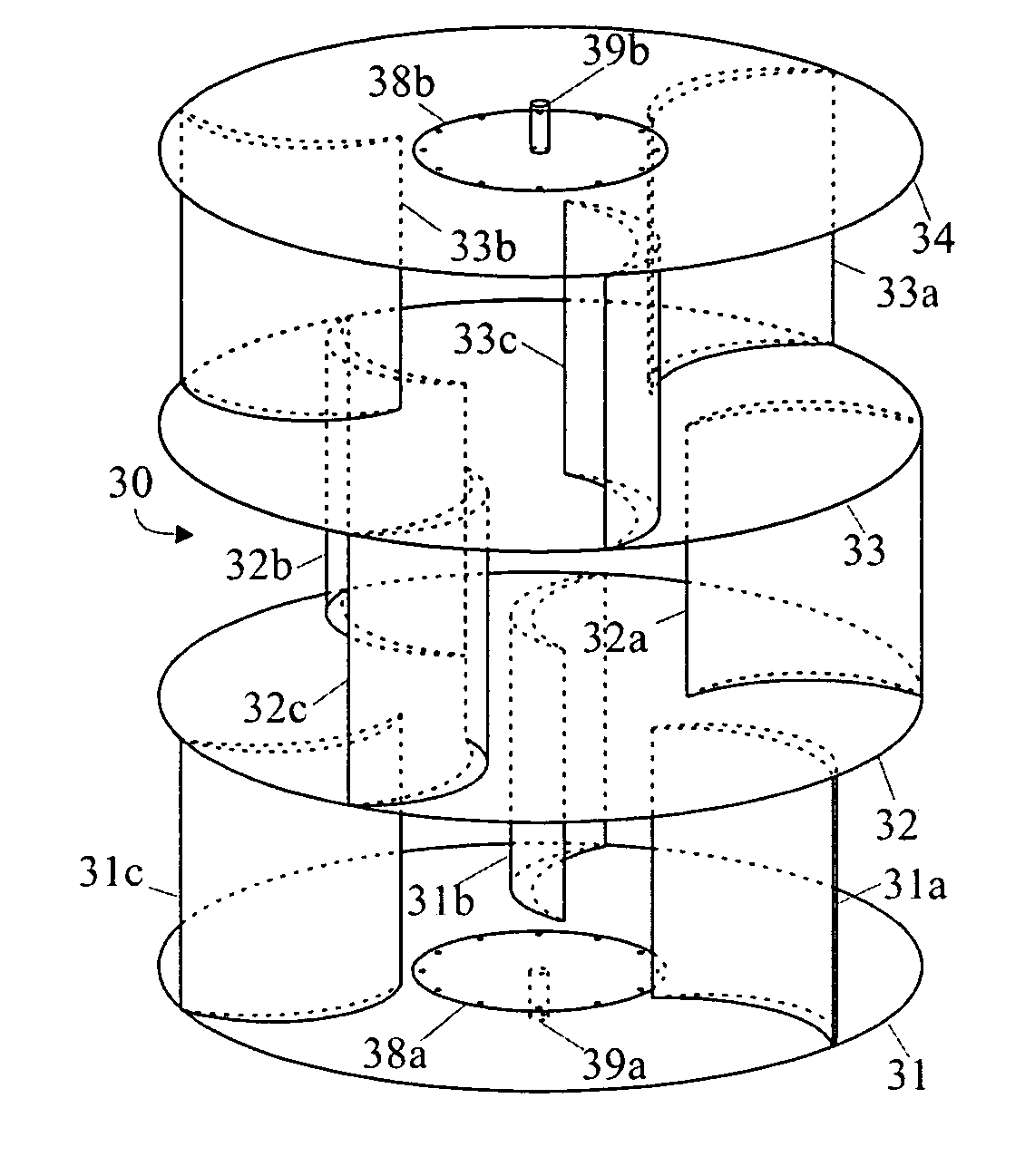
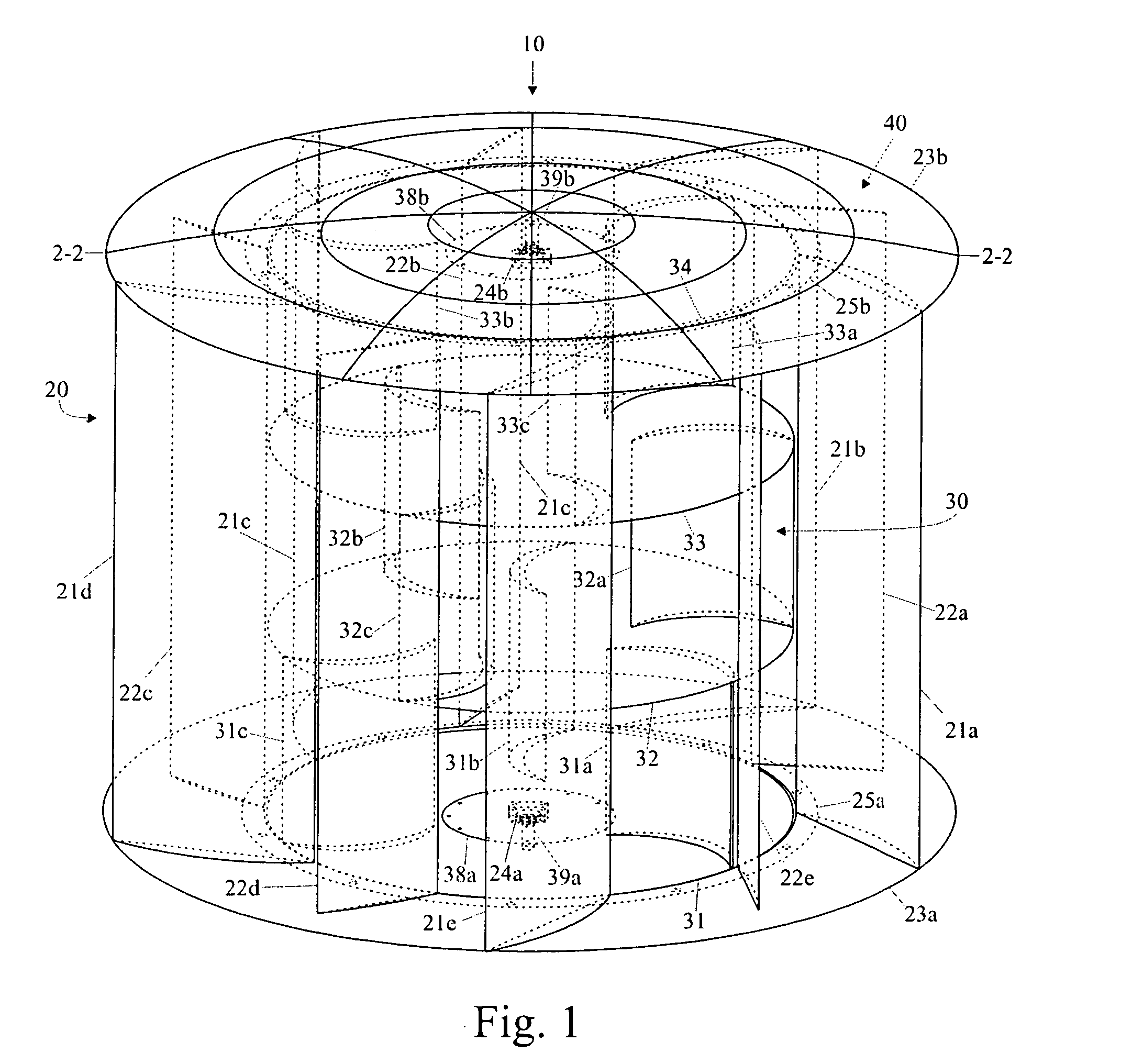
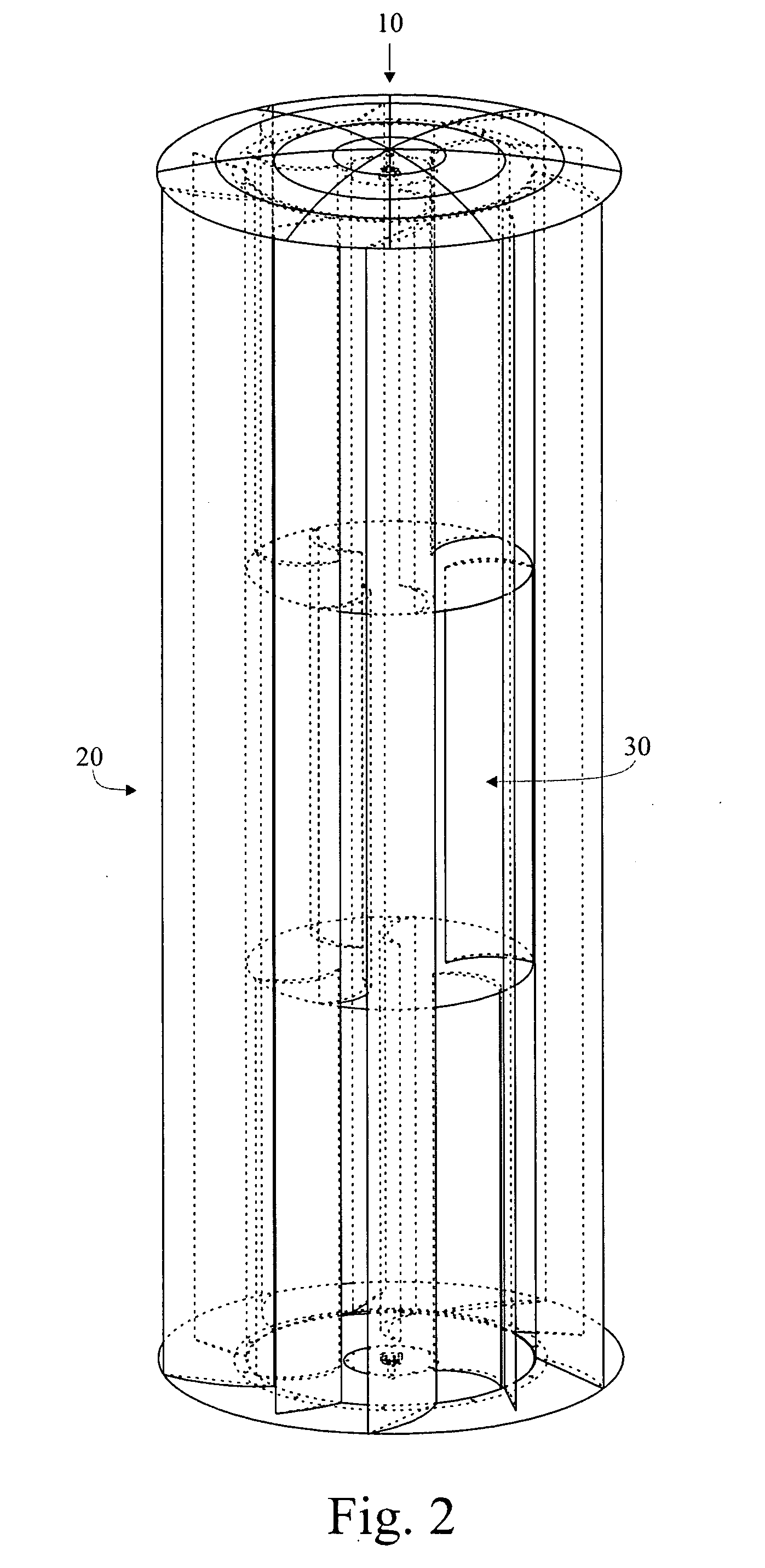
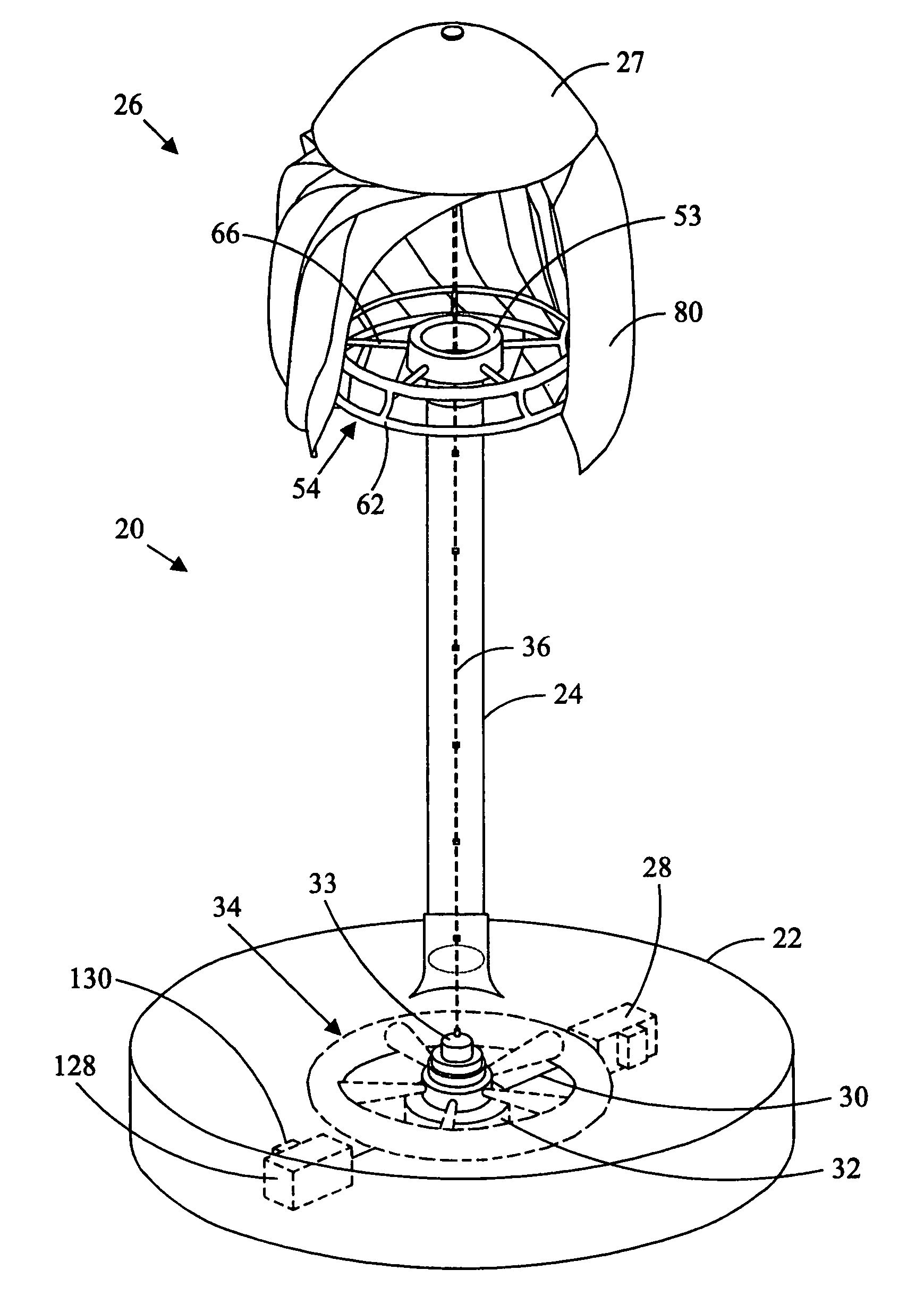
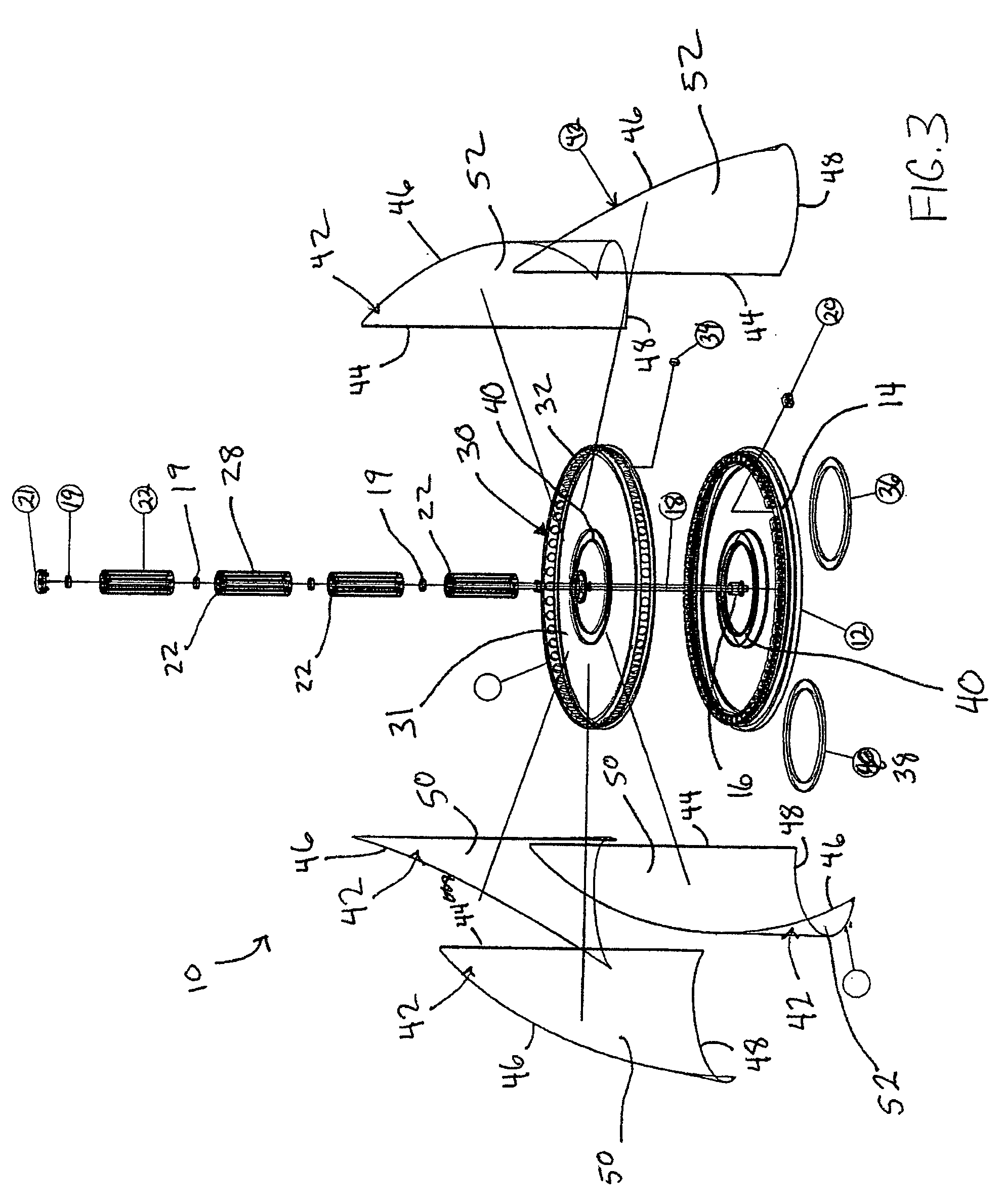
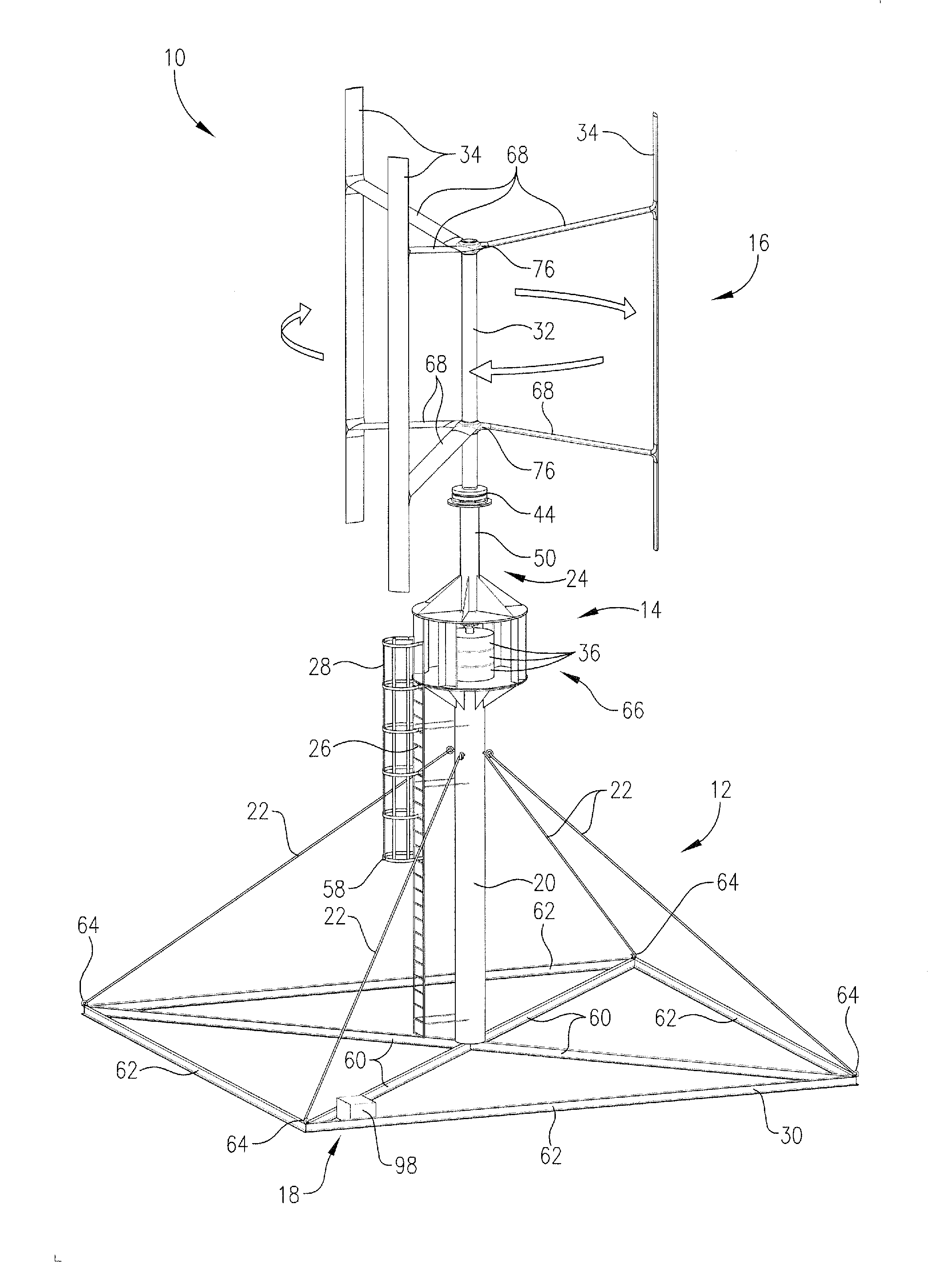
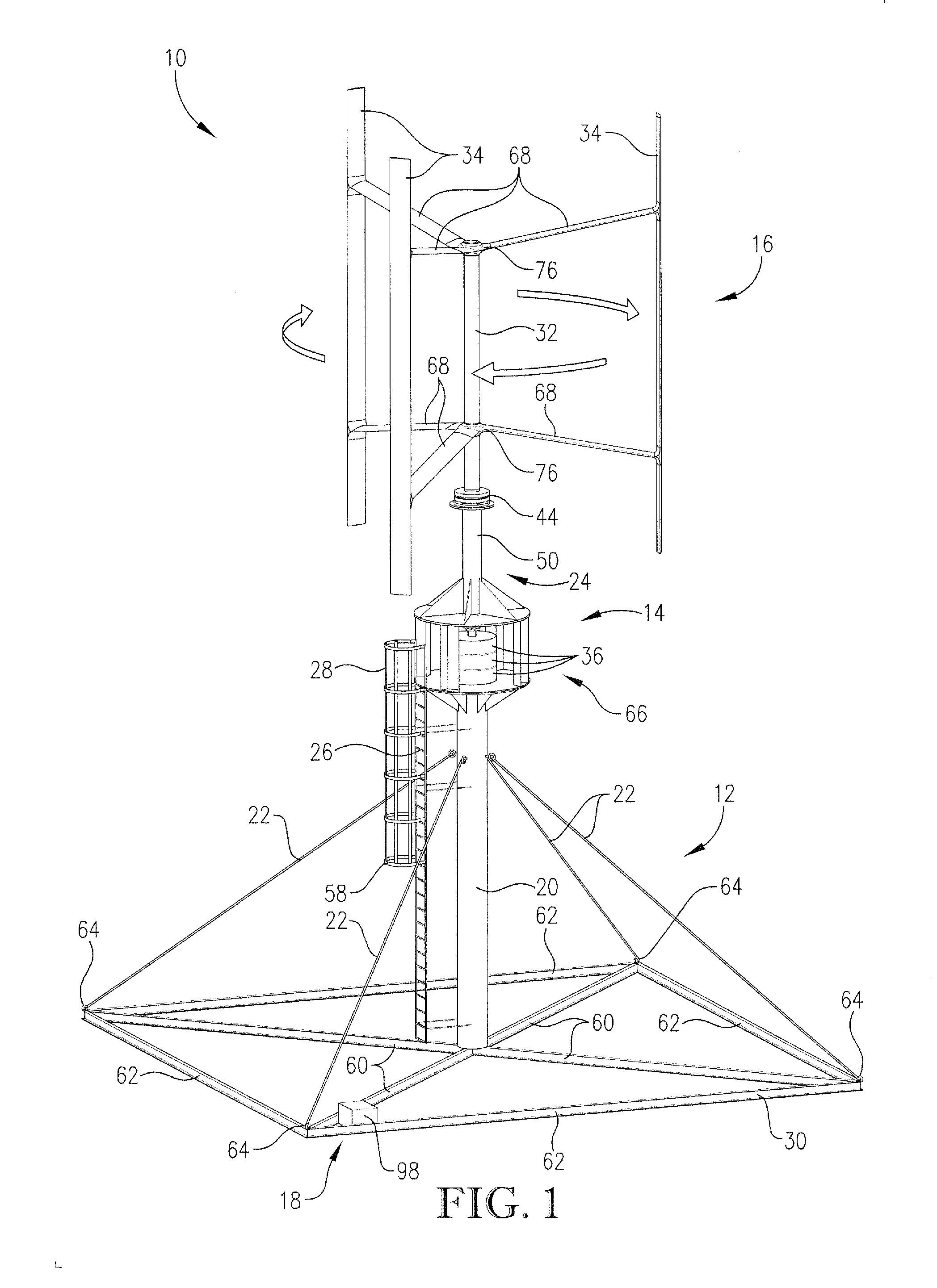
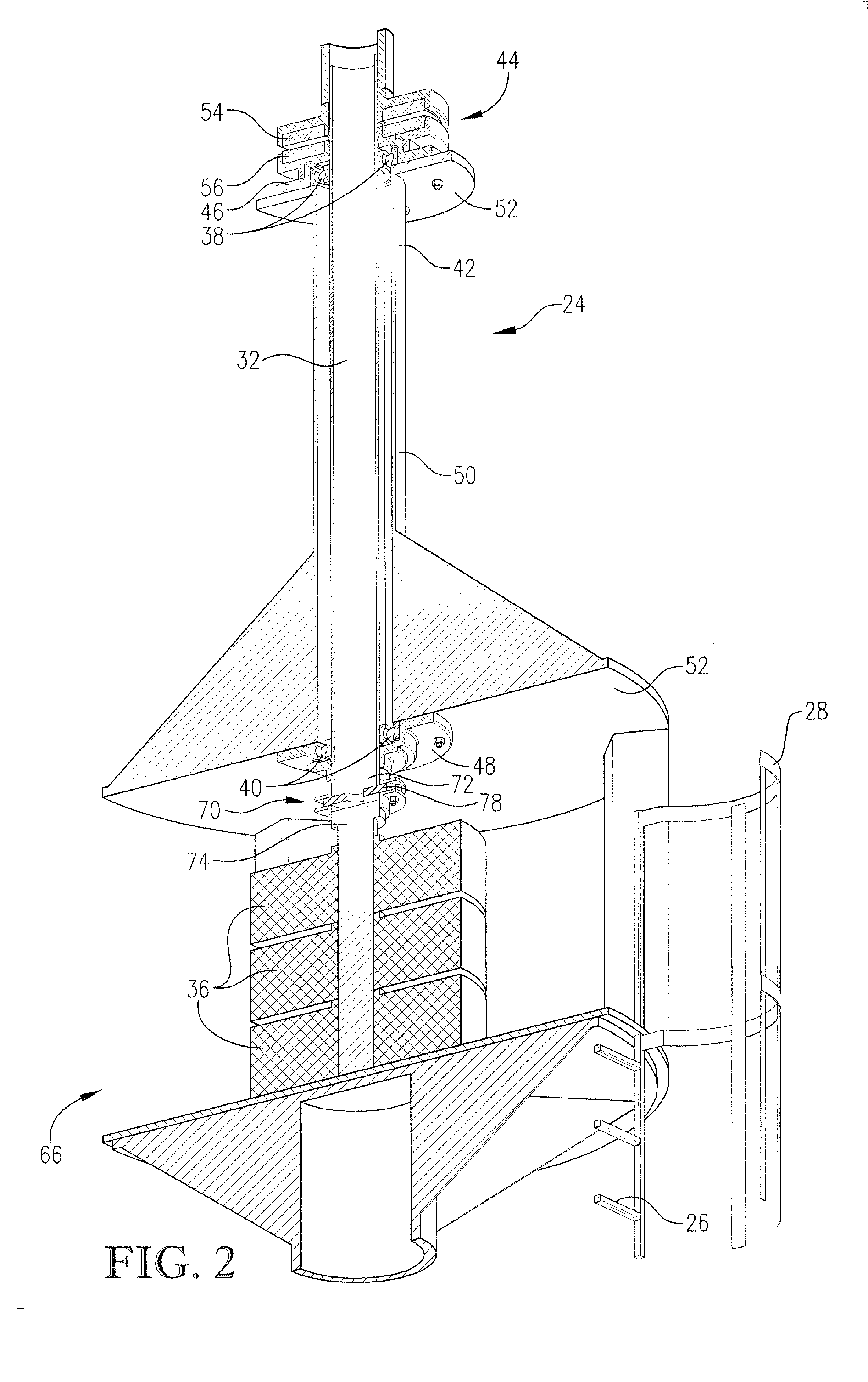
Patents
Literature
1431 results about "Vertical axis wind turbine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
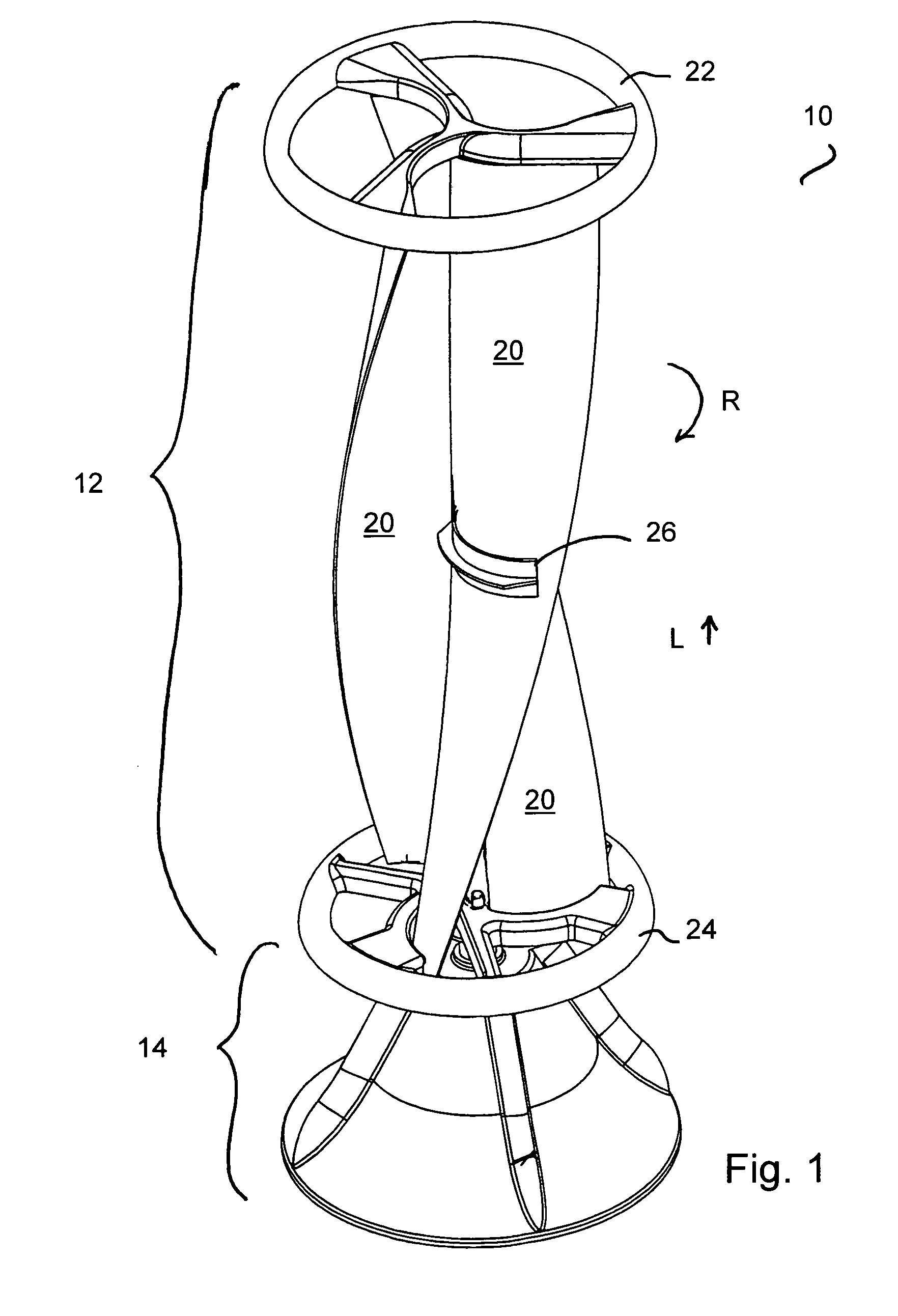
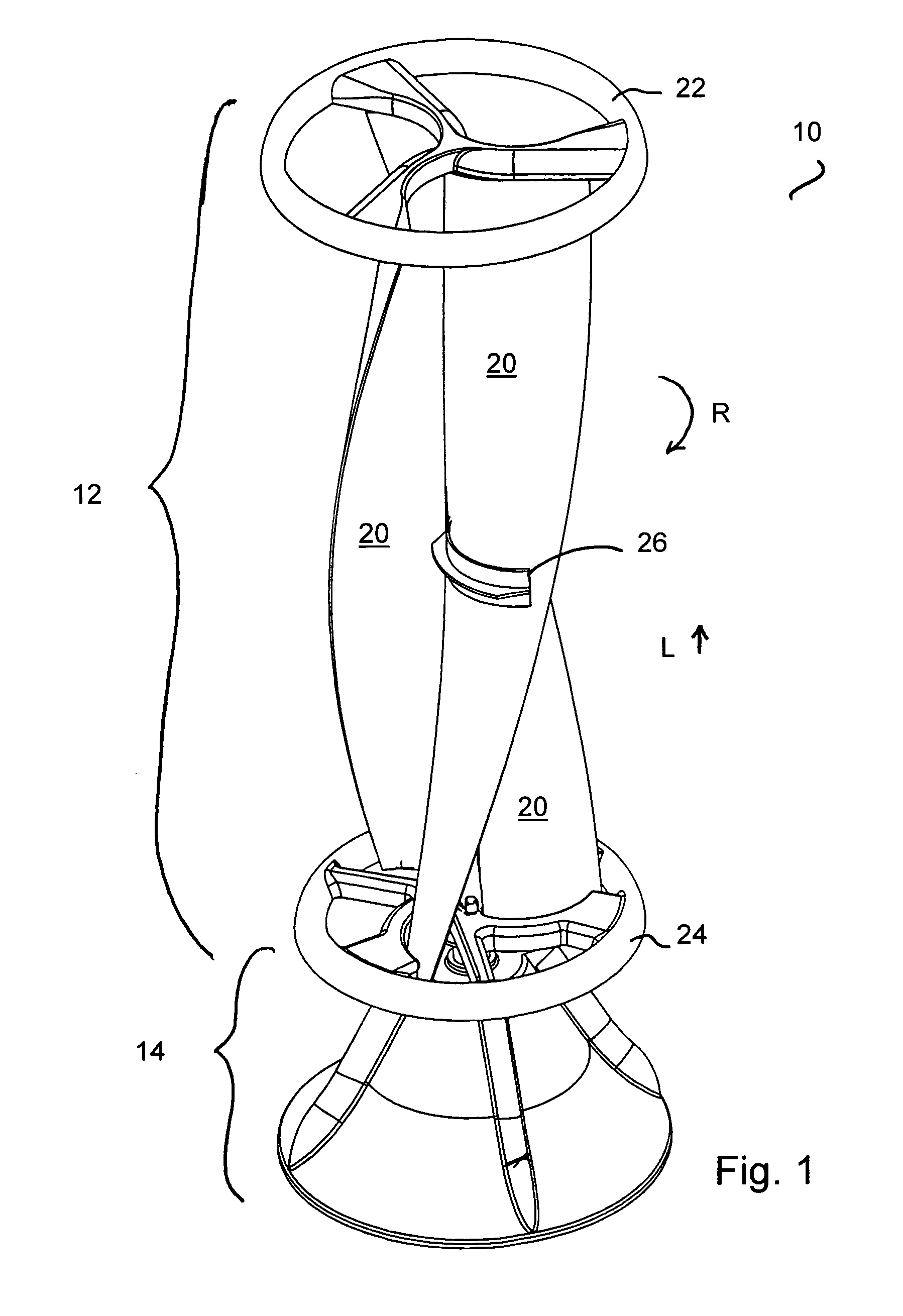
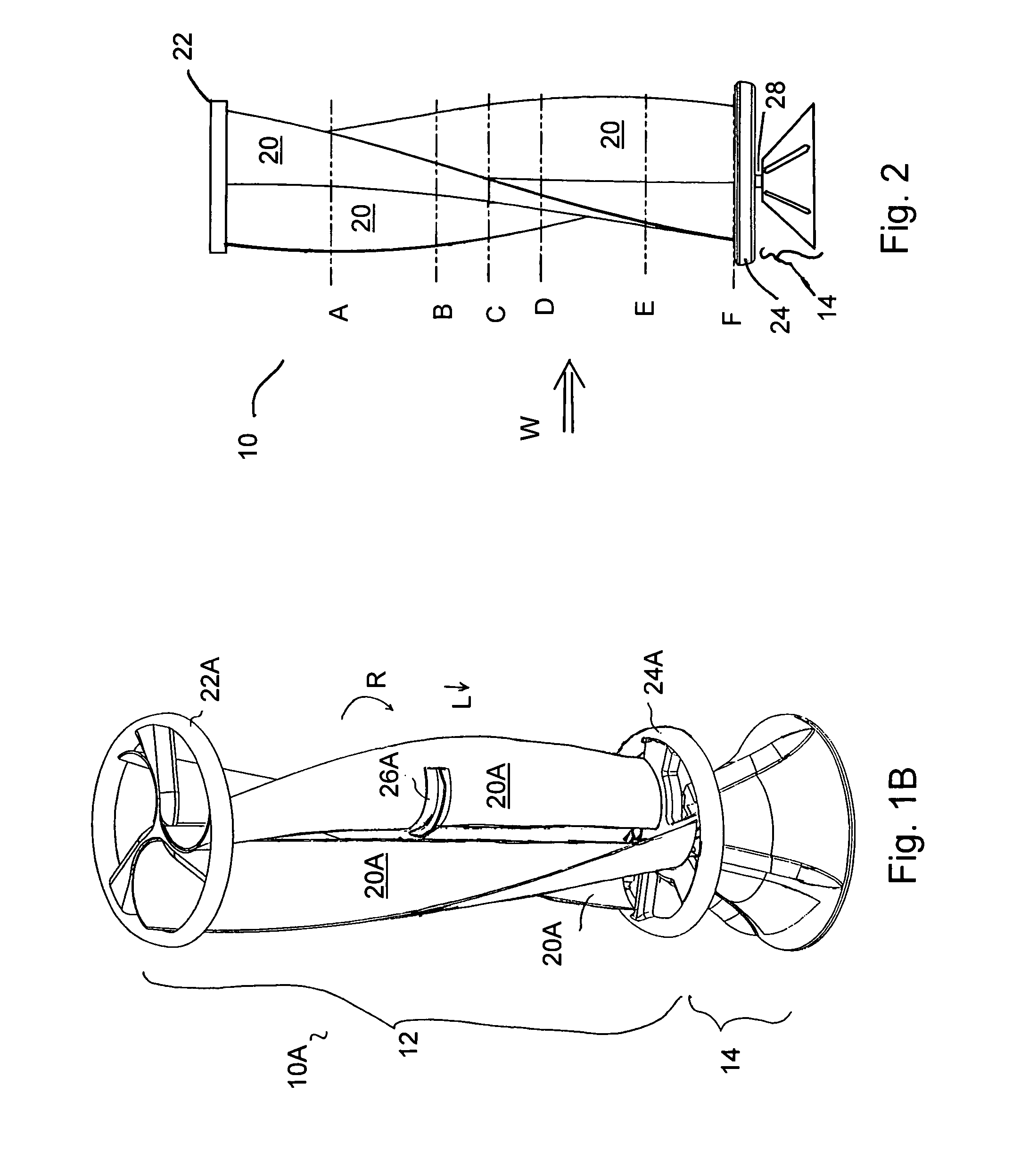
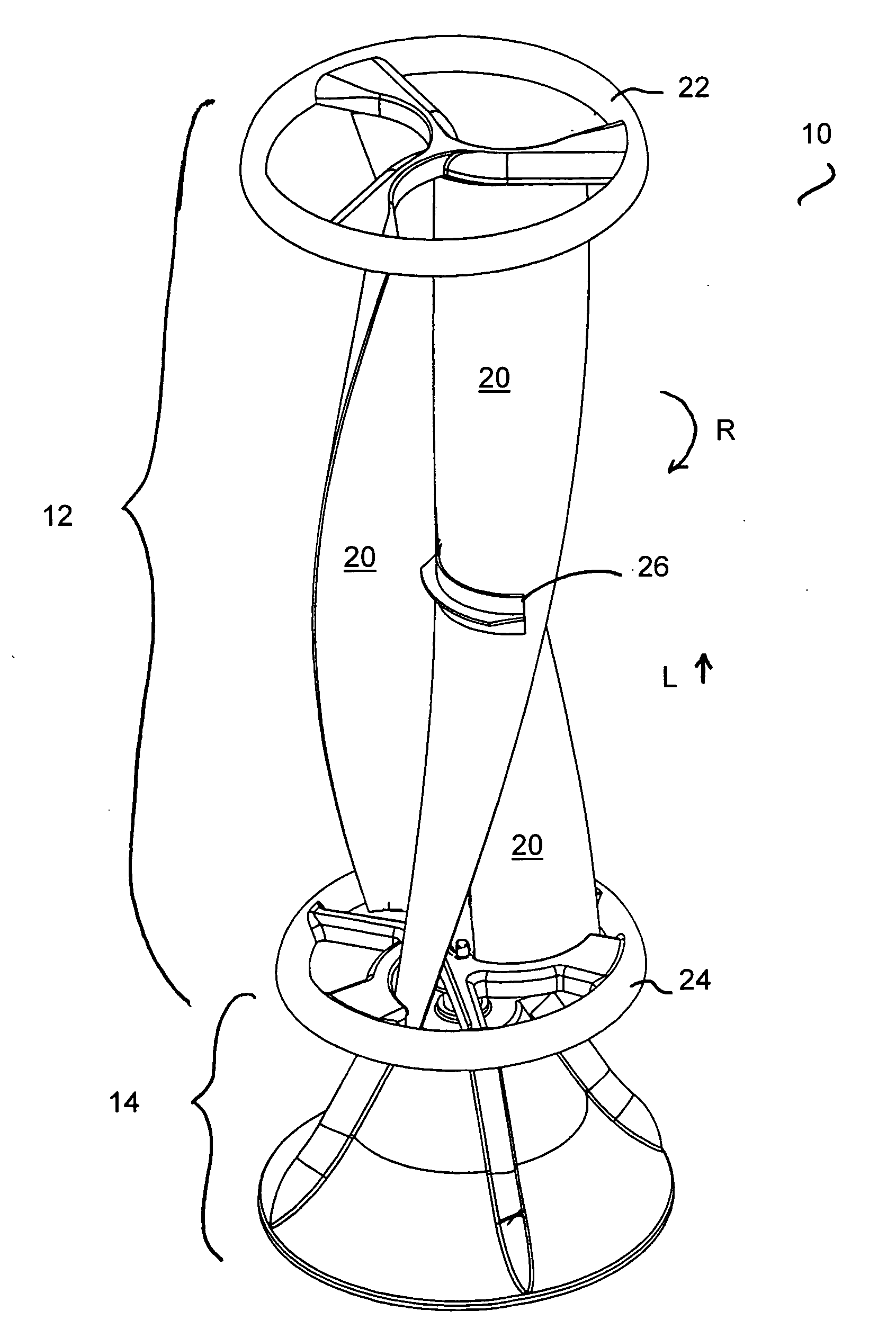
A vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWT) is a type of wind turbine where the main rotor shaft is set transverse to the wind (but not necessarily vertically) while the main components are located at the base of the turbine. This arrangement allows the generator and gearbox to be located close to the ground, facilitating service and repair. VAWTs do not need to be pointed into the wind, which removes the need for wind-sensing and orientation mechanisms. Major drawbacks for the early designs (Savonius, Darrieus and giromill) included the significant torque variation or "ripple" during each revolution, and the large bending moments on the blades. Later designs addressed the torque ripple issue by sweeping the blades helically (Gorlov type).
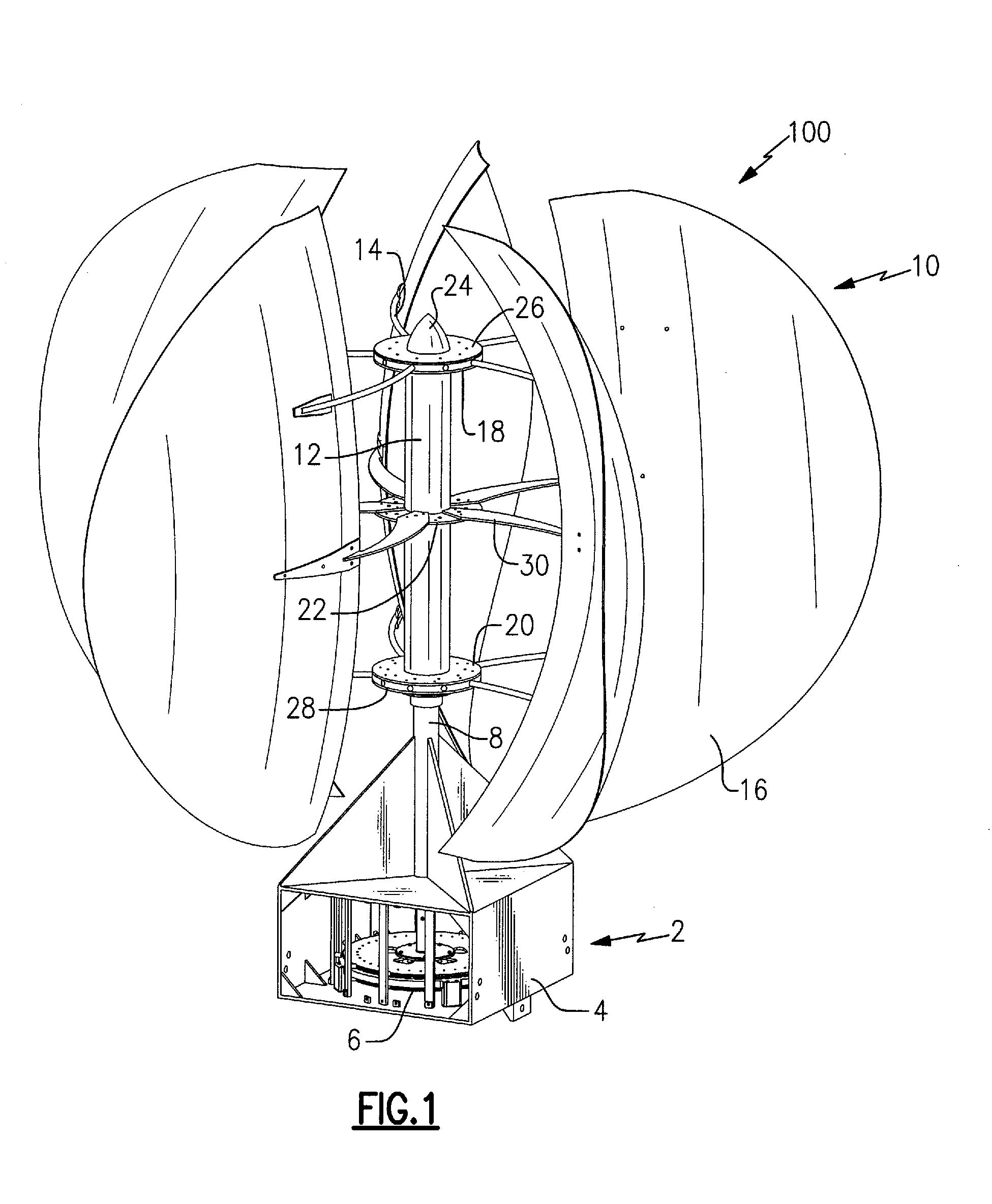
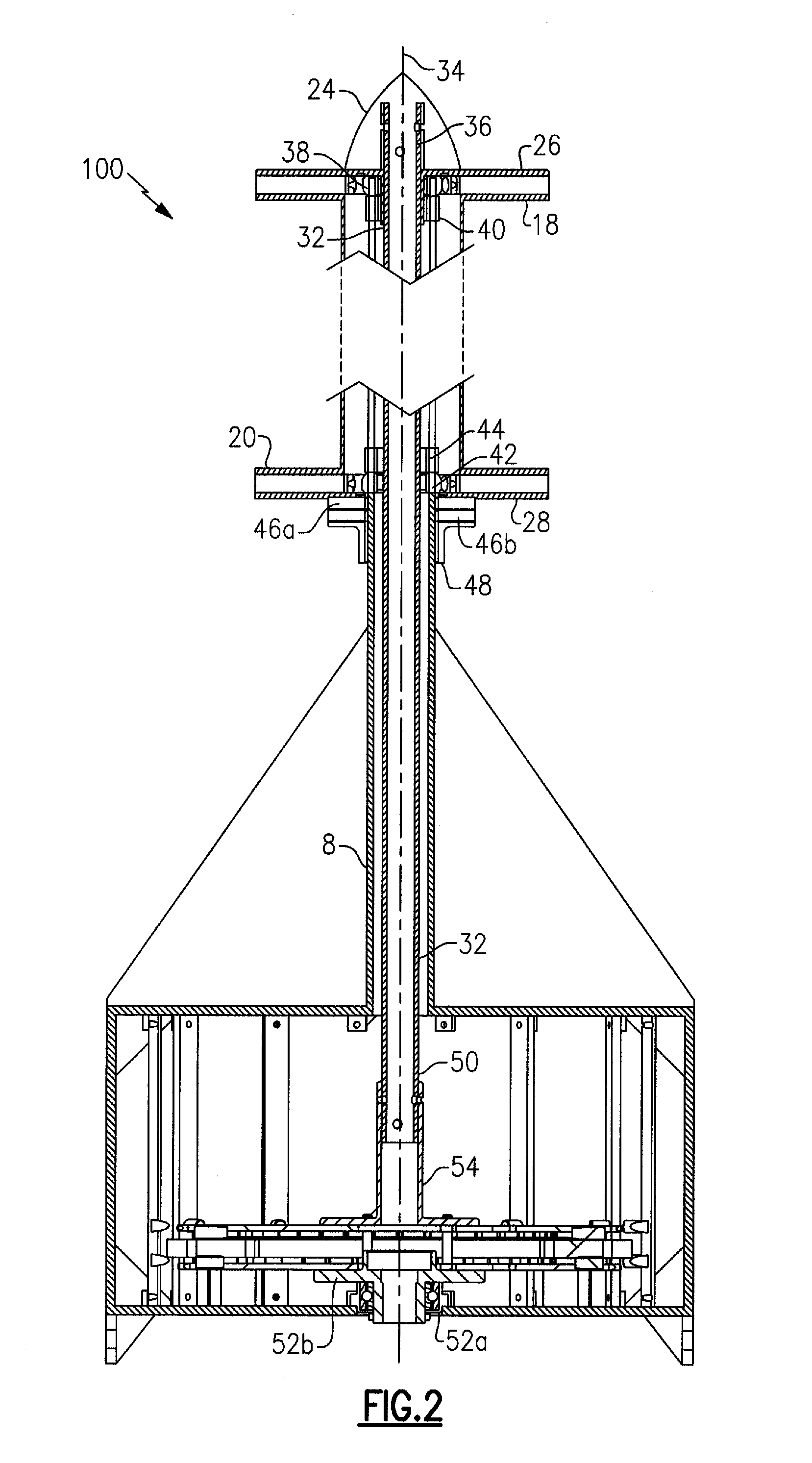
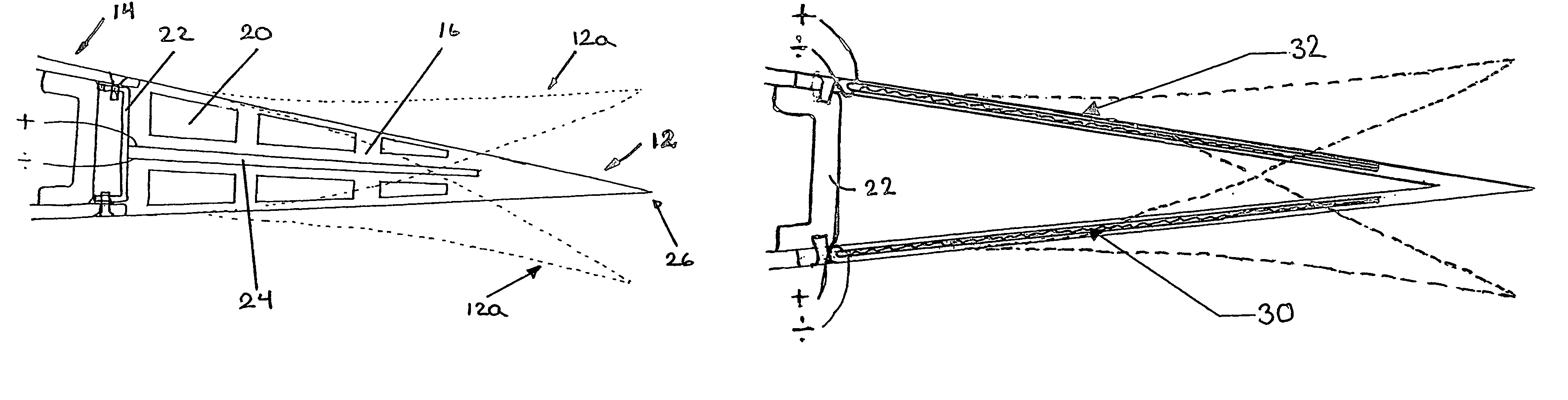
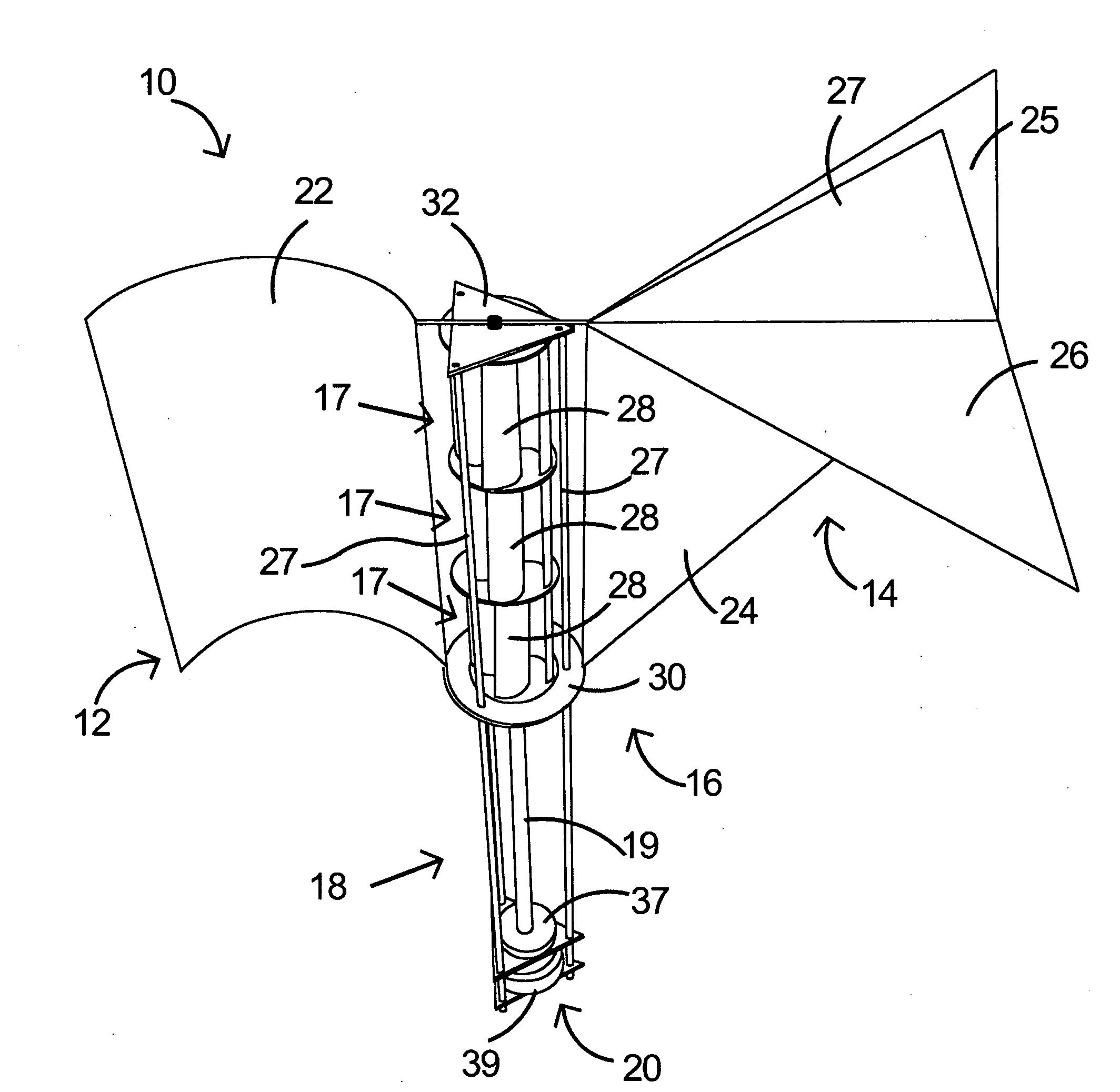
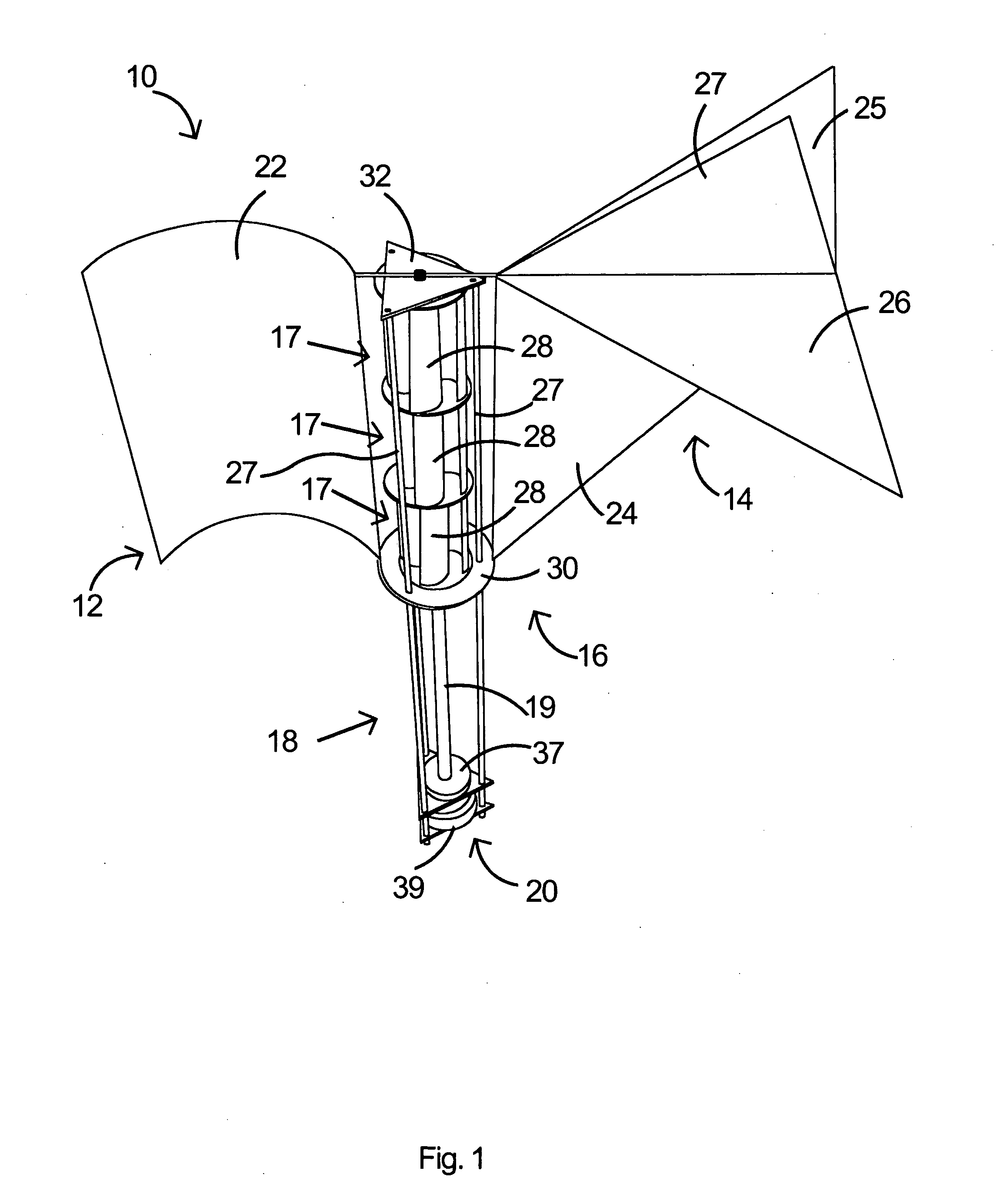
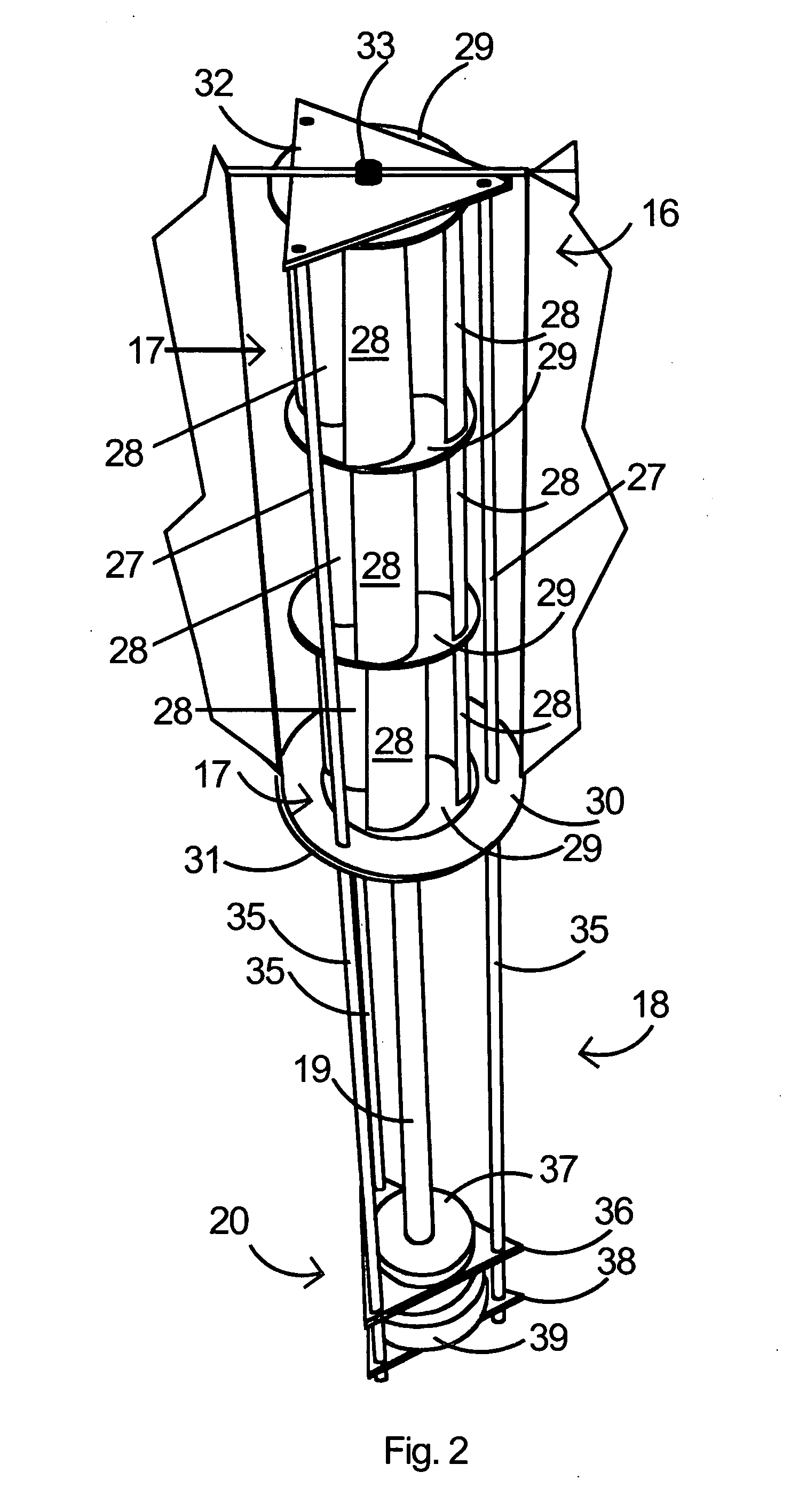
Aerodynamic-hybrid vertical-axis wind turbine
InactiveUS20060275105A1Eliminating salient back pressureEffectively and efficiently harnessingWind motor controlWind motor supports/mountsConvex sideVertical axis wind turbine
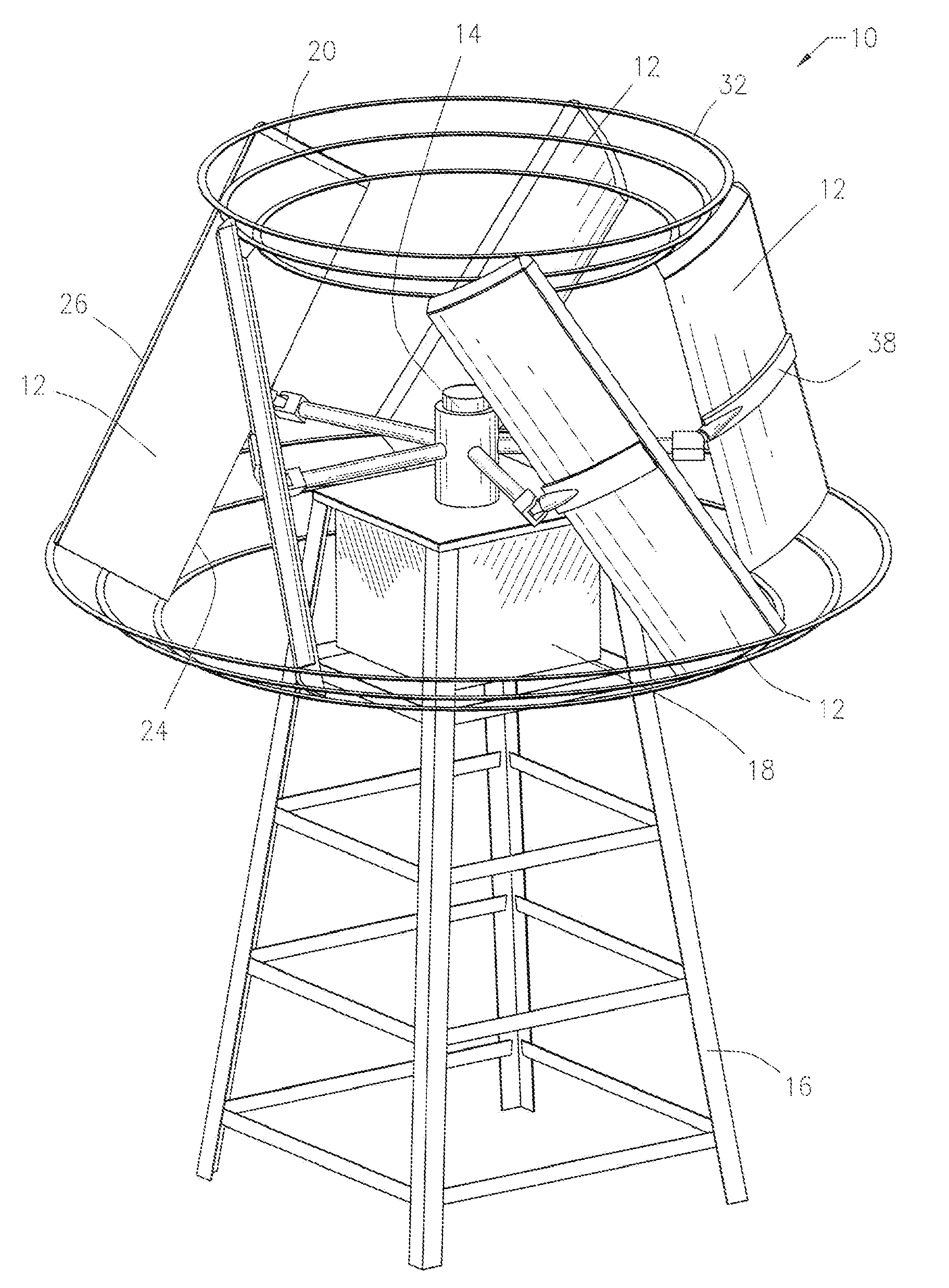
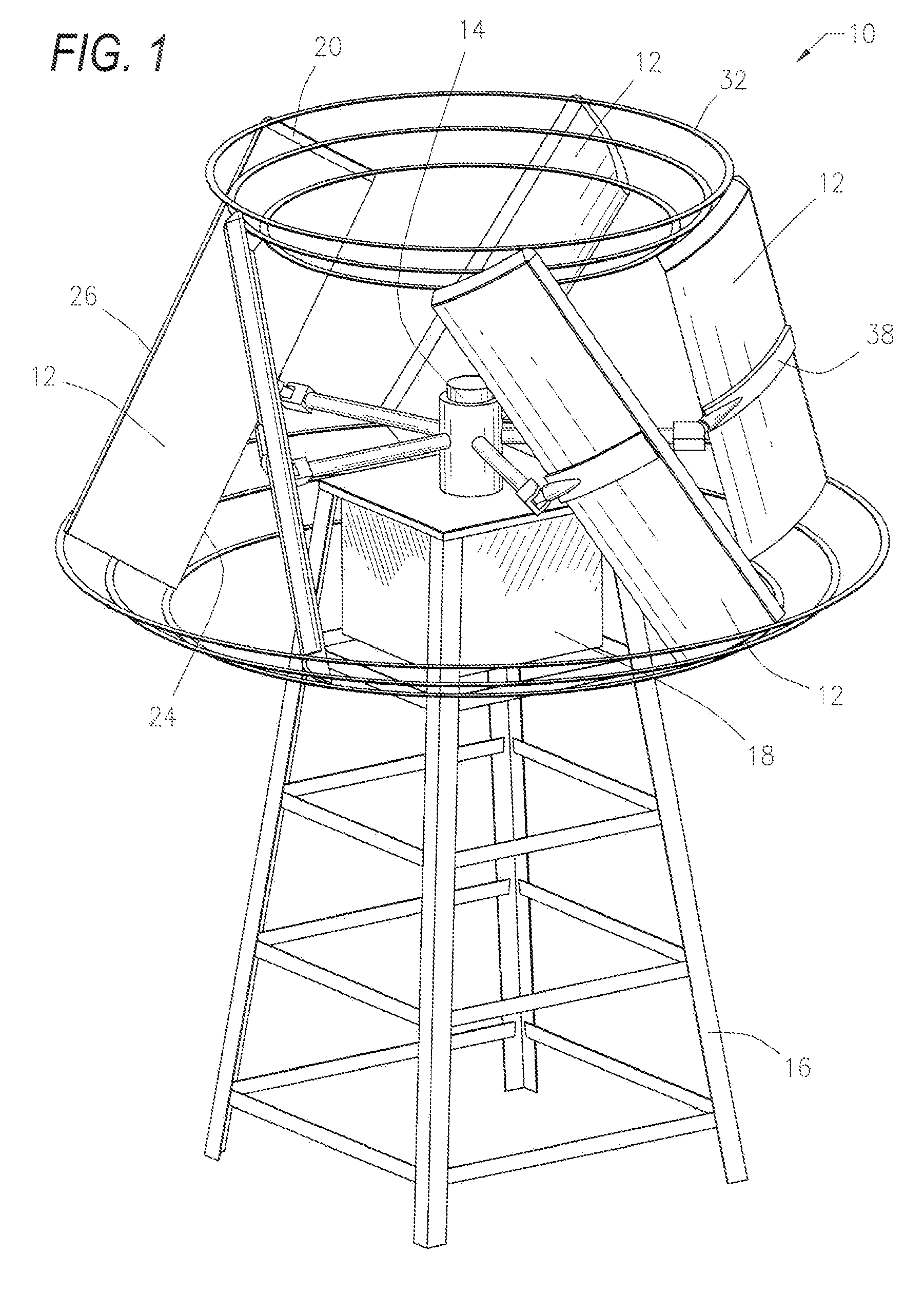
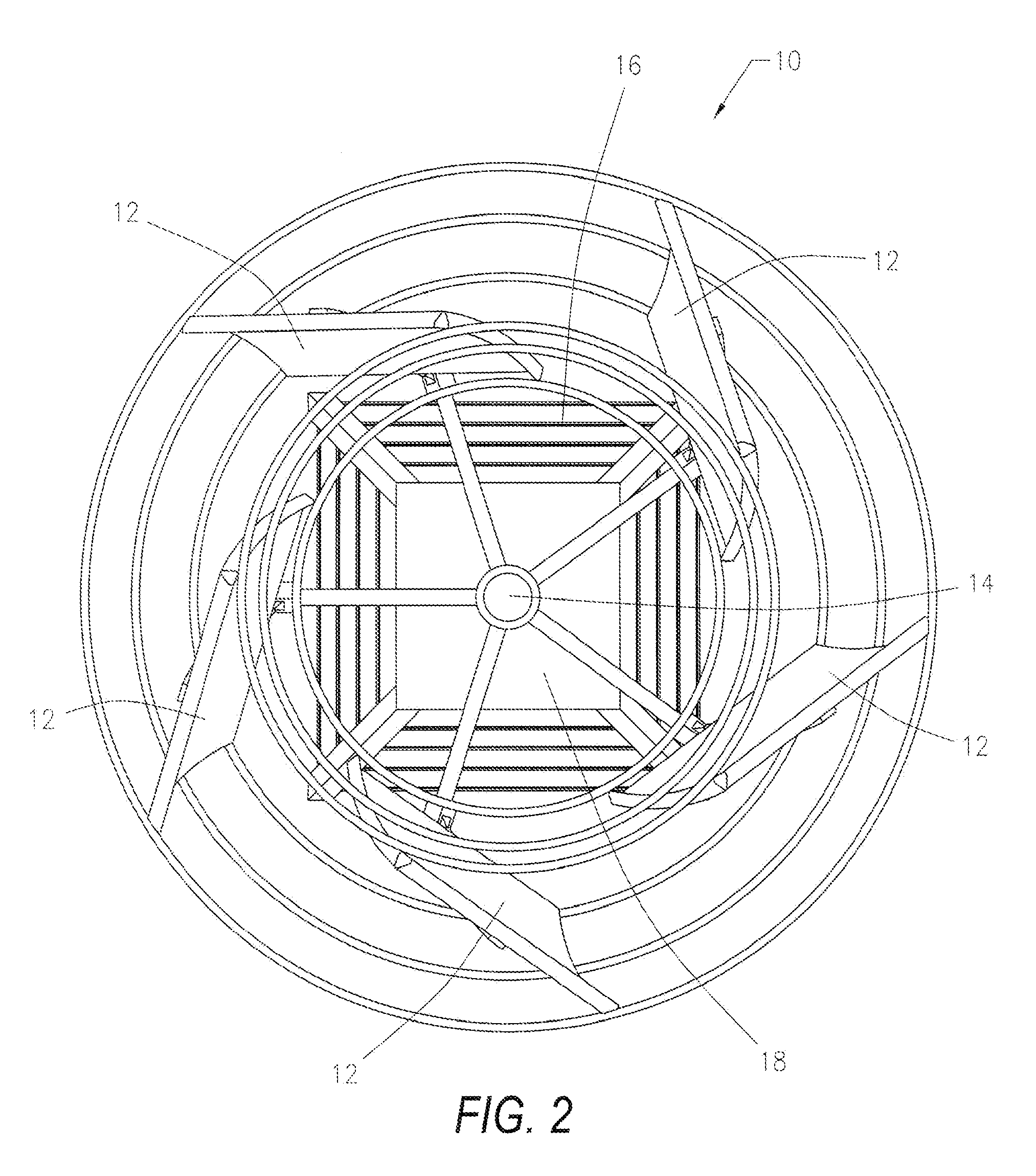
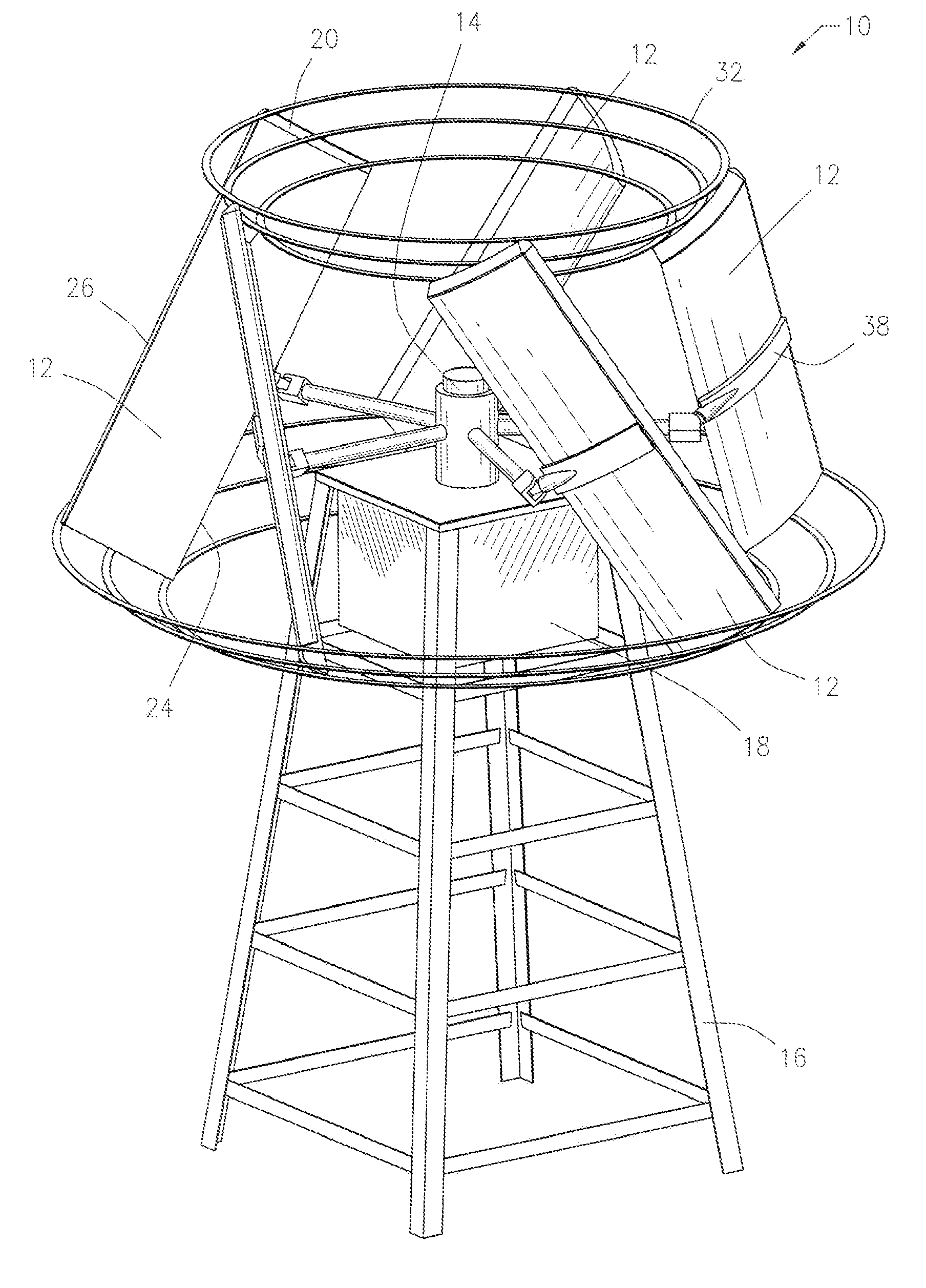
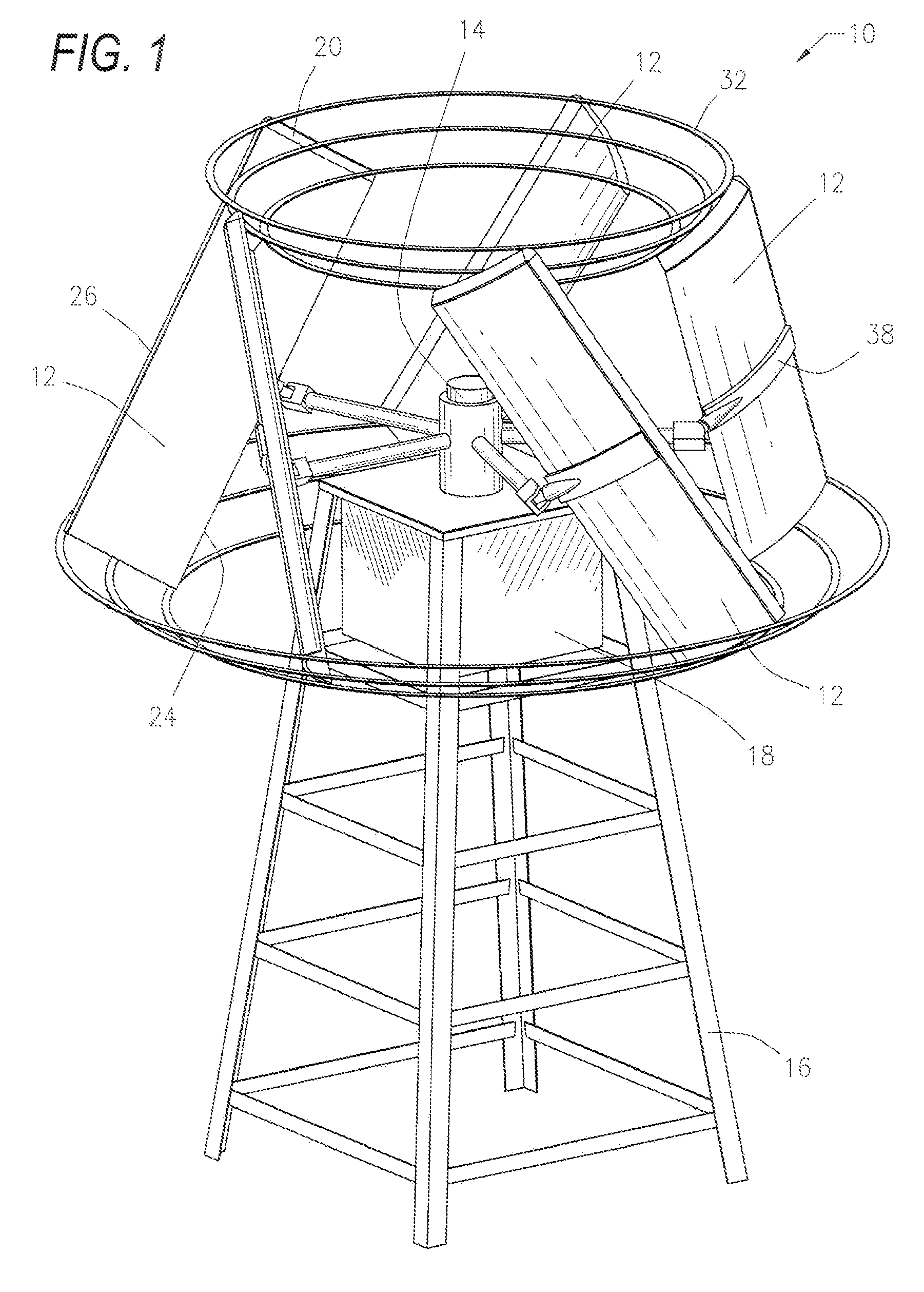
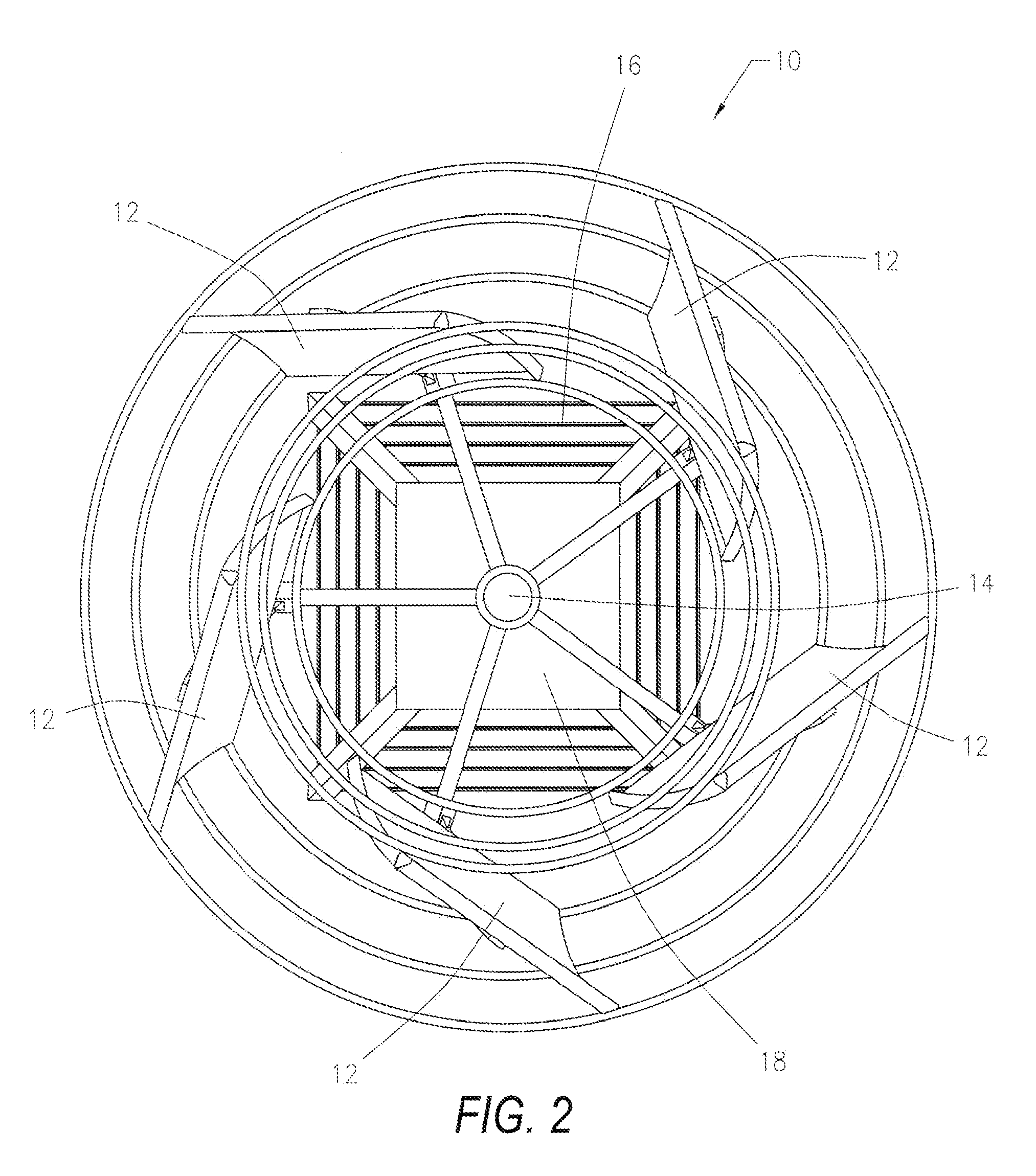
An aerodynamic-hybrid, vertical-axis wind turbine which includes a rotor airfoil and stator blade combination which maximizes energy production by increasing wind velocity and pressure while eliminating back pressure and improving the laminar flow of wind both around and through the device. The rotor airfoils have a horizontal cross-section with a crescent shape including a convex leading side and a concave trailing side with a thicker middle section that tapers to narrower sections at ends. The stator blades have a horizontal cross-section with a planar side and a convex side. Rotor airfoil and stator blade combinations are secured between upper and lower annular sails.
Owner:NOVASTRON
Wind turbine
A wind turbine operable as either a vertical axis wind turbine or a horizontal axis wind turbine is disclosed.
Owner:KANE VIC
Protective wind energy conversion chamber
ActiveUS7215037B2Improve efficiencyWind motor combinationsMachines/enginesHorizontal axisVertical axis wind turbine
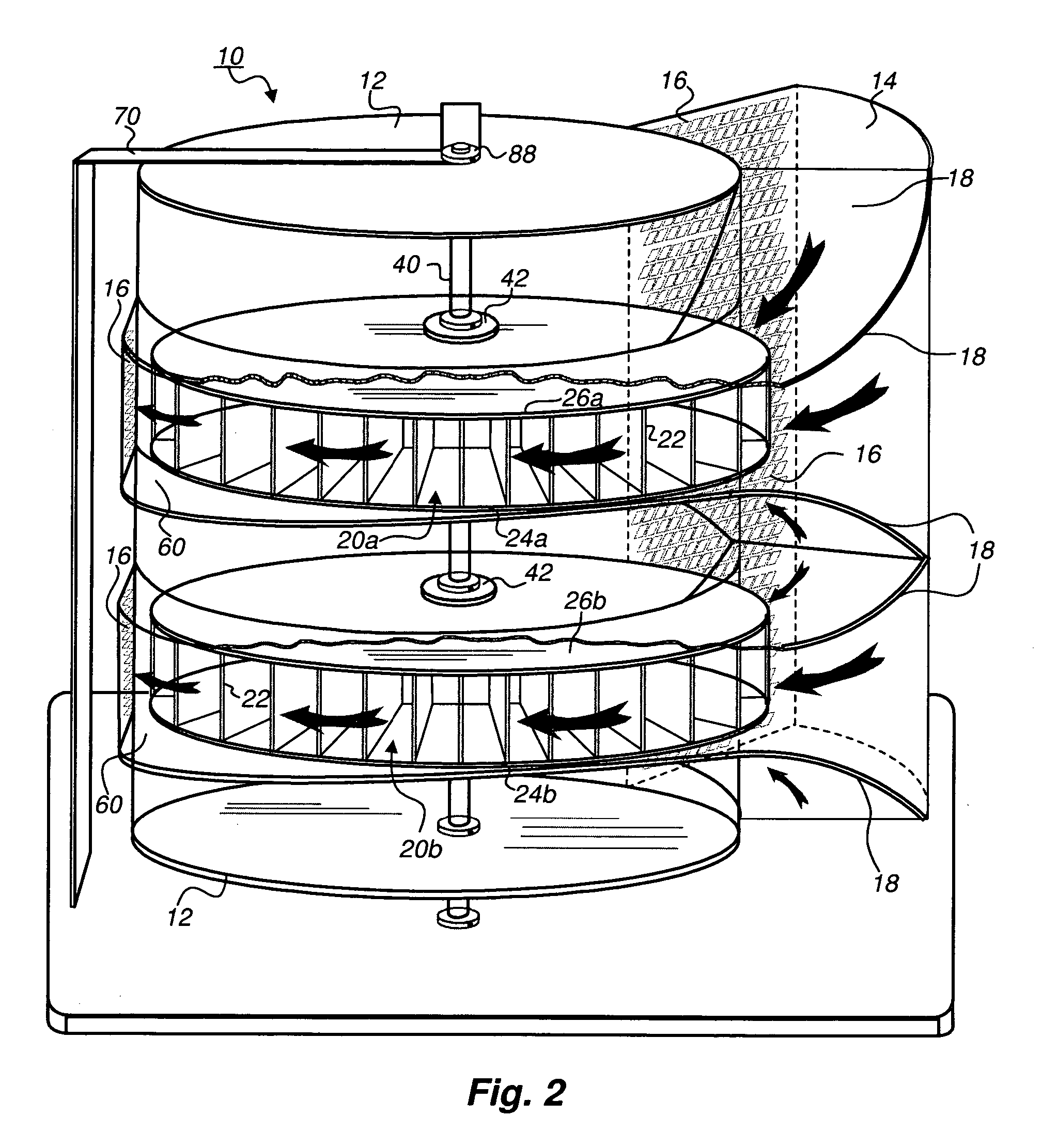
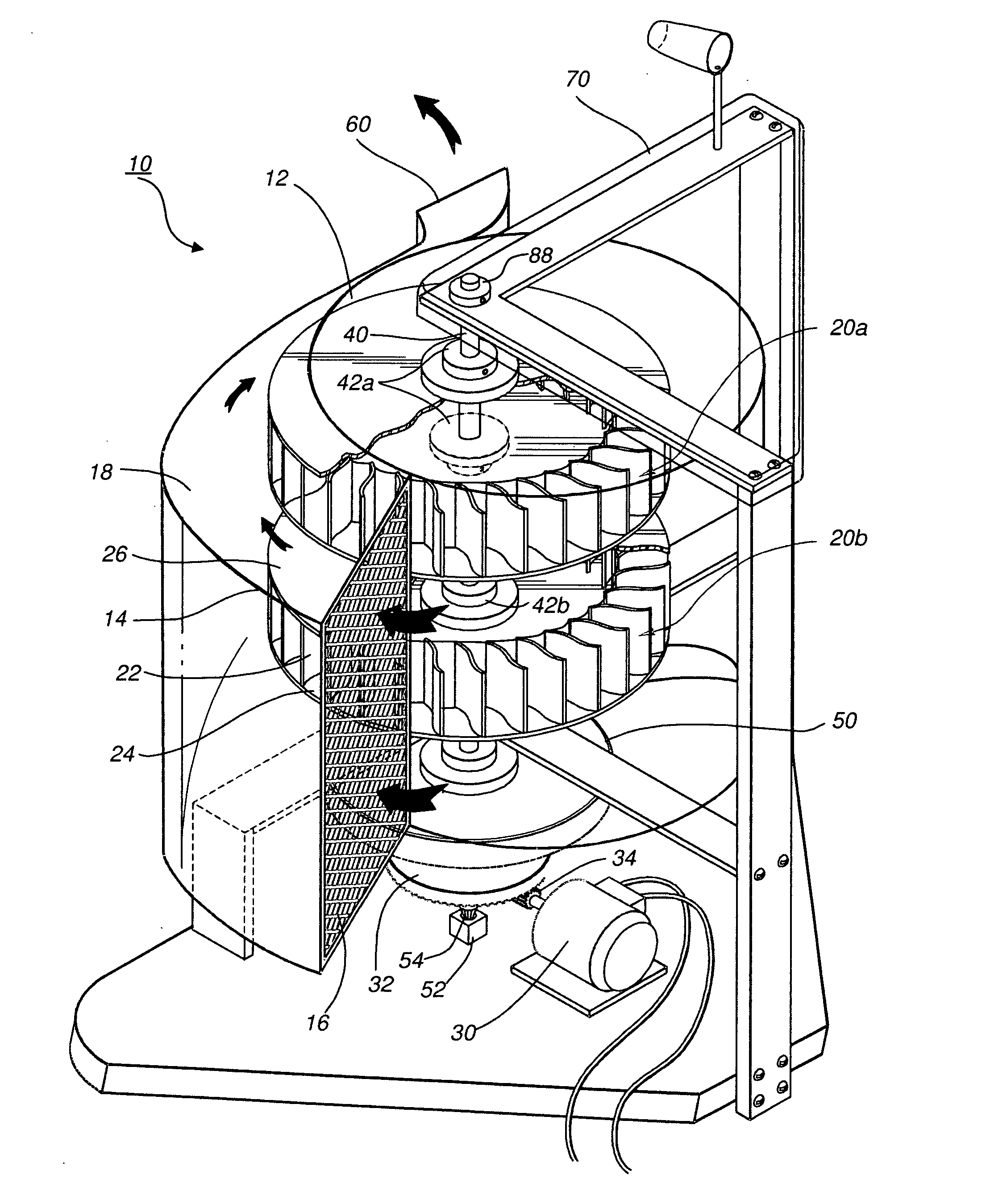
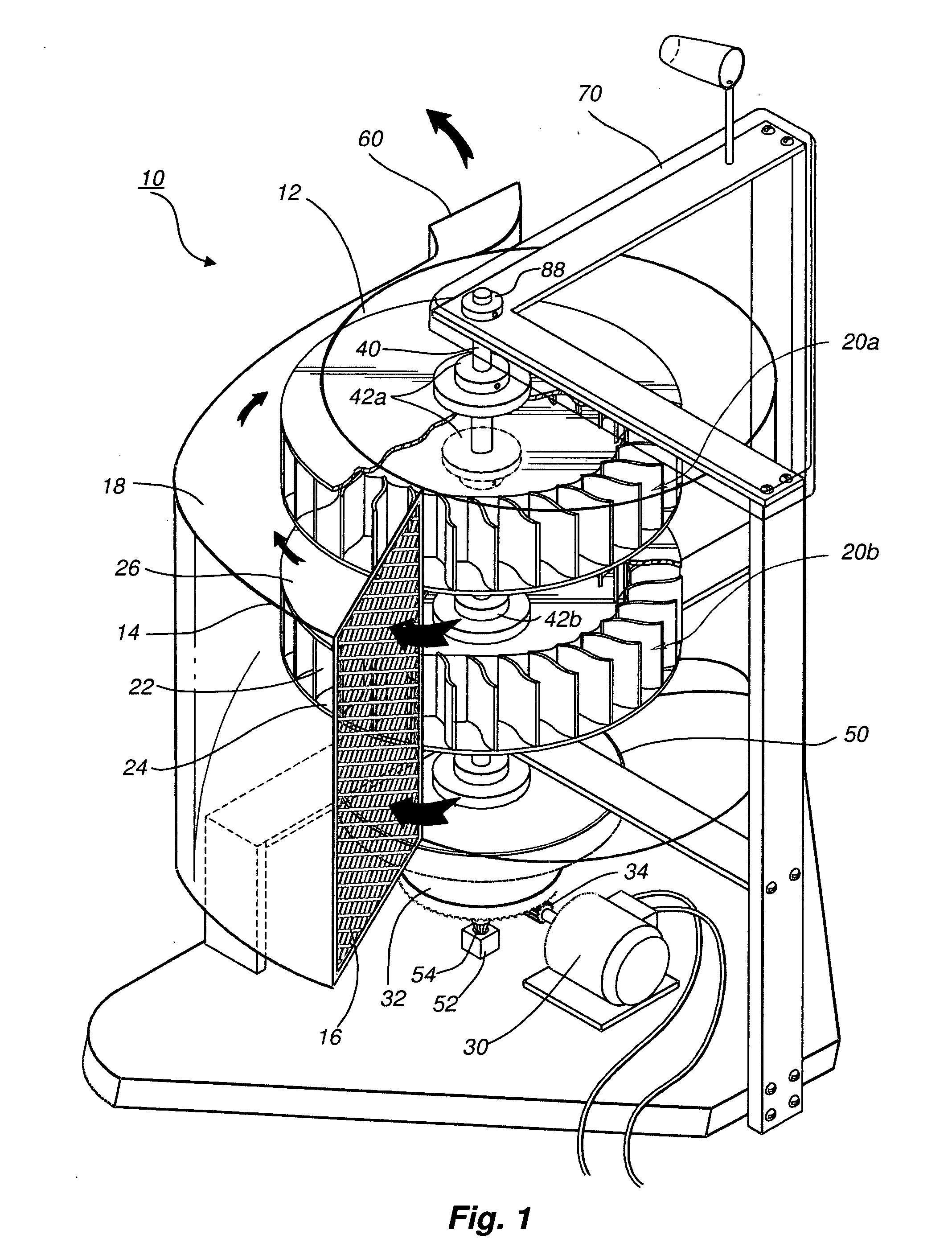
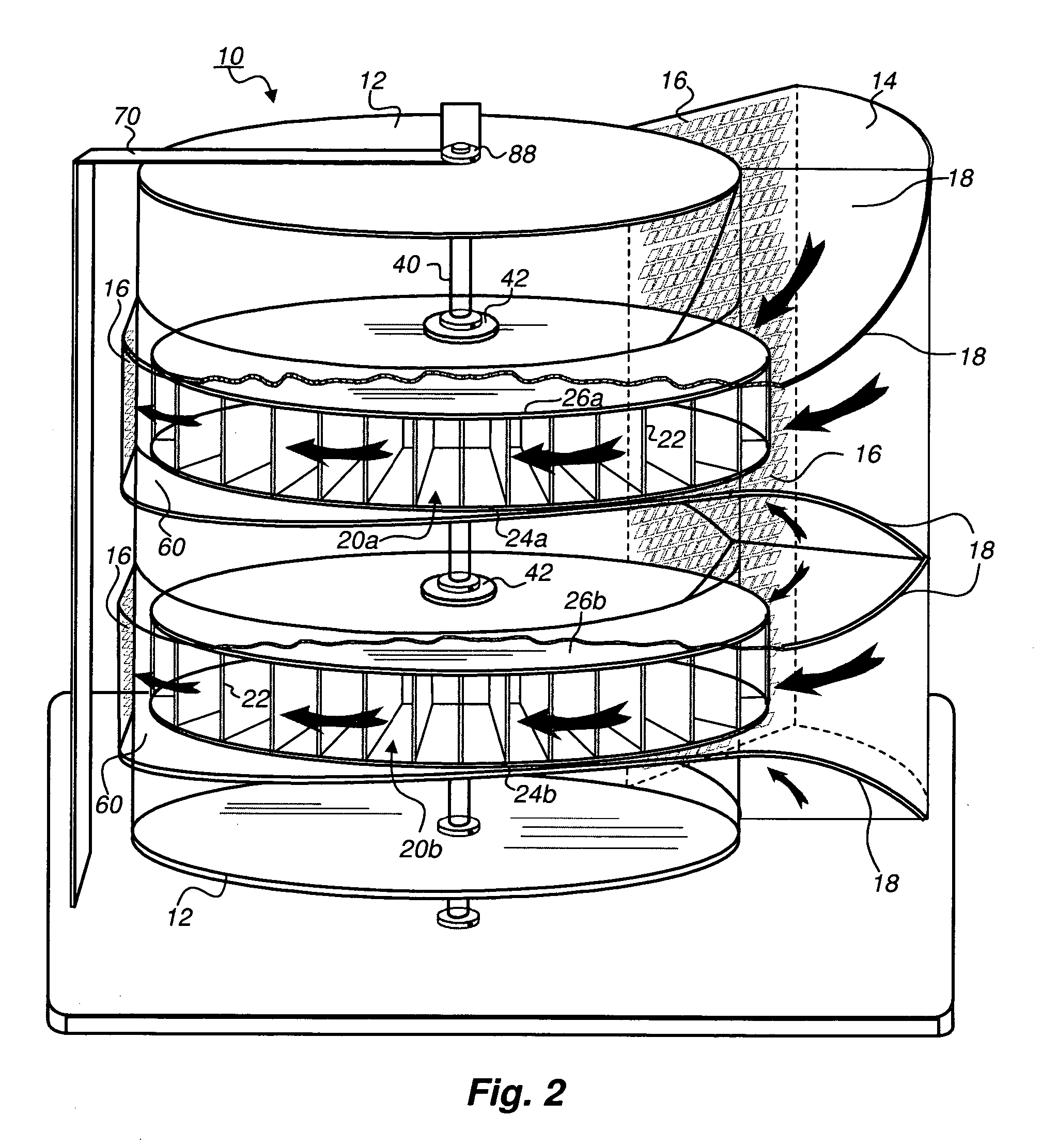
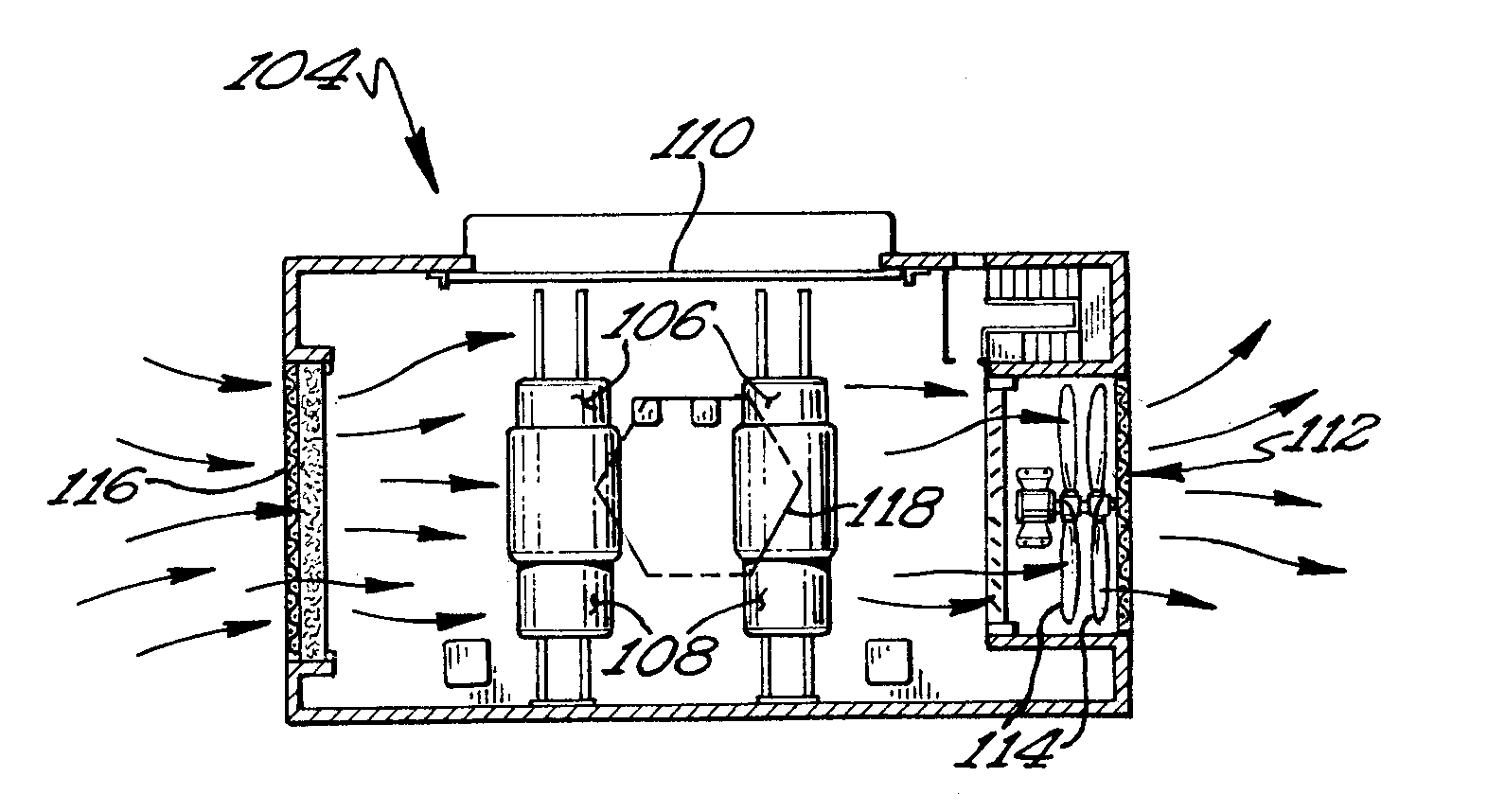
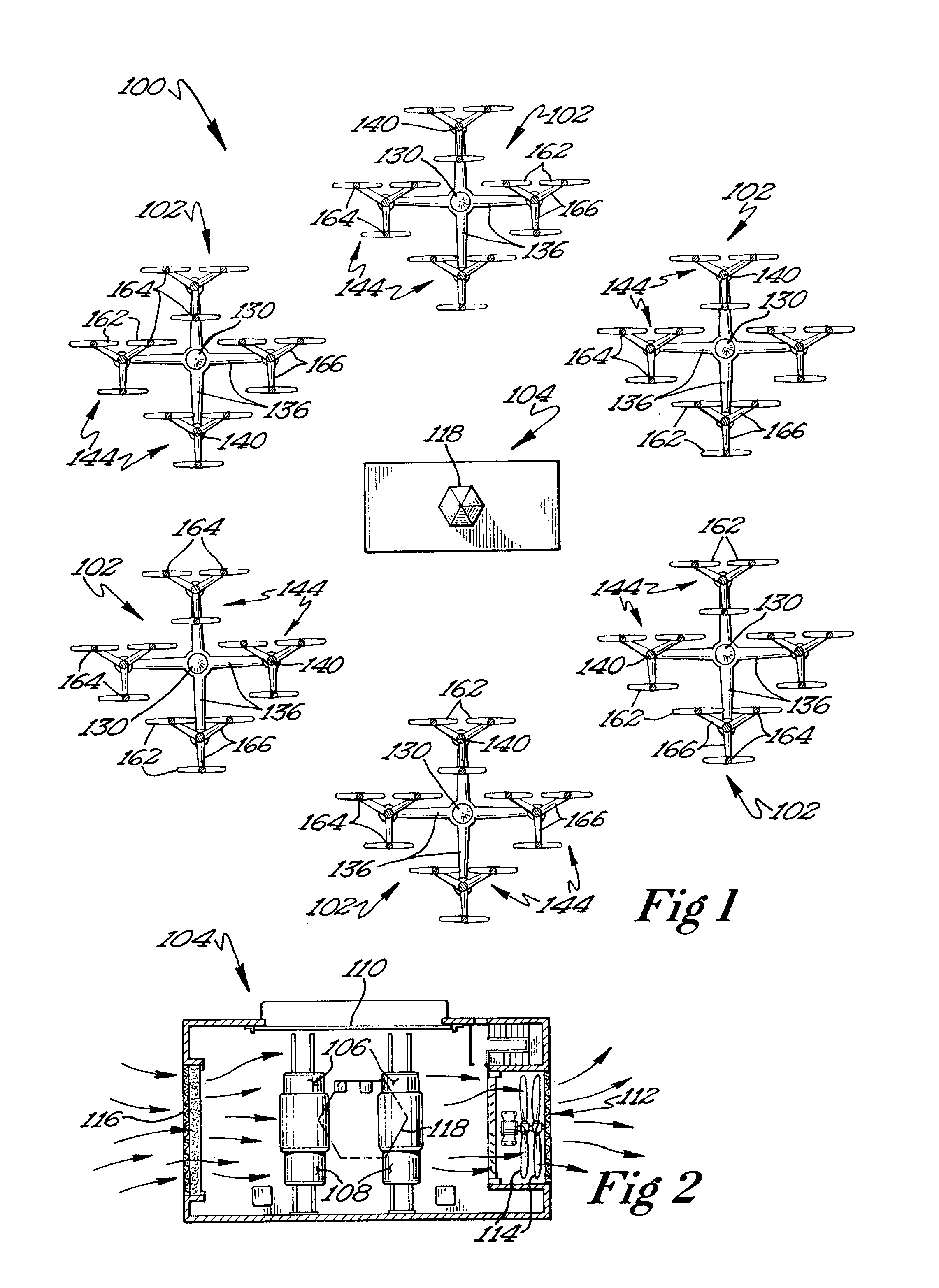
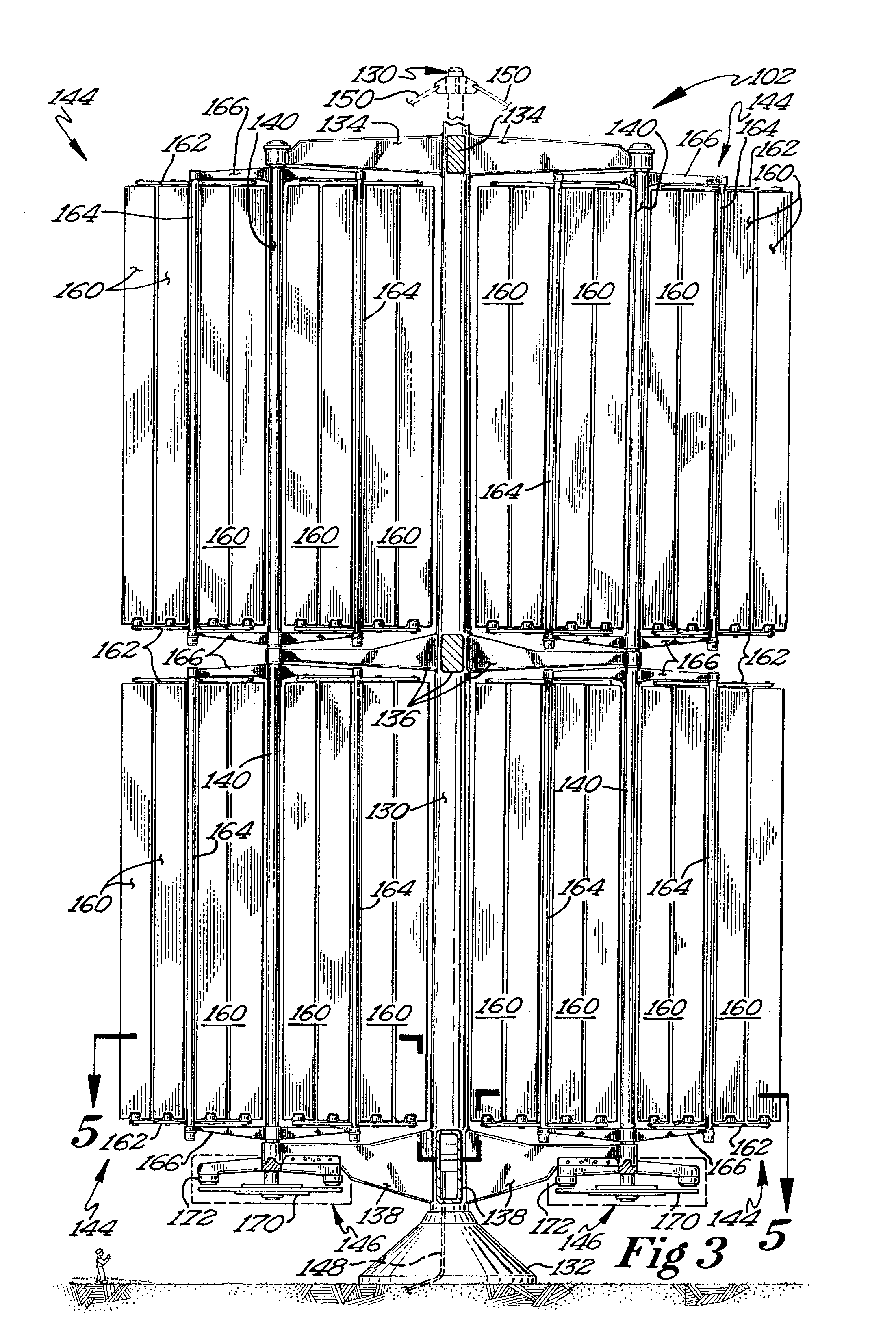
A protective wind energy conversion chamber provides a protected multiple turbine mechanism axially aligned to convert kinetic energy of a moving fluid (e.g., wind) into rotational mechanical power by the reaction of the moving fluid with the turbine. The conversion chamber may either be configured as a vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) or horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT). The conversion chamber repositions an intake windward to collect and concentrate the wind prior to converting the wind into energy via the axially aligned multi-turbine mechanism. The remaining wind is released via a leeward-facing exhaust. Completely enclosed by the protective wind energy conversion chamber, the axially aligned multi-turbine mechanism avoids interference by birds and other outside objects.
Owner:SCALZI SAVERIO
Aerodynamic-hybrid vertical-axis wind turbine
InactiveUS7329965B2Eliminate back pressureEffective forceWind motor controlWind motor supports/mountsConvex sideVertical axis wind turbine
An aerodynamic-hybrid, vertical-axis wind turbine which includes a rotor airfoil and stator blade combination which maximizes energy production by increasing wind velocity and pressure while eliminating back pressure and improving the laminar flow of wind both around and through the device. The rotor airfoils have a horizontal cross-section with a crescent shape including a convex leading side and a concave trailing side with a thicker middle section that tapers to narrower sections at ends. The stator blades have a horizontal cross-section with a planar side and a convex side. Rotor airfoil and stator blade combinations are secured between upper and lower annular sails.
Owner:NOVASTRON
Helical wind turbine
InactiveUS7344353B2Efficient captureLower resistanceWind motor controlPump componentsLinear configurationWing configuration
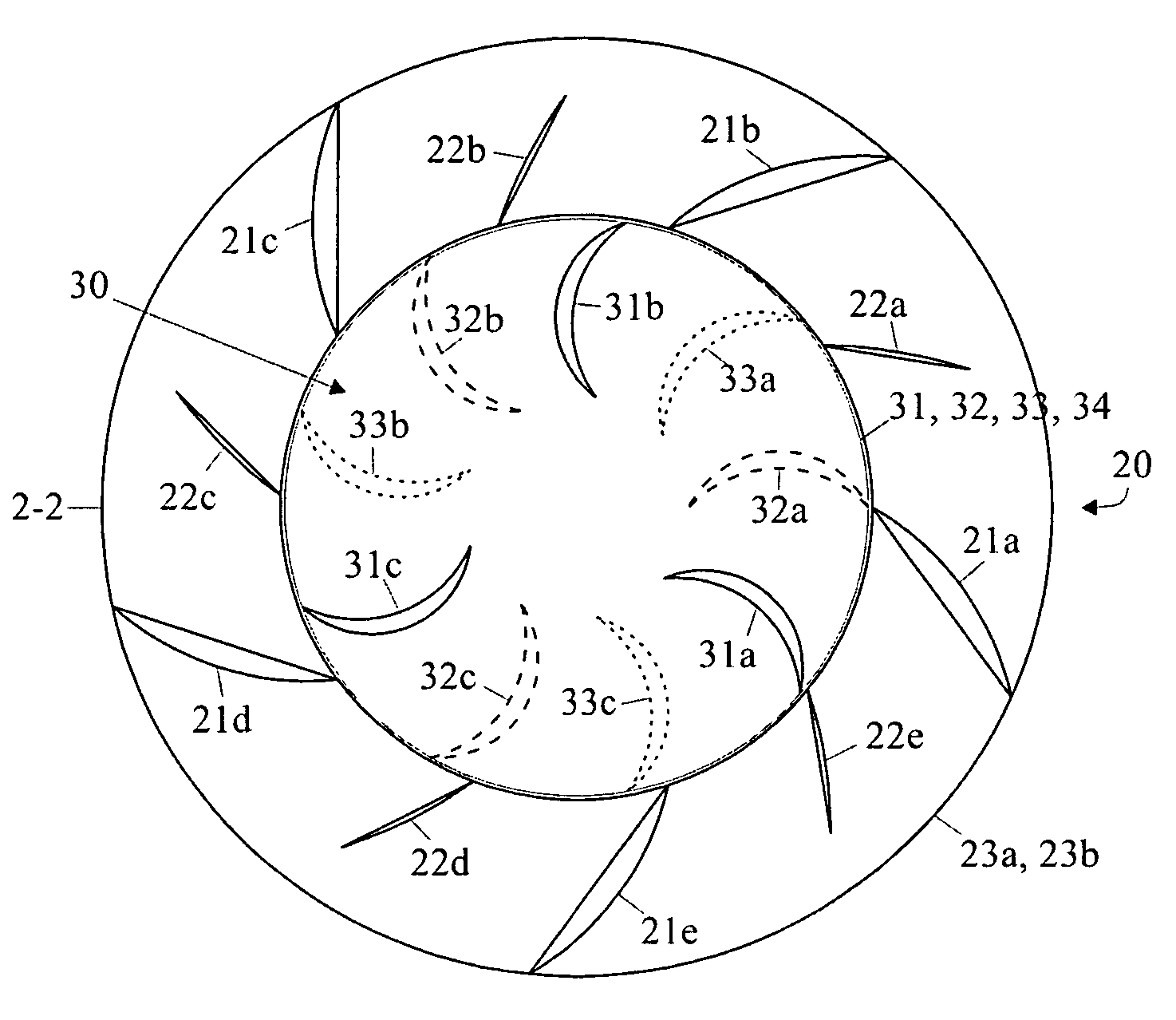
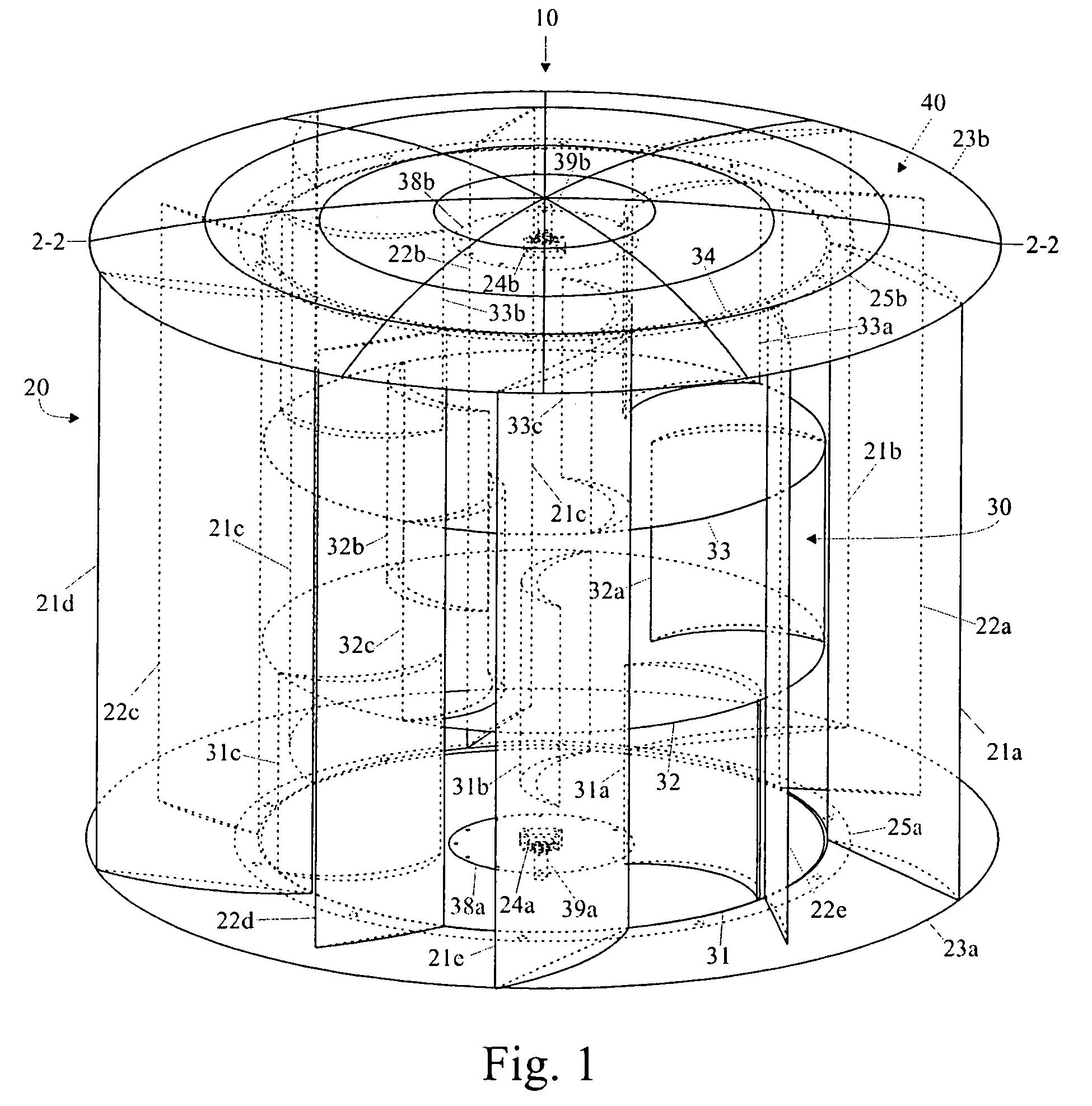
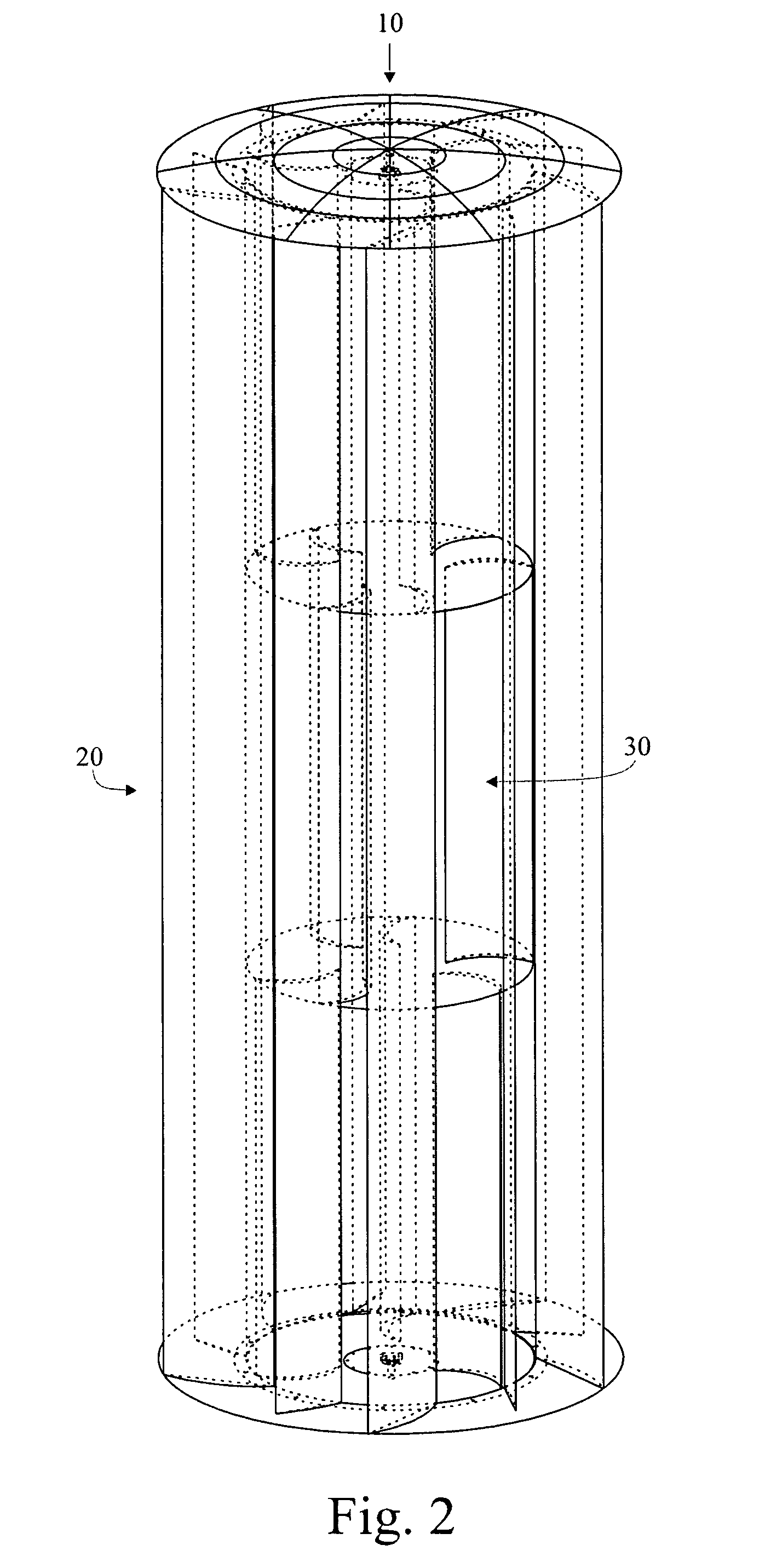
A vertical axis wind turbine wherein the blades of the rotor section of the wind turbine comprise at least sections wherein the blades have a non-linear configuration in the “z” axis. In a preferred embodiment, the blades of the rotor section have a linear trailing edge with a non-linear, and preferably helical, surface configuration. This particular design allows the blades to provide both a rotational force and a positive or negative lift component. Further, the blades define an open area in the center of the rotor section through which air flow can pass in order to create a vertical vortex of air. As such, a more efficient vertical axis wind turbine provided.
Owner:ARROWIND CORP
Helical wind turbine
InactiveUS20060257240A1Efficient captureLower resistancePump componentsWind motor controlLinear configurationSpecial design
A vertical axis wind turbine wherein the blades of the rotor section of the wind turbine comprise at least sections wherein the blades have a non-linear configuration in the “z” axis. In a preferred embodiment, the blades of the rotor section have a linear trailing edge with a non-linear, and preferably helical, surface configuration. This particular design allows the blades to provide both a rotational force and a positive or negative lift component. Further, the blades define an open area in the center of the rotor section through which air flow can pass in order to create a vertical vortex of air. As such, a more efficient vertical axis wind turbine provided.
Owner:ARROWIND CORP
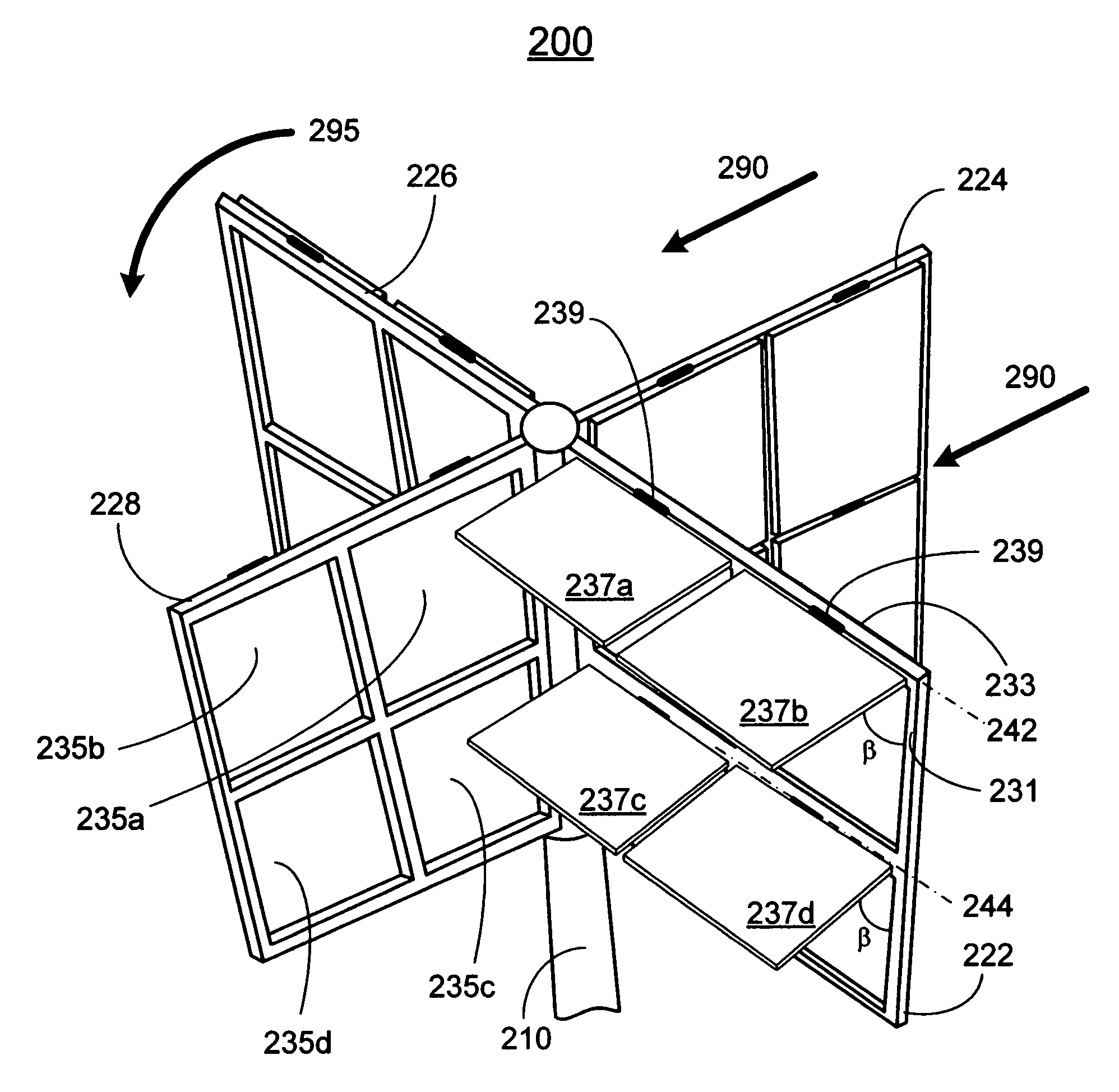
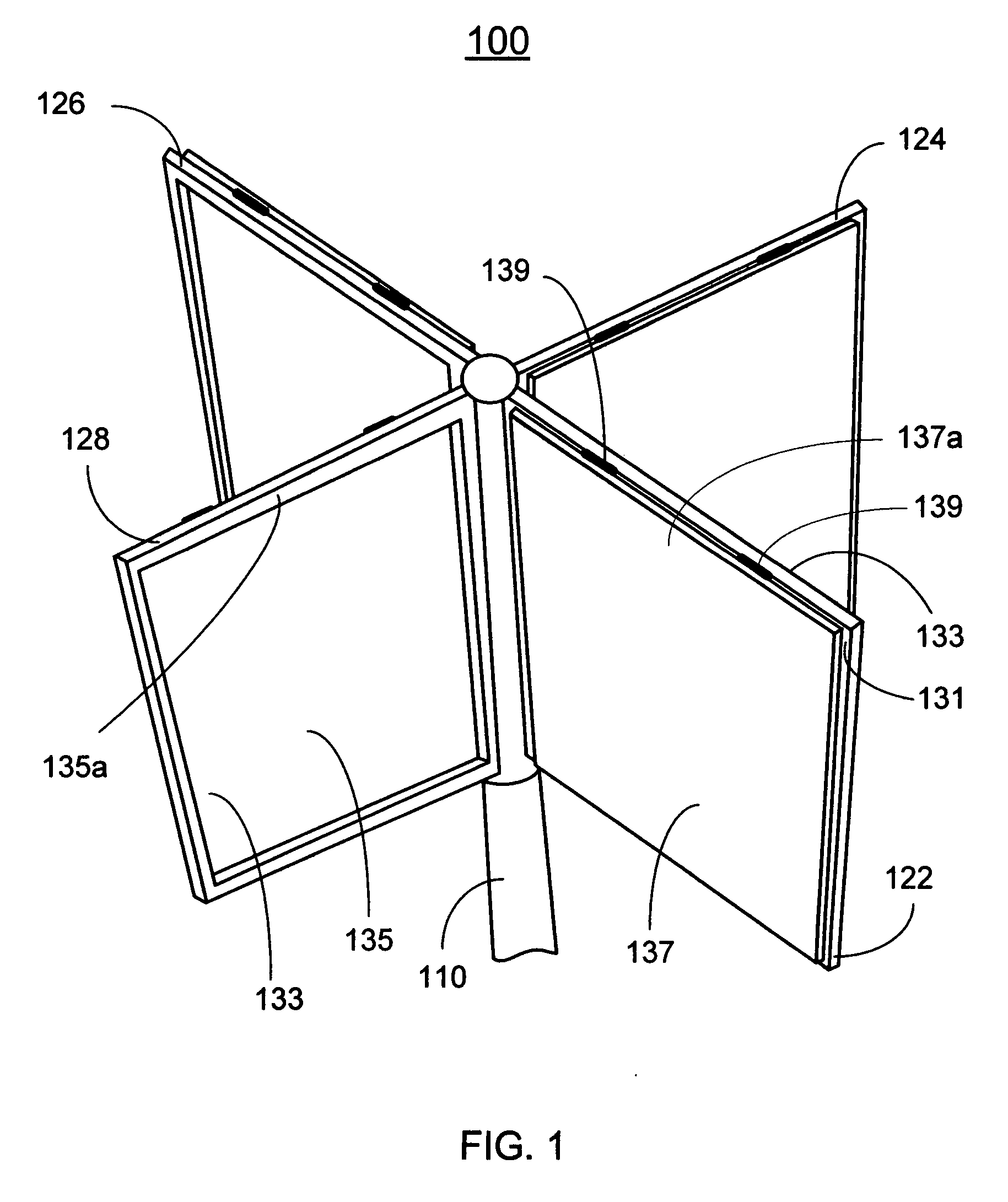
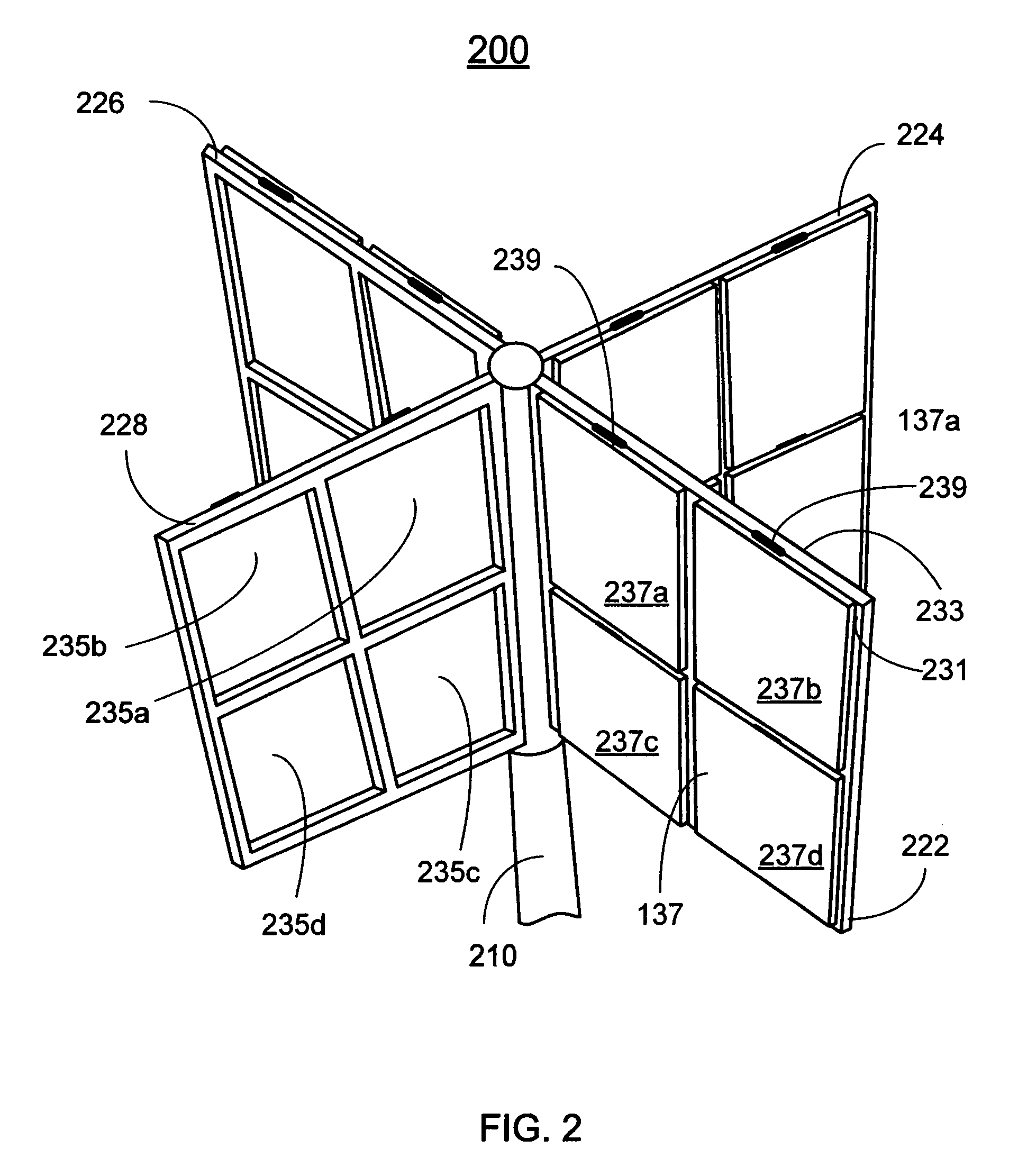
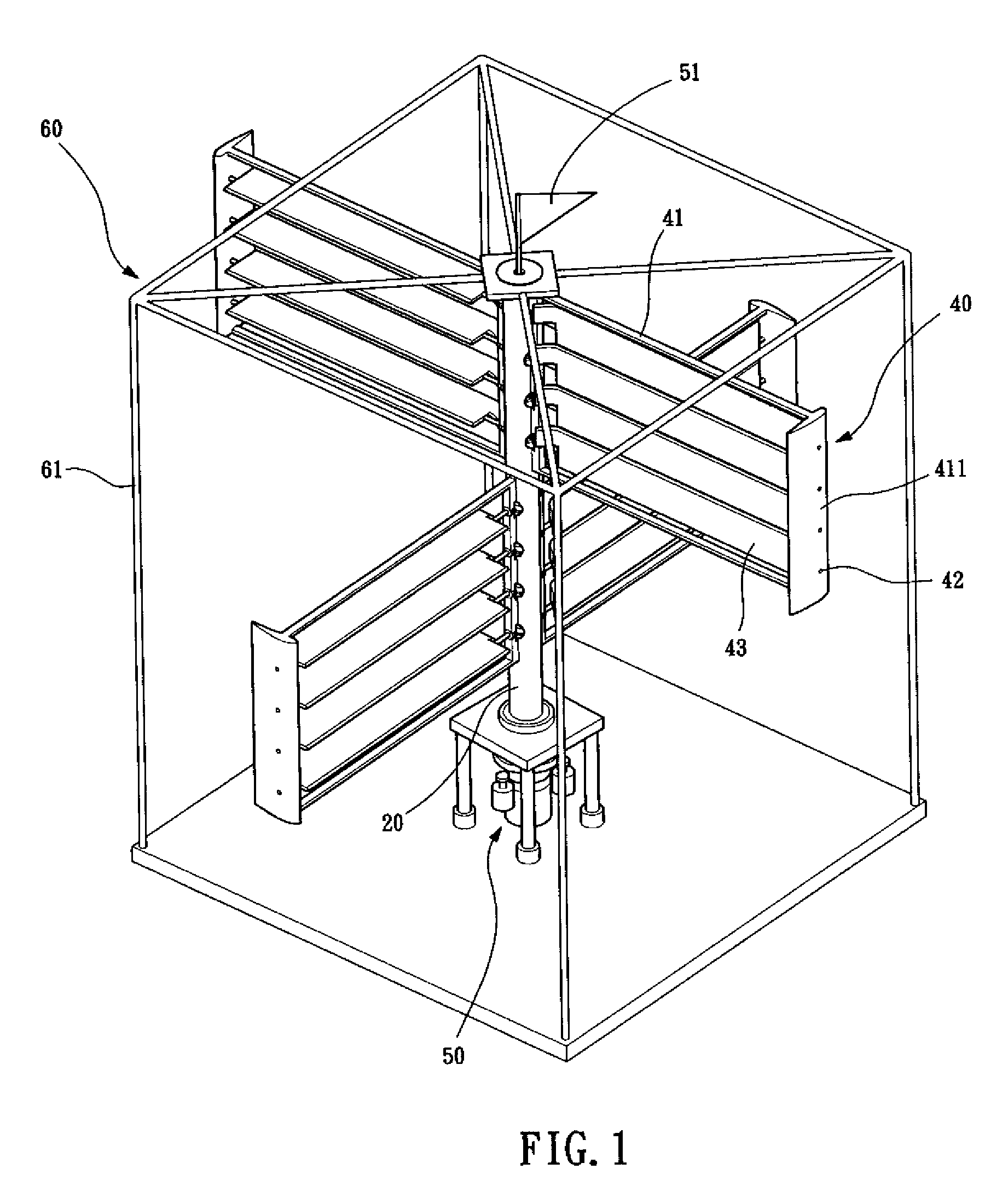
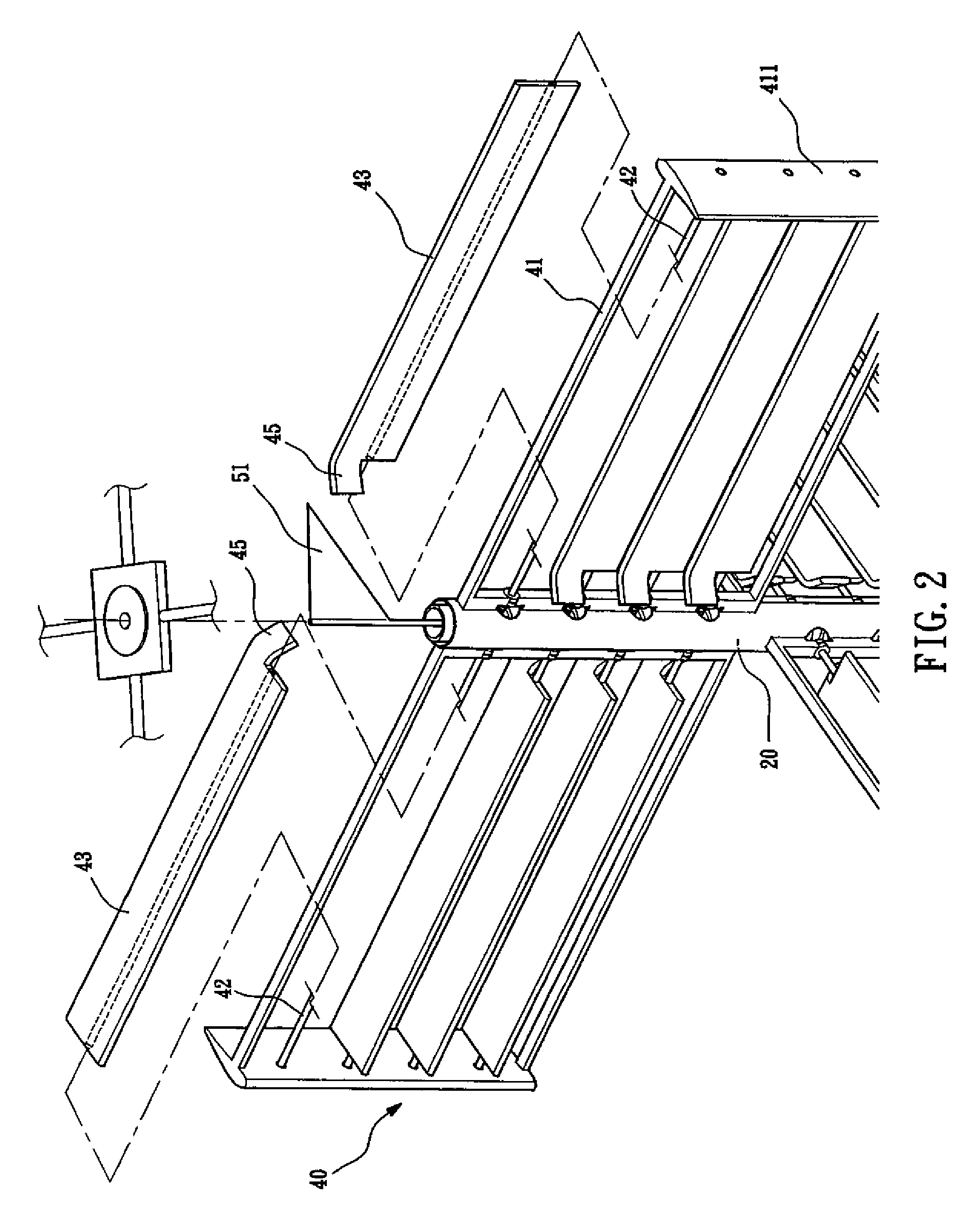
Vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS6942454B2Improve efficiencyPropellersWind motor controlAxis of symmetryVertical axis wind turbine
The vertical axis wind turbine has two counter-rotating rotors mounted on first and second spaced apart vertical axes. Each rotor has a plurality of rotor blades extending generally inwardly from an outer circumference, the vertical axes being mounted on a support structure which is in turn rotatable on a third vertical axis on a platform. The third axis is spaced from a point midway between the first and second axes in a direction at 90 degrees to and forward from a line between the first and second axes. The vertical axis wind turbine further has a guide vane mounted on the support structure, having a vertex forward of the third vertical axis in the direction at 90 degrees from a line between the first and second axes. The guide vane has left and right symmetrical vane portions extending towards the rotors so as to direct airflow from wind primarily towards portions of the rotors outboard of the first and second axes. The guide vane also tends to keep the vertical axis wind turbine oriented with the guide vane's axis of symmetry pointing forwardly into the wind. Movable deflector flaps pivotally mounted adjacent opposite ends of the vane portions can deflect air at least partially away from the rotors. The structure of the wind turbine can support an unrelated structure such as a restaurant.
Owner:OHLMANN HANS ARMIN
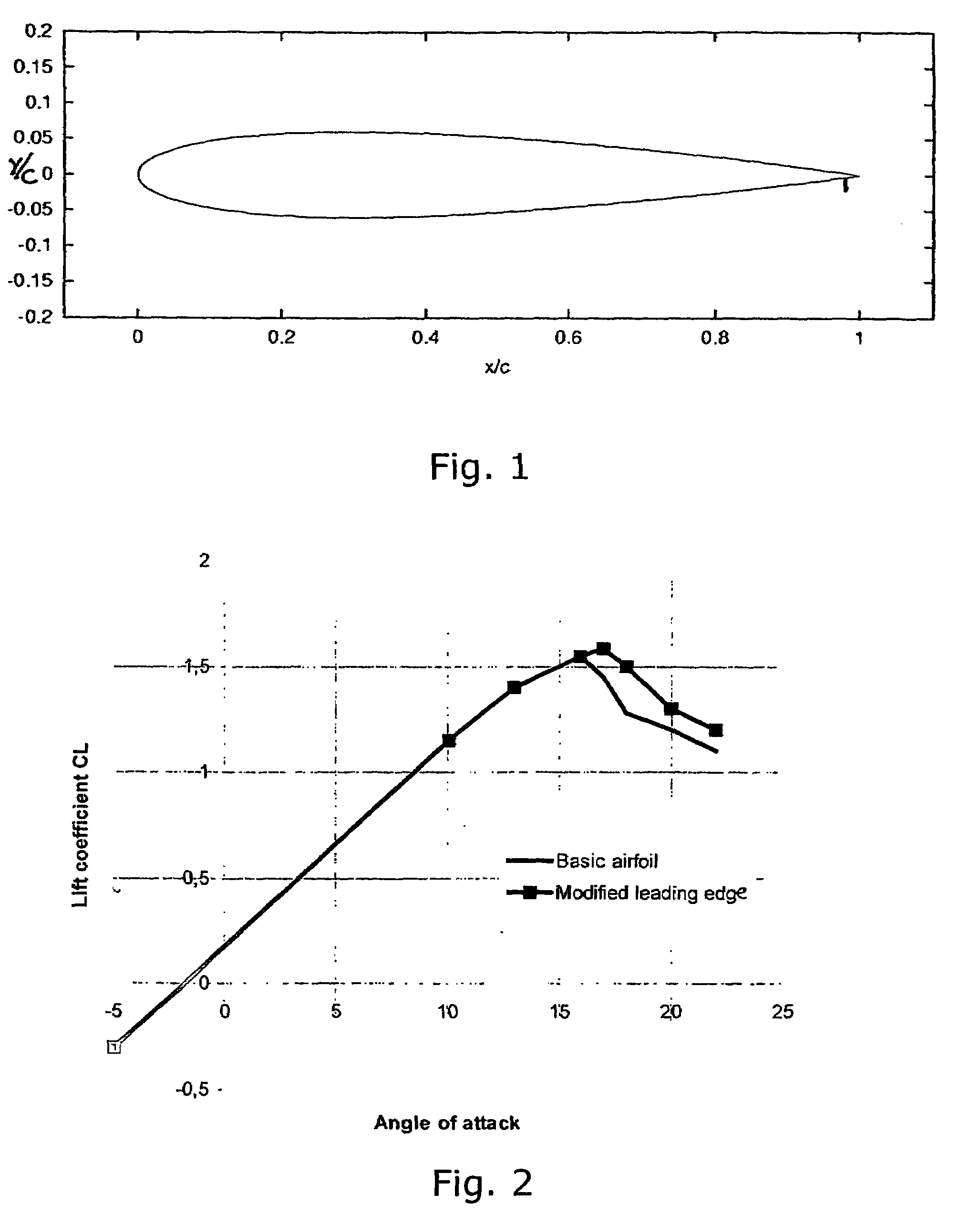
Vertical axis wind turbine with optimized blade profile
InactiveUS20070104582A1Wind motor controlOther chemical processesLeading edgeVertical axis wind turbine
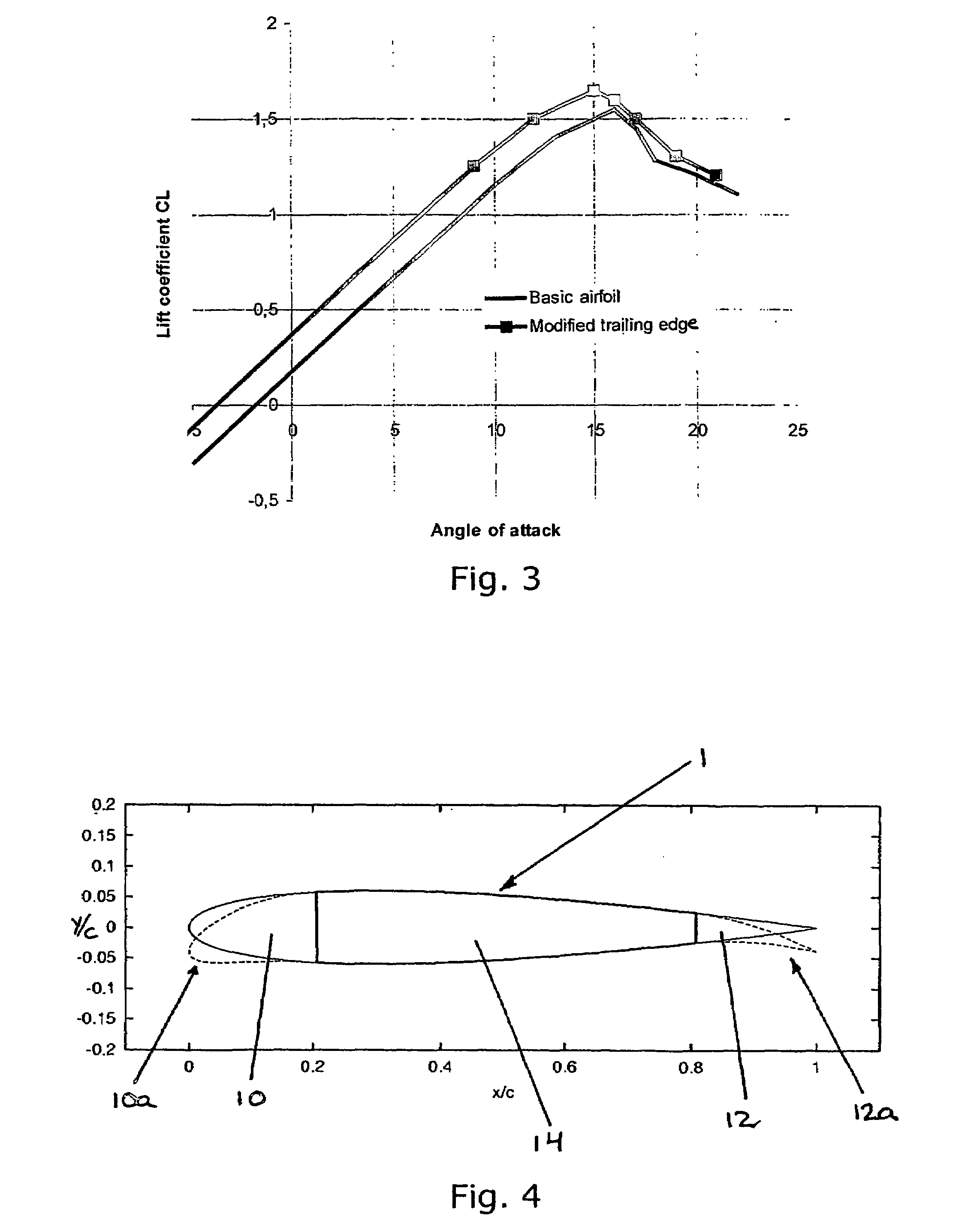
A high efficiency vertical axis wind turbine includes an optimized blade shape for increased torque output. The shape of the optimized profile includes a camber portion at a leading edge region of the blade with a maximum height to chord ratio (Y / C) at when the non-dimensional chord length (X / C) is approximately one third. An intermediate region follows the leading edge region and is characterized by a shallow convex region, followed by a flow reattachment surface at the trailing edge region characterized by a second concave region and a local maximum of the height to chord ratio at approximately four fifths of the non-dimensional chord length.
Owner:VIA VERDE LTD
Vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS6242818B1Rotational speed controlWind motor controlVertical axis wind turbineGravitational force
A vertical axis wind turbine having a plurality of blades around its periphery and a pivotable door associated with each blade. Each door has a pivot axis that is inclined outwardly toward the bottom of the turbine so that gravitational forces will pull the doors toward an open position. The doors are designed to move toward a closed position to at least partially block wind forces from the blades when the rotor rotates at potentially damaging speeds. The turbine has mating coils on the rotor and the support column to generate electrical energy when the rotor rotates.
Owner:SMEDLEY RONALD H
Vertical axis wind turbine and generator therefore
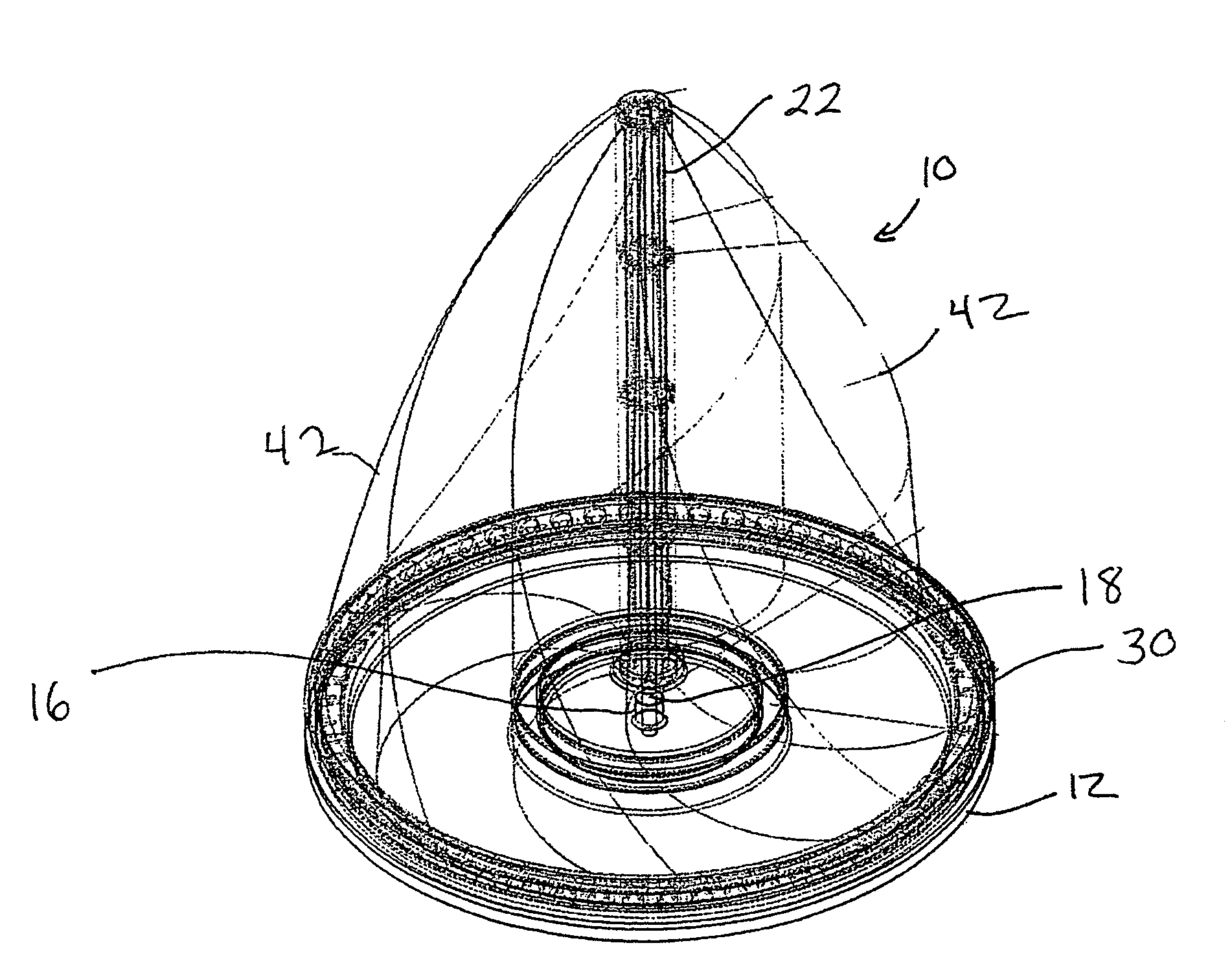
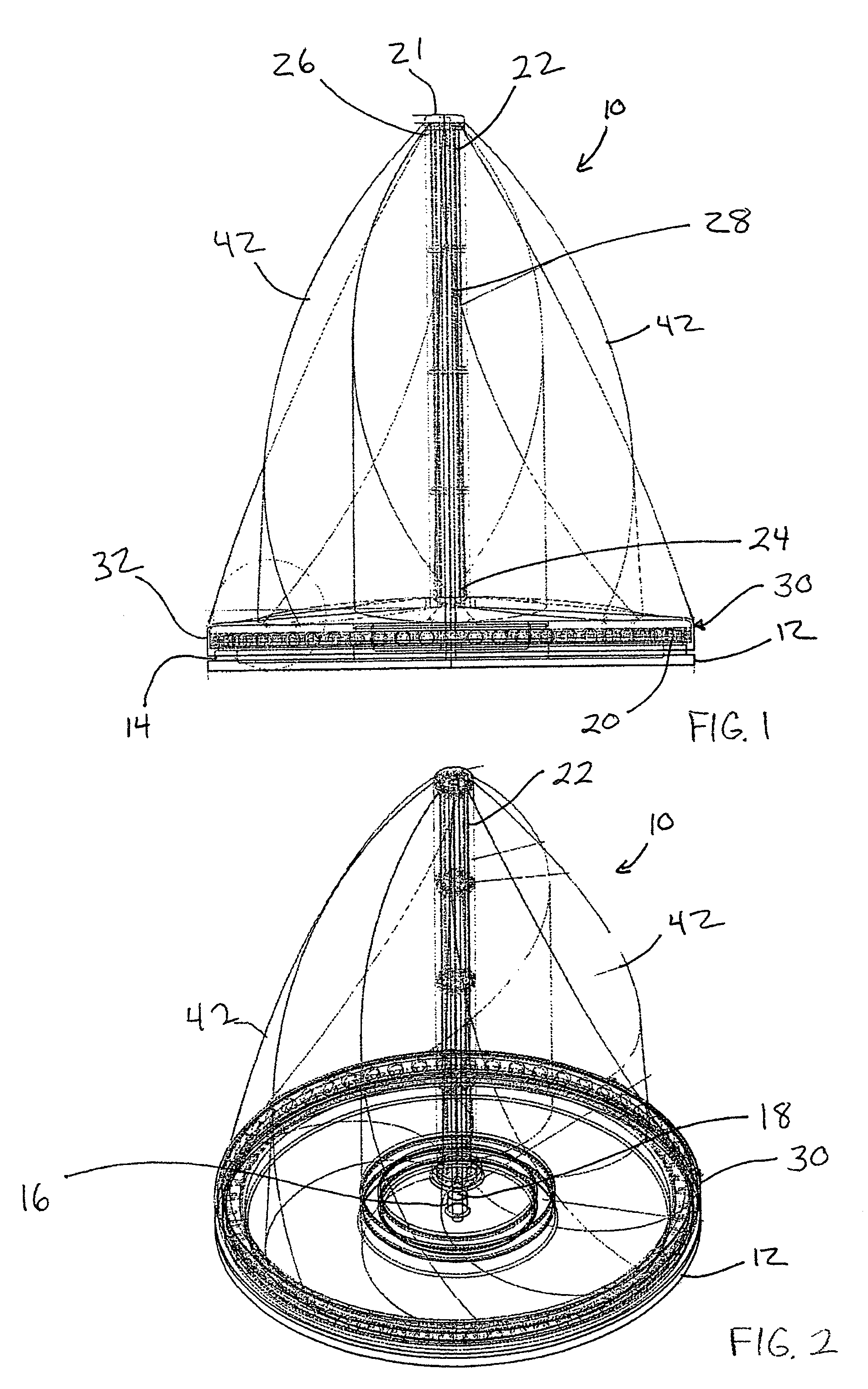
A vertical wind turbine is provided that includes a support base defined about an axis, a bearing assembly, a drive shaft having a proximal end and an opposing distal end, and a multistage axial flux generator. The bearing assembly includes a fixed ring and a rotating ring, wherein the fixed ring is coupled to the support base. The drive shaft is coupled to the rotating ring of the bearing assembly, and a plurality of sails are coupled to the drive shaft. The multistage axial flux generator includes a rotor assembly coupled to the drive shaft and a stator assembly coupled to the support base. The rotor assembly includes a plurality of permanent magnets, and the stator assembly includes a plurality of coils defining at least two voltage output stages. The permanent magnets on the rotor assembly are close-coupled to the coils on the stator assembly.
Owner:GRASSMAN DEREK
Control of power, loads and/or stability of a horizontal axis wind turbine by use of variable blade geometry control
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Protective wind energy conversion chamber
ActiveUS20060108809A1Improve efficiencyImprove environmental safetyMachines/enginesWind motor combinationsHorizontal axisVertical axis wind turbine
A protective wind energy conversion chamber provides a protected multiple turbine mechanism axially aligned to convert kinetic energy of a moving fluid (e.g., wind) into rotational mechanical power by the reaction of the moving fluid with the turbine. The conversion chamber may either be configured as a vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) or horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT). The conversion chamber repositions an intake windward to collect and concentrate the wind prior to converting the wind into energy via the axially aligned multi-turbine mechanism. The remaining wind is released via a leeward-facing exhaust. Completely enclosed by the protective wind energy conversion chamber, the axially aligned multi-turbine mechanism avoids interference by birds and other outside objects.
Owner:SCALZI SAVERIO
Broad speed range generator
InactiveUS20100283252A1Harvest sustainable mechanical powerWide speed rangeWindingsMagnetic circuitPower qualityDc current
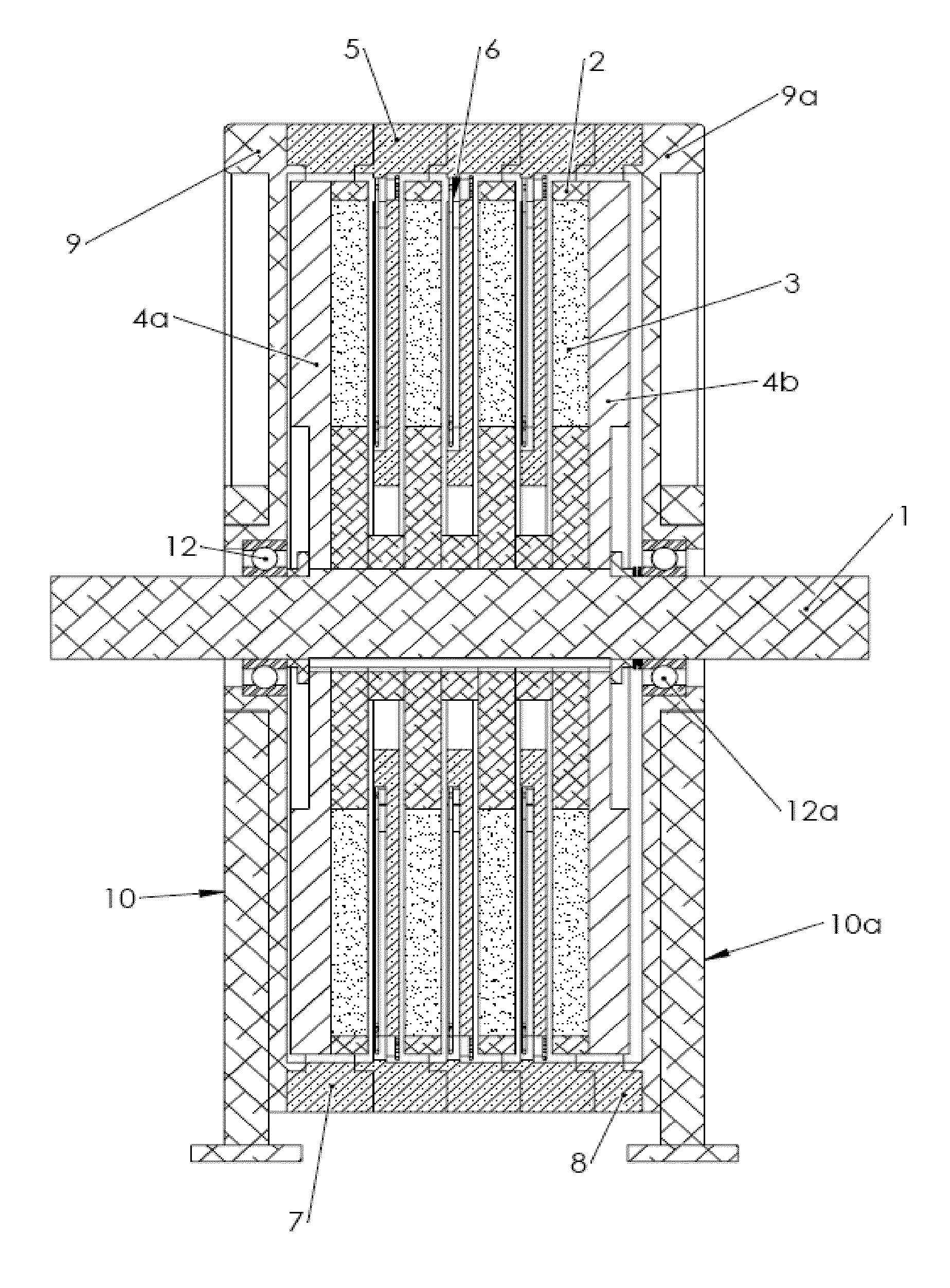
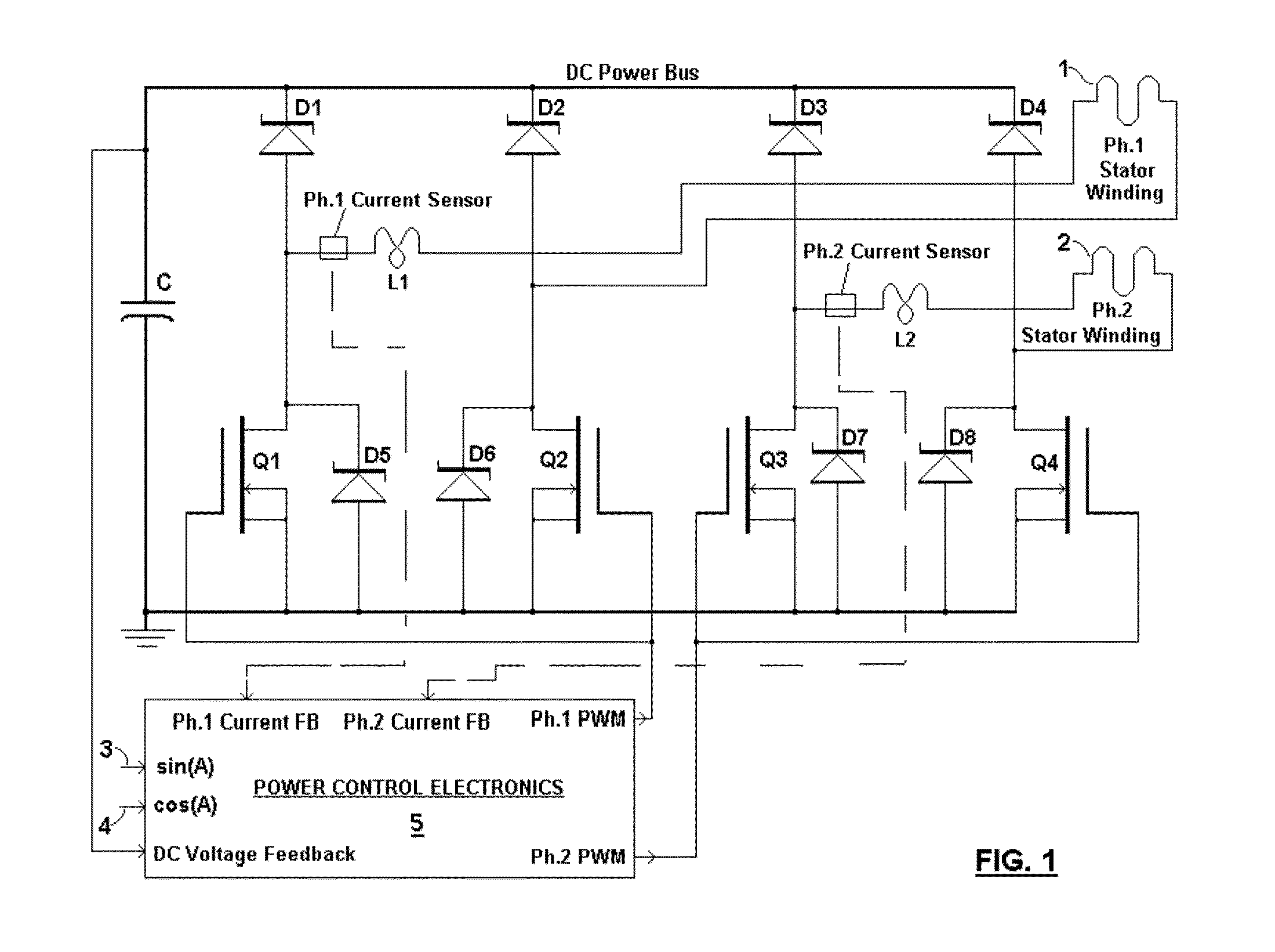
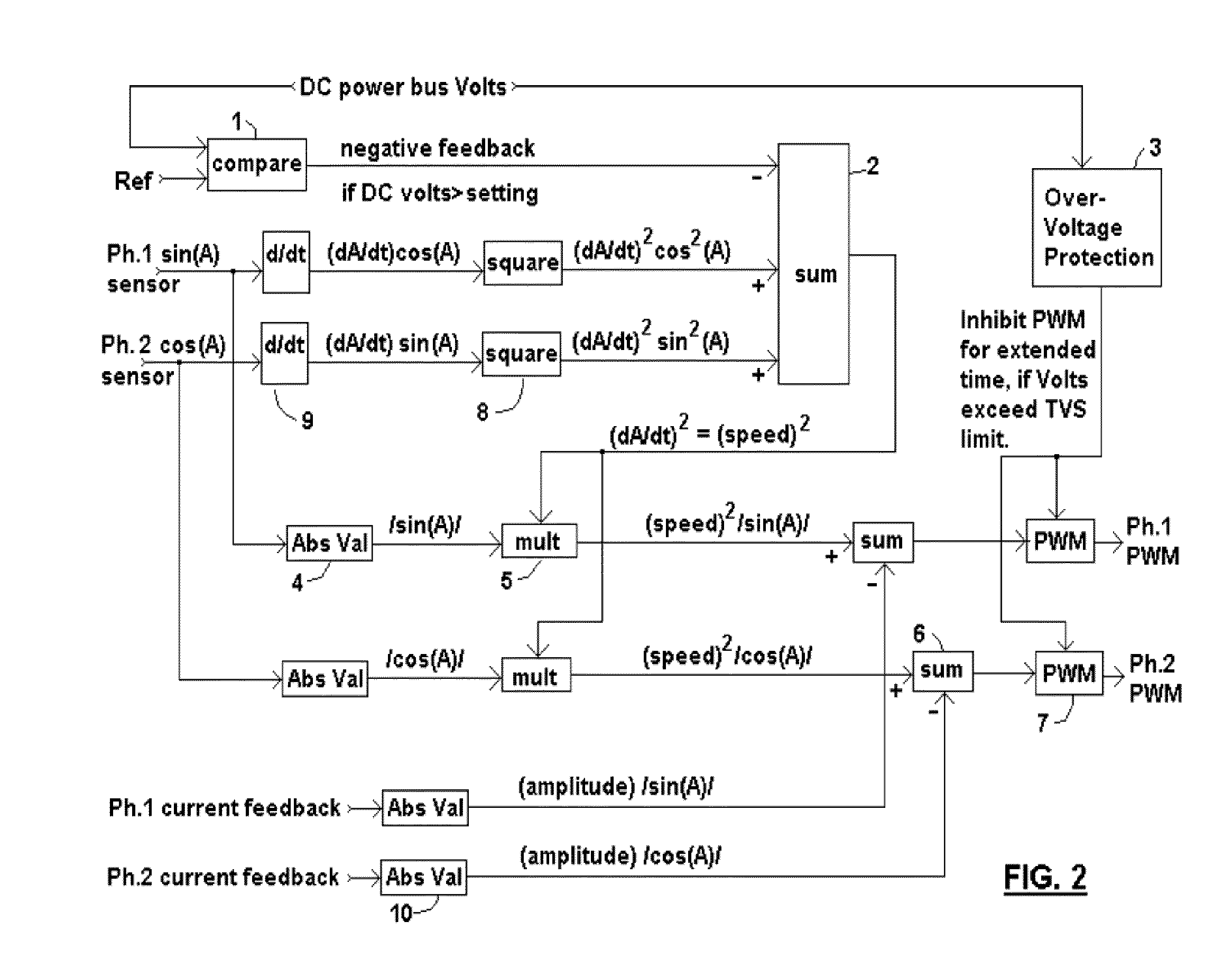
A brushless generator with permanent-magnet multi-pole rotor disks and coreless stator winding disks includes integral electronics to efficiently generate regulated DC current and voltage from shaft input power over a broad speed range. Its power rating is scalable, and it incurs no cogging torque, or friction from gearing. Integral power control electronics includes high-frequency pulse-width-modulated boost regulation, which provides regulated current at requisite voltage over its broad speed range. A main embodiment to produce DC power at widely variable speeds includes signal processing so output power varies according to the third power of speed. A version for use with vertical-axis wind turbines has a relatively large diameter to facilitate a large number of poles. Combined boost-regulation, zero cogging torque, and no gearing, enable a wide speed range, for better power quality and higher wind energy yields. An alternate embodiment is intended to produce DC power from a variety of shaft drive sources, with selectable shaft torque.
Owner:FRADELLA RICHARD B
Leveredged wind turbine w/ multiple generators
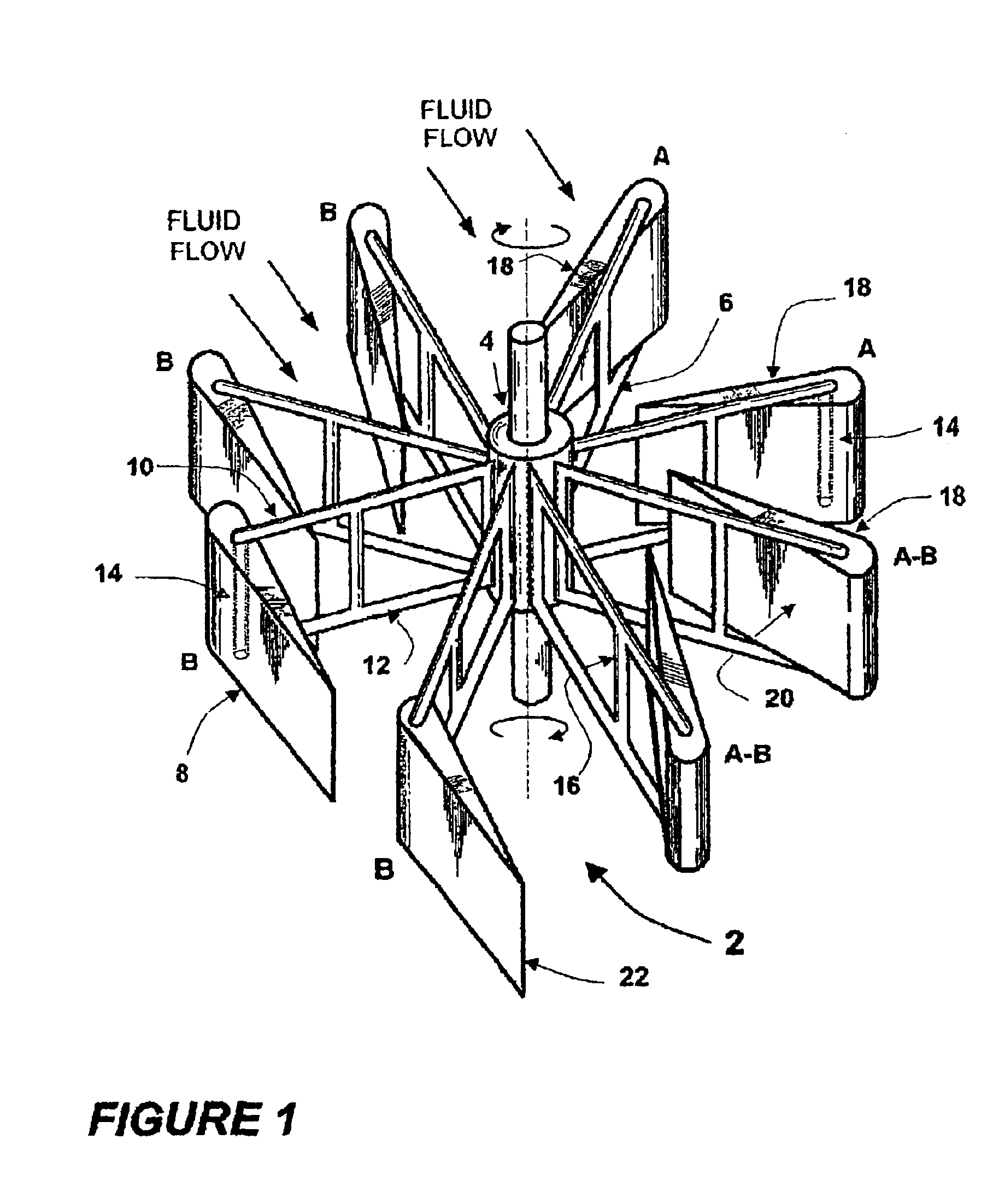
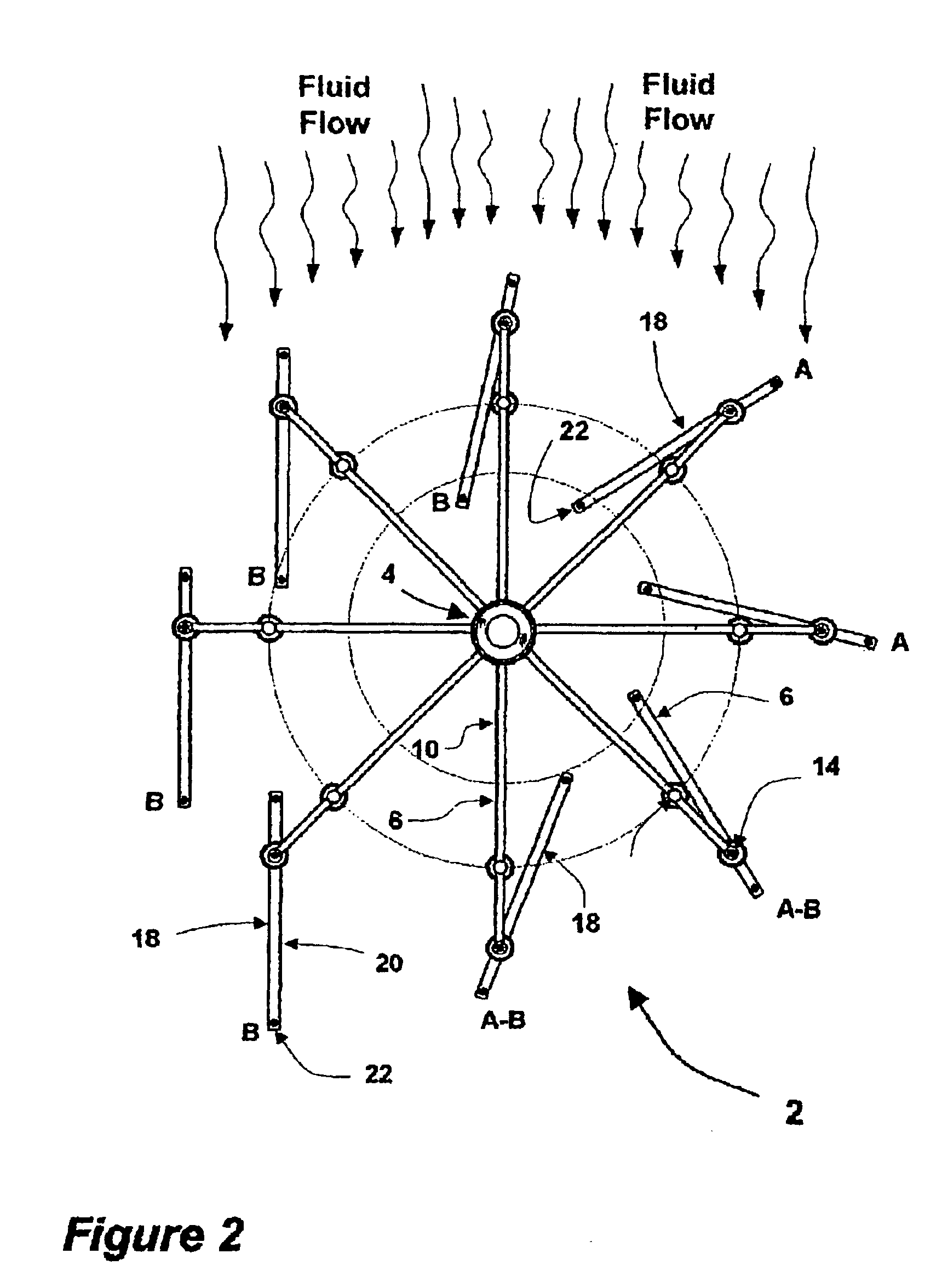
The invention is a vertical axis wind turbine that utilizes leverage to compound the force from the wind, thereby creating exstordinary power, enough to turn a plurality of generators, thereby reducing the cost per kilowatt of electricity. It has wind blocking means that when struck by the wind from behind they shift to a position to block the wind to absorb energy from the wind thereby causing the turbine to revolve. At the same time, the wind blocking means on the opposite side of the turbine are being struck by the wind on their front leading edge causing them to rotate up to a position where they do not block wind. The result is that one half of the turbine is always being driven by the wind to cause rotation while the opposite side of the turbine is always allowing wind to pass through it. It doesn't matter which direction the wind is coming from.
Owner:PAGE JOHN S JR
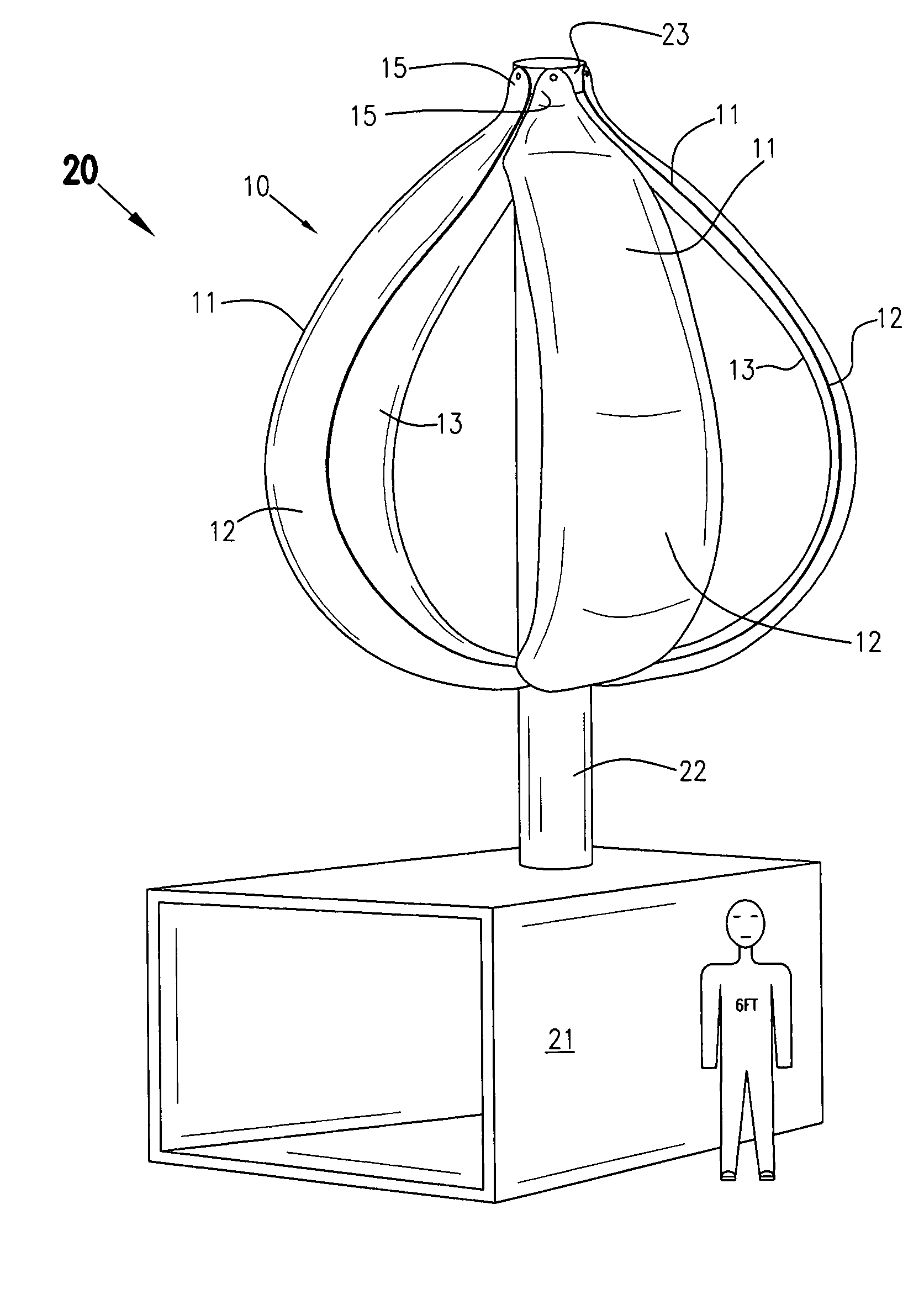
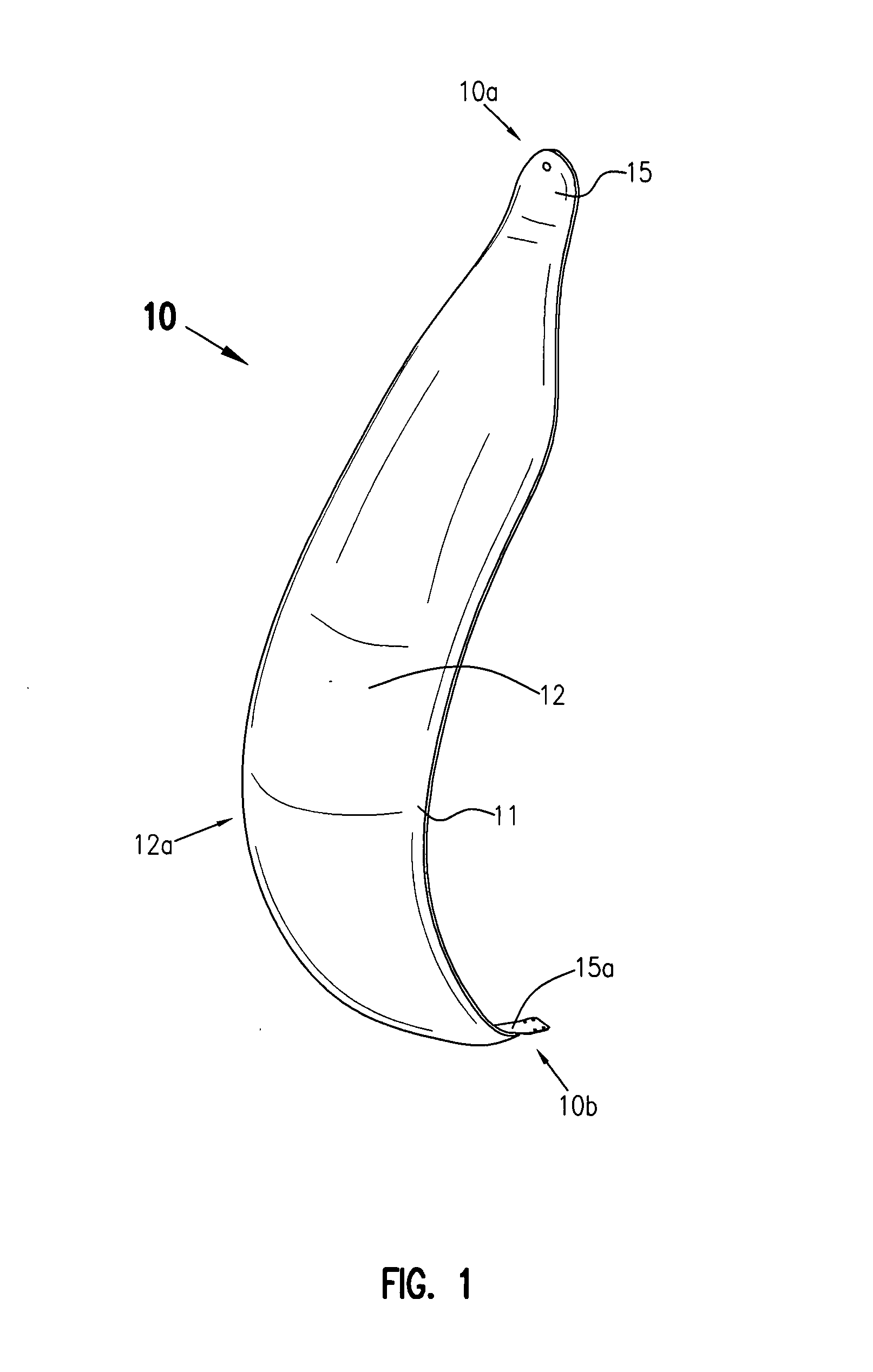
Magnetic vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS7303369B2Reduce frictionMaximize operation of systemPropellersWind motor controlElectricityAlternator
A lift and drag-based vertical axis wind turbine in which the vertical axis and foils mounted thereon are magnetically levitated above the turbine's base, thereby reducing friction within the system. The foils or vanes are three-dimensionally shaped about the vertical axis so as to resemble the billowed sail of a sailing ship and capture wind through 360 degrees of rotation under any wind condition. The system has an axial flux alternator using variable resistance coils which can be individually and selectively turned on or off depending on wind conditions and electrical draw requirements. The coils can also be used to produce mechanical drag on the system as desired to brake the turbine in high wind conditions or for maintenance. The system may be programmed to assess whether electricity generated by the system can be or should be transmitted to a public grid or stored locally on a chargeable battery system.
Owner:NIAGARA CENT RES
Vertical axis wind turbine
ActiveUS20110133474A1Increase torqueReduce resistanceWind motor controlRenewable energy generationVertical axis wind turbineVertical axis
A vertical axis wind turbine includes an upstanding support structure, a plurality of generators disposed on the support structure, a central shaft in rotatable communication with the generators and positioned along a central axis of the vertical-axis wind turbine, a plurality of struts extending from the central shaft, and a plurality of blades, each blade positioned at an end of a corresponding strut and oriented substantially vertically. The vertical axis wind turbine optionally includes strut ailerons, blade extension elements, or blade ailerons to increase the efficiency and duty cycle of the wind turbine.
Owner:JONATHAN HAAR
Vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS20070243066A1Less susceptible to flexion and extensionReduce maintenancePropellersPump componentsHydraulic pumpVertical axis wind turbine
A vertical axis sail-type wind turbine includes an array of sail-like structures that are mounted on rotating main masts. The sail-like structures can be oriented to interact with the wind. For example, when the sail-like structures are moving in a downwind direction, they are oriented to present a flat surface that is perpendicular to the wind direction. On the other hand, when the sail-like structures are moving in an upwind direction, they are oriented to present a surface that is at an angle that creates an upwind vector. The sail-like structures rotate about the sail masts, which are mounted to transverse mounting arms that are firmly mounted to a main mast. The main mast rotates, transferring power through a gear and shaft drive to hydraulic pumps in the tower. This hydraulic fluid pressure is then used to drive an electrical generator.
Owner:BARON RICHARD
Vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS7083382B2Reduce resistanceReduces the drag on the prime moverPropellersPump componentsRotational axisVertical axis wind turbine
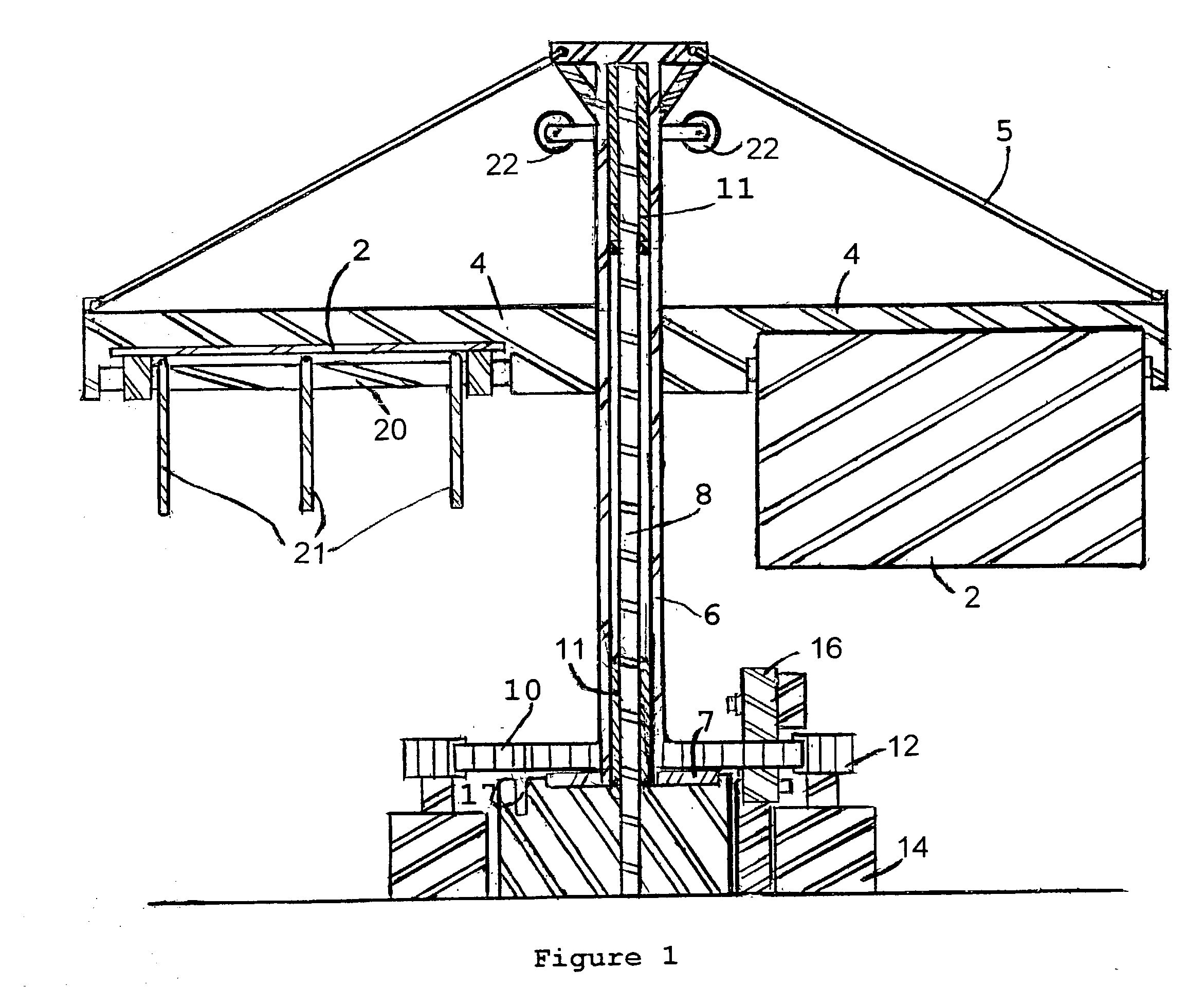
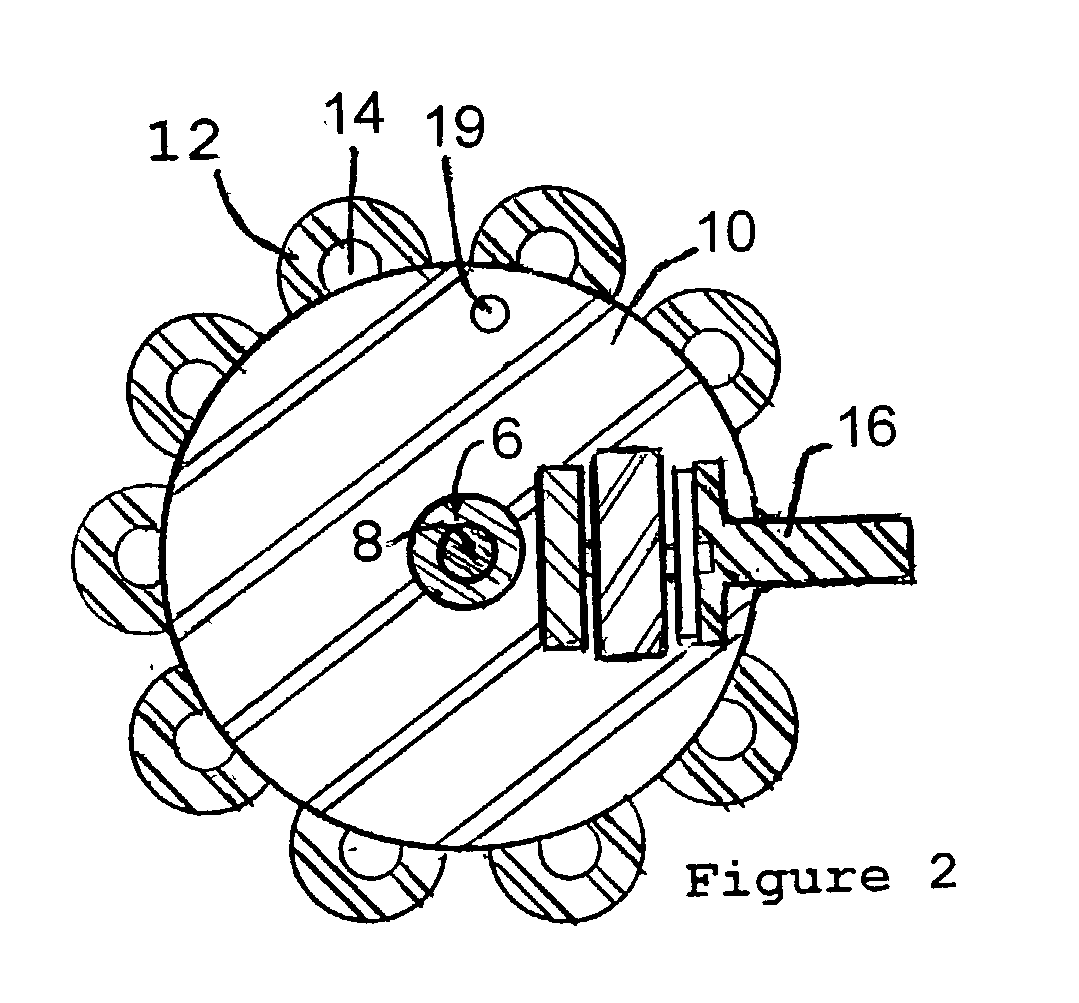
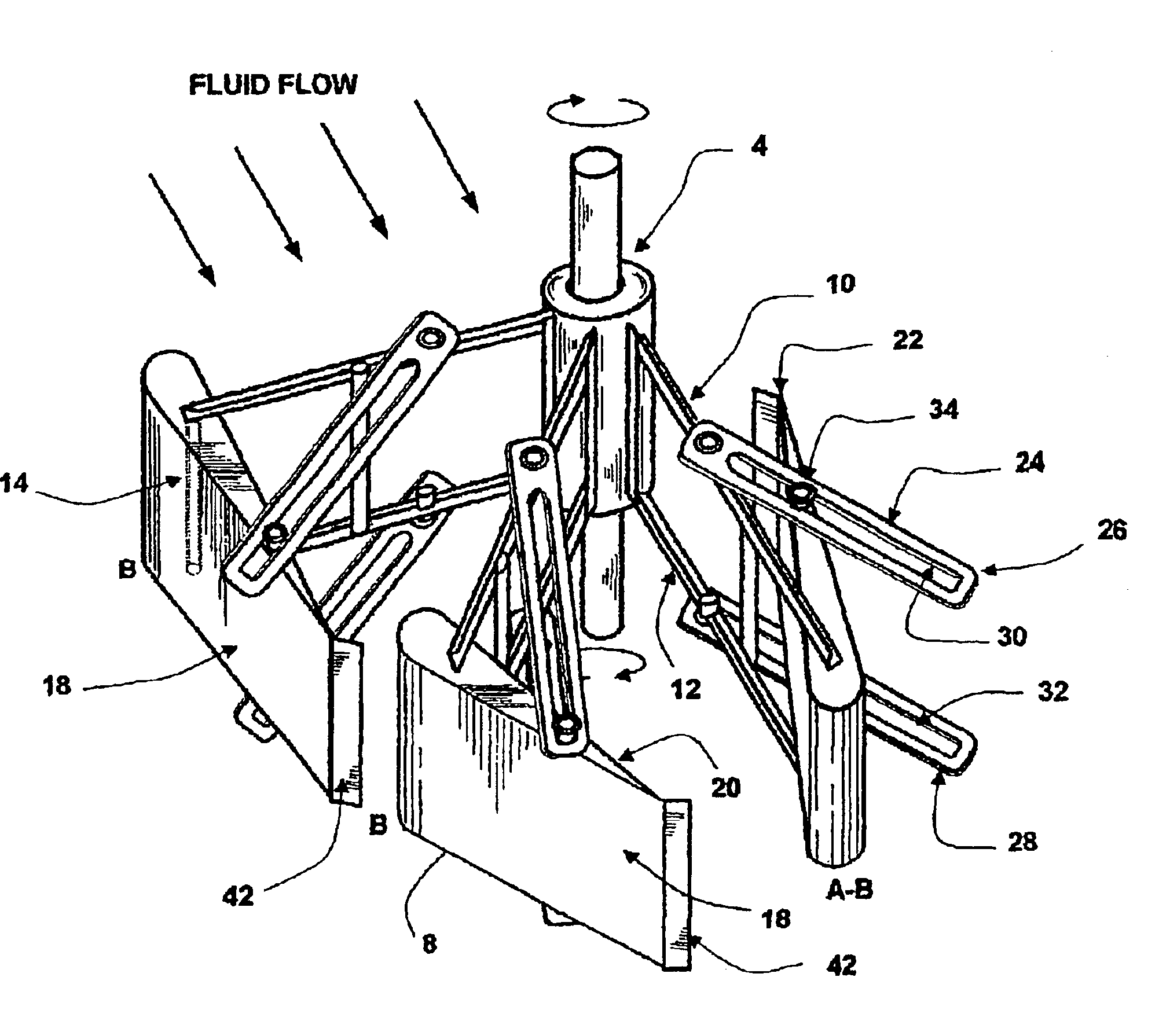
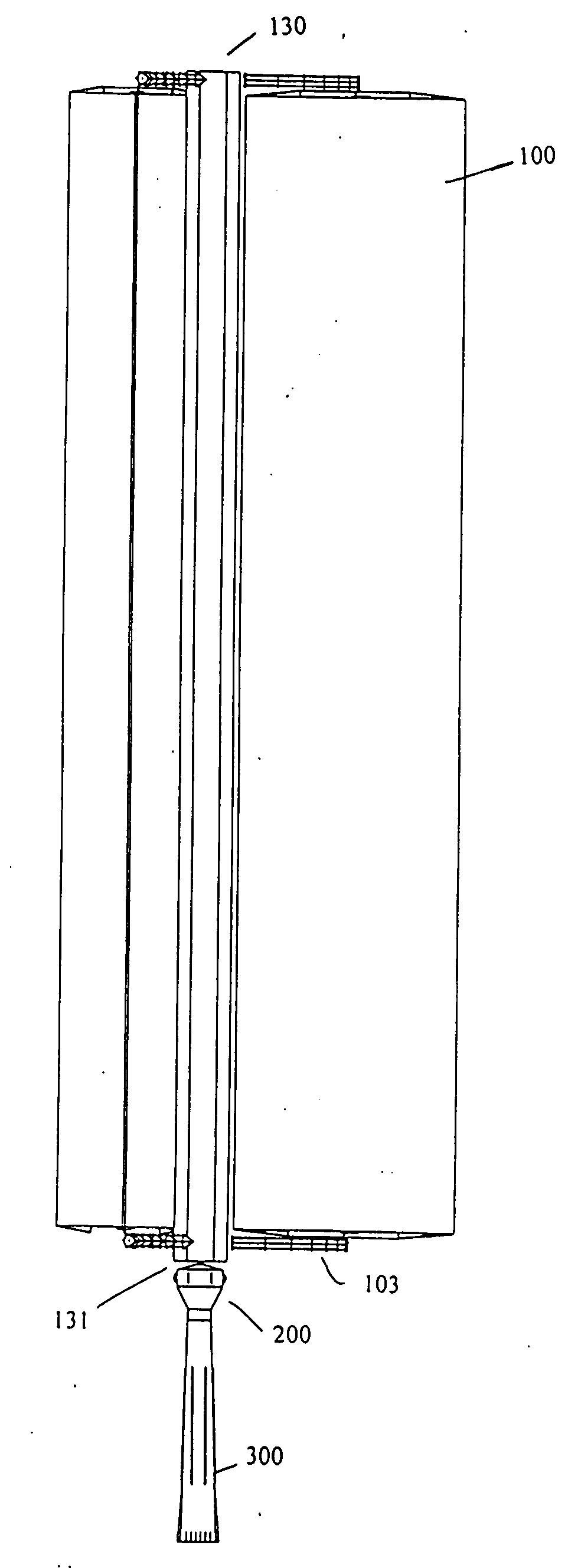
The present invention provides a prime mover (2) for harnessing energy from a flow of fluid, the prime mover (2) comprising a shaft (4) having a rotational axis, arranged to be rotatably mounted to a substructure, the shaft (4) comprising at leas one arm (6) extending radially from the shaft (4), the or each arm (6) comprising at least one blade (8) wherein the or each blade (8) is oriented such that flow action on the blade (8) effects rotation of the shaft (4), characterized in that the or each blade (8) is movably mounted on an arm (6) and wherein each blade (8) is movable from a first position, having a first drag, to a second position, having a second drag, wherein the first drag is higher than the second drag. The prime mover (2) of the invention provides substantially reduced drag in a flow of fluid, and an increased torque output, compared to prior art prime movers.
Owner:US ISIDRO U
Vertical axis wind turbine with controlled gybing
InactiveUS6926491B2Efficient capturePropellersWind motor controlElectricityVertical axis wind turbine
A device for generating electricity in which wind blowing from any direction causes the rotation of sails around a vertical tower. As the sails rotate the sails moving toward the wind are automatically feathered, and the sails moving away from the direction of the wind are prevented from being feathered by sail restraints. An inner sail restraint positions each sail so that the sail gybes at an earlier time than would otherwise occur. An outer sail restraint “catches” the sail as it gybes, capturing much of the energy of the gybe, adding additional rotational force. The device may be used to extract energy from the wind to produce electricity.
Owner:MIGLER BERNARD
Multi-Axis Wind Turbine With Power Concentrator Sail
InactiveUS20090191057A1Effective and reliableAvoid disruptionPropellersPump componentsVisibilityAir movement
A wind energy to electrical power conversion device provides a protected multiple turbine mechanism axially aligned to convert kinetic energy of air movement, i.e. wind (or other moving fluid such as water), into rotational mechanical power to directly create electrical energy by the reaction of the wind with the turbine. The present wind energy to electrical power conversion device may either be configured as a vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) or horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT). An associated wind gathering sail automatically repositions itself to maximize wind intake and to collect and concentrate the wind prior to converting the wind into energy via the axially aligned multi-turbine mechanism into electrical energy. The remaining wind is released via a leeward-facing exhaust. The present axially aligned multi-turbine mechanism avoids interference by birds and other outside objects due to its inherent structural visibility.
Owner:KNUTSON ROGER C
Wind turbine mounted on power transmission tower
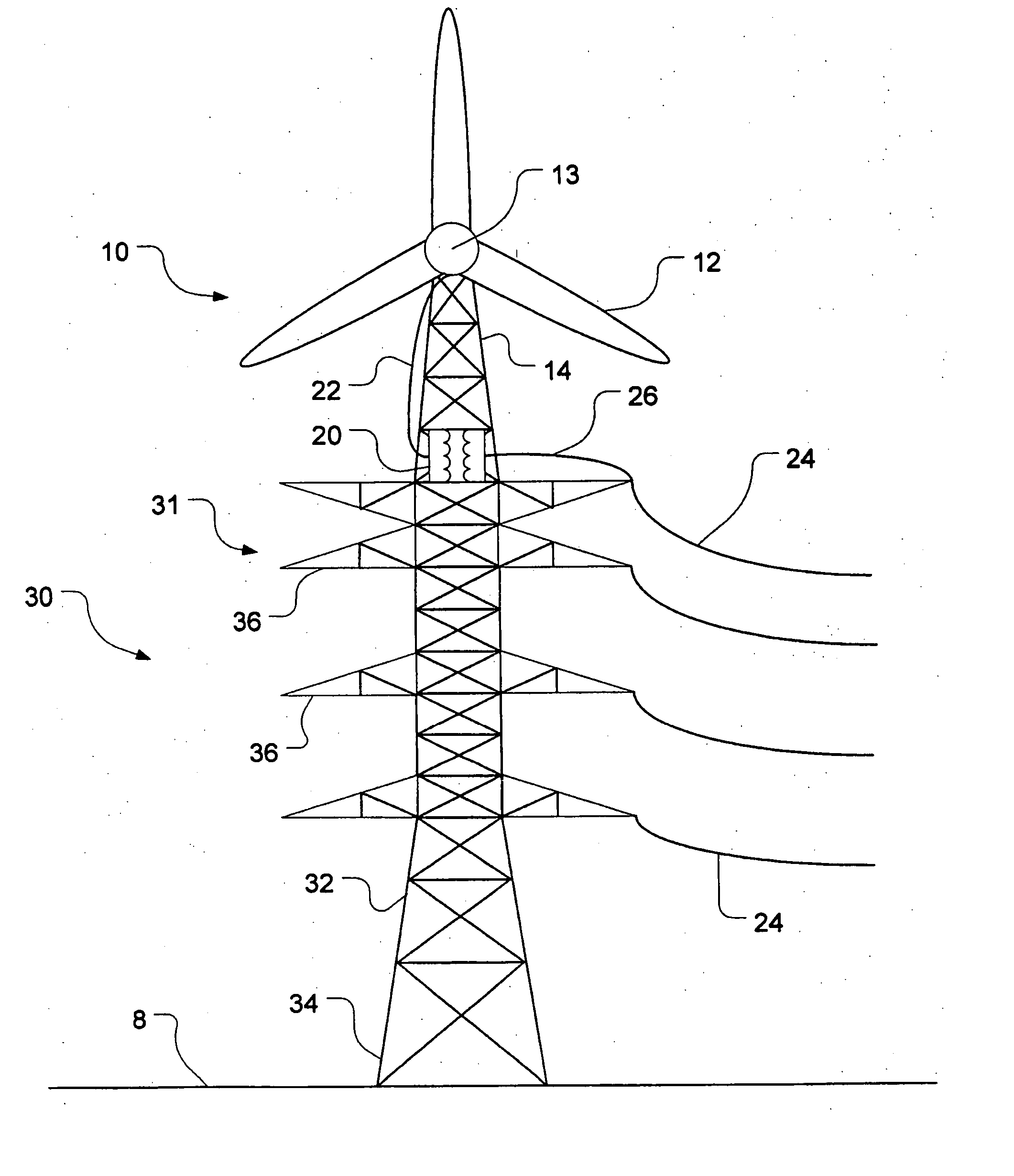
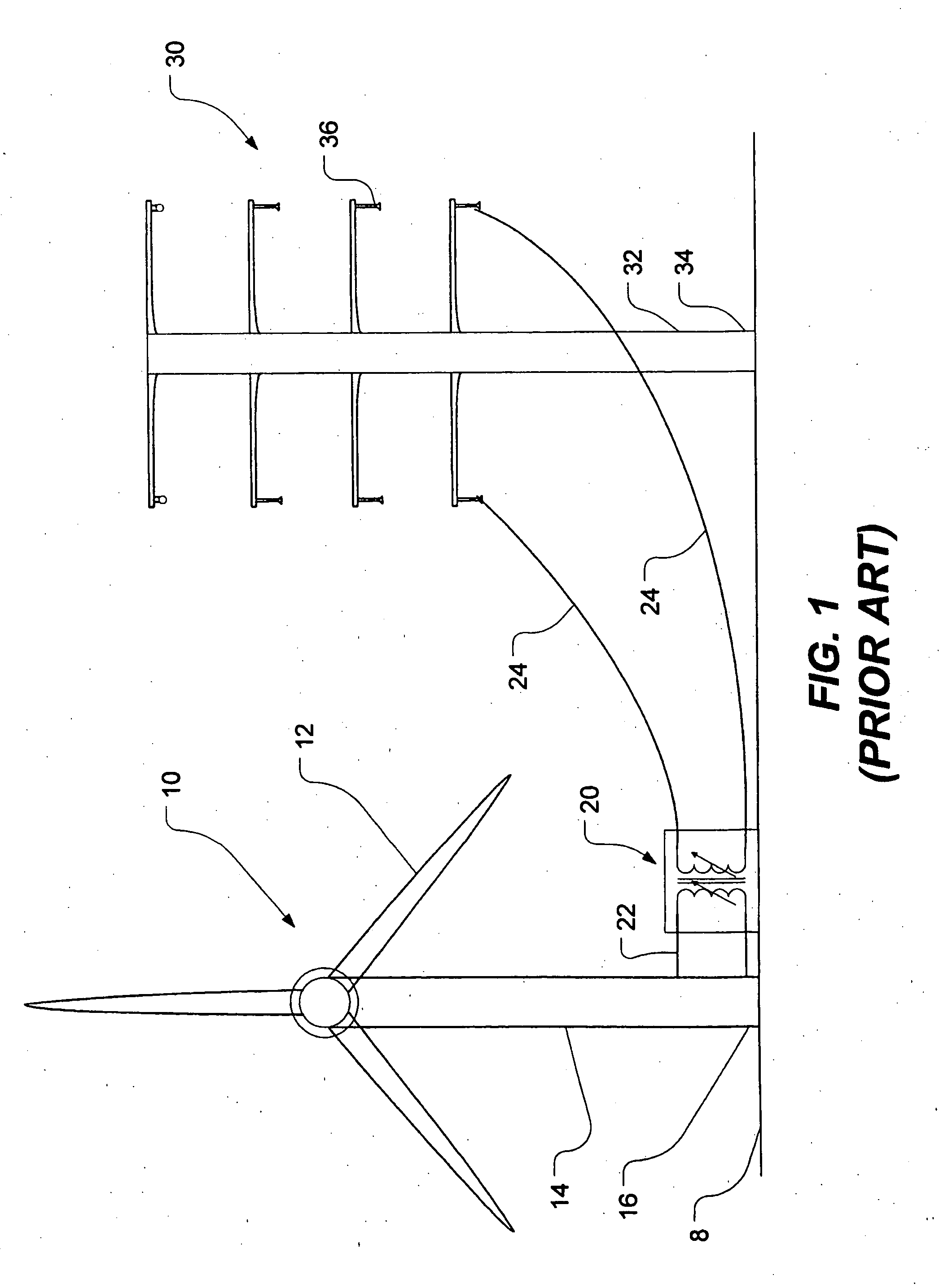
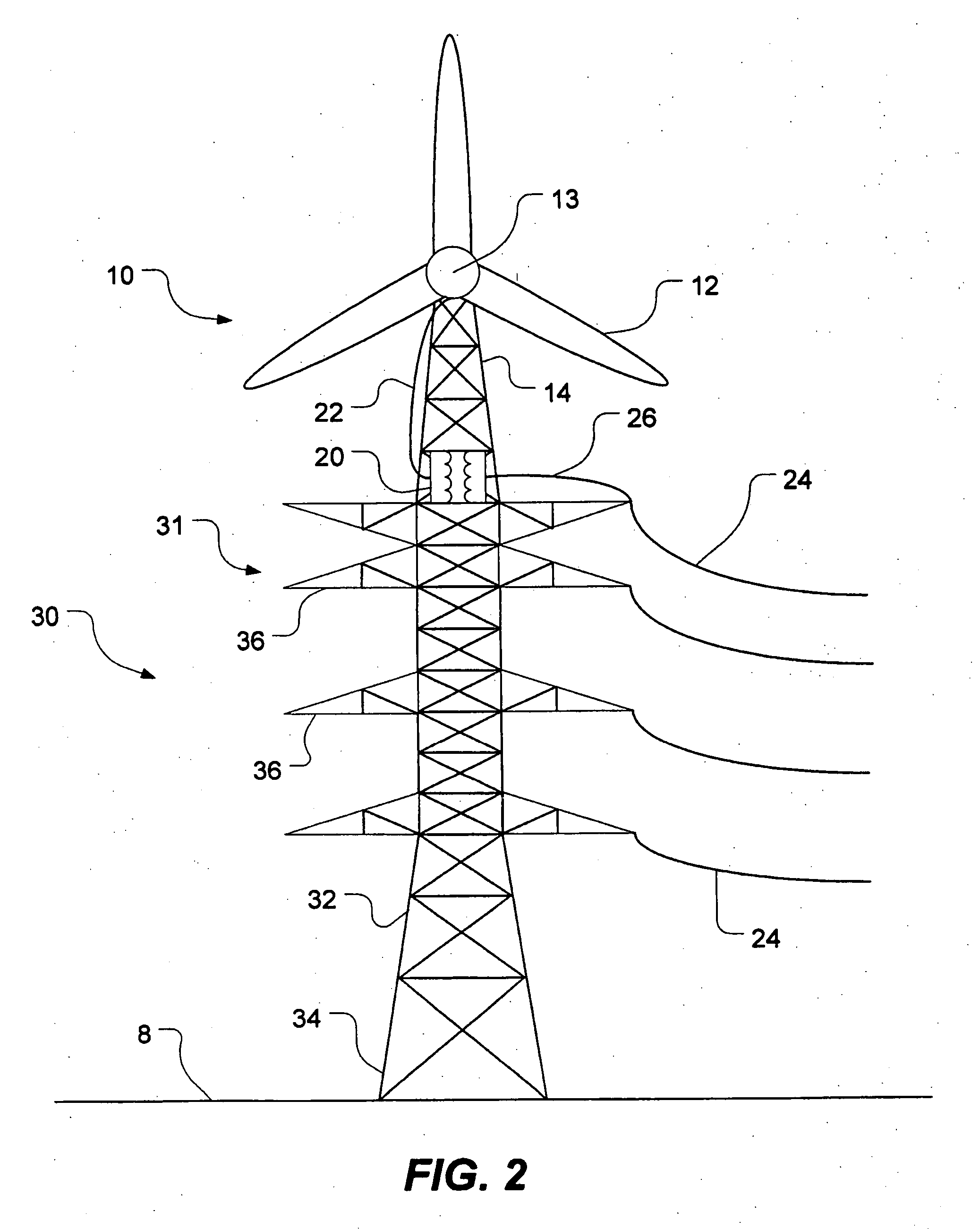
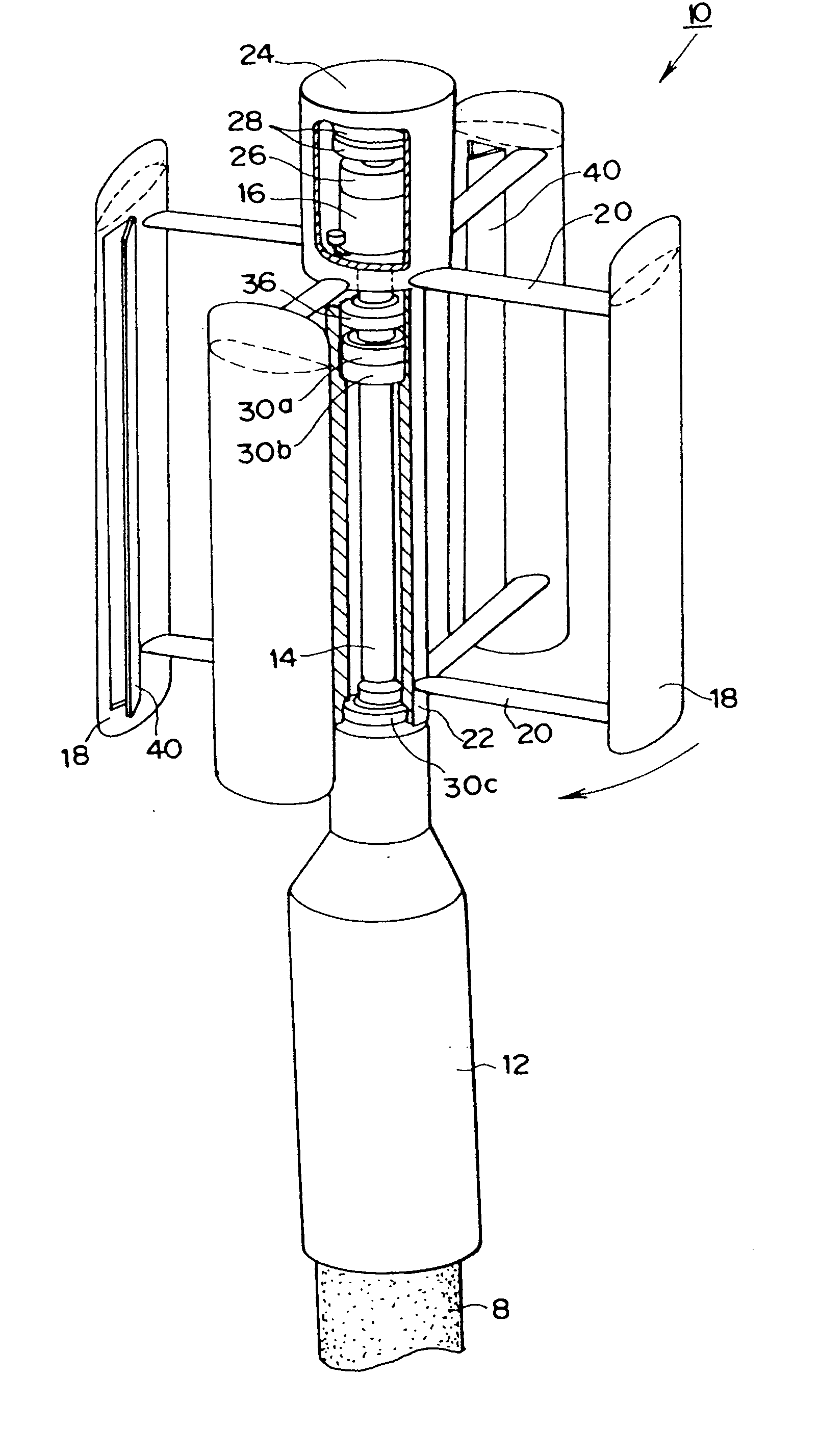
InactiveUS20050230980A1Reduce construction costsMinimises aesthetic impactWind motor supports/mountsWind motor combinationsTransformerHorizontal axis
A power transmission tower carrying power lines has a wind turbine mounted to an upper portion of the tower. The wind turbine has a rotor which drives a generator for generating electric power. The generated power is stepped up using a transformer before being fed into one of the power lines. Optionally, electric power generated by a plurality of such wind turbines could be accumulated downstream and then transformed and fed into the grid at multiple-tower intervals. The wind turbine can be mounted on a lattice tower, a monopole tower or a hybrid tower. The wind turbine has either a fixed horizontal axis or a variable (but non-vertical) axis. Alternatively, a vertical-axis wind turbine may be used provided the generator is mounted at or near the top of the tower. Using existing infrastructure, the present invention supplements the capacity of a power grid with environmentally friendly power generation.
Owner:BRUNET ANDRE
Vertical axis wind turbine and wind turbine blade
InactiveUS20070177970A1Improve lifting performanceImprove startup performanceWind motor controlMachines/enginesTurbine bladeVertical axis wind turbine
It is an object of the invention is to provide a vertical axis wind turbine and a wind turbine blade, which are excellent in self-starting performance and have a high torque constant. Since the present invention comprises a wind receiving plate 40 having a wind receiving surface and an openable and closable pivot 42, which wind receiving plate 40 is operated to close in the direction in which the centrifugal force is produced in proportion to the revolution of a blade 18 generating a lifting power, and an energizing means (such as spring 44) for energizing an opening force to open the wind receiving plate to the wind receiving side, the starting performance of the lift type wind turbine can be improved by means of the wind receiving plate 40, which opens at a low revolution of the blade 18 so as to function as a drag type wind turbine, and automatically closes at a high revolution of the blade 18 so as to function as a lift type wind turbine.
Owner:INTPROP BANK CORP (JP)
Magnetic vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS20070098563A1Reduce frictionMaximize operation of systemOther chemical processesPump componentsElectricityAlternator
A lift and drag-based vertical axis wind turbine in which the vertical axis and foils mounted thereon are magnetically levitated above the turbine's base, thereby reducing friction within the system. The foils or vanes are three-dimensionally shaped about the vertical axis so as to resemble the billowed sail of a sailing ship and capture wind through 360 degrees of rotation under any wind condition. The system has an axial flux alternator using variable resistance coils which can be individually and selectively turned on or off depending on wind conditions and electrical draw requirements. The coils can also be used to produce mechanical drag on the system as desired to brake the turbine in high wind conditions or for maintenance. The system may be programmed to assess whether electricity generated by the system can be or should be transmitted to a public grid or stored locally on a chargeable battery system.
Owner:NIAGARA CENT RES
Vertical axis wind turbine with articulating rotor
A VAWT wind engine includes a support structure, an articulating rotor mounted on the support structure for rotation about a vertically extending axis, and at least one airfoil on the rotor for rotor-powering purposes. The articulating rotor is mounted in a manner enabling tilting movement of the rotor during rotation so that the airfoil produces rotor rotation and rotor tilt as the airfoil orbits the rotational axis. At least one mechanical linkage is included to actively vary airfoil pitch according to rotor tilt. The partially articulating rotor of a teetering-rotor embodiment seesaws up and down about a horizontally extending pivotal axis. The fully articulating rotor of another embodiment supports three airfoils as it tilts in any direction by virtue of a gimbal or other rotor hub assembly providing a 360-degree swiveling action, while furling hinges help protect the airfoils against damaging winds during wind engine shutdown.
Owner:BOATNER BRUCE E
Vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS20080187432A1Wind motor controlRenewable energy generationLeading edgeVertical axis wind turbine
A vertical axis wind turbine having a plurality of blades spaced from a rotatable around a rotor shaft vertical to the ground. The plurality of blades are arranged in a helical pattern about the rotor shaft. Each blade is flexible to move in response to wind and has a top, bottom, leading edge, and trailing edge wherein the leading edge is in the shape of an airfoil. A hub having a plurality of blade attachment rods radially extending from the rotor wherein in one blade is secured to one of the attachment arms. The hub has a plurality of attachment rods radially extending from the rotor wherein one blade is secured to one of the attachment rods near the center and wherein the top of each blade is closer to the rotor than the bottom of each blade.
Owner:PREFERRED ENERGY
Vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS20060188364A1Not consume valuable irreplaceable resourceNegative impactWind motor with solar radiationWind motor controlVertical axis wind turbineFlywheel
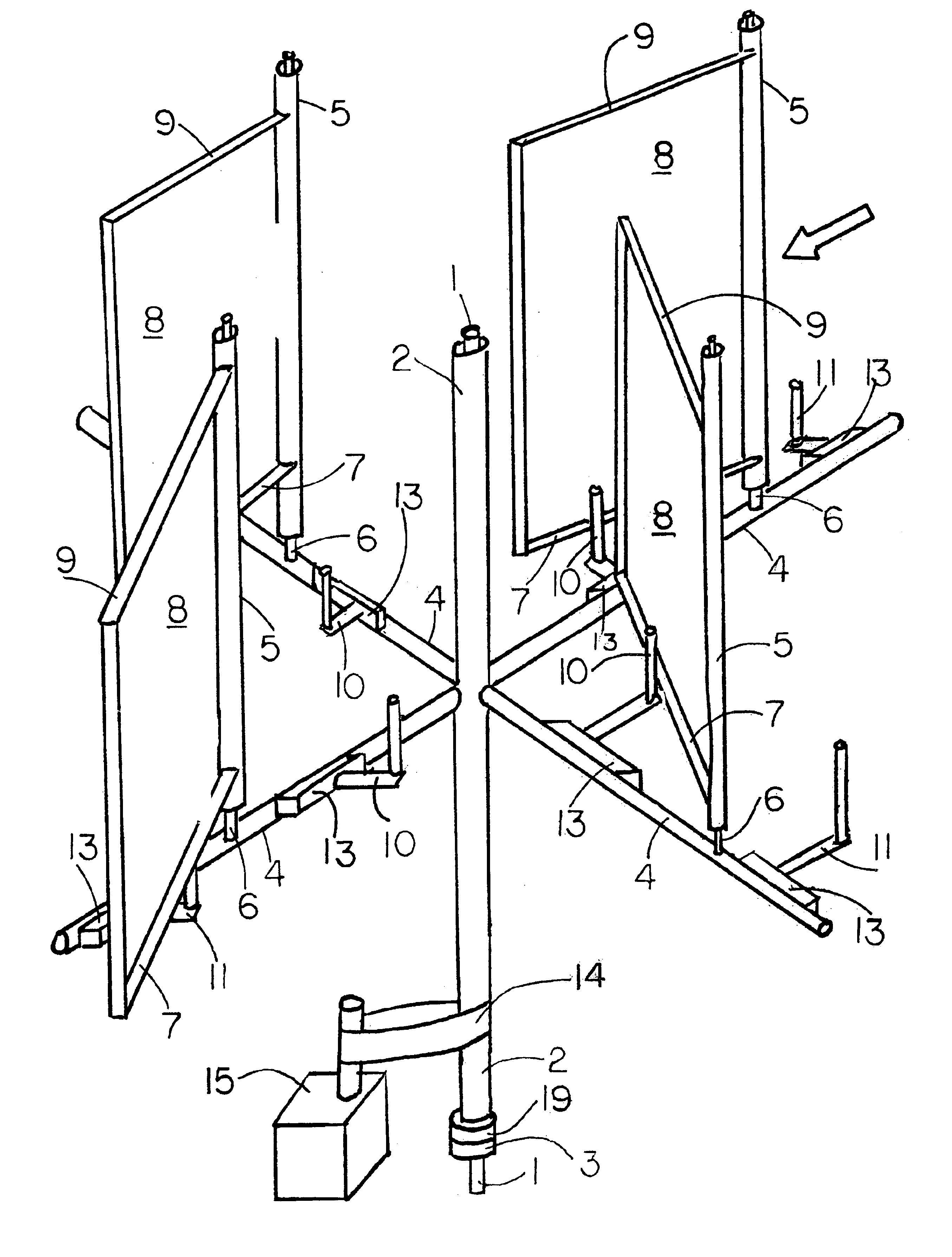
The United States of America consumes nearly 20 million barrels of oil a day, 6.6 billion per year. This depleting chemical composition, in part, ends up in our air, on our trees, on our clothing, in our lungs, in our blood streams. A large portion of this oil is imported causing a dependency on foreign countries and a significant economic burden to this country. Clean, renewable, domestic energy is a necessity, not a luxury. The Z-333 Energy Management System is an answer to this challenge. There have been many Vertical Axis Wind Turbine patents issued since Mr. Elhanan L. Stoners' patent in 1891. However it appears that none has yet manifested itself into a large scale economic reality. The Z-333 Energy Management System is the latest of a series of improved Vertical Axis Wind Turbine designs which will make that reality come to pass. The Z-333 Energy Management System includes several novel changes to previously patented designs, plus incorporates totally new accessories to make man's continuing conquest of wind an actuality. These innovations include; Aerodynamic “balanced” wings. Tightly stretched fabric-only wings strengthening the overall structure, and at the same time, drastically lower the cost of construction. Flexible photovoltaic cells cover the aforementioned fabric-only-wings. A rotating tower that is flexible and safer. A unique high winds shut off switch. A multi-generator braking system maintains the shaft at a constant RPM. Generators and gears mounted to removable panels. Rubber-like covered shaft and large ring transmission. A low cost switch that controls the angle of attack of the wing with less problems and cost. A tower made of prefabricated interchangeable modules that can be used as a home, water tank, storage room, shop, and / or a shed. A base which is also a large battery and / or a control box shell. A programmable intelligent control box, which notifies the owner by cell phone, of battery fast charge / discharge, vandalism, key energy indicators, integrates a multi-circuit station timer, plus provides an electric-fence-like shock protection from animals and vandals. Low cost, multi-pancake generator that is highly efficient. A shaft centered flywheel. A shaft centered centrifugal pump. A sea base with ballast for low cost erection. A sea base with desalinization equipment built inside. A sea base with integrated hydrogen and oxygen producing equipment.
Owner:FRITZ MIKE J
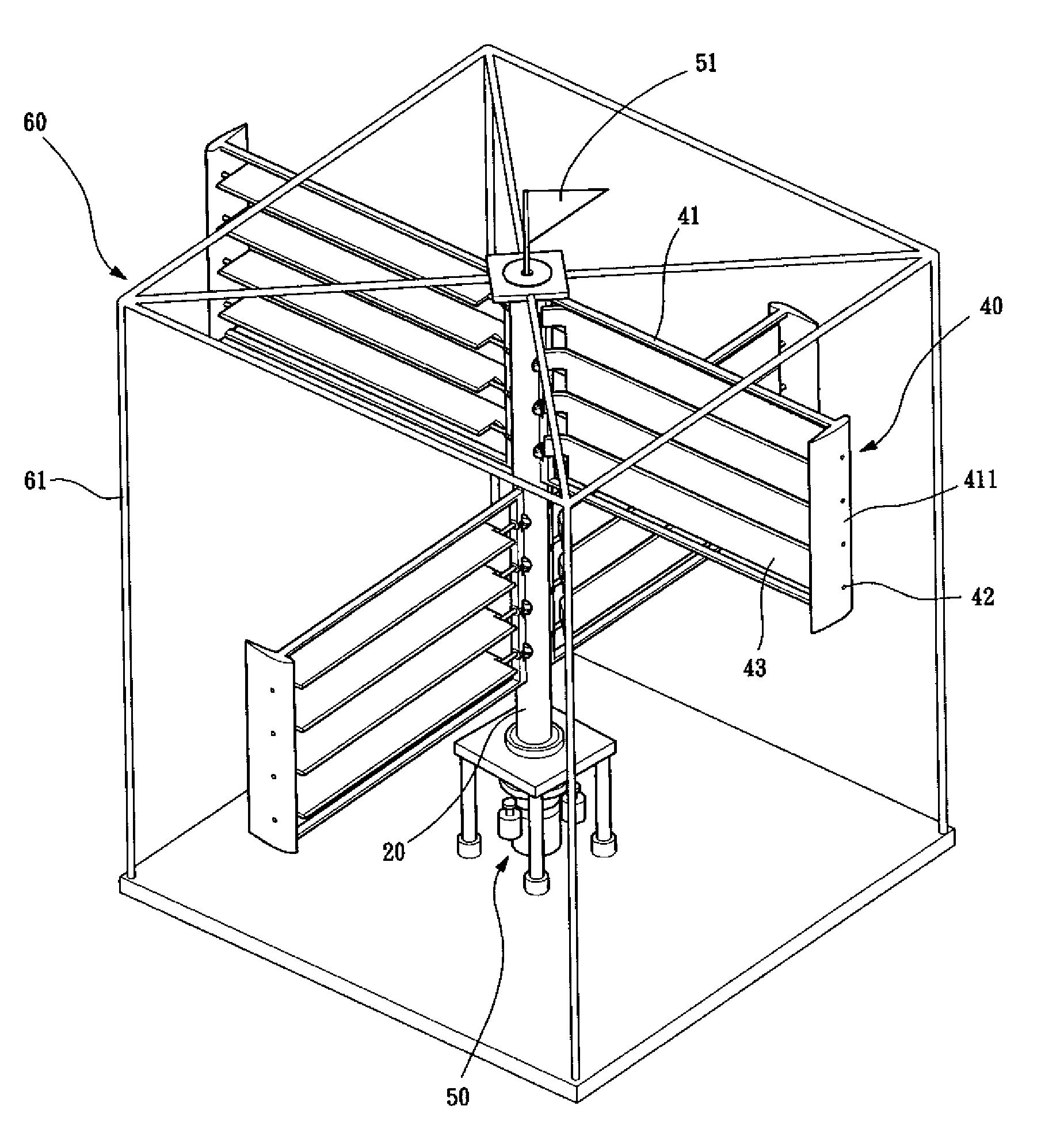
Vertical axis wind turbine
One aspect of the present invention relates to a vertical axis wind turbine. In one embodiment, the vertical axis wind turbine comprises a rotor comprising a vertical oriented shaft, and a plurality of vertical oriented blades angle-equally and radially secured to the vertical aligned shaft. Each of the plurality of vertical oriented blades has a face side, a back side, at least one window and at least one pane pivotally mounted onto the at least one window on the face side such that the at least one pane is rotatable between a closed position and an opening position around a pivotal axis responsive to a wind condition thereof. The pivotal axis is substantially perpendicular to the vertical oriented shaft.
Owner:LIANG RAY HUNG
Vertical axis wind turbine with wingletted cam-tiltable blades
InactiveUS20090035134A1Easy to set upIncrease motivationPropellersWind motor controlVertical axis wind turbineCam
A vertical axis wind turbine with wingletted cam-tiltable blades is provided, including: a generator, a shaft interconnected with the generator, and a plurality of blade sets coupled to the shaft. Cam members are provided inside the shaft and have guide sections of predetermined shapes. The blade set includes blades that are coupled to crank arms in contact with the guide sections. Thus, when the blades are located in a windward position and a leeward position respectively, the blades are caused by the guide sections to automatically and easily set at an optimum pressure-receiving condition and a least wind-resistance condition respectively, for receiving wind energy from variable directions so that the shaft can be rotated in low wind speed conditions to drive the generator for power generation.
Owner:SEVEN STARS WORLDWIDE
Vertical axis wind turbine system
InactiveUS20080145224A1Improve powerImprove efficiencyPropellersWind motor controlTurbine bladeVertical axis wind turbine
The present invention is a vertical wind turbine having a turbine with a plurality of blades or wind vanes. The blades are constructed and attached to the shaft of the turbine so as to allow them to twist open to present more surface area to wind currents when a threshold rotational velocity is reached. Also presented are a novel outer shell that is placed over at least part of the shaft and a novel turbine blade.
Owner:SRI VAWT
Vertical axis wind turbine
A vertical axis wind turbine having a plurality of blades spaced from a rotatable around a rotor shaft vertical to the ground. The plurality of blades are arranged in a helical pattern about the rotor shaft. Each blade is flexible to move in response to wind and has a top, bottom, leading edge, and trailing edge wherein the leading edge is in the shape of an airfoil. A hub having a plurality of blade attachment rods radially extending from the rotor wherein in one blade is secured to one of the attachment arms. The hub has a plurality of attachment rods radially extending from the rotor wherein one blade is secured to one of the attachment rods near the center and wherein the top of each blade is closer to the rotor than the bottom of each blade.
Owner:PREFERRED ENERGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com