Patents
Literature
2456 results about "Convex side" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bell-shaped having a convex shape that resembles a bell convex on both sides; shaped like a lentil (of a ship) so weakened as to sag at each end convex on one side and concave on the other with the convexity being greater than the concavity (used of the moon) more than half full having the convex shape of a helmet
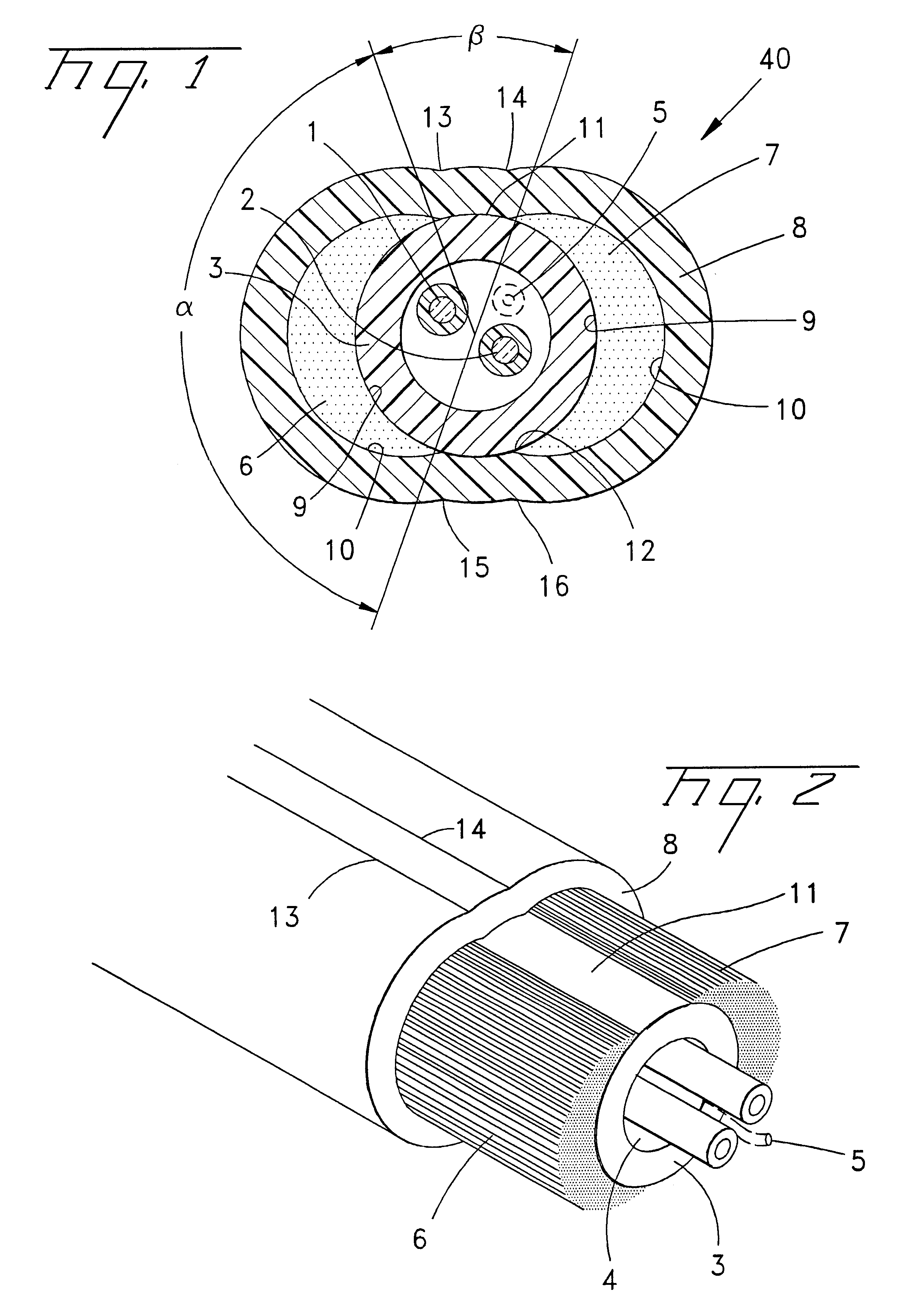
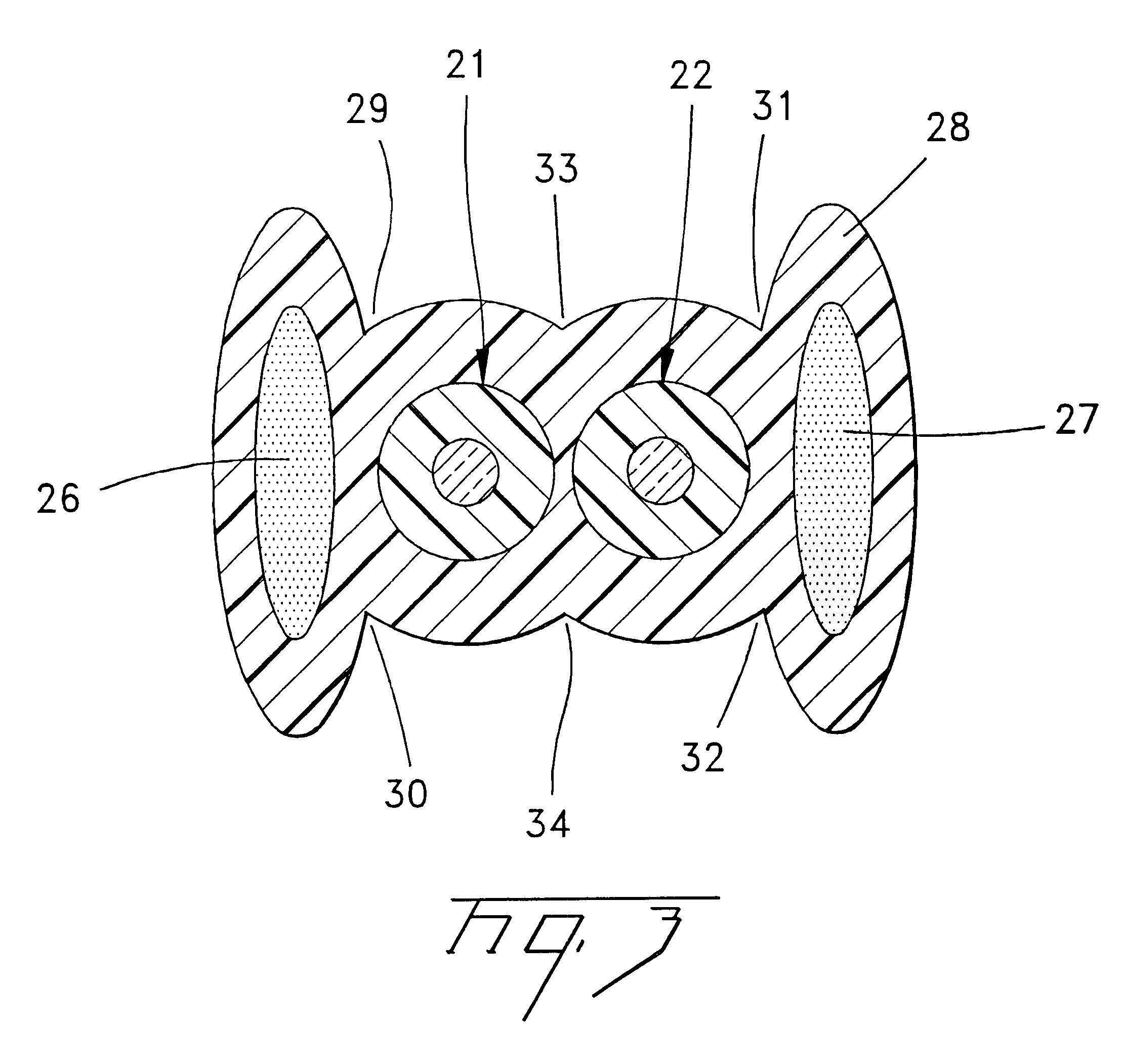
Blades with functional balance asymmetries for use with ultrasonic surgical instruments
InactiveUS6976969B2Correct the imbalanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesCurve shapeEngineering
Disclosed is an ultrasonic surgical instrument that combines end-effector geometry to best affect the multiple functions of a shears-type configuration. The shape of the blade is characterized by a radiused cut offset by some distance to form a curved geometry. The cut creates a curved surface with multiple asymmetries causing multiple imbalances within the blade. Imbalance due to the curve of the instrument is corrected by a non-functional asymmetry proximal to the functional asymmetry. Imbalance due to the asymmetric cross-section of the blade is corrected by the appropriate selection of the volume and location of material removed from a functional asymmetry. The shape of the blade in one embodiment of the present invention is characterized by two radiused cuts offset by some distance to form a curved and potentially tapered geometry. These two cuts create curved surfaces including a concave surface and a convex surface. The length of the radiused cuts affects, in part, the acoustic balancing of the transverse motion induced by the curved shape.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Surgical stapling instrument
A surgical stapling instrument having a staple fastening assembly including a curved cartridge device. The device has at least one curved open row of staples having a first and second ends and having a concave side and a convex side. Opposite to the cartridge device there is a curved anvil for forming the ends of the staples. The instrument also includes a moving device adapted to move the anvil with respect to the cartridge device in a parallel relationship. The instrument also includes a staple driving device adapted to drive the staples out of the cartridge device towards the anvil, and a knife. The knife has opposing first and second sides and is contained in the cartridge device. There is also a knife actuating device adapted to move the knife towards the anvil. The instrument includes staple fastening assembly having a retaining pin which moves between the cartridge device to align them. The retaining pin is located on the second side of the knife in an intermediate region between the first end and second ends of the curved row of staples.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Ultrasonic medical device and method
InactiveUS7285895B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerConvex side
Owner:CRESCENDO TECH
Blades with functional balance asymmetries for use with ultrasonic surgical instruments
Disclosed is an ultrasonic surgical instrument that combines end-effector geometry to best affect the multiple functions of a shears-type configuration. The shape of the blade is characterized by a radiused cut offset by some distance to form a curved geometry. The cut creates a curved surface with multiple asymmetries causing multiple imbalances within the blade. Imbalance due to the curve of the instrument is corrected by a non-functional asymmetry proximal to the functional asymmetry. Imbalance due to the asymmetric cross-section of the blade is corrected by the appropriate selection of the volume and location of material removed from a functional asymmetry. The shape of the blade in one embodiment of the present invention is characterized by two radiused cuts offset by some distance to form a curved and potentially tapered geometry. These two cuts create curved surfaces including a concave surface and a convex surface. The length of the radiused cuts affects, in part, the acoustic balancing of the transverse motion induced by the curved shape.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Forward-directed atherectomy catheter
InactiveUS20060229646A1Great relative stretch forceReduce the cross-sectional areaCannulasExcision instrumentsAtherectomyDrive shaft
Owner:SPARKS KURT D
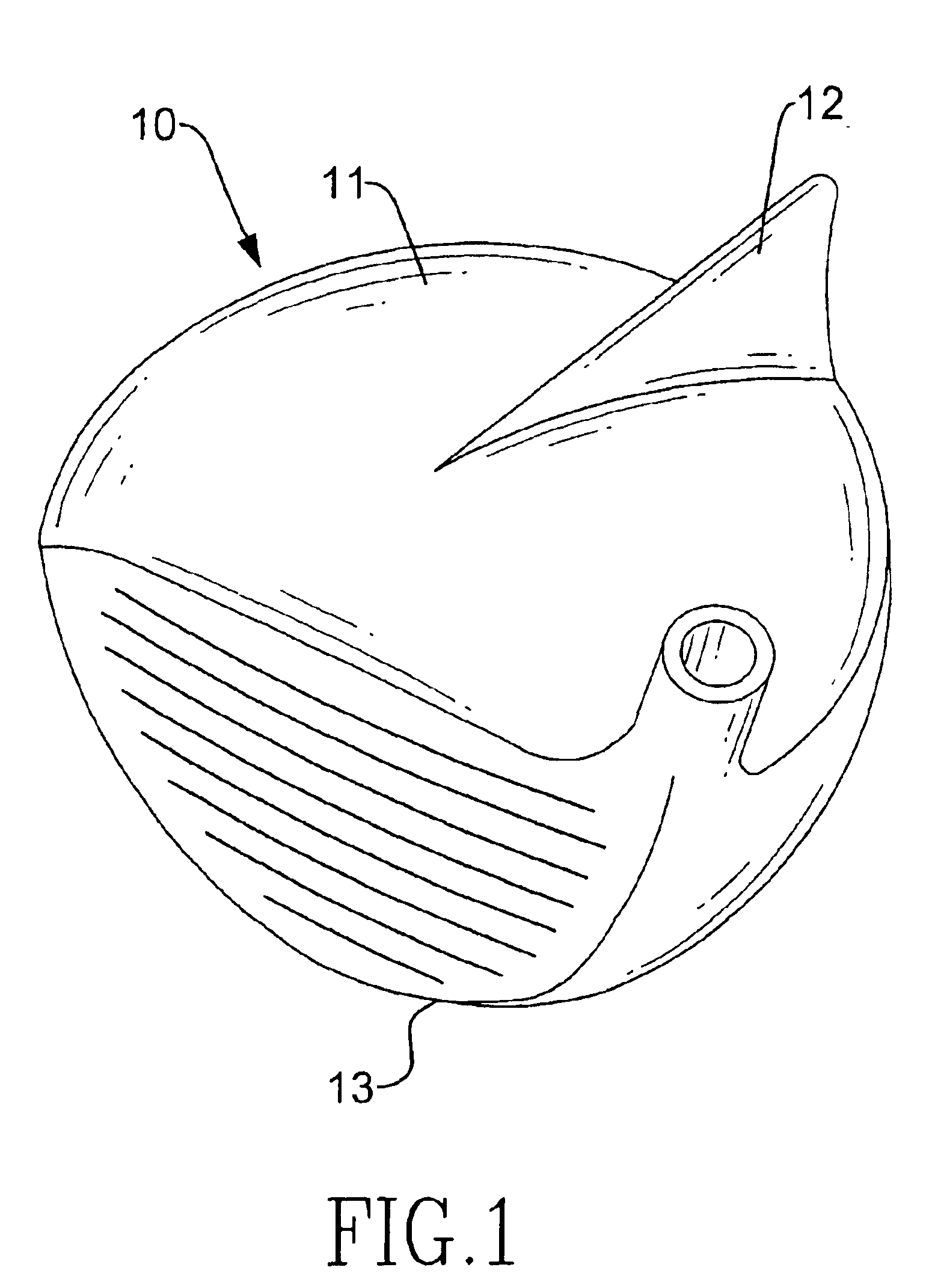
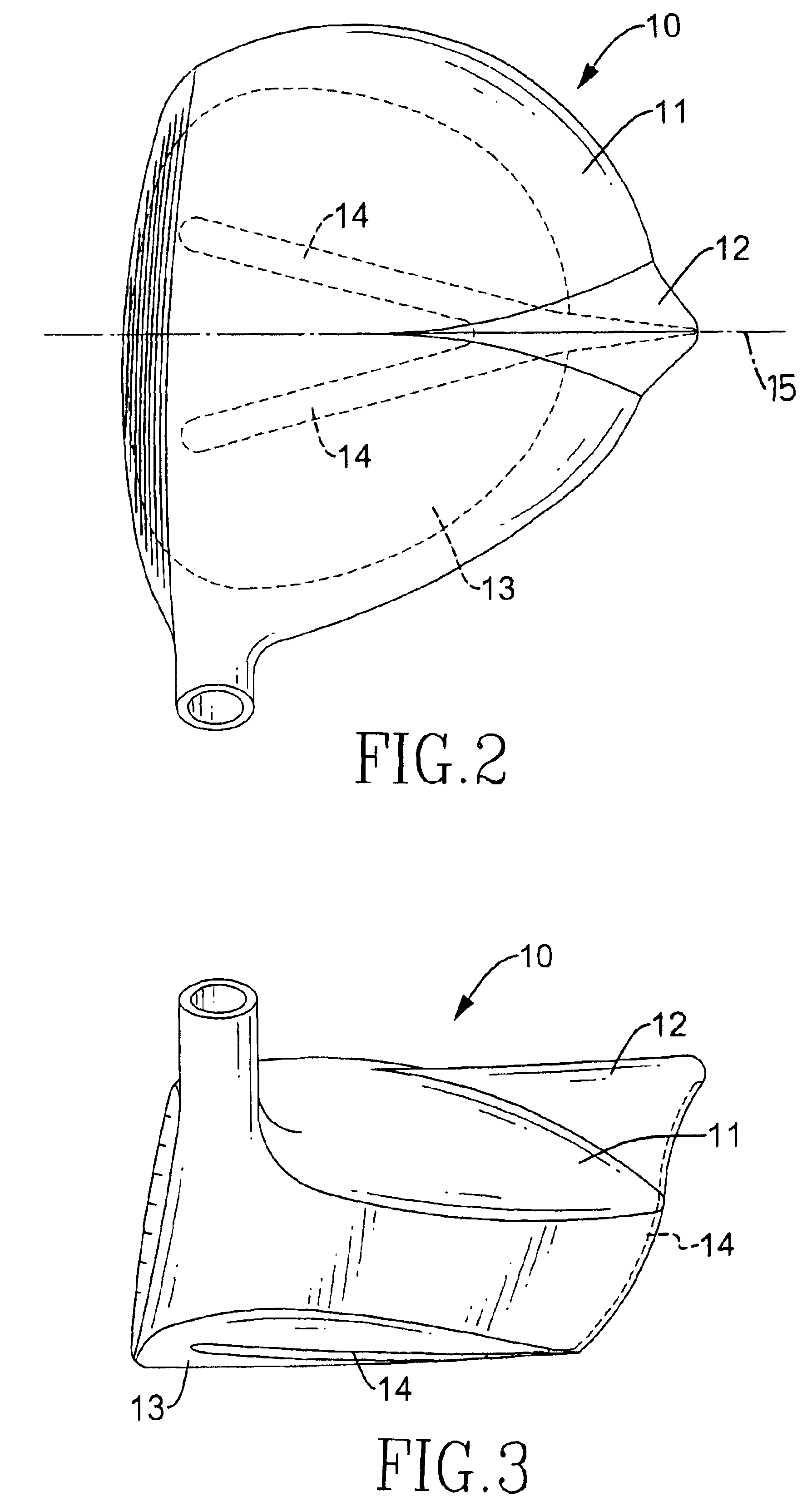
Wood type golf club head
A wood type golf club head has a hollow body, an air fin and air guides. The hollow body has a front, a rear, a crown and a sole. The crown has a top convex surface with a symmetric central line. The air fin is formed perpendicularly from the convex top surface of the crown from the front to the rear of the hollow body along the symmetric central line of the convex top surface. The air guides are defined on the sole with a forked configuration and are extended to the air fin. The air fin and the air guides will reduce external airflow effects during the golf club head moving. Consequently, the motion and direction of the motion of the golf club head will be stable such that a golfer will swing successfully to hit a golf ball.
Owner:O TA PRECISION IND
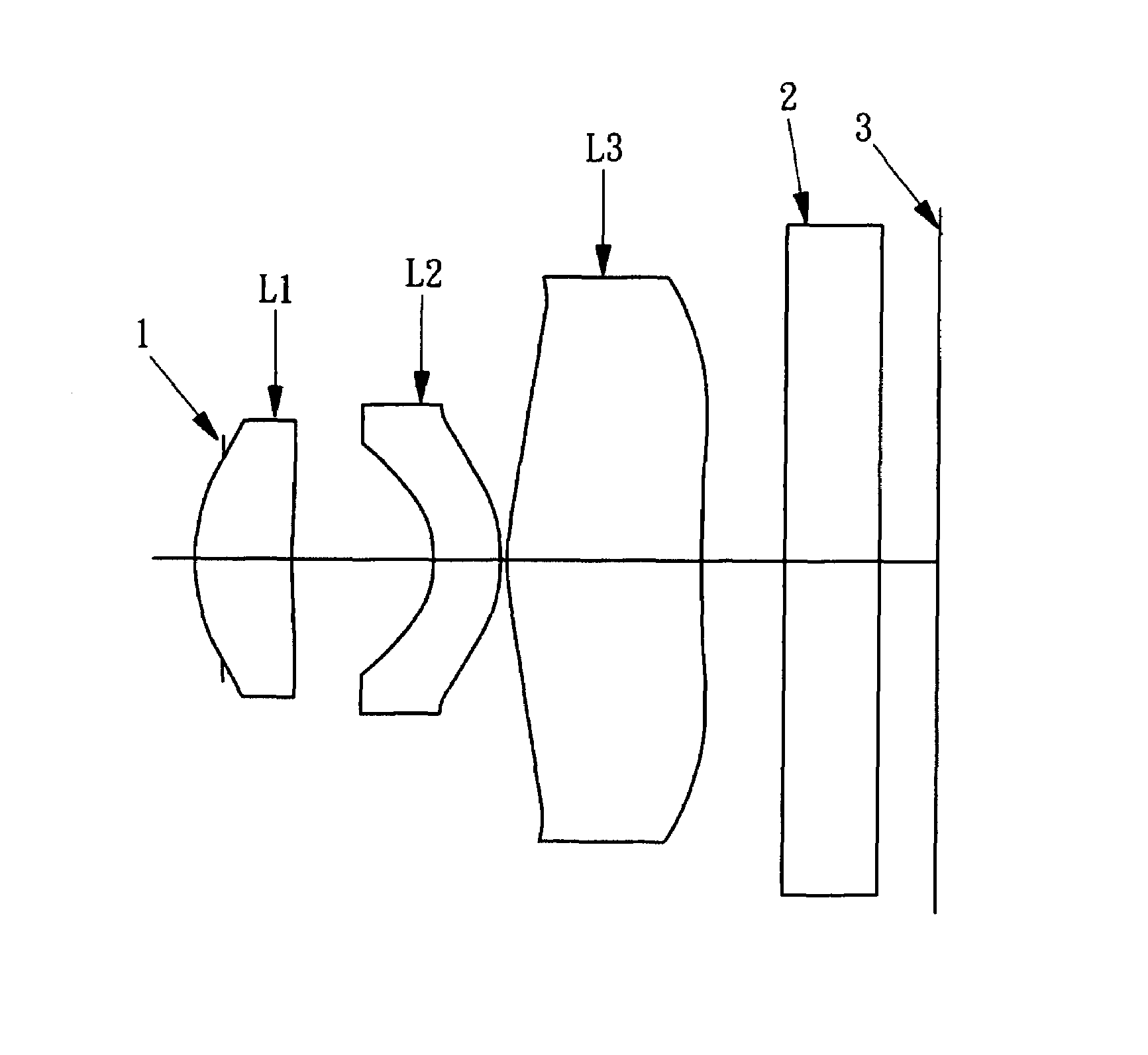
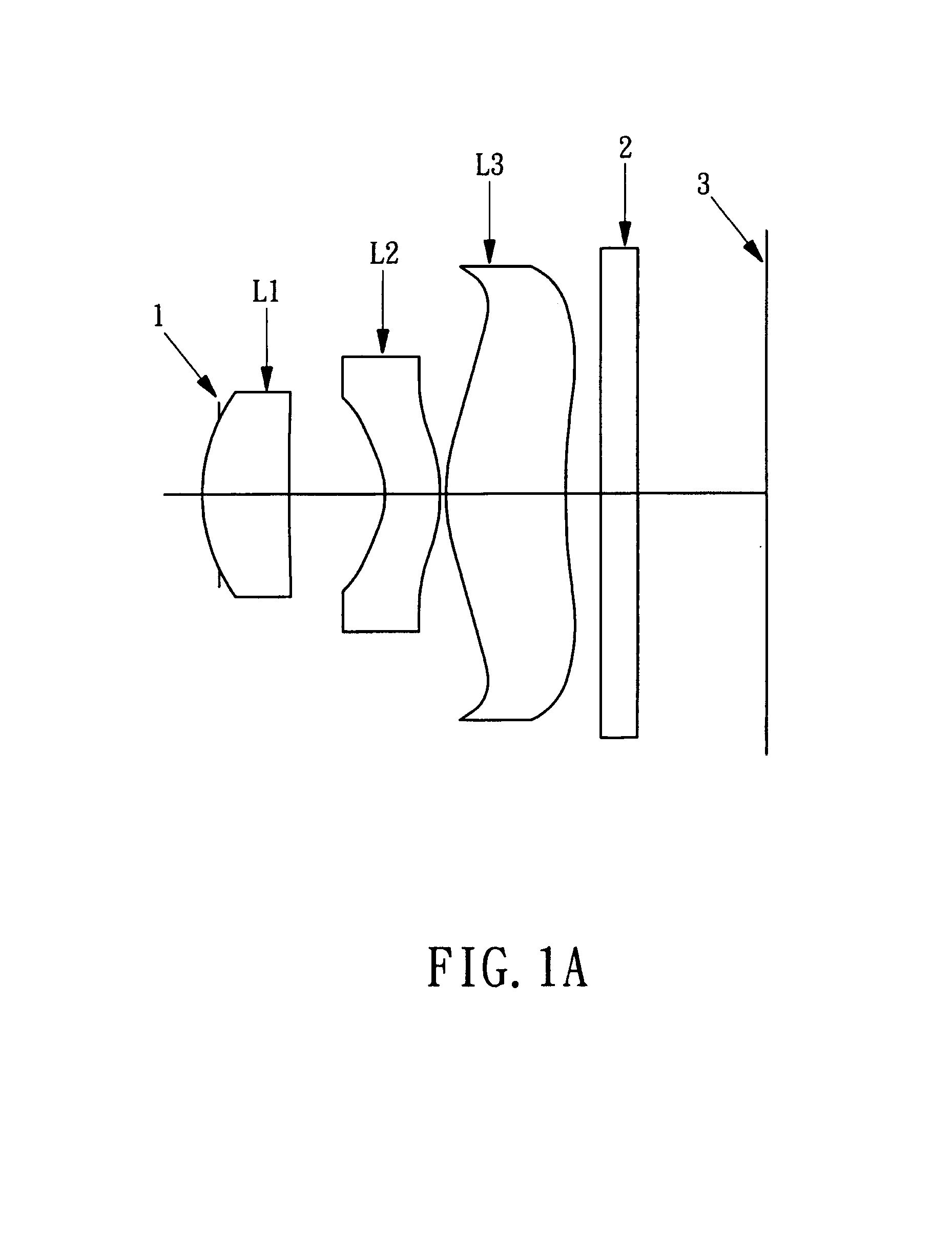
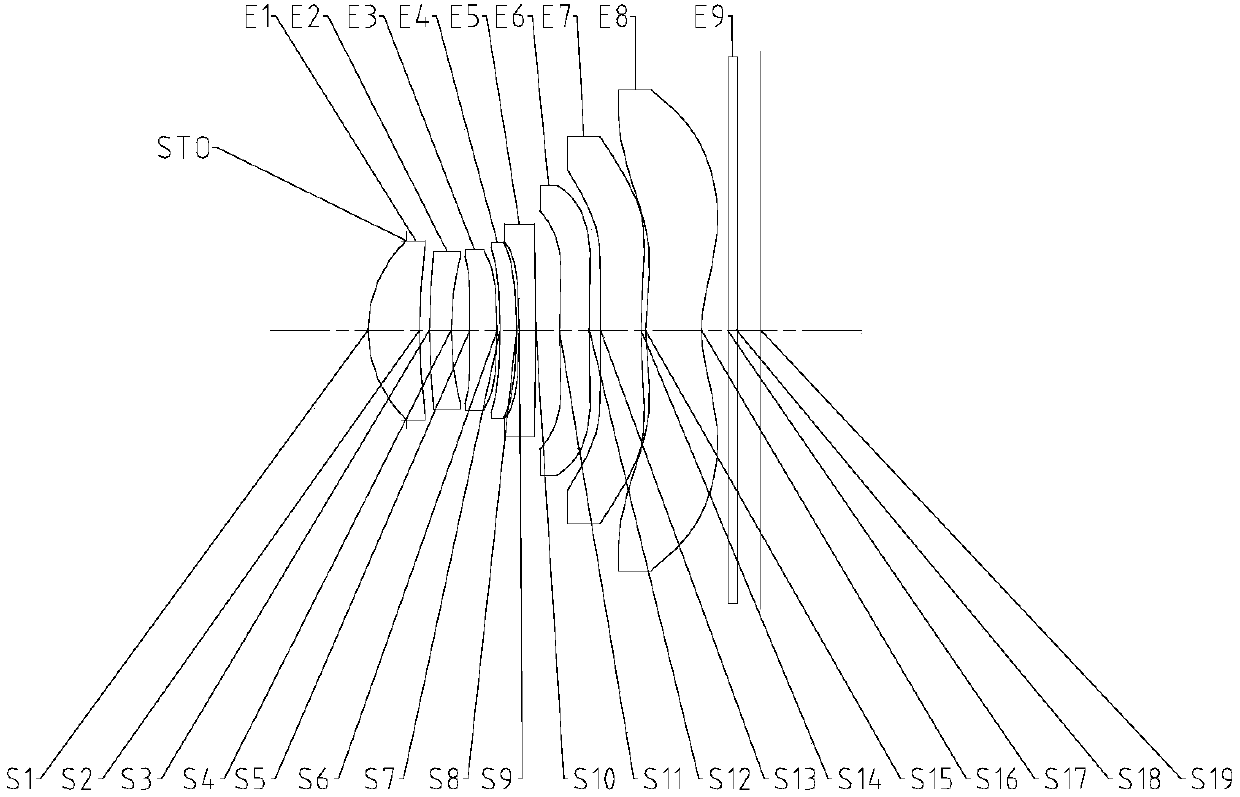
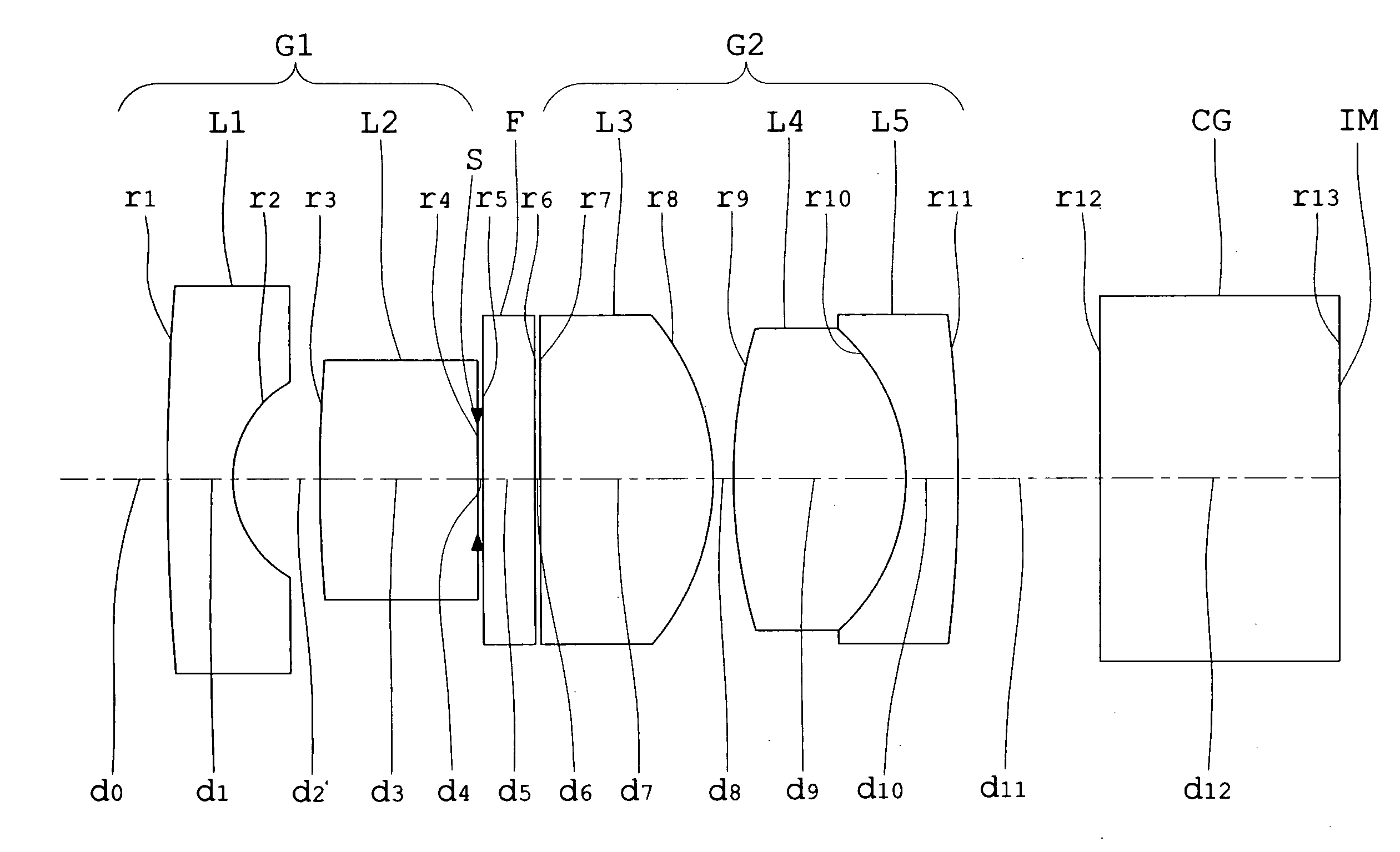
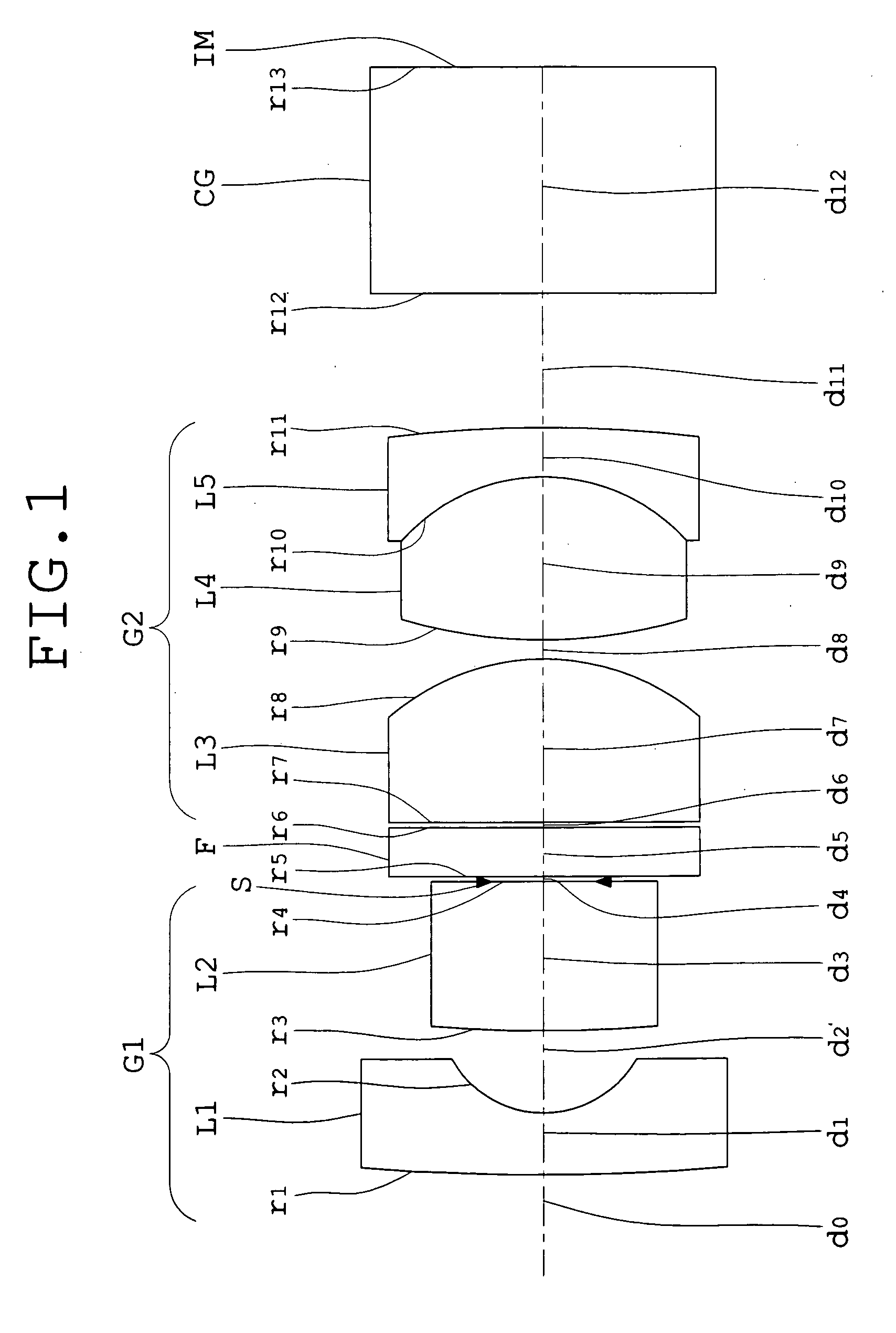
Lens assembly for an image sensor
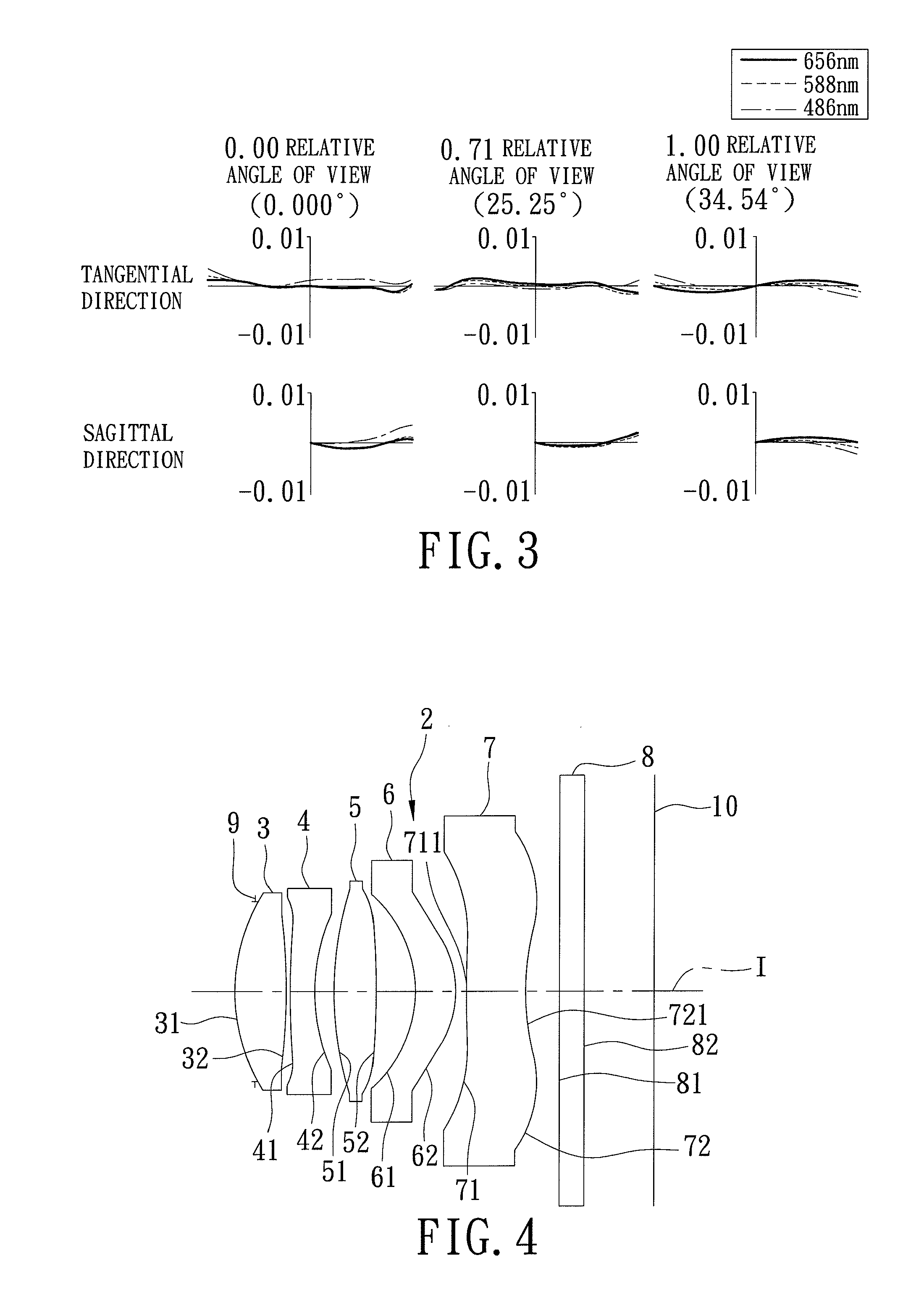
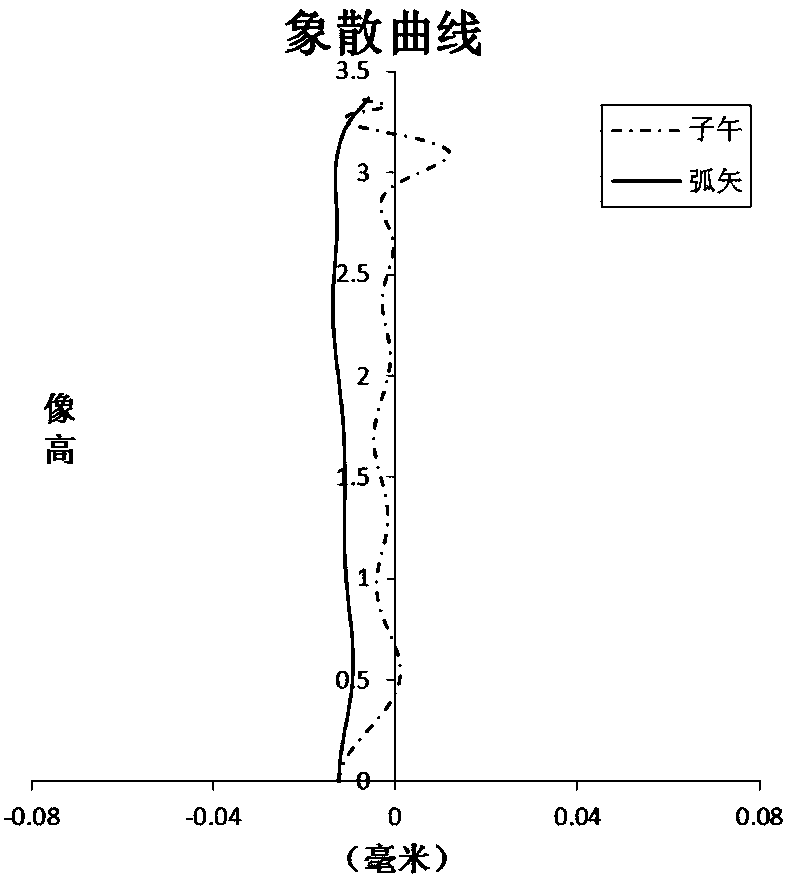
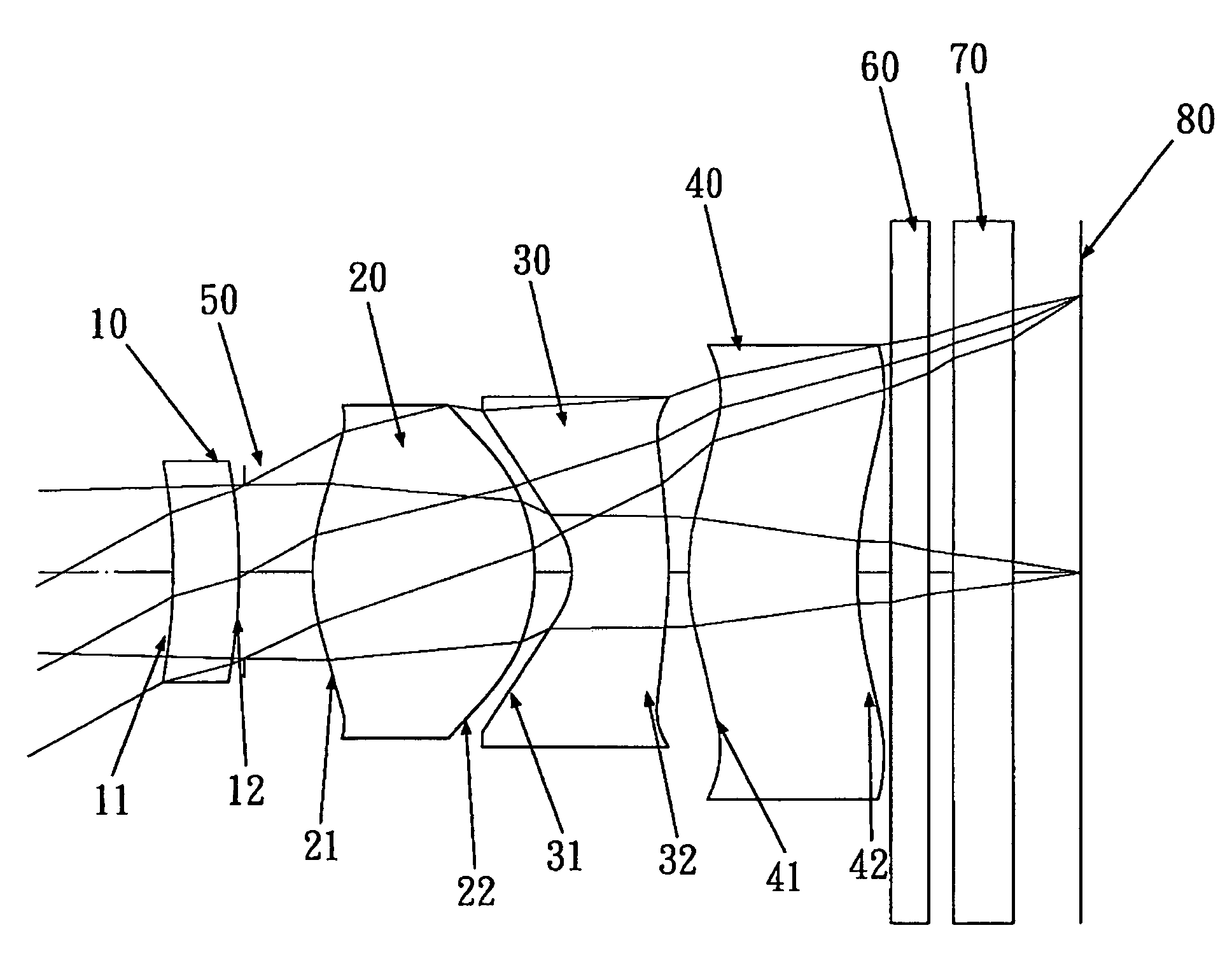
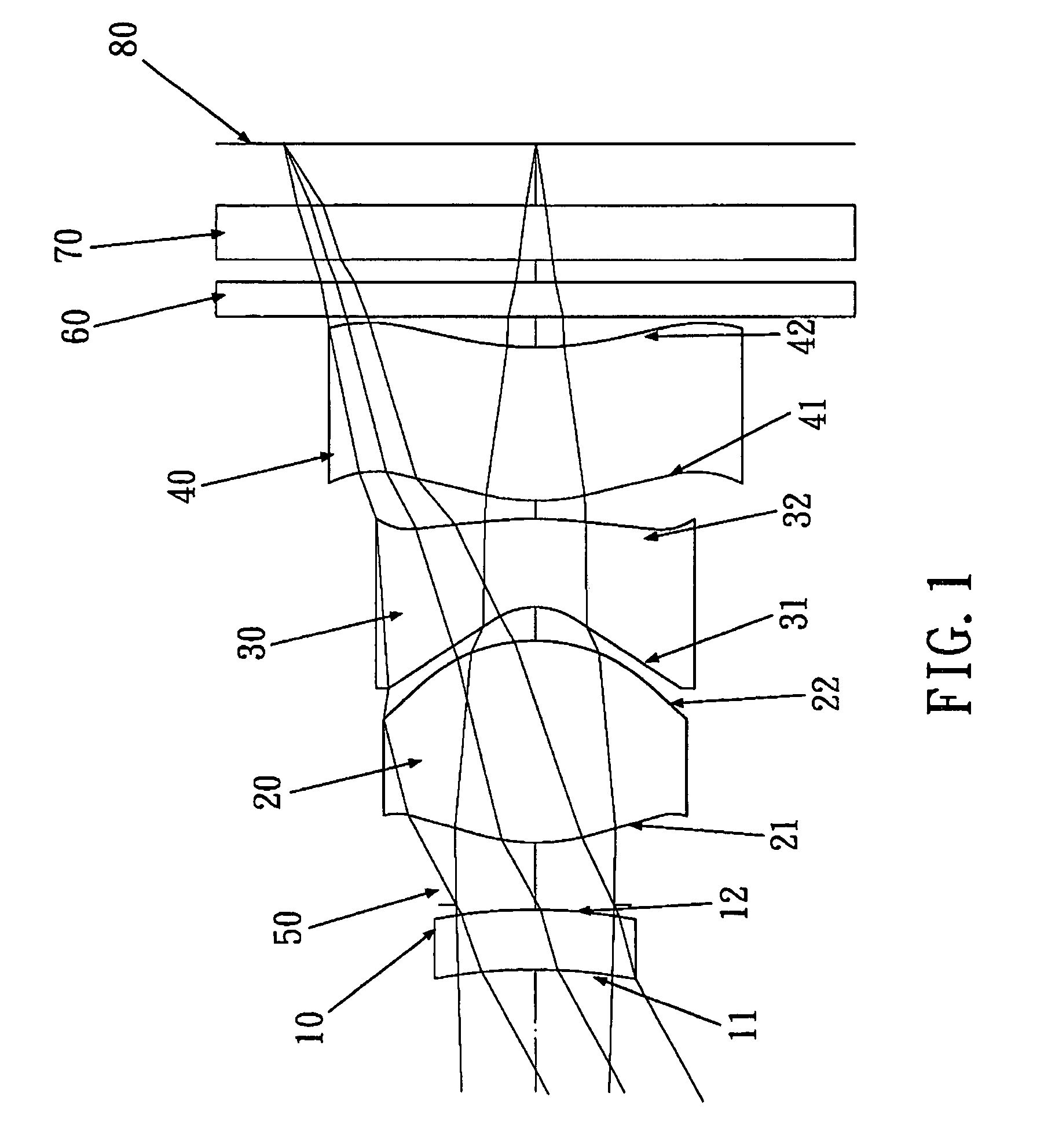
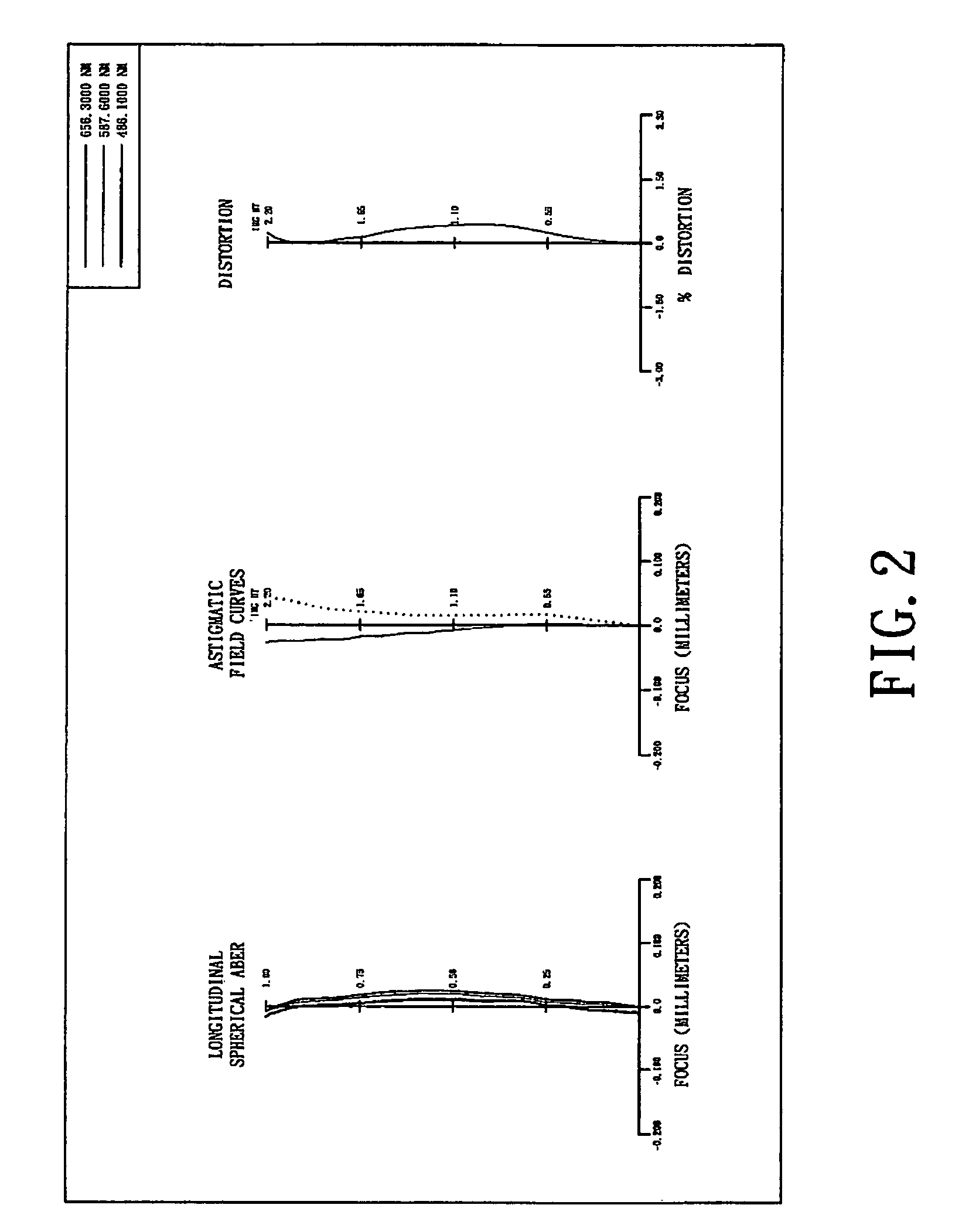
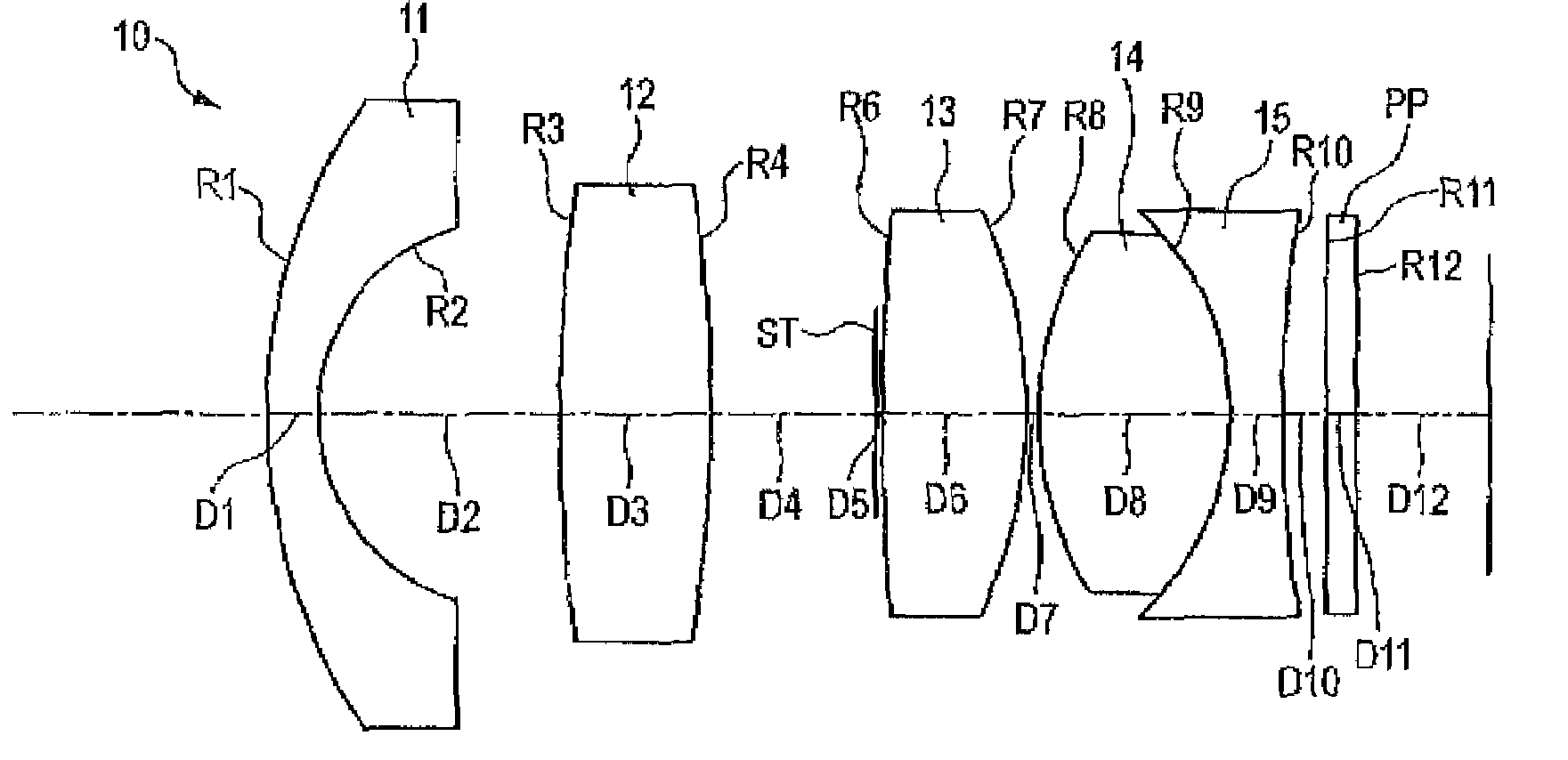
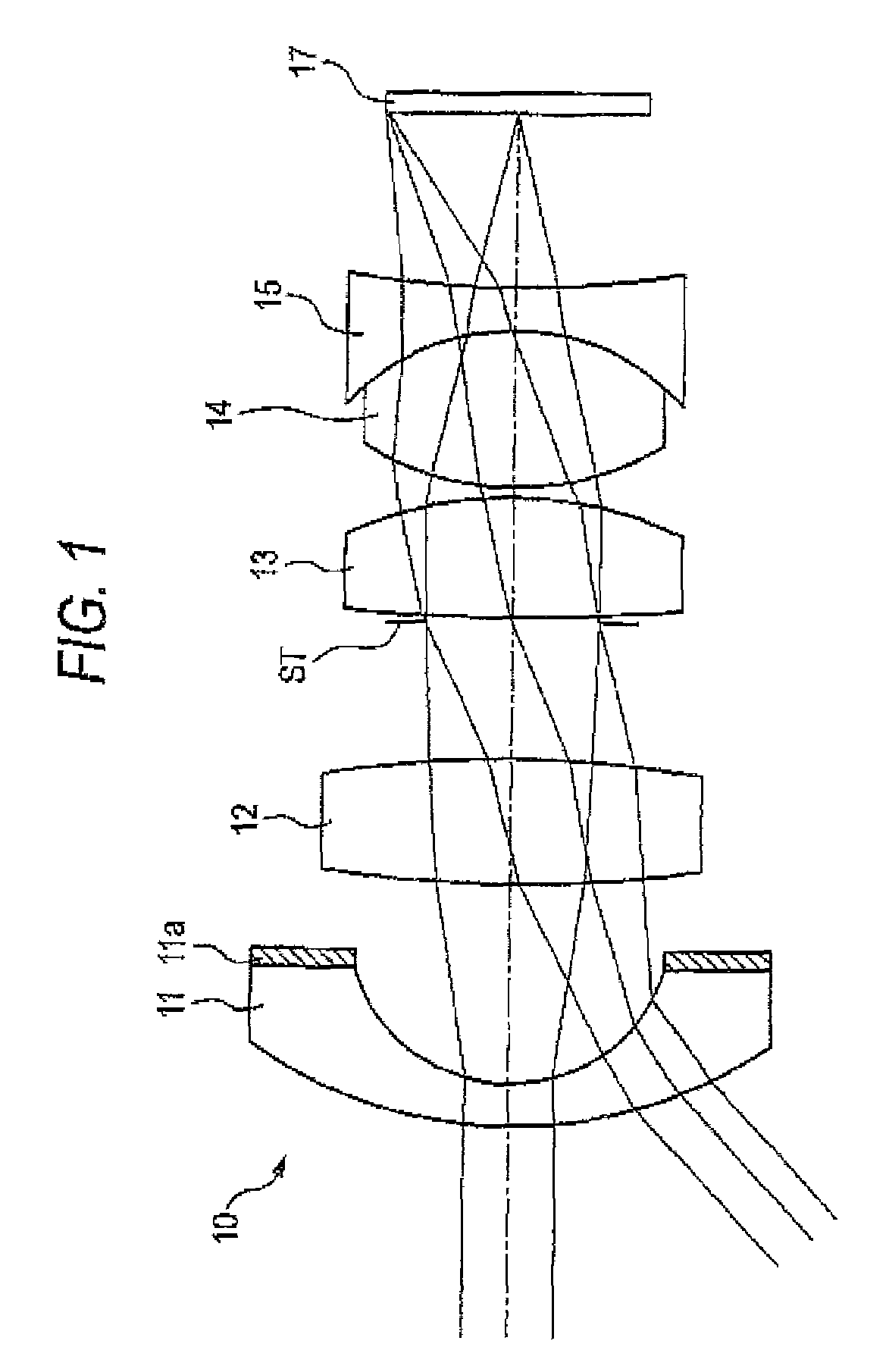
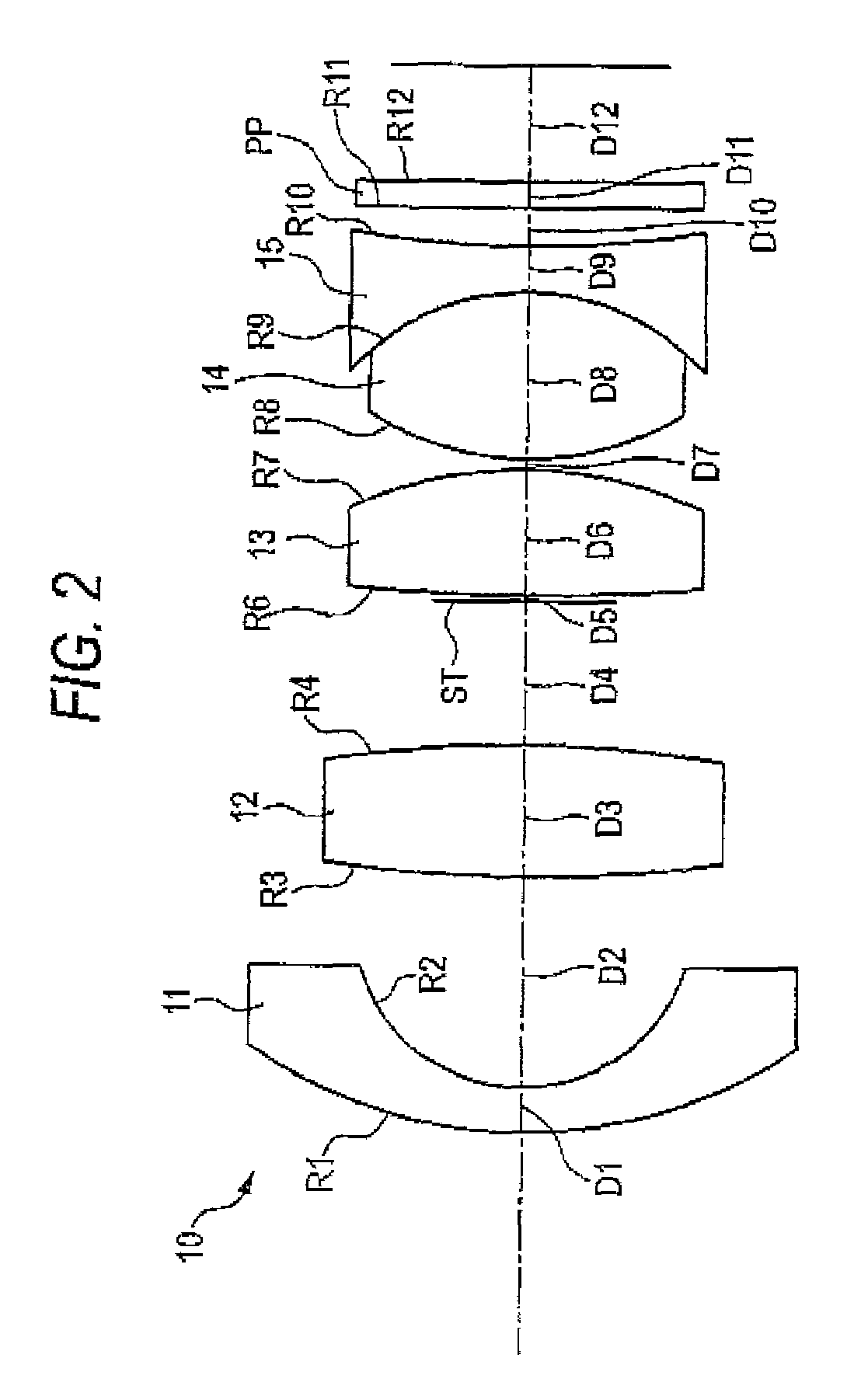
ActiveUS7145736B2Reduce sensitivityImproved capability of restraining powerLensCamera lensConvex side
A lens assembly for an image sensor comprises an aperture, a first lens, a second lens and a third lens, which are arranged sequentially from the object side. The first lens is a planoconvex lens or a positive meniscus lens whose convex surface faces the object side; the second lens is a negative meniscus lens with a convex surface facing the image side and at least has an aspherical surface; and the third lens is a positive meniscus lens with a convex surface facing the object side and, at least, has an aspherical surface. The sensitivity of decentration and the aberration-correction effect of the whole lens assembly in accordance with the present invention can be effectively improved.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Imaging lens
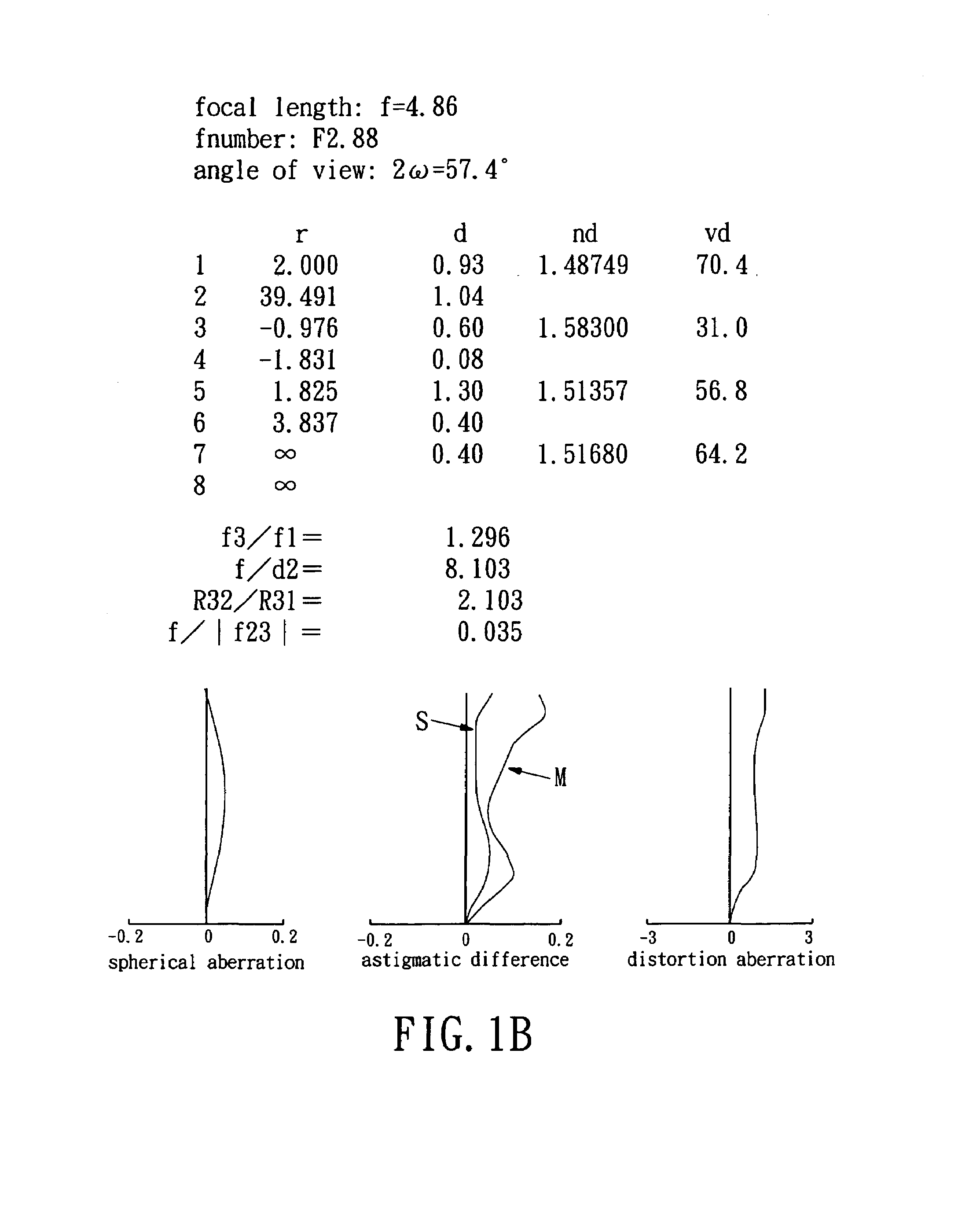
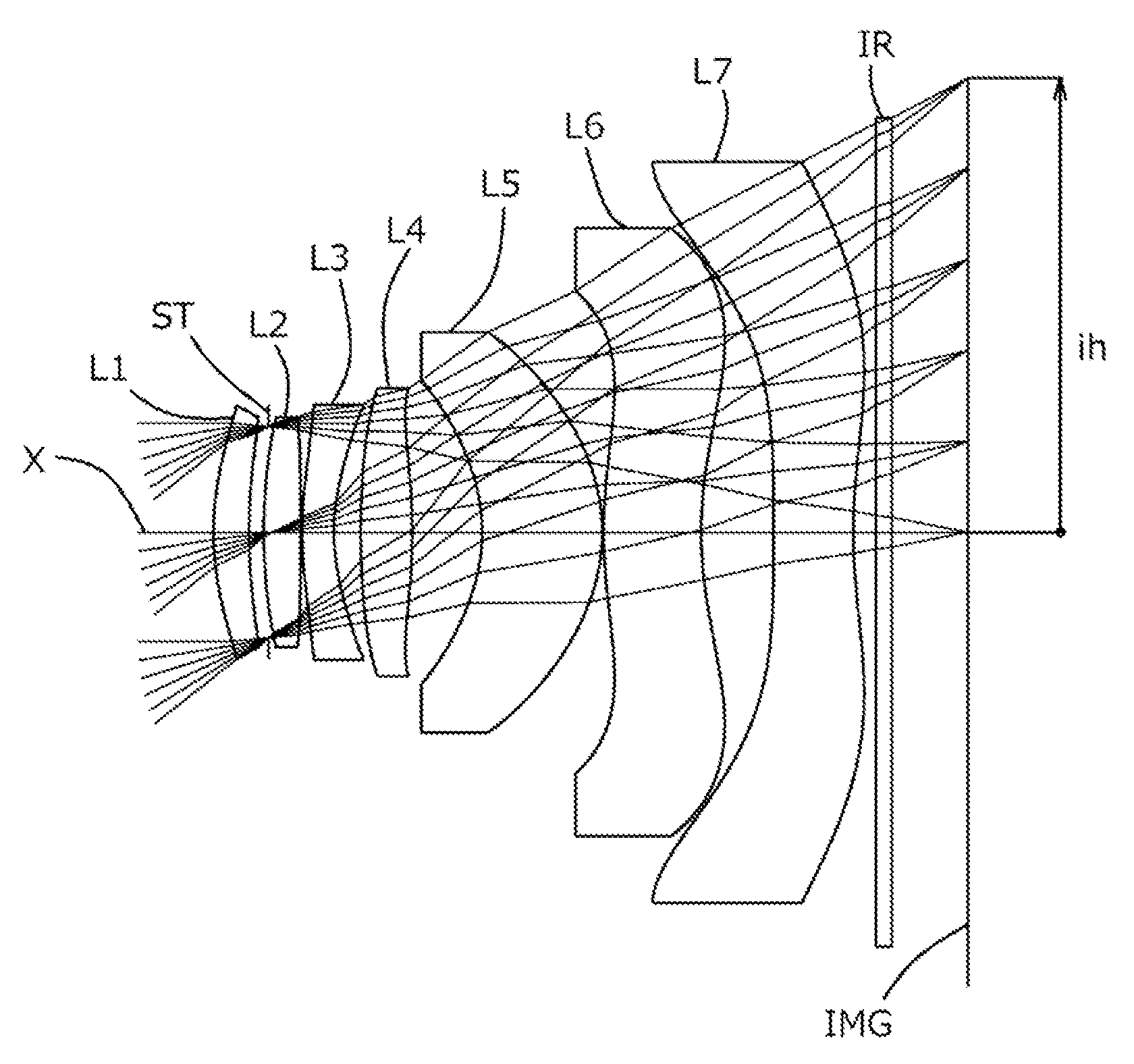
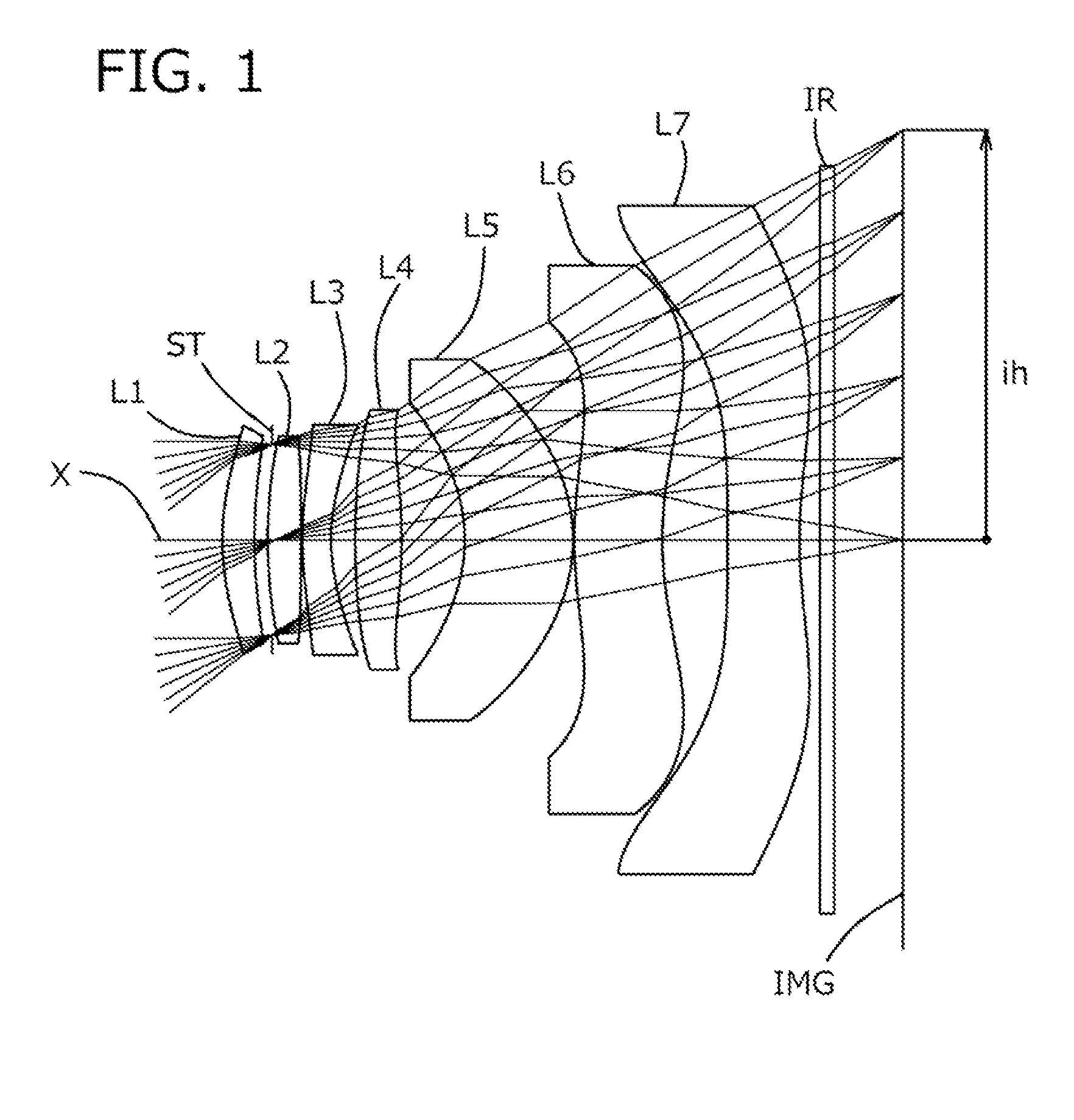
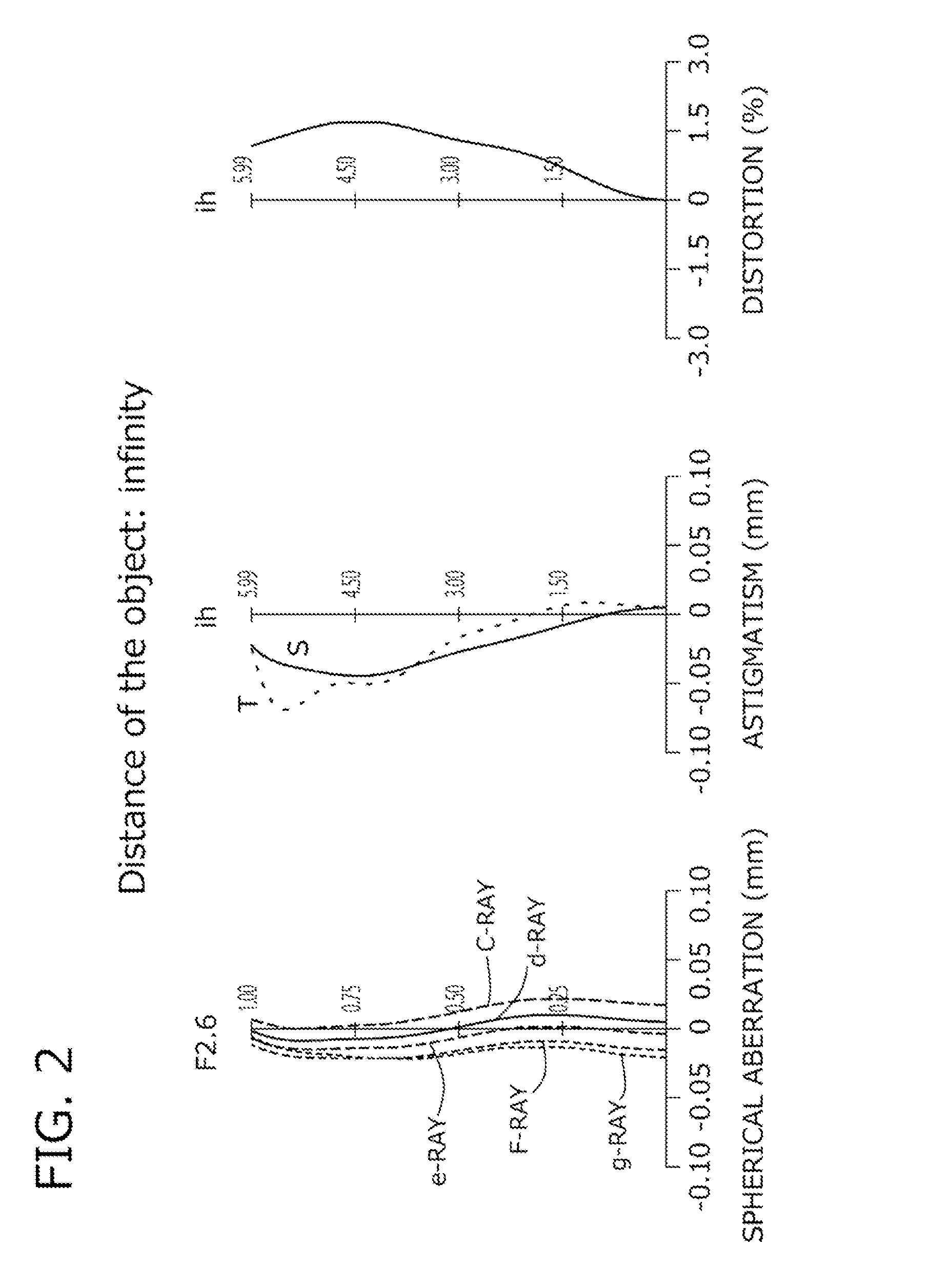
ActiveUS20150070783A1Good optical performanceVarious aberrationImage enhancementStatic indicating devicesWide fieldAspheric lens
An imaging lens which uses a larger number of constituent lenses for higher performance and features compactness and a wide field of view. The imaging lens is composed of seven lenses to form an image of an object on a solid-state image sensor. The constituent lenses are arranged in the following order from an object side to an image side: a first lens with positive refractive power; a second lens with positive or negative refractive power; a third lens with negative refractive power; a fourth lens with positive or negative refractive power as a double-sided aspheric lens; a meniscus fifth lens having a convex surface on the image side; a sixth lens with positive or negative refractive power as a double-sided aspheric lens; and a seventh lens with negative refractive power, in which an air gap is provided between lenses.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Aerodynamic-hybrid vertical-axis wind turbine
InactiveUS20060275105A1Eliminating salient back pressureEffectively and efficiently harnessingWind motor controlWind motor supports/mountsConvex sideVertical axis wind turbine
An aerodynamic-hybrid, vertical-axis wind turbine which includes a rotor airfoil and stator blade combination which maximizes energy production by increasing wind velocity and pressure while eliminating back pressure and improving the laminar flow of wind both around and through the device. The rotor airfoils have a horizontal cross-section with a crescent shape including a convex leading side and a concave trailing side with a thicker middle section that tapers to narrower sections at ends. The stator blades have a horizontal cross-section with a planar side and a convex side. Rotor airfoil and stator blade combinations are secured between upper and lower annular sails.
Owner:NOVASTRON
Imaging Lens, Imaging Device and Portable Terminal
ActiveUS20110134305A1Improve image qualityExcellently correctedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensLens speed
Provided is a small-sized five-element image pickup lens which ensures a sufficient lens speed of about F2 and exhibits various aberrations being excellently corrected. The image pickup lens is composed of, in order from the object side, a first lens with a positive refractive power, including a convex surface facing the object side; a second lens with a negative refractive power, including a concave surface facing the image side; a third lens with a positive or negative refractive power; a fourth lens with a positive refractive power, including a convex surface facing the image side; and a fifth lens with a negative refractive power, including a concave surface facing the image side. The image-side surface of the fifth lens has an aspheric shape, and includes an inflection point at a position excluding an intersection point with the optical axis.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Aerodynamic-hybrid vertical-axis wind turbine
InactiveUS7329965B2Eliminate back pressureEffective forceWind motor controlWind motor supports/mountsConvex sideVertical axis wind turbine
An aerodynamic-hybrid, vertical-axis wind turbine which includes a rotor airfoil and stator blade combination which maximizes energy production by increasing wind velocity and pressure while eliminating back pressure and improving the laminar flow of wind both around and through the device. The rotor airfoils have a horizontal cross-section with a crescent shape including a convex leading side and a concave trailing side with a thicker middle section that tapers to narrower sections at ends. The stator blades have a horizontal cross-section with a planar side and a convex side. Rotor airfoil and stator blade combinations are secured between upper and lower annular sails.
Owner:NOVASTRON
Fisheye lens and imaging device using it
A fisheye lens with a field angle of at least one hundred sixty degrees is formed of two lens groups, arranged in order from the object side, as follows: a first lens group having negative refractive power and a second lens group having positive refractive power. The first lens group includes, arranged in order from the object side, two lens elements, each having negative refractive power and a meniscus shape with the convex surface on the object side, a lens element having negative refractive power with a concave surface on the image side, and two lens elements of opposite refractive powers. The second lens group includes, arranged in order from the object side, two lens elements of opposite refractive powers, a stop, and two lens elements of opposite refractive powers. The fisheye lens preferably satisfies specified conditions related to spacings of lens surfaces and to distortion characteristics of the fisheye lens.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Imaging lens
A low-cost imaging lens which corrects aberrations properly with a small F-value, ensures high performance with a larger number of constituent lenses and has a more low-profile design than before. The constituent lenses are arranged in the following order from an object side to an image side: a positive (refractive power) first lens having a convex object-side surface near an optical axis; a positive second lens having convex object-side and image-side surfaces near the optical axis; a negative third lens having a concave image-side surface near the optical axis; a fourth lens having at least one aspheric surface; a meniscus fifth lens having a concave object-side surface near the optical axis; a sixth lens as a double-sided aspheric lens; and a negative seventh lens as a double-sided aspheric lens having a concave image-side surface near the optical axis. These constituent lenses are not joined to each other.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Optical cables with flexible strength sections
A fiber optic cable (40) having at least one optical component (1,2,3) therein, and a cable jacket (8) surrounding the optical component. Strength sections (6,7) are defined between the optical-component and the cable jacket, the strength sections comprising generally crescent-like cross sections. The generally crescent-like cross sections have respective generally concave and generally convex faces (9,10). The generally concave face (9) has a general center that is preferably aligned with the longitudinal axis of the cable, and the generally convex face (10) has a general center that is preferably offset from a longitudinal.axis of the fiber optic cable. The convex faces subtend respective angles (prop) of about 45° to about 160°. The cable jacket (8) defining contact interfaces (11,12) with the optical component, the contact interfaces being respectively disposed between the strength sections (6,7). A fiber optic cable having relatively large, force-absorbing transverse dimensions is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING CABLE SYST LLC
Imaging lens
An imaging lens includes plastic-made first, second, third, fourth, and fifth lens elements arranged in the given order from an object side to an imaging side, each having object-side and imaging-side surfaces facing toward the object and imaging sides, respectively. The first lens element has a positive focusing power, and the object-side surface thereof is a convex surface. The second lens element has a negative focusing power, and the imaging-side surface thereof is a concave surface. The third lens element has a positive focusing power, and each of the imaging-side and object-side surfaces thereof is a convex surface. The fourth lens element is a meniscus lens, and the imaging-side surface thereof is a convex surface. The imaging-side surface of the fifth lens element has a concave area in a vicinity of an optical axis of the fifth lens element.
Owner:GENIUS ELECTRONICS OPTICAL CO LTD
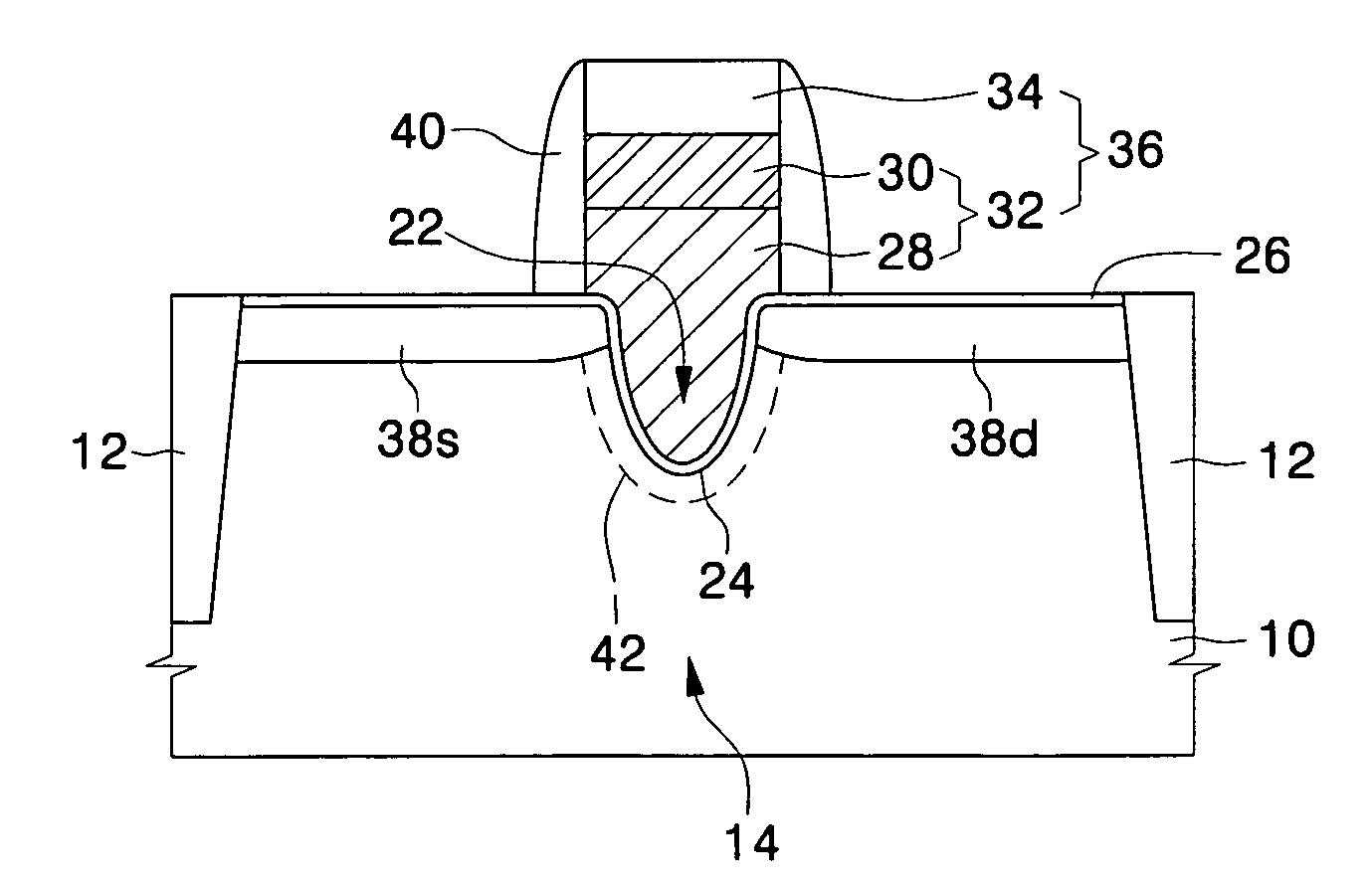
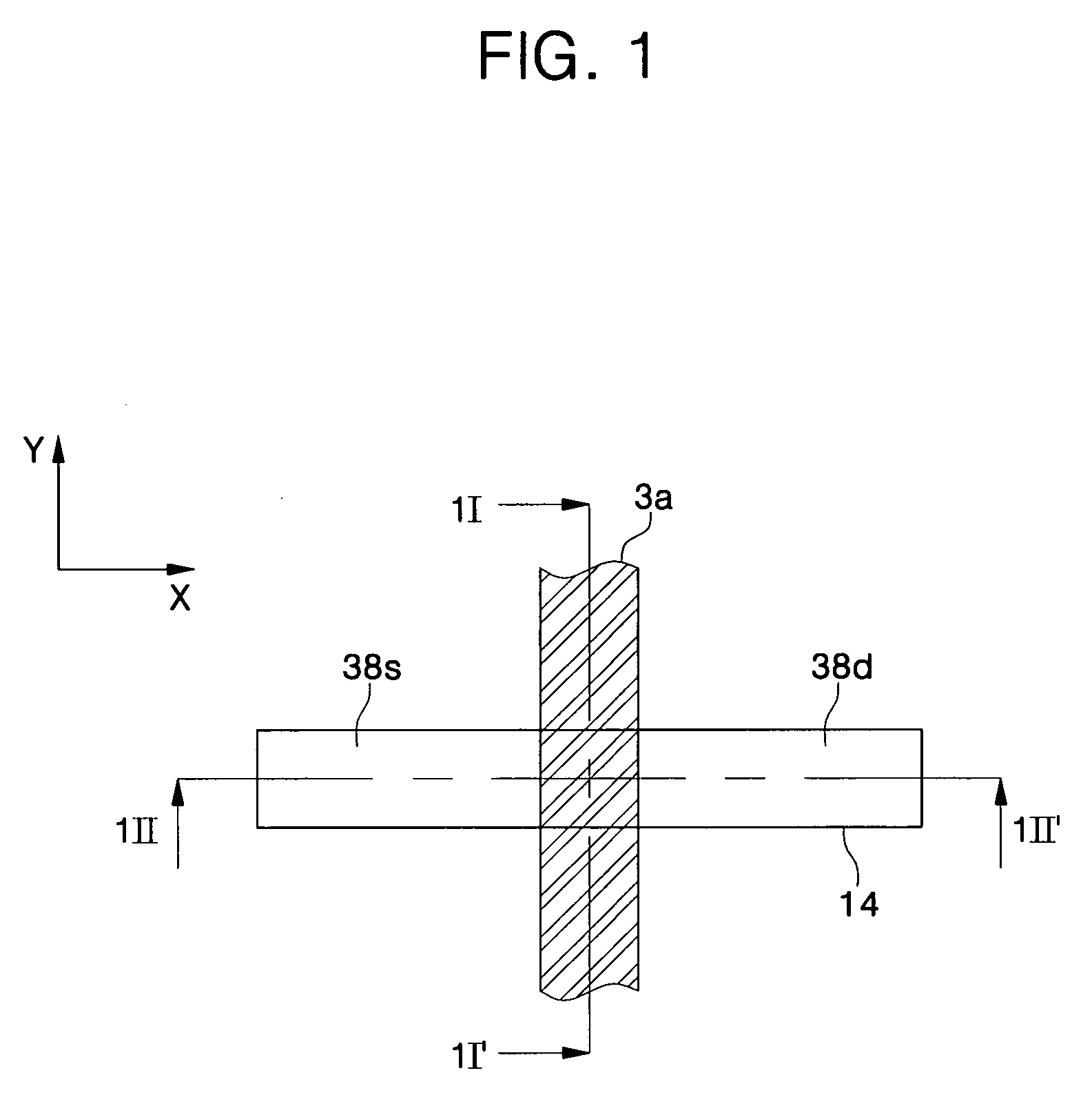
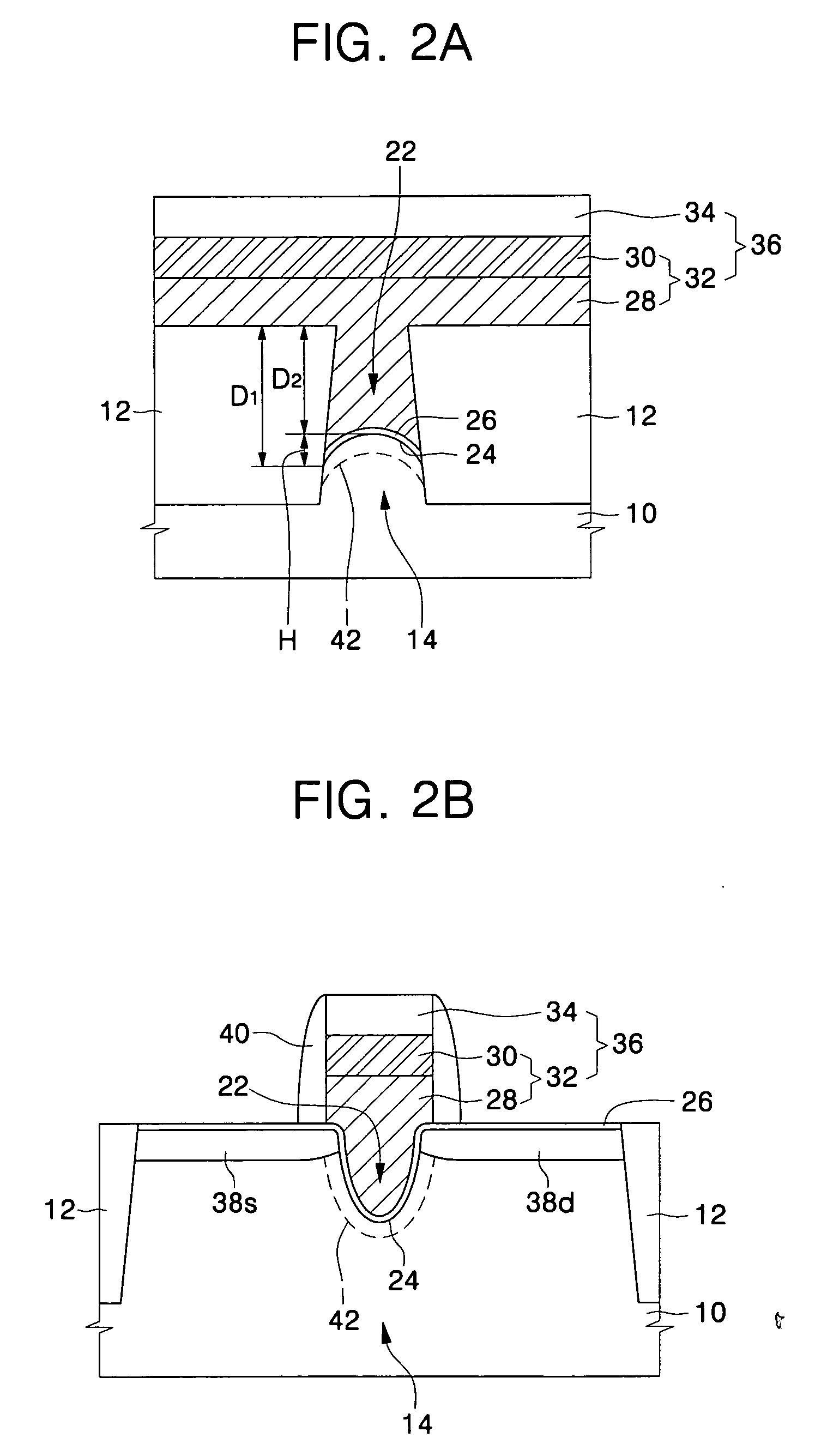
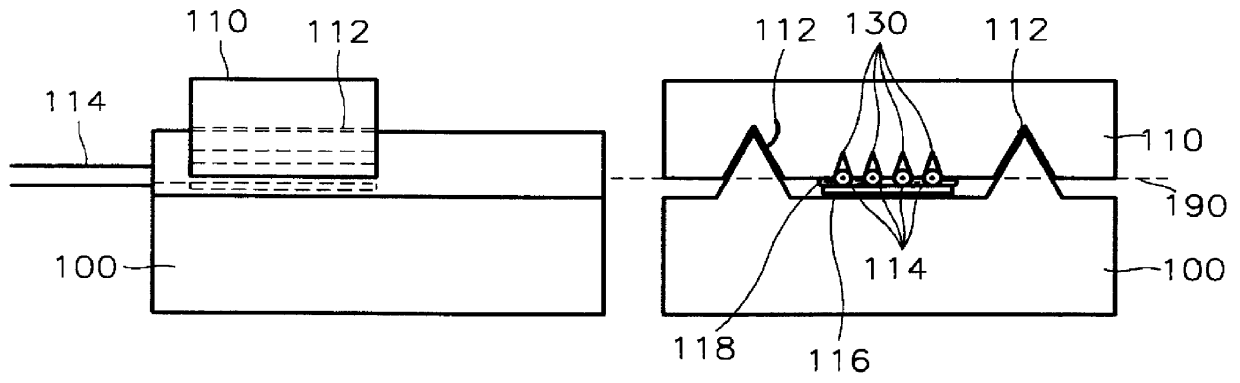
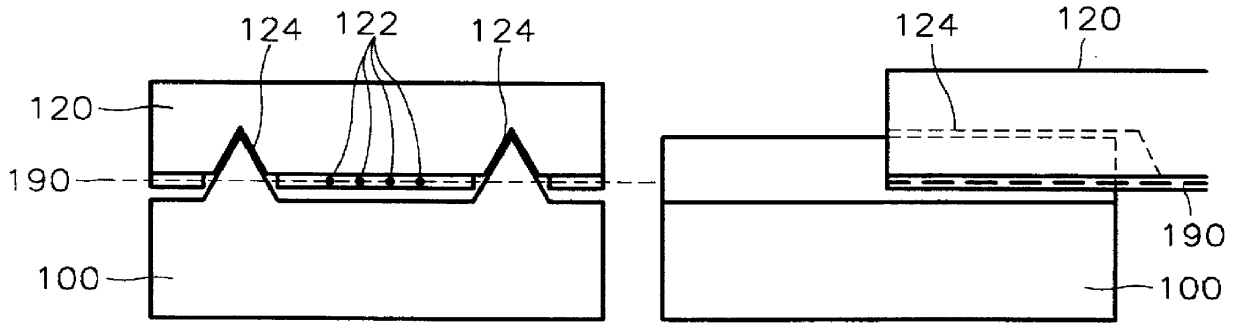
Metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistors having a recessed gate electrode and methods of fabricating the same
A metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) includes an isolation layer disposed in a semiconductor substrate to define an active region. A source region and a drain region are disposed on both sides of the active region such that a first direction is defined from the source region to the drain region. A channel recess is disposed in the active region between the source and drain regions. The channel recess has a convex surface when viewed from a cross-sectional view taken along a second direction orthogonal to the first direction. A gate electrode fills the channel recess and crosses the active region in the second direction. A gate insulating layer is interposed between the gate electrode and the active region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
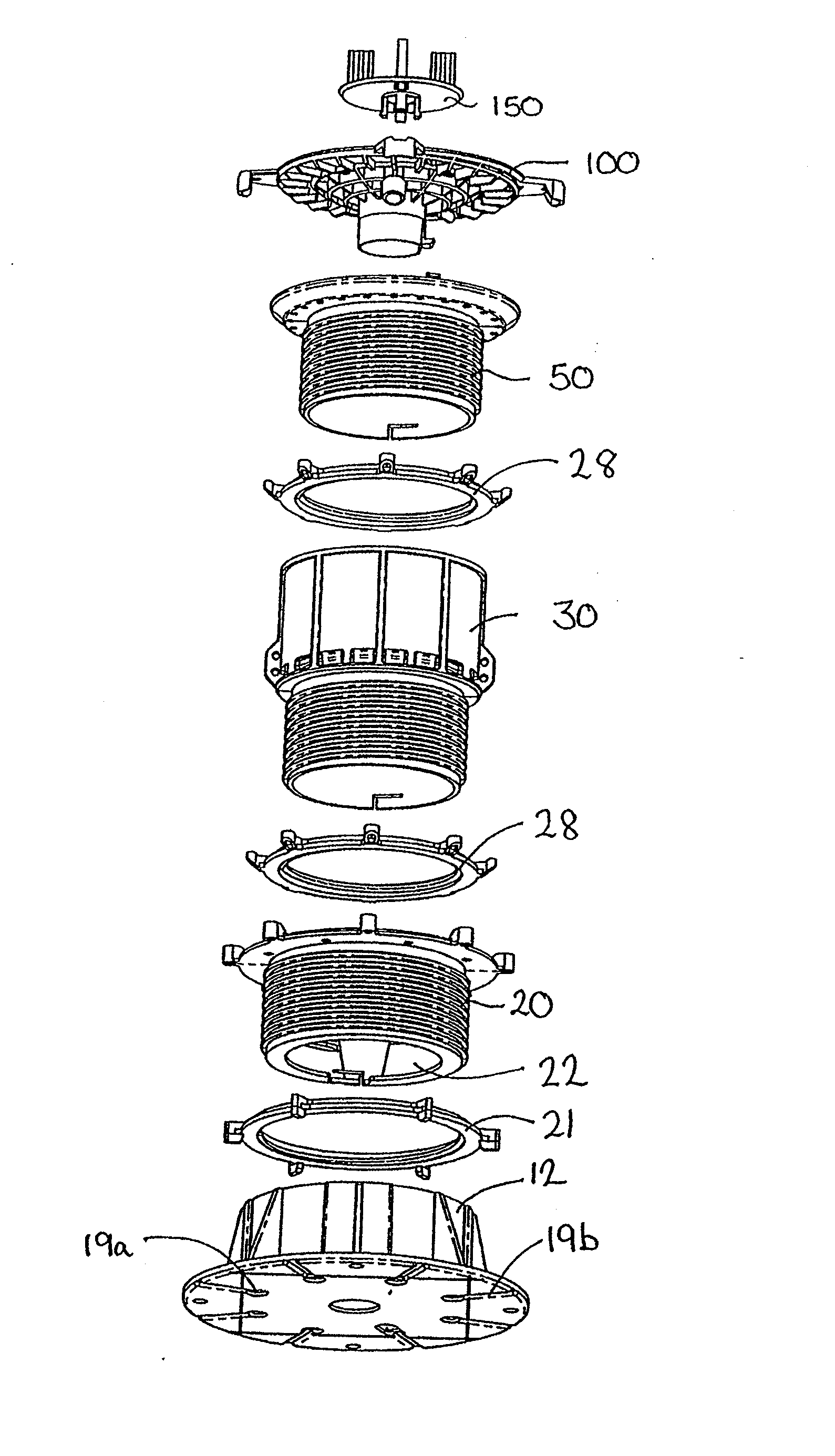
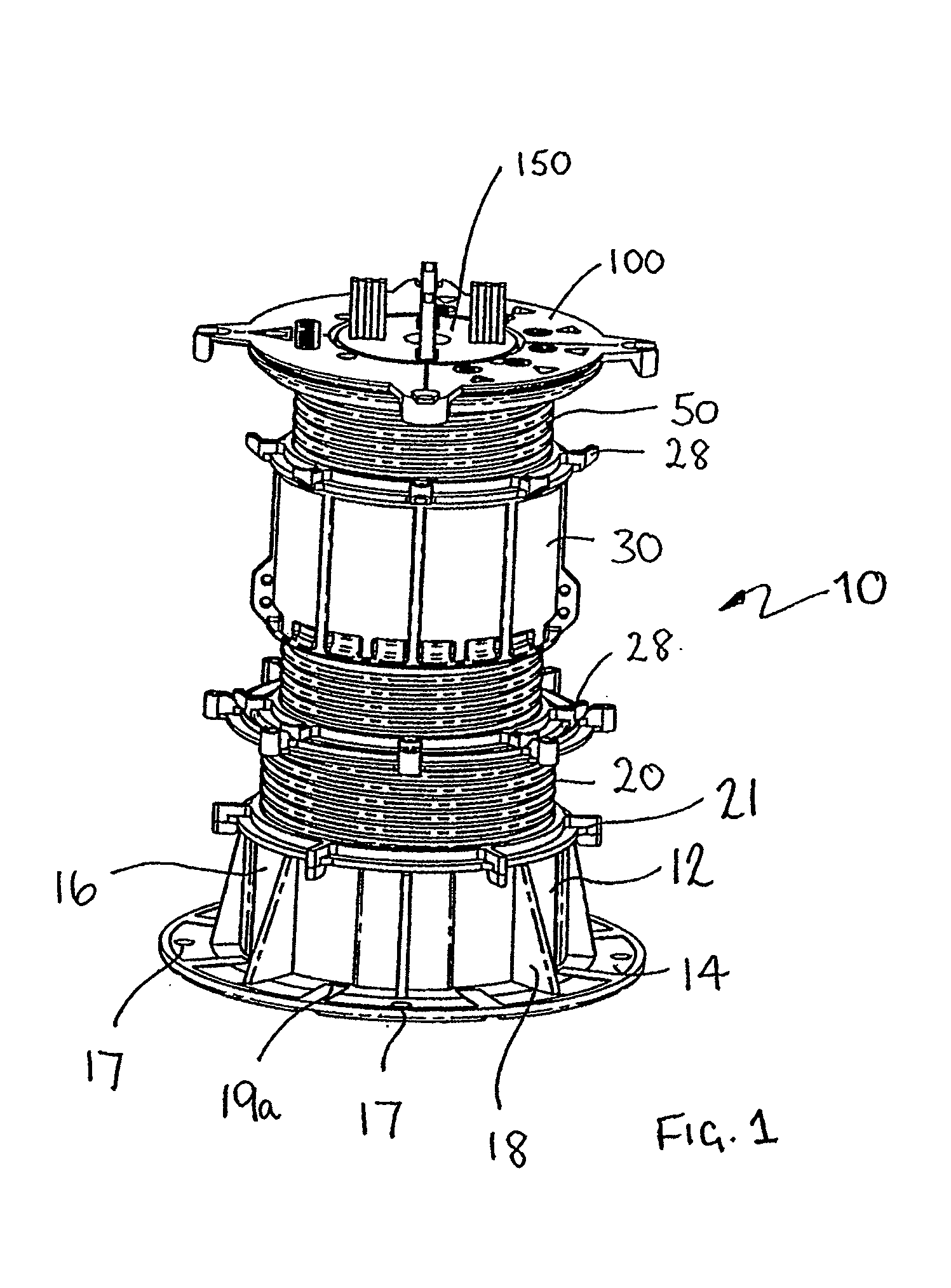
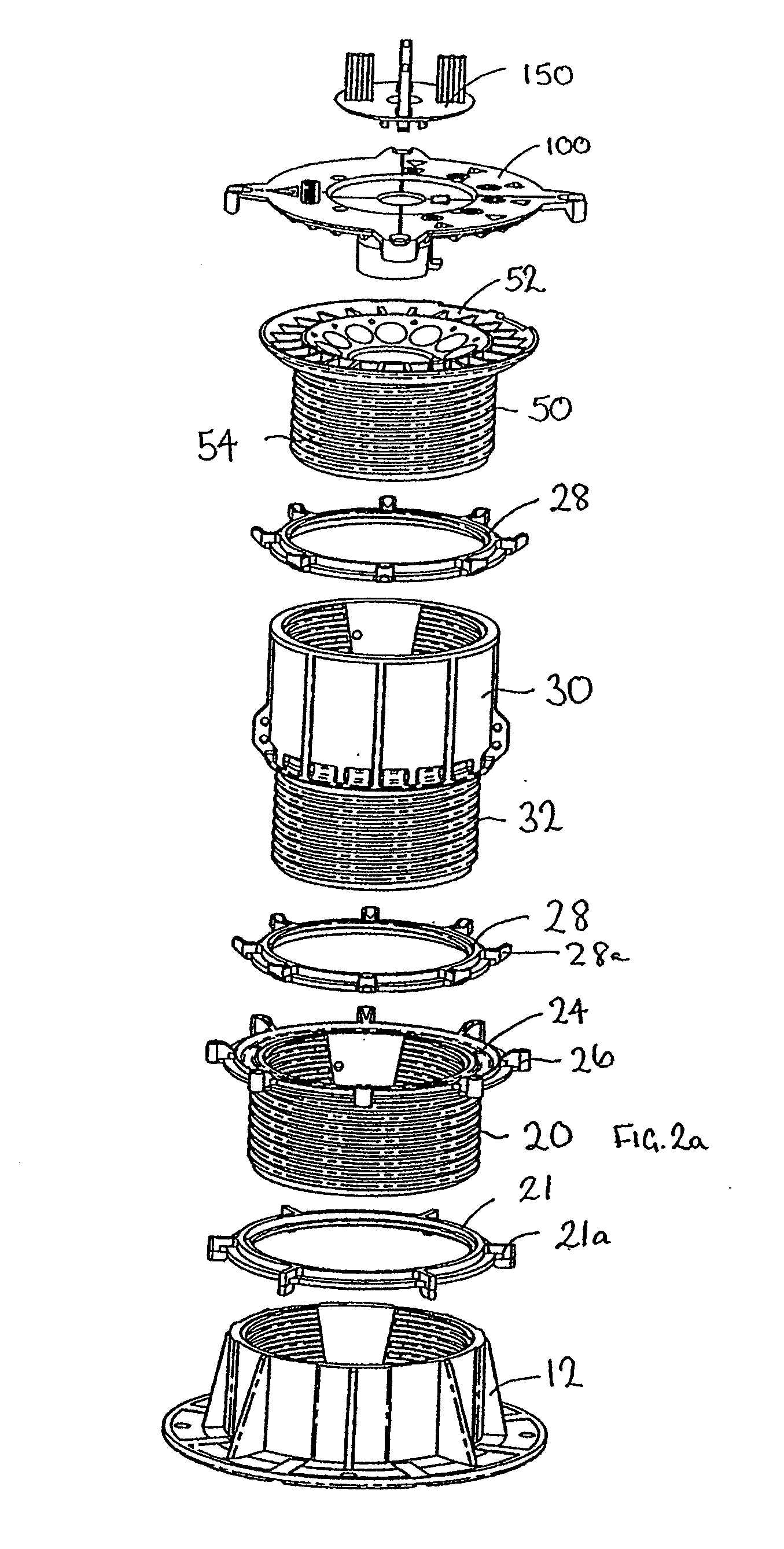
Slope compensator for pedestal for elevated floors
InactiveUS20080222973A1Reduce prevent relative movementImprove stabilityBuilding roofsCeilingsConvex sideEngineering
A slope adjustable head for an adjustable pedestal (10) for supporting beams, panel members, typically pavers, in accurate edge aligned relation, in a level plane is disclosed. The pedestal (10) includes a base block (12) and a series of inter-engaging threaded annular elements (20, 30) which can be rotated relative to each other to adjust the height of the top of the pedestal in a screw jack fashion. A slope compensator is located at the top of the pedestal and comprises a slope compensation plate (100) and a head member (50). The head member (50) defines a concave surface having a defined radius of curvature. The slope compensation plate (100) defines a corresponding convex surface having the same radius of curvature and sits on top of the head member. The pedestal (10) is calibrated to allow adjustment for typically zero to five percent in one percent increments. The top member defines a central aperture (56) and a series of holes (72) arranged in a spiral around the central aperture. The adjustment member defines a depending central cylindrical portion (110) which locates in the central aperture (56) and two diametrically opposed depending pegs (132, 134) spaced either side of the central cylindrical portion which locate in the holes of the top member. Rotation of the slope compensation plate (100) about its centre of curvature causes the angle of the adjustment plate relative to the vertical axis to change thus allowing for compensation for the slope of the surface on which the pedestal is standing.
Owner:LEE IN OK
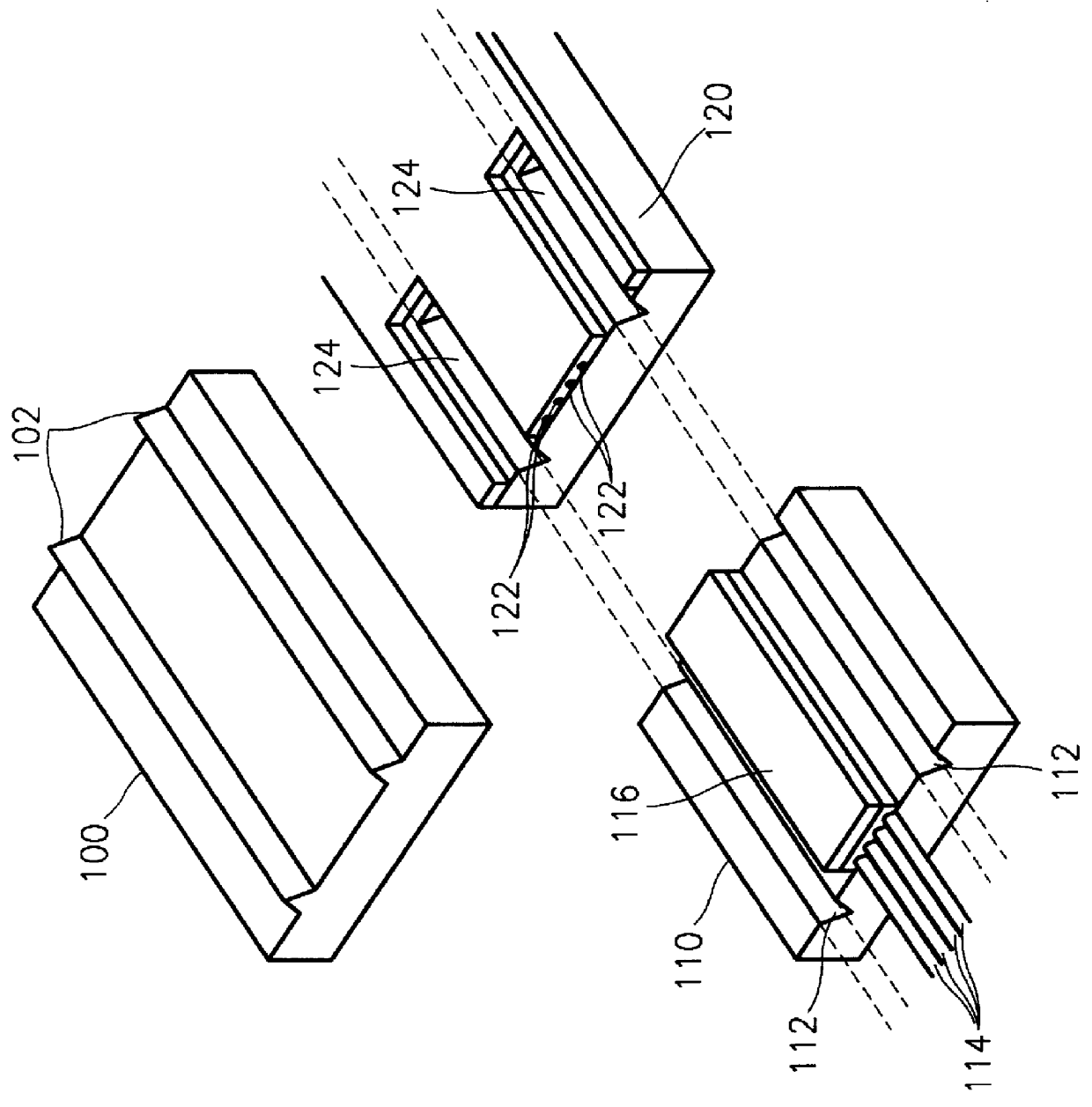
Apparatus and method for combining optical waveguide and optical fiber
An apparatus and a method for combining an optical waveguide and optical fibers are provided. The apparatus includes an apparatus for combining optical fibers with an optical waveguide device, including a guide rail portion for alignment including guide rails for alignment spaced apart from each other by a predetermined distance, on a flat substrate, an optical fiber array portion put on the guide rail portion for alignment when the optical fibers are combined with the optical waveguide device, including an array of grooves for arranging the optical fibers spaced apart from each other by a predetermined distance in an array pattern, and including guide grooves for alignment having a concavo-convex relationship with the guide rail portion for alignment, and an optical waveguide device chip put on the guide rail portion when the optical fibers are combined with the optical waveguide, including the optical waveguide connected to the optical fibers of the optical fiber array portion, and including guide grooves for alignment spaced apart from each other by the same distance as that by which the rails of the guide rail portion are spaced apart from each other and having a concavo-convex relationship with the guide rail portion for alignment, to the outside of an optical waveguide area in which the cores of the optical fibers of the optical fiber array portion respectively coincide with those of the optical waveguide. According to the present invention, a light source and a photodetector (required for active alignment) are not necessary. A complicated alignment process of performing an alignment with respect to an alignment axis having six degrees of freedom with submicron precision is not necessary. Also, it is possible to save time and money when attaching the optical fibers to the optical waveguide device chip.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Super wide angle optical system
There is provided a super wide angle optical system including, arranged about an optical axis: a first lens having a negative refractive power and having a meniscus shape with a convex object-side surface; a second lens having a negative refractive power and having a meniscus shape with a convex object-side surface; a third lens having a positive refractive power and having both convex surfaces; a fourth lens having a positive refractive power; a fifth lens having a negative refractive power; and a sixth lens having a positive refractive power and having both convex surfaces.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Imaging optical system
InactiveUS20160124192A1Correct abaxial aberrationMinimization requirementsLensOptical axisConvex side
An imaging optical system includes a positive first lens element having a convex surface on the object side, a negative second lens element having a concave surface on the image side, a third lens element, a positive fourth lens element, a fifth lens element, and a negative sixth lens element provided with at least one aspherical surface that has inflection points other than at an optical axis thereof. The following conditions (1) and (2) are satisfied:0.86<f / f12<1.20 (1), and−0.71<(r11−r12) / (r11+r12)<−0.20 (2),wherein f designates the focal length of the imaging optical system, f12 designates the combined focal length of the first and second lens elements, and r11 and r12 designate the radius of curvatures of surfaces on the object side and image side of the first lens element, respectively.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Gas turbine blade cooling circuits
InactiveUS6705836B2Temperature controlExtended service lifePump componentsEngine fuctionsLeading edgeConvex side
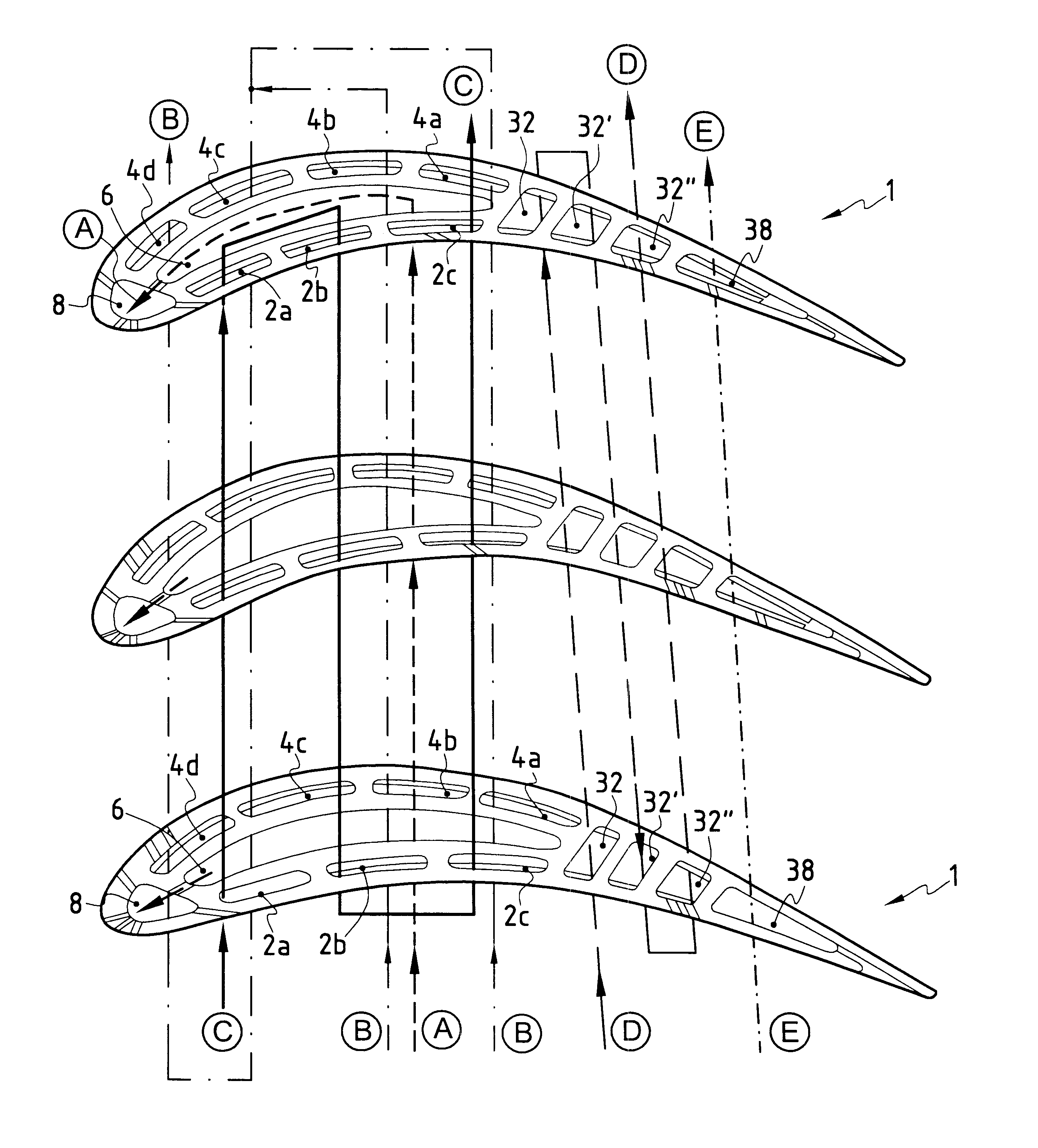
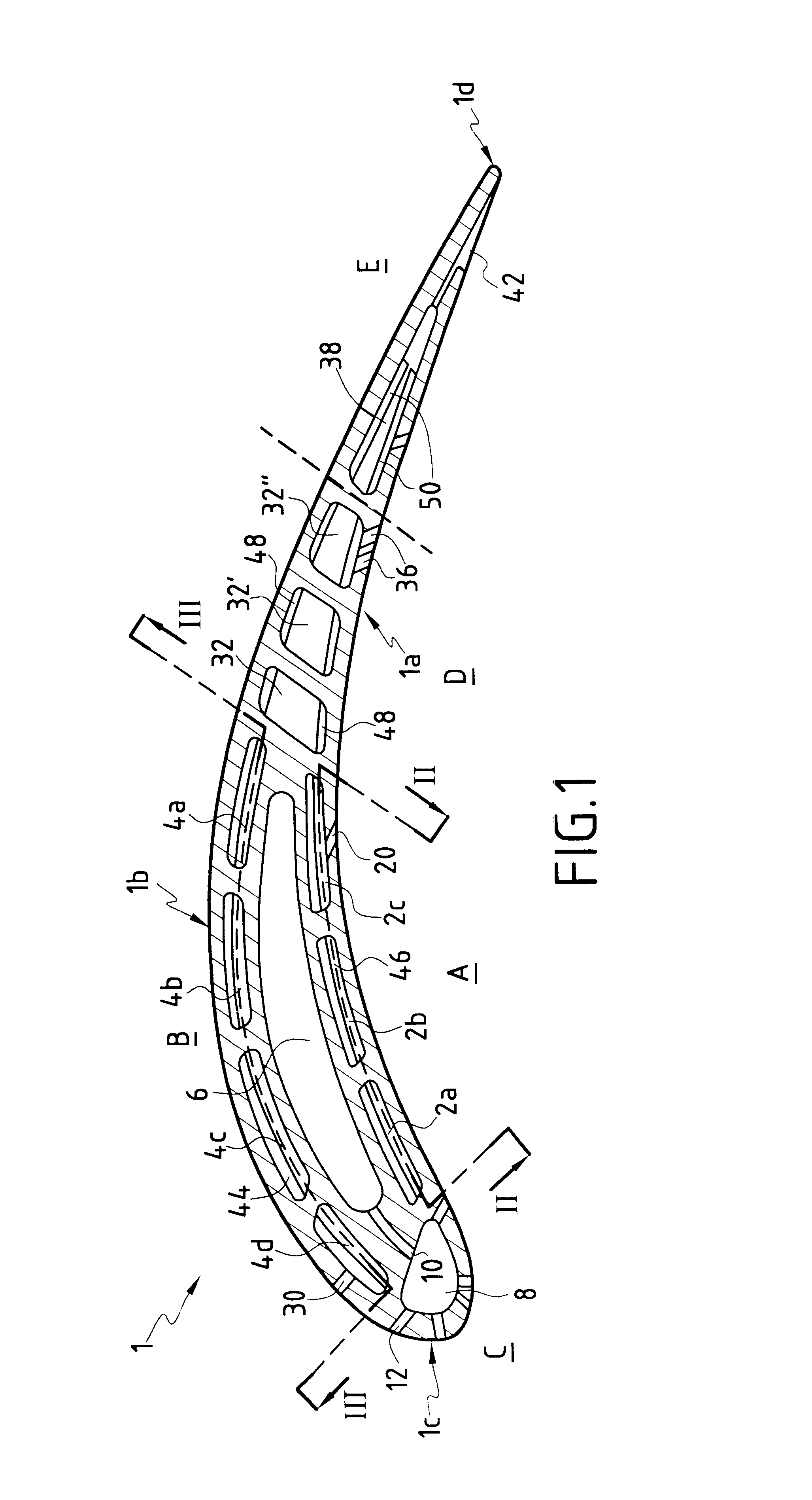
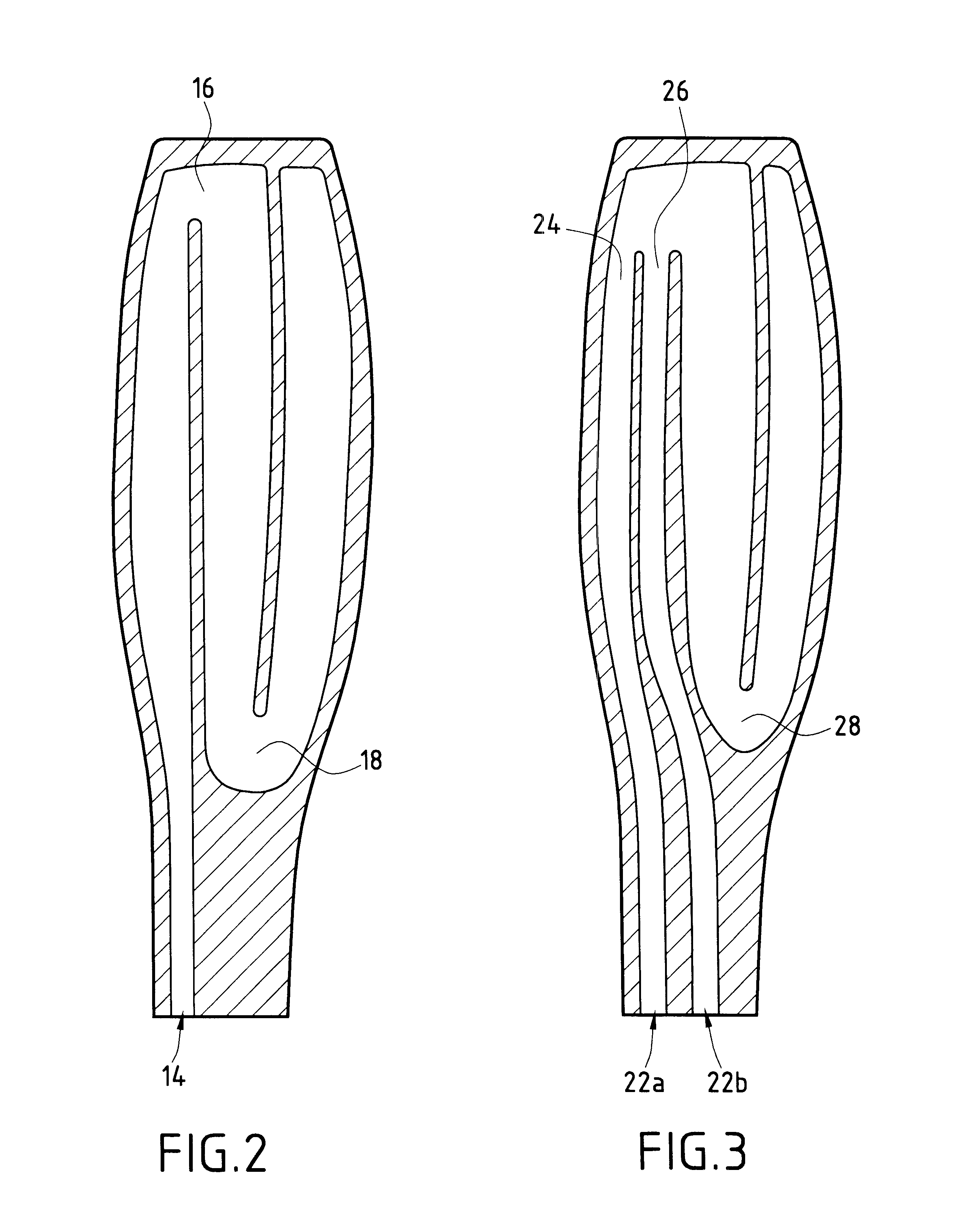
A gas turbine blade for an airplane engine, the blade comprising at least a first cooling circuit comprising at least a concave side cavity extending radially beside the concave face of the blade, at least a second cooling circuit comprising at least one convex side cavity extending radially beside the convex face of the blade, and at least one third cooling circuit comprising at least one central cavity situated in the central portion of the blade between the concave side cavity and the convex side cavity, at least one leading edge cavity situated in the vicinity of the leading edge of the blade, communication orifices opening out into the central cavity and into the leading edge cavity, and outlet orifices opening out into the leading edge cavity and through the leading edge of the blade.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
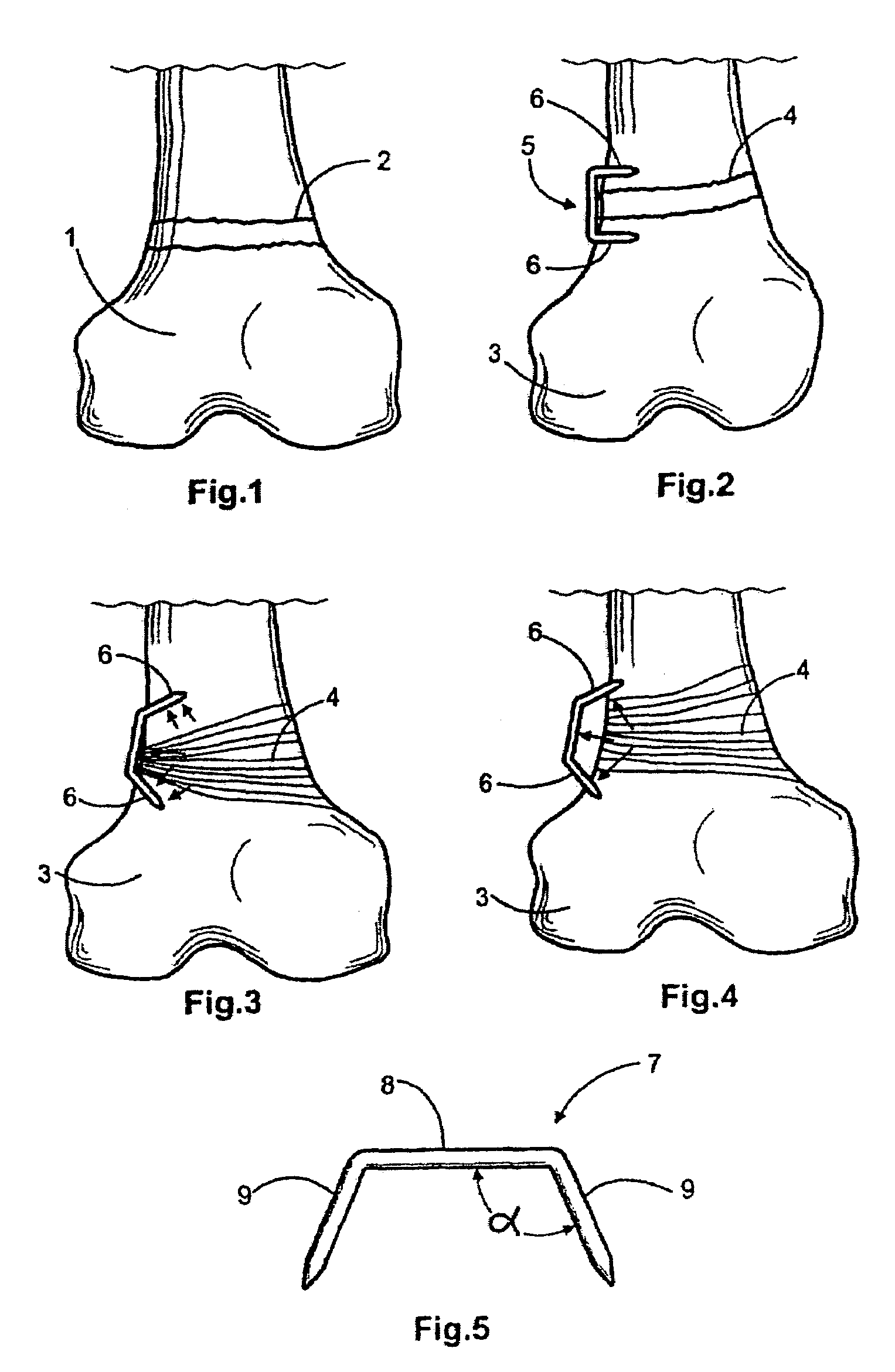
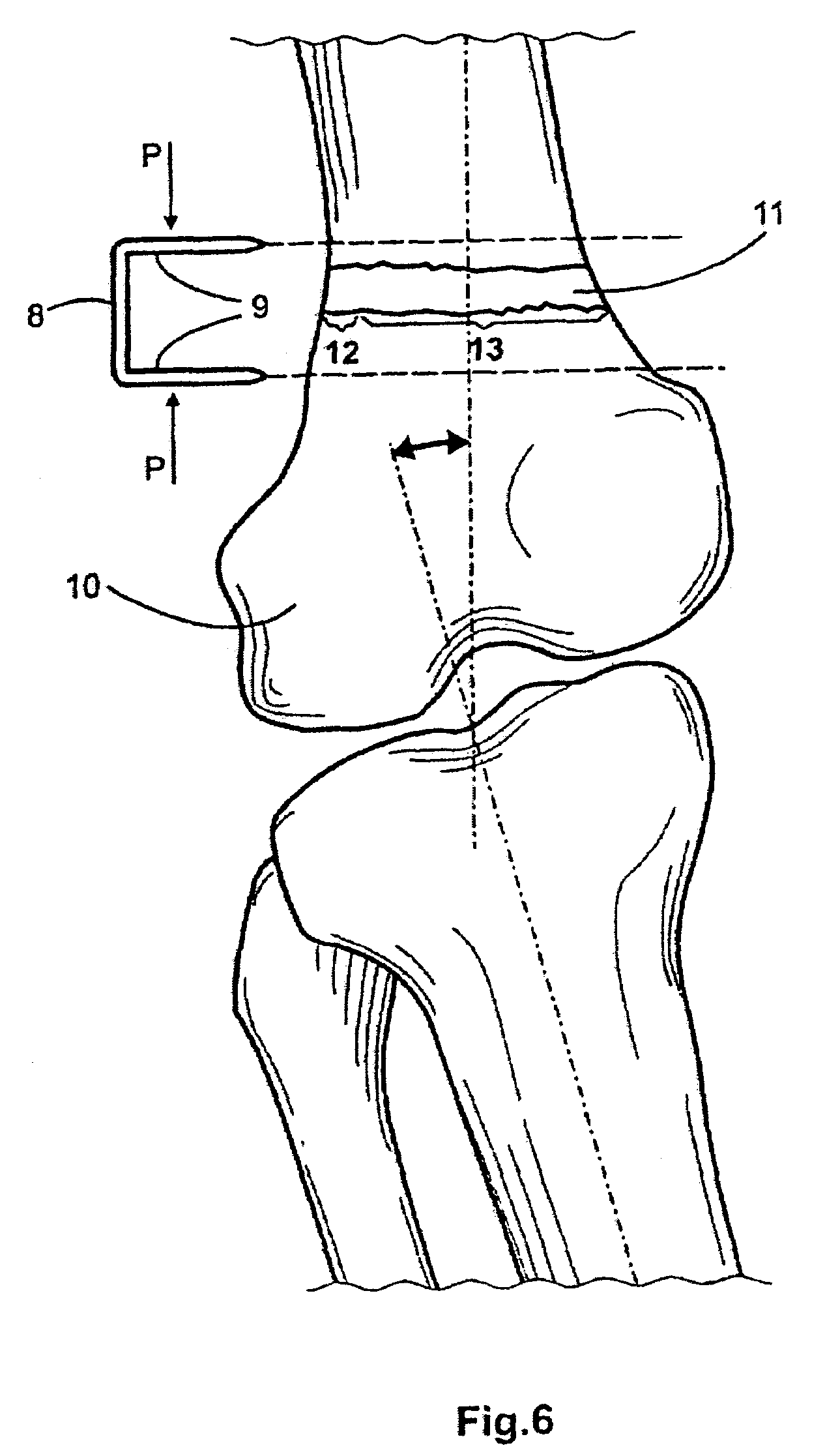
Bone staple and methods for correcting spine disorders
A method and staple for correcting an abnormally curved bone, such as a spinal column having a concave side and a convex side, the method comprising providing a staple having a central portion and a pair of legs with a first memorized shape and a second deformed shape and implanting the staple, in the second shape, at the convex side of the spinal column in a manner that the legs extend close to the concave side, such that the legs exert a distraction force at the concave side of the spinal column.
Owner:GROISO JORGE ABEL
Optical imaging camera lens
The invention discloses an optical imaging camera lens. The camera lens comprises a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens, a sixth lens, a seventh lens and an eighth lens in sequence from the object side to the image side along the optical axis. The first lens has positive focal power, and the object side is the convex side; the second lens has negative focal power;the second lens has positive focal power; the fourth lens has positive focal power or negative focal power, the object side is the concave side, and the image side is the convex side; the fifth lens has positive focal power or negative focal power; the sixth lens has positive focal power or negative focal power, and the object side is the convex side; the seventh lens has positive focal power or negative focal power; the eighth lens has negative focal power.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUNNY OPTICAL CO LTD
Optical lens system for taking image
An optical lens system for taking image comprises four lens elements with refractive power, from the object side to the image side: a first meniscus lens element with negative refractive power; a second lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side and a convex image-side surface; a third lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a fourth lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface; and an aperture stop located between the object and the second lens element. The above arrangements effectively reduce the volume of the optical lens system while providing a relatively high resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Imaging lens and camera system including the same lens
An imaging lens comprises, in order from an object side: a first lens having a negative refractive power with a concave surface directed to an image side thereof; a second lens having a positive refractive power with a convex surface directed to an image side thereof and having an absolute value of a radius of curvature on the image side is equal to or smaller than that on an object side thereof; an aperture stop; a third lens which is a planoconvex lens having a plane on an object side thereof or a double-convex lens having on an object side thereof a surface of which an absolute value of a radius of curvature is larger than that on an image side thereof; and a compound lens of a fourth lens and a fifth lens, the compound lens having a positive composite power.
Owner:TIANJIN OFILM OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
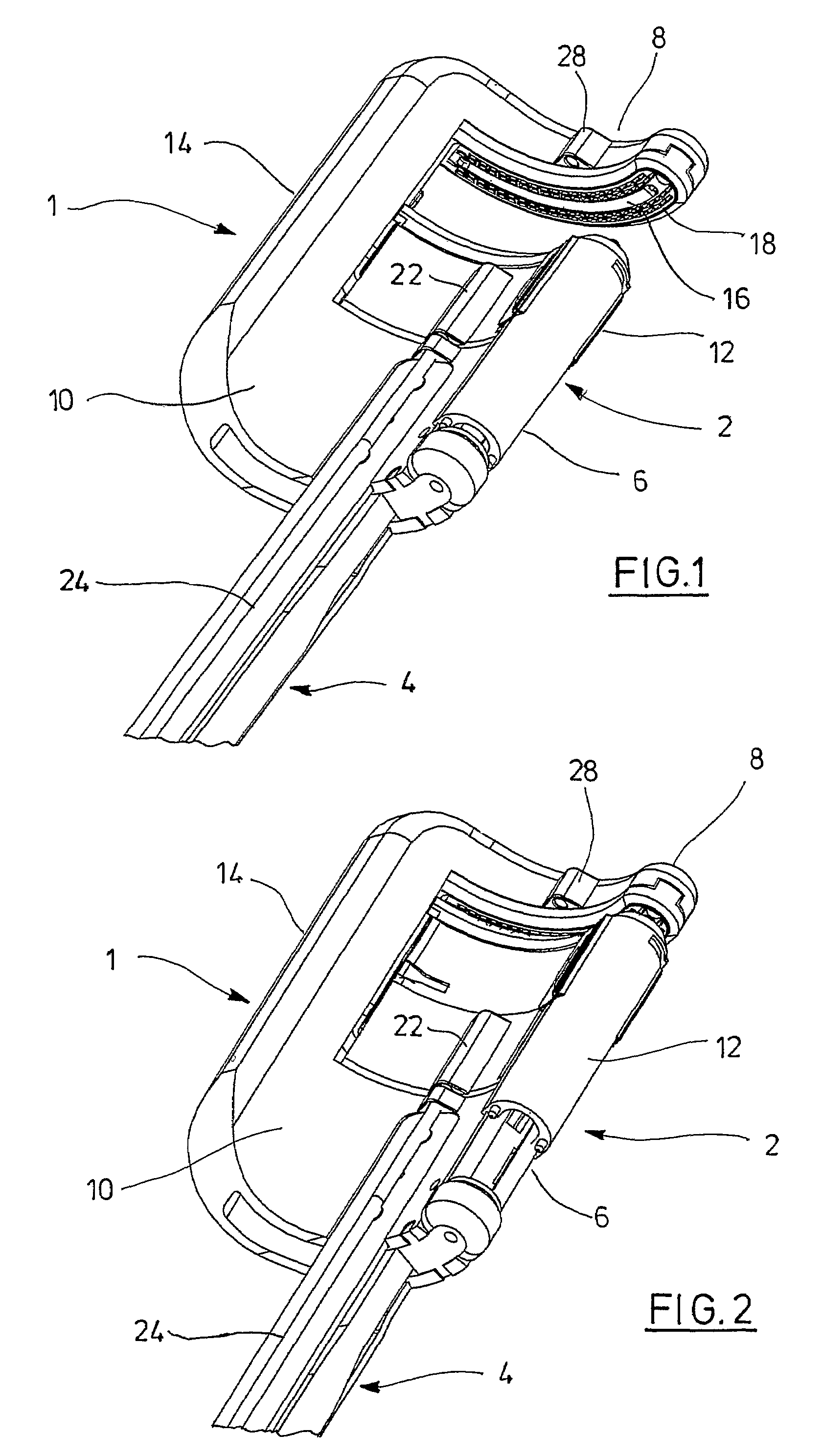
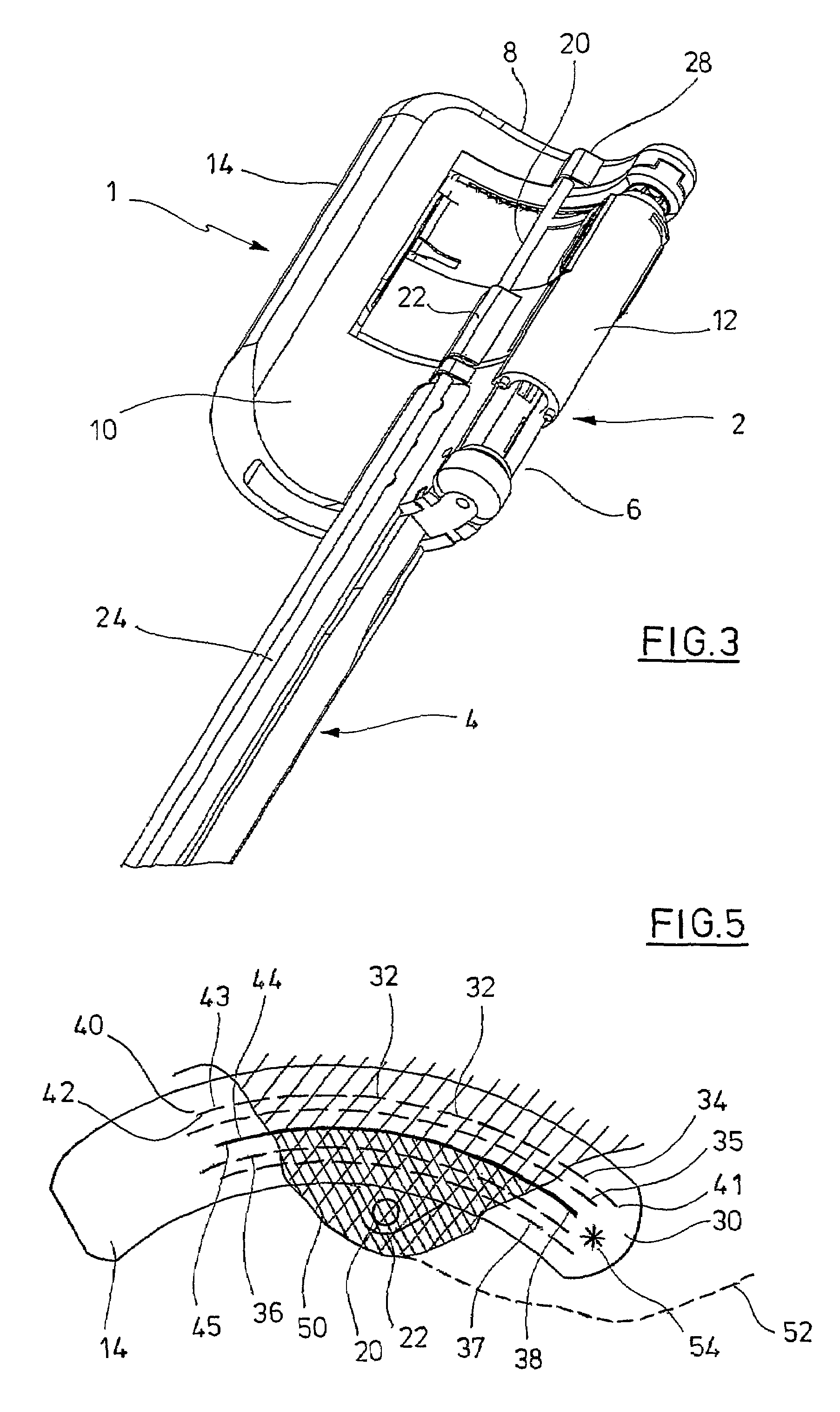
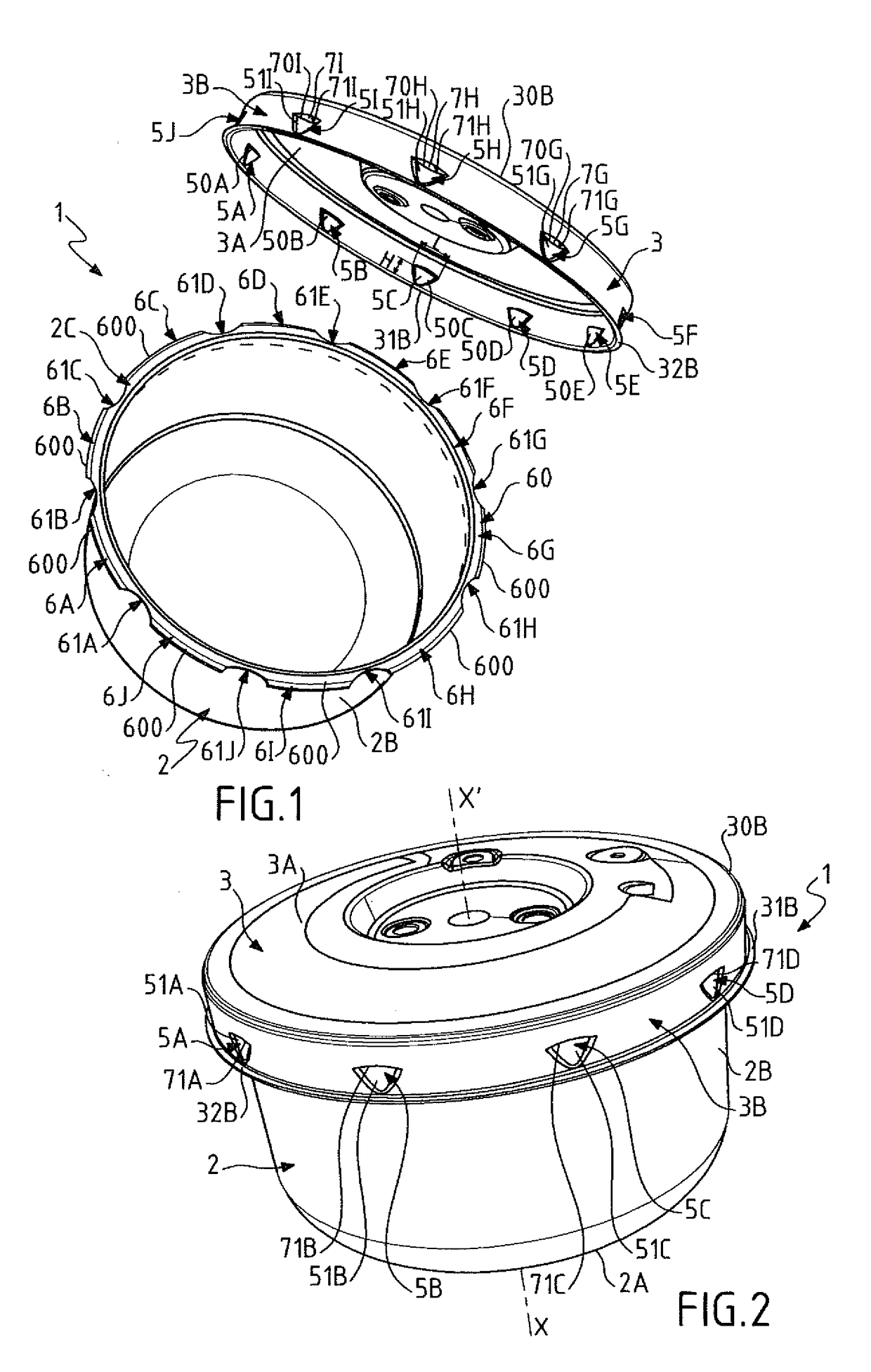
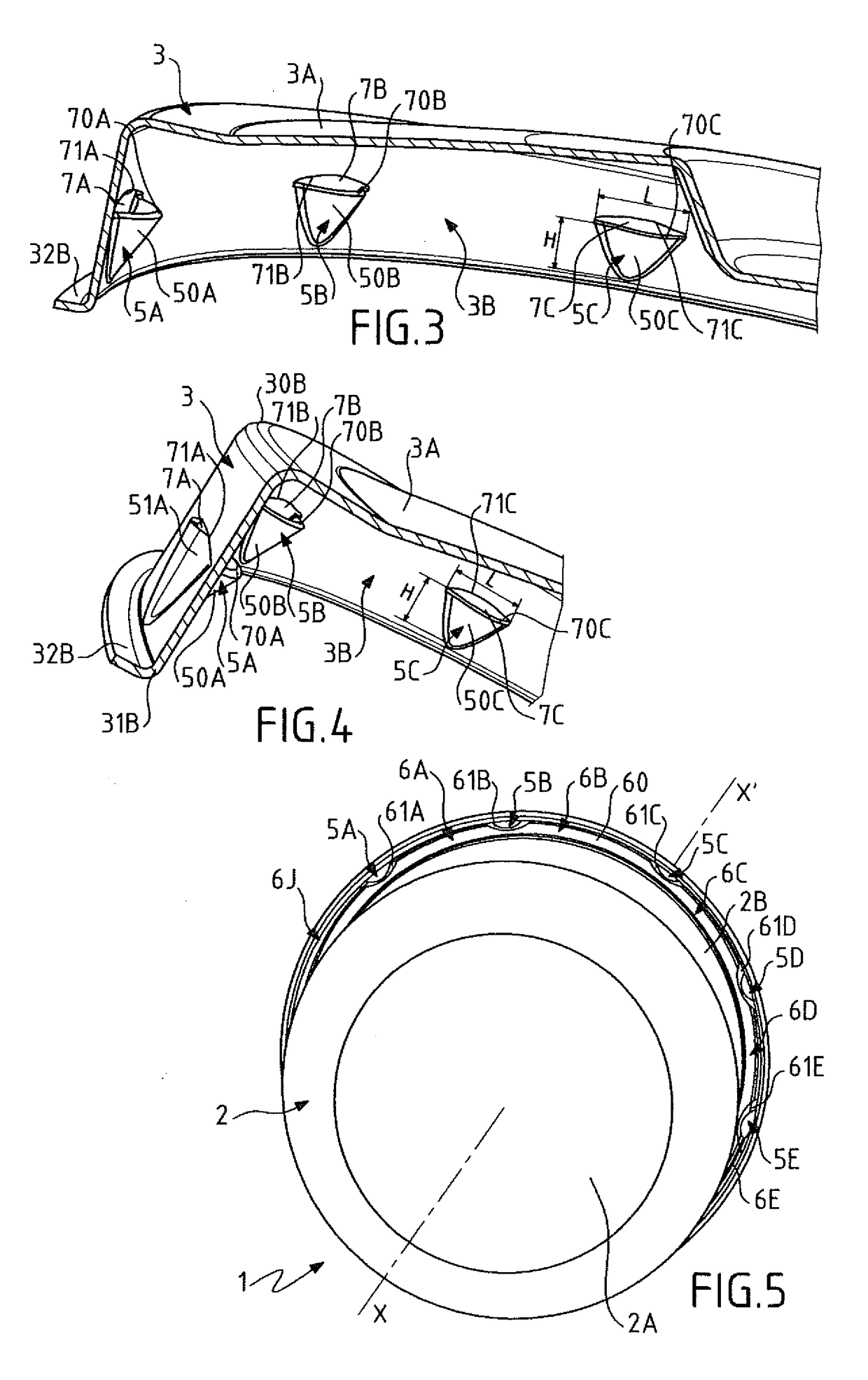
Pressure cooker having bayonet mount and related manufacturing method
ActiveUS20170172335A1Light weightEasy to handleCooking-vessel lids/coversRefuse receptaclesConvex sidePressure cooking
The invention relates to a food pressure cooking appliance including a bowl and a lid intended to be locked relative to the bowl to form with the latter a cooking chamber adapted to rise in pressure. The appliance also including bayonet locking means forming first and second series of protrusions that are integral with the envelope of the lid and the envelope of the bowl, respectively, and that are intended to cooperate with each other to ensure the locking of the lid relative to the bowl. Each protrusion of at least one of said series is consisted by a volume element that has opposite convex and concave faces, and that is formed by a localized radial deformation of the corresponding envelope.
Owner:SEB SA
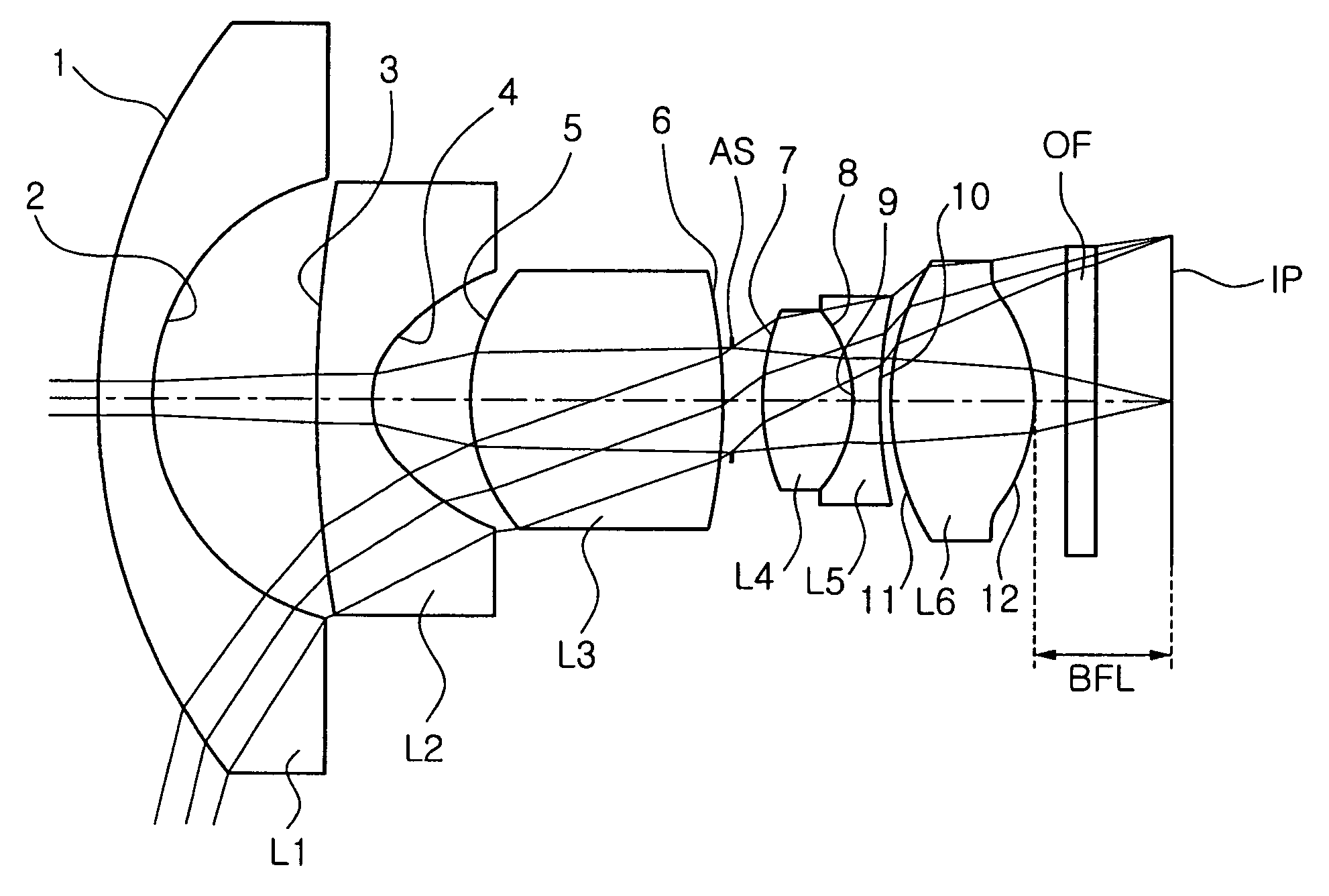
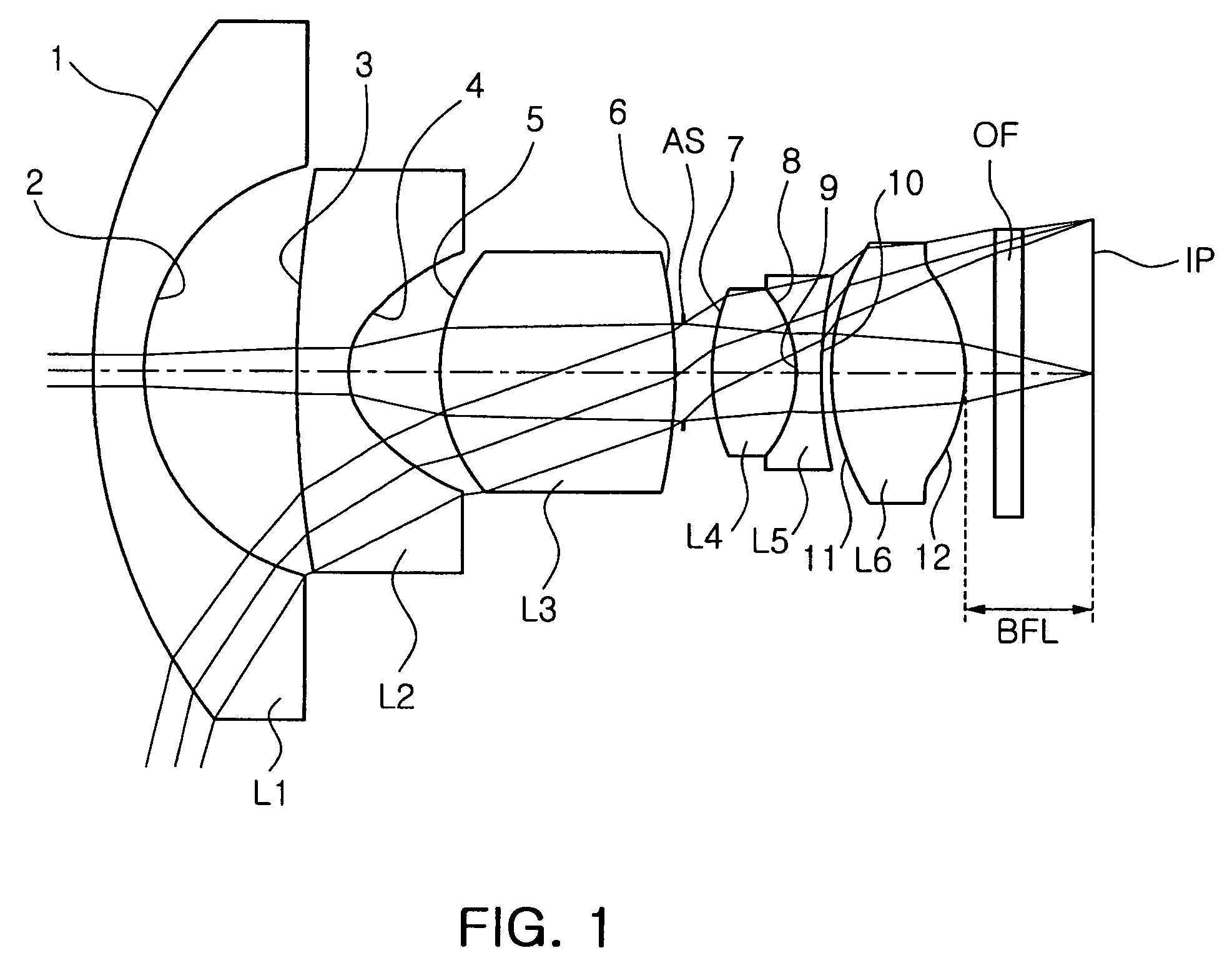
Objective lens for endoscopes
ActiveUS20090161234A1Improve image qualityCompact design can be attainedMicroscopesTelescopesConvex sideOptoelectronics
An objective lens for endoscopes has a front lens unit and a rear lens unit with an aperture stop between them. The front lens unit includes a first lens element with negative refracting power of a meniscus shape, with a convex surface facing the object side and a second lens element with positive refracting power, and the rear lens unit includes a third lens element with positive refracting power, with a surface of the minor radius of curvature facing the image side and a cemented lens component of a fourth lens element with positive refracting power and a fifth lens element with negative refracting power. The objective lens satisfies the following conditions:−2<SF<−0.90.94<D / (f×sin θ)<1.70.86<(D1+D2−f1) / (2×f3)<1.13where SF is the shape factor of the first lens element and is a value expressed by SF=(R2+R1) / (R2−R1) when the radius of curvature of the object-side surface is denoted by R1 and the radius of curvature of the image-side surface is denoted by R2; D is a distance (an equivalent-air medium length) from the vertex of the image-side surface of the first lens element to the aperture stop; f is the combined focal length of the entire system; θ is a half angle of view; D1 is an actually measured distance from the vertex of the object-side surface of the first lens element to the aperture stop; D2 is a distance (an equivalent-air medium length) from the aperture stop to the image-side surface of the third lens element; f1 is the focal length of the first lens element; and f3 is the focal length of the third lens element.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Mounting bracket for electronic device having dimensional inserts
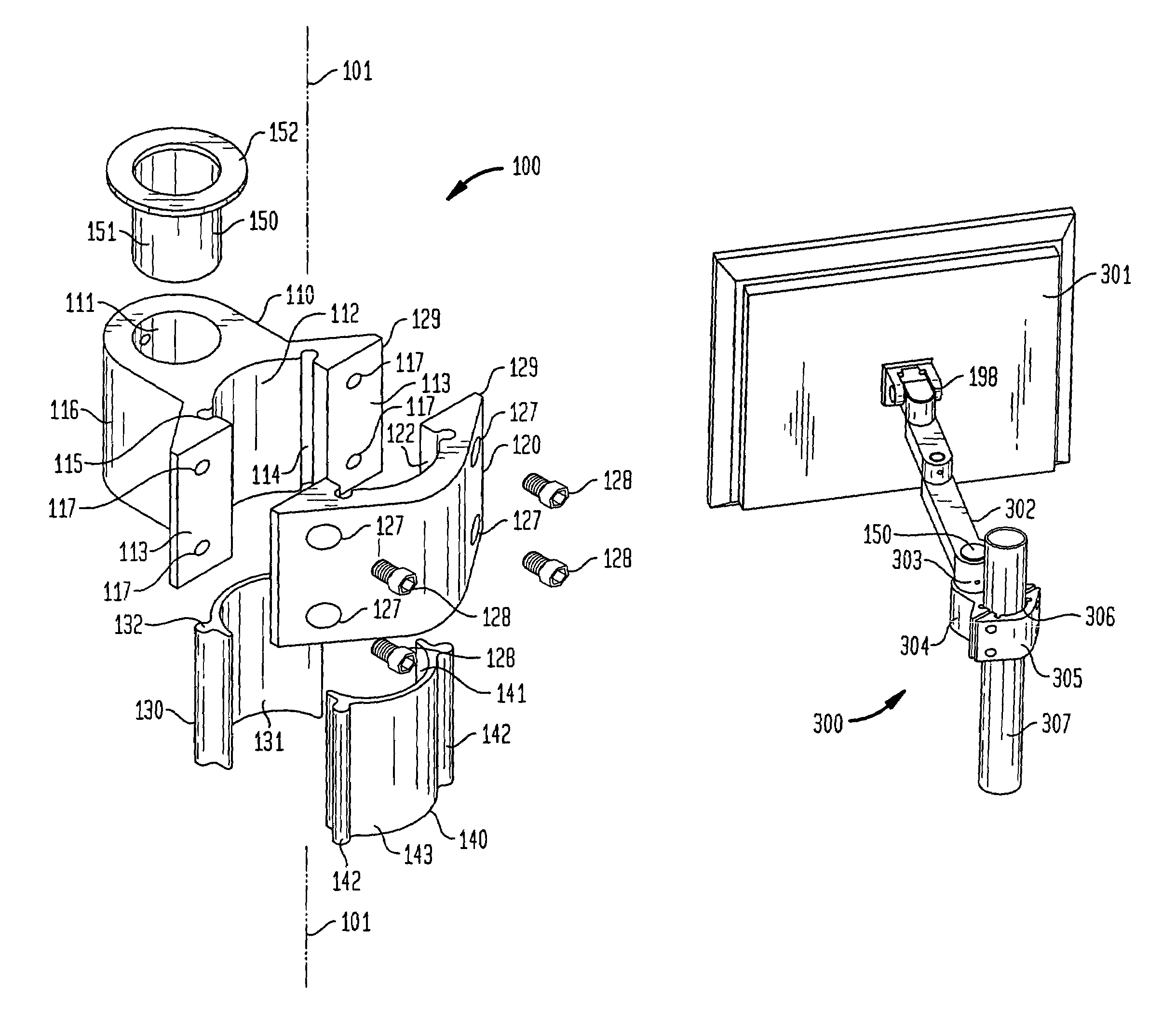
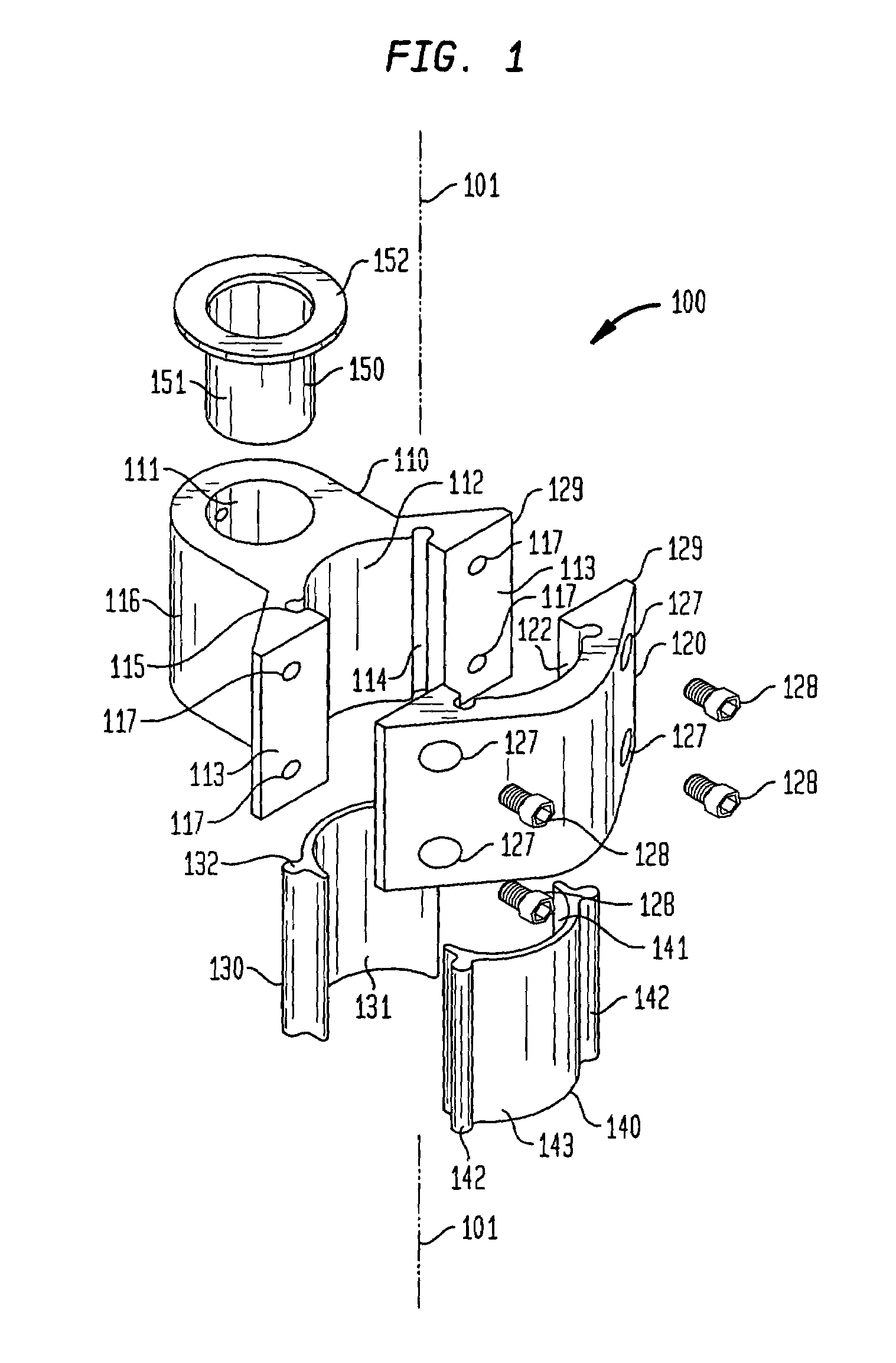
A mounting bracket and insert for use in mounting mountable devices to a mounting pole including a first section and a second section, each of said first and second sections having a concave surface, each concave surface having at least a one longitudinally extended groove, the first and second sections being joinable to one another, with such joining forming a cylindrical area between the first and second sections, said cylindrical area formed by said concave surfaces, and at least a pair of inserts, each insert having a convex surface sized to fit within the concave surface of one of the two sections, the convex surface of each insert having at least one protrusion aligned along the longitudinal axis of the insert and shaped to fit into at least one groove of the concave surfaces of the sections is described.
Owner:INNOVATIVE OFFICE PROD LLC
Structure support apparatus and structure installation method
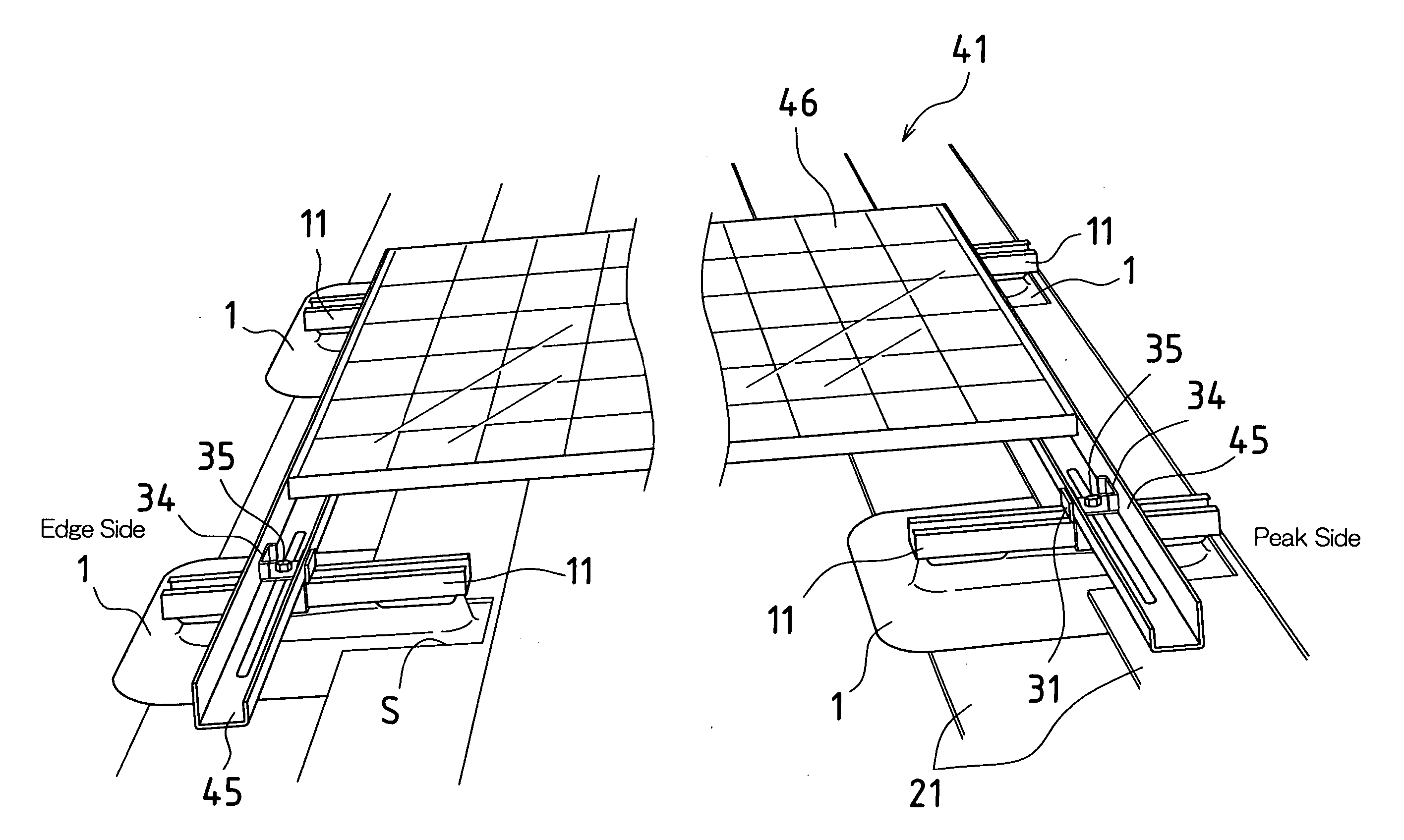
InactiveUS20080053008A1High strengthIncreased durabilityPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyConvex sideEngineering
According to an embodiment of the present invention, a structure support apparatus for anchoring and supporting a structure upon a roof comprises a bowed plate having a dome-shaped convex portion formed in the center of the bowed plate projecting from the concave side toward the convex side of the bowed plate. A screw hole is formed in the dome-shaped convex portion, penetrating the center of the bowed plate, and the structure is supported by the apex of the dome-shaped convex portion.
Owner:SHARP KK
Image pickup lens, image pickup unit and cellphone terminal equipped therewith
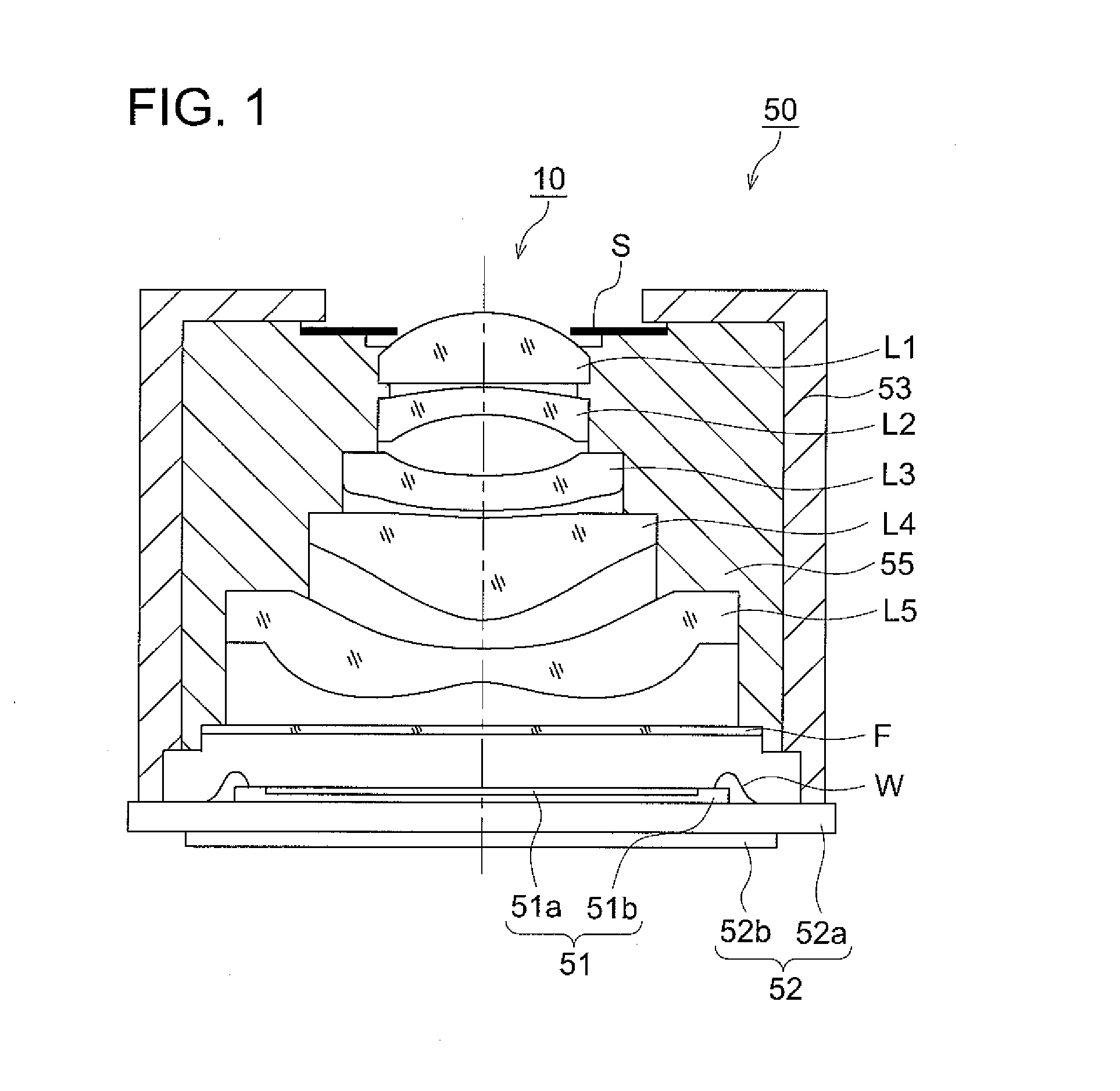
InactiveUS6885508B2Shorten the lengthEasy to fixTelevision system detailsColor television detailsConvex sidePhysics
An image pickup lens that has therein, in the order named from an object side, an aperture stop, a meniscus-shaped first lens having positive refracting power whose convex surface faces an object and a second lens having positive or negative refracting power whose convex surface faces the object, wherein each of the first lens and the second lens has at least one aspheric surface and satisfies the following condition expression f1 / |f2|<1.0 wherein, f1 is a focal length of the first lens, f2 is a focal length of the second lens and f is a focal length of the entire system of the image pickup lens.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com