Patents
Literature
6417 results about "Duration time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Duration may refer to: The amount of elapsed time between two events. Duration (music) – an amount of time or a particular time interval, often cited as one of the fundamental aspects of music. Duration (philosophy) – a theory of time and consciousness first proposed by Henri Bergson.
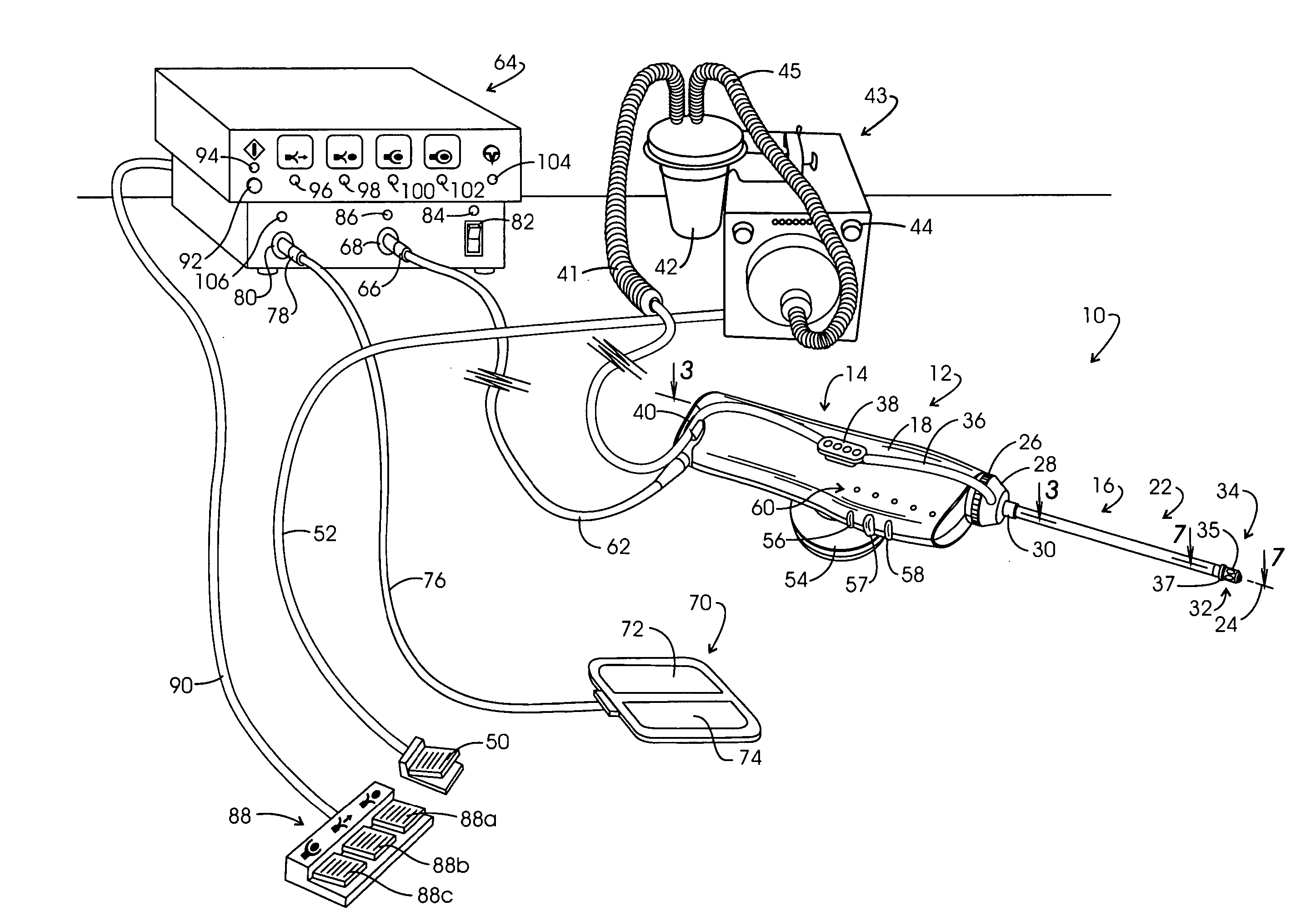
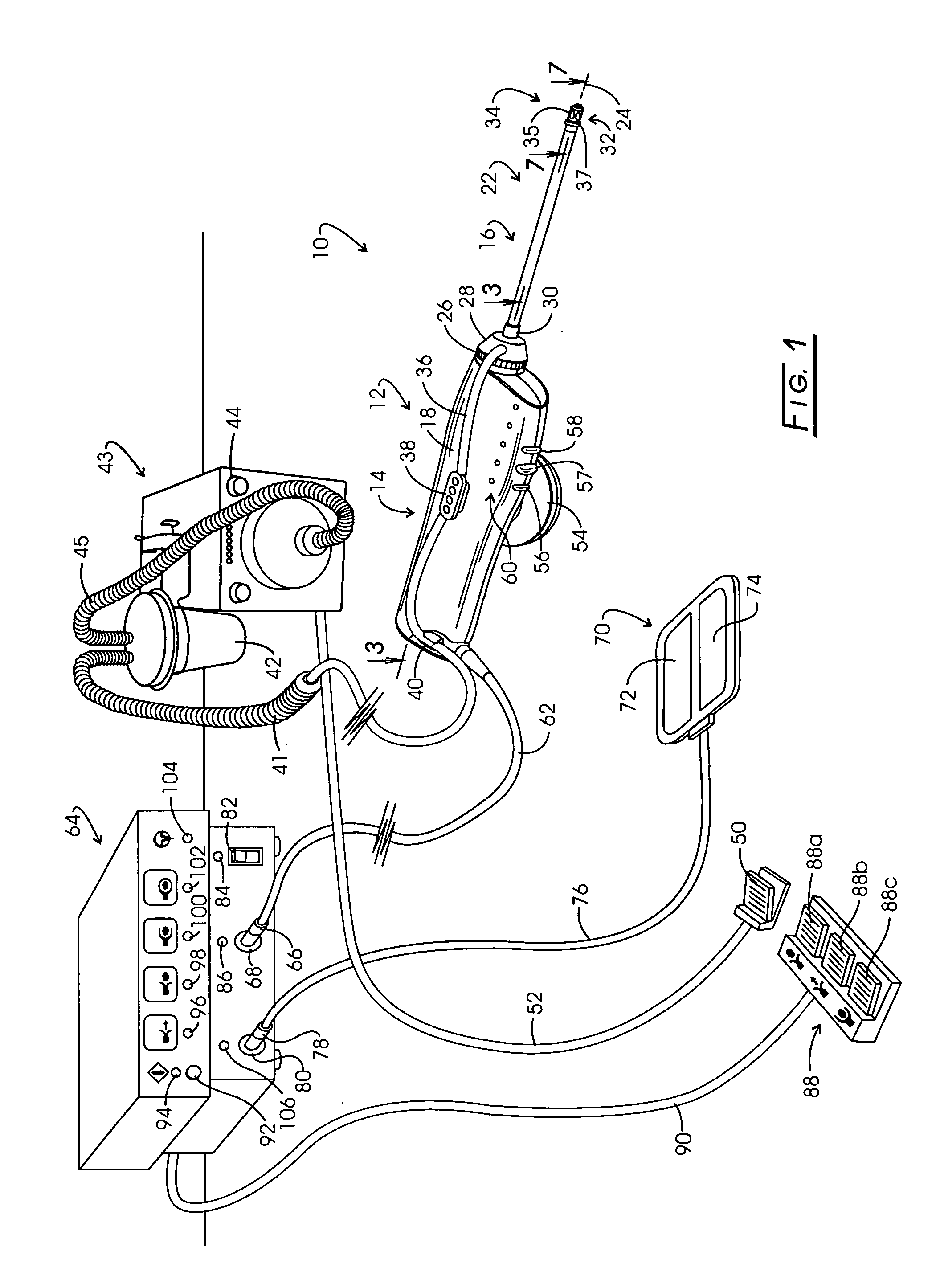
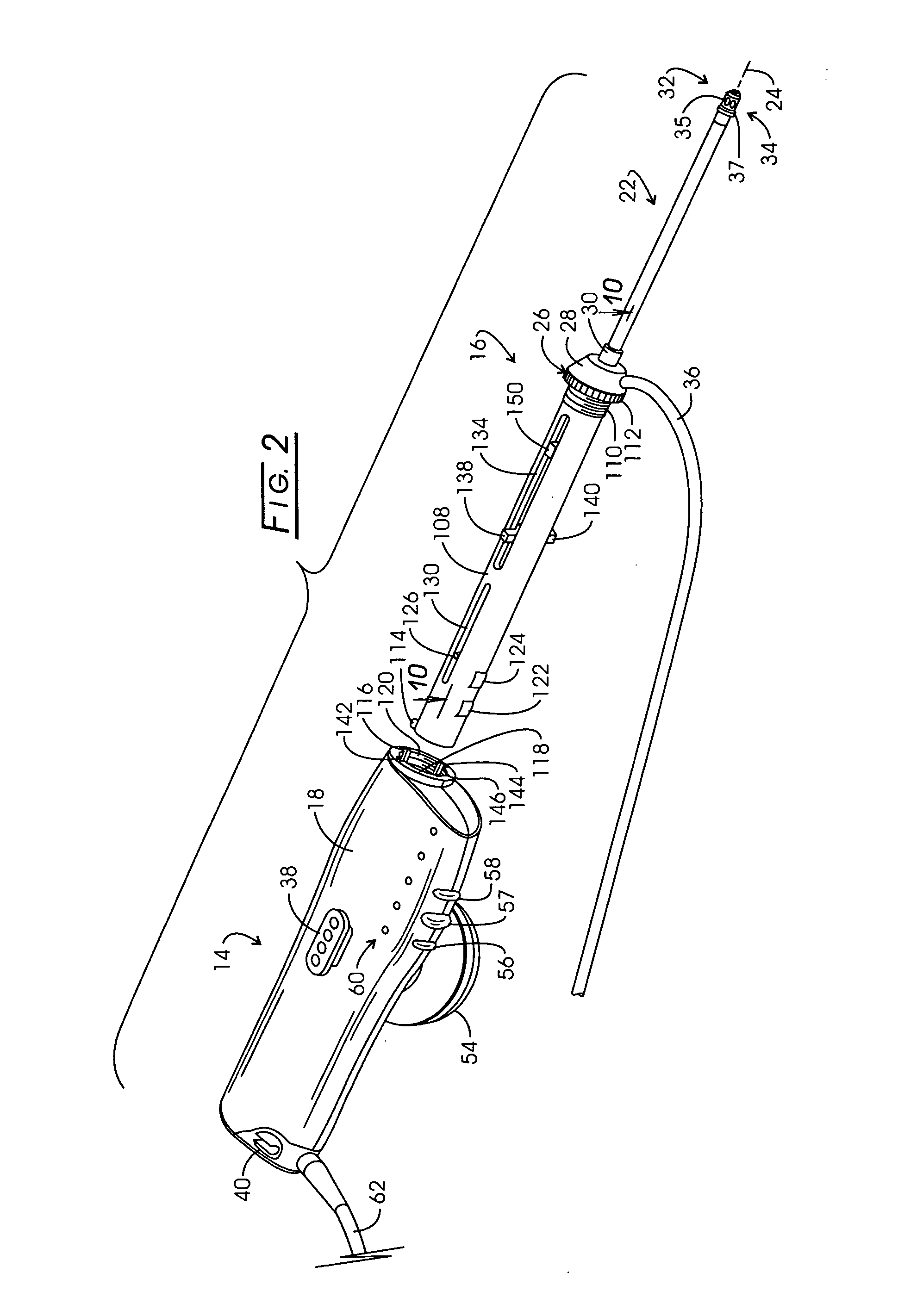
Electrosurgery with infiltration anesthesia
InactiveUS20050267455A1Reliable formationAnaesthesiaSurgical instruments for heatingElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrosurgery
Method for carrying out the recovery of an intact volume of tissue wherein a delivery cannula tip is positioned in confronting adjacency with the volume of tissue to be recovered. The electrosurgical generator employed to form an arc at a capture component extending from the tip is configured having a resistance-power profile which permits recovery of the specimen without excessive thermal artifact while providing sufficient power to sustain a cutting arc. For the recovery procedure, a local anesthetic employing a diluent which exhibits a higher resistivity is utilized and the method for deploying the capture component involves an intermittent formation of a cutting arc with capture component actuation interspersed with pauses of duration effective to evacuate any accumulation or pockets of local anesthetic solution encountered by the cutting electrodes.
Owner:INTACT MEDICAL
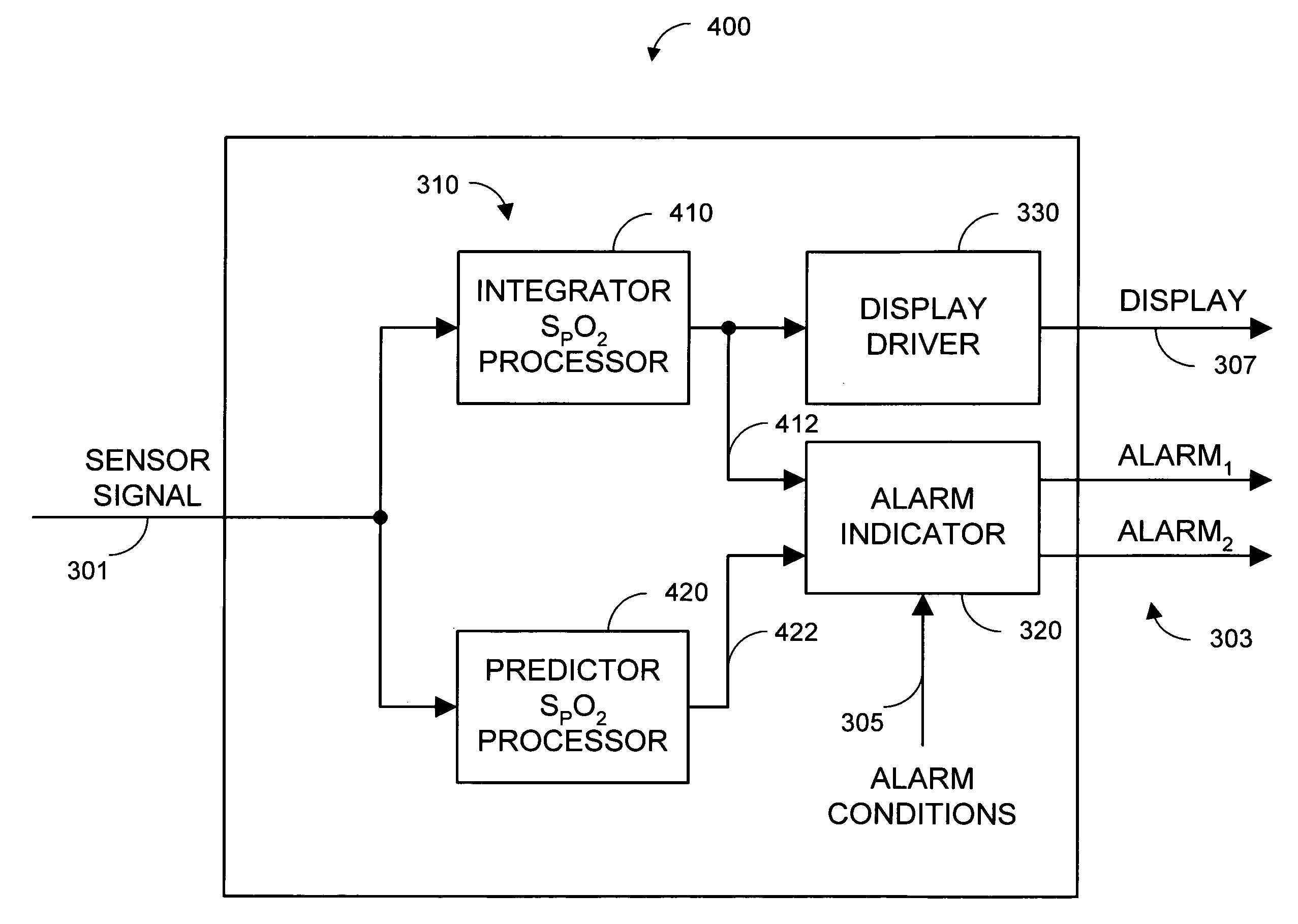
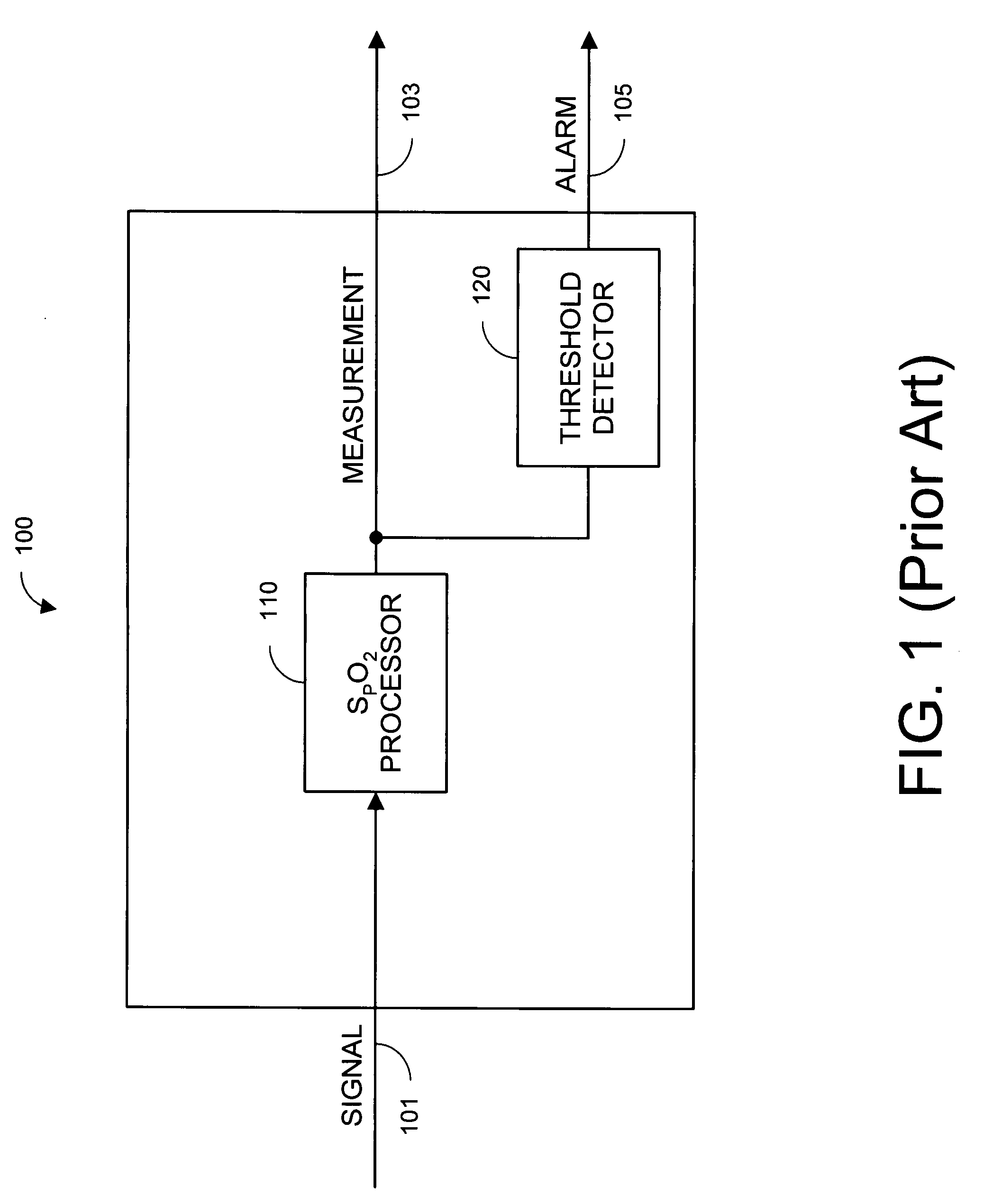
Parallel alarm processor
InactiveUS7355512B1Waste caregiver resourcesReduce false alarm rateEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsLower limitOxygen Saturation Measurement
A parallel alarm processor has a threshold detector, a pattern extractor, a predetermined reference pattern, a first alarm and a second alarm. The threshold detector has a first output responsive to relatively long duration oxygen desaturations. The pattern extractor has a second output responsive to relatively short duration oxygen desaturations. The predetermined reference pattern is indicative of a series of intermittent oxygen desaturations. A first alarm is triggered when the first output crosses a lower limit threshold. A second alarm is triggered when the second output matches the predetermined reference pattern. In an embodiment, an integrator inputs smoothed oxygen saturation measurements to the threshold detector, and a predictor inputs predictive oxygen saturation measurements to the pattern extractor.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
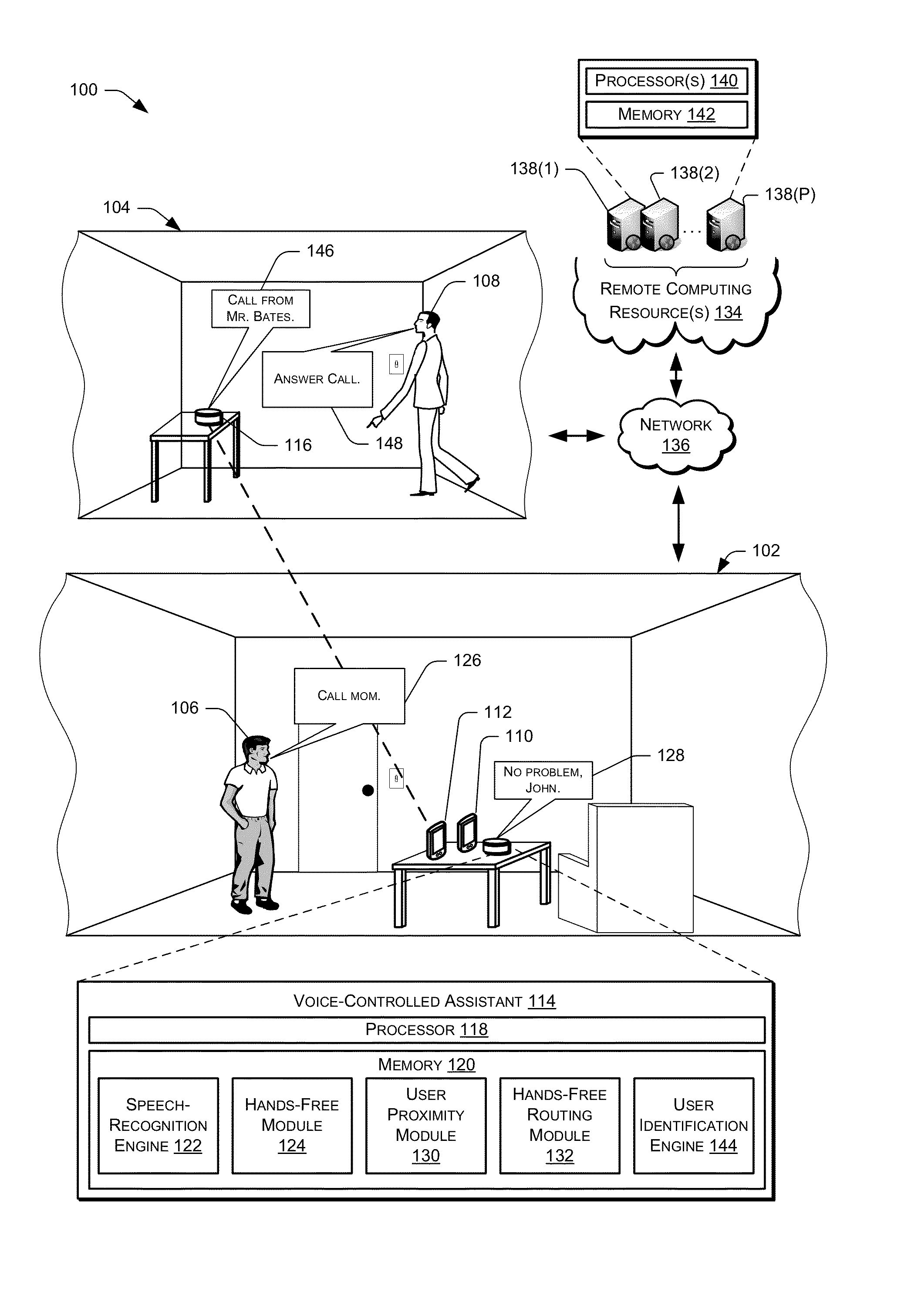
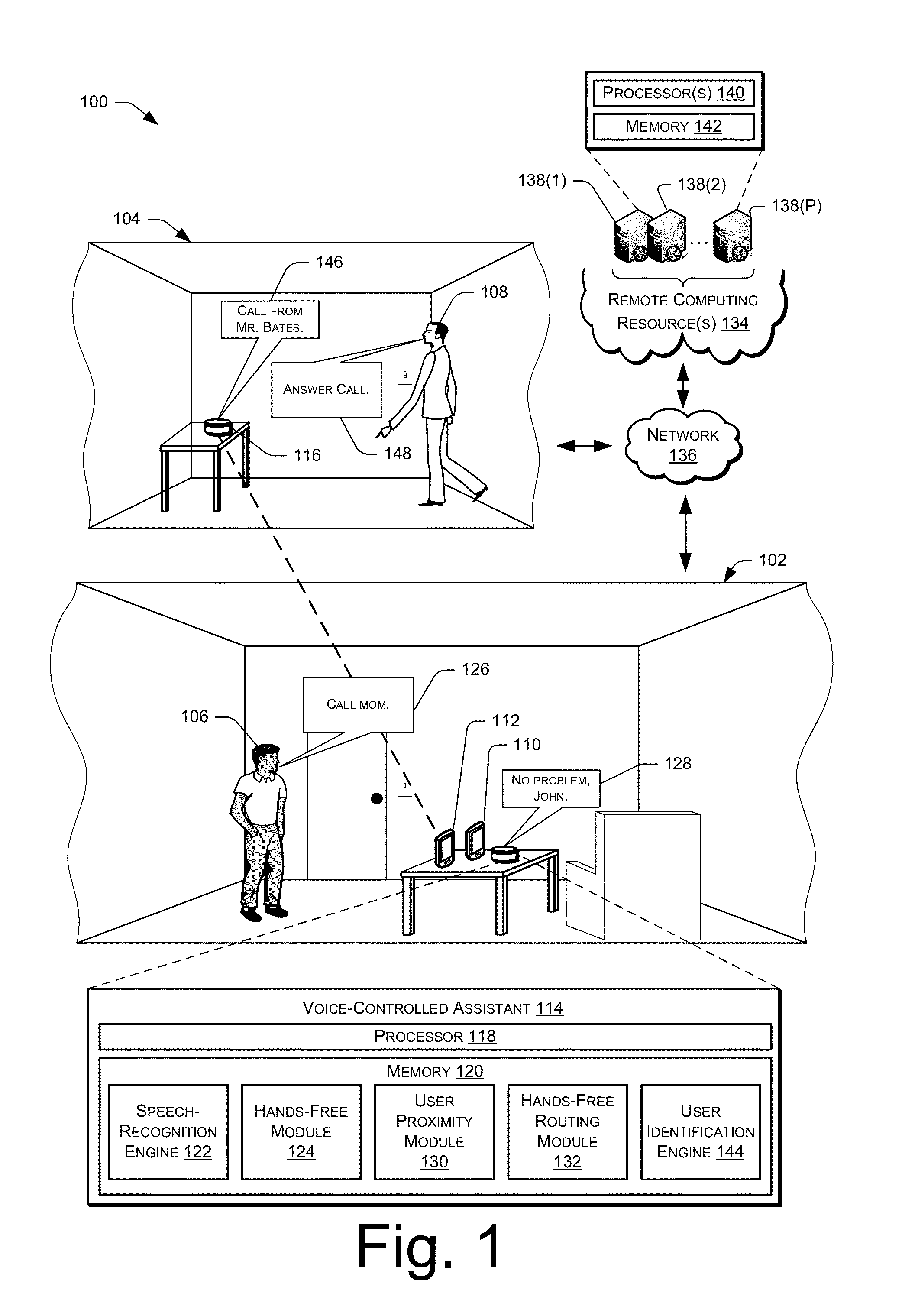
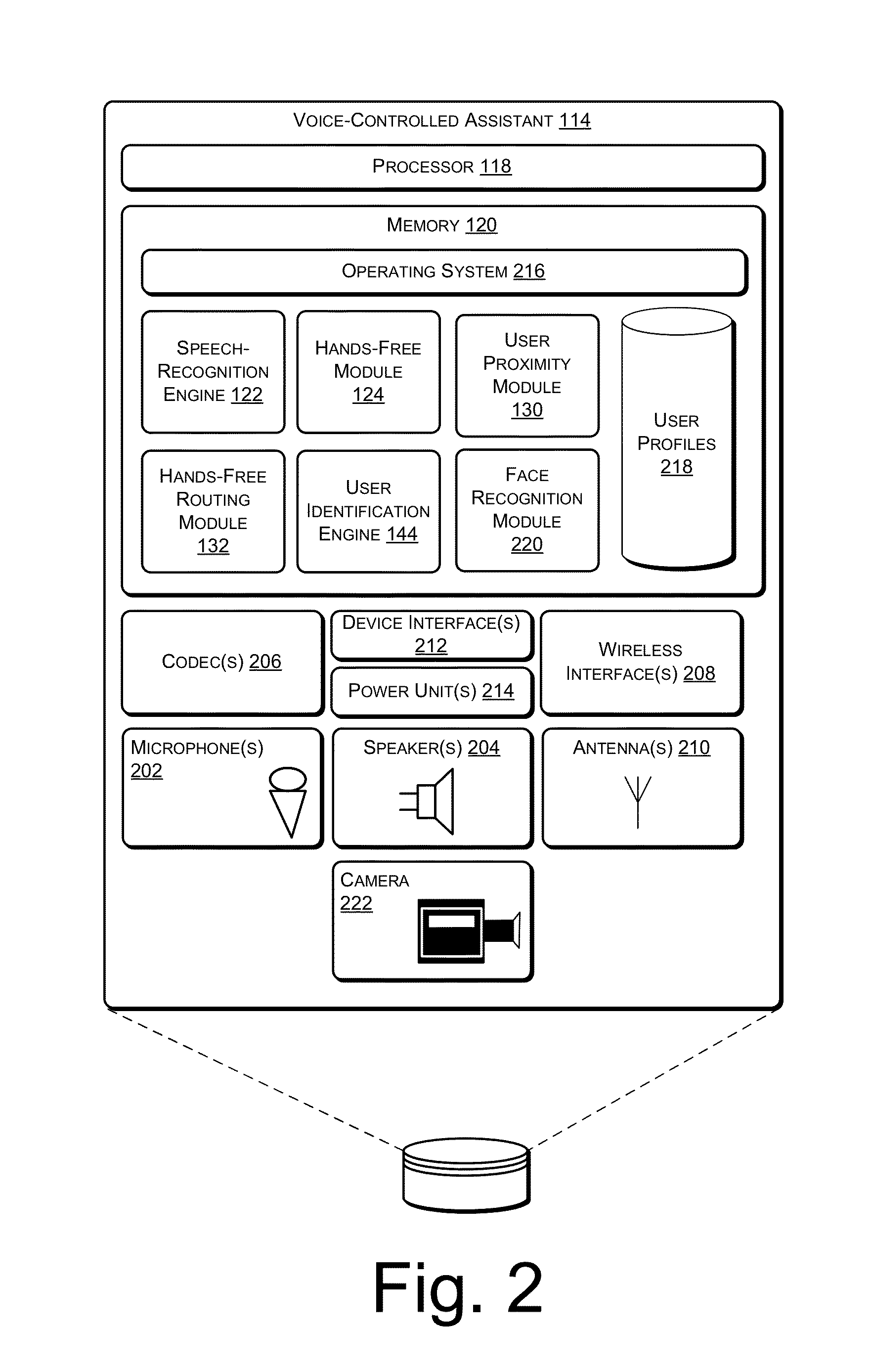
Providing hands-free service to multiple devices
ActiveUS8983383B1Devices with voice recognitionSubstation speech amplifiersComputer moduleHands free
Techniques for providing audio services to multiple devices are described. For instance, connections between a hands-free unit and multiple wireless devices are established. The connections are themselves used to establish active communication channels, such as active audio communication channels, between the hands-free unit and the wireless devices, such as during a phone call. Upon establishment of an active communication channel with one of the wireless devices, the connections to the other wireless devices are disconnected—and / or additional connections refused—for the duration of the active communication channel. Furthermore, a routing module in various embodiments permits multiple hands-free units to route active communication channels to each other depending on user location.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
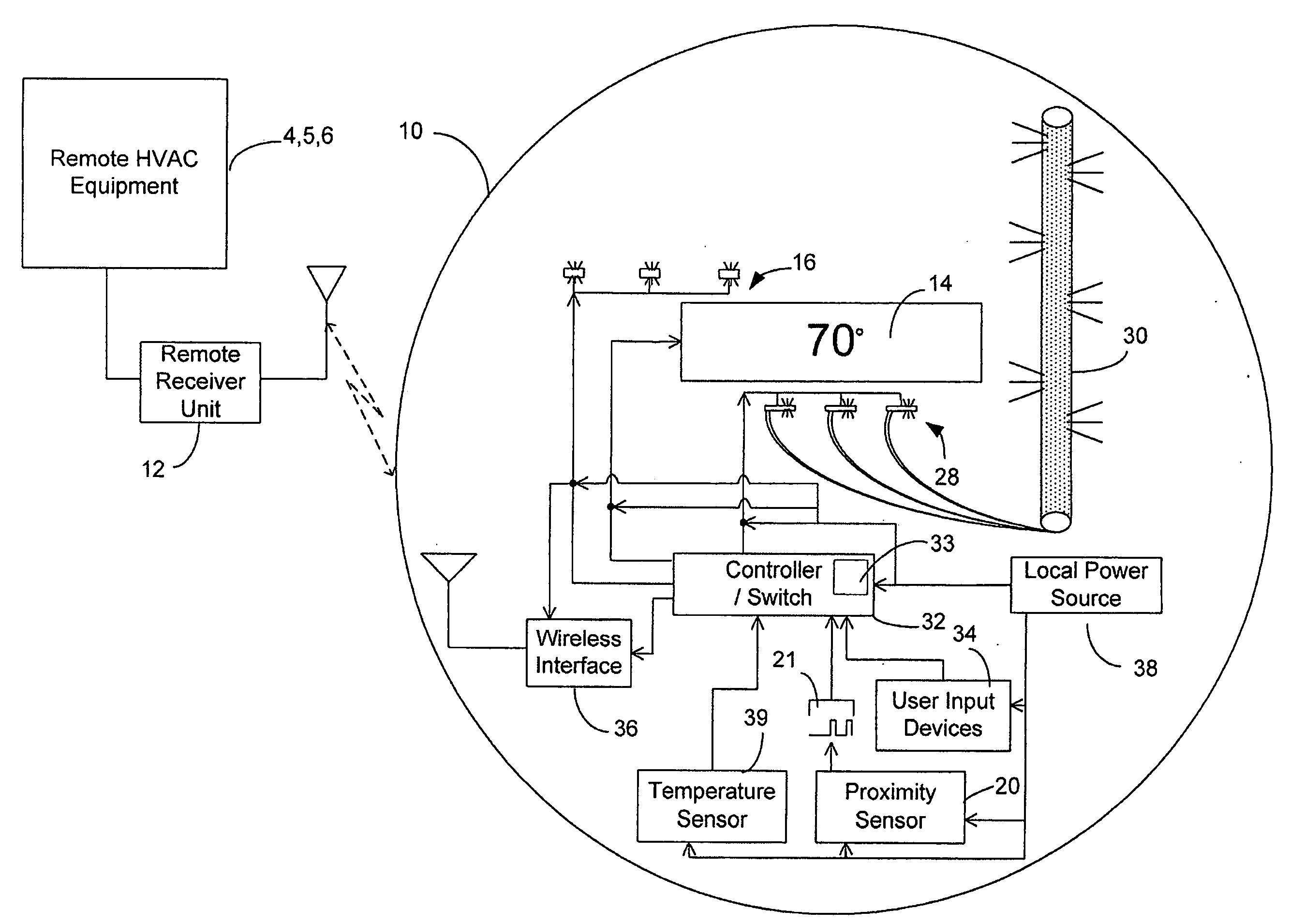
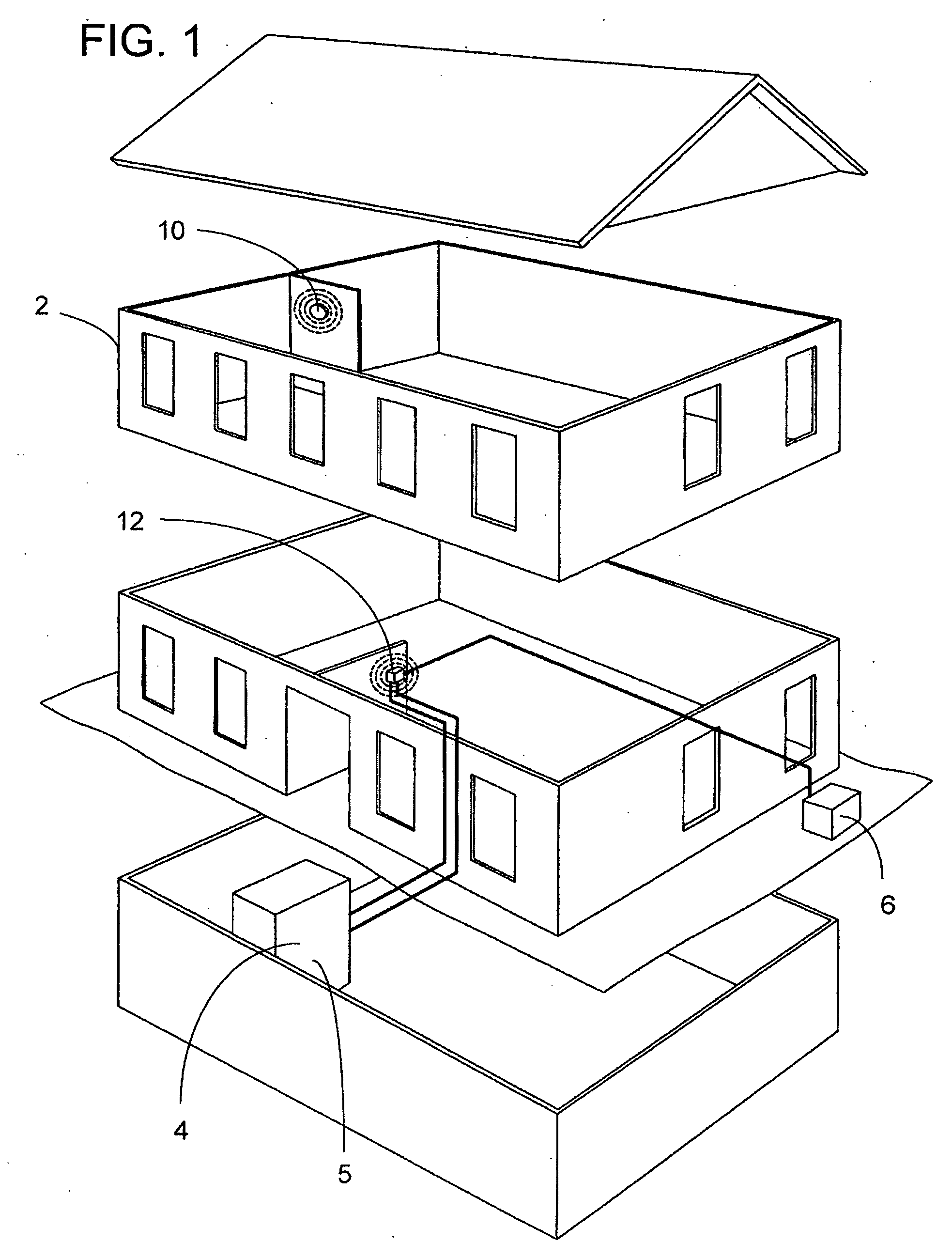
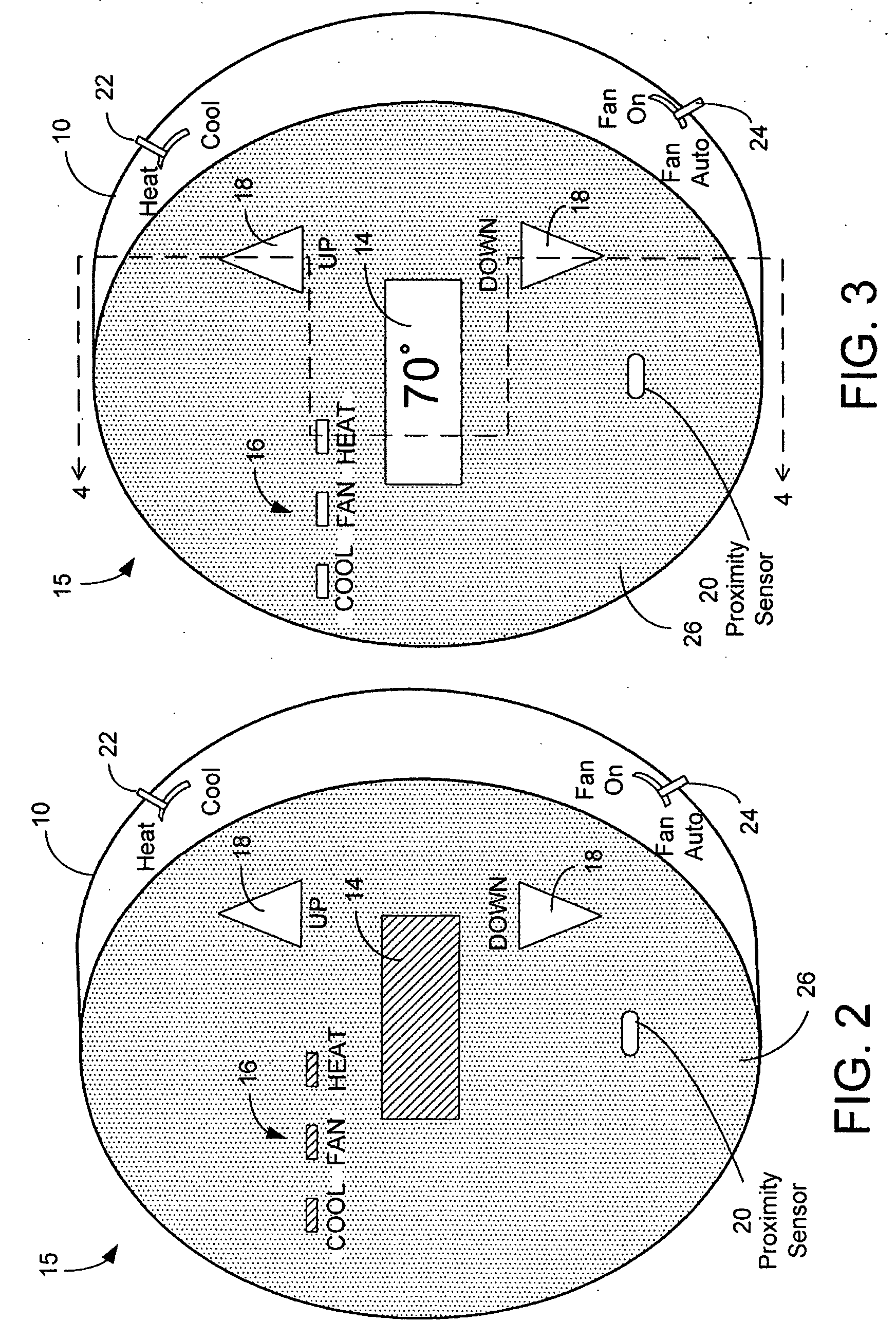
Management of a thermostat's power consumption
InactiveUS20070241203A1Reduce energy consumptionAdditional level of power conservationTemperature control without auxillary powerMechanical apparatusProximity sensorUser input
An HVAC system comprises a programmable wireless thermostat and a remote receiver unit. The thermostat includes a user interface having one or more displays, user input devices, such as buttons, sliders, or a touch screen, and a backlight. The thermostat may include a proximity sensor, wherein the user interface is controlled based on a user's presence near the thermostat. A thermostat controller enters into a reduced energy consumption mode and switches the user interface to an idle state when the proximity sensor indicates a lack of user proximity for a predetermined duration. When the proximity sensor indicates user proximity, the controller exits the reduced energy consumption mode and switches the user interface to an active state. During the reduced energy consumption mode, the user interface may be concealed when the user interface is in a housing which is transparent when backlit but is opaque otherwise.
Owner:RANCO OF DELAWARE
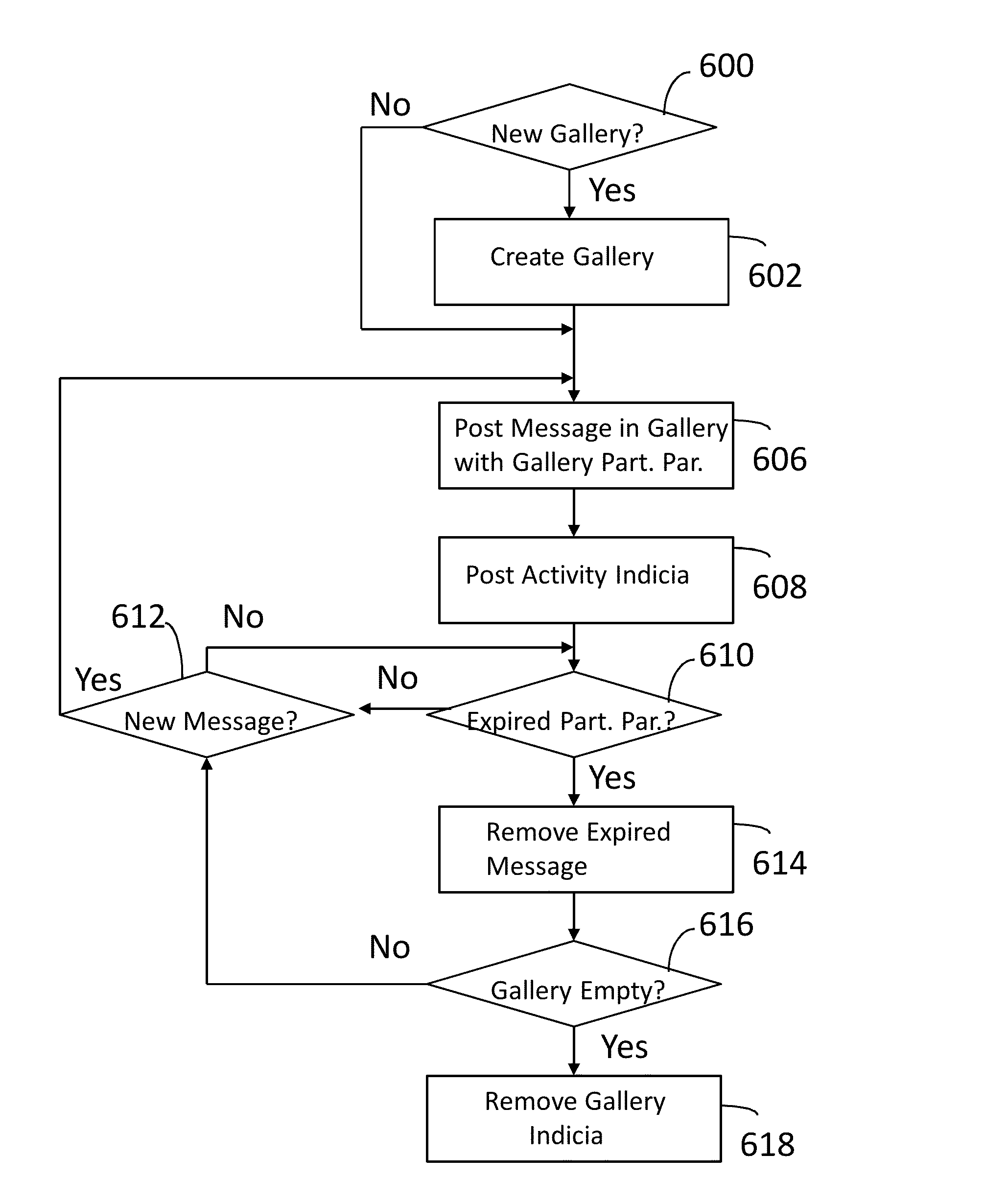
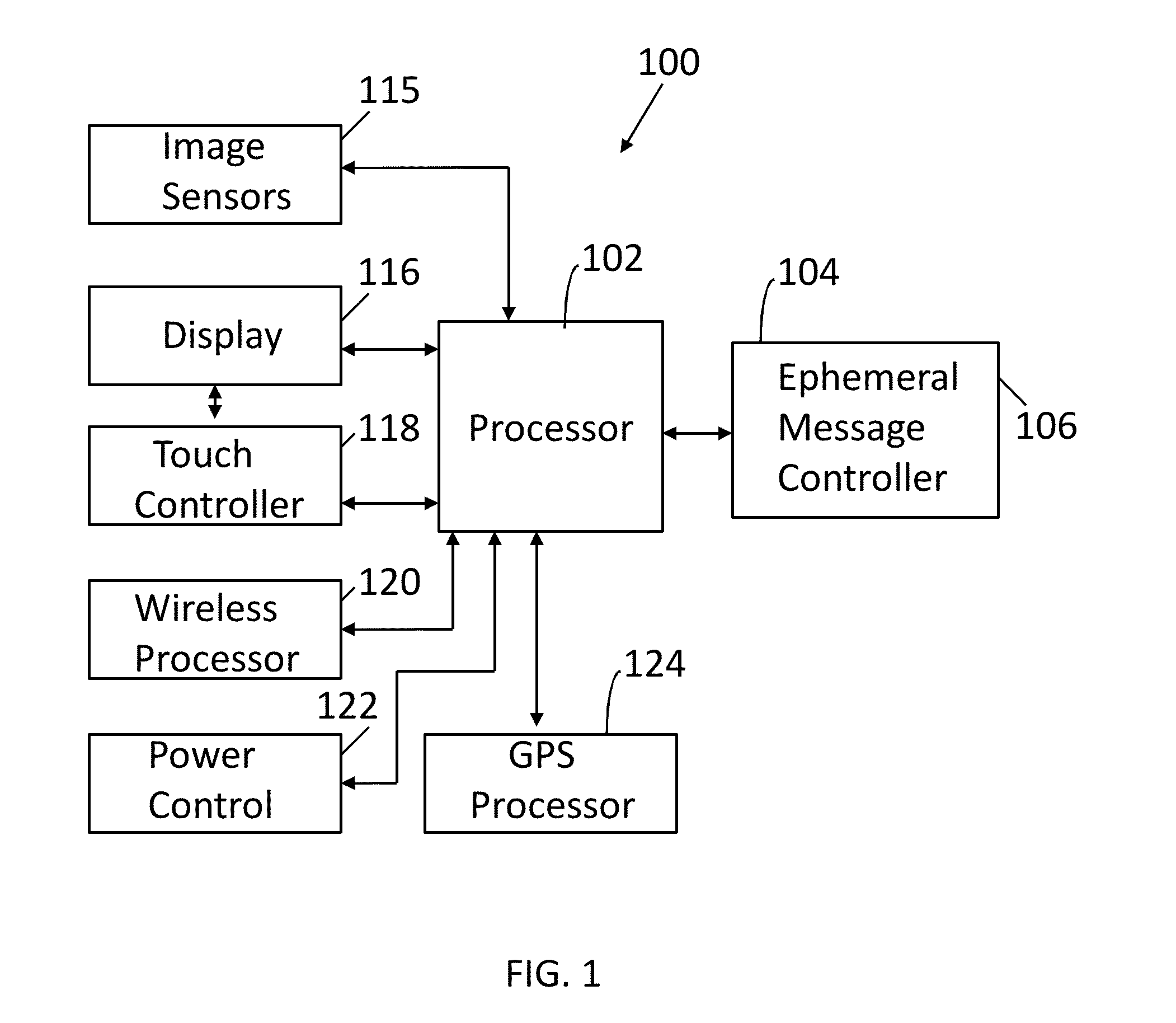
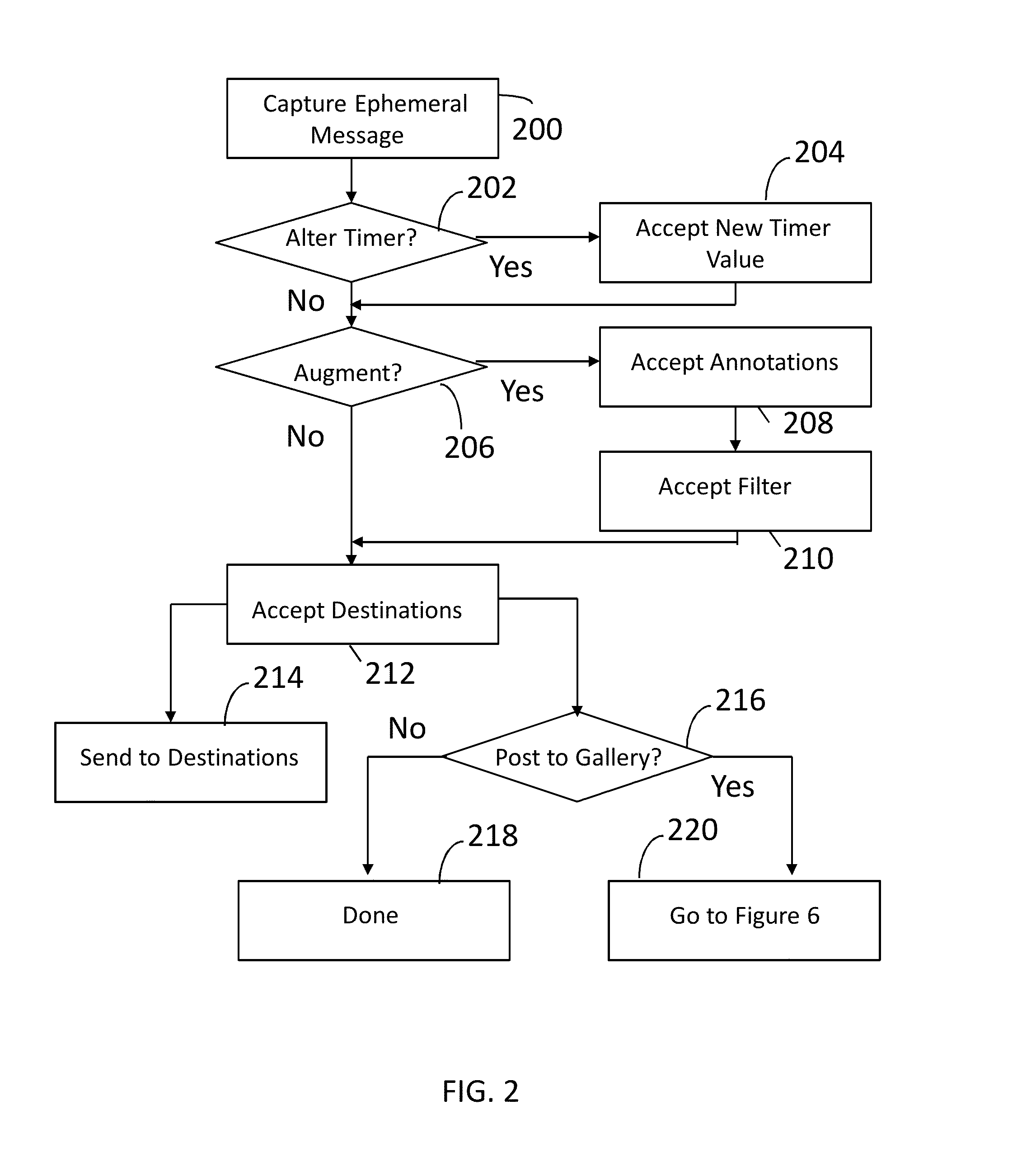
Ephemeral Gallery of Ephemeral Messages
ActiveUS20160099901A1Data processing applicationsDigital data protectionComputer scienceStore instruction
A server has a processor and a memory storing instructions executed by the processor to maintain an ephemeral gallery of ephemeral messages. An ephemeral message is posted to the ephemeral gallery. The ephemeral message has an associated message duration parameter and a gallery participation parameter. An ephemeral message is removed from the ephemeral gallery in response to the identification of an expired gallery participation parameter.
Owner:SNAP INC
Method and system of program transmission optimization using a redundant transmission sequence
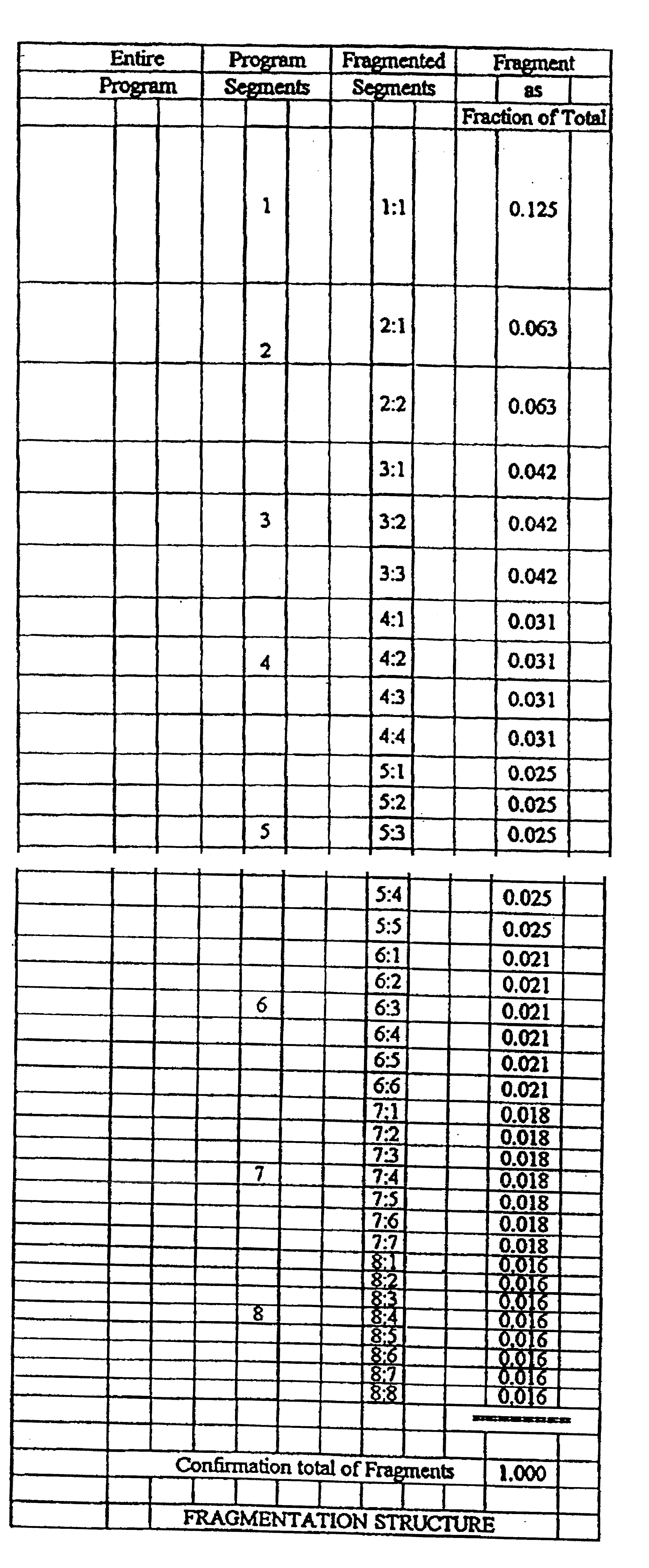
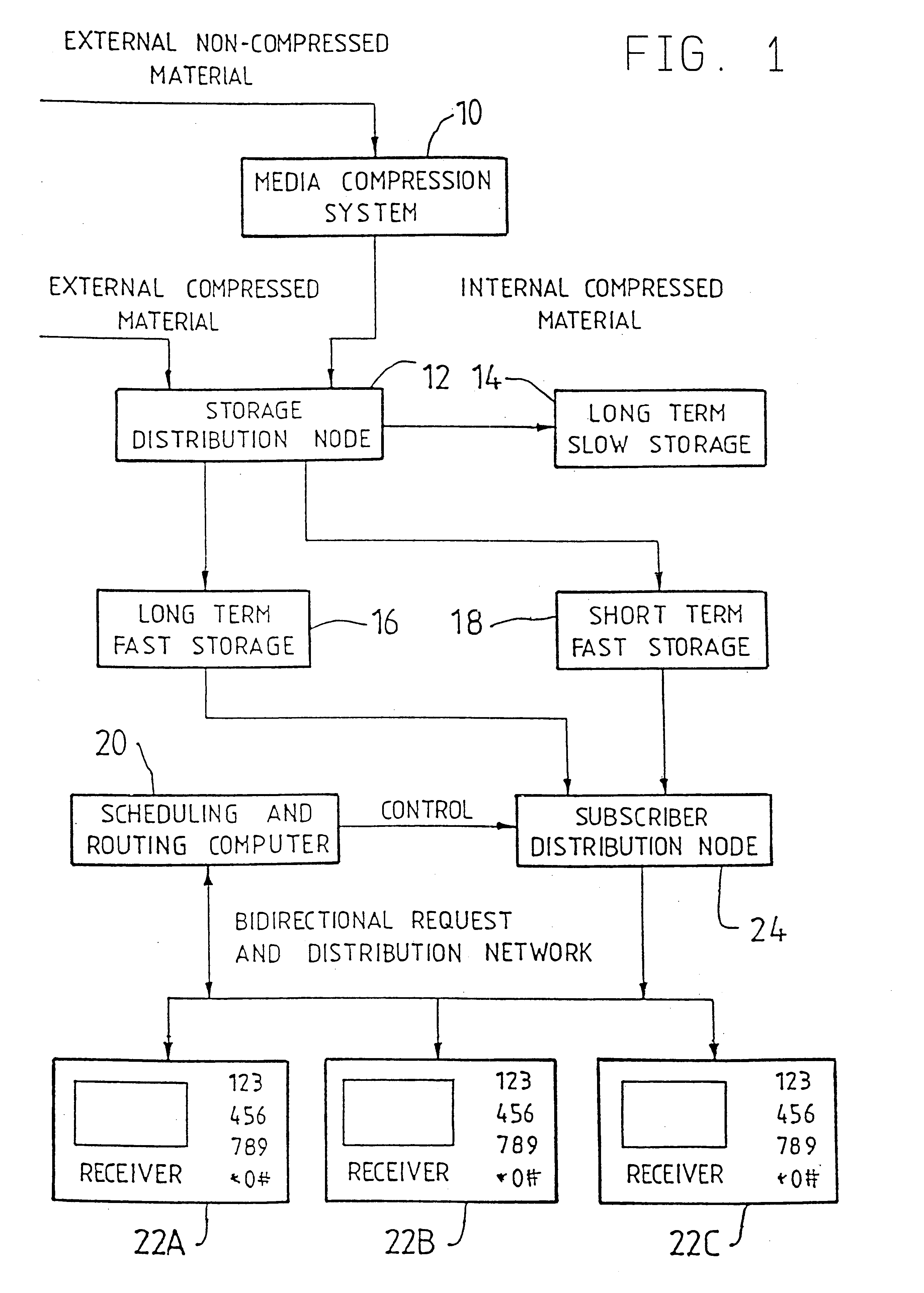
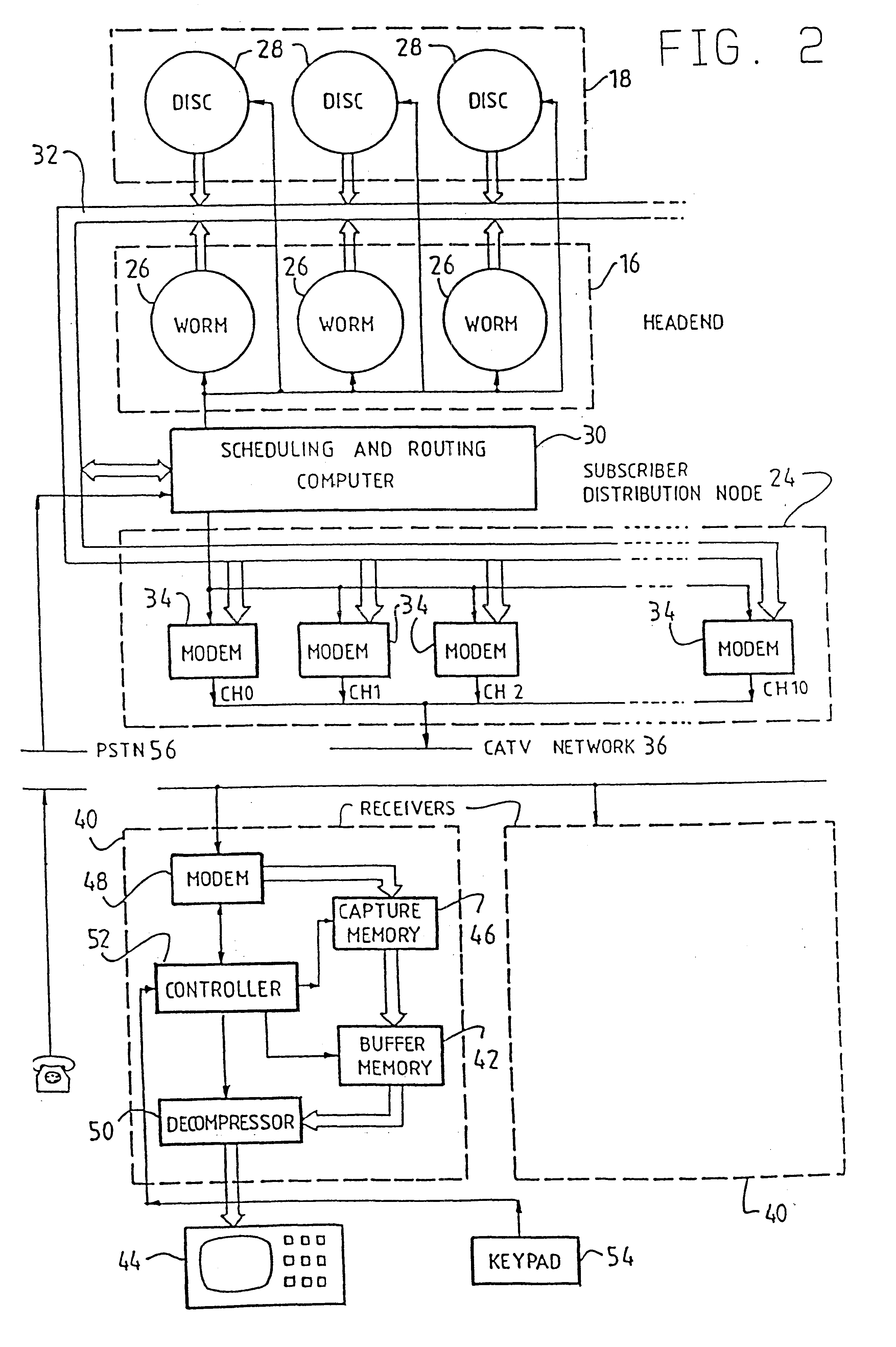
A system and method of optimizing transmission of a program to multiple users over a distribution system, with particular application to video-on-demand for a CATV network. The system includes, at a head end of the CATV network a scheduling and routing computer for dividing the video program stored in long term fast storage or short term fast storage into a plurality of program segments, and a subscriber distribution node for transmitting the program segments in a redundant sequence in accordance with a scheduling algorithm. At a receiver of the CATV network there is provided a buffer memory for storing the transmitted video program segments for subsequent playback whereby, in use, the scheduling algorithm can ensure that a user's receiver will receive all of the program segments in a manner that will enable continuous playback in real time of the program. Under the control of controller the receiver distinguishes received program segments by a segment identifier so that redundant segments captured in capture memory are then stored in buffer memory from which the segments can be retrieved and decompressed in data compressor for immediate or subsequent viewing. In one embodiment, the method of this invention includes dividing at least some segments into fragments, and transmitting one fragment of each segment during a playback interval of a duration, for example, equal to a playback time of a segment.
Owner:DETA TECH DEV
Electrophoretic displays using gaseous fluids
InactiveUS20080024429A1Reduce the impactIncrease the lengthStatic indicating devicesElectrophoresisDisplay device
An electrophoretic display comprises a pair of facing substrates, at least one of which is transparent, a plurality of particles and a gas between the substrates, and means for applying an electric field to cause the particles to move and thus change the electro-optic state of the display. The electric field means is arranged to increase the impulse applied to the display with increasing time since a reference time, or with increasing number of images written on the display. In another embodiment, an alternating current pulse is applied to the display, and the duration and / or amplitude of the alternating current pulse is increased with increasing time since a reference time.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
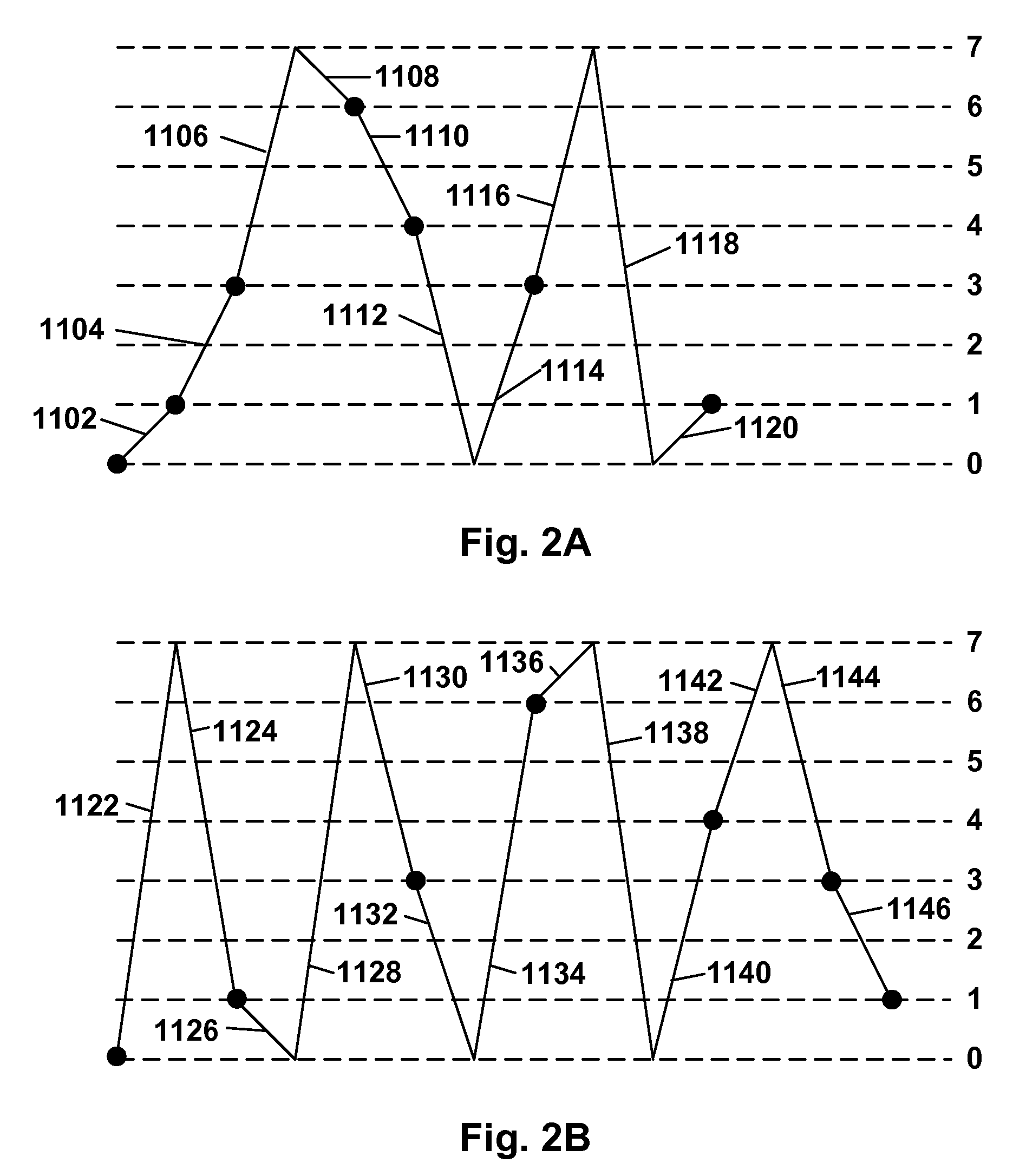
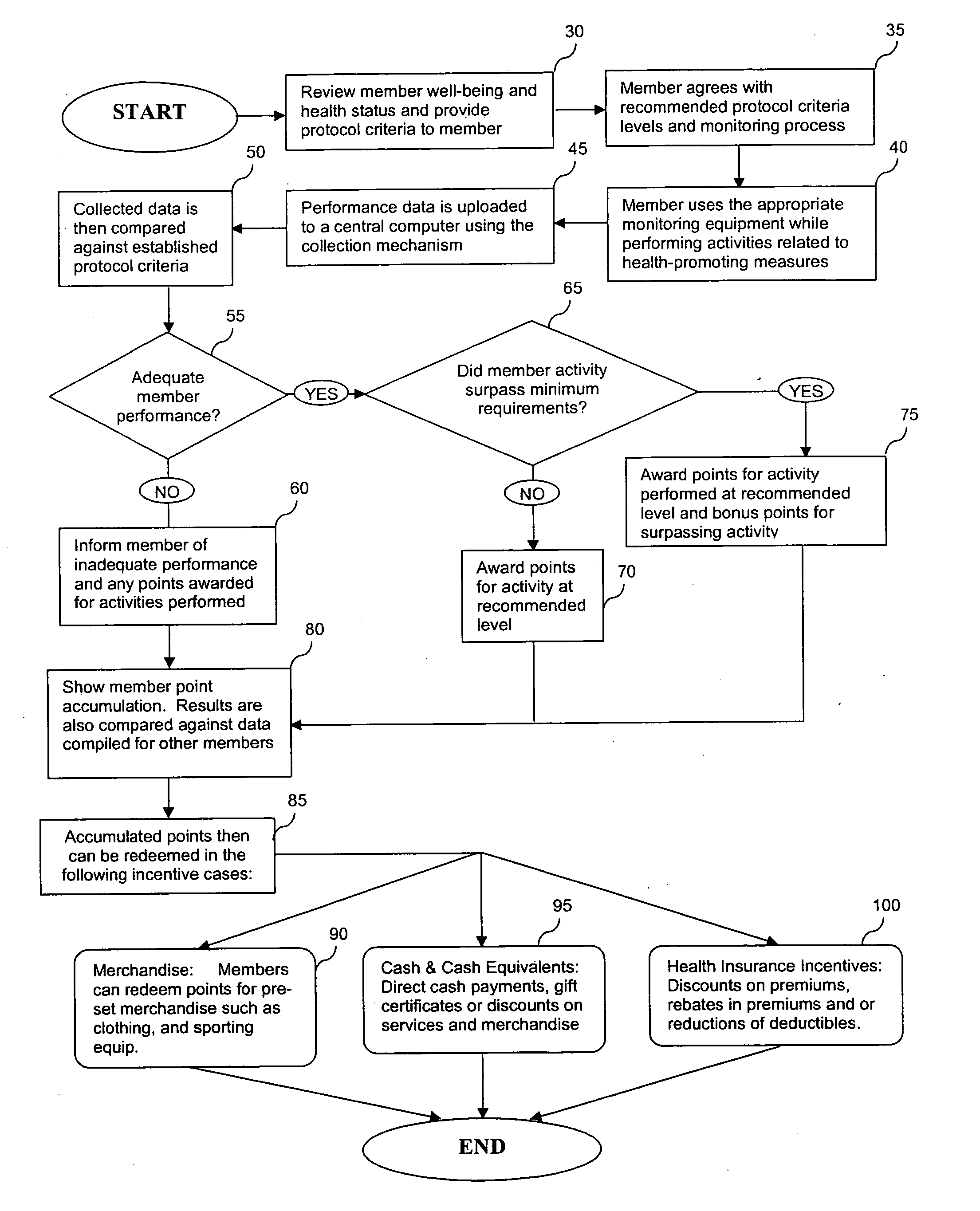
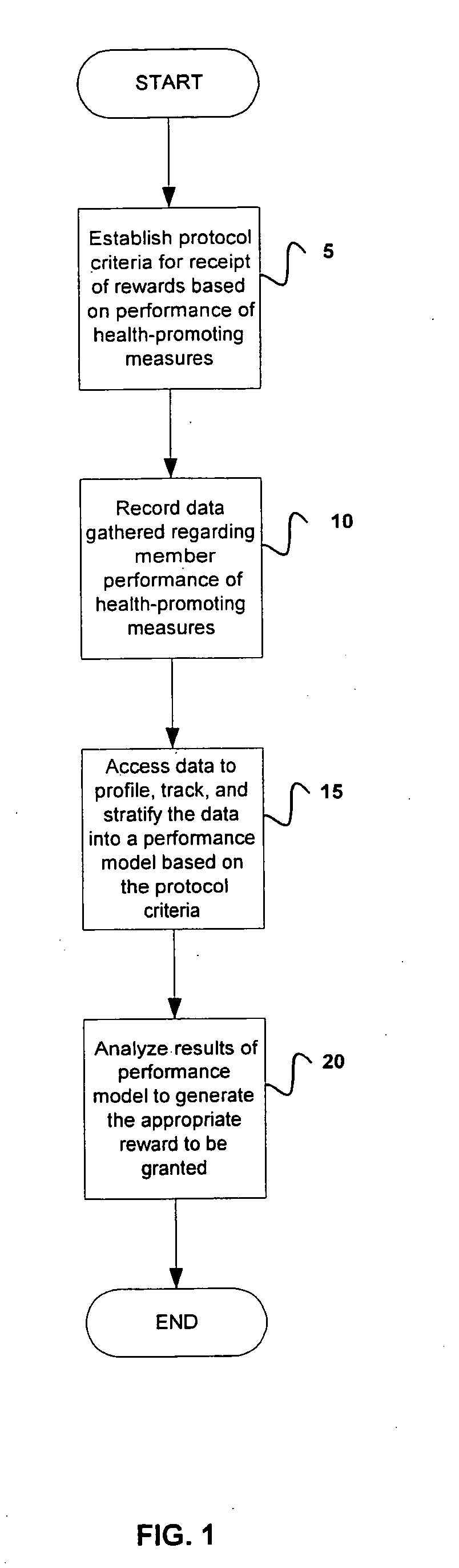
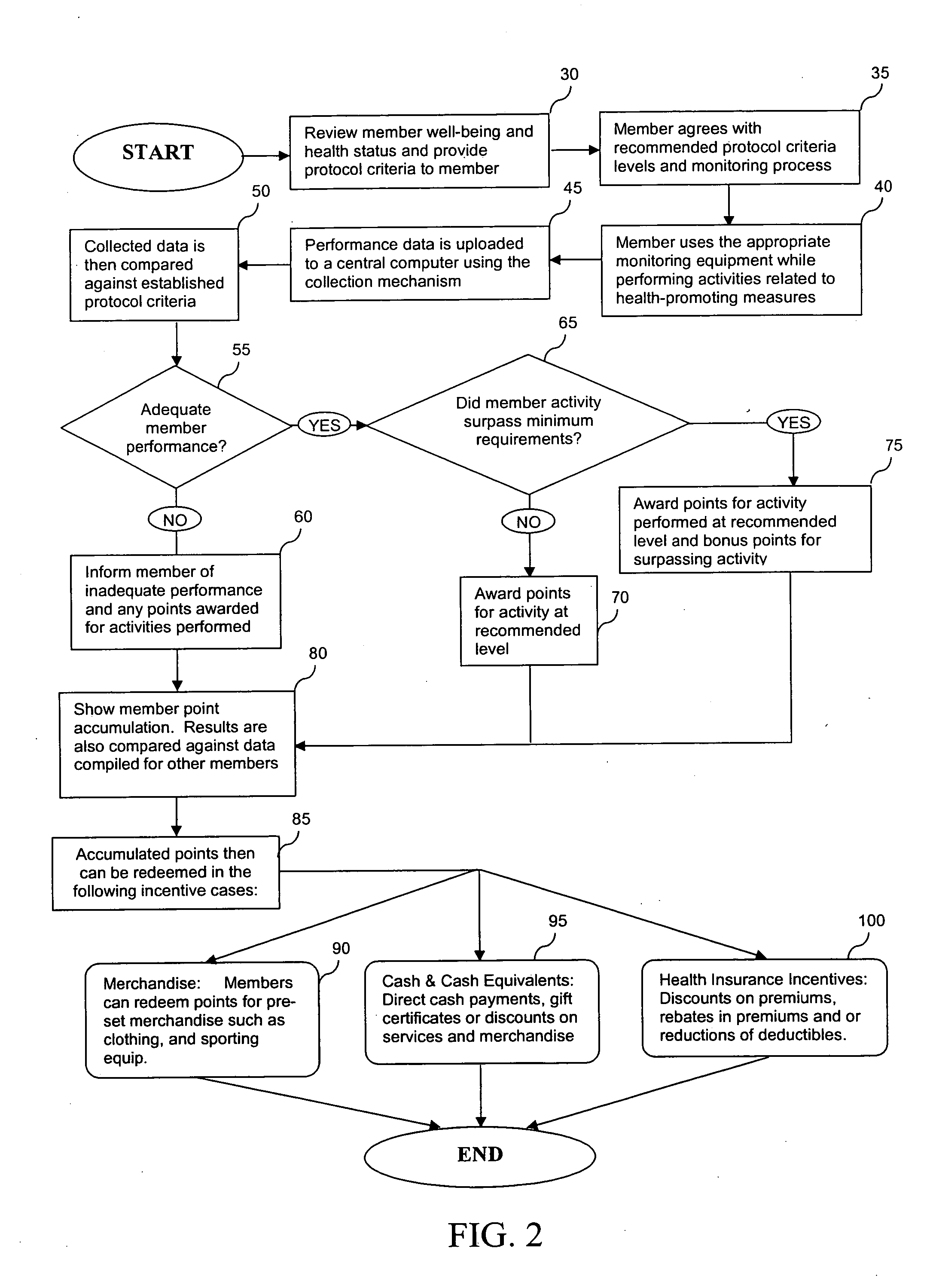
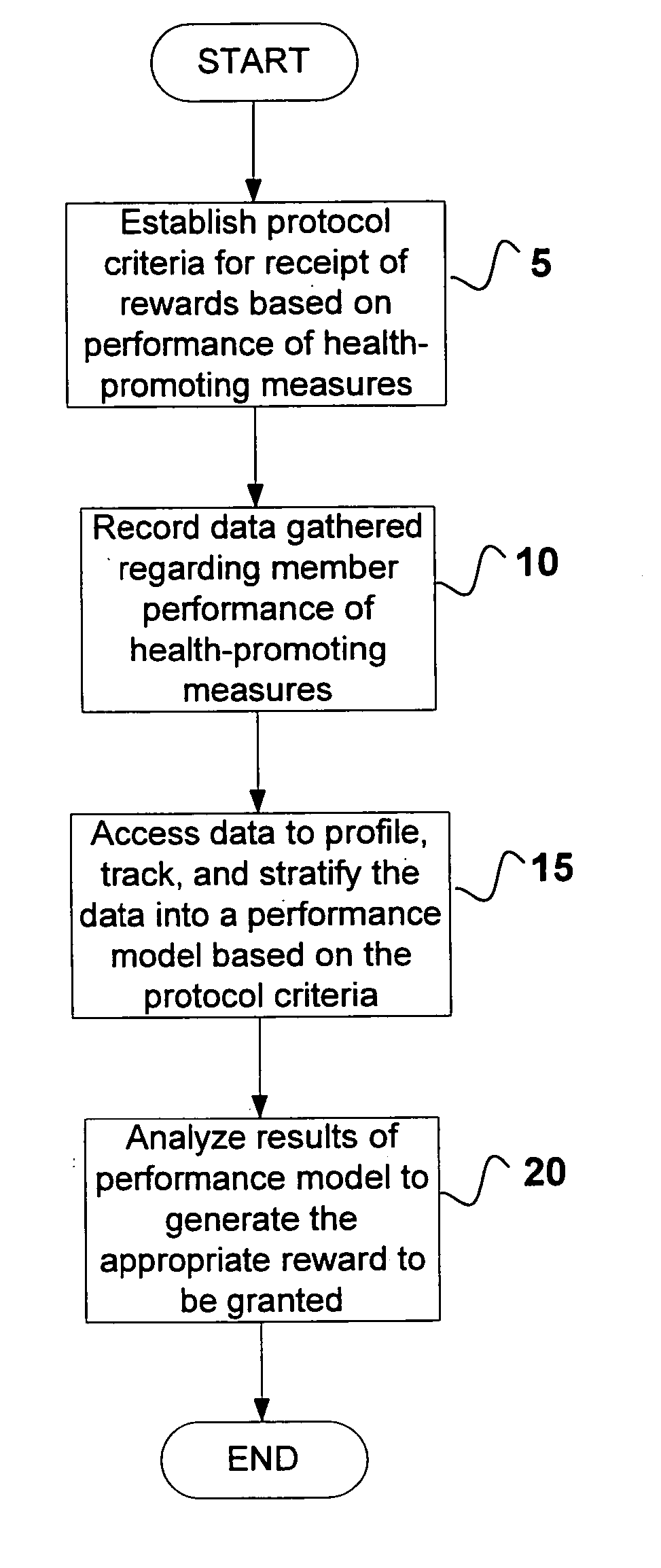
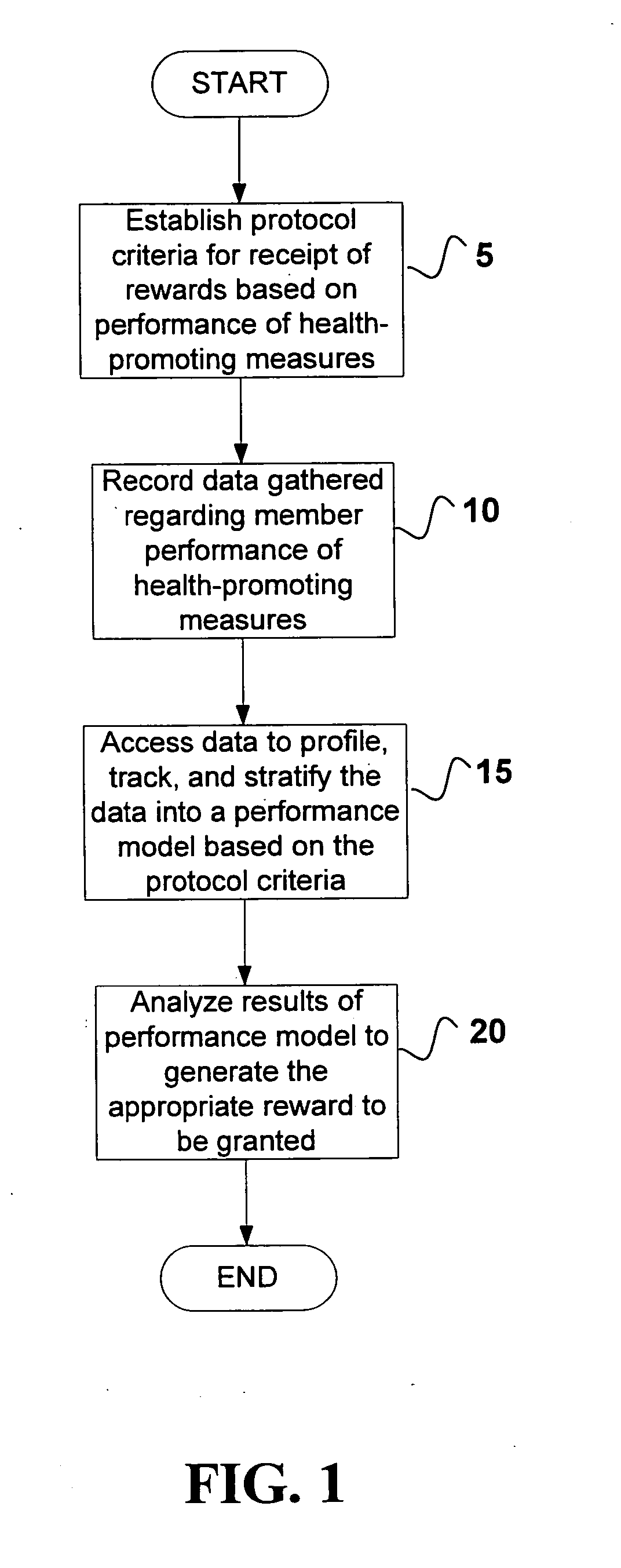
System and method for encouraging performance of health-promoting measures
InactiveUS20060111944A1Easy to modifyPhysical therapies and activitiesDiscounts/incentivesHealth related informationHealth promotion
The present invention relates to systems and methods for monitoring and promoting behavioral modification with regard to an individual's health. In particular, the present invention provides a means for monitoring an individual's performance of health-promoting measures and, based on the member compliance to health-promoting measures, issuing tangible and / or intangible incentive products. In one embodiment, exercise / activity monitors are worn by members to verify their identity and to record and transmit member compliance in performing health-promoting measures (i.e., heart rate, type of exercise, exercise intensity and duration). All health-related information, including physical examination results and recorded participation in health-promoting measures, are used to determine appropriate incentives (i.e., subsidize membership fees for health club) to be rewarded to said member.
Owner:SIRMANS JAMES R JR +1
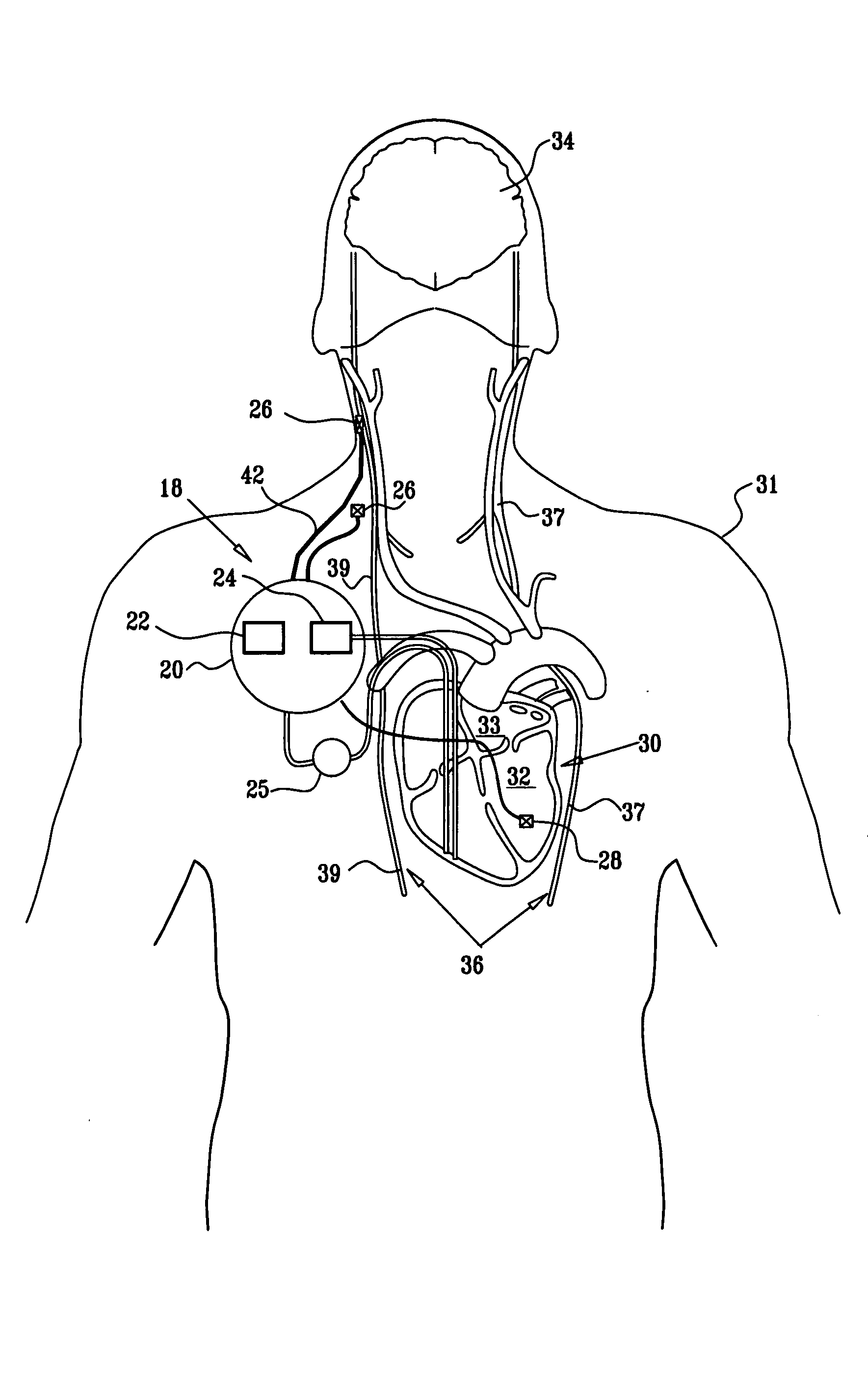
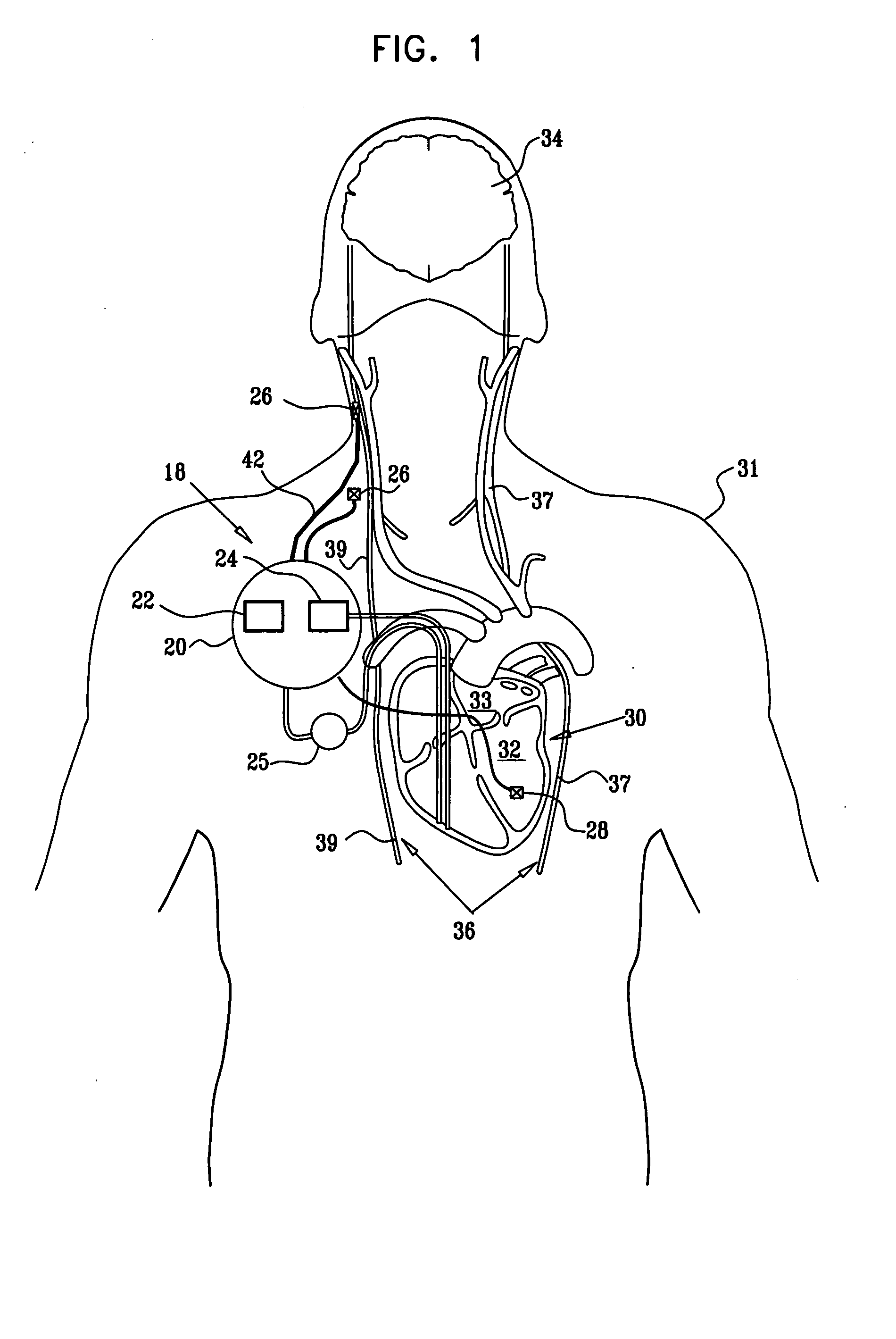
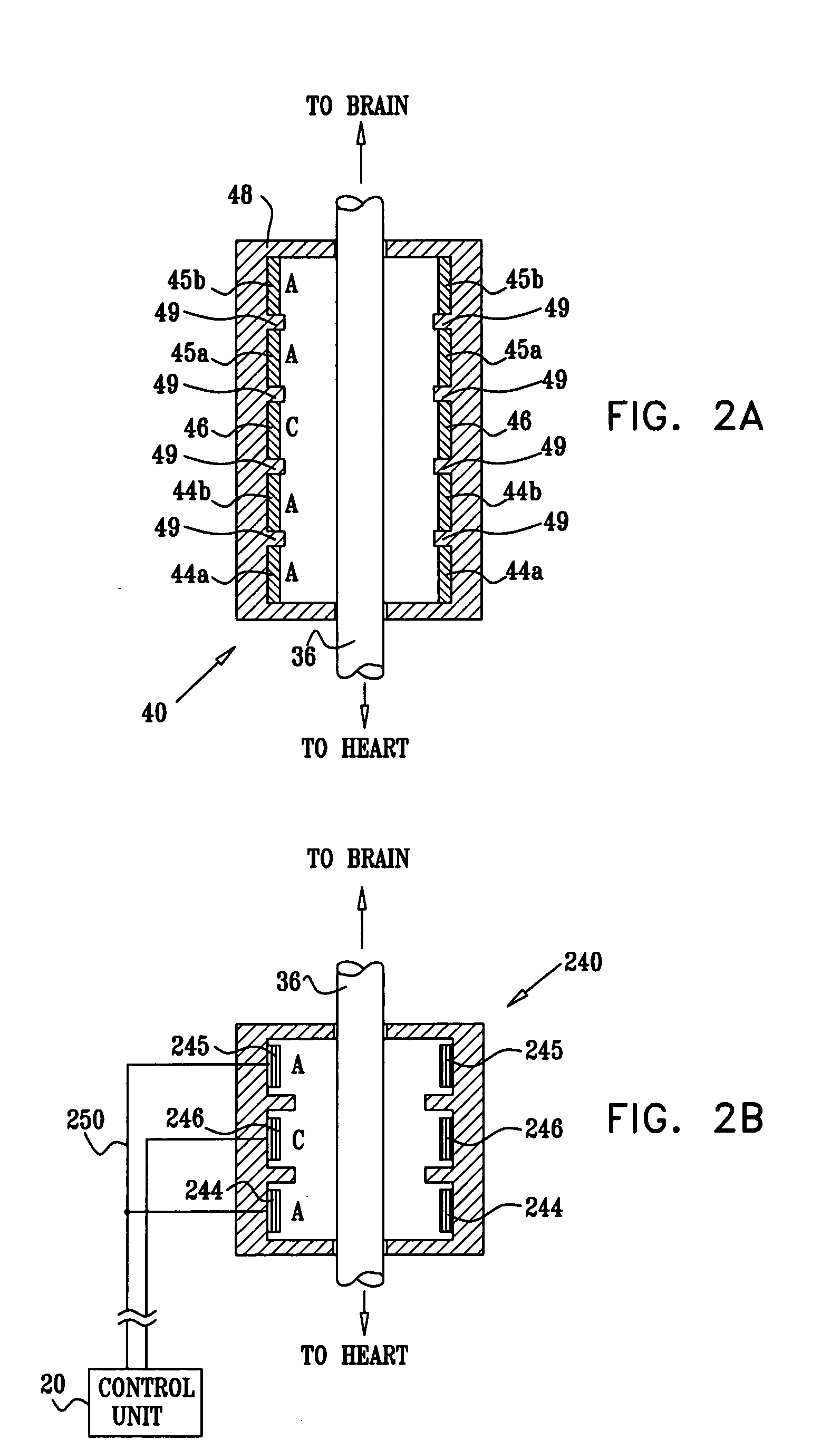
Techniques for applying, calibrating, and controlling nerve fiber stimulation
InactiveUS20050197675A1Reduce riskFew potential side effectSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsNerve fiber bundleFiber
Apparatus is provided including an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a site of a subject; and a control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply a current to the site intermittently during alternating “on” and “off”periods, each of the “on” periods having an “on” duration equal to between 1 and 10 seconds, and each of the “off” periods having an “off”duration equal to at least 50% of the “on” duration. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
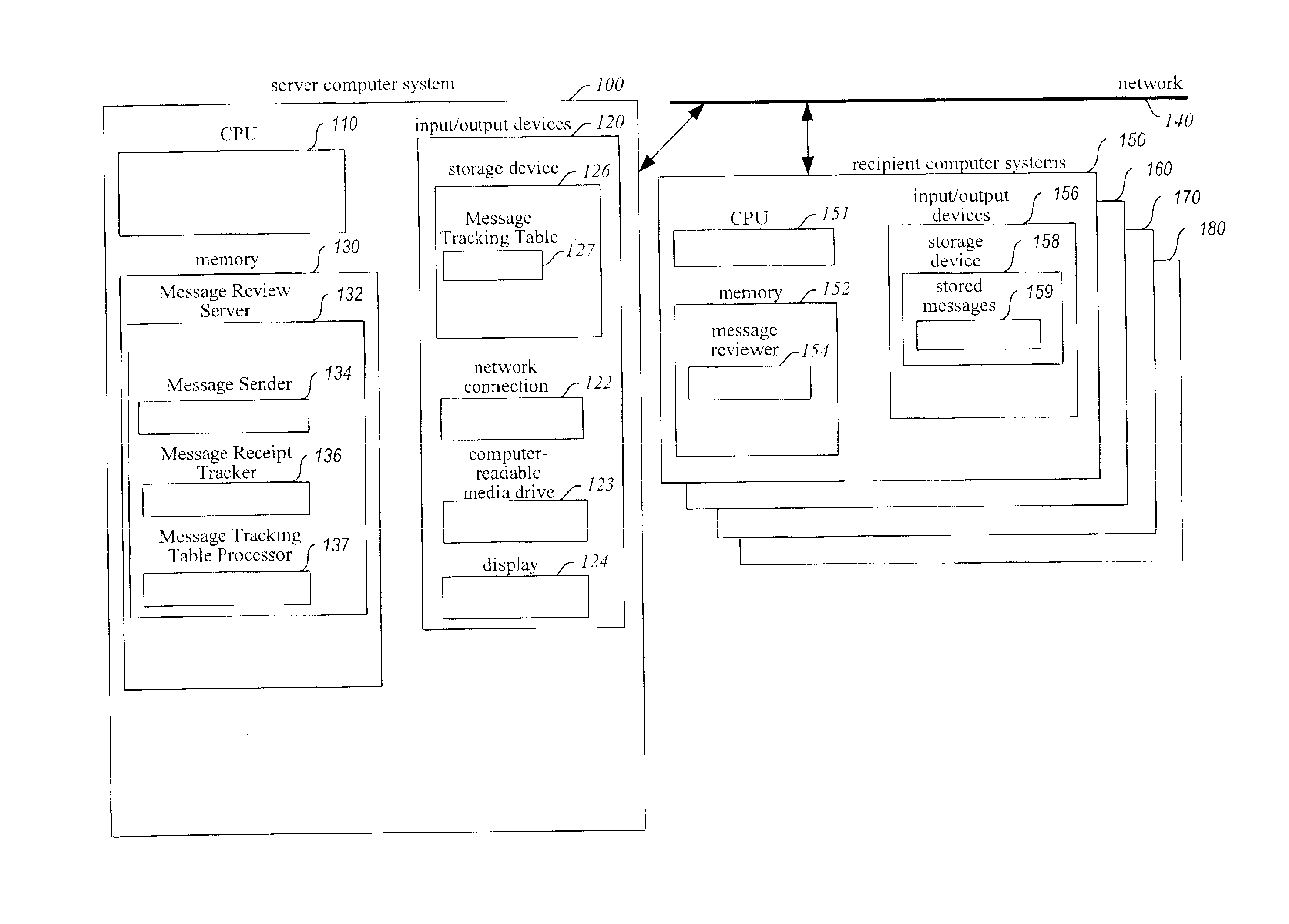
Method and system for enhancing reliability of communication with electronic messages
InactiveUS6854007B1Improve reliabilitySpecific activityMultiple digital computer combinationsPersonalizationComputer hardware
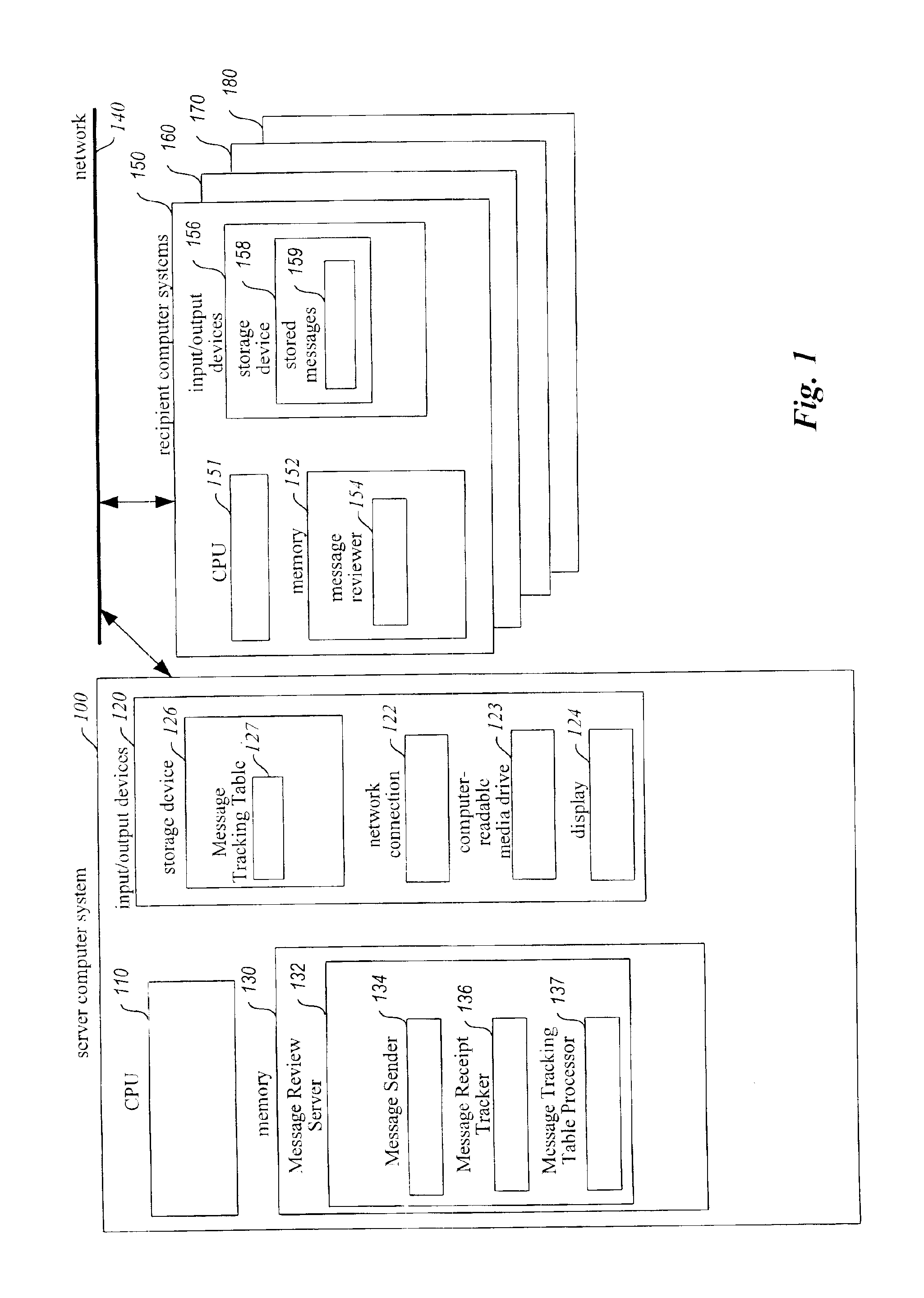
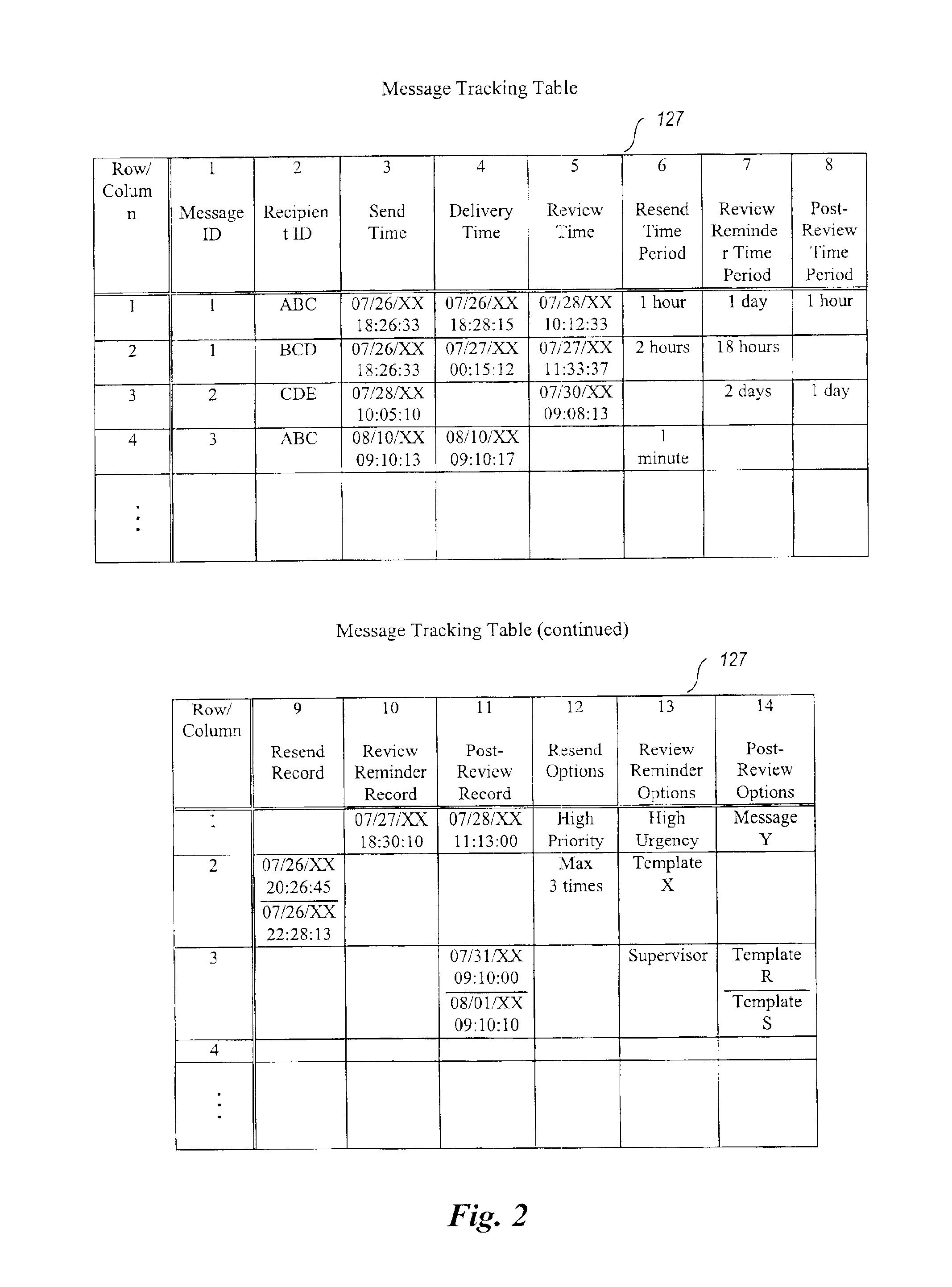
A system for enhancing the reliability of communicating with electronic messages. The system sends an electronic message to designated recipients, and then automatically helps ensure that each message has been successfully delivered within a specified period of time and that each message has been reviewed within a specified period of time. In addition, the system automatically performs specified activities after review of a message takes place. The sender of an electronic message initiates reliability-enhanced messaging by specifying message delivery information and message review information. The sender can specify that if delivery or review notifications are not received within specified periods of time, the message will be resent to the recipient or a reminder message will be sent to the recipient or to another user. The message information can include various frequency and duration options, such as resending a message only once or resending it every 2 hours for a week. Message information can also specify to resend the message with a higher transmission priority or review urgency so that its delivery and review is more likely, or could specify to use a different recipient system for the recipient (e.g., to a second email address if a first address fails, or to a pager if a cellular phone is not available). Each recipient of a message can have individualized message delivery information. The system tracks whether each message has been delivered to each recipient, and uses the message delivery information to resend the messages whose delivery and review was not confirmed.
Owner:MEI CALIFORNIA
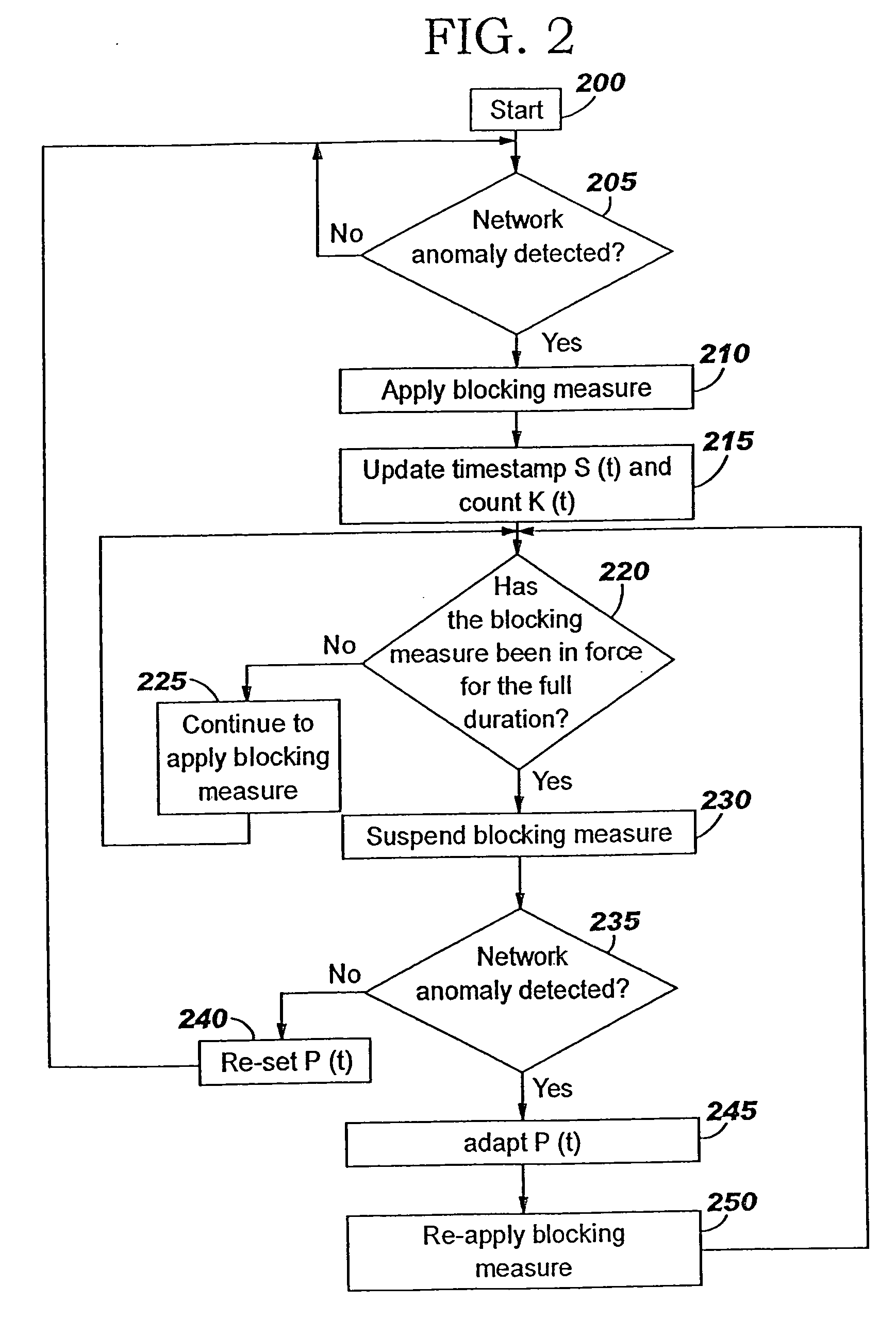
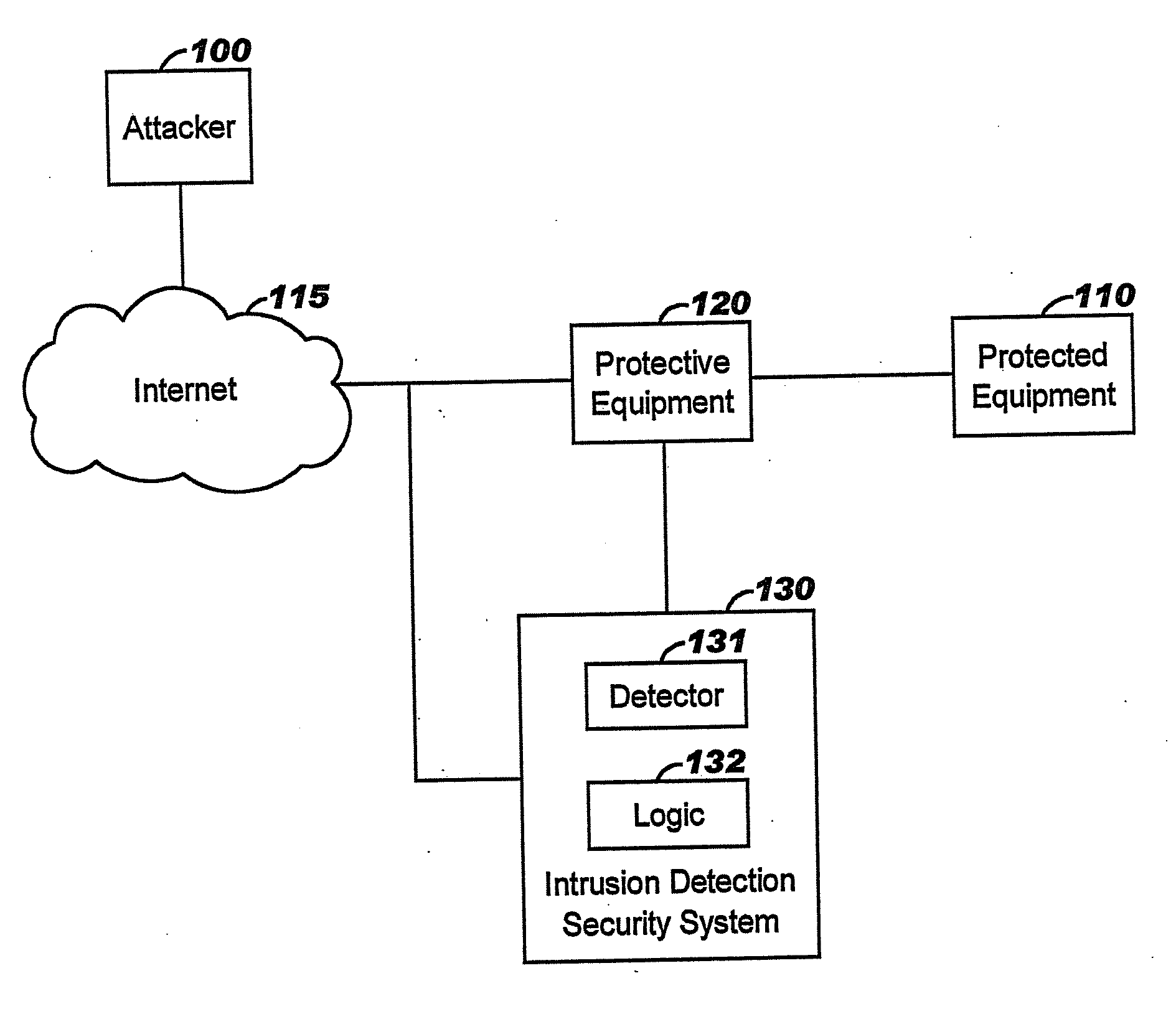
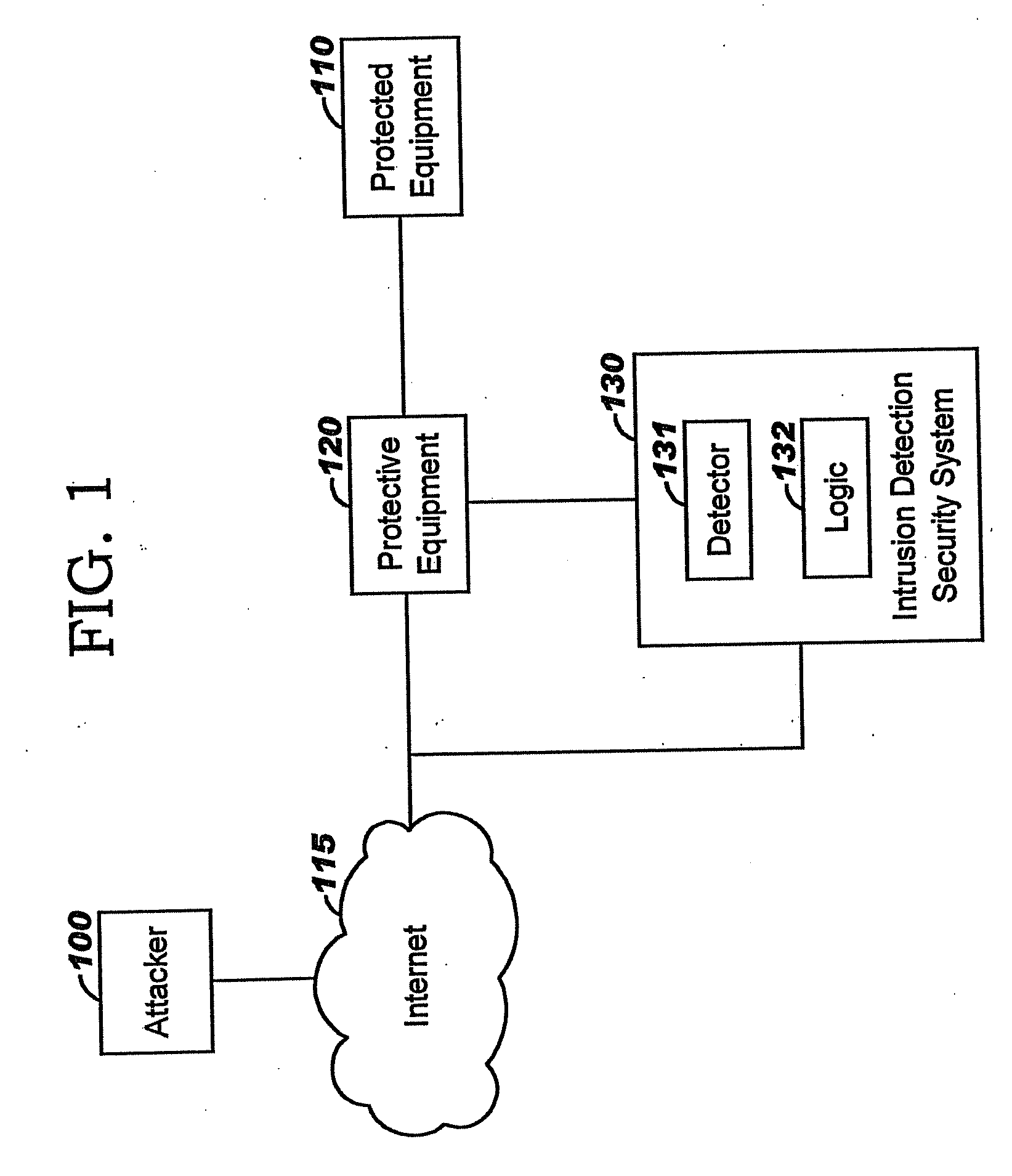
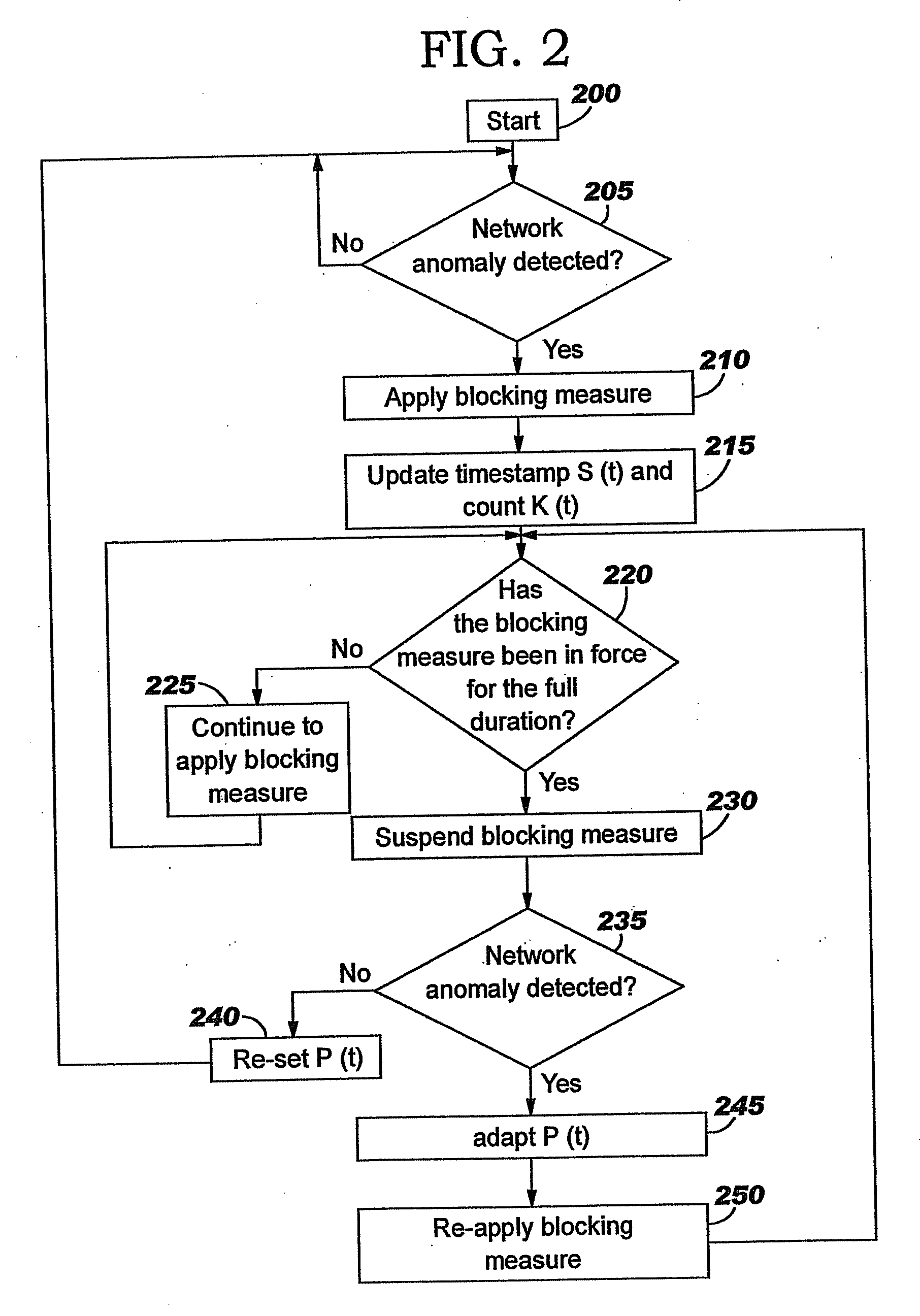
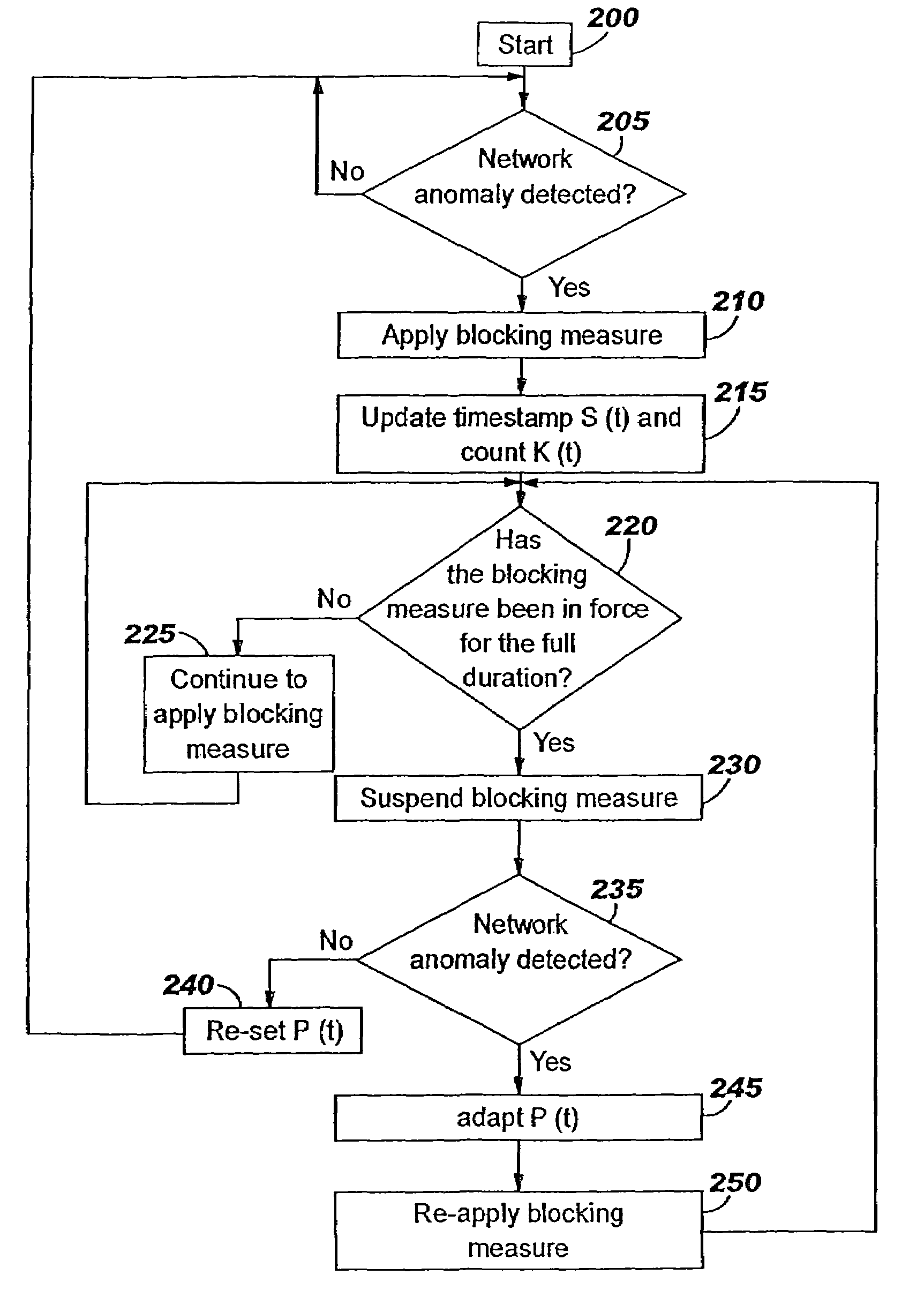
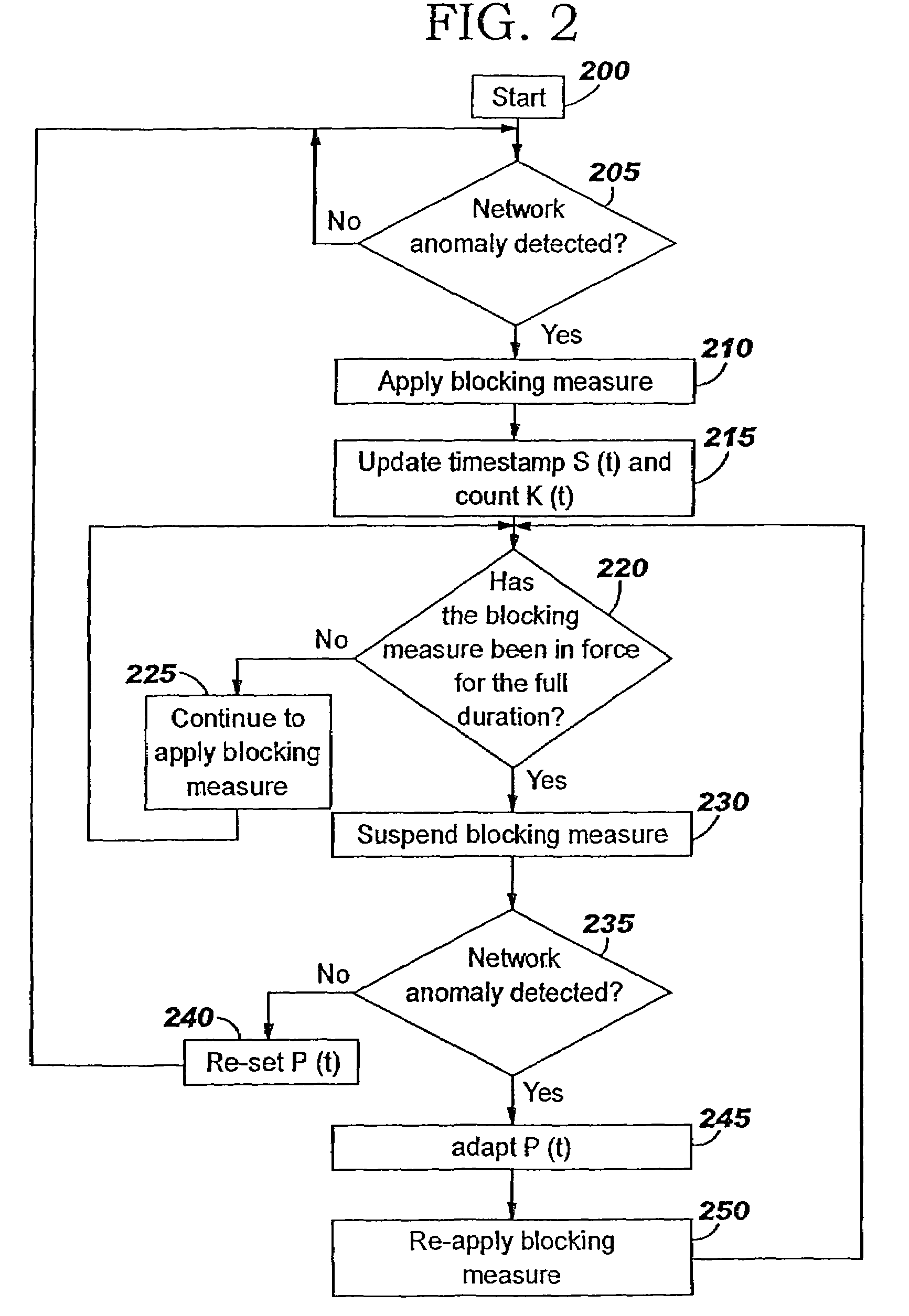
Applying blocking measures progressively to malicious network traffic
InactiveUS20060075496A1Minimizing adverse consequenceMinimize consequencesMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionResponse methodFalse positives and false negatives
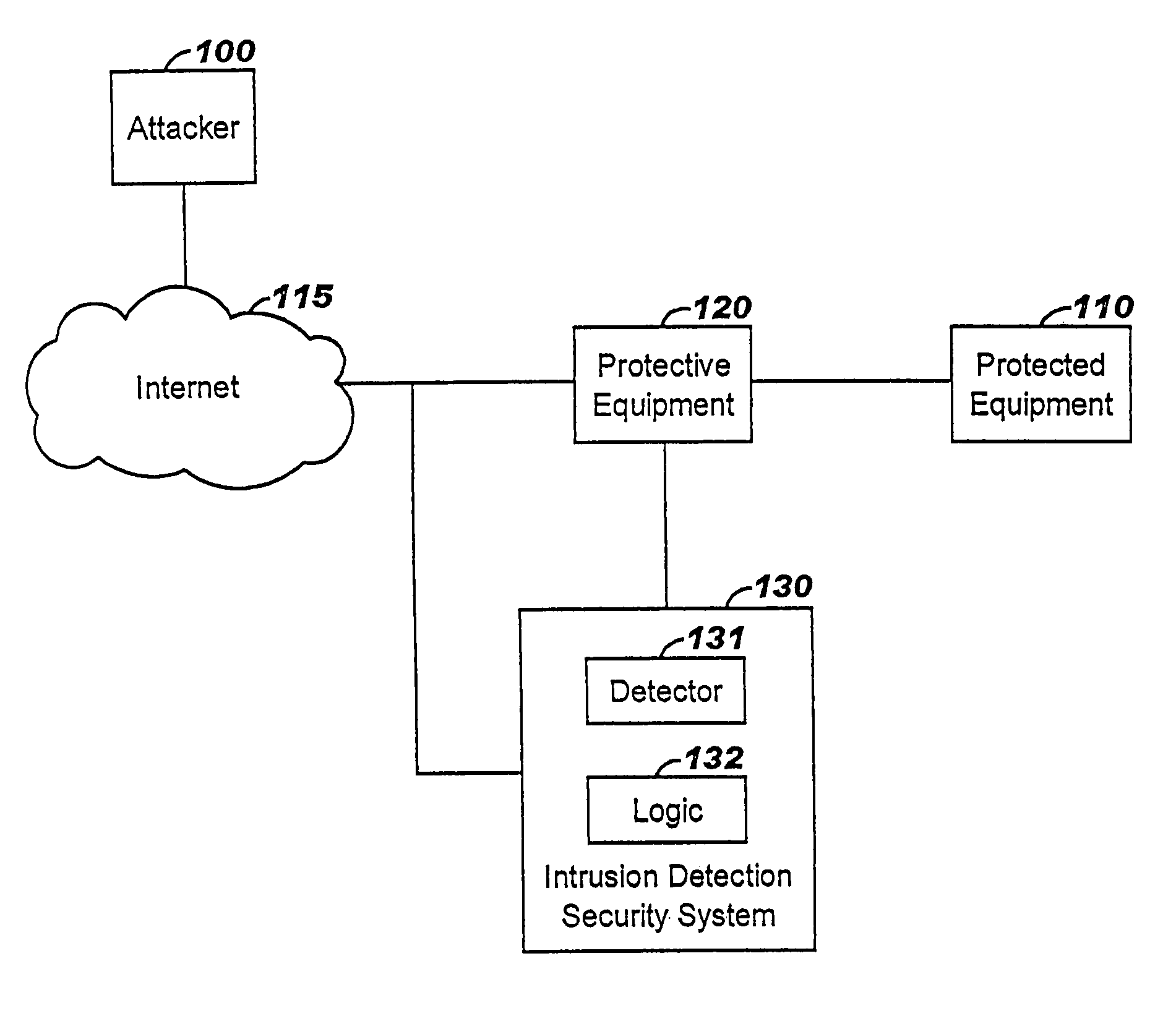
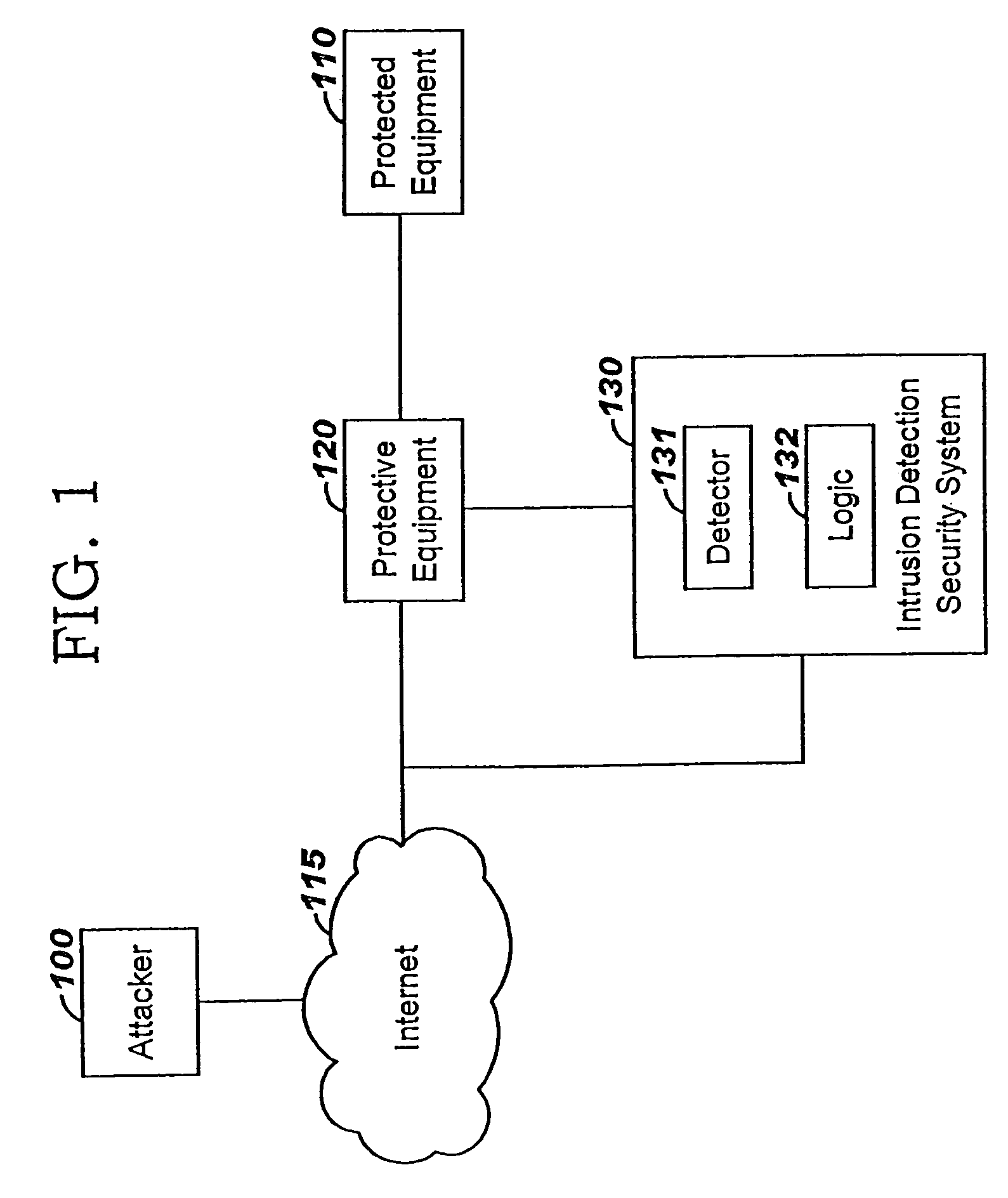
A method of progressive response for invoking and suspending blocking measures that defend against network anomalies such as malicious network traffic so that false positives and false negatives are minimized. When a truncated secure session attack is detected, the detector notifies protective equipment such as a firewall or a router to invoke a blocking measure. The blocking measure is maintained for an initial duration, after which it is suspended while another test for the anomaly is made. If the attack is no longer evident, the method returns to the state of readiness. Otherwise, a loop is executed to re-applying the blocking measure for a specified duration, then suspend the blocking measure and test again for the attack. If the attack is detected, the blocking measure is re-applied, and its duration is adapted. If the attack is no longer detected, the method returns to the state of readiness.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
Applying blocking measures progressively to malicious network traffic
InactiveUS20080072326A1Minimizing adverse consequenceMinimize consequencesMemory loss protectionDigital computer detailsResponse methodFalse positives and false negatives
A method of progressive response for invoking and suspending blocking measures that defend against network anomalies such as malicious network traffic so that false positives and false negatives are minimized. When an anomaly is detected, the detector notifies protective equipment such as a firewall or a router to invoke a blocking measure. The blocking measure is maintained for an initial duration, after which it is suspended while another test for the anomaly is made. If the anomaly is no longer evident, the method returns to the state of readiness. Otherwise, a loop is executed to re-applying the blocking measure for a specified duration, then suspend the blocking measure and test again for the anomaly. If the anomaly is detected, the blocking measure is re-applied, and its duration is adapted. If the anomaly is no longer detected, the method returns to the state of readiness.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of responding to a truncated secure session attack
InactiveUS7464404B2Minimizing adverse consequenceMinimize consequencesMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionTraffic capacityFalse positives and false negatives
A method of progressive response for invoking and suspending blocking measures that defend against network anomalies such as malicious network traffic so that false positives and false negatives are minimized. When a truncated secure session attack is detected, the detector notifies protective equipment such as a firewall or a router to invoke a blocking measure. The blocking measure is maintained for an initial duration, after which it is suspended while another test for the anomaly is made. If the attack is no longer evident, the method returns to the state of readiness. Otherwise, a loop is executed to re-applying the blocking measure for a specified duration, then suspend the blocking measure and test again for the attack. If the attack is detected, the blocking measure is re-applied, and its duration is adapted. If the attack is no longer detected, the method returns to the state of readiness.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
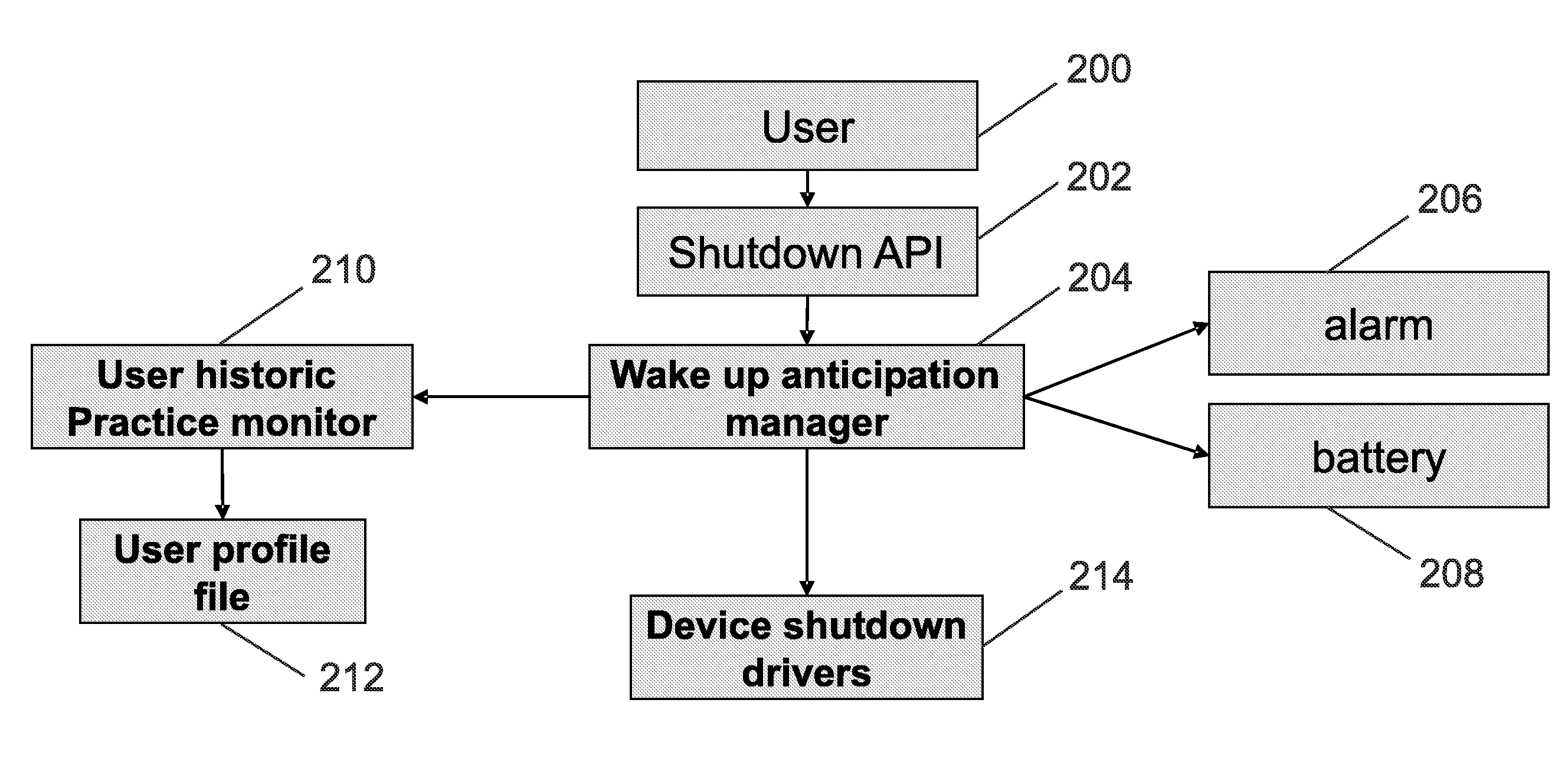
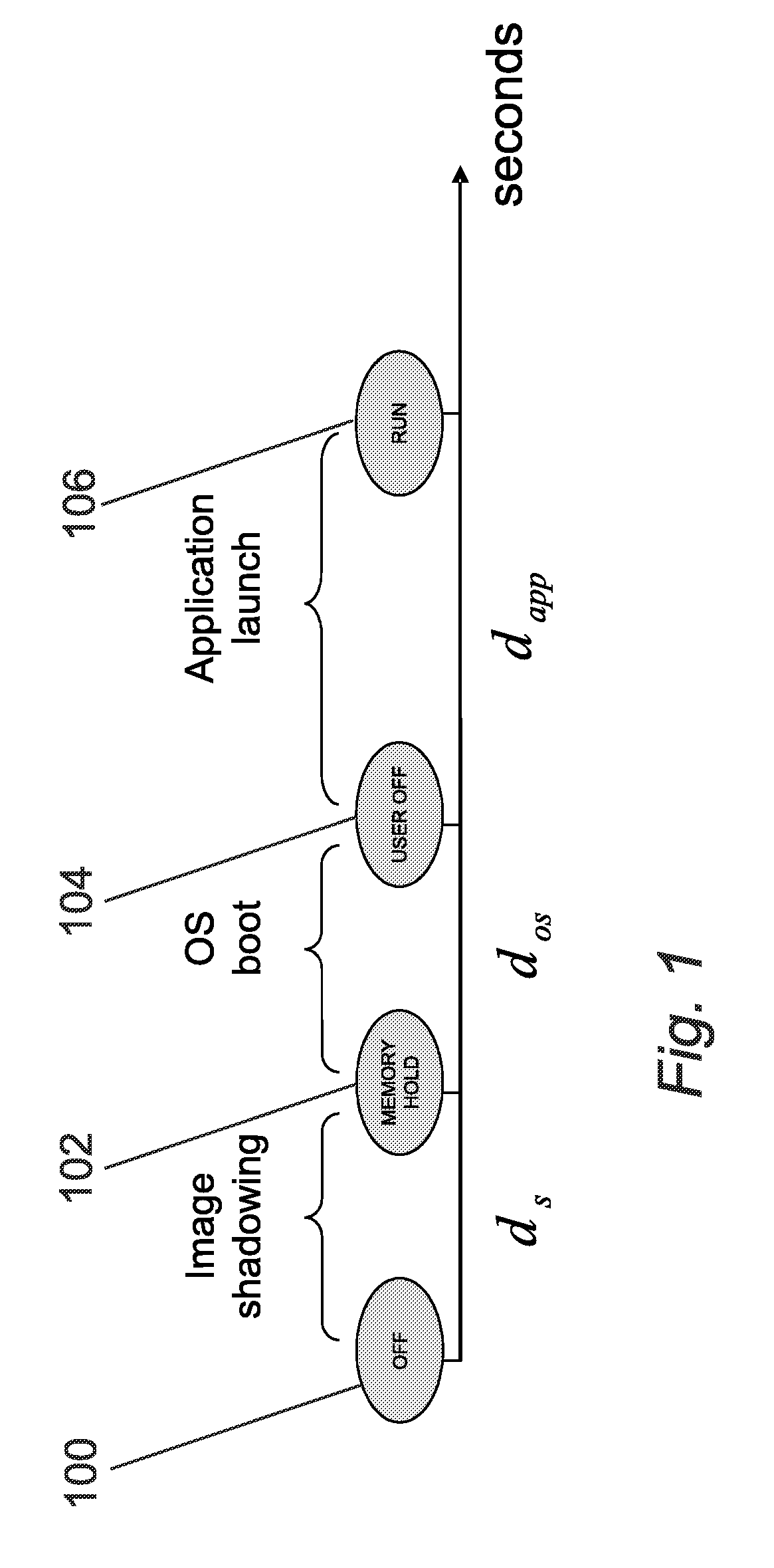
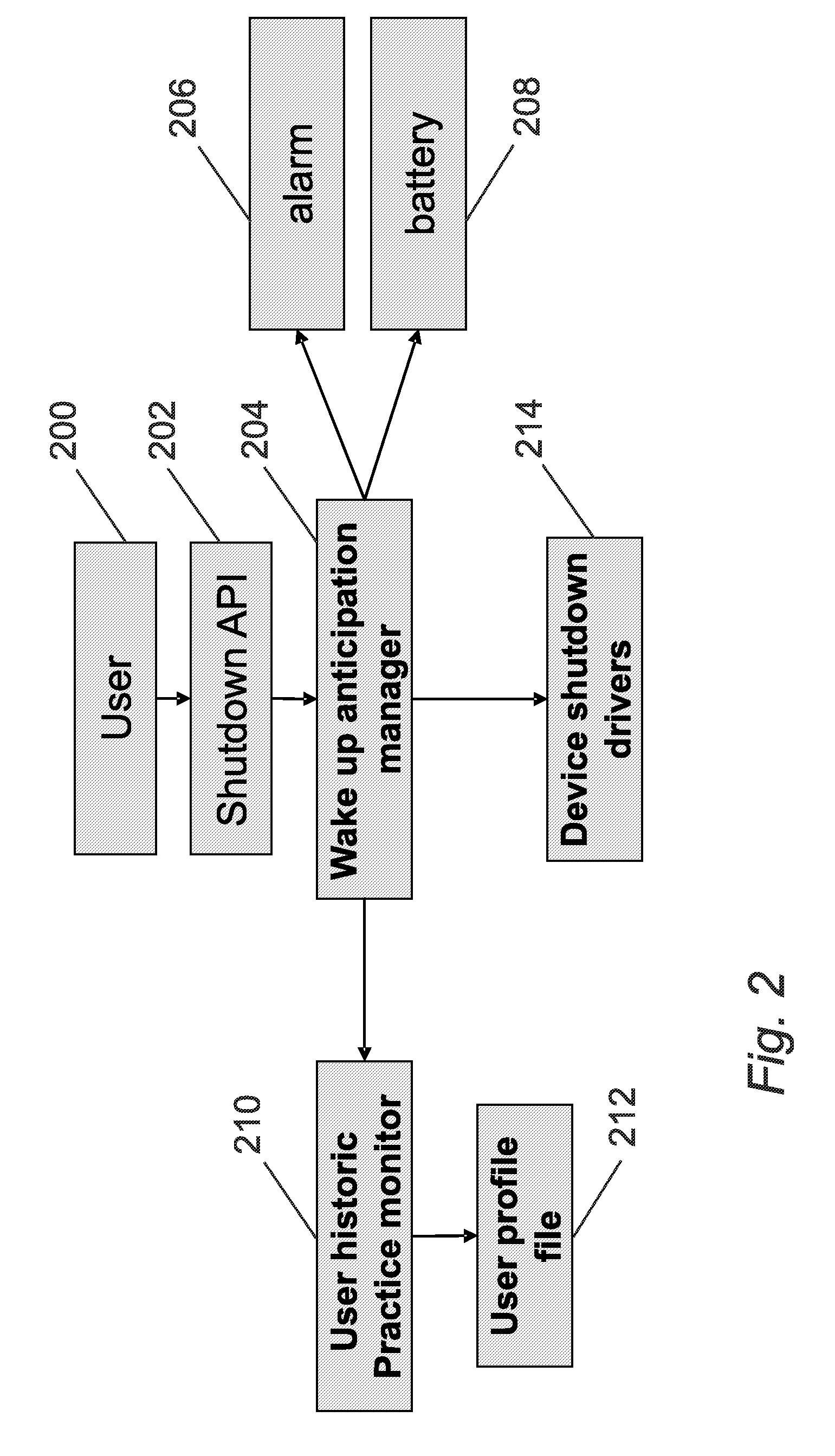
Anticipation of power on of a mobile device
A method of managing the power up of a device that has power down state; and at least two power up states, wherein the method includes the following steps:statistically analysing the power up time profile of the device;determining one or more predetermined statistical indicators associated with the stored power up time profile;calculating an anticipated start up time from the statistical indicators;at the anticipated start up time changing the device state from the power down state to a pre-determined one of the power up states depending on the statistical indicators;maintaining the device at pre-determined power up states for a predetermined duration;returning the device to the power down state if there is no user interaction with the device during the predetermined duration.
Owner:NXP USA INC
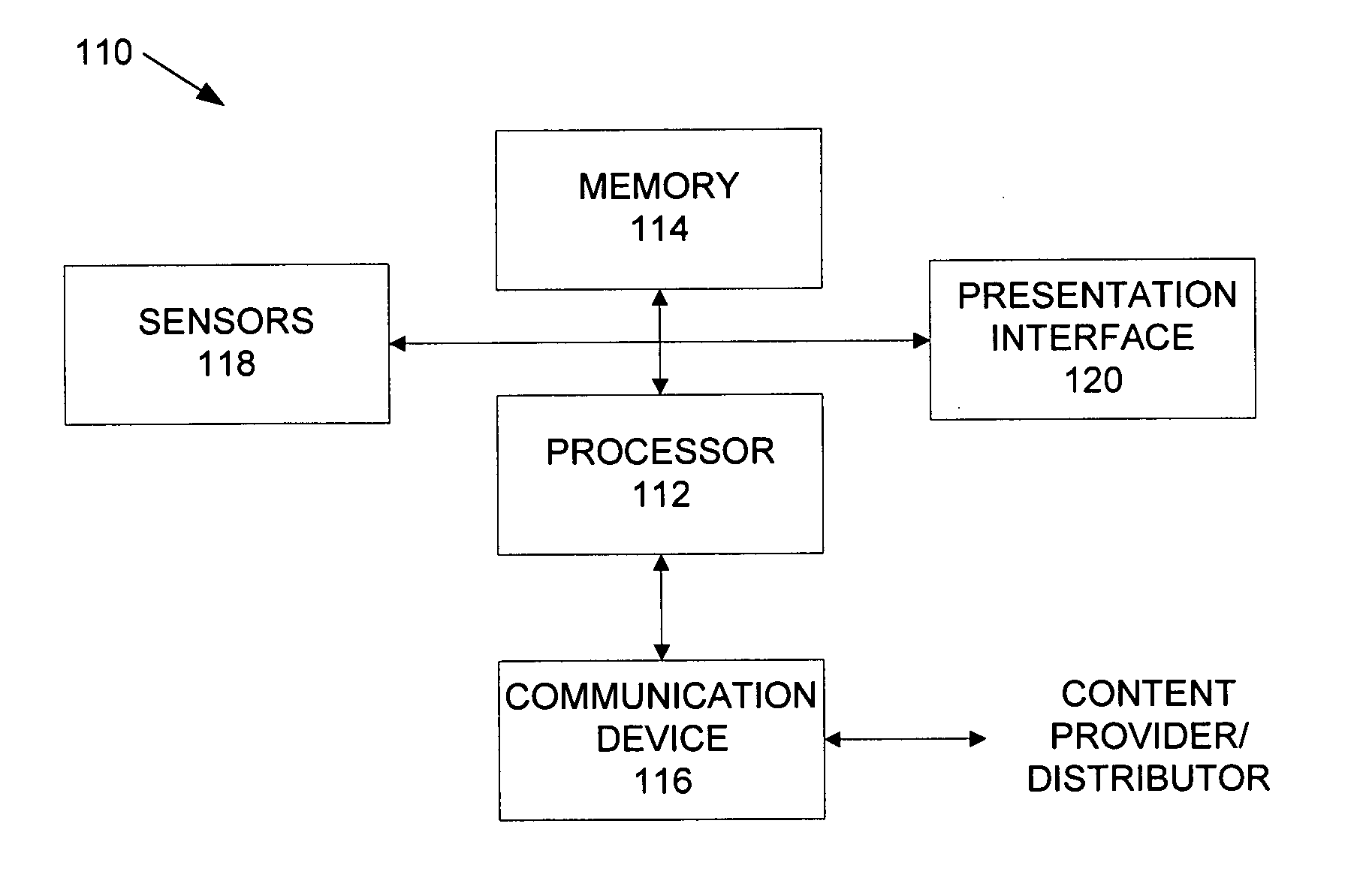
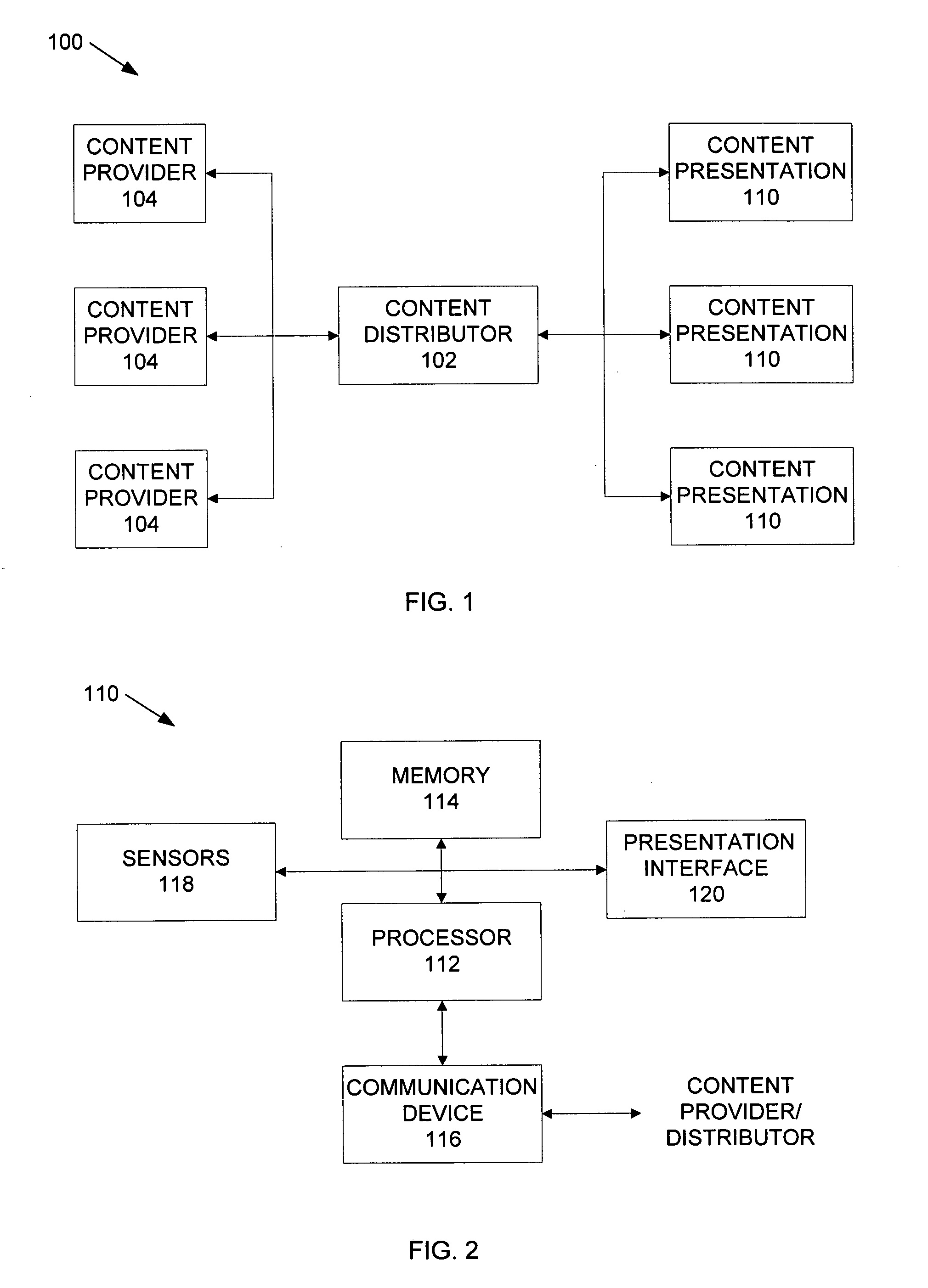
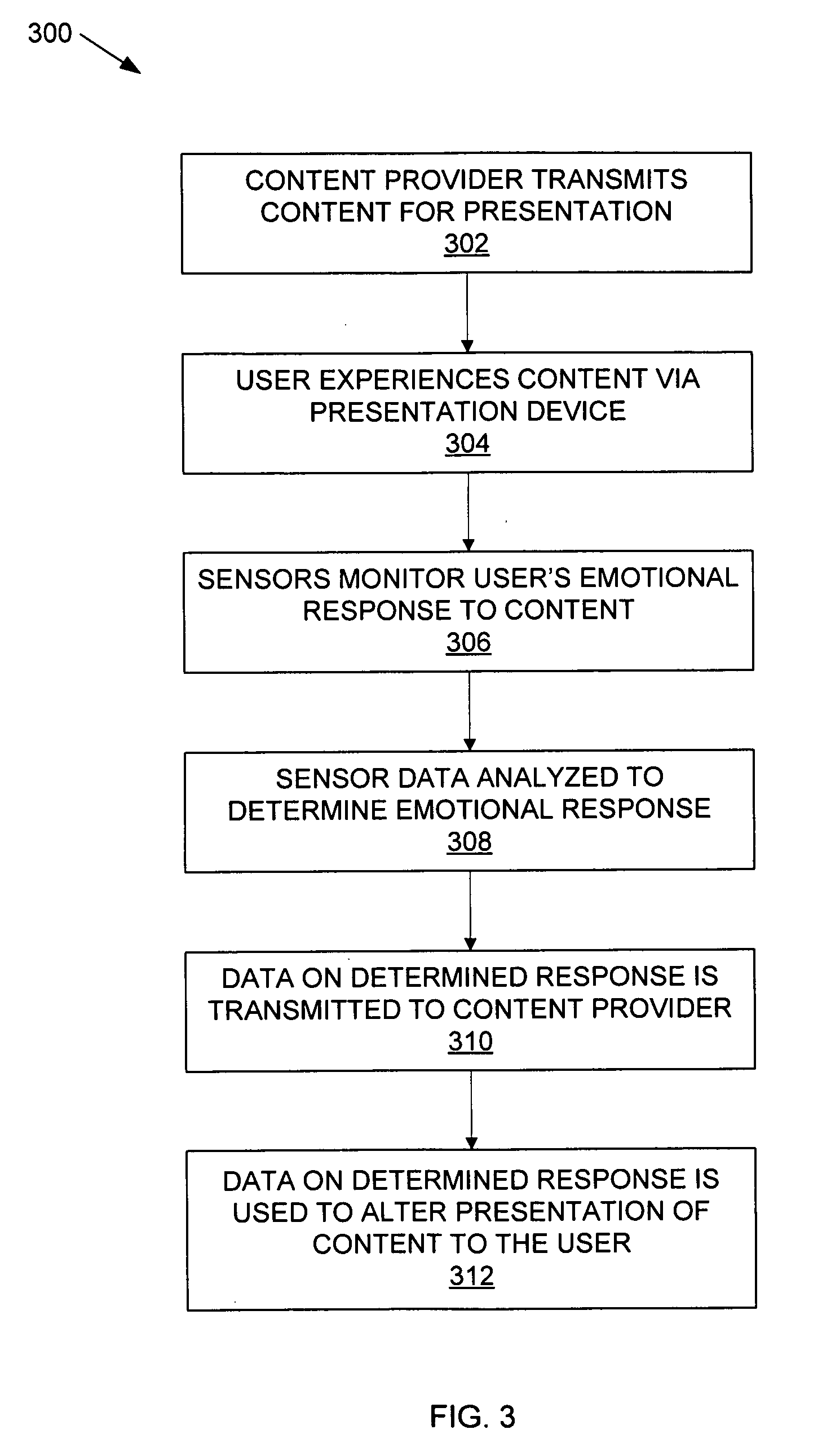
Using sensors to provide feedback on the access of digital content
InactiveUS20070150916A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast components for monitoring/identification/recognitionGraphicsDigital content
A system according to the present disclosure presents content to a user and provides feedback to a content provider without requiring the viewer to explicitly take action. A content presentation unit, such as a digital picture frame or public display, may be any device that continuously and / or sequentially displays graphical, audio and other presentations that may be sensed by a user, generally without intervention by the user. The unit may include sensors that detect when a human expresses interest in specific content, and in various embodiments, determines a type of emotional response experienced by the user regarding the content. Particular sensors may include eye-contact, touch, motion and voice, though other sensors may also be used. The response information can be combined to provide feedback to the content provider that the content was experienced, and may determine various data, such as the duration of attention to the content and any detected emotional response to it.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
System and method for evaluating insurance member activity and pricing insurance products
InactiveUS20050102172A1Reduced premiumFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsHealth related informationProduct base
The present invention relates to systems and methods for evaluating and establishing pricing of insurance products based on insured member compliance to health-promoting measures. Member participation in health-promoting measures are monitored and used as a basis for establishing incentives (i.e., reduction in insurance premiums) for said member. In one embodiment, exercise / activity monitors are worn by members to verify their identity and to record insurance member compliance in performing health-promoting measures (i.e., heart rate, type of exercise, exercise intensity and duration). All health-related information, including physical examination results and recorded participation in health-promoting measures, are used to determine appropriate incentives (i.e., subsidize membership fees for health club) to be rewarded to said member.
Owner:SIRMANS JAMES R JR
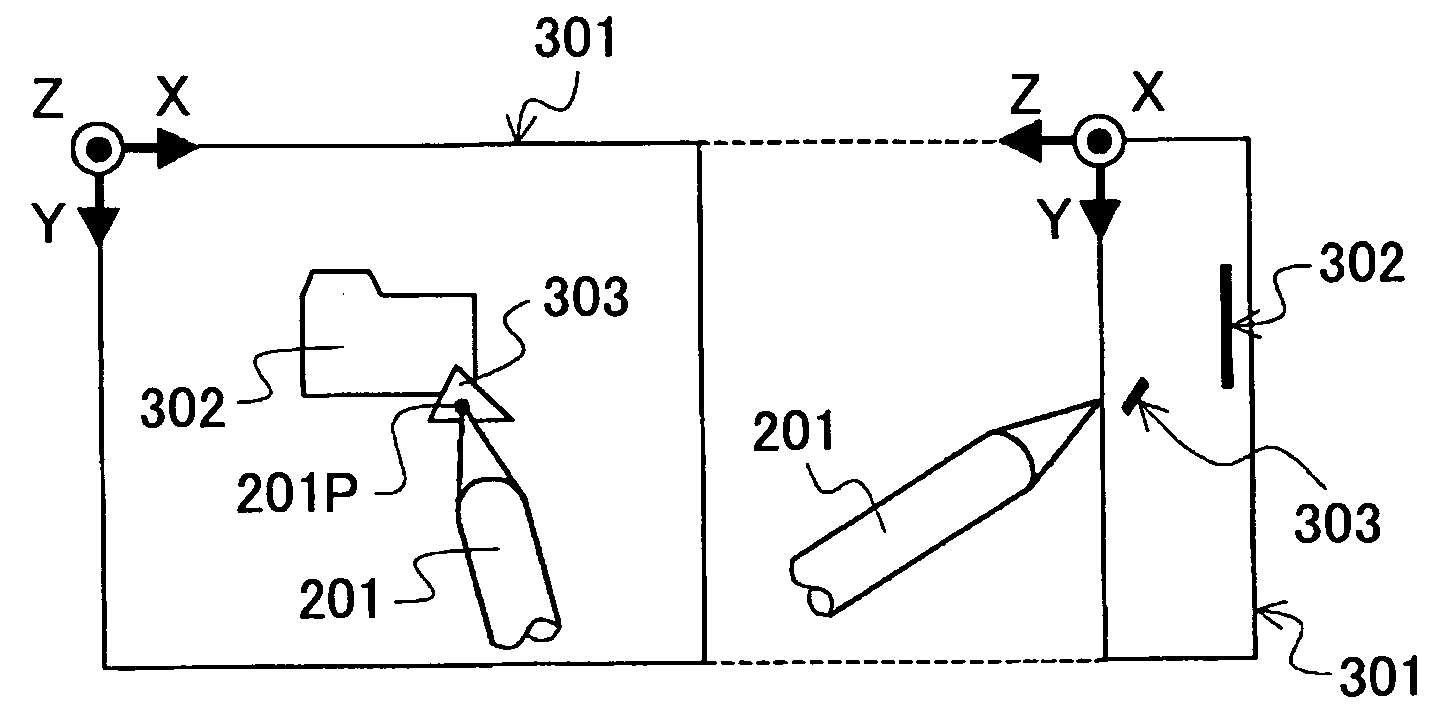
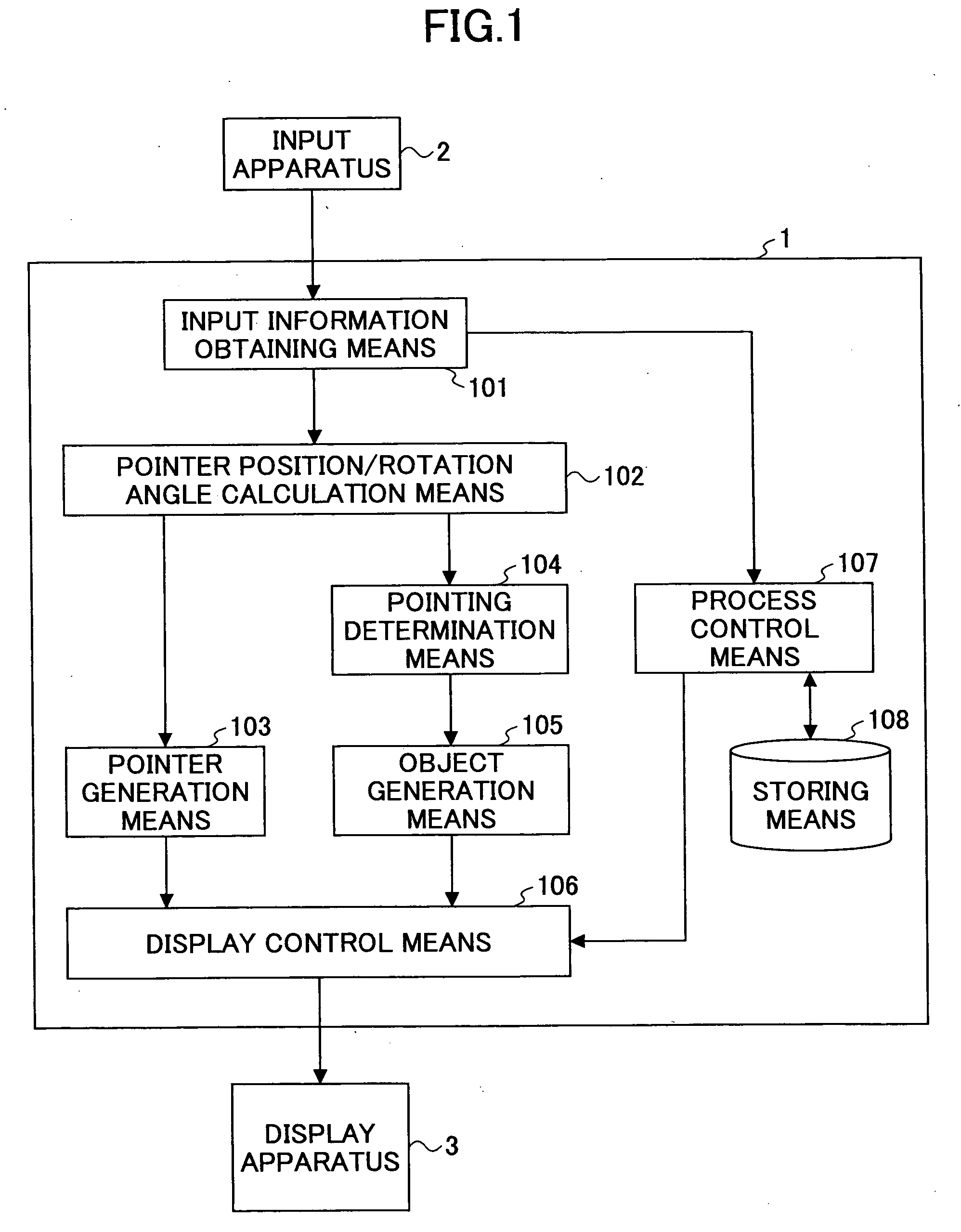
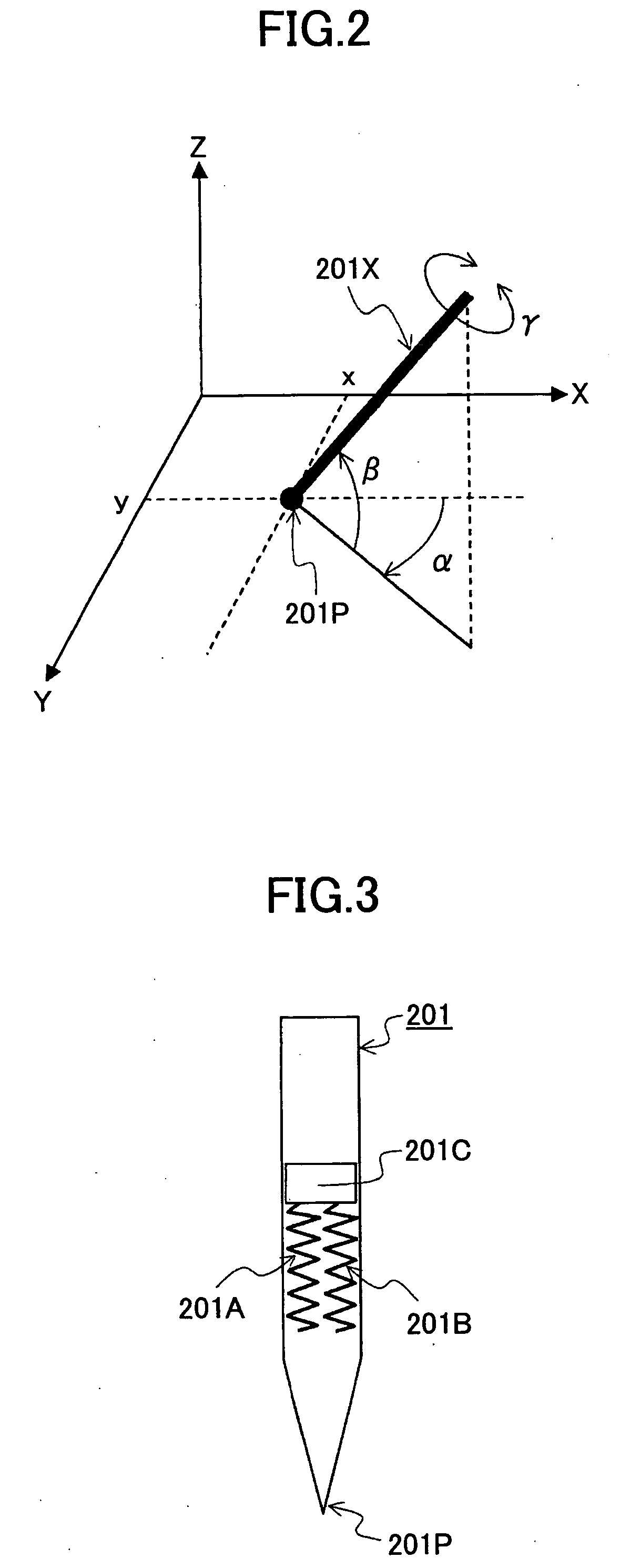
3D Pointing Method, 3D Display Control Method, 3D Pointing Device, 3D Display Control Device, 3D Pointing Program, and 3D Display Control Program
InactiveUS20080225007A1Easy to operateReduce fatigueInput/output processes for data processing3D modellingThree-dimensional spacePointing device
A three-dimensional pointing method is disclosed. In the three-dimensional pointing method of the present invention, a desired point in a three-dimensional space represented on a display apparatus is pointed at based on two-dimensional coordinates of a position that is pointed at by a pen tip of an input pen on a predetermined detection plane, and, based on pen pressure that is pressure applied to the pen tip of the input pen, time for continuing to point or operation of an operation means provided in the input pen. In addition, in the three-dimensional pointing method of the present invention, a depth direction coordinate of a three-dimensional pointer to be displayed in the three-dimensional space is changed according to the pen pressure of the input pen, the time for continuing to point or the operation of the operation means provided in the input pen, and the three-dimensional pointer is displayed.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
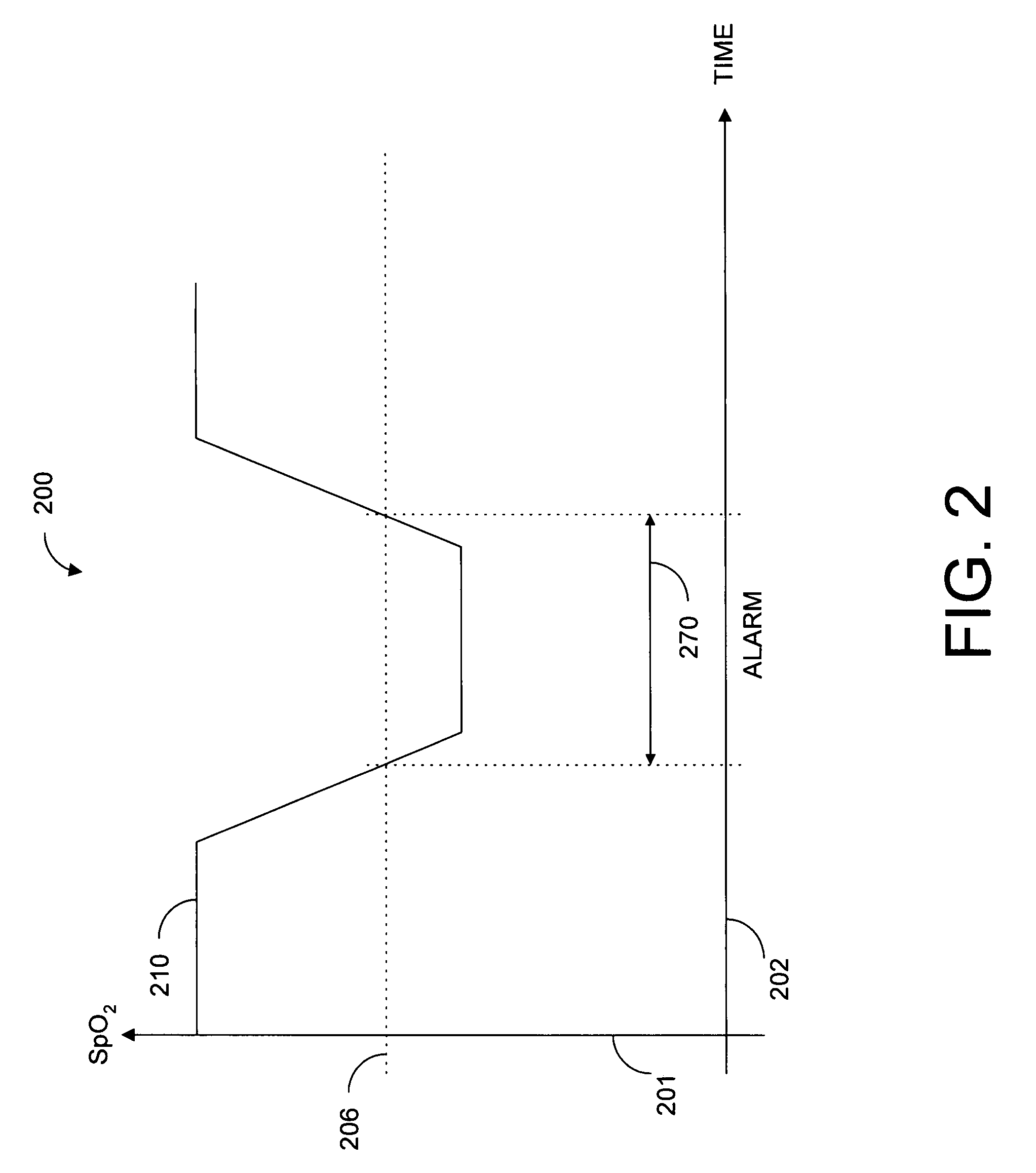
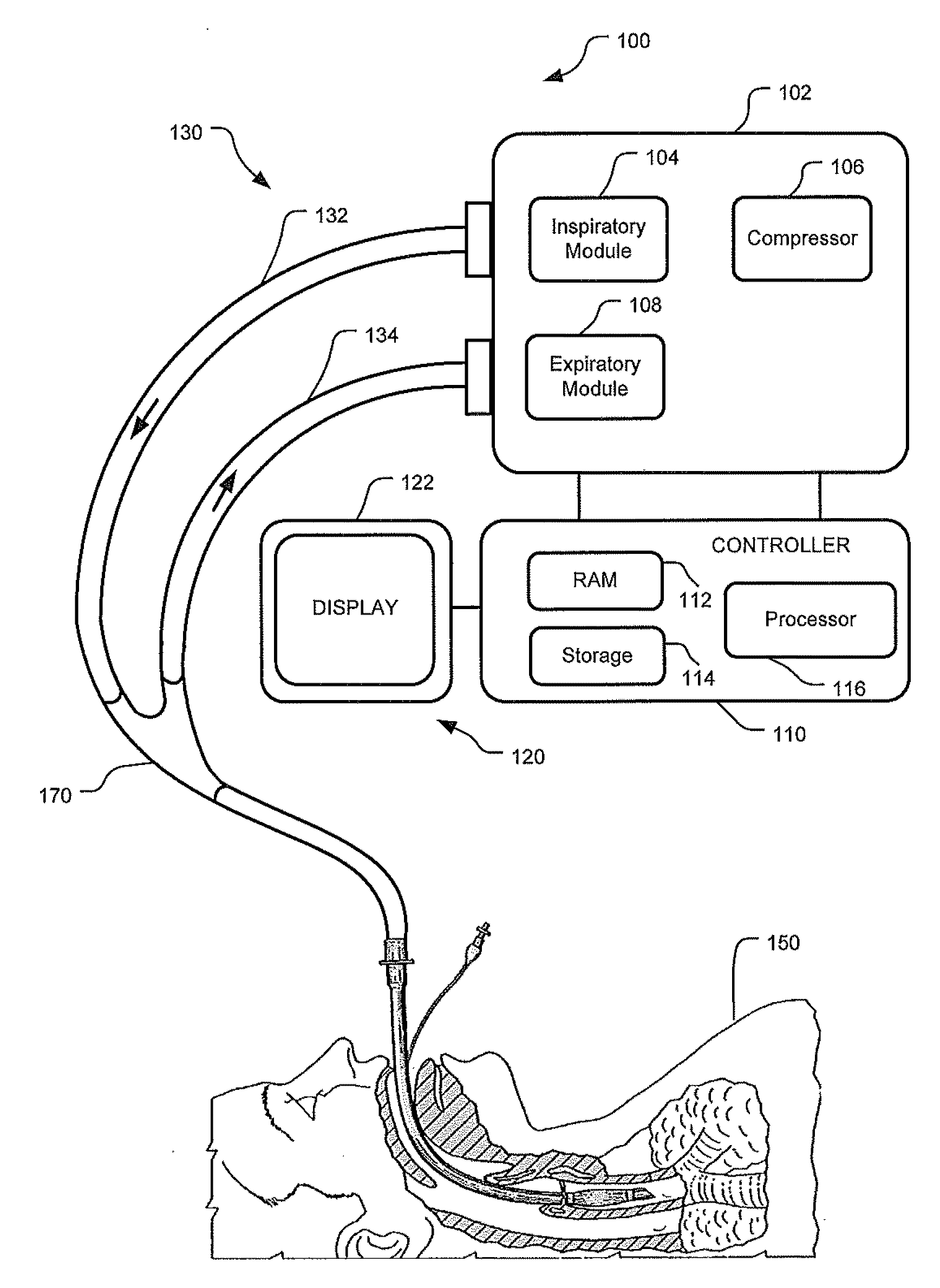
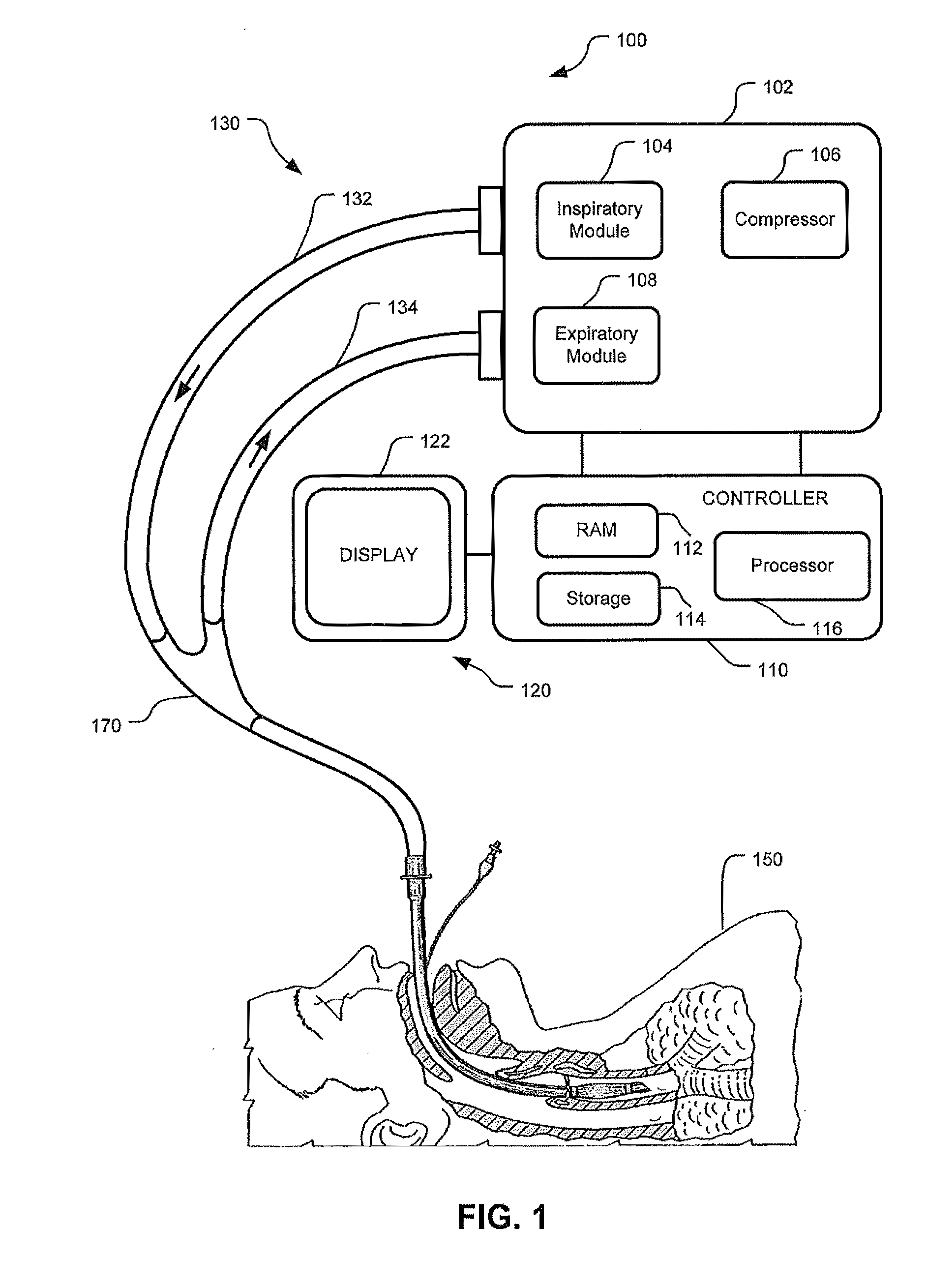
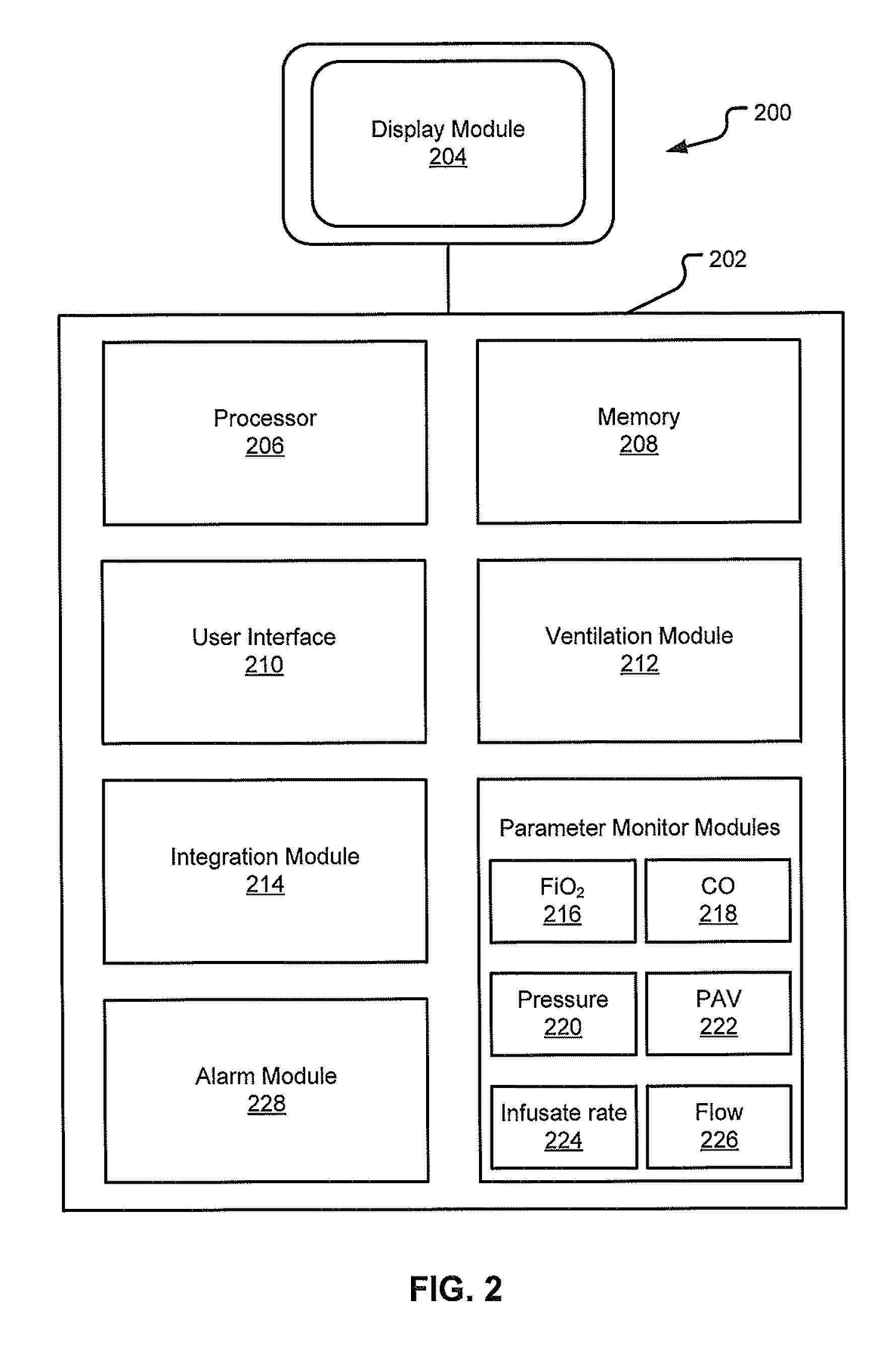
Nuisance Alarm Reduction Method For Therapeutic Parameters
ActiveUS20110175728A1Mitigate nuisance alarmsReduce nuisance alarmRespiratorsBreathing masksMedicineDuration time
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
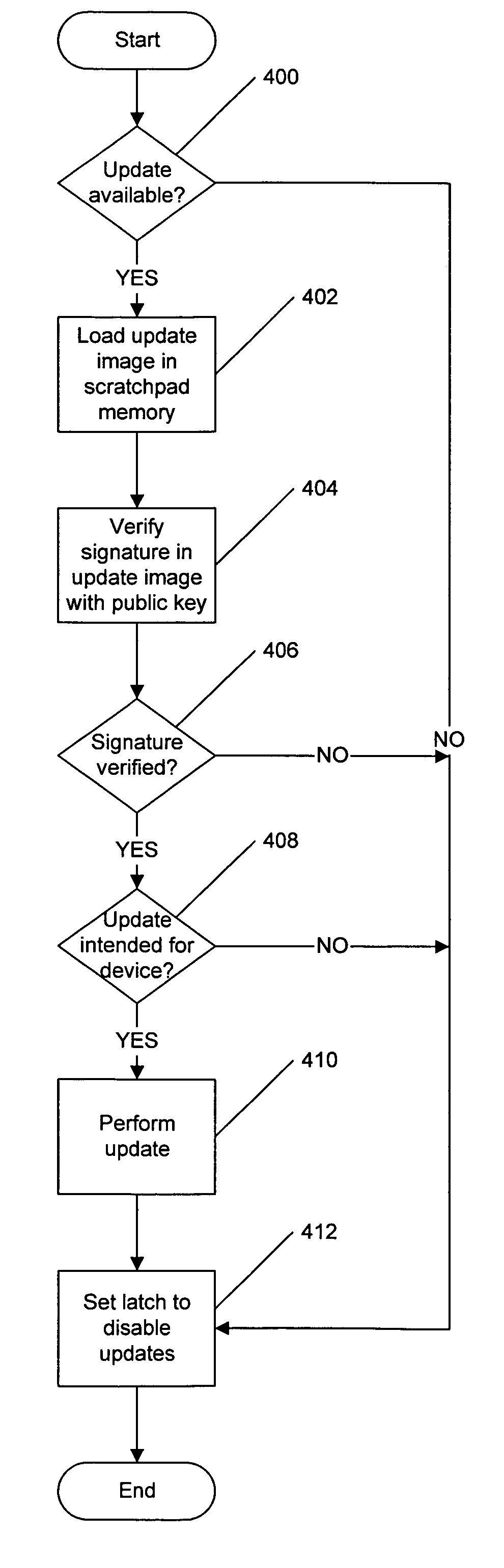
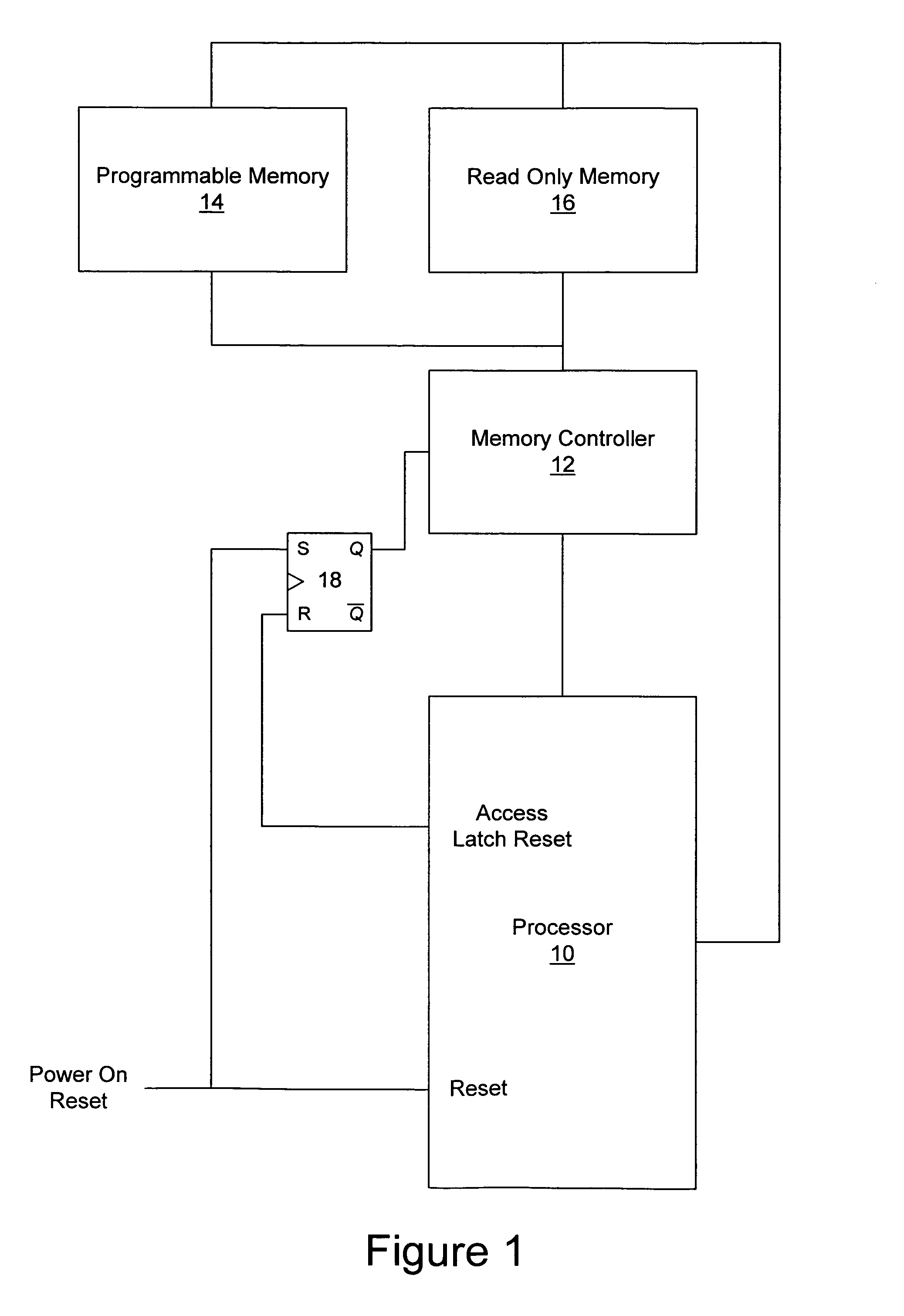
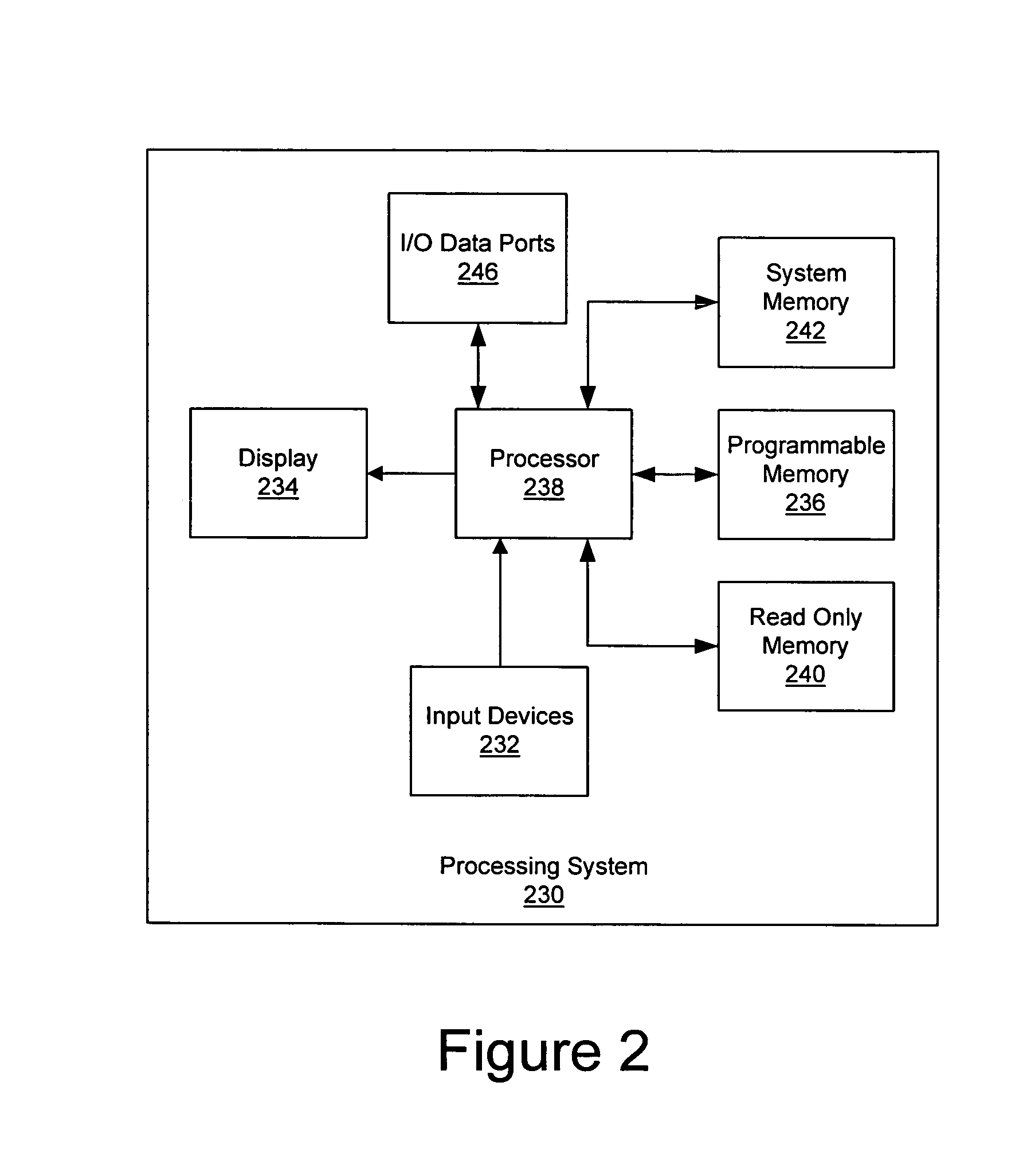
Methods, systems and computer program products for secure firmware updates
ActiveUS7069452B1Avoid accessReduce stepsDigital computer detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionData storeControl equipment
Methods, systems and computer program products which provide secure updates of firmware (i.e. data stored in a programmable memory device of a processing system) are disclosed. Updates of a programmable memory of a device may be controlled by providing an update window of finite duration during which the programmable memory may be updated. Access to the programmable memory may be based on the state of an access latch. The access latch may be set to allow access after a hardware reset of the device. An update control program may be executed to control access to the programmable memory and the latch reset to prevent access upon completion of the update control program. Verification of the update may be provided through encryption techniques and rules incorporated in certificates for application of updates to provide for selectively updating devices. Also disclosed are methods of securely providing differing functionality to generic devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for funds management
Owner:UBS BUSINESS SOLUTIONS AG
Safety indicator and method
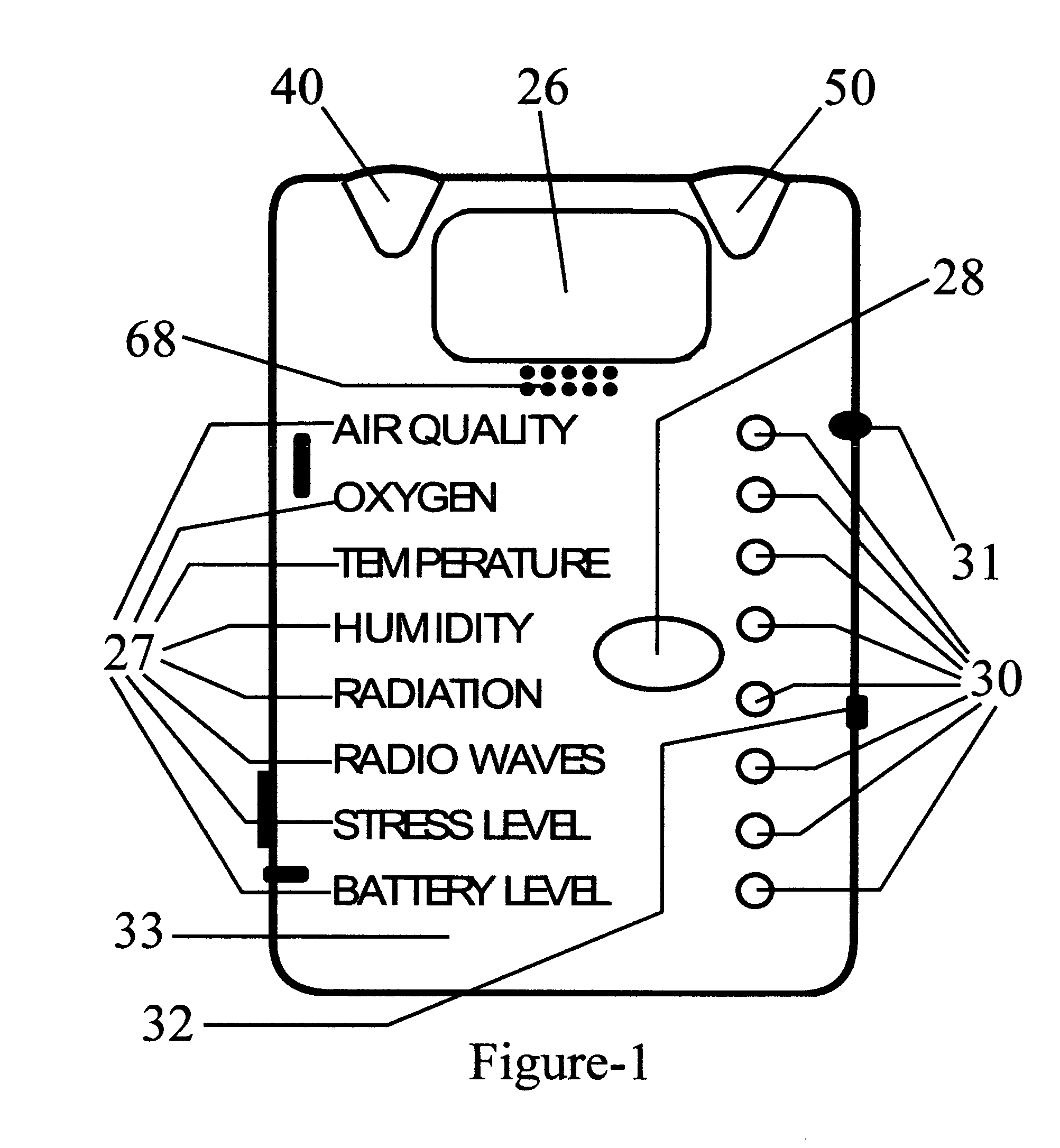
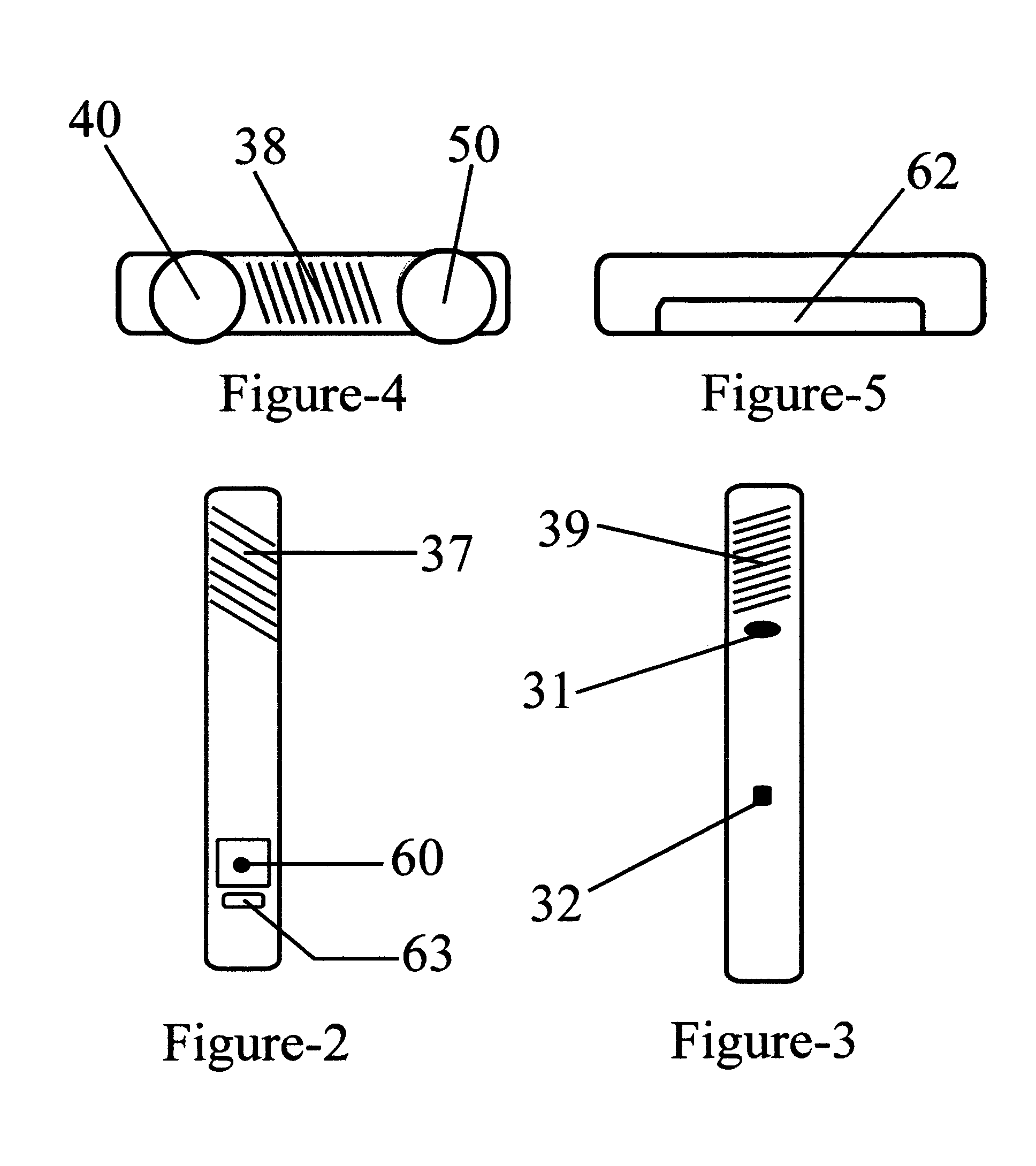
InactiveUS7378954B2Eliminate saturationReduce the noise floorDosimetersPhotometryExposure durationRadiation exposure
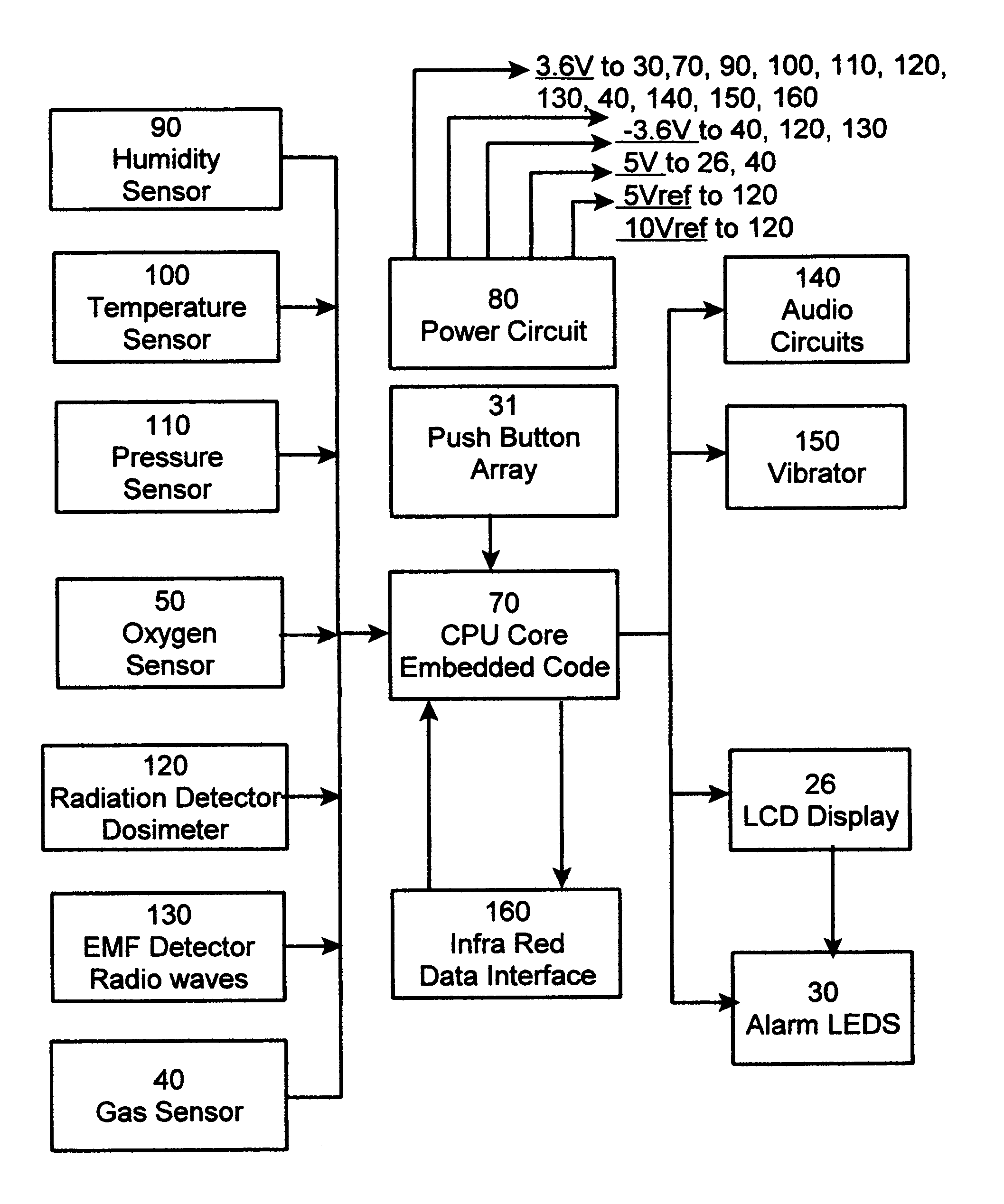
A safety indicator monitors environment conditions detrimental to humans e.g., hazardous gases, air pollutants, low oxygen, radiation levels of EMF or RF and microwave, temperature, humidity and air pressure retaining a three month history to upload to a PC via infra red data interface or phone link. Contaminants are analyzed and compared to stored profiles to determine its classification and notify user of an adversity by stored voice messages from, via alarm tones and associated flashing LED, via vibrator for silent operation or via LCD. Environmental radiation sources are monitored and auto-scaled. Instantaneous radiation exposure level and exposure duration data are stored for later readout as a detector and dosimeter. Scans for EMF allow detection with auto scaling of radiation levels and exposure durations are stored for subsequent readout. Electronic bugs can be found with a high sensitivity EMF range setting. Ambient temperature measurements or humidity and barometric pressure can be made over time to predict weather changes. A PCS RF link provides wireless remote communications in a first responder military use by upload of alarm conditions, field measurements and with download of command instructions. The link supports reception of telemetry data for real time remote monitoring of personnel via the wrist band for blood pressure, temperature, pulse rate and blood oxygen levels are transmitted. Commercial uses include remote environmental data collection and employee assignment tasking. GPS locates personnel and reporting coordinates associated with alarm occurrences and associated environmental measurements.
Owner:NTCG
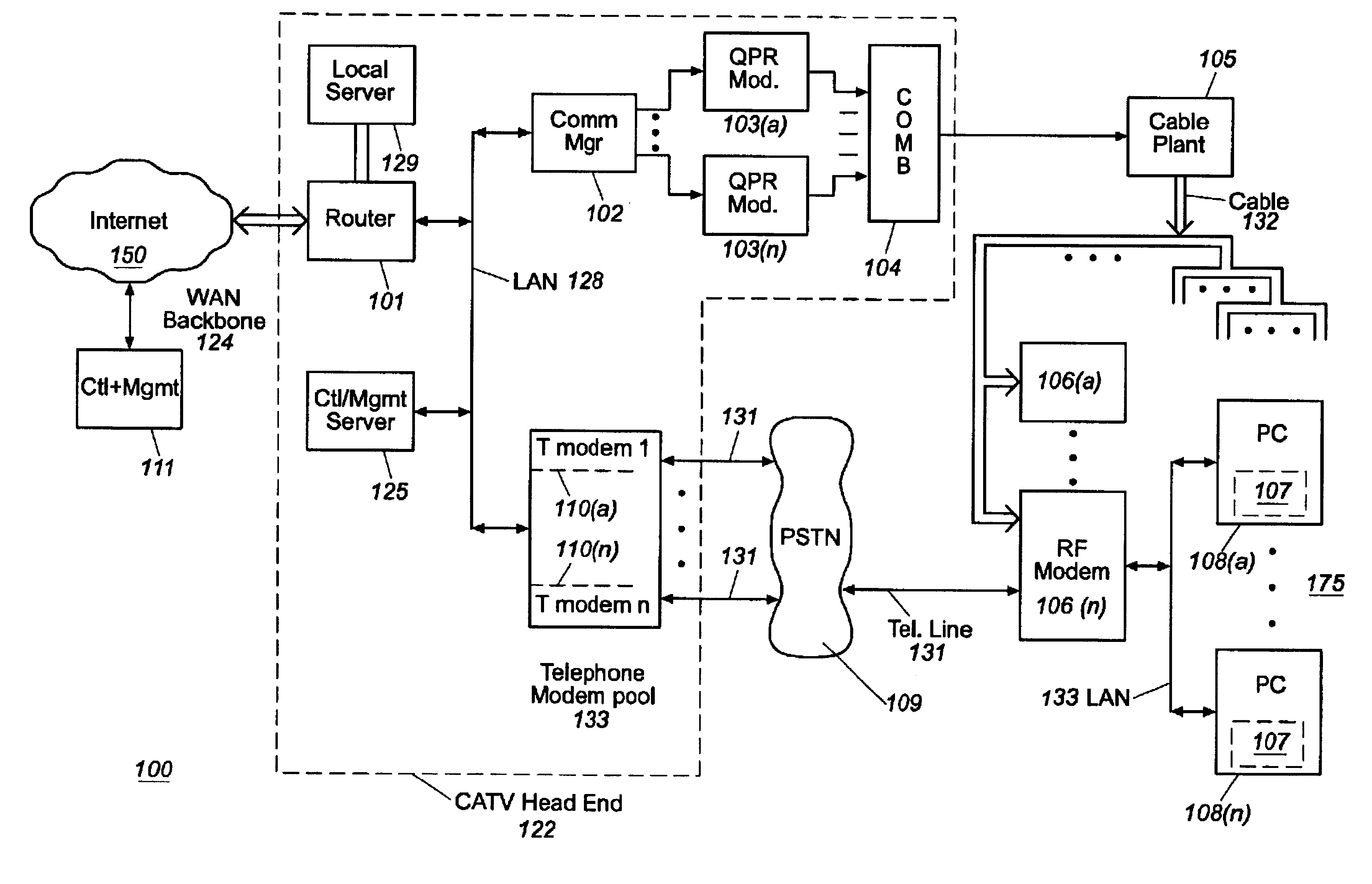
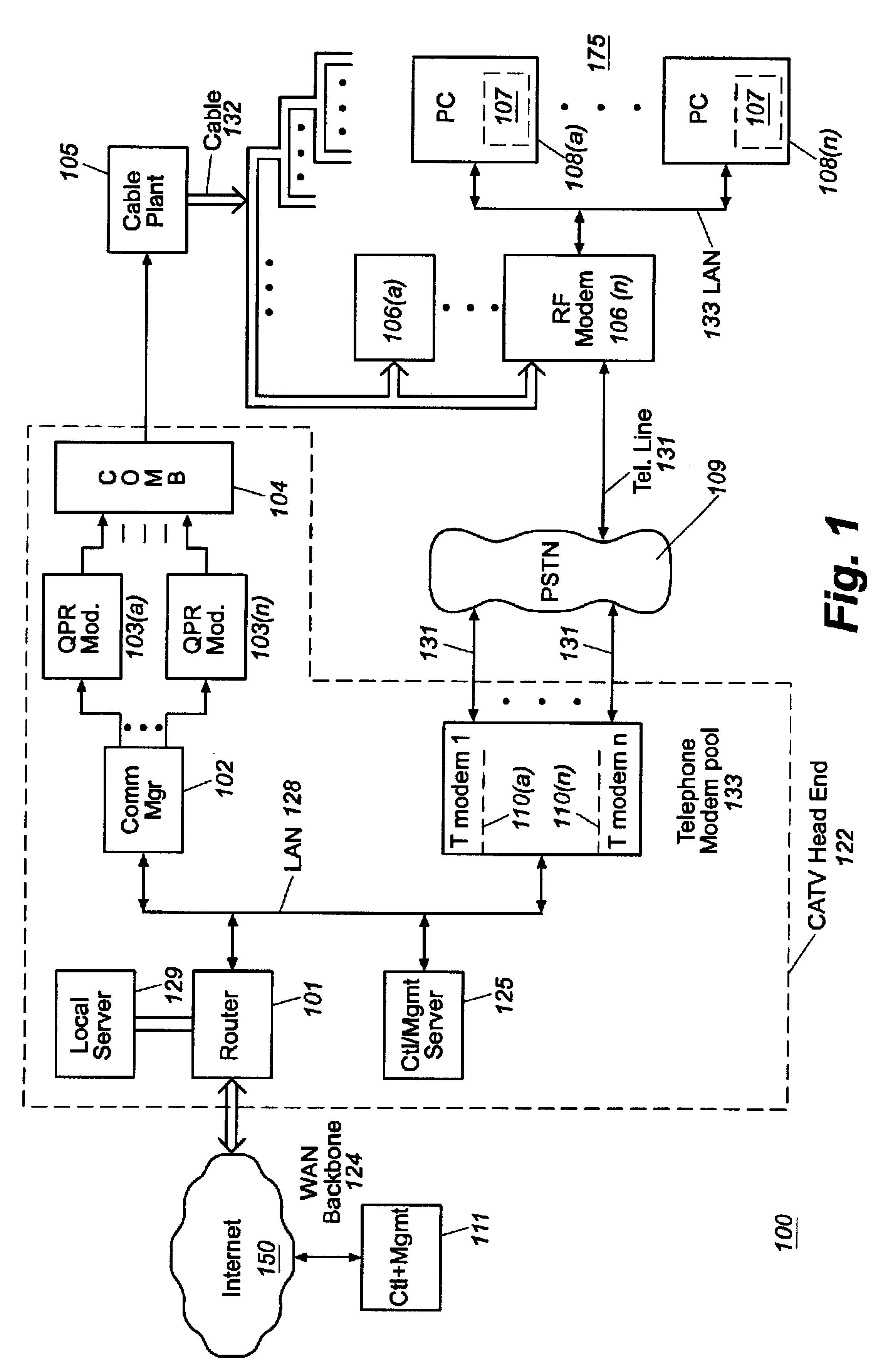
Usage statistics collection for a cable data delivery system
InactiveUS6308328B1Broadband local area networksBroadcast transmission systemsData connectionNetwork management
Apparatus for recording and collecting usage and other statistical data from components of a cable data network comprises a network manager for maintaining and collecting the statistics. Internet protocol addresses are associated with components of the network. The component maintains a software agent that manages a statistics database. Responsive to a manager request generated at a service provider defined time interval, the component software agent provides the usage statistics to the network manager in real-time during an Internet session with a host. When the host to Internet or other data connection is torn down due to failure, disconnect or inactivity time-out, remaining usage statistics data is collected and the session duration updated with the time of tear down. Usage statistics collected include the amount of data transferred to / from a host, the amount of data that is discarded due to insufficient resource capacity and amount of data that cannot be corrected despite forward error correction used in a downstream high capacity channel to the host. Data traps may be defined and downloaded to components of the network for implementation. As a result, billing of users of the cable data network can be usage sensitive and determined based on actual data transferred (including credit given for errored data) and / or time sensitive based on session duration.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
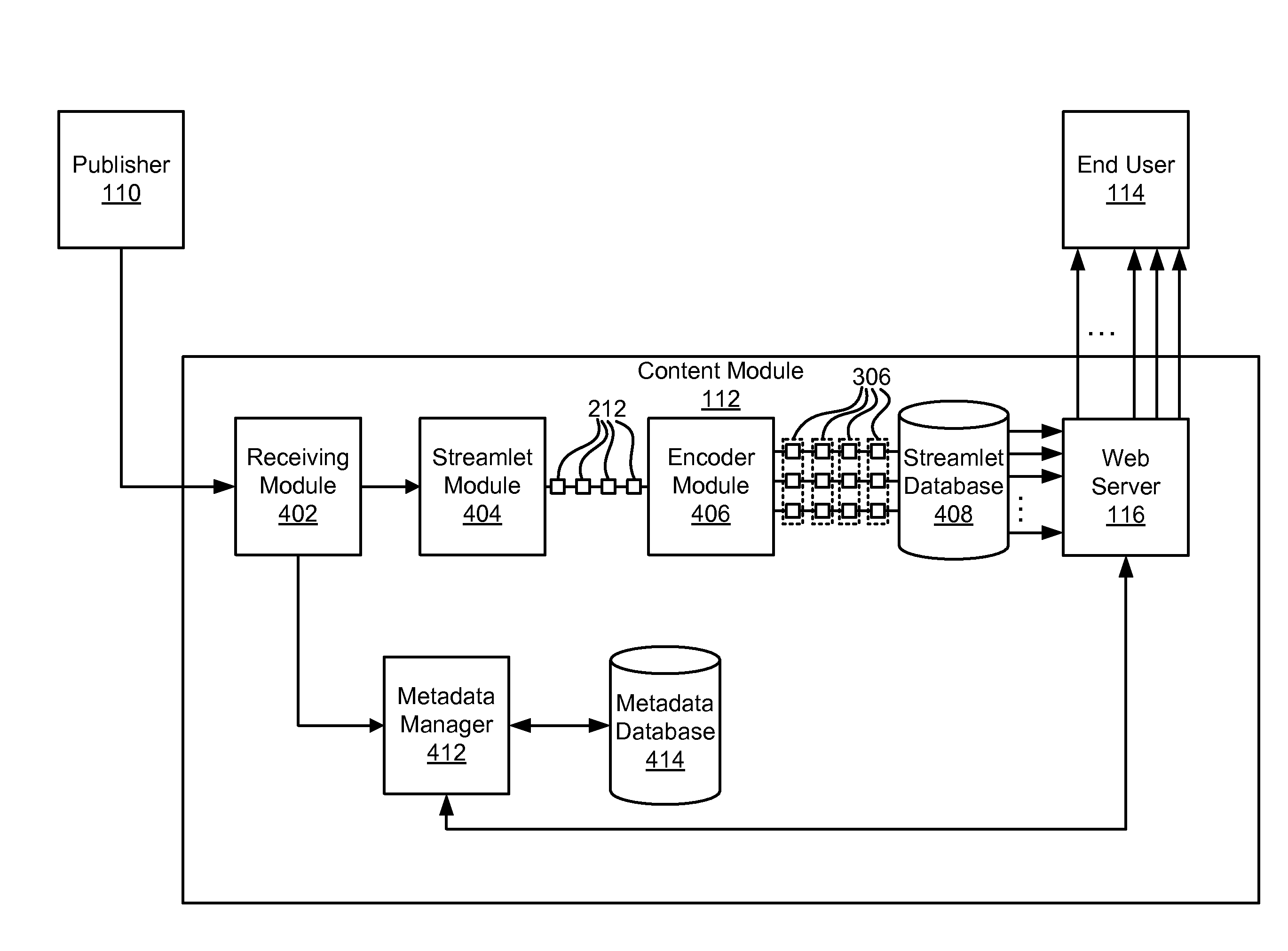
Apparatus, system, and method for multi-bitrate content streaming
ActiveUS20080195743A1Overcomes shortcomingVideo data indexingPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime indexBit rate
An apparatus for multi-bitrate content streaming includes a receiving module configured to capture media content, a streamlet module configured to segment the media content and generate a plurality of streamlets, and an encoding module configured to generate a set of streamlets. The system includes the apparatus, wherein the set of streamlets comprises a plurality of streamlets having identical time indices and durations, and each streamlet of the set of streamlets having a unique bitrate, and wherein the encoding module comprises a master module configured to assign an encoding job to one of a plurality of host computing modules in response to an encoding job completion bid. A method includes receiving media content, segmenting the media content and generating a plurality of streamlets, and generating a set of streamlets.
Owner:DISH TECH L L C
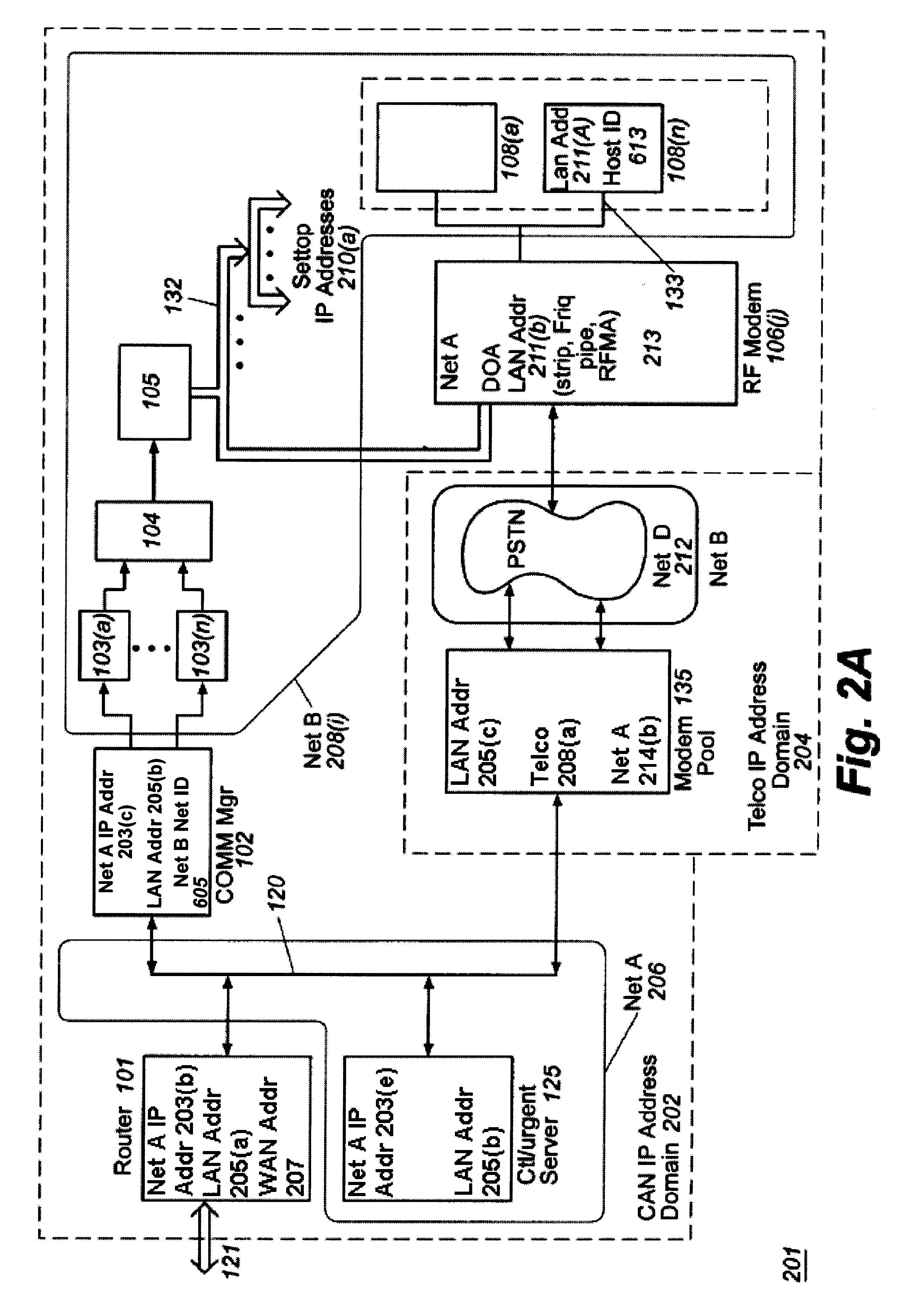
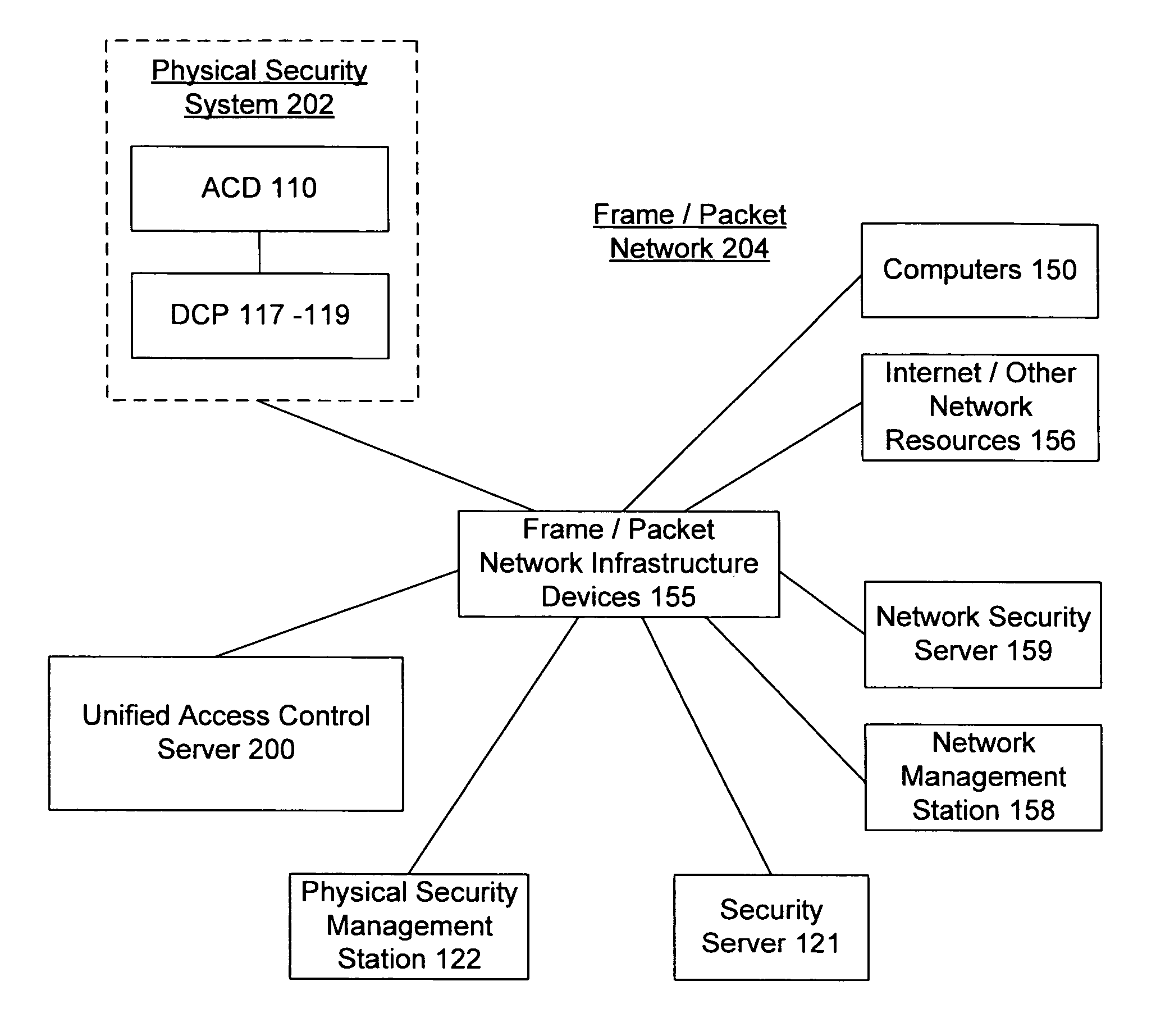
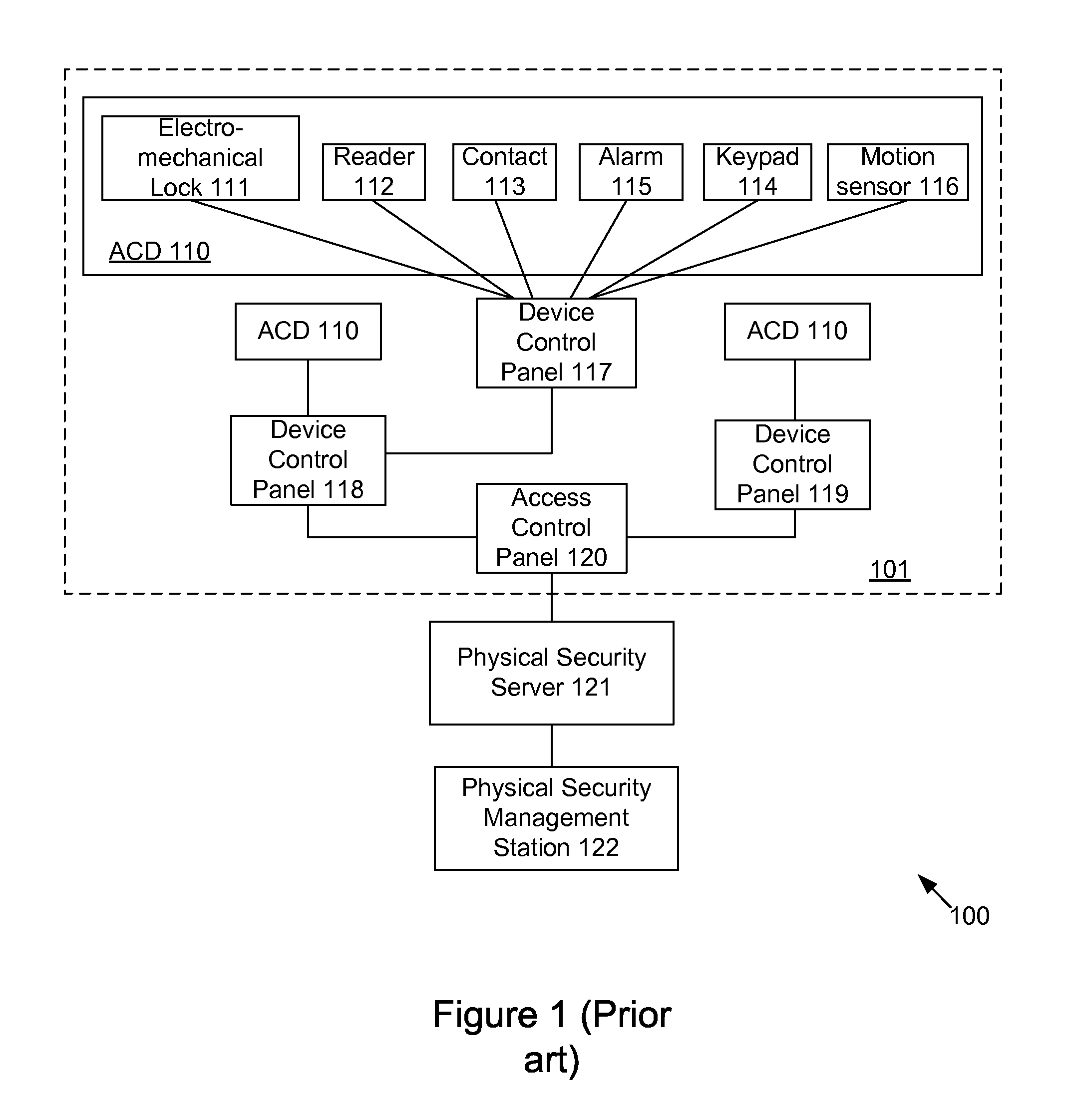
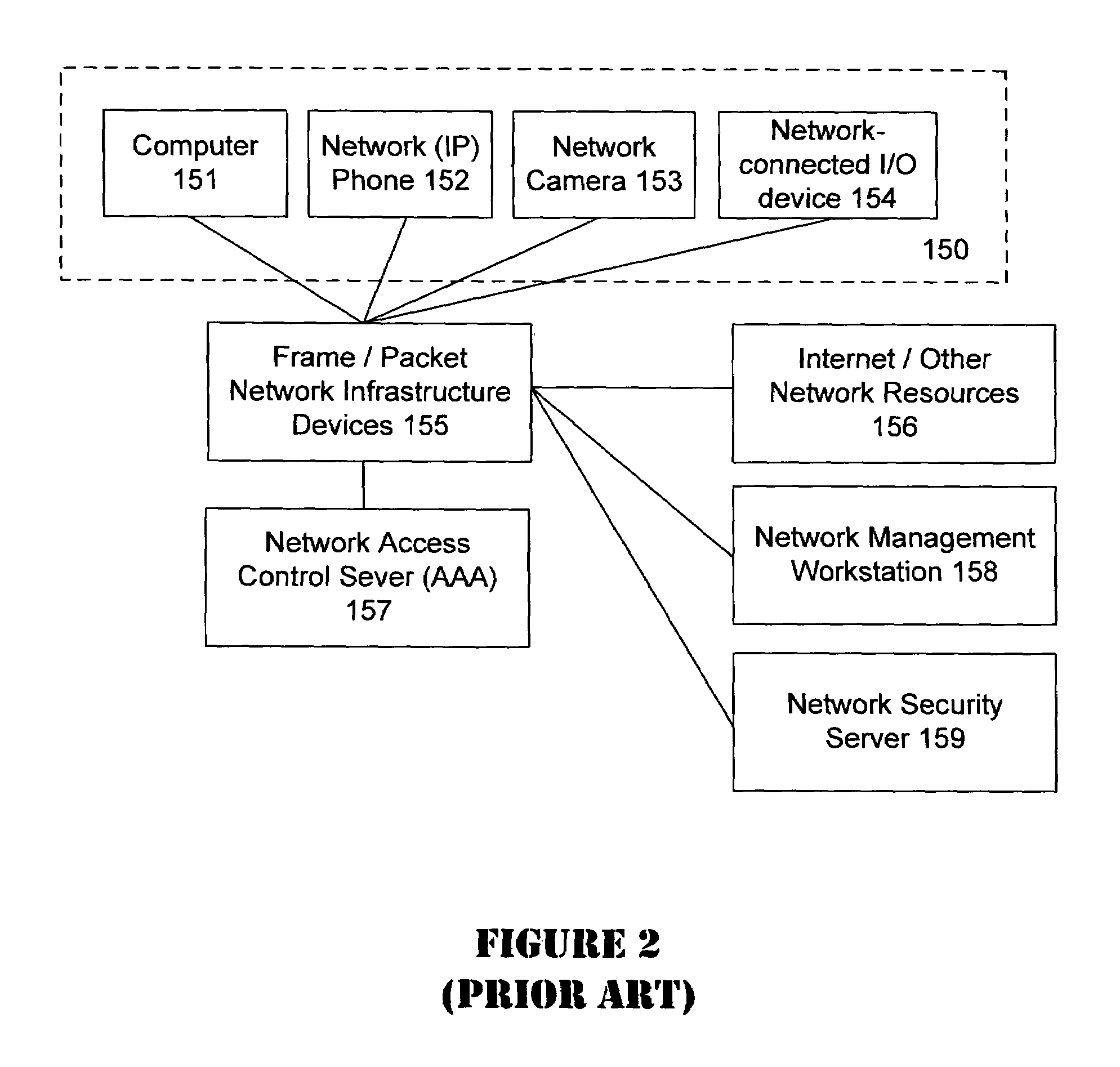
Unified network and physical premises access control server
ActiveUS7437755B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTime of dayNetwork Access Device
The present invention provides an access control server that holds information pertaining to both network access and facility access. The access control server enforces policies based on location, type of resource, time of day, duration, or other events, and logs all successful and unsuccessful attempts to access a given resource whether it be on the network or at the facility. The access control server operates off a common list or table of attributes and policies, or separate lists or tables of attributes and policies that are arbitrated by a credential verification and policy engine. This unified access control server implements protocols that work with network and / or physical premises-based devices. The unified access control server allows events in the facility to be associated with events on the network and vice versa and direct policies that may be executed in the physical or network realm.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus, system, and method for multi-bitrate content streaming
ActiveUS7818444B2Video data indexingPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime indexBit rate
Owner:DISH TECH L L C
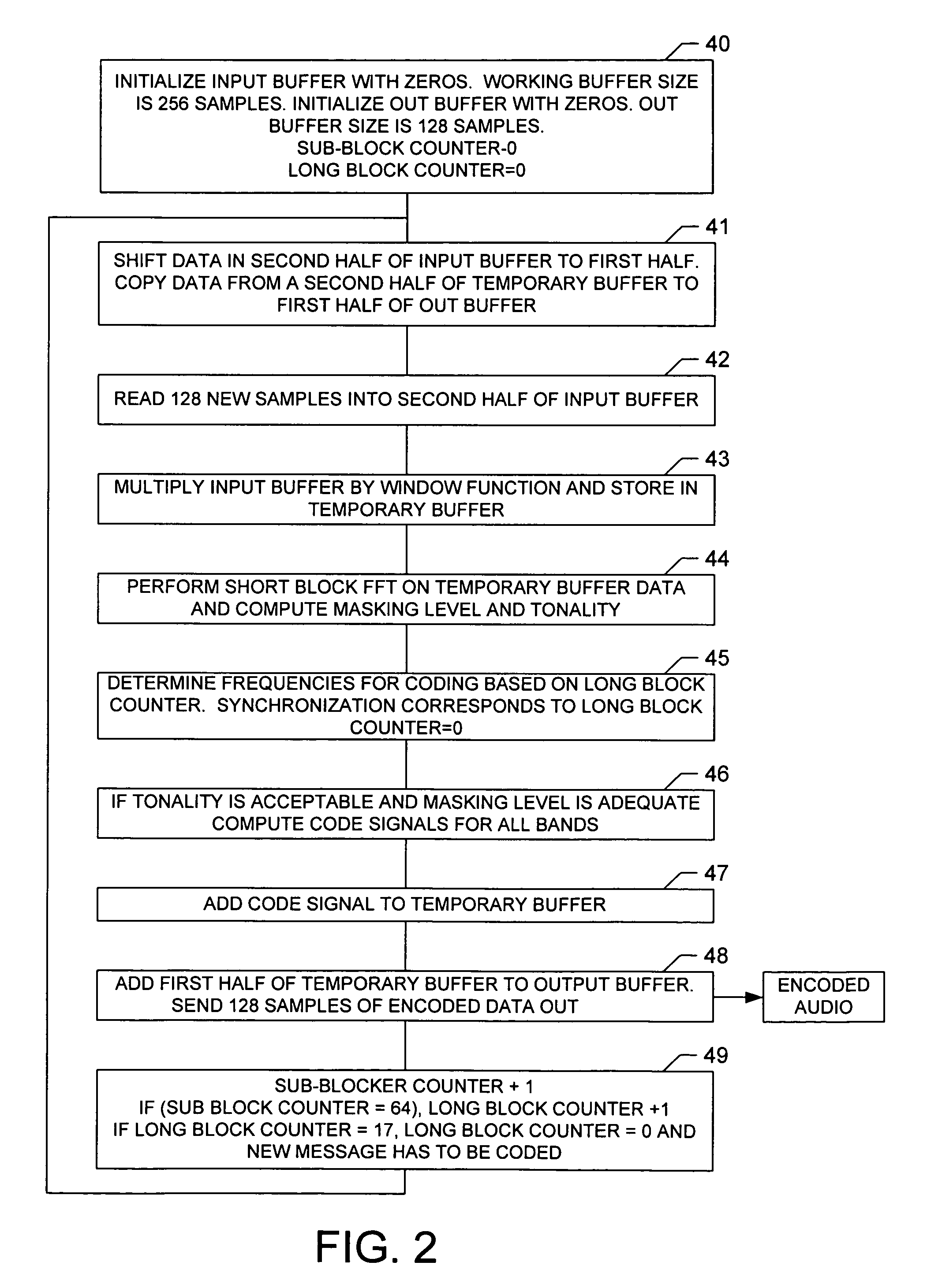
Multi-band spectral audio encoding
An encoder includes a sampler that samples an audio signal and that generates from the samples a plurality of short blocks of sampled audio. Each of the short blocks has a duration less than a minimum audibly perceivable signal delay. A processor combines the plurality of short blocks into a long block. The long block is transformed into a frequency domain signal having a plurality of independently modulatable frequency indices. The frequency difference between adjacent indices is determined by the minimum duration and the sampling rate of the sampler. A neighborhood of frequency indices is selected so that the frequency difference between a lowest index and a highest index within the neighborhood is less than a predetermined value. Two or more of the indices are modulated in the neighborhood so as to make a selected one of the indices an extremum while keeping the total energy of the neighborhood constant. A plurality of frequency bands are so coded. A decoder decides that a bit or bits have been received if, in a majority of the frequency bands, the decoder detects a modulated index.
Owner:NIELSEN COMPANY US LLC THE A DELAWARE LIMITED LIABILITY
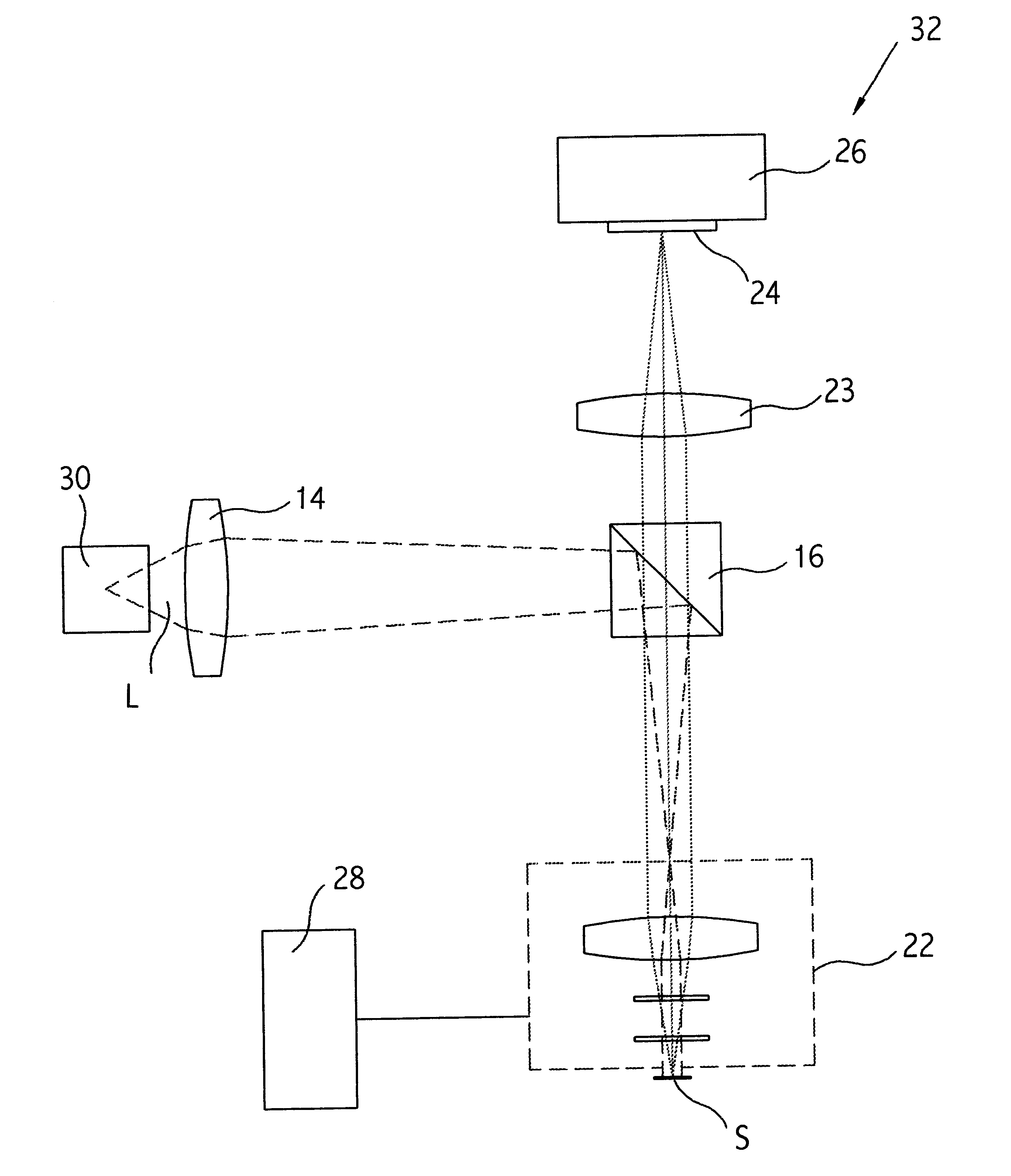
Pulsed source scanning interferometer
InactiveUS6556305B1Improve signal utilizationChange is minimalUsing optical meansPhase shiftedCombined use
A pulsed light source in used conjunction with a ramping scanning mechanism for phase-shift and vertical-scanning interferometry. The pulse length and the scanning velocity are selected such that a minimal change in OPD occurs during the pulse. As long as the duration of the pulse is shorter than the detector's integration time, the effective integration time and the corresponding phase shift are determined by the length of the pulse, rather than the detector's characteristics. The resulting minimal phase shift produces negligible loss of fringe modulation, thereby greatly improving signal utilization during phase-shifting and vertical-scanning interferometry.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Generating, transporting, processing, storing and presenting segmentation information for audio-visual programs
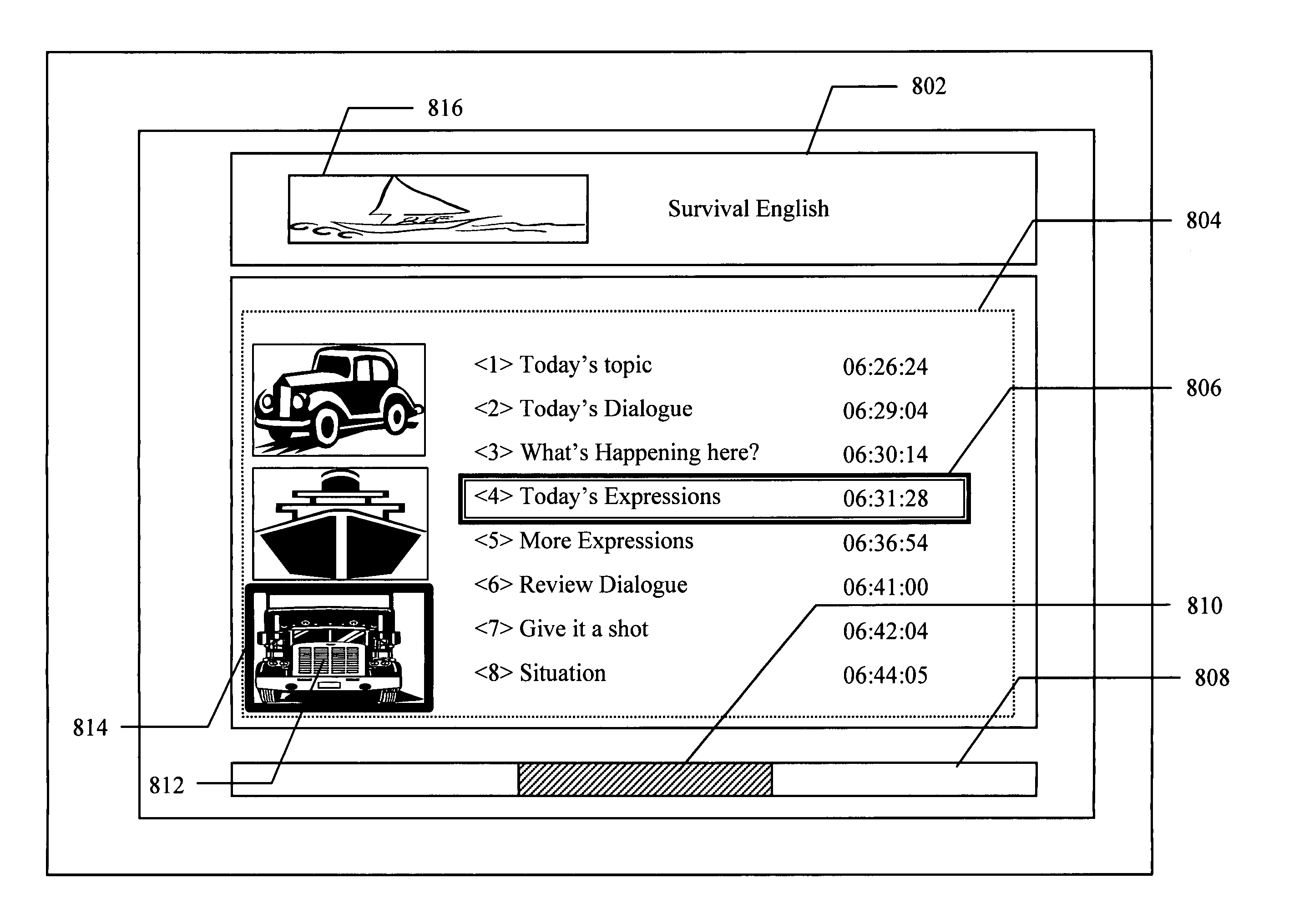
InactiveUS20050193408A1Efficient deliveryDisc-shaped record carriersPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesInteractive graphicsGraphical user interface
Techniques (method, apparatus, system) are provided for efficiently delivering segmentation information of broadcast or other delivered programs to DVRs and the like associated with a conventional type program guide (for example, ATSC-PSIP or DVB-SI EPGs) for efficient random accessing to segments of a program which may be recorded in DVRs using the delivered segmentation information. The segmentation information may include segment titles, temporal start positions and durations of the segments of broadcast programs. Additionally, an interactive graphical user interface (GUI) is generated for browsing based on received segmentation information using thumbnail images from specific positions of a video file which can be generated either by hardware (H / W) or software (S / W) or firmware (F / W), or a combination thereof.
Owner:VIVCOM INC
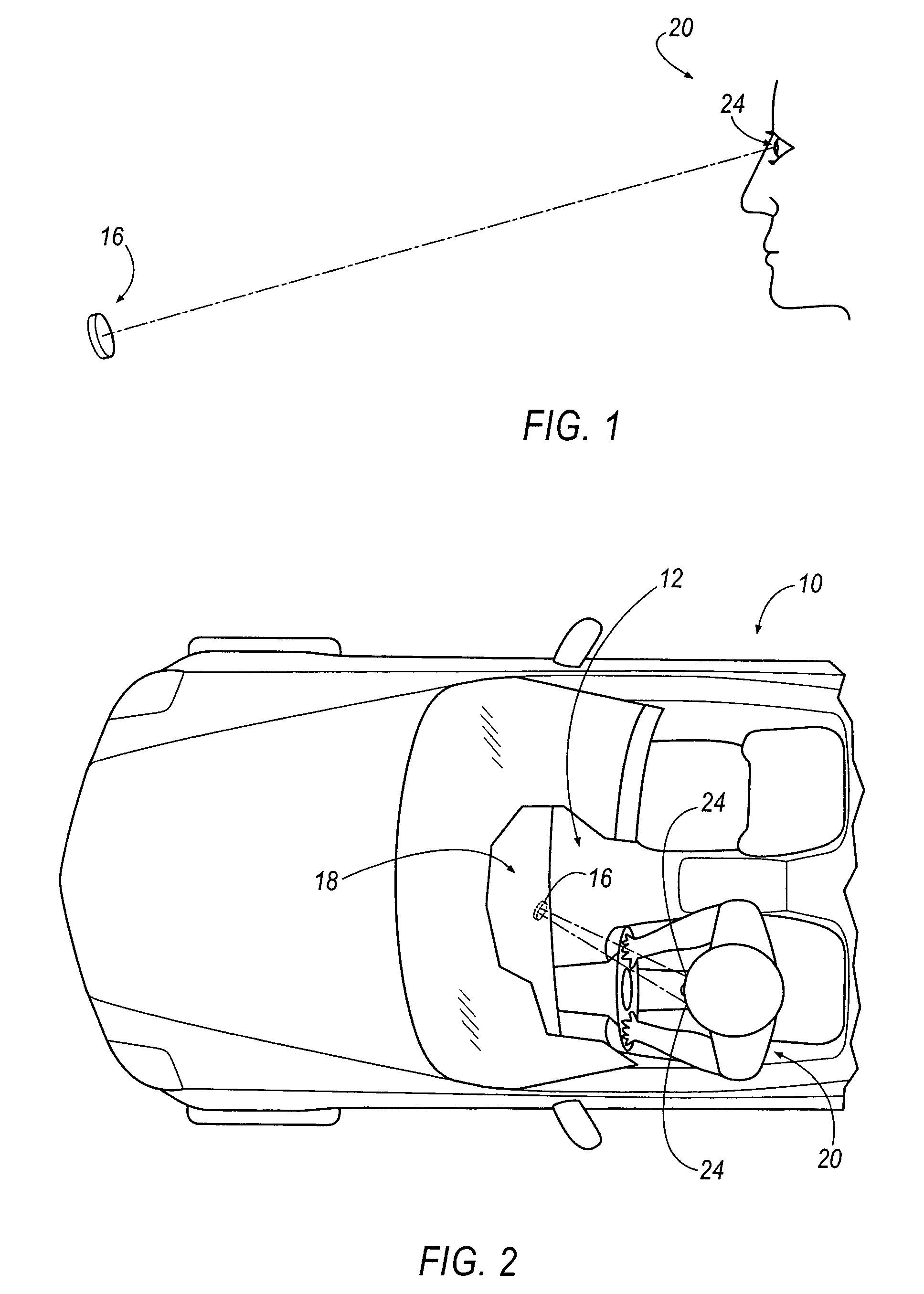
Method of mitigating driver distraction
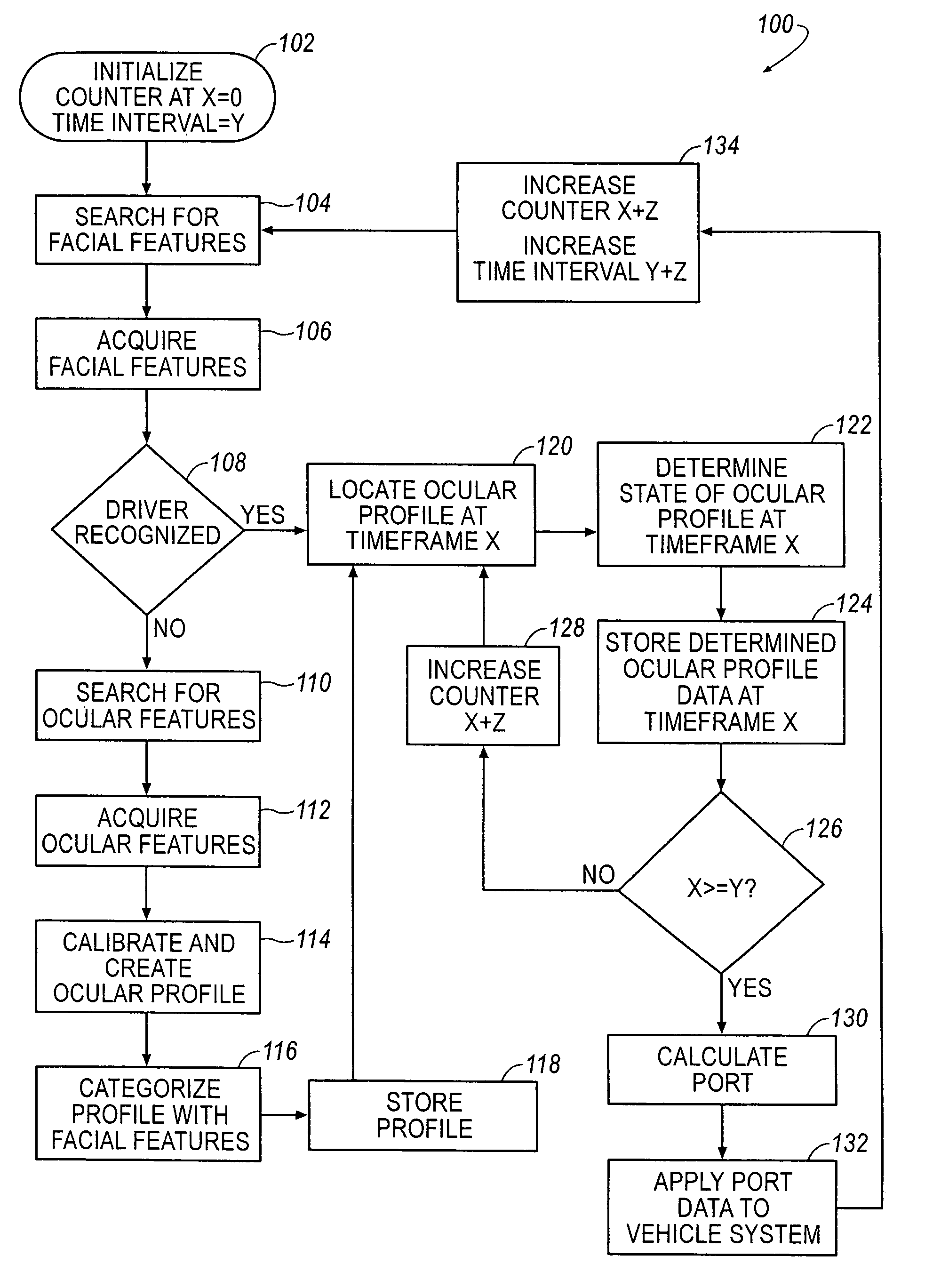
ActiveUS7835834B2Reduce distractionsDigital data processing detailsAcquiring/recognising eyesDriver/operatorIn vehicle
A driver alert for mitigating driver distraction is issued based on a proportion of off-road gaze time and the duration of a current off-road gaze. The driver alert is ordinarily issued when the proportion of off-road gaze exceeds a threshold, but is not issued if the driver's gaze has been off-road for at least a reference time. In vehicles equipped with forward-looking object detection, the driver alert is also not issued if the closing speed of an in-path object exceeds a calibrated closing rate.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
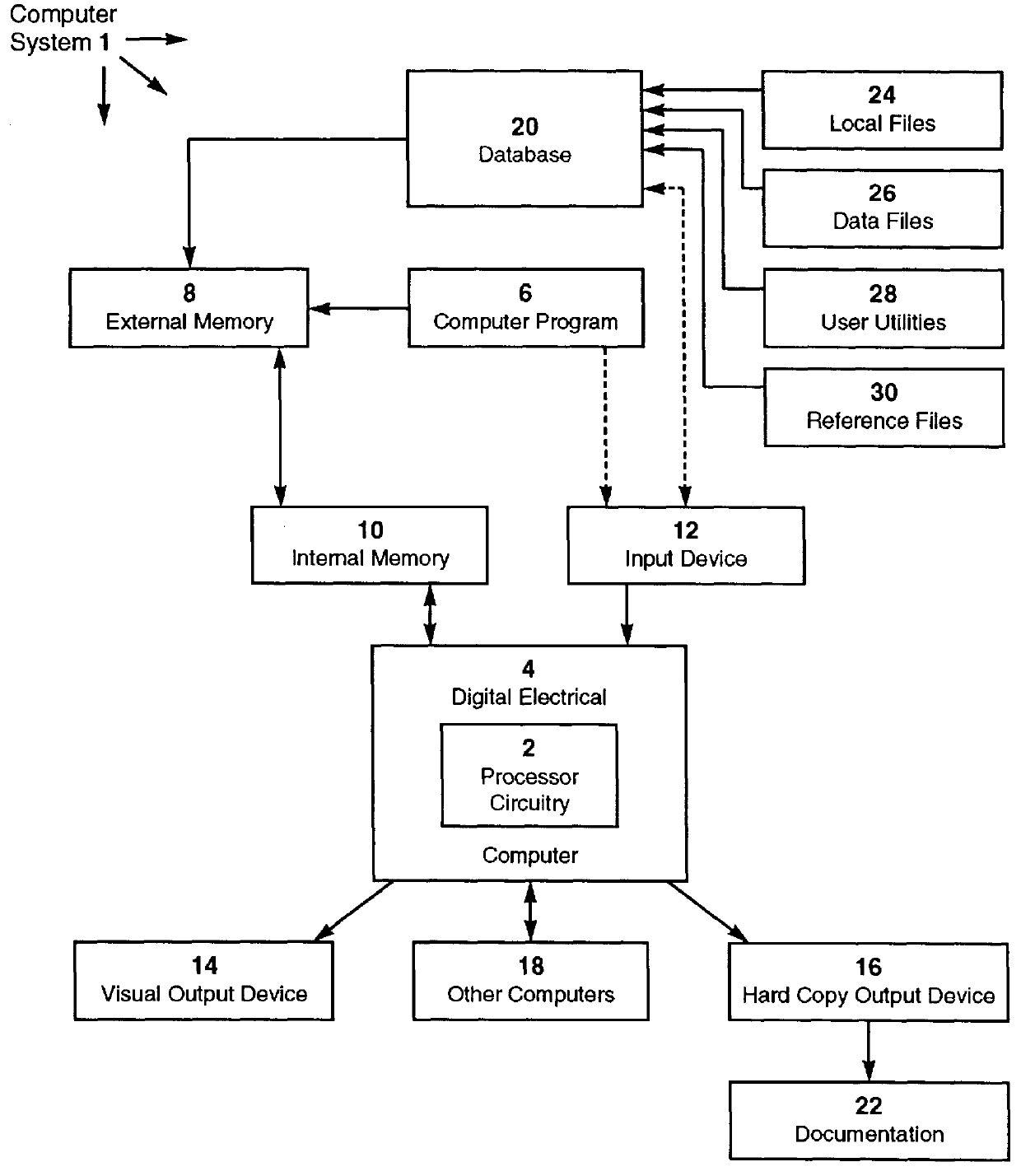
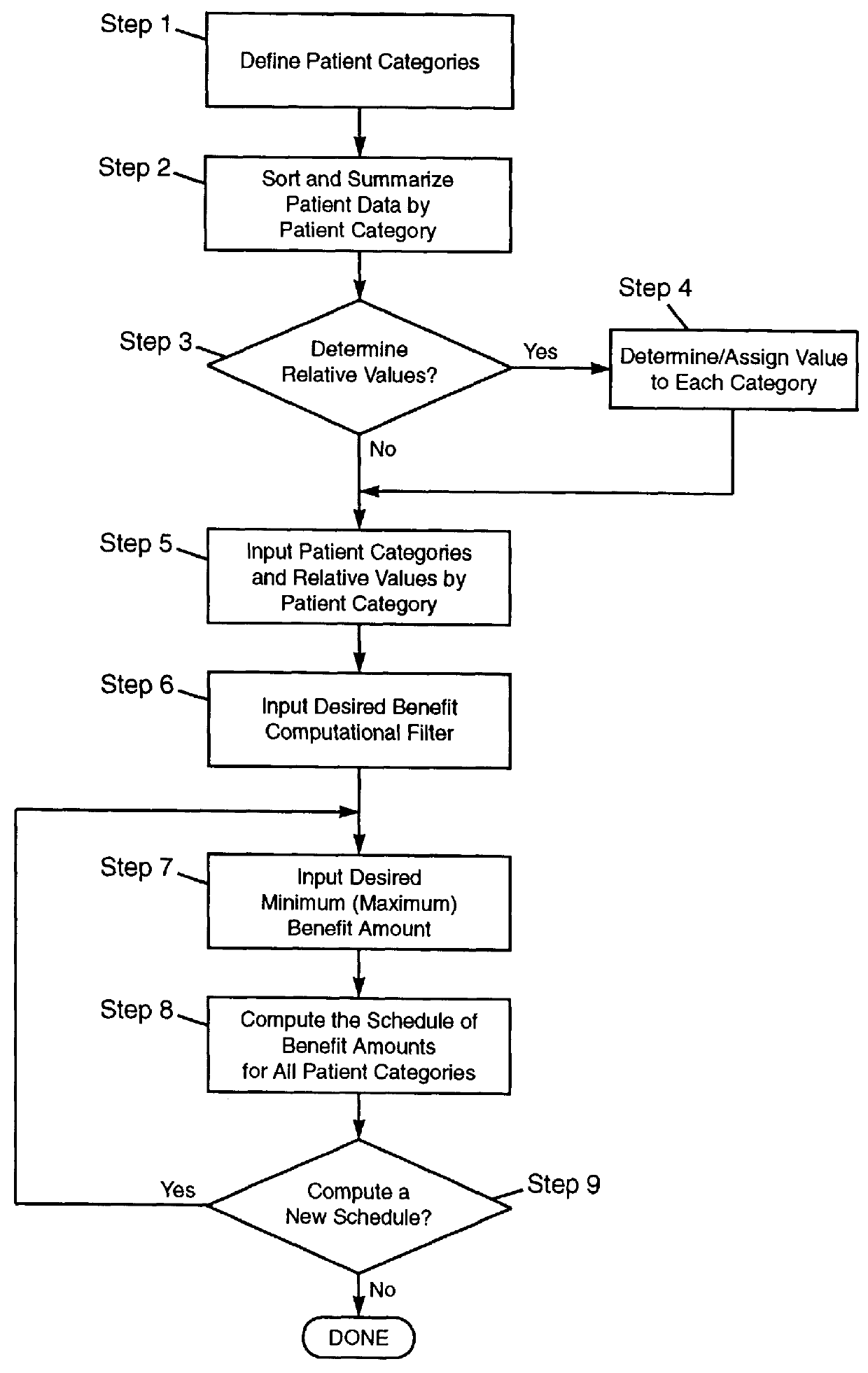
Apparatus and method for determining insurance benefit amounts based on groupings of long-term care patients with common characteristics
InactiveUS6014632AEfficient productionDecreased quality of careFinanceOffice automationVisual presentationDocumentation procedure
A method for using a digital electrical apparatus to electrically process signals in generating output for insurance documentation, the method including the steps of: in a digital electrical computer apparatus comprising a digital computer having a processor, the processor electrically connected to a memory device for storing and retrieving operations including machine-readable signals in the memory device, to an input device for receiving input data and converting the input data into input electrical data, to a visual display unit for converting output electrical data into output having a visual presentation, to a printer for converting the output electrical data into printed documentation, wherein the processor is programmed to control the apparatus to receive the input data and to produce the output data by steps including: defining a plurality of patient categories; and for each of the categories, determining a periodic duration-specific insurance benefit amount for long-term care patients; the method further including the step of inserting the periodic duration-specific insurance benefit amounts in a long-term care insurance policy.
Owner:FINANCIAL GROWTH RESOURCES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com