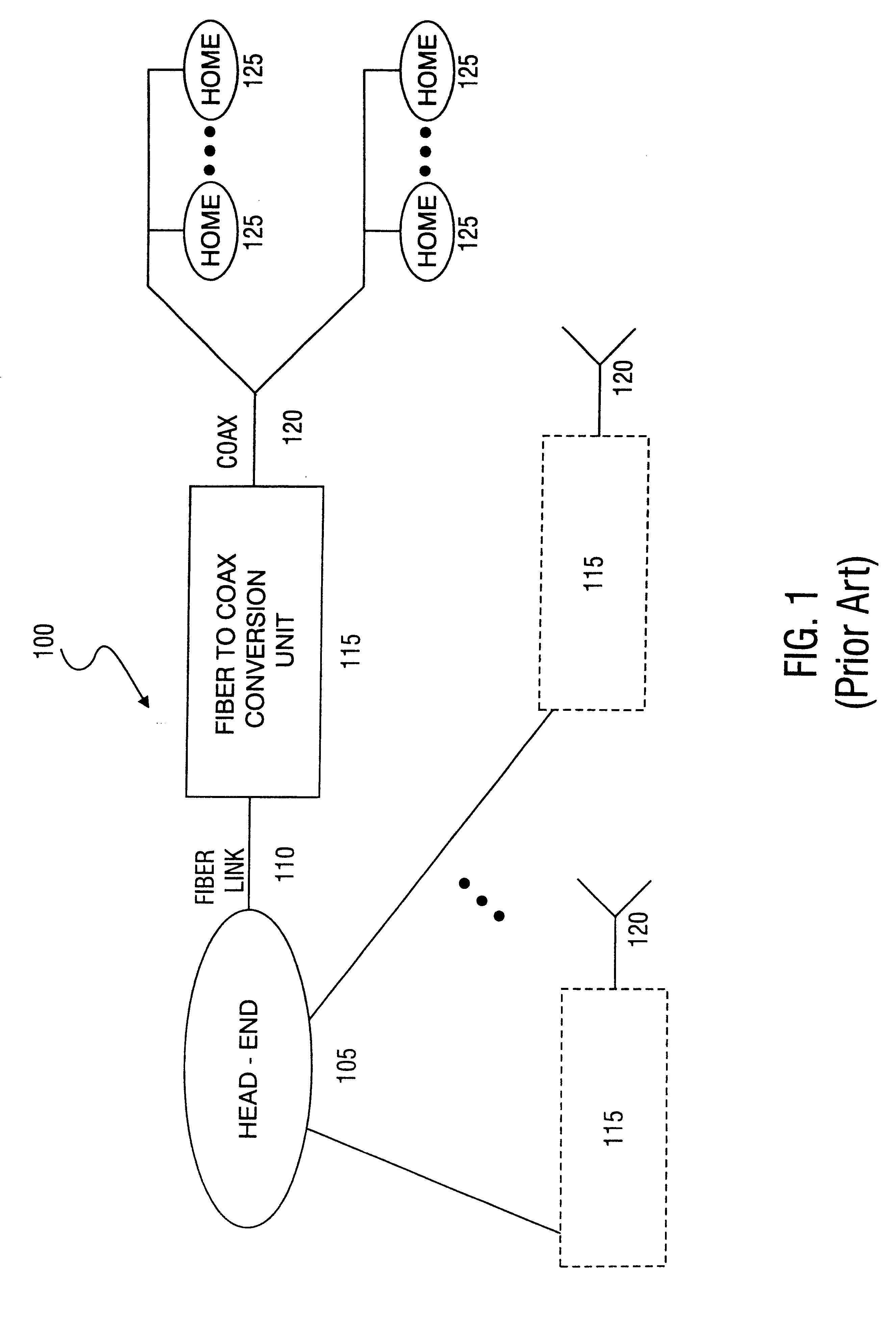
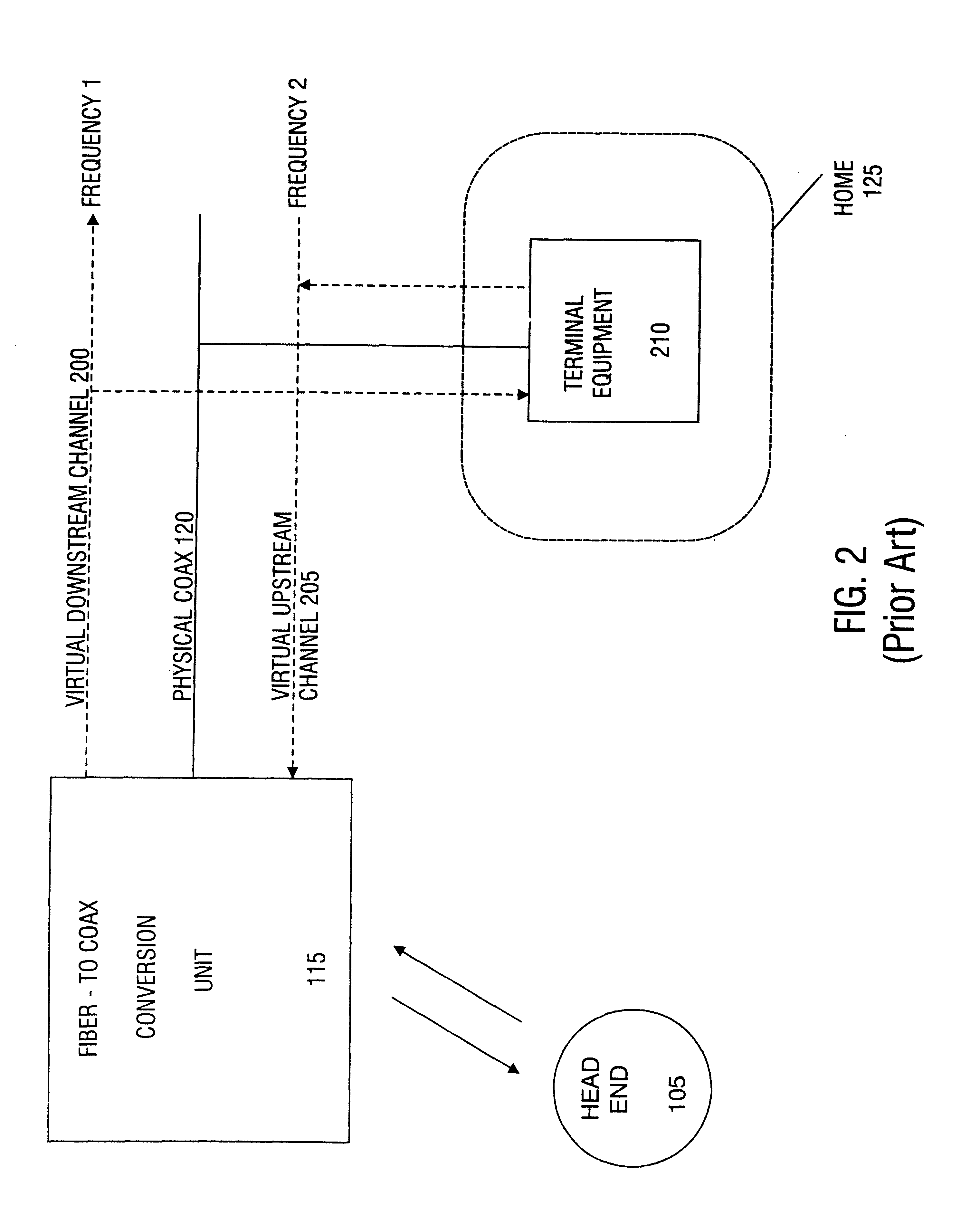
Patents
Literature
1364results about "Broadband local area networks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
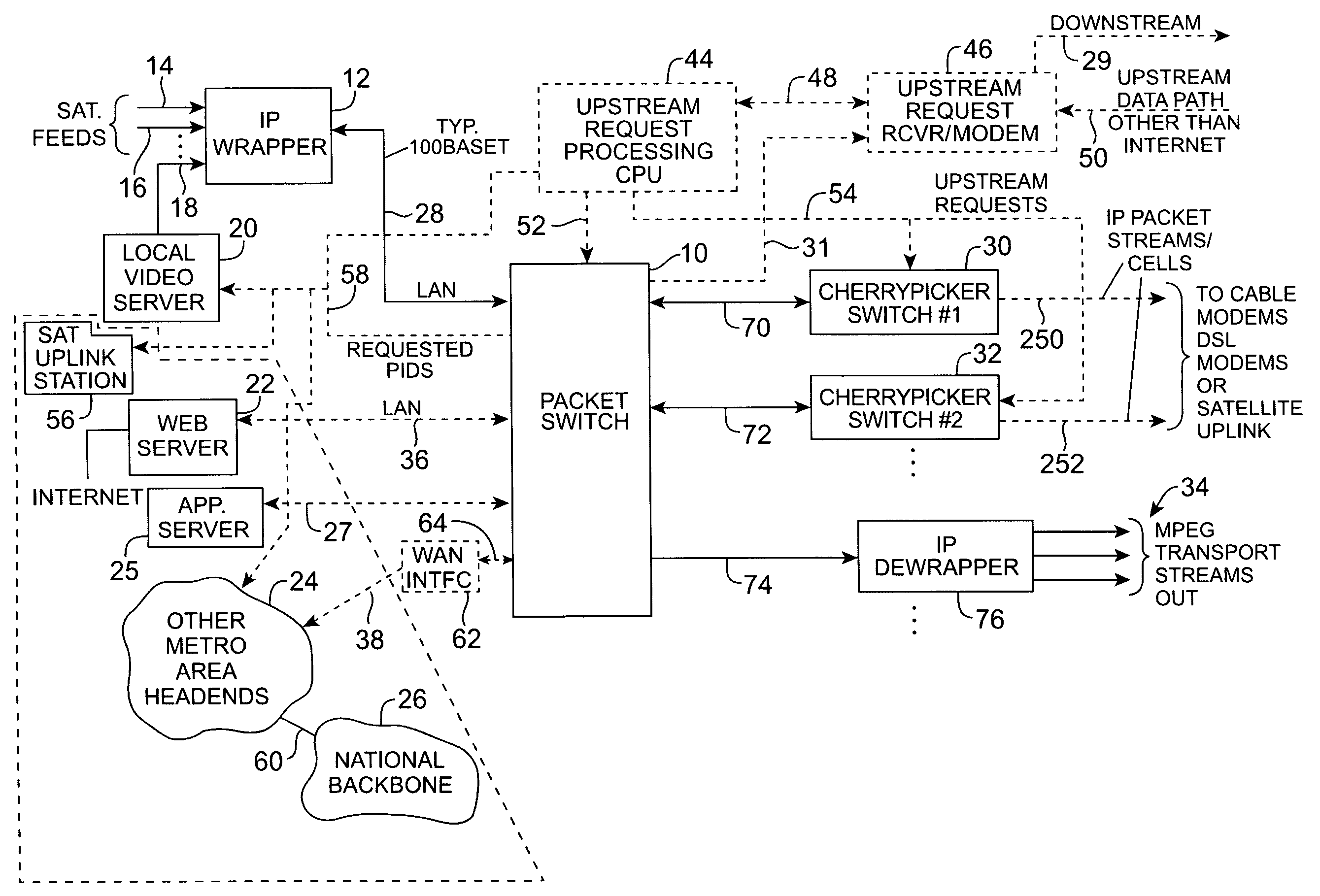
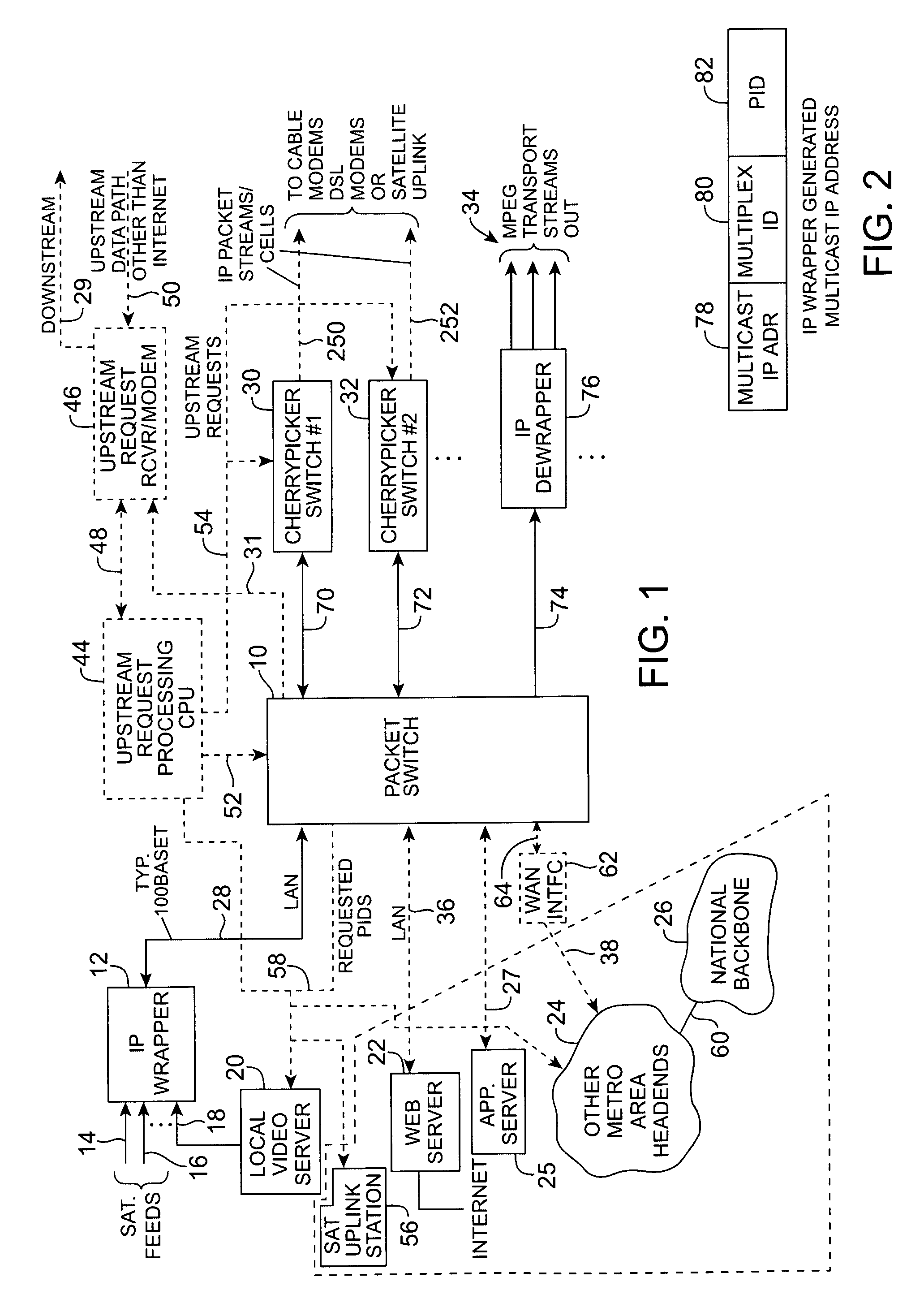
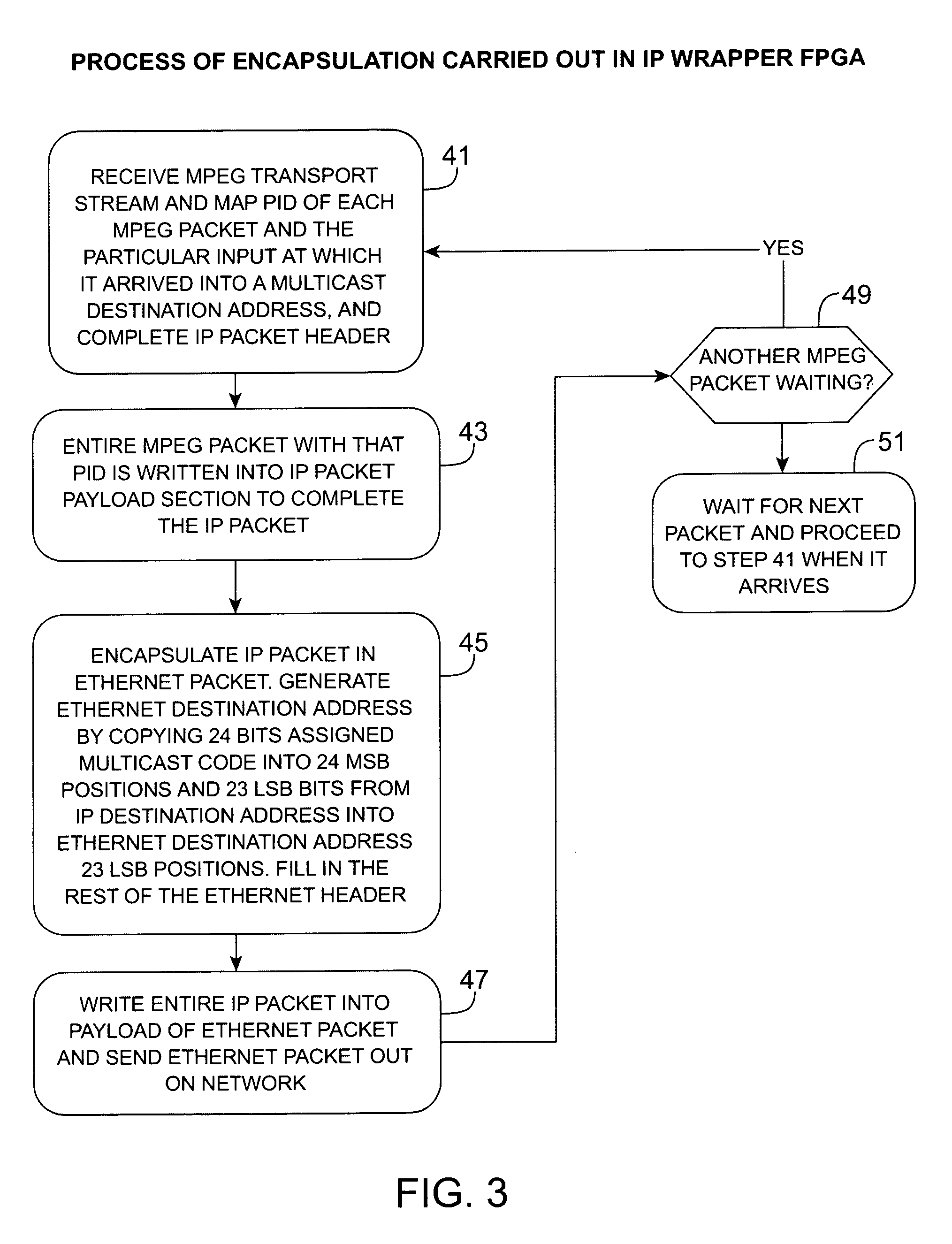
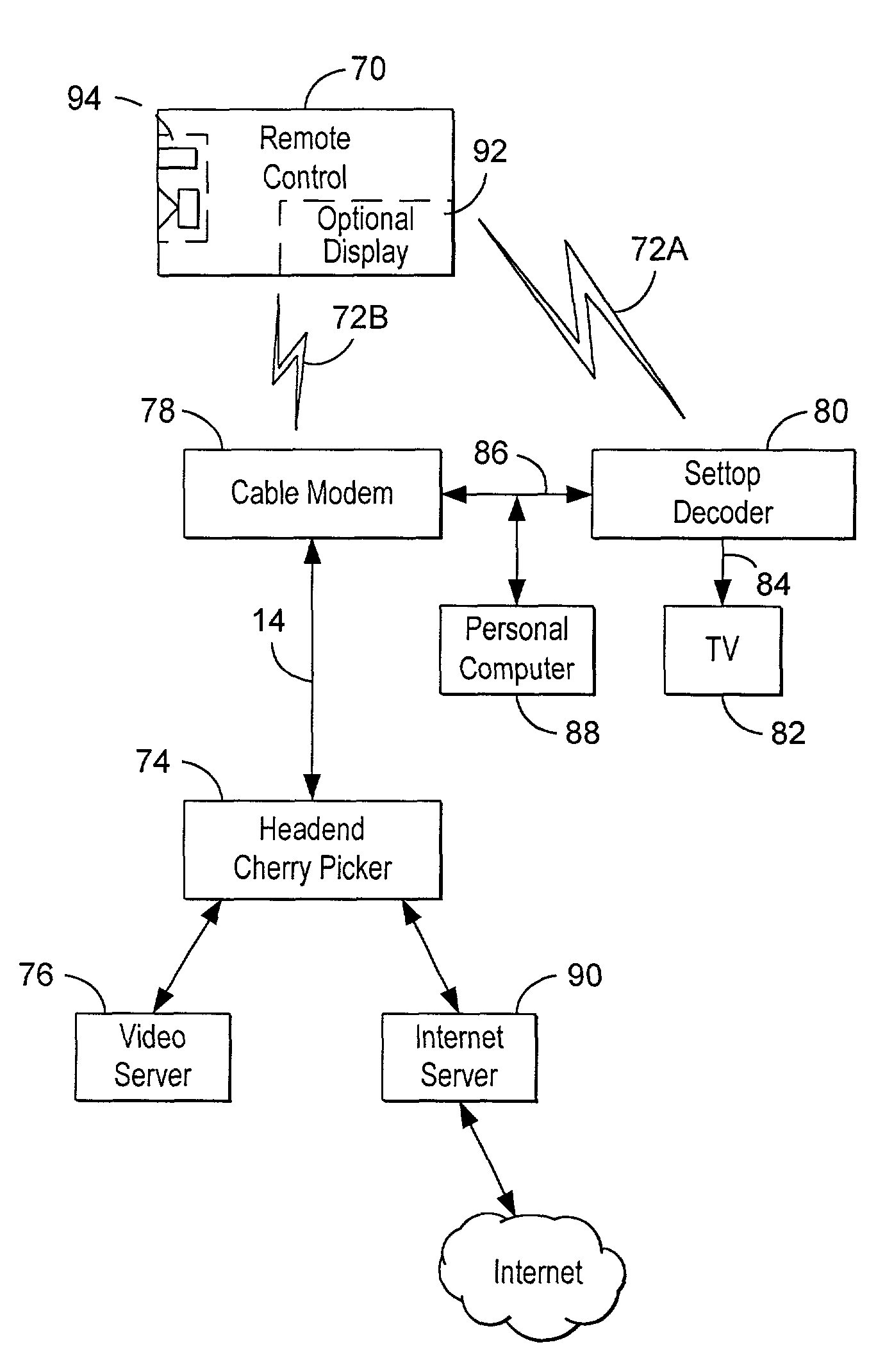
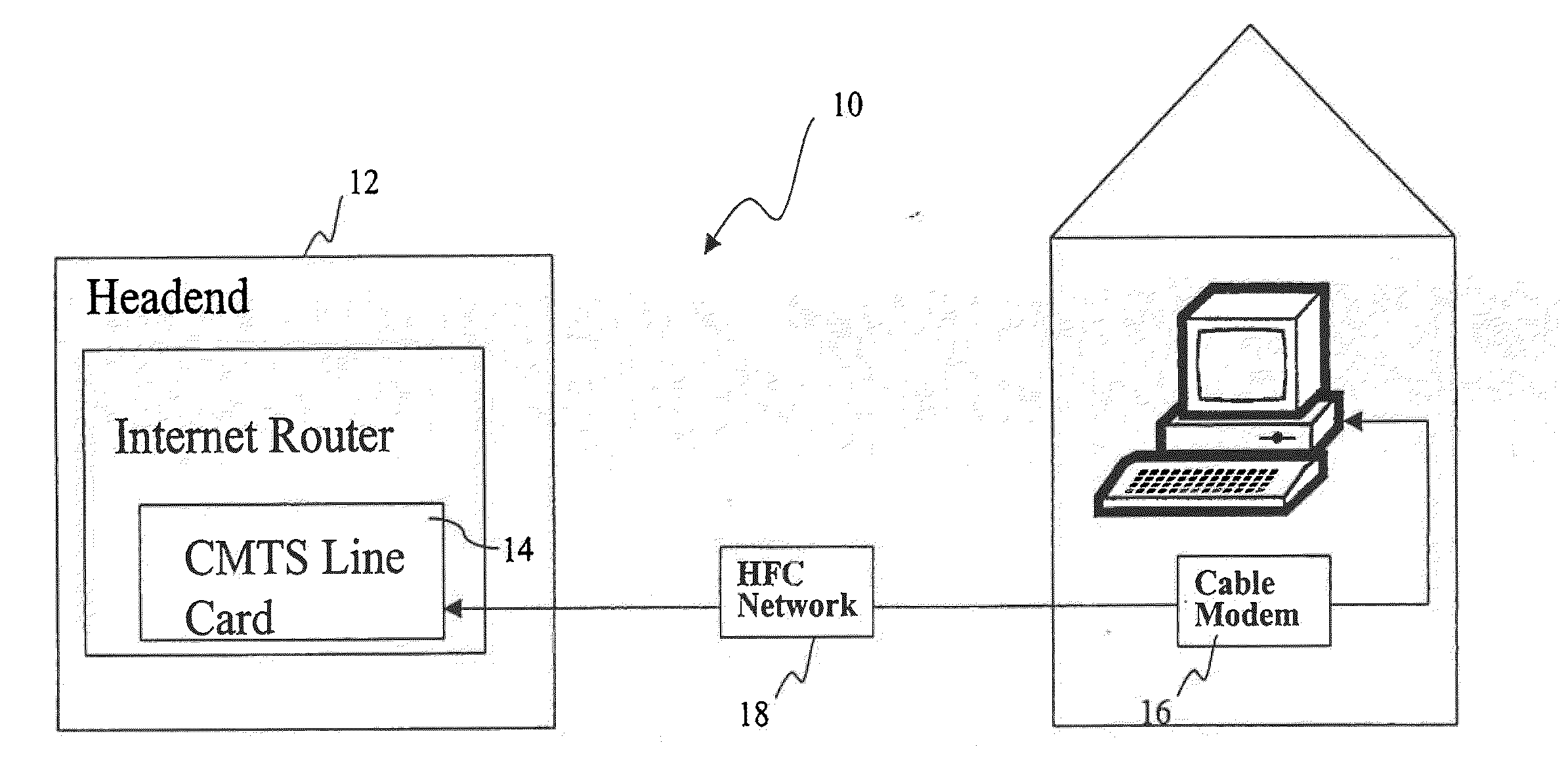
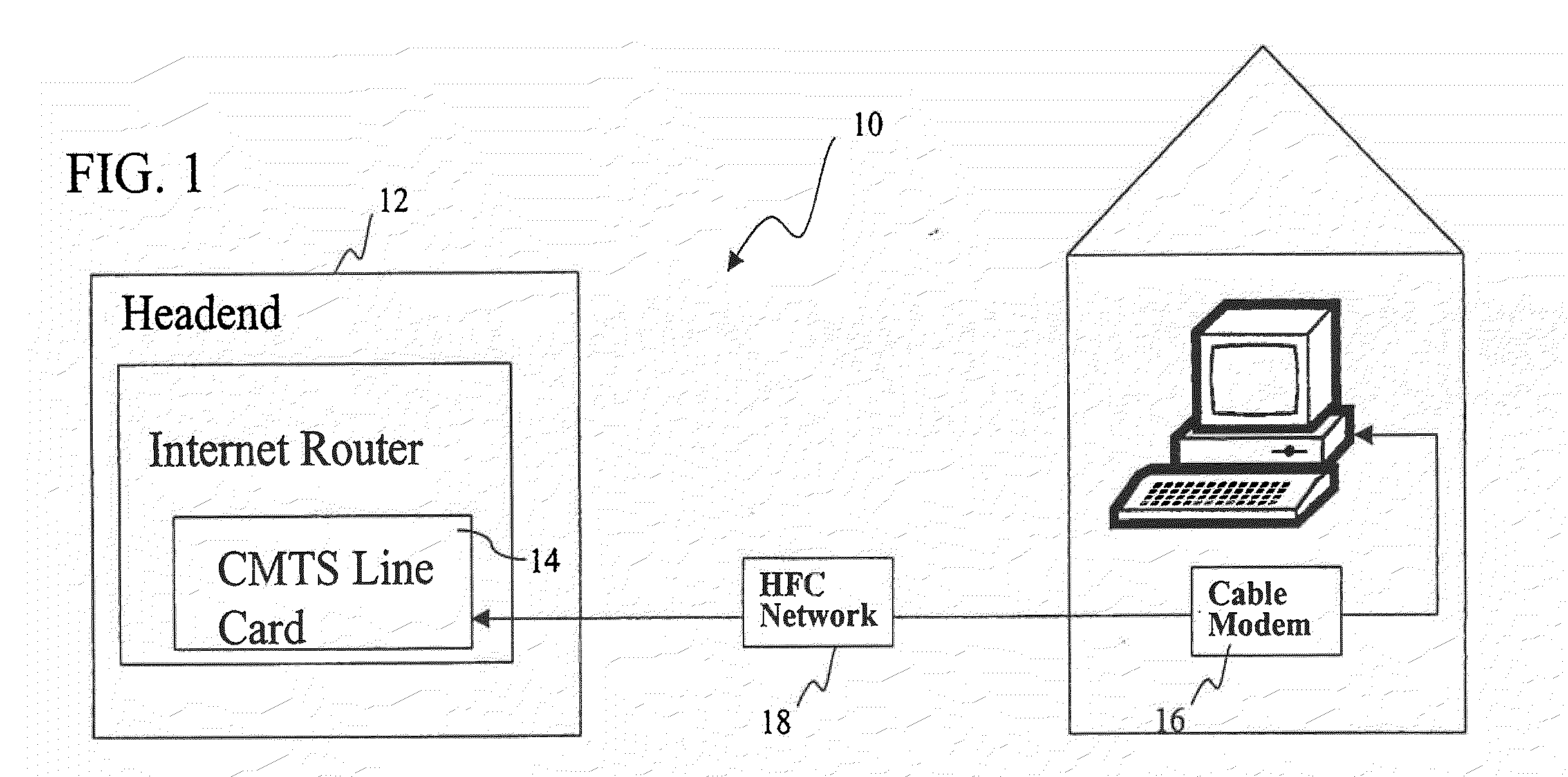
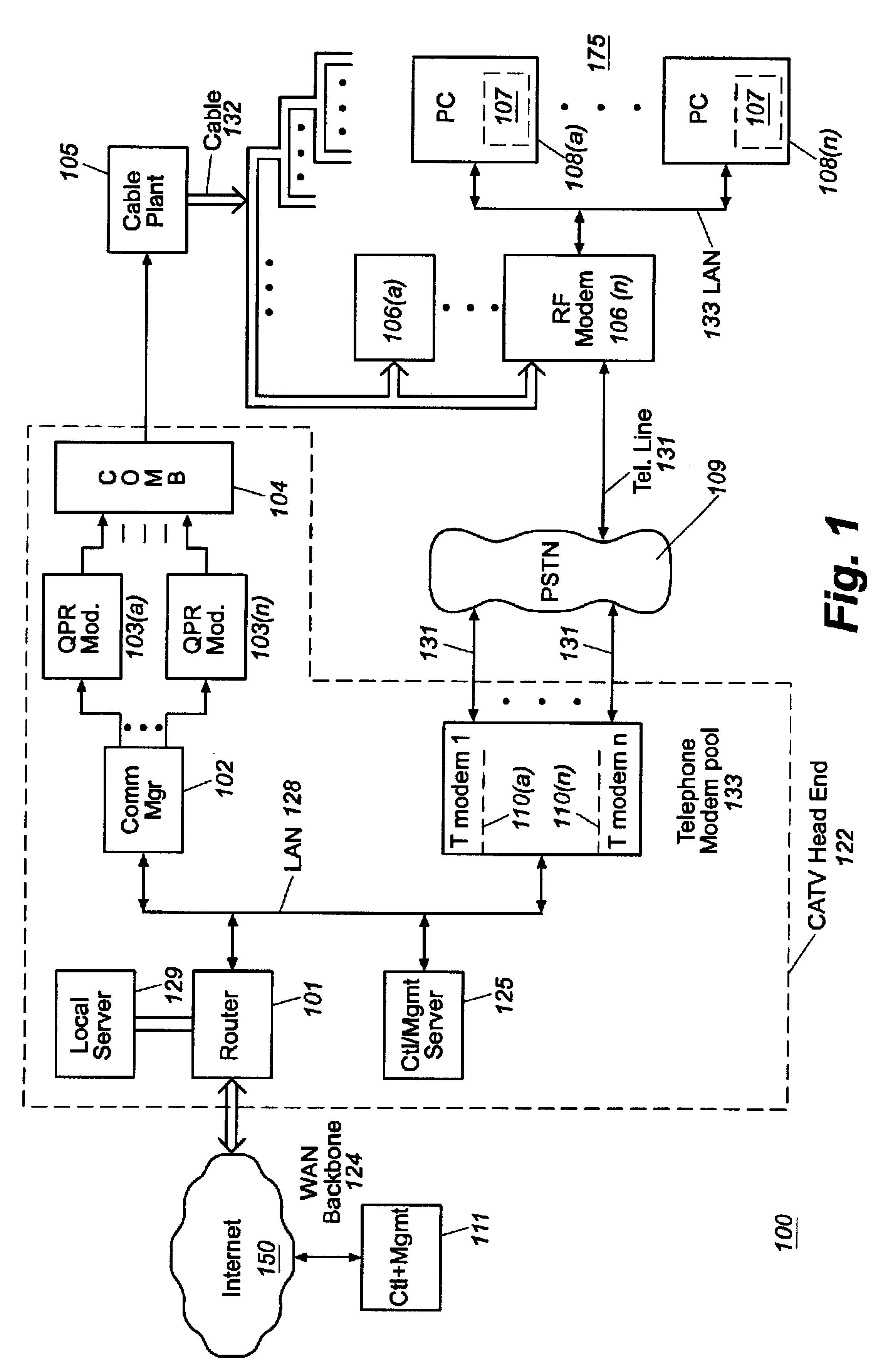
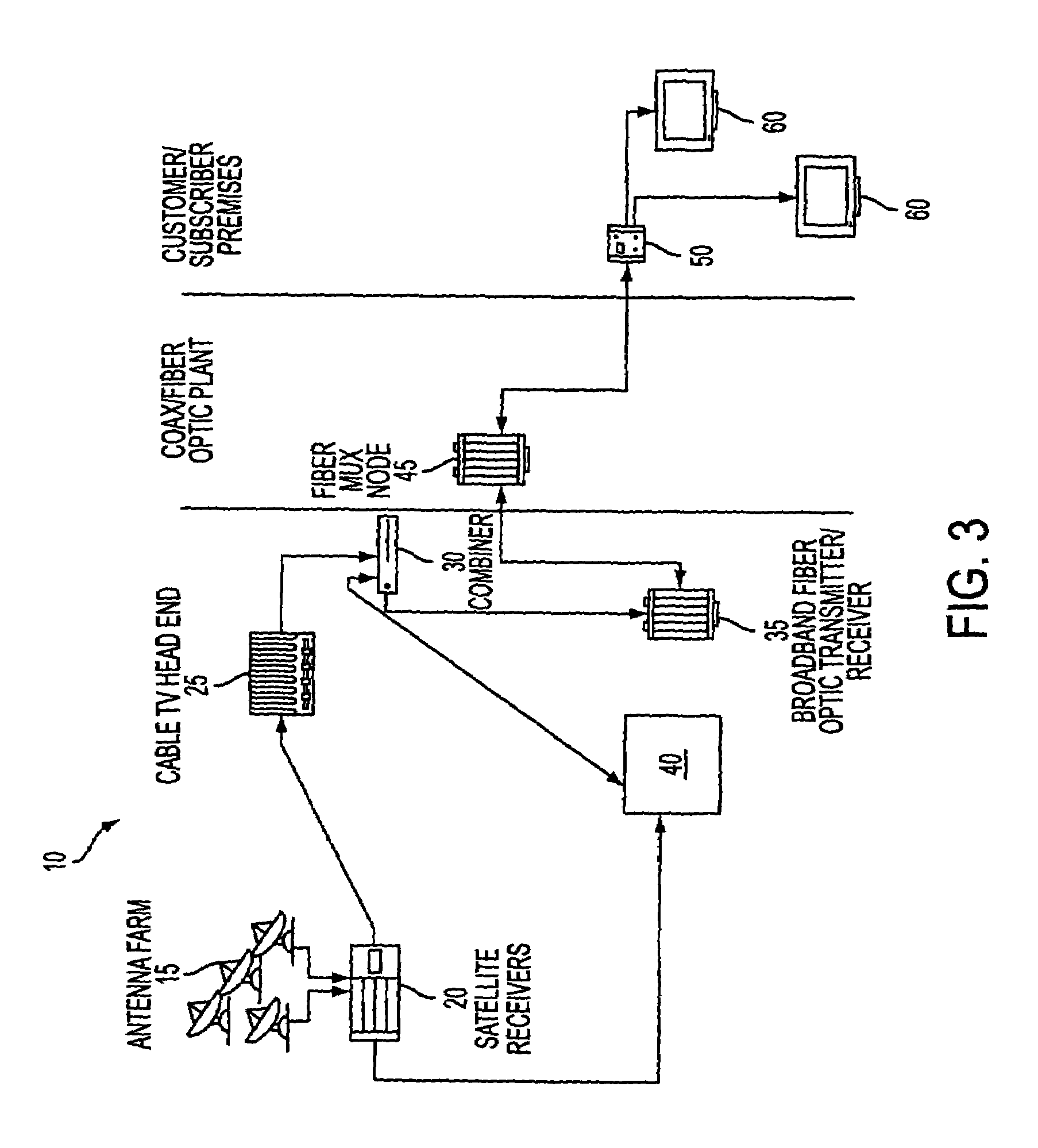
Headend cherrypicker multiplexer with switched front end
InactiveUS7039048B1Low costEasily scaledBroadband local area networksTime-division multiplexMPEG transport streamModem device
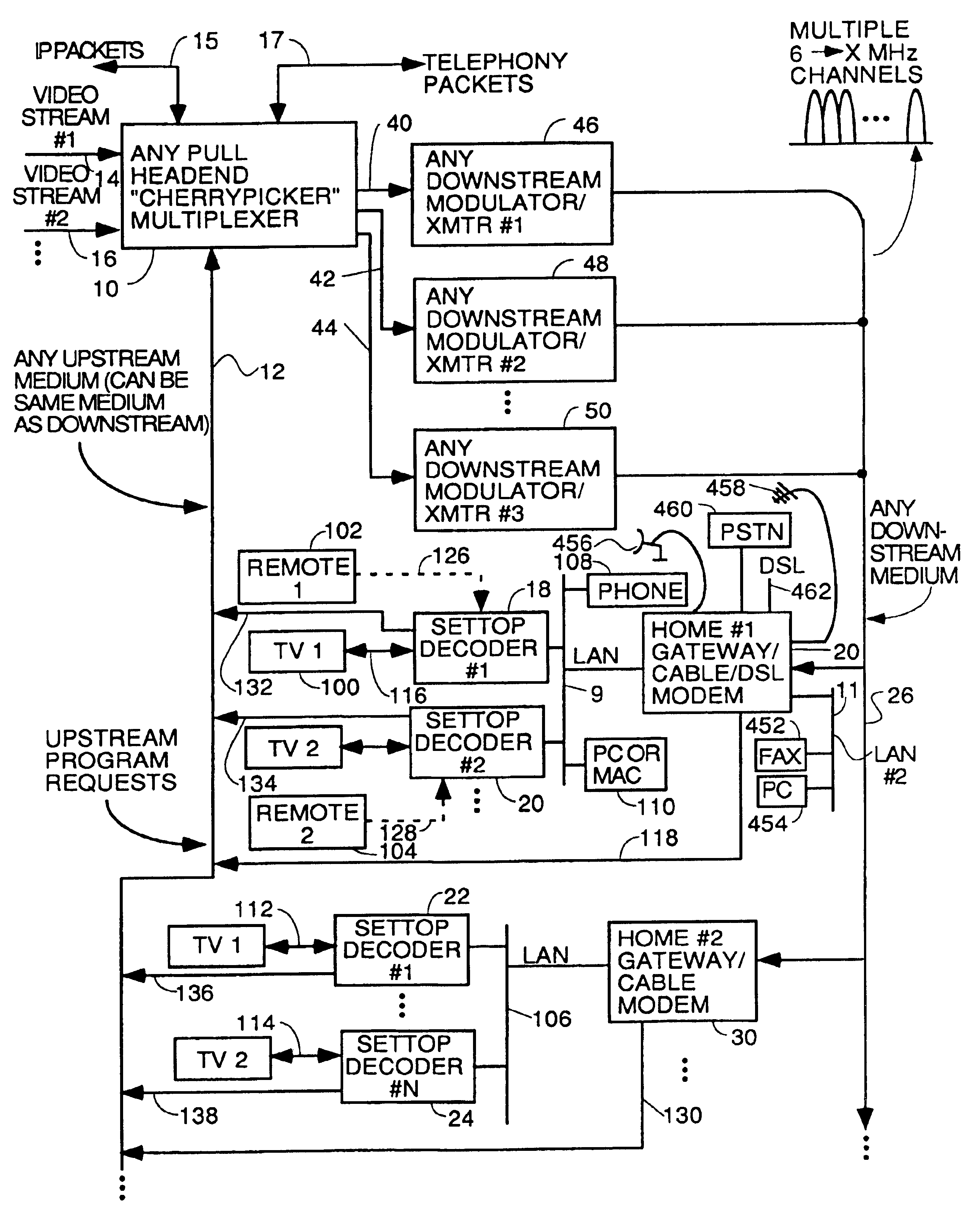
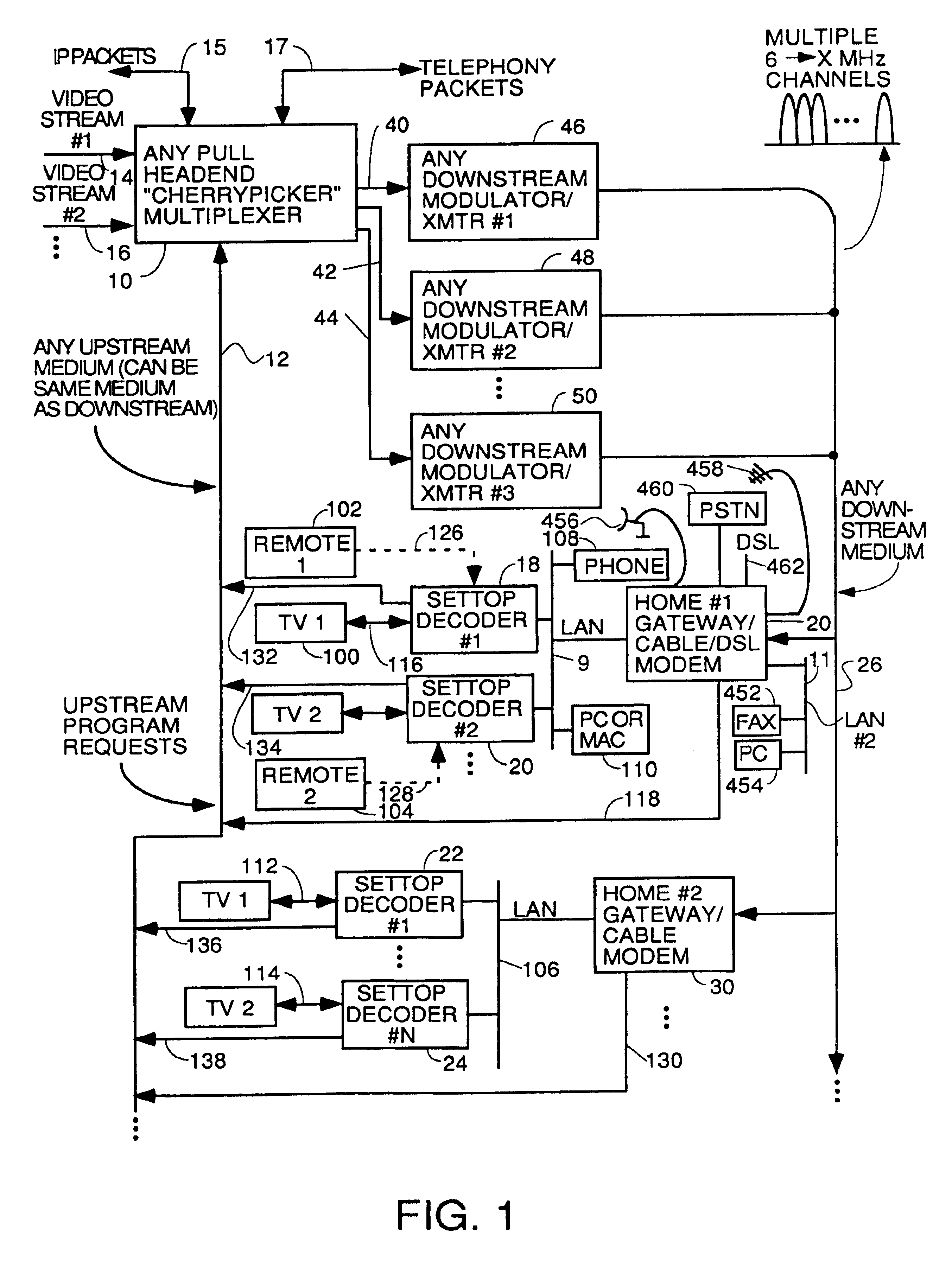
A headend or central office or satellite uplink facility for receiving upstream video-on-demand requests and MPEG transport streams containing video program data and packetizing said video data into TCP / IP or UDP / IP packets and LAN packets and routing them through a switch to one or more cherrypicker multiplexers. Each cherrypicker multiplexer receives LAN packets, depacketizes the MPEG data, partially or fully decompresses the data and recompresses the data to another smaller bandwidth, and repacketizes the data into MPEG packets or TCP / IP or UDP / IP packets. The repacketized TCP / IP or UDP / IP packets are transmitted directly to the customer as TCP / IP or UDP / IP packet data. MPEG packets generated by the cherrypicker multiplexer are, optionally, encapsulated in LAN packets addressed to an IP dewrapper circuit. There, they are depacketized back to MPEG packets and transmitted to the appropriate transmitter or modem for transmitting to a customer. Internet data and data from application servers, referred to as iData, can also be transmitted to customers through the cherrypicker multiplexers or a downstream modem, and upstream iData can be received through the modem.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
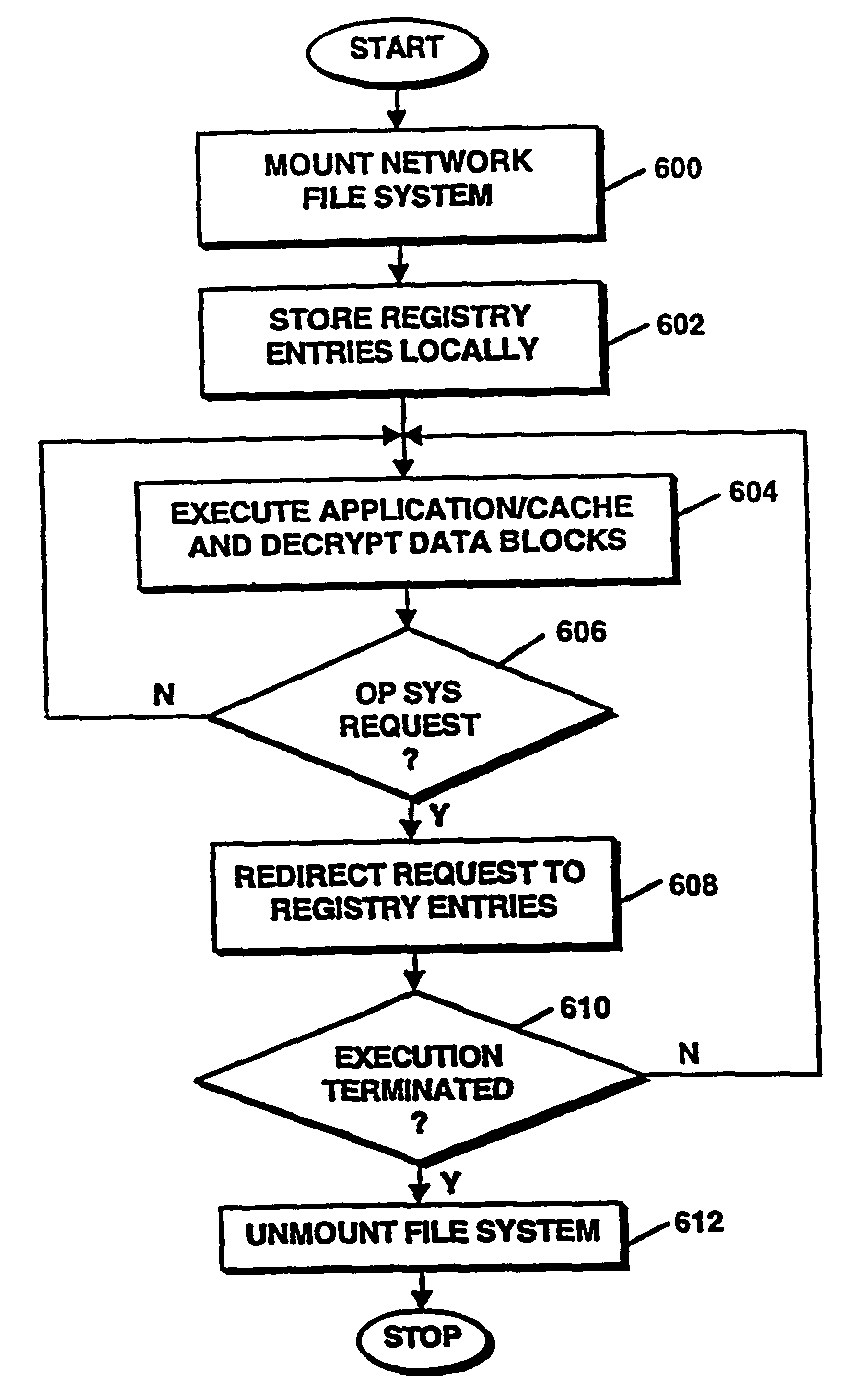
Method and apparatus for installation abstraction in a secure content delivery system
InactiveUS6374402B1Expand accessAvoid leverageTelevision system detailsBroadband local area networksOperational systemNetwork addressing
A system for secure delivery of on-demand content over broadband access networks includes a client application executing on a user's local computer system. The client application interacts with a content server on which a plurality of selectable titles are stored and further interacts with an access server which provides the network address of a title and keying data necessary for to the client process access and execute the title. The client process utilizes an installation abstraction which enables a title to be executed on the local computer system without ever being installed. The abstraction is achieved by mounting a network file system and storing a set of registry entries related to the title on the local computer system. Portions of the title are retrieved from the content server and executed by the local operating system. During title execution, requests from the local operating system are intercepted and redirected to the set of registry entries, as applicable. The times at which the client process may retrieve the title data from the content server are defined by the access server through use of an activator and token.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
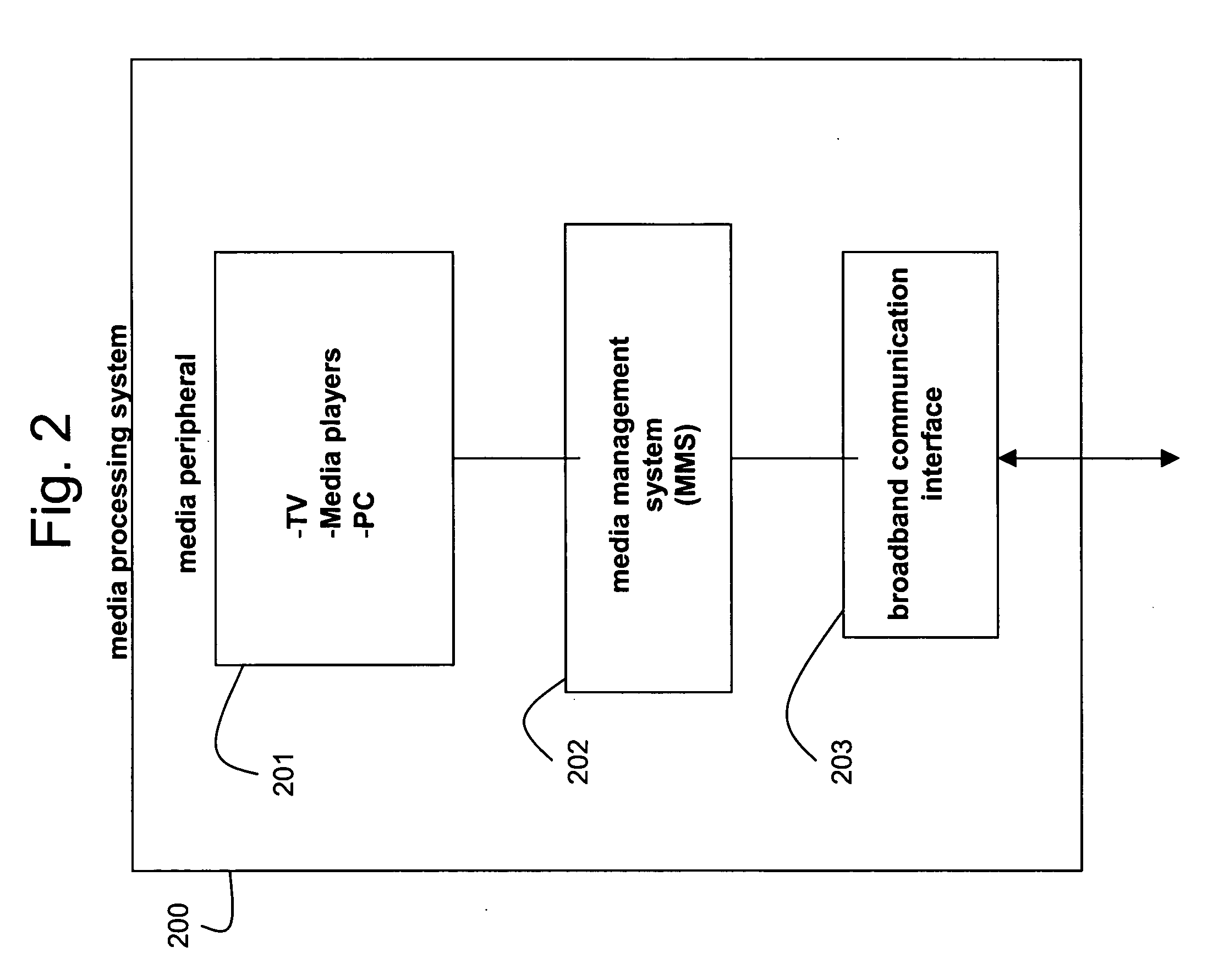
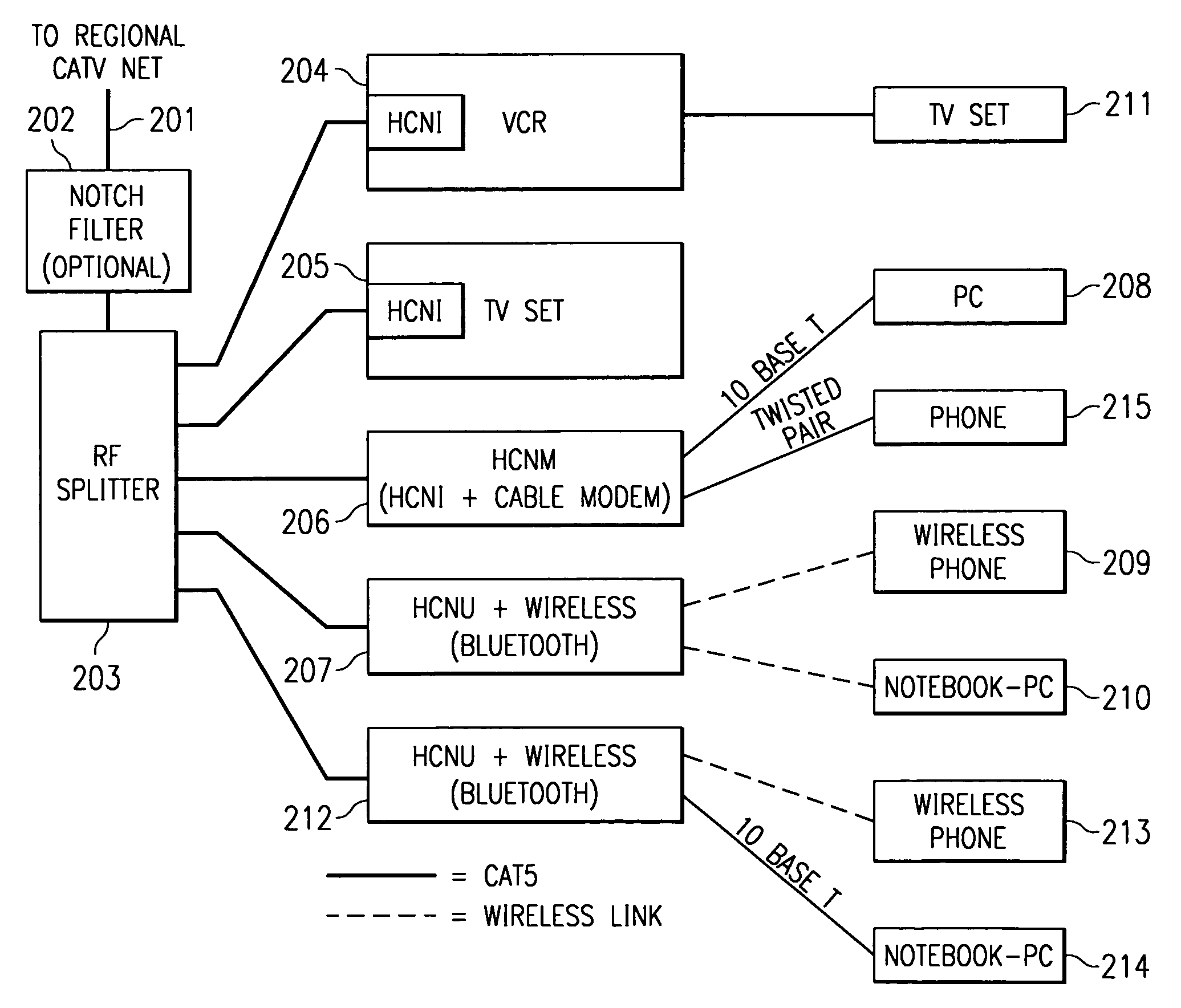
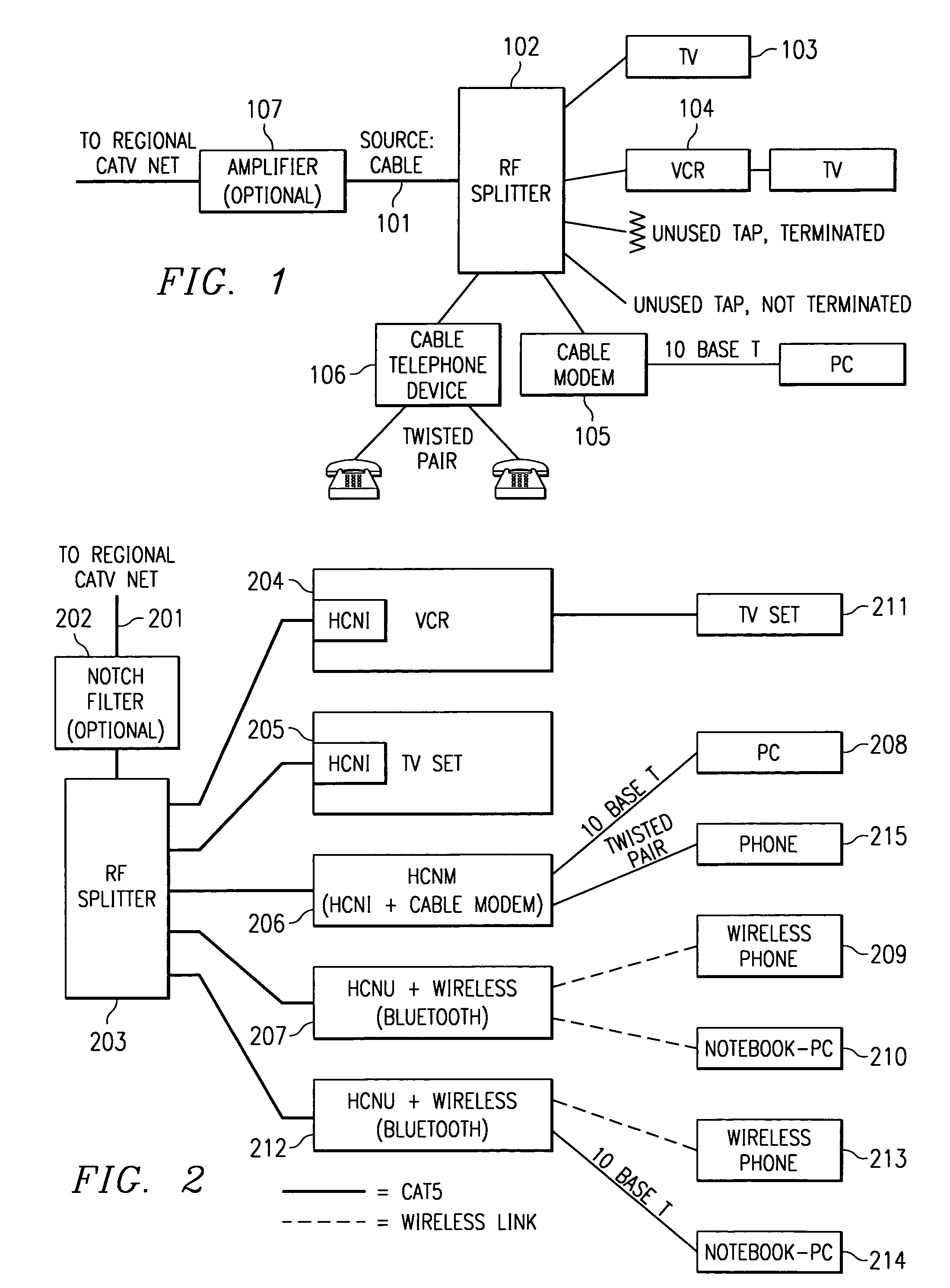
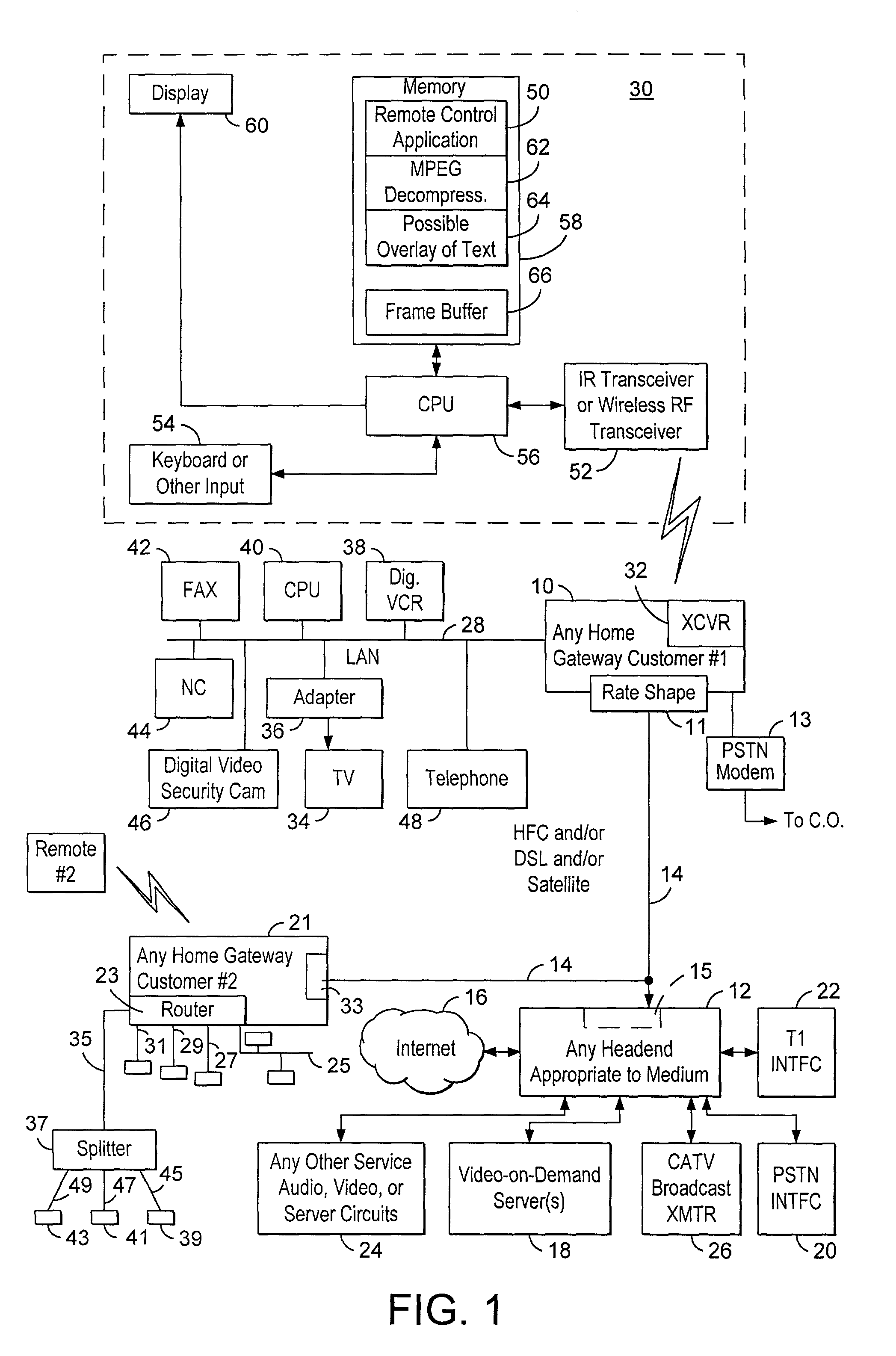
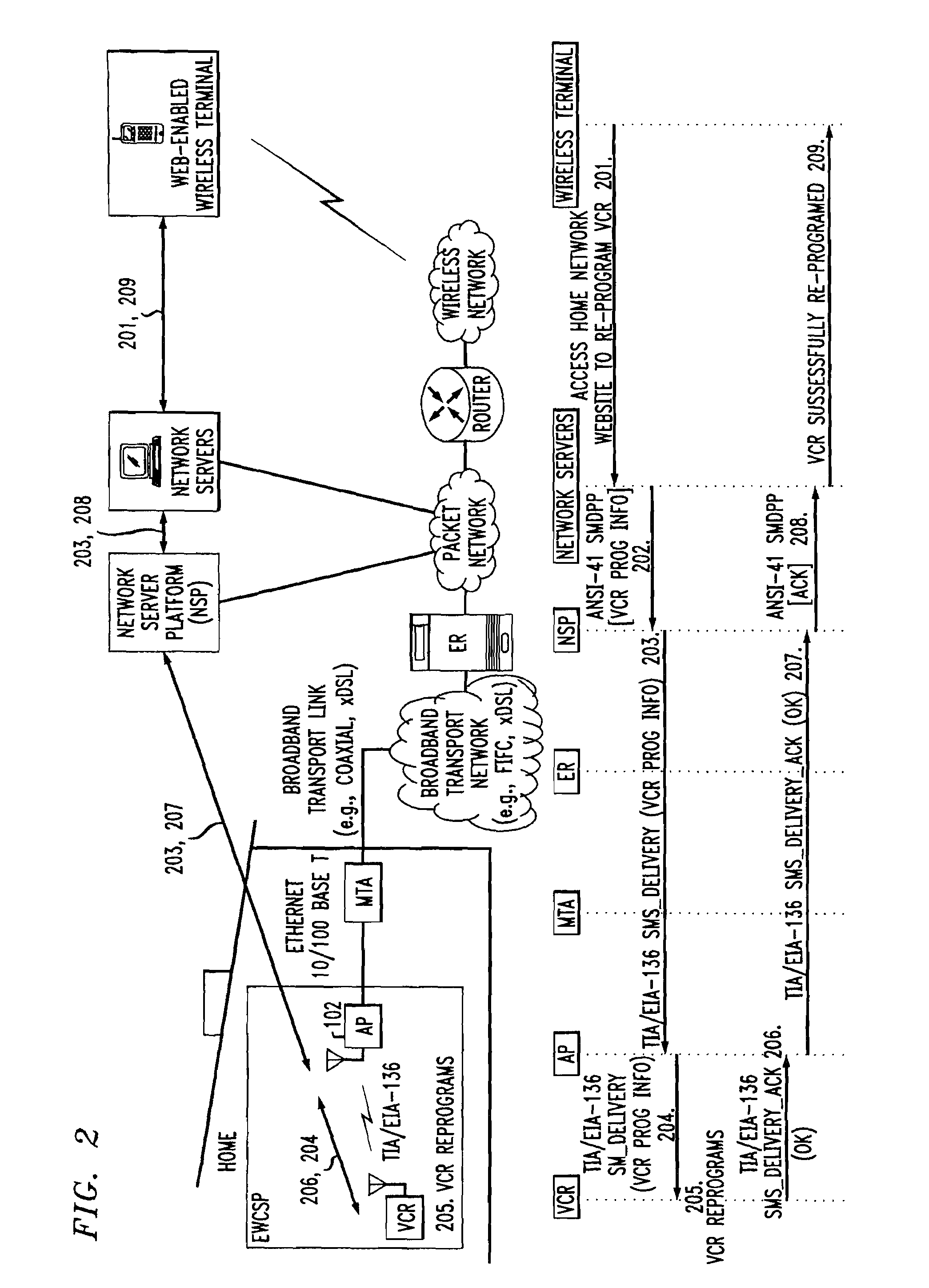
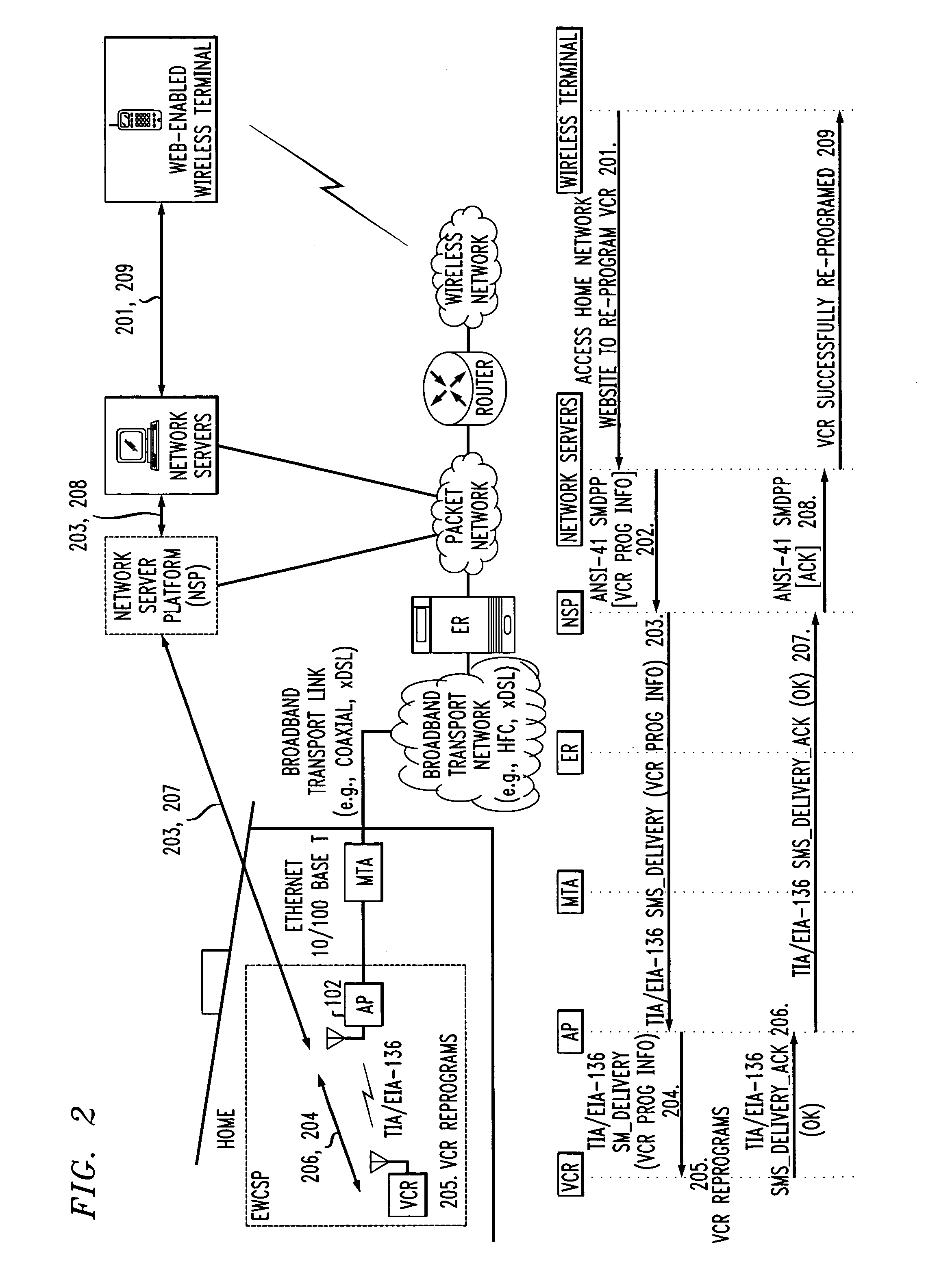
Home network for receiving video-on-demand and other requested programs and services
InactiveUS6889385B1Reduce quality problemsReduce bandwidth consumptionBroadband local area networksAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsVideocassette recorderTransceiver
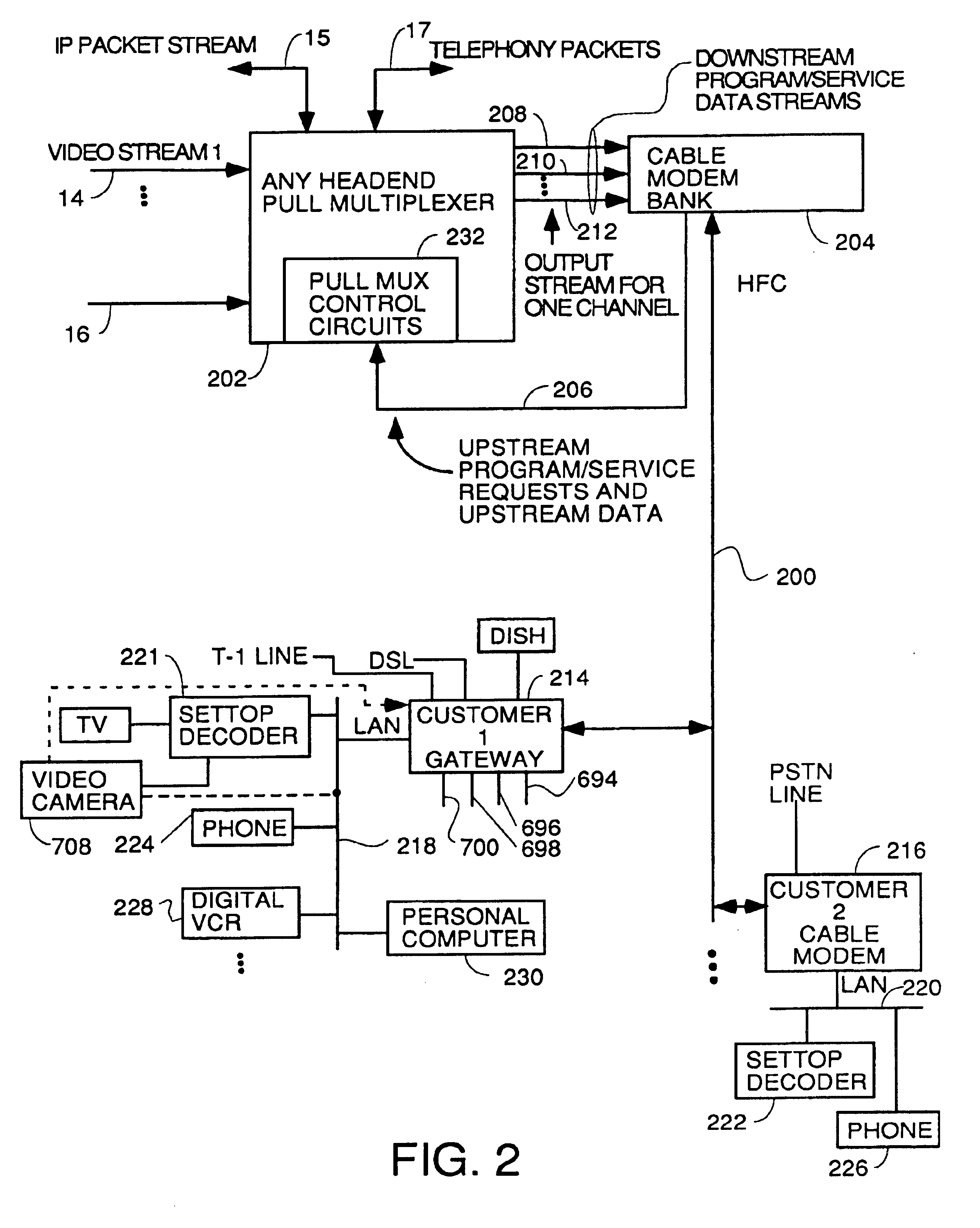
A system for providing video-on-demand service, broadband internet access and other broadband services over T-carrier systems including a pull multiplexer cherrypicker at the head end is disclosed. The pull multiplexer receives upstream requests and cull out MPEG or other compressed video packets, IP packets and other data packet types to satisfy the requests or to send pushed programming downstream. The downstream can be DSL or HFC. Each customer has a cable modem, DSL modem or a gateway which interfaces multiple signal sources to a LAN to which settop decoders, digital phones, personal computers, digital FAX machines, video cameras, digital VCRs etc. can be attached. Each gateway can coupled the LAN to a DSL line or HFC through a cable modem or a satellite dish through a satellite transceiver. A PSTN and conventional TV antenna interface is also provided.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
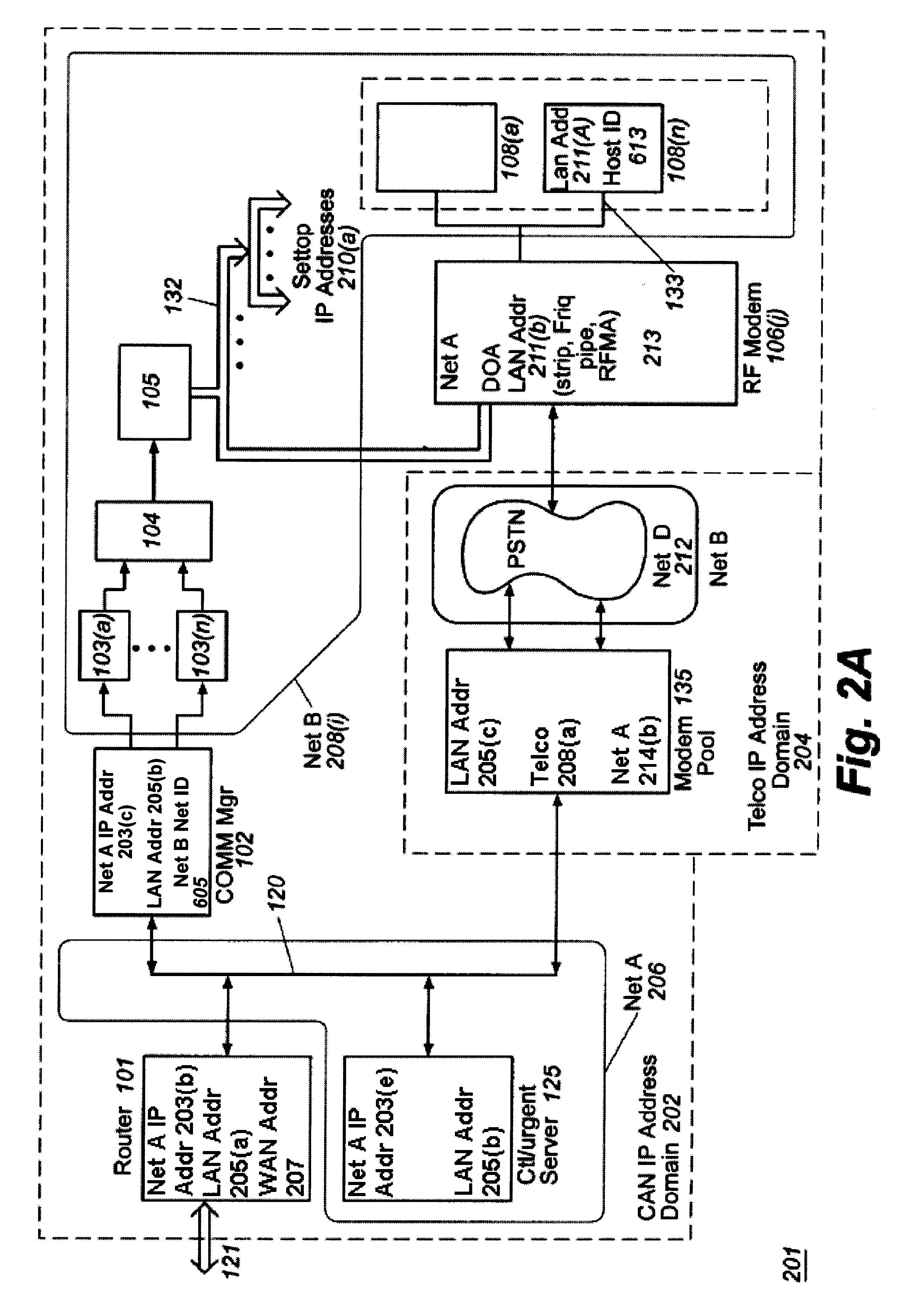
Cable modem map display for network management of a cable data delivery system
InactiveUS6272150B1Broadband local area networksBroadcast-related systemsTransport systemModem device
Apparatus for recording and collecting the installed location of cable modems in a cable data network comprises a network manager for maintaining and collecting cable modem location information. Components of the network manager maintains a software agent that manages a database of modem installation and status information. Responsive to a manager request, the component software agent provides the installation and status information to the network manager. The information is displayed as a map which can show the topology of the cable modem's location in the network with respect to other modems and other components of the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
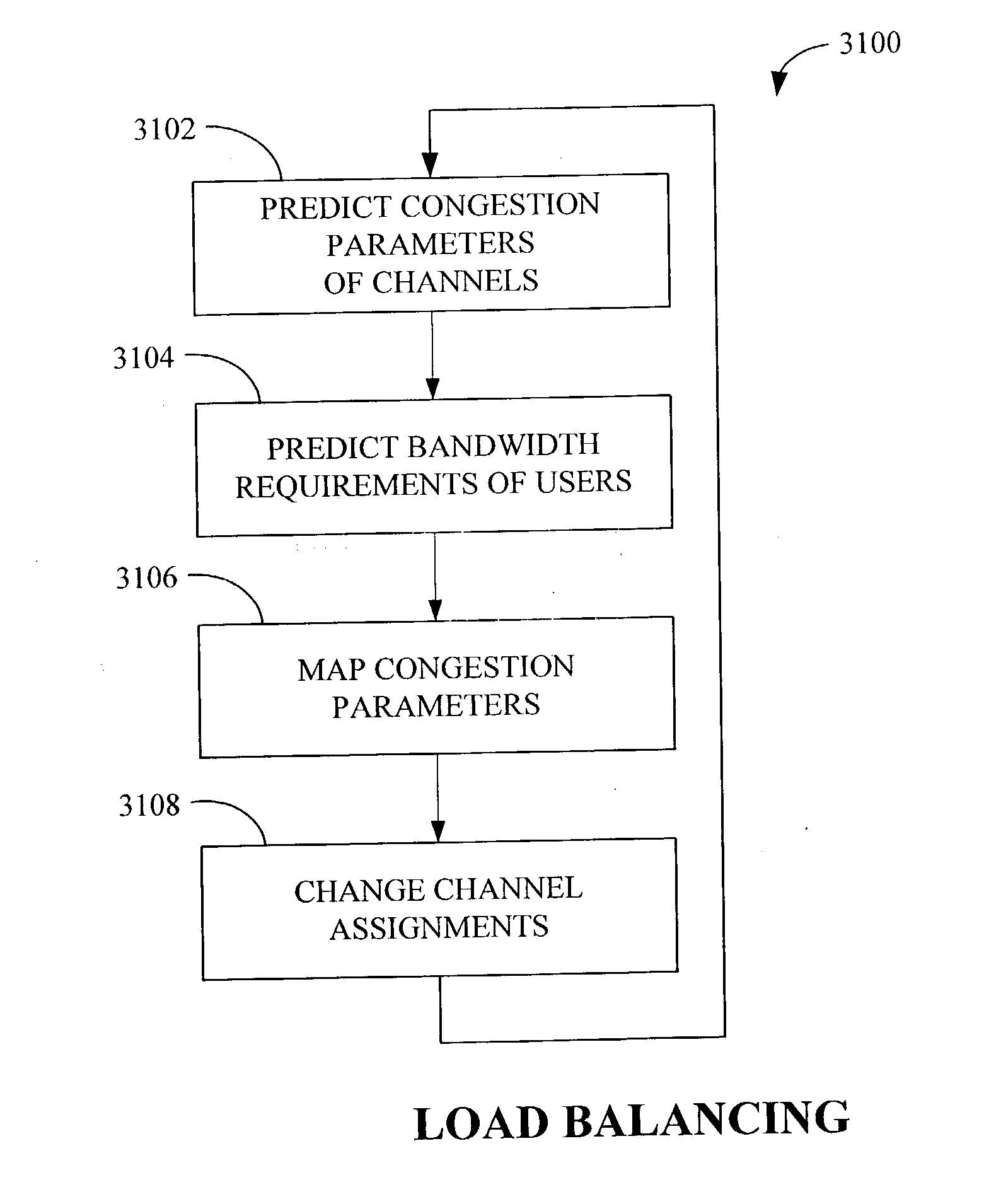
Apparatus and methods for incorporating bandwidth forecasting and dynamic bandwidth allocation into a broadband communication system
InactiveUS20060120282A1Energy efficient ICTError preventionDynamic bandwidth allocationComputer network
A method for providing network access to a shared access communications medium for a plurality of users includes the steps of conducting predictive admission control by arbitrating user requests for access to the shared medium based on predicted aggregate demands, conducting lookahead scheduling for use in making user channel assignments by forecasting schedule transmission opportunities one or more channels of the shared medium, and balancing load by making channel assignments such that a plurality users are each assigned a respective channel of the shared medium based upon a predicted need. Congestion parameters can predicted for each channel of the shared medium and mapped to a congestion measure using a mathematical function that takes into account packet loss rate, packet delay, packet delay jitter, and available capacity.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
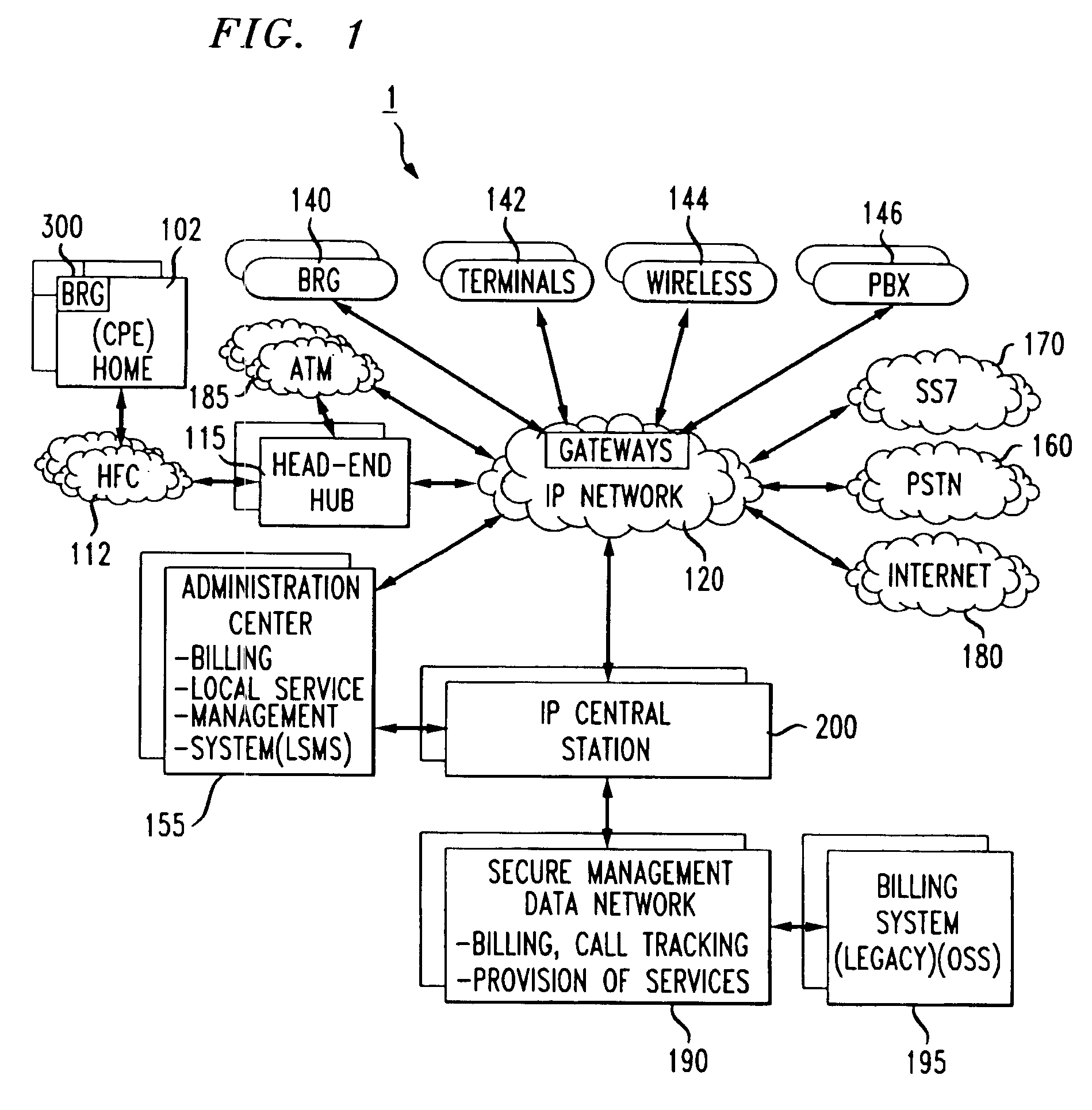
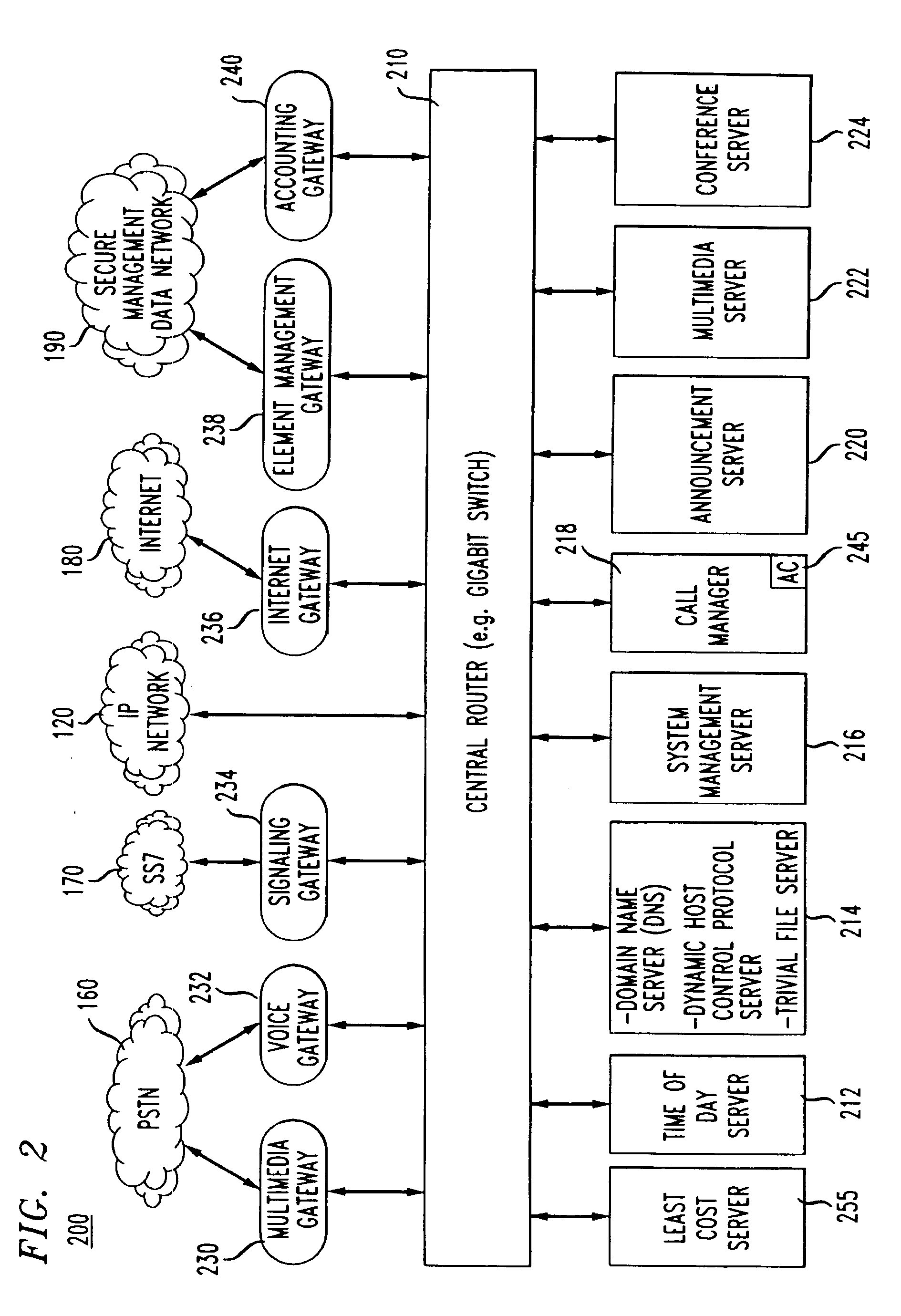
Broadband cable telephony network architecture IP ITN network architecture reference model
InactiveUS7120139B1Easy to deployMinimal costTelephone data network interconnectionsBroadband local area networksVoice communicationNetwork architecture
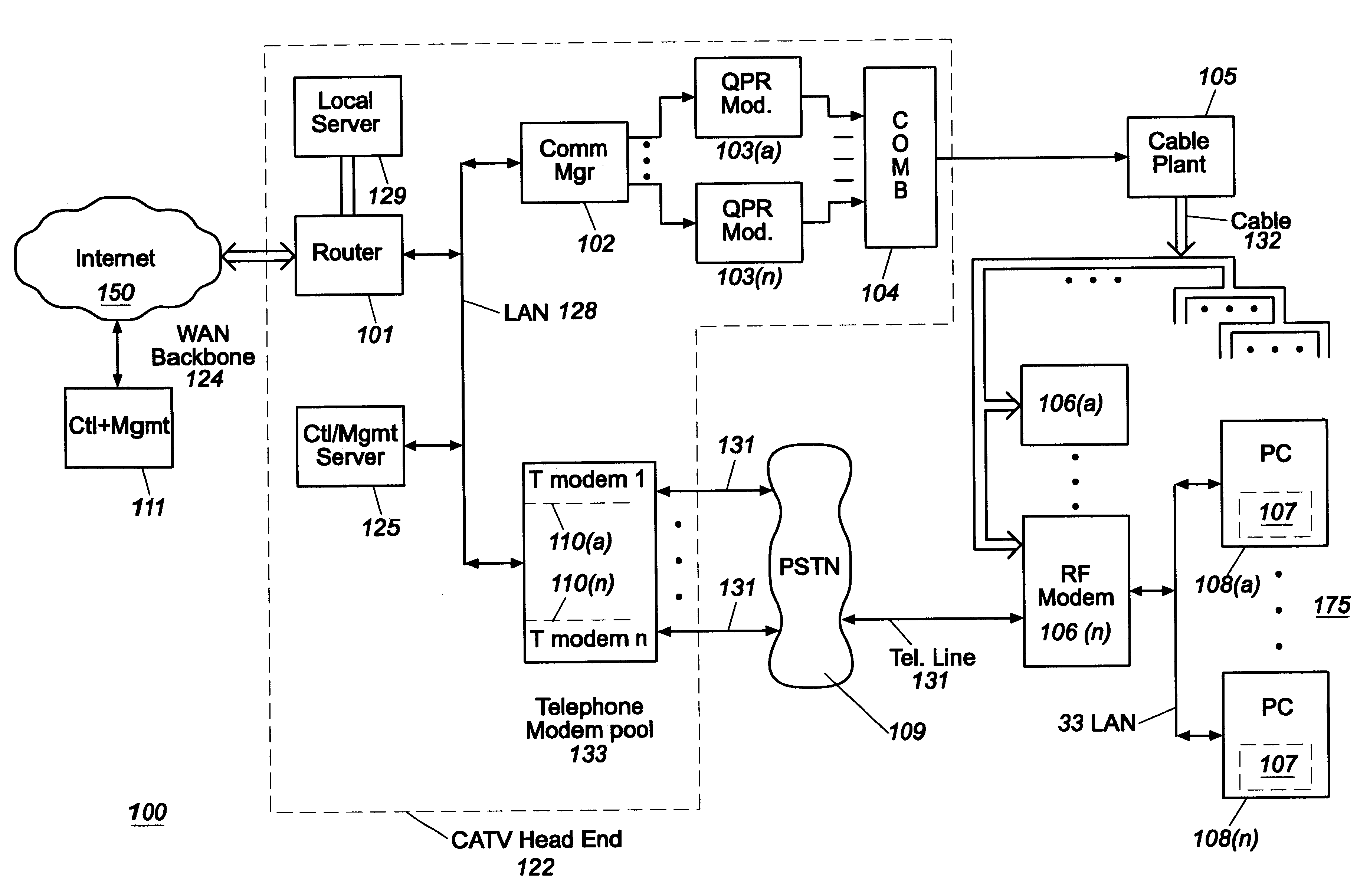
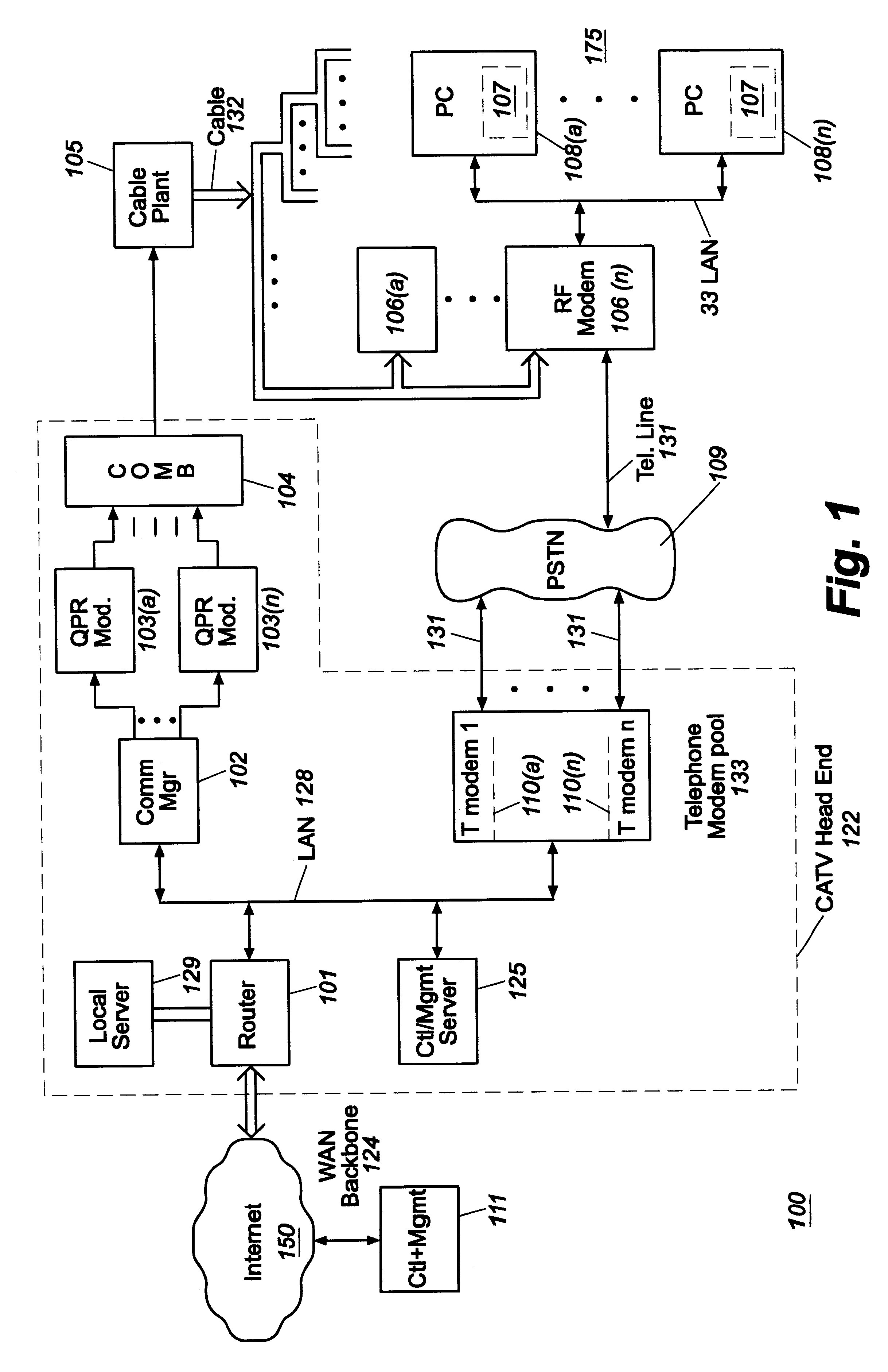
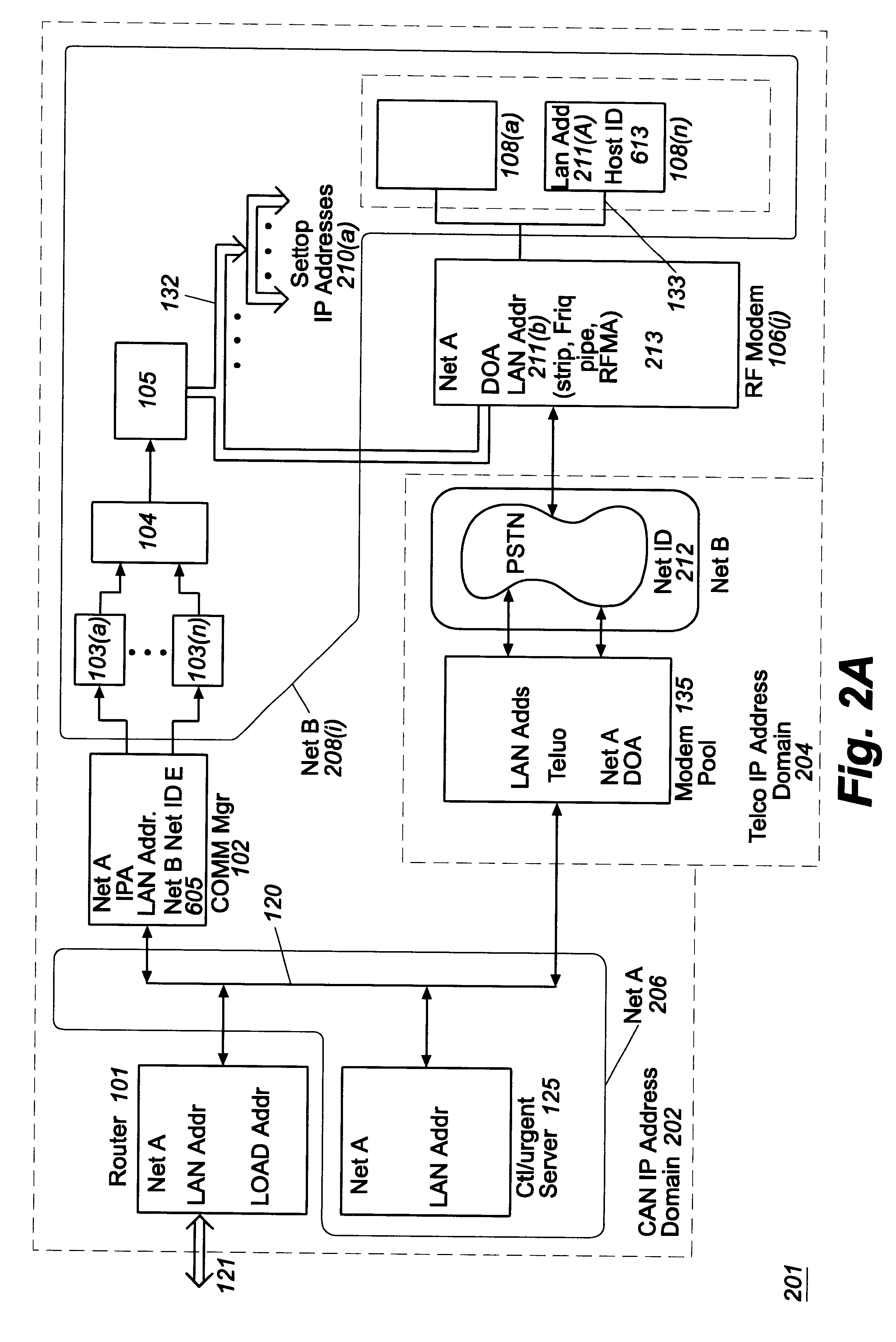
The present invention provides a system and method for a reliable, low-cost, secure Internet Protocol (IP) based network that provides broadband-based voice communications as well as video and data communications. The IP network is arranged to function with the infrastructure of the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), to control telephone calls in SS7 type networks and to provide the features, applications, and services of the typical SS7 networks in a voice over IP network. The present invention supports large effective call volumes, allows accommodation of a wide range of broadband-based service platforms, provides flexibility to support current and future calling feature services, and provides high quality voice transmission.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
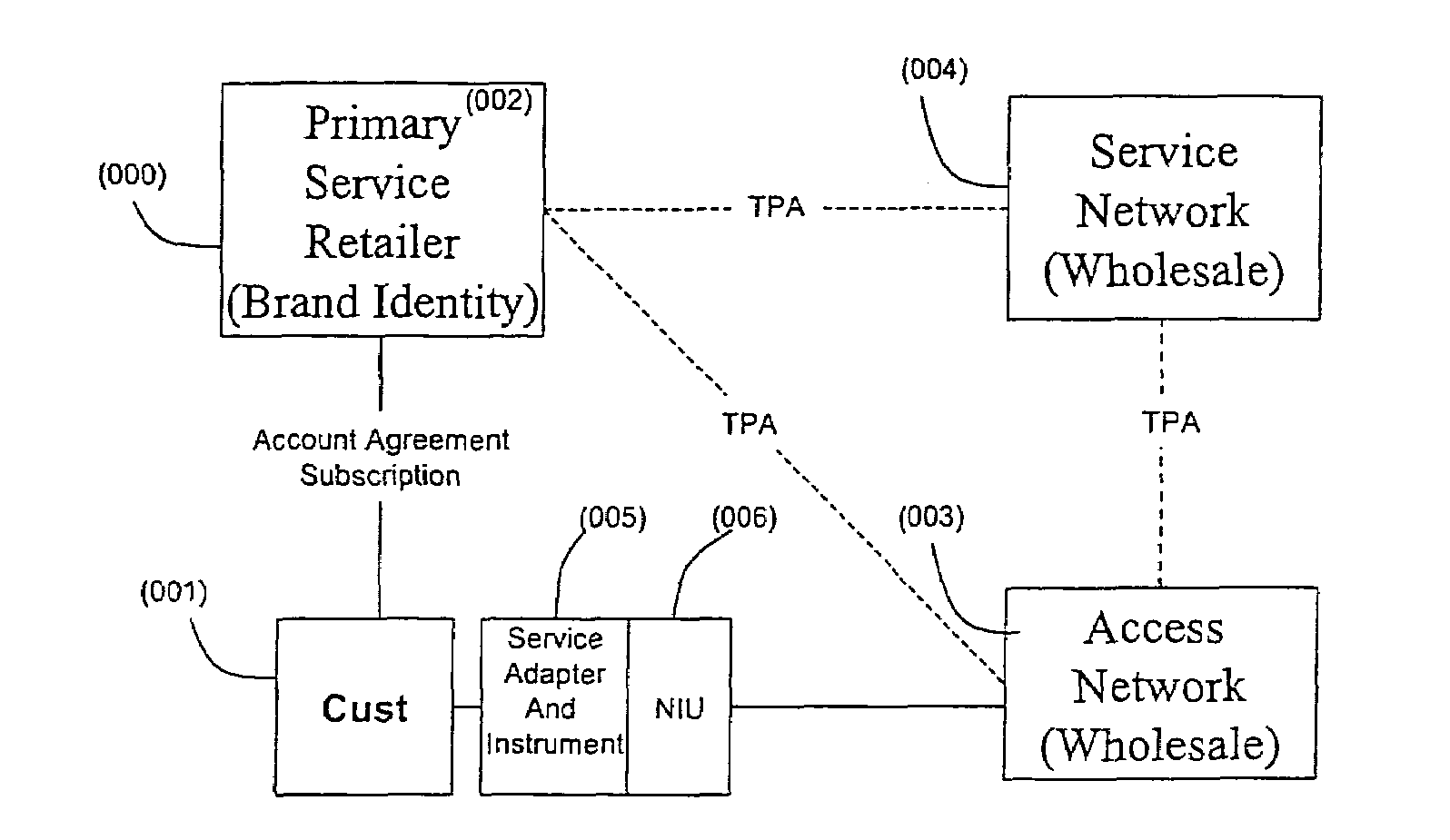
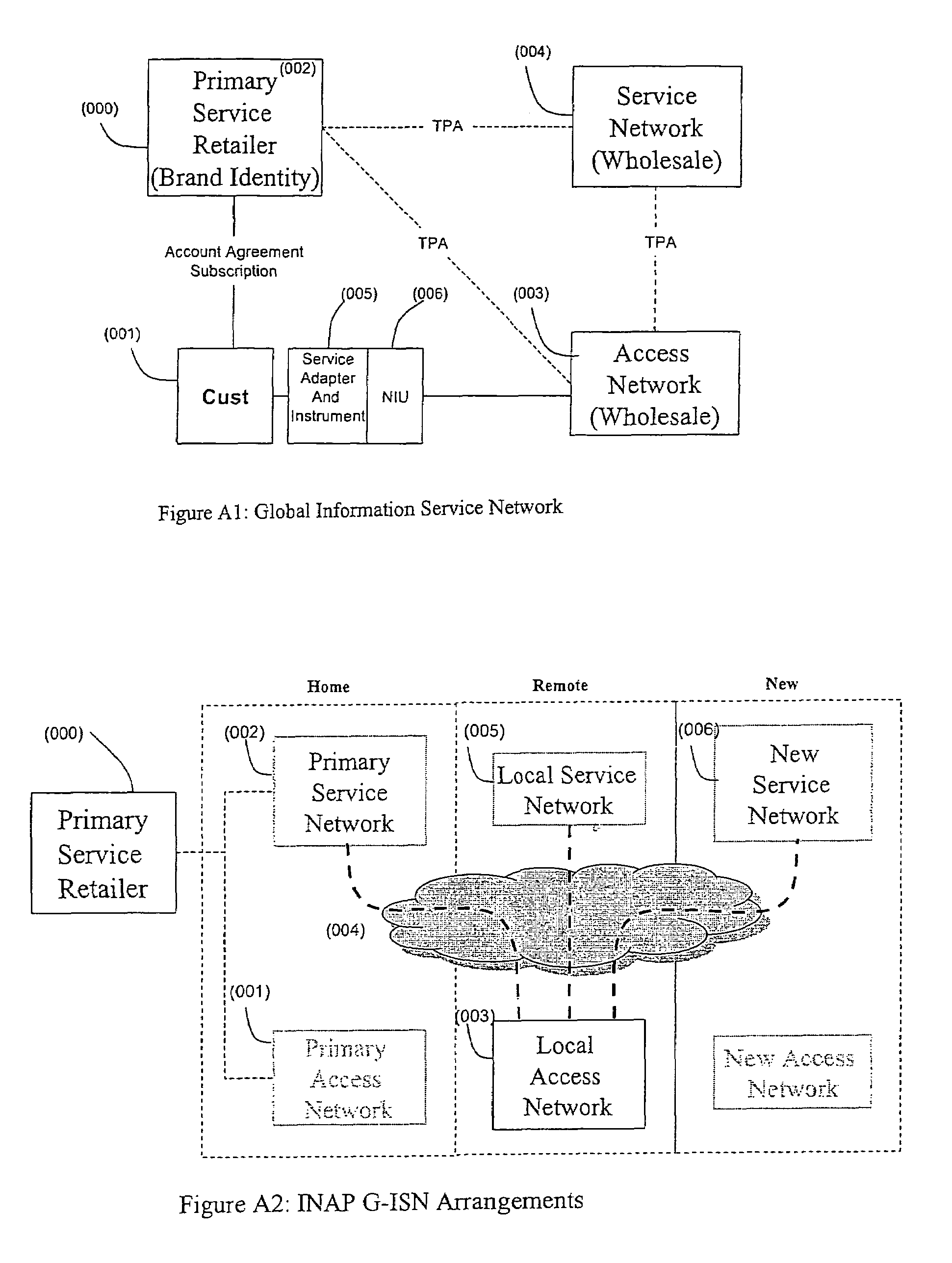
Intelligent network providing network access services (INP-NAS)
InactiveUS7496652B2Efficient use ofConsiderable timeBroadband local area networksMultiple digital computer combinationsIntelligent NetworkSmart network
An open Information Services network architecture is disclosed which enables multiple business entities to assume specialized roles of access provider, service provider, and service retailer. The disclosed technology provides instant plug-and-play service, decouples access and service networks and provides seamless (single step) access enabling customers to maintain a service account regardless of location. The benefits of the disclosed technology, among others, include: Multi-level and multi-service registration; Broker Services providing customers with a choice of provider; Security Services relating to distribution; Revenue Assurance services, Gentle Reminder / Gentle Touch; Revenue Assurance services pertaining to usage integrity verification upon registration; mobile services derived from G-ISN; and claim benefits pertaining to LNP services derived from G-ISN.
Owner:AI-CORE TECH LLC +1
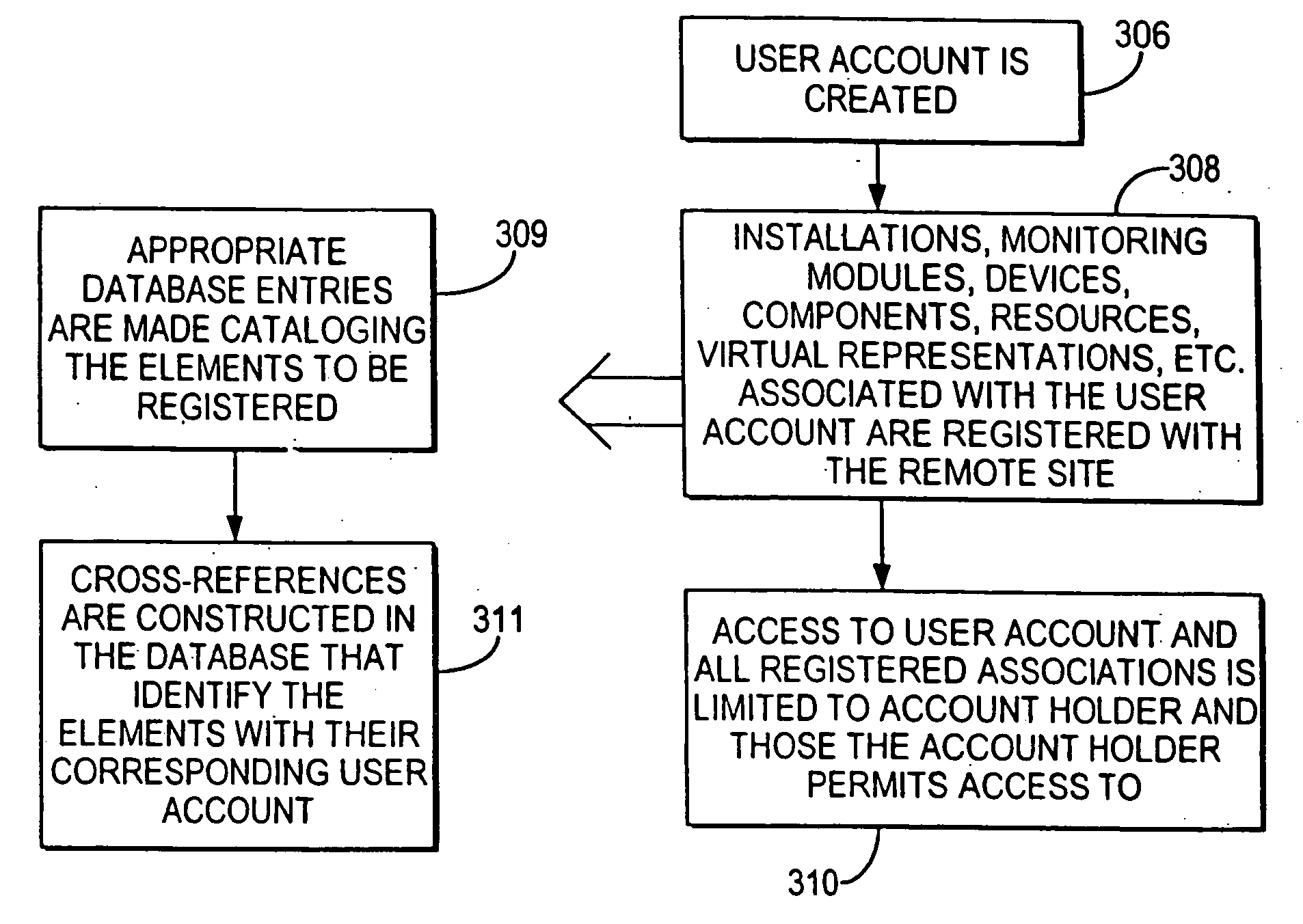
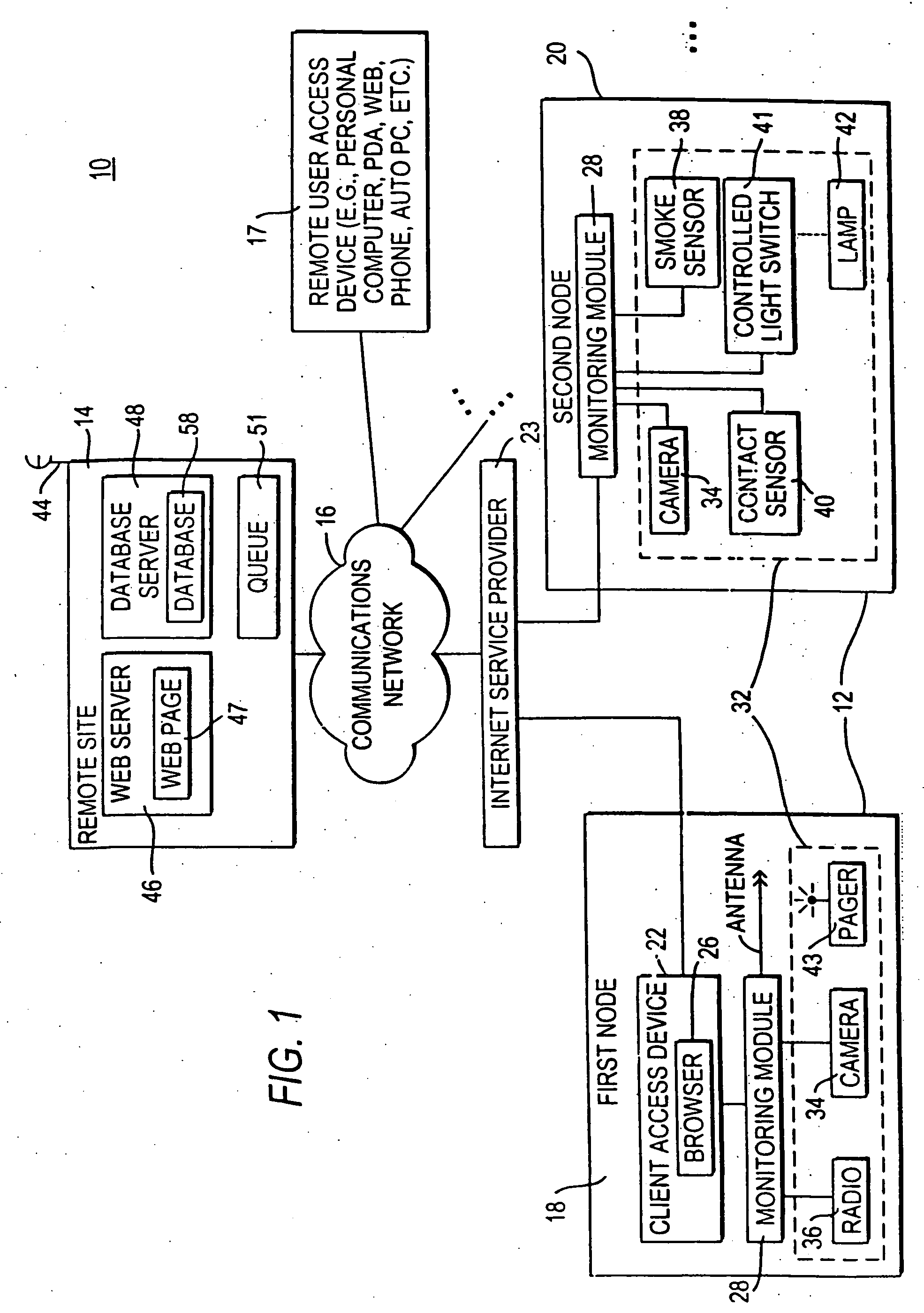
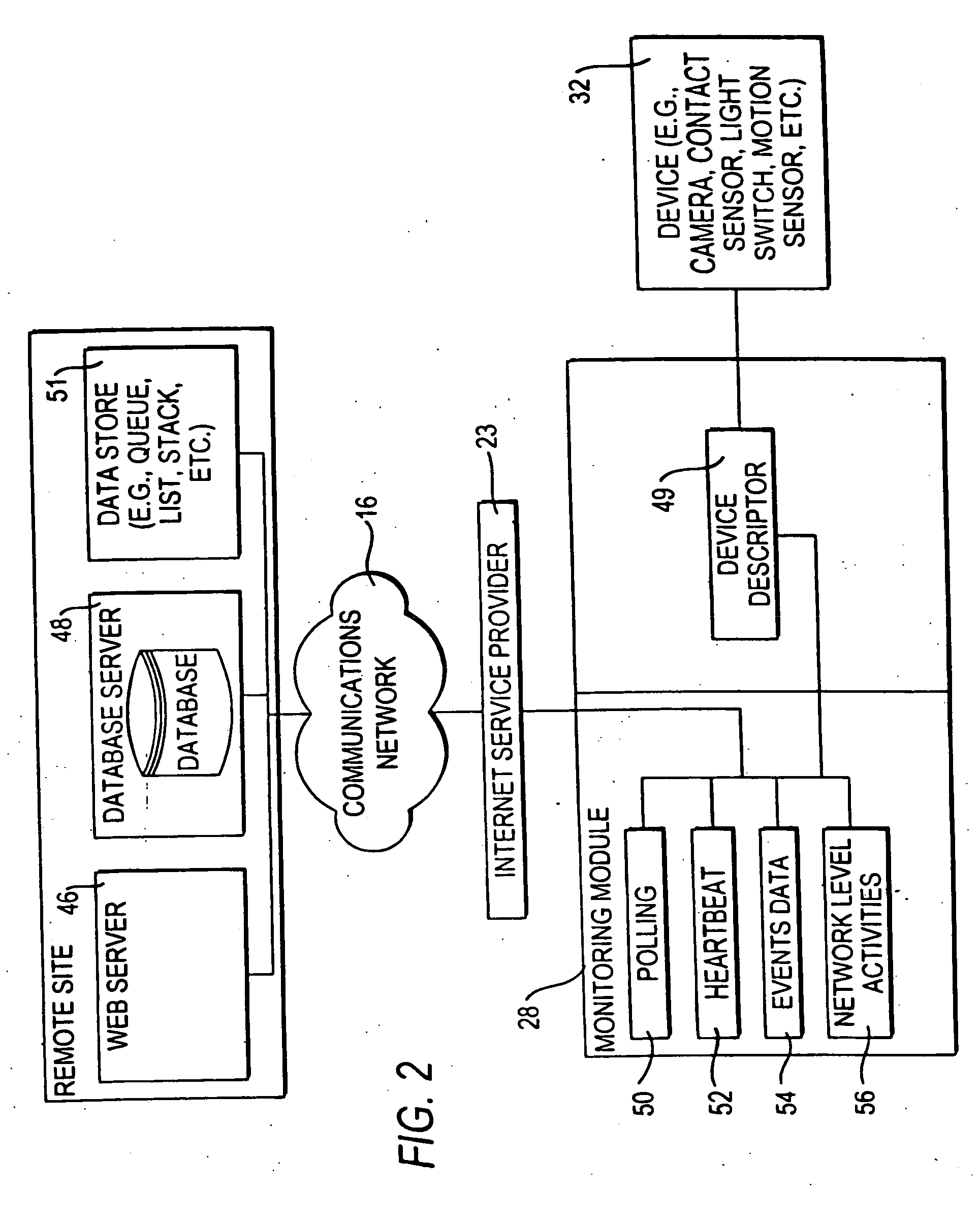
Systems and methods for the automatic registration of devices
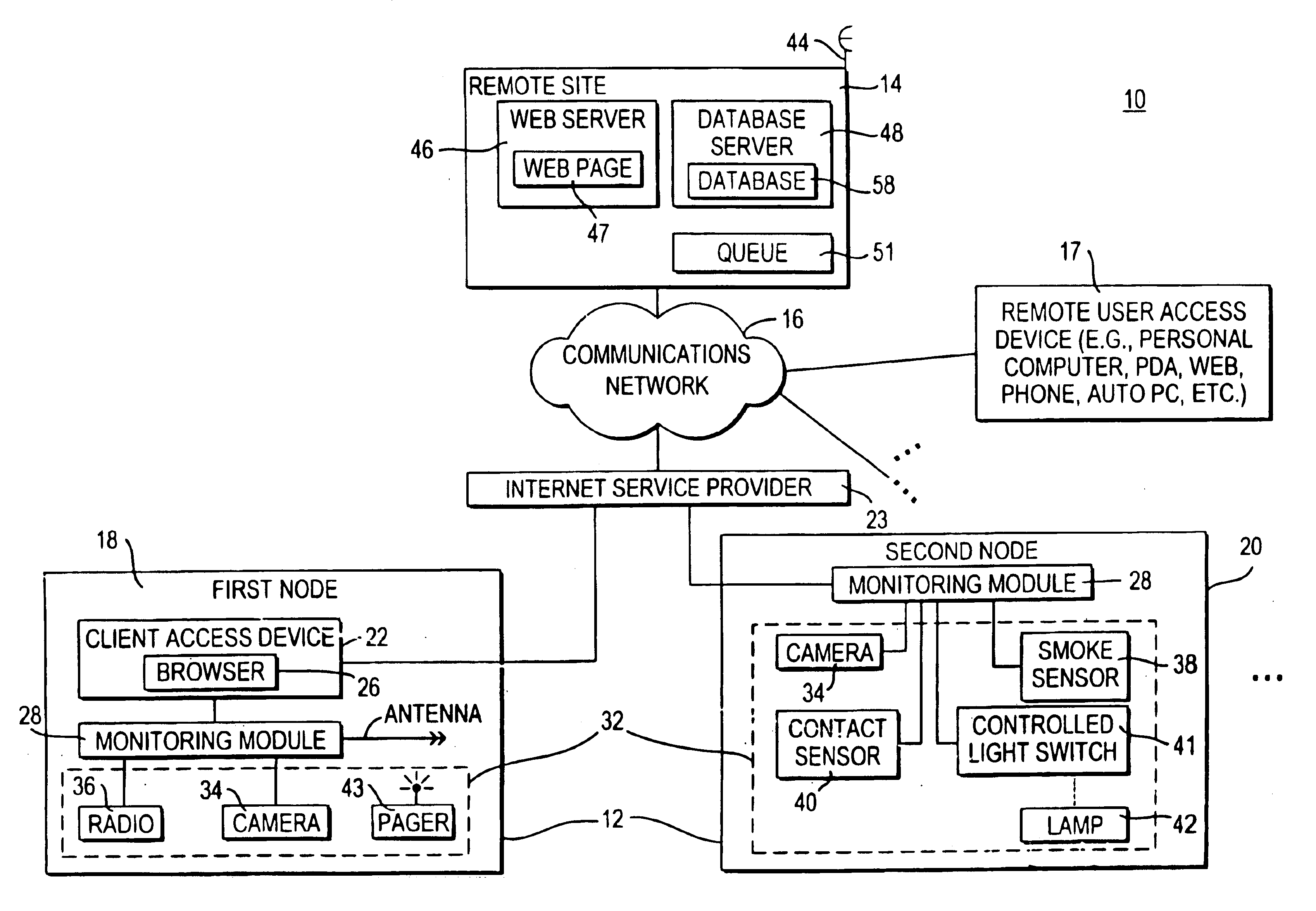
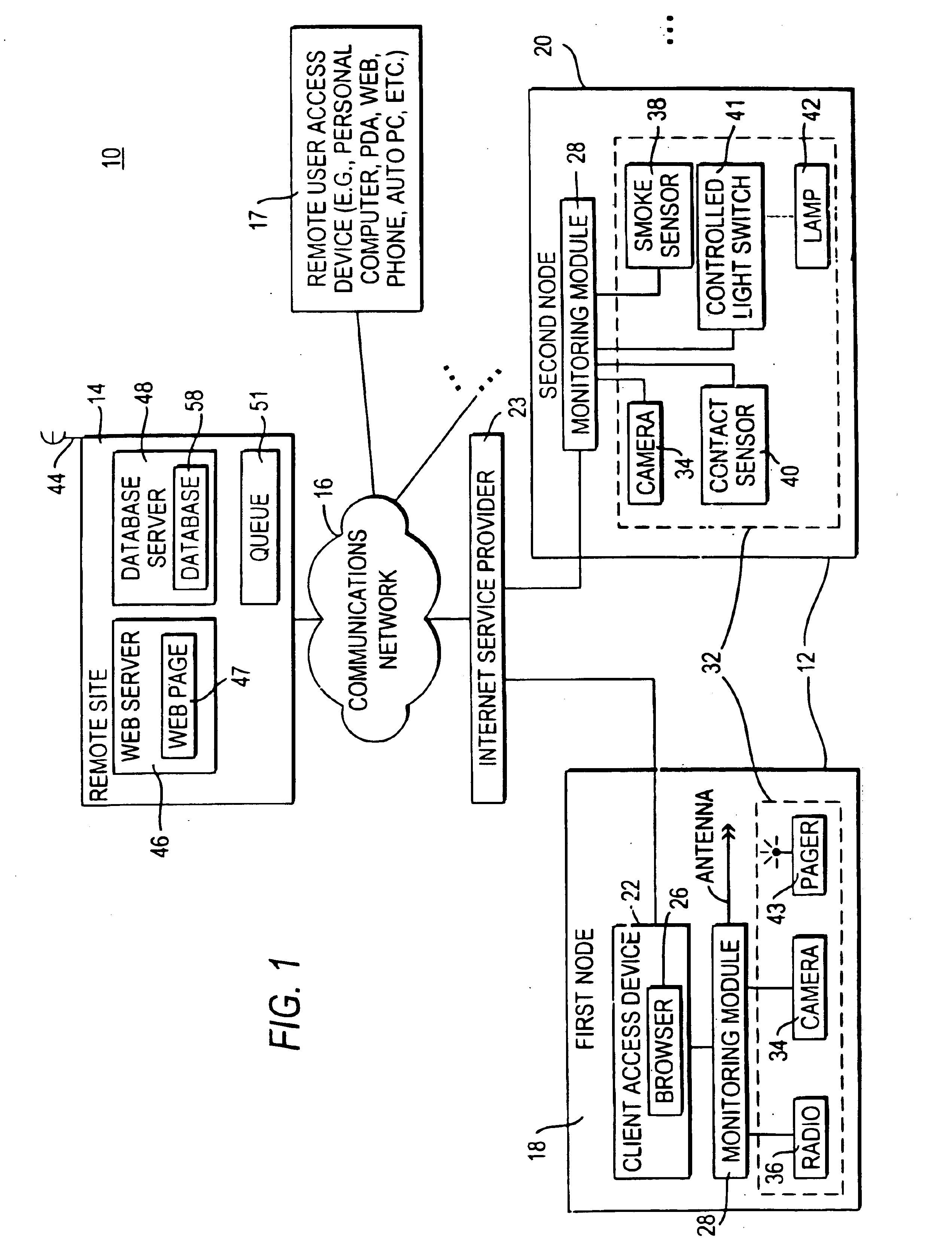
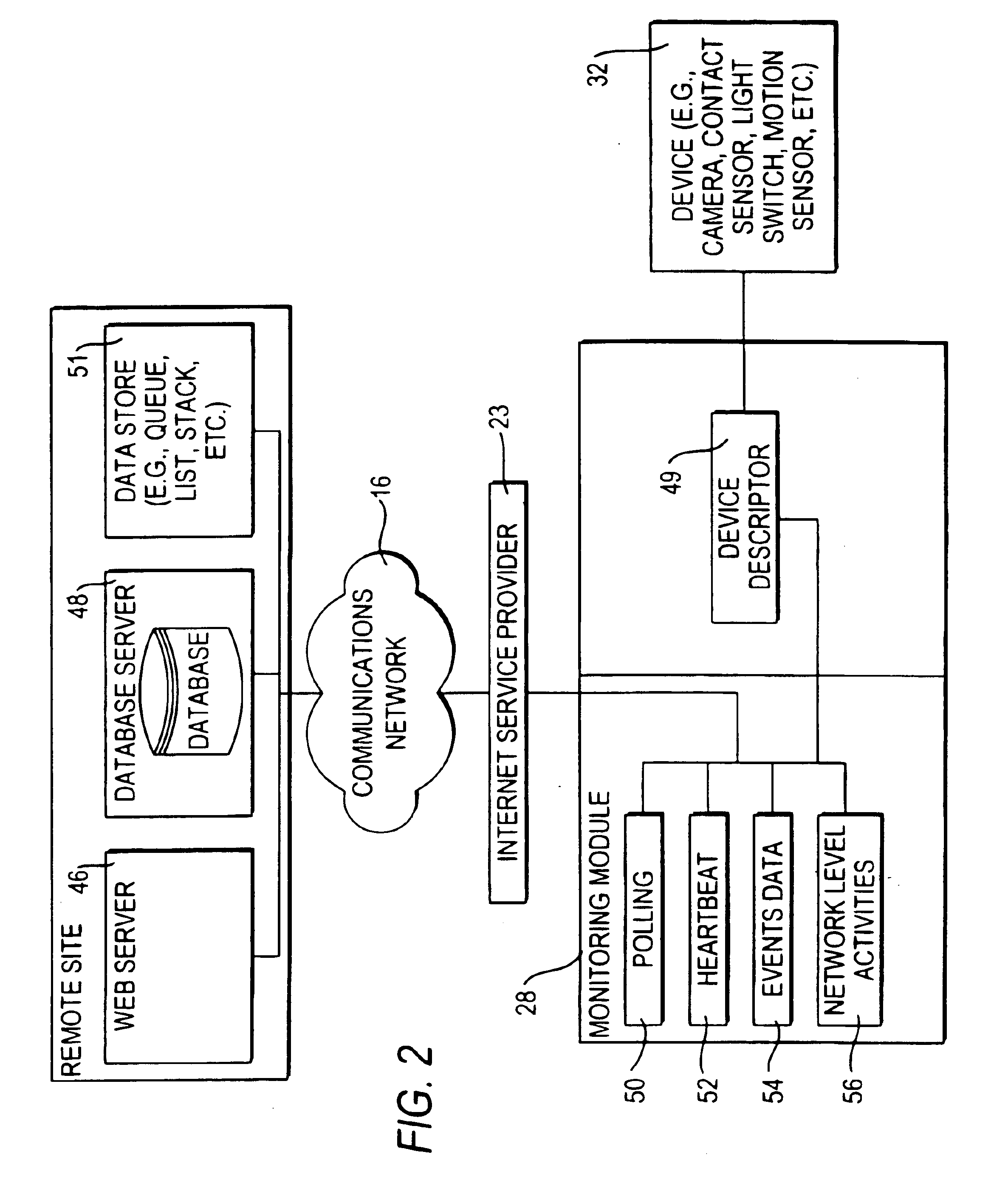
InactiveUS6943681B2Not automaticallyBroadband local area networksElectric testing/monitoringDatabase serverData library
Systems and methods for providing registration at a remote site that may include, for example, a monitoring module that may communicate with a remote site. A registration protocol may be used by the monitoring module and the remote site in generating the messages communicated during the registration process. The monitoring module may gather and generate various identification information to be included in the registration protocol messages. The registration information provided by the monitoring module may be stored at the remote site in a database server having a database. A confirmation message may be communicated from the remote site to the monitoring module that may either acknowledge successful registration or report that an error occurred during the registration process.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Multi-channel support for virtual private networks in a packet to ATM cell cable system
InactiveUS6917614B1Avoid compromiseExtension of timeBroadband local area networksFrequency-division multiplexQuality of serviceScheduling function
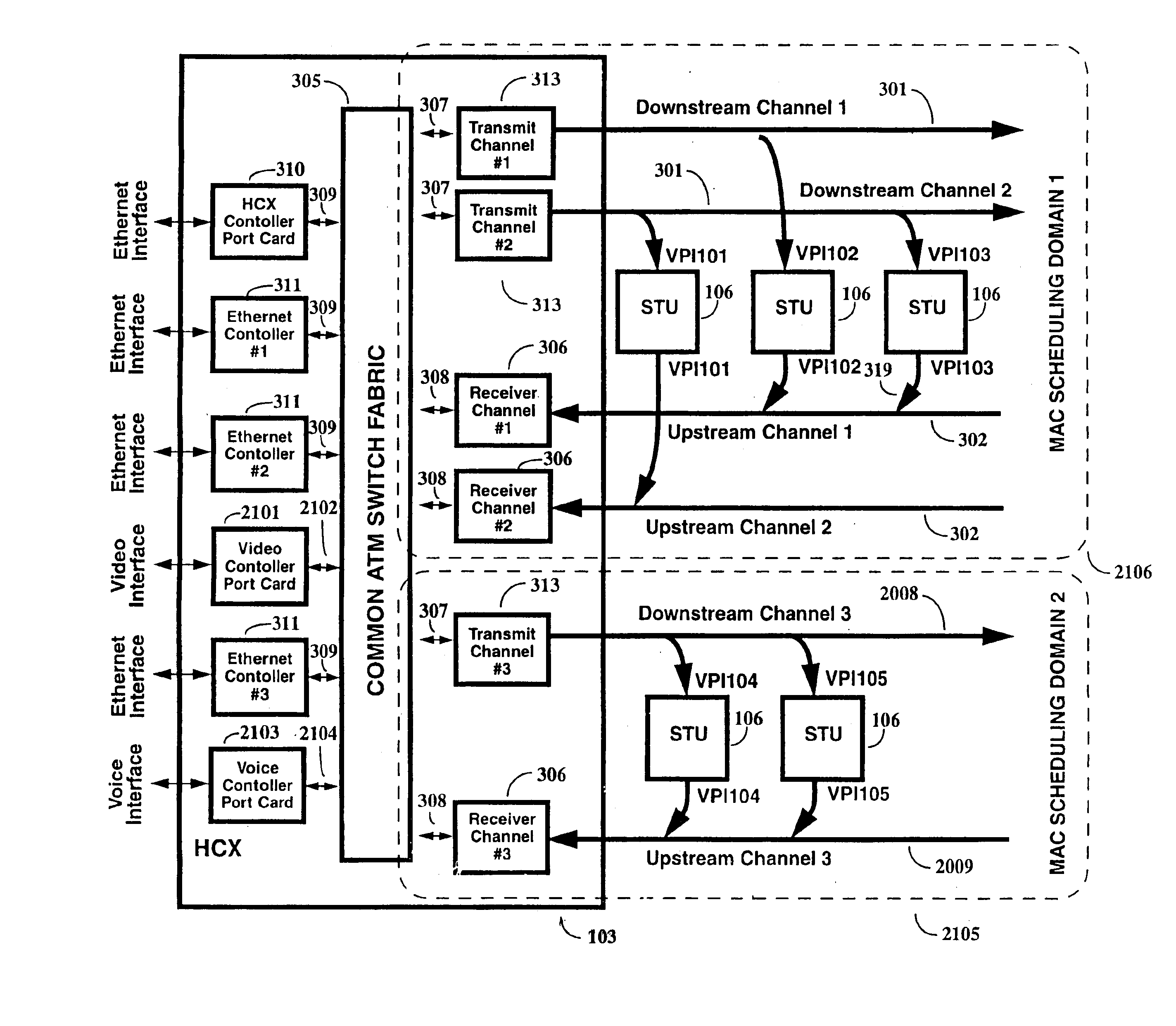
A two-way cable network offering high-speed broadband communications delivered via virtual private networks over a multi-channel shared media system. Bi-directional transmission of packet to ATM cell based communications is established between a head end communication controller and a number of subscriber terminal units, whereby individual cells are prioritized and routed according to a virtual connection. Virtual connections are organized to support multiple virtual private networks in a shared media CATV system. The virtual private network to which a particular STU belongs is user selectable and has the flexibility of handling multi up / downstream channels with different MAC domains. The present invention can also handle non-ATM MAC domains via the same common ATM switch. To overcome the limited number of addresses inherent to common ATM switches, a mapping / remapping function is implemented in the port cards. Furthermore, downstream as well as upstream traffic are filtered at each STU. In one embodiment, information pertaining to downstream traffic is used to implement predictive scheduling in order to improve the timing associated with the request / grant cycle. In another embodiment, a user has the ability to select a quality of service that best suits the needs of the current application. In a further embodiment, the scheduling function is associated with each of the receivers in order to provide improved scalability.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
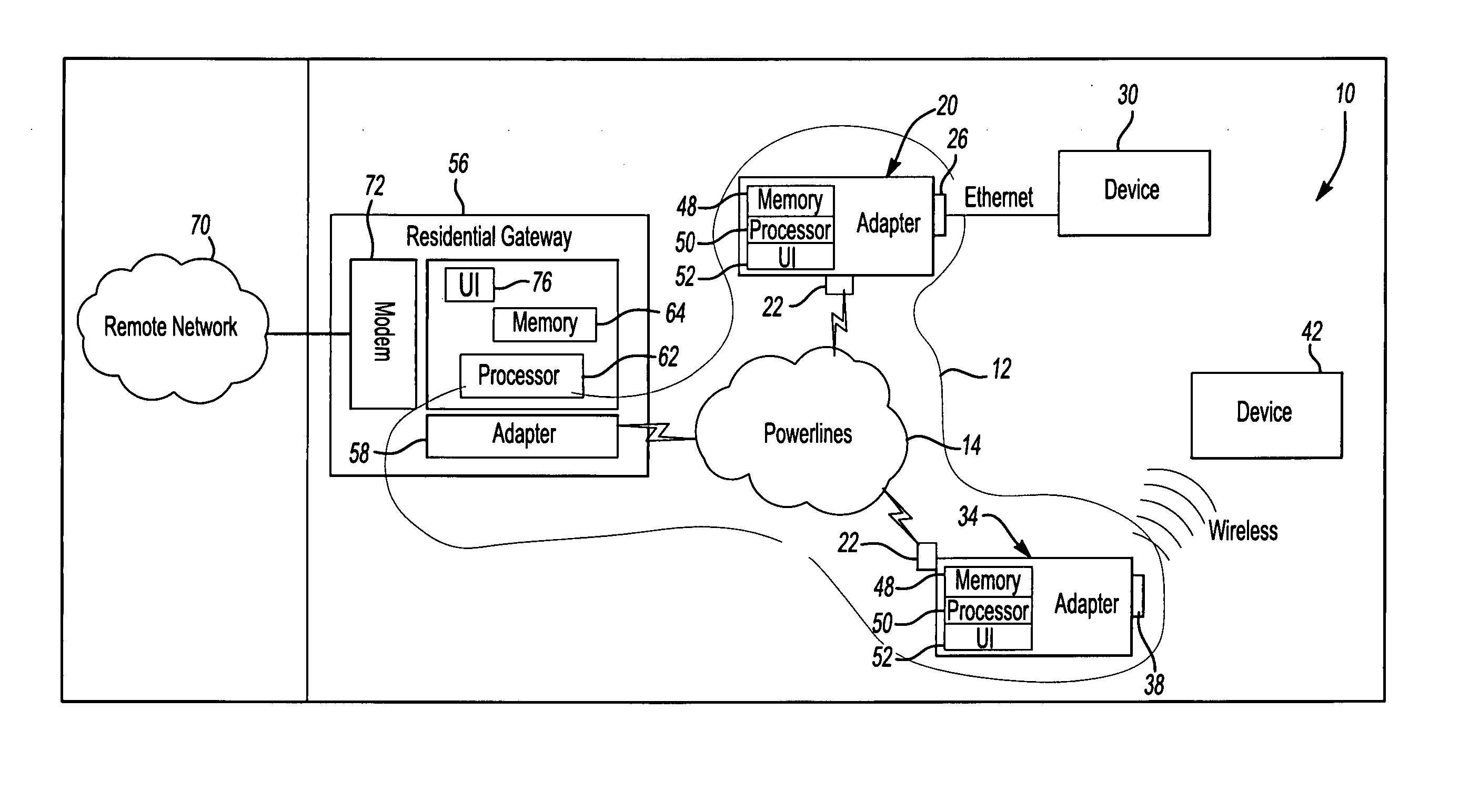
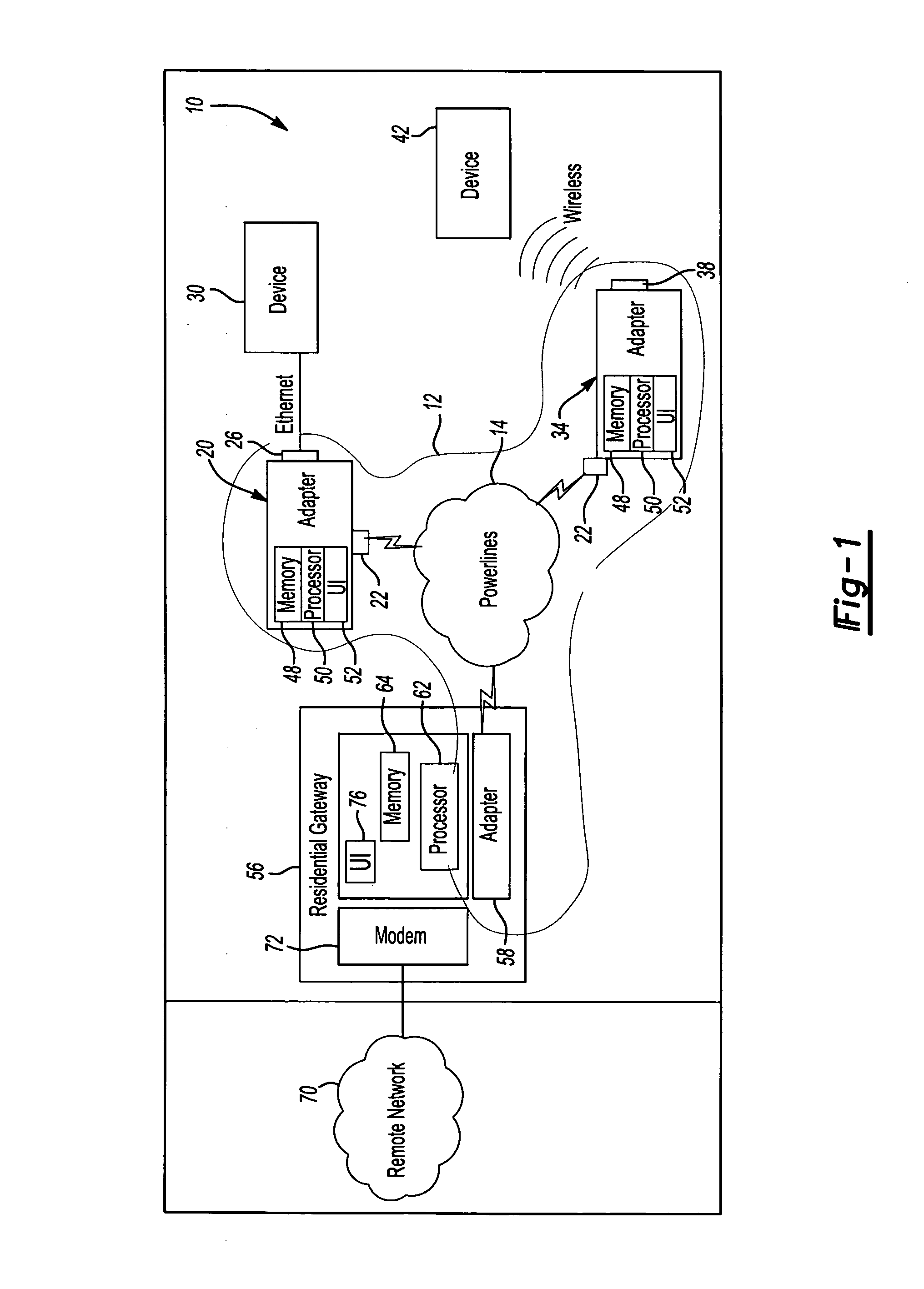
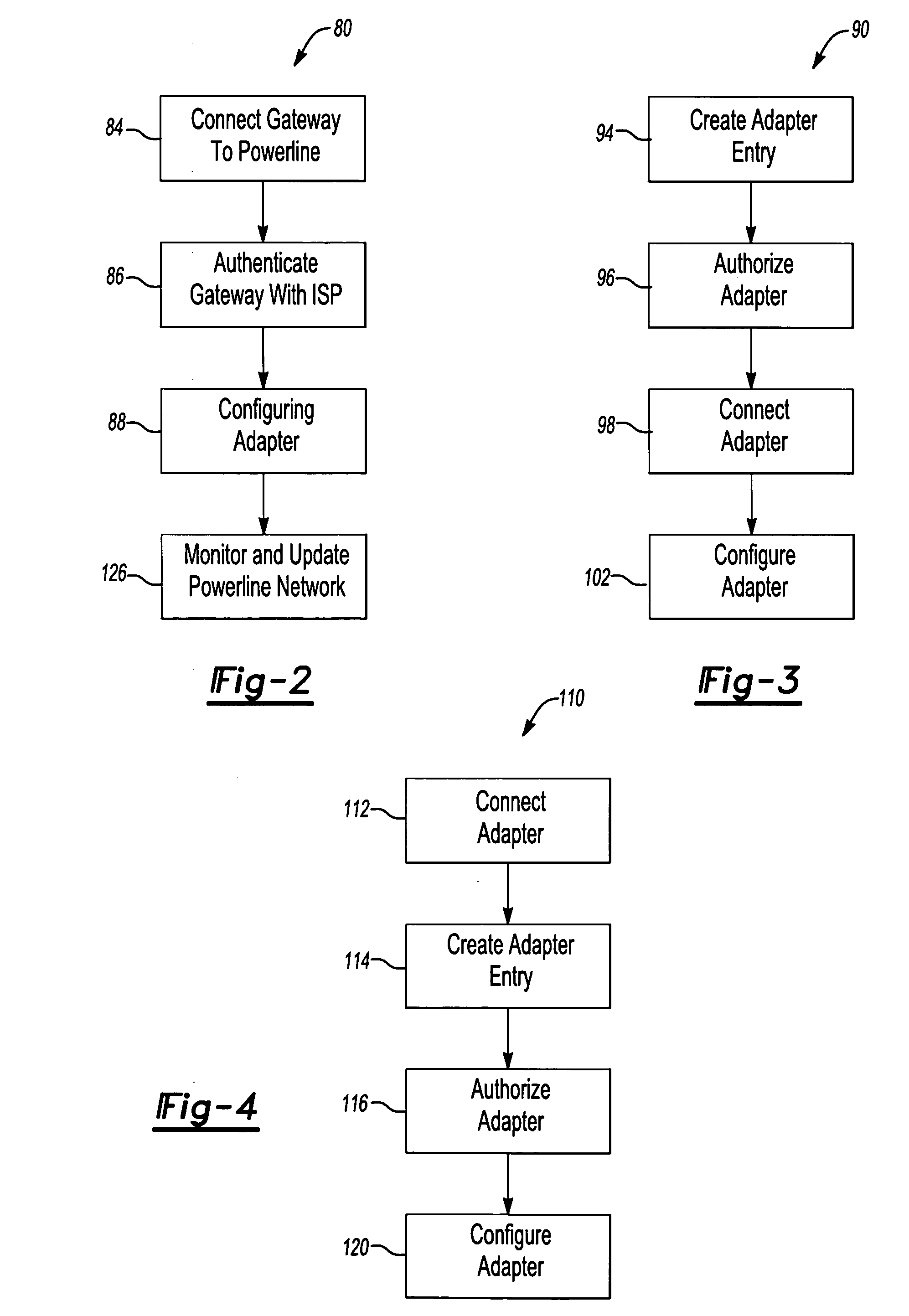
Method and system for powerline networking
InactiveUS20060018328A1Improve securityEasy to changeBroadband local area networksBroadcast transmission systemsComputer network
A method and system for powerline networking. The method and system include an adapter and a gateway connected to powerlines. The gateway is operable for configuring the adapter for powerline networking by communicating configuration signals to the adapter over the powerlines. A powerline network is defined by the configuring of the adapter to communicate with the gateway over the powerlines.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
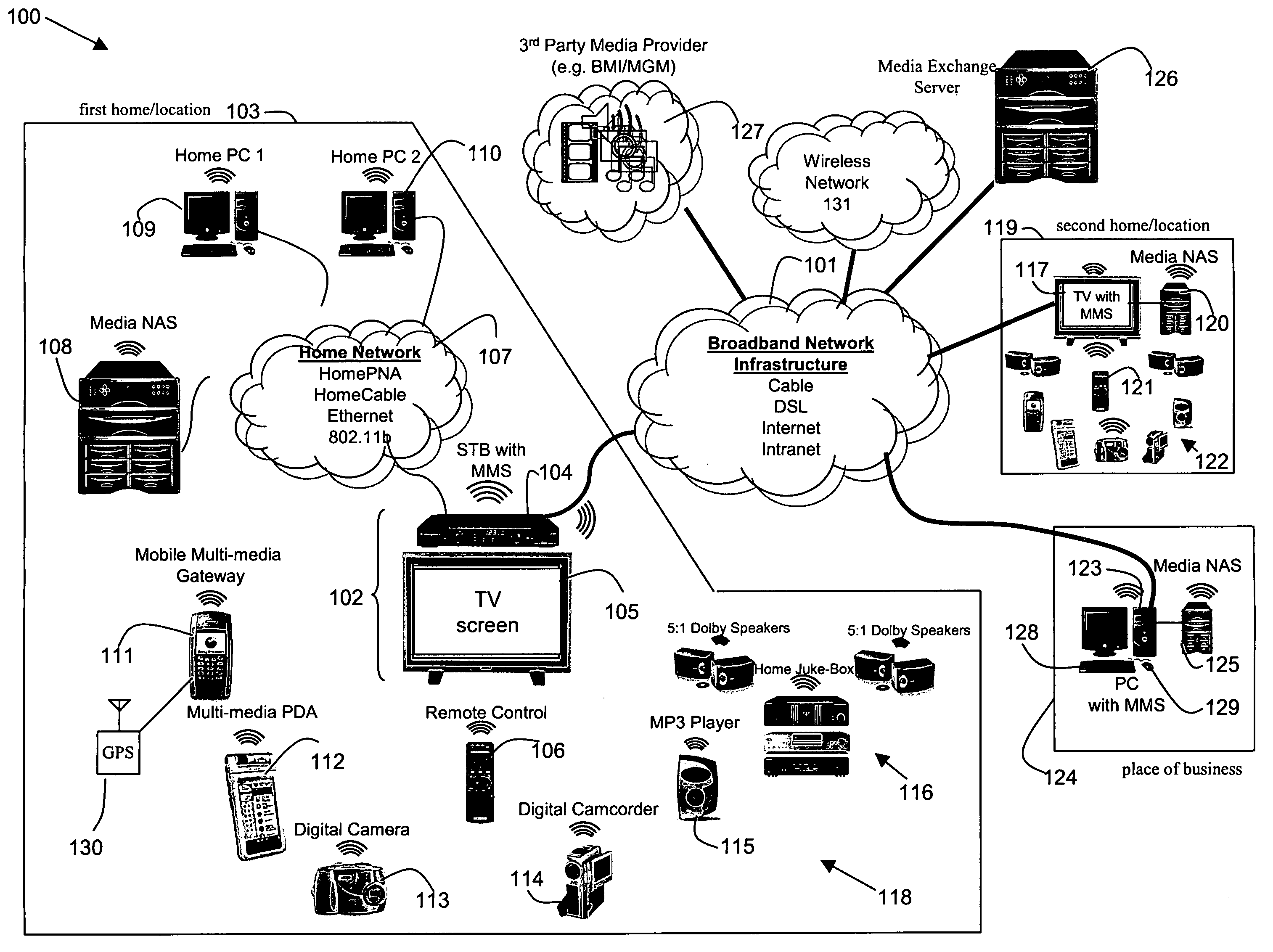
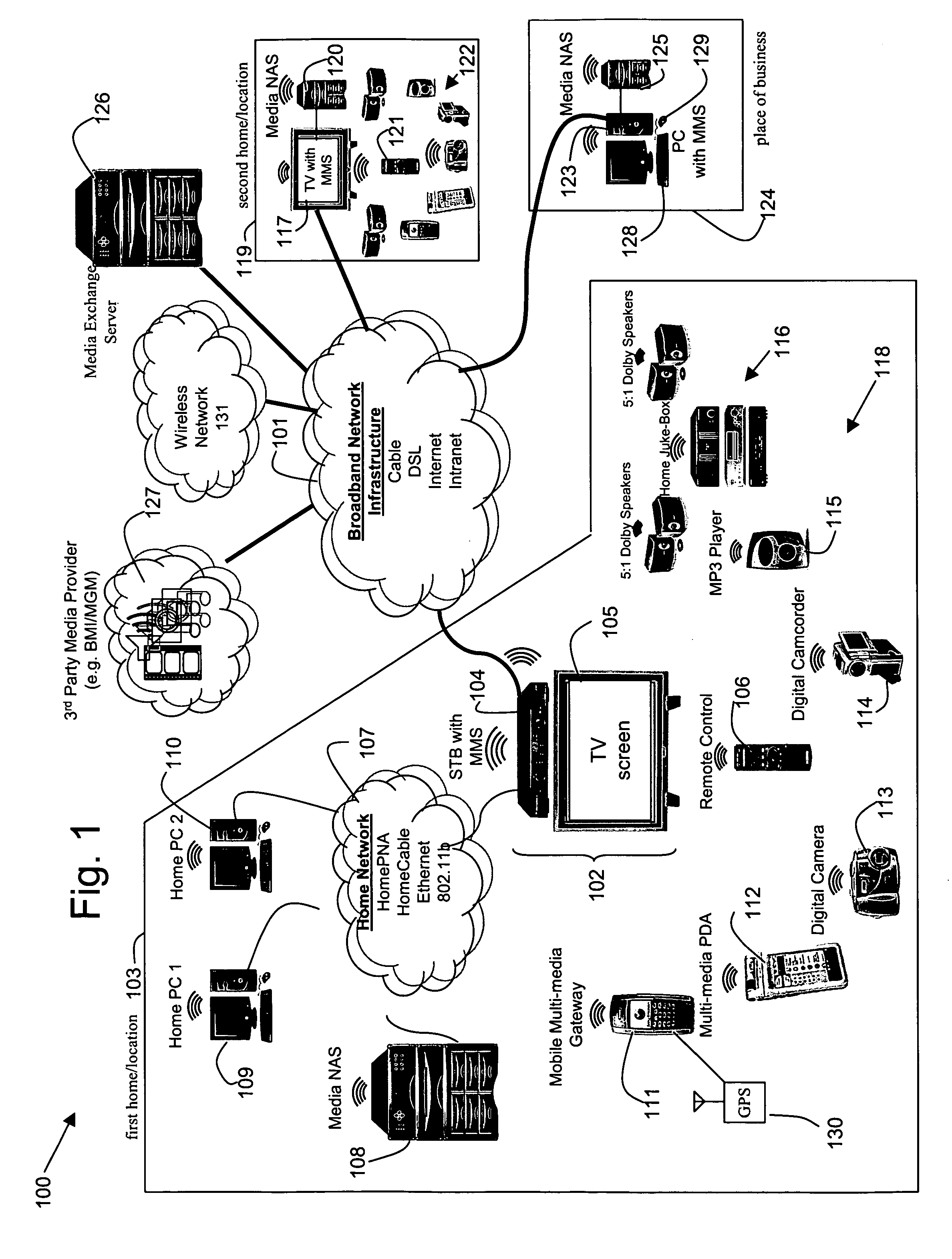
System, method, and apparatus for secure sharing of multimedia content across several electronic devices
InactiveUS20060020960A1Broadband local area networksMultimedia data retrievalComputer securityDigital video
Disclosed herein is a secure, media exchange network and a method of securely exchanging media between electronic devices across the network. In an embodiment according to the present invention, media may be securely and simultaneously exchanged between friends, family members, business associates, government entities, military entities, law enforcement entities, and 3rd party media providers over a closed and secure media exchange network. The media may include, for example, digital video, digital audio, digital images, digital data, or any other form of digital information. Security features may include security techniques, associated security hardware, and associated security software.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
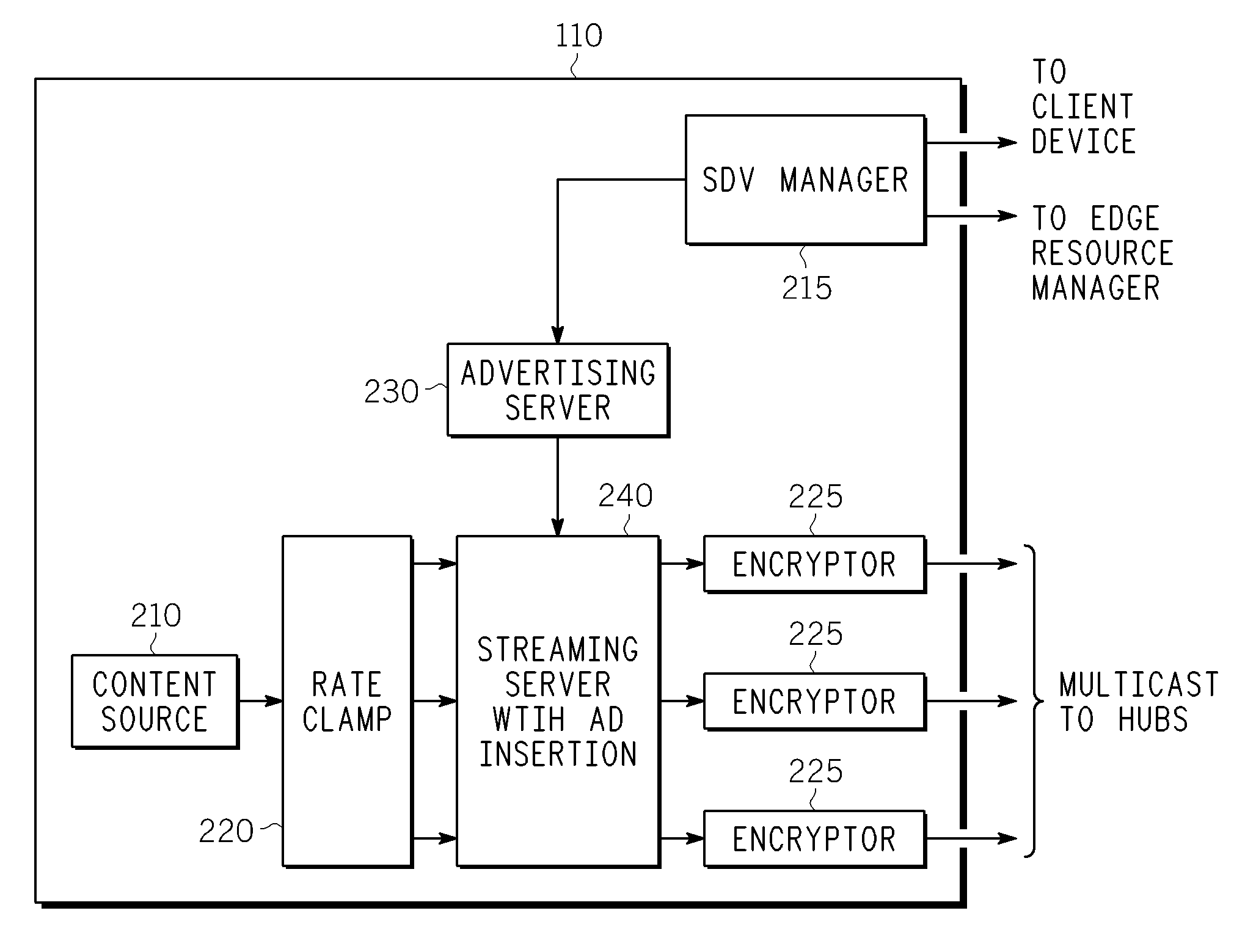
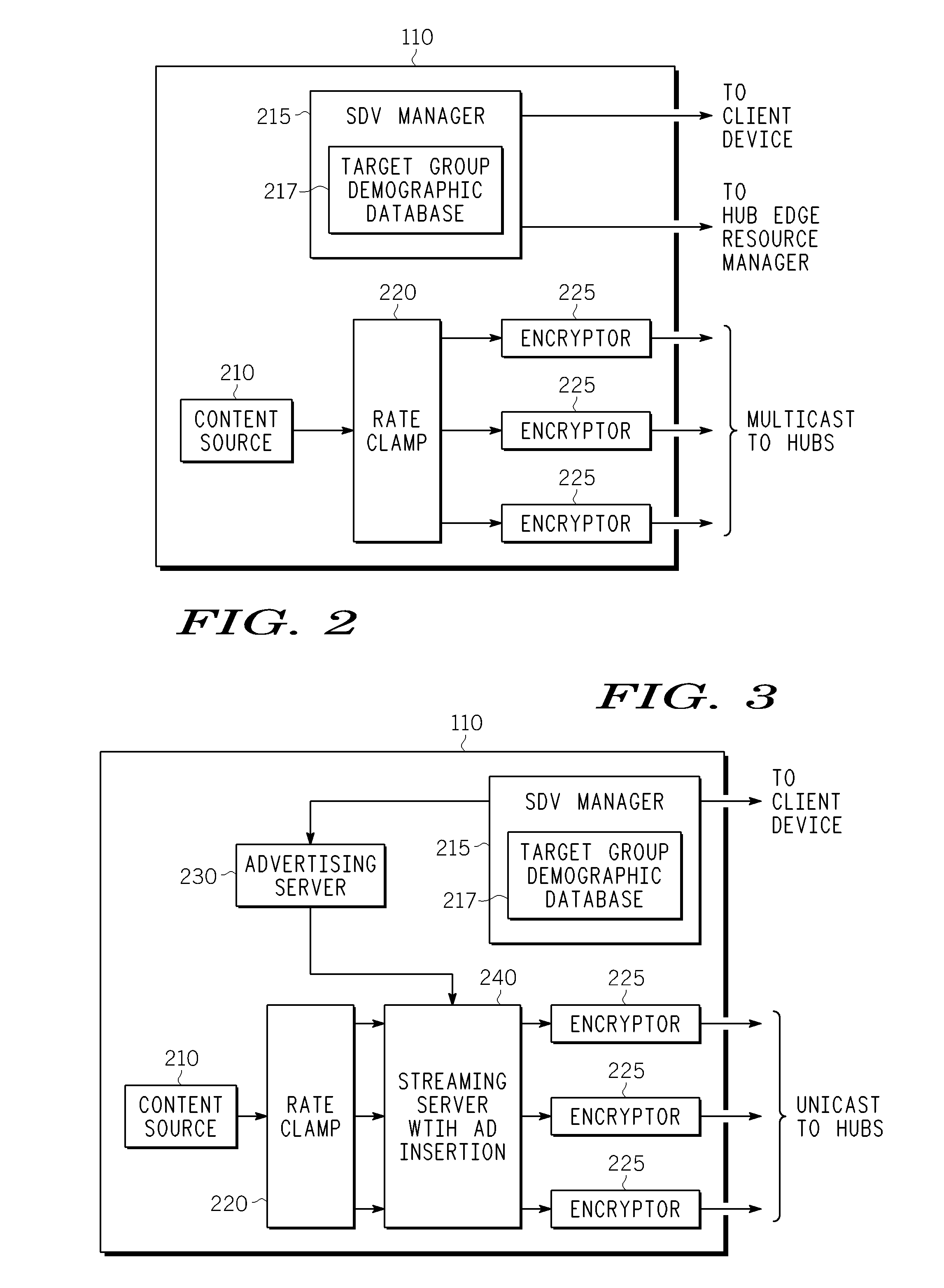
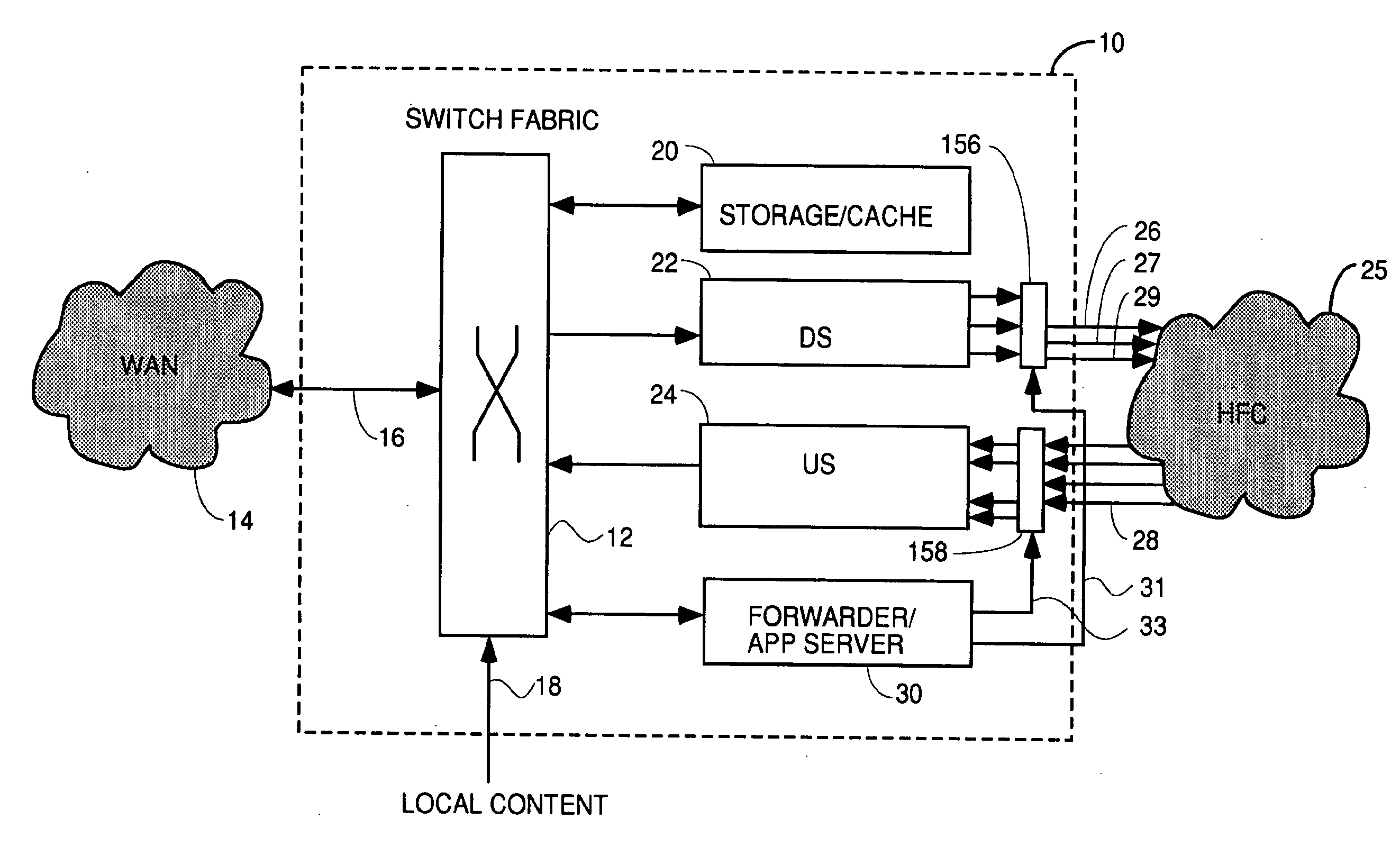
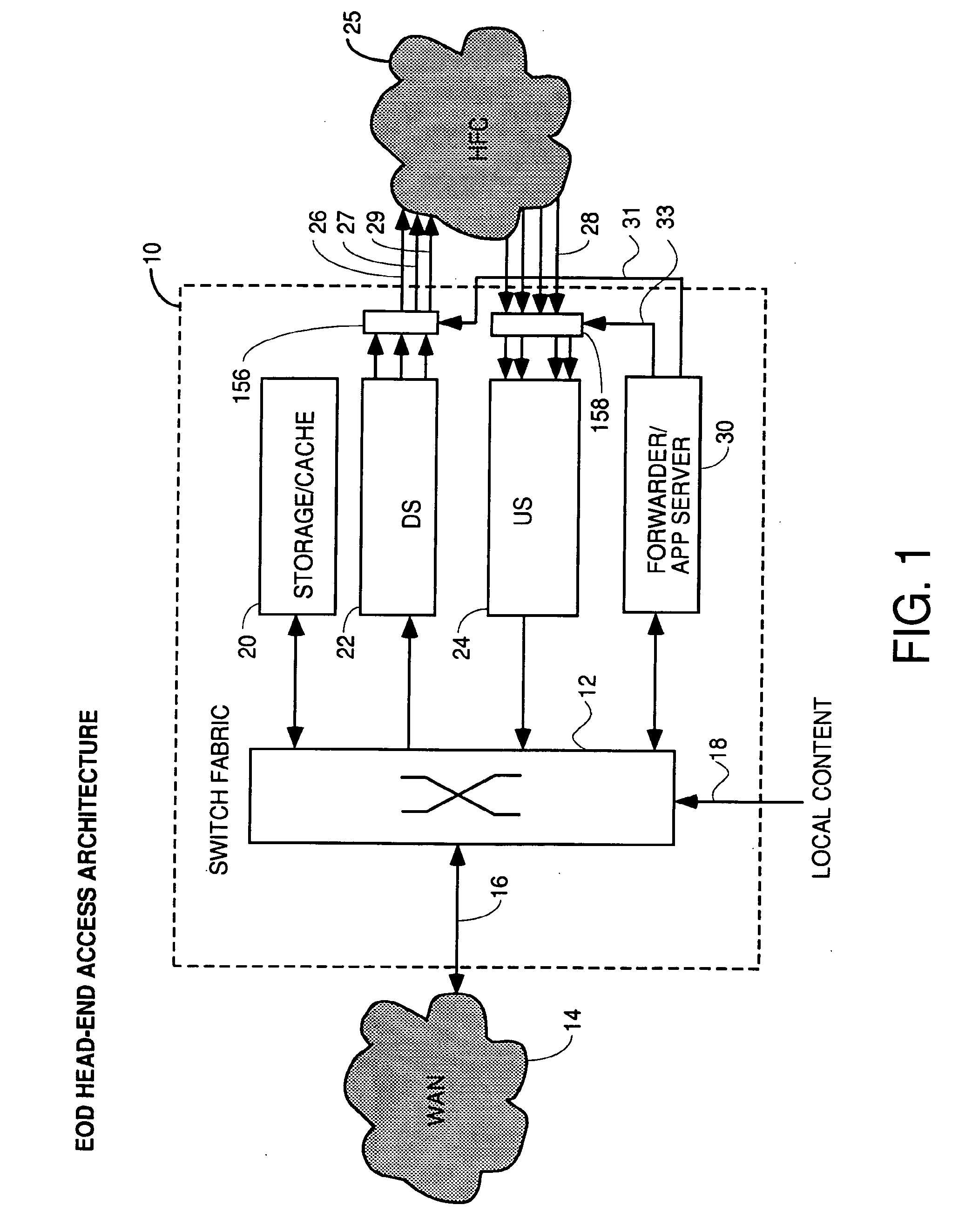
Method And Apparatus For Delivering SDV Programming With Targeted Advertising To Selected Groups Of Subscribers
InactiveUS20090150926A1Broadband local area networksTwo-way working systemsAccess networkDigital video
A switched digital video (SDV) system includes an SDV manager for coordinating a SDV session requested by a subscriber terminal and a storage medium on which resides content to be transmitted during the SDV session. The system also includes a plurality of edge devices for receiving a transport stream that includes content provided by the storage medium and transmitting the transport stream over an access network to the subscriber terminal on one of a plurality of SDV channels. The SDV manager is configured to cause different renditions of an SDV program to be provided by the edge devices to subscriber terminals associated with different target groups. The target groups each include a plurality of subscriber terminals that is less than a number of subscriber terminals serviced by a distinct edge device or devices.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
System and methods for home network communications
InactiveUS7127734B1Low costBroadband local area networksClosed circuit television systemsEngineeringNetwork communication
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and System for Selecting a Wireless Network for Offloading
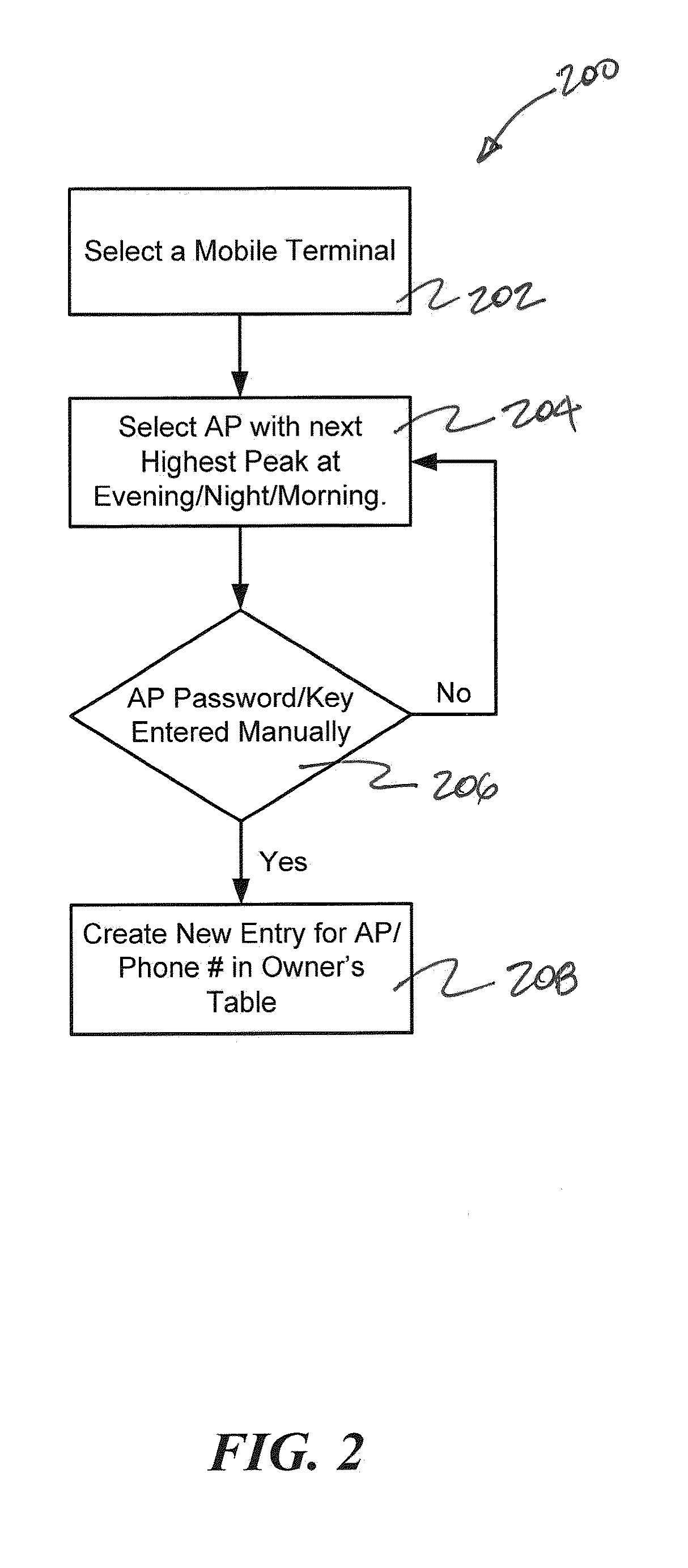
ActiveUS20130084835A1Good choicePrecise managementBroadband local area networksNetwork traffic/resource managementTraffic capacityWifi network
The present invention is directed to a method and system for selecting a wireless network for offloading network traffic from another network. In one embodiment, a method and system for offloading network traffic in a wireless user terminal from a first network, such as cellular network, onto a second network, such as a WiFi network, includes determining a measure of the relationship between the user of the wireless user terminal and the owner of the access point for the second network. The measure of the relationship can be used to provide an indication of the likelihood that the owner of the access point will grant access to the user of the wireless user terminal.
Owner:WEFI
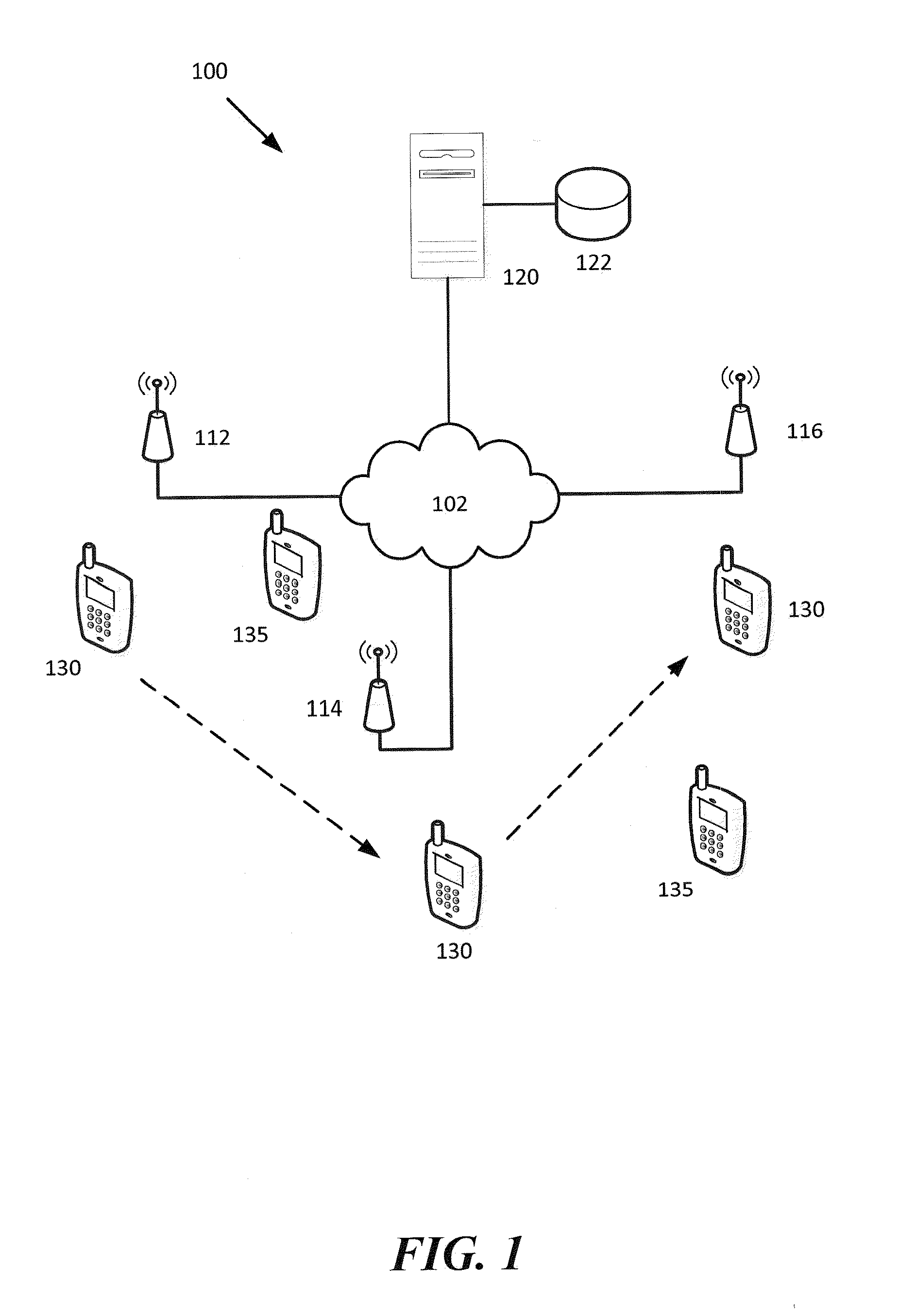
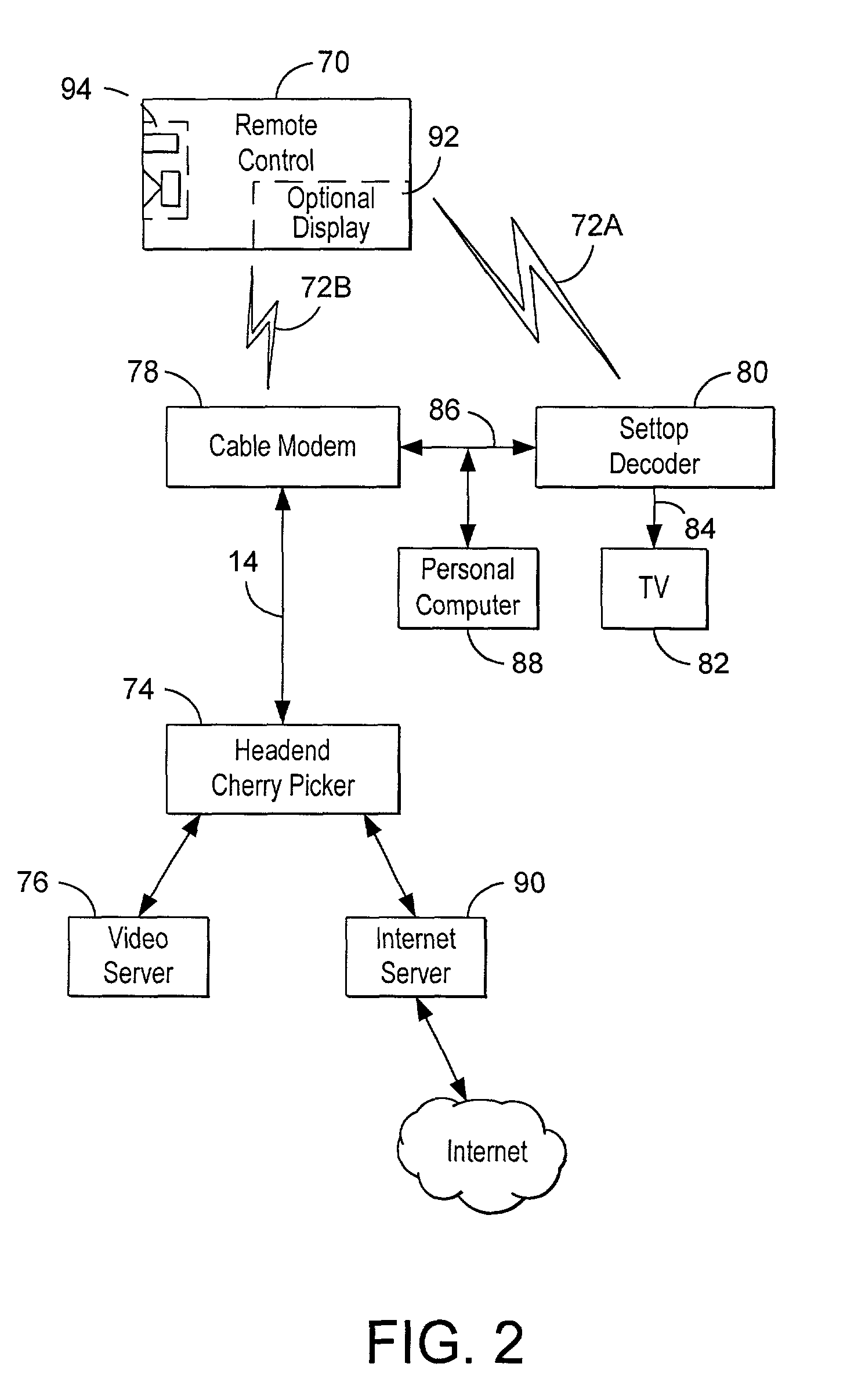
Remote control for wireless control of system including home gateway and headend, either or both of which have digital video recording functionality
ActiveUS8151306B2Television system detailsBroadband local area networksDigital videoWireless control
A system for wireless remote control of a gateway and ordering or invocation of services provided by a headend. The remote control includes a video display and user input device or keyboard and can decompress and display compressed streaming video in some embodiments. Some species of the remote control can act as web browsers, appliance control, TIVO function control, an IP telephony telephone, a cellular telephone and / or an MP3 player. In some embodiments, the gateway and / or headend can implement TIVO-like functions under control from a wireless remote of custom design or implemented on a Personal Digital Assistant.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
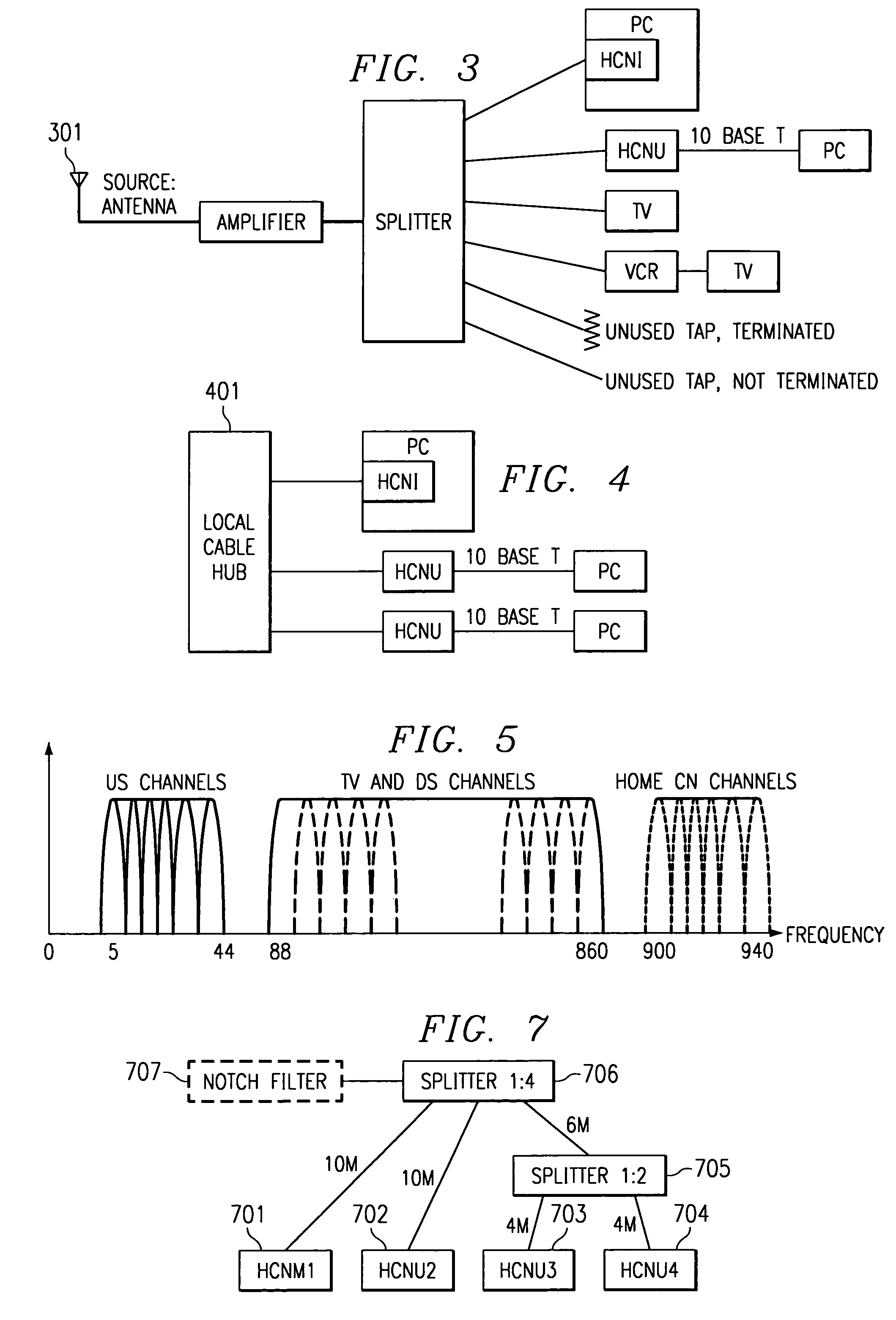
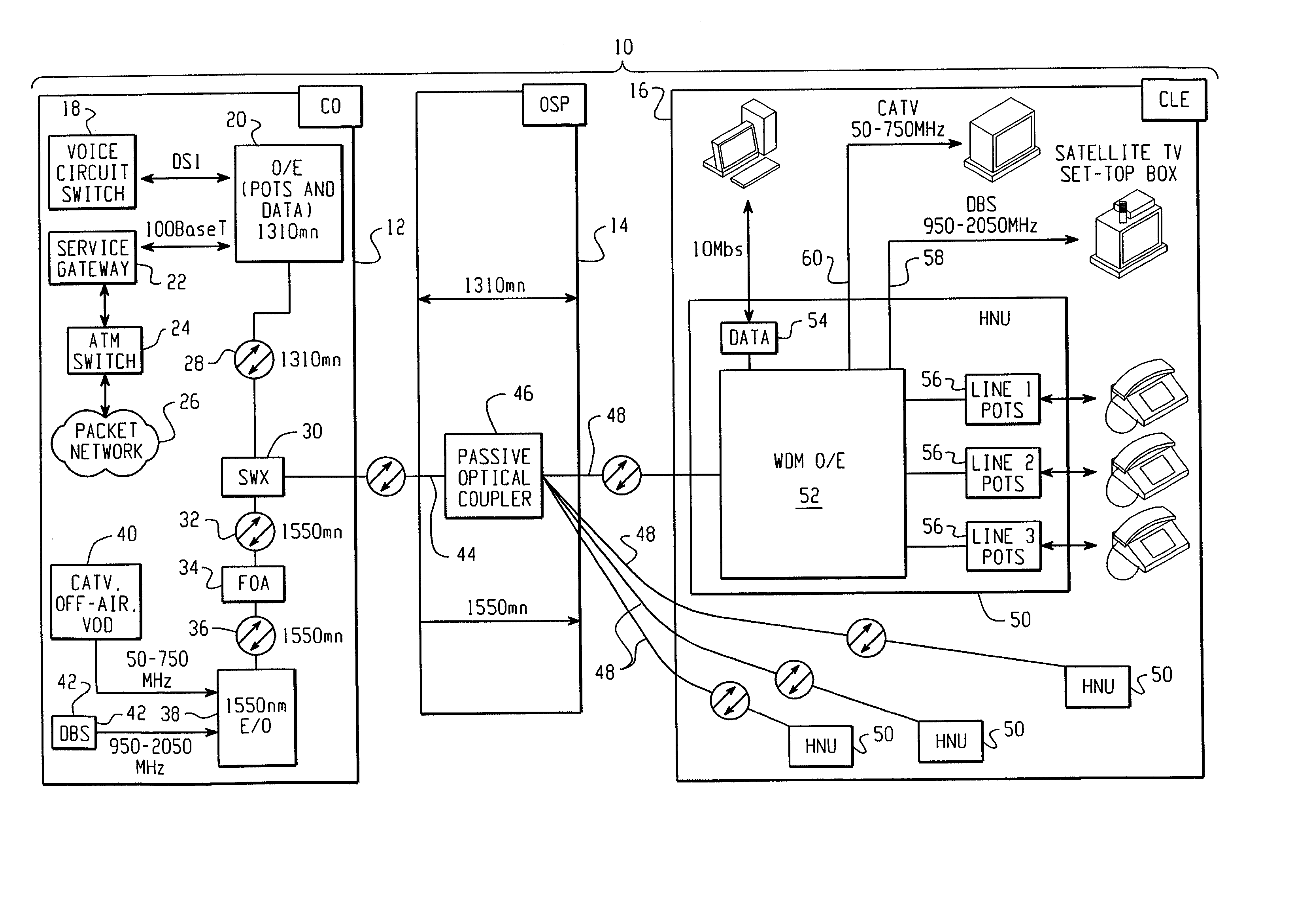
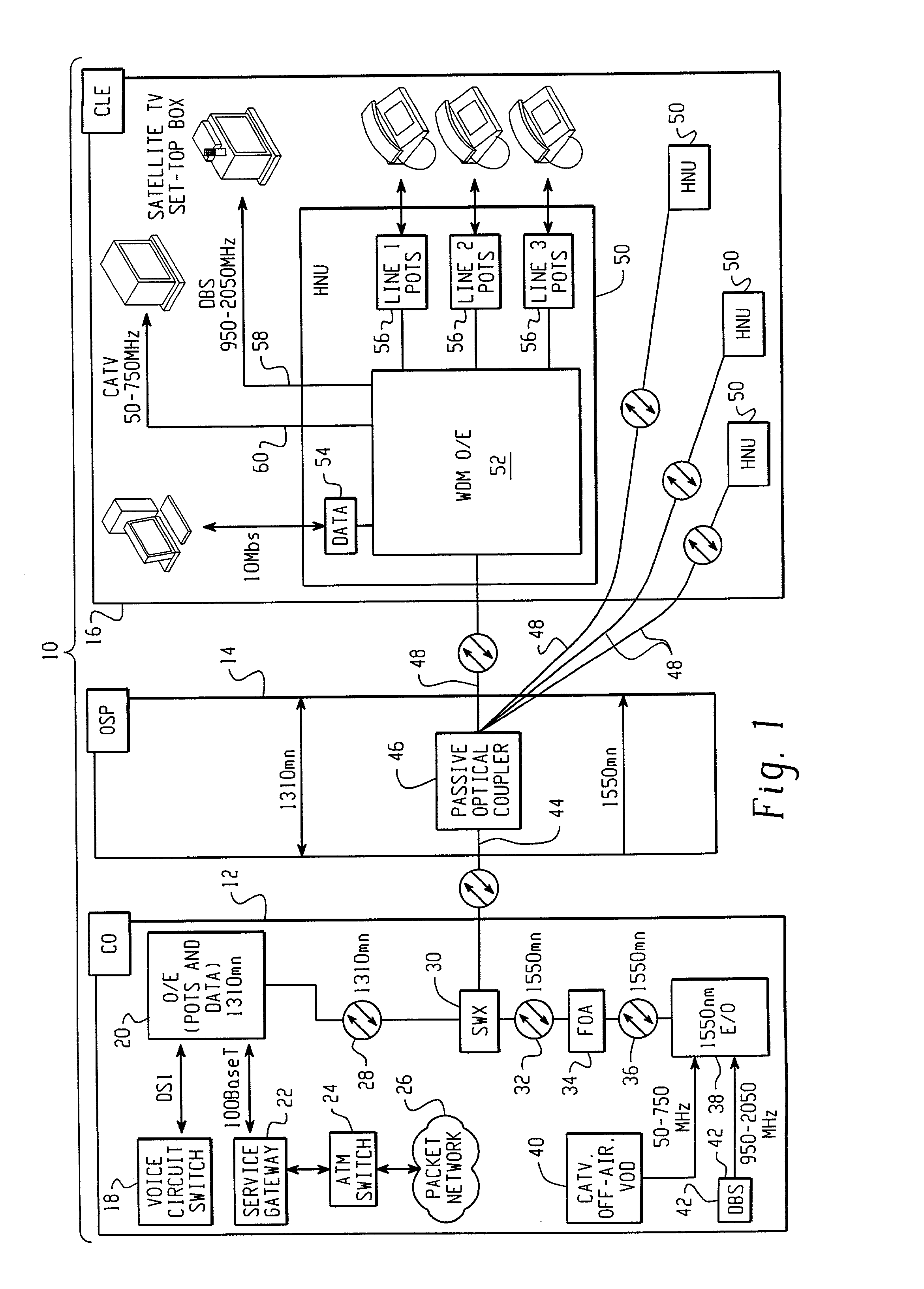
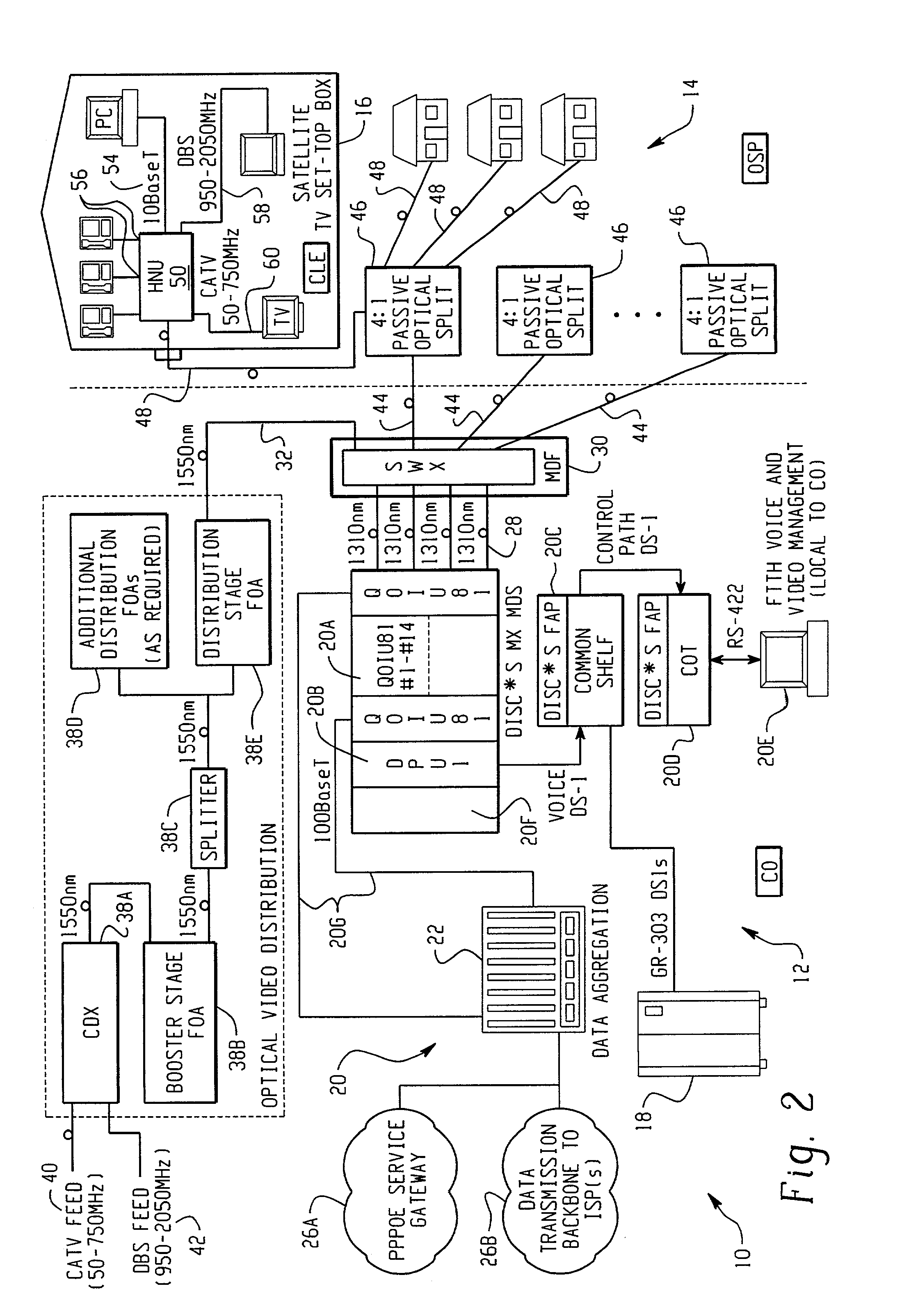
Fiber to the home (FTTH) multimedia access system with reflection PON
InactiveUS20020063924A1Inexpensive, easy-to-serviceEasy to scaleBroadband local area networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingData signal
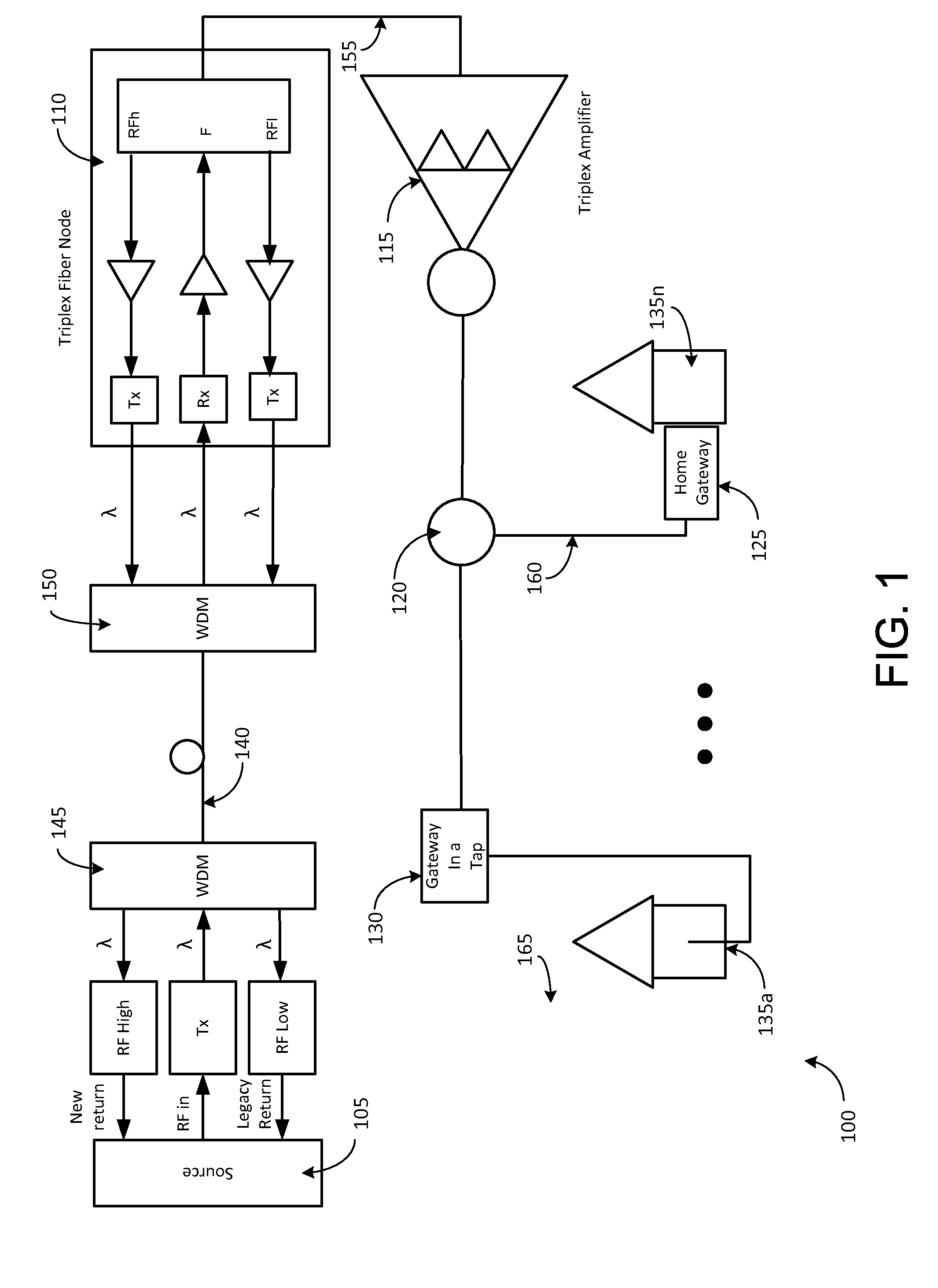
A Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) multi-media access system and method are provided in which voice, video and data signals are transported over a passive optical network (PON) between a central office location and a plurality of subscriber home network units (HNUs). Optical video distribution circuitry and telephony / data distribution circuitry at the central office location are included in the system and operate to send and receive CATV video, PBS video television, telephony and Packet data signals to and from the HNUs via the PON. Optical multiplexing / demultiplexing circuitry operating at the central office combines the video signals, which are operating at one optical wavelength, with the telephony / data signals, which are operating at a second, distinct optical wavelength. These combined optical signals are then transported over the PON to the HNUs. The PON includes a plurality of distribution fibers coupled to a plurality of passive optical splitters, which are each coupled to a plurality of drop fibers that connect to the HNUs. The HNUs receive the combined optical signals, demultiplex and convert the optical signals into corresponding electrical signals, which are in turn coupled through the HNU to the video, data and telephony networks within the home. The HNUs also receive upstream electrical signals from devices within the home, multiplex and convert these electrical signals into upstream optical signals, and transmit these upstream optical signals to the central office.
Owner:ADVANCED FIBER ACCESS CORP
Latency Reduction In A Low Power Mode
InactiveUS20110172000A1Lower latencyFacilitate communicationEnergy efficient ICTBroadband local area networksPower modeCommunications system
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
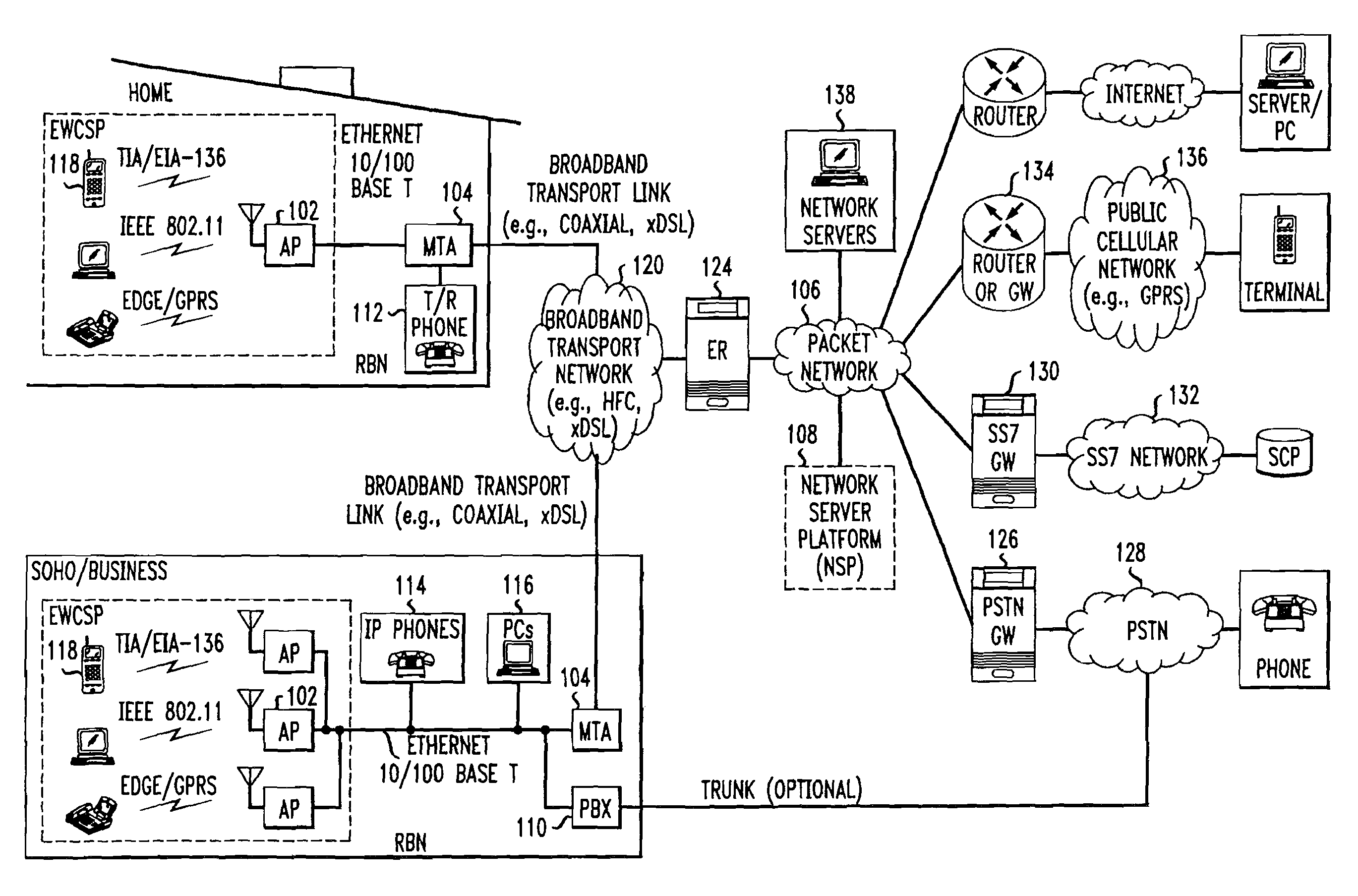
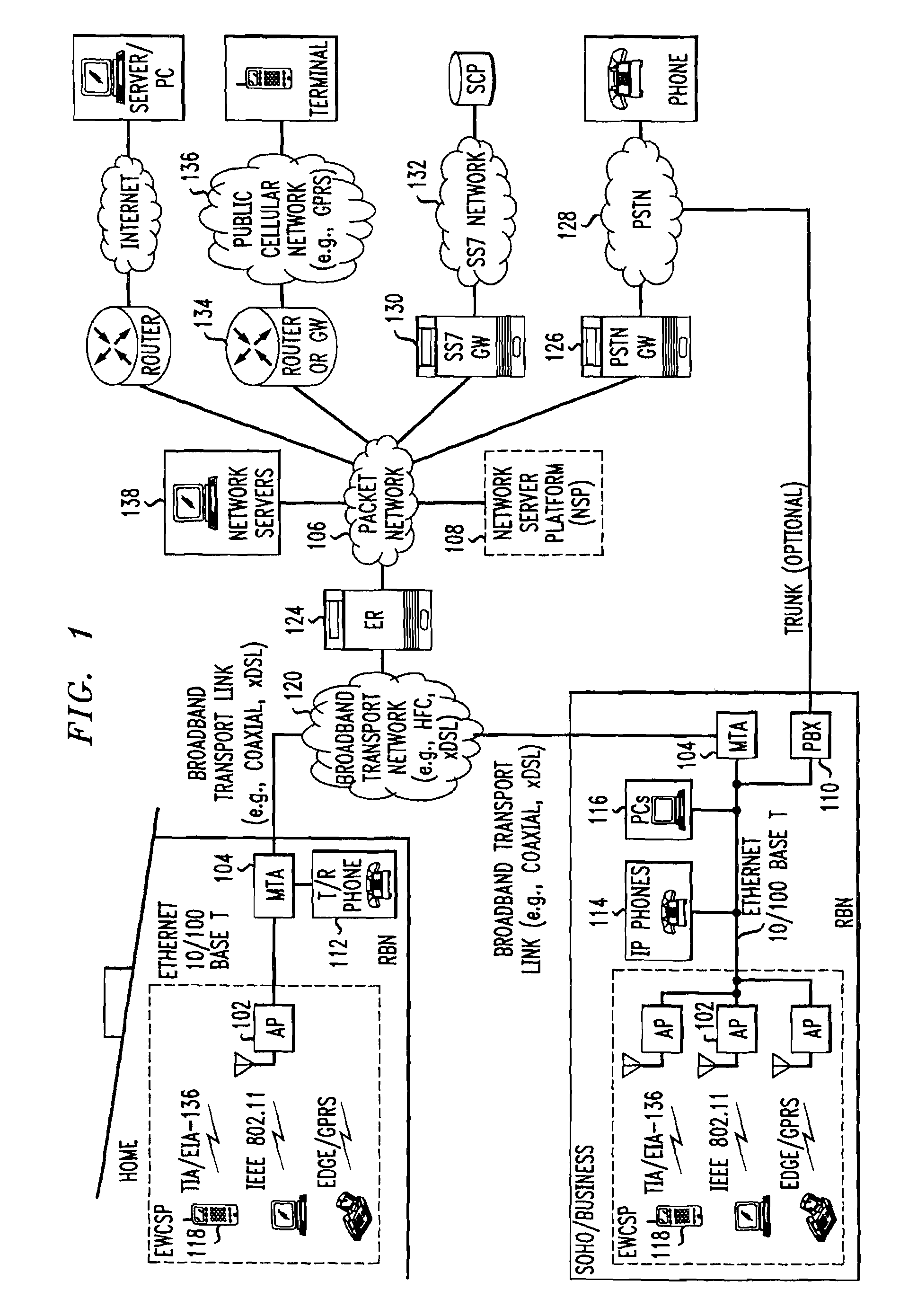
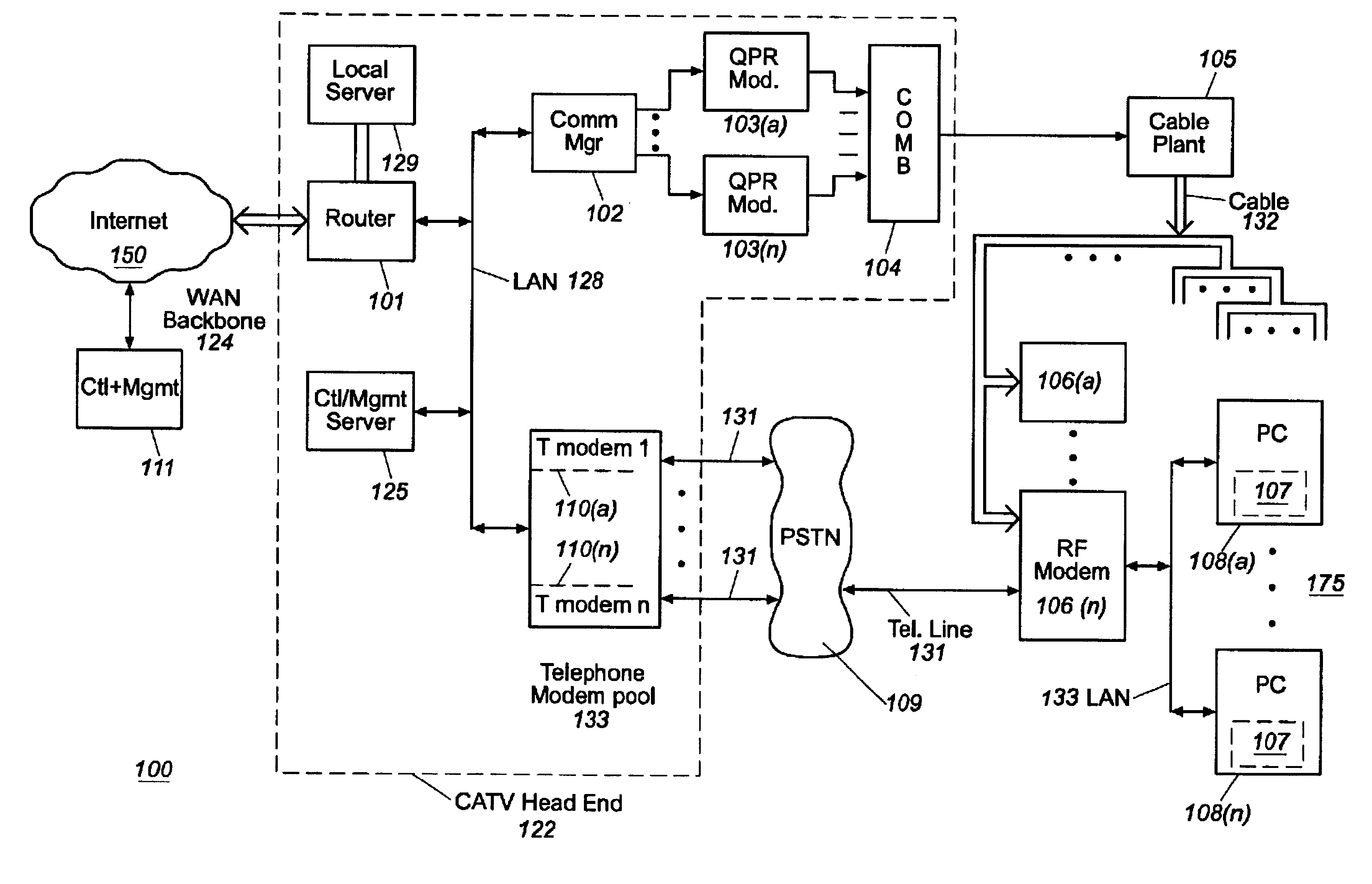
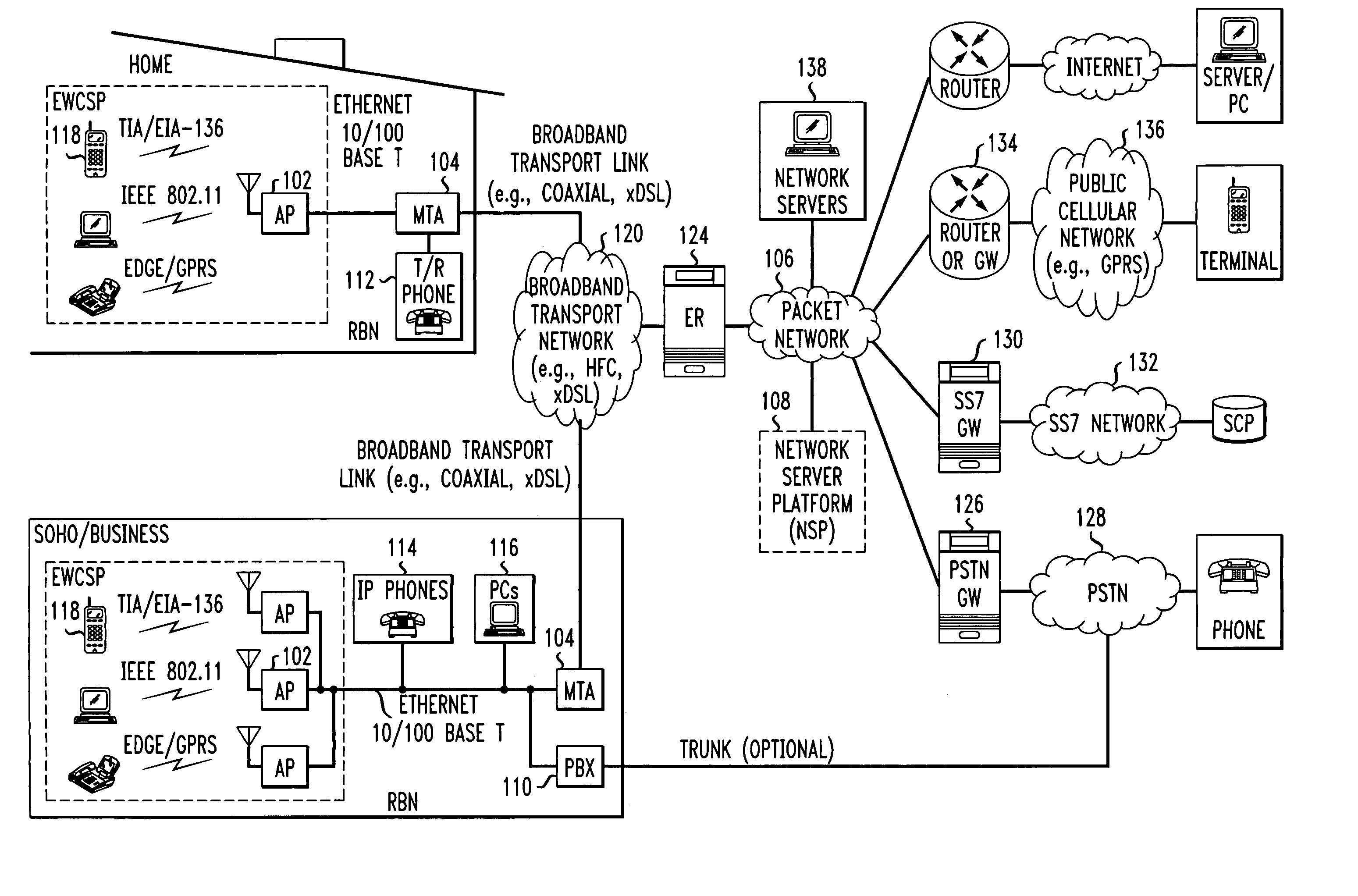
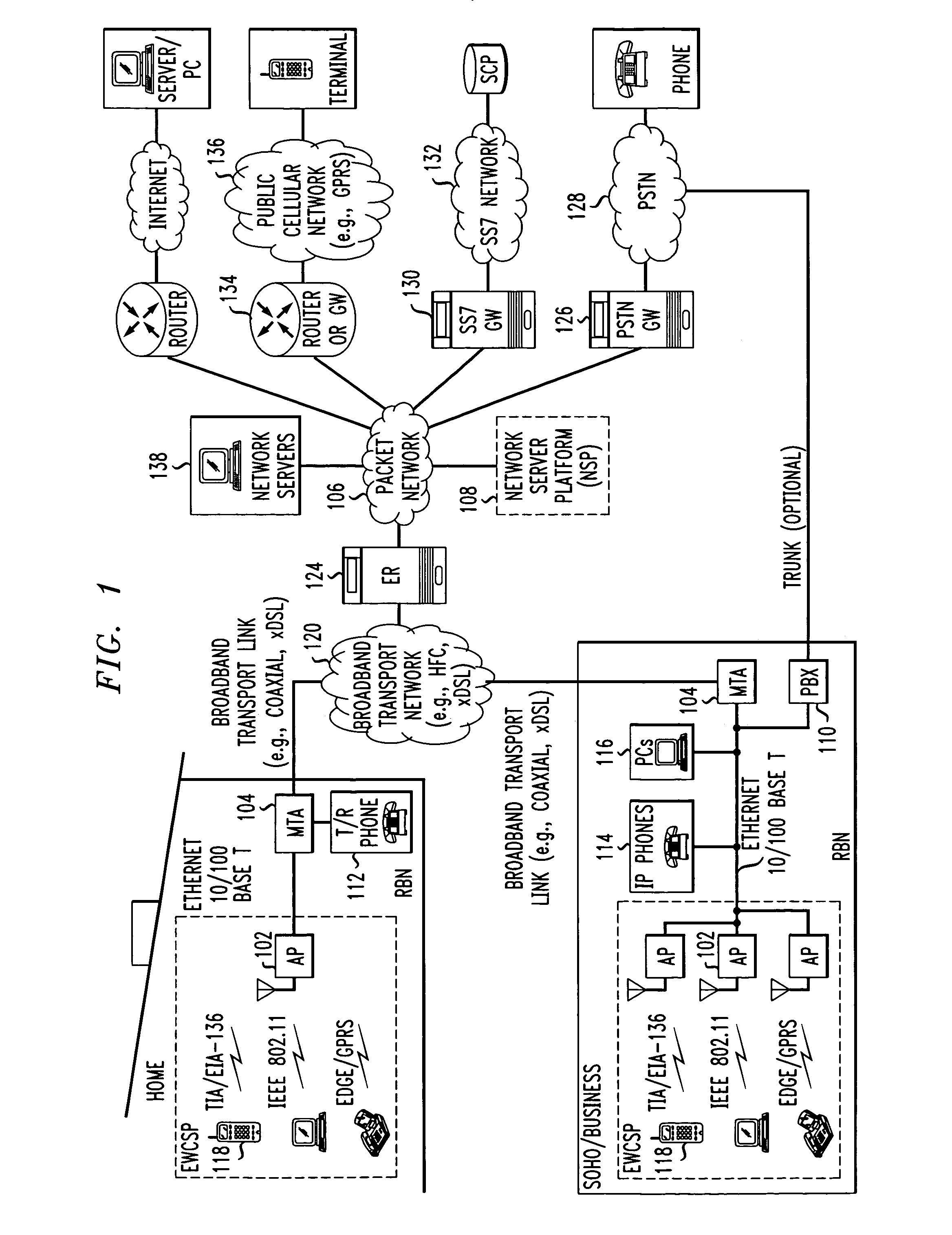
Computer readable medium with embedded instructions for providing communication services between a broadband network and an enterprise wireless communication platform within a residential or business environment
InactiveUS8155155B1Easy maintenanceCost-effectivelyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsModem deviceBroadband transmission
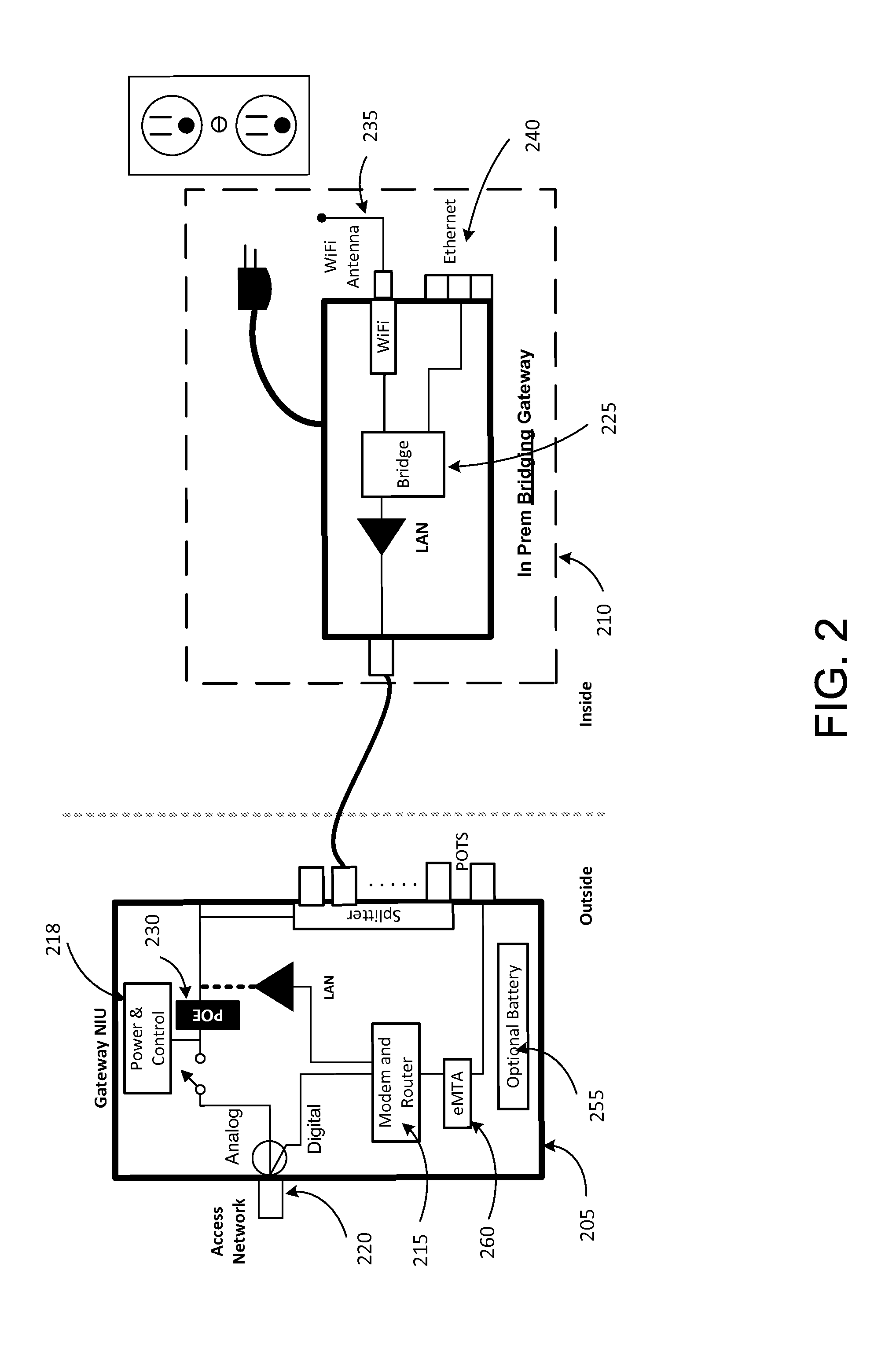
The present invention sets forth computer-readable non-transitory medium having computer-executable instructions for providing network-centric service distribution method that integrates a wireless access system / service with conventional telecommunications services in the residence, SOHO, business or public environment through the use of a local broadband network, such as a Residential-Business Broadband Network (RBN). The RBN communicates with the service provider's broadband transport network and broadband packet network to facilitate end-to-end packet telecommunication services. Signals from a plurality of wireless devices are accepted and forwarded to an IEEE 802.11b interface for a wireless modem and / or to an Ethernet interface for a Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP) / Ethernet Processor, where the forwarded signals comprise intranet telephony and data.
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
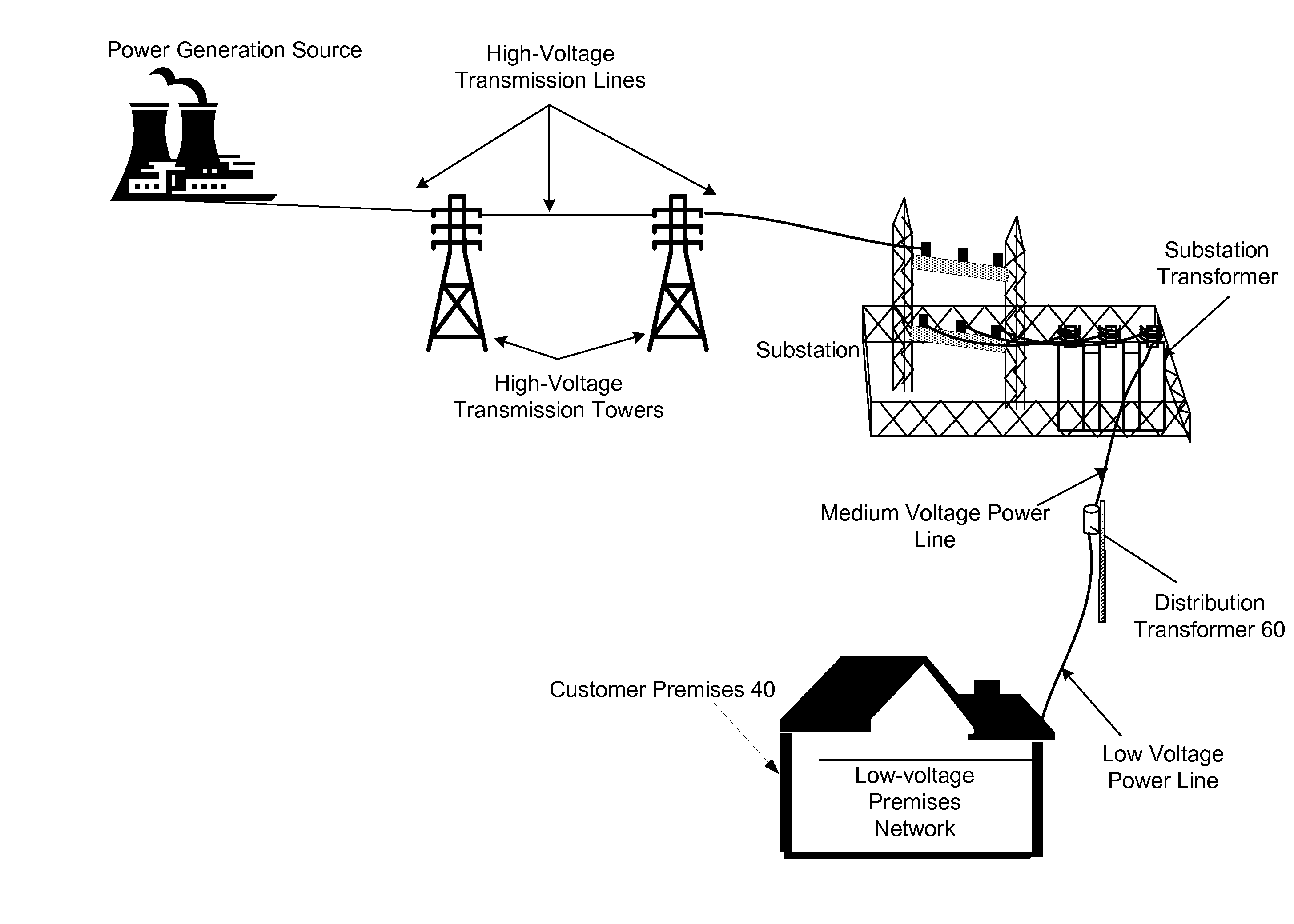
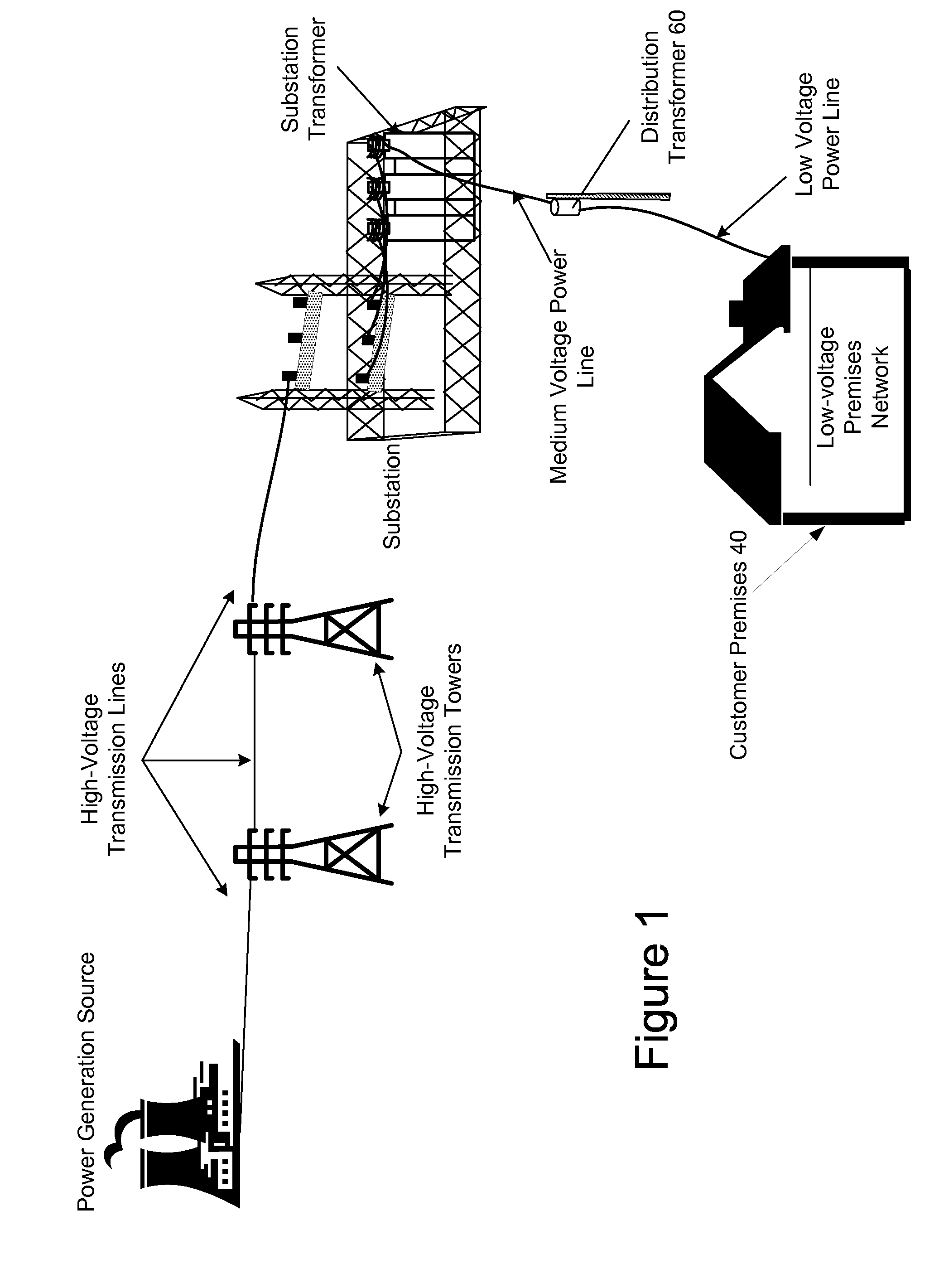
Power Line Communications System and Method
InactiveUS20070268124A1Electric signal transmission systemsBroadband local area networksData packUser device
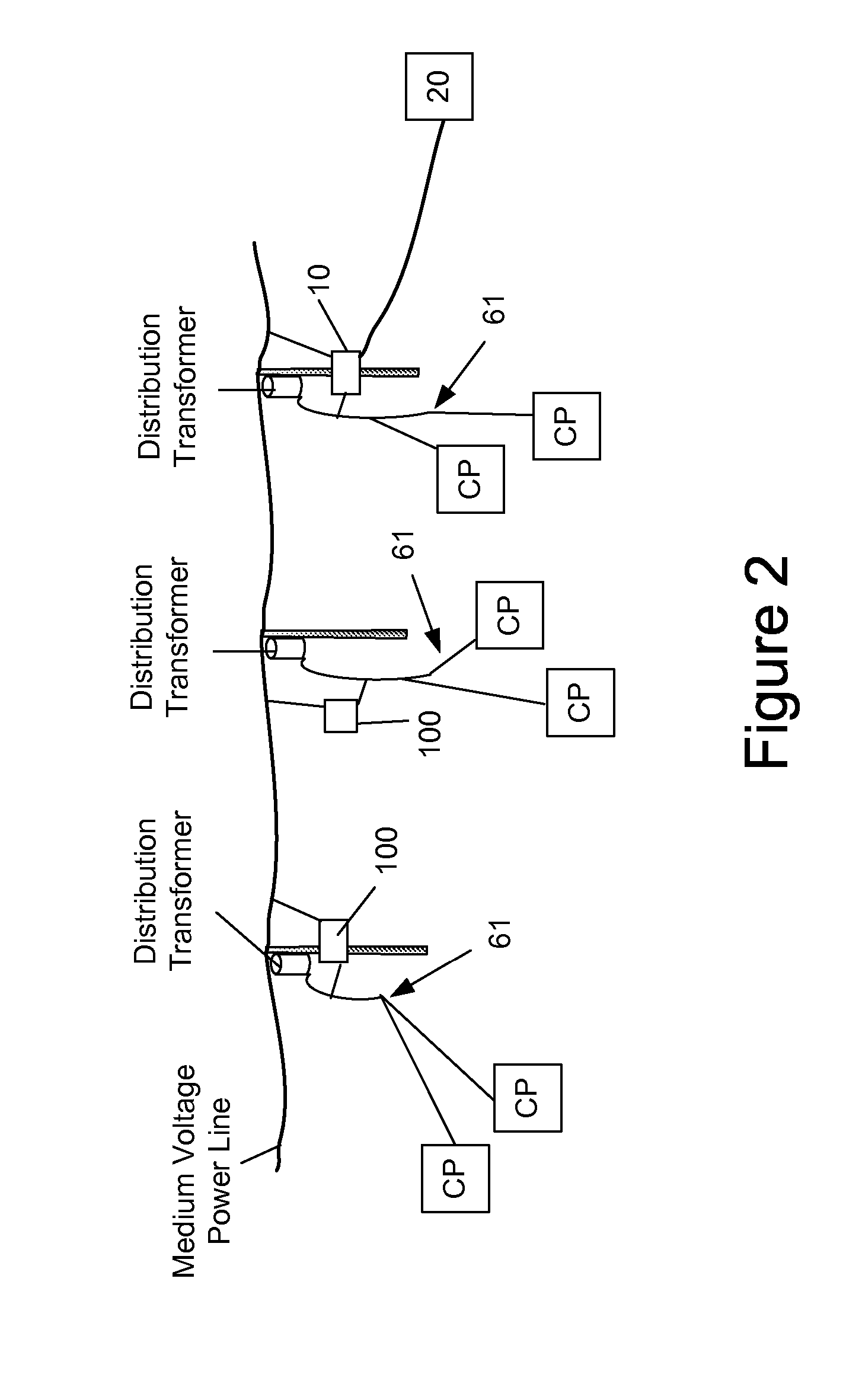
A power line communications system (PLCS) that provides communications to one or more user devices by repeating data packets on the power distribution network is provided. The PLCS may employ any or all of the MV power line conductors and / or the neutral conductor and be dynamically and remotely transitioned to one of a plurality of potential configurations.
Owner:CURRENT TECH
Systems and methods for providing broadband communication
InactiveUS20140355989A1To offer comfortIncreased return signal capabilityBroadband local area networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringLight signal
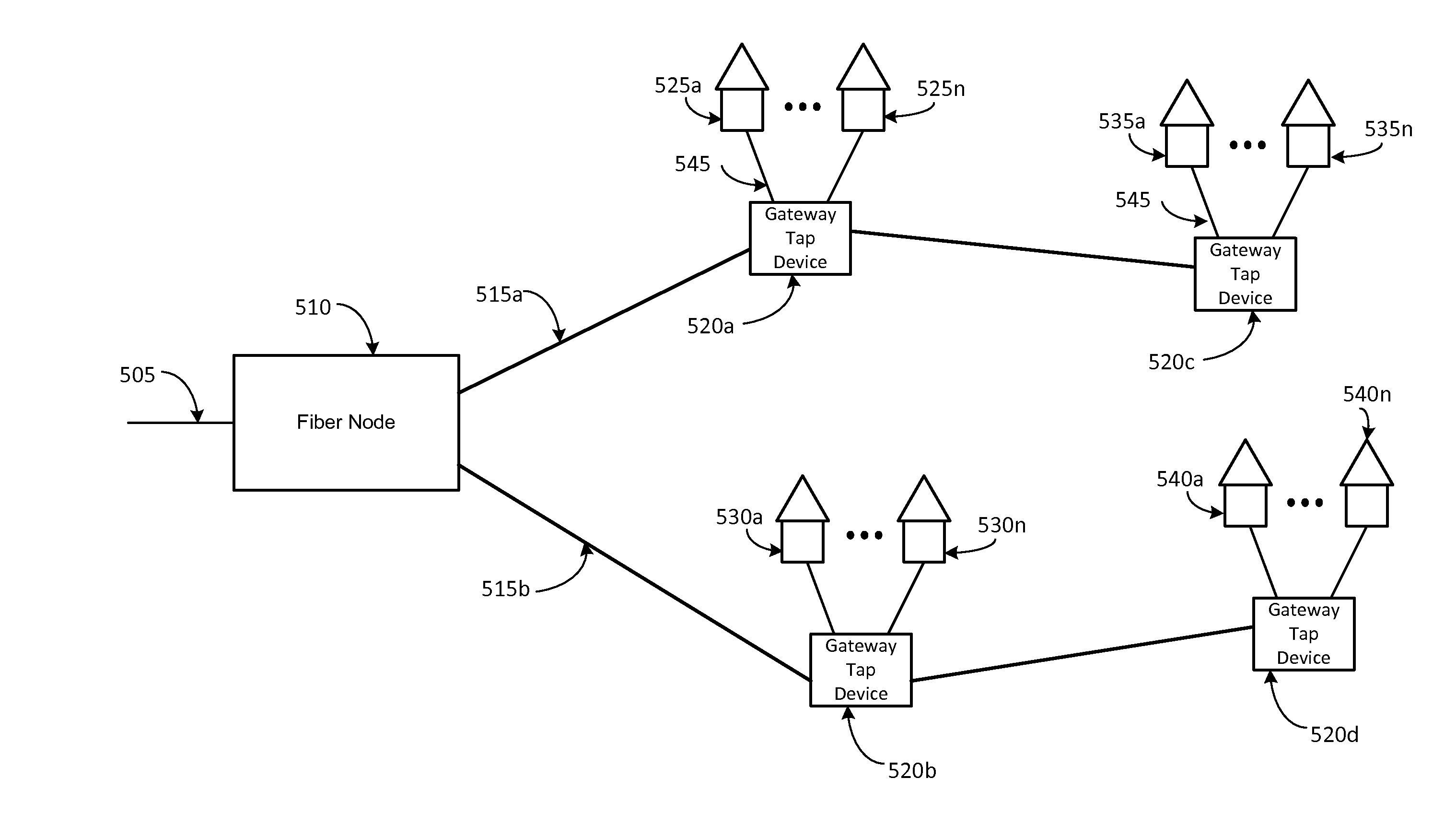
Systems and methods for providing broadband communication are provided. An optical fiber node may be coupled to a source component. The optical fiber node may receive, from the source component, a downstream light signal via at least one input optical fiber, and transmit the downstream light signal to a plurality of output optical fibers. A tap device may be coupled to the optical fiber node via at least on optical fiber. The tap device may receive the downstream light signal via the at least one output optical fiber, convert the downstream light signal into a radio frequency downstream signal, and transmit the radio frequency downstream signal to a plurality of cable lines. The plurality of cable lines may be coupled to one or more customer premises.
Owner:COX COMMUNICATIONS
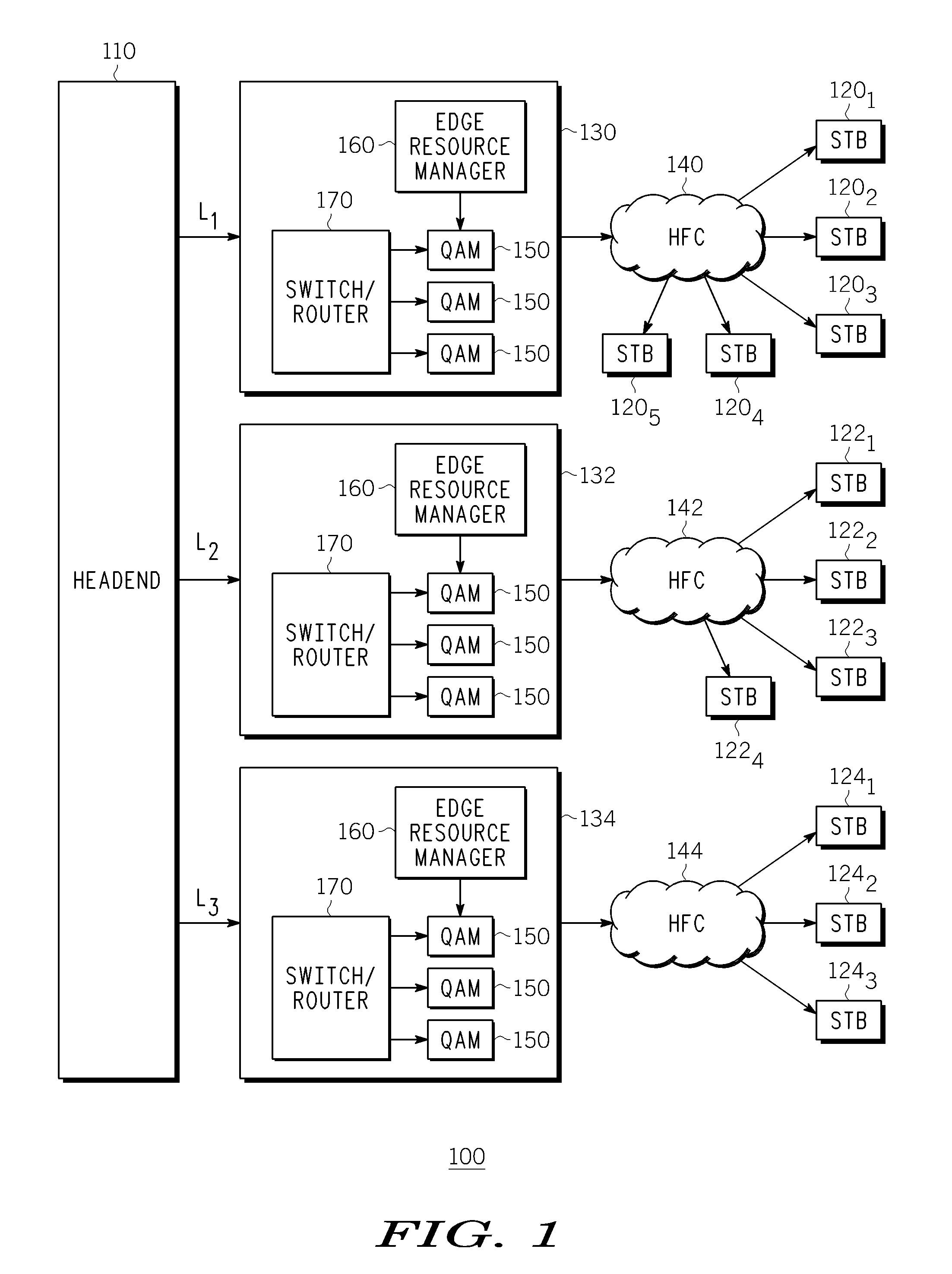
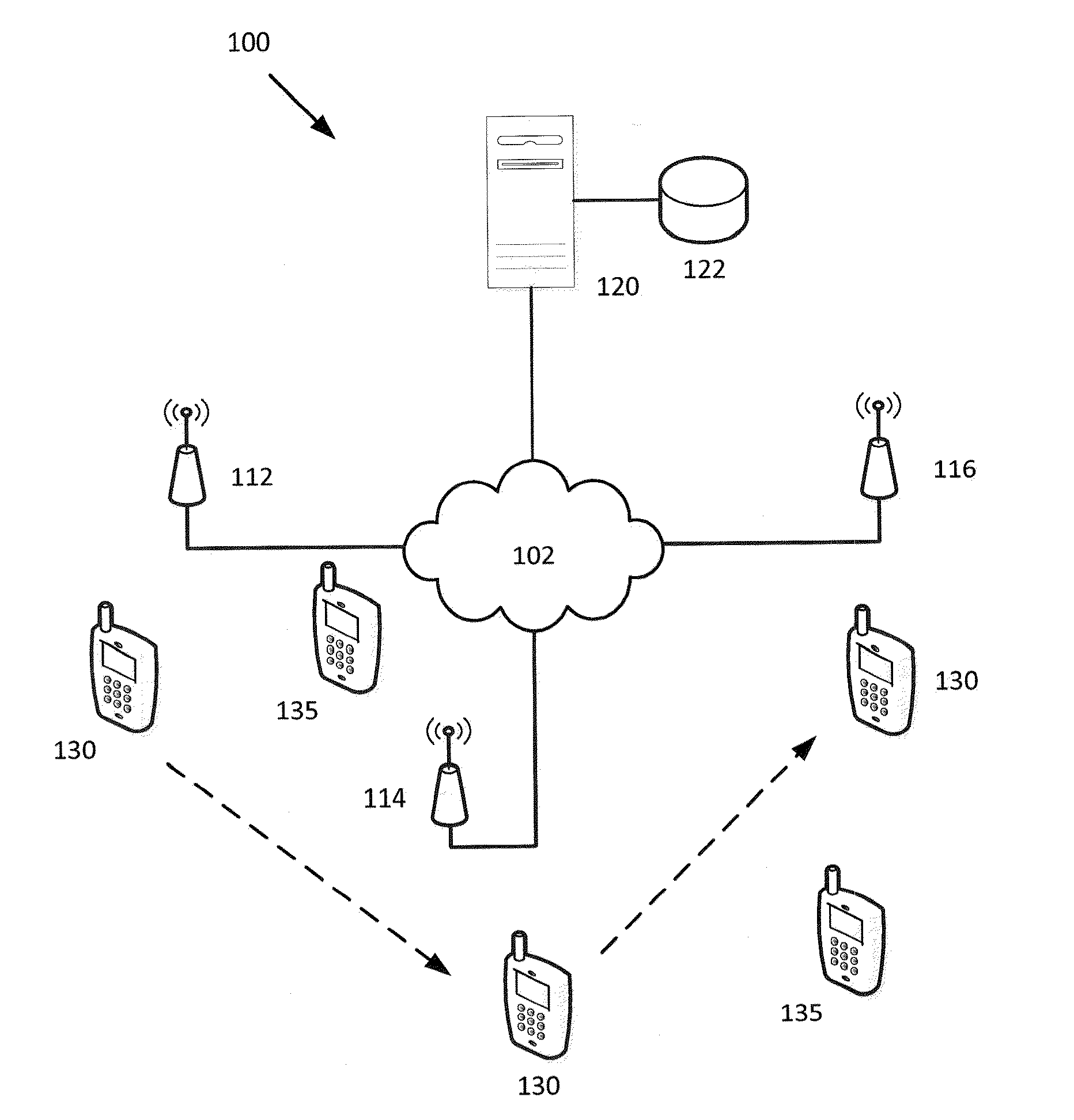
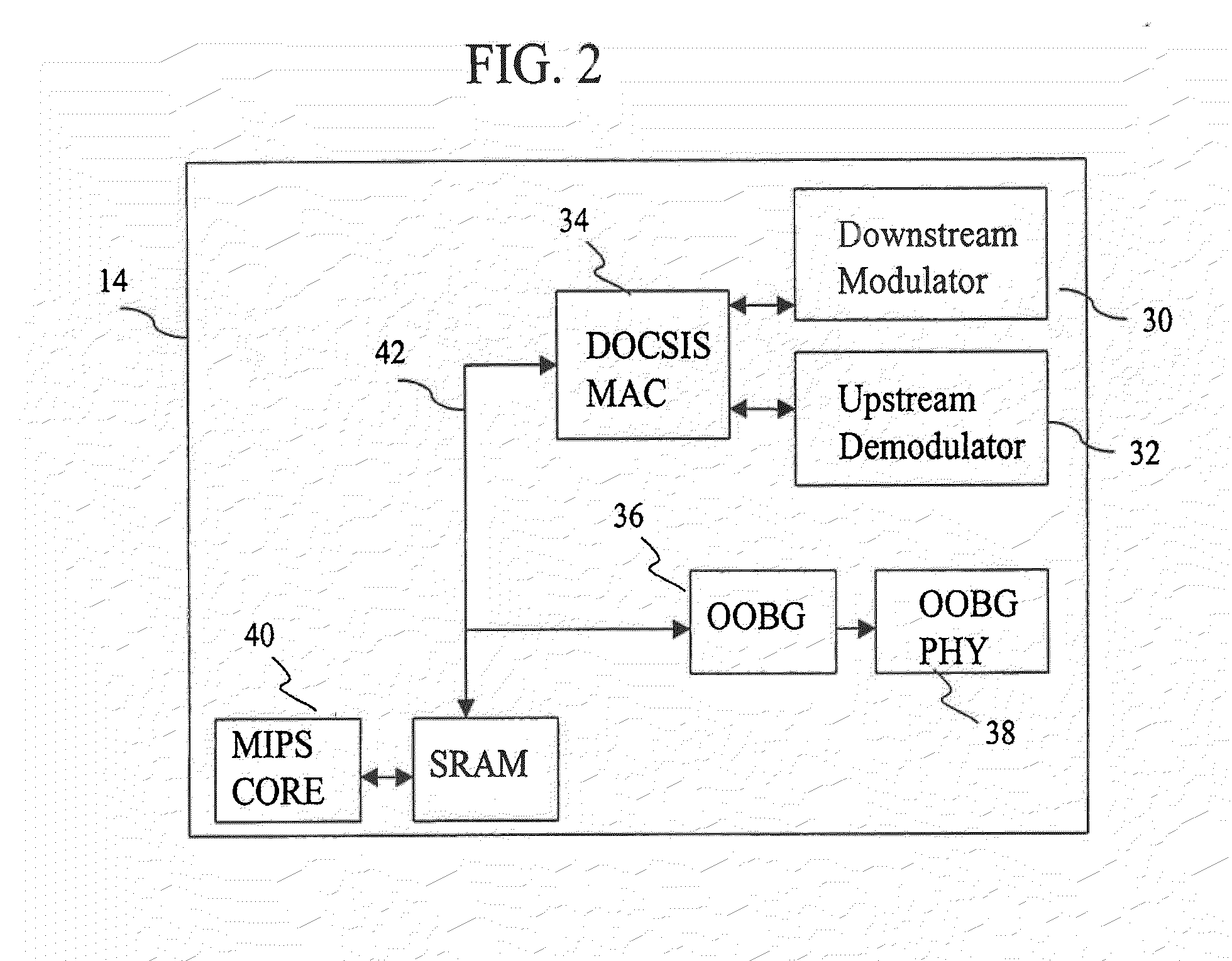
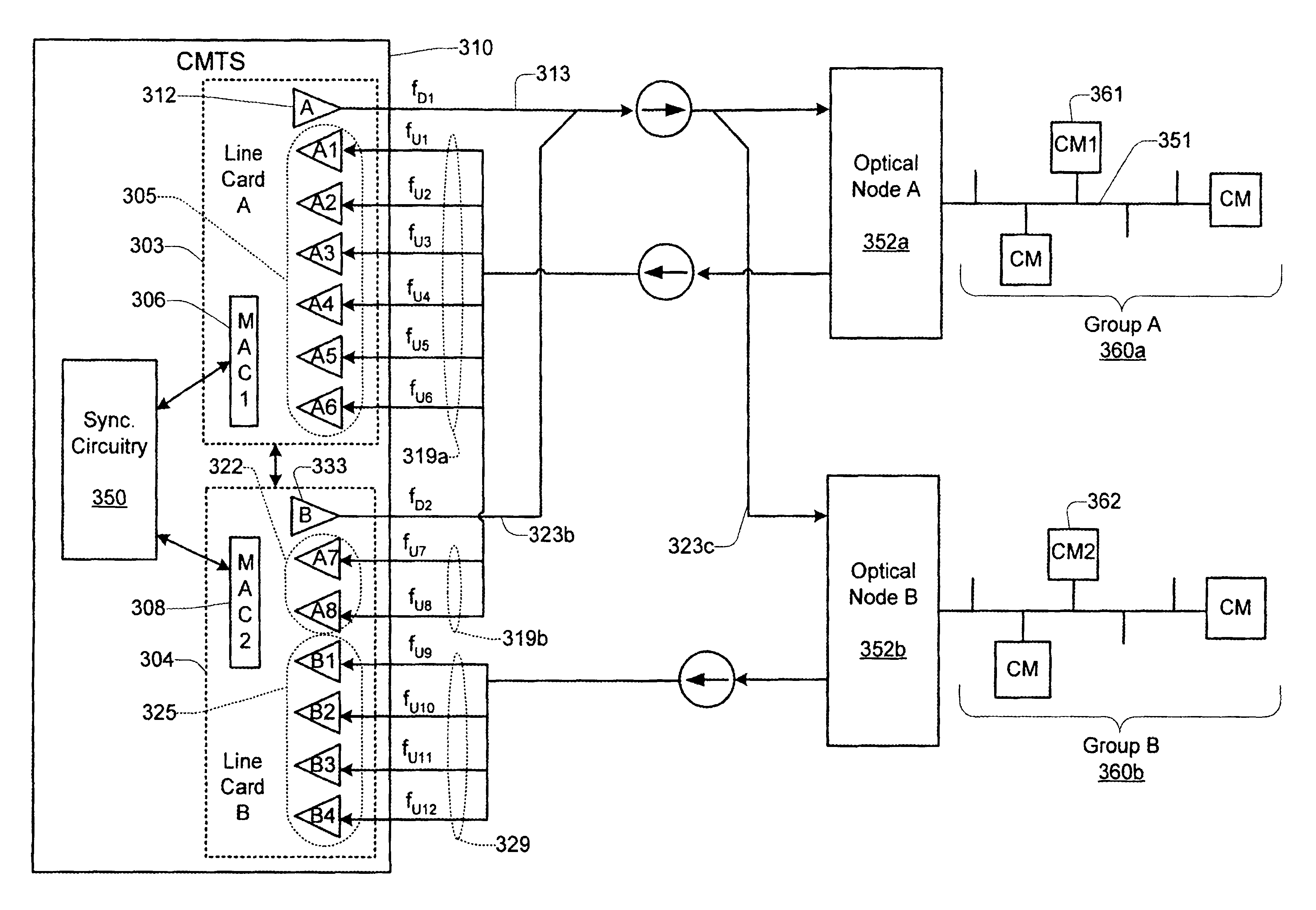
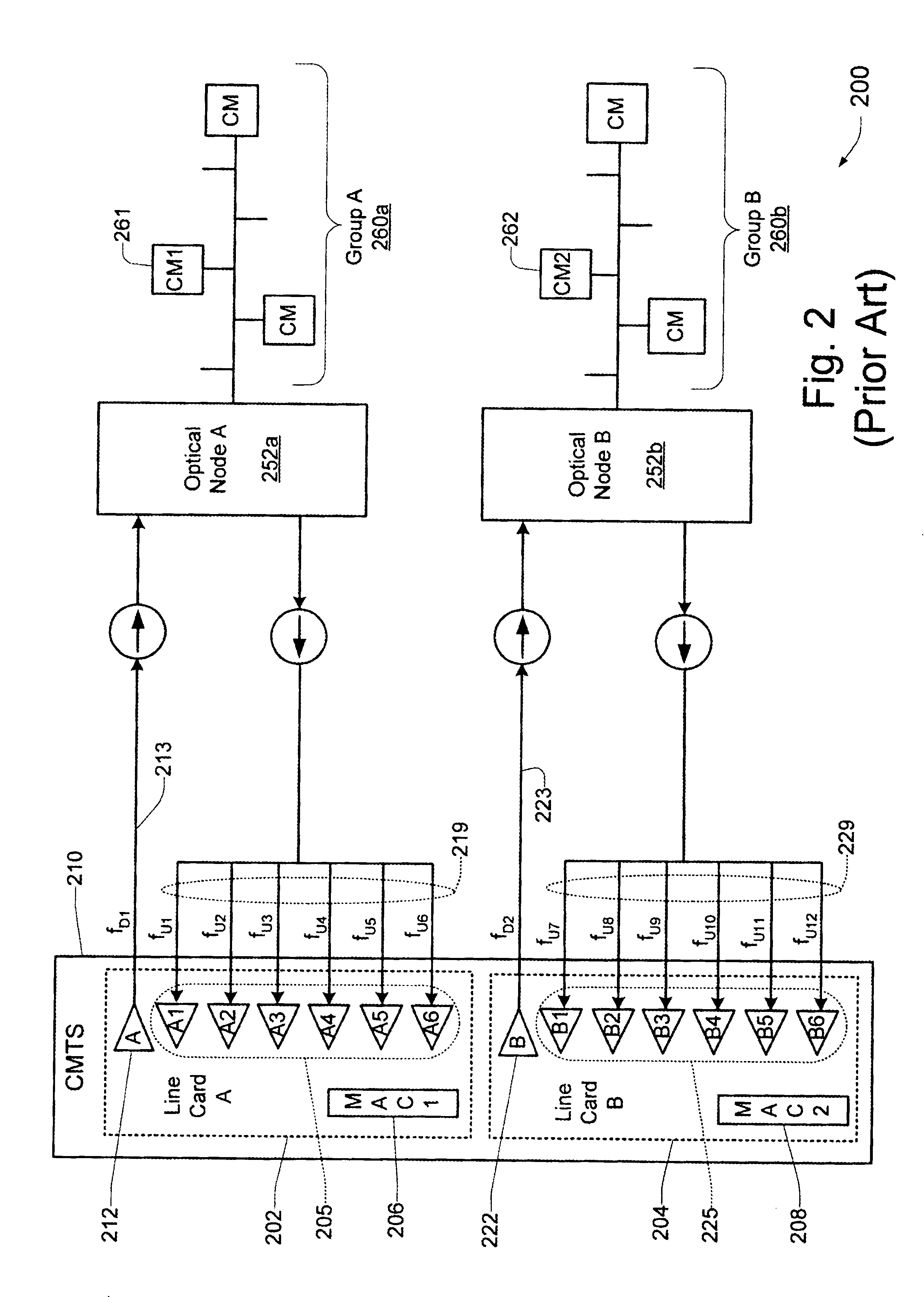
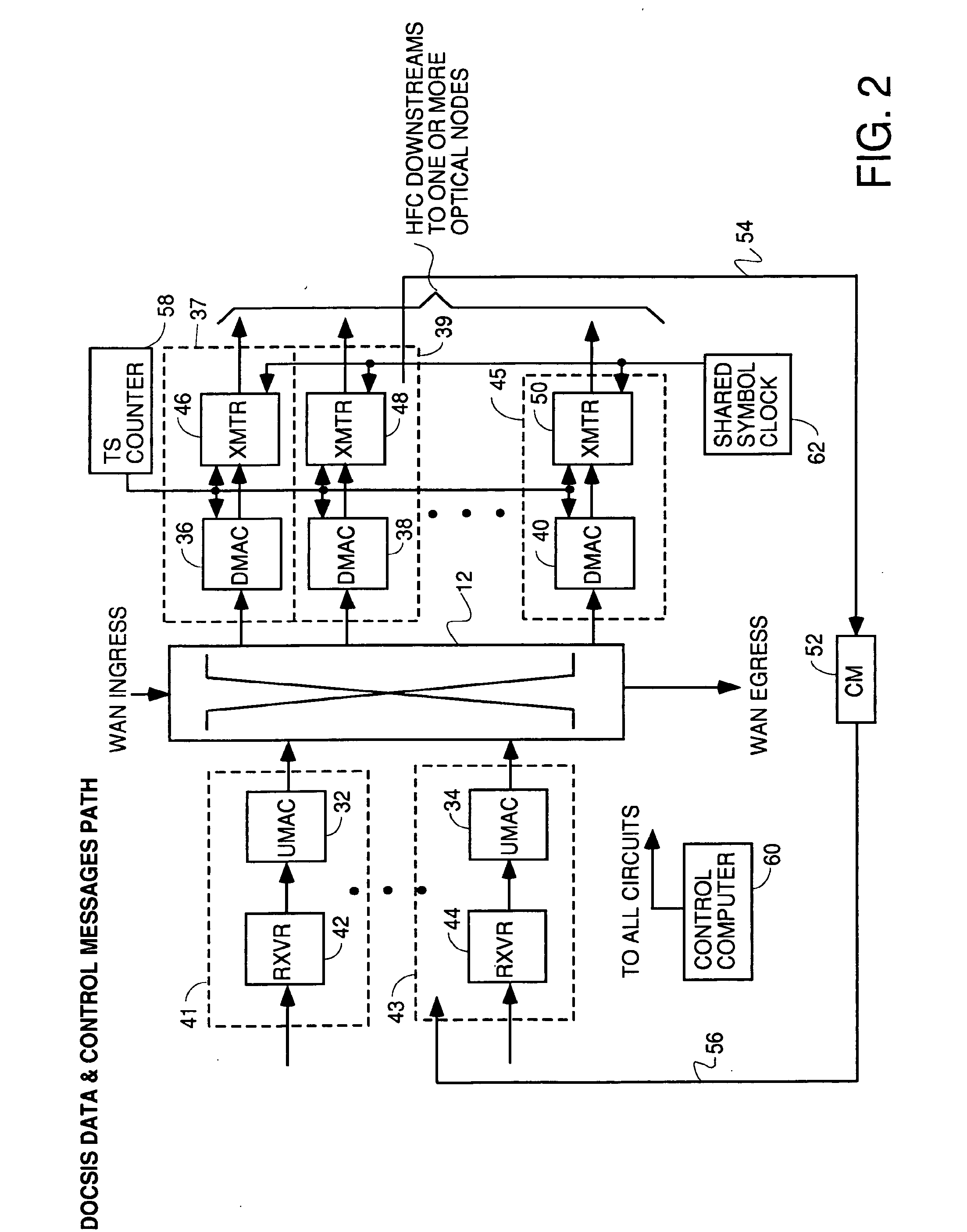
Technique for synchronizing multiple access controllers at the head end of an access network
InactiveUS7065779B1Broadband local area networksAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsAccess networkTimestamp
A technique is described which may be used to synchronize a plurality of different access controllers which control a plurality of distinct ports at the Head End of an access network. In the context of a cable network, the technique of the present invention may be used to synchronize desired upstream and / or downstream channels across different line cards within a Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS). The technique involves utilizing a master time reference device which maintains and updates a current time reference, and periodically distributes synchronization signals to desired line cards in the system in order to synchronize these line cards. In a specific embodiment, the synchronization signals include current timestamp data generated from the master time reference device and distributed to all (or selected) line cards in the system. A slave time reference device on each of the line cards receives the periodic synchronization updates and uses the synchronization data to remain synchronized with the master time reference device. There are also provisions in this protocol to allow for hot insertion and removal of line cards, software reset or loading of the master and / or slave time reference devices, and redundant master time reference devices, including master time reference device fault detection and automatic fail over.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Usage statistics collection for a cable data delivery system
InactiveUS6308328B1Broadband local area networksBroadcast transmission systemsData connectionNetwork management
Apparatus for recording and collecting usage and other statistical data from components of a cable data network comprises a network manager for maintaining and collecting the statistics. Internet protocol addresses are associated with components of the network. The component maintains a software agent that manages a statistics database. Responsive to a manager request generated at a service provider defined time interval, the component software agent provides the usage statistics to the network manager in real-time during an Internet session with a host. When the host to Internet or other data connection is torn down due to failure, disconnect or inactivity time-out, remaining usage statistics data is collected and the session duration updated with the time of tear down. Usage statistics collected include the amount of data transferred to / from a host, the amount of data that is discarded due to insufficient resource capacity and amount of data that cannot be corrected despite forward error correction used in a downstream high capacity channel to the host. Data traps may be defined and downloaded to components of the network for implementation. As a result, billing of users of the cable data network can be usage sensitive and determined based on actual data transferred (including credit given for errored data) and / or time sensitive based on session duration.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Broadband network with enterprise wireless communication method for residential and business environment
InactiveUS7010002B2Easy to optimizeCost-effective deploymentMultiplex system selection arrangementsTelephone data network interconnectionsModem deviceBroadband transmission
The present invention sets forth a network-centric service distribution architecture and method that integrates a wireless access system / service in the residence, SOHO, business or public environment through the use of a local broadband network, such as a Residential-Business Broadband Network (RBN), to the service provider's broadband transport network and to a service provider's broadband packet network that facilitates end-to-end packet telecommunication services. Access functions for connecting said service provider's broadband packet network to the RBN via said service provider's broadband transport network are provided. Call and service termination functions to a plurality of local RBN devices are also provided. Signals from a plurality of wireless devices are accepted and forwarded to an IEEE 802.11b interface for a wireless modem and / or to an Ethernet interface for a Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP) / Ethernet Processor, where the forwarded signals comprise intranet telephony and data. Voice signals are also accepted from a plurality of tip / ring interfaces and forwarded to a broadband transport interface for back haul of data and voice packets. A service provider can deploy services in an integrated voice, data and multimedia environment cost-effectively based on one broadband packet network.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Systems and methods for the automatic registration of devices
InactiveUS20060010078A1Broadband local area networksPayment architectureDatabase serverComputer science
Systems and methods for providing registration at a remote site that may include, for example, a monitoring module that may communicate with a remote site. A registration protocol may be used by the monitoring module and the remote site in generating the messages communicated during the registration process. The monitoring module may gather and generate various identification information to be included in the registration protocol messages. The registration information provided by the monitoring module may be stored at the remote site in a database server having a database. A confirmation message may be communicated from the remote site to the monitoring module that may either acknowledge successful registration or report that an error occurred during the registration process.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
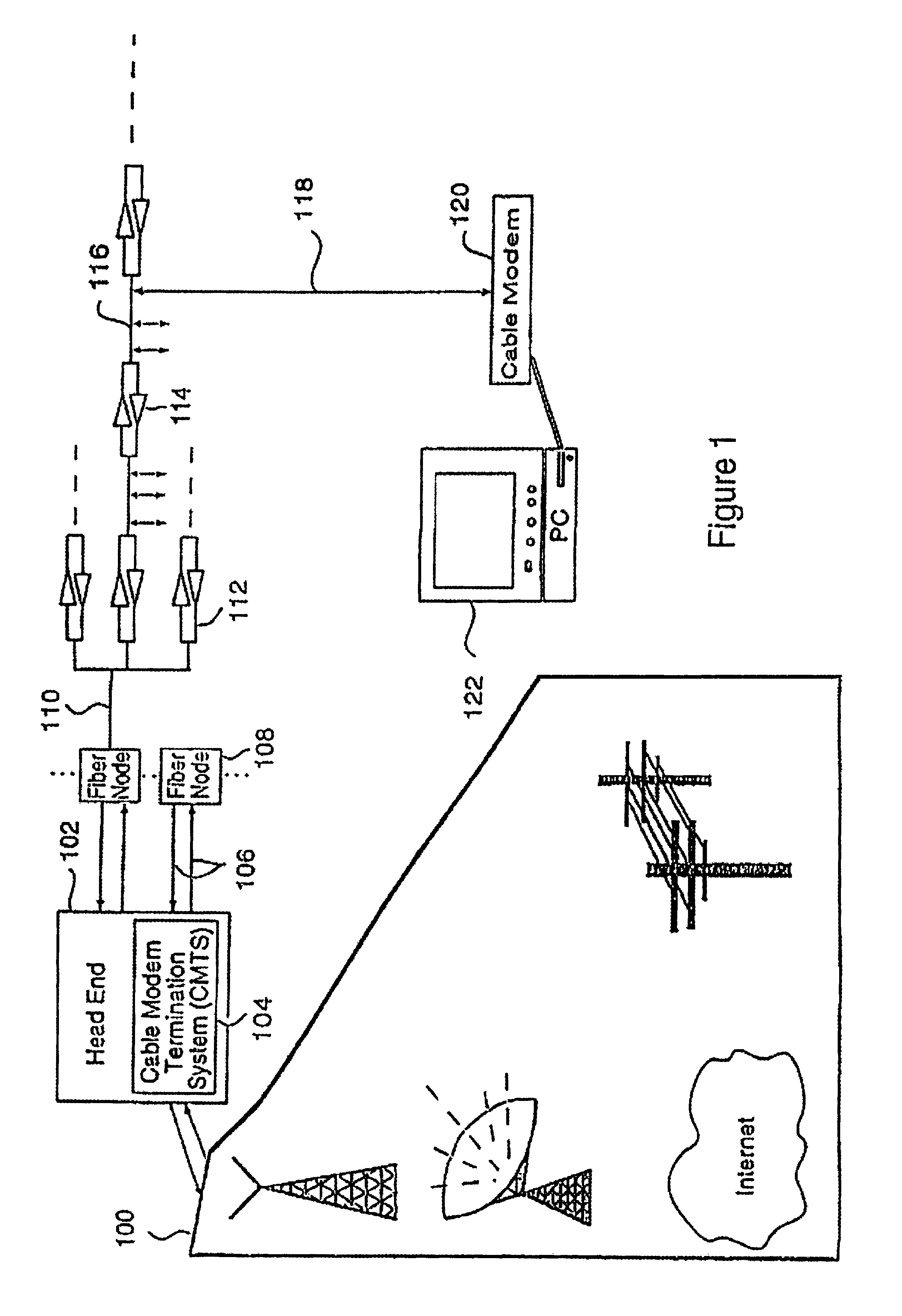
System and method for delivering high-performance online multimedia services
InactiveUS6370571B1Easy to scaleIncrease speedSpecial service provision for substationResource allocationFiberCoaxial cable
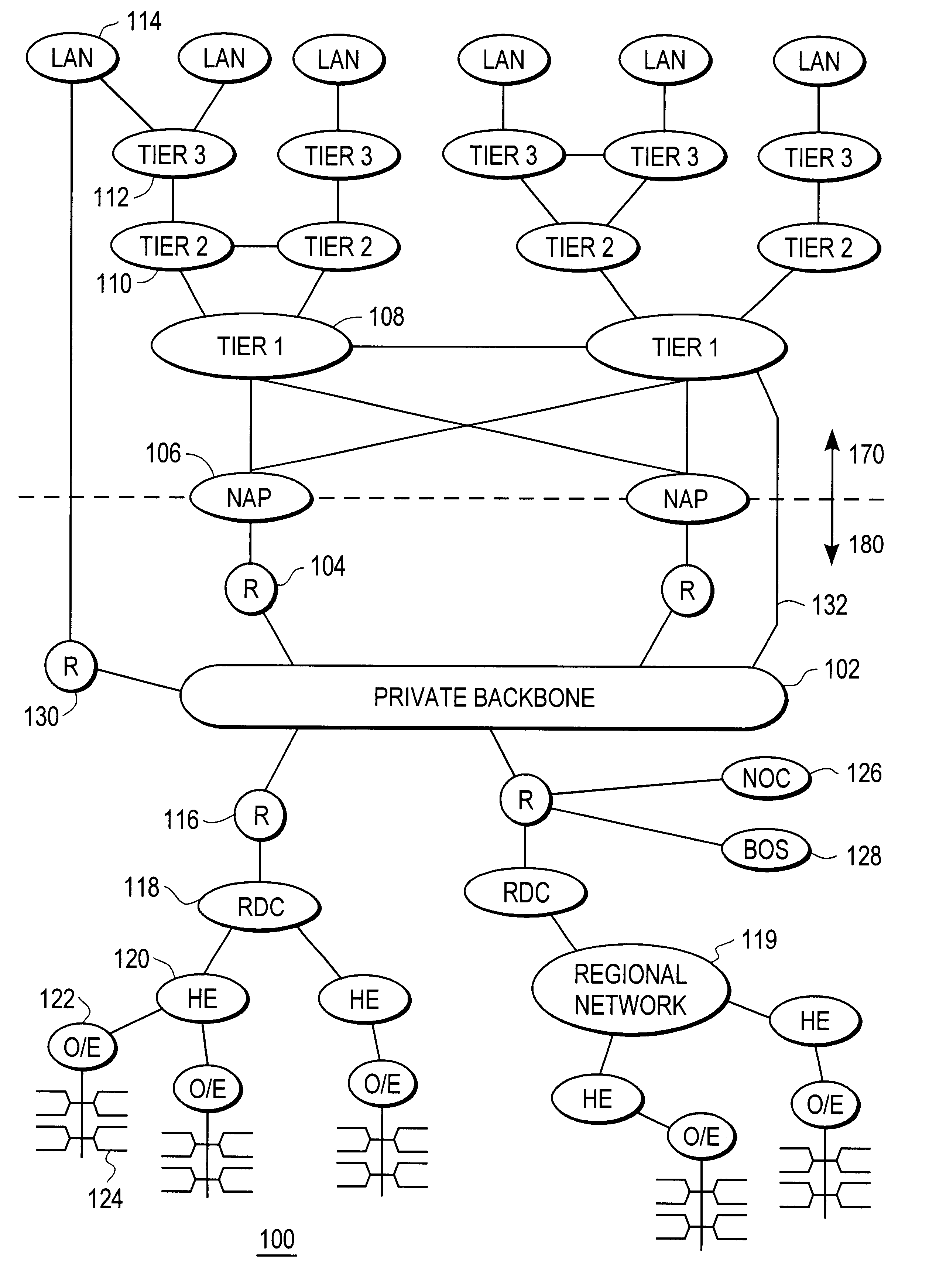
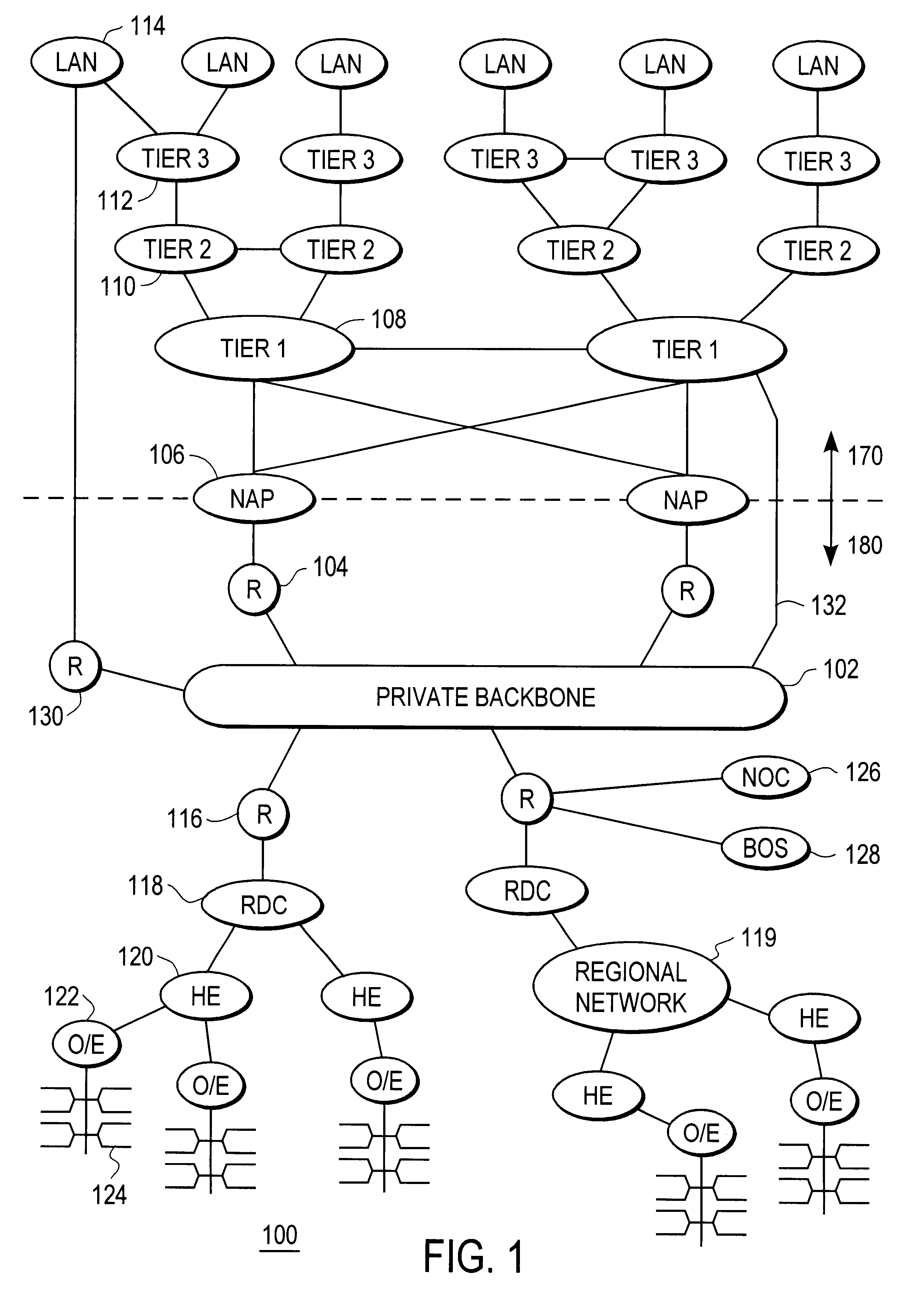
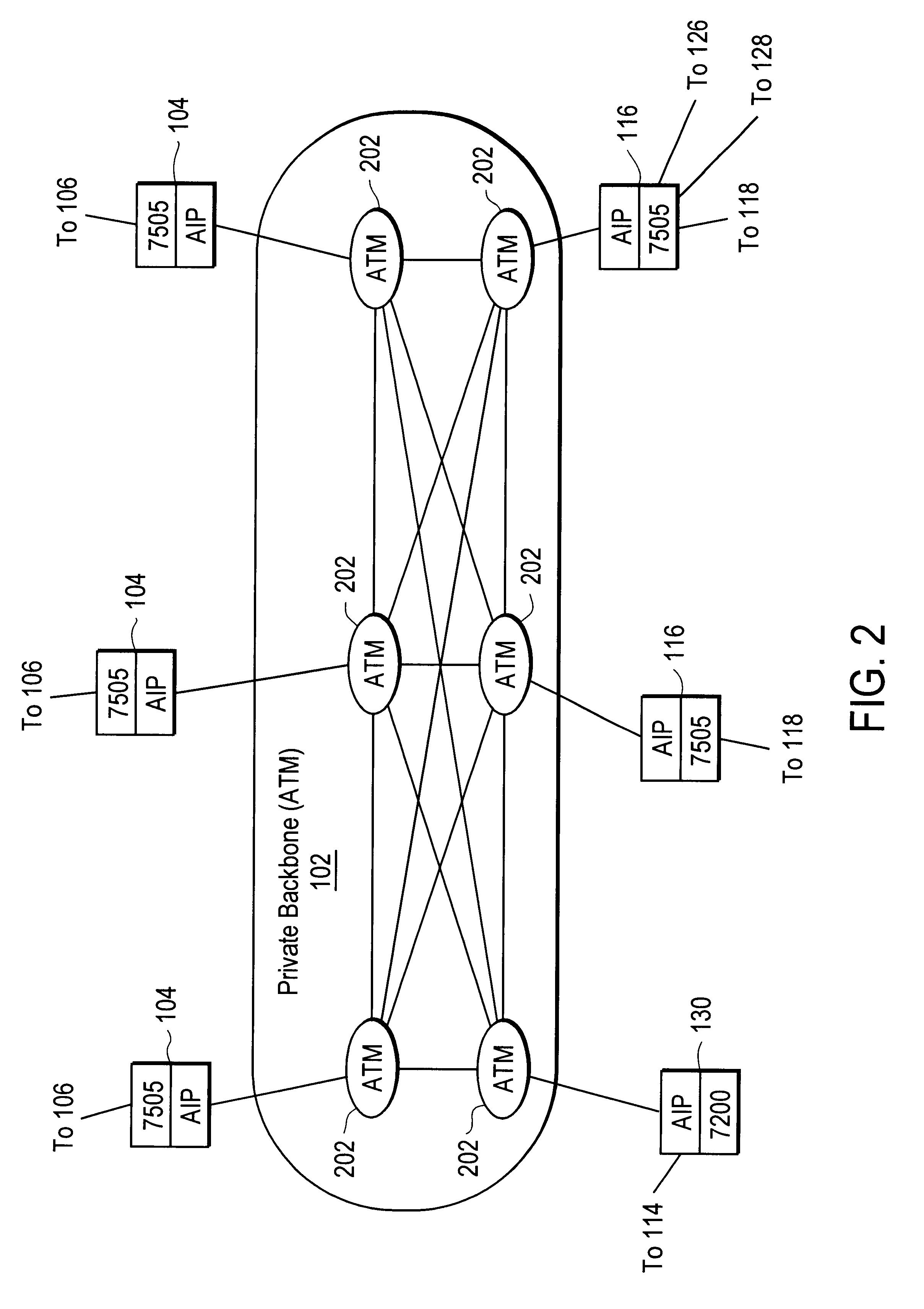
Disclosed is a scalable, hierarchical, distributed network architecture and processes for the delivery of high-performance, end-to-end online multimedia services, including Internet services such as World Wide Web access. The network architecture connects a high-speed private backbone to multiple network access points of the Internet, to a network operation center, to a back office system, and to multiple regional servers in regional data centers. Each of the regional servers connects to several caching servers in modified head-ends, which in turn connect via fiber optics to many neighborhood nodes. Finally, each node connects via coaxial cable to multiple end-user systems. The processes include those for replicating and caching frequently-accessed content, and multicasting content customized per region or locality.
Owner:AT HOME BONDHOLDERS LIQUIDATING TRUST +1
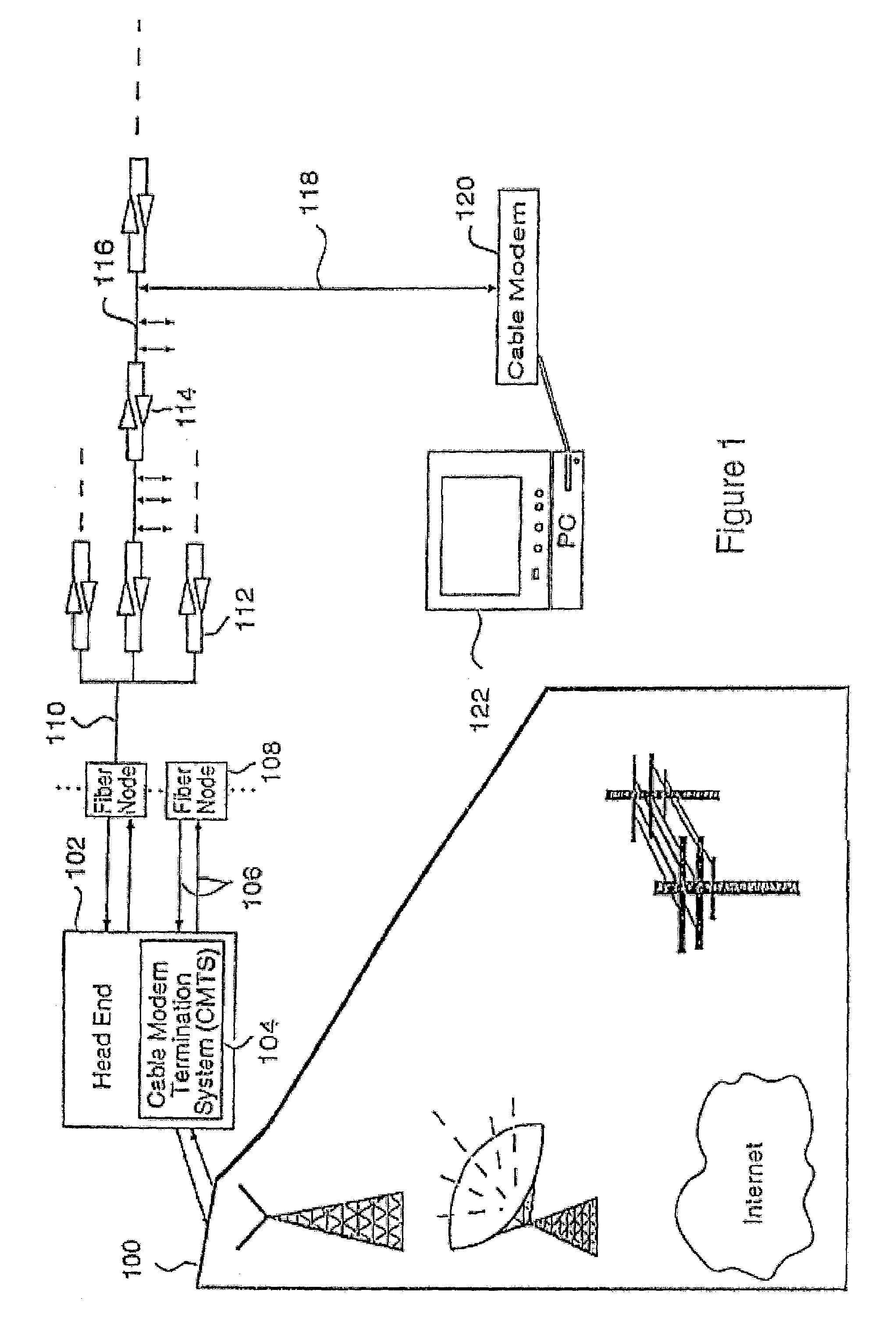
Downstream channel change technique implemented in an access network
A dynamic channel change technique is disclosed which may be implemented between nodes and a Head End of an access network. Initially a network device may communicate with the Head End via a first downstream channel and a first upstream channel. When the network device receives a dynamic channel change request which includes instructions for the network device to switch to a second downstream channel, the network device may respond by switching from the first downstream channel to the second downstream channel. Thereafter, the network device may communicate with the Head End via the second downstream channel and first upstream channel. Further, according to a specific embodiment, the dynamic channel change request may also include an upstream channel change request for causing the network device to switch from a first upstream channel to a second upstream channel.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
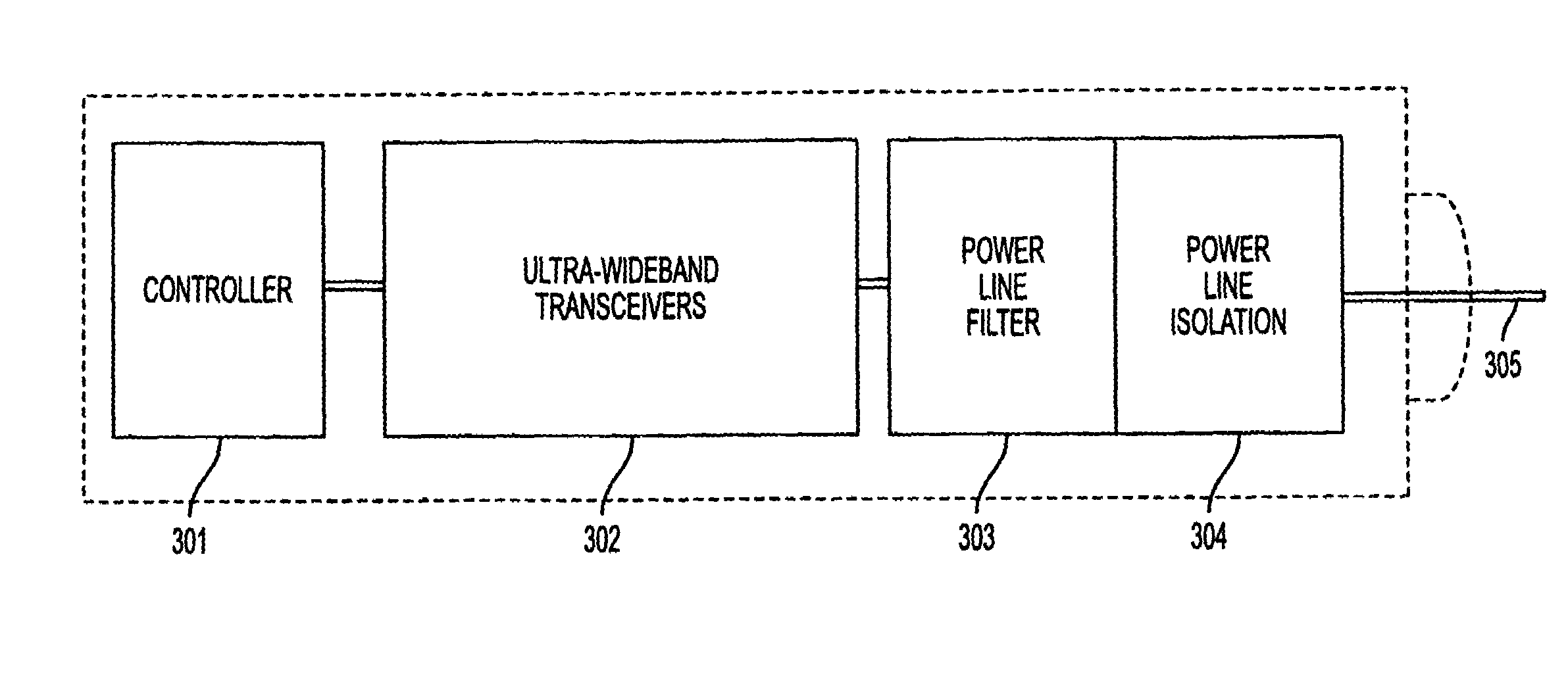
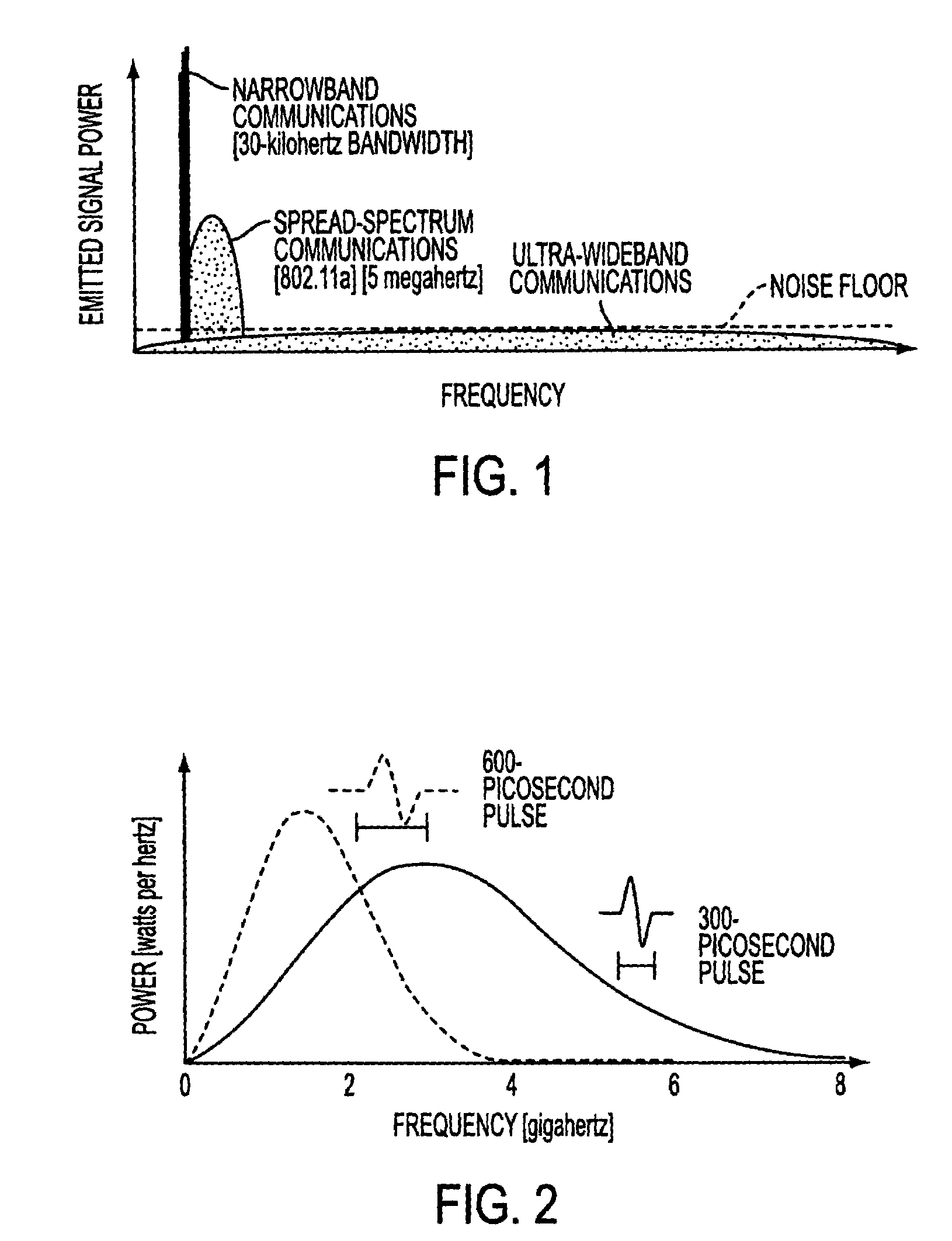
Ultra-wideband communication through local power lines
InactiveUS7027483B2Transmission/receiving by adding signal to waveBroadband local area networksUltra-widebandSubject matter
A system, method and apparatus structured to transmit a plurality of ultra-wideband pulses through an electric power medium is provided. One embodiment of the method comprises an ultra-wideband transmitter structured to transmit the plurality of ultra-wideband pulses through the electric power medium and an ultra-wideband receiver structured to receive the plurality of ultra-wideband pulses from the electric power medium. Another embodiment of the present invention comprises a power supply that provides ultra-wideband communications to devices that obtain power from the power supply. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
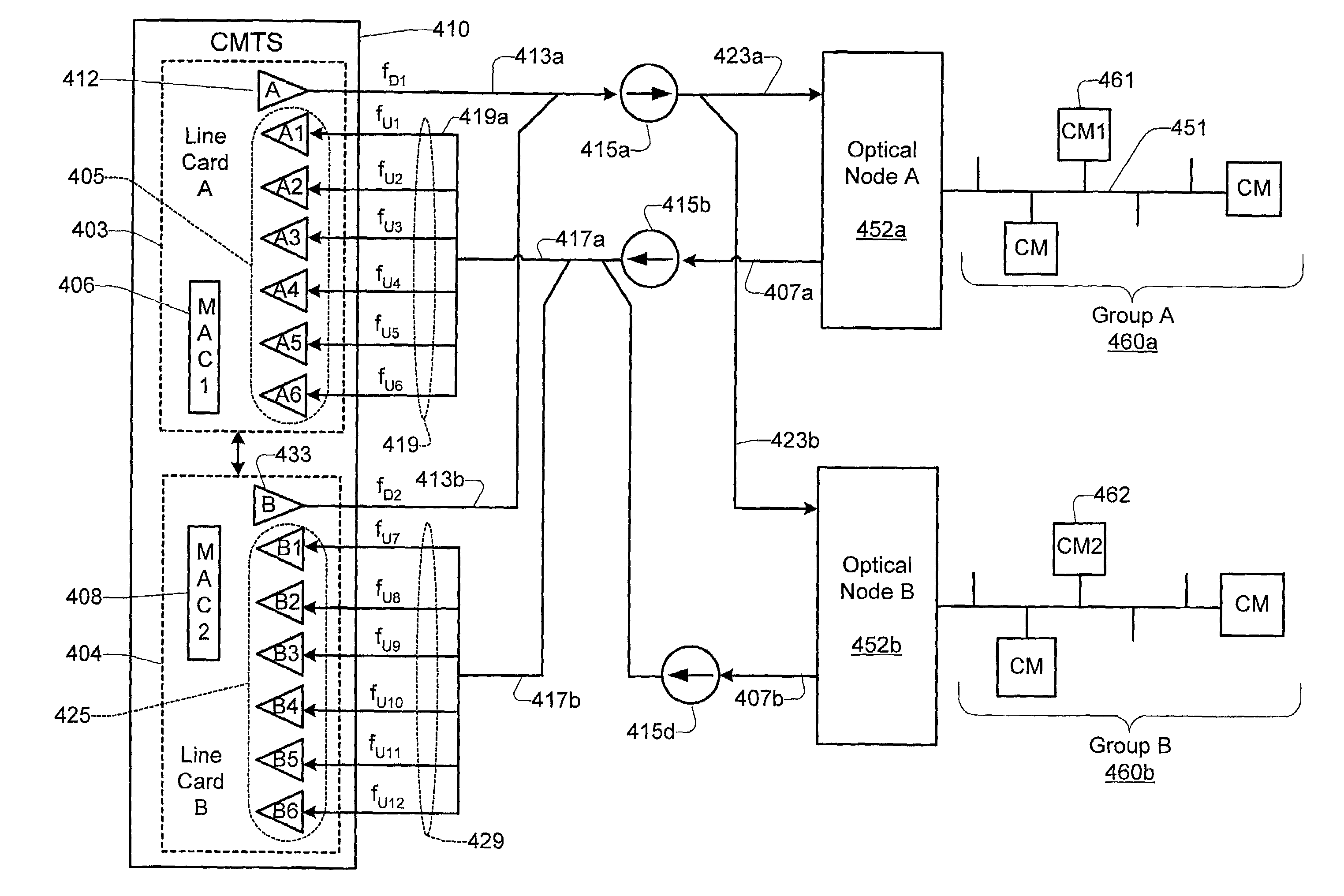
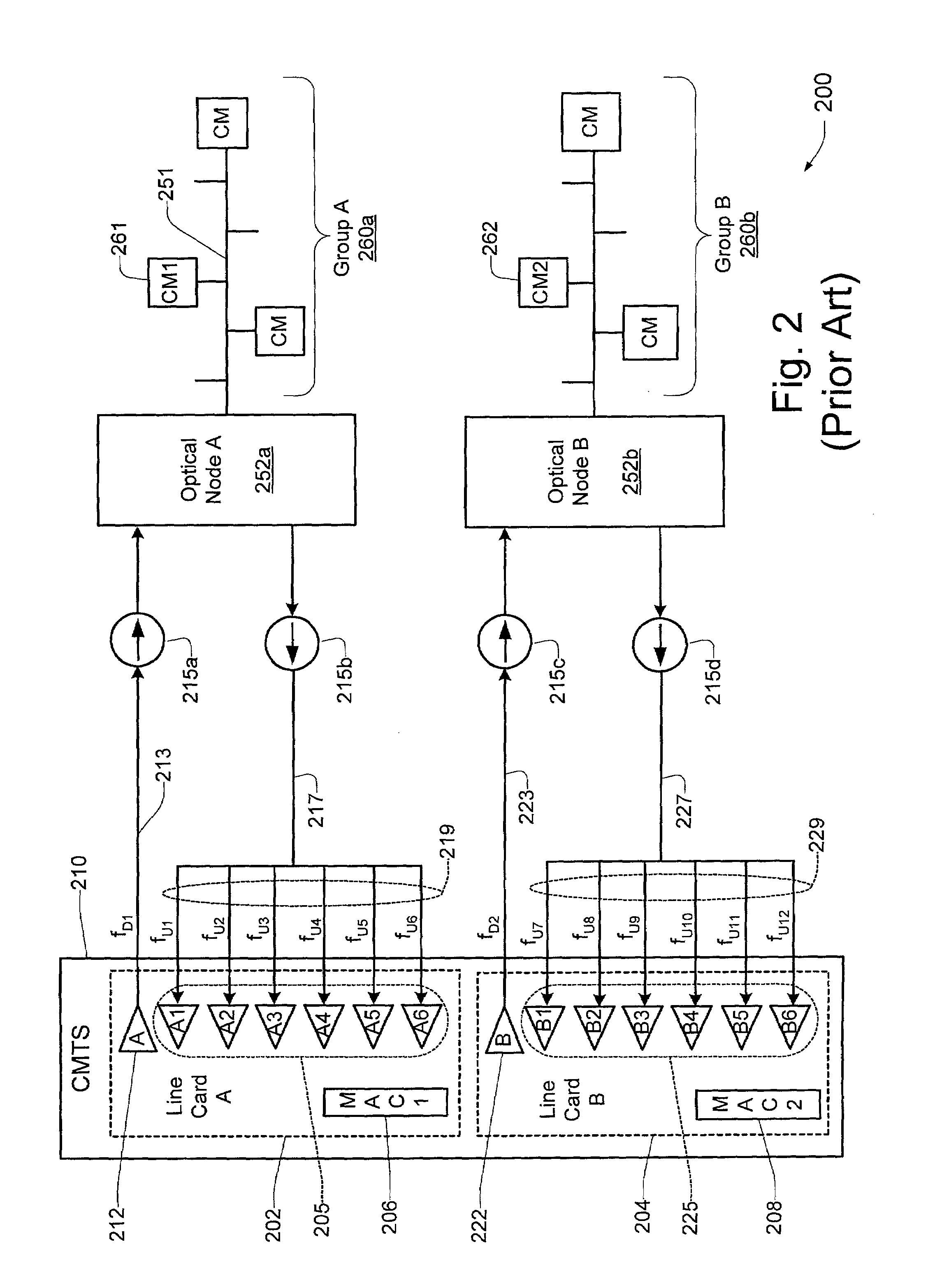
System for low noise aggregation in DOCSIS contention slots in a shared upstream receiver environment
InactiveUS20080170853A1Reduce the amount requiredMore noise tolerantBroadband local area networksTime-division multiplexLow noiseModem device
A cable modem termination system is disclosed with flexible mapping of upstreams to downstreams and flexible mapping of downstreams to optical nodes and optical nodes to upstream receivers and the ability to add singe upstreams or downstreams as needed for load balancing. Multiple downstreams can share the same upstream. Multiple receivers can be coupled to the same upstream. Monitoring of upstream performance for overperforming or underperforming modems can be carried out, and new upstreams with higher and / or lower throughtput can be created to service the overperformers and / or underperformers. Modems can be grouped into logical groups with different performance levels and serviced by different upstreams or different upstream logical channels on the same upstream physical channel. An upstream linecard with a digital crosspoint switch is disclosed with the switch operated during contention intervals to allow reception with or without aggregation of noise where multiple upstream share the same receiver.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Radio communication system, radio communication control apparatus, radio communication control method, and computer program
InactiveUS20030169697A1Broadband local area networksNetwork topologiesCommunications systemCommunication control
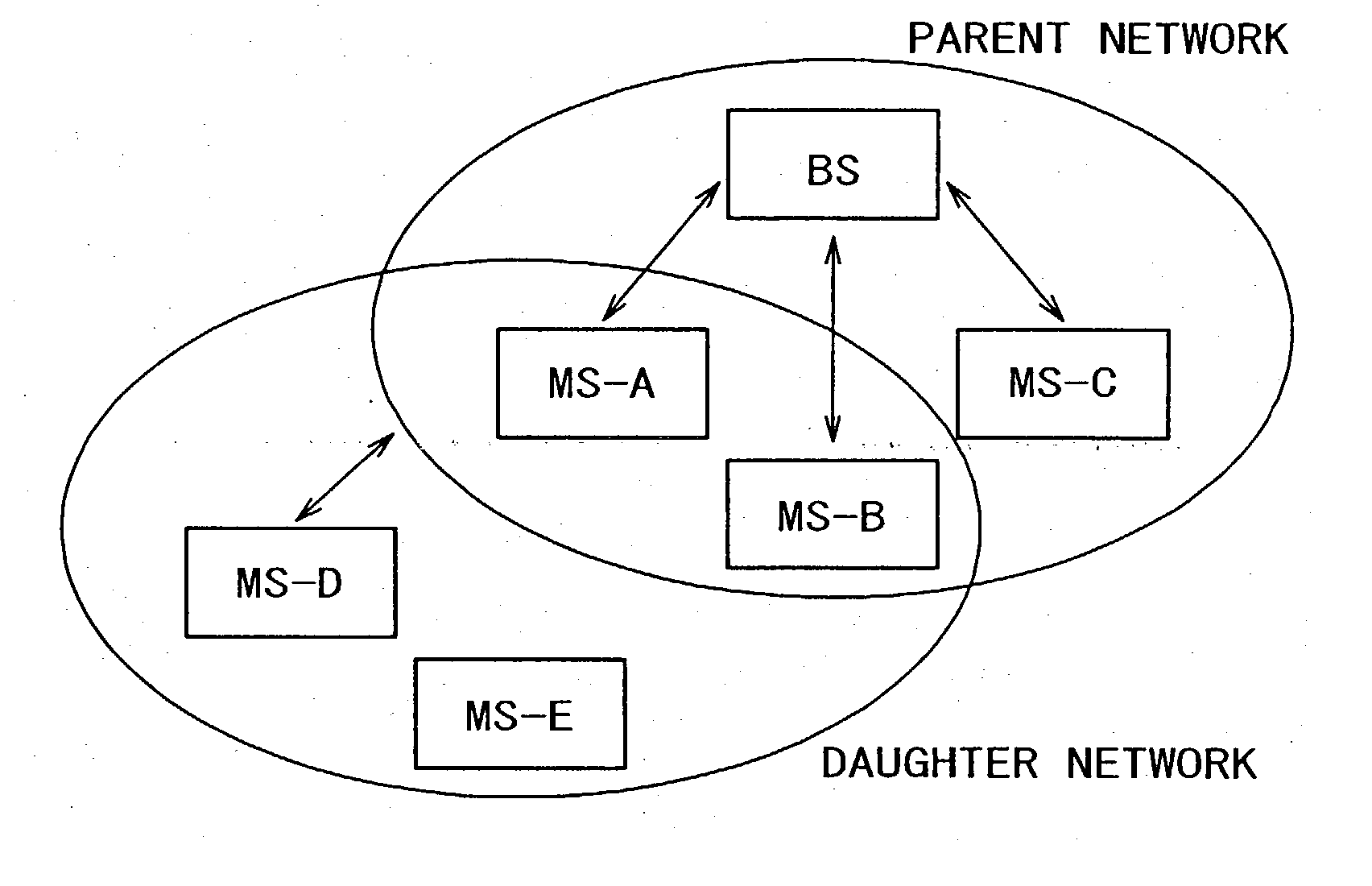
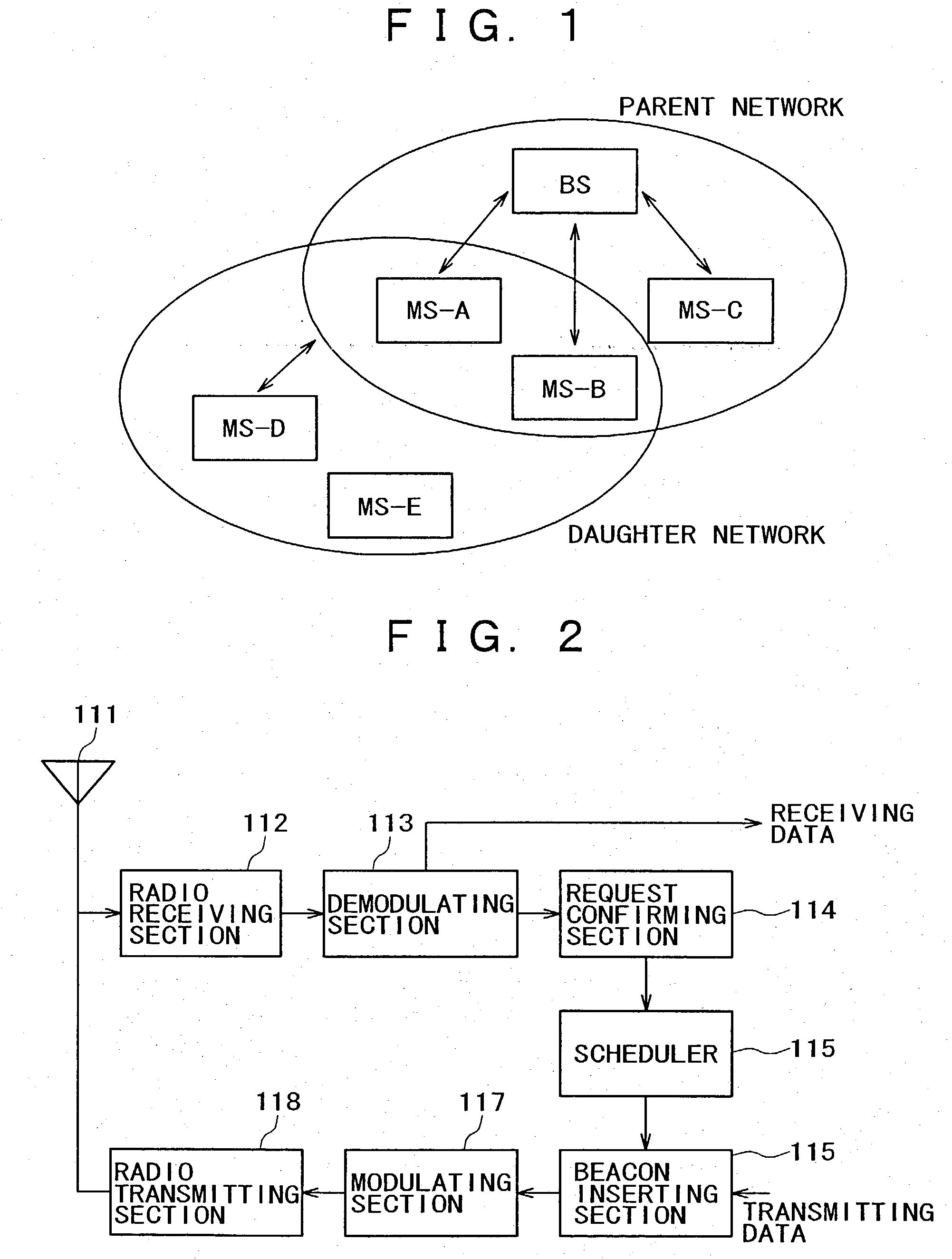
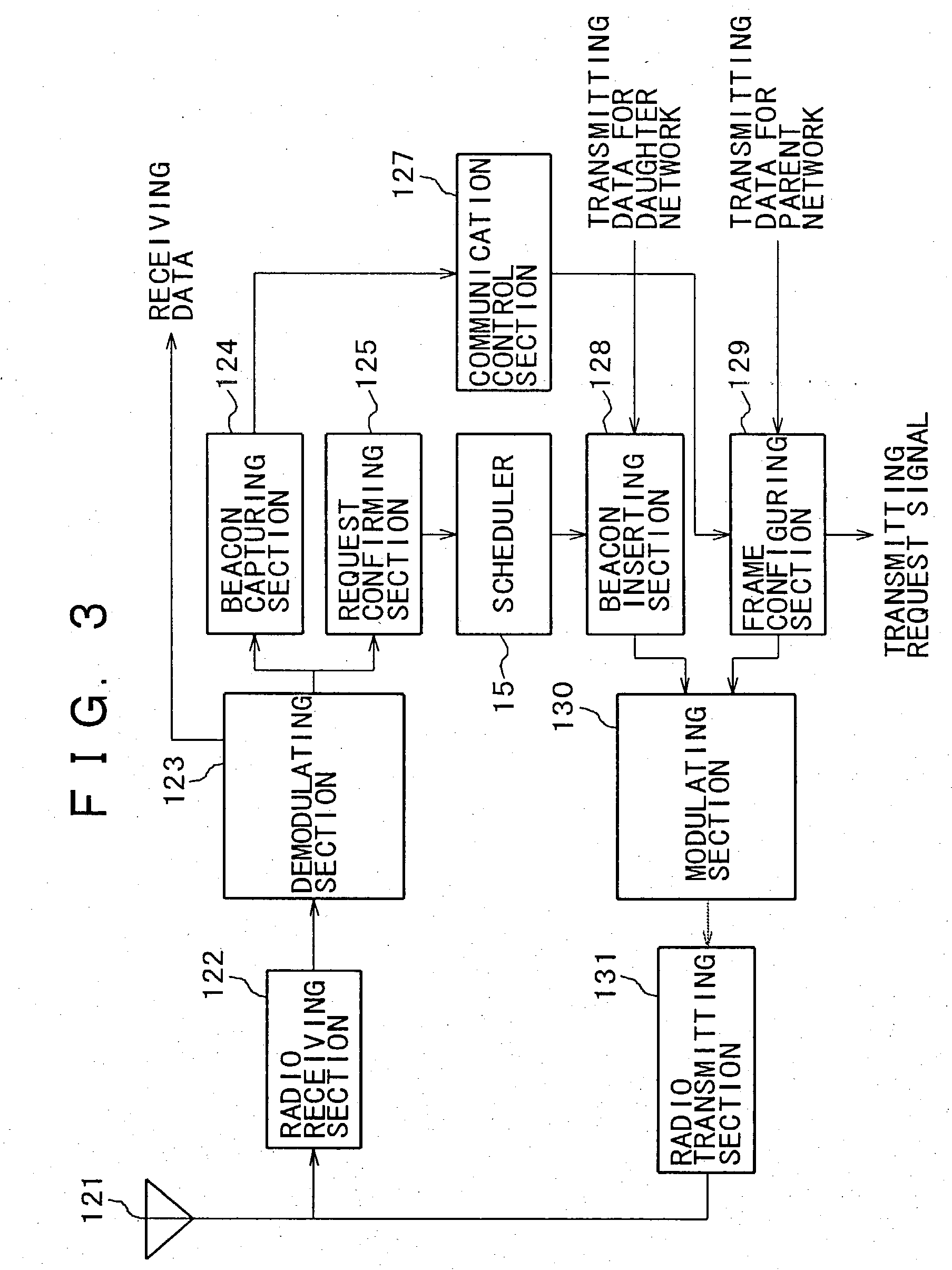
A communication terminal under the control of a wireless base station recursively has wireless base station capabilities in a parent network, constructs a daughter network within a scope of resources of the own apparatus assigned by the wireless base station, and assigns the resources to an other communication terminal under the control of the communication terminal having base station capabilities. This novel constitution allows to configure two or more networks guaranteed not to interfere each other, thereby allowing the coexistence of a plurality of personal area networks on a same frequency channel. At the same time, the novel constitution allows expanding a network area without increasing the scale of equipment.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for providing integrated packet services over a shared-media network
InactiveUS6563829B1Good serviceError preventionTransmission systemsQos quality of serviceExchange network
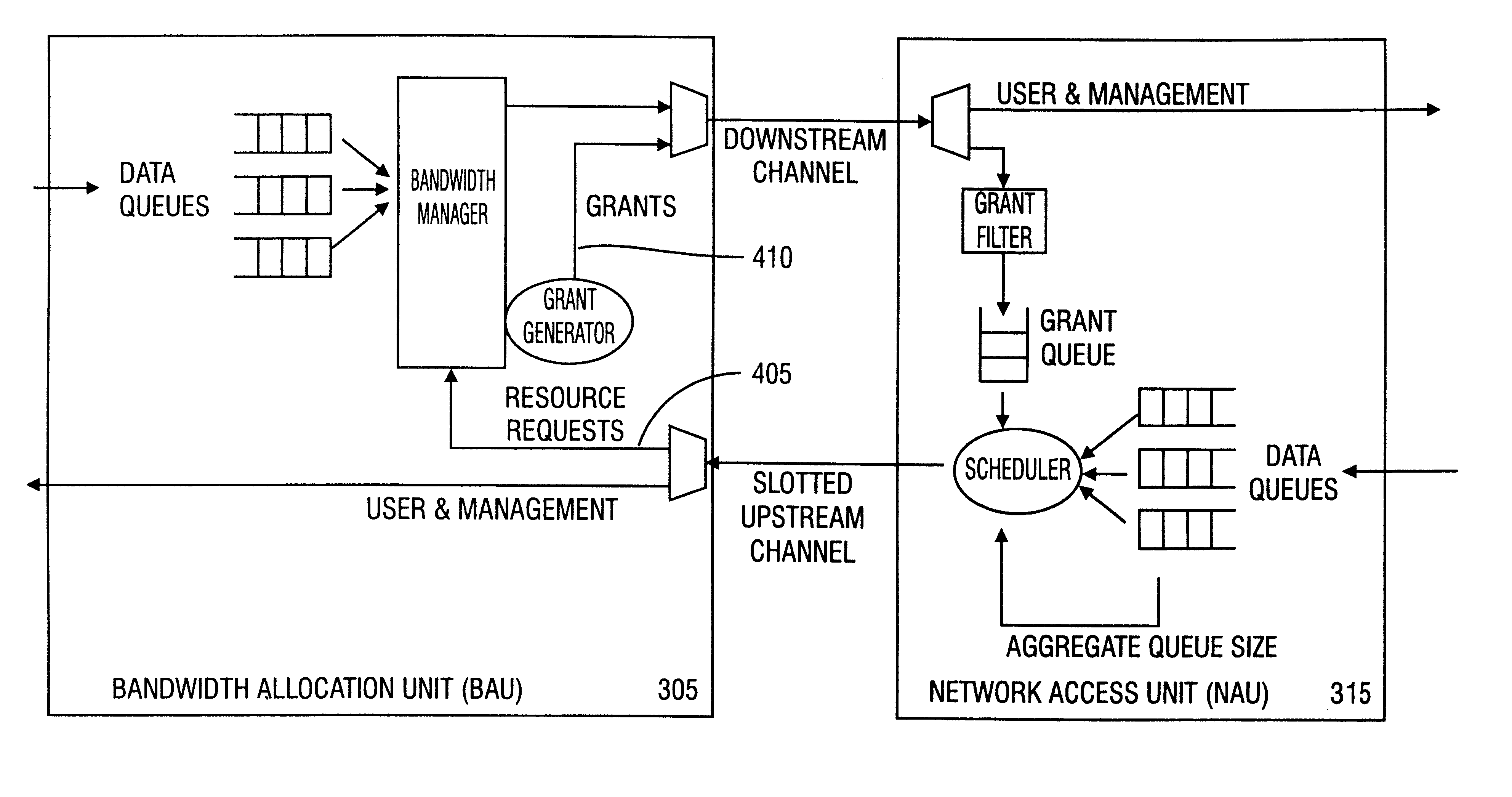
A method in accordance with the invention allocates bandwidth, fairly and dynamically, in a shared-media packet switched network to accommodate both elastic and inelastic applications. The method, executed by or in a head-end controller, allocates bandwidth transmission slots, converting requests for bandwidth into virtual scheduling times for granting access to the shared media. The method can use a weighted fair queuing algorithm or a virtual clock algorithm to generate a sequence of upstream slot / transmission assignment grants. The method supports multiple quality of service (QoS) classes via mechanisms which give highest priority to the service class with the most stringent QoS requirements.
Owner:AMERICAN CAPITAL FINANCIAL SERVICES
Popular searches
Selective content distribution Digital data processing details User identity/authority verification Color television details Buying/selling/leasing transactions Program/content distribution protection Special data processing applications Program loading/initiating Networks interconnection Memory systems
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com