Patents
Literature
242 results about "Induced stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stress-induced asthma can be triggered by anything that causes stress, such as: pressure at work. difficulties in school. conflict in a personal relationship. financial frustrations. any significant life-changing event.
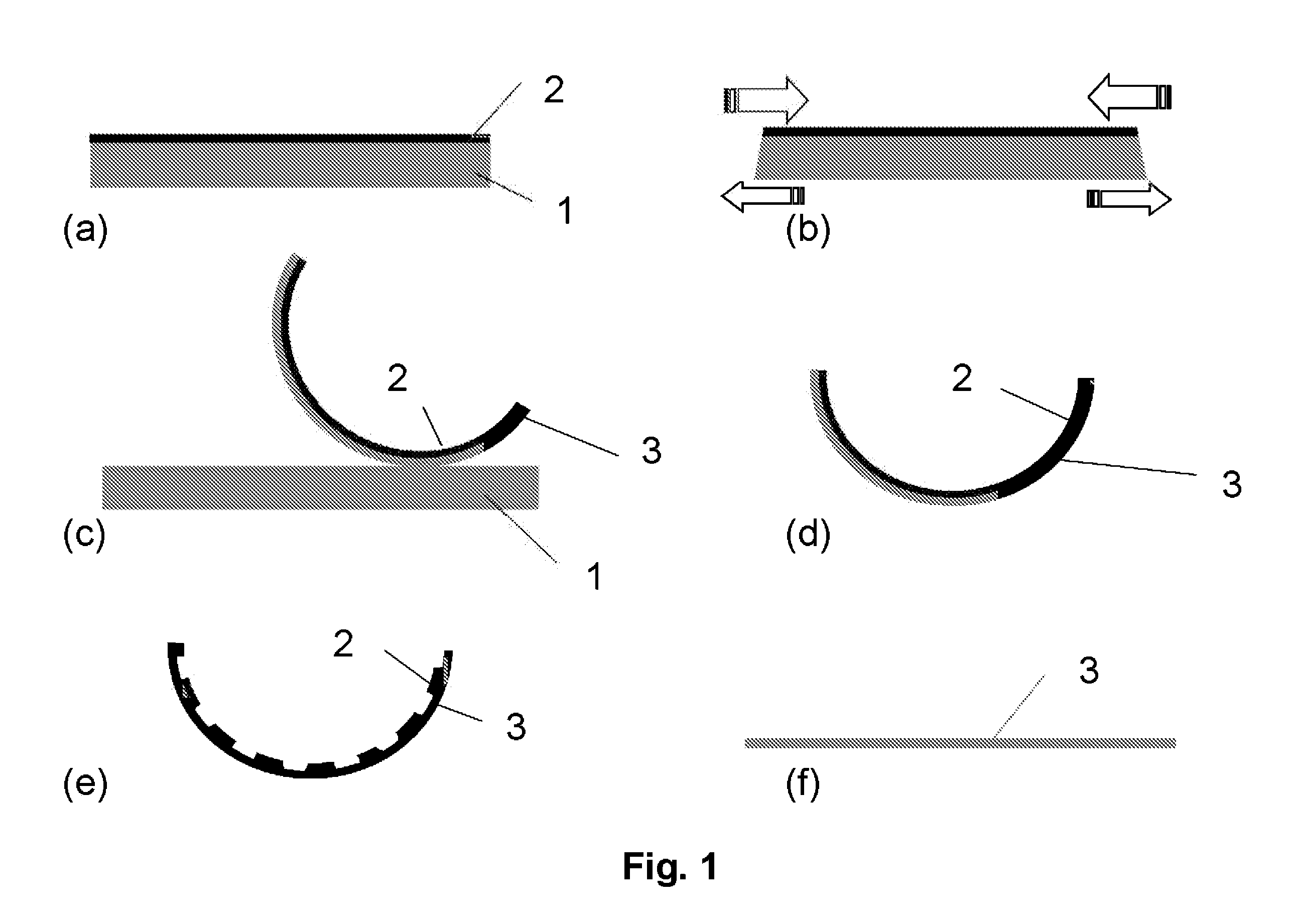
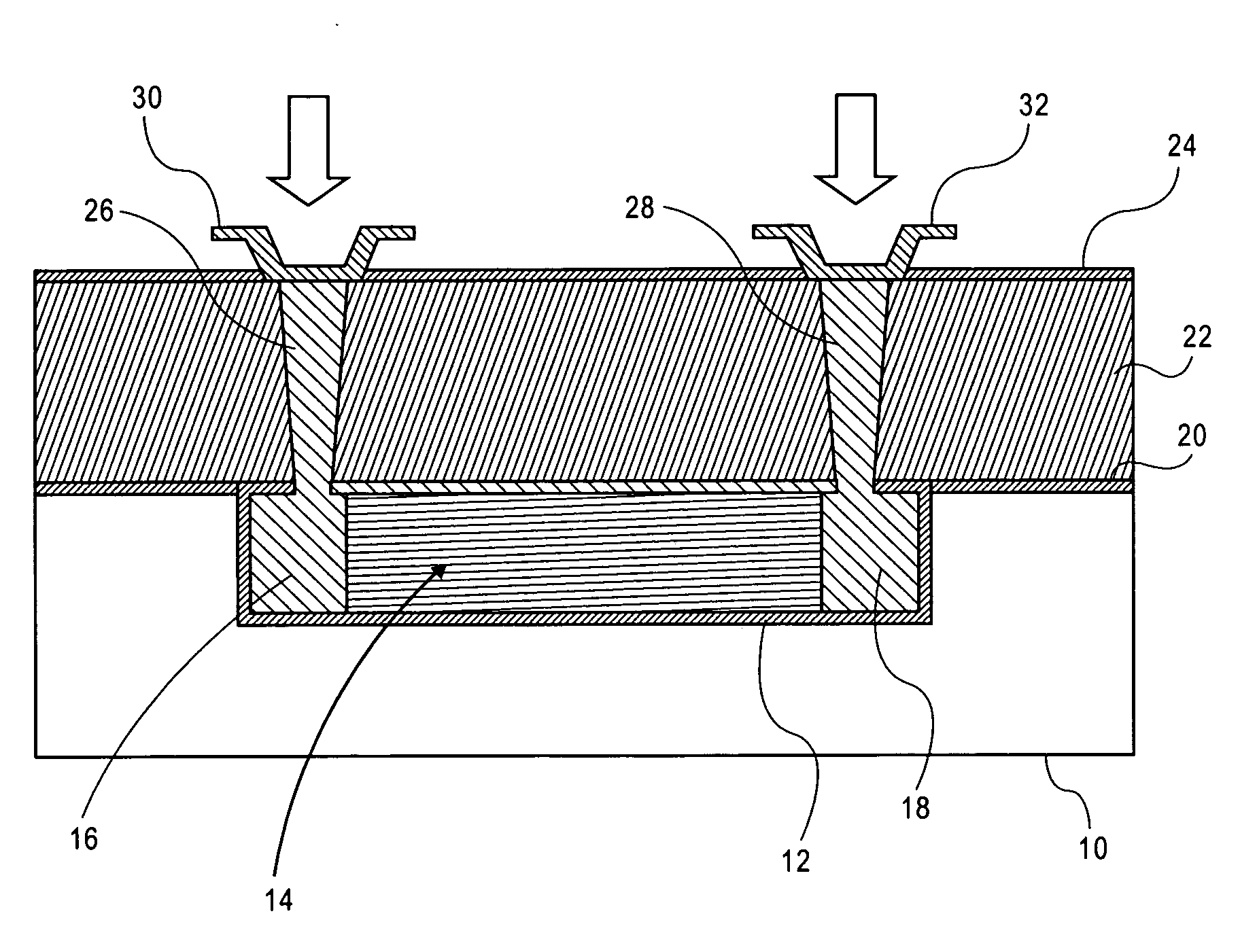
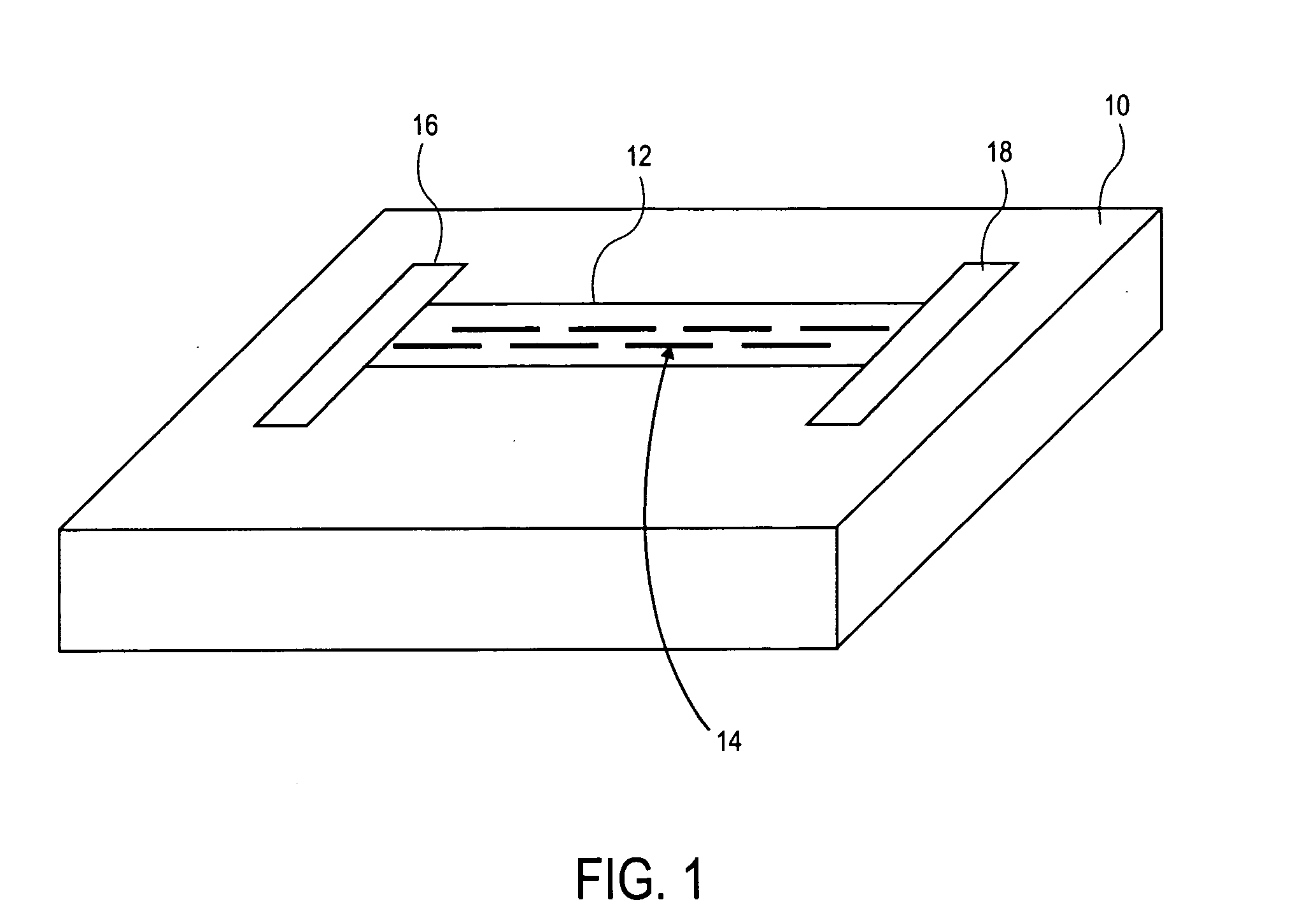
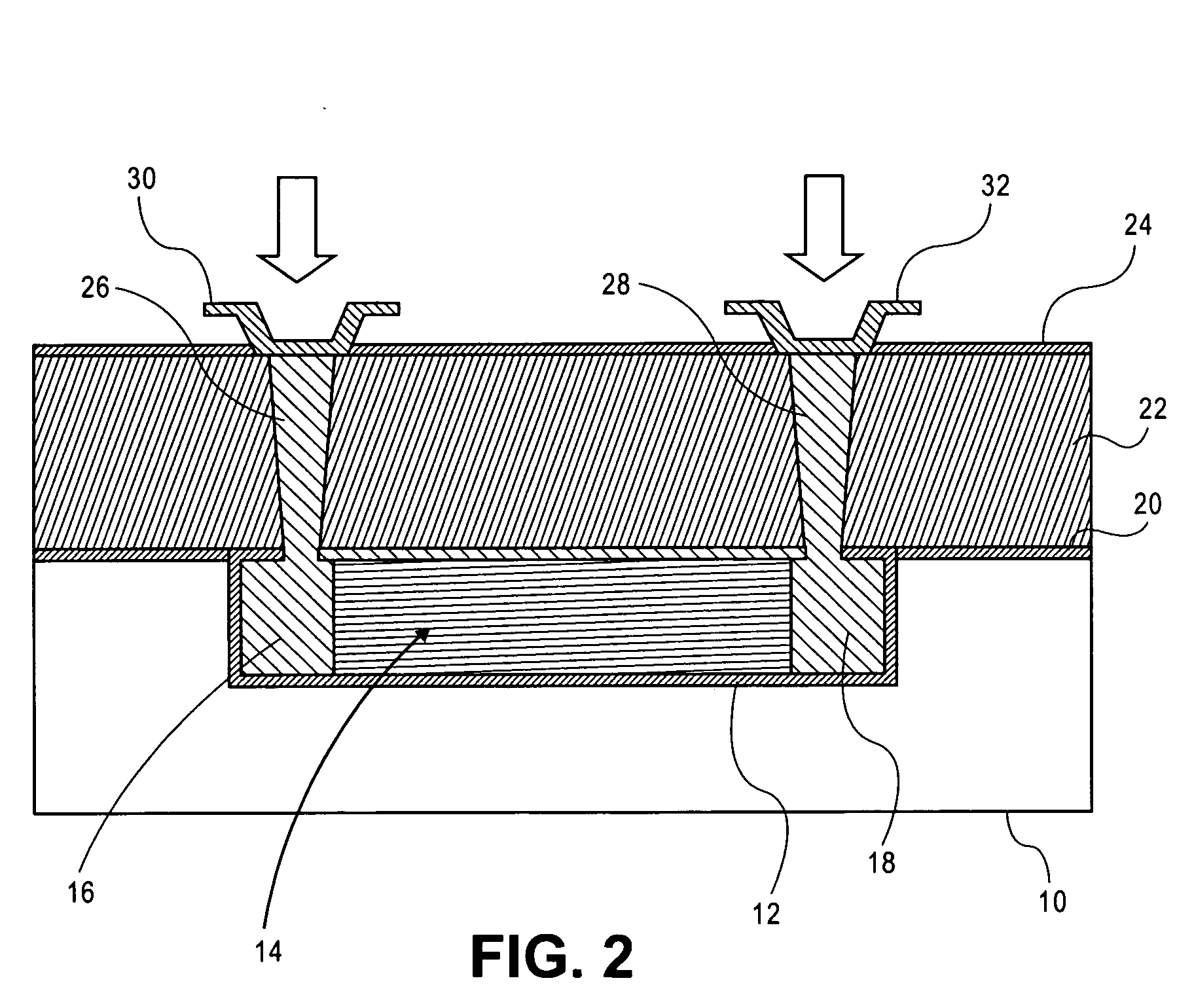
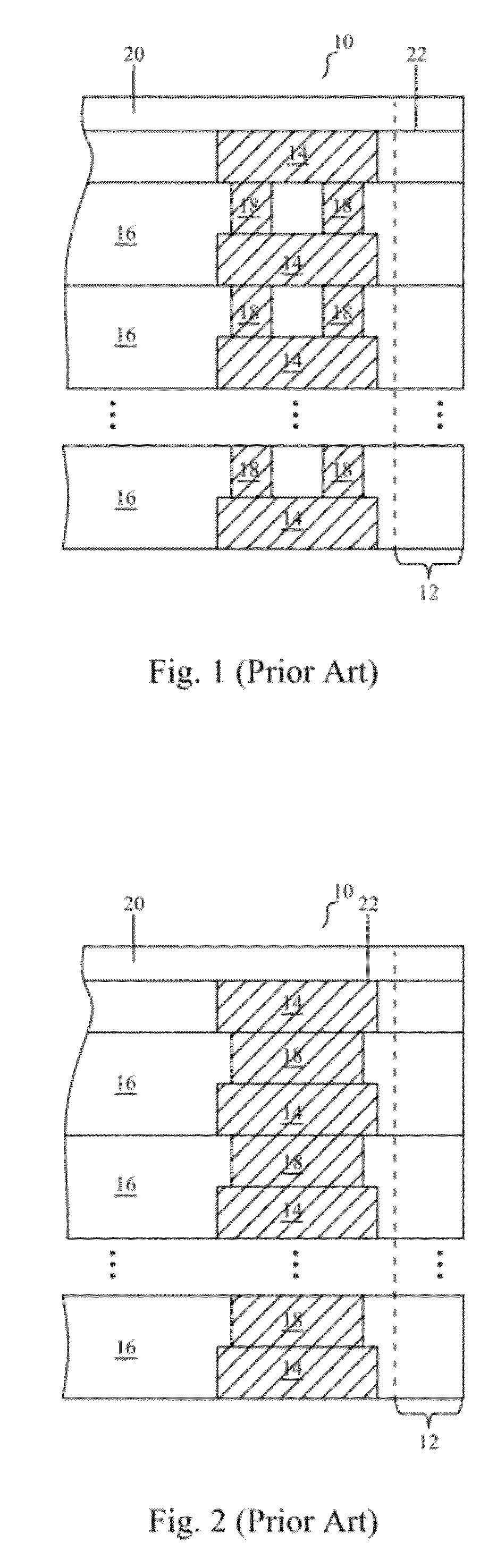
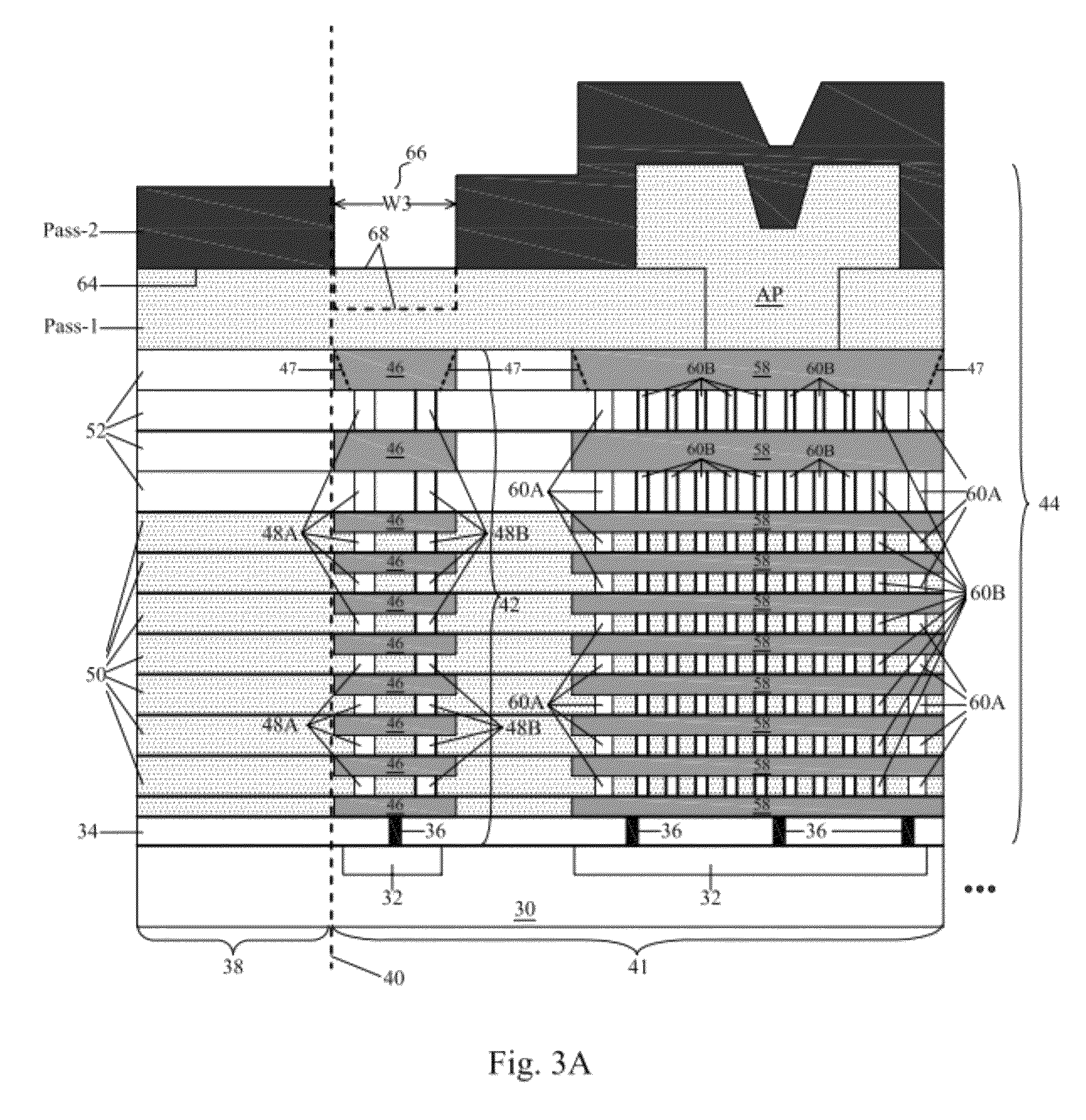
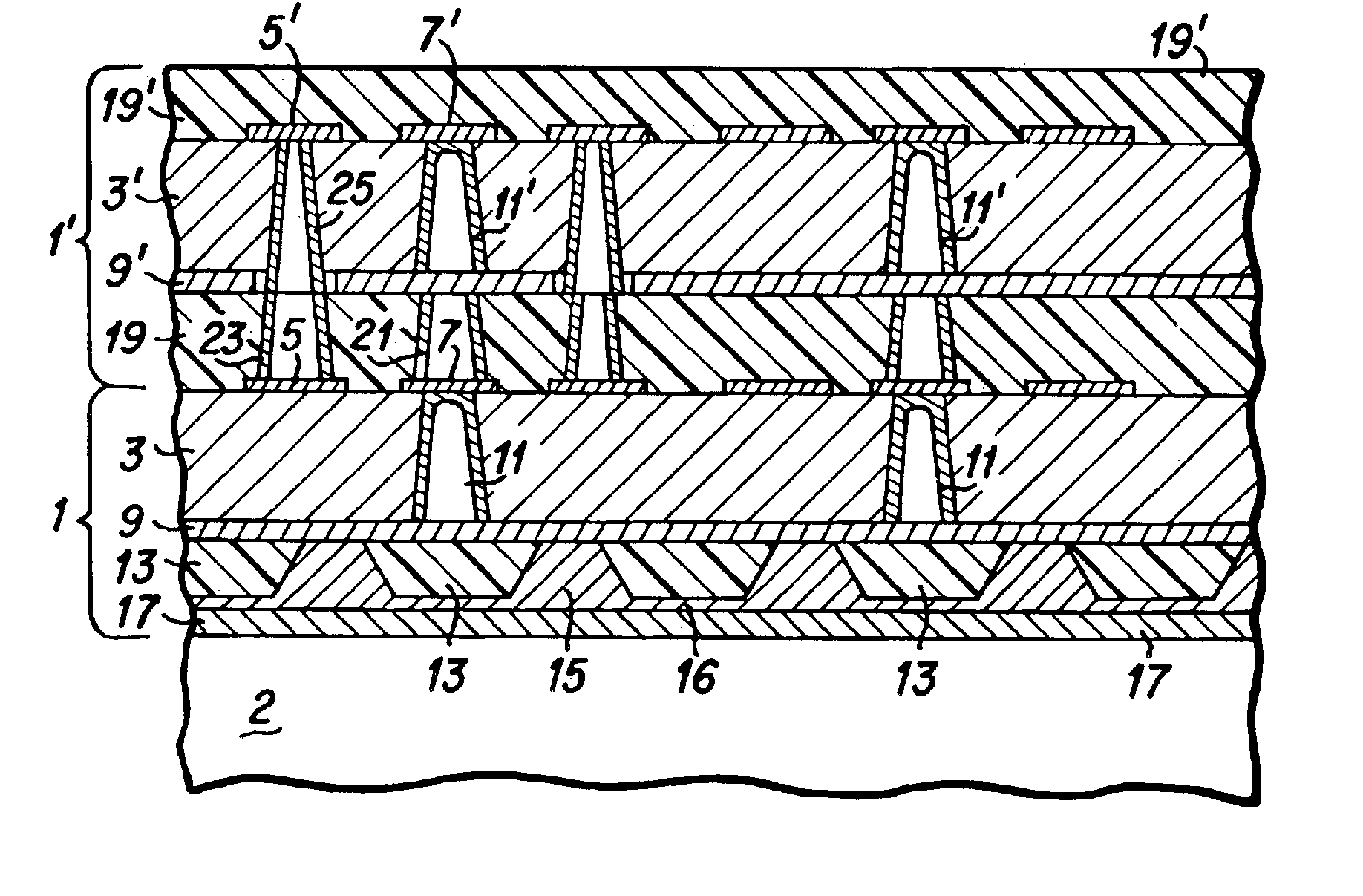
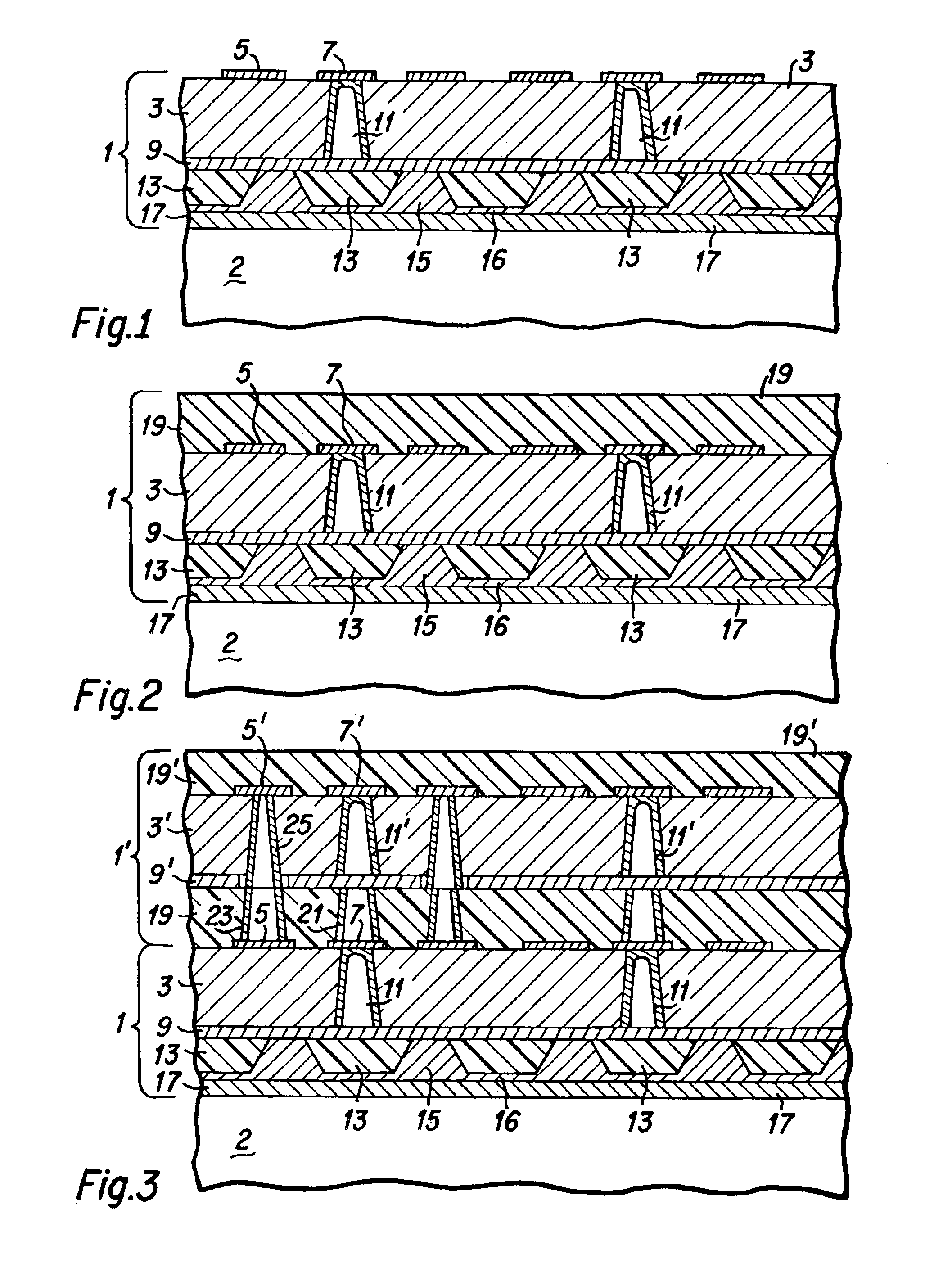
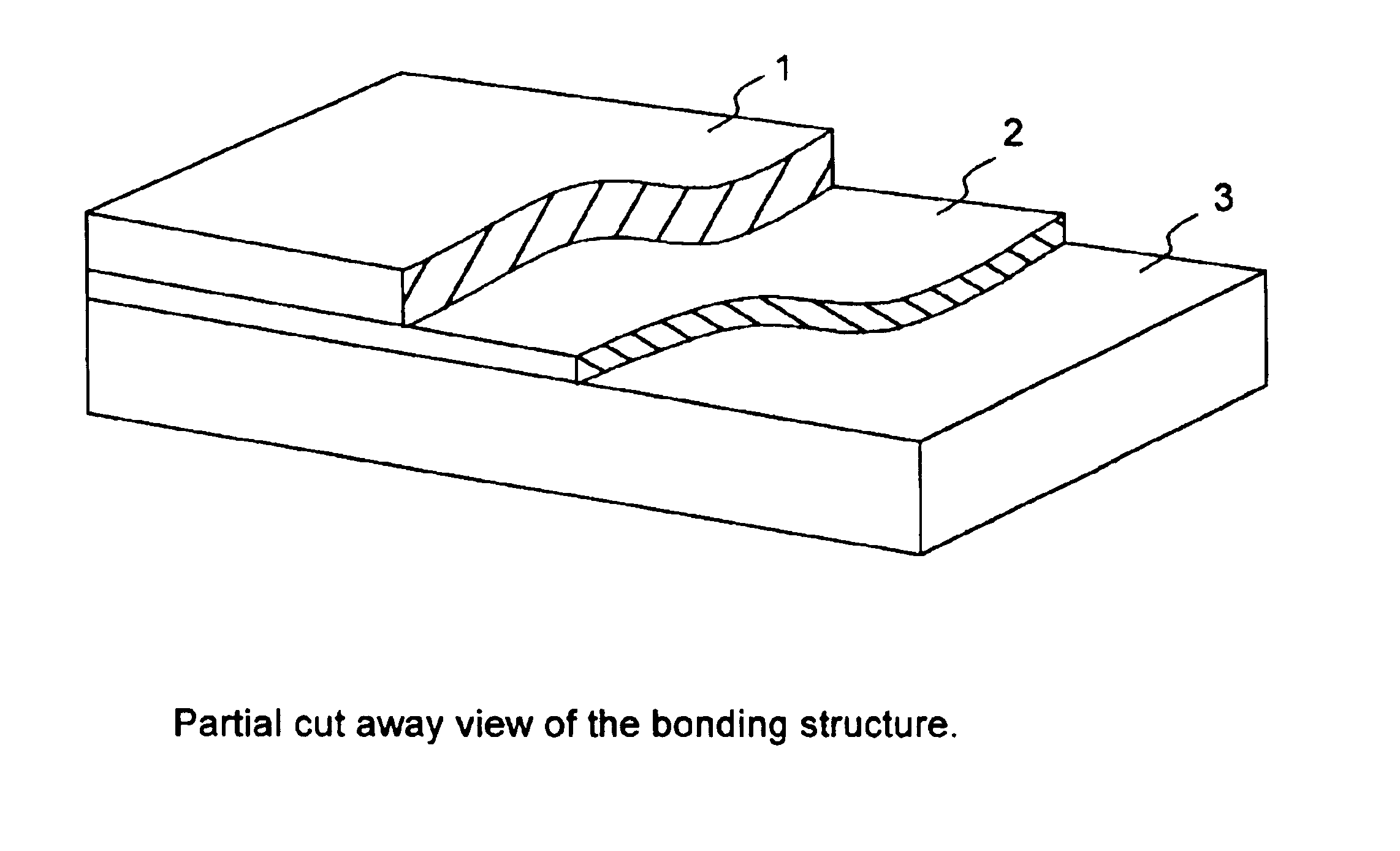
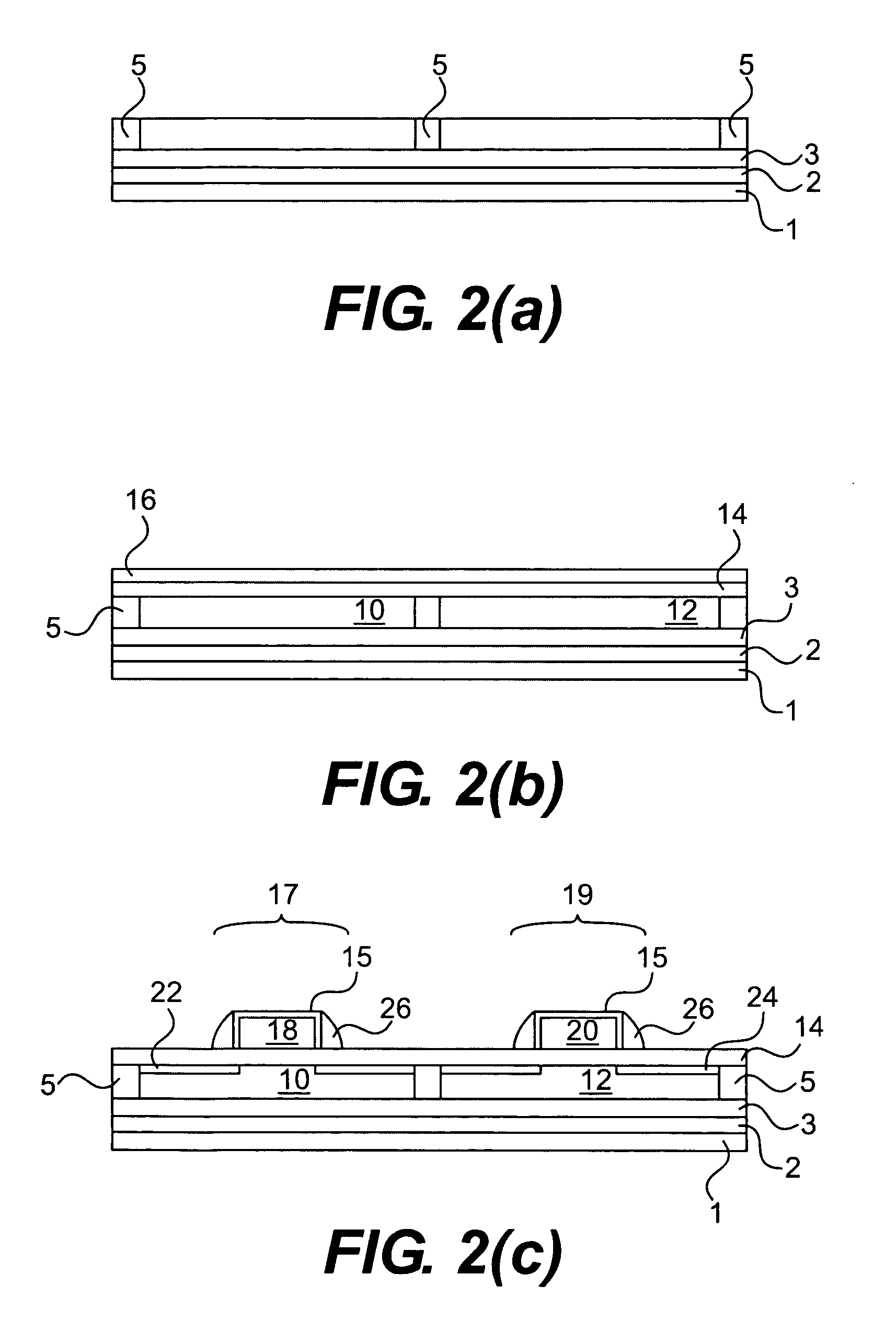
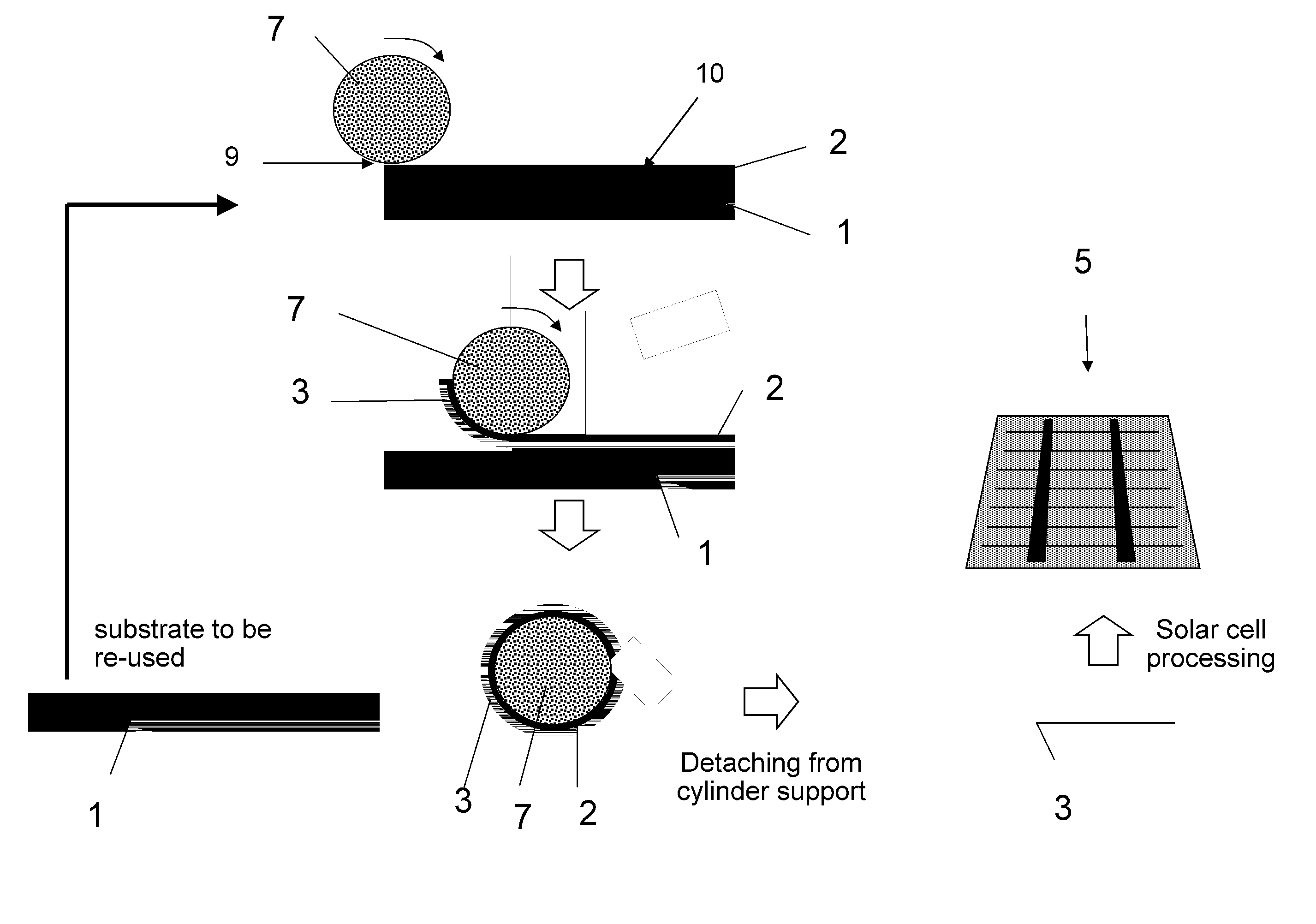
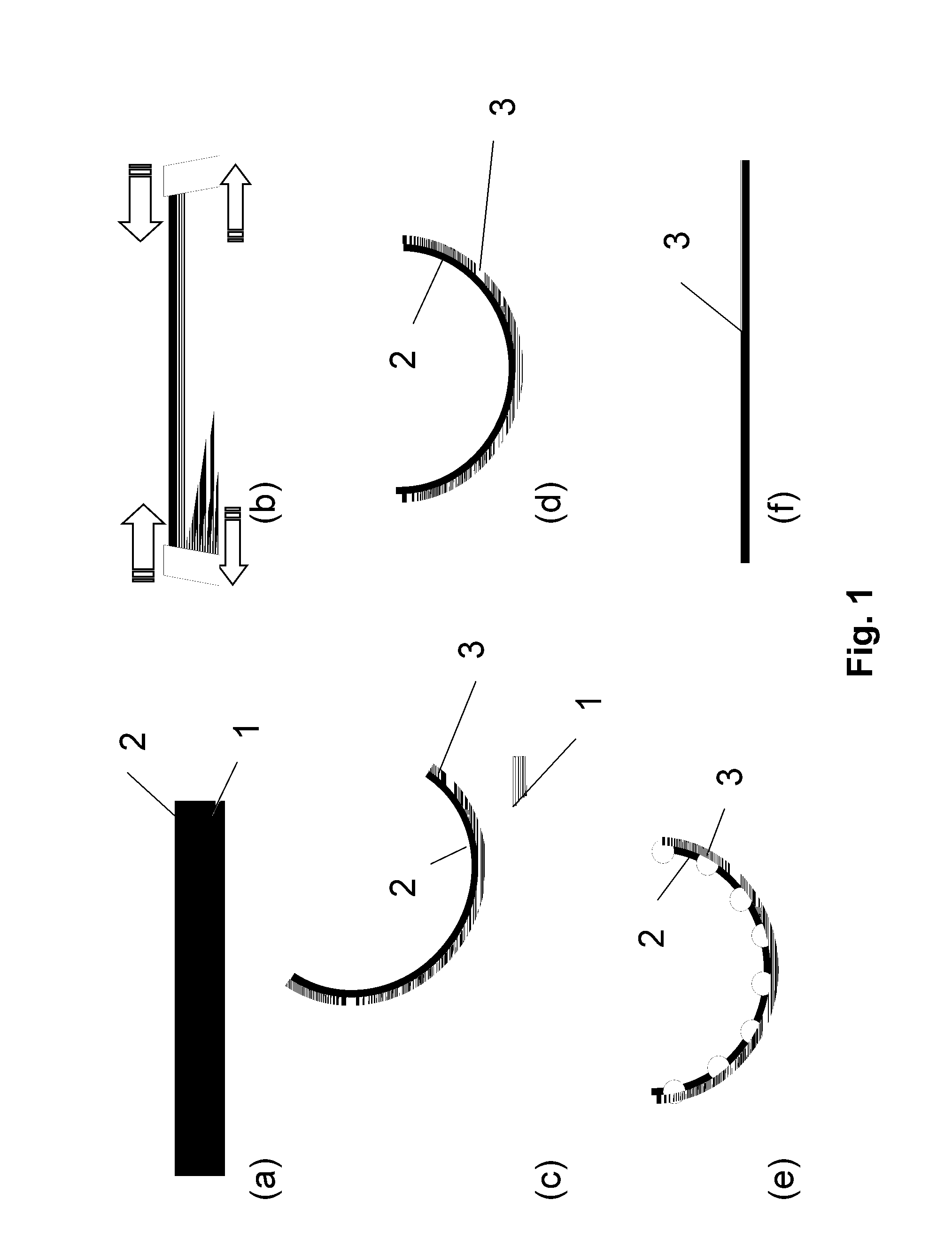
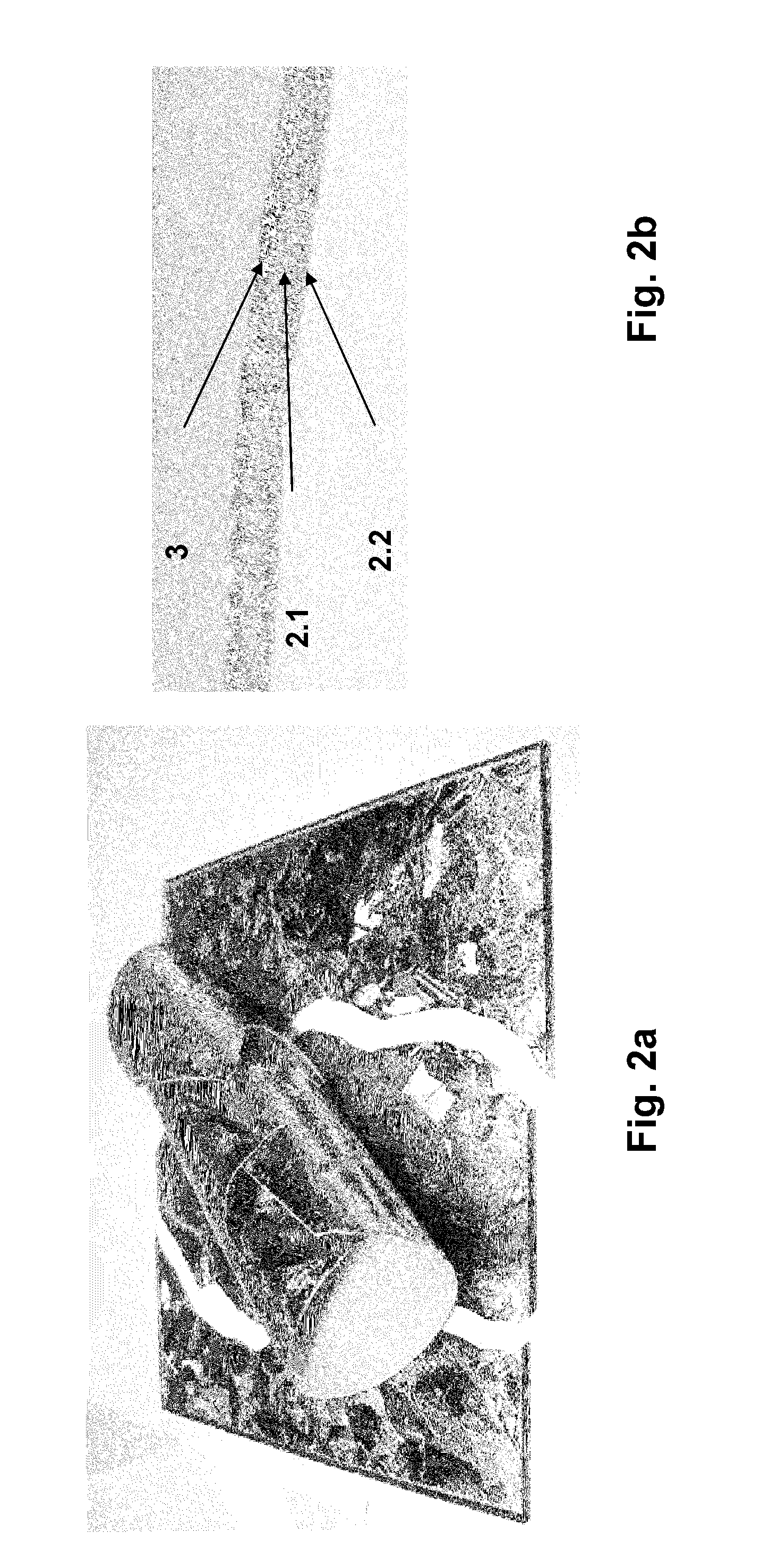
Method for the production of thin substrates
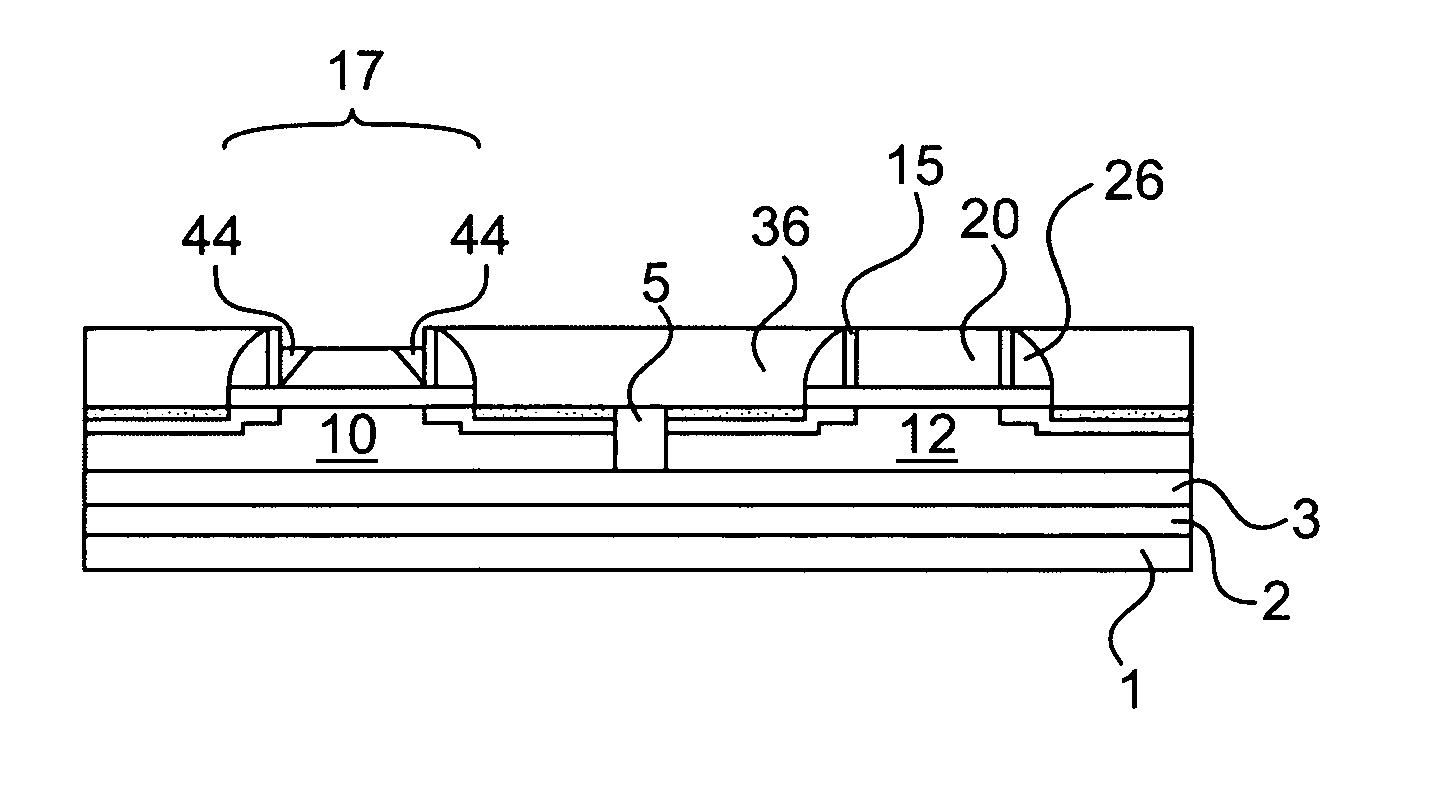
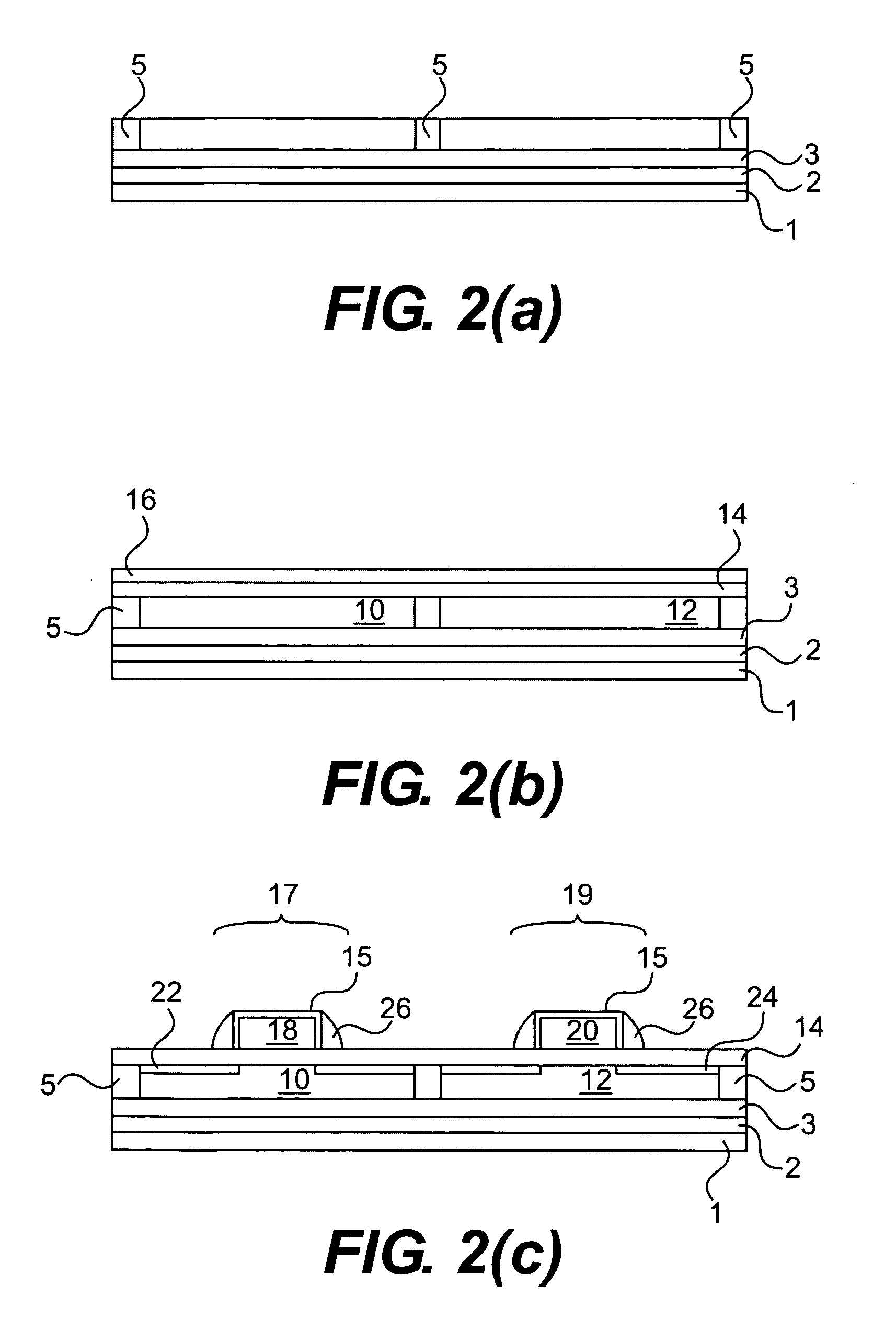
InactiveUS20070249140A1Improve efficiencyLarge thicknessFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolar cellInduced stress
A method is provided for producing a thin substrate with a thickness below 750 microns, comprising providing a mother substrate, the mother substrate having a first main surface and a toughness; inducing a stress with predetermined stress profile in at least a portion of the mother substrate, said portion comprising the thin substrate, the induced stress being locally larger than the toughness of the mother substrate at a first depth under the main surface; such that the thin substrate is released from the mother substrate, wherein the toughness of the mother substrate at the first depth is not lowered prior to inducing the stress. The method can be used in the production of, for example, solar cells.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
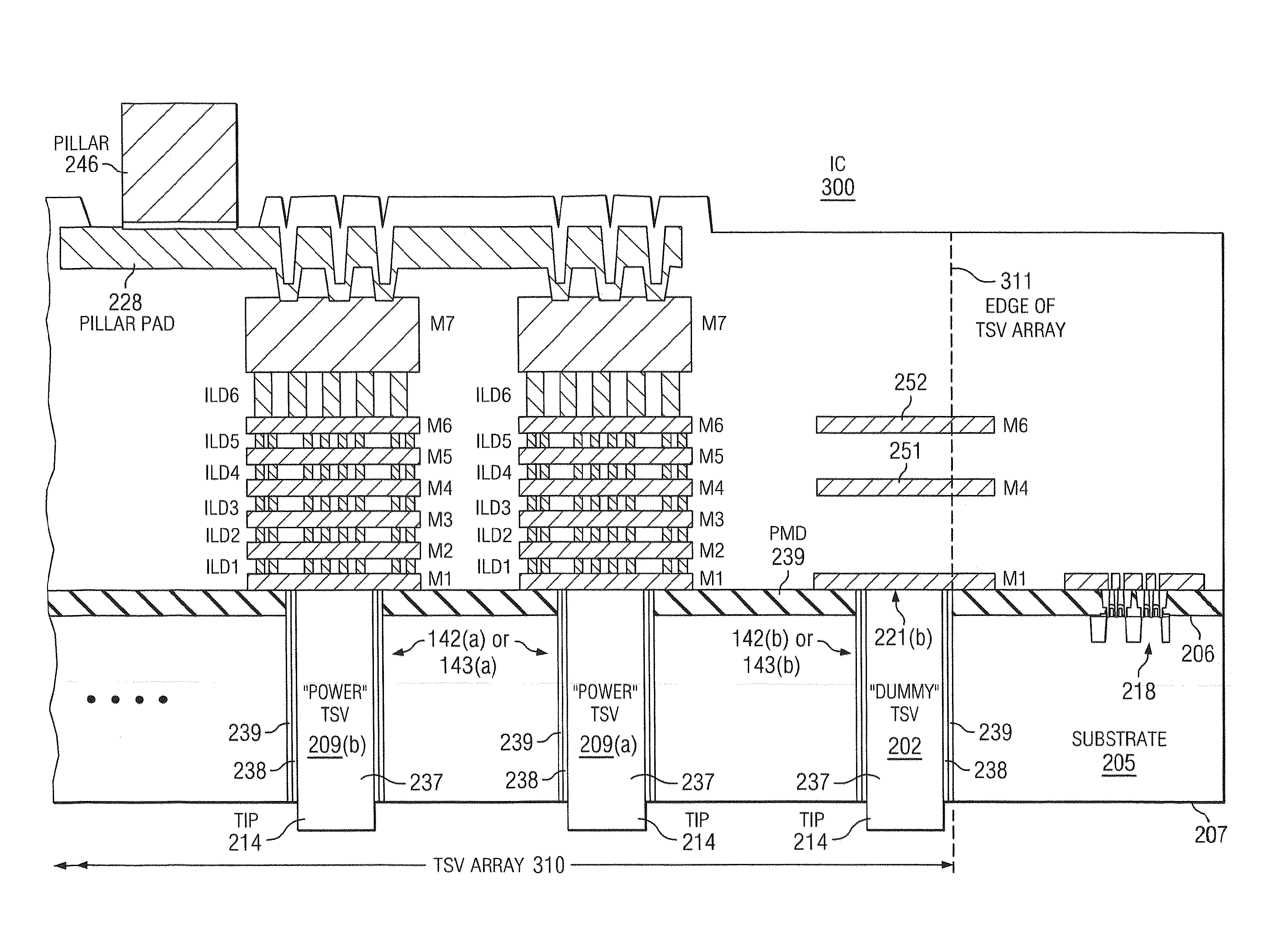
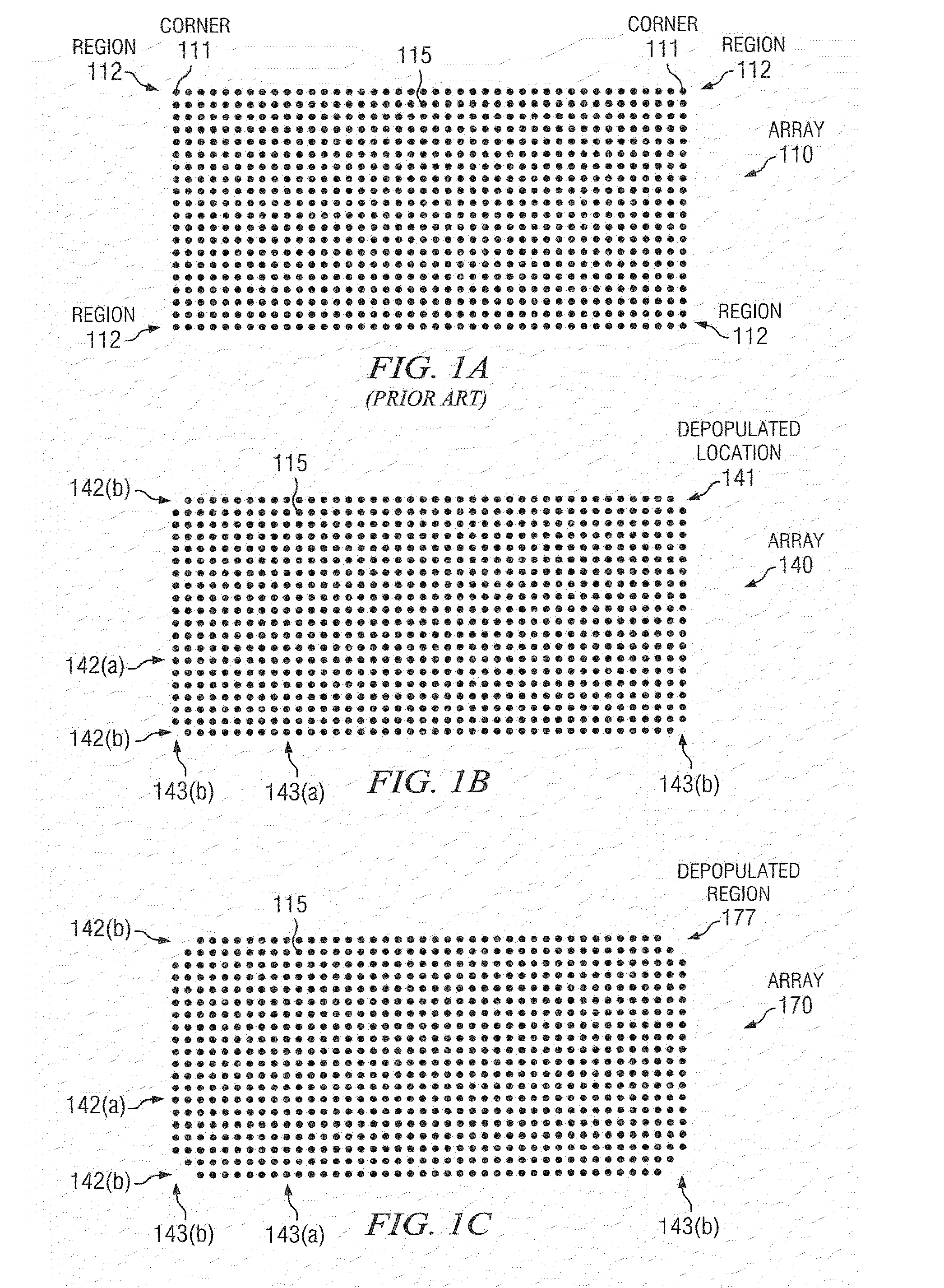
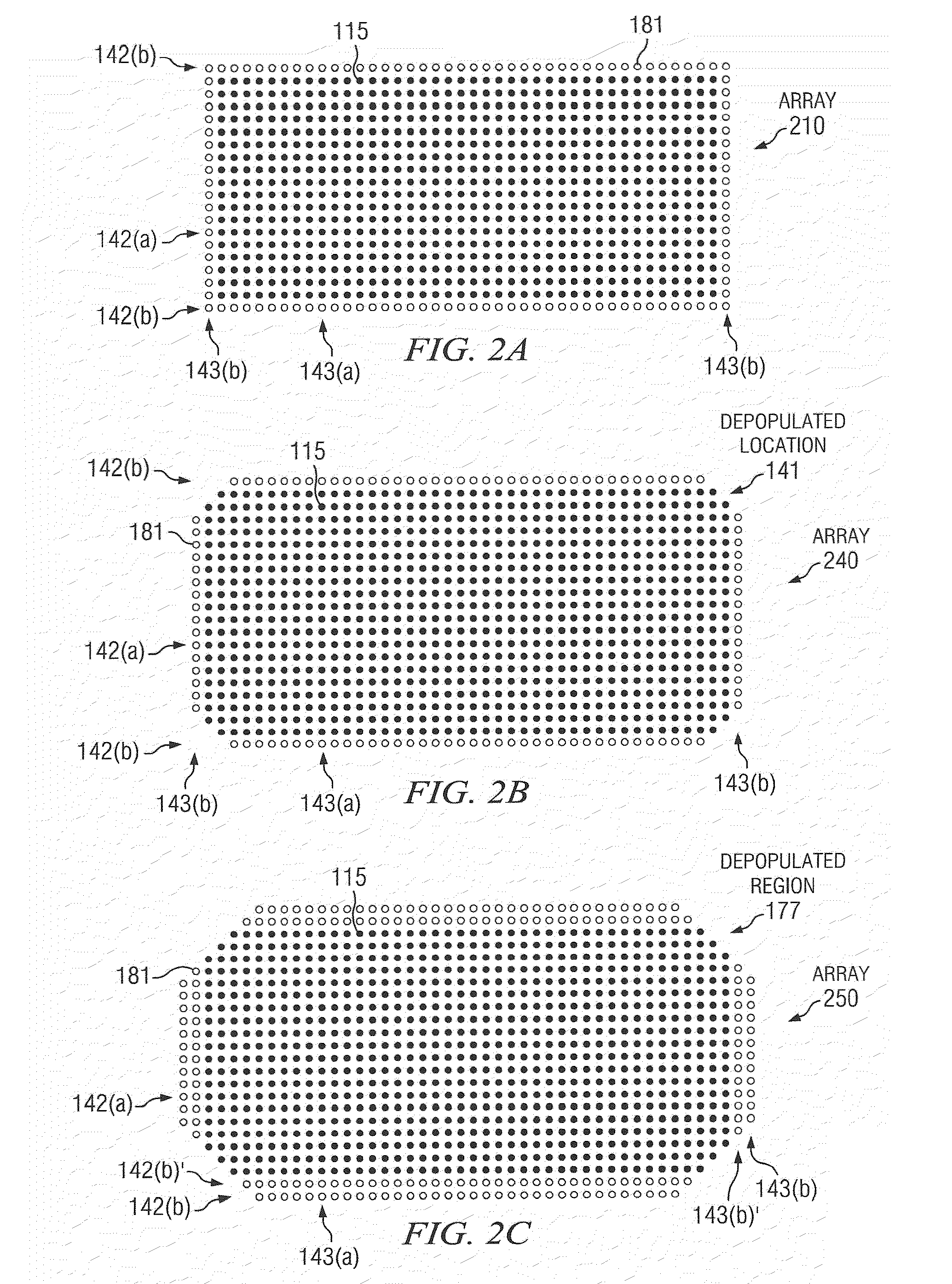
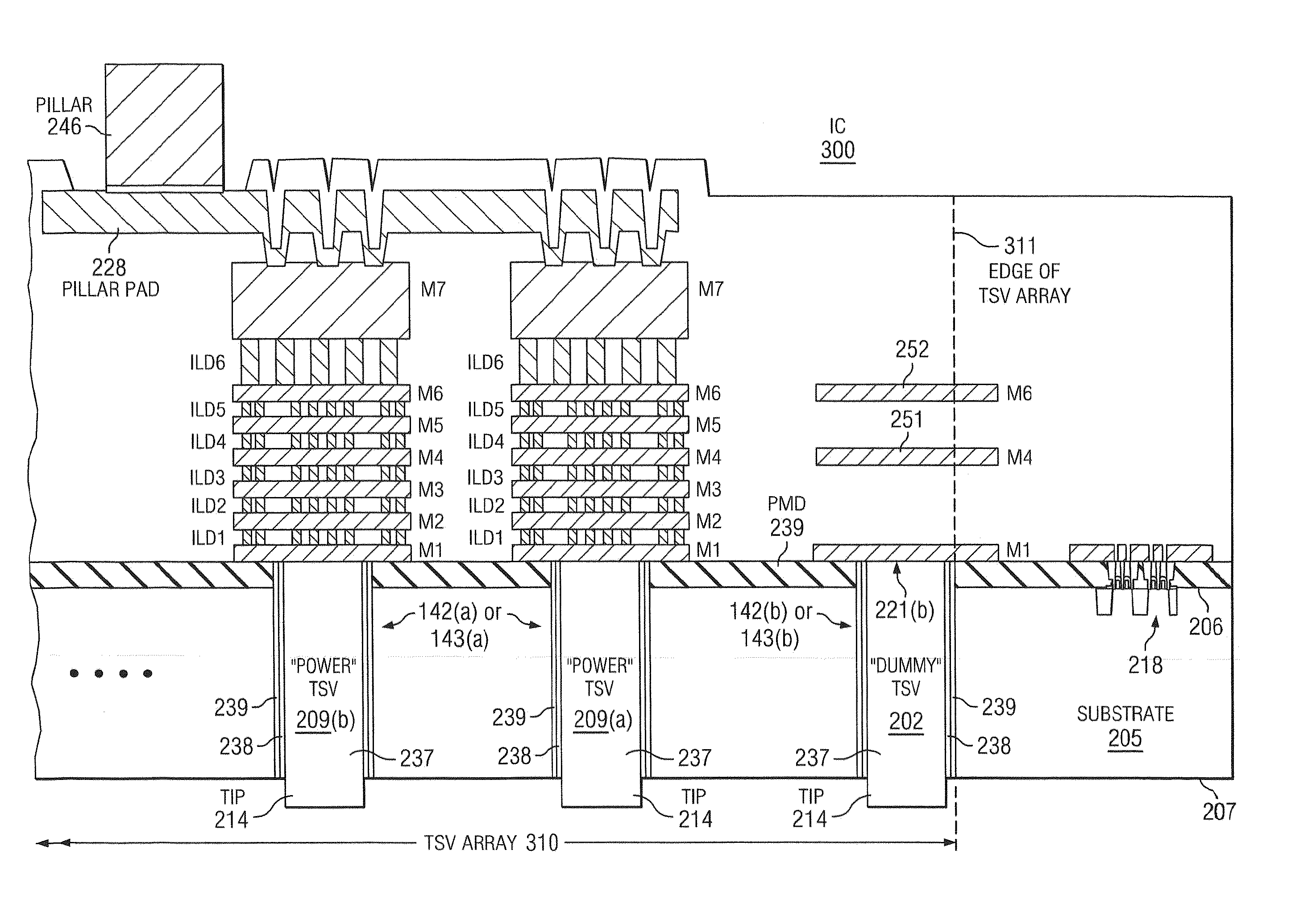
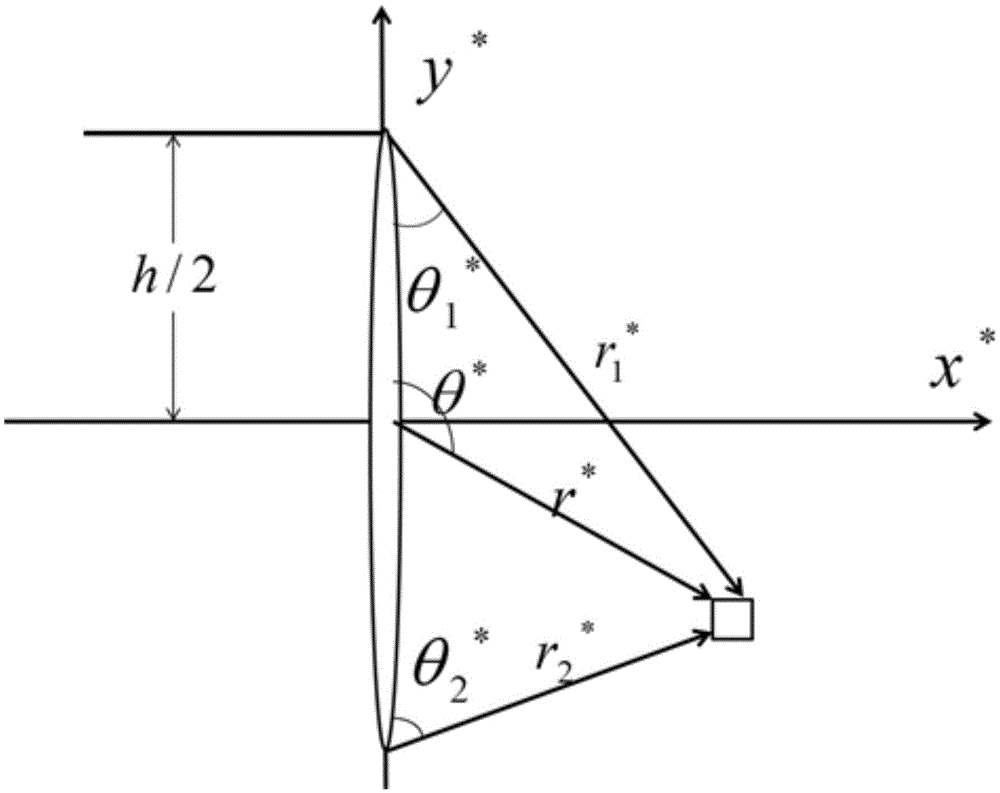
IC having TSV arrays with reduced TSV induced stress
ActiveUS20100171226A1Increase the areaEliminate needSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal interconnectEngineering
An integrated circuit (IC) includes a substrate having a top side having active circuitry thereon including a plurality of metal interconnect levels including a first metal interconnect level and a top metal interconnect level, and a bottom side. At least one TSV array includes a plurality of TSVs. The TSVs are positioned in rows including a plurality of interior rows and a pair of exterior rows and a plurality of columns including a plurality of interior columns and a pair of exterior columns. At least a portion of the TSVs in the array are electrically connected TSVs that are coupled to a TSV terminating metal interconnect level selected from the plurality of metal interconnect levels. At least one of the exterior rows or exterior columns include a lower number of electrically connected TSVs compared to a maximum number of electrically connected TSVs in the interior rows and interior columns, respectively.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
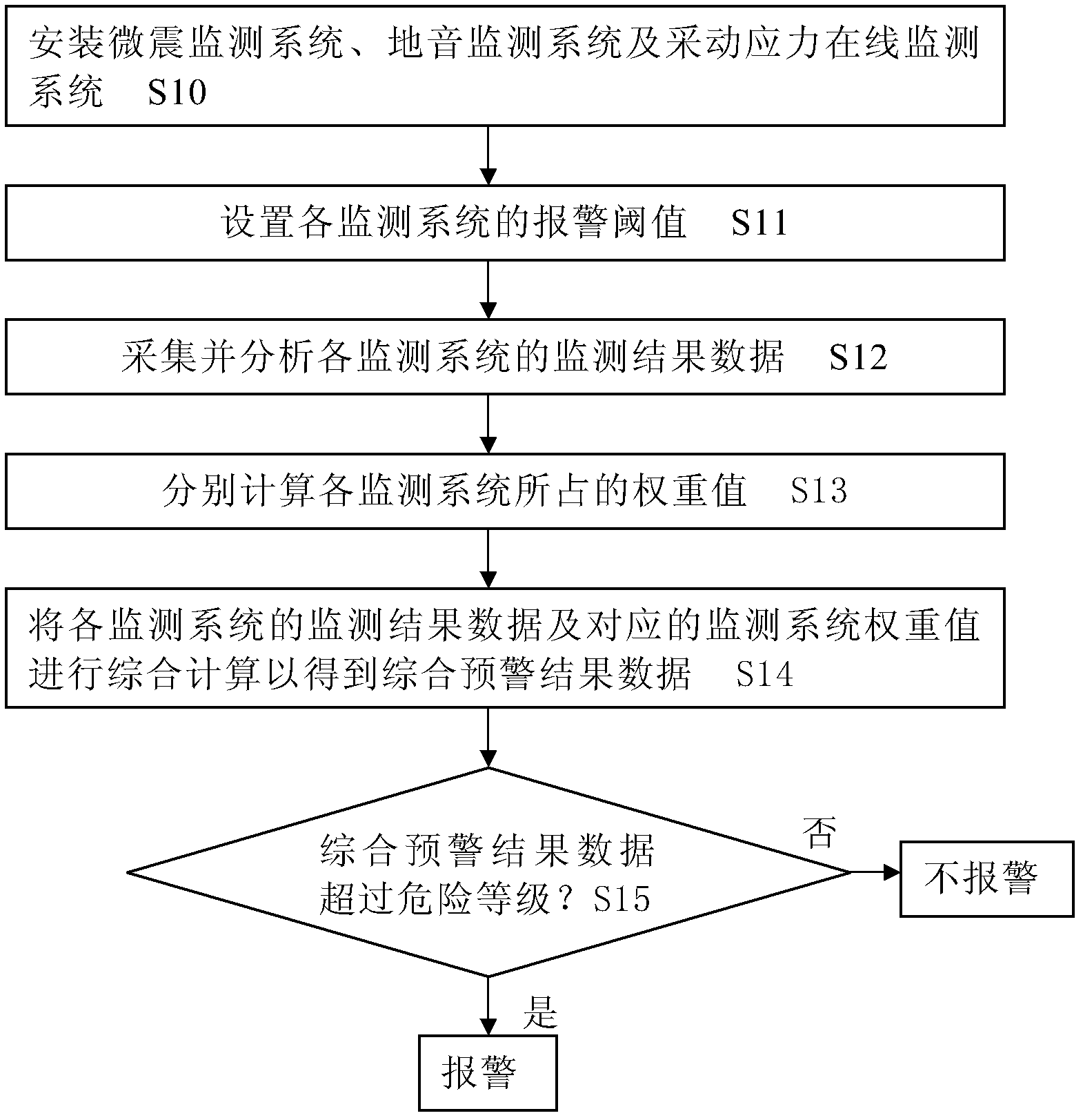
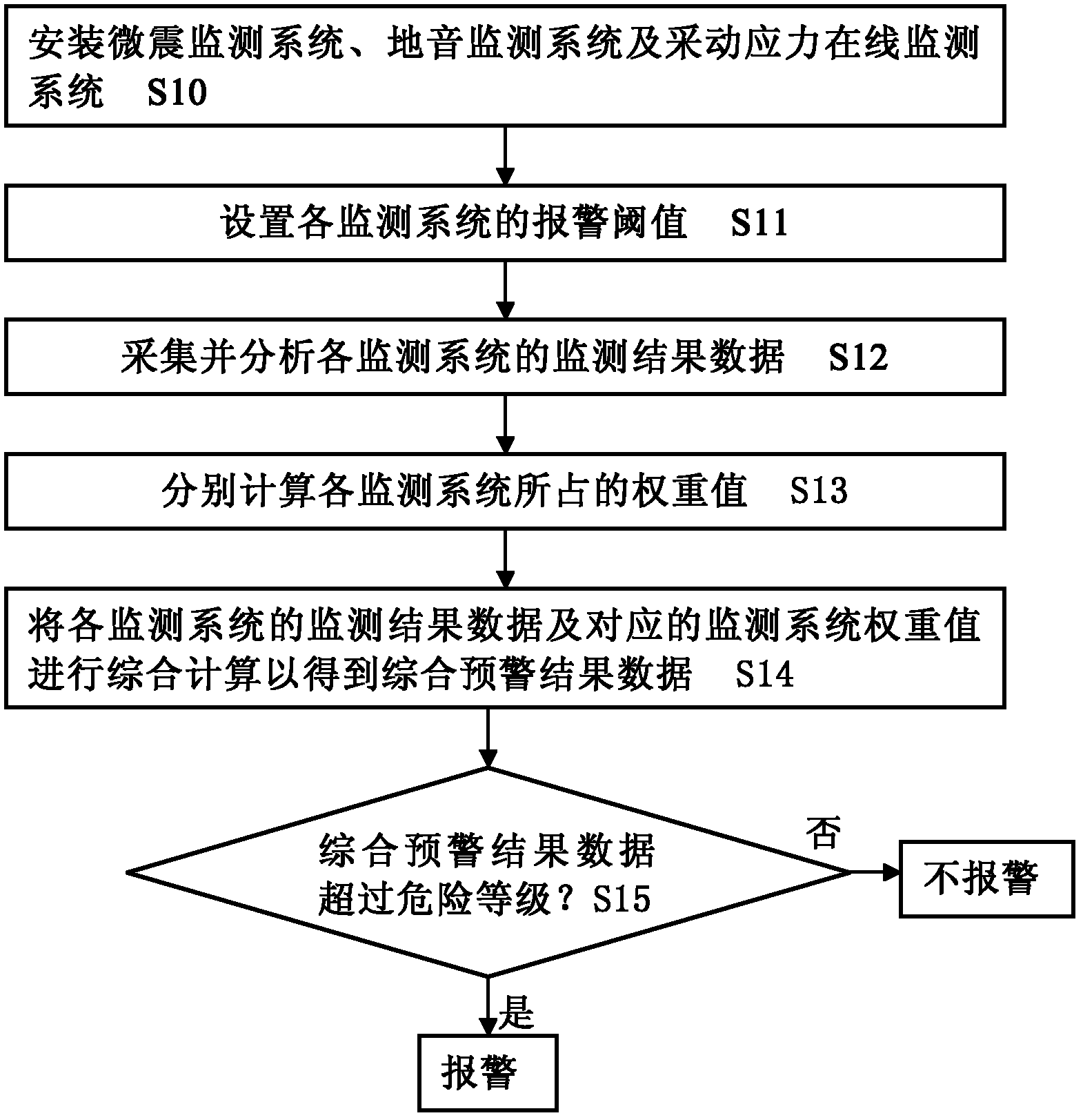
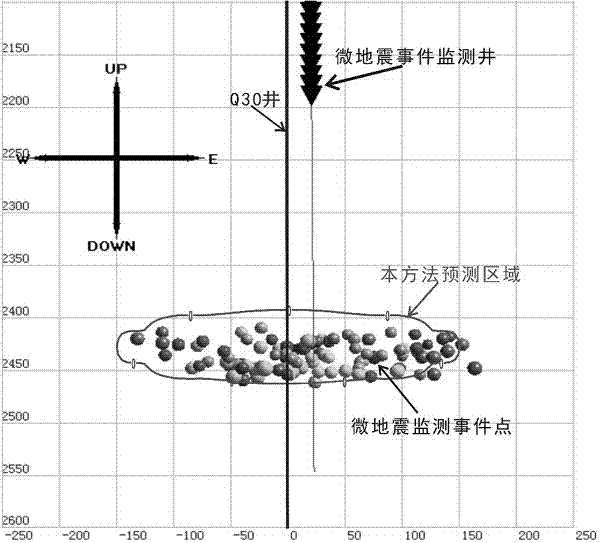
Impact ground pressure split source comprehensive early-warning method of coal mine
ActiveCN102628373AEffective monitoring and early warningAddress abuseMining devicesNoise monitoringMonitoring system
The invention discloses an impact ground pressure split source comprehensive early-warning method of a coal mine which is capable of carrying out split source monitoring early warning by aiming at different load sources of induced impact ground pressure from different space ranges. The method comprises the steps of: installing a microquake monitoring system, a rock noise monitoring system and a mining-induced stress on-line monitoring system; respectively setting the warning threshold value of each monitoring system; collecting and analyzing the monitoring result data of each monitoring system; respectively calculating the weight value occupied by each monitoring system according to the relative importance degree of each monitoring system in the impact ground pressure early warning and the danger level corresponding to the monitoring result data of each monitoring system; comprehensively calculating the monitoring result data of each monitoring system and the weight value of the corresponding monitoring system to obtain the comprehensive early-warning result data; and judging whether the comprehensive early-warning result data exceeds the preset impact ground pressure damager level or not, if so, carrying out the warning, and if not, avoiding the warning. The method has the advantages that missing warning and error warning can be avoided, the operability is high, and in addition, labor and material sources can be saved.
Owner:TIANDI SCI & TECH CO LTD
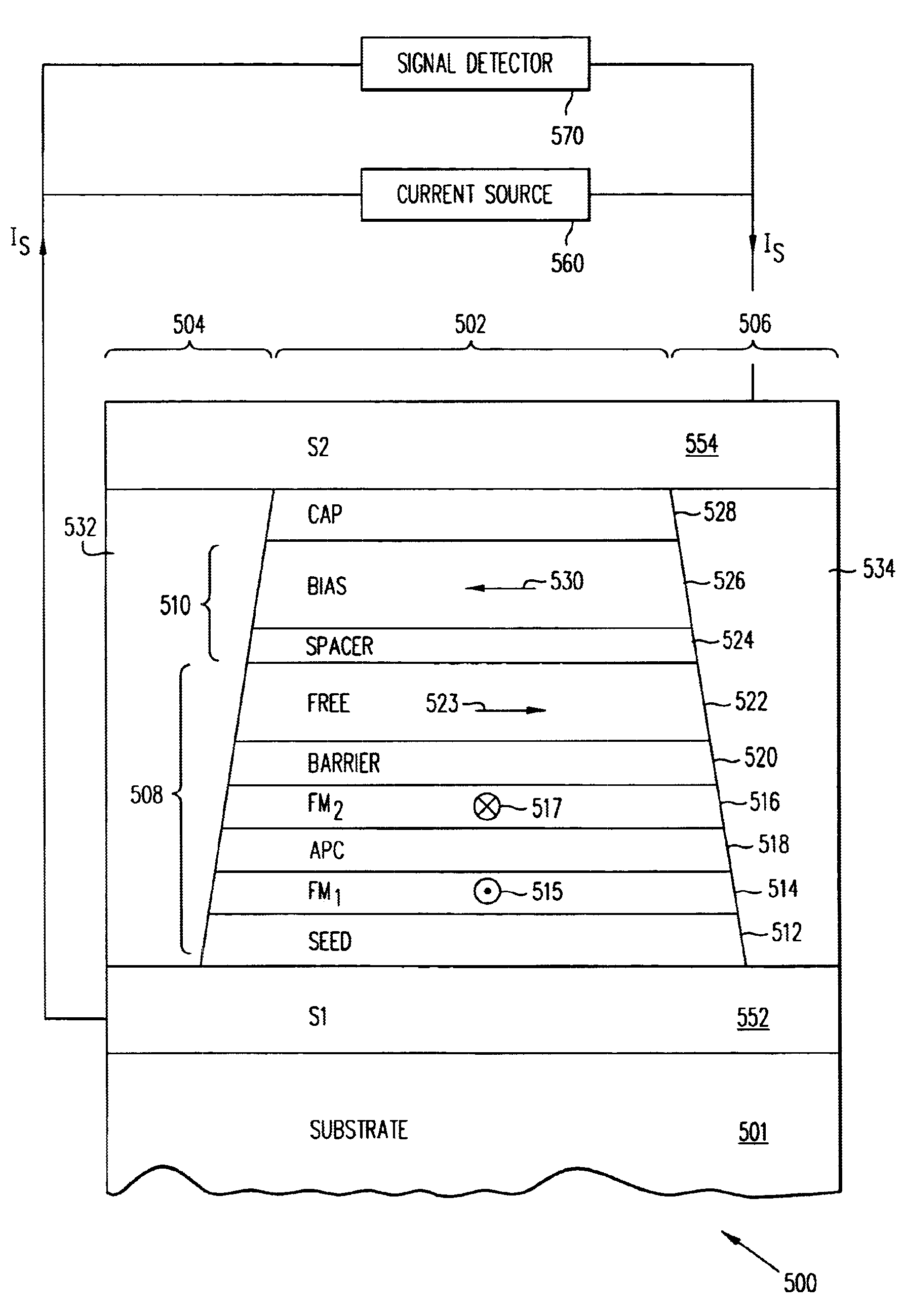
Self-pinned in-stack bias structure for magnetoresistive read heads
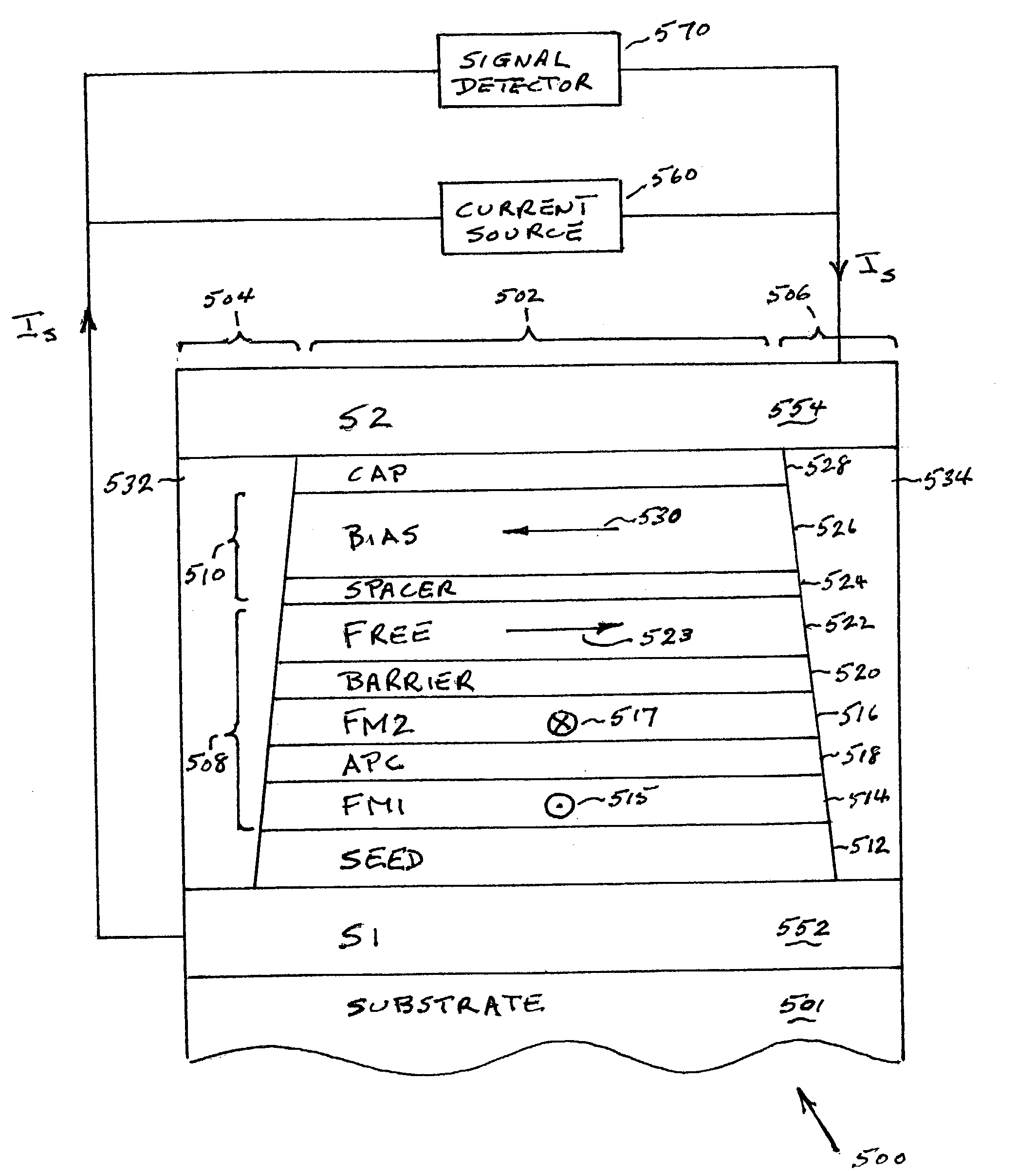
A current-perpendicular-to-the plane magnetoresistive sensor with a self-pinned in-stack longitudinal bias structure is provided comprising a ferromagnetic bias layer formed of material having a negative magnetostriction coefficient and a spacer layer for antiparallel coupling to a free layer. The negative magnetostriction of the bias layer interacts with the lapping-induced stress anisotropy of the sensor stack to provide strong pinning of the magnetization of the bias layer in a direction parallel to the ABS and antiparallel to the direction of the magnetization of the free layer. Magnetostatic coupling of the bias layer magnetization with the free layer provides a longitudinal bias field to stabilize the free layer magnetization.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
IC having TSV arrays with reduced TSV induced stress
ActiveUS8097964B2Increase the areaWide operating temperature rangeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal interconnectInduced stress
An integrated circuit (IC) includes a substrate having a top side having active circuitry thereon including a plurality of metal interconnect levels including a first metal interconnect level and a top metal interconnect level, and a bottom side. At least one TSV array includes a plurality of TSVs. The TSVs are positioned in rows including a plurality of interior rows and a pair of exterior rows and a plurality of columns including a plurality of interior columns and a pair of exterior columns. At least a portion of the TSVs in the array are electrically connected TSVs that are coupled to a TSV terminating metal interconnect level selected from the plurality of metal interconnect levels. At least one of the exterior rows or exterior columns include a lower number of electrically connected TSVs compared to a maximum number of electrically connected TSVs in the interior rows and interior columns, respectively.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
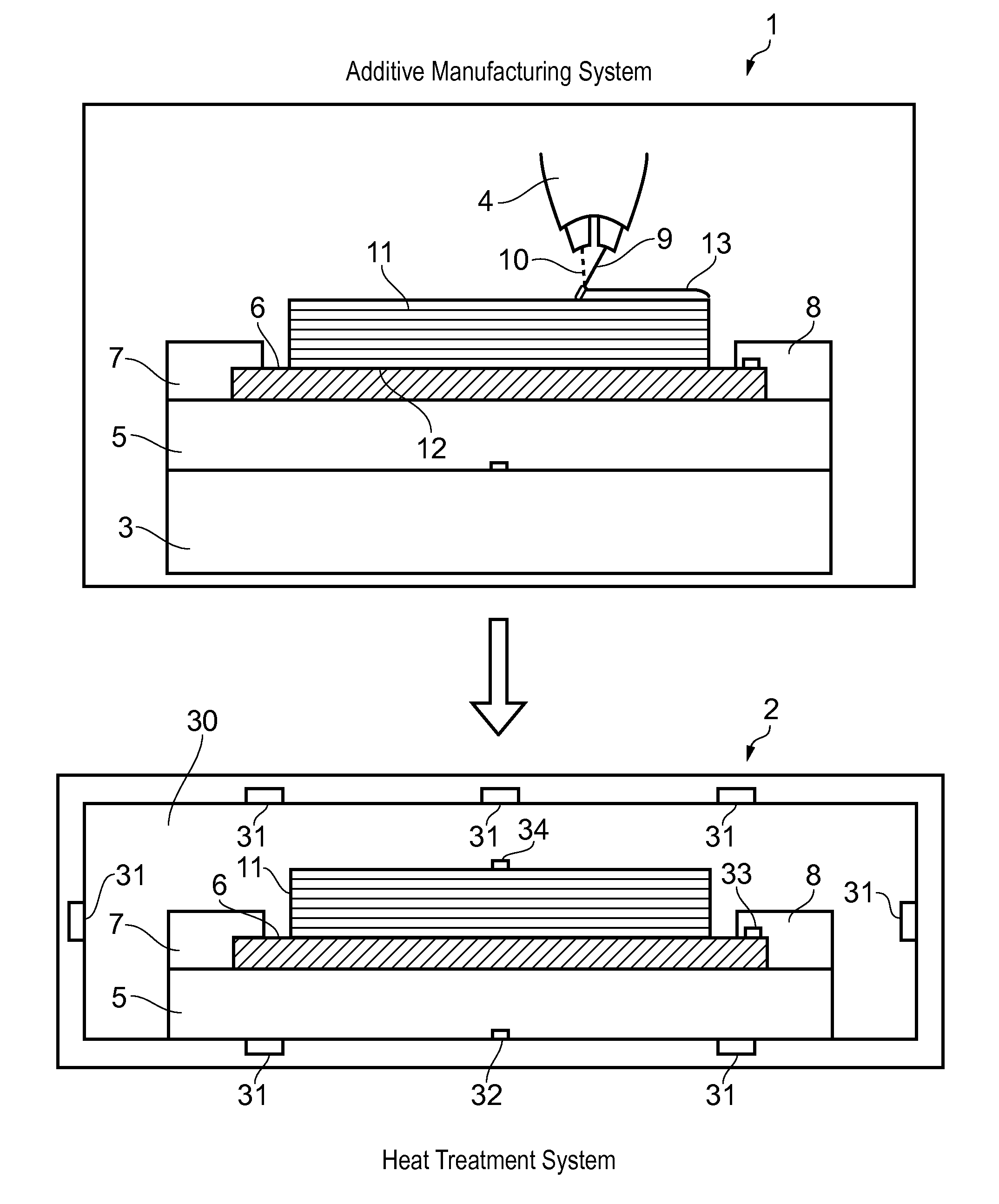
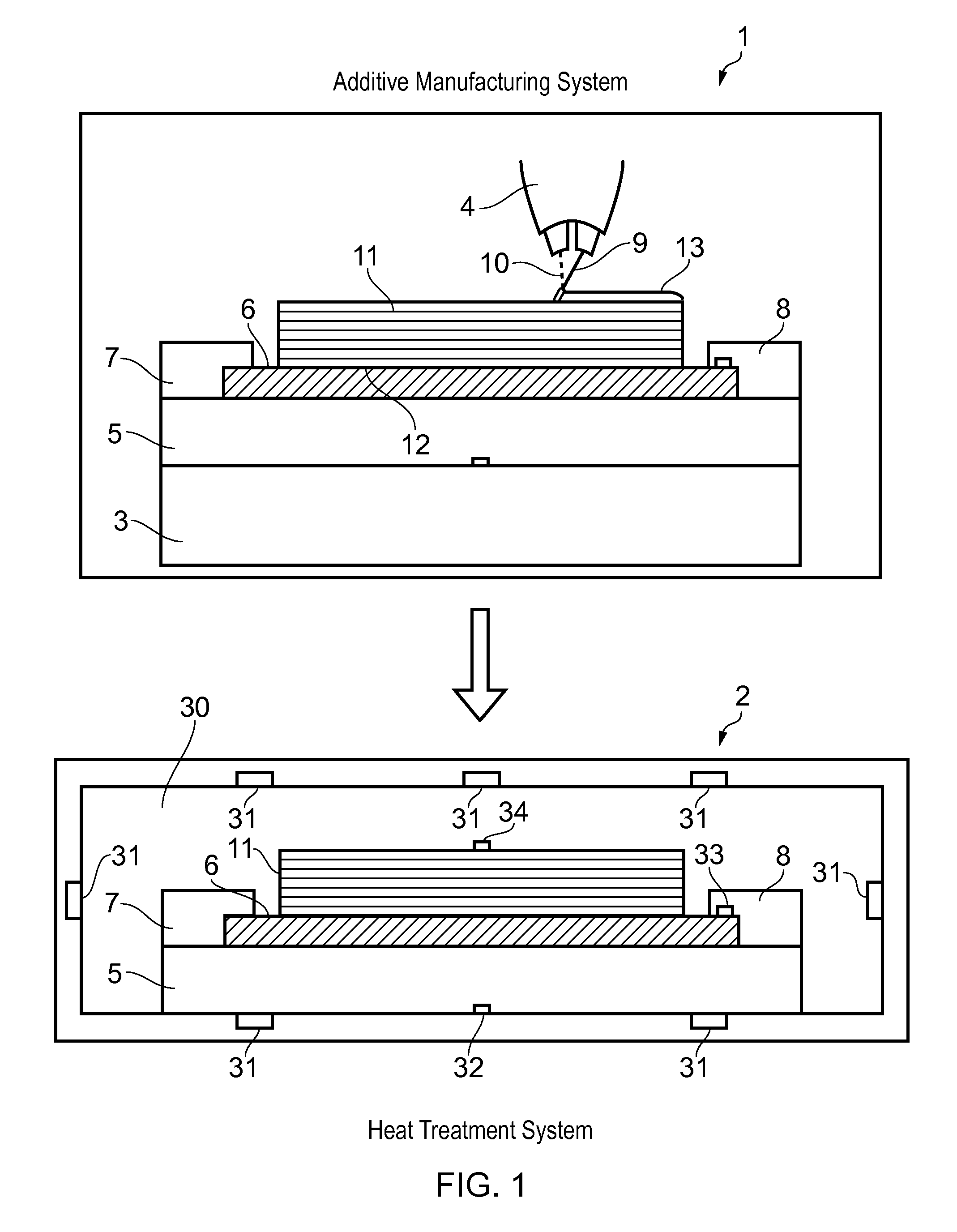
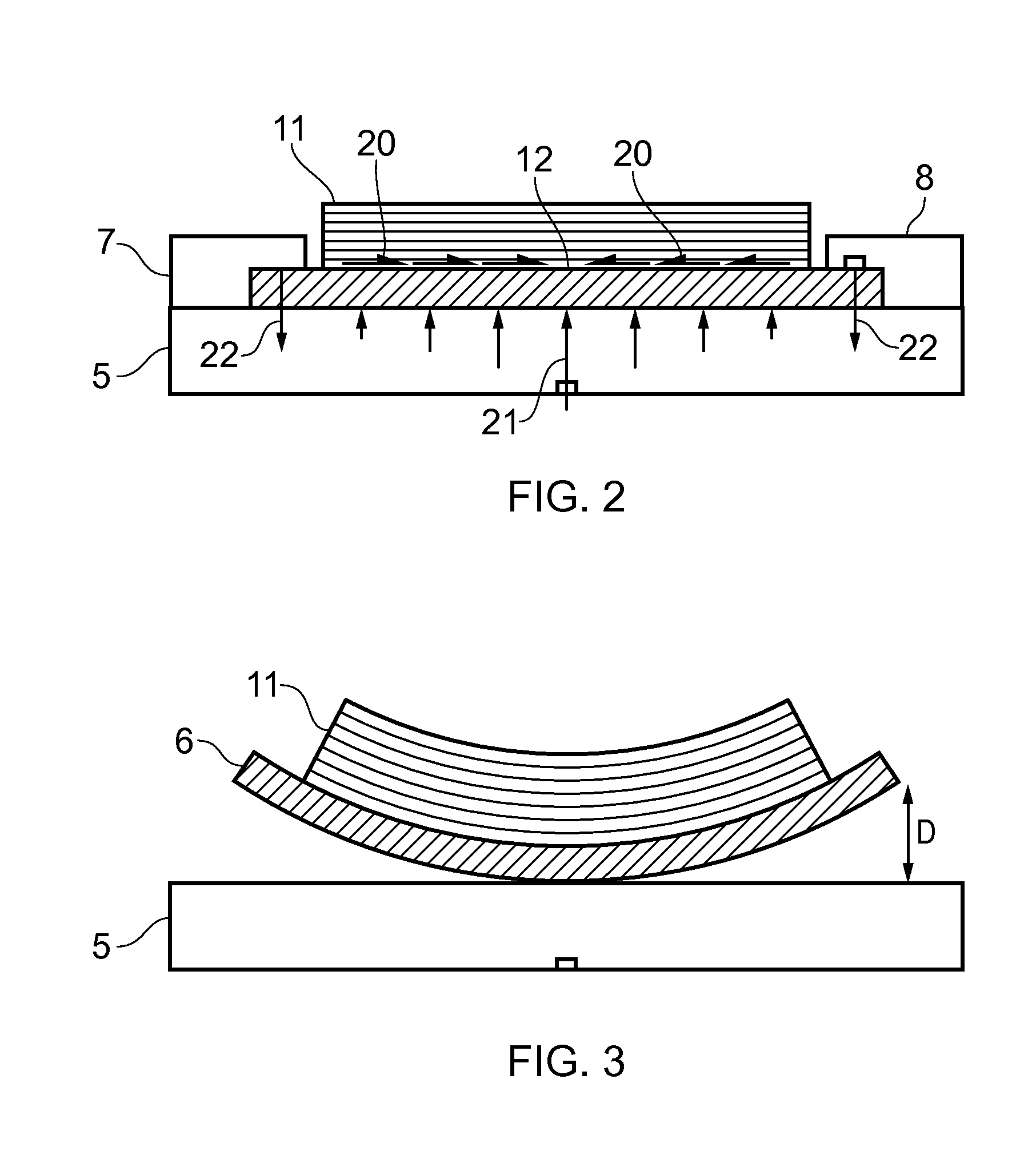
Method of Additive Manufacturing and Heat Treatment
ActiveUS20160108483A1Easy transferImprove performanceManufacturing platforms/substratesWelding/cutting auxillary devicesInduced stressManufacturing systems
A method of additive manufacturing and heat treatment. A substrate is secured to a fixture and an additive manufacturing system is operated to perform a build process by building a part on the substrate secured to the fixture, the part being built by forming a series of layers of metallic material on the substrate, the metallic material melting and solidifying during the build process thereby bonding the part to the substrate and creating thermally induced stress in the part. The part, the substrate and the fixture are moved together from the additive manufacturing system to a heat treatment system, wherein the substrate remains secured to the fixture and the part remains bonded to the substrate as they are moved. The heat treatment system is operated to perform a heat treatment process by heating the part, the substrate and the fixture together thereby relieving the thermally induced stress in the part, the substrate remaining secured to the fixture during the heat treatment process. Finally the substrate is released from the fixture and the part and the substrate are removed from the fixture. The part remains bonded to the support as they are removed from the fixture.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
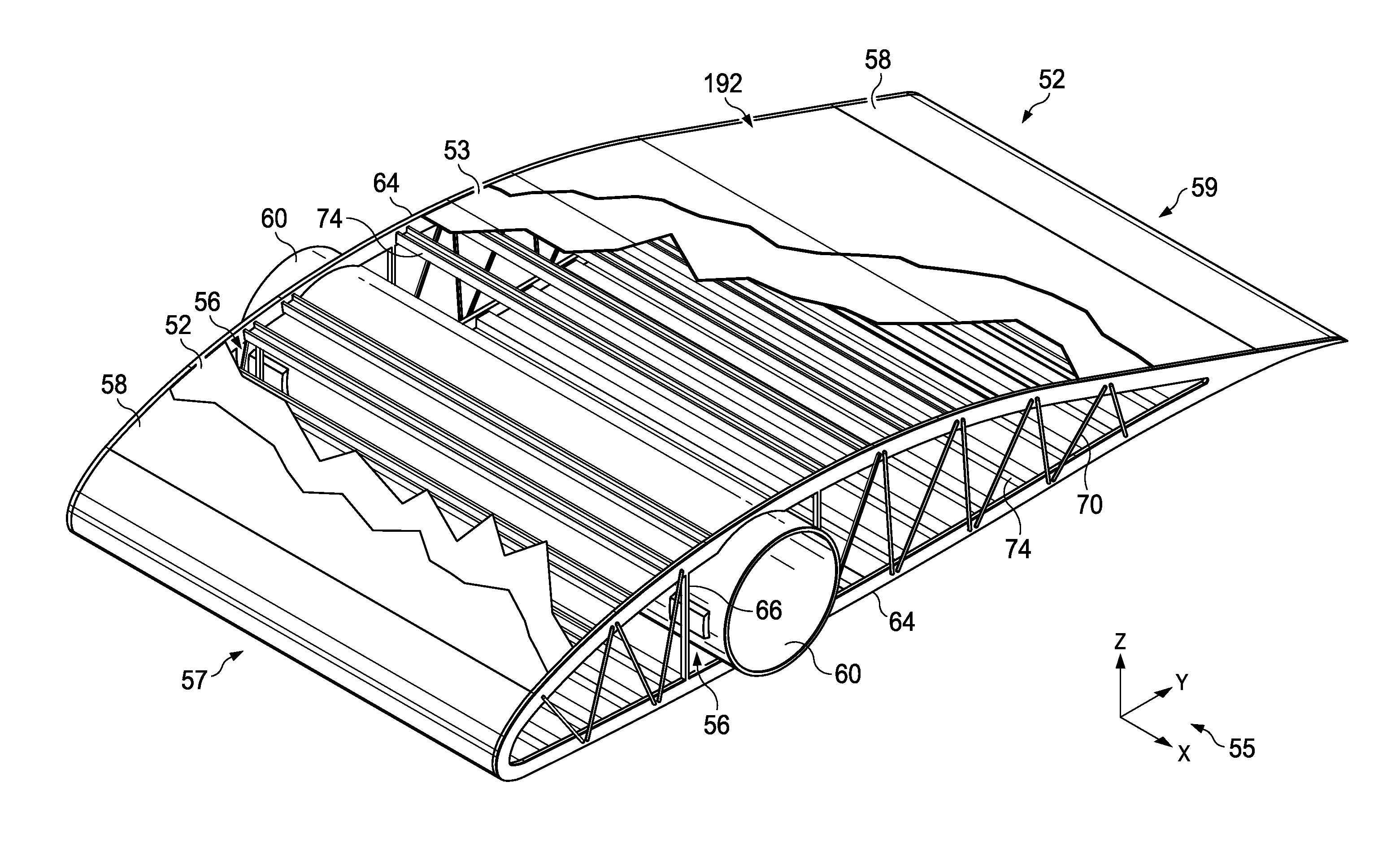
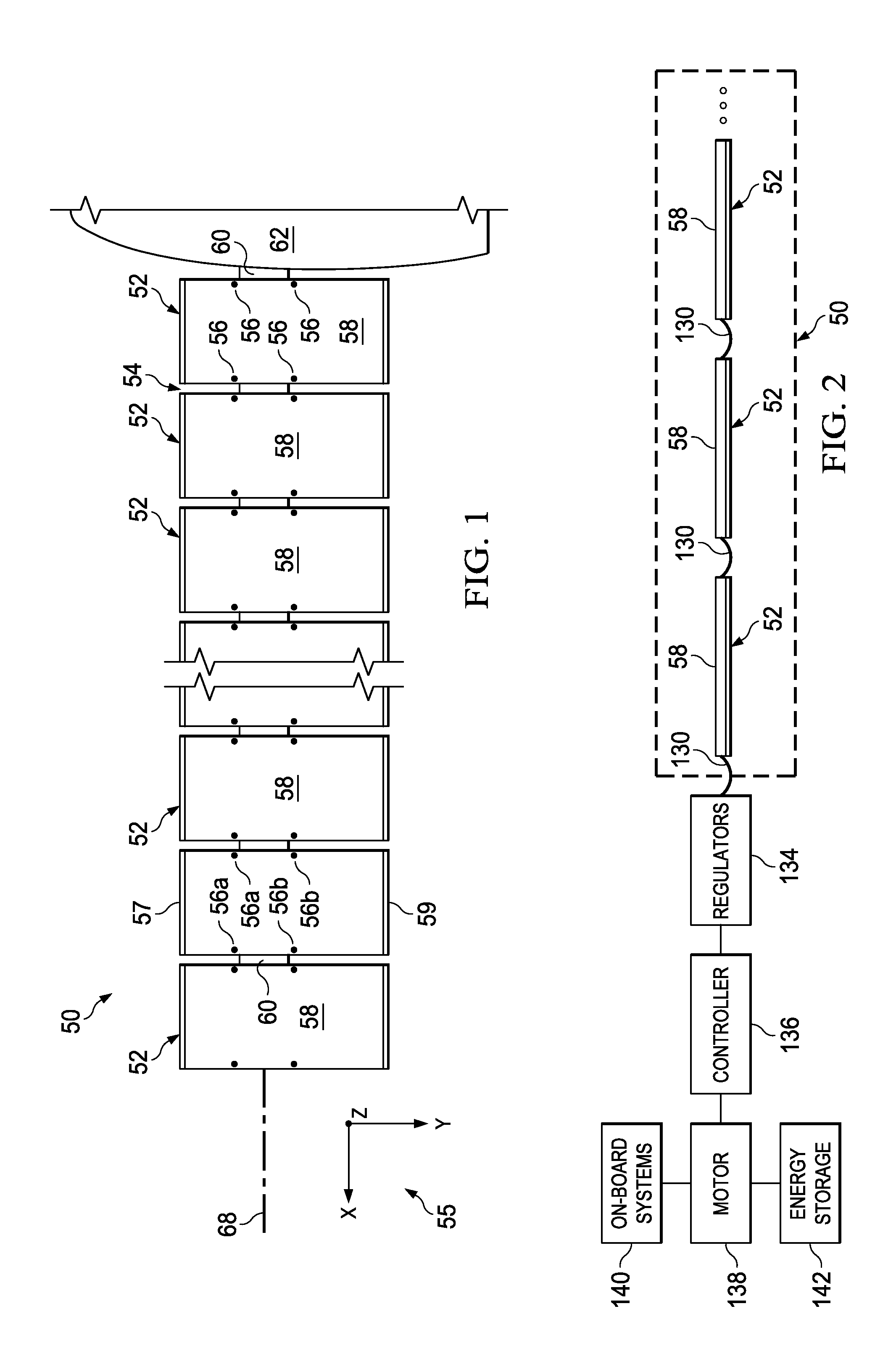
Segmented Aircraft Wing Having Solar Arrays
ActiveUS20130099063A1Long wingspanLow strain levelSpars/stringersSolar panel attachmentsThermal expansionInduced stress
An aircraft wing has a plurality of wing segments mounted on a wing spar by joints that allow relative movement between the spar and the wing segments. Tuning of coefficients of thermal expansion is employed to reduce induced stresses from changes in temperature.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Stress sensor for in-situ measurement of package-induced stress in semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20080067619A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectricityCarbon nanotube
A stress sensor is disclosed herein. The stress sensor includes a plurality of carbon nanotubes in a substrate, and first and second contacts electrically connectable with the plurality of carbon nanotubes. Methods of making and using the stress sensor are also disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Tight reservoir horizontal well volume fracturing process
InactiveCN103527163AIncrease success rateSolve the problem of inadequate transformationFluid removalBottom hole pressureWell logging
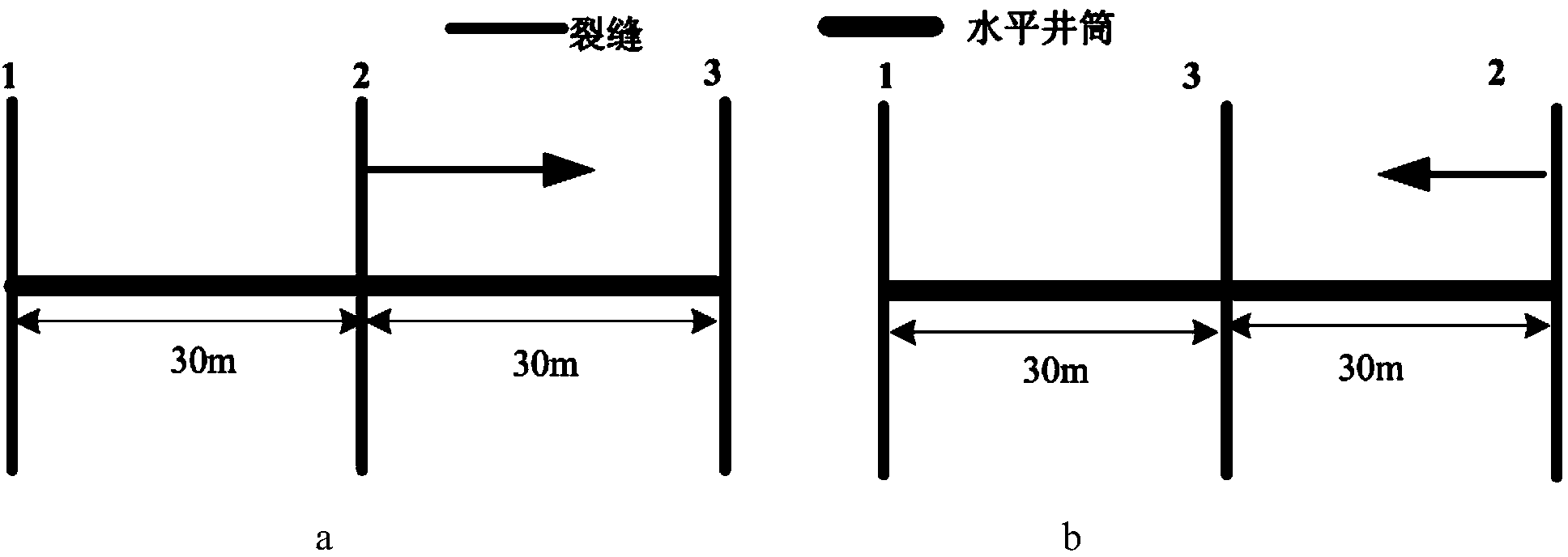
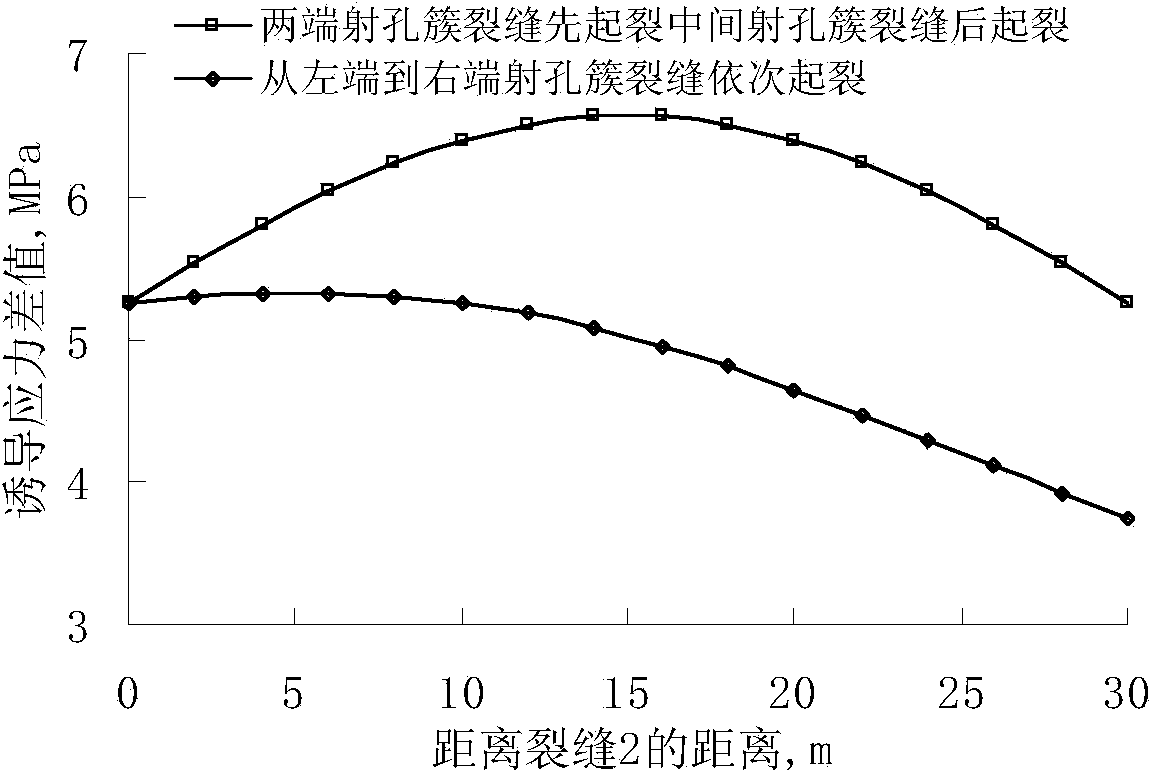
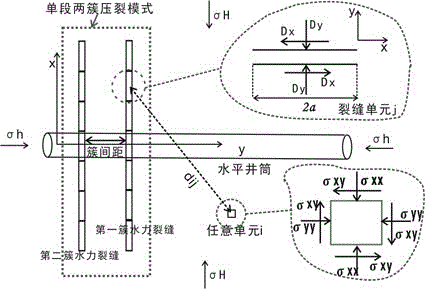
The invention relates to a tight reservoir horizontal well volume fracturing process. Data including in-situ stress magnitude and direction, horizontal well azimuth and length, reservoir Young moduli, a Poisson ratio, a well logging interpretation result and the like are collected and used as basic parameters for calculating induced stress needed for generation of complex cracks in tight reservoir horizontal well volume fracturing; according to reservoir physical characteristics, induced stress difference value variation conditions of three or more perforation clusters in the same fracturing segment according to different crack initiation sequences are contrasted, and preference is given to the perforation cluster crack initiation sequences with the maximal induced stress difference value as the target; preference is given to perforation cluster gaps so that the complex cracks can be formed through fracturing in the same fracturing segment of a horizontal well; in cooperation with perforation parameter optimization and with bottom hole pressure control as the target, the effect that the cracks of the perforation clusters at the two ends are initiated and extended for a certain distance through discharge capacity adjustment and then the discharge capacity is improved to utilize perforation friction for pressing open the cracks of the perforation clusters in the middle is achieved; then, prepad fluid and sand-carrying fluid containing a propping agent are poured into the cracks in sequence to realize transformation of the shape of the complex cracks of the fractured horizontal well.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Volume alternating fracturing method of horizontal well in experimental shale reservoir
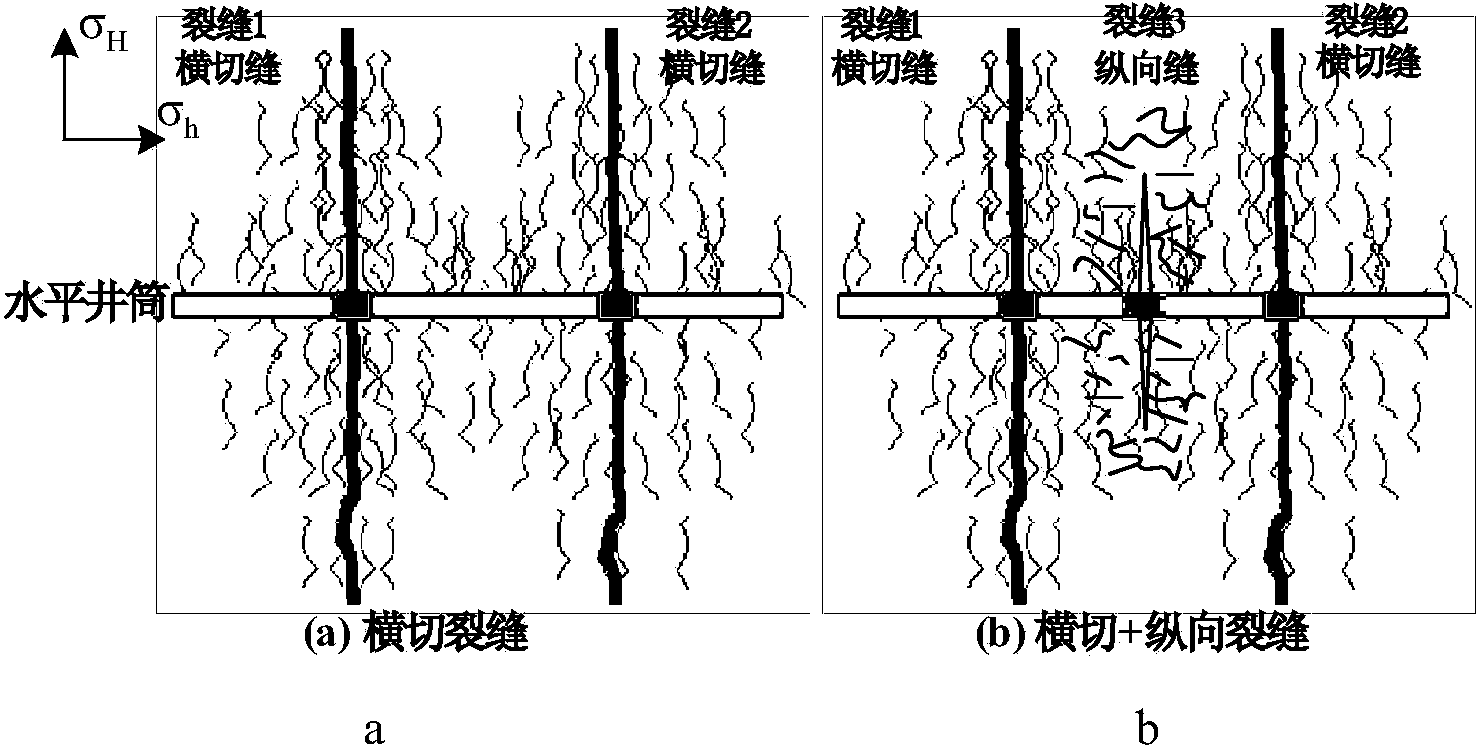
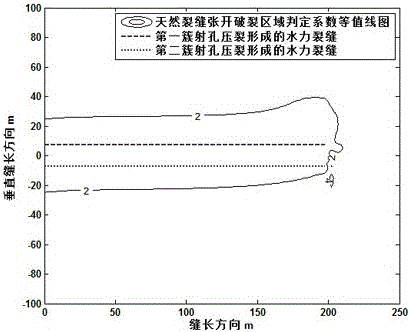
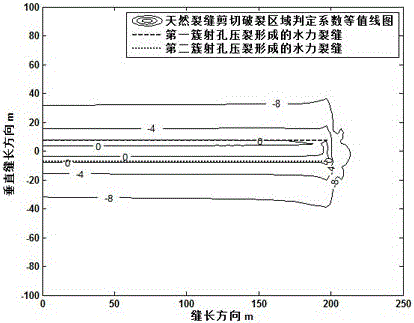
The invention discloses a volume alternating fracturing method of a horizontal well in an experimental shale reservoir. The method comprises the following steps: collecting the stratum parameter, the natural fracture parameter and the hydraulic fracture basic parameter of a reservoir; establishing stretching, shearing and pass through failure criterions of a natural fracture when a hydraulic fracture and the natural fracture are interacted, and quantitatively analyzing the influence on the natural fracture failure by a horizontal principal stress difference; establishing a hydraulic fracture induced stress calculation model, and computing the influence on the induced stress of a middle perforation cluster fracture elongated area by gaps among different perforation cluster fractures and fracture extended lengths; optimally selecting a shale reservoir horizontal well volume fracturing perforation cluster gap and perforation cluster extended lengths at the two ends, so as to promote a middle perforation cluster hydraulic fracturing fracture to be extended and interactively produce stretching, shearing and pass through failure modes with the natural fracture at the same time to form a complex fracture. According to the method, induced stress field produced through the extension of the hydraulic fracture, perforation gaps within the same fracturing section and the extended fracture lengths are organically combined, and the horizontal well volume fracturing technology is properly perfected.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
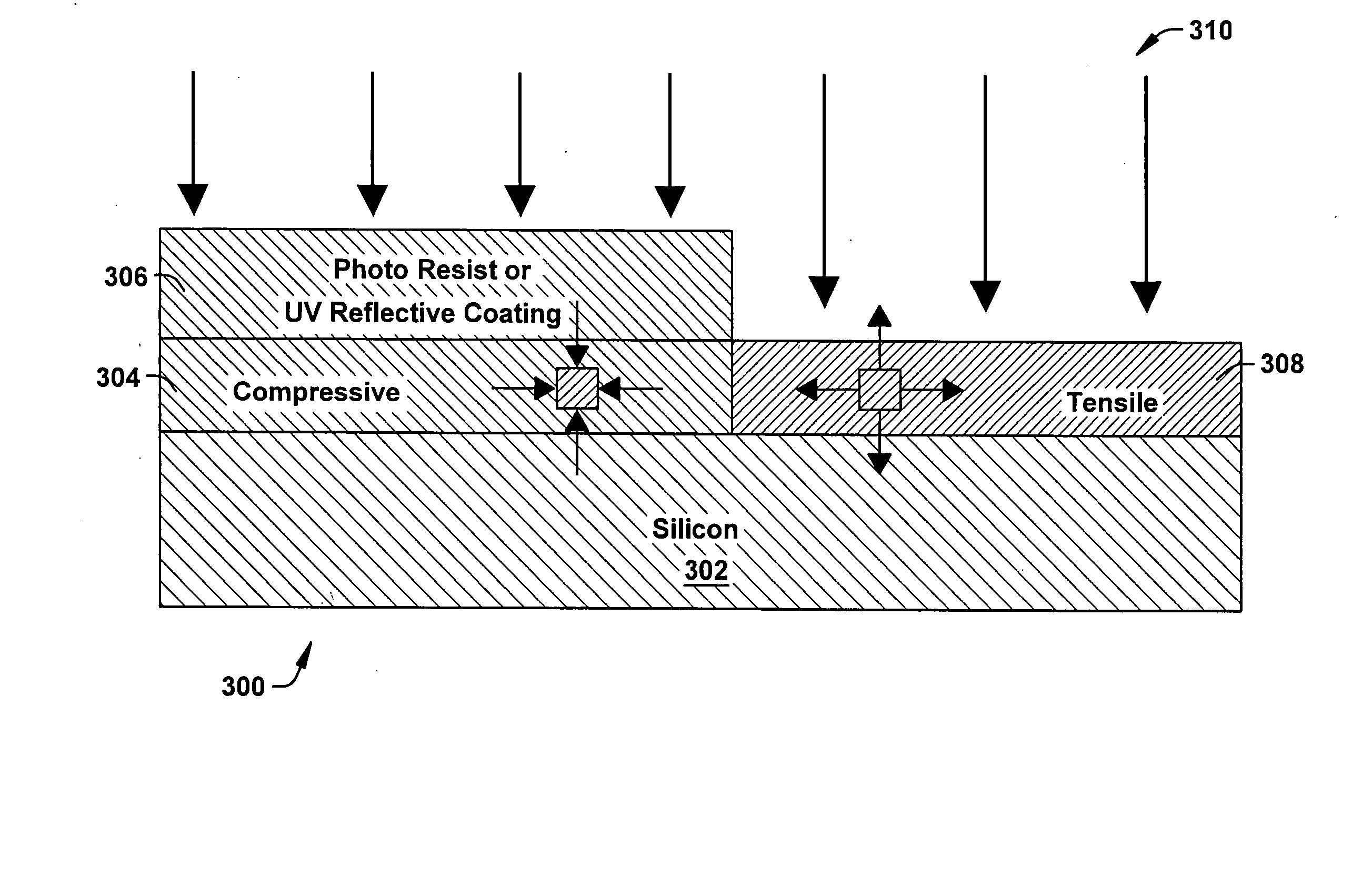
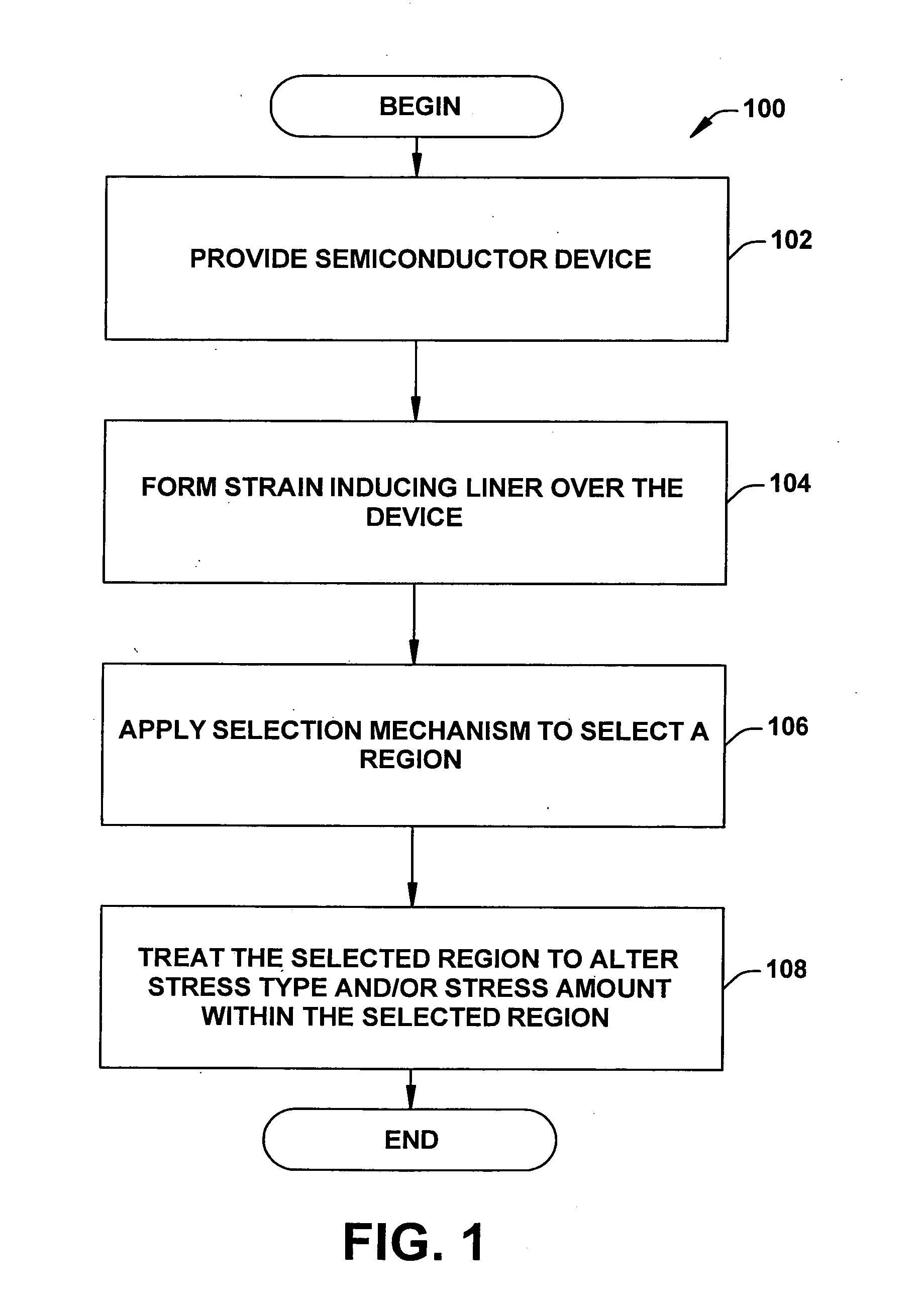
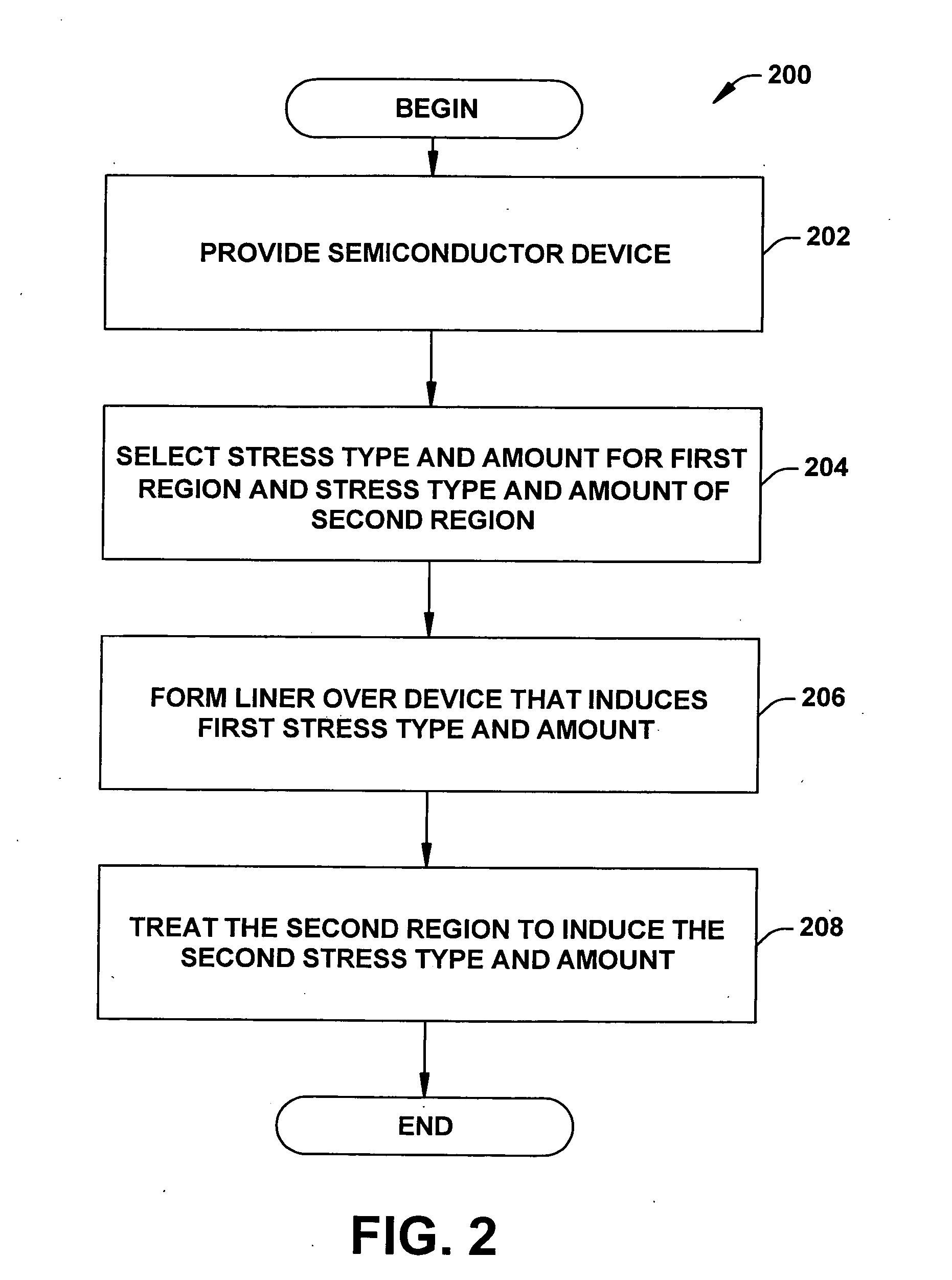
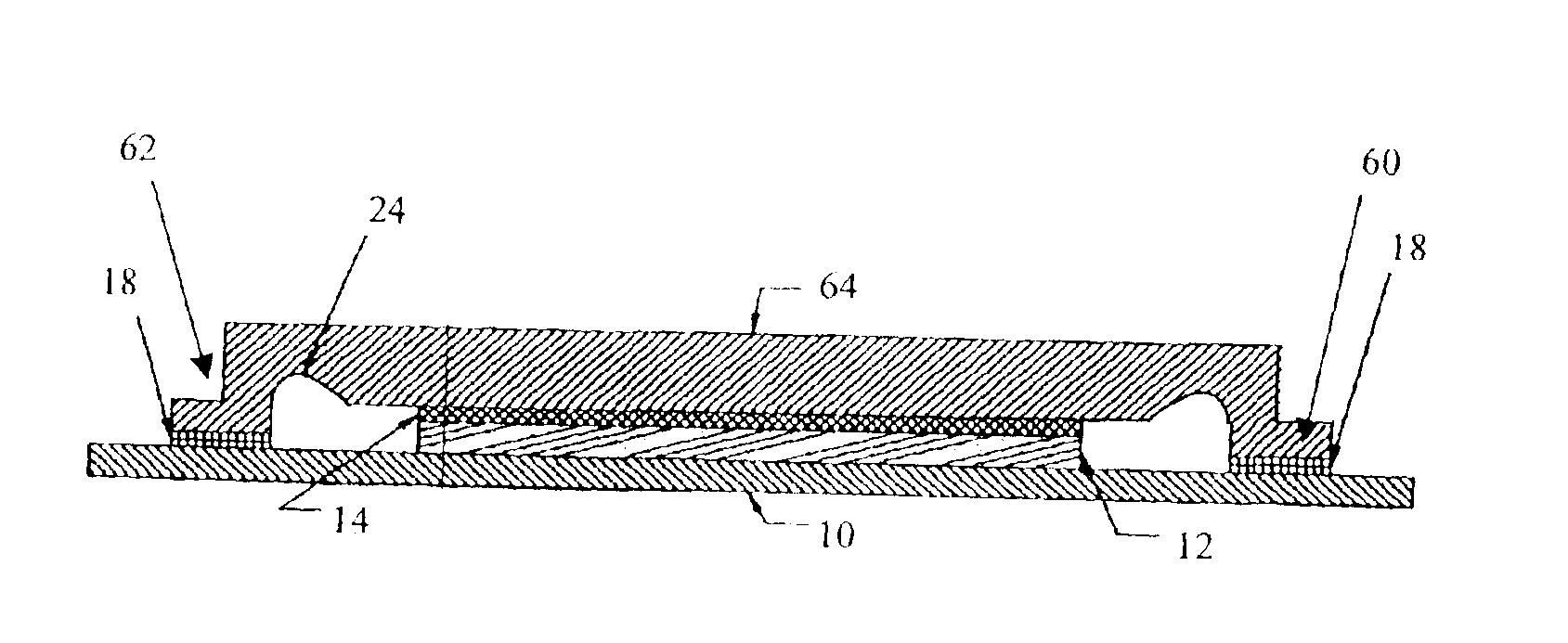
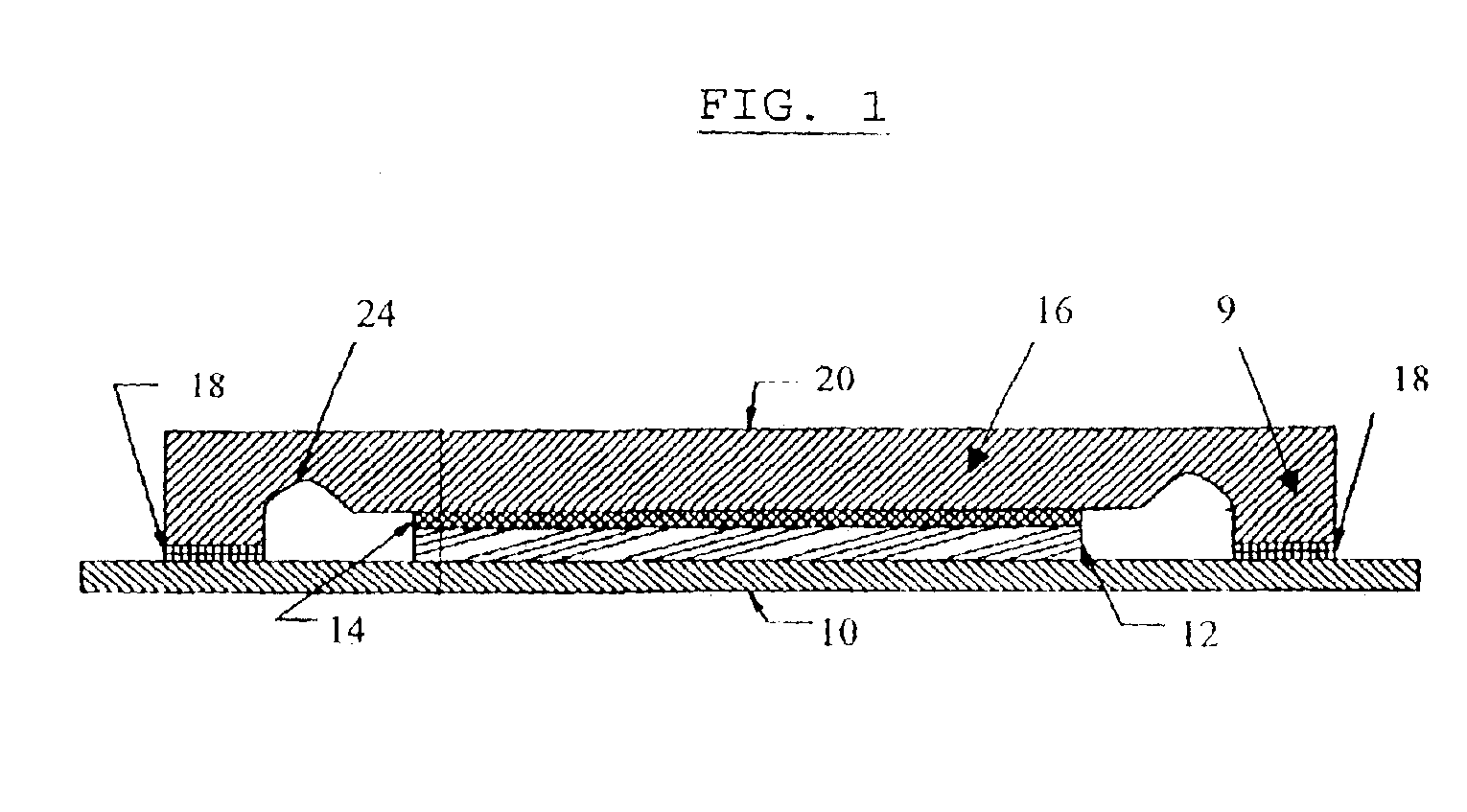
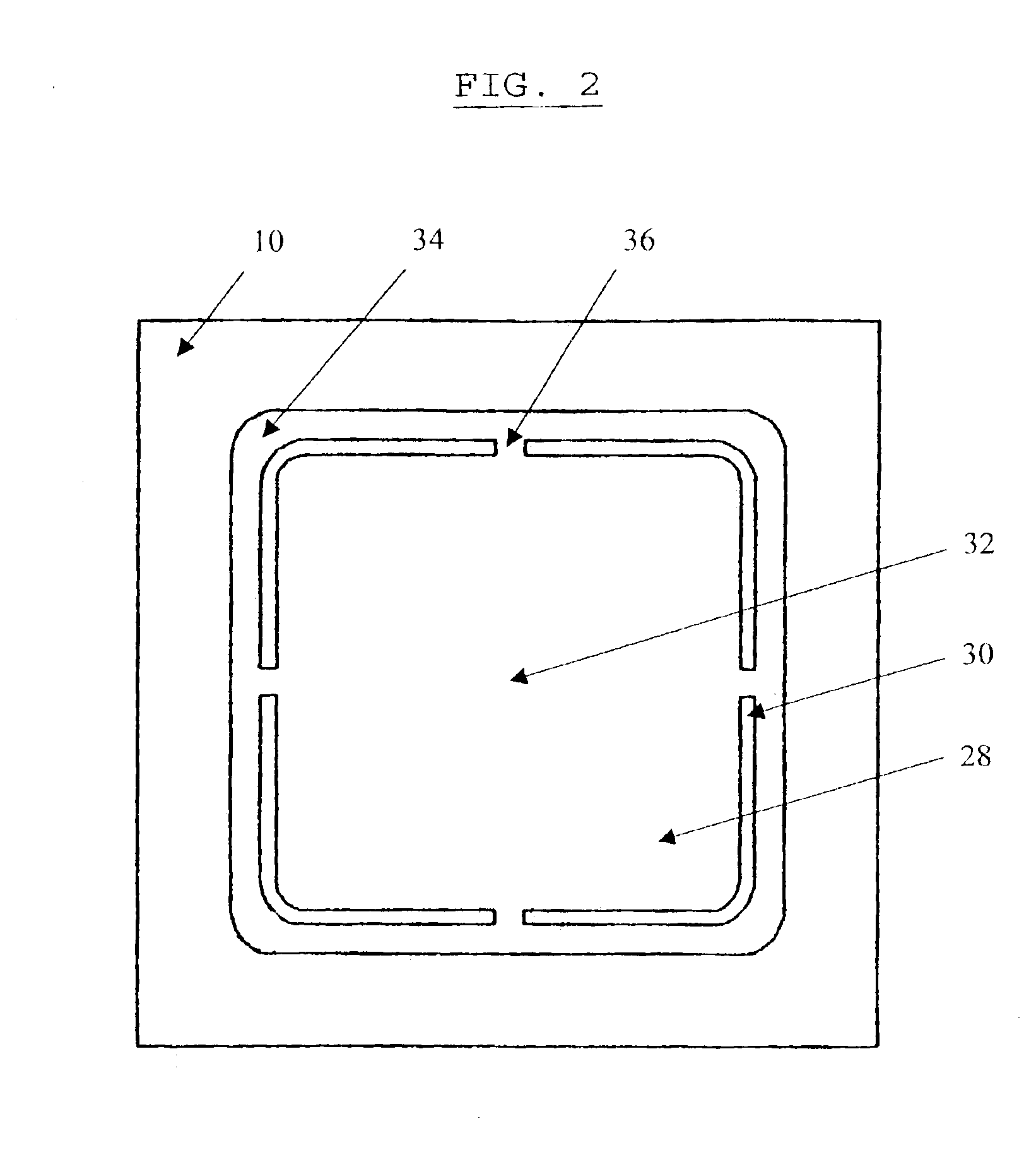
Systems and methods that selectively modify liner induced stress
ActiveUS20060172481A1Facilitates semiconductor fabricationFacilitating device operationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialUltraviolet
The present invention facilitates semiconductor fabrication by providing methods of fabrication that selectively apply strain to multiple regions of a semiconductor device. A semiconductor device having one or more regions is provided (102). A strain inducing liner is formed over the semiconductor device (104). A selection mechanism, such as a layer of photoresist or UV reflective coating is applied to the semiconductor device to select a region (106). The selected region is treated with a stress altering treatment that alters a type and / or magnitude of stress produced by the selected region (108).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Integrated heat spreader lid
InactiveUS6906413B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsEngineeringThermal expansion
A heat spreader lid includes an outer periphery region having a lip for bonding to an underlying substrate board, a center region, and one or more strain isolation regions. The strain isolation regions are located between the center region and the outer periphery region and may comprise a number of slots cut partially or completely through the lid in a pattern surrounding or partially surrounding the center region. The strain isolation regions provide isolation of strain and relief of stress due to thermal expansion of the lid despite constraint at its periphery by the bonded lip, resulting in less thermally-induced warping of the center region, less thermally-induced stress on the bond between the lip and the substrate board, and / or less thermally-induced deflection of the substrate board. The reduced warping, stress, and / or deflection increases the reliability of the system by reducing the propensity for delamination or separation in the interface between the lid and the die, and / or by reducing the chance of structural failure in the bond between the lid and the substrate board.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Cluster interval optimizing method for segmental multi-cluster fracturing of horizontal well of low-permeability oil and gas reservoir
The invention discloses a cluster interval optimizing method for segmental multi-cluster fracturing of a horizontal well of a low-permeability oil and gas reservoir. The cluster interval optimizing method for segmental multi-cluster fracturing of the horizontal well of the low-permeability oil and gas reservoir sequentially comprises the following steps that (1) the induced stress generated by hydraulic fractures in a stratum is calculated; (2) the formation pore pressure after fracturing liquid is leaked off is calculated; (3) formation pore elastic stress after the fracturing liquid is leaked off is calculated; (4) the three induced stress fields and the original ground stress field are superposed, so that a new ground stress field is obtained; (5) facture network waves and the region area are calculated; and (6) a relation curve chart of the fracture cluster interval, the fracture network waves and the region area is drawn with the cluster interval being used as x-coordinates and the fracture network waves and region areas being used as y-coordinates, and the optimal cluster interval is determined. According to the cluster interval optimizing method for segmental multi-cluster fracturing of the horizontal well of the low-permeability oil and gas reservoir, the interference effect of the hydraulic fractures on the original ground stress field is considered, the expanding and shear fracturing behaviors of natural fractures under a complex ground stress field condition are also considered, and the novel cluster interval optimizing method is formed with the optimization goal of obtaining the maximum fracture network wave and the maximum region area; and the novel cluster interval optimizing method is more objective, accurate and practical.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Self-diagnosis system for wind-induced cumulative fatigue damage of pull lug node substructure of mast structure
InactiveCN101825522AEnsure safetyMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesForce measurementFatigue damageReal time analysis
The invention discloses a self-diagnosis system for wind-induced cumulative fatigue damages of a pull lug node substructure of a mast structure. The system comprises a displacement measuring apparatus, a pull rope tension determination module, a welding residual stress determination module, a pull lug substructure wind-induced stress field determination module, a fatigue crack initiation degree real-time analysis module and a man-machine interaction interface, so that the system can timely inform a user of the degree of the cumulative fatigue at the danger point position of the pull lug node substructure of the mast structure and the time when the cumulative fatigue crack initiation occurs and make early warning on cumulative fatigue cracks when the pull lug node substructure of the mast structure is in a good condition. In addition, the system also comprises an acoustic emission sensor, a strain transducer, a fatigue crack growth determination module and an ultimate crack length and fracture analysis module, so that the system can timely inform the user of the degree of the cumulative fatigue crack growth and the time when the fracture occurs, timely repair the crack and ensure the safety of the mast structure when the cumulative fatigue cracks of pull lug node substructure of the mast structure occur.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
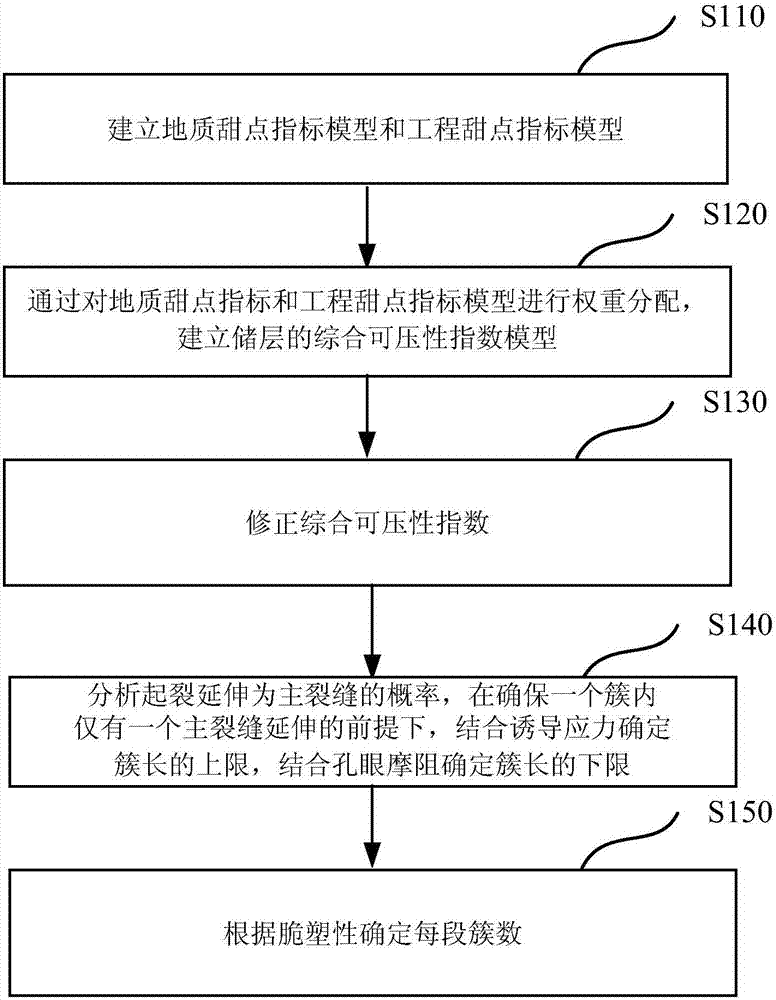
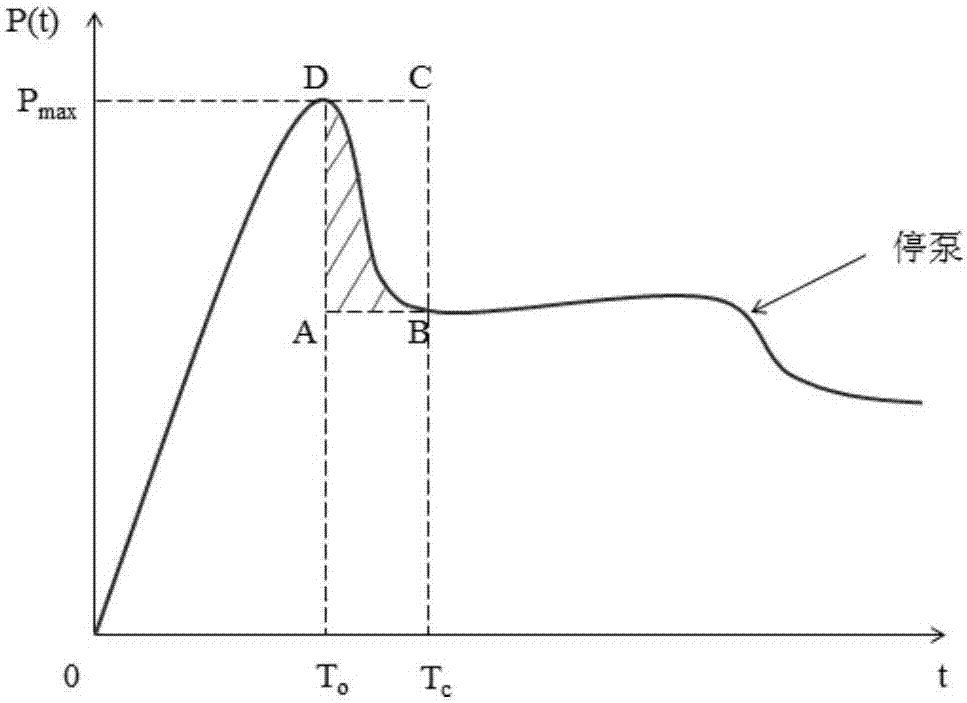
Method for optimizing perforation schemes of staged fracturing clusters of horizontal wells
ActiveCN107229989AOptimal Cluster Perforation ParametersScientific and reasonable designForecastingFluid removalExtension principleHorizontal wells
The invention discloses a method for optimizing perforation schemes of staged fracturing clusters of horizontal wells. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a comprehensive compressibility index model which considers geological dessert and engineering dessert of a reservoir at the same time; determining a dessert position and brittle-plasticity of the reservoir by utilizing the model; and comprehensively determining an optimum cluster length and an optimum cluster number by combining an induced stress and a hole friction resistance according to a major fracture randomness extension principle. According to the method, the risk of causing ineffective and low-efficiency fractures can be reduced, accurate guidance can be provided for setting perforation schemes of staged fracturing clusters of horizontal wells, and the optimization result can greatly increase the reformation volume and remarkably improve the construction effect so as to obtain maximum economic benefit.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
NFETs using gate induced stress modulation
InactiveUS20050064646A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialField-effect transistor
A method for manufacturing an integrated circuit comprising a plurality of semiconductor devices including an n-type field effect transistor and a p-type field effect transistor by covering the p-type field effect transistor with a mask, and oxidizing a portion of a gate polysilicon of the n-type field effect transistor, such that tensile mechanical stresses are formed within a channel of the n-type field effect transistor.
Owner:IBM CORP
Self-pinned in-stack bias structure for magnetoresistive read heads
A current-perpendicular-to-the plane magnetoresistive sensor with a self-pinned in-stack longitudinal bias structure is provided comprising a ferromagnetic bias layer formed of material having a negative magnetostriction coefficient and a spacer layer for antiparallel coupling to a free layer. The negative magnetostriction of the bias layer interacts with the lapping-induced stress anisotropy of the sensor stack to provide strong pinning of the magnetization of the bias layer in a direction parallel to the ABS and antiparallel to the direction of the magnetization of the free layer. Magnetostatic coupling of the bias layer magnetization with the free layer provides a longitudinal bias field to stabilize the free layer magnetization.
Owner:IBM CORP
Protective seal ring for preventing die-saw induced stress
ActiveUS8334582B2Crack-propagation caused by die-sawing is reducedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipEngineering
A semiconductor chip includes a semiconductor substrate; a plurality of low-k dielectric layers over the semiconductor substrate; a first passivation layer over the plurality of low-k dielectric layers; and a second passivation layer over the first passivation layer. A first seal ring is adjacent to an edge of the semiconductor chip, wherein the first seal ring has an upper surface substantially level to a bottom surface of the first passivation layer. A second seal ring is adjacent to the first seal ring and on an inner side of the semiconductor chip than the first seal ring. The second seal ring includes a pad ring in the first passivation layer and the second passivation layer. A trench ring includes at least a portion directly over the first seal ring. The trench ring extends from a top surface of the second passivation layer down to at least an interface between the first passivation layer and the second passivation layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
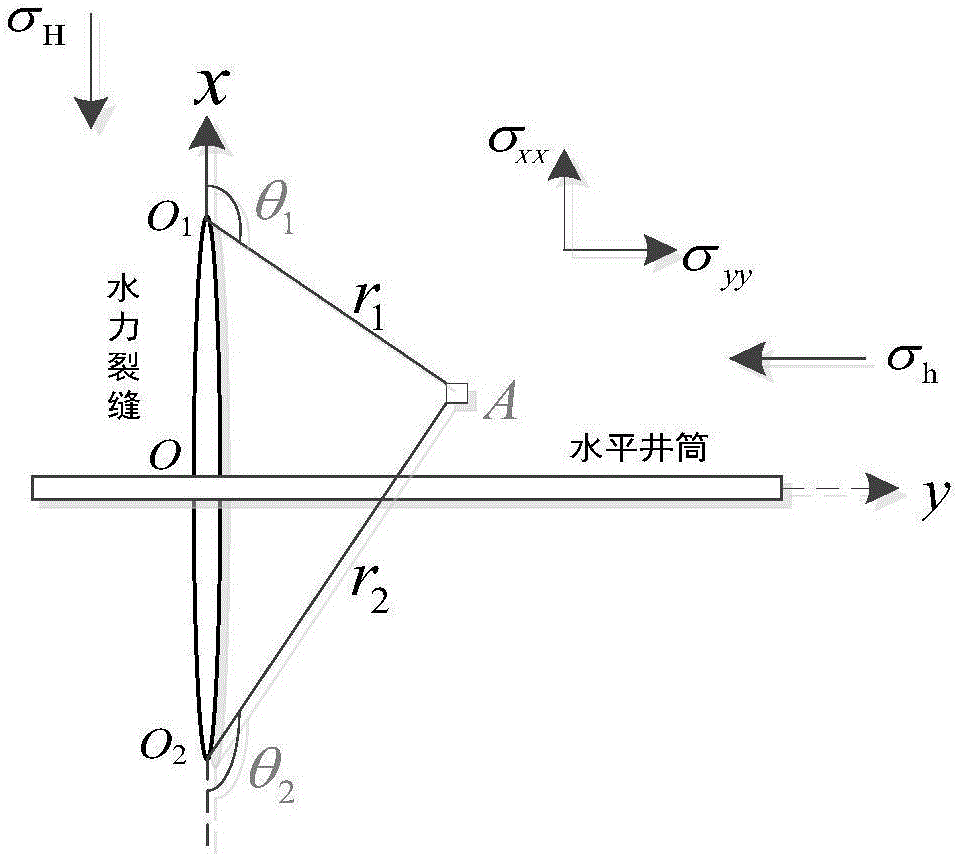
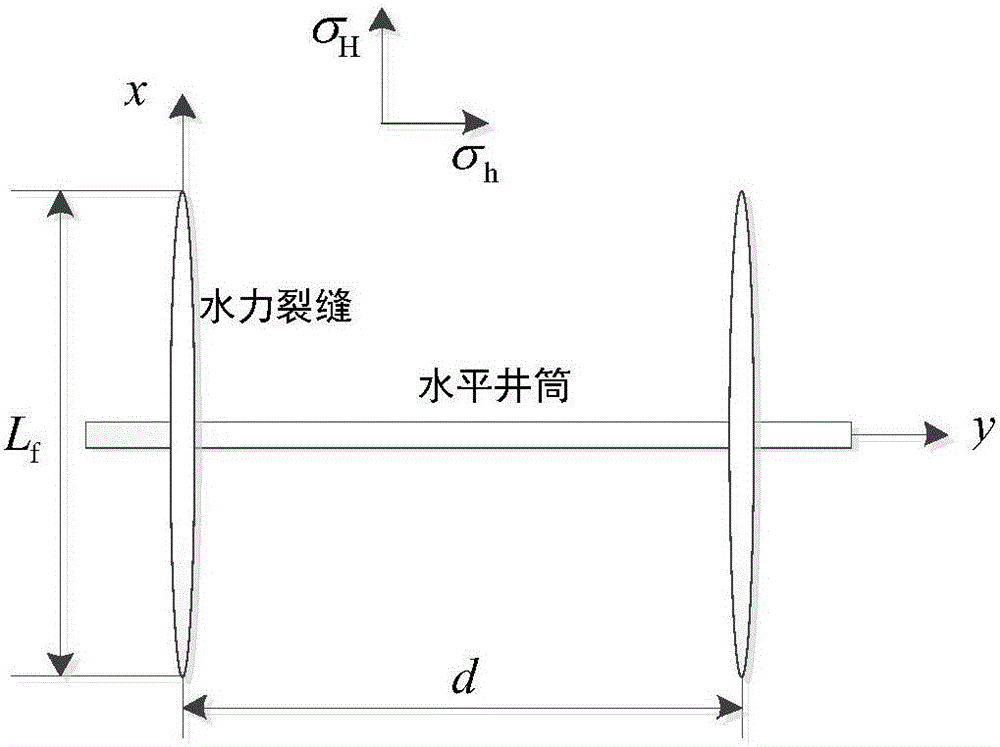
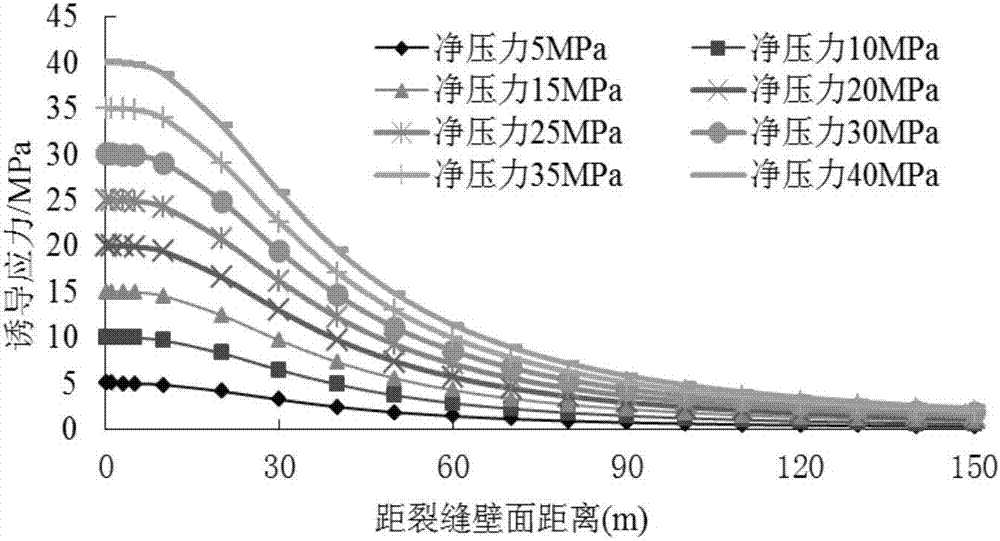
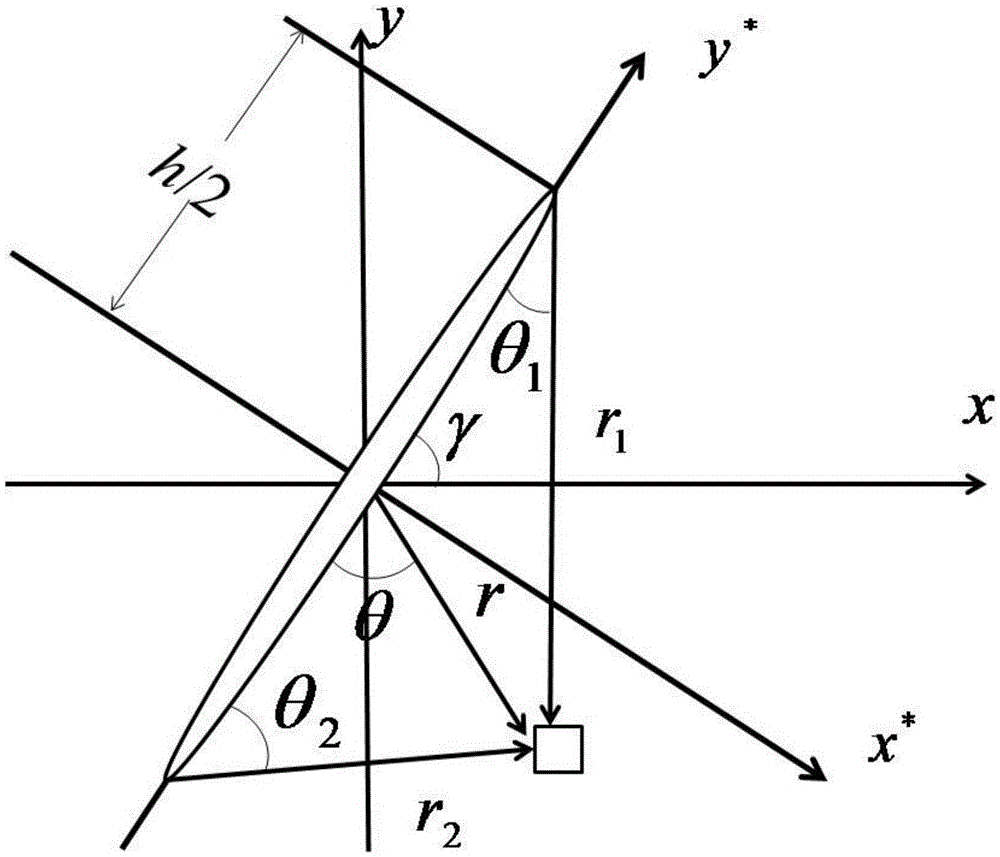
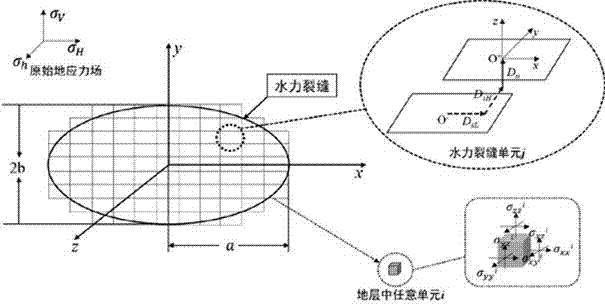
Method for calculating hydraulic fracturing inclined crack induced stress of shale reservoir
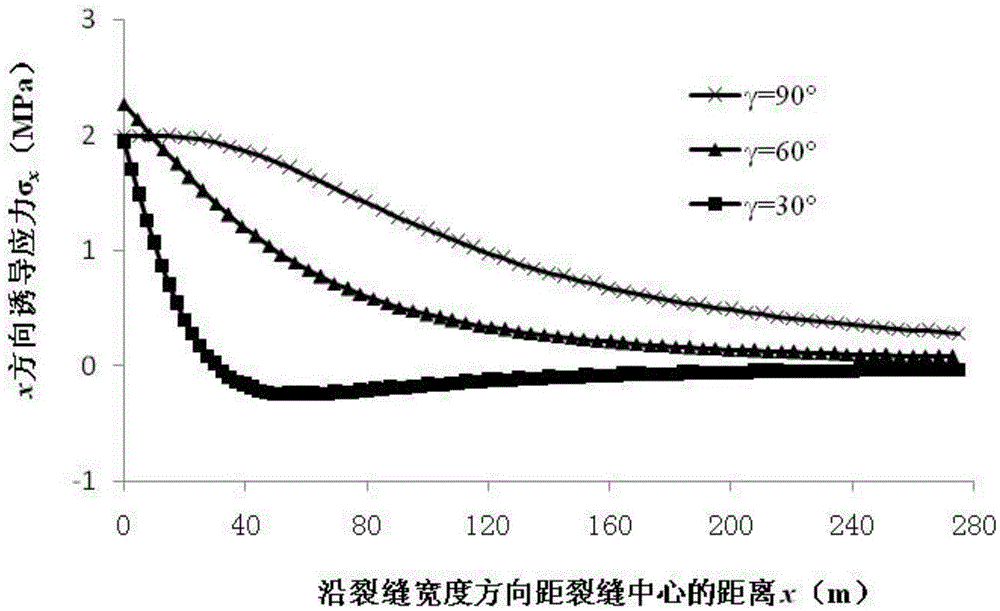
ActiveCN105550410AImprove fracturing effectSpecial data processing applicationsHydraulic fracturingInduced stress
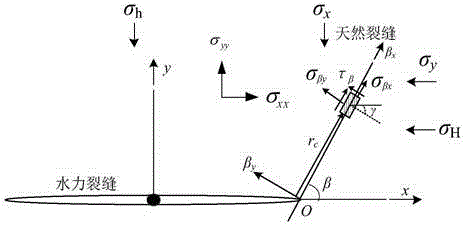
The application discloses a method for calculating a hydraulic fracturing inclined crack induced stress of a shale reservoir. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, collecting basic parameters of the shale reservoir and a hydraulic crack; 2, establishing a calculation model of the hydraulic fracturing inclined crack induced stress of the shale reservoir; and 3, calculating the hydraulic fracturing inclined crack induced stress of the shale reservoir, and by analyzing change rules of the inclined crack induced stress in an x crack width direction and a z crack length direction, determining a stress inverted region. According to the method disclosed by the application, aiming at the inclined crack induced stress formed in the horizontal well fracturing process of the shale reservoir, simulation is carried out, and an induced stress field distribution condition under the inclined crack is analyzed, so that guidance is provided for optimization of a hydraulic crack position where the complex crack is formed by a fracturing horizontal well of the shale reservoir, and a fracturing effect of the shale gas reservoir is improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
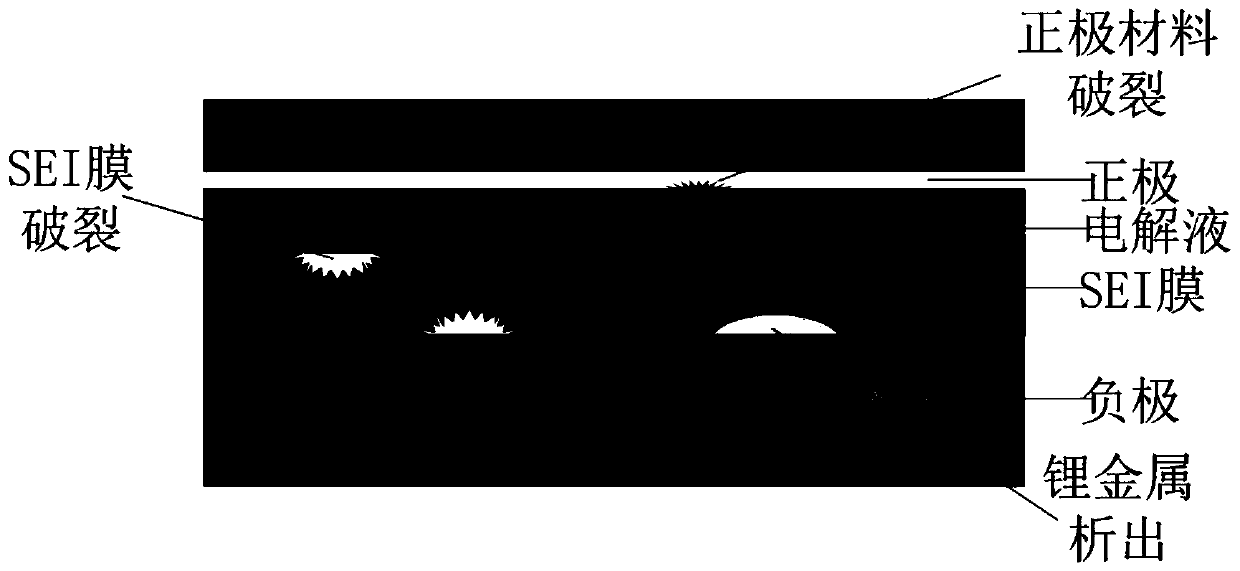
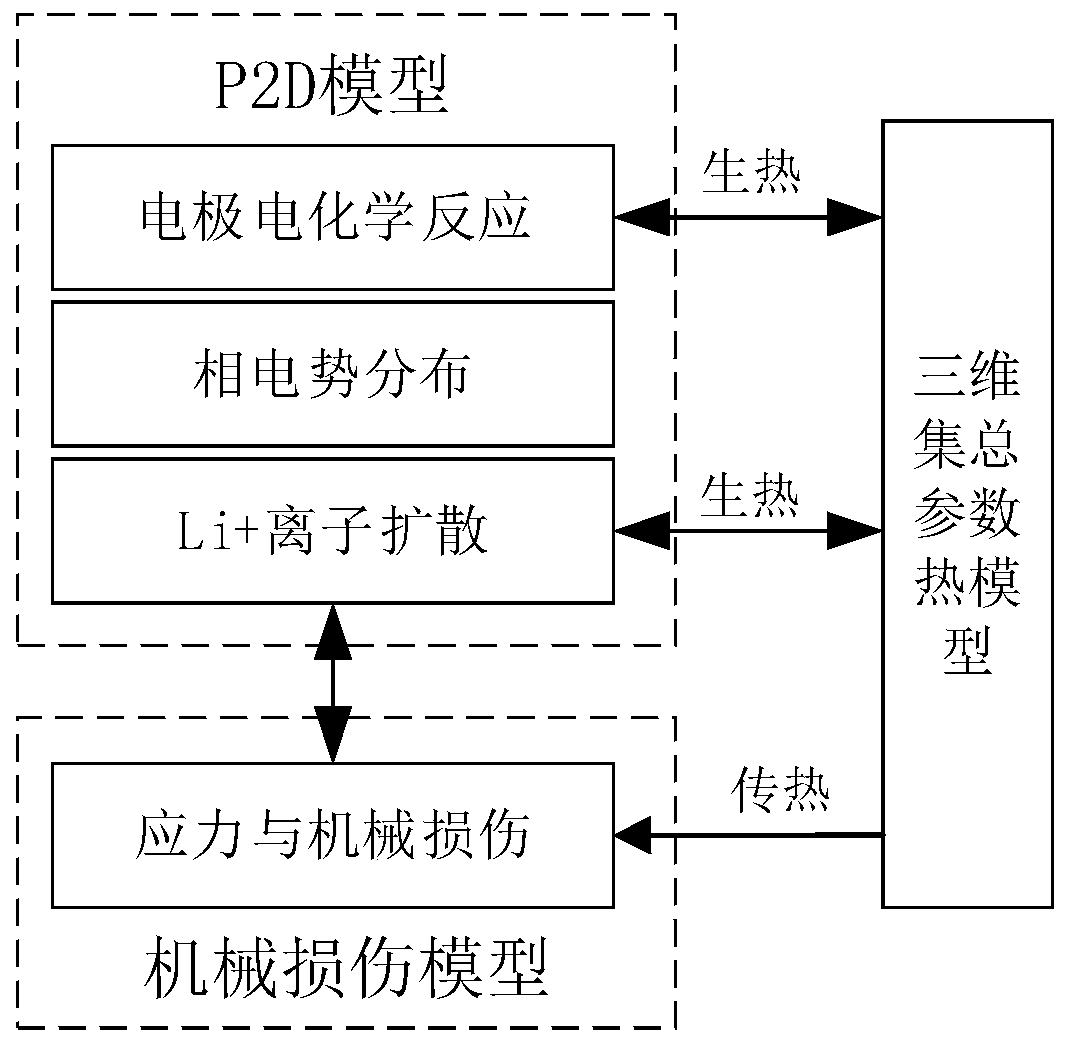
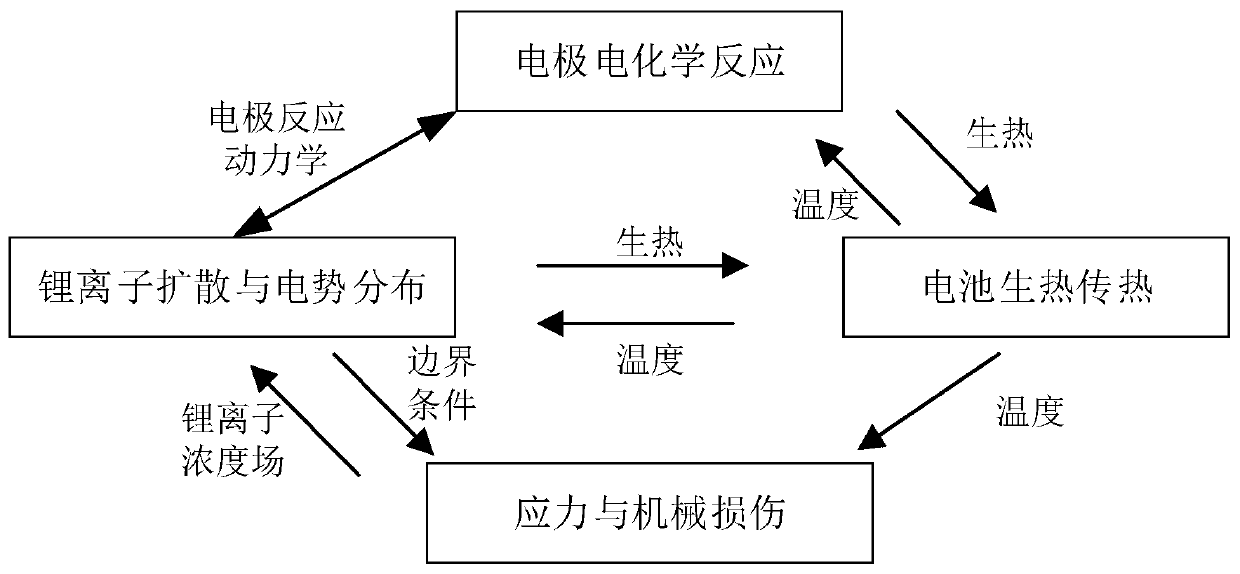
Electrochemical-thermal-mechanical coupling model of lithium ion battery and modeling method
InactiveCN110457742ADelay agingImprove performanceComputational theoretical chemistrySpecial data processing applicationsElectrochemical responseCyclic process
The invention relates to an electrochemical-thermal-mechanical coupling model of a lithium ion battery and a modeling method. Based on a classic electrochemical quasi-two-dimensional model of the lithium ion battery, heat generated by electrochemical reaction of the battery in use is introduced; meanwhile, a three-dimensional lumped parameter thermal model is adopted to simulate temperature changein the battery cycle process, a mechanical damage model of the battery in the whole life cycle is established to describe the influence of ion diffusion induced stress on the service life of the battery in the charging and discharging process of the battery, and a dynamic parameter compensation method is utilized to couple the models. The lithium ion battery electrochemical-thermal-mechanical coupling model generated by using the model building method can be used for estimating and predicting the monomer temperature of a battery thermal management system (BTM) and researching the physical property change and thermal runaway of the battery; a basis is provided for research on the performance evolution law of the lithium ion battery, and the method has important significance in slowing downbattery aging and prolonging the service life.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
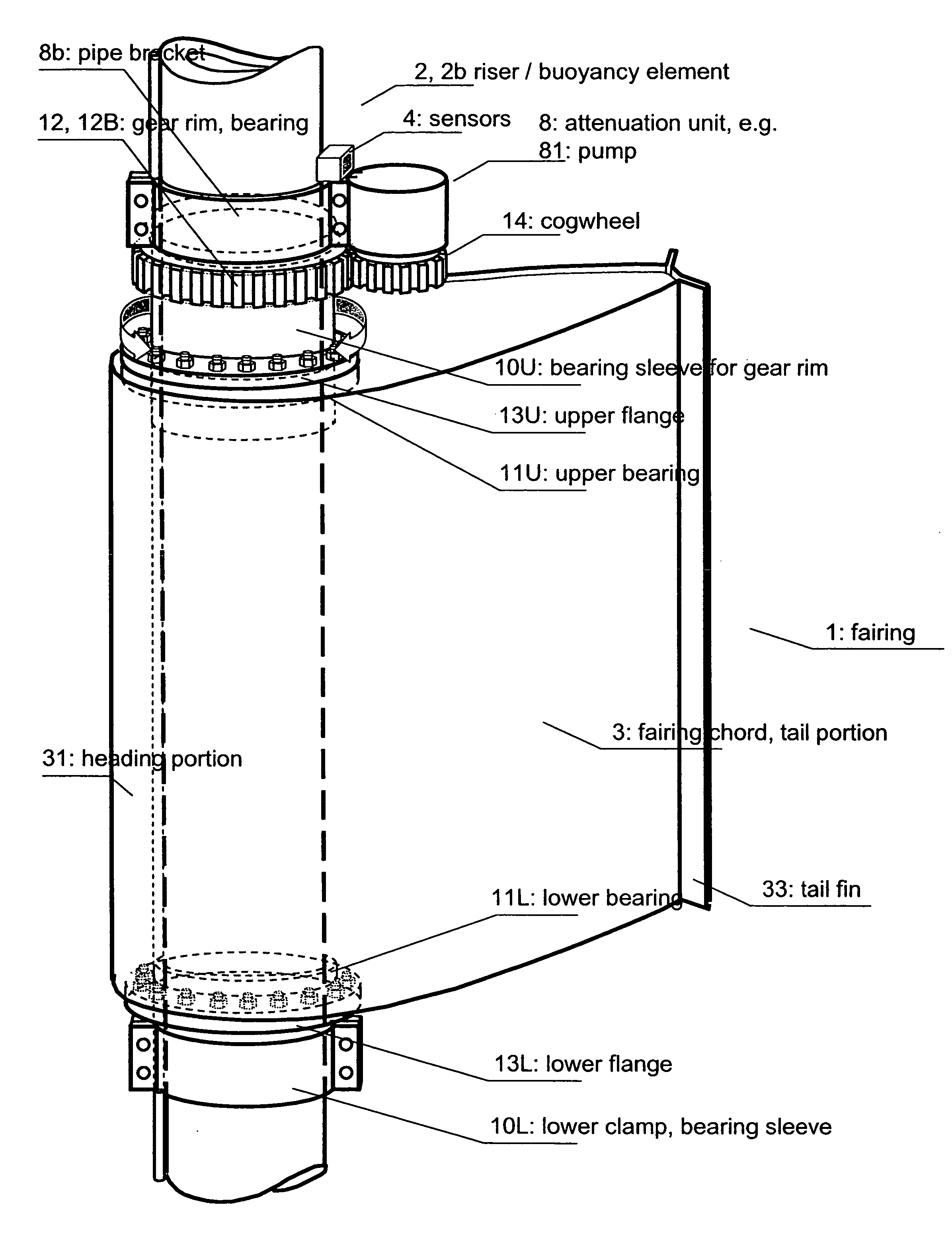
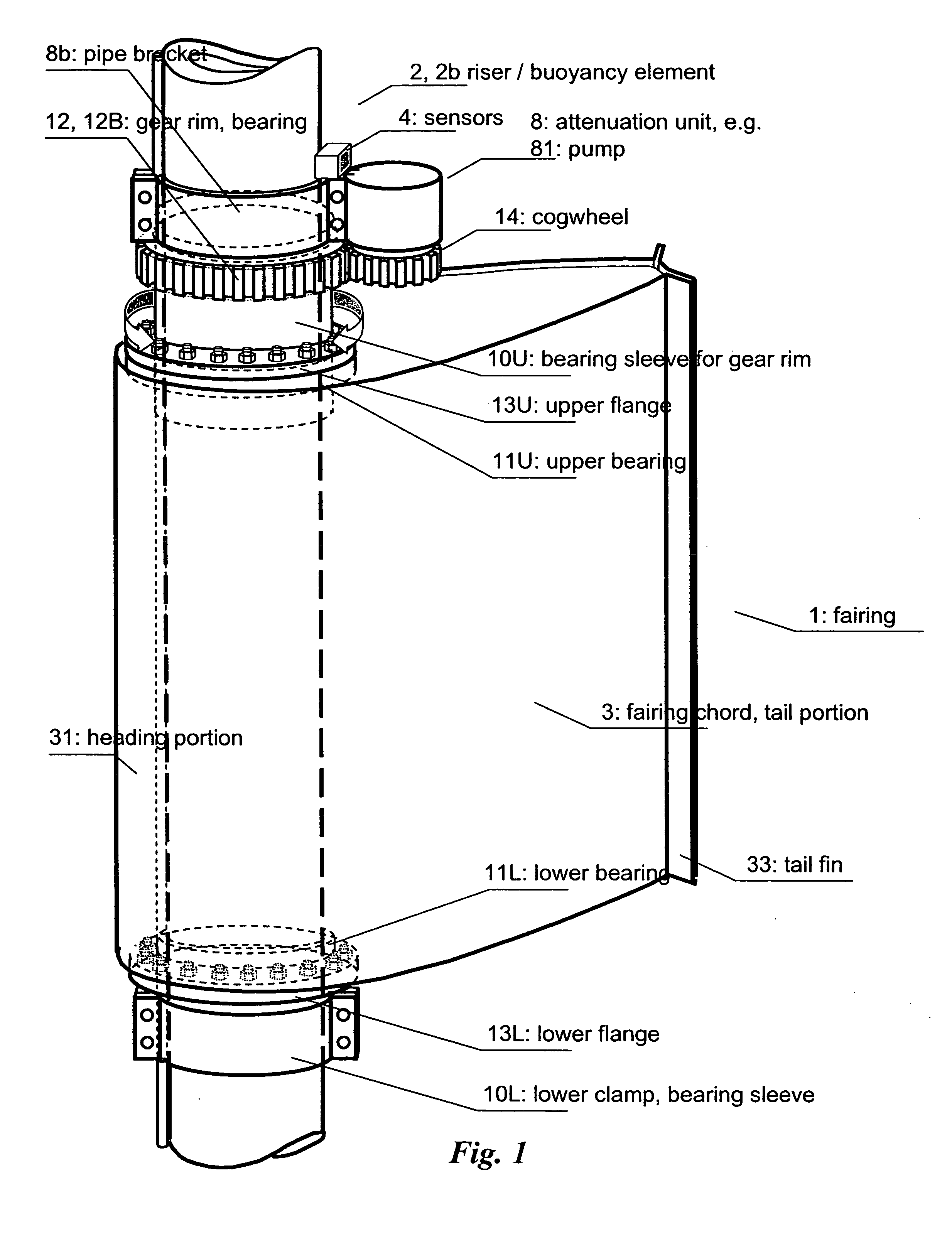
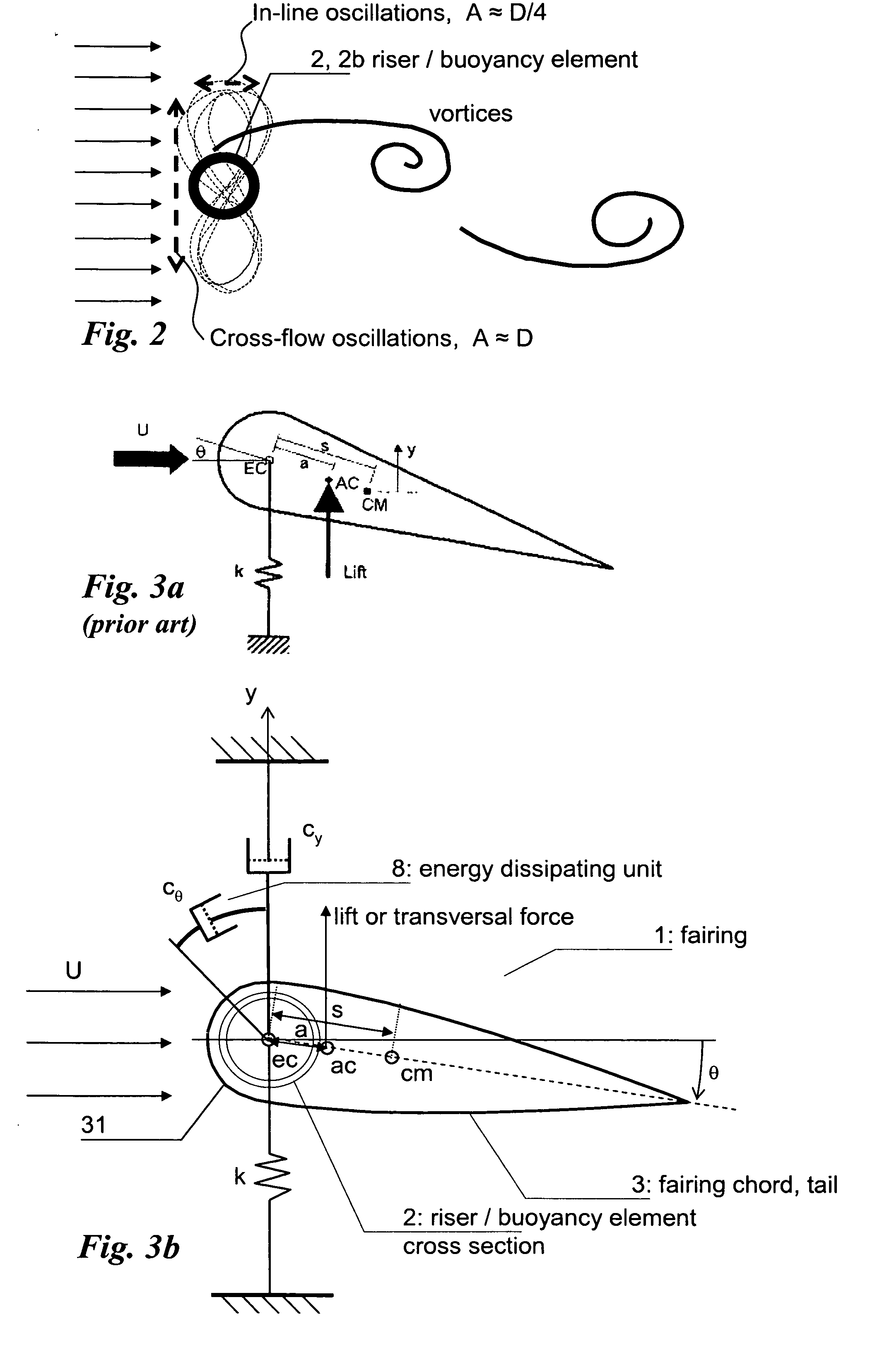
Fairing for reducing watercurrent-induced stresses on a marine riser
InactiveUS20070215028A1Reduce frictionAvoid vibrationDrilling rodsOffensive equipmentUltrasound attenuationWater flow
The invention relates to a rotatable fairing (1) for a marine riser (2) or other slender marine structure. The fairing (1) is arranged on the riser for reducing watercurrent-induced stresses on said riser (2), said fairing (1) having a tail portion (3) for trailing generally in the downstream direction behind said riser. The fairing (1) is provided with an attenuation unit (8) for counteracting the unstable rotation of said fairing (2) relative to said riser (2), in order to prevent undesired vibrations of said riser (2). The fairing is provided with one or more clamps (10) for attachment to and around a periphery of said riser (2), said clamps (10) arranged with a gear rim (12) for engagement with an actuating cogged wheel (14) of said attenuation unit (8).
Owner:SINTEF TTO AS
Method for predicting vertical well volume fractured reservoir reform volume of low permeable reservoir
The invention discloses a method for predicting vertical well volume fractured reservoir reform volume of low permeable reservoir. The method sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) calculating the induced stress produced by hydraulic fracture in a three-dimensional space; (2) calculating the formation pore pressure obtained after leak-off of fracturing fluid; (3) calculating the formation pore elastic stress obtained after the leak-off of the fracturing fluid; (4) overlapping the stress fields obtained in the step (1), (2) and (3) with an in-situ stress field to obtain a new crustal stress field, and calculating the magnitude and direction of three-way principal effective stress in the overlapped reservoir space; (5) calculating the open fracture determination coefficient M of a natural fracture in the reservoir space and the shear fracture region determination coefficient S of the natural fracture so as to predict the volume fractured reservoir reform volume. The method is used for predicting the reservoir reform volume after vertical well volume fracturing, is better in operability and accuracy, provides a favorable theoretical basis for effect evaluation and yield prediction after vertical well volume fracturing of the low permeable reservoir, and overcomes the defects of the prior art.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Inexpensive wafer level MMIC chip packaging
ActiveUS6888253B1Firm packagingCheap packagingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipEngineering
An inexpensive package for a semiconductor chip (1) that incorporates a stress relief buffer (13) between a side of the chip and the metal carrier layer (2) to absorb thermally induced stress produced by significantly different rates of thermal expansion of the wafer and the metal carrier. The buffer (13) is formed by a polymer that is flexible and can be etched, contains a coefficient of thermal expansion that does not significantly differ from that of the chip and / or a combination of CET and elasticity that retains a physical connection with the side of the chip and the metal carrier over the temperature range of operation anticipated for the chip. Polyimide or paraylene are preferred examples. Vias (15) extend through the buffer to place the metal carrier electrically in common with the metal layer (5) found on the back surface of the wafer so that an electrical ground applied to the metal carrier layer (2) may extend through to that surface.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
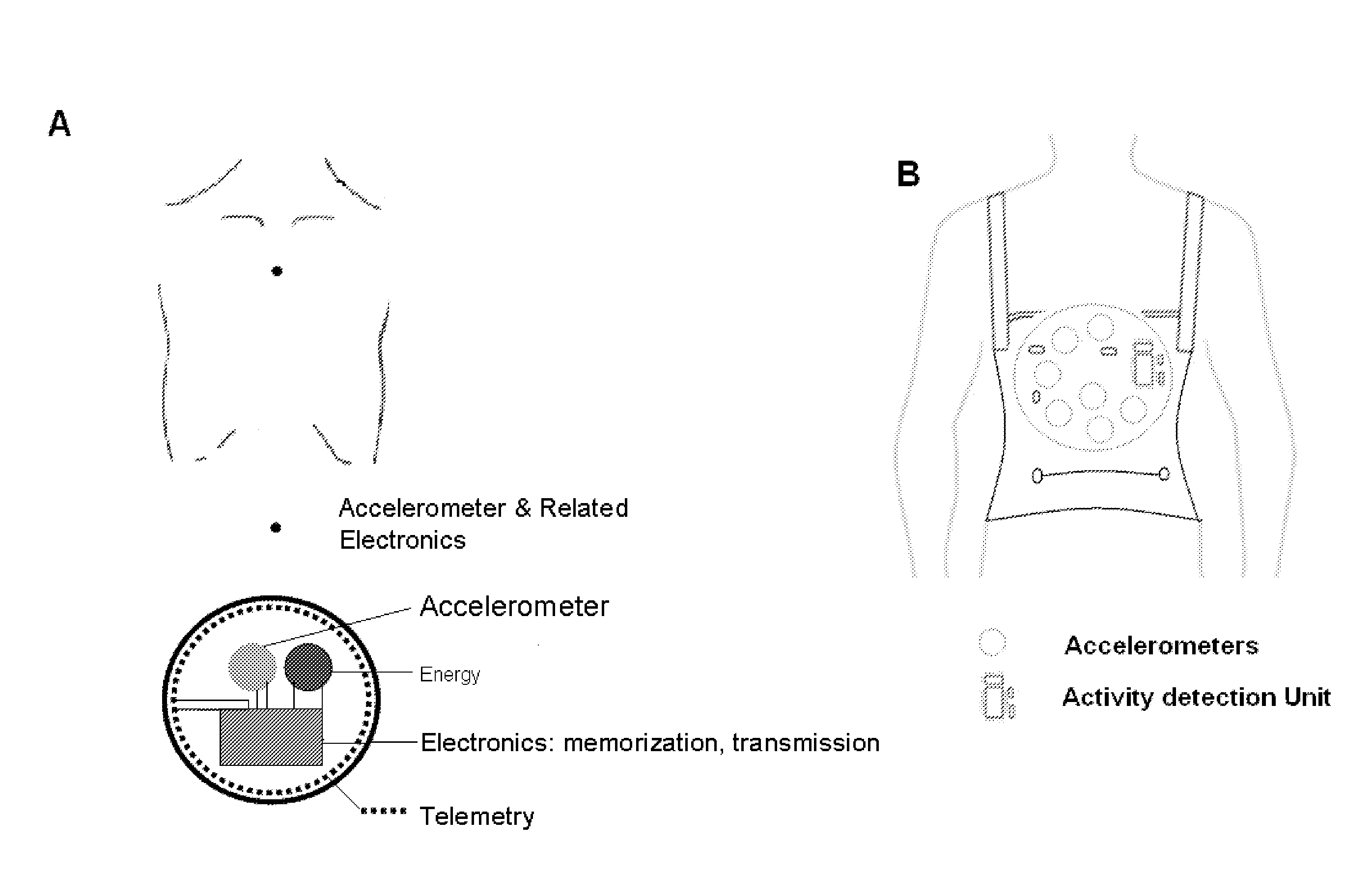
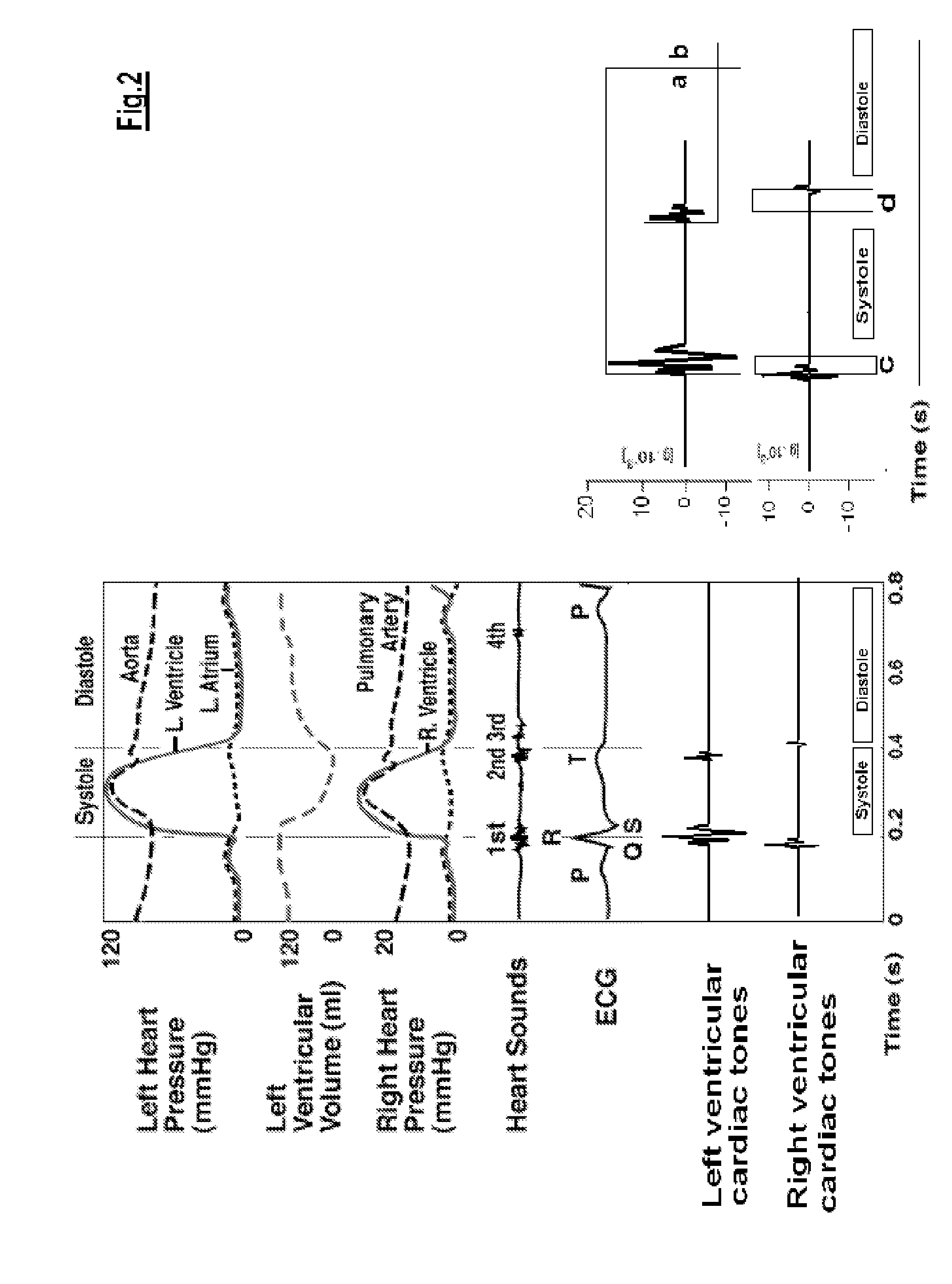
Device for quantification and monitoring of cardiovascular function during induced stress or physical activity and at rest
InactiveUS20110208016A1Easy to distinguishEasy to calculateEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsMedicineInduced stress
Method and device for the quantification and monitoring of cardiovascular function comprising continuous determination of significant individual cardiovascular function parameters through a multisensory, operator-independent platform during a sample period at rest, recording the data determined, continuously monitoring these data during pharmacological stress or exercise activity, comparing the memorized data with those determined during the same time span of the sample period and comparing the changes in cardiovascular function occurring during stress or exercise vs rest, and comparing the changes in cardiovascular function occurring during recovery vs rest and vs stress or exercise.
Owner:BOMBARDINI TONINO
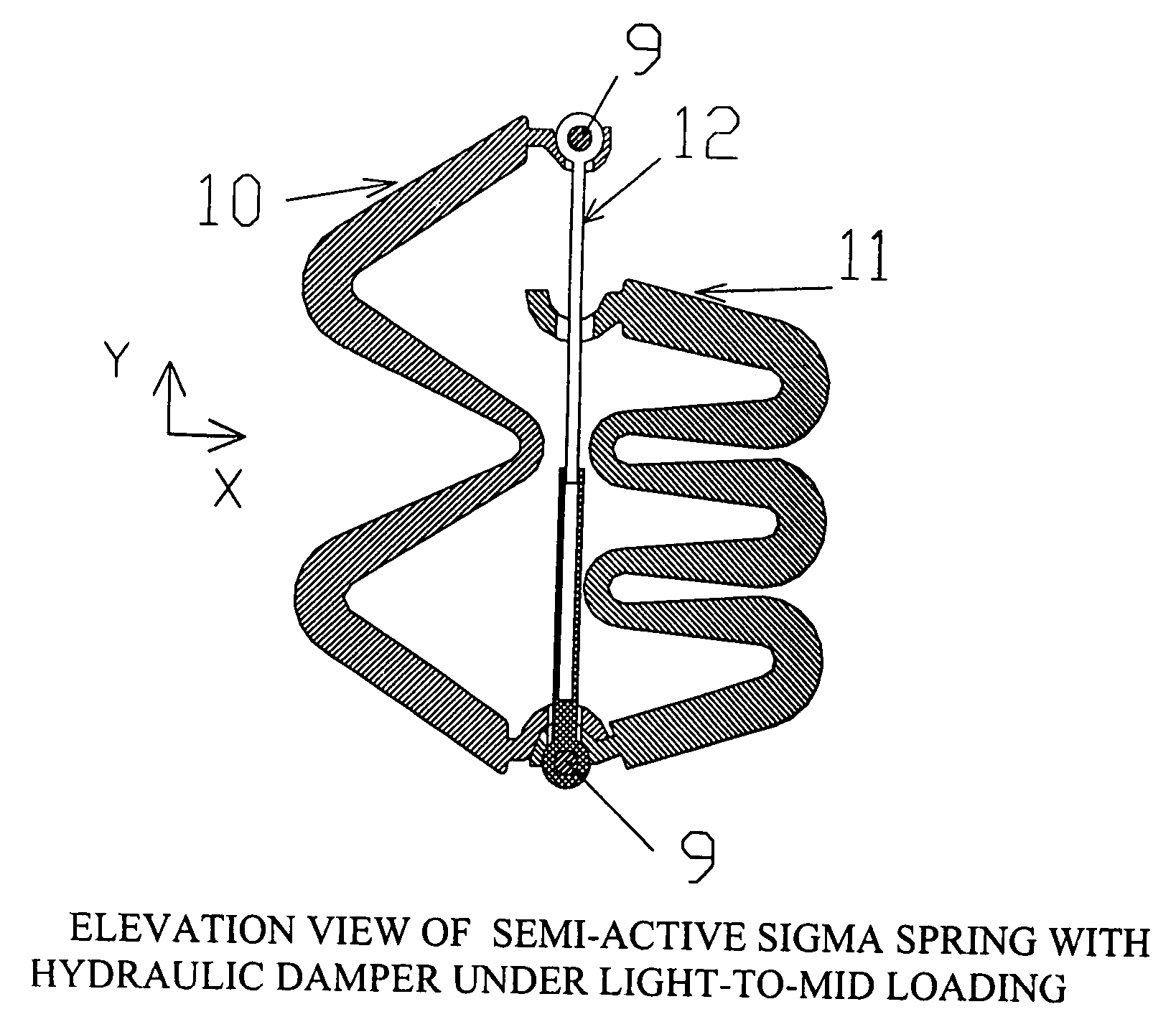
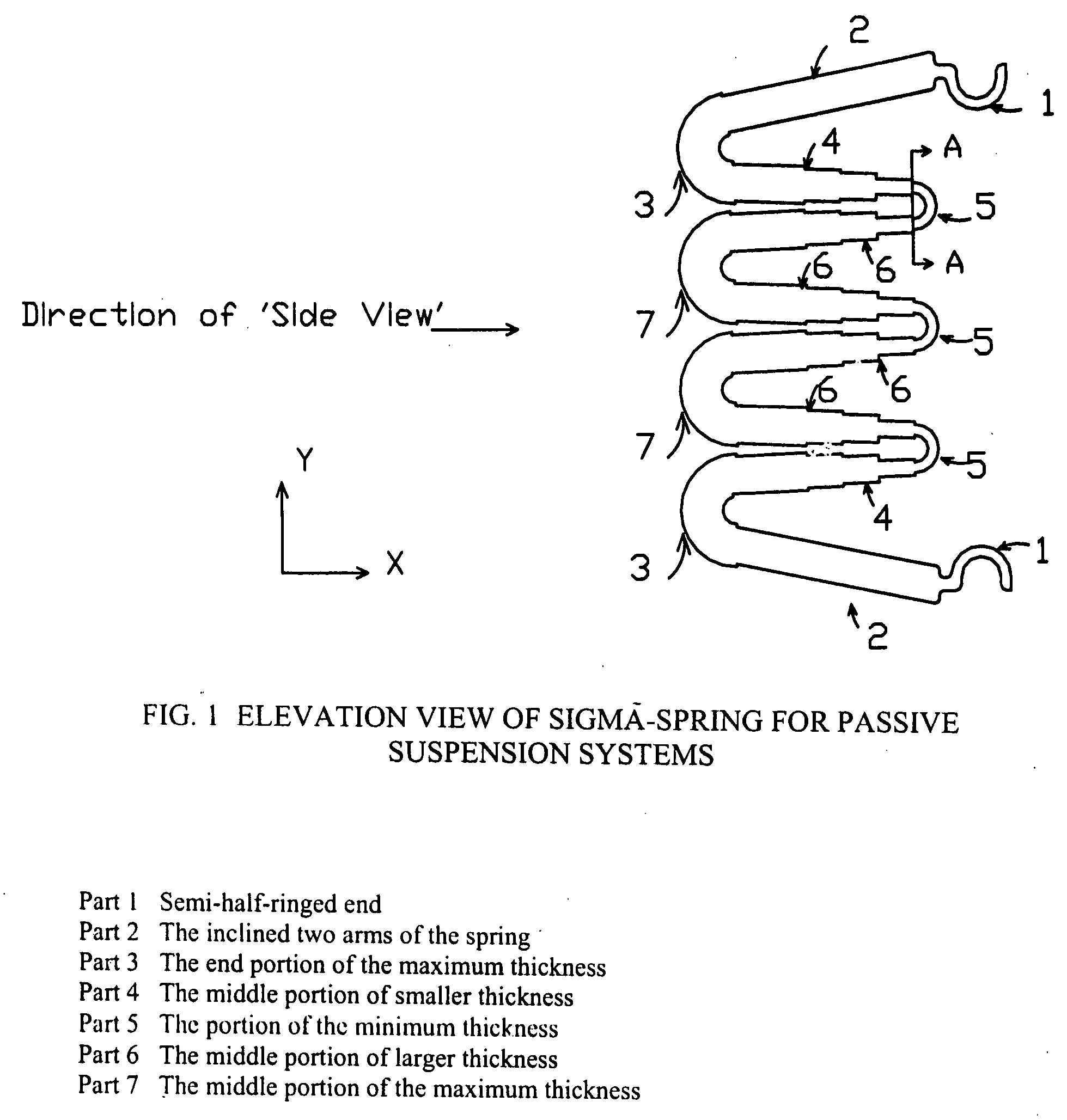
Sigma-springs for suspension systems
InactiveUS20070267792A1Improve rendering capabilitiesQuality improvementLeaf springsResilient suspensionsGlass fiberSemi active
Sigma-spring can be used as a passive vehicle suspension system of built-in damping, a passive vehicle suspension system with hydraulic damper, a semi-active vehicle suspension system of two opposite Sigma-springs (10,11) of built-in damping, or a semi-active vehicle suspension system of two opposite Sigma-springs (10,11) penetrated at line of external loading by hydraulic damper (12). The Sigma-spring is a spring of a special Sigma-shape above which mass can be suspended vertically while under static or dynamic loading conditions. The outer two arms of the Sigma-shape of the spring are inclined such that to be horizontal while fully loaded ensuring safe compression pattern. The Sigma-shape has two opposite sets of turns of different sizes one of small radius of curvature at the side of line of the applied external load and the opposite one has large radius of curvature in order to maximize spring vertical deflection capability. Thickness throughout the Sigma-spring developed length is graduated in order to minimize induced stresses, weight, and cost. Stiffness of the Sigma-spring can be nonlinear in order to provide improved vibration isolation and can be adjusted for same compact space allowance through increasing or decreasing its number of turns. The Sigma-spring can be made of Polymeric Matrix Composite of resin strengthened at nano-scale by nanometer-sized powder E-glass fibers. Moreover, the Sigma-spring can be made of Metallic Matrix Composite or of whole metallic monolithic material.
Owner:ELMOSELHY SALAH AHMED MOHAMED
Bonding of parts with dissimilar thermal expansion coefficients
InactiveUS6897123B2Long lasting bondIncrease stiffnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin material handlingThermal expansionInduced stress
A method for bonding materials with different thermal expansion coefficients is provided. An intermediary layer of glass, ceramics, polymers, metals or composites is inserted between the materials to be bonded; this intermediary layer has a compositional gradient that could have been formed through diffusion processes. The coefficient of thermal expansion changes across the intermediary layer and on each side it is not substantially different from the coefficient of thermal expansion of the material that the layer is facing. In that manner there is nowhere within the intermediate layer or on the interfaces to the materials being bonded that thermally induced stress will cause fractures or significant permanent plastic deformation. The thickness of the intermediary layer depends on the difference in the coefficient of thermal expansion between the two materials being bonded, the temperature range the bond will be exposed to and the elasticity.
Owner:AGITYNE CORP
NFETs using gate induced stress modulation
InactiveUS7144767B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesField-effect transistorInduced stress
A method for manufacturing an integrated circuit comprising a plurality of semiconductor devices including an n-type field effect transistor and a p-type field effect transistor by covering the p-type field effect transistor with a mask, and oxidizing a portion of a gate polysilicon of the n-type field effect transistor, such that tensile mechanical stresses are formed within a channel of the n-type field effect transistor.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
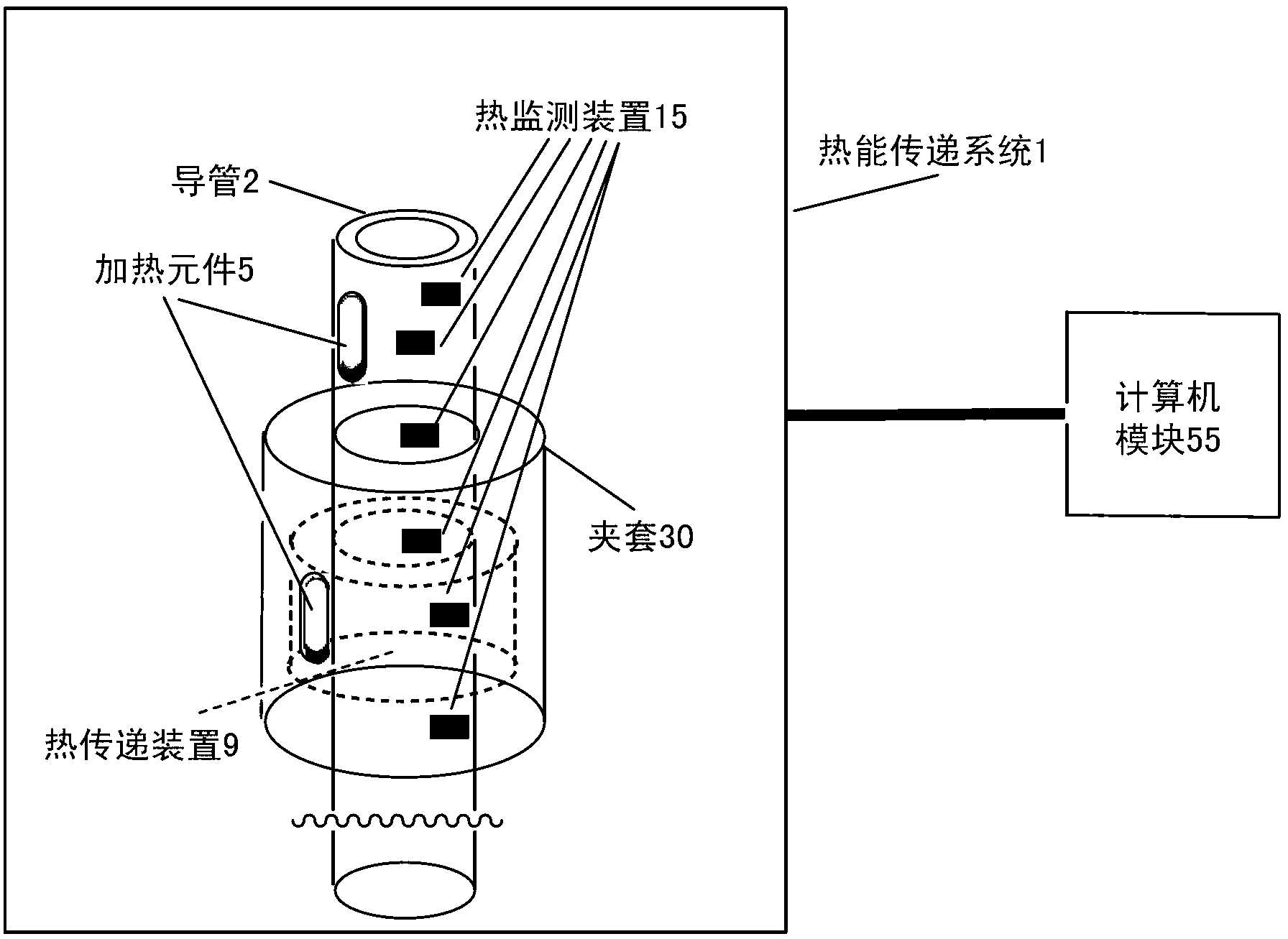
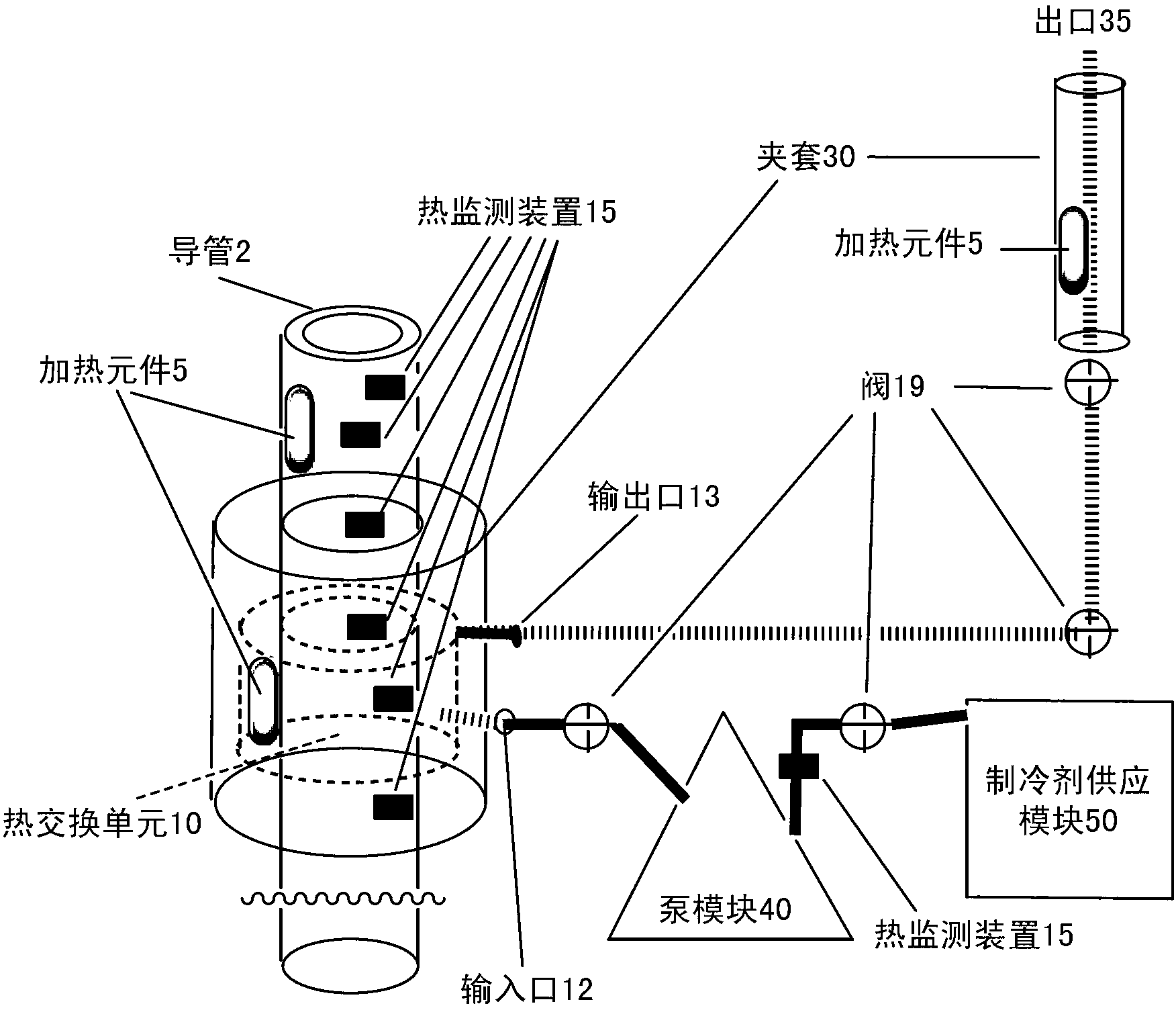
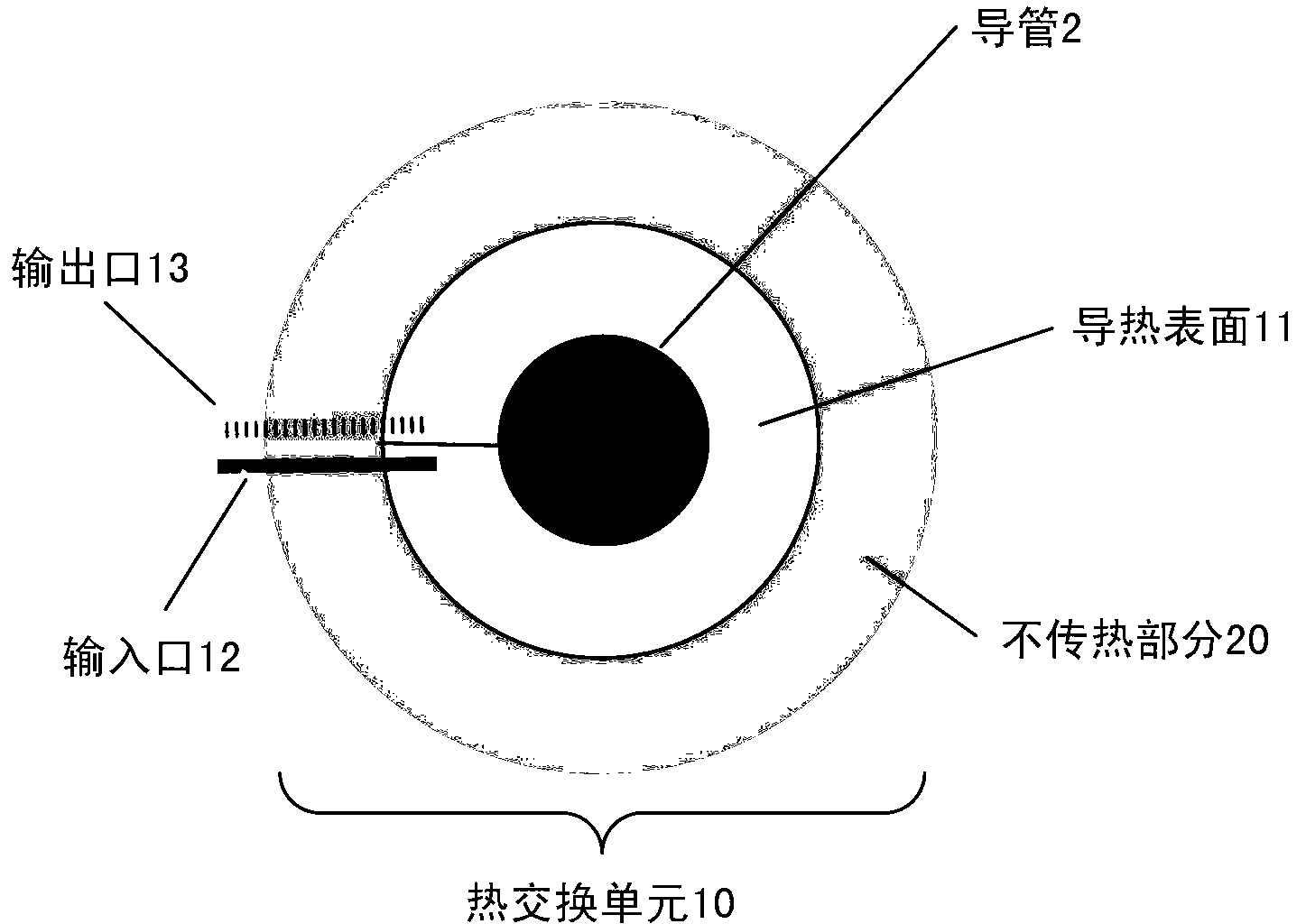
Methods, devices systems for extraction of thermal energy from a heat conducting metal conduit
Provided are methods, devices and systems for controlled removal of thermal energy from a fluid within a thermally conducting metal conduit. The system allows for the in situ formation of a reversible plug that can stop the flow of fluid through the conduit, particularly without inducing thermally induced stress fractures or breaches in the conduit. The devices and systems include a thermal transfer device that can be adapted to be in thermal communication with a thermal conducting metal conduit containing a fluid, particularly a flowing fluid. The devices and systems allows for controlled re-heating of the conduit without inducing thermally induced stress fractures or breaches in the conduit to restore fluid flow through the conduit.
Owner:BIOFILM IP
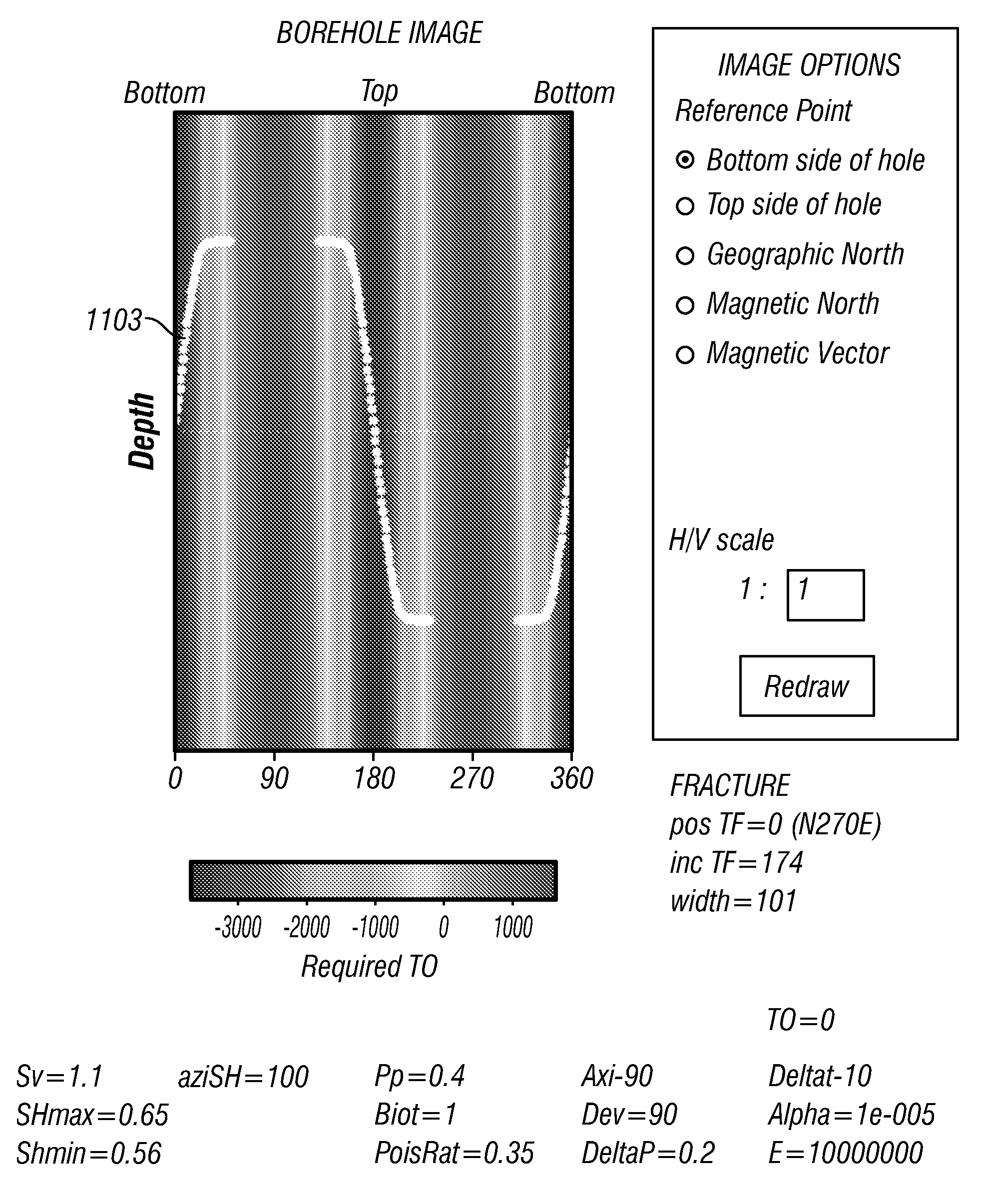
System and Method for Stress Field Based Wellbore Steering
A system, method and computer-readable medium for developing an earth formation is disclosed. A tool conveyed in a borehole induces a stress in the earth formation proximate a borehole. A sensor assembly obtains a measurement of a physical property of the borehole at a plurality of azimuthal locations in the borehole. The values of the physical property are indicative of the induced stress in the formation. A processor forms an image of the borehole using the obtained measurements of the physical property, estimates an azimuthal variation with borehole depth of the induced stress in the formation from the formed image, and alters an operational parameter of a device for developing the earth formation using the estimated azimuthal variation with depth of the induced stress in the formation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
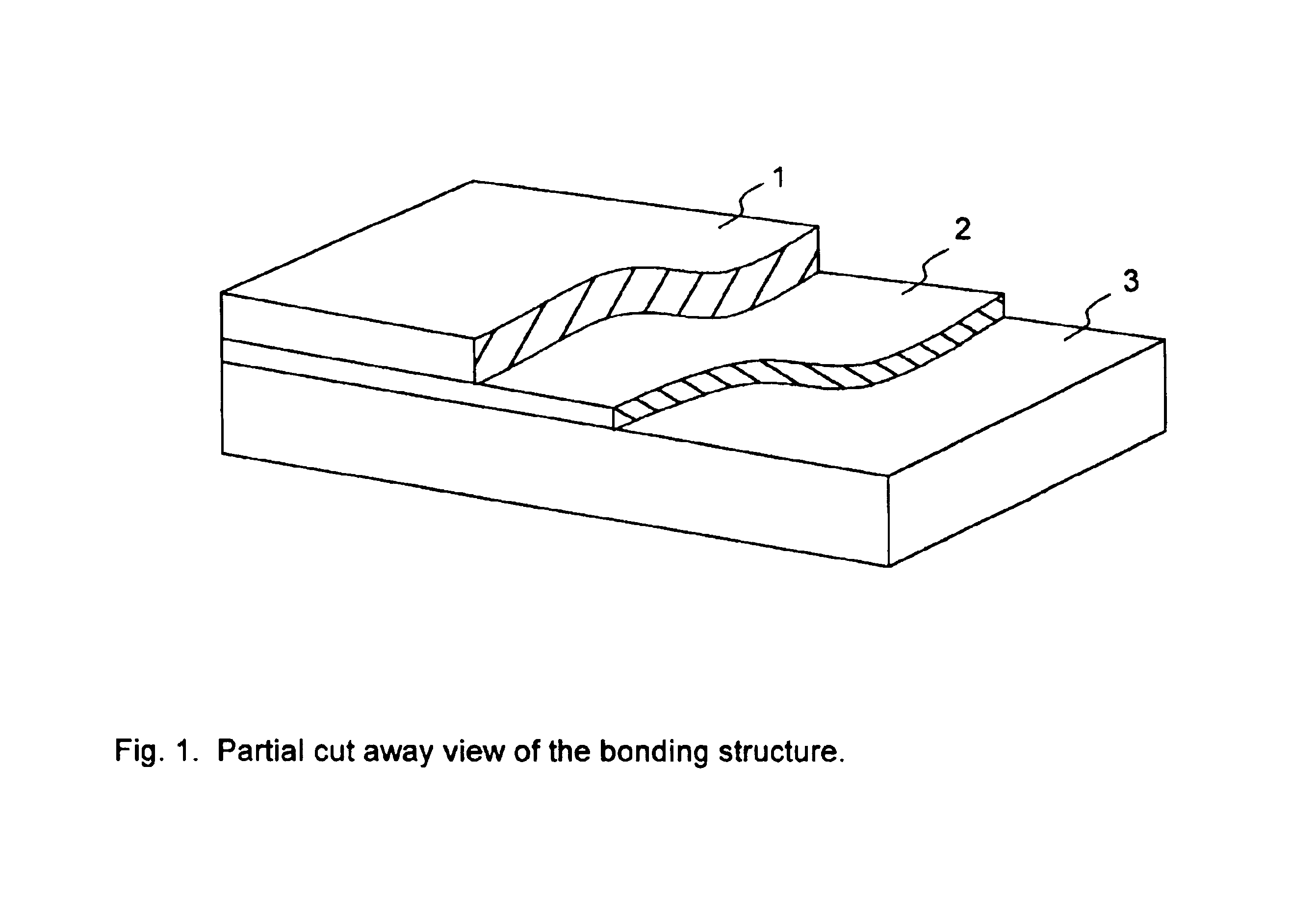
Method for the production of thin substrates
InactiveUS20100323472A1Easy to controlLow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolar cellInduced stress
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com