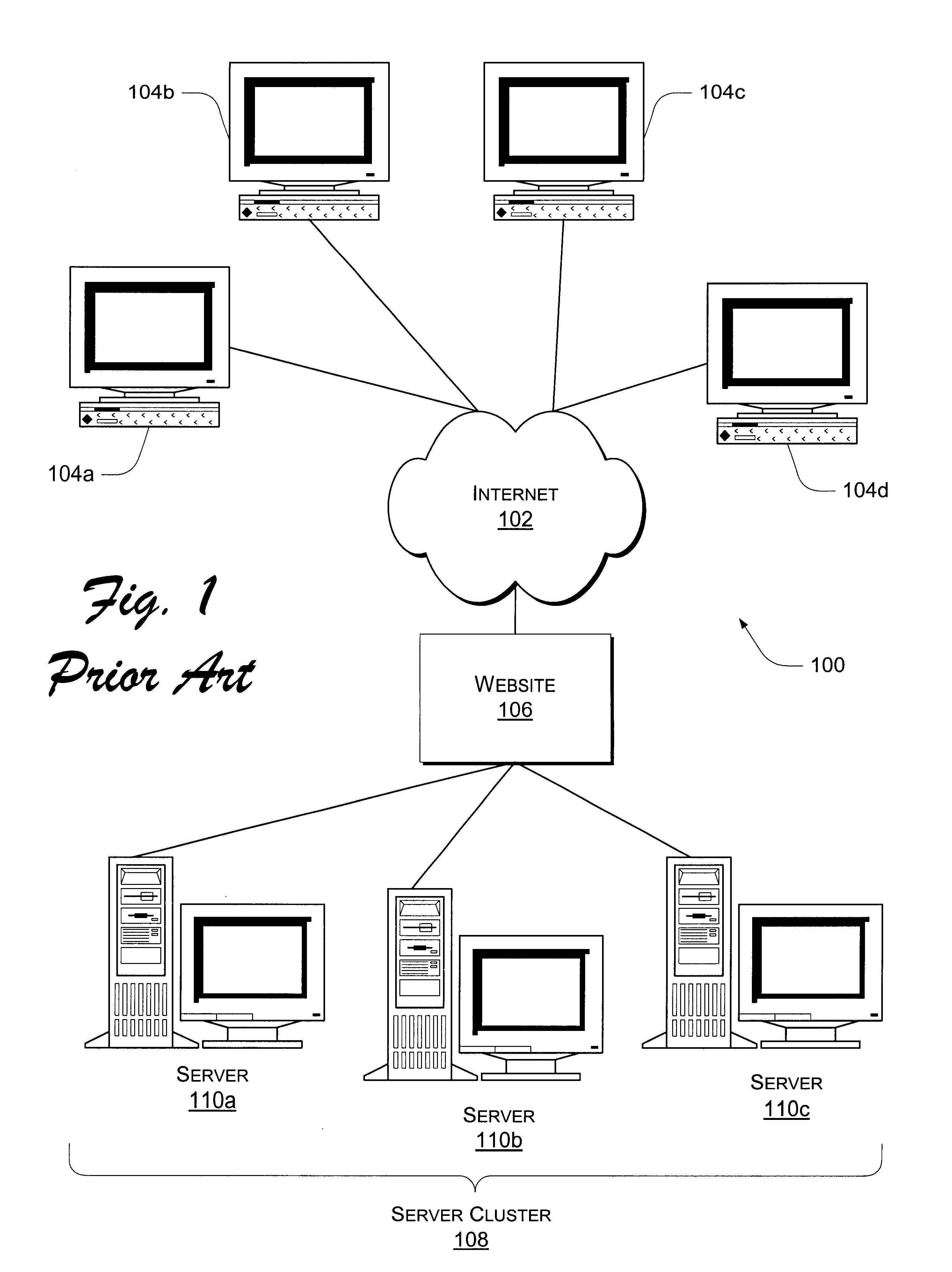
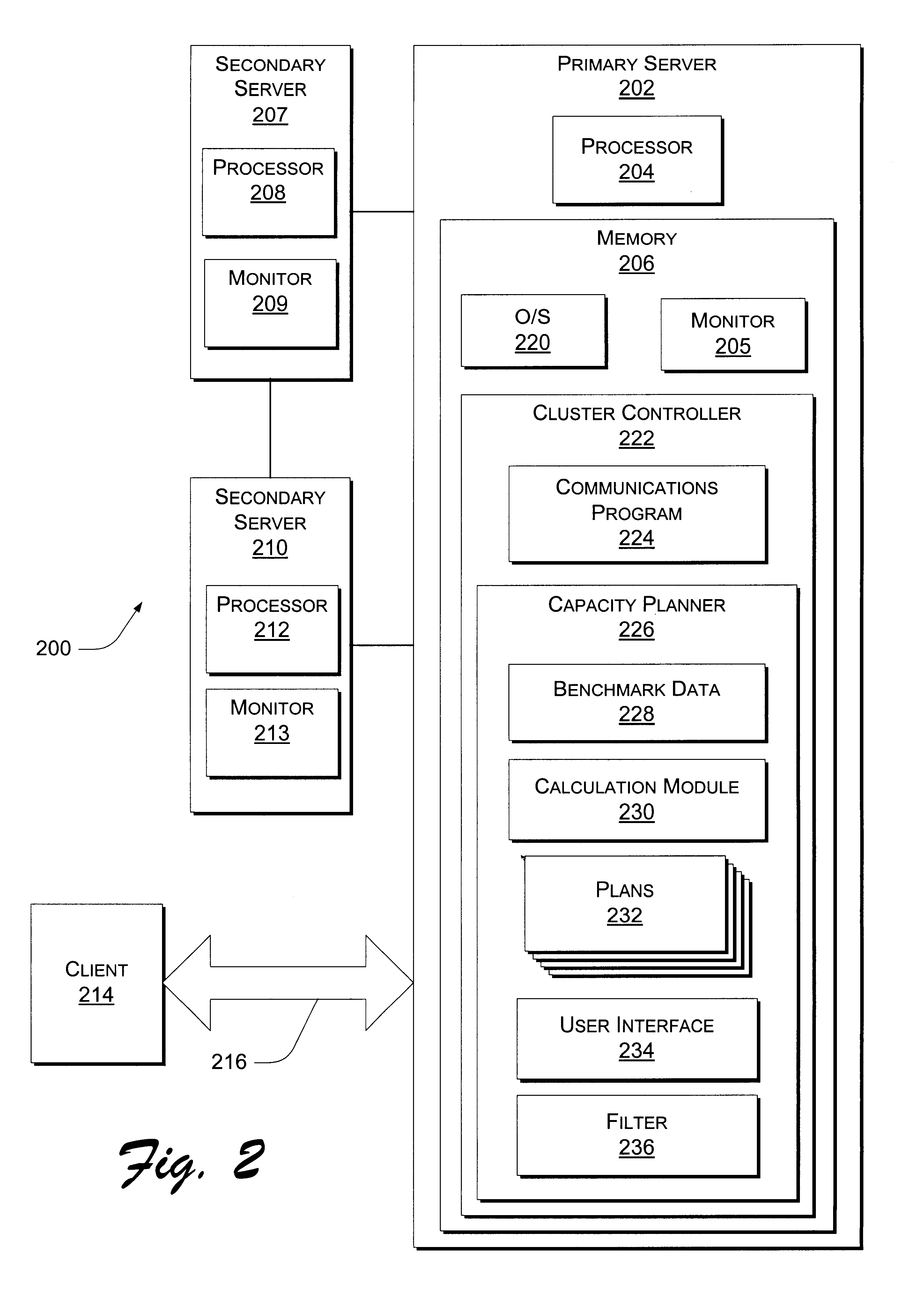
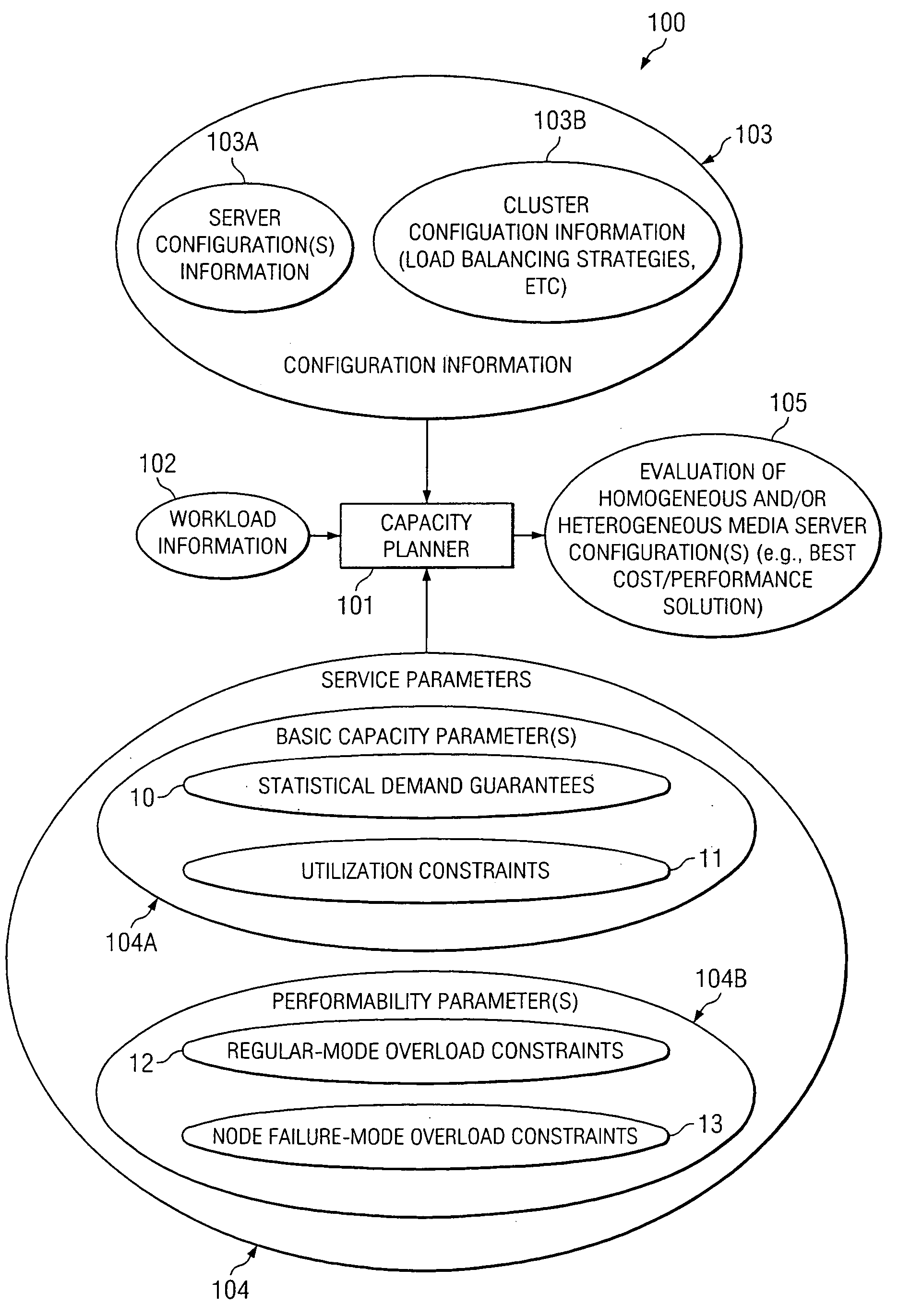
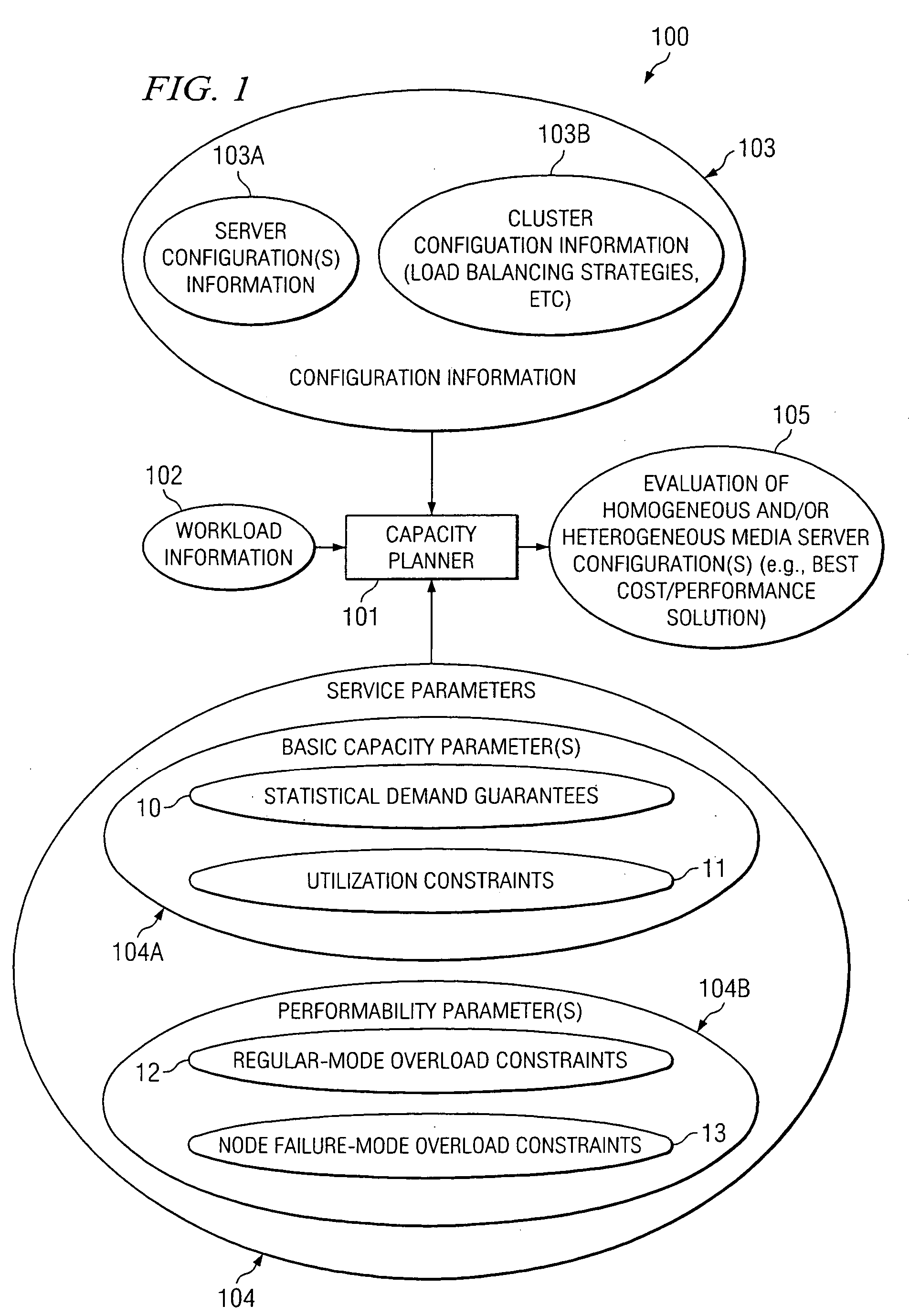
Patents
Literature
309 results about "Capacity planning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Capacity planning is the process of determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands for its products. In the context of capacity planning, design capacity is the maximum amount of work that an organization is capable of completing in a given period. Effective capacity is the maximum amount of work that an organization is capable of completing in a given period due to constraints such as quality problems, delays, material handling, etc.
Method and storage and manipulation of storage system metrics
InactiveUS7082441B1Promote generationEasy accessData processing applicationsError detection/correctionData operationsData description
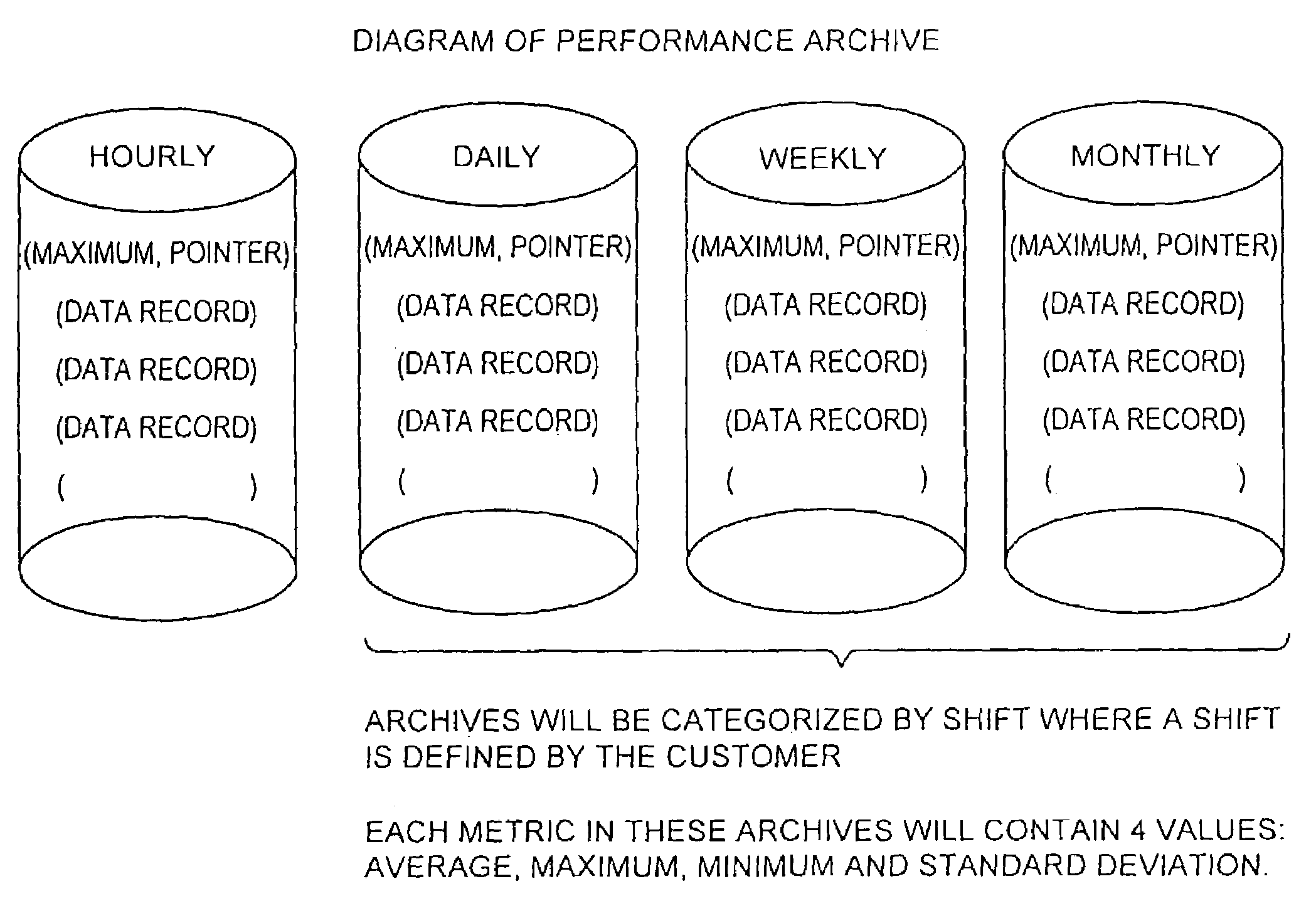
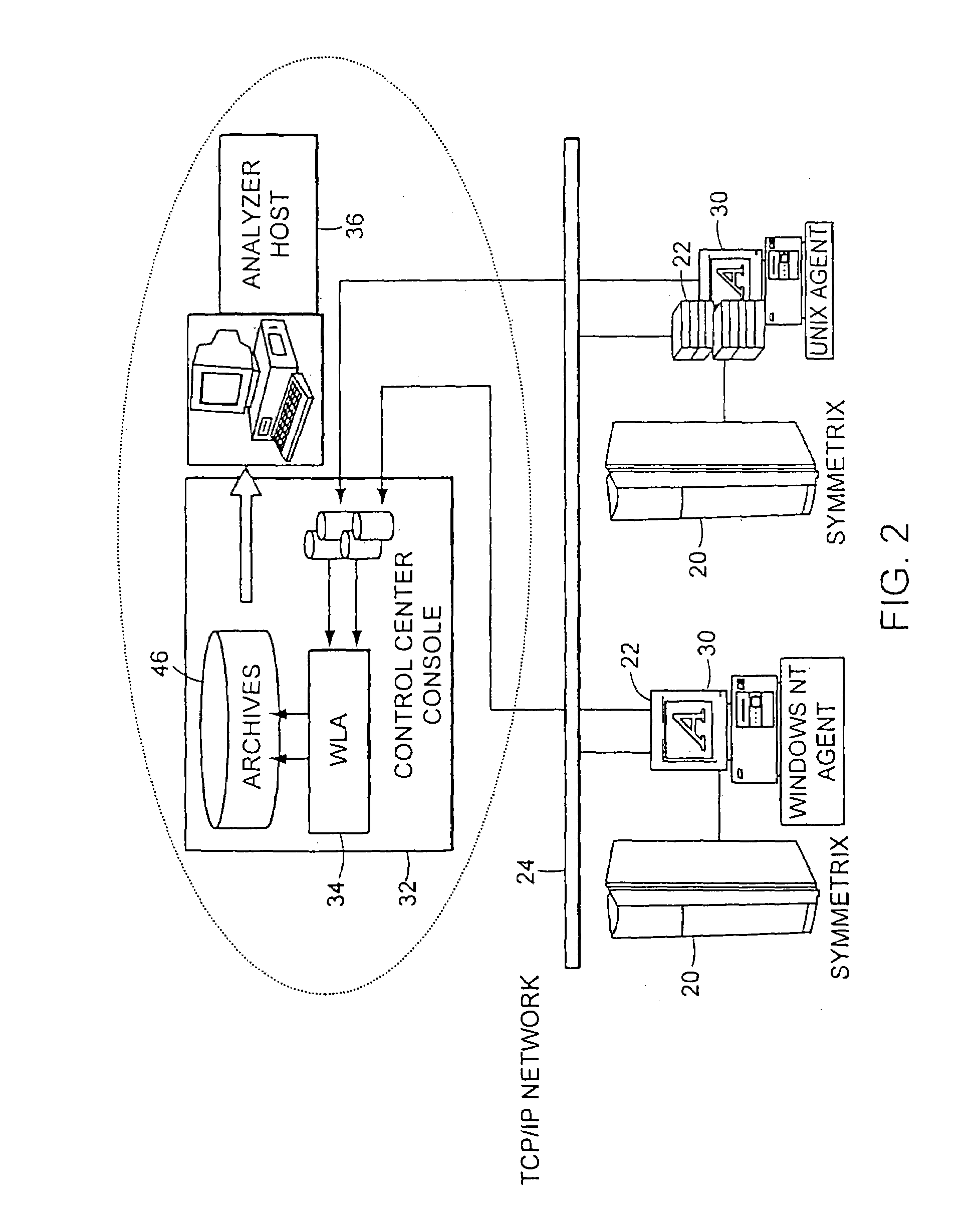
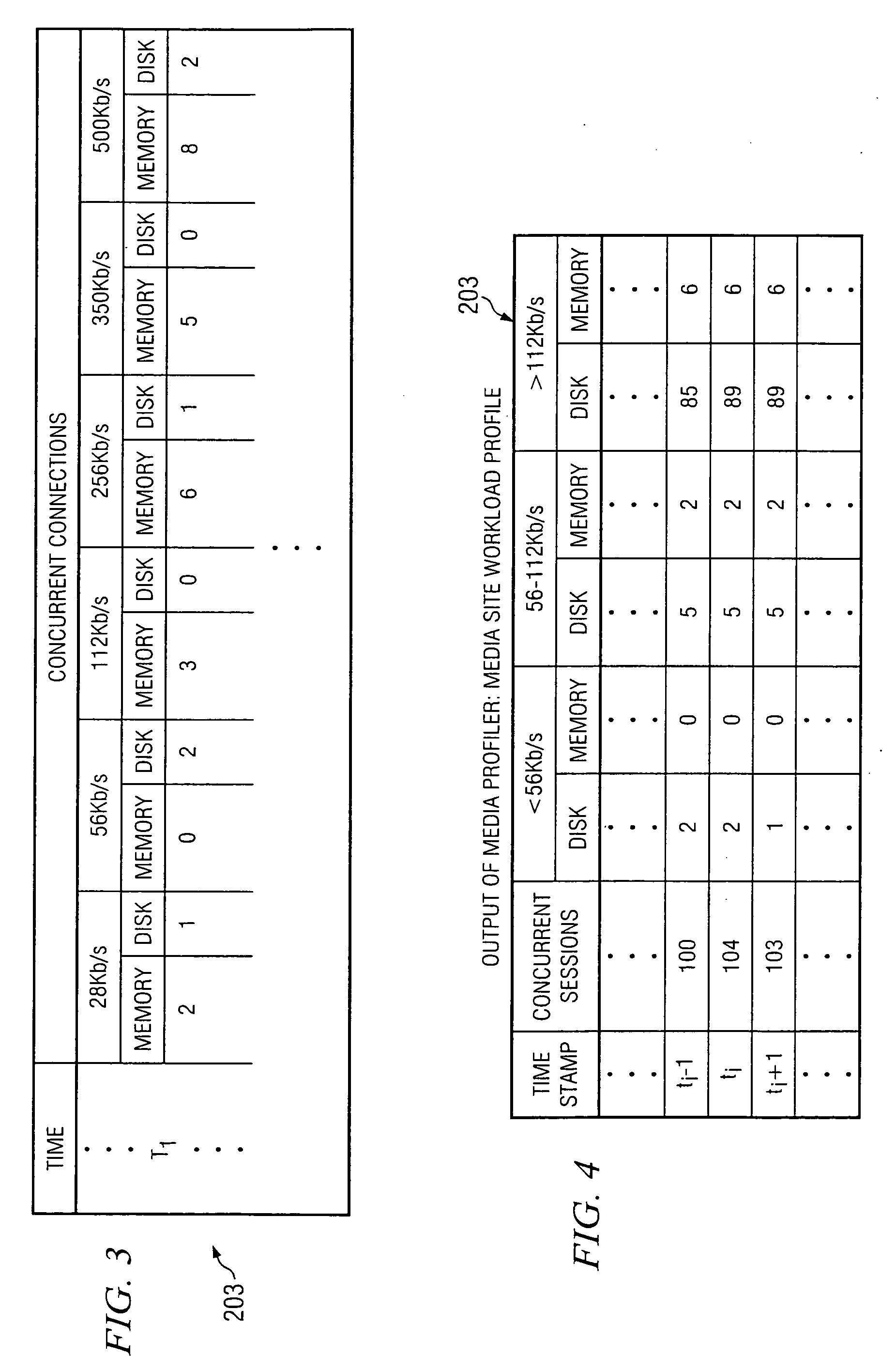
A method for storage and manipulation of storage system metrics incorporates a self-describing format wherein each data file includes a header block that contains the description and order of the periodic data. The header block is followed by a data block in which the data items are presented in the order that they appear in the data description block for that category. Two types of data are managed, including Base Metrics and Derived Metrics. Base Metrics are metrics that appear in the data file sent by an agent. Derived Metrics are computed based on a set of functions that derive new metrics from the base metrics as well as from previously defined derived metrics. A subset of the data block or file describes the configuration of the storage system at the time that the data file was created. Thus the data file contains a header section that in addition to describing the metrics also describes the configuration. A performance view component a user interface that facilitates access to the archives, and data manipulation effecting enhanced performance analysis, workload characterization and capacity planning. The performance view component facilitates generation of factory and user defined views of monitored metrics / parameters. Metrics from a storage system can be correlated using the performance view features, and parameters across machines can be correlated as well. System configuration(s) can be viewed and changed via the performance view user interface.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Storage area network (SAN) forecasting in a heterogeneous environment
InactiveUS20090077340A1Meet expectationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTransmissionStorage area networkProgram assurance
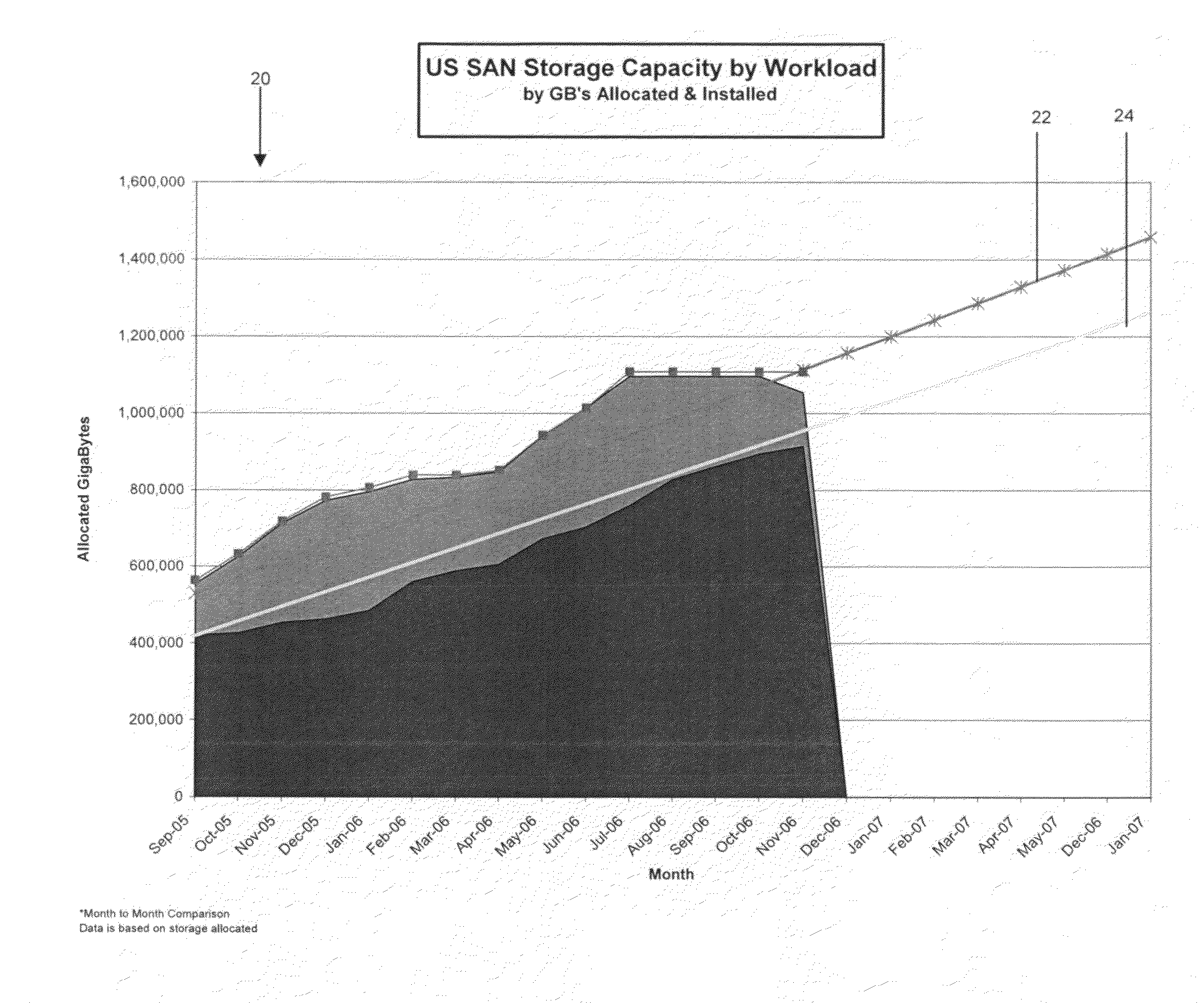
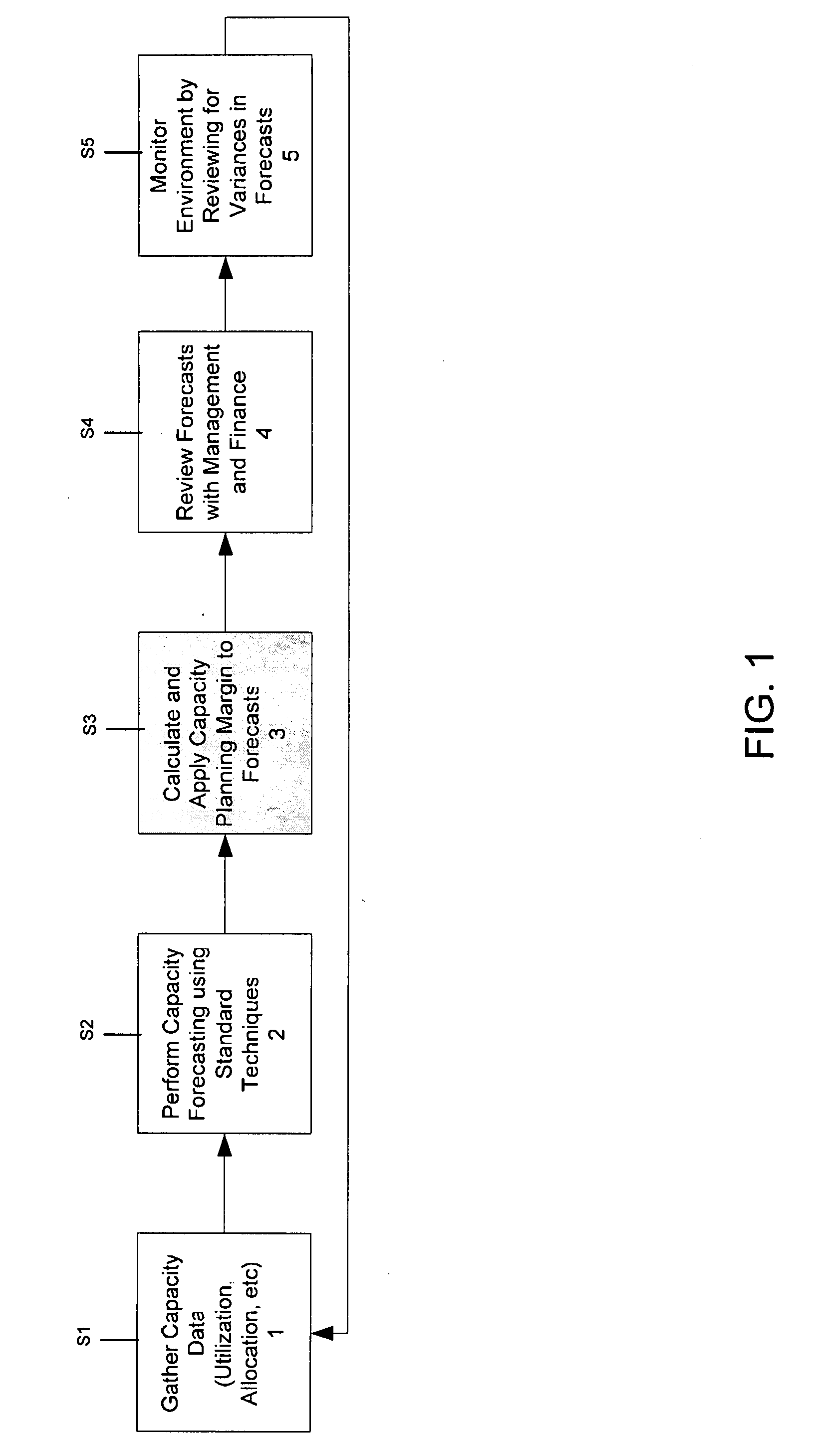
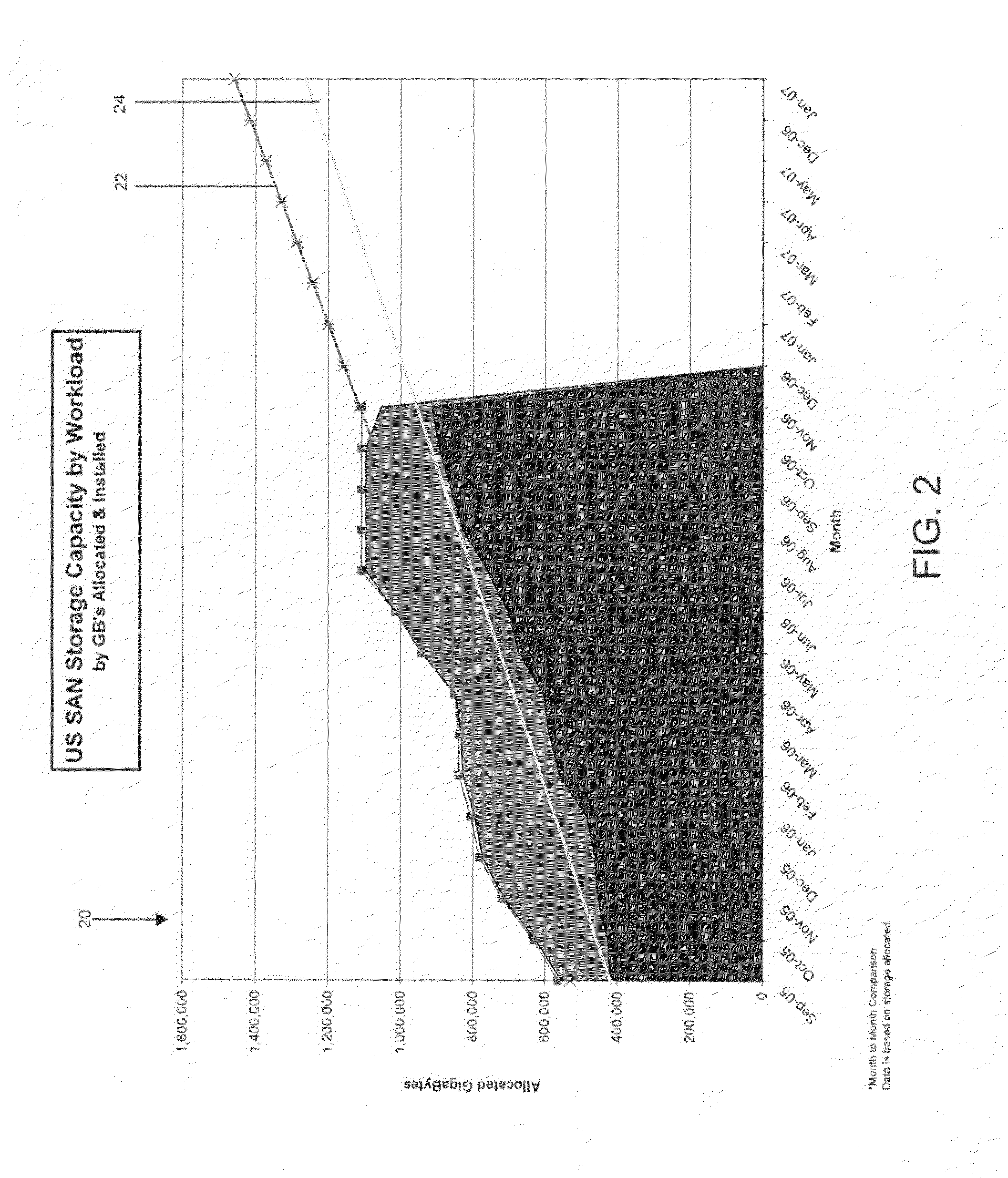
The present invention provides an approach for SAN forecasting in a heterogeneous environment. Specifically, under the present invention capacity data on the heterogeneous environment is gathered. Capacity management techniques will then be used to analyze the SAN utilization, identify growth trends and patterns. Proactively, plans are made to account for these changes. Thereafter, a Capacity Planning Margin (CPM) will be applied to the forecast to reflect actual customer usage. The CPM adjusted forecasts will then be reviewed. Then, the SAN environment can be monitored by comparing actual vs. planned and return to adjust the forecast accordingly.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and apparatus for allocating resources in the presence of uncertainty
InactiveUS6219649B1ResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsOrganizational resourceDeterministic method
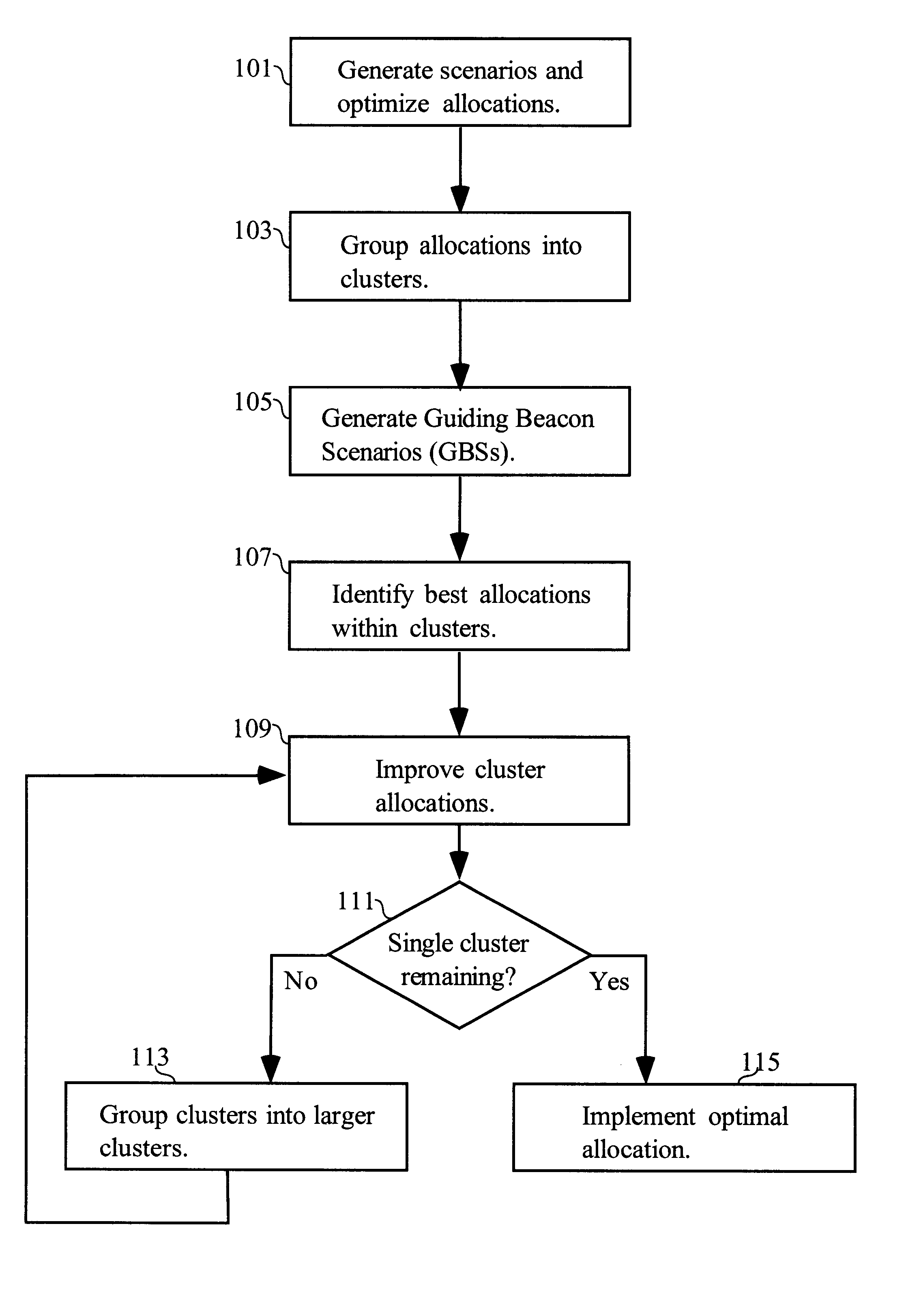
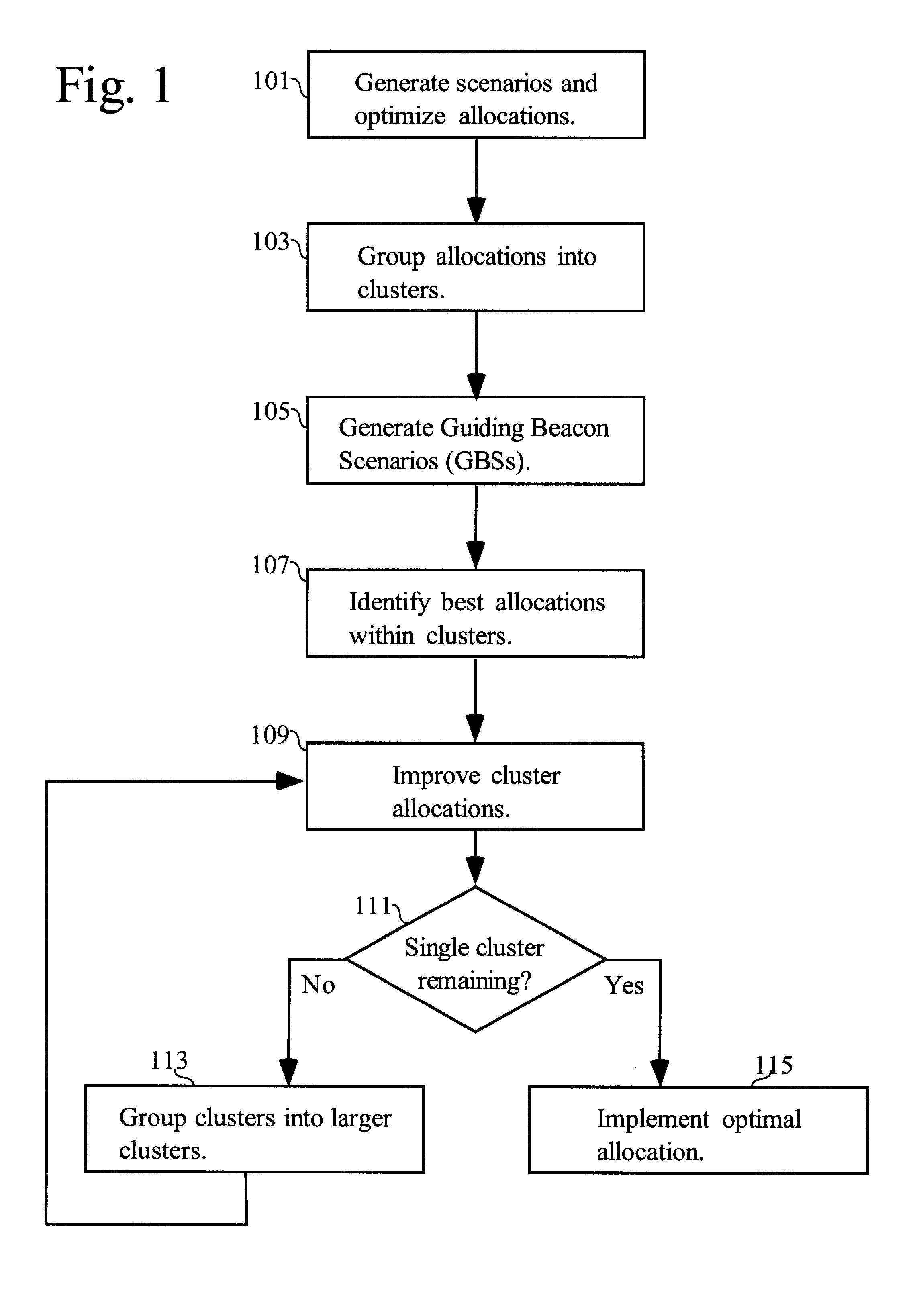
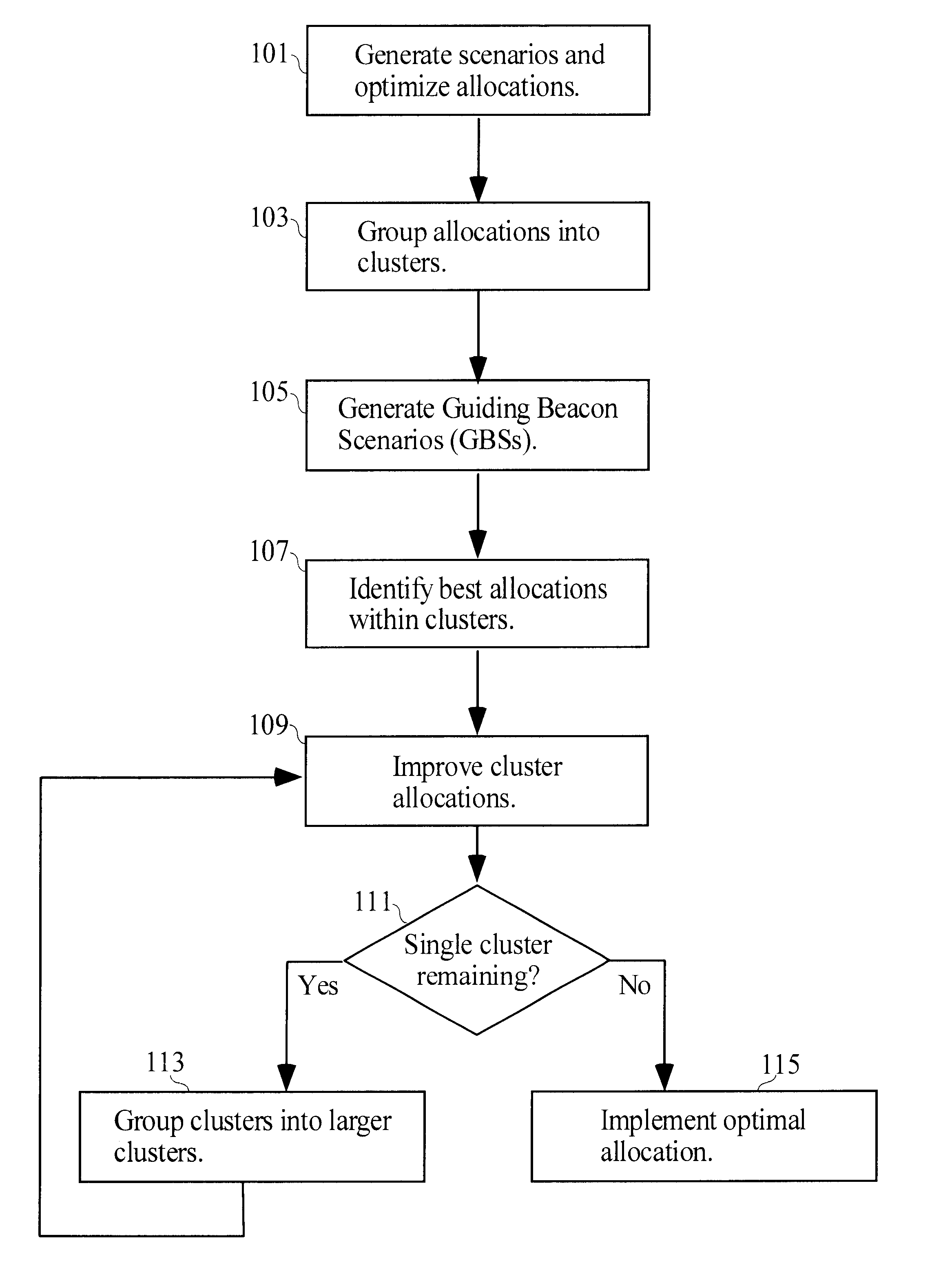
A method of allocating resources in the presence of uncertainty is presented. The method builds upon deterministic methods and initially creates and optimizes scenarios. The invention employs clustering, line-searching, statistical sampling, and unbiased approximation for optimization. Clustering is used to divide the allocation problem into simpler sub-problems, for which determining optimal allocations is simpler and faster. Optimal allocations for sub-problems are used to define spaces for line-searches; line-searches are used for optimizing allocations over ever larger sub-problems. Sampling is used to develop Guiding Beacon Scenarios that are used for generating and evaluating allocations. Optimization is made considering both constraints, and positive and negative ramifications of constraint violations. Applications for capacity planning, organizational resource allocation, and financial optimization are presented.
Owner:JAMESON JOEL
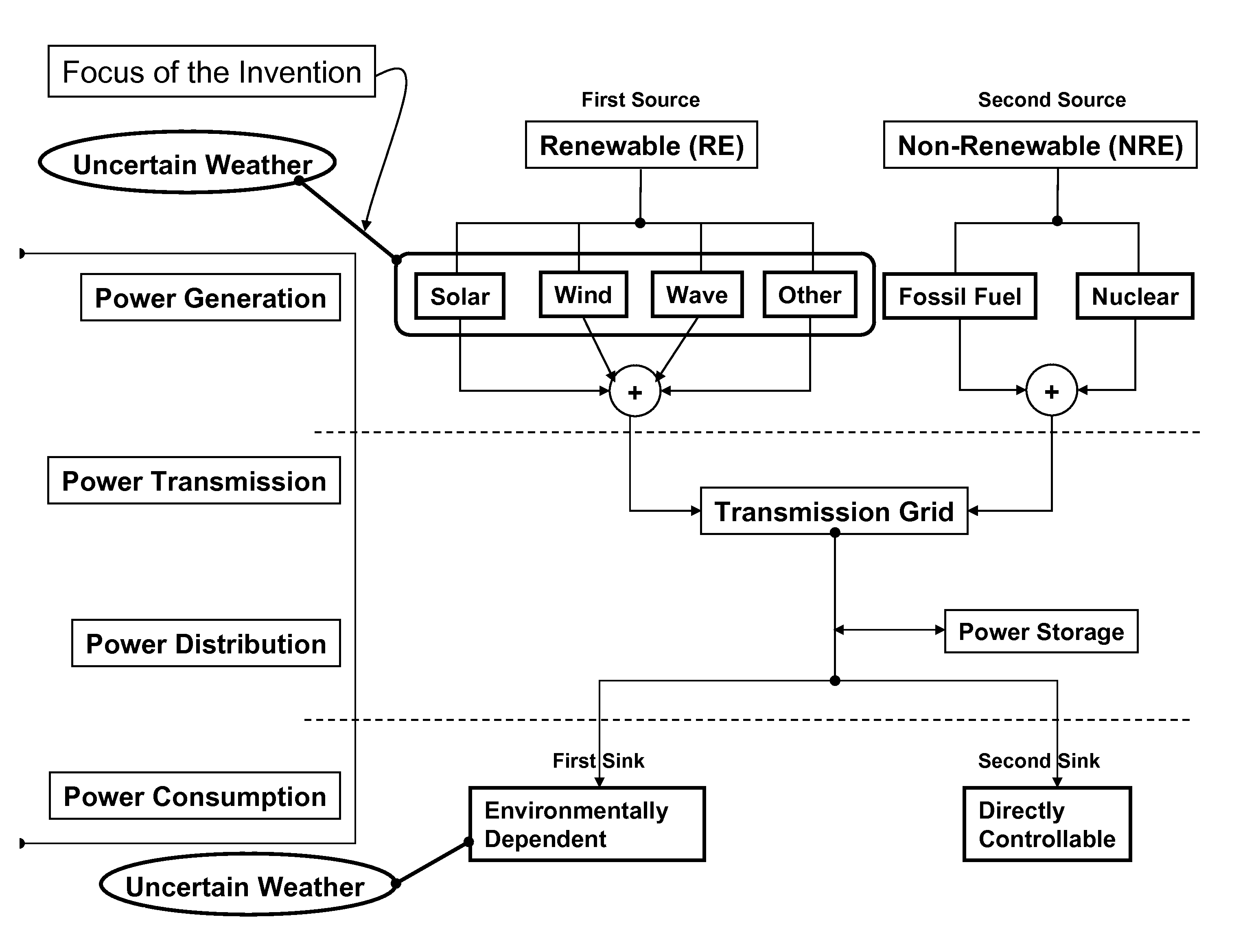
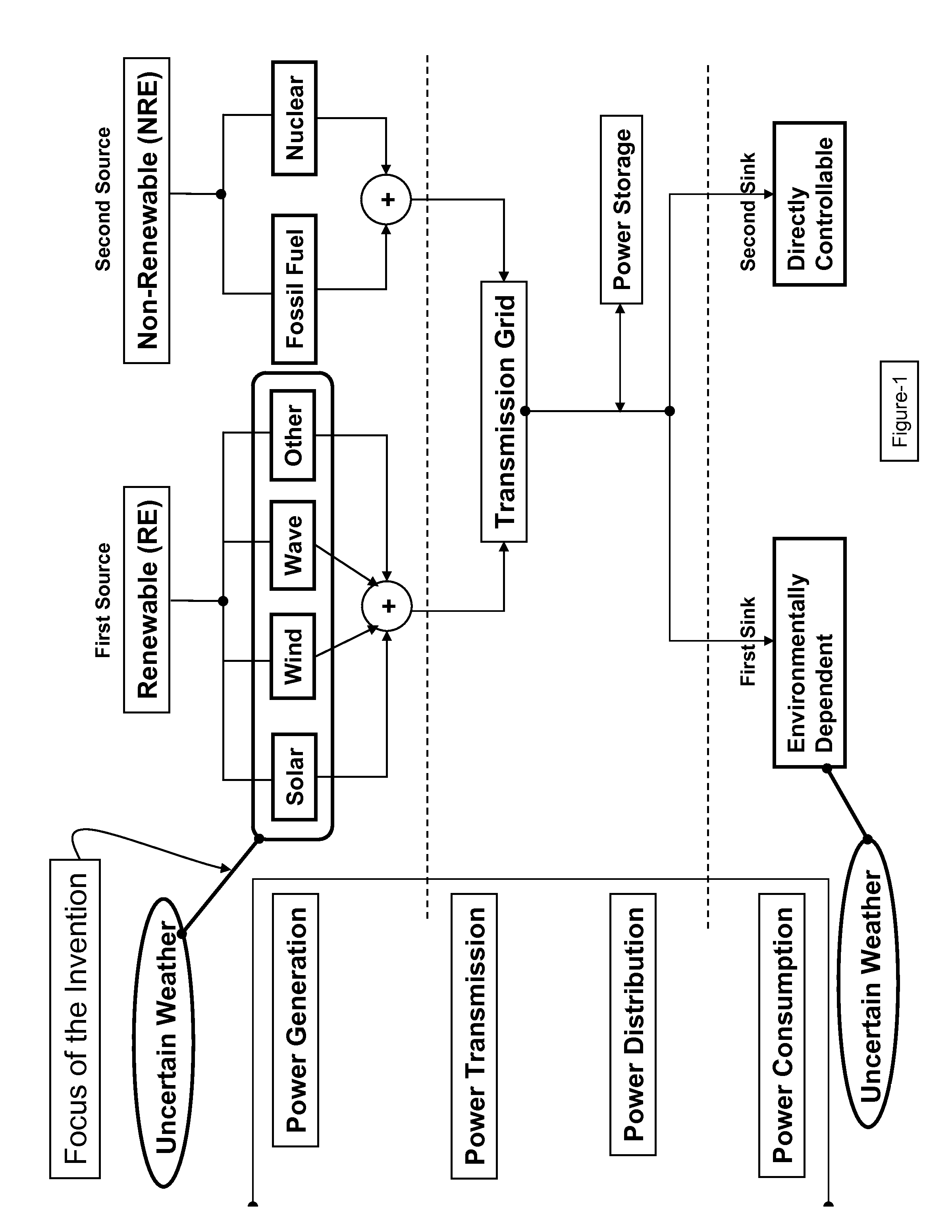
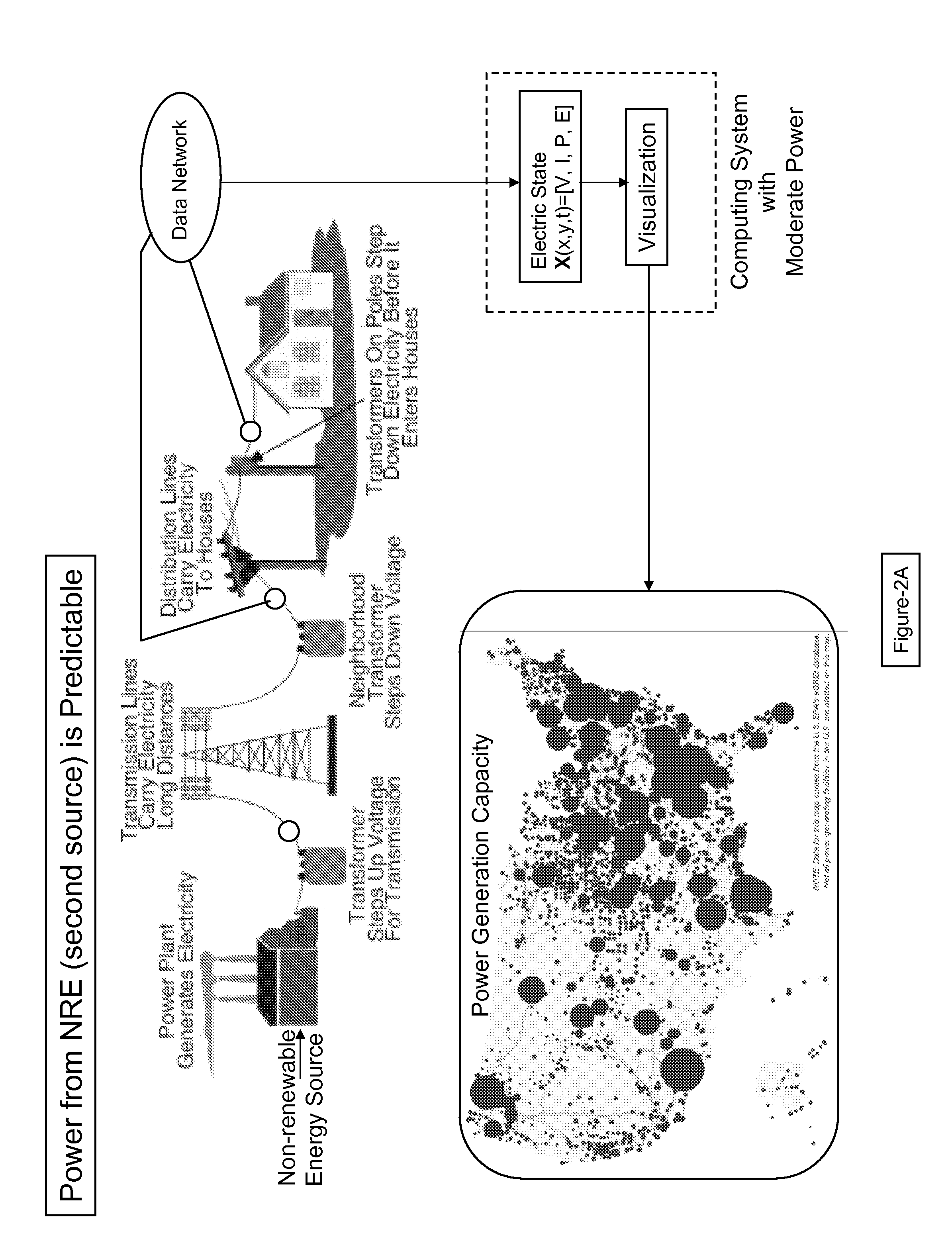
Smarter-Grid: Method to Forecast Electric Energy Production and Utilization Subject to Uncertain Environmental Variables
InactiveUS20110307109A1Improve accuracyMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlSmart gridEngineering
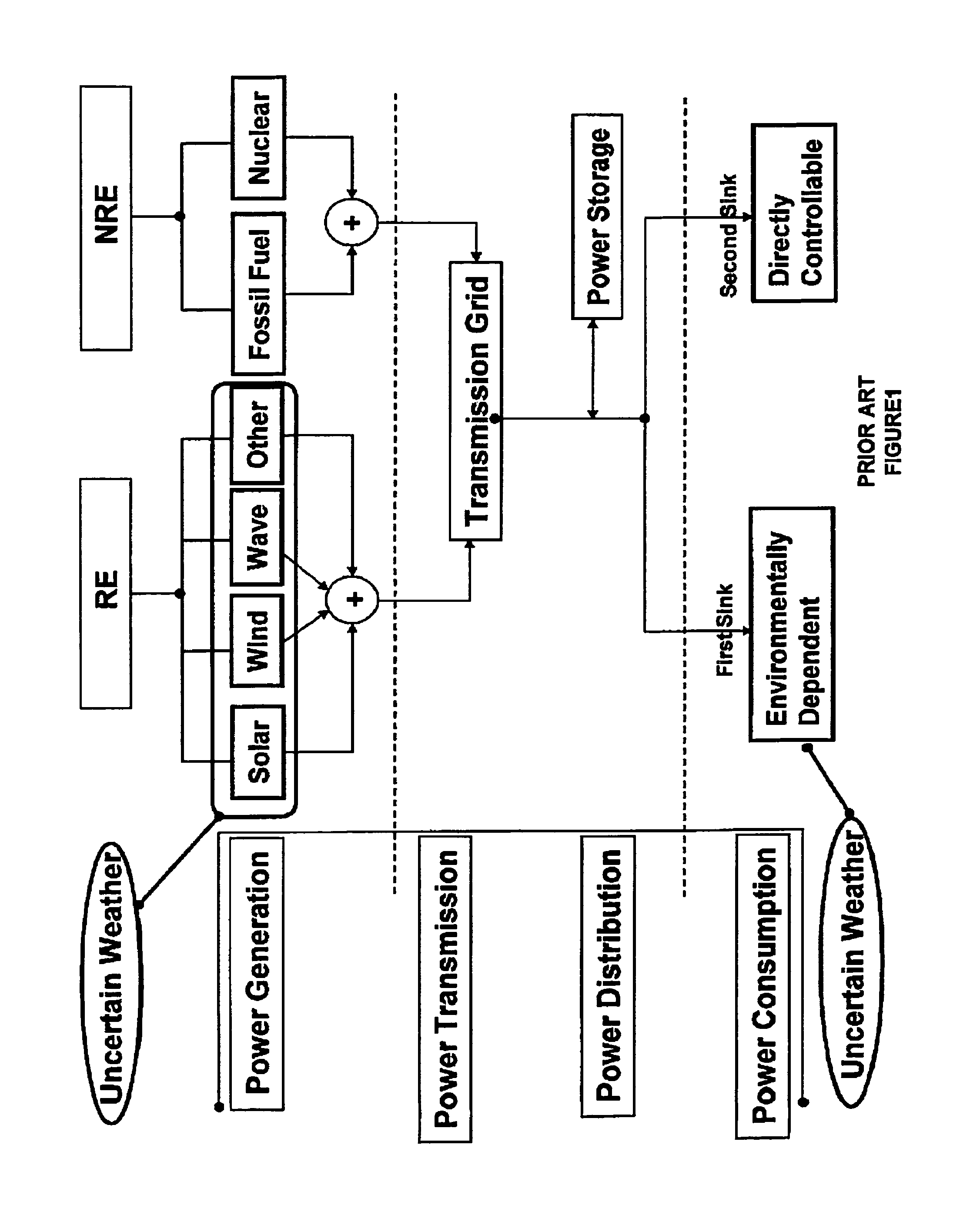
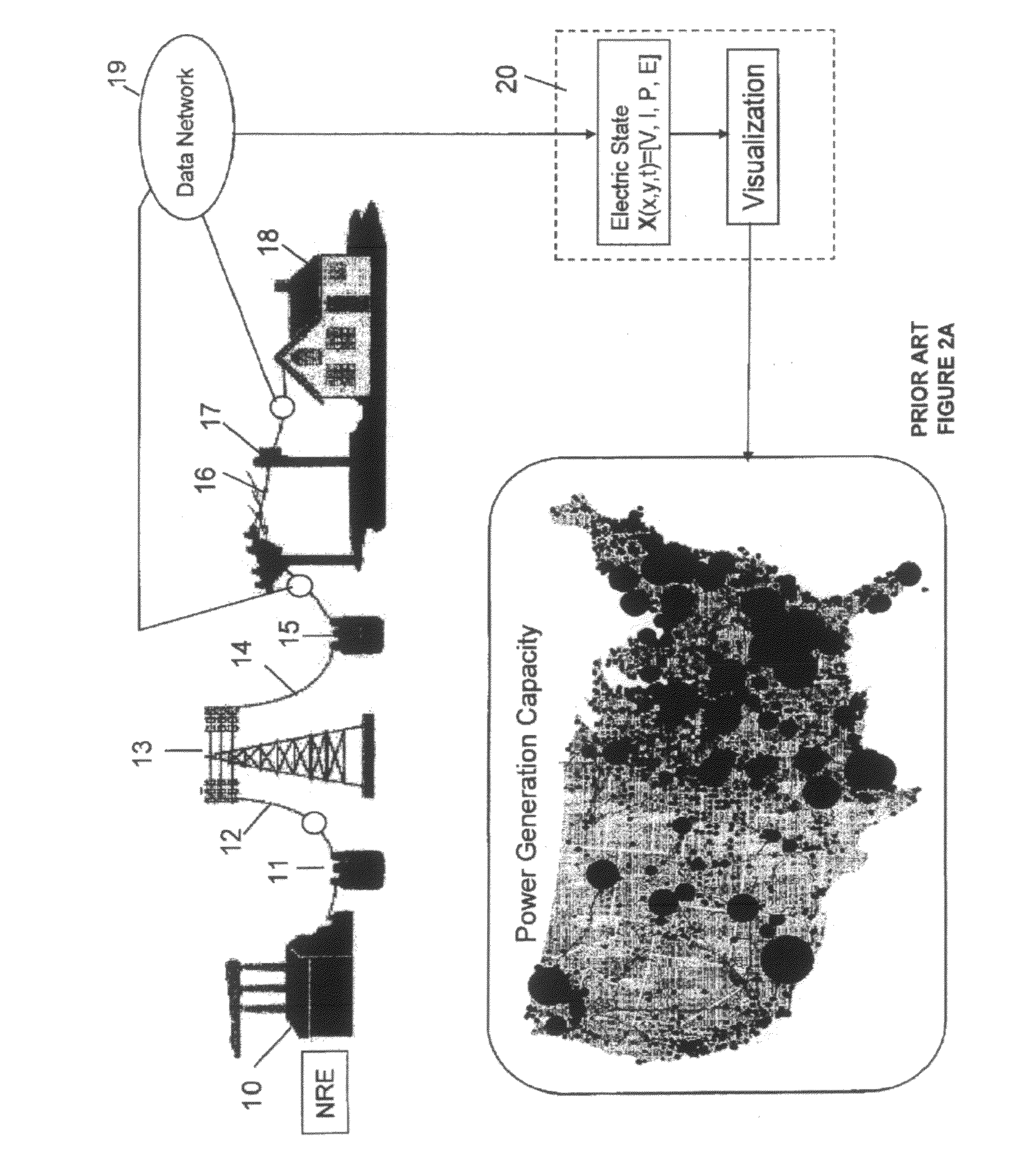
A method to forecast the energy sources and energy sinks to facilitate continuous capacity planning, regulation and control of energy state of an entity under variable weather condition is established. Energy sources of specific focus are related to renewable energy forms from wind, solar and wave that are highly dependent on prevailing weather conditions.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
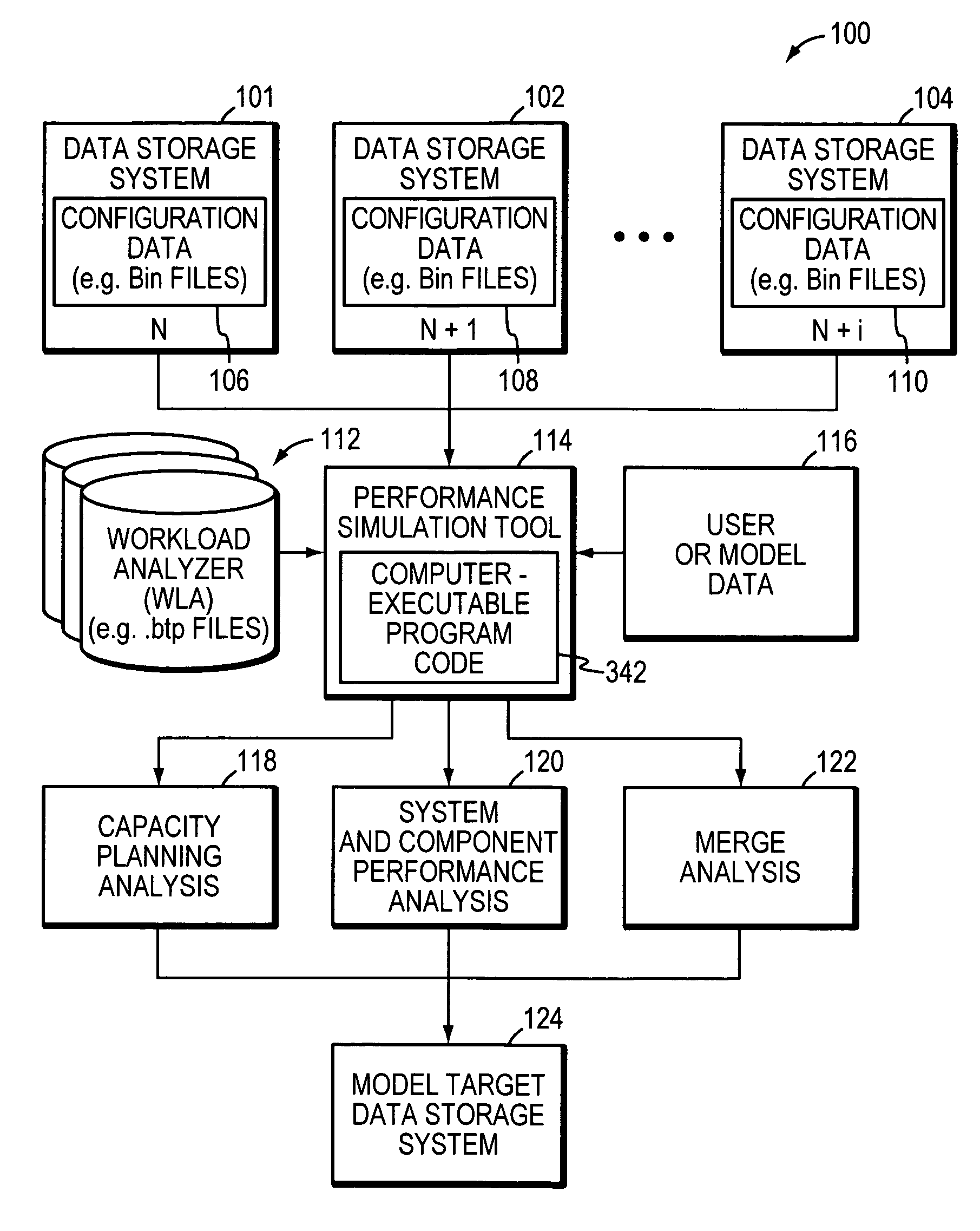
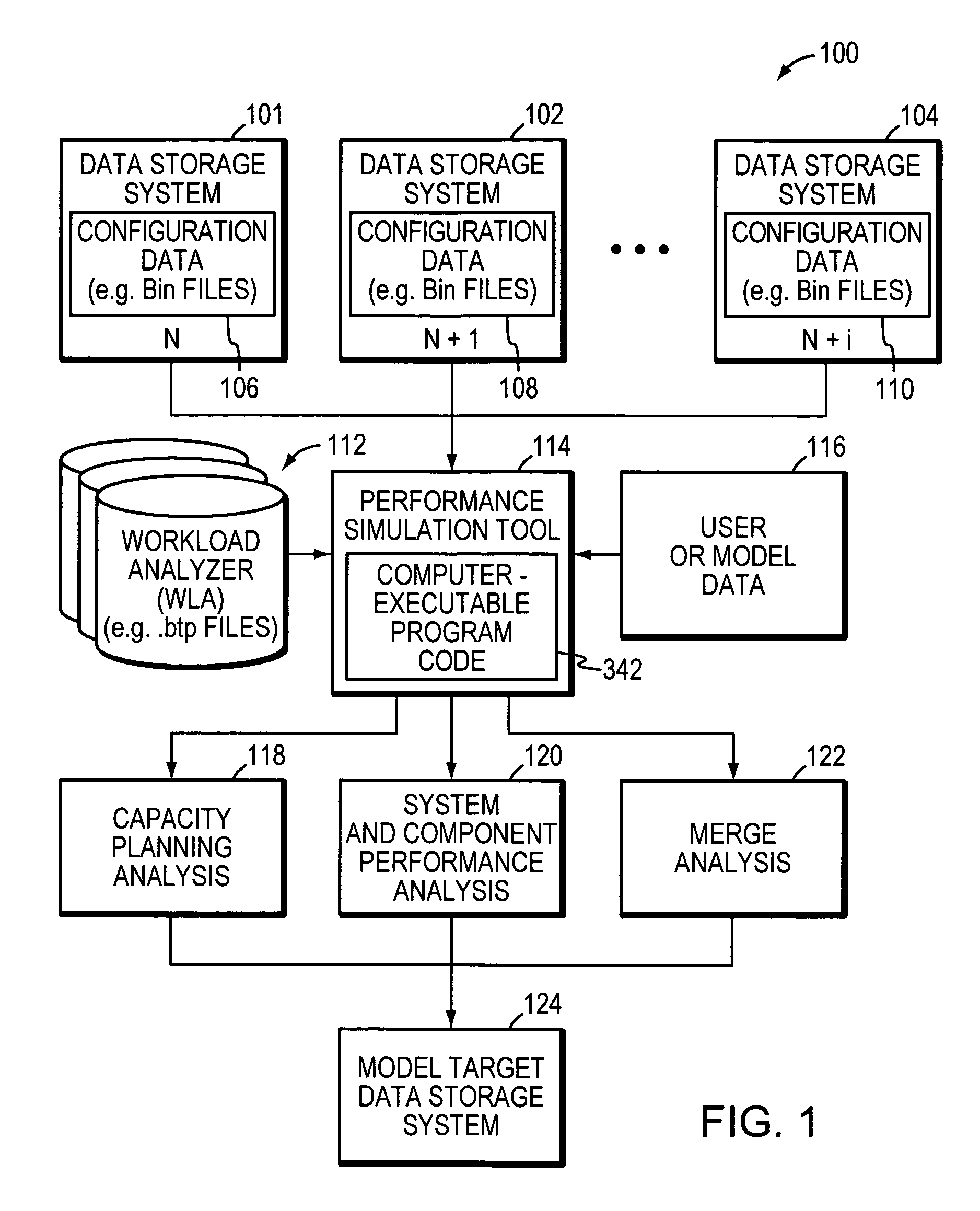
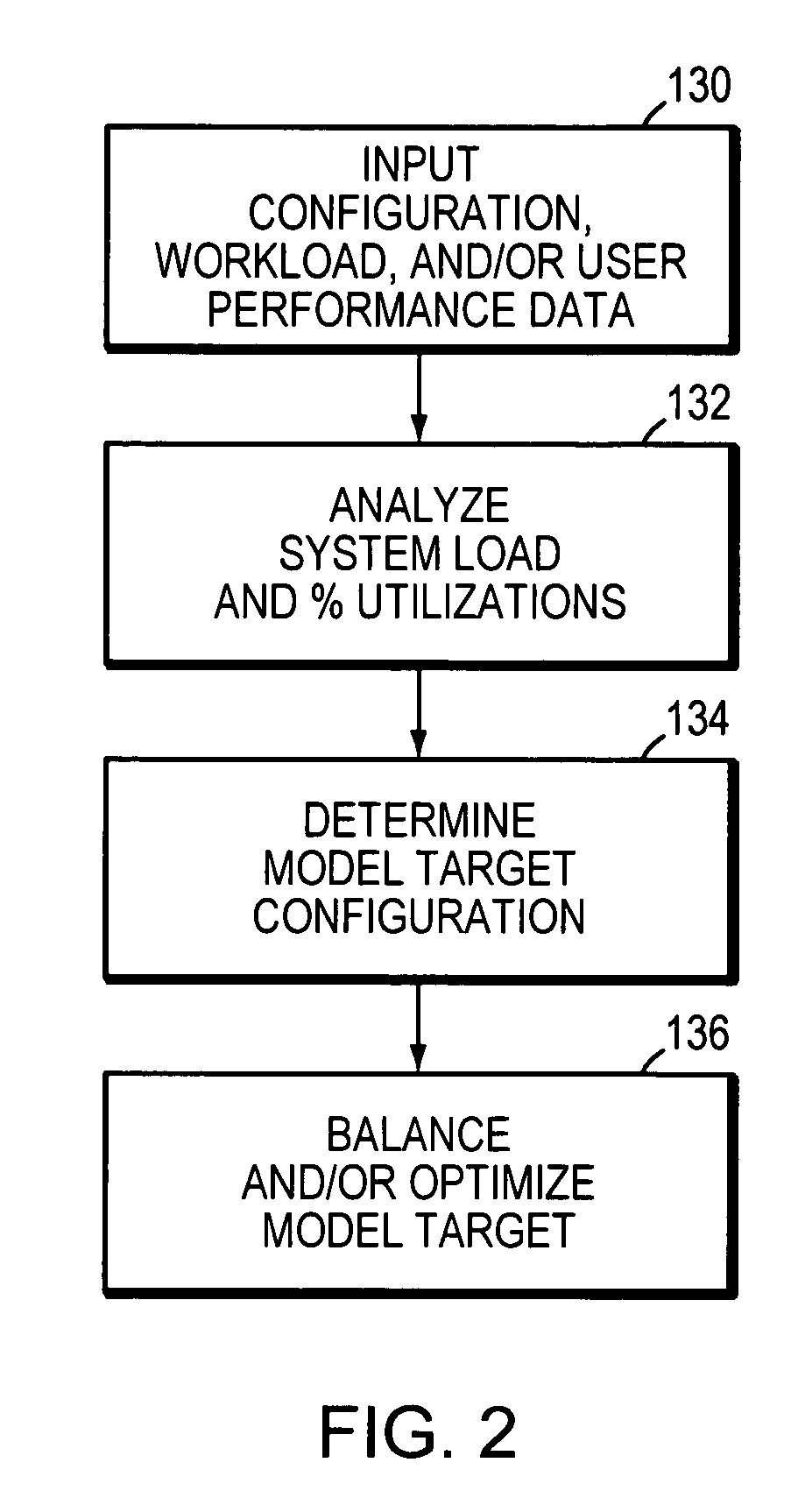
Method and system for capacity planning and configuring one or more data storage systems
This invention is a system and method for determining configuration or simulating performance of one or more data storage systems. This invention may be used in many useful ways including for configuring or modeling a data storage environment, problem isolation, and general design.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
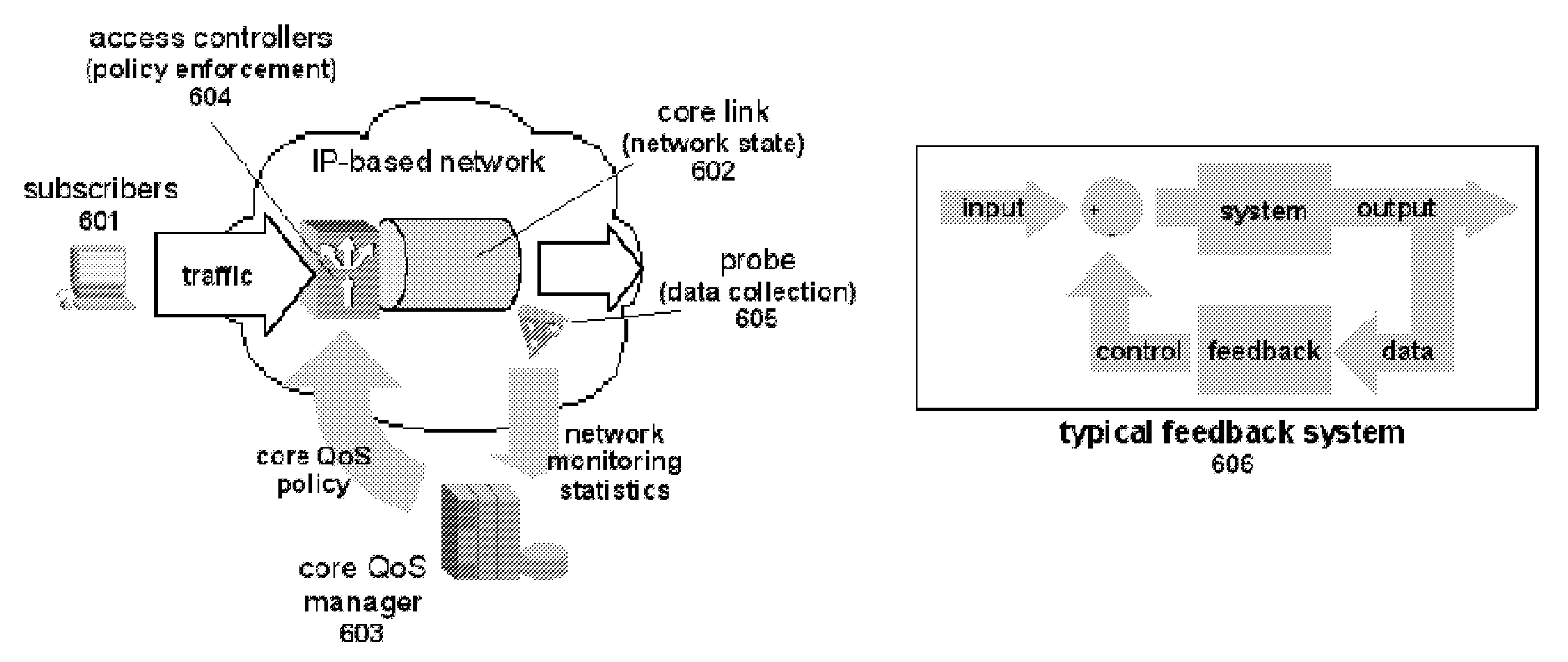
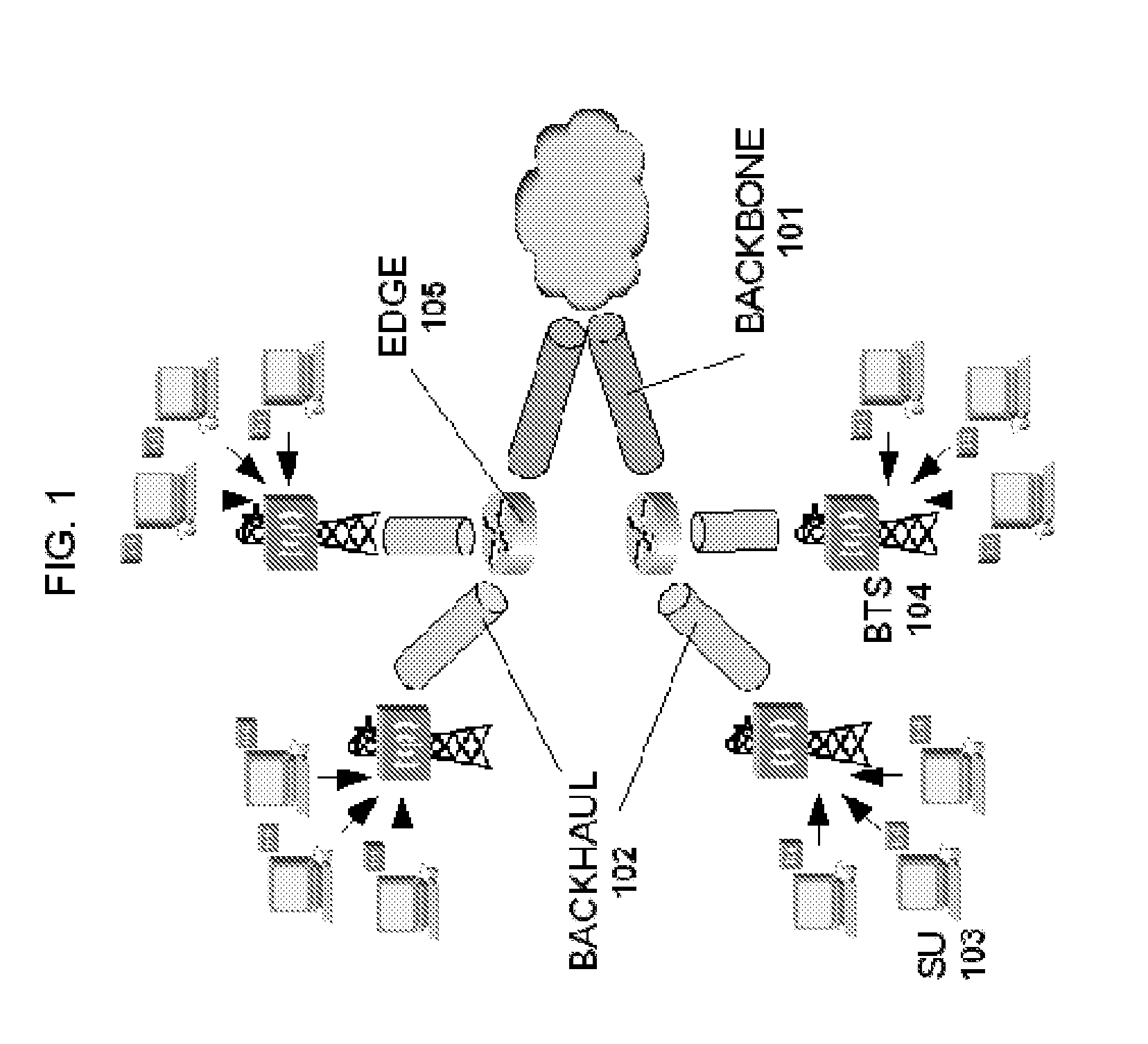
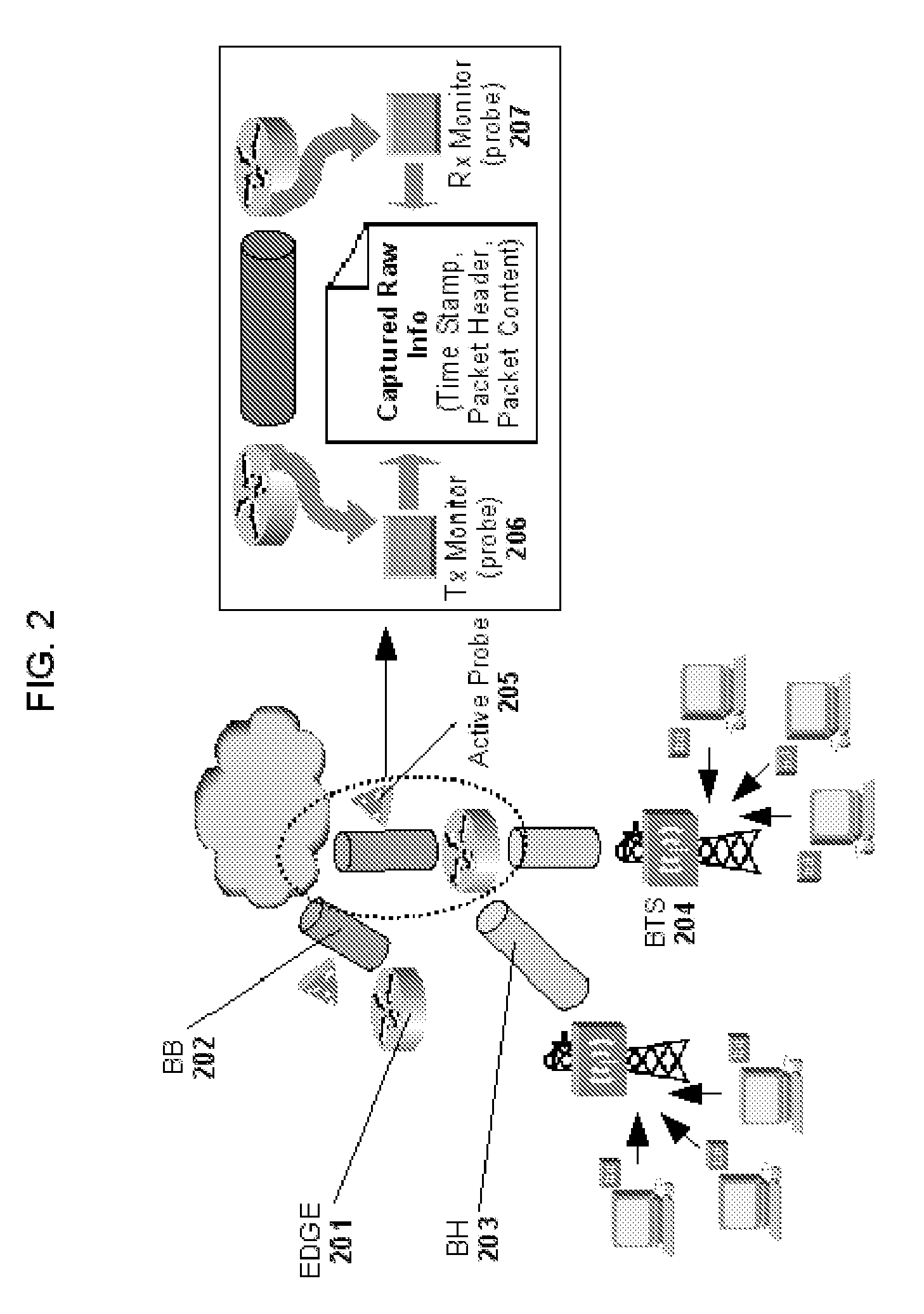
Methods and systems for providing quality of service in packet-based core transport networks
InactiveUS7599290B2Effective carryFair sharingEnergy efficient ICTError preventionService-level agreementTraffic capacity
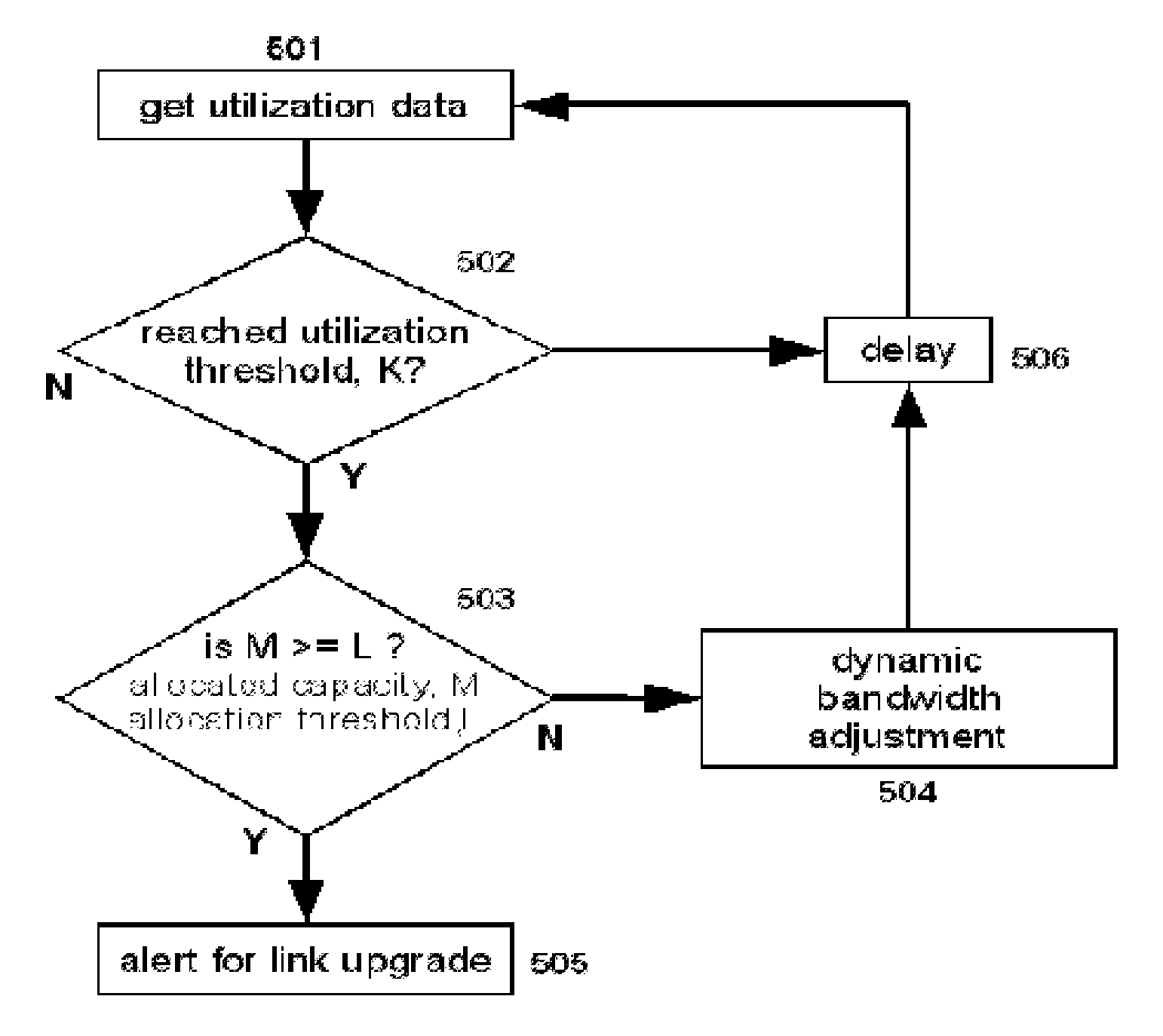
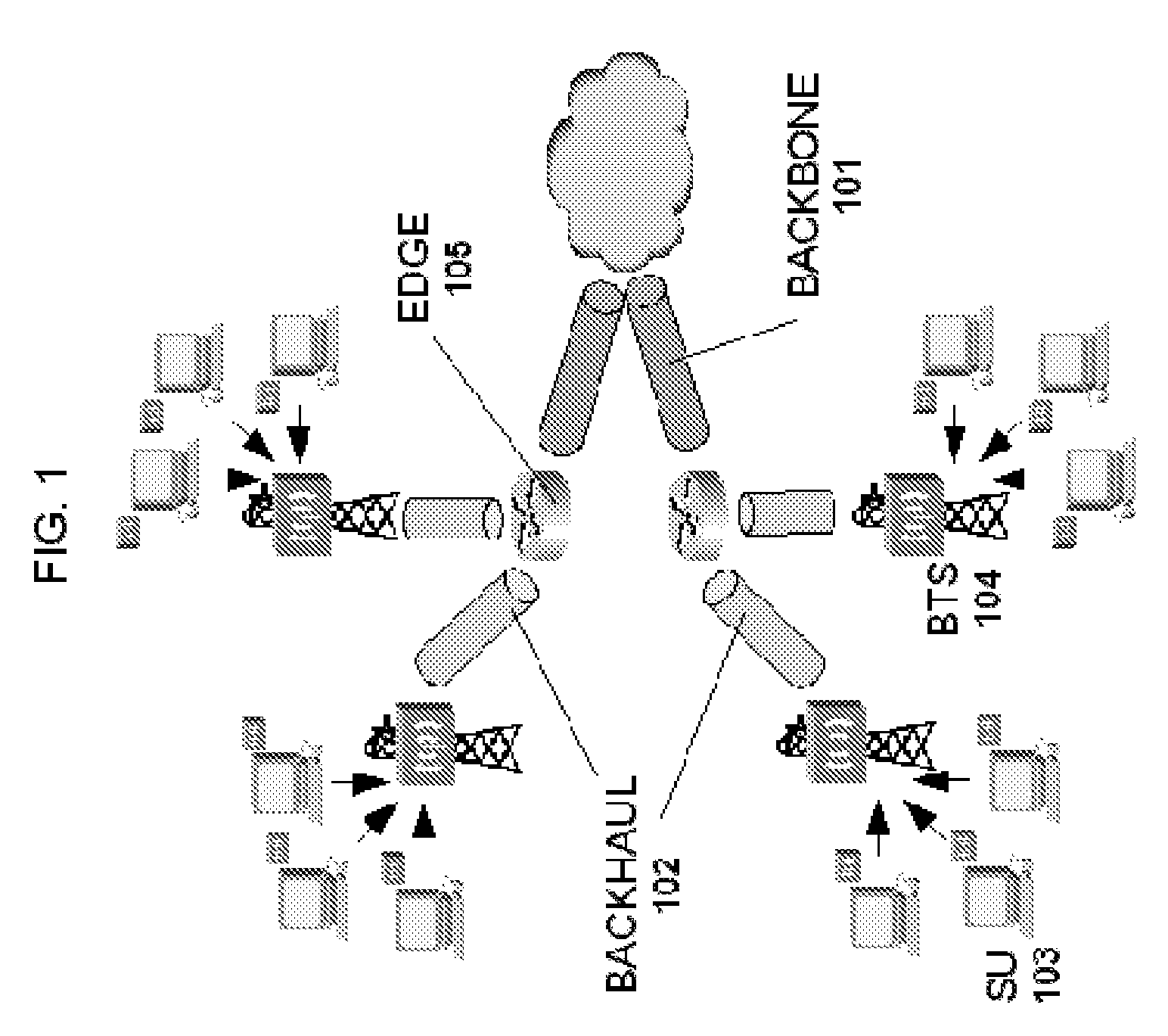
Methods and systems for providing necessary and sufficient quality-of-service (QoS), in a packet-based core transport network that utilizes dynamic setting of bandwidth management pipes or thresholds to obviate link congestion are disclosed. Congestion avoidance is a necessary and sufficient requirement in order to guarantee Quality of Service (QoS) in packet-based core networks.A typical network is composed of a plurality of backbone links connecting edge nodes where backhaul links are aggregated. The backhaul links connect the backbone links to the remote sites serving the subscribers. In order to enforce bandwidth management policies, Access Controllers, which perform traffic shaping, are situated on each remote site.In the event of a violation of certain link threshold settings, dynamic adjustment of the bandwidth management policies on affected Access Controllers is enforced. Various algorithms in determining the correlation between the link nearing congestion and the source or destination of traffic streams are also discussed. This invention implements a feedback control loop wherein probes at various points in the network checks for congestion states to guide bandwidth management threshold decisions in order to maintain the condition of non-congestion throughout the network. Capacity planning and congestion avoidance mechanisms work hand-in-hand to fulfill Service Level Agreements (SLA).
Owner:LATITUDE BROADBAND
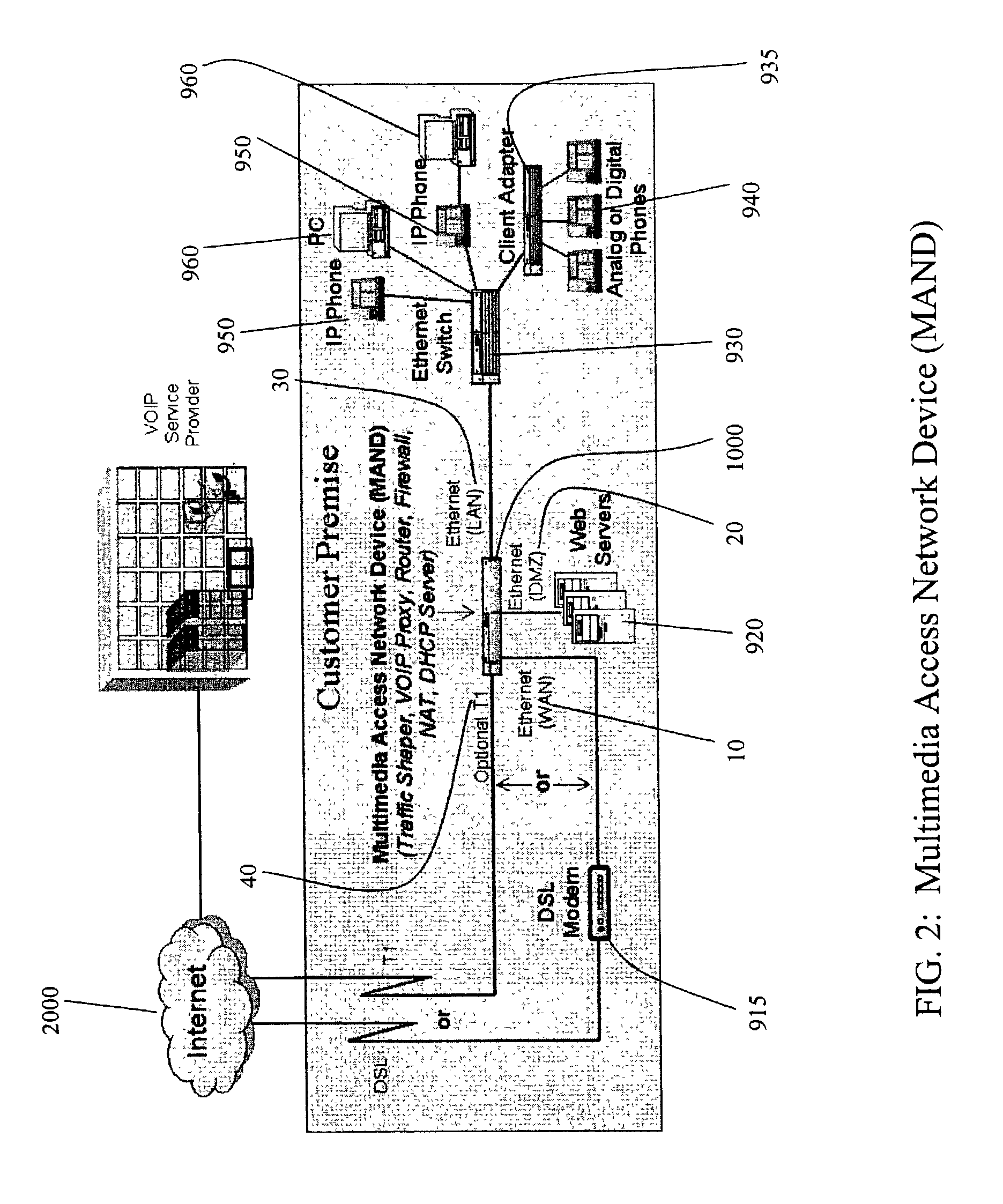
Method and system for implementing and managing a multimedia access network device
ActiveUS7274684B2Telephonic communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork address translationAuthentication
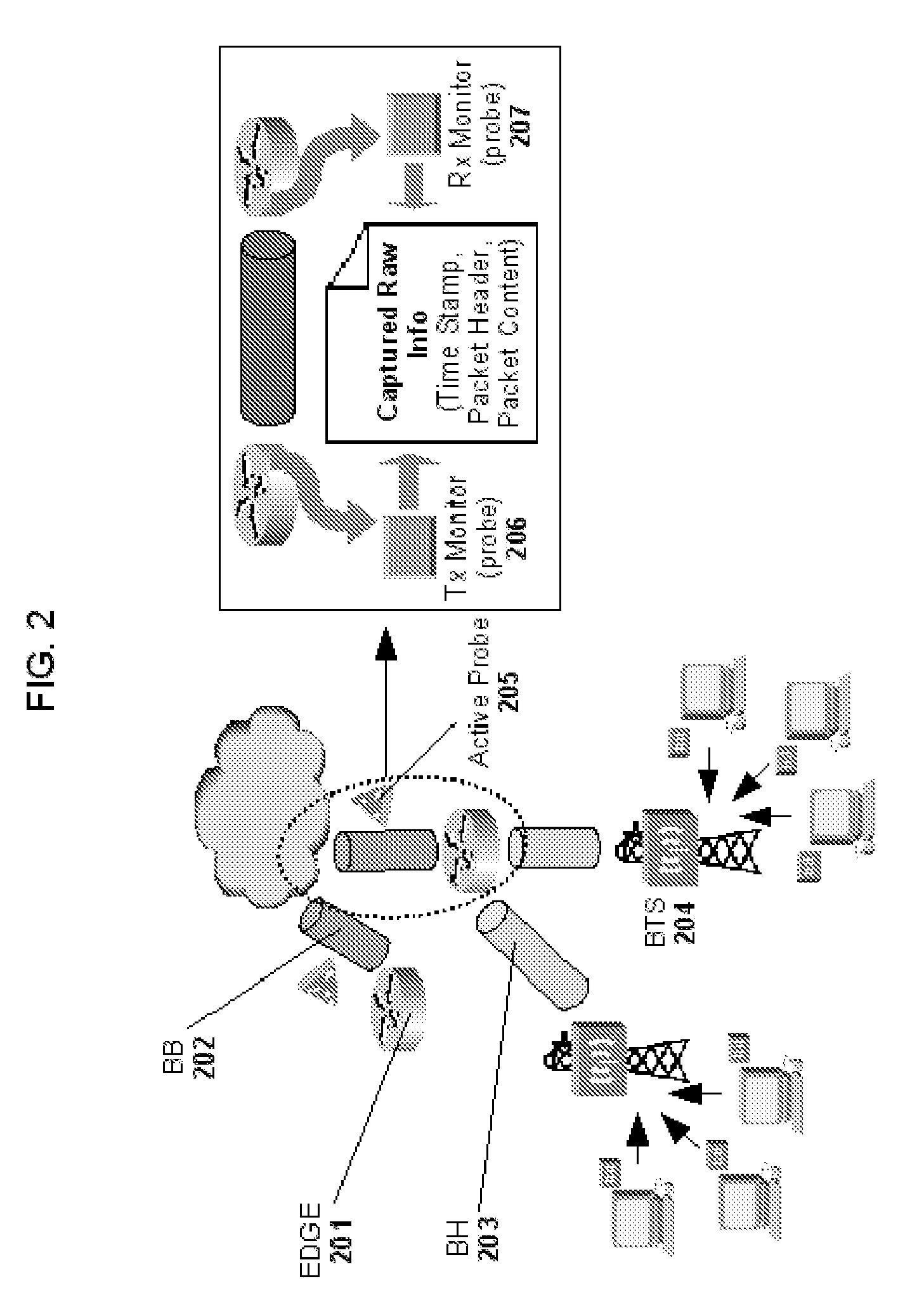
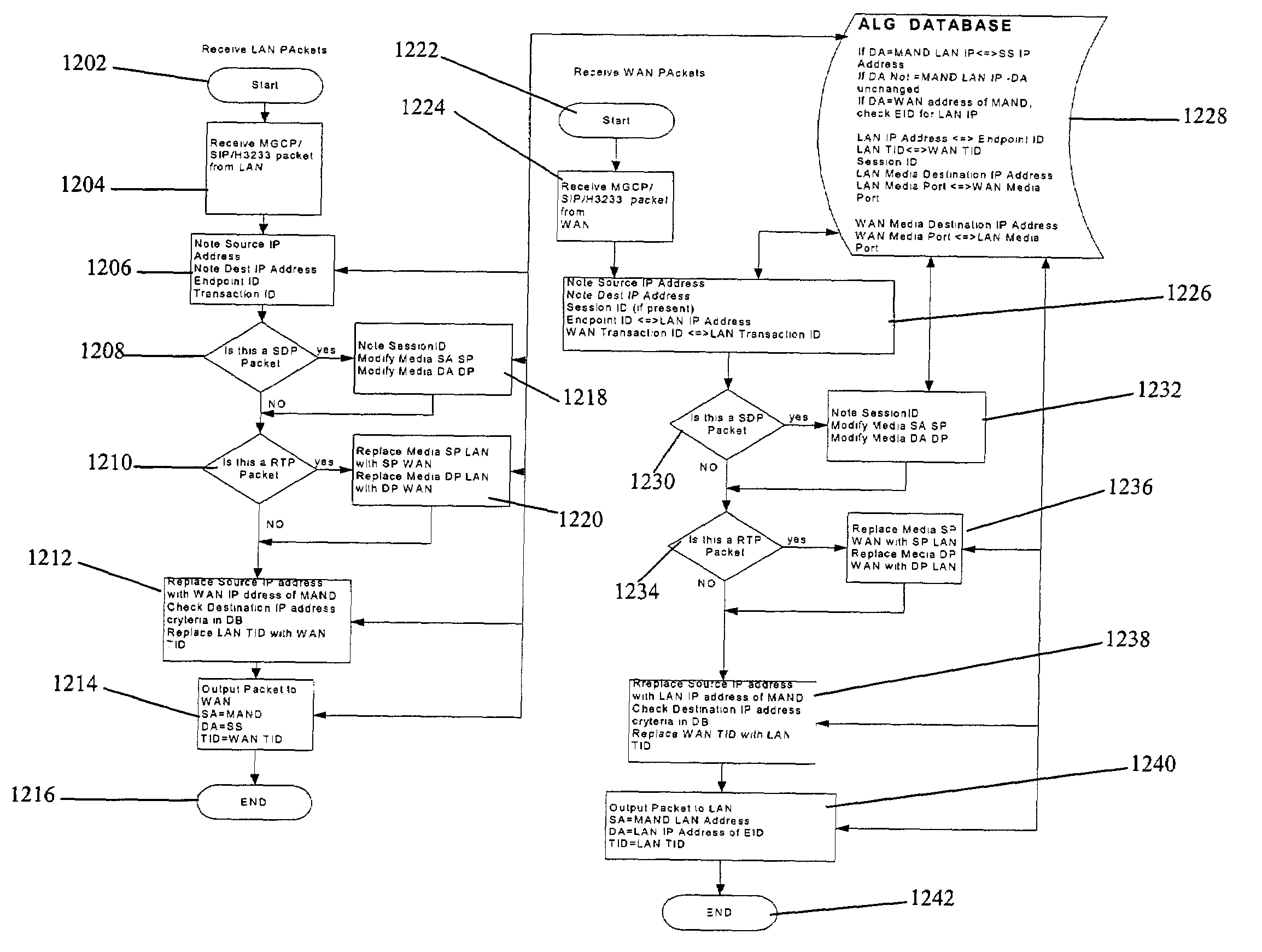
In a complete network-in-a-box system acting as an enterprise network demarcation point, packets such as voice, video and data packets, are routed over common network connections, such as LAN and WAN. The packets are mapped from a public address field (such as an IP address) and port number to a private address field and port number, the mapping process typically being handled by a NAT (Network Address Translation). The packets are also prioritized, by marking the packets for priority queuing and routing, and configuring the bandwidths of the WAN traffic and the voice traffic to predetermined quantities and configuring the address fields of the voice devices. Simultaneous transmission of the various packets can be limited to predetermined quantities, typically by utilizing a CAC (Client Access Control). Secure firewalls are also included as well as a performance test client application that provides a defined workload generated across the WAN interface for capacity planning measurements and allows remote monitoring of the QoS (Quality of Service) data, such as latency, jitter, lost packets and MOS scores. Optionally, a simple, common remote management interface is included, allowing service providers to configure, upgrade and manage the system. Additionally, address fields can be provided to voice, video or data devices attached to a LAN port. VPN authentication and encrypted sessions can be tunneled through the firewall for access to an internal network by using a VPN terminator. For power outages and other emergency purposes, additional ports that connect to PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) analog telephone lines as well as other analog telephones or devices, can be provided. Another advantageous element is that most of the above components or features may be enabled or disabled.
Owner:EDGEWATER NETWORKS
Methods And Systems For Providing Quality Of Service In Packet-Based Core Transport Networks
InactiveUS20080037552A1Effective carryFair sharingEnergy efficient ICTError preventionService-level agreementTraffic capacity
Methods and systems for providing necessary and sufficient quality-of-service (QoS), in a packet-based core transport network that utilizes dynamic setting of bandwidth management pipes or thresholds to obviate link congestion are disclosed. Congestion avoidance is a necessary and sufficient requirement in order to guarantee Quality of Service (QoS) in packet-based core networks.A typical network is composed of a plurality of backbone links connecting edge nodes where backhaul links are aggregated. The backhaul links connect the backbone links to the remote sites serving the subscribers. In order to enforce bandwidth management policies, Access Controllers, which perform traffic shaping, are situated on each remote site.In the event of a violation of certain link threshold settings, dynamic adjustment of the bandwidth management policies on affected Access Controllers is enforced. Various algorithms in determining the correlation between the link nearing congestion and the source or destination of traffic streams are also discussed. This invention implements a feedback control loop wherein probes at various points in the network checks for congestion states to guide bandwidth management threshold decisions in order to maintain the condition of non-congestion throughout the network. Capacity planning and congestion avoidance mechanisms work hand-in-hand to fulfill Service Level Agreements (SLA).
Owner:LATITUDE BROADBAND
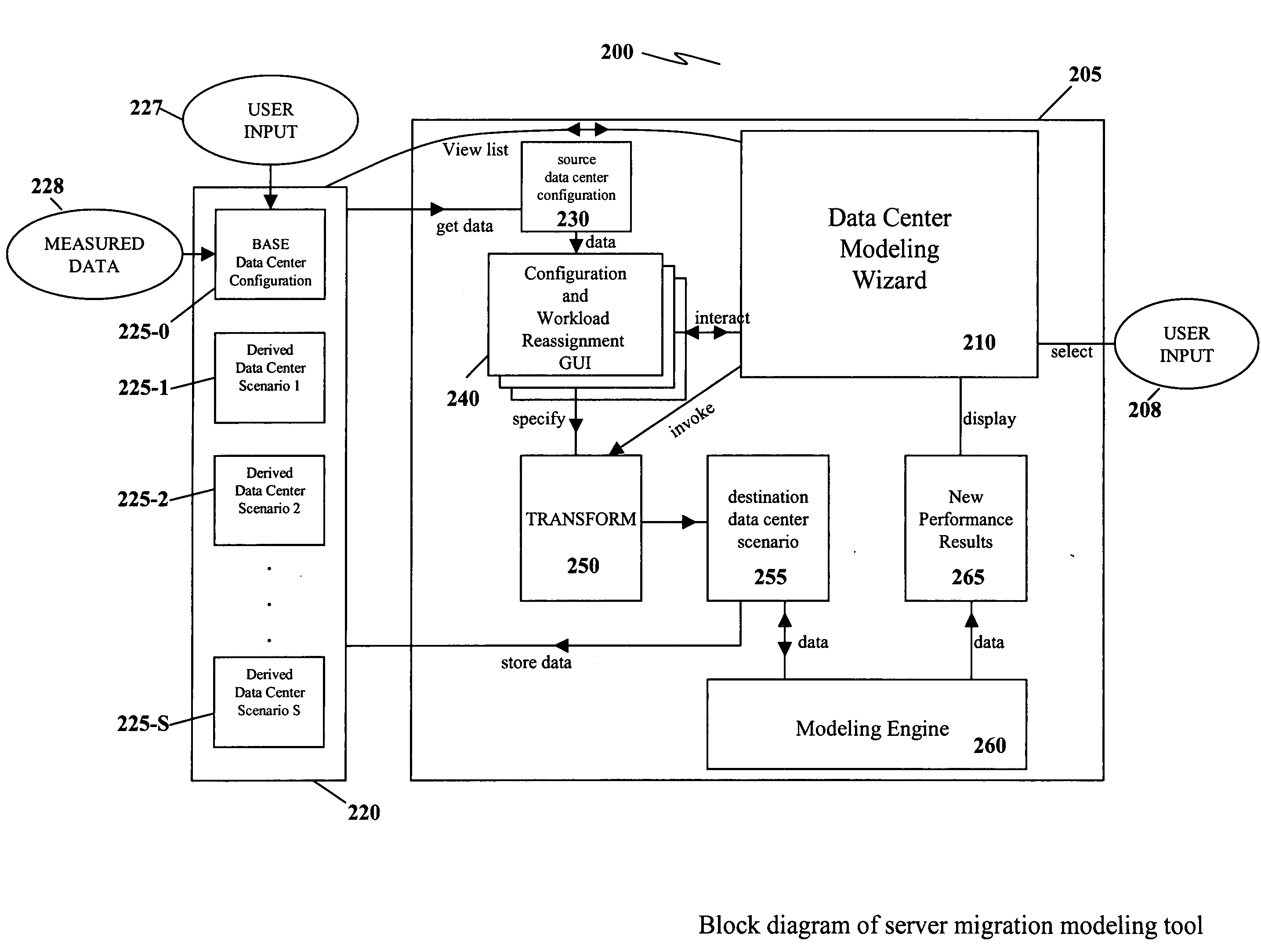
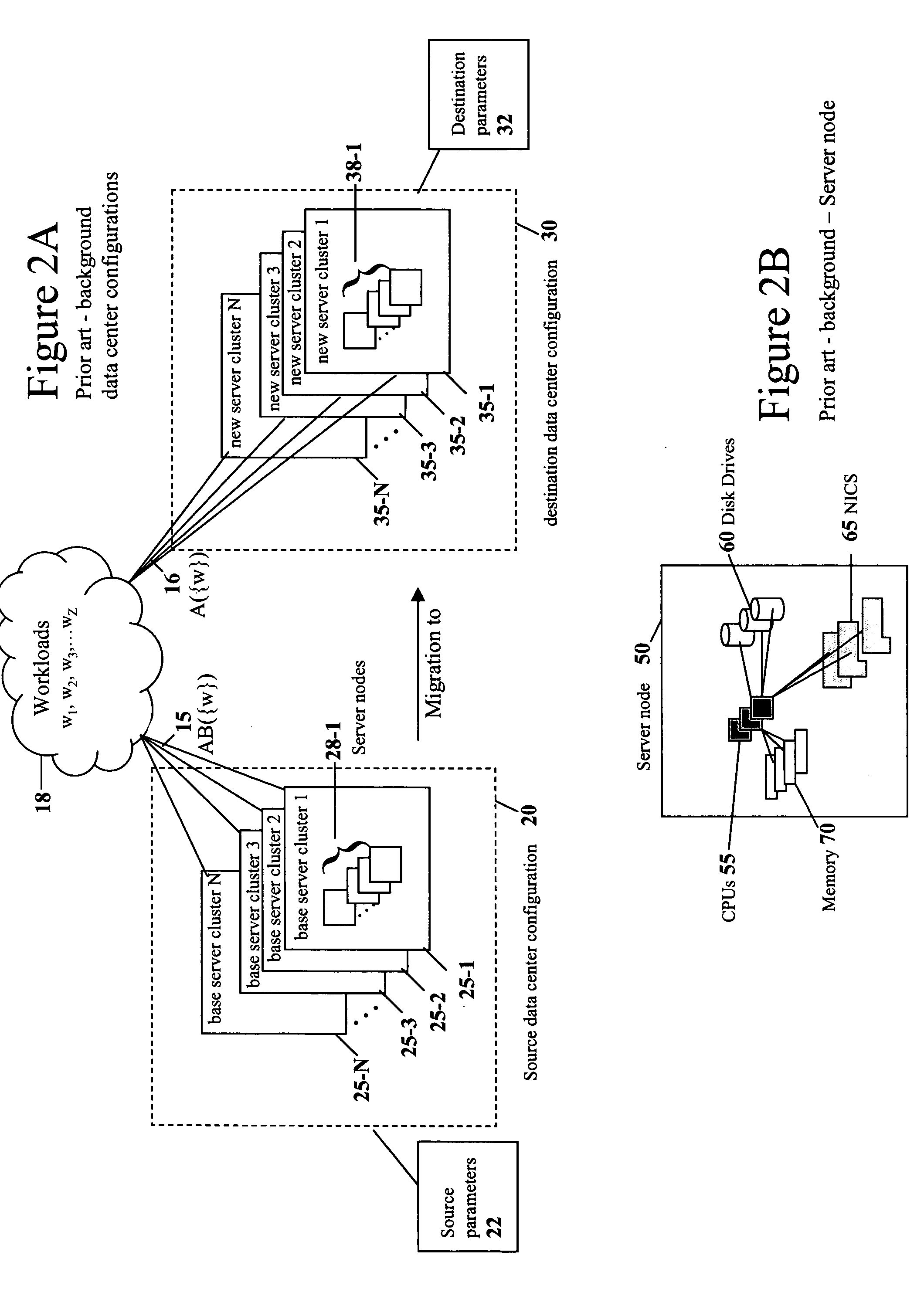
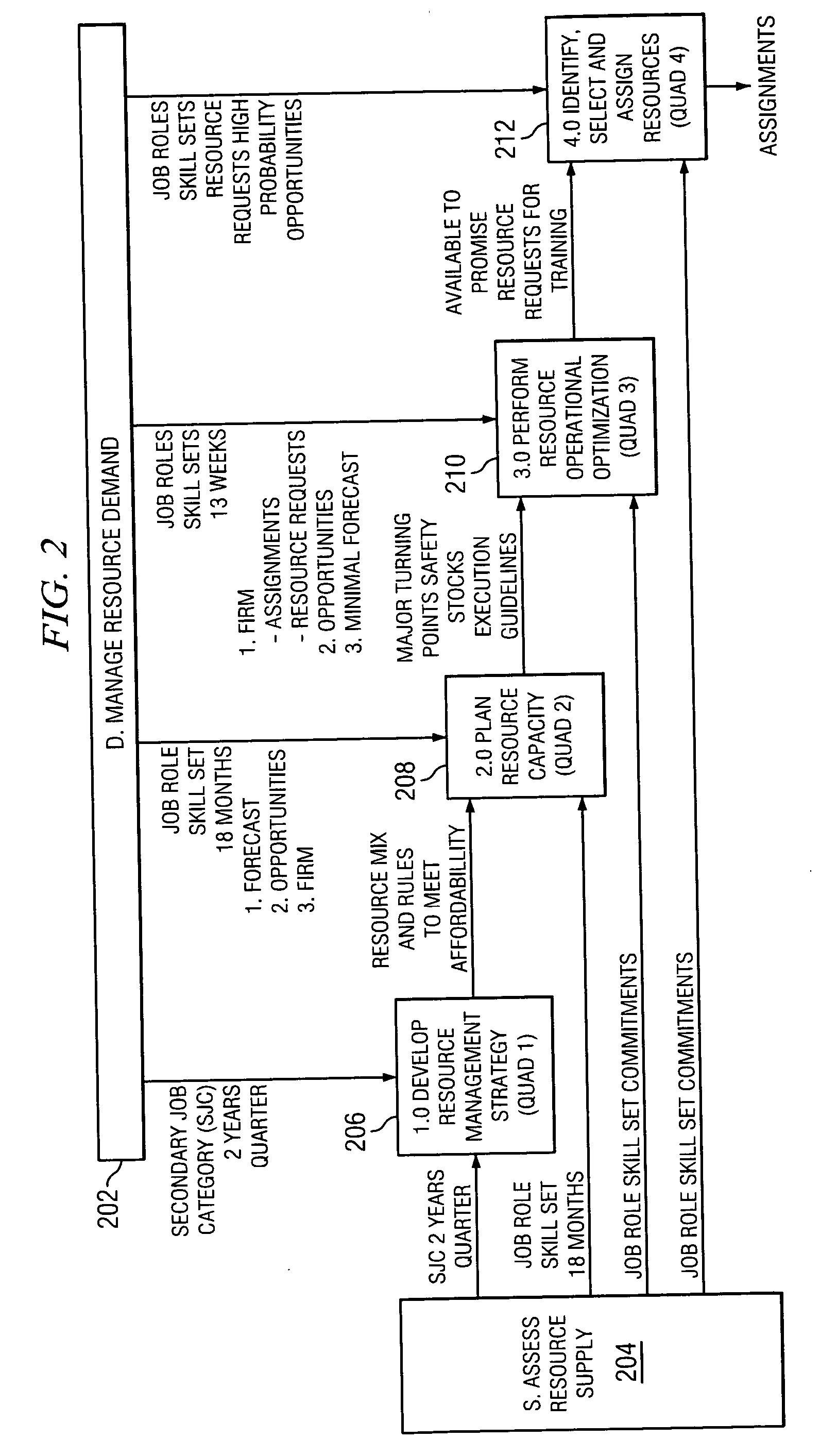
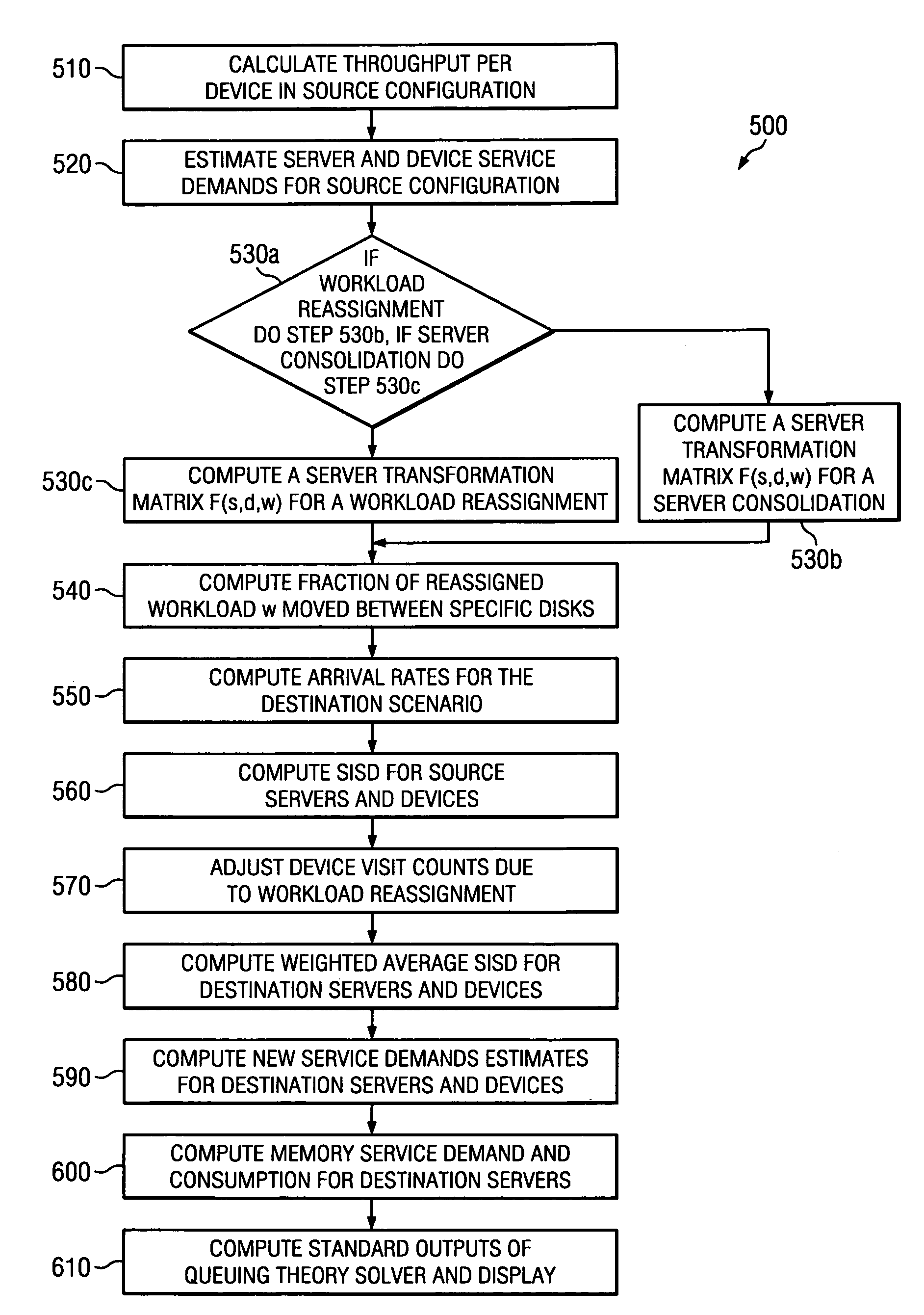
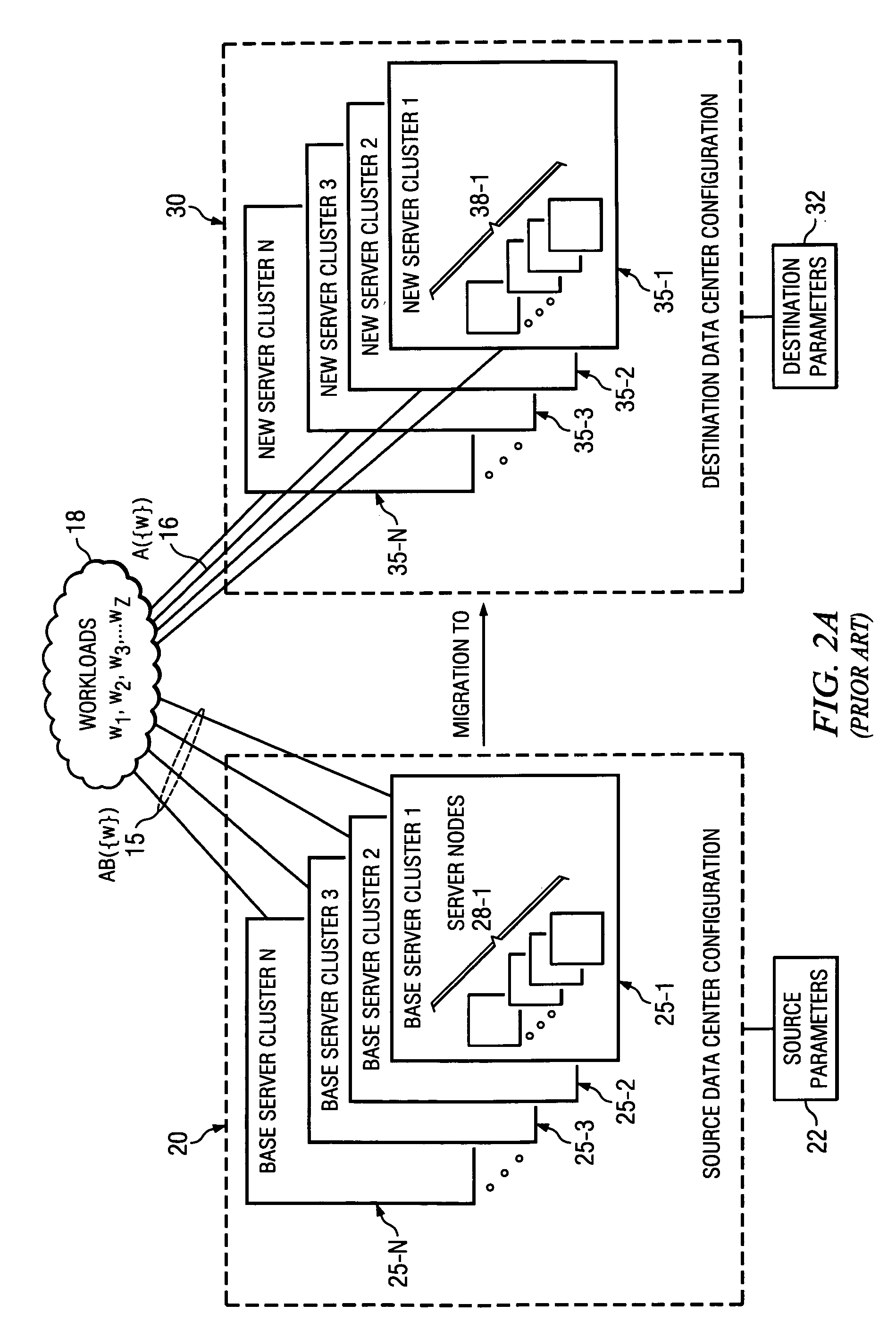
Apparatus and method for capacity planning for data center server consolidation and workload reassignment
InactiveUS20080077366A1Improve ease of useIncrease flexibilityAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDigital computer detailsCapacity planningWorkload
A server migration tool used to construct data center migration scenarios allowing for a user to rapidly manipulate a large number of input parameters required to describe a transformation from one data center configuration to a new data center configuration. The tool then performs the transformation and allows the user to interact with new data center configuration to understand its performance. A novel parameterization, speed independent service demand (SISD), greatly facilitates scaling performance metrics between different hardware platforms.
Owner:HYPERFORMIX
Capacity planning for server resources
InactiveUS6862623B1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsResource utilizationCapacity planning
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for evaluating a heterogeneous cluster for supporting expected workload in compliance with at least one service parameter
ActiveUS20050278453A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsHeterogeneous clusterWorkload
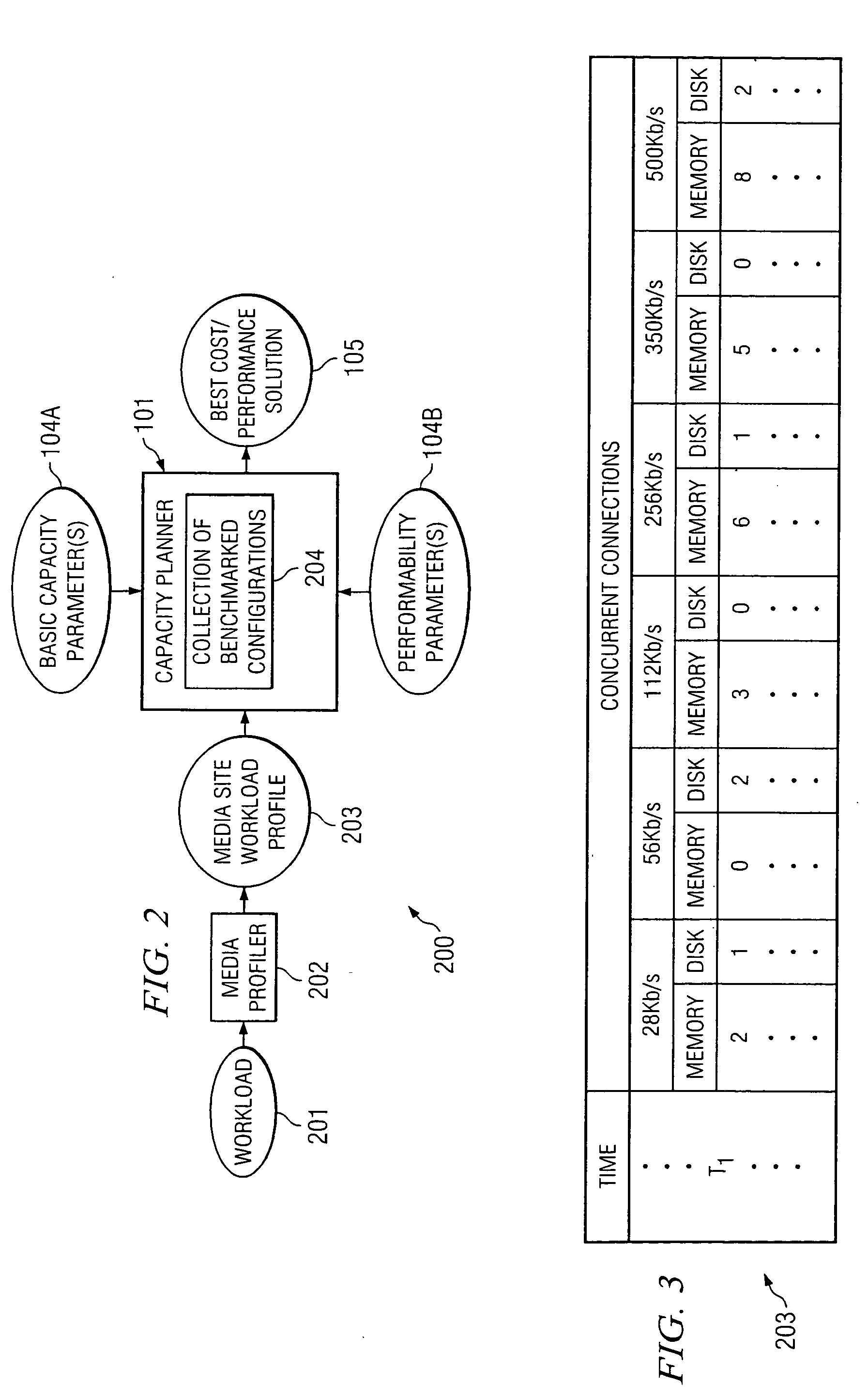
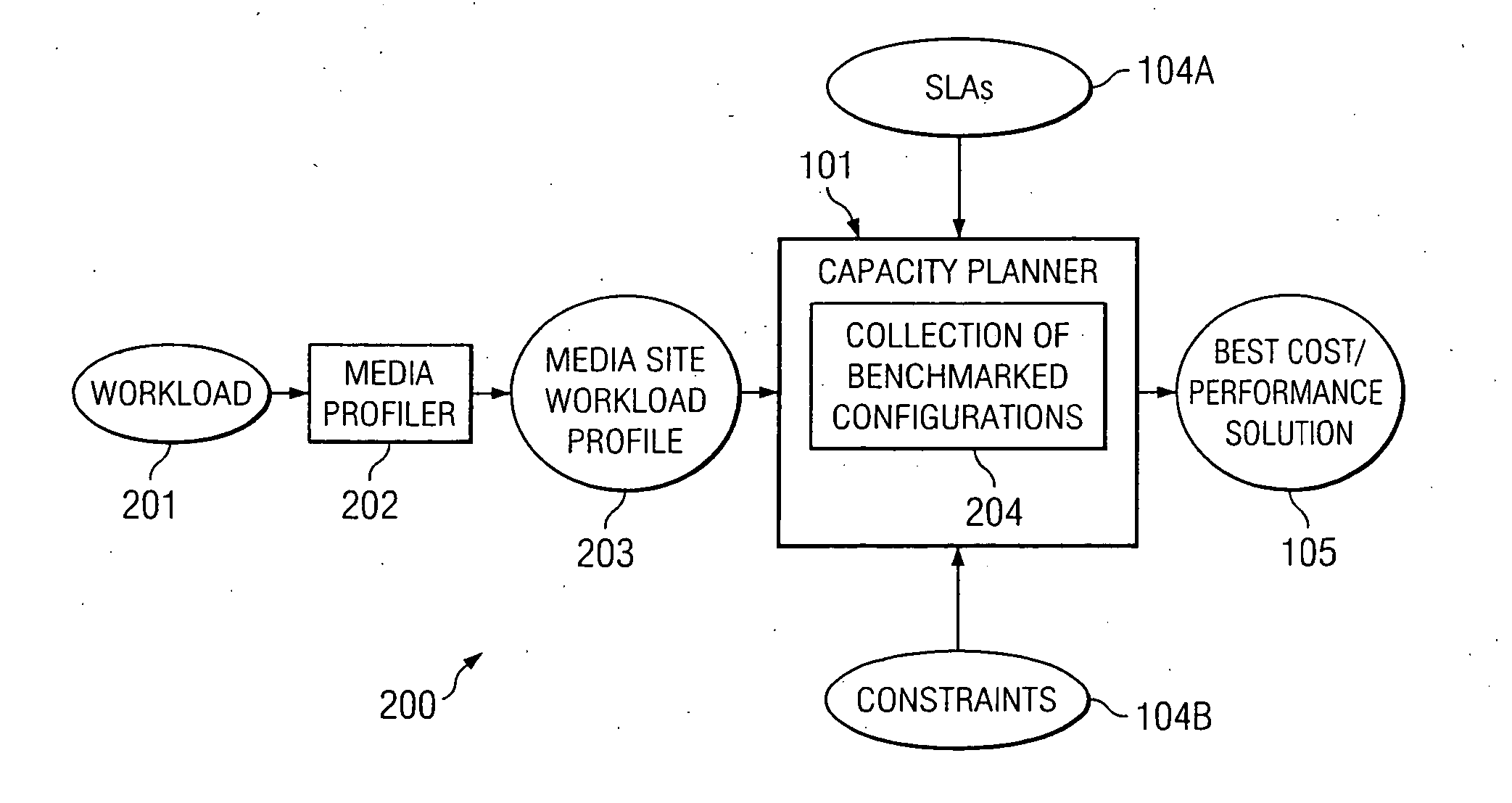
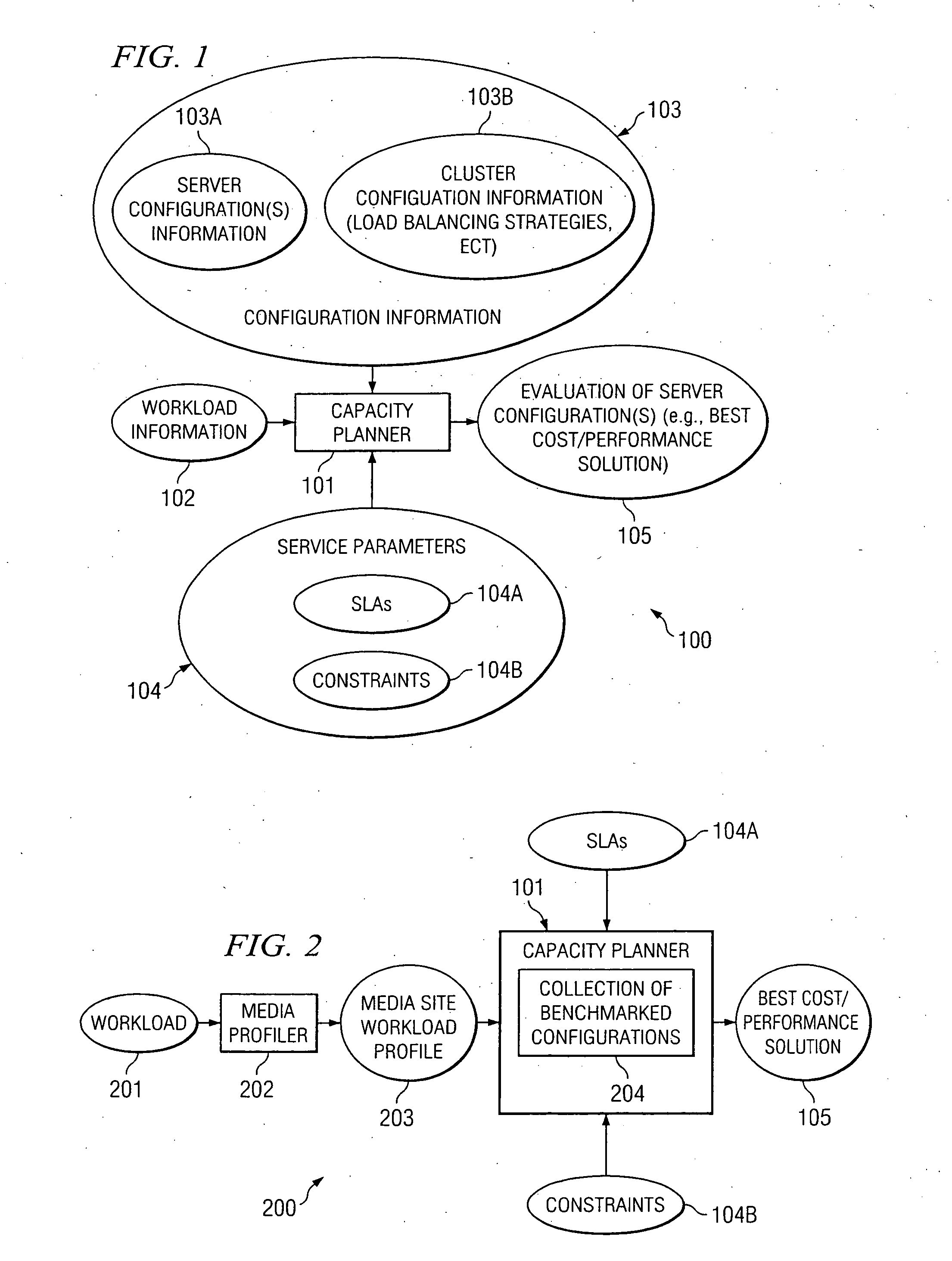
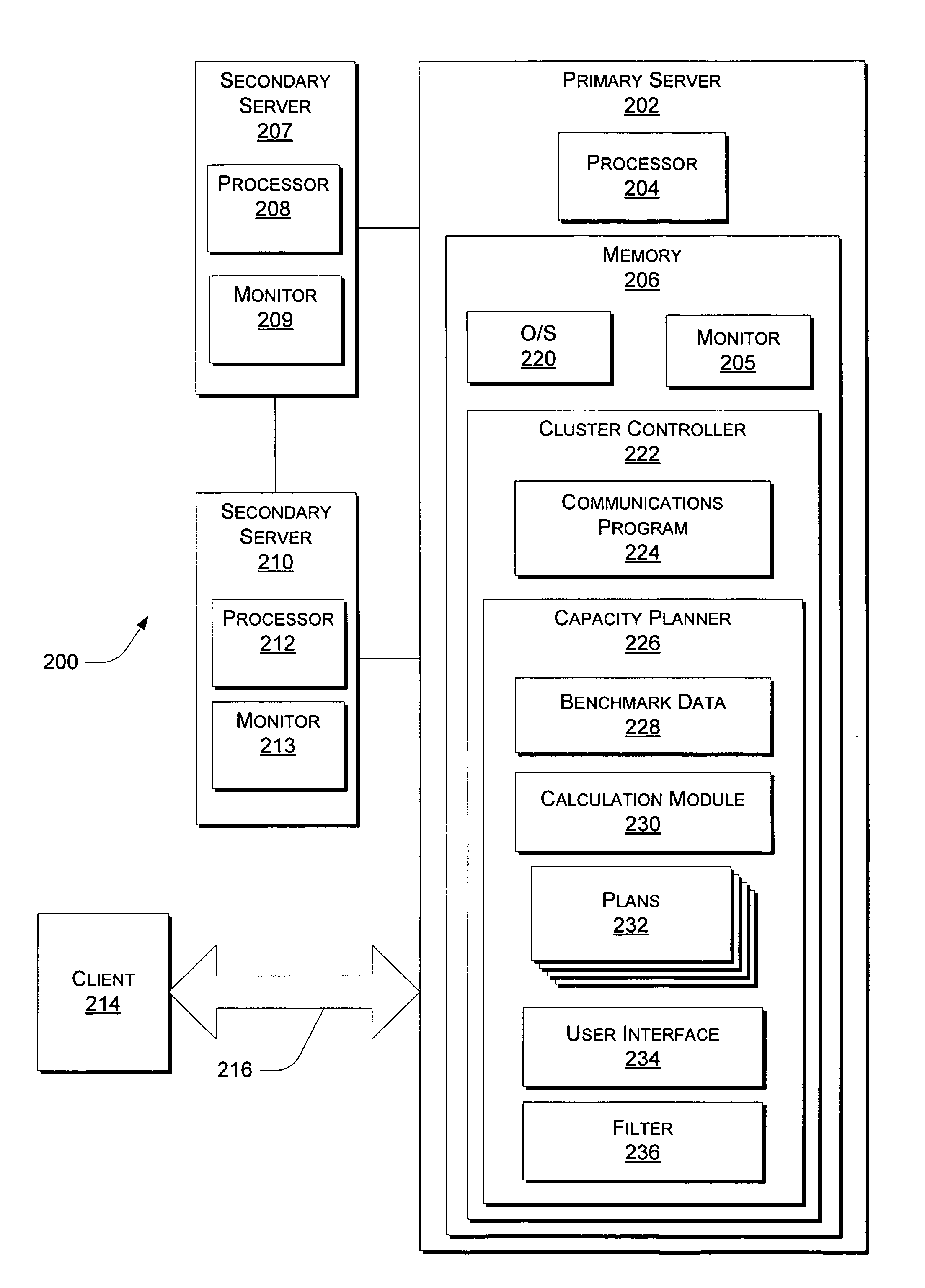
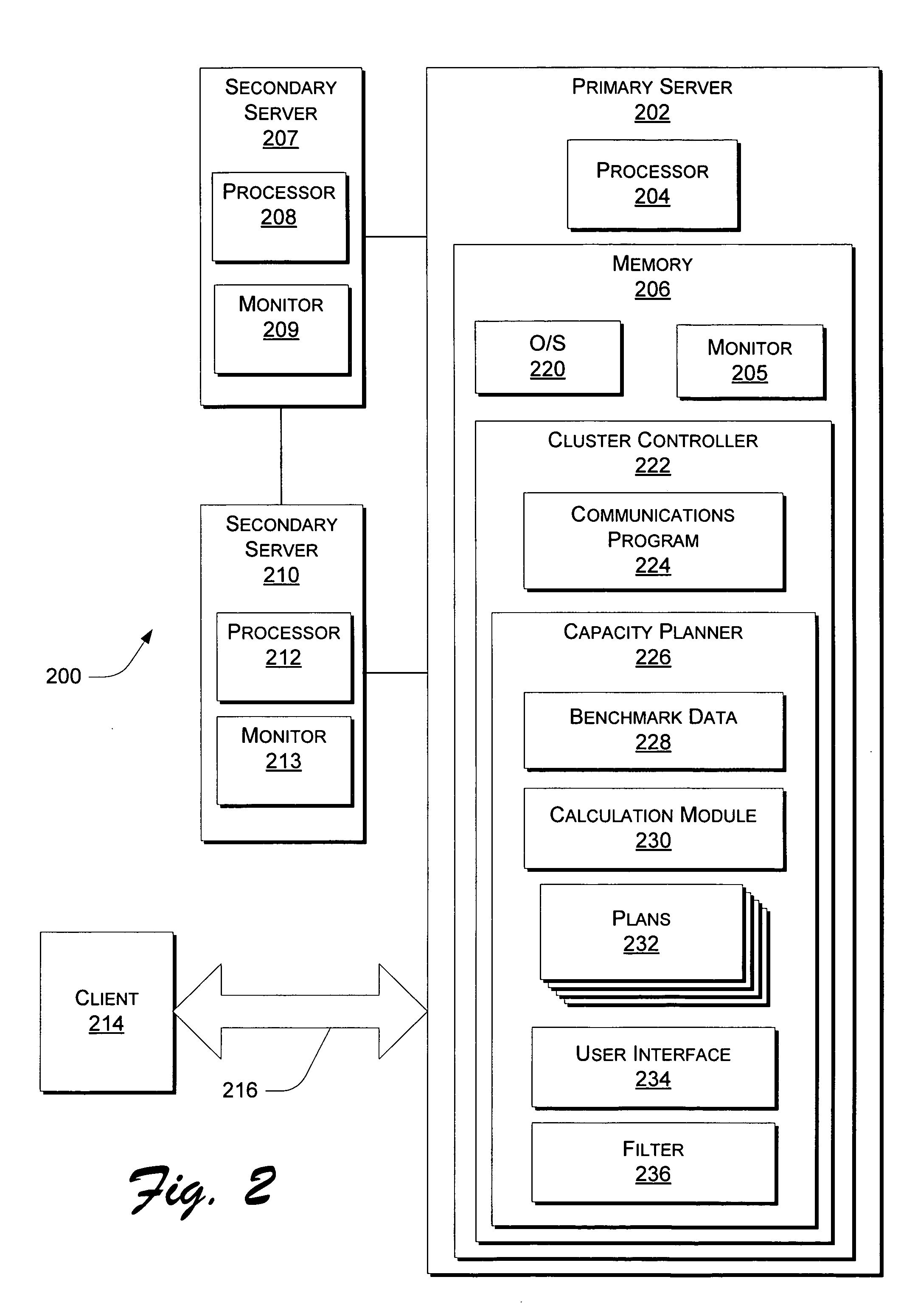
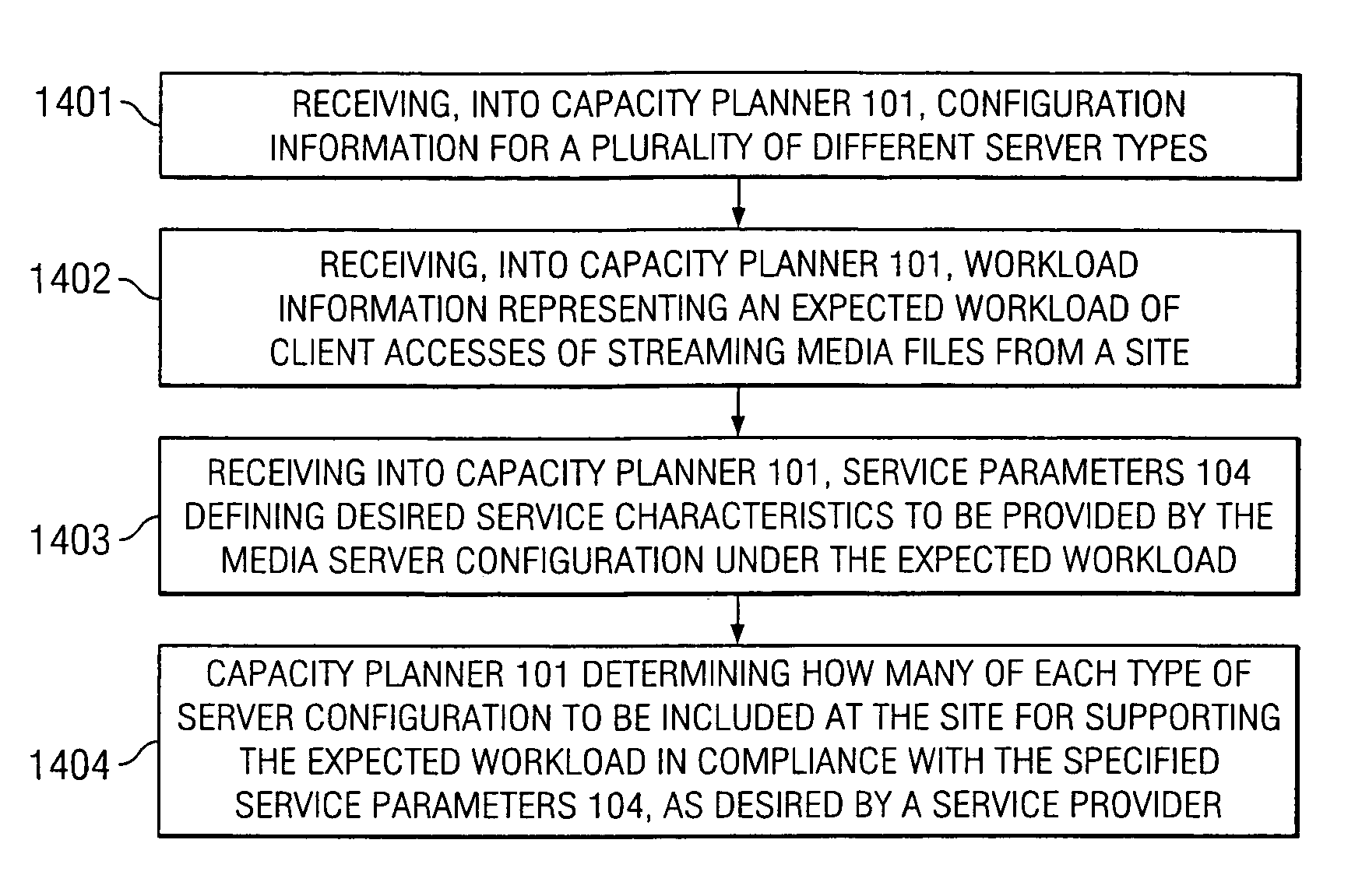
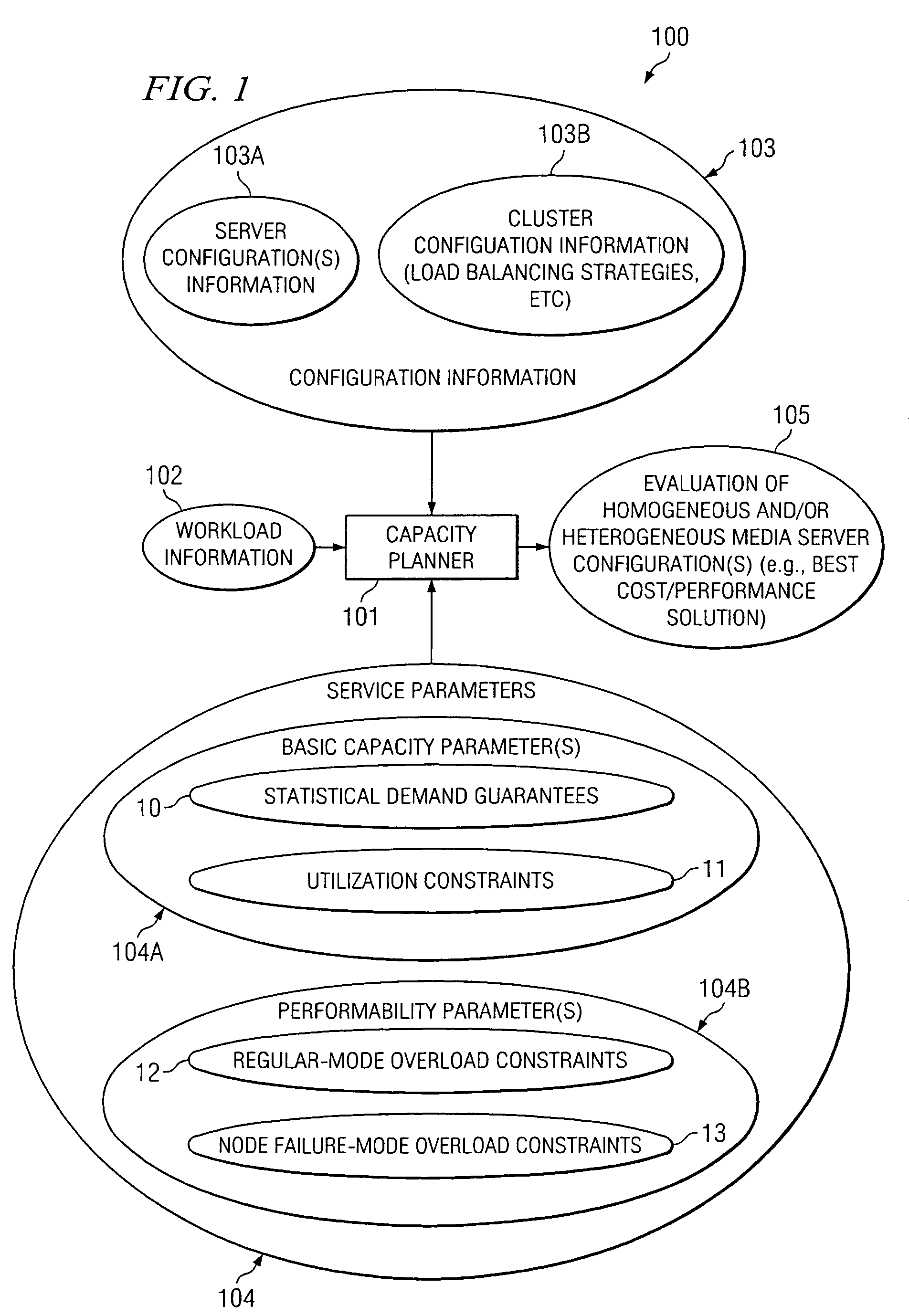
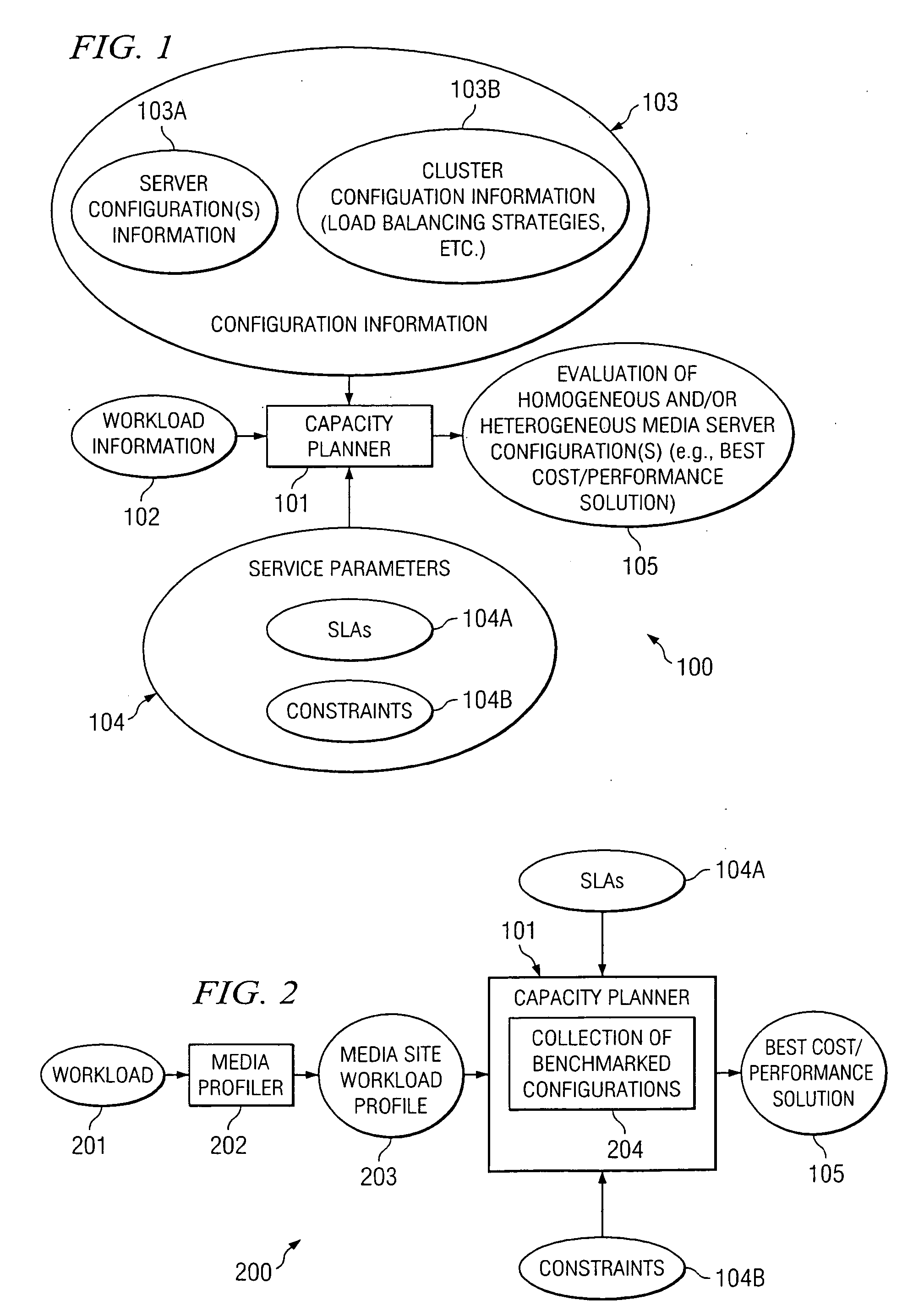
According to at least one embodiment, a method comprises receiving, into a capacity planning system, workload information representing an expected workload of client accesses of streaming media files from a site. The method further comprises receiving, into the capacity planning system, at least one service parameter that defines a desired service characteristic to be provided by a heterogeneous cluster of servers under the expected workload. The capacity planning system evaluates whether the heterogeneous cluster, having a plurality of different server configurations included therein, is capable of supporting the expected workload in compliance with the at least one service parameter.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Optimized capacity planning
InactiveUS20110202925A1Resource allocationError detection/correctionResource poolService-level agreement
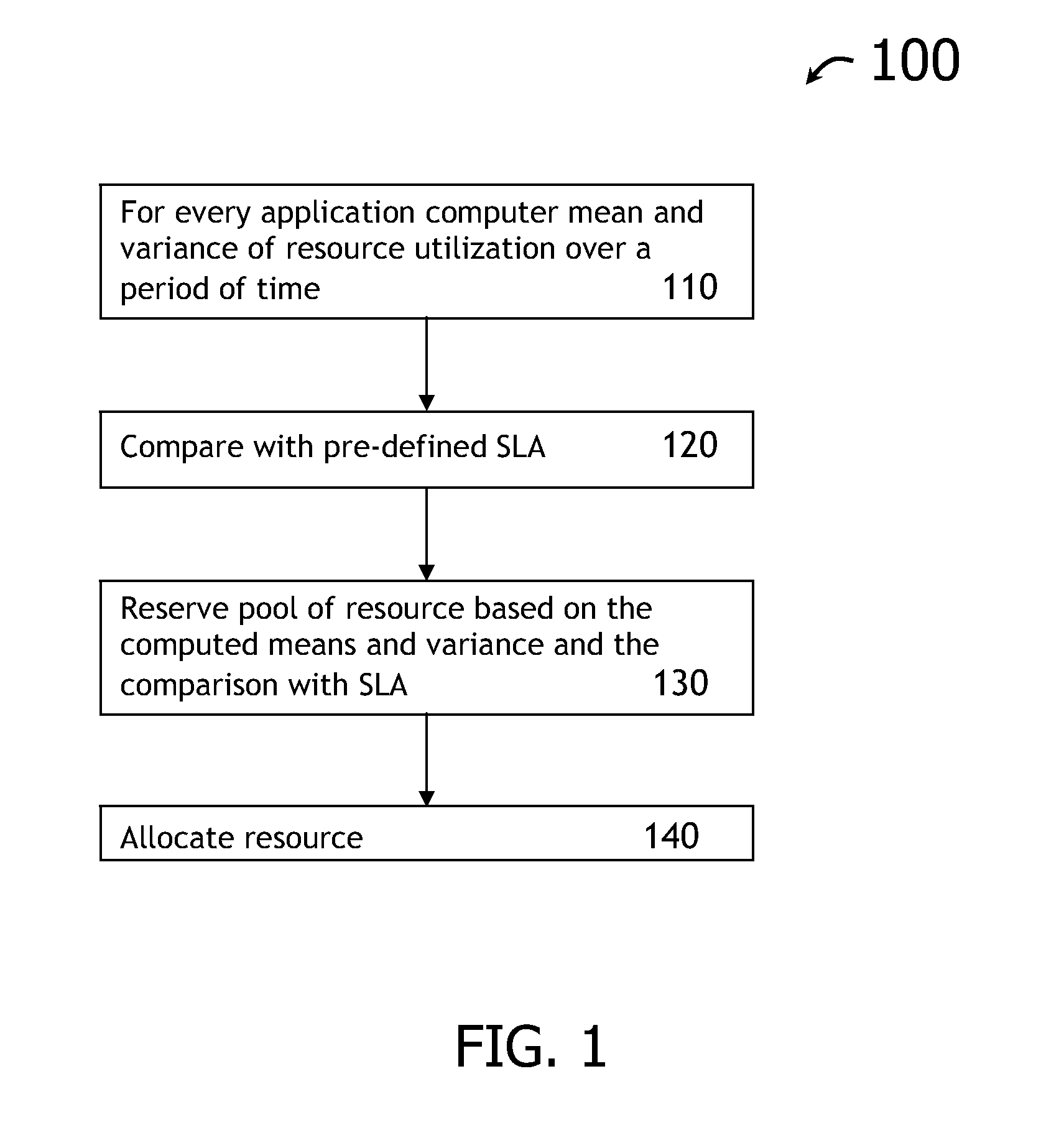
A computer implemented method, system and / or program product determine capacity planning of resources allocation for an application scheduled to execute on a virtual machine from a set of multiple applications by computing a mean associated with a pool of pre-defined resources utilization over a time interval; computing a variance associated with the pool of pre-defined resources utilization over the same time interval; identifying a set of resource to execute the scheduled application from the pool of pre-defined resources, wherein the pool of pre-defined resources is created from a pre-defined Service Level Agreement (SLA); and allocating a set of fixed resources from the pool of pre-defined resources to execute the application based on the mean resource utilization.
Owner:IBM CORP
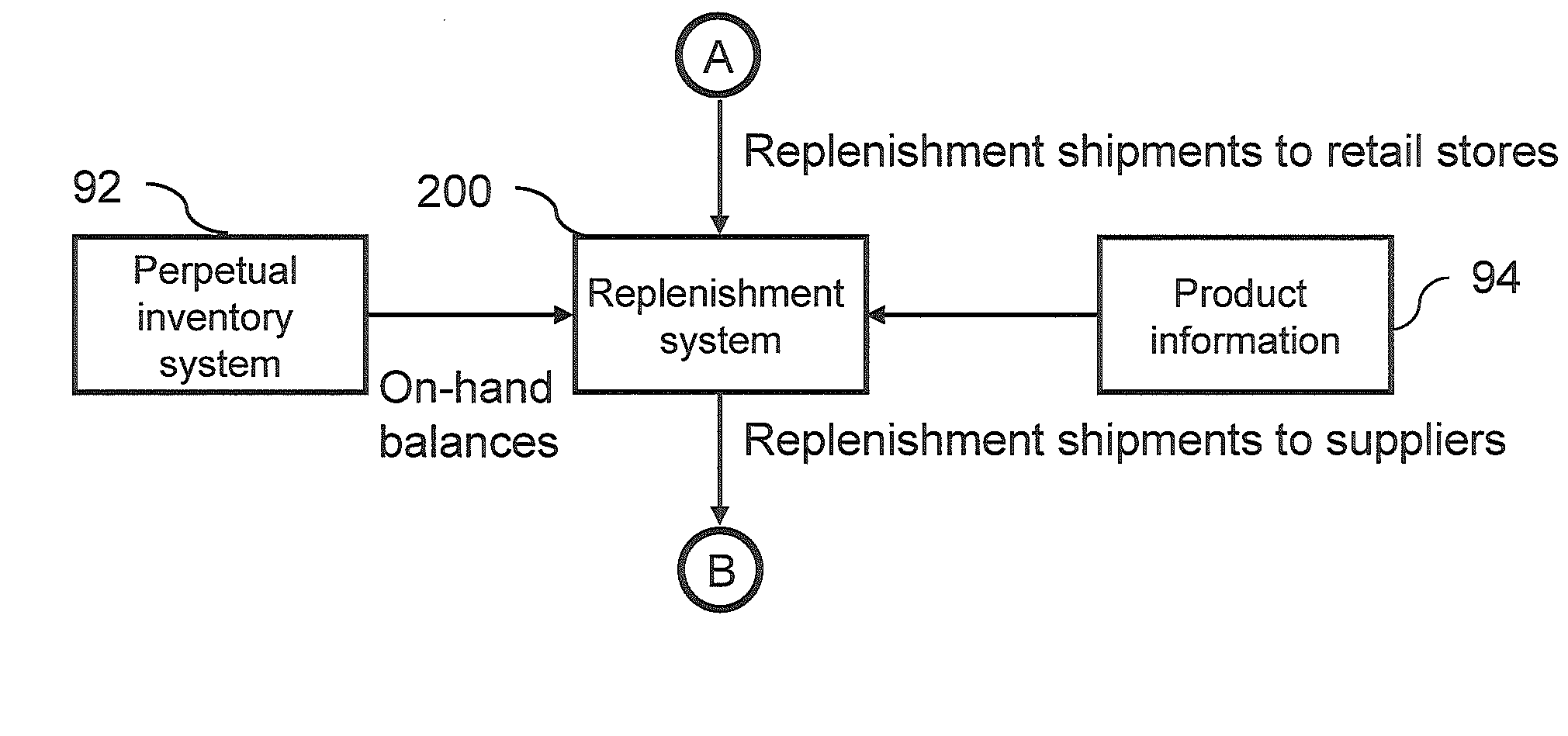
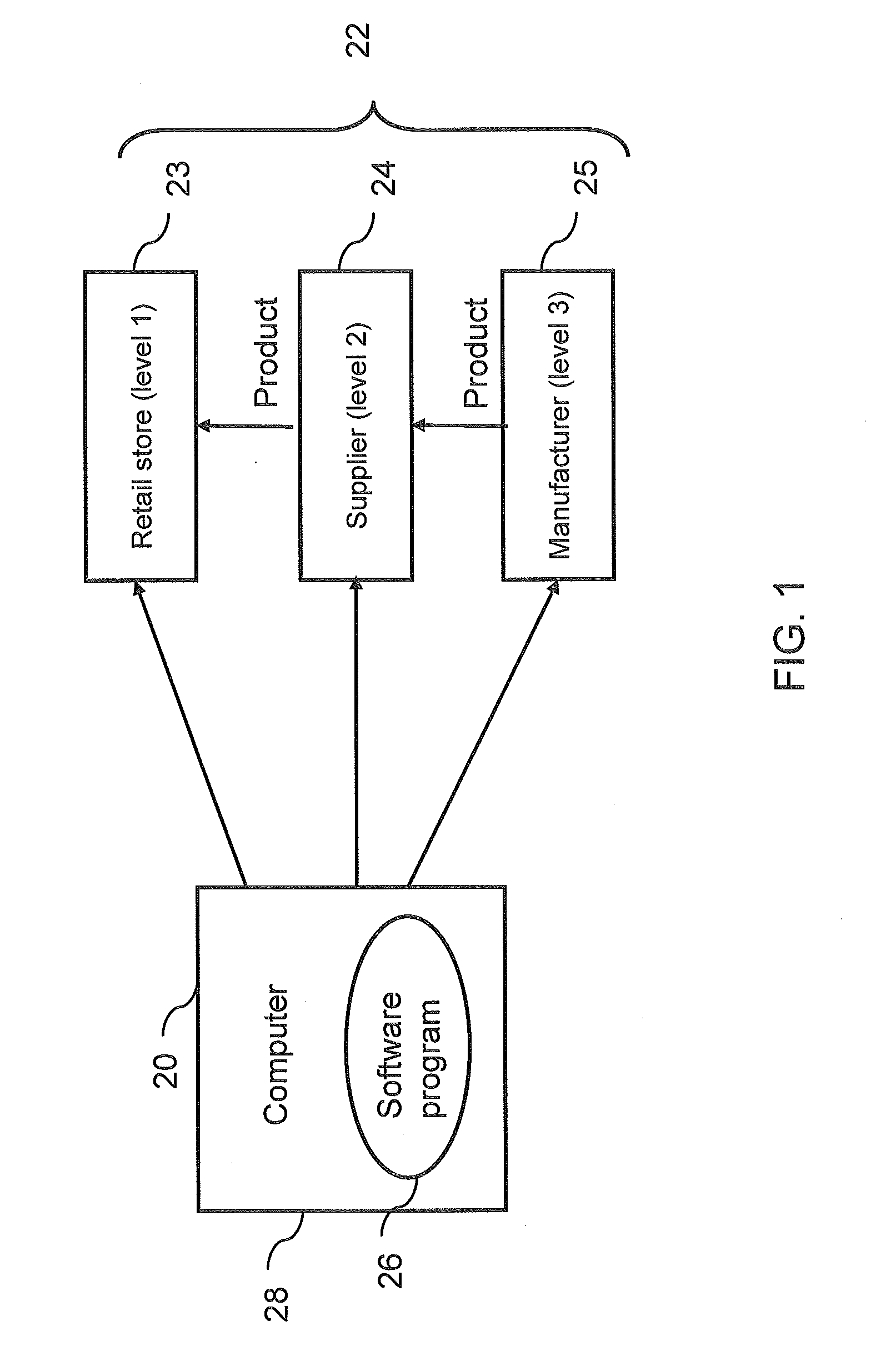
Method and system for retail store supply chain sales forecasting and replenishment shipment determination
ActiveUS7552066B1Lower the volumeCommerceSpecial data processing applicationsSystems designTransportation planning
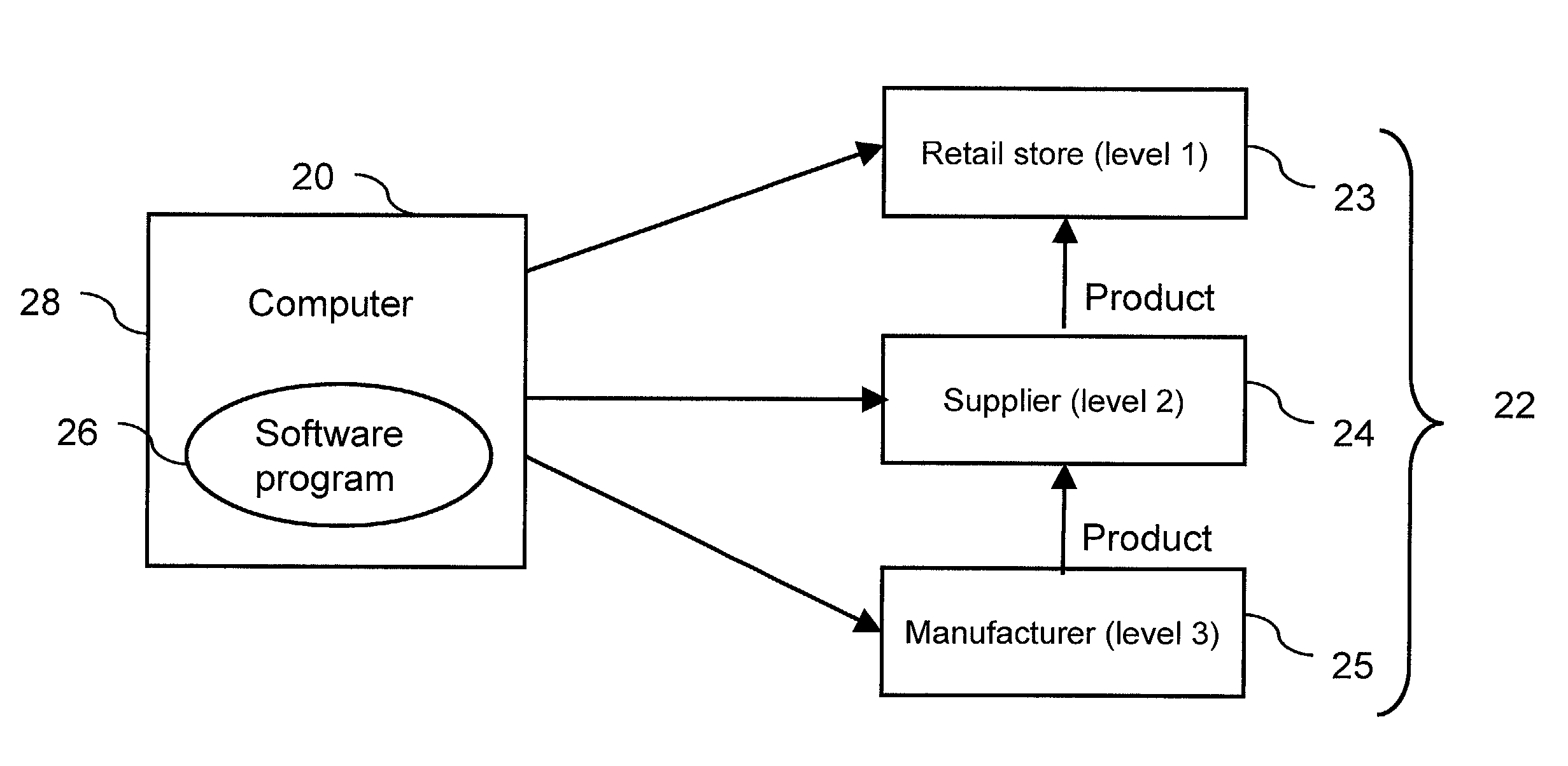
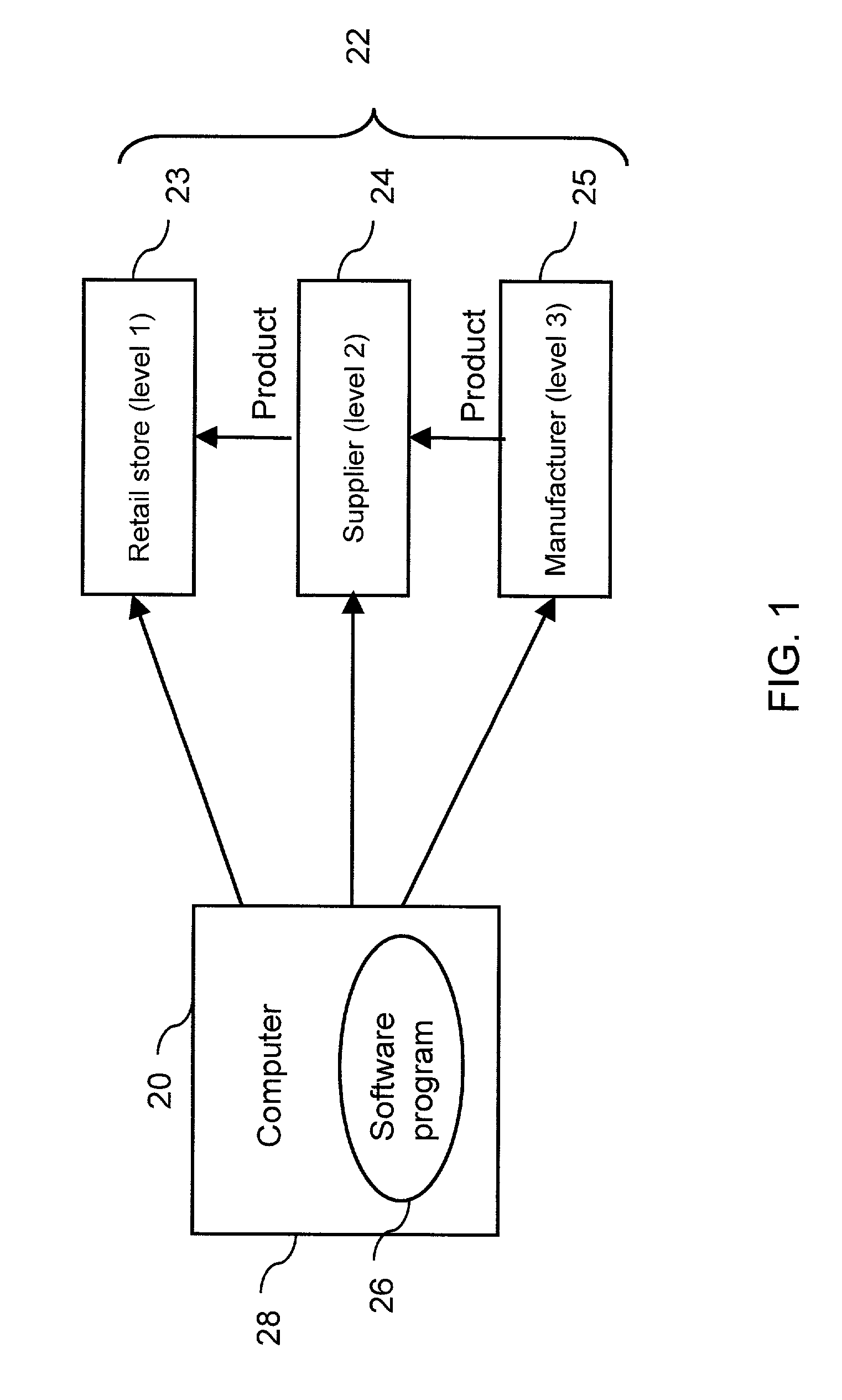
A time-phased forecasting and replenishment system (20) for a retail supply chain for inventory management, financial management, capacity planning and transportation planning. A computer(s) (28) create time-phased plans for one or more retail facilities, such as various types of retail stores (23) and / or various types of suppliers (24). The system calculates projected sales for each product at each facility and calculates projected replenishment shipments between facilities and suppliers a specified number of weeks into the future. The calculated forecasts and replenishments are done in ways that account for the unique needs of retail organizations, and allow efficient processing and storage of the large data volumes typical in many retail organizations. In particular the system has specified logic for handling low-volume products, and has a transportation and capacity planning component that benefits retail stores. Also, the system is designed to operate on a continuous basis if desired.
Owner:BLUE YONDER GRP INC
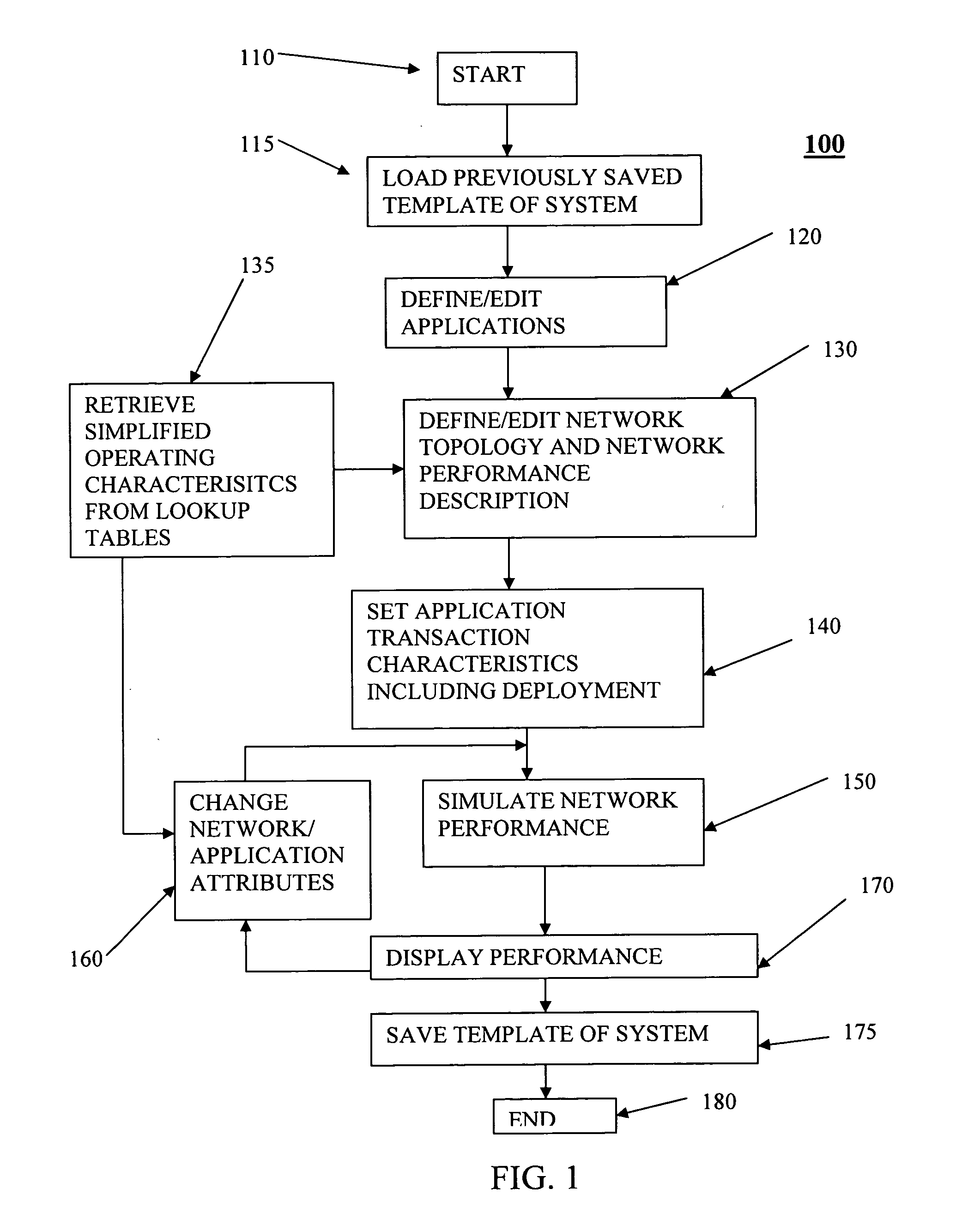
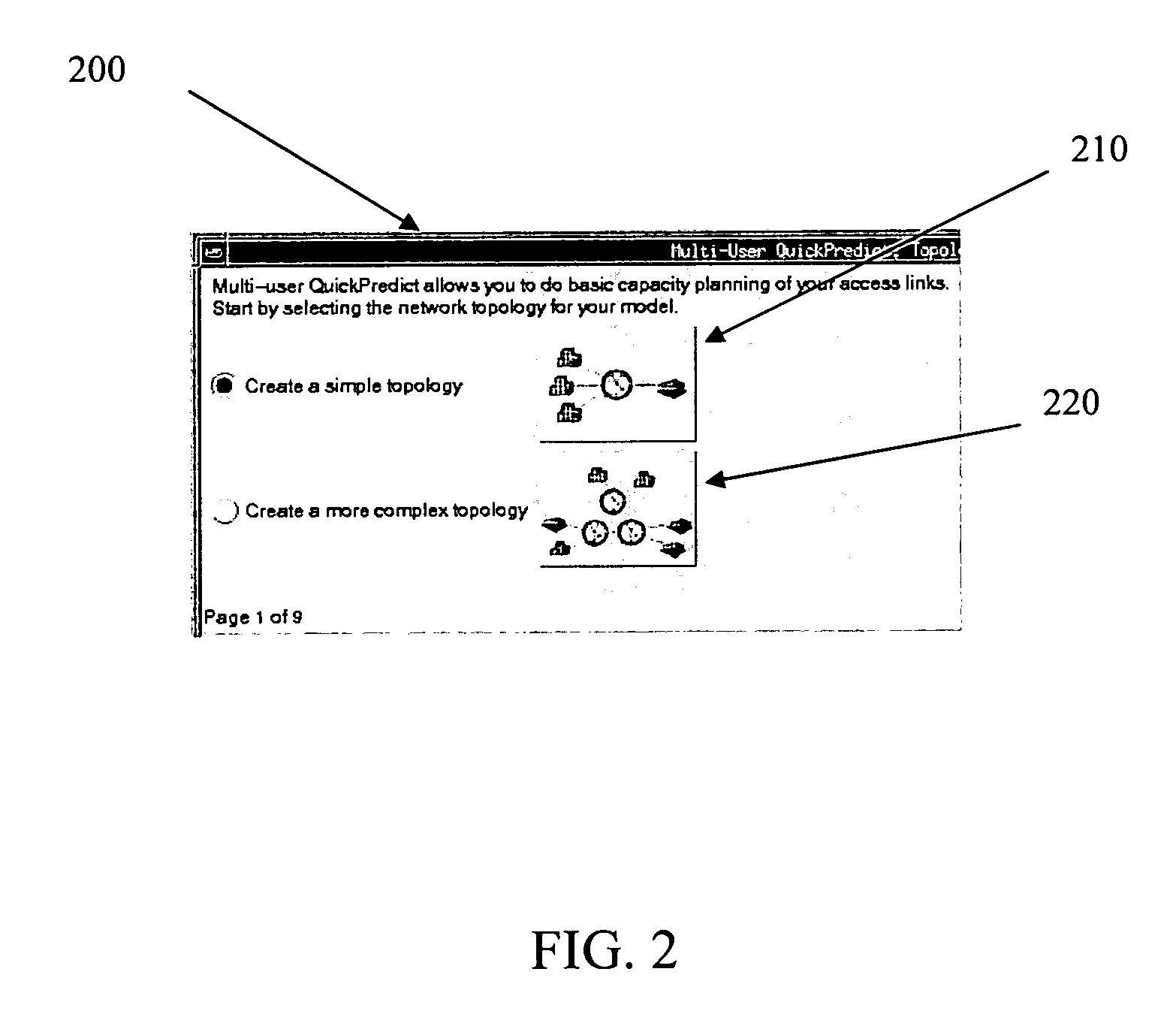
Network capacity planning
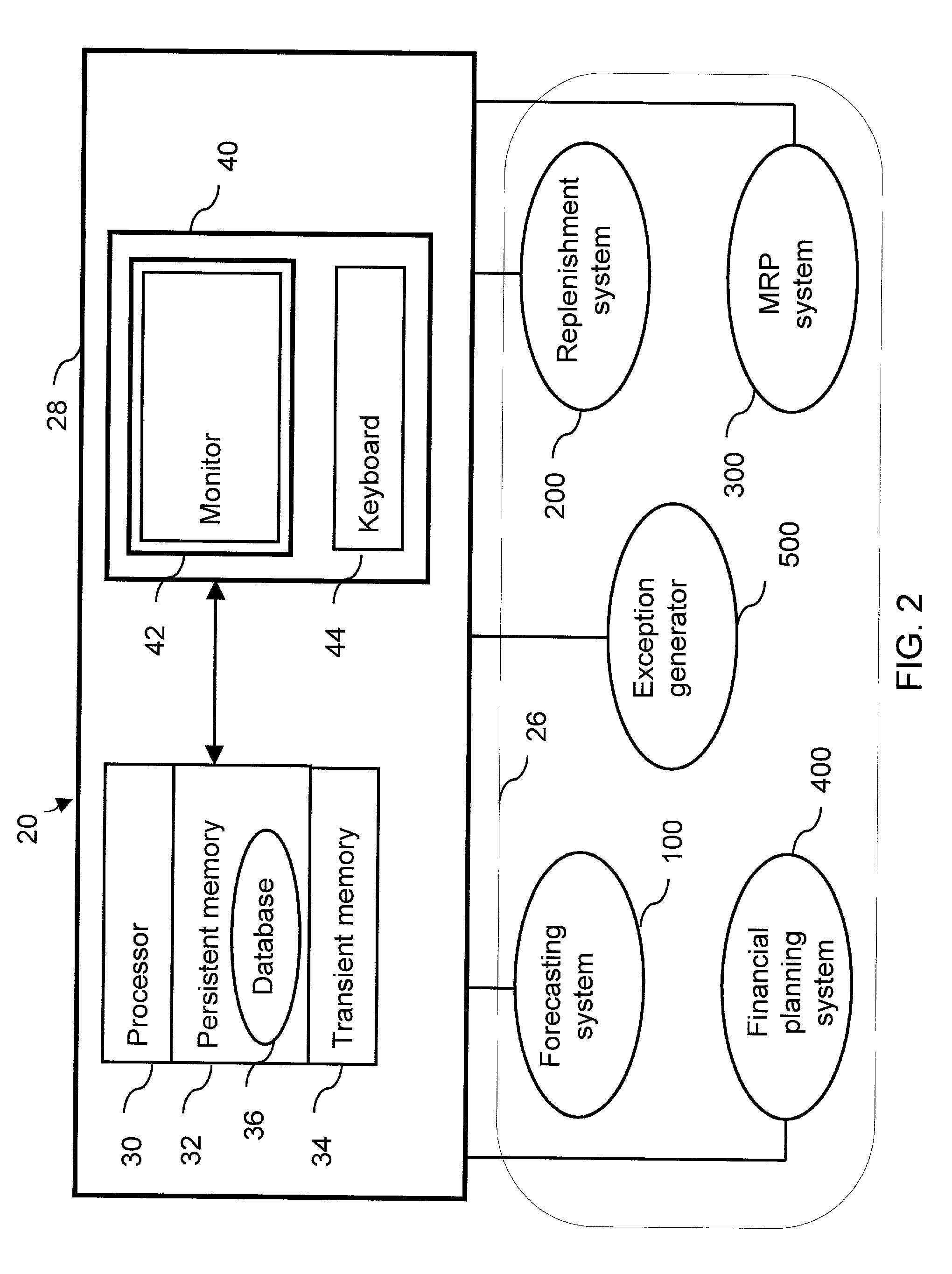
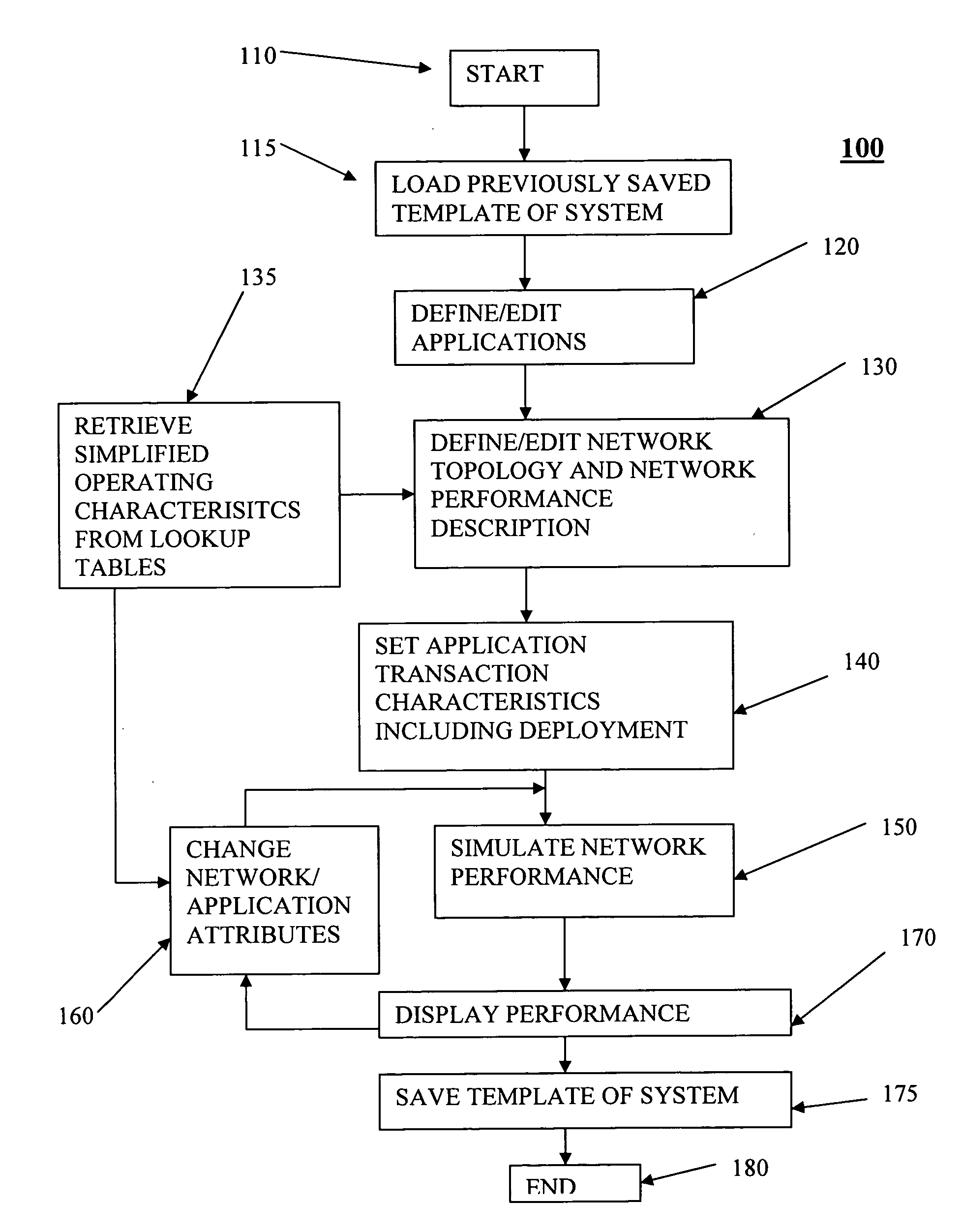
Data representing application deployment attributes, network topology, and network performance attributes based on a reduced set of element attributes is utilized to simulate application deployment. The data may be received from a user directly, a program that models a network topology or application behavior, and a wizard that implies the data based on an interview process. The simulation may be based on application deployment attributes including application traffic pattern, application message sizes, network topology, and network performance attributes. The element attributes may be determined from a lookup table of element operating characteristics that may contain element maximum and minimum boundary operating values utilized to interpolate other operating conditions. Application response time may be derived using an iterative analysis based on multiple instances of one or more applications wherein a predetermined number of iterations is used or until a substantially steady state of network performance is achieved.
Owner:OPNET TECH LLC
Method and System For Retail Store Supply Chain Sales Forecasting and Replenishment Shipment Determination
A time-phased forecasting and replenishment system (20) for a retail supply chain for inventory management, financial management, capacity planning and transportation planning. A computer(s) (28) create time-phased plans for one or more retail facilities, such as various types of retail stores (23) and / or various types of suppliers (24). The system calculates projected sales for each product at each facility and calculates projected replenishment shipments between facilities and suppliers a specified number of weeks into the future. The calculated forecasts and replenishments are done in ways that account for the unique needs of retail organizations, and allow efficient processing and storage of the large data volumes typical in many retail organizations. In particular the system has specified logic for handling low-volume products, and has a transportation and capacity planning component that benefits retail stores. Also, the system is designed to operate on a continuous basis if desired.
Owner:JDA SOFTWARE GROUP
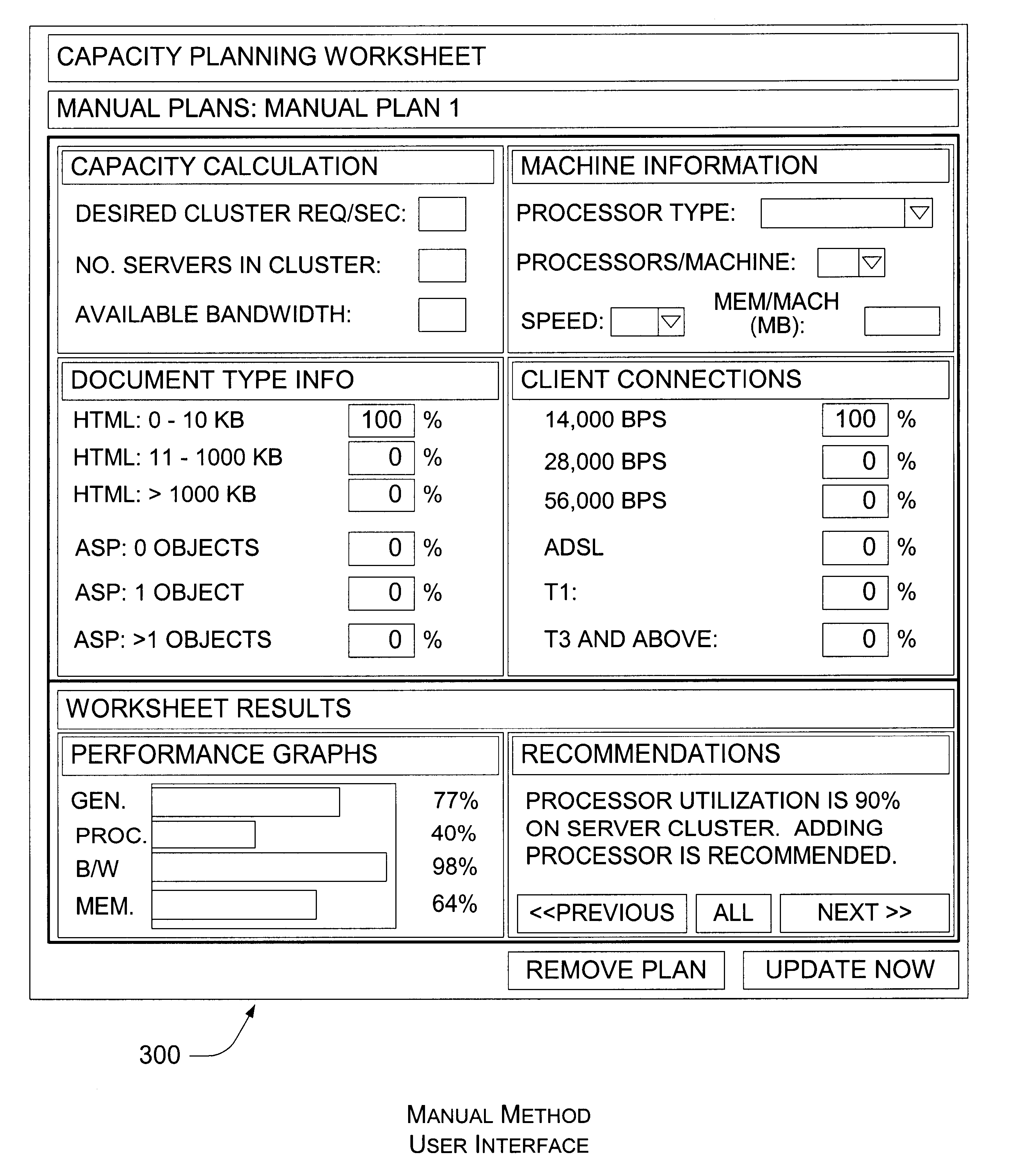
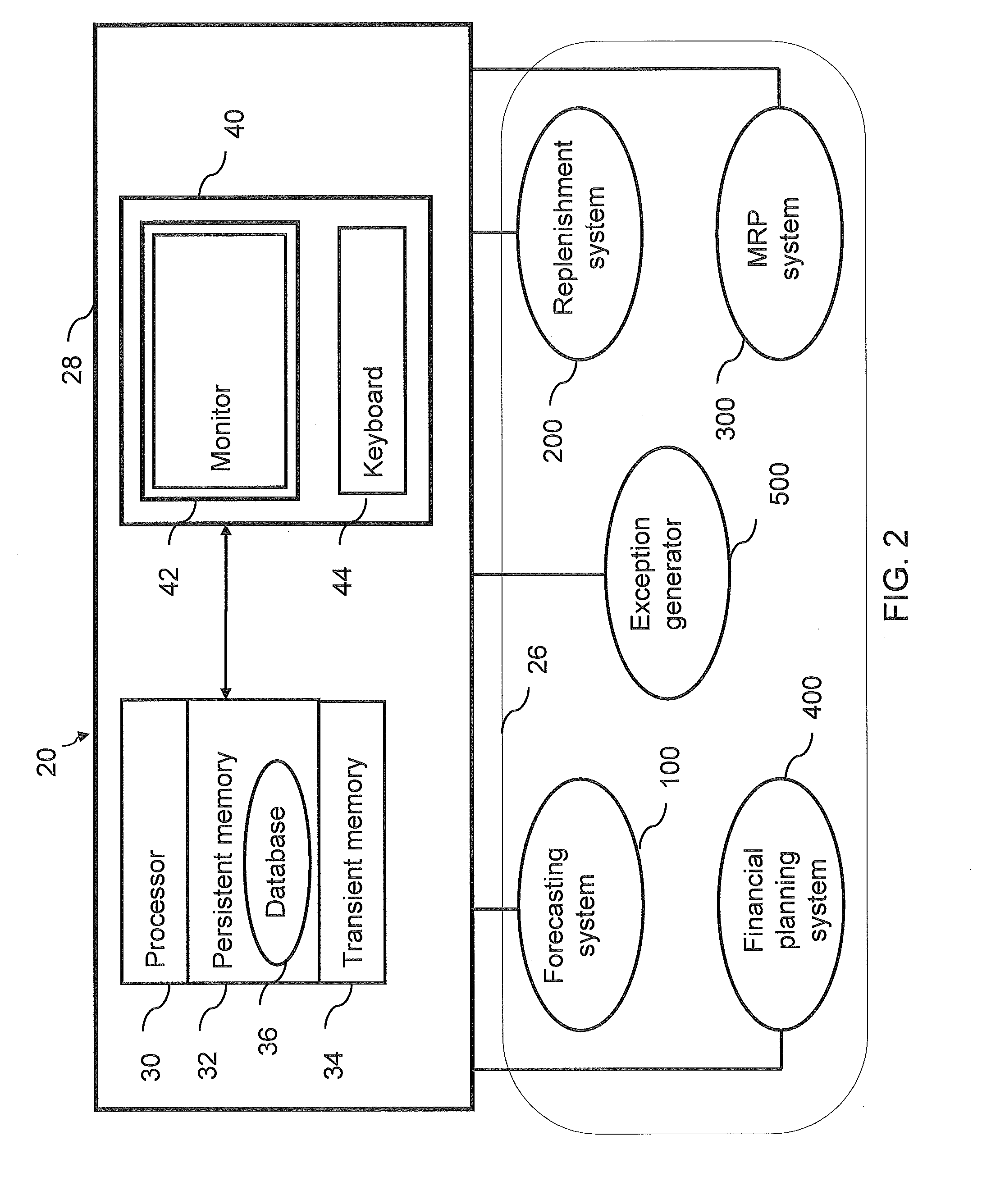
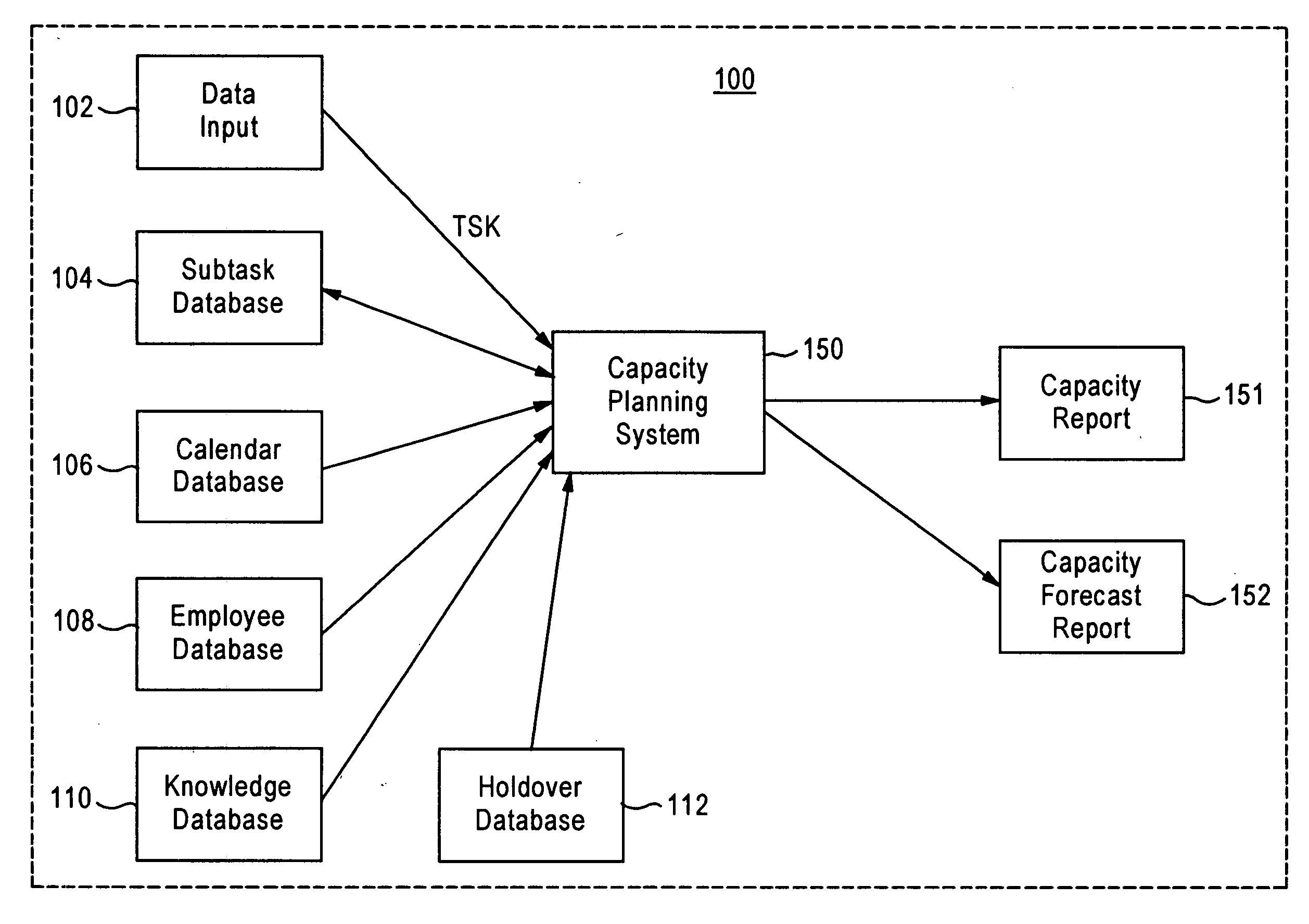
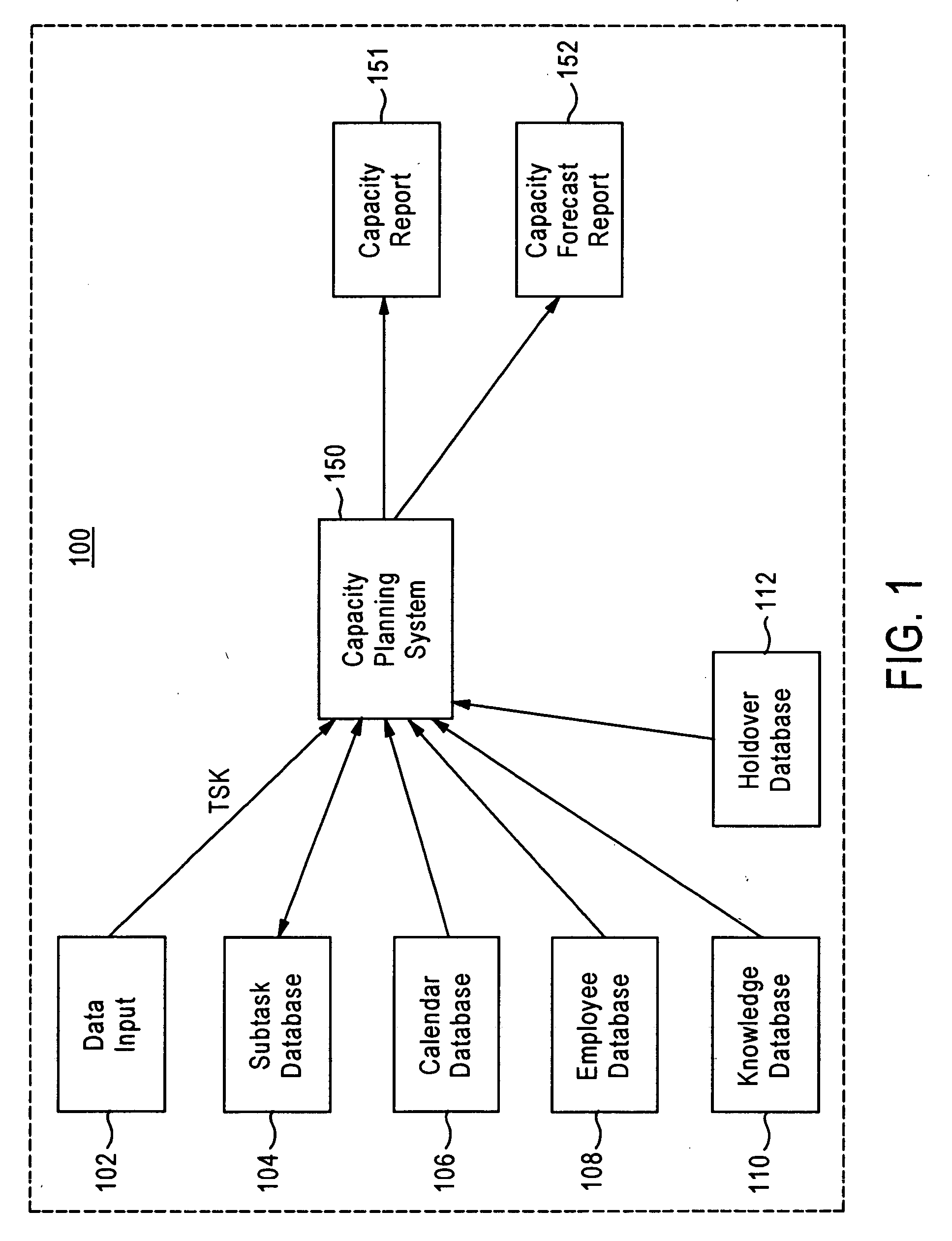
Capacity planning method and system with approved accuracy and confidence indication
A capacity planning method and system that dynamically determine staff capacity based on staff availability, work schedule, and holdover information, also provides a confidence indication to assist determination of report accuracy. The system calculates a workload of a task, and the amount of time or the number of staff needed to perform the tasks. A capacity report is generated based on the workload and staff availability. The task includes data obtained or generated from different sources and / or various methods. Respective trustworthiness scores associated with the data obtained or generated from different sources and / or methods are obtained to calculate an index of confidence indicating the reliability of information included in the capacity report.
Owner:PERSHING INVESTMENTS
System and method for determining how many servers of at least one server configuration to be included at a service provider's site for supporting an expected workload
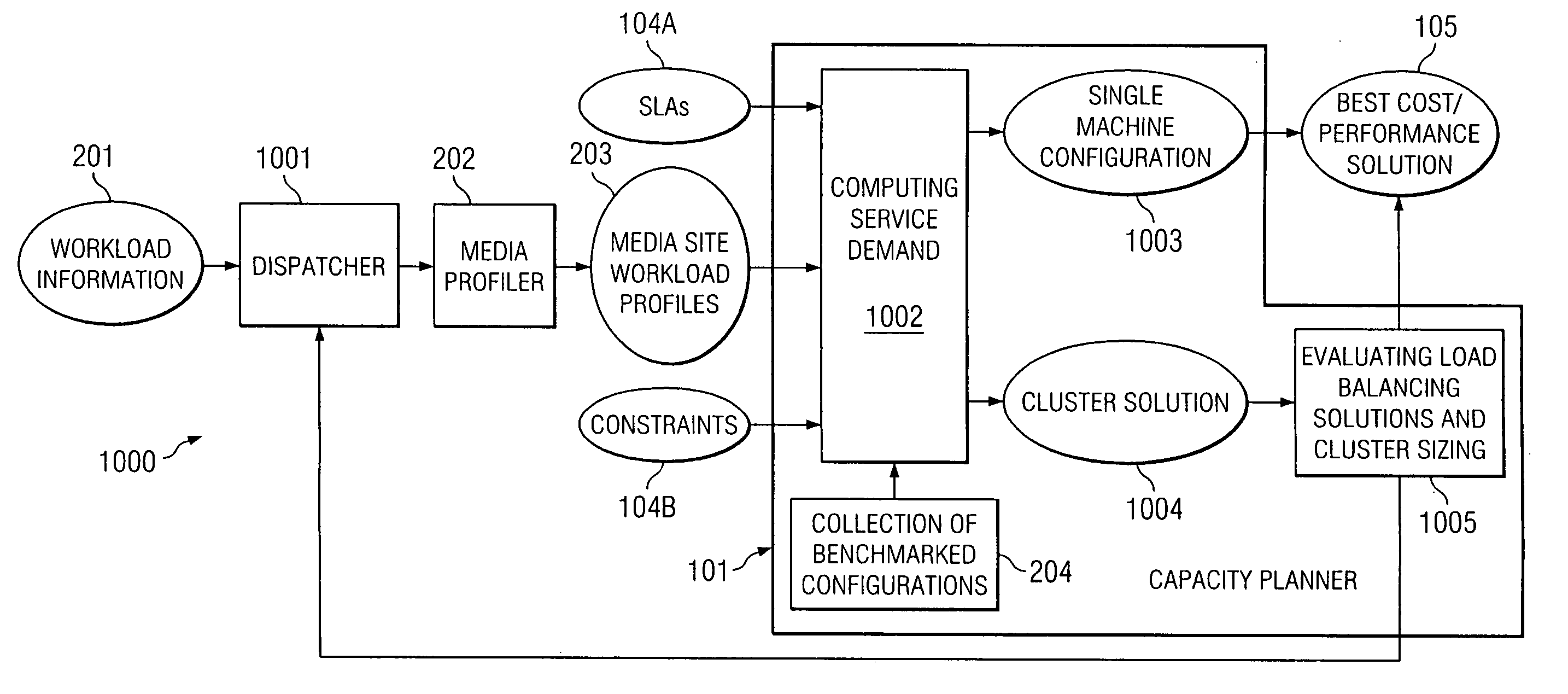
ActiveUS20050138170A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsService provisionWorkload
A method comprises receiving, into a capacity planning system, workload information representing an expected workload of client accesses of streaming media files from a site. The method further comprises the capacity planning system determining, for at least one server configuration, how many servers of the at least one server configuration to be included at the site for supporting the expected workload in a desired manner.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Design method for integrated energy system with source-load-storage coordination and interaction
ActiveCN108494015APreserve the properties of uncertain probability distributionsReduce computational complexitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network load balancingElement modelIntegrated energy system
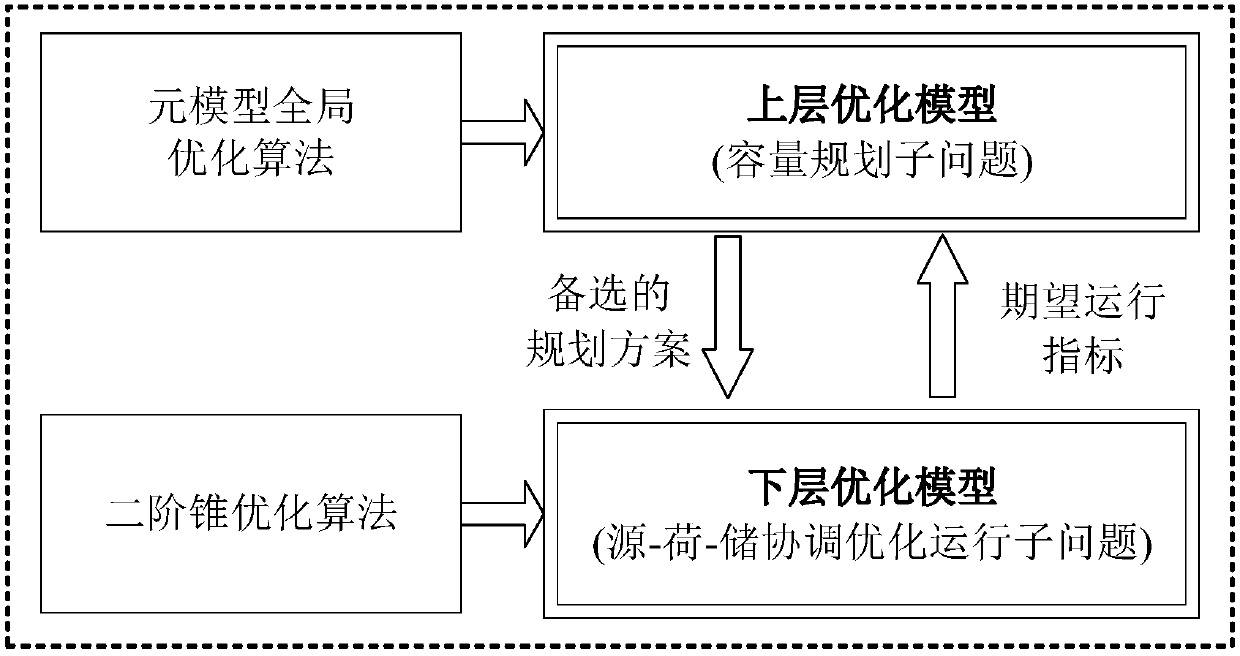
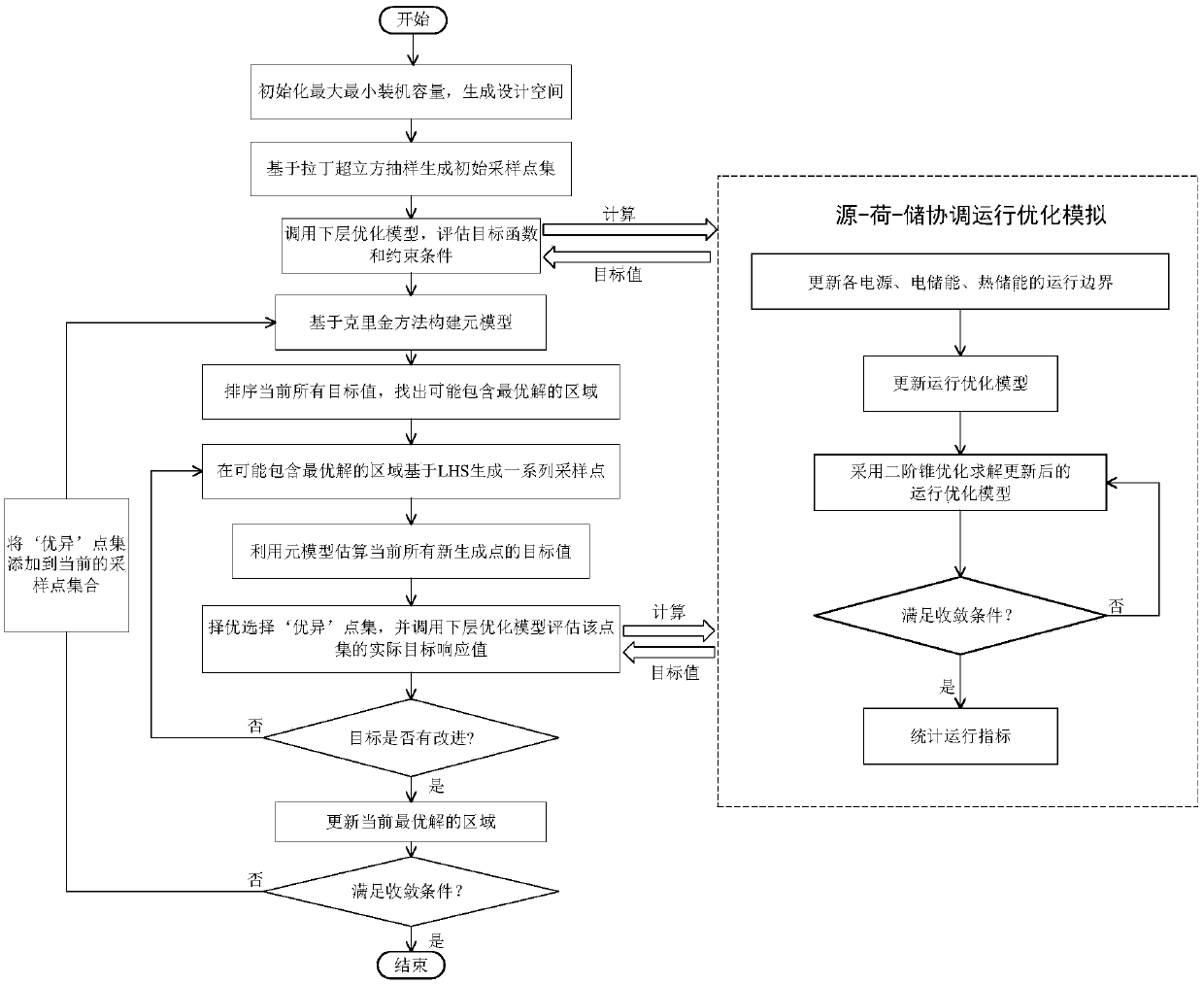
The invention relates to a design method for an integrated energy system with source-load-storage coordination and interaction. A lot of source-load output scenes are generated via Latin hypercube sampling, and a few of specific probability of planning scenes in which original scene characteristics are reserved are obtained via cluster analysis combined with a scene reduction method. An installedcost model and an operation cost model are established for each piece of equipment, an upper-level optimization model is optimized to minimize the sum of the annual investment conversion cost and theannual operation cost in different probability scenes, a lower-level optimization model is optimized to minimize the annual operation cost in different probability scenes a double-layer planning modelof the integrated energy system with source-load-storage coordination and interaction is established, and different reliable and safe operation constraints are met. The upper-level and lower-level optimization models are solved by an element model global optimization algorithm and a second-order conic optimization method respectively, solving is carried out by interactive iteration till convergence, and the installed capacity and optimal operation scheme of each piece of equipment of the integrated energy system are obtained by optimization. The method can be applied to capacity planning andoptimized design of the multiple energy complementary integrated energy system.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and apparatus for allocating resources in the presence of uncertainty
InactiveUS6625577B1ResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsOrganizational resourceDeterministic method
A method of allocating resources in the presence of uncertainty is presented. The method builds upon deterministic methods and initially creates and optimizes scenarios. The invention employs clustering, line-searching, statistical sampling, and unbiased approximation for optimization. Clustering is used to divide the allocation problem into simpler sub-problems, for which determining optimal allocations is simpler and faster. Optimal allocations for sub-problems are used to define spaces for line-searches; line-searches are used for optimizing allocations over ever larger sub-problems. Sampling is used to develop Guiding Beacon Scenarios that are used for generating and evaluating allocations. Optimization is made considering both constraints, and positive and negative ramifications of constraint violations. Applications for capacity planning, organizational resource allocation, and financial optimization are presented.
Owner:JAMESON JOEL
System and method for capacity planning for computing systems
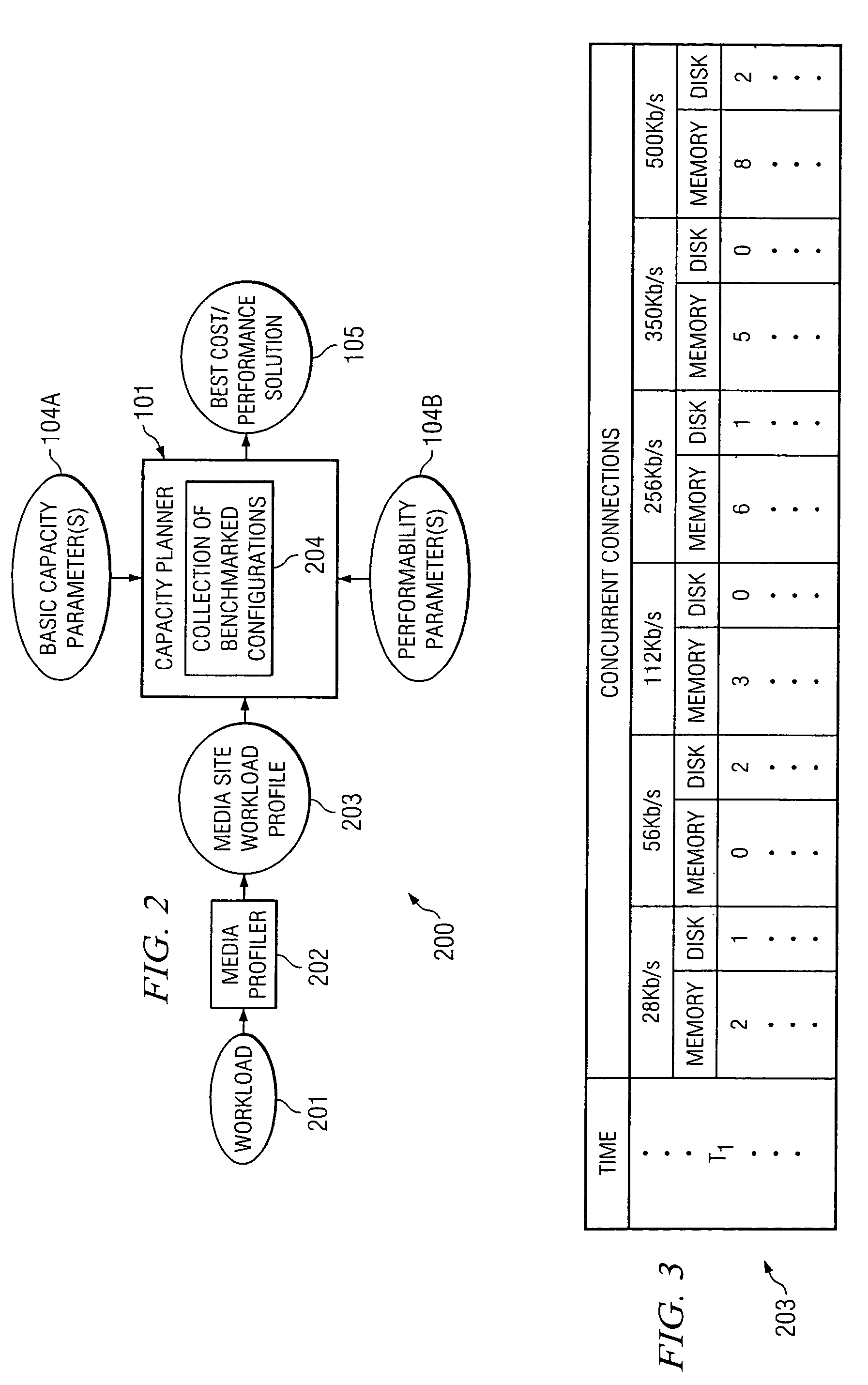
ActiveUS20080221941A1Error detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsWorkload profilingCapacity planning
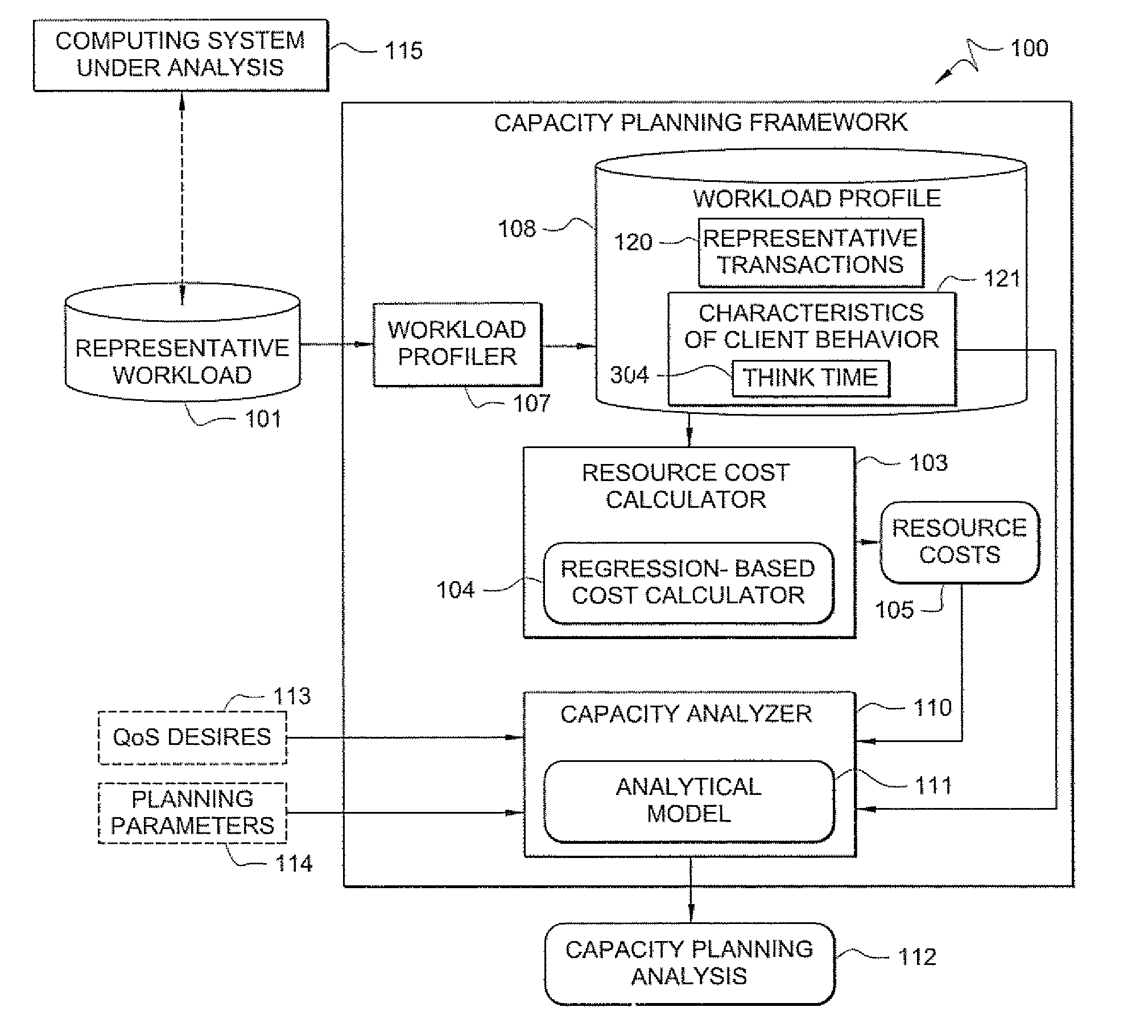
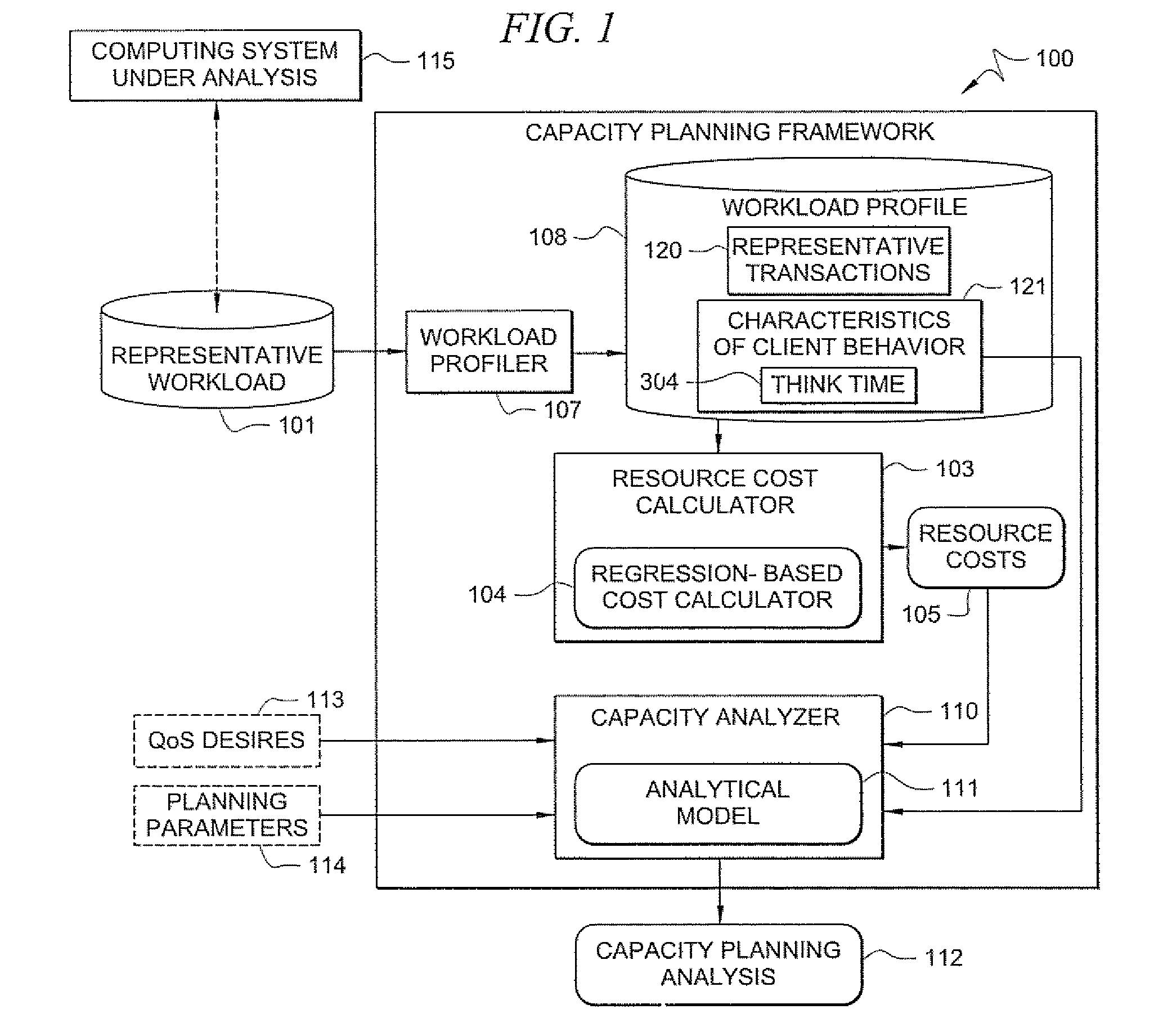
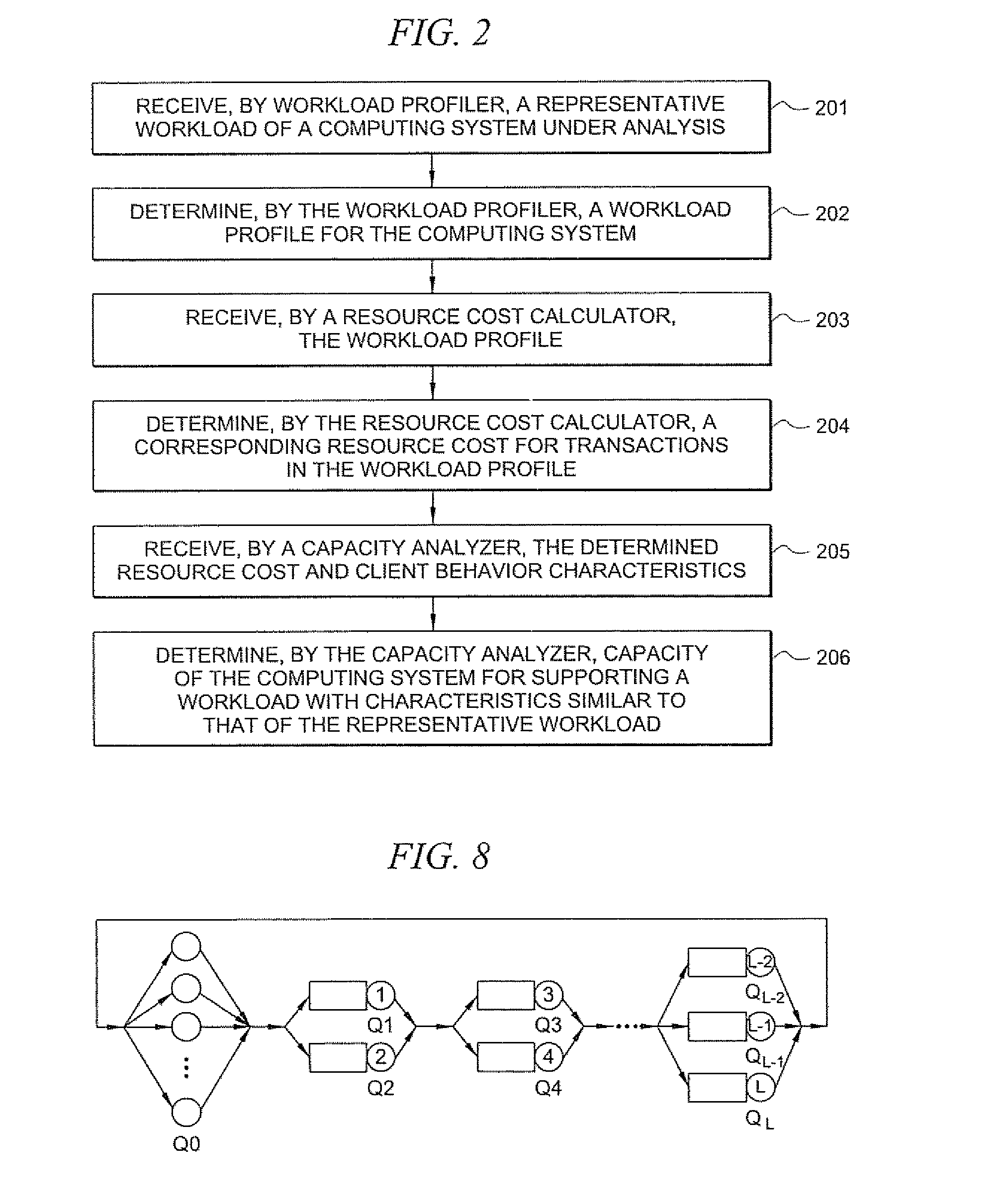
A method comprises receiving, by a workload profiler, a representative workload of a computing system under analysis. The workload profiler determines a workload profile of the computing system that reflects a transaction mix that varies over times. A capacity analyzer receives the workload profile, and determines a maximum capacity of the computing system under analysis for serving the workload profile while satisfying a defined quality of service (QoS) target.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
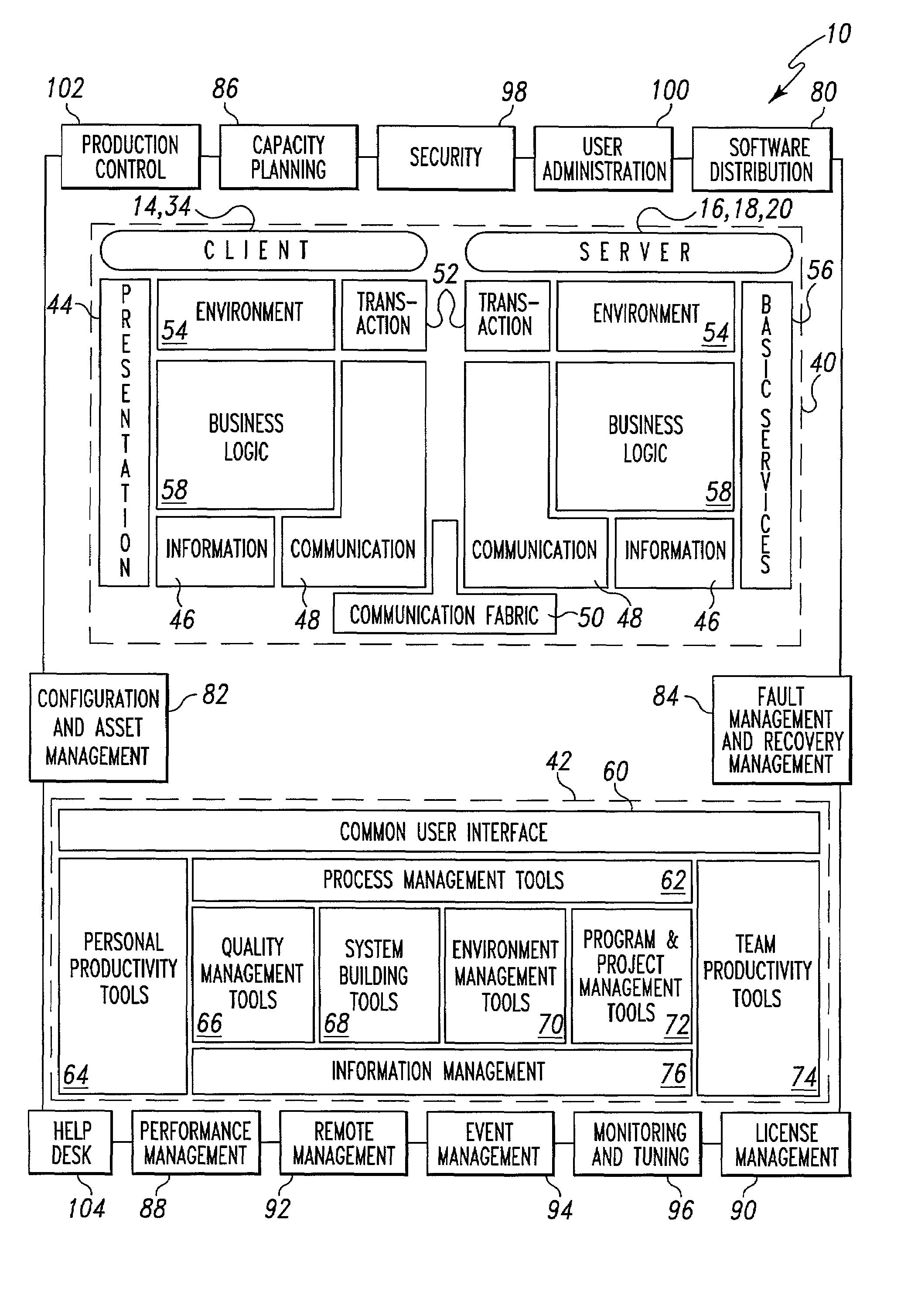
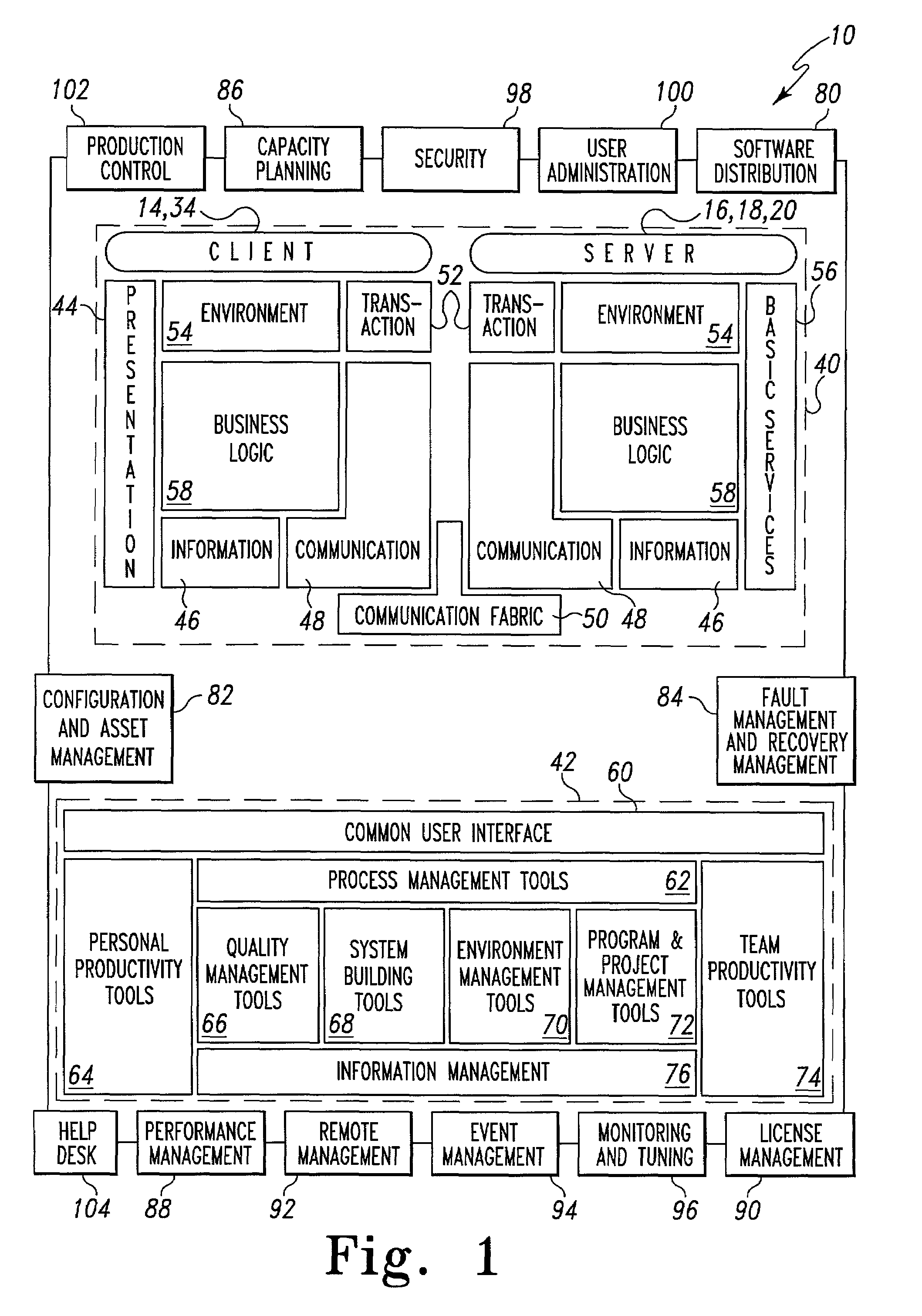
Operations architectures for netcentric computing systems
InactiveUS7415509B1Data processing applicationsWeb data retrievalManagement toolSoftware distribution
An operations architecture for a netcentric computing system including a server connected with a client. The preferred operations architecture includes a software distribution tool, a configuration and asset management tool, a fault management and recovery management tool, a capacity planning tool, a performance management tool, a license management tool, a remote management tool, a event management tool, a systems monitoring and tuning tool, a security tool, a user administration tool, a production control application set and a help desk tool that support the server and the client in the netcentric computing system.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
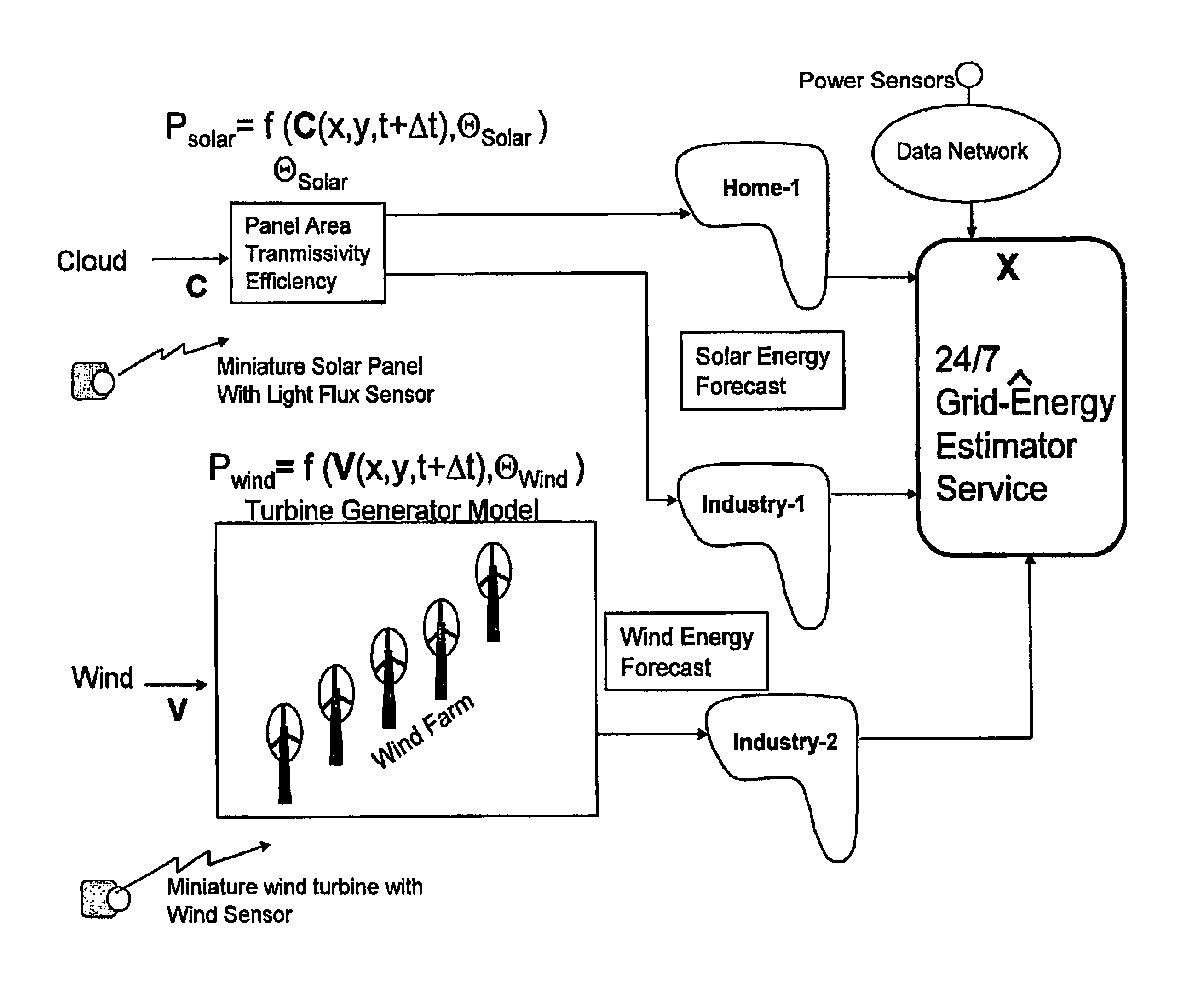
Smarter-grid: method to forecast electric energy production and utilization subject to uncertain environmental variables
InactiveUS8600572B2Improve accuracyMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlSmart gridEngineering
A method to forecast the energy sources and energy sinks to facilitate continuous capacity planning, regulation and control of energy state of an entity under variable weather condition is established. Energy sources of specific focus are related to renewable energy forms from wind, solar and wave that are highly dependent on prevailing weather conditions.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Resource capacity planning
InactiveUS20070073576A1Reduce laborResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsProgram planningCapacity planning
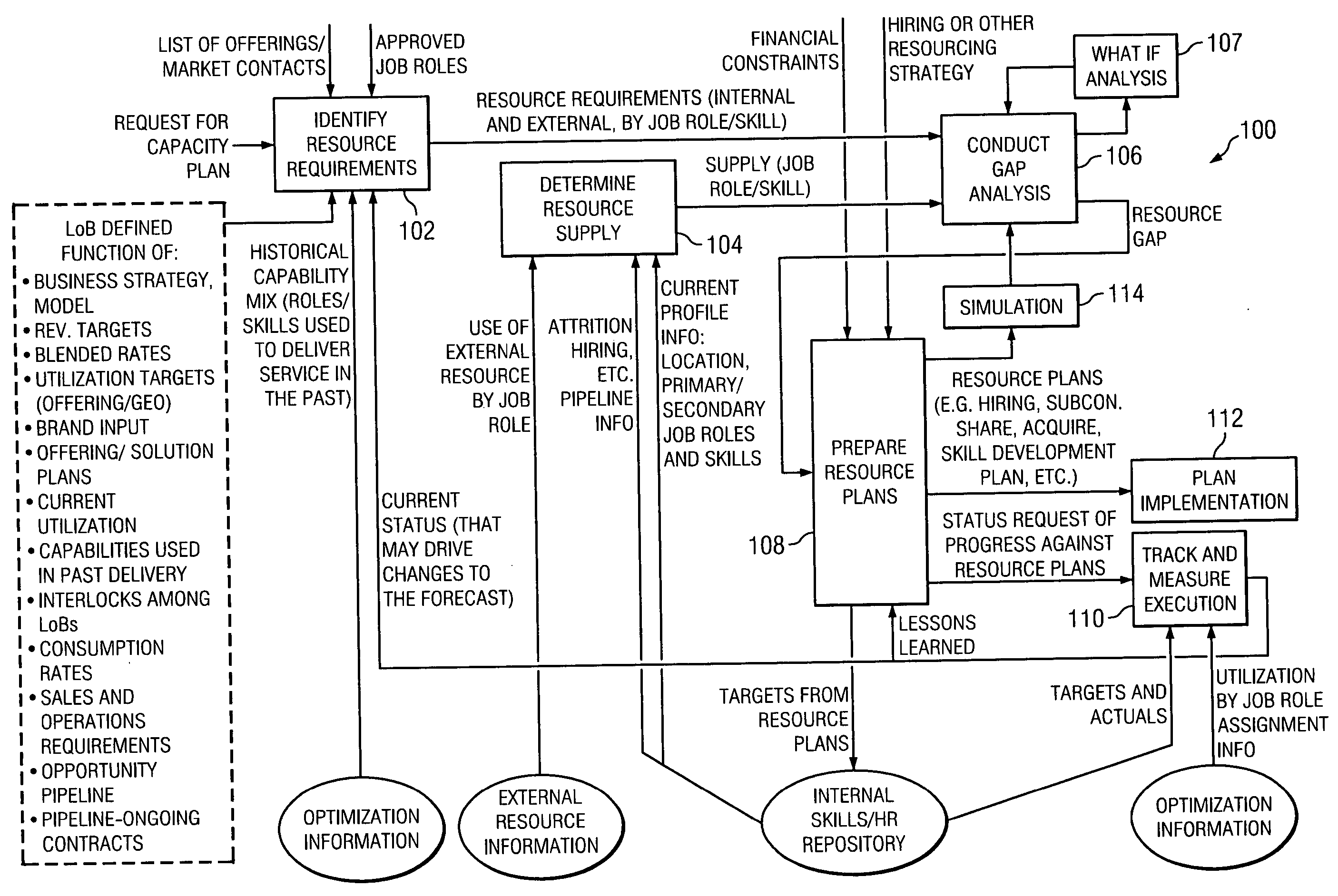
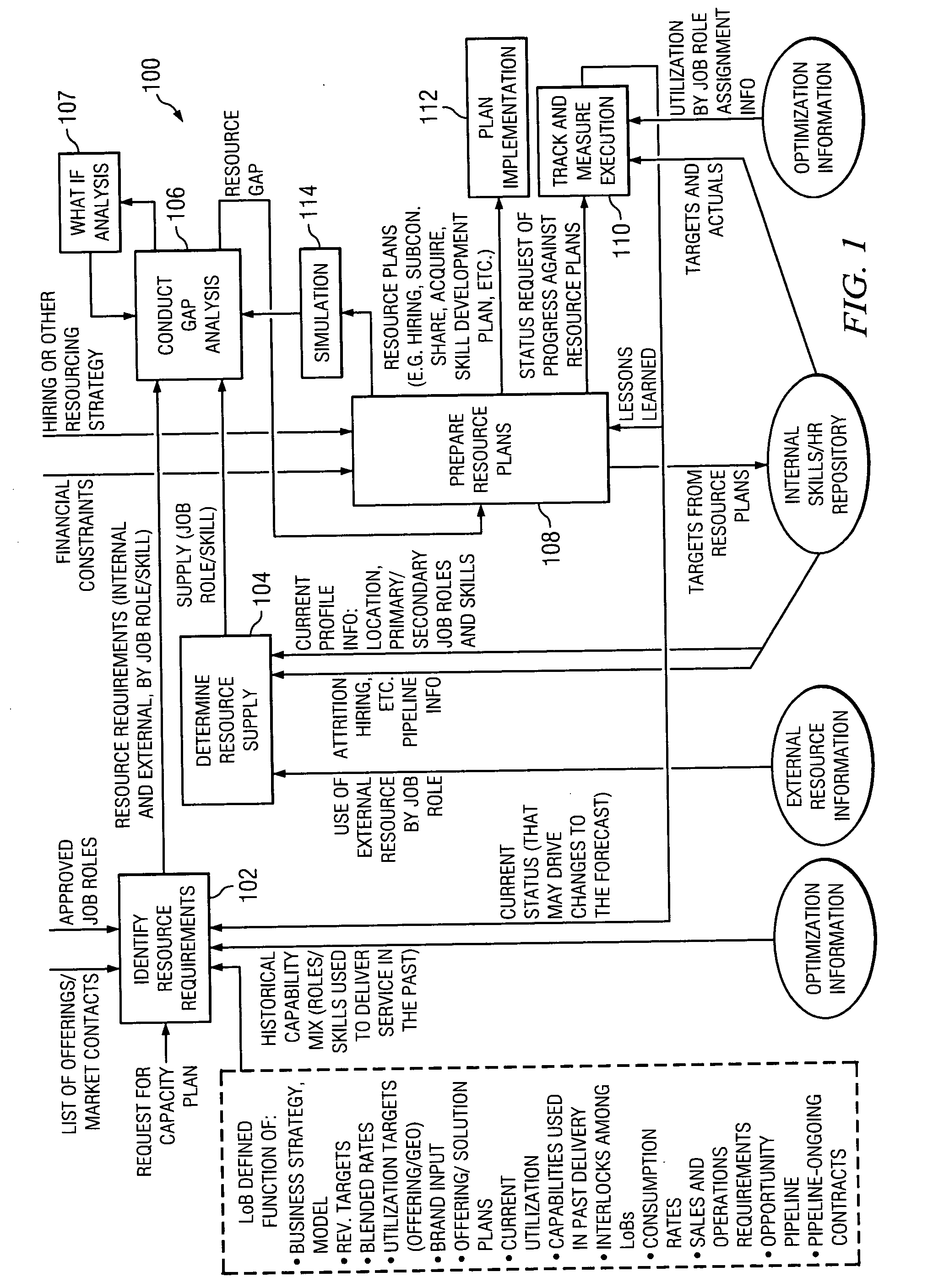
An integrated Resource Capacity Planning (RCP) process and tool program is presented. The RCP program includes identifying future labor needs and predicted labor supply. A gap analysis between the predicted future needs and supply is performed. Based on the gap analysis, resource actions are planned and taken to alleviate predicted future labor shortages. The predicted gap analysis is later compared with actual future needs / supply to evaluate the effectiveness of the parameters used in the RCP program. The RCP program is enterprise-independent, thus permitting re-use of data and parameters, and allowing the RCP program to be scalable.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for capacity planning for data center server consolidation and workload reassignment
A server migration tool used to construct data center migration scenarios allowing for a user to rapidly manipulate a large number of input parameters required to describe a transformation from one data center configuration to a new data center configuration. The tool then performs the transformation and allows the user to interact with new data center configuration to understand its performance. A novel parameterization, speed independent service demand (SISD), greatly facilitates scaling performance metrics between different hardware platforms.
Owner:HYPERFORMIX
Capacity planning for server resources
InactiveUS20050005012A1Fully processedThe result is accurateMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsResource utilizationCapacity planning
Methods and systems for capacity planning of server resources are described wherein fixed resources of a server cluster are used in comparison to similar server cluster benchmarks to determine the maximum load—requests per second—that can be handled by the server cluster. The maximum load is used to determine utilization of server resources and to provide estimates of server resource utilization for hypothetical loads. A recommendation as to changes to server resources to handle the hypothetical loads is displayed to the user.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for evaluating a heterogeneous cluster for supporting expected workload in compliance with at least one service parameter
ActiveUS7953843B2Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsHeterogeneous clusterWorkload
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
System and method for evaluating capacity of a heterogeneous media server configuration for supporting an expected workload
According to at least one embodiment, a method comprises receiving, into a capacity planning system, workload information representing an expected workload of client accesses of streaming media files from a site. The capacity planning system evaluates whether a heterogeneous cluster having a plurality of different server configurations included therein is capable of supporting the expected workload in a desired manner.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method and system for orchestrating system resources with energy consumption monitoring
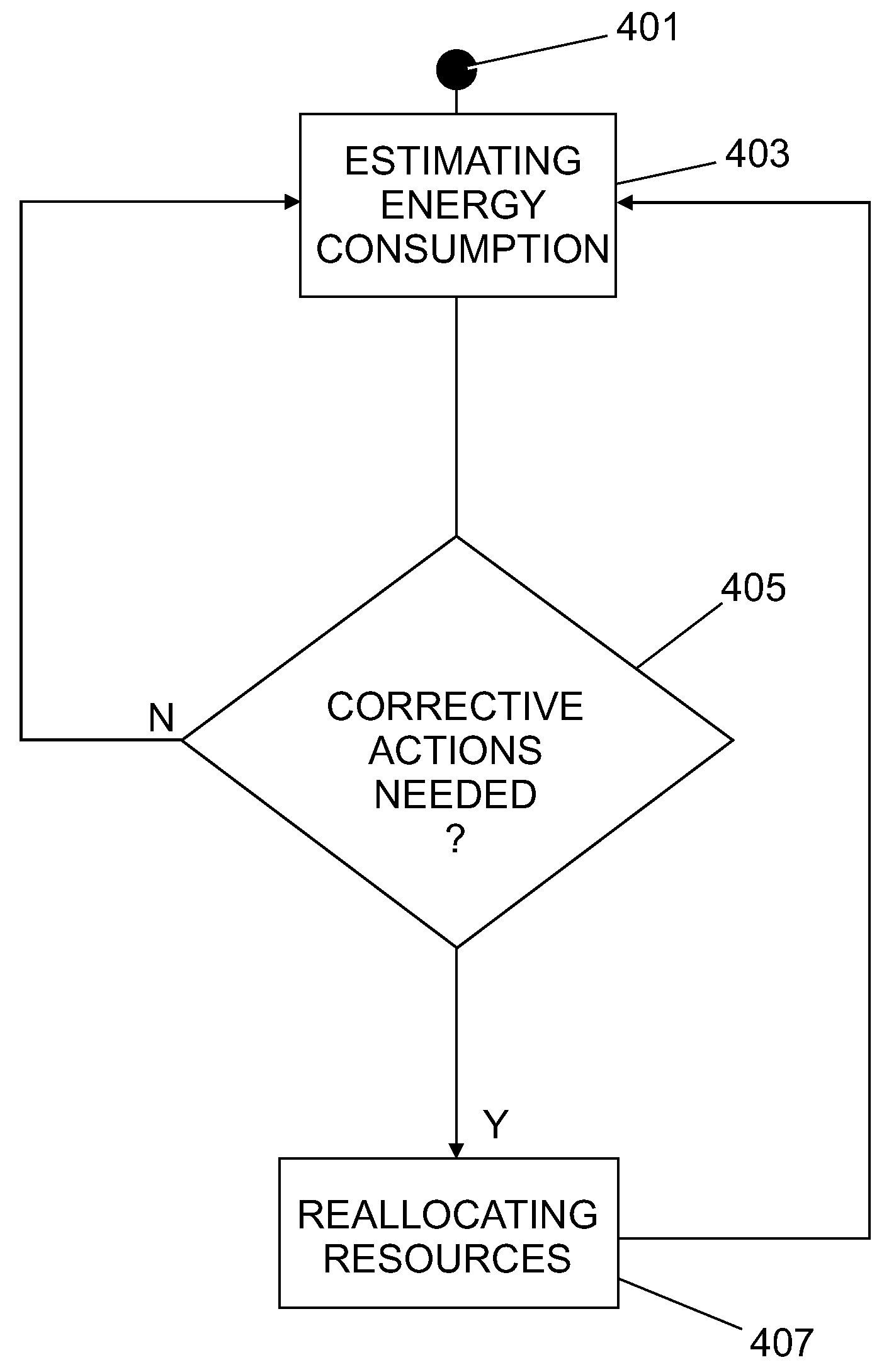
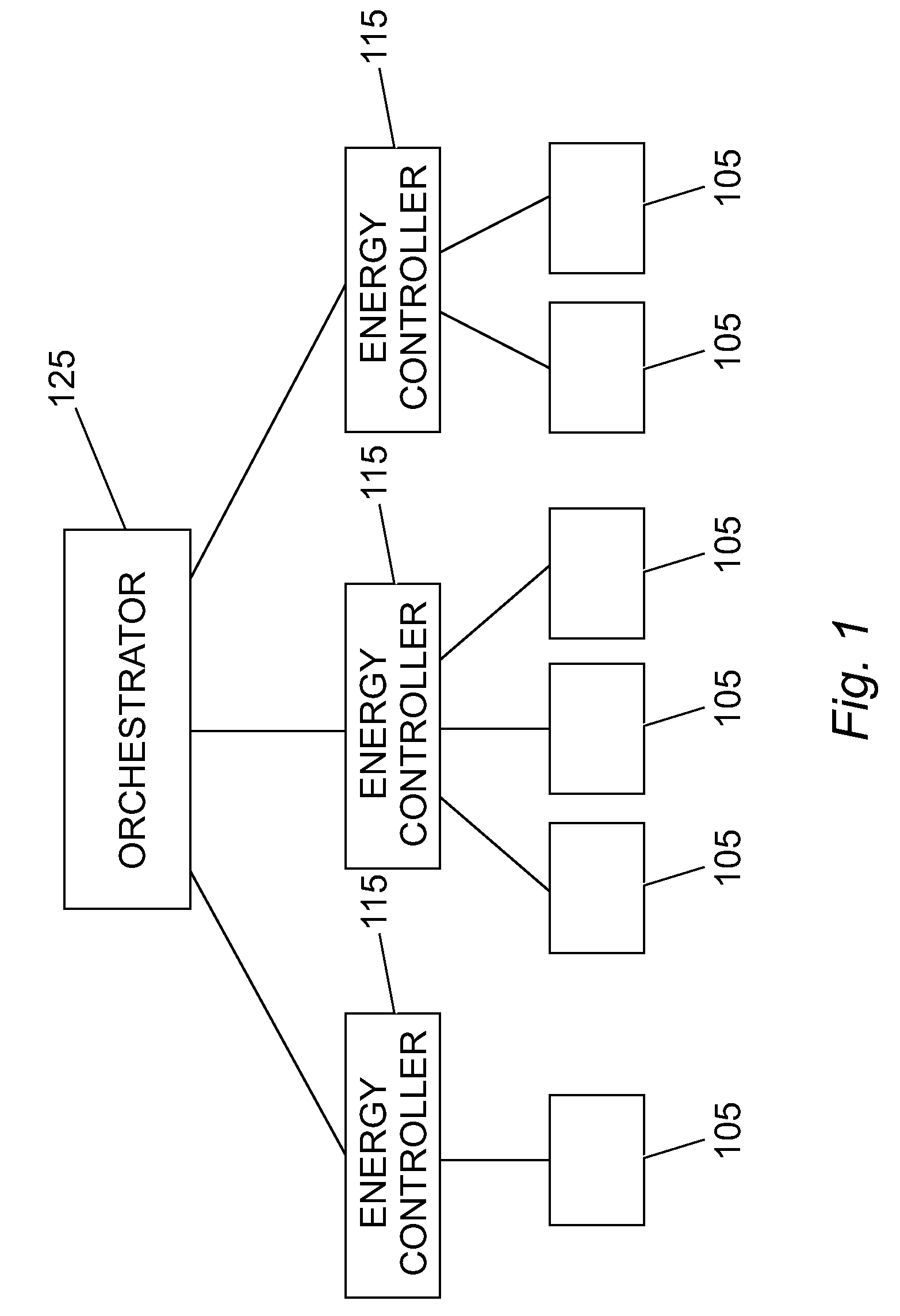
InactiveUS20090007128A1Energy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsEngineeringCapacity planning
A method and system for orchestrating system resources including provisioning process, performance measurement, capacity planning and infrastructure deployment. An integrated solution is provided which could help monitoring the system power consumption and applying corrective rebalancing actions. Such orchestrating and rebalancing activity is performed by the system taking into account the estimated power consumption of the single SW applications.
Owner:IBM CORP
Traffic matrix computation for a backbone network supporting virtual private networks
InactiveUS7027396B1Shorten the timeView accuratelyError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityInternet traffic engineering
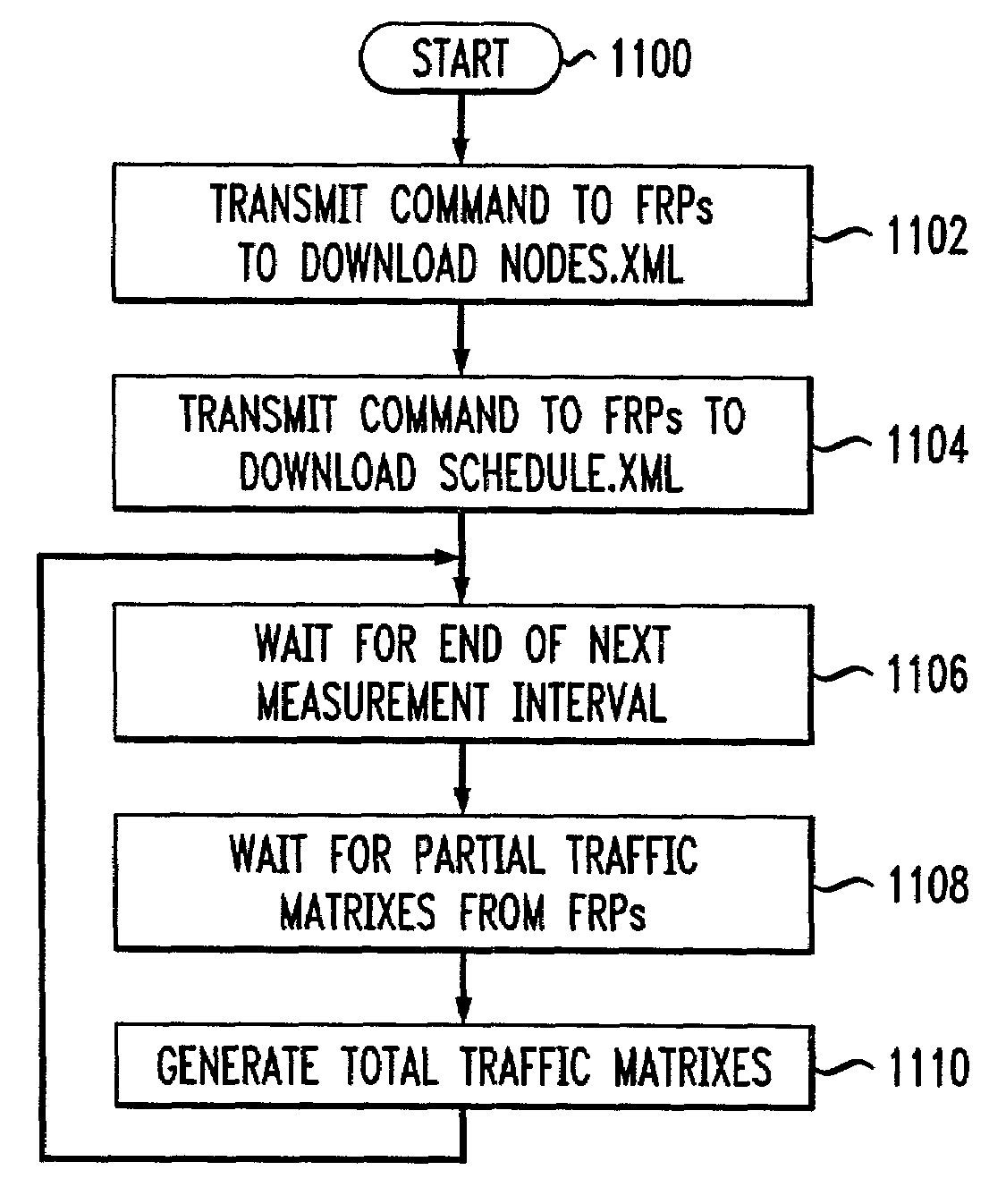
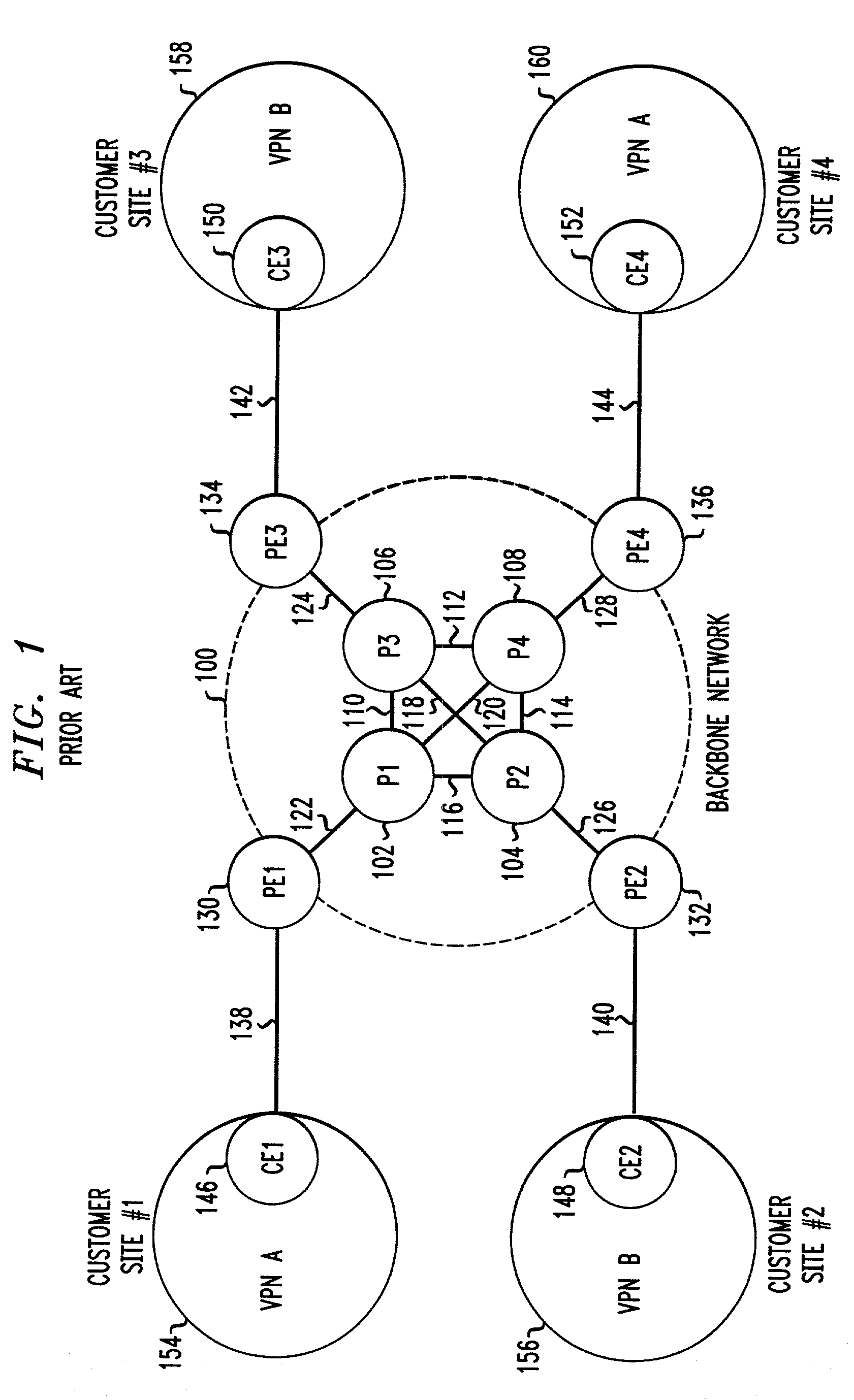
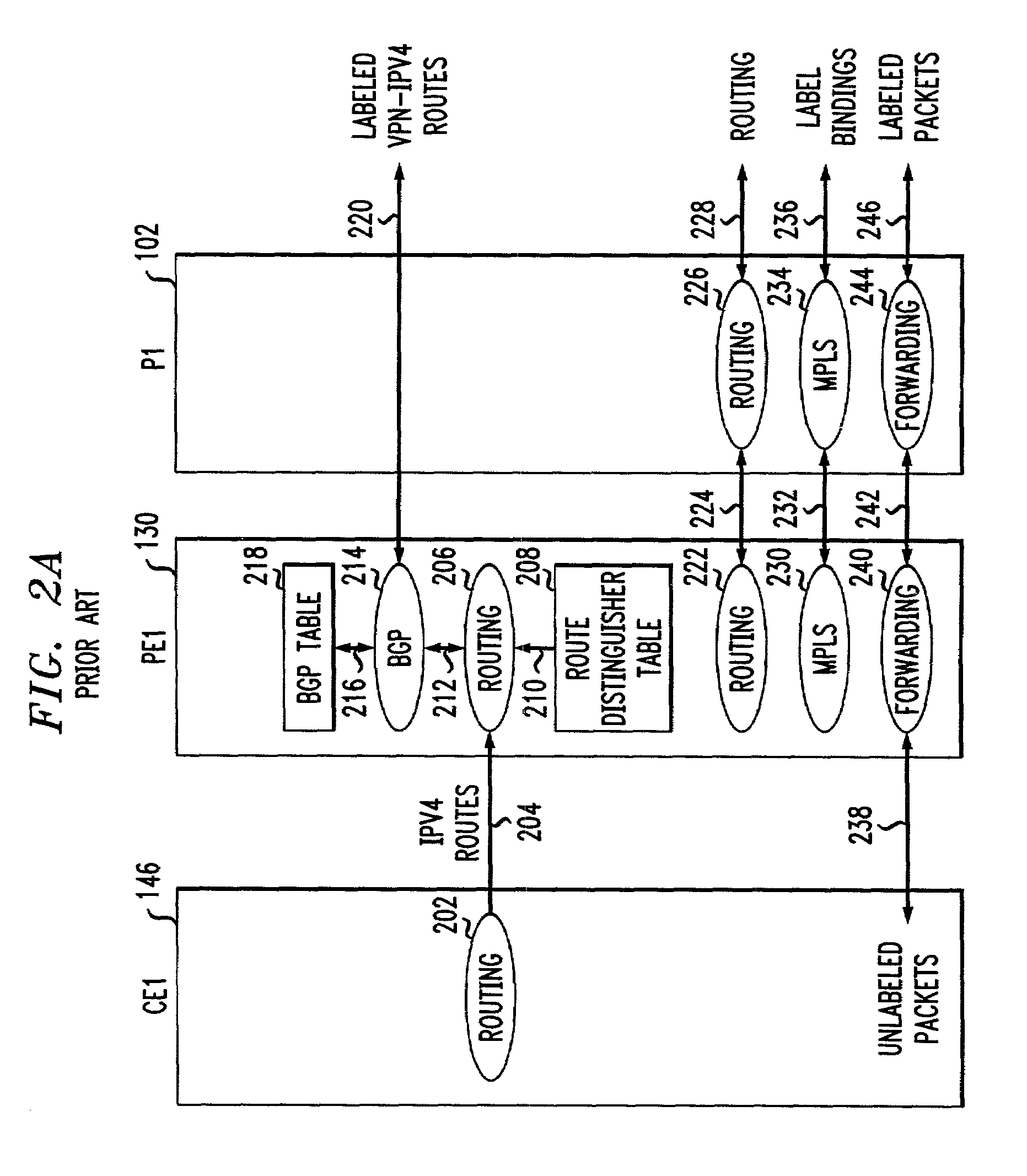
This invention provides a more effective method for capacity planning and traffic engineering of packet networks that connect Virtual Private Network (VPN) sites. A distributed architecture efficiently computes traffic matrixes that show the number of bytes and / or packets exchanged among provider edge (PE) routers and / or service nodes. Each PE router in a service node is exports flow records to a Flow Record Processor (FRP) in the same location. The FRPs use these records in conjunction with configuration data extracted from the PE routers to compute partial traffic matrixes. The partial traffic matrixes are uploaded to a Matrix Generator to create a total traffic matrix. The total traffic matrix is essential input for capacity planning or traffic engineering tools.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method of allocating work in capacity planning
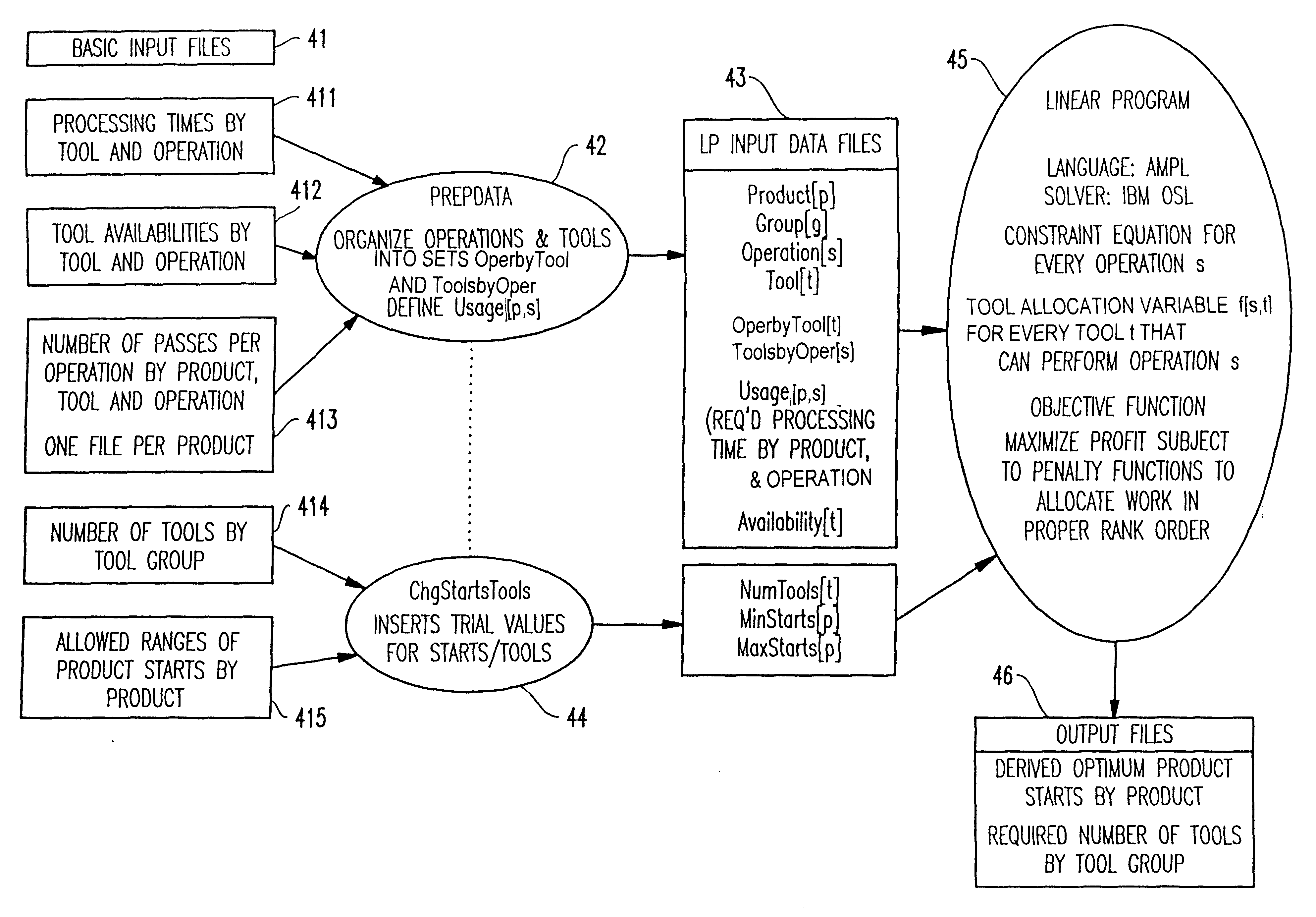
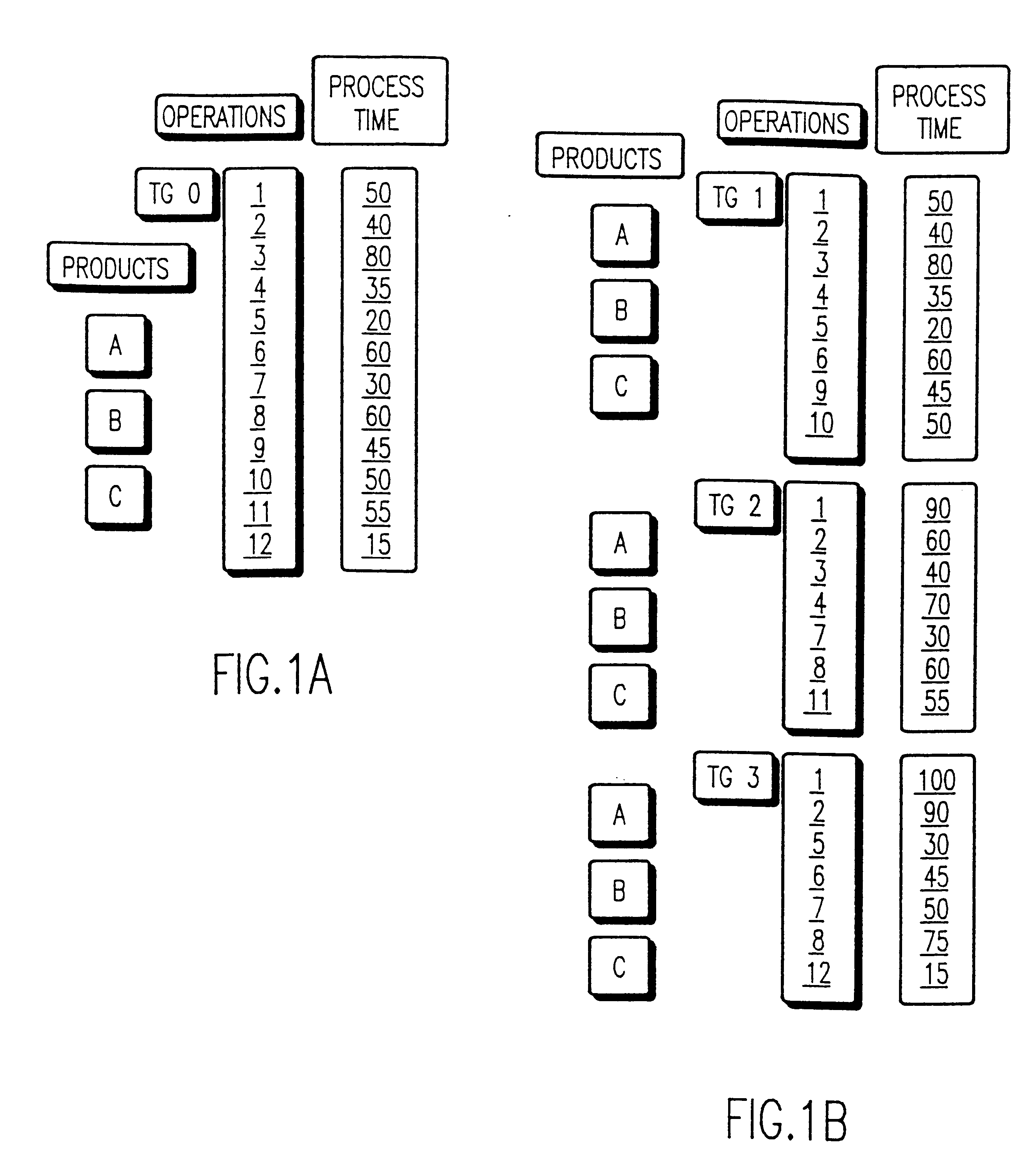
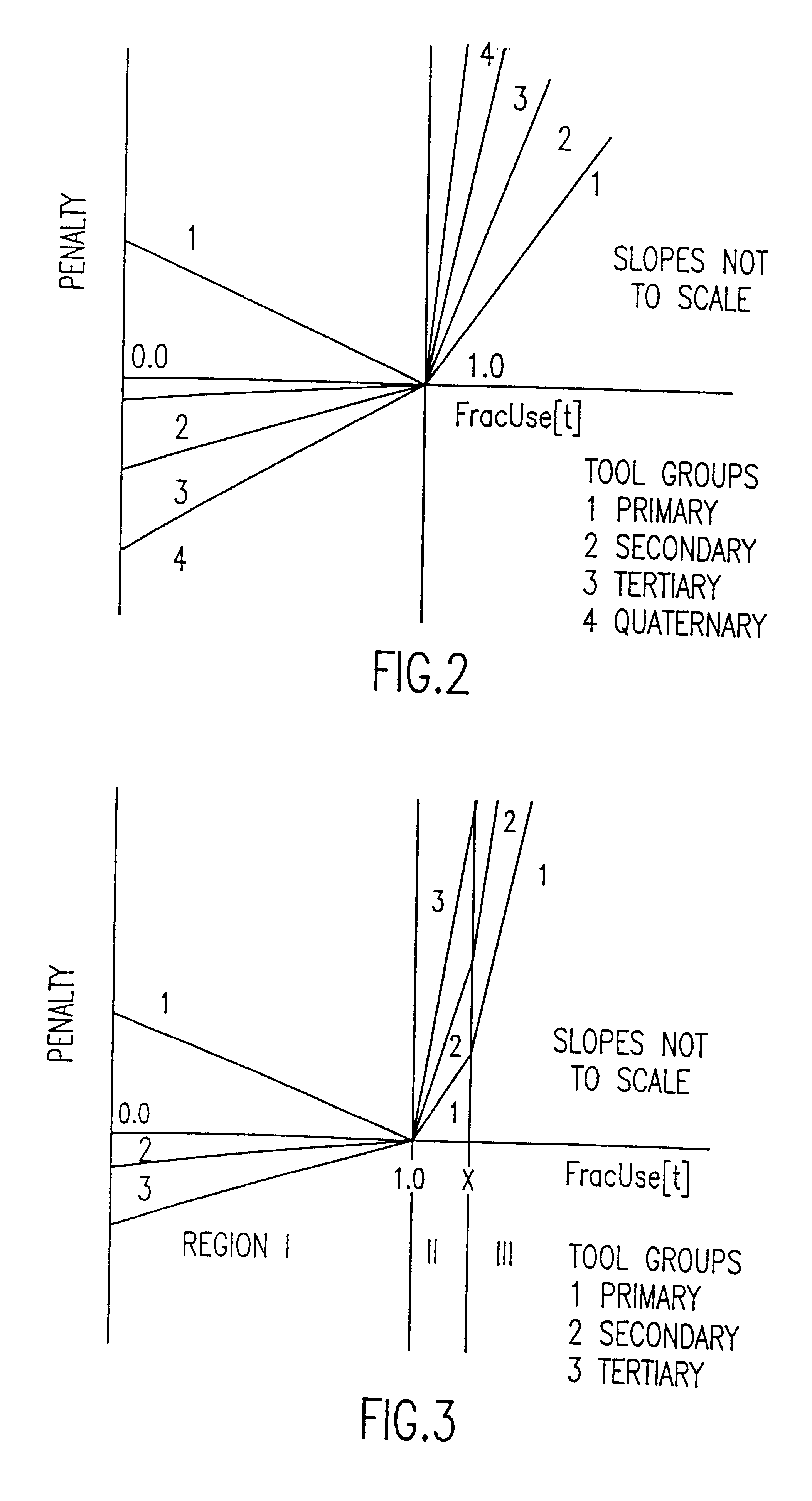
A computer implemented method provides accurate capacity planning for manufacturing environments comprising parallel, unrelated tools that can process the same operations at different rates and with preferences for the sequence in which those tools are selected to accommodate the workload. The method reliably determines precisely what are the gating tools among sets of parallel, unrelated tools in a complex manufacturing environment in which different tools can perform the same or similar sets of operations, generally at different rates. The primary, secondary, etc. tool groups in each cascade set are explicitly kept track of in order to enable the correct penalty function to be associated, in one implementation with the appropriate tool group, and in another implementation with the tool allocation variables. The end user may also interact with the input data through a Menu Program or through a Graphical User Interface (GUI) and modify the data for "what-if" analyses.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com