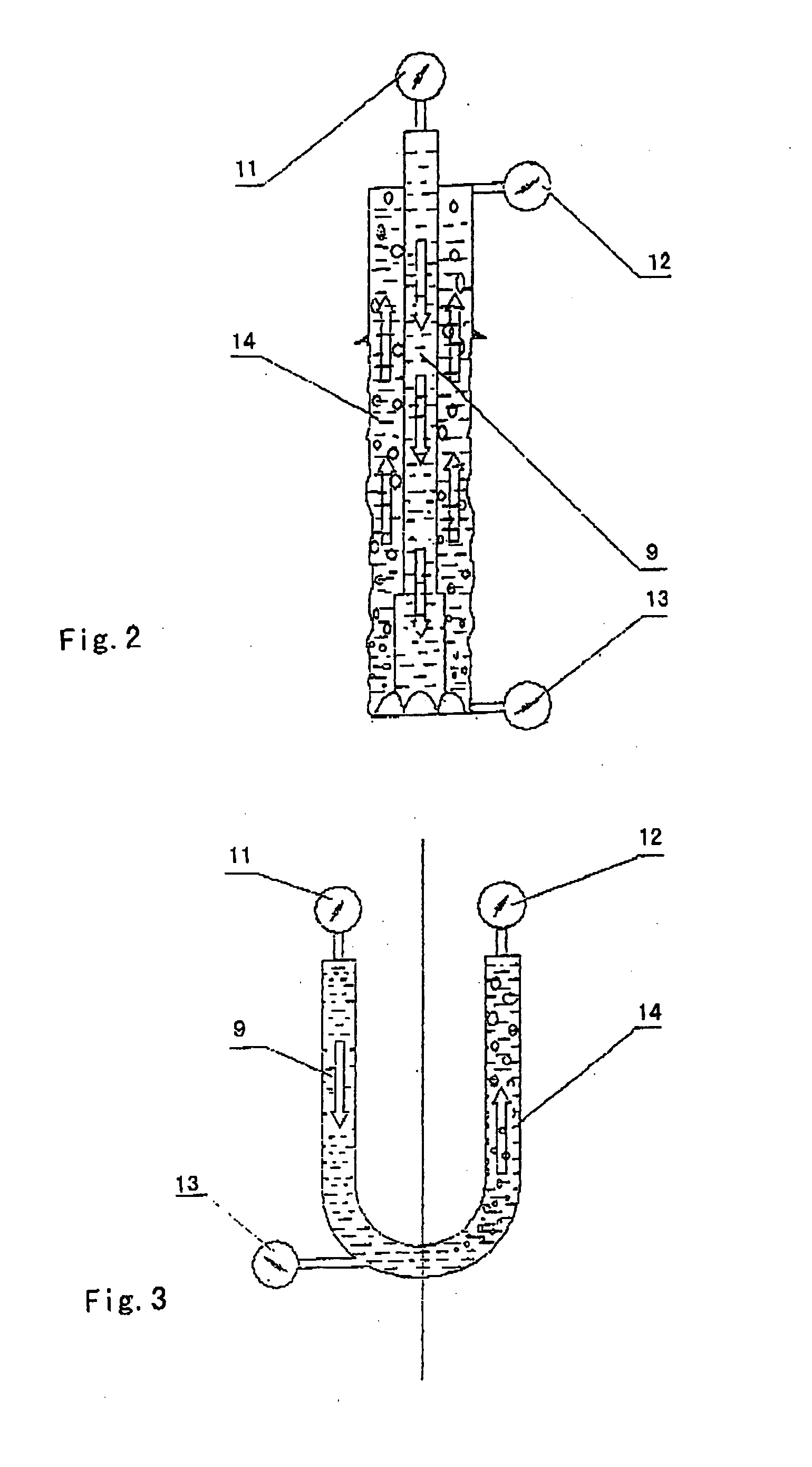
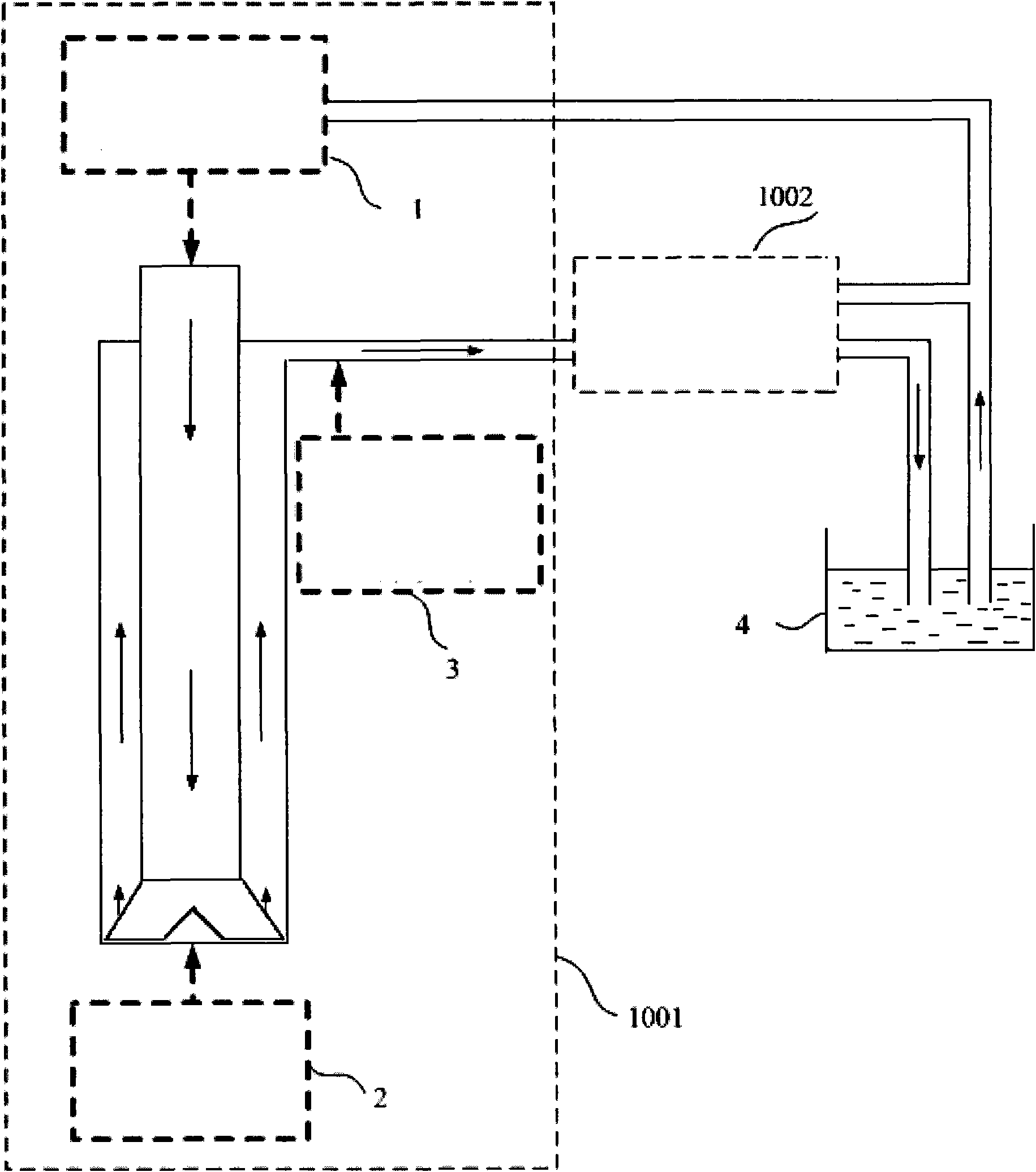
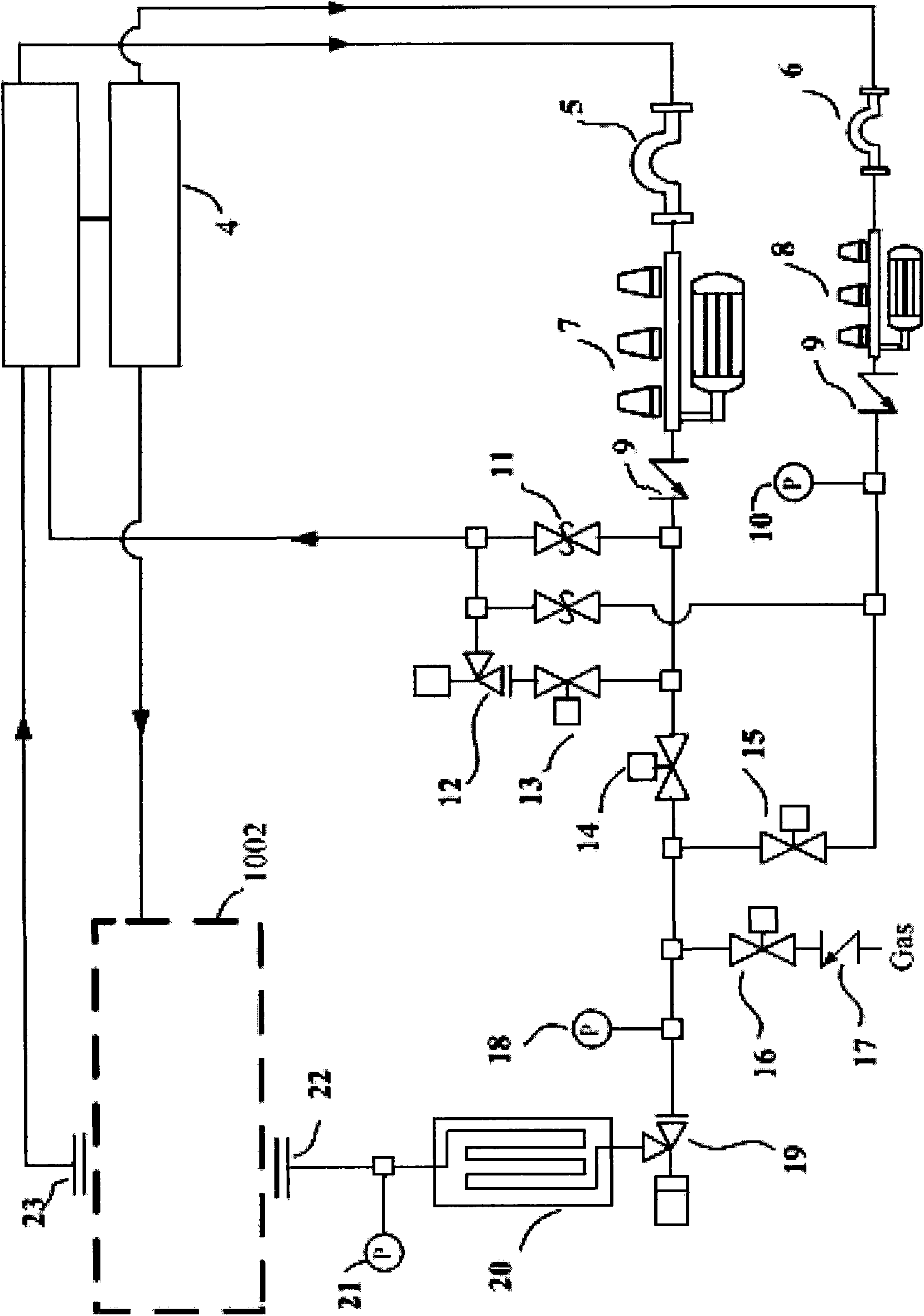
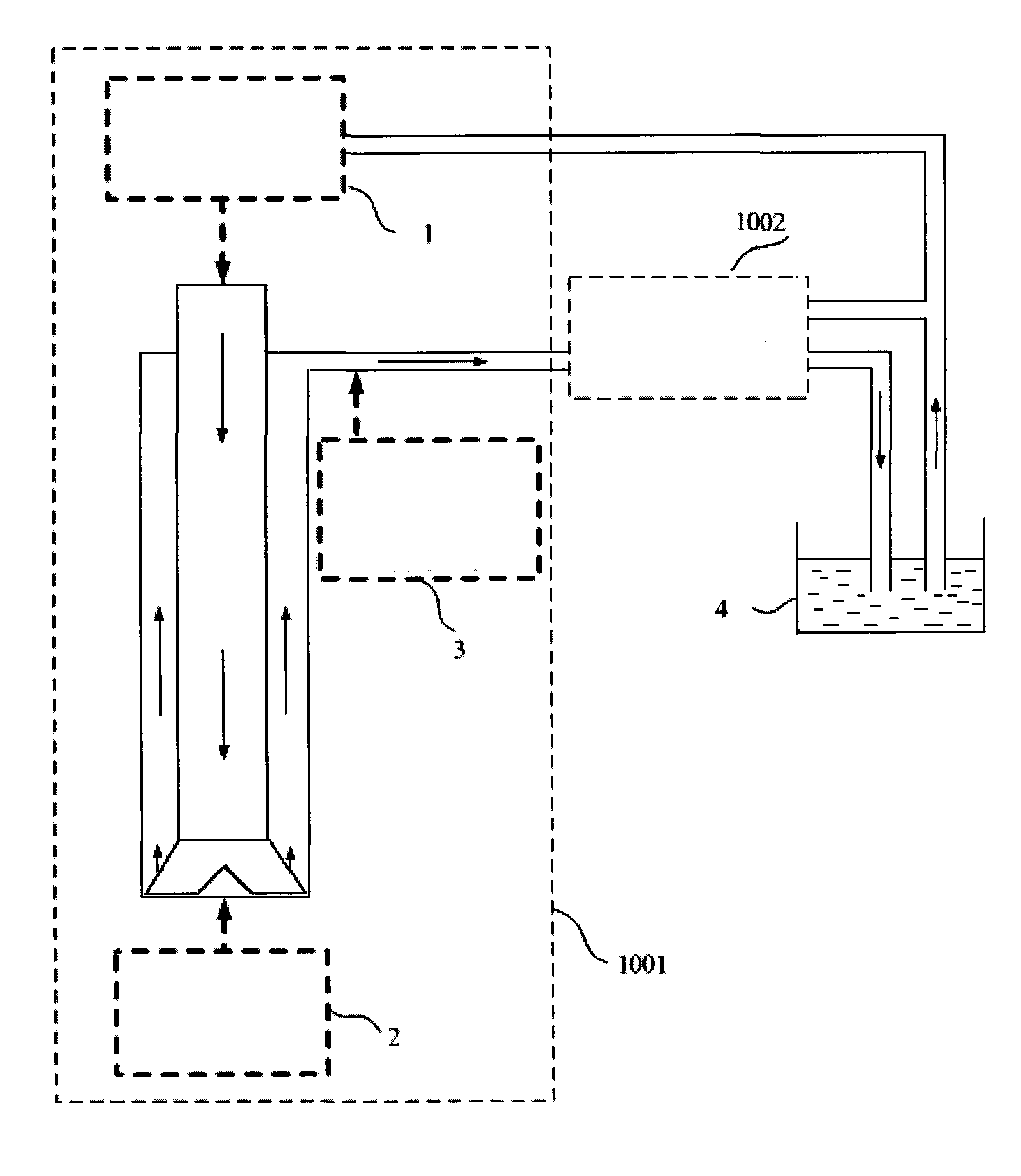
Patents
Literature
404 results about "Bottom hole pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
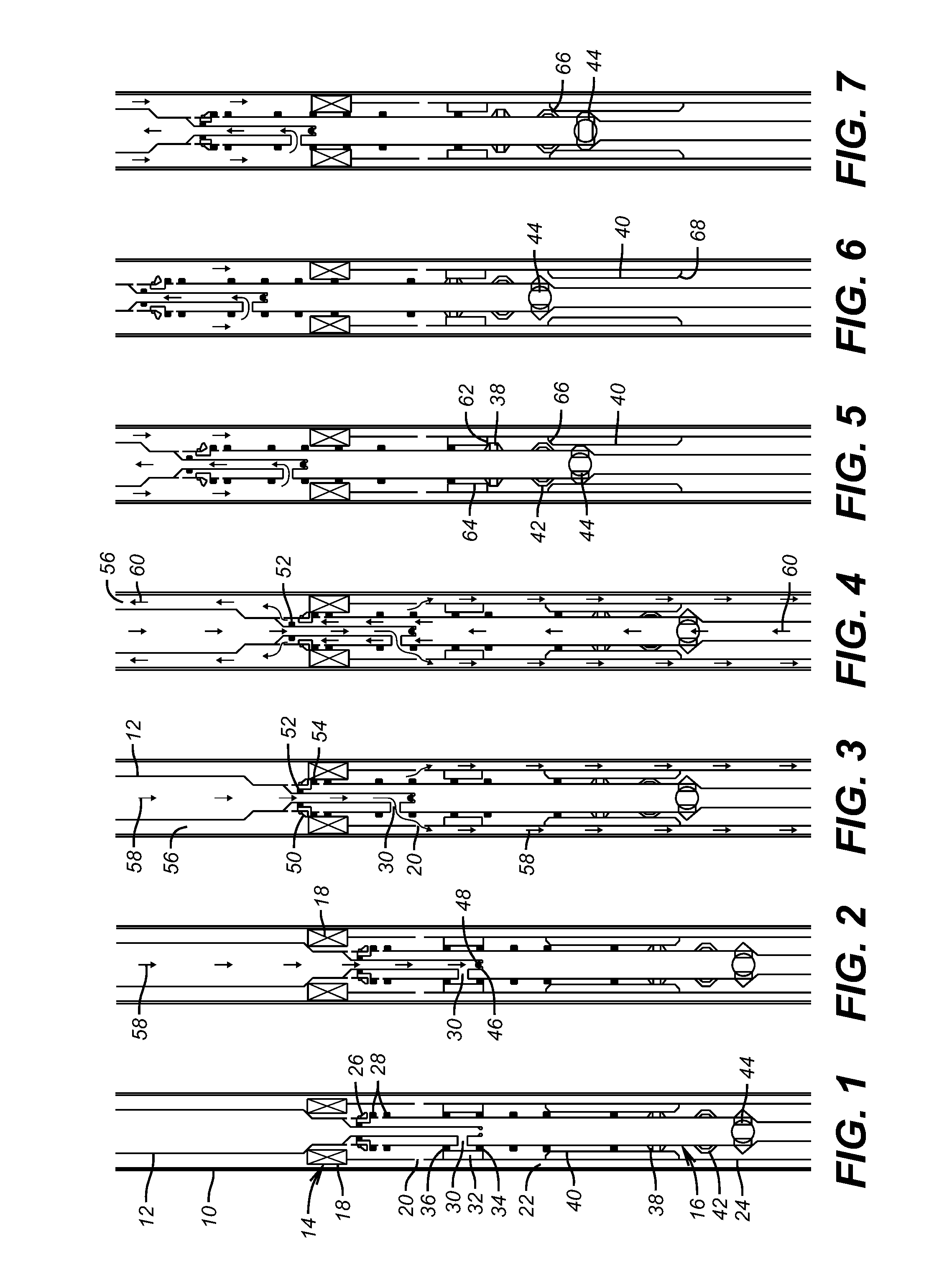
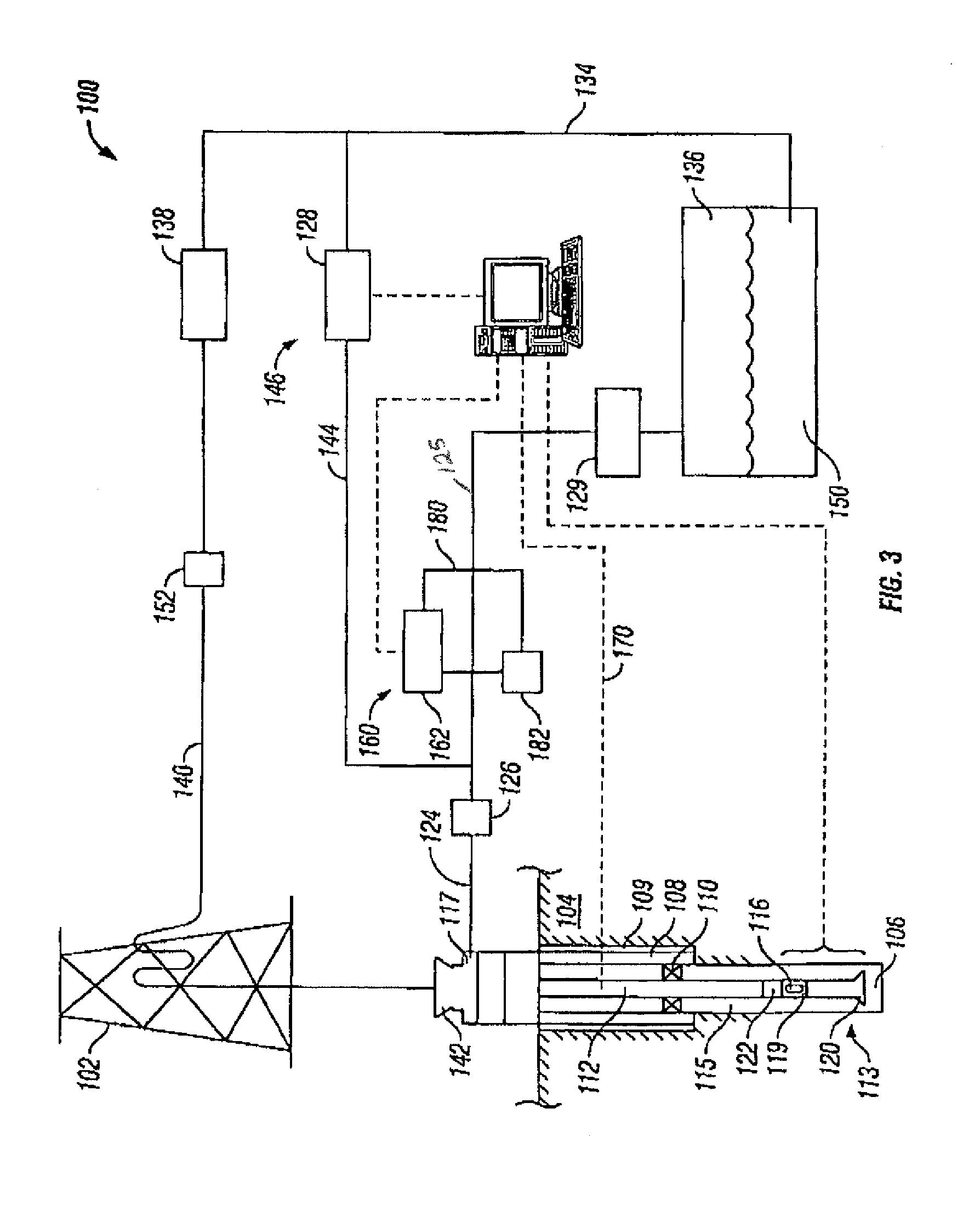
Drilling system and method for controlling equivalent circulating density during drilling of wellbores
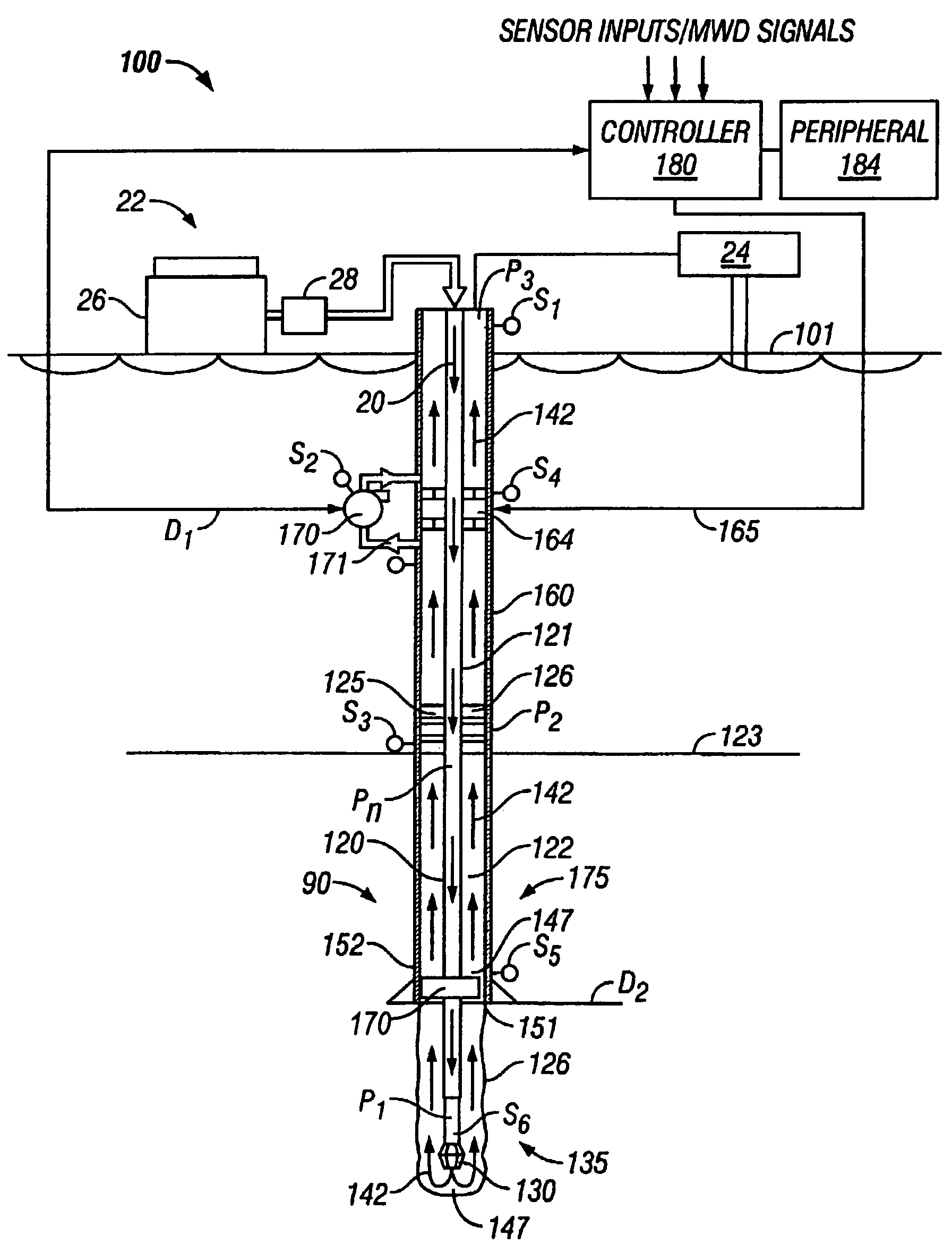
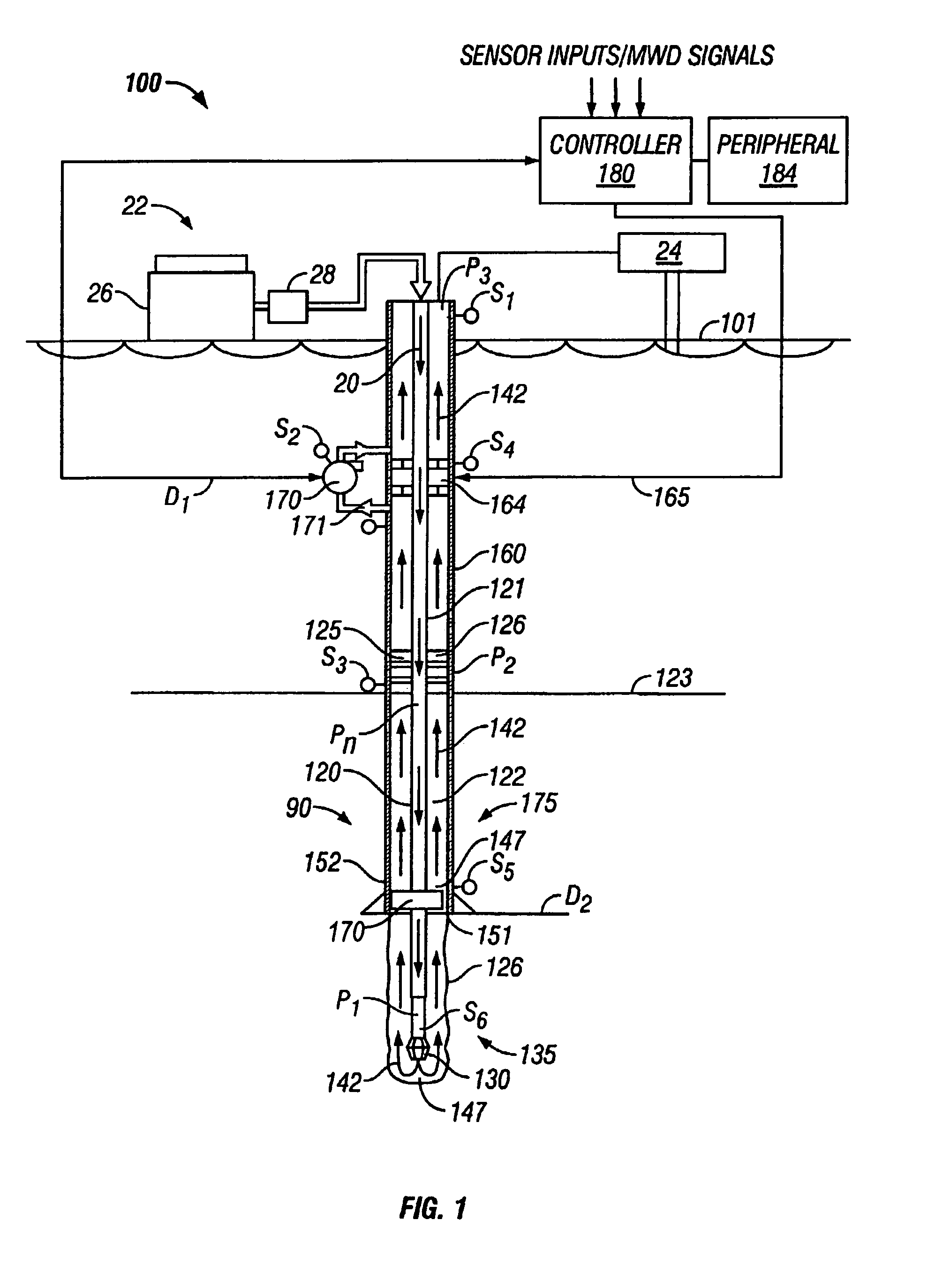
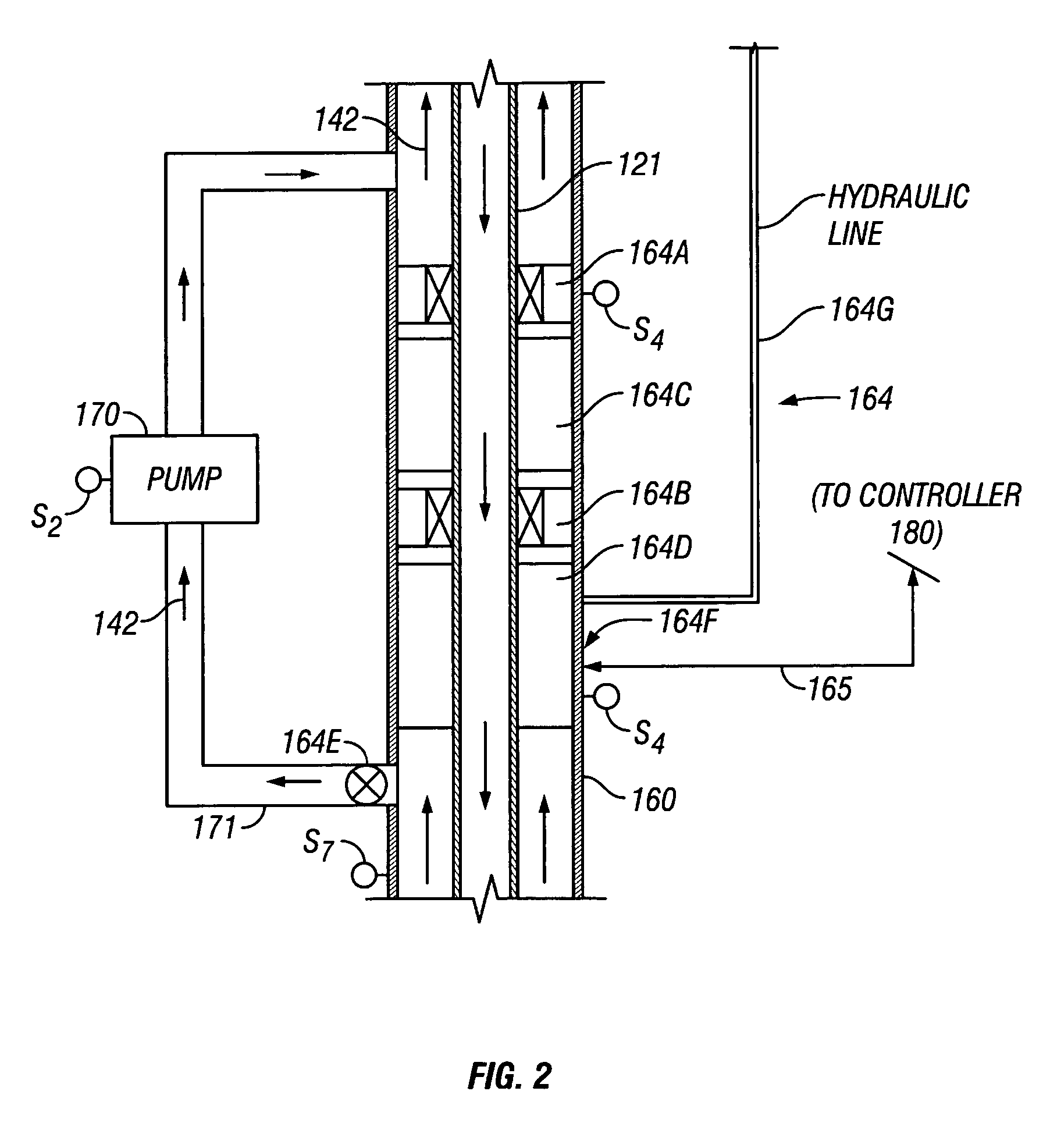
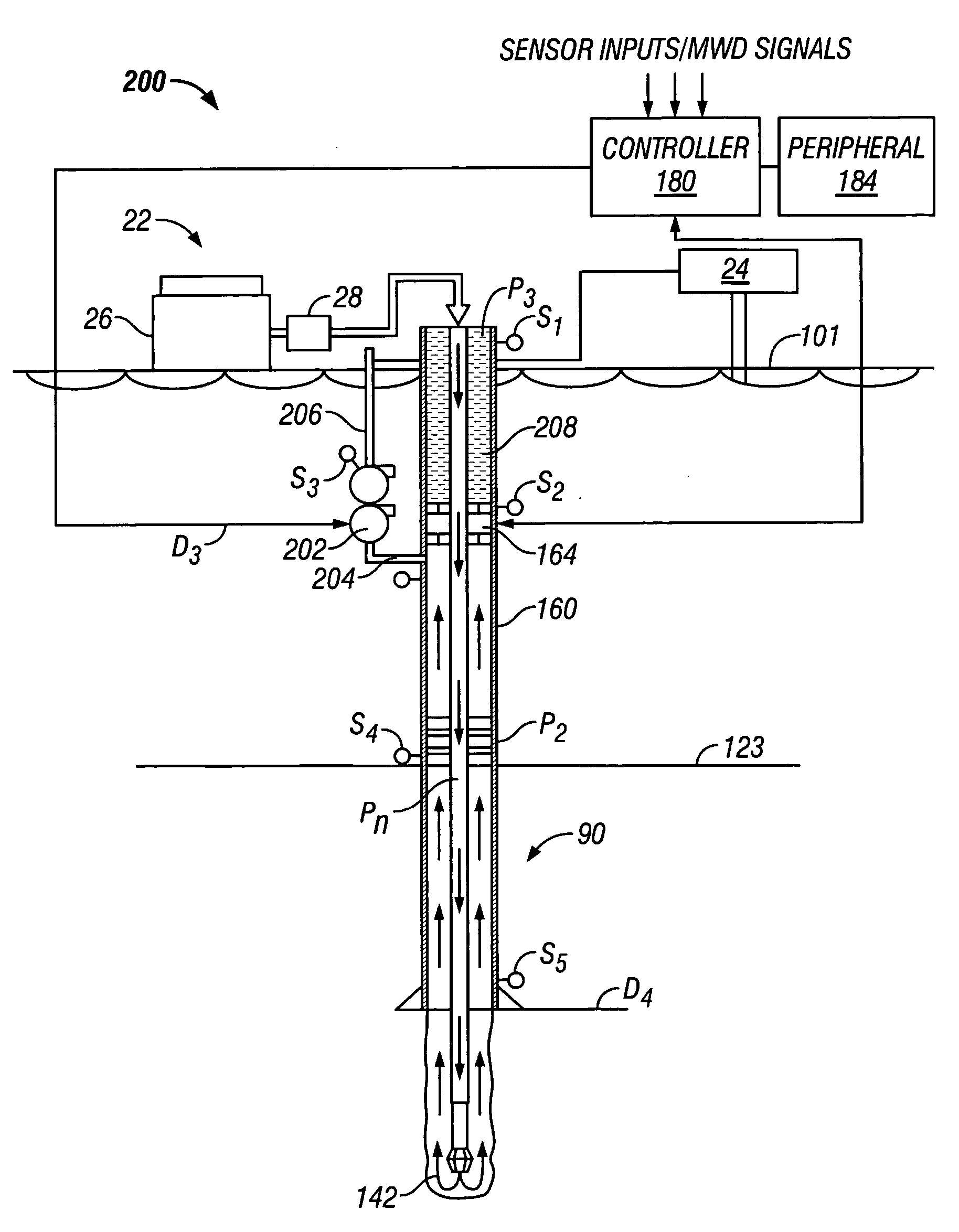
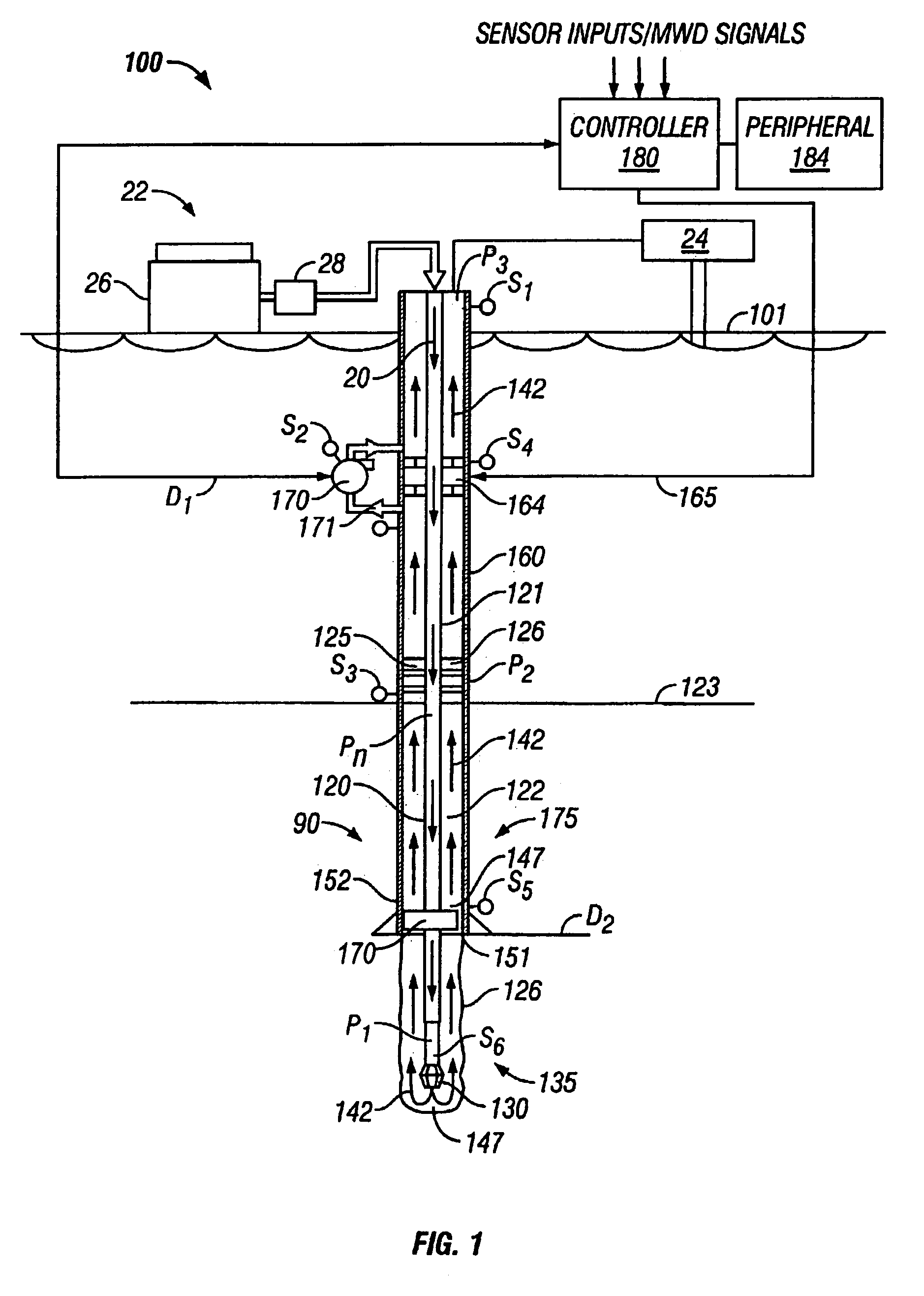
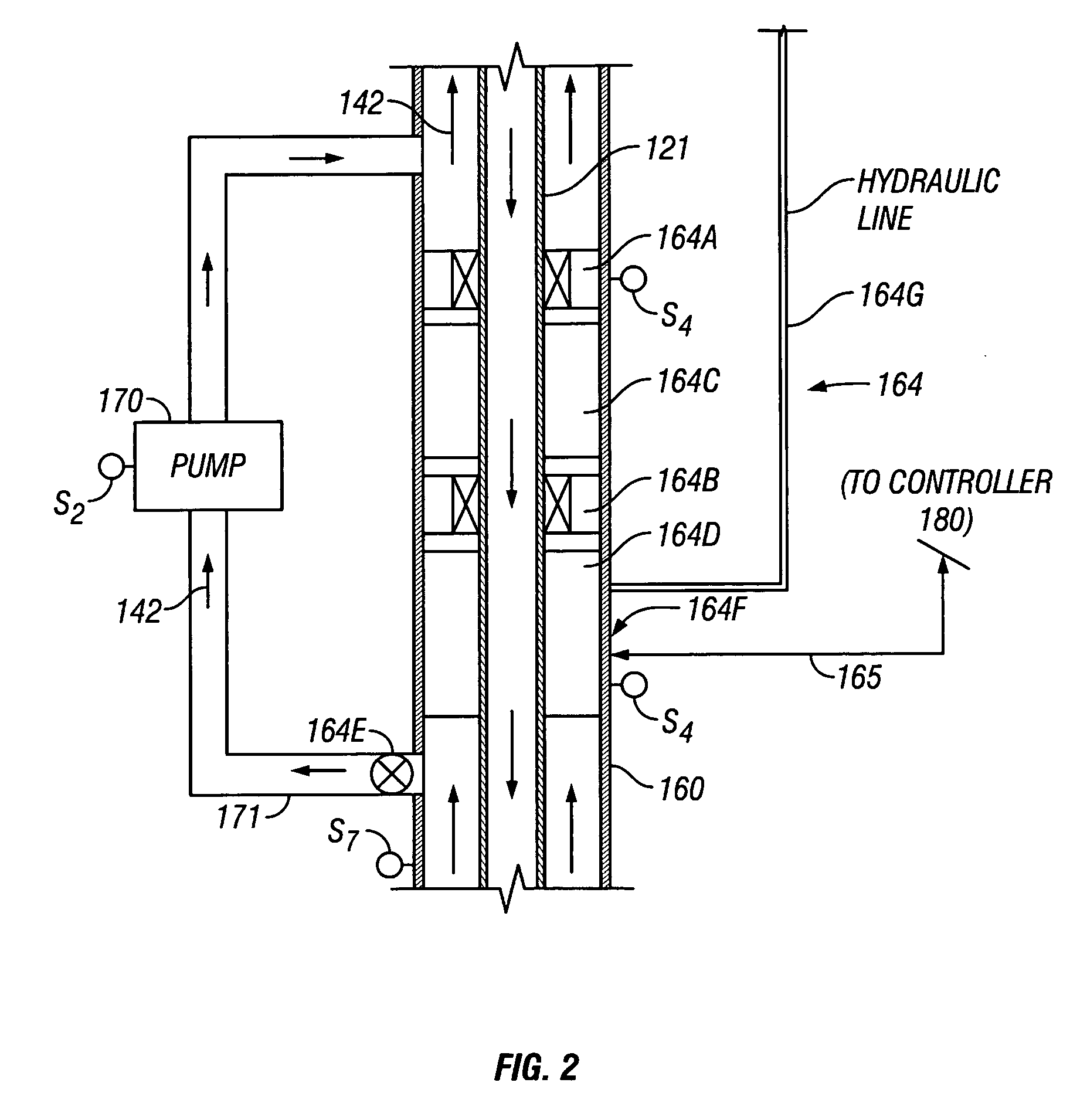
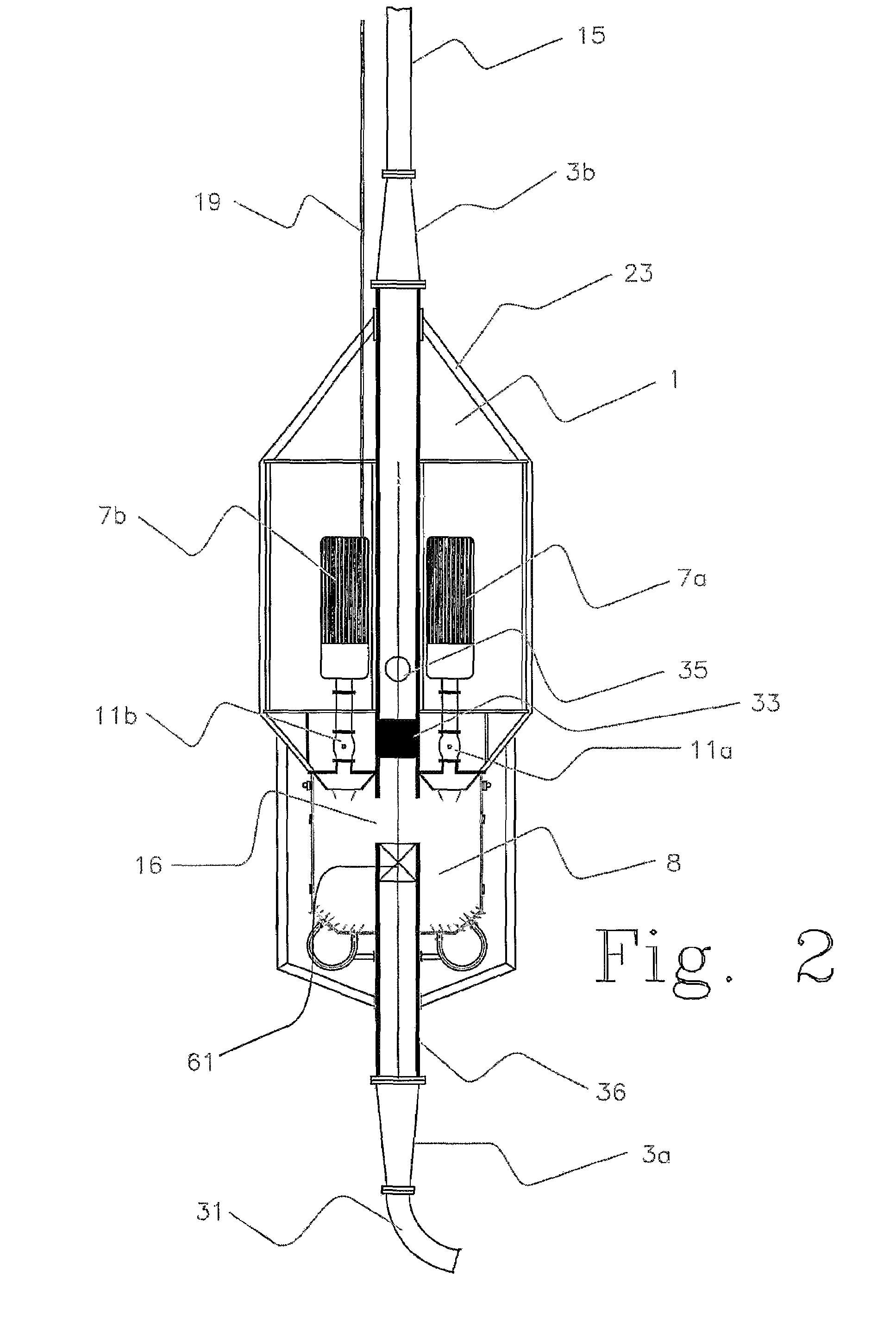
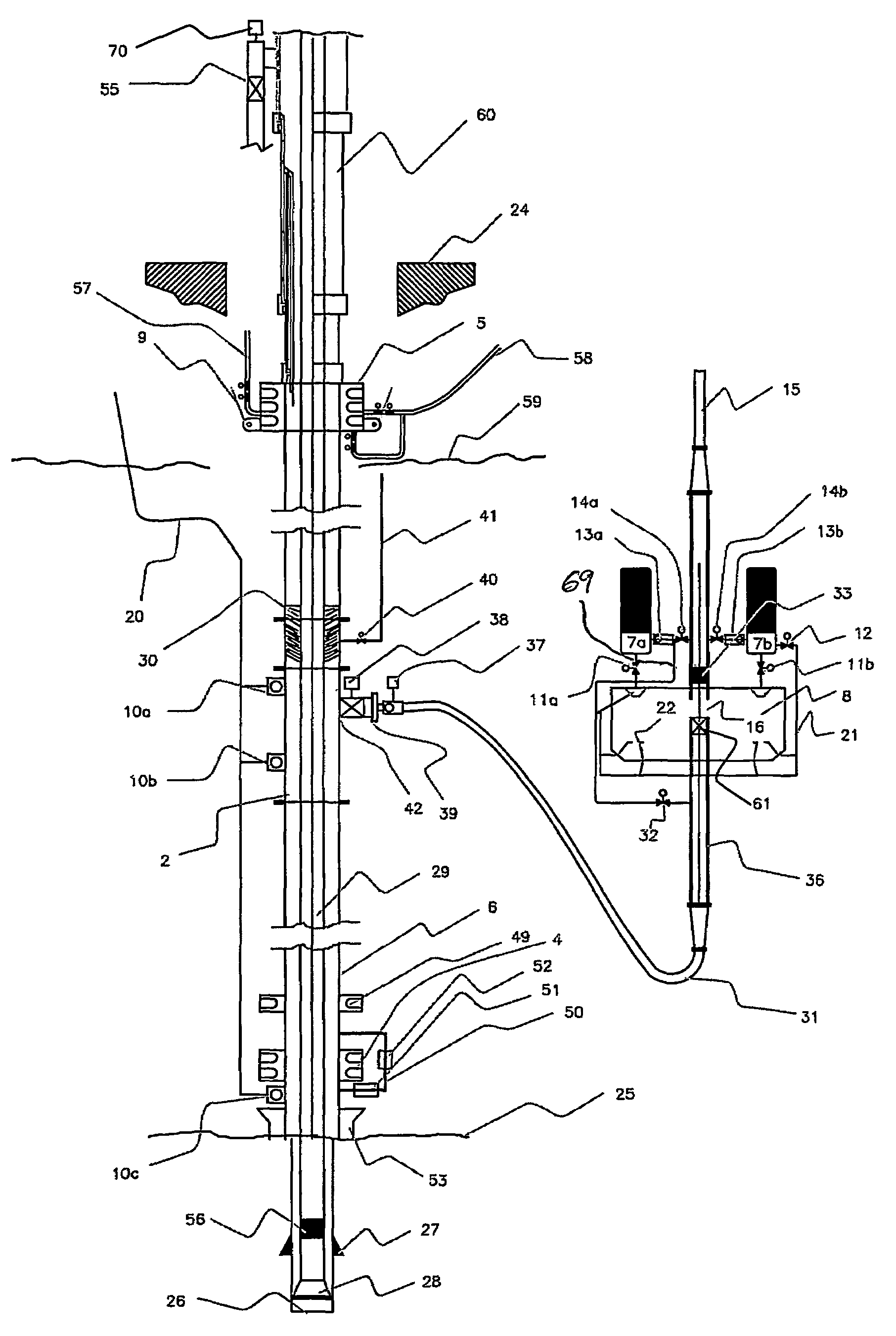
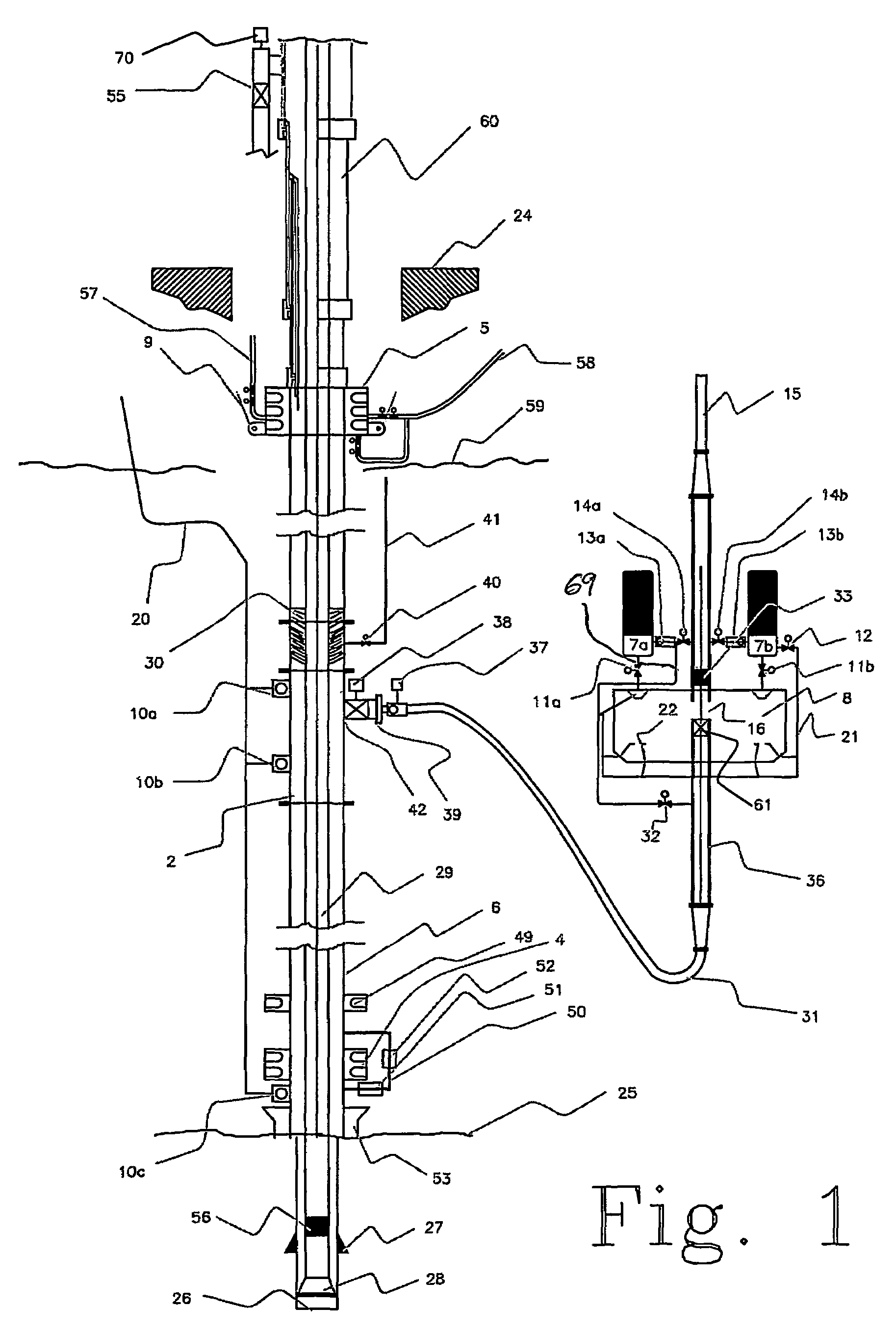
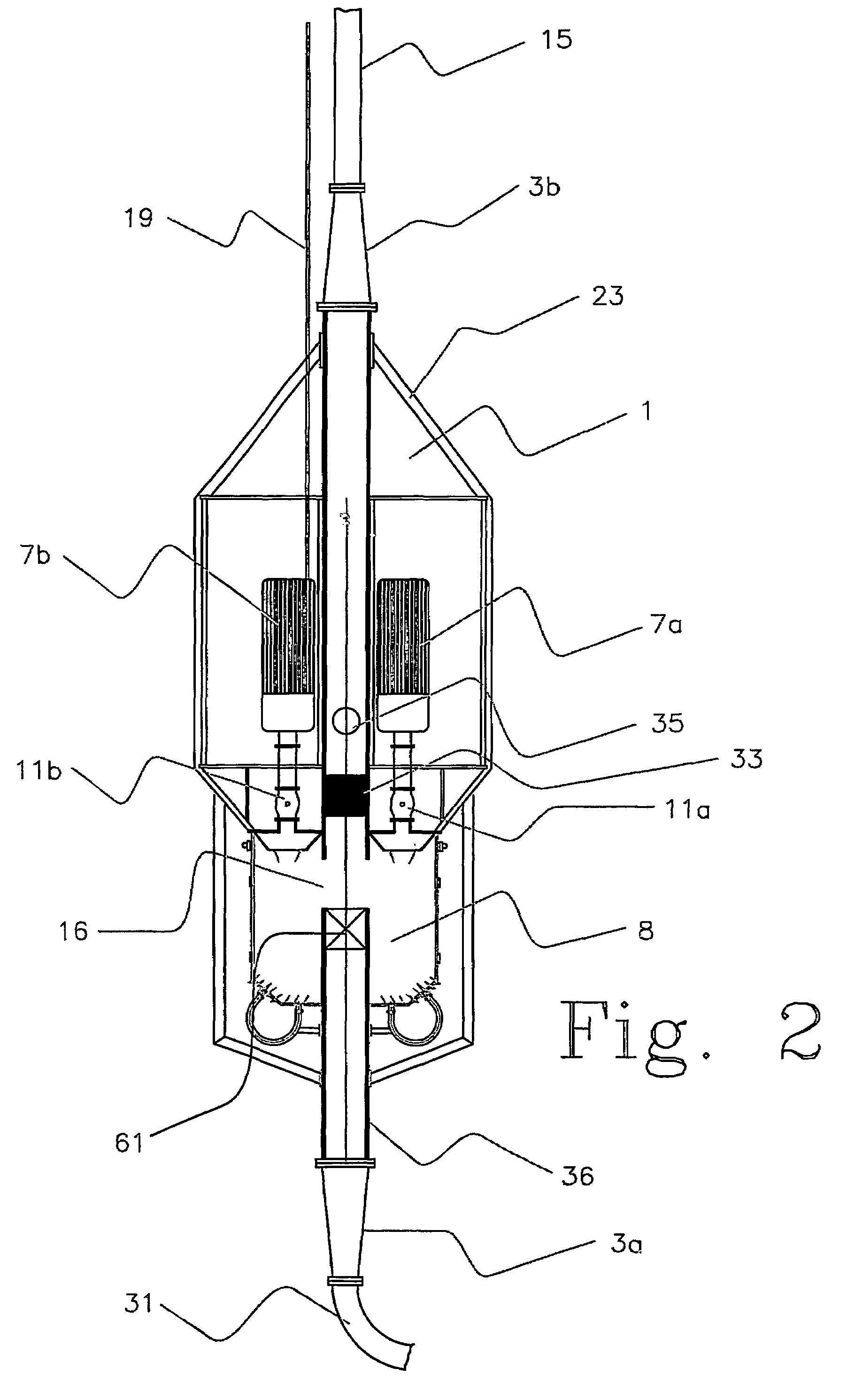
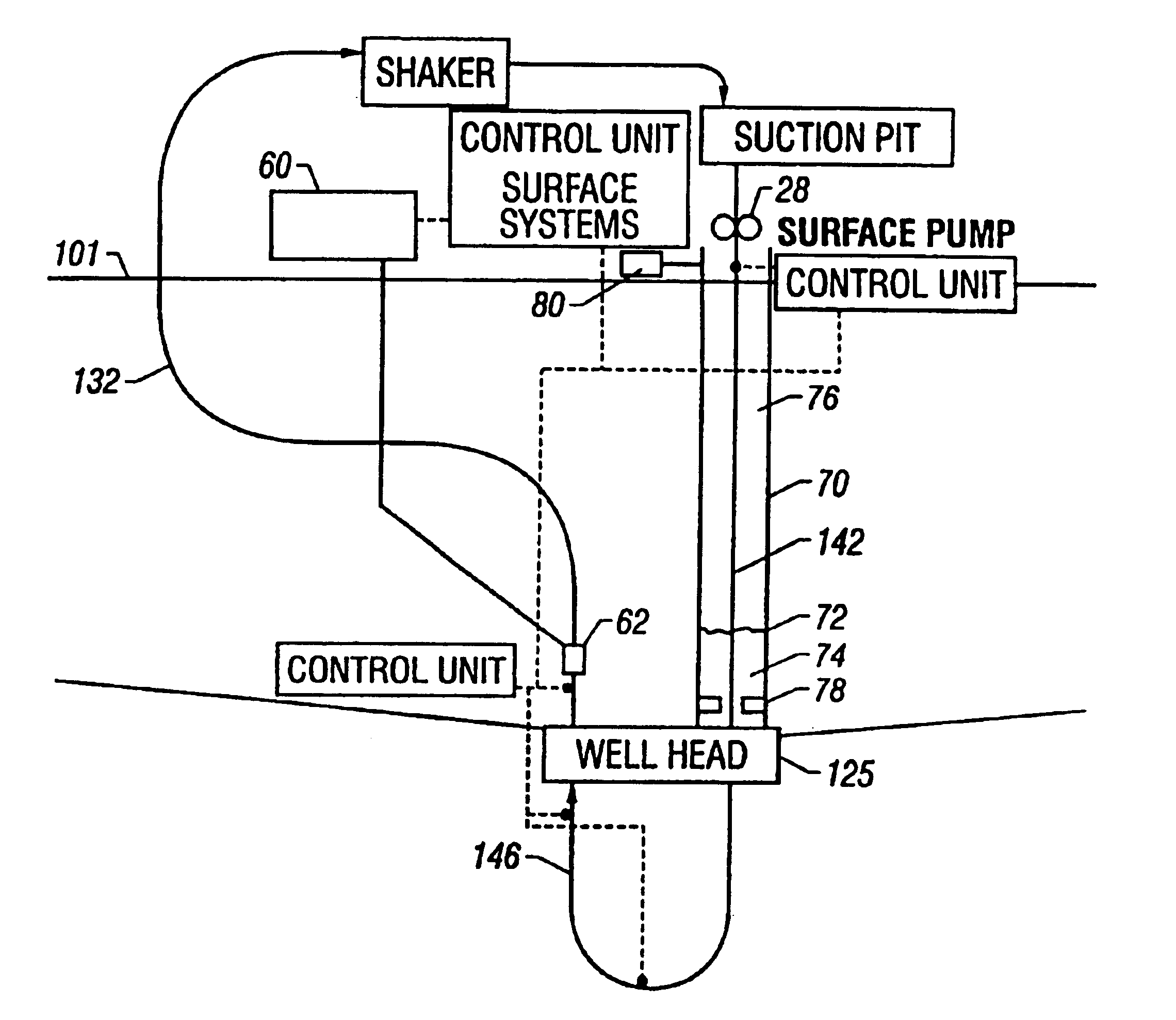
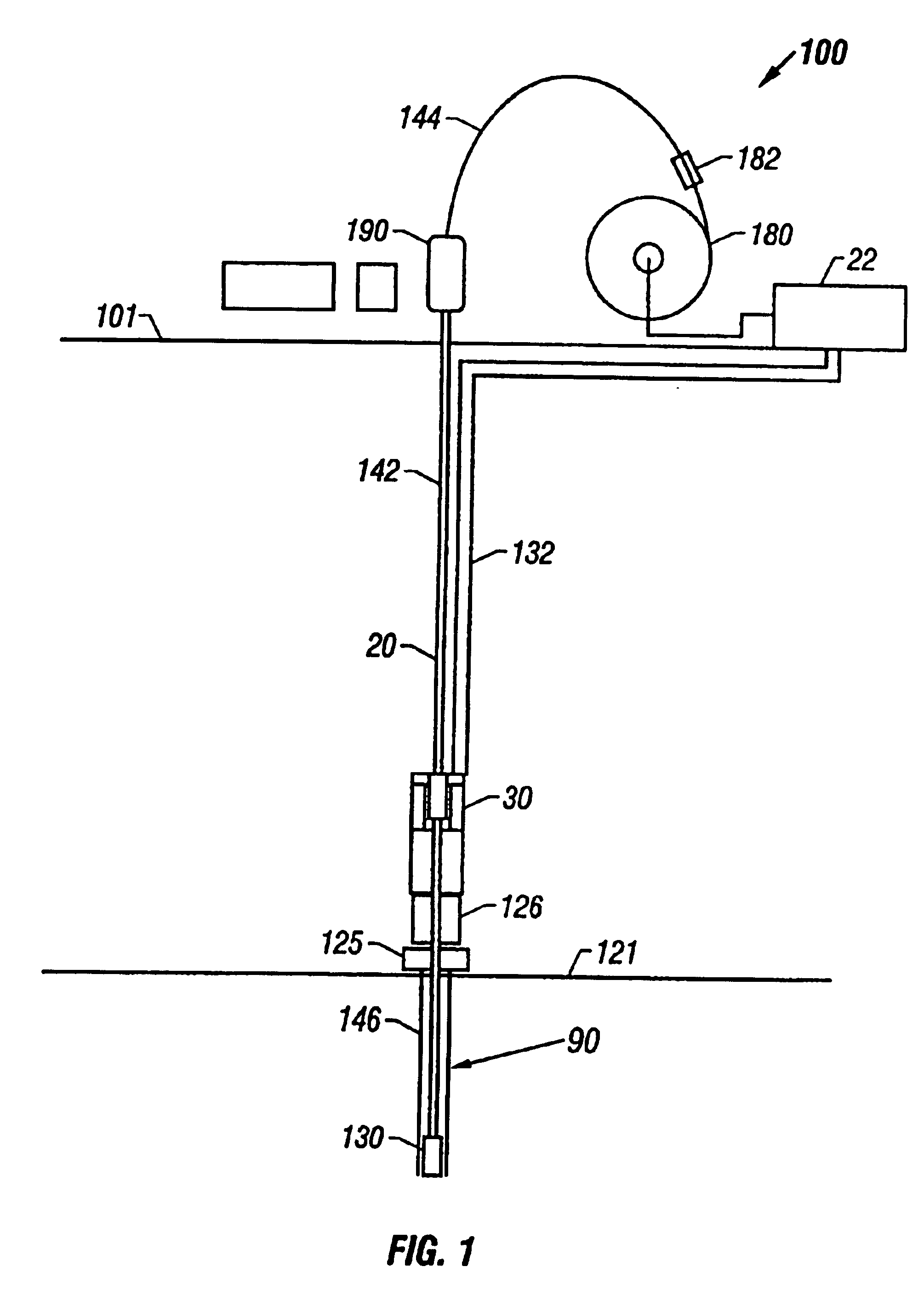
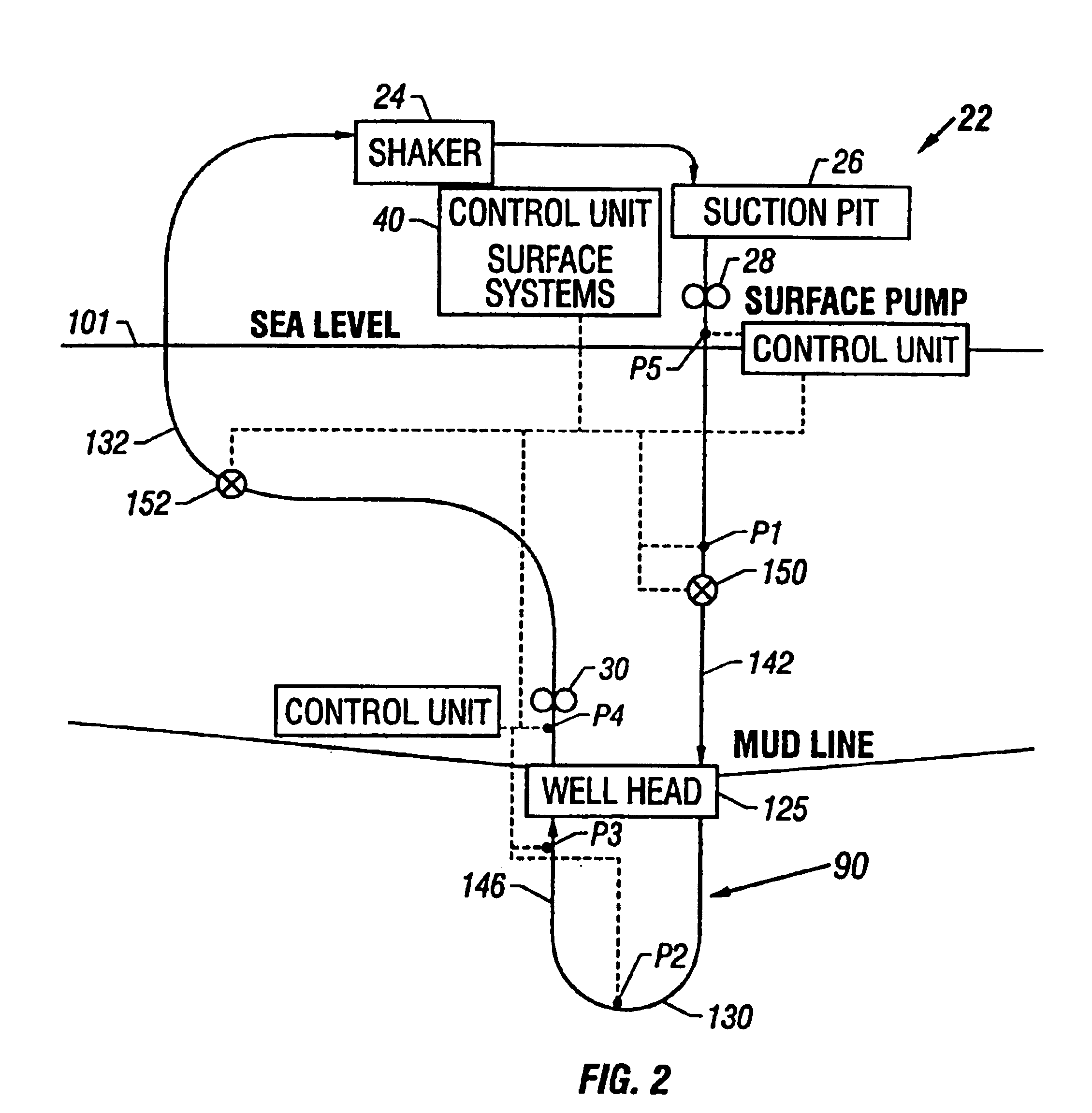
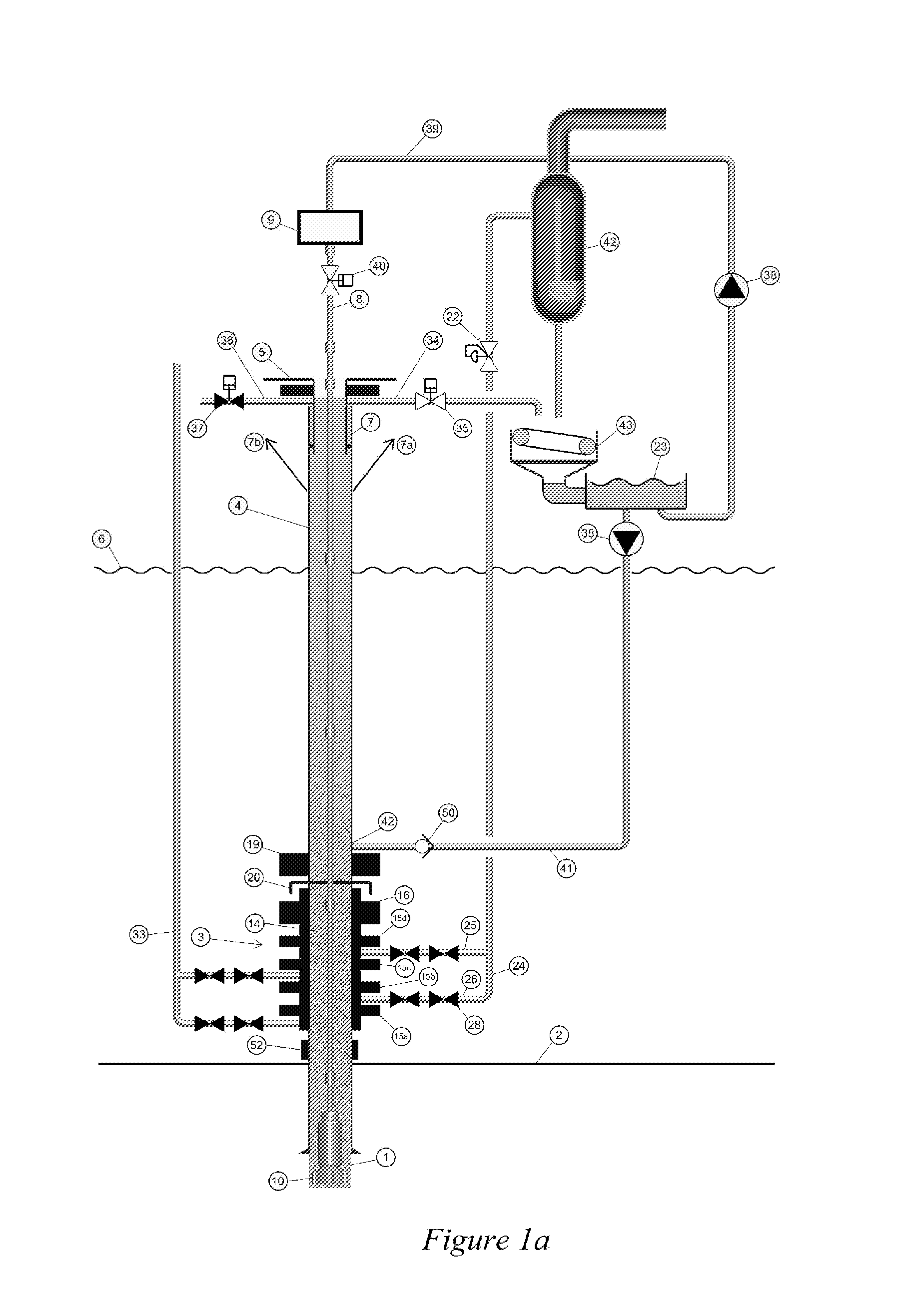
A drilling system for drilling subsea wellbores includes a tubing-conveyed drill bit that passes through a subsea wellhead. Surface supplied drilling fluid flows through the tubing, discharges at the drill bit, returns to the wellhead through a wellbore annulus, and flows to the surface via a riser extending from the wellhead. A flow restriction device positioned in the riser restricts the flow of the returning fluid while an active fluid device controllably discharges fluid from a location below to just above the flow restriction device in the riser, thereby controlling bottomhole pressure and equivalent circulating density (“ECD”). Alternatively, the fluid is discharged into a separate return line thereby providing dual gradient drilling while controlling bottomhole pressure and ECD. A controller controls the energy and thus the speed of the pump in response to downhole measurement(s) to maintain the ECD at a predetermined value or within a predetermined range.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
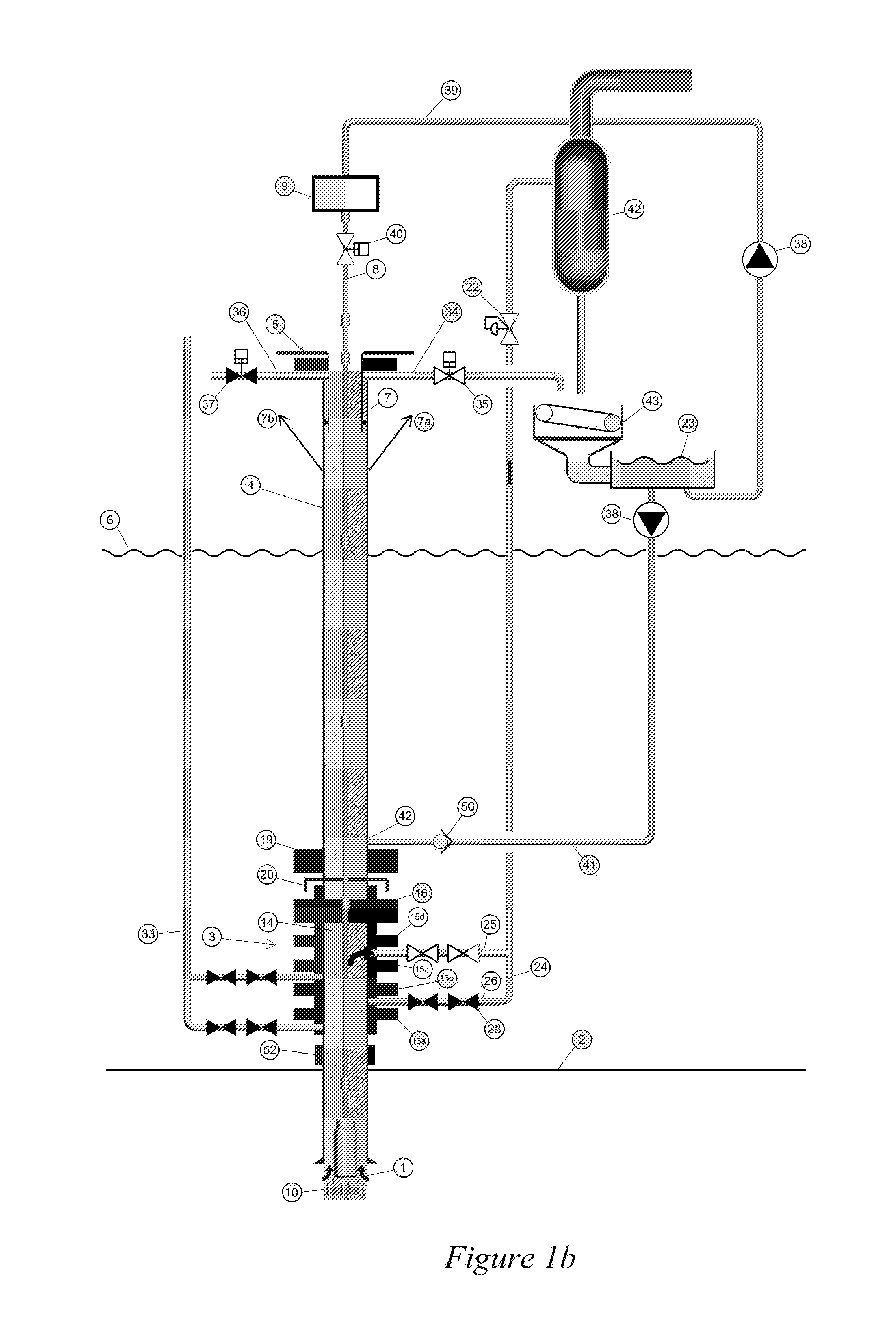
Drilling system and method for controlling equivalent circulating density during drilling of wellbores
A drilling system for drilling subsea wellbores includes a tubing-conveyed drill bit that passes through a subsea wellhead. Surface supplied drilling fluid flows through the tubing, discharges at the drill bit, returns to the wellhead through a wellbore annulus, and flows to the surface via a riser extending from the wellhead. A flow restriction device positioned in the riser restricts the flow of the returning fluid while an active fluid device controllably discharges fluid from a location below to just above the flow restriction device in the riser, thereby controlling bottomhole pressure and equivalent circulating density (“ECD”). Alternatively, the fluid is discharged into a separate return line thereby providing dual gradient drilling while controlling bottomhole pressure and ECD. A controller controls the energy and thus the speed of the pump in response to downhole measurement(s) to maintain the ECD at a predetermined value or within a predetermined range.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
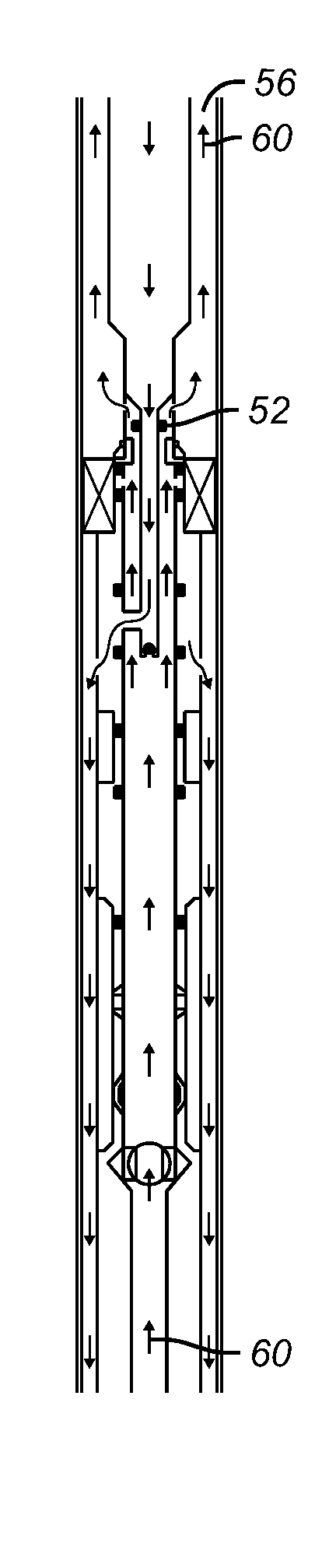
Arrangement and method for controlling and regulating bottom hole pressure when drilling deepwater offshore wells
InactiveUS7497266B2Handling is restrictedReduce pressureDrilling rodsConstructionsBottom hole pressureLine tubing
An arrangement and method for controlling and regulating bottom hole pressure in a well during subsea drilling in deep water involves adjustment of a liquid / gas interface level in a high pressure drilling riser up or down to change the slope and offset of the pressure gradient in the well. The arrangement may include a surface BOP and gas bleeding outlet at the upper end of the drilling riser, a lower BOP with a by-pass line, and an outlet at a depth below the water surface that is connected to a pumping system with a flow return conduit running back to a drilling vessel or platform.
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
Arrangement and method for regulating bottom hole pressures when drilling deepwater offshore wells
InactiveUS7264058B2Improve abilitiesChange densityDrilling rodsConstructionsBottom hole pressureLine tubing
An arrangement and a method to control and regulate the bottom hole pressure in a well during subsea drilling at deep waters: The method involves adjustment of a liquid / gas interface level in a drilling riser up or down. The arrangement comprises a high pressure drilling riser and a surface BOP at the upper end of the drilling riser. The surface BOP havs a gas bleeding outlet. The riser also comprises a BOP, with a by-pass line. The drilling riser has an outlet at a depth below the water surface, and the outlet is connected to a pumping system with a flow return conduit running back to a drilling vessel / platform.
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
Subsea wellbore drilling system for reducing bottom hole pressure
InactiveUS6854532B2Easy to deployFaster and effective subsea downhole operationDrilling rodsConstructionsDelivery systemBottom hole assembly
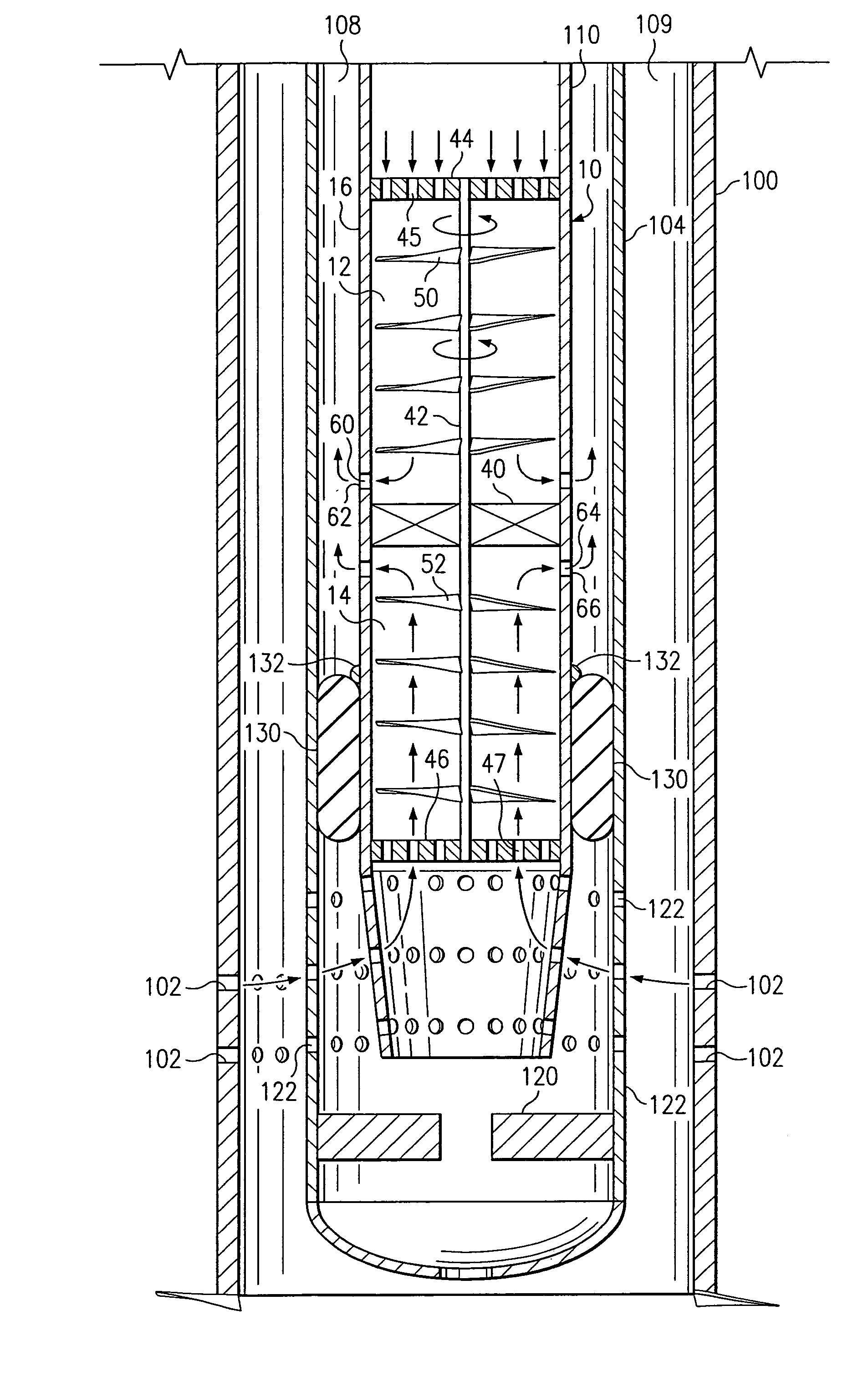
The present invention provides drilling systems for drilling subsea wellbores. The drilling system includes a tubing that passes through a sea bottom wellhead and carries a drill bit. A drilling fluid system continuously supplies drilling fluid into the tubing, which discharges at the drill bit bottom and returns to the wellhead through an annulus between the tubing and the wellbore carrying the drill cuttings. A fluid return line extending from the wellhead equipment to the drilling vessel transports the returning fluid to the surface. In a riserless arrangement, the return fluid line is separate and spaced apart from the tubing. In a system using a riser, the return fluid line may be the riser or a separate line carried by the riser. The tubing may be coiled tubing with a drilling motor in the bottom hole assembly driving the drill bit. A suction pump coupled to the annulus is used to control the bottom hole pressure during drilling operations, making it possible to use heavier drilling muds and drill to greater depths than would be possible without the suction pump. An optional delivery system continuously injects a flowable material, whose fluid density is less than the density of the drilling fluid, into the returning fluid at one or more suitable locations the rate of such lighter material can be controlled to provide supplementary regulation of the pressure. Various pressure, temperature, flow rate and kick sensors included in the drilling system provide signals to a controller that controls the suction pump, the surface mud pump, a number of flow control devices, and the optional delivery system.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Downhole well pump
The pump and pump system of the present invention is designed to remove liquids, gas, sand and coal fines from gas and / or oil well bores. There is a need in the oil and gas industry to develop a more efficient operating pump that is capable of operating in wells that do not have enough bottom hole pressure to lift liquids to the surface causing the well to log off with fluids and if not economic, potentially be plugged prematurely. Additionally, this design will allow the producer the ability to conduct well bore maintenance such as acid flushes for perforation cleaning and scale batch treating for continued scale treatment.
Owner:BURLINGTON RESOURCES OIL & GAS LP
Well drilling method and system
Methods and systems are provided for drilling a well bore 60 through a subterranean formation using a drilling rig 25 and a drill string 50, whereby the bottom hole pressure while circulating drilling fluid ("ECD") may be substantially maintained when circulation is interrupted or altered, such as when adding a joint of drill pipe to or removing a joint of drill pipe from the drill string. The method includes controllably applying and maintaining a desired variable annulus fluid pressure in the well bore, and thereafter controllably releasing the pressure from the well bore 60. In addition, methods and systems are provided for rotating the drill string while trapping, maintaining and / or releasing the well bore pressure. A substantially constant ECD pressure may be maintained on a formation, thereby facilitating the use of a lower density drilling fluid than may otherwise be required to maintain well control. In one embodiment, a drill pipe connection may be made up and / or broke out while the drill string continues to rotate.
Owner:VAREO SHAFFER
Method for calculating staged fracturing productivity of compact reservoir horizontal well
ActiveCN105840187ACalculations are reliableGood application effectInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsBottom hole pressureMultiple fracture
The invention relates to the technical field of oil fracturing, in particular to a method for calculating the staged fracturing productivity of a compact reservoir horizontal well. The method is characterized by including the steps of firstly, dividing a reservoir infiltration area into four parts; secondly, obtaining the equivalent hole diameter of each fracture; thirdly, obtaining the yield of each fracture during multiple fracture disturbance; fourthly, coupling the yield of each fracture with the hydraulic pressure drop flow model in a horizontal wellbore to obtain a group of bottom hole pressure, iteratively solving until the bottom hole pressure difference of the previous step and the next step is smaller than tolerance, namely convergence, and taking the determined group of yield as the fracture-control yield of each fracture and the sum of the fracture-control yield of the fractures as the total yield of the horizontal well. The method is real and reliable in calculation result and good in application effect.
Owner:RES INST OF SHAANXI YANCHANG PETROLEUM GRP
System and method for drilling a subsea well
ActiveUS20120227978A1Increase the differential pressureFluid removalUnderwater drillingBottom hole pressureSuction stress
A subsea mud pump can be used to return heavy drilling fluid to the surface. In order to provide a less stringent requirement for such a pump and to better manage the bottom hole pressure in the case of a gas kick or well control event, the gas should be separated from the drilling fluid before the drilling fluid enters the subsea mud pump and the pressure within the separating chamber. The mud pump suction should be controlled and kept equal or lower than the ambient seawater pressure. This can be achieved within the cavities of the subsea BOP by a system arrangement and methods explained. This function can be used with or without a drilling riser connecting the subsea BOP to a drilling unit above the body of water.
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
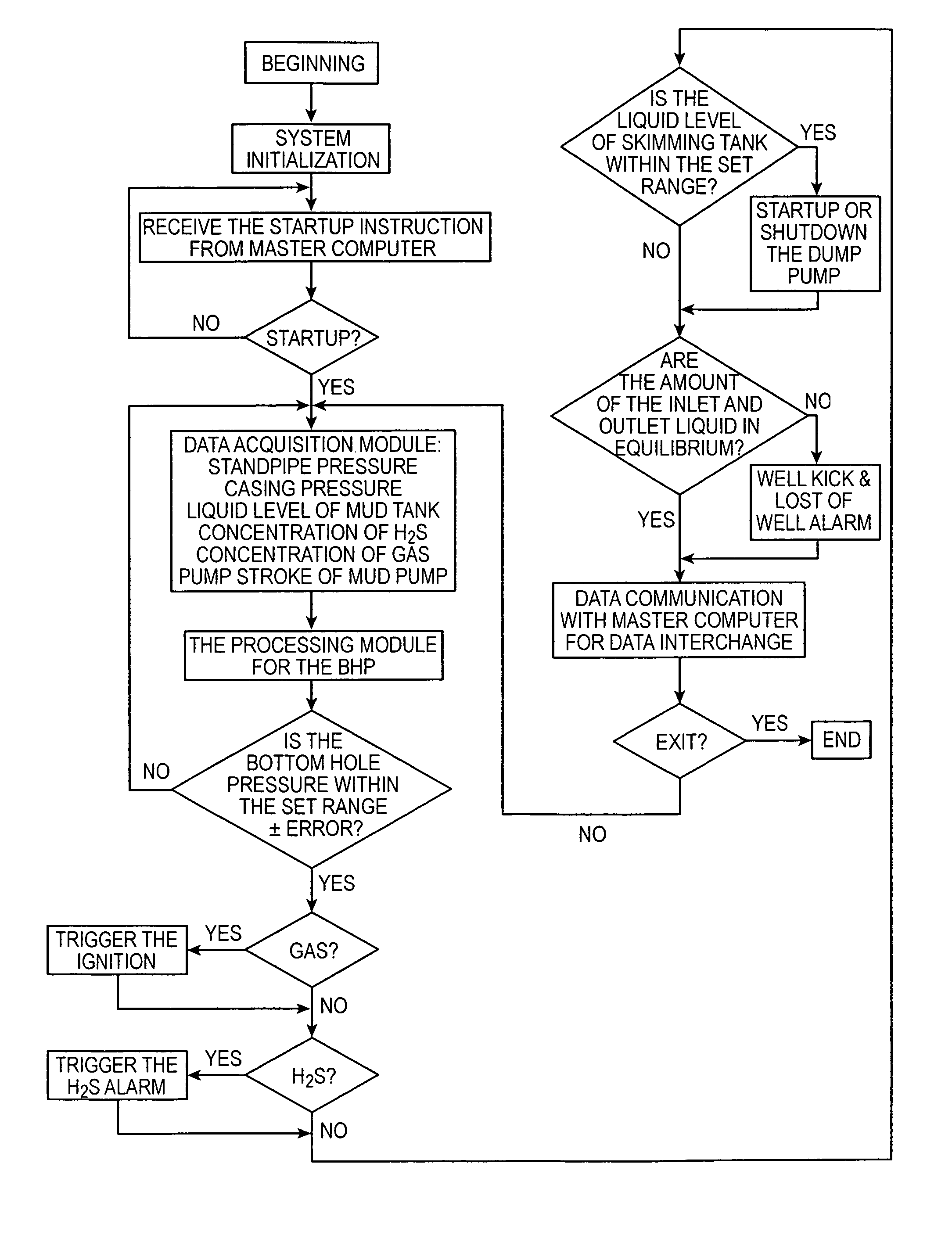
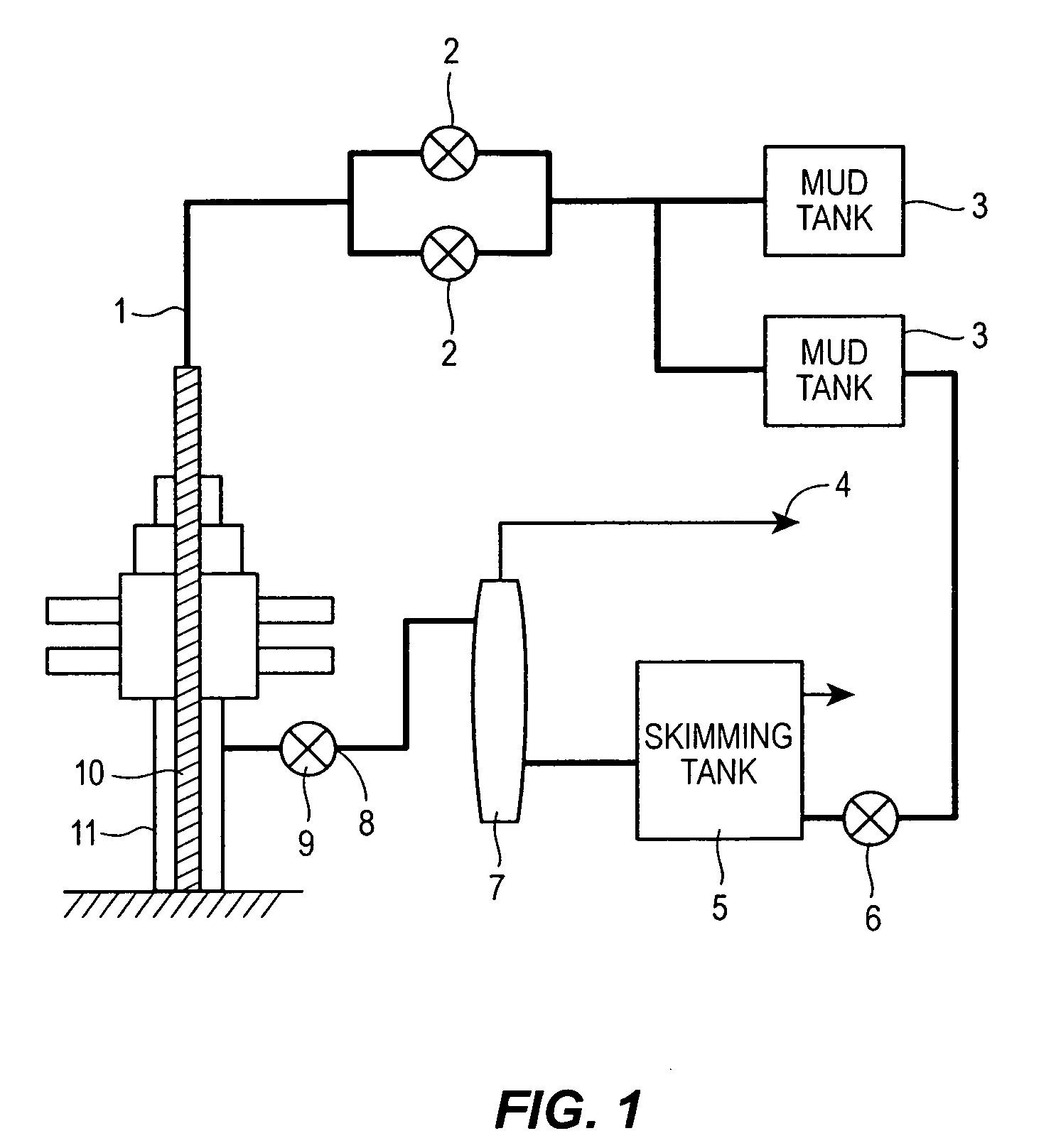
Automatic control system and method for bottom hole pressure in the underbalance drilling
ActiveUS20050096848A1Easy to controlHigh adjustment accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsAutomatic controlEngineering
This invention provides an automatic control system and method for bottom hole pressure (BHP) in the underbalance drilling. It relates to a computer automatic control technology. The automatic control system according to the invention includes a processing module for the BHP based on the mechanisms of hydraulics. The BHP in the underbalance drilling is calculated from the acquired standpipe pressure (SPP), the calculated circulating pressure loss in the drilling tools, drill bit pressure drop and the fluid column pressure in the drill string. The resulting BHP is then compared with the set pressure value of the system. In case that the BHP is higher or lower than the set pressure, an instruction to regulate throttle valve opening will be issued in order to bring the BHP back to the set pressure range and complete BHP monitoring and control. The automatic control system and method according to the invention enable real-time tracking of the changes in BHP and achieve accurate and timely adjustment and control of BHP. The automatic control system and method improve the level of automation in the underbalance drilling process, and also enhance the reliability and safety in the underbalance drilling operation, which have wide foreground for application.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Underground working condition simulation method for controlled pressure drilling experiment and test
The invention relates to an underground working condition simulation method and a device for a controlled pressure drilling experiment and a test, wherein the underground working condition simulation device is connected with controlled pressure drilling equipment in series to perform the experiment and the test. The underground working condition simulation device simulates changes of underground working conditions, including a plurality of types of working conditions such as normal drilling, switching slurry pumping, pipe tripping, circulation loss, well kick and the like; and the controlled pressure drilling equipment automatically judges and identifies the working conditions and controls pressure changes according to the changes of the working conditions, and keeps the simulated bottom hole pressure constant to avoid abnormal conditions such as the circulation loss, the well kick and the like. The bottom hole pressure fluctuations are simulated by adjusting the opening of a throttlevalve B according to the flow and the density of a drilling fluid input by a slurry pump A; a choke manifold simulates the bore hole annular pressure loss; the opening of a throttle valve A is adjusted to simulate a circulation loss working condition; and a slurry pump B or an air source is started and the input flow is controlled to simulate a well kick working condition. By adopting the method and the device, the controlled pressure drilling parameters are precisely grasped, and the controlled pressure drilling equipment is debugged delicately.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
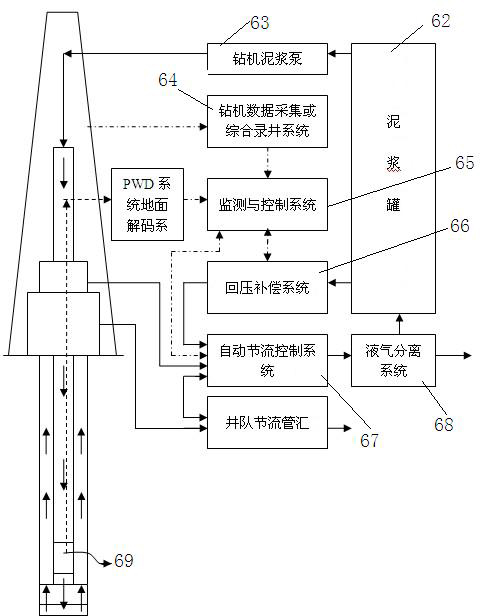
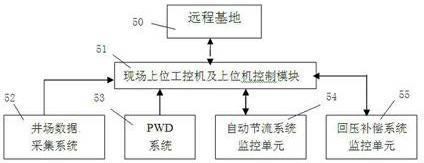
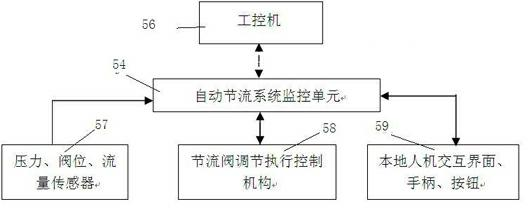
Closed-loop controlled-pressure well drilling system
The invention discloses a closed-loop controlled-pressure well drilling system, which comprises an annular pressure monitoring system, a rotary control head, a liquid-gas separation system, a monitoring and controlling system, an automatic throttle control system and a back pressure compensation system, wherein the monitoring and controlling system is respectively connected with the automatic throttle control system and the back pressure compensation system; the monitoring and controlling system comprises a superior industrial control detection mechanism, an automatic throttle system monitoring unit and a back pressure compensation system monitoring unit; and the superior industrial control detection mechanism is respectively connected with the automatic throttle system monitoring unit and the back pressure compensation system monitoring unit. Through precise pressure control, bottom-hole pressure is precisely controlled to reach a target pressure.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
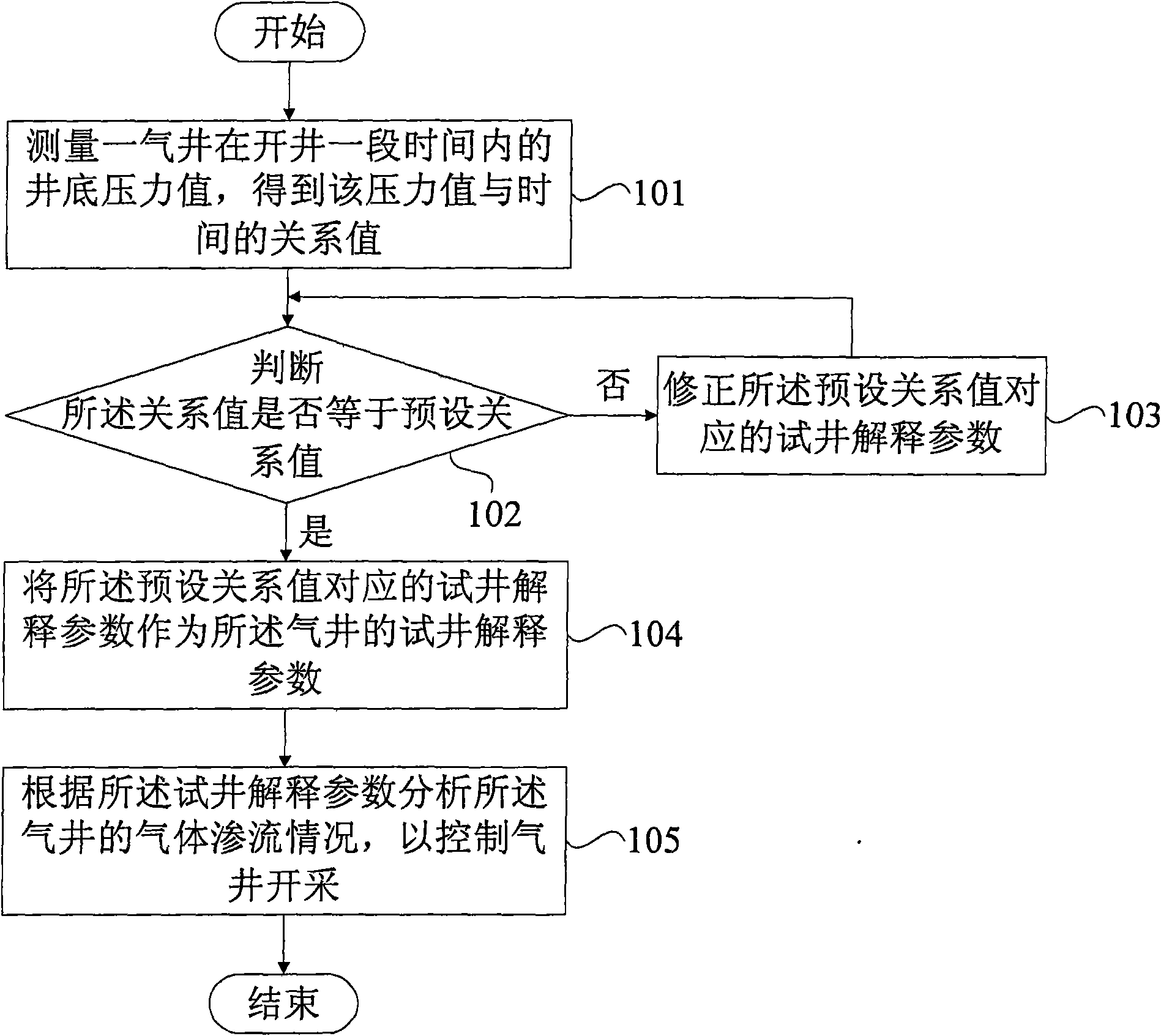
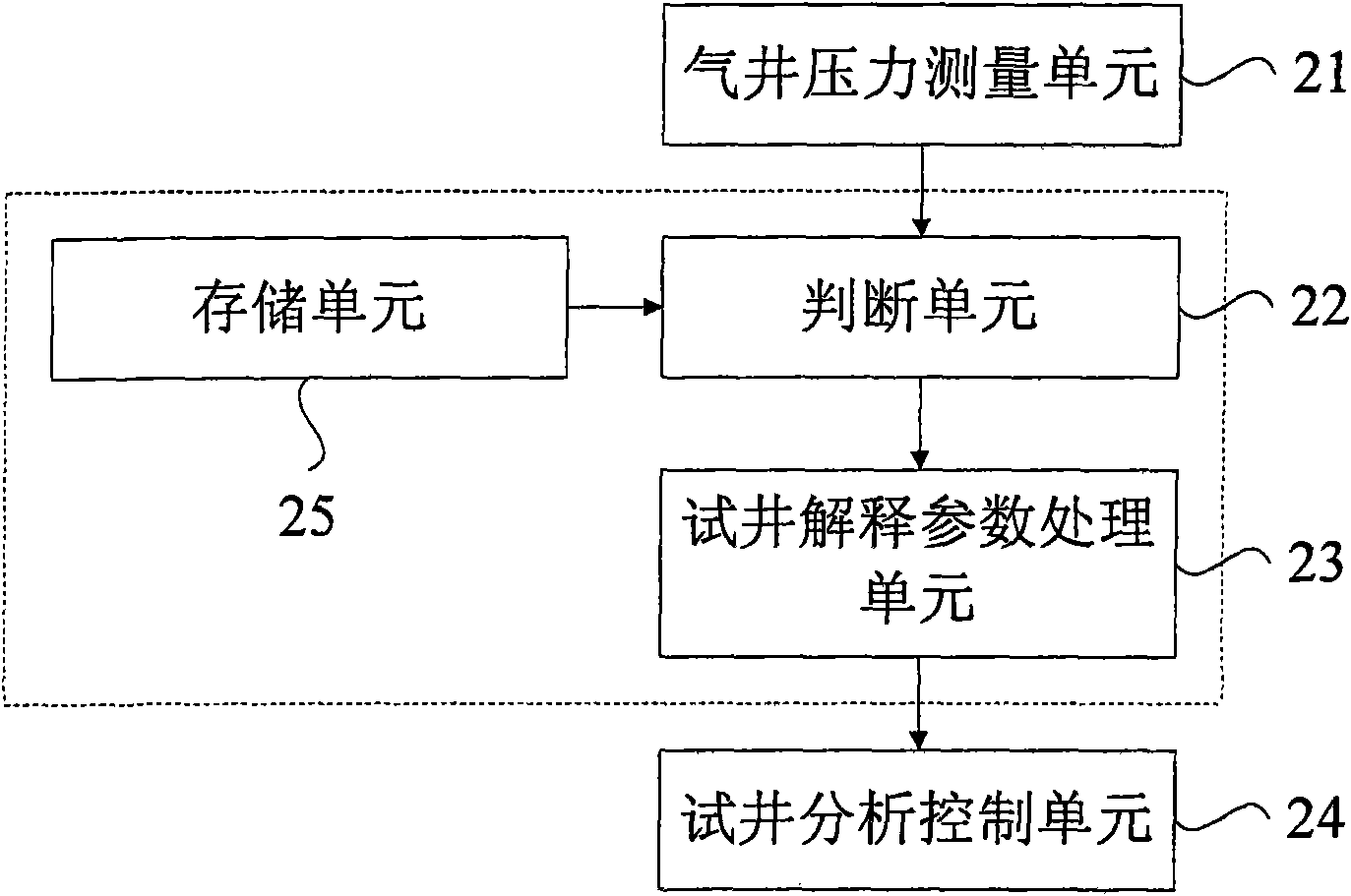
Well test analysis control method for low permeability gas reservoir and method thereof
InactiveCN101560879AOvercome the shortcoming of small test rangeHigh precisionBorehole/well accessoriesSkin factorBottom hole pressure
The invention provides a well test analysis control system for a low permeability gas reservoir and a method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: measuring bottom hole pressure value of a gas well in a period after well startup to obtain a relation value between pressure difference and time; judging whether the relation value equals a preset relation value, if yes, performing the next step, or correcting well test interpretation parameters corresponding to the preset relation value; taking the well test interpretation parameters corresponding to the preset relation value as the well test interpretation parameters of the gas well; analyzing gas permeation situation of the gas well according to the well test interpretation parameters so as to control exploitation of the well gas; wherein, the well test interpretation parameters comprise gas slip factor, low level permeability, skin factor, well bore storage coefficient, flow coefficient and formation pressure. The well testinterpretation according to the method perfectly accords with actual condition of the gas reservoirs, accurately describe the gas reservoirs, and provide a reference for determining production system.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Automatic control system and method for bottom hole pressure in the underbalance drilling
ActiveUS7158886B2Accurate calculationRelatively small errorElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsAutomatic controlAutomated control system
This invention provides an automatic control system and method for bottom hole pressure (BHP) in the underbalanced drilling. It relates to a computer automatic control technology. The automatic control system according to the invention includes a processing module for the BHP based on the mechanisms of hydraulics. The BHP in the underbalanced drilling is calculated from the acquired standpipe pressure (SPP), the calculated circulating pressure loss in the drilling tools, drill bit pressure drop and the fluid colunm pressure in the drill string. The resulting BHP is then compared with the set pressure value of the system. In case that the BHP is higher or lower than the set pressure, an instruction to regulate throttle valve opening will be issued in order to bring the BHP back to the set pressure range and complete BHP monitoring and control.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Tight reservoir horizontal well volume fracturing process
InactiveCN103527163AIncrease success rateSolve the problem of inadequate transformationFluid removalBottom hole pressureWell logging
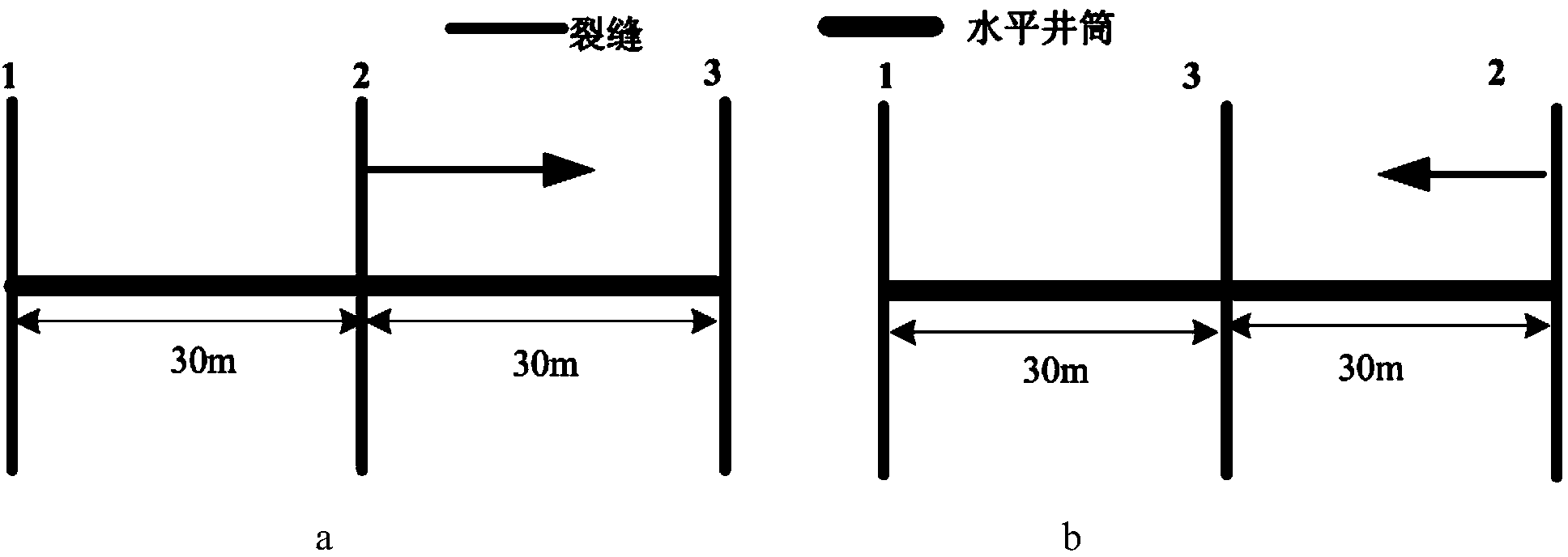
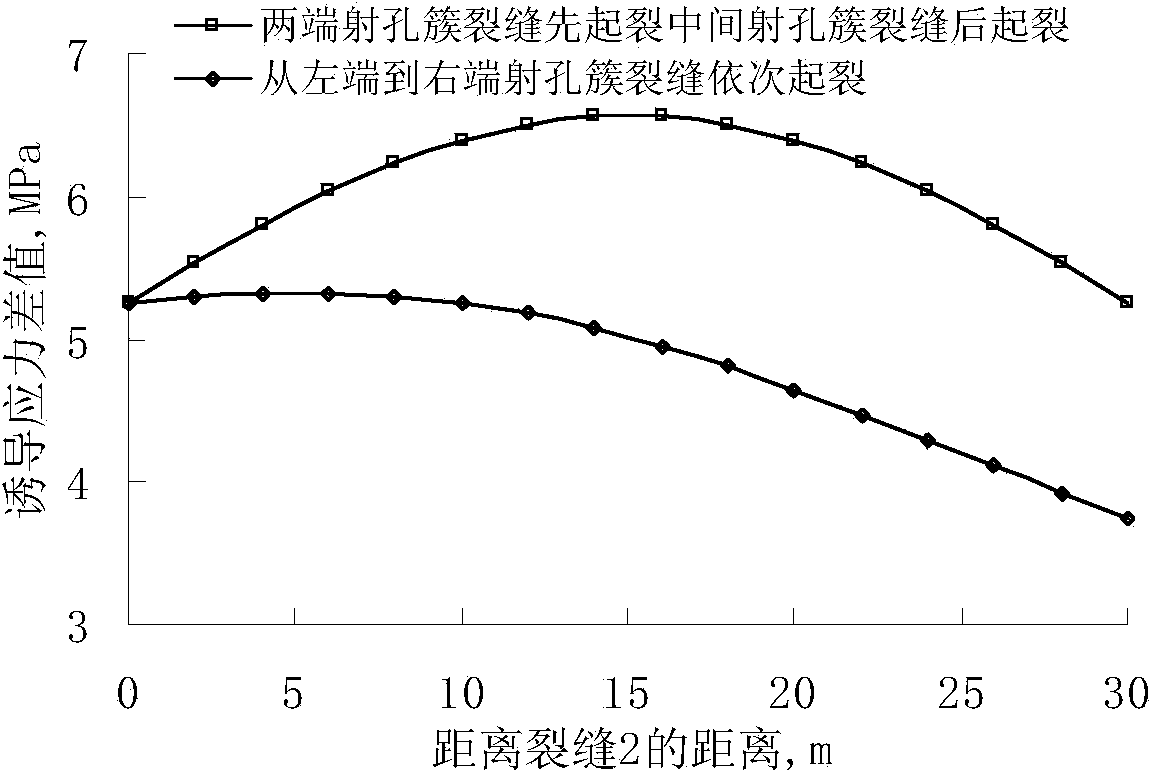
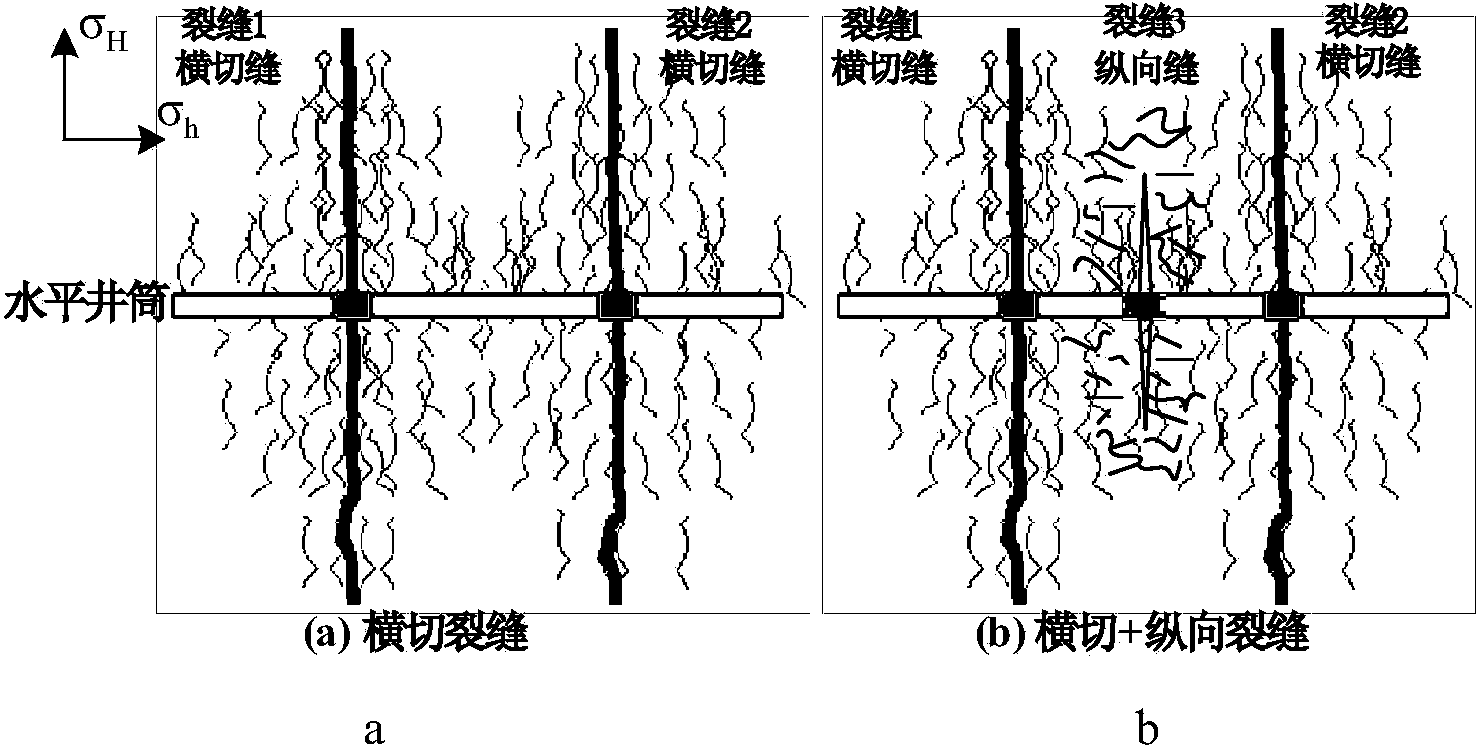
The invention relates to a tight reservoir horizontal well volume fracturing process. Data including in-situ stress magnitude and direction, horizontal well azimuth and length, reservoir Young moduli, a Poisson ratio, a well logging interpretation result and the like are collected and used as basic parameters for calculating induced stress needed for generation of complex cracks in tight reservoir horizontal well volume fracturing; according to reservoir physical characteristics, induced stress difference value variation conditions of three or more perforation clusters in the same fracturing segment according to different crack initiation sequences are contrasted, and preference is given to the perforation cluster crack initiation sequences with the maximal induced stress difference value as the target; preference is given to perforation cluster gaps so that the complex cracks can be formed through fracturing in the same fracturing segment of a horizontal well; in cooperation with perforation parameter optimization and with bottom hole pressure control as the target, the effect that the cracks of the perforation clusters at the two ends are initiated and extended for a certain distance through discharge capacity adjustment and then the discharge capacity is improved to utilize perforation friction for pressing open the cracks of the perforation clusters in the middle is achieved; then, prepad fluid and sand-carrying fluid containing a propping agent are poured into the cracks in sequence to realize transformation of the shape of the complex cracks of the fractured horizontal well.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Live bottom hole pressure for perforation/fracturing operations
ActiveUS8607864B2Improve efficiencyImprove optimizationSurveyFlow control using electric meansBottom hole pressureHydraulic fracturing
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
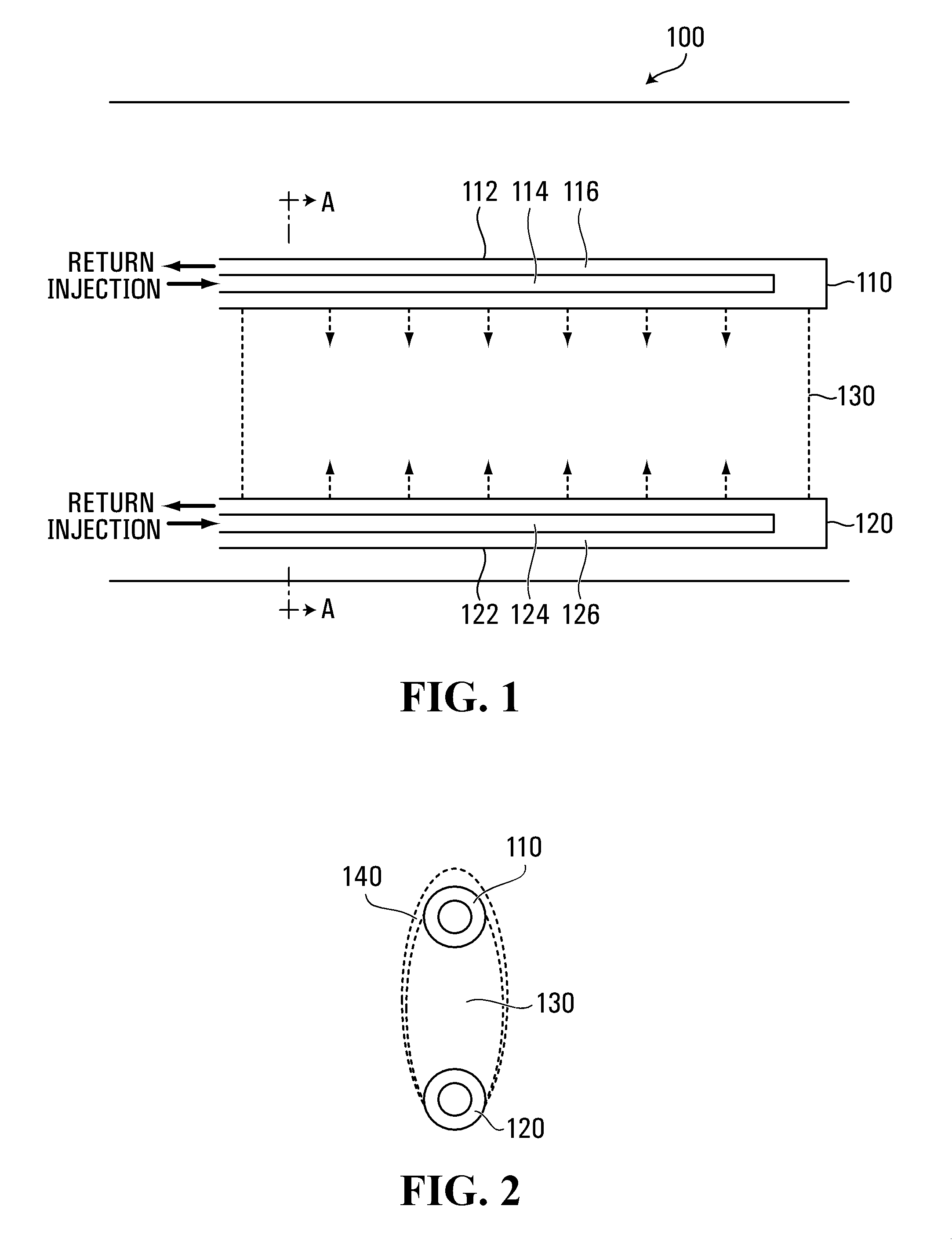
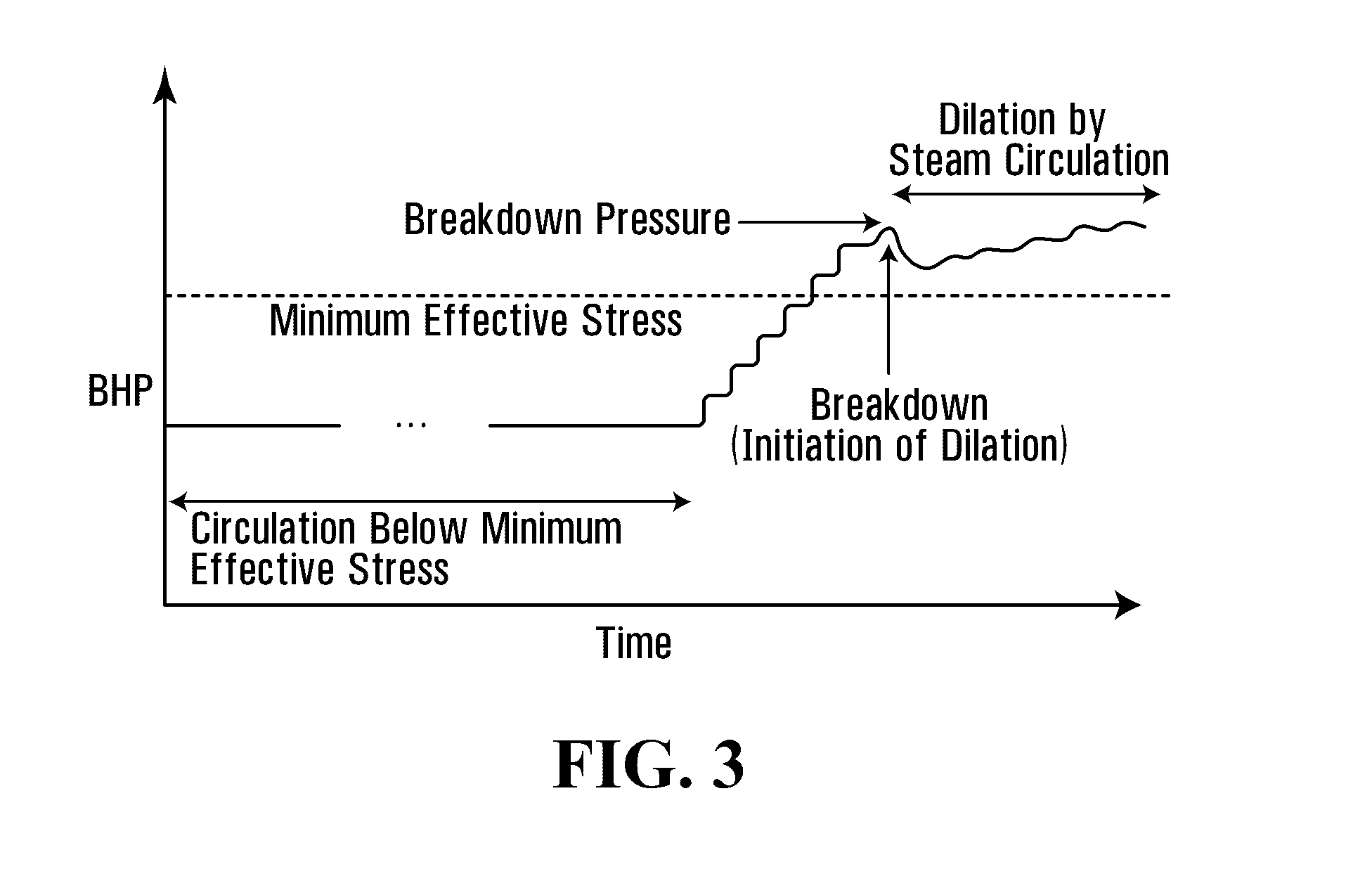
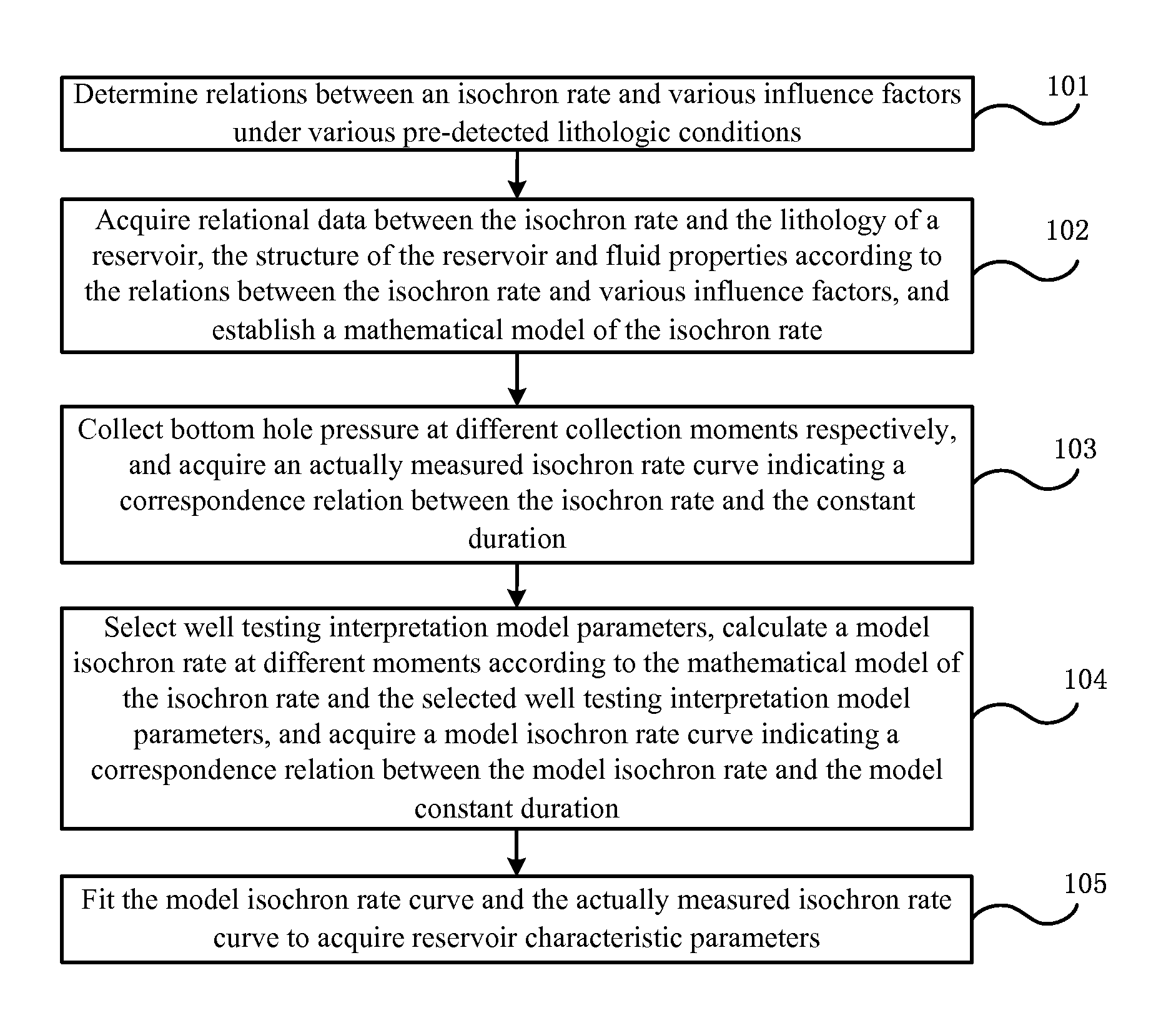
Establishing communication between well pairs in oil sands by dilation with steam or water circulation at elevated pressures
ActiveUS20130032336A1Increase steam pressureReduce steam pressureSurveyConstructionsBottom hole pressureWater circulation
A method of establishing fluid communication between a well pair in an oil-sand reservoir is provided, where dilatable oil sands in the reservoir form a barrier to fluid communication between the well pair. Steam or water is circulated within at least one well to apply a steam or water pressure to a region of the oil sands adjacent to the well. The steam or water pressure is increased to a dilation pressure sufficient to dilate the oil sands in the region. While circulating steam or water within the well at a substantially steady state, the steam or water pressure is maintained at a level sufficient to enlarge the dilated region, until detection of a signal indicative of fluid communication between the well pair. The rates of steam or water injection and production may be monitored and adjusted, and the steam or water pressure may be controlled by adjusting the rate of steam or water injection or production to vary a bottom-hole pressure in the well.
Owner:FCCL PARTNERSHIP
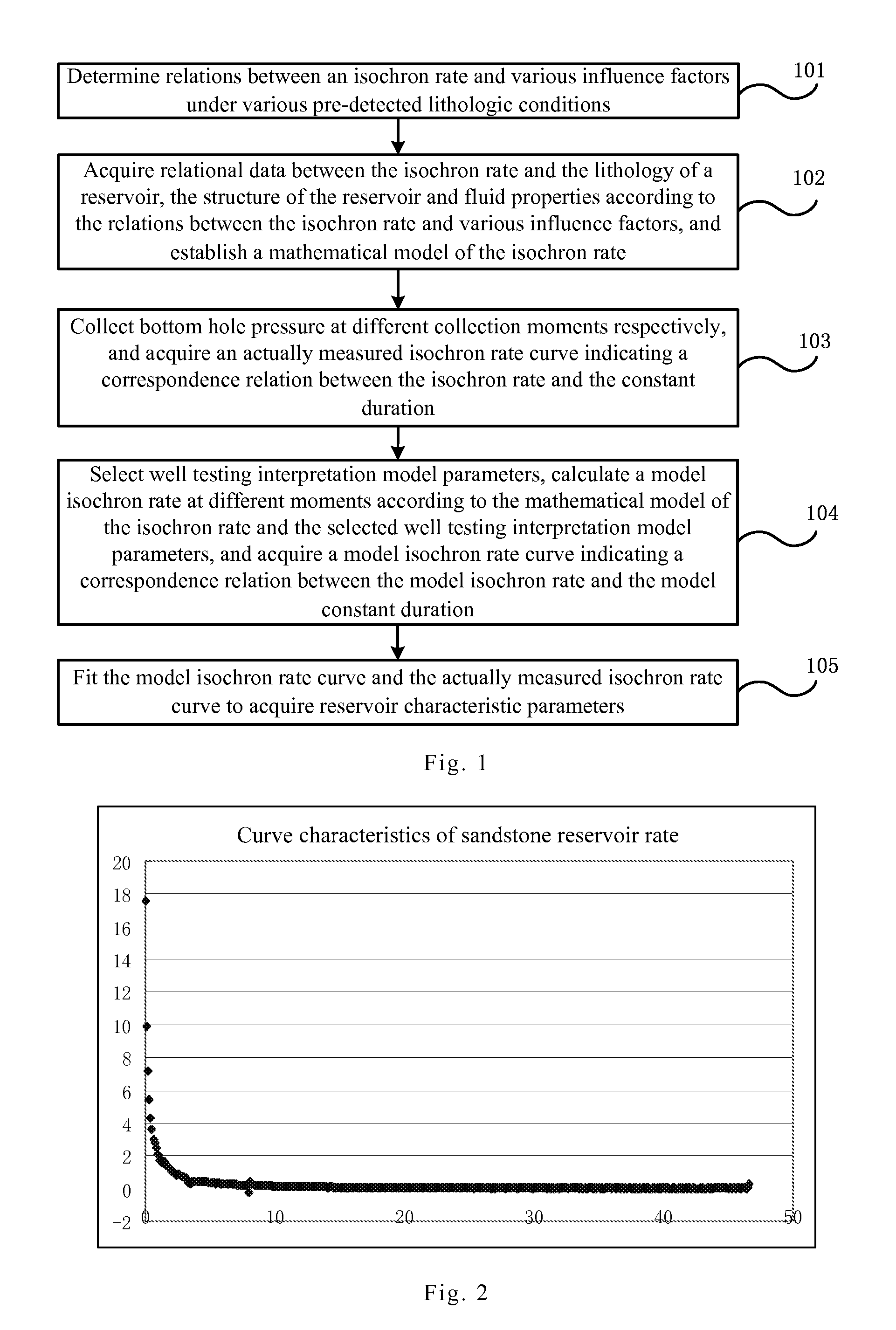
Method and system for analyzing and processing continued flow data in well testing data
InactiveUS20150066372A1Easy to analyzeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyBottom hole pressureLithology
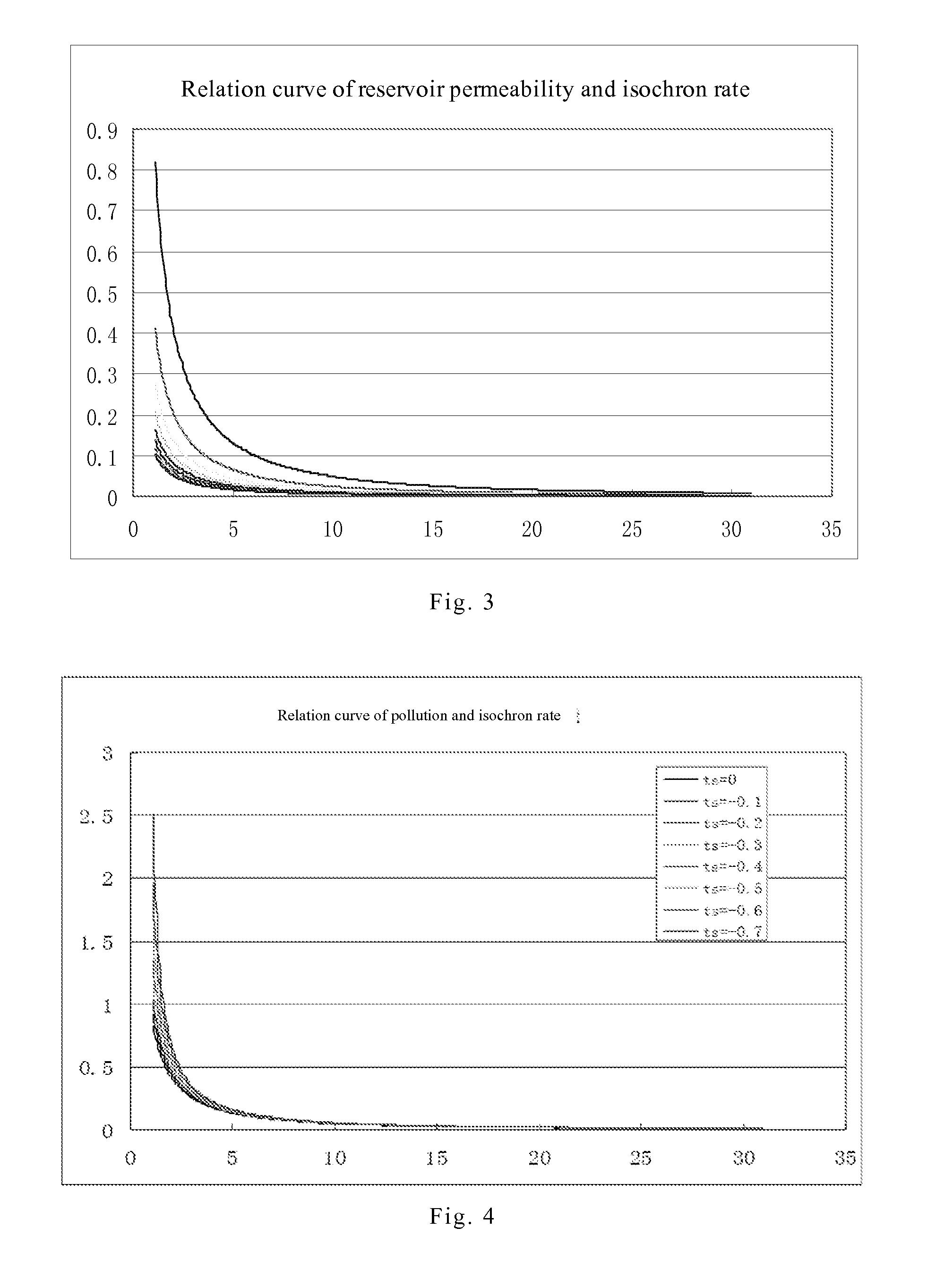
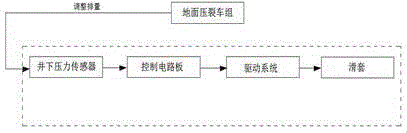
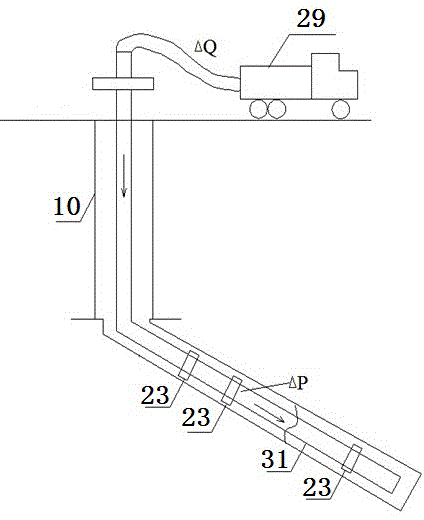
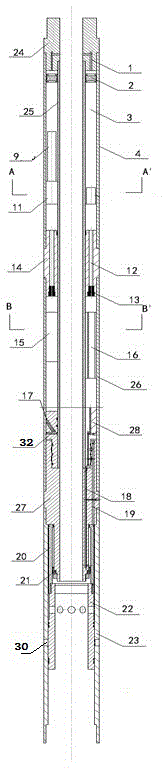
Methods and systems analyze continued flow data in well testing data. Embodiments can determine relations between an isochron rate and influence factors under pre-detected lithologic conditions, acquire relational data between the isochron rate and the lithology of a reservoir, the structure of the reservoir, and fluid properties; establish a mathematical model of the isochron rate; collect bottom hole pressure at different collection moments respectively during the reservoir well testing process; acquire a measured isochron rate curve between the isochron rate Vp and the constant duration t; select well testing interpretation model parameters; calculate a model isochron rate Vp′ at different moments according to the mathematical model of the isochron rate and the selected well testing interpretation model parameters; acquire a model isochron rate curve between Vp′ and the model constant duration t′; and fit the model isochron rate curve and the measured isochron rate curve to acquire reservoir characteristic parameters.
Owner:IDS NEW TECH
Method for controlling underground sliding sleeves by ground pressure waves
ActiveCN104088603AReal-time control switch actionShorten the timeFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsControl theoryGround pressure
The invention discloses a method for controlling underground sliding sleeves by ground pressure waves. The method comprises the steps as follows: the ground pumping displacement is adjusted regularly to enable underground pressure to change according to the same rule, that is, a pressure fluctuation signal comprising a control command is transmitted to the underground; a receiving device arranged on each sliding sleeve receives the ground control command, and the ground control command is compared with command information assigned by the sliding sleeve; if the ground control command is different from the command information assigned in each sliding sleeve, the sliding sleeve does not act and waits for a next ground control command; and if the ground control command is the same as the command information assigned in each sliding sleeve, the sliding sleeve acts and finishes the opening or closing operation required by the control command. According to the method for controlling the underground sliding sleeves by the ground pressure waves, the underground pressure changes regularly according to regular adjustment of the ground pumping displacement, opening and closing actions of the underground sliding sleeves are remotely controlled by recognizing the signals transmitted through regular pressure change, and opening and closing of the sliding sleeves can be controlled in real time.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Multi-acting Circulation Valve
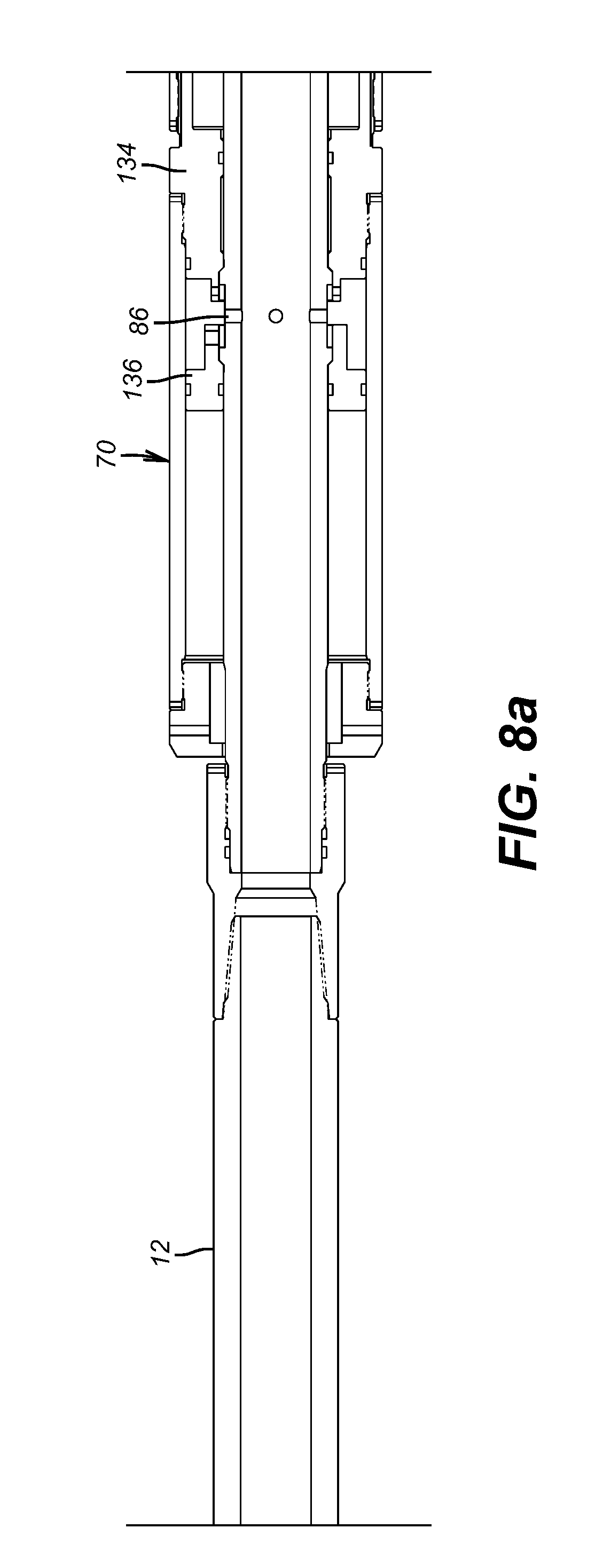
ActiveUS20110048723A1Prevent fluid lossAvoid scrubbingConstructionsFluid removalBottom hole pressureEngineering
A fracturing and gravel packing tool has features that prevent well swabbing when the tool is picked up with respect to a set isolation packer. An upper or multi-acting circulation valve allows switching between the squeeze and circulation positions without risk of closing the low bottom hole pressure ball valve. The multi-acting circulation valve can prevent fluid loss to the formation when being set down with the crossover tool supported or on the reciprocating set down device and the multi-acting circulation valve is closed without risk of closing the wash pipe valve.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
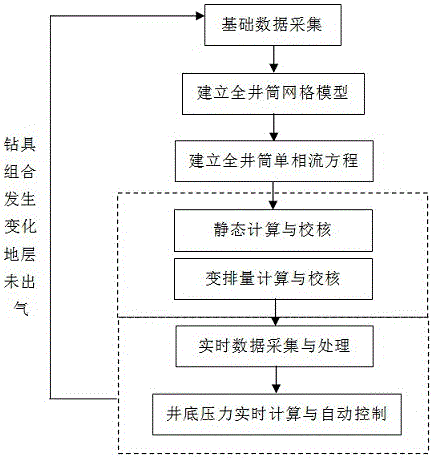
Bottom hole pressure real-time prediction and control method
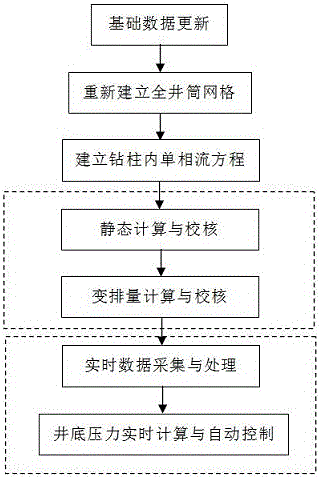
The invention discloses a bottom hole pressure real-time prediction and control method. The method includes the following steps that a, essential data are acquired, wherein bottom hole pressure meter data in the test drilling process are obtained, and the essential data of a well are obtained; b, a whole-shaft grid model is established; c, a whole-shaft single-phase flow equation is established; d, static computation and checking are conducted; e, variable displacement computation and checking are conducted; f, real-time data acquisition and processing are conducted; and g, bottom hole pressure real-time computation and automatic control are conducted, wherein the step g includes the content that all the data are called for conducting bottom hole pressure real-time computation and control. By the adoption of the method, the problems that a multi-phase flow model is complex, a flow pattern is difficult to distinguish, and key coefficients are difficult to determine due to the utilization of annulus multi-phase flow pressure loss computation traditionally can be solved, and the computation accuracy of the bottom hole pressure is improved.
Owner:CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP CHUANQING DRILLING ENG CO LTD
Well drilling device and method for controlling bottom hole pressure by monitoring flow
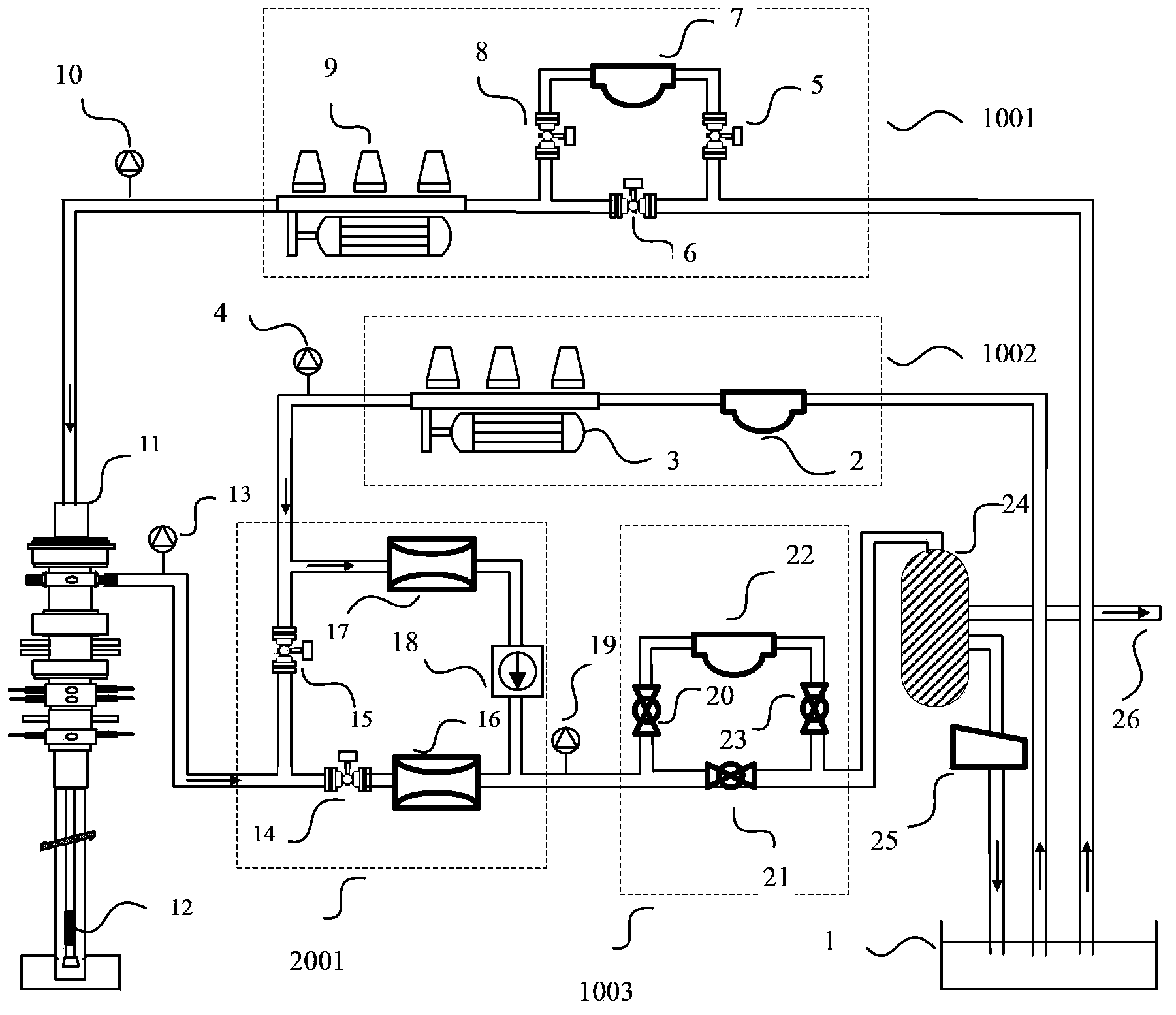
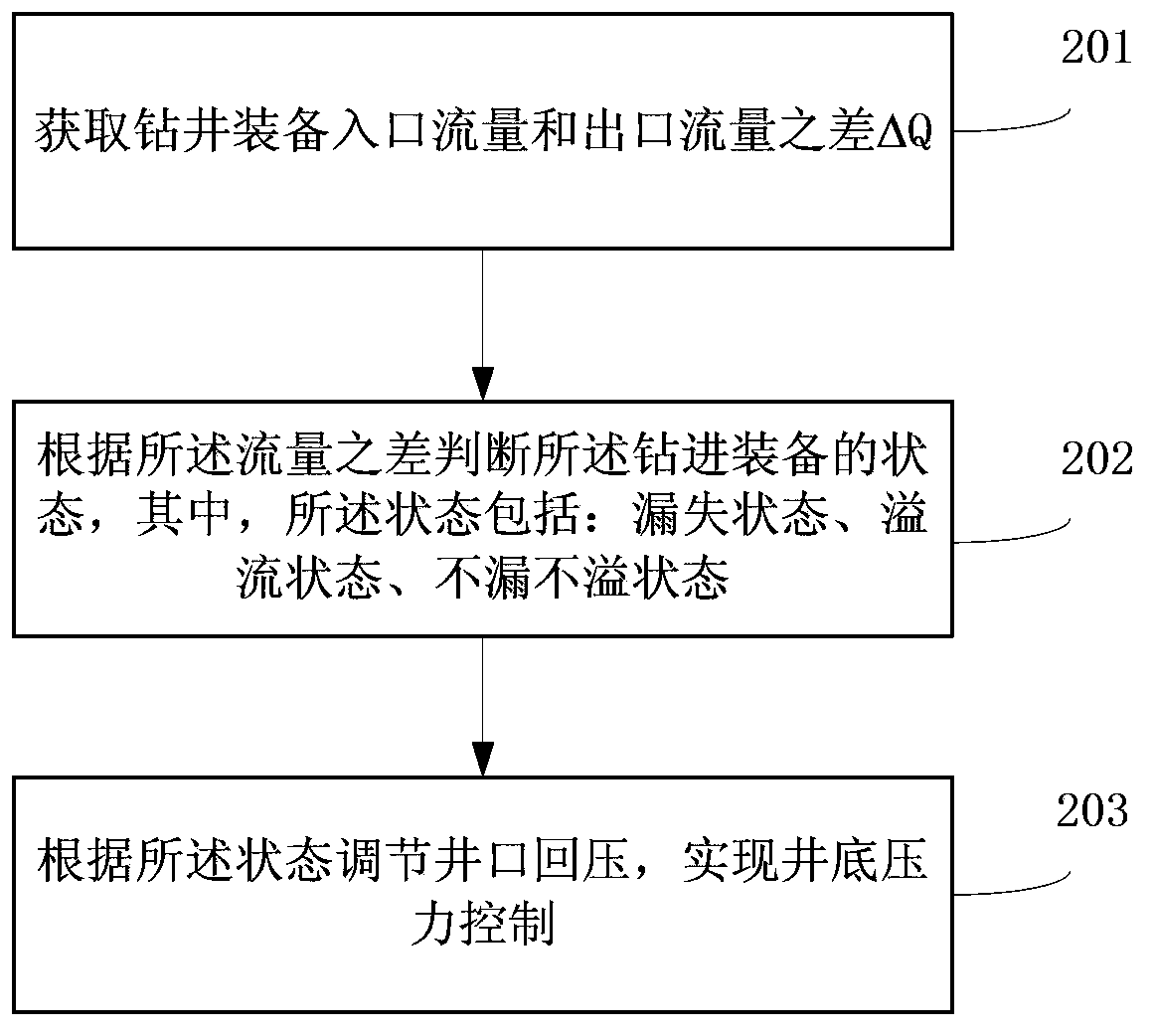
ActiveCN103510893AGood Pressure Control RequirementsControl or eliminate leaksFlushingBottom hole pressureCombustion
The invention discloses a well drilling device and method for controlling bottom hole pressure by monitoring flow. The well drilling device comprises a slime pump inlet flow measuring system, a return pressure pump inlet flow measuring system, a drilling liquid reversing-out flow measuring system, an automatic throttling pipe converging system, a rotation control head, a liquid-gas separator and a vibration screen. The inlet of the slime pump inlet flow measuring system is connected to a slime tank through a pipeline. The outlet of the slime pump inlet flow measuring system is connected to a drilling rod through a pipeline, reaches the rotation control head from a drill and a borehole by passing the bottom of the drilling rod in an annular space mode, and is communicated with an inlet pipeline of the automatic throttling pipe converging system and an outlet pipeline of the return pressure pump inlet flow measuring system. The return pressure inlet flow measuring system is connected to the slime tank through a pipeline. The outlet of the automatic throttling pipe converging system is connected with the inlet of the drilling liquid reversing-out flow measuring system. The outlet of the drilling liquid reversing-out flow measuring system is connected with the inlet of the liquid-gas separator through a pipeline. The liquid-gas separator is provided with two branches, wherein one branch is connected to the vibration screen and connected to the slime tank through the vibration screen and the other branch is connected to a combustion opening. The well drilling device and method for controlling the bottom hole pressure by monitoring the flow can effectively control or eliminate adverse affection on well drilling, wherein the adverse affection is caused by shaft bottom leakage and losses or overflowing which can cause.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Live Bottom Hole Pressure for Perforation/Fracturing Operations
ActiveUS20090218094A1Improve treatment efficiencyImproved reservoir optimizationSurveyFlow control using electric meansBottom hole pressureHydraulic fracturing
A method of determining when to stop pumping proppant during hydraulic fracturing in a wellbore is described. By accurately detecting tip screen-out with a bottom hole pressure gauge mounted to a perforating gun, the optimal amount of proppant can be supplied to a fracture while avoiding the risks associated with wellbore screen-out.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
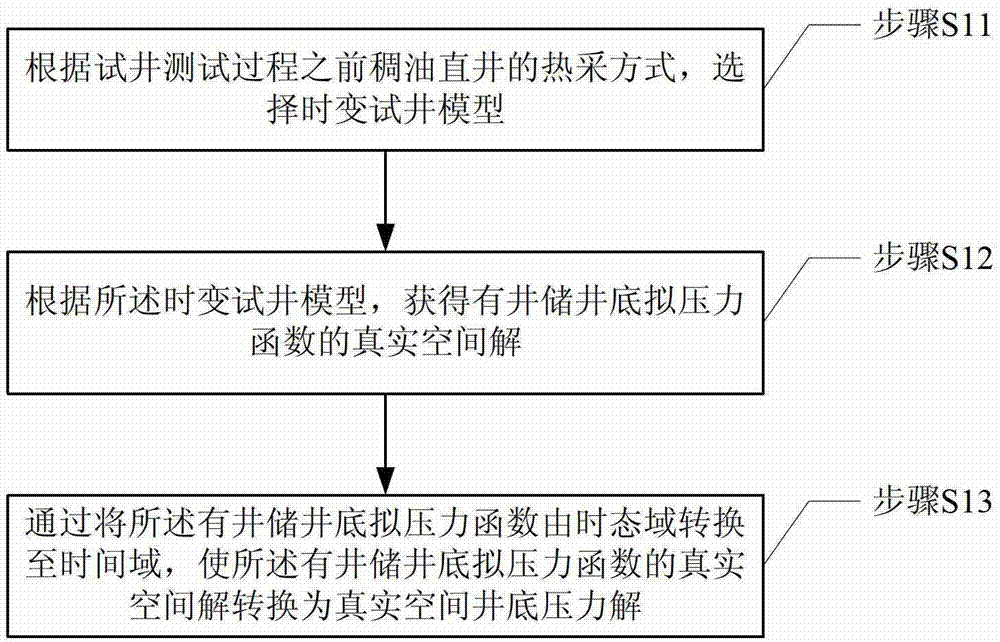
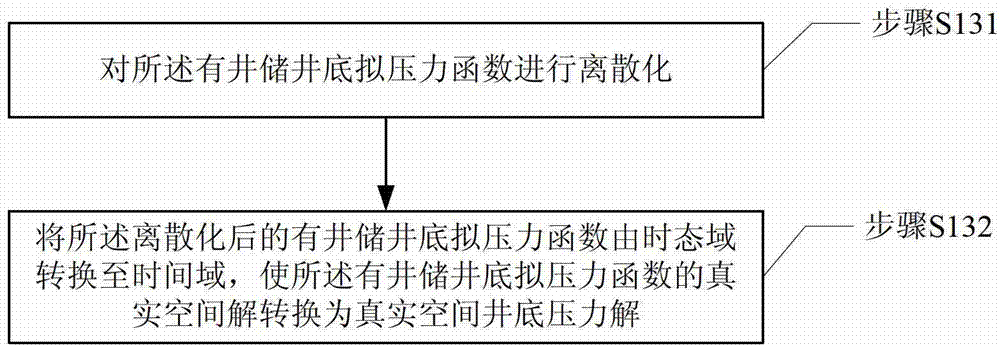
Well test interpretation method of vertical well for thickened oil thermal recovery
InactiveCN103161435ASolve problems that are difficult to solve exactlyCalculation structure is simpleSurveyFluid removalBottom hole pressureTime domain
The invention provides a well test interpretation method of a vertical well for thickened oil thermal recovery. The method comprises: choosing a time varying well test model according to a thickened oil vertical well thermal recovery mode before a well test process; obtaining a real space solution of a bottom pseudopressure function with well storage according to the time varying well test model; and converting the real space solution of the bottom pseudopressure function with the well storage into a real space bottom hole pressure solution through converting the bottom pseudopressure function with the well storage from a temporal domain into a time domain. The temporal domain is a multi-dimensional space, and arguments of the temporal domain are time, pressure and temperature. The time domain is a one-dimensional space, and an argument of the time domain is time. The well test interpretation method is simple in computation structure, the problem that a thermal recovery well test mathematical model is different to solve accurately is solved, and accurate inversion of oil deposit dynamic parameters through the thermal recovery well test is achieved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
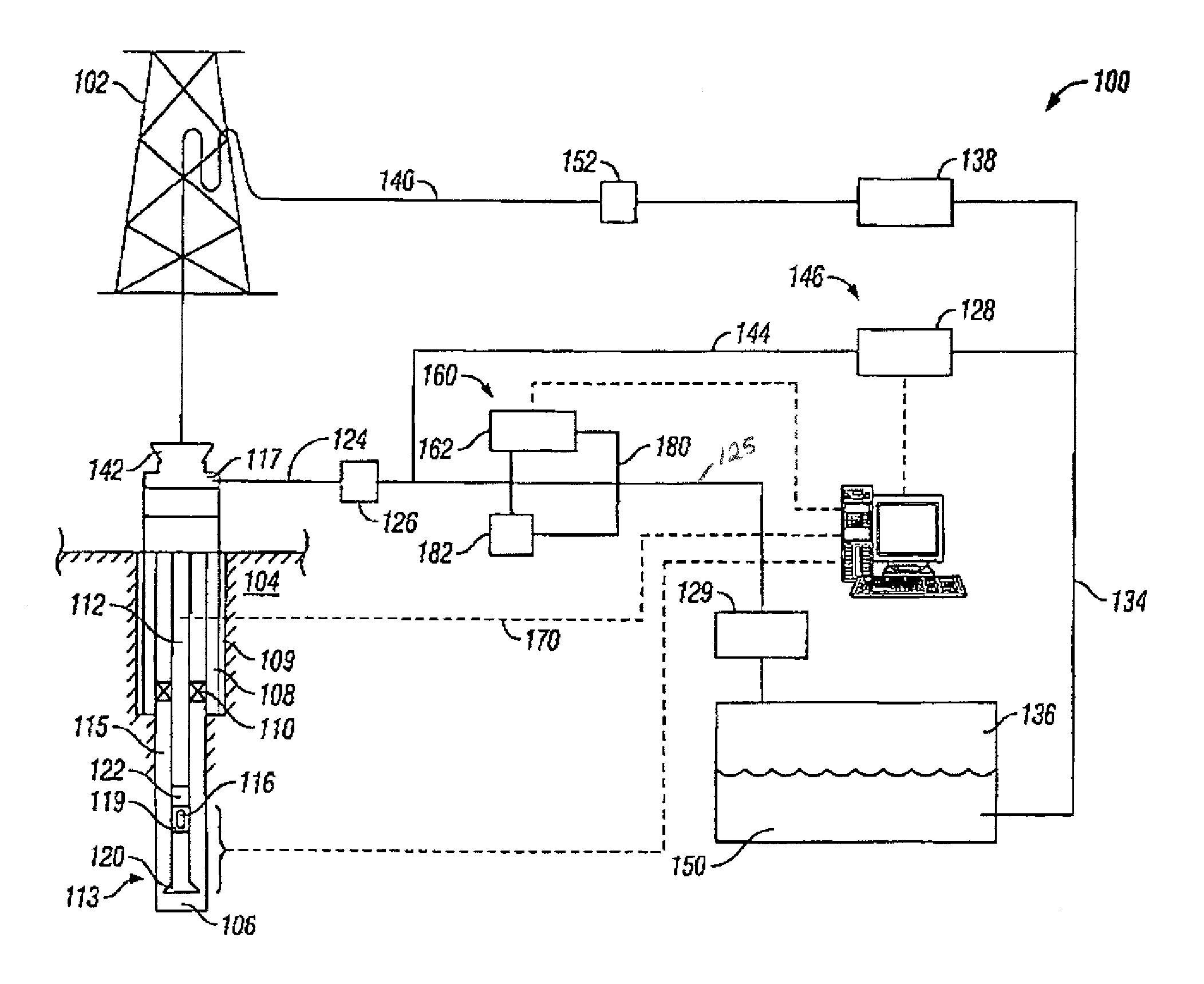
Method and apparatus for controlling bottom hole pressure in a subterranean formation during rig pump operation
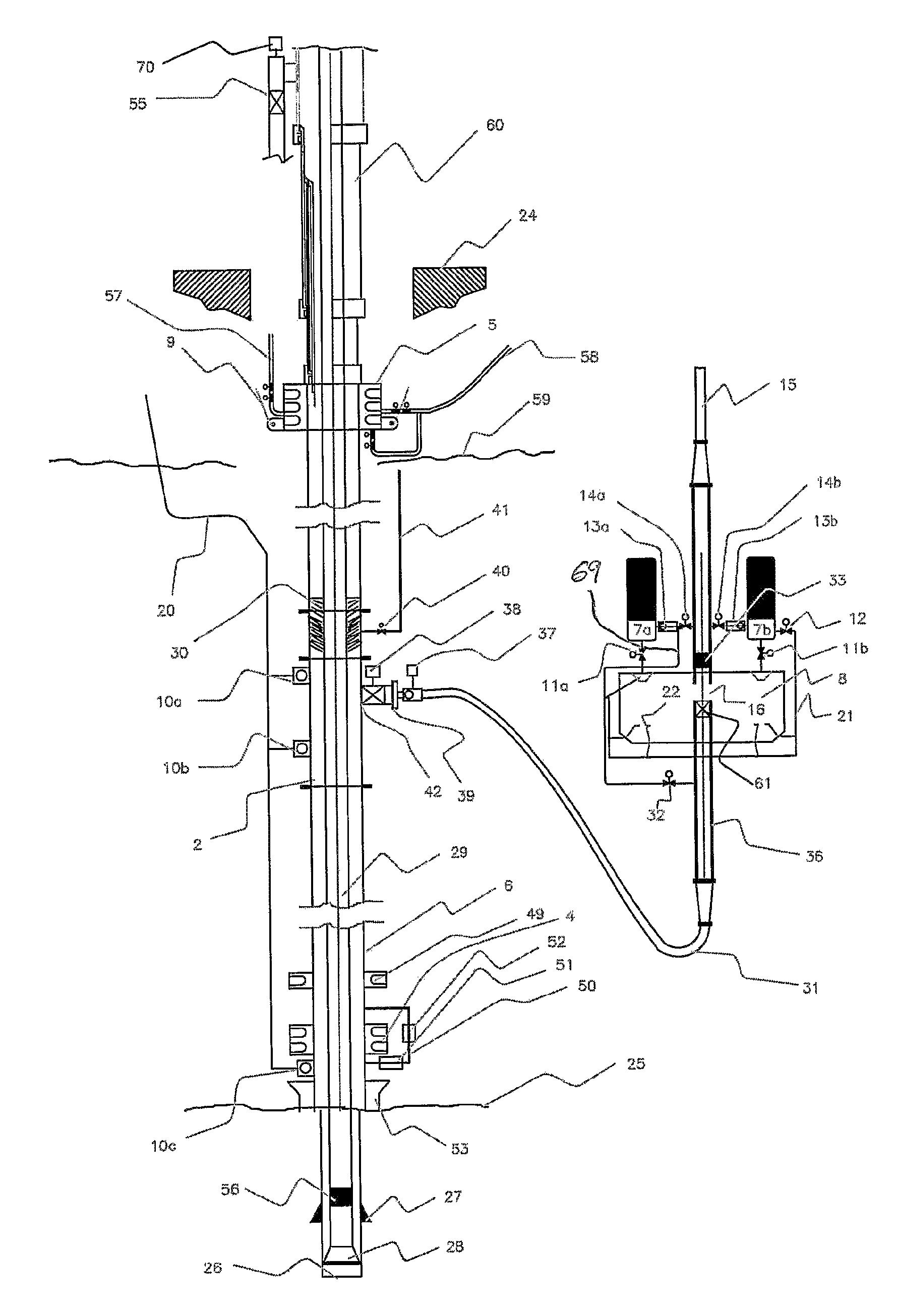
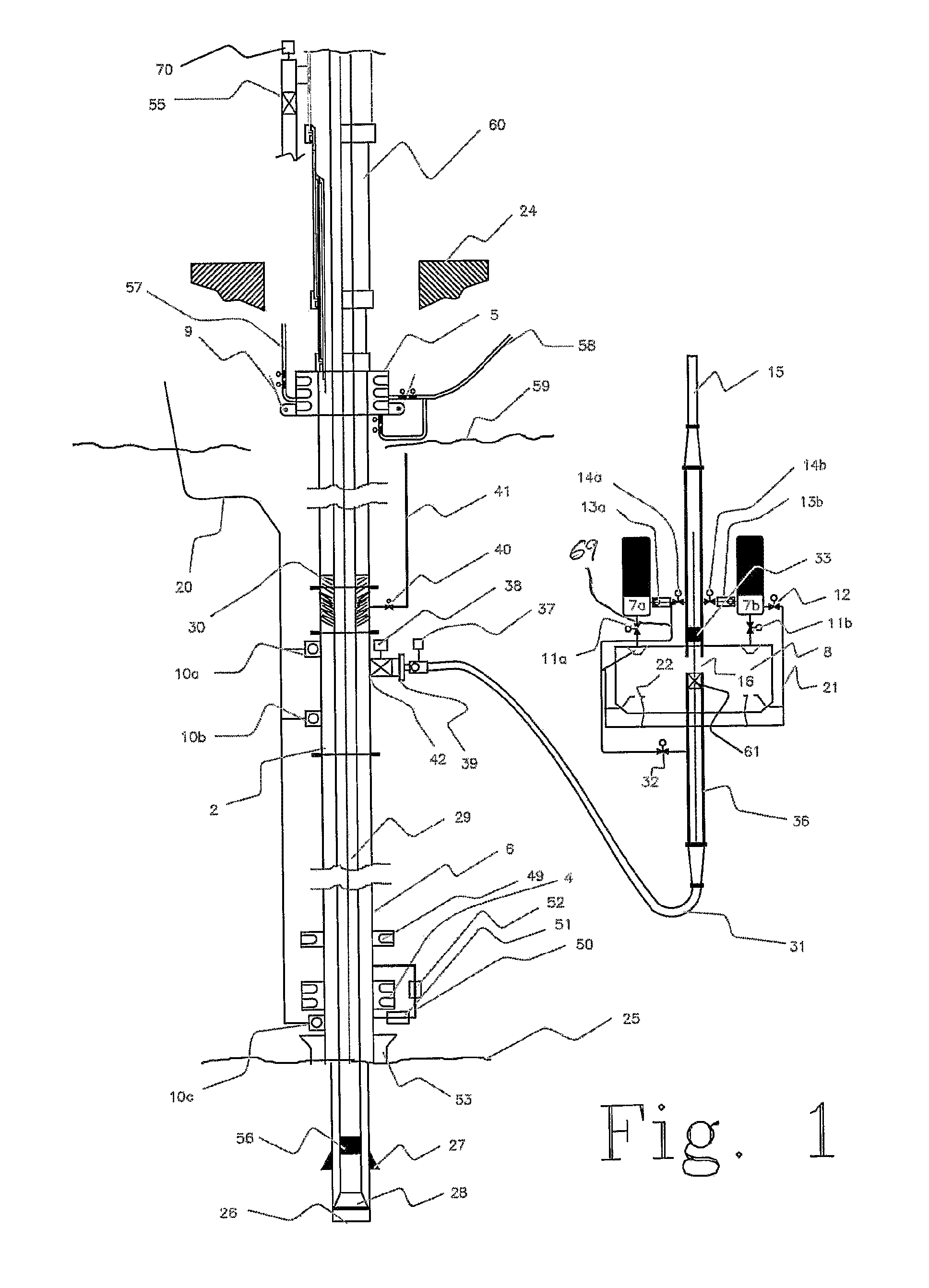
A method for maintaining pressure in a wellbore during drilling operations includes the steps of providing fluid from a reservoir through a drill string, circulating the fluid from the drill string to an annulus between the drill string and the wellbore, isolating pressure in the annulus, measuring pressure in the annulus, calculating a set point backpressure, applying back pressure to the annulus based on the set point back pressure, diverting fluid from the annulus to a controllable choke, controllably bleeding off pressurized fluid from the annulus, separating solids from the fluid, and directing the fluid back to the reservoir. An apparatus for maintaining pressure in a wellbore during drilling operations includes an adjustable choke for controllably bleeding off pressurized fluid from the wellbore annulus, a backpressure pump for applying a calculated set point backpressure, and a processor for controlling the adjustable choke and backpressure pump.
Owner:MI +1
Drilling power tool, drilling tool and drilling method for forming boreholes
ActiveCN102705140AImprove rock breaking efficiencyReduce wearDrilling rodsMachines/enginesEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention discloses a drilling power tool, a drilling tool and a drilling method for forming boreholes. The drilling power tool comprises an energy conversion mechanism and a valve shaft system. The energy conversion mechanism is a rotary generator. The valve shaft system comprises a stator, a rotor, a movable valve sheet assembly, a fixed valve sheet assembly and a shaft assembly, wherein the rotor makes a reciprocating motion right and left and drives the movable valve sheet assembly directly connected with the rotor. The energy conversion mechanism is a screw rod or a turbine or an impeller. According to the invention, when a drilling bit is rotated, the drilling pressure at the drilling bit and the drilling pressure at the bottom of a drilling well are similar to the continuous gentle change of the sine law, which is favorable for the strength reduction of surrounding rocks and the development of fractures, so that the rock breaking efficiency can be improved obviously. In addition, because the pressure at the drilling bit and at the bottom of the drilling well is changed periodically, the negative-pressure injection and the high-pressure injection are generated alternately; and when the pressure becomes lower, the well drilling in an underbalance manner or by using the gas drilling fluid is carried out, so that the surrounding rock environment is changed, and the mechanical drilling rate is improved obviously.
Owner:SINOPEC OILFIELD EQUIP CORP +1
Method for predicting wellbore pressure and temperature field simulation as well as hydrate through deep-water test
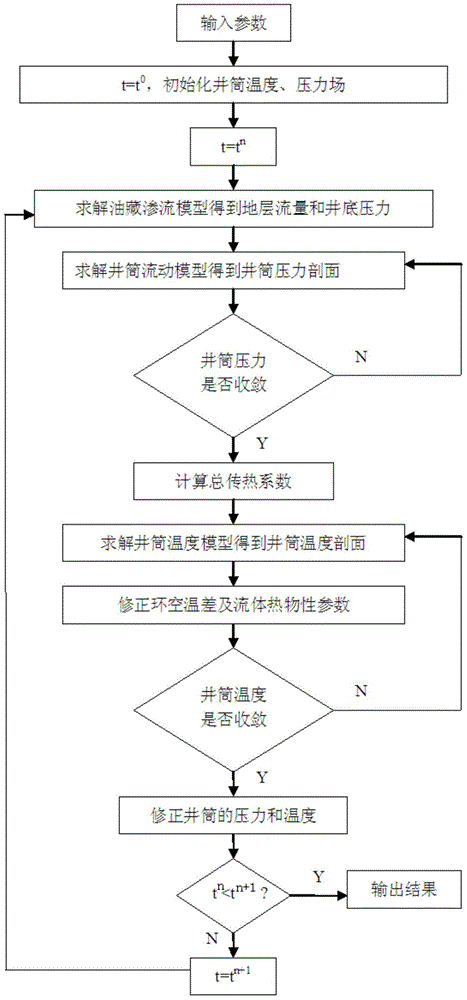
ActiveCN104895560AReliable calculationPressure results are reliableSurveyConstructionsBottom hole pressureMathematical model
The invention relates to a method for predicting wellbore pressure and temperature field simulation as well as hydrate through deep-water test. The method comprises the following steps: preparing parameters; initializing a wellbore temperature field and pressure field; solving formation flow and bottom-hole pressure distribution information by using a seepage flow mathematical model for gas reservoir; inputting the formation flow and bottom-hole pressure distribution information into a wellbore flow model for iteration to solve a wellbore pressure profile and determine whether the wellbore pressure is converged or not; calculating thermophysical parameters, and calculating a total heat transfer coefficient of a formation section and a seawater section; substituting the wellbore pressure and the total heat transfer coefficient into a wellbore temperature field model to calculate the wellbore temperature profile of each node; determining whether the wellbore temperature profile is converged; determining whether tn is less than (tn+1) or not, if yes, outputting a well temperature-well depth curve and a hydrate generation temperature-well depth curve corresponding to the wellbore pressure, and determining whether a hydrate is generated according to the curves; or else, returning to predict the conditions of wellbore pressure and temperature field simulation as well as hydrate. According to the invention, the method can be widely used in the oil exploration process.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Overall process under-balance drilling pressure compensation system and method
InactiveCN101929331APressure balanceEnsure safe implementationFlushingSealing/packingHigh pressureBlowout preventer
The invention relates to an overall process under-balance drilling pressure compensation system and a method for oil and gas drilling, an underground casing valve (10) is connected on a superior casing string, a wellhead rotary blowout preventer (11) is arranged at an upper end of a wellhead blowout preventer group and is connected with an under-balance throttle manifold (8) through a high-pressure hose (9), a well control manifold (12) which is connected out of a normal wellhead control device by four-pass is connected with a drilling fluid continuous pouring system in parallel by two-pass; and drilling is pulled to the front of the underground casing valve (10), the drilling fluid continuous pouring system grouts, the under-balance throttle manifold (8) controls the pressure in a shaft, and the drilling fluid which is circulated out enters a normal drilling fluid circulating system. In the drilling pulling process, the drilling fluid can be continuously poured into the shaft by a ground pressure compensation system and the bottom-hole pressure can be dynamically controlled simultaneously, thus effectively preventing formation fluid from intruding into the shaft in the drilling pulling process and keeping the steady under-balance state of the shaft.
Owner:中国石油集团西部钻探工程有限公司克拉玛依钻井工艺研究院
Well bottom booster pump and its supercharging method
ActiveCN101403279AIncrease drilling speedGood value for moneyFluid-pressure convertersFlushingBottom hole pressurePrice ratio
The invention discloses a bottom hole pressure pump and a pressurizing method thereof, wherein, the pressure pump mainly comprises a filter screen assembly, an upper end connector, a shell, a lower end fastening and an assorted double-channel drill bit. A change valve, a reversing control device, a power cylinder and a pressure cylinder are arranged in the shell sequentially, the lower end of the filter screen assembly is connected with the upper end connector by threads, the lower end of the upper end connector is connected with the shell by threads and sealed, the lower end fastening is connected with the shell by threads and sealed, and the left end of the lower end fastening props against the right end of the pressure cylinder, and presses and connects the change valve, the power cylinder and the pressure cylinder in the shell with a locking part arranged in the upper end connector. The invention can drastically improve the drilling speed, reduce the drilling cost and shorten the drilling period, and has relatively simple structure, short total length, low movement velocity, long service life, low manufacturing cost and high performance-price ratio.
Owner:ZHONGCHAO LIANHE ENERGY SCI & TECH BEIJING CO LTD
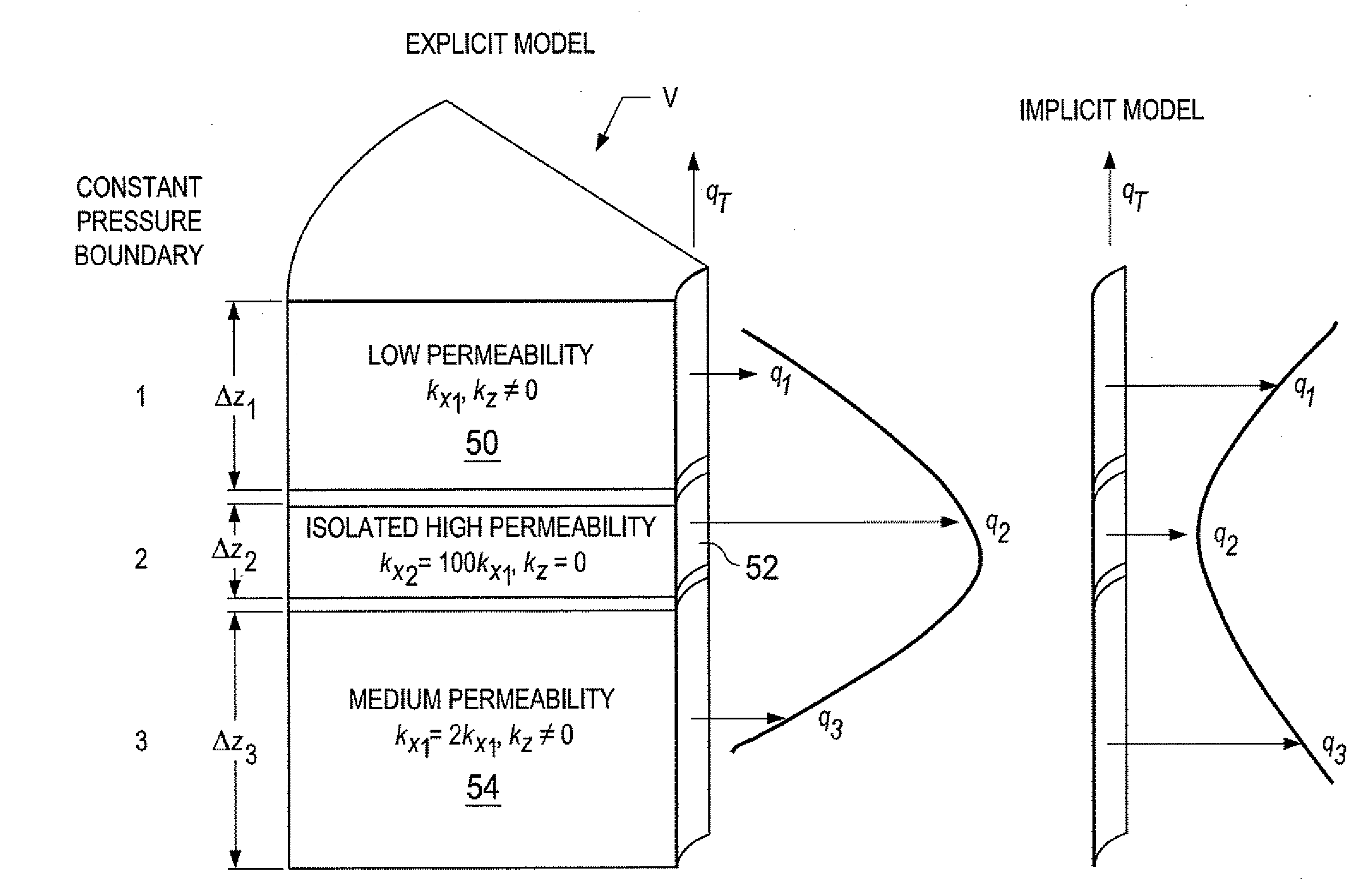
Sequential Fully Implicit Well Model for Reservoir Simulation
A subsurface hydrocarbon reservoir with wells is simulated by simultaneous solution of reservoir and well equations which simulate flow profiles along a well without requiring an unstructured coefficient matrix for reservoir unknowns. An analytical model of the reservoir is formed using the known or measured bottom hole pressure. Where several layers in an interval in the reservoir are present between vertical flow barriers in the reservoir, and communicate vertically with others, the communicating layers are combined for analytical modeling into a single layer for that interval for simulation purposes. The matrix of equations defining the unknown pressures and saturations of the intervals of combined layers in the reservoir are solved in the computer, and a perforation rate determined for each such interval of combined layers. Rates for the intervals in the reservoir are then combined to determine total well rate.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com