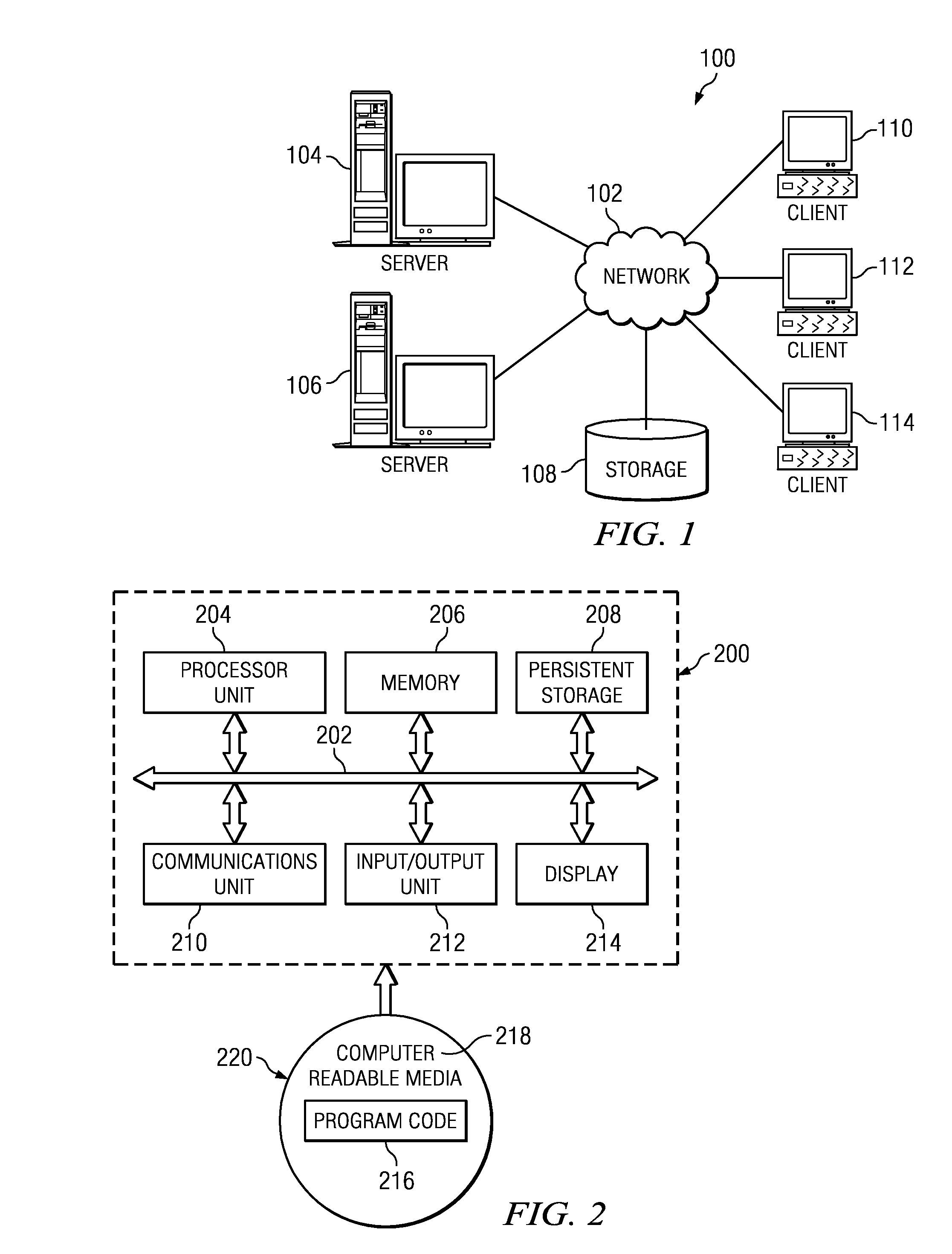
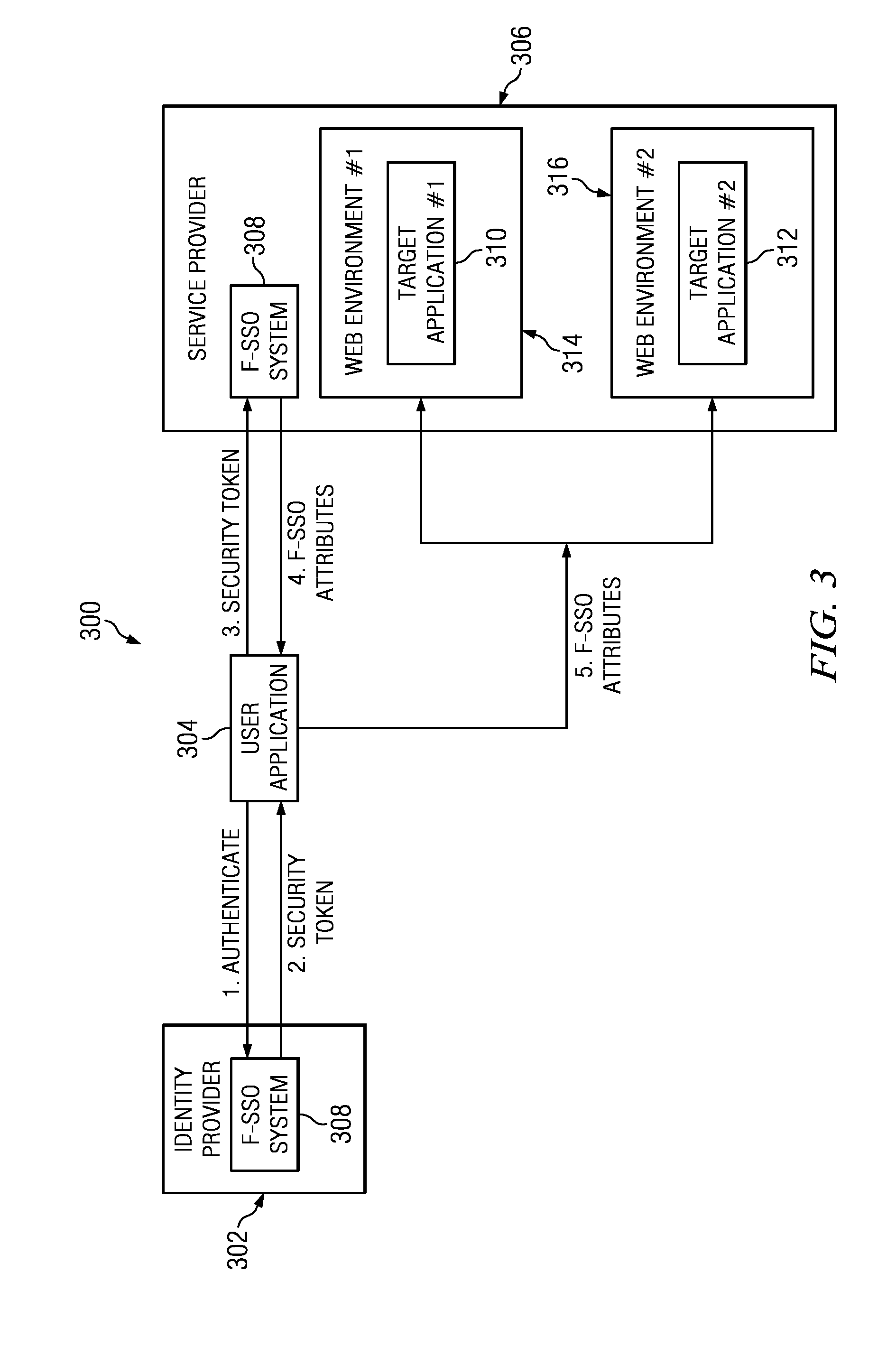
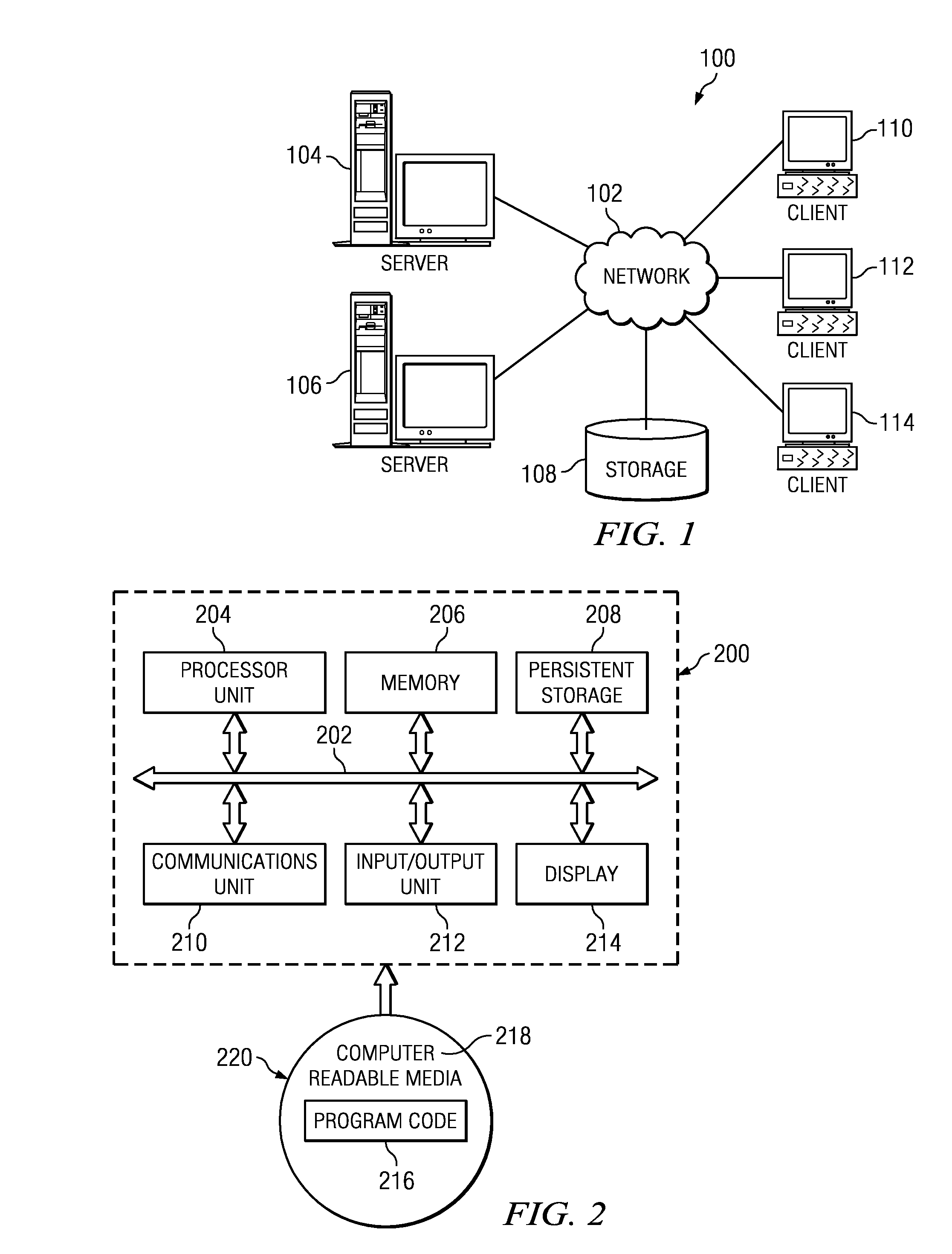
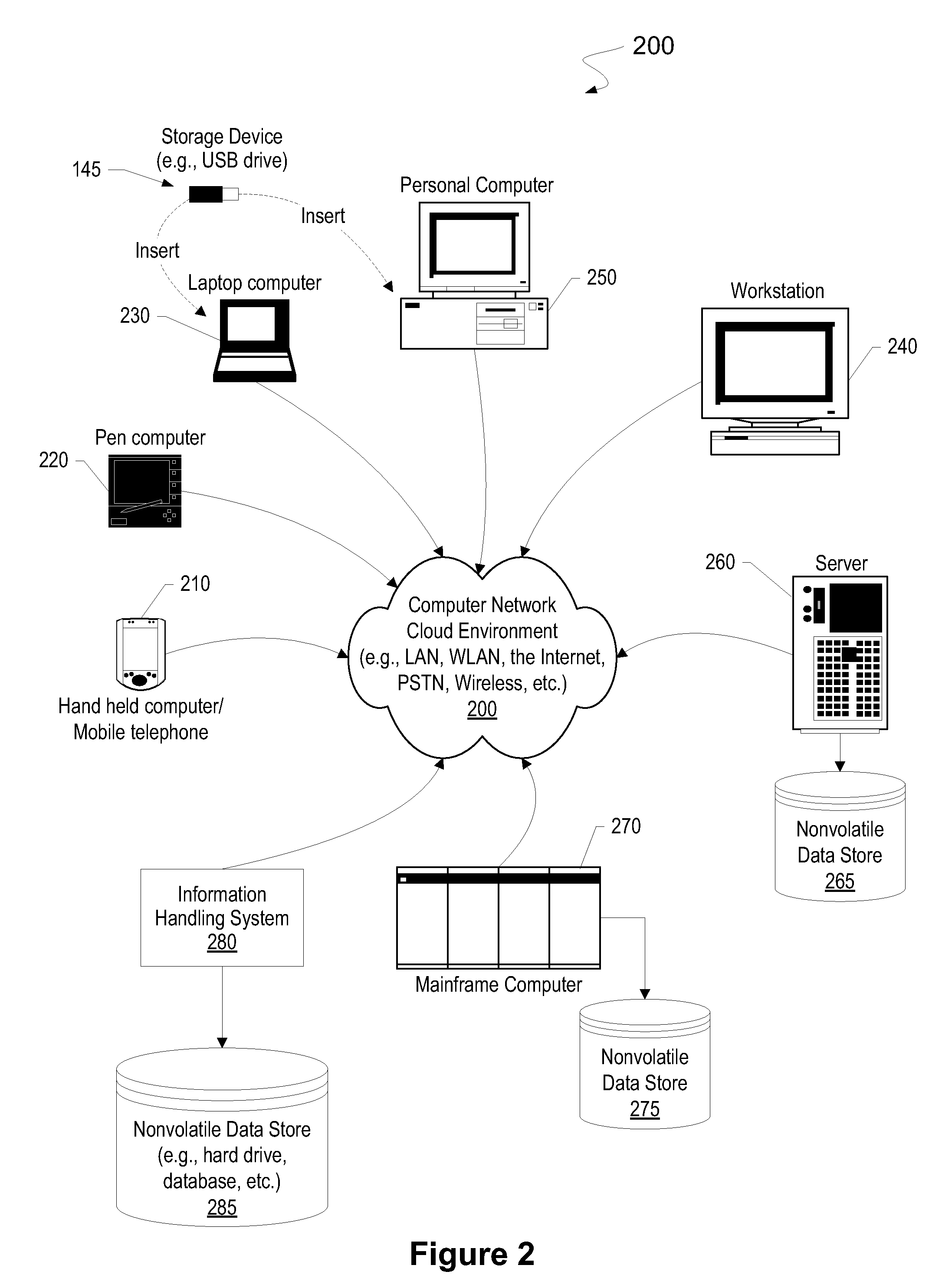
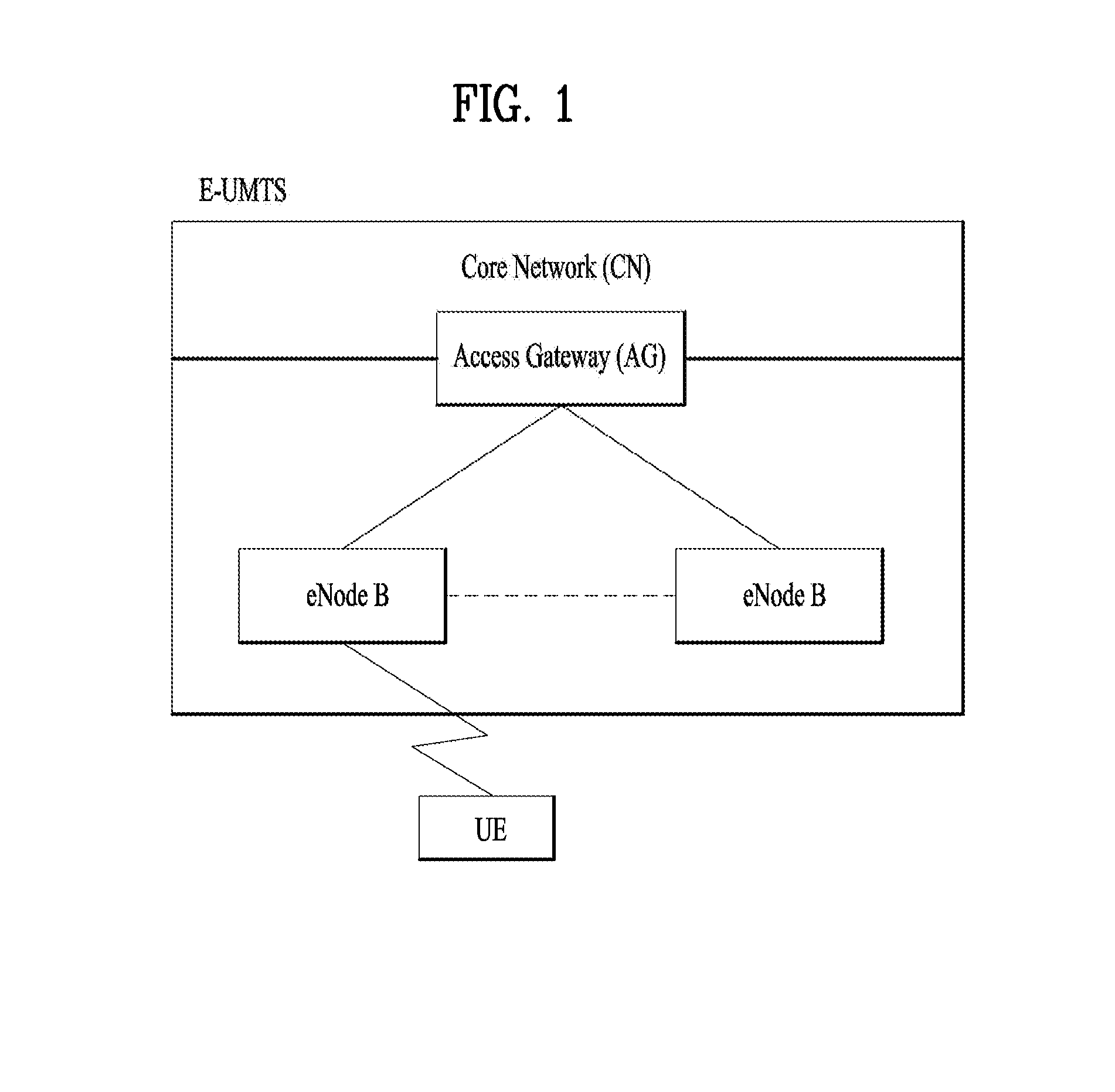
Patents
Literature
3930 results about "Resource pool" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
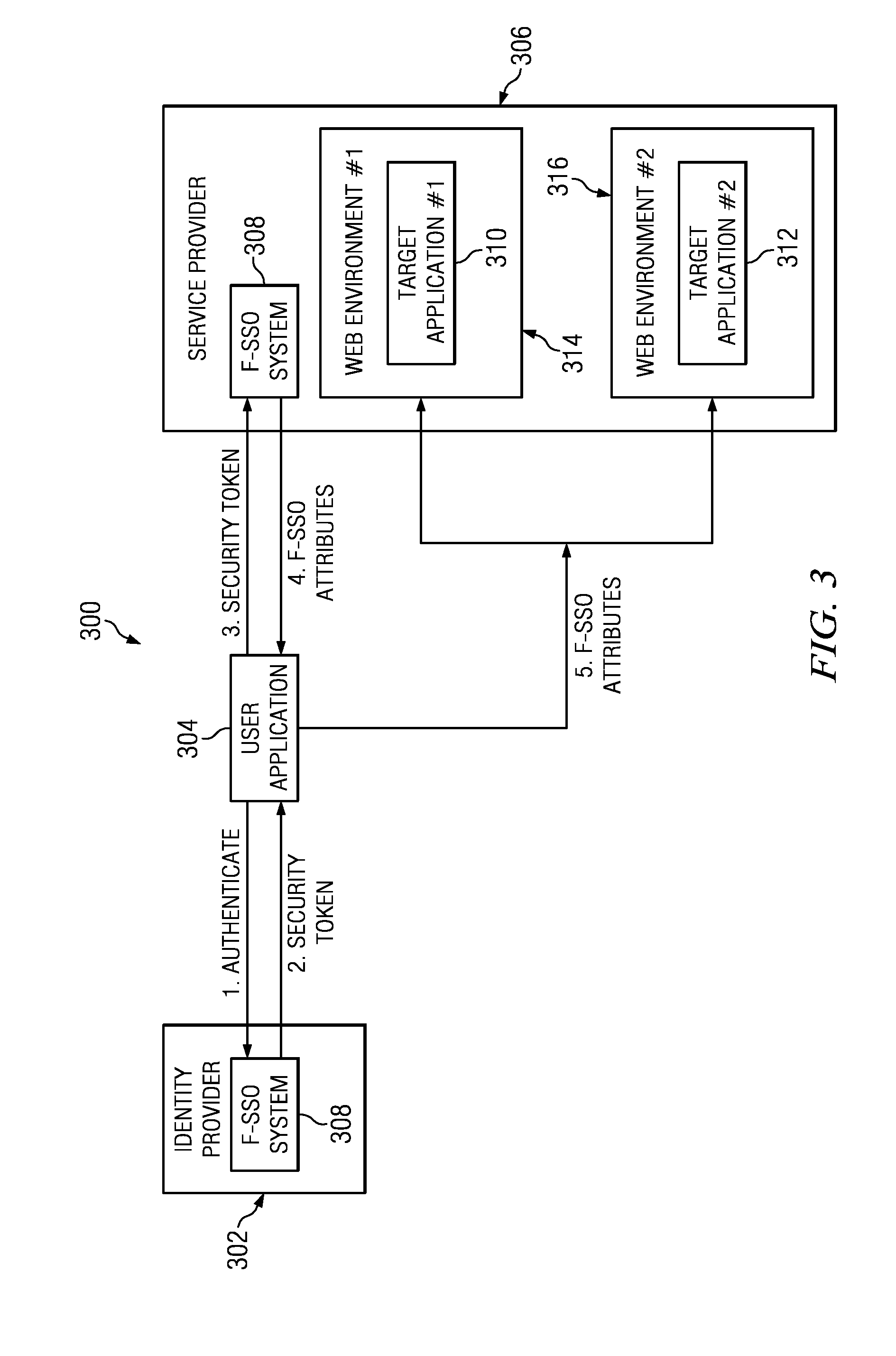
System and Method for Distributed Denial of Service Identification and Prevention
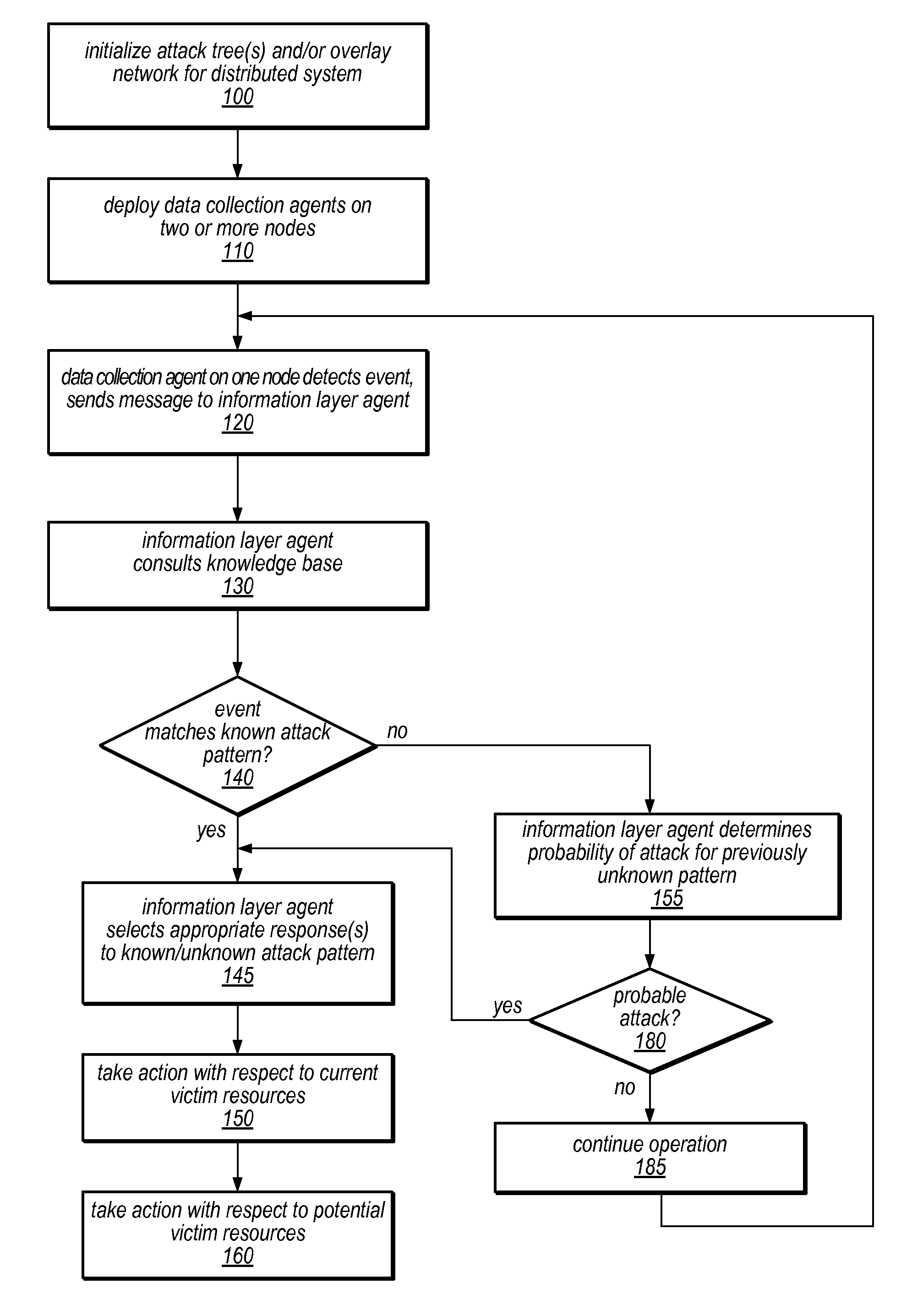
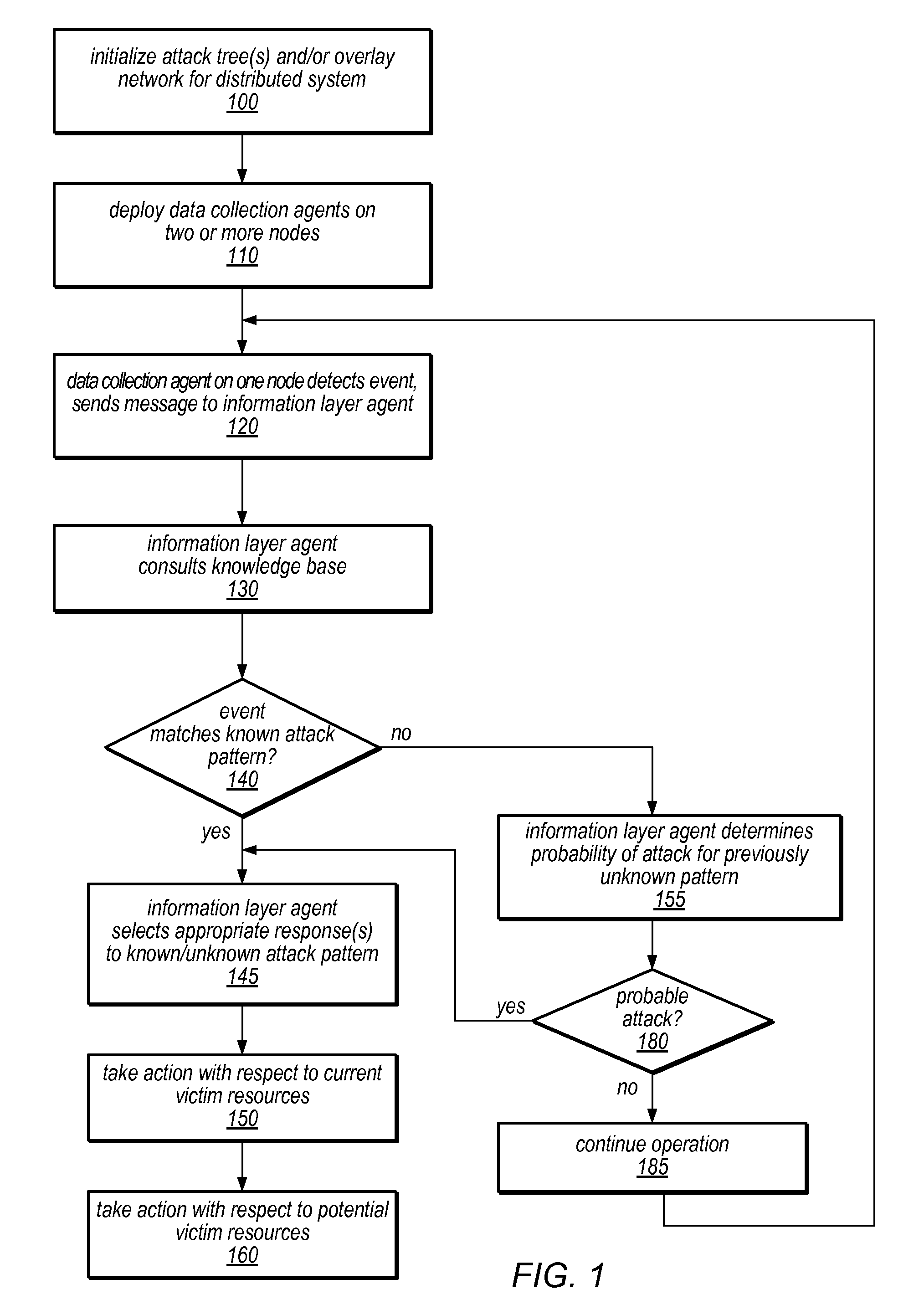
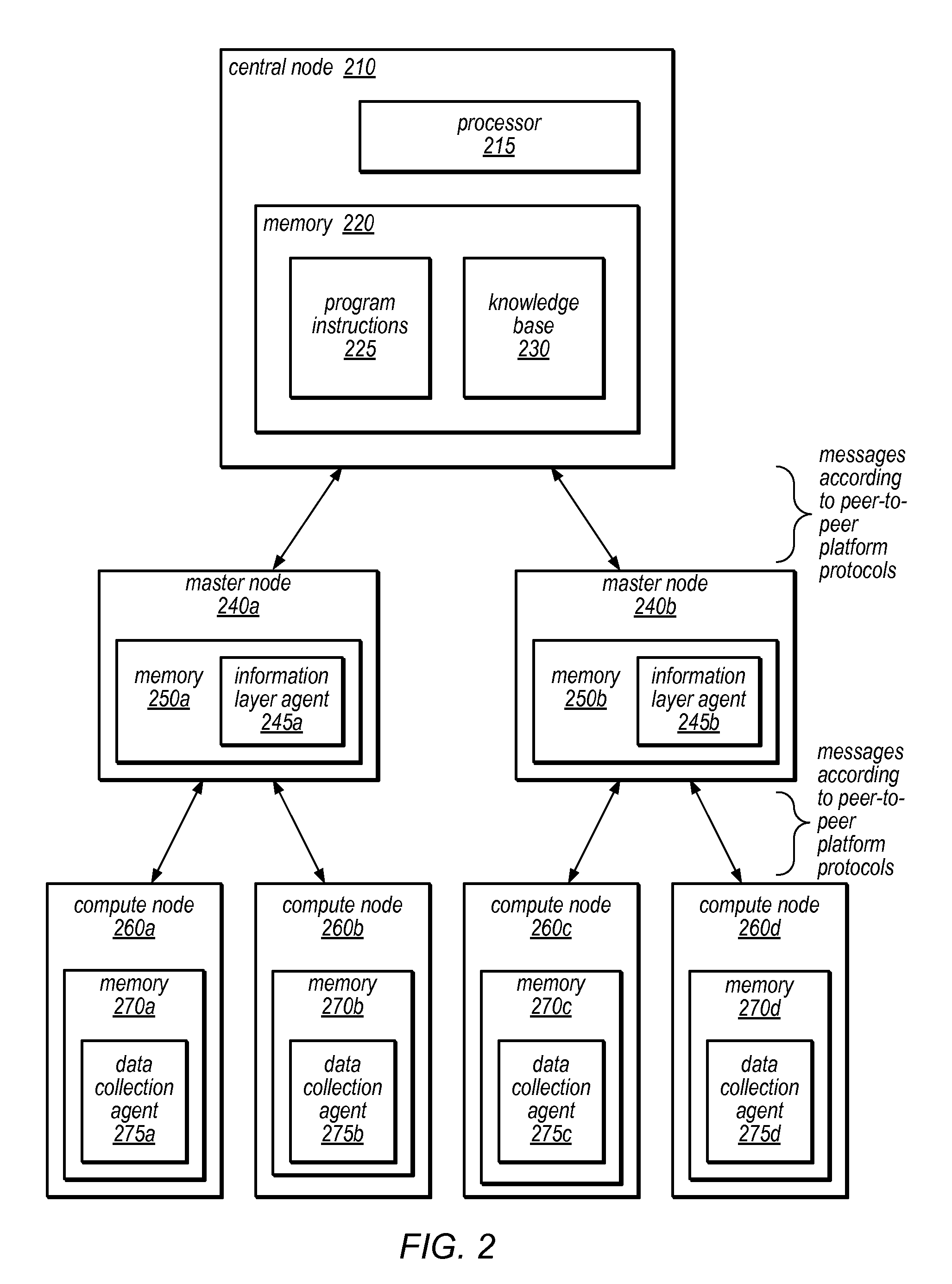
Systems and methods for discovery and classification of denial of service attacks in a distributed computing system may employ local agents on nodes thereof to detect resource-related events. An information later agent may determine if events indicate attacks, perform clustering analysis to determine if they represent known or unknown attack patterns, classify the attacks, and initiate appropriate responses to prevent and / or mitigate the attack, including sending warnings and / or modifying resource pool(s). The information layer agent may consult a knowledge base comprising information associated with known attack patterns, including state-action mappings. An attack tree model and an overlay network (over which detection and / or response messages may be sent) may be constructed for the distributed system. They may be dynamically modified in response to changes in system configuration, state, and / or workload. Reinforcement learning may be applied to the tuning of attack detection and classification techniques and to the identification of appropriate responses.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Authentication and authorization methods for cloud computing security
ActiveUS8769622B2Retain controlKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsResource poolThird party
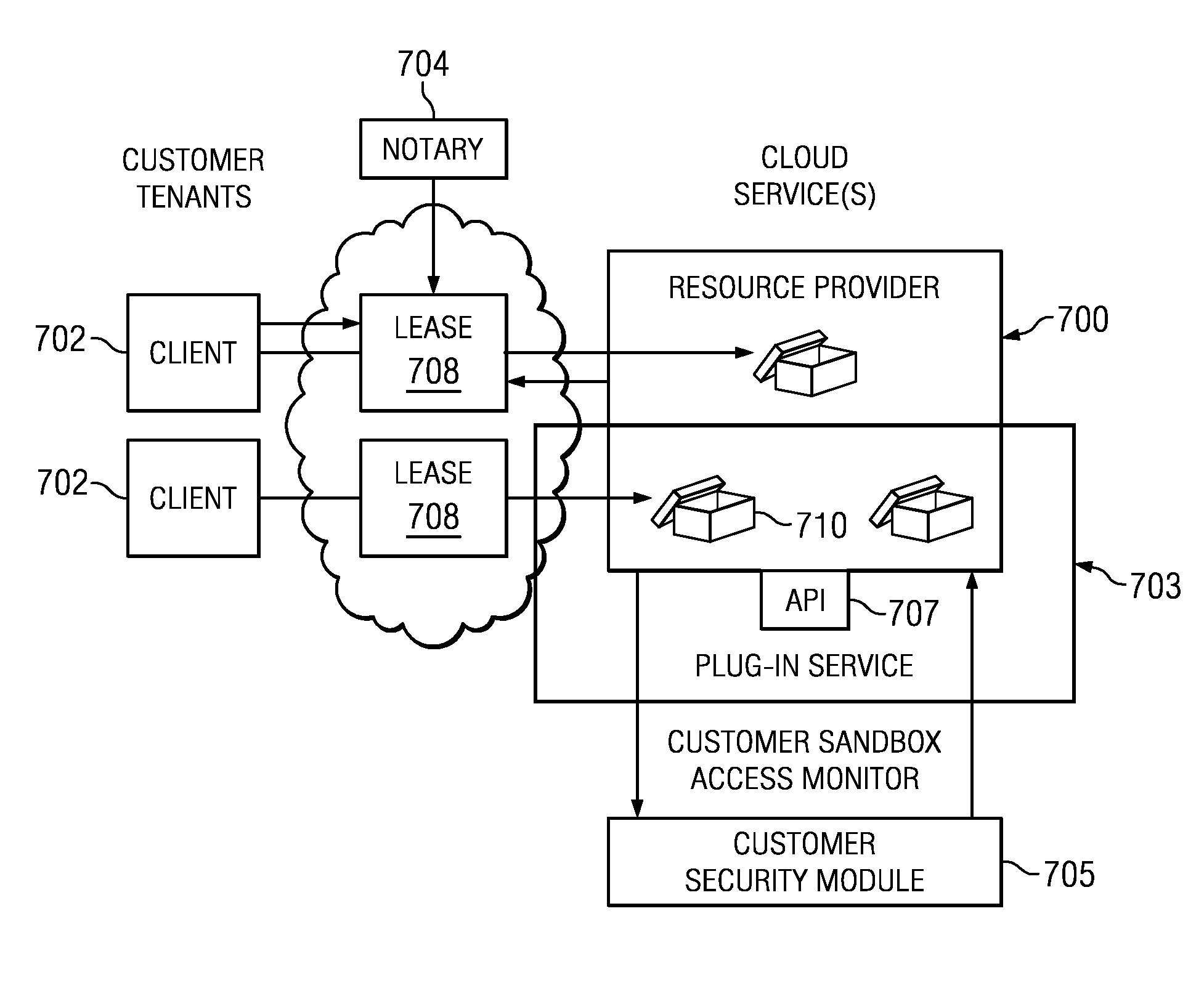
An authentication and authorization plug-in model for a cloud computing environment enables cloud customers to retain control over their enterprise information when their applications are deployed in the cloud. The cloud service provider provides a pluggable interface for customer security modules. When a customer deploys an application, the cloud environment administrator allocates a resource group (e.g., processors, storage, and memory) for the customer's application and data. The customer registers its own authentication and authorization security module with the cloud security service, and that security module is then used to control what persons or entities can access information associated with the deployed application. The cloud environment administrator, however, typically is not registered (as a permitted user) within the customer's security module; thus, the cloud environment administrator is not able to access (or release to others, or to the cloud's general resource pool) the resources assigned to the cloud customer (even though the administrator itself assigned those resources) or the associated business information. To further balance the rights of the various parties, a third party notary service protects the privacy and the access right of the customer when its application and information are deployed in the cloud.
Owner:IBM CORP
Authentication and authorization methods for cloud computing security platform
ActiveUS20130007845A1Retain controlDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationThird partyResource pool
An authentication and authorization plug-in model for a cloud computing environment enables cloud customers to retain control over their enterprise information when their applications are deployed in the cloud. The cloud service provider provides a pluggable interface for customer security modules. When a customer deploys an application, the cloud environment administrator allocates a resource group (e.g., processors, storage, and memory) for the customer's application and data. The customer registers its own authentication and authorization security module with the cloud security service, and that security module is then used to control what persons or entities can access information associated with the deployed application. The cloud environment administrator, however, typically is not registered (as a permitted user) within the customer's security module; thus, the cloud environment administrator is not able to access (or release to others, or to the cloud's general resource pool) the resources assigned to the cloud customer (even though the administrator itself assigned those resources) or the associated business information. To further balance the rights of the various parties, a third party notary service protects the privacy and the access right of the customer when its application and information are deployed in the cloud.
Owner:IBM CORP
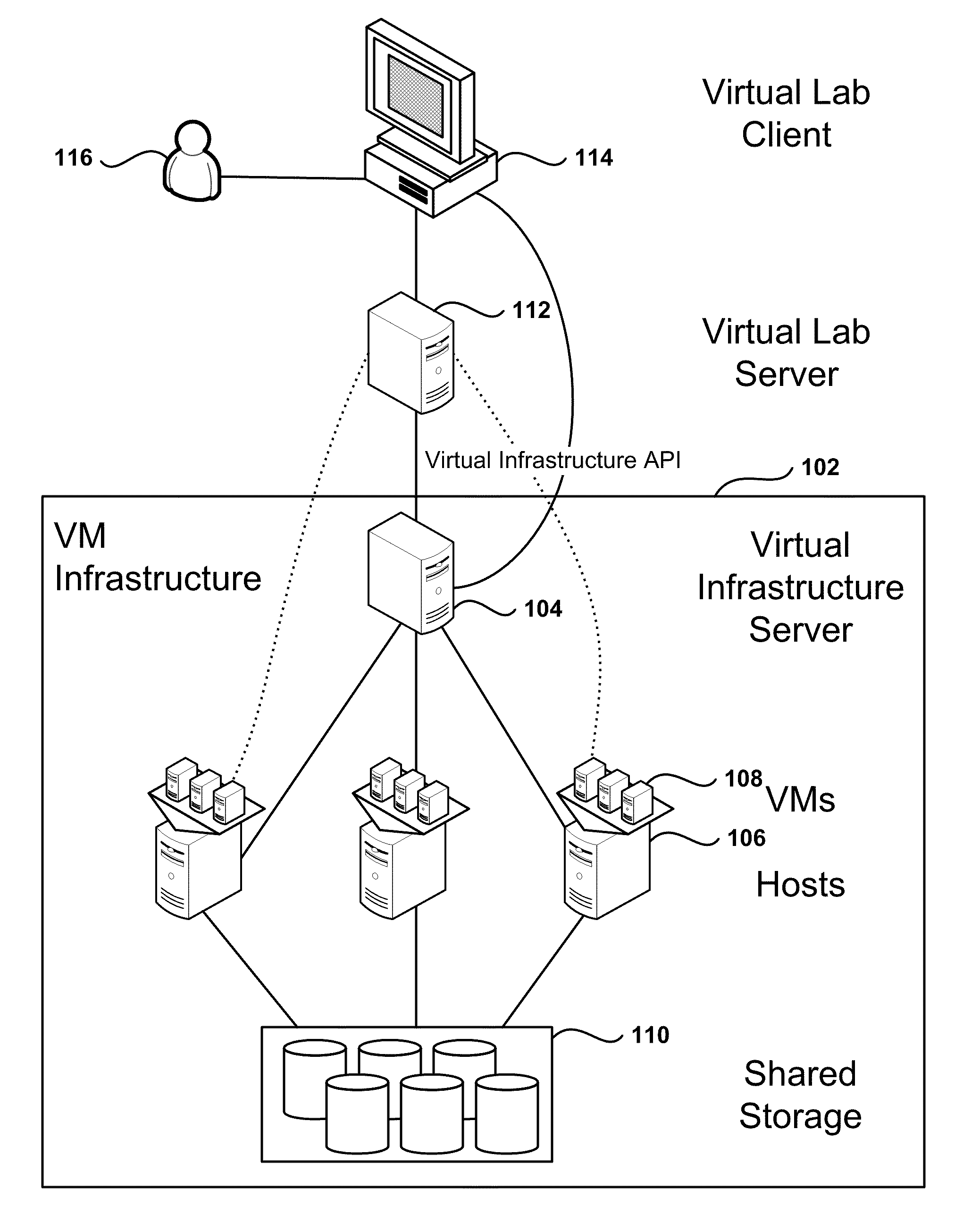
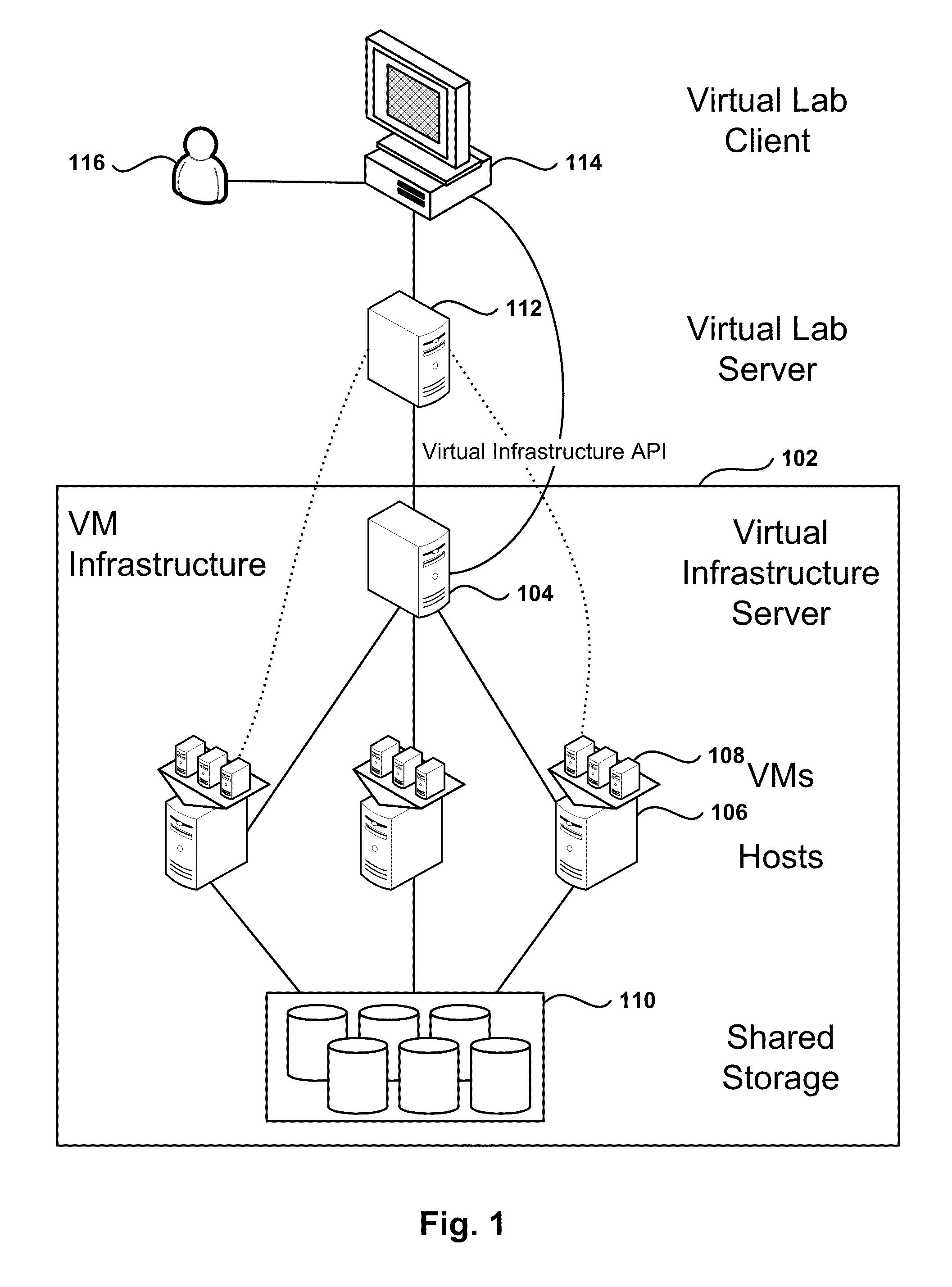
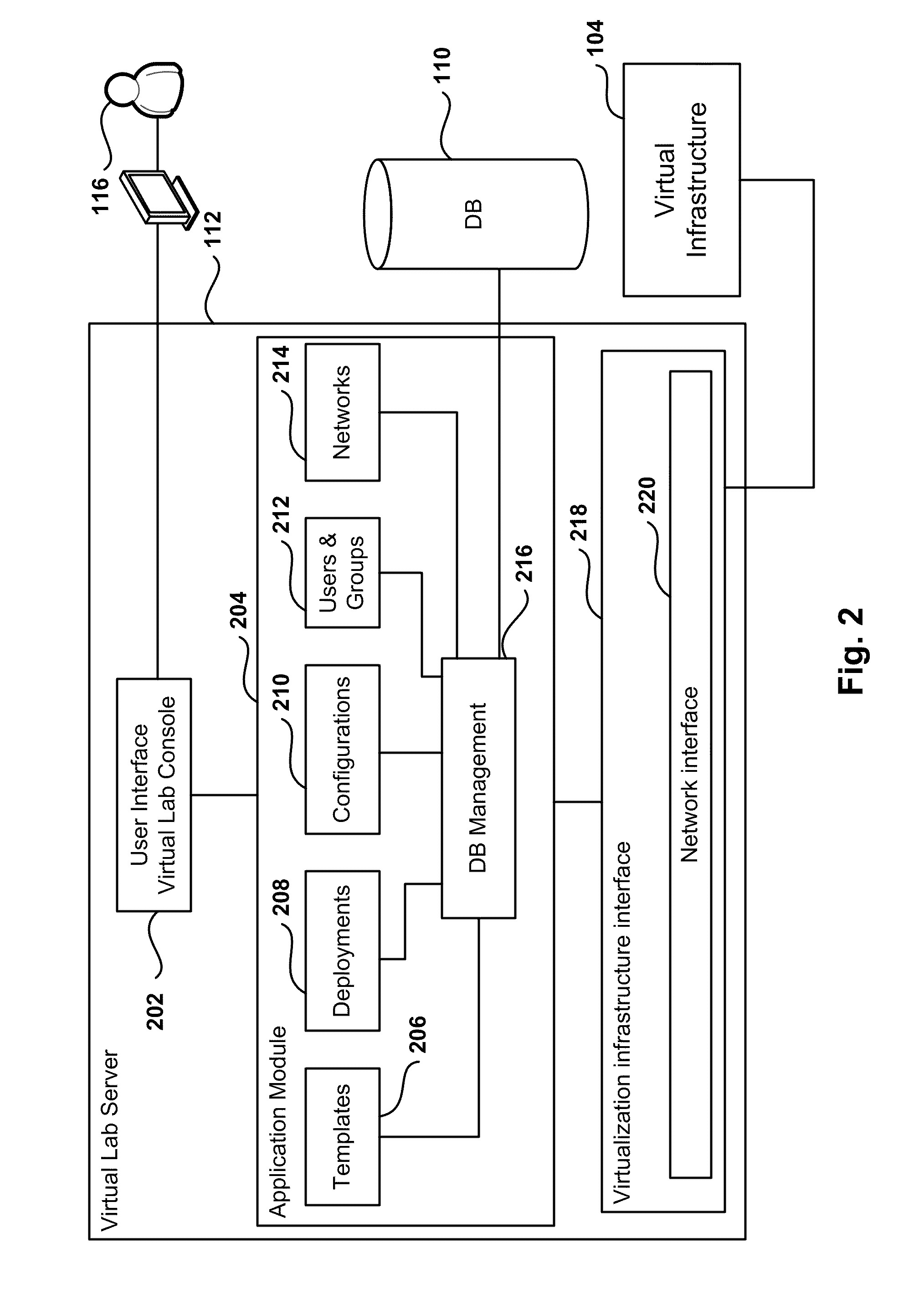
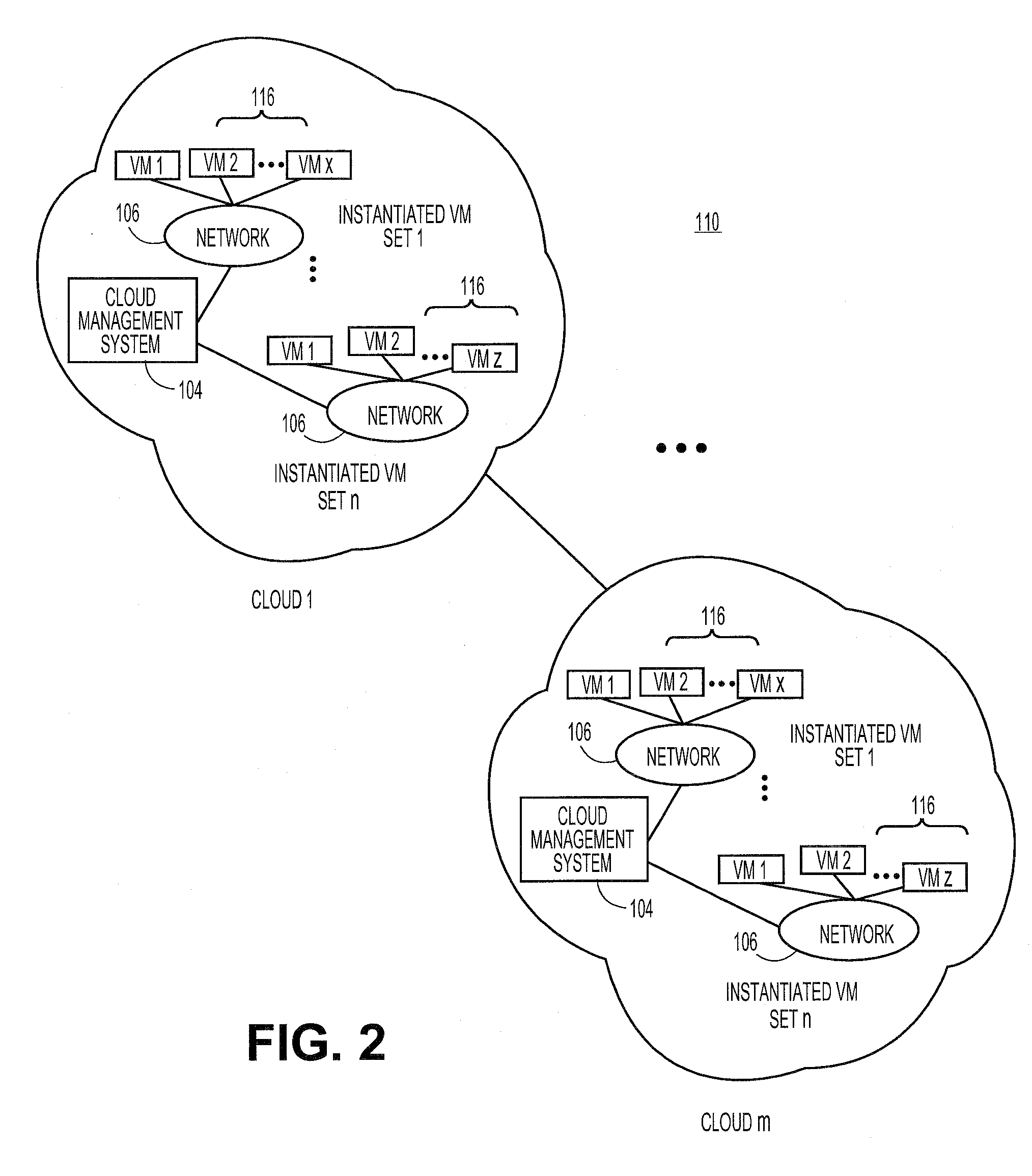
Automated Network Configuration of Virtual Machines in a Virtual Lab Environment
Methods, systems, and computer programs for creating virtual machines (VM) and associated networks in a virtual infrastructure are presented. The method defines virtual network templates in a database, where each virtual network template includes network specifications. A configuration of a virtual system is created, which includes VMs, virtual lab networks associated with virtual network templates, and connections from the VMs to the virtual lab networks. Further, the configuration is deployed in the virtual infrastructure resulting in a deployed configuration. The deployment of the configuration includes instantiating in the virtual infrastructure the VMs of the configuration, instantiating in the virtual infrastructure the virtual lab networks, retrieving information from the database, and creating and executing programming instructions for the VMs. The database information includes the network specifications from the virtual network templates associated with the virtual lab networks, and network resources for the virtual lab networks from a pool of available network resources. The programming instructions are created for the particular Guest Operating System (GOS) running in each VM based on the GOS and on the retrieved database information. When executed in the corresponding VM GOS, the programming instructions configure the VMs network interfaces with the corresponding network specifications.
Owner:NICIRA
Resource scheduling method and system
ActiveUS20070021998A1Reduce the amount of calculationIncrease opportunitiesDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsResource poolDistributed computing
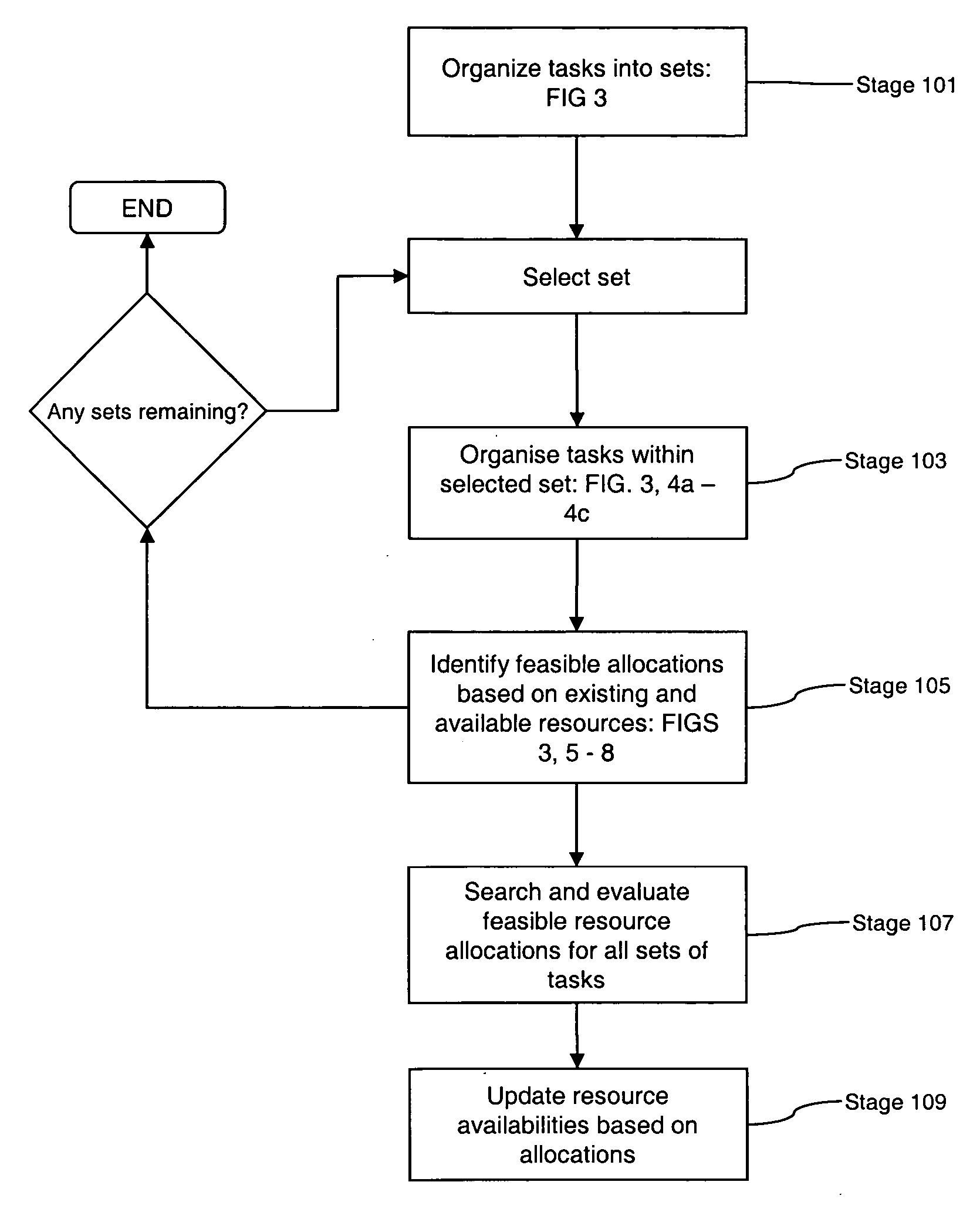
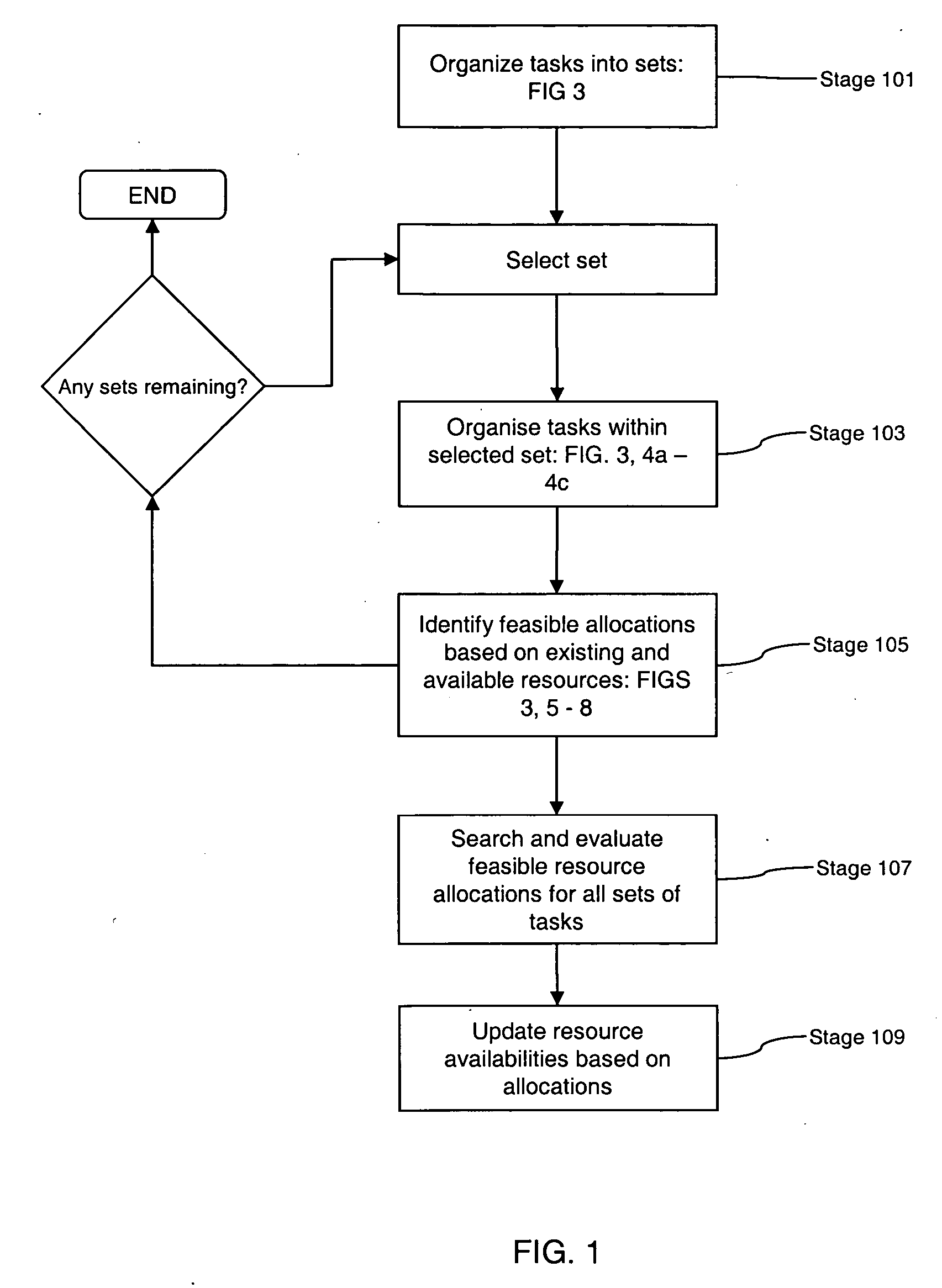
Embodiments of the invention are concerned with scheduling resources to perform tasks requiring a plurality of capabilities or capabilities and capacities, and has particular application to highly changeable or uncertain environments in which the status and the composition of tasks and / or resources changes frequently. Embodiments provide a method for use in a scheduling process for scheduling allocation of resources to a task, each resource having a plurality of attributes, wherein the task has one or more operational constraints including a required plurality of capabilities, and a performance condition associated therewith. The method comprises: receiving data indicative of a change to the status of the scheduling process; in response to receipt of the status data, reviewing the attributes of individual resources so as to identify combinations of resources able to collectively satisfy said capability requirements of the task; evaluating each identified combination of resources in accordance with a performance algorithm so as to identify an associated performance cost; selecting a combination of resources whose identified performance cost meets the performance condition; and scheduling said task on the basis of said selected combination of resources. In embodiments of this aspect of the invention, changes to resource configurations are effected as part of the scheduling process. These changes can be made dynamically, in response to the occurrence of events that have a bearing on the scheduling process, and involve aggregating resources together so as to create, essentially, a new resource pool from which selection can be made.
Owner:TRIMBLE MRM
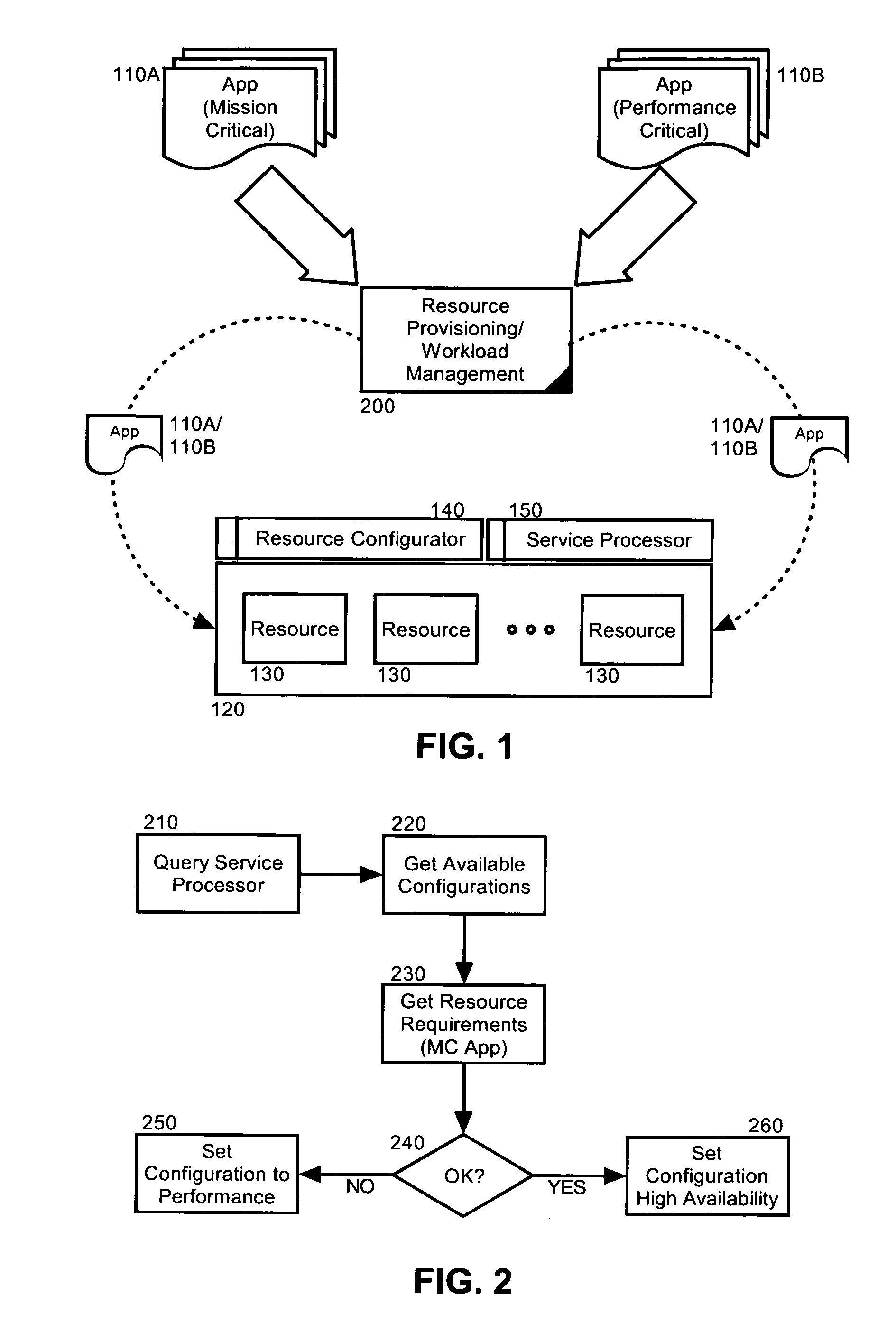
Dynamic resource allocation for disparate application performance requirements
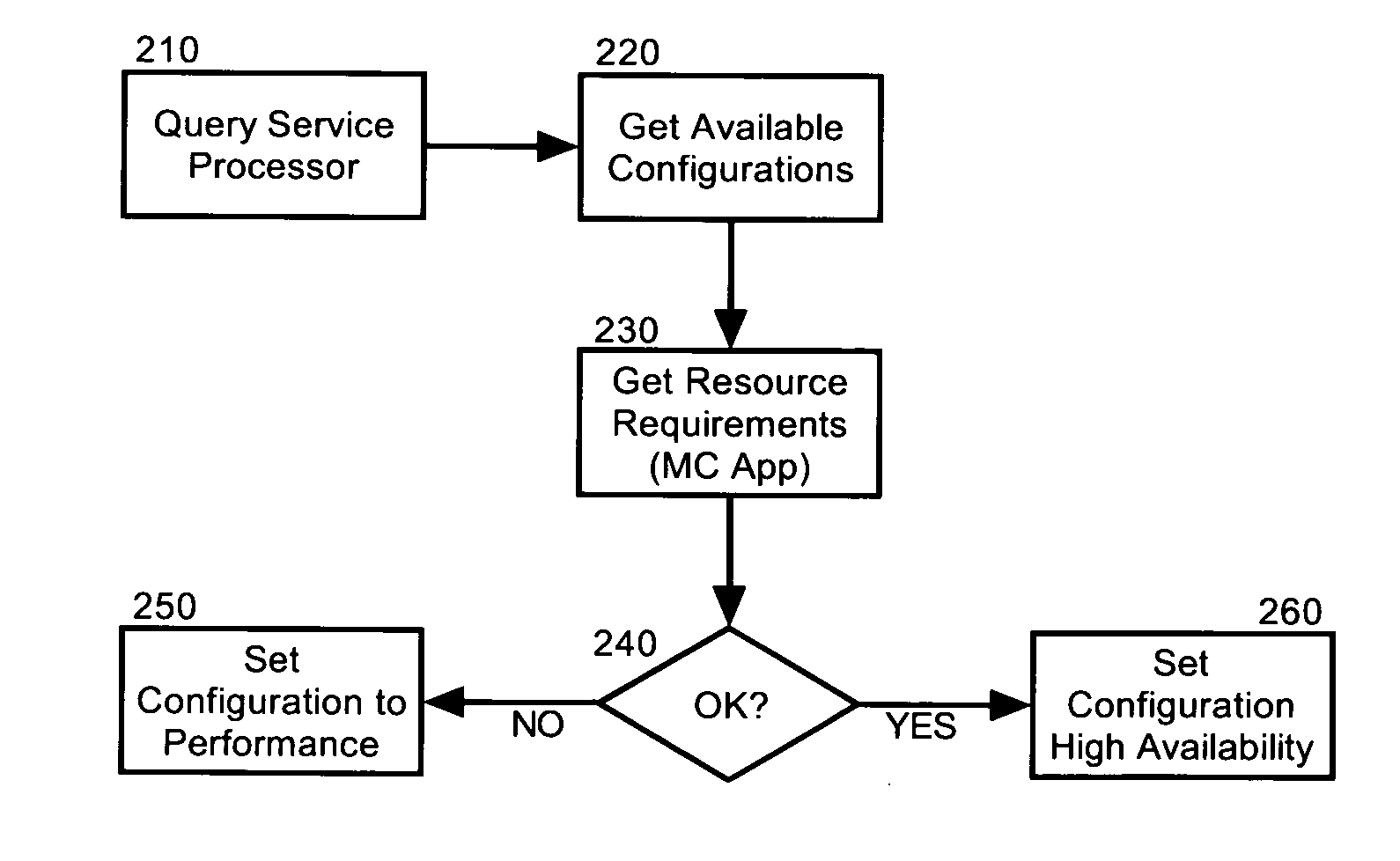
InactiveUS20070198982A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsResource poolData processing system
Embodiments of the invention address deficiencies of the art in respect to dynamic computing resource allocation, and provide a method, system and computer program product for dynamic resource allocation for disparate application performance requirements. In one embodiment of the invention, a resource allocation data processing system can include a shared resource pool including resources and a resource configurator coupled to the shared resource pool. The system further can include a service processor coupled to the resource configurator, wherein the service processor can include an application programming interface (API) exposing methods for commanding the resource configurator to configure the resources in the shared resource pool.
Owner:LENOVO ENTERPRISE SOLUTIONS SINGAPORE
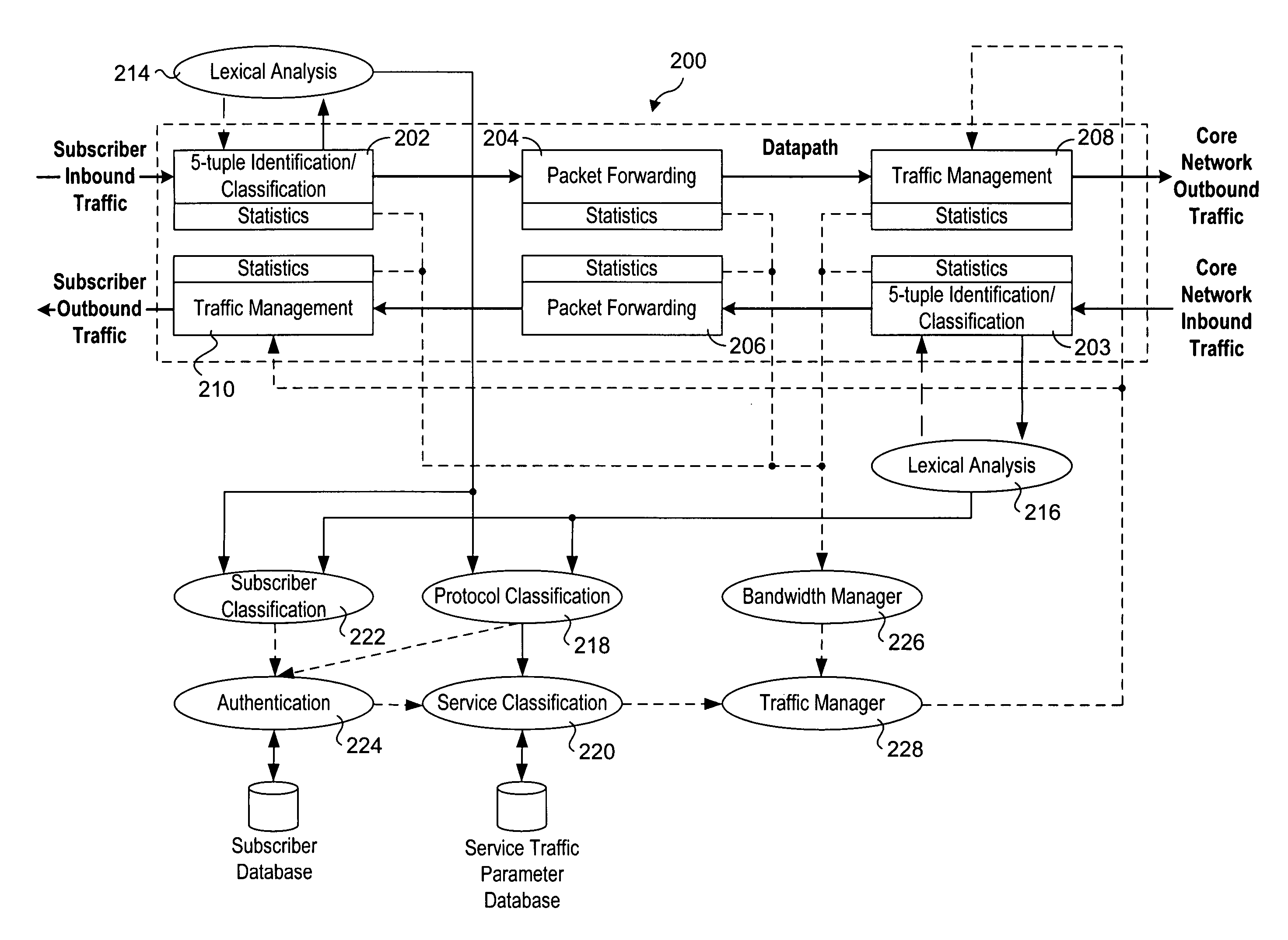
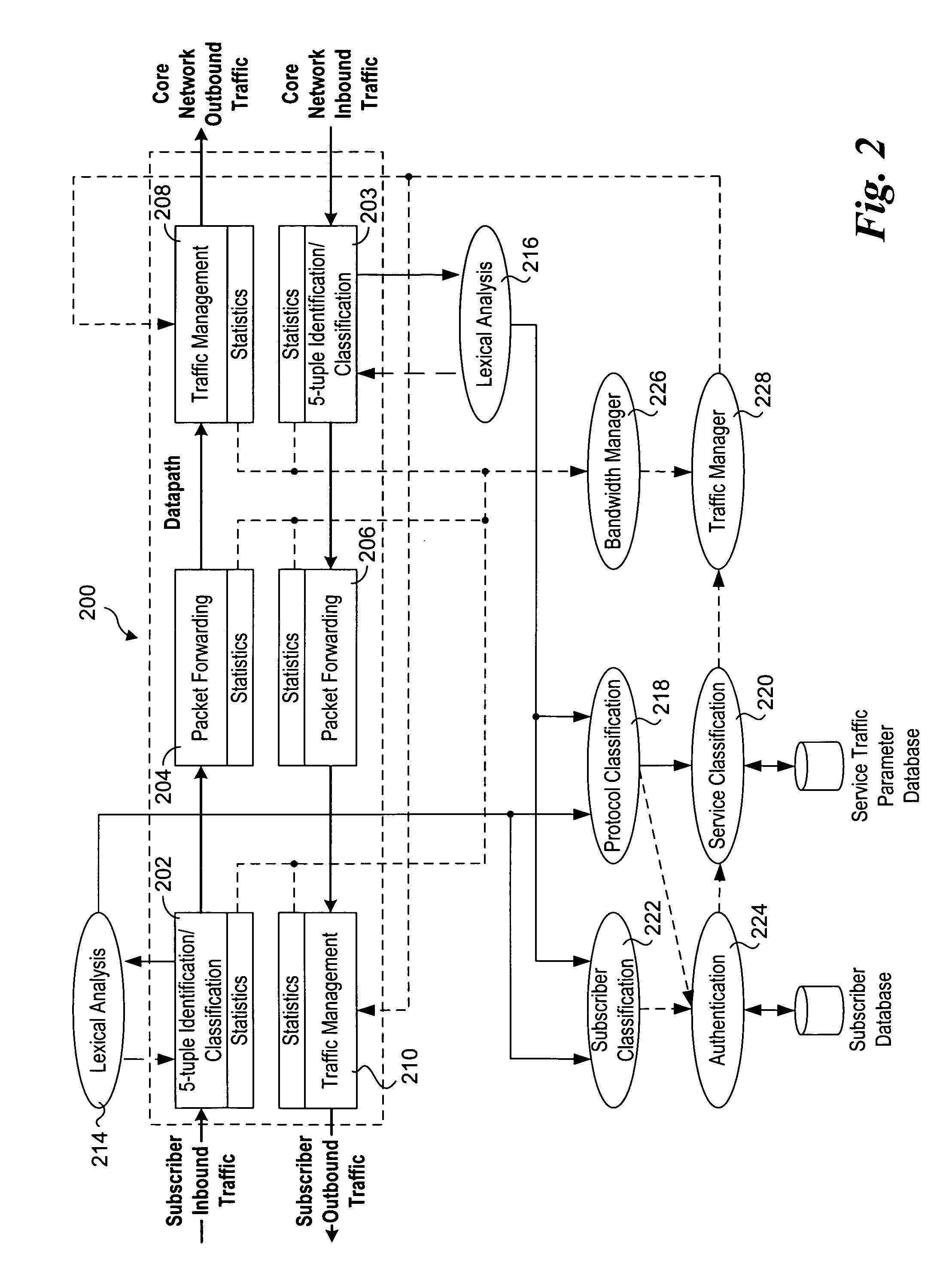
Methods and apparatus to support dynamic allocation of traffic management resources in a network element
Methods and apparatus to support dynamic allocation of traffic management resources in a network element. Shared pools of traffic management resources comprising an aggregation of local line card resources distributed across the line cards or a network element maintained by apparatus software. Incoming packets are classified into subscriber flows using a hierarchical classification scheme. In view of subscriber services and flow application types, traffic management resources are dynamically allocated from the shared pools, and traffic management policies associated with the subscriber services and application types are applied to the subscriber flows via the allocated resources. In response to detecting a subscriber flow has terminated, the allocated resources are release and made available to be dynamically re-allocated to subsequent subscriber flows.
Owner:TELLABS COMM CANADA
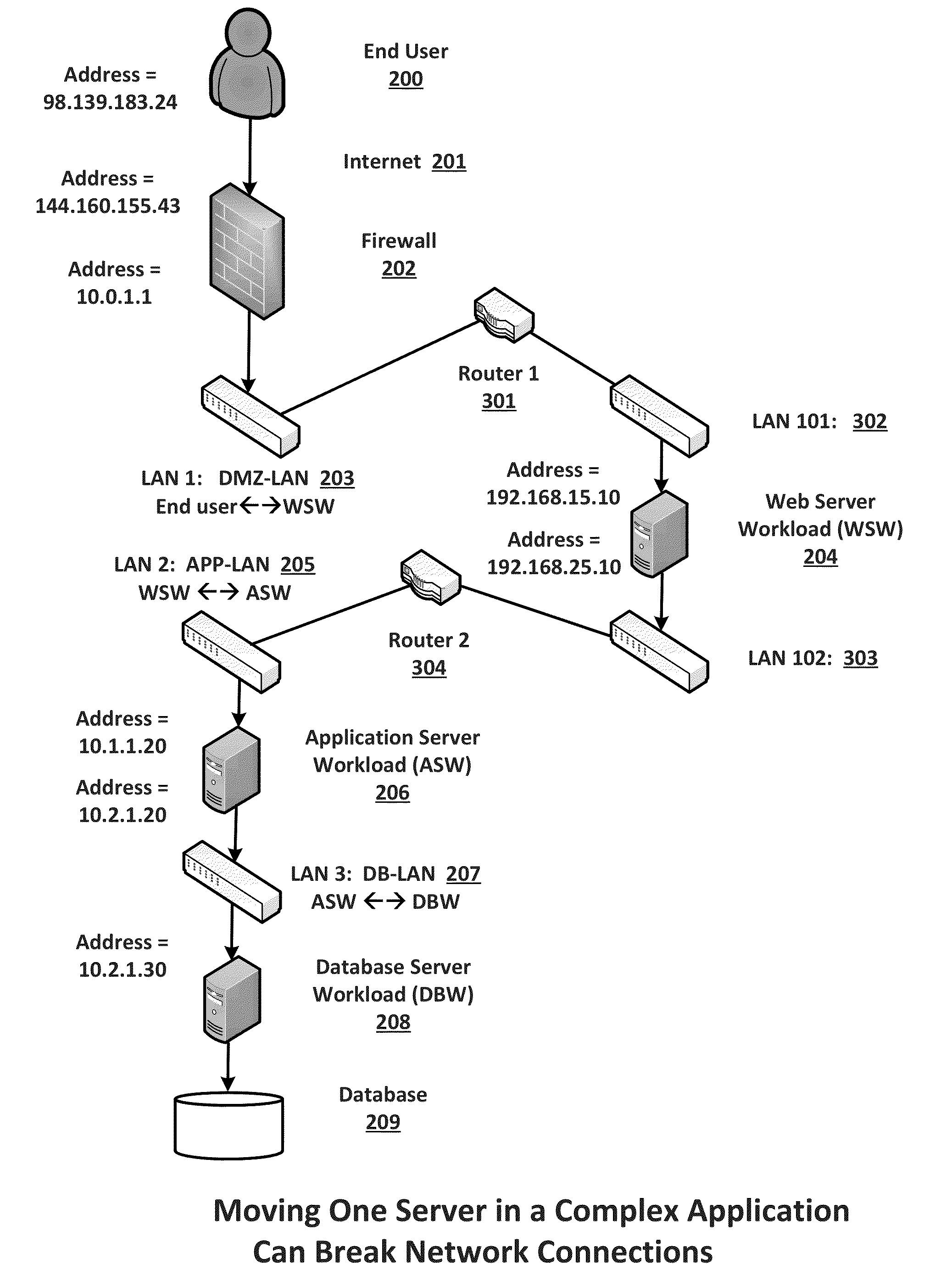
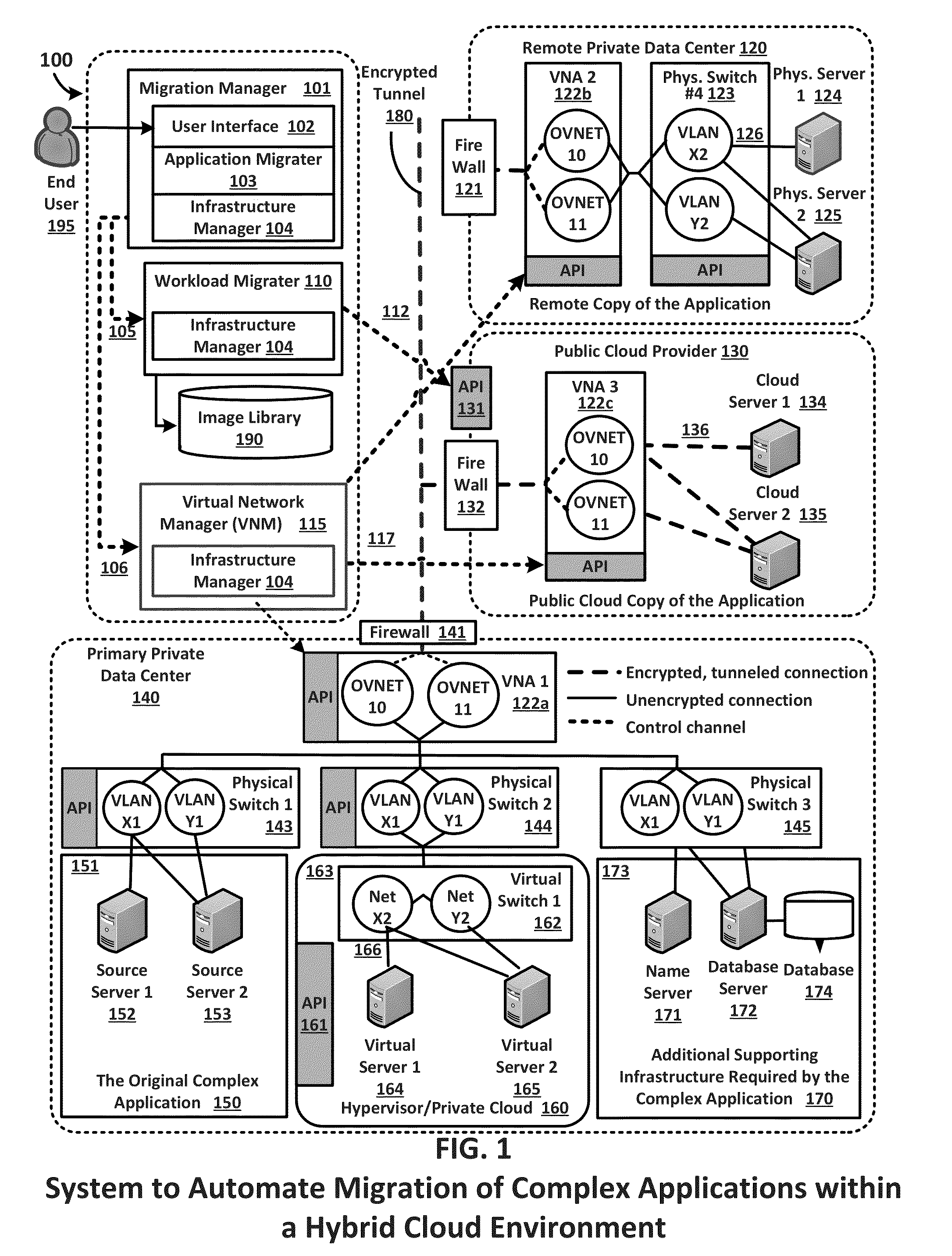
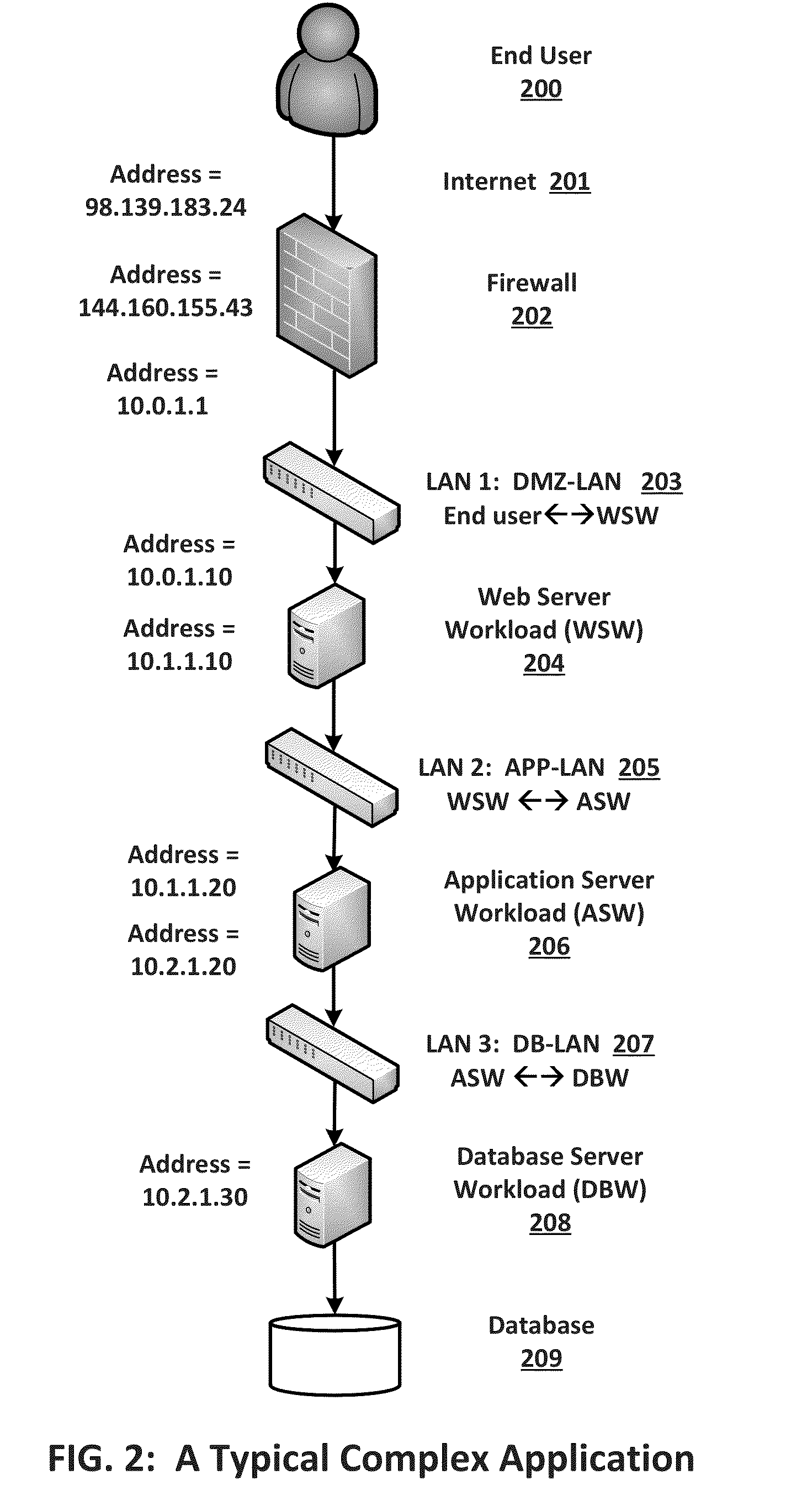
Migration of complex applications within a hybrid cloud environment
ActiveUS20150096011A1Increase the number ofFully automatedMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlResource poolData center
A system and methods for the migration of complex computer applications and the workloads comprising them between physical, virtual, and cloud servers that span a hybrid cloud environment comprising private local and remote customer data centers and public cloud data centers, without modification to the applications, their operational environments, or user access procedures. A virtual network manager securely extends the subnets and VLANS within the customer's various data center across the distributed, hybrid environment using overlay networks implemented with virtual network appliances at nodes of the overlay network. A server migrater migrates individual workloads of servers used by the complex application from one pool of server resources to another. A migration manager application provides a control interface, and also maps and manages the resources of the complex application, the hybrid environment, and the virtual network spanning the hybrid cloud environment.
Owner:RACEMI
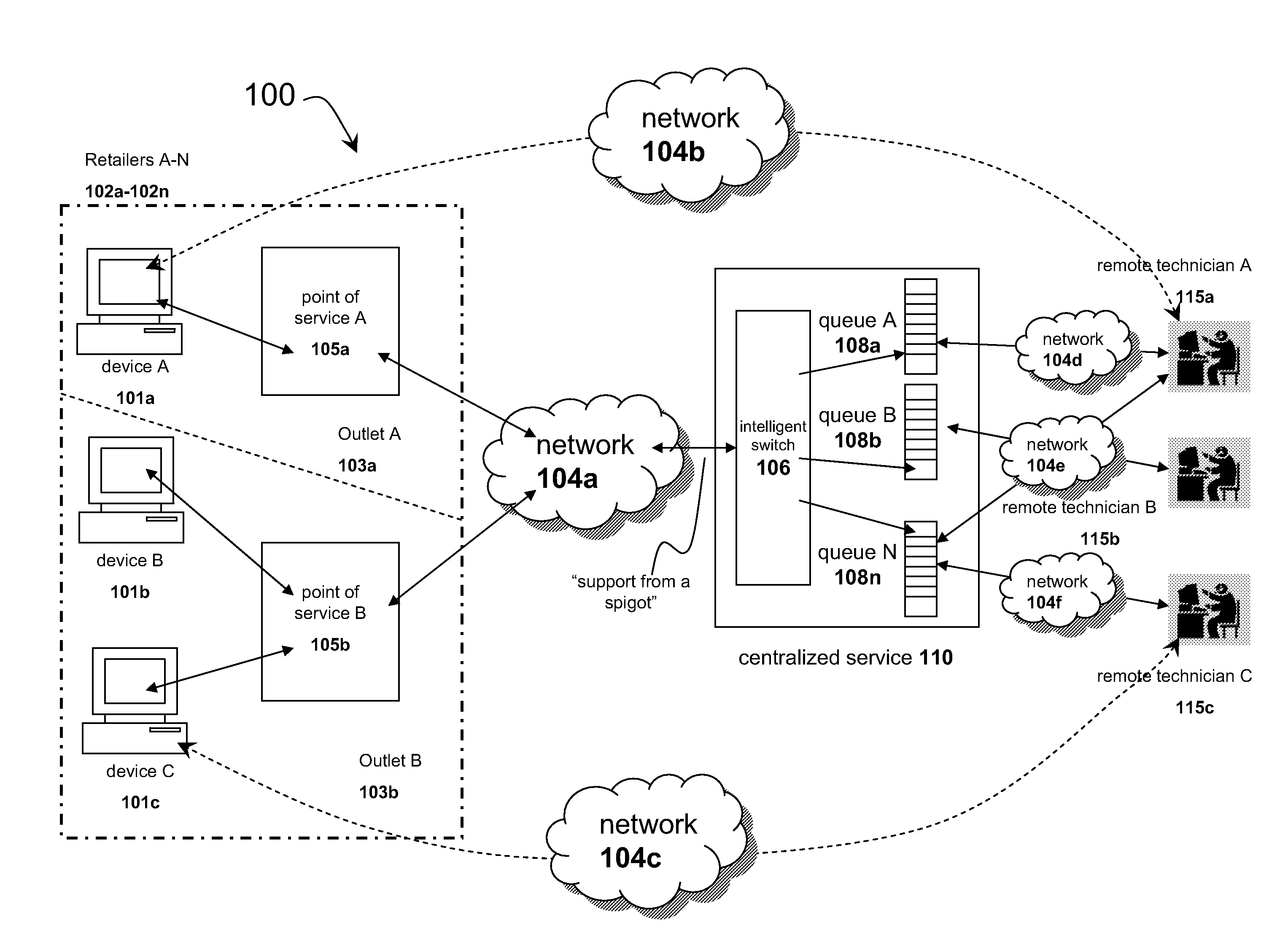
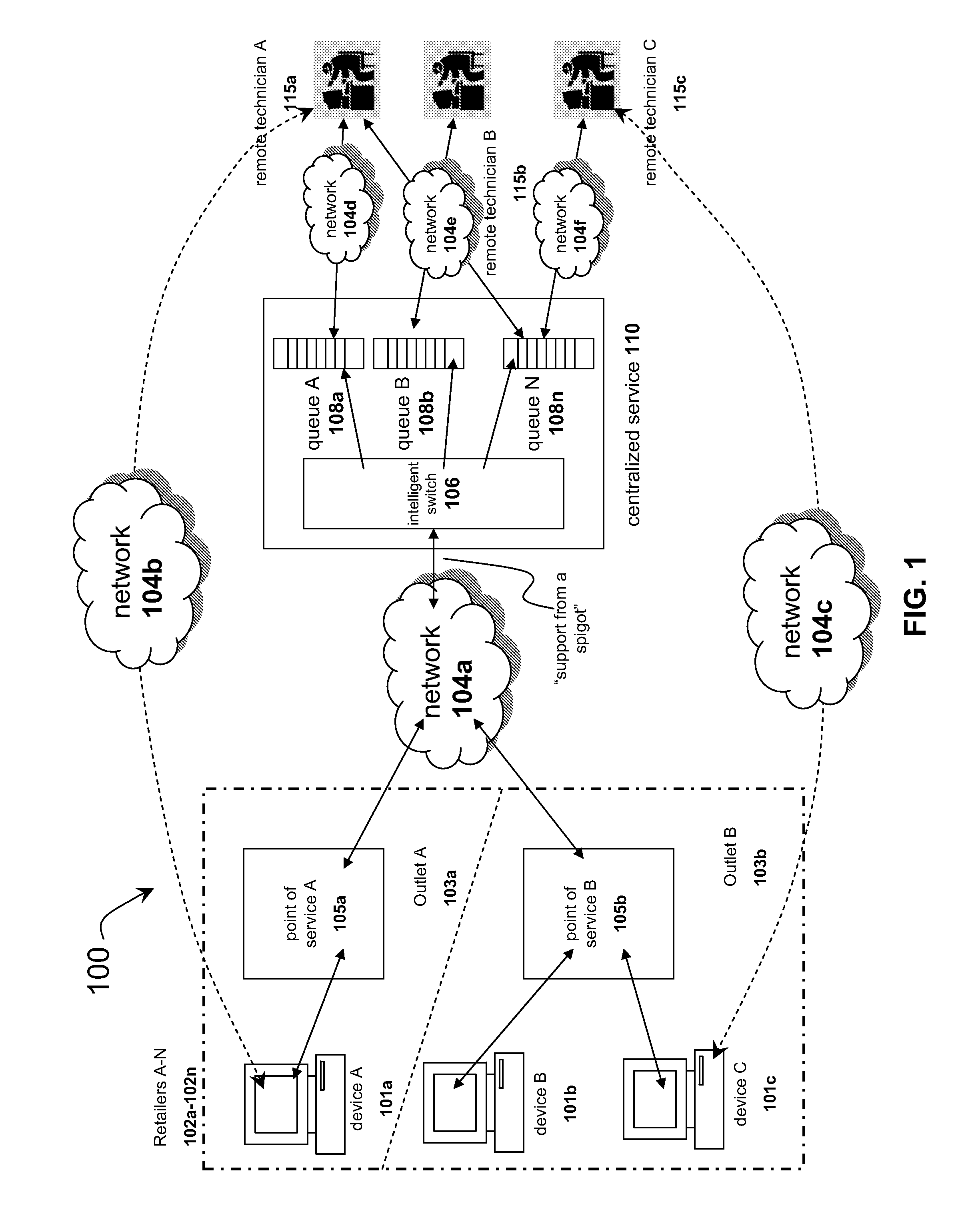
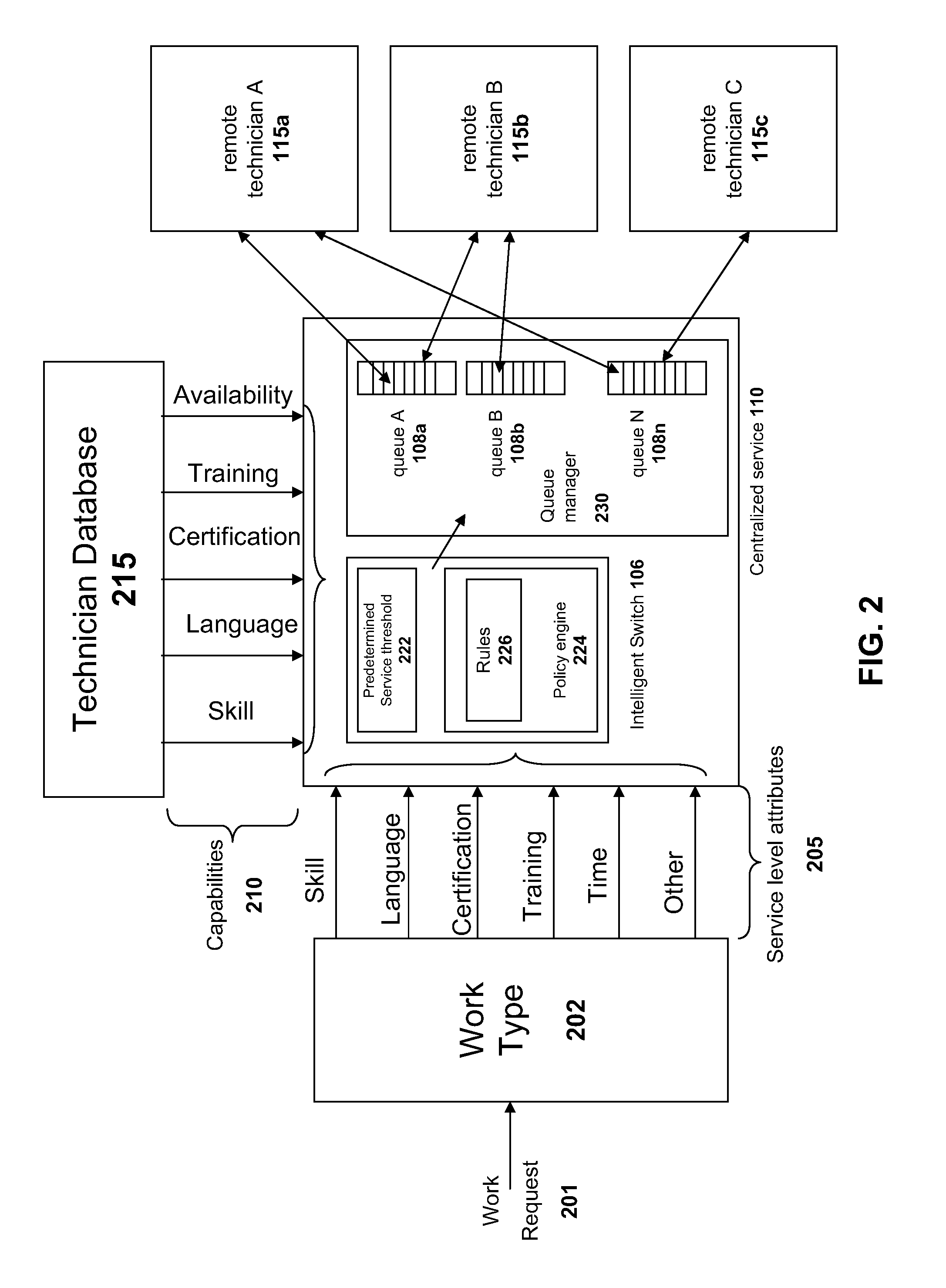
Systems and methods for distributing remote technical support via a centralized service
InactiveUS20090125608A1Quality improvementLow costMultiple digital computer combinationsManual exchangesResource poolService personnel
The solution described herein provides an innovative use of remote services technology integrated with service personnel onsite at the point of service, such as a consumer repair outlet, to provide a pool of technical support resources to service a widely distributed resource need, such as support and repair resource needs of a chain of consumer outlets or an aggregated group of single proprietor consumer outlets. With this solution, qualified technical resources are provided from a central location to service a widely distributed retail environment. This is on-demand online remote support service is called or referred to as “support from a spigot.” The distribution method enables the delivery of higher quality, more reliable and overall lower cost services. Instead of requiring dedicated technical resources at each location, lower skilled labor may be deployed at the location to enable the remote technical support services process.
Owner:PLUMCHOICE
Methods and systems for providing access control to user-controlled resources in a cloud computing environment
A cloud computing environment can be configured to allow third party, user-controlled resources to be included in the pool of resources available in the cloud. The user-controlled resources can include a cloud application to communicate with a cloud management system to coordinate access to the user-controlled resources. The cloud application allows the user to specify the specific set of resources that the cloud can access, such as specific hardware and software resources.
Owner:RED HAT
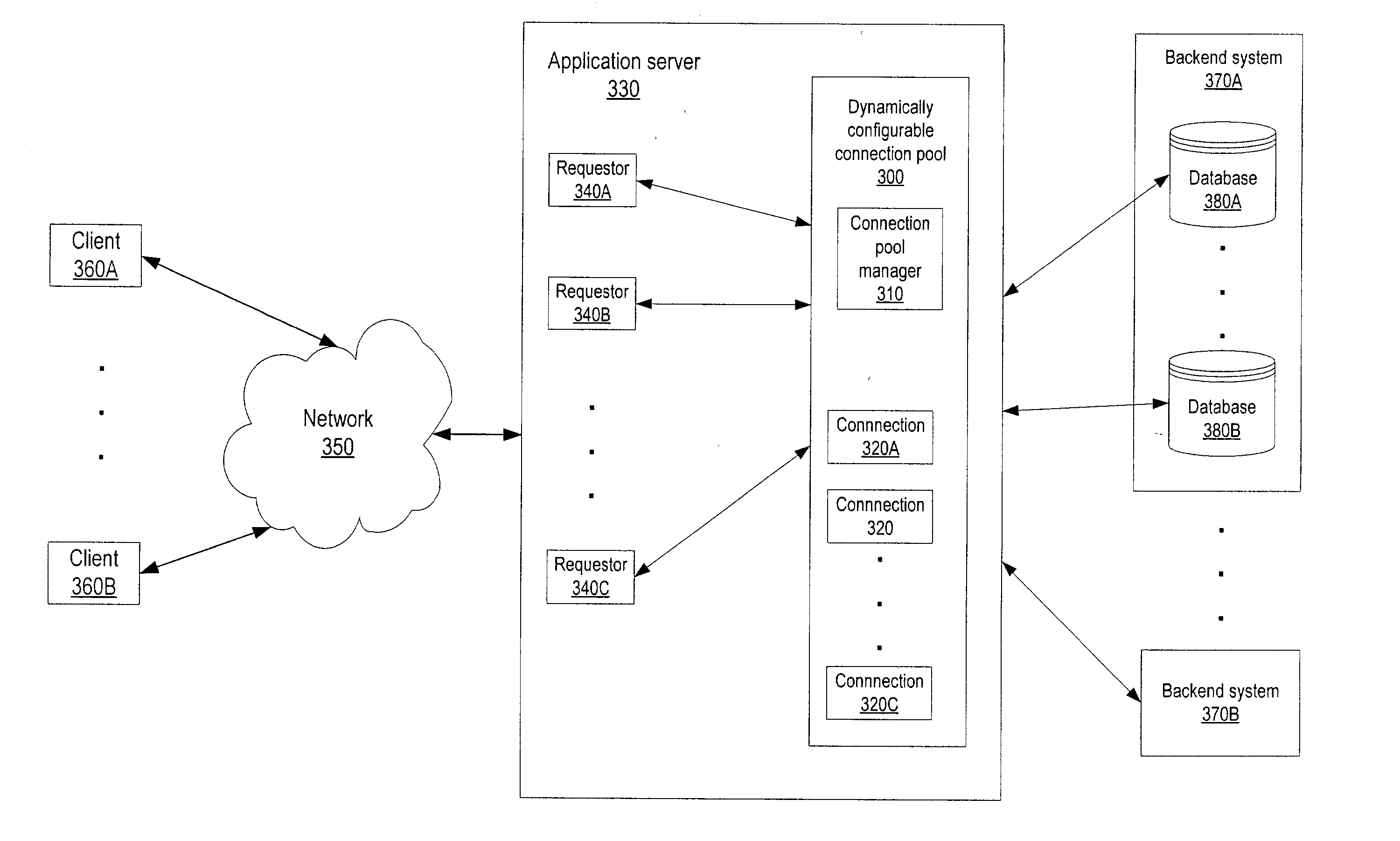
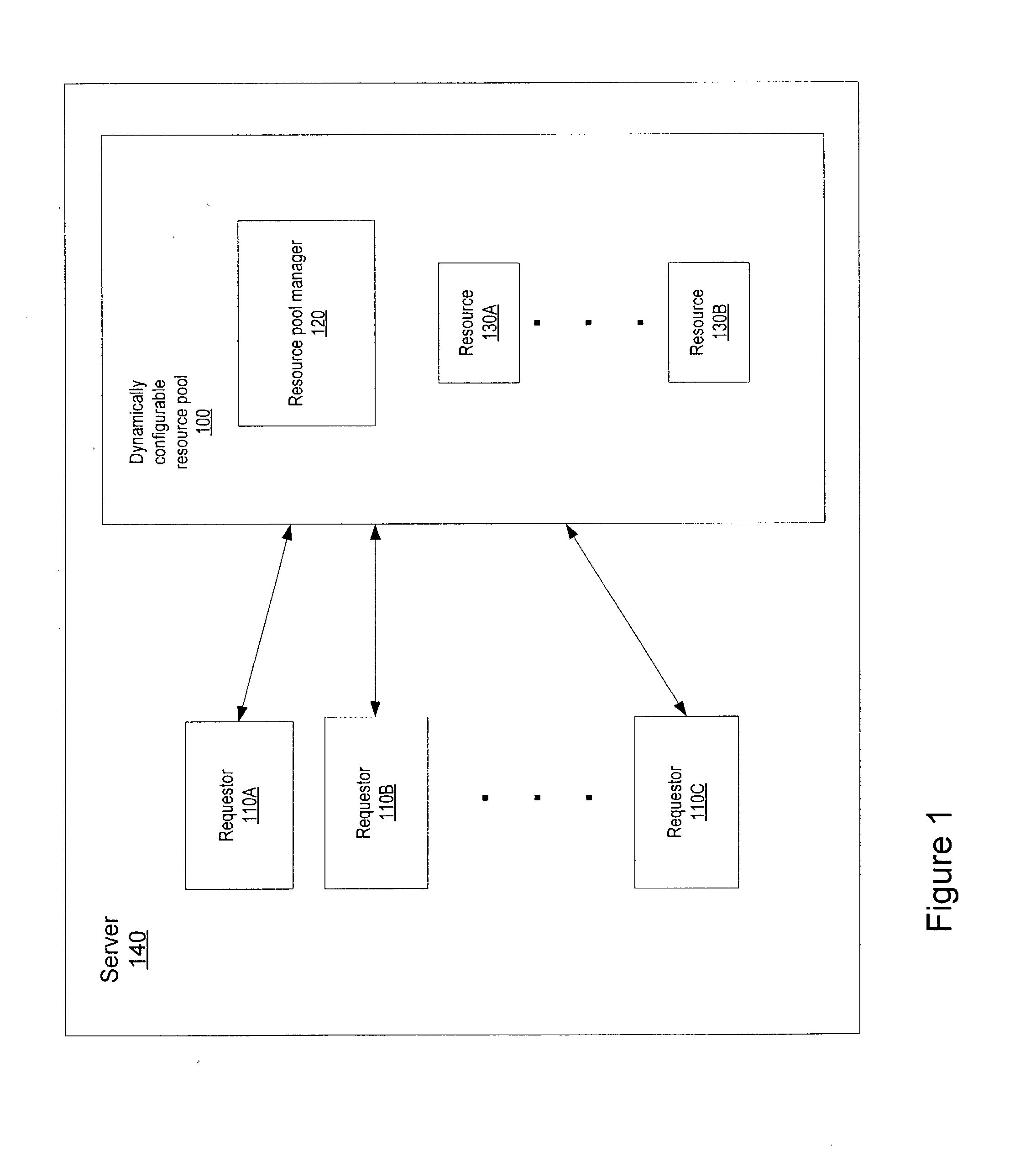
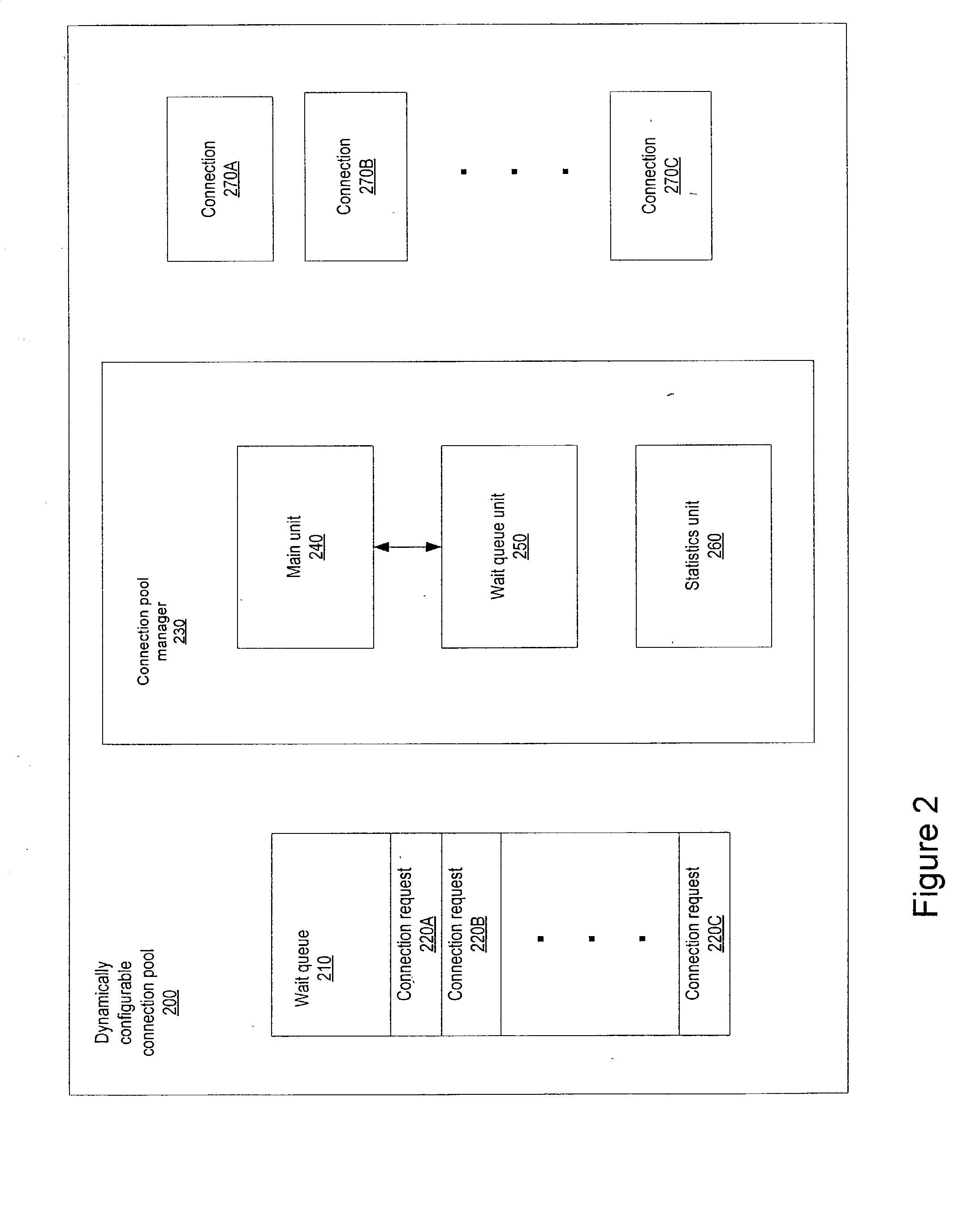
Dynamically configurable resource pool
ActiveUS20040088413A1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsResource poolWeb service
A dynamically configurable resource pool may provide a pool of computing resource for use in a computing system or application, such as a connection pool or a thread pool for server systems such as application and web server systems. In one embodiment, a server may include a resource pool configured to provide a plurality of computing resources. Other components in the server may be configured to request use of one of the computing resources from the connection pool. The resource pool may include a resource pool manager configured to service requests for the computing resources. The resource pool manager may manage configuration of the resource pool. The resource pool manager may also be configured to receive a configuration change request to change the configuration of the resource pool while the resource pool is available for use.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
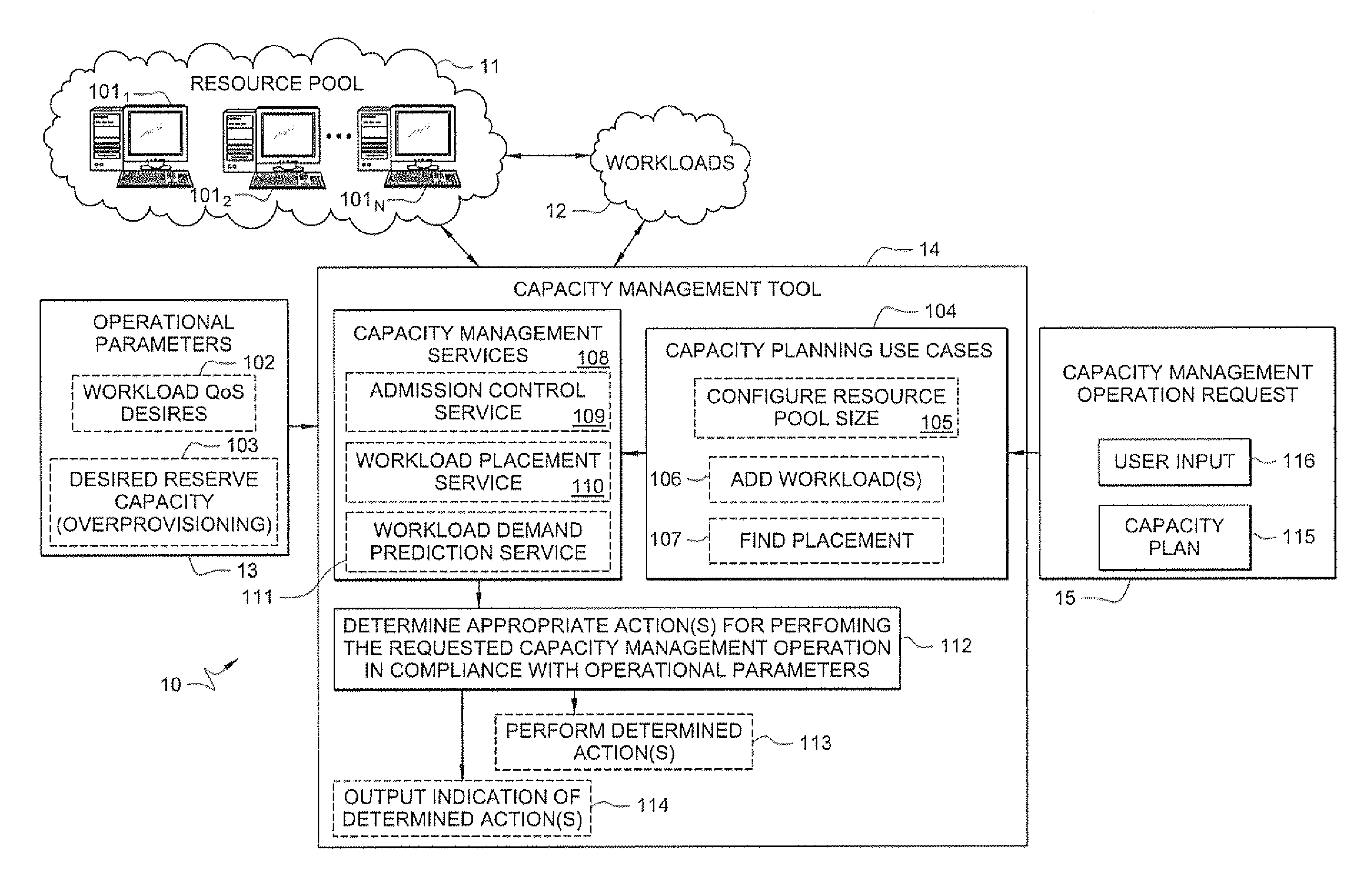
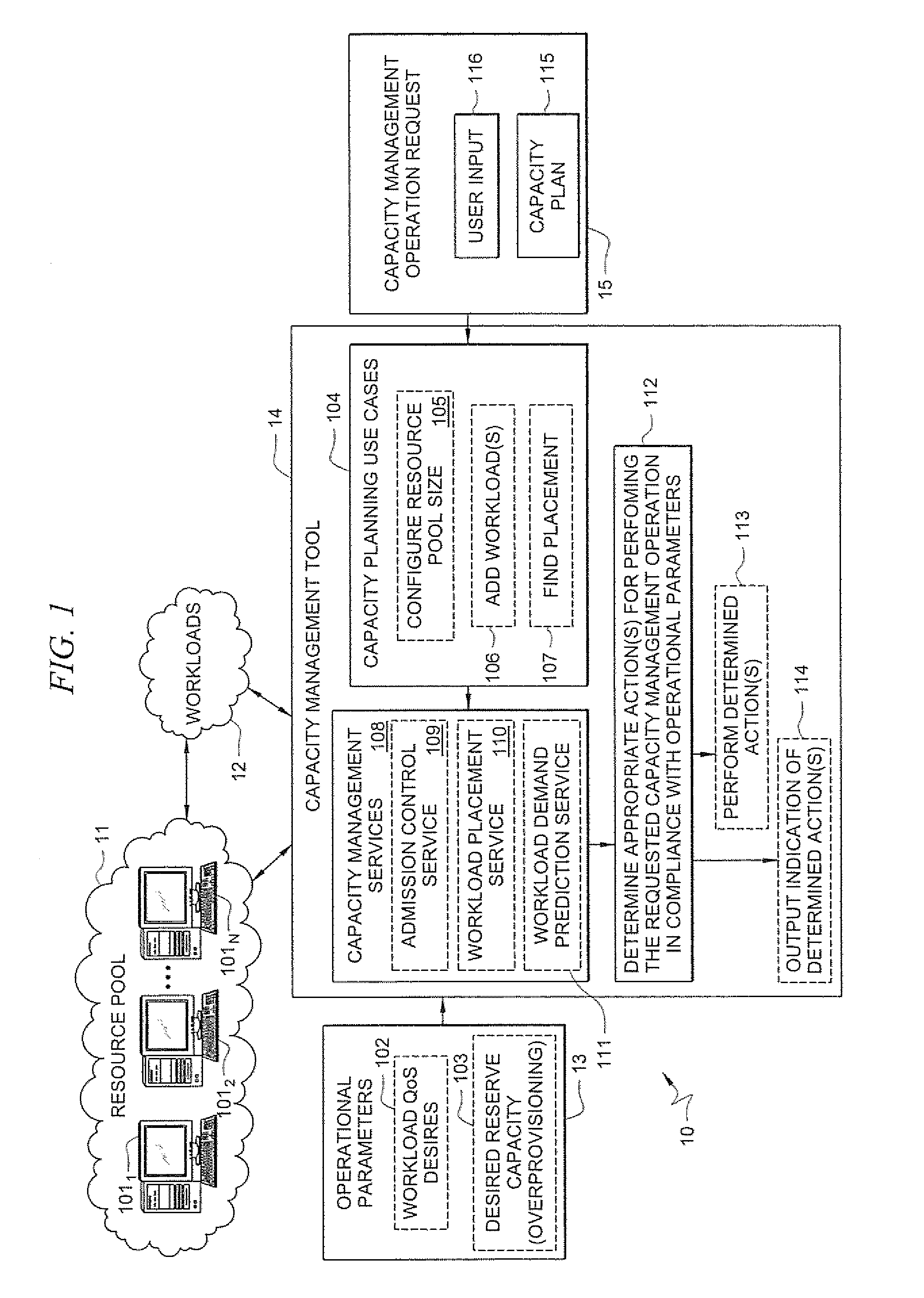
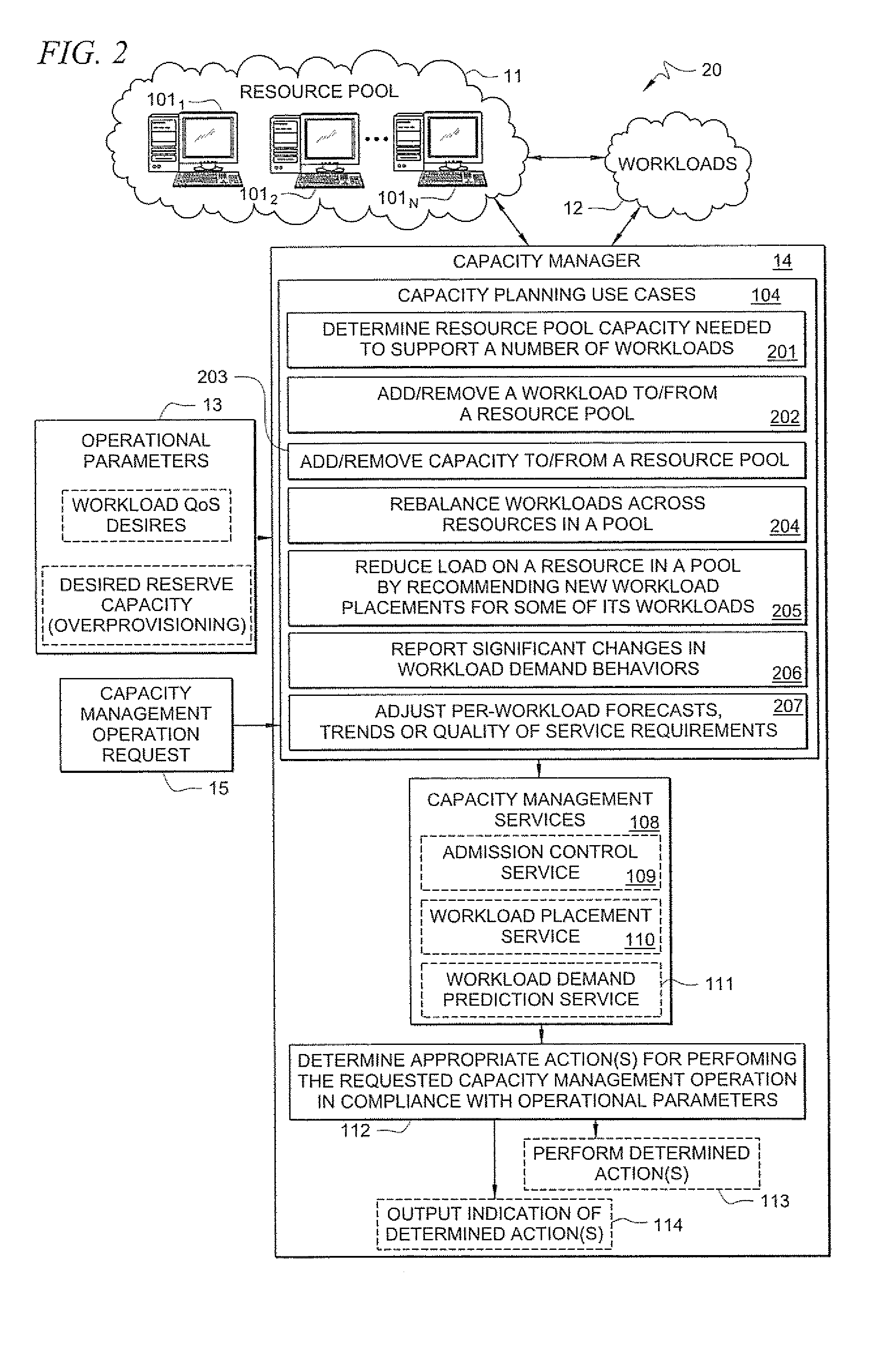
Systems and methods for providing capacity management of resource pools for servicing workloads
A method comprises receiving, by a capacity management tool, a capacity management operation request that specifies a resource pool-level operation desired for managing capacity of a resource pool that services workloads. The capacity management tool determines, in response to the received request, one or more actions to perform in the resource pool for performing the requested capacity management operation in compliance with defined operational parameters of the workloads. The method further comprises performing the determined one or more actions for performing the requested capacity management operation.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
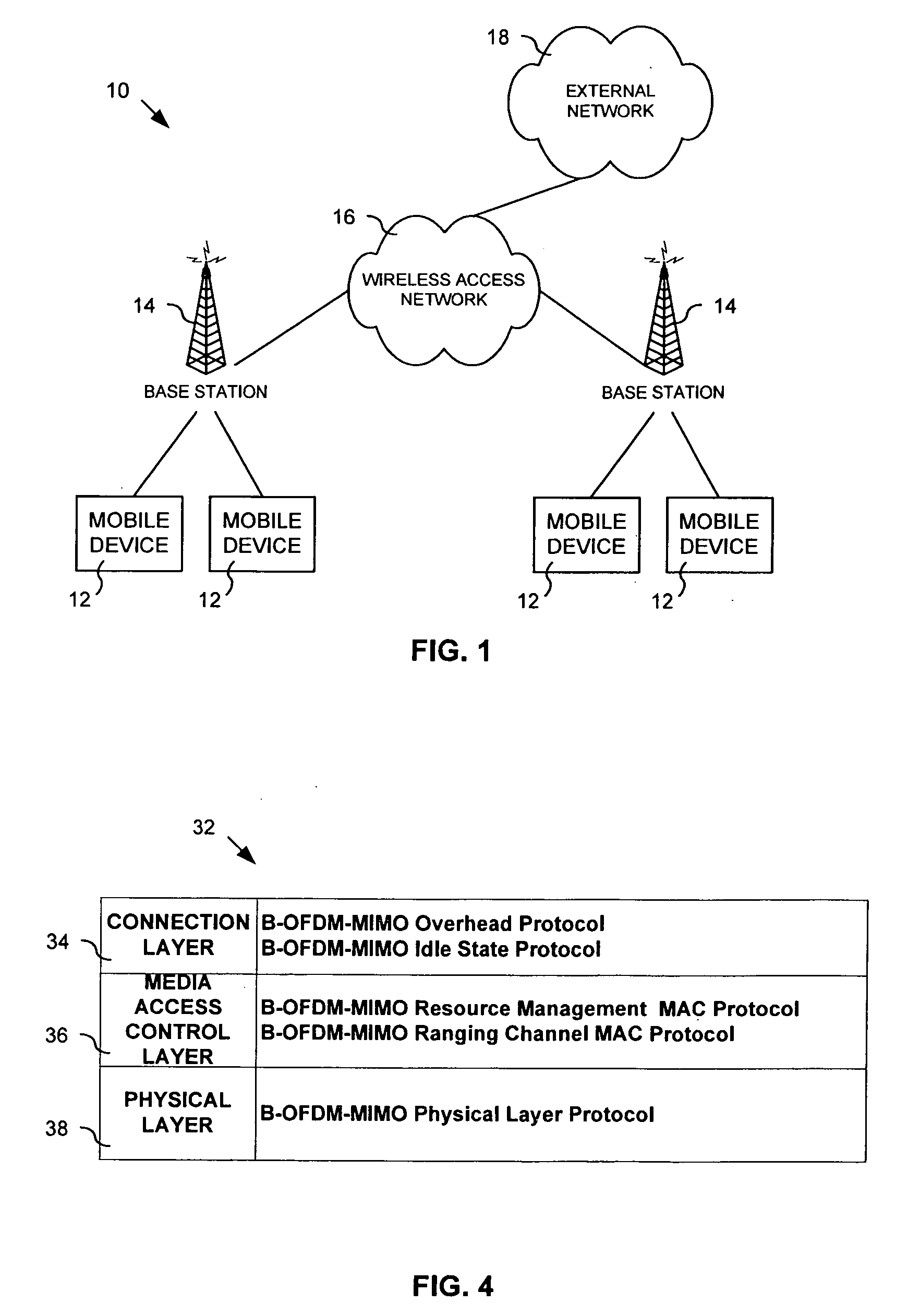
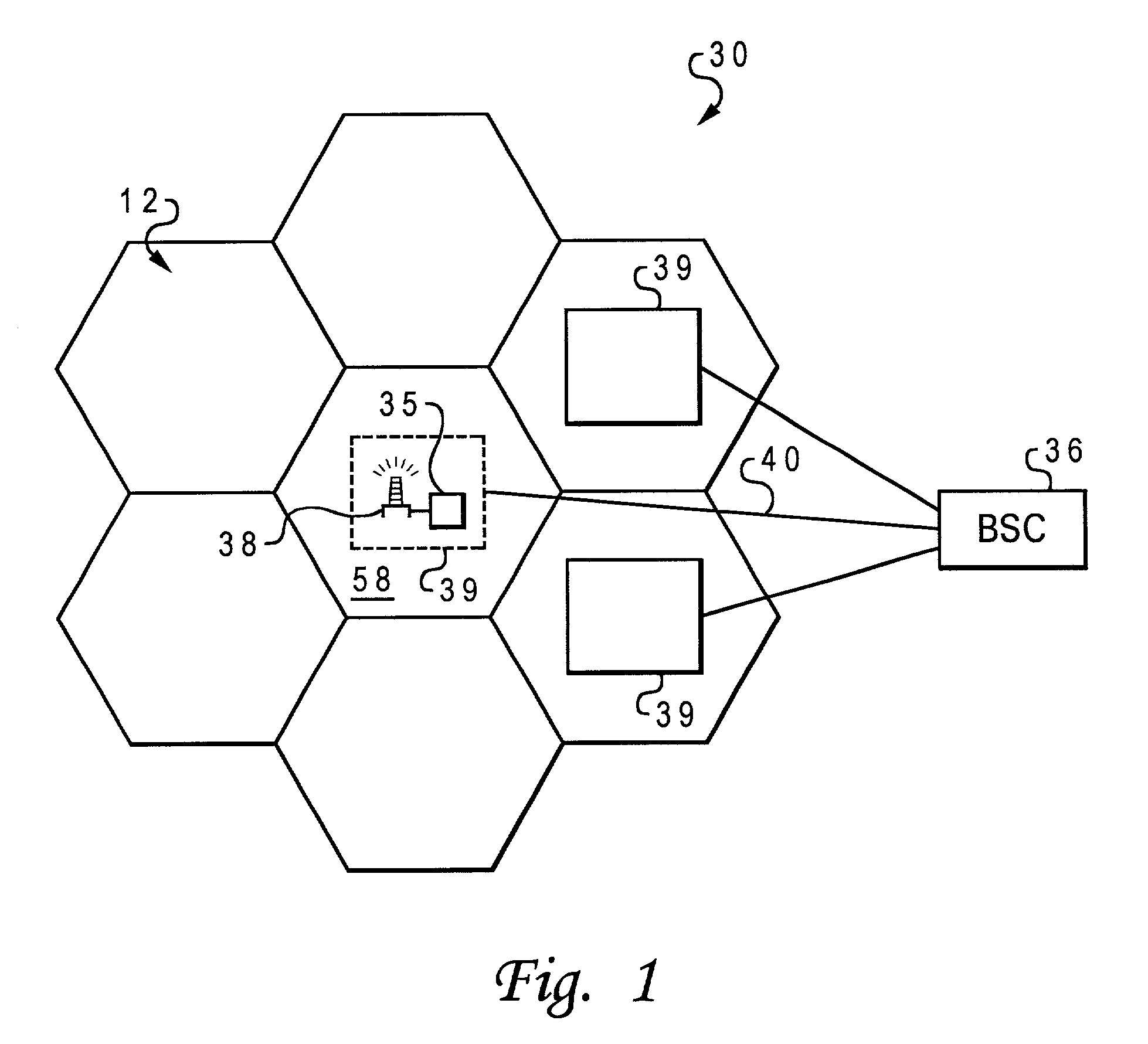
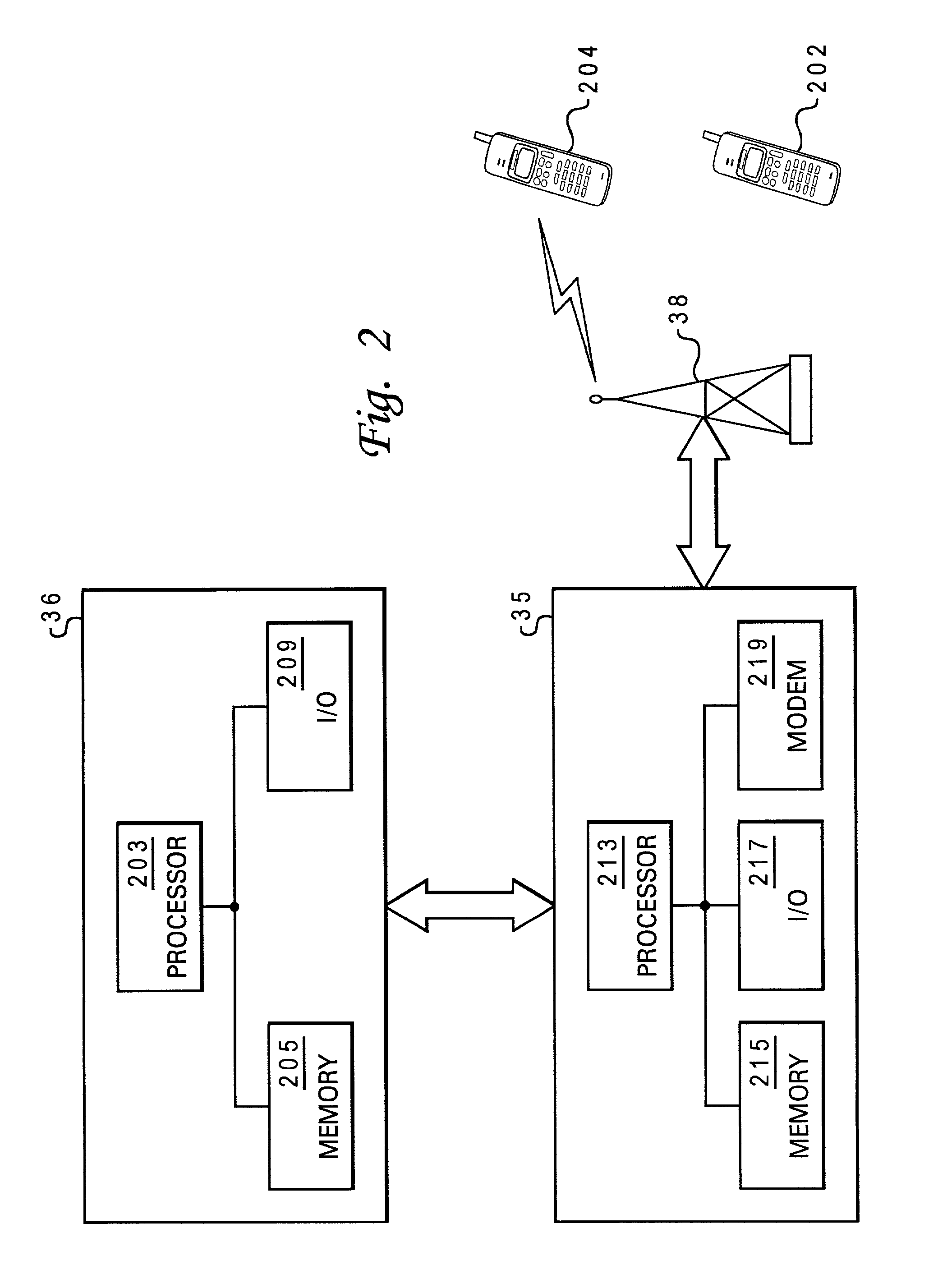
Method and system for allocating media access control layer resources in a wireless communication environment
ActiveUS20060264218A1Effective distributionError preventionModulated-carrier systemsResource poolWireless transmission
A method and system for allocating shareable wireless transmission resources. A resource pool is established. The resource pool is divided into a plurality of physical layer allocation units usable for wirelessly transmitting control information and traffic data. The allocation units are assigned at the media access control layer for the wireless transmission of the control information and traffic data. The system and method of the present invention also allows mobile stations to be dynamically grouped into multicast groupings to reduce system overhead resource requirements.
Owner:APPLE INC
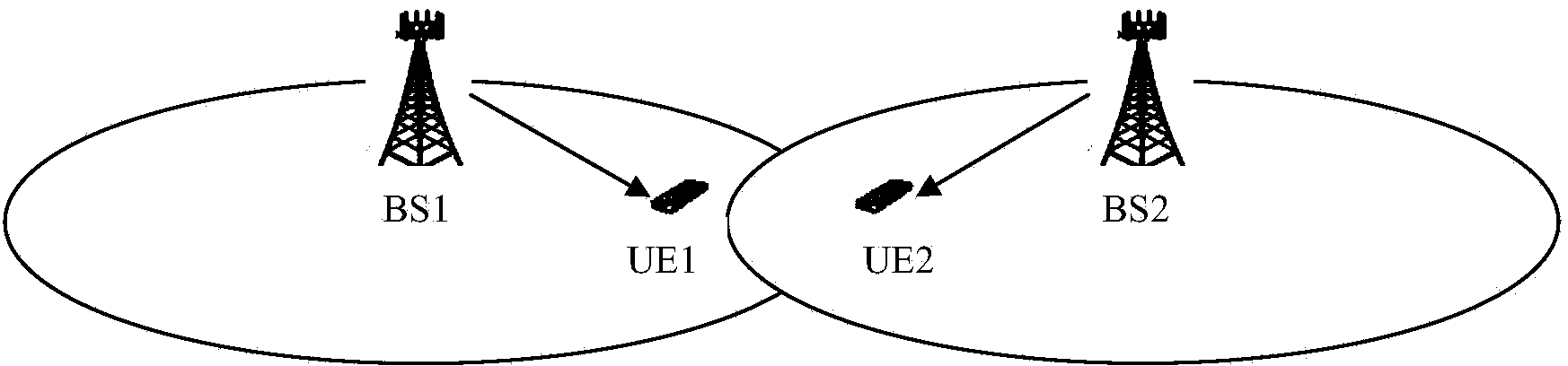
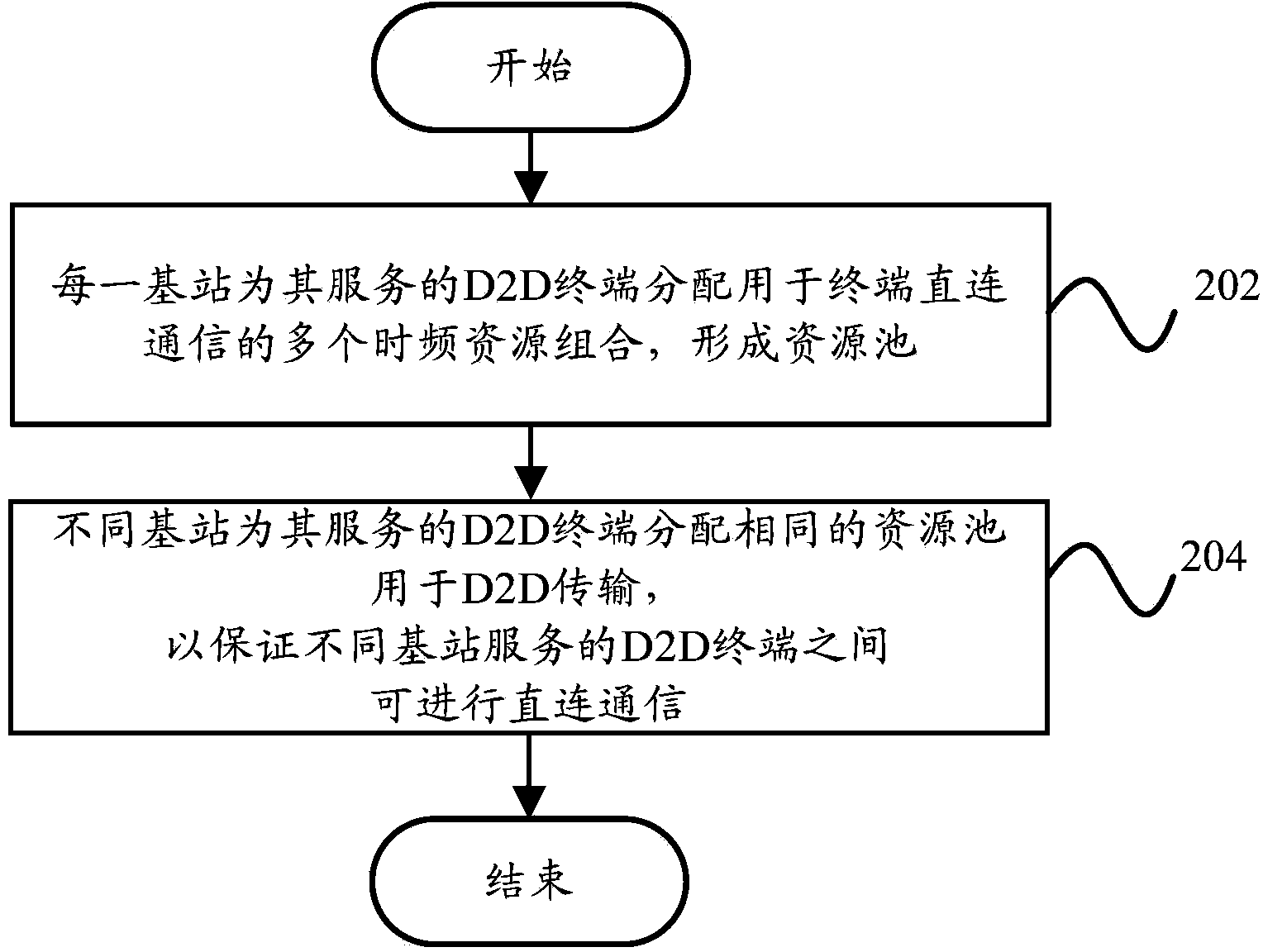
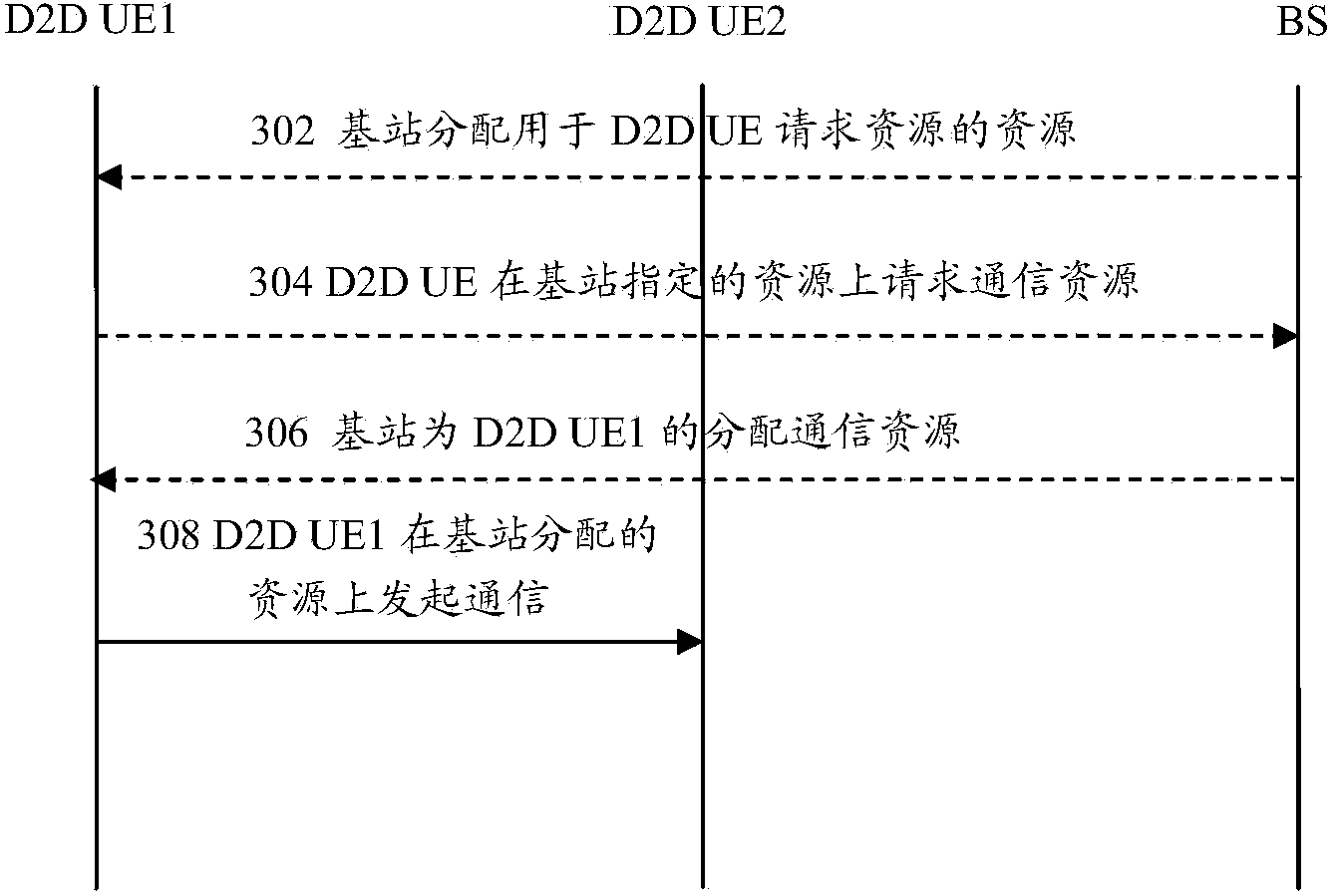
Terminal D2D communication method and terminal D2D communication system
InactiveCN103841649ASolve communication problemsConnection managementResource poolCommunications system
The invention provides a terminal D2D communication method and a terminal D2D communication system. The terminal D2D communication method includes the steps that each base station distributes a plurality of time-frequency resource combinations used for terminal D2D communication for a D2D terminal which is served by the base station, so that a resource pool is formed; different base stations distribute the same resource pool for the D2D terminals which are served by different base stations for D2D transmission so as to ensure that the D2D terminals which are served by different base stations can be in D2D communication. According to the technical scheme, the problem that adjacent cell edge terminals cannot be in communication due to different communication resources can be solved.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
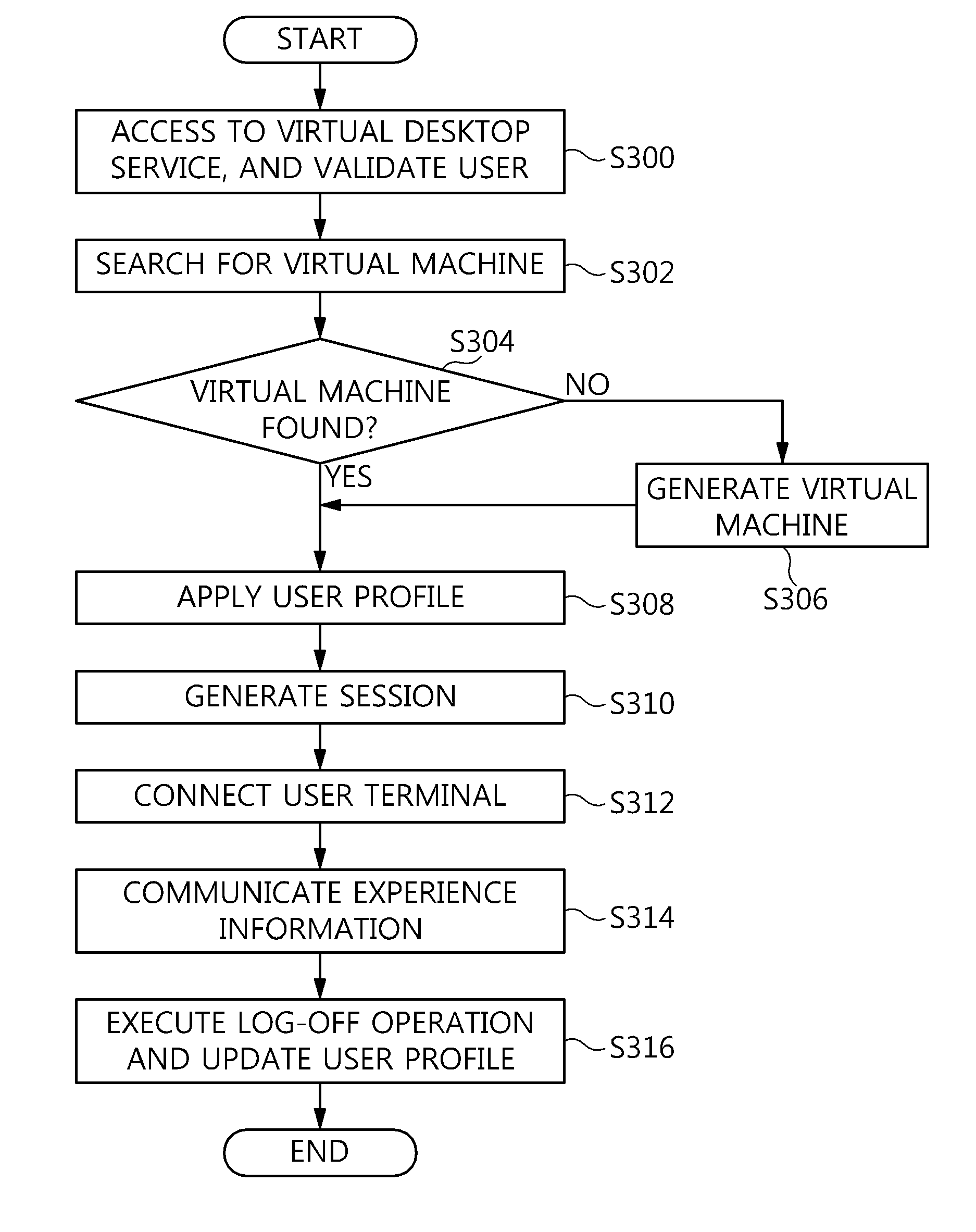
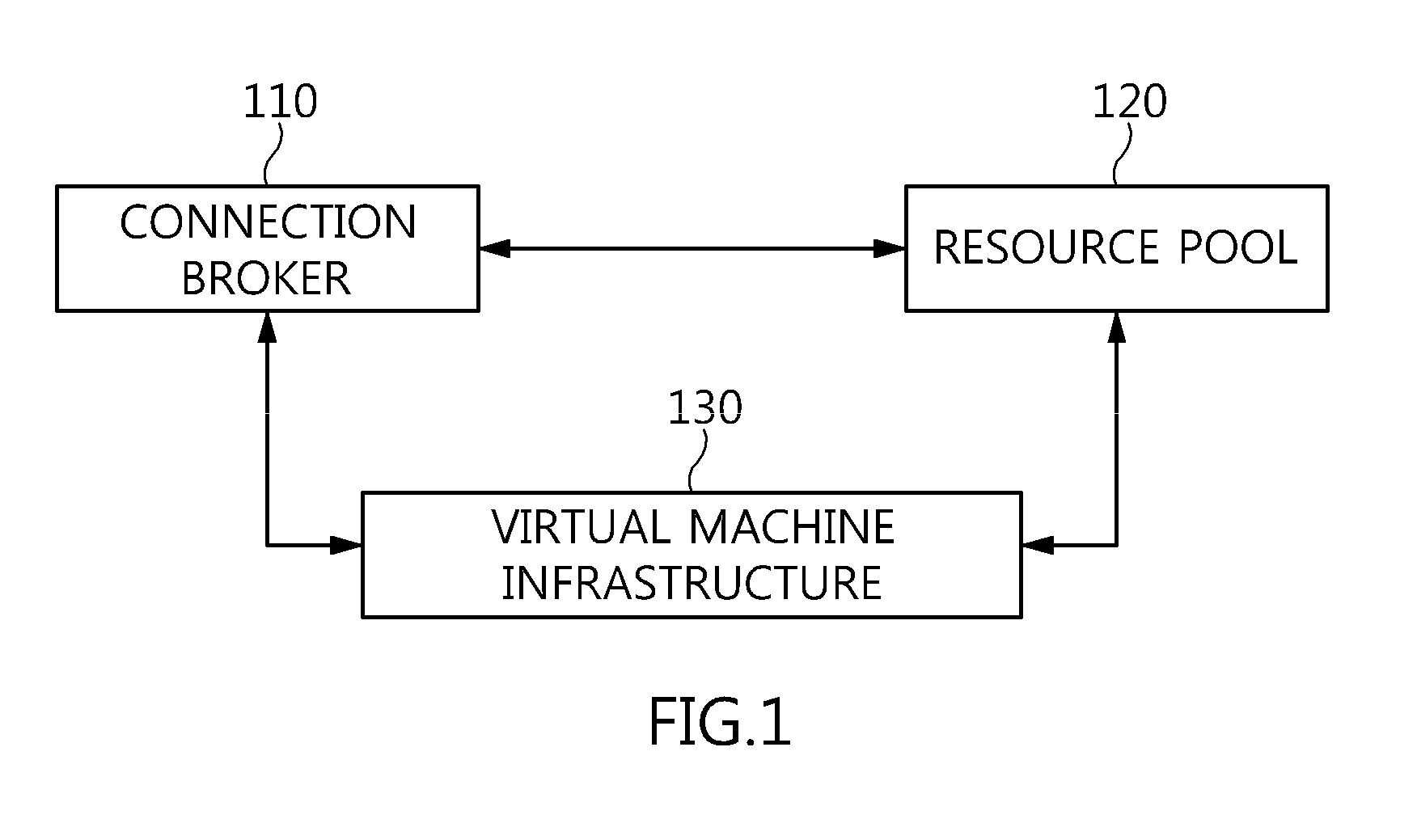
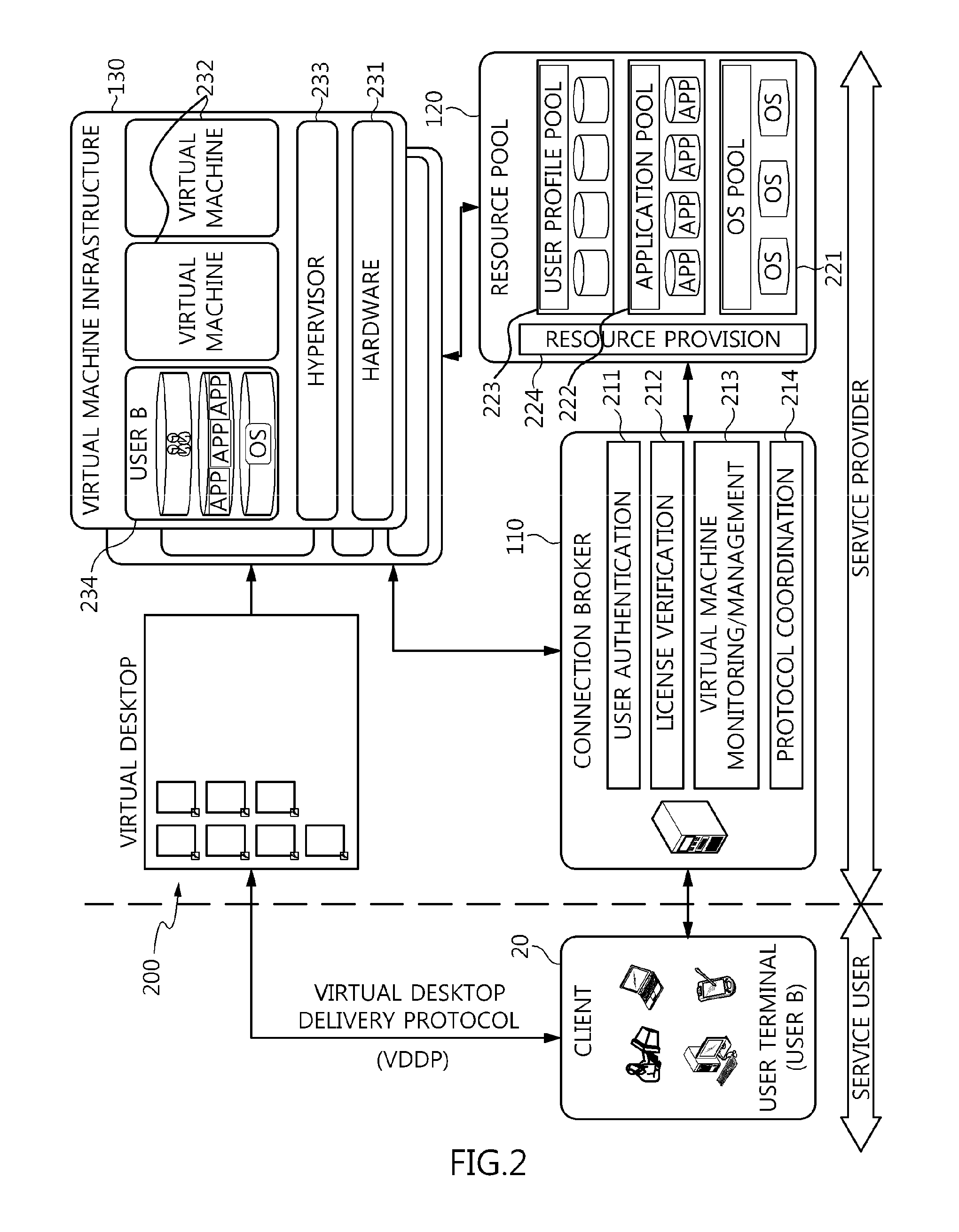
Method and architecture for virtual desktop service
ActiveUS9086897B2Efficiently provideAvoid lossMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital data authenticationResource poolOn demand
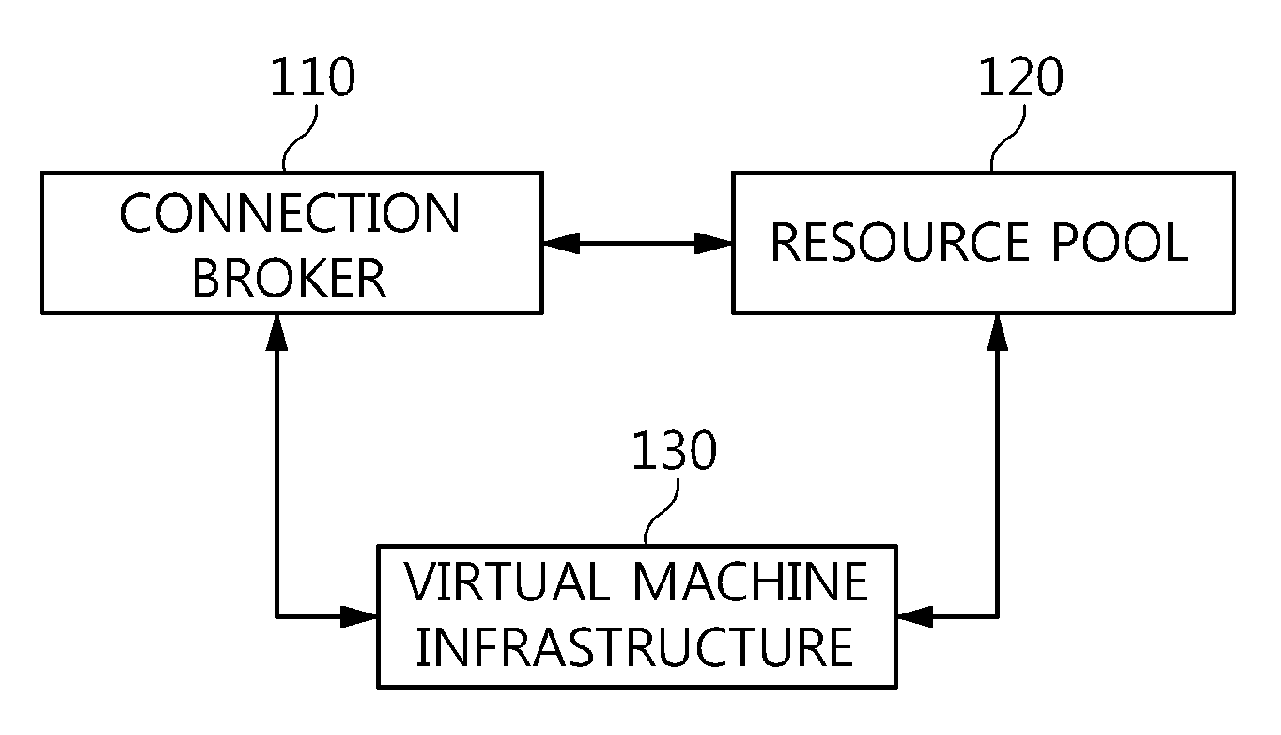
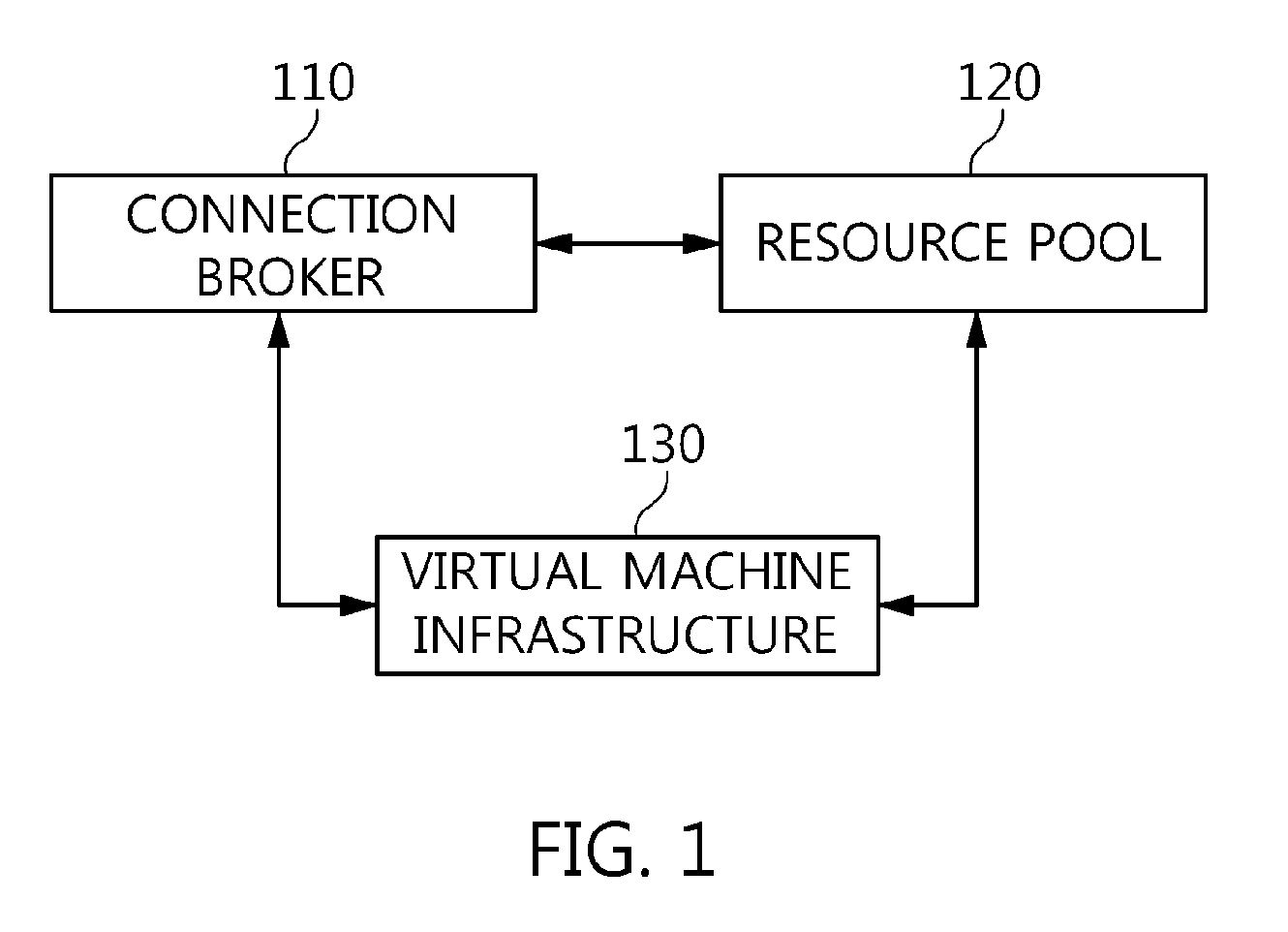
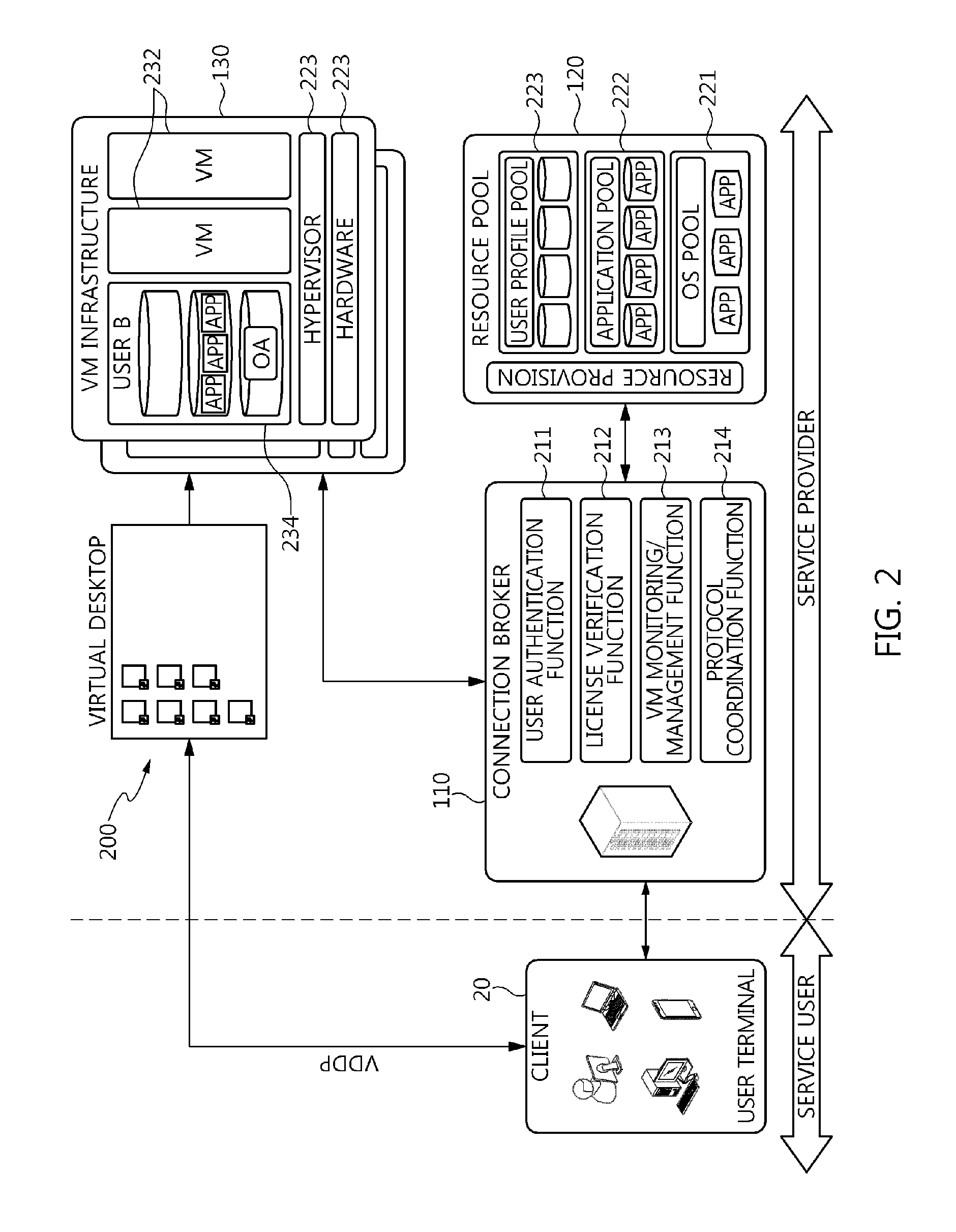
The present invention relates to a method and an architecture capable of efficiently providing a virtual desktop service. The service architecture for the virtual desktop service includes a connection broker for performing the management of virtual machines, a server monitoring function, and a protocol coordination function. A resource pool is configured to manage software resources that are transferred to a specific virtual machine in a streaming form at a predetermined time and that are executed on the specific virtual machine and to provide provision information about the managed software resources at the request of the connection broker, in order to provide an on-demand virtual desktop service. A virtual machine infrastructure is configured to support hardware resources, generate virtual machines in which the software of the user terminal is operated, and provide the virtual machines as virtual desktops.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and system for digital rendering over a network
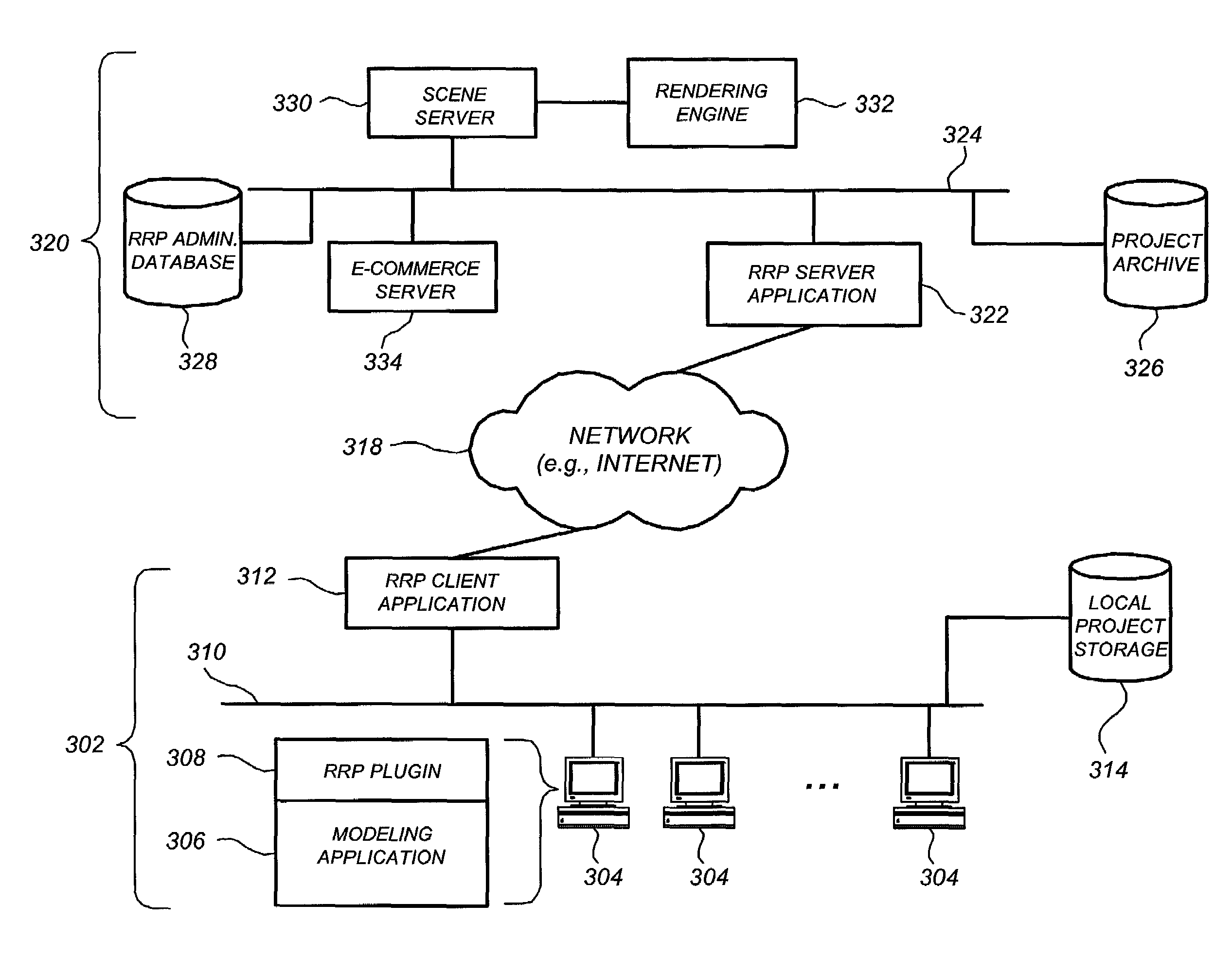
InactiveUS7266616B1BandwidthSave bandwidthMultiple digital computer combinationsImage data processing detailsClient-sideResource pool
Digital rendering over a network is described. Rendering resources associated with a project are stored in a project resource pool at a rendering service site, and for each rendering request received from a client site the project resource pool is compared to current rendering resources at the client site. A given rendering resource is uploaded from the client site to the rendering service only if the project resource pool does not contain the current version, thereby conserving bandwidth. In one embodiment, redundant generation of raw rendering resource files is avoided by only generating those raw rendering resource files not mated with generated rendering resource files. Reducing redundant generation of raw resources is also described, as well as statistically reducing the number of raw resource files required to be uploaded to the rendering service for multi-frame sessions.
Owner:DATACLOUD TECH LLC
Optimized capacity planning
InactiveUS20110202925A1Resource allocationError detection/correctionResource poolService-level agreement
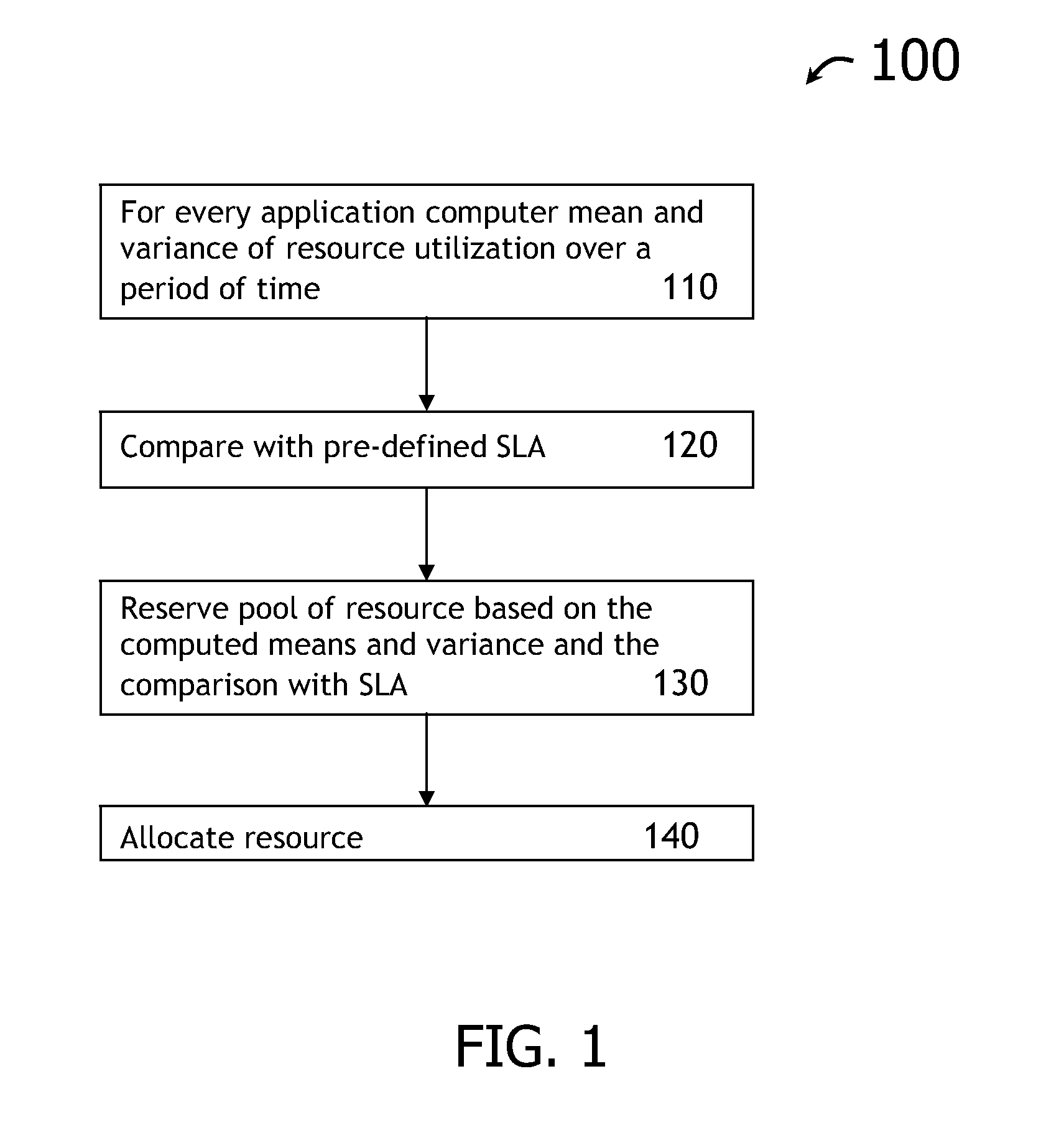
A computer implemented method, system and / or program product determine capacity planning of resources allocation for an application scheduled to execute on a virtual machine from a set of multiple applications by computing a mean associated with a pool of pre-defined resources utilization over a time interval; computing a variance associated with the pool of pre-defined resources utilization over the same time interval; identifying a set of resource to execute the scheduled application from the pool of pre-defined resources, wherein the pool of pre-defined resources is created from a pre-defined Service Level Agreement (SLA); and allocating a set of fixed resources from the pool of pre-defined resources to execute the application based on the mean resource utilization.
Owner:IBM CORP
Cloud database sharing
InactiveUS20130031136A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsAuthorization certificateResource pool
A method, system and computer program product is provided achieving database sharing by providing an interface to contribute a database and a set of resources to a resource pool in a first cloud environment. The interface further allowing a user to input parameters identifying a database, a set of resources, a set of authorization credentials, and a sharing policy. The interface further comprising responsive to the user using the interface and providing the interface parameters which identify the database, the set of resources, the set of authorization credentials, and the sharing policy, adding the database, the set of resources, the set of authorization credentials, and the sharing policy to the database resource pool in the cloud environment, sharing the database, the set of resources, according to the sharing policy, and utilizing the set of authorization credentials.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
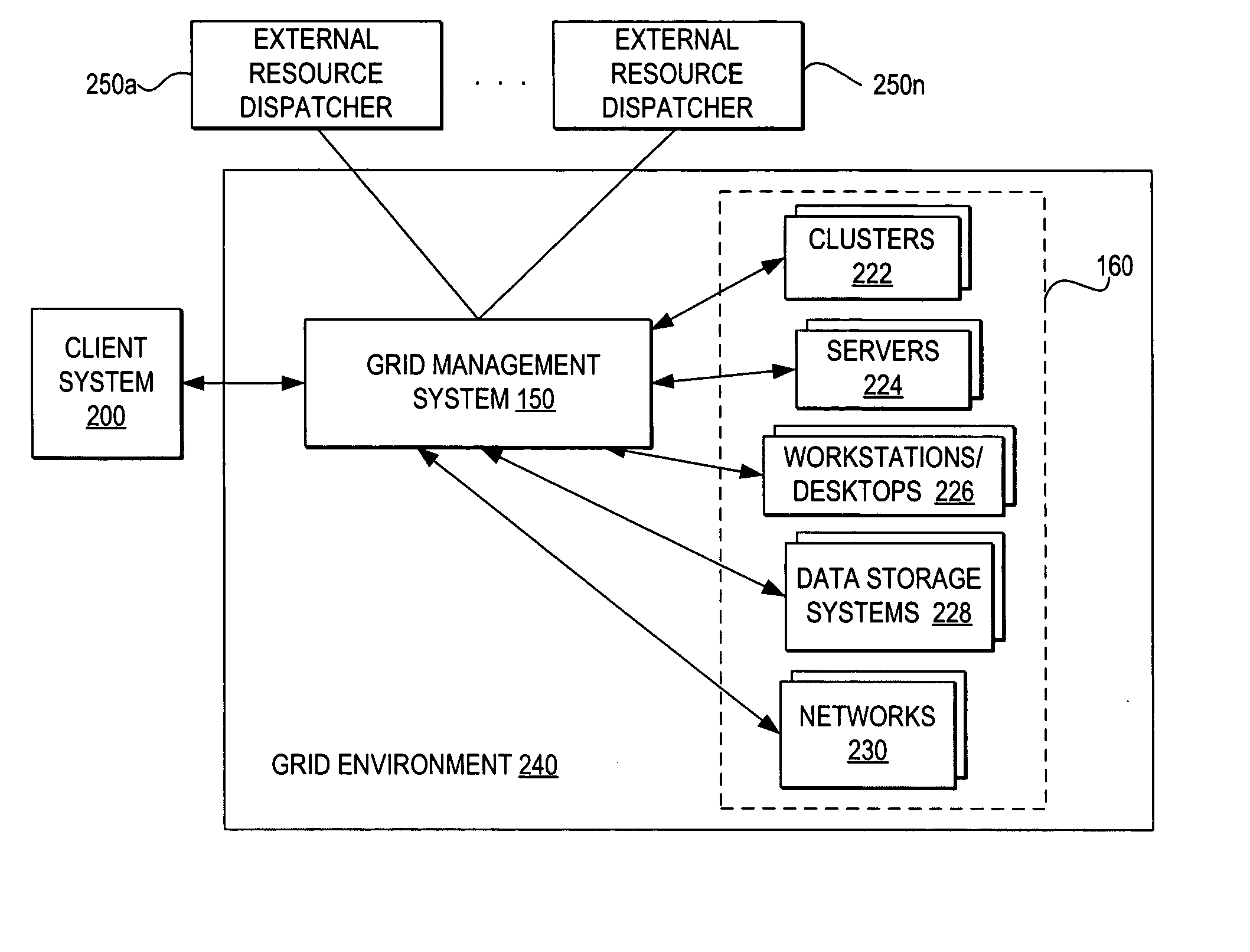
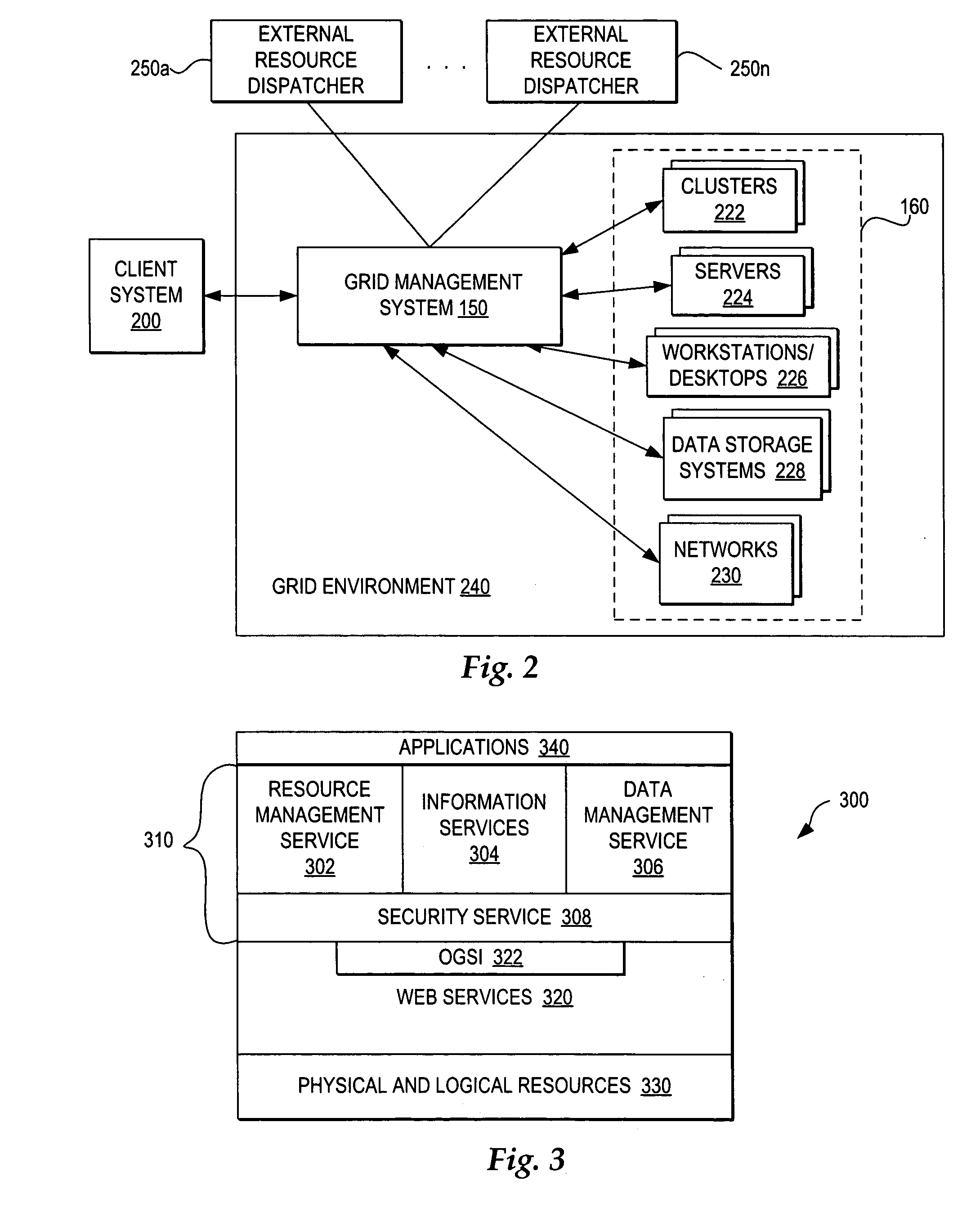
Coordinating use of independent external resources within requesting grid environments
InactiveUS20050278441A1Improve performanceEnergy efficient ICTError preventionResource poolGrid management
A method, system, and program for coordinating use of independent external resources within requesting grid environments. A external resource dispatcher receives requests for use of external resources. The external resource dispatcher controls the dispatch of a pool of external resources hidden from the grid management systems of requesting grid clients. In particular, the external resource dispatcher coordinates dispatch of a selection of the external resources for temporary registration with a requesting grid client management system. The requesting grid client management system registers the external resources for use within the grid client and monitors whether the external resources are still needed. When a requesting grid client no longer needs a dispatched external resource, the external resource dispatcher controls detachment of the dispatched external resource and returns the external resource to the available pool of external resources.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Apparatus and method for virtual desktop service
ActiveUS9489227B2Efficiently providedResource allocationPlatform integrity maintainanceResource poolSpecific time
Disclosed herein are a method and architecture capable of efficiently providing virtual desktop service. A service architecture for virtual desktop service according to the present invention includes a connection broker configured to perform authentication, manage virtual machines, and perform a server monitoring and protocol coordination function, a resource pool configured to manage software resources that are delivered to a specific virtual machine in a streaming form on a specific time in order to provide on-demand virtual desktop service and are executed on the specific virtual machine and to provide provision information about the managed software resources in response to a request from the connection broker, and a virtual machine infrastructure configured to support hardware resources, generate virtual machines in which the software of a user terminal is executed, and provide the generated virtual machine as virtual desktops.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for device-to-device communication in wireless communication system and apparatus therefor
Disclosed are a method for device-to-device communication in a wireless communication system, and an apparatus therefor. Specifically, the present invention relates to a method for performing device-to-device (D2D) communication by a terminal in a wireless communication system, the method comprising the steps of: receiving, from a base station, physical sidelink control channel (PSCCH) resource pool setting information; receiving, from the base station, downlink control information (DCI) including the PSCCH resource allocation information; and sending the PSCCH on the basis of the PSCCH resource allocation information, wherein a first PSCCH time-frequency resource and a second PSCCH time-frequency resource for sending the PSCCH are determined on the basis of a value indicated in the PSCCH resource allocation information within the PSCCH resource pool, and the PSCCH may be sent in the first PSCCH time-frequency resource and the second PSCCH time-frequency resource.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and system for self-adaptive on-demand resource allocation in a virtualized environment
ActiveCN102279771AReduce maintenance costsAdaptableProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationVirtualizationResource pool
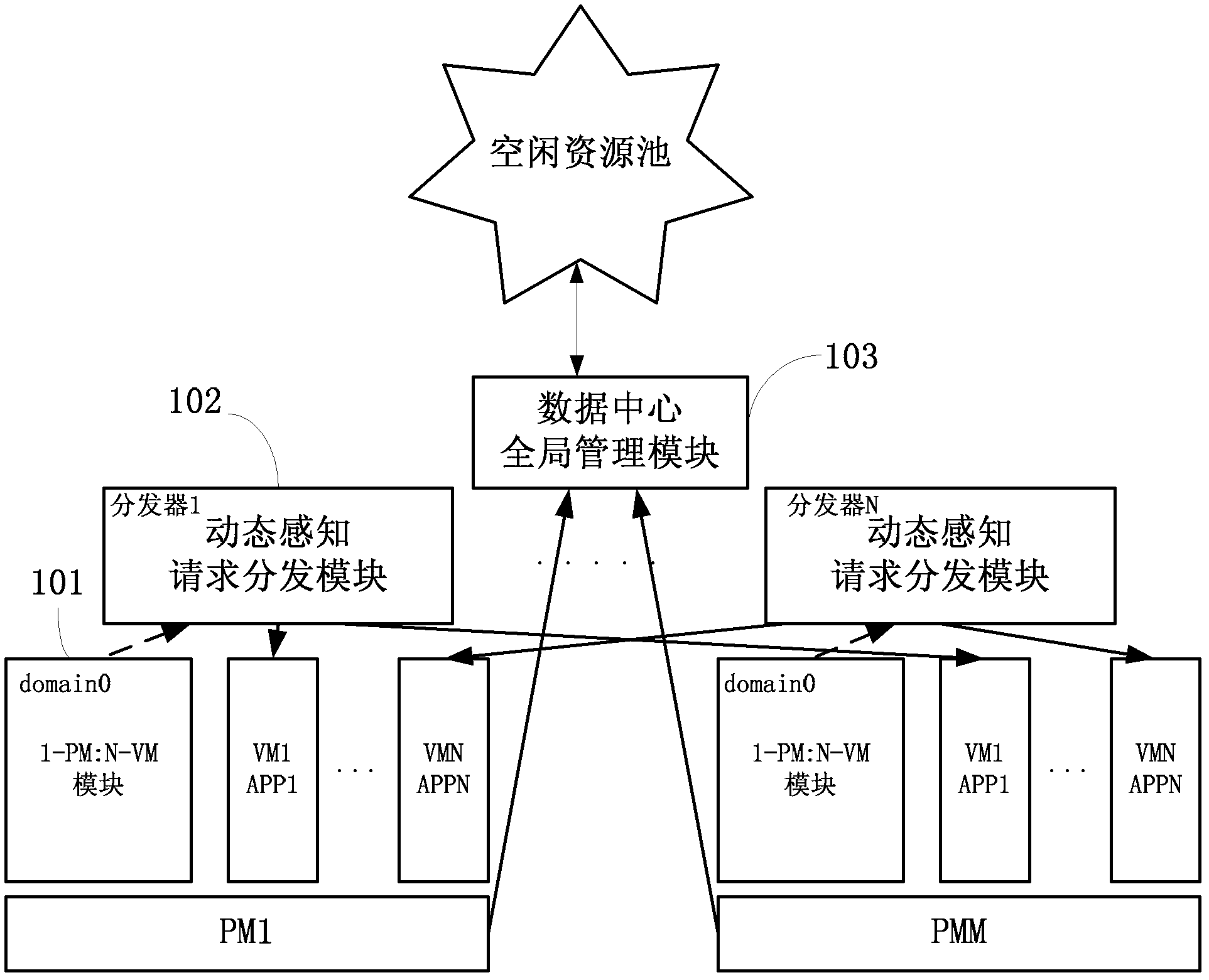
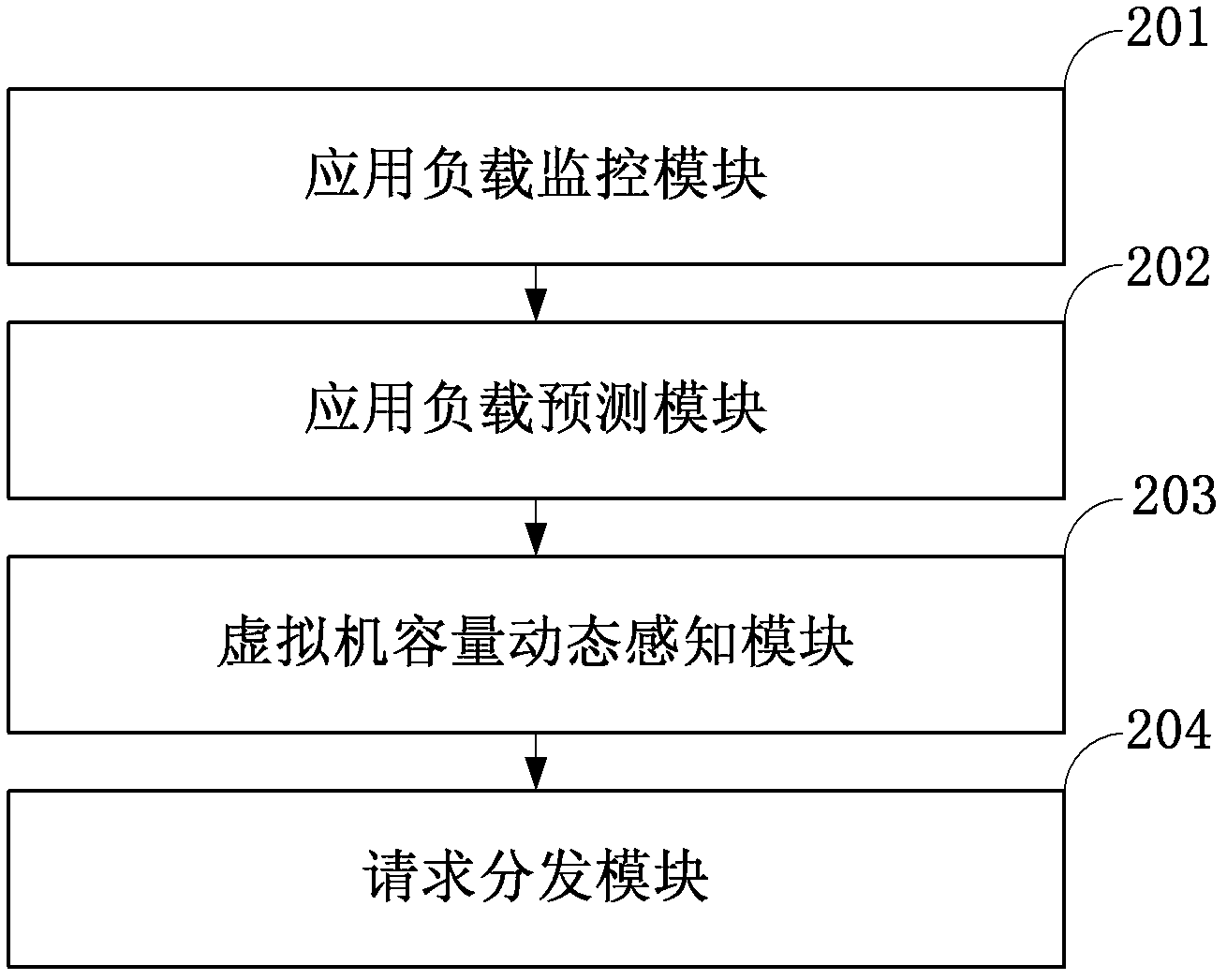
The invention discloses a system for adaptively allocating resources as required in a virtualization environment. The system comprises a dynamic perception request distribution module, a 1-physical machine (PM):N-virtual machine (VM) module and a data center global management module, wherein the 1-PM:N-VM module allocates the resources on a PM according to user experiences which are collected in real time; the dynamic perception request distribution module distributes loads to proper VMs according to monitored application request load information and VM volume information and responds to requests; and the data center global management module judges whether the VMs are required to migrate between the PMs to be re-placed according to collected PM resource load information, and judges whether a new PM is released or applied to an idle resource pool to quit or enter application service when the PM is excess or insufficient. The invention also discloses a method for adaptively allocating the resources as required in the virtualization environment. The method comprises an adaptive VM dynamic volume perception request distribution strategy, a 1-PM:N-VM resource allocation strategy and a VM migration strategy. The invention has an application prospect in the technical field of computers.
Owner:日照育成科技咨询服务有限责任公司
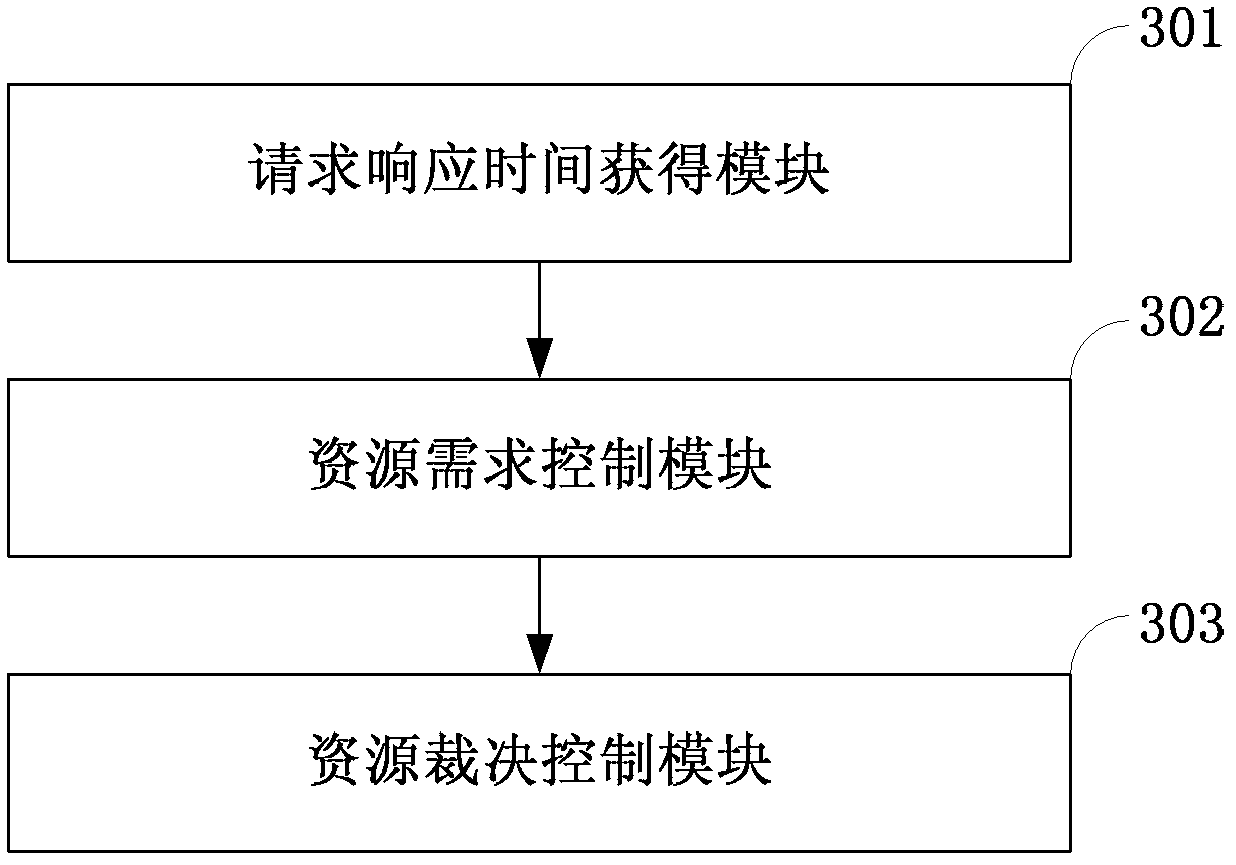
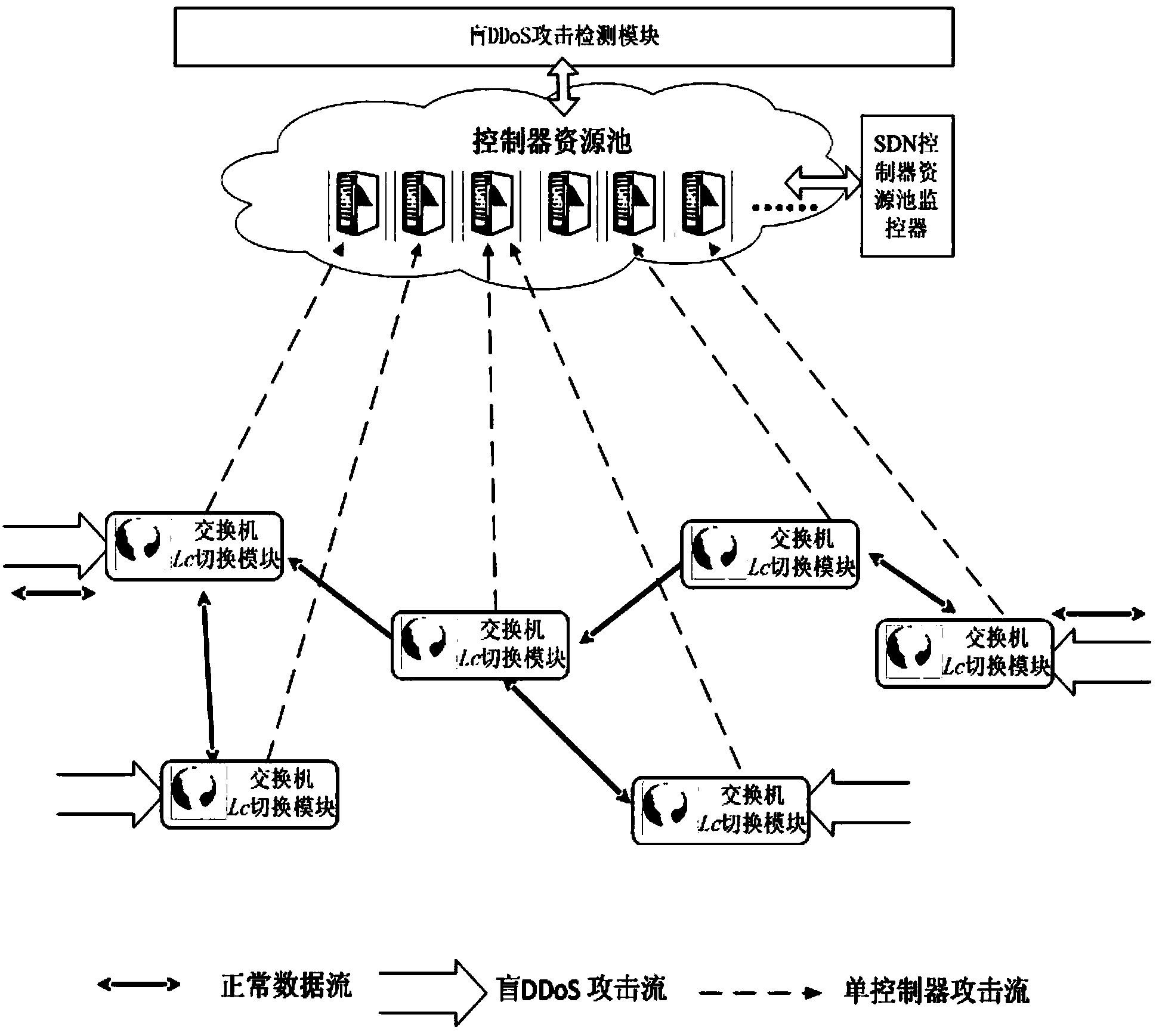
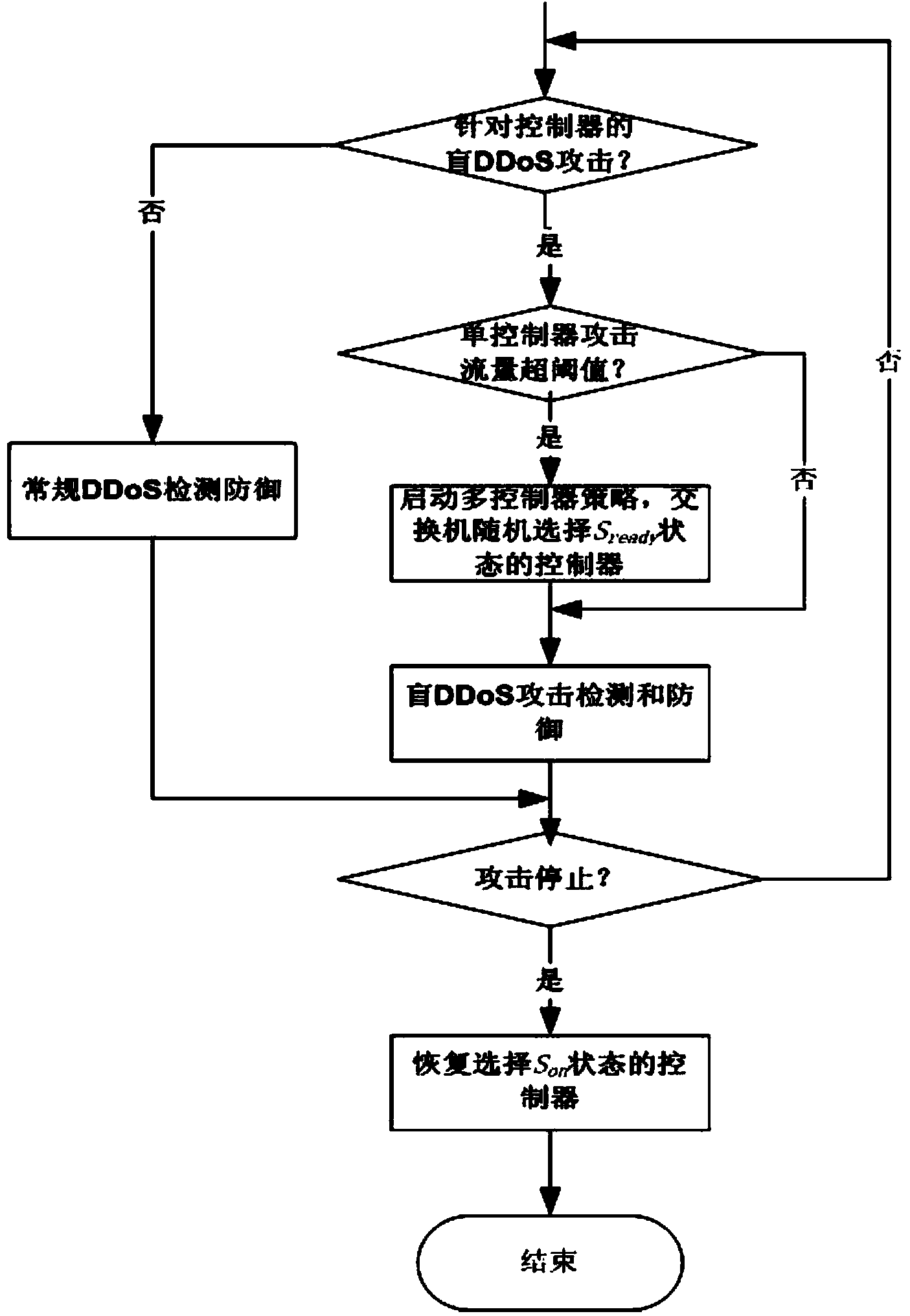
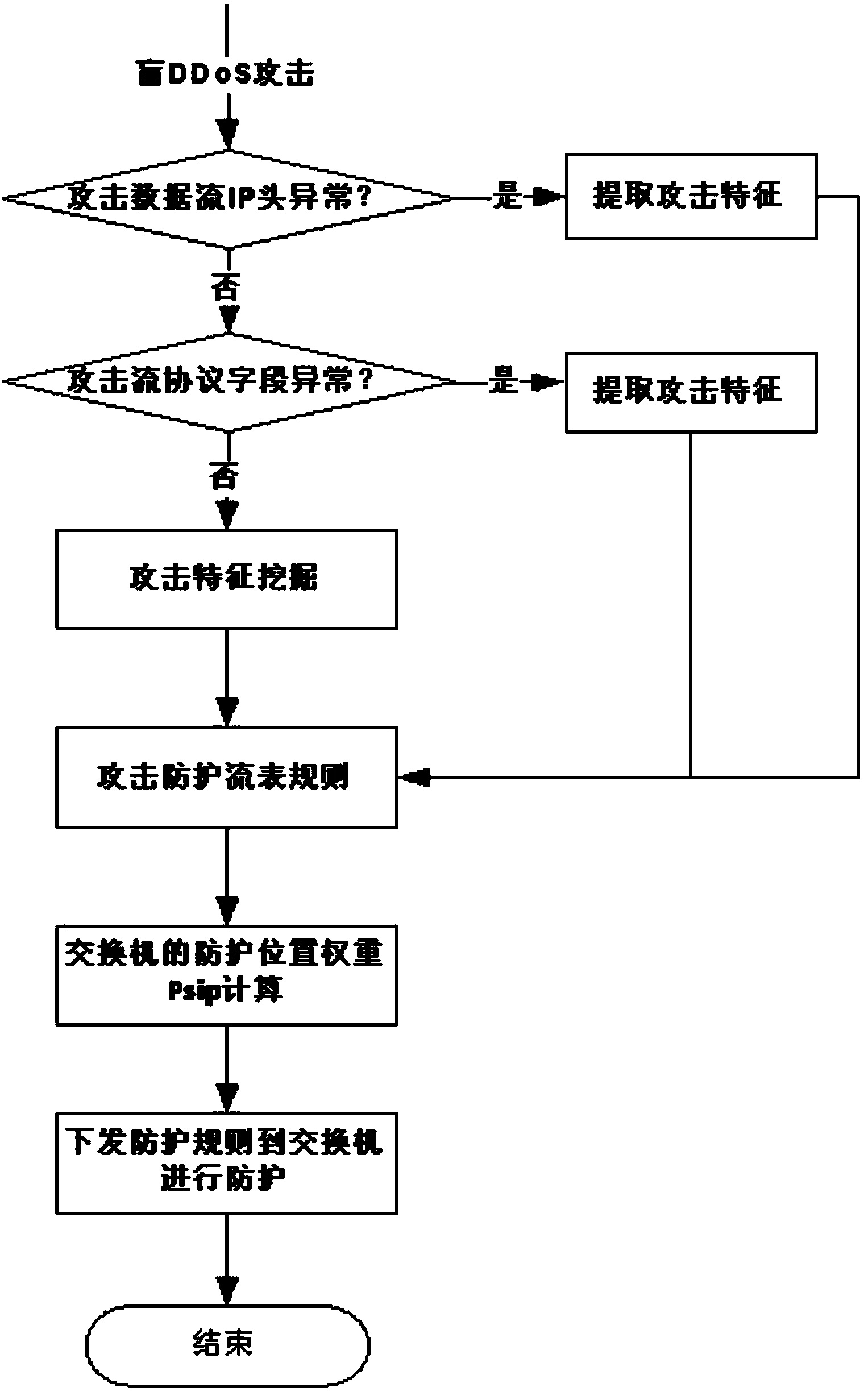
Method and system for preventing blind DDoS attacks on SDN controllers
The invention relates to a method and system for preventing blind DDoS attacks on SDN controllers. The system comprises an SDN controller resource pool monitor, a controller list dynamic switching module deployed on an SDN switch and an attack detection application module, and the attack detection application module and the controllers carry out data interaction through data interfaces. The SDN controller resource pool monitor is used for maintaining the establishment of a plurality of physical machine and / or virtual machine controllers, data synchronism, IP address distribution and state lists to be issued to the switch. The attack detection application module detects the communication data streams of the controllers and the switch in an SDN network, and when blind DDoS attack streams on the controllers are detected, the SDN controller resource pool monitor dynamically adjusts the number of the controllers according to attack flow generated when the blind DDoS attacks occur. The method can dynamically adjust the number of the controllers, the blind DDoS attacks on the controllers can be effectively prevented, and the usability of the SDN network is guaranteed.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for dynamically adjusting resources assigned to plurality of customers, for meeting service level agreements (SLAs) with minimal resources, and allowing common pools of resources to be used across plural customers on a demand basis
InactiveUS20060129687A1Easy to usePrevent crashError preventionTransmission systemsResource poolService-level agreement
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Data backup system and method for virtual infrastructure
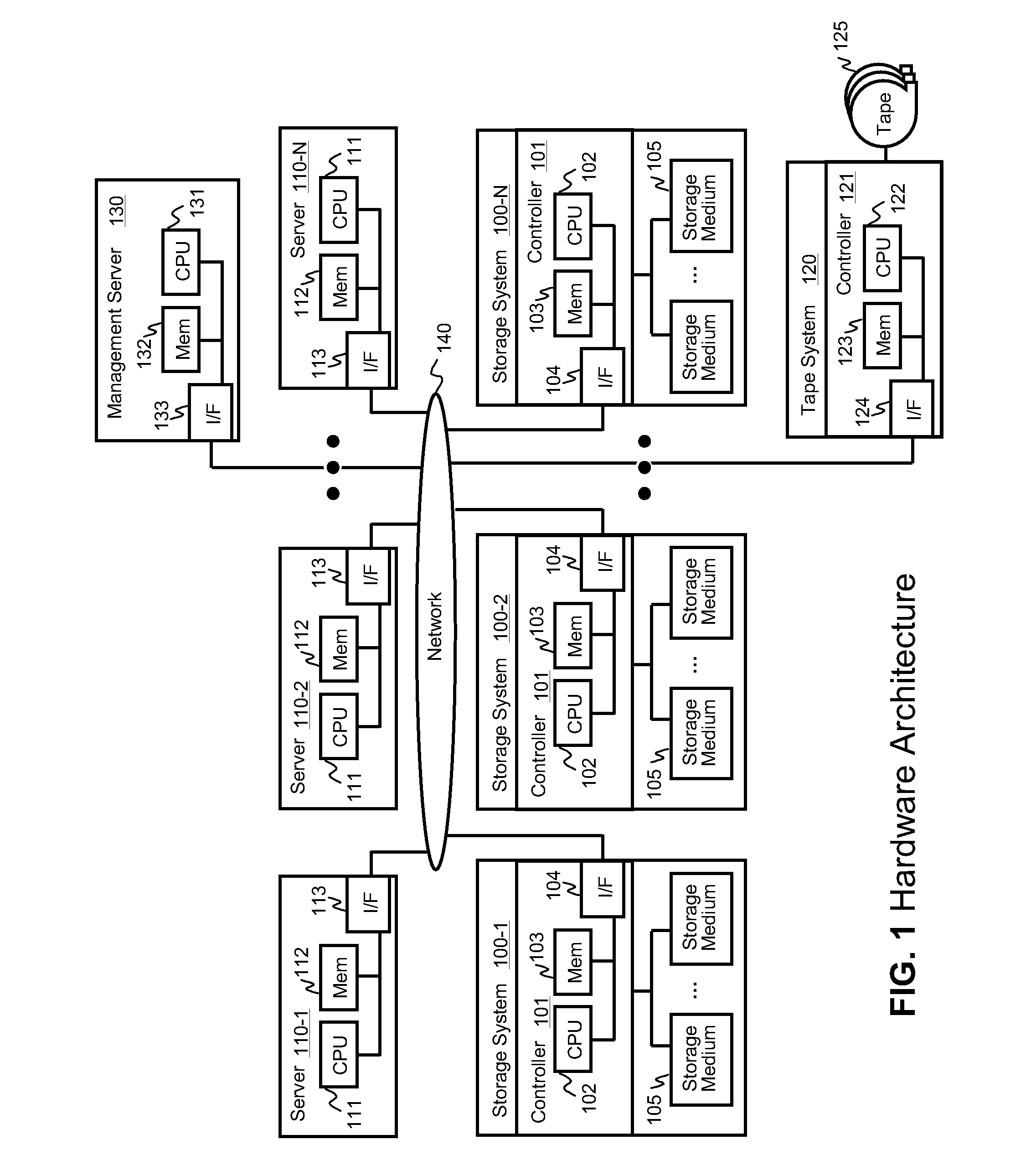
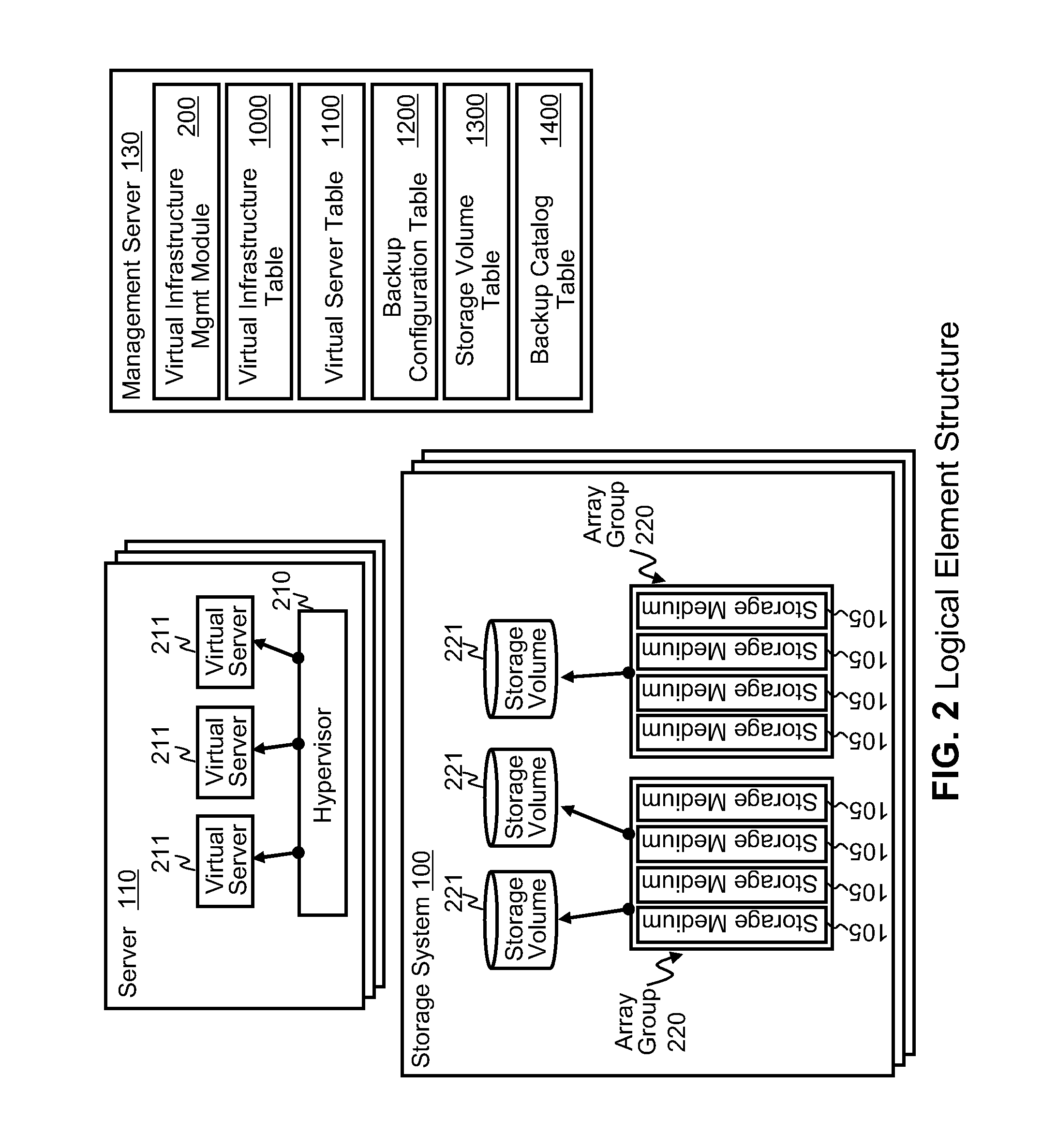
InactiveUS20100125712A1Reduce in quantityMinimize the numberMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsResource poolData center
Systems for backing up the data of an IT system by utilizing server or storage virtualization technology to create and move logical IT infrastructures dynamically. A virtualized IT system provides a server resource pool and a storage resource pool composed from multiple physical devices either within a datacenter or a globally located plurality of datacenters. The virtual server and the storage volume provisioned from those pools will be paired to form the virtual infrastructure. In other words, the virtual infrastructure becomes a logical IT environment build with the required computing and storage resources needed in order to execute specific applications. The virtual infrastructure can also be migrated within / among datacenter sites.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and system for dispatching cloud computed resources
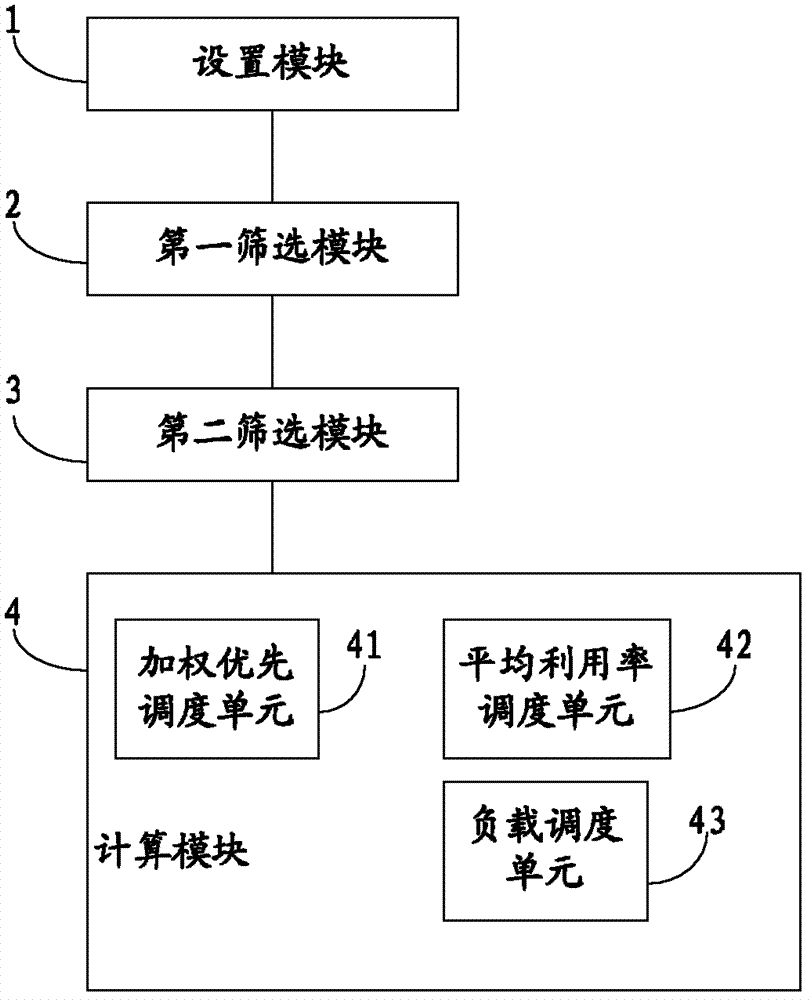
The invention provides a method and system for dispatching cloud computed resources. The method comprises the following steps: a resource allocating strategy and a resource dispatching strategy of cloud computing are arranged; the resource allocating strategy is arranged to appoint a resource pool of cloud computed resources used for creating a virtual machine; the arranged resource dispatching strategy is used for sifting a host machine meeting requirements in the resource pool; available host machine information in the resource pool is confirmed and a host machine list is generated according to the resource allocating strategy selected by a user when the virtual machine is created; a host machine conform to the resources for creating the virtual machine is sifted from the host machine list according to the resource dispatching strategy selected by the user, so as to obtain a residual host machine list; and optimized host machines and optimized storage of the residual host machine list are obtained through computing, and are allocated to the virtual machine. The system comprises an arranging module, a first sifting module, a second sifting module and a computing module. The method and system for dispatching cloud computed resources can effectively realize the reasonable dispatch of resources.
Owner:BEIJING TEAMSUN TECH
Method for selecting of sidelink grant for a d2d ue in a d2d communication system and device therefor
The present invention relates to a wireless communication system. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method and a device for selecting of sidelink grant for a D2D UE in a D2D communication system, the method comprising: configuring a resource pool in which the UE selects a sidelink grant for transmitting sidelink data; and selecting a first set of sidelink grants for a first SC period from the resource pool to transmit a sidelink data; and selecting a second set of sidelink grants for a second SC period from the resource pool if amount of available sidelink data cannot be transmitted using remaining sidelink grants among the first set of sidelink grants in the first SC period.
Owner:TAISSA RES LLC
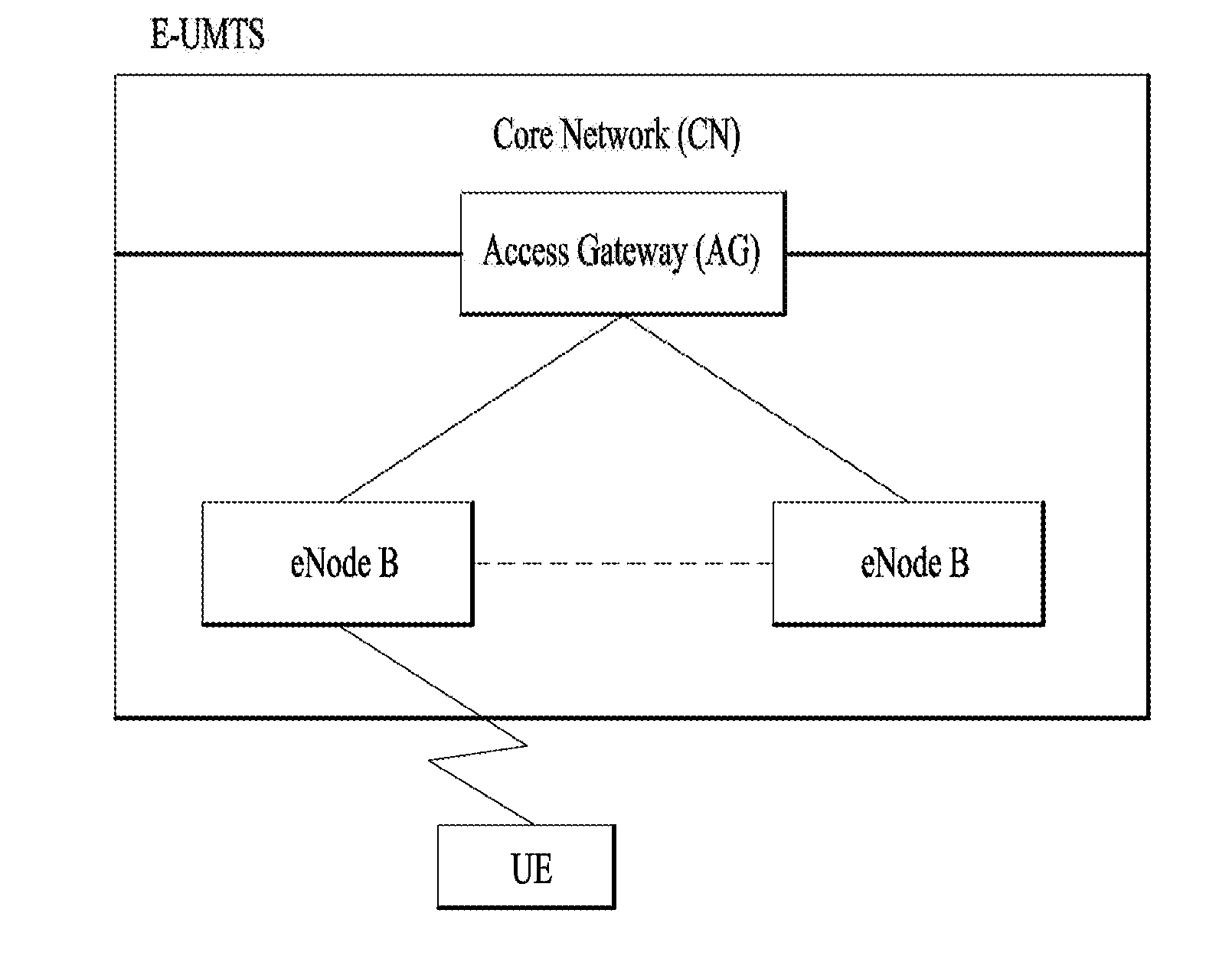
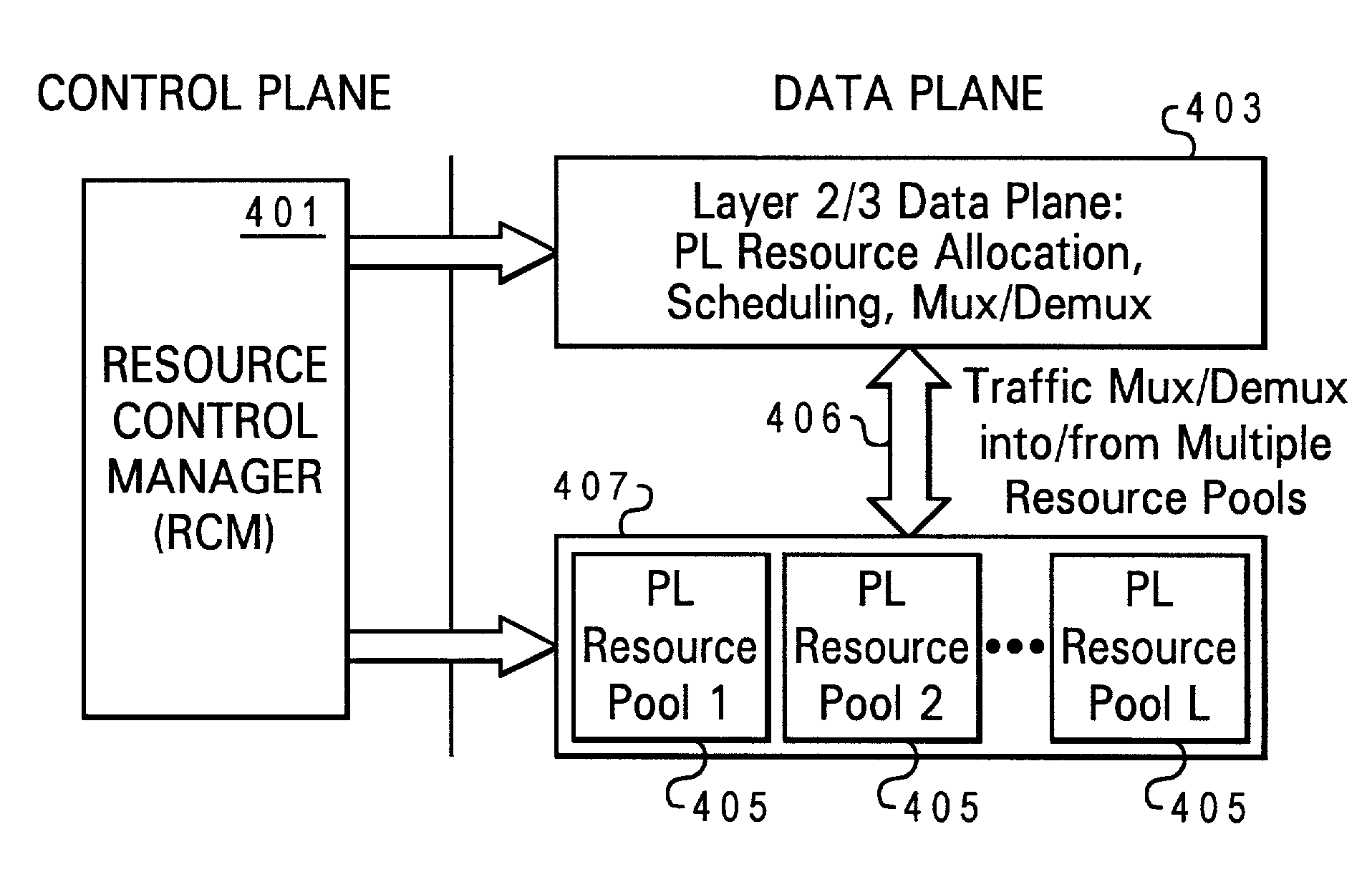
Service-driven air interface protocol architecture for wireless systems
ActiveUS7492737B1Time-division multiplexTransmission path multiple useQuality of servicePublic interface
Disclosed is an air interface protocol architecture for a multi-carrier wireless communications network having a plurality of carriers. The protocol architecture comprises a common layer 2 / 3 protocol for each of the carriers. The common layer 2 / 3 protocol provides a common interface with wireline upper level protocols. In addition to the common layer 2 / 3 protocol, the architecture comprises a multimode physical layer for each of the carriers. The protocol architecture enables the physical layer of each carrier may have a different protocol configuration for each mobile station serviced by the carrier. Each air interface protocol instance includes one or more resource pools. The resource pools each includes: (1) a quality of service (QoS) supported; (2) a list of manageable resources; (3) a carrier identification; and (4) an air interface configuration. Additionally, the layer 2 protocol of the common layer 2 / 3 protocol includes one or more Radio Link Protocol (RLP) instances (or a QoS Link Protocol) and one or more Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer instances.
Owner:APPLE INC
Network slice manager and management method thereof
ActiveCN106549806AMaximize UtilizationIncrease profitData switching networksAccess networkResource pool
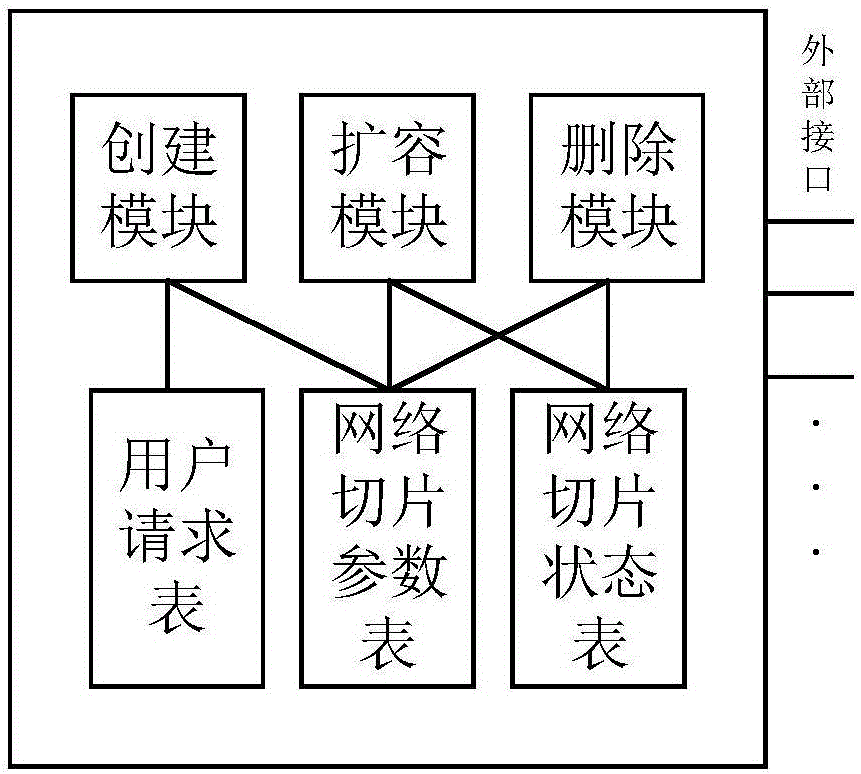
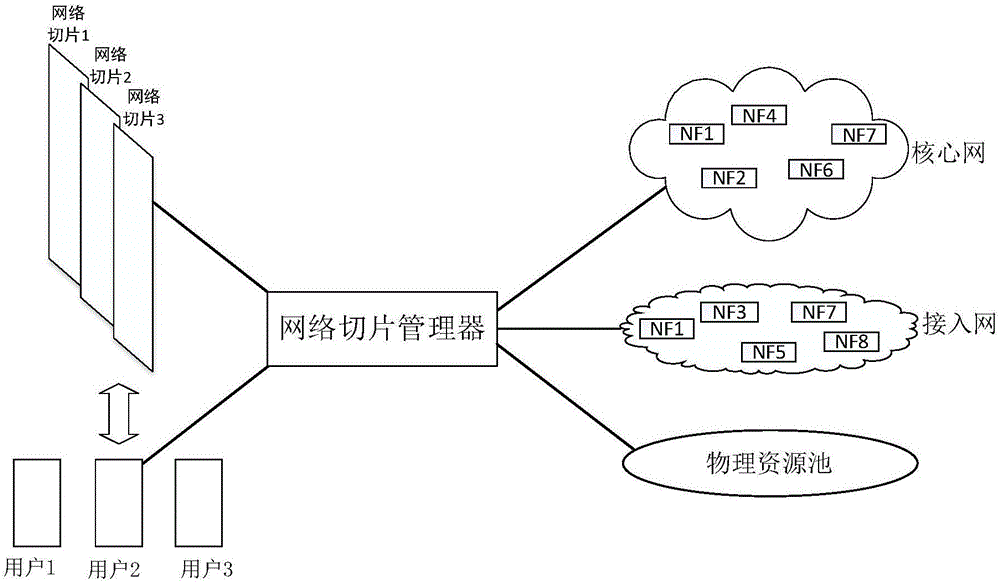
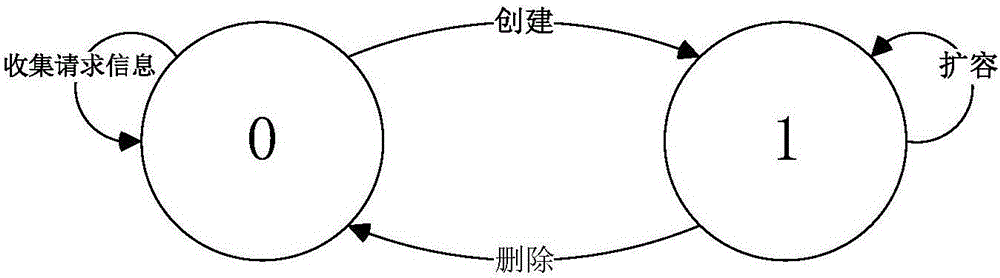
The invention discloses a network slice manager and a management method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of communication. The manager comprises a creation module, an expansion module, a deletion module, a user request table, a network slice parameter table, a network slice state table and a plurality of external interfaces, wherein the creation module is respectively connected with the user request table and the network slice parameter table; both the expansion module and the deletion module are respectively connected with the network slice parameter table and the network slice state table; the creation module is connected with a core network, an access network, a physical resource pool and a user by the external interfaces; the expansion module is connected with an existing network slice and the physical resource pool by the external interfaces; and the deletion module is connected with the existing network slice by the external interface. The management method of the manager comprises three parts of creation, expansion and deletion of the network slice. According to the network slice manager and the management method thereof, which are disclosed by the invention, the network slice which meets requirements can be created according to user demands, and a utilization rate of the network slice is effectively maximized, so that a utilization rate of network resources is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Majority consistent escape error processing device based on mimicry security defense zero-day attack and method thereof
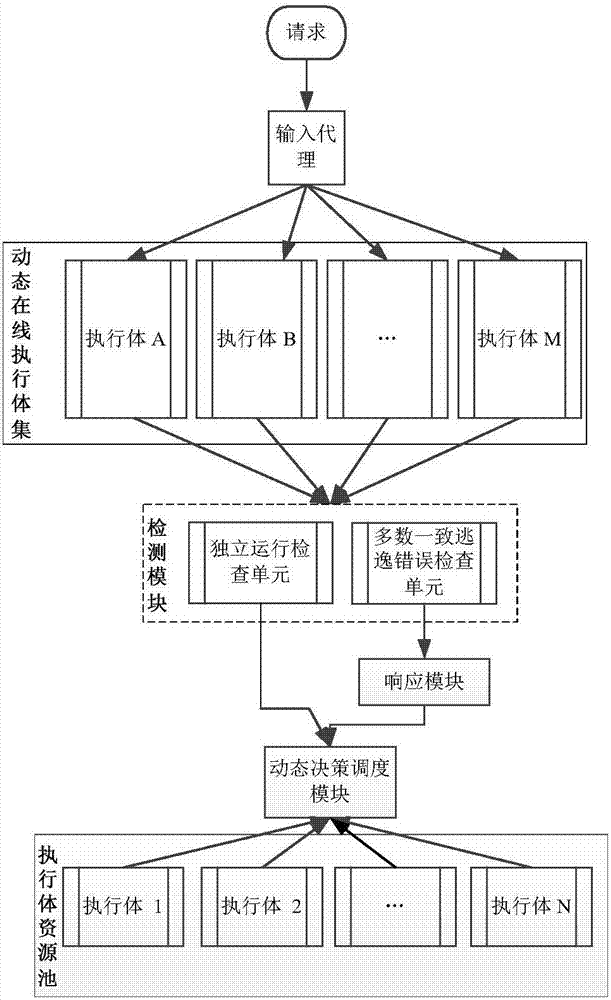
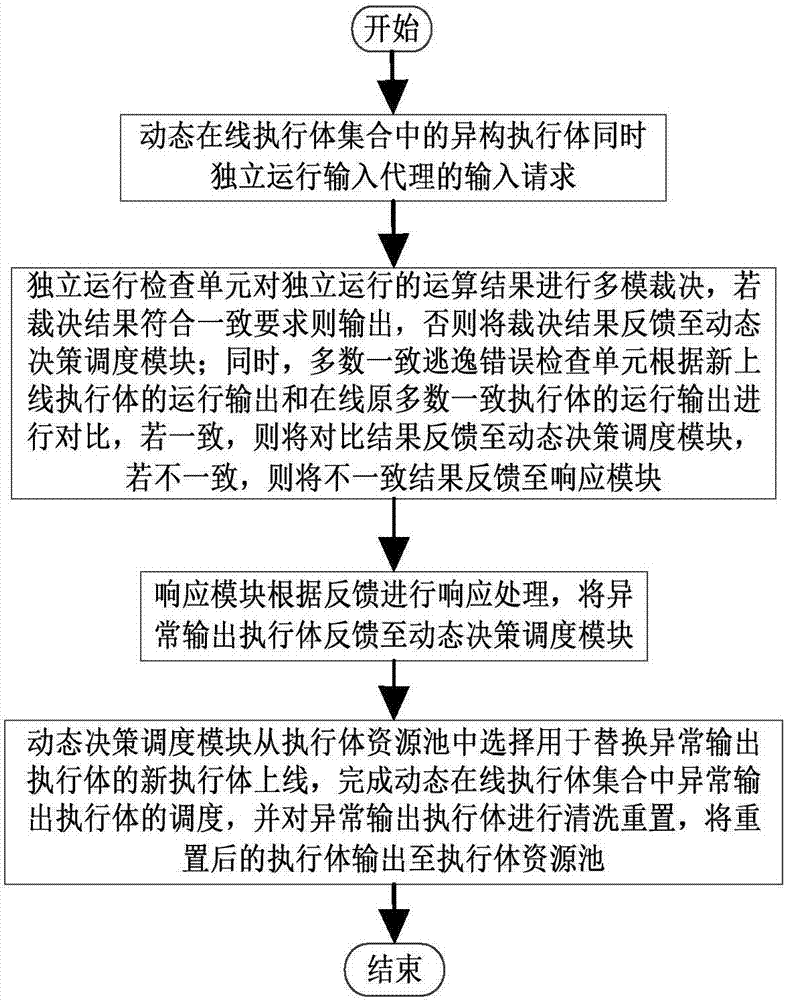
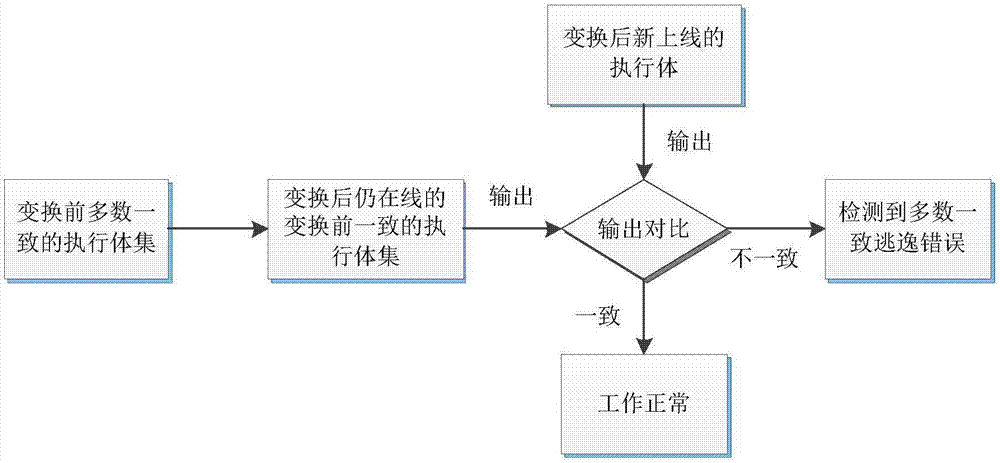
ActiveCN106874755AGuaranteed robustnessGuaranteed survivabilityPlatform integrity maintainanceResource poolError processing
The invention relates to a majority consistent escape error processing device based on mimicry security defense zero-day attack and a method thereof. The method comprises: a heterogeneous executive in a dynamic online executive assembly independently operating an input request; performing multimode adjudication on an operation result, if an adjudication result meets a consistency requirement, outputting the adjudication result, if not, feeding back the adjudication result to a dynamic decision dispatching module; comparing new online executive operation output with online original majority consistent executive operation output, respectively feeding back results to the dynamic decision dispatching module and a responding module; the responding module processing the response according to feedback, and feeding back abnormal output executive to the dynamic decision dispatching module; and the dynamic decision dispatching module selecting new executive to be online from an executive resource pool, and cleaning and resetting offline executives. The method is used to provide means of detection and response when majority of mimicry defense online executives are attacked, and solves security threat a mimicry defense system faces, so as to enhance robustness of the mimicry system.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com