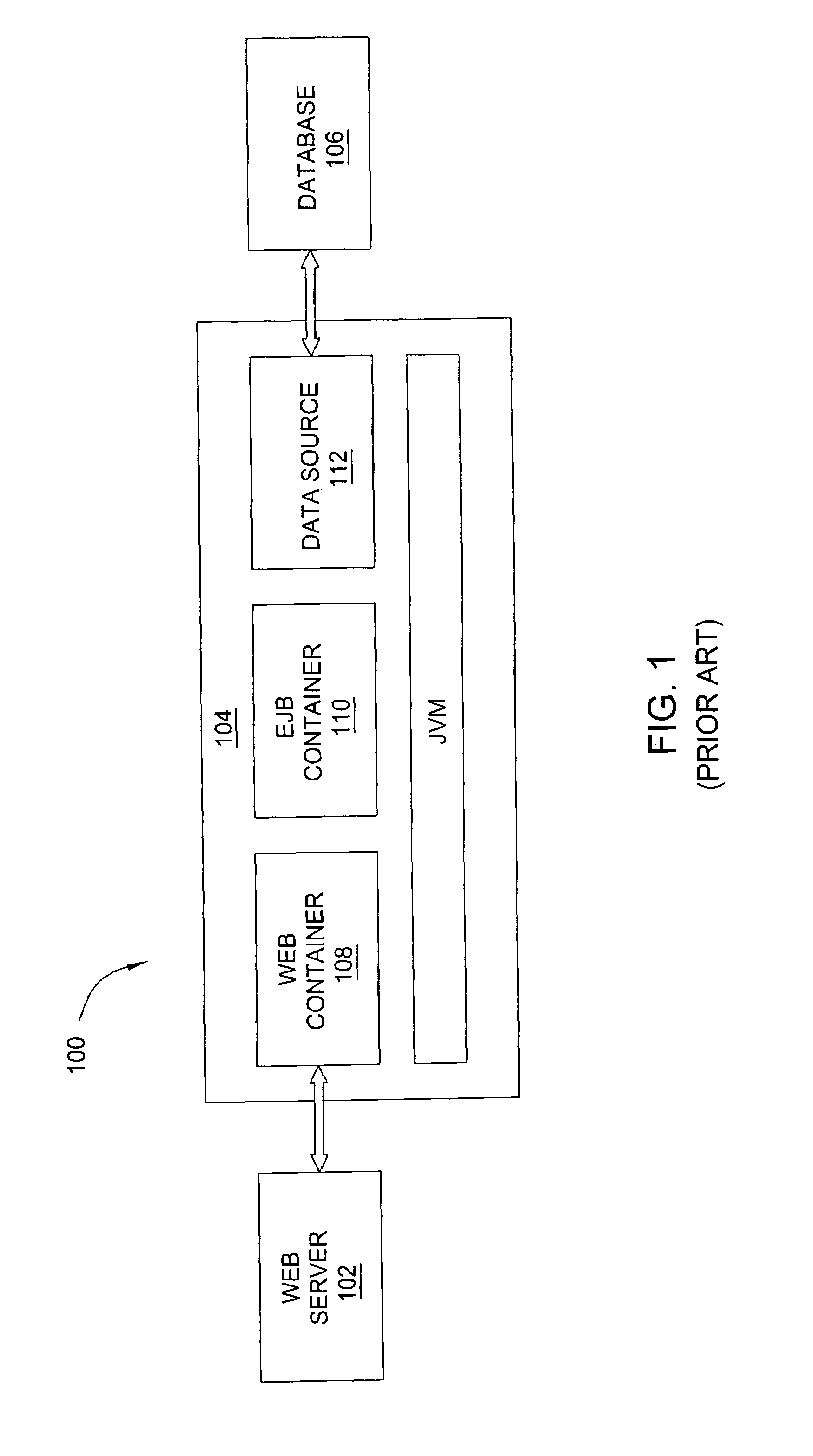
Patents
Literature
240 results about "Hypercube" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In geometry, a hypercube is an n-dimensional analogue of a square (n = 2) and a cube (n = 3). It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1-skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions, perpendicular to each other and of the same length. A unit hypercube's longest diagonal in n dimensions is equal to √(n). An n-dimensional hypercube is more commonly referred to as an n-cube or sometimes as an n-dimensional cube.
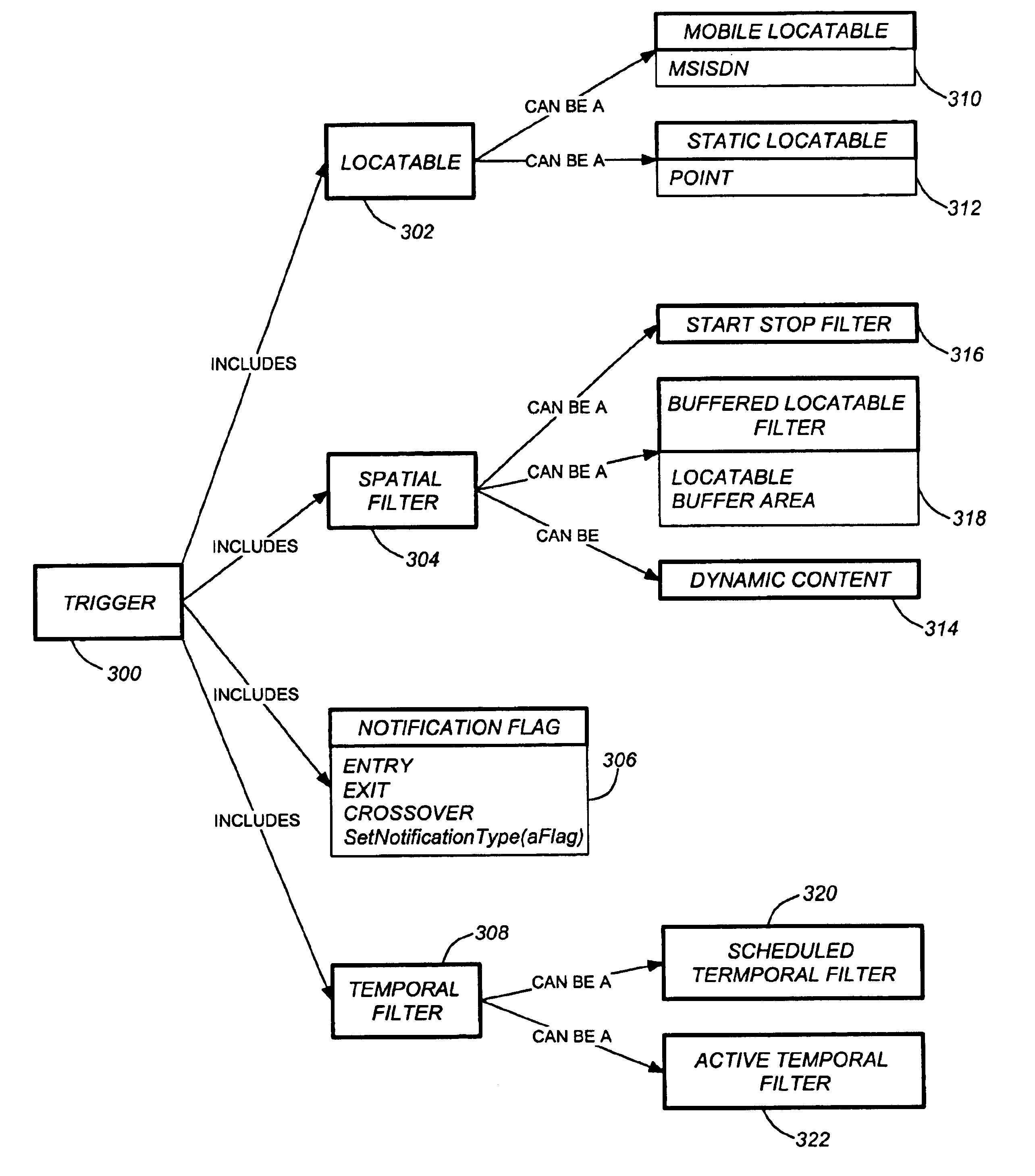
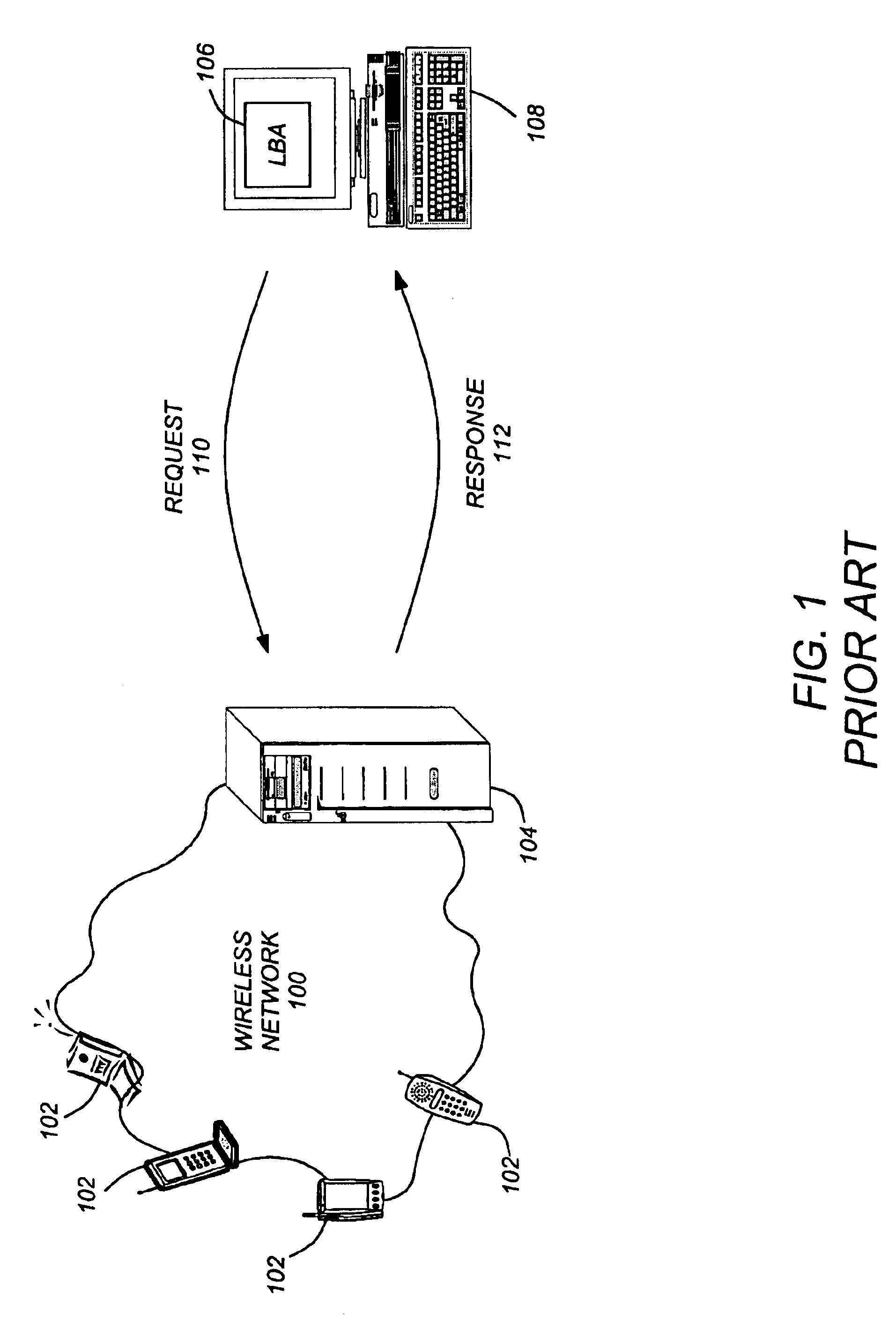
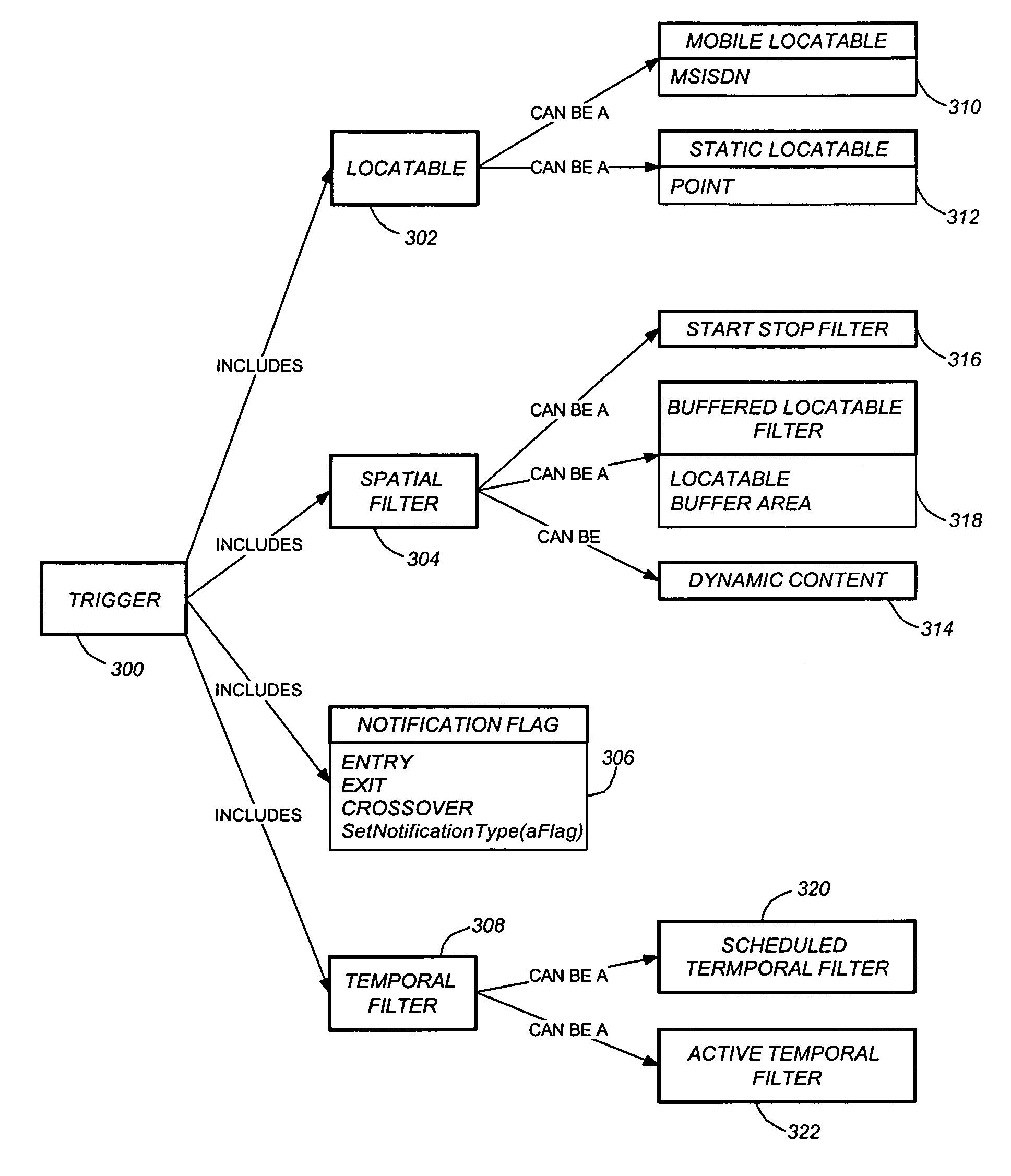
Use of triggers and a location hypercube to enable push-based location applications
ActiveUS6985747B2Minimizing pollingImprove performanceTelephonic communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTemporal informationComputer science
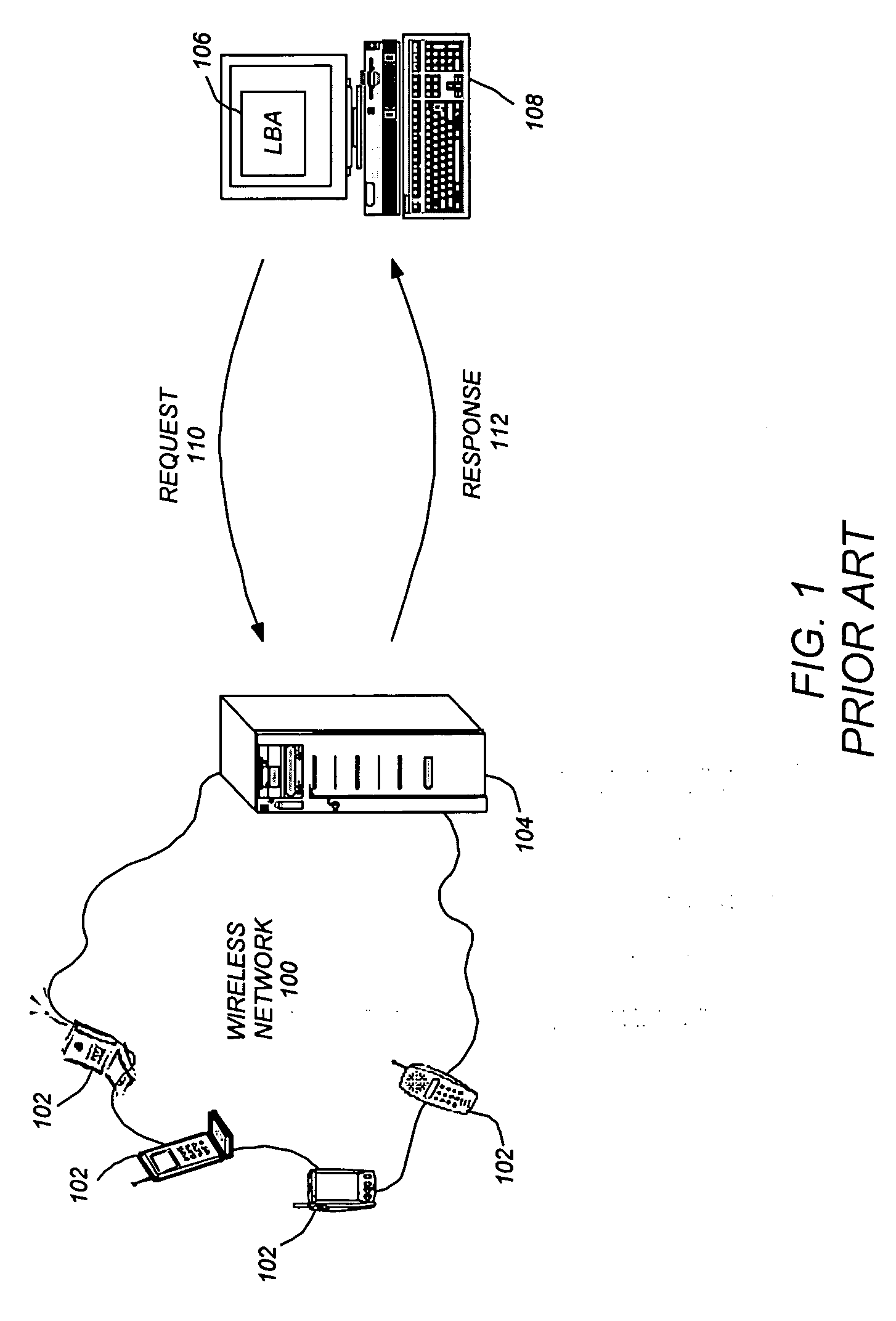
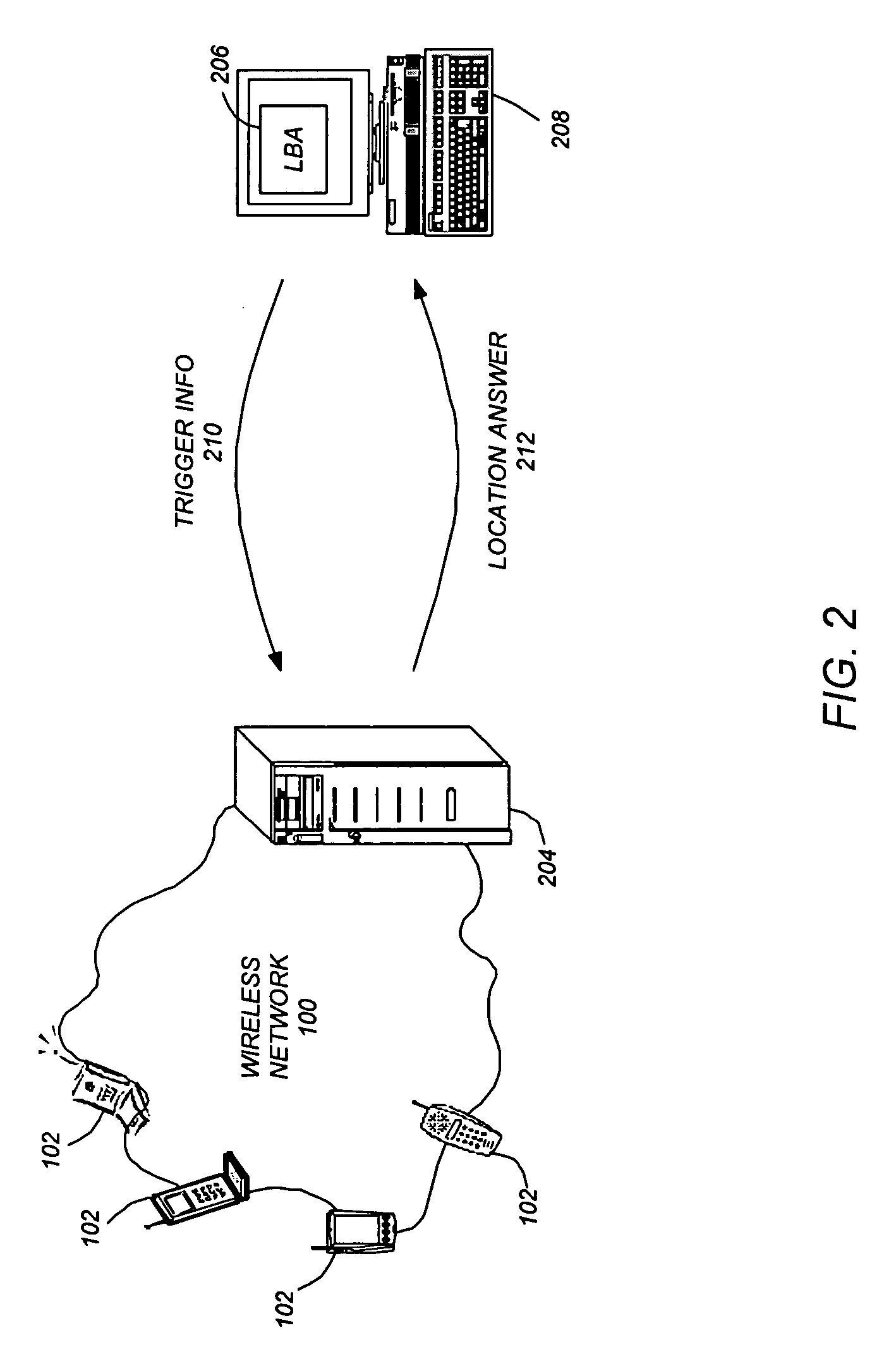
A method, system, and article of manufacture enable the use of location based applications (LBA). A location server (LS) on a wireless network receives trigger information from a LBA that is located outside of the wireless network. The trigger information defines a source locatable, spatial information (defining spatial criteria for a target locatable), a notification flag (describing) an interaction between the source locatable and the spatial criteria), and temporal information (defining a time period the trigger will be active). The LS determines if the triggers are active based on the temporal information and obtains updated locations if the trigger is active. Active triggers are evaluated to determine if a trigger alert has been caused by the locatables interacting with each other pursuant to the spatial information and notification flag. A location answer is pushed to the LBA if a trigger alert has been caused.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
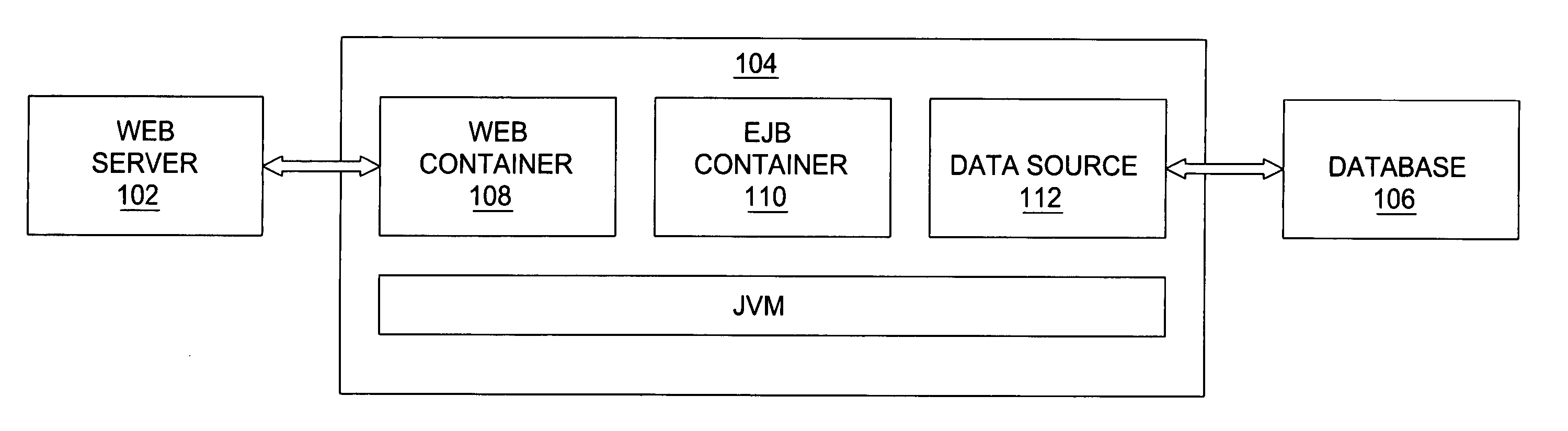
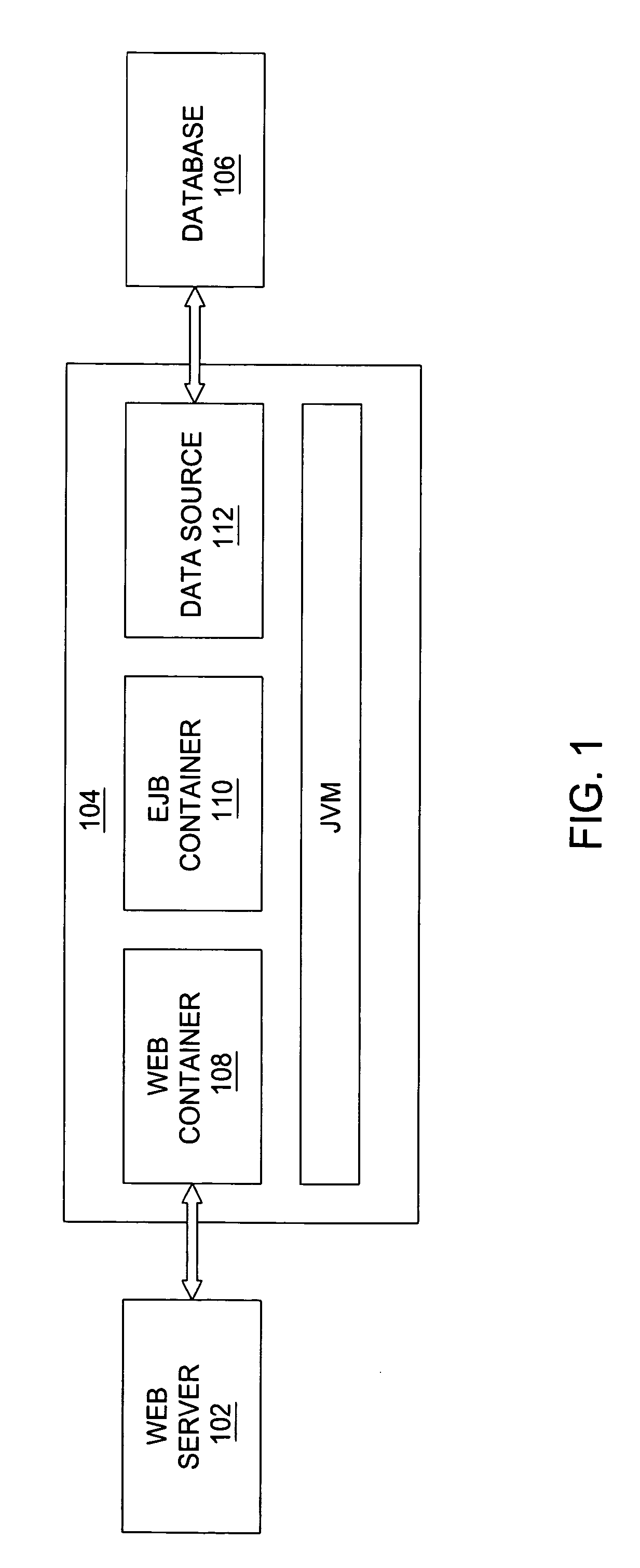
Method and apparatus for three dimensional internet and computer file interface
InactiveUS6938218B1Input/output processes for data processing3D-image renderingOperator interfaceDisplay device
A method and apparatus for geometrically organizing, interfacing to, surfing, authoring, converting and viewing computer files such as pages on the World Wide Web or operator interface windows of application software. A plurality of related Web pages or windows are organized and presented for view on a computer display in an apparent three or four dimensional relationship to each other with a front, right, left, top, and bottom face (page). A back face may be accessed by a button. Each face and its corresponding page / file can be further spatially related to five other faces and their corresponding pages / files in the same manner ad infinitum. The related pages are organized as a matrix of three dimensional cubes or four dimensional hypercubes.
Owner:NOLEN JAMES A III
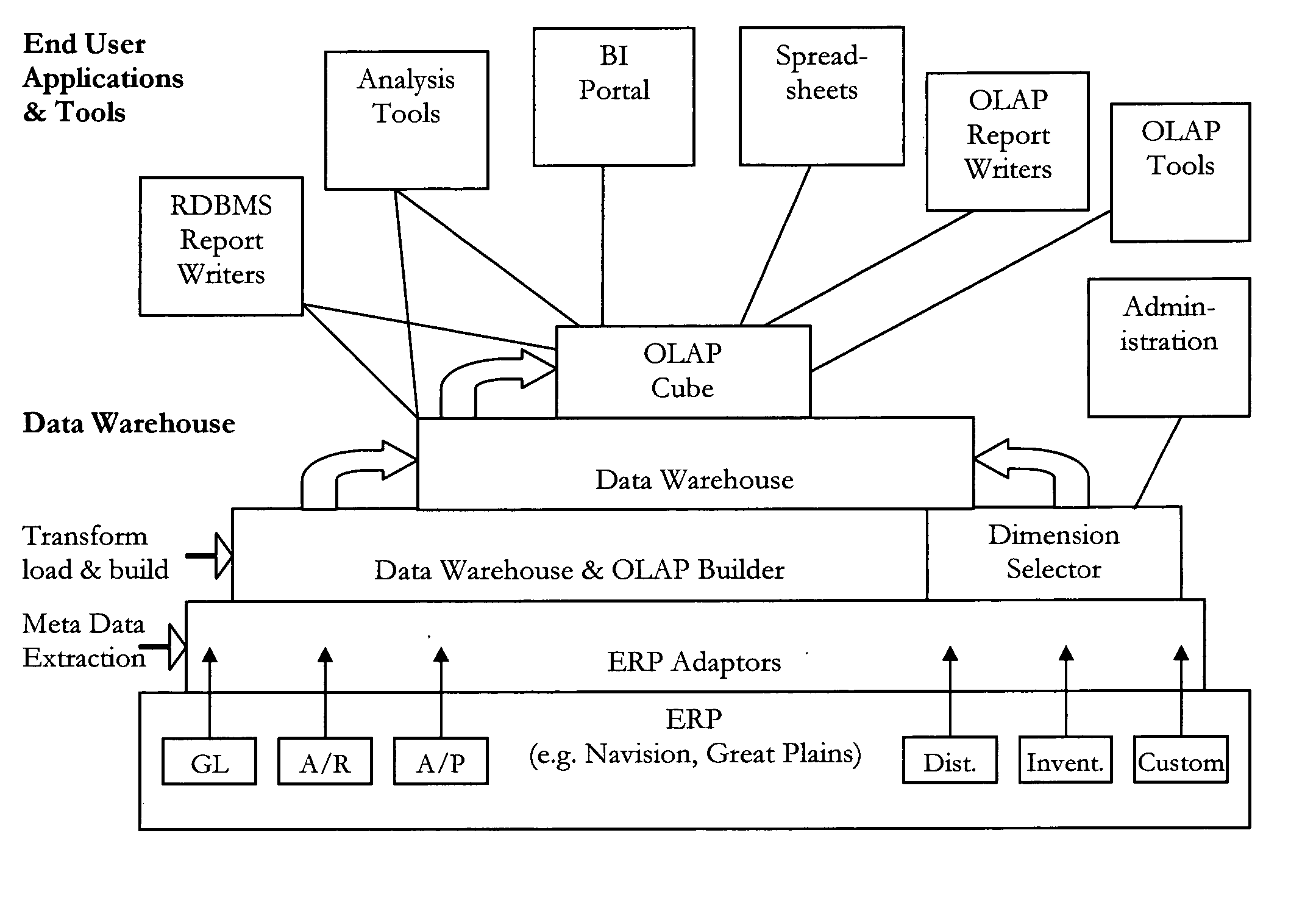
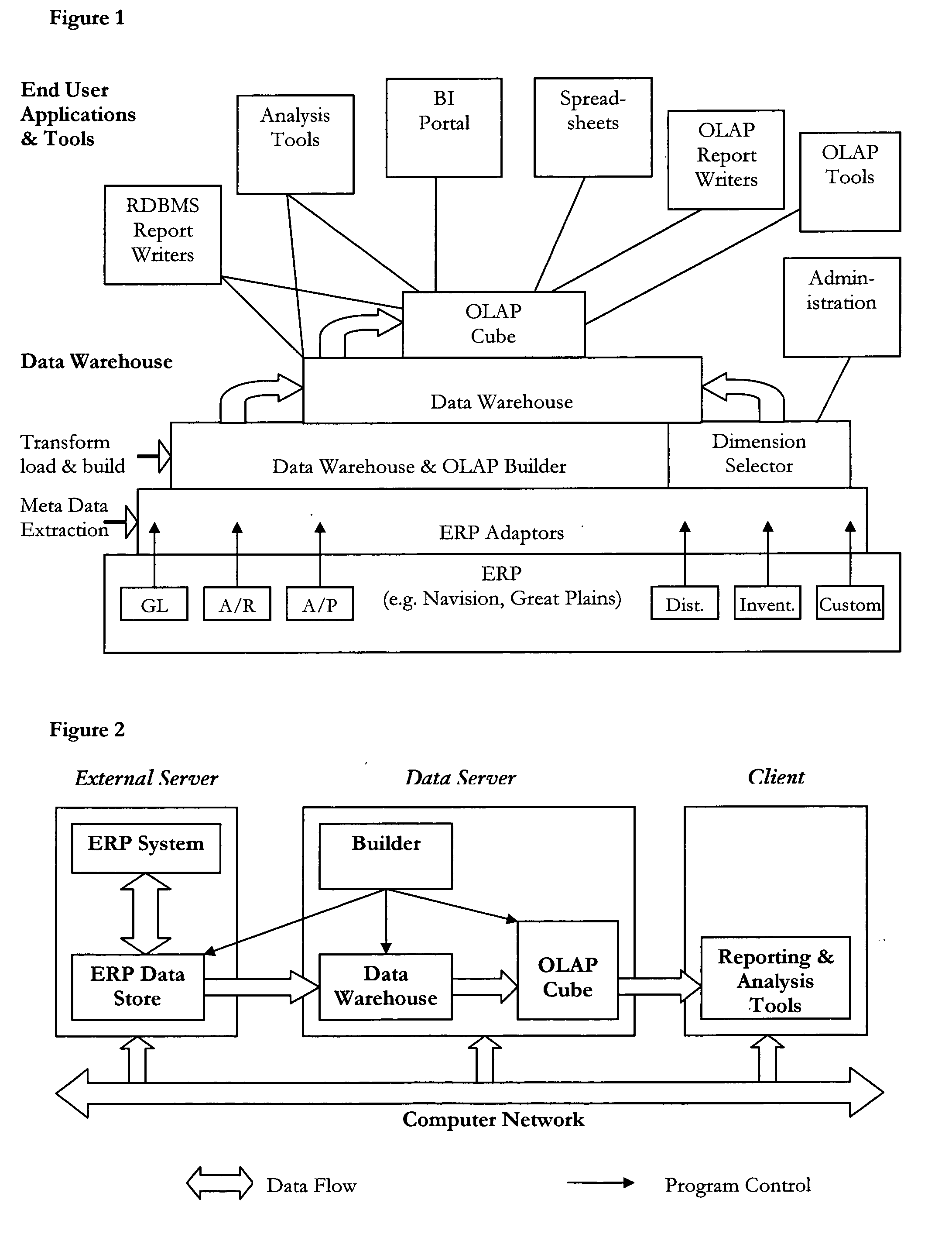
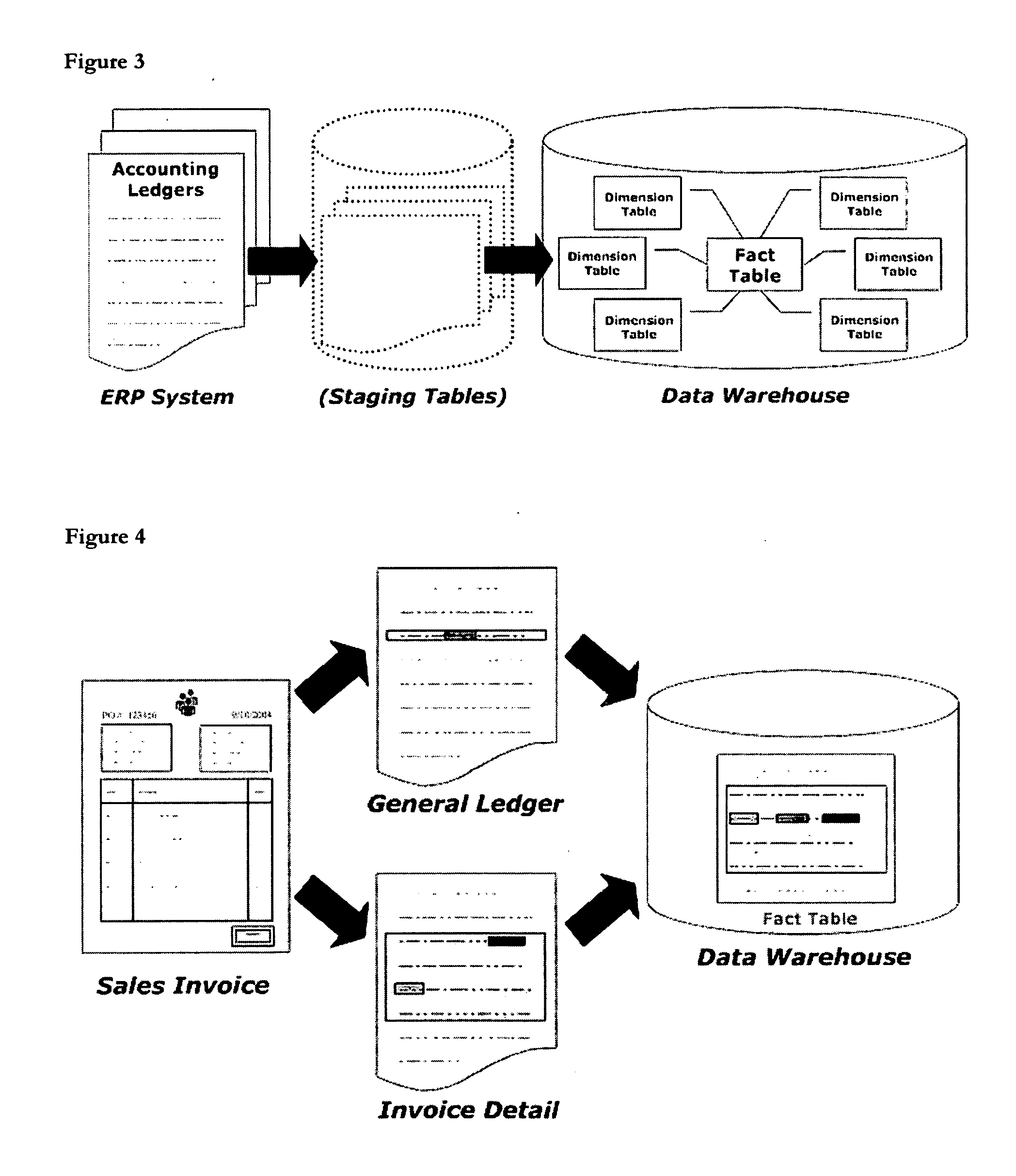
Method and apparatus for automatically creating a data warehouse and OLAP cube
ActiveUS20050246357A1Facilitate efficient retrievalEasy to analyzeDigital data processing detailsMulti-dimensional databasesData warehouseData set
A data warehouse design that combines data from multiple source ledgers or modules is constructed and from that an associated, single physical Star or Snow-Flake schema and OLAP hyper-cube analytic structure is generated to enable cross-functional analysis of any those multiple source ledgers or modules. The step of constructing the data warehouse or the step of generating the associated OLAP cube is achieved without significant human intervention using software. The present invention is based on the insight that the technical bias against generating individual data marts and OLAP cubes from multiple source ledgers is not well founded. Previously, the norm has been to generate a single physical OLAP cube for each individual ledger—hence one for the General Ledger, a further one for sales order processing etc. This prior art approach makes cross functional analysis multiple source ledgers and sub-ledgers difficult since it requires the creation of a further level of physical or virtual cubes across multiple physical cubes and complex querying. This is no longer necessary with the present invention.
Owner:ANALYSOFT DEV
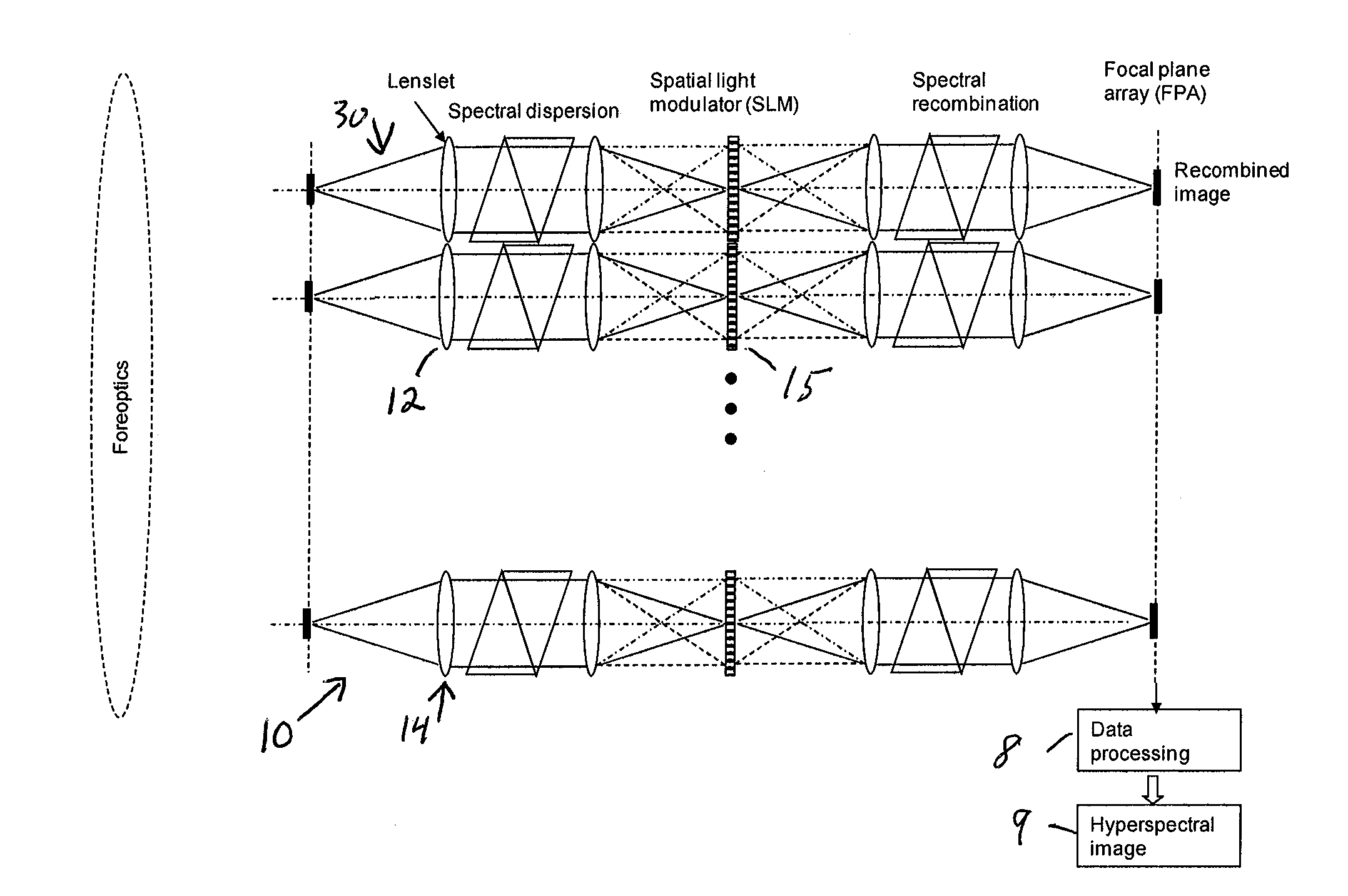
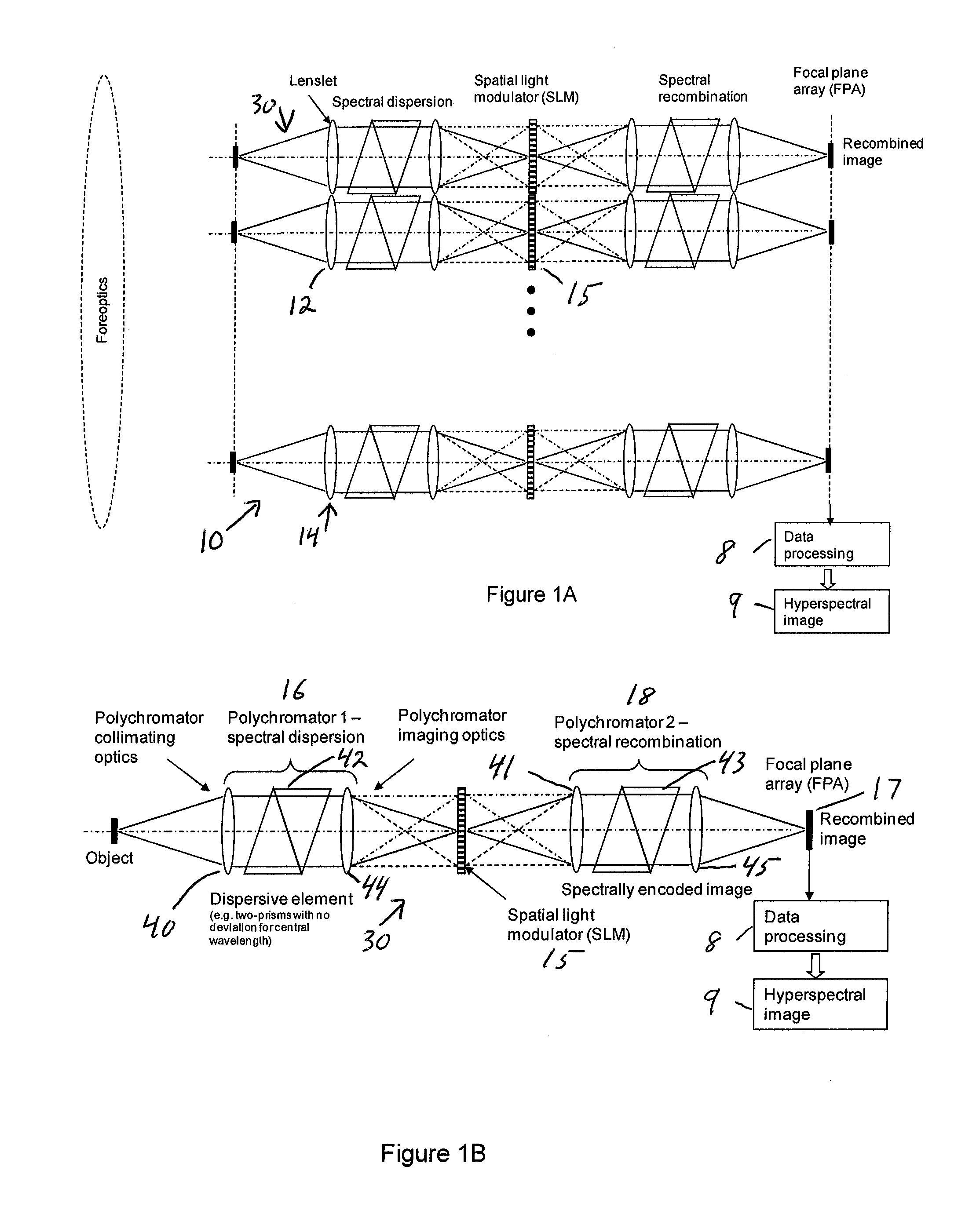
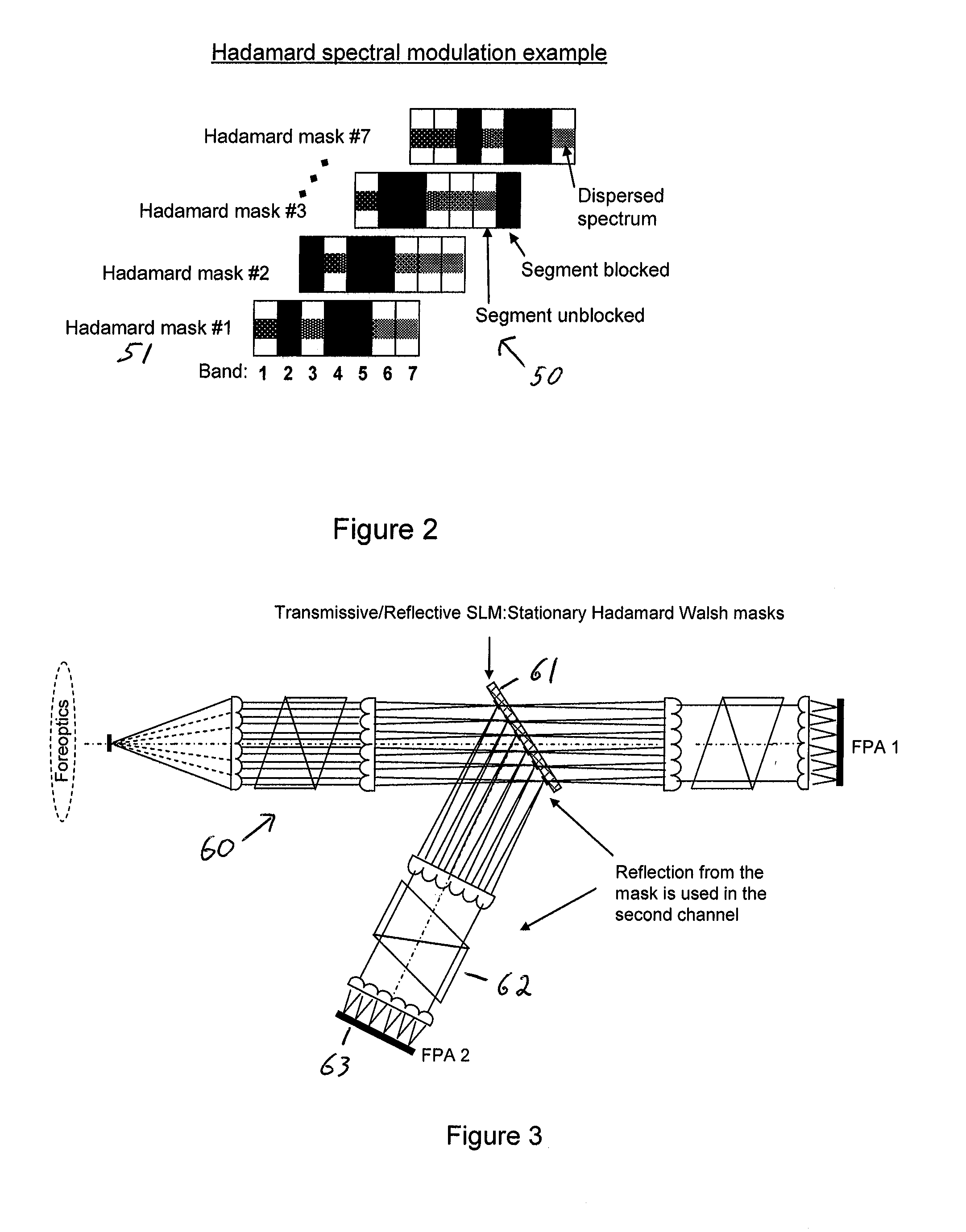
Single-Shot Spectral Imager
ActiveUS20100309467A1Improve spatial resolutionEasy to useRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using refracting elementsMultiplexingSpatial light modulator
A single-shot spectral imager or imaging system which acquires multiplexed spatial and spectral data in a single snapshot with high optical collection efficiency and with the speed limited only by the readout time of the detector circuitry. The imager uses dispersive optics together with spatial light modulators to encode a mathematical transform onto the acquired spatial-spectral data. A multitude of encoded images is recorded simultaneously on a focal plane array and subsequently decoded to produce a spectral / spatial hypercube.
Owner:SPECTRAL SCI
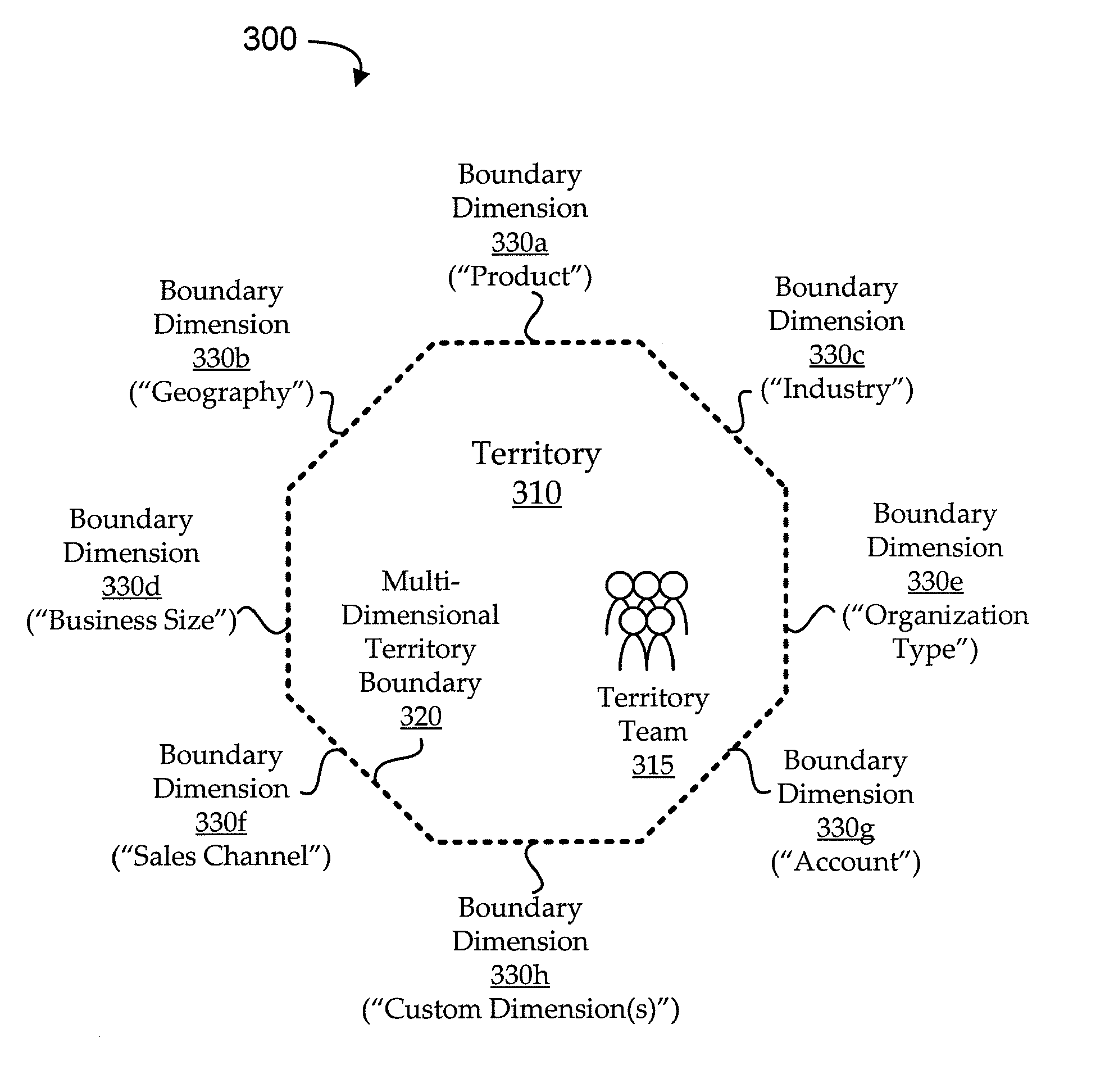
Reassignment and reconciliation for multi-dimensional sales territories
InactiveUS20110040697A1Minimizing and eliminating needImprove efficiencyResourcesData miningMulti dimensional
Embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for using multi-dimensional modeling techniques to handle gaps, overlaps, and reassignments of opportunities for sales territory management. Embodiments use multi-dimensional modeling to define territories in such a way that accounts for applicable territory criteria as sets with logical boundaries, rather than as a defined rule-based architecture (e.g., as dimensions in a territory hypercube). The multi-dimensional model is de-normalized to capture the multi-dimensional nature of the sales territory definitions while, for example, flattening hierarchical trees and minimizing or eliminating the need for ordinal processing of the data. In some embodiments, the de-normalized territory definitions are used to facilitate efficient and reliable gap and / or overlap processing (e.g., detection, reconciliation, etc.). In other embodiments, the de-normalized territory definitions are used to optimize identification of territory regions where reassignment of opportunities is appropriate and / or to reassign opportunities in those regions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
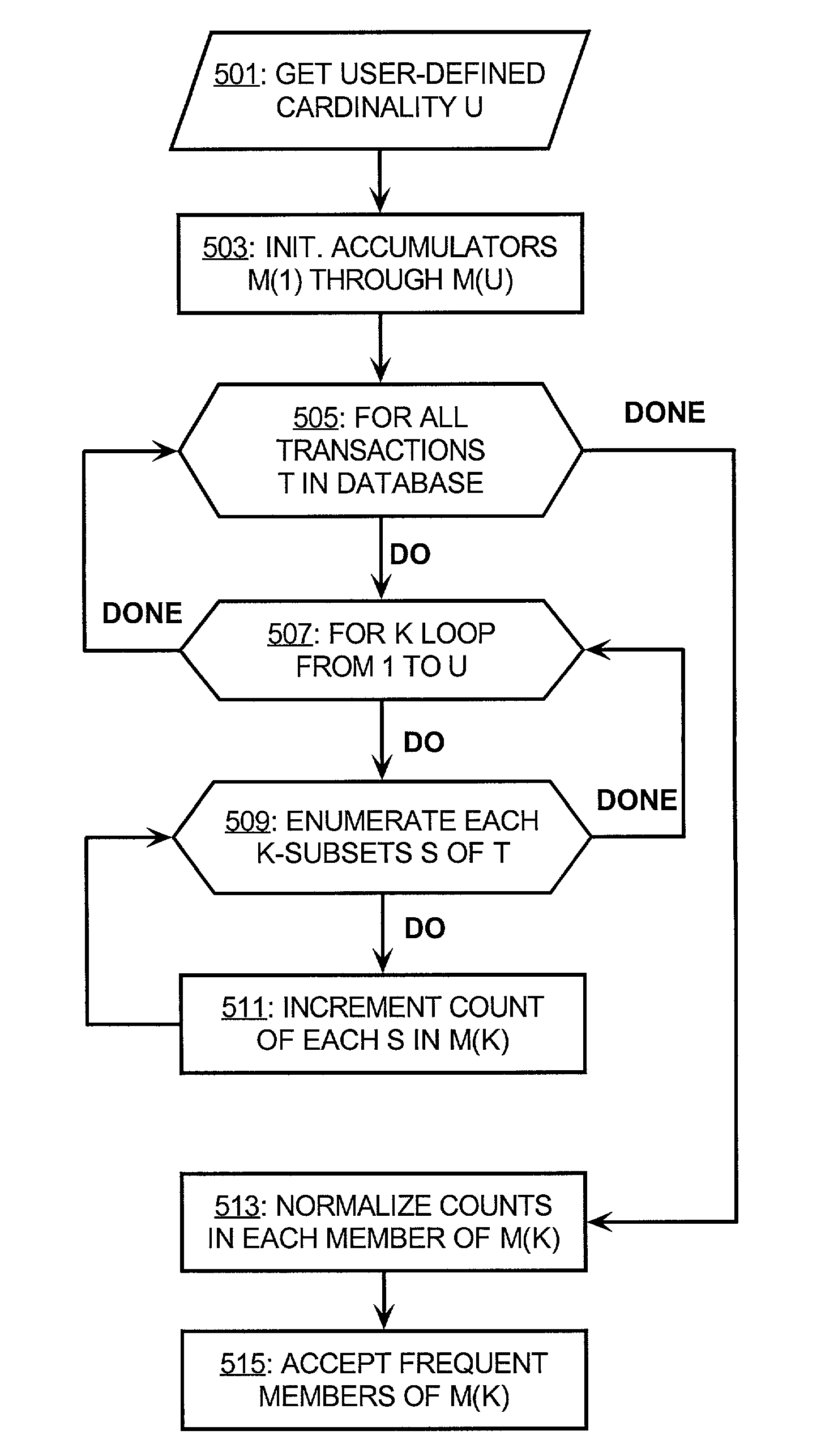
Method for extracting association rules from transactions in a database
ActiveUS7370033B1Lower performance requirementsPerformance penaltyDigital data processing detailsMulti-dimensional databasesDirect computationComputation complexity
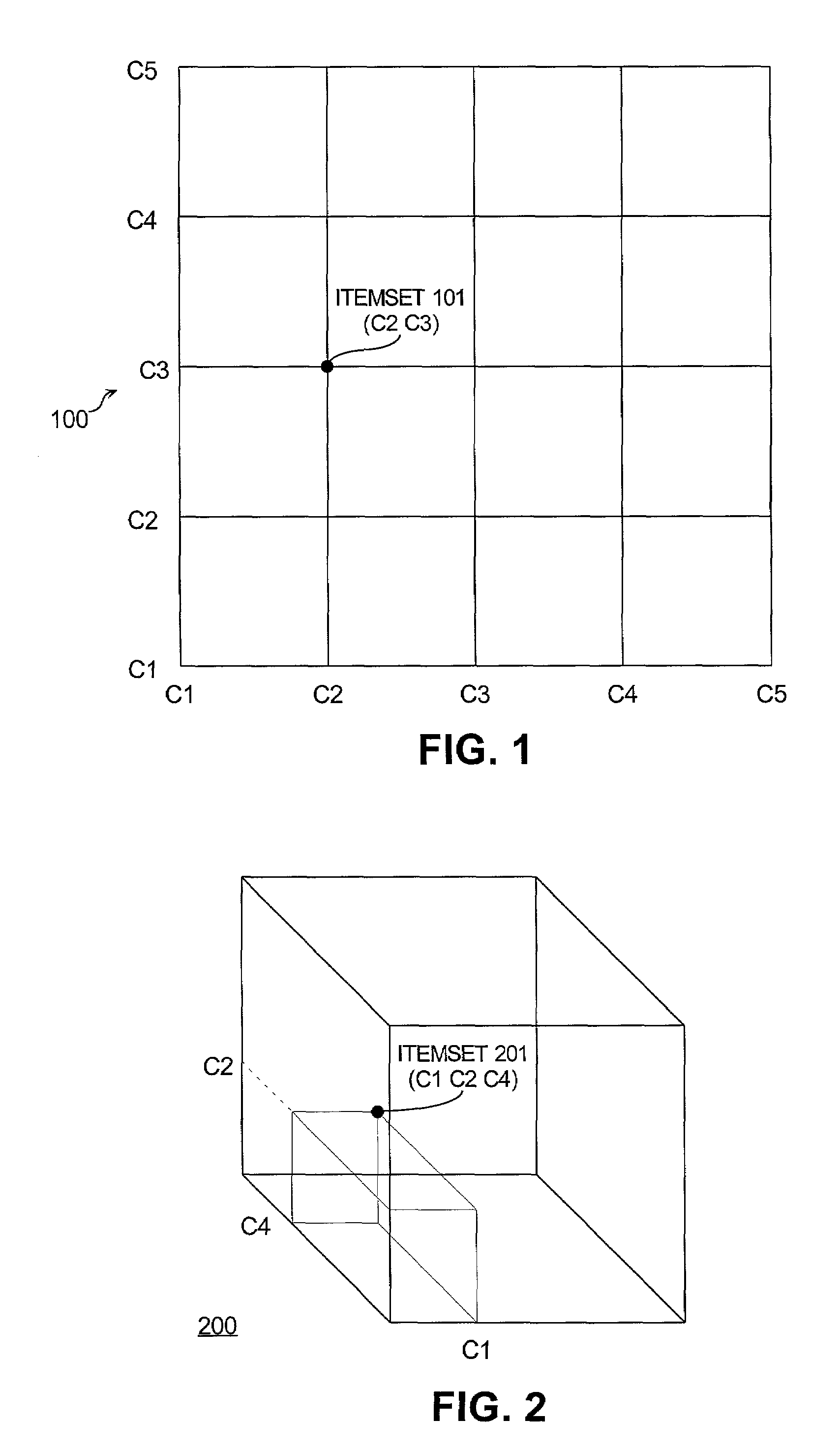
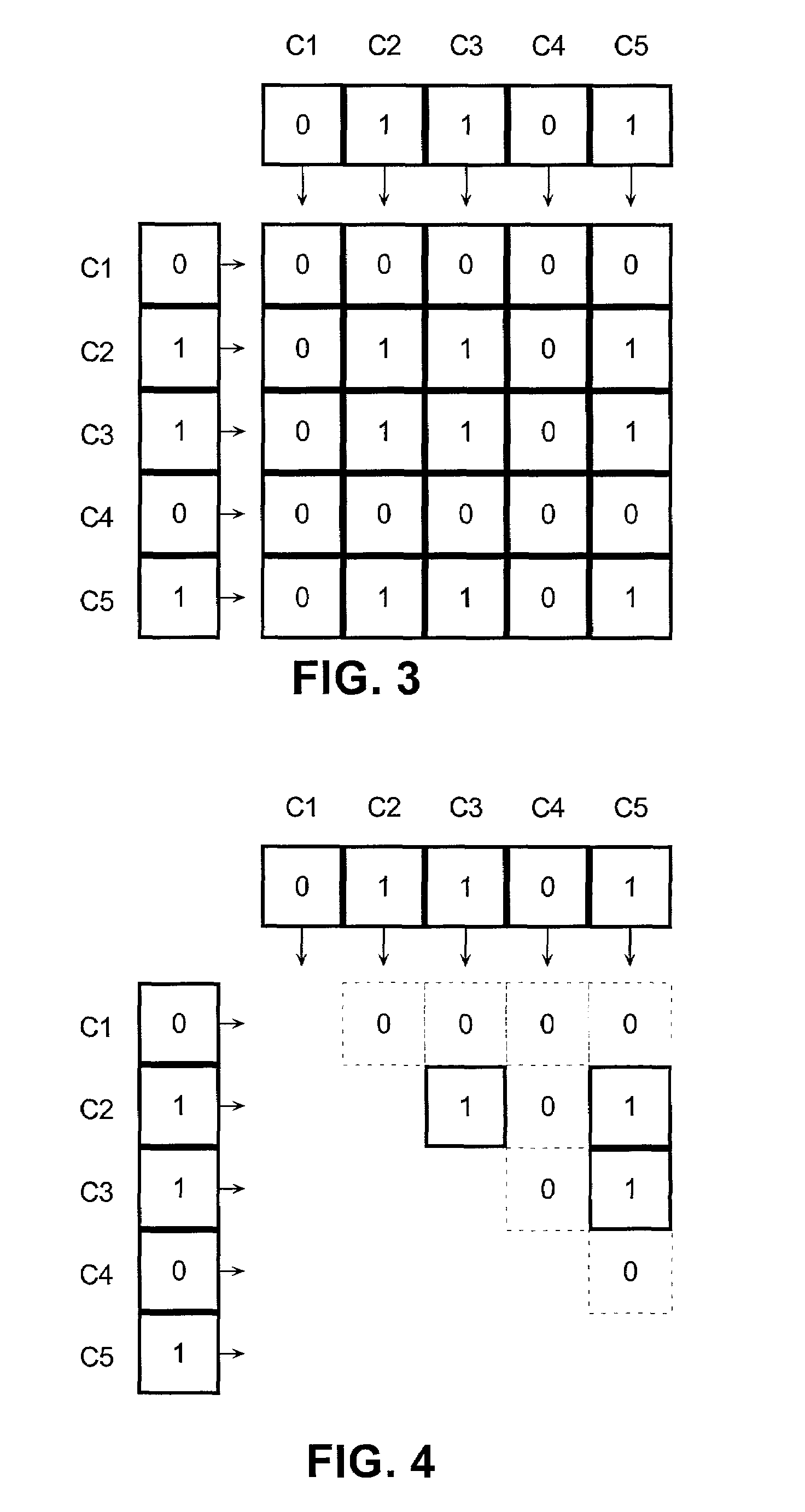
Apriori algorithms are popular data mining techniques for extracting association rules from a body of data. The computational complexity of these algorithms is reduced by representing itemset information at cells of a hypercube. The cells encode associations between the items of each transaction. Direct computation of a cell as a lexicographic combination of items accelerates the computation of itemsets, and thereby improves the computational runtime complexity of the apriori algorithm that discovers association rules. Even faster computation is achieved by a user selected cardinality that limits the maximum size of the itemsets.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
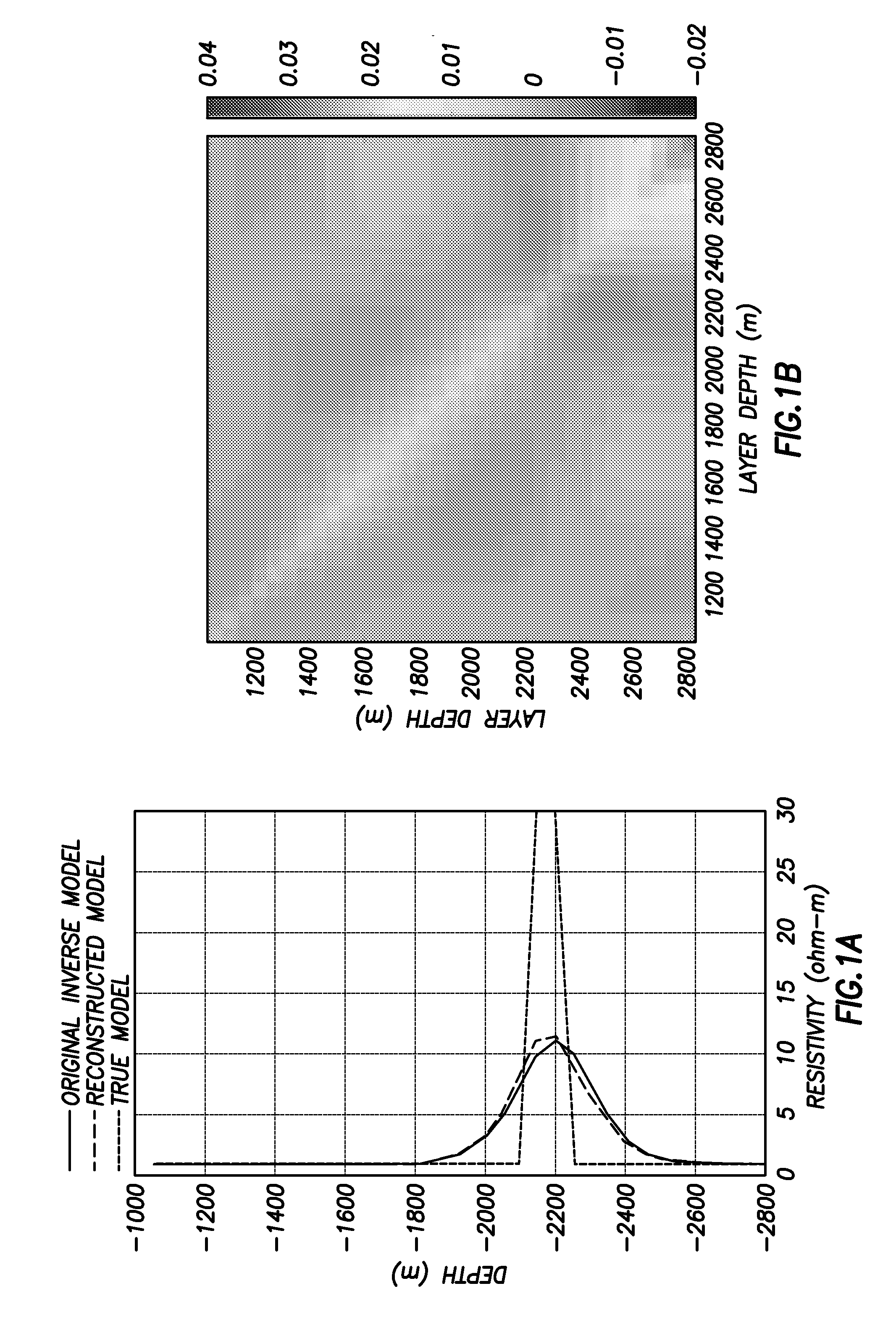
Uncertainty estimation for large-scale nonlinear inverse problems using geometric sampling and covariance-free model compression
ActiveUS20130185033A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationModel sampleModel parameters
A method for uncertainty estimation for nonlinear inverse problems includes obtaining an inverse model of spatial distribution of a physical property of subsurface formations. A set of possible models of spatial distribution is obtained based on the measurements. A set of model parameters is obtained. The number of model parameters is reduced by covariance free compression transform. Upper and lower limits of a value of the physical property are mapped to orthogonalspace. A model polytope including a geometric region of feasible models is defined. At least one of random and geometric sampling of the model polytope is performed in a reduced-dimensional space to generate an equi-feasible ensemble of models. The reduced-dimensional space includes an approximated hypercube. Probable model samples are evaluated based on data misfits from among an equi-feasible model ensemble determined by forward numerical simulation. Final uncertainties are determined from the equivalent model ensemble and the final uncertainties are displayed in at least one map.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
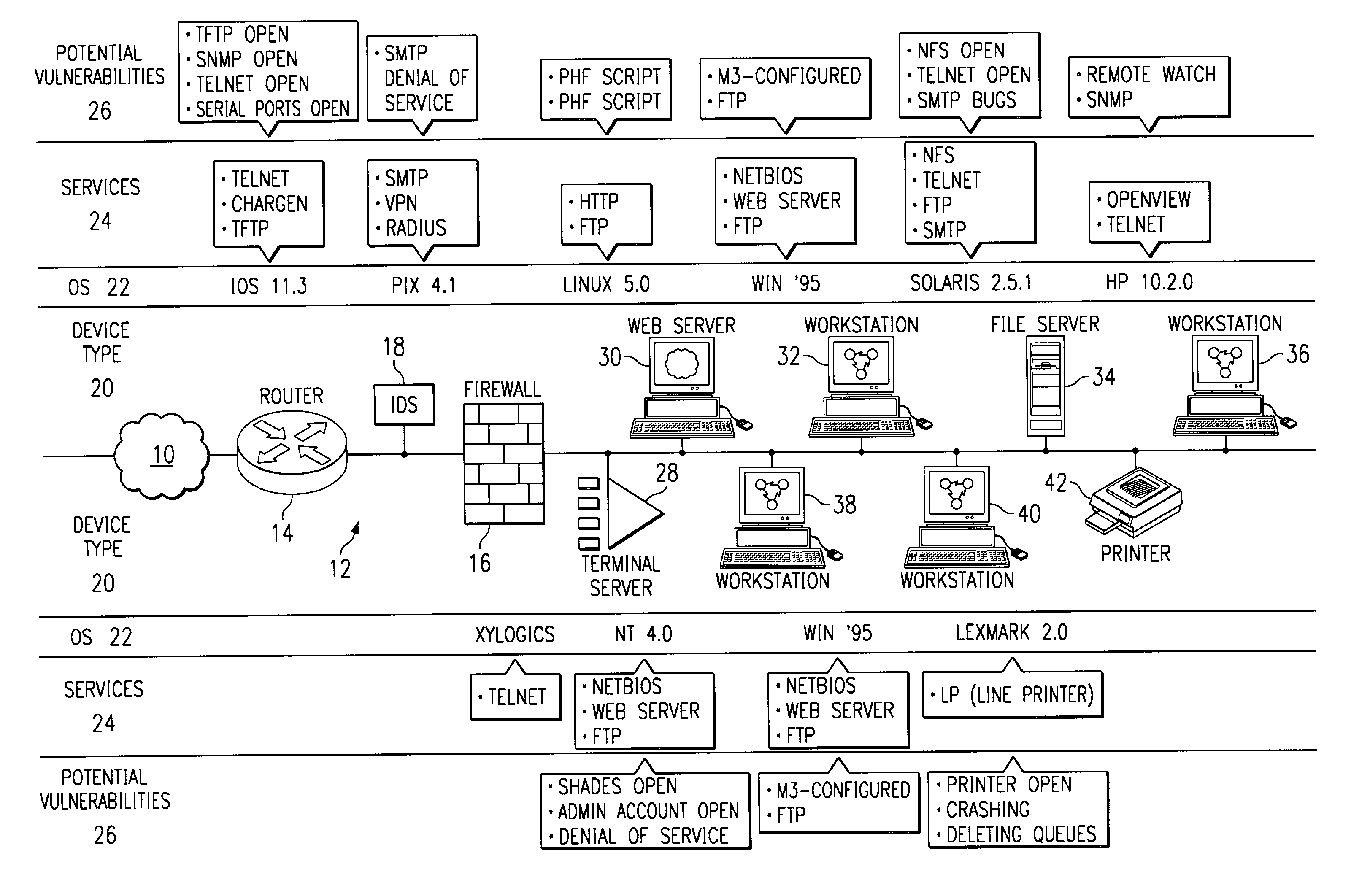
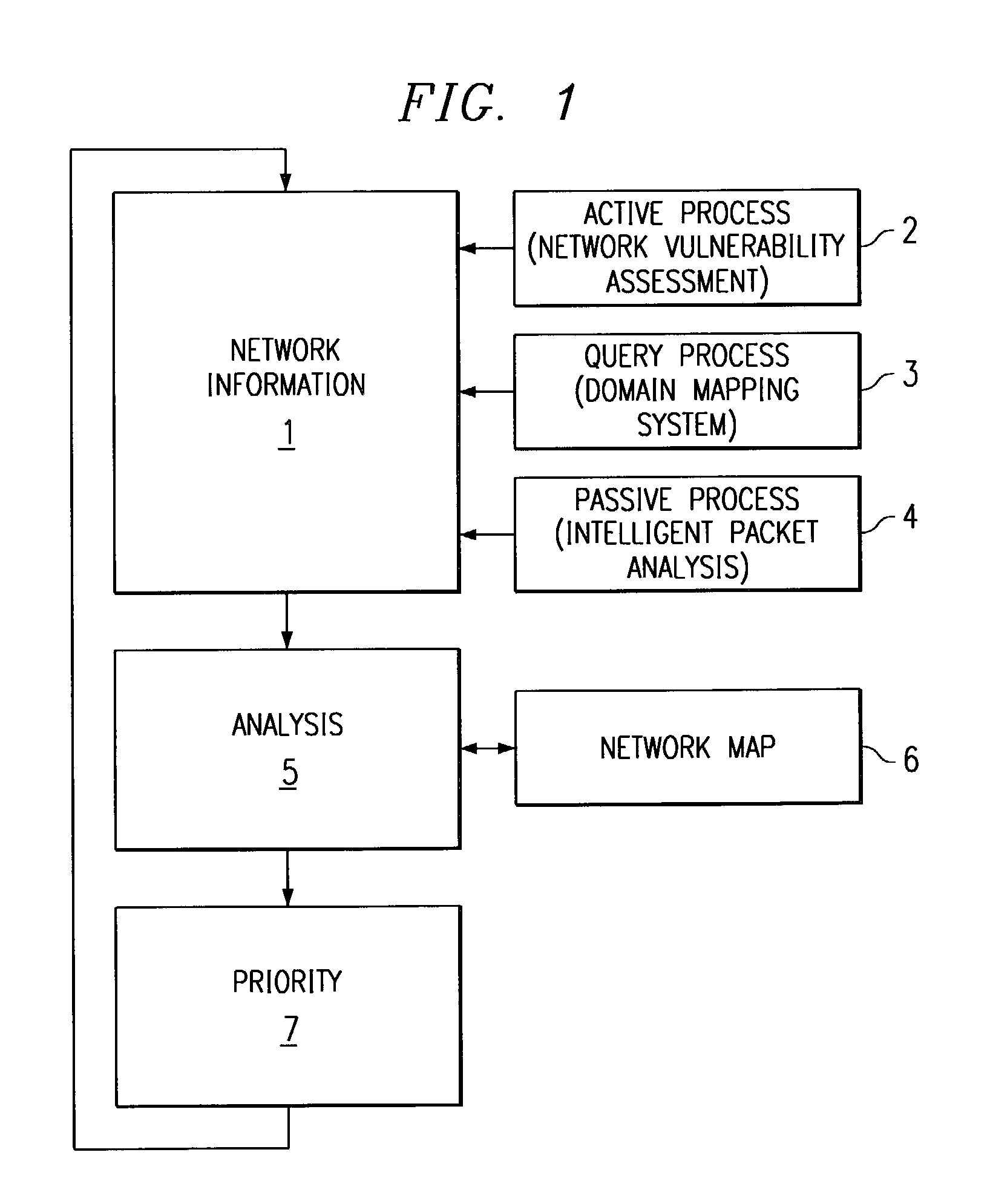
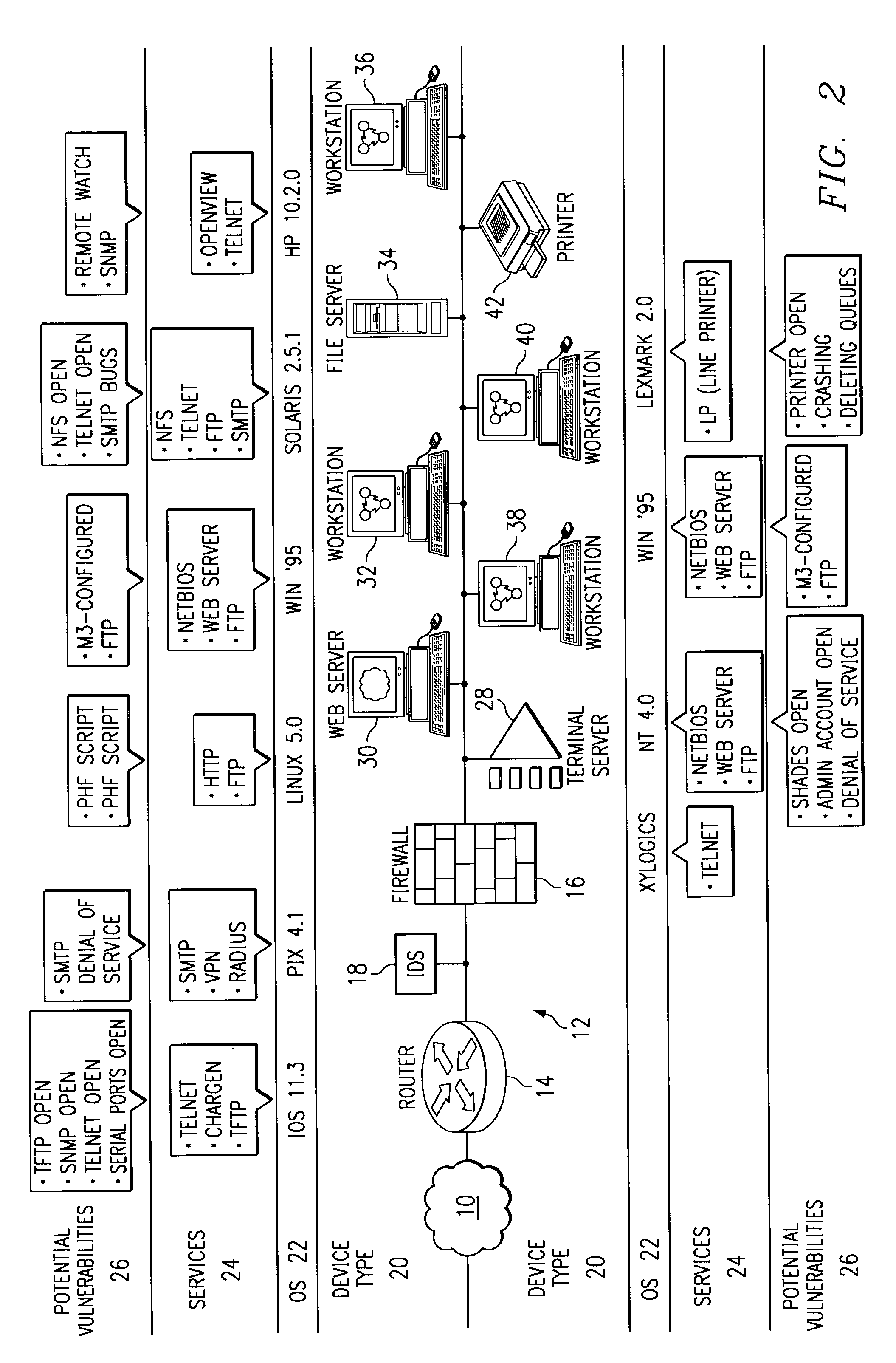
Method and system for mapping a network for system security
InactiveUS6968377B1Reduce overheadShorten the timeDigital computer detailsData switching networksDevice typeOperational system
A method and system for mapping a network domain provides a centralized repository for network information to support network devices, including an intrusion detection system. A domain mapping device includes an acquisition engine for acquiring network information, hypercube storage for storing network information, and a query engine for responding to queries from network devices for network information. The acquisition engine acquires network information by active scanning of network devices, passive scanning of network devices, polling of network devices, or receiving network information pushed from network devices. The network information includes device type, operating system, service and vulnerability information. The query engine provides network information in response to queries from network devices, such as intrusion detection devices that use the data to detect attacks on the vulnerabilities of the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
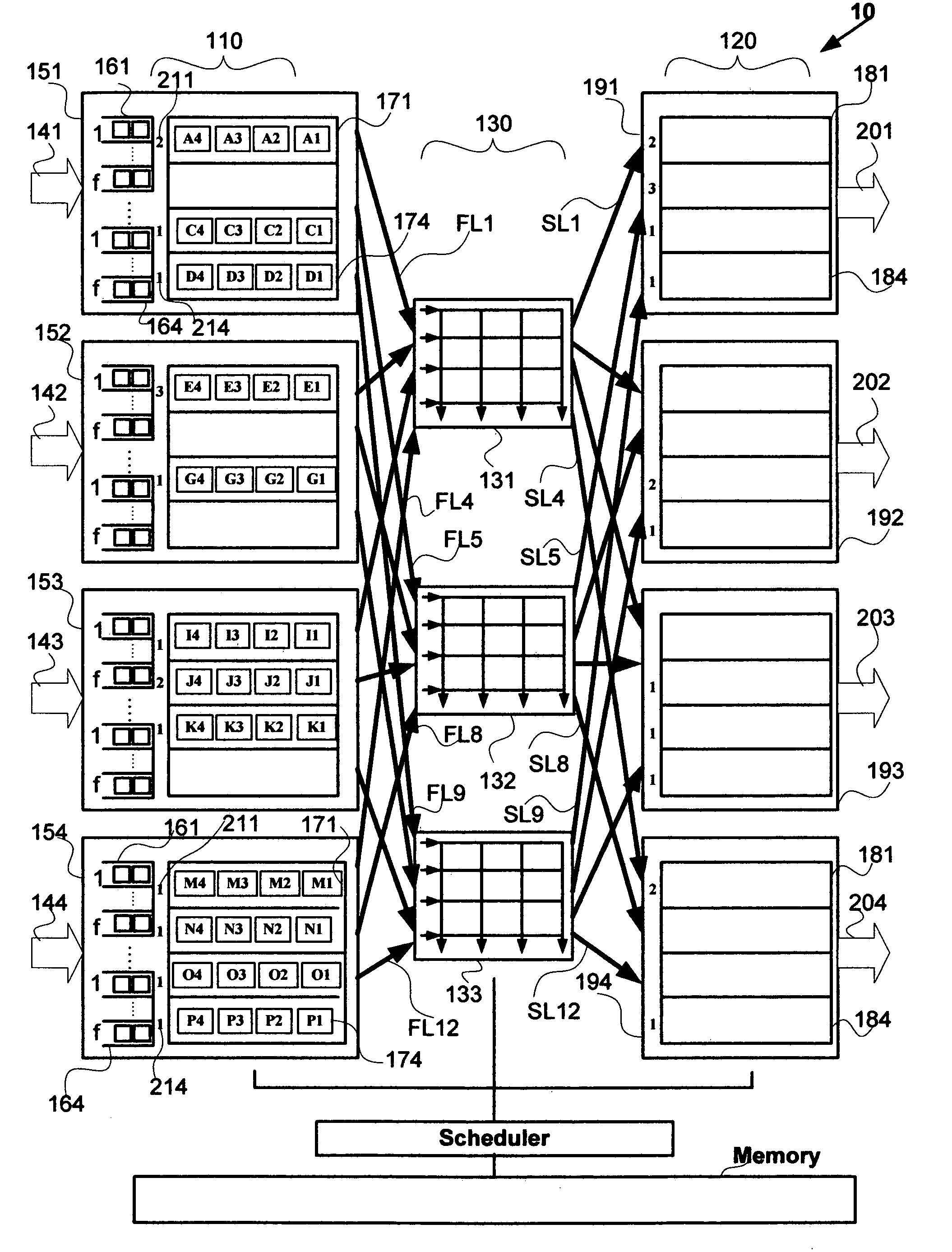
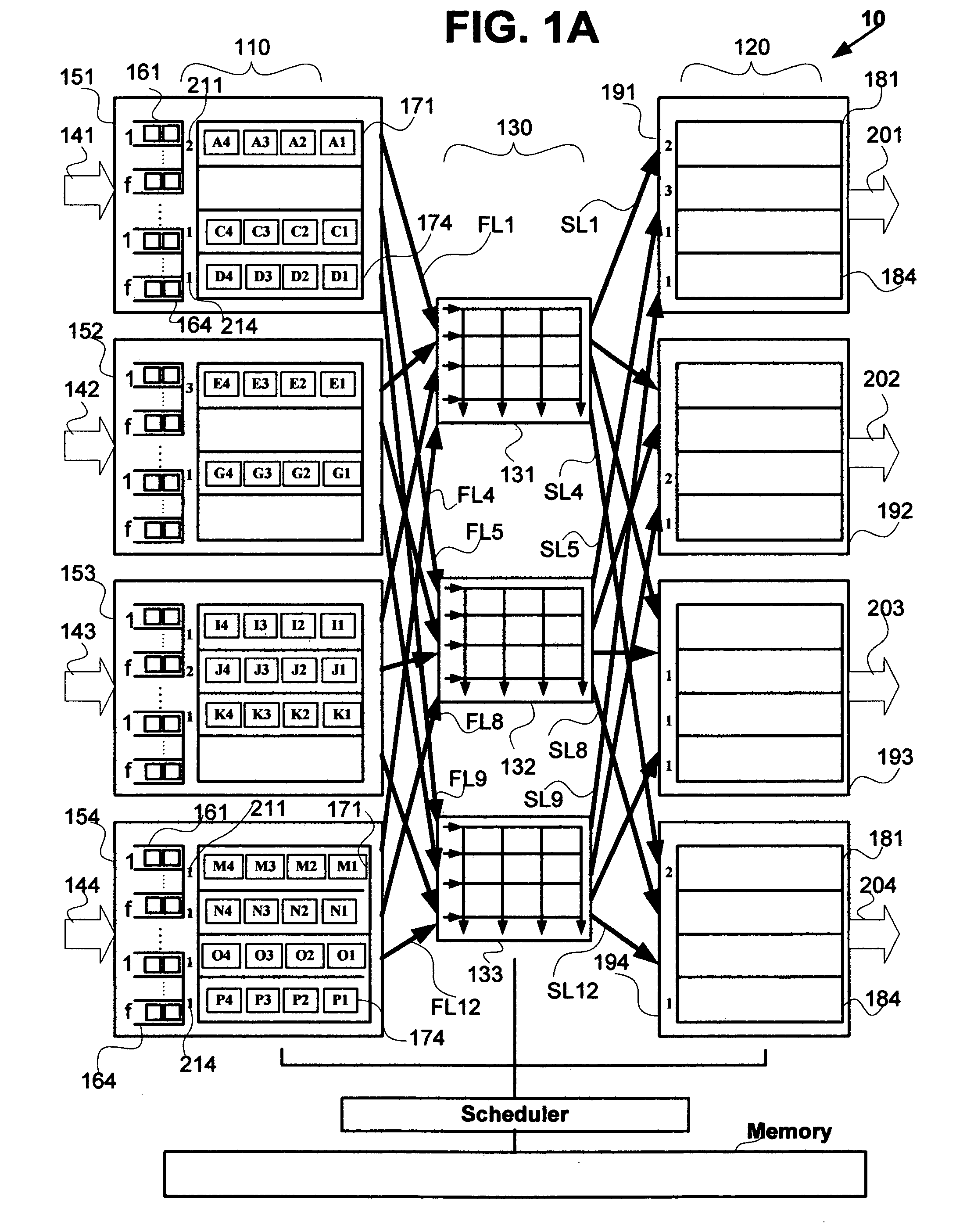
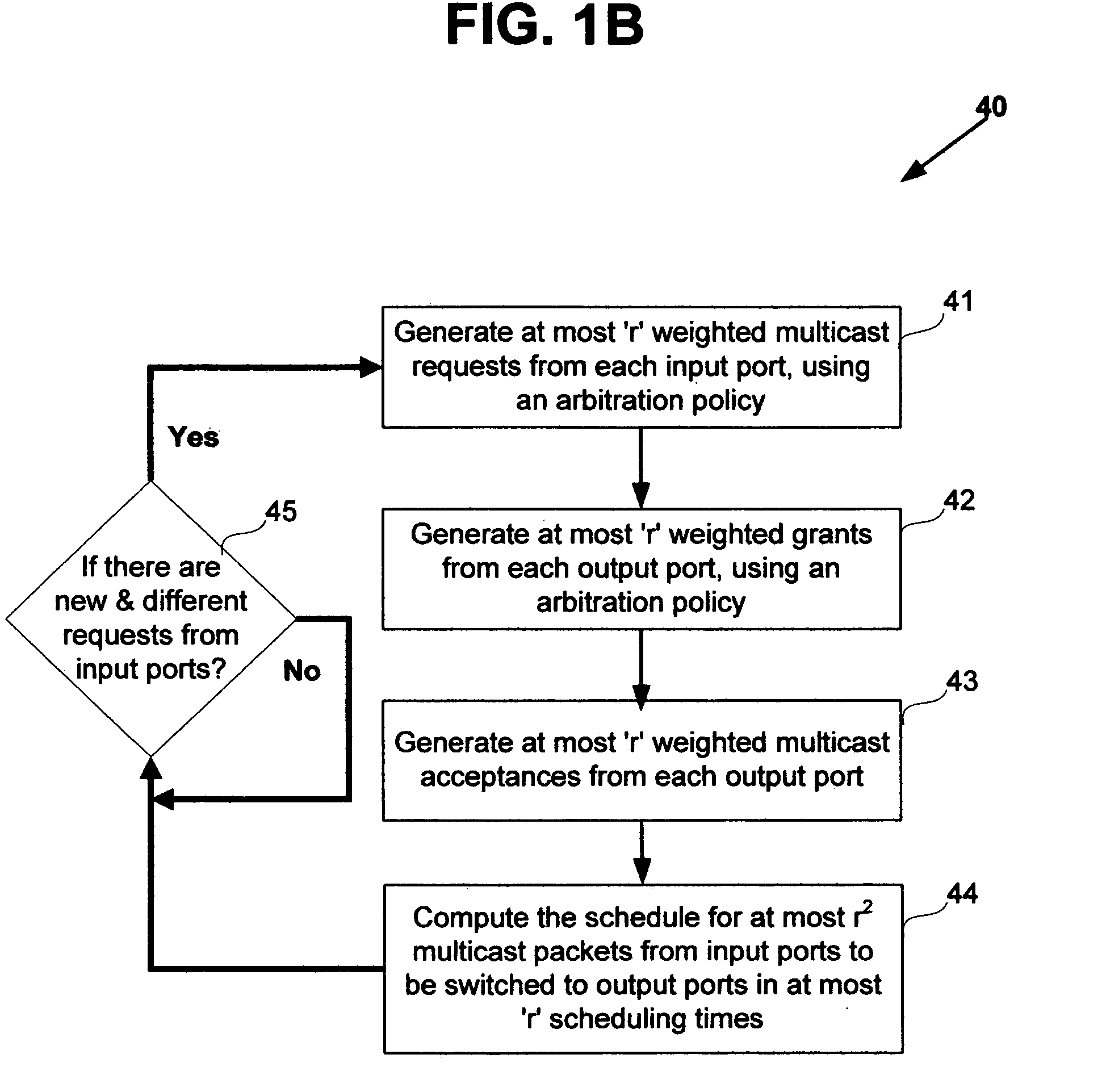
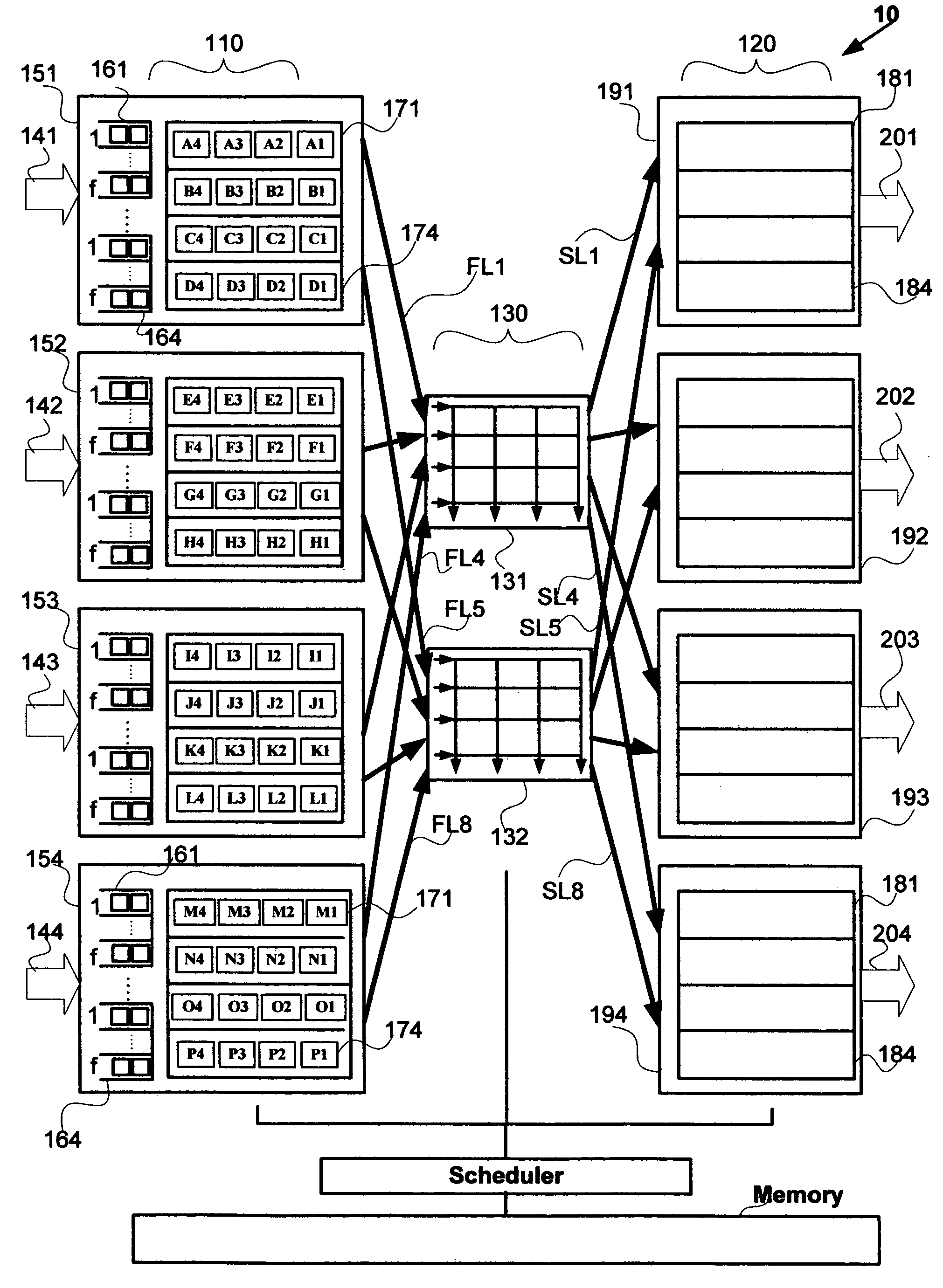
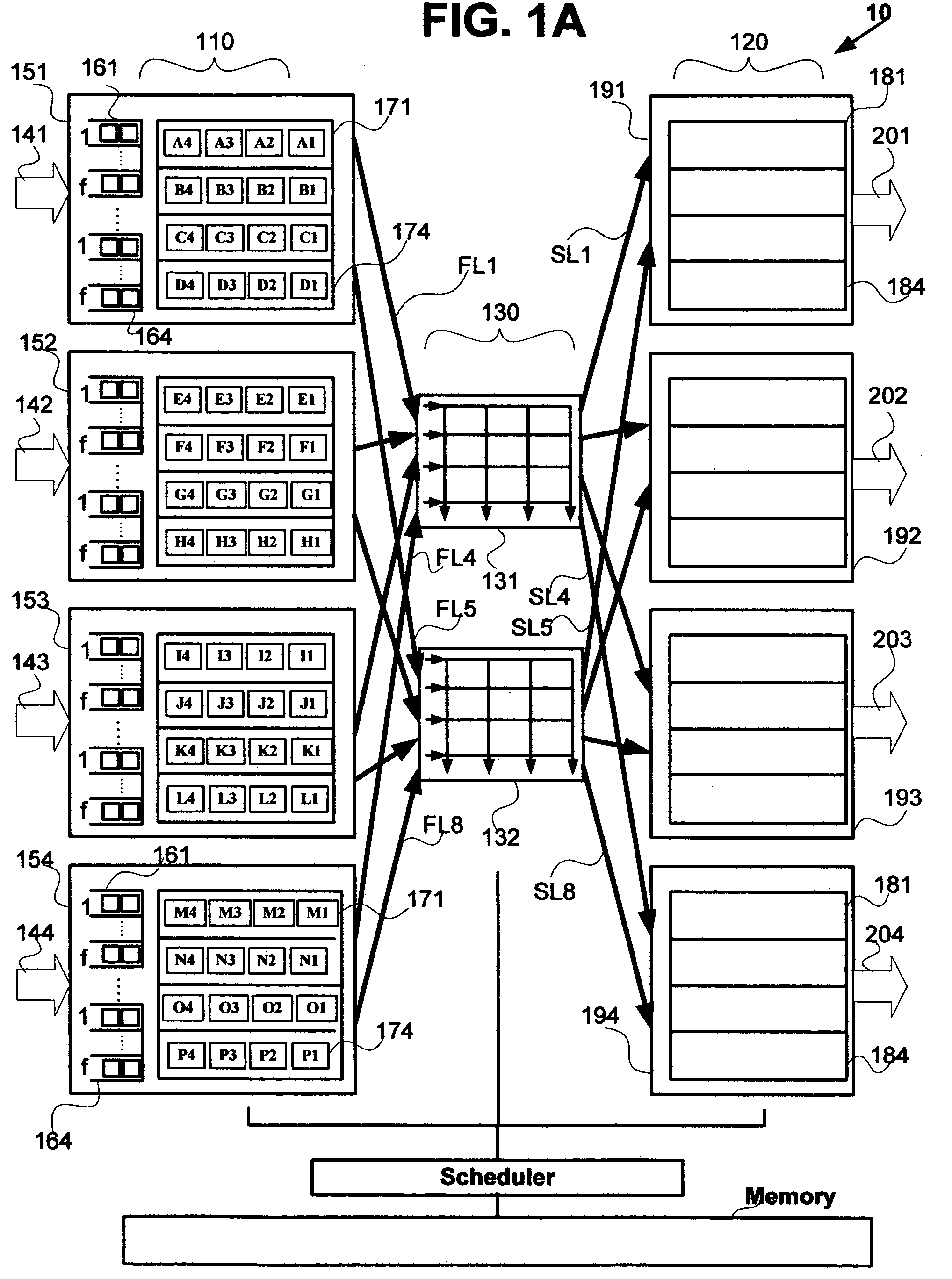
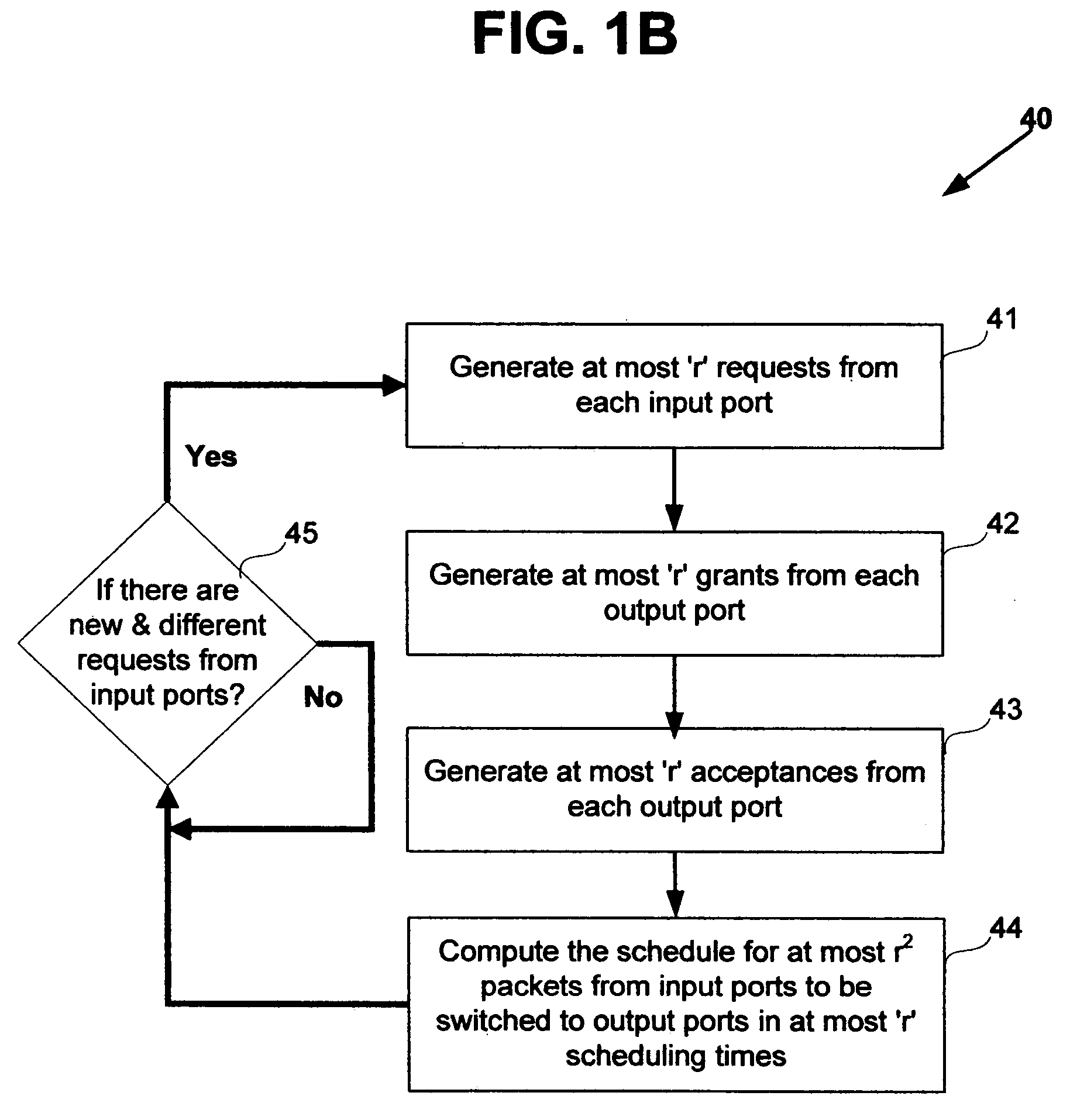
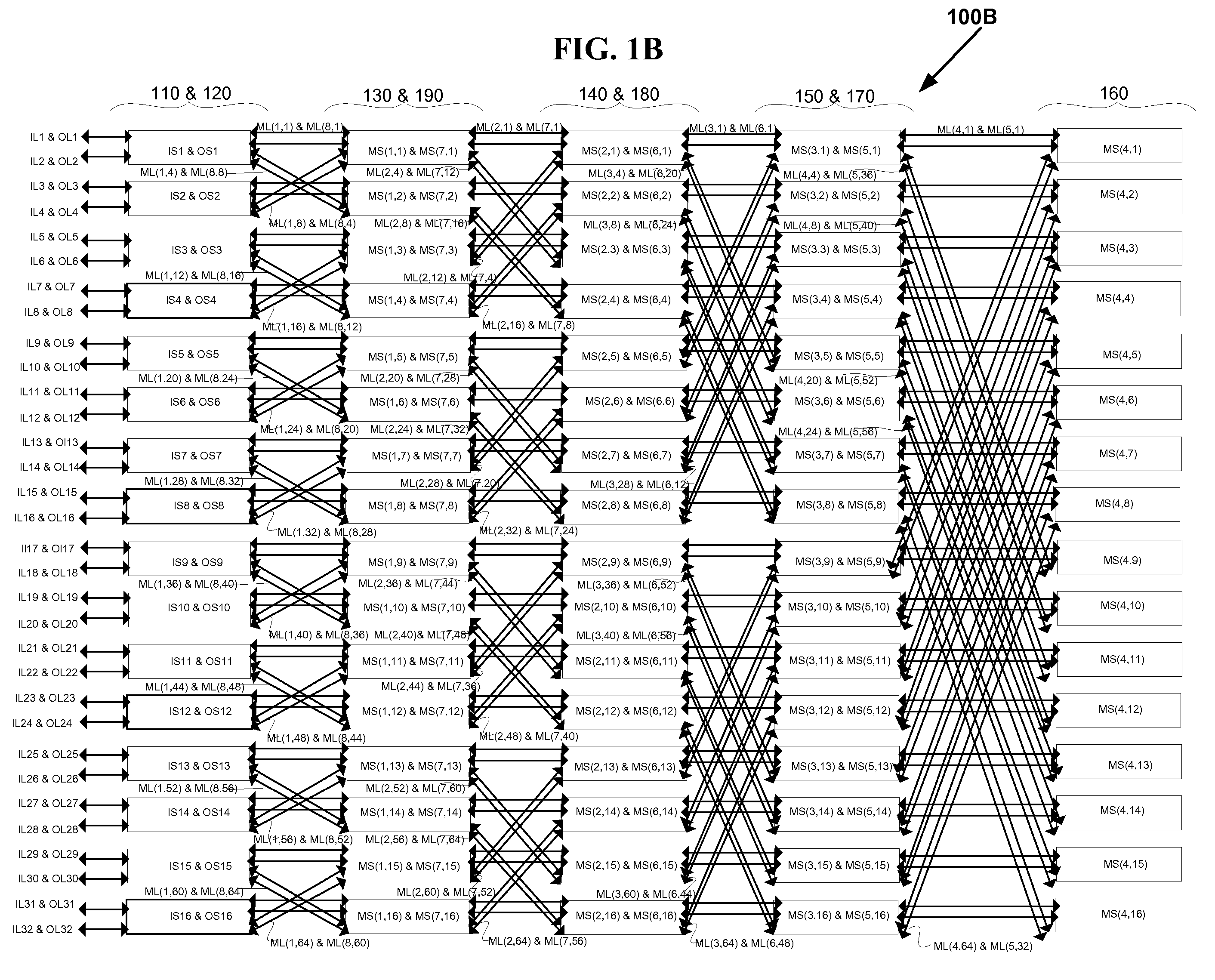
Nonblocking and deterministic multirate multicast packet scheduling
InactiveUS20070053356A1Guaranteed bandwidthGuaranteed LatencyData switching by path configurationSwitching timeMulti rate
A system for scheduling multirate multicast packets through an interconnection network having a plurality of input ports, a plurality of output ports, and a plurality of input queues, comprising multirate multicast packets with rate weight, at each input port is operated in nonblocking manner in accordance with the invention by scheduling corresponding to the packet rate weight, at most as many packets equal to the number of input queues from each input port to each output port. The scheduling is performed so that each multicast packet is fan-out split through not more than two interconnection networks and not more than two switching times. The system is operated at 100% throughput, work conserving, fair, and yet deterministically thereby never congesting the output ports. The system performs arbitration in only one iteration, with mathematical minimum speedup in the interconnection network. The system operates with absolutely no packet reordering issues, no internal buffering of packets in the interconnection network, and hence in a truly cut-through and distributed manner. In another embodiment each output port also comprises a plurality of output queues and each packet is transferred corresponding to the packet rate weight, to an output queue in the destined output port in deterministic manner and without the requirement of segmentation and reassembly of packets even when the packets are of variable size. In one embodiment the scheduling is performed in strictly nonblocking manner with a speedup of at least three in the interconnection network. In another embodiment the scheduling is performed in rearrangeably nonblocking manner with a speedup of at least two in the interconnection network. The system also offers end to end guaranteed bandwidth and latency for multirate multicast packets from input ports to output ports. In all the embodiments, the interconnection network may be a crossbar network, shared memory network, clos network, hypercube network, or any internally nonblocking interconnection network or network of networks.
Owner:TEAK TECH
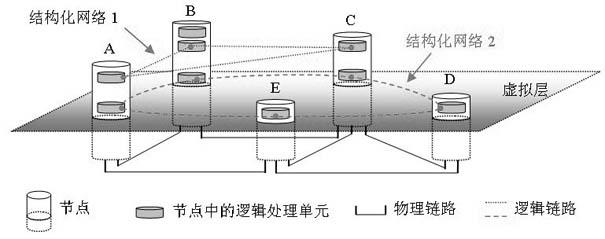
Structured network system applicable to future internet
InactiveCN102523166AEliminate blockingLoad balancingData switching networksContent distributionScale structure
The invention provides a structured network system applicable to the future internet, which constructs and maintains a plurality of concomitant structured networks (SNs) on a physical network through a virtual layer. The system can construct the structured future internet on a large-scale structure-free network, adopt globally unified and simple addressing, route and inquiring mechanisms, and enable route inquiring time, network interoperability or interconnection, content distribution efficiency and service obligation to be greatly improved. Practical examples of the structured network comprise hypercube networks, artificial neural networks and Batcher networks. Achieved functions comprise content / service addressing, semanteme searching, and mobile supporting, safe service based on positions, multicast, intrusion detection, network measurement, data fusion, webpage grading and flow load balancing.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
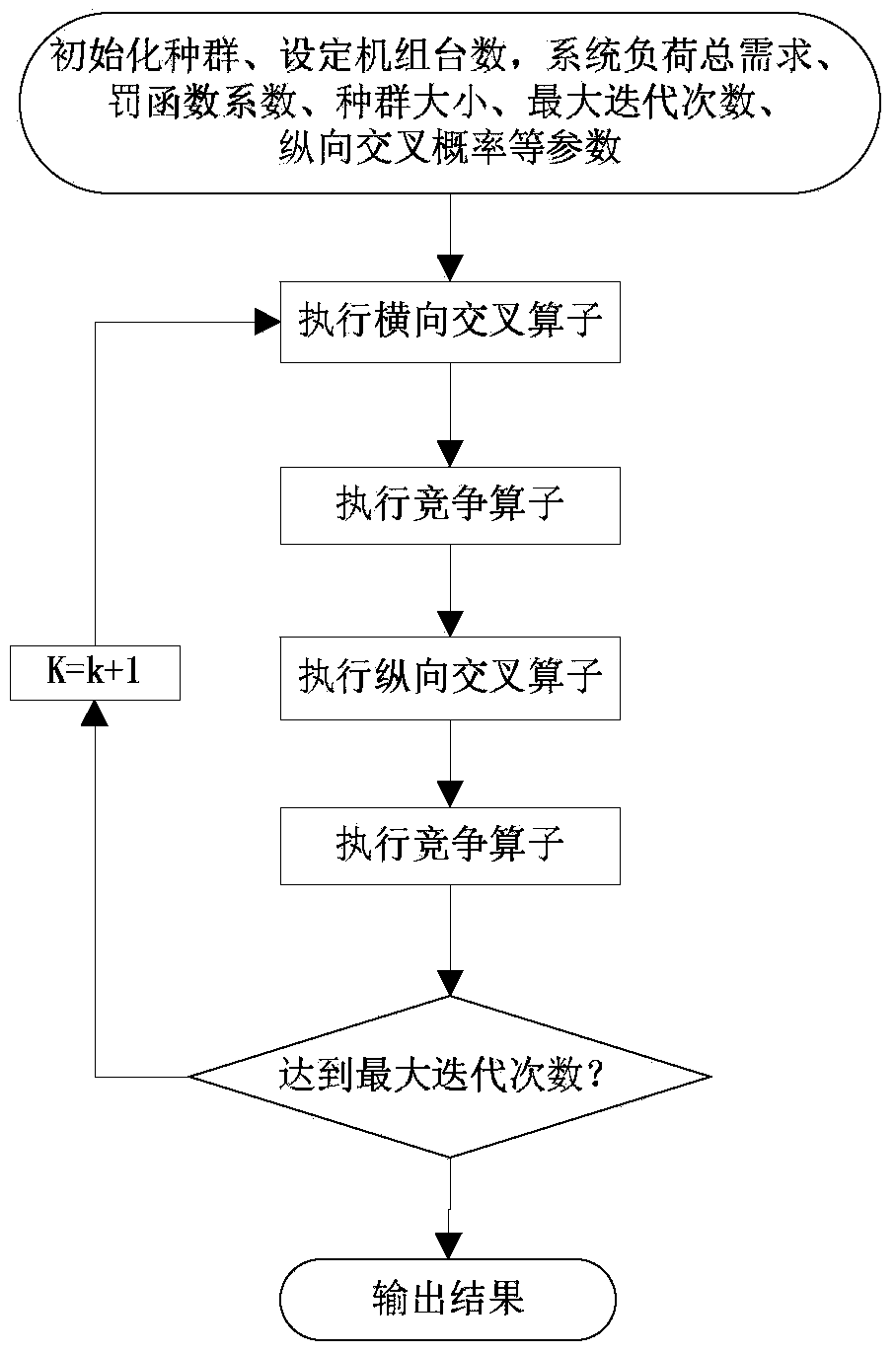
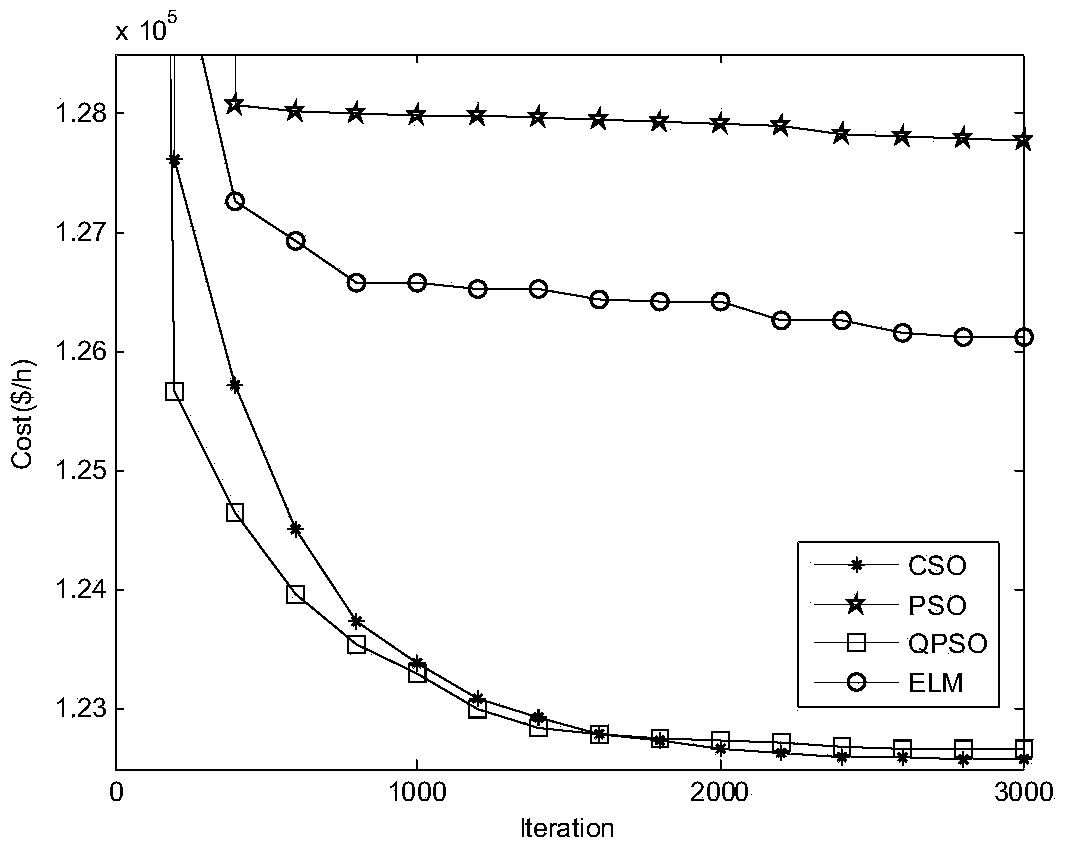
Electric system economic dispatching optimization method based on criss-cross algorithm
InactiveCN104239961ASimple stepsFew control parametersForecastingSystems intergating technologiesHypercubeCriss-cross algorithm
The invention discloses an electric system economic dispatching optimization method based on a criss-cross algorithm. The criss-cross algorithm is a brand new swarm intelligence optimization algorithm and mainly comprises a horizontal cross operator and a longitudinal cross operator, wherein a multi-dimensional optimizing space is divided into hypercubes with half of the population size through horizontal cross, and each pair of paired parent particles searches for filial generations in its hypercube subspace and the periphery of the hypercube subspace; arithmetic cross search is executed on different dimensions in the population with a certain probability through longitudinal cross; a domination solution obtained from a moderate solution generated through two kinds of cross through a competition operator will rapidly spread into the whole population in a chain reaction mode, so that the evolution speed is greatly increased. The electric system economic dispatching optimization method based on the criss-cross algorithm has the advantages of being high in global searching ability and high in convergence rate through the criss-cross algorithm, applicable to optimizing a non-linear high-dimensional function and also applicable to achieving large-scale complex optimization in practical engineering.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
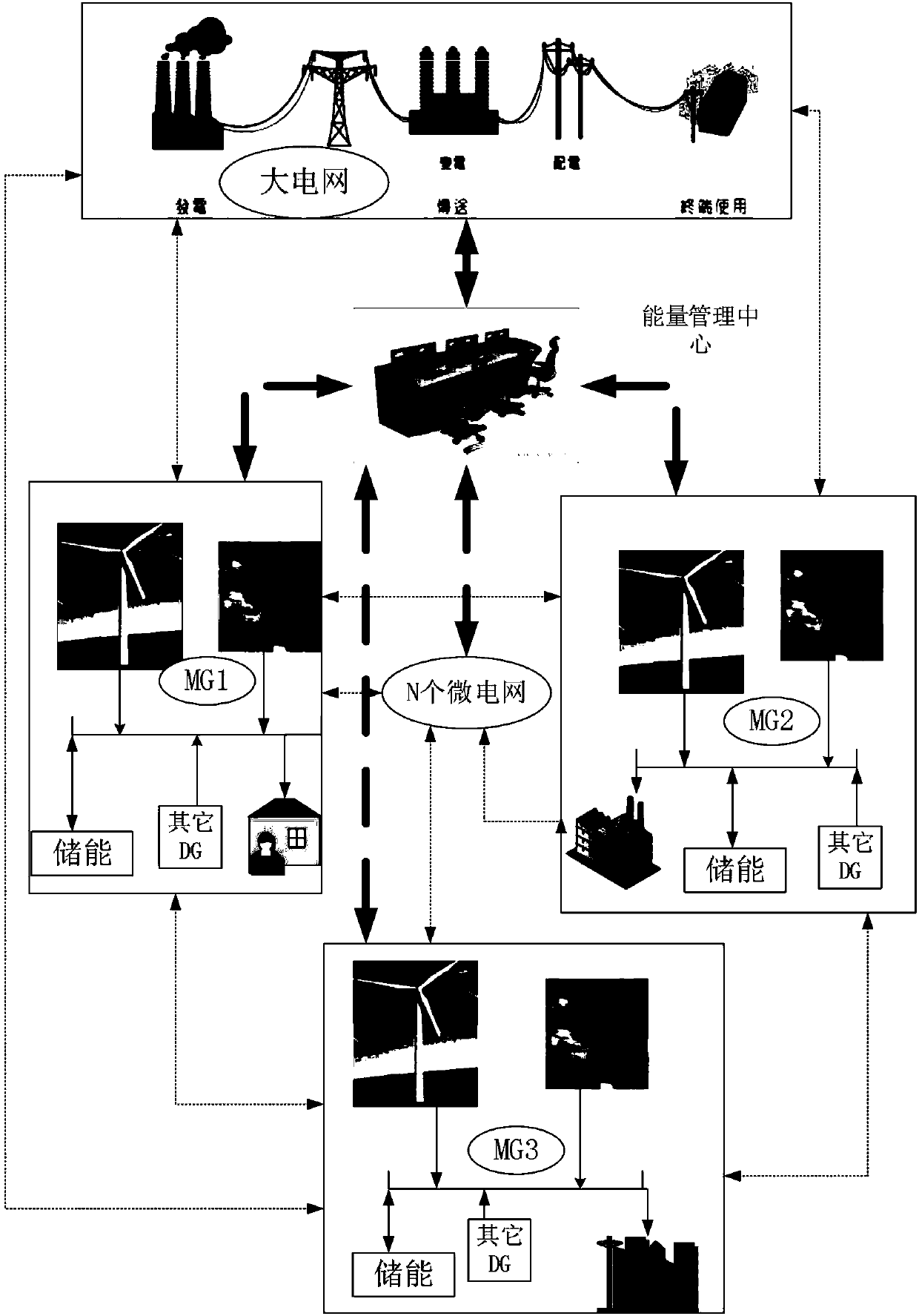
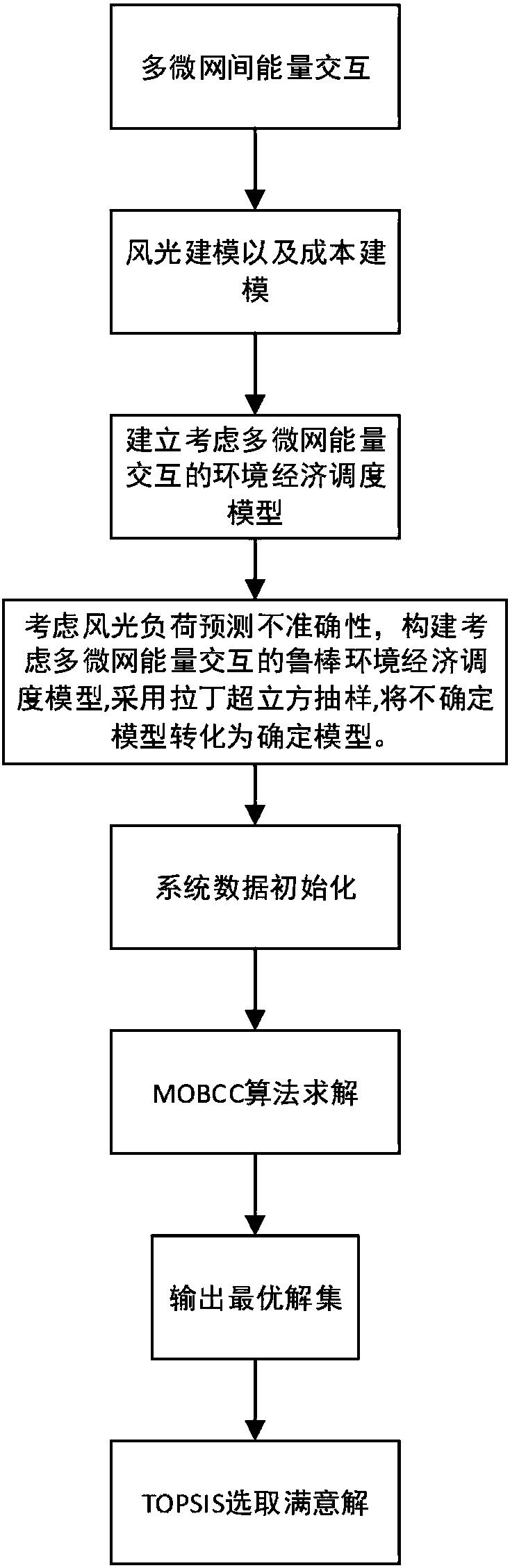
Robust environment economic scheduling method considering multi-microgrid energy interaction
InactiveCN107622324ALow costThe result is accurateSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsForecastingMicrogridLoad forecasting
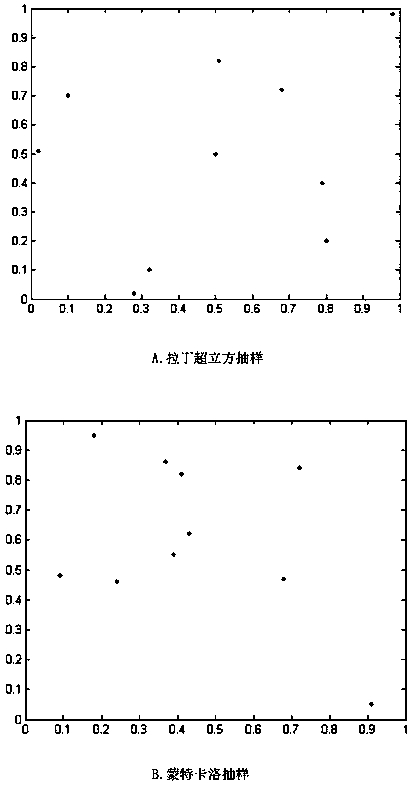
The invention discloses a robust environment economic scheduling method considering multi-microgrid energy interaction. The method comprises the following steps: in the background of supporting the rapid development of an active distribution network by microgrids, the energy interaction among multiple microgrids is thoroughly considered; a renewable energy generation model and a cost model in themicrogrid are built; an environment economic scheduling model considering multi-microgrid energy interaction is built; the uncertainty of renewable energy and load is considered, a robust environmenteconomic scheduling model considering multi-microgrid energy interaction is built, a Latin hypercube method is adopted for sampling, and the robust environment economic scheduling model is converted to a robust certainty model; and a multi-objective chemotaxis algorithm is adopted to solve the above robust certainty model, and the Pareto optimal solution is found out. The uncertainty of renewableenergy and load prediction is thoroughly considered, the energy interaction among multiple microgrids is considered, the calculation result is closer to the actual situation, the rationality is strong, and reliable basis is provided for the economic operation of the power system.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
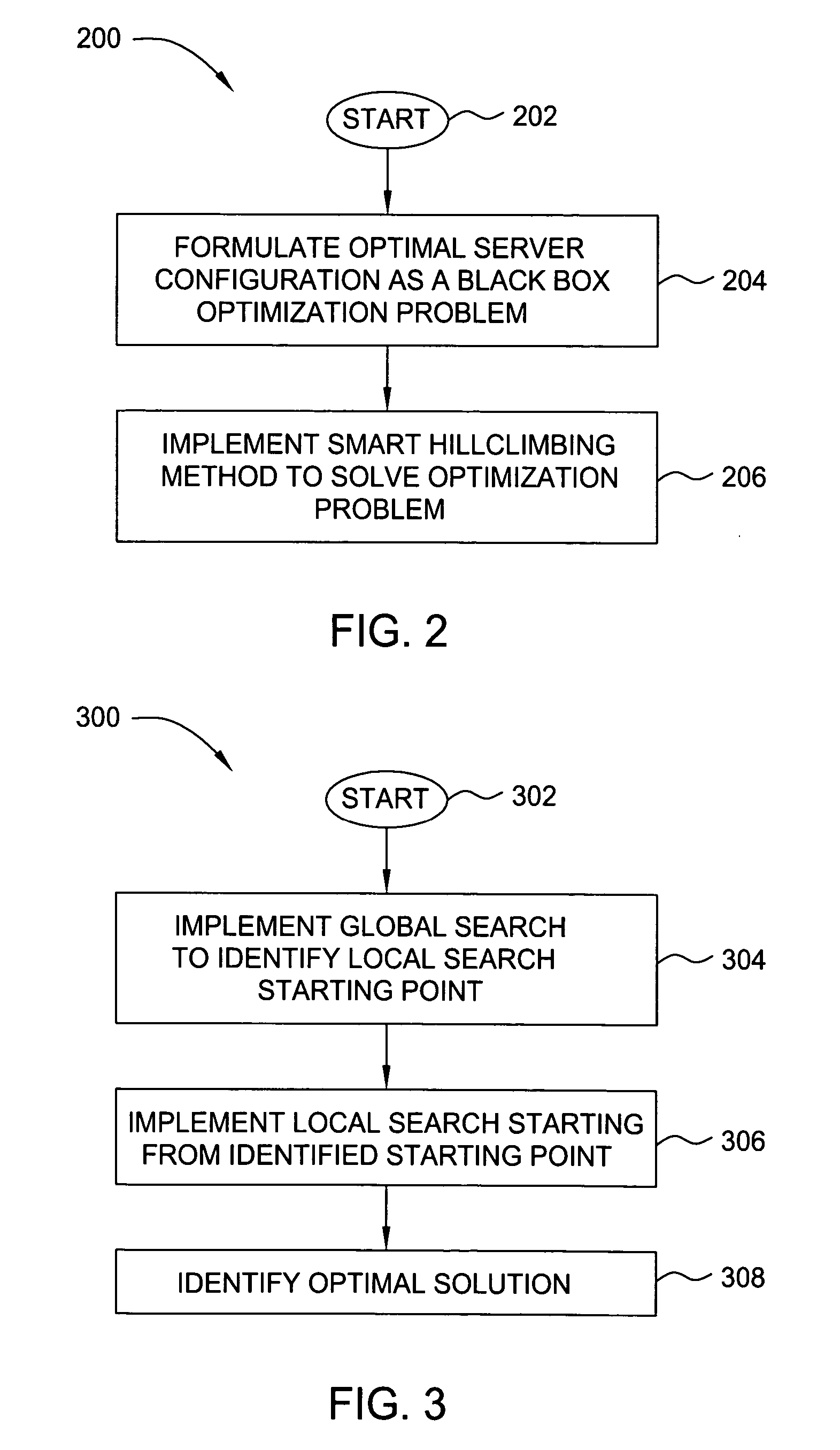
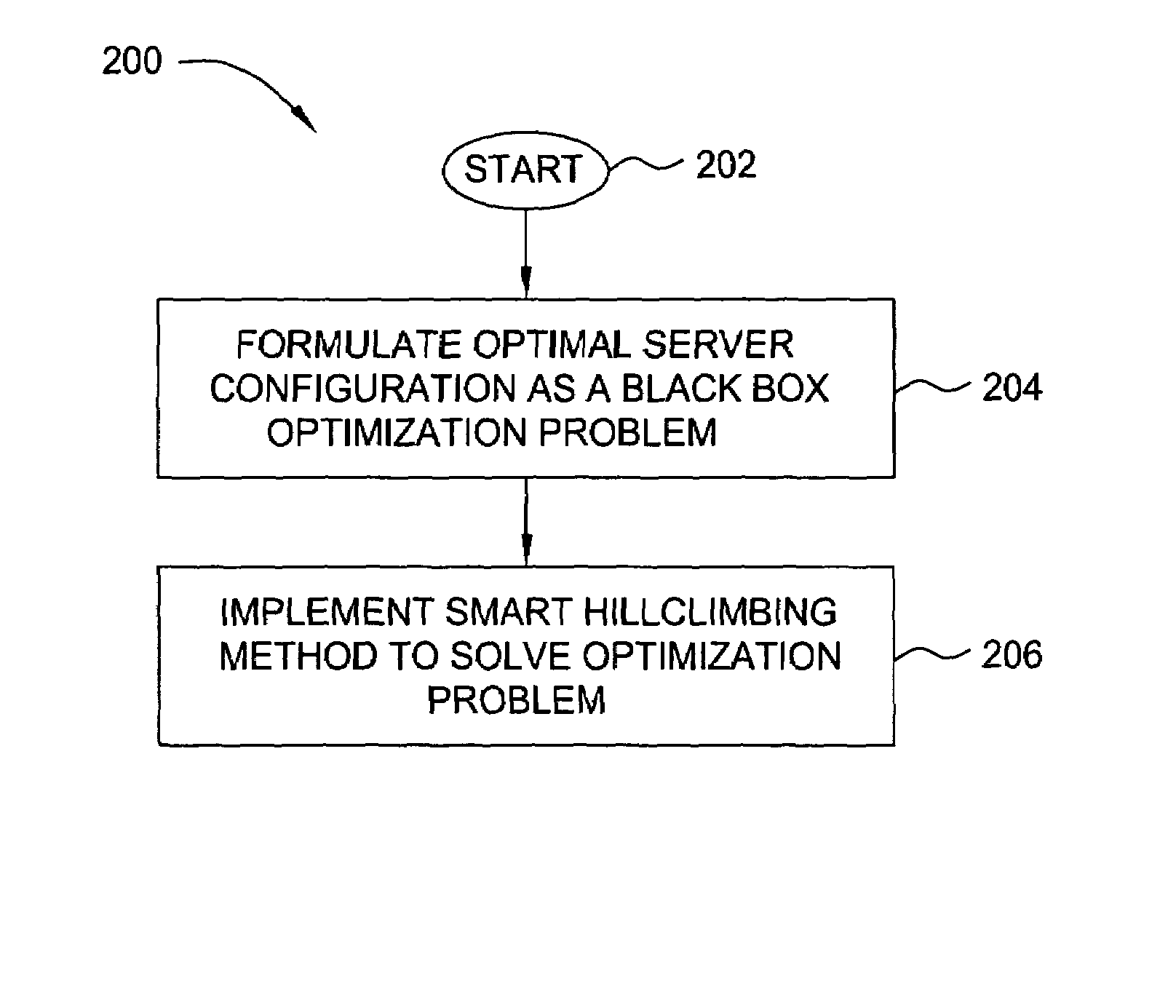
Methods and apparatus for automatic system parameter configuration for performance improvement
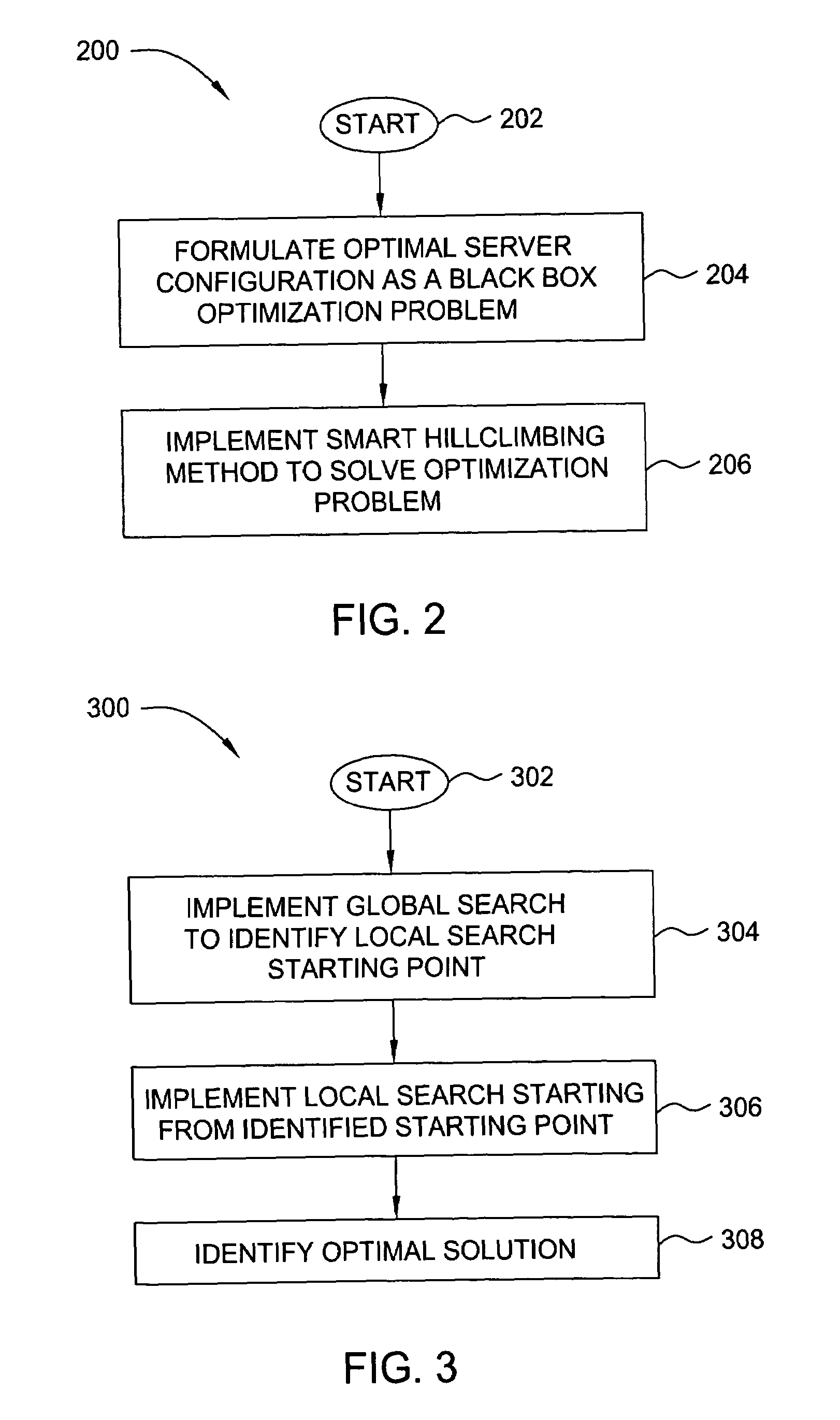
InactiveUS20050262230A1Handy search resultsImprove performanceData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsData miningOptimization problem
In one embodiment, the present invention is a method and apparatus for automatic system parameter configuration for performance improvement. One embodiment of the inventive method involves formulating a black box optimization problem, and solving the optimization problem using an enhanced smart hill climbing method. The smart hill climbing method includes both a global and a more precise local search to identify an optimal solution. In one embodiment, one or both of the global and local searches employs a weighted Latin Hypercube Sampling method in combination with importance sampling techniques to yield improved search results
Owner:IBM CORP
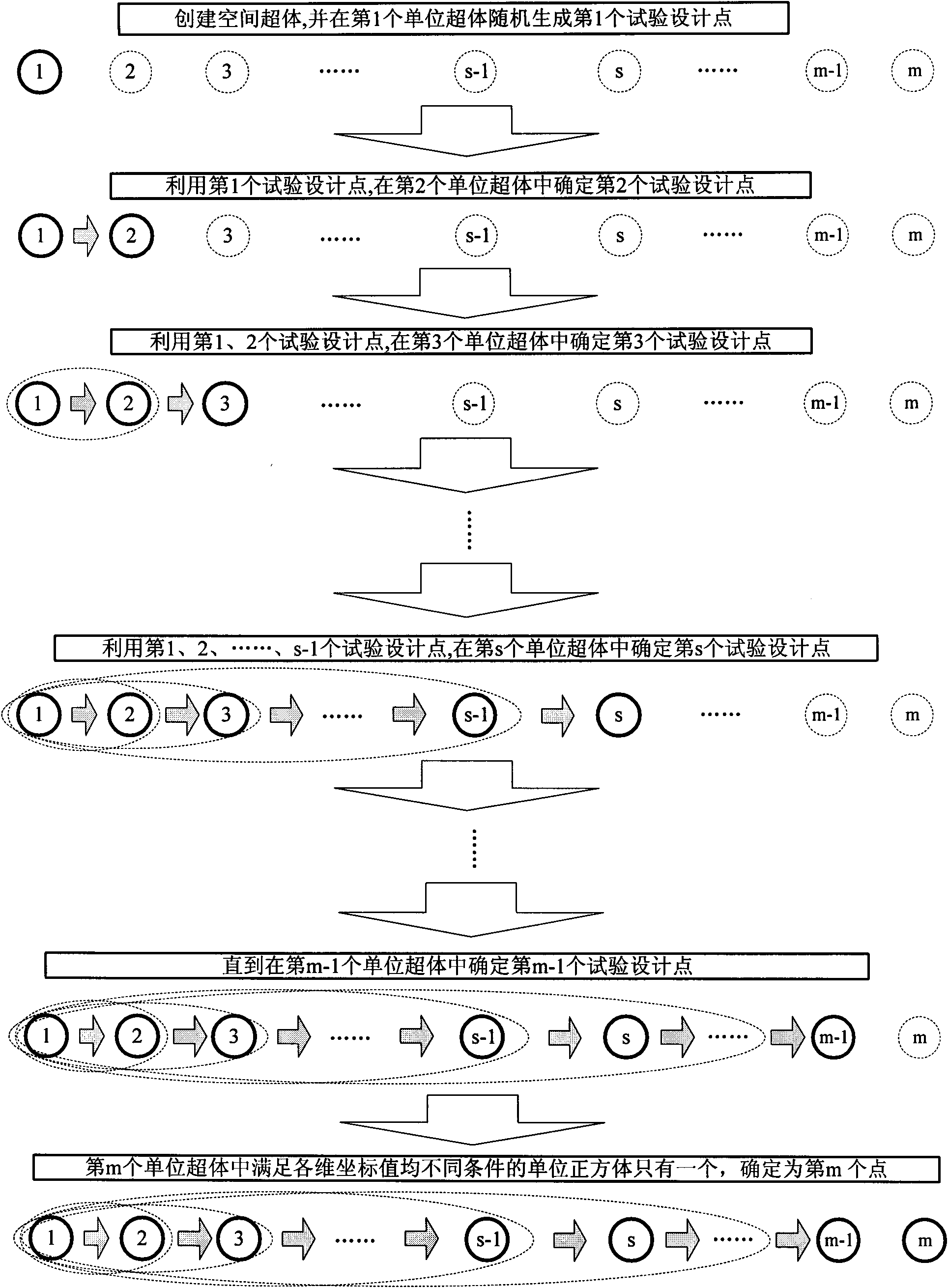
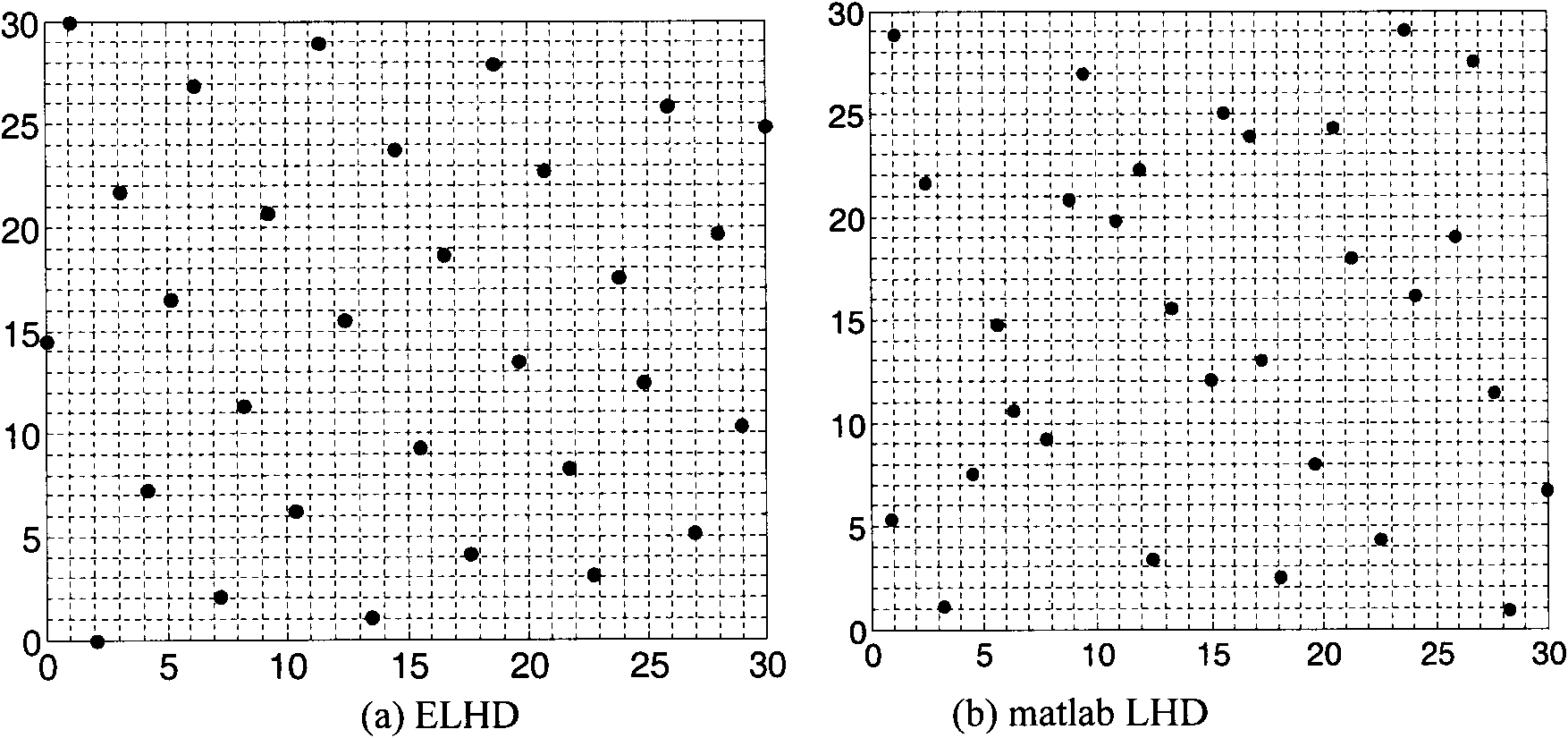
High-efficiency Latin hypercube experimental design method
InactiveCN101923590AImprove sampling efficiencySimple designSpecial data processing applicationsPartition of unityEngineering
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
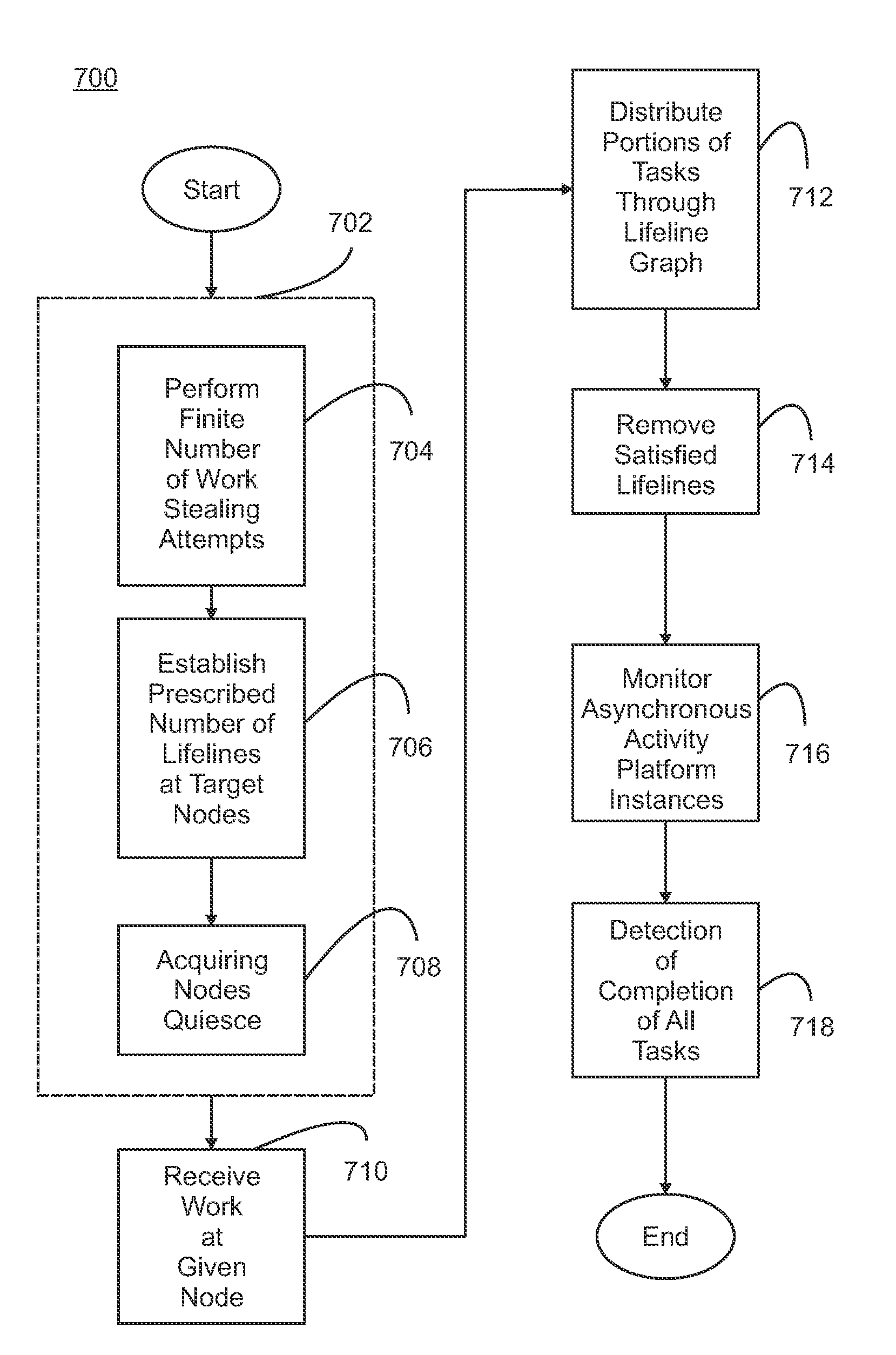
Lifeline-based global load balancing
InactiveUS20120304192A1Extend work-stealingEffective expansionMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsDistributed memoryDistributed computing
Work-stealing is efficiently extended to distributed memory using low degree, low-diameter, fully-connected directed lifeline graphs. These lifeline graphs include k-dimensional hypercubes. When a node is unable to find work after w unsuccessful steals, that node quiesces after informing the outgoing edges in its lifeline graph. Quiescent nodes do not disturb other nodes. Each quiesced node reactivates when work arrives from a lifeline, itself sharing this work with its incoming lifelines that are activated. Termination occurs when computation at all nodes has quiesced. In a language such as X10, such passive distributed termination is detected automatically using the finish construct.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and camera for the real-time acquisition of visual information from three-dimensional scenes
ActiveUS20110032337A1High resolutionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex amplitudeSpatial correlation
The invention relates to a method for calculating the focal stack associated with an object space from the plenoptic function thereof, using a sum transform along the length of constrained planes in discrete hypercubes, which allows the computing time to be considerably reduced. The invention also relates to a method for increasing the resolution of the focal stack obtained. In addition, the invention relates to two methods for the real-time recovery of the depths and moduli and phases of the complex amplitude of the wavefront respectively in each position of the surfaces of a three-dimensional scene and to a system adapted for carrying out the aforementioned methods.
Owner:UNIV DE LA LAGUNA
Nonblocking and deterministic unicast packet scheduling
InactiveUS20050117575A1Guaranteed bandwidthElectronic switchingData switching by path configurationCrossbar switchPacket scheduling
A system for scheduling unicast packets through an interconnection network having a plurality of input ports, a plurality of output ports, and a plurality of input queues, comprising unicast packets, at each input port is operated in nonblocking manner in accordance with the invention by scheduling at most as many packets equal to the number of input queues from each input port to each output port. The system is operated at 100% throughput, work conserving, fair, and yet deterministically thereby never congesting the output ports. The system performs arbitration in only one iteration, with mathematical minimum speedup in the interconnection network. The system operates with absolutely no packet reordering issues, no internal buffering of packets in the interconnection network, and hence in a truly cut-through and distributed manner. In another embodiment each output port also comprises a plurality of output queues and each packet is transferred to an output queue in the destined output port in nonblocking and deterministic manner and without the requirement of segmentation and reassembly of packets even when the packets are of variable size. In one embodiment the scheduling is performed in strictly nonblocking manner with a speedup of at least two in the interconnection network. In another embodiment the scheduling is performed in rearrangeably nonblocking manner with a speedup of at least one in the interconnection network. The system also offers end to end guaranteed bandwidth and latency for packets from input ports to output ports. In all the embodiments, the interconnection network may be a crossbar network, shared memory network, clos network, hypercube network, or any internally nonblocking interconnection network or network of networks.
Owner:TEAK TECH
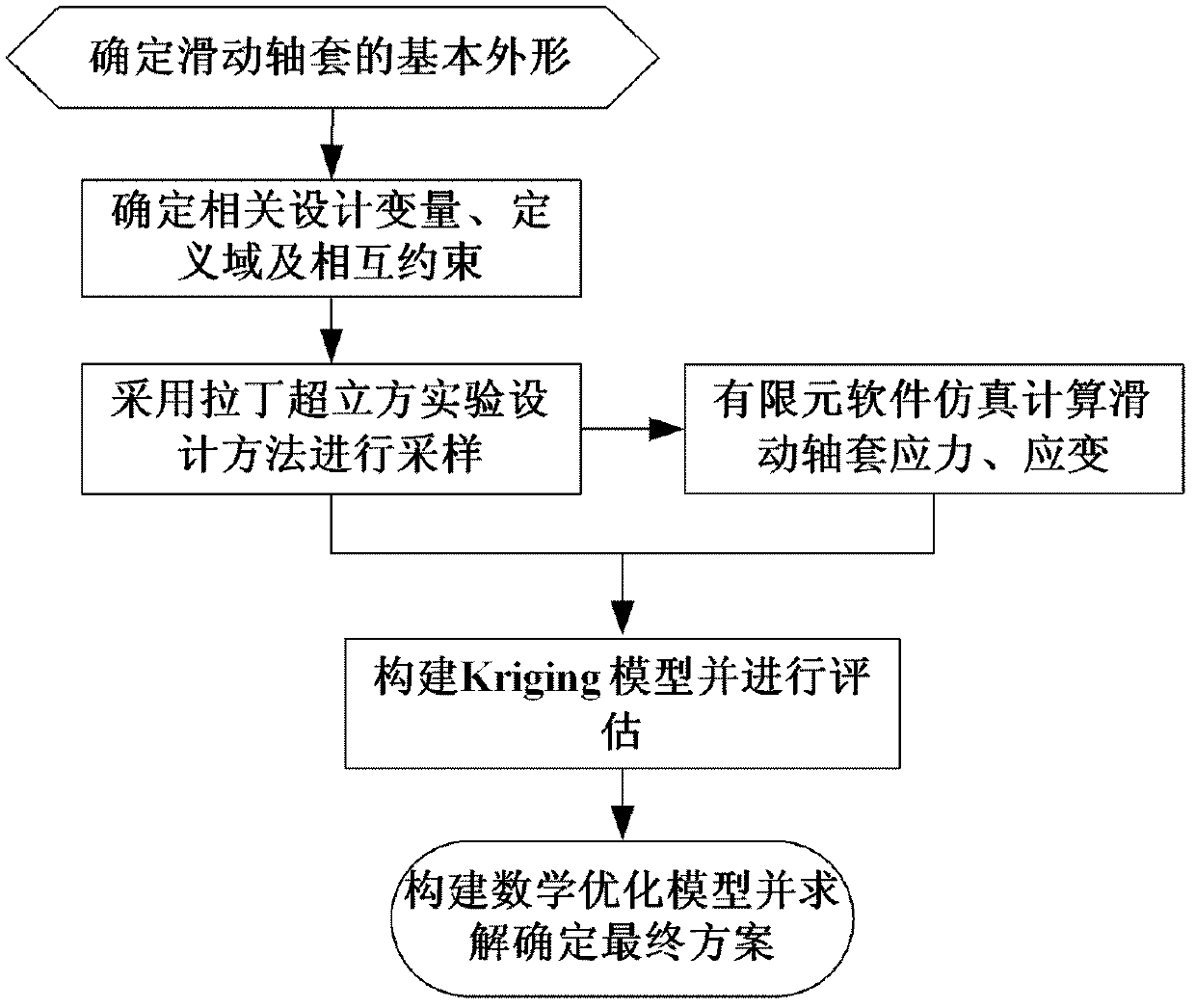
Method for optimally designing structure of sliding shaft sleeve based on Kriging model
InactiveCN102360403ACalculation speedTime consumingSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmControl engineering
The invention relates to a method for optimally designing the structure of a sliding shaft sleeve based on a Kriging model. By using an unbiased optimal estimation theory of the Kriging model, the optimal design scheme of the sliding shaft sleeve is predicted and solved. The method comprises the following steps of: determining the basic appearance of the sliding shaft sleeve; analyzing and defining a design variable and a definition domain, which influence the shape of the sliding shaft sleeve; sampling a design space by using a Latin hypercube experiment design method; calculating the stress response of the sliding shaft sleeve by using a finite element method; constructing the Kriging model, and performing accuracy estimation; and constructing a mathematical optimization model, solving the optimal design scheme of the sliding shaft sleeve, and validating by using the finite element method. By using the design variable correlation and variability characteristic of the Kriging model, the unbiased optimal estimation is performed, and guidance is provided for optimal design of the structure of the sliding shaft sleeve. Compared with the conventional method, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high calculation speed, optimal scheme design and high reliability.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
Network topology structure based on fat tree high scalability hypercube
InactiveCN103957163AImprove scalabilityHigh bandwidth throughputData switching networksFault tolerancePath network
The invention is applied to the field of network communication, and provides a network topology structure based on a fat tree high scalability hypercube. The network topology structure comprises multiple switches and multiple servers. The switches employ a recursion unit hierarchical mode to form a topology network. A lowest recursion unit employs an m-port n- tree fat tree network structure, and the number of servers supported by the lower recursion unit is: g0=2*(m / 2)n, wherein m is the number of ports of the switches in a fat tree, and n is the number of layers of the fat tree structure. In a network topology, the k-th port of the i-th switch at a highest layer is interconnected with the k-th server of the i-th subunit for realizing a multipath network topology structure, wherein i and k belong to a set of {1,2, ..., gk-1}. Through fusing a fat tree network topology in hierarchical recursion, the high scalability of the network topology is realized, at the same time, the characteristics of equal bandwidth and multipath performance of a fat tree network are also inherited, the bandwidth throughput is quite large, the fault tolerance is quite good, and the average time delay is quite small.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
VLSI layouts of fully connected generalized networks
ActiveUS8269523B2Low pour pointReduce signal delaySolid-state devicesComputer aided designCross-linkMulti link
Owner:KONDA VENKAT
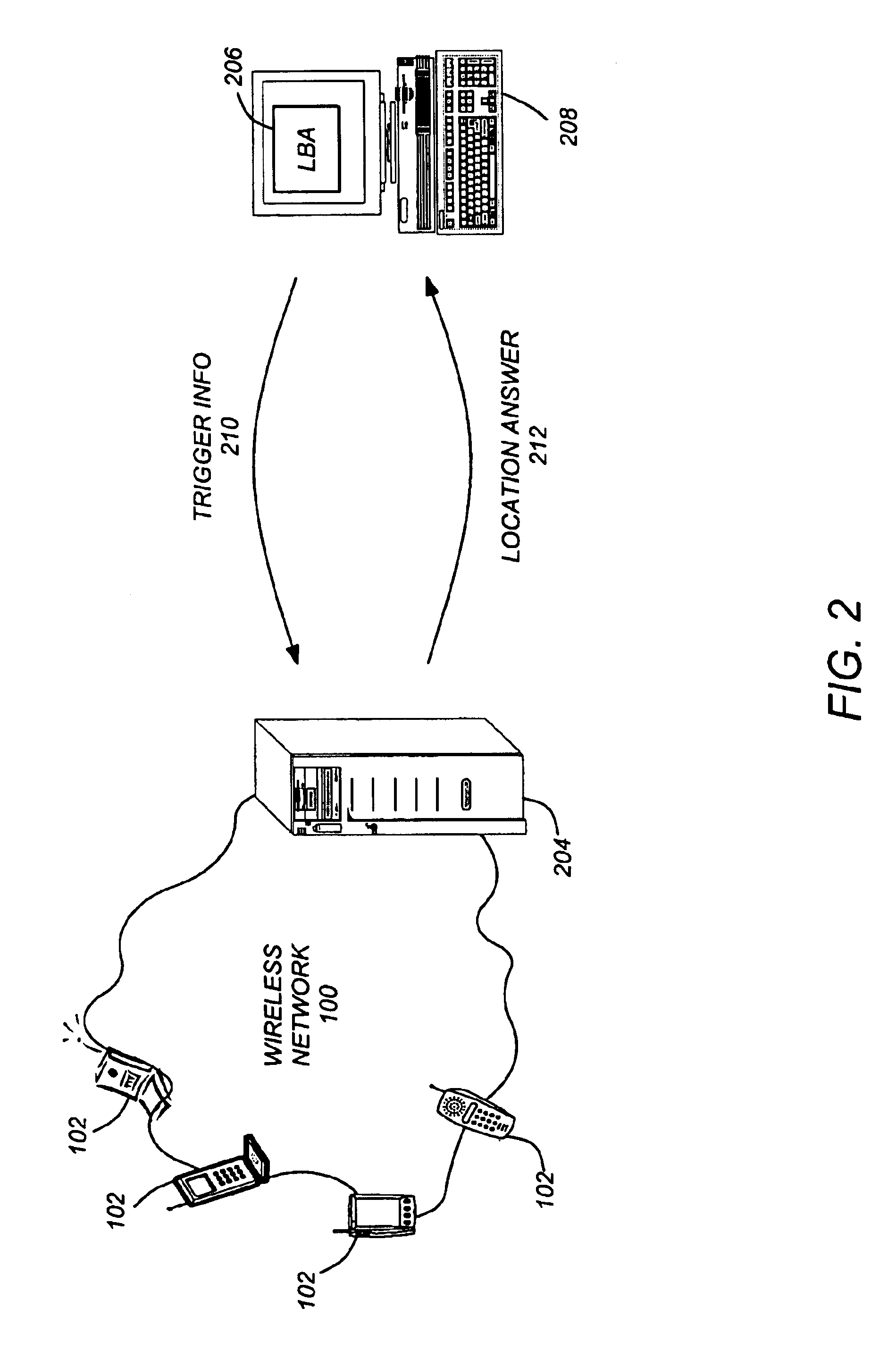
Use of triggers and a location hypercube to enable push-based location applications
InactiveUS20060111126A1Minimizing pollingImprove performanceRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsLocation information based serviceComputer scienceHypercube
A method, system, and article of manufacture enable the use of location based applications (LBA). A location server (LS) on a wireless network receives trigger information from a LBA that is located outside of the wireless network. The trigger information defines a source locatable and spatial information (defining spatial criteria for a target locatable). Triggers are evaluated to determine if a trigger has been activated by the locatables interacting with each other pursuant to the spatial information / criteria. A location answer is pushed to a location based application outside of the network if a trigger has been activated (i.e., if the source and target locatables comply with the spatial criteria).
Owner:LONGHORN ACQUISITION
Information processing device, information processing method, and recording medium storing program
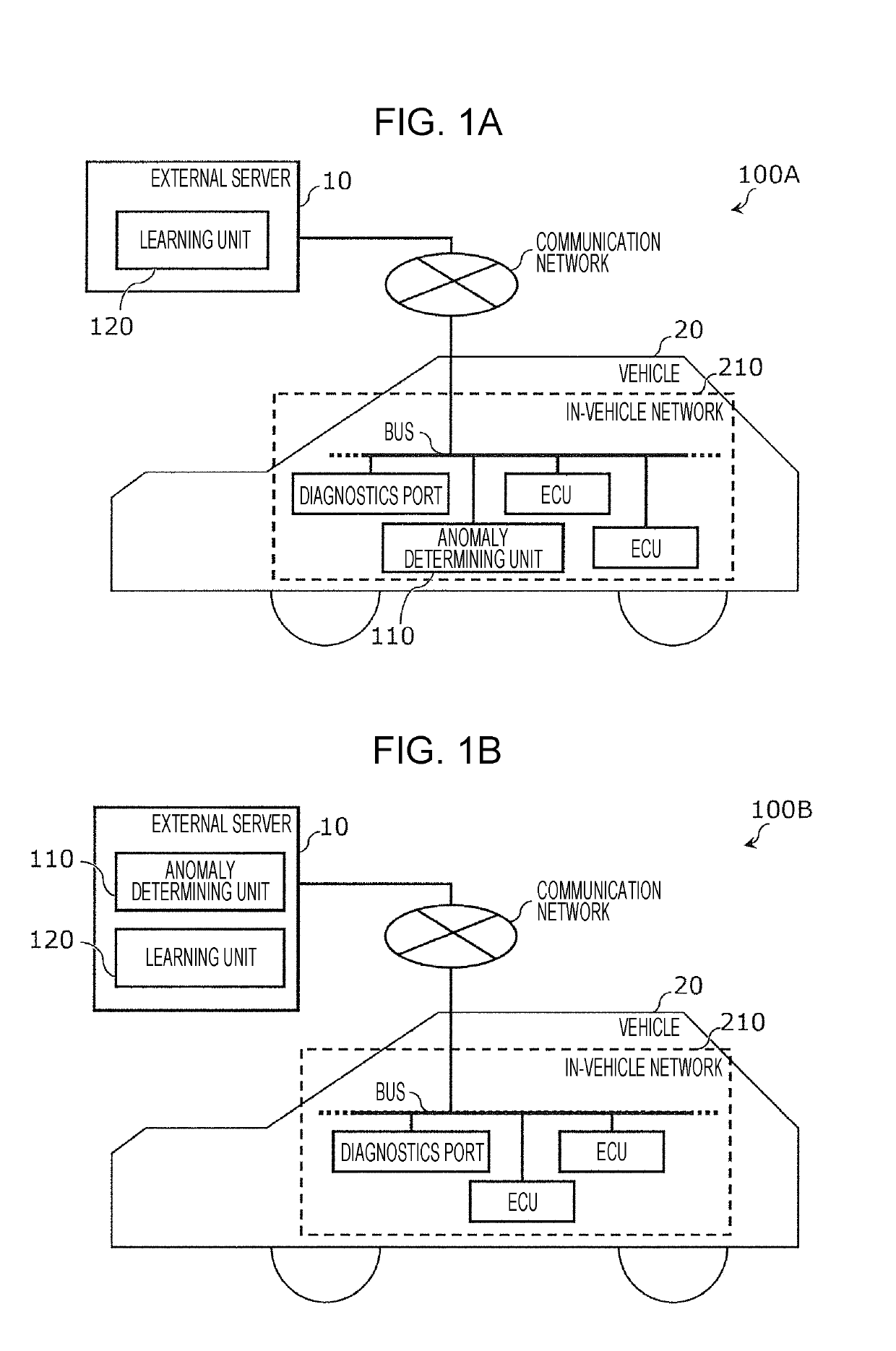
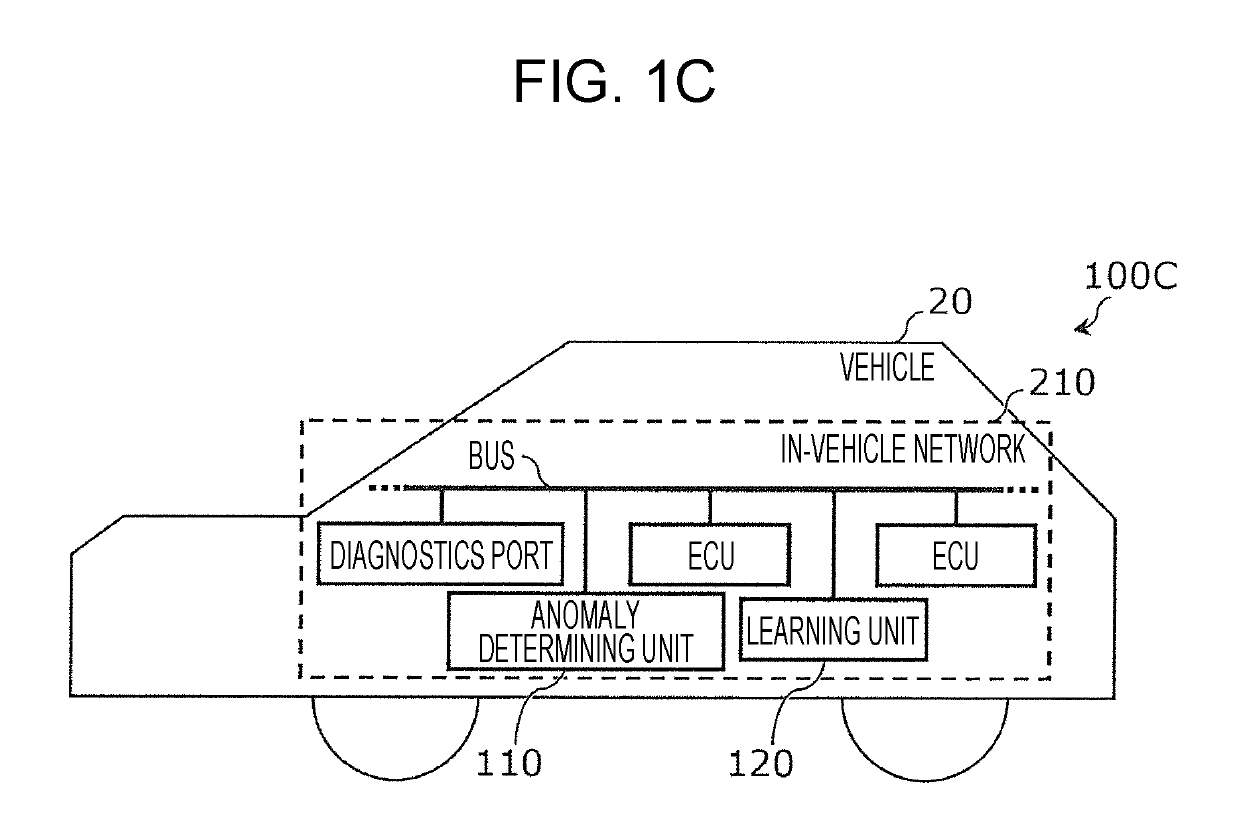
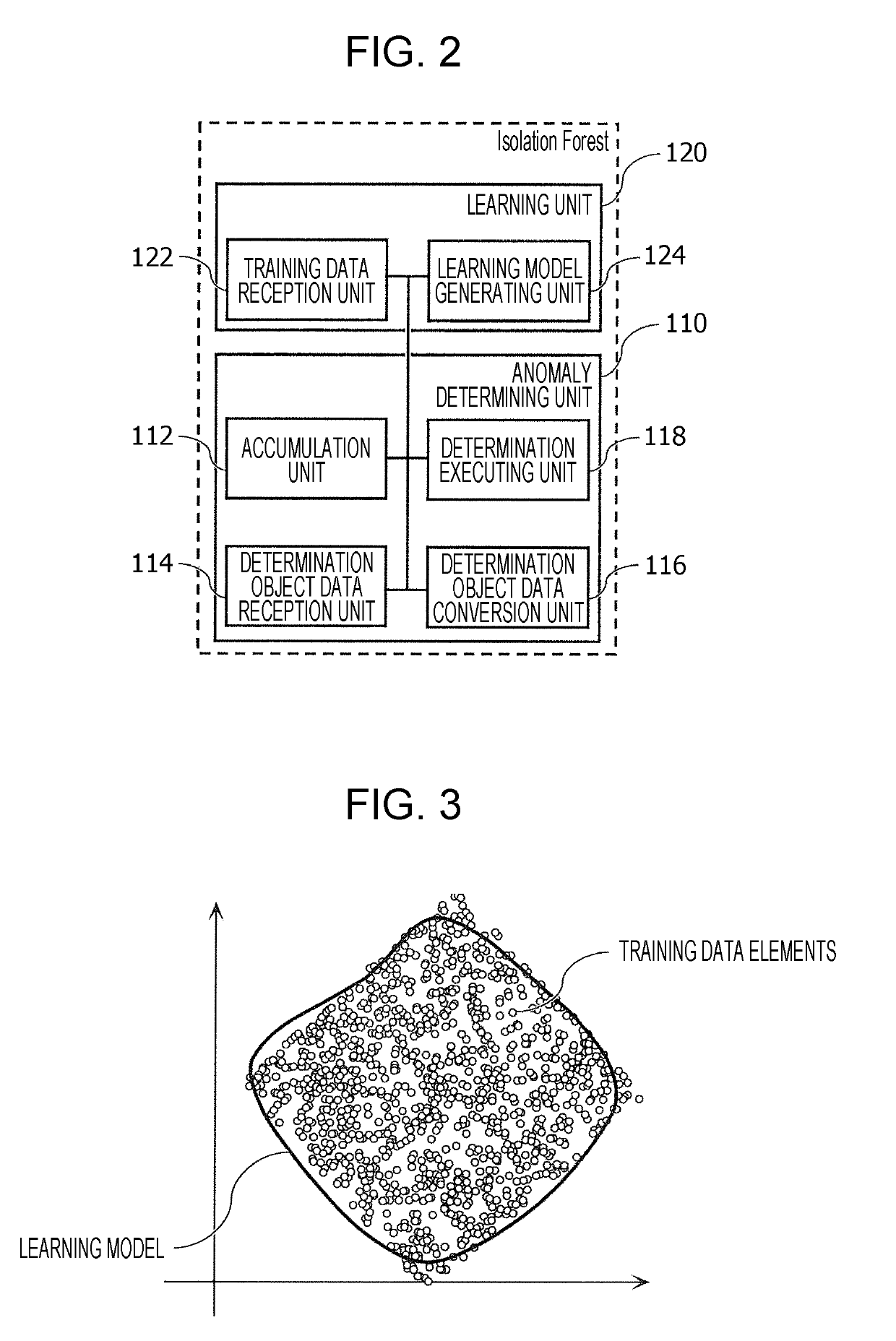
ActiveUS20190173902A1Suppressed erroneous detection rateRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEnsemble learningInformation processingIn vehicle
Provided is an information processing device that includes a processor and has a capability to detect abnormalities on an in-vehicle network that may be caused by an attack. The processor receives input of data elements to be used as training data, normalizes the training data so as to be distributed within a first region, divides a multi-dimensional second region that encompasses the first region into third regions that are hypercubes of equal sizes, obtains S data elements that are contained by each of the third regions, and for each third region that includes a number of data elements that is less than a first threshold value T, adds noise elements that are vectors with a uniform distribution to the third regions, generates noise-added training data including the vectors in the second region, and generates and outputs Isolation Forest learning model data by using the generated noise-added training data.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
VLSI layouts of fully connected generalized networks
ActiveUS20110037498A1Low pour pointReduce signal delaySolid-state devicesComputer aided designCross-linkMulti link
In accordance with the invention, VLSI layouts of generalized multi-stage networks for broadcast, unicast and multicast connections are presented using only horizontal and vertical links. The VLSI layouts employ shuffle exchange links where outlet links of cross links from switches in a stage in one sub-integrated circuit block are connected to inlet links of switches in the succeeding stage in another sub-integrated circuit block so that said cross links are either vertical links or horizontal and vice versa. In one embodiment the sub-integrated circuit blocks are arranged in a hypercube arrangement in a two-dimensional plane. The VLSI layouts exploit the benefits of significantly lower cross points, lower signal latency, lower power and full connectivity with significantly fast compilation.The VLSI layouts presented are applicable to generalized multi-stage networks V(N1, N2, d, s), generalized folded multi-stage networks Vfold(N1, N2, d, s), generalized butterfly fat tree networks Vbft(N1, N2, d, s), generalized multi-link multi-stage networks Vmlink(N1, N2, d, s), generalized folded multi-link multi-stage networks Vfold-mlink(N1, N2, d, s), generalized multi-link butterfly fat tree networks Vmlink-bft(N1, N2, d, s), and generalized hypercube networks Vhcube(N1, N2, d, s) for s=1, 2, 3 or any number in general. The embodiments of VLSI layouts are useful in wide target applications such as FPGAs, CPLDs, pSoCs, ASIC placement and route tools, networking applications, parallel & distributed computing, and reconfigurable computing.
Owner:KONDA VENKAT
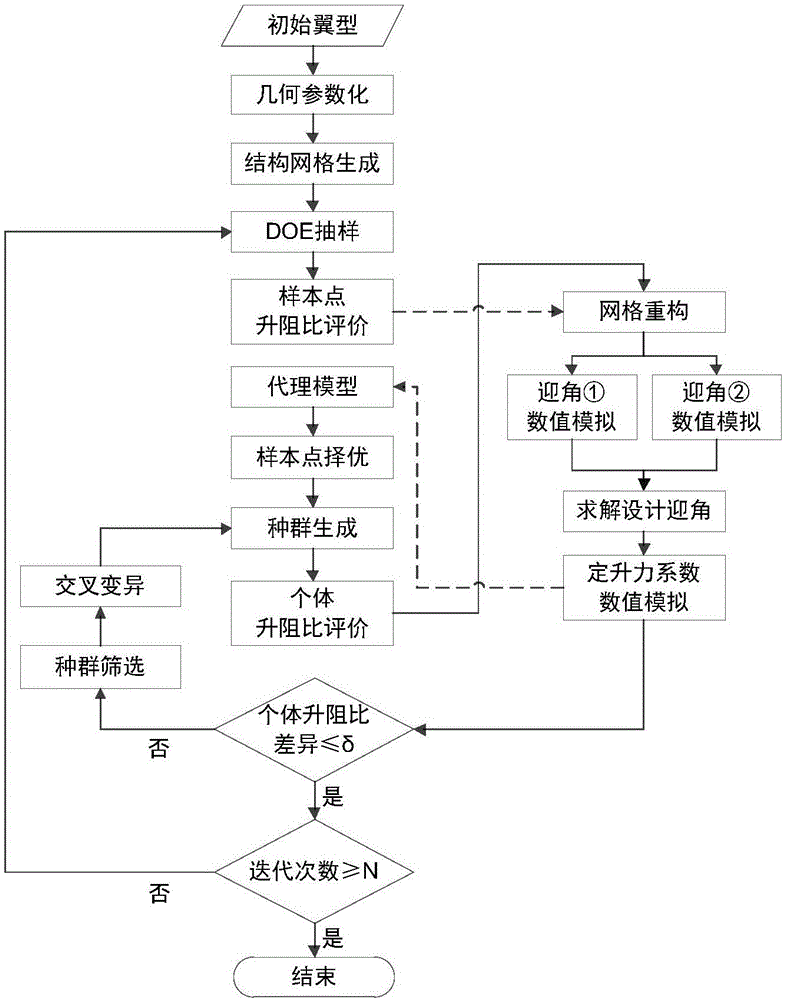
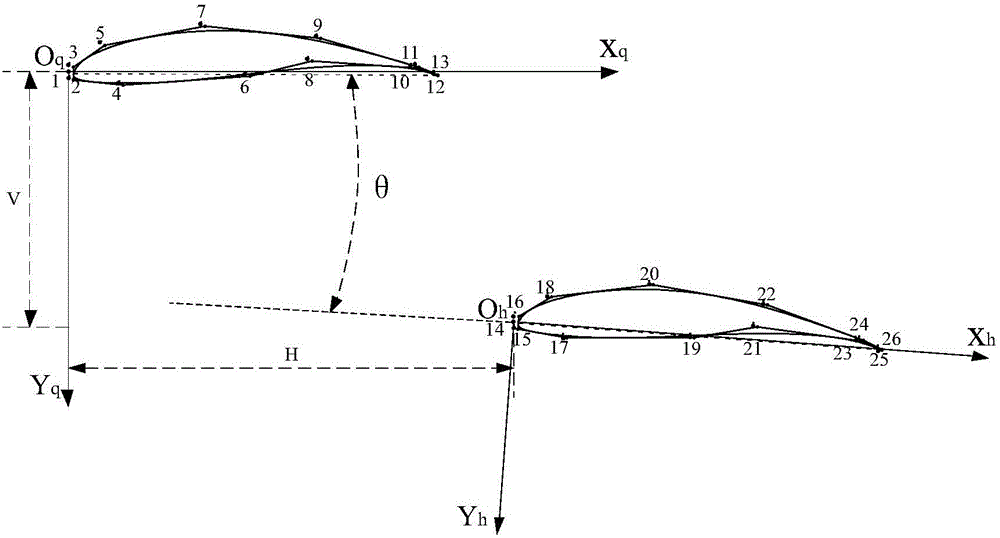
Optimization design method for wing types of low-Reynolds-number staggered-floor wings
ActiveCN106547954AAvoid changeImprove calculation accuracyGeometric CADSustainable transportationFlight vehicleGenetic algorithm
The invention discloses an optimization design method for wing types of low-Reynolds-number staggered-floor wings, and belongs to the technical field of flight vehicle design. Specific to the staggered-floor wings, the wing types are subjected to parameterization by adopting an NURBS curve fitting method, and 13 control points are selected on front and back wings for control separately; computational grids are generated by adopting an automatic grid reconstruction technology, and numerical value simulation on a flow field is carried out based on a <gamma>-Re<theta> transition model which is coupled with a k-<ohms> SST turbulence model; and optimization is carried out by a combined optimization strategy by combination of DOE sampling and a multi-island genetic algorithm as follows: uniform sampling in a designed space is performed by optimal Latin hypercube design, an most effective design region in the overall design space is captured, and then optimization design is performed in the most effective design region by adopting the multi-island genetic algorithm. By performing optimization on the wing types of the staggered-floor wings, unfavorable pneumatic interference of the staggered-floor wings is lowered, lift-drag ratio is improved, the calculated amount is reduced on the basis of ensuring the calculation precision, and the optimization efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Optimization design method for air vehicle lifting surface structure
ActiveCN102789539AReduce computing costImprove optimization efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringDesign space
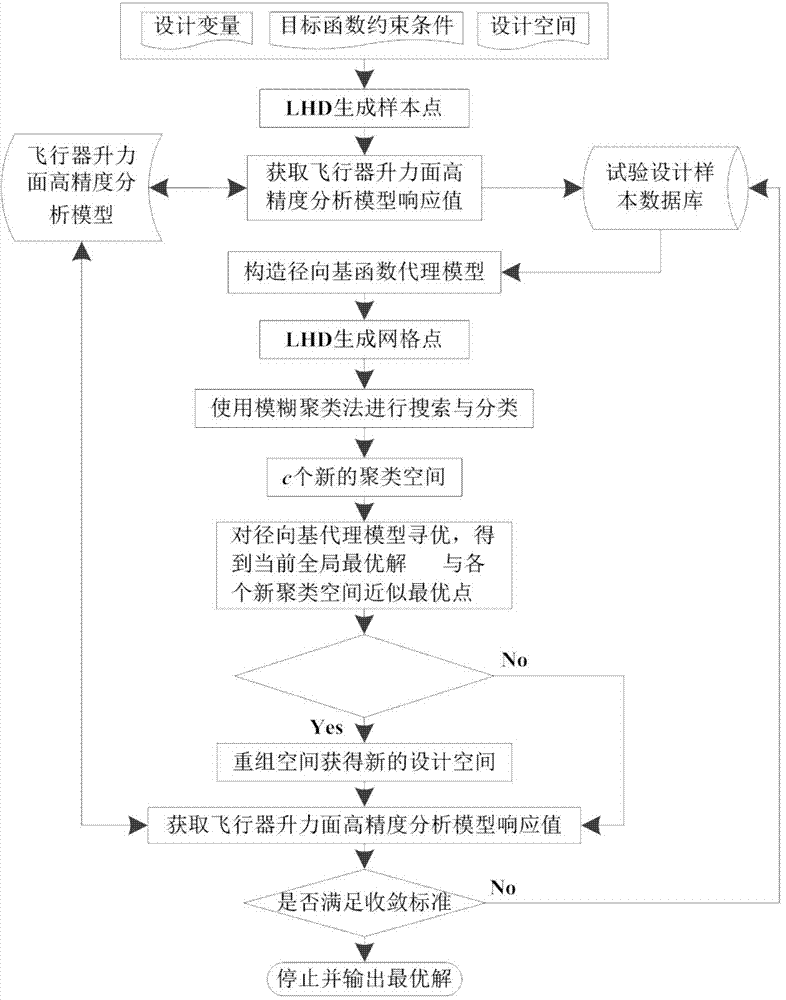
Disclosed is an optimization design method for an air vehicle lifting surface structure. The method includes utilizing a Latin hypercube design (LHD) method to extract experiment design samples and obtain a high-accuracy analysis model response value of an air vehicle lifting surface; constructing a radial basis function (RBF) broker model; generating a certain amount of grid points randomly by using the LHD method in design space, and calculating a corresponding response value of the RBF broker model; setting a global space reduction rate M1% and a local space reduction rate M2%, and performing two times of pseudo reduction; optimizing the RBF broker model by using a genetic algorithm in each clustering space; obtaining the space distance between an optimal point and a last-time space global approximate optimal point, and deleting the current space to obtain novel space if reduction criteria are met; and obtaining an actual response value of a current global approximate optimal solution, determining whether the value is convergent, and stopping optimizing if the value is convergent, otherwise, performing iteration repeatedly till the optimal solution is found. According to the optimization design method for the air vehicle lifting surface structure, the optimization efficiency is improved, and the optimization design cost of the air vehicle lifting surface structures saved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
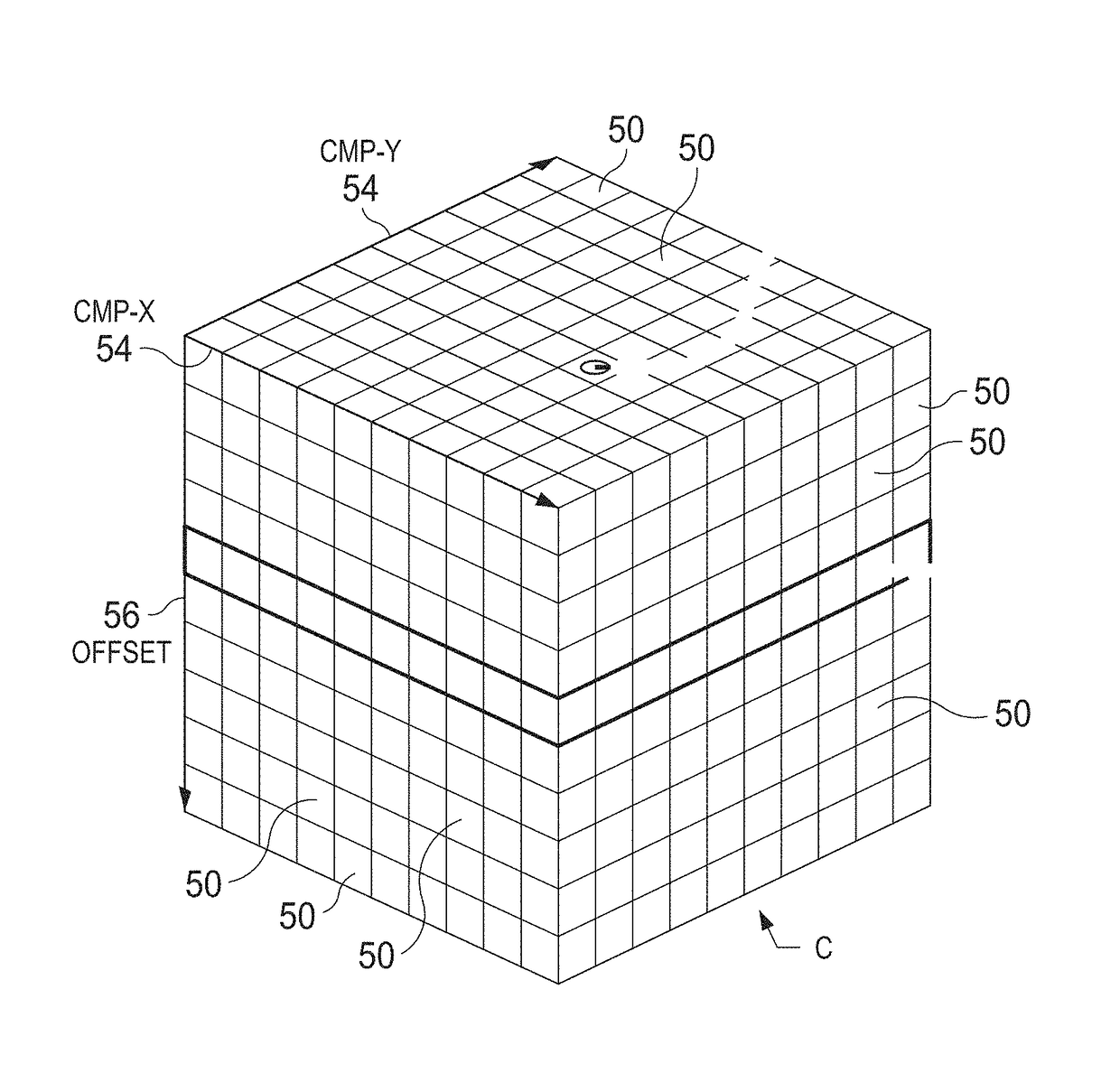
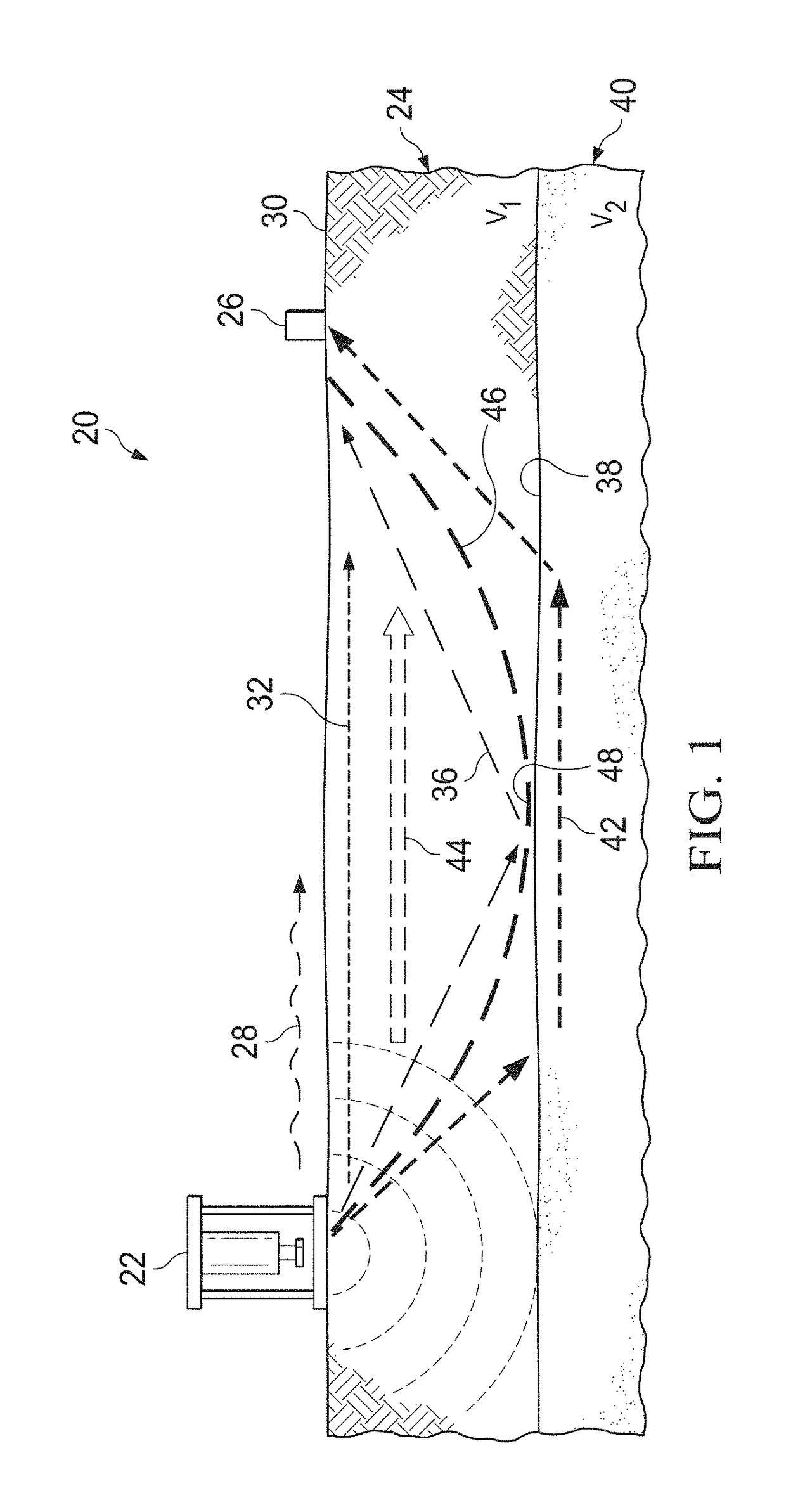
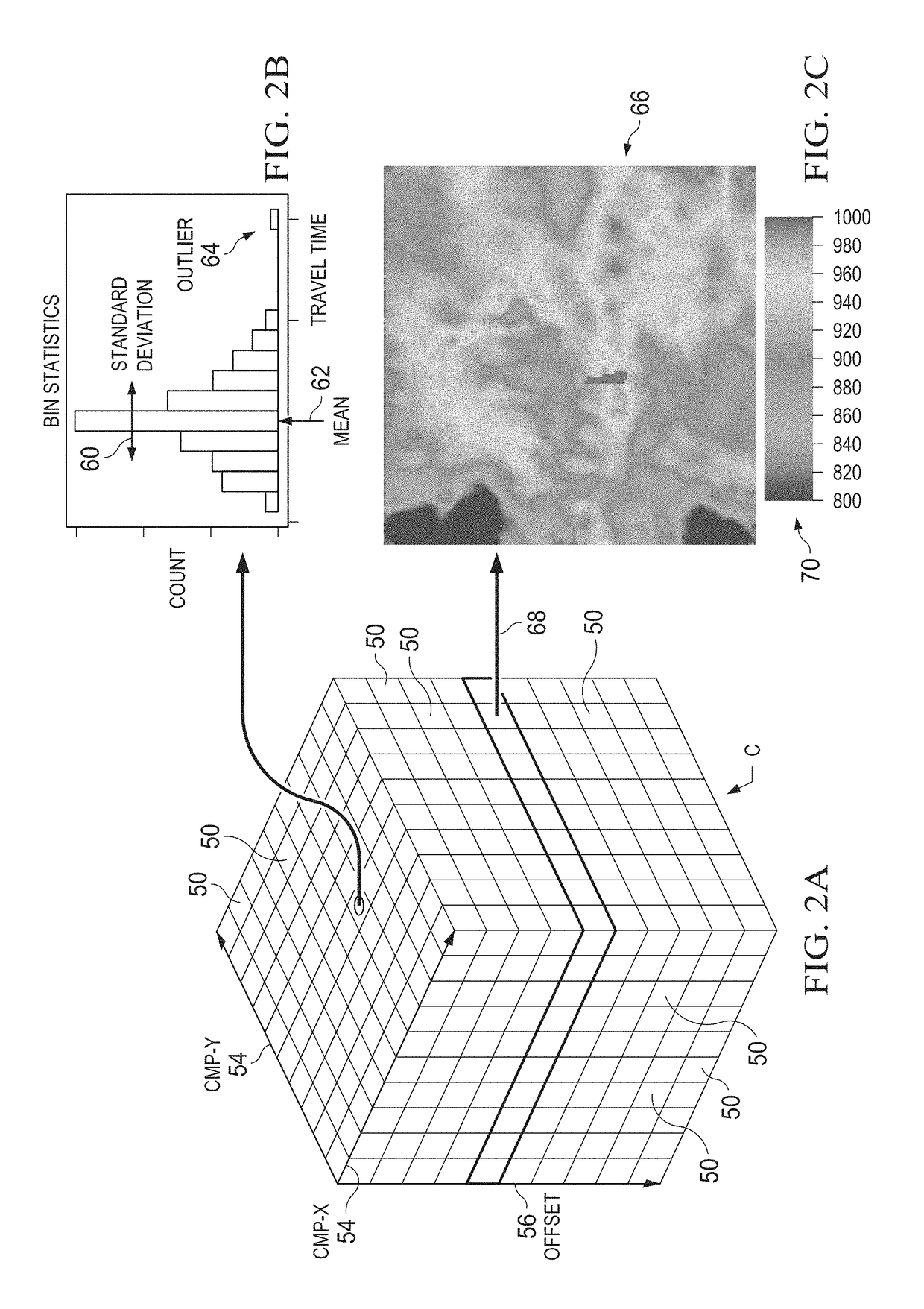
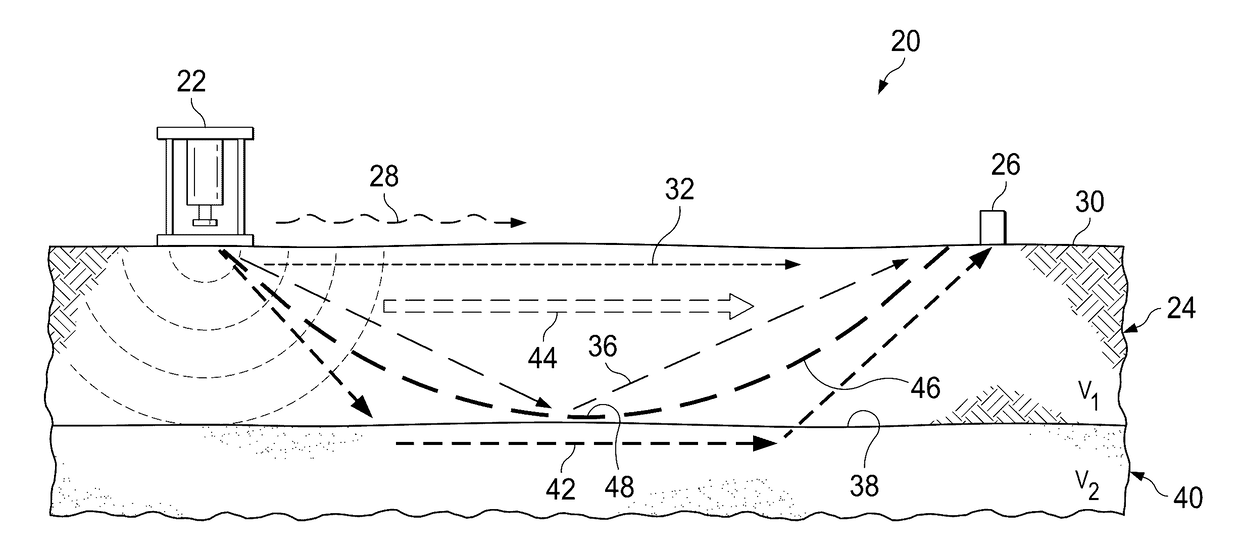
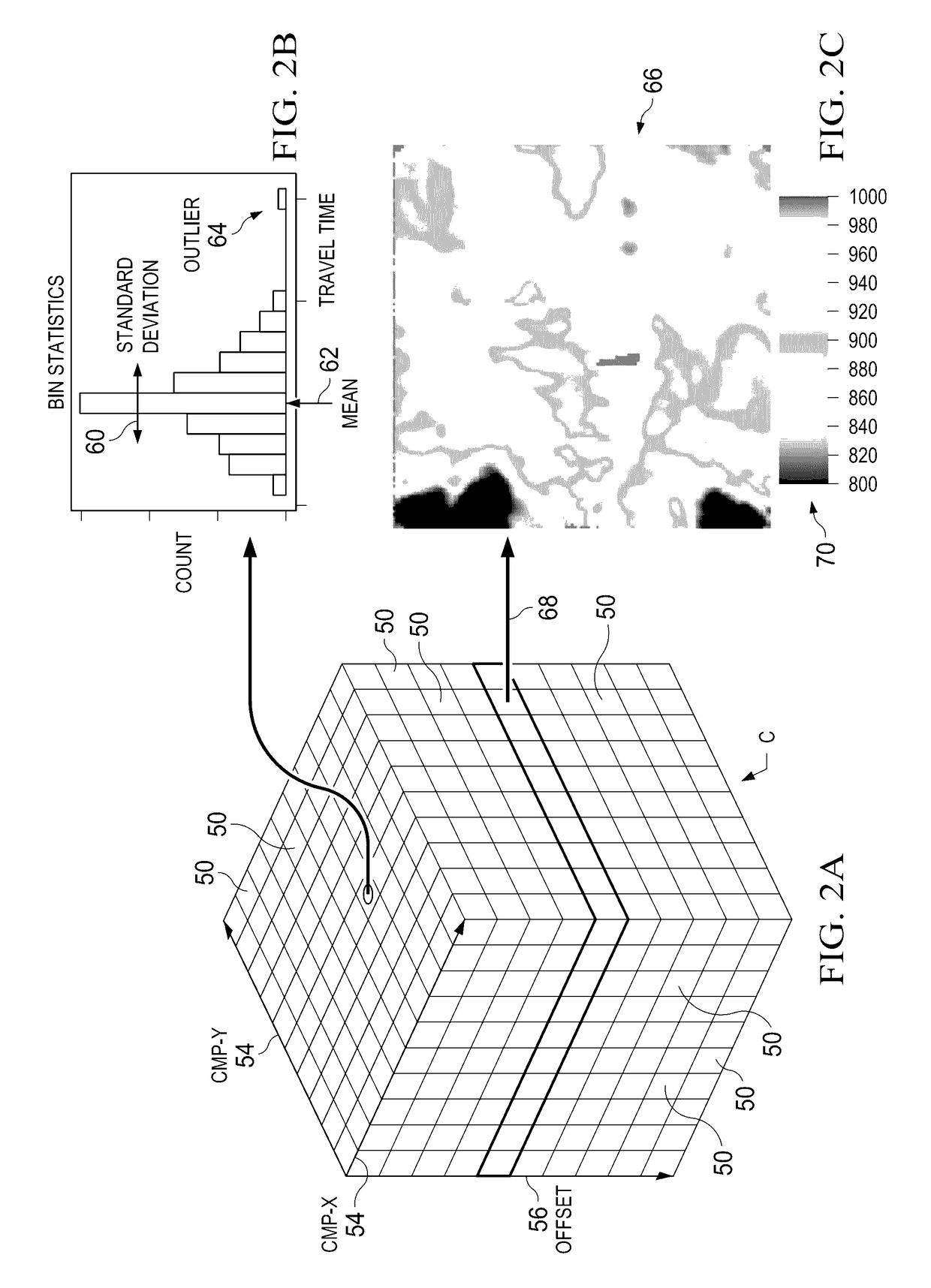
Automatic quality control of seismic travel time
Seismic data from seismic exploration surveys are mapped into a hypercube of bins or voxels in a four-dimensional space (X, Y, Offset, and Azimuth) according to Common Mid-Point (or CMP) between source and receivers. The mapped data from individual voxels or bins is then analyzed by multimodal statistics. Robust estimates of first break picks are obtained from the analysis. The first break picks are then used to as seed inputs for autopicking iteration, which proceeds to convergence. Estimates of confidence levels in the data are provided for re-picking to reduce computer processing time in successive autopicking iterations. Analysis is provided of different seismic attributes such as azimuthal velocity variations indicative of anisotropy, positioning errors of sources / receivers, geometry errors, and three dimensional distribution of inversion residuals. Analysis is also performed of standard deviation of the travel time data useful for estimating data errors in the inversion covariance matrix.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
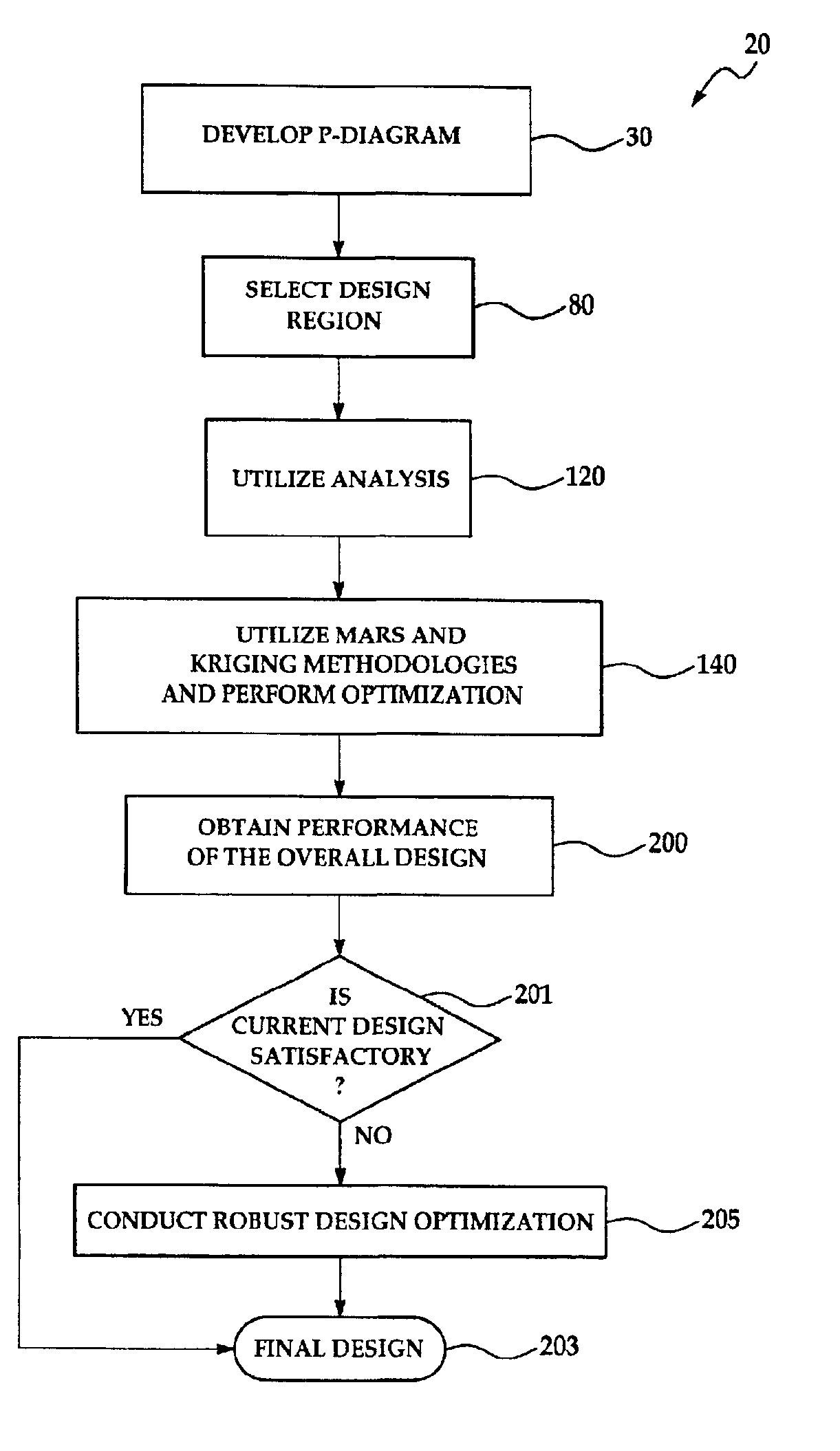
Method and apparatus for analyzing a design
InactiveUS6931366B2Overcomes drawbackImprove reliabilityDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringEngineeringAnalysis design
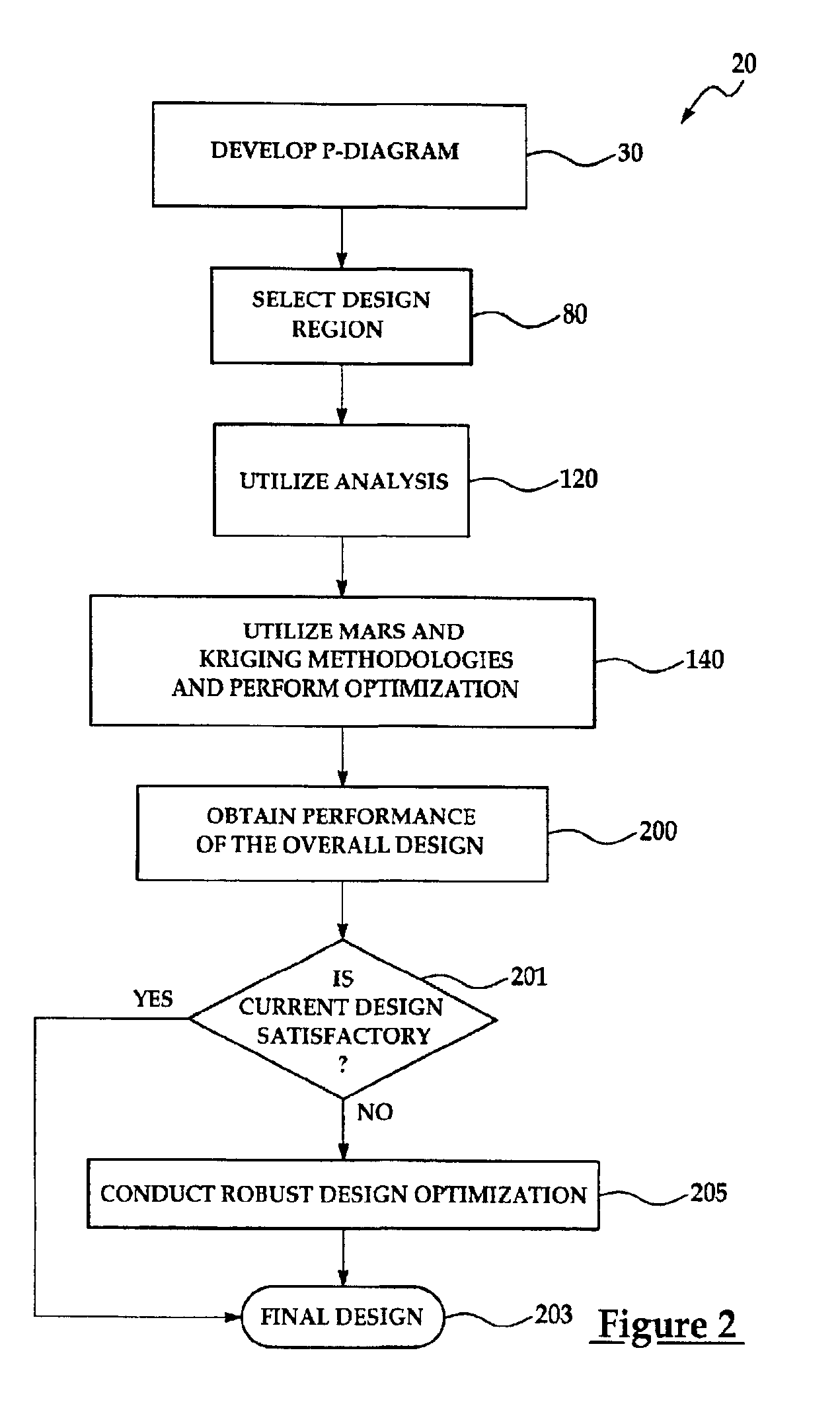
A system 10, which receives a computer, aided model or design 18 and which probabilistically analyzes the model 18 by use of a modified Latin Hypercube sampling technique and combined MARS and Kriging simulation methodologies, thereby allowing a simulation to be conducted at a most probable point of operation and allowing products having desired characteristics and attributes to be created.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
Optimizing method for multi-flexible dynamic structure of bridge crane
ActiveCN106202731ASmall amount of calculationFast structure optimizationGeometric CADConstraint-based CADDynamic modelsLinear relationship
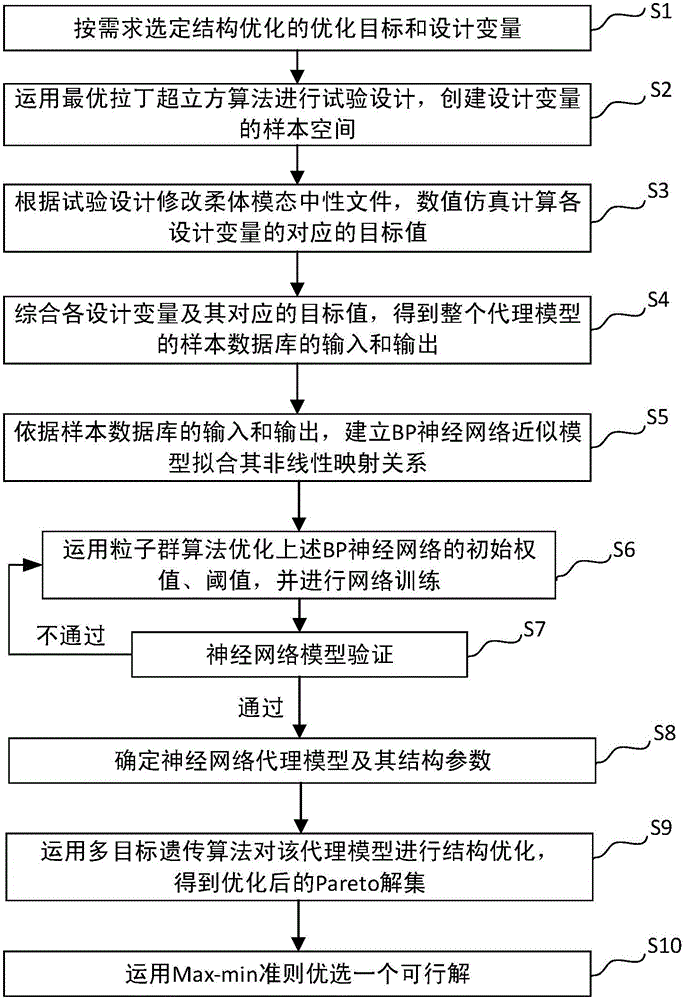
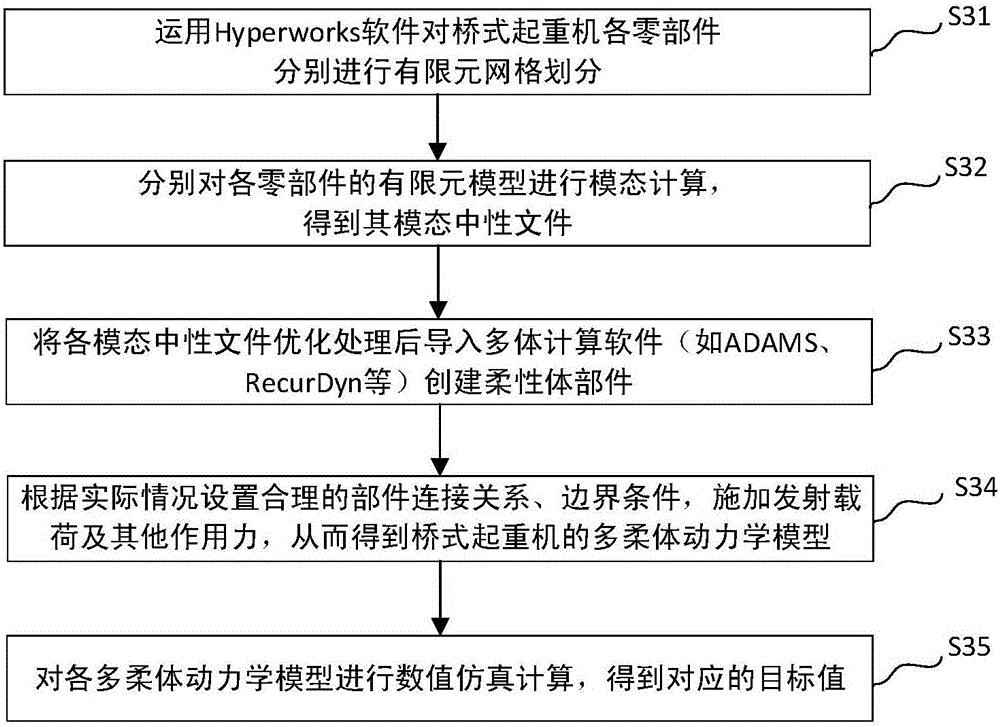
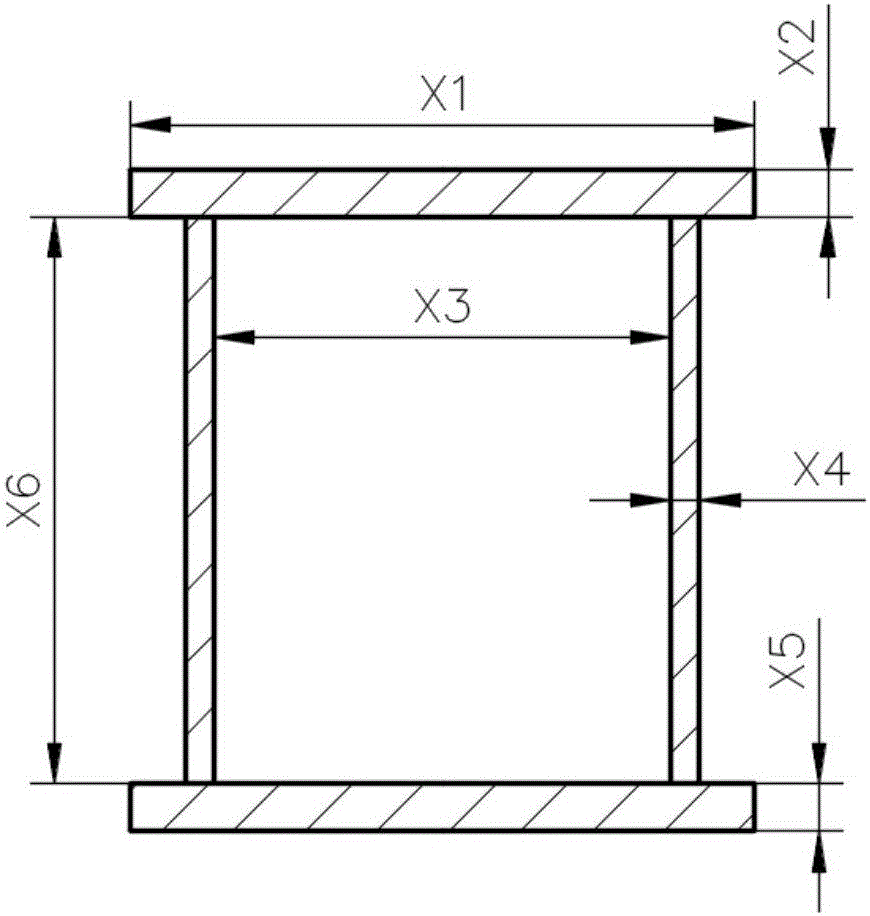
The invention discloses an optimizing method for a multi-flexible dynamic structure of a bridge crane. A multi-flexible dynamic technology, an optimal Latin hypercube algorithm, a neural network model optimized through particle swarm optimization, a NSGA-II algorithm and Maxi-min criterion are adopted for solving the problem of difficulty in optimizing the flexible part in the previous multi-flexible dynamic optimization process. According to the method, design variable values in a dynamic model are changed by altering a finite element parameter for changing modal neutral file information; a BP neural network optimized by the particle swarm optimization is introduced for establishing a surrogate model; the non-linear relationship between the design variable values of the flexible body and the optimized target value in the multi-flexible dynamic model is fit; the NSGA-II genetic algorithm is adopted for performing multi-target optimization on the surrogate model, thereby acquiring a Pareto solution set; the Maxi-min criterion is adopted for finding a feasible solution considering all the optimized targets.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Automatic quality control of seismic travel time
Seismic data from seismic exploration surveys are mapped into a hypercube of bins or voxels in a four-dimensional space (X, Y, Offset, and Azimuth) according to Common Mid-Point (or CMP) between source and receivers. The mapped data from individual voxels or bins is then analyzed by multimodal statistics. Robust estimates of first break picks are obtained from the analysis. The first break picks are then used to as seed inputs for autopicking iteration, which proceeds to convergence. Estimates of confidence levels in the data are provided for re-picking to reduce computer processing time in successive autopicking iterations. Analysis is provided of different seismic attributes such as azimuthal velocity variations indicative of anisotropy, positioning errors of sources / receivers, geometry errors, and three dimensional distribution of inversion residuals. Analysis is also performed of standard deviation of the travel time data useful for estimating data errors in the inversion covariance matrix.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Methods and apparatus for automatic system parameter configuration for performance improvement
InactiveUS7272707B2Simple methodHandy search resultsData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsData miningOptimization problem
In one embodiment, the present invention is a method and apparatus for automatic system parameter configuration for performance improvement. One embodiment of the inventive method involves formulating a black box optimization problem, and solving the optimization problem using an enhanced smart hill climbing method. The smart hill climbing method includes both a global and a more precise local search to identify an optimal solution. In one embodiment, one or both of the global and local searches employs a weighted Latin Hypercube Sampling method in combination with importance sampling techniques to yield improved search results
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com