Patents
Literature
1144 results about "Change request" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
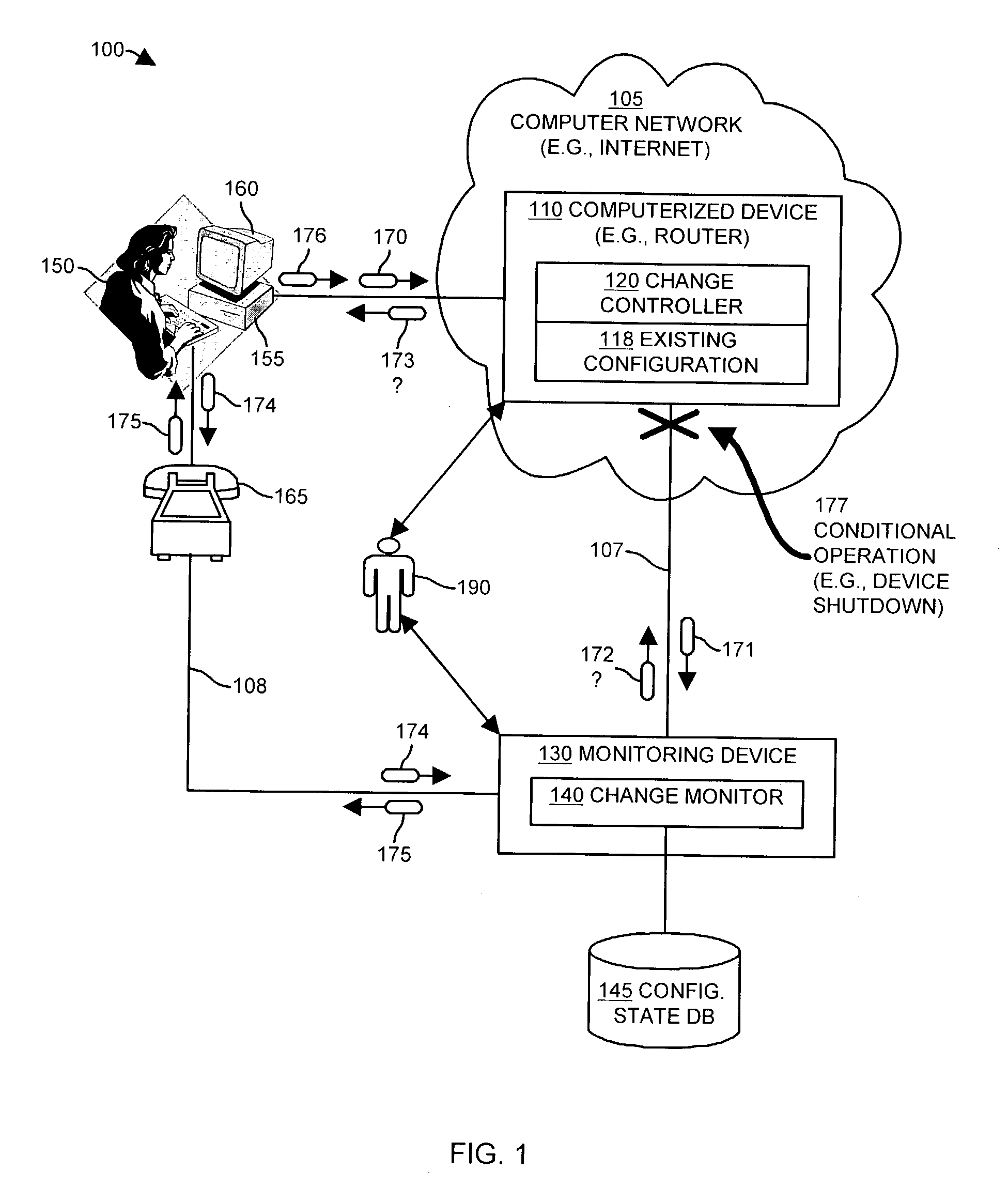
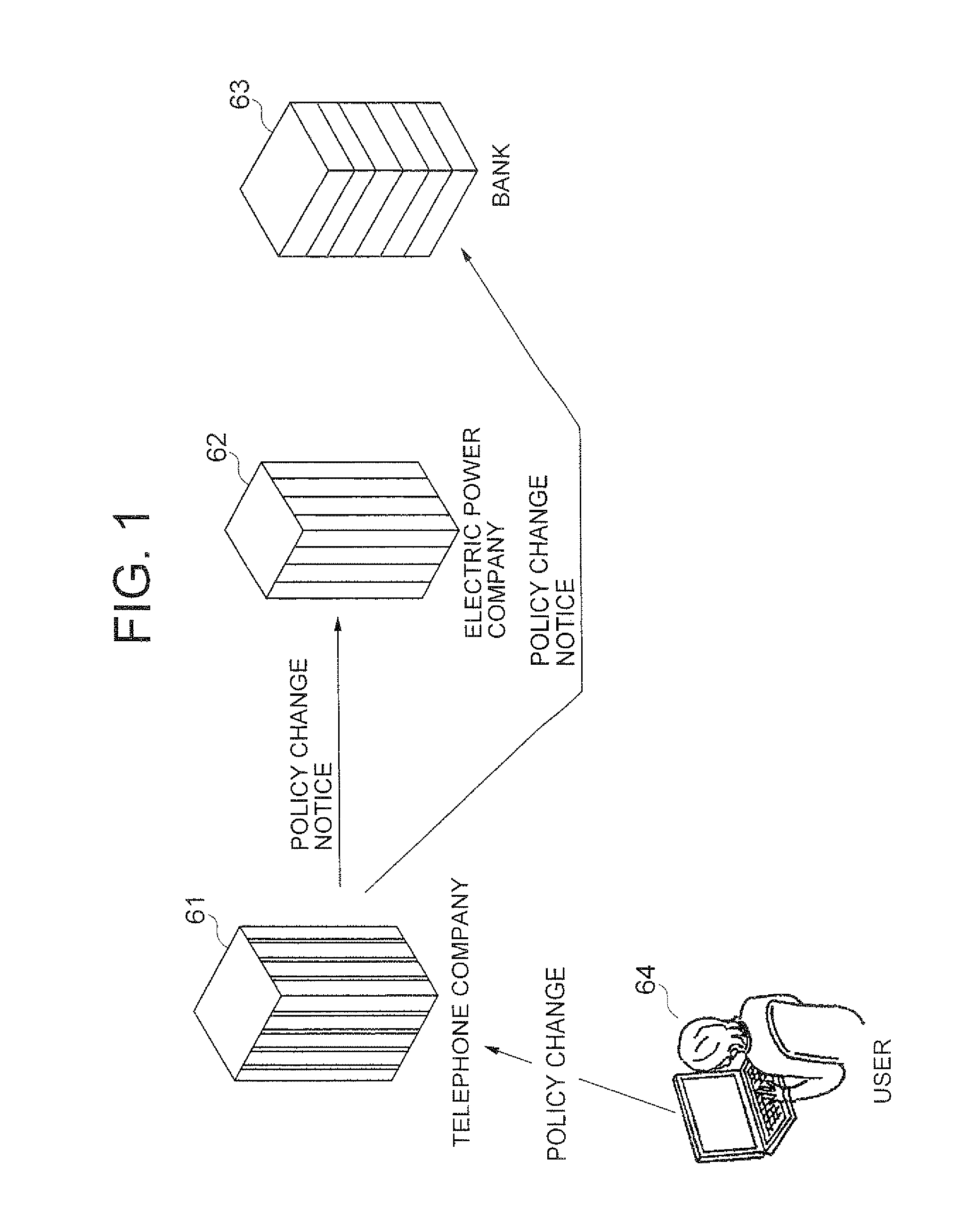
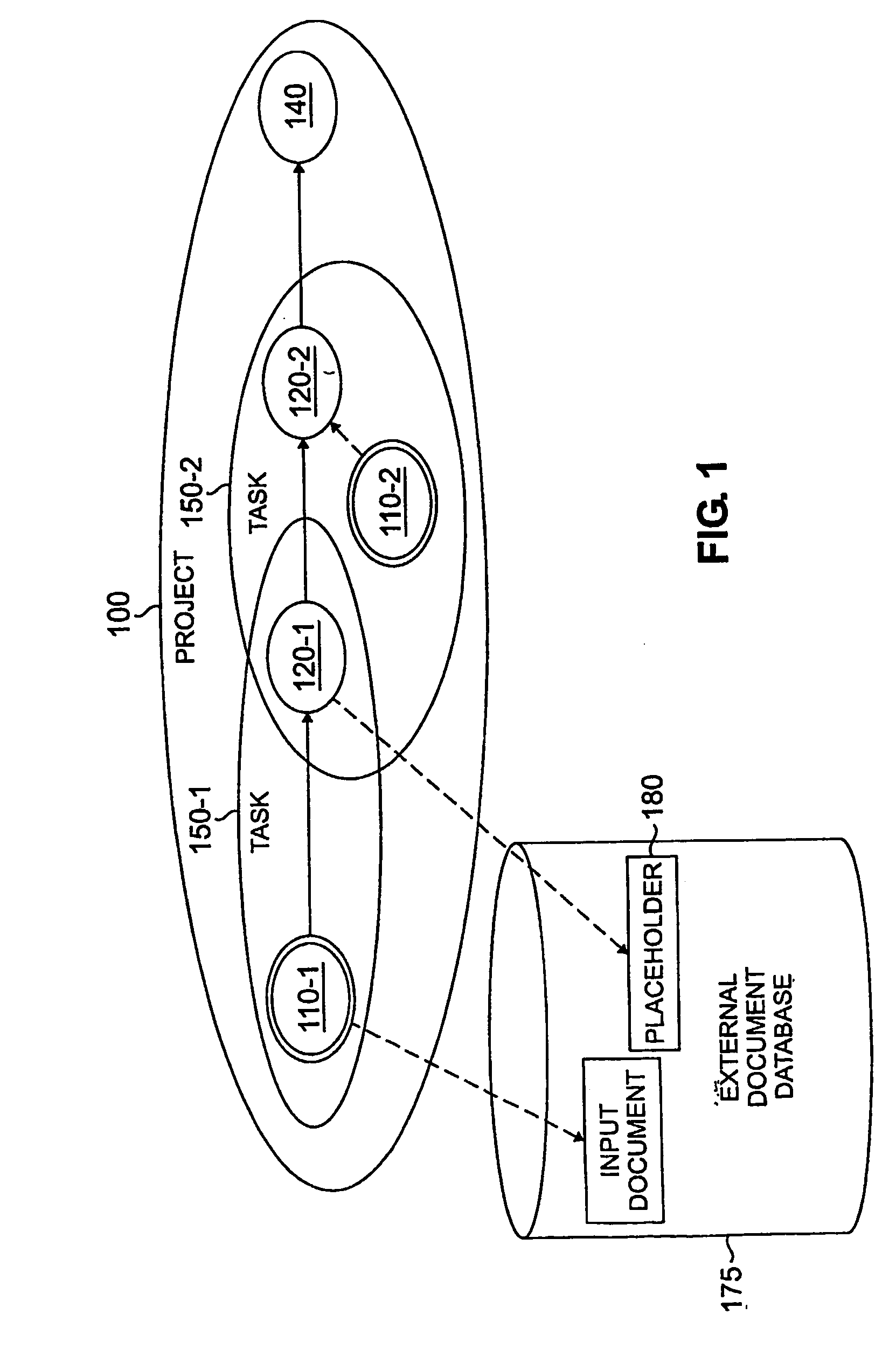
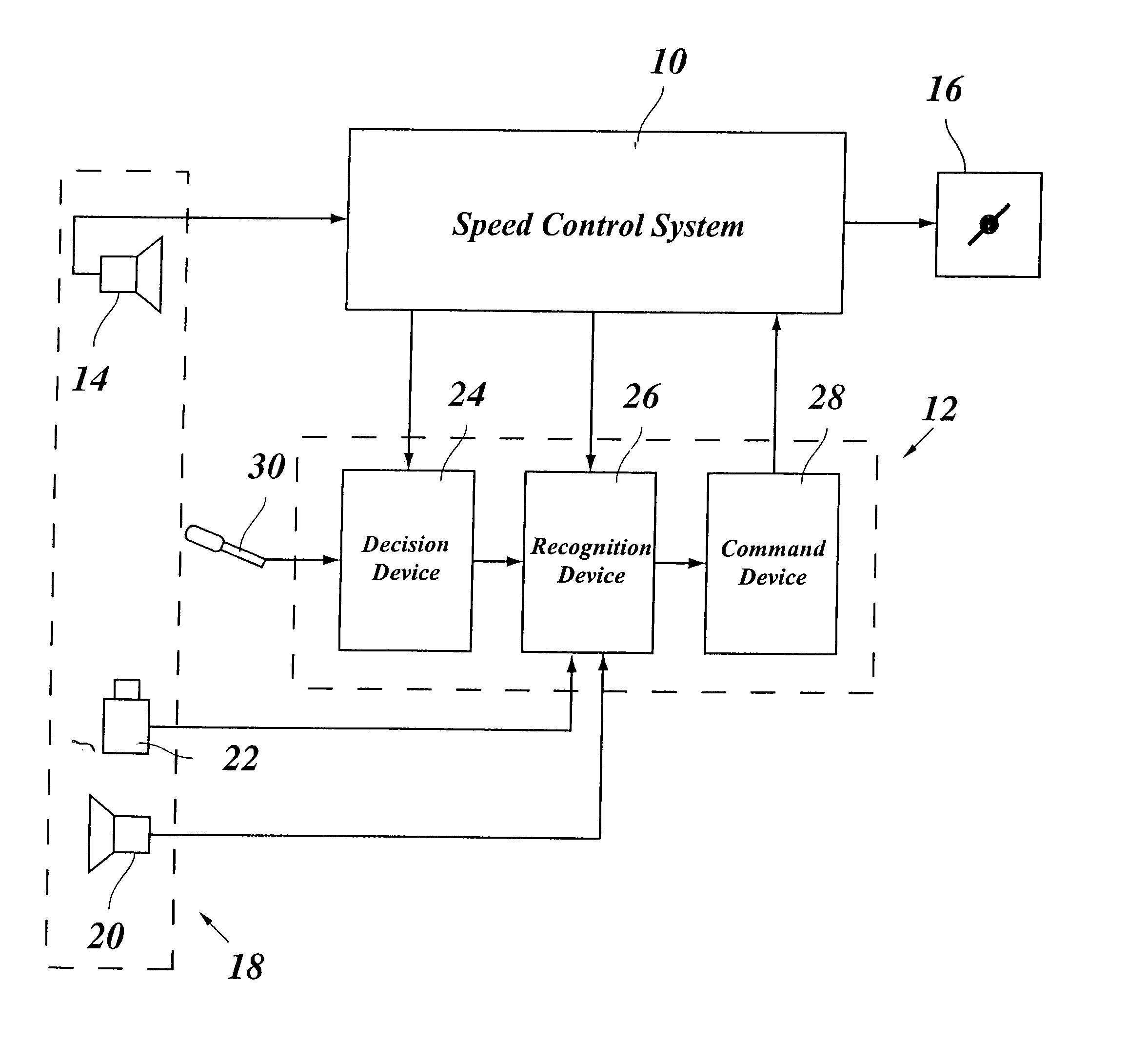
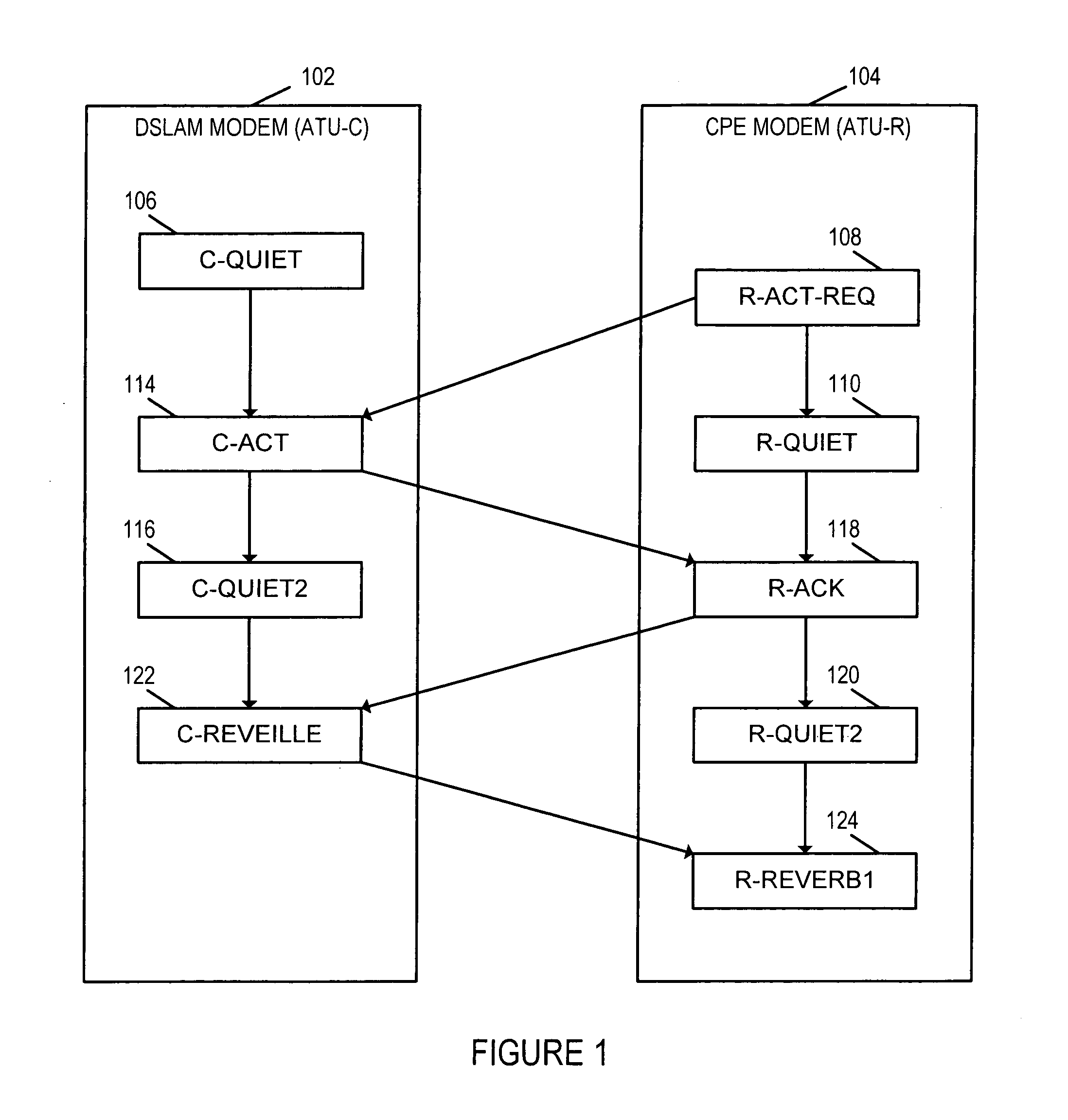
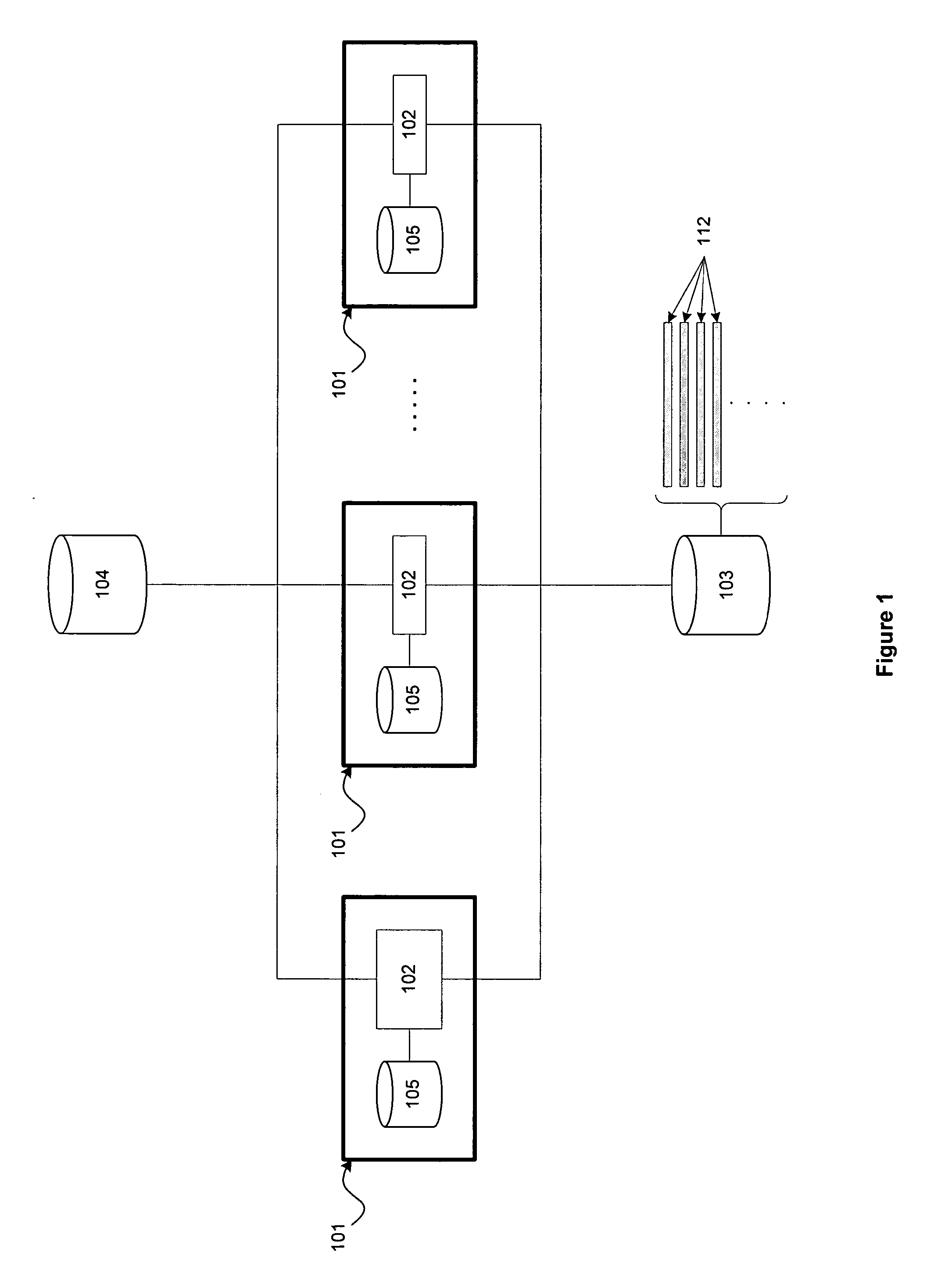
A change request is a document containing a call for an adjustment of a system; it is of great importance in the change management process. A change request is declarative, i.e. it states what needs to be accomplished, but leaves out how the change should be carried out. Important elements of a change request are an ID, the customer (ID), the deadline (if applicable), an indication whether the change is required or optional, the change type (often chosen from a domain-specific ontology) and a change abstract, which is a piece of narrative (Keller, 2005). An example of a change request can be found in Figure 1 on the right.
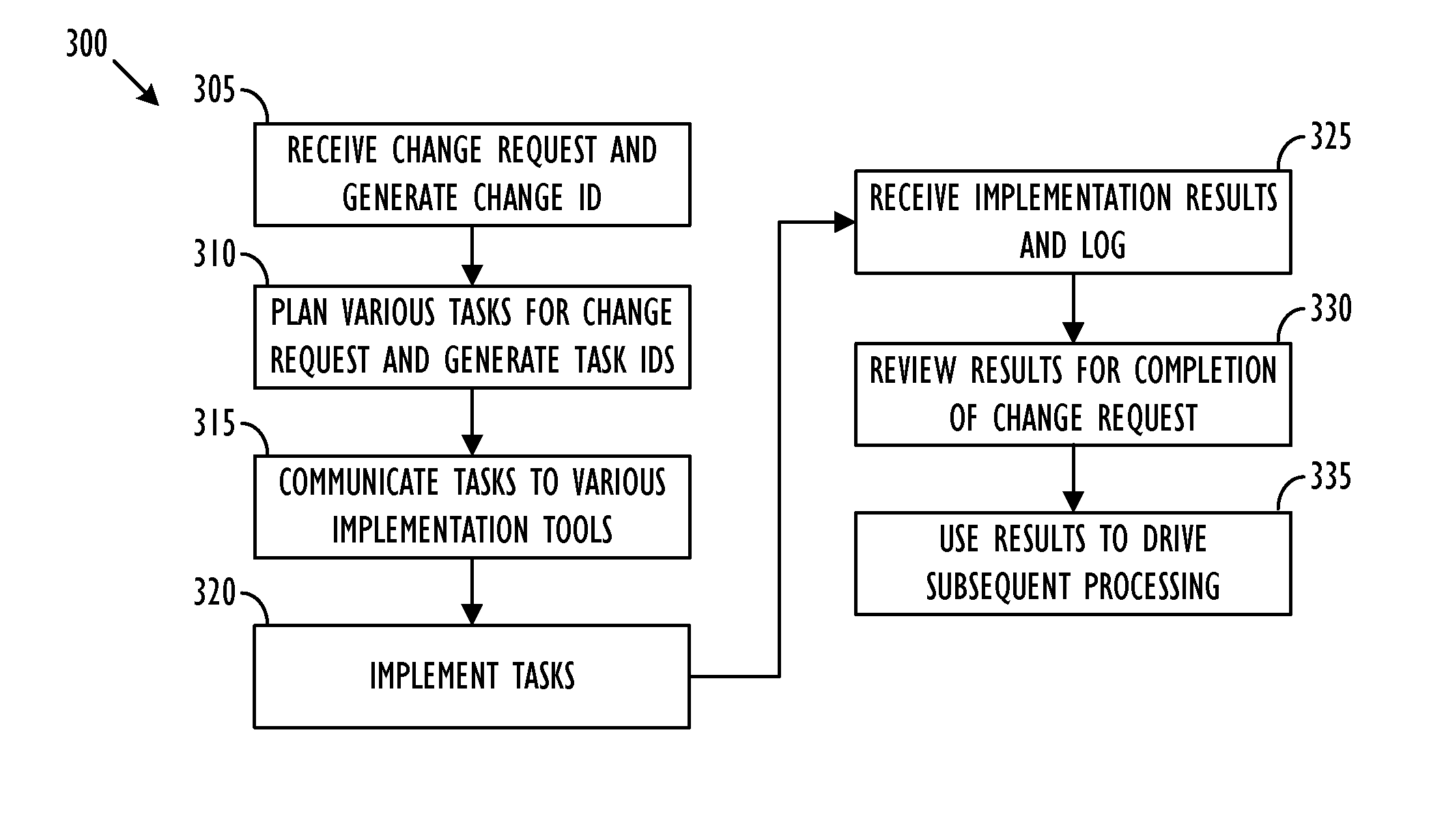
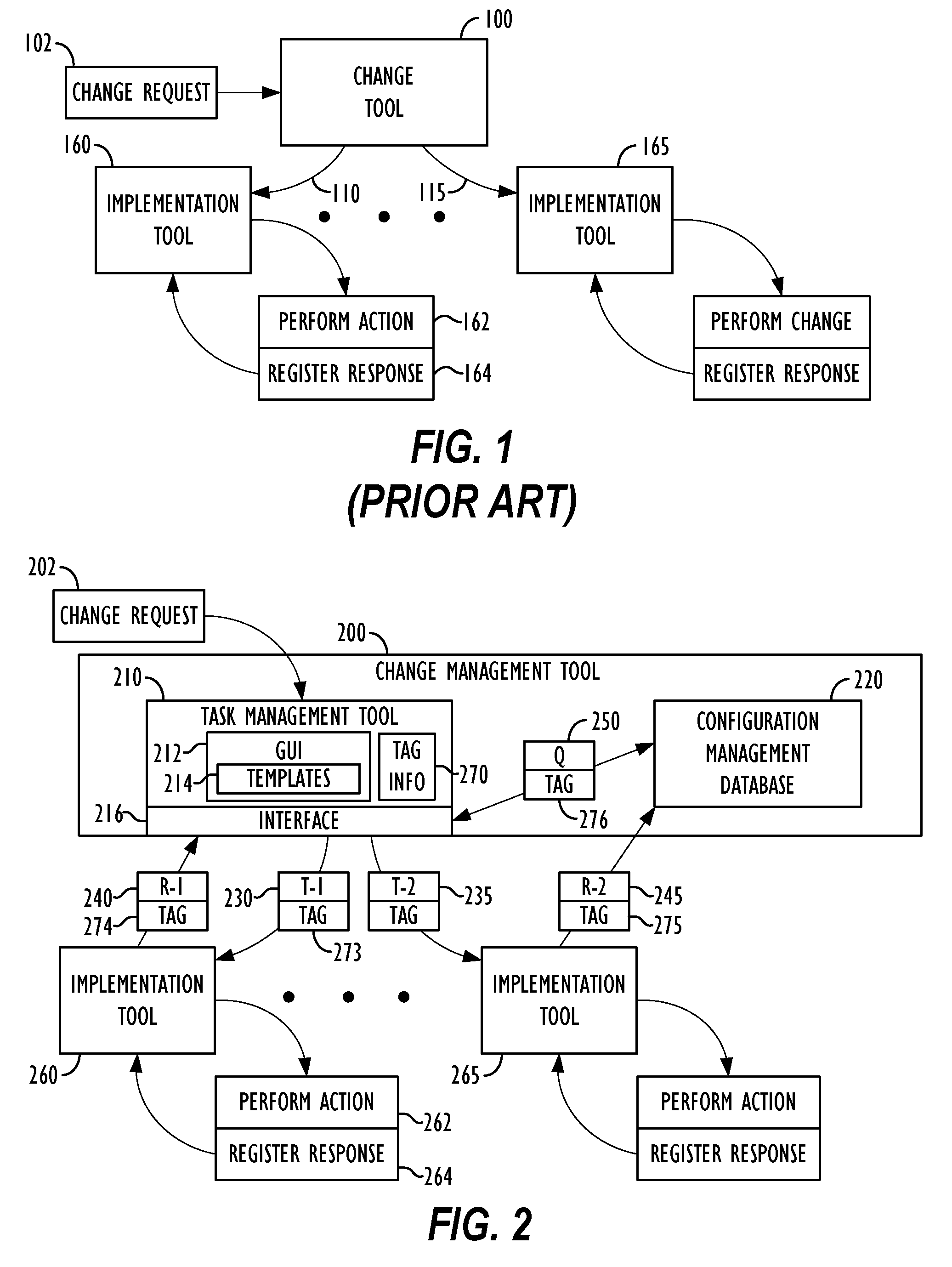
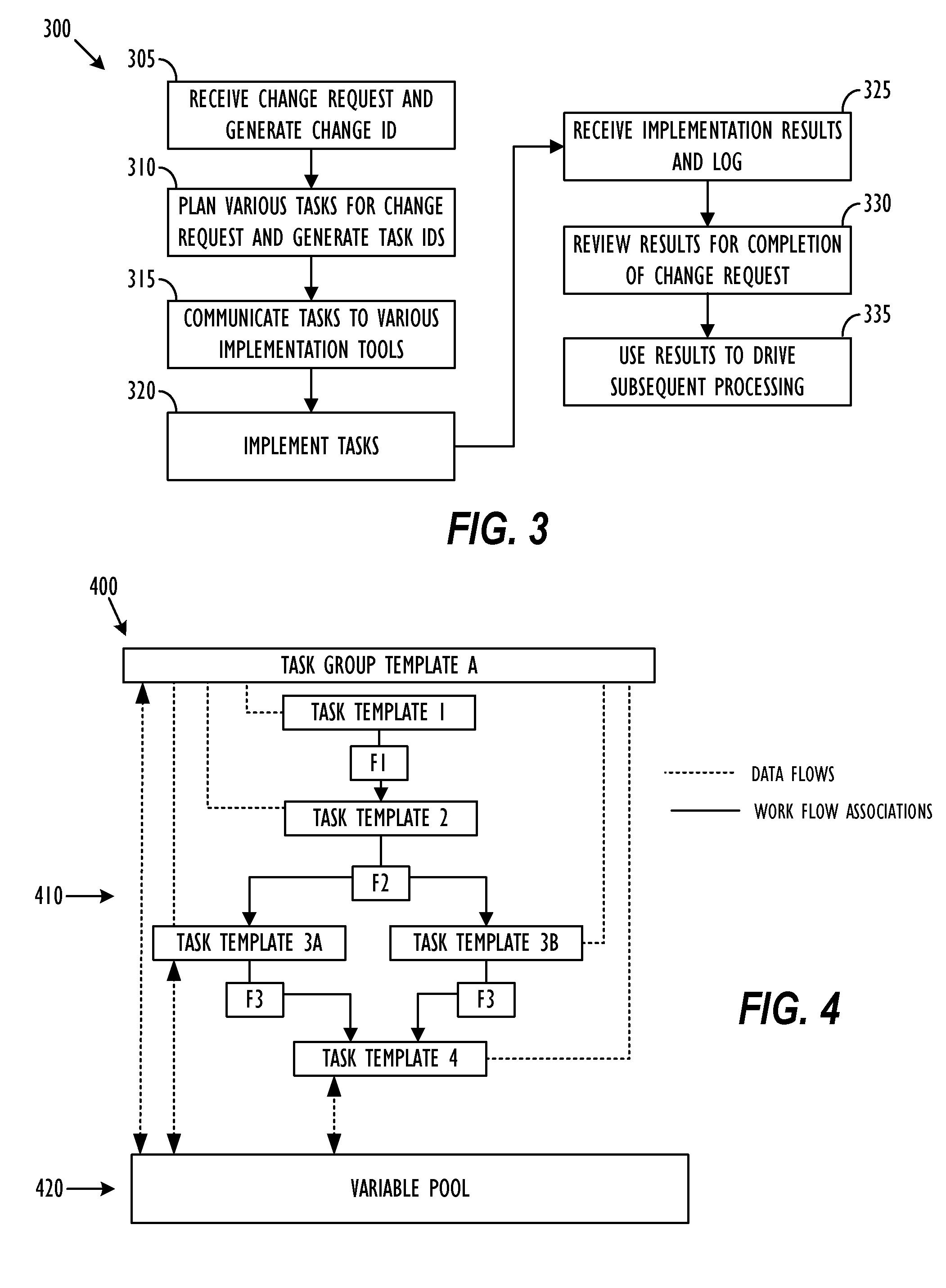
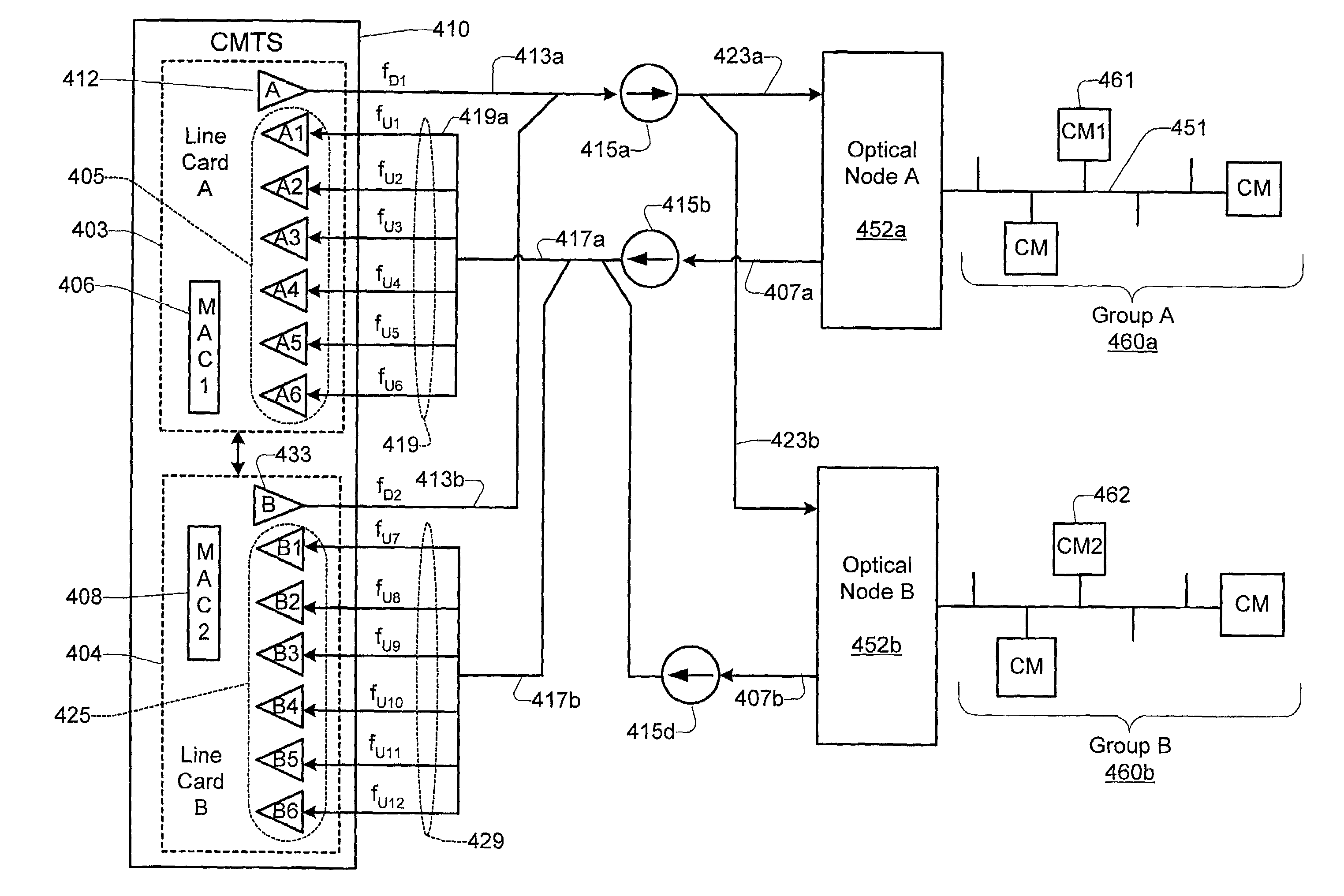
Bi-directional communication between change management tool and implementation tools
ActiveUS8887133B2Version controlSpecific program execution arrangementsChange managementManagement tool
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
Methods and apparatus for auditing and tracking changes to an existing configuration of a computerized device
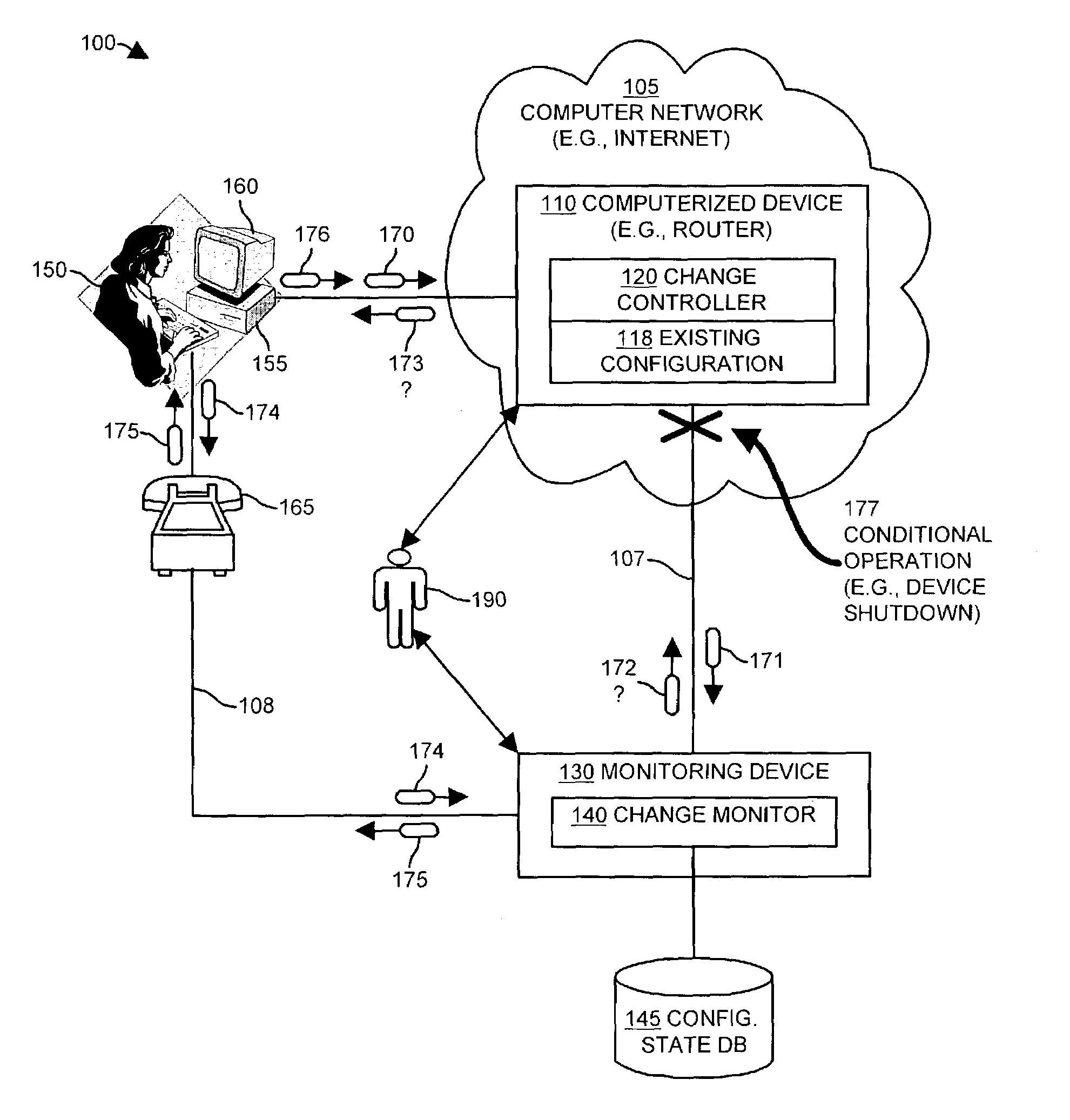
InactiveUS7024548B1Maliciously compromisedOvercome deficienciesMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionNotification ReceiverChange control
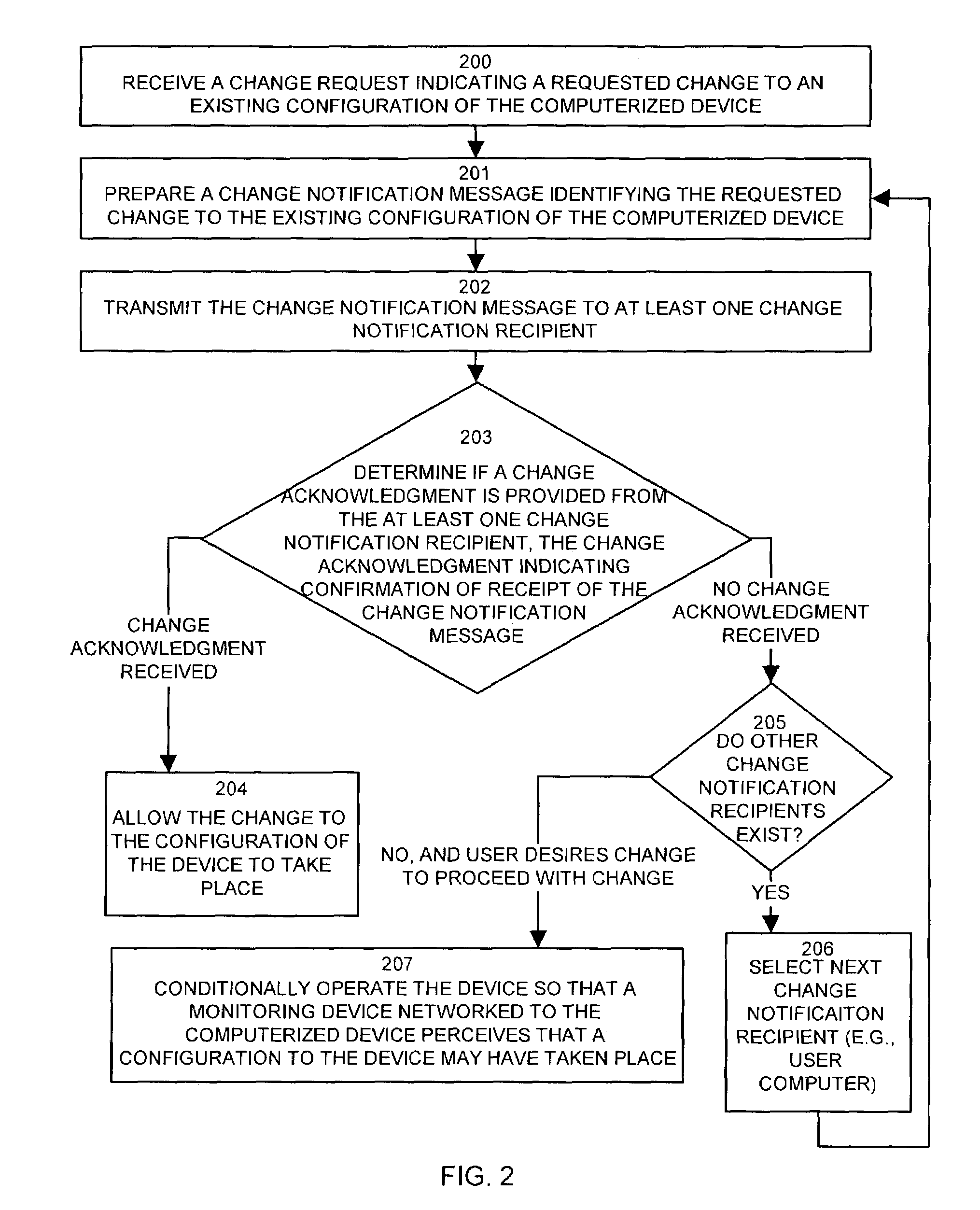
A change controller application, process and system tracks modification to a configuration of a computerized device by receiving a change request indicating a requested change to an existing configuration of the computerized device and preparing a change notification message identifying the requested change to the existing configuration of the computerized device. The change controller transmits the change notification message to at least one change notification recipient and determines if a change acknowledgement is provided in response. If a change acknowledgement is provided from a change notification recipient that indicates confirmation of receipt of the change notification message, the system allows the requested change to the configuration of the computerized device to take place. If the change acknowledgement is not provided from a change notification recipient, the system conditionally operates the computerized device so that a monitoring device networked to the computerized device perceives that a configuration change to the computerized device may have taken place.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
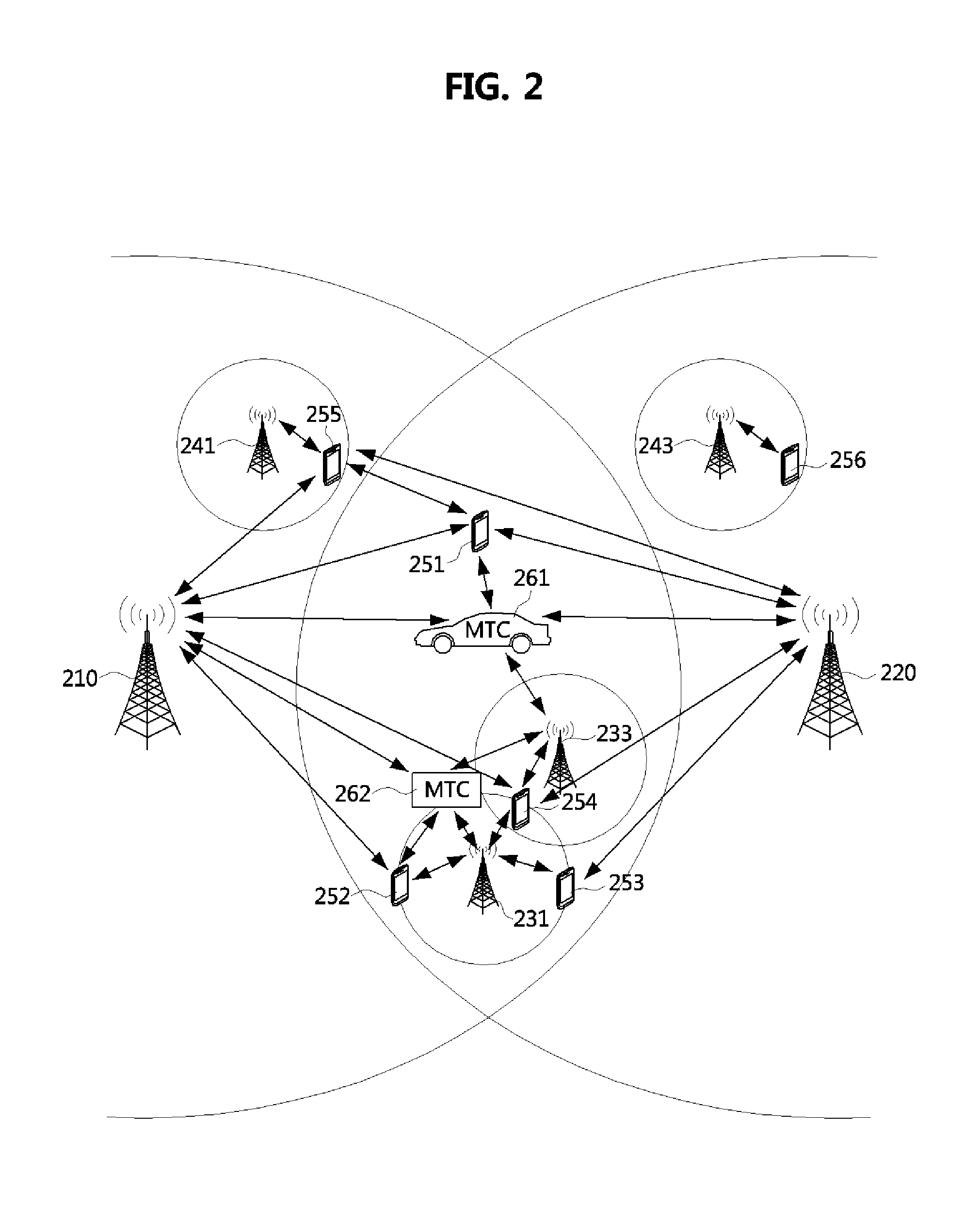
Methods of managing terminal performed in base station and terminal
InactiveUS20130229931A1Easy to moveEnsure continuityError preventionTransmission systemsHeterogeneous networkConnection control
Provided are methods of managing a terminal in a heterogeneous network (HetNet) environment. Between the methods, a method of managing a terminal performed in a base station includes determining whether or not a measurement change request event has occurred, and when a measurement change request event has occurred, transmitting a control message for instructing a change of a measurement operation to the terminal. Accordingly, it is possible to improve a measurement operation and discontinuous reception (DRX) operation control procedure necessary for connection control between one or more base stations and a terminal in a HetNet environment, and thereby performance of a system can be improved.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
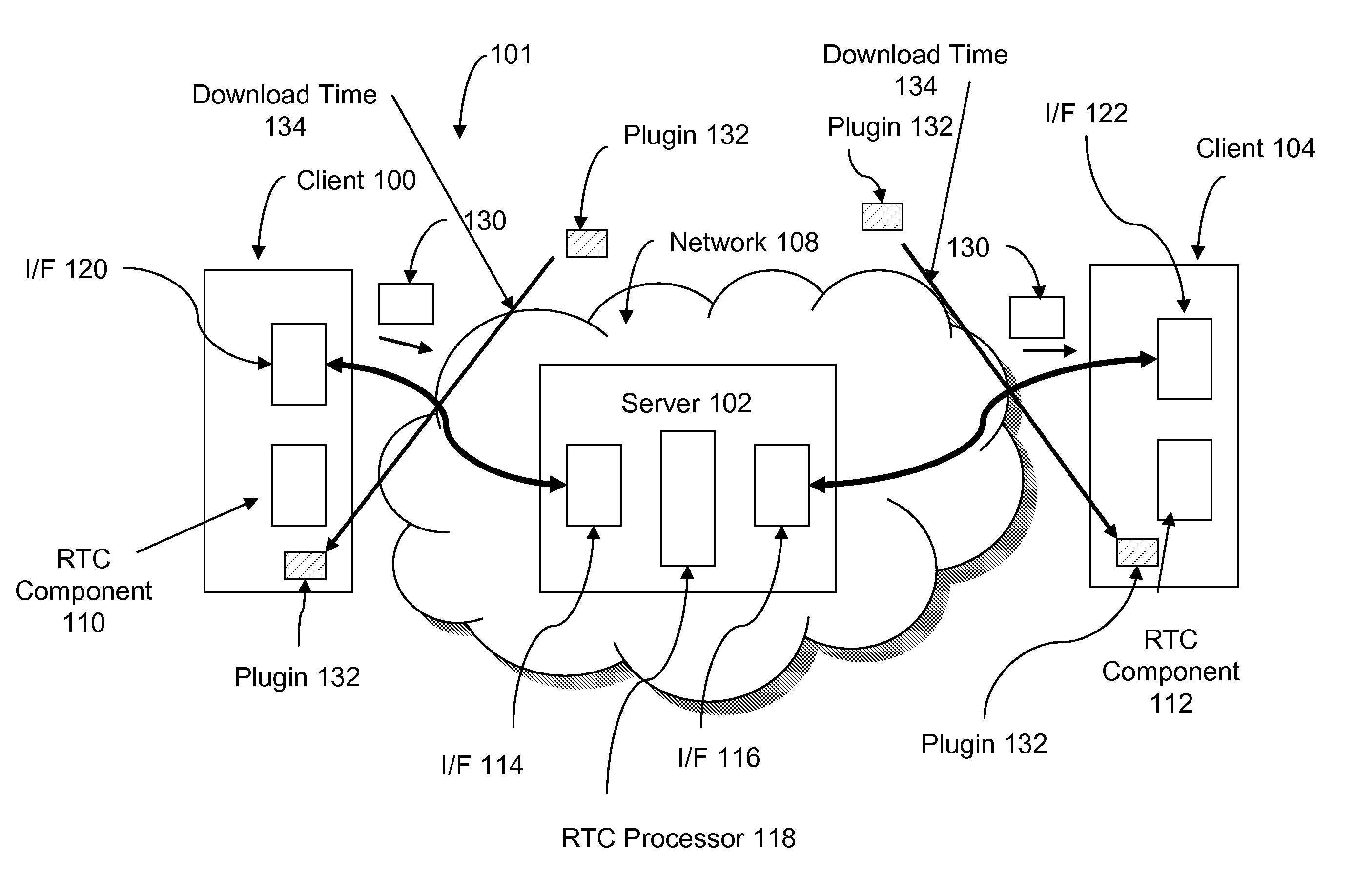
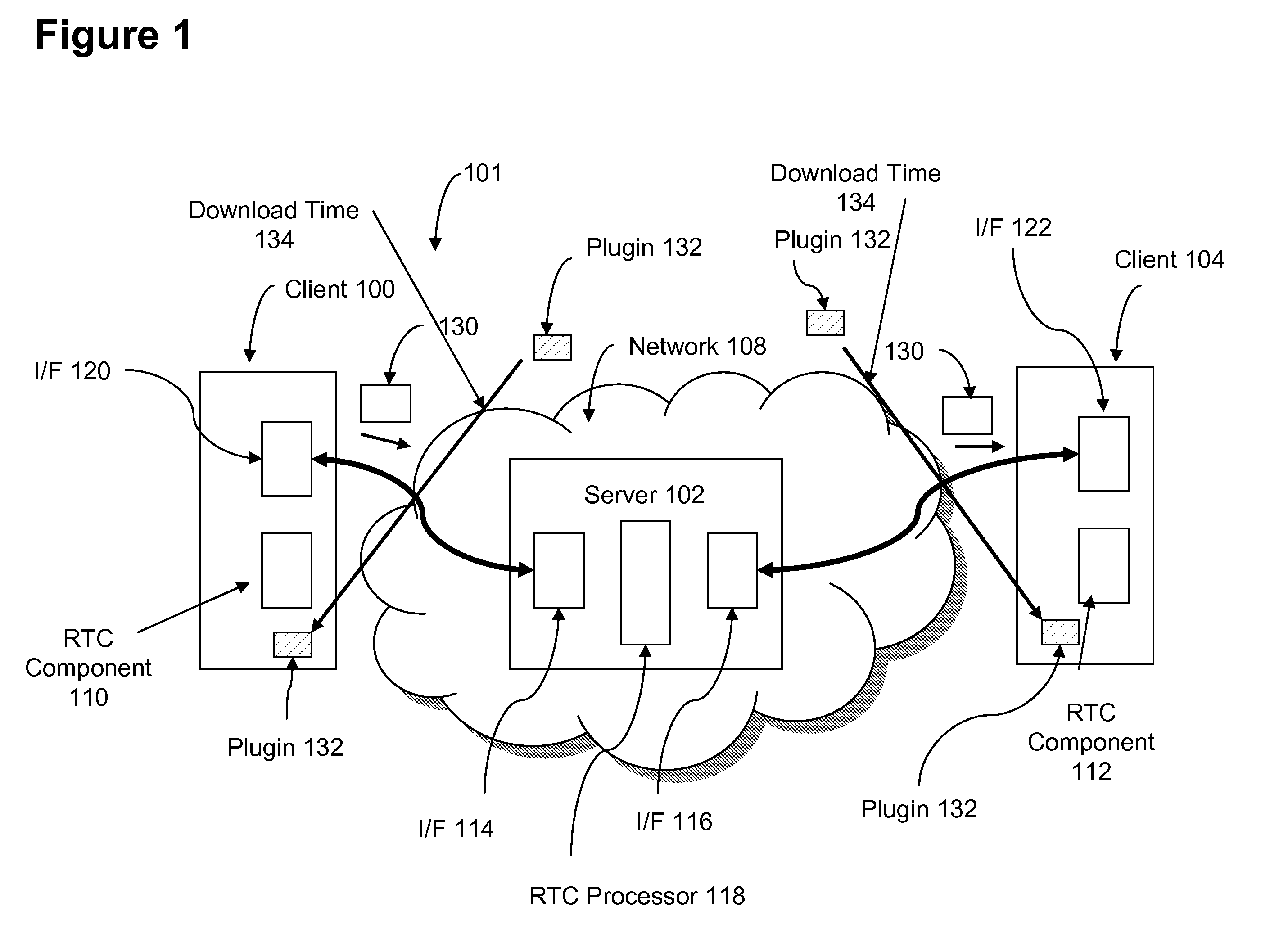
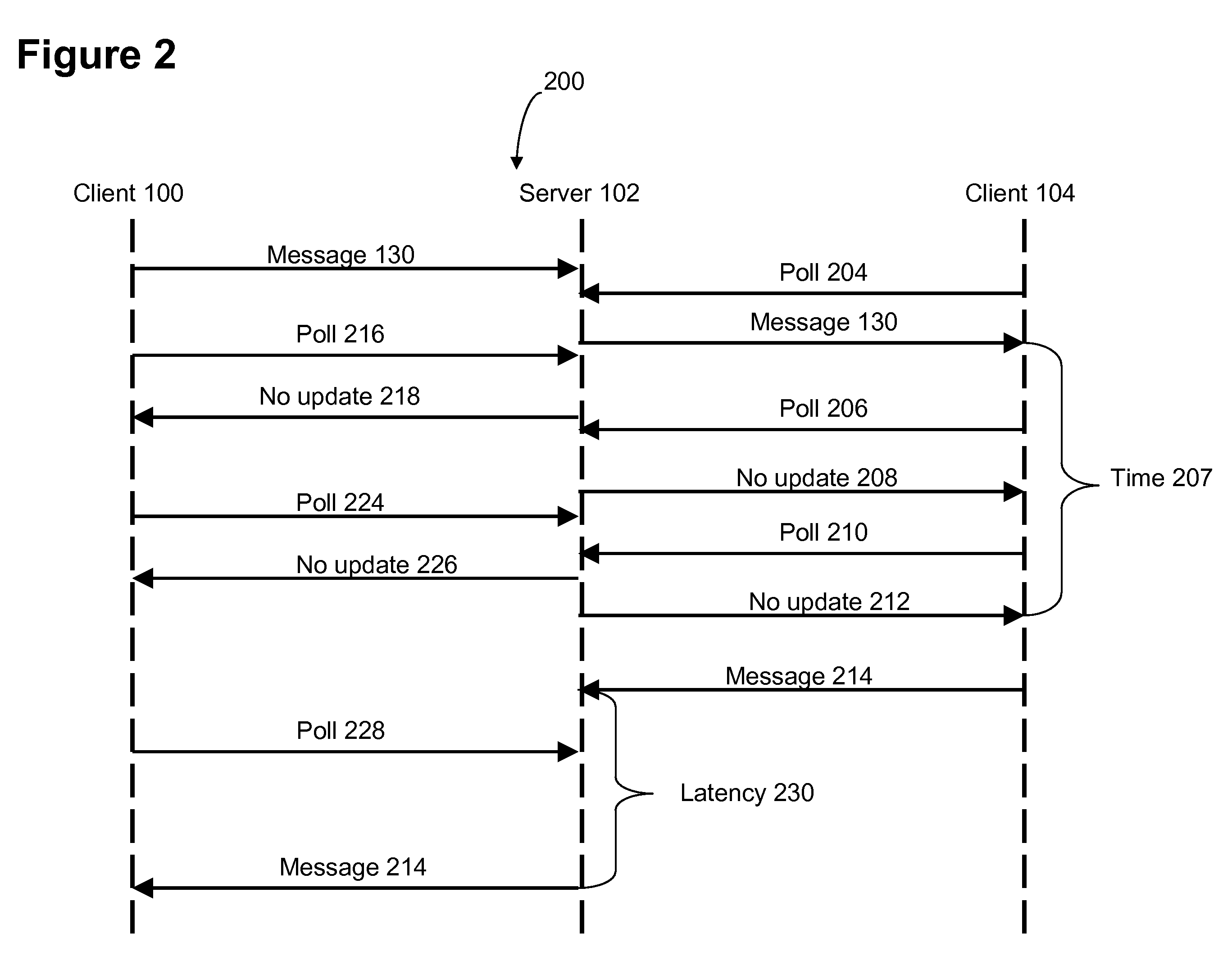
System and method for achieving highly scalable real-time collaboration applications using HTTP
InactiveUS20080147834A1Highly scalable and highly responsiveHighly scalable and highly responsive RTC serviceDigital computer detailsTransmissionApplication serverApplication software
A highly scalable and highly responsive RTC system uses asynchronous or non-blocking I / O and HTTP response queuing to avoid server overload. The system distinguishes between two types of requests: an update request and a change request. An update request is a request used to fetch an update or change notification. A change request is a request to change some data related to the real-time session. For a given RTC session, the server first checks whether any updates exist for an update request. If an update exists, the server code can send an immediate response to the client. However, if no update exists, the server code application sets a well-defined HTTP response header, and then responds. Once the server code application responds, all application server resources are freed, and the application server is free to handle the next requests without blocking any thread. The existence of the well-defined response header, allows the lower level networking code to queue the response, allowing it to be later addressed by the RTC session ID. This way, the HTTP response can be delayed (queued) without blocking a thread in the application server. A Change Request is a request used to change some data related to the real-time session. Such requests would typically be tied to an action within a given RTC session (e.g., adding text to a chat, changing a slide, etc.). When these actions are sent to the server, the server-side application can determine whether the request affects the queued responses that are awaiting change notifications. In the case of a change, the notification response is computed, and then an API call into the lower-level network flushes all queued responses awaiting updates in the session. Therefore this mechanism is used to trigger the responses to complete, thus providing immediate updates to clients.
Owner:IBM CORP
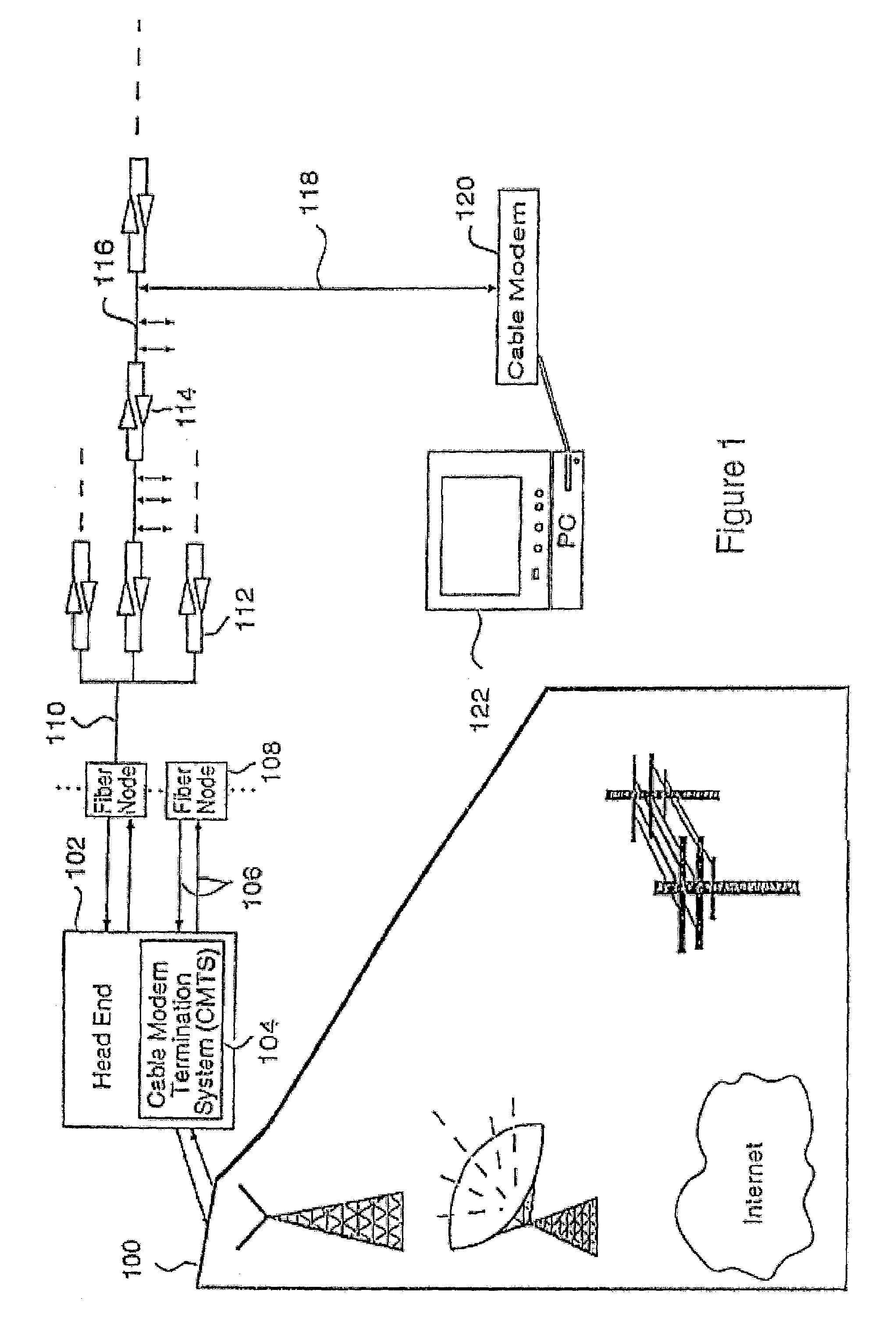
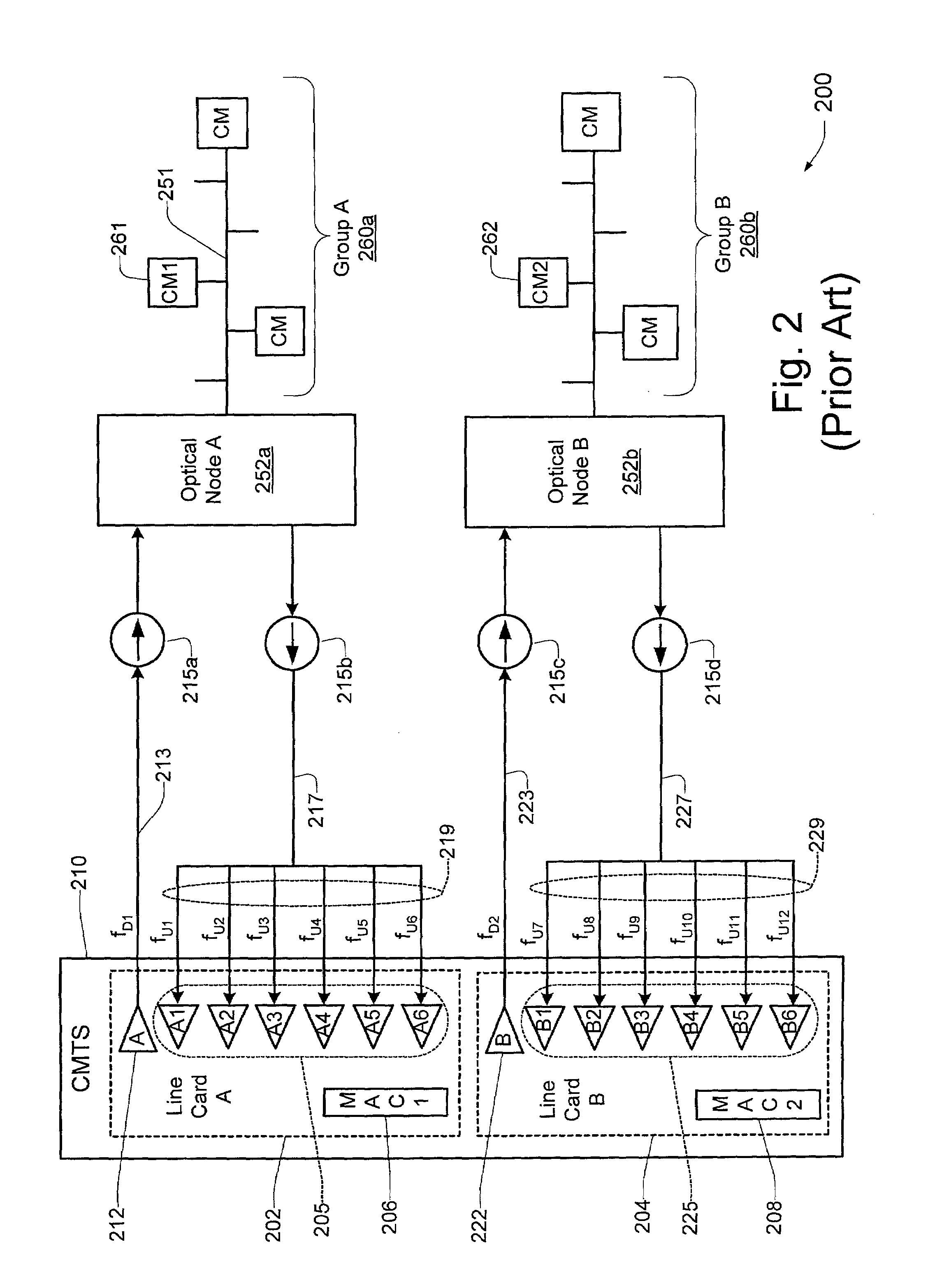
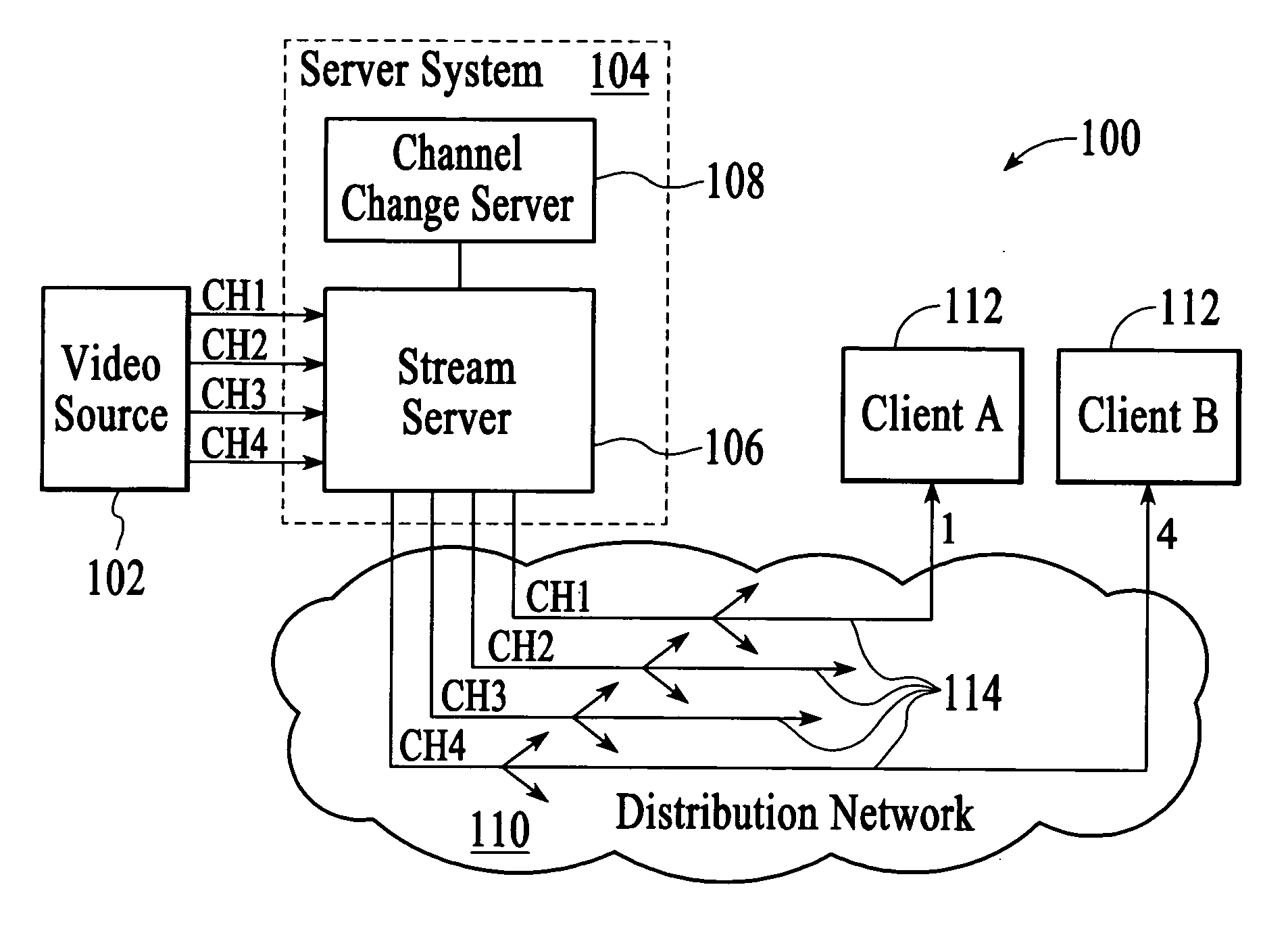
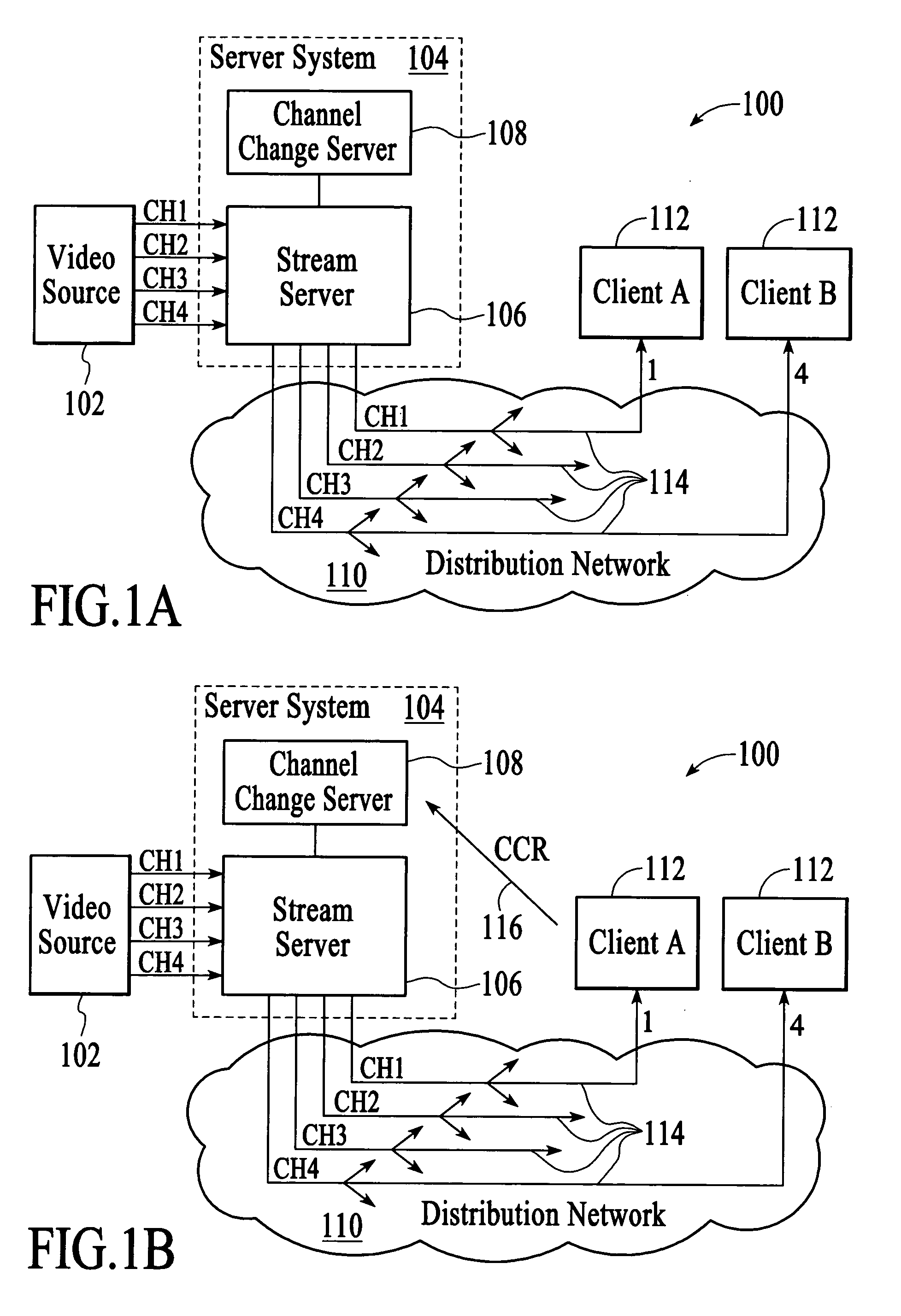
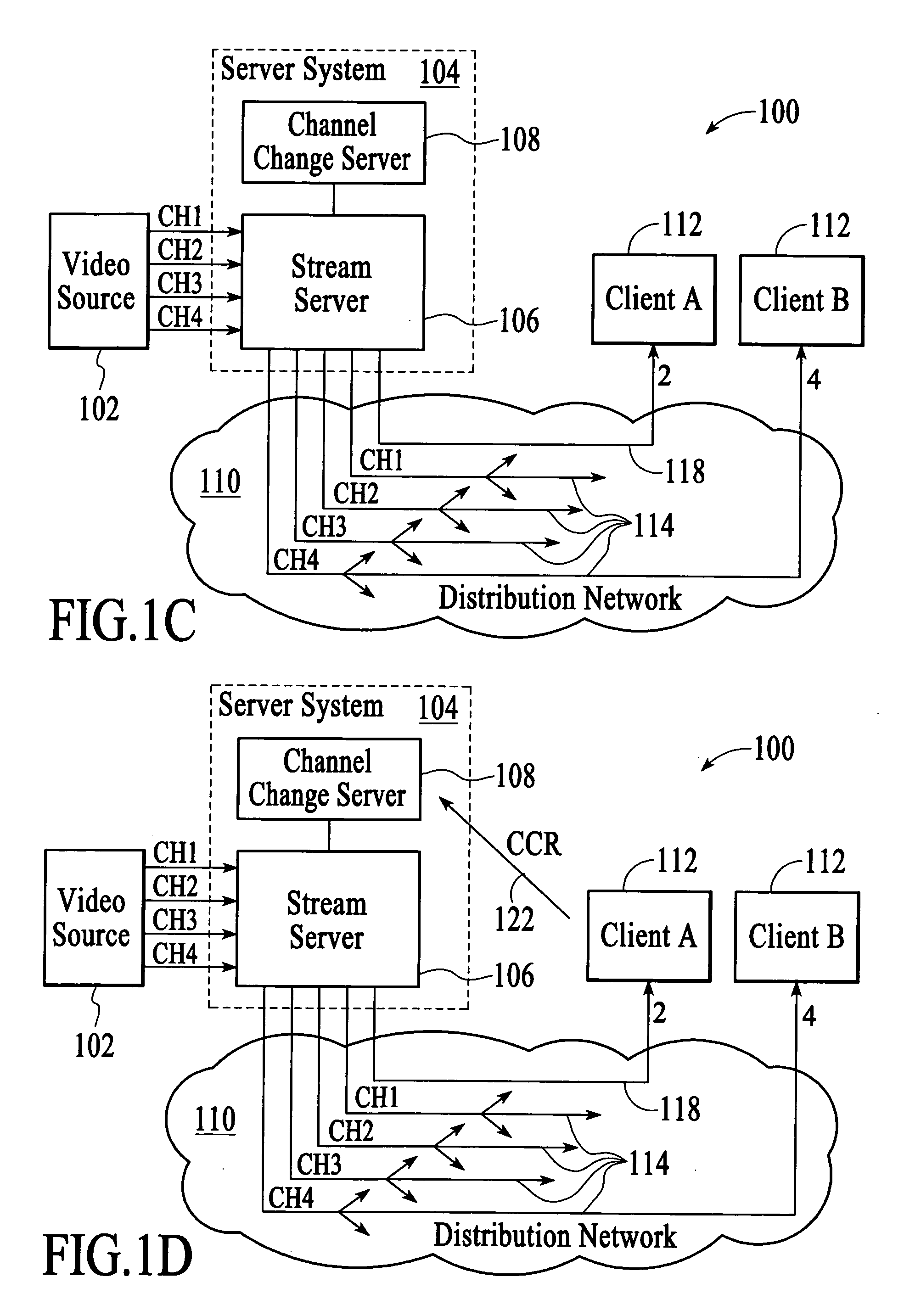
Downstream channel change technique implemented in an access network
A dynamic channel change technique is disclosed which may be implemented between nodes and a Head End of an access network. Initially a network device may communicate with the Head End via a first downstream channel and a first upstream channel. When the network device receives a dynamic channel change request which includes instructions for the network device to switch to a second downstream channel, the network device may respond by switching from the first downstream channel to the second downstream channel. Thereafter, the network device may communicate with the Head End via the second downstream channel and first upstream channel. Further, according to a specific embodiment, the dynamic channel change request may also include an upstream channel change request for causing the network device to switch from a first upstream channel to a second upstream channel.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
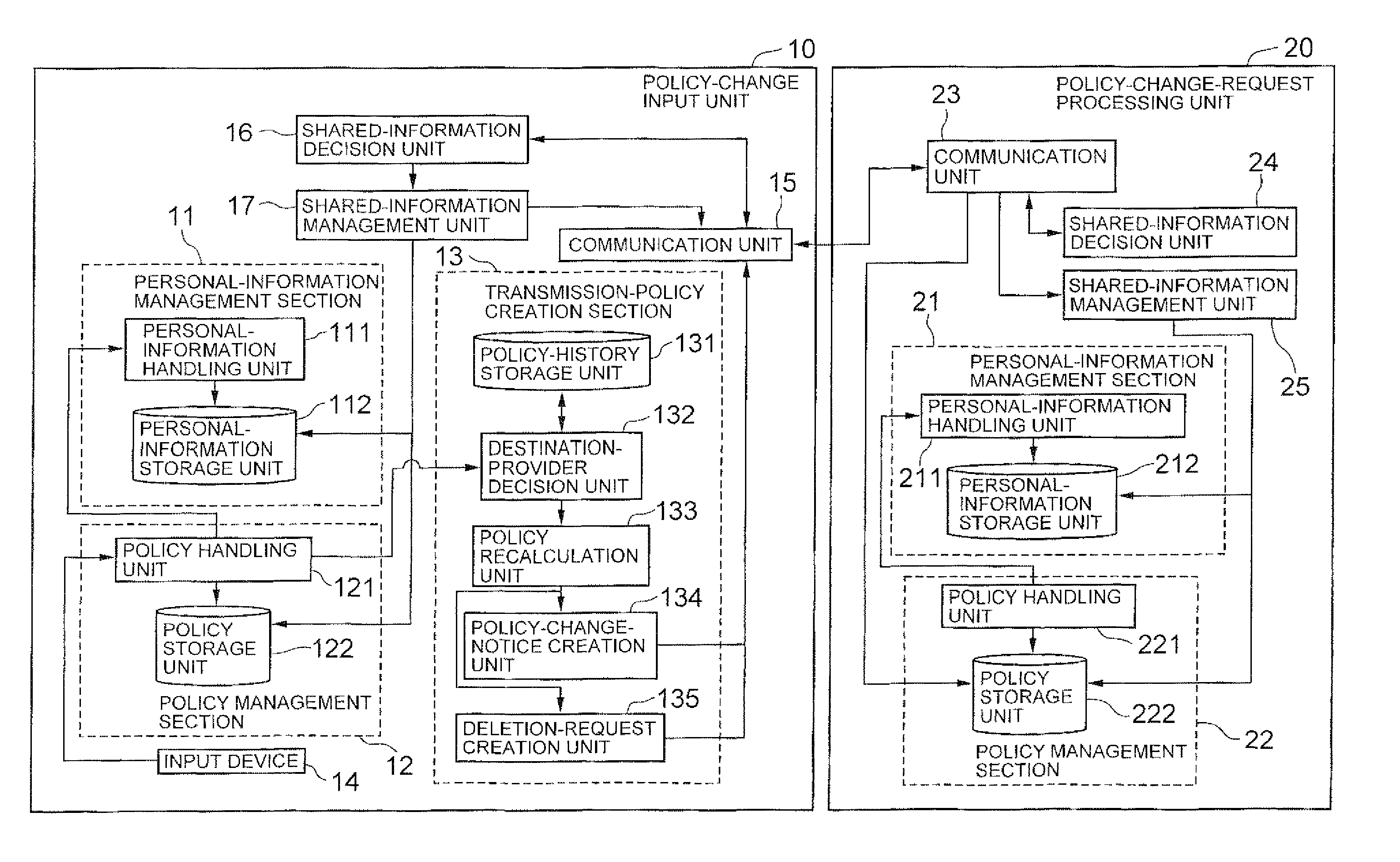
Sharing management system, sharing management method and program
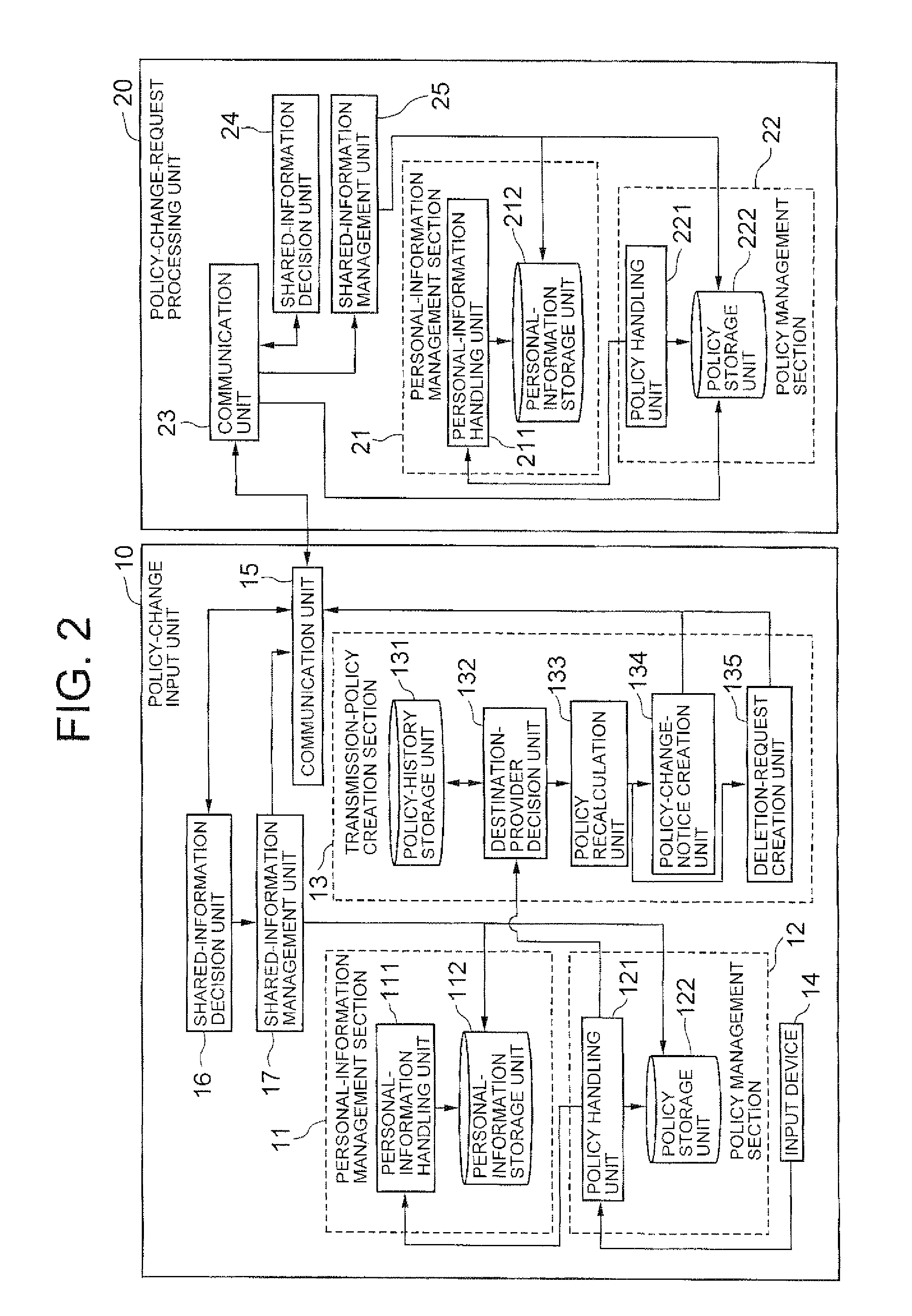
In a policy-change input unit (10), a policy recalculation unit (133) compares, upon occurring of a change request of a privacy policy from a user, an existing policy against an updating policy, recalculates a transmission policy to be transmitted to other providers based on the result of comparison, and transmits the recalculated policy to the other policy. The policy recalculation unit (133) transmits a deletion request of personal information to another provider by using a deletion-request creation unit, upon judging that the another provider cannot use the personal information due to the change of privacy policy.
Owner:NEC CORP
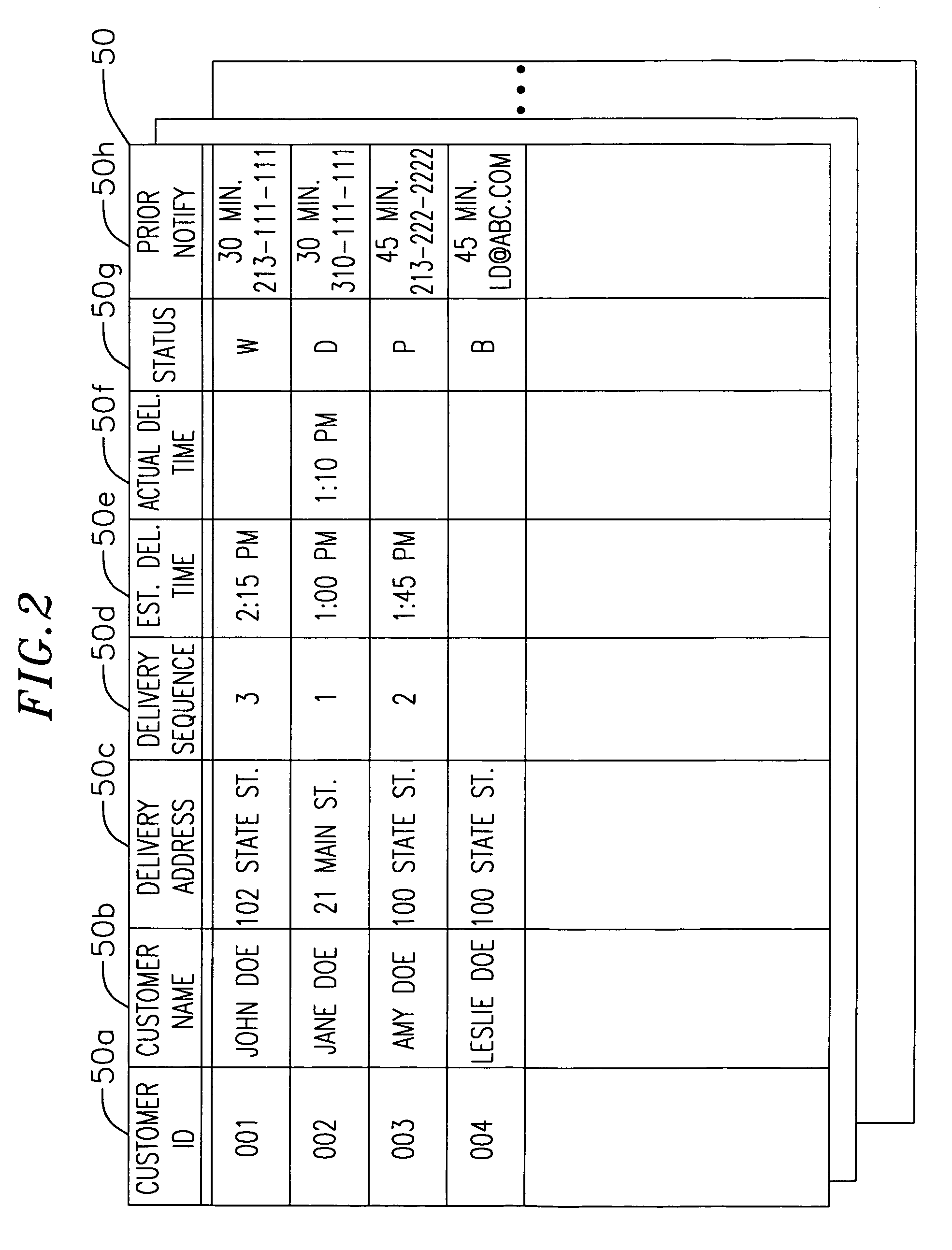
System and method for continuous delivery schedule including automated customer notification
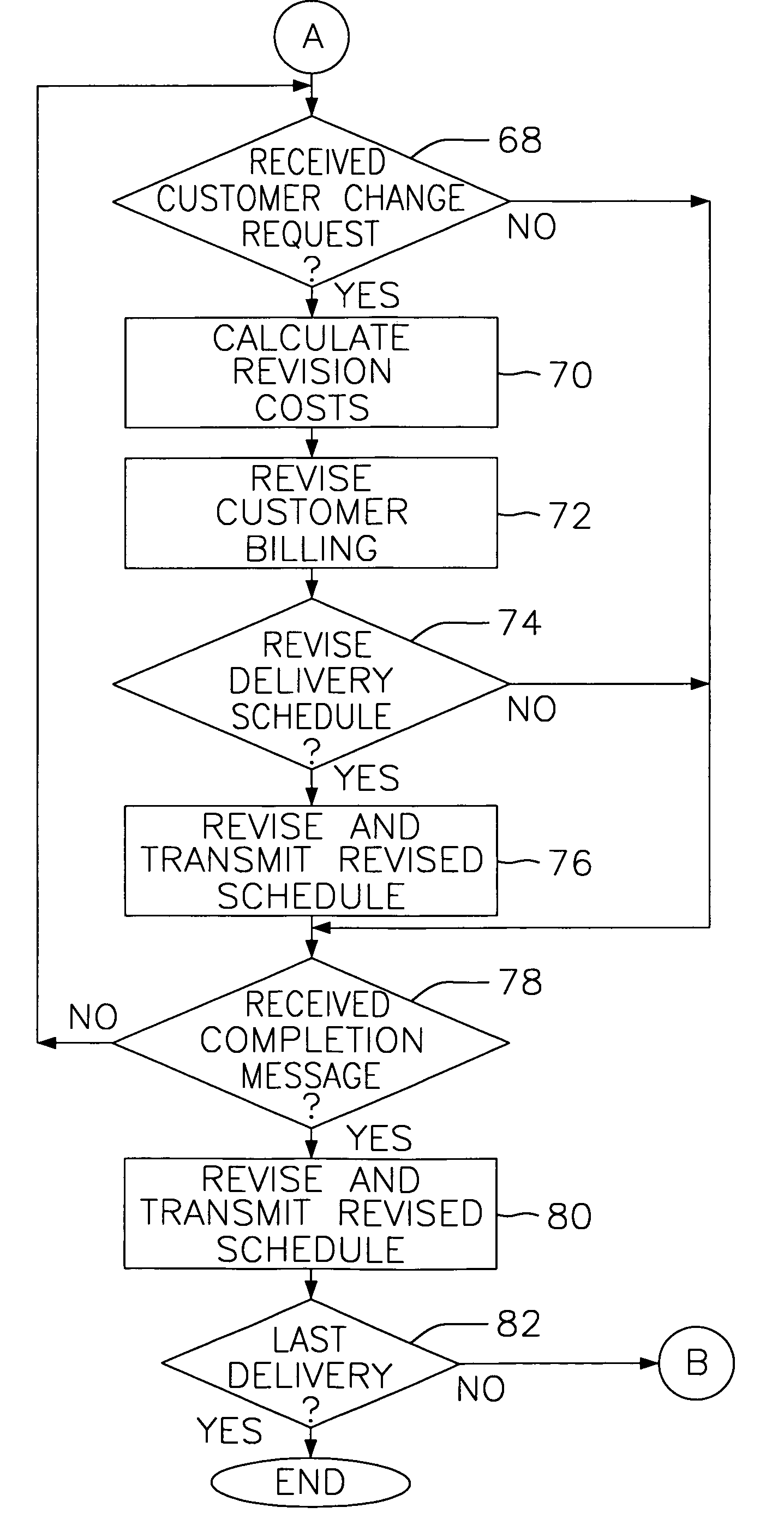
A system and method for continuously monitoring and updating delivery schedules based on completed deliveries and customer modifications. A delivery scheduling computer stores and updates delivery schedule information, notifying the customer prior to a scheduled delivery of an estimated time of delivery. The notification is made to a customer's PC, browser-based client, hand-held computer or set-top box, or by conventional communication methods such as a telephone, pager, or cellular phone. If the customer desires to change the time or location of the delivery, the customer transmits a delivery change request and the schedule is modified accordingly. Employees use a hand-held computer or a browser-based client to receive updated delivery schedule information, as well as to transmit a delivery completion message to the delivery scheduling computer. The message includes an actual delivery time which the delivery scheduling computer uses to update the estimated delivery times of the remaining deliveries.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
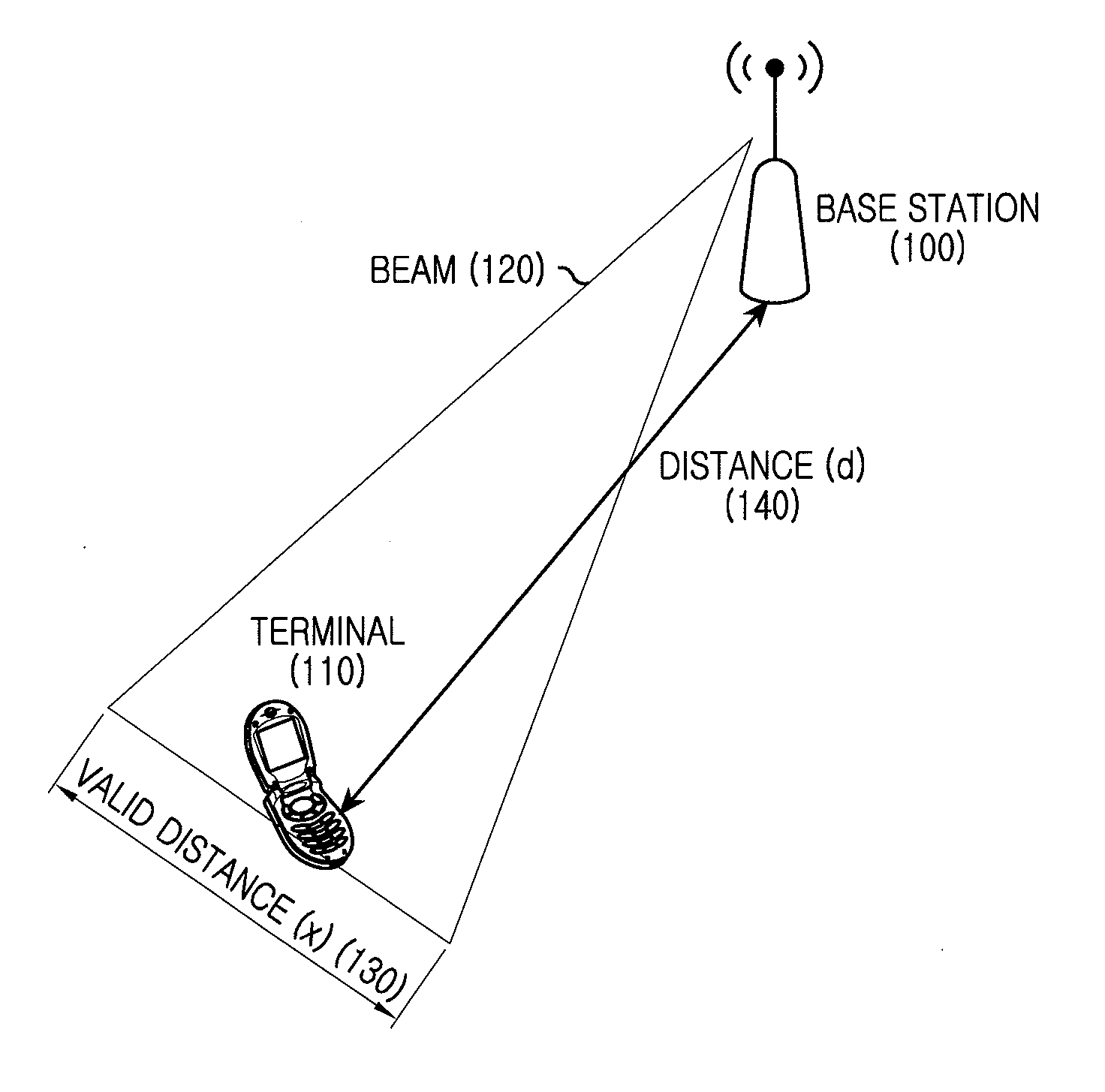
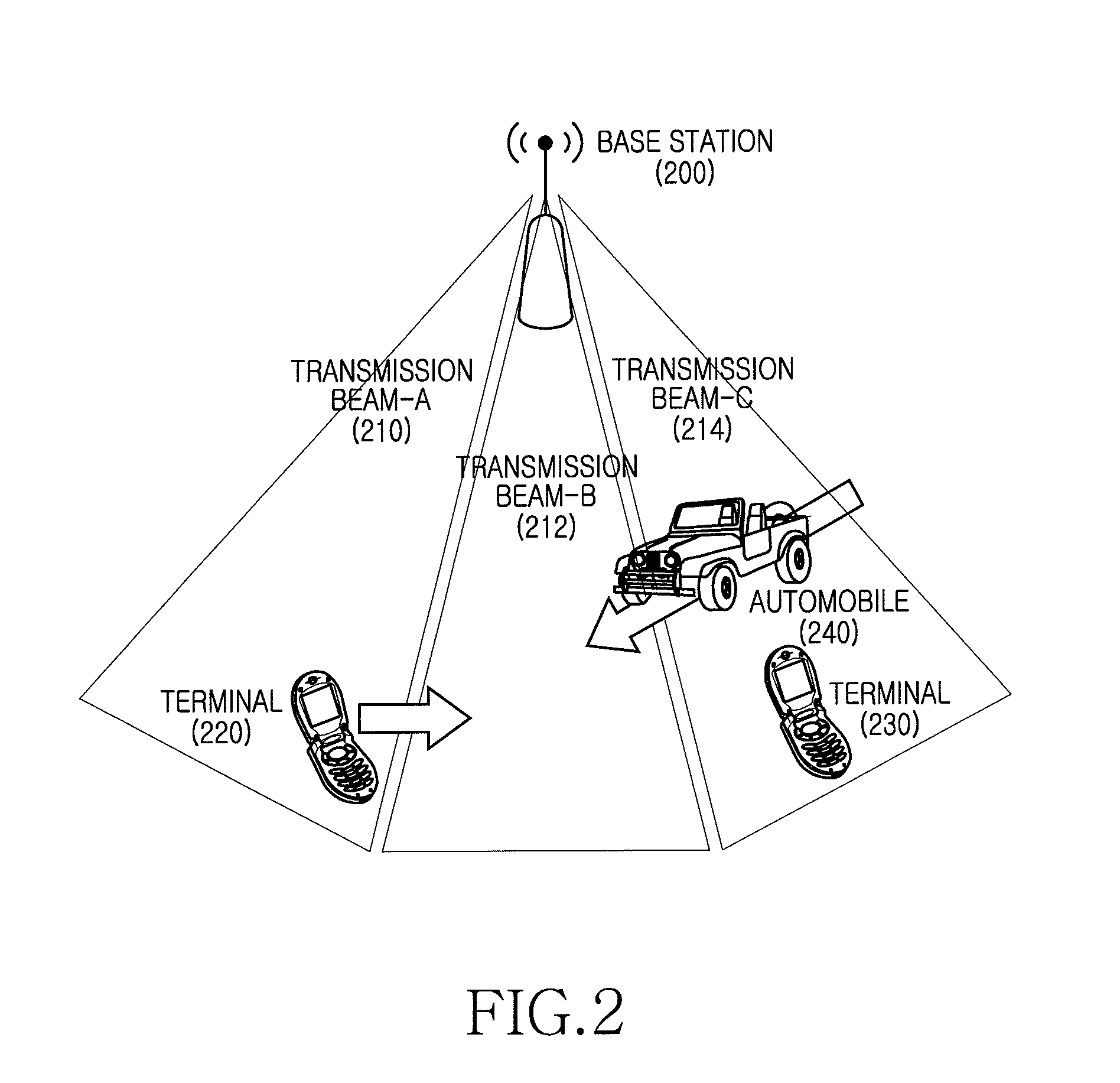
Apparatus and method for adaptive beam-forming in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20130039345A1Effectively performing beam-formingImprove performanceError preventionNetwork topologiesCommunications systemTelecommunications
Apparatuses and methods for maintaining an optimal beam direction in a wireless communication system are provided. The method for operating a receiving node in a wireless communication system includes, determining a first transmission beam is determined as a preferred transmission beam using a plurality of reference signals transmitted by a transmitting node, generating preferred transmission beam information, transmitting the preferred transmission beam information to the transmitting node, receiving transmissions from the transmitting node via the first transmission beam, and determining whether a change of a transmission beam is necessary. When the change of the transmission beam is determined to be necessary, generating a beam change request and transmitting the beam change request to the transmitting node.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
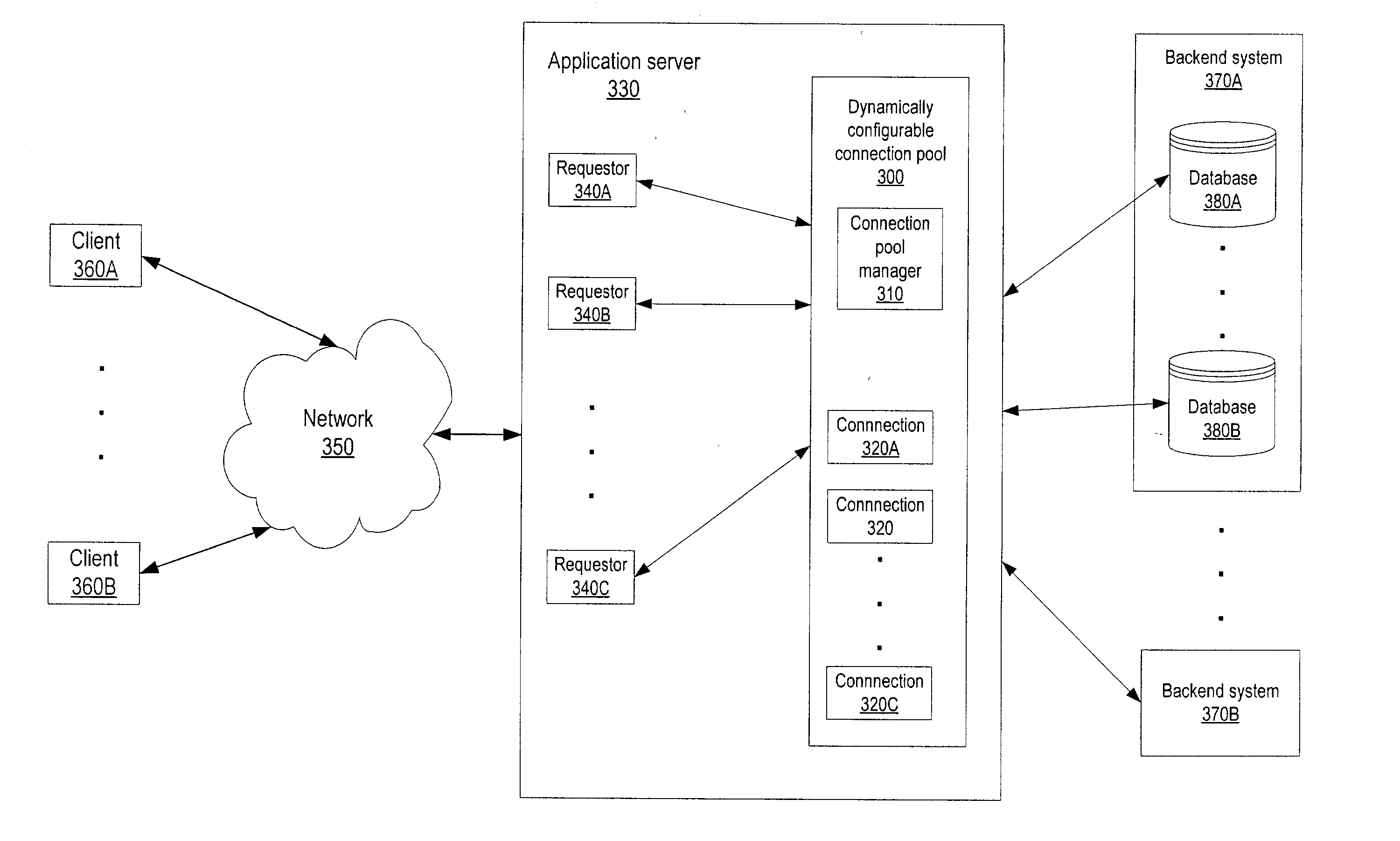
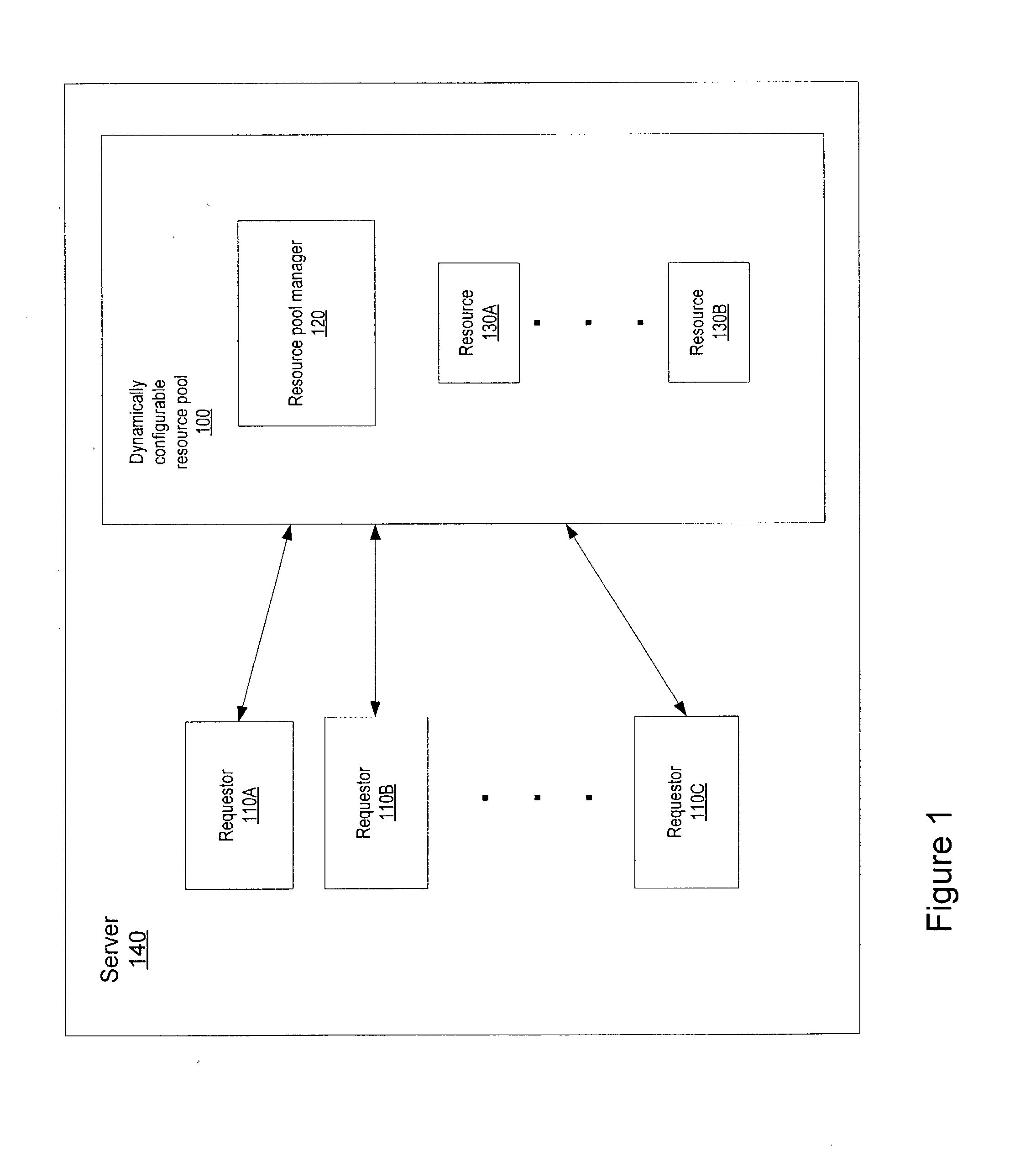
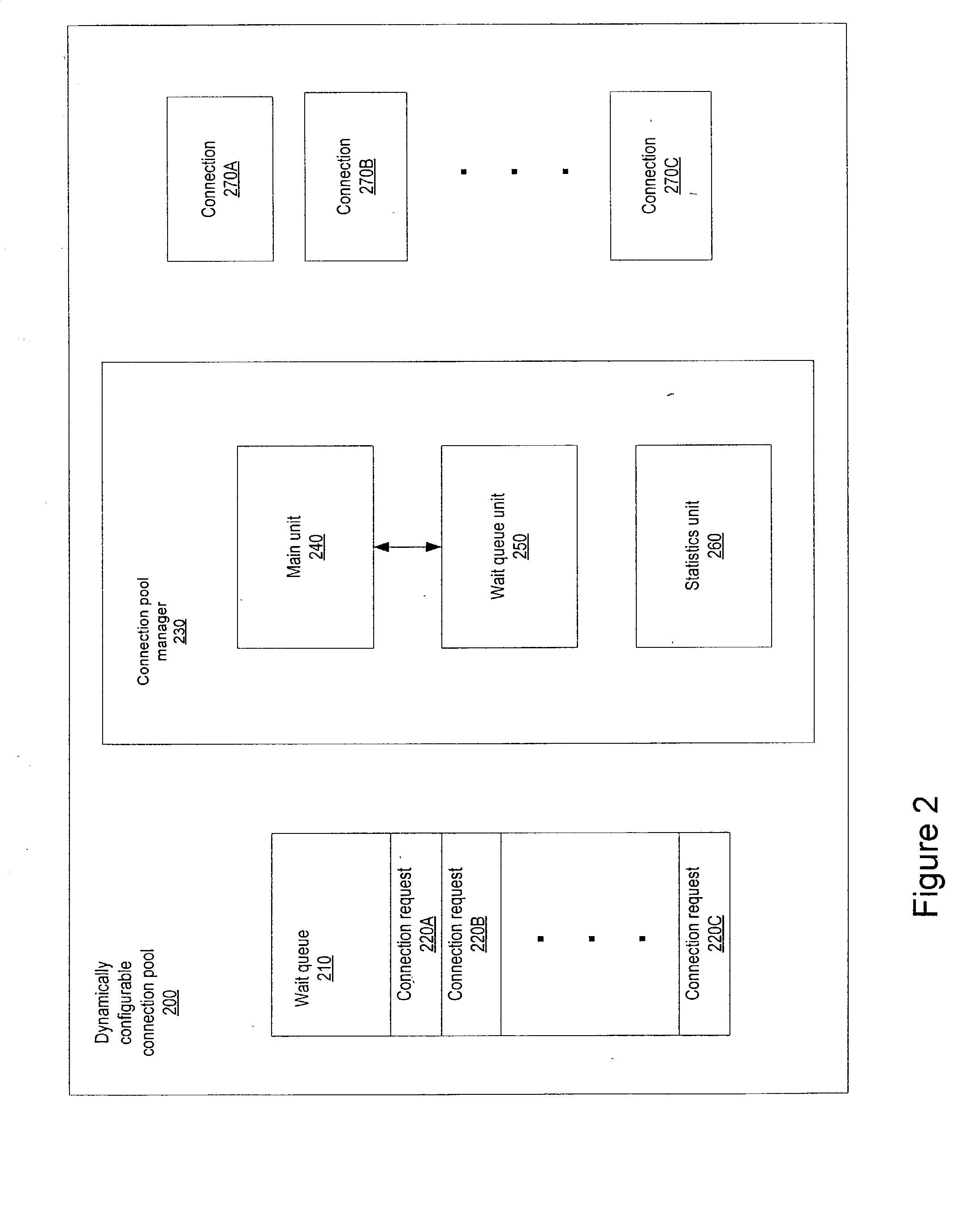
Dynamically configurable resource pool
ActiveUS20040088413A1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsResource poolWeb service
A dynamically configurable resource pool may provide a pool of computing resource for use in a computing system or application, such as a connection pool or a thread pool for server systems such as application and web server systems. In one embodiment, a server may include a resource pool configured to provide a plurality of computing resources. Other components in the server may be configured to request use of one of the computing resources from the connection pool. The resource pool may include a resource pool manager configured to service requests for the computing resources. The resource pool manager may manage configuration of the resource pool. The resource pool manager may also be configured to receive a configuration change request to change the configuration of the resource pool while the resource pool is available for use.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Network management apparatus, network management method, and network management system
InactiveUS20140064056A1Improve network use efficiencyEasy to identifyError preventionTransmission systemsNetwork managementChange request
A network management apparatus is designed so that when reassigning the existing address, the network management apparatus extracts a link with the largest link cost from among links comprising the network based on the network configuration information and specifies a flow routed though the extracted link based on the statistic information; when receiving a path change request and a via link request to request a via link with respect to the specified flow from an external terminal, the network management apparatus selects either one of addresses of an address pair of the specified flow as a change target address; and when changing the selected change target address, the network management apparatus changes the change target address to a candidate address to be assigned by selecting an address, which is routed through a link included in the via link request and has not been assigned, as the candidate address to be assigned.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
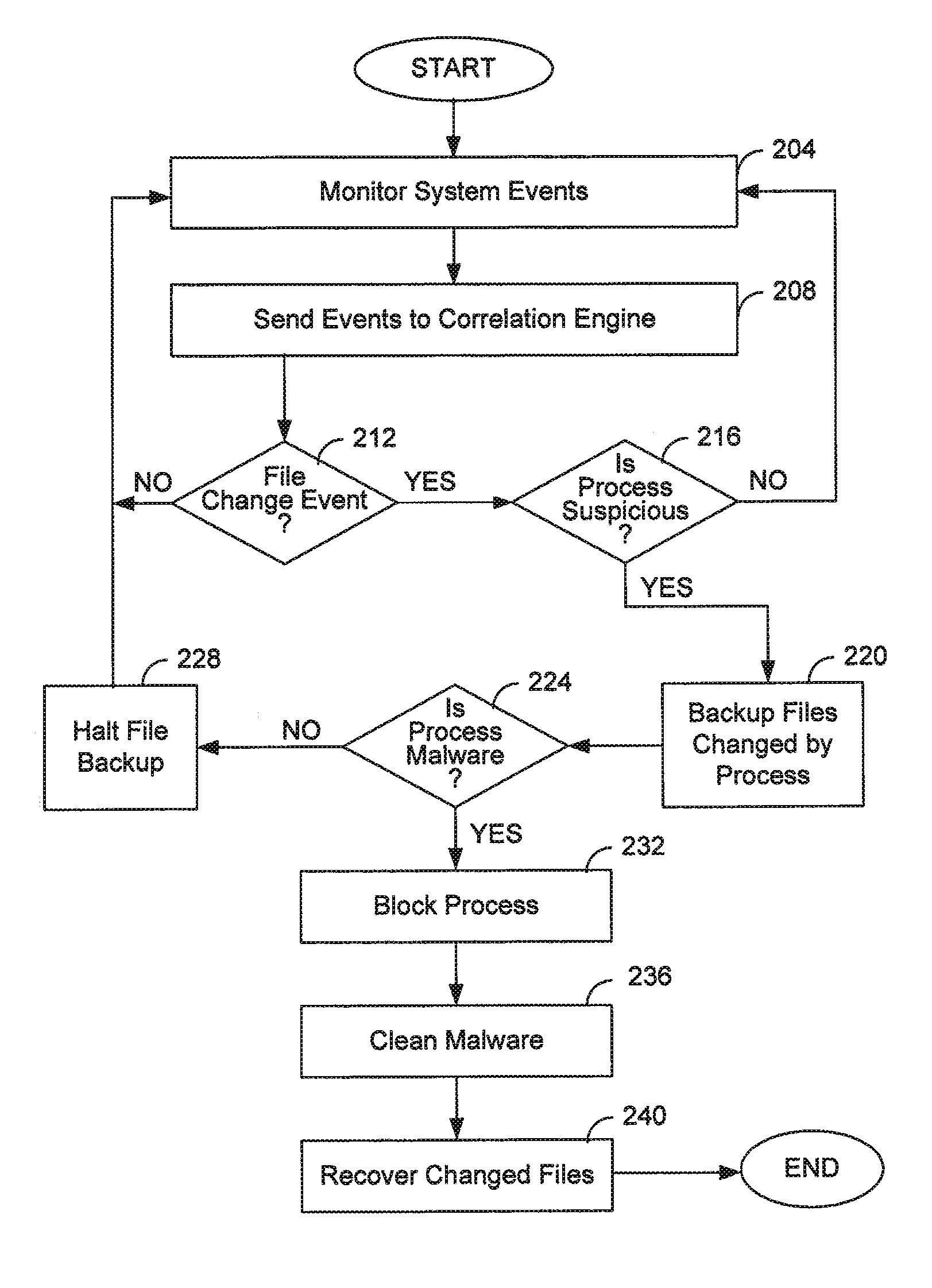
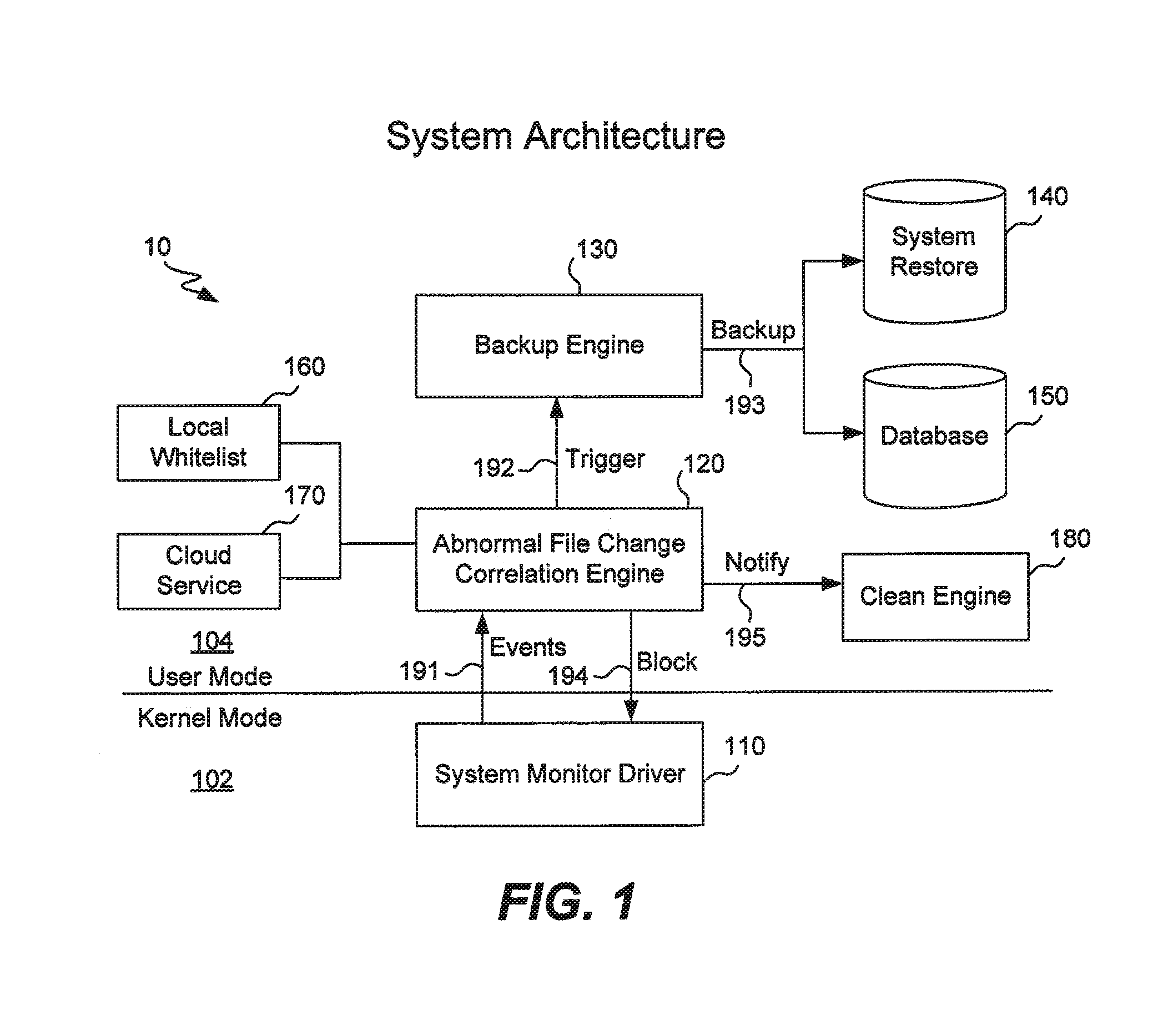
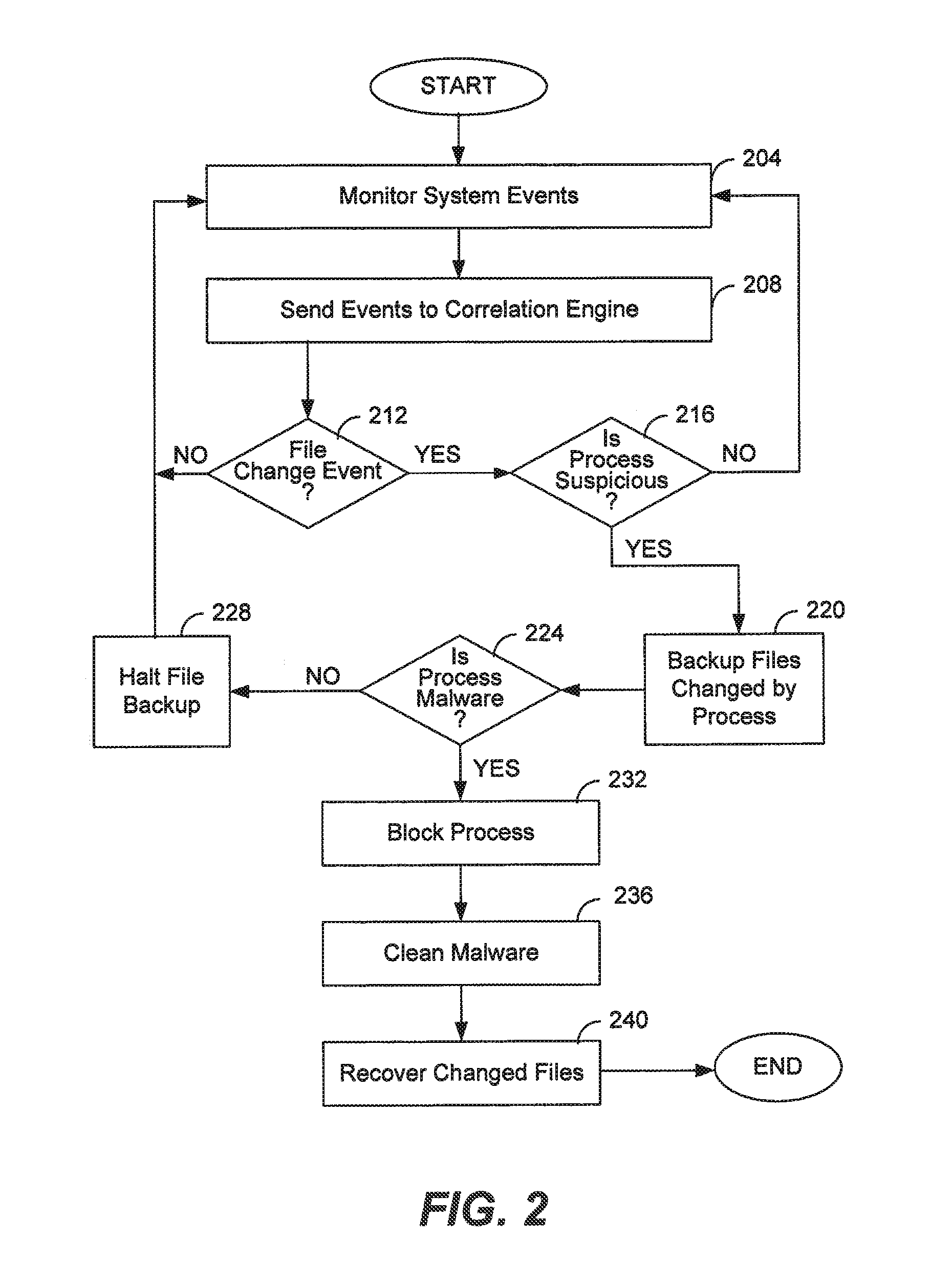
File backup to combat ransomware
ActiveUS9317686B1Prevent encryptionLimited impact on system performancePlatform integrity maintainanceRedundant operation error correctionOperational systemFilename extension
Operating system events are monitored and a file change request of a process is detected. If the process is suspicious, then the file to be changed is backed up and then the process is allowed to change the file as requested. If it is later determined that the process is ransomware, the process is blocked and further file backups are halted. The original file is recovered and the encrypted file is discarded. If it is later determined that the process is not malicious, then further file backups are halted. Any backup files are discarded. Ransomware may be detected by comparing a file extension of the process with file extensions of any files requested to be changed, by comparing file extensions of any files requested to be changed, or by an analysis of behavior of the process itself.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
Method for implementing dynamic virtual lane buffer reconfiguration
InactiveUS20050060445A1Without effectOvercome disadvantagesData switching networksInput/output processes for data processingProcessor registerChange request
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided for implementing dynamic Virtual Lane buffer reconfiguration in a channel adapter. A first register is provided for communicating an adapter buffer size and allocation capability for the channel adapter. At least one second register is provided for communicating a current port buffer size and one second register is associated with each physical port of the channel adapter. A plurality of third registers is provided for communicating a current VL buffer size, and one third register is associated with each VL of each physical port of the channel adapter. The second register is used for receiving change requests for adjusting the current port buffer size for an associated physical port. The third register is used for receiving change requests for adjusting the current VL buffer size for an associated VL.
Owner:IBM CORP
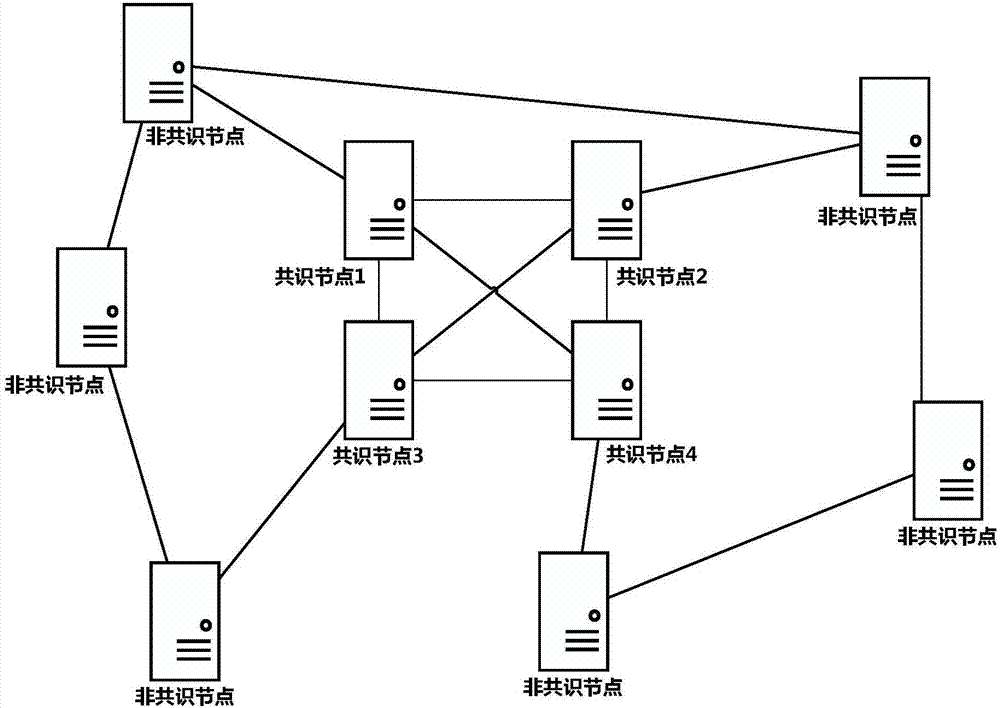
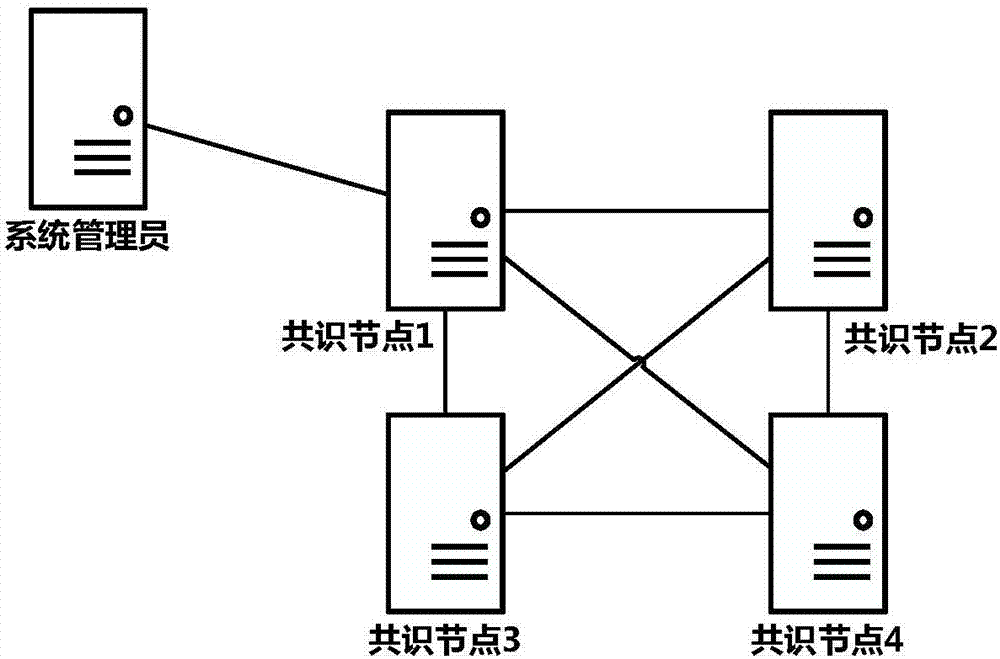
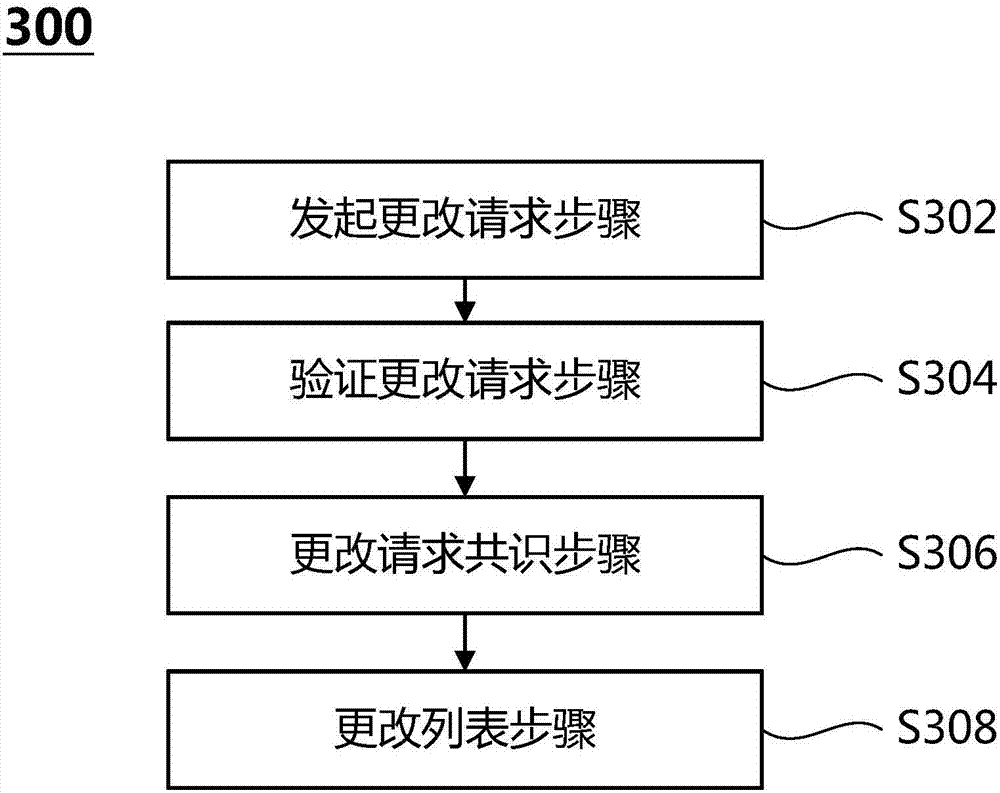
Method for dynamically changing consensus node in practical Byzantine fault tolerant consensus mechanism
ActiveCN107579848ASafe and reliable dynamic changesDynamically change the implementationFault responseData switching networksByzantine fault toleranceSmart contract
The invention provides a method for dynamically changing a consensus node in a practical Byzantine fault tolerant consensus mechanism. The method comprises the following steps: a system administratorinitiates a change request of increasing or decreasing the consensus node to the consensus node as a system-level transaction, and the change request is signed by using a private key of the system administrator; the consensus node verifies the change request, if the verification is successful, a special system transaction head is added to the change request, the change request is broadcast, and each consensus node puts the change request into a priority transaction queue; a new round of consensus operation is performed, a selected proposal node proposes a proposal block including the change request and broadcasts the proposal block to all consensus nodes, all the consensus nodes verify transactions in the proposal block, firstly verify the transaction heads of the transactions, and enter system transaction operation logic rather than smart contracts when a special system transaction head is verified; and after reaching a consensus, the node executes the change request and updates a consensus node set list, and the updated consensus node set list is stored to a local file of the nodes.
Owner:上海保险交易所股份有限公司
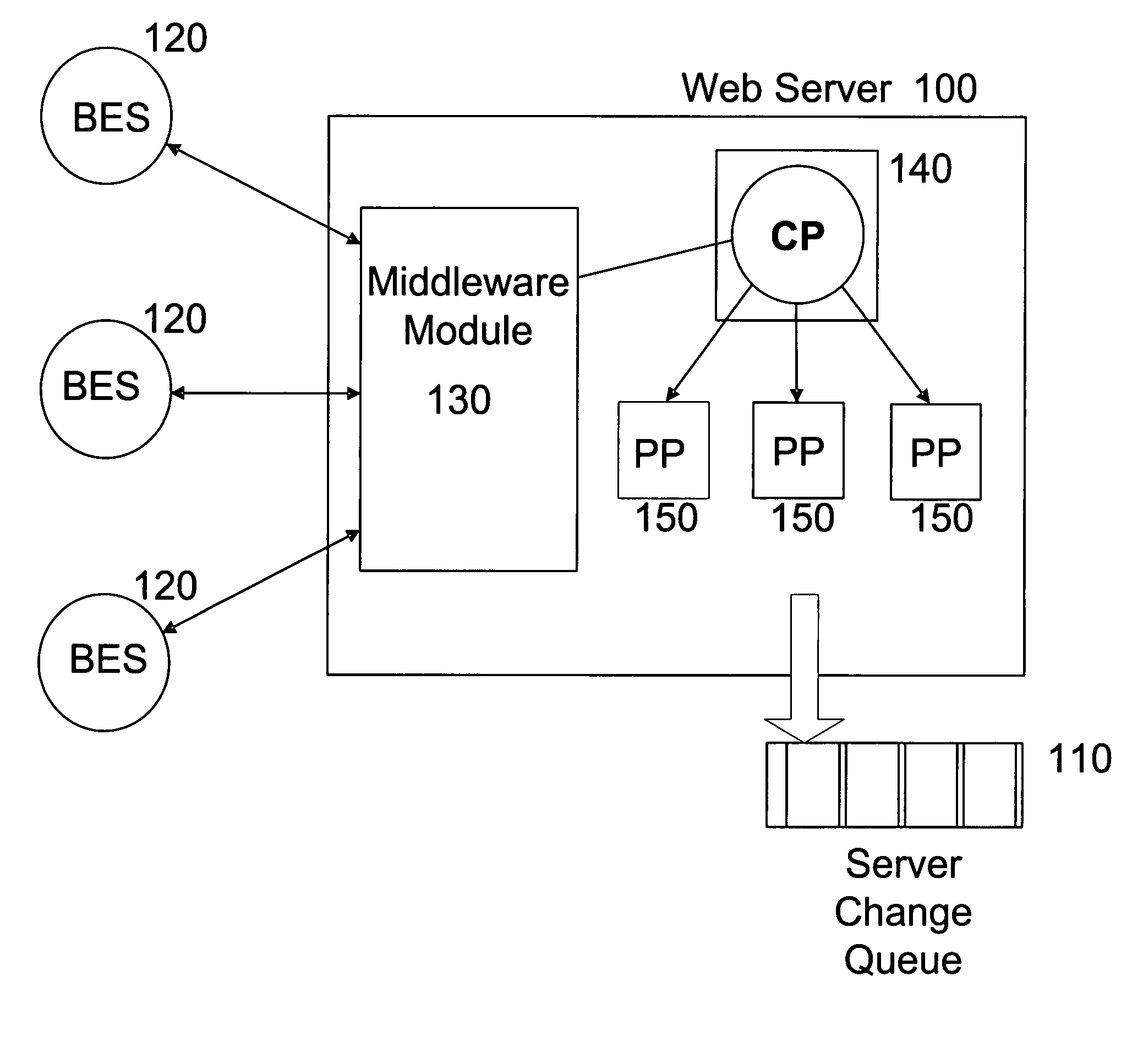
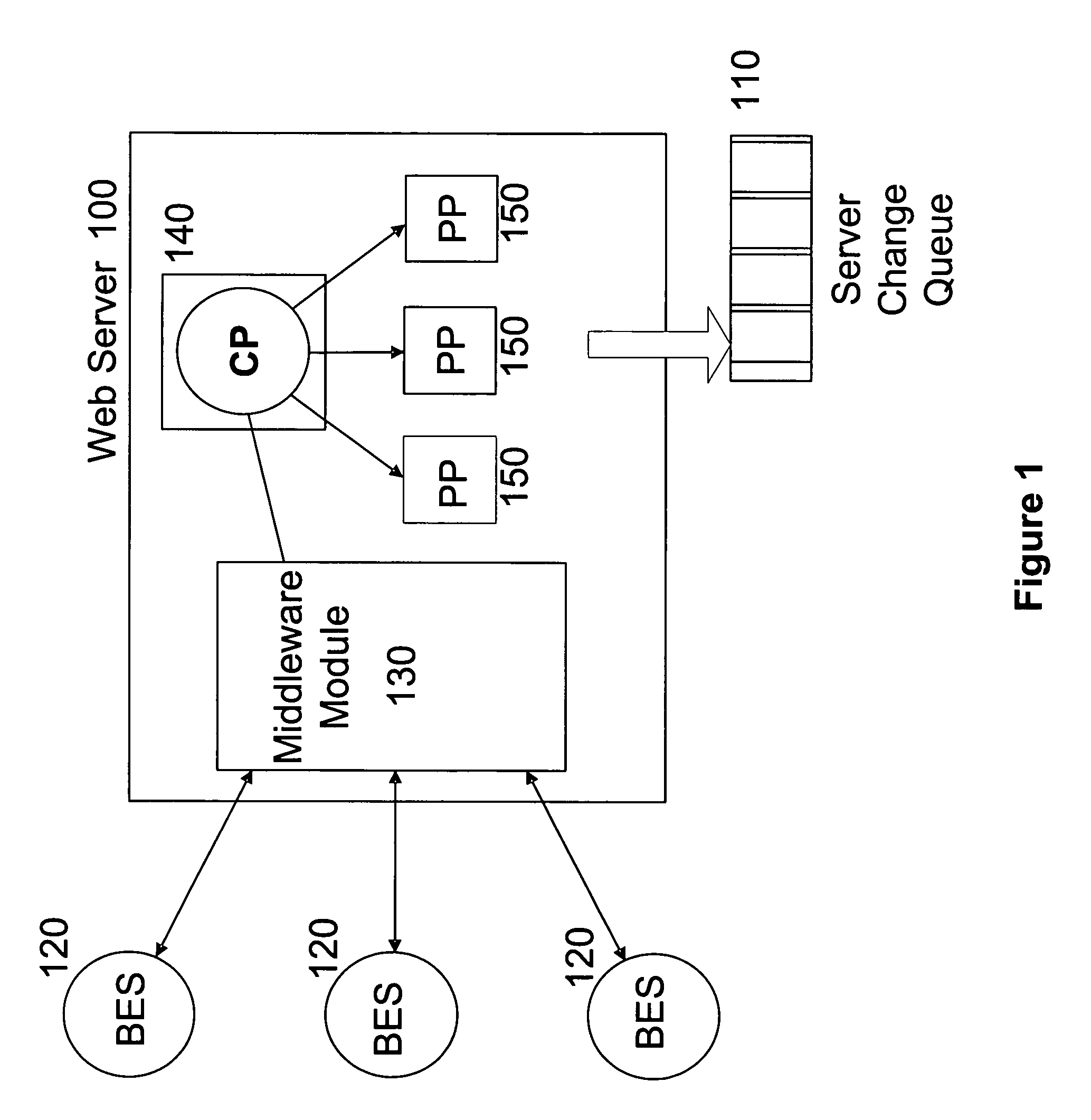
Method and apparatus for prioritizing data change requests and maintaining data consistency in a distributed computer system equipped for activity-based collaboration
InactiveUS6859821B1Substantial consistency of dataDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsChange requestCollaboration
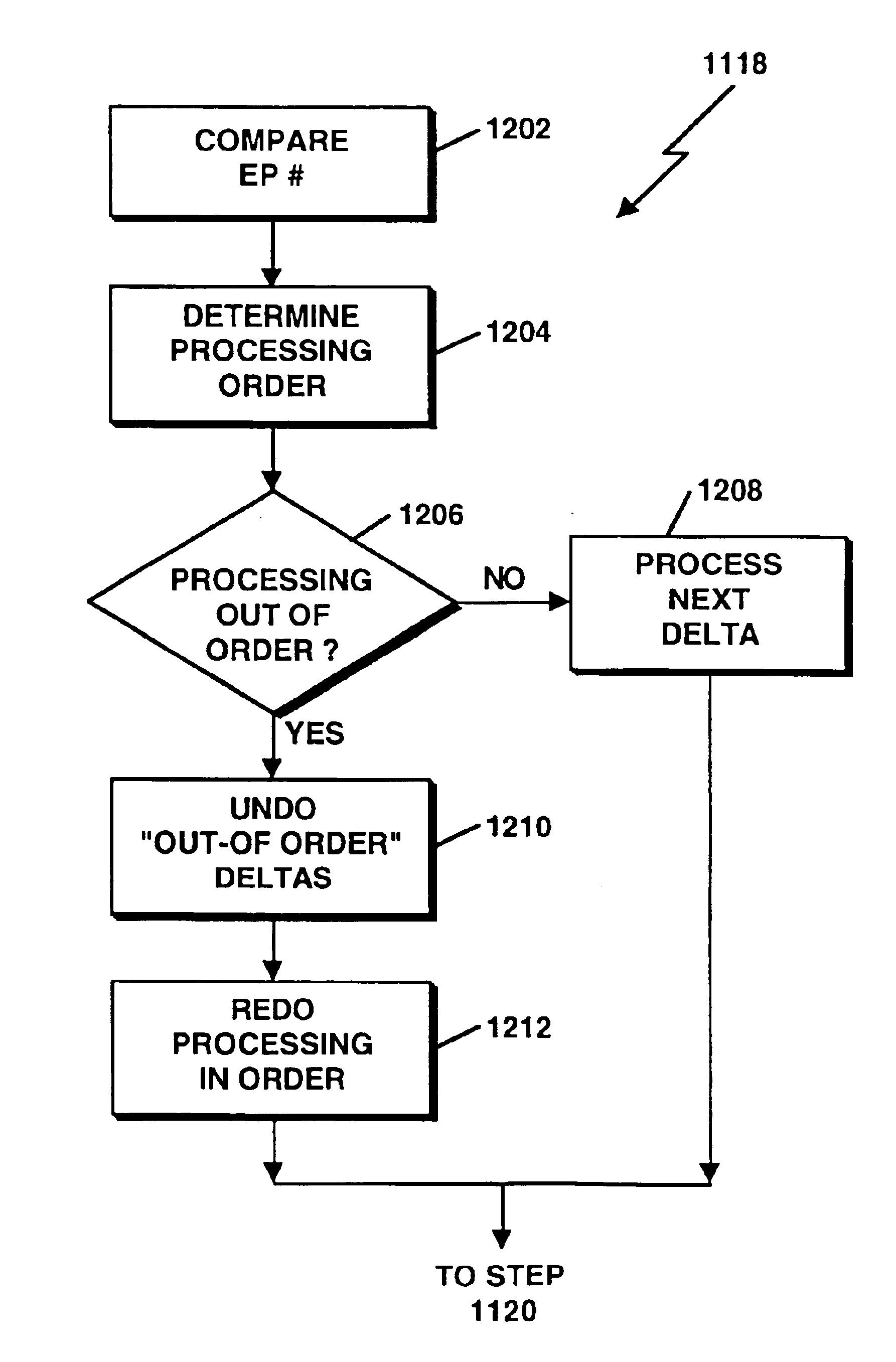
A distributed, activity-based collaboration system can employ a data change request priority scheme for determining an order of execution of data change requests in effecting changes to local copies of data so as to optimize data consistency for collaborative activities. The data change request priority scheme can entail encoding sequence number information and dependency information in the data change requests, responsive to which data changes can be made, unmade and remade to the data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
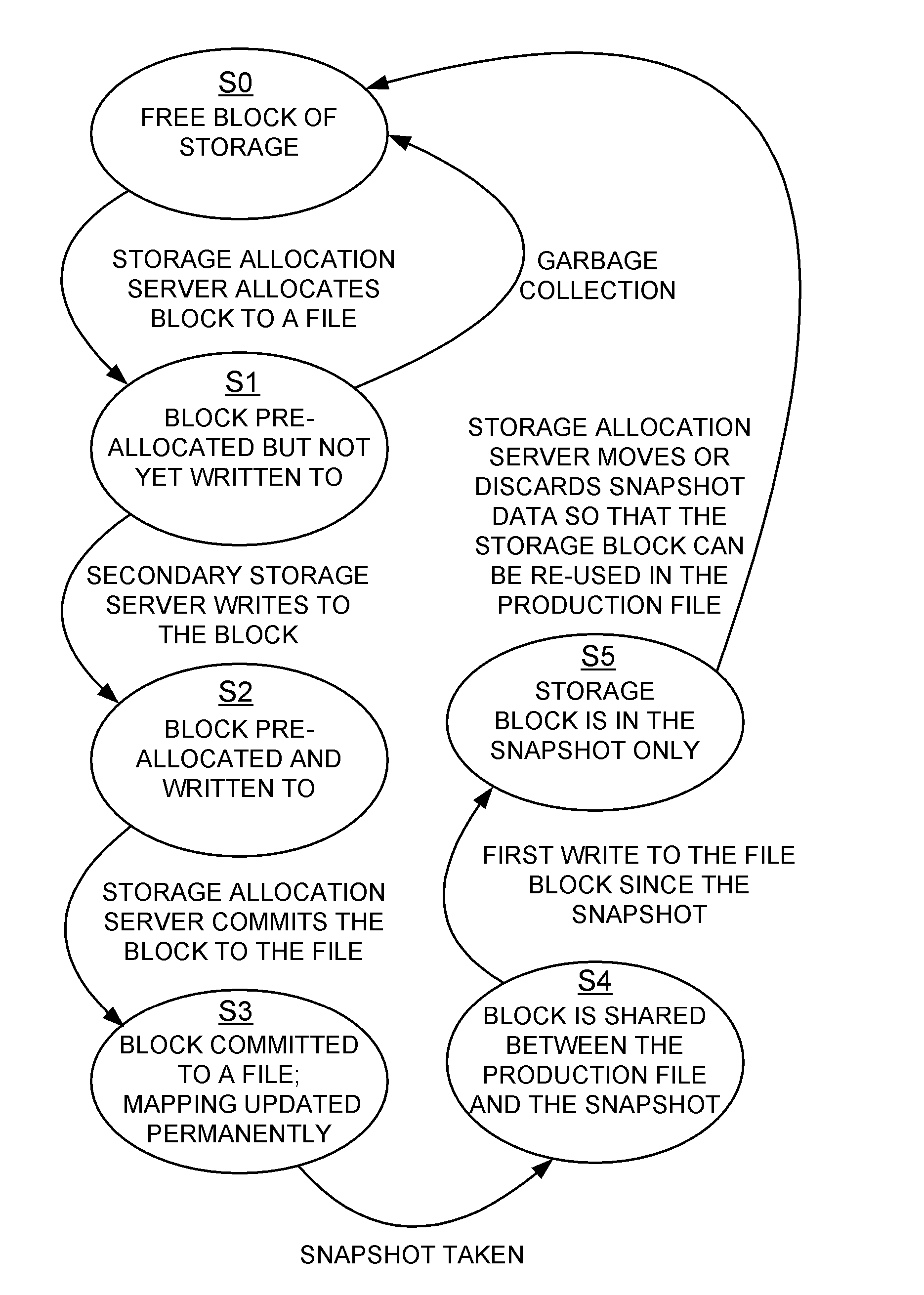
Distributed maintenance of snapshot copies by a primary processor managing metadata and a secondary processor providing read-write access to a production dataset
ActiveUS20070260830A1Degrades I/O performanceImprove I/O performanceMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsData setCoprocessor
A primary processor manages metadata of a production dataset and a snapshot copy, while a secondary processor provides concurrent read-write access to the primary dataset. The secondary processor determines when a first write is being made to a data block of the production dataset, and in this case sends a metadata change request to the primary data processor. The primary data processor commits the metadata change to the production dataset and maintains the snapshot copy while the secondary data processor continues to service other read-write requests. The secondary processor logs metadata changes so that the secondary processor may return a “write completed” message before the primary processor commits the metadata change. The primary data processor pre-allocates data storage blocks in such a way that the “write anywhere” method does not result in a gradual degradation in I / O performance.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Flexible traffic management and shaping processing for multimedia distribution
InactiveUS8214868B2Efficient deliveryReduce delaysMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsTime segmentData rate
Owner:INTEL CORP
Fast channel change with conditional return to multicasting
ActiveUS20070107026A1Efficient use of resourcesManagement intelligenceData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital videoClient-side
In a digital video network that is capable of distributing digital video content to a client via multicasting and unicasting, servicing a channel change request from a client involves switching from providing the digital video content to the client via multicasting to providing the digital video content to the client via unicasting and continuing to provide digital video content to the client via unicasting until a pre-established condition is met. Continuing to provide digital video content to the client via unicasting until a pre-established condition is met allows the network to opportunistically switch the client from unicasting back to multicasting.
Owner:SYNAMEDIA LTD
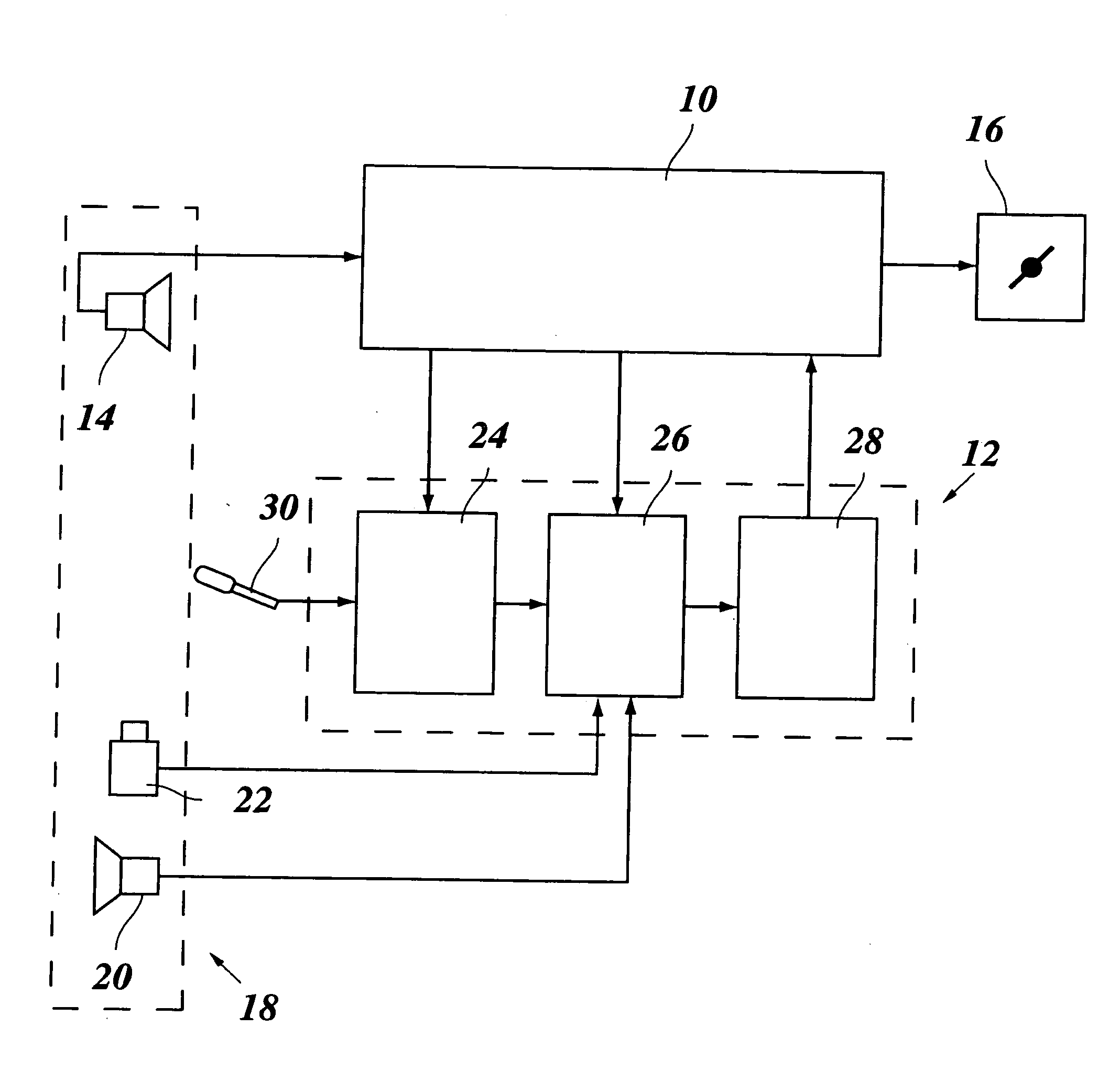
Lane changing assistant for motor vehicles
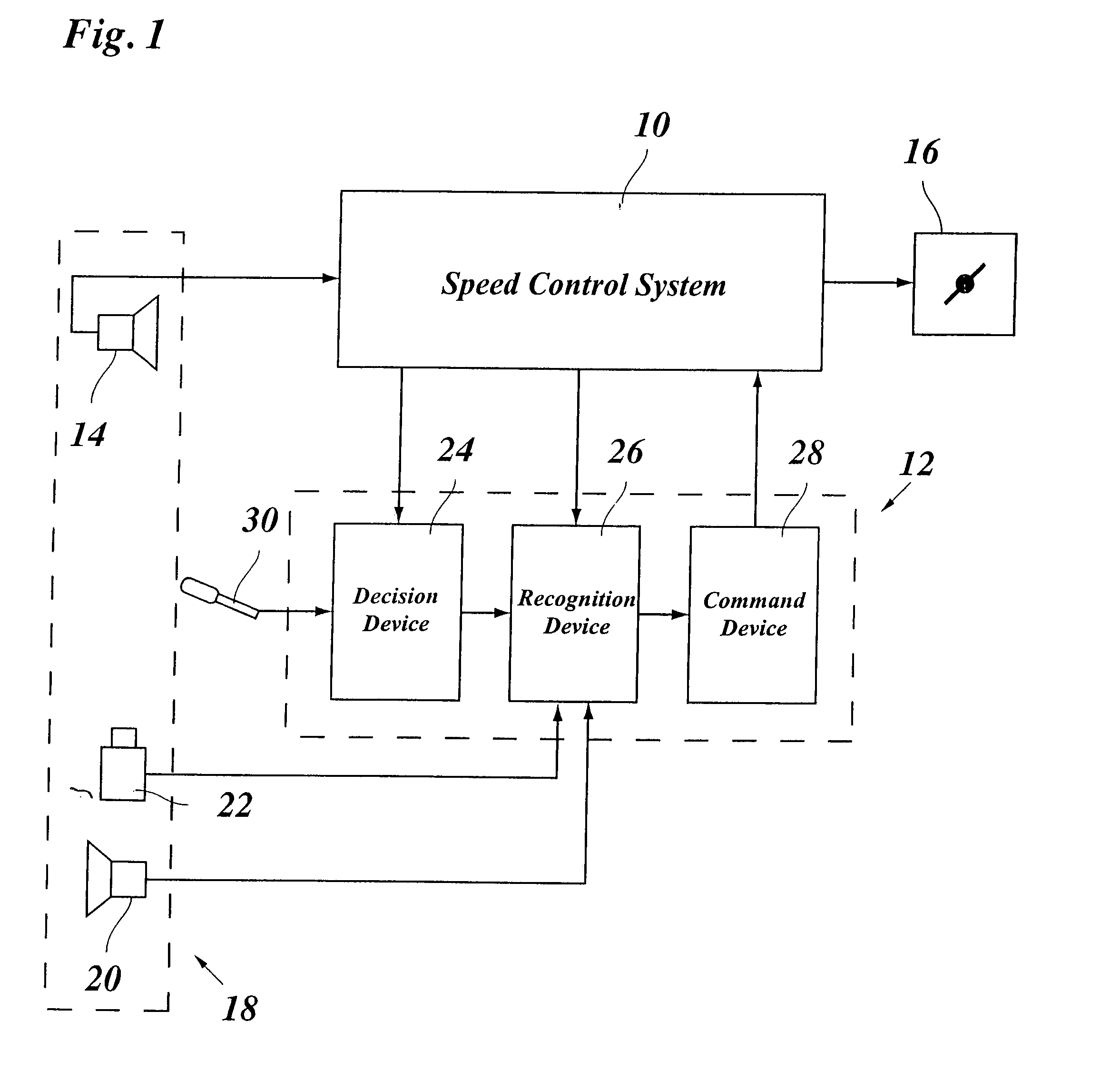
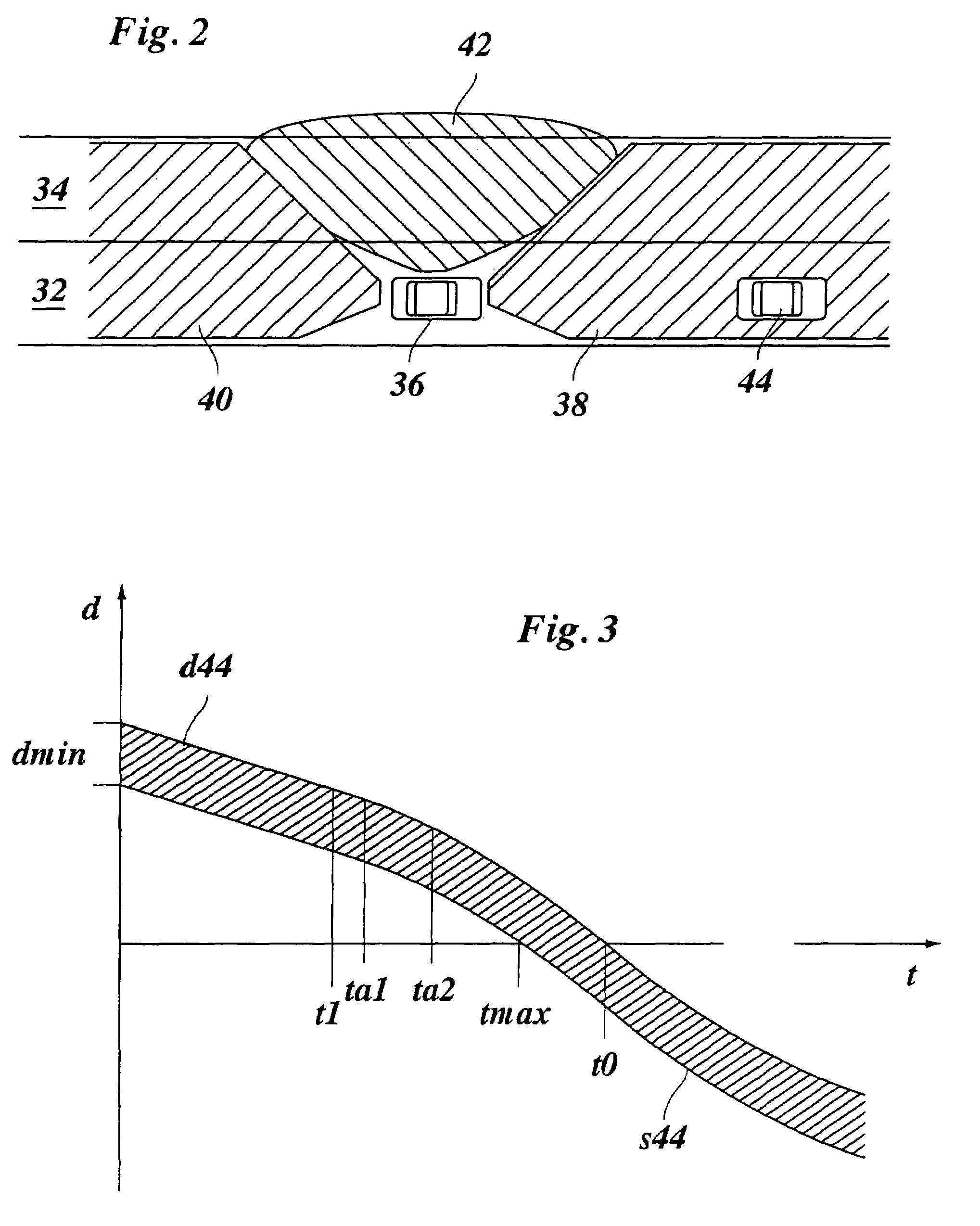
ActiveUS20060009910A1Easy to changeAvoid stimulationVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsDriver/operatorControl system
A lane changing assistant for motor vehicles, having a speed control system and a surroundings sensor system for recording the traffic environment including the traffic in an adjacent lane, having a decision device for deciding whether a lane changing request of the driver is to be accepted, and having a command device for issuing an acceleration command to the speed control system in the case of a lane changing request, wherein a recognition device is developed to recognize a window for swinging into the adjacent lane without danger, in the light of the data of the surroundings sensor system; and the command device is developed to compute an acceleration strategy adjusted to the window, including a point in time for the beginning of the acceleration.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
System and mehtod for dynamically allocating resources in a mobile communication system employing orthogonal frequency division multiple access
InactiveUS20050063336A1Network traffic/resource managementFrequency-division multiplexMobile communication systemsOrthogonal frequency-division multiple access
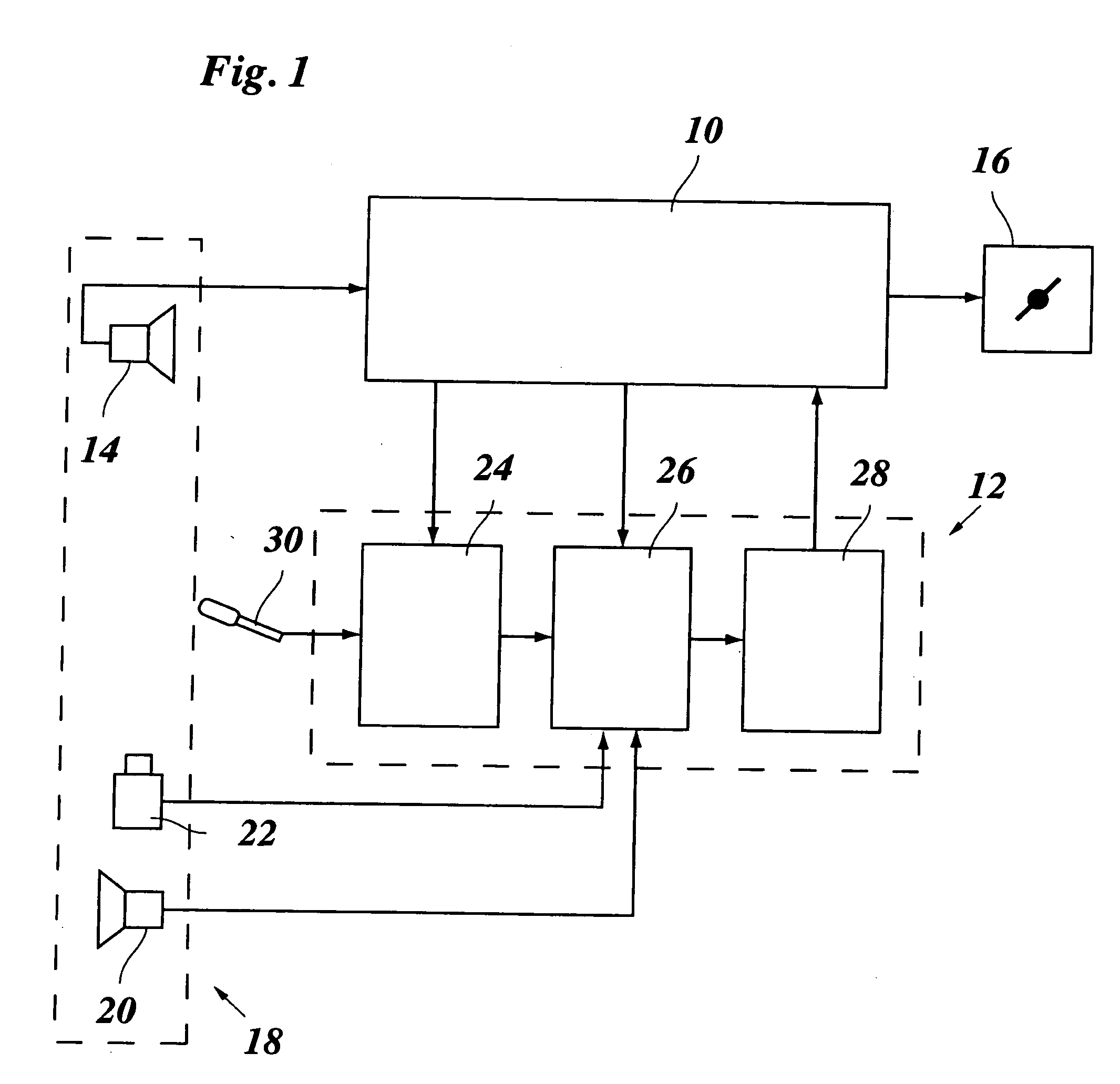
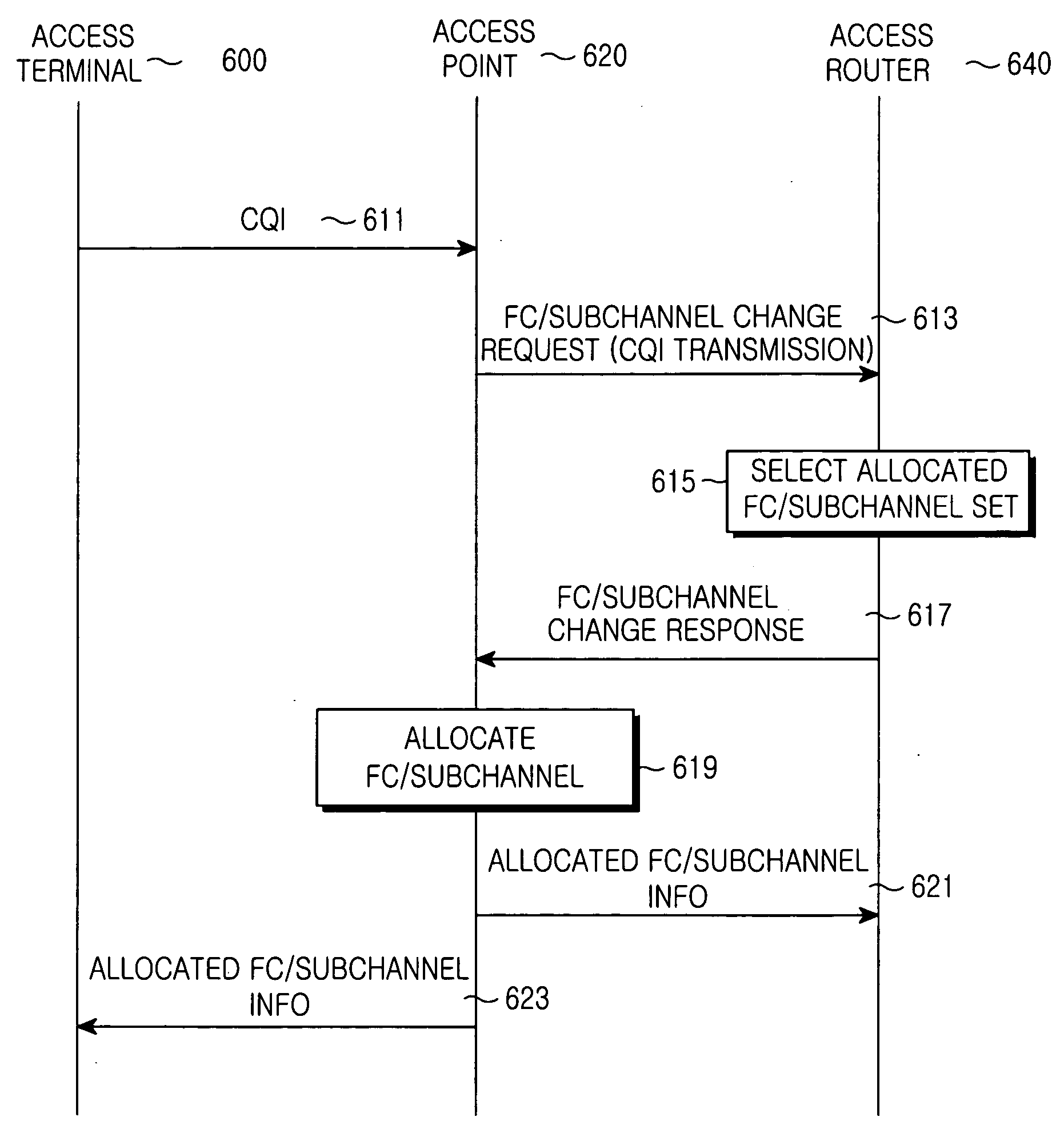
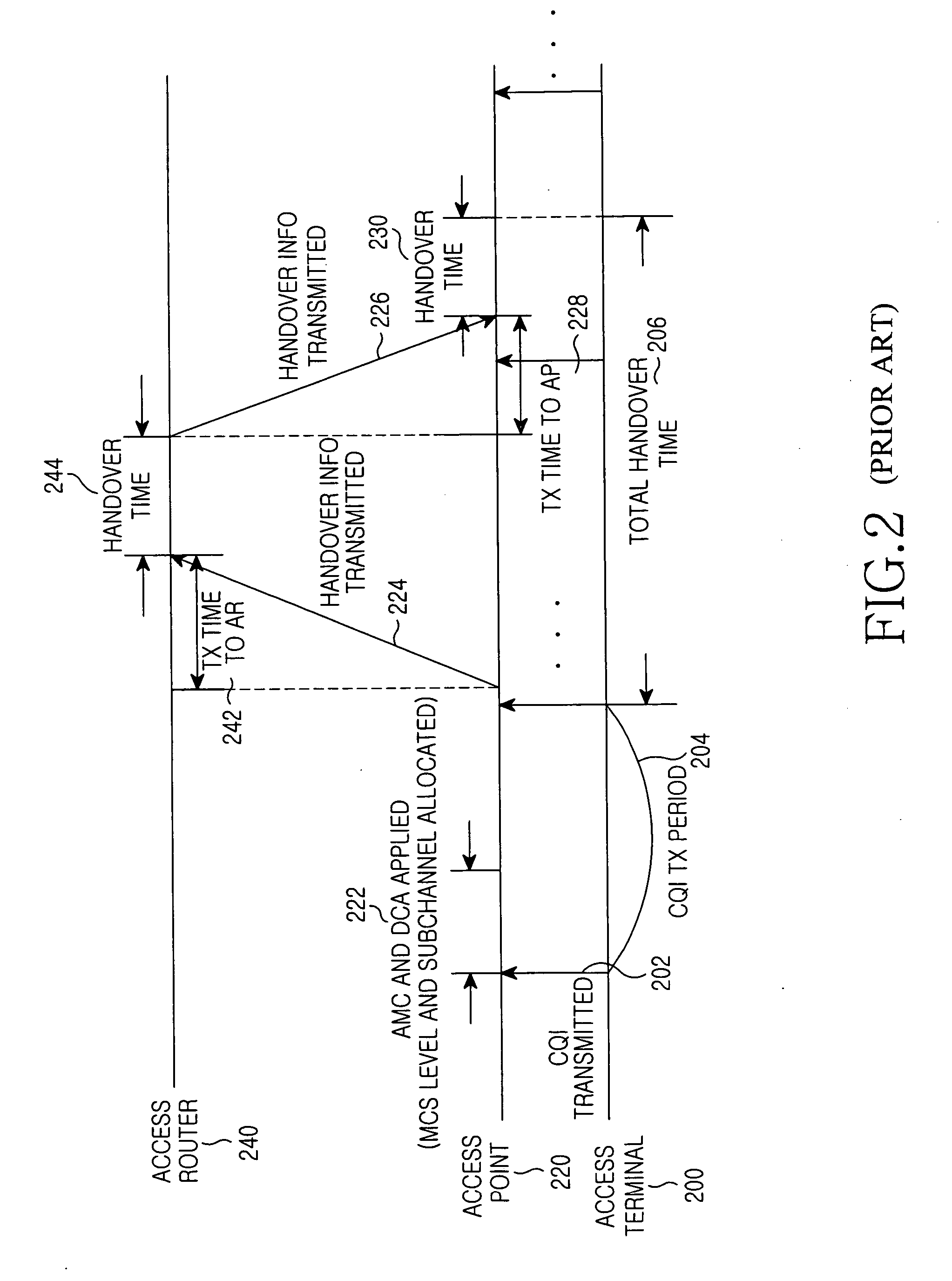
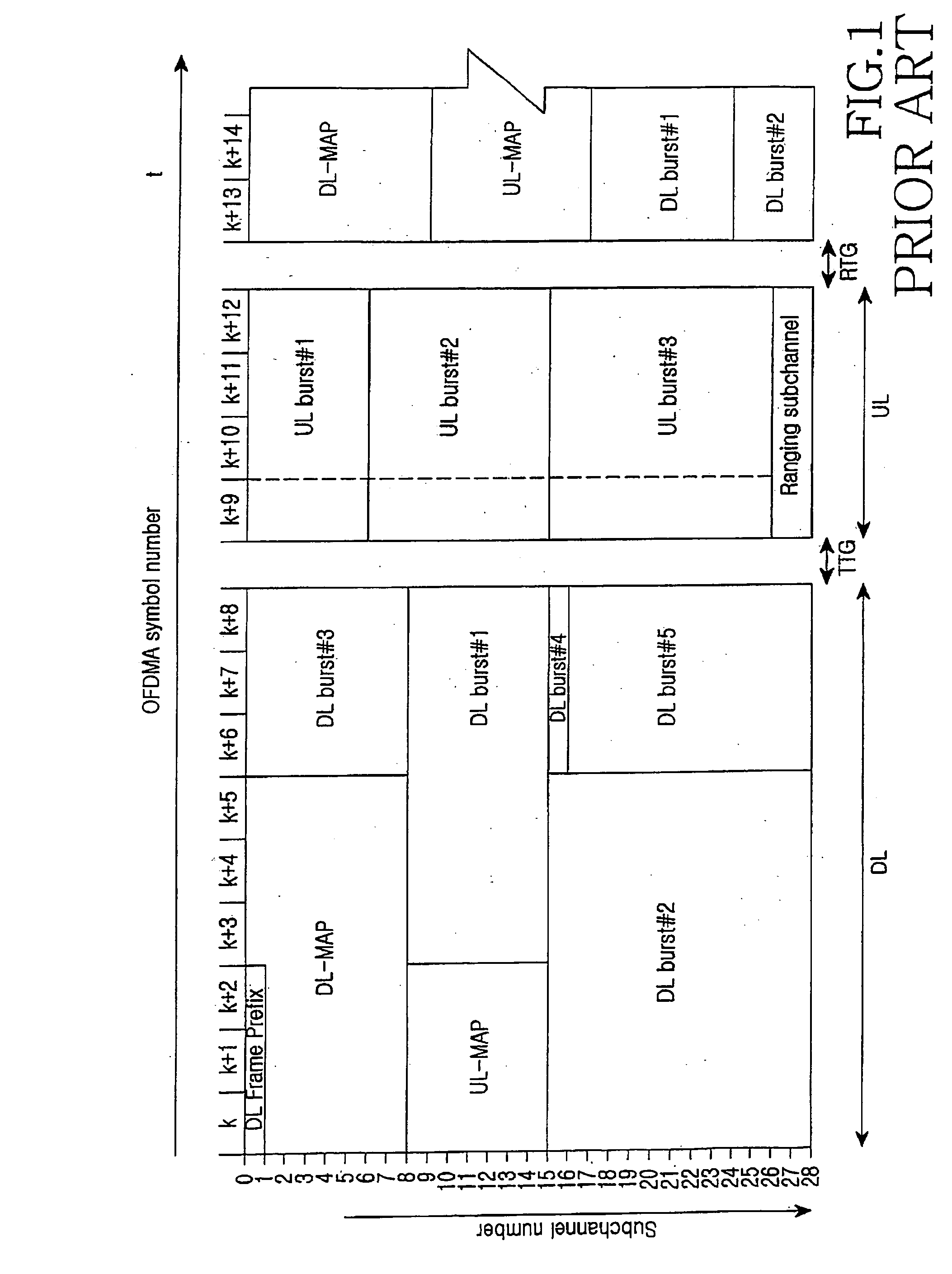
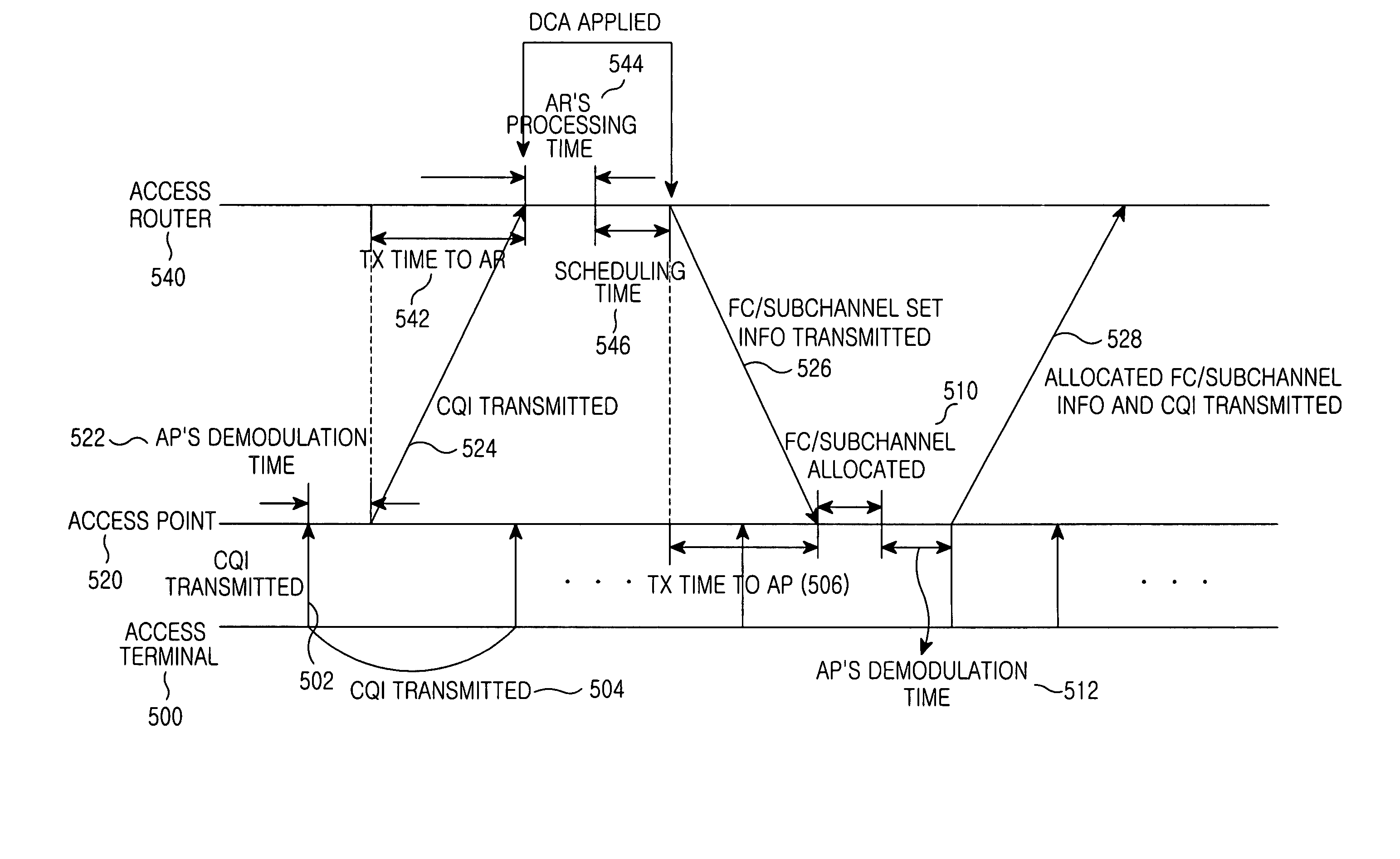
Dynamically allocating a frame cell (FC) / subchannel in a mobile communication system by an access point that receives channel quality information (CQIs) fed back from access terminals, determines a modulation and coding scheme (MCS) to be applied to the access terminals based on the CQIs, and if access terminals whose FCs / subchannels must be changed are detected from the access terminals, sends an FC / subchannel change request to an access router. The access router allocates an FC / subchannel set by selecting a number of FCs / subchannels according to the FC / subchannel change request, and transmits information on the allocated FC / subchannel set to the access point. The access point selects and allocates a particular FC / subchannel from among FCs / subchannels in the FC / subchannel set information to the access terminals whose FCs / subchannels must be changed, based on CQIs last received from the access terminals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
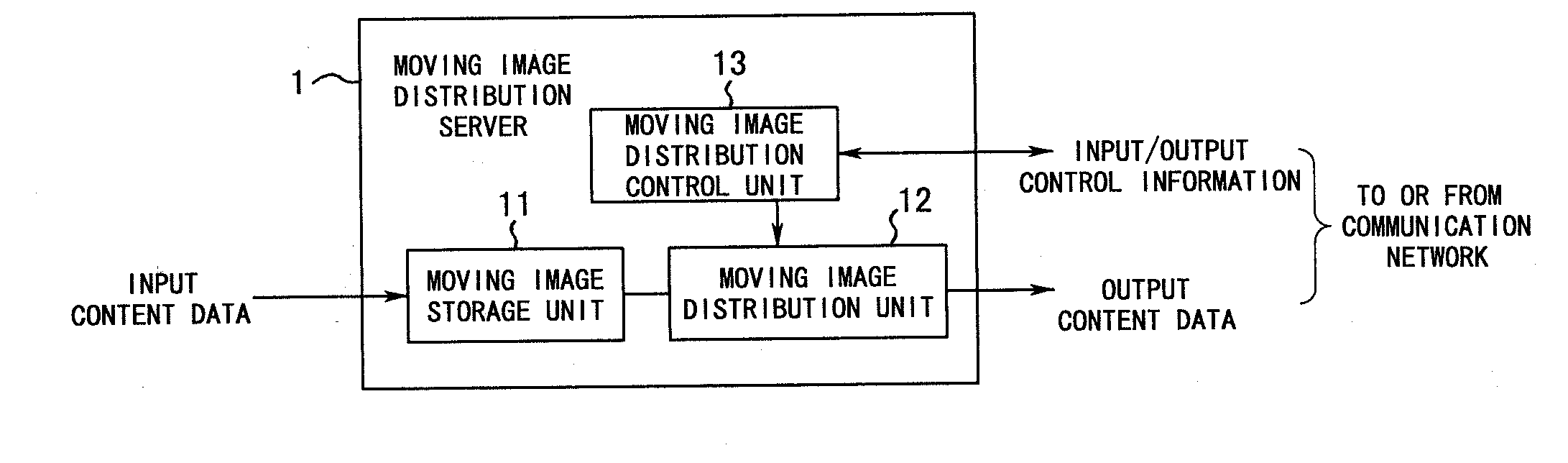
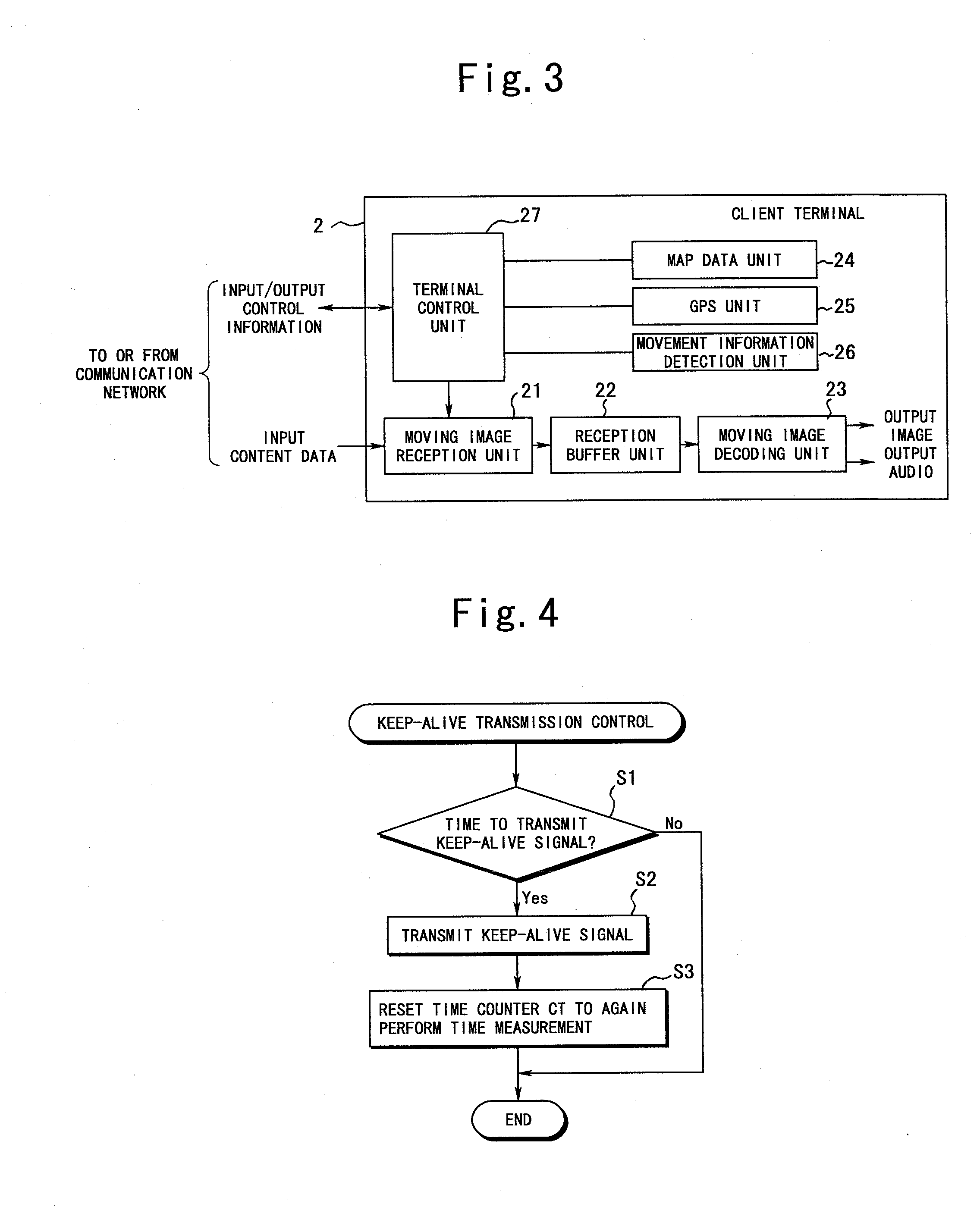
Content distribution system and its control method
InactiveUS20100228863A1Easy to confirmInhibition can be terminatedNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementContent distributionComputer hardware
A content distribution system in which, when it is detected that an incommunicable area is present in a moving direction of a client terminal, the client terminal transmits a change request signal, requesting an increase of the confirmation interval of a keep-alive signal, to the content distribution server before the client terminal enters the incommunicable area. When the change request signal is received during distribution of content data, the content distribution server increases the confirmation interval of the keep-alive signal, thereby allowing the session of content distribution to be maintained while the client terminal is in motion within the incommunicable area.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Method and apparatus for synchronous project collaboration
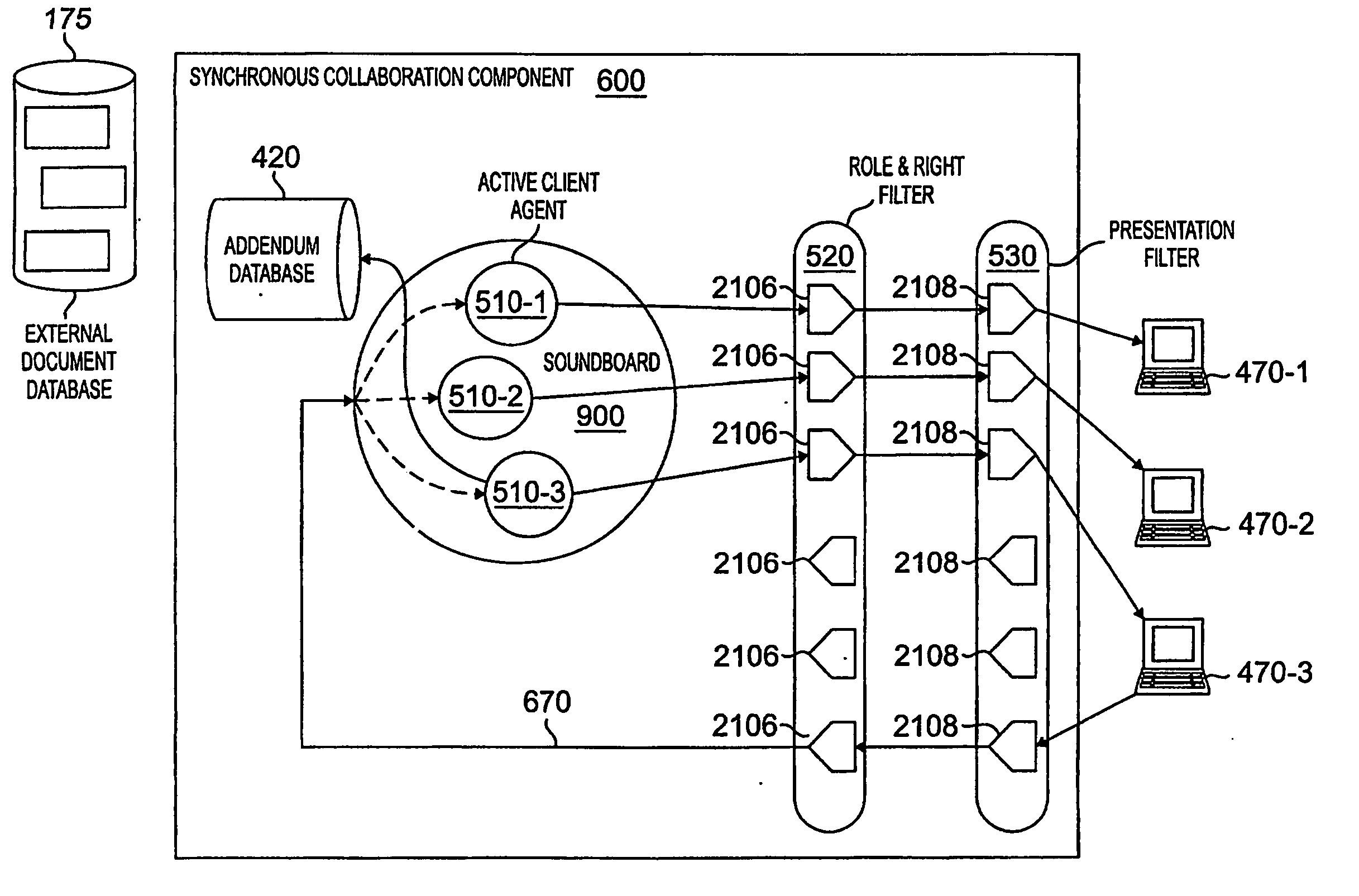
InactiveUS20060136441A1Easy transitionOffice automationSpecial data processing applicationsBroadcastingDocumentation
A disclosed project management system allows one or more team members to share documents in asynchronous and synchronous collaboration modes. A synchronous collaboration system is provided as an incremental addition that extends a conventional asynchronous collaboration system. One or more users can transition between asynchronous and synchronous collaboration modes. A plurality of users can interact in a synchronous collaboration mode to create and modify documents and perform other project tasks without requiring a token. A serializer initially receives each of the change requests and serializes them. The serialized requests are then sent to a broadcaster that broadcasts the requests to all users. Each user implements the broadcast change requests to the document as they are received so that shared documents are presented to each user in the same way at any given time.
Owner:JUBA HISASHI
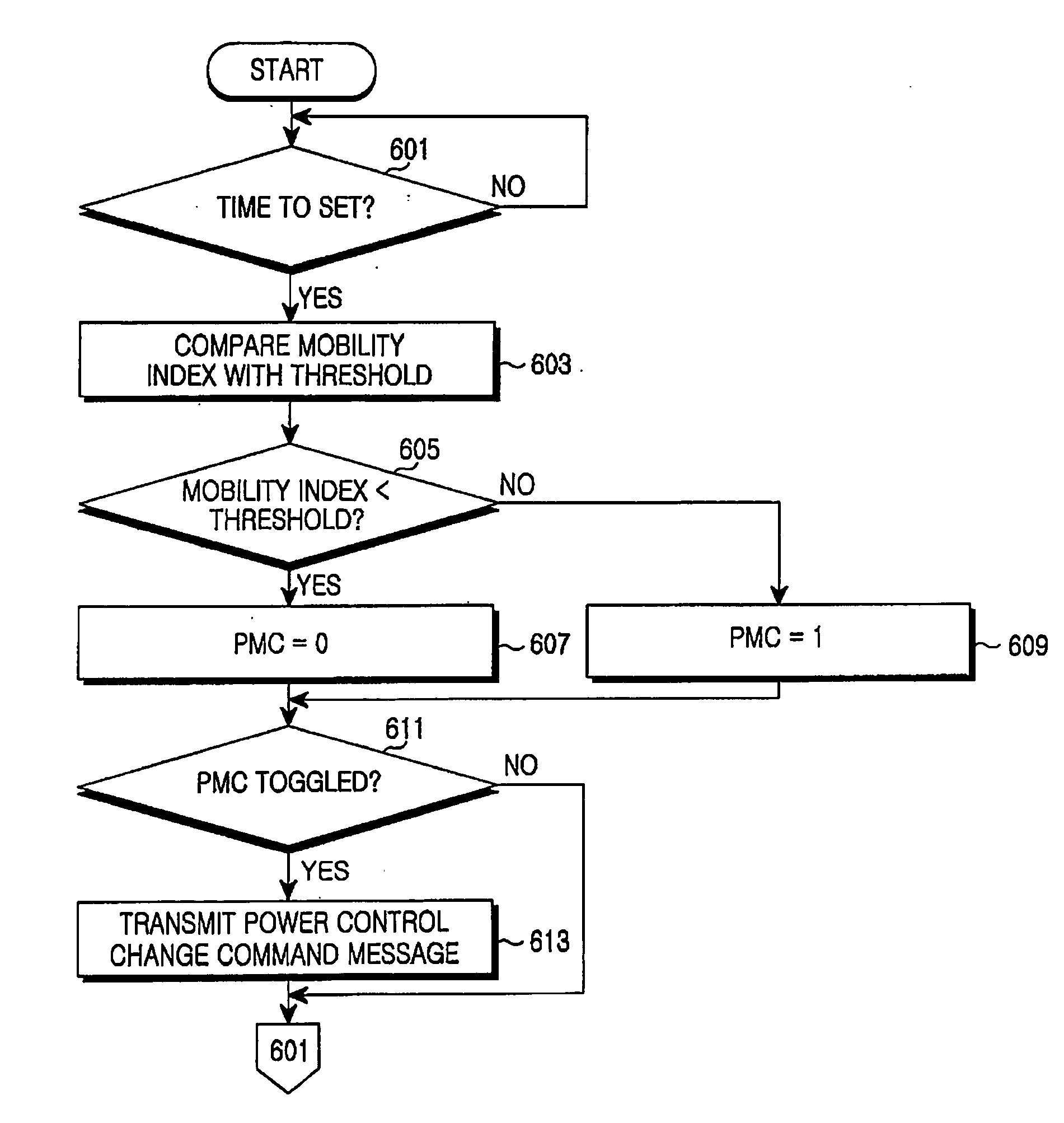
Apparatus and method for adaptively changing uplink power control scheme according to mobile status in a TDD mobile communication system
ActiveUS20060040619A1Power managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile communication systemsSelf adaptive
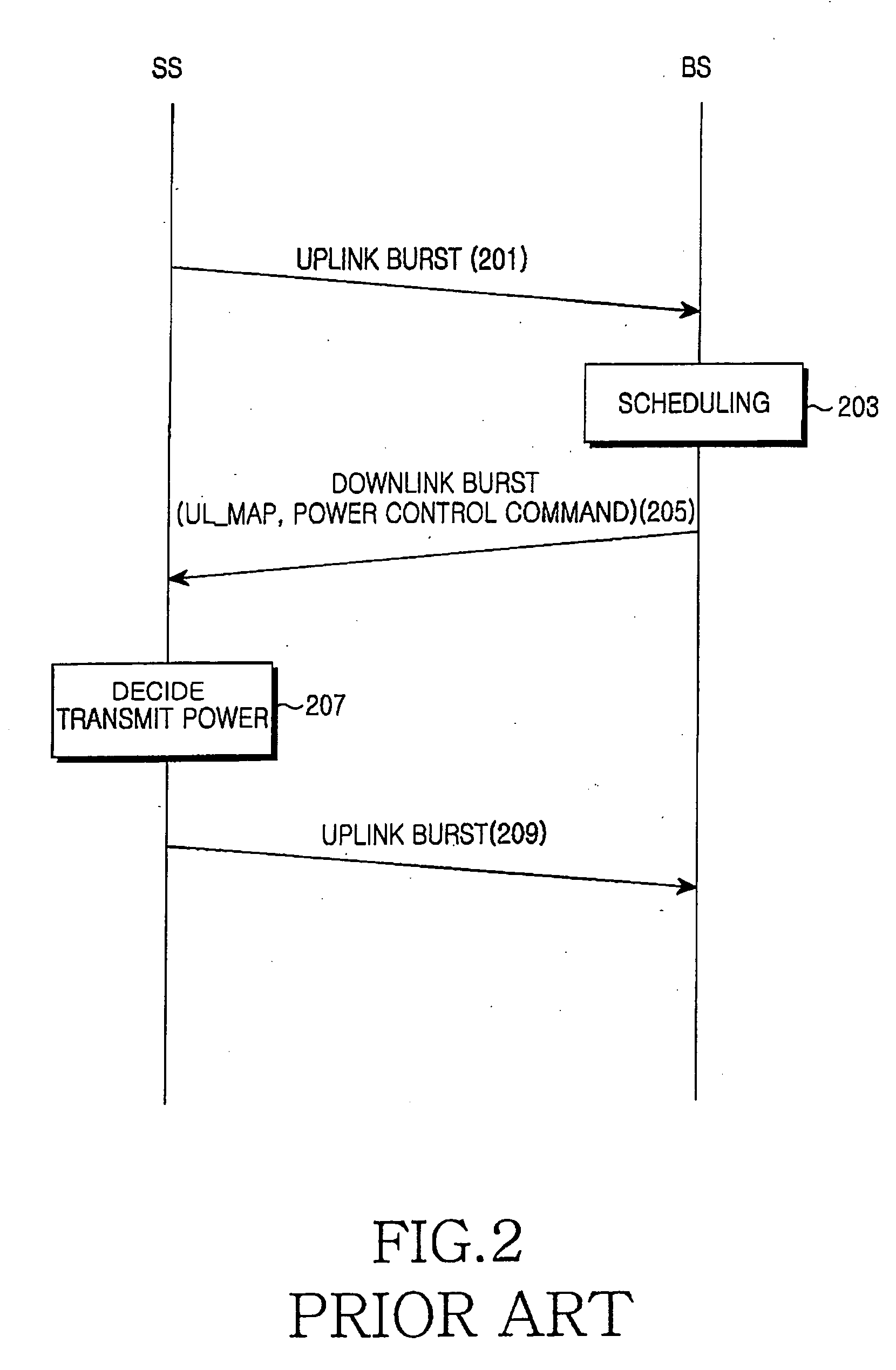
An apparatus and method for changing an uplink power control scheme according to mobile status in a TDD mobile communication system are provided. A subscriber station transmits to a base station a power control change request message including information about a requested power control scheme. Upon receipt of the power control change request message, the base station selects a power control scheme for the uplink of the subscriber station and transmits to the subscriber station a power control change command message including information about the selected power control scheme. The subscriber station extracts, upon receipt of the power control change command message from the base station, the power control scheme information from the power control change command message and selects a power control scheme according to the extracted information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
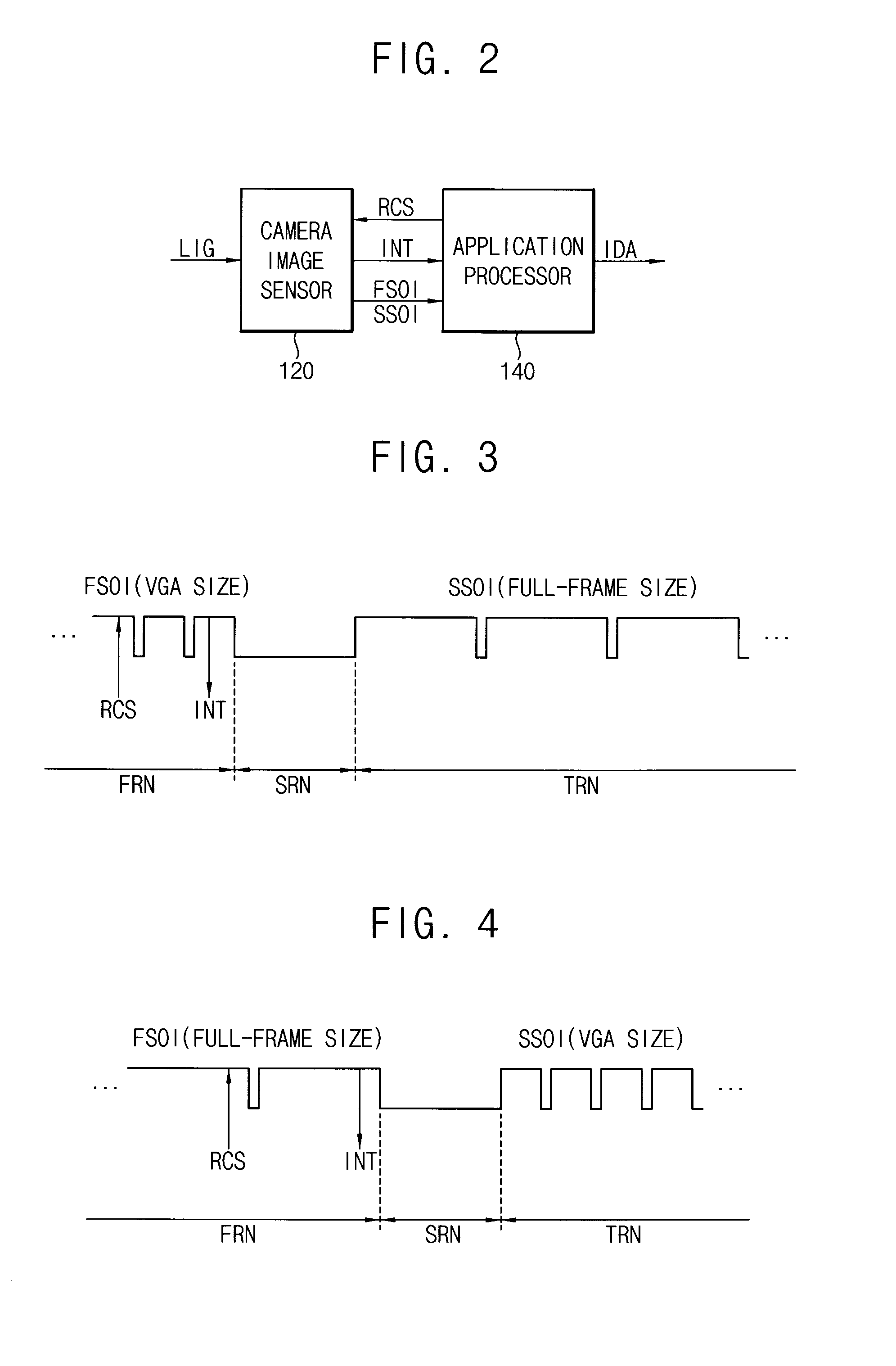
Method of changing an operation mode of a camera image sensor
InactiveUS20130201360A1Precise changeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera imageImage resolution
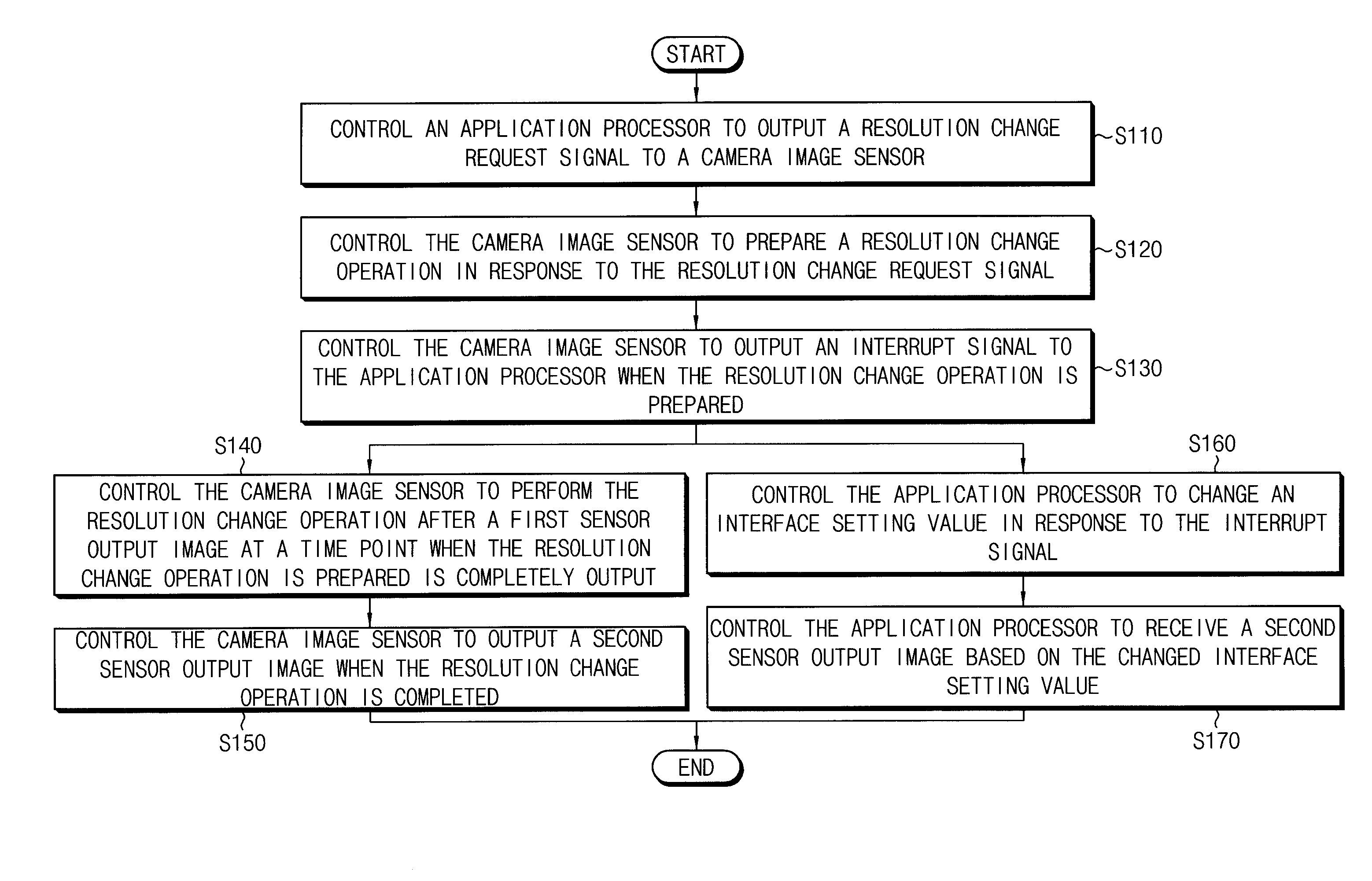
By a method of changing an operation mode of a camera image sensor, an application processor outputs a resolution change request signal to the camera image sensor when an operation mode change signal is generated while the camera image sensor outputs a first sensor output image. The camera image sensor prepares a resolution change operation in response to the resolution change request signal, outputs an interrupt signal to the application processor when the resolution change operation is prepared, performs the resolution change operation after the first sensor output image is output, and outputs a second sensor output image when the resolution change operation is completed. The application processor changes an interface setting value in response to the interrupt signal, and receives the second sensor output image based on the changed interface setting value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
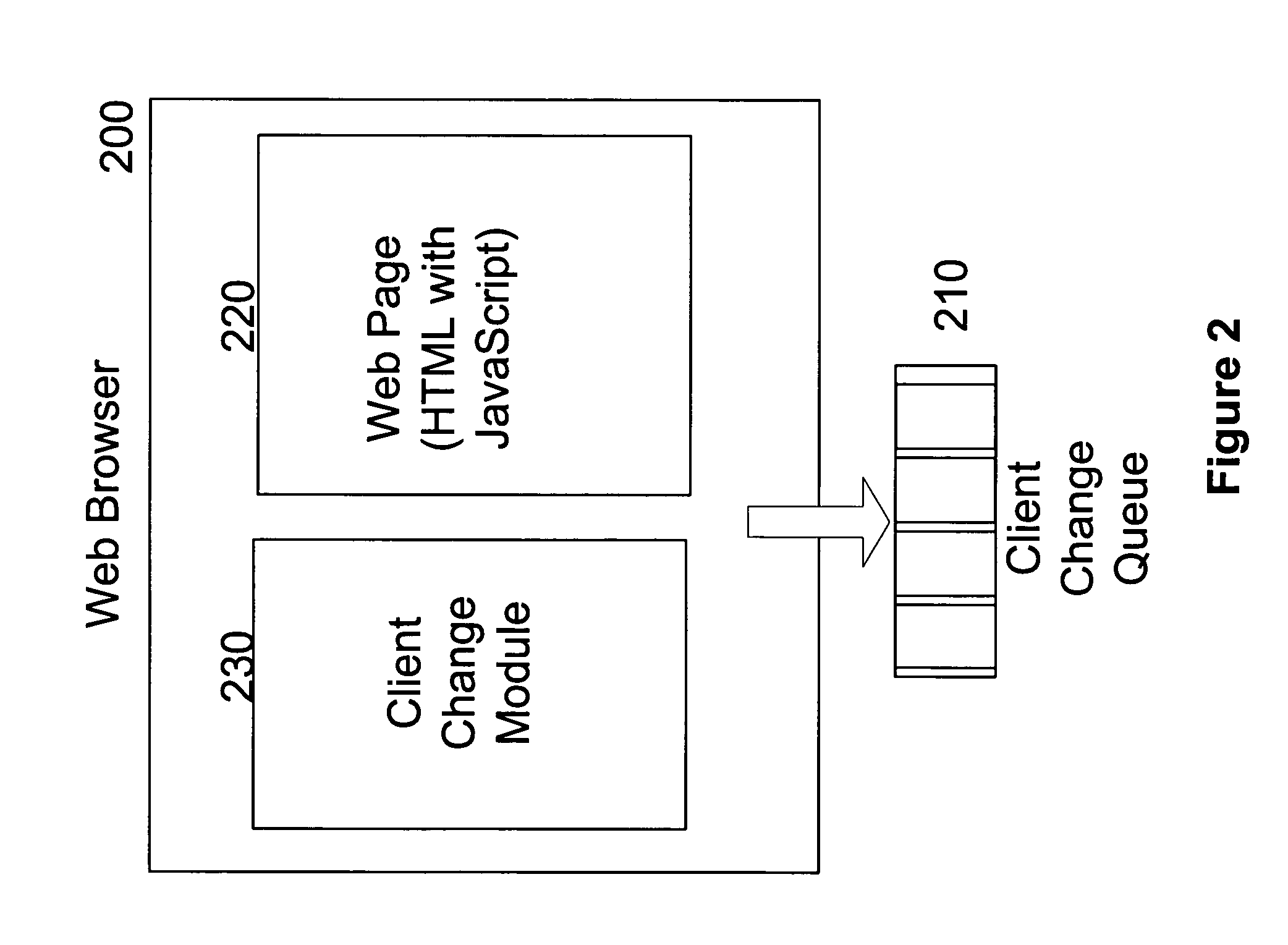
Method and apparatus for partial updating of client interfaces
ActiveUS20050204047A1Good flexibilityDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsPaper documentDocument preparation
A method and apparatus for partial updating of client interfaces in a client-server environment. The client updates the corresponding server-side through a middleware “engine.” Individual interface element change requests may be queued. Programmatically defined events may trigger processing of the change request queue on the client, resulting in partial updating of an interface container, such as a Web page or XML document, in the client interface context. Processing may occur on the server, where resultant client update requests are likewise queued. Alternative programmatically defined events may trigger the return of the server change queue to the client. Only those elements of the interface container affected by changes in the queue are updated. This partial updating method replaces the need for refreshing an entire interface, thus affording a more desktop-like look and feel.
Owner:III HLDG 3
Lane changing assistant for motor vehicles
ActiveUS7363140B2Easy to changeAvoid stimulationVehicle fittingsAnalogue computers for trafficMobile vehicleDriver/operator
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Lane change control device and control method
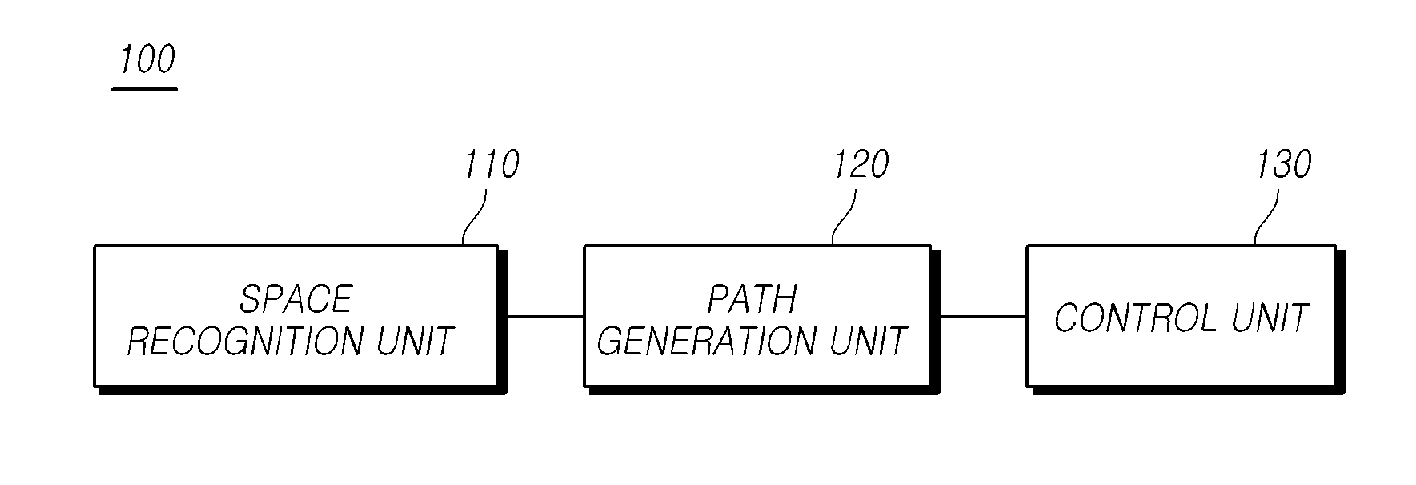
ActiveUS20160185388A1Provide securityTelevision system detailsVehicle fittingsSteering anglePath generation
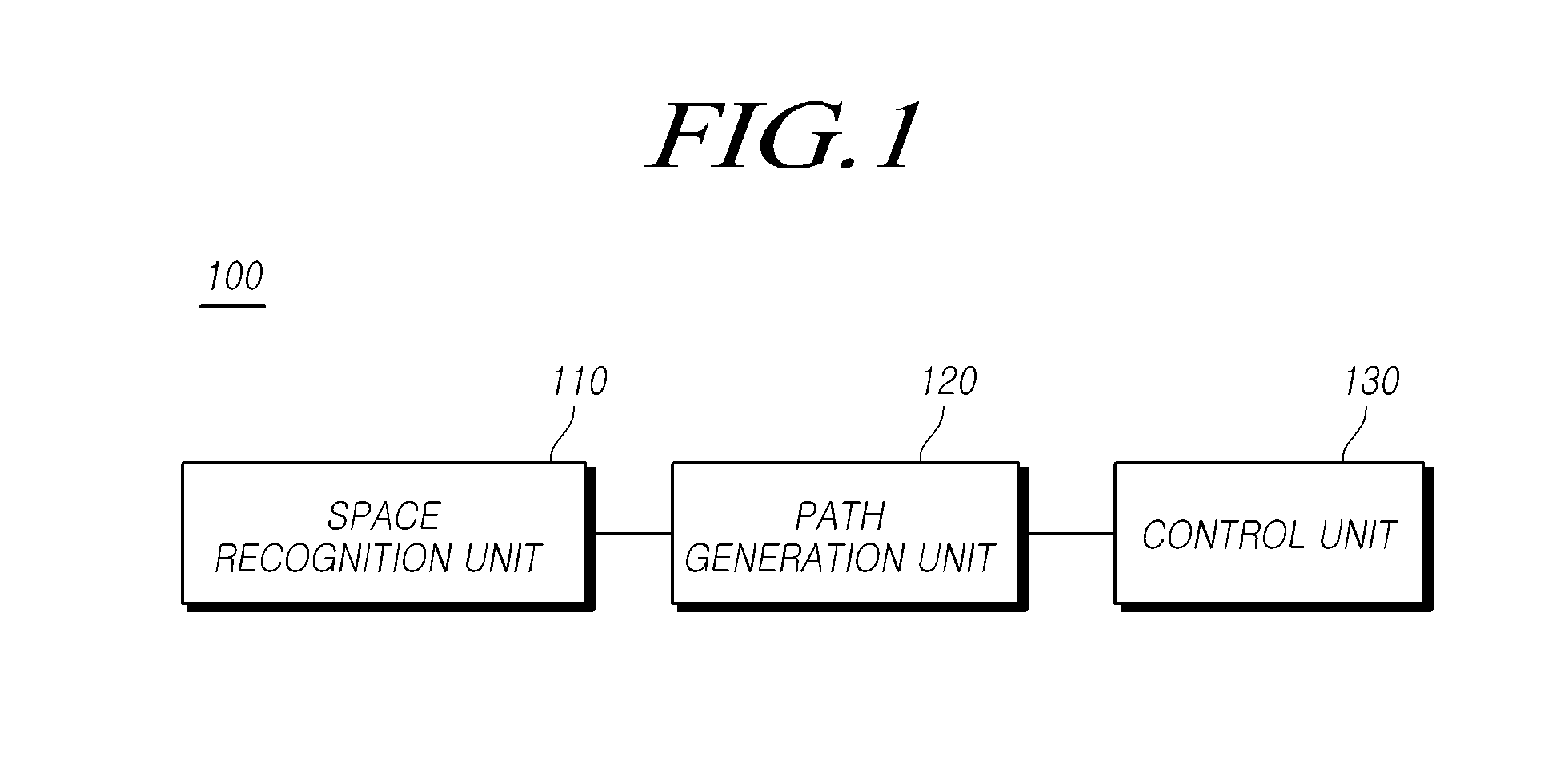
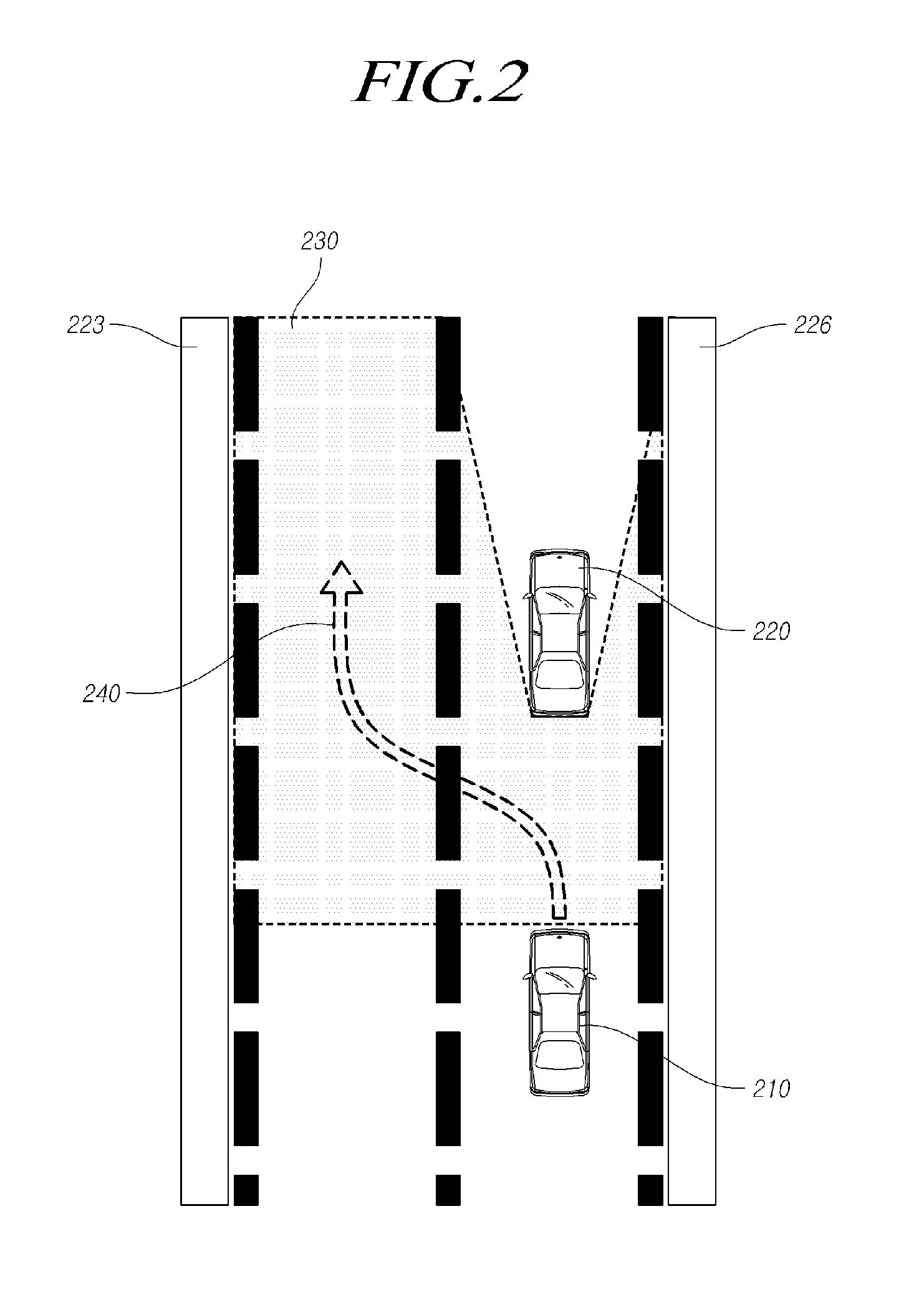
The present disclosure relates to an automatic lane change control of a vehicle is possible using a lane change control device including: a space recognition unit that detects a front object using a camera sensor of a vehicle, recognizes an empty space, and determines a target position, within the empty space on the basis of a lane modeling equation determined from a lateral offset, the vehicle's traveling velocity (V), and a lane change request time (t); a path generation unit that generates a path for moving from a current vehicle position to the target position; and a control unit that performs a lane change control that controls at least one of the vehicle's steering angle and a vehicle velocity such that the vehicle moves to the target position along the path.
Owner:HL KLEMOVE CORP
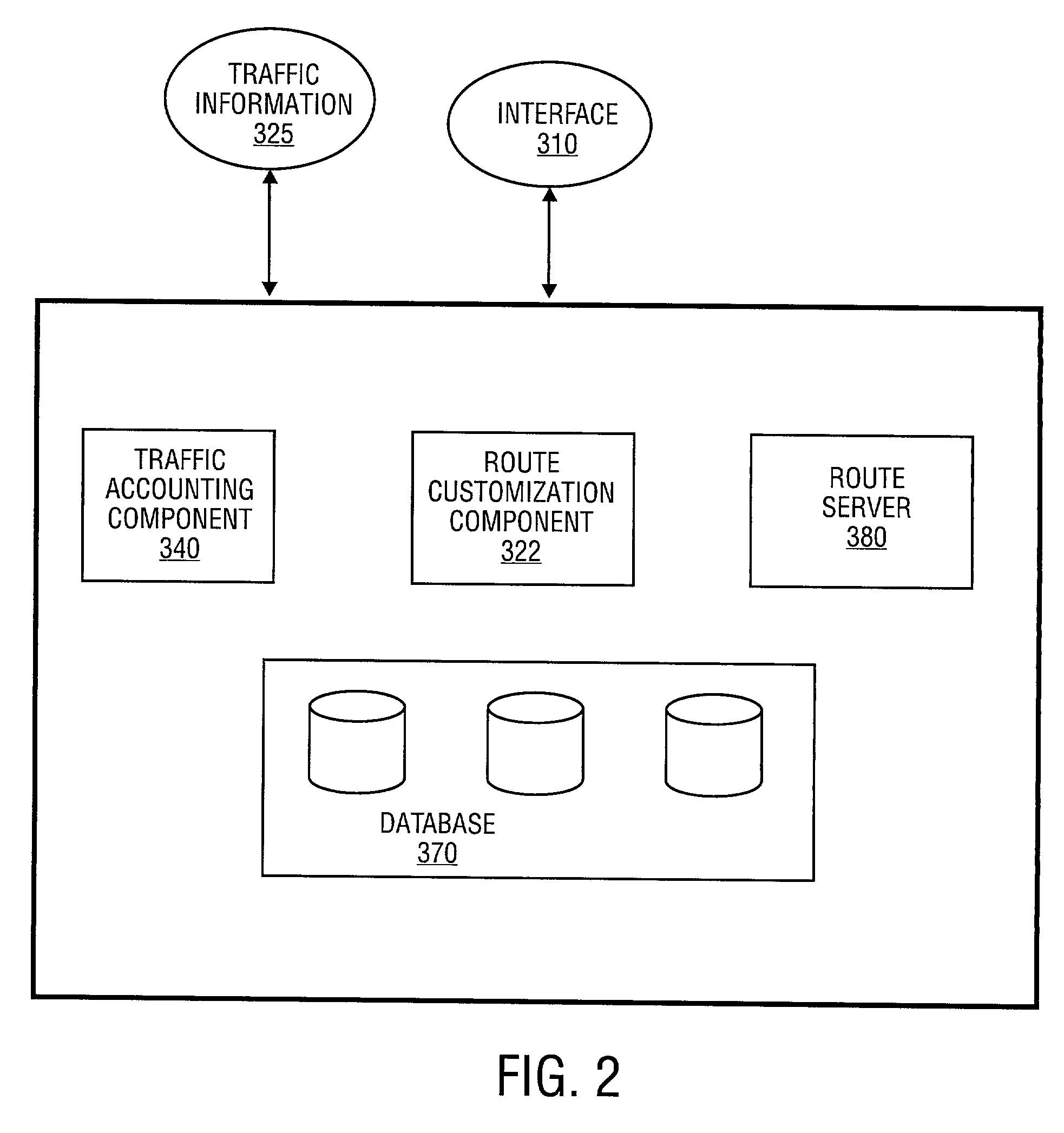
System and method for traffic accounting and route customization of network services
ActiveUS7577154B1Metering/charging/biilling arrangementsTelephonic communicationTraffic capacityMedia access control
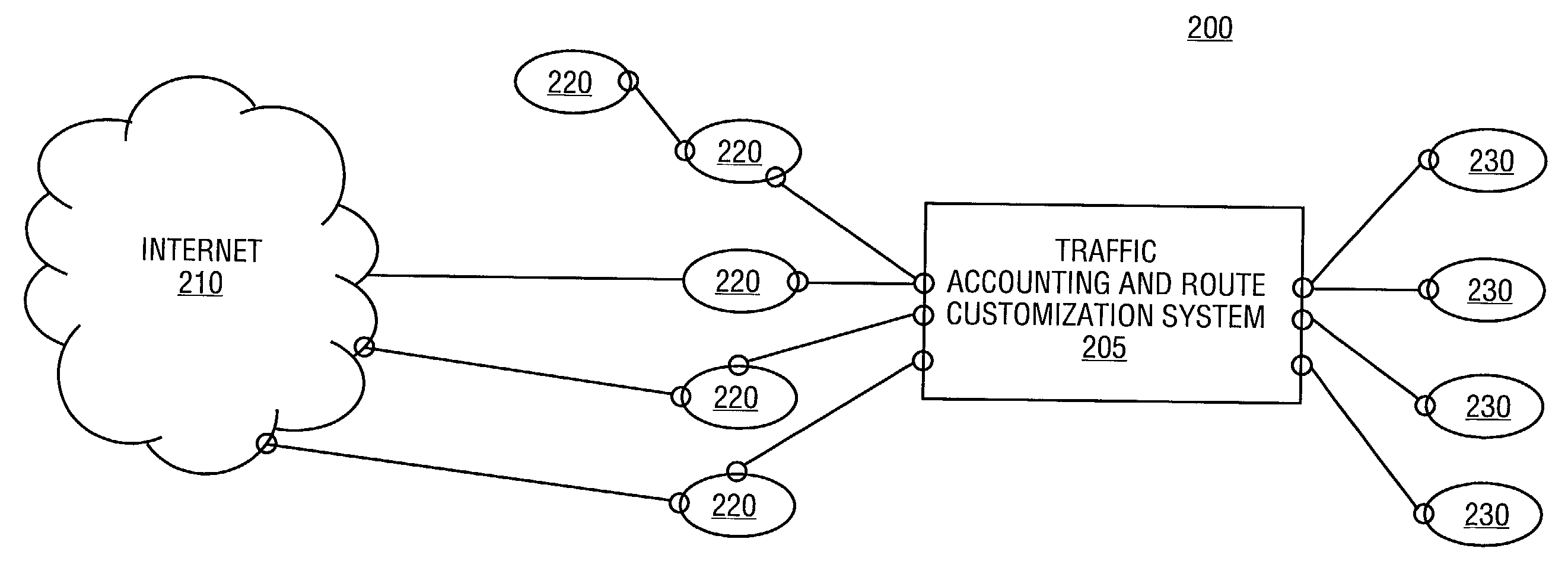
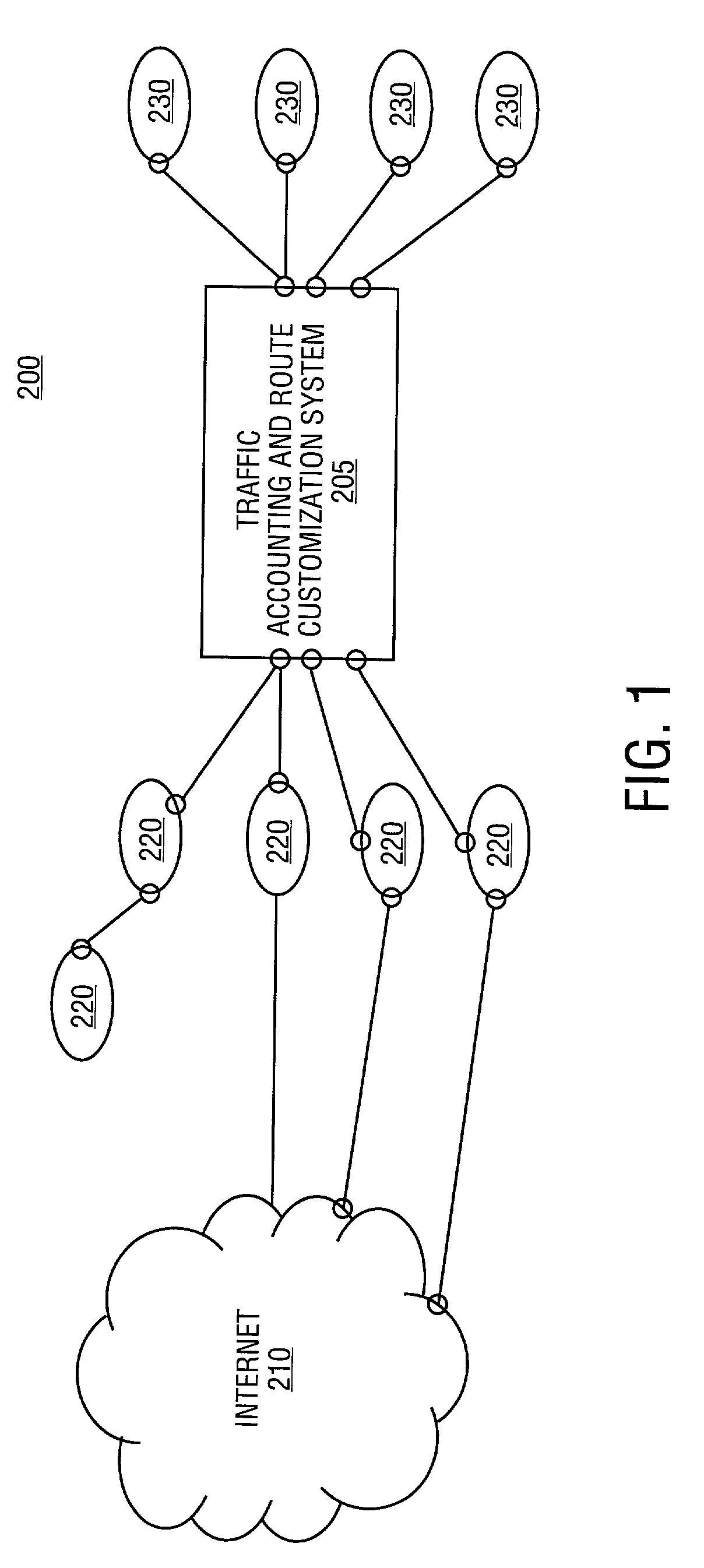
Traffic accounting and route customization of network services is described. According to one embodiment of the invention, a route customization server selects one or more network service providers to provide network services for one of a plurality of network users. The selection is based on a change request being provided by the one of the plurality of users. In another embodiment of the invention, a traffic accounting server provides billing information to the one of the plurality of users based on one or more media access control (MAC) addresses included in the network traffic of the one of the plurality of users.
Owner:EQUINIX
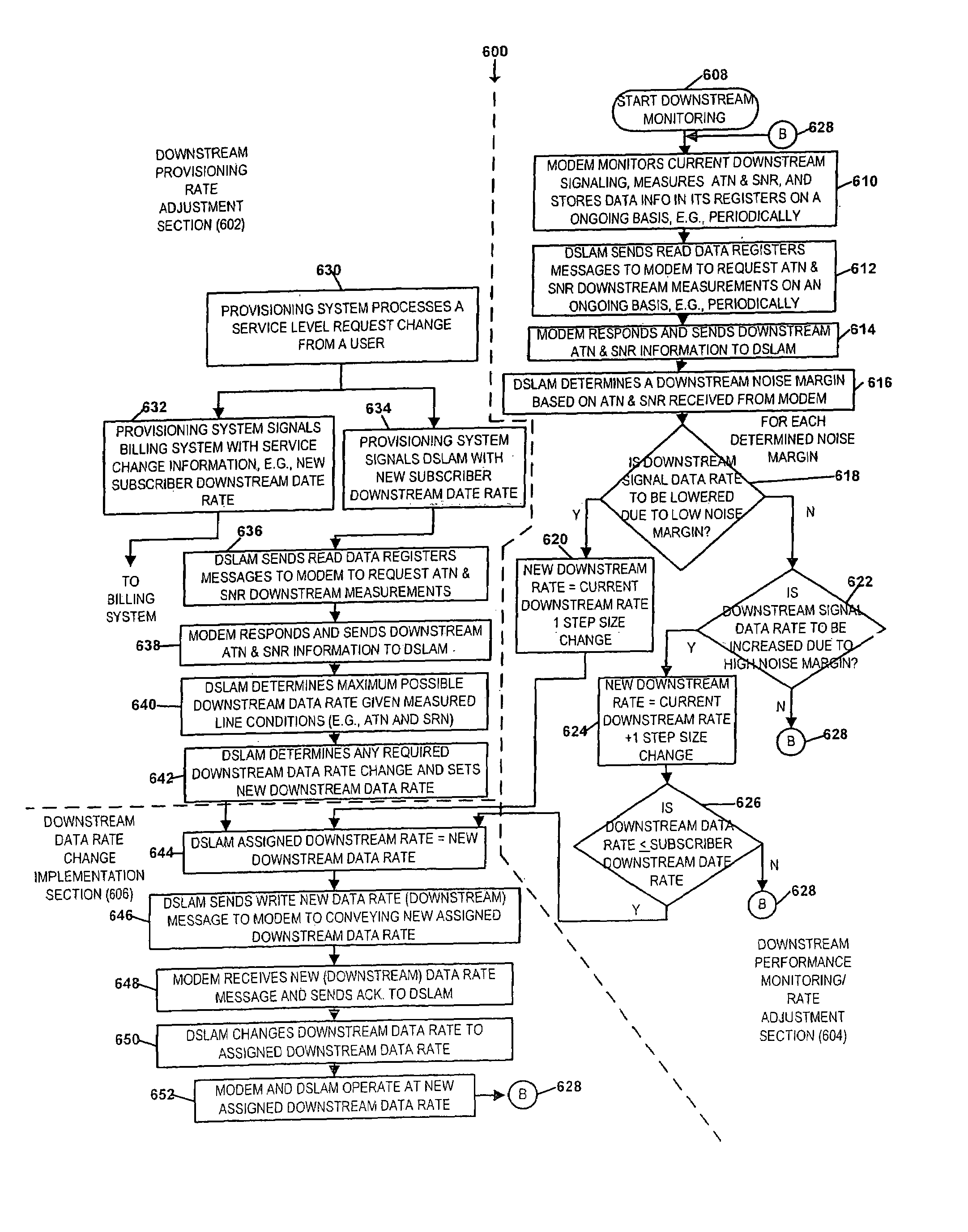
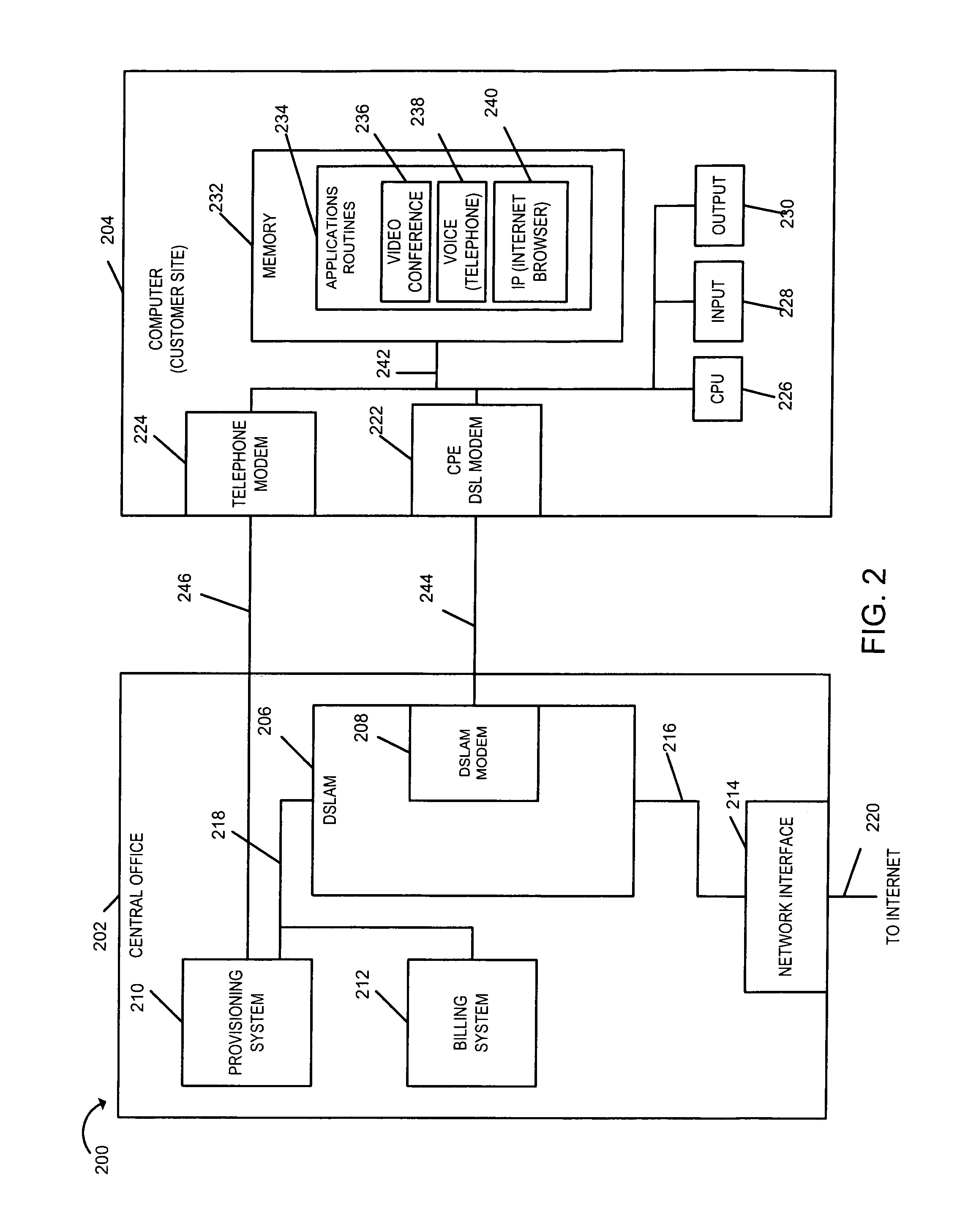
Rate agile rate-adaptive digital subscriber line
ActiveUS7317754B1Line rate can be increasedHigh achievable data rateEnergy efficient ICTSignal allocationModem deviceRate change
Methods and apparatus for maintaining the maximum achievable data rate on a DSL line, up to and including a rate to which a user subscribes is described. Performance monitoring is conducted on the DSL line on an ongoing basis to determine noise margins in each direction. Each noise margin is compared against pre-determined decreasing / increasing thresholds to determine whether the line characteristics dictate a data rate change without loss of synchronization. The invention supports dynamic provisioning changes including application driven service level change requests, e.g., new bandwidth-on demand services. In some embodiments, a combination of existing and new embedded operations channel (EOC) messages are used to implement the modem data rate changes. New EOC messages may be implemented using some of the reserved and / or vendor proprietary Opcodes currently permitted. Modem assigned data rate changes are implemented without a disruption of service, e.g., without the need for re-initialization and / or re-synchronization.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
System and method for dynamically allocating resources in a mobile communication system employing orthogonal frequency division multiple access
InactiveUS20050111429A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMobile communication systemsOrthogonal frequency-division multiple access
A system and method for dynamically allocating a frame cell (FC) and subchannel (FC / subchannel) is disclosed. An access point receives channel quality information (CQIs) which is fed back from a plurality of access terminals on an FC-by-FC basis, and determines a modulation and coding scheme (MCS) to be applied to each of the access terminals. If access terminals whose FCs / subchannels must be changed are detected from the plurality of the access terminals, the access point sends an FC / subchannel change request for the detected access terminals to an access router. The access router generates weights for all FCs, allocates an FC / subchannel set by selecting a predetermined number of FCs / subchannels considering the weights of the FCs for the access terminals corresponding to the received FC / subchannel change request, and transmits information on the allocated FC / subchannel set to the access point. The access point selects and allocates a particular FC / subchannel from among FCs / subchannels in the FC / subchannel set information received from the access router for the access terminals whose FCs / subchannels must be changed, based on CQIs last received from the access terminals whose FCs / subchannels must be changed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Enforcing alignment of approved changes and deployed changes in the software change life-cycle
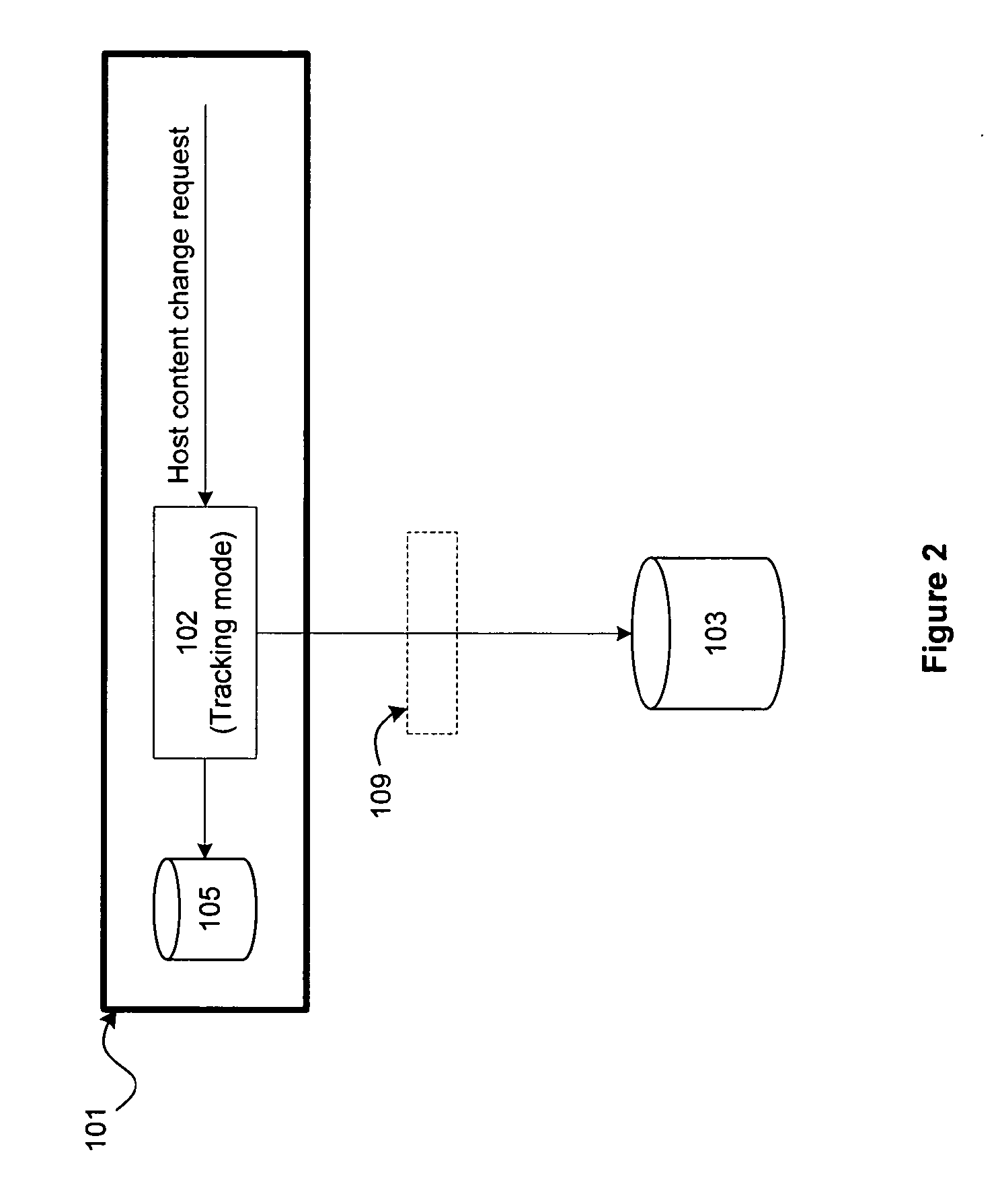
On a host, host content change requests are intercepted in real-time. In a tracking mode, the change requests are logged and allowed to take effect on the host. In an enforcement mode, the change requests are logged and additionally compared against authorized change policies and a determination is made whether to allow the change to take effect or to block the changes, thereby enforcing the authorized change policies on the host. Tracking and enforcement can be done in real-time. In either mode and at any time, the logged changes can be reconciled against a set of approved change orders in order to identify classes of changes, including changes that were deployed but not approved and changes that were approved but not deployed.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com