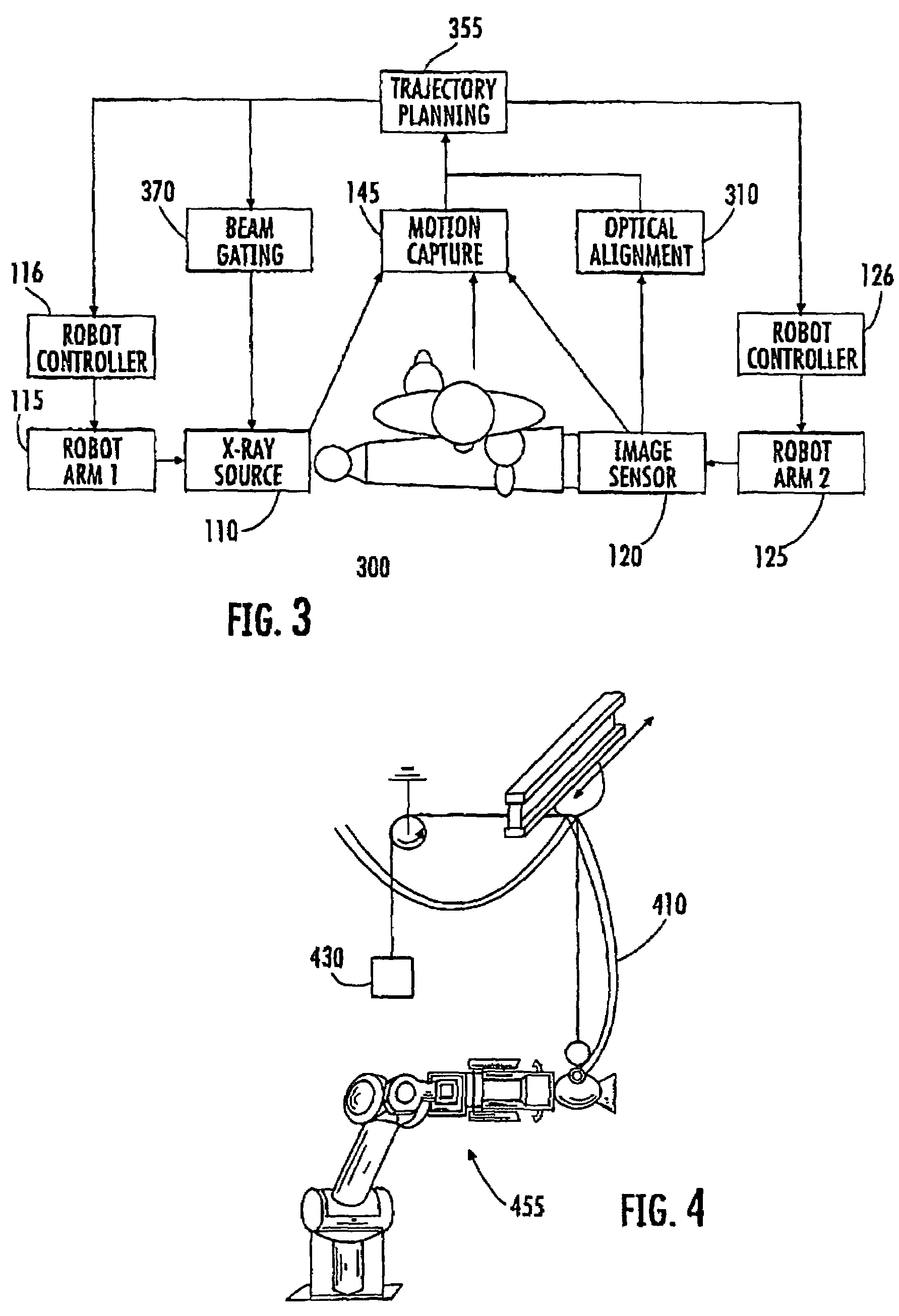
Radiographic medical imaging system using robot mounted source and sensor for dynamic image capture and tomography
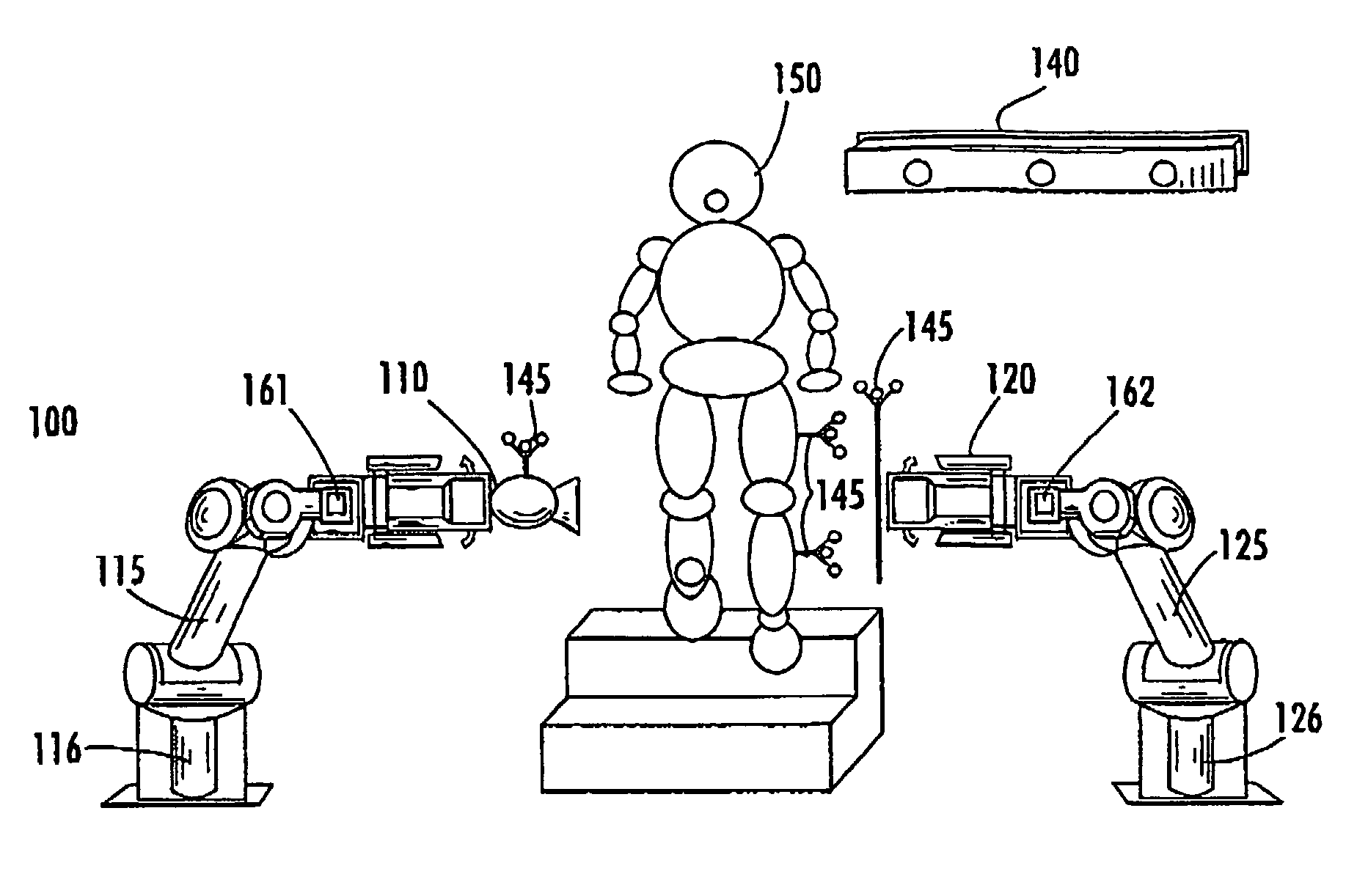
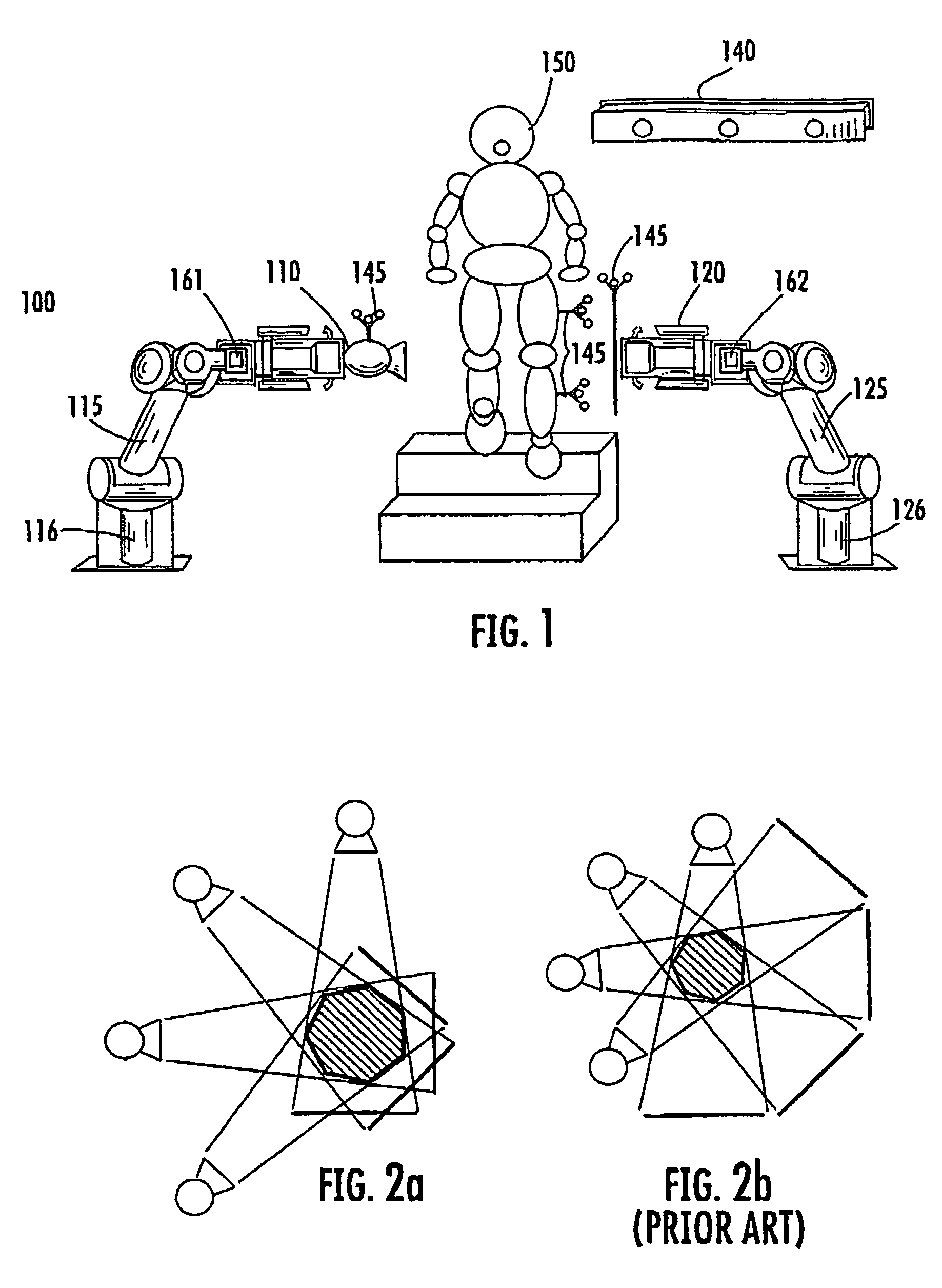
ActiveUS7441953B2Image analysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRobotic armEngineering
A radiographic imaging system includes (100) a penetrating radiation source (110) including a first translating device (115), the first translating device (115) comprising a first controller (116) for positioning the radiation source. A radiation detector (120) includes second translating device (125) comprising a second controller for positioning the detector (120). A motion capture device (140) is communicably connected to both the first and second controllers. The motion capture device (140) tracks a position of the subject being imaged and provides position information to both the first controller (116) and second controllers (126) for dynamically coordinating trajectories for both the radiation source (110) and the radiation detector(120). The first and second translating devices preferably comprise robotic arms.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
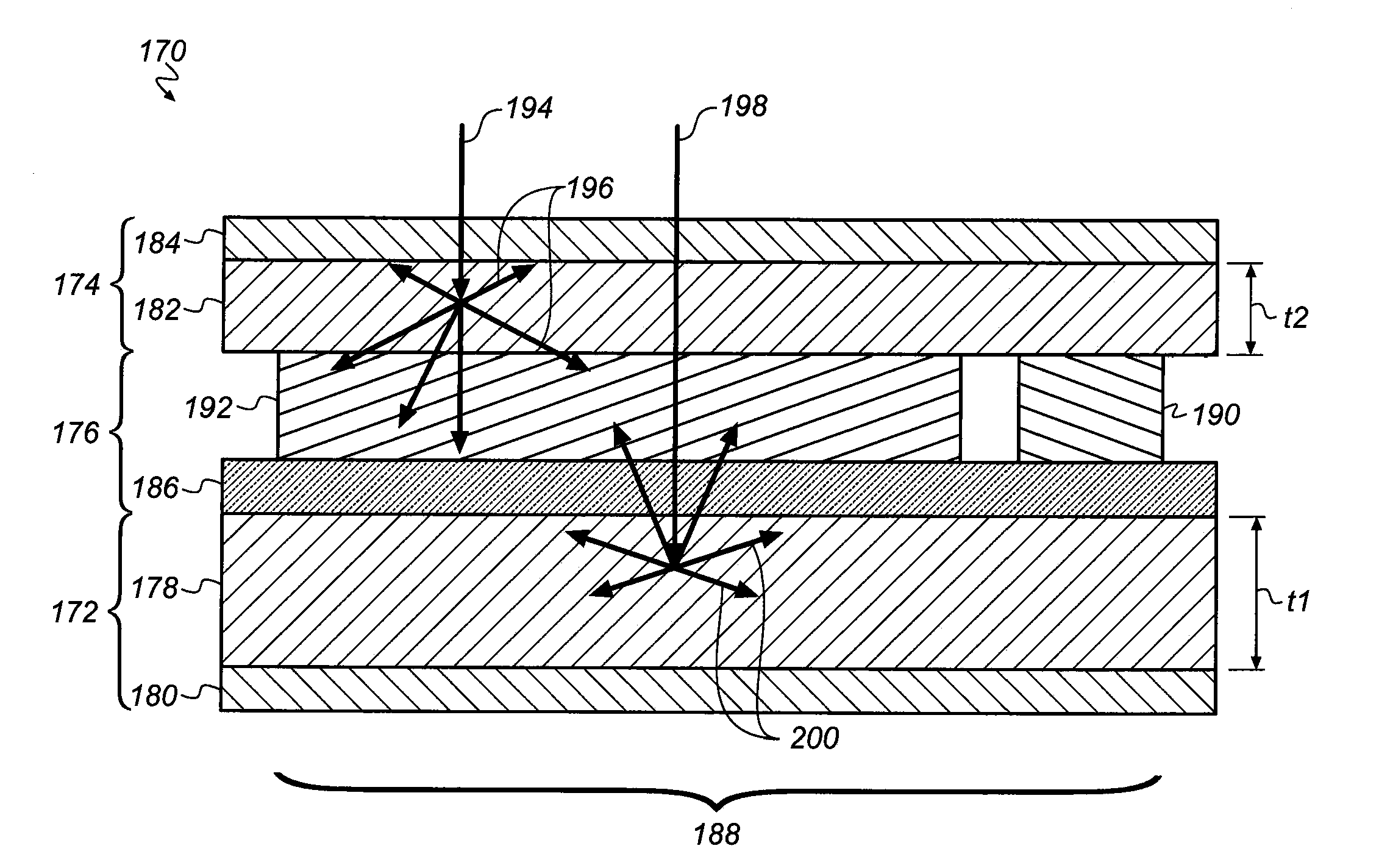
Dual-screen digital radiographic imaging detector array
ActiveUS20080245968A1Quality improvementClear imagingTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhosphorDetector array
A radiographic imaging device has a first scintillating phosphor screen having a first thickness and a second scintillating phosphor screen having a second thickness. A transparent substrate is disposed between the first and second screens. An imaging array formed on a side of the substrate includes multiple photosensors and an array of readout elements.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Imaging protocols
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
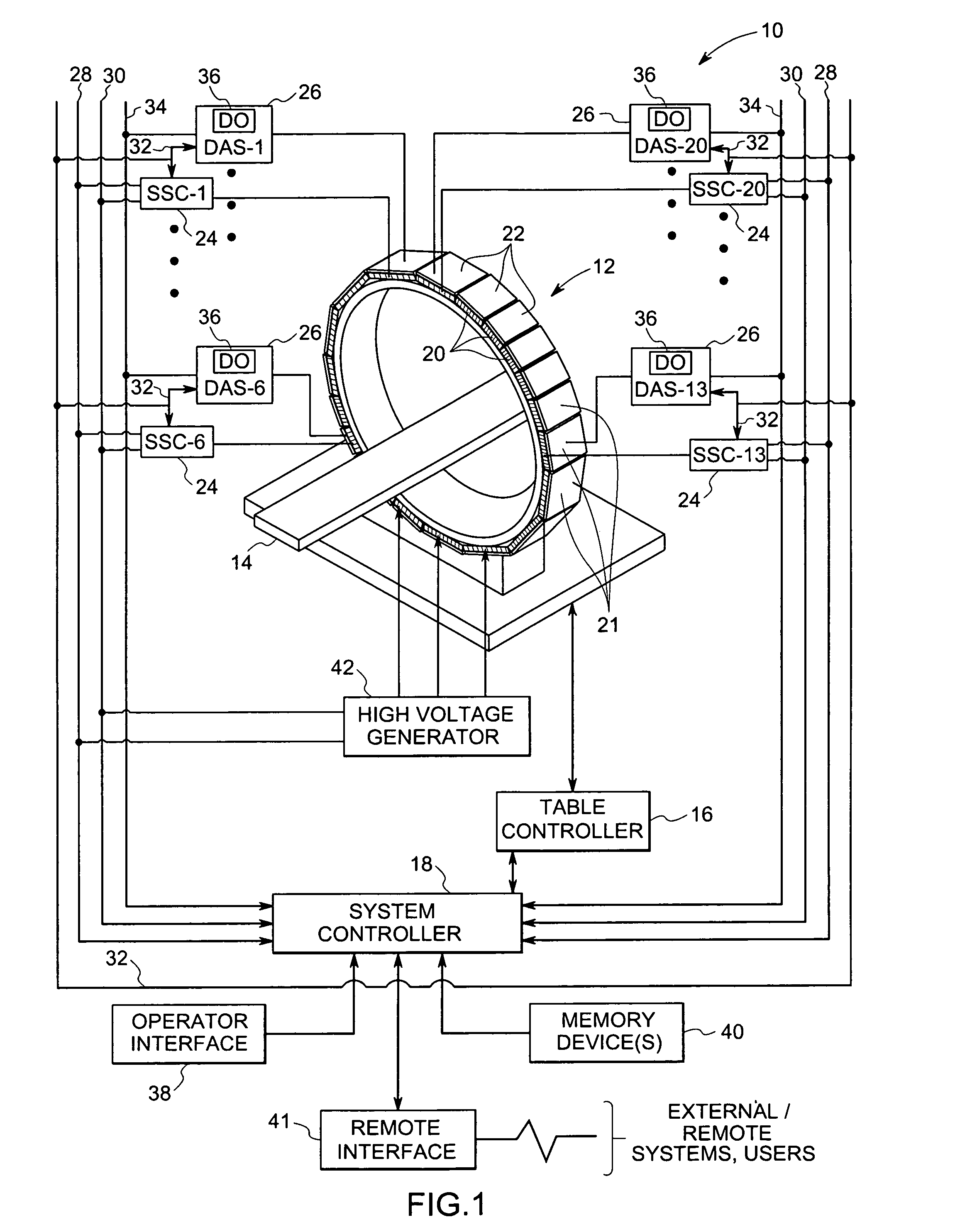
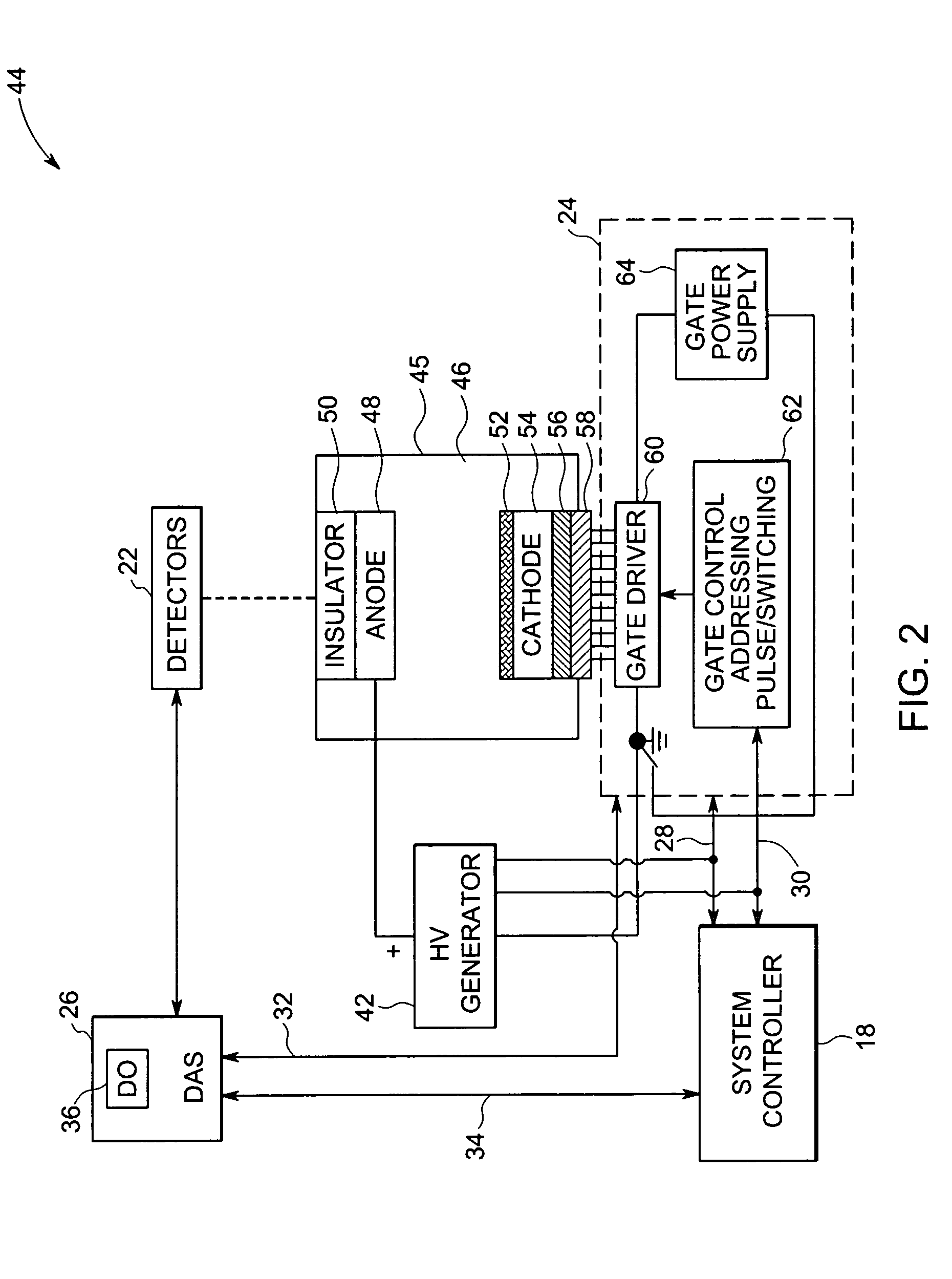
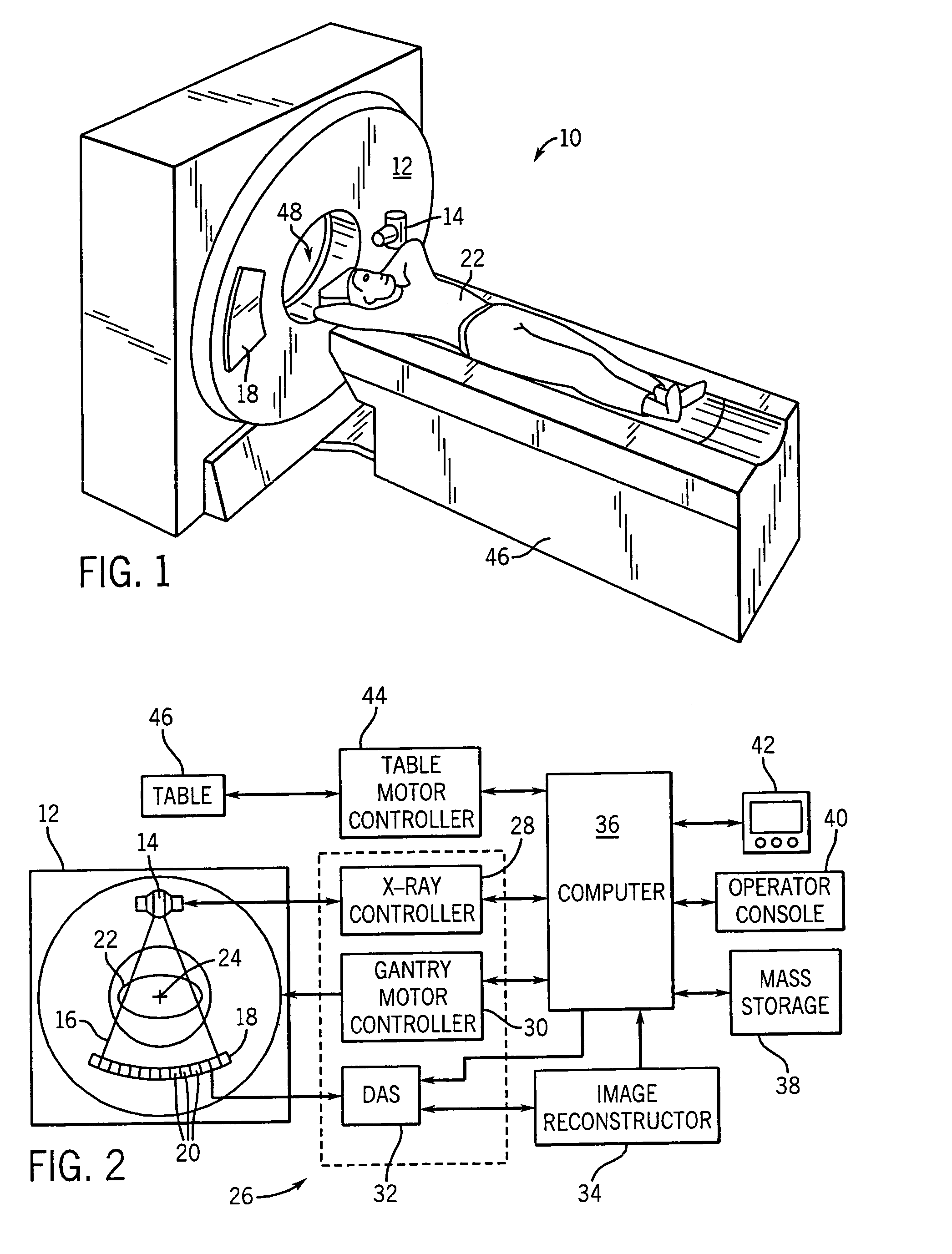
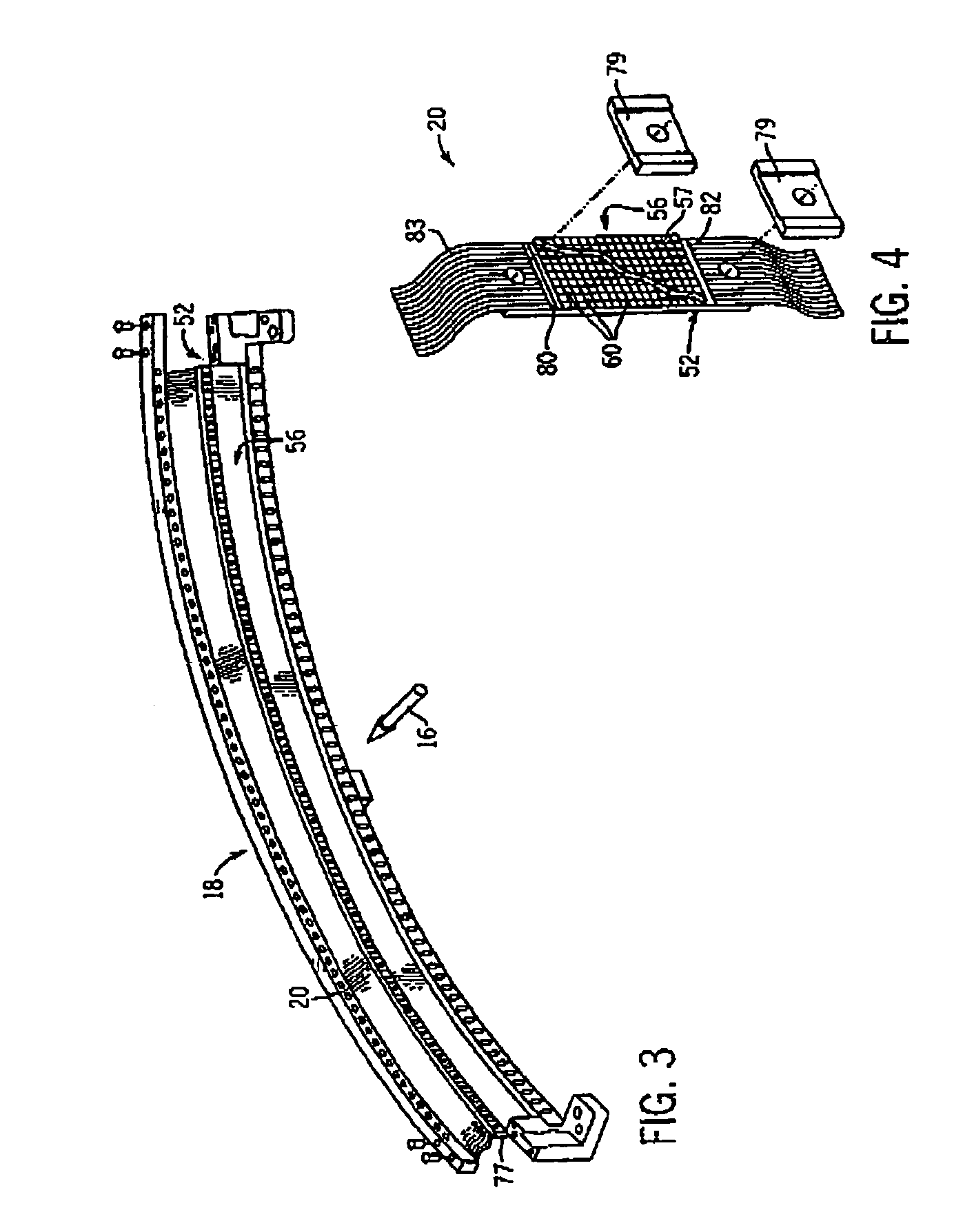
Stationary computed tomography system and method
ActiveUS7295651B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTelecommunications linkX-ray
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
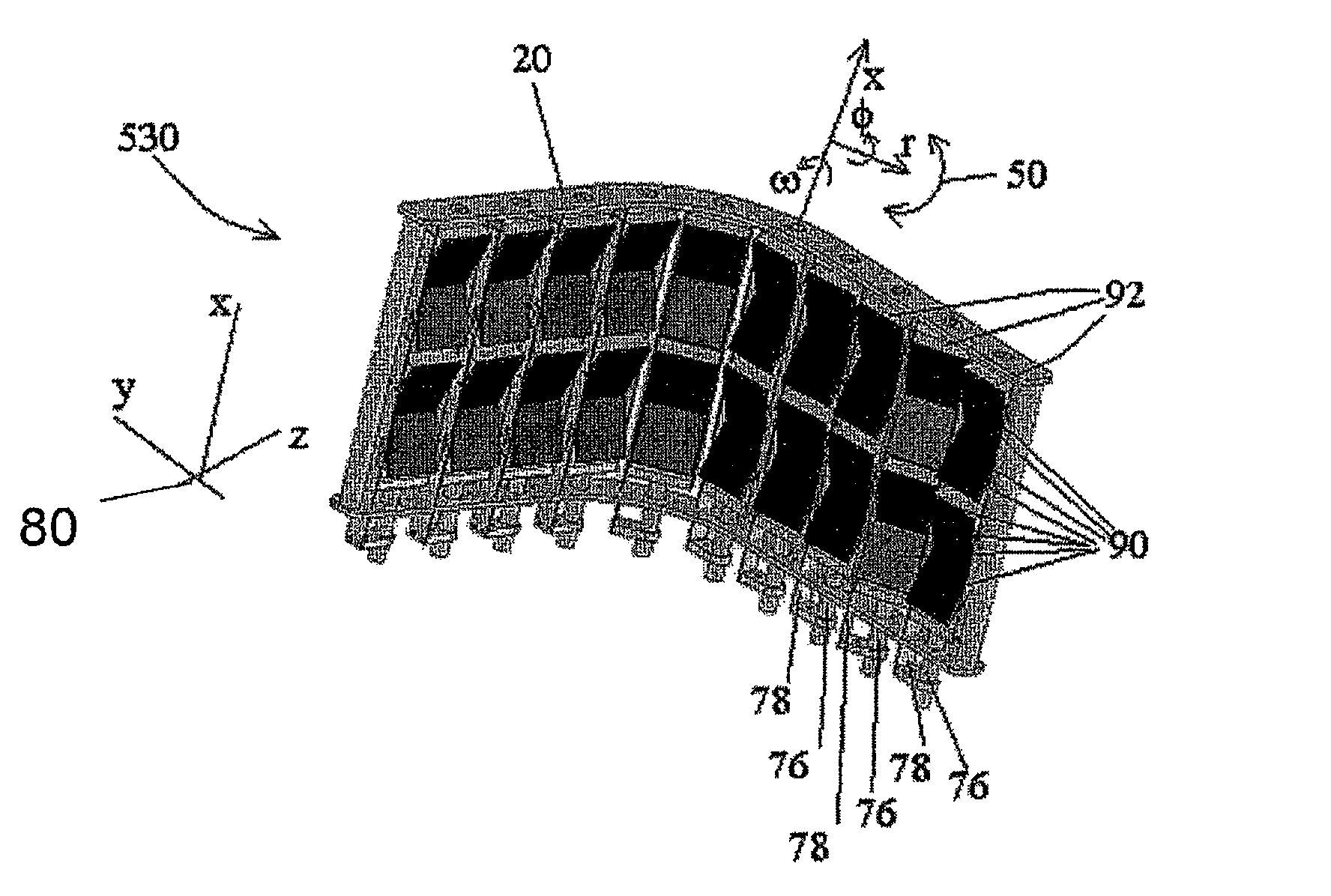
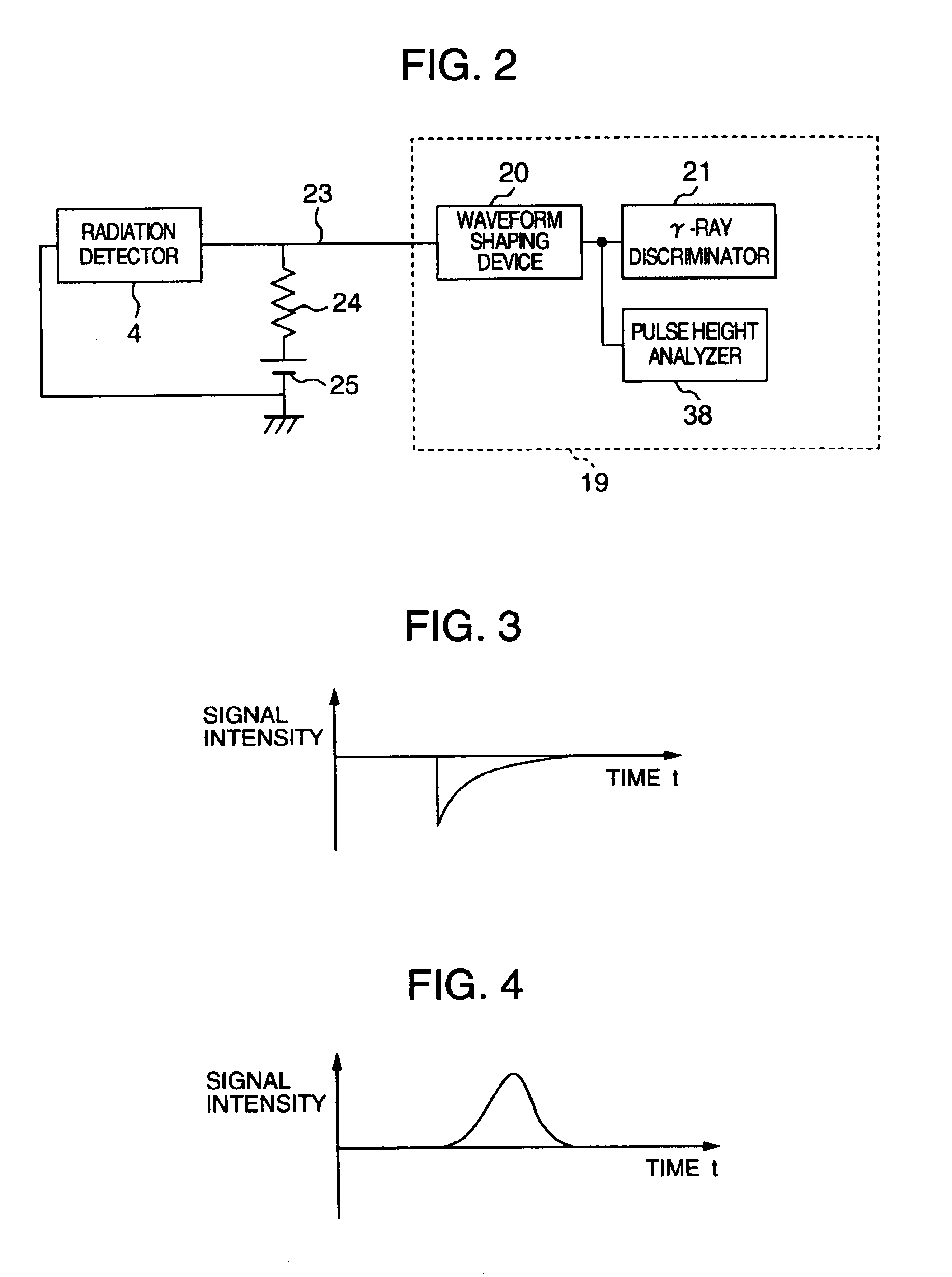
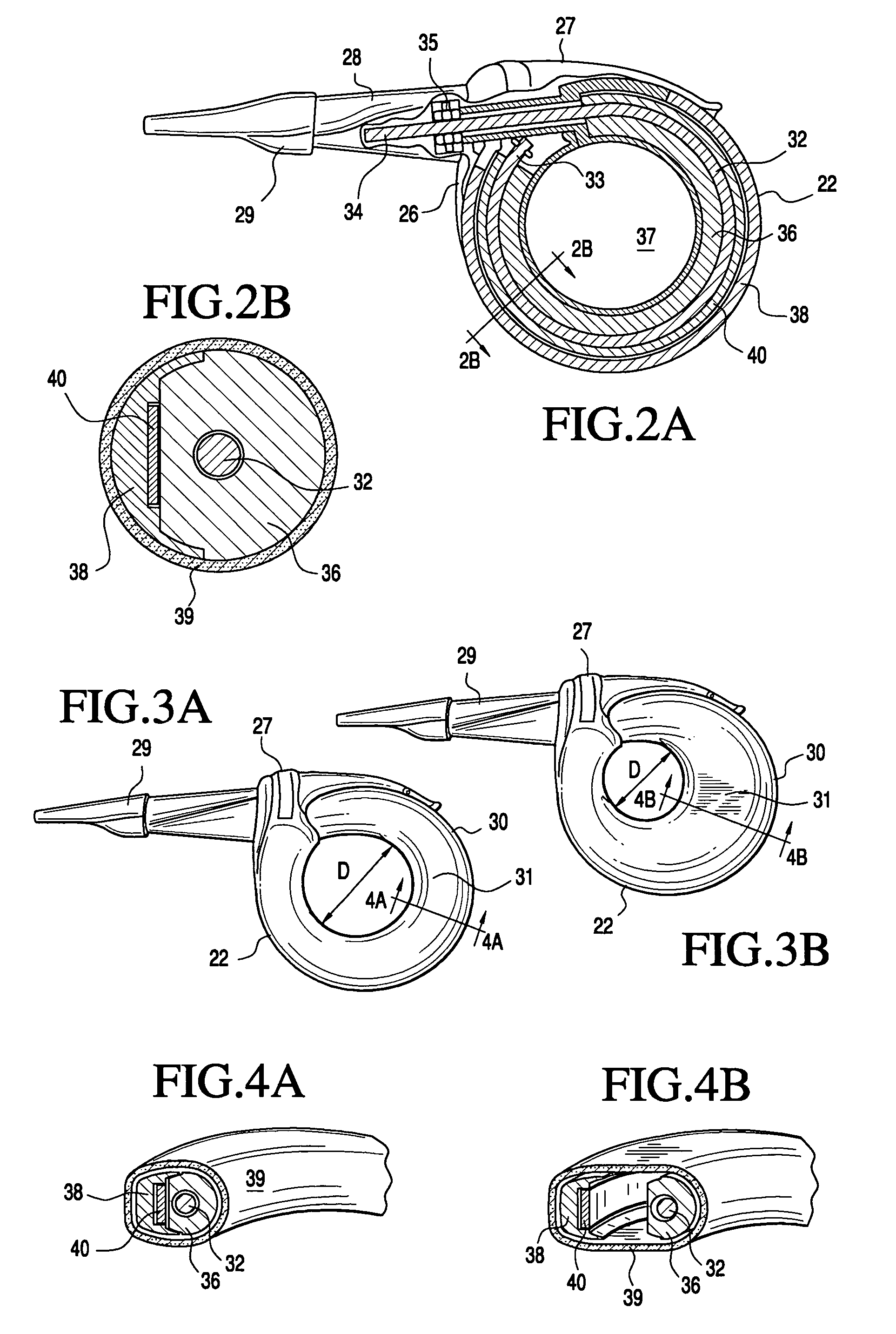
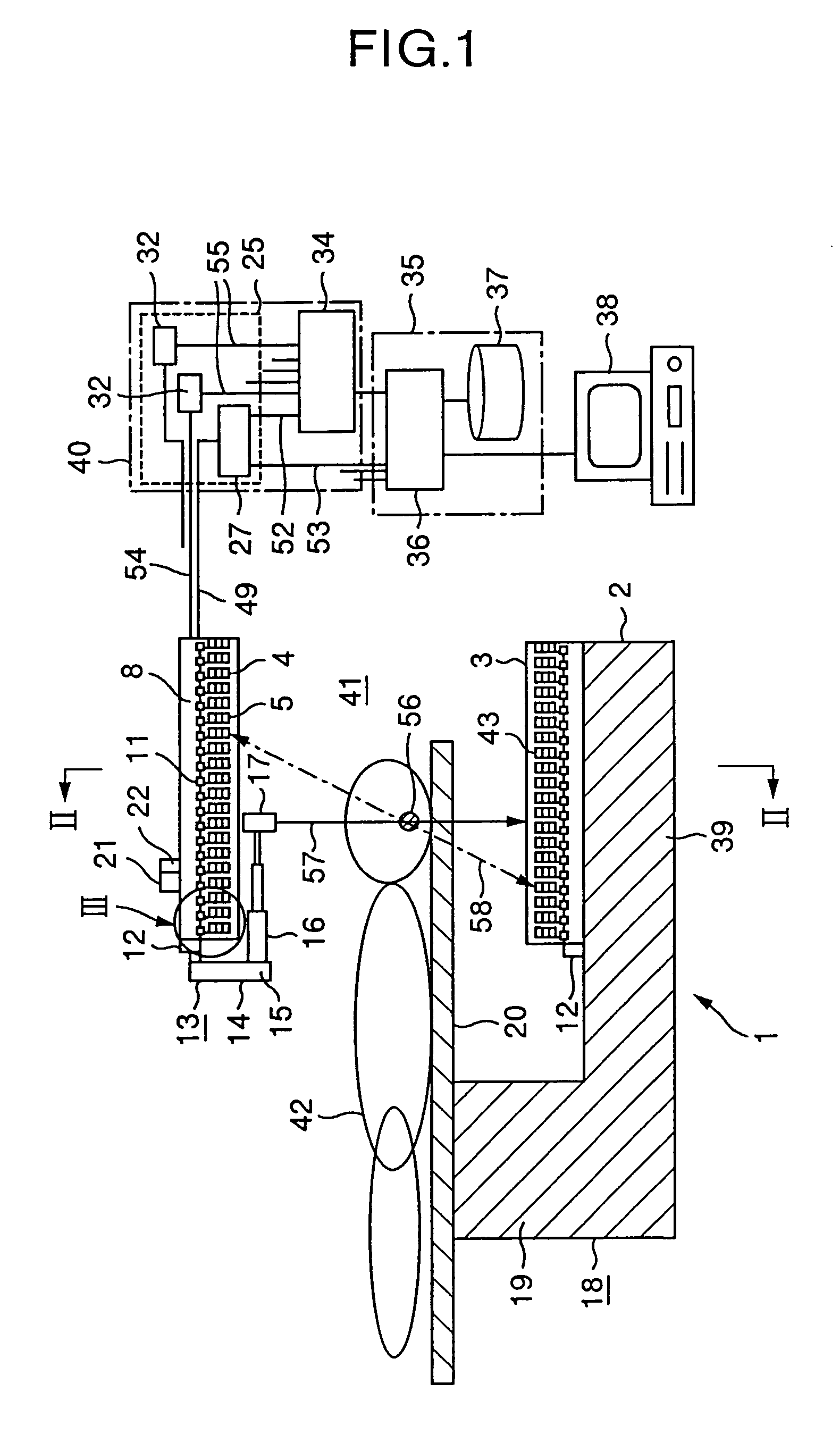
Radiological imaging apparatus and radiological imaging method
InactiveUS6965661B2Simple configurationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
An image pickup apparatus of a radiological imaging apparatus includes a plurality of radiation detectors arranged in a ring form around a through hole section formed on a casing into which an examinee is inserted. An X-ray source unit having an X-ray source moves in a circumferential direction of the through hole section along a ring-shaped guide rail provided on the casing. Each radiation detector outputs both an X-ray detection signal which is a detection signal of X-rays that have passed through the examinee and a γ-ray detection signal which is a detection signal of γ-rays radiated from the examinee caused by radiopharmaceutical. A computer creates an X-ray computed tomographic image data based on the X-ray detection signal and a PET image data based on the γ-ray detection signal and creates fused tomographic image data using the X-ray computed tomographic image data and the PET image data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
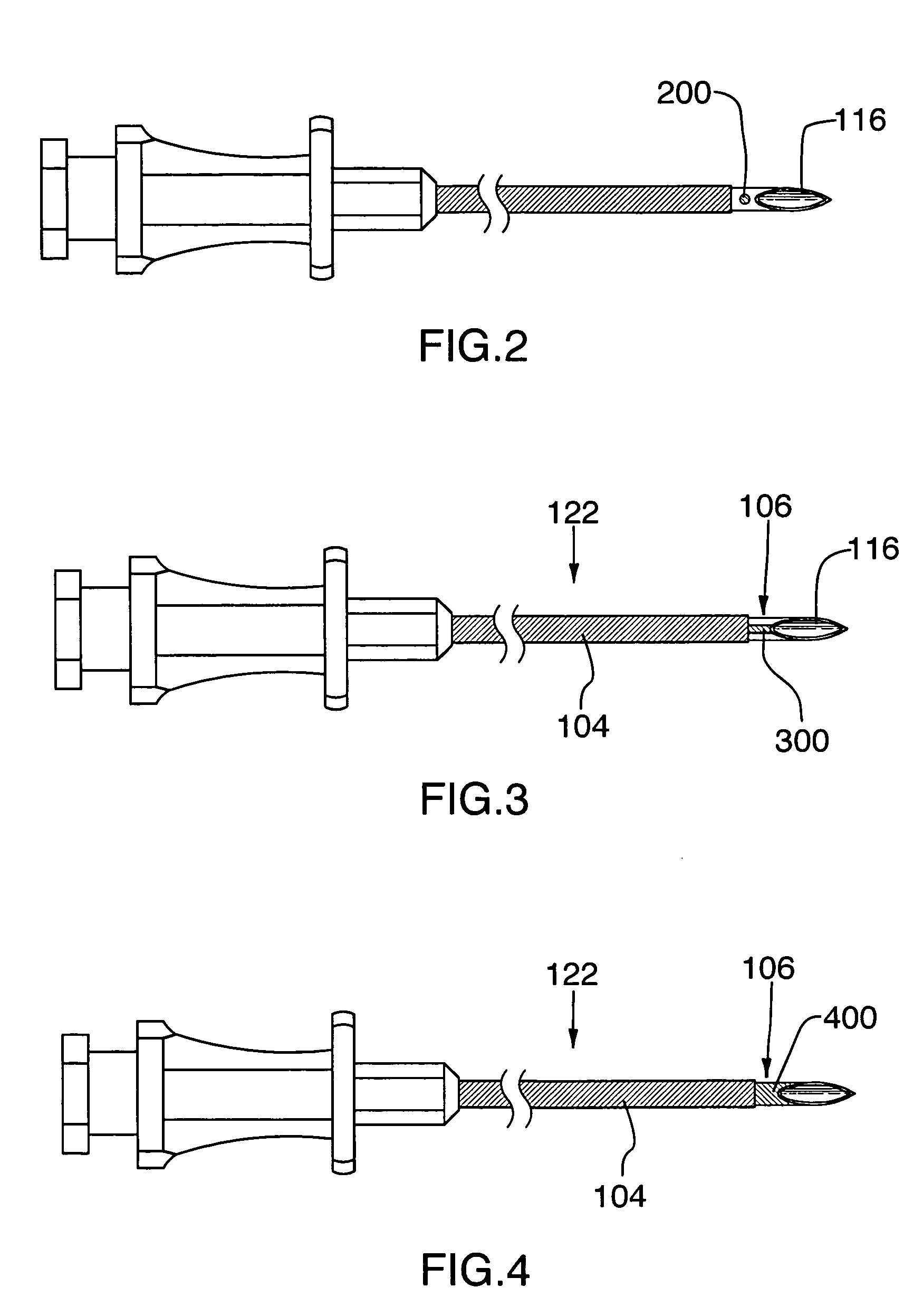
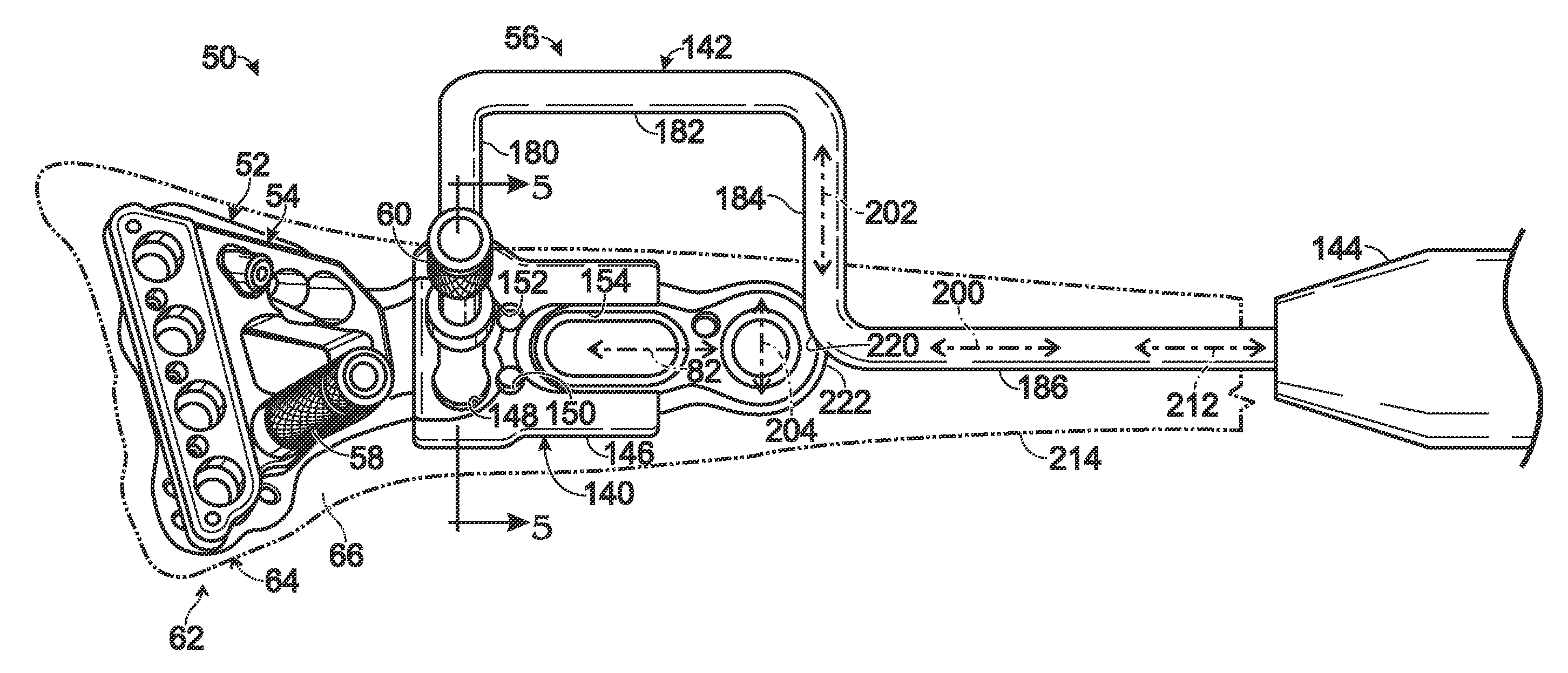
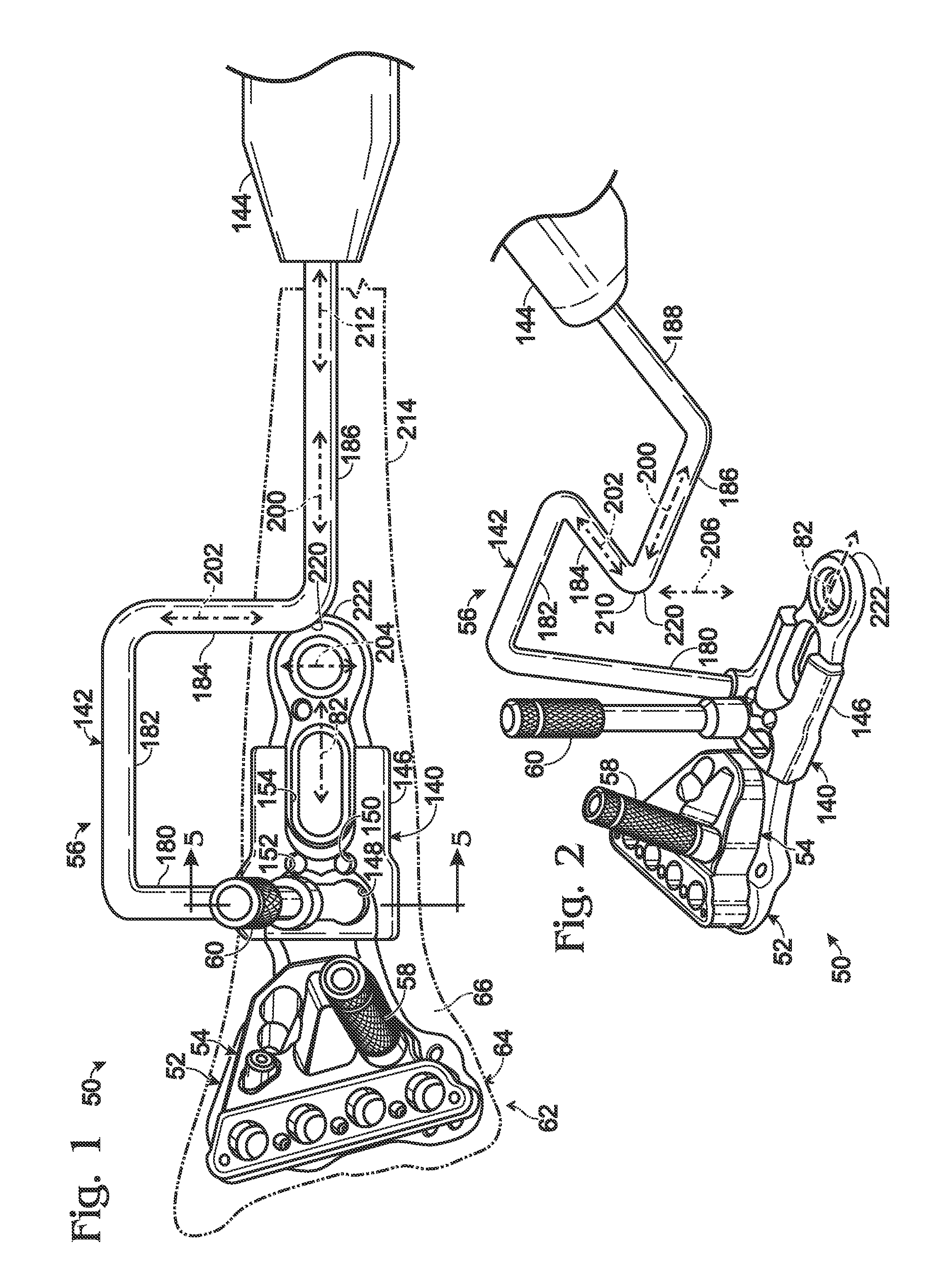
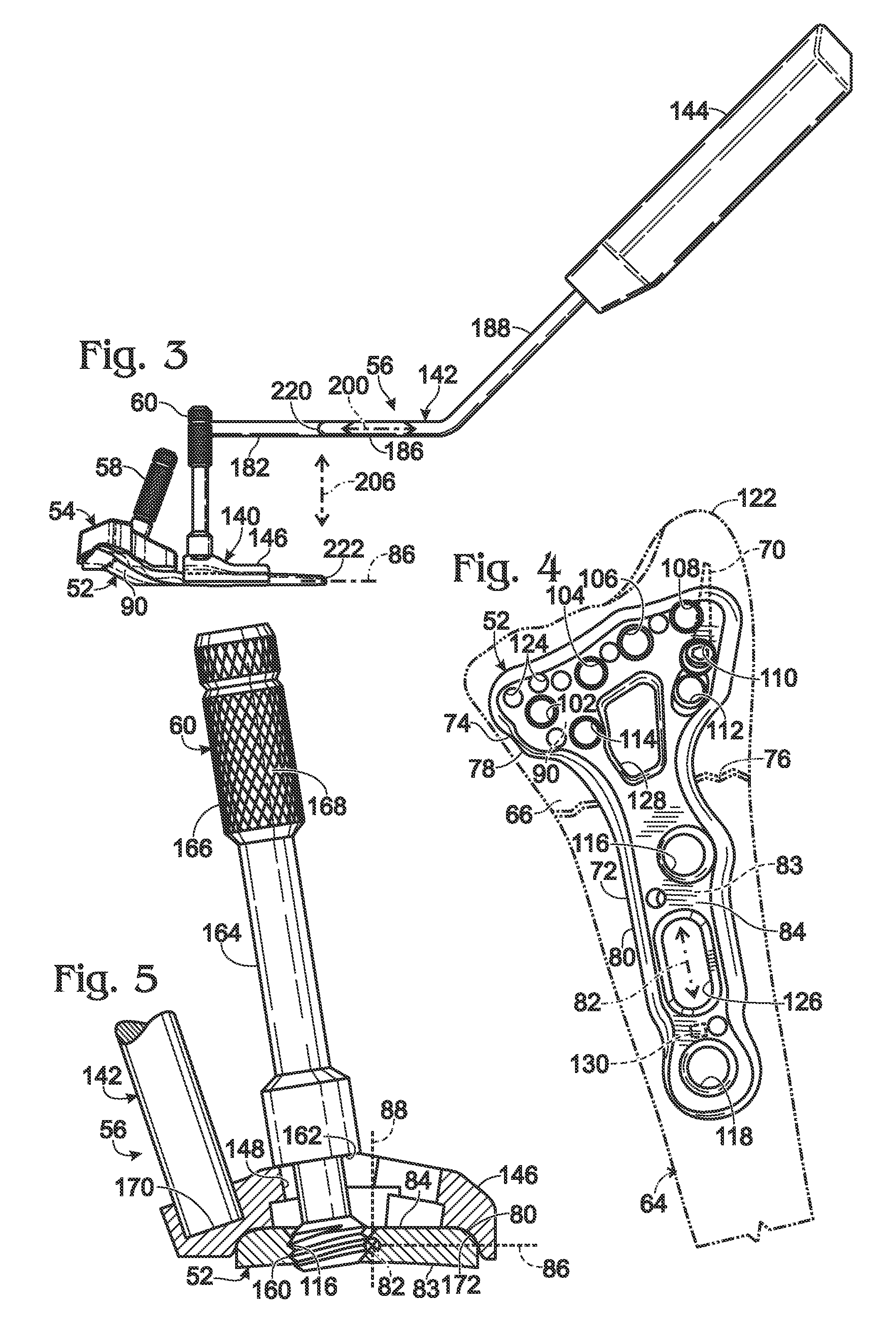
Targeting guide with a radiopaque marker to facilitate positioning a bone plate on bone
Bone fixation system, including methods, apparatus, and kits, and comprising a bone plate and at least one instrument that attaches to the bone plate and provides at least one radiopaque region to facilitate positioning the bone plate on bone visualized by radiographic imaging. The instrument may be a handle assembly and / or a targeting guide.
Owner:ACUMED
On-demand cleavable linkers for radioconjugates for cancer imaging and therapy
InactiveUS20050255042A1Improving site-specific deliveryGood removal effectRadioactive preparation carriersRadiation therapyAbnormal tissue growthRadiation therapy
The present invention provides compositions comprising a biological agent, a targeting moiety, and a peptide linker attaching the biological agent to the targeting moiety, wherein the peptide linker is selectively cleaved by a protease. Efficient methods are provided for administering the compositions of the present invention for treating cancer or imaging a tumor, organ, or tissue in a subject. Kits are also provided for administering the compositions of the present invention for radiotherapy or radioimaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Alignment apparatus for x-ray imaging system
A method for aligning a radiation source with a portable image receiver in a radiographic imaging system generates a magnetic field with a predetermined field pattern and with a time-varying vector direction at a predetermined frequency from an emitter apparatus that is coupled to the radiation source, wherein the generated magnetic field further comprises a synchronization signal. Sensed signals from the magnetic field are obtained from a sensing apparatus that is coupled to the image receiver, wherein the sensing apparatus comprises three or more sensor elements, wherein at least two of the sensor elements are arranged at different angles relative to each other and are disposed outside the imaging area of the image receiver. An output signal is indicative of an alignment adjustment according to the amplitude and phase of the obtained sensed signals relative to the synchronization signal.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Electrosurgical device with improved visibility
InactiveUS7593778B2Little strengthImproving radiographic visualizationSurgical needlesDiagnostic markersVisibilityProximate
A method and apparatus are disclosed for improving accuracy of placement of a cannula during delivery of electrical energy proximate to bodily tissue, e.g. neural structures. The apparatus optionally includes a cannula operable to deliver electrical current where a portion of the cannula is electrically insulated and a portion of the cannula is exposed and electrically conductive. The cannula further includes a radiopaque marker to identify a specific portion of the cannula, for example to differentiate the electrically insulated region from the electrically exposed region, by allowing it to be more clearly delineated using fluoroscopy or other radiographic imaging techniques. The radiopaque marker is optionally tapered in order to reduce the force required to insert a cannula comprising a radiopaque marker into the patient's body.
Owner:AVENT INC
Targeting guide with a radiopaque marker to facilitate positioning a bone plate on bone
Bone fixation system, including methods, apparatus, and kits, and comprising a bone plate and at least one instrument that attaches to the bone plate and provides at least one radiopaque region to facilitate positioning the bone plate on bone visualized by radiographic imaging. The instrument may be a handle assembly and / or a targeting guide.
Owner:ACUMED
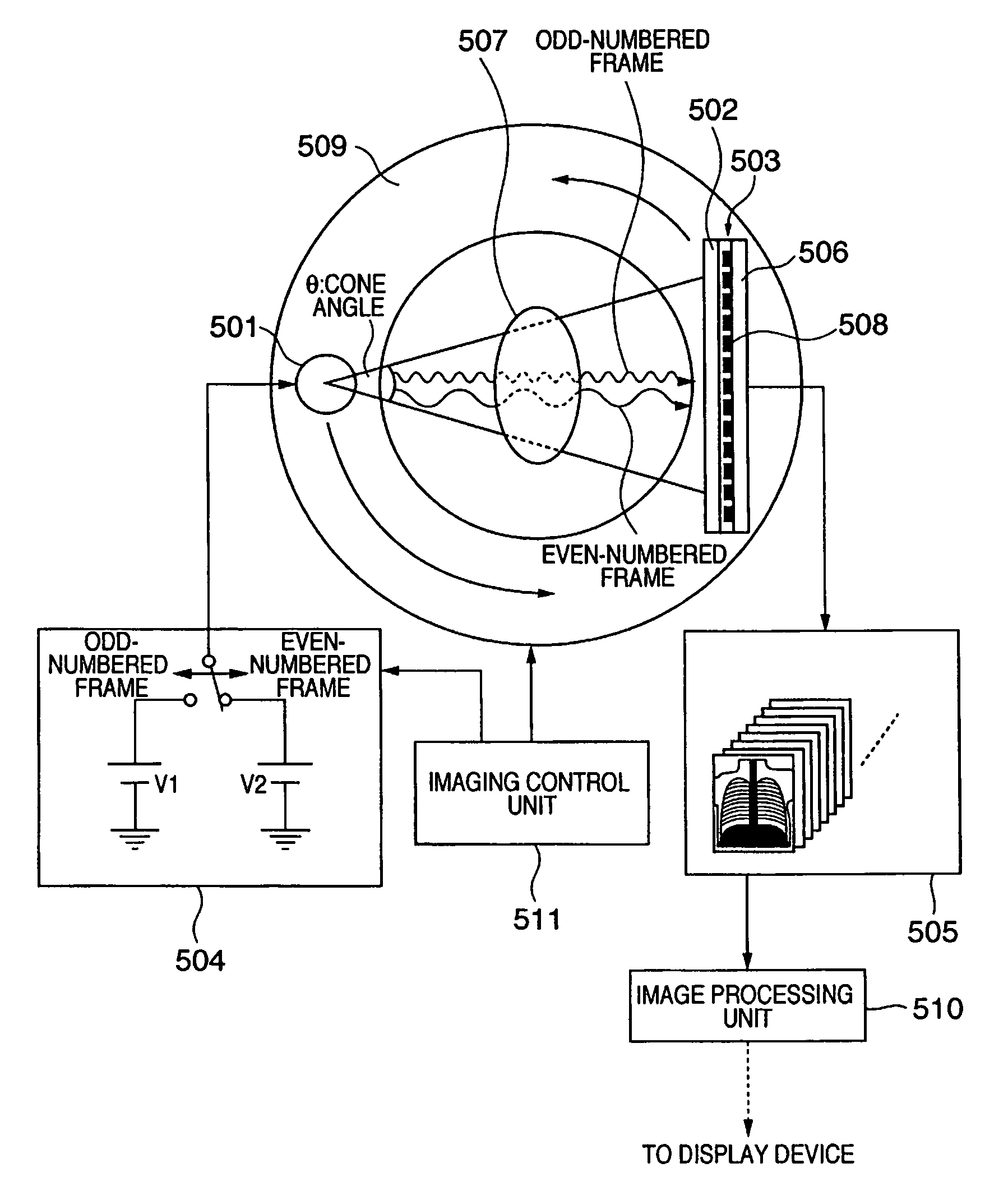
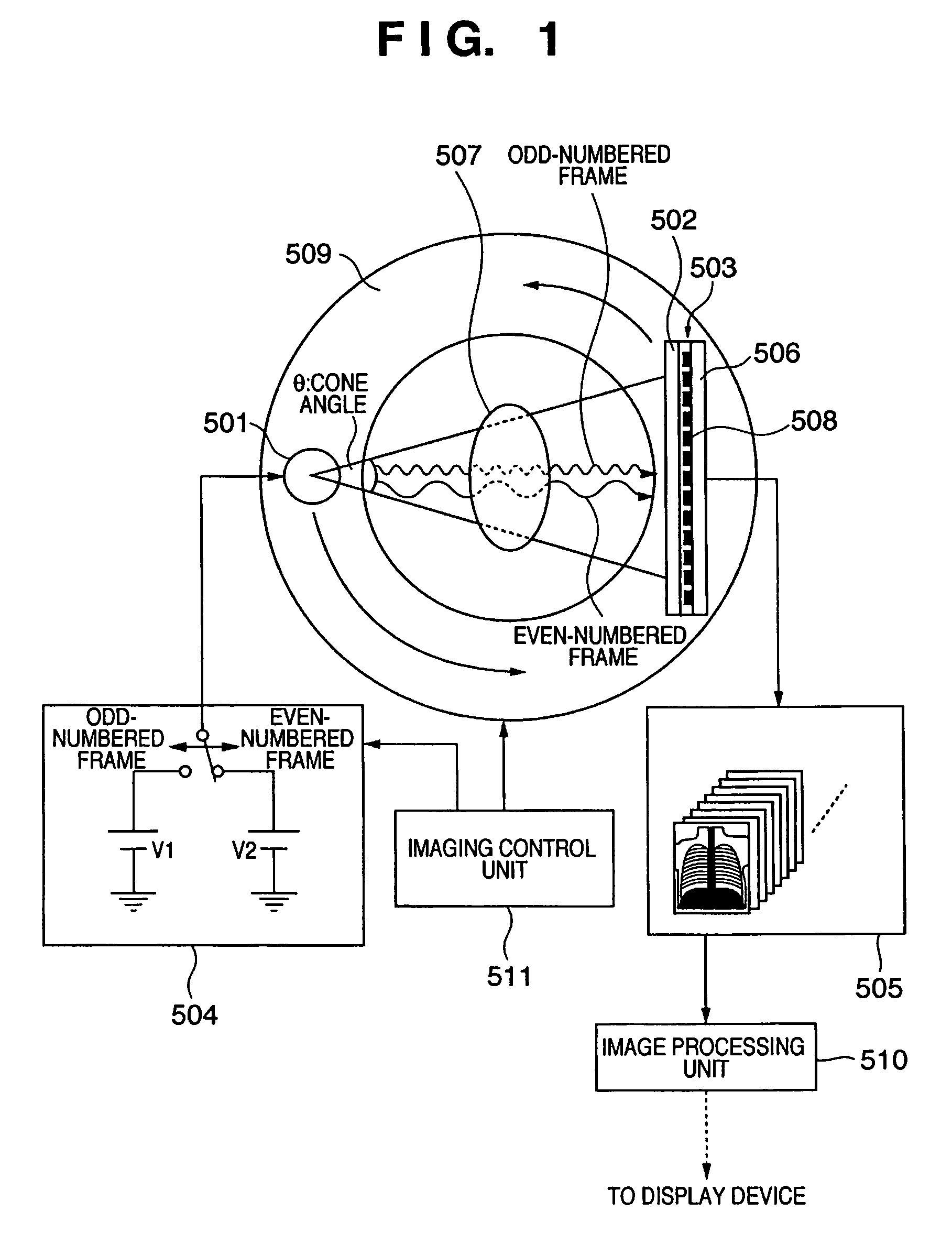
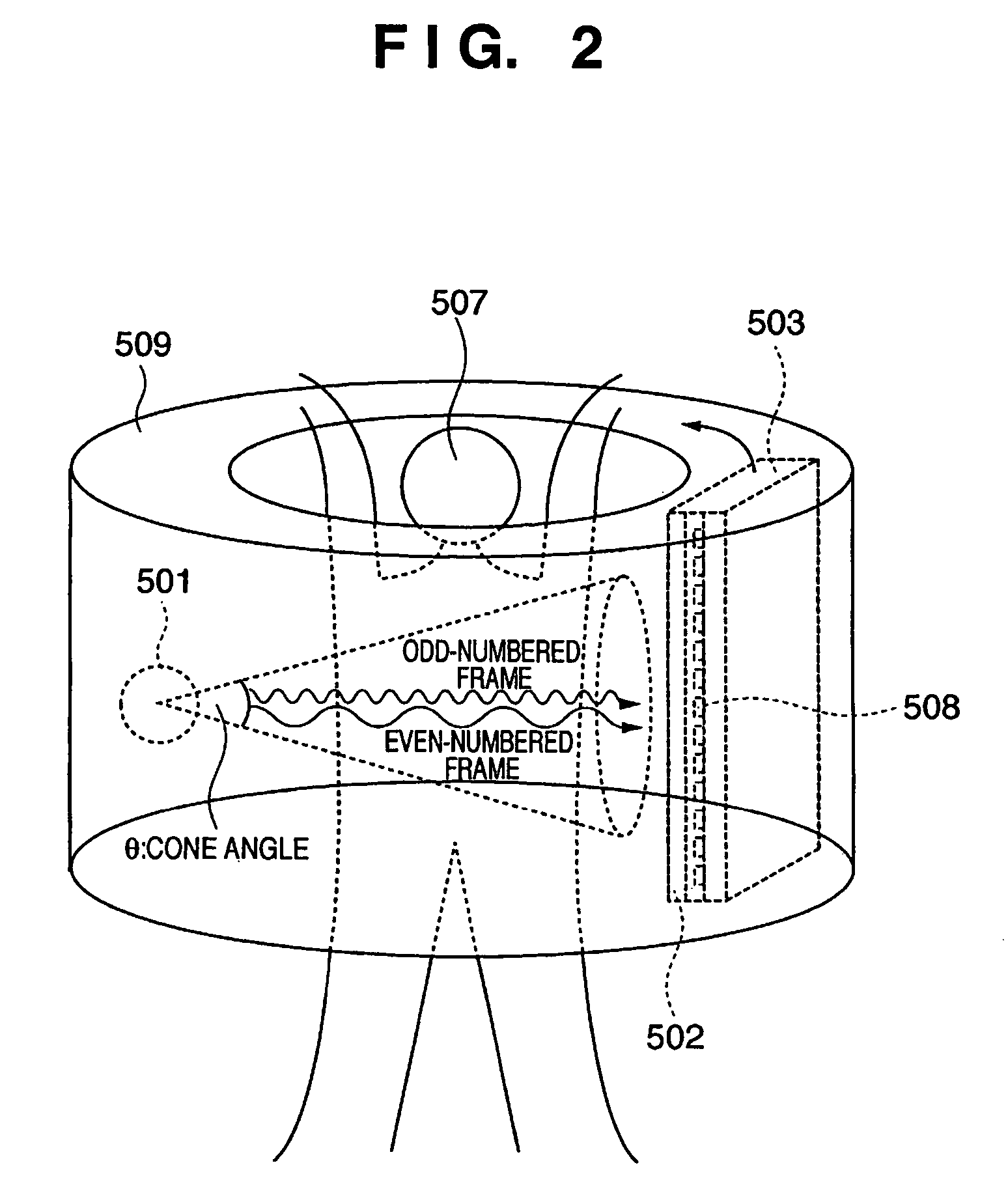
Radiographic imaging apparatus, control method thereof, and radiographic imaging system
InactiveUS7386089B2Reduce contrastImprove diagnostic efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingImaging processing3d image
A radiographic imaging apparatus includes a radiation detection circuit with elements arranged two-dimensionally to convert radiation into an electrical signal, a driving mechanism which changes a positional relationship between the components, a memory which stores that electrical signal, an imaging controller to control the radiation source so as to emit a first radiation pulse at a first energy for a first frame and to emit a second radiation pulse at a second energy for a second frame, controlling the driving mechanism to maintain the positional relationship during the first radiation pulse and the second radiation pulse and to change the positional relationship in a period between the first period and the second period. The frames are different and sequentially imaged, and an image processing unit for subtraction processing of the first and second frames in memory to generate a processed image, then generate a tomographic and a 3D image.
Owner:CANON KK
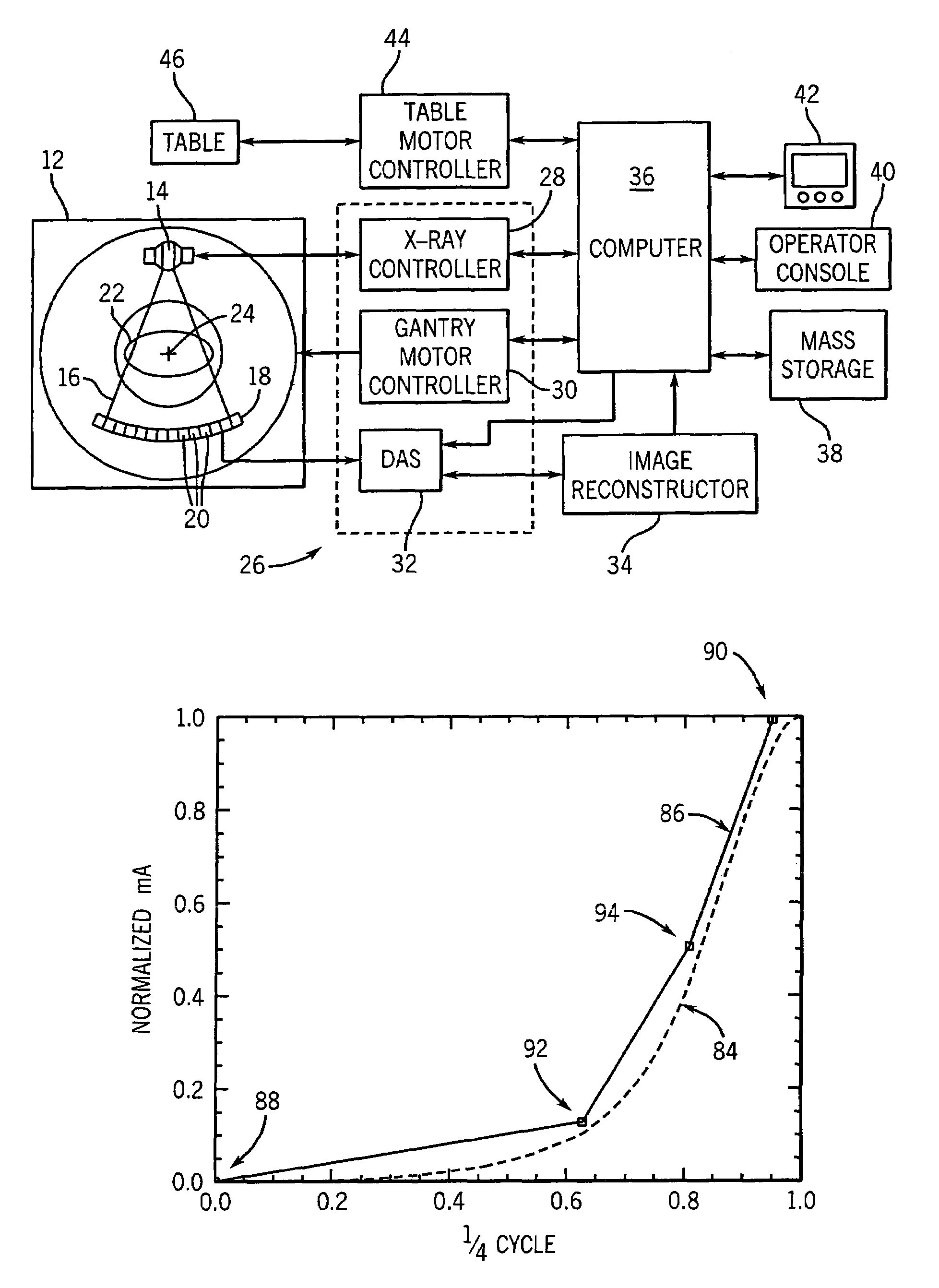
Method and apparatus to determine tube current modulation profile for radiographic imaging
A method and apparatus is disclosed to acquire scout scan data of a subject and analyzed to determine a peak-to-peak modulation amplitude of a normalized waveform indicative of subject size and shape. The scout scan data provides a representation of patient size and shape that is associated with an ideal tube current modulation waveform or profile. The ideal tube current modulation profile may then be sampled or approximated at various points to determine a tube current modulation profile for implementation to acquire CT data with reduced dose but without sacrificing image quality.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
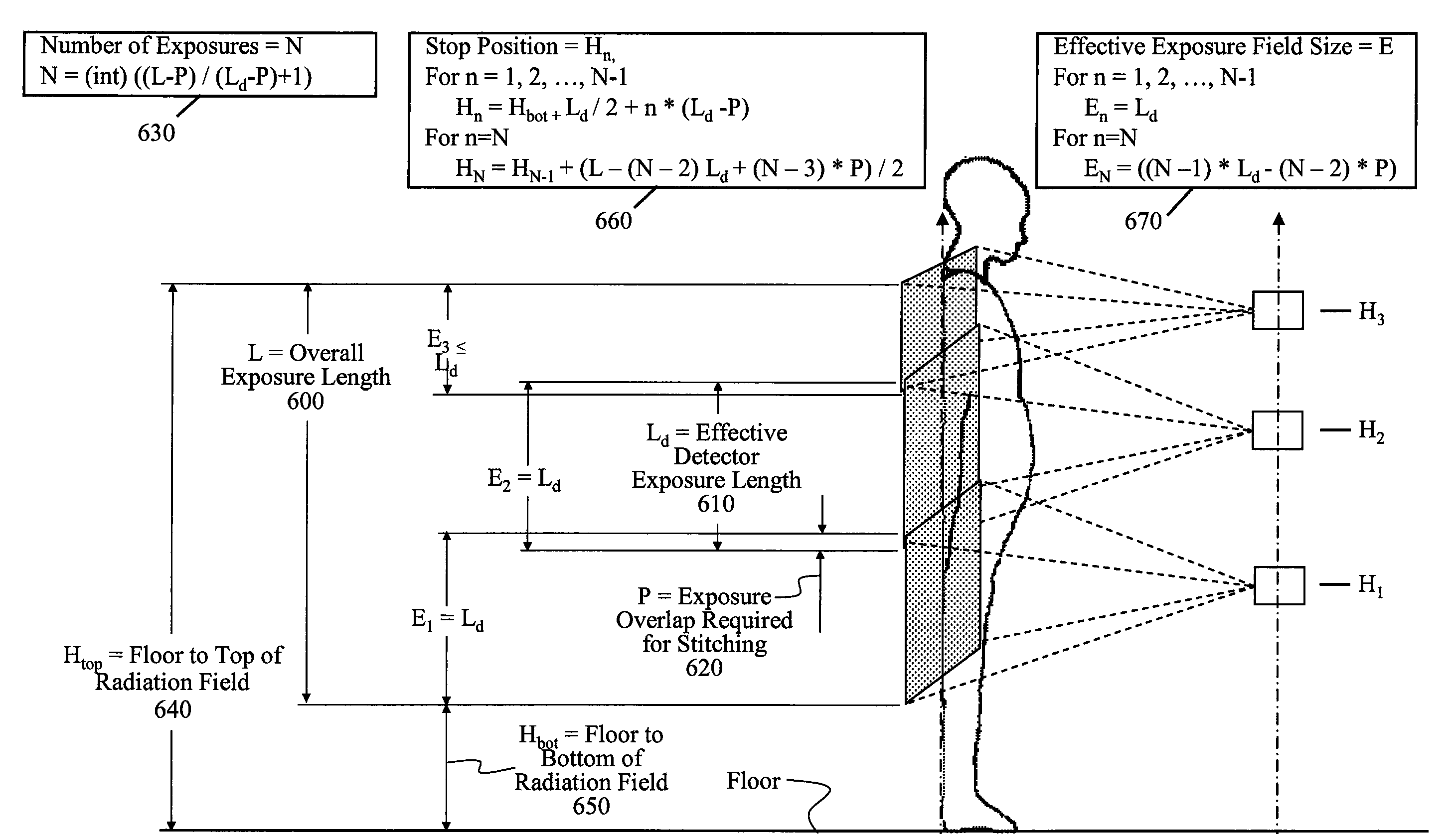
Long length imaging using digital radiography
InactiveUS7555100B2Reduce needSimplifies the long length imaging processTelevision system detailsTomographyLeg lengthDigital radiography
A method for long length imaging with a digital radiography apparatus. Setup instructions are obtained for the image and a set of imaging positions is calculated for an exposure series according to the setup instructions. An operator command is obtained to initiate an imaging sequence. The imaging sequence is executed for each member of the set of imaging positions in the exposure series by automatically repeating the steps of positioning a radiation source and a detector at a location corresponding to the specified member of the set of imaging positions and obtaining an image from the detector at that location and storing the image as a partial image. The long length image is generated by combining two or more partial images.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Mastopexy and Breast Reconstruction Prostheses and Method
InactiveUS20120158134A1Easy to handleResistant to biodegradationMammary implantsCell-Extracellular MatrixMastopexy
Mastopexy and breast reconstruction prostheses and implantation method that allow for radiographic imaging of the breast tissue. The prostheses are arcuate and elongate optionally meshed to conform with breast tissue when implanted. Prostheses are made from naturally occurring extracellular matrix, primarily collagen, that, allows for mammographic imaging without interference as is expected from synthetic materials.
Owner:CODORI HURFF JEANNE +1
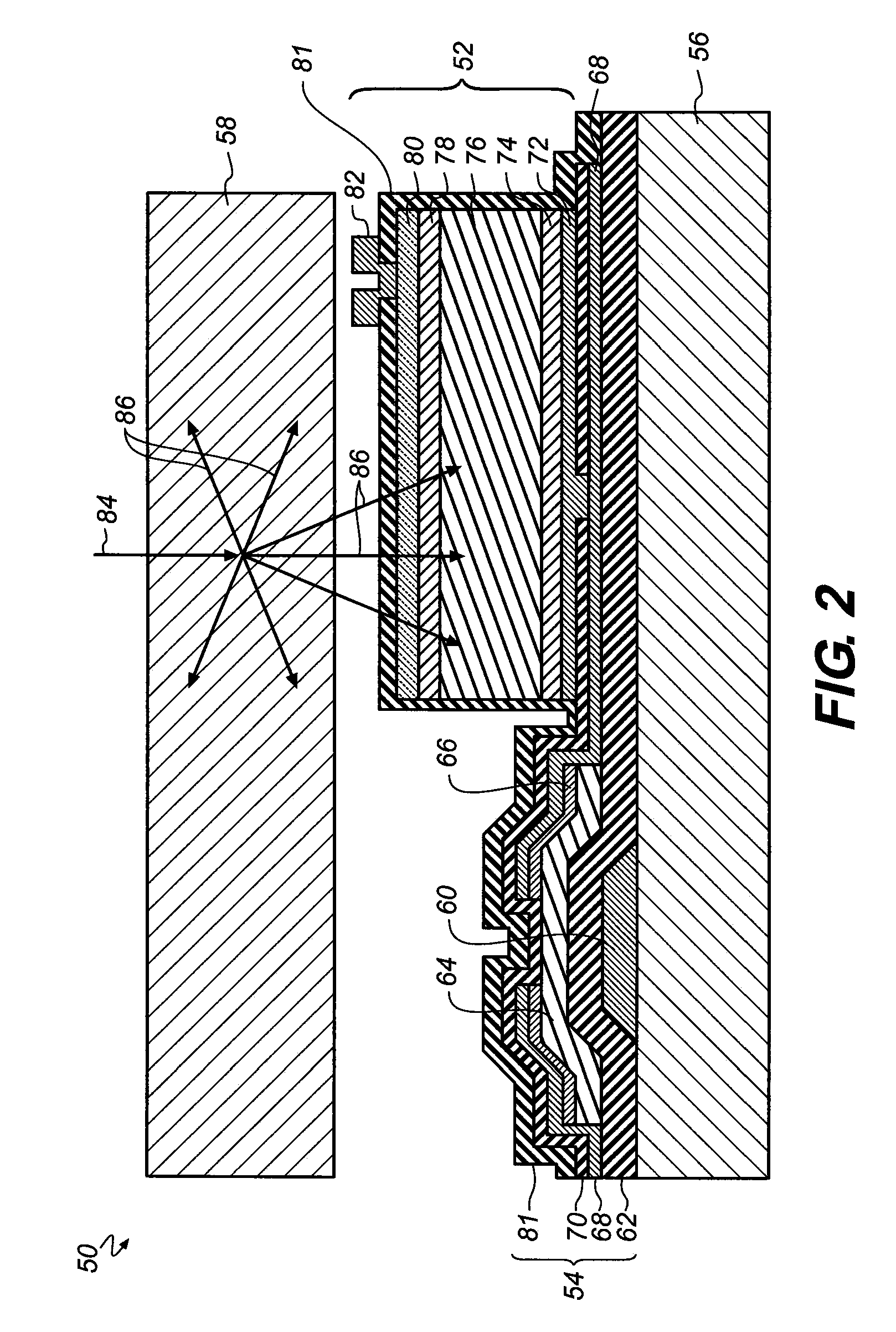
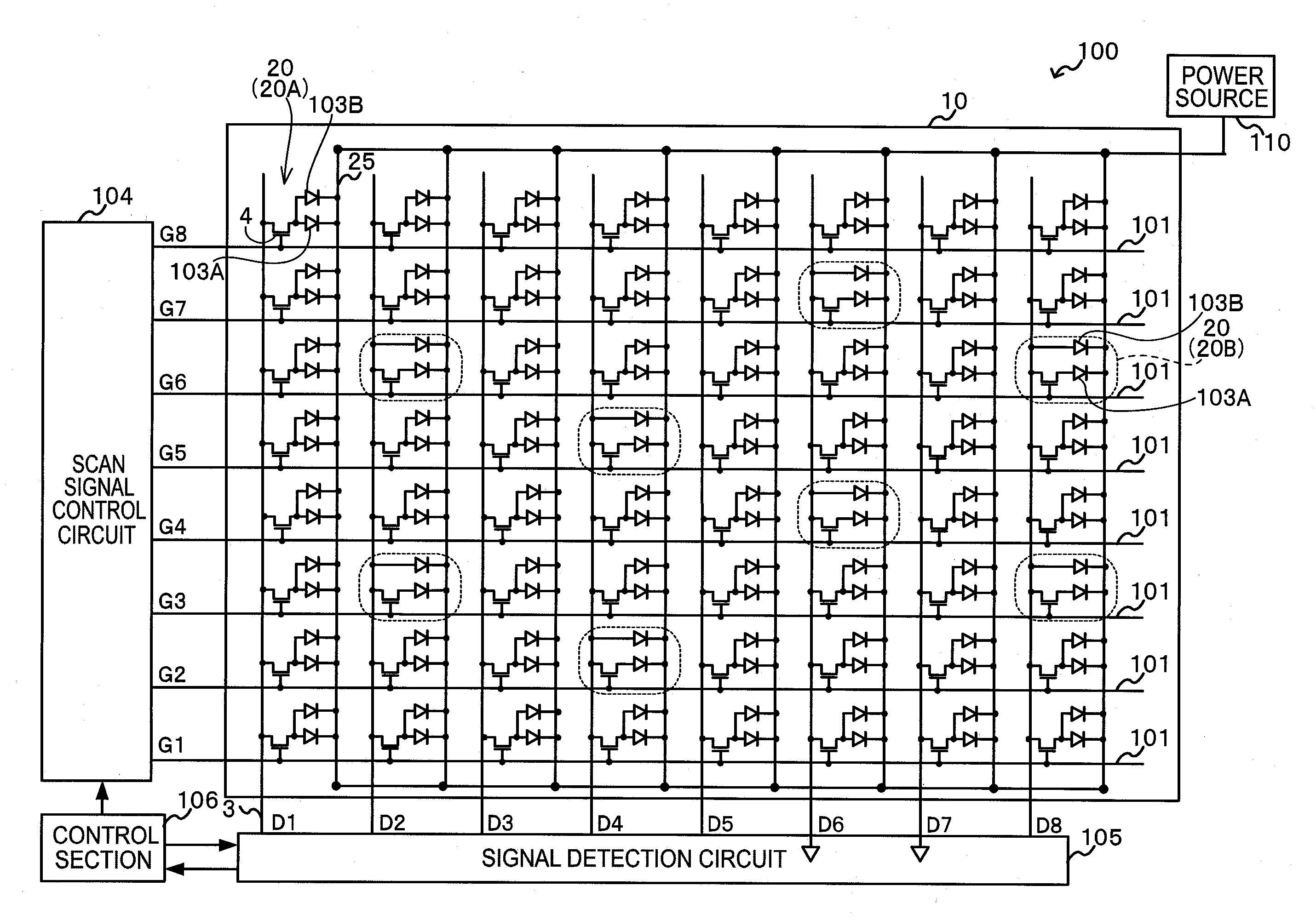
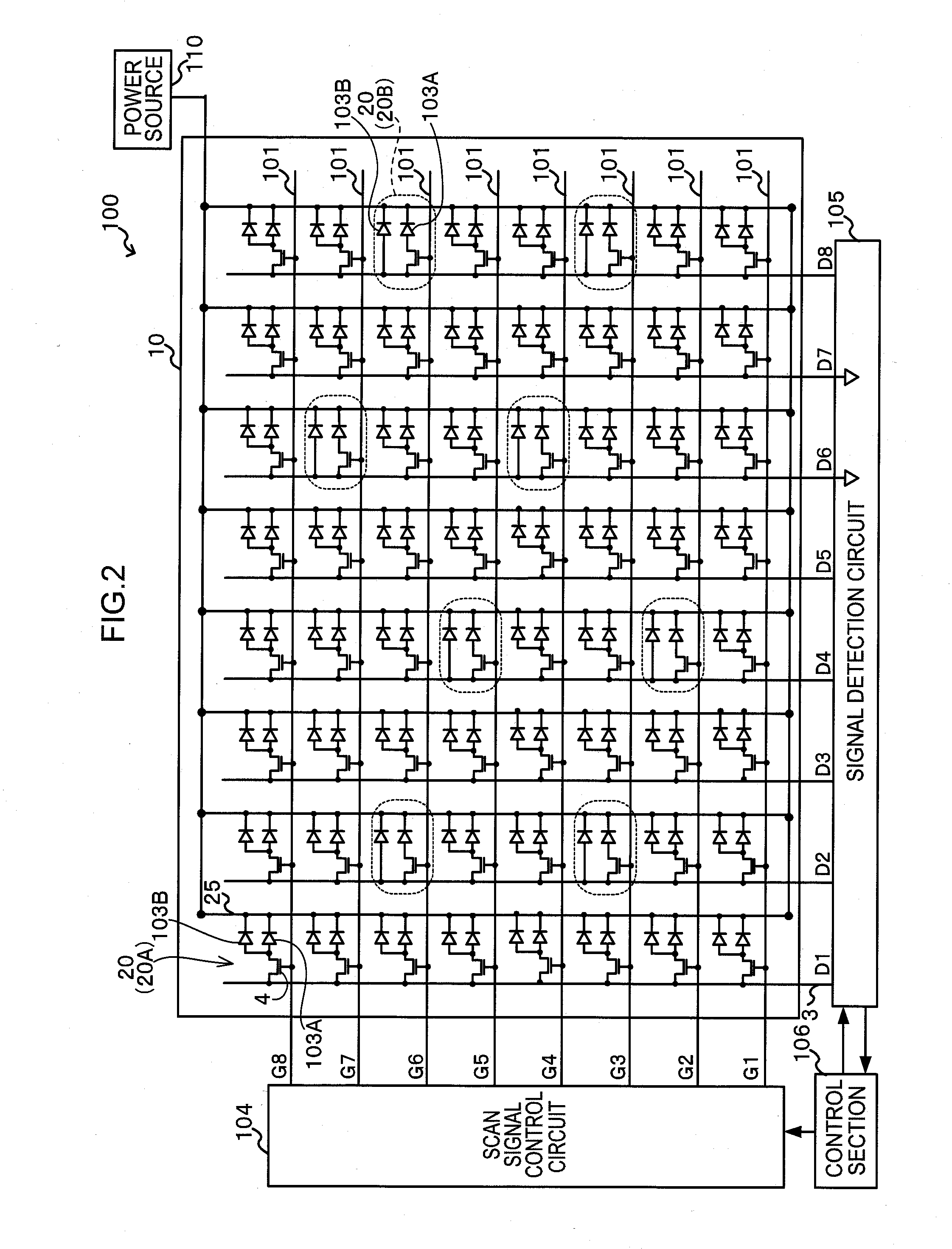
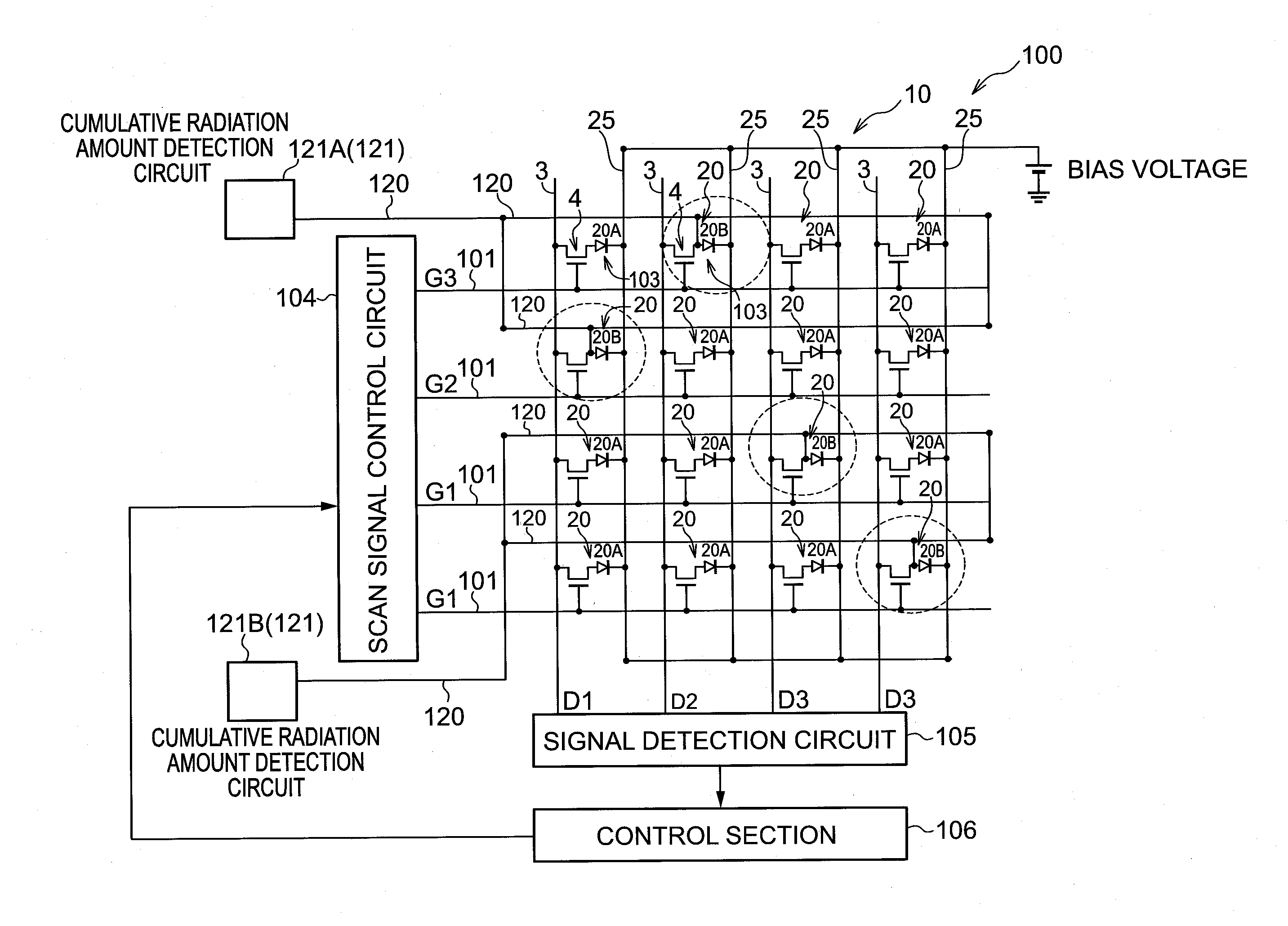
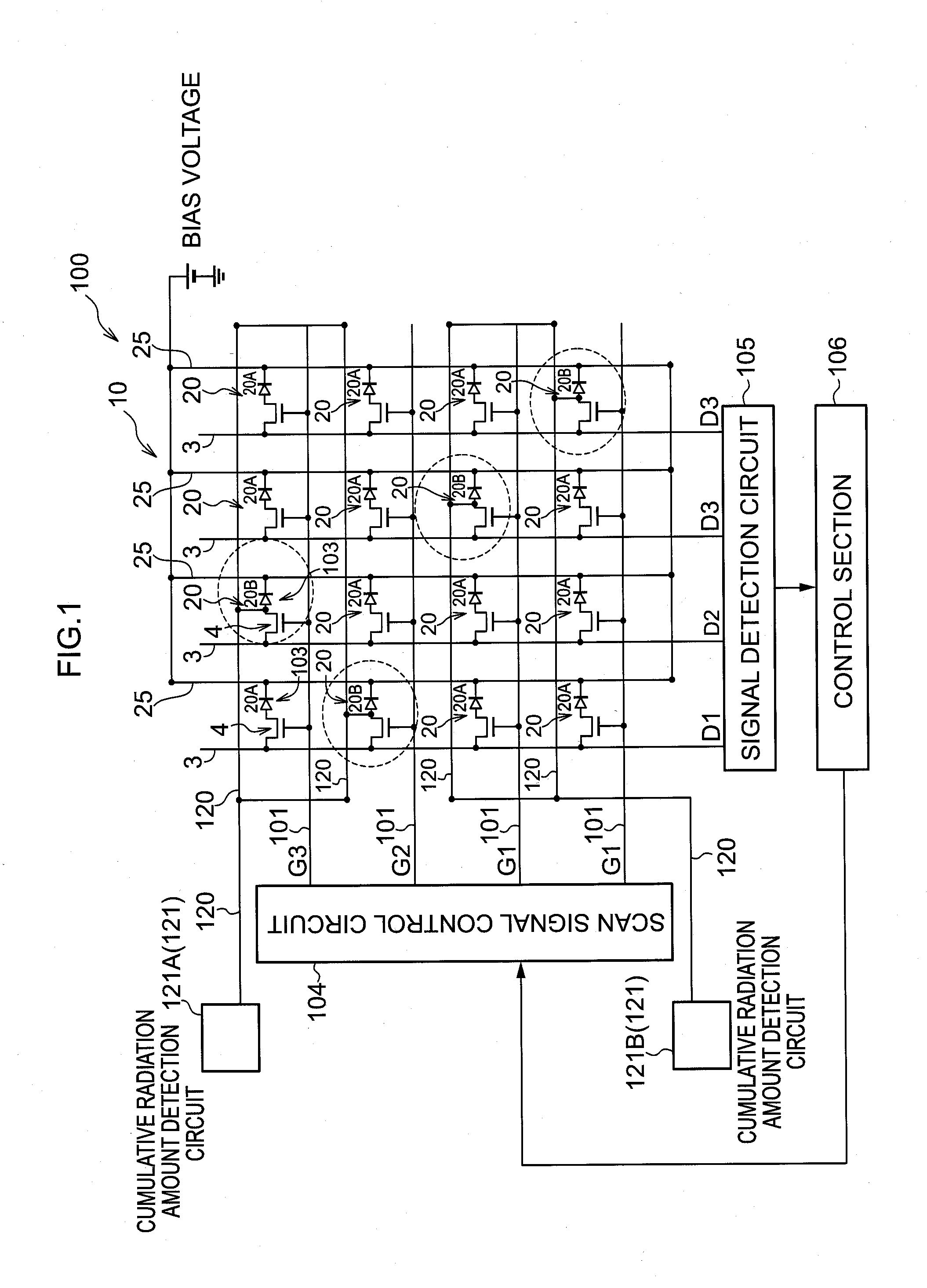
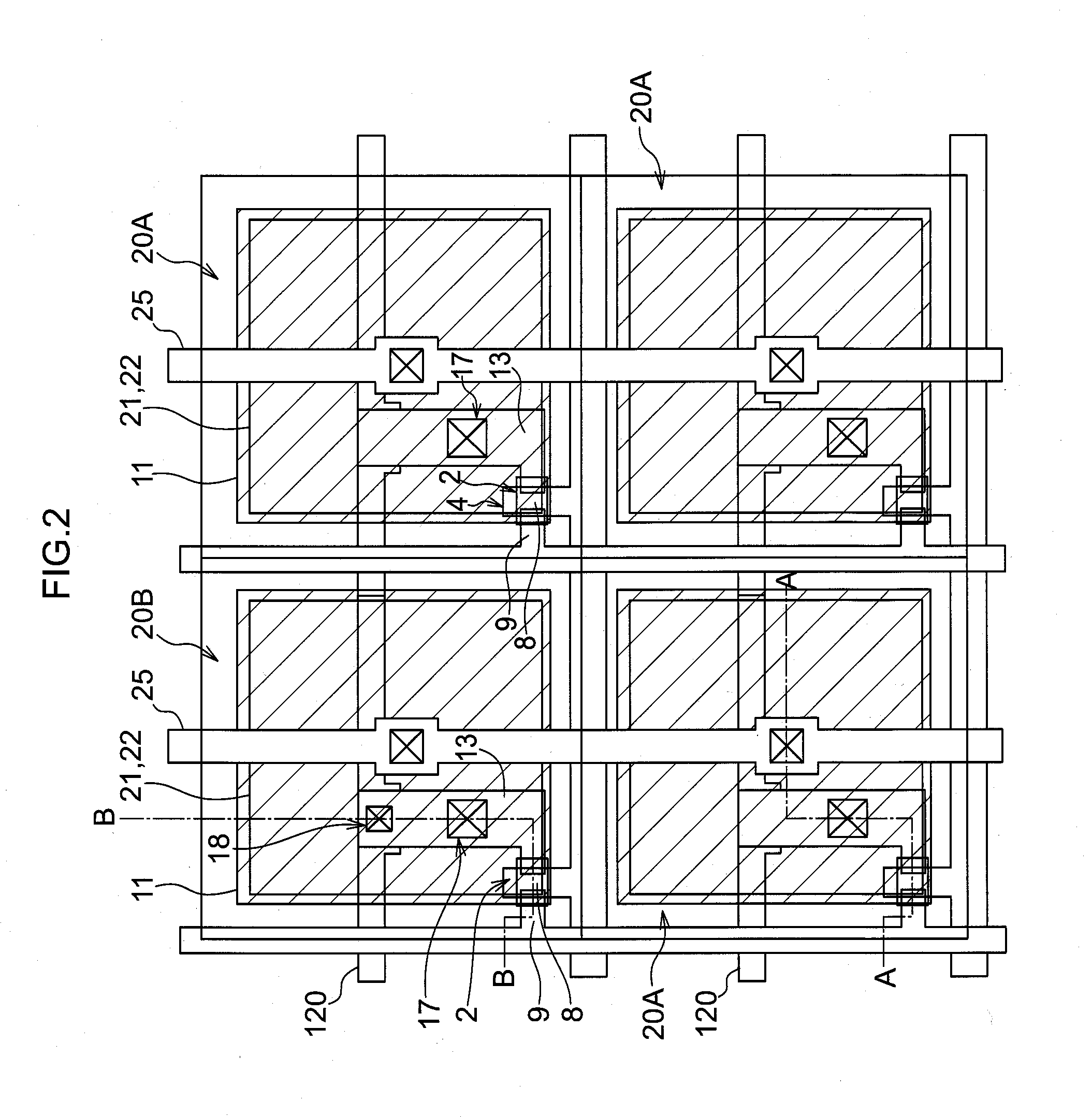
Radiation detector, radiographic imaging device and radiographic imaging system
ActiveUS20130009069A1Good precisionEasy to testSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiographyImage system
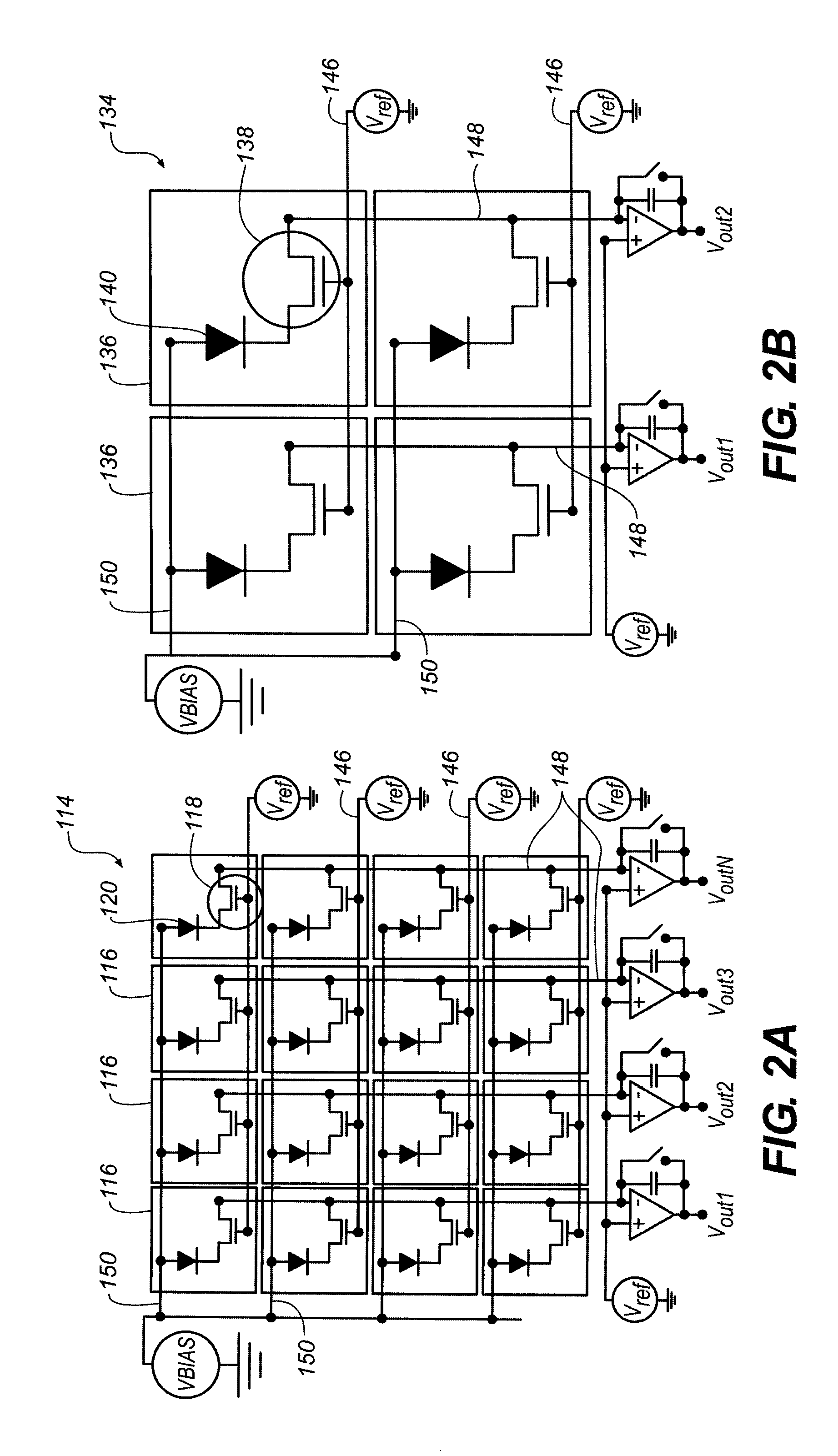
The present invention provides a radiation detector, a radiographic imaging device, and a radiographic image system that may be easily tested and may precisely detect radiation. Namely, pixels each includes a sensor portion A and a sensor portion B. In imaging pixels, the sensor portion A and the sensor portion B are connected by a connection line, and charges generated in the sensor portion A and in the sensor portion B are read by a TFT switch and output to a signal line. In radiation detection pixels, charges generated in the sensor portion A are read by a TFT switch and output to a signal line. Further, in the radiation detection pixels, the sensor portion B and the signal line are directly connected by a connection line, and the charges generated in the sensor portion B are output to the signal line as they arise.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
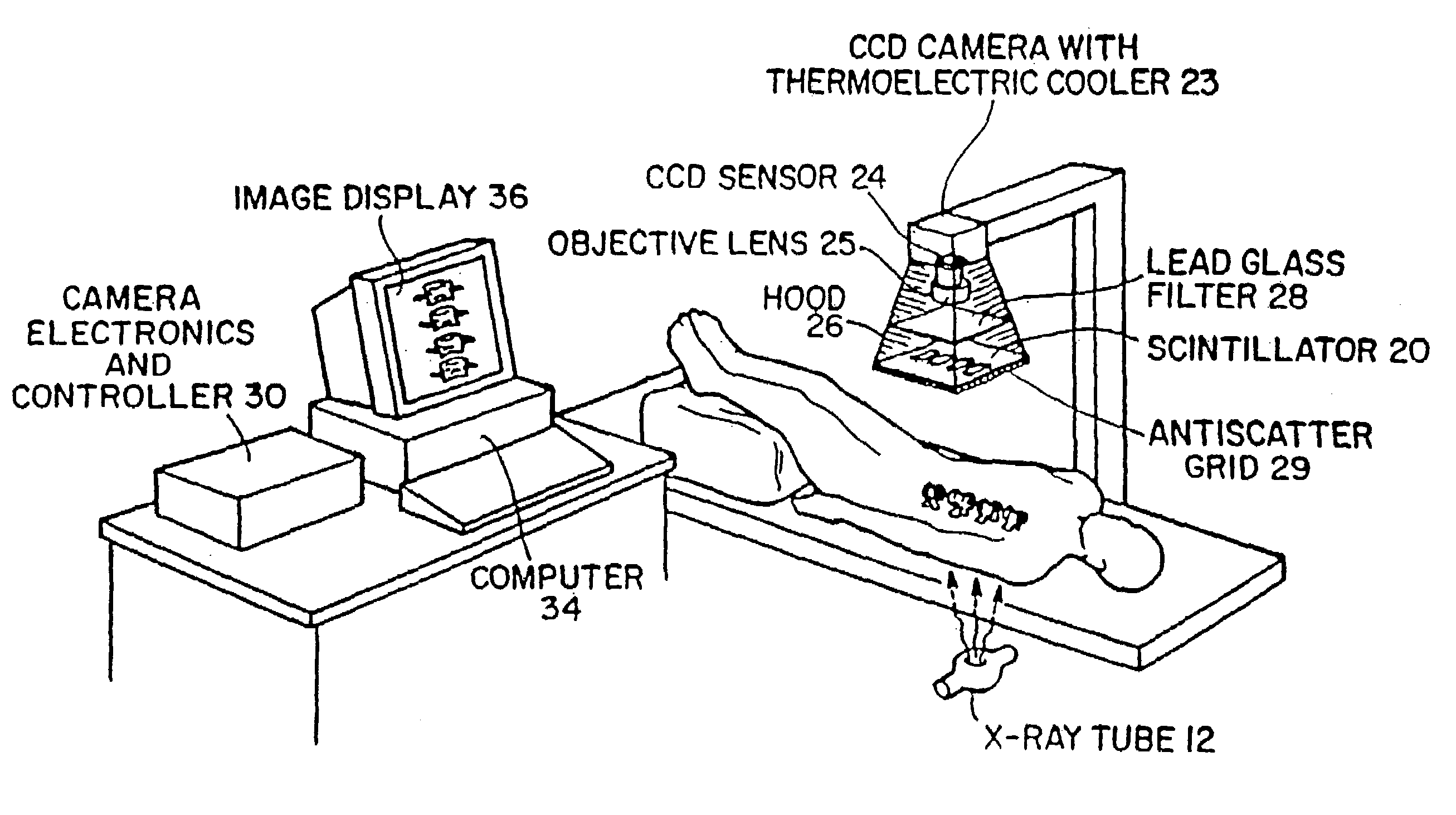
System for quantitative radiographic imaging
InactiveUS7330531B1Reduce and eliminate scattered radiationSuitable for applicationTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayDual energy
A system for spectroscopic imaging of bodily tissue in which a scintillation screen and a charged coupled device (CCD) are used to accurately image selected tissue. Applications include the imaging of radionuclide distributions within the human body or the use of a dual energy source to provide a dual photon bone densitometry apparatus that uses stationary or scanning acquisition techniques. An x-ray source generates x-rays which pass through a region of a subject's body, forming an x-ray image which reaches the scintillation screen. The scintillation screen reradiates a spatial intensity pattern corresponding to the image, the pattern being detected by a CCD sensor. The image is digitized by the sensor and processed by a controller before being stored as an electronic image. A dual energy x-ray source that delivers two different energy levels provides quantitative information regarding the object being imaged using dual photon absorptiometry techniques. Dual scintillation screens can be used to simultaneously generate images of low-energy and high-energy x-ray patterns. Each image is directed onto an associated respective CCD or amorphous silicon detector to generate individual electronic representations of the separate images.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS MEDICAL CENT
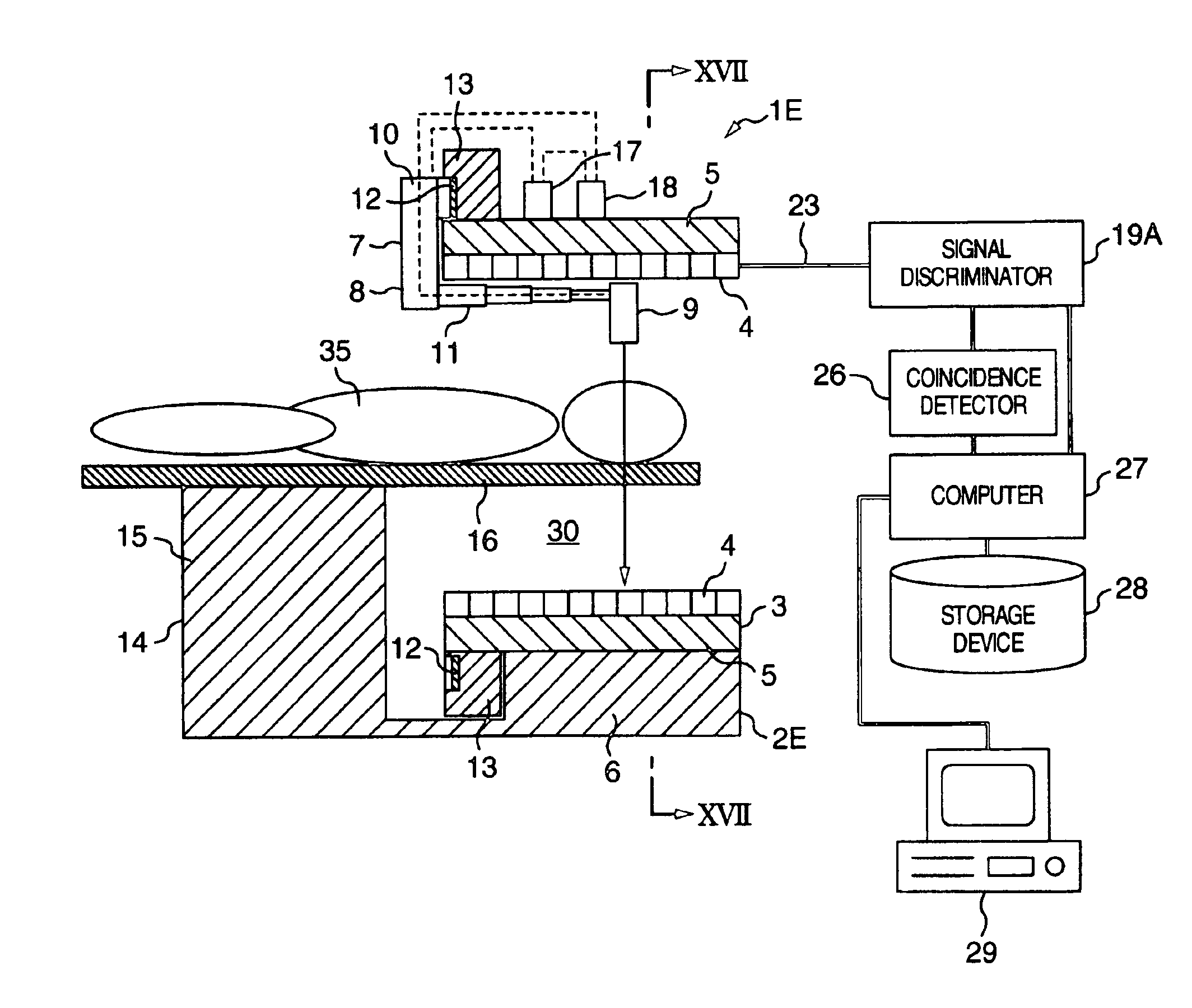
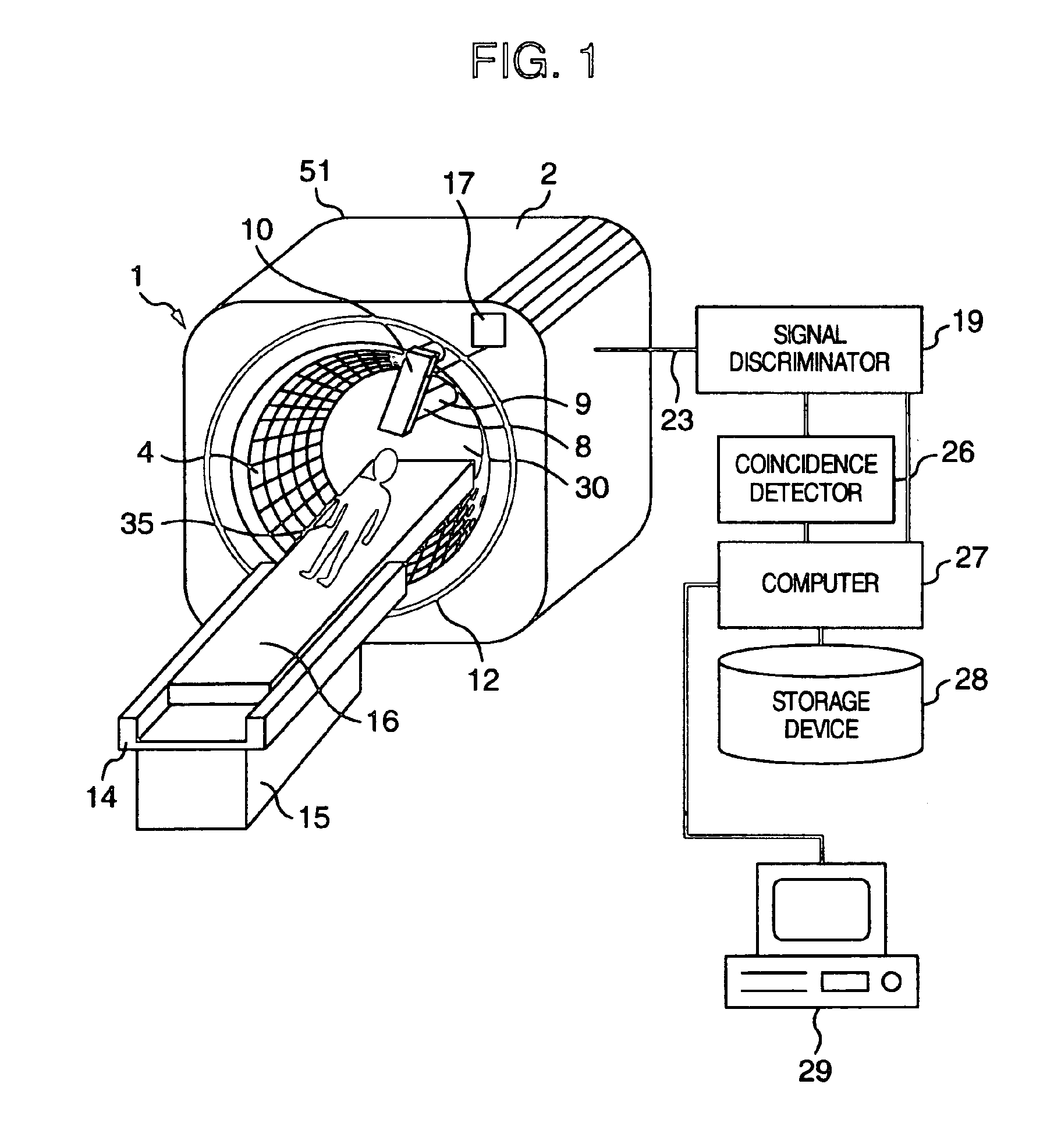
Method of radiographic imaging for three-dimensional reconstruction, and a computer program and apparatus for implementing the method
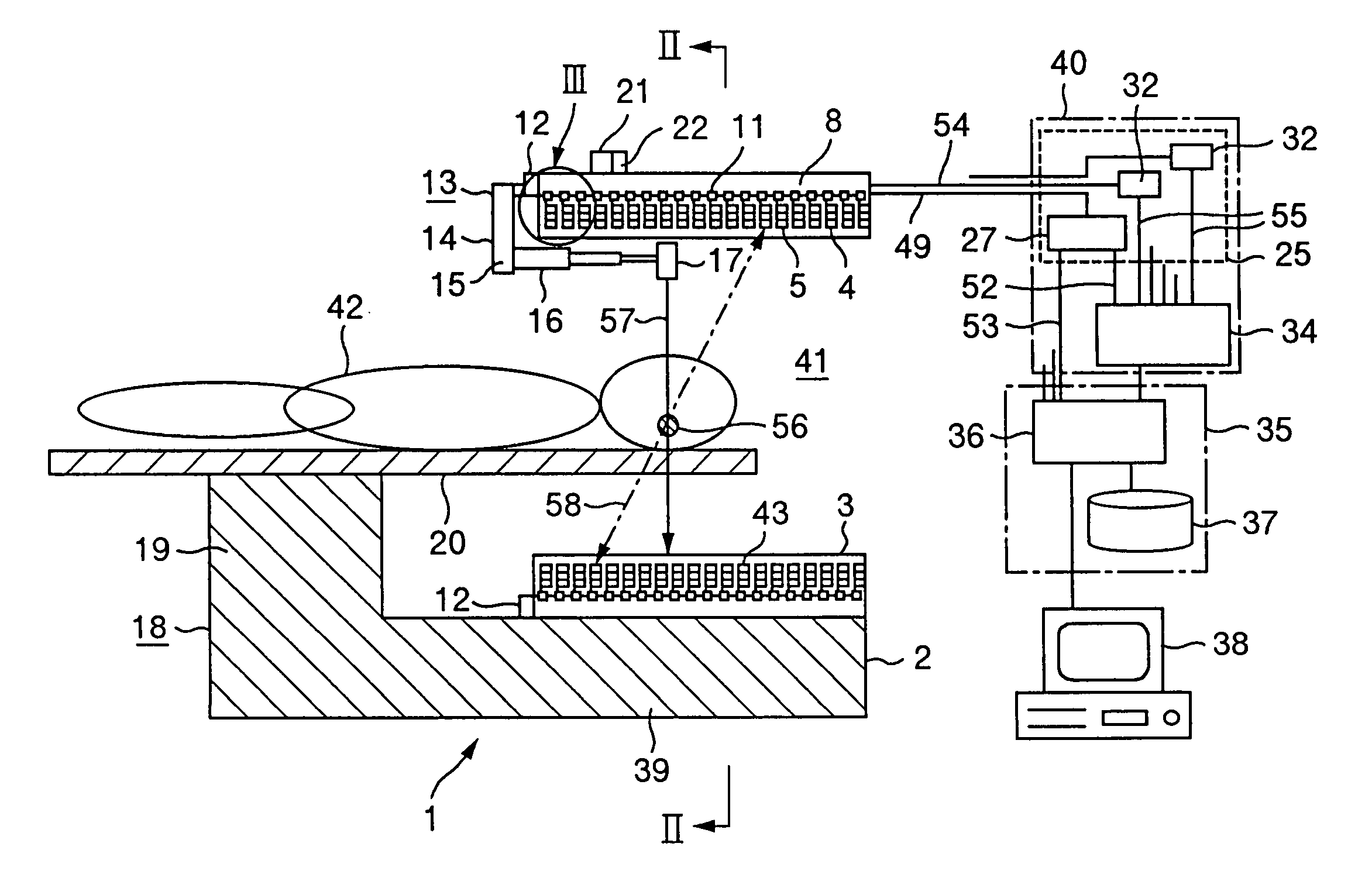
ActiveUS7639866B2Quick and easy to recover shapeImage enhancementImage analysisGeometric modelingThree dimensional shape
Owner:EOS IMAGING
Sterile radiological imaging unit drape and method of providing a sterile surface therewith
A surgical radiological C-arm imaging unit drape configured to provide a sterile outer surface about an end portion of a C-arm imaging unit and method of providing a sterile surface about an end of a C-arm imaging unit is provided. The drape includes a flexible enclosure having an upper wall with a pair of sidewalls and a rear side extending downwardly from the upper wall. The upper wall and the side walls are extendible between expanded and collapsed positions. When in the expanded position, a pocket sized for receipt of the end portion of the imaging unit beneath the upper wall is formed. The upper wall has a sterile outer surface configured to face away from and overlie the end portion of the imaging unit to maintain sterility in a sterile zone above an operating table. When in the collapsed position, the sterile outer surface shielded from external contamination.
Owner:TIDI PROD LLC
Radiographic imaging device and radiographic imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20110180717A1Improve image qualityEasy to detectTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityControl signal
The present invention provides a radiographic imaging device including: plural pixels disposed in a matrix, each pixel including a sensor section that generates charges based on irradiation of radiation, or on illumination of light that has been converted from radiation; plural scan lines through which a control signal flows for switching switch elements included in pixels that are employed as radiographic imaging pixels out of the plural pixels; plural signal lines through which electrical signal flow corresponding to the charge that has been accumulated in the radiographic imaging pixels according to the switching state of the switch elements; and one or more radiation detection line through which an electrical signal flows corresponding to the charge that has been generated in the sensor sections of the radiation detection pixels out of the plural pixels.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
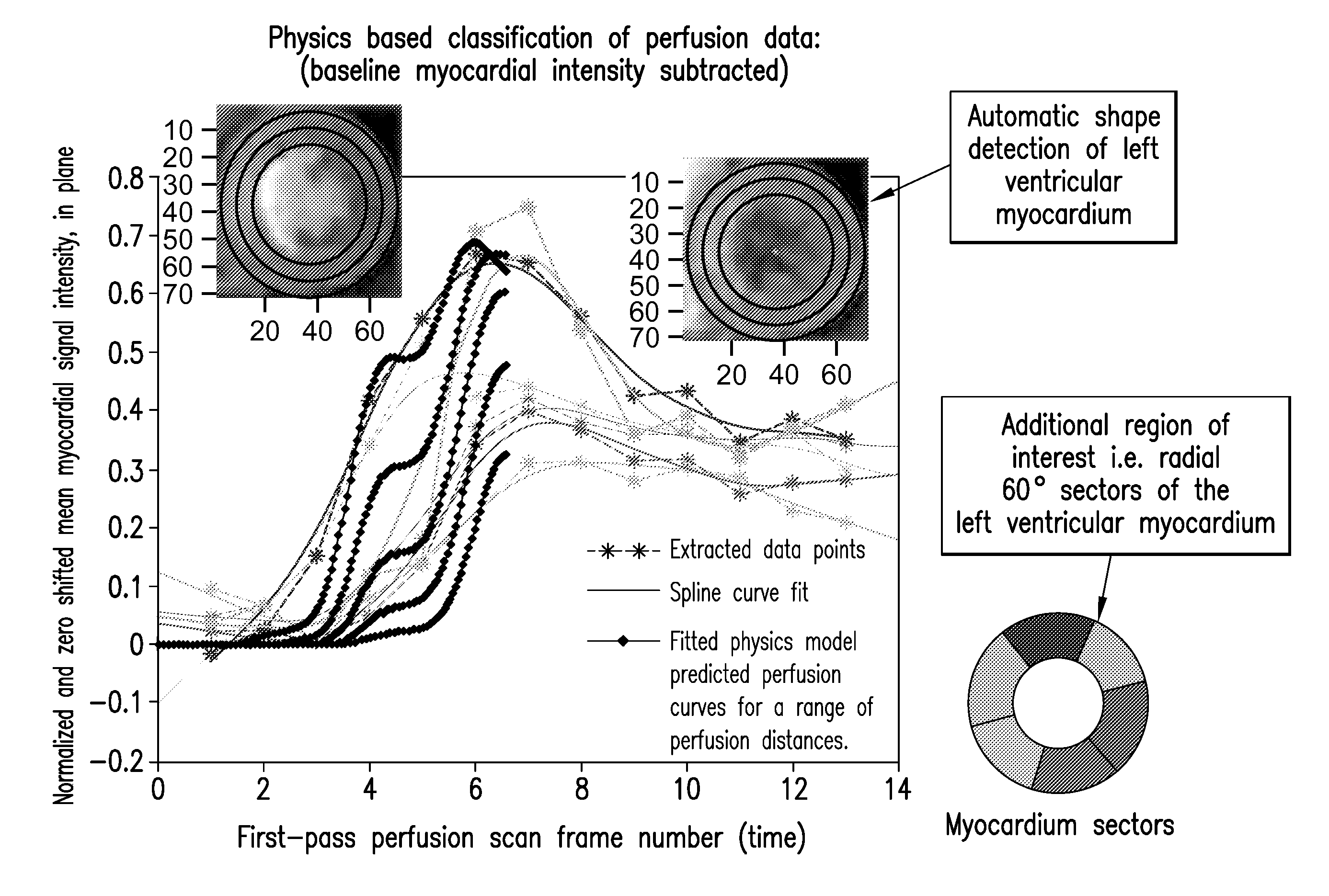
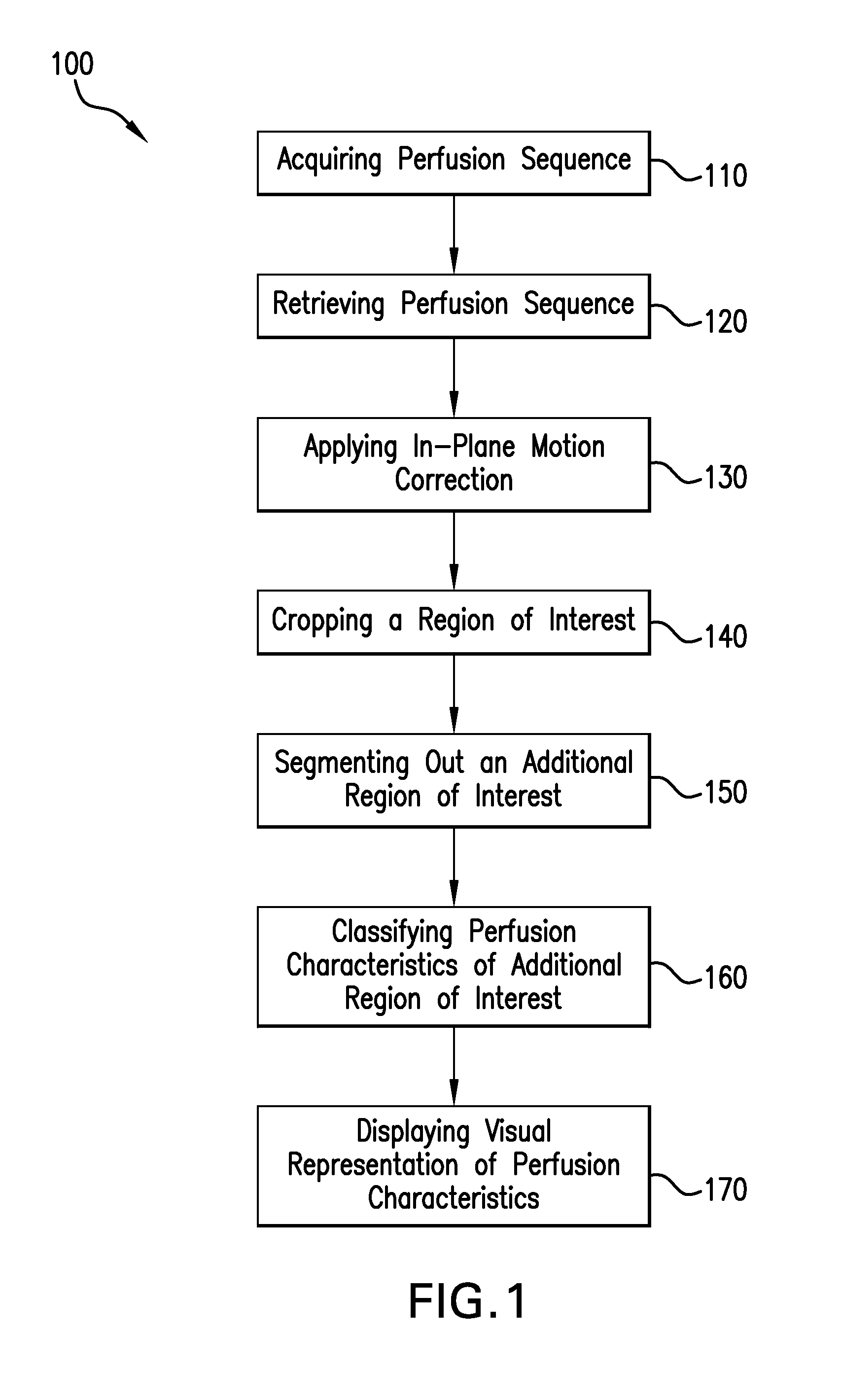
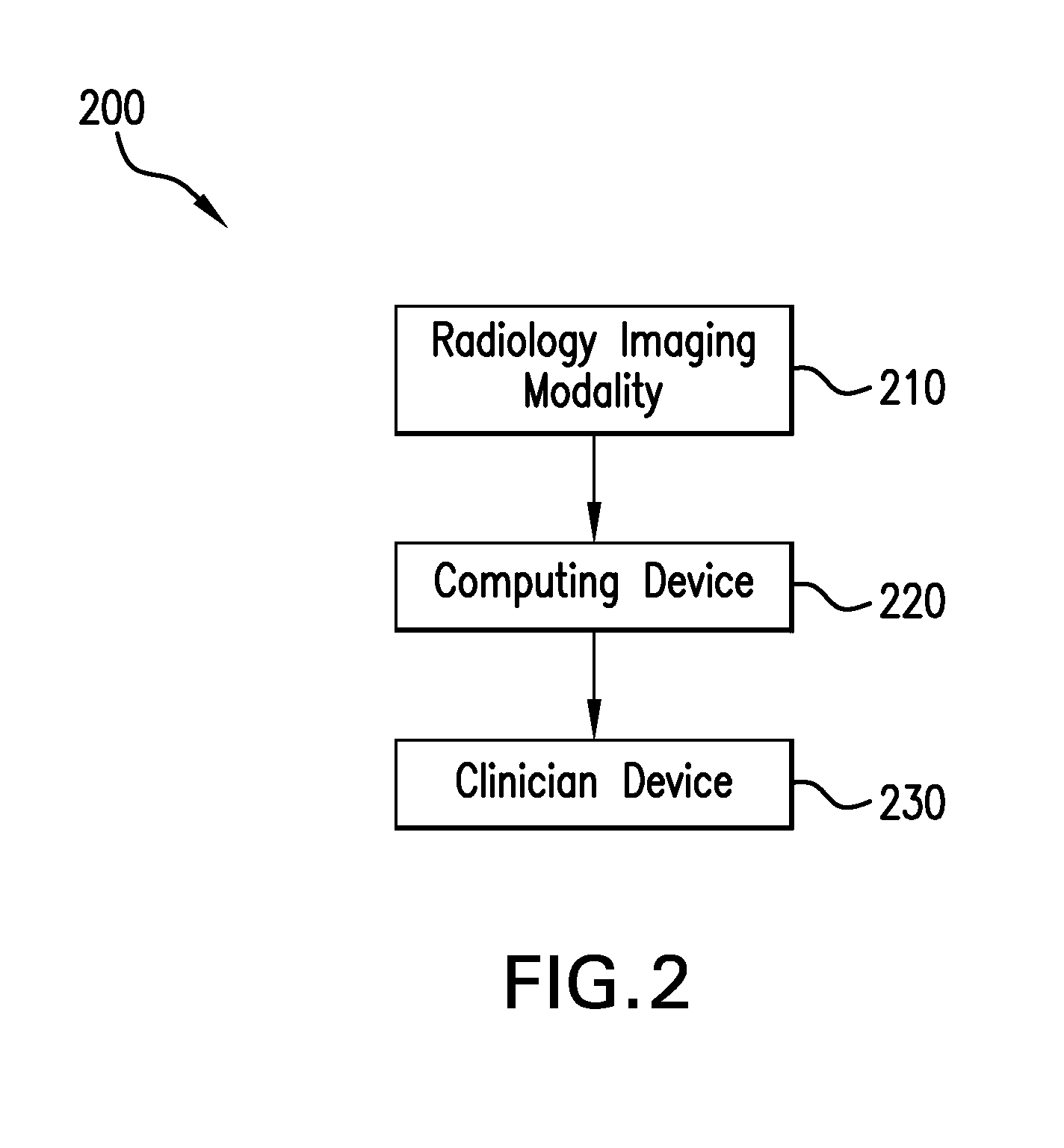
Physics based image processing and evaluation process of perfusion images from radiology imaging
ActiveUS20120323118A1Accurate detectionBlood flow measurement devicesHealth-index calculationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPhysics based
A process and a system for assisting a clinician in identification and evaluation of perfusion characteristics of an organ are disclosed. The process and system may be used to extend clinical diagnosis capabilities by augmenting the ability to analyze perfusion images acquired from a radiology imaging modality through the use of the quantification technology as described. Classification of perfusion characteristics of a region of interest is facilitated through the use of a quantitative spatial perfusion characteristics map. The map is generated by a computing device which applies at least one physics-based image processing technique. This map is displayed on a clinician device for review by the clinician to assist in the spatial identification of perfusion abnormalities.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
Telemetrically controlled band for regulating functioning of a body organ or duct, and methods of making, implantation and use
InactiveUS7901419B2Accurate degreeDesired level of constrictionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesObesity treatmentBody organsEngineering
Apparatus and methods are provided comprising an implantable non-hydraulic ring that encircles and provides a controllable degree of constriction to an organ or duct and an external control that powers and controls operation of the ring. The ring includes a rigid dorsal periphery that maintains a constant exterior diameter, and a compliant constriction system that reduces intolerance phenomena. A high precision, energy efficient mechanical actuator is employed that is telemetrically powered and controlled, and maintains the ring at a selected diameter when the device is unpowered, even for extended periods. The actuator provides a reversible degree of constriction of the organ or duct, which is readily ascertainable without the need for radiographic imaging. Methods of use and implantation also are provided.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
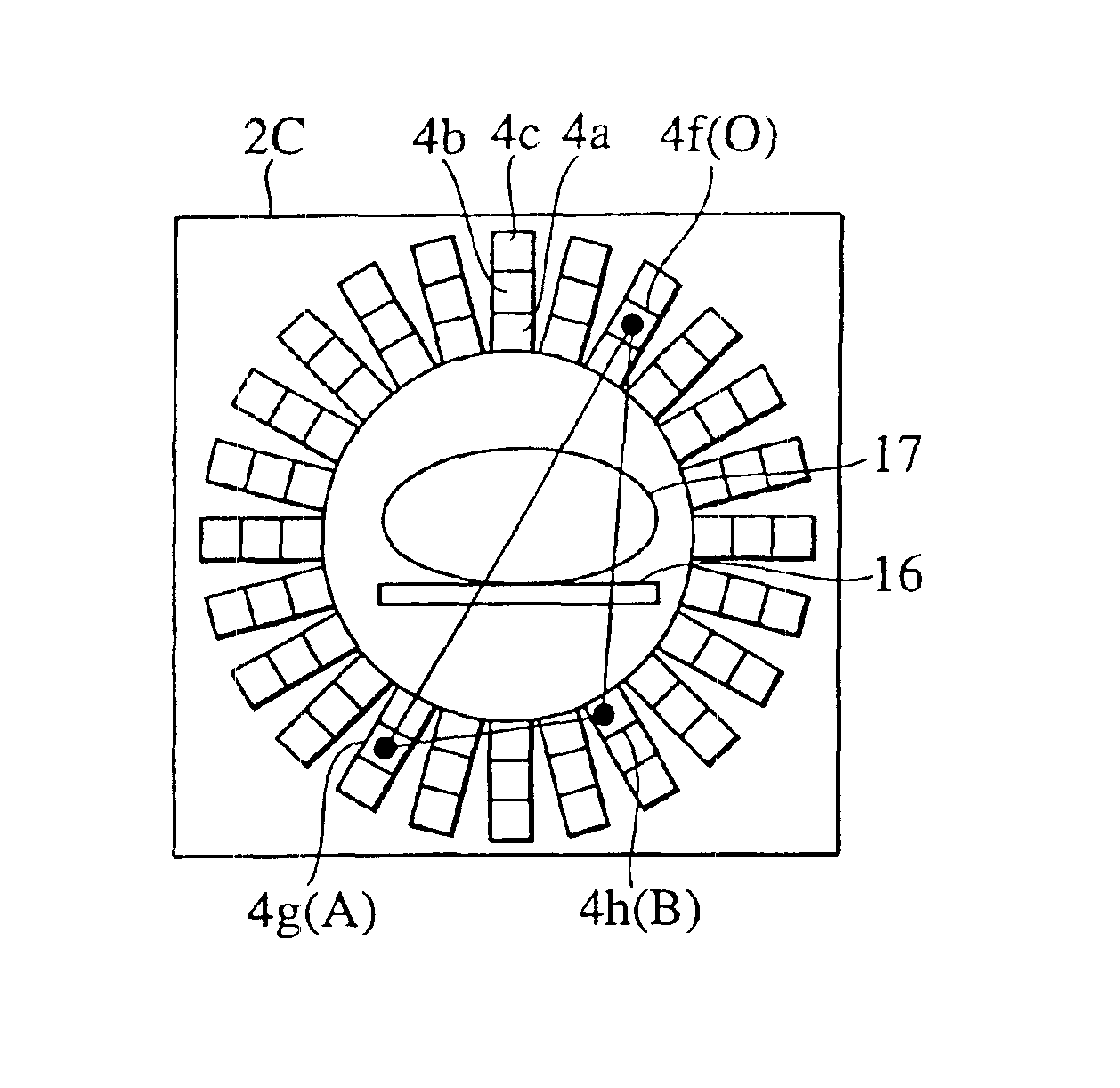
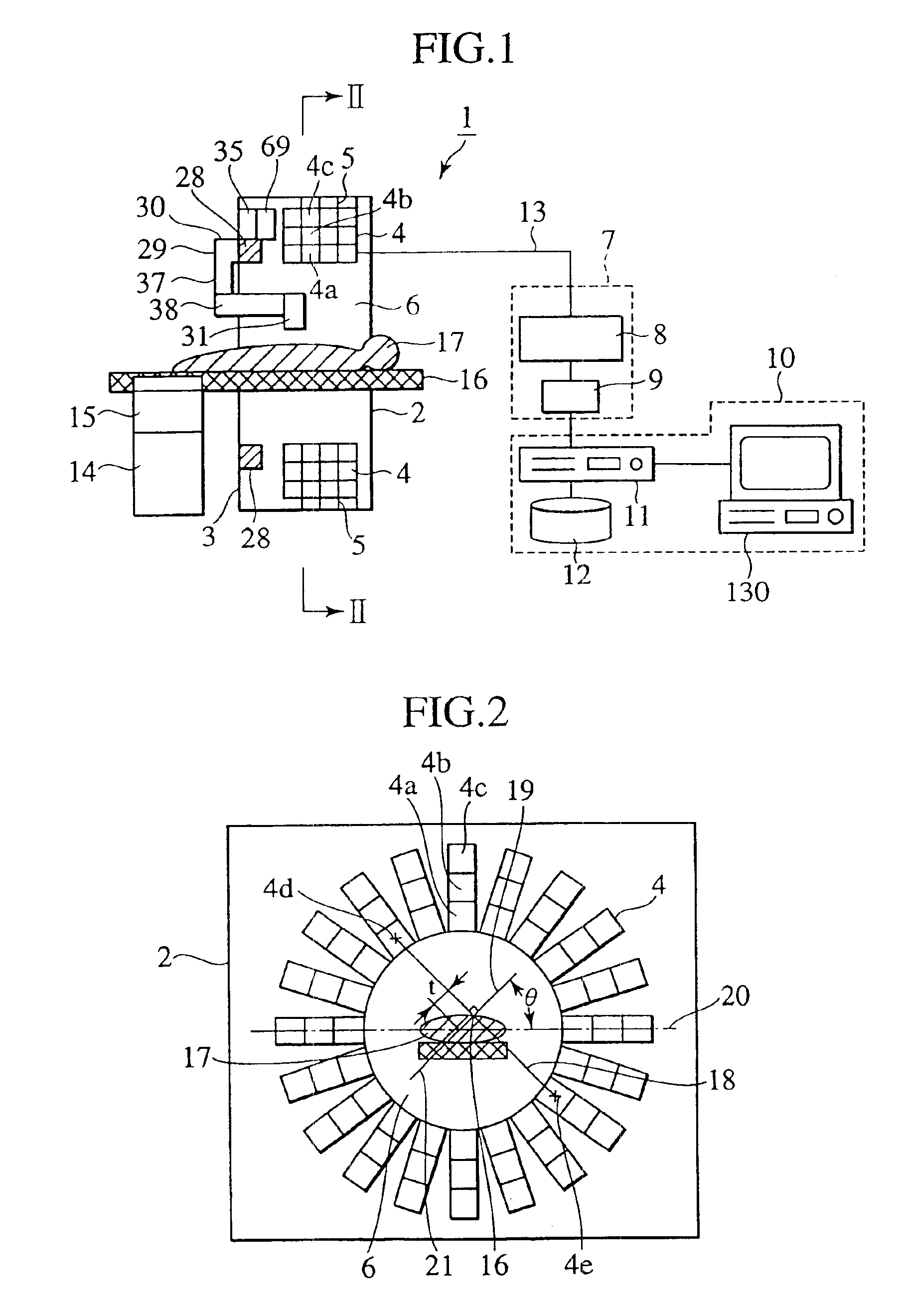
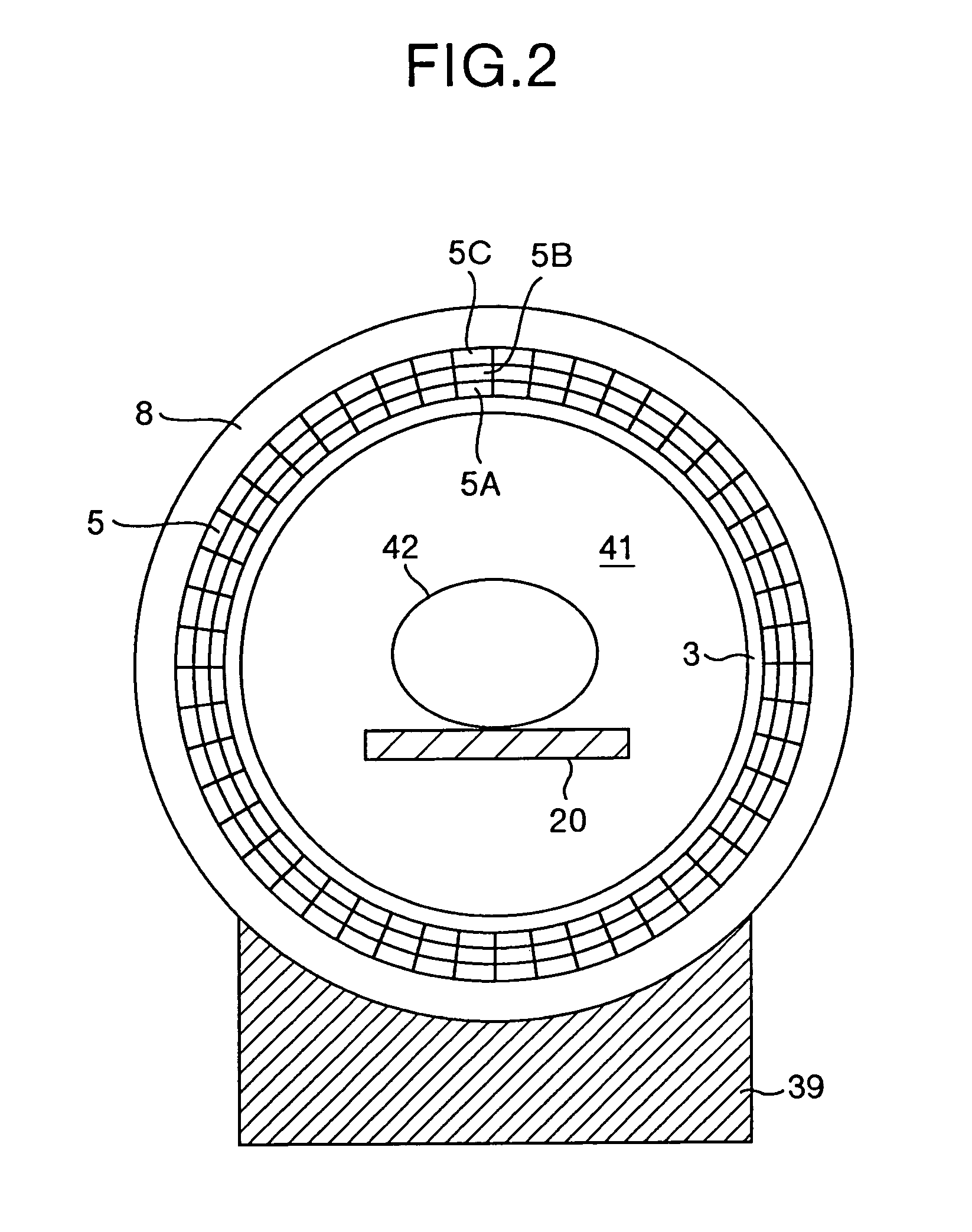
Radiological imaging apparatus
InactiveUS7026622B2High precisionImprove accuracyRadiation/particle handlingSolid-state devicesTomographic imageMedical treatment
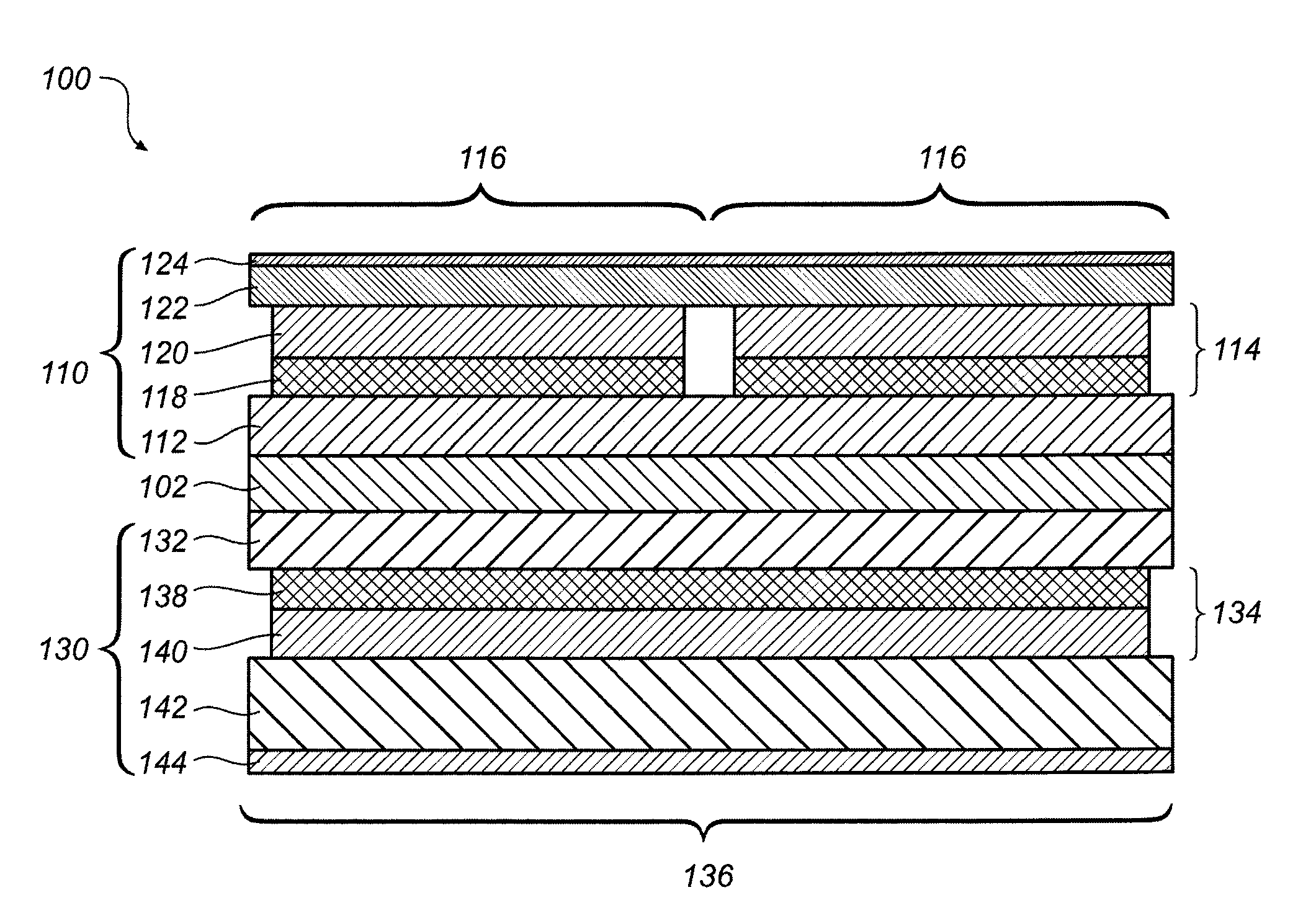
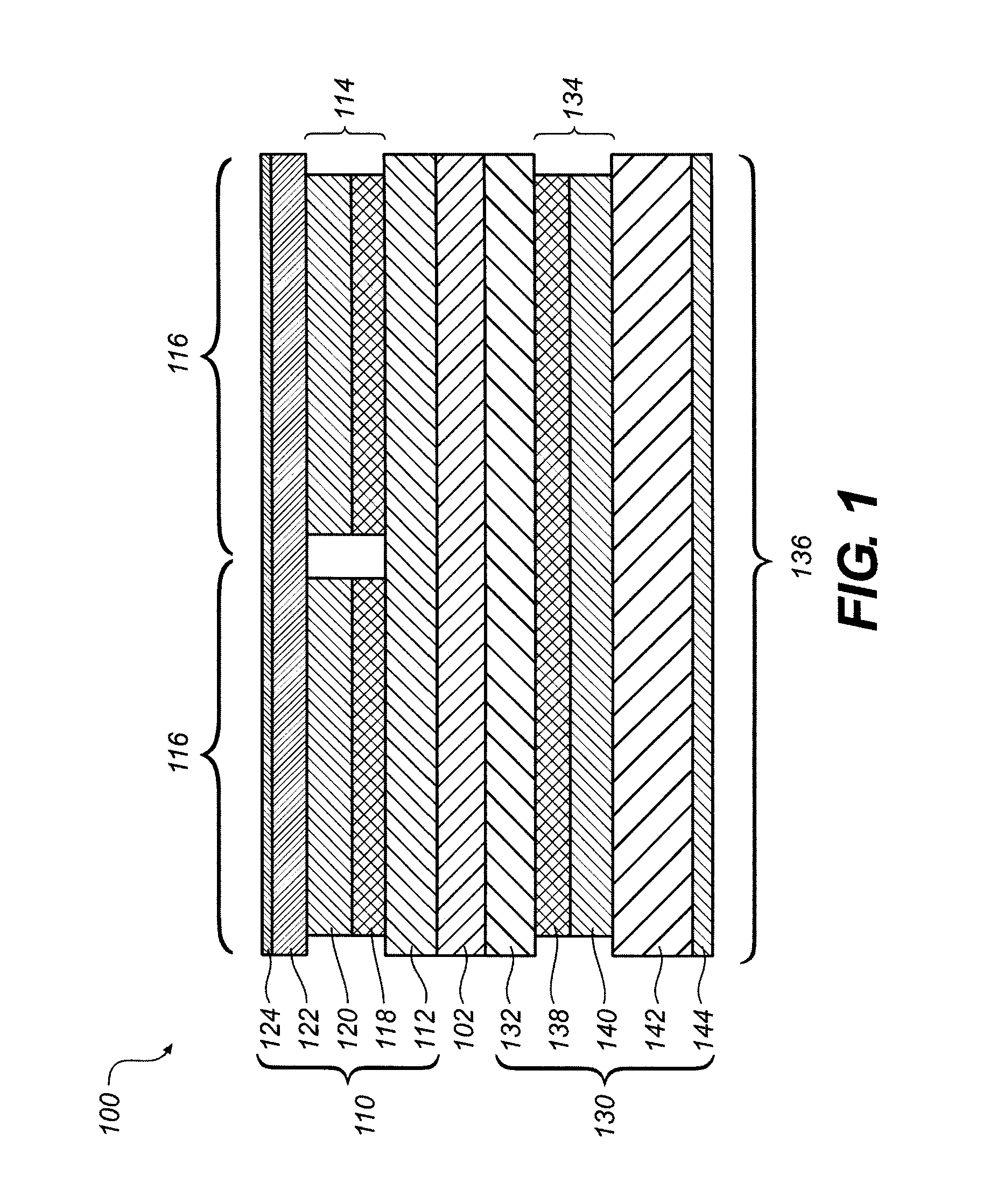
A radiological imaging apparatus of the present invention comprises an image pickup device and a medical examinee holding device that is provided with a bed. The image pickup device includes a large number of radiation detectors and radiation detector support plates. A large number of radiation detectors are mounted around the circumference of a through-hole and arranged in the axial direction of the through-hole. The radiation detectors are arranged in three layers formed radially with respect to the center of the through-hole and mounted on the lateral surfaces of the radiation detector support plates. Since the radiation detectors are not only arranged in the axial direction and circumferential direction of the through-hole but also arrayed in the radial direction, it is possible to obtain accurate information about a γ-ray arrival position in the radial direction of the through-hole (the positional information about a radiation detector from which a γ-ray image pickup signal is output). The use of accurate information about γ-ray arrival increases the tomogram accuracy. As a result, the present invention enhances the tomogram accuracy, that is, the PET examination accuracy.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Dual screen radiographic detector with improved spatial sampling
ActiveUS20110303849A1Need be addressMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementScintillatorPhysics
Embodiments of radiographic imaging apparatus and methods for operating the same can include a first scintillator, a second scintillator, a plurality of first photosensitive elements, and a plurality of second photosensitive elements. The plurality of first photosensitive elements receives light from the first scintillator and has first photosensitive element characteristics chosen to cooperate with the first scintillator properties. The plurality of second photosensitive elements are arranged to receive light from the second scintillator and has second photosensitive element characteristics different from the first photosensitive element characteristics and chosen to cooperate with the second scintillator properties. Further, the first scintillator can have first scintillator properties and the second scintillator can have second scintillator properties different from the first scintillator properties.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
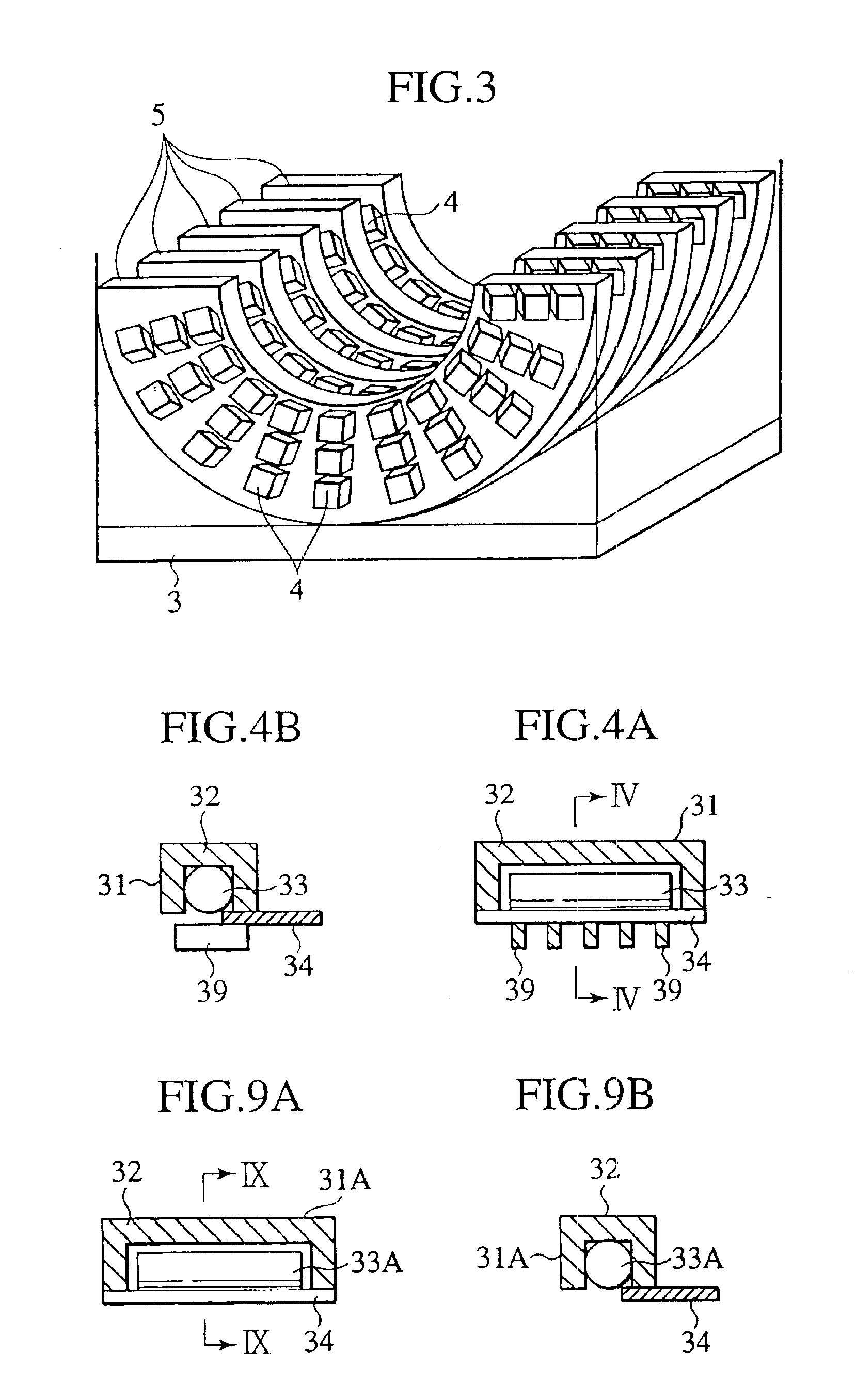
Radiological imaging apparatus
InactiveUS7154989B2Improve accuracyImprove positionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayDetector cell
The image pickup apparatus of the radiological imaging apparatus of the present invention includes many detector units, a ring-shaped detector support member and an X-ray source circumferential transport apparatus. Each of the detector units is attached to the detector support section in a detachable manner. A plurality of radiation detectors provided for the detector units are arranged in three layers in the radius direction of the detector support member and in three columns in the axial direction of the detector support member. Since the radiation detectors are arranged in three layers in the radius direction, it is possible to recognize the detection position of radiation in the radius direction in detail. Furthermore, since the detector units are attached in a detachable manner, it is easy to replace damaged radiation detectors.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com