Patents
Literature
877 results about "Finite element method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
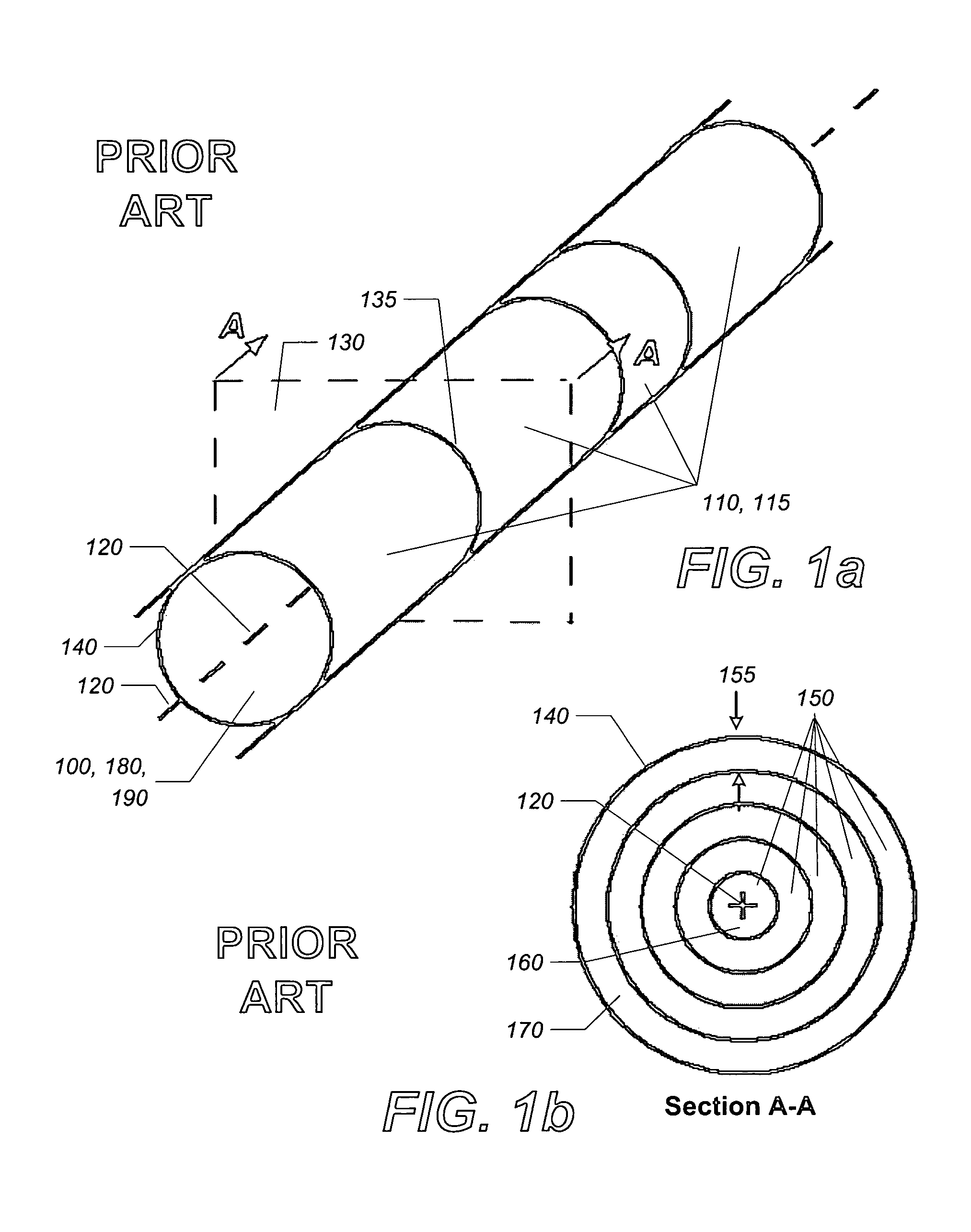
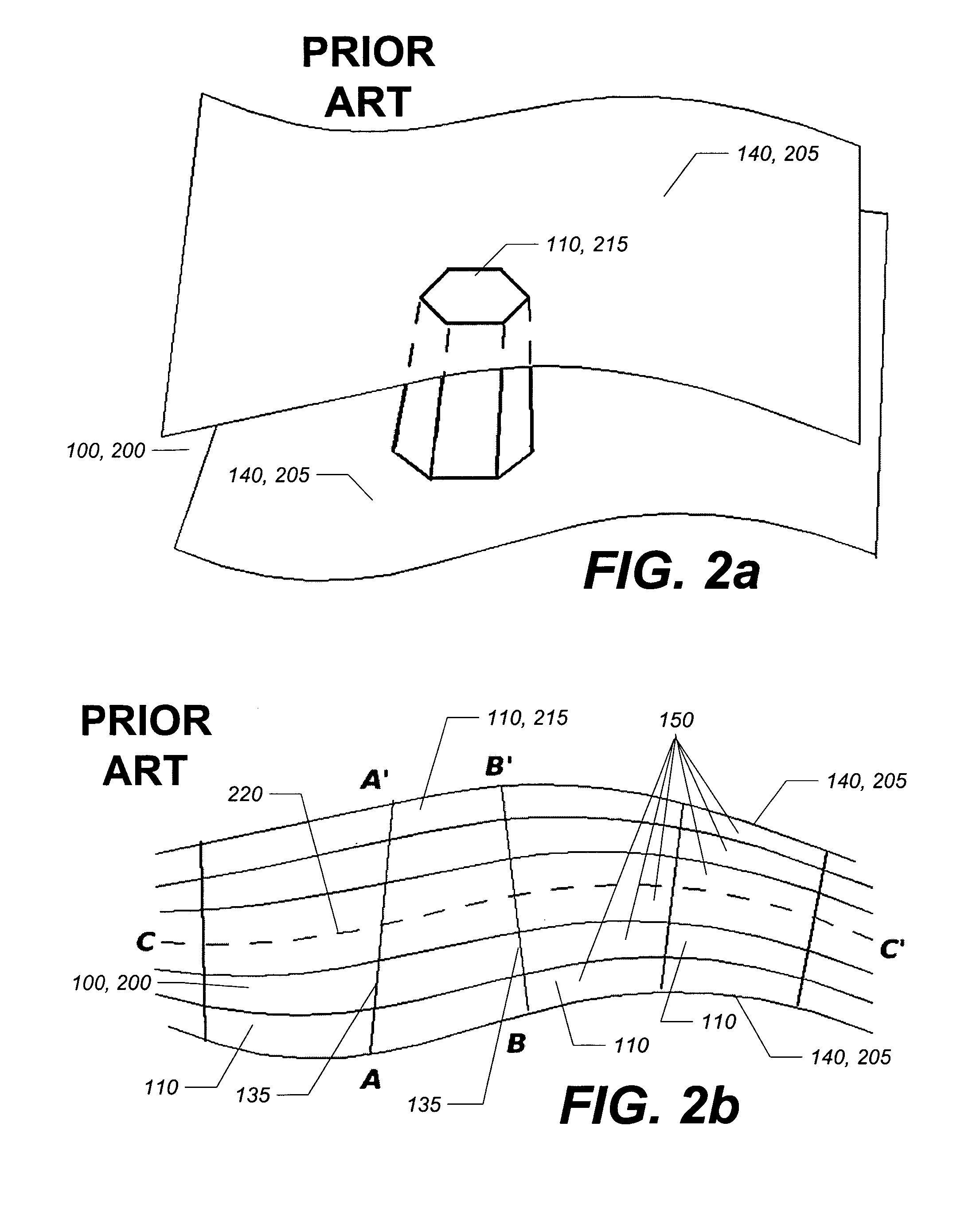
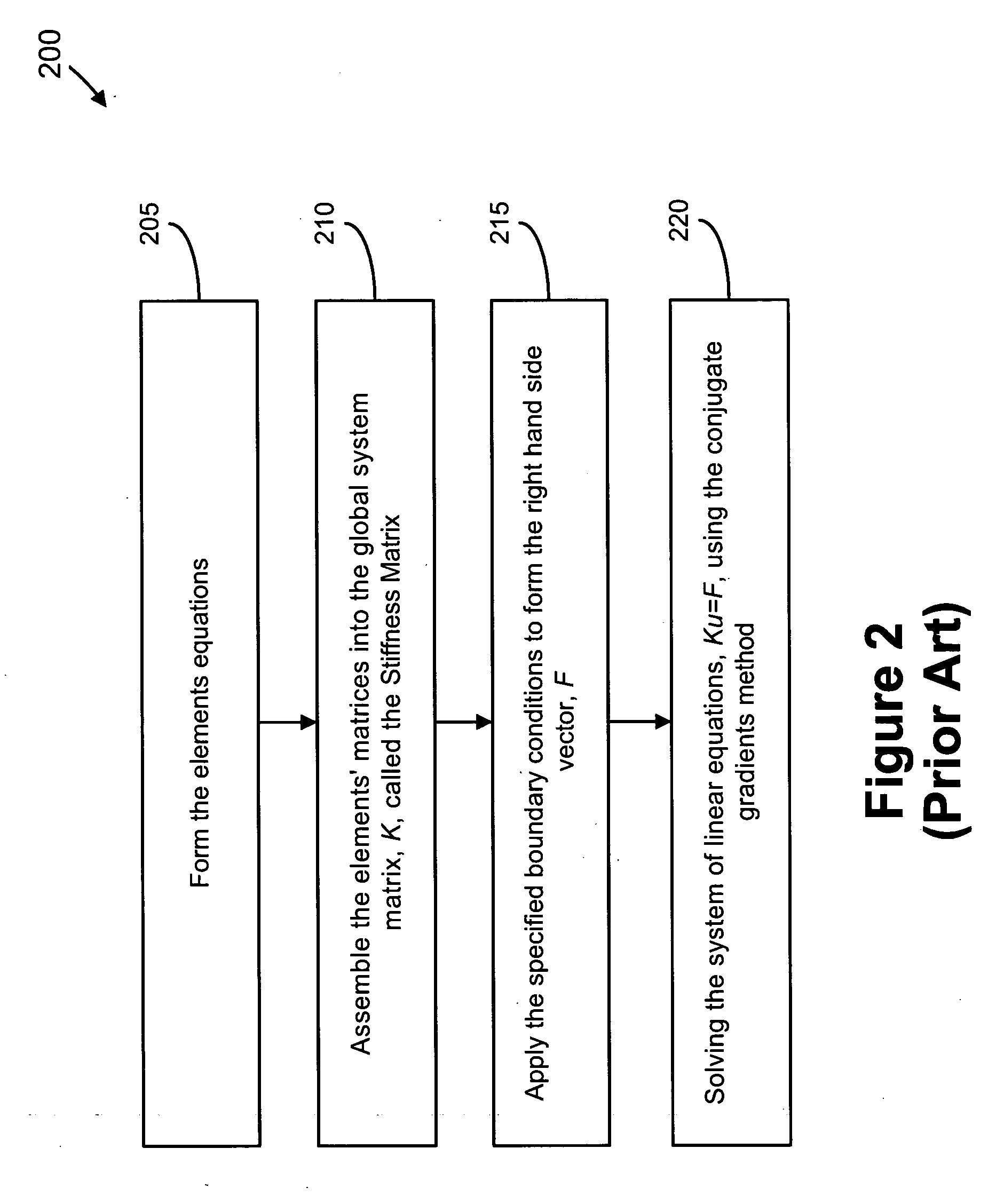
The finite element method (FEM) is a numerical method for solving problems of engineering and mathematical physics. Typical problem areas of interest include structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential. The analytical solution of these problems generally require the solution to boundary value problems for partial differential equations. The finite element method formulation of the problem results in a system of algebraic equations. The method approximates the unknown function over the domain. To solve the problem, it subdivides a large system into smaller, simpler parts that are called finite elements. The simple equations that model these finite elements are then assembled into a larger system of equations that models the entire problem. FEM then uses variational methods from the calculus of variations to approximate a solution by minimizing an associated error function.
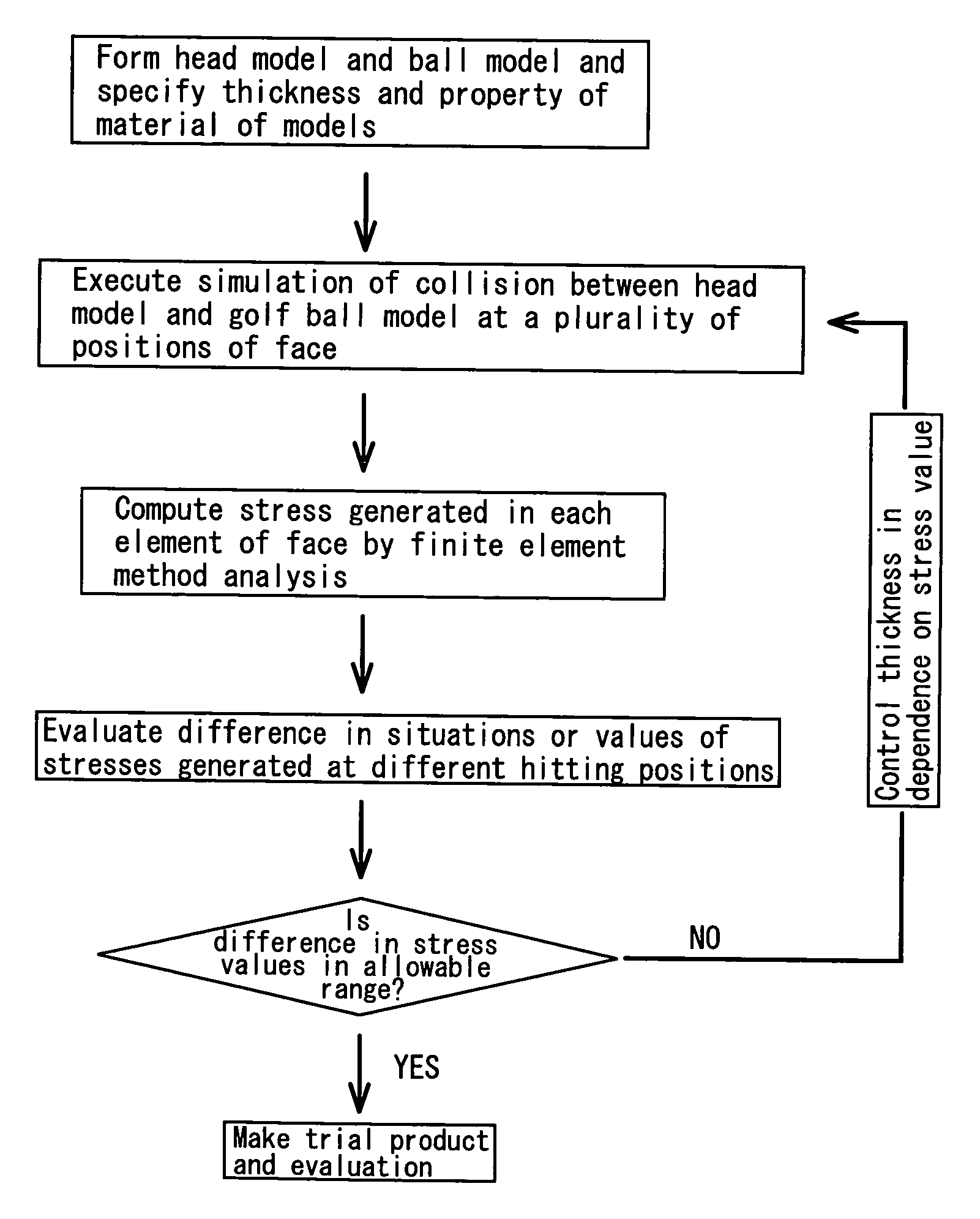
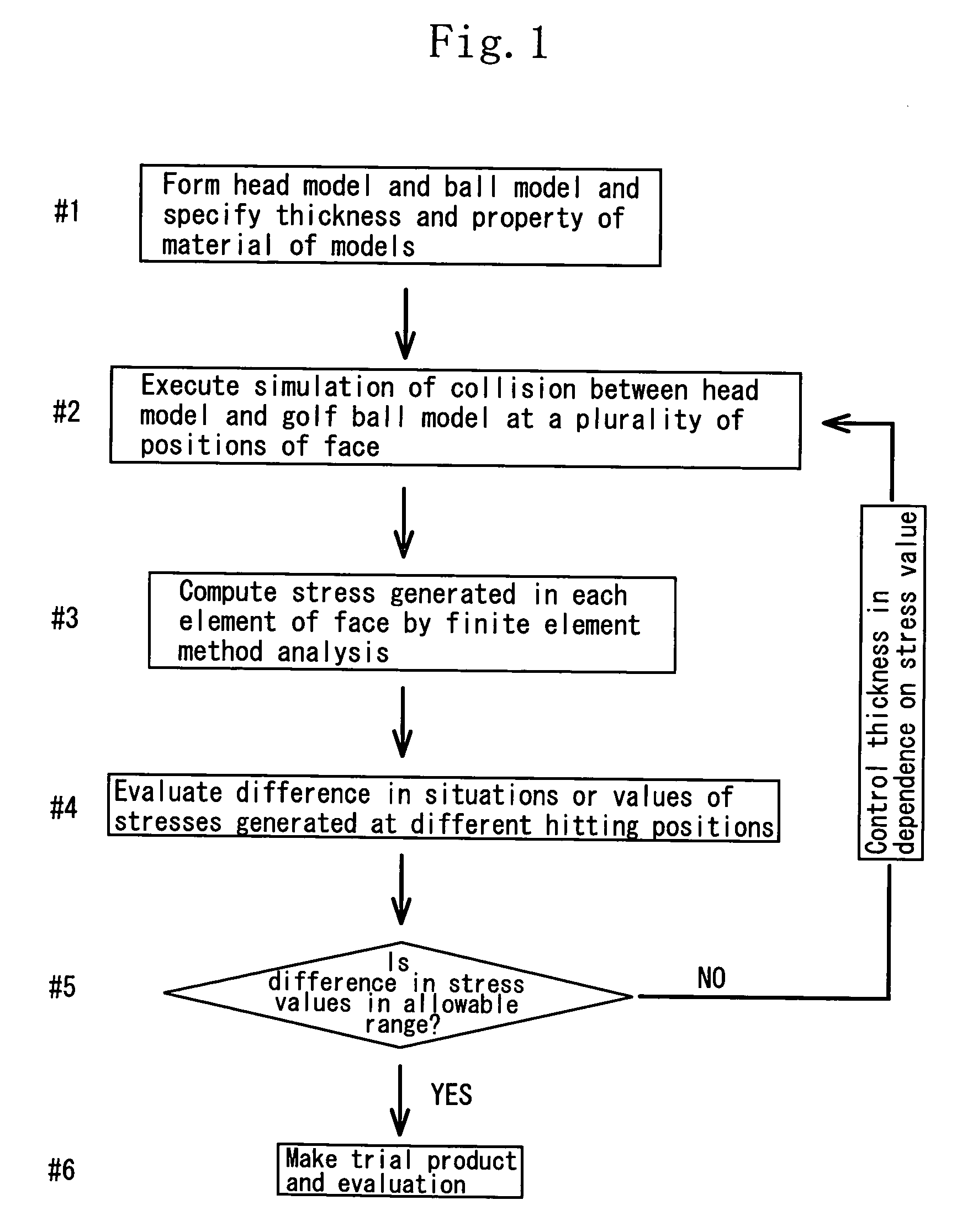
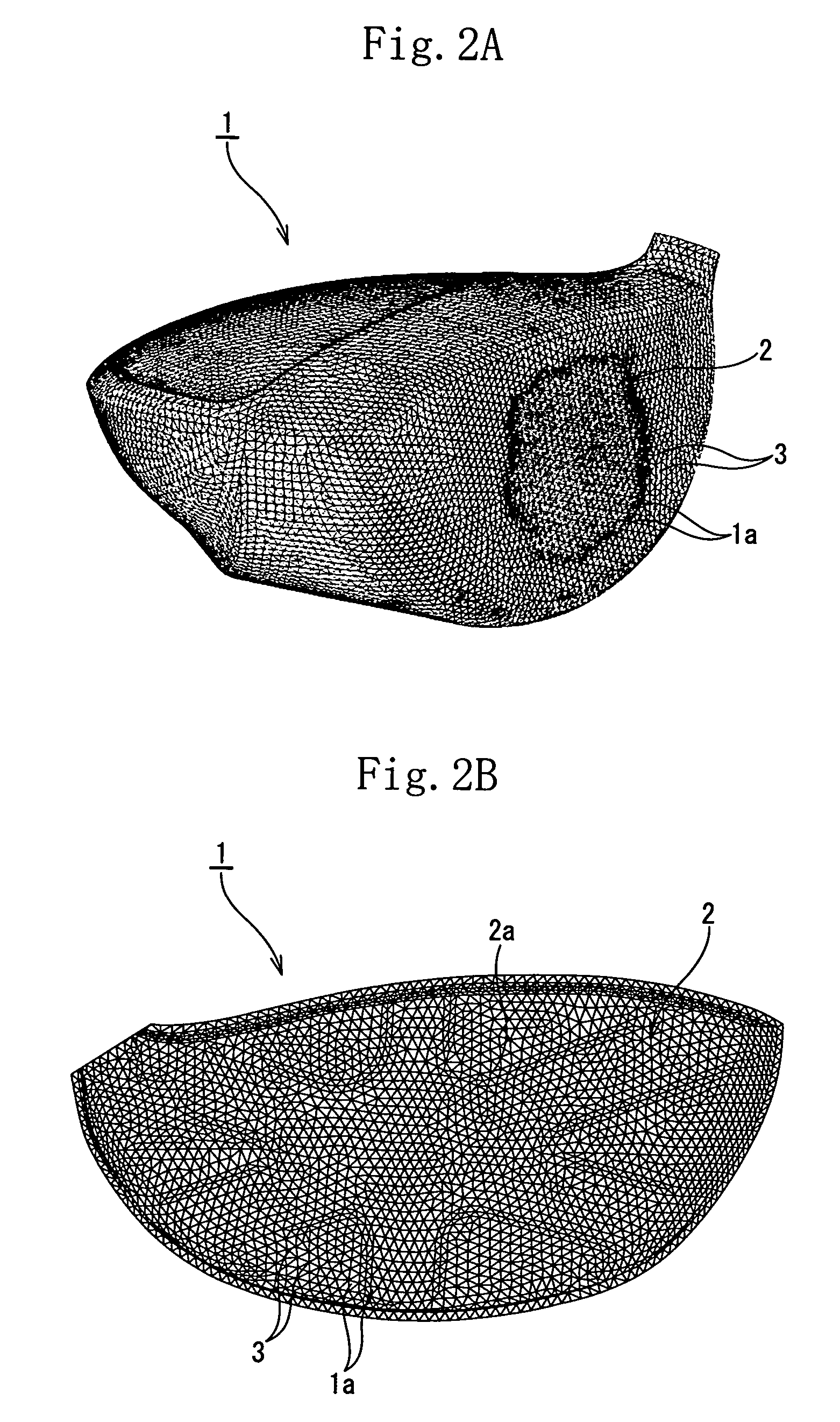
Method of designing golf club and golf club head
InactiveUS20070015601A1Reduce expensesSimple designDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFinite element methodGolf Ball
A method for designing a golf club head by using a computer. A golf club head model in which the rear surface of a face part is provided with reinforcing ribs and a golf ball model to be analyzed by using a finite element method (FEM) are prepared. Conditions including the positions of the reinforcing ribs and the configurations thereof including the sectional areas and heights are adjusted to set the maximum value of the Mises stresses generated by the collision between the golf ball model and the golf club head model at any off-center positions of said front surface of said face part thereof to less than 1.3 times the maximum value of the Mises stress generated by the collision between the golf ball model and the golf club head model at the center of said front surface of said face part thereof.
Owner:DUNLOP SPORTS CO LTD
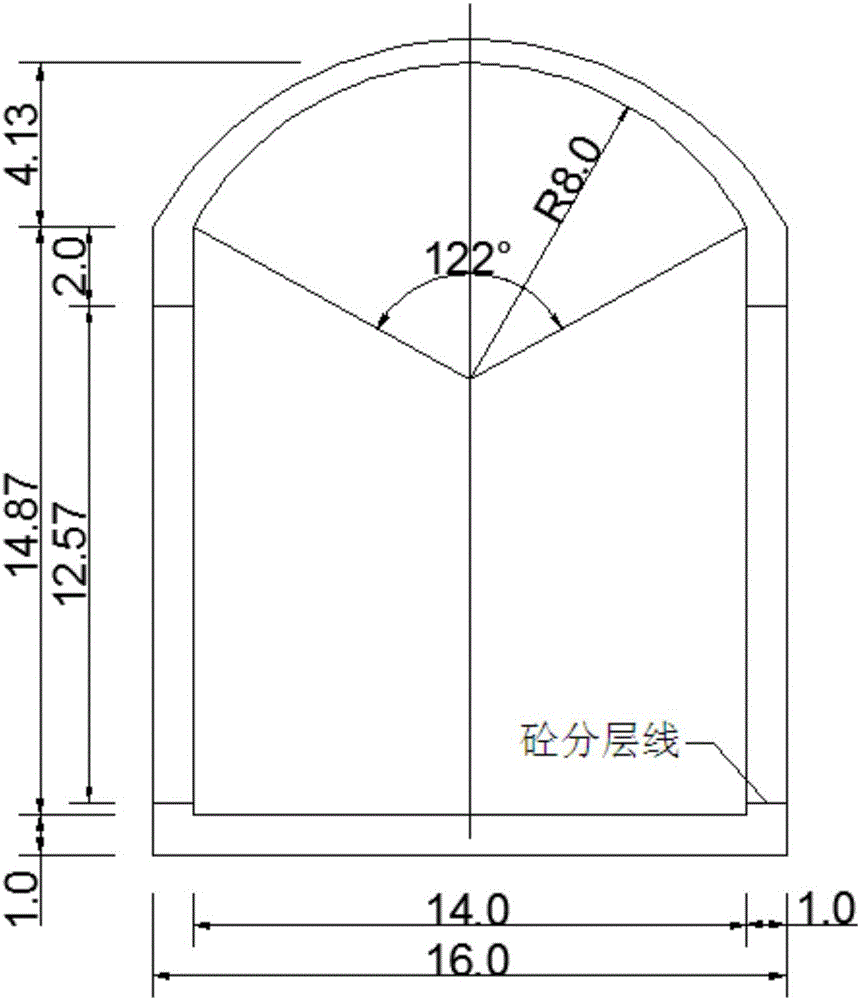
Large diameter tunneling close range down-traversing small diameter subway tunnel distortion control method
InactiveCN101215969AGuarantee smooth constructionEnsure safetyTunnelsUnderground tunnelFinite element method
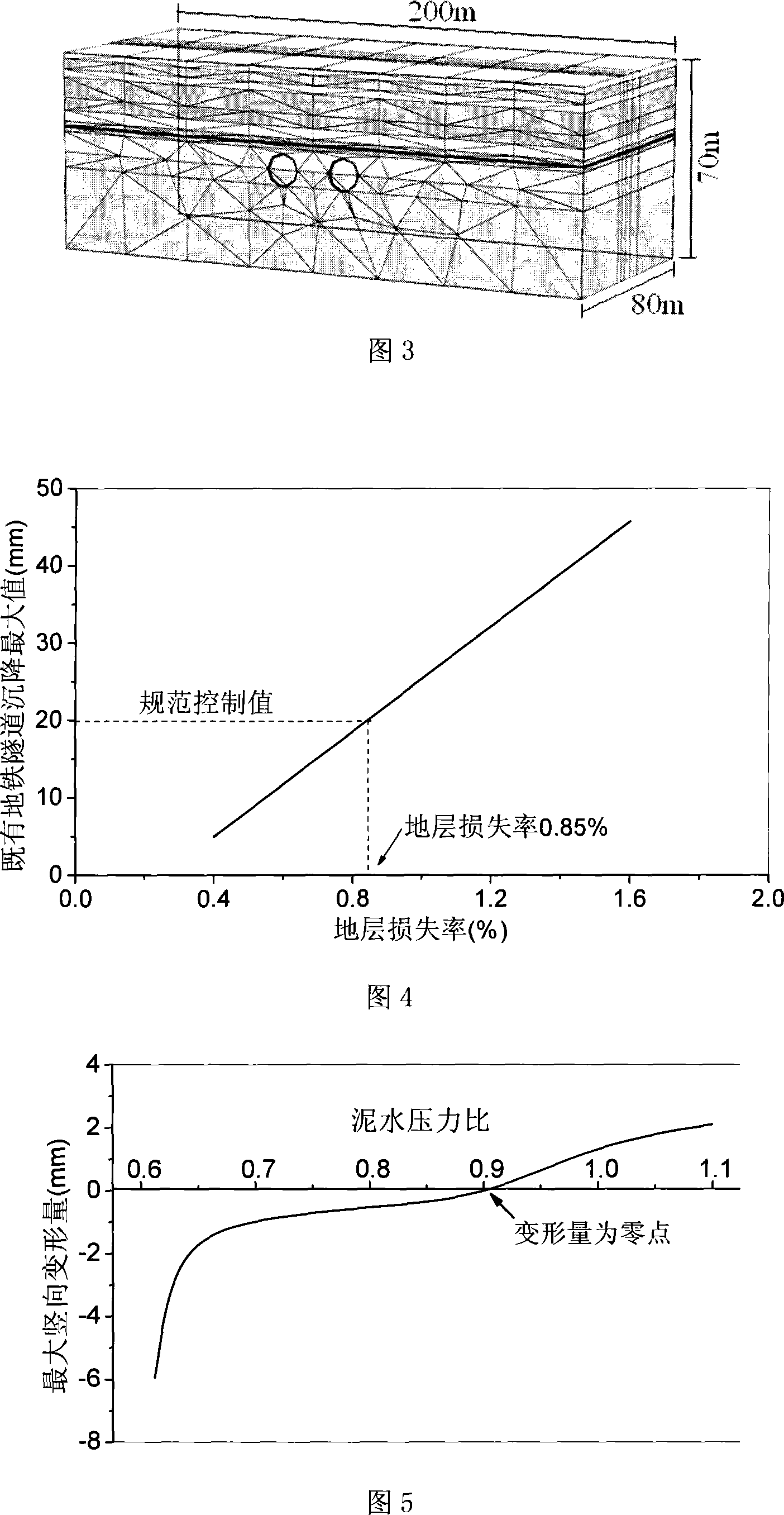
The invention discloses a method for controlling distortion for deep large diameter shield tunnels to under-pass small diameter tunnels, which pertains to the technical field of tunnel engineering. According to the method, the control range of the stratum loss ratio of newly established tunnels and the optimum value of the support pressure of the shield cut surface are acquired by using the finite-element method; soil pressure in front of the shield cut surface is kept relatively balanced by setting the optimal value of the support pressure, and the support pressure fluctuation range of the cut surface is controlled to range from minus 10kPa to plus 10kPa; the stratum loss ratio of the newly established tunnels is controlled within the allowed range. According to the construction technique measures, a test propelling area is arranged before the shield reaches a cross position. In the area, construction is carried out according to the situation of the existing underground tunnels above; and construction parameters are controlled and regulated to adjust the support pressure, the propulsive velocity and the amount of the grout to be injected in time; the shield passes through the cross position in combination with the optimal values of the construction parameters of the test propelling area. The invention can not only ensure the construction of tunnels to be carried out safely and smoothly, but also minimize the influence of construction on ambient environment.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Data measuring and calculating method for uniaxial tensile test
InactiveCN101975693AReduce calculation precisionDiscovery of the intensity effectMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesLength effectEnergy absorption
The invention discloses a data measuring and calculating method for a uniaxial tensile test, which comprises the following steps of: marking a measuring point; measuring test data; calculating real breaking strain stress; and drawing an engineering and real stress strain curve. The method of the invention can obtain engineering and real stress strain curves in different reference lengths in the same uniaxial tensile test, establishes a corresponding relationship between the reference length effect and the mesh size effect and provides a thorough solution for the mesh size effect problem in a finite element method, i.e. a real stress strain curve in the equal reference lengths is defined for the same material with different mesh sizes. Meanwhile, theoretical explanation is provided for the practical problems, such as mesh size effect, energy absorption, material strain invalidation, and the like according to a uniaxial tensile basic theory provided by the invention, therefore, the invention has important theory and engineering practical significance.
Owner:肖锋
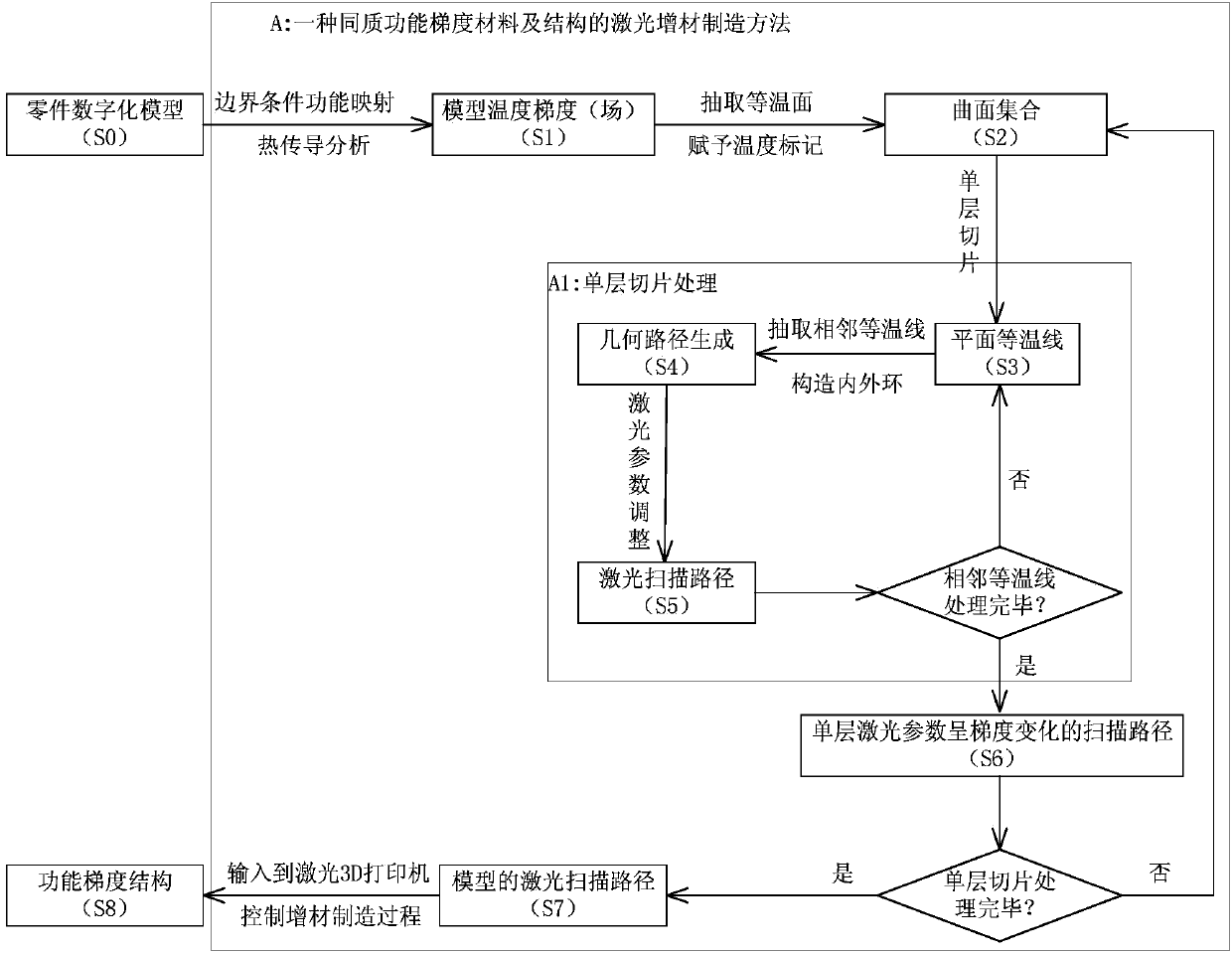
Laser additive manufacturing method for homogeneous functionally graded material and structure
ActiveCN104190930AOvercome functionOvercome structureIncreasing energy efficiencyLaser scanningOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a laser additive manufacturing method for a homogeneous functionally graded material and structure. The method includes the following steps that different functions are mapped into different temperatures which serve as boundary conditions to be exerted on different parts of a three-dimensional model; a three-dimensional finite element method is used for calculating a heat conduction equation of the model, inner temperature graded distribution, namely the temperature field of a model, is obtained, that is a temperature field of the model is obtained; an isothermal surface of the model is extracted, and a curved surface set with different temperature marks is obtained; slicing is conducted on the curved surface set, the intersection outline of each layer and the isothermal surface is obtained, in other words, plane isothermal lines are obtained; slices of each layer are processed, and a scanning route with laser parameters of the single layer in graded variation is obtained; the steps are repeatedly conducted until slicing is completed and a laser scanning route of the model is obtained; the generated laser scanning route is input into a laser 3D printing machine to control the additive manufacturing process, and the homogeneous functionally graded structure is obtained. According to the additive manufacturing method, the fact that the homogeneous functionally graded material and the homogeneous functionally graded structure can be manufactured in an additive mode is achieved, and the fact cannot be achieved through a current laser additive manufacturing method.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for analyzing vortex vibration and fatigue of depth tension-type vertical pipe
A method for analyzing vortex vibration and fatigue of a depth tension-type vertical pipe, which relates to the field of depth vertical pipe design, comprises the following specific steps of: step 1. obtaining flow field data; step 2. substituting the flow field data into vertical pipe vibration equations 6 and 7; step 3. solving the equations 6 and 7 by using a finite element method, and obtaining calculation results including displacement, velocity, accelerated velocity and stress time interval; and step 4. counting stress cycle number n(i) of an amplitude within a certain time by adopting a rain-flow counting method according to the calculation results, and substituting the n(i) into a fatigue damage calculation formula 8 to calculate the fatigue damage. The method for analyzing vortex vibration and fatigue of the depth tension-type vertical pipe improves the accuracy of stress calculation by adopting a practical pipe-in-pipe model and simultaneously considering direct flow vibration and cross flow vibration.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
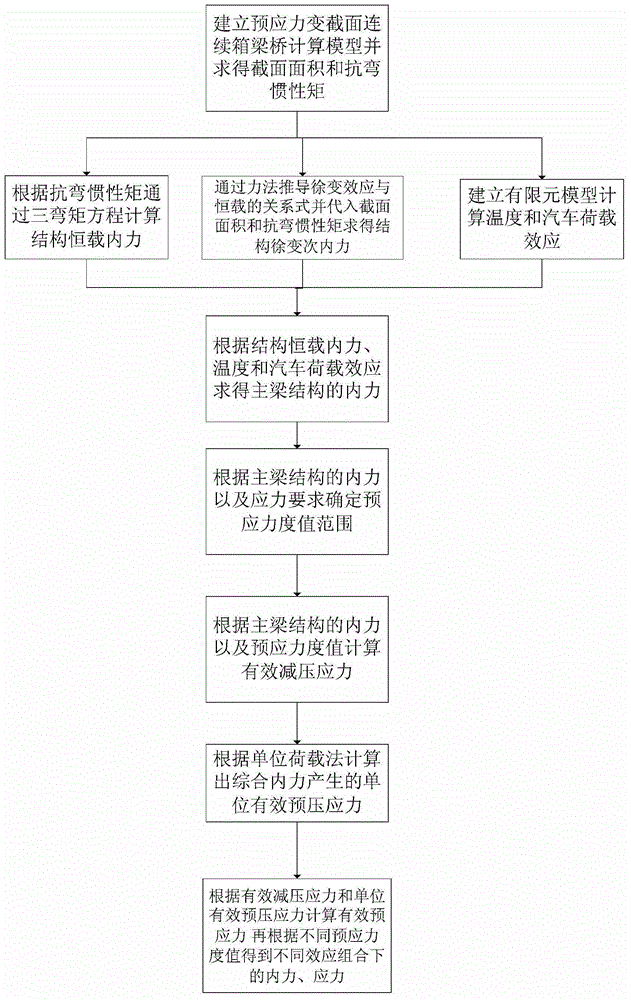
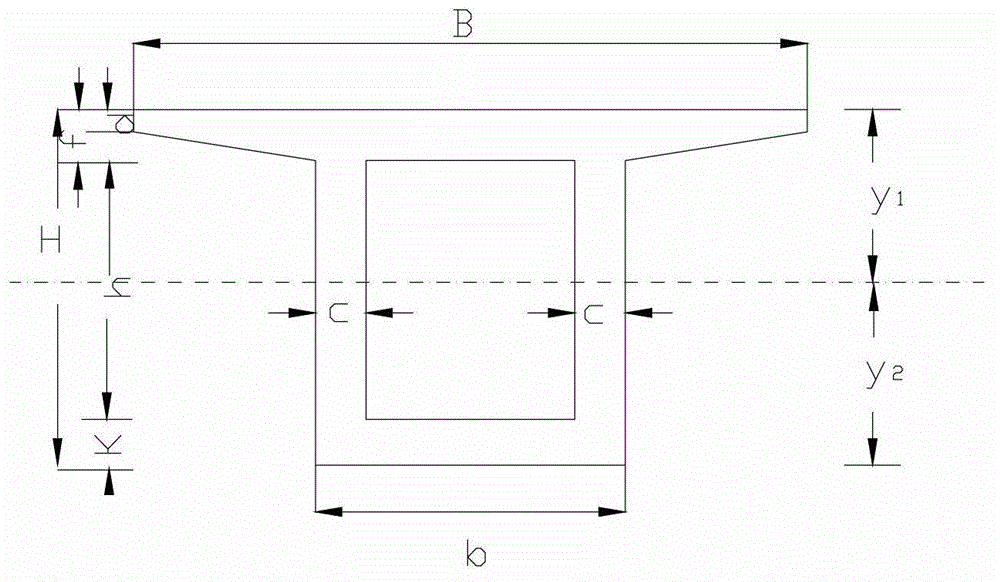
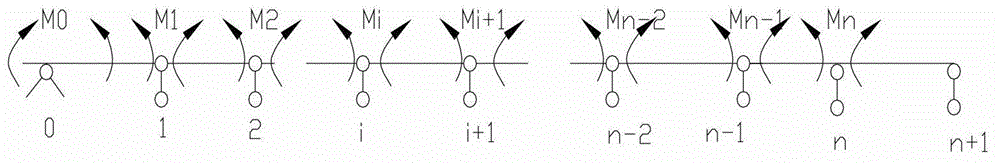
Design method for longitudinal pre-stressing tendons of variable-cross-section pre-stressed concrete continuous bridge
InactiveCN103065035ADevelop longitudinal prestressDevelopment of Analytical Computational MethodsSpecial data processing applicationsBridge materialsStress ratioPre stressing
The invention discloses a design method for longitudinal pre-stressing tendons of a variable-cross-section pre-stressed concrete continuous bridge. The optimization design method for the longitudinal pre-stressing tendons of the pre-stressed concrete continuous bridge is built based on the design principle of the pre-stressed degree and through combining an analytic method with a finite element method and compressively considering dead load and live load action effects. A three moment equation of the variable-cross-section pre-stressed concrete continuous box girder bridge is established to solve the internal force of the structure under the action of the self weight on the basis of the average bending moment method. A calculation formula of pre-stressed effective pre-pressure is built through a load equal effect method and a unit load method; a creep effect calculation formula is built through a force method; the temperature effect and the automobile load effect are calculated through the finite element method; and a variable-cross-section statically indeterminate structure pre-stressing tendon reinforcement calculation formula is obtained through combination of the stress ratio with the definition of the competitive pre-stressed degree.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Automated generation of lean models for injection molding simulation
ActiveUS7574339B2Preserve efficiencyPreserve spiritComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer resourcesKey innovation
The present invention is a method and system for simulating fluid flow in a cavity, having relevance to the modeling of viscous flows within thin cavities of complex shapes in which heat exchange with the cavity walls may be a governing factor, as in injection molding of plastic parts. Its automated discretization scheme, in which the model cavity is partitioned into macrocells, each macrocell having substantial contact areas with the model cavity walls, eliminates the need for time consuming and expensive manual model configuration required by some modeling methods. Because of the simplicity of the discretization, models based on the invention are less demanding on computer resources then conventional finite element methods, and execute more quickly. A key innovation of the method is a function characterizing the shape of a macrocell that appears in a coefficient in equations governing the flow. As a consequence of the improvements offered by the invention, molds for complex parts can be fabricated more rapidly, with the resulting parts having high quality.
Owner:PROTOMOLD CO THE
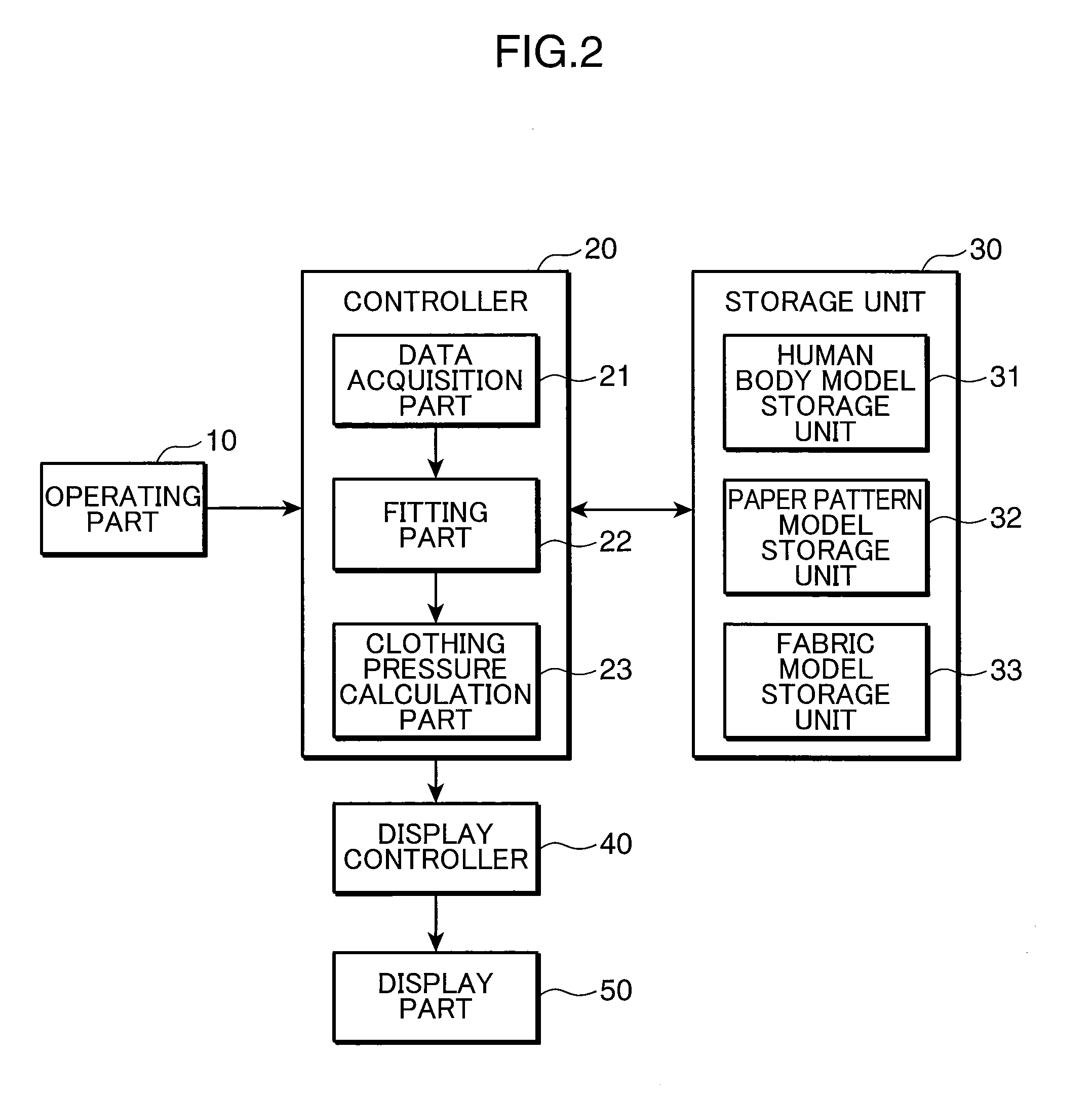
Clothing simulation apparatus, clothing simulation program, and clothing simulation method
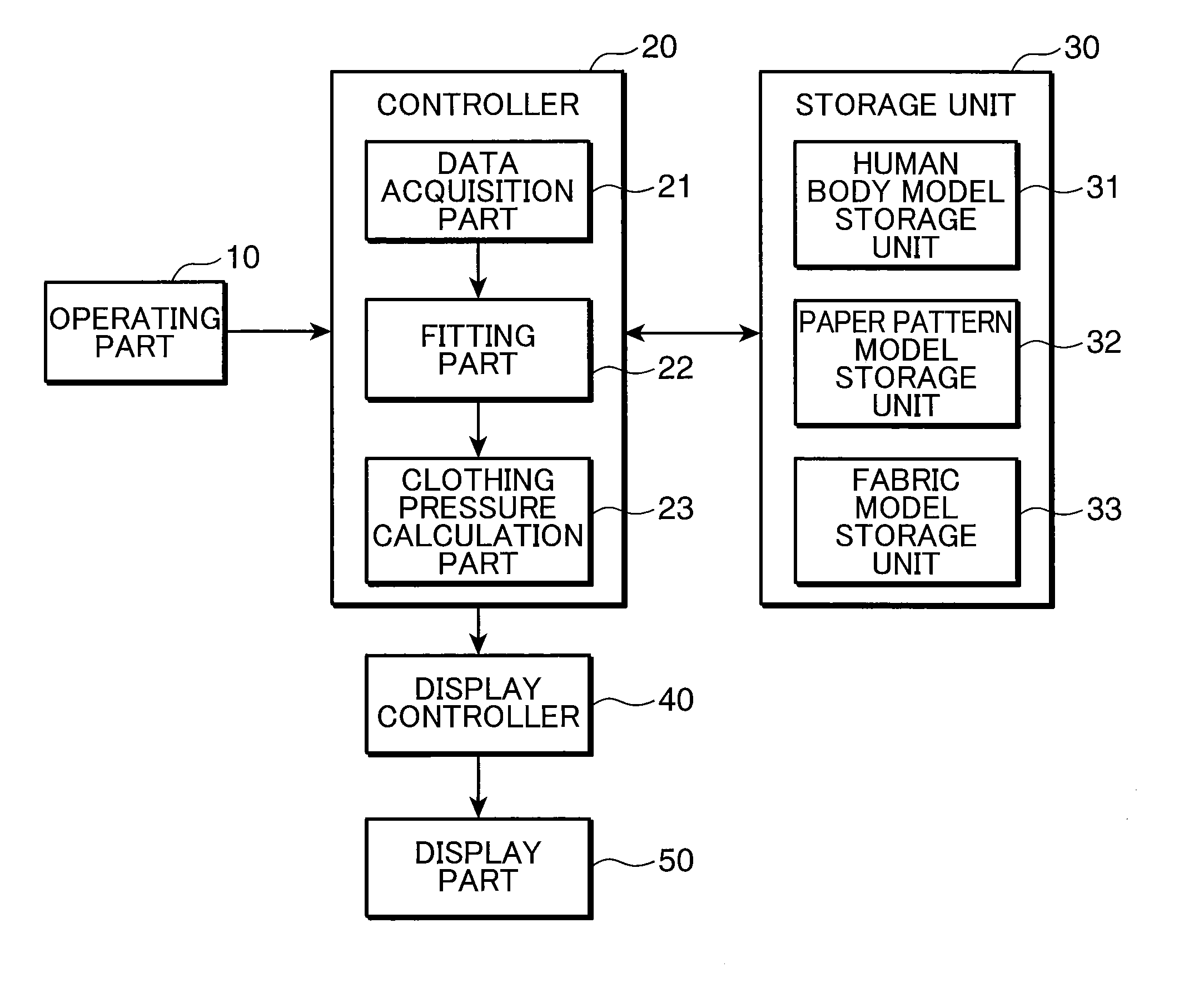
InactiveUS20110022372A1Accurate acquisitionClothing pressureAnalogue computers for chemical processesDesign optimisation/simulationHuman bodyFinite element method
A clothing simulation apparatus precisely determines clothing pressure for bringing a clothing into tight contact with a human body. A fitting part 22 divides a paper pattern model into a plurality of elements, imparts dynamic characteristics shown by a fabric model to each element, deforms the paper pattern model by solving the motion equation of each element using a finite element method, and then fits the clothing virtually to a human body model. The fitting part 22 sets a temporary model to cover a predetermined section of the human body model, deforms the paper pattern model to bring the paper pattern model into contact with the temporary model, and thereafter deforms the paper pattern model to bring the paper pattern model into contact with the human body model.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
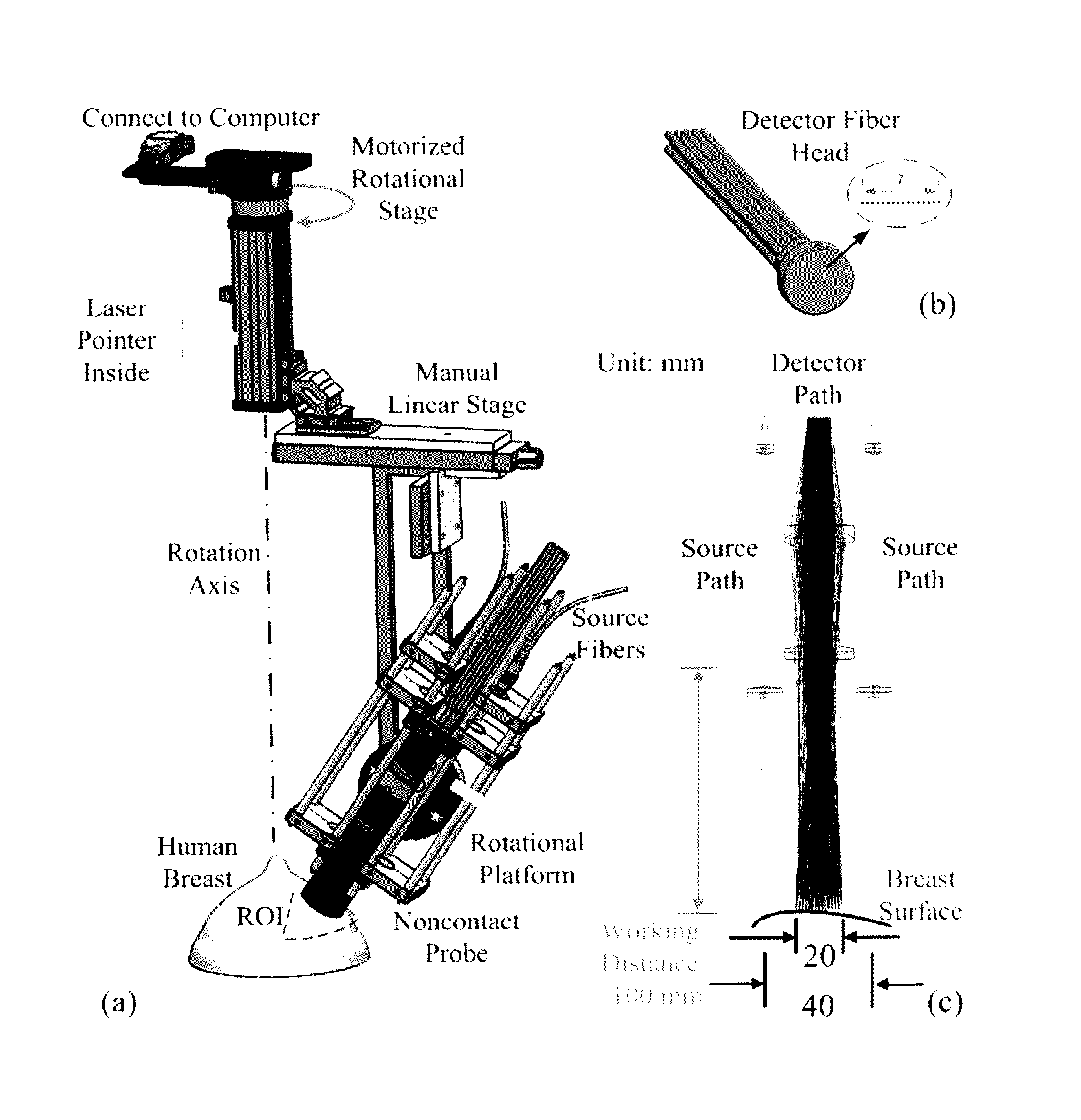
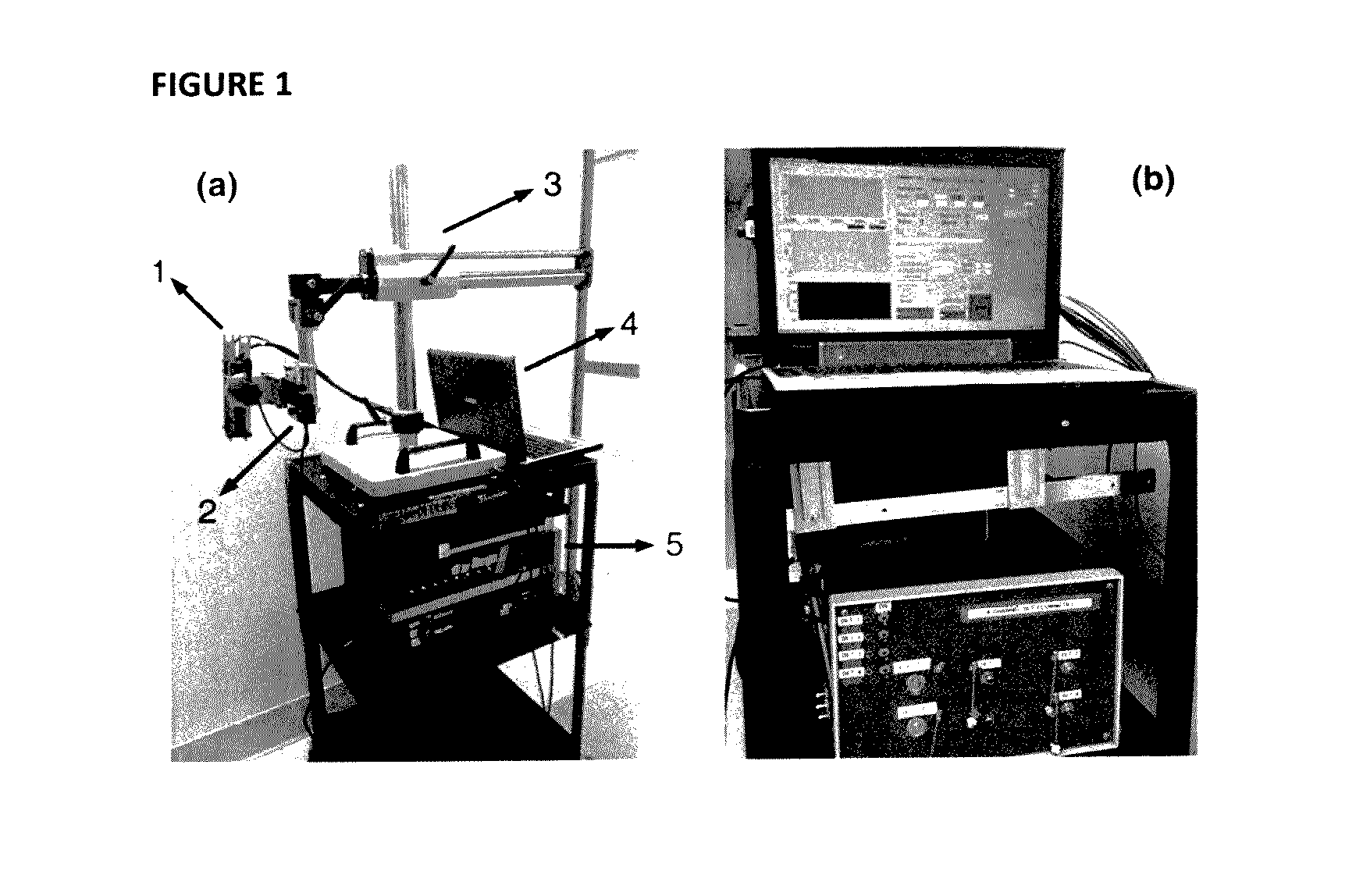
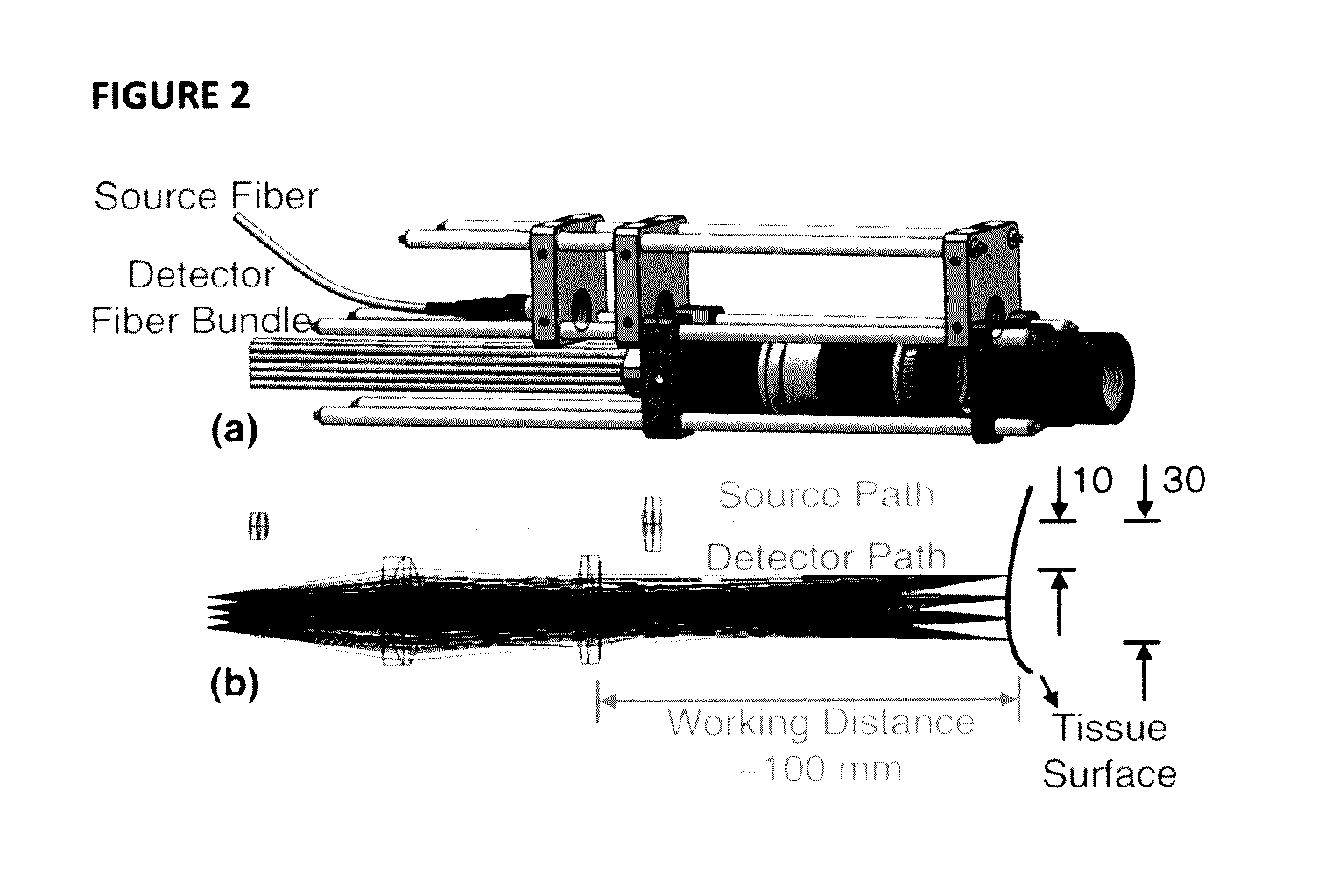
Noncontact Three-dimensional Diffuse Optical Imaging of Deep Tissue Blood Flow Distribution
ActiveUS20160278715A1Avoid contactMedical simulationDiagnostics using spectroscopyFinite element methodDeep tissue
The present invention provides for three-dimensional reflectance diffuse optical imaging of deep tissue blood flow distribution that removes the need for probe-tissue contact, thereby allowing for such technology to be applied to sensitive, vulnerable, damaged, or reconstructive tissue. The systems utilize noncontact application and detection of near-infrared light through optical lens and detection through a linear array or two-dimensional array of avalanche photodiodes or a two-dimensional array of detectors provided by charge-coupled-device (CCD). Both further feature a finite-element-method (FEM) based facilitation to provide for three-dimensional flow image reconstruction in deep tissues with arbitrary geometries.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
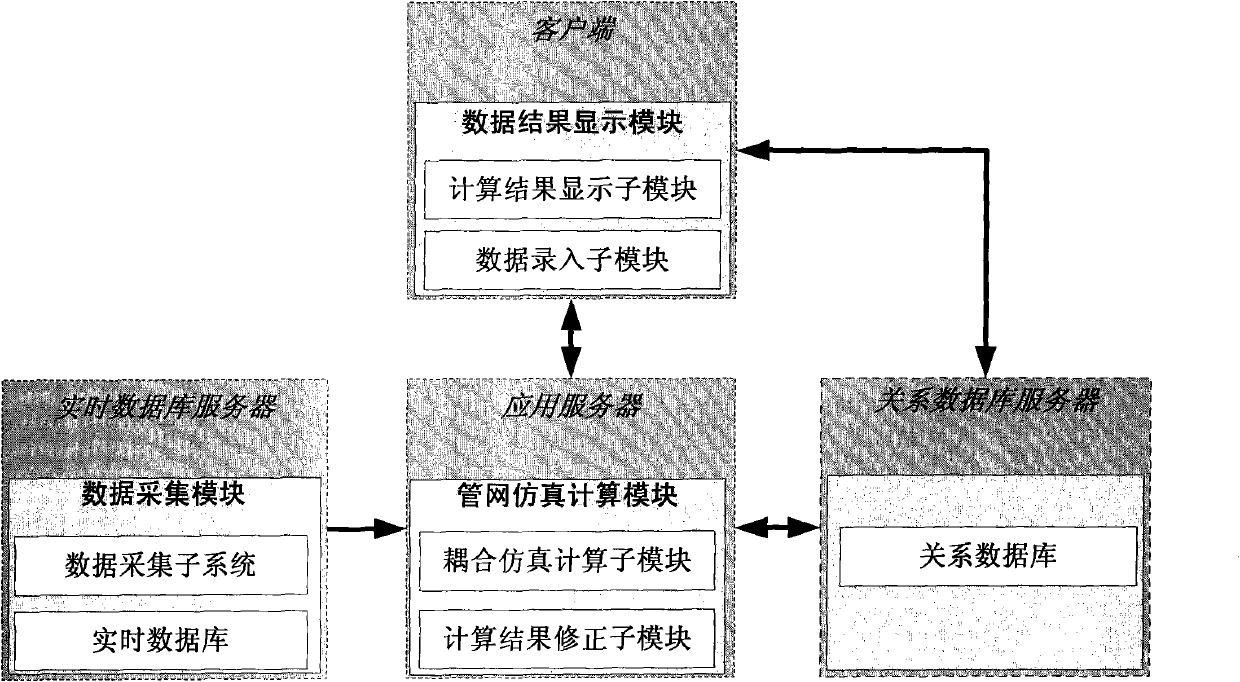
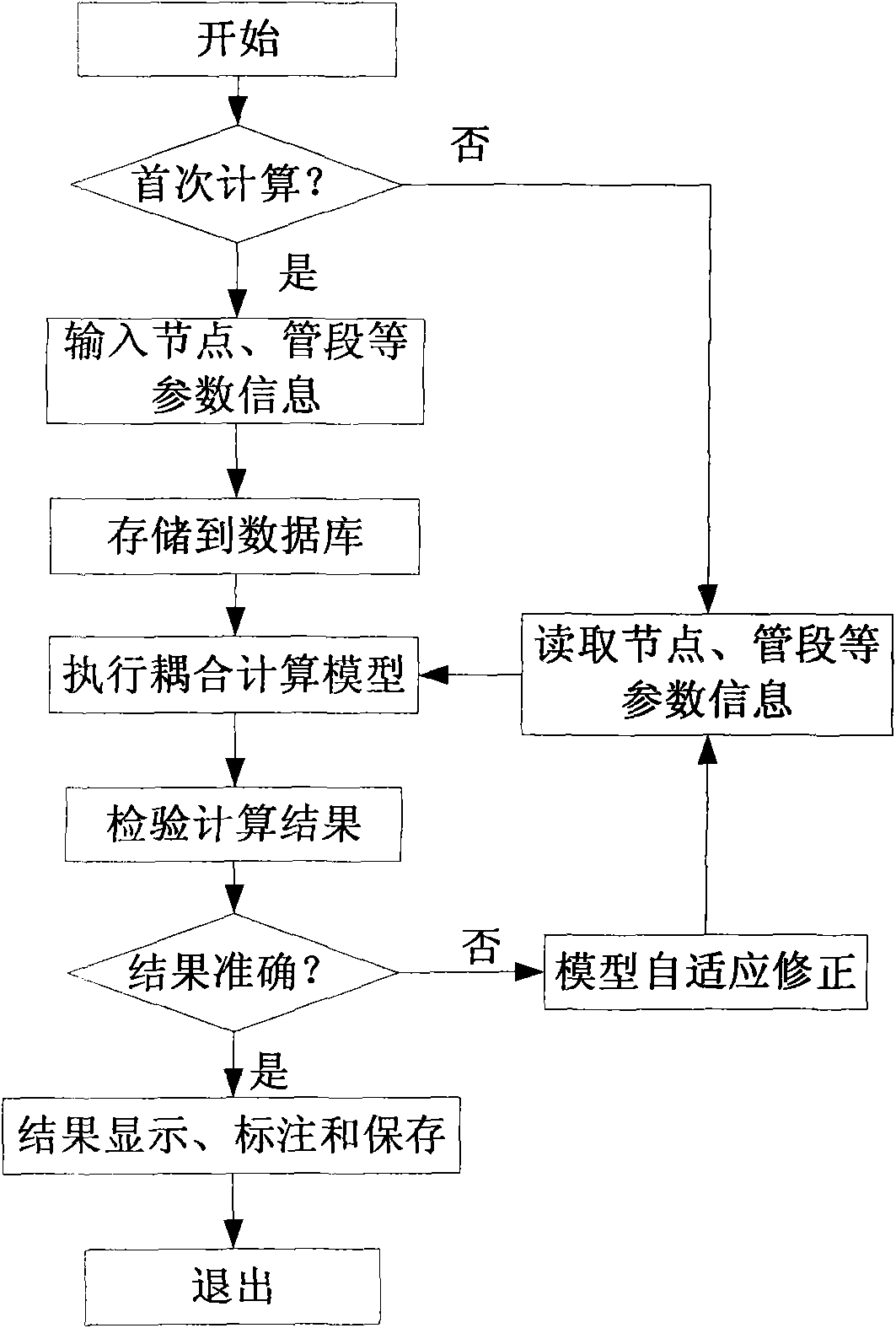
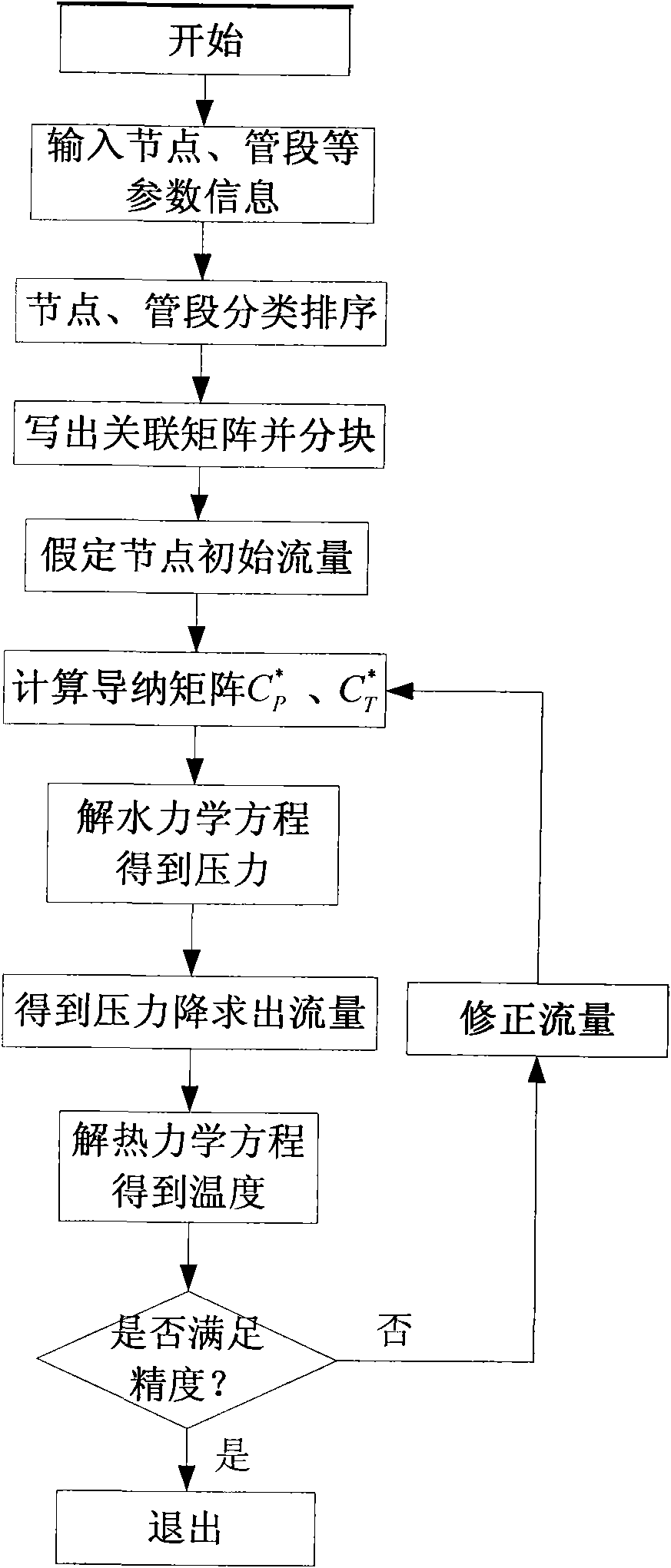
Multi-gas-source steam pipe network computing system of hydraulic thermal-coupling simulation model
InactiveCN102063566AHigh precisionThe calculation result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsRelational databaseState parameter
The invention relates to a multi-gas-source steam pipe network computing system of a hydraulic thermal-coupling simulation model, belonging to the technical field of energy pipe network simulation calculation. The system provided by the invention comprises a relation database, a data acquisition module, a data result display module and a pipe network simulation calculation module, wherein the data acquisition module comprises a real-time database and a data acquisition subsystem; the data result display module comprises a data input submodule and a calculation result display submodule, and the pipe network simulation calculation module comprises a coupling simulation calculation submodule and a calculation result correction submodule. The system provides a modeling reference for multi-gas-source calculation through describing the topological structure of the pipe network by using a graph theory method, is coupled with hydraulic and thermodynamic calculation models, solves the modules by using a finite element method, and can trigger result correction when the pipe network environment is changed, and the data result display module can be displayed in a view control fitting of the pipe network in a visualization mode. The invention has the advantages of improving the calculation accuracy of state parameters and solving the calculation problems of the multi-gas-source pipe network model.
Owner:AUTOMATION RES & DESIGN INST OF METALLURGICAL IND
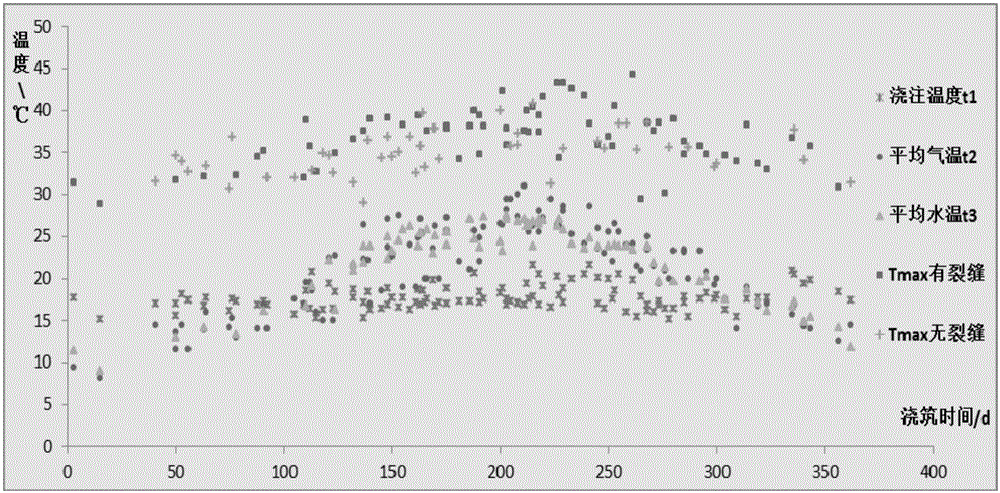
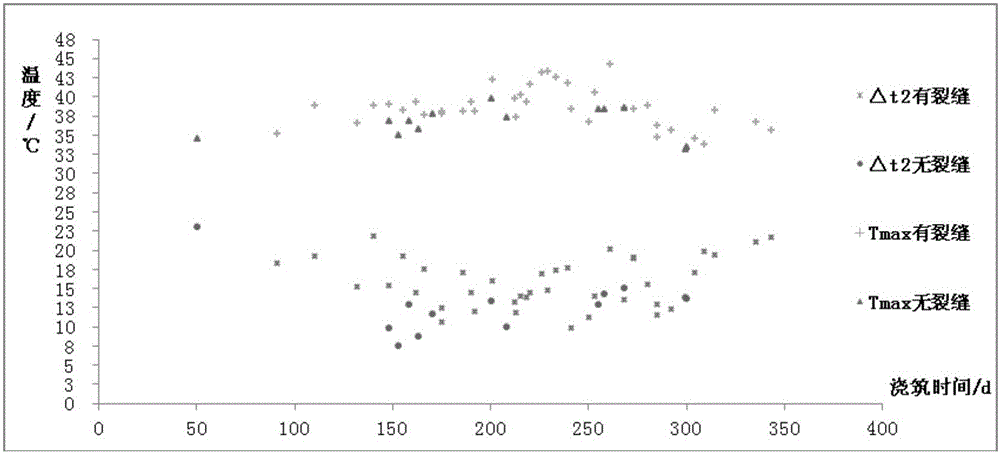
Temperature control and crack prevention design calculating method used for lining concrete of door-opening-shaped section structure
ActiveCN105672187AThe calculation formula is simpleQuick calculation of maximum temperatureGeometric CADHydraulic engineering apparatusTemperature controlFinite element method
The invention discloses a temperature control and crack prevention design calculating method used for lining concrete of a door-opening-shaped section structure. The method comprises the following steps of (1) determining a temperature control and crack prevention target, (2) calculating the permitted maximum temperature and (3) making a temperature control scheme, specifically, the maximum temperature inside the concrete is calculated, and on the premise that the worked-out maximum temperature is smaller than or equal to the permitted maximum temperature, the temperature control and crack prevention scheme is designed. The calculation formula of the method is simple, the influences of surrounding rock performance, the lining structure size, concrete strength, intro-opening air temperature, water-introducing cooling and water temperature thereof, pouring temperature and the like can be reasonably reflected, the permitted maximum temperature of pouring construction each month in the construction period of the lining concrete of the door-opening-shaped section structure can be rapidly calculated, the maximum temperature inside the lining concrete is calculated rapidly for different temperature control schemes, and a temperature control and crack prevention construction scheme suitable for a project is provided under the conditions that the inside maximum temperature is smaller than or equal to the permitted maximum temperature and economy is achieved. The error is smaller than 3% compared with the simulation calculation result of a finite element method, and the temperature control and crack prevention design calculating method is particularly suitable for optimization and adjustment of primary design and an on-site construction scheme.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
High-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method based on H matrix algorithm
InactiveCN102033985AQuick solveDiscrete Fit ExactSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexityDecomposition
The invention discloses a high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method based on an H matrix algorithm, which can realize electromagnetic simulation on a large three-dimensional target. In the method, a time domain finite element method (TDFEM) is used as a background, a low-rank compression technique is used as a core, and a tree structure is used as a basis for carrying out logical unit (LU) decomposition on a sparse matrix generated by the TDFEM by a four arithmetic algorithm corresponding to the H matrix. The acquired upper and lower triangular factors have low-rank compressible characteristics, and the compressed matrix equation can realize quick solution of high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation by the H matrix algorithm. The high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method has the advantages of fast computation speed, low memory consumption, controllable computation accuracy, good stability and the like, can reduce the complexity of computation to O(Nlog<2>N) and reduce the memory consumption to O(NlogN), can be widely applied to the solution of a large sparse linear system of equations during high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation, and can provide important reference for analyzing the electromagnetic property of the large three-dimensional target.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Simulation method of low-permeability reservoir crude oil boundary layer
InactiveCN104331579AShorten the timeIn line with the actual situationSpecial data processing applicationsThroatRock core
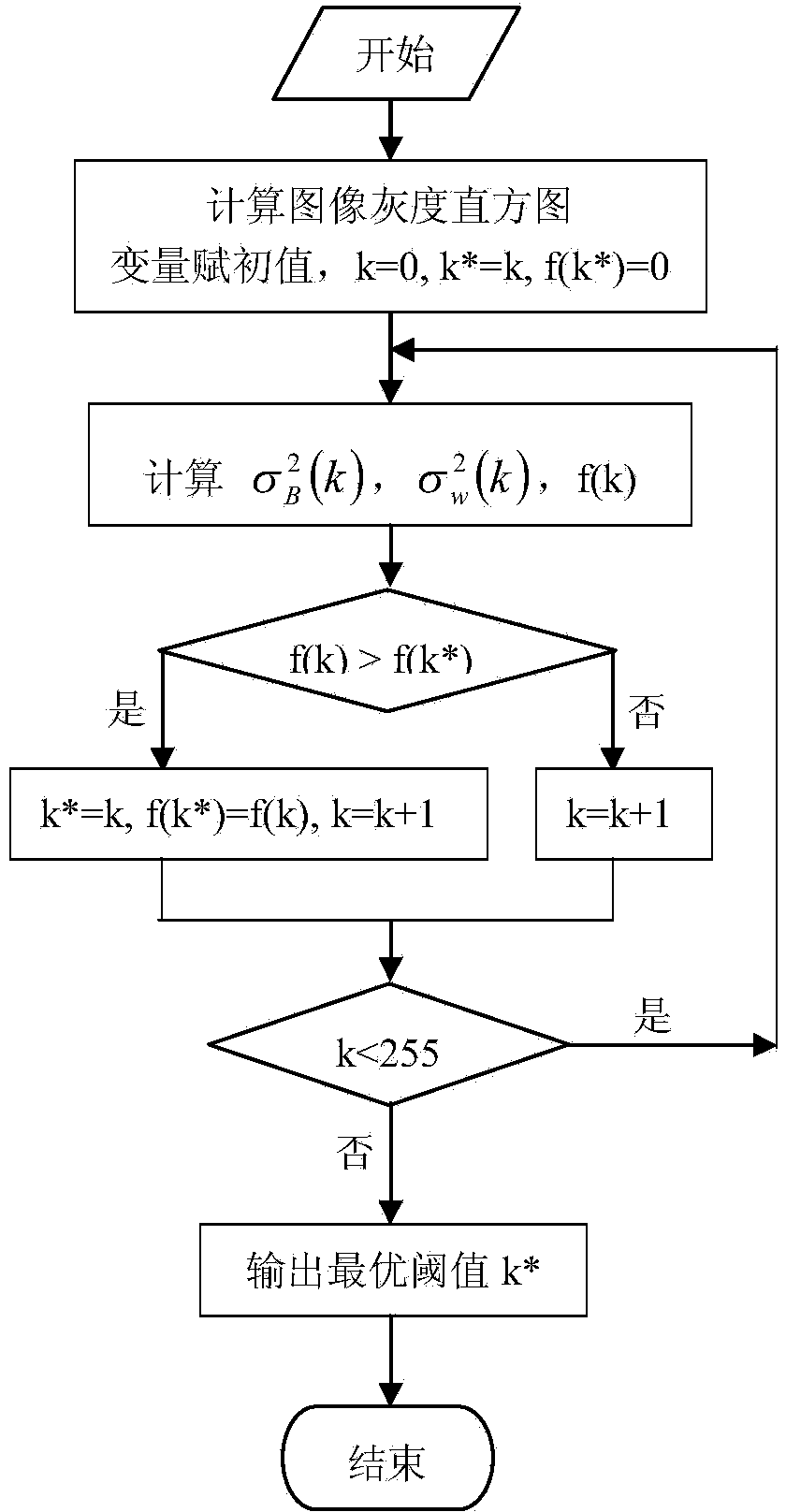
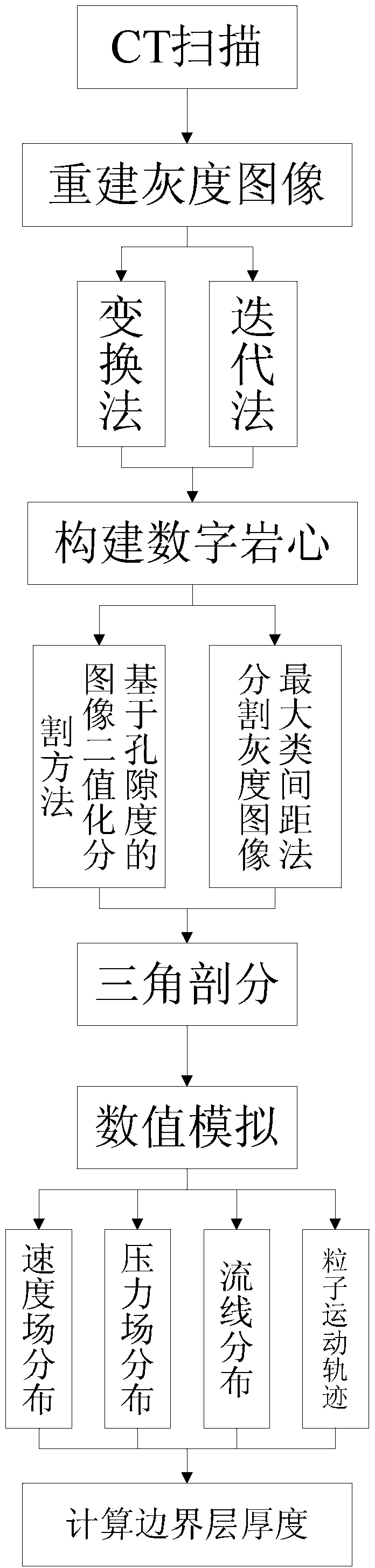
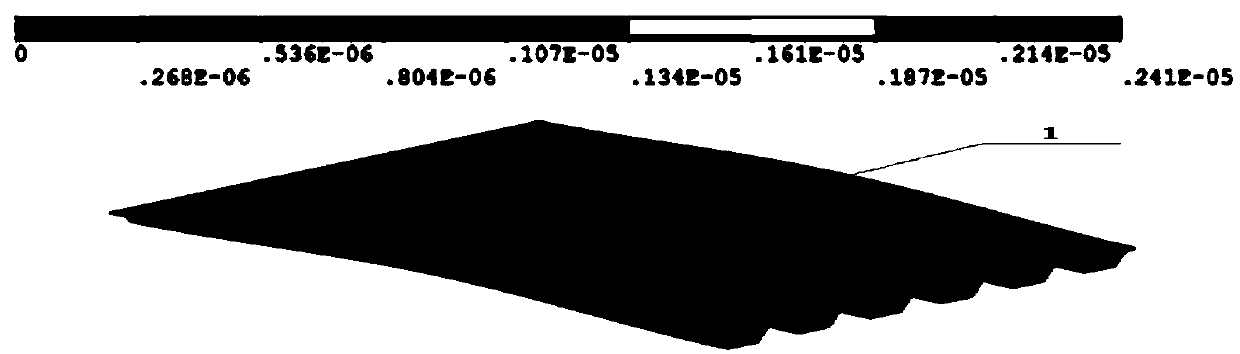
The invention discloses a simulation method of a low-permeability reservoir crude oil boundary layer. The simulation method comprises the following steps: (1) building a digital rock core by a CT (Computed Tomography) scanning method; (2) dividing the built digital rock core by a Delauny triangular dividing algorithm to obtain a three-dimensional geometric model; and (3) carrying out numerical simulation of the divided three-dimensional description geometric model of the fluid by using a finite element method under the condition that the boundary layer influence is considered, namely solving an incompressible equation which is N-S equation of the fluid with micro flowing in holes to obtain a flowing rate field and a pressure distribution field of the fluid. According to the simulation method of the low-permeability reservoir crude oil boundary layer, comsol simulation is used; the manpower, material resources and time can be saved; a regular hole mesh model is used, the pore throat condition of the real rock core can be accurately simulated; the condition is more accordance with the actual condition; data results are processed, the thickness of the boundary layer can be accurately calculated and is closer to the thickness of the crude oil boundary layer of the real rock core.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Bridge damage identification method based on neural network
InactiveCN104200005AOptimal initial weight thresholdDamage identification results are stableBiological neural network modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionMomentum
The invention discloses a bridge damage identification method based on a neural network. The method includes the following steps of firstly, constructing sample data, wherein a bridge model is established with a finite element method, simulation strain data are obtained under the condition that a bridge is complete and under the condition that the bridge is differently damaged, and the strain change rates serve as the sample data of the BP neural network; secondly, determining a network topology structure, wherein the number of hidden layers of the BP neural network and the number of nerve cells contained on each layer are determined, and meanwhile the weight threshold value of the neural network is initialized; thirdly, conducting training and testing, wherein the BP neural network is trained through a gradient descent momentum algorithm, and the neural network is tested through a testing sample; fourthly, identifying the damage, wherein the damage of the bridge is identified by inputting the real-time train data of the bridge into the trained BP neural network. The bridge is identified through stress parameters, and therefore bridge damage identification accuracy is improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
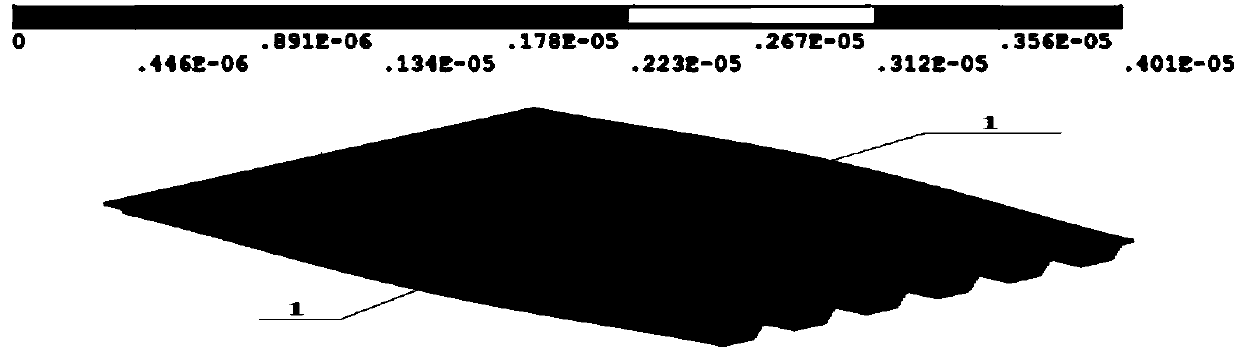
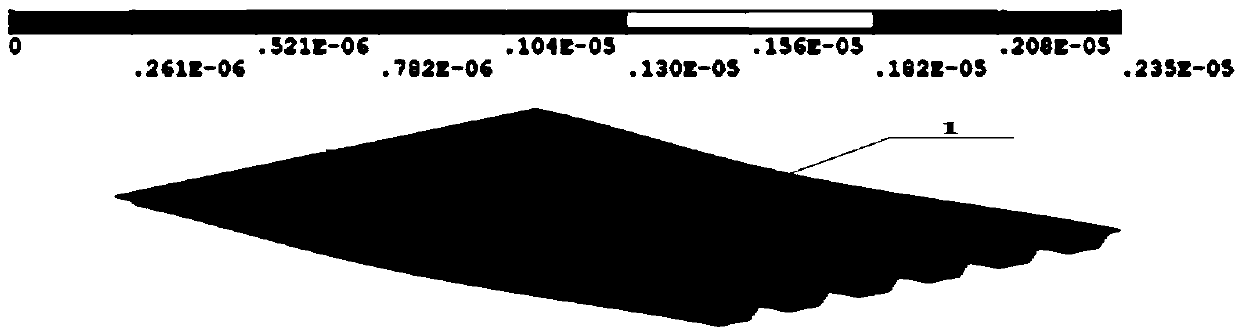
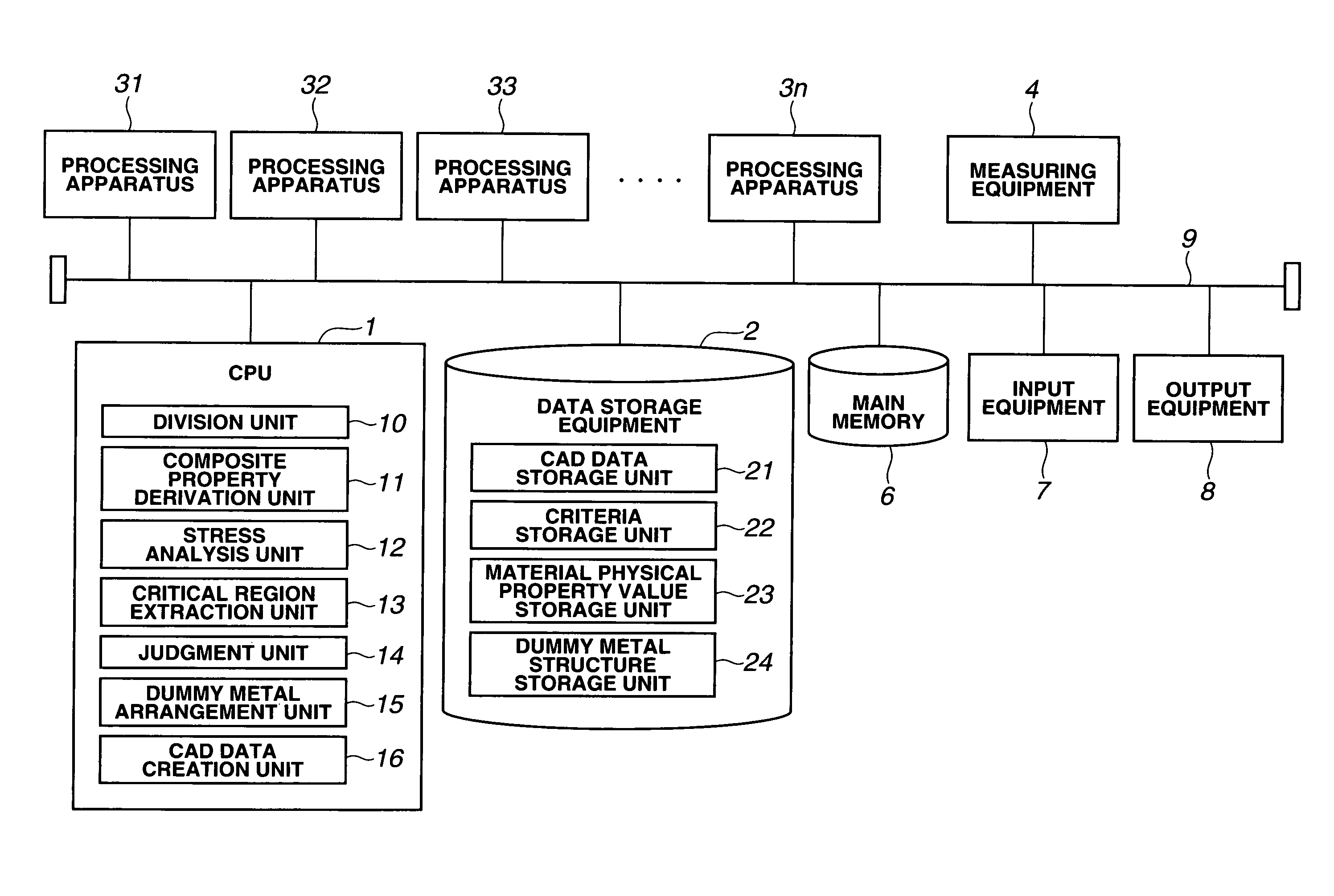
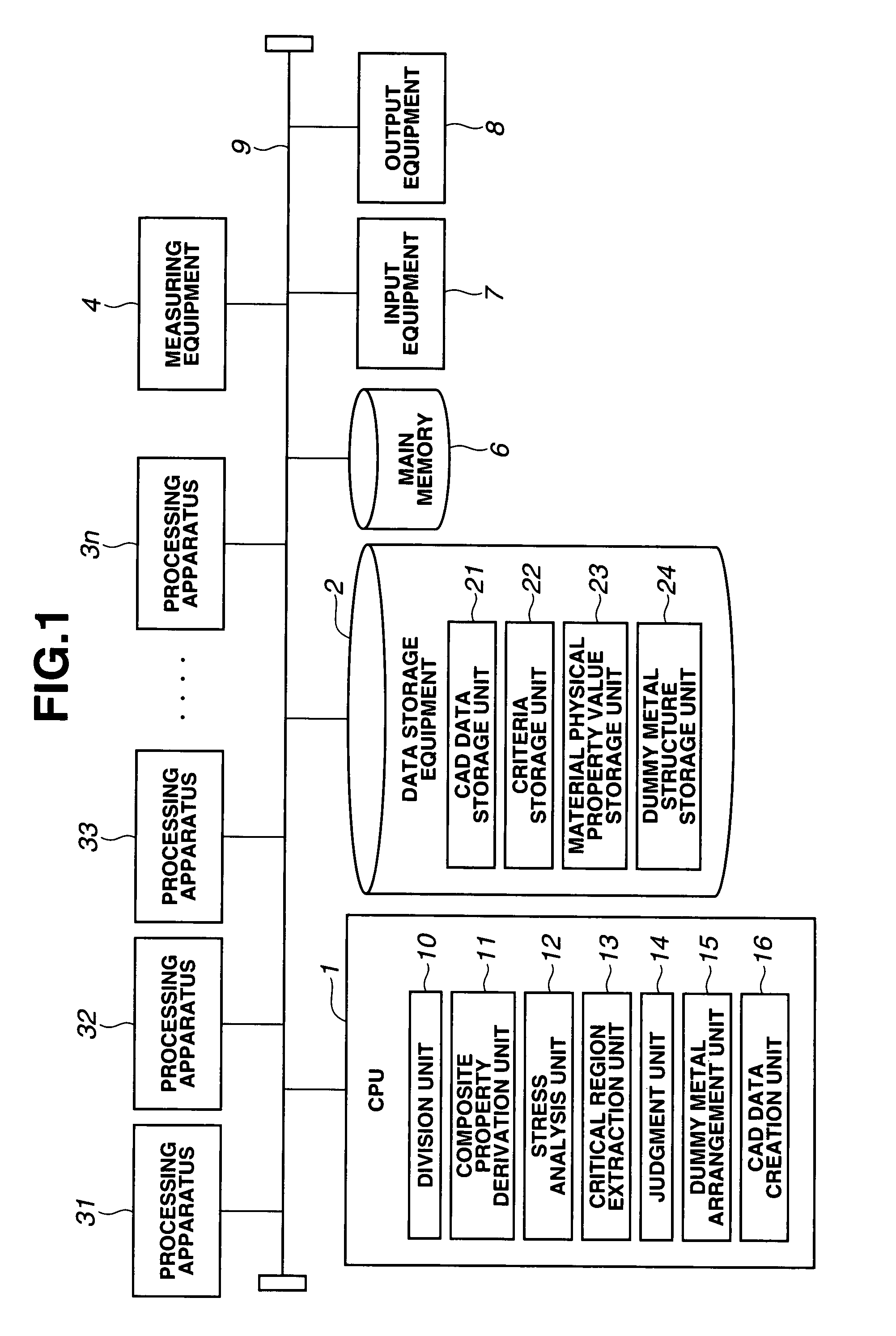
Stress analysis method, wiring structure design method, program, and semiconductor device production method
ActiveUS7921401B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsDetecting faulty computer hardwareFinite element methodEngineering
A stress analysis method is provided: including dividing, by using a division unit, an inside of a chip into a plurality of analysis areas, deriving, by using a composite property derivation unit, a composite property into which physical property values of a plurality of materials included in an analysis area are compounded, about each of the plurality of analysis areas on the basis of wiring structure data for each of the plurality of analysis areas, and creating, by using a stress analysis unit, a three-dimensional model of a finite element method which uses each analysis area as an element, to apply the composite property to each element, and to perform a stress analysis.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
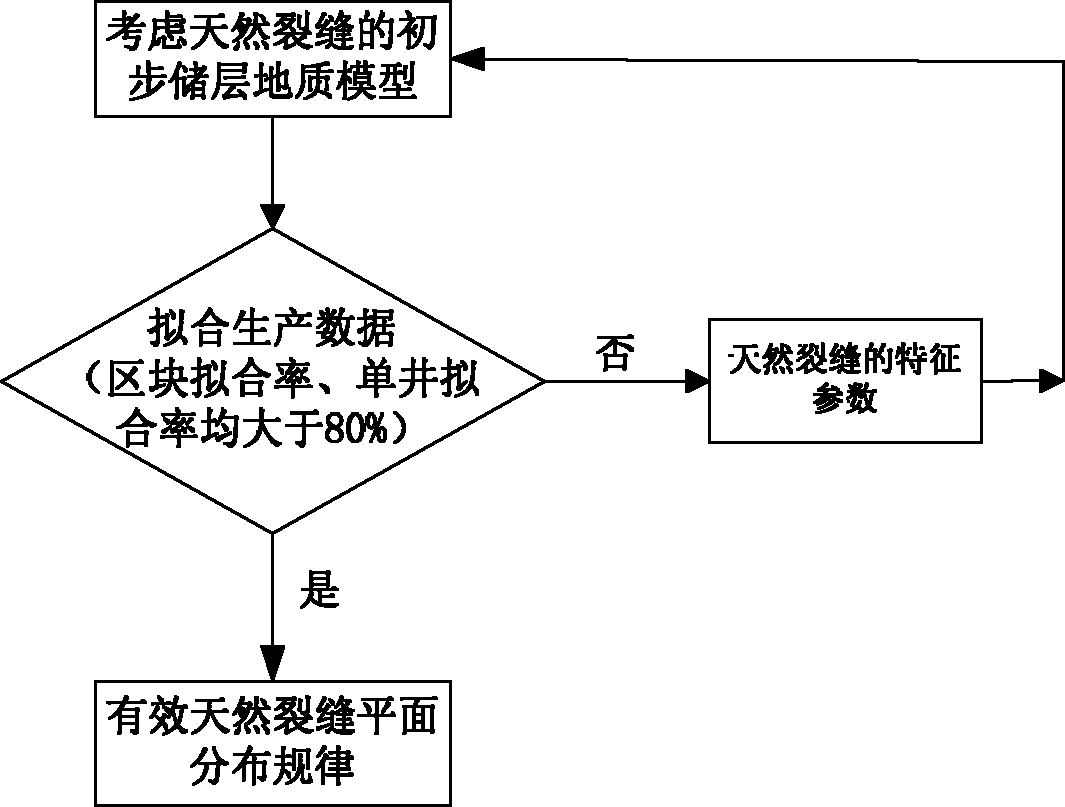
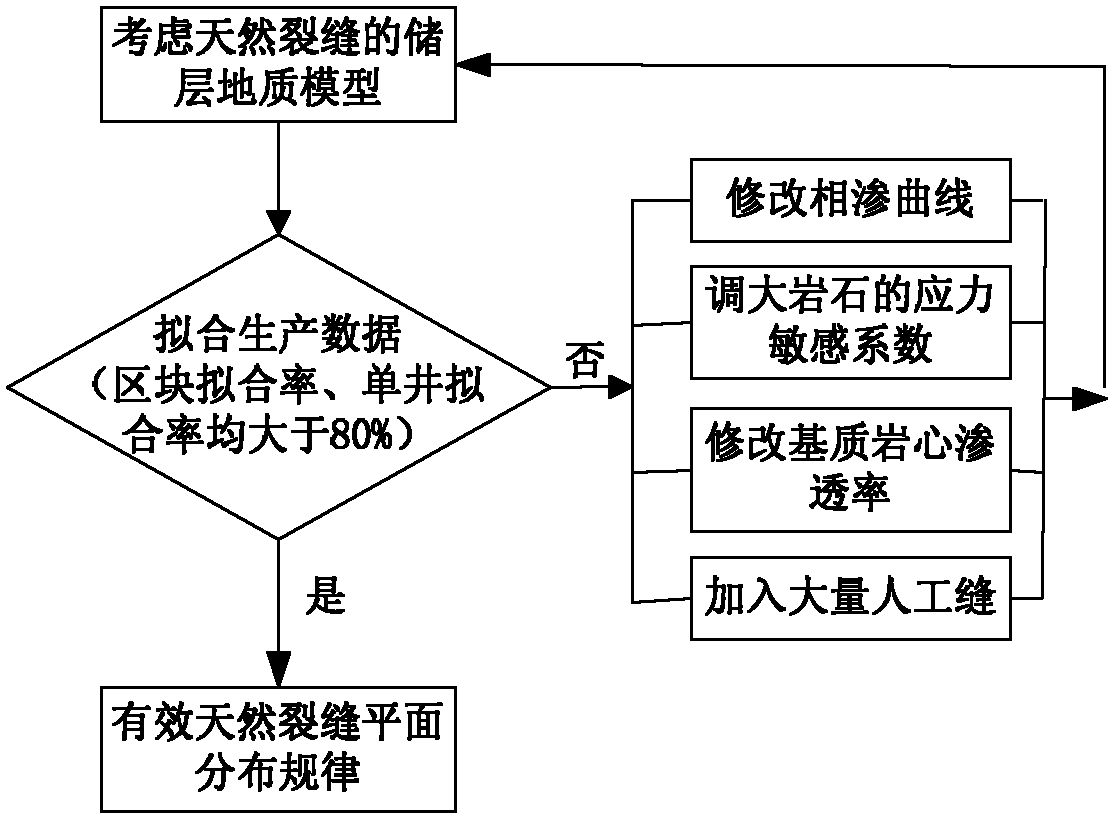
Method for predicting plane distribution law of effective natural fissures of oil reservoir
ActiveCN103324770AAccurately reflectSolve the phenomenon that the predicted fracture density distribution is too largeSpecial data processing applicationsSoil scienceFinite element method
The invention discloses a method for predicting the plane distribution law of the effective natural fissures of an oil reservoir and belongs to the field of natural fissure research. The method comprises the following steps: according to the conventional fissure recognition and description technologies, preliminarily determining the characteristic parameters of the natural fissures of the ultra-permeability dense oil reservoir; acquiring the preliminary distribution law of the natural fissures according to the finite element method; according to the characteristic parameters and the preliminary distribution law, building a reservoir-bed fissure geologic model; according to the sequence stratigraphy and the phase-controlled modeling technology, building a reservoir bed matrix geologic model; according to development conditions of the natural fissures in different matrixes, combining the reservoir bed fissure geologic model and the reservoir bed matrix geologic model and building a preliminary reservoir bed geologic model taking the natural fissures into consideration; on the basis of the preliminary reservoir bed geologic model taking the natural fissures into consideration, acquiring the plane distribution law of the effective natural fissures by adjusting the characteristic parameters to be fitted with production data. The method provides a reliable basis for optimizing a development technology policy.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Damage-tolerance testing method for whole wing spar of airplane
InactiveCN101561365ASolve scalabilitySolve the strength problemStructural/machines measurementJet aeroplaneResidual strength
The invention pertains to airplane fatigue and damage-tolerance testing technologies, and relates to a damage-tolerance testing method for the whole wing spar of an airplane. The method comprises the steps of: (I) choosing a part with large load from the whole wing spar for serving as a testing part examining segment, (II) producing two same testing parts according to the examining segment, (III) reserving an interval of 20 to 30mm between the two back-to-back testing parts which are respectively provided with a coating in the upper part and the lower part (the coating is connected with an upper spar edge strip and a lower spar edge strip to form a case segment), (IV) fixing the root of the testing case segment completing assembly on a load-bearing wall, (V) exerting concentrated load at one end of the testing parts to simulate the bending moment of the spar at the testing segment and the shearing force of a web, without considering the influence of the shearing flow of the coating and (VI) using a finite element method to conduct damage tolerance analysis on the testing parts and comparing testing results. The method solves the difficulty that the crack expansion and remaining strength of the present airplane whole wing spar structure lack theoretical evidence; and the design of the testing parts adopts a method of simultaneously conducting tests to the two back-to-back testing parts, thereby eliminating the distortion of a single spar.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Temperature control and crack prevention design calculation method for lining concrete with round cross section structure
ActiveCN105155542AThe calculation formula is simpleQuickly calculate the maximum temperatureWater-power plantsHydro energy generationTemperature controlFinite element method
The invention discloses a temperature control and crack prevention design calculation method for lining concrete with a round cross section structure. The temperature control and crack prevention design calculation method comprises the following steps of determining a temperature control and crack prevention target; calculating a permitted highest temperature; drafting a temperature control scheme; calculating the highest temperature inside the concrete; and designing a temperature control and crack prevention scheme on the premise that the calculated highest temperature is smaller than or equal to the permitted highest temperature. According to the method, calculation formulas are simple; influences of surrounding rock performance, lining thickness, concrete strength, air temperature in a tunnel, water cooling and water temperature, pouring temperature and the like can be reflected reasonably; the permitted highest temperature of pouring construction in each month of the construction period of the lining concrete with the round cross section structure can be calculated rapidly; the temperature control and crack prevention construction scheme applicable to a project is provided on the condition that the inside highest temperature is smaller than or equal to the permitted highest temperature and the economic requirement is met; the error between the result of the method and the result of simulating calculation of a finite element method is smaller than 5%; and the temperature control and crack prevention design calculation method is particularly applicable to primary design and optimization and adjustment on an on-site construction implementation scheme.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for setting high-pressure high-power thyristor electrothermic model
ActiveCN101587507ASave timeSave costThyristorSpecial data processing applicationsPspice softwareJunction temperature
The invention relates to a method for setting a high-pressure high-power thyristor electrothermic model and a simulating method. In the invention, first a thermal impedance model of a thyristor is calculated and set according to the finite element method, and a Foster network thermal impedance model is expressed by the identical transformation, subsequently a thyristor equivalent electric model is set by using the mathematical method. The loss Pave(t) is determined by the switch-on forward voltage drop Vtm and the working current IA, an electrothermic model of the thyristor is set by connecting the relation of the variants such as the switch-on forward voltage drop Vtm, the working current IA, the loss Pave(t), the junction temperature TJ and the like, then the simulation is conducted on a Pspice software. The model of the invention contains a thermodynamics and electrics model, which can provides the dynamic relationship between the heating parameters and the electric parameters, can be used for simulating the transient and steady junction temperature change and predicting whether the thyristor works in the safe area, also used for insulating the junction temperature change under the sine semi-wave surge current surge and predicting whether the thyristor fail.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Springback compensation in formed sheet metal parts
ActiveUS20150134093A1Constant adjustability for curvesGeometric CADProgramme controlLeading edgeFinite element method
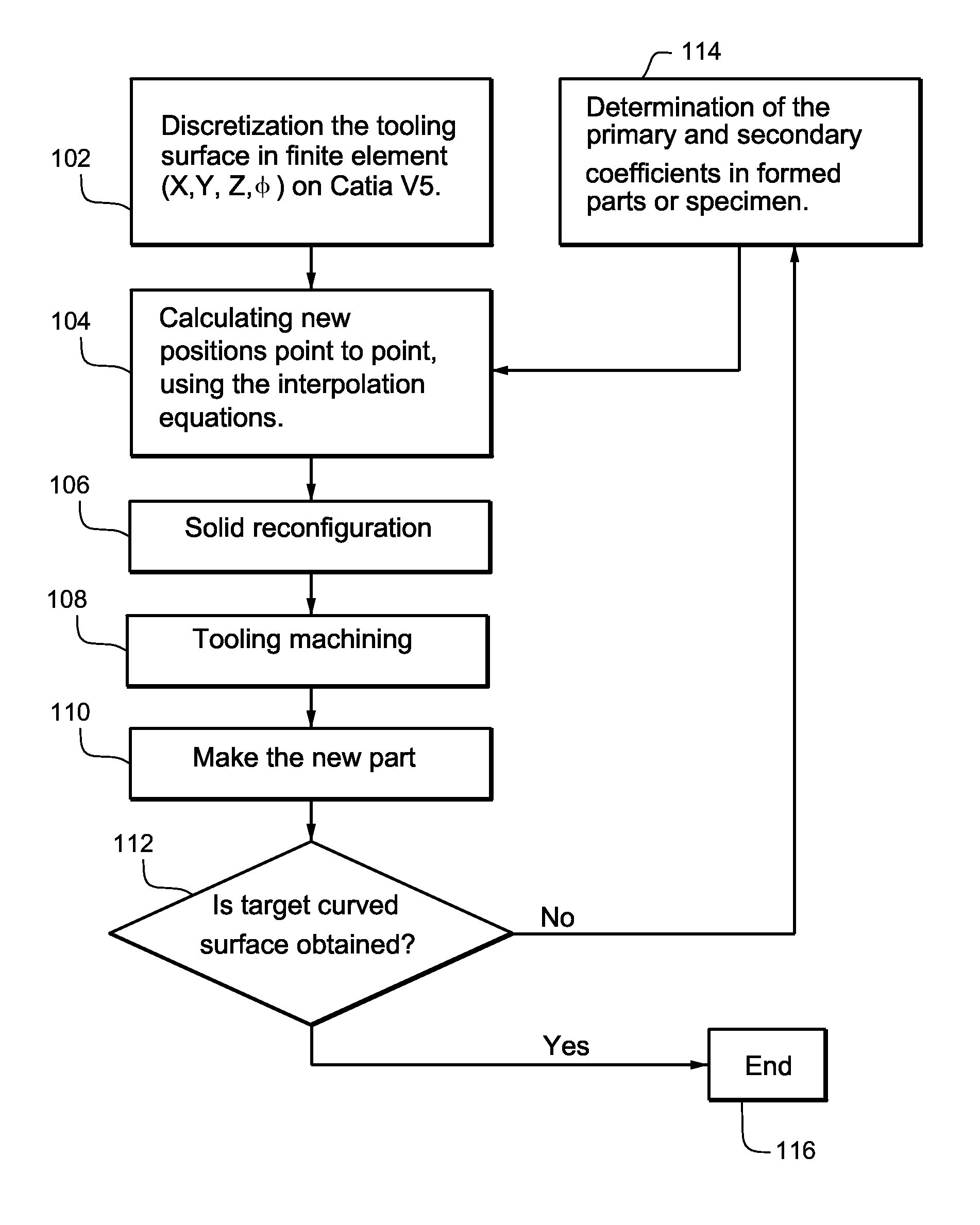
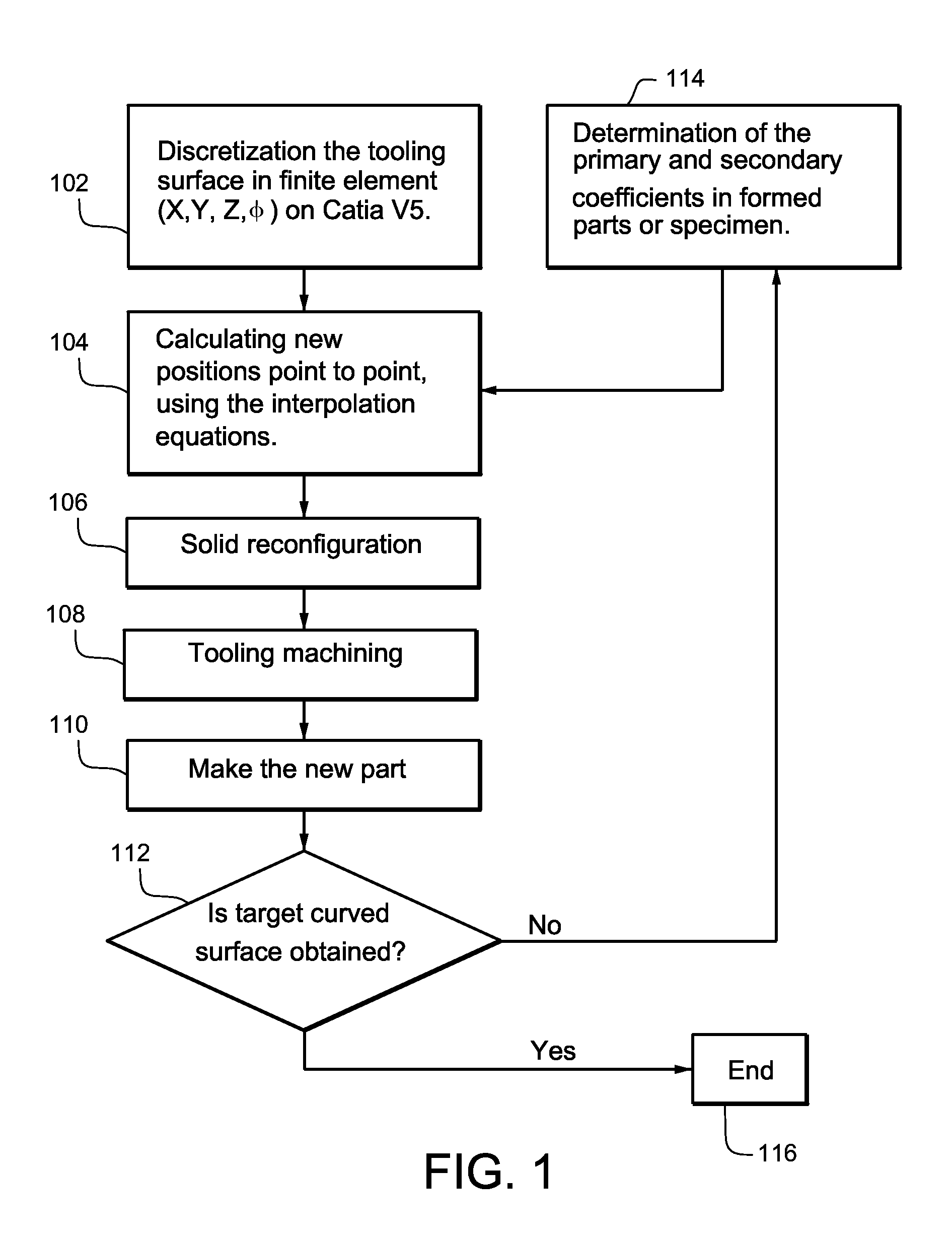
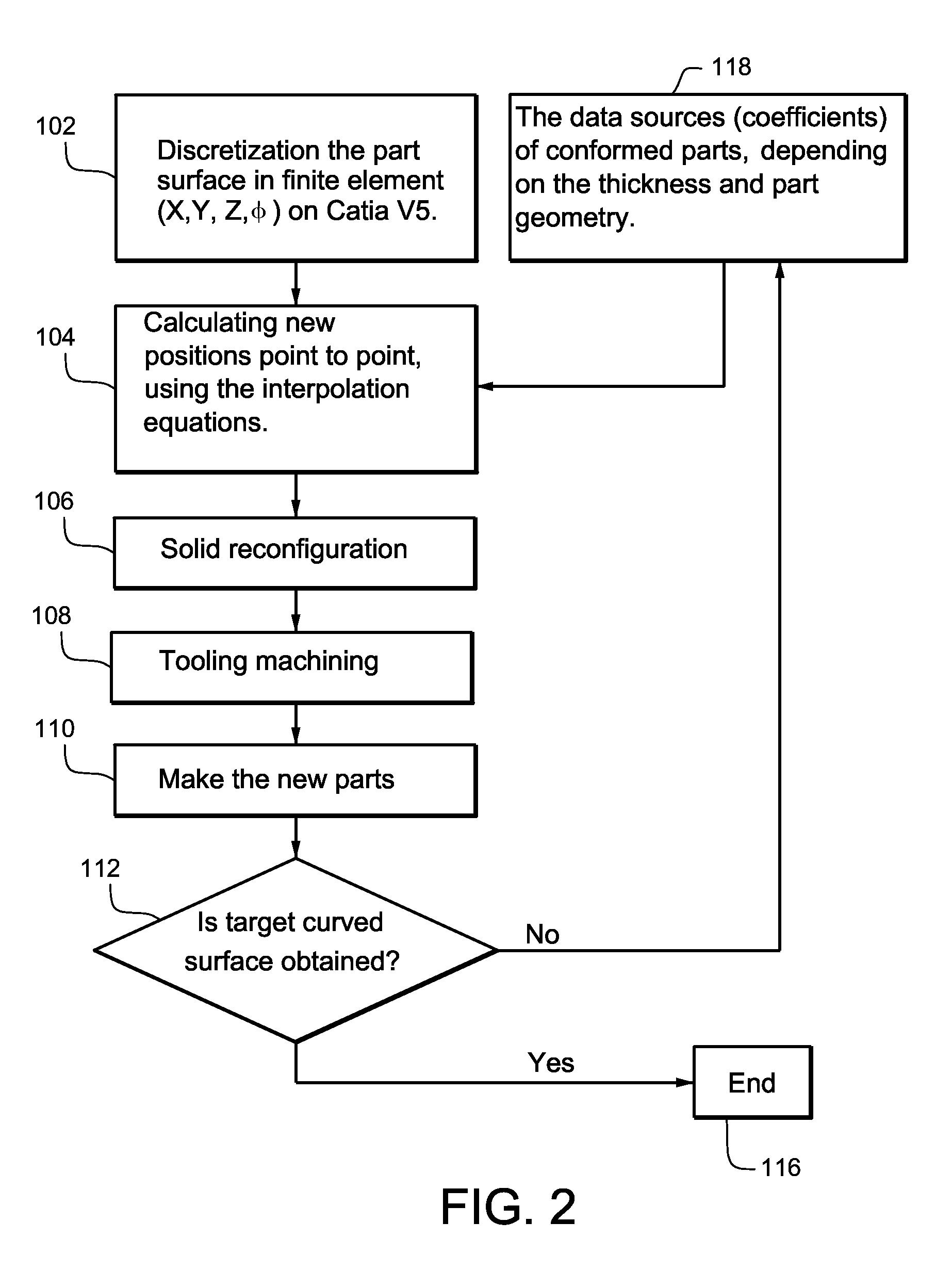
Finite element methods for compensating for springback in aircraft parts meet the visual appearance and aerodynamics of complex parts including those made of fabricated sheet metal. The methods can be used to make narrow parts (e.g., leading edge and slats) and double negative curvature parts, and do not need to leave marks on the surface of the sheet so that visual aspects are not adversely affected. The compensation technique, point to point uses approach equations with constant adjustable for curves. The constant(s) used depend on geometry and type of forming (e.g., stretch or hydraulic press). This example non-limiting process does not need to use mechanical properties of the material.
Owner:EMBRAER SA
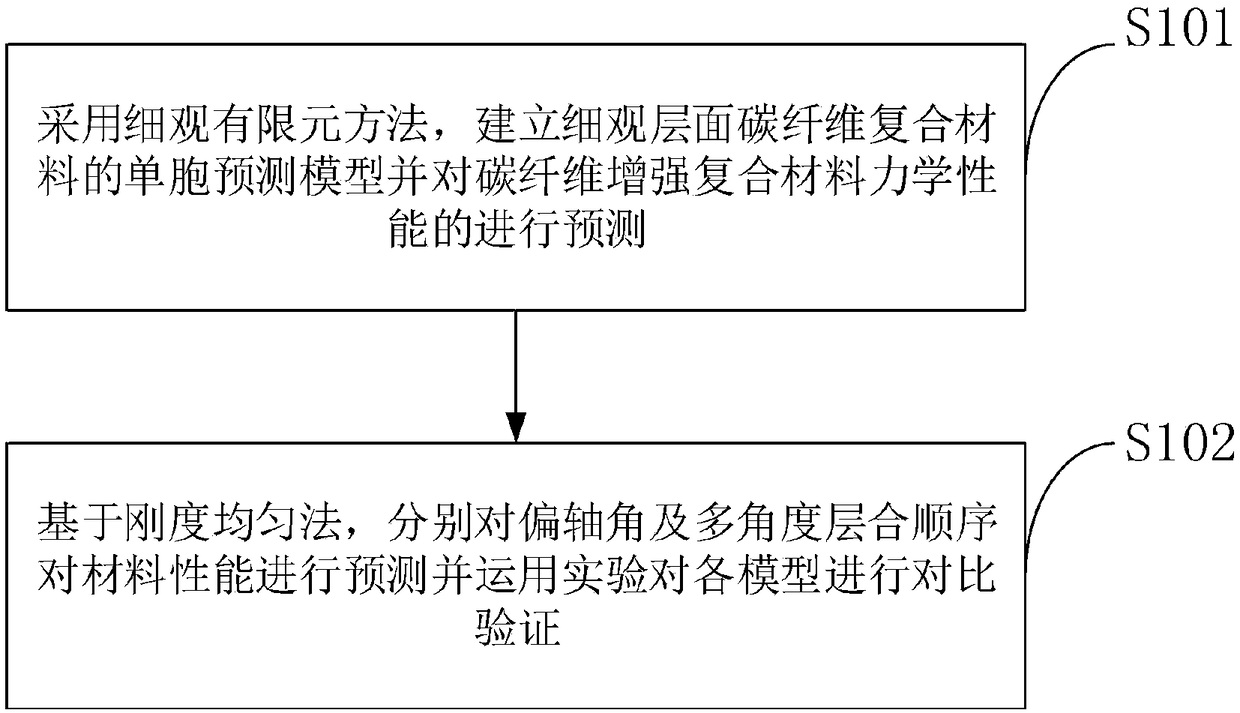
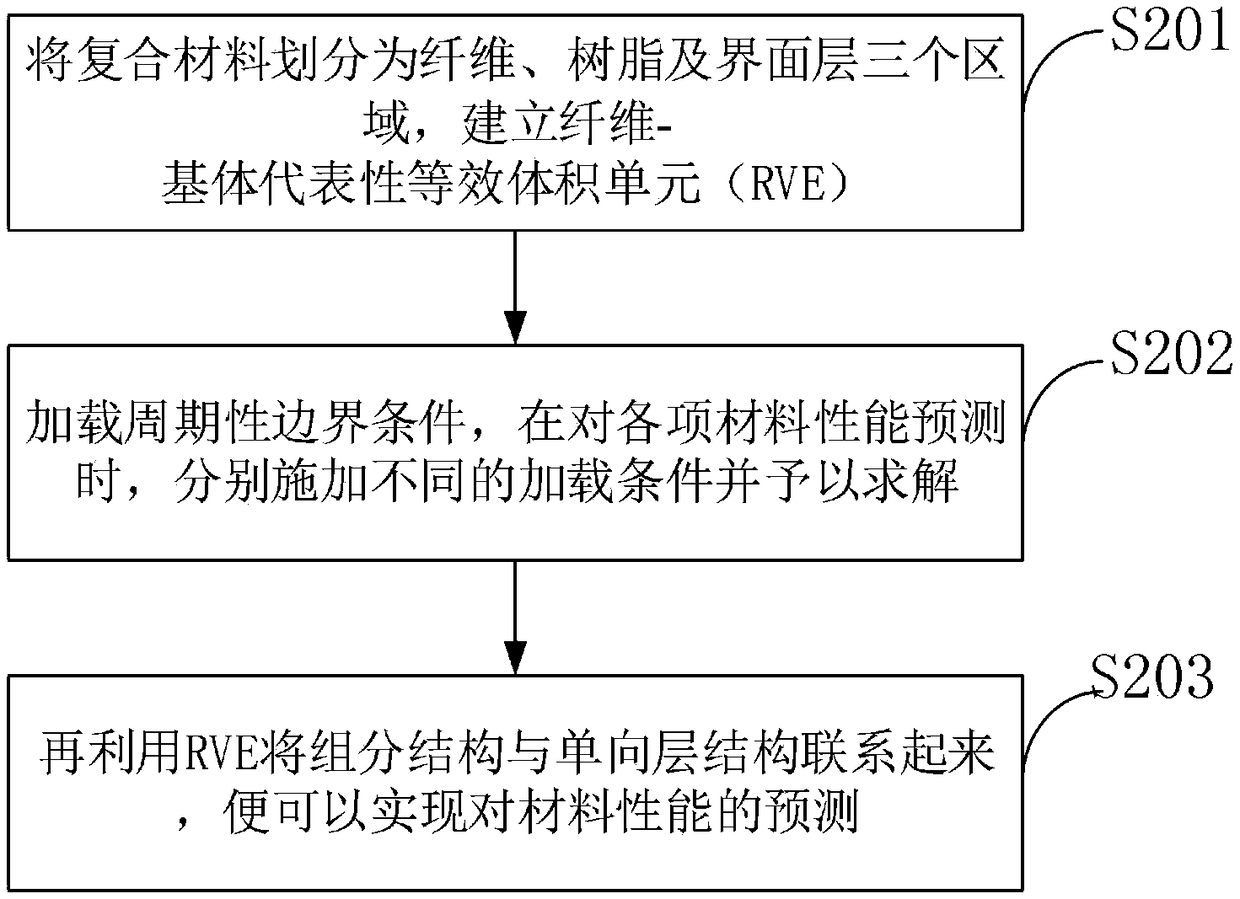
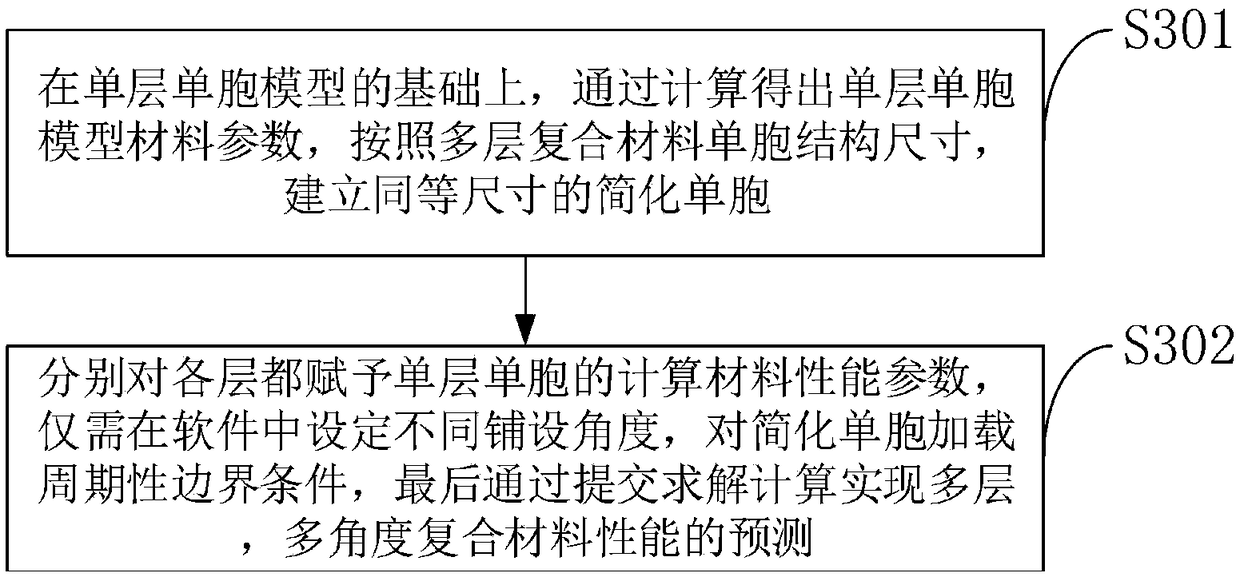
Carbon fiber reinforced composite material mechanical performance prediction method based on cross-scale simulation
ActiveCN109241650AImprove mechanical propertiesSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationPredictive methodsFinite element method
The invention belongs to the technical field of composite material prediction, and discloses a carbon fiber reinforced composite material mechanical performance prediction method based on cross-scalesimulation. The prediction method comprises the following steps: adopting a meso-finite element method, establishing a single cell prediction model of a meso-level carbon fiber composite material andpredicting the mechanical performance of the carbon fiber reinforced composite material; Based on the stiffness homogeneity method, predicting the off-axis angle and multi-angle lamination sequence and verifying the models by experiments. The invention provides a method for predicting the mechanical properties of the composite material, and the experimental results are consistent with the theoretical model.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
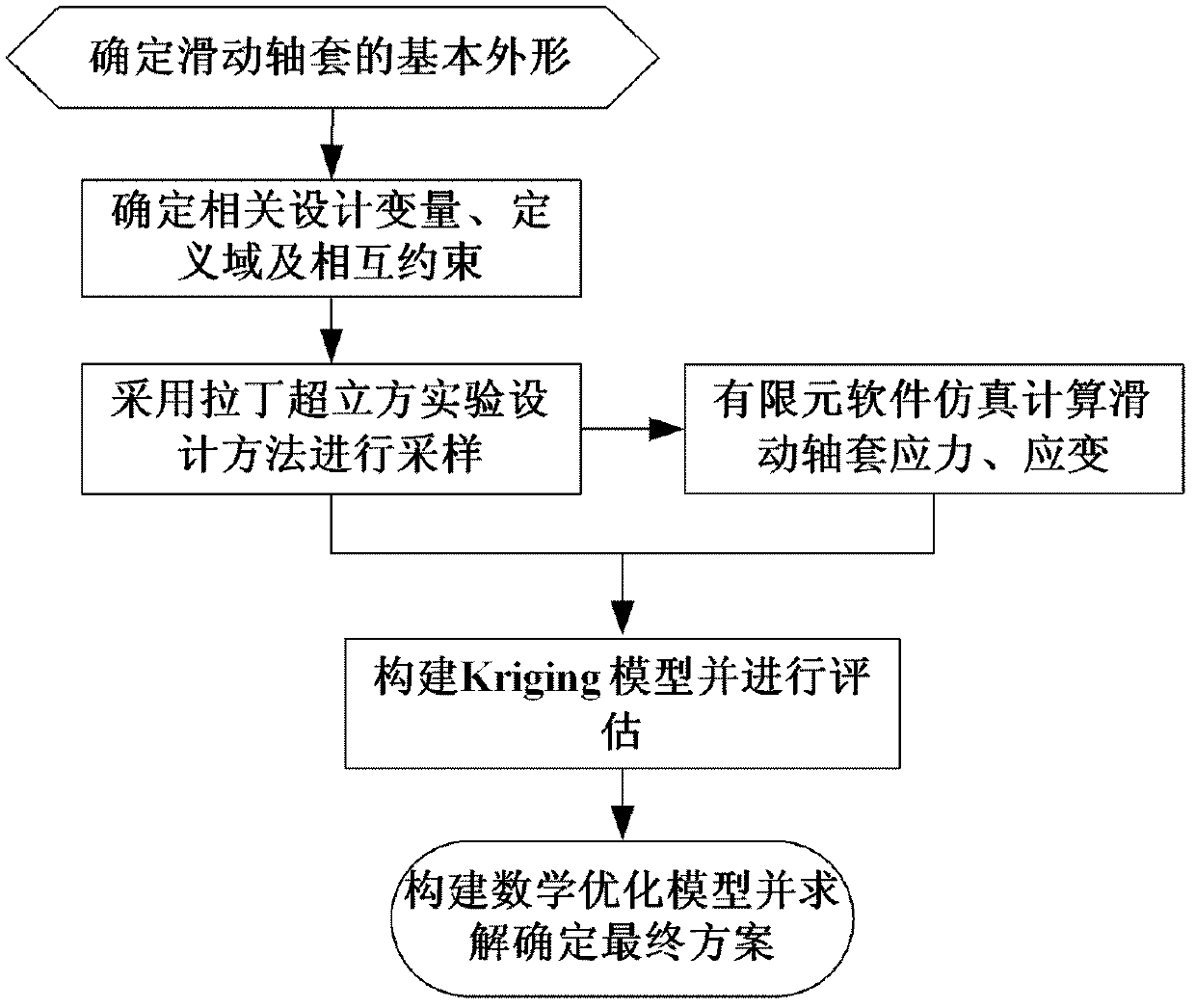
Method for optimally designing structure of sliding shaft sleeve based on Kriging model
InactiveCN102360403ACalculation speedTime consumingSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmControl engineering
The invention relates to a method for optimally designing the structure of a sliding shaft sleeve based on a Kriging model. By using an unbiased optimal estimation theory of the Kriging model, the optimal design scheme of the sliding shaft sleeve is predicted and solved. The method comprises the following steps of: determining the basic appearance of the sliding shaft sleeve; analyzing and defining a design variable and a definition domain, which influence the shape of the sliding shaft sleeve; sampling a design space by using a Latin hypercube experiment design method; calculating the stress response of the sliding shaft sleeve by using a finite element method; constructing the Kriging model, and performing accuracy estimation; and constructing a mathematical optimization model, solving the optimal design scheme of the sliding shaft sleeve, and validating by using the finite element method. By using the design variable correlation and variability characteristic of the Kriging model, the unbiased optimal estimation is performed, and guidance is provided for optimal design of the structure of the sliding shaft sleeve. Compared with the conventional method, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high calculation speed, optimal scheme design and high reliability.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
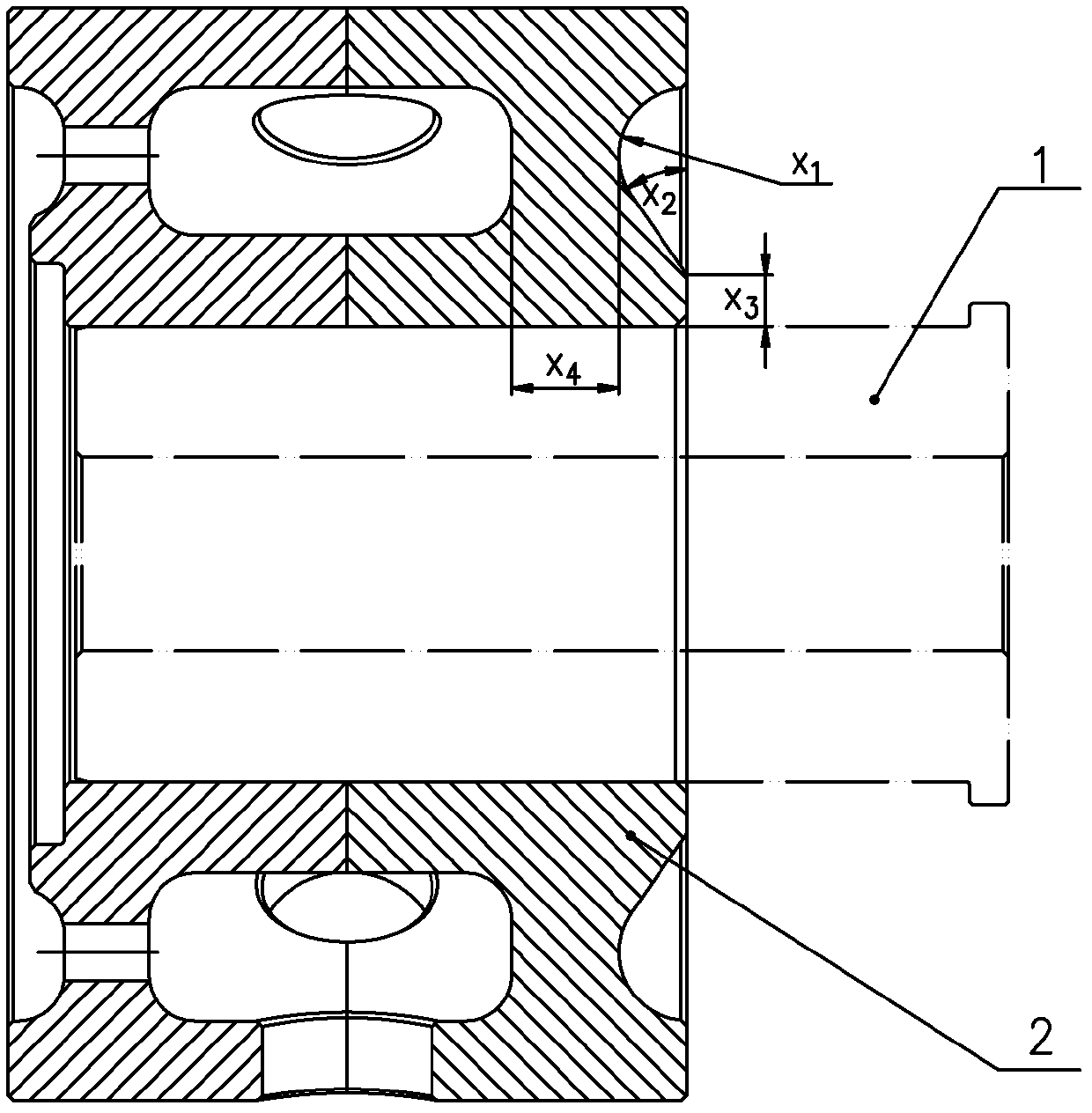
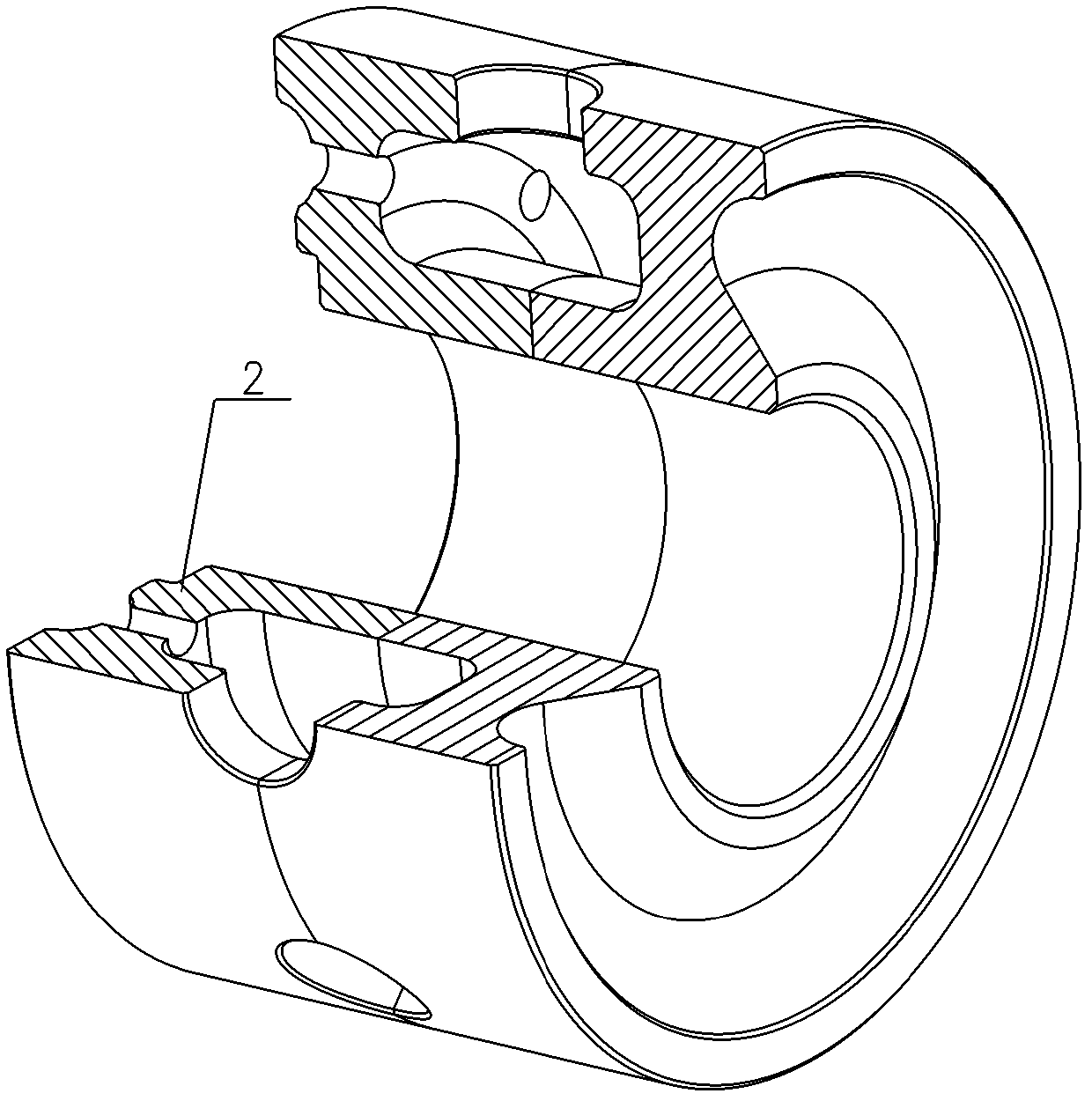
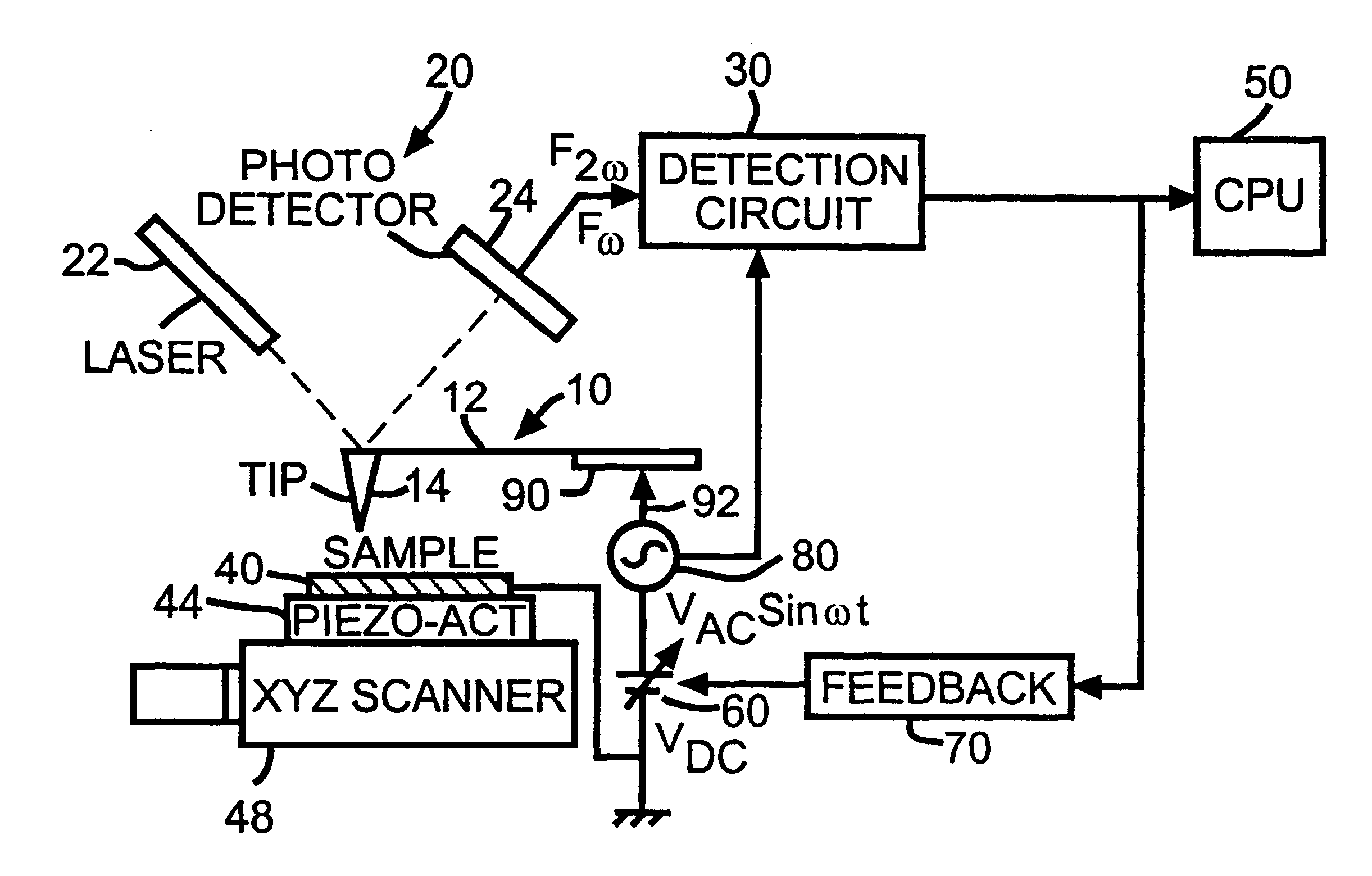
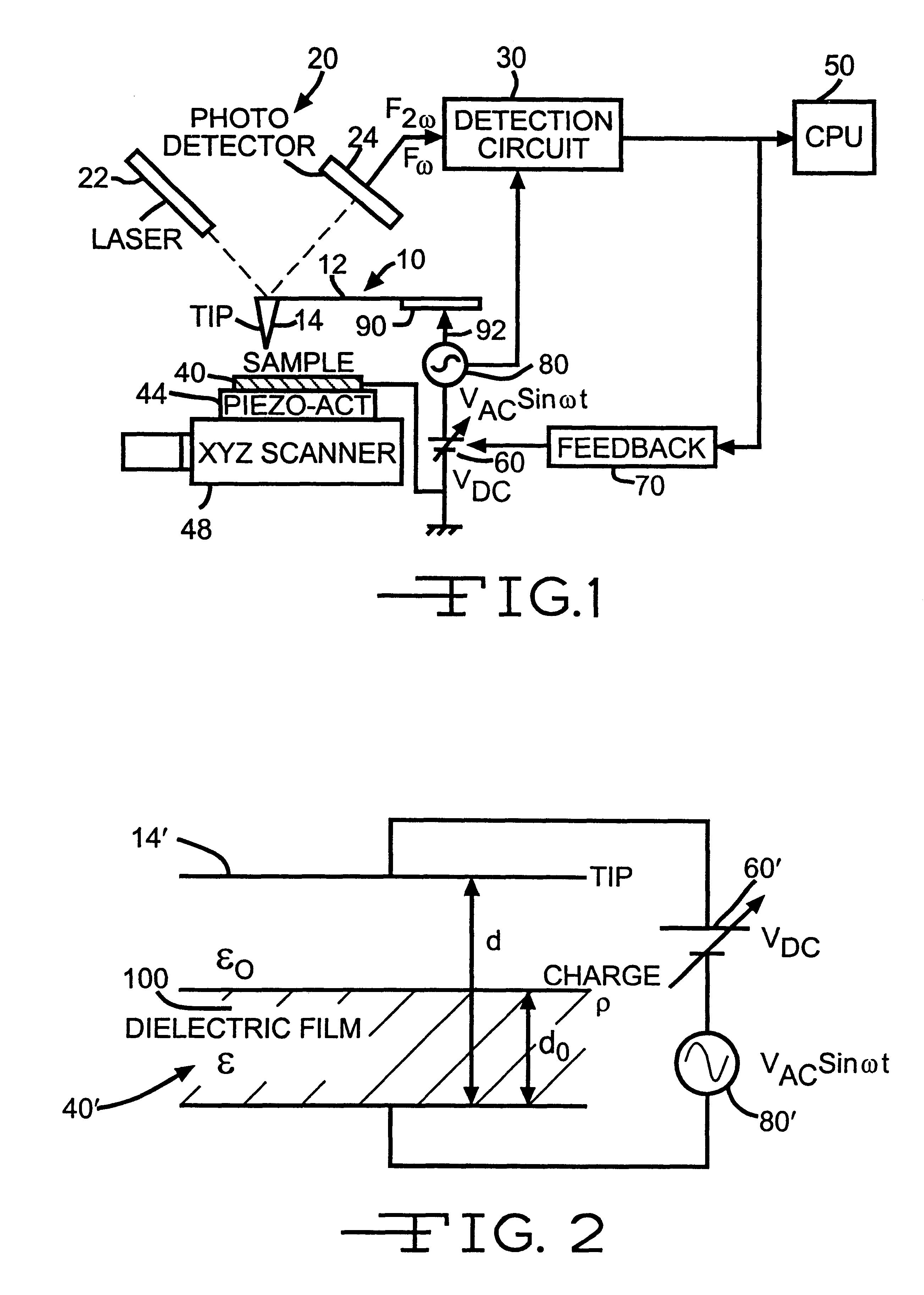
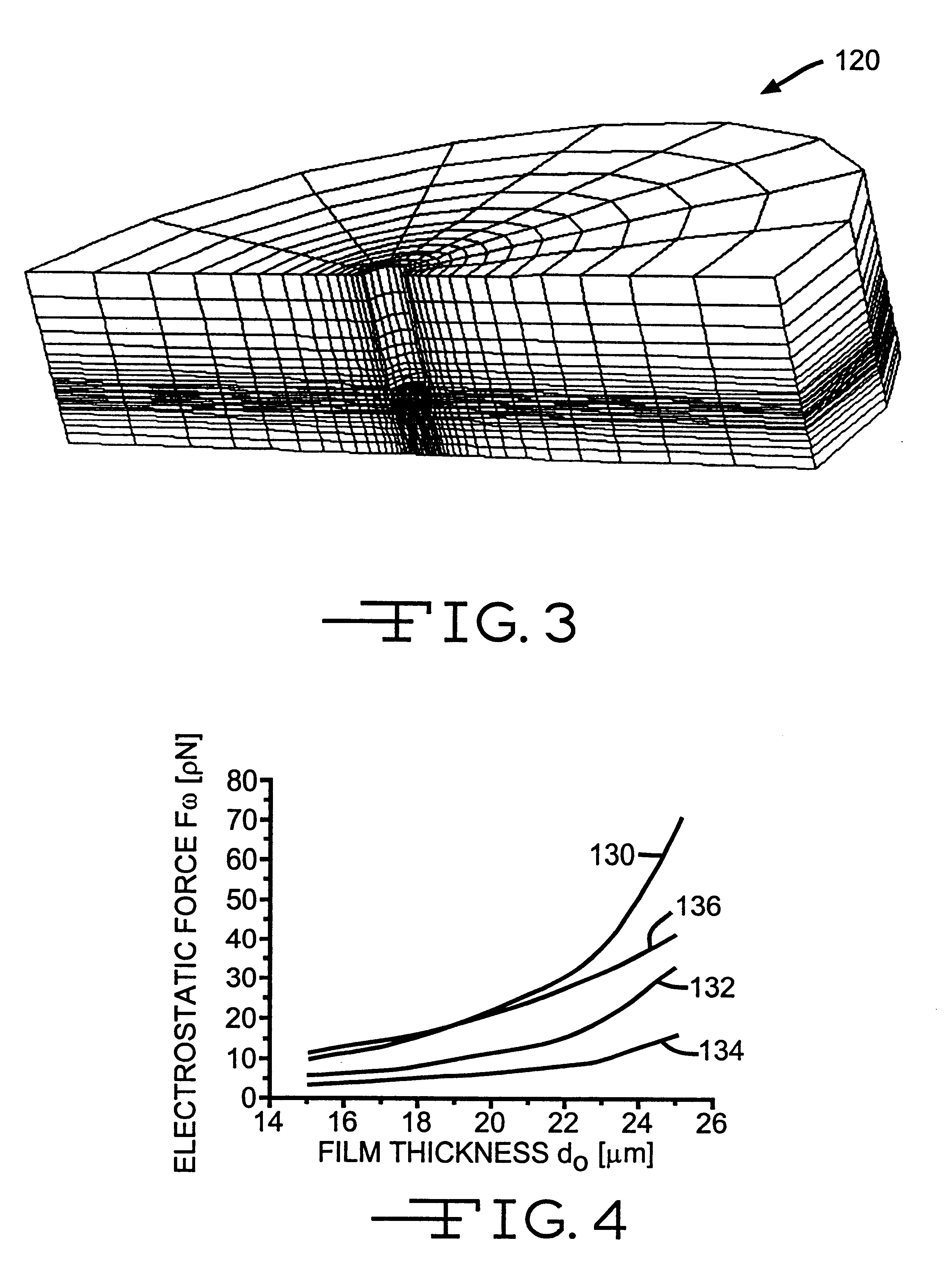
Electrostatic force detector with cantilever for an electrostatic force microscope
InactiveUS6507197B1Reduce errorsSimultaneous measurementNanotechMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansParallel plateImage resolution
An electrostatic force microscope wherein electrostatic force applied to the detector is determined through obtaining the field distribution on several different shaped detectors with the calculation of the voltage distribution near the detector with the Finite Element Method to direct the measurement of the absolute charge amount on surface under test so that one can define the differences between the analysis and the results from the parallel plate model. Of interest is how large the error in the charge detection occurs in conjunction with thickness change of dielectric materials to be tested. There is provided a detector with cantilever which has proper shape for the spatial resolution of 10mu made out of nickel foil for an electrostatic force microscope and the electrostatic force which appeared on it has been calculated.
Owner:TREK BICYCLE CORPORATION
Parallel workflow finite element pre-processing method
ActiveUS20140222387A1CAD network environmentDesign optimisation/simulationComputational sciencePretreatment method
A method for collaborative analysis pre-processing of electronic models of engineering objects includes assigning a first user to de-feature a model of an engineering object during a first session to provide a de-featured model of an engineering object, assigning a second user to conduct other FEA pre-processing operations on the model of the engineering object during a second session, and applying the other FEA pre-processing operations for the model of the engineering object to the de-featured model of the engineering object. Example of other FEA pre-processing operations include applying a material definition to a geometry, pre-meshing a geometry, initiating automated meshing of a geometry, validating automated meshing of a geometry, editing a mesh for a geometry, manually meshing a geometry, and defining one or more boundary conditions for a geometry. The second session and the first session may be conducted concurrently. A corresponding system and apparatus are also disclosed herein.
Owner:COLLAB SYST LLC
Electrochemical corrosion processing method with micro fine cylindrical group electrode
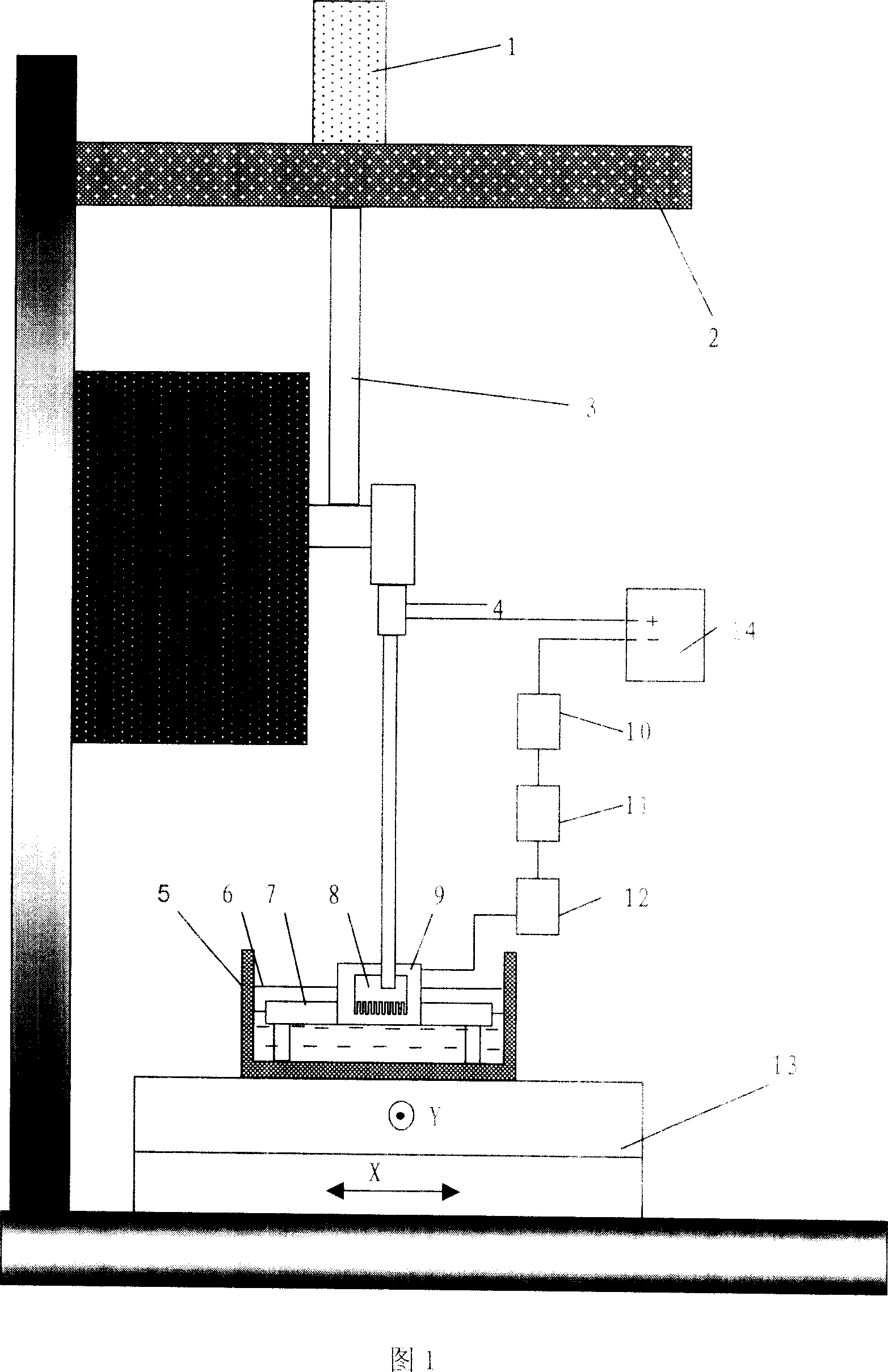
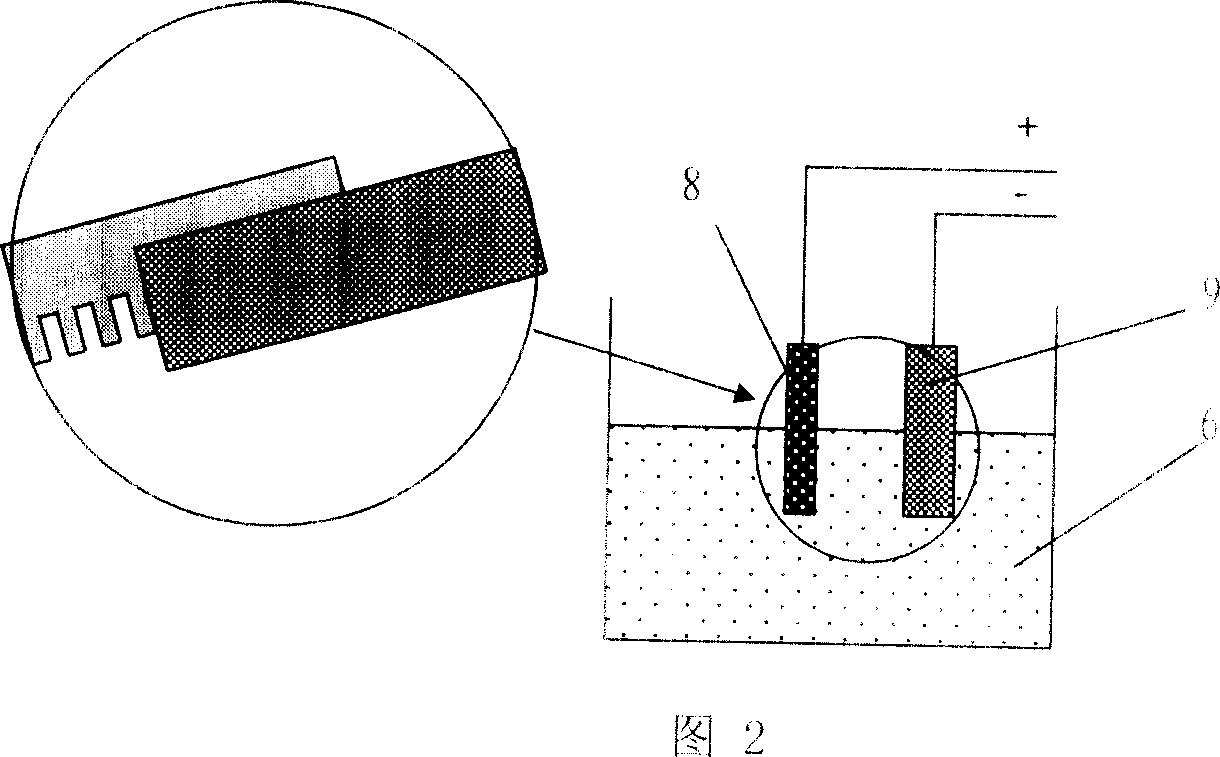
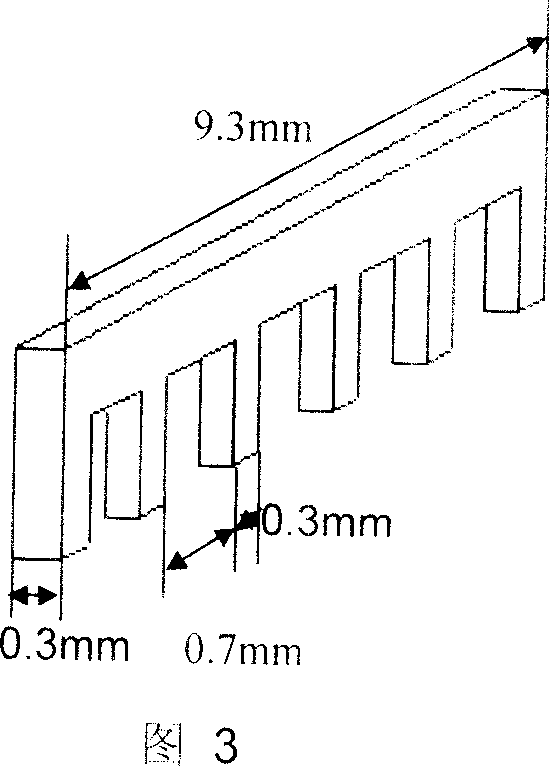
ActiveCN1943950AUniform current densityImprove processing efficiencyMachining electrodesElectrical-based machining electrodesElectrolysisControl manner
The electrochemical corrosion processing method for micro cylindrical group electrode belongs to the field of electrolysis processing technology. The method includes the following steps: 1. making group electrode blank with several single electrodes through wire electric cutting or micro milling; 2. designing and making tool cathode for electrochemical erosion in finite element method; 3. soaking the group electrode blank as the anode for electrochemical erosion and the cathode into electrolyte vertically and parallelly; and 4. applying voltage for processing the group electrode blank via electrochemical erosion and controlling the shape and size of the group electrode via constant voltage method and the charge method. The present invention has simple processing apparatus and control, high processing efficiency, high processing quality and low production cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
GPU-based Finite Element
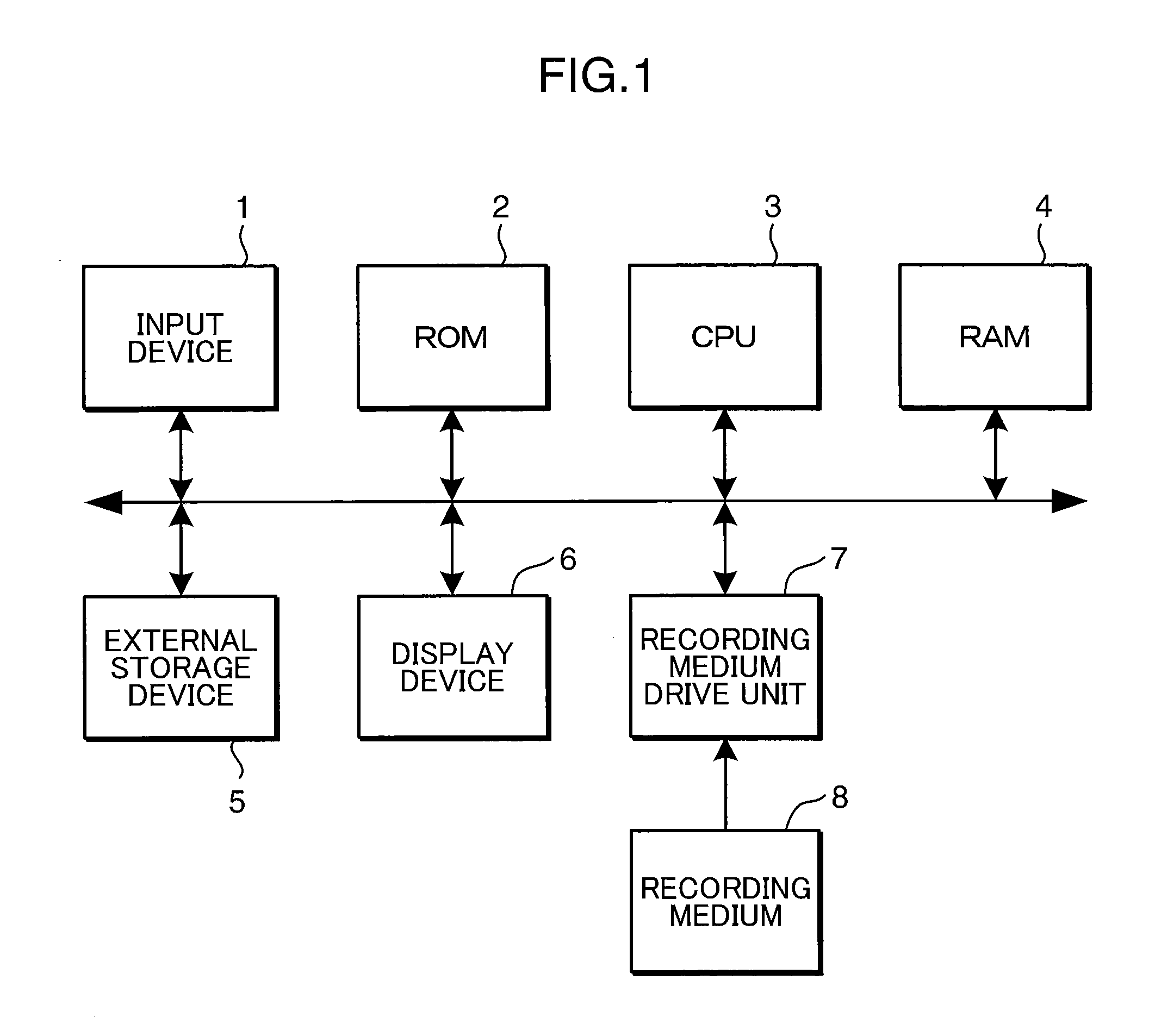
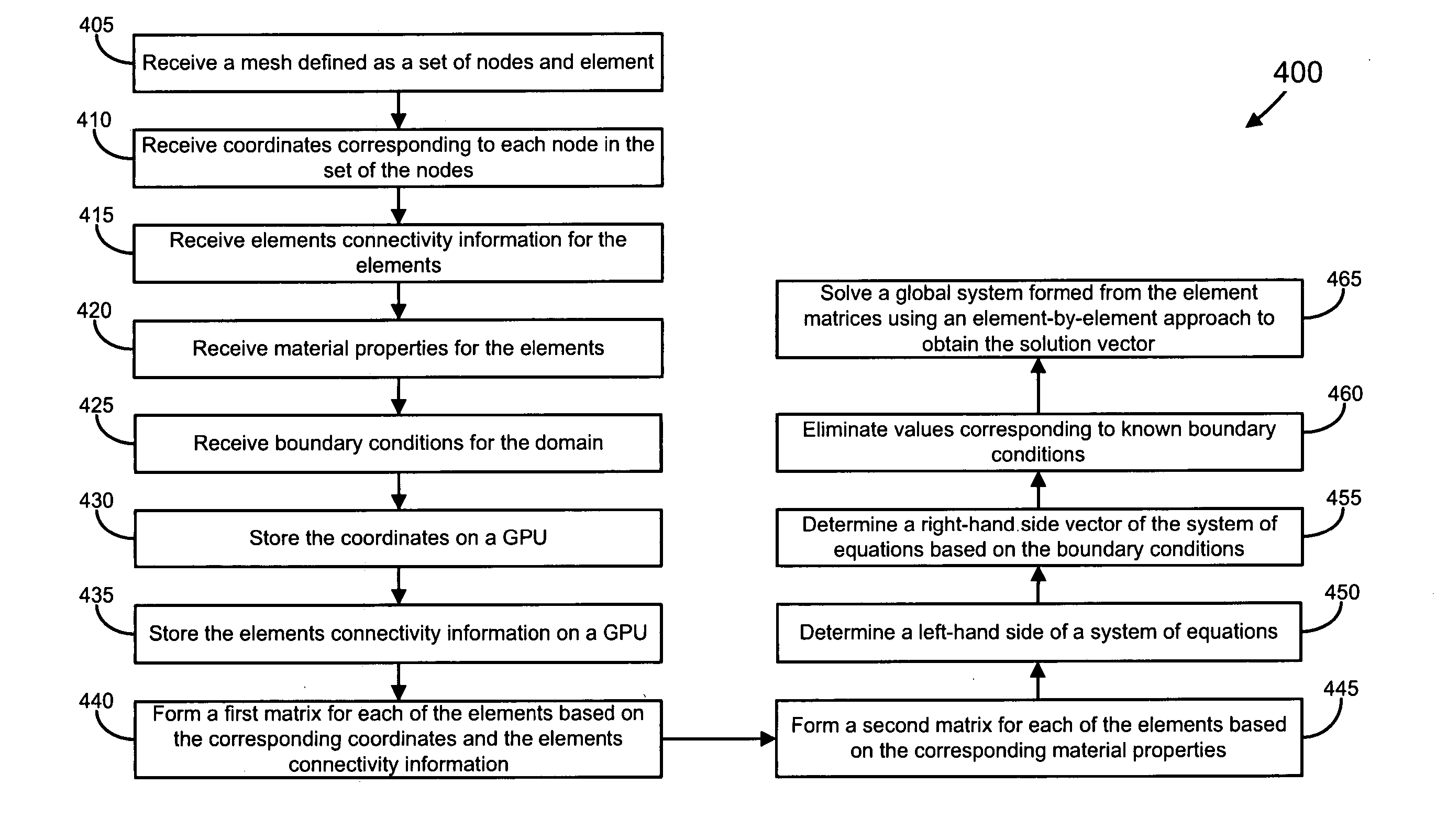
InactiveUS20050243087A1Special data processing applications3D modellingComputational scienceGraphics
Exemplary methods and systems are provided for performing the Finite Element Method. An exemplary method includes the steps of transferring a set of nodes and elements (i.e., a mesh) from a memory to a graphics processing unit (GPU); and performing the Finite Element Method on the set of nodes and elements using only the GPU. An exemplary system includes a central processing unit (CPU); a memory operatively connected to the CPU; and a graphics processing unit (GPU) operatively connected to the CPU; wherein the CPU transfers a set of nodes and elements from the memory to the GPU; and wherein the GPU performs the Finite Element Method on the set of nodes and elements.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
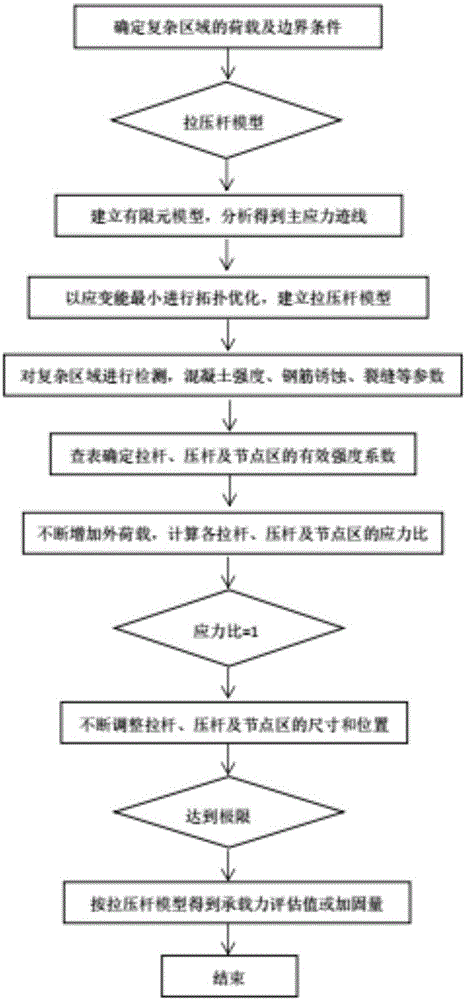
Bearing capacity assessment and reinforcement calculation method for complex region of existing concrete bridge
InactiveCN105956256AAddress usability issuesSolve complexitySpecial data processing applicationsNODALCarbonization
The invention discloses a bearing capacity assessment calculation method for a complex region of an existing concrete bridge. The method comprises the steps of determining load and boundary conditions of the complex region for diseases such as reinforcement corrosion, concrete cracking, carbonization and the like appearing in the complex region; establishing a pull rod model and a press rod model of the complex region; according to a detection result, further determining reduction coefficients of a pull rod, a press rod and a joint after the diseases are considered; making a calculation according to a pull rod strength control rule, a press rod strength control rule and a joint strength control rule to obtain a minimum bearing capacity value; and finally, according to a bearing capacity assessment result, determining a reinforcement load transfer model, continuously adjusting the positions of the reinforced pull rod, press rod and joint, or continuously increasing the reinforcement amounts of the pull rod and the press rod until the usage requirements are met. According to the method, the problems of inapplicability of a section method in calculating the complex region of concrete, complex calculation for a finite element method and difficulty in arrangement of reinforcement are solved and the bearing capacity of a complex region of an old bridge can be accurately estimated.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
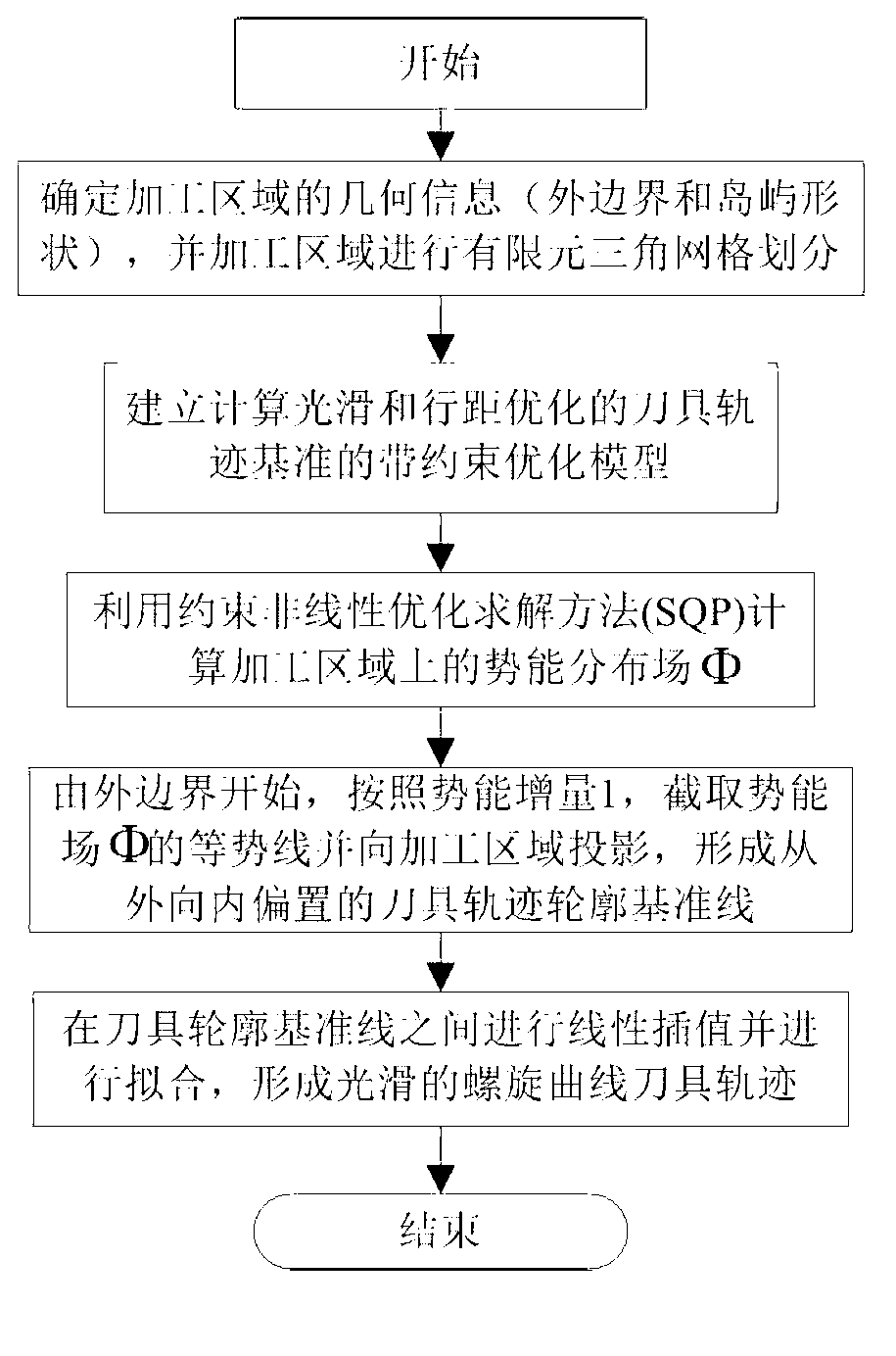
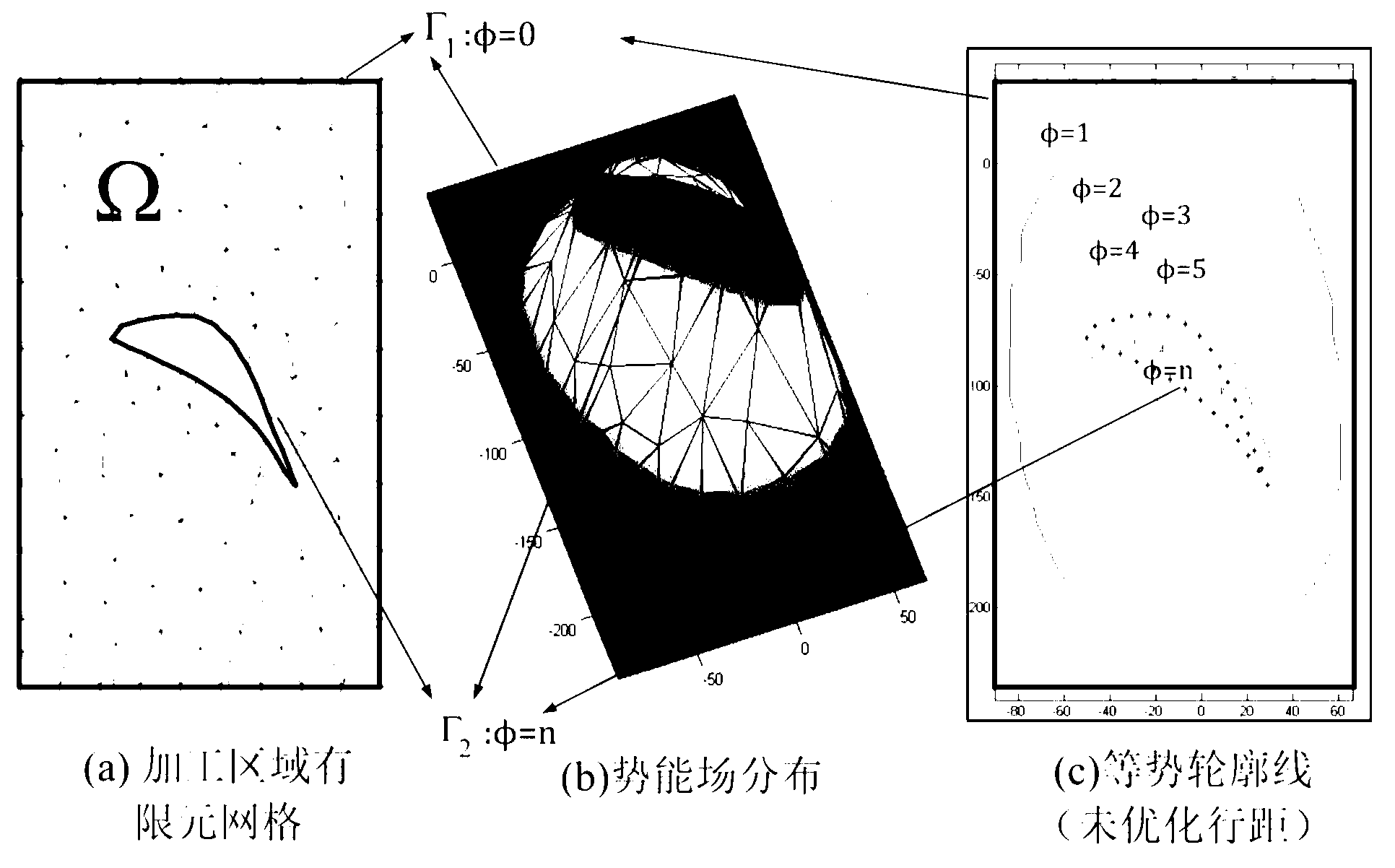
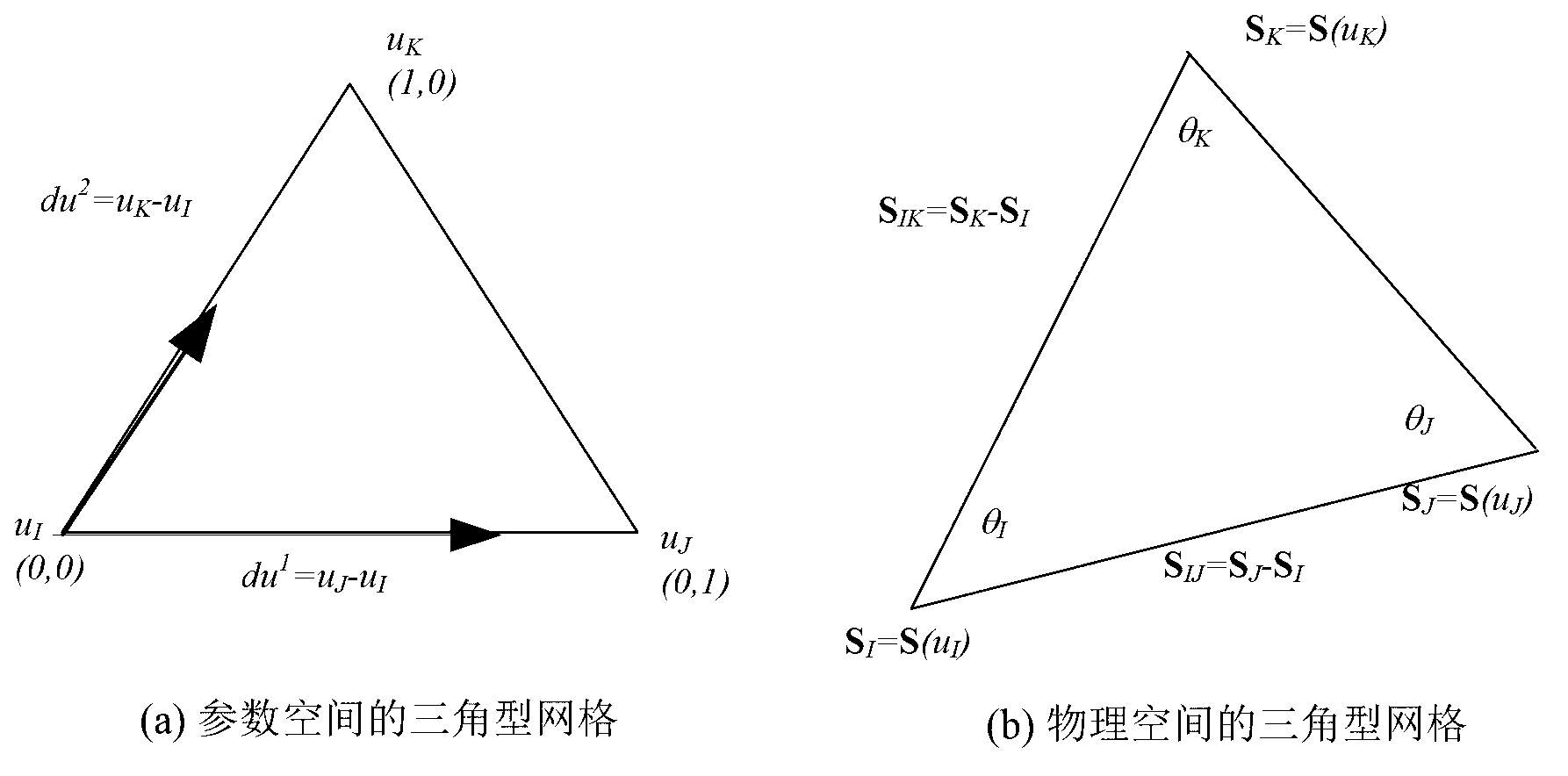
Cutter track generating method based on potential energy field and energy functional optimization
The invention discloses a cutter track generating method based on a potential energy field and energy functional optimization. The cutter track generating method based on the potential energy field and the energy functional optimization comprises an energy functional, boundary conditions and line width constraint conditions. A method of finite elements is used to obtain a numerical approximation computational formula of a cutting track optimization calculating model, wherein the numerical approximation computational formula is based on a triangular discrete grid. An approximate value phi Phi on each node I where the potential energy field template Phi exists is obtained according to the cutter track calculating model. Contour lines of a volcanic vent are sectioned and images are cast on a machining zone omega Omega. Approximate tracks of equipotential contours are formed and smoothing and sampling are performed on the approximate tracks of the equipotential contours. Cutter track contour datum lines which are arranged from the exterior to the interior in an inclined mode are obtained. Linear interpolation is performed among the cutter track contour datum lines and a segment of a spiral cutter track is formed. All spiral cutter tracks are connected to form a spiral track. Curve fitting is performed on the spiral track to form a geometry second order continuous B spline cutter track. The cutter track generating method based on the potential energy field and the energy functional optimization achieves high-speed machining, optimizes cutting force distribution and improves quality of surface machining.
Owner:武汉智能控制工业技术研究院有限公司
Finite-element reconstruction method for space weighting of auto-fluorescence imaging
InactiveCN101539518AHigh speedSolving Quantitative Reconstruction Problems2D-image generationDiagnostic recording/measuringNumerical stabilityOptical tomography
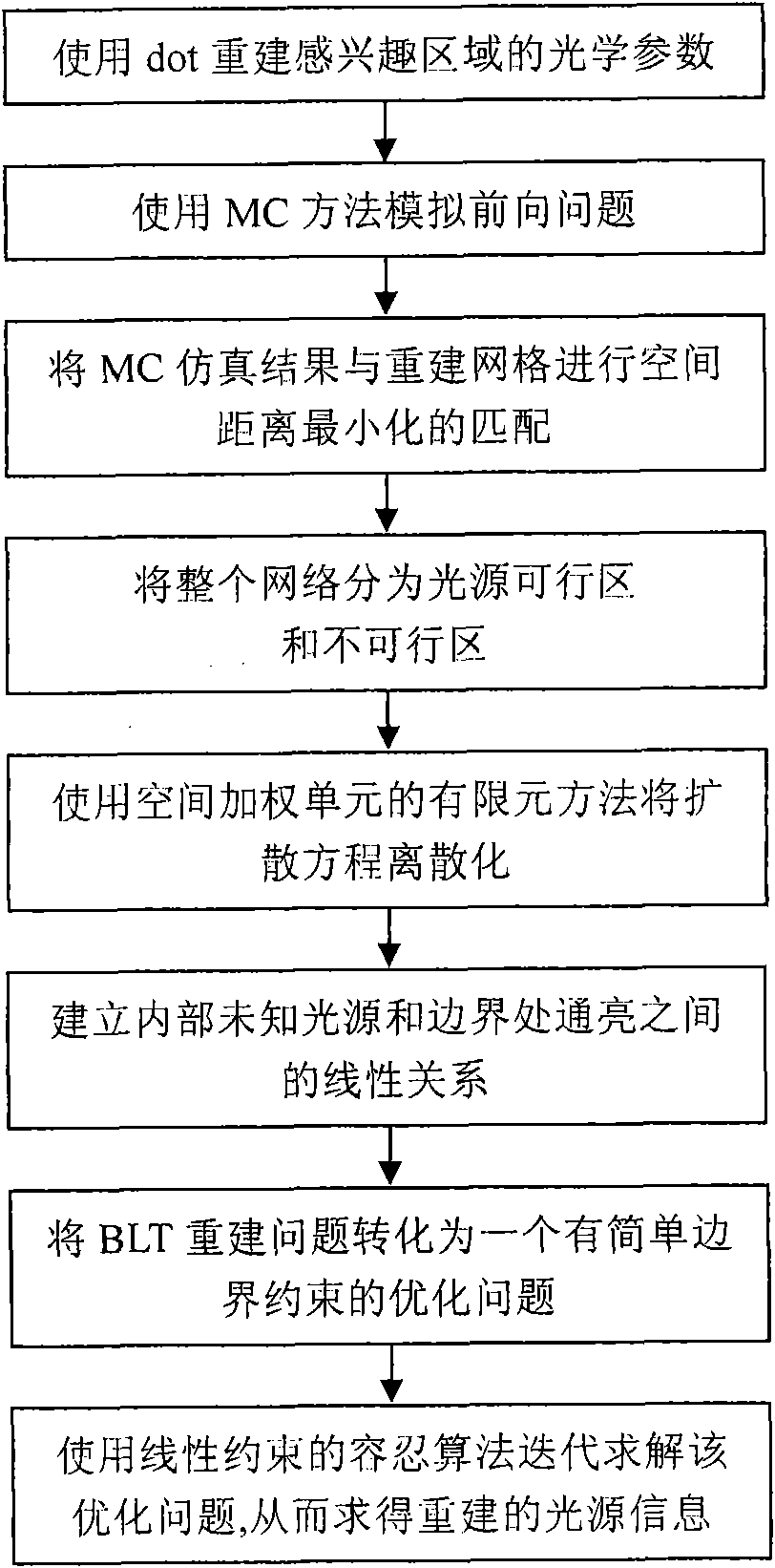
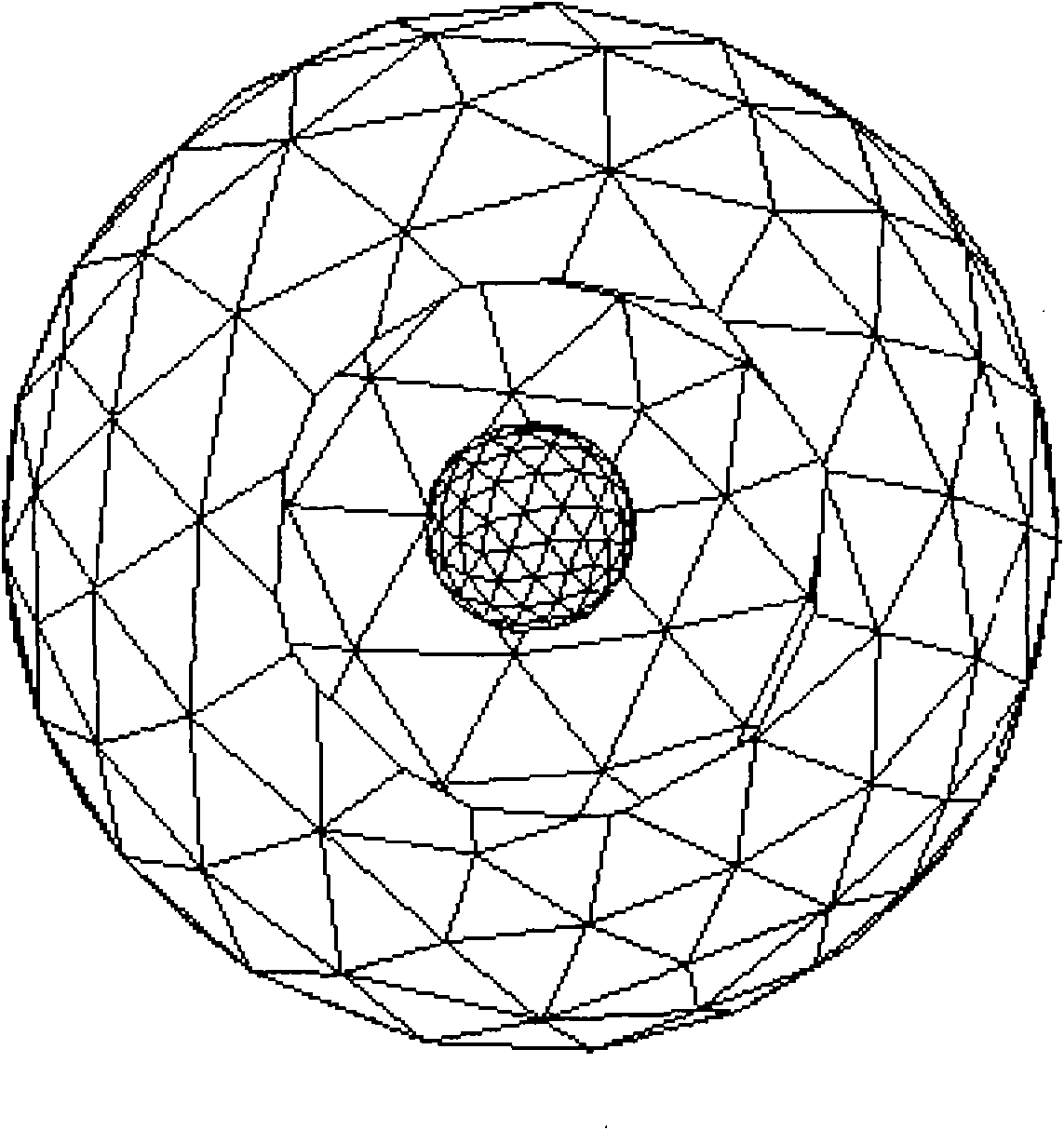
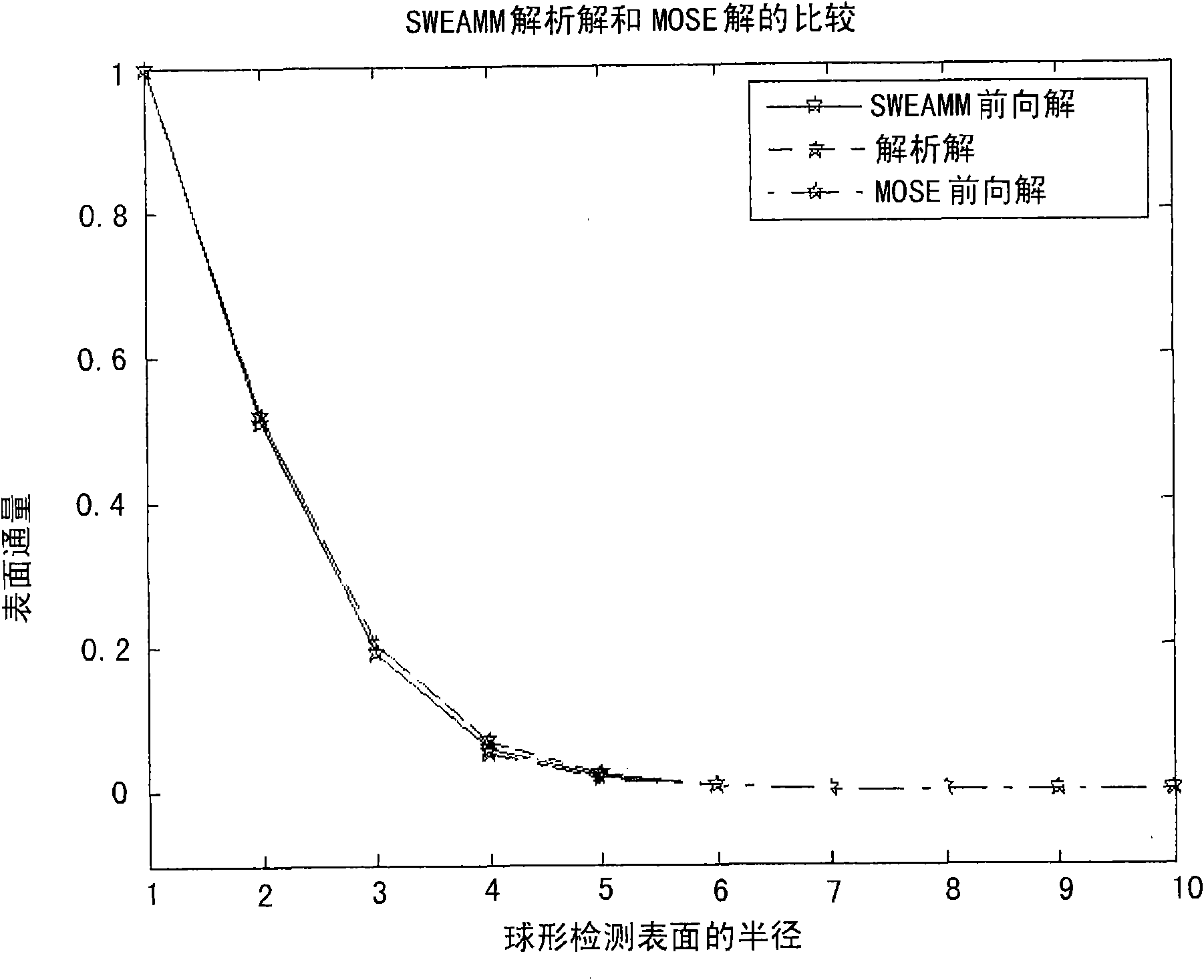
The invention puts forward a finite-element reconstruction method for space weighting of auto-fluorescence imaging. The method uses a diffuse optical tomography (DOT) technique to precisely reconstruct optical parameters of main biological tissue. The method limits a possible real light-source region, and divides a whole reconstruction region into a light-source possible region and a light-source impossible region so as to improve the numerical stability and effectiveness of reconstruction problems and reduce the ill-conditioned property of BLT reconstruction problems. In order to avoid famous 'Inverse Crime' problems, the method adopts a Monte Carlo (MC) random method to simulate the process of transmitting light in the biological tissue. Then the invention puts forward a finite-element method based on a space-weighting unit and adopts a tolerant algorithm for linear constrained optimization problems to reconstruct light-source information.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
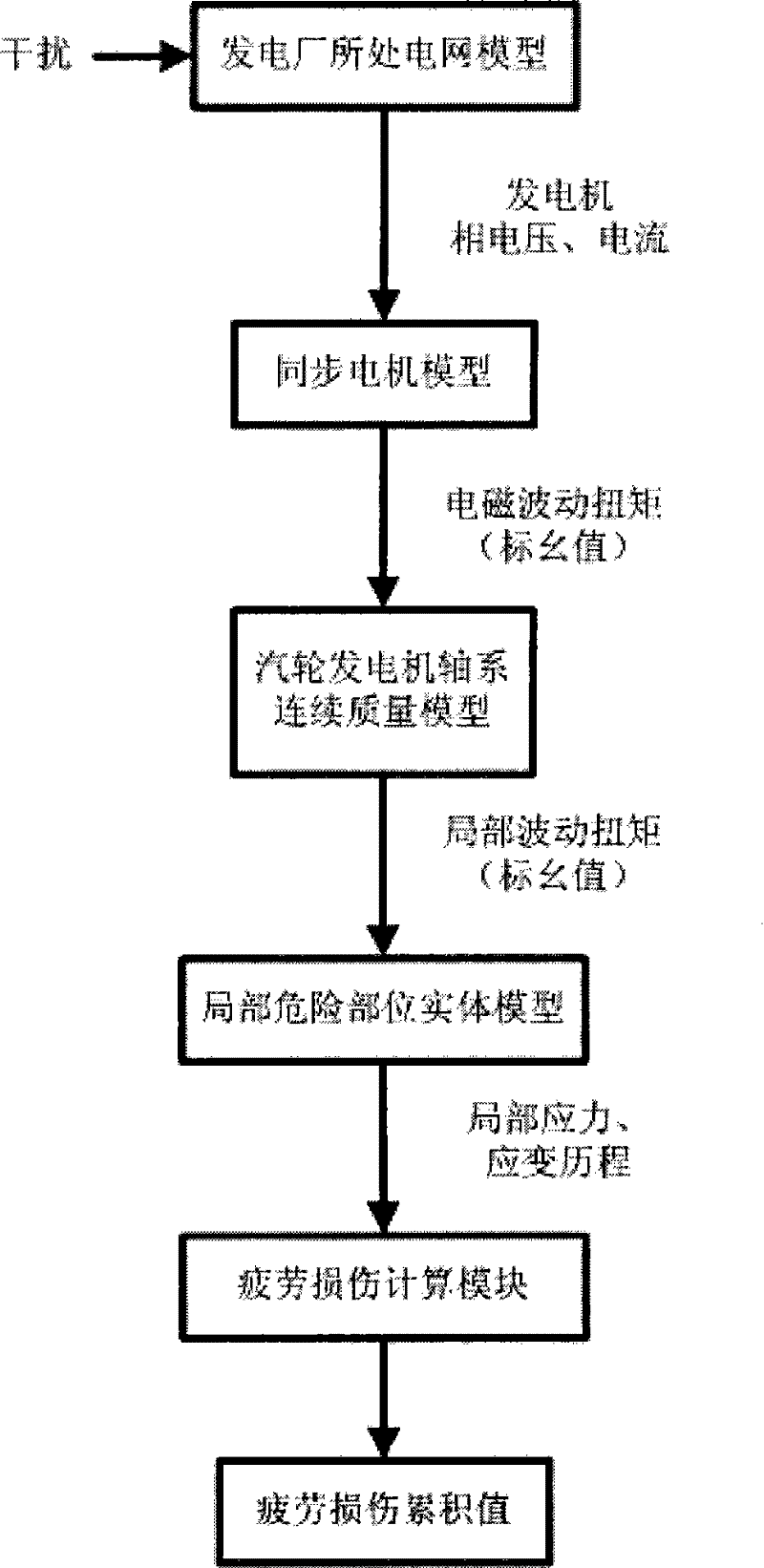
Online analysis method for turbonator shafting fatigue damage caused by subsynchronous oscillation
ActiveCN101750216AFine modelingHigh solution accuracyMachine bearings testingEngine testingFatigue damagePhase currents
The invention relates to an online analysis method for the turbonator shafting fatigue damage caused by the subsynchronous oscillation, which confirms the subsynchronous oscillation amplitude by actually sensing the phase voltage and the phase current. A four-stage synchronous electric motor model is adopted to confirm the change process of the electromagnetic torque of an electric motor; a turbonator shafting continuous quality model is adopted to confirm the change process of the shafting transient state torque; a finite element method is adopted to build a partial dangerous section physical model so as to confirm the maximum fatigue damage section; and a high-cycle fatigue damage norm is adopted to confirm the shafting fatigue damage value. A fatigue damage database is built to store the calculating data of each process so as to confirm the online analysis method for the turbonator shafting fatigue damage caused by the subsynchronous oscillation. The invention can be used for analyzing the turbonator shafting fatigue damage caused by subsynchronous oscillation on line, enhances the evaluation level for the electric network subsynchronous and the electric generating set correlation and effect, and effectively avoids the electric generating set fatigue damage and accumulation caused by the subsynchronous oscillation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com