Patents
Literature
222 results about "Radiation pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
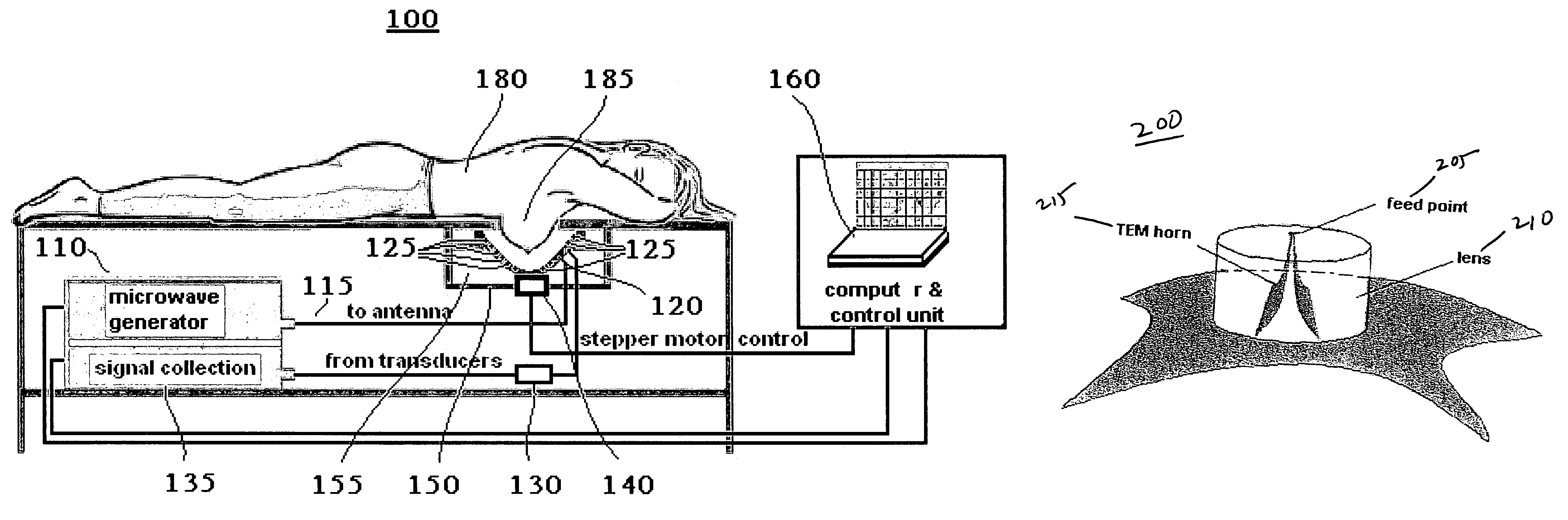
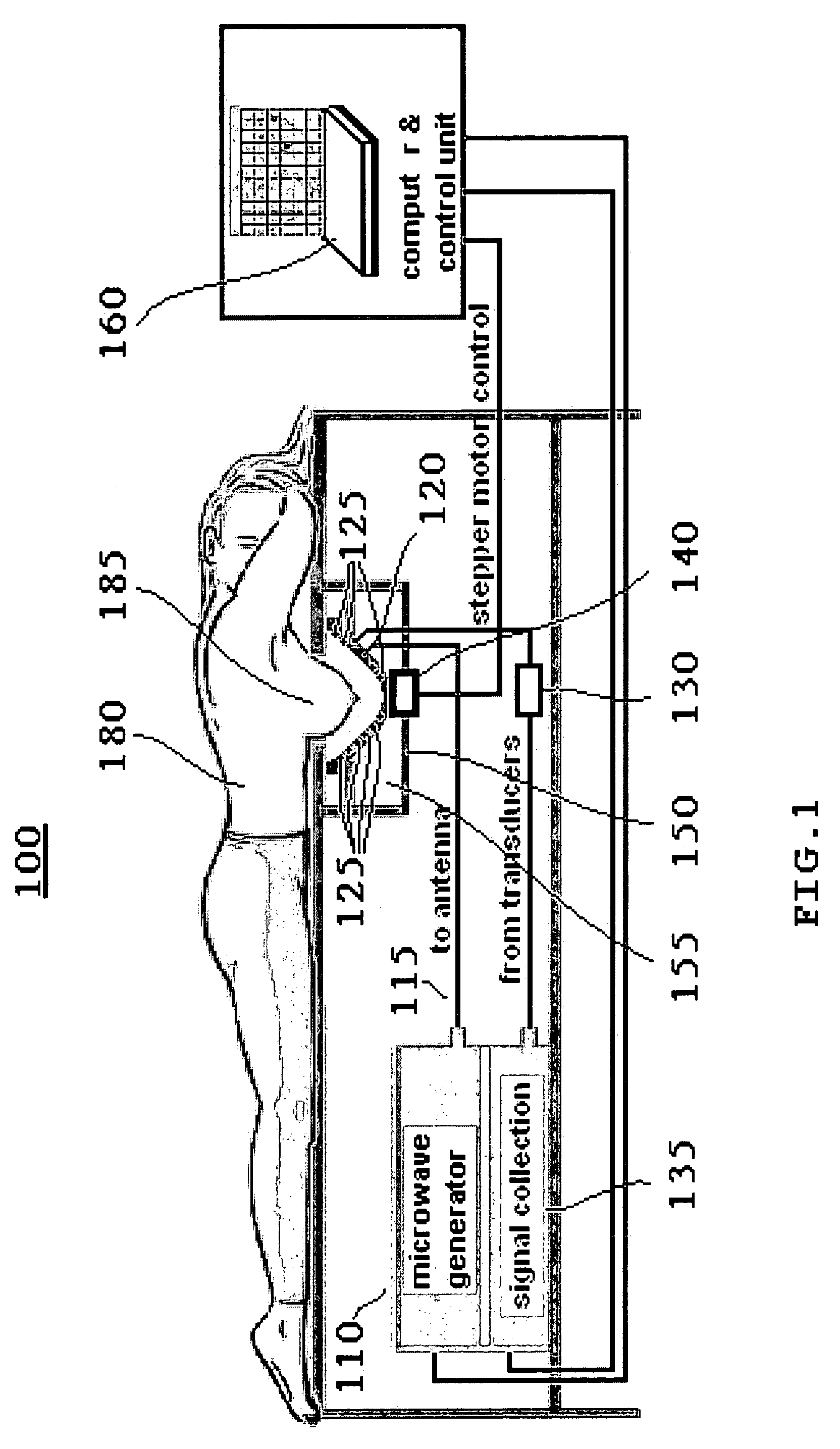
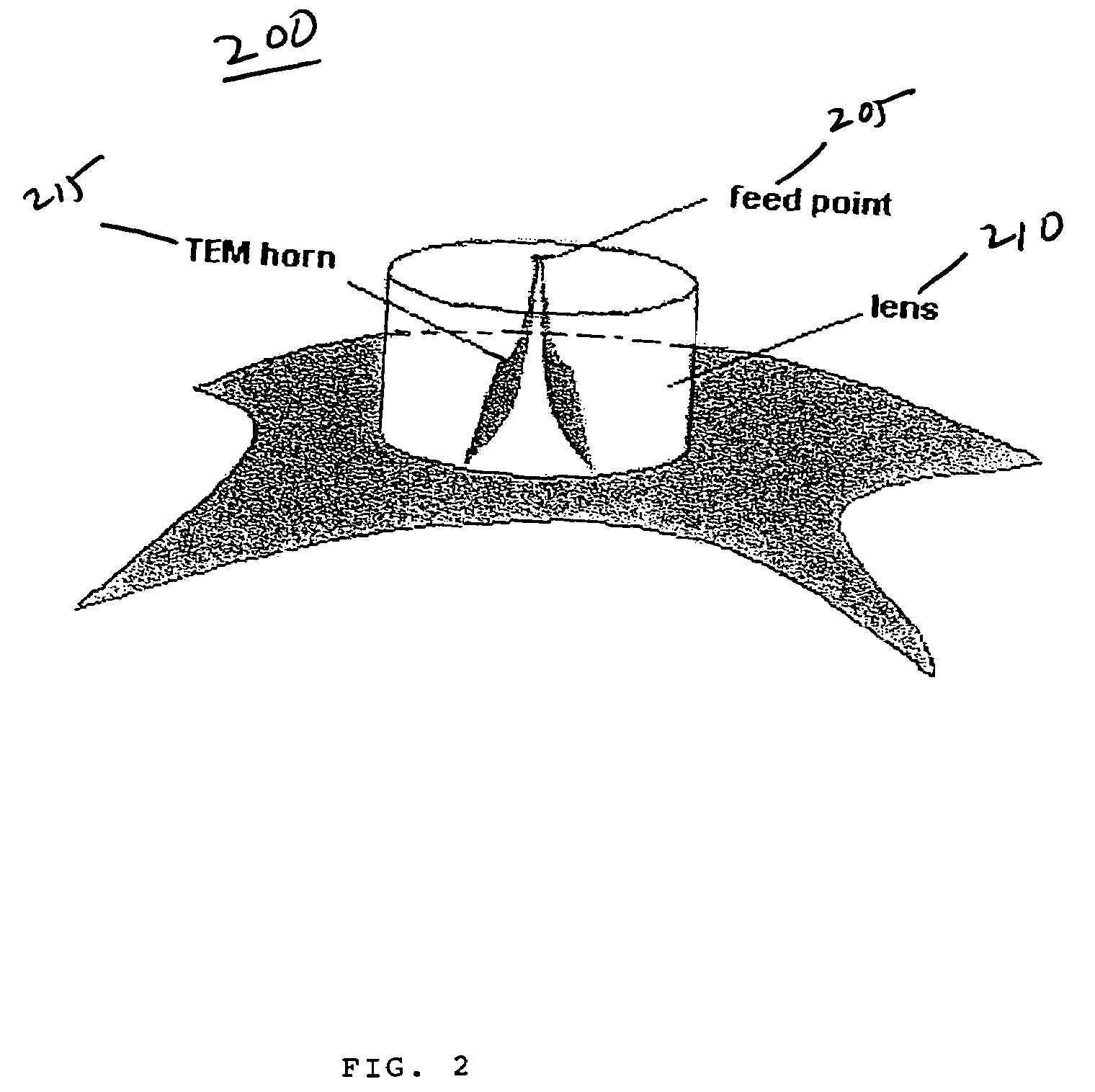
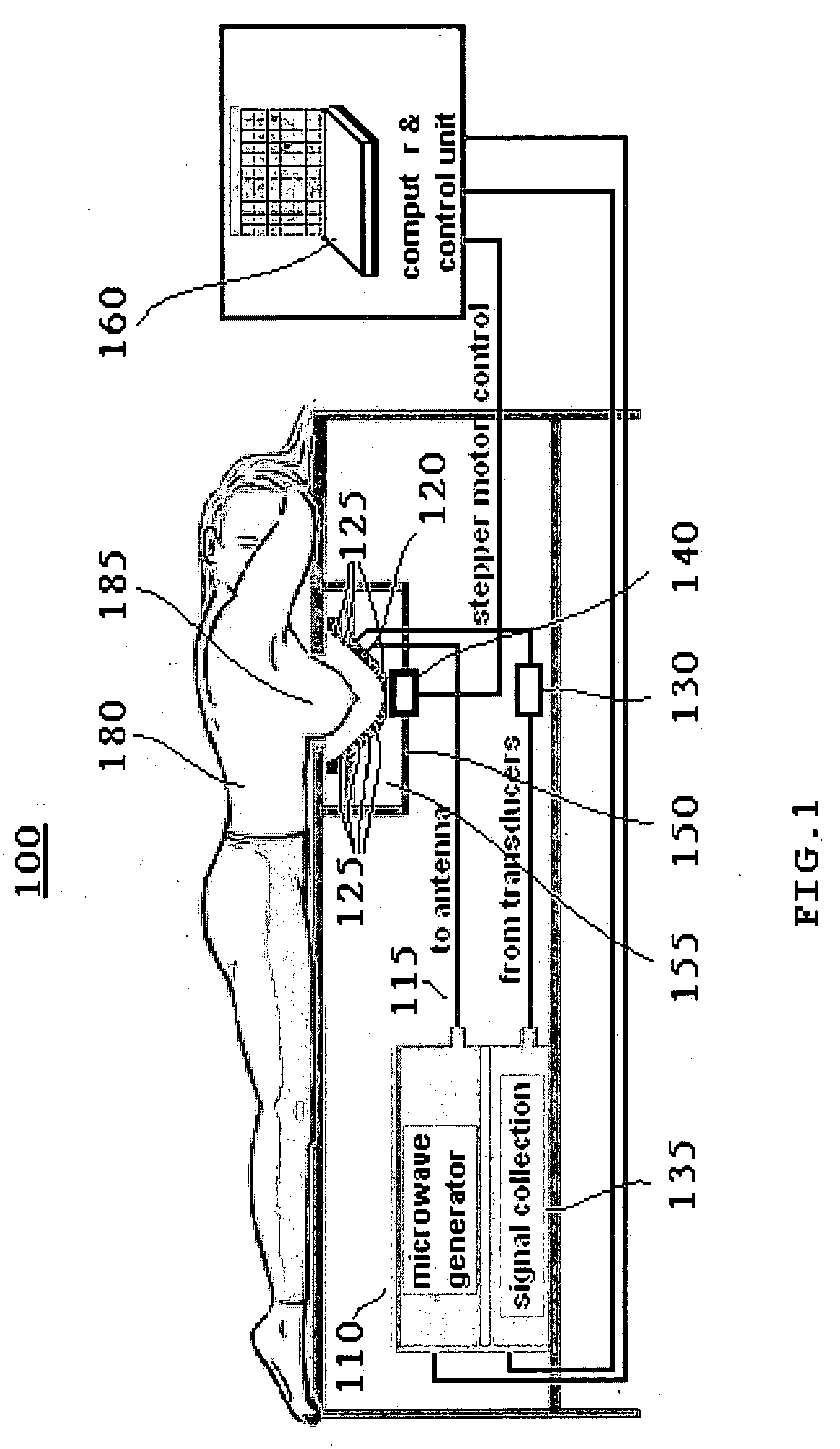
Multi-frequency microwave-induced thermoacoustic imaging of biological tissue
A method and system for examining biological tissue includes the steps of radiating a tissue region with a plurality of microwave radiation pulses. The microwave pulses are swept across a range of microwave frequencies. In response to the swept frequency microwave pulses, the tissue region emits a plurality of thermoacoustic signals. At least one image of the tissue region is formed from the plurality of thermoacoustic signals. The signals can be ultrawideband signals.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
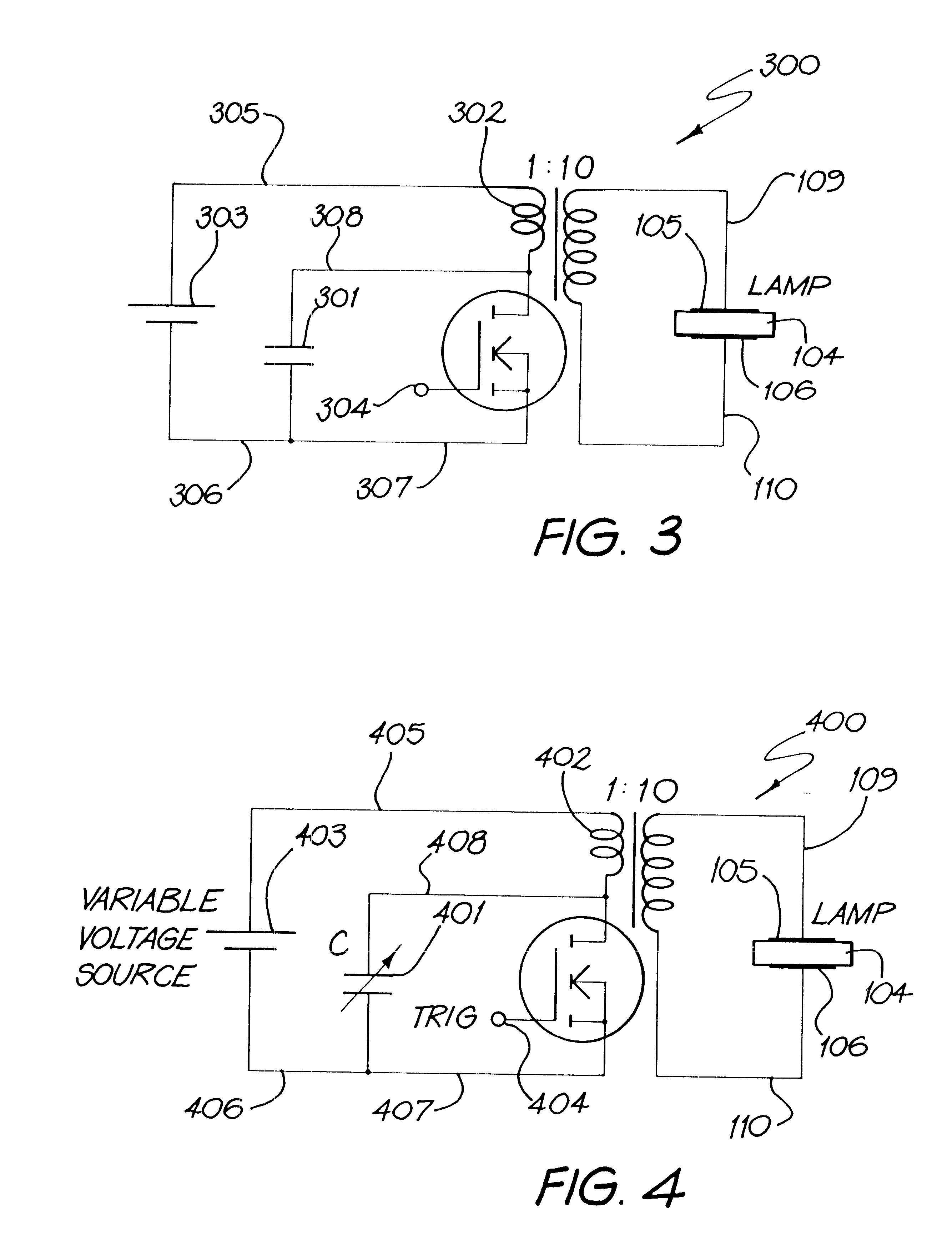
Methods for eyeglass lens curing using ultraviolet light
InactiveUS6022498AControl generationControl releaseOther chemical processesOptical articlesUV curingRadiation pulse
Method and apparatus for making [and coating] a plastic lens is provided. [Oxygen barrier containing photoinitiator is used to cure incompletely cured lens portions. Radiation pulses are used to control lens curing rate. Lens is postcured while in a mold cavity using a conductive heat source.] More particularly, the invention relates to applying alternating periods of ultraviolet light to lens forming composition. Such composition is cured while controlling the rate of heat generation and / or dissipation via manipulation of the duration of the radiation or the cooling in the curing chamber. The ultraviolet light is directed toward the lens forming composition which is preferably disposed in a mold cavity formed by two mold members. The ultraviolet light may be directed in pulses or continuously.
Owner:Q2100
Photoacoustic removal of occlusions from blood vessels
Partial or total occlusions of fluid passages within the human body are removed by positioning an array of optical fibers in the passage and directing treatment radiation pulses along the fibers, one at a time, to generate a shock wave and hydrodynamic flows that strike and emulsify the occlusions. A preferred application is the removal of blood clots (thrombi and emboli) from small cerebral vessels to reverse the effects of an ischemic stroke. The operating parameters and techniques are chosen to minimize the amount of heating of the fragile cerebral vessel walls occurring during this photoacoustic treatment. One such technique is the optical monitoring of the existence of hydrodynamic flow generating vapor bubbles when they are expected to occur and stopping the heat generating pulses propagated along an optical fiber that is not generating such bubbles.
Owner:SELVA MEDICAL +2
Laser cutting of stents and other medical devices
A desired pattern may be cut into a stent preform by impinging a laser beam onto the stent preform. The laser beam is formed using a laser system comprising a resonator cavity for resonating laser radiation, a gain medium contained in the resonator cavity, a pump for periodically pumping the gain medium and an electro-optical modulator in communication with the resonator cavity. The laser system produces a radiation pulse for each pump period. Each radiation pulse is conditioned by suppressing at least a portion of the pulse. The pulse may also be modulated with an electro-optical modulator to produce a pulse train of ordered pulses of radiation. Each pulse train is output from the optical cavity as an output laser beam which is directed at the stent preform to cut a desired pattern in the stent preform.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
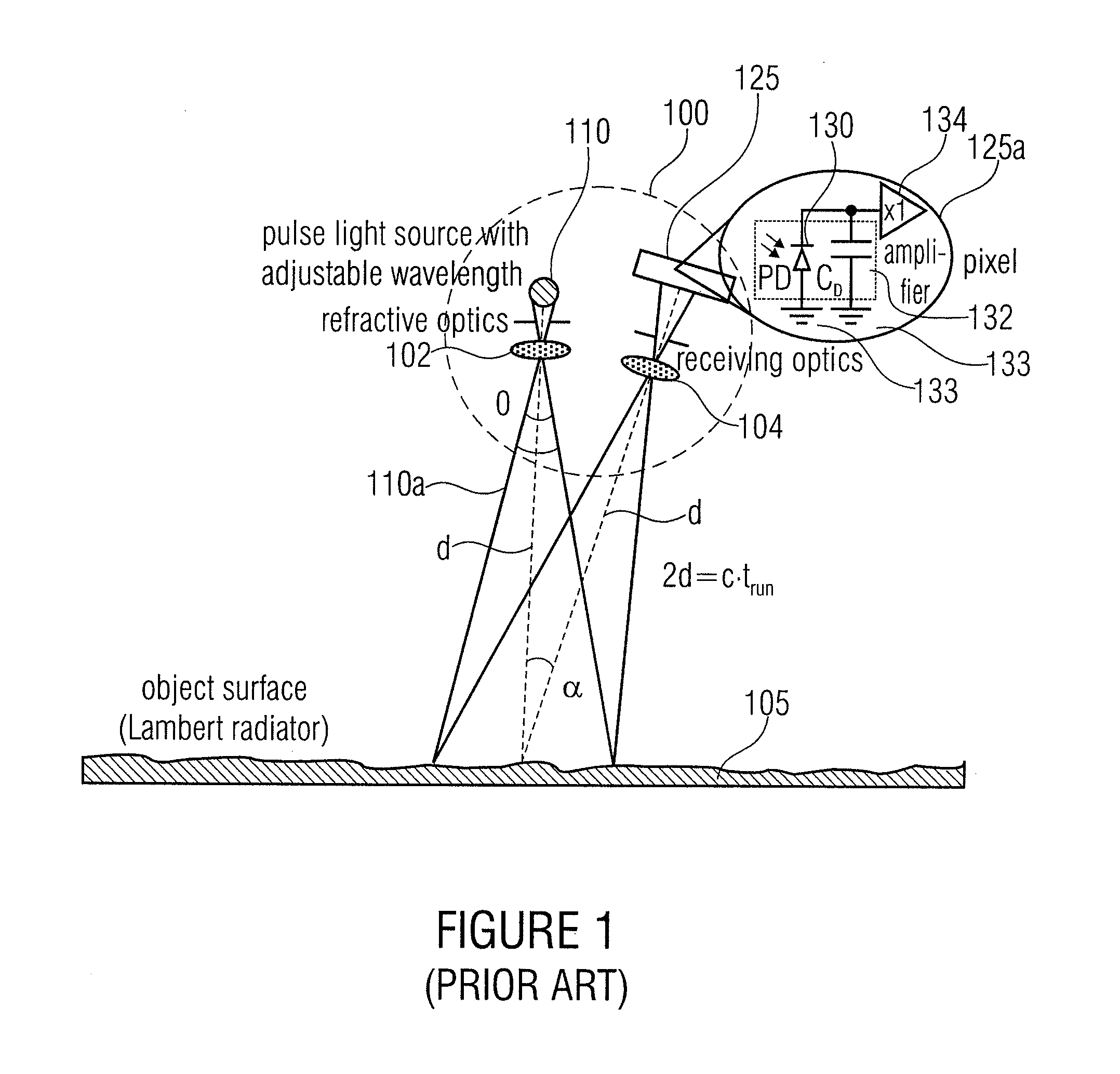
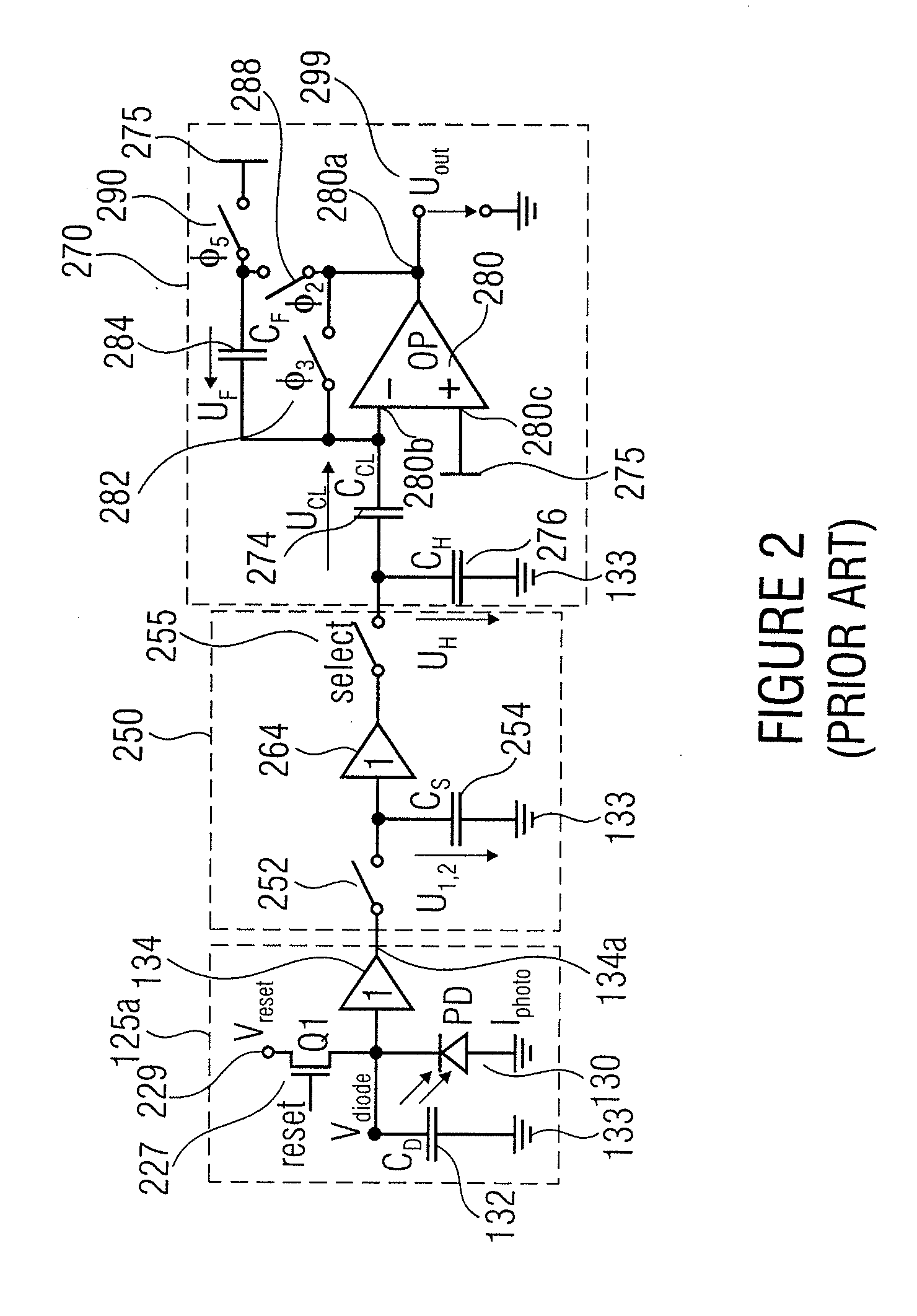
Concept for optical distance measurement
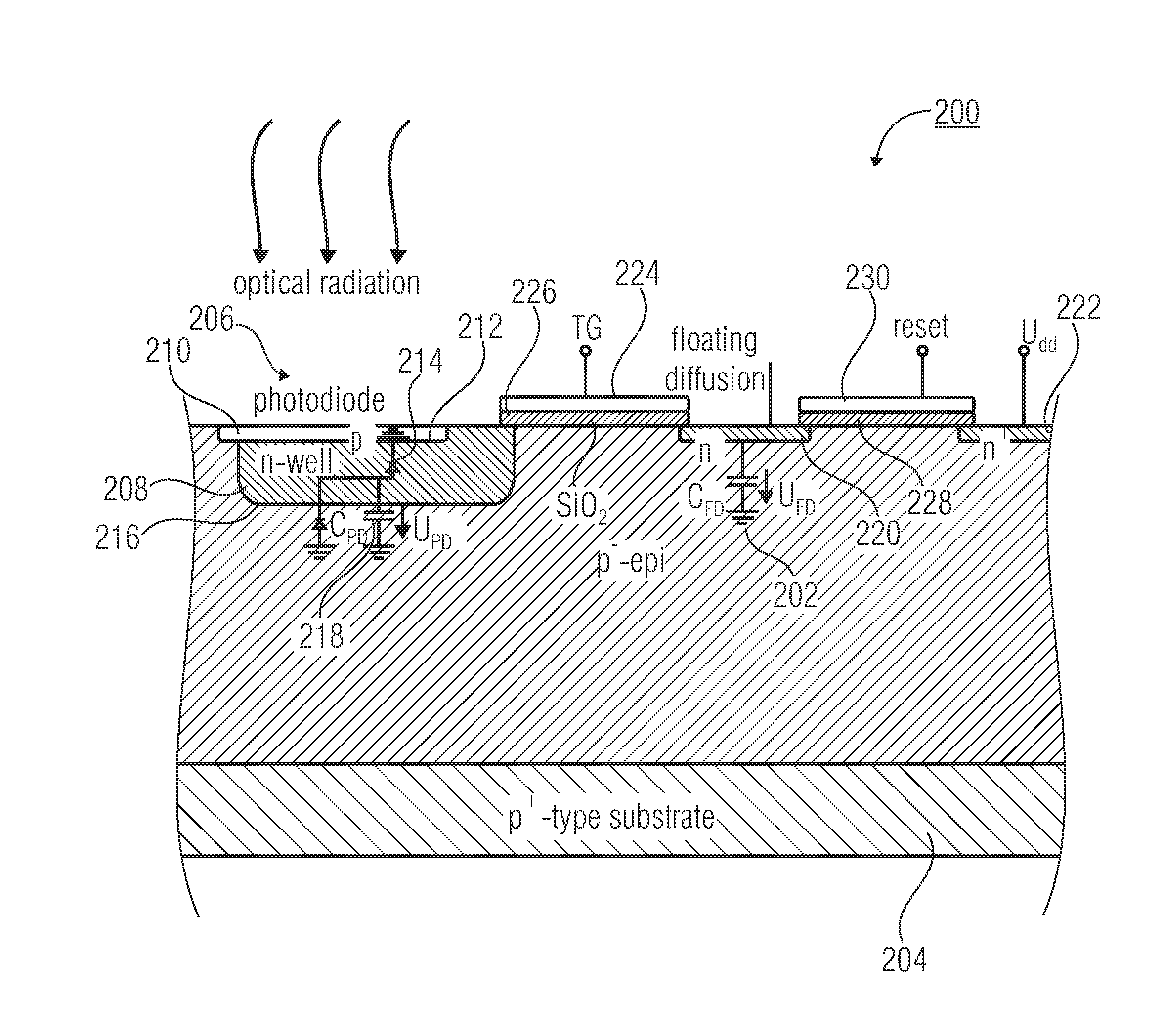
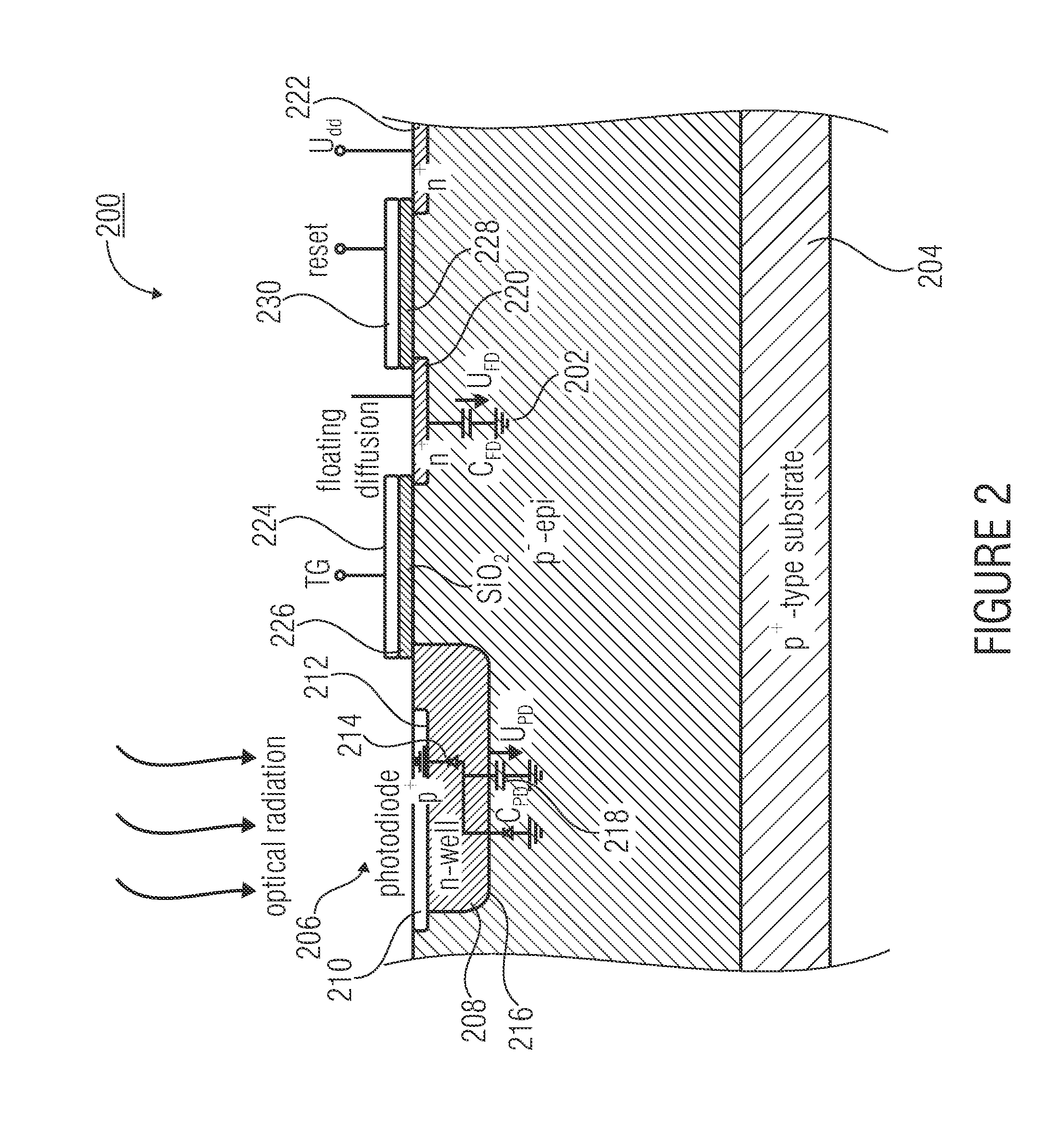
ActiveUS20110037969A1Halving laser energyDoubling measuring speedOptical rangefindersDiodeCharge-carrier densityCharge carrier
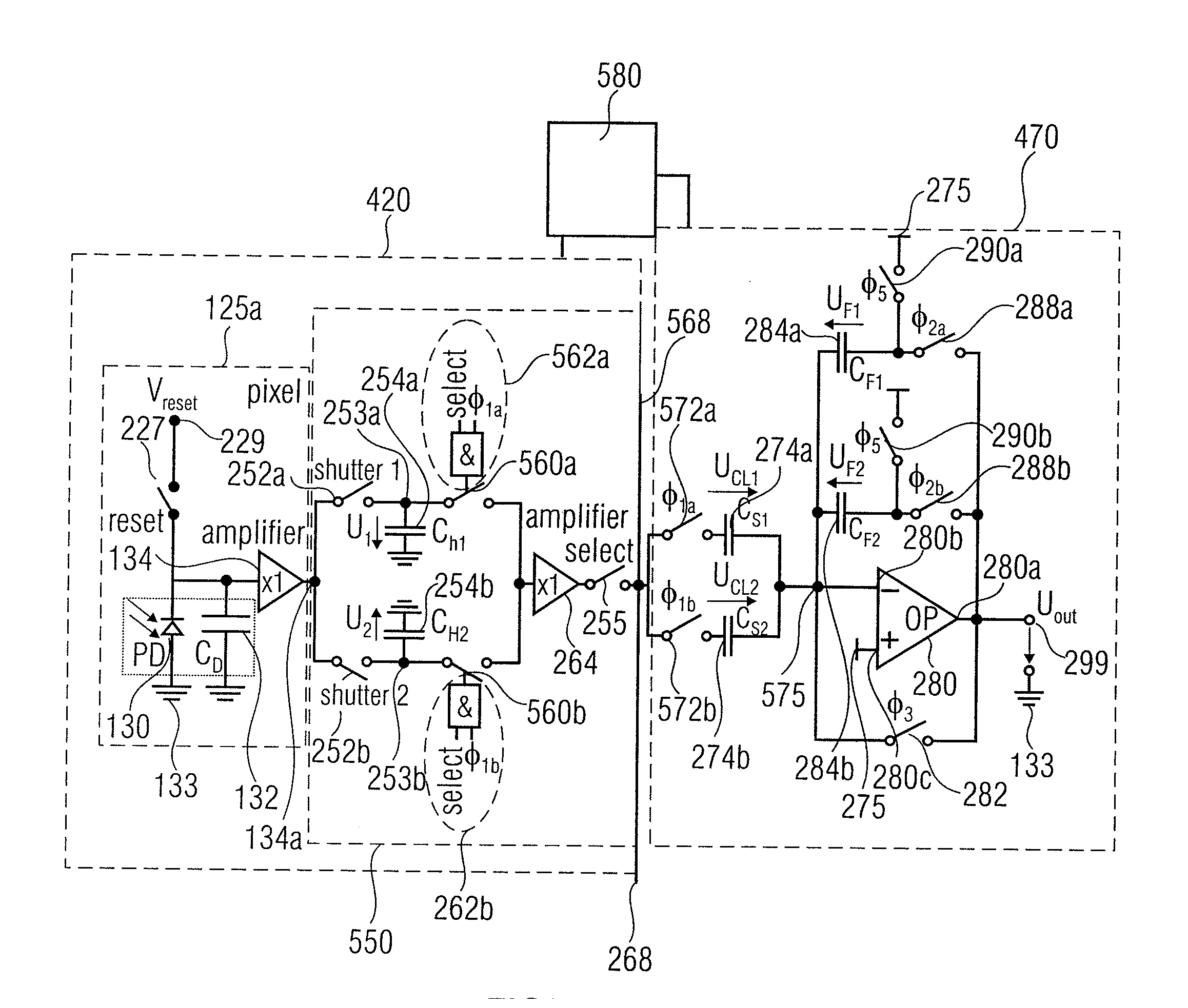
The present invention relates to a concept for optical distance measurement, wherein a radiation pulse is emitted in the direction of an object of measurement. At least two different transfer gates which couple a photoactive region to at least two different evaluating capacities are driven during different drive intervals so that charge carriers generated during the drive intervals by a radiation pulse reflected from the object of measurement and / or by ambient radiation can be transported from the photoactive region to the evaluating capacities each coupled to the at least two transfer gates. Another transfer gate is driven during a time outside the drive intervals of the at least two transfer gates to connect the photoactive region to a reference potential terminal acting as a charge carrier sink during the time outside the drive intervals of the at least two transfer gates.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
Multi-frequency microwave-induced thermoacoustic imaging of biological tissue
InactiveUS20050107692A1Improving Impedance MatchingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsThermoacousticsRadiation pulse
A method and system for examining biological tissue includes the steps of radiating a tissue region with a plurality of microwave radiation pulses. The microwave pulses are swept across a range of microwave frequencies. In response to the swept frequency microwave pulses, the tissue region emits a plurality of thermoacoustic signals. At least one image of the tissue region is formed from the plurality of thermoacoustic signals. The signals can be ultrawideband signals.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods and apparatus for eyeglass lens curing using ultraviolet light and improved cooling
InactiveUS6086799AControl generationControl releaseOther chemical processesOptical articlesUltraviolet lightsRadiation pulse
Method and apparatus for making and coating a plastic lens. Oxygen barrier containing photoinitiator is used to cure incompletely cured lens portions. Radiation pulses are used to control lens curing rate. Lens is postcured while in a mold cavity using a conductive heat source. Air may be directed toward the mold cavity to help remove heat from the lens. An in-mold scratch resistant coating may be formed from two separate material which both contain a photoinitiator.
Owner:Q2100
Laser scanning apparatus and methods for thermal processing
InactiveUS20040084427A1Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser scanningProcess region
Apparatus and methods for thermally processing a substrate with scanned laser radiation are disclosed. The apparatus includes a continuous radiation source and an optical system that forms an image on a substrate. The image is scanned relative to the substrate surface so that each point in the process region receives a pulse of radiation sufficient to thermally process the region.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
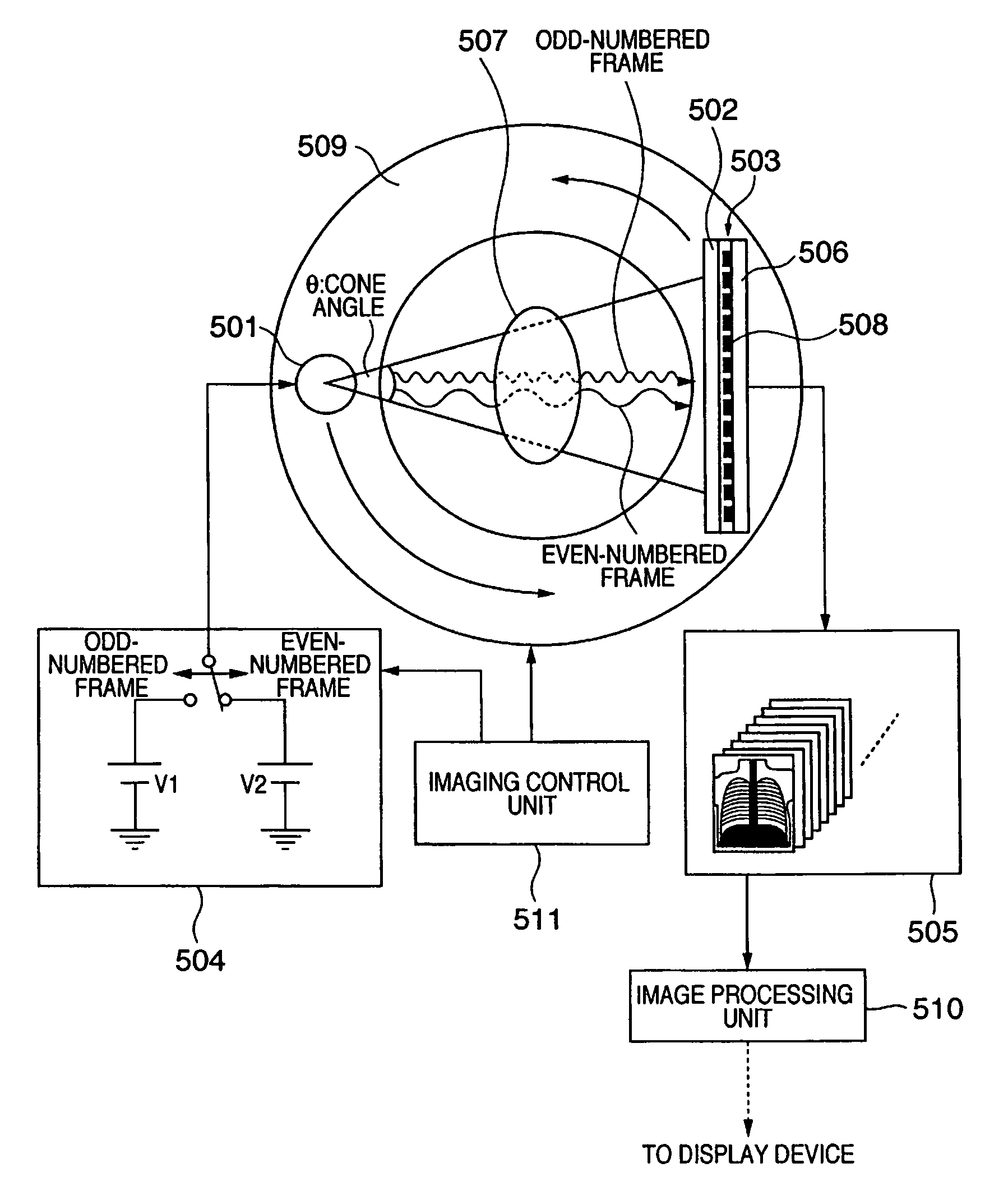
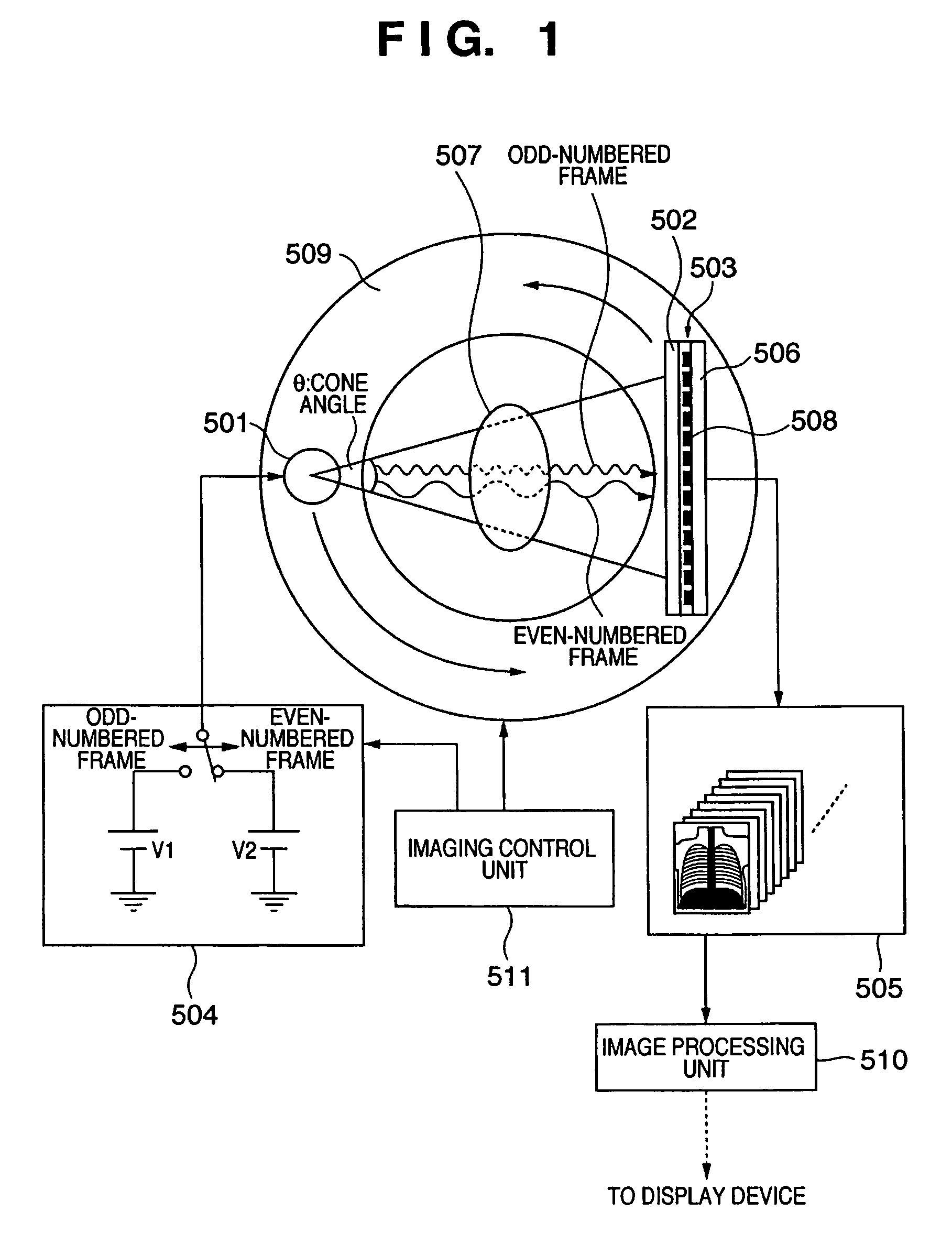
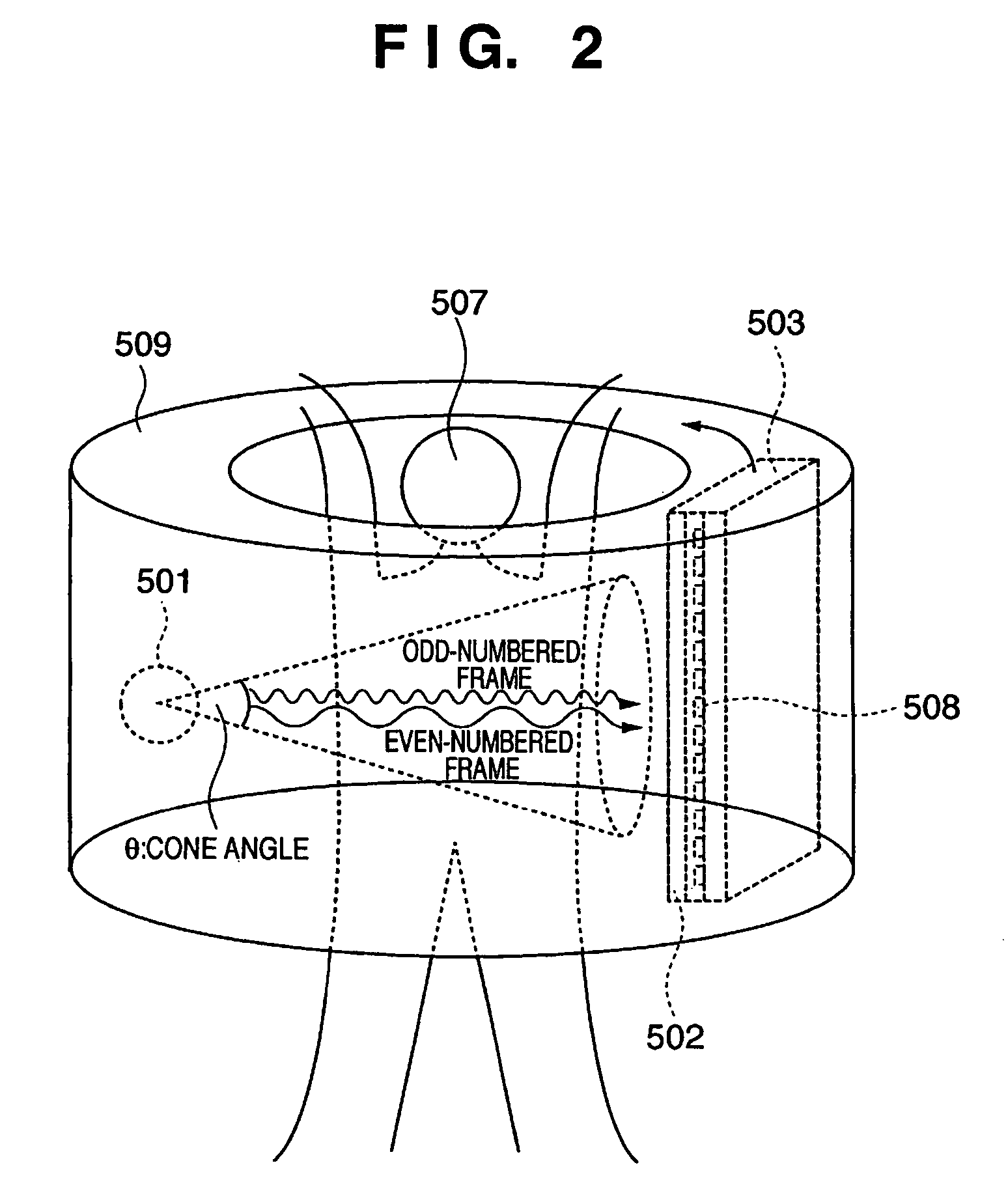
Radiographic imaging apparatus, control method thereof, and radiographic imaging system
InactiveUS7386089B2Reduce contrastImprove diagnostic efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingImaging processing3d image
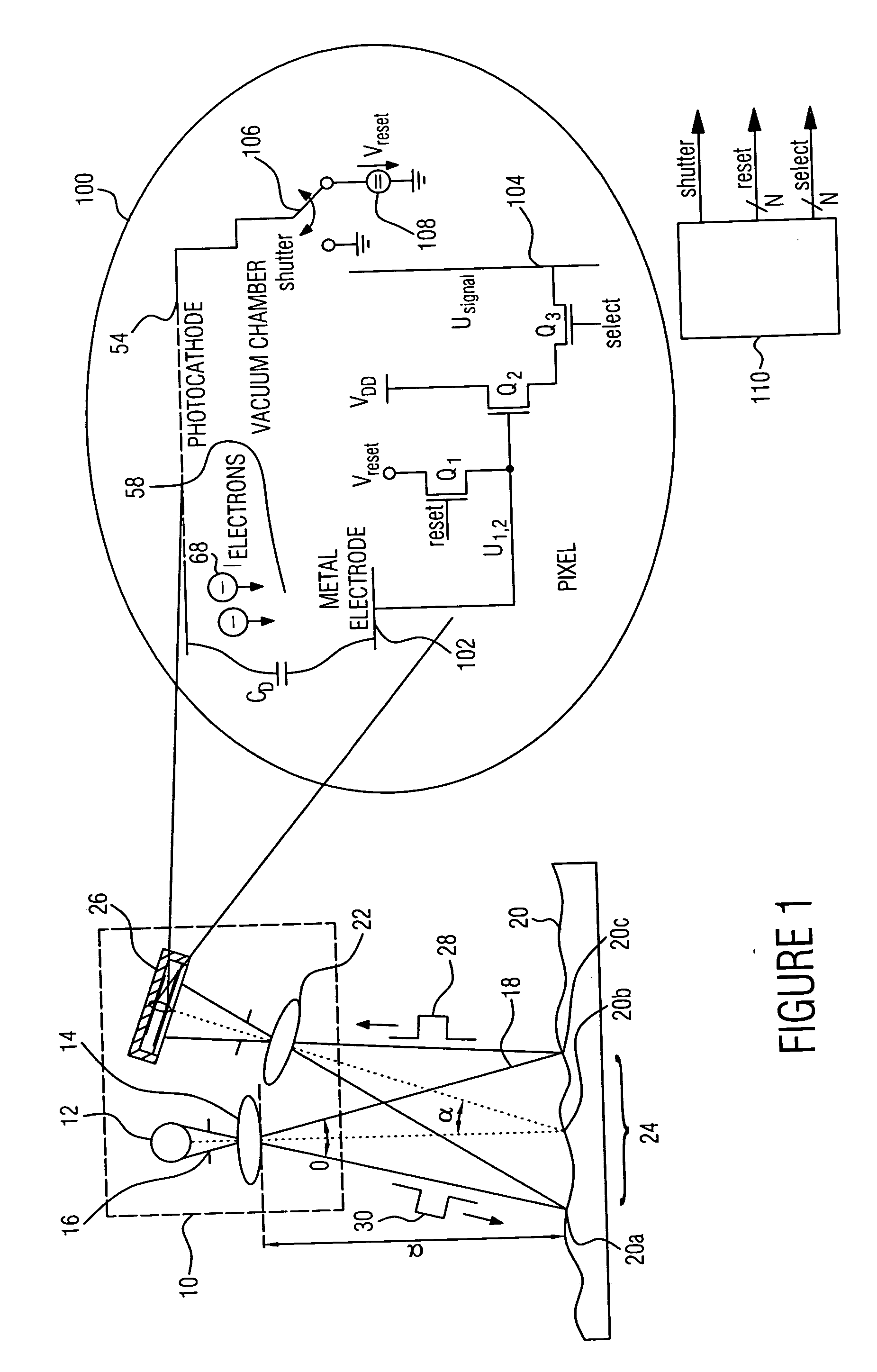
A radiographic imaging apparatus includes a radiation detection circuit with elements arranged two-dimensionally to convert radiation into an electrical signal, a driving mechanism which changes a positional relationship between the components, a memory which stores that electrical signal, an imaging controller to control the radiation source so as to emit a first radiation pulse at a first energy for a first frame and to emit a second radiation pulse at a second energy for a second frame, controlling the driving mechanism to maintain the positional relationship during the first radiation pulse and the second radiation pulse and to change the positional relationship in a period between the first period and the second period. The frames are different and sequentially imaged, and an image processing unit for subtraction processing of the first and second frames in memory to generate a processed image, then generate a tomographic and a 3D image.
Owner:CANON KK
Distance sensor and method for detecting a distance
ActiveUS20060214121A1Improve reliabilityImprove precisionInvestigating moving sheetsElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadiation pulseUsability
An indirect detection of the reflected radiation pulses, when measuring a distance by means of the photoeffect, allows considerably expanding the usability of the distance sensor and the distance measuring method, wherein the adaption to a new field of application only requires little design changes. Since in the external photoeffect the photoelectrons are ejected from the material irradiated photon by photon or quantum by quantum and the photons, when being ejected, only require a certain minimum energy and correspondingly the radiation used for irradiation only requires a sufficiently small wavelength, the external photoeffect allows detecting radiation over a large spectral range. When interferences occur in a certain wavelength range in a certain field of application, the operating wavelength range of the distance sensor technology may at first simply be set to another spectral range by using such an irradiation source having a spectrum outside the spectral range containing the interferences.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
Light treatments for acne and other disorders of follicles
InactiveUS20100204686A1Good curative effectReduce unevennessSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyDiseaseLight treatment
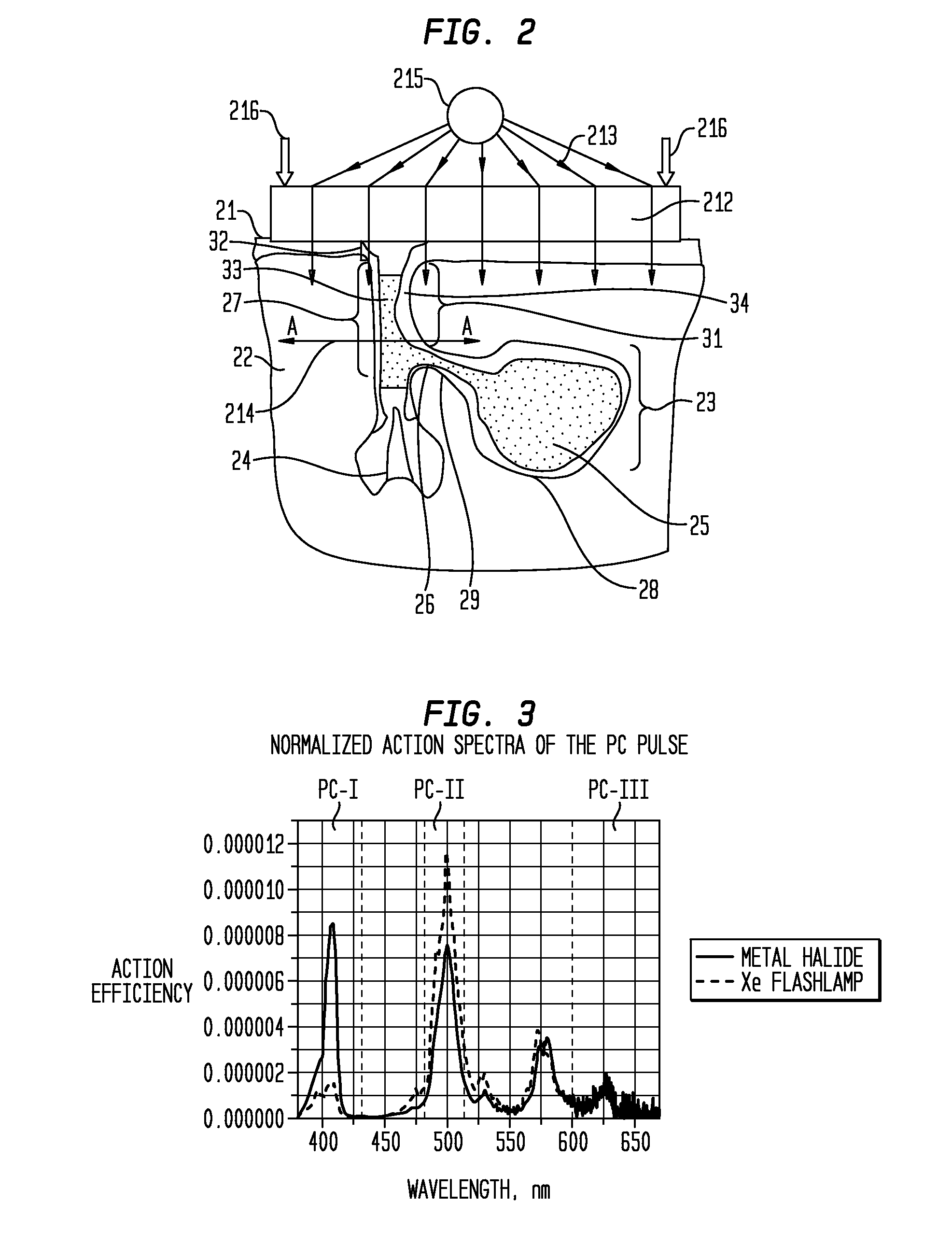
The present invention provide methods for treating acne by exposing affected follicles to at least one, and preferably two or all three, of the following radiation pulses: a radiation pulse (PC pulse) having a wavelength components in a range of about 360-700 nm; a radiation pulse (PTV pulse) having wavelength components in a range of about 470 nm to 650 nm and / or in a range of about 500 nm to about 620 nm; and a radiation pulse (PTIR pulse) having wavelength components in a range of about 900 nm to about 1800 nm. The irradiated treatment region is preferably maintained at a temperature of about 38 to 43 C in order to enhance the efficacy of the treatment.
Owner:PALOMAR MEDICAL TECH
Laser scanning apparatus and methods for thermal processing
InactiveUS20040188396A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser scanningProcess region
Apparatus and methods for thermally processing a substrate with scanned laser radiation are disclosed. The apparatus includes a continuous radiation source and an optical system that forms an image on a substrate. The image is scanned relative to the substrate surface so that each point in the process region receives a pulse of radiation sufficient to thermally process the region.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Semi solid rheoforming method for metal parts and device therefor
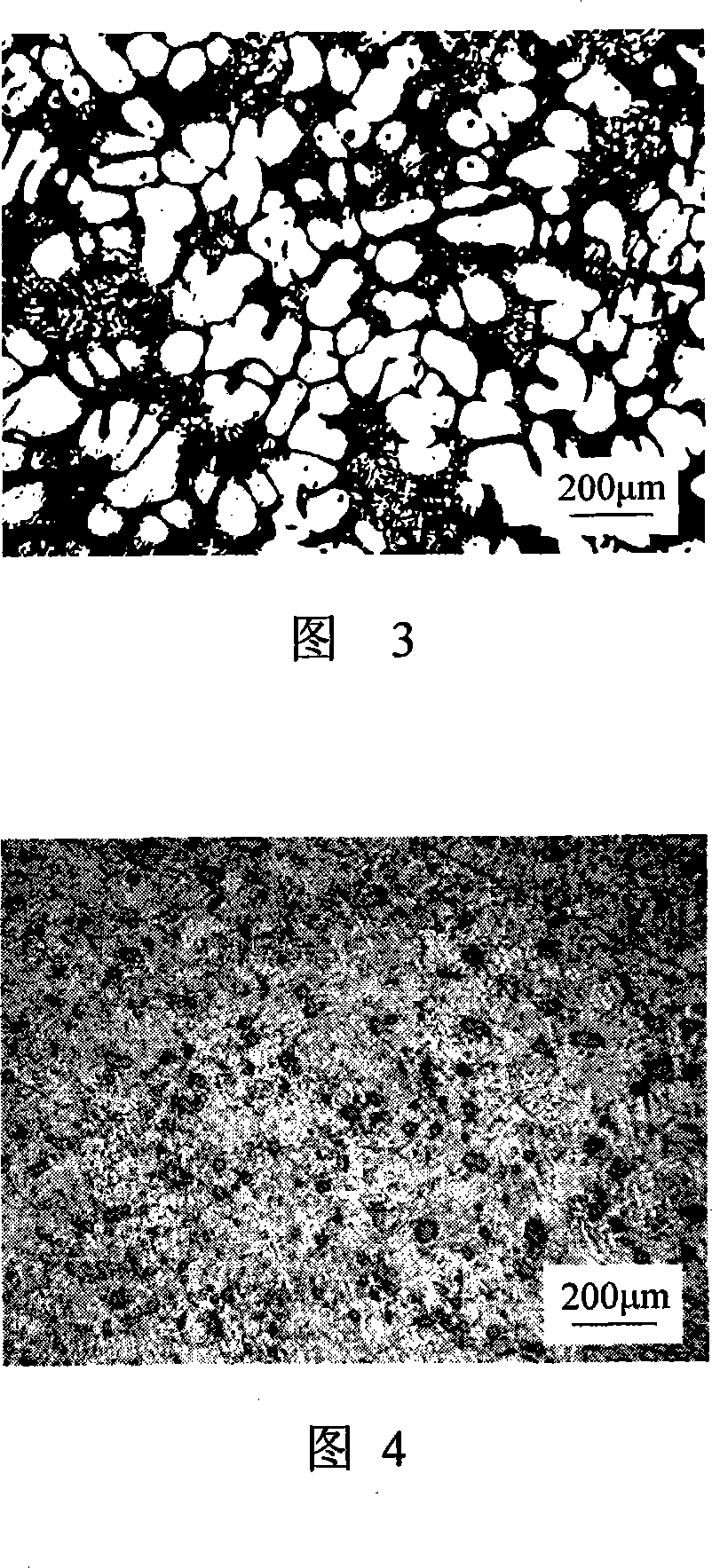
The invention relates to a semi-solid fluidized molding method and a device for metal parts. Liquid metal with the temperature from 0 to 40 DEG C above liquid phase is guided into a pulp container, and then an ultrasonic radiation is lowered down to 1 to 30mm above the liquid surface, ultrasonic radiation is started, and the slurry is cooled at the speed ranging from 0.1 DEG C per second to 3 DEG C per second. The ultrasonic radiation can be pulse radiation or non-radiation pulse with ultrasonic frequency ranging from 12kHz to 80kHz, radiation volume power 5W / cm<3> to 100W / cm<3>, and radiation time from 15s to 1000s; the slurry is poured into molding equipment to be molded into parts after the radiation. The molded part has dense organization, fine and equally distributed grains. The device of the invention comprises a pulp container, a thermostat, an ultrasonic generation and a control unit, a sleeve, and a mold and an injection rod and a molding device. The fluidized molding method and device can be used for fluidized molding of various alloy parts made from aluminum, magnesium, tin, copper and iron etc. The method has the advantages of non-contaminated pulp, long service life of ultrasonic equipment and high part production efficiency.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optical Distance Measuring Device and Method for Optical Distance Measurement
ActiveUS20120268727A1Fast measurement speedReduce radiant energyOptical rangefindersMaterial analysis by optical meansObject basedRadiation pulse
The present invention describes an optical distance measuring device having a pulsed radiation source that is implemented to transmit, in a temporally contiguous radiation pulse period, a radiation pulse having a pulse duration tp that is shorter than the radiation pulse period, and to transmit no radiation pulse in a temporally contiguous dark period. Further, the optical distance measuring device includes a detector for detecting different amounts of radiation in two overlapping detection periods during the radiation pulse period to capture reflections of the radiation pulse at an object surface and a background radiation and / or in two overlapping detection periods during the dark period to capture background radiation. The optical distance measuring device further includes an evaluator determining a signal depending on a distance of the optical distance measuring device to an object based on the detected amount of radiation. Further, the present invention provides a method for optical distance measurement and for multiple sampling.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
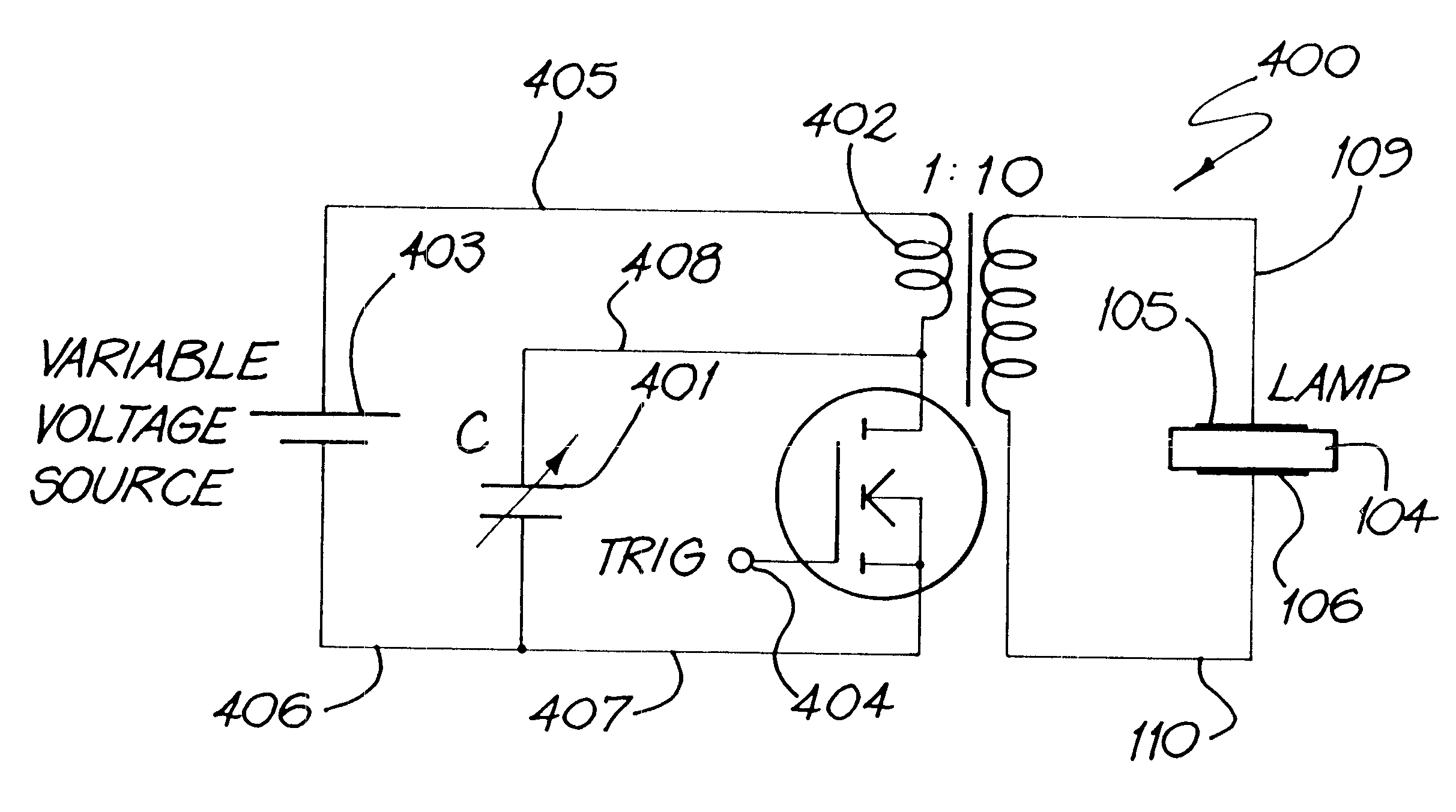
Methods and systems for providing emission of incoherent radiation and uses therefor
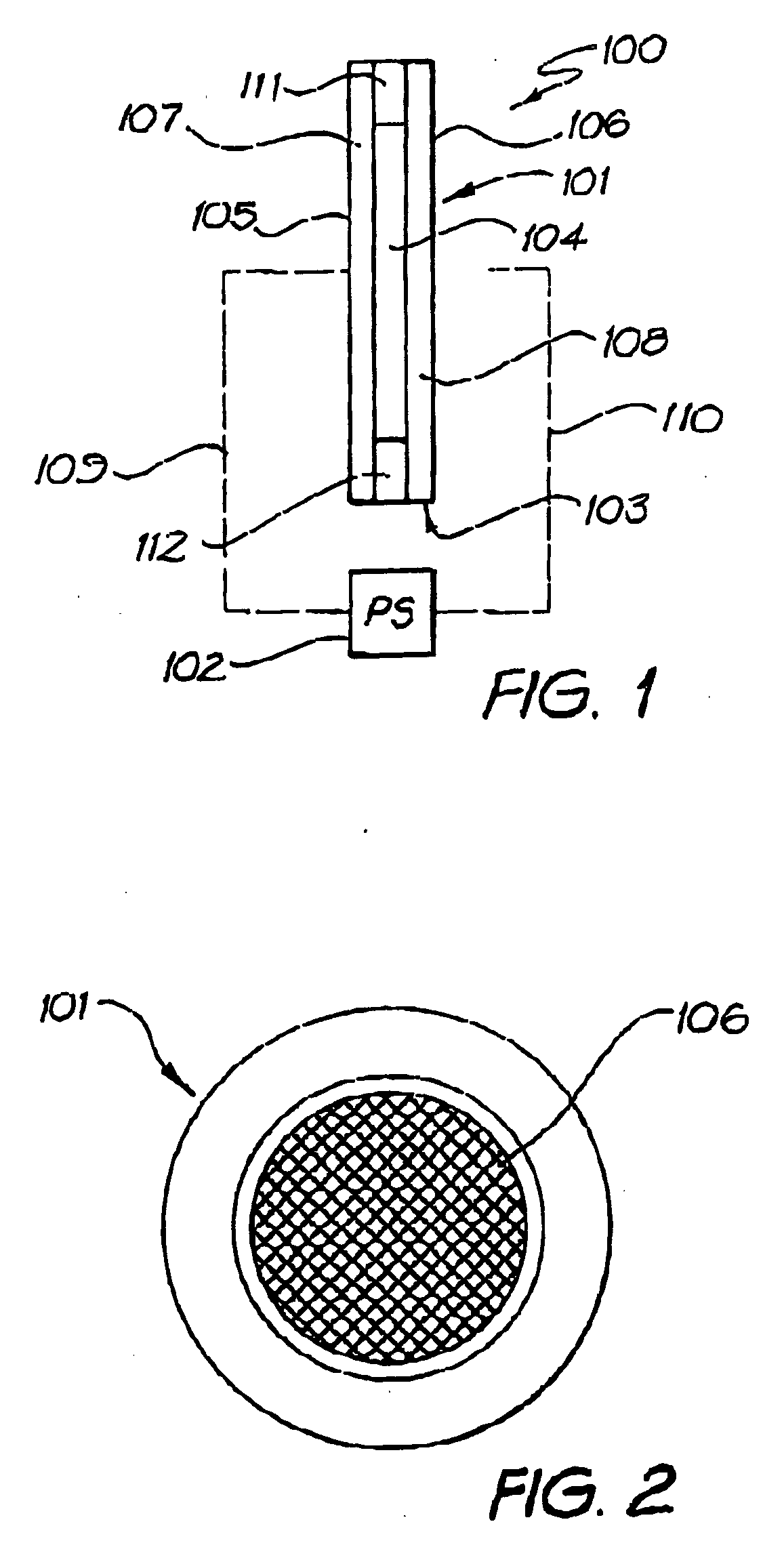
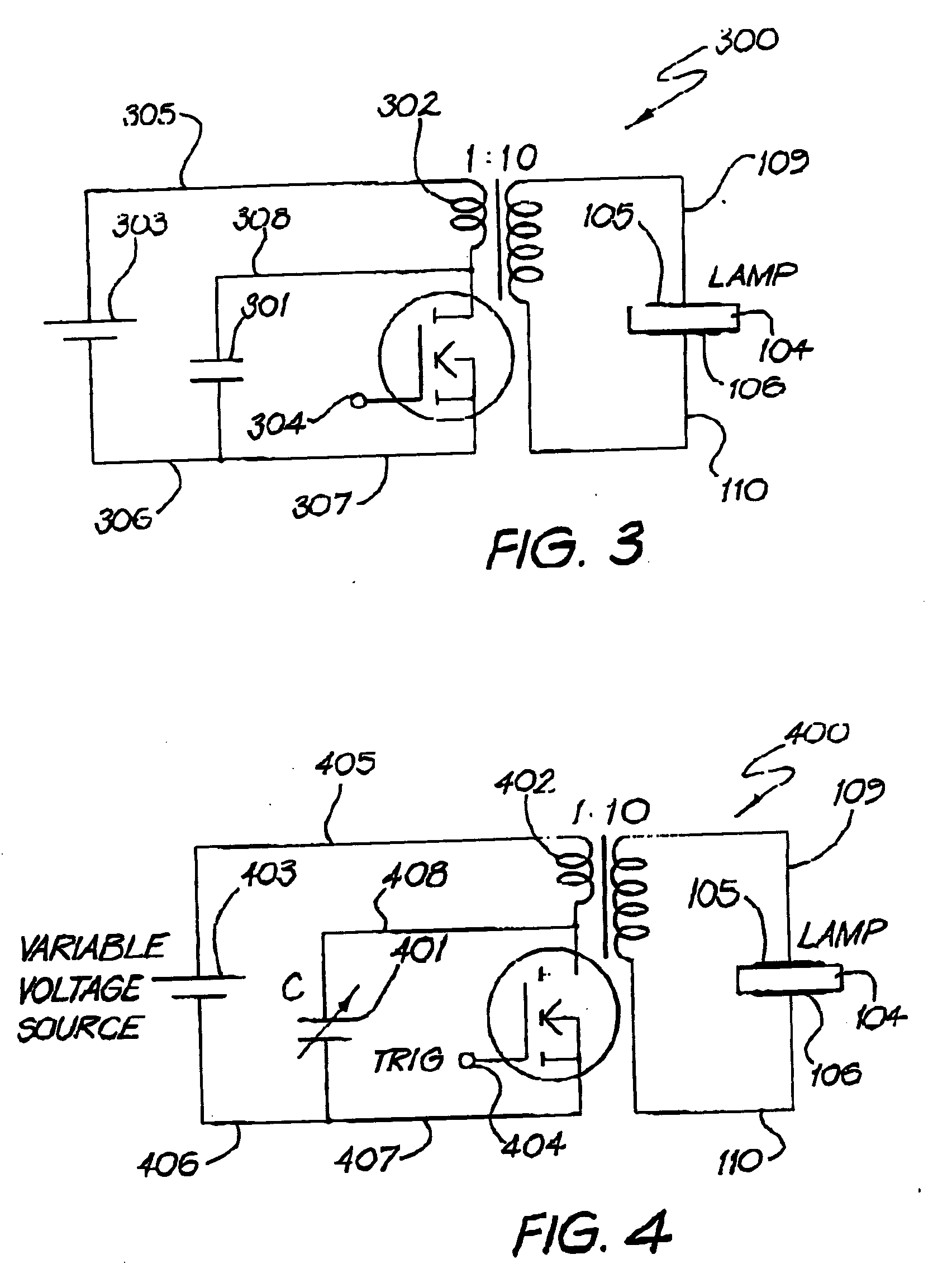
InactiveUS6541924B1High outputPower maximizationGas-filled discharge tubesStatic indicating devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage pulse
Methods and systems for providing emission of incoherent radiation and uses therefor are disclosed. A system for providing emission of high peak power (in watts) incoherent radiation, comprises an electrically impeded discharge lamp linked to an electrical energy supply. The lamp comprises a discharge chamber which is at least partially transparent to the incoherent radiation, a discharge gas in the chamber, two electrodes disposed with respect to the chamber for discharging electrical energy therebetween, at least one dielectric barrier disposed between the two electrodes to electrically impede electrical energy passing between the two electrodes, an electrical energy supply capable of providing fast risetime, high peak power unipolar linking the electrodes with the supply, the energy supply being capable of providing a sequence of high peak power unipolar voltage pulses from the energy supply to the electrodes and means to control (i interpulse period, and (ii) pulse risetime, whereby, in use, a substantially homogeneous discharge occurs between the two electrodes which causes emission of incoherent radiation pulses of high peak power from the lamp.
Owner:MACQUARIE RES
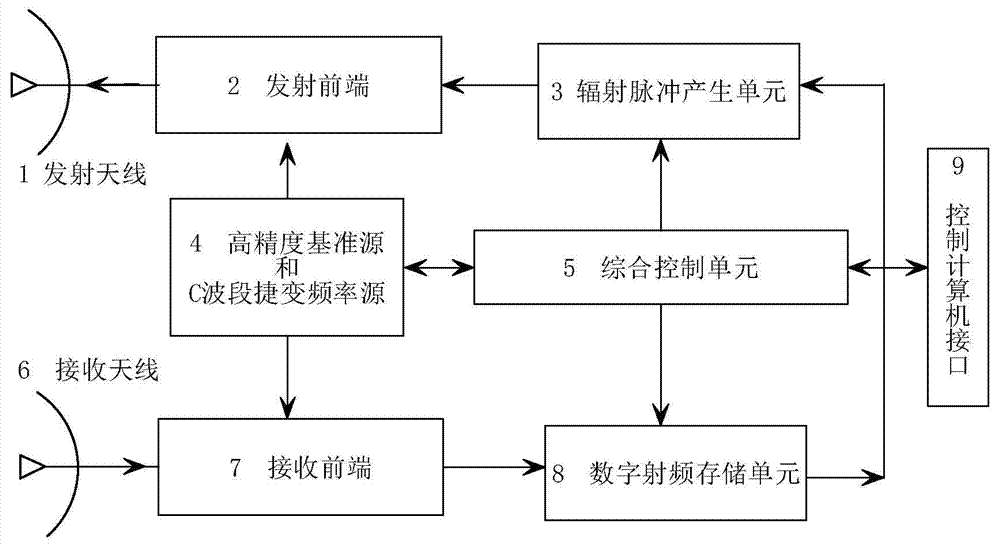
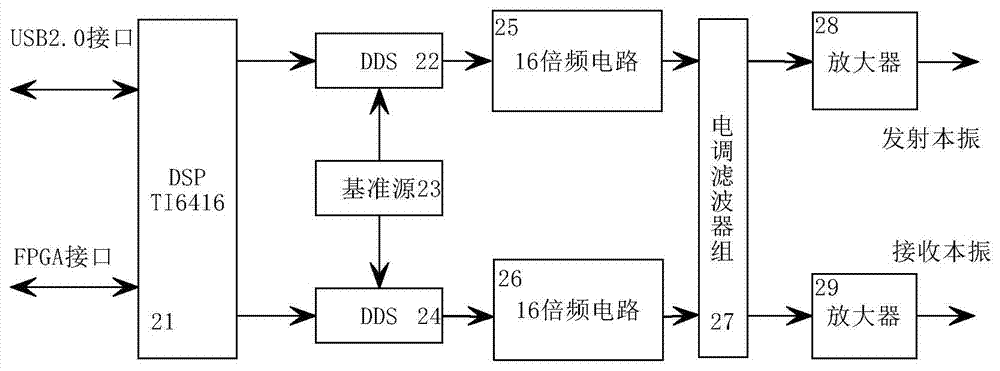
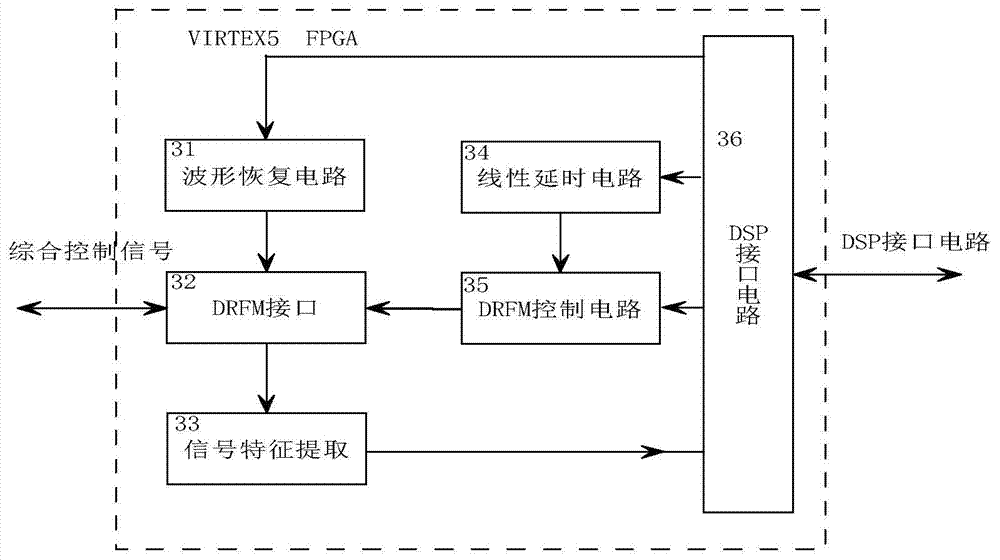
Object indication radar object simulator
The invention discloses an object indication radar object simulator which is mainly applied to simulating radar reflection echoes of a missile type object and an airplane type object in a real state close to reality. The object indication radar object simulator comprises an emission antenna, an emission front end, a radiation pulse generation unit, a high precision reference source and C-wave band agility frequency source, a comprehensive control unit, a digital radio frequency memory unit, a receiving front end and a receiving antenna. Radar signals, after being converted down to an intermediate frequency through the receiving front end, penetrate into the radio frequency memory unit and are stored there, the comprehensive control unit performs control according to an object batch, a speed and distance information which are to be simulated, the radio frequency memory unit generates intermediate frequency signals of object echoes, then the radiation pulse generation unit and the emission front end simulate magnitude information and Doppler information of the echoes, and final, the emission antenna performs emission. The stimulator can simulate radar echo information of a real object and is mainly applied to dynamic object simulation, outfield test simulation, integrated practice and testing of a radar system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
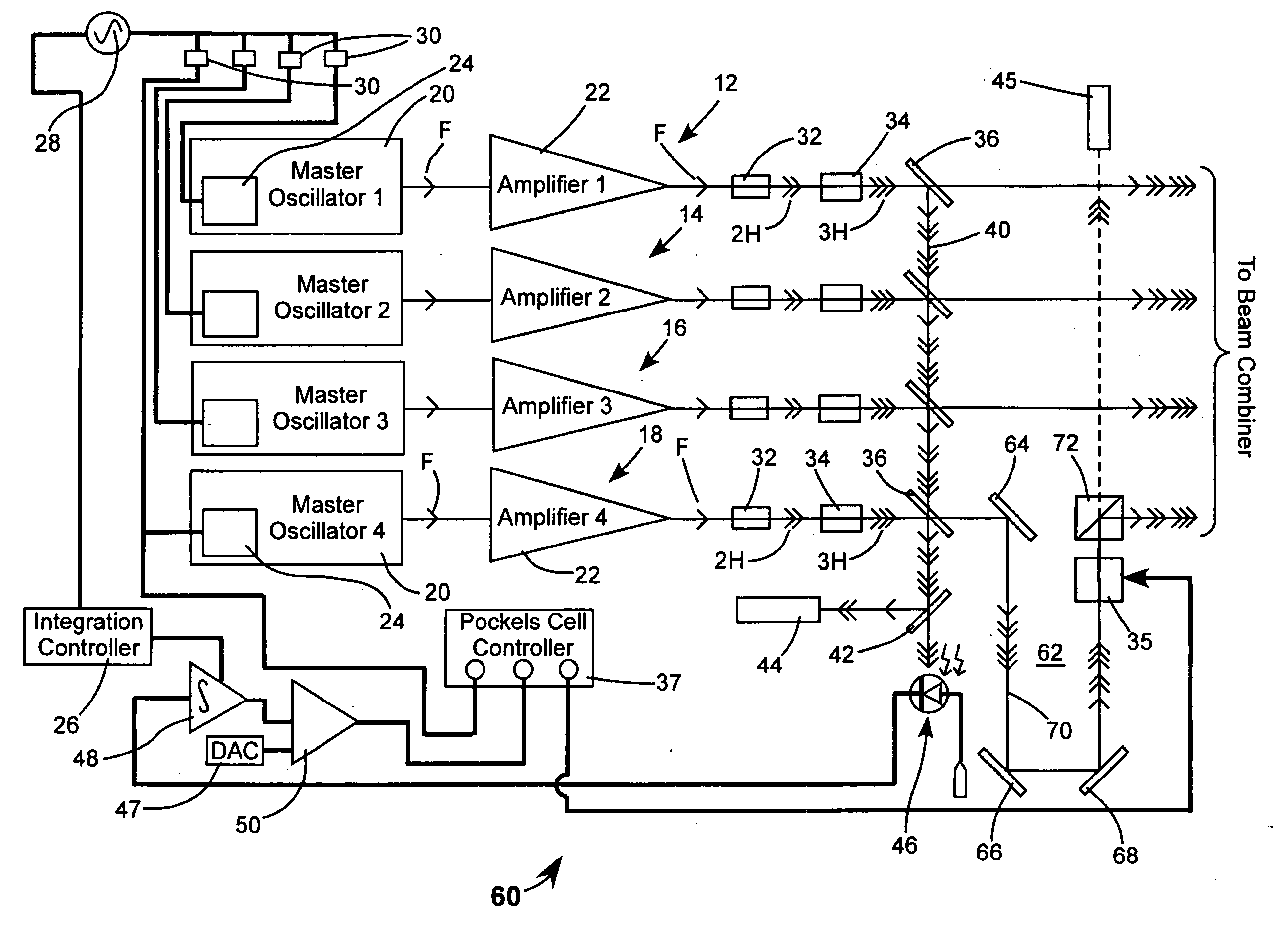
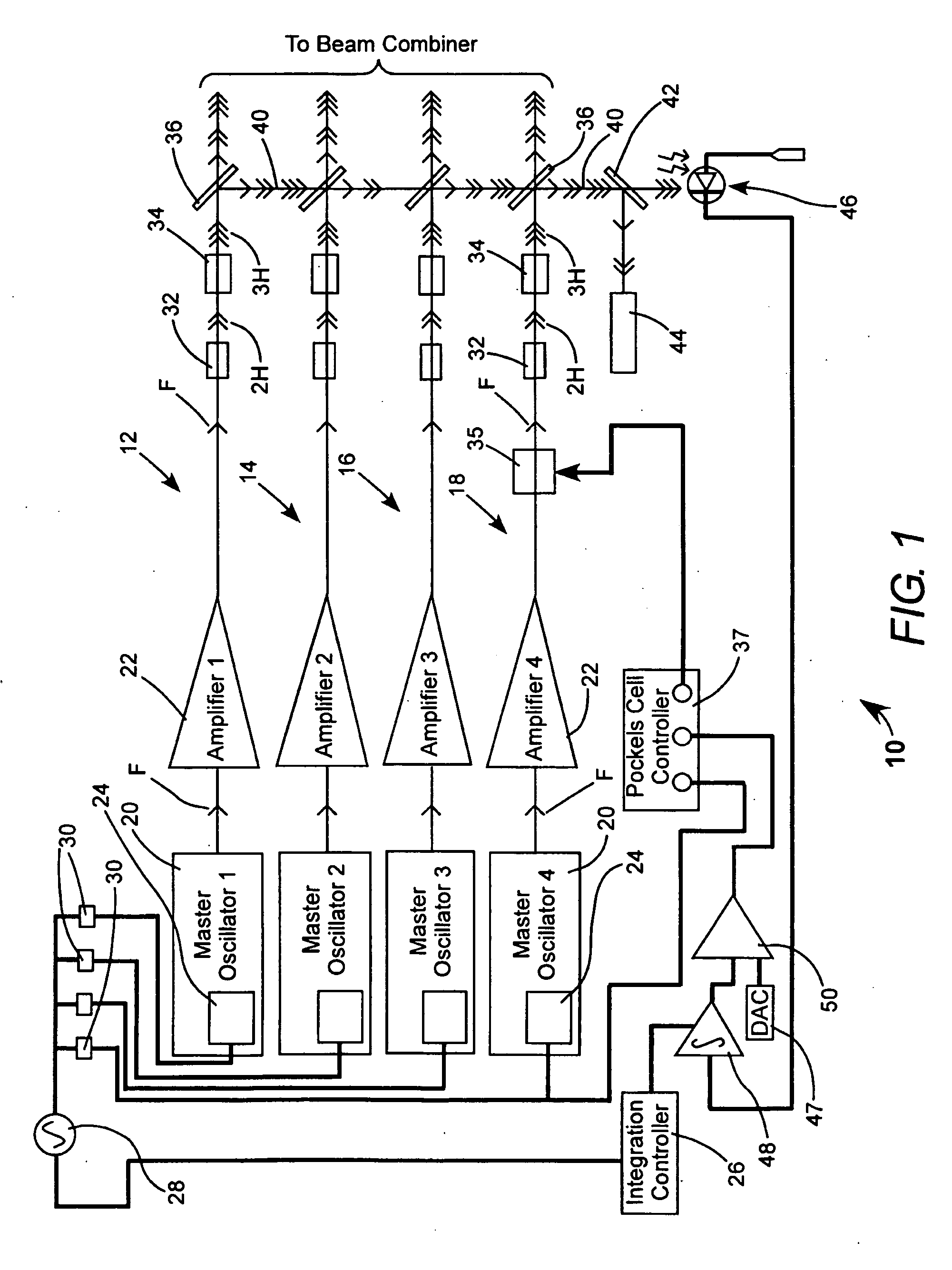
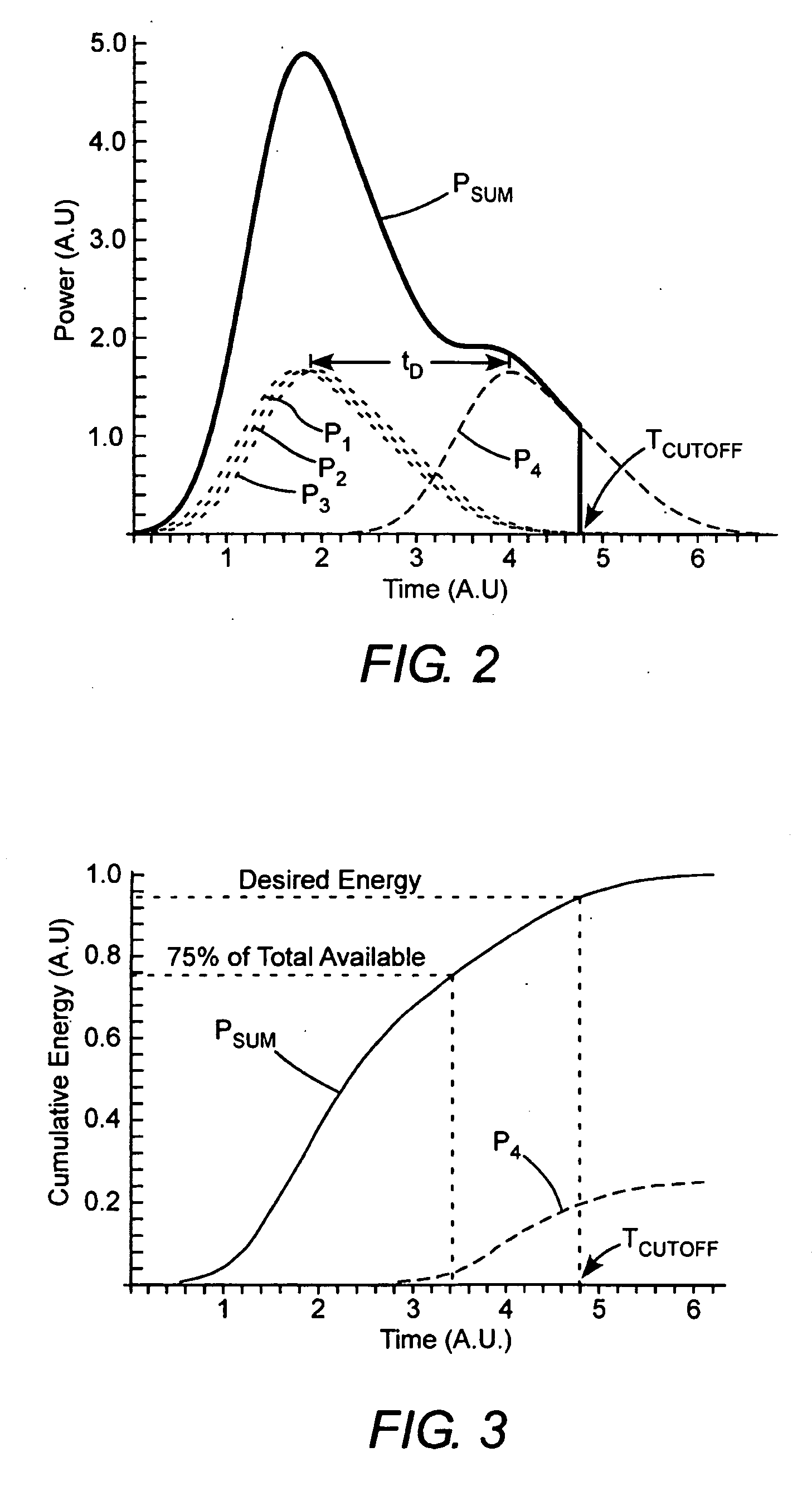
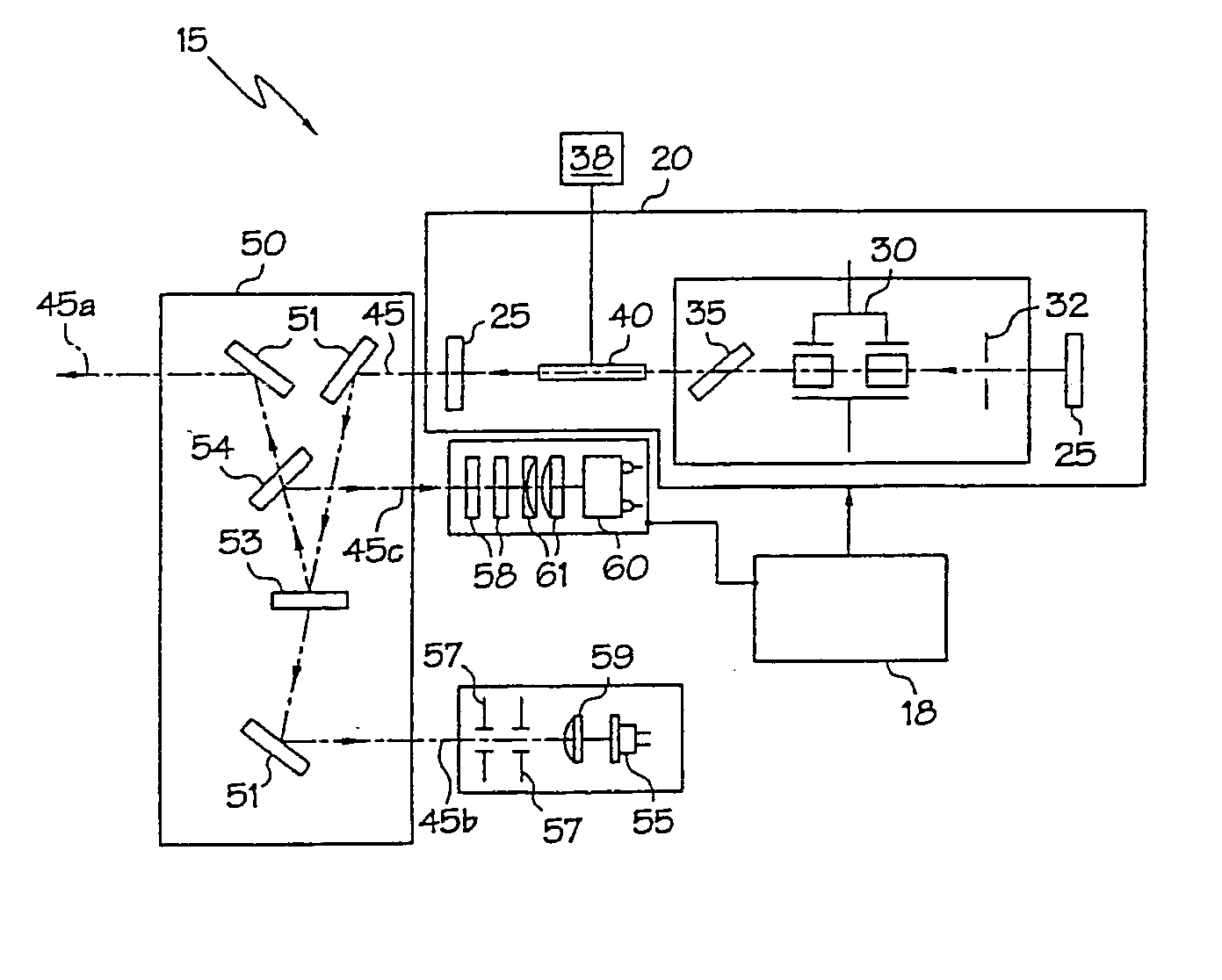
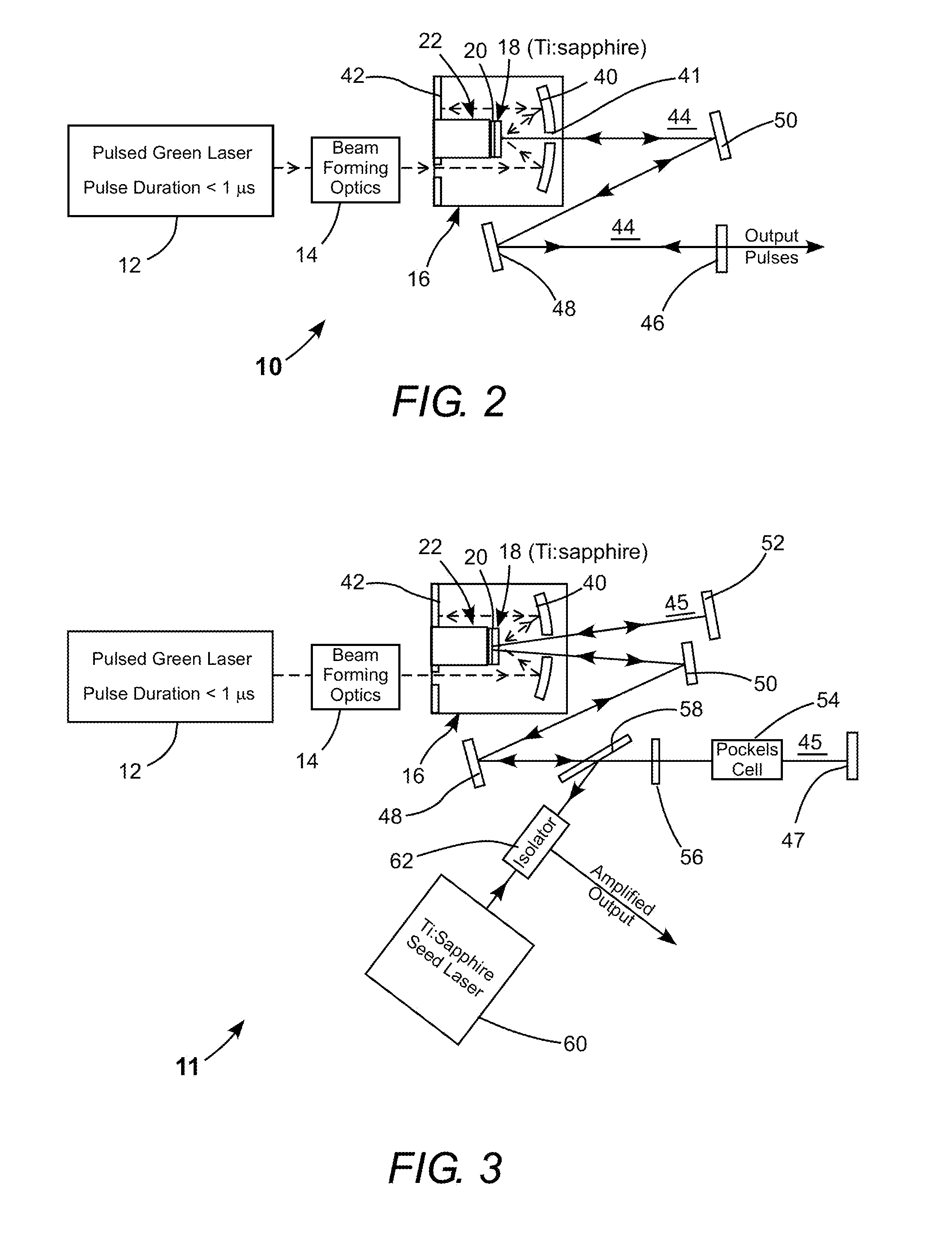
Energy stabilization of combined pulses from multiple lasers
A combined radiation pulse of a predetermined energy is provided by temporally and spatially overlapping four pulses from four extra-cavity, frequency-tripled lasers. Frequency tripling is effected in each laser by a second-harmonic generating crystal followed by a third-harmonic generating crystal. One of the lasers includes a Pockels cell preceding the second-harmonic generating crystal. The third harmonic pulse from this laser is the fourth and last delivered in the sequence. The total available energy in three of the pulses is less than the predetermined energy. The cumulative integrated energy of the pulses is determined while the pulses are being delivered. When the energy is determined to have reached the predetermined value, the Pockels cell is activated to rotate the polarization plane of fundamental radiation entering the second-harmonic generating crystal, thereby terminating generation of the fourth pulse and delivering the combined radiation pulse at the predetermined energy.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Laser cutting of stents and other medical devices
A desired pattern may be cut into a stent preform by impinging a laser beam onto the stent preform. The laser beam is formed using a laser system comprising a resonator cavity for resonating laser radiation, a gain medium contained in the resonator cavity, a pump for periodically pumping the gain medium and an electro-optical modulator in communication with the resonator cavity. The laser system produces a radiation pulse for each pump period. Each radiation pulse is conditioned by suppressing at least a portion of the pulse. The pulse may also be modulated with an electro-optical modulator to produce a pulse train of ordered pulses of radiation. Each pulse train is output from the optical cavity as an output laser beam which is directed at the stent preform to cut a desired pattern in the stent preform.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
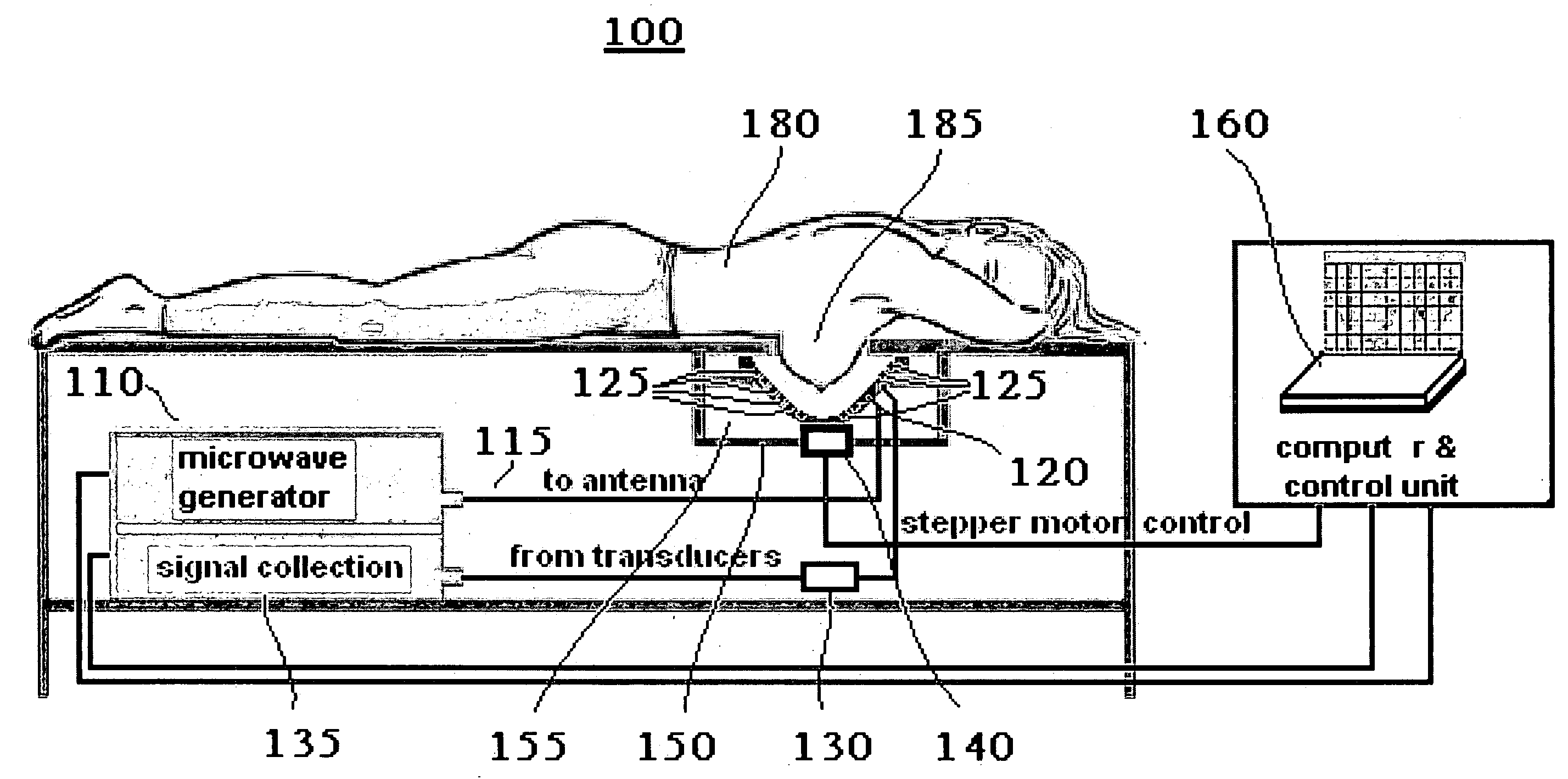
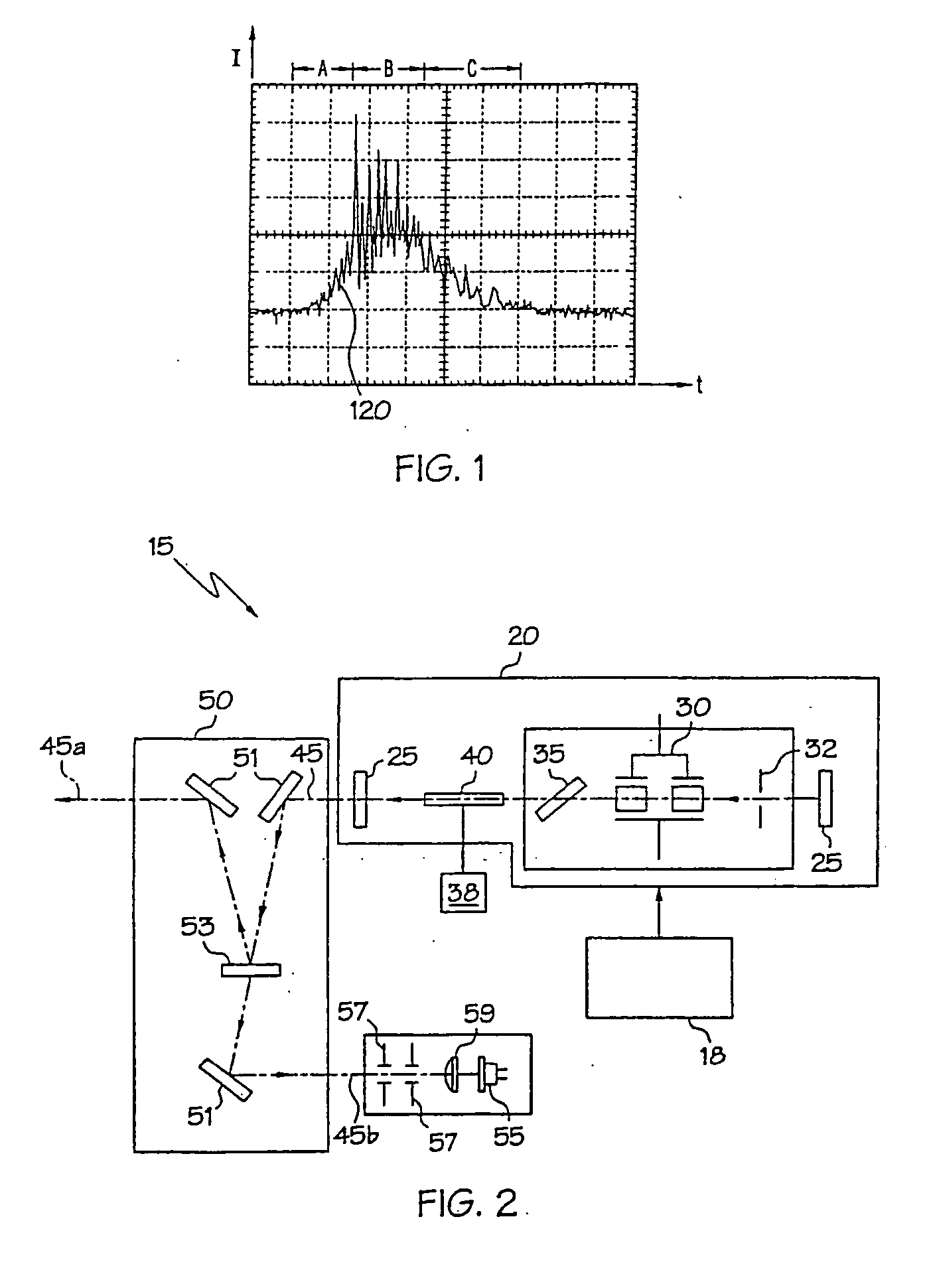
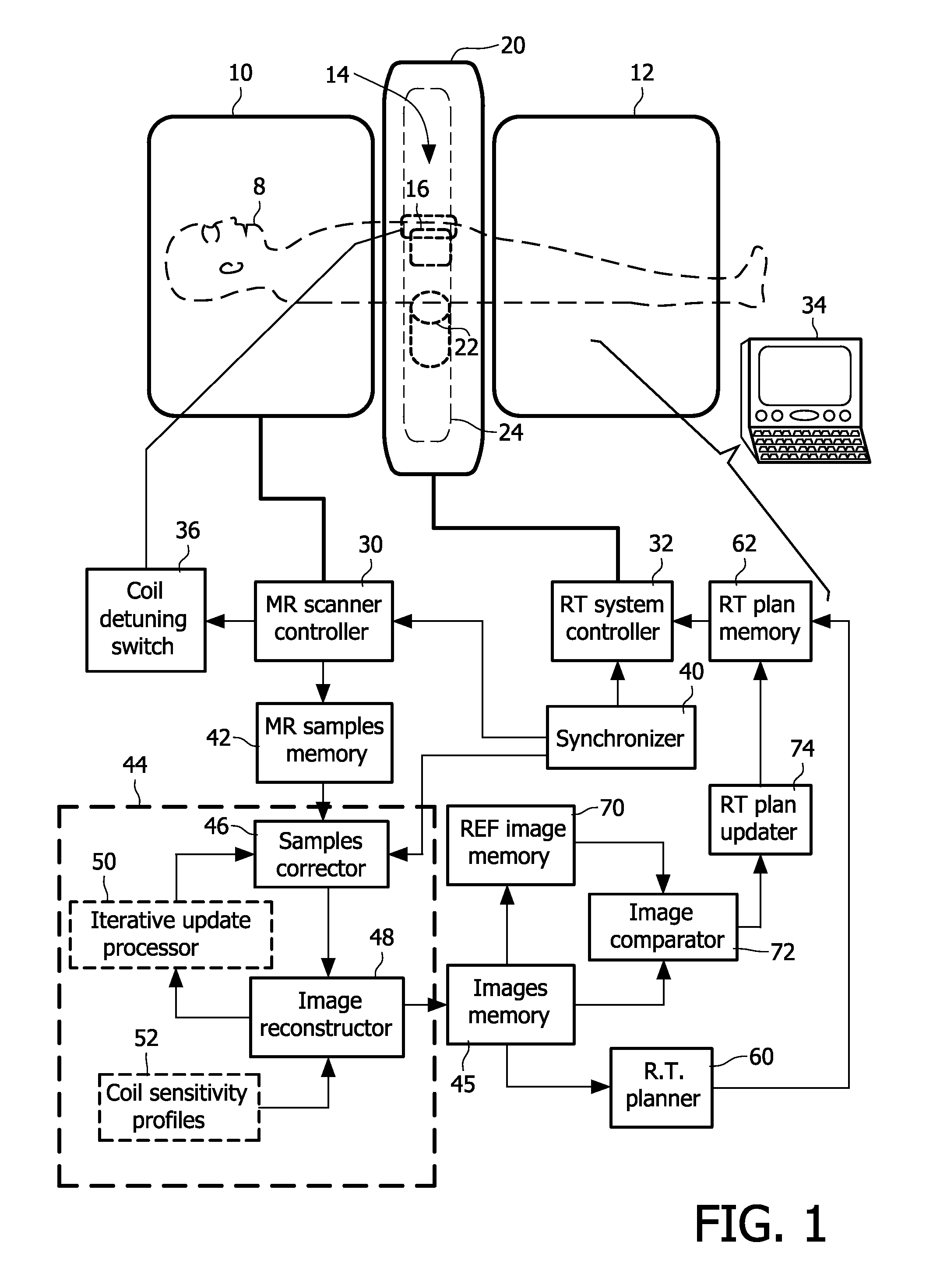
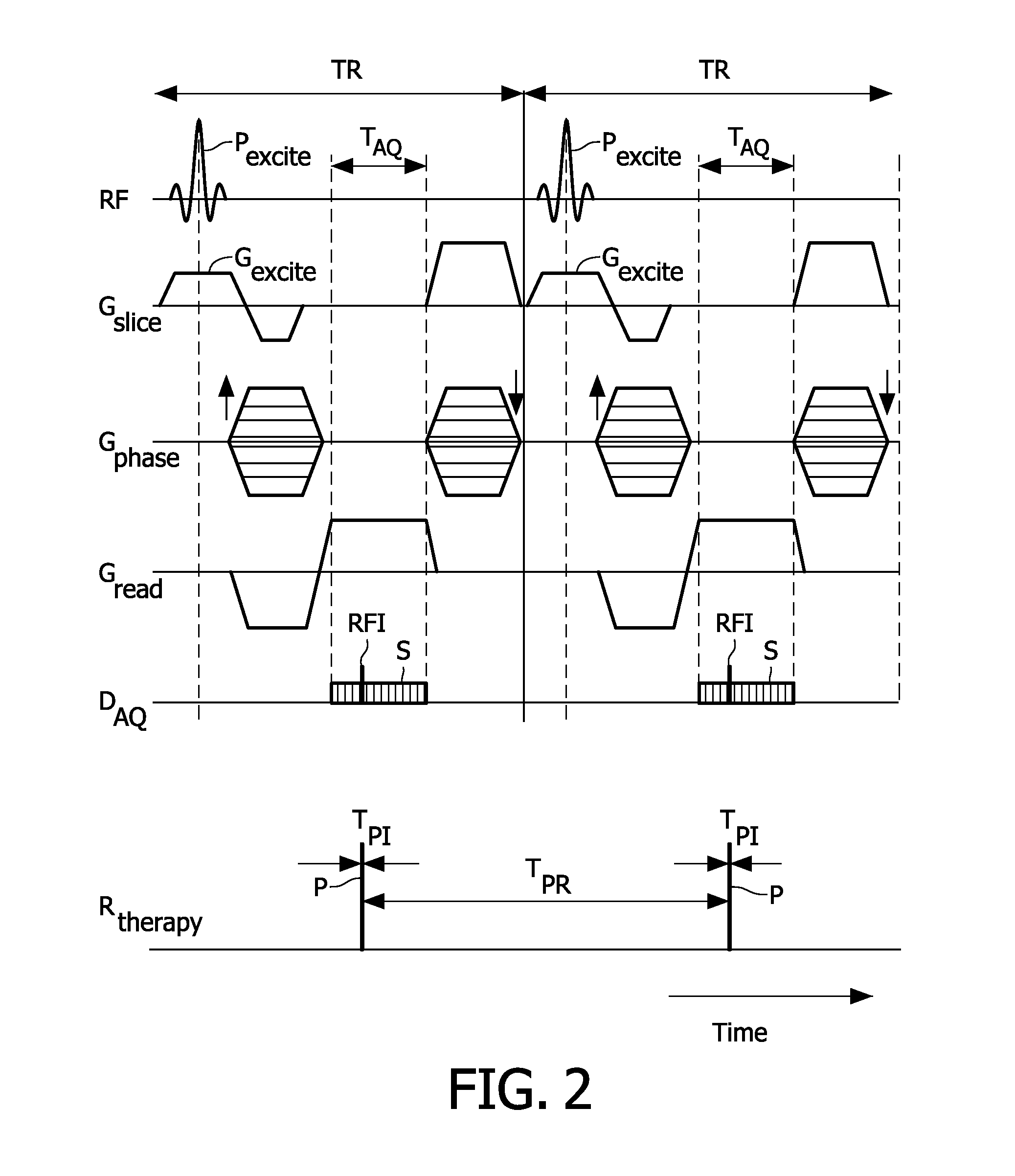
Radiation therapy system with real time magnetic resonance monitoring
ActiveUS20110087090A1Short radiation therapy sessionDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData setMedicine
A radiation therapy system comprises: a radiation therapy subsystem (20, 22, 32) configured to perform radiation therapy by applying radiation pulses to a region of a subject at pulse intervals (Tpi); a magnetic resonance (MR) imaging subsystem (10, 16, 30, 36) configured to acquire a dataset of MR imaging data samples from the region of the subject over one or more MR sampling intervals (TAQ) that are longer than the pulse intervals, the one or more MR sampling intervals overlapping at least some of the pulse intervals; a synchronizer (40) configured to identify MR imaging data samples of the dataset whose acquisition times overlap pulse intervals; and a reconstruction processor (44) configured to reconstruct the dataset without the measured values for the MR imaging data samples identified as having acquisition times overlapping pulse intervals to generate a reconstructed MR image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
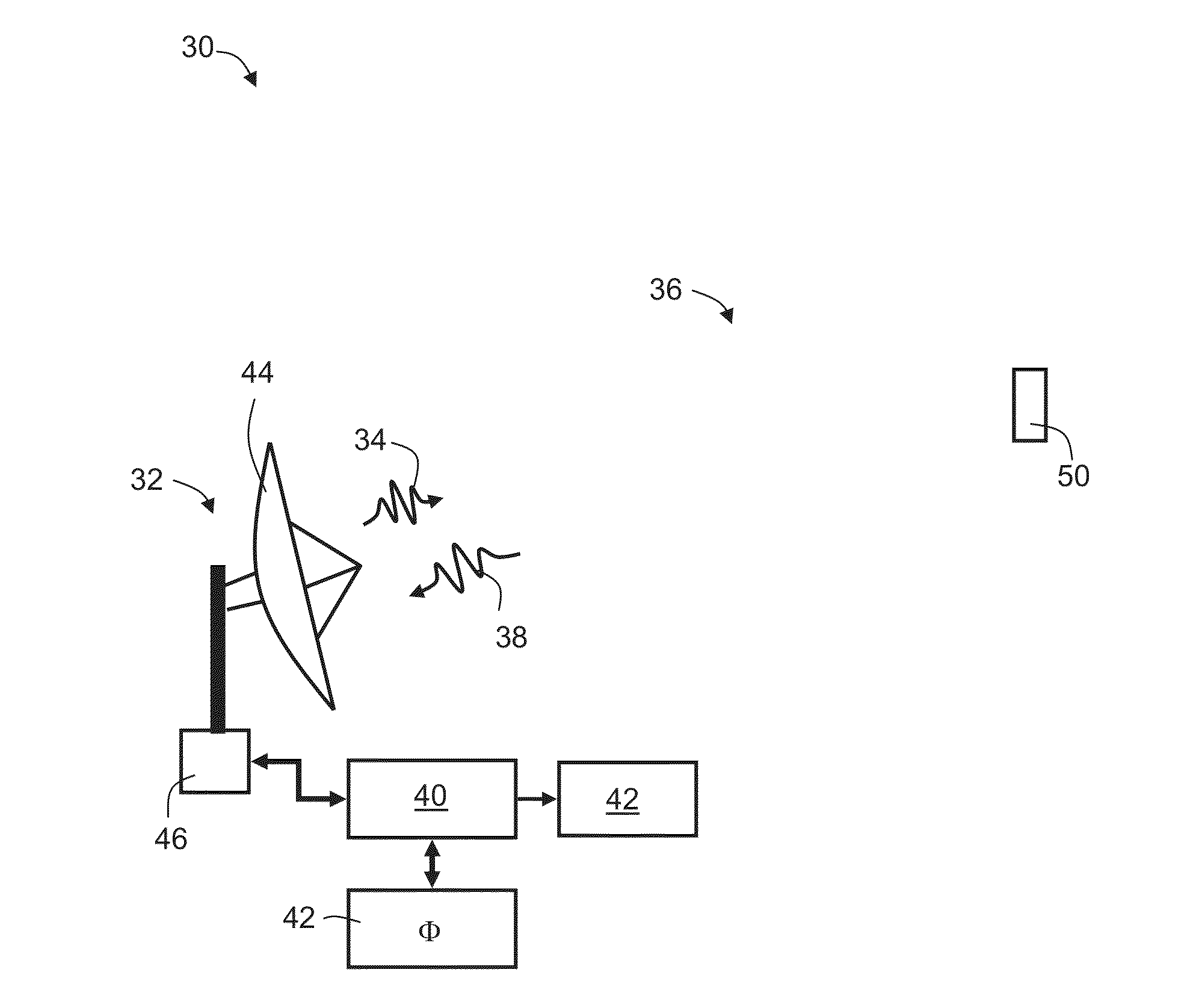
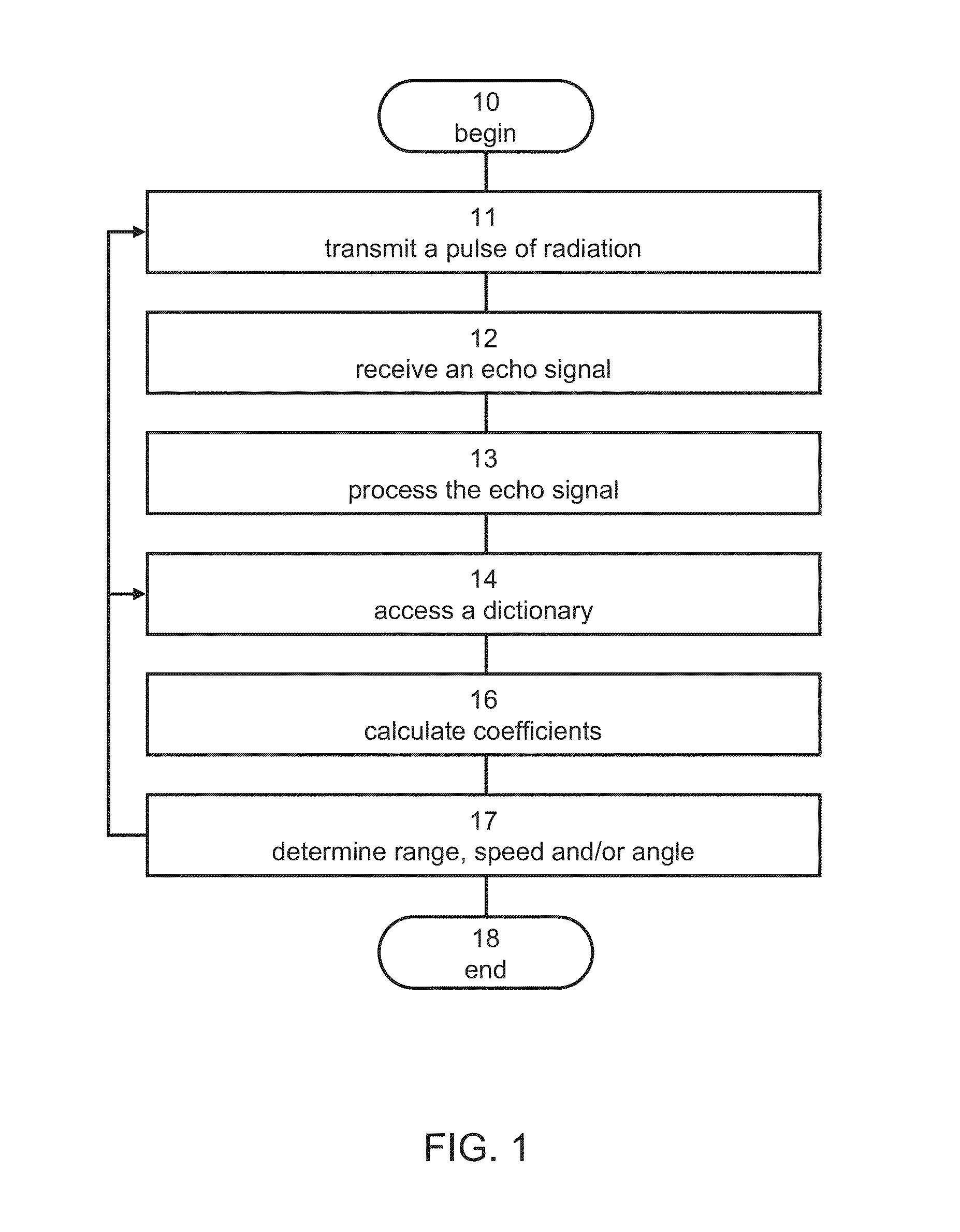
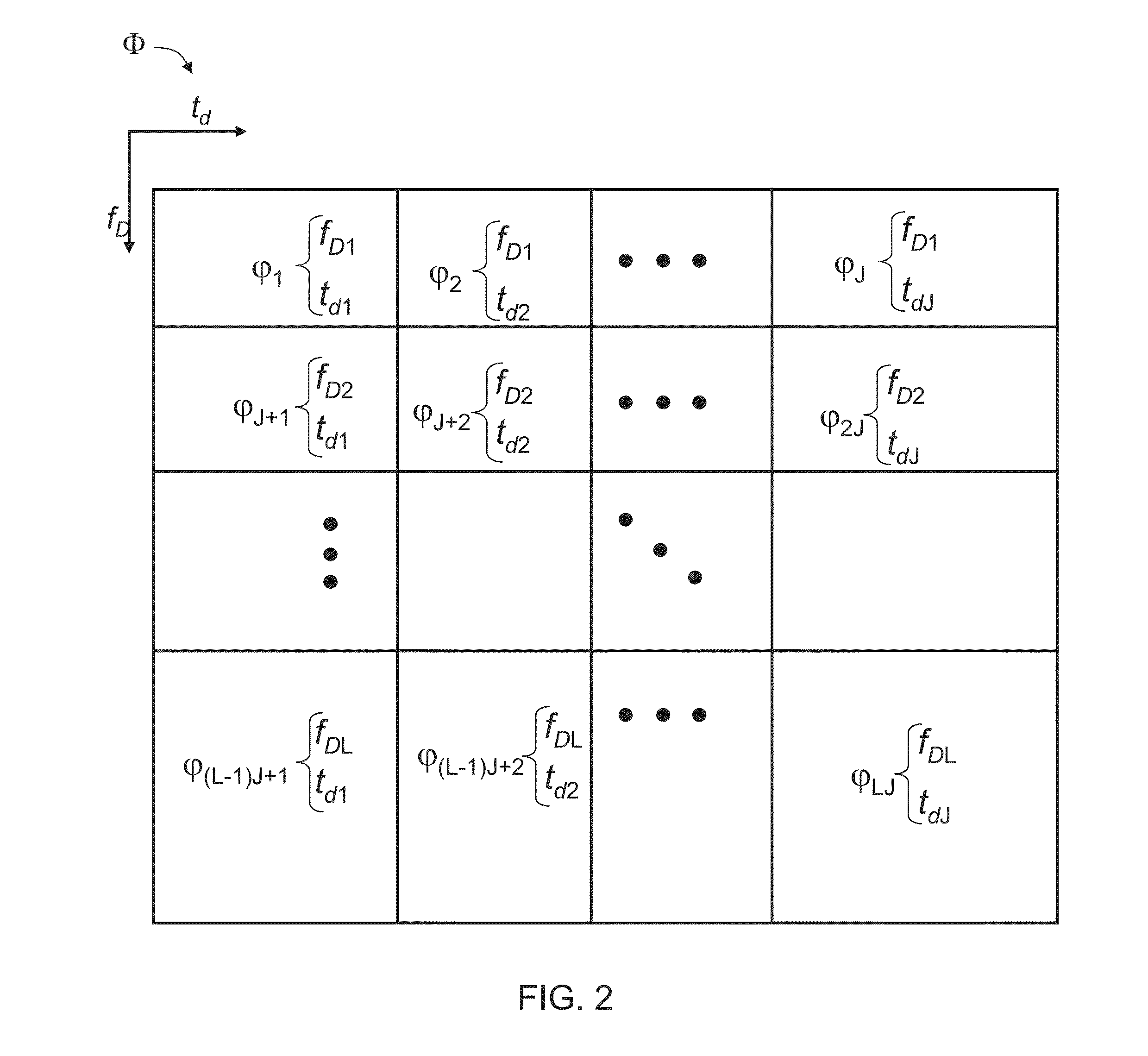
Method and system for target detection
ActiveUS20140035776A1Electromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime delaysRadiation pulse
A method of detecting a physical target in a region-of-interest is disclosed. The method comprises: transmitting a pulse of radiation into the region-of-interest; receiving an echo signal from the region-of-interest; accessing a computer readable medium storing a dictionary defined over a plurality of dictionary atoms each describing a dictionary function corresponding to at least a time delay and a Doppler shift; calculating a coefficient for each dictionary function using the echo signal, thereby providing a plurality of coefficients, wherein a linear combination of all dictionary functions respectively weighted by the coefficients does not reconstruct the echo signal; and determining at least one of a range and a speed of the target based on the coefficients.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Optical pulse calibration for quantum key distribution
InactiveUS7242775B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsOptical radiationUltrasound attenuation
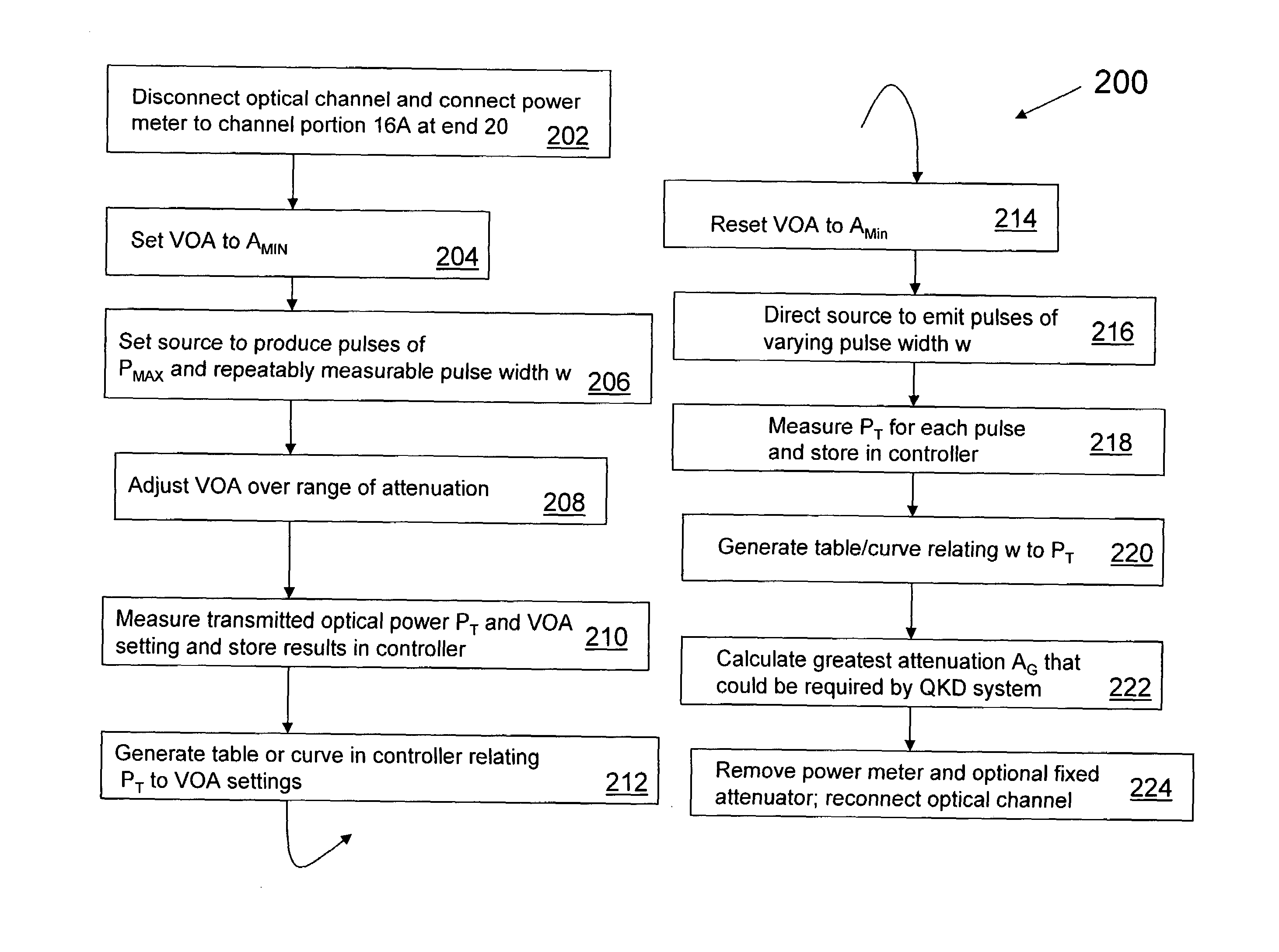
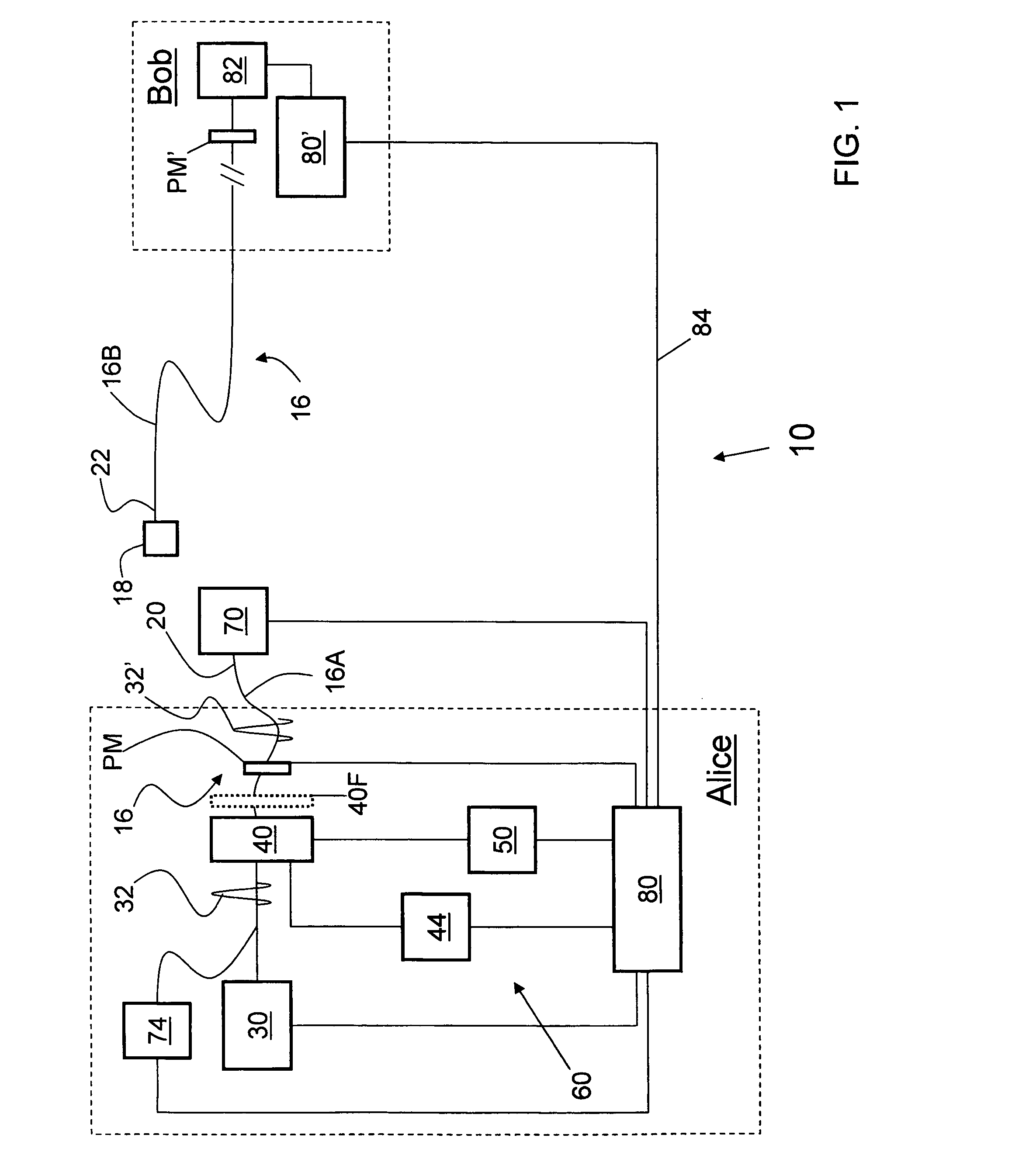
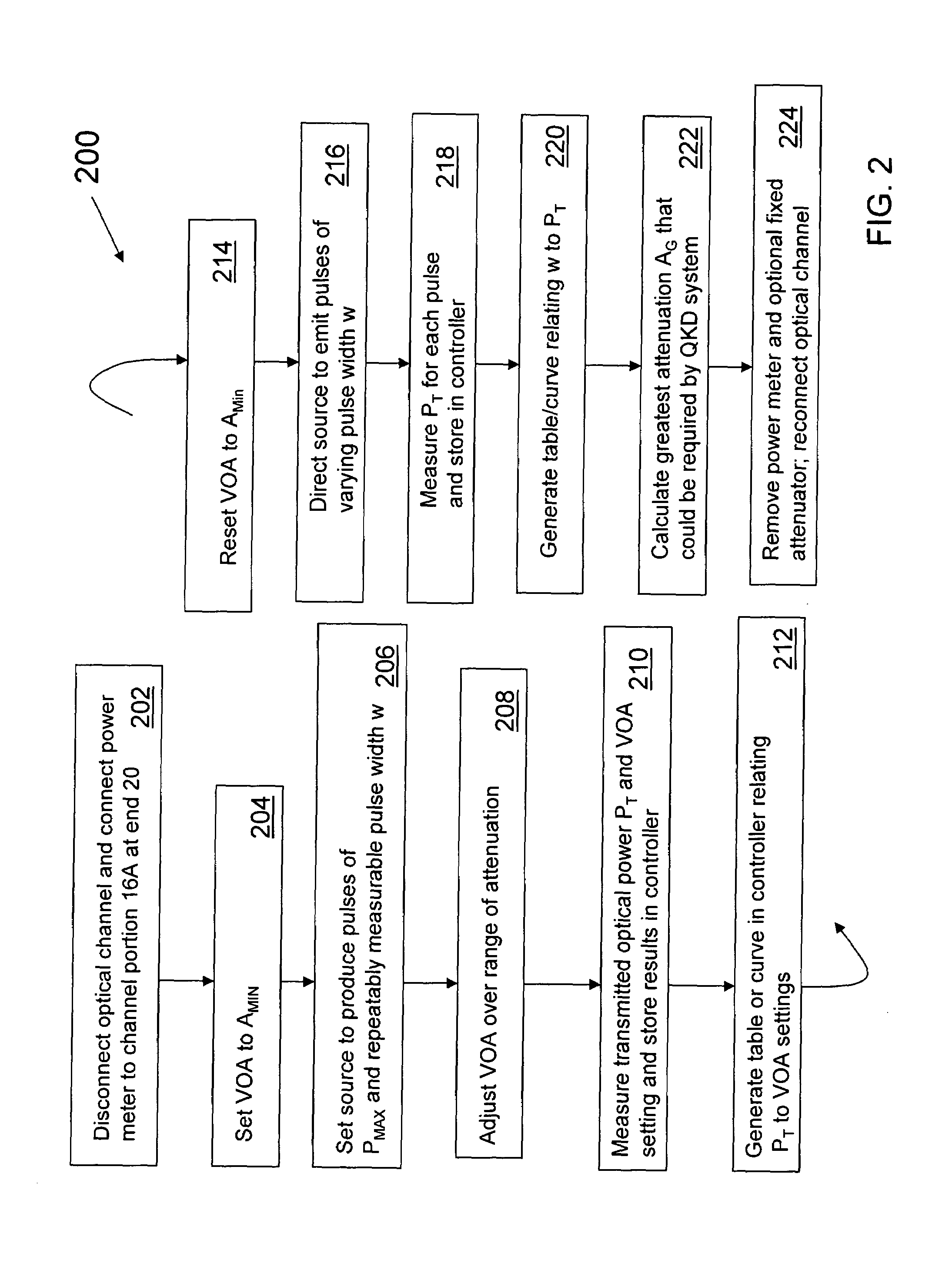
Methods and systems for generating calibrated optical pulses in a QKD system. The method includes calibrating a variable optical attenuator (VOA) by first passing radiation pulses of a given intensity and pulse width through the VOA for a variety of VOA settings. The method further includes resetting the VOA to minimum attenuation and sending through the VOA optical pulses having varying pulse widths. The method also includes determining the power needed at the receiver in the QKD system, and setting the VOA so that optical pulses generated by the optical radiation source are calibrated to provide the needed average power. Such calibration is critical in a QKD system, where the average number of photons per pulse needs to be very small—i.e., on the order of 0.1 photons per pulse—in order to ensure quantum security of the system.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Methods and systems for providing emission of incoherent radiation and uses therefor
InactiveUS20040183461A1High peak power UV outputMaximizes peak powerElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
Methods and systems for providing emission of incoherent radiation and uses therefor are disclosed. A system for providing emission of high peak power (in watts) incoherent radiation, comprises an electrically impeded discharge lamp linked to an electrical energy supply. The lamp comprises a discharge chamber which is at least partially transparent to the incoherent radiation, a discharge gas in the chamber, two electrodes disposed with respect to the chamber for discharging electrical energy therebetween, at least one dielectric barrier disposed between the two electrodes to electrically impede electrical energy passing between the two electrodes, an electrical energy supply capable of providing test risetime, high peak power unipolar voltage pulses, means of electrically linking the electrodes with the supply, the energy supply being capable of providing a sequence of high peak power unipolar voltage pulses from the energy supply to the electrodes and means to control (i interpulse period, and (ii) pulse risetime, whereby, in use, a substantially homogeneous discharge occurs between the two electrodes which causes emission of incoherent radiation pulses of high peak power from the lamp.
Owner:MACQUARIE RES
Transition-metal-doped thin-disk laser
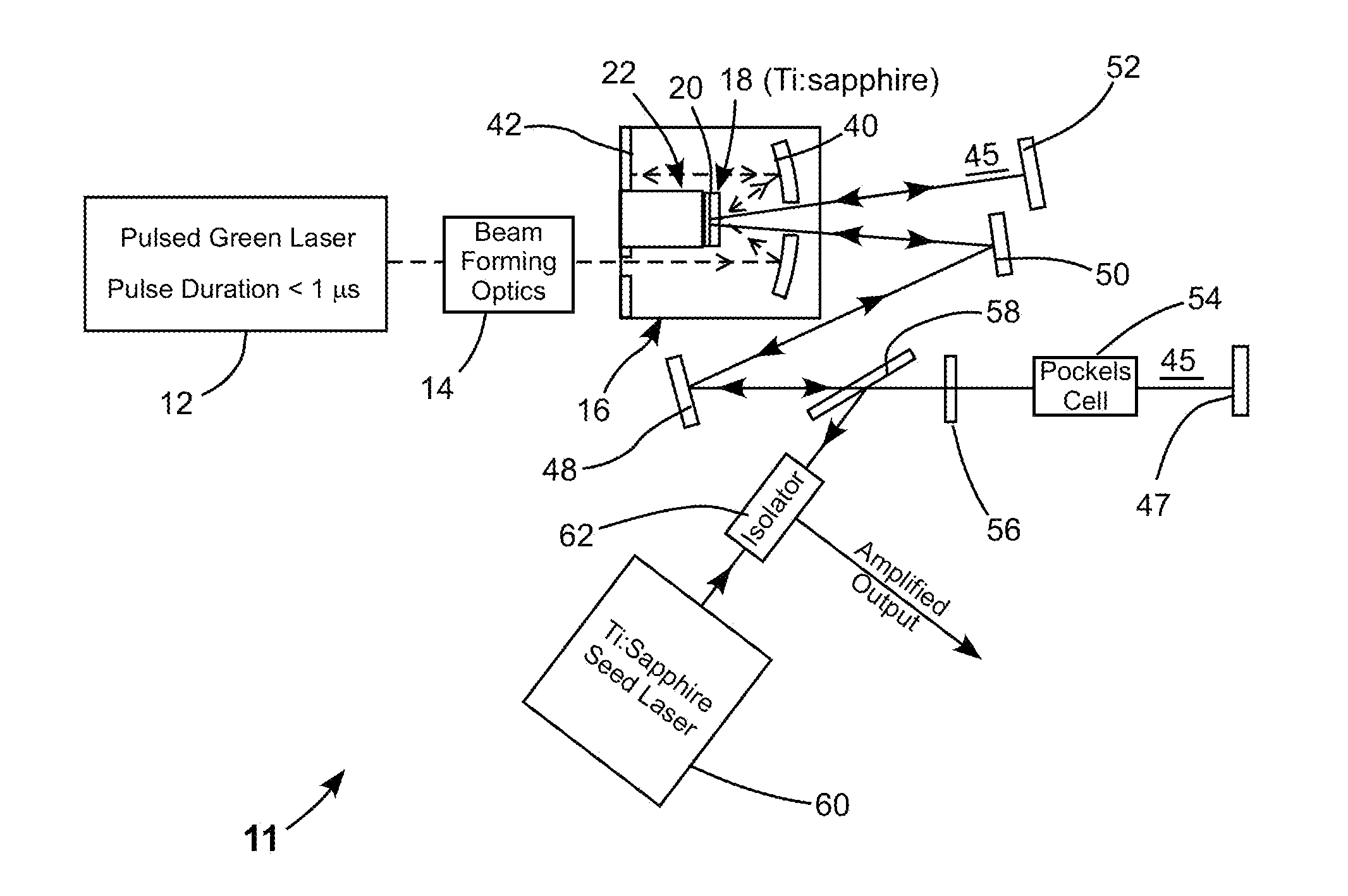
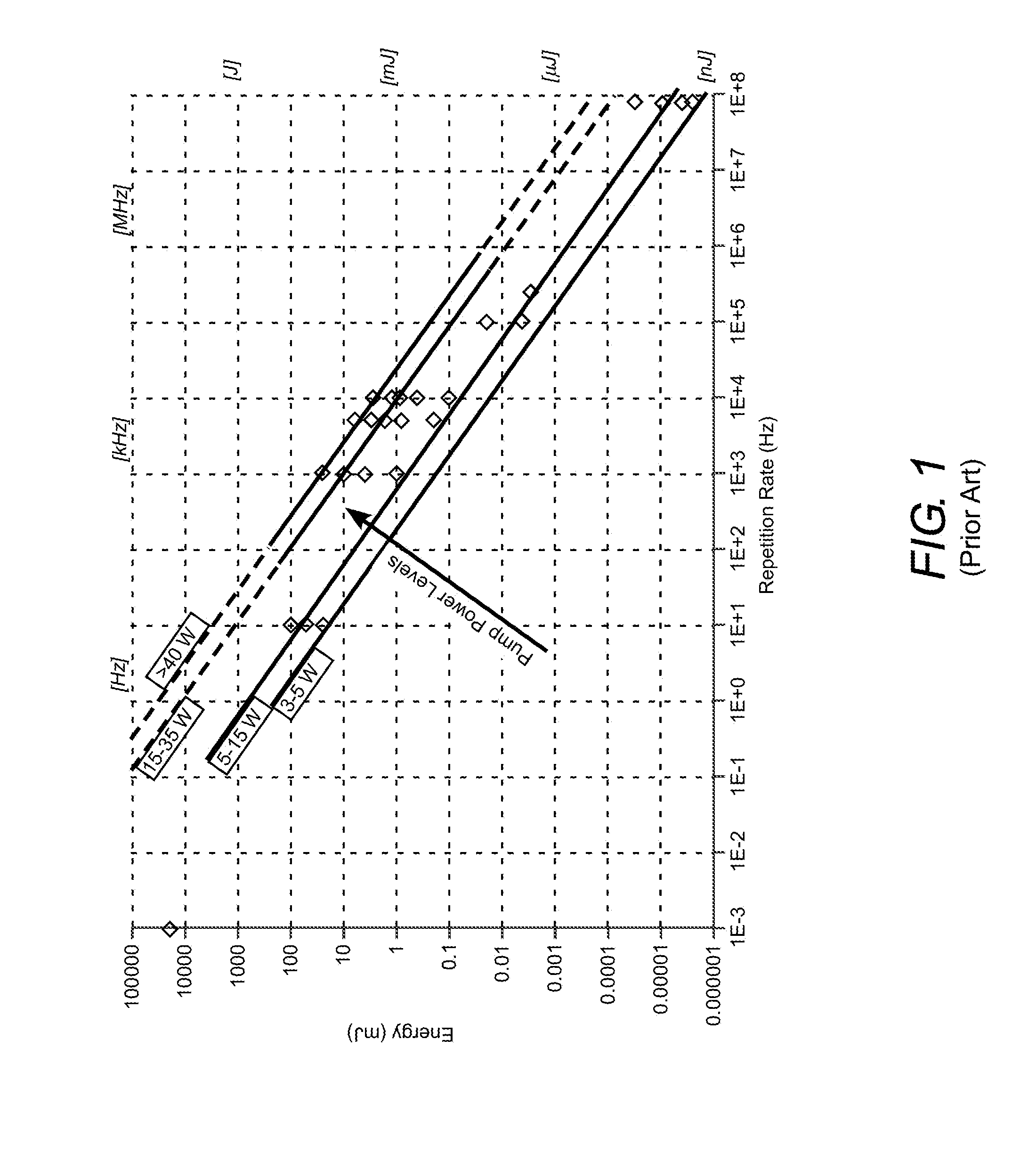
A laser includes a Ti:sapphire gain-medium in the form of a thin-disk. The thin-disk gain-medium is optically pumped by pump-radiation pulses having a wavelength in the green region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The pump-radiation pulses have a duration less than twice the excited-state lifetime of the gain-medium.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Laser scanning apparatus and methods for thermal processing
InactiveUS20070051708A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser scanningRadiation pulse
Apparatus and methods for thermally processing a substrate with scanned laser radiation are disclosed. The apparatus includes a continuous radiation source and an optical system that forms an image on a substrate. The image is scanned relative to the substrate surface so that each point in the process region receives a pulse of radiation sufficient to thermally process the region.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
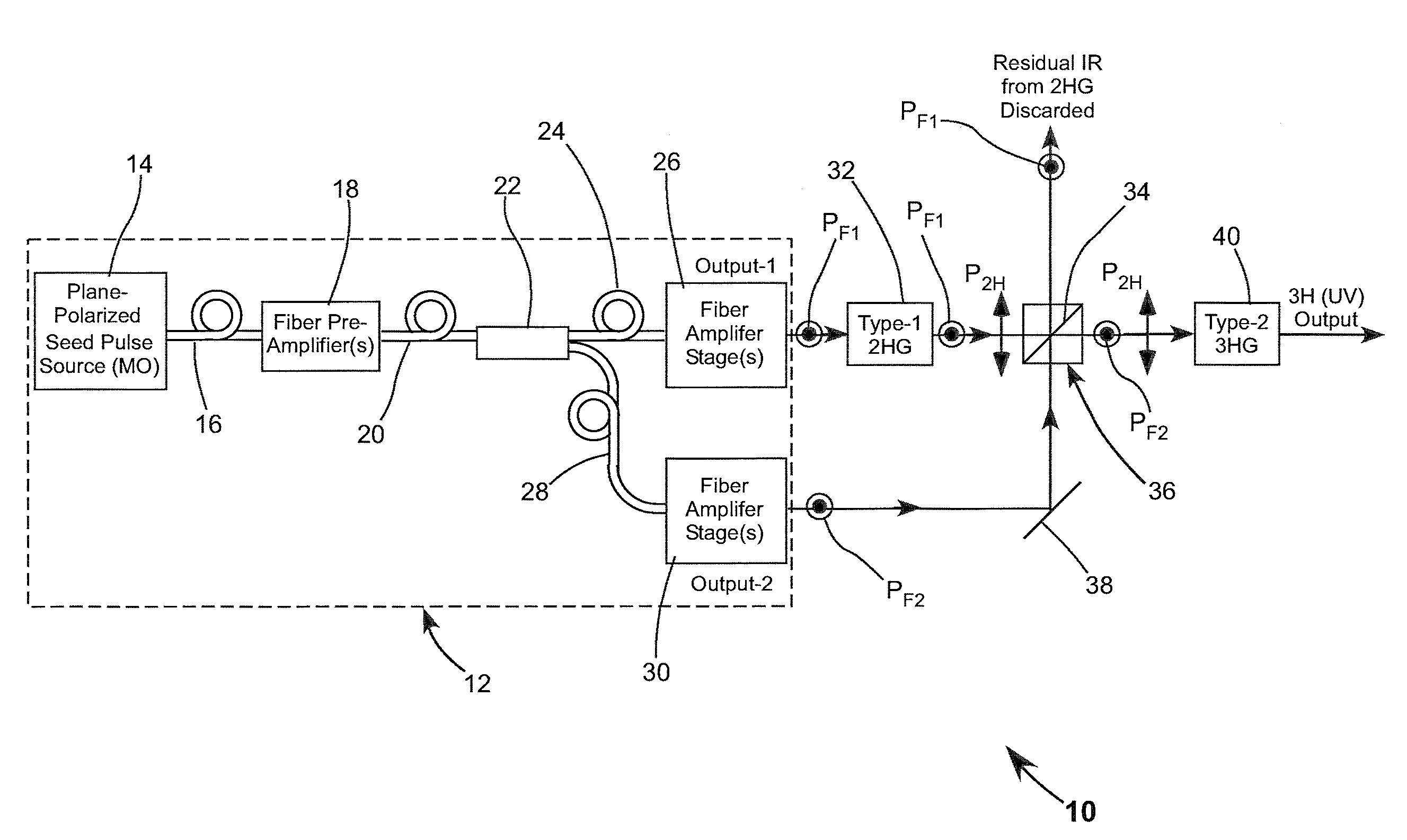
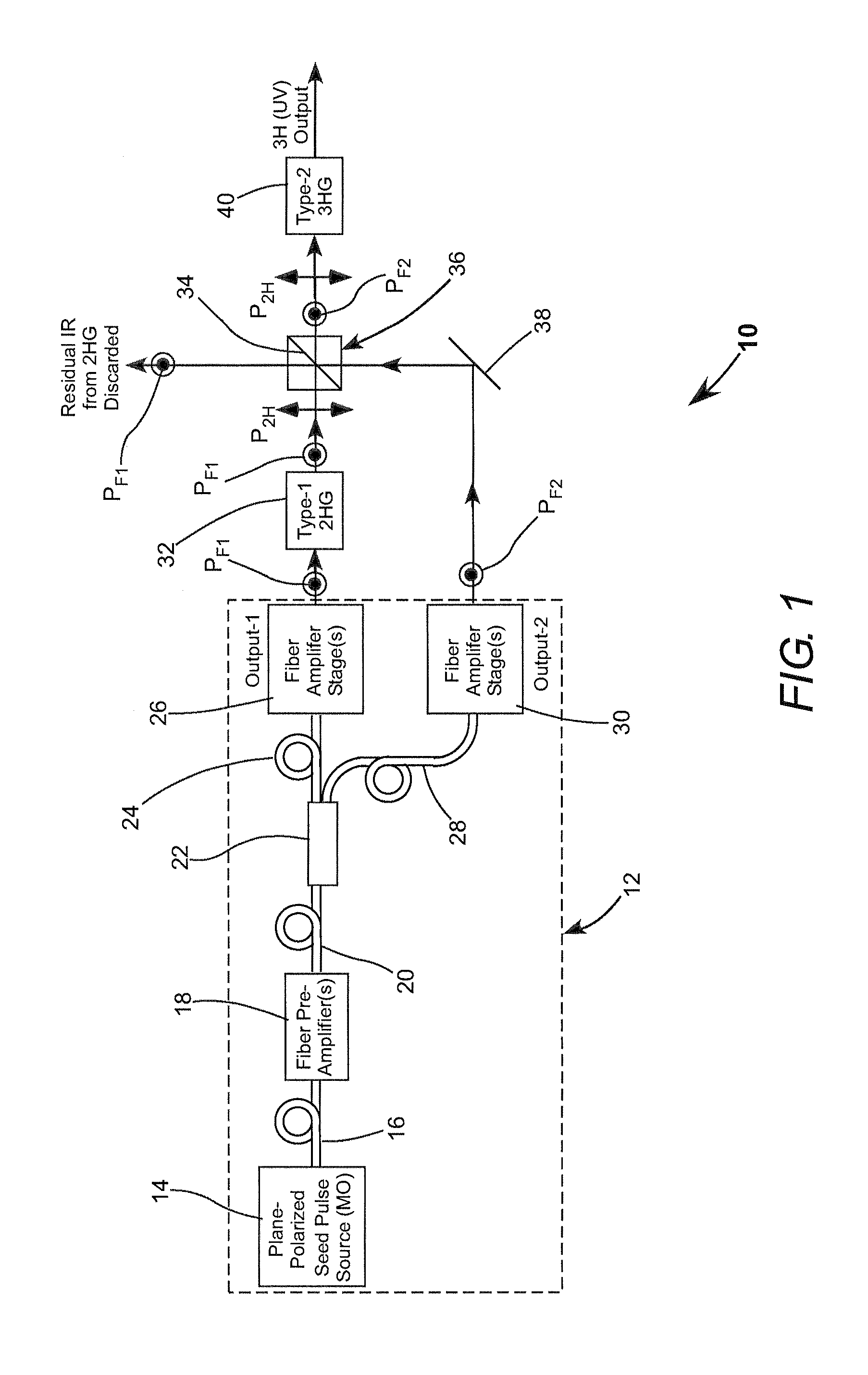
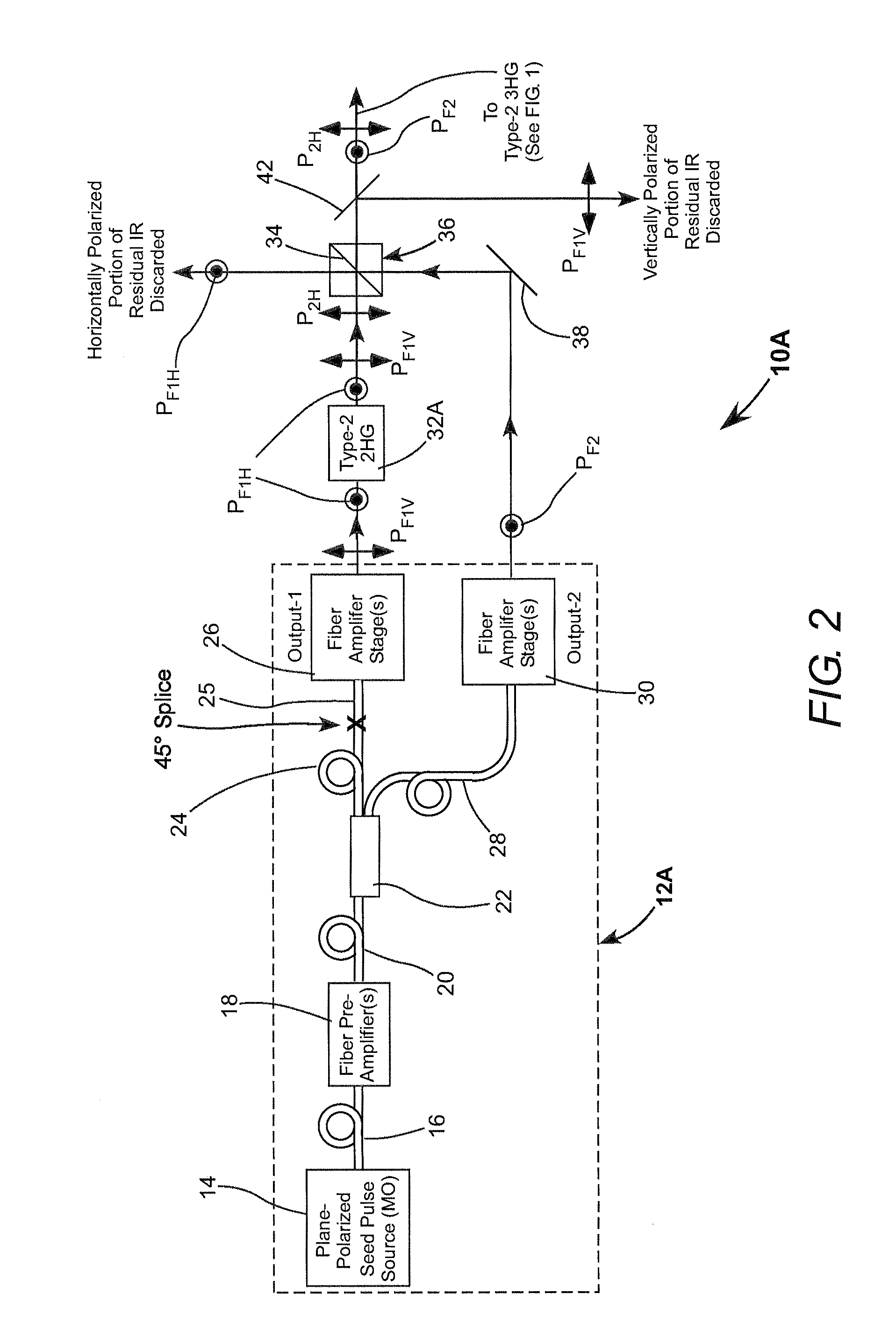
Frequency-tripled fiber mopa
Fundamental-wavelength pulses from a fiber a laser are divided into two portions and the two portions are separately amplified. One of the amplified fundamental-wavelength pulse-portions is frequency-doubled. The frequency doubled portion is sum-frequency mixed with the other amplified fundamental wavelength pulse-portions to provide third-harmonic radiation pulses.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Full-lightning positioning system with combination of very-low frequency and very-high frequency
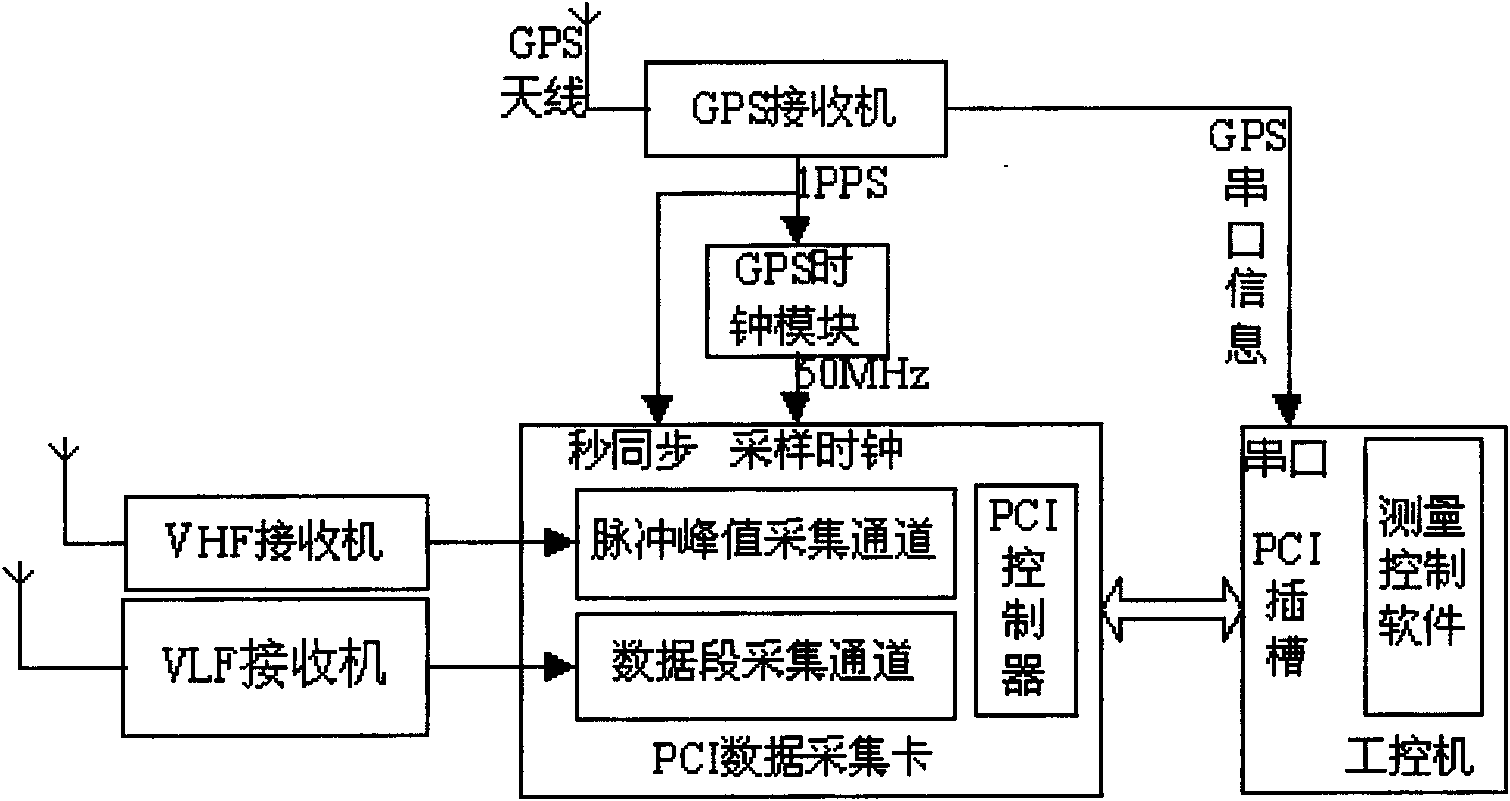
InactiveCN101609145ALightning Activity WarningWeather condition predictionPosition fixationThe InternetRadiation pulse
The invention relates to a full-lightning positioning system with combination of very-low frequency and very-high frequency (VHF). The full-lightning positioning system is characterized by comprising at least four lightning positioning monitoring stations which are respectively provided with a very-low frequency lightning radiation receiver, a very-high frequency lightning radiation receiver, a GPS receiver and an industrial computer; the station utilizes time reference provided by the GPS receiver and obtains the time and waveform that the change pulse of a lightning electric field and VHF radiation pulse reach all the stations, utilizes the industrial computer to preprocess the obtained waveform data, then transmits the obtained data in real time to the industrial computer for analyzing and processing the pulse waveform by an internet, and realizes real-time monitoring and three-dimensional positioning to lightning discharge events. Under the matching of the above hardware and software, the system can be used for determining the quantity, types, characteristic parameters and statistical characteristics of lightning discharge events occurring in a specified area, and carries out monitoring and early warning to the activities of thunder and lightning.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF METEOROLOGICAL SCI
Arrangement for the generation of EUV radiation with high repetition rates
InactiveUS6946669B2Increased electrode wearEasy to wearRadiation pyrometryNuclear explosivesOptical axisPulse energy
The arrangement for generating EUV radiation based on electrically triggered gas discharges with high repetition rates and high average outputs. The object of the invention, to find a novel possibility for generating EUV radiation based on a gas discharge pumped plasma which permits the generation of EUV pulse sequences with a pulse repetition frequency of greater than 5 kHz at pulse energies of at least 10 mJ / sr without having to tolerate increased electrode wear, is met according to the invention in that a plurality of source modules of identical construction, each of which generates a radiation-emitting plasma and has bundled EUV radiation, are arranged in a vacuum chamber so as to be uniformly distributed around an optical axis of the source in its entirety in order to provide successive radiation pulses at a point on the optical axis, so that a reflector device which is supported so as to be rotatable around the optical axis deflects the radiation delivered by the source modules in the direction of the optical axis successively with respect to time. A synchronization device triggers the source modules in a circularly successive manner depending upon the actual rotational position of the reflector device and adjusts a preselected pulse repetition frequency by means of the rotating speed.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Periodic lighting device
InactiveUS20110109236A1Prevent penetrationSimplify disassemblyAnimal huntingBaitBiological bodyRadiation pulse
There is presented a detailed electronic method for simulation of a firefly, other insects, or organisms producing bioluminescence and with light radiation functions similar to a real firefly, other insects, or organisms producing bioluminescence. An illuminated artificial firefly, other insects, or organisms producing bioluminescence can be placed on trees and shrubs in landscape, or at home to produce radiation, at night time, and blinking a gradually decaying light. More particularly it relates to a decorative type of device in the form of a firefly, other insects, or organisms producing bioluminescence and with light radiation functions similar to a real firefly, other insects, or organisms producing bioluminescence. The light is simulated by an electronics program that is a part of compact device with the form of a real firefly, other insects, or organisms producing bioluminescence. Short radiation pulses of microsecond-millisecond duration time in violet and ultraviolet range of radiation wavelengths can be utilized for scaring birds or other animals from undesirable or dangerous places of human activity, such as airports, contaminated ponds, wind turbines, electorized fences and antennas.
Owner:SCHAAL HERBERT RUDOLF +1
Systems and methods for generating high power, wideband microwave radiation using variable capacitance voltage multiplication
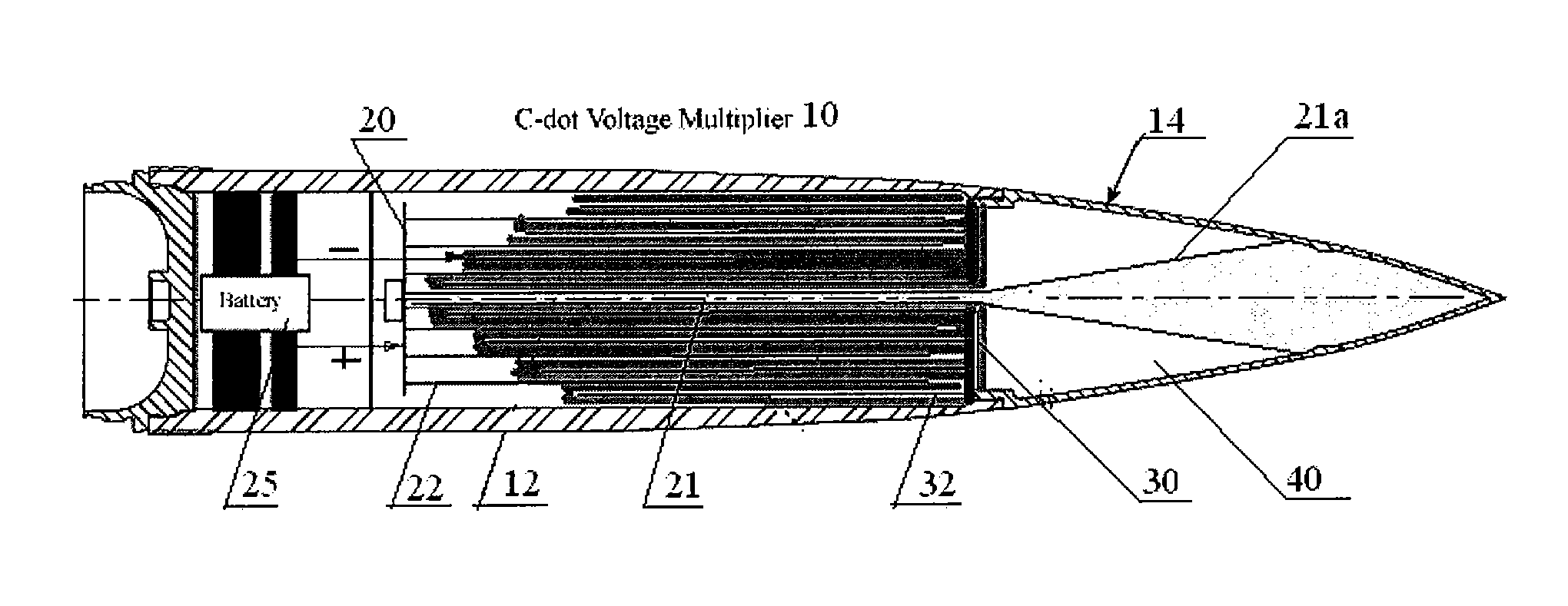
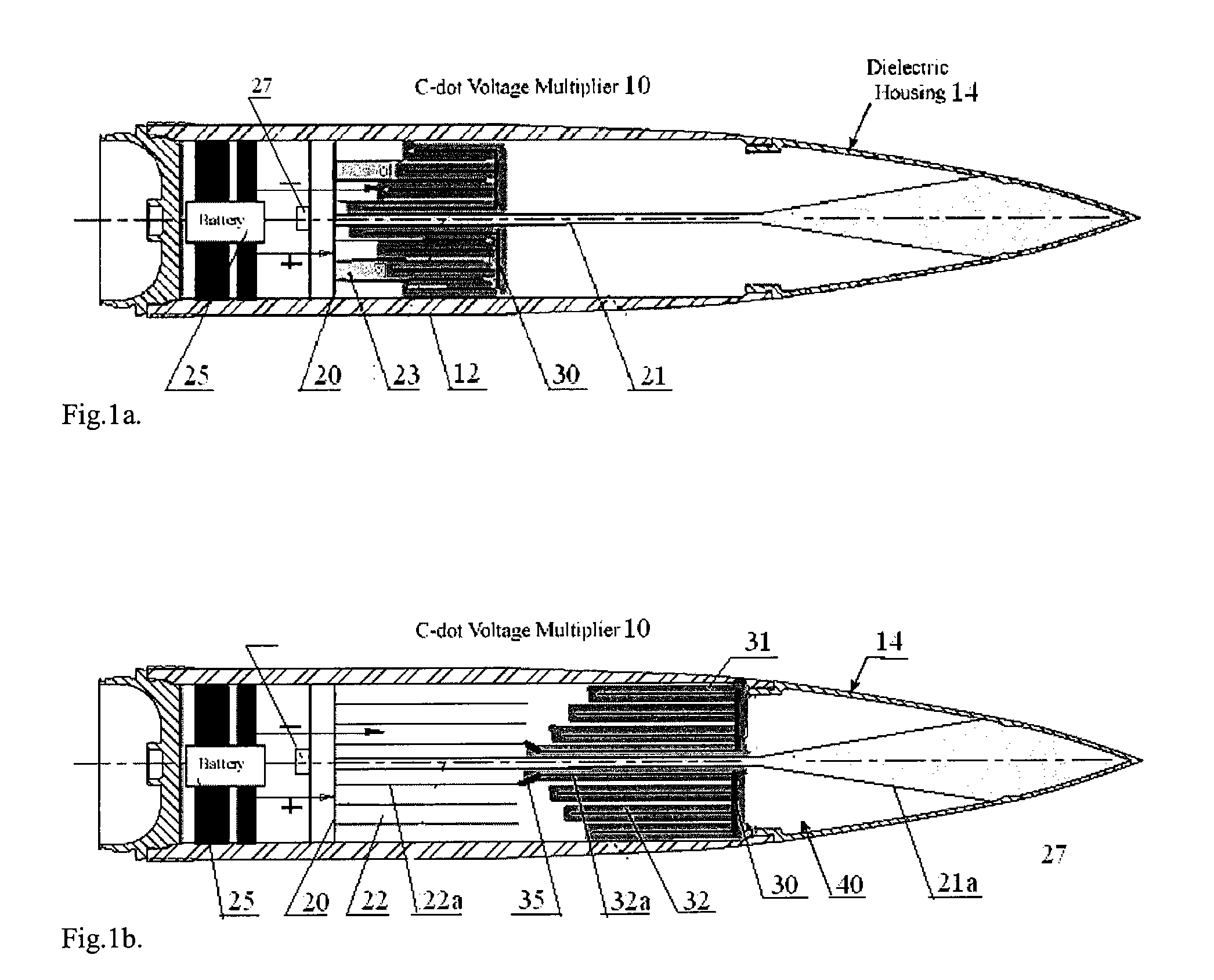
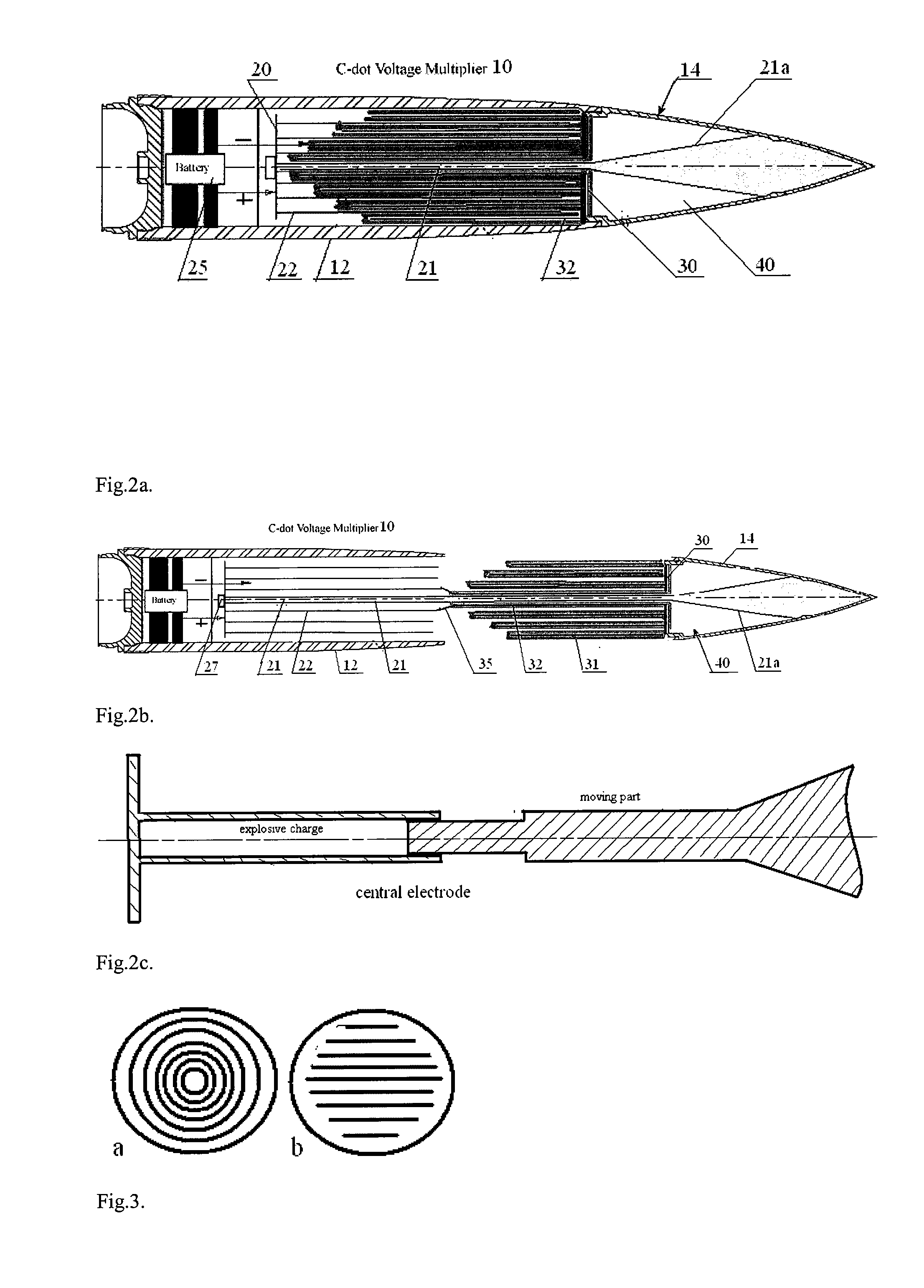
InactiveUS20090224610A1Reduce capacitanceIncrease distanceAmmunition projectilesPulse train generatorRadiation pulseElectromagnetic pulse
Systems and methods for generating high power, wideband microwave radiation pulses. A pulse generating device includes a capacitor as a primary electric energy store, a source of mechanical or chemical energy for modifying the capacitance of the capacitor, which then connects to a transmission line or pulse forming line (PFL) with many times increased electromagnetic energy, a switch and a broadband radiating element such as an antenna. A high voltage pulse and accordingly a high amount of electromagnetic energy is formed owing to decreasing the capacitance of an initially charged capacitor by dynamically changing a configuration of capacitor electrodes using mechanical work. The final configuration forms a transmission line, with the voltage and electric energy increased by the ratio of initial capacitance to final capacitance when the charge on the modifying capacitor is conserved. A switch connects opposite charged parts of the transmission line, and the resulting high voltage in the form of a pulse or multiple pulses propagates along the transmission line to a load (antenna) to generate one or more electromagnetic pulses.
Owner:MICROWAVE SCI
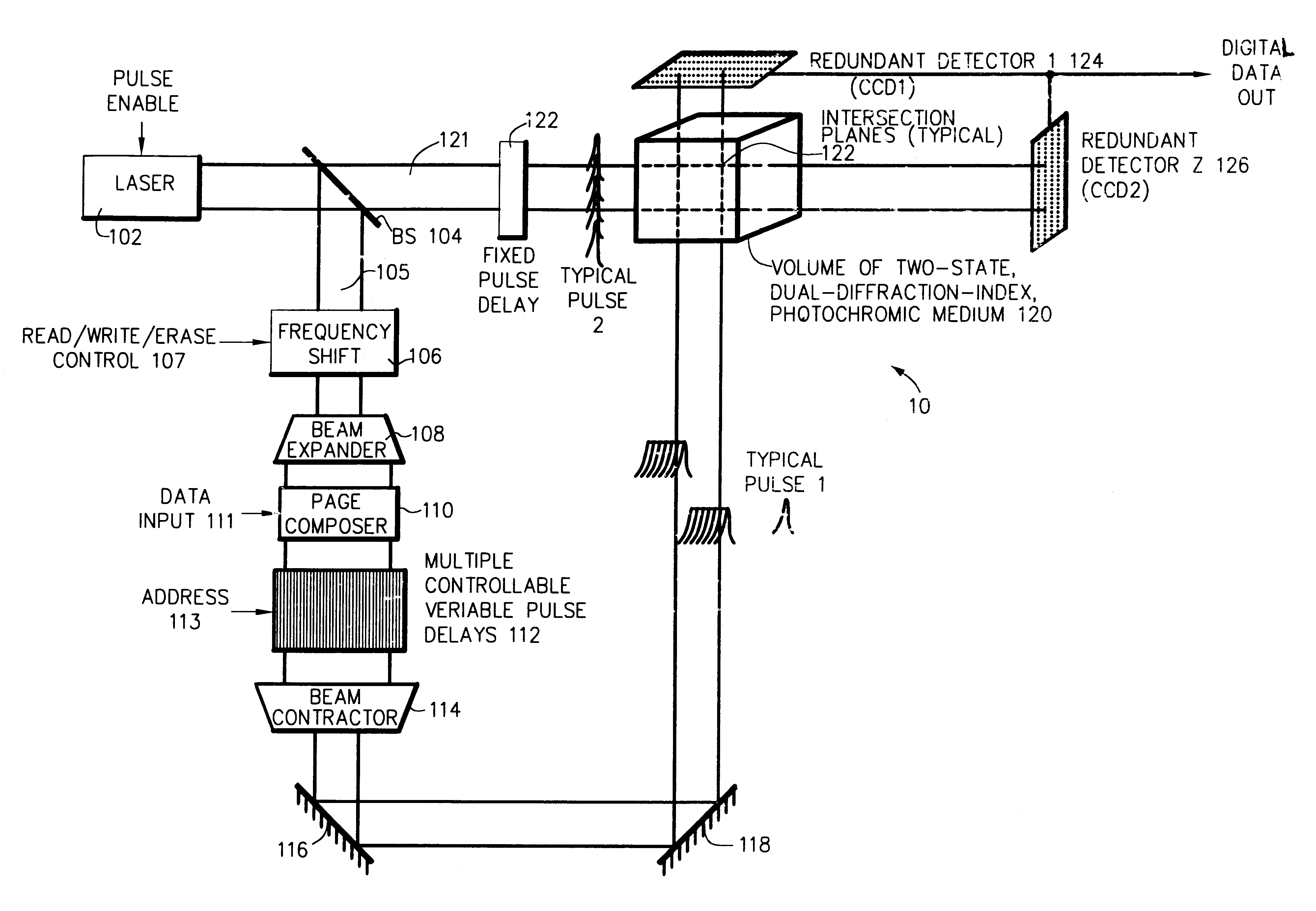
Two-photon four-dimensional optical memory
InactiveUS6608774B1Accurate resolutionRecording involving hole burningNanoinformaticsSpatial light modulatorFluorescence
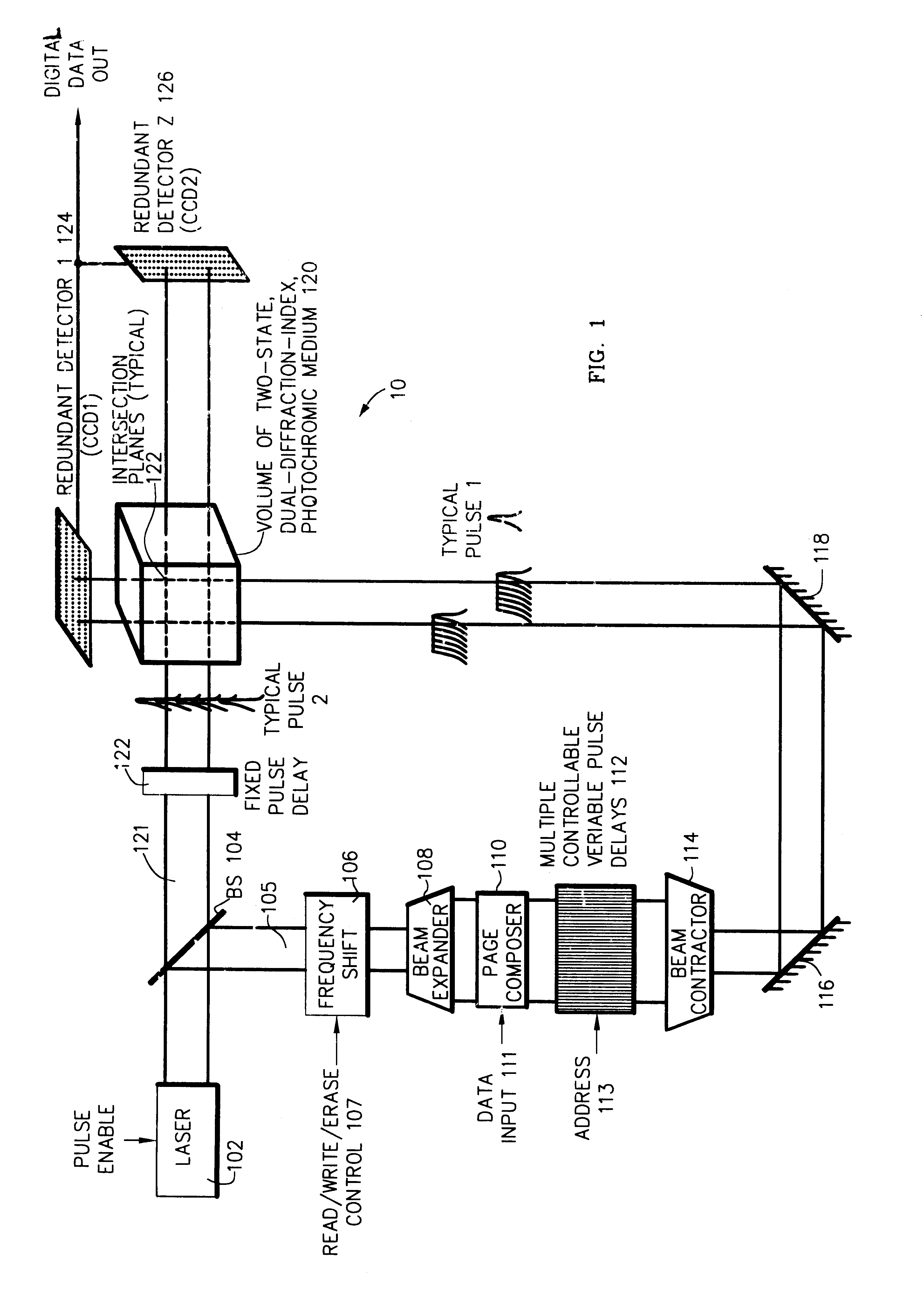
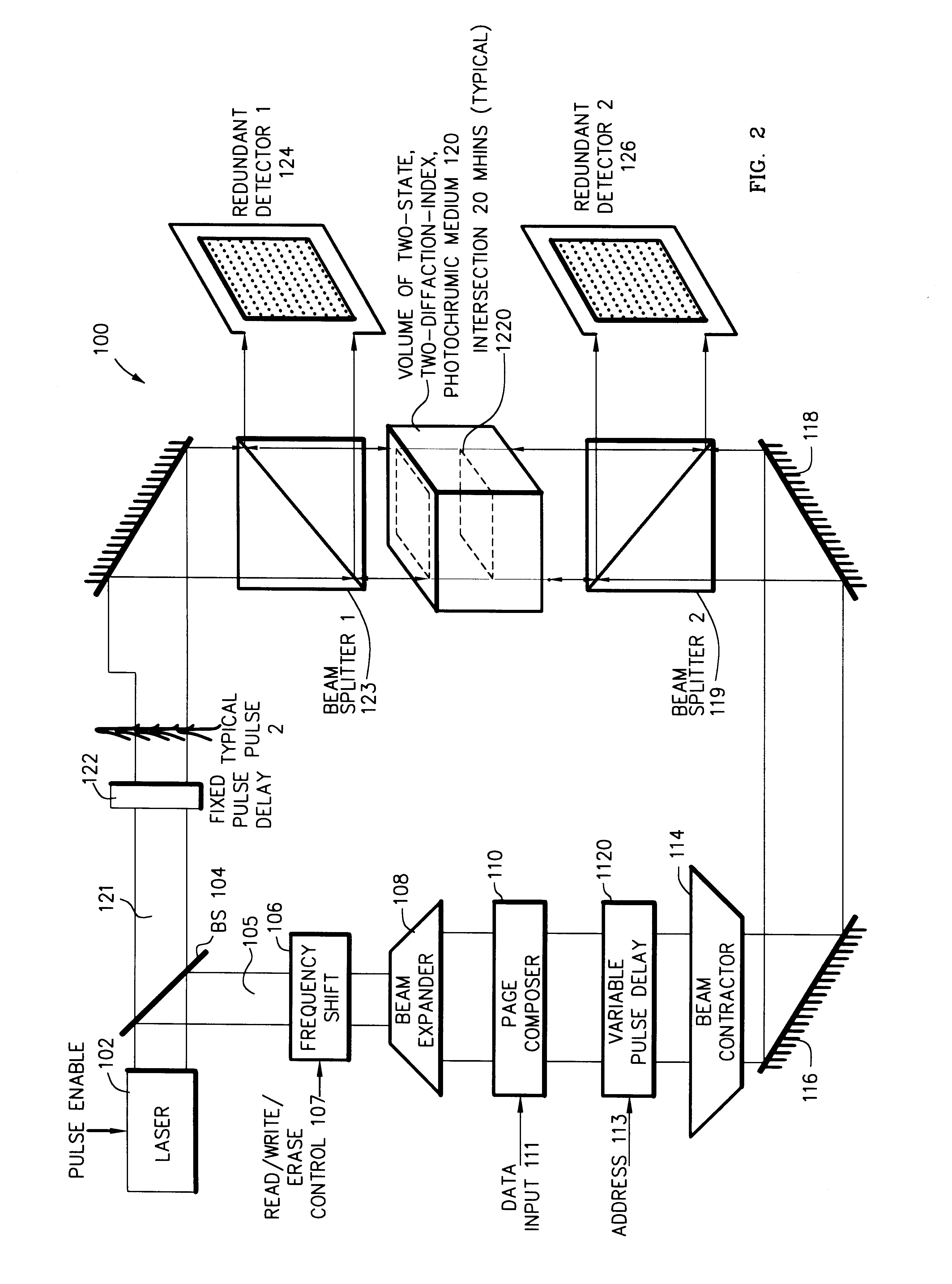
Selected domains, normally 2x103x2x103 such domains arrayed in a plane, within a three-dimensional (3-D) volume of radiation-sensitive medium, typically 1 cm3 of spirobenzopyran containing 2x103 such planes, are temporally and spatially simultaneously illuminated by two radiation pulses, normally laser light pulses in various combinations of wavelengths 532 nm and 1024 nm, in order, dependent upon the particular combination of illuminating light, to either write binary data to, or read binary data from, the selected domains by process of two-photon (2-P) interaction / absorption. One laser light pulse is preferably directed to illuminate all domains during its propagation along one directional axis of the volume. The other laser light pulse is first spatially encoded with binary information by 2-D spatial light modulator, and is then (i) directed and (ii) time sequenced to intersection with the other light pulse in a locus of intersection domains. During writing the selected, simultaneously illuminated, intersection domains change their index of refraction, attendant upon a change in isomeric molecular form, by process of 2-P absorption. During reading selected intersection domains selectively refract each of two read light pulses identically-as well as fluoresce-dependent upon their individually pre-established, written, states. The selective refraction of each read pulse in its passage straight through the volume is sensed in a detector array. I / O bandwidth to each cm3 of radiation-sensitive medium is on the order of 1 Gbit / sec to 1 Tbit / sec.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com