Patents
Literature
6790 results about "Back pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Back pressure (or backpressure) is a resistance or force opposing the desired flow of fluid through pipes, leading to friction loss and pressure drop. The term back pressure is a misnomer, as pressure is a scalar quantity, so it has a magnitude but no direction. The fluid is what is directed, tending to flow away from high-pressure regions and toward low-pressure regions. If the low-pressure space is more high-pressure than intended (e.g. due to obstructions or tight bends in an exhaust pipe) or the high-pressure space is more low-pressure than intended, this opposes the desired flow and reduces the discharge. Similarly, bending or other operations on a pipe (such as a stock car exhaust system with a particularly high number of twists and bends) can reduce flow rate.
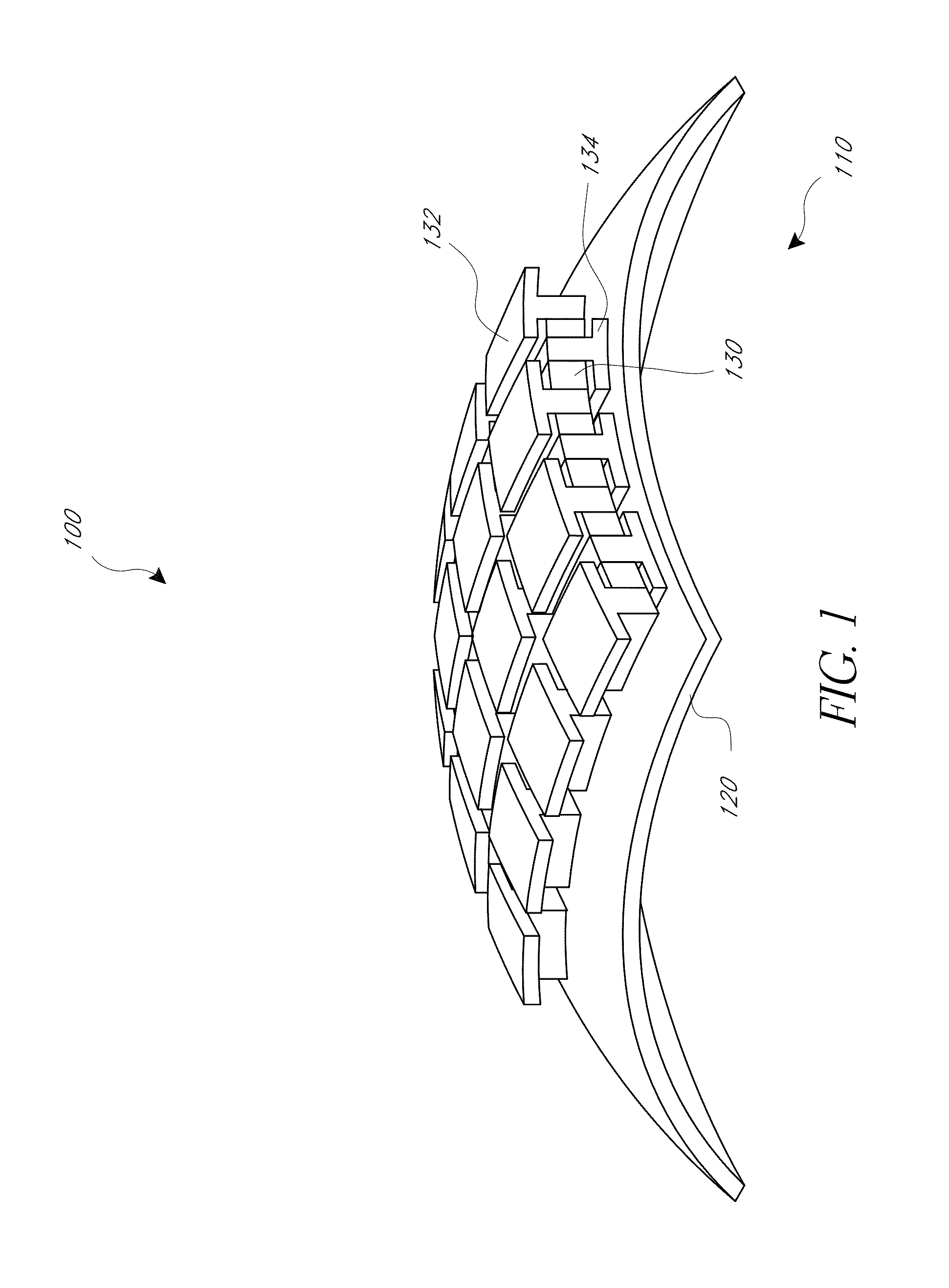
Printing semiconductor elements by shear-assisted elastomeric stamp transfer
ActiveUS8506867B2Sacrificing printing yield and accuracyIncrease chanceConfectionerySolid-state devicesEngineeringVertical displacement
Provided are methods and devices for transfer printing of semiconductor elements to a receiving surface. In an aspect, the printing is by conformal contact between an elastomeric stamp inked with the semiconductor elements and a receiving surface, and during stamp removal, a shear offset is applied between the stamp and the receiving surface. The shear-offset printing process achieves high printing transfer yields with good placement accuracy. Process parameter selection during transfer printing, including time varying stamp-backing pressure application and vertical displacement, yields substantially constant delamination rates with attendant transfer printing improvement.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
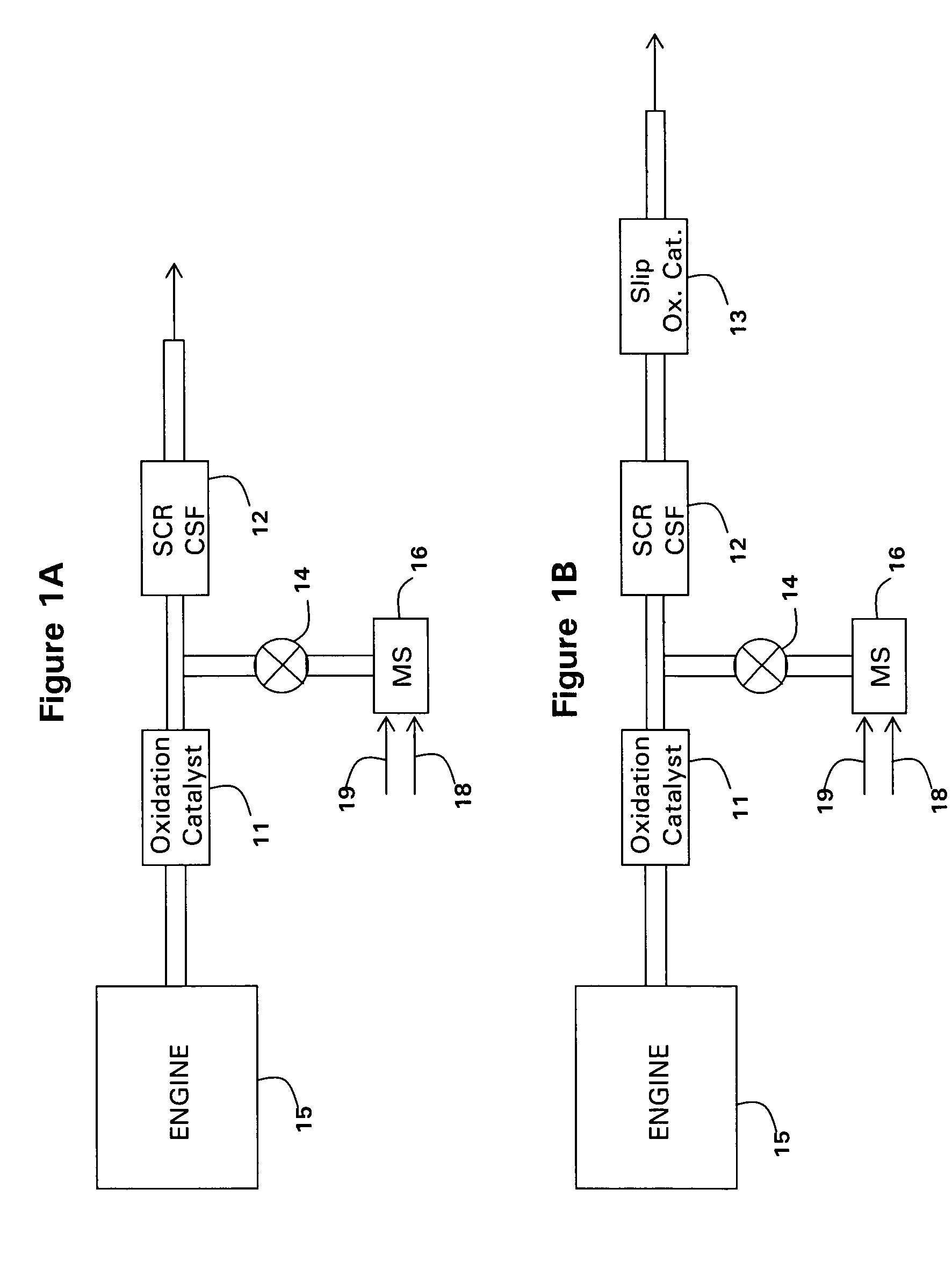
Catalyzed SCR filter and emission treatment system
ActiveUS7229597B2Reduce the temperaturePromote regenerationCombination devicesLiquid degasification with auxillary substancesNitrogen oxideSoot
Provided is an emission treatment system and method for simultaneously remediating the nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter, and gaseous hydrocarbons present in diesel engine exhaust streams. The emission treatment system has an oxidation catalyst upstream of a soot filter coated with a material effective in the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) of NOx by a reductant, e.g., ammonia. Also provided is a method for disposing an SCR catalyst composition on a wall flow monolith that provides adequate catalyst loading, but does not result in unsuitable back pressures in the exhaust.
Owner:BASF CORP
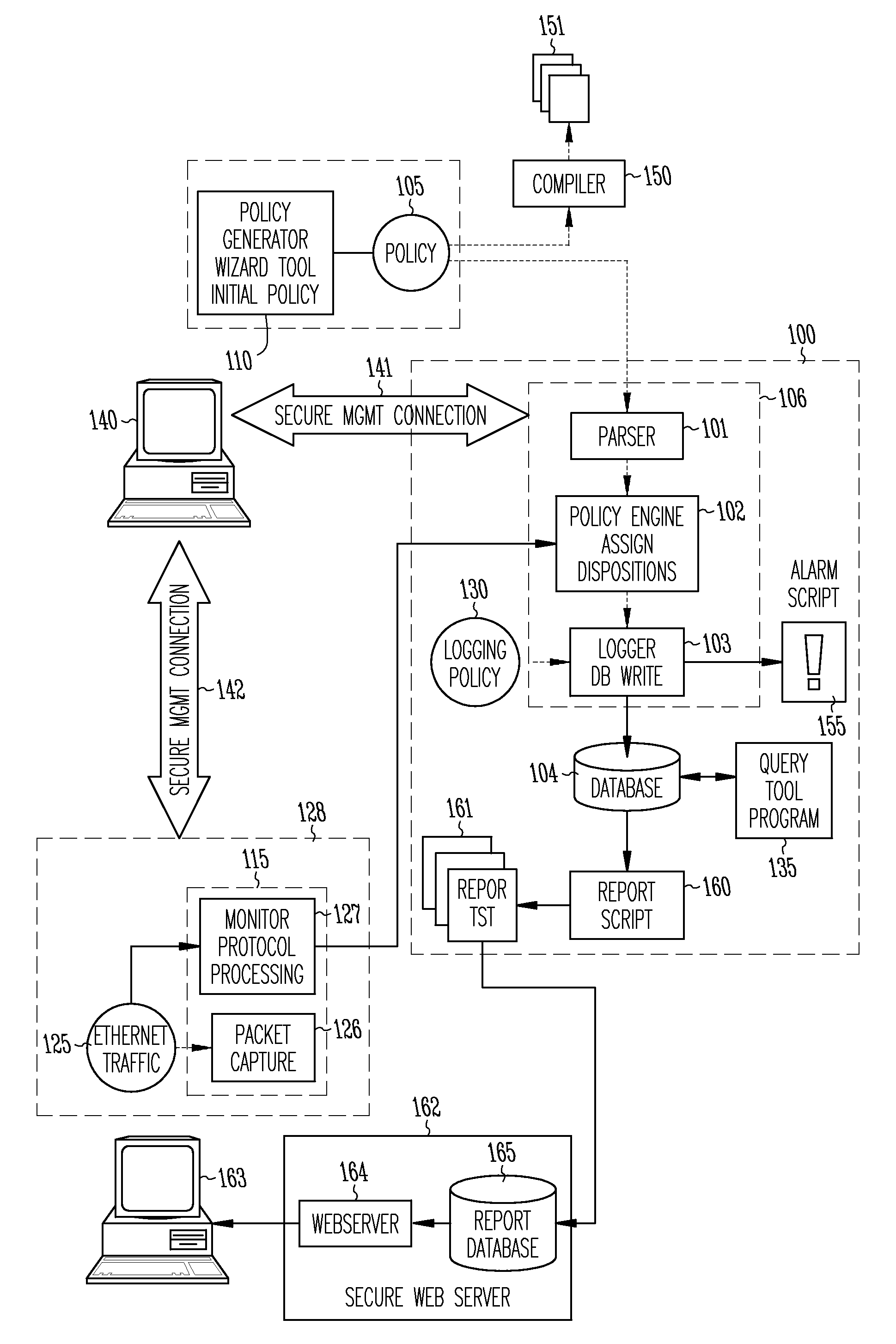
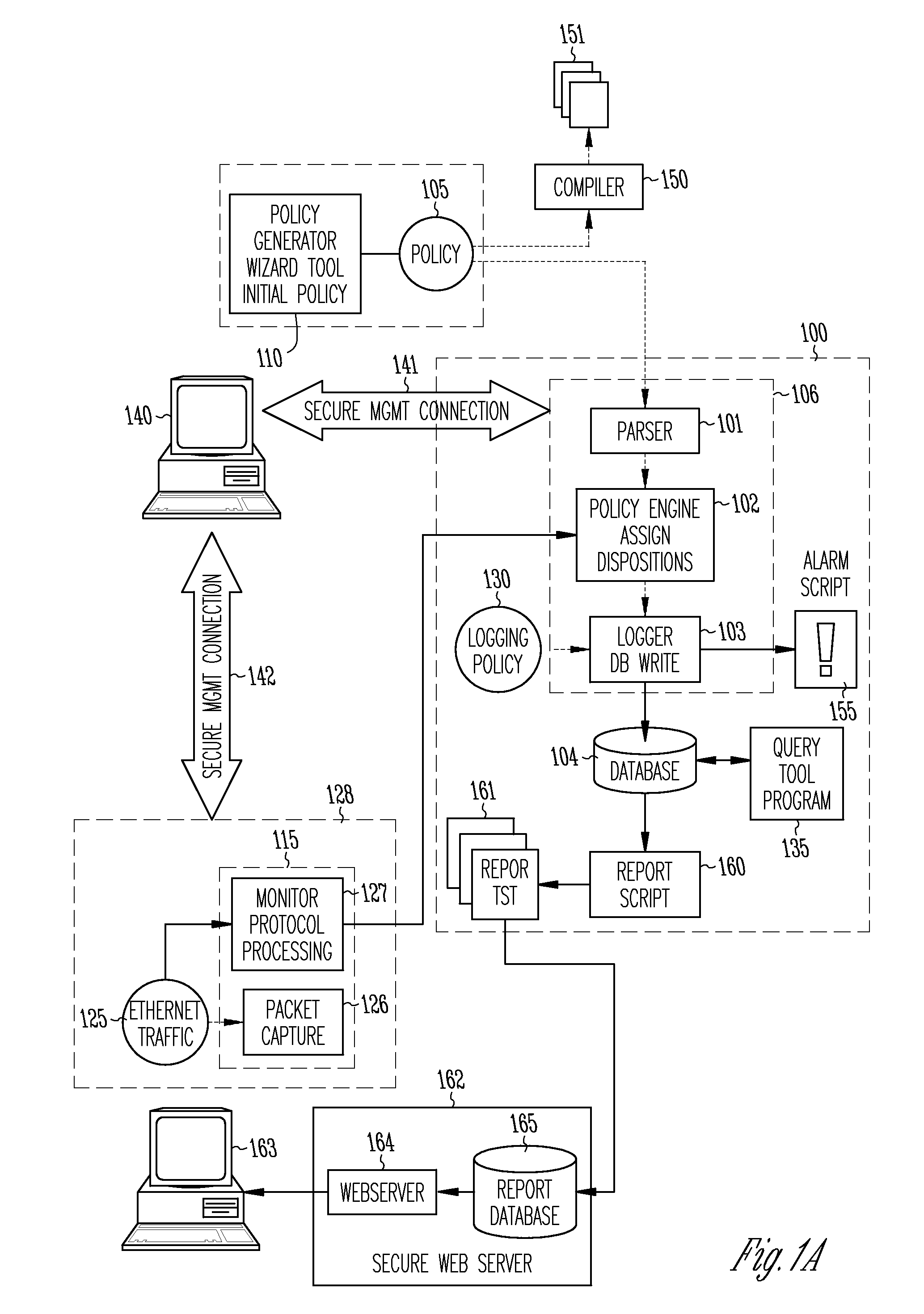
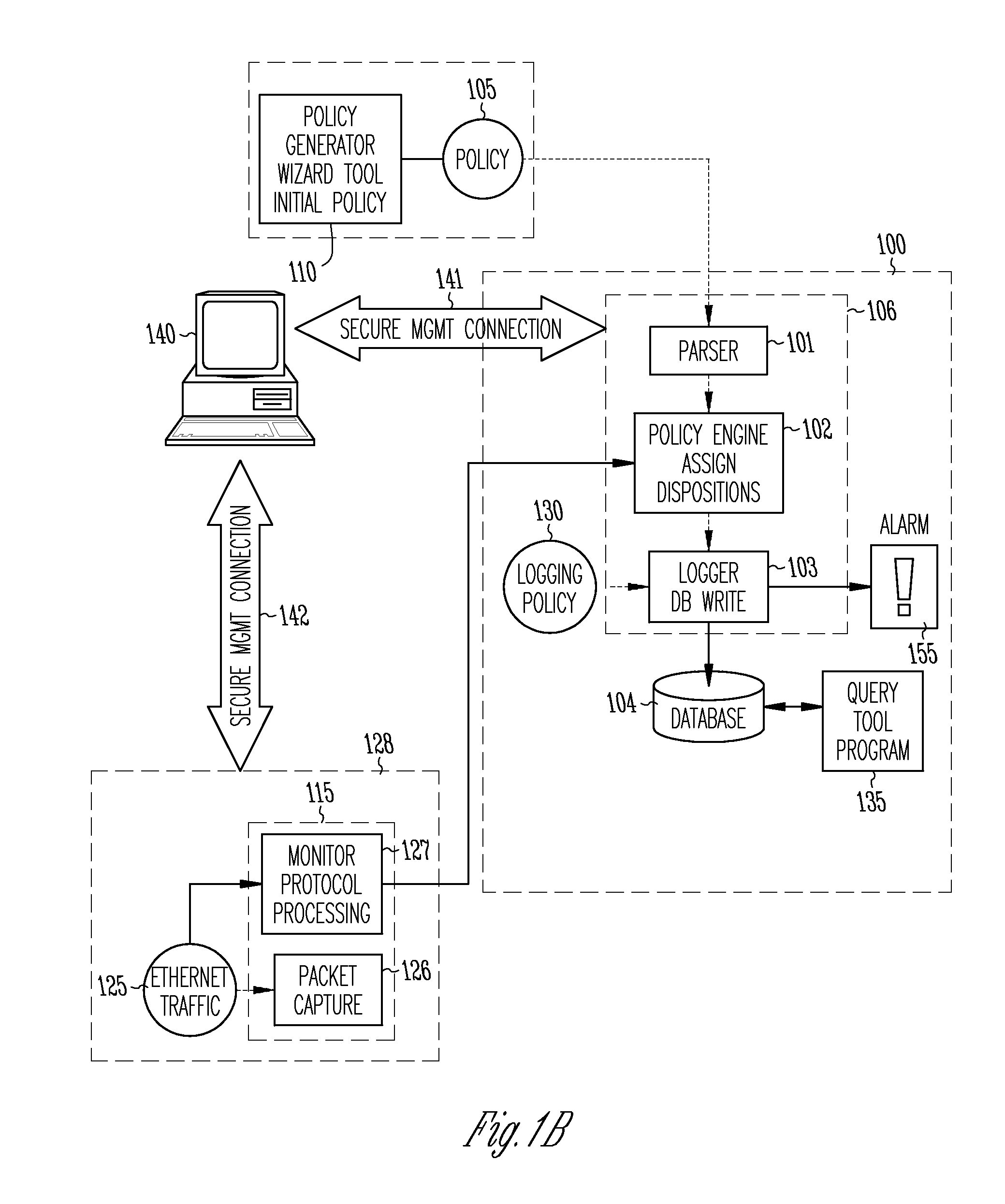
Method and apparatus for enterprise management
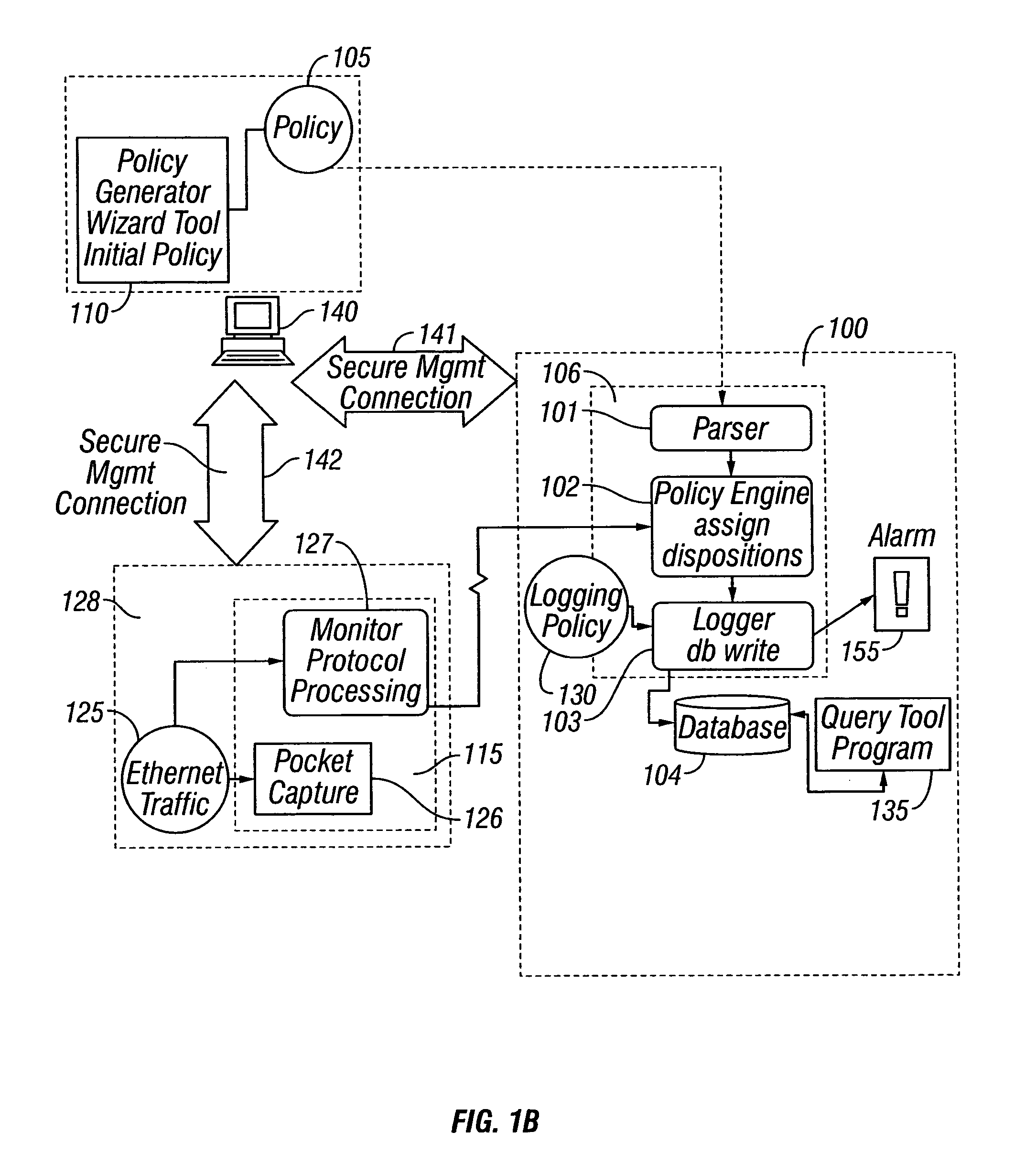
A method and apparatus for a network monitor internals mechanism, which serves to translate packet data into multiple concurrent streams of encoded network event data, to contribute to enterprise management, reporting, and global mechanisms for aggregating monitors at a centralized aggregation point, and to facilitate rate limiting techniques because such monitors are not in control (i.e. cannot back pressure flow) is provided.
Owner:SECURIFY
Dynamic annular pressure control apparatus and method
InactiveUS6904981B2Increased annular pressureBuildFluid removalFlushingPressure controlled ventilationPressure control
A system and method for controlling formation pressures during drilling of a subterranean formation utilizing a selectively fluid backpressure system in which fluid is pumped down the drilling fluid return system in response to detected borehole pressures. A pressure monitoring system is further provided to monitor detected borehole pressures, model expected borehole pressures for further drilling and control the fluid backpressure system.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Slurry mixer outlet
InactiveUS6874930B2Unwanted premature setting is preventedReduce generationFlow mixersDischarging apparatusSlurryReducer
An apparatus configured for connection to a mixer for receiving a slurry and altering the flow characteristics of the slurry includes a conduit having a main inlet in slurry receiving communication with the mixer outlet and extending to a spout for discharging the slurry, at least one conduit restrictor associated with the conduit for creating back-pressure between the conduit restrictor and the mixer outlet for keeping the mixer full, and at least one pressure reducer associated with the discharge spout and configured for reducing the pressure of the slurry dispensed from the discharge spout. The apparatus is configured for maintaining a generally laminar flow from the mixer outlet to the discharge spout.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
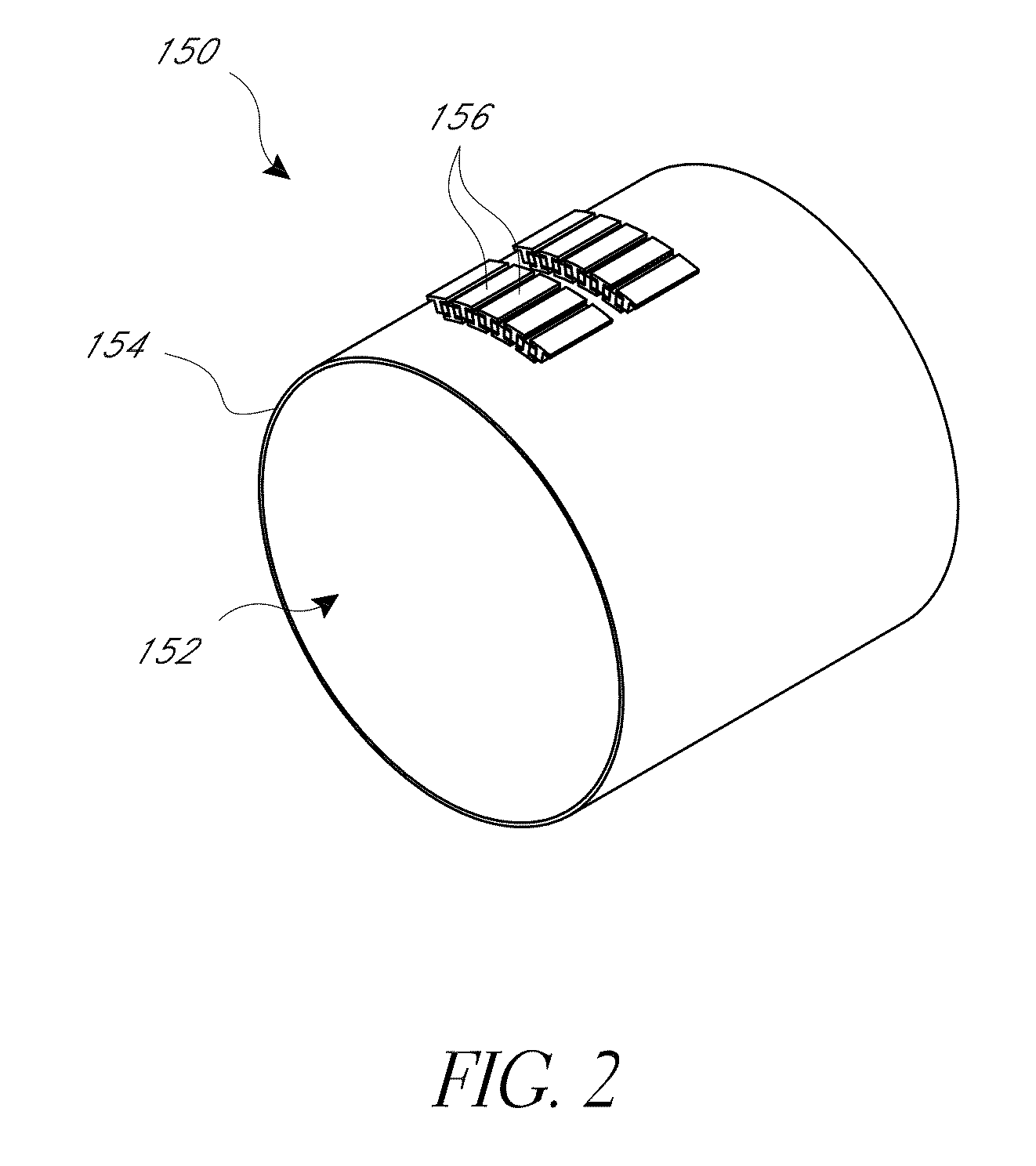
Printing Semiconductor Elements by Shear-Assisted Elastomeric Stamp Transfer
ActiveUS20100123268A1High delamination rateSacrificing printing yieldConfectionerySolid-state devicesBack pressureEngineering
Provided are methods and devices for transfer printing of semiconductor elements to a receiving surface. In an aspect, the printing is by conformal contact between an elastomeric stamp inked with the semiconductor elements and a receiving surface, and during stamp removal, a shear offset is applied between the stamp and the receiving surface. The shear-offset printing process achieves high printing transfer yields with good placement accuracy. Process parameter selection during transfer printing, including time varying stamp-backing pressure application and vertical displacement, yields substantially constant delamination rates with attendant transfer printing improvement.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
Method and apparatus for rate limiting
A method and apparatus for a network monitor internals mechanism, which serves to translate packet data into multiple concurrent streams of encoded network event data, to contribute to enterprise management, reporting, and global mechanisms for aggregating monitors at a centralized aggregation point, and to facilitate rate limiting techniques because such monitors are not in control (i.e. cannot back pressure flow) is provided.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Gas flow control method in a blower based ventilation system
ActiveUS7487773B2Accurate predictionRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesControl systemFeedback controller
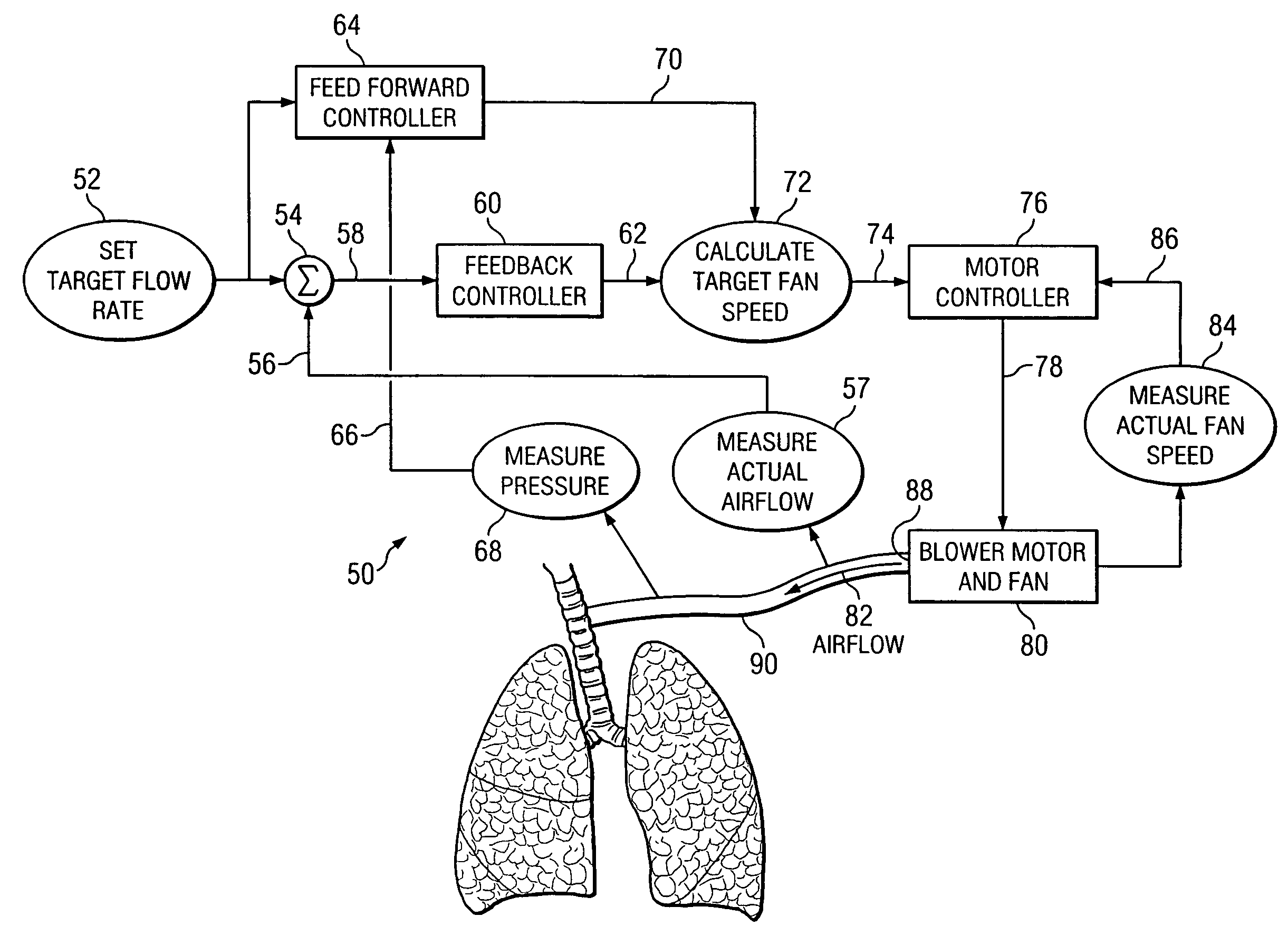
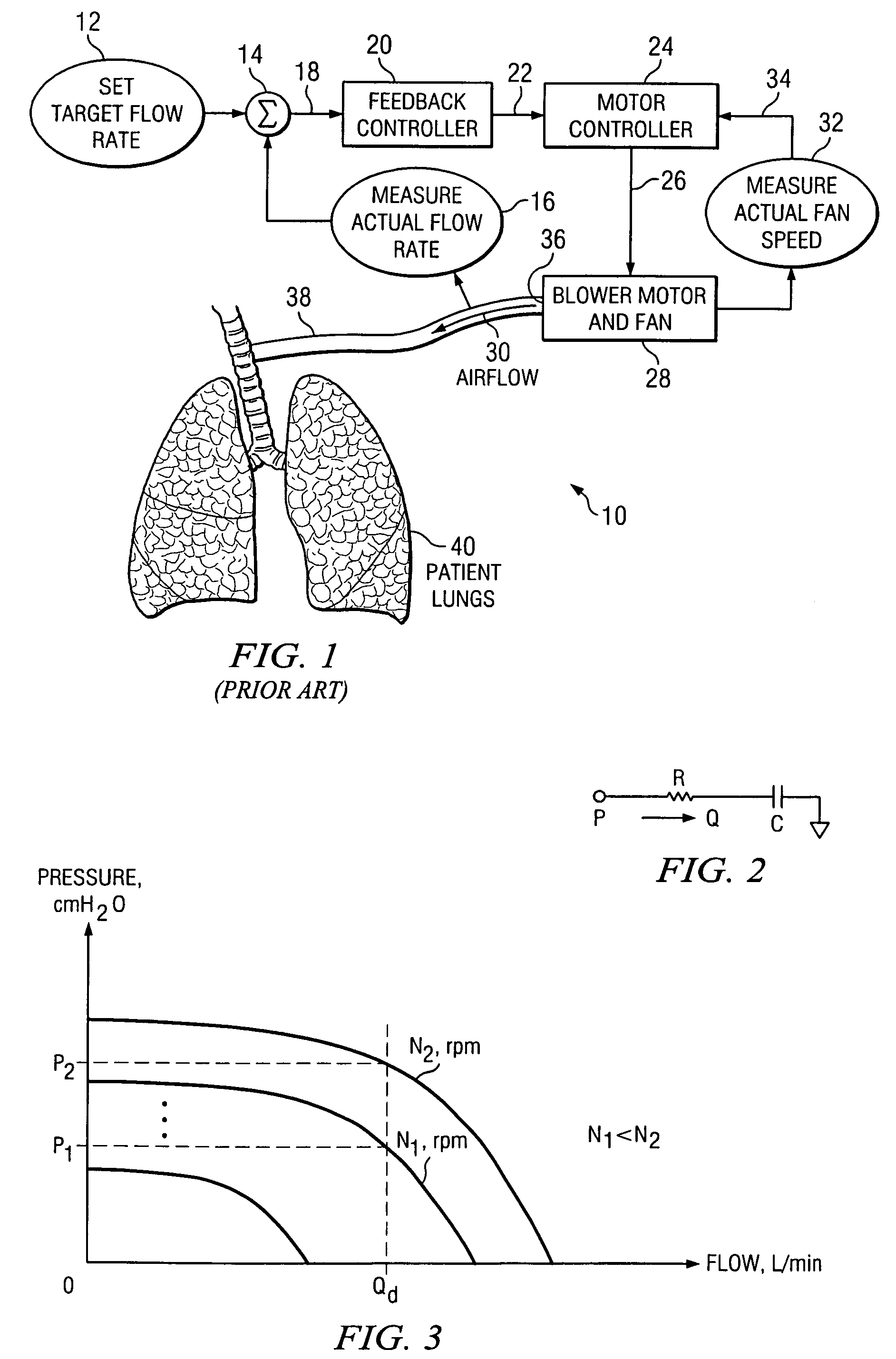
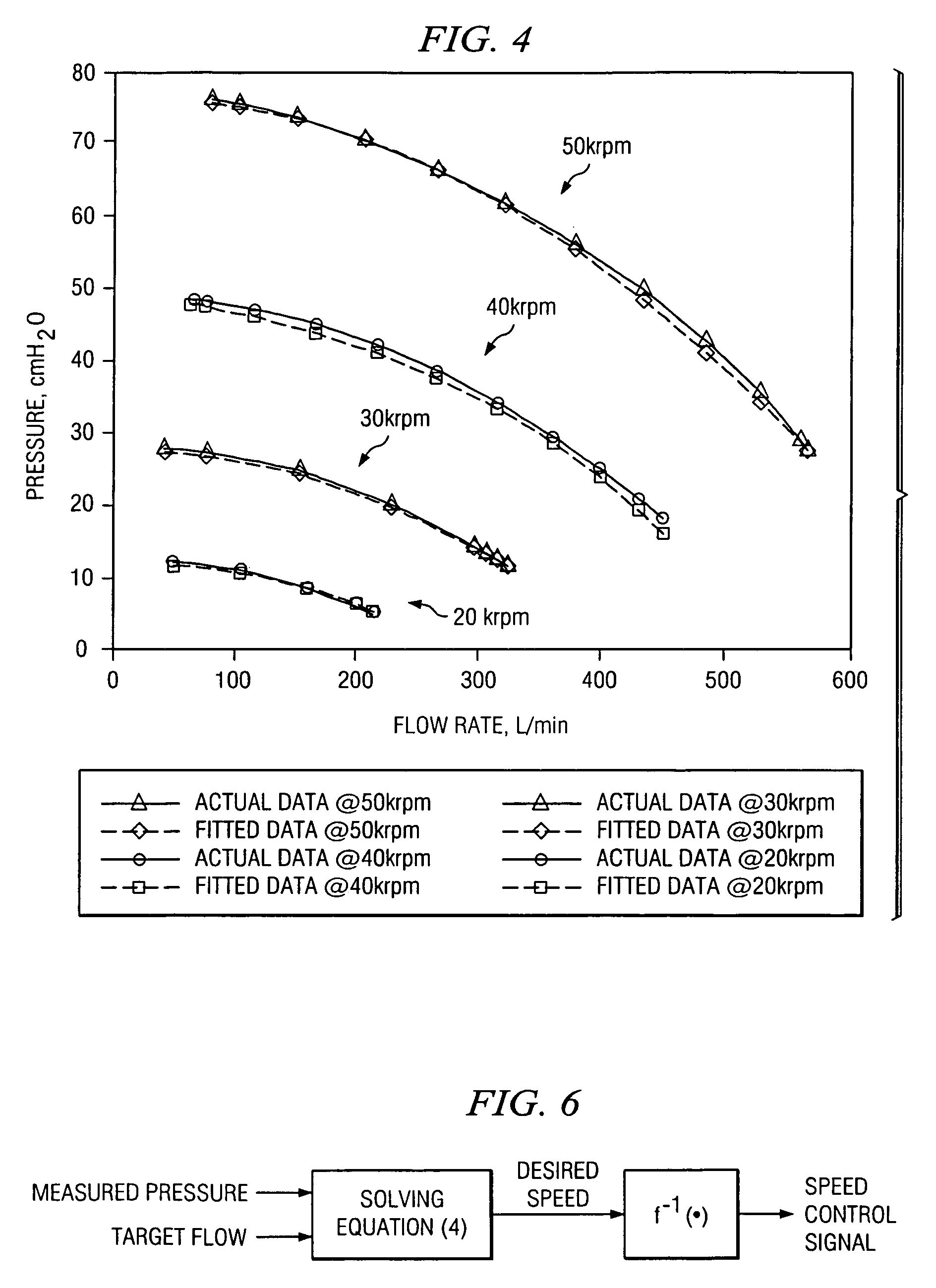
The invention is directed to a system and method for controlling the flow of gas from a medical ventilator into a patient's lungs. The control system provides for a non-linear feedforward controller to correct for disturbances caused by back pressure at the outlet of the blower of the medical ventilator. For this purpose, a pressure transducer is provided to measure the back pressure. Additionally, the invention allows for a feedback controller to correct for the differences between the rate of the actual gas flow and the targeted gas flow rate. For this purpose a flow rate transducer is provided. The control system may account for each of the gas flow rate error and the back pressure disturbance to provide for a quick and accurate adjustment to achieve the targeted gas flow rate.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and apparatus for rate limiting
A method and apparatus for a network monitor internals mechanism, which serves to translate packet data into multiple concurrent streams of encoded network event data, to contribute to enterprise management, reporting, and global mechanisms for aggregating monitors at a centralized aggregation point, and to facilitate rate limiting techniques because such monitors are not in control (i.e. cannot back pressure flow) is provided.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Drilling system and method
InactiveUS20030079912A1Accurate calculationImprove securityConstructionsFlushingWell drillingEngineering
A closed-loop circulating system for drilling wells has control of the flow rates in and out of the wellbore. Kicks and fluid losses are quickly controlled by adjusting the backpressure. Kick tolerance and tripping margins are eliminated by real-time determination of pore and fracture pressure. The system can incorporate a rotating BOP and can be used with underbalanced drilling.
Owner:SECURE DRILLING INT
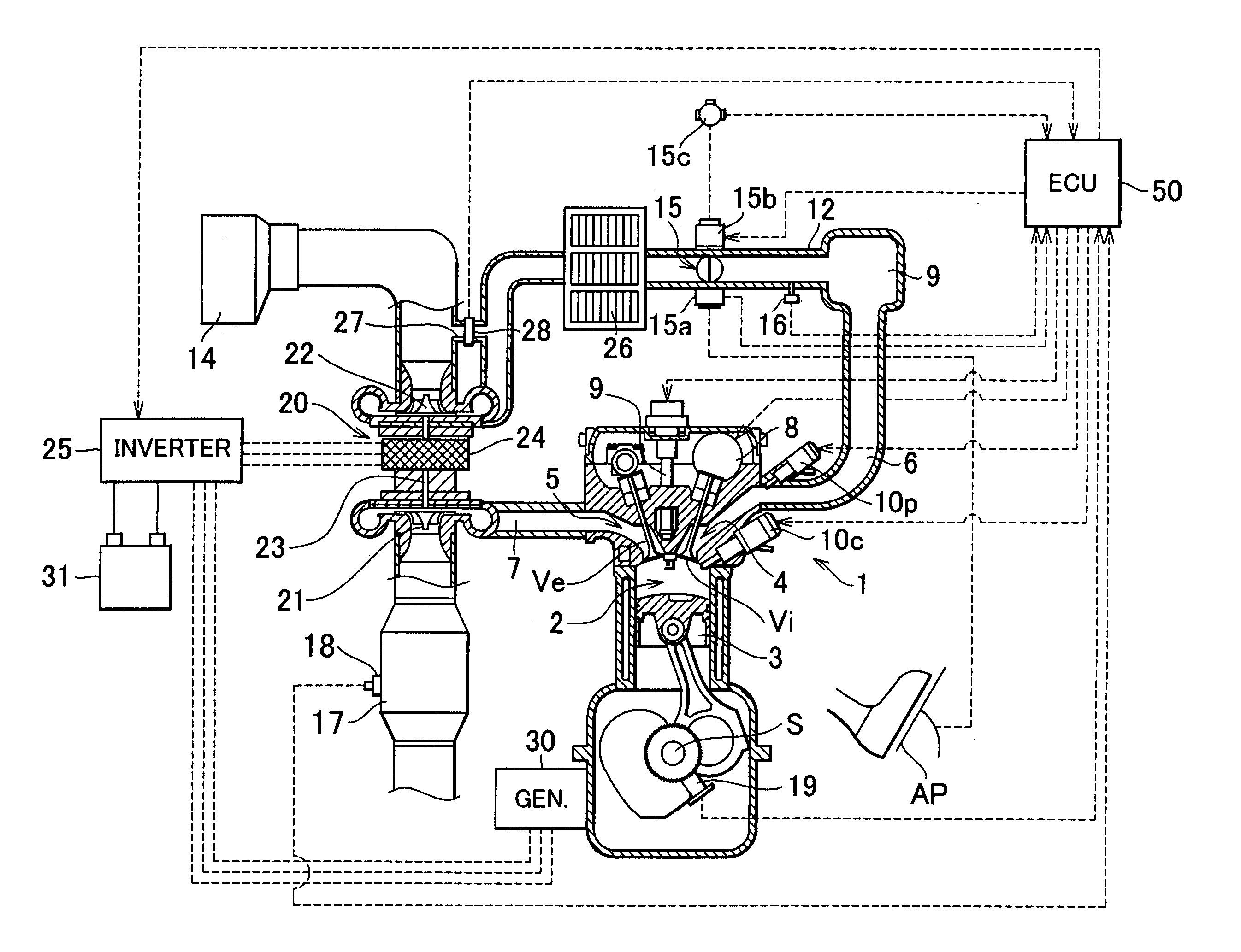
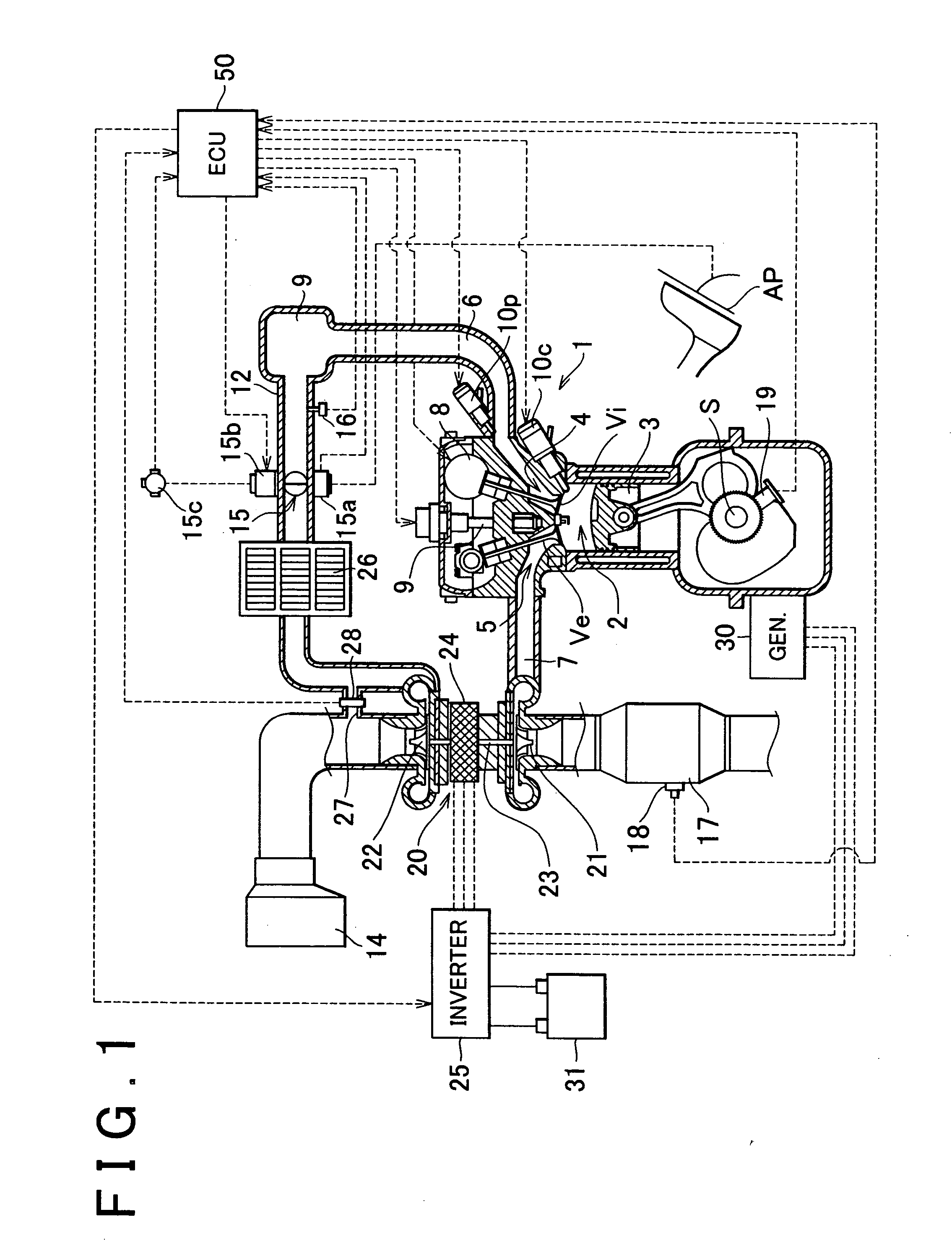
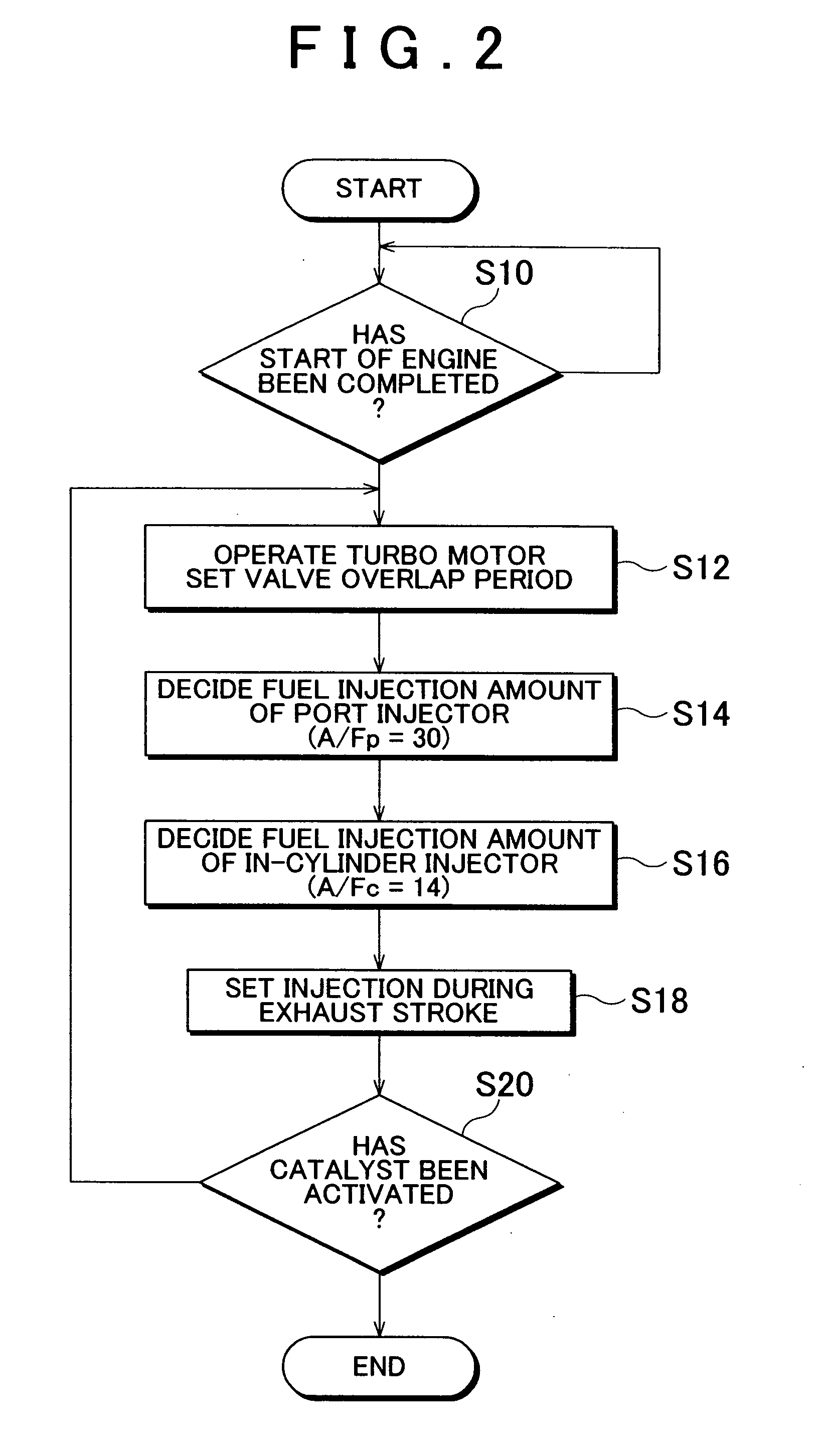
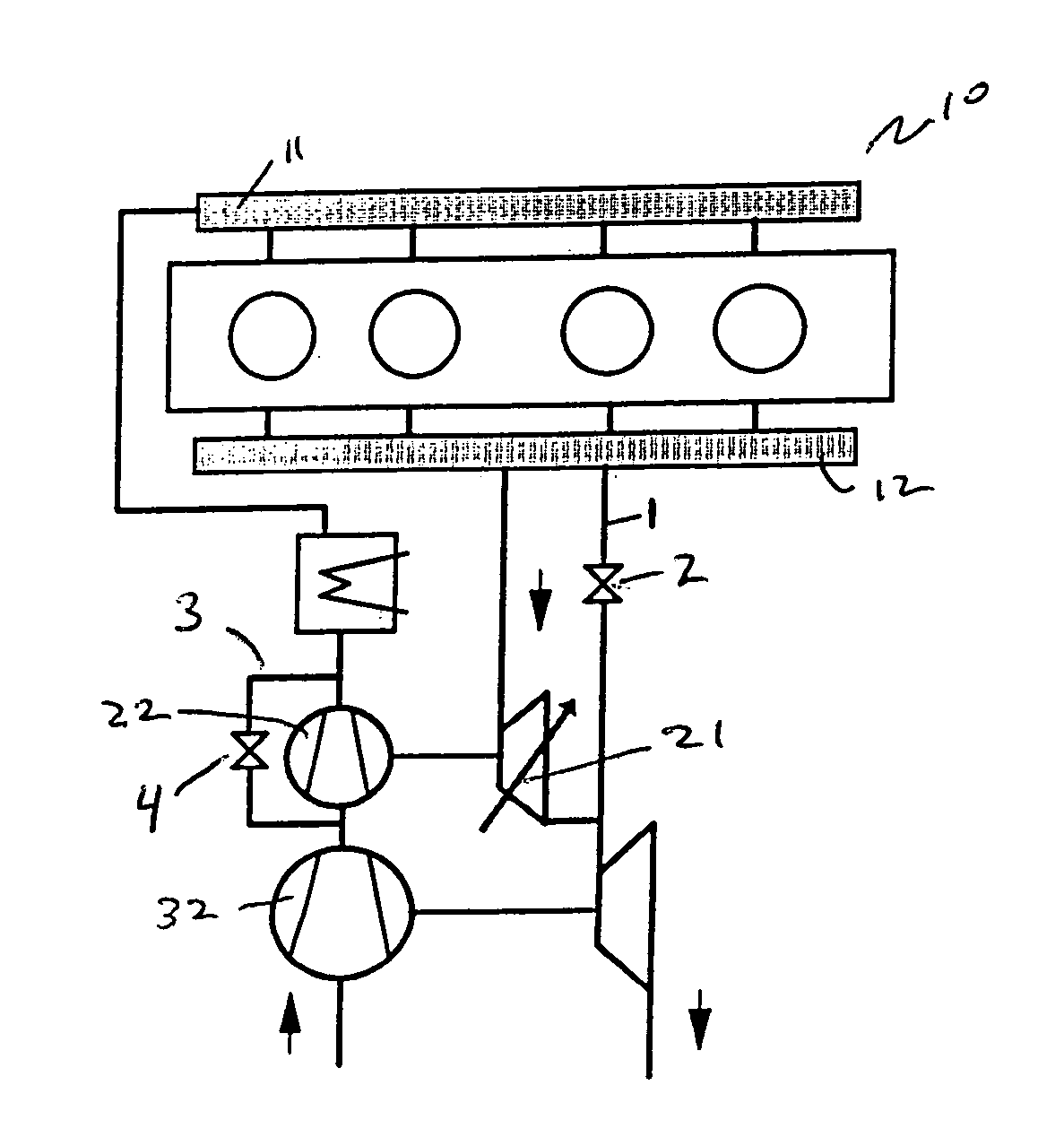
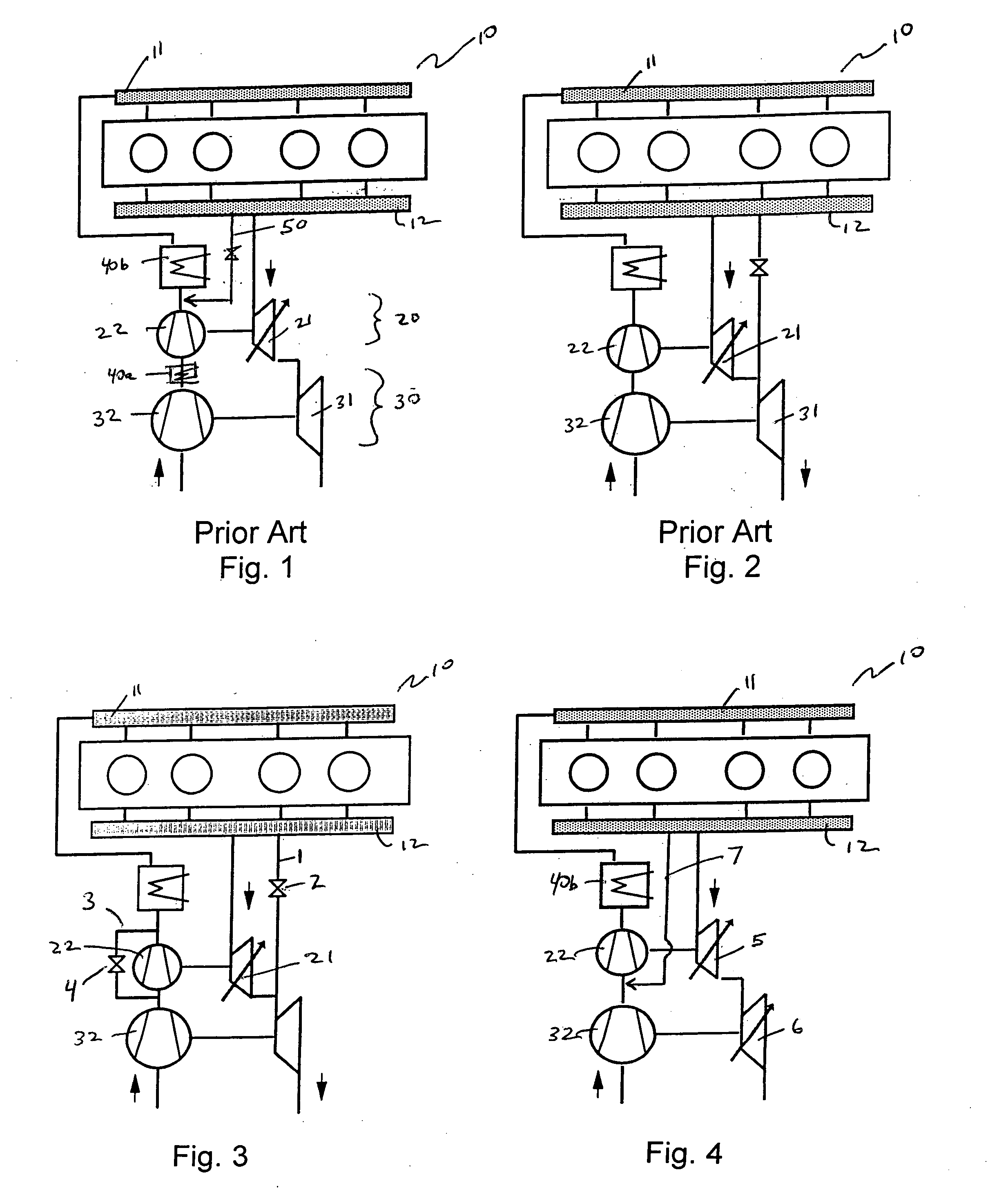
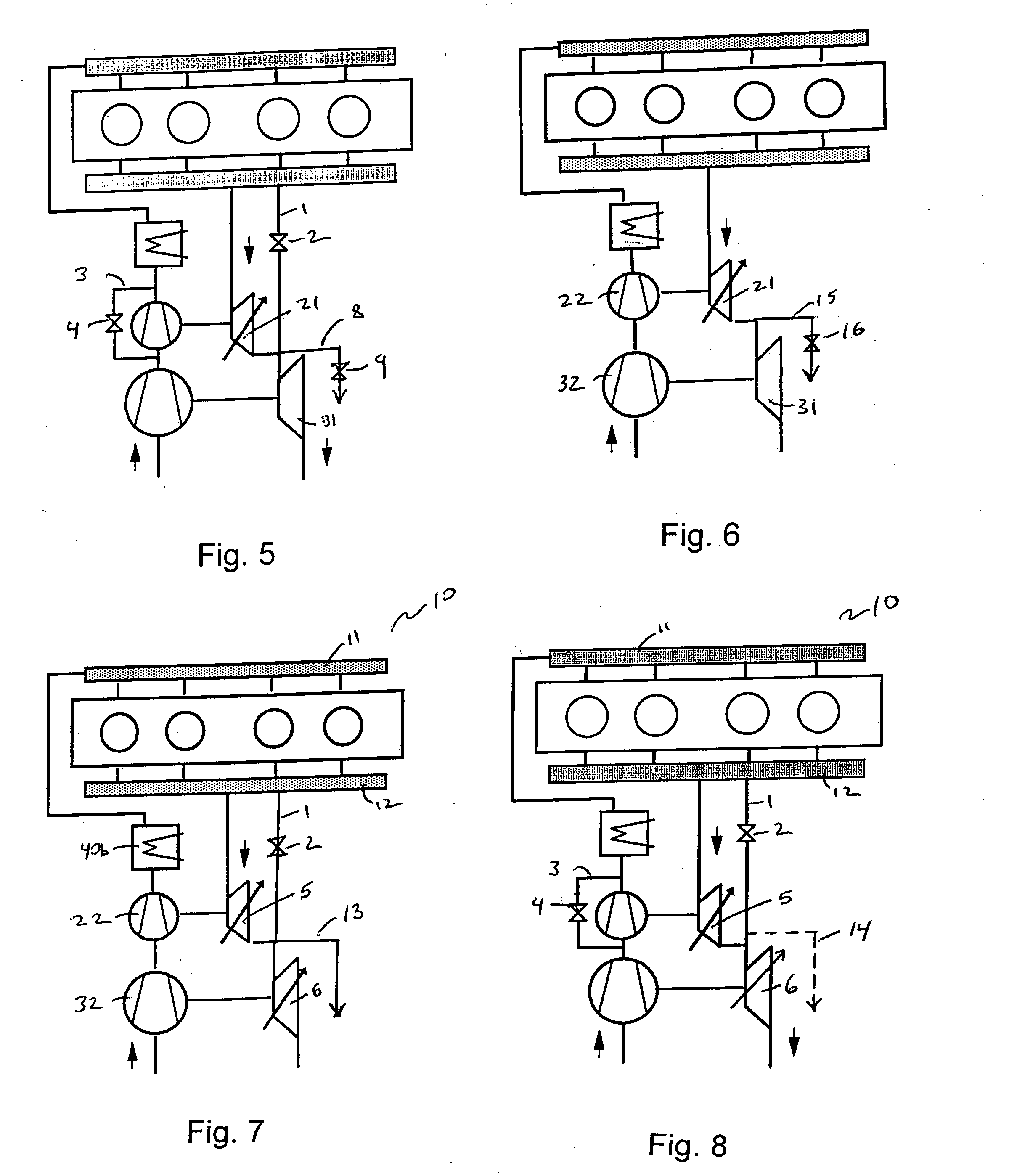
Internal combustion engine and control method thereof
InactiveUS20050097888A1Reliably activatedReduce exhaust emissionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberExhaust valve
An internal combustion engine in which power is generated by burning a mixture of fuel supplied from a port injector and / or an in-cylinder injector and air in a combustion chamber, includes a valve drive mechanism which can change a valve opening characteristic of at least one of an intake valve and an exhaust valve; a turbocharger which supercharges air taken into the combustion chamber; a turbo motor which changes supercharging pressure generated by the turbocharger; a catalyst device including a catalyst which purifies exhaust gas discharged from the combustion chamber; and an ECU which controls the turbo motor such that pressure of the air taken into the combustion chamber becomes larger than back pressure until it is determined that the catalyst has been activated, and which sets a valve overlap period during which both of the intake valve and the exhaust valve are opened.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Check valve
InactiveUS20110186151A1Maximum vacuum boostIncrease airflowCheck valvesEqualizing valvesEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A check valve which is positioned in the vacuum air line of an internal combustion engine. The check valve includes a single-piece valve body having an outlet port and two or more inlet ports, with one outlet port located substantially in line with the inlet port and connected by a venturi tube. The second inlet port is separated from the main air flow line by the valve stem and a diaphragm which allows communication there between and prevents back pressure. The second inlet port communicates with the outlet port through the valve stem and a second venturi tube which provides a vacuum boost to a device, usually vehicle brakes, connected to the inlet. The use of seal diaphragms having a non-constant radius allows for faster recovery time for replenishment than prior art devices.
Owner:TECHNIPLAS US LLC
Heart valve prosthesis and method of manufacture
ActiveUS20060290027A1Easy to cleanRelieving problemHeart valvesPharmaceutical containersProsthesisThrombus
A cardiac valve prosthesis having a frame and two or more leaflets (preferably three) attached to the frame. The leaflets are attached to the frame between posts, with a free edge which can seal the leaflets together when the valve is closed under back pressure. The leaflets are created in a mathematically defined shape allowing good wash-out of the whole leaflet orifice, including the area close to the frame posts, thereby relieving the problem of thrombus deposition under clinical implant conditions.
Owner:AORTECH INT
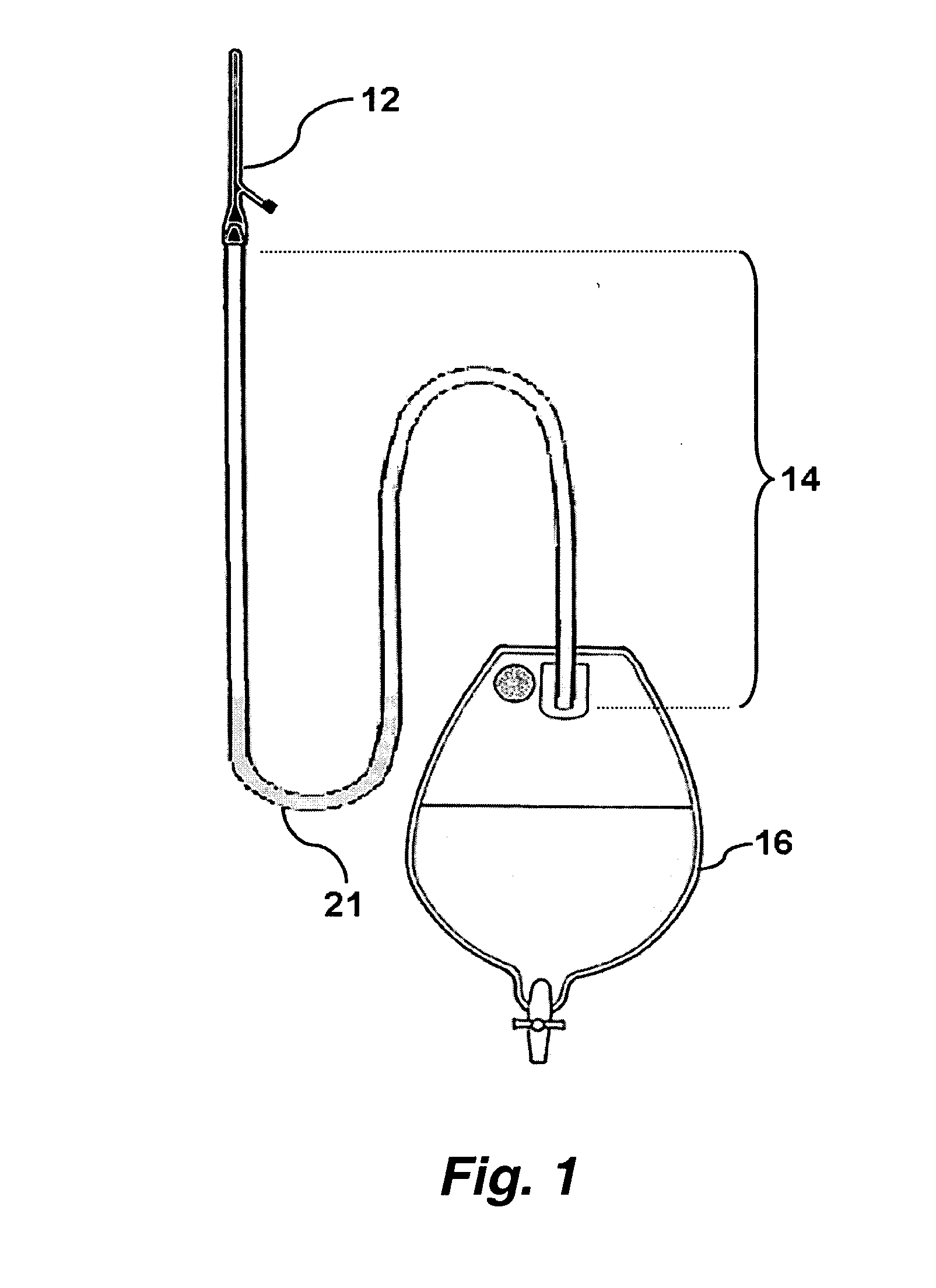
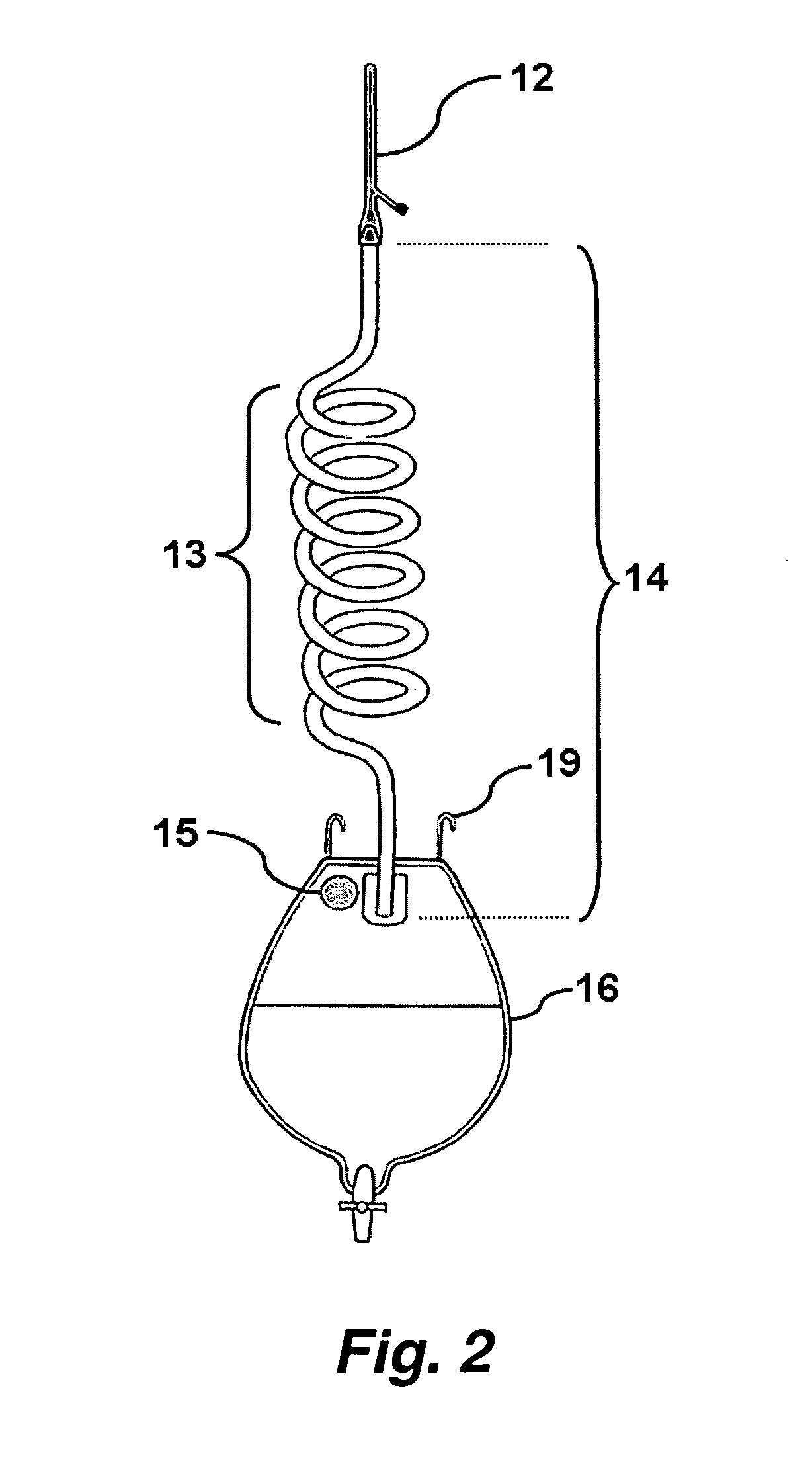
Drainage system
InactiveUS20060271019A1Easy to drainReducing and eliminating airlockWound drainsCatheterBladder drainageUrine output
This invention provides improved medical drainage devices. In certain embodiments this invention provides a system for improved drainage from a bladder in a patient where the system comprises: a fluid collection apparatus; a drainage receptacle; and a connecting tube comprising a means for reducing or eliminating airlocks in the connecting tube and thereby providing sufficiently low backpressure such that a patient having a urinary bladder drained with said system maintains an average residual bladder urine volume of less than about 50 cubic centimeters over a period of at least four hours after initial drainage without manipulation of components of said system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
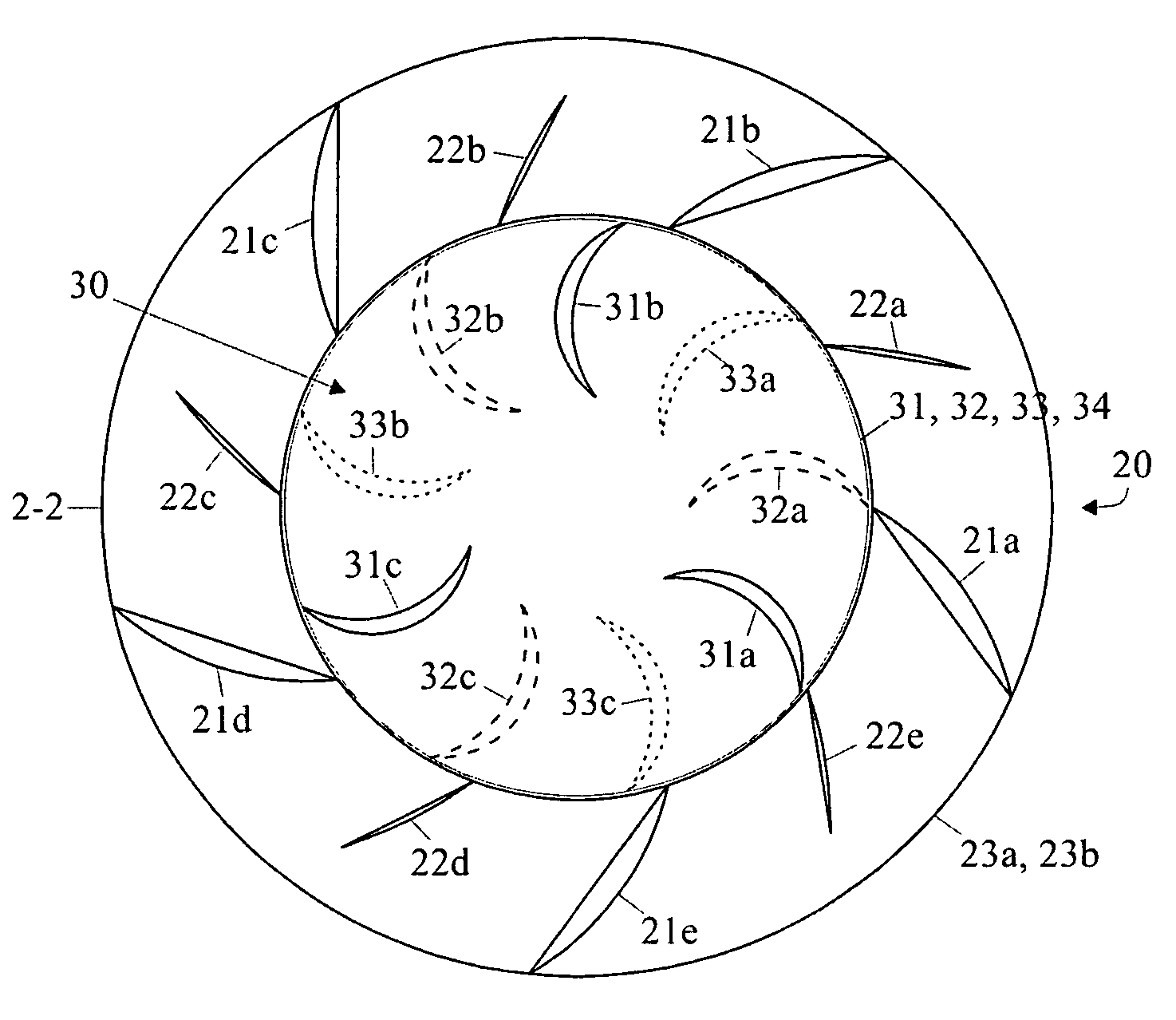
Aerodynamic-hybrid vertical-axis wind turbine
InactiveUS20060275105A1Eliminating salient back pressureEffectively and efficiently harnessingWind motor controlWind motor supports/mountsConvex sideVertical axis wind turbine
An aerodynamic-hybrid, vertical-axis wind turbine which includes a rotor airfoil and stator blade combination which maximizes energy production by increasing wind velocity and pressure while eliminating back pressure and improving the laminar flow of wind both around and through the device. The rotor airfoils have a horizontal cross-section with a crescent shape including a convex leading side and a concave trailing side with a thicker middle section that tapers to narrower sections at ends. The stator blades have a horizontal cross-section with a planar side and a convex side. Rotor airfoil and stator blade combinations are secured between upper and lower annular sails.
Owner:NOVASTRON
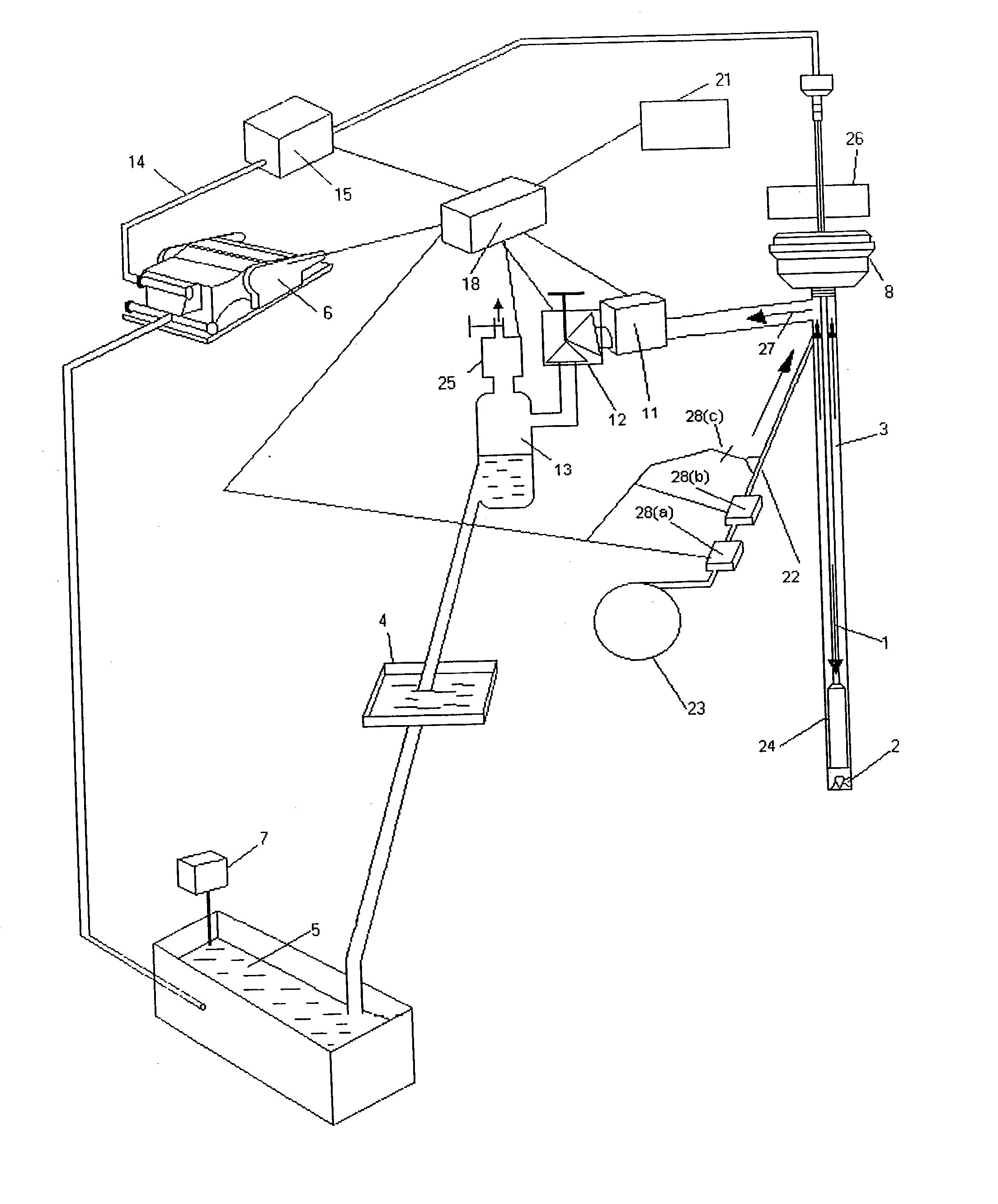
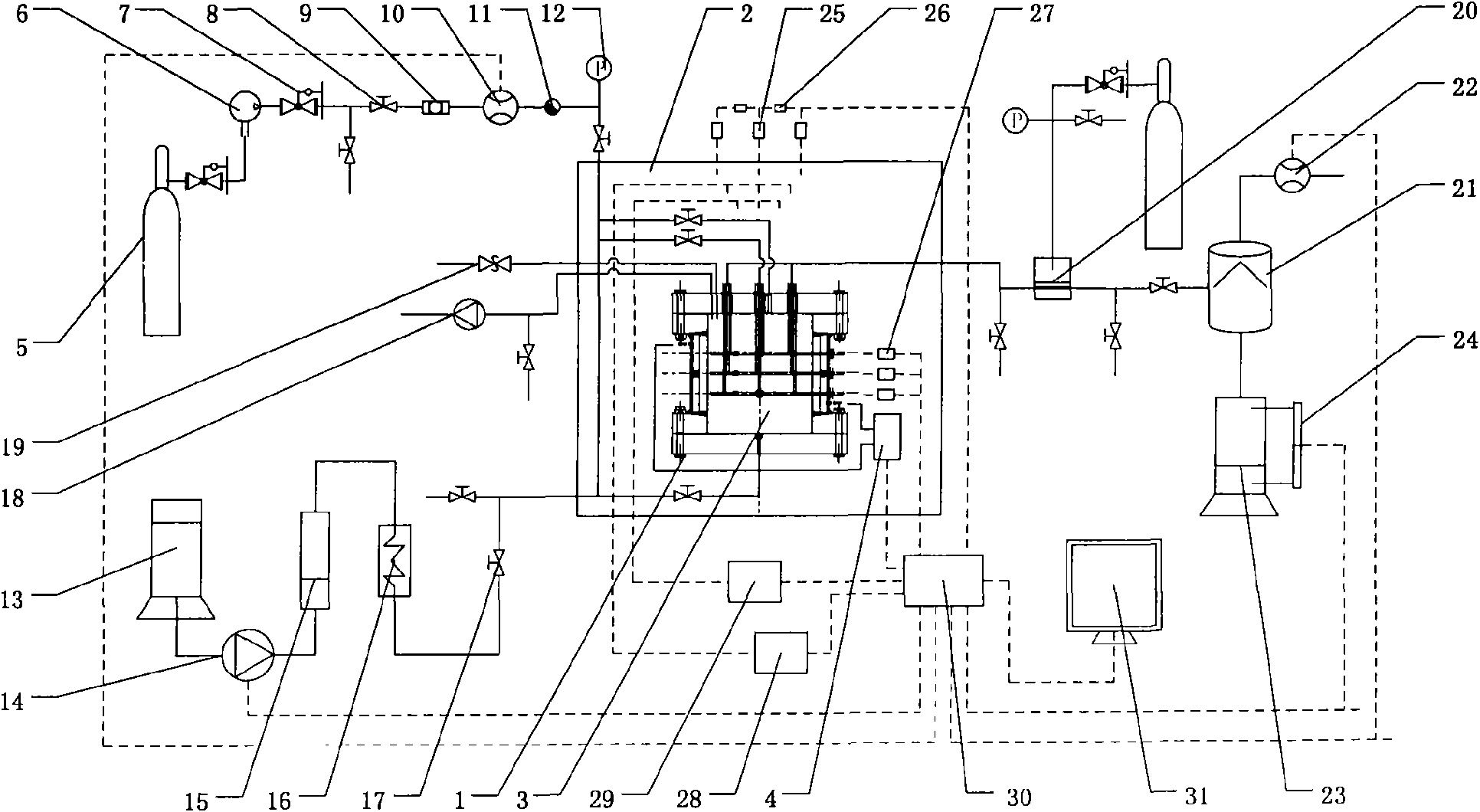
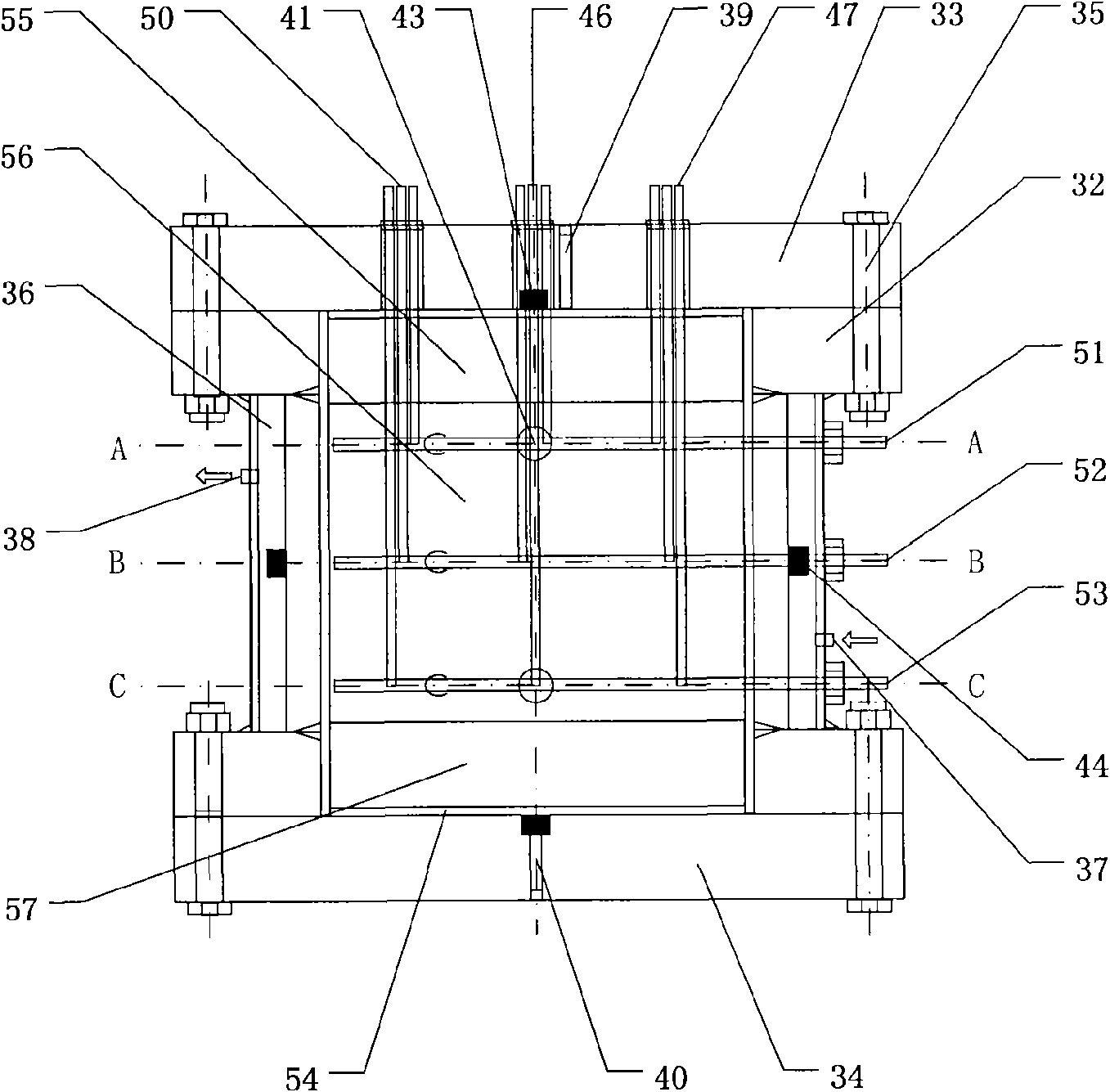
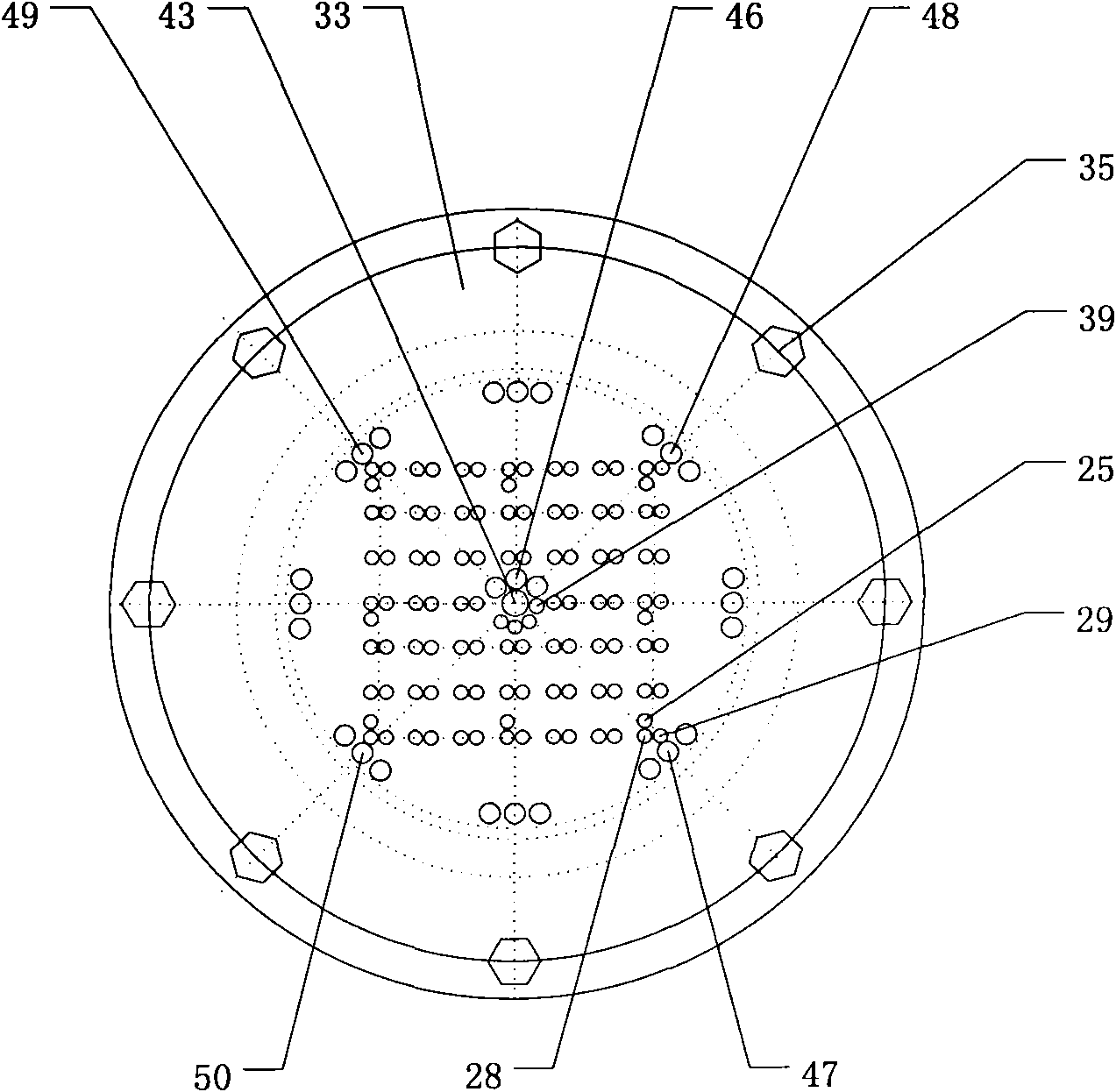
Three-dimensional exploitation simulated experiment apparatus for natural gas hydrate
The objective of the present invention is to provide a simulated experiment apparatus of comprehensive study various exploitation mechanism, exploitation dynamic, and proceeding optimizing and comprehensive evaluation to various exploitation methods. The apparatus includes three-dimensional model, natural gas supply unit, working solution supply unit, back pressure control unit, environment control unit and postprocessing unit. Applying the experimental apparatus can simulate vertical well cluster and horizontal well cluster simultaneity, utilizing visual window and optical fibre endoscope observing and simulating hydrated compound status inside the cavity, proceeding comprehensive evaluation to exploitation process and exploitation impression, being able to provide guide for gas hydrate exploitation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
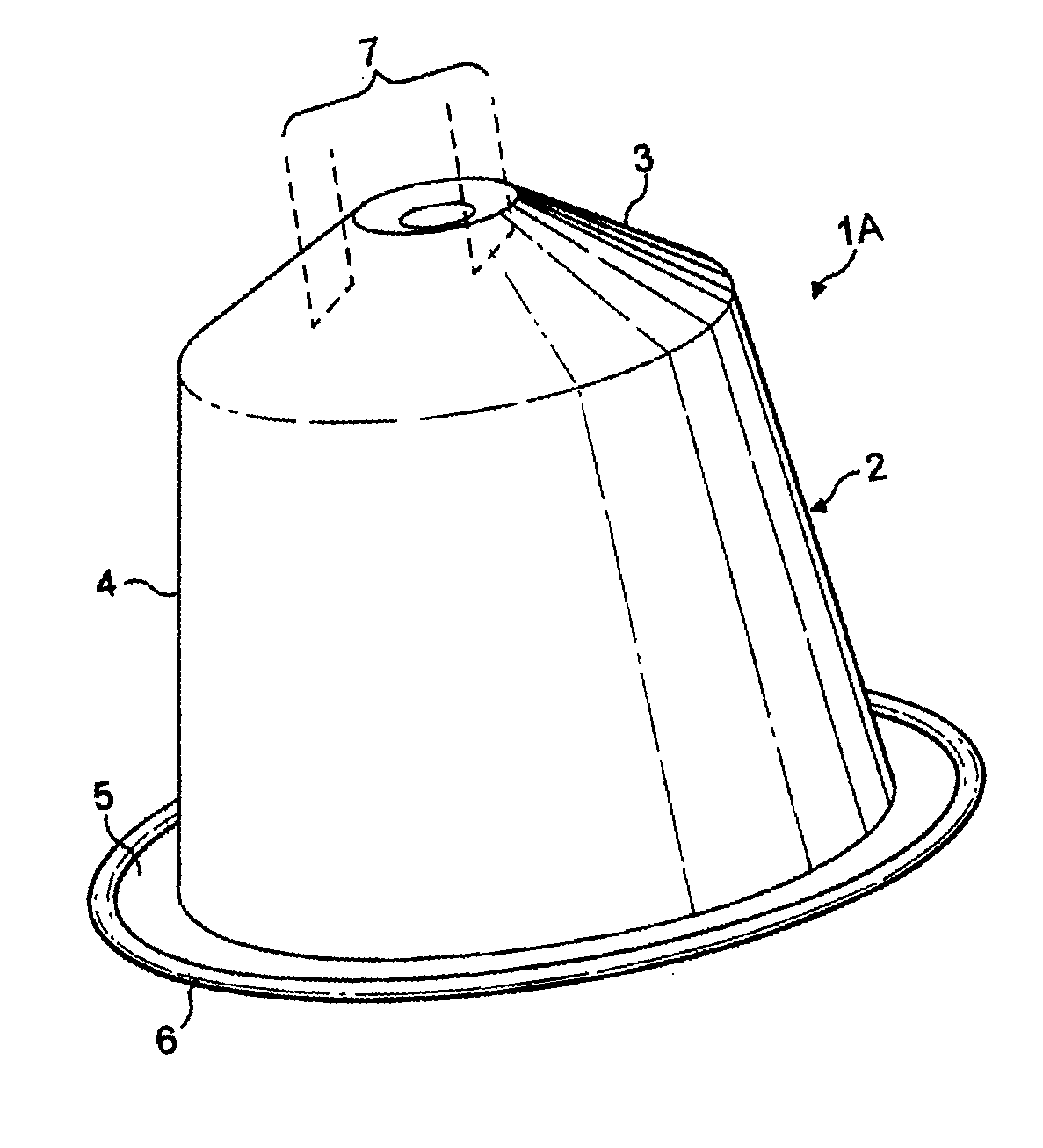
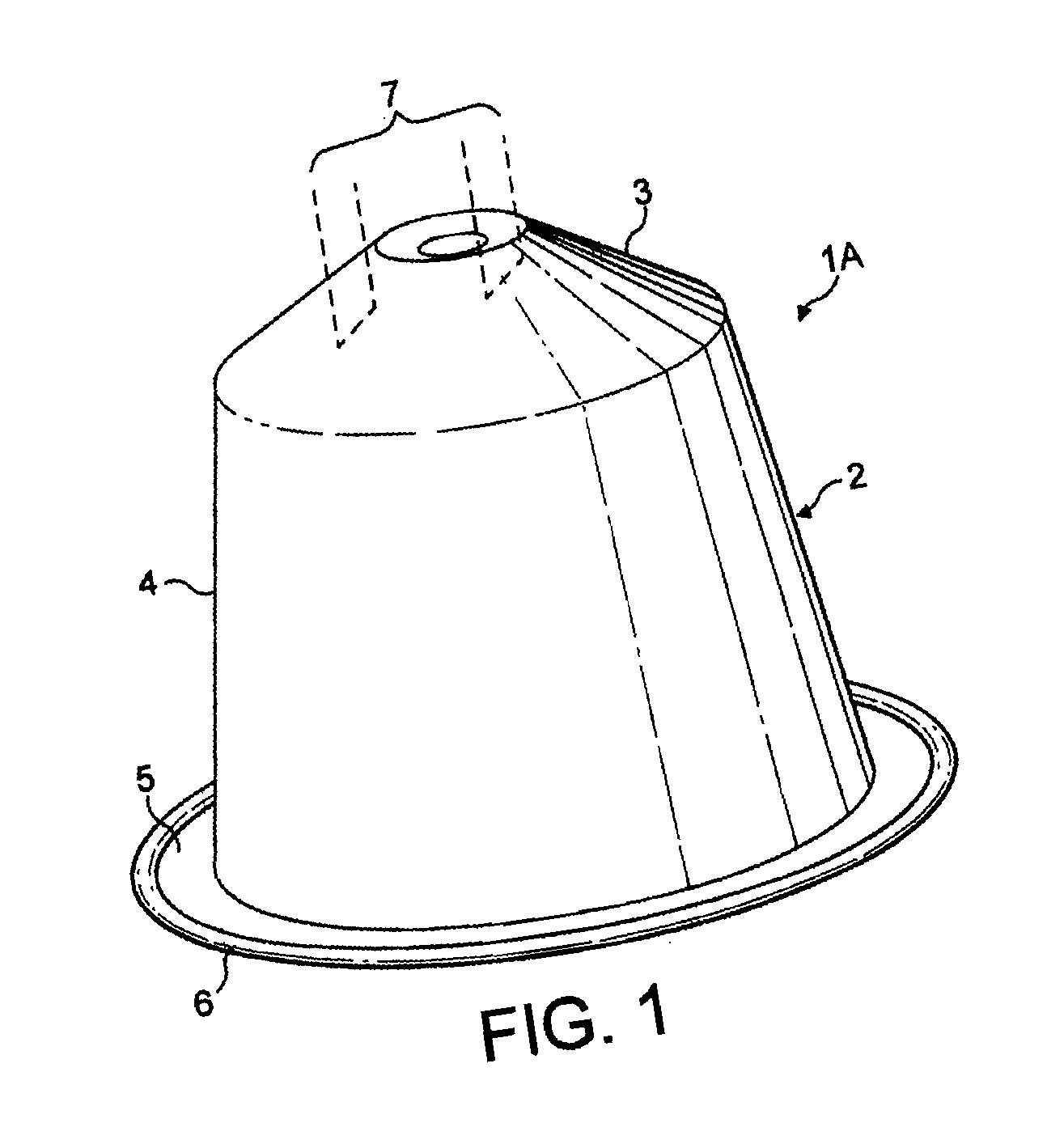
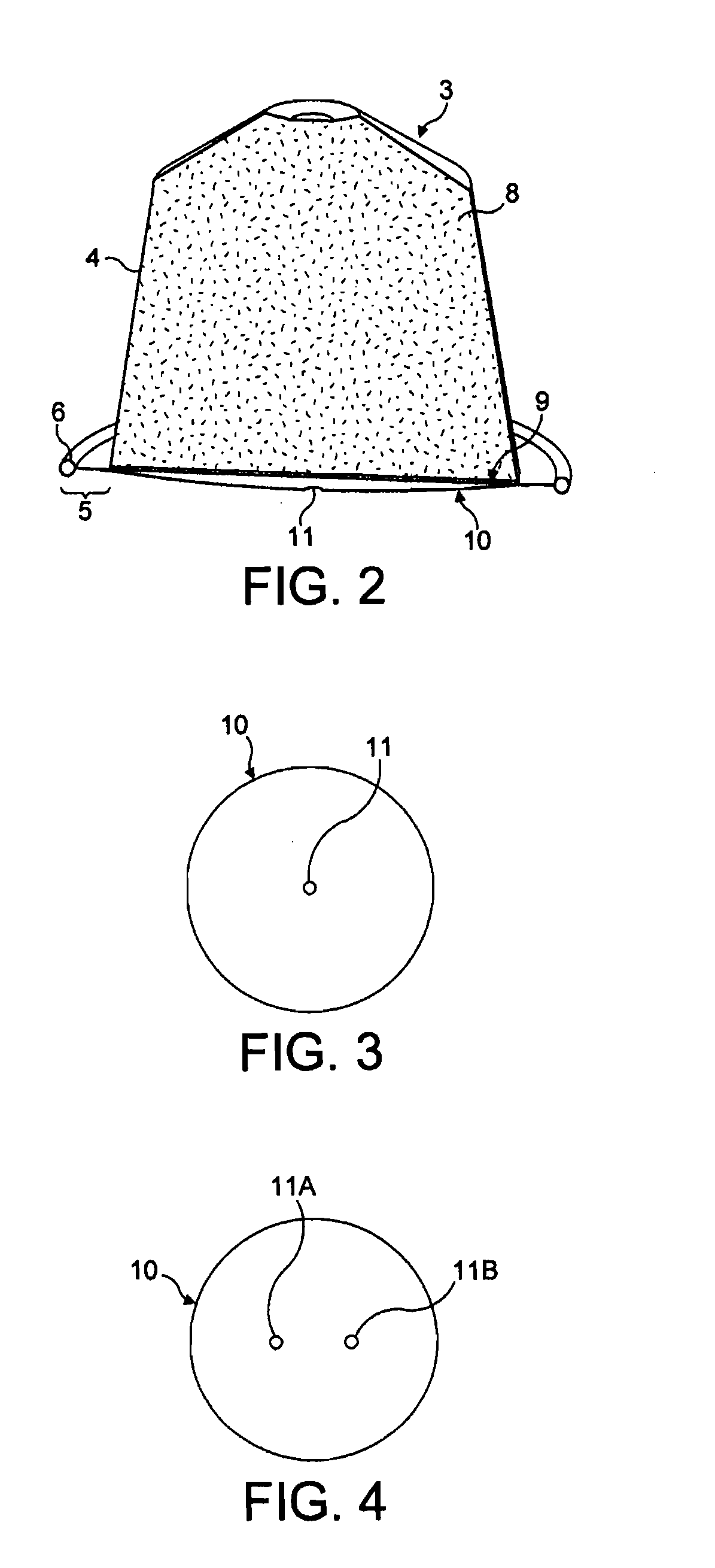
Capsule for preparing coffee in a device comprising a cartridge holder with relief and recessed elements
ActiveUS20100239717A1Consistent flowBeverage vesselsPackaging foodstuffsAdditive ingredientEngineering
A capsule for the production of a beverage in a beverage production machine comprising a capsule holder with relief and recessed elements. The capsule includes an inverted cup-shaped body forming a chamber containing beverage ingredients; a bottom injection wall; a sidewall; and a delivery wall which is sealed to the body. The delivery wall is configured and dimensioned to include a calibrated orifice or perforating means to provide a calibrated orifice with the beverage delivery wall not being tearable against the capsule holder during extraction. The wall also provides through the restriction created by the calibrated orifice a certain back pressure which generates an elevated pressure in the capsule during extraction. Also, a system and method for producing a beverage from the capsules of the invention.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Thermoelectric-based power generation systems and methods
InactiveUS20110067742A1Lower overall pressure dropInternal combustion piston enginesRecuperative heat exchangersExhaust valveEngineering
Some embodiments provide a waste heat recovery apparatus including an exhaust tube having a cylindrical outer shell configured to contain a flow of exhaust fluid; a first heat exchanger extending through a first region of the exhaust tube, the first heat exchanger in thermal communication with the cylindrical outer shell; a second region of the exhaust tube extending through the exhaust tube, the second region having a low exhaust fluid pressure drop; an exhaust valve operatively disposed within the second region and configured to allow exhaust fluid to flow through the second region only when a flow rate of the exhaust fluid becomes great enough to result in back pressure beyond an allowable limit; and a plurality of thermoelectric elements in thermal communication with an outer surface of the outer shell.
Owner:GENTHERM INC
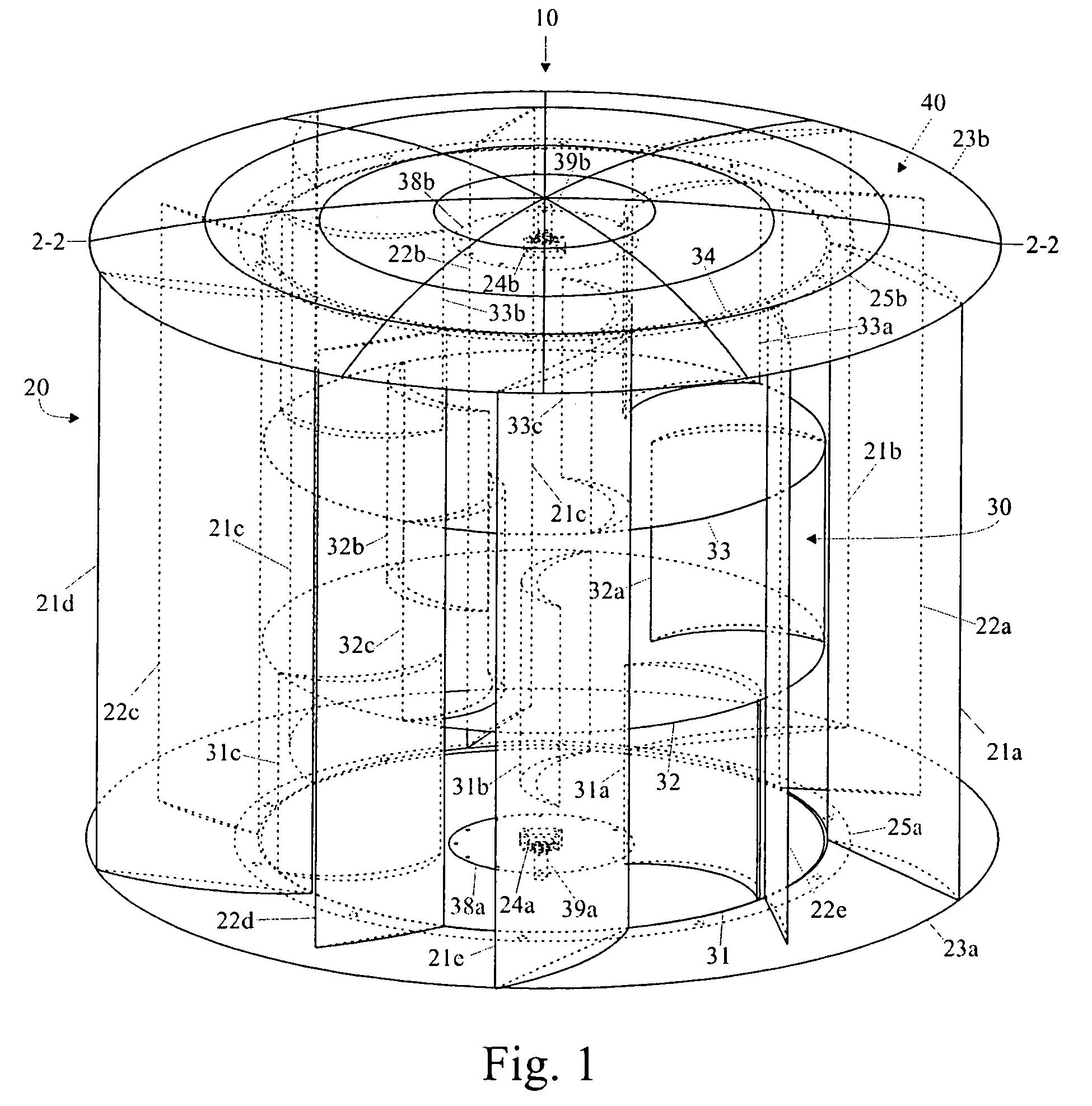
Aerodynamic-hybrid vertical-axis wind turbine
InactiveUS7329965B2Eliminate back pressureEffective forceWind motor controlWind motor supports/mountsConvex sideVertical axis wind turbine
An aerodynamic-hybrid, vertical-axis wind turbine which includes a rotor airfoil and stator blade combination which maximizes energy production by increasing wind velocity and pressure while eliminating back pressure and improving the laminar flow of wind both around and through the device. The rotor airfoils have a horizontal cross-section with a crescent shape including a convex leading side and a concave trailing side with a thicker middle section that tapers to narrower sections at ends. The stator blades have a horizontal cross-section with a planar side and a convex side. Rotor airfoil and stator blade combinations are secured between upper and lower annular sails.
Owner:NOVASTRON
Earphone
ActiveUS8712087B2Reduce pressureImprove fidelityEar supported setsIntra aural earpiecesEngineeringHeadphones
The earphone includes a driver unit; a housing accommodating the driver unit, the housing having a front face serving as a sound emitting surface and a bowl shaped rear face; a hollow casing provided separately from the housing, the casing being configured to increase an internal volume adjacent to the rear side of a vibrating plate and to reduce the back pressure of the vibrating plate; and a connecting channel connecting the rear face of the housing and the casing such that the housing is in communication with the internal space of the casing, in which the housing includes a sound emitting tube protruding from the front face thereof so as to be fitted into an external auditory meatus.
Owner:AUDIO-TECHNICA
Direct drive fan system with variable process control
ActiveUS20140244051A1System smoothReduce vibrationTransportation and packagingEngine fuctionsCooling towerHigh torque
The present invention is directed to a direct-drive fan system and a variable process control system for efficiently managing the operation of fans in a cooling system such a as wet-cooling tower or air-cooled heat exchanger (ACHE), HVAC systems, mechanical towers or chiller systems. The present invention is based on the integration of key features and characteristics such as tower thermal performance, fan speed and airflow, motor torque, fan pitch, fan speed, fan aerodynamic properties, and pump flow. The variable process control system processes feedback signals from multiple locations in order control a high torque, variable speed, permanent magnet motor to drive the fan. Such feedback signals represent certain operating conditions including motor temperature, basin temperature, vibrations, and pump flow rates. Other data processed by the variable process control system in order to control the motor include turbine back pressure set-point, condenser temperature set-point and plant part-load setting. The variable process control system processes this data and the aforesaid feedback signals to optimize the operation of the cooling system in order to prevent disruption of the industrial process and prevent equipment (turbine) failure or trip. The variable process control system alerts the operators for the need to conduct maintenance actions to remedy deficient operating conditions such as condenser fouling. The variable process control system increases cooling for cracking crude and also adjusts the motor RPM, and hence the fan RPM, accordingly during plant part-load conditions in order to save energy.
Owner:PRIME DATUM
Backpressure adaptor pin and methods of use
A tubing assembly including a tubing string and tubing hanger provides a fluid passage with backpressure threads for securing a backpressure plug in a fluid-tight seal below the tubing hanger, so that the tubing hanger can be removed from the tubing string. The back pressure threads are preferably incorporated in a backpressure adapter pin connected between the tubing string and the tubing hanger. The adapter pin may also incorporate external weight-bearing shoulders for snubbing and / or suspending the tubing assembly. The backpressure plug is inserted or removed using a backpressure plug tool that slides through a packing in a pressurized casement that maintains pressure in an axial passage through a control stack of the wellhead.
Owner:STINGER WELLHEAD PROTECTION
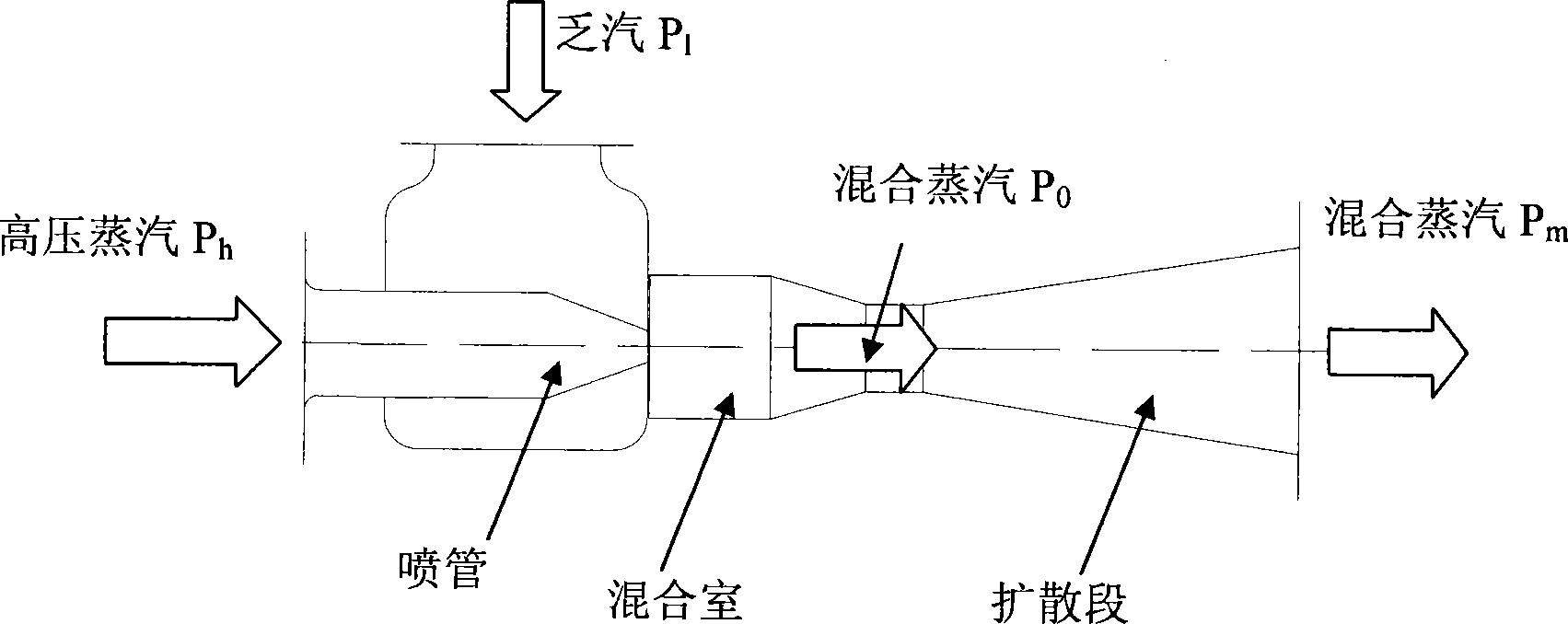
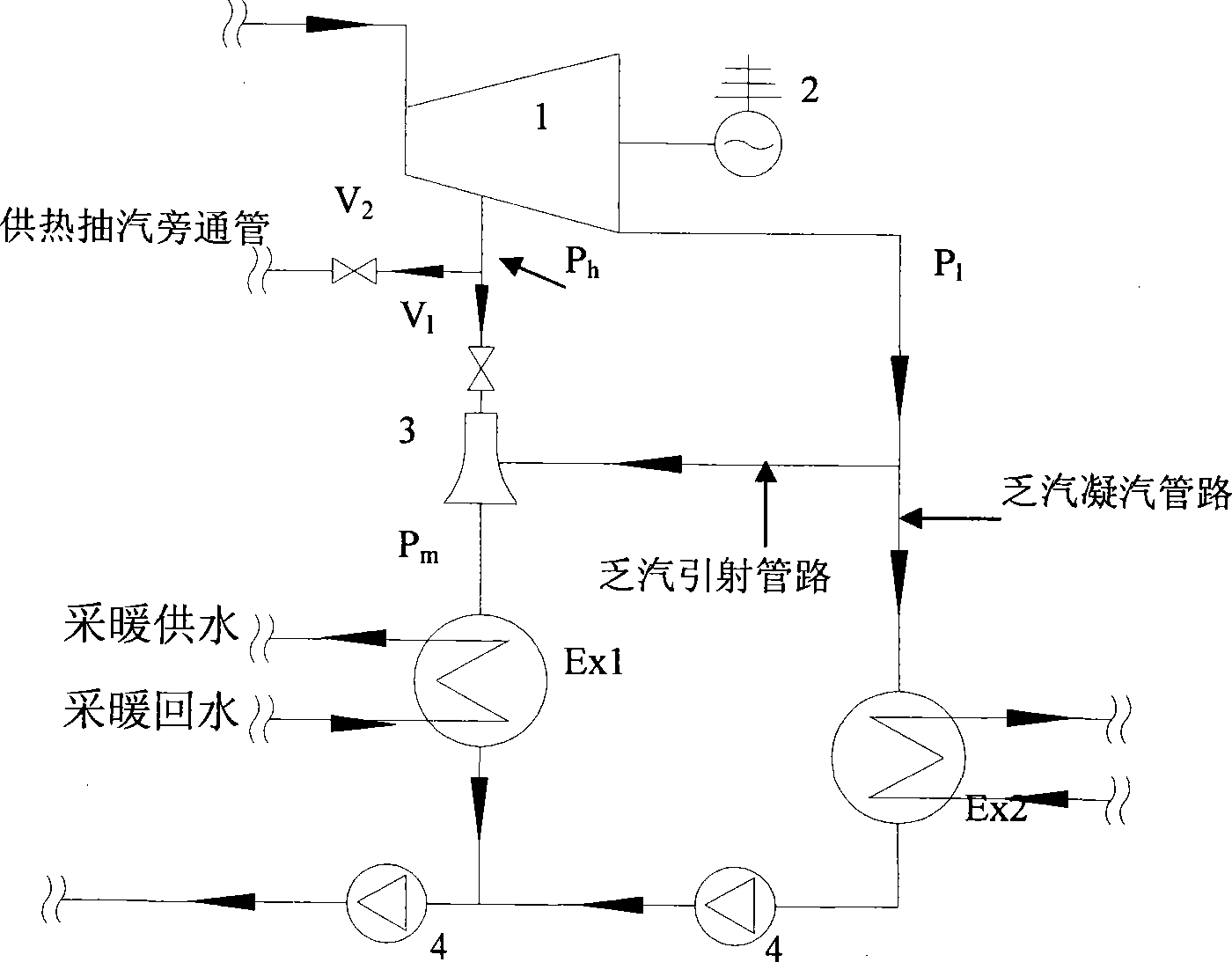
Steam jet type heat pump heat distribution system for recovering thermal power plant condensing residual heat
InactiveCN101240909AEasy to manufactureImprove heat transfer effectFeed water supplyEnergy efficient heating/coolingLow voltageCore component
The present invention provides a steam injection heatpump heating system. The technical solution is that the system is composed of a steam injector, a high voltage steam pipeline, a low voltage steam pipeline, a throttling gear and a bypass connecting pipe. The high voltage steam enters in the heat exchanger heaing backwater after injecting lower steam turbine voltage condensing in low temperature, this realises waste heat recovery in low temperature condensing steam of the steam turbine. The core component is the steam injector, the high voltage heat supplying pumping is used as high-velocity jet acceleratively formed in the injecting tube of the working steam, and lower voltage steam turbine is rolled in the mixing room as injected flow, mixing steam in the expanding section of the steam injector is decelerately compressed in a certain back pressure, then sending to the heat interchanger for heating backwater, a certian back pressure mixing steam condenses to water after heat releasing in the exchanger, returning to the backwater system of electrical factory, completing thermal circuit of the combined heat and power generation set.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Multi-stage turbocharging system utilizing VTG turbine stage(s)
InactiveUS20060070381A1Improve fuel economyEmission reductionInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelWastegateInternal combustion engine
Multi-stage turbocharging, and more particularly, an advanced multi-stage turbocharging system using the variable turbine power of one or more variable turbine geometry (VTG) turbochargers to adjust compressor boost and exhaust back pressure to engine operating demands. The invention further relates to a turbocharged internal combustion engine, in particular a turbocharged internal combustion engine with at least one high-pressure turbine stage and one downstream low-pressure turbine stage, wherein the high-pressure turbine may be a single-flow or double-flow type, wherein the high pressure or low pressure compressor may be variable geometry, wherein the high pressure or low pressure compressor may be variably bypassed, and wherein the high pressure or low pressure turbine may be provided with an active control variable bypass or wastegate.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
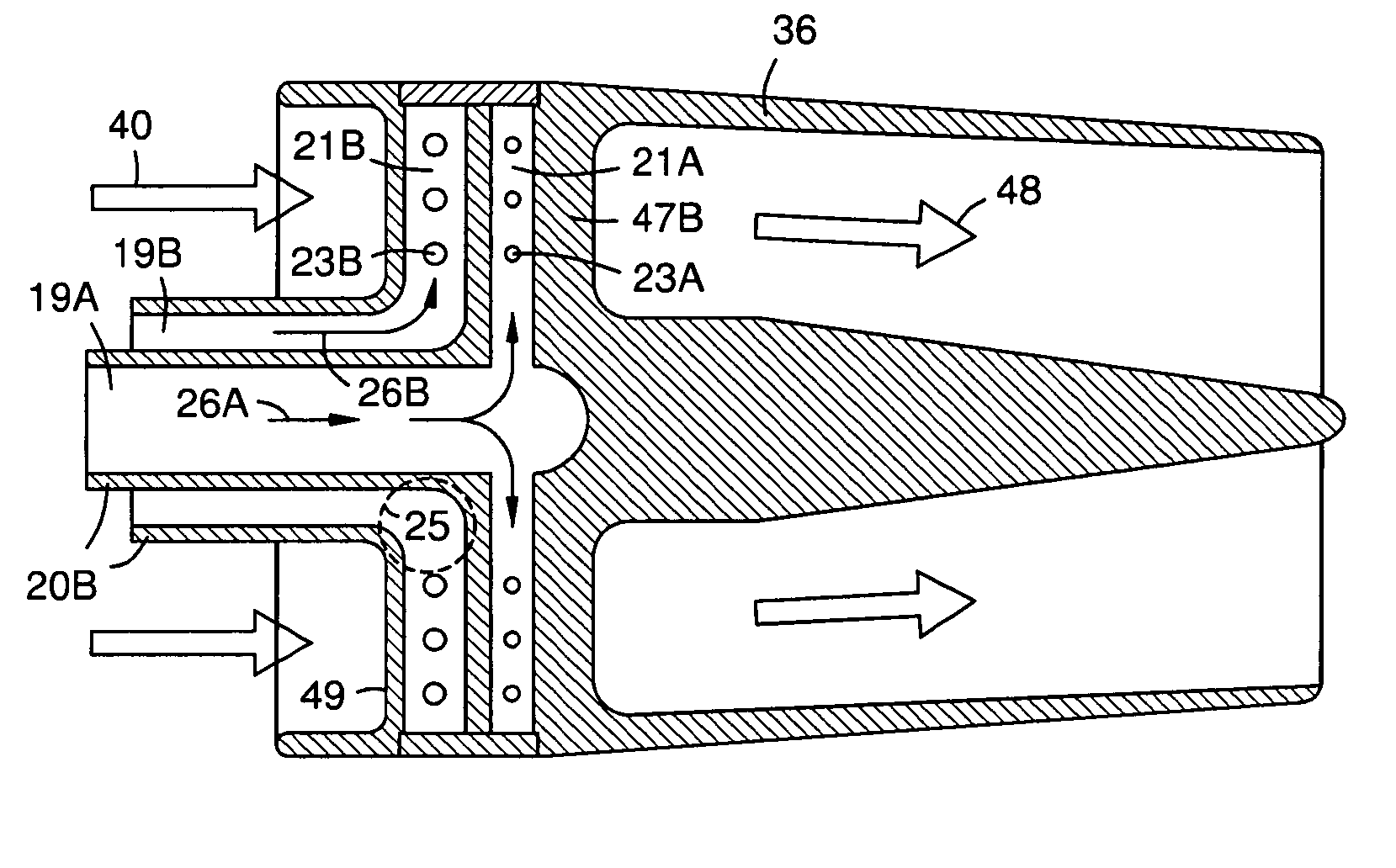
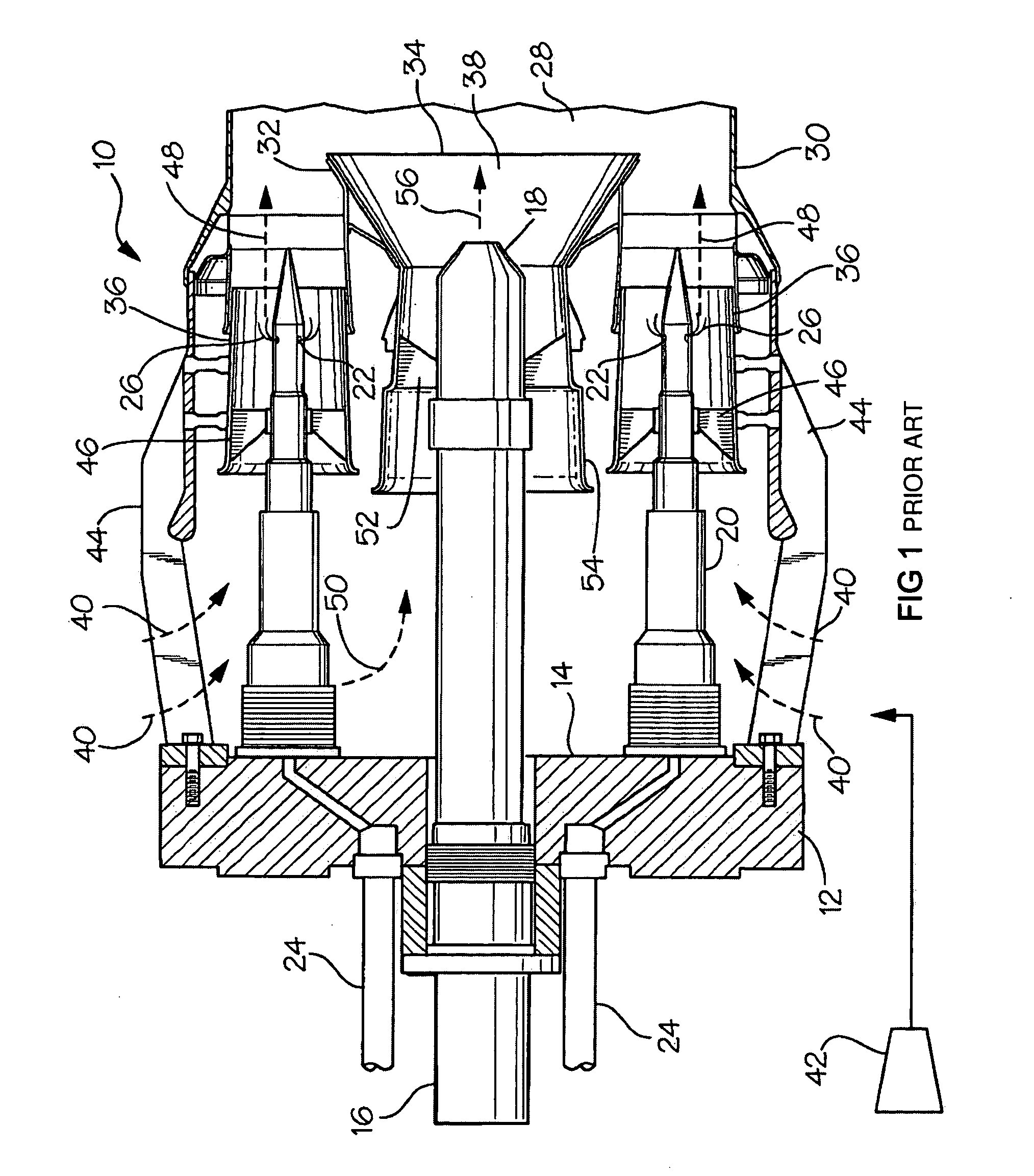
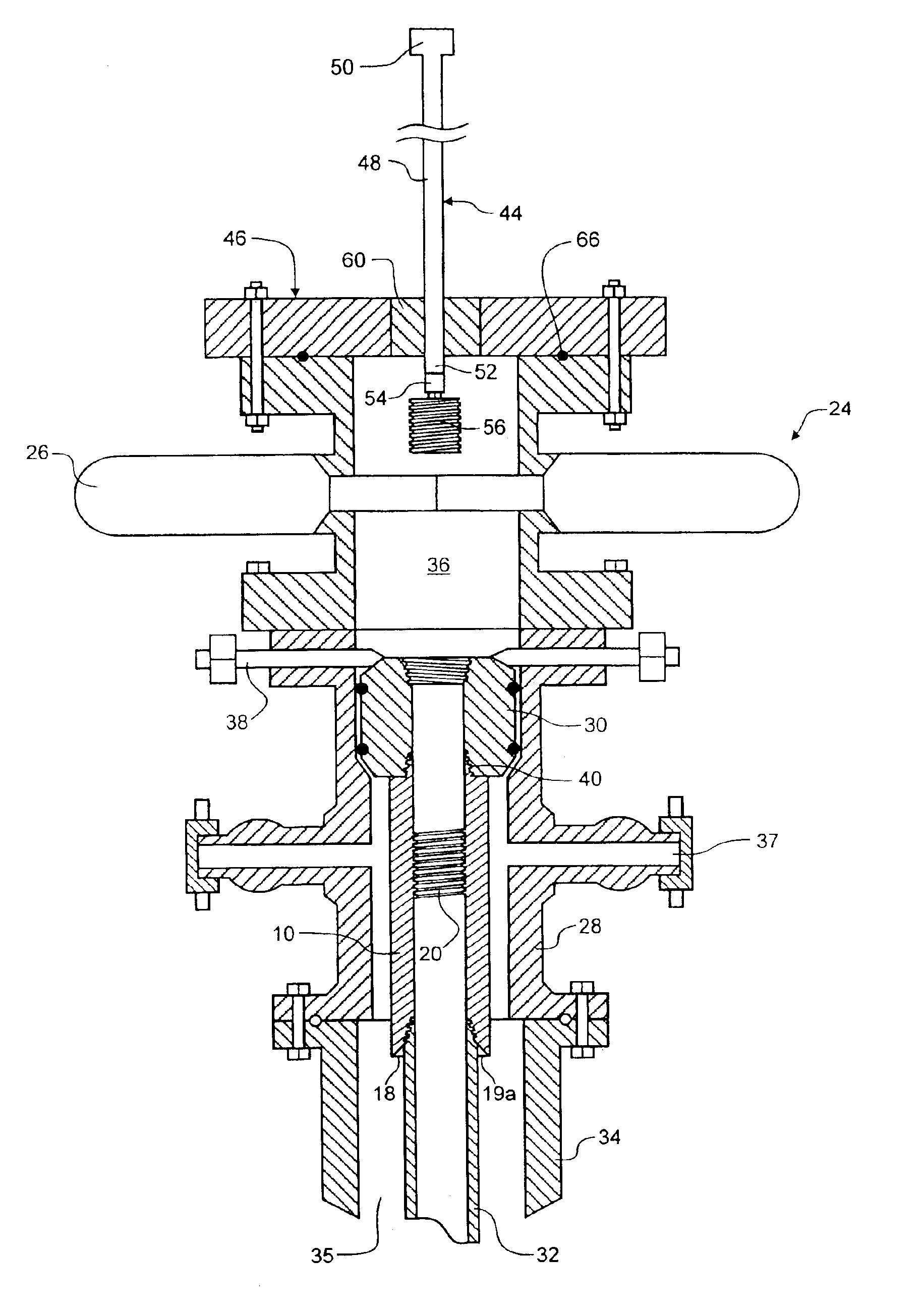
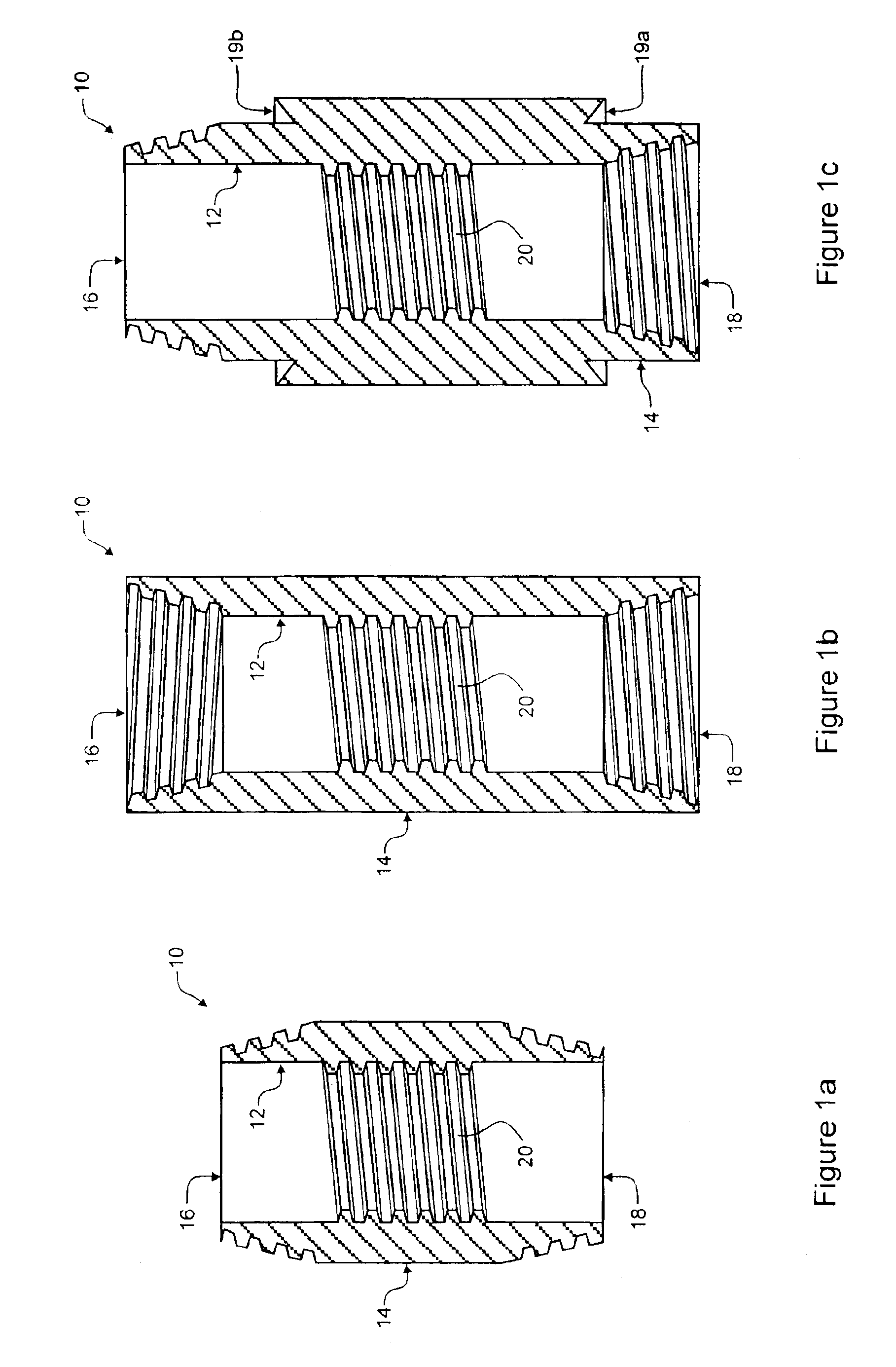
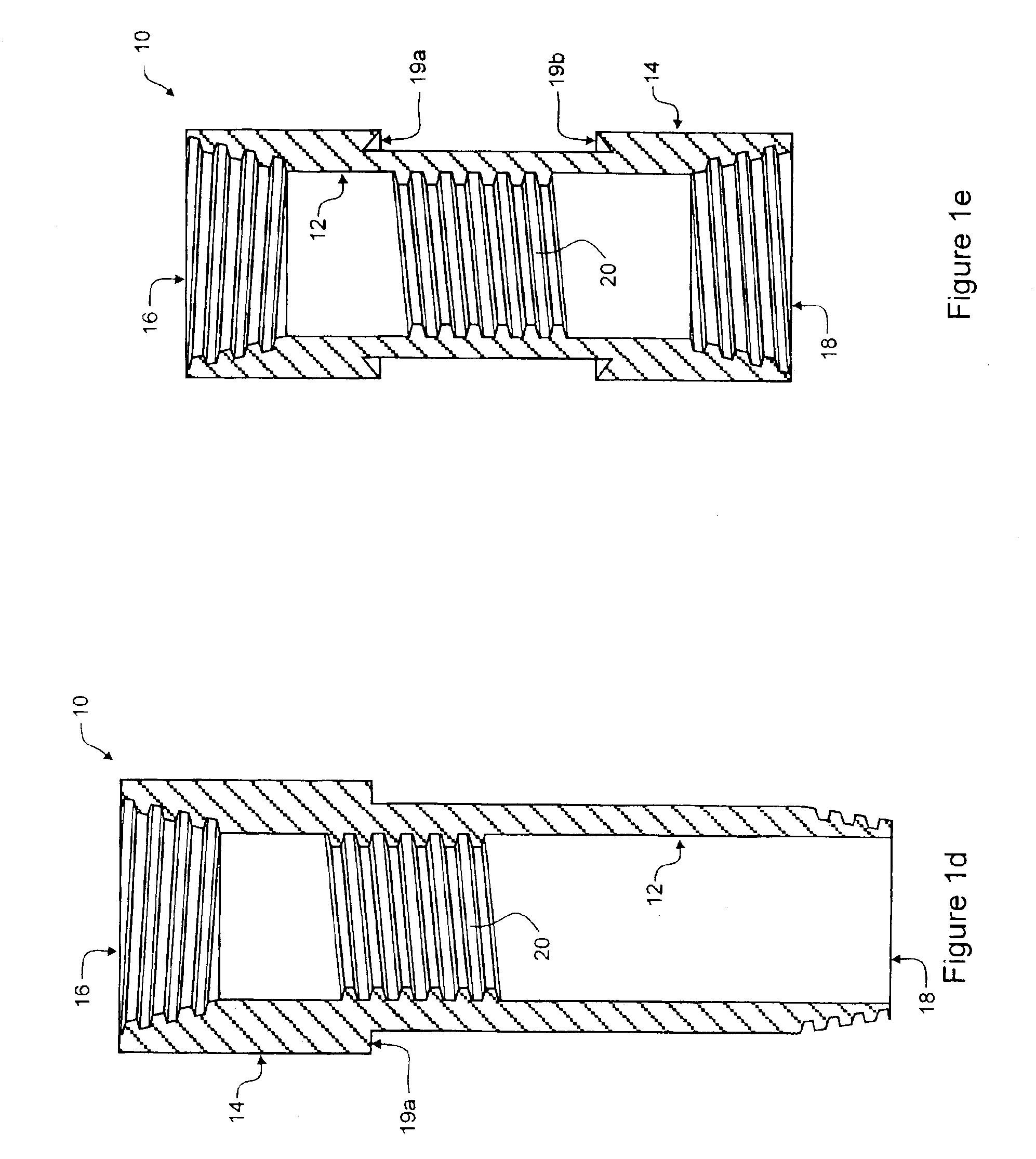
Flex-Fuel Injector for Gas Turbines
A fuel injector (36) for alternate fuels (26A, 26B) with energy densities that differ by at least about a factor of two. Vanes (47B) extend radially from a fuel delivery tube structure (20B) with first and second fuel supply channels (19A, 19B). Each vane has first and second radial passages (21A, 21B) communicating with the respective fuel supply channels, and first and second sets of apertures (23A, 23B) between the respective radial passages and the surface (49) of the vane. The first fuel supply channel, first radial passage, and first apertures form a first fuel delivery pathway providing a first fuel flow rate at a given backpressure. The second fuel supply channel, second radial passage, and second apertures form a second fuel delivery pathway providing a second fuel flow rate that may be at least about twice first fuel flow rate at the given backpressure.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Backpressure adapter pin and methods of use
A tubing assembly including a tubing string and tubing hanger provides a fluid passage with backpressure threads for securing a backpressure plug in a fluid-tight seal below the tubing hanger, so that the tubing hanger can be removed from the tubing string. The back pressure threads are preferably incorporated in a backpressure adapter pin connected between the tubing string and the tubing hanger. The adapter pin may also incorporate external weight-bearing shoulders for snubbing and / or suspending the tubing assembly. The backpressure plug is inserted or removed using a backpressure plug tool that slides through a packing in a pressurized casement that maintains pressure in an axial passage through a control stack of the wellhead.
Owner:STINGER WELLHEAD PROTECTION
Pressure regulator adaptable to compressed gas cartridge
ActiveUS7334598B1Reduce manufacturing costImprove reliabilityContainer filling methodsGas handling applicationsEngineeringHigh pressure
This pressure regulator is specifically designed to operate with a portable compressed gas cartridge thus reducing the high vapor pressure found in compressed gas cartridges down to a substantially consistent outlet pressure. Due to the nature of the crowded regulator art, the soon to be embodied pressure regulator has been specifically embodied for use in the portable compressed gas cartridge harnessing art and this specific use is carried into the claims. Exemplified in the pressure regulator embodiments is a reduced amount of components over existing designs. Additionally, safety and reliability features have been integrated into the design and will shortly be taught in the following paragraphs. A burp-off feature in all embodiments will be exemplified that vents back-pressure spikes as well as a method of adjusting the burp-off back-pressure spikes independent of regulated pressure in some embodiments.
Owner:HOLLARS ANTHONY SCOTT
Pressure control device
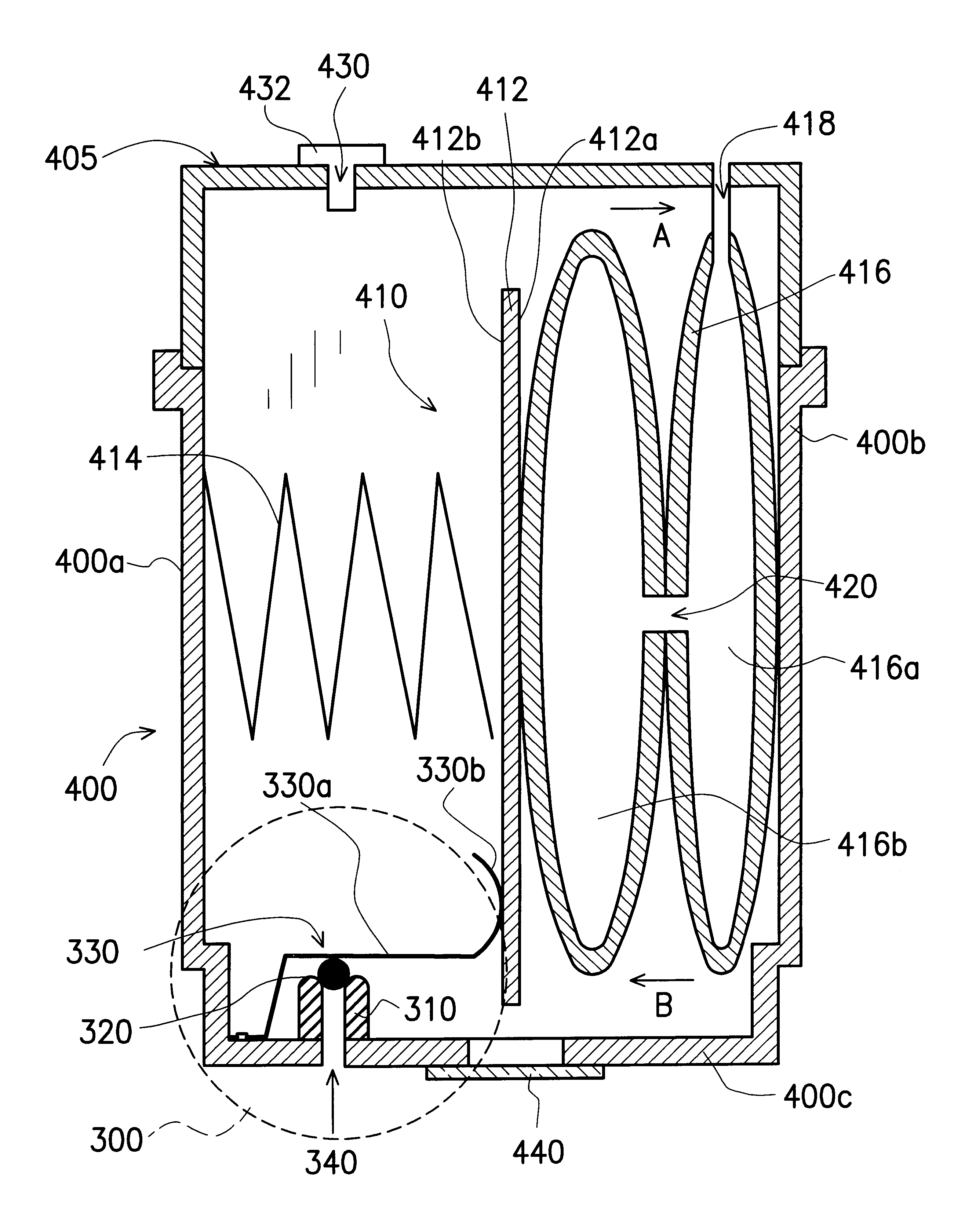
A pressure control device installed at the bottom of the reservoir of an ink-jet pen. The device has a tubular boss whose upper end has an arc surface and that a sphere sits on the arc surface. Ideally, the sphere makes a line contact with the arc surface of the boss. The device also has a spring with one end mounted to the bottom of the reservoir. The spring has two portions together. The first portion of the spring presses tightly against the sphere while the second portion touches a pressure plate inside the reservoir. The reservoir further contains an expandable bag. When the bag inside the reservoir expands, the pressure plate attached to the bag will push the second portion of the spring such that its first portion will move away from the sphere. Due to the presence of a back pressure within the reservoir, the sphere will be afloat briefly permitting ambient air to enter the reservoir. Consequently, back pressure within the reservoir is regulated.
Owner:TRANSPACIFIC IP LTD
Vaporizing assembly and vapor generating device
ActiveUS20170208864A1Reduce the amount requiredTobacco devicesOhmic-resistance heatingElectrical and Electronics engineeringBack pressure
A heater assembly for a vaporizing device, a vaporizing device containing the heater assembly, and a method for vaporizing fluid ejected by an ejection head. The heater assembly for the vaporizing device includes a vapor inlet end and a vapor outlet end, positive and negative electrodes for contact with positive and negative heater terminals on a vaporizing heater, an insulator disposed between the positive and negative electrodes, and a wick disposed between the insulator and the vaporizing heater for dispersion of liquid to be vaporized by the vaporizing heater and for back pressure control of the vaporizing device.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
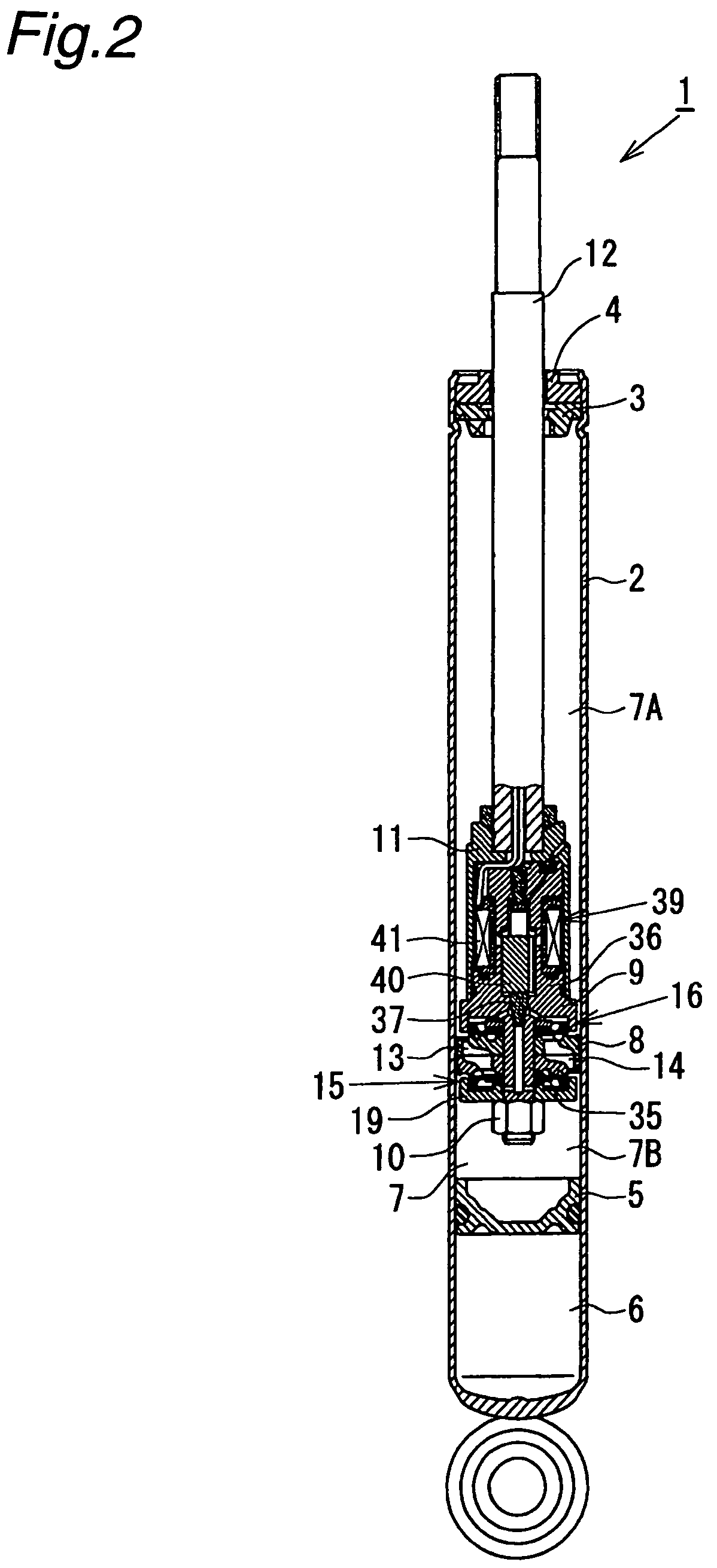
Controllable damping force hydraulic shock absorber
A controllable damping force hydraulic shock absorber including a pilot type damping valve having a back-pressure chamber for each of an extension stroke and a compression stroke. A piston connected to a piston rod is fitted into a sealed cylinder in which a hydraulic fluid is contained. During an extension stroke of the piston rod, the hydraulic fluid in an upper cylinder chamber flows to a lower cylinder chamber through an extension-side hydraulic fluid passage, an extension-side orifice hydraulic fluid passage, an extension-side back-pressure chamber, an axial hydraulic fluid passage, a radial hydraulic fluid passage, a compression-side back-pressure chamber, an extension-side check valve and a compression-side hydraulic fluid passage. During a compression stroke, the hydraulic fluid in the lower cylinder chamber flows to the upper cylinder chamber through the compression-side hydraulic fluid passage, the compression-side orifice passage, the compression-side back-pressure chamber, the radial hydraulic fluid passage, the axial hydraulic fluid passage, the extension-side back-pressure chamber, the compression-side check valve and the extension-side hydraulic passage. The hydraulic fluid passage for an extension stroke and the hydraulic fluid passage for a compression stroke have some elements in common, thus simplifying the structure of the controllable damping force hydraulic shock absorber.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com