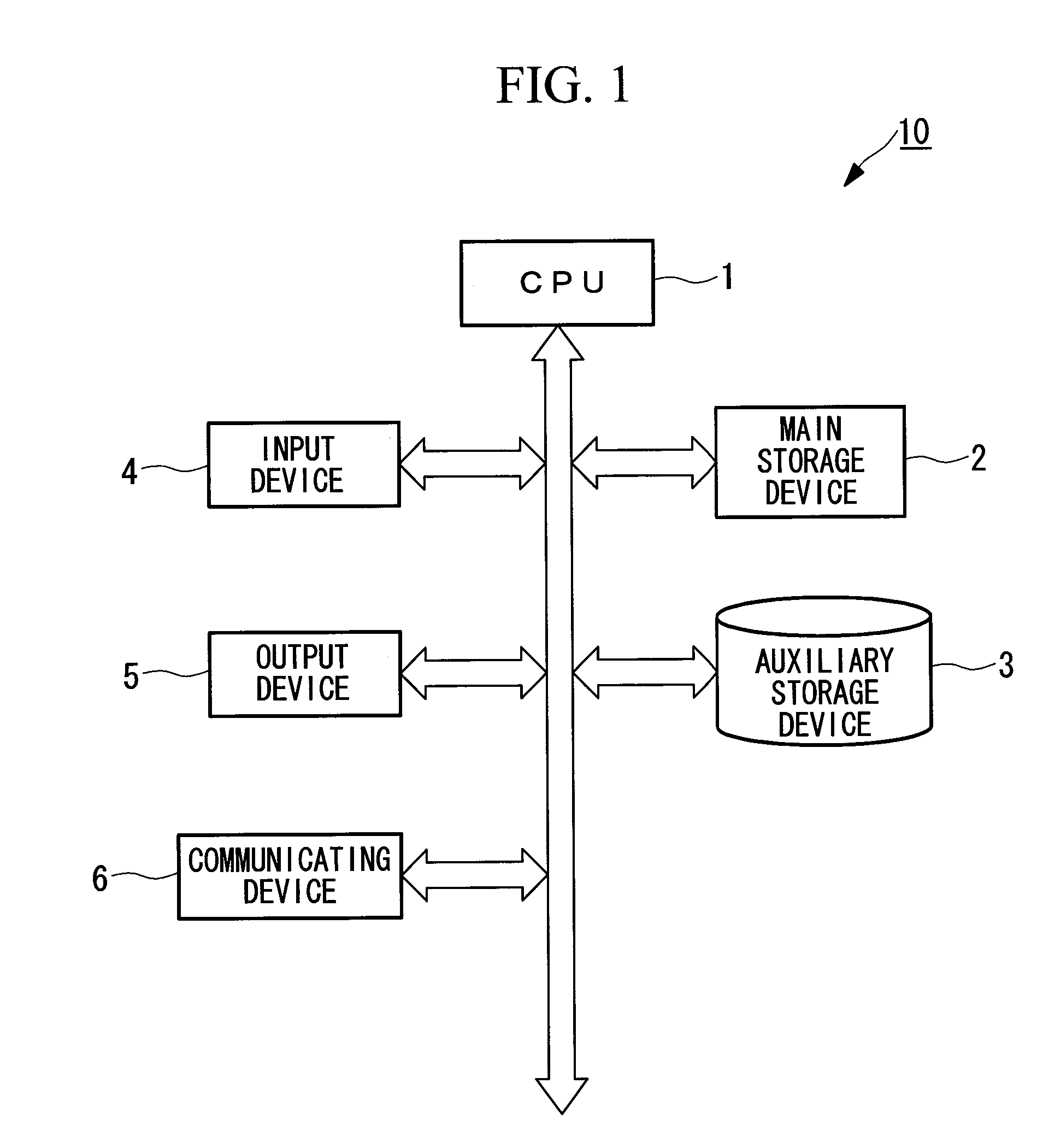
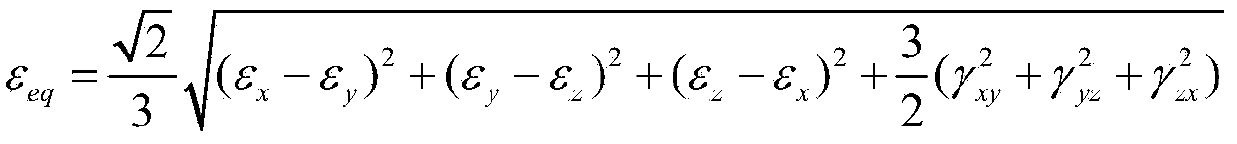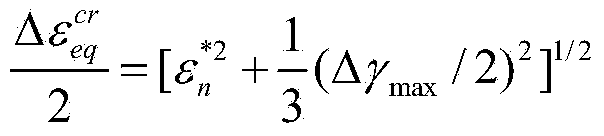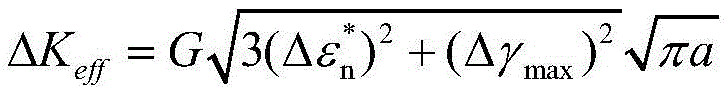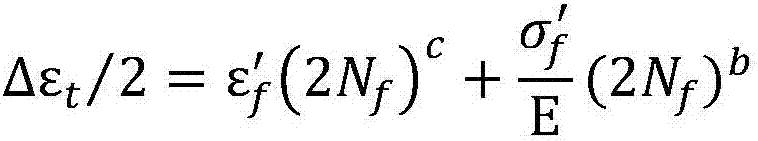Patents
Literature
1618 results about "Fatigue damage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
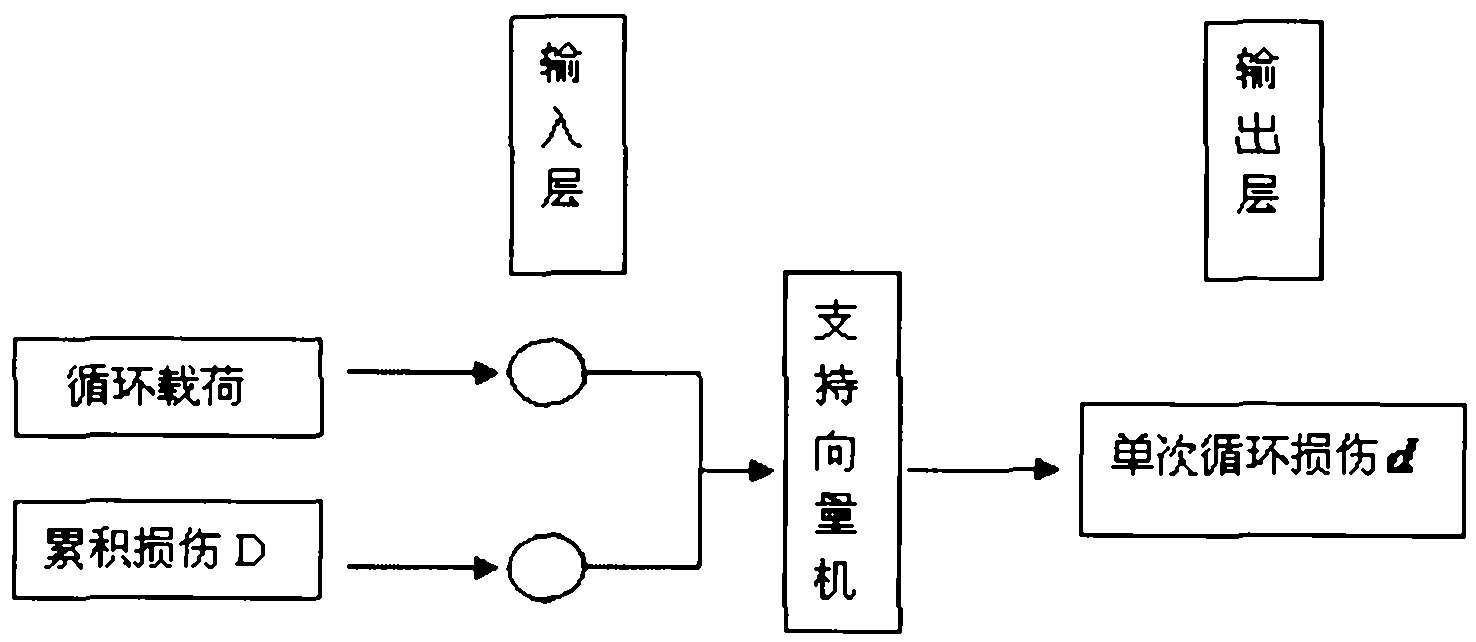
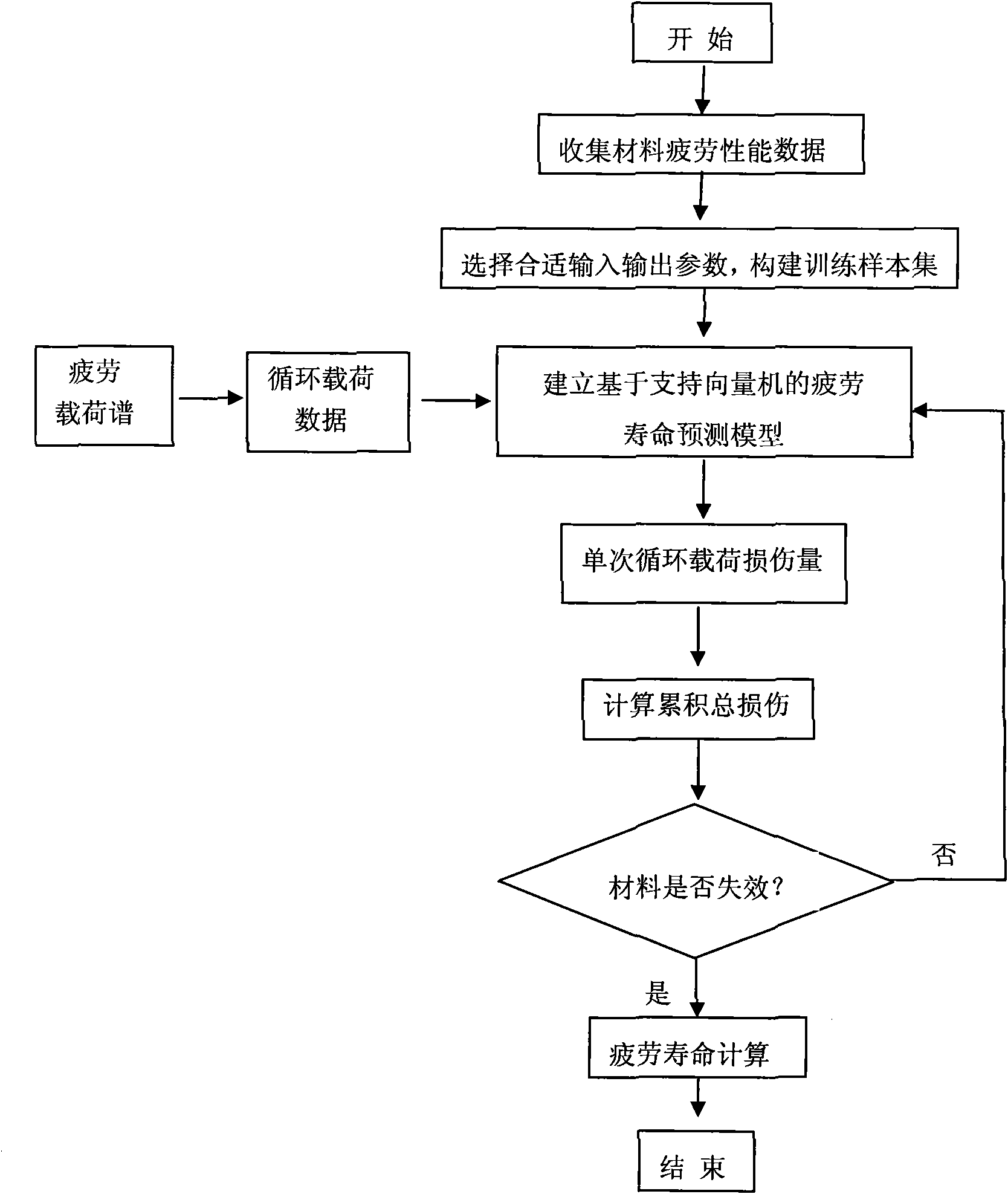
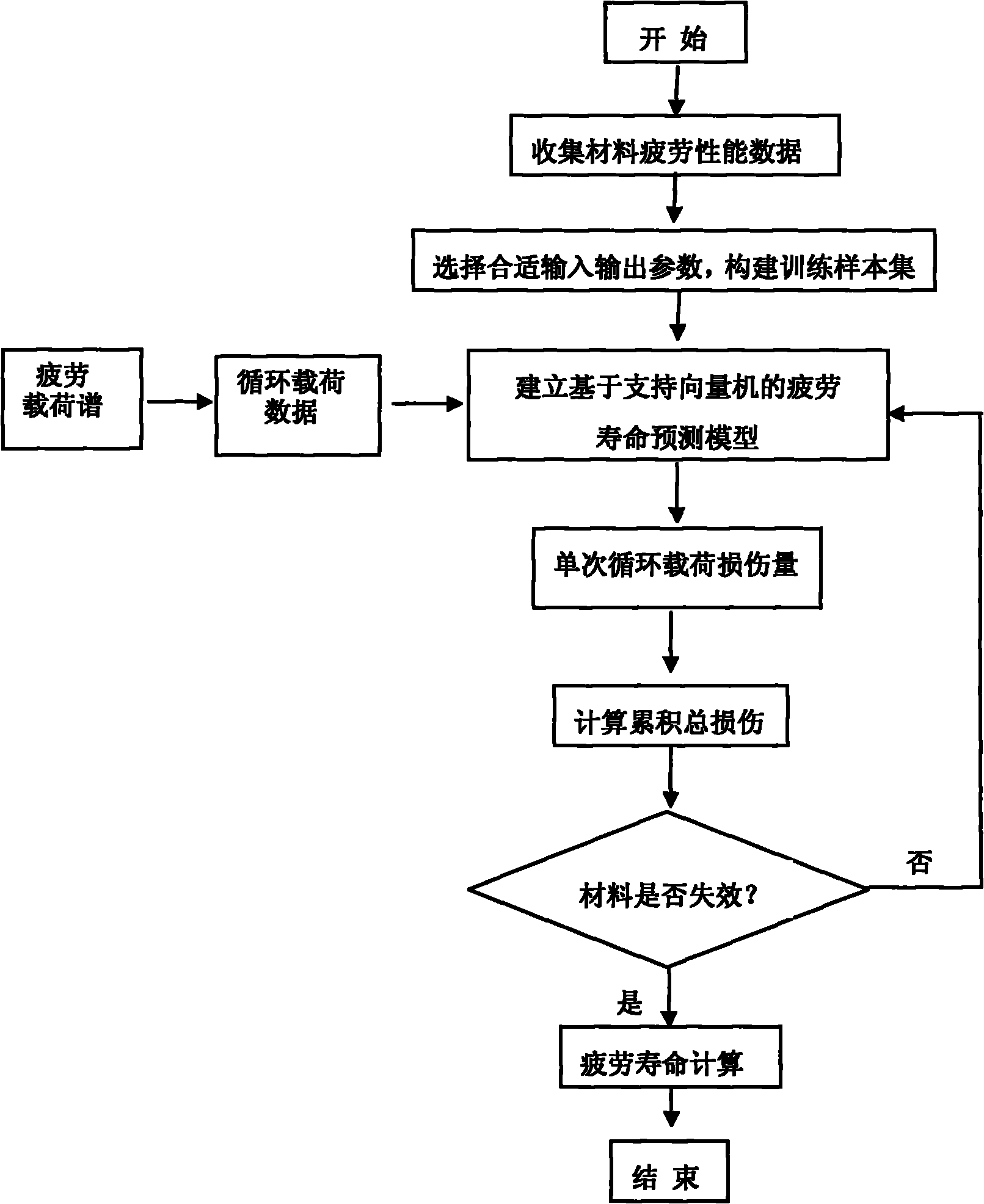
Material fatigue-life predicting method based on support vector machine
InactiveCN102081020ASave fatigue experimentsExtended service lifeStrength propertiesFatigue damageSupport vector machine
The invention relates to a material fatigue-life predicting method based on a support vector machine, and discloses a method for predicting the fatigue service life of a structural material, which comprises the steps of: obtaining material fatigue performance data, selecting a proper input and output parameter to construct a training sample set, establishing a fatigue-life predicting model based on the support vector machine, preprocessing a fatigue load, and calculating the fatigue life. The material fatigue-life predicting method has the advantages of realizing the nonlinear accumulation of fatigue damages by using less material fatigue performance data, and improving the accuracy of predicting the life. The method provided by the invention is suitable for the structural material fatigue life estimation and the life prolonging analysis, and has an important theoretical significance and an actual application value in formulating a reasonable maintenance plan for prolonging the service life of the material.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
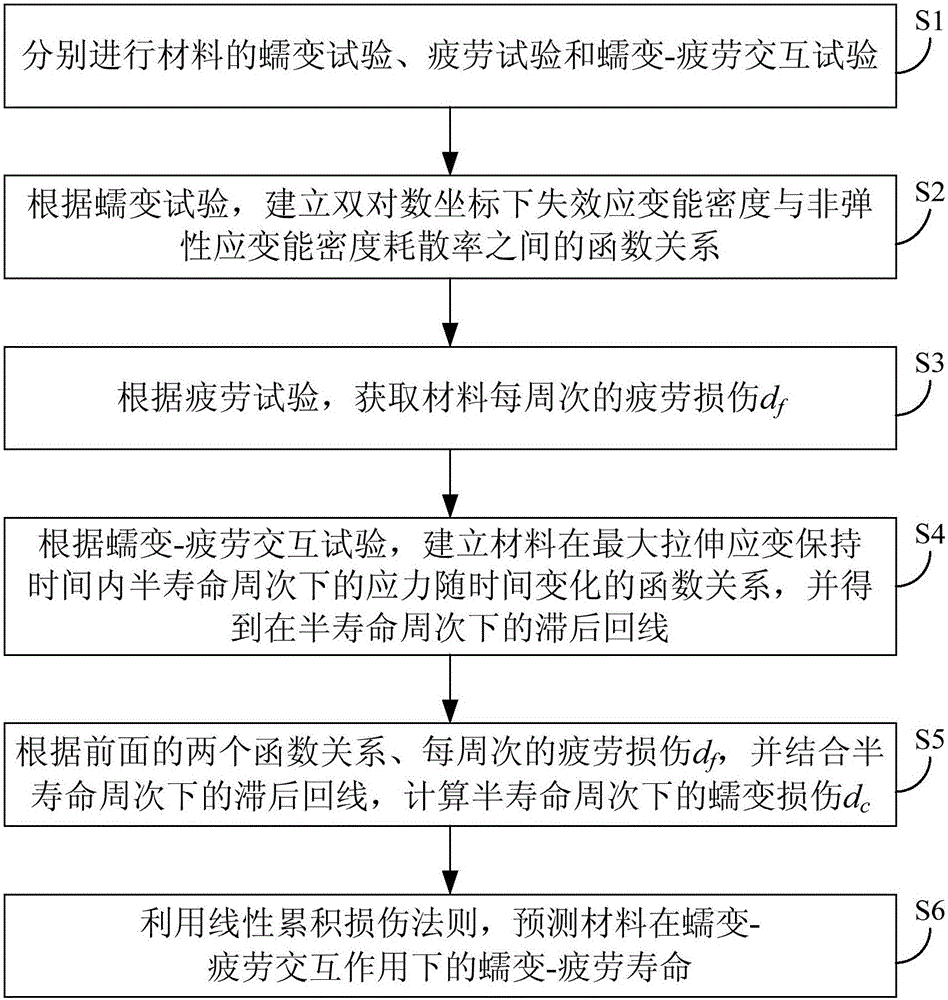
Forecasting method for creep-fatigue life of material
ActiveCN105158084ALife expectancyReal-time Damage DetectionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFatigue damageHysteresis
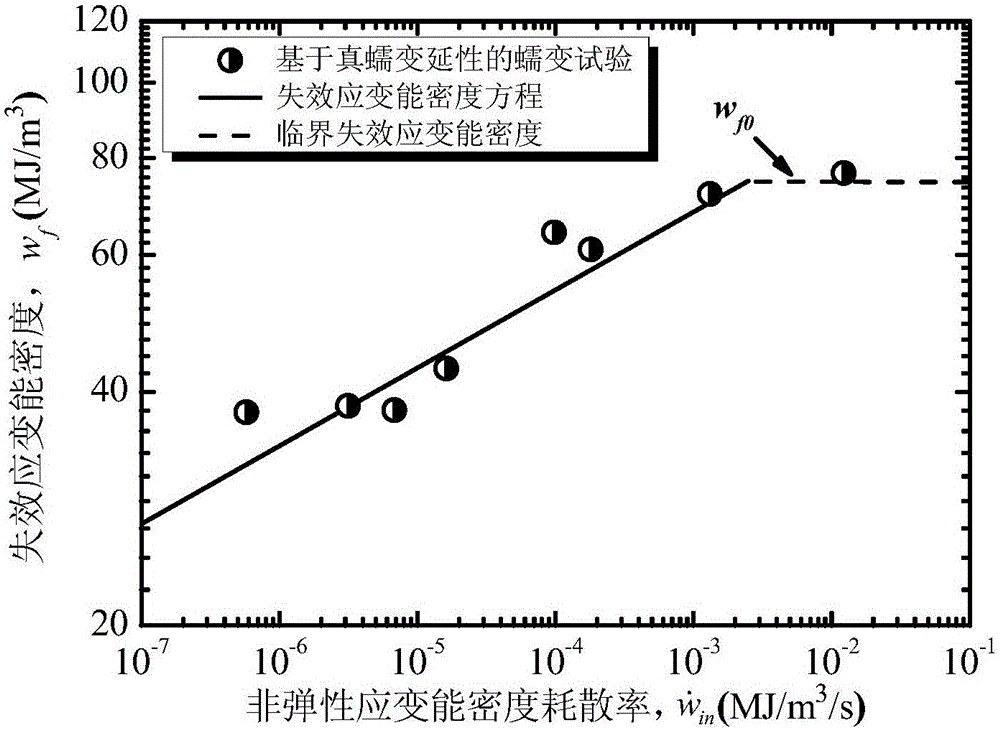
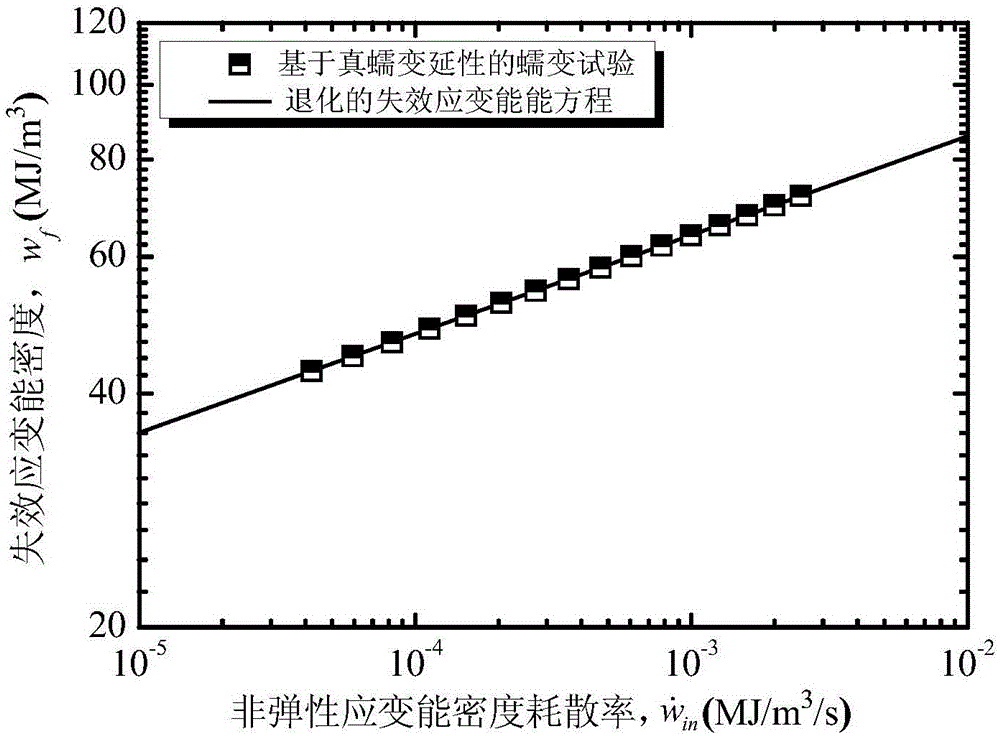
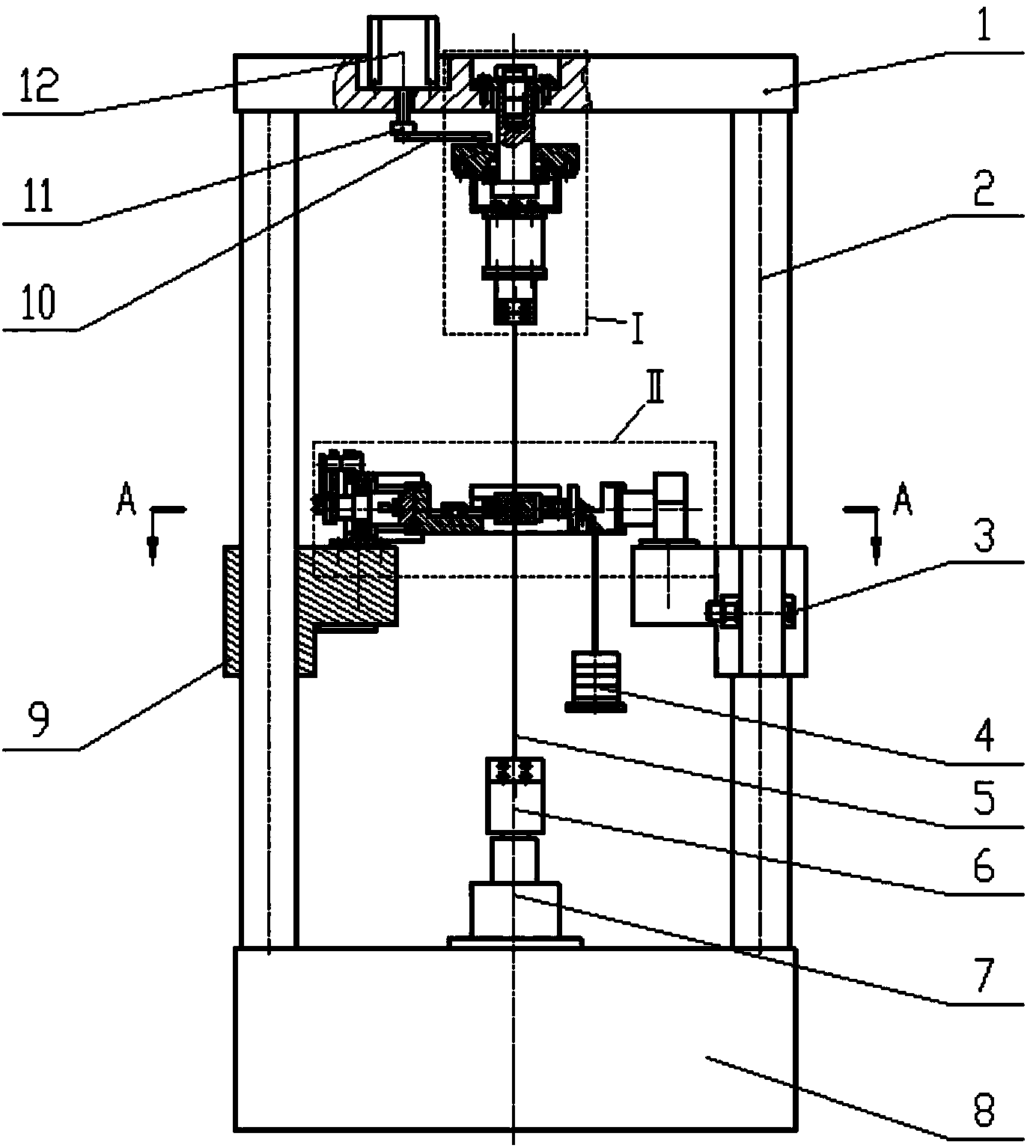
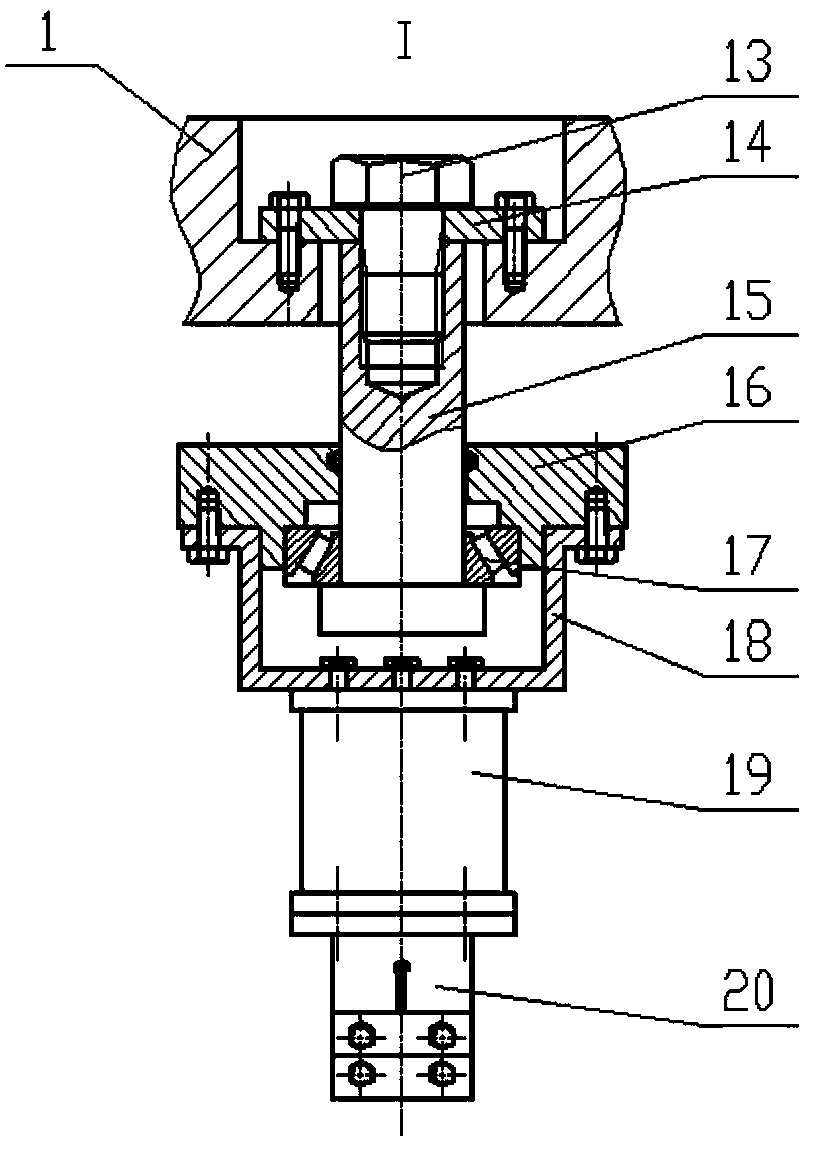
The invention provides a forecasting method for creep-fatigue life of a material. The method comprises the following steps: respectively performing a creep test, a fatigue test and a creep-fatigue interaction test for the material at a same test temperature; establishing a relation between the failure strain energy density wf and a non-elastic strain energy density dissipation rate of the material under a log-log coordinate according to the creep test; acquiring the fatigue damage df of the material per period according to the fatigue test; acquiring a hysteresis loop under a half-life period according to the creep-fatigue interaction test and establishing a function relation of the change of the stress Sigma (t) of the material under the half-life period within the maximum tensile strain maintaining time along with the change of time t; calculating the creep damage dc under the half-life period by combining with the hysteresis loop and based on the relation between wf and the function as shown in the specification and the relation of change of the fatigue damage df and the stress Sigma (t) along with the change of time t; and utilizing a linear accumulating damage rule to forecast the creep-fatigue life of the material under a creep-fatigue interaction. According to the method provided by the invention, the life of the material under the creep-fatigue interaction can be accurately forecasted.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
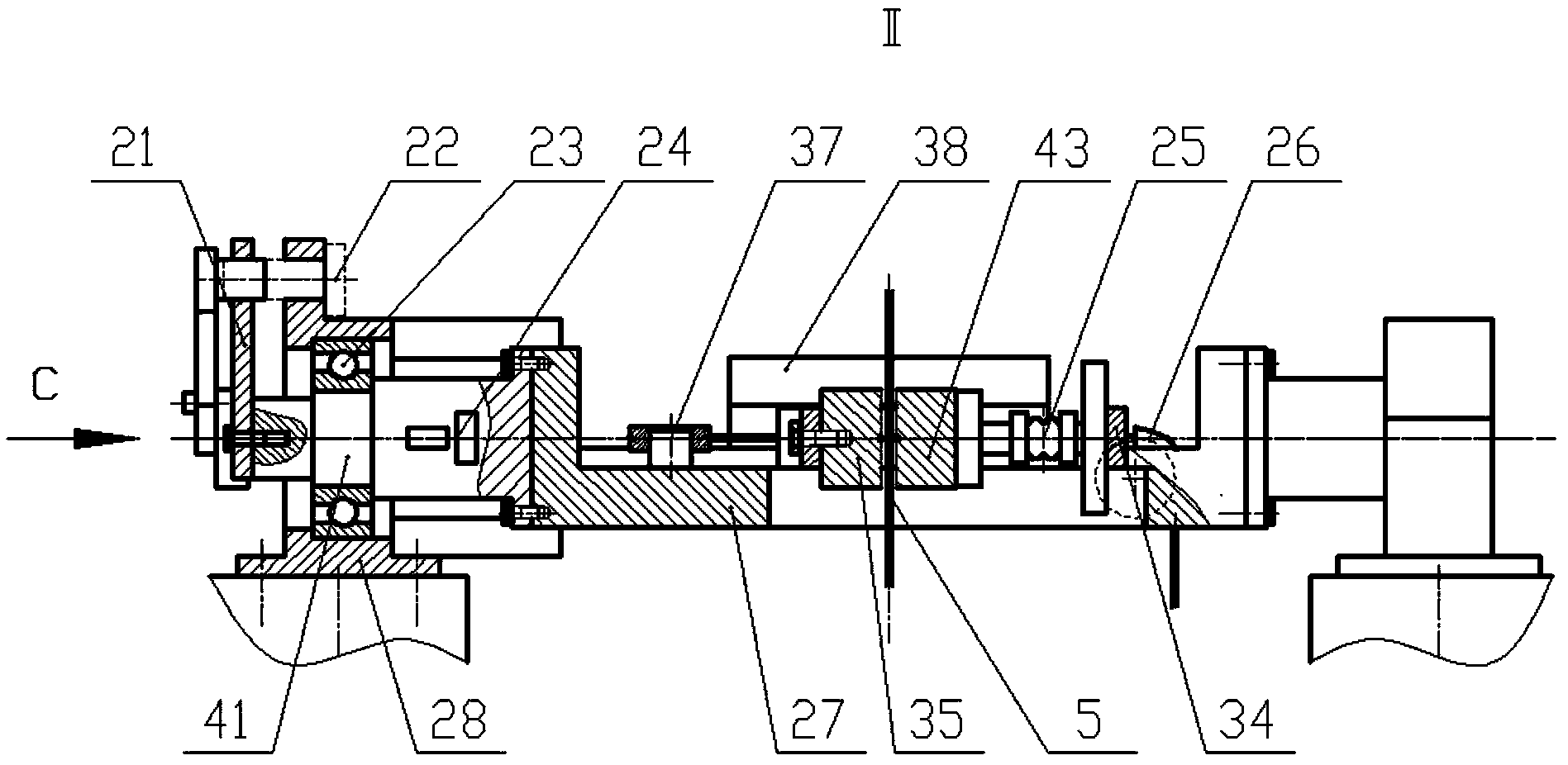
Device and method for multi-axis fretting fatigue test of steel wire
ActiveCN104297046AImprove multi-axis fretting fatigue damage characteristicsAdjust relative position in real timeMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFatigue damageSupporting system
The invention relates to a device and a method for a multi-axis fretting fatigue test of a steel wire. The device comprises a base frame, a pull-torsion fatigue system, a swing loading system and a condition monitoring system, wherein the base frame comprises a base, support stand columns, bearing beams and support fixture blocks, the support stand columns are symmetrically arranged on the base; the bearing beams are respectively arranged on the tops of the support stand columns; the support fixture blocks are respectively arranged in the middle parts of the support stand columns; the pull-torsion fatigue system comprises a support system, a torsion driving system and a pull-pull fatigue system; the swing loading system comprises a swing driving system and a loading system; the condition monitoring system comprises a fretting measurement system, an axial fatigue load measurement system, a torsion measurement system and a swing measurement system. The torsion angle of the fatigue steel wire can be obtained through a crank-link mechanism by adjusting the eccentric position of an eccentric block; the multi-axis fretting fatigue test of the steel wire can be realized in the composite motion modes such as pull-pull fatigue, torsion and variable crossing angle swing and the like; the device and the method are used for disclosing the multi-axis fretting fatigue fracture mechanism of the steel wire, and carrying out quantitative evaluation on multi-axis fretting fatigue damage evolution and multi-axis fretting fatigue life of the steel wire.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
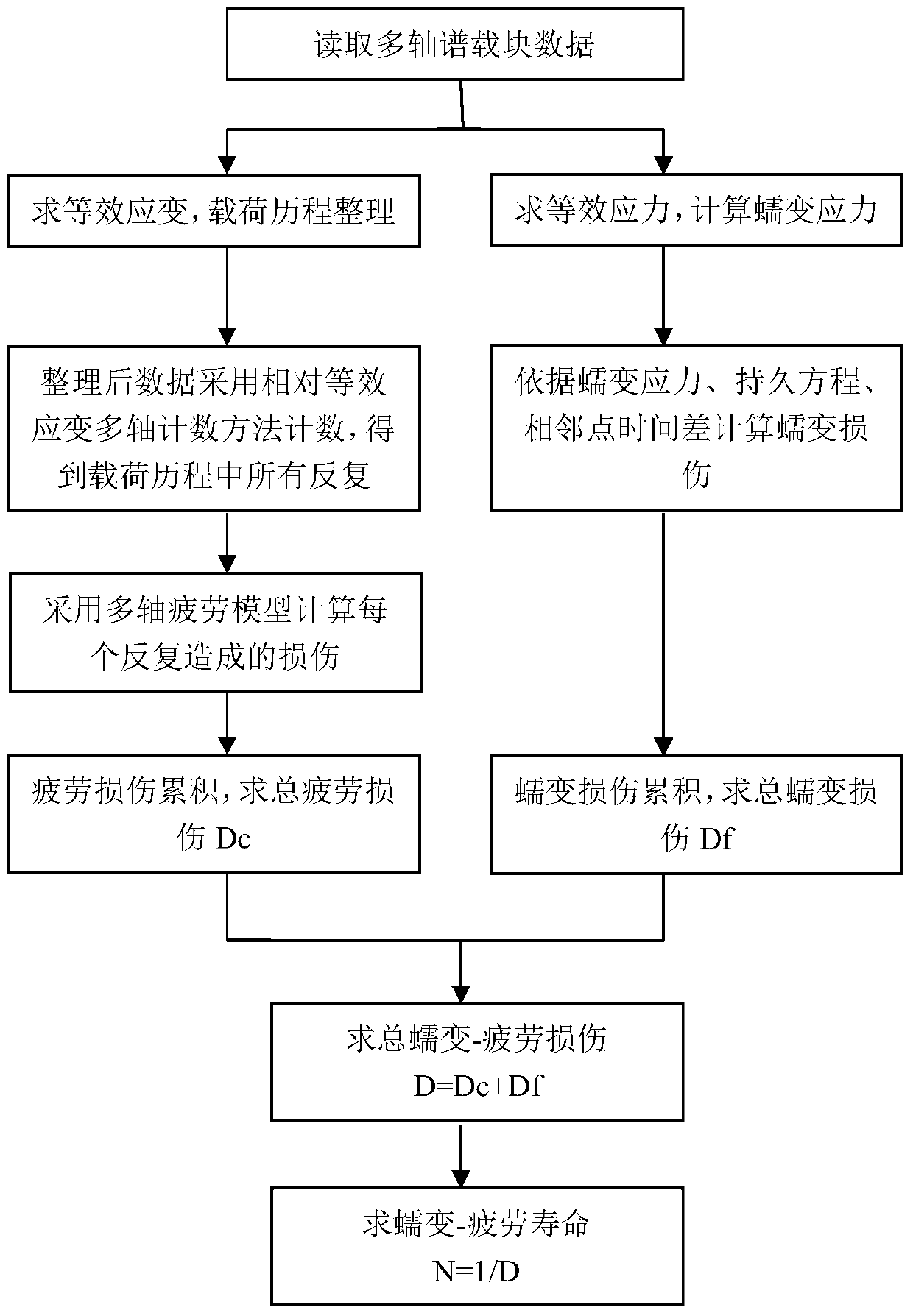
Low-cycle creep and fatigue life evaluation method under conditions of high temperature and multiaxial spectrum load
ActiveCN103926152AEasy accessReduce testing costsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFatigue damageCreep stress
The invention relates to a low-cycle creep and fatigue life evaluation method under the conditions of high temperature and multiaxial spectrum load. The method comprises the following steps of reading a stress strain history in a multiaxial loading spectrum data block, working out equivalent strain, and finishing a loading history; repeatedly extracting by adopting a relative equivalent strain multi-axis counting method; working out all repeated fatigue damage by adopting a unified multiaxial fatigue damage life prediction model; accumulating the fatigue damage to work out the total fatigue damage; working out equivalent creep stress by utilizing the original loading history; working out creep damage Dc according to the equivalent creep stress and the stress history by combining a creep lasting equation; working out the total damage D caused by a multiaxial load spectrum block at the high temperature; and estimating the multiaxial creep and fatigue life. According to the method, the fatigue damage under the multiaxial stress and the creep damage under the multiaxial stress can be respectively calculated in the whole loading spectrum data block, the fatigue material constant at the room temperature is adopted in the calculation of the fatigue damage, and lasting equation material constant recommended by specification is adopted in the calculation of the creep damage; through experimental verification, the method has a good prediction effect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
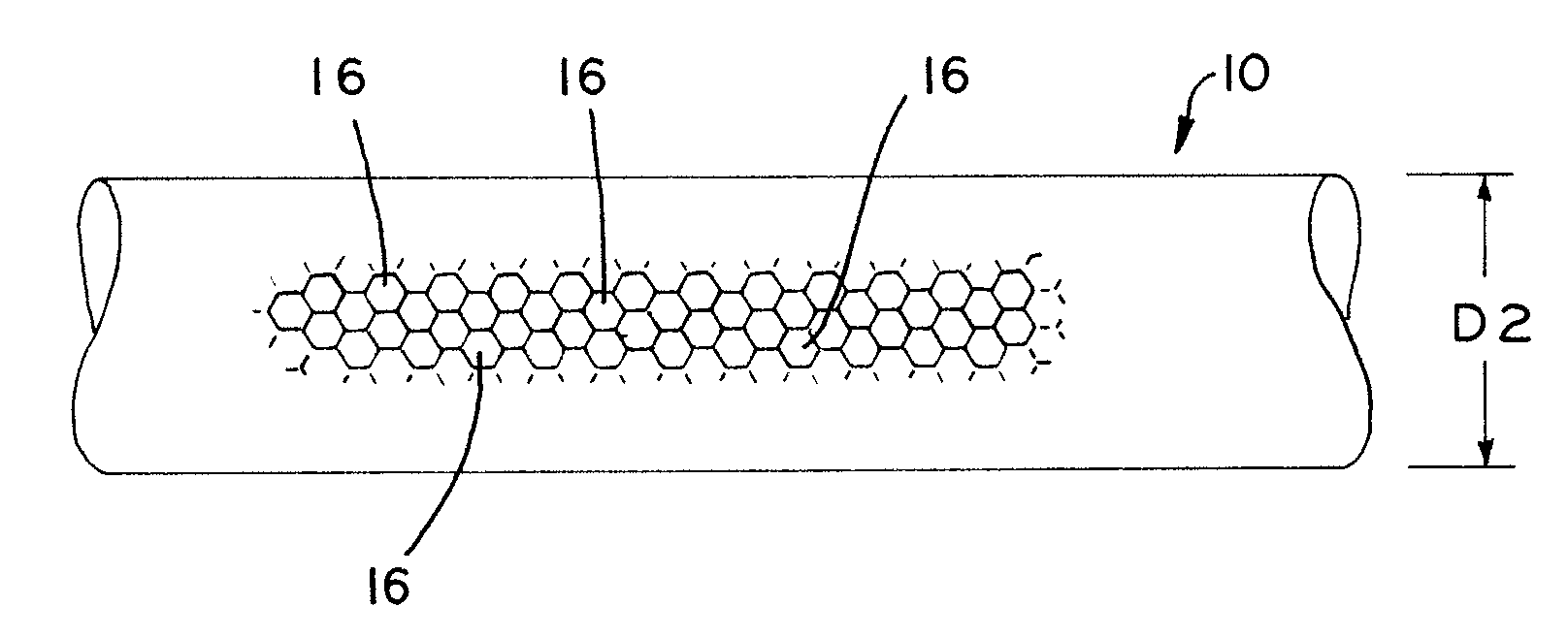
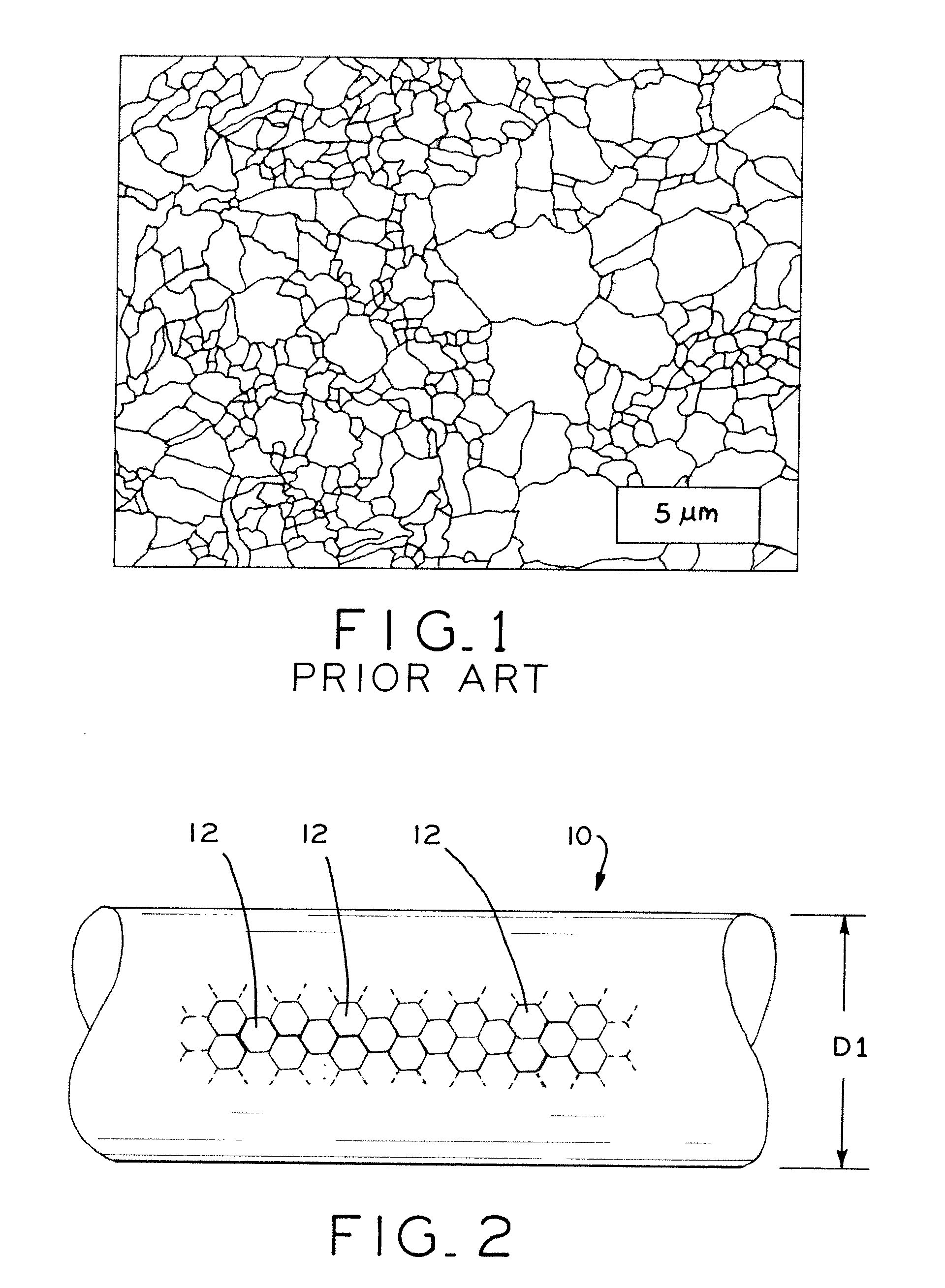
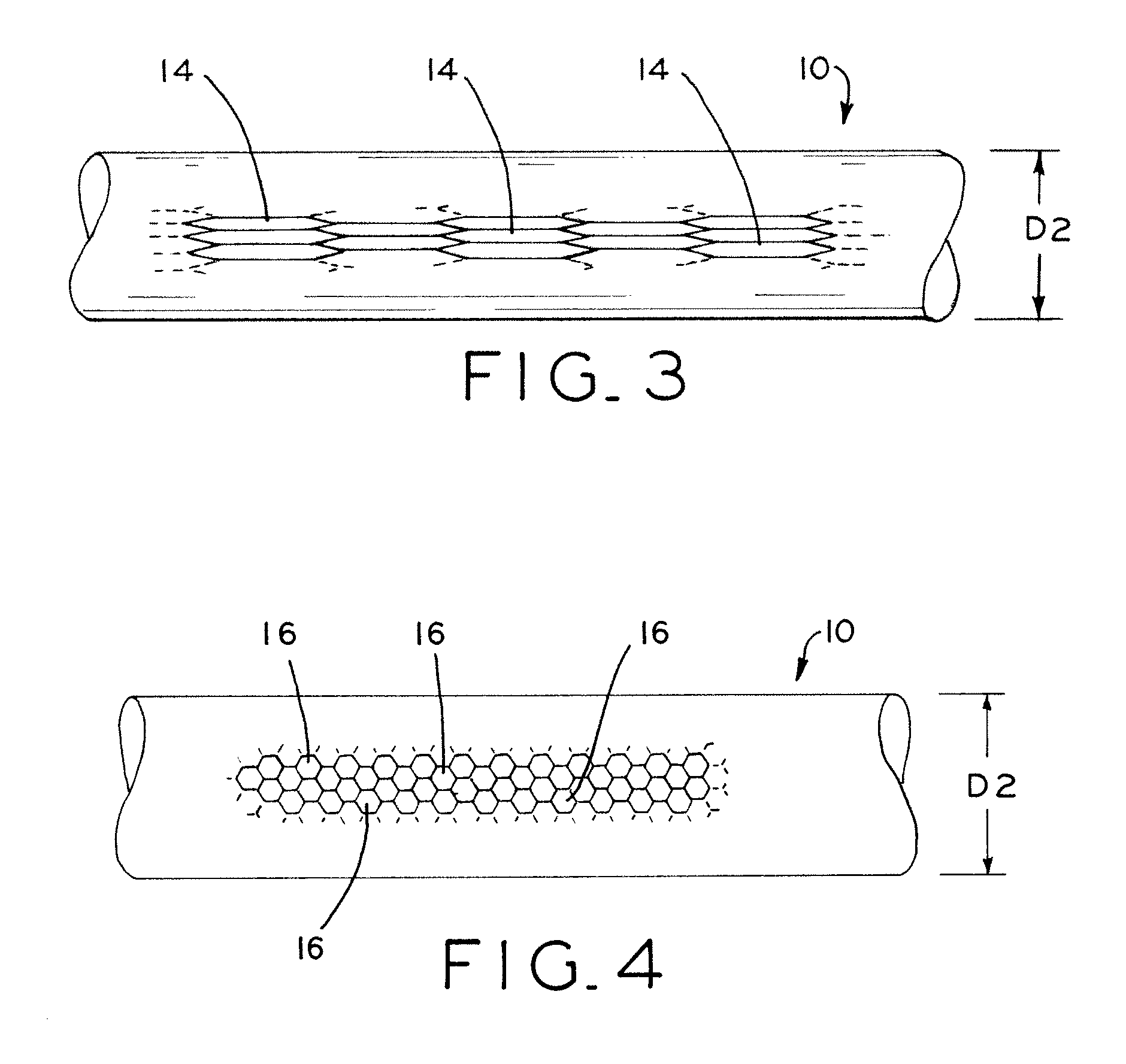
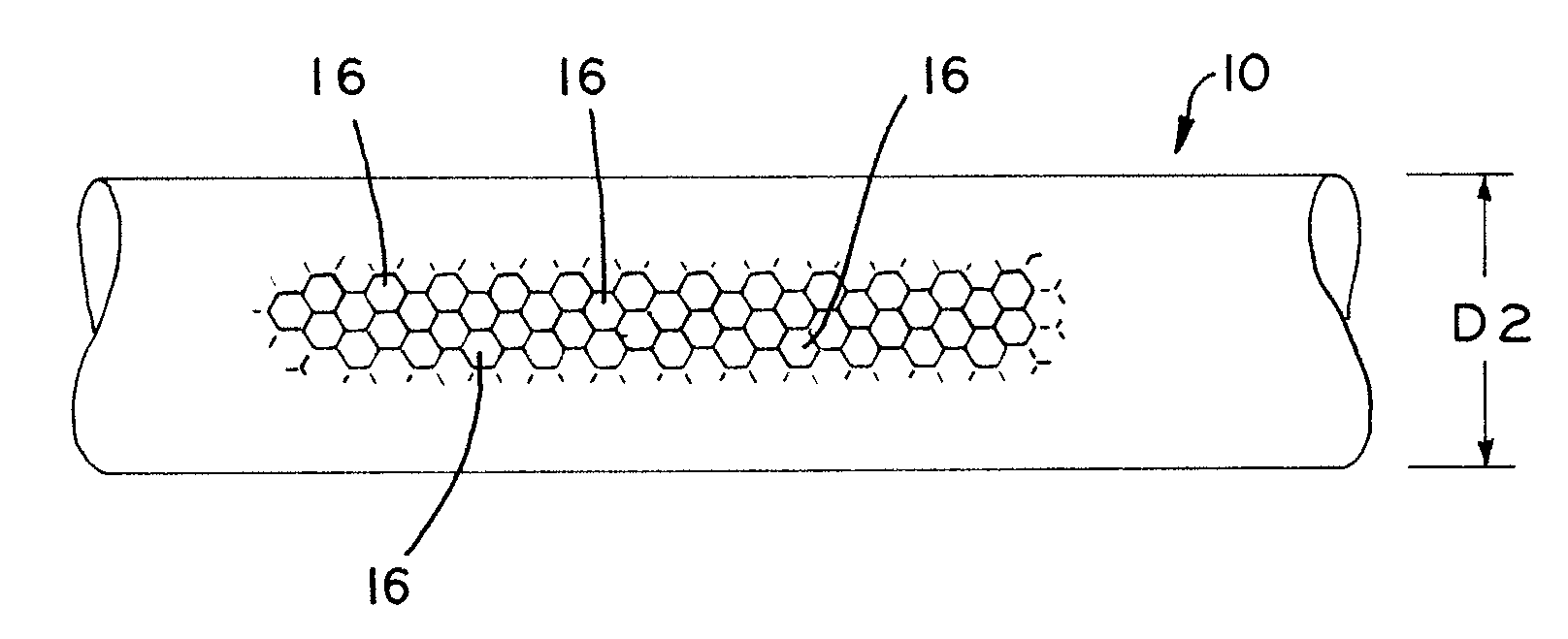
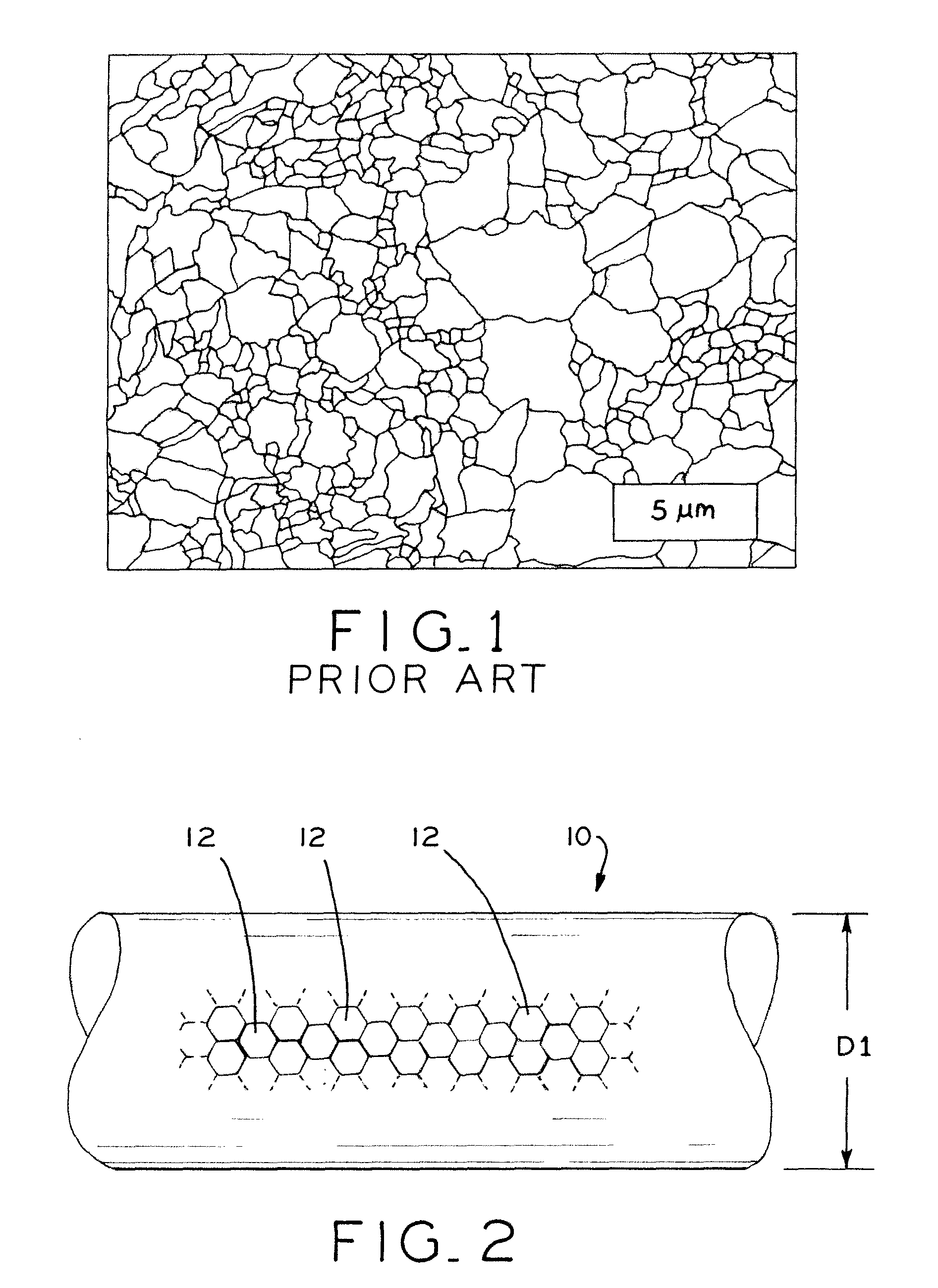
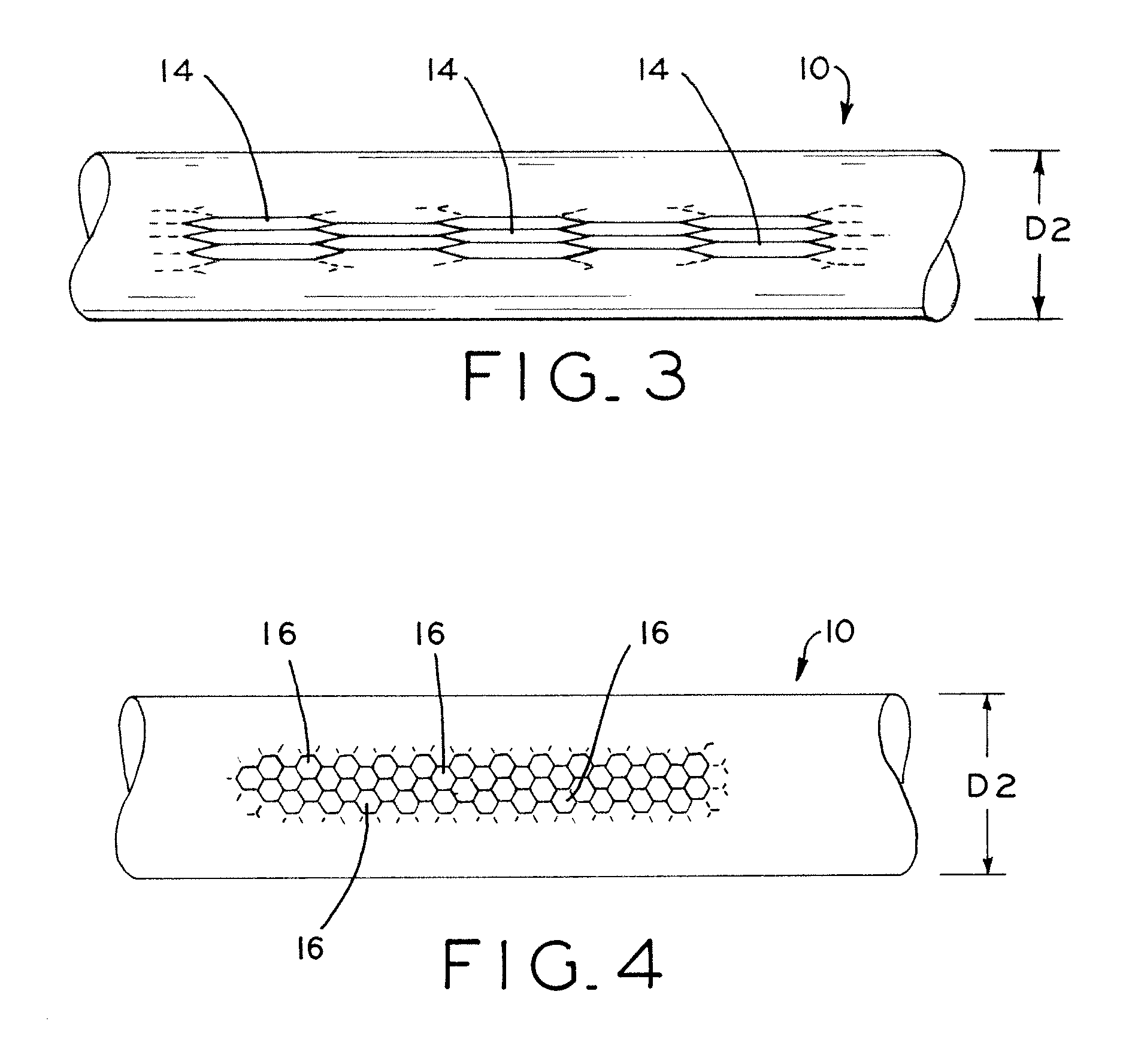
Fatigue damage resistant wire and method of production thereof
ActiveUS20100075168A1Improve resistance to fatigue damageImprove material performanceStentsPig casting plantsFatigue damageWire rod
Fatigue damage resistant metal or metal alloy wires have a submicron-scale or nanograin microstructure that demonstrates improved fatigue damage resistance properties, and methods for manufacturing such wires. The present method may be used to form a wire having a nanograin microstructure characterized by a mean grain size that is 500 nm or less, in which the wire demonstrates improved fatigue damage resistance. Wire manufactured in accordance with the present process may show improvement in one or more other material properties, such as ultimate strength, unloading plateau strength, permanent set, ductility, and recoverable strain, for example. Wire manufactured in accordance with the present process is suitable for use in a medical device, or other high end application.
Owner:FORT WAYNE METALS RES PROD LLC
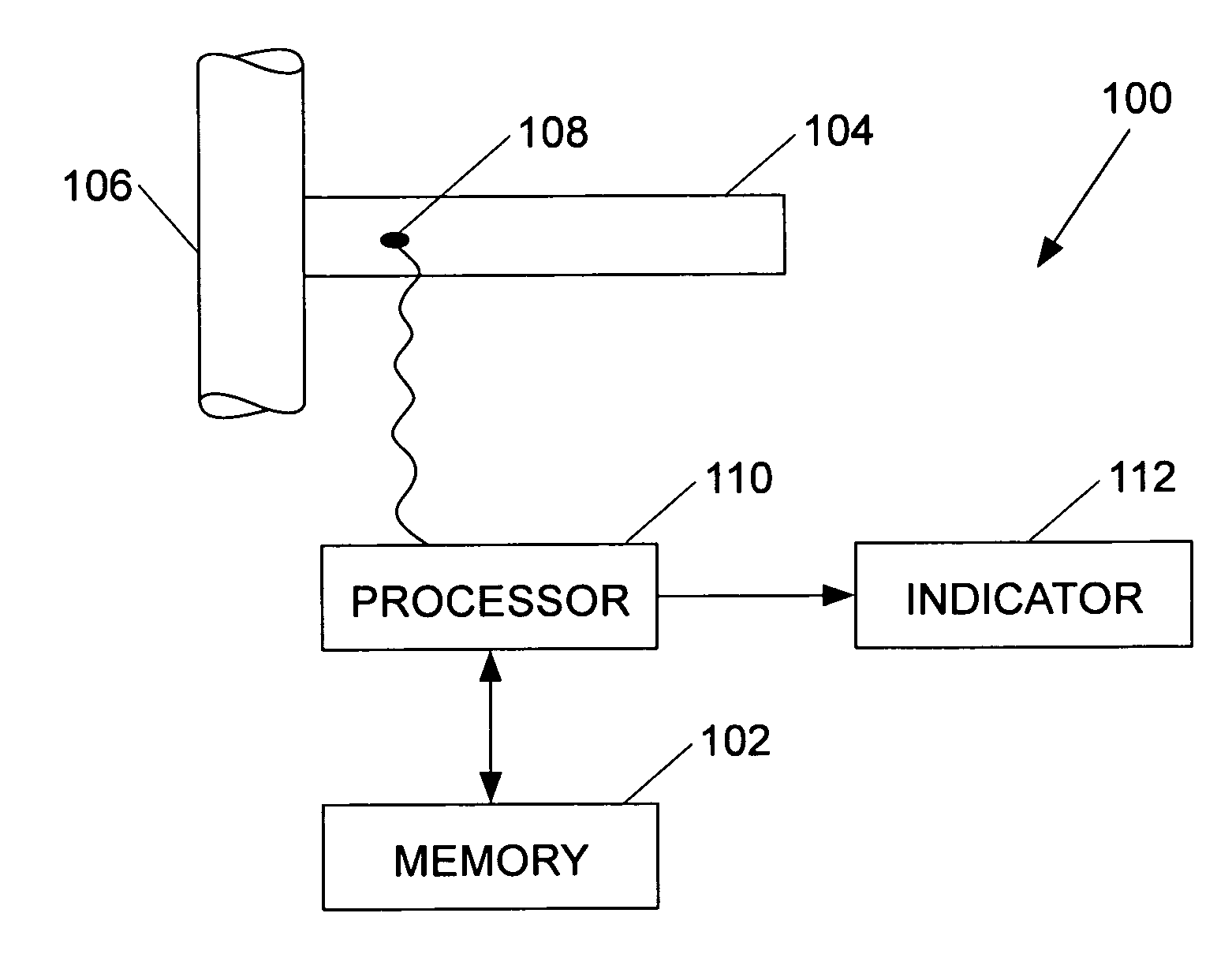
Determination of remaining useful life of gas turbine blade
InactiveUS20070272018A1Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFatigue damageTurbine blade
A system may be used to indicate a need for replacement of a vibrating structure and includes a sensor, an indicator, and a processor. The sensor senses a frequency of vibration of the vibrating structure. The indicator is controlled to provide an indication of the need for replacement of the vibrating structure. The processor compares the frequency of vibration of the vibrating structure to data that relates the vibration frequency of the vibrating structure to fatigue damage of the vibrating structure, and controls the indicator based on the comparison.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
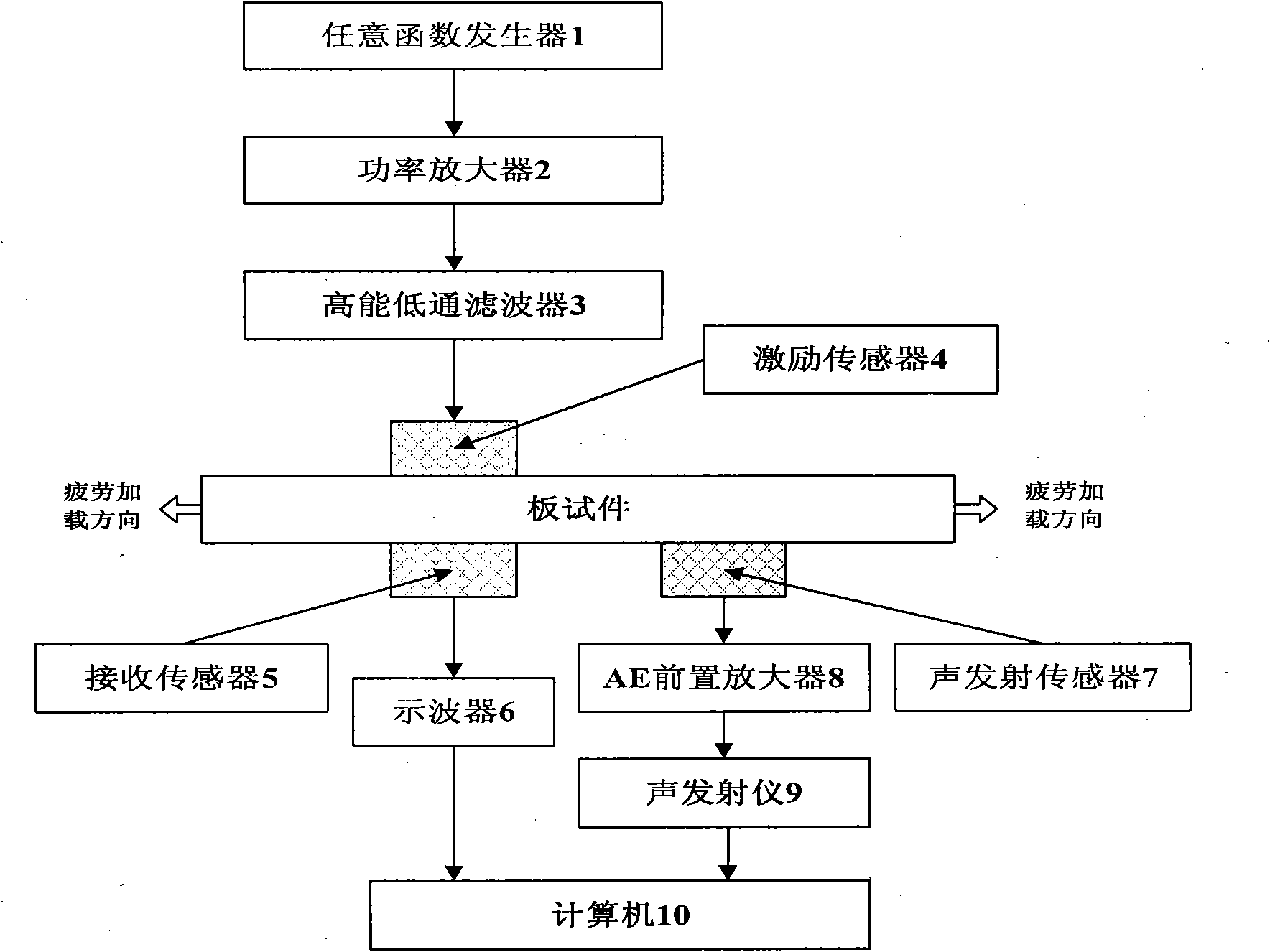
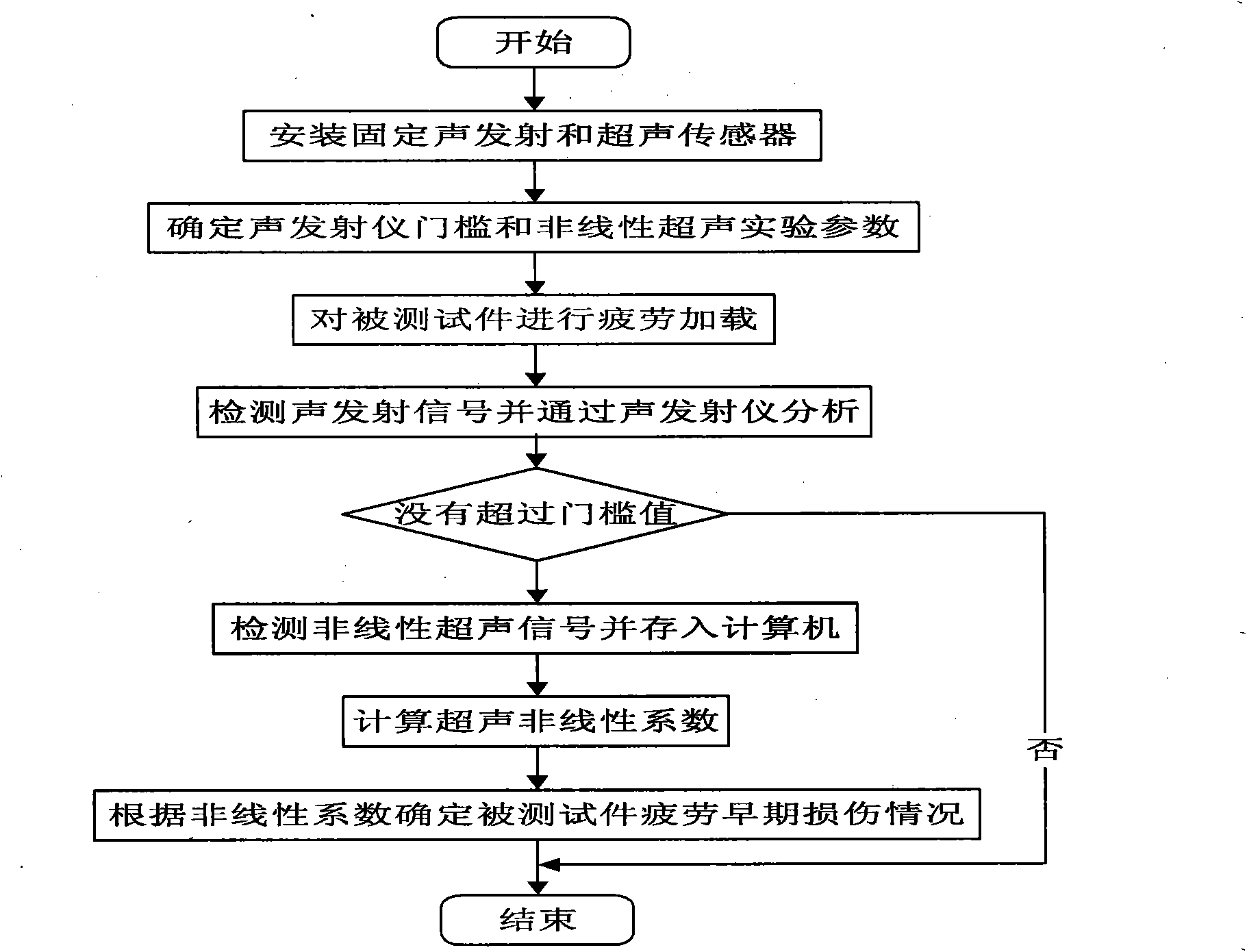
Method for non-linear ultrasonic online detection of early fatigue damage to metal material
InactiveCN101806778ARealize the whole process of fatigue detectionSolve misjudgmentMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesFatigue damageSonification
A method for the non-linear ultrasonic online detection of early fatigue damage to a metal material belongs to the field of nondestructive detection. The method comprises the following steps: determining an excitation signal parameter according to the thickness of a tested piece and inputting the parameter to an arbitrary function generator to generate a sound signal; determining a threshold value of an acoustic emission instrument according to the amplitude of a no-load noise signal; performing fatigue loading on the tested piece, continuously detecting an acoustic emission signal in real time with an acoustic emission sensor, amplifying the acoustic emission signal, inputting the acoustic emission signal into the acoustic emission instrument, and judging ring with the acoustic emission instrument when the amplitude of the acoustic emission signal exceeds the preset the threshold value of the acoustic emission instrument; detecting a non-linear ultrasonic signal at equal time interval if the acoustic emission instrument does not display the ring or the times of the continuous ring is not more than an empirical value; and stopping detection if the displayed ring times is more than the empirical value, because fatigue cracks are generated and develop. On the basis of non-linear ultrasonic nondestructive detection, the method of the invention introduces acoustic emission technique, so the method does not make incorrect judgment when detecting the early fatigue damage to the metal material and realizes continuous online detection.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
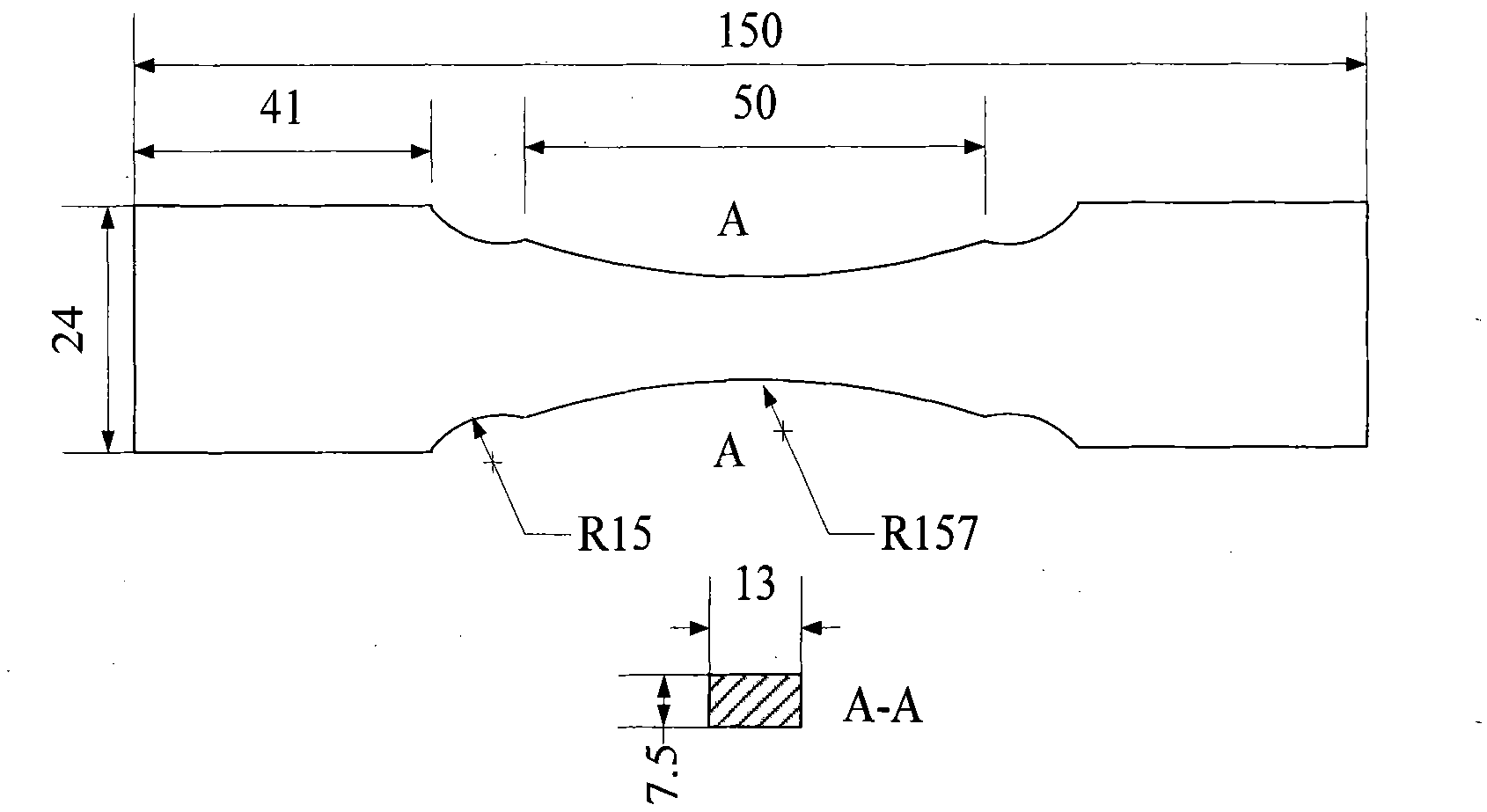
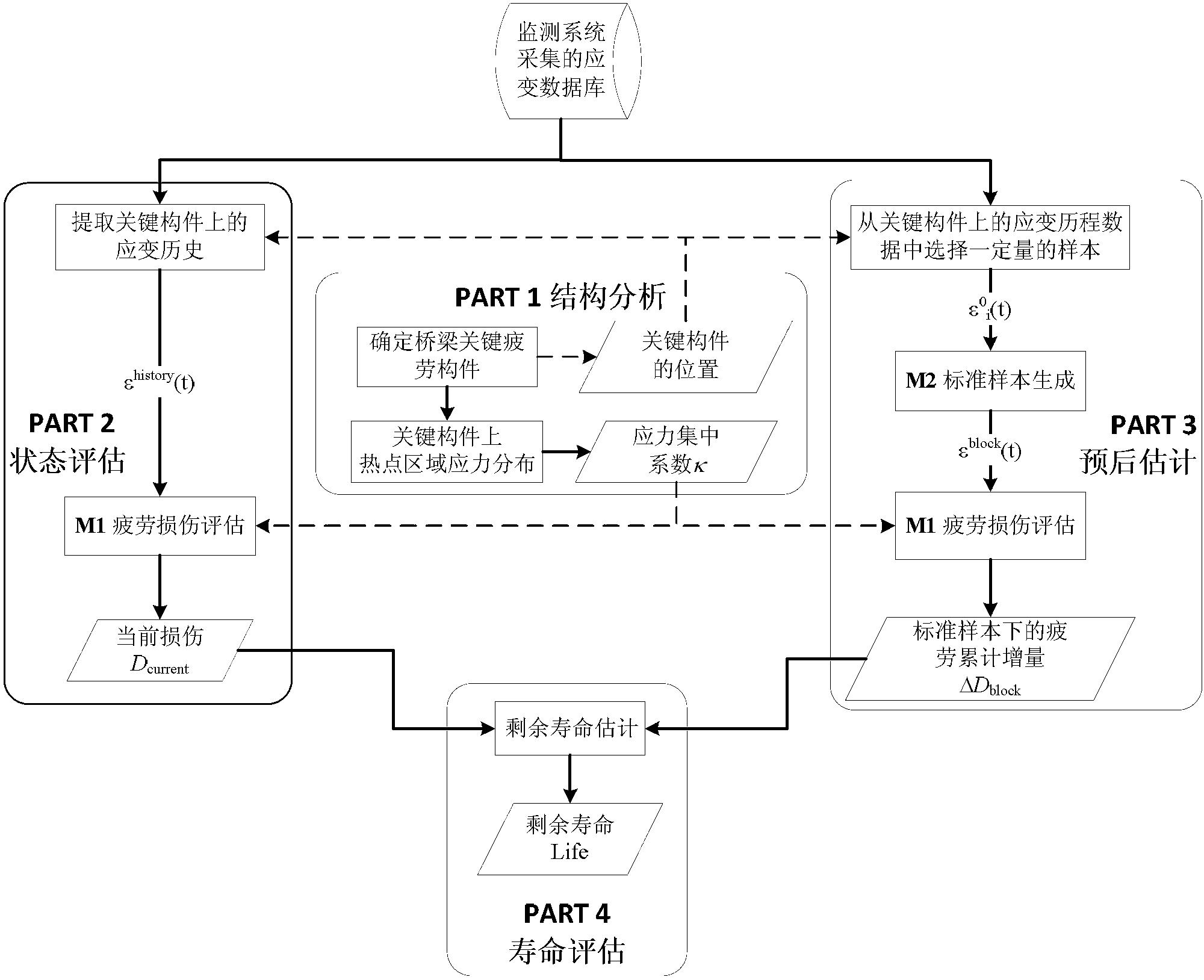
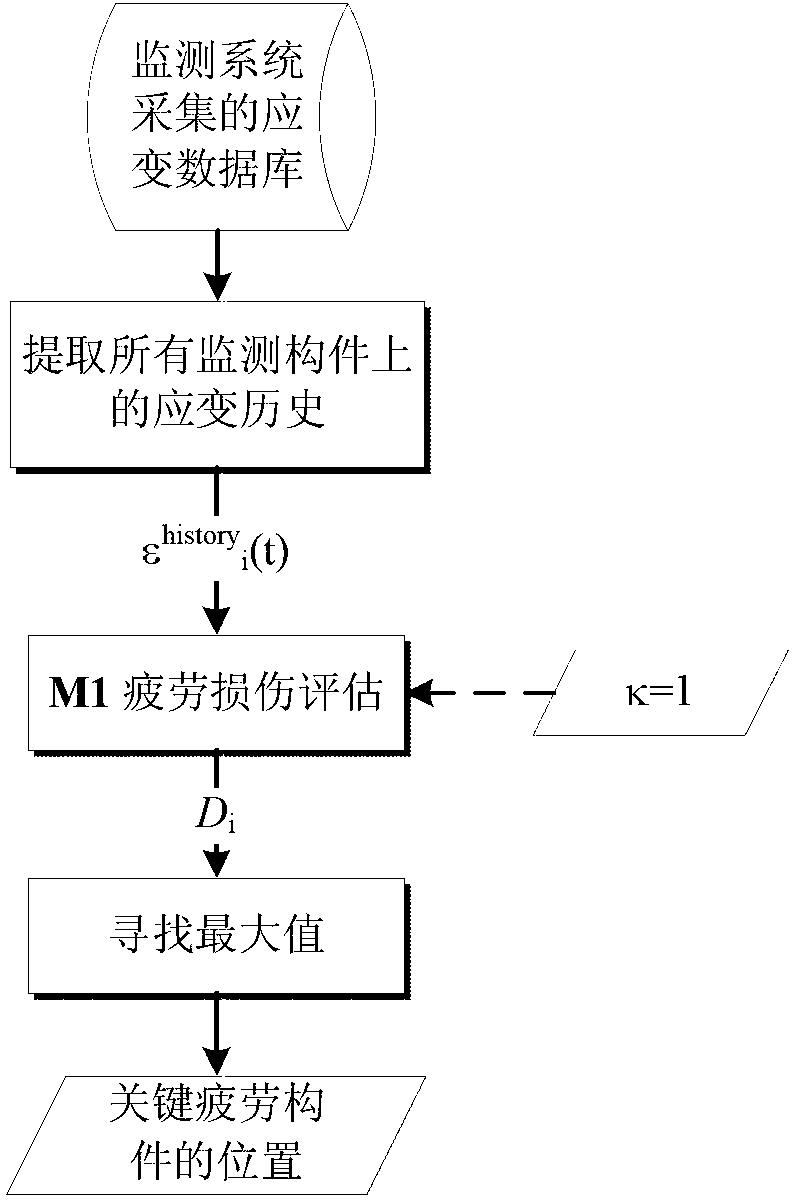
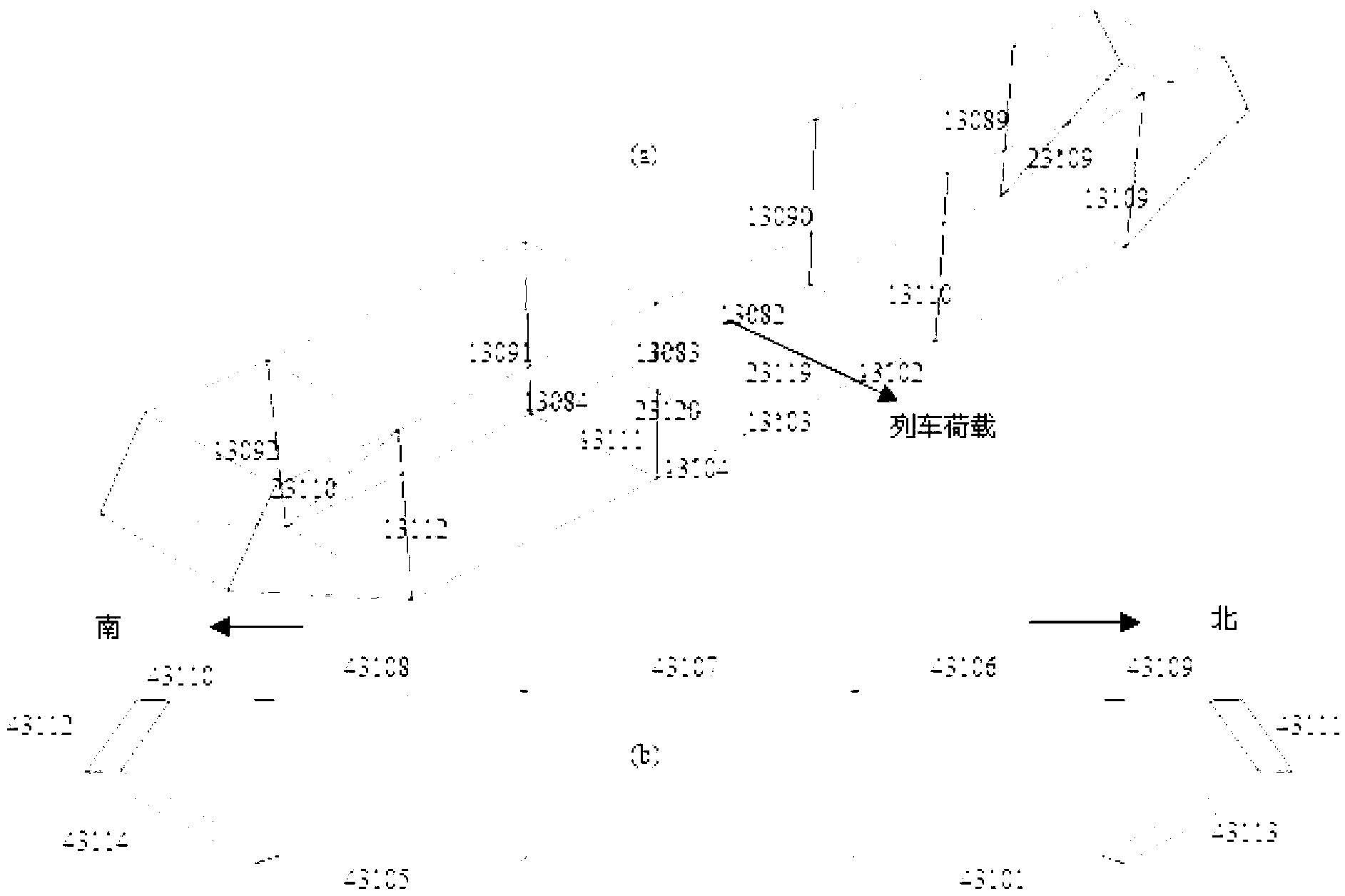
Bridge fatigue damage state and residual life evaluating method
InactiveCN103293014AEstimated remaining lifeStructural/machines measurementFatigue damageEvaluation result
The invention discloses a bridge fatigue damage state and residual life evaluating method which is used for evaluating fatigue damage states of a bridge on the basis of acquired strain data of a large-span bridge health testing system and estimating the residual life of the bridge through prognostic estimation. The bridge fatigue damage state and residual life evaluating method includes mutually linked steps of P1) analysis of bridge structure; P2) evaluation of the current damage state of the bridge; P3) prognostic estimation of the bridge damages; P4) evaluation of the residual life of the bridge, wherein the fatigue damage state obtained in the P2) and the residual fatigue life obtained in the P4) are evaluation results. The bridge fatigue damage state and residual life evaluating method can regularly evaluate and update the fatigue damage states of the bridge and simultaneously estimates the residual life of the bridge in the bridge operating environment, and provide reference for decision making of bridge operators. Furthermore, the evaluation results are beneficial for verification and correction design requirements.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
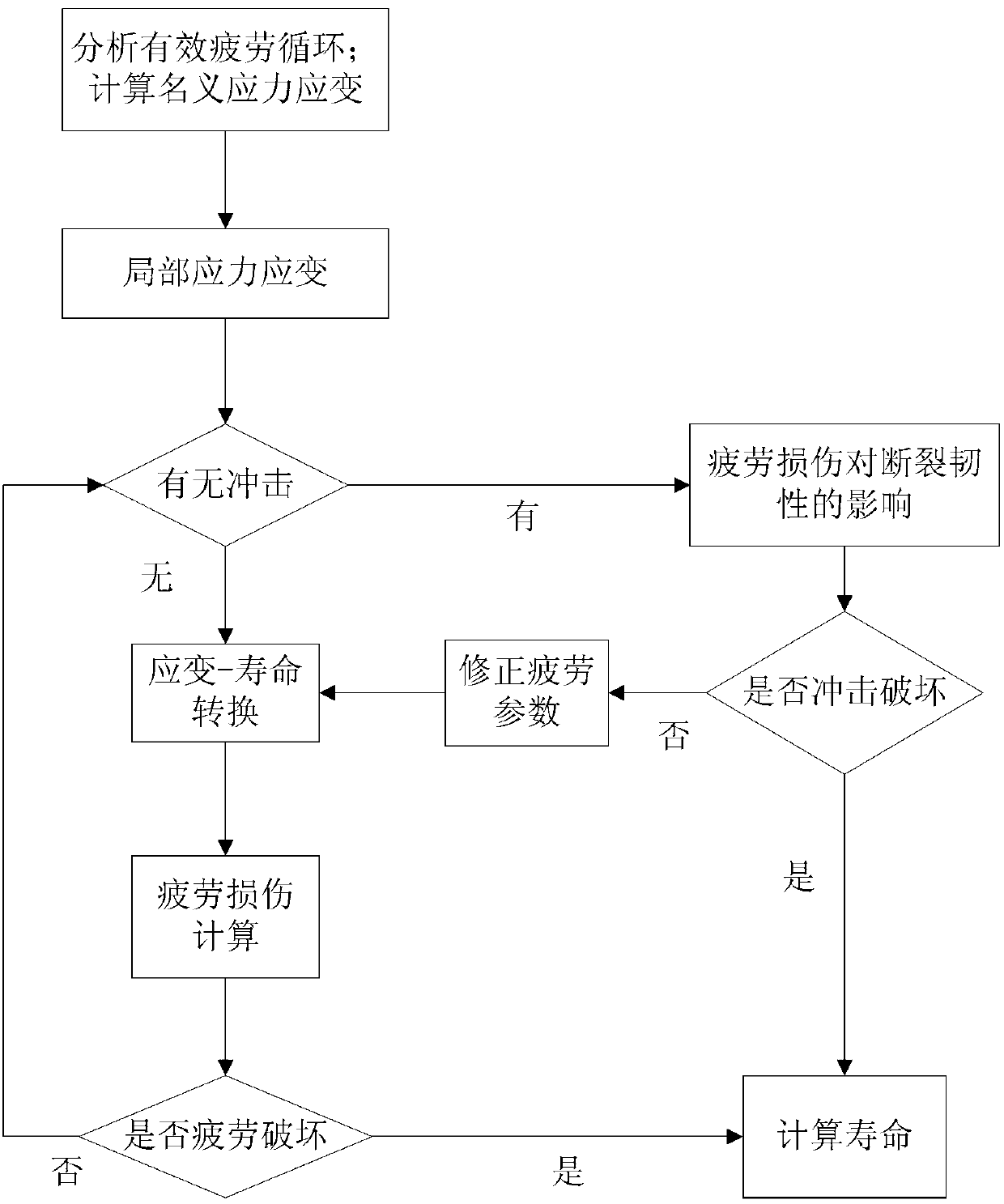
Damage calculation method for low-cycle fatigue and high-strength impact coupling based on local stress strain method
InactiveCN103344515AAccurate fatigue damage analysis resultsMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesFatigue damageFatigue loading
The invention relates to a damage calculation method for low-cycle fatigue and high-strength impact coupling based on a local stress strain method. The damage calculation method comprises the following steps of: (1) analyzing a fatigue load spectrum, calculating nominal stress strain of each stage of multiple stages of amplitude-variable fatigue load spectra, and converting the nominal stress strain into local stress strain; (2) calculating fatigue life and damage corresponding to each stage of fatigue load local strain when a product is impacted; (3) calculating the fatigue life and the damage corresponding to each stage of the fatigue load local strain when the product is impacted and the impact is in an influence range, and considering the damage probability in a fatigue circulation unit when the product is impacted; (4) calculating impact performance influenced by fatigue accumulated damage; and (5) calculating comprehensive degree of reliability. Compared with a conventional fatigue damage calculation method, the damage calculation method has the advantages that the influence of high-strength impact on the fatigue damage, the influence of fracture failure caused by direct impact to the life of the product and the influence of the fatigue accumulated damage to the shock resistance of the product are considered, and the fatigue-impact life and the degree of reliability of the product can be well evaluated under a complex environment.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and device for determining foreign matter or defect of multiple filled containers
ActiveCN101061382AImage analysisOptically investigating flaws/contaminationFatigue damageForeign matter
A method for repairing a damaged portion of a combustor inner liner assembly. The method includes removing the combustor from a gas turbine engine. After inspecting the combustor to determine whether cracks exists in portions of the inner liner assembly, the method includes removing a cracked inner liner assembly from the combustor. Then the portion of the inner liner assembly, comprising a multi-hole panel region, an aft lip region, an aft seal flange region and an aft panel support leg are separated from the inner liner assembly. The multi-hole panel region and aft lip, where fatigue damage typically exists, along with the aft seal flange region, are discarded and a new aft lip region / aft seal flange region and multi-hole panel region are provided. The new parts are joined to the aft panel support leg and the inner liner assembly aft of forward bolt flange region after these parts are refurbished. The inner liner assembly is then reattached to the combustor and reassembled into the engine.
Owner:MOELLER & DEVICON
Method for analyzing vortex vibration and fatigue of depth tension-type vertical pipe
A method for analyzing vortex vibration and fatigue of a depth tension-type vertical pipe, which relates to the field of depth vertical pipe design, comprises the following specific steps of: step 1. obtaining flow field data; step 2. substituting the flow field data into vertical pipe vibration equations 6 and 7; step 3. solving the equations 6 and 7 by using a finite element method, and obtaining calculation results including displacement, velocity, accelerated velocity and stress time interval; and step 4. counting stress cycle number n(i) of an amplitude within a certain time by adopting a rain-flow counting method according to the calculation results, and substituting the n(i) into a fatigue damage calculation formula 8 to calculate the fatigue damage. The method for analyzing vortex vibration and fatigue of the depth tension-type vertical pipe improves the accuracy of stress calculation by adopting a practical pipe-in-pipe model and simultaneously considering direct flow vibration and cross flow vibration.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
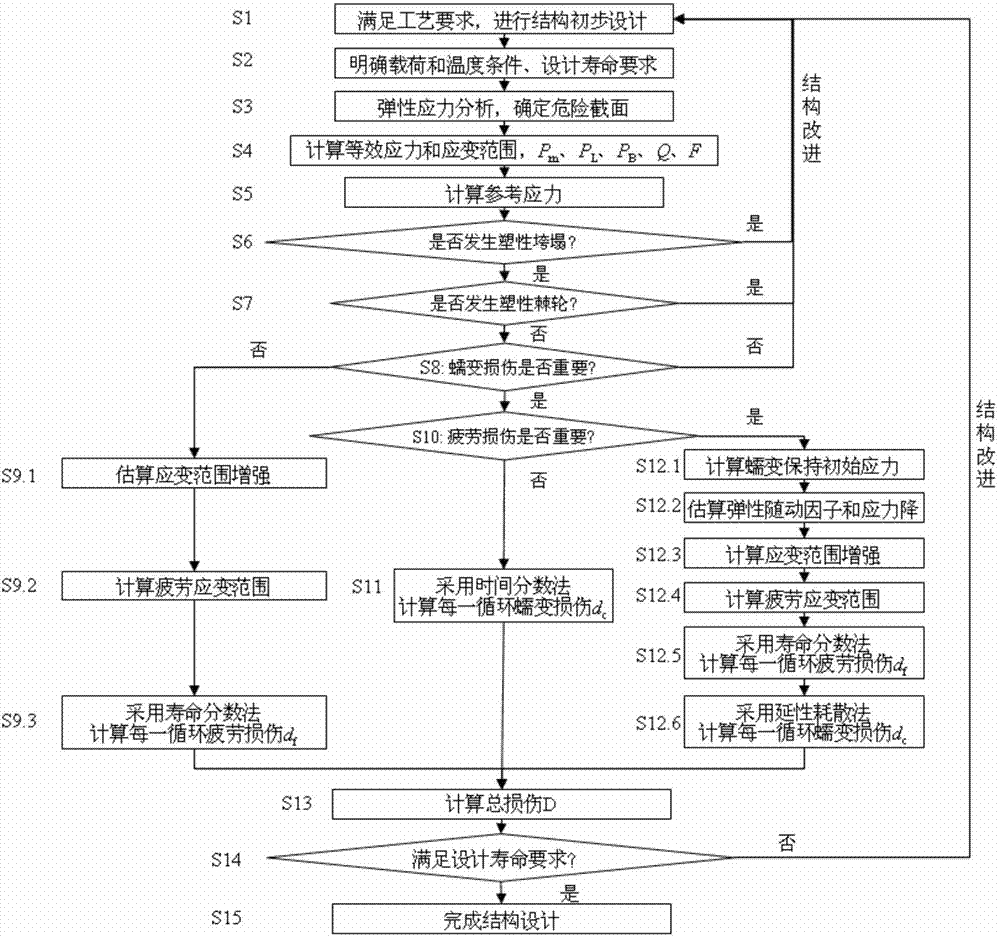
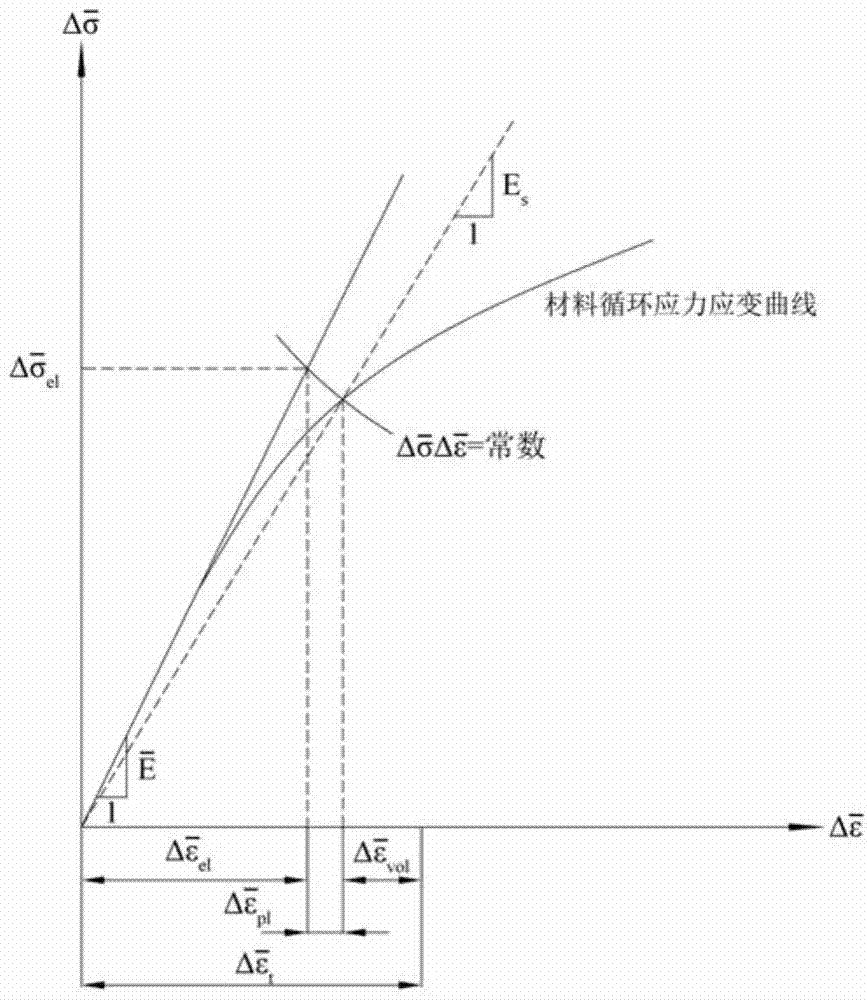
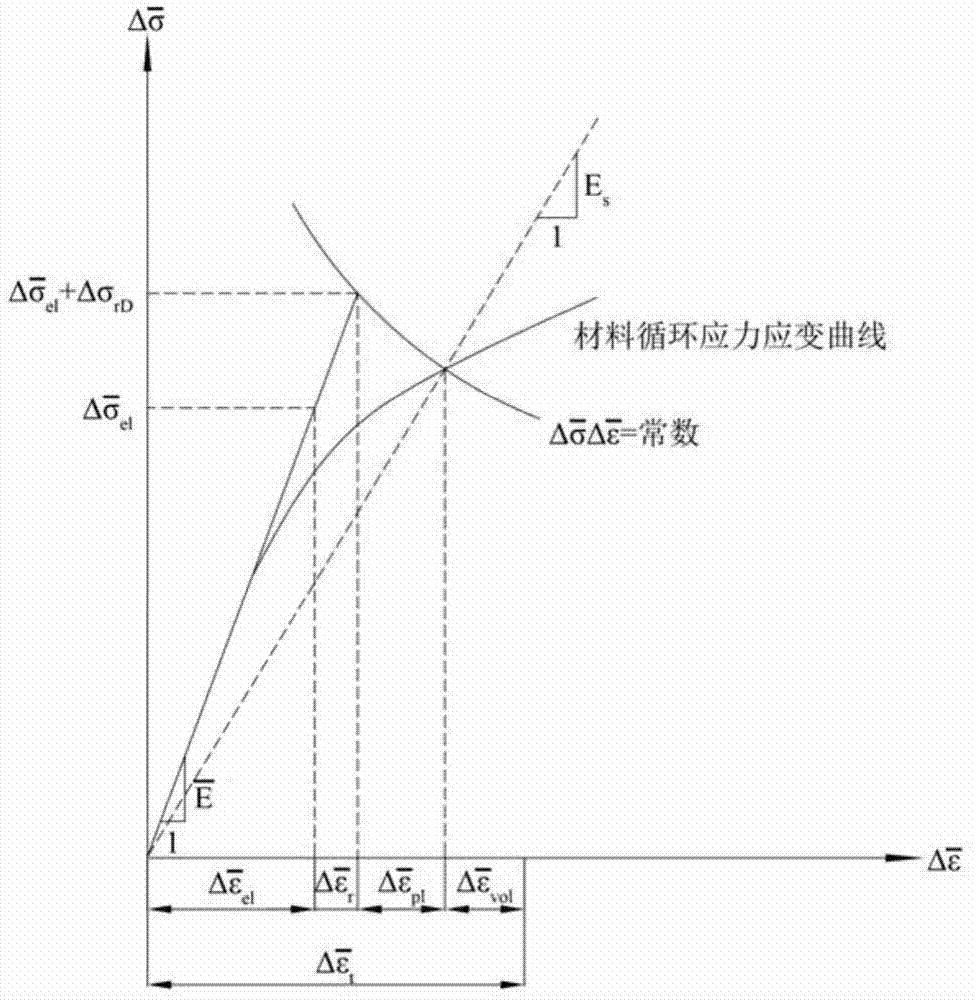
Service life based high-temperature container creep fatigue strength design method
The invention discloses a service life based high-temperature container creep fatigue strength design method. The method comprises the steps of 1, performing structure preliminary design; 2 determining load and temperature conditions and the design service life requirement; 3, determining dangerous sections; 4, calculating the equivalent stress and strain range; 5, calculating reference stress; 6, determining whether plastic collapse occurs; 7 determining whether the plastic ratchet occur; 8, determining whether creep damage is important; 9, estimating fatigue damage of each cycle when the creep damage is not important; 10, determining whether the fatigue damage is important; 11, estimating the creep damage when the fatigue damage is not important; 12, estimating damage of each cycle when the creep damage and the fatigue damage are non-ignorable; 13, estimating creep-fatigue total damage; 14, performing result analysis and structural design improvement; 15, completing structural design. According to the method, the foundation is laid for national establishing of creep and fatigue failure mode based high-temperature pressure container design standards and achieving design and manufacture of high-temperature pressure containers according to the service life.
Owner:HEFEI GENERAL MACHINERY RES INST
Asphalt mixture life prediction method considering fatigue-creep interaction damage effect
InactiveCN103630450AImprove scienceEasy to determineMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesFatigue damageRoad engineering
The invention relates to an asphalt mixture life prediction method considering a fatigue-creep interaction damage effect, and belongs to the field of road engineering. The method comprises the following steps: (1) determining a complex modulus of an asphalt mixture under the action of a period load; (2) determining a damage variable of the asphalt mixture; (3) building a creep damage equation and a fatigue damage equation of the asphalt mixture respectively; (4) building an asphalt mixture life prediction model under the combined action of creep damage and fatigue damage. Compared with a conventional asphalt mixture life prediction method, the viscoelastic behavior of the asphalt mixture is considered and a more accurate prediction model is built. The method accurately describes asphalt mixture damage failure process and rule, has the advantages of wide application range and reliable calculation results, and provides a more reliable method for structural design of an asphalt pavement.
Owner:云南交投集团公路建设有限公司
Pearlite steel rail of high internal hardness type excellent in wear resistance and fatigue failure resistance and process for production of the same
ActiveCN101646795AStable manufacturingExcellent wear resistanceFurnace typesMetal rolling arrangementsFatigue damageHardness
The invention provides a pearlite steel rail of high internal hardness type which is excellent in both wear resistance and fatigue failure resistance and a process suitable for the production of the rail. Specifically, a pearlite steel rail which has a composition containing by mass C: 0.73 to 0.85%, Si: 0.5 to 0.75%, Mn: 0.3 to 1.0%, P: 0.035% or below, S: 0.0005 to 0.012% and Cr: 0.2 to 1.3% with the balance consisting of Fe and unavoidable impurities and having a ¢%Mn! / ¢%Cr! ratio of 0.3 or above and below 1.0 (wherein ¢%Mn! is Mn content and ¢%Cr! is Cr content) and whose railhead exhibitsan internal hardness of Hv380 or above and below Hv480 in terms of Vickers hardness (Hv)in a depth range of at least 25mm from the railhead surface.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Recuperator and turbine support adapter for recuperated gas turbine engines
A recuperator and turbine support adapter for securing a recuperator to a combustor case is provided. The recuperator and turbine support adapter comprises an outer strutted body, an inner strutted body and a thermal spring. The thermal spring allows for thermal expansion of the recuperator and turbine support adapter while alleviating any stress or fatigue damage to the adapter. Each of the outer strutted bodies further comprises an outer ring and an inner ring connected by a plurality of struts. The recuperator and turbine support adapter also provides a means of directing the flow of cold compressed air to the recuperator and the return of the recuperator heated air to the combustor / turbine module.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Fatigue damage resistant wire and method of production thereof
Fatigue damage resistant metal or metal alloy wires have a submicron-scale or nanograin microstructure that demonstrates improved fatigue damage resistance properties, and methods for manufacturing such wires. The present method may be used to form a wire having a nanograin microstructure characterized by a mean grain size that is 500 nm or less, in which the wire demonstrates improved fatigue damage resistance. Wire manufactured in accordance with the present process may show improvement in one or more other material properties, such as ultimate strength, unloading plateau strength, permanent set, ductility, and recoverable strain, for example. Wire manufactured in accordance with the present process is suitable for use in a medical device, or other high end application.
Owner:FORT WAYNE METALS RES PROD CORP
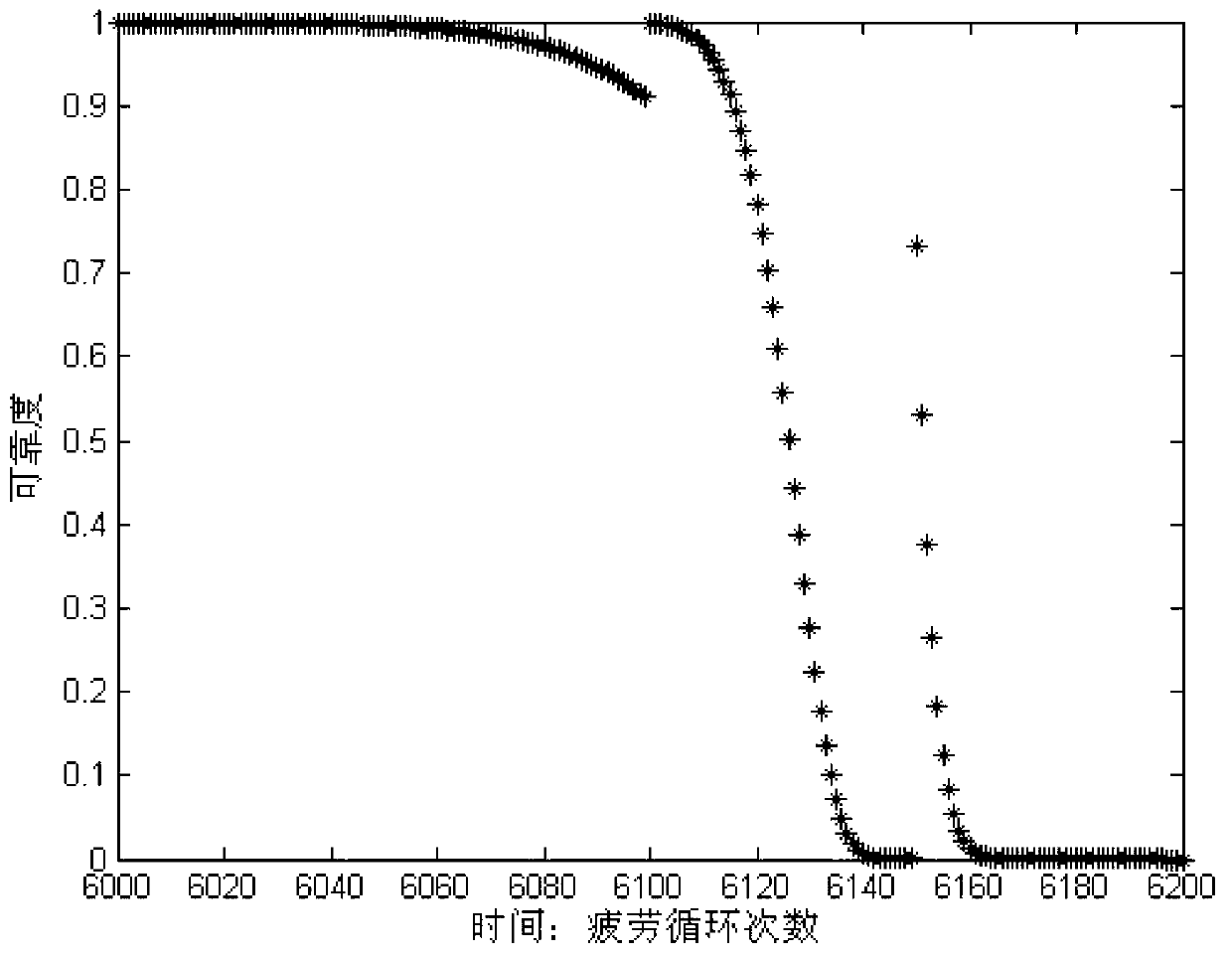
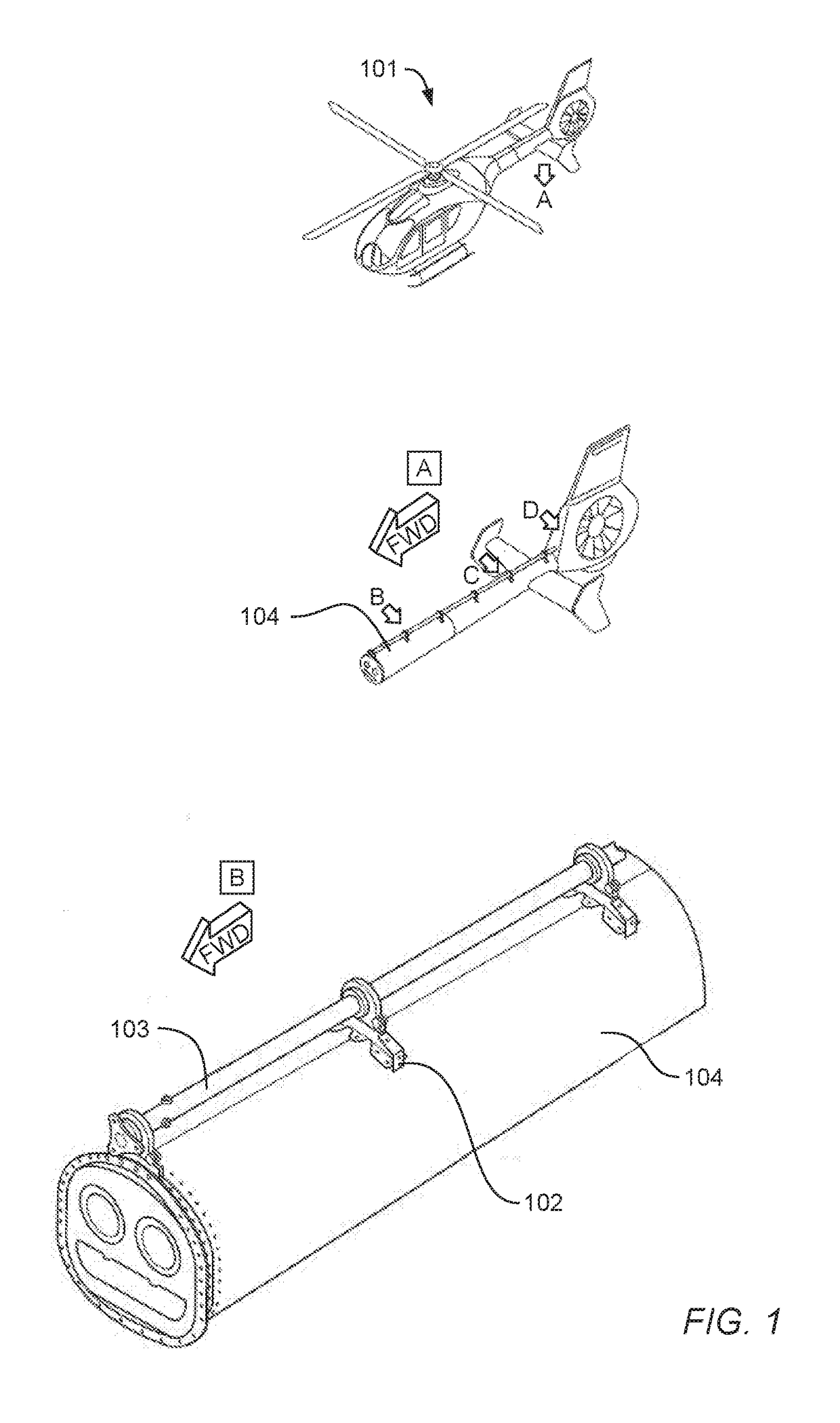
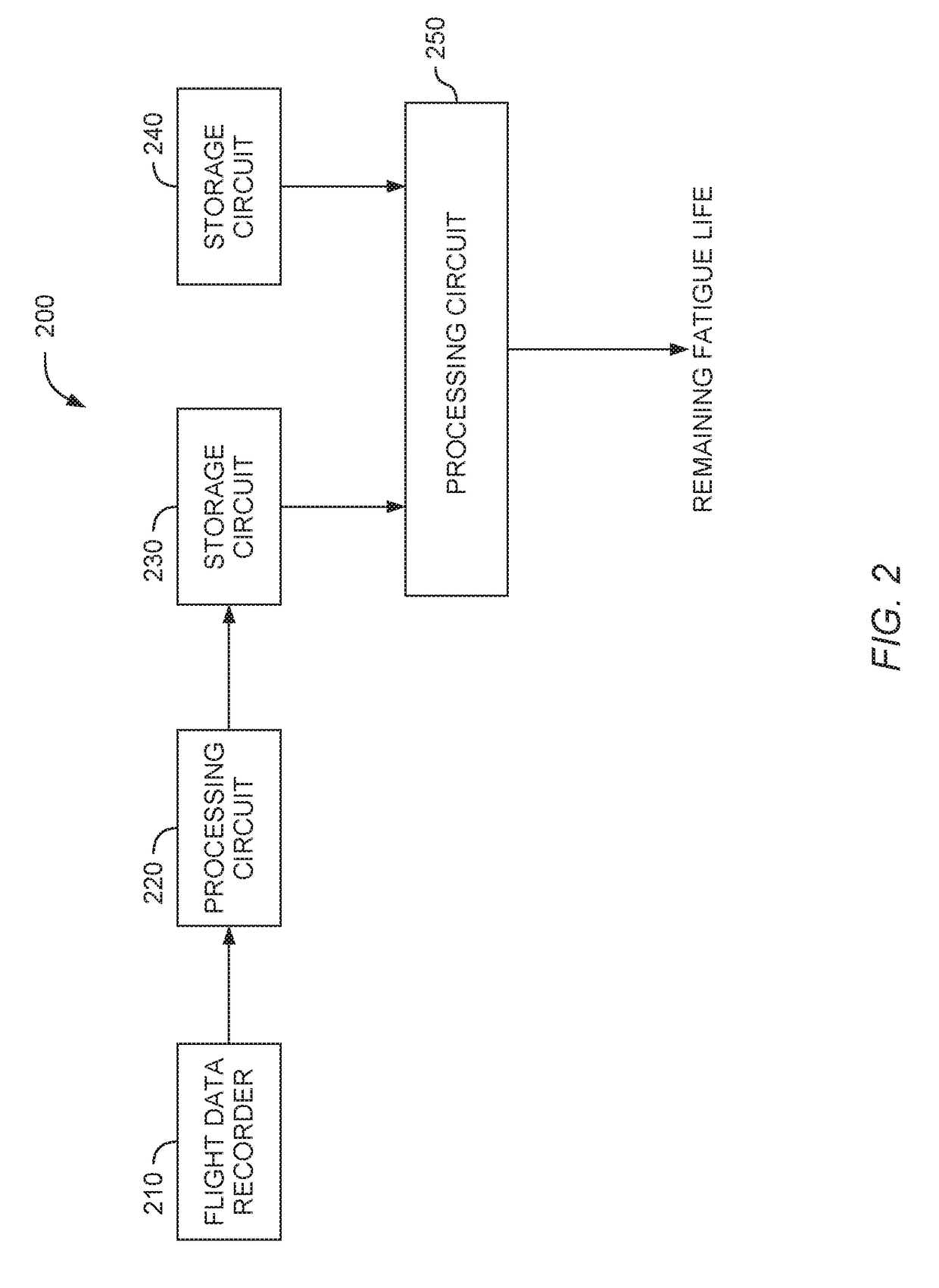
Probabilistic load and damage modeling for fatigue life management
A fatigue life management system for determining a remaining fatigue life of a component of an aircraft. The fatigue life management system may generate probability density functions of minimum load, maximum load, and timeframe damage for predetermined time intervals based on selected flight data of the aircraft and regression models for probabilistic prediction of minimum load, maximum load, and timeframe damage of the component. The fatigue life management system may further compute an accumulated fatigue damage estimation based on the probability density functions and a probabilistic fatigue strength model. The fatigue life management system may then generate a distribution of the accumulated fatigue damage estimation of the component. If desired, the processing circuit may compare the distribution of the accumulated fatigue damage estimation with a reliability requirement to determine the remaining fatigue life of the component.
Owner:AIRBUS HELICOPTERS DEUT GMBH
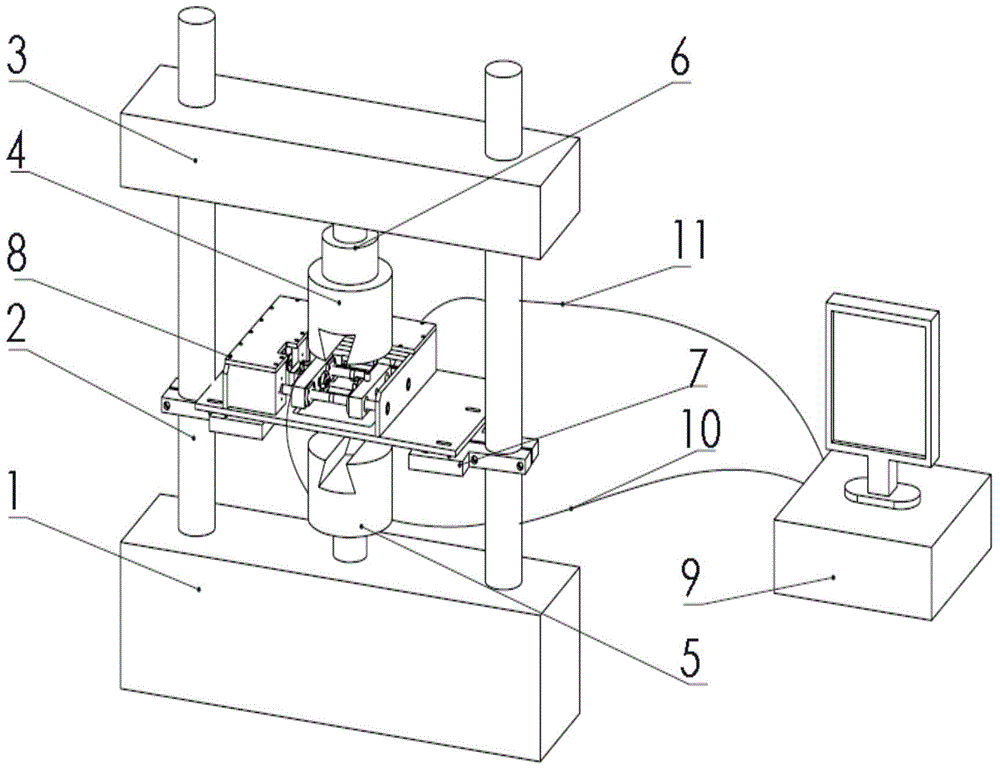
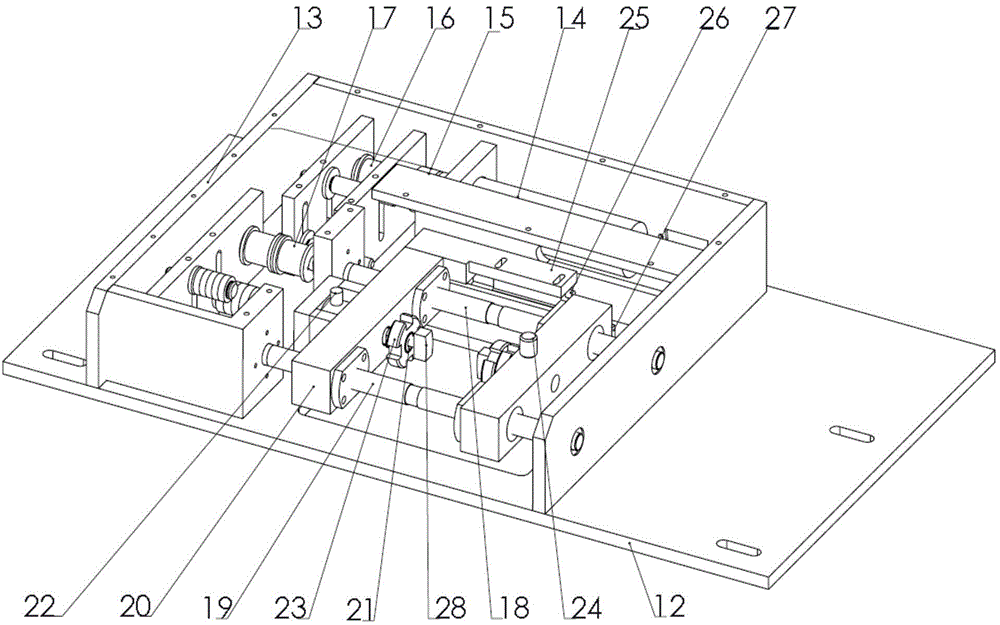
Fretting fatigue testing method allowing contact load to be adjusted in real time and testing machine adopting fretting fatigue testing method
InactiveCN104931366ASolve the problem that the fretting fatigue test that cannot simulate the component subjected to alternating contact loadsGood repeatabilityMachine part testingMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesFatigue damageMotor drive
The invention relates to a fretting fatigue testing method allowing a contact load to be adjusted in real time and a testing machine adopting the fretting fatigue testing method. The testing machine comprises an electronic-hydraulic servo fatigue testing machine, fretting supporting platforms, a fretting device and a computer testing and controlling system, wherein the fretting supporting platforms are fixed on supporting stand columns of the fatigue testing machine; the fretting device is horizontally arranged on the fretting supporting platform; the fatigue testing machine comprises an upper clamp and a lower clamp which are used for fixing a test piece; a contact load sensor, a motor drive signal and a displacement signal of the fretting device are connected with a computer data acquisition control system. Two fretting pad clamps are fixed in middles of two lead screw cross beams, and two opposite fretting pads are mounted at two ends of each fretting pad clamp. A fretting fatigue test with the contact load changing in real time is performed through the fretting fatigue testing machine, influences of the contact load on fretting fatigue damage are researched, meanwhile, fretting fatigue tests at different amplitudes and frequencies can be researched, and an experiment method is provided for deeper understanding of a fretting fatigue damage mechanism.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Evaluation method for fatigue damage and service life of horizontal axis wind turbine blade
ActiveCN102607831AGet actual lifespanShort cycleMachine part testingStrength propertiesFatigue damageImpeller
The invention discloses a test method for the fatigue damage and the service life of a horizontal axis wind turbine blade, aiming to obtain a more exact blade fatigue performance parameter by adopting a test detection and computational analysis means having low cost and high efficiency so as to meet the requirements of blade design, research and development and detection. The method is characterized in that on the basis of the characteristic that the impeller speed of a horizontal axis wind turbine is lower, and the period change frequency of various fatigue loads is also lower, a series of steps of carrying out static loading testing on the wind turbine blade to obtain a stress / strain amplitude distribution condition under the effect of various fatigue loads and analyzing by combining a material property curve and a cumulative damage theory are adopted to realize the evaluation to the blade fatigue performance. Compared with the traditional horizontal axis wind turbine blade fatigue testing technology, the method has the advantages of short period, low cost, capability of obtaining a final service life parameter of the blade, and the like.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
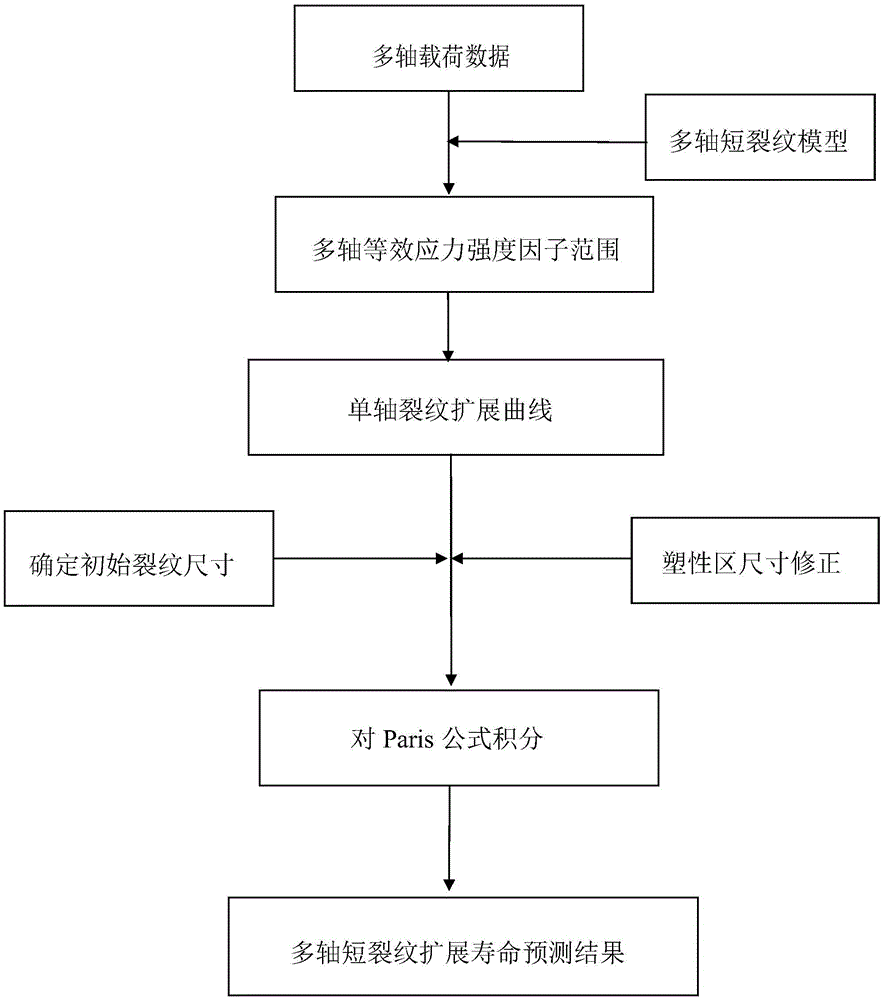
Multiaxial short crack propagation life prediction method based on critical surface method
ActiveCN105466772APromote engineering applicationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady torsional forcesFatigue damageEngineering
The present invention provides a multiaxial short crack propagation life prediction method based on a critical surface method, and relates to the field of multiaxial fatigue strength theory. The algorithm comprises the steps of: (1) selecting a plane, which contains the maximum shearing strain range, as a critical surface, and using the damage parameters on the critical surface to characterize a short crack propagation driving force; (2) based on the shear-type multiaxial fatigue damage parameters, establishing an equivalent crack stress intensity factor applicable to the multiaxial stress state; (3) fitting the short crack propagation rate data under uniaxial loading to obtain an uniaxial short crack propagation curve; and (4) carrying out plastic zone size correction on the crack tip, and calculating the short crack propagation life by a fracture mechanics method. The method can well descript the influence of non-proportional loading on crack propagation. The results show that the method can well predict the short crack propagation life under multiaxial proportional and non-proportional loading.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
A multi-axis creep fatigue prediction method based on ABAQUS
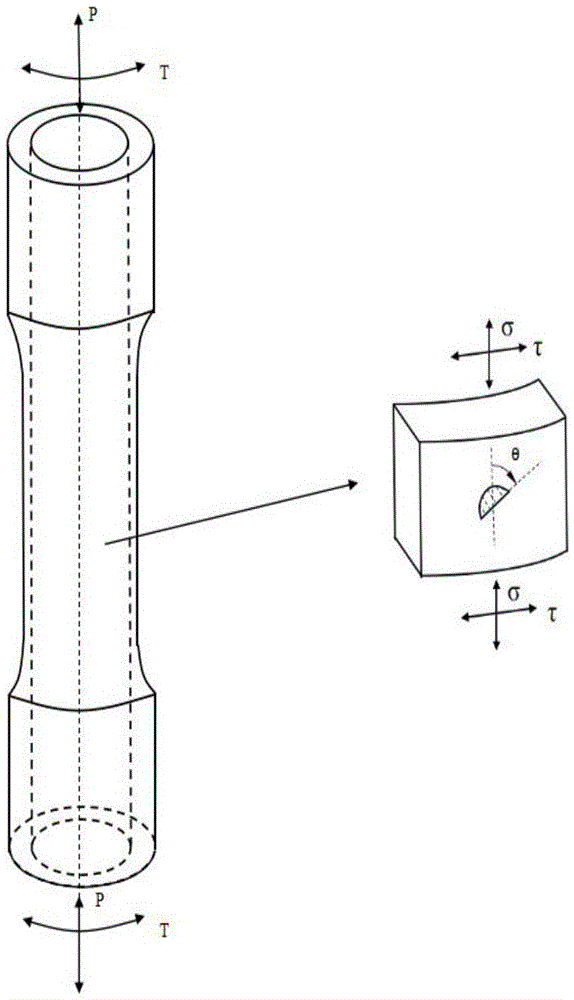
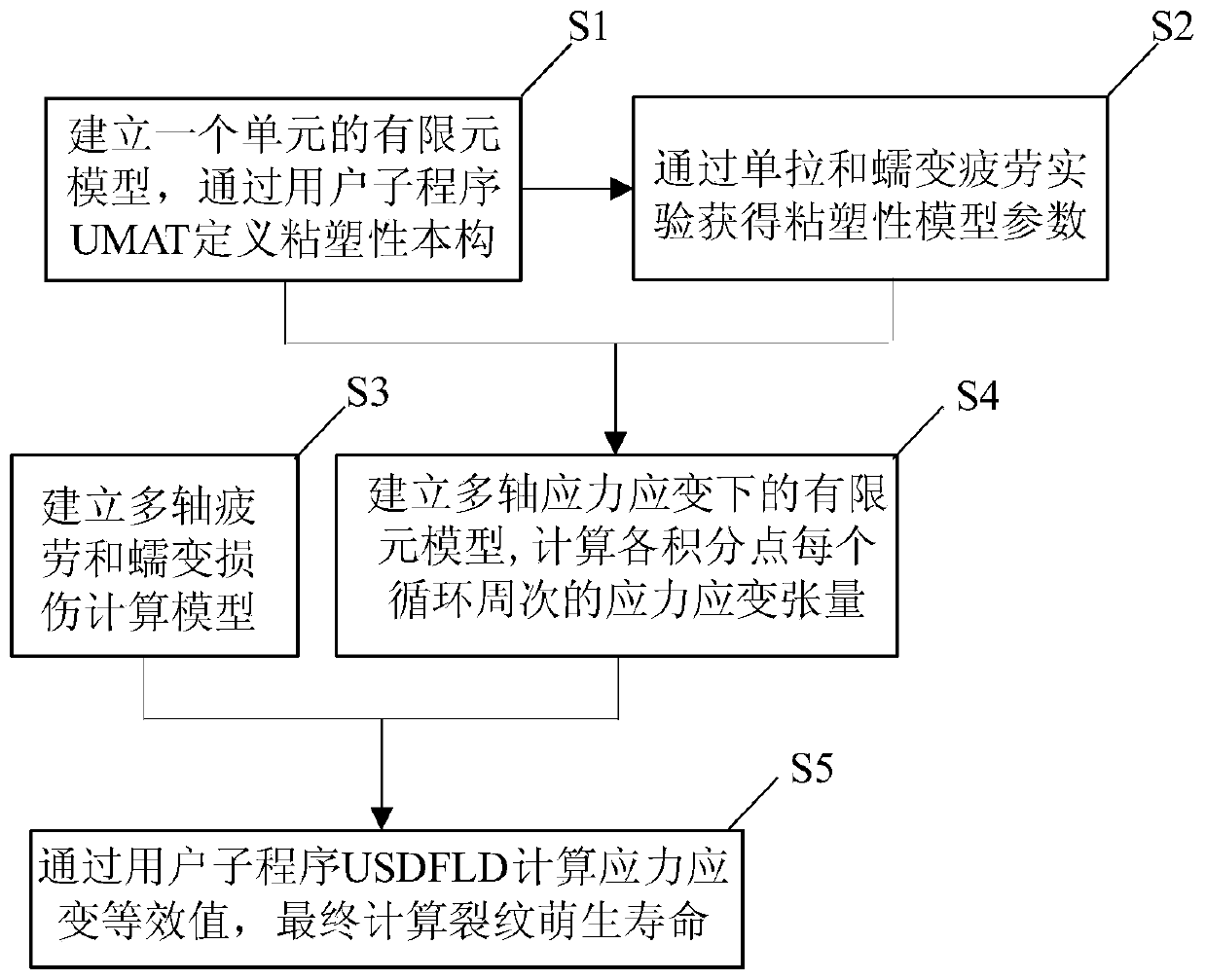
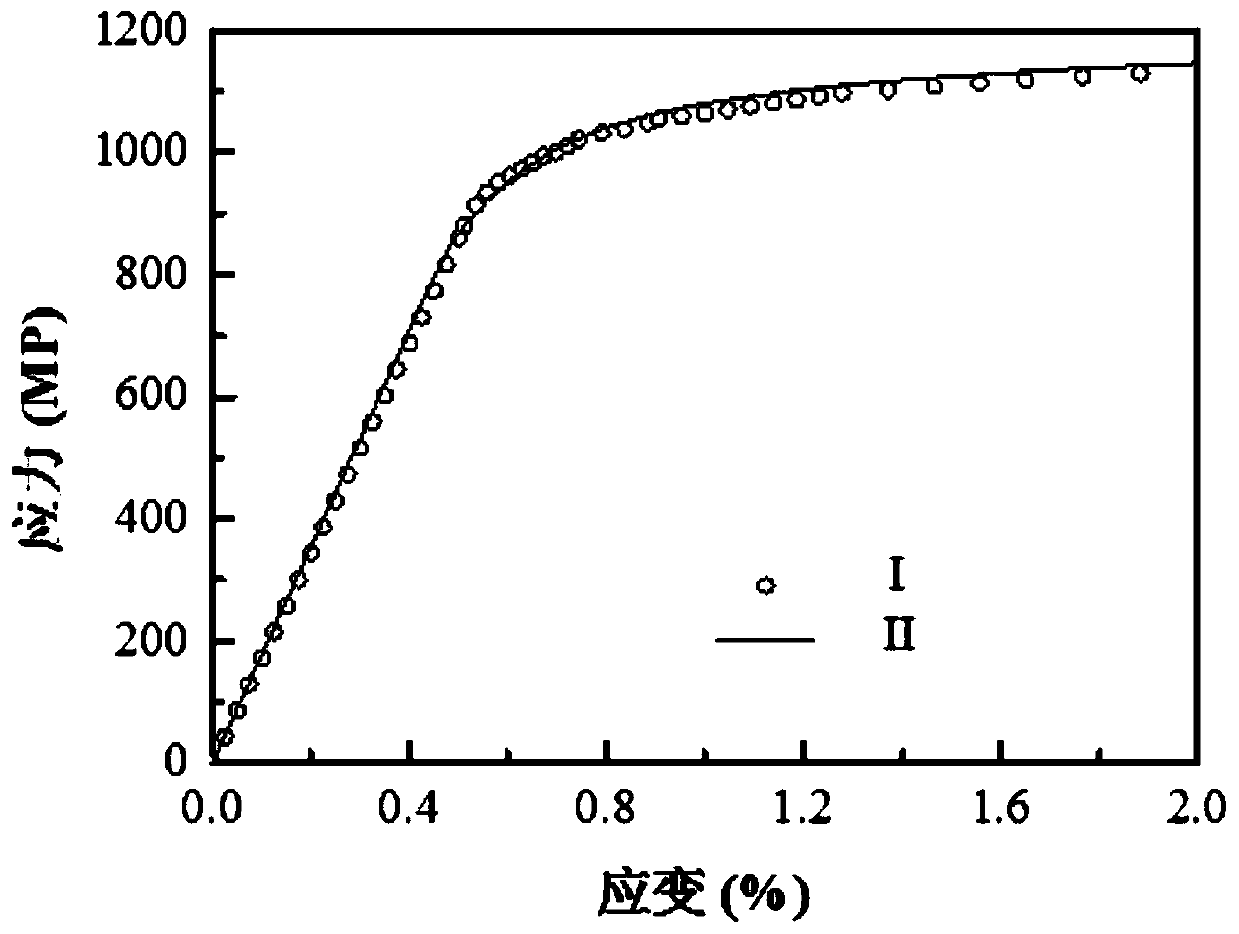
ActiveCN109885874AGain creep damageIntuitiveMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesDesign optimisation/simulationFatigue damageElement model
The invention discloses a multi-axis creep fatigue prediction method based on ABAQUS, and the method comprises the steps of S1, building an ABAQUS finite element model, and defining a viscoplastic constitutive equation of a to-be-tested material through a user subprogram UMAT; S2, determining model parameters required by the viscoplastic constitutive equation; S3, establishing a fatigue damage calculation model and a creep damage calculation model of the multi-axis stress-strain state of the to-be-tested material; S4, establishing an ABAQUS finite element model in a multi-axis stress-strain state, and calculating to obtain a stress-strain tensor of each cycle on the basis of the defined viscoplastic constitutive equation and model parameters; and S5, calculating equivalent stress and equivalent plastic strain through a user subprogram USDFLD, and superposing fatigue damage and creep damage of each cycle through a linear cumulative damage criterion on the basis of the fatigue damage calculation model and the creep damage calculation model in combination with the stress strain tensor to obtain the crack initiation life.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fatigue analysis method and fatigue analysis device of structural member in wind generating set
ActiveCN104573172AStress calculation results are accurateReflect changes in stress stateSpecial data processing applicationsFatigue damageElement model
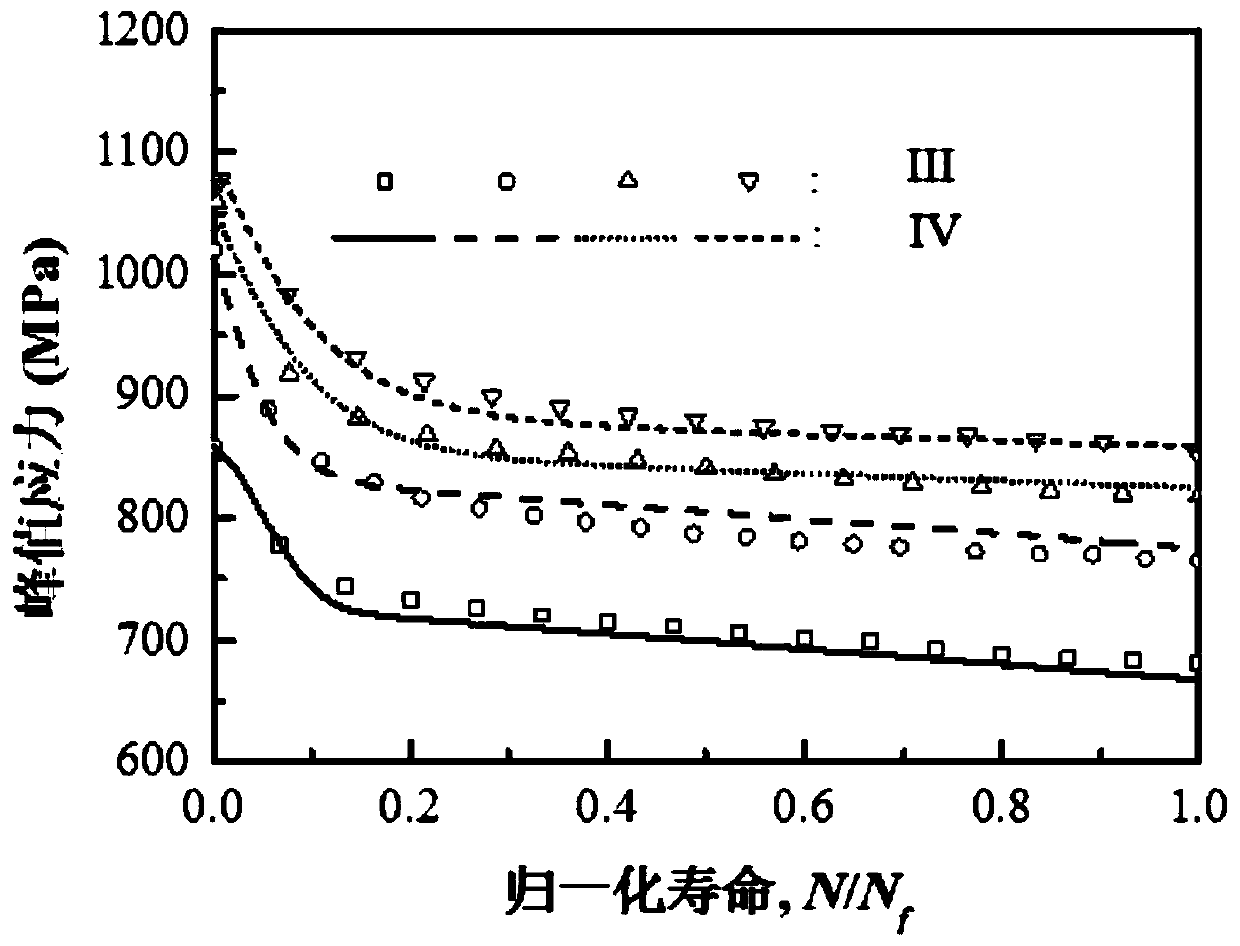
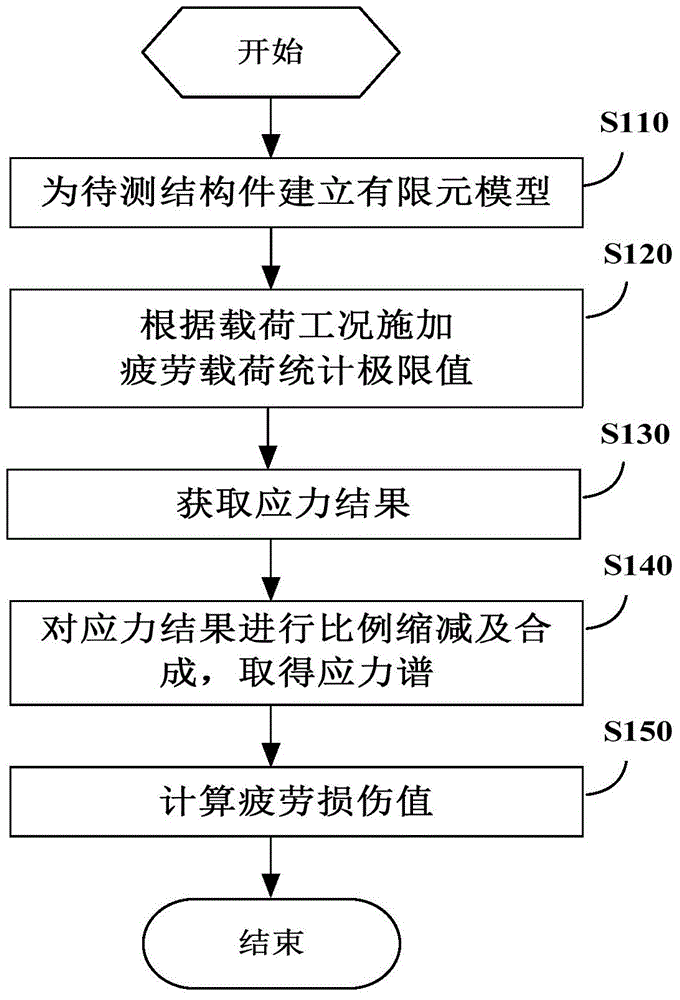
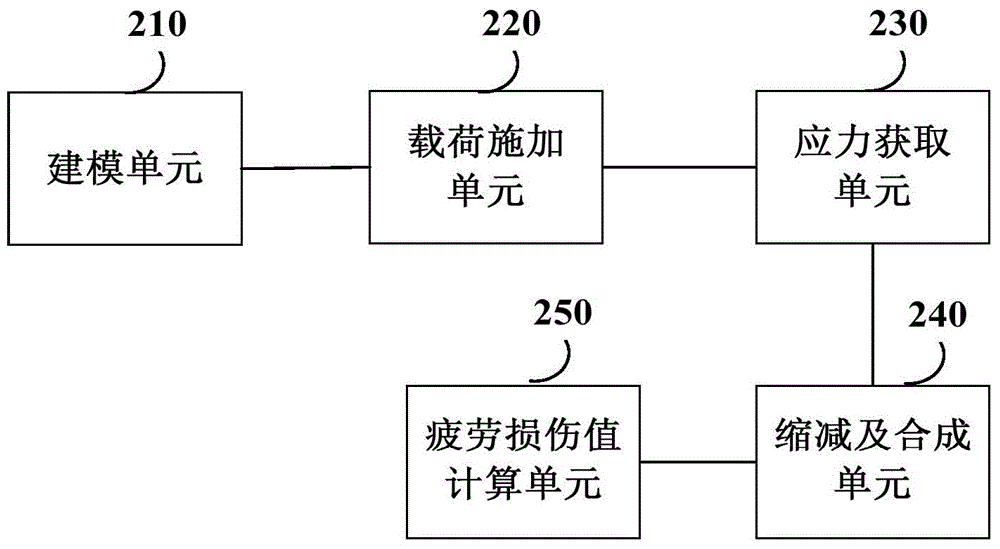
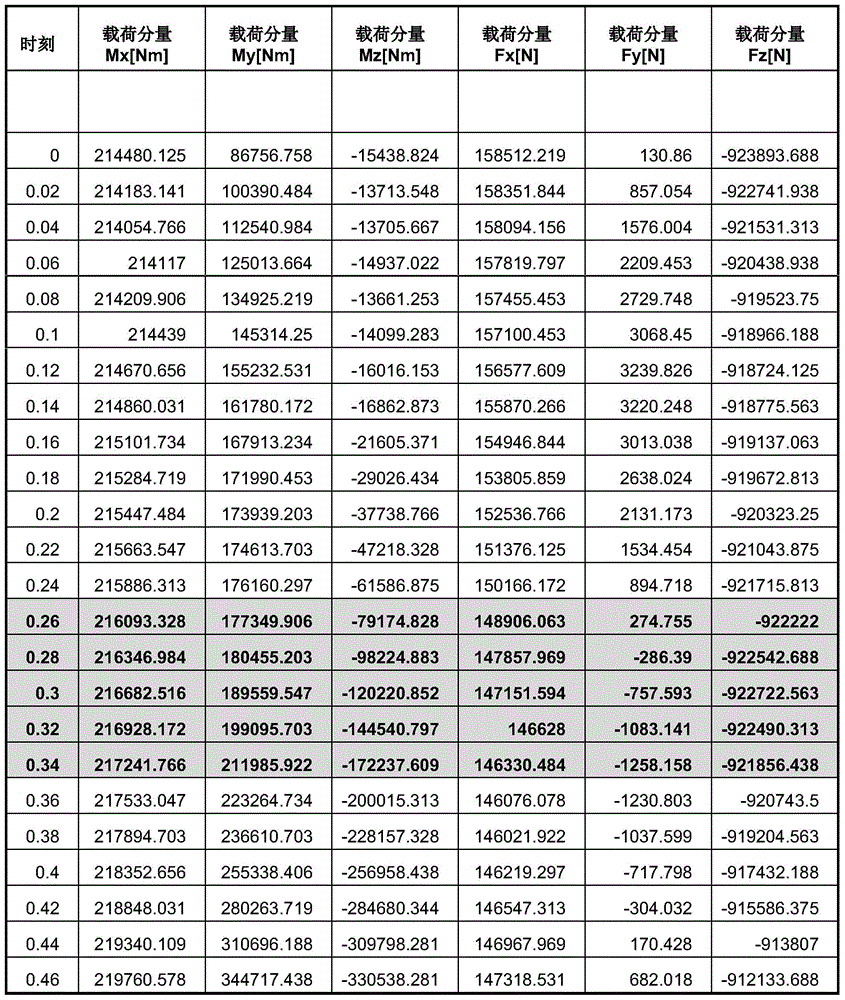
The invention provides a fatigue analysis method and a fatigue analysis device of a structural member in a wind generating set. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a finite element model for a to-be-measured structural member involving bearing connection and related structural members thereof; applying load to the finite element model according to various preset load working conditions respectively; acquiring each node stress result of the to-be-measured structural member under each load working condition through finite element analysis; scaling down the acquired stress results by taking a fatigue load sequence which is pretreated through regularization as a coefficient; synthesizing the stress results under the different load components after scaling down to obtain a stress spectrum of each node of the finite element model of the to-be-measured structural member; calculating a fatigue damage value of the to-be-measured structural member according to the stress spectrum of each node and the stress-life curve of the to-be-measured structural member. By applying the method and the device, the fatigue analysis result of the structural member in the wind generating set is more accurate.
Owner:XINJIANG GOLDWIND SCI & TECH
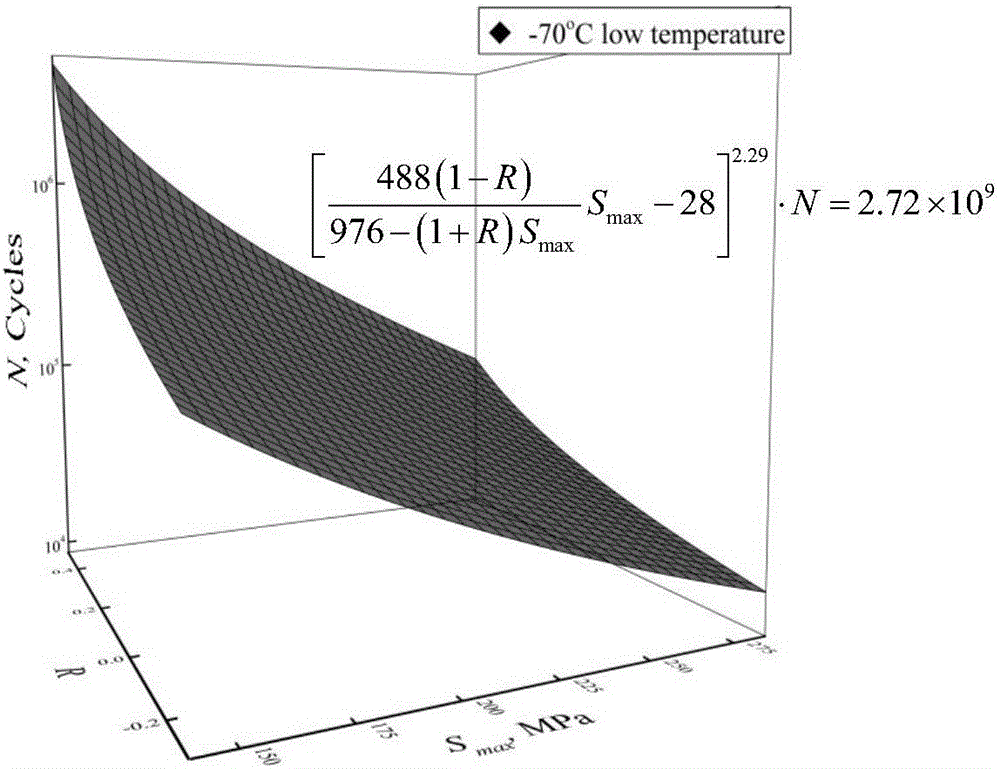
Low-temperature fatigue property characterization and life estimation method
The invention discloses a low-temperature fatigue property characterization and life estimation method. The method comprises three major steps of step 1, through considering the influence of a stress ratio, deriving an S-N-R curved surface characterizing the fatigue property by adopting a Goodman equilife curve based on a three-parameter power function expression, and performing data processing by virtue of a linear regression theory; step 2, through considering an interaction effect of loads under spectrum loading, proposing a corrected spectrum loading fatigue life estimation model based on a Willenborg / Chang model and a crack tip plastic zone theory, and giving out a fatigue damage increment representation method; and step 3, calculating the low-temperature spectrum loading fatigue life of a material by adopting an accumulative damage theory. The method is simple and practical; and a low-temperature fatigue property characterization model can be constructed only by a constant-load fatigue property curved surface and an actually measured flight load spectrum of the material in a low-temperature environment, and the spectrum loading fatigue life is estimated, so that the method has important academic meanings and engineering application values.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
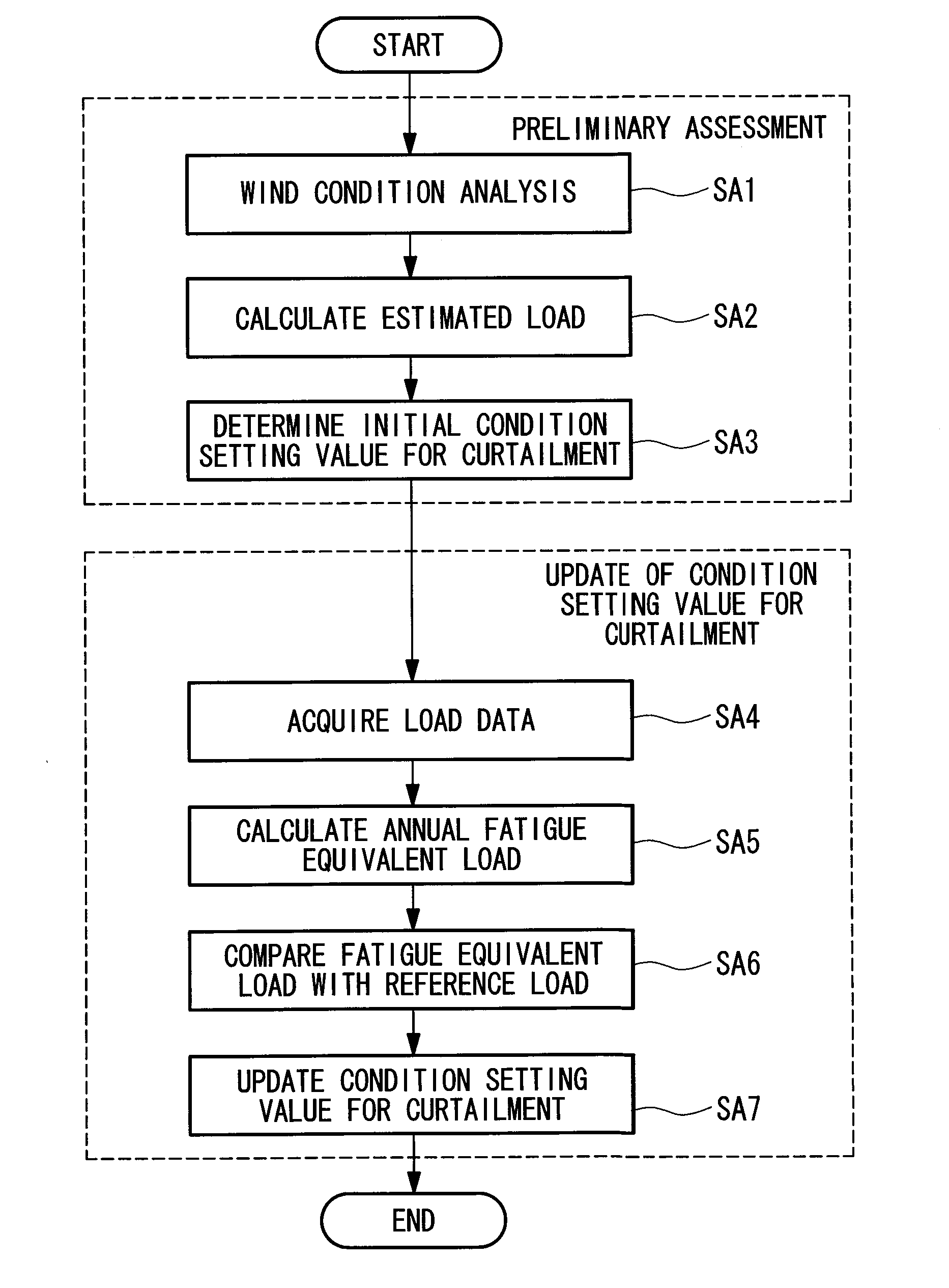
Device and method of adjusting curtailment strategy for wind turbine, and program
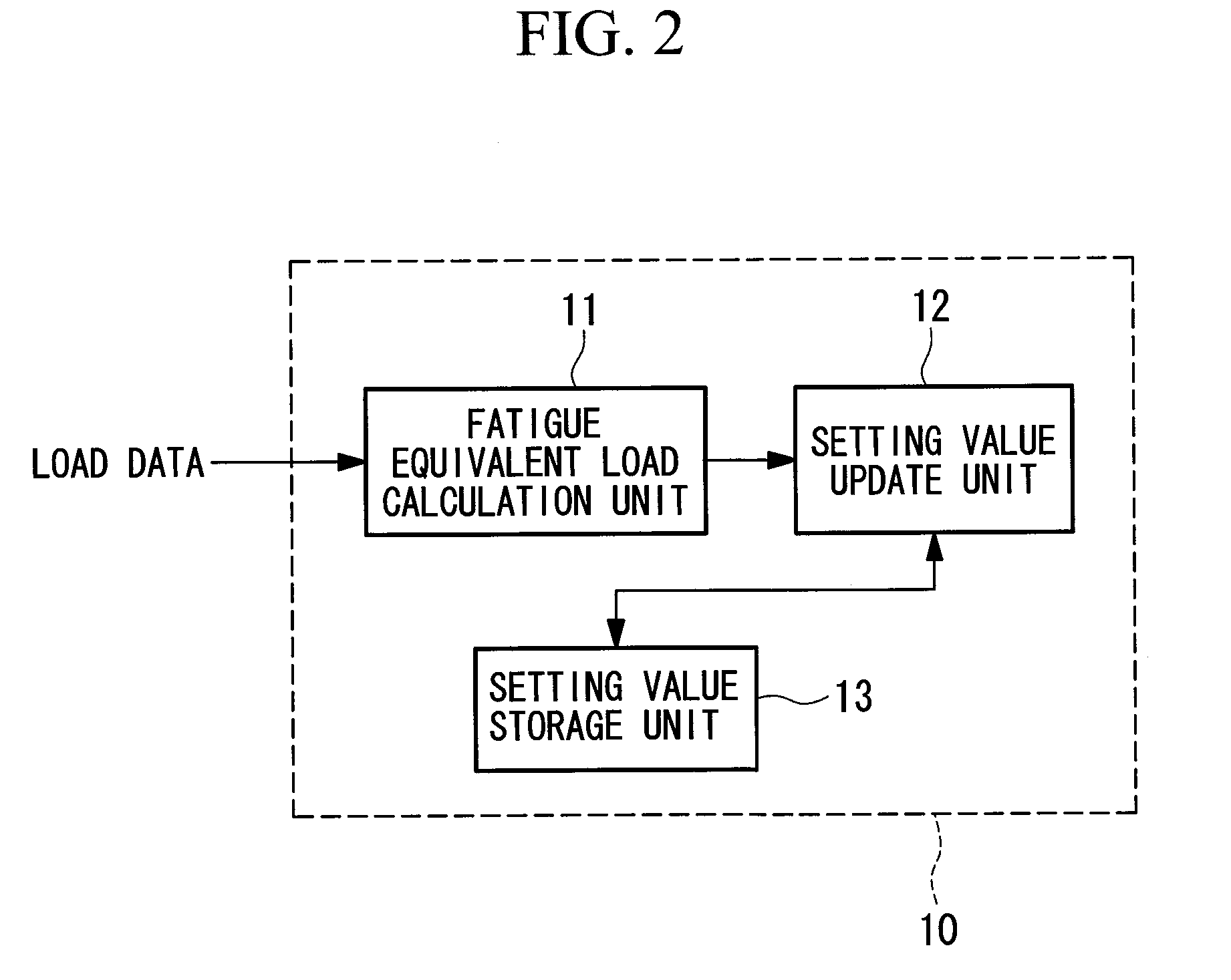
ActiveUS20110018271A1Inhibition decreasedWind motor controlWind motor combinationsFatigue damageTurbine
An object is to suppress reduction of energy production as much as possible while ensuring an expected lifetime. There is provided a device of adjusting a curtailment strategy for a wind turbine, the device including: a fatigue equivalent load calculation unit that calculates a fatigue equivalent load for evaluating a fatigue damage of the wind turbine in a predetermined time period by using load data of the wind turbine; and a setting value update unit that compares the fatigue equivalent load with a reference load determined by an expected lifetime of the wind turbine, and, when a difference between the fatigue equivalent load and the reference load exceeds a predetermined threshold value, updates the condition setting value for the curtailment that is currently employed according to the difference.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
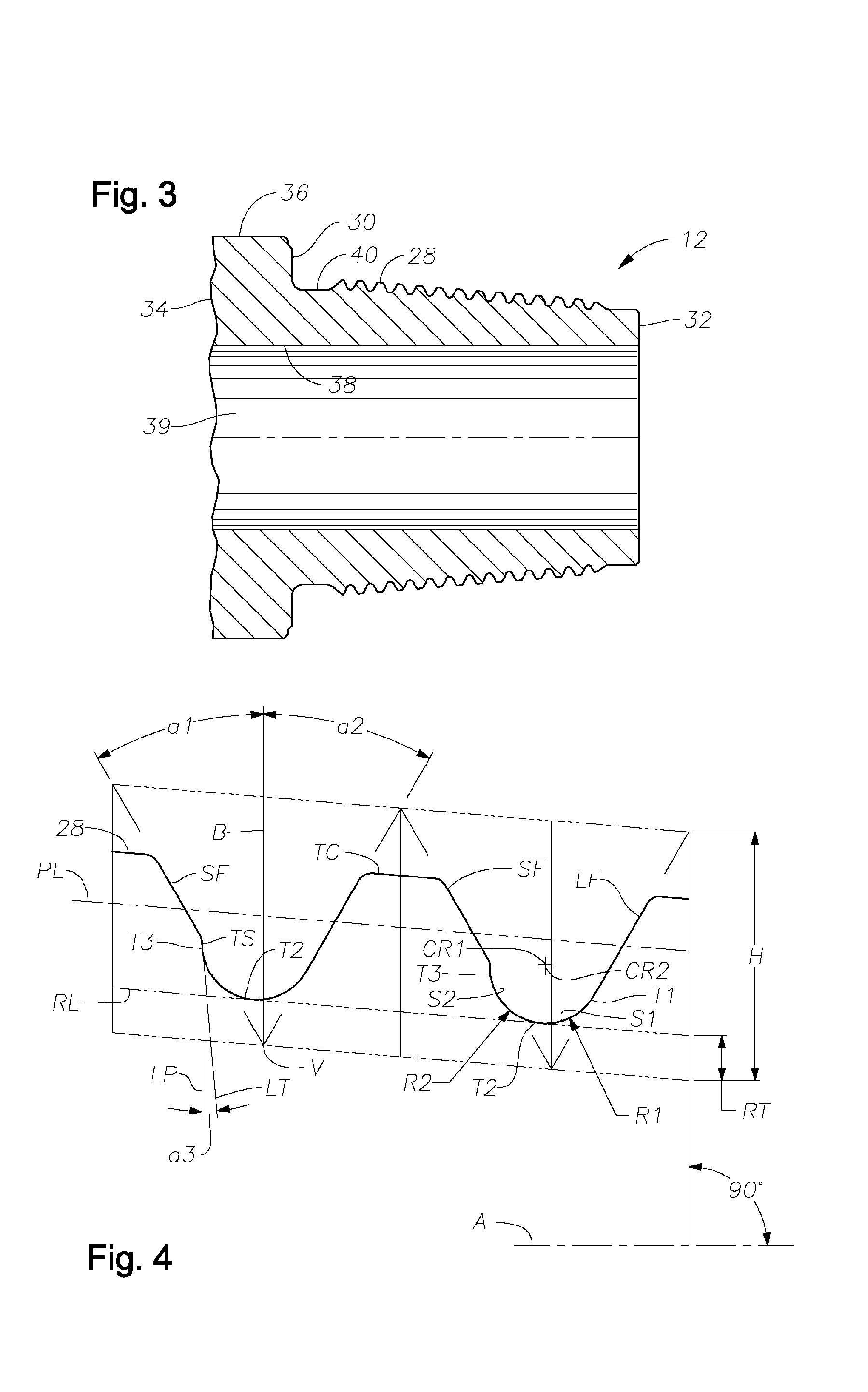
Fatigue Resistant Rotary Shouldered Connection and Method
InactiveUS20060214421A1Space maximizationImprove operational capabilitiesDrilling rodsHose connectionsHigh resistanceFatigue damage
Threaded connections are provided with a thread form that permits the construction of enlarged root radii between adjacent threads. Relatively coarse thread leads formed along conical surfaces with relatively extended tapers cooperate with relatively tall thread heights and an enlarged root radius (or radii) to produce a fatigue resistant, rotary-shouldered connection that can be assembled with reasonably attainable high torque forces. The ratios between the thread lead, measured in threads per inch, as the numerator, and denominators comprising the untruncated thread height of the thread, and / or the root truncation and / or the root radius (or radii) are maintained at low values compared to those existing in conventional prior art connections. The ratio of the untruncated thread height to the root radius (or radii) is also retained at a relatively low value as compared to that existing in many prior art configurations. The connection design produces an unexpectedly high resistance to fatigue damage or failure. The connection may be employed in any rotary-shouldered connection and is particularly effective in preventing fatigue damage in the stiffer components of drill stem assemblies including single shoulder and double shoulder drill collar connections.
Owner:GRANT PRIDECO LP
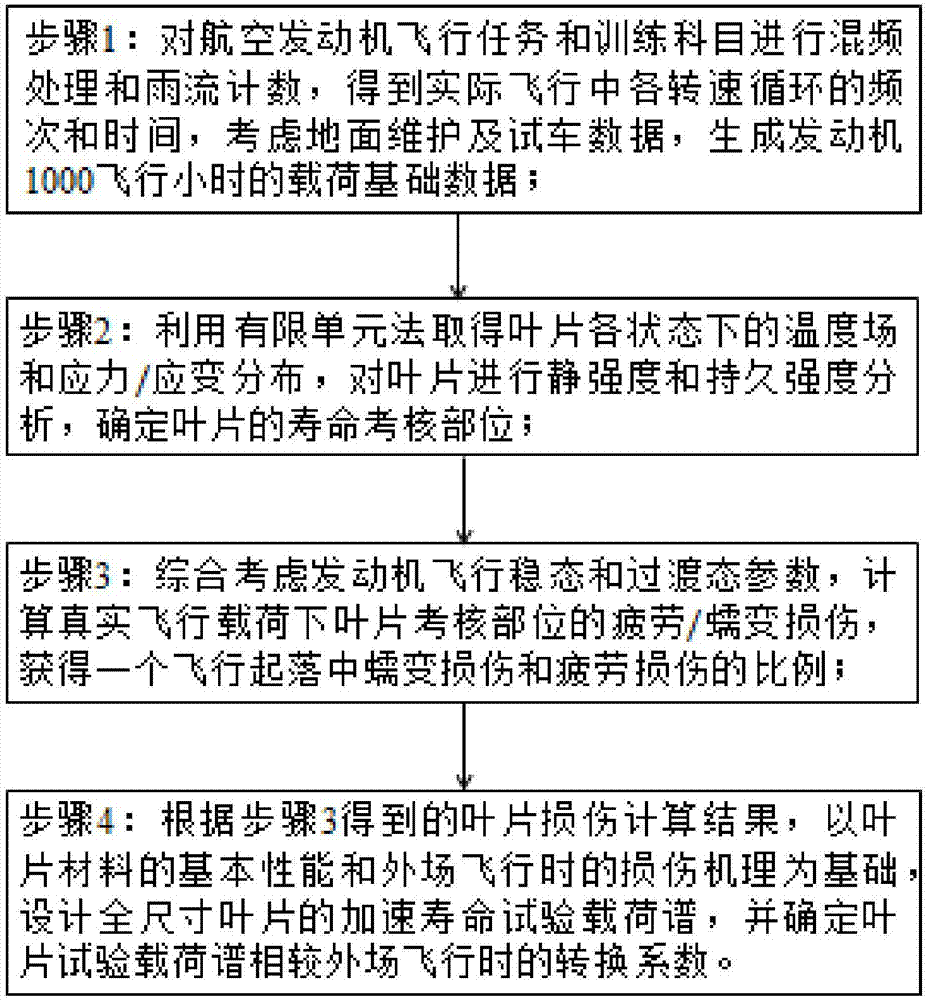
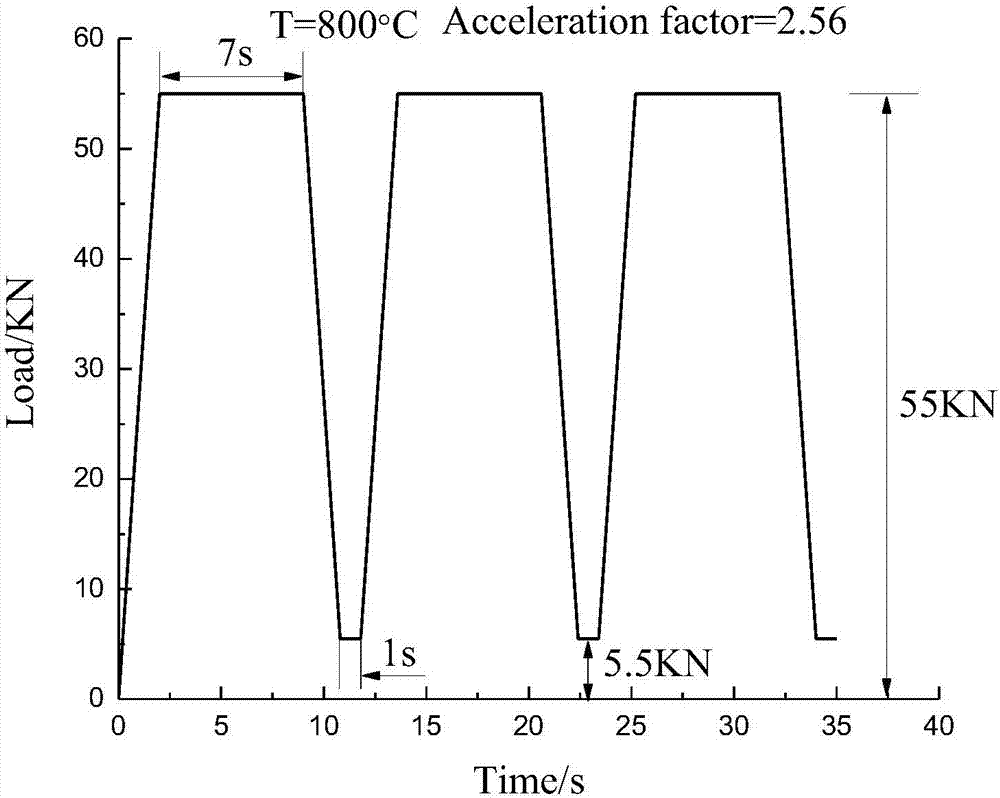
Turbine rotor blade accelerated life test load design method taking regard of flight damage
PendingCN107247002ADamage reasonably characterizedLife assessmentMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesDesign optimisation/simulationFatigue damageAviation
The invention relates to a turbine rotor blade accelerated life test load design method taking regard of flight damage. The method includes: 1) conducting frequency mixing treatment and rain flow counting on aeroengine flight missions and training subjects to acquire the frequency and time of each rotation speed cycle in actual flight, thus obtaining the load basic data of an engine within certain flight hours; 2) acquiring the temperature field and stress strain distribution of the blade under all states by finite element method, analyzing the blade static strength and endurance, and determining a lifetime testing part of the blade; 3) calculating the fatigue damage and creep damage of the blade testing part under a true flight load to acquire a ratio of creep damage and fatigue damage during rise and fall of a flight; and 4) designing a accelerated life test load spectrum of a full-size blade, and determining a conversion coefficient of the blade test load spectrum relative to out-field flight. The method provided by the invention can be used for acquiring the technical life of the blade and studying the remaining life of the blade, and saves time and economic cost for the fatigue-creep lifetime test of the blade.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Self-diagnosis system for wind-induced cumulative fatigue damage of pull lug node substructure of mast structure
InactiveCN101825522AEnsure safetyMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesForce measurementFatigue damageReal time analysis
The invention discloses a self-diagnosis system for wind-induced cumulative fatigue damages of a pull lug node substructure of a mast structure. The system comprises a displacement measuring apparatus, a pull rope tension determination module, a welding residual stress determination module, a pull lug substructure wind-induced stress field determination module, a fatigue crack initiation degree real-time analysis module and a man-machine interaction interface, so that the system can timely inform a user of the degree of the cumulative fatigue at the danger point position of the pull lug node substructure of the mast structure and the time when the cumulative fatigue crack initiation occurs and make early warning on cumulative fatigue cracks when the pull lug node substructure of the mast structure is in a good condition. In addition, the system also comprises an acoustic emission sensor, a strain transducer, a fatigue crack growth determination module and an ultimate crack length and fracture analysis module, so that the system can timely inform the user of the degree of the cumulative fatigue crack growth and the time when the fracture occurs, timely repair the crack and ensure the safety of the mast structure when the cumulative fatigue cracks of pull lug node substructure of the mast structure occur.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
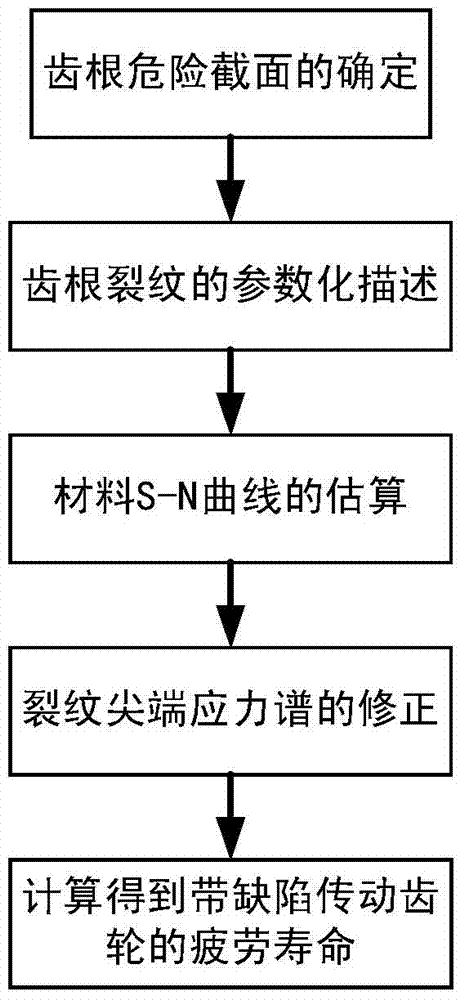
Transmission gear fatigue life assessment method based on defect modeling
InactiveCN103616179AImprove fatigue analysis efficiencyReduce fatigue life analysis complexityMachine gearing/transmission testingFatigue damageEstimation methods
The invention discloses a transmission gear fatigue life assessment method based on defect modeling. The method includes the following steps that (1), crack occurrence rules and reasonable crack forms are analyzed, and the method for introducing cracks into a gear model is researched; (2), material fatigue characteristic parameters are obtained through test data fitting or a numerical value estimation method; (3), a stress spectrum under the condition of working situations of a gear containing the cracks is calculated by using a finite element method, and the stress spectrum is corrected according to obtaining conditions of the material fatigue characteristic parameters; (4), fatigue life under the condition of working situations of a gear containing the cracks is calculated by using the reasonable fatigue damage accumulation theory. The fatigue life assessment method based on defect modeling is provided for the transmission gear, and an effective detection basis is provided for the remanufacturing process of a gear recycled part.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Offshore wind power spar buoyant foundation capable of towing
ActiveCN105438411AReduce resistanceSkip the dry mopping processFoundation engineeringFloating buildingsStress concentrationFatigue damage
The invention relates to an offshore wind power buoyant foundation form and in particular relates to an offshore wind power spar buoyant foundation capable of towing, which comprises a connecting column and is characterized in that the upper end of the connecting column is connected with a fan through a flange ring, a plurality of flat columnar closed air flotation boxes are arranged at the middle part of the connecting column, the closed air flotation boxes are not communicated with the connecting column, and the bottom of the connecting column is communicated with a loading cabin; a column body of the connecting column is provided with a detachable gear required for towing; and a mooring rope is arranged at the center of gravity of the buoyant foundation. Compared with the prior art, the offshore wind power spar buoyant foundation provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the construction is convenient, rolling towage can be realized, the resistance of a wave flow is reduced, the stress concentration and fatigue damage caused by the traditional spar foundation in a wet towing process are avoided, the construction difficulty and construction cost are greatly reduced, and the offshore wind power spar buoyant foundation can be recycled. The additional mass and viscous damping of heave motion are effectively improved by virtue of the flat air flotation boxes, the water surface profile area of a buoy is effectively increased by virtue of the flat air flotation boxes on the water surface, a relatively large restoring moment is provided, the structure stability is relatively good, the center of gravity is lower than the center of flotation, and the resistance to capsizing is good.
Owner:CEEC JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER DESIGN INST
Life prediction method used for nickel-base superalloy blade under thermal mechanical fatigue load
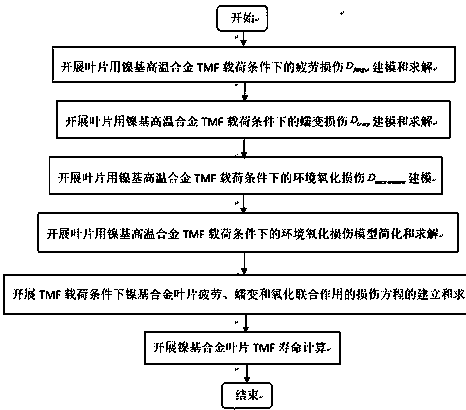
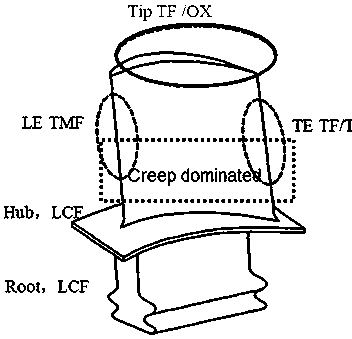
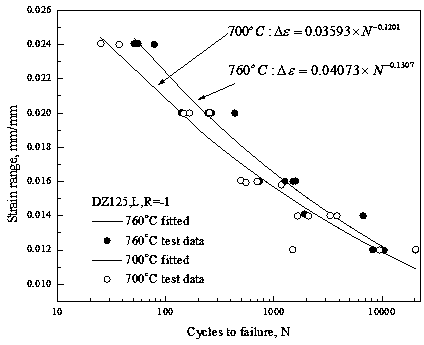
InactiveCN108170905AThe modeling process is clearFully combine structural featuresDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFatigue damageTime function
The invention discloses a life prediction method used for a nickel-base superalloy blade under a thermal mechanical fatigue load. The problems of life prediction and joint representation of low cyclefatigue damage, creep damage and oxidation environment damage of the nickel-base superalloy blade under the TMF load are effectively solved; according to isothermal low cycle fatigue life data of nickel-base alloy under the condition of not causing high-temperature effects of creep, oxidation and the like, fitting is performed to obtain a strain life equation; in combination with a fatigue damagelinear accumulation theory, a fatigue damage model is obtained; a creep damage model is represented as temperature, stress and time functions; the oxidation environment damage is modeled based on an oxidation-cracking mechanism with a continuous oxidation layer at a crack tip; a continuous damage accumulation mechanism is adopted for the three models; and by virtue of stress, strain and temperature data of dangerous position points of the blade, accurate and reliable unified representation of fatigue, creep and oxidation interactive damage, and life prediction of a combined damage model to a nickel-base superalloy member under the thermal mechanical fatigue load is realized.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com