Patents
Literature
1364 results about "Angle of attack" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
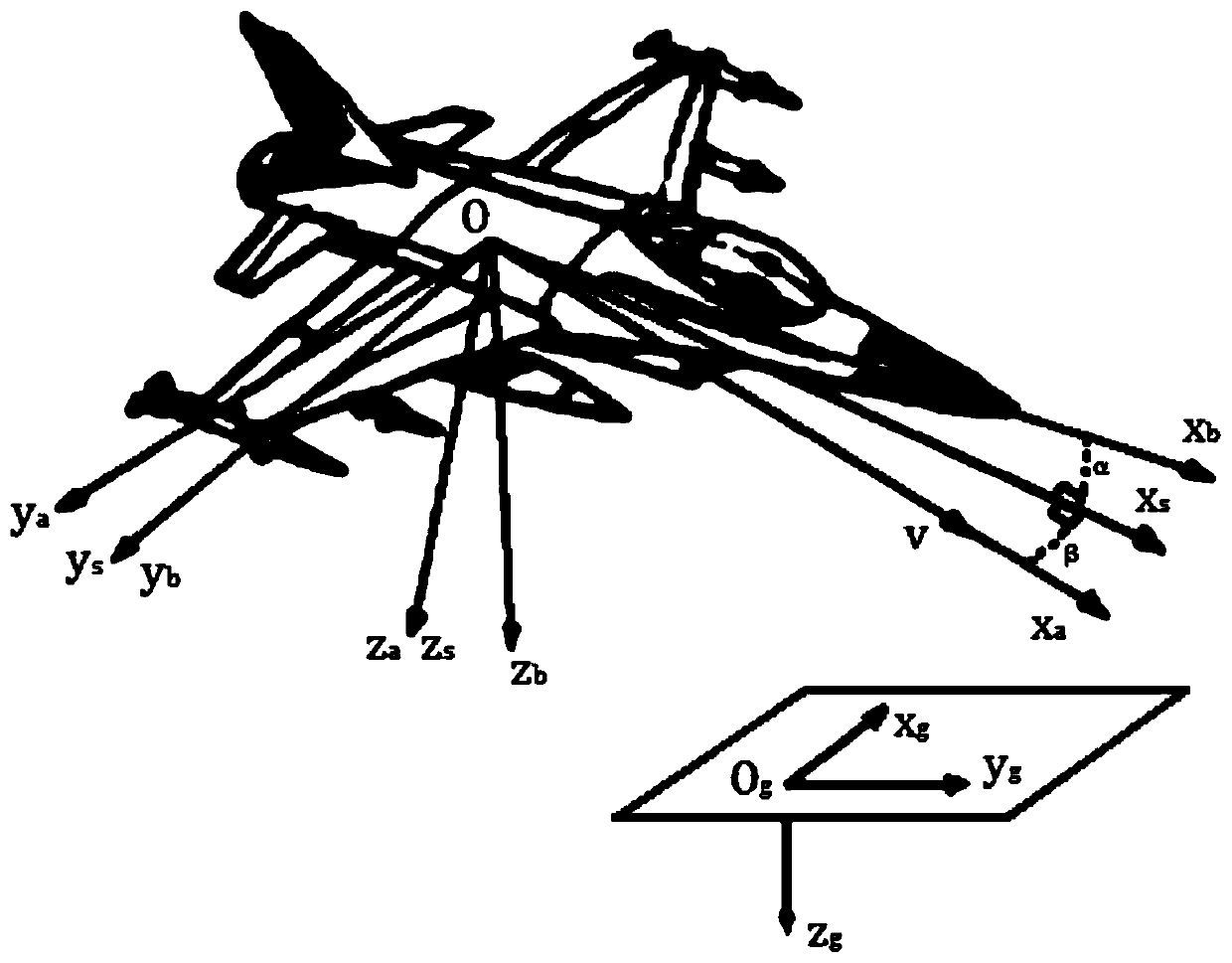
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or α) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air.
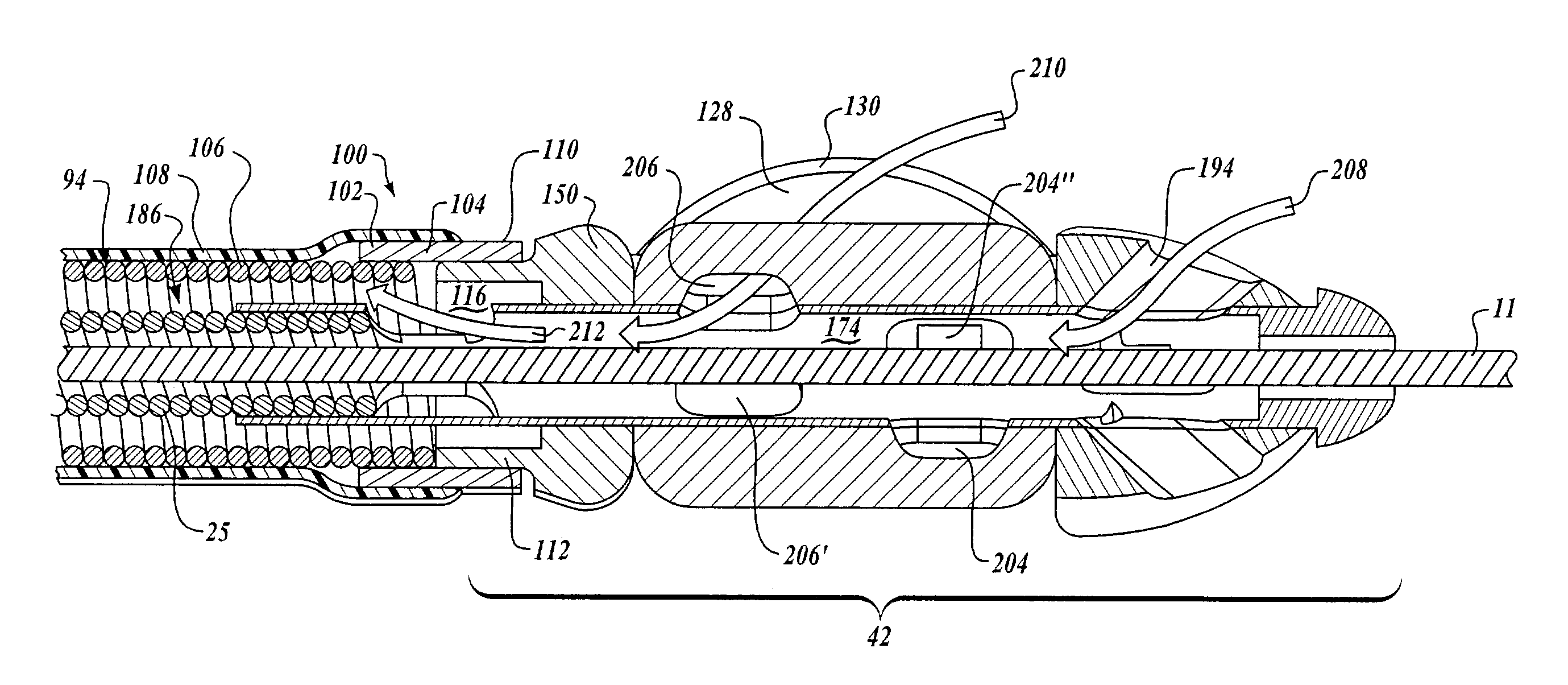
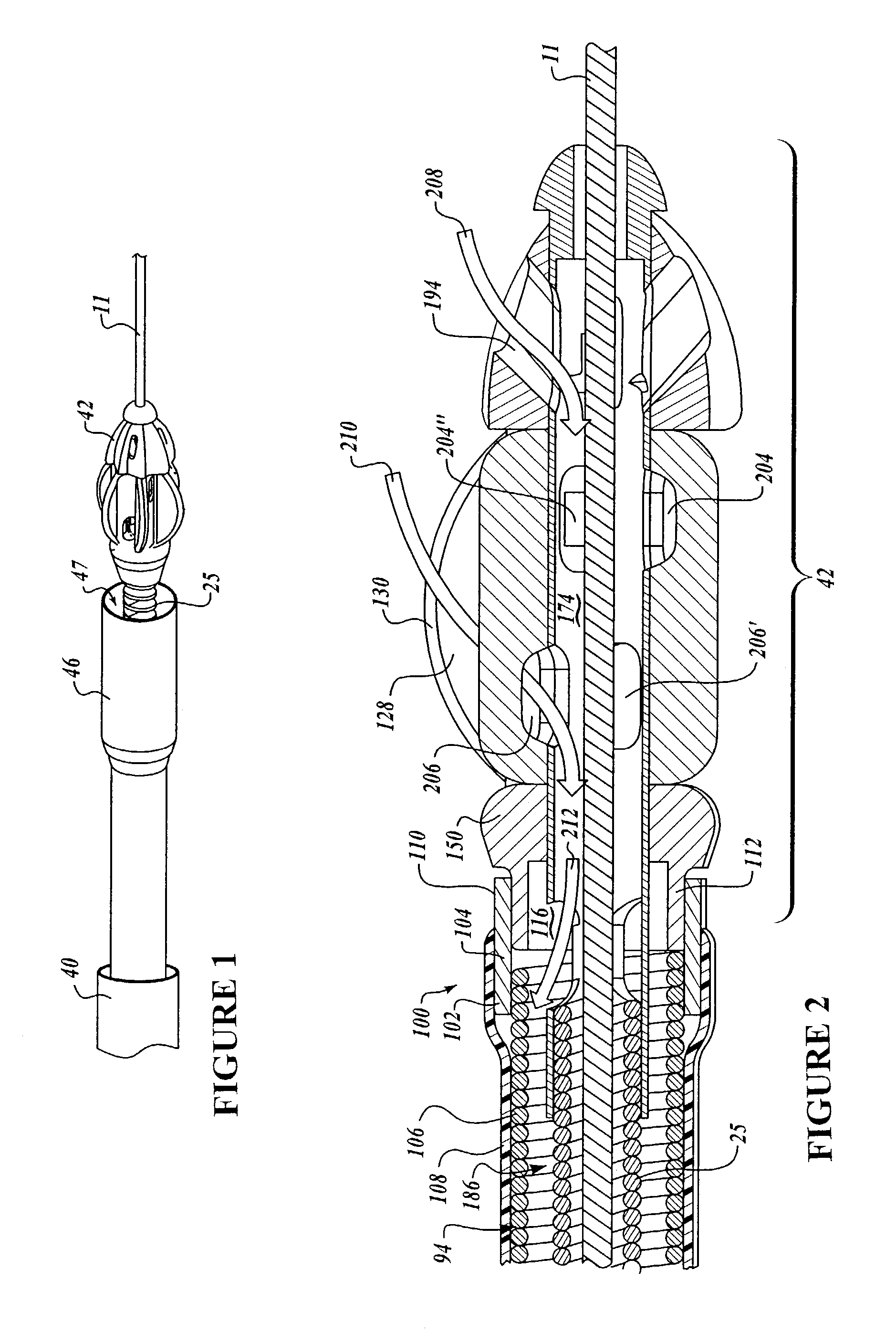
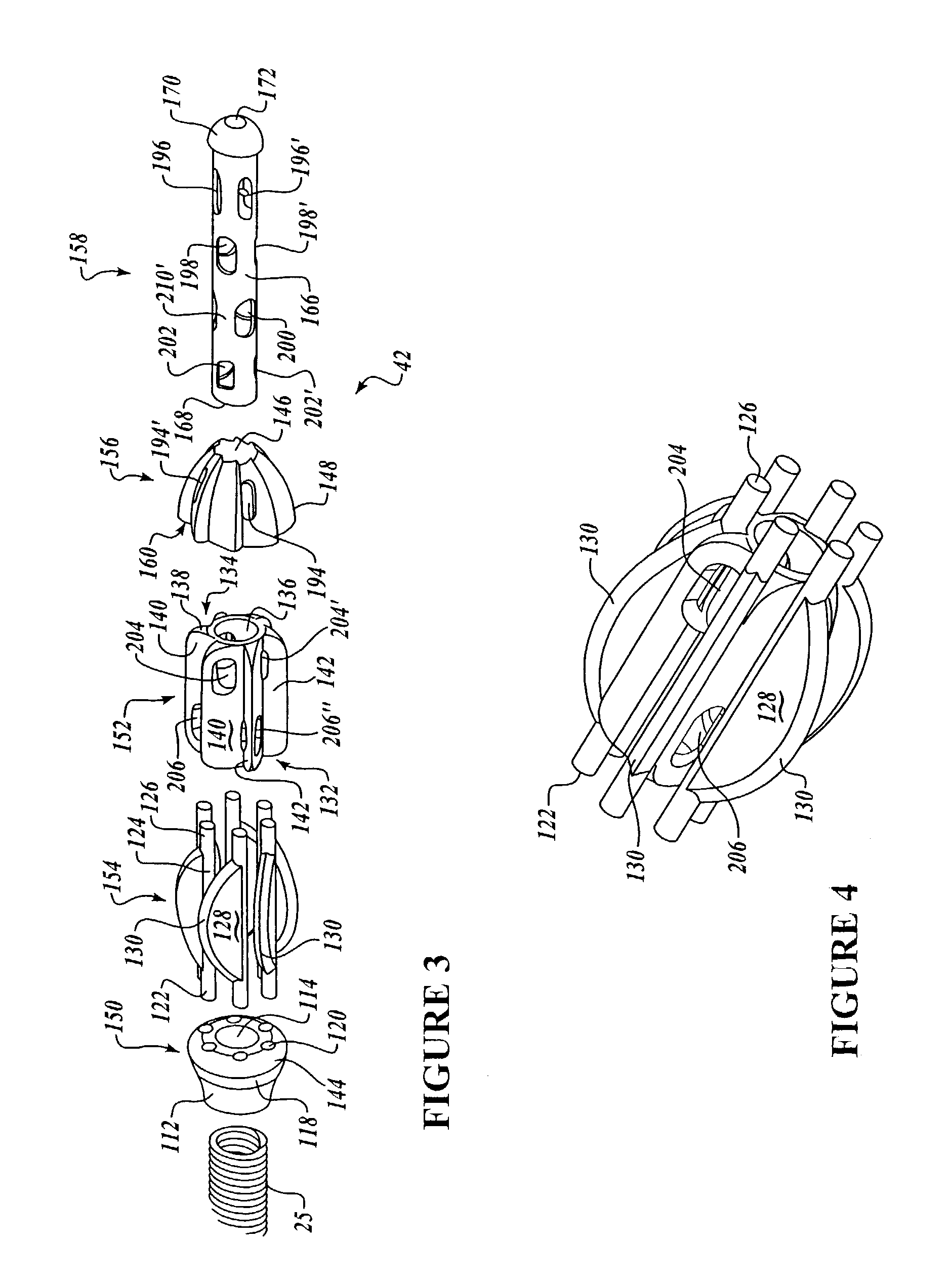
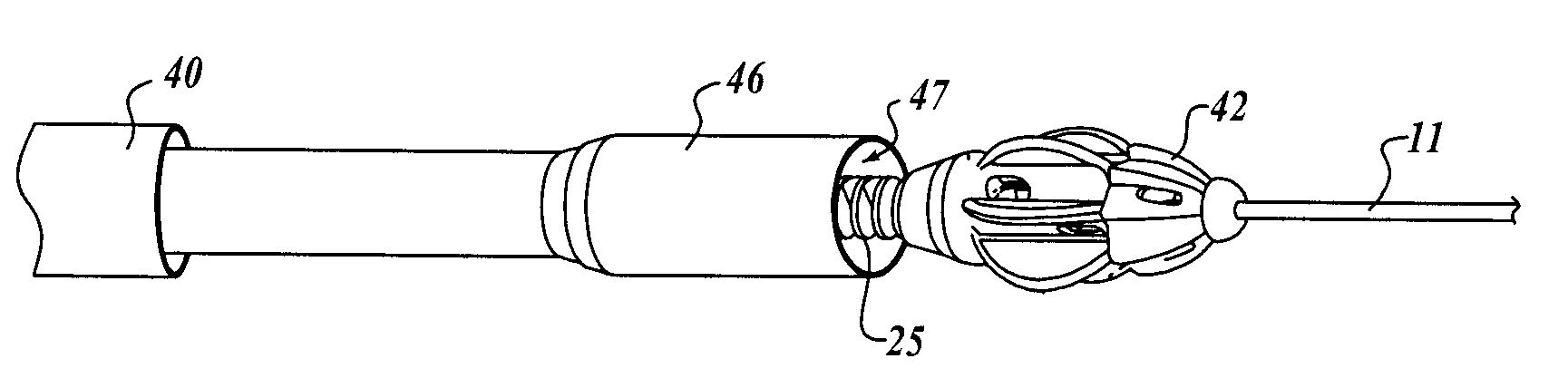
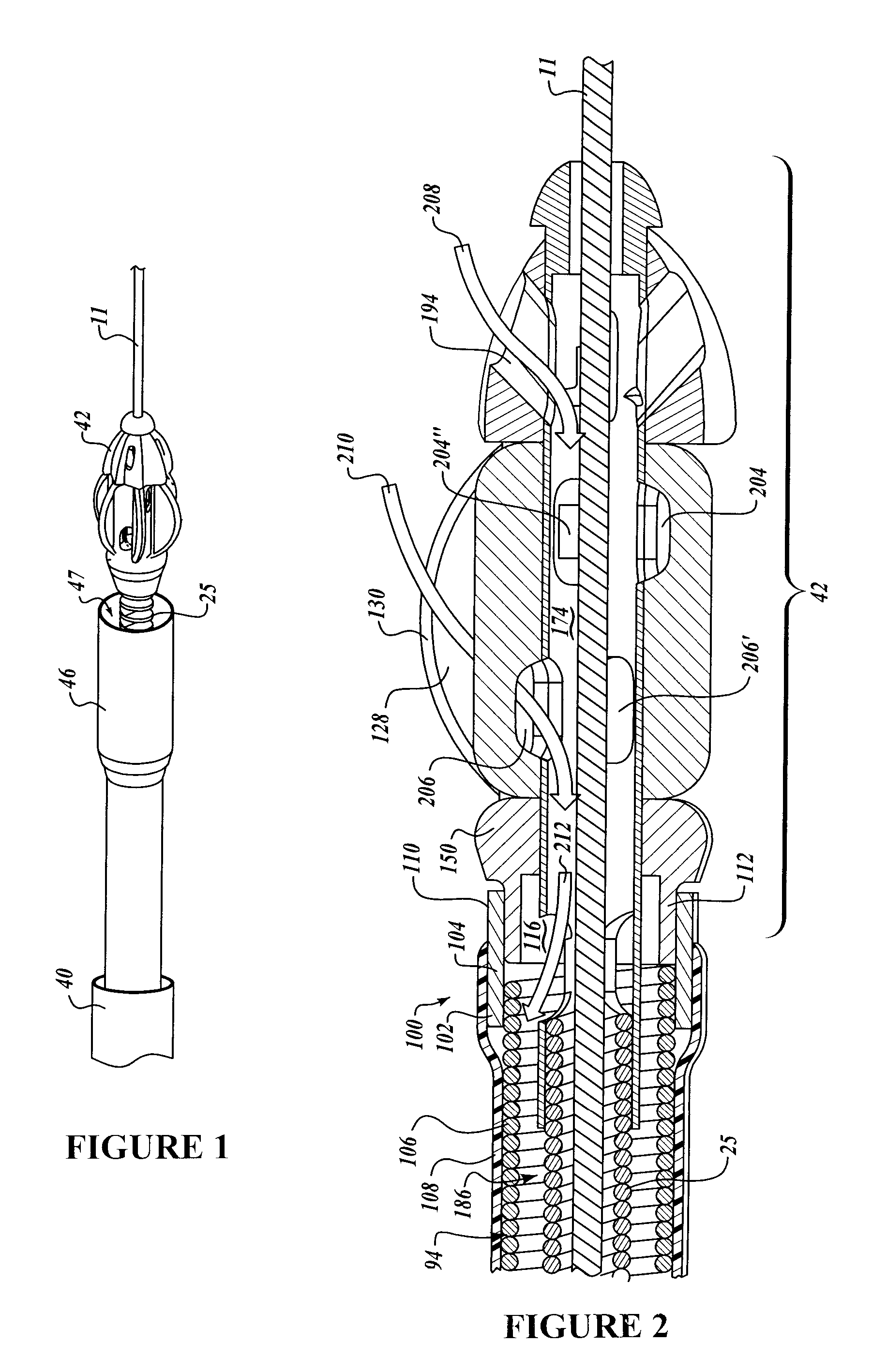
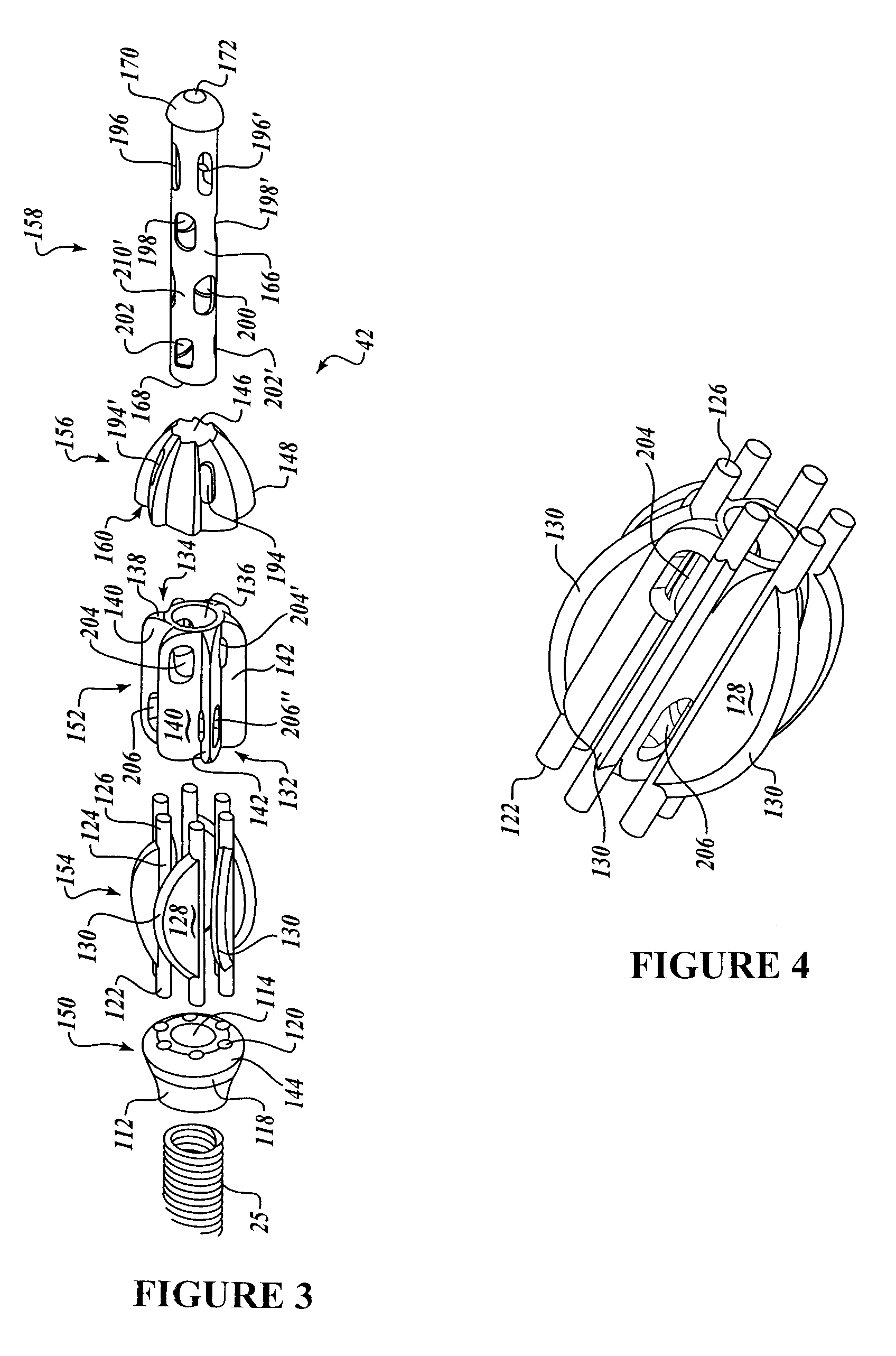
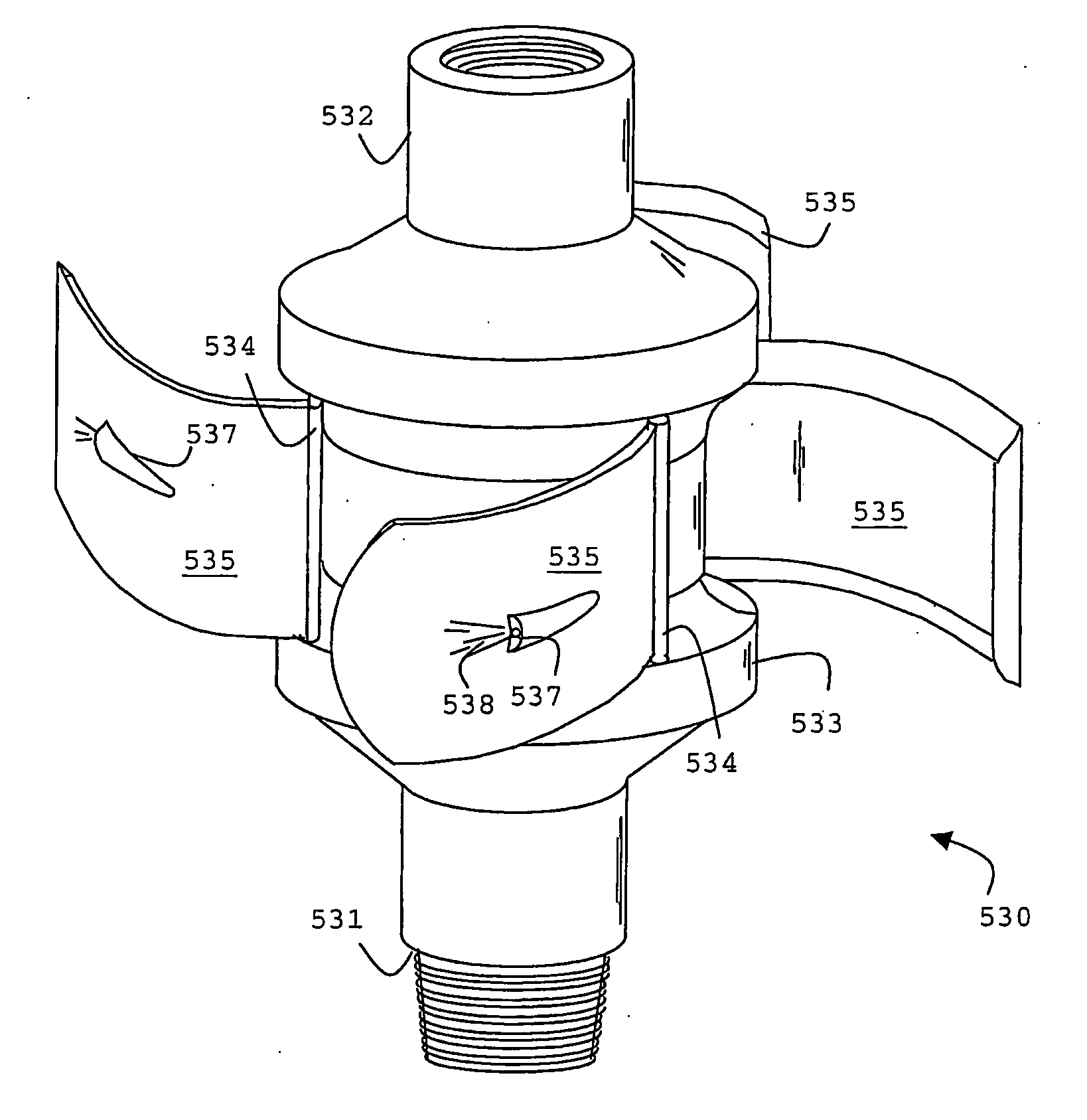
Intralumenal material removal using a cutting device for differential cutting
InactiveUS7344546B2Minimal damageFacilitates translation and navigationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasDrive shaftMaterial removal
Intralumenal material removal systems are provided using an advanceable and rotatable cutter assembly designed for differential cutting. The intralumenal material removal system includes a cutter assembly positionable in the body cavity of a mammalian subject. One embodiment of the cutter assembly includes a cutter with blades that are designed and arranged to form an acute blade angle of attack with the matter-to-be-removed. The cutter assembly is axially advanceable by translating the drive shaft and rotatable by rotating the drive shaft. The occlusive material is scraped by the cutter assembly and may be aspirated to remove the material from the body cavity. The cutter assembly may provide aspiration ports positioned between facing surfaces of the blades.
Owner:BOSTON SCI LTD
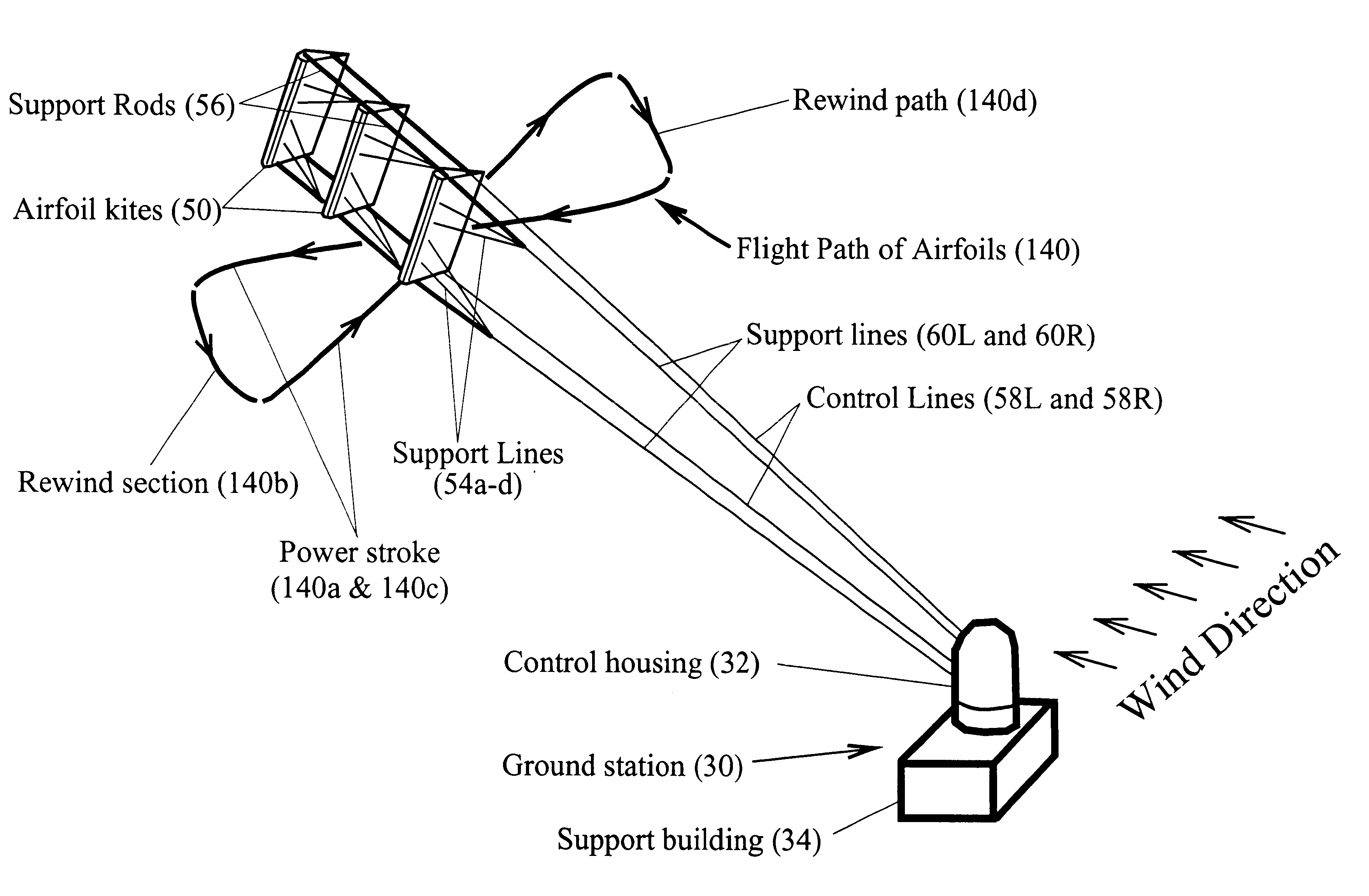
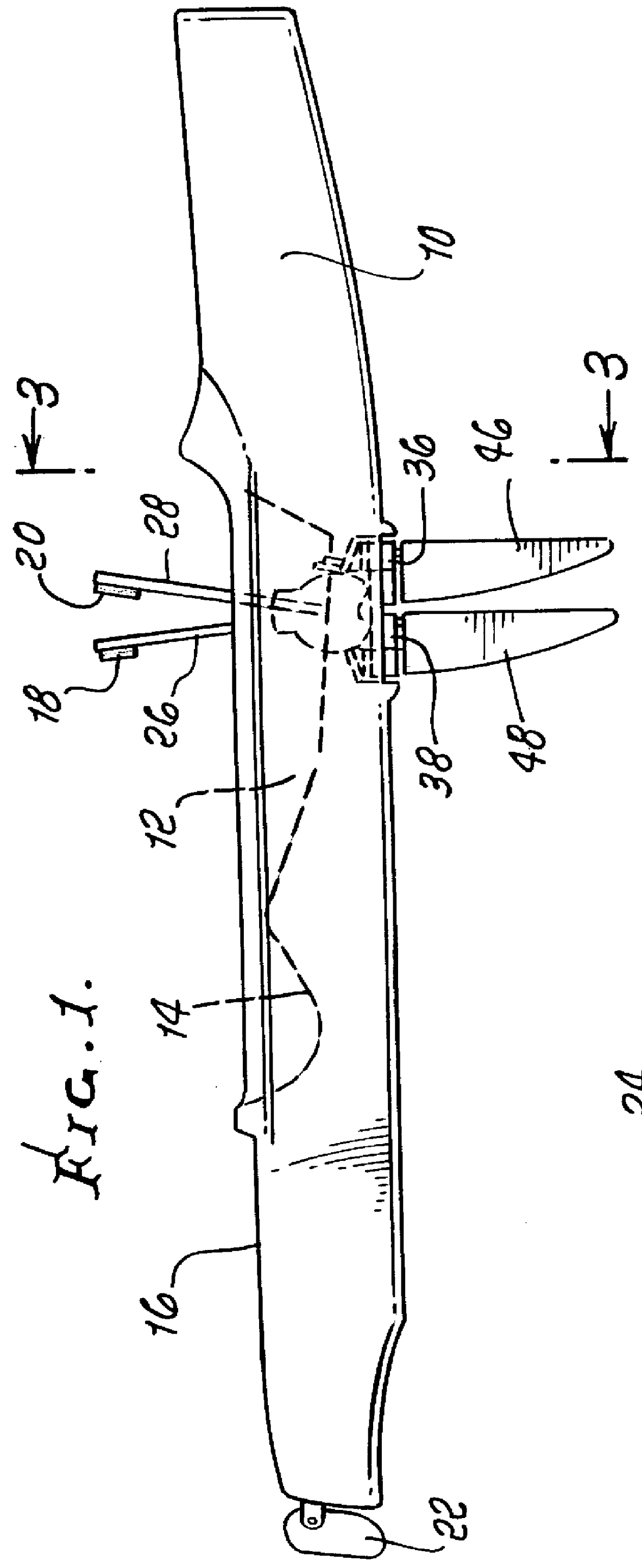
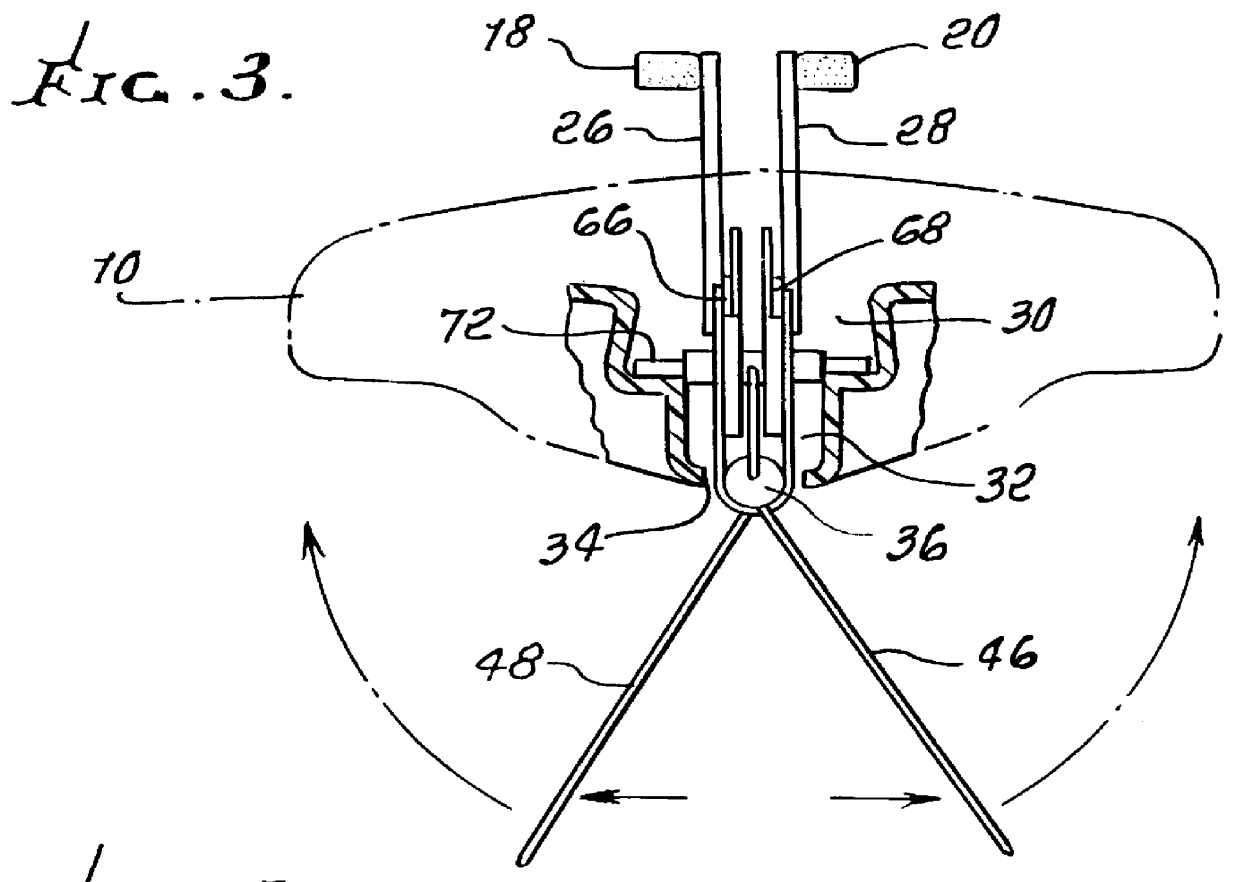
Axial-mode linear wind-turbine
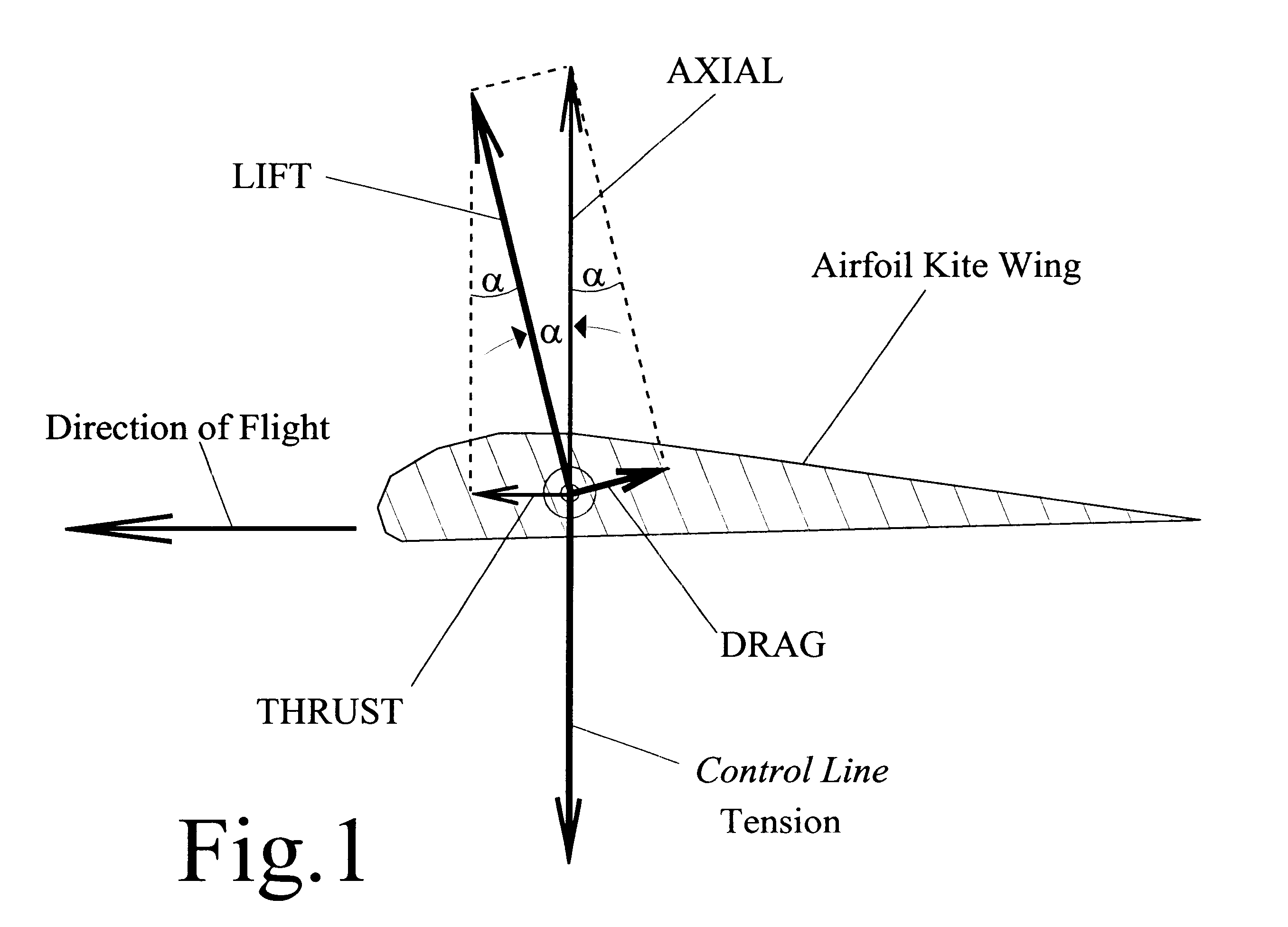
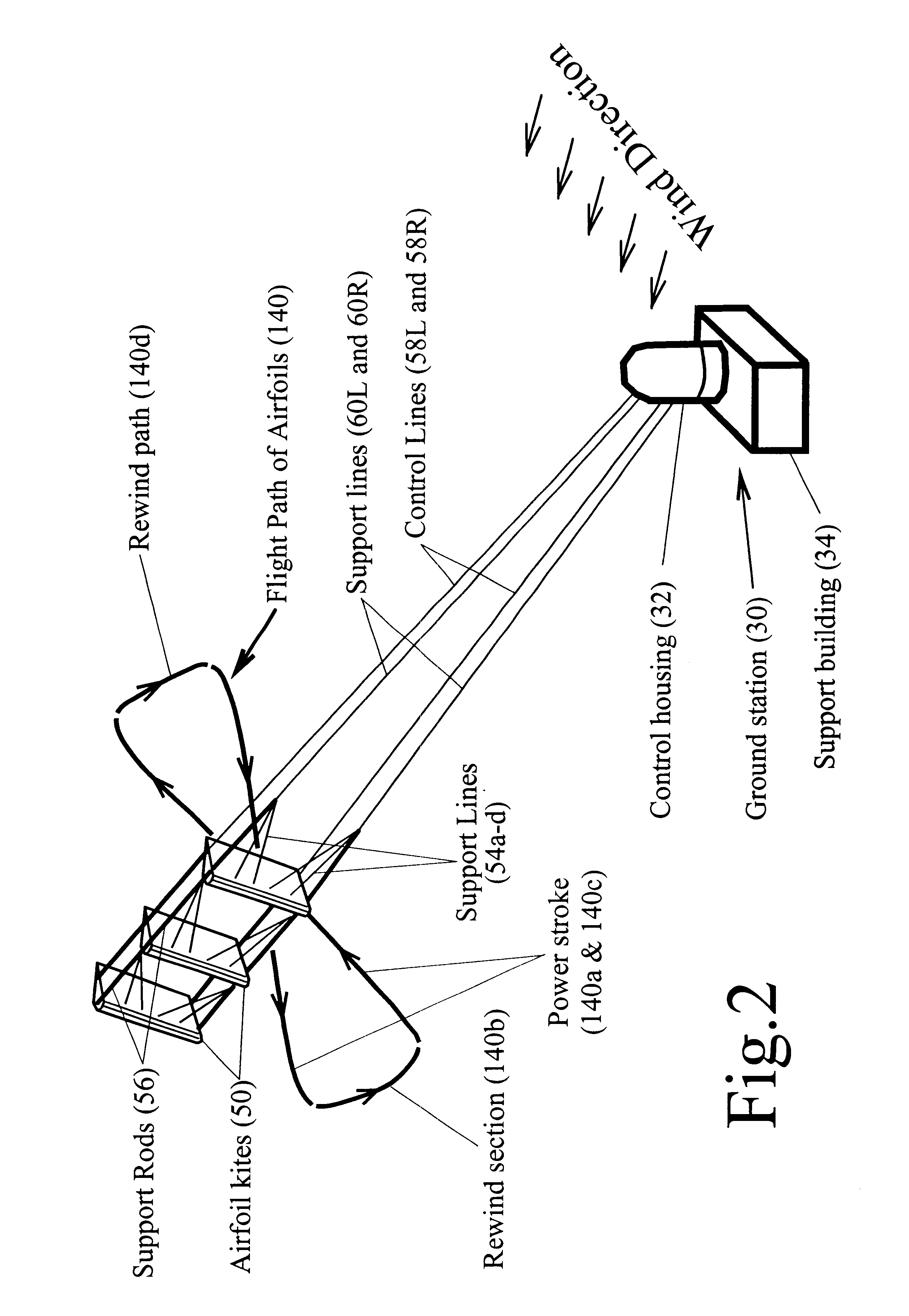
A wind harnessing system using a plurality of self supporting airfoil kites 50 for production of useful power. The system comprising multiple airfoil kites 50 in tandem attached to a pivotal control housing 32 by control lines 58L and 58R and support lines 60L and 60R. Control lines 58L and 58R can change length with respect to the length of support lines 60L and 60R to control the airfoil kites' 50 angle-of-attack, pitch angle, direction of flight, and flight speed. The length of control lines 58L and 58R are controlled from ground station 30 by a movable pulley system in control housing 32 to adjust the airfoils' direction to follow a specific flight path 140. Control lines 58R and 58L and support lines 60R and 60L are also wound on a power shaft and pulley system in control housing 32. As the airfoil kites are propelled by the wind at very-high speed, the airfoils generate a powerful AXIAL force. The control lines 58L and 58R and support lines 60L and 60R are then reeled-out under this AXIAL tension causing the power shaft and pulley system in control housing 32 to turn a generator to generate electricity. After airfoil kites 50 have finished their reel-out power stroke 140a, the airfoil's pitch angle is made negative so they can be reeled-in by their control and support lines using a minimum of force along path 140b. Once the airfoils have been rewound to the proper distance, the airfoils are again angled for high-speed operation to generate powerful AXIAL force and reeled-out along 140c to provide another power stroke. The airfoil kites are then reeled-in again along path 140d and the entire process repeats starting with power stroke 140a. Since the force to rewind the airfoils is much less than the force generated during reel-out, there is net power generated.
Owner:RAGNER GARY DEAN
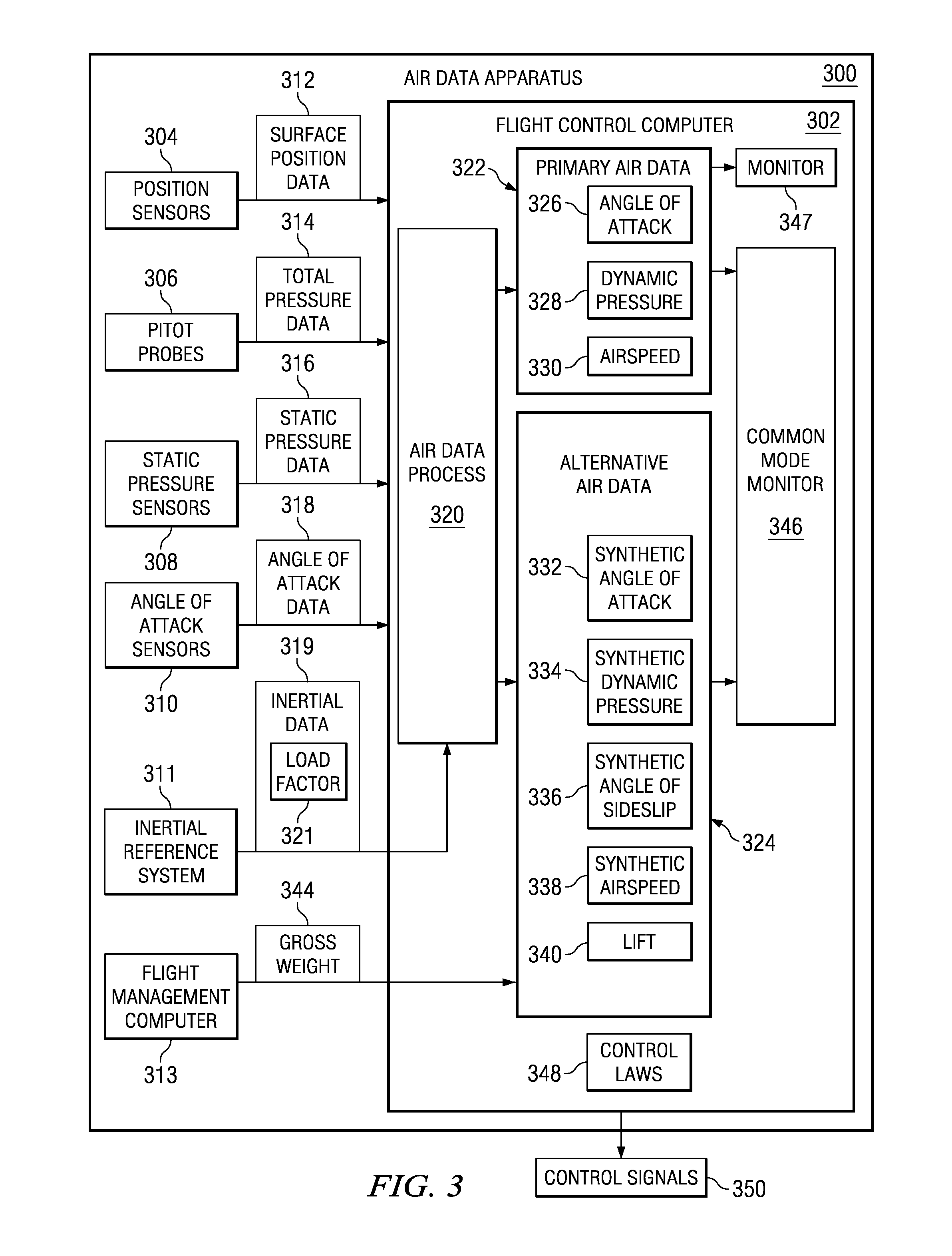
Alternative method to determine the air mass state of an aircraft and to validate and augment the primary method
ActiveUS20100100260A1Aircraft controlDigital data processing detailsFlight vehicleAlternative methods
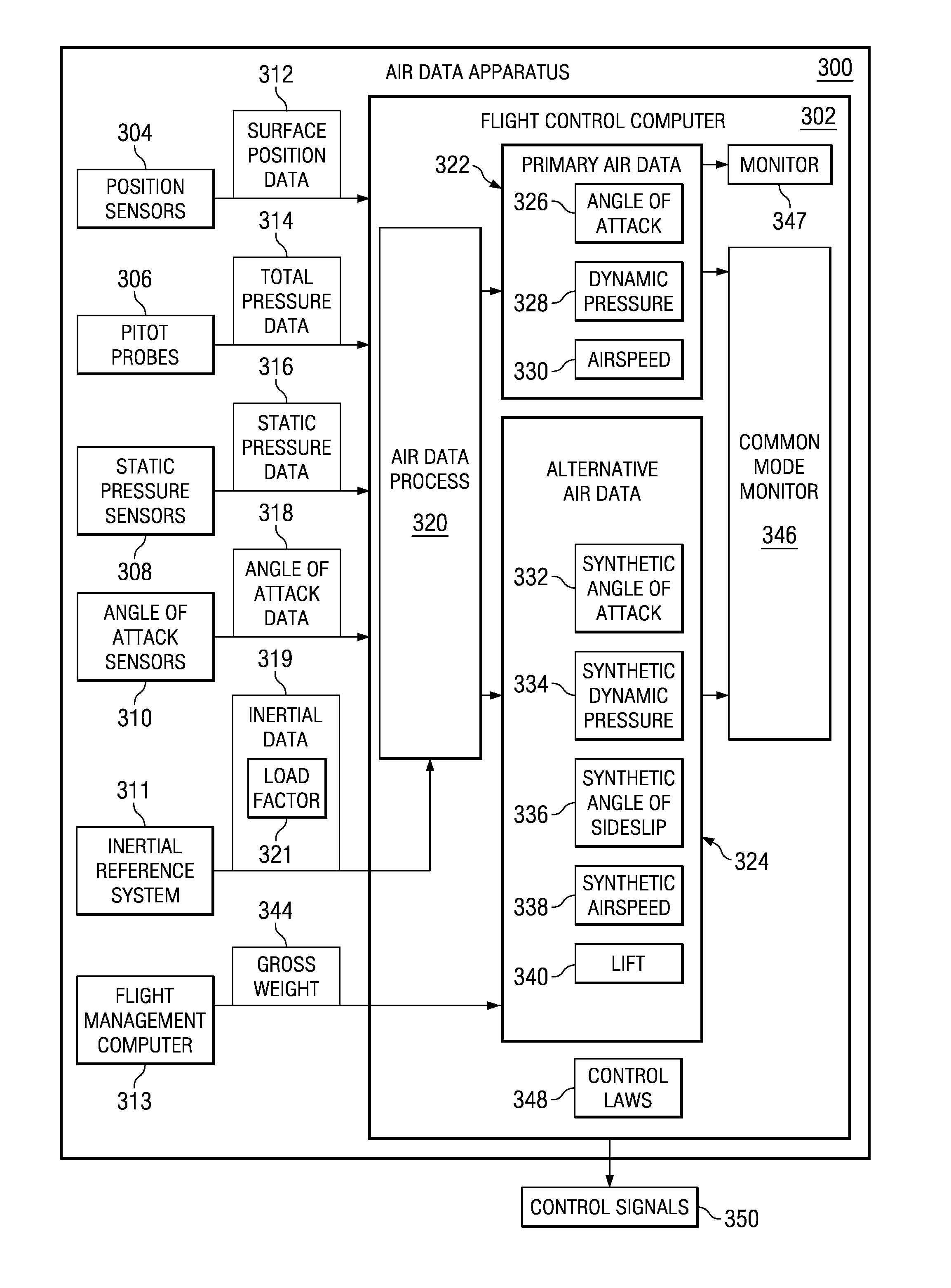
A method, apparatus, and computer program product for identifying air data for an aircraft. The lift for the aircraft is identified. The number of surface positions for the aircraft is identified. The angle of attack during flight of the aircraft is identified. A synthetic dynamic pressure is computed from the lift, the number of surface positions, and the angle of attack.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
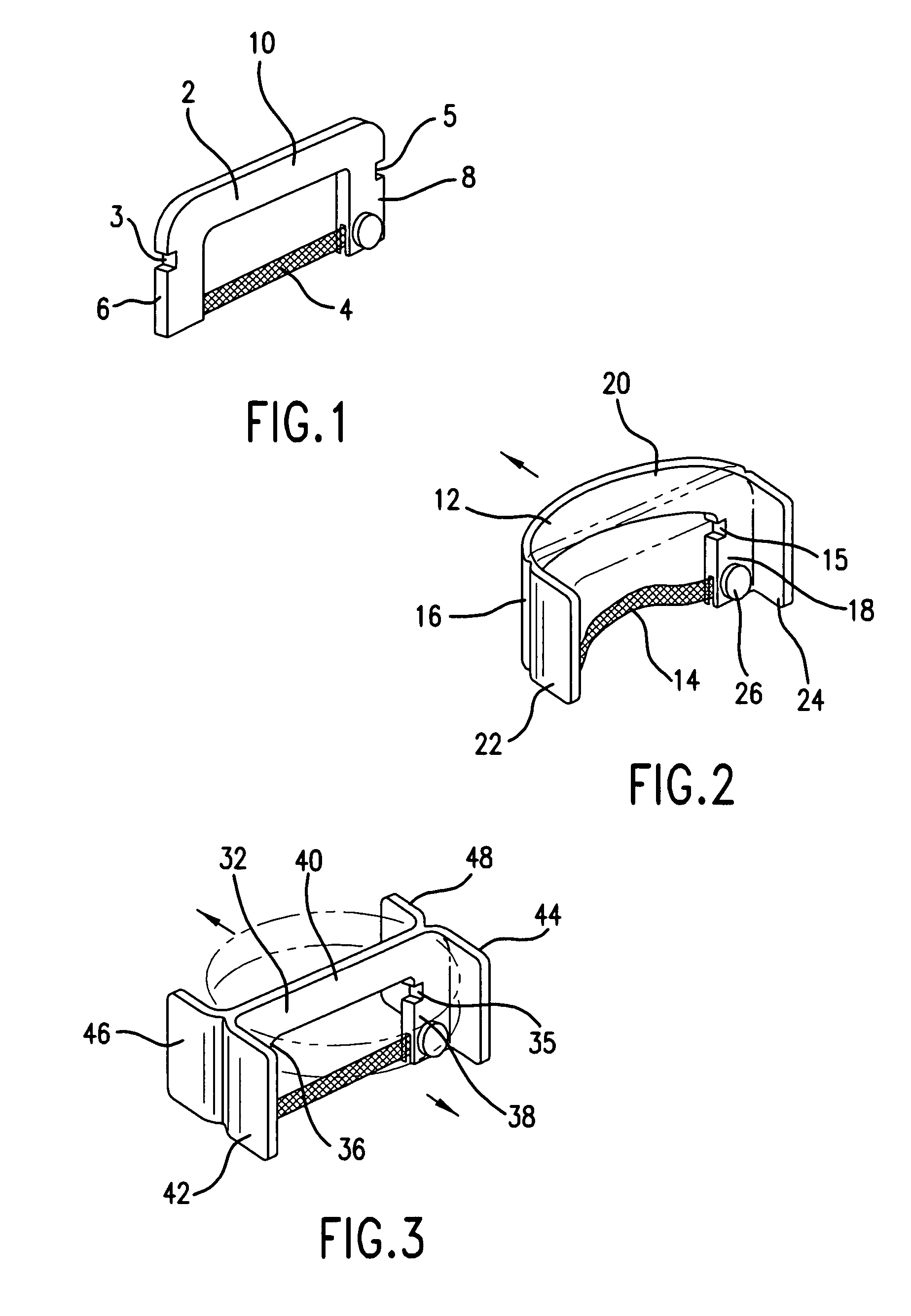
Interproximal devices and methods of using same
ActiveUS7455521B2Facilitates quick and easy interchangeIncrease variabilityTooth sawsGum massageEngineeringAngle of attack
A loop is formed by a bow having across one side a strip or blade. The bow has flexure and memory. The flexure and memory of the bow are imparted to the strip, enabling the strip to be either taut or loose, depending on the pressure exerted by the operator upon the bow. The bow is held and manipulated by the operator with the thumb and finger. The strip is positioned under tension. A holder for the device allows additional variability in the angle of attack of the strip, and facilitates quick and easy interchange of the strips. A holder avoids insertion of fingers far back in the mouth, where working space is limited.
Owner:FISHBURNE JR COTESWORTH
Intralumenal material removal using a cutting device for differential cutting
InactiveUS20080228208A1Minimal damageFacilitates translation and navigationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasMaterial removalDrive shaft
Owner:PATHWAY MEDICAL TECH
System and method for extracting power from fluid using a tesla-type bladeless turbine
InactiveUS20100129193A1Reduce lossesOptimal longitudinal spacingWind motor controlPump componentsSurface oceanViscous shear
Smooth, preferably variable-sweep fluid collection device surfaces disposed into opposition with wind, river, surf, ocean or tidal currents generate enhanced velocity fluid flows at length driven into onboard work-extracting disc turbines at advantageous angles of attack. Keyed to shafts turning freely through optionally extendable volutes, disc turbines comprising a dense population of smooth, axially fixed or adjustably spaced discs conducting preferably laminar flow between adjacent elements develop significant torque through boundary layer adhesion and viscous shear-stress between fluid layers. Exhaust of disc turbine throughput into divergent channels drafting into external currents of initially higher than ambient velocity and lower pressure may reduce turbine discharge backpressure, rapidly clear system throughput, and allow normally disadvantageous drag to be utilized to develop greater work generation. Gainfully turning with, instead of at odds to natural or anthropogenic currents provided, disc turbines utilized as disclosed may provide unprecedented renewable energy from fluids in motion.
Owner:SHERRER GORDON DAVID
Power loss reduction in turbulent wind for a wind turbine using localized sensing and control
InactiveUS20080317598A1Reduce impactMinimize the differencePropellersWind motor controlTurbine bladeAngle of attack
A wind turbine blade assembly includes at least one local load sensor disposed on and / or within a surface of the wind turbine blade and at least one active flow modification device disposed on and / or within a surface of the wind turbine blade and configured to alter the aerodynamics of the wind turbine blade in response to real time local load sensor measurements such that a difference between a current angle of attack and an optimum angle of attack on the wind turbine blade is substantially minimized.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
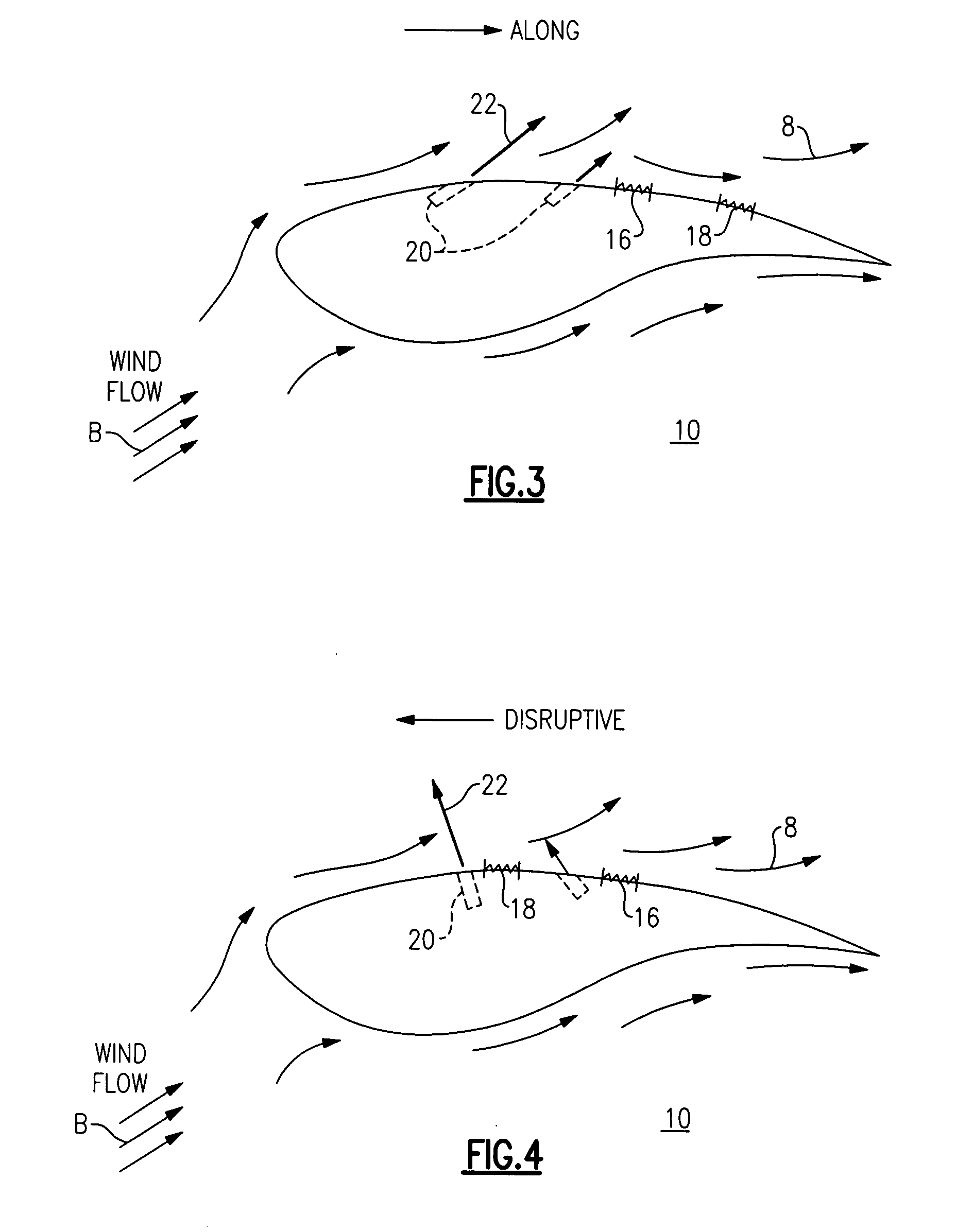
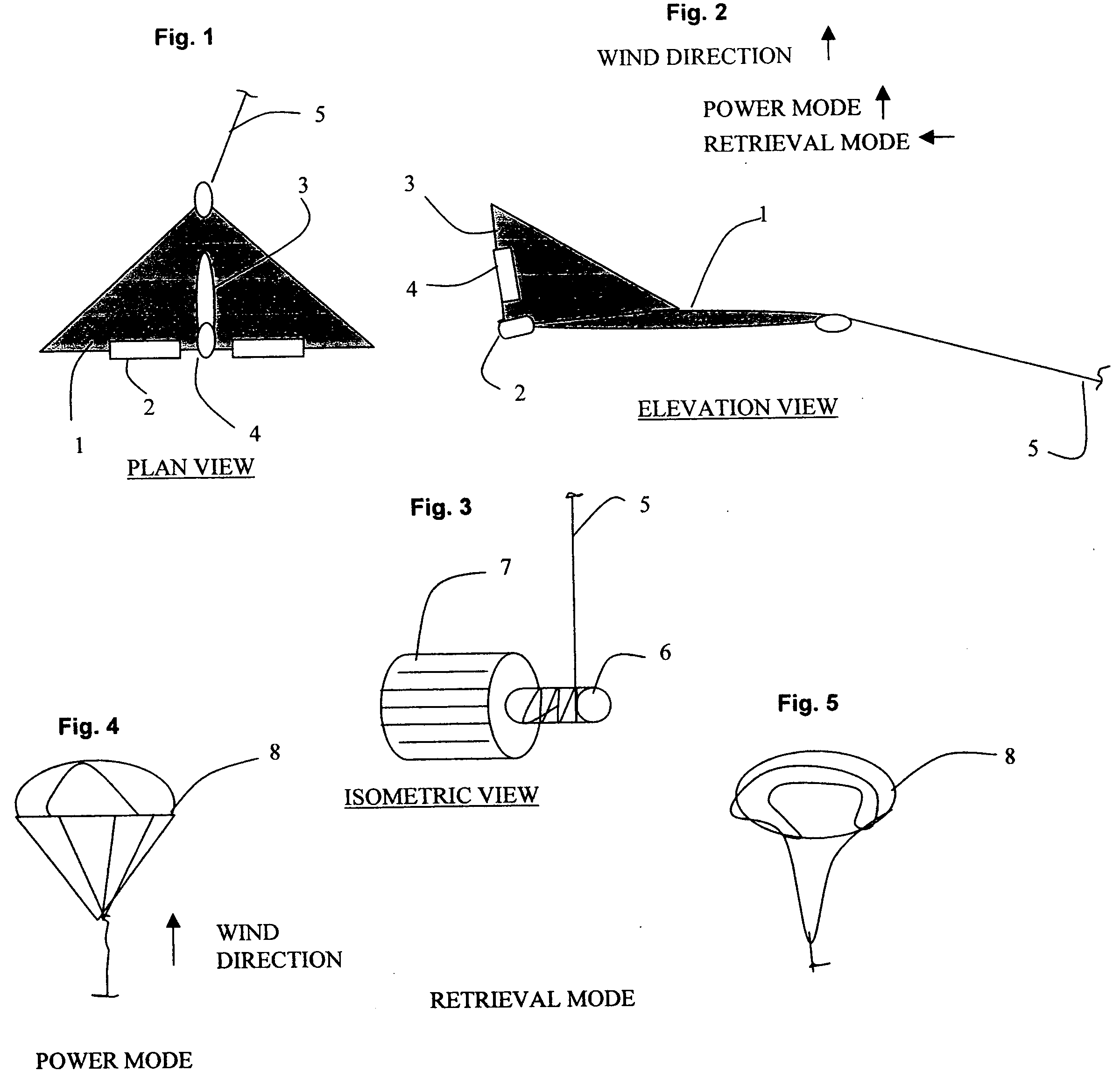
Wind energy production using kites and ground mounted power generators
Systems and methods are described for creating low cost energy using kites connected to ground mounted equipment. In power mode the kites generate maximum energy by positioning the kite at a high angle of attack relative to wind direction. The kite is allowed to travel a distance limited only by the length of line attached. The opposite end of the line is attached to a reel capable of turning a shaft to create mechanical or electrical energy. Upon reaching a controlled length, the kite is repositioned to a minimum angle of attack relative to the wind to minimize energy required to retrieve the kite. The shaft rotation is then reversed thereby winding the line on the reel. Energy is expended in retrieval mode. The difference in energy during power and retrieval mode is the net energy gain available for useful work.
Owner:KINGSLEY GORDON BRUCE
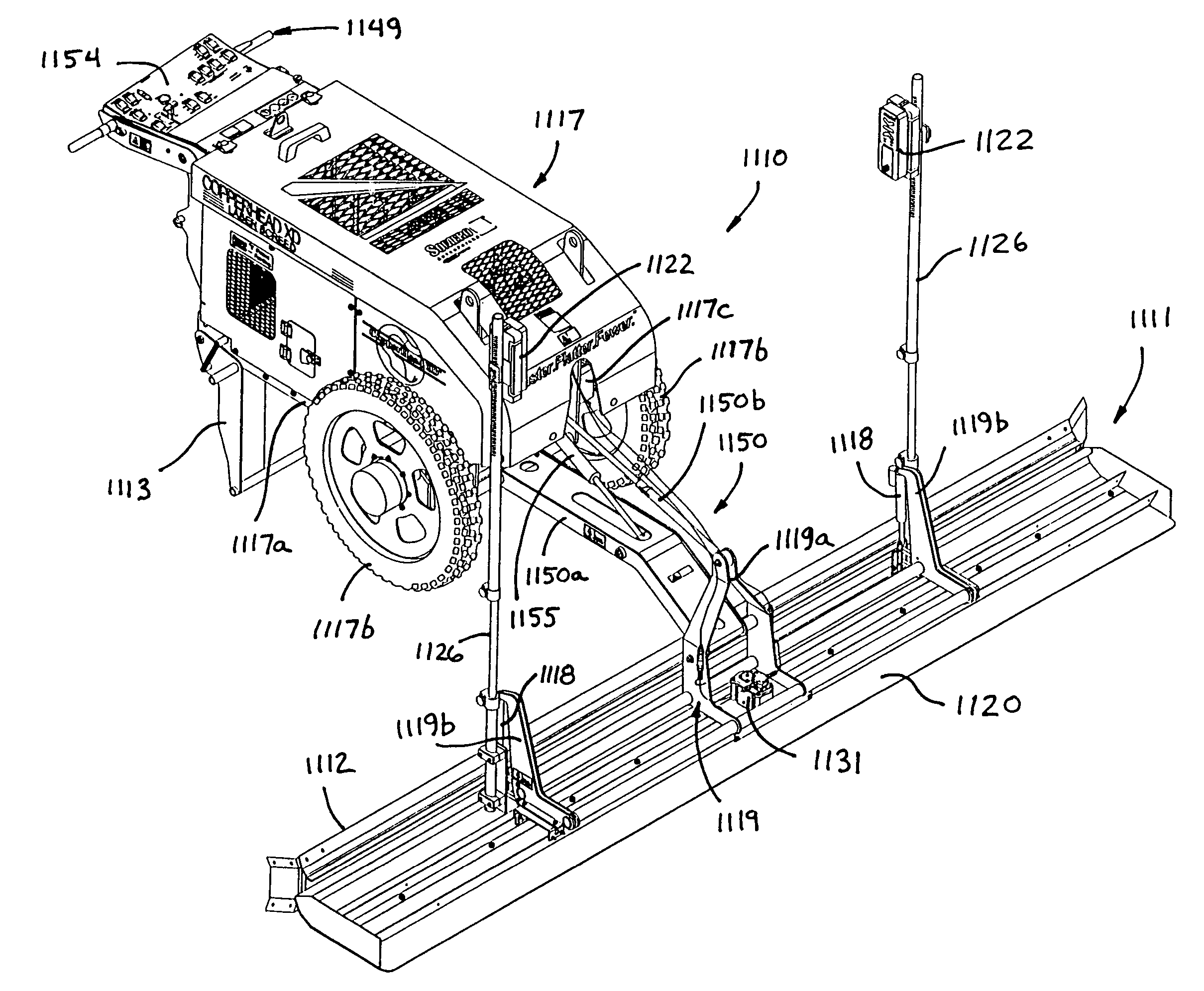
Apparatus for screeding uncured concrete surfaces
InactiveUS7121762B2Improve accuracyEasy to operateRoads maintainenceBuilding material handlingControl systemEngineering
A screeding apparatus for screeding and smoothing an uncured concrete surface includes a vibrating member and a grade setting device adjustably mounted to said vibrating member. The screeding apparatus may include a wheeled support which at least partially supports the vibrating member and / or the grade setting device. The grade setting device is vertically adjustable, such as via a laser plane responsive control system, to set or indicate the desired grade of the concrete surface as the screeding apparatus is moved over and through the uncured concrete. The level of the screeding apparatus may be automatically adjustable to maintain a desired level and angle of attack of the vibrating member. The vibrating member may be activated only when the screeding apparatus is moved in a screeding direction so as to reduce depressions that otherwise may occur if the vibrating member vibrates on the uncured concrete when not moving.
Owner:SOMERO ENTERPRISES INC
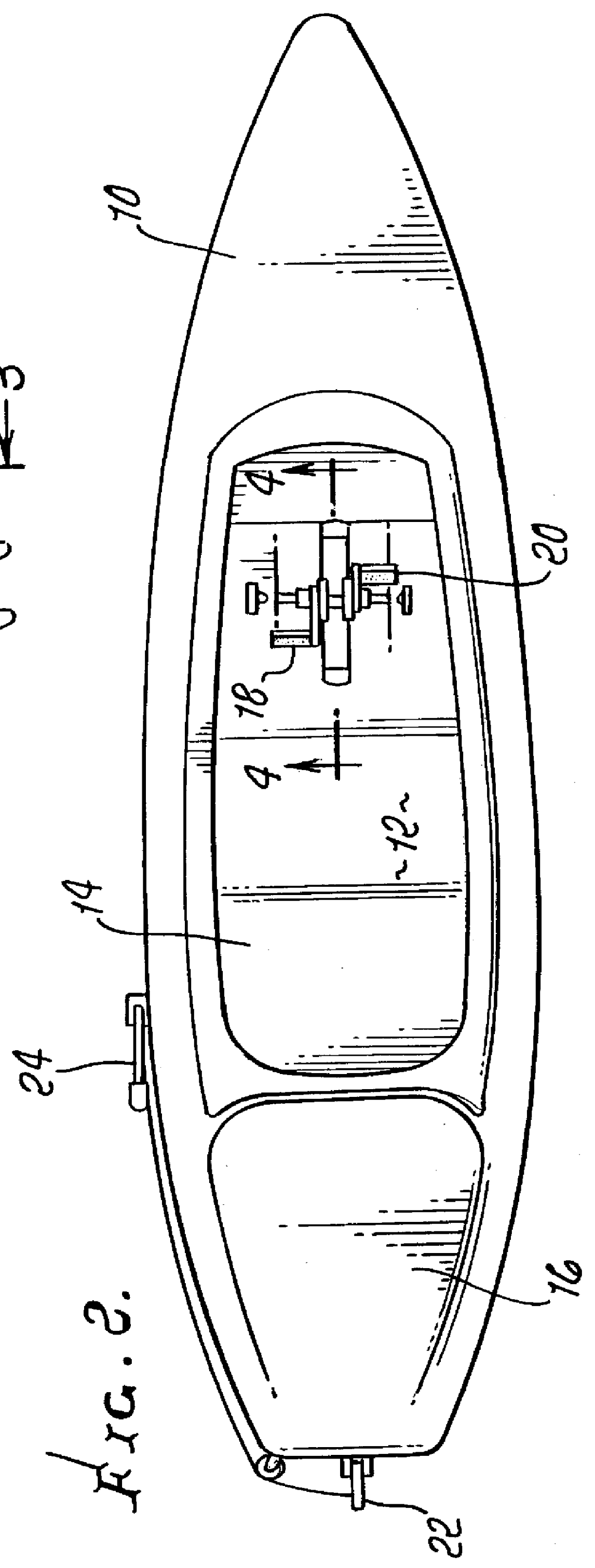
Watercraft
InactiveUS6022249APropulsive elements of non-rotary typeMuscle power acting propulsive elementsKeelWatercraft
A novel water craft, which may include a hull with a keel, having propulsion means extending below the water line. The propulsion means comprises a pair of flappers each adapted to oscillate through an arcuate path in a generally transverse direction with respect to the central longitudinal dimension of the watercraft. Means are operatively associated with the propulsion means for applying input force to the propulsion means. The flappers twist to form an angle of attack for providing forward thrust with respect to the longitudinal dimension of the watercraft while moving in both directions along the arcuate path.
Owner:R R SAIL
High efficiency fluid movers
Fluid movers produce at least predominantly laminar flow internally in an axial or a radial direction in a rotor. A fluid mover rotor comprises a matrix of passages of appropriate size to produce at least predominantly laminar flow spaced circumferentially around the rotor. The passages may provide axial, radial or mixed flow. “Appropriate” dimensions may be selected for a specified volume flow rate. In a radial embodiment, a matrix of radially extending passages could comprise walls having an axial height projecting from an annular disk. The passages may be offset with respect to the radial direction to provide an angle of attack that minimizes incidence losses. The matrix structure allows the use of thin-walled passages to minimize blockage of entering air.
Owner:HILL ENG
Apparatus for screeding uncured concrete surfaces
InactiveUS20050069385A1Improve accuracyEasy to operateRoads maintainenceBuilding material handlingControl systemMechanical engineering
A screeding apparatus for screeding and smoothing an uncured concrete surface includes a vibrating member and a grade setting device adjustably mounted to said vibrating member. The screeding apparatus may include a wheeled support which at least partially supports the vibrating member and / or the grade setting device. The grade setting device is vertically adjustable, such as via a laser plane responsive control system, to set or indicate the desired grade of the concrete surface as the screeding apparatus is moved over and through the uncured concrete. The level of the screeding apparatus may be automatically adjustable to maintain a desired level and angle of attack of the vibrating member. The vibrating member may be activated only when the screeding apparatus is moved in a screeding direction so as to reduce depressions that otherwise may occur if the vibrating member vibrates on the uncured concrete when not moving.
Owner:SOMERO ENTERPRISES INC
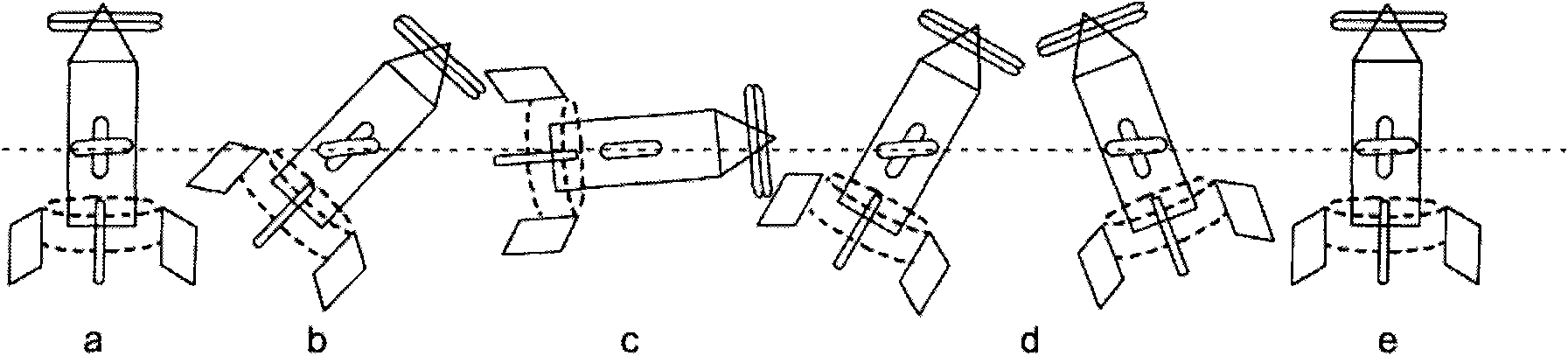
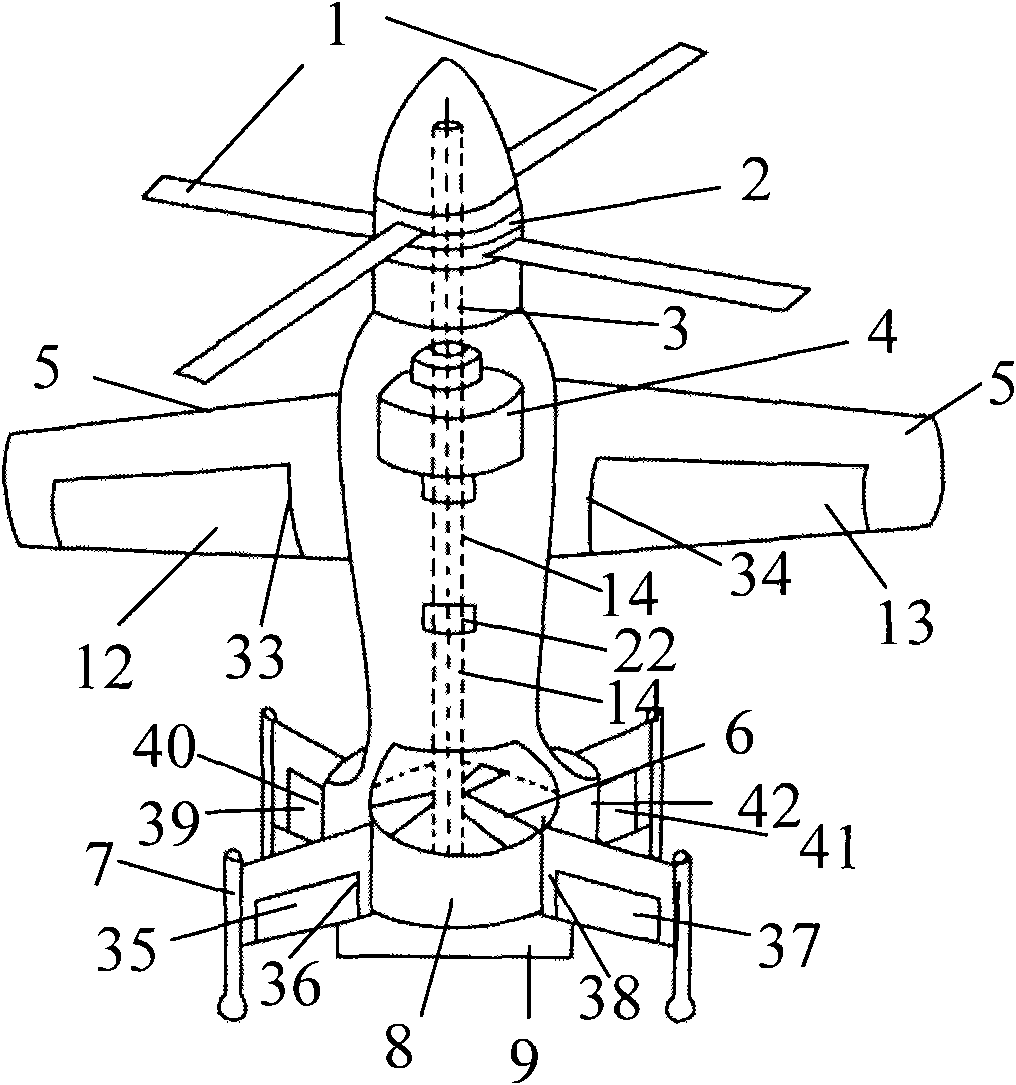
A composite rotating fixed-wing aircraft and its design method
InactiveCN101549754APrevent rolloverPrevent sideslipVehicle position/course/altitude controlGround installationsStarter generatorMotor drive
The composite rotating fixed-wing aircraft consists of the coaxial counter-paddle, reverse gear, engine output shaft, engine with a starter-generator, wings, tail blades, landing device, culvert, steering gear, fairing, fuselage, motor, motor drive shaft, wing control unit of small angle of attack, aileron rudder surface, and tailplane rudder surface. Co-axial counter-blade is located in the upper part of the aircraft, which connects with the engine output shaft; the reverse gear is installed between the co-axial counter-propellers; the motor connects with motor drive shaft powered by the starter-generator of the engine; the wings are located on both sides of aircraft and connect with the fuselage; the tail blades are located at the aircraft tail, which are installed behinde motor drive shaft; the landing device is located under the lower part of the fuselage and fixed with it; the culvert connects with the landing device; the fairing is installed in the culvert and connects with the steering gear; the wing control unit of small angle of attack is installed on the wing. The aircraft design method has six steps with strict scientific idea; this invention has a wide range of practical value and application prospect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
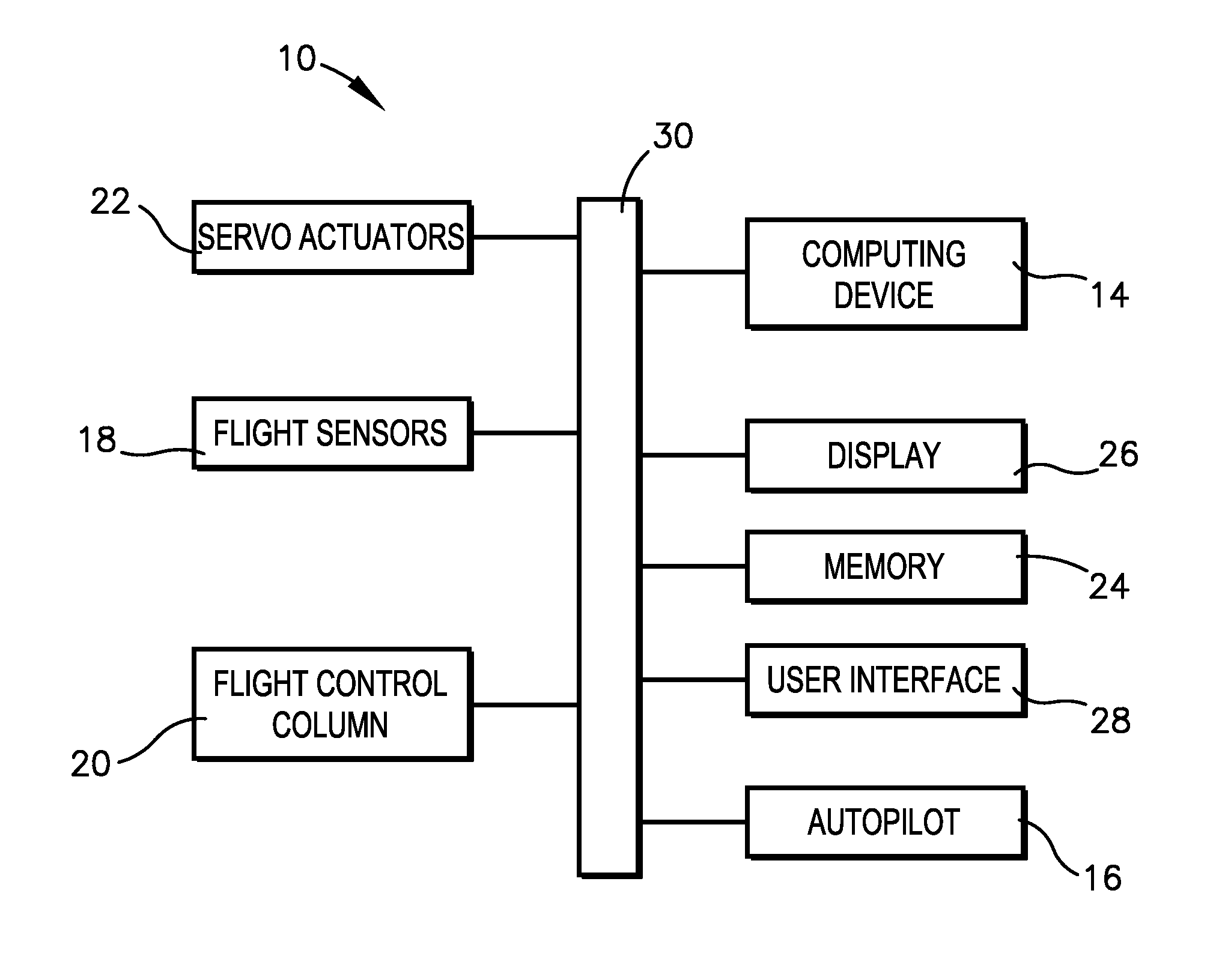
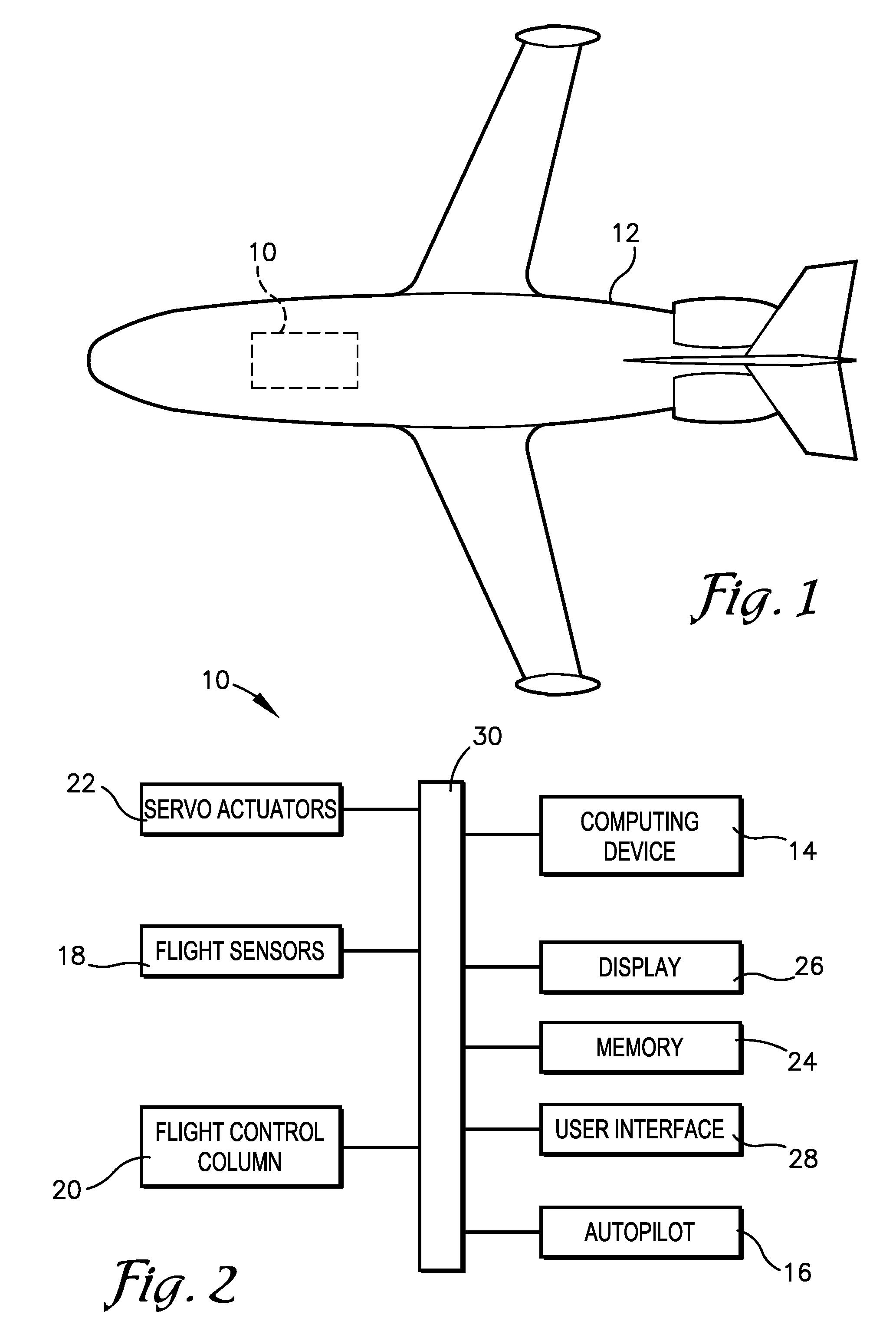
Envelope protection for mechanically-controlled aircraft
An avionics system for a mechanically-controlled aircraft configured to provide envelope protection for deterring a pilot from flying outside of acceptable flight parameter limits for flight parameters such as banking angle, pitch attitude, g loading, proximity to terrain and / or obstacles, angle of attack, and / or airspeed. The avionics system may comprise at least one servo actuator and a computing device. The computing device may engage envelope protection by engaging the at least one servo actuator if the aircraft reaches a maximum or minimum limit for any of the flight parameters, such that the at least one servo actuator provides a force to urge a flight control device in a direction to bring the aircraft back within the acceptable flight parameter limits. The servo actuator may be disengaged when the aircraft flight parameters reach an end value corresponding to the start value that triggered envelope protection to engage.
Owner:GARMIN INT
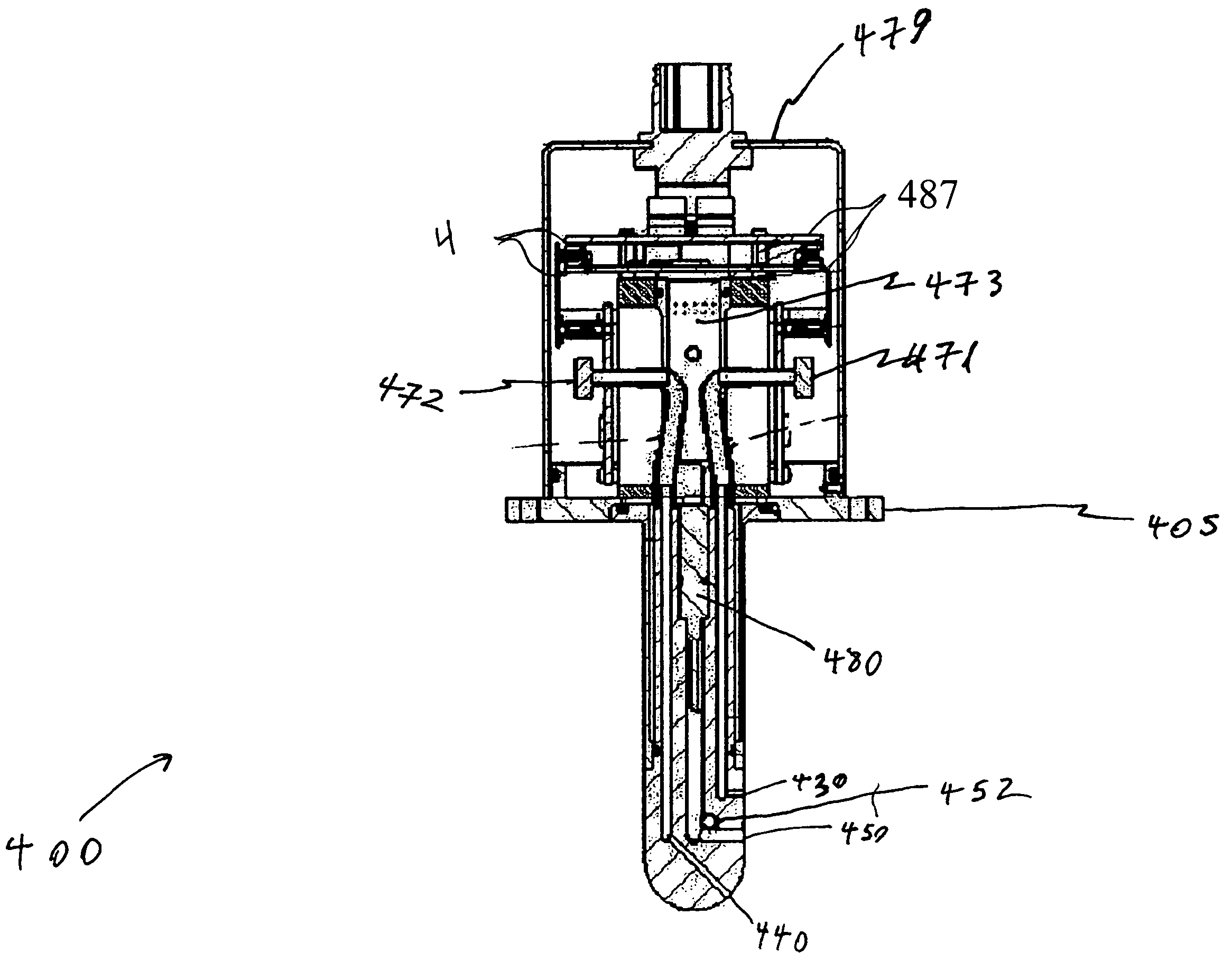
Scale measuring device for pitching dynamic derivative experiment
InactiveCN101726401AAccurate detectionDesign scienceSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementAerodynamic testingMeasurement deviceDrive shaft
The invention provides a scale measuring device for a pitching dynamic derivative experiment. An electric motor is arranged in a motor support rod; a motor output shaft is connected with a transmission shaft via a speed reducer and a shaft coupling; the transmission shaft is rotationally connected with a scale support rod; the rear end of the scale support rod is fixedly connected with the front end of the motor support rod; the front end of the transmission shaft is provided with an eccentric wheel which is provided with a lug; the lug is inserted into a sliding chute of a slide block; upper and lower cross springs of a cross spring scale have a crisscross structure respectively, and the front and rear ends thereof are fixedly connected with a scale frame via a front seat; and central positions of the upper and lower cross springs are provided with supporting cylinders. The scale measuring device for the pitching dynamic derivative experiment is a novel pitching dynamic derivative scale device. A pitching direct derivative of an aerial craft and a rolling crossover derivative induced by yaw oscillation can be measured under a big attack angle by designing a special vibrating mechanism, the cross spring scale and a pitching five-component scale structure. The scale measuring device for the pitching dynamic derivative experiment can meet the requirement of a wind tunnel trial.
Owner:SHENGYANG AERODYNAMIC INST AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
Device to aid in placing tracheal tubes
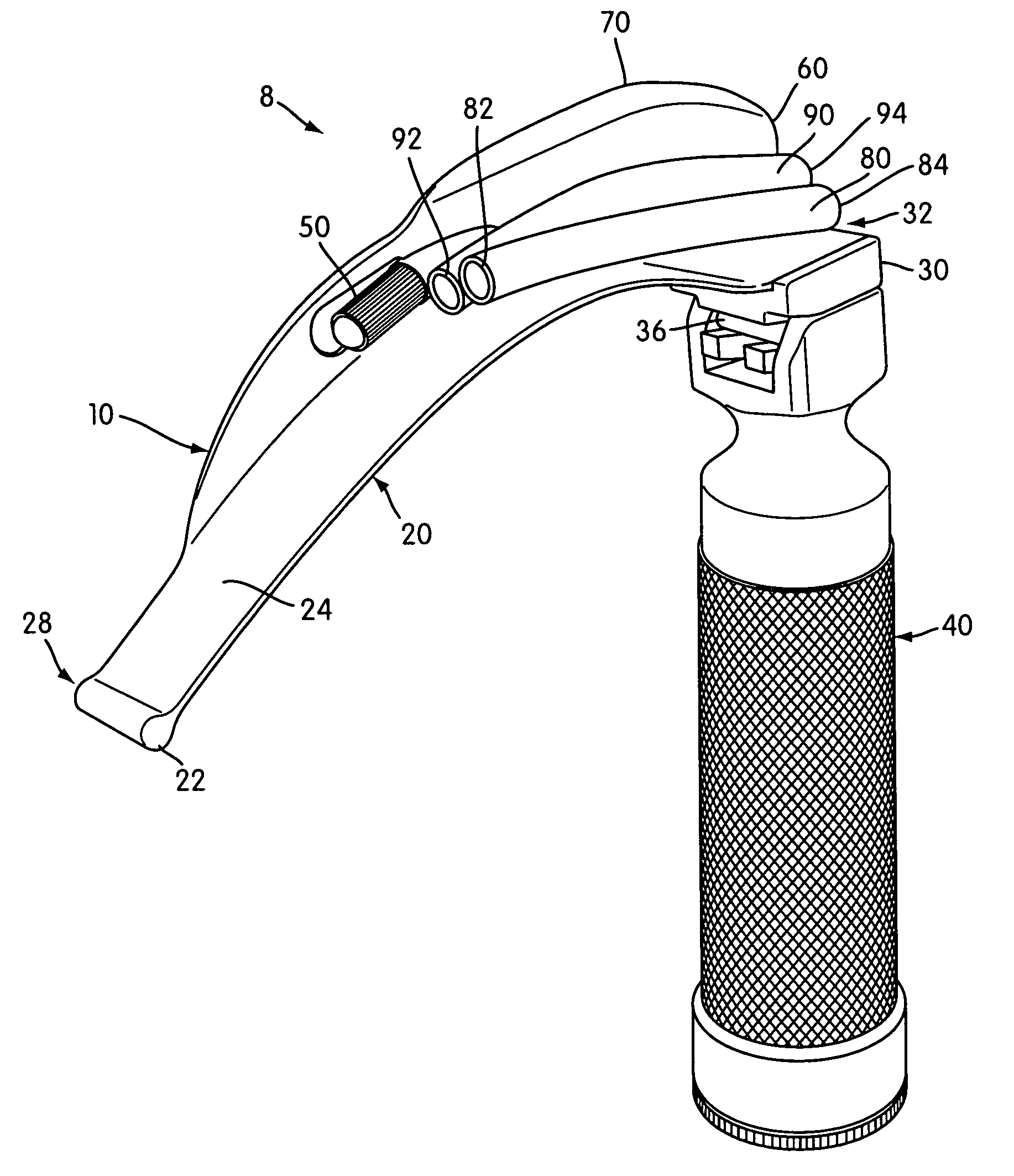
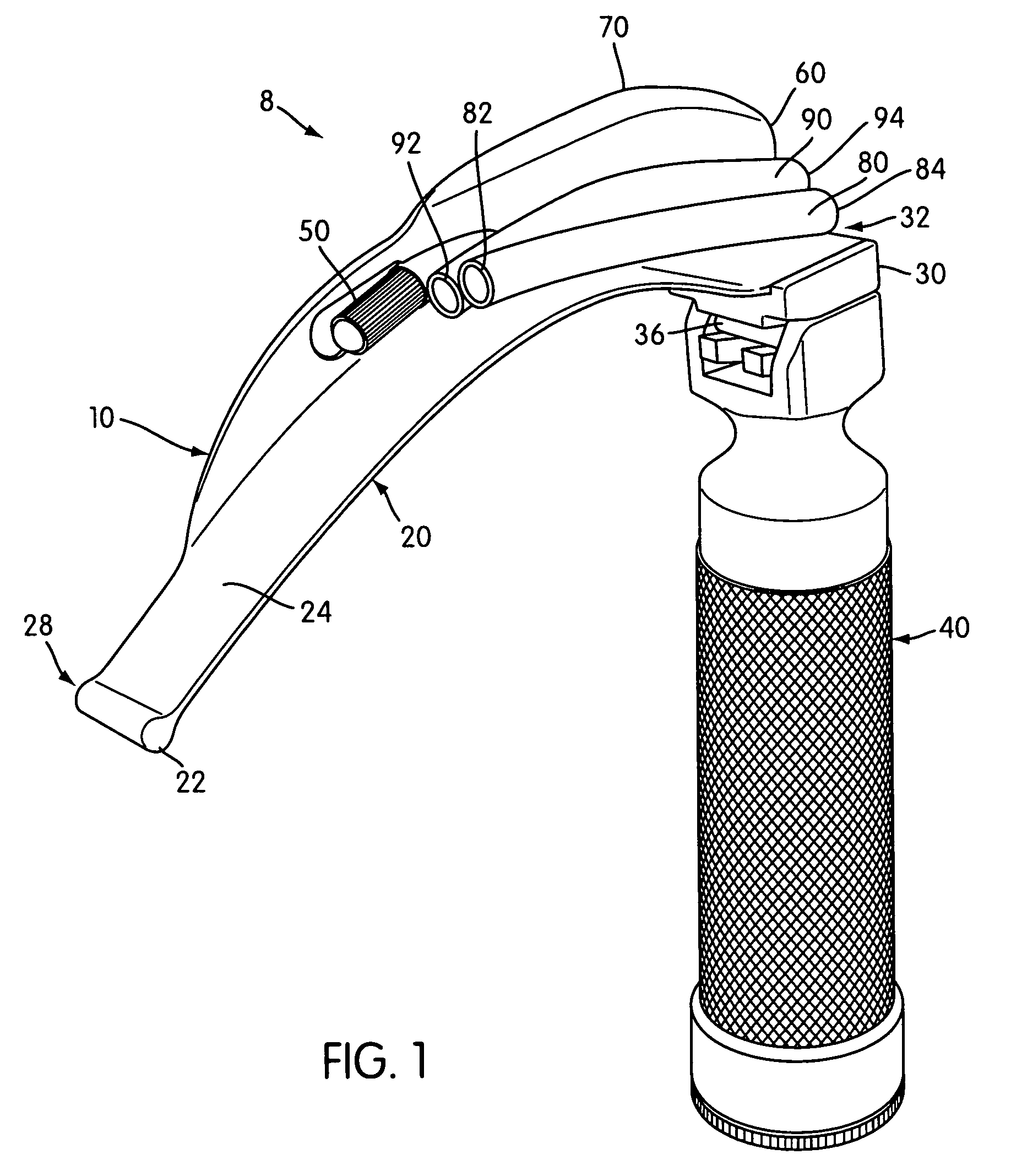
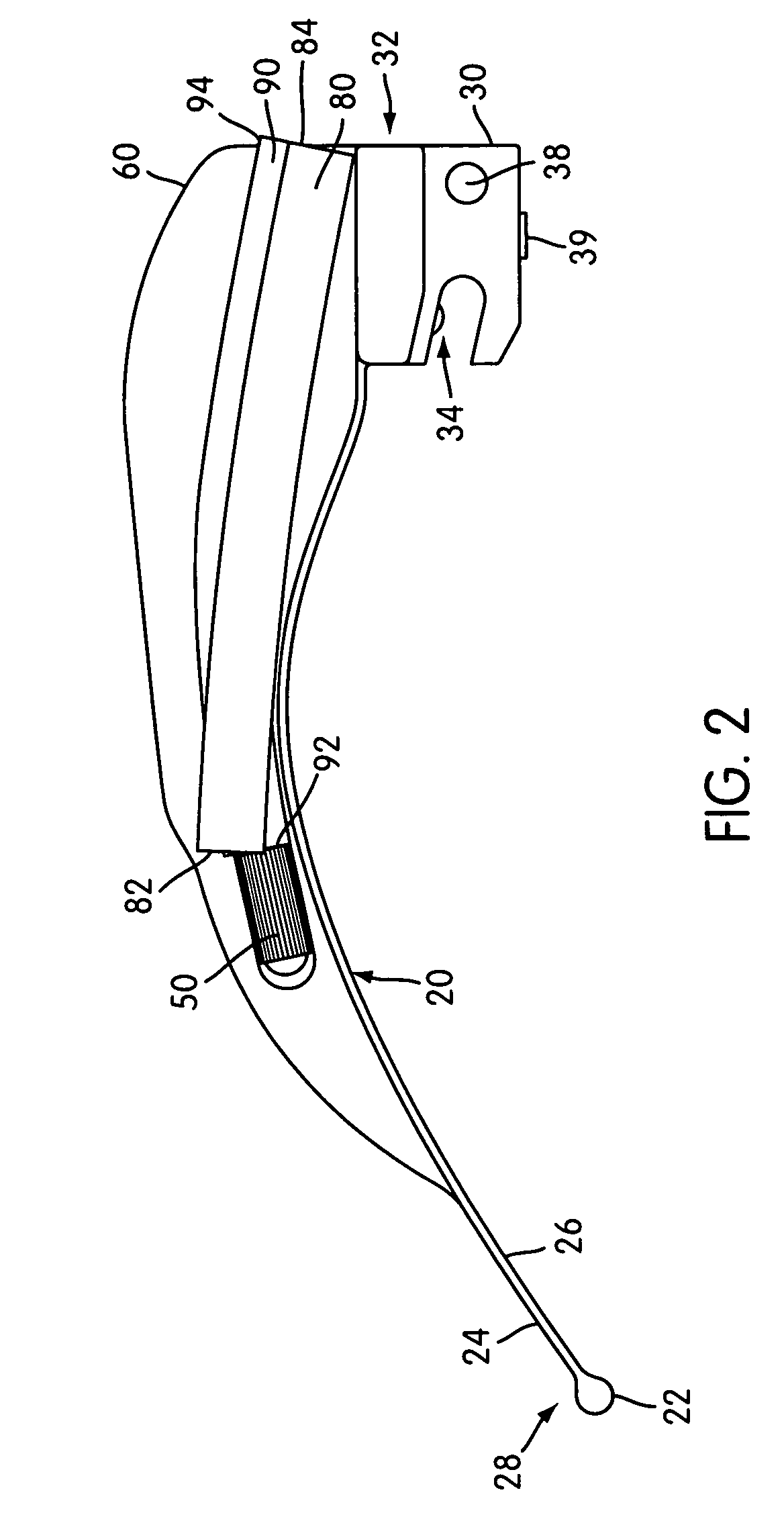
A laryngoscope includes a blade assembly with a base that is coupled to a handle. Attached to the blade assembly are two hollow guide tubes that generally follow along the longitudinal axis of the blade assembly. The two tubes are oriented at different angles of attack for directing aspirating and / or oxygenating tubes into different regions of the patient's oral cavity. The handle has an ergonomic shape to conform to the user's hand, thereby facilitating the user's application of a downward force necessary to effect laryngeal suspension. A tube extension / retraction mechanism effects user-controlled powered movement of an aspiration / oxygenation tube into or out of the patient's oral cavity. A bayonette connection is provided for connecting the blade assembly to the handle.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Network defense strategy selection method and apparatus based on Markov evolutionary game
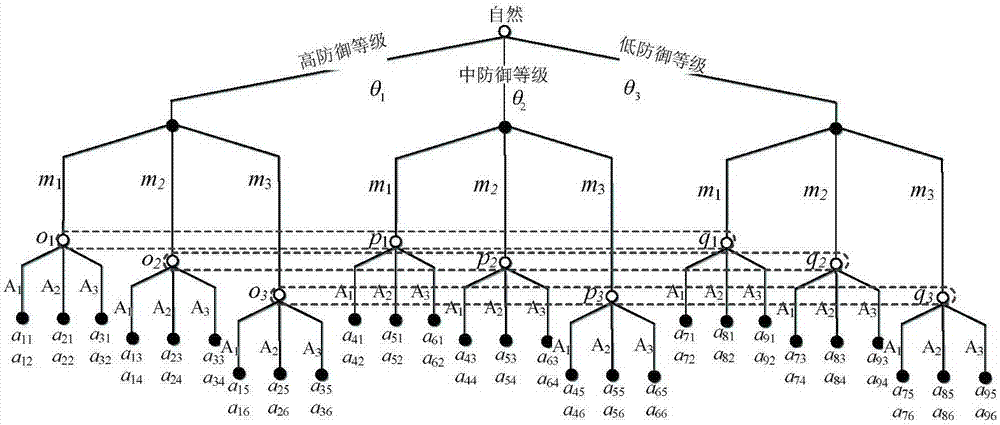
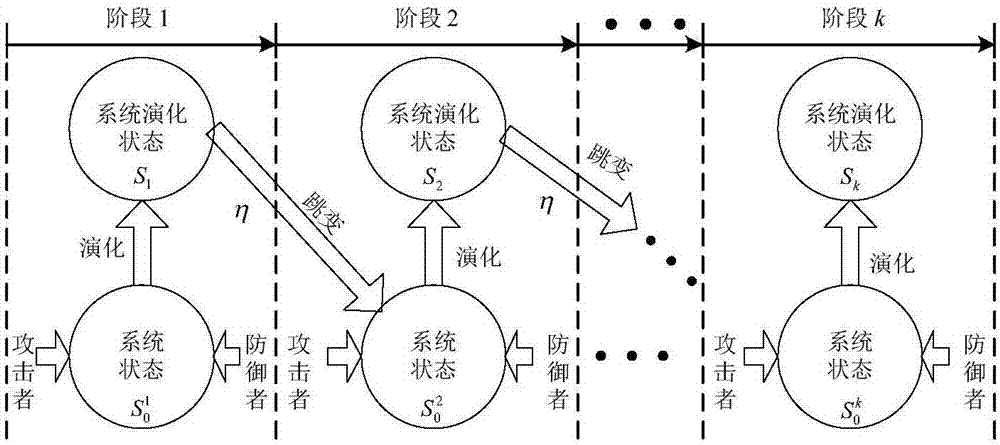
The invention relates to a network defense strategy selection method and apparatus based on Markov evolutionary game. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a multi-stage Markov attack and defense evolutionary game model according to dynamic attack and defense game in a network attack and defense process, wherein the model contains a plurality of sub game stages; solving and outputting optimal defense strategies of the stages of the attack and defense game by using an optimal defense strategy selection algorithm for the multi-stage Markov attack and defense evolutionary game model. According to the network defense strategy selection method and apparatus provided by the invention, a dynamic evolution process of network attack and defense in view of the multi-stage Markov attack and defense evolutionary game model, the state skip of the evolutionary stages is described as a random process from the angle of attack and defense confrontation, and the multi-stage Markov evolutionary game is constructed on the basis of the Markov process; the total discount gain of the game is used as a target function, a discount factor eta is imported to perform discount processing on the game gains of different stages, a network security analysis method and a defense technology system are researched and searched, and thus the network defense strategy selection method and apparatus have important practical significance.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Active flow control for wind turbine blades
InactiveUS20070231151A1Increase angle of attack rangeIncrease angle of attackWind motor controlBlade accessoriesTurbine bladeActuator
A method for operating a wind turbine with at least one blade includes providing at least one blade with an active flow control actuator configured to increase an angle of attack range in which the blade or blades can generate torque without flow separation, and using the flow control actuator to adjust this angle of attack range in accordance with load.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wellbore consolidating tool for rotary drilling applications
InactiveUS20060144620A1Increase resistance against wearIncrease tear downholeDrilling rodsCleaning apparatusWell drillingAngle of attack
A subpart (430) of a drill string (211) is described having an outer circumferential surface which is contoured and adapted to engage the wall of the borehole with a small angle of attack while exerting during rotary drilling operations an compacting pressure on mud cake and / or cuttings present in the annulus between the drill string and the borehole.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Interproximal devices and methods of using same
ActiveUS20050271999A1Facilitates quickFacilitates easy interchangeTooth sawsGum massageEngineeringAngle of attack
A loop is formed by a bow having across one side a strip or blade. The bow has flexure and memory. The flexure and memory of the bow are imparted to the strip, enabling the strip to be either taut or loose, depending on the pressure exerted by the operator upon the bow. The bow is held and manipulated by the operator with the thumb and finger. The strip is positioned under tension. A holder for the device allows additional variability in the angle of attack of the strip, and facilitates quick and easy interchange of the strips. A holder avoids insertion of fingers far back in the mouth, where working space is limited.
Owner:FISHBURNE JR COTESWORTH
Vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS20060188364A1Not consume valuable irreplaceable resourceNegative impactWind motor with solar radiationWind motor controlVertical axis wind turbineFlywheel
The United States of America consumes nearly 20 million barrels of oil a day, 6.6 billion per year. This depleting chemical composition, in part, ends up in our air, on our trees, on our clothing, in our lungs, in our blood streams. A large portion of this oil is imported causing a dependency on foreign countries and a significant economic burden to this country. Clean, renewable, domestic energy is a necessity, not a luxury. The Z-333 Energy Management System is an answer to this challenge. There have been many Vertical Axis Wind Turbine patents issued since Mr. Elhanan L. Stoners' patent in 1891. However it appears that none has yet manifested itself into a large scale economic reality. The Z-333 Energy Management System is the latest of a series of improved Vertical Axis Wind Turbine designs which will make that reality come to pass. The Z-333 Energy Management System includes several novel changes to previously patented designs, plus incorporates totally new accessories to make man's continuing conquest of wind an actuality. These innovations include; Aerodynamic “balanced” wings. Tightly stretched fabric-only wings strengthening the overall structure, and at the same time, drastically lower the cost of construction. Flexible photovoltaic cells cover the aforementioned fabric-only-wings. A rotating tower that is flexible and safer. A unique high winds shut off switch. A multi-generator braking system maintains the shaft at a constant RPM. Generators and gears mounted to removable panels. Rubber-like covered shaft and large ring transmission. A low cost switch that controls the angle of attack of the wing with less problems and cost. A tower made of prefabricated interchangeable modules that can be used as a home, water tank, storage room, shop, and / or a shed. A base which is also a large battery and / or a control box shell. A programmable intelligent control box, which notifies the owner by cell phone, of battery fast charge / discharge, vandalism, key energy indicators, integrates a multi-circuit station timer, plus provides an electric-fence-like shock protection from animals and vandals. Low cost, multi-pancake generator that is highly efficient. A shaft centered flywheel. A shaft centered centrifugal pump. A sea base with ballast for low cost erection. A sea base with desalinization equipment built inside. A sea base with integrated hydrogen and oxygen producing equipment.
Owner:FRITZ MIKE J
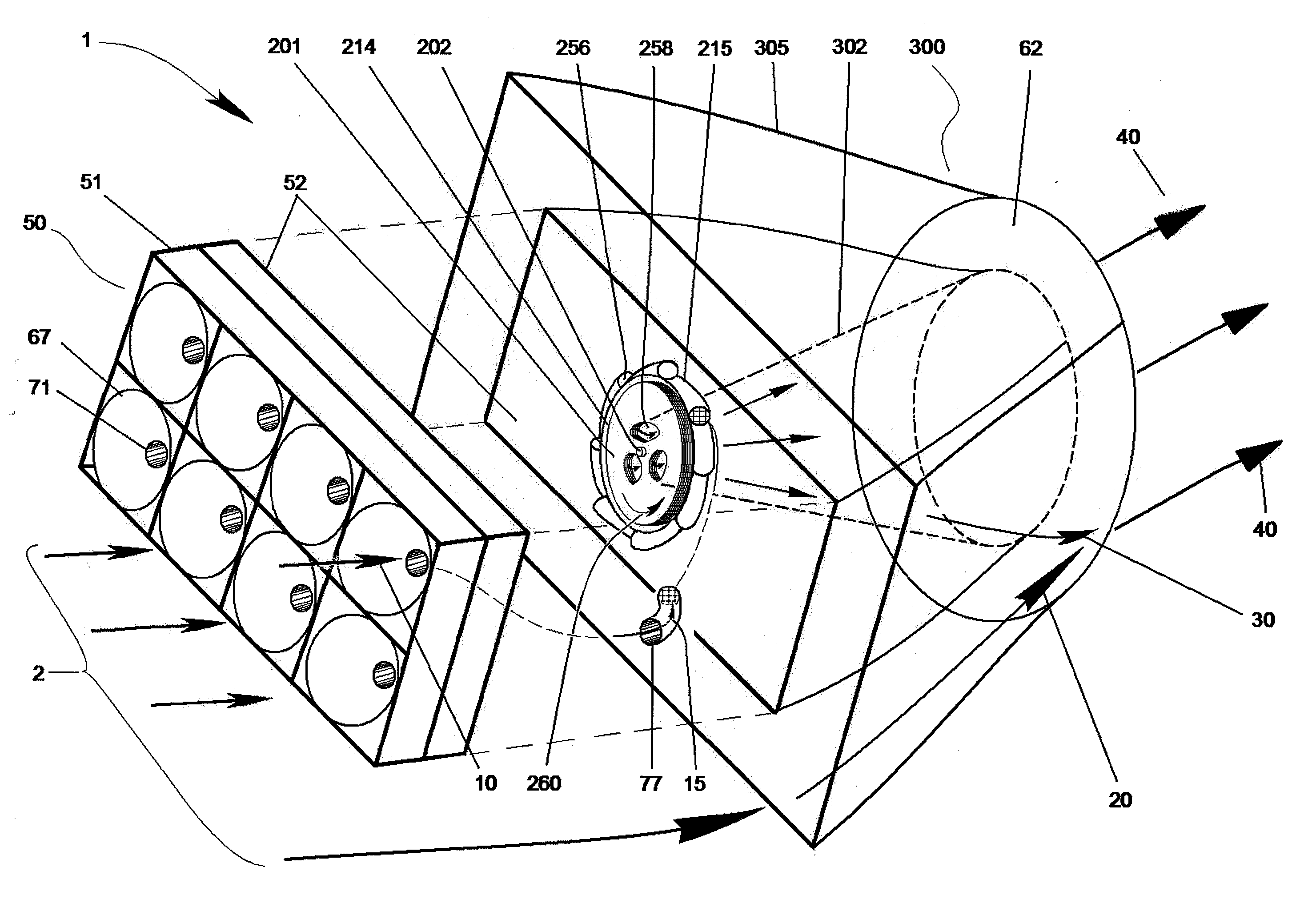
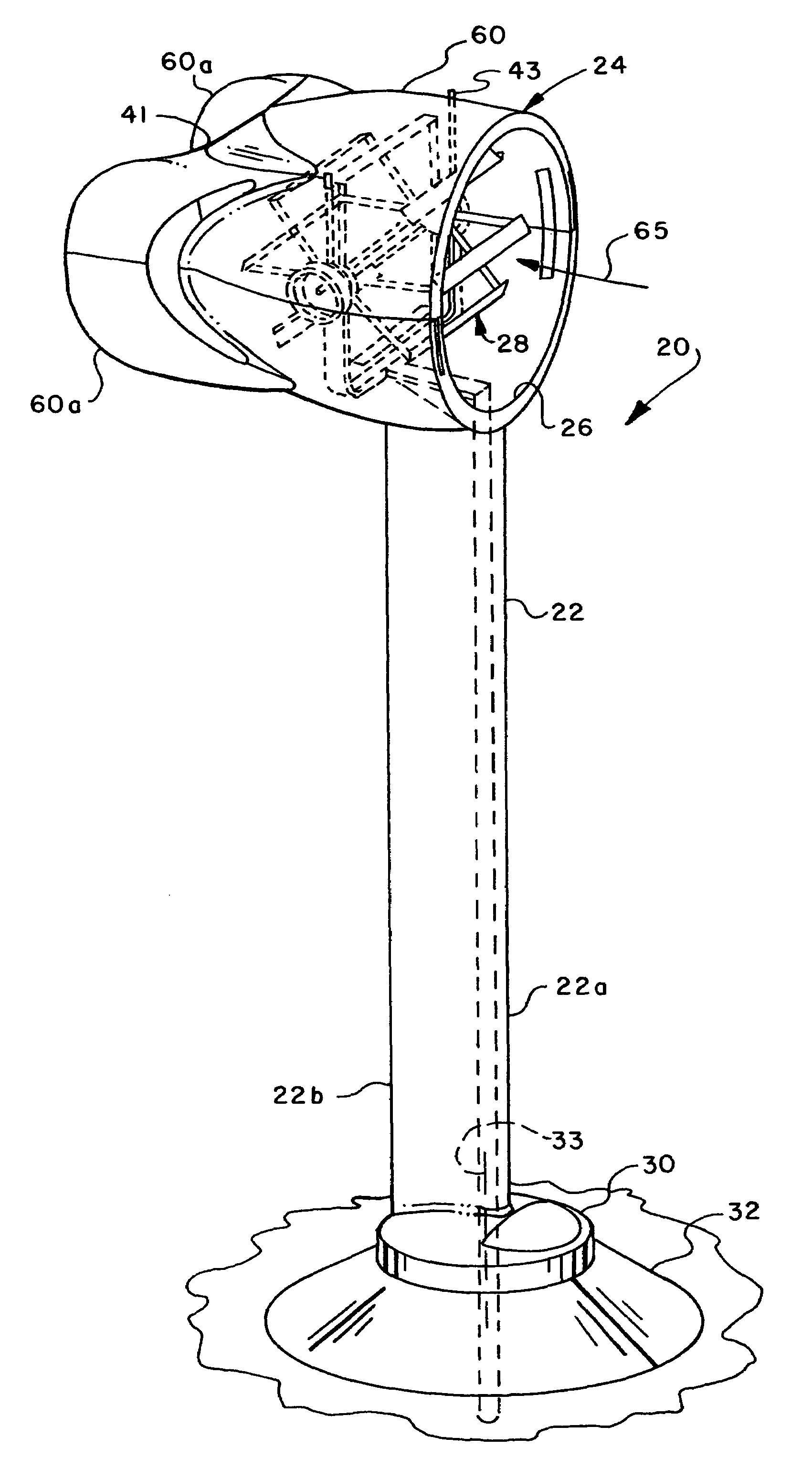
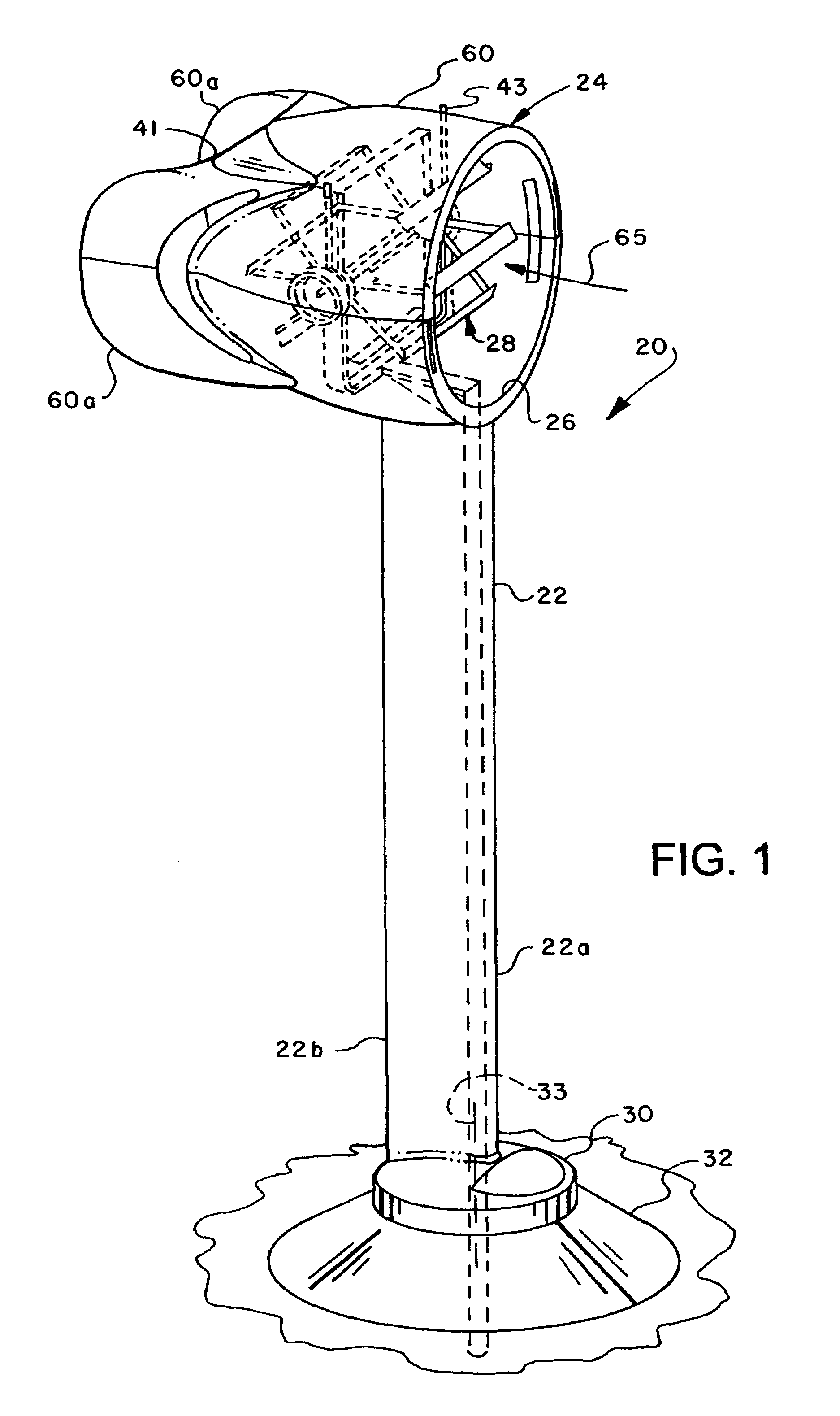
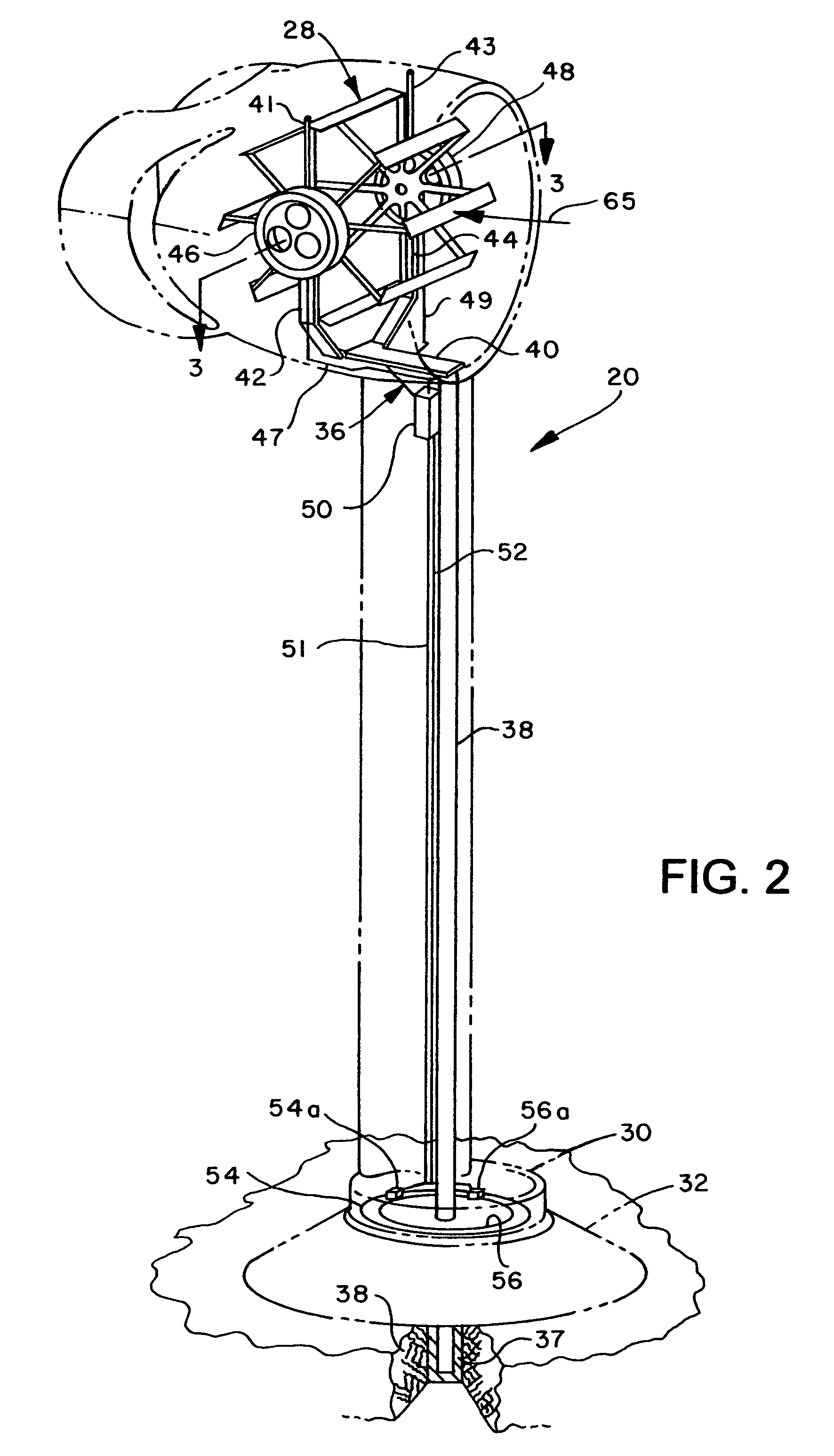
Wind driven power generator
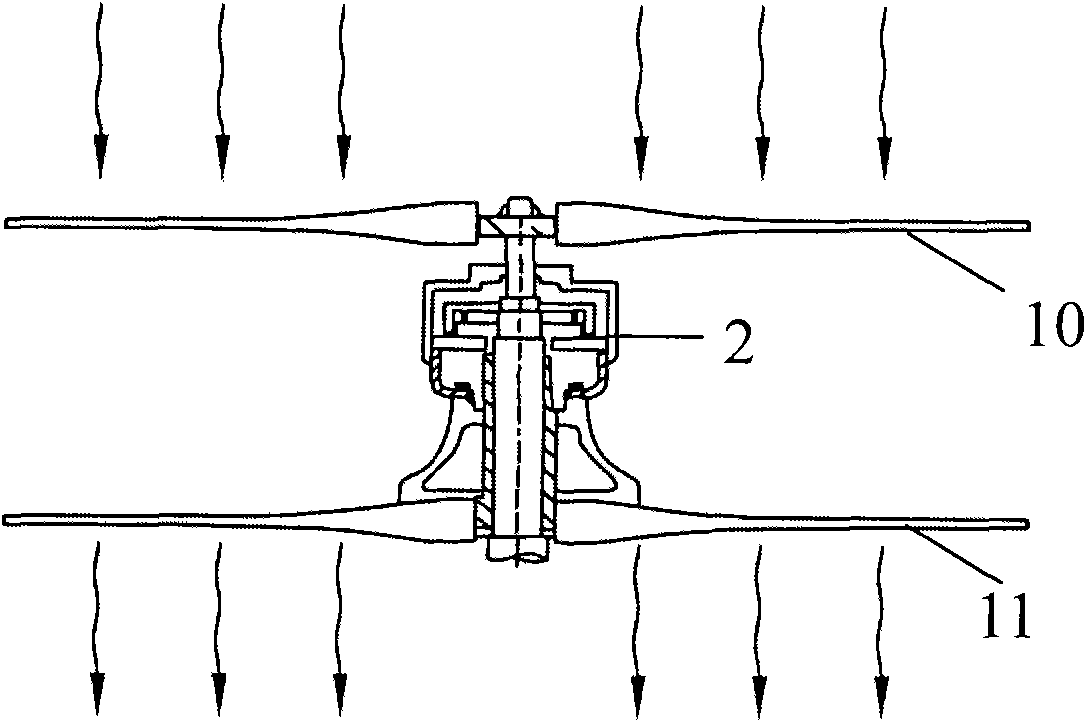
InactiveUS7365448B2Less obtrusiveMinimizing to bird lifeEngine fuctionsWind motor supports/mountsWind drivenHorizontal axis
A wind driven generator includes a rotor disposed in a cylindrical duct and supported by a frame for rotation in response to wind flowing through the duct. The rotor includes plural circumferentially spaced paralleled rotor blades supported for rotation about a generally horizontal axis. Each blade is supported for pivotal movement to change blade pitch, angle of attack or camber as the rotor rotates. A pitch or camber control motor or self-governing wind vane mechanism is operable to move a circular cam to vary blade pitch or camber to control rotor speed. The duct is mounted on a mast having a base supported on a foundation for pivotal movement to face the wind for maximizing air flow through the duct. Electric power generators are connected to opposite ends of the rotor at respective power output or drive shafts.
Owner:BROADSTAR INVESTMENT COMPANY
High volume low speed fan
An HVLS fan system uses STOL technology for airfoils and angle of attack thus optimizing air movement efficiency and reducing drag. The HVLS fan system includes wingtip fence end caps to the airfoils for improving efficiency by reducing drag. The HVLS fan system also includes an interconnection of the airfoils to a securing plate thus providing a failsafe and reduced potential for damage or injury resulting from failure of the connection between the airfoil array and a drive unit such as an electric motor and associated gearing.
Owner:SKYBLADE FAN
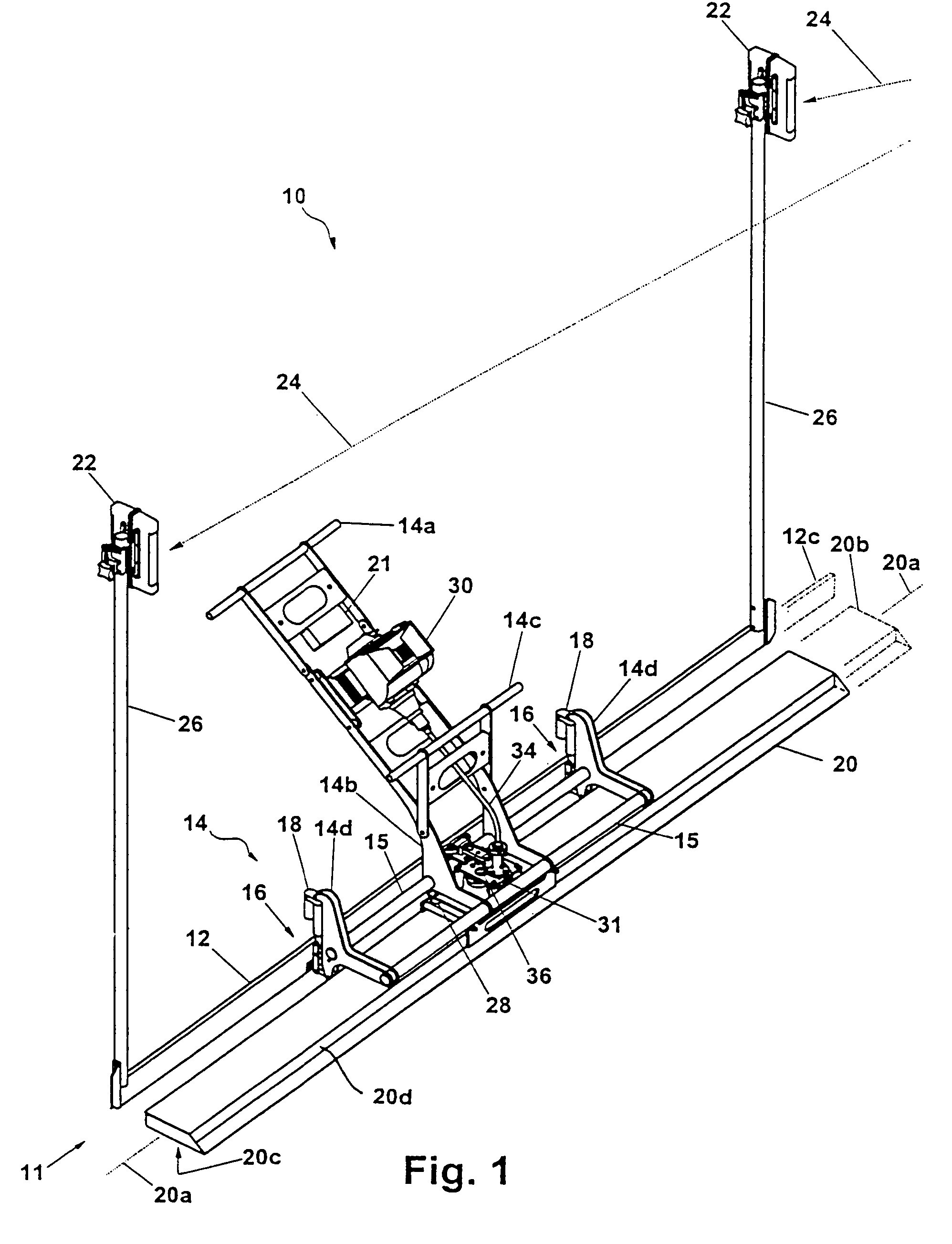
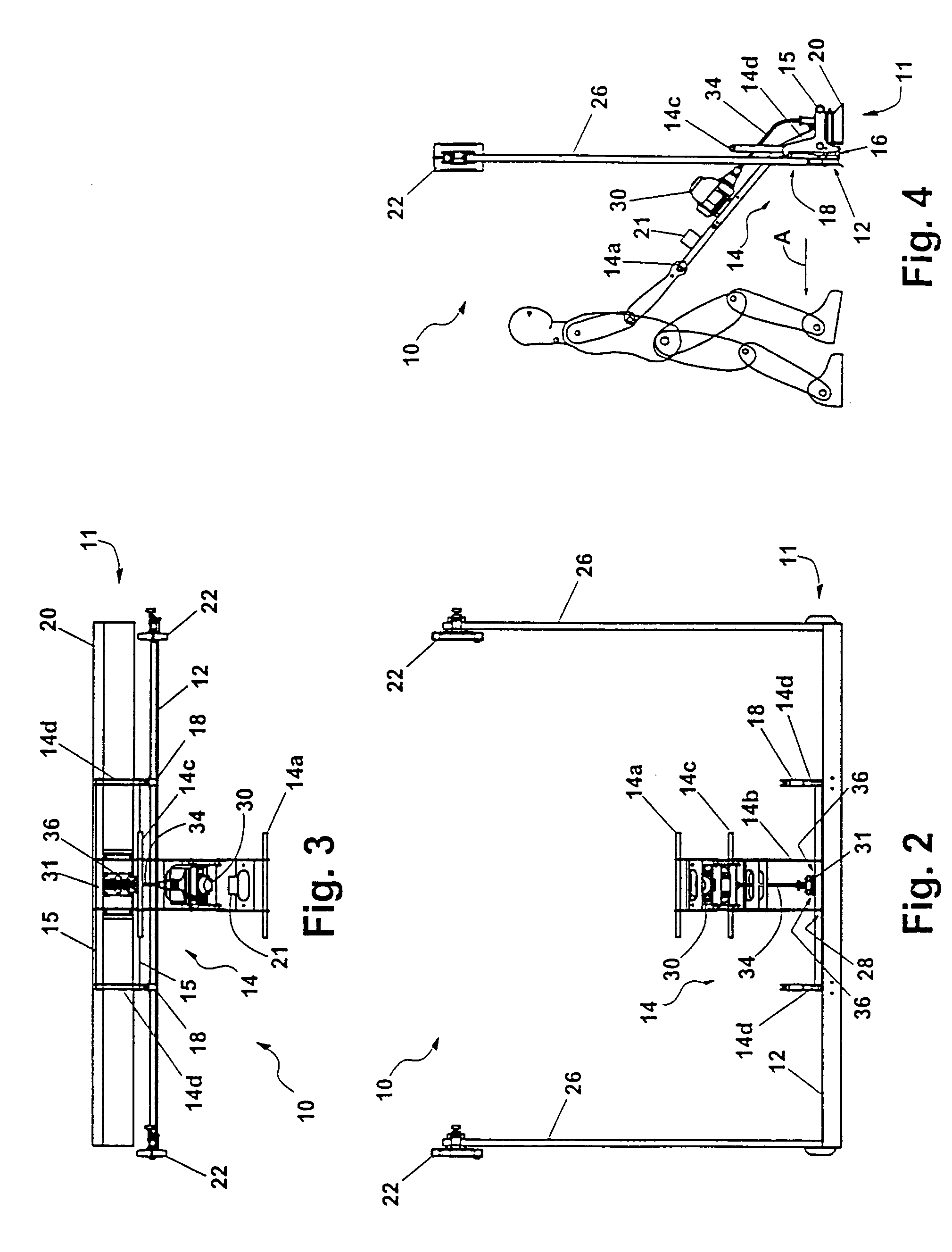
Methods for creating consistent large scale blade deflections
Methods are disclosed to design resilient hydrofoils (164) which are capable of having substantially similar large scale blade deflections under significantly varying loads. The methods permit the hydrofoil (164) to experience significantly large-scale deflections to a significantly reduced angle of attack under a relatively light load while avoiding excessive degrees of deflection under increased loading conditions. A predetermined compression range on the lee portion of said hydrofoil (164) permits the hydrofoil (164) to deflect to a predetermined reduced angle of attack with significantly low bending resistance. This predetermined compression range is significantly used up during the deflection to the predetermined angle of attack in an amount effective to create a sufficiently large leeward shift in the neutral bending surface with the load bearing portions of the hydrofoil (164) to permit the hydrofoil (164) to experience a significantly large increase in bending resistance as increased loads deflect the hydrofoil (164) beyond the predetermined reduced angle of attack. The shift in the neutral bending surface causes a significant increase in the elongation range required along an attacking portion of the hydrofoil (164) after the predetermined angle of attack is exceed. Methods are also disclosed for designing the hydrofoil (164) so that it has a natural resonant frequency that is sufficiently close the frequency of the reciprocating strokes used to attain propulsion in an amount sufficient to create harmonic wave addition that creates an amplified oscillation in the free end of the reciprocating hydrofoil (164).
Owner:MCCARTHY PETER T
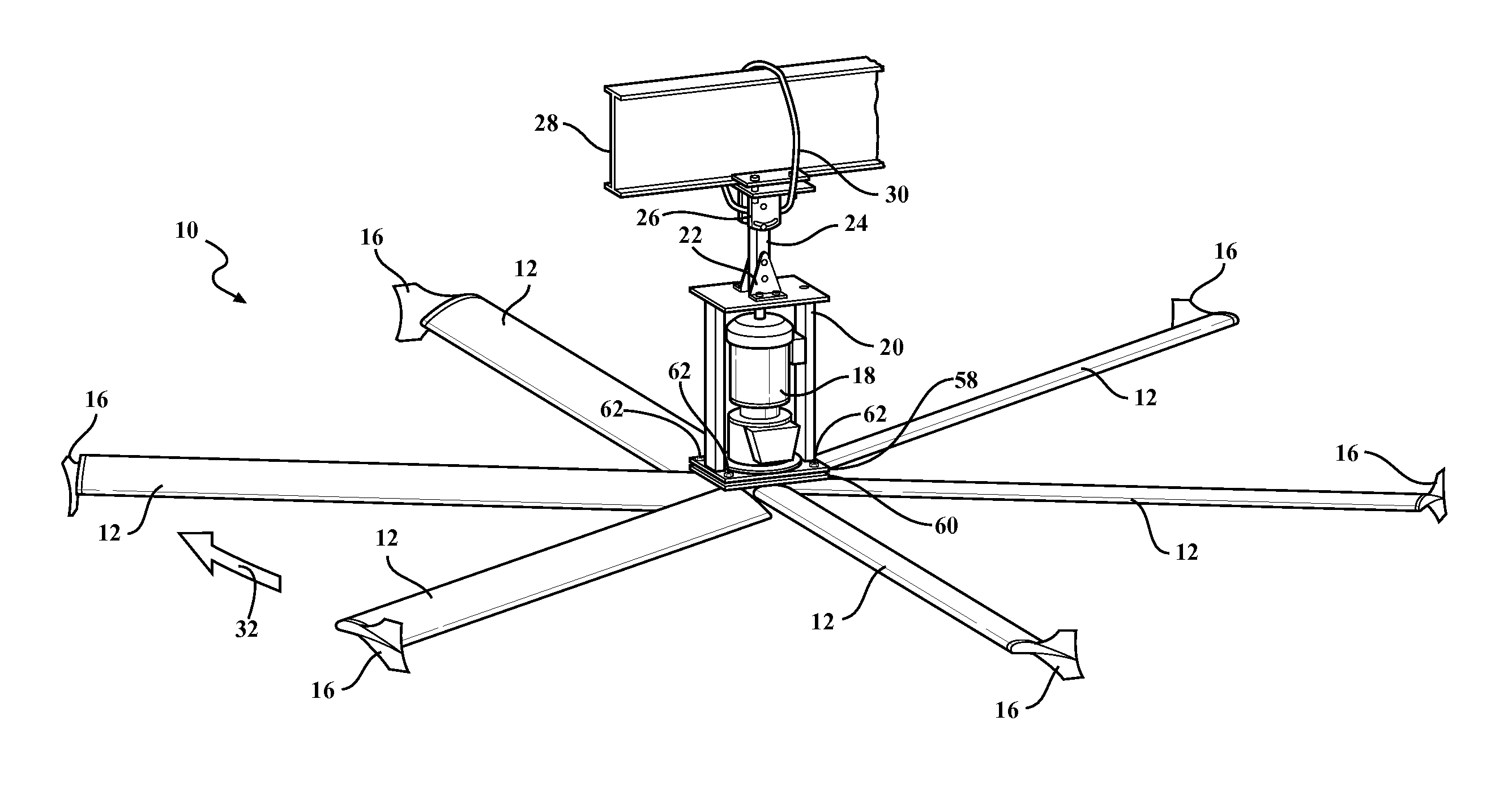
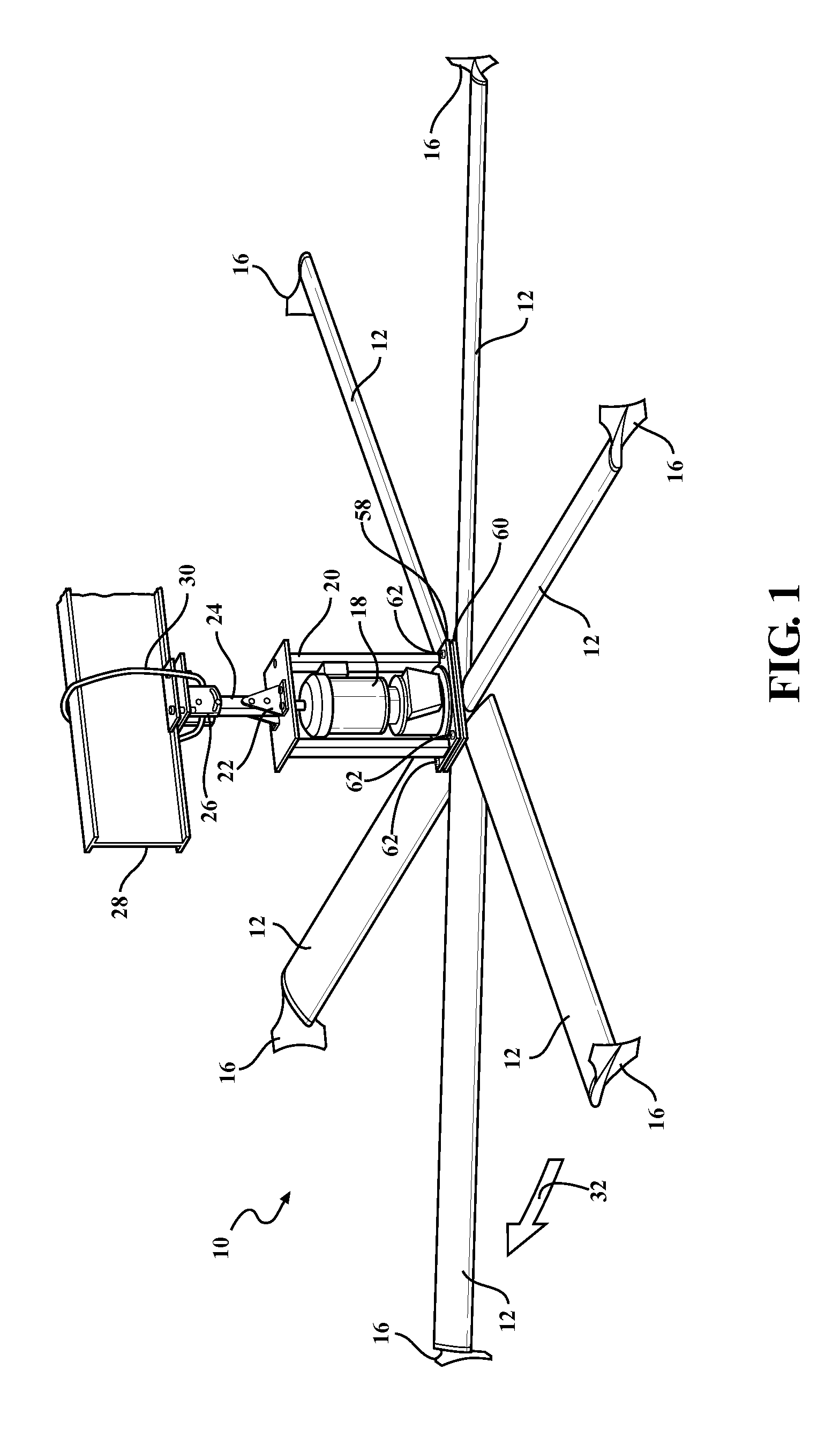
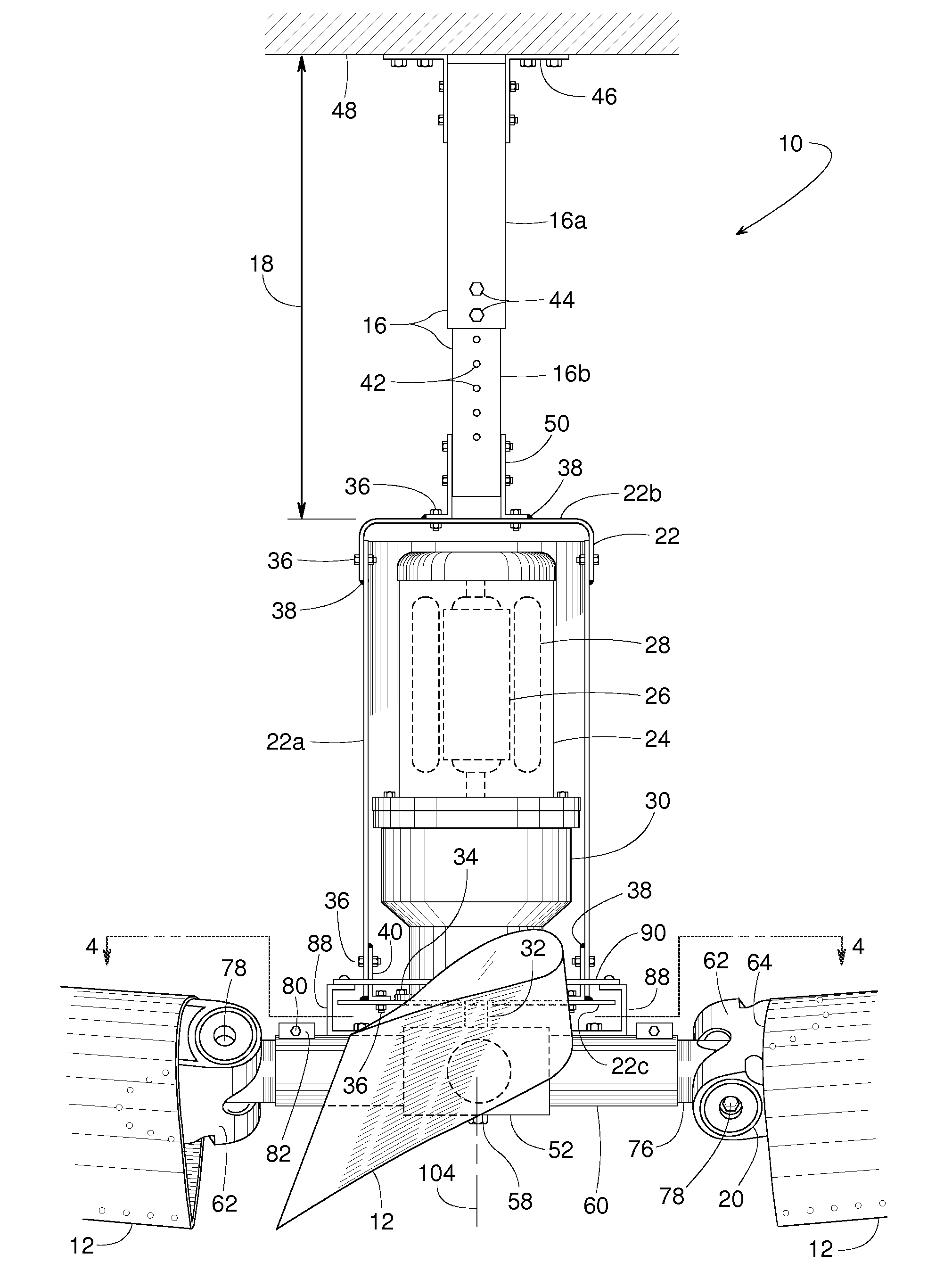
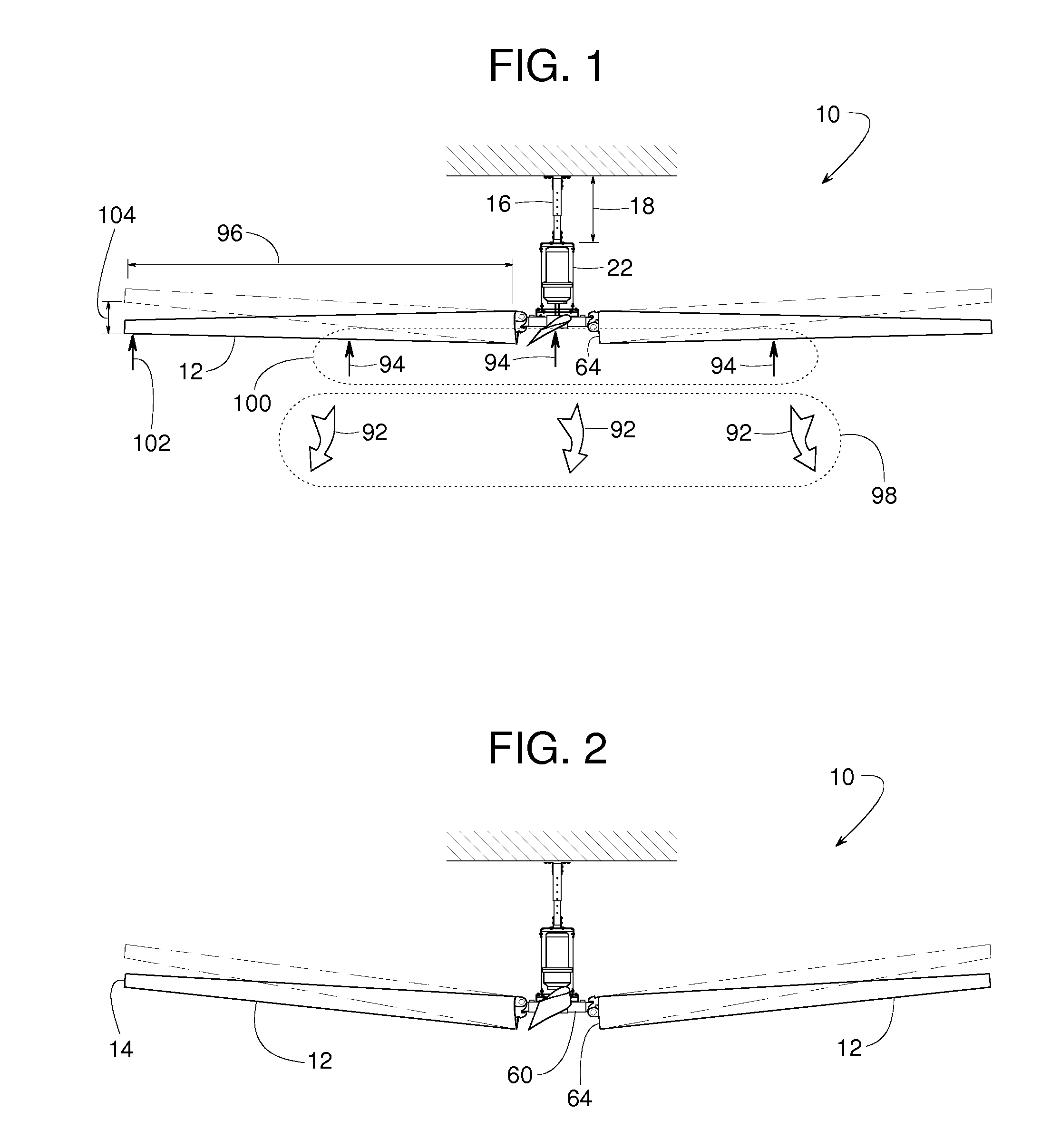
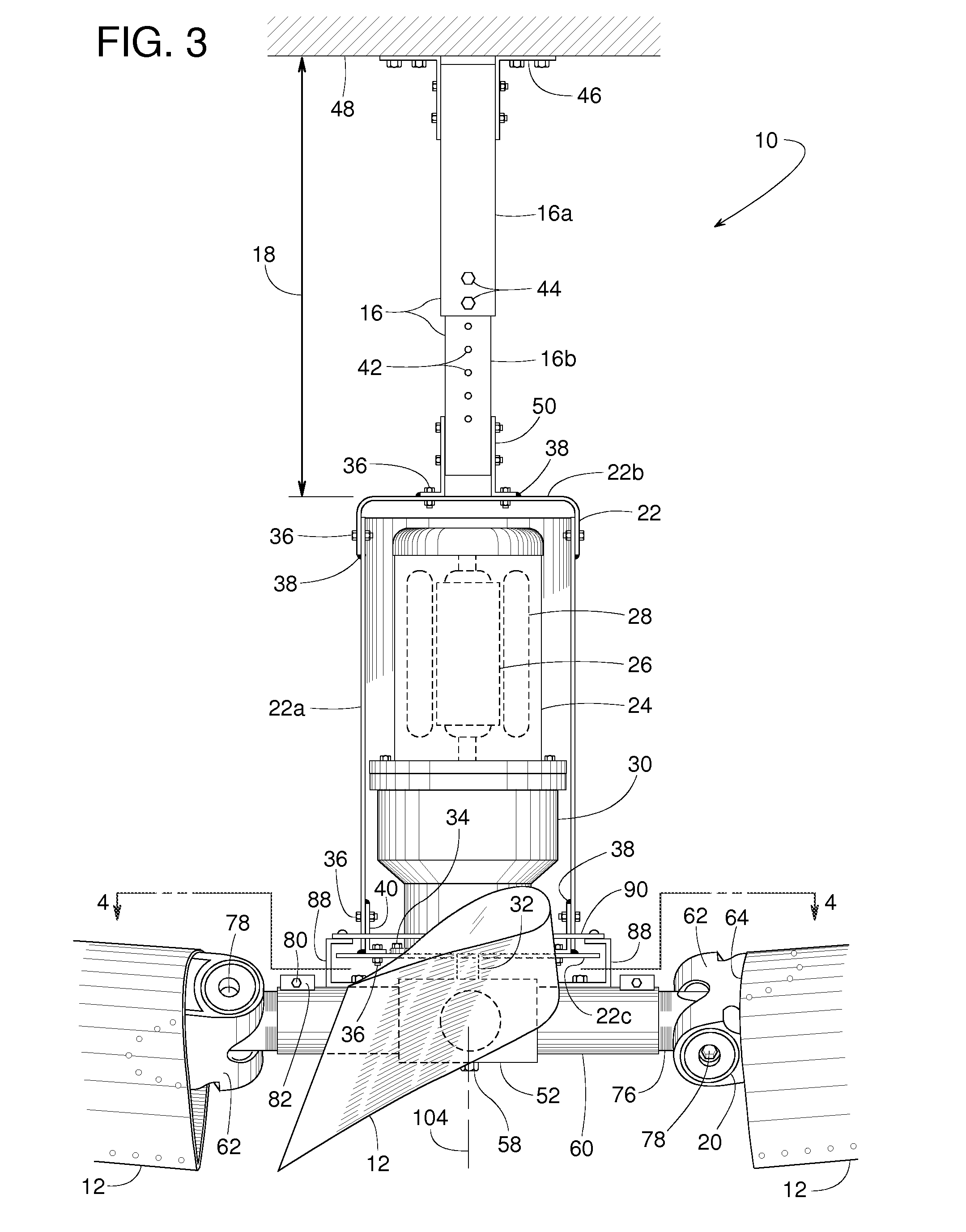
Industrial ceiling fan
A large industrial ceiling fan includes exceptionally long fan blades with blade tips that can be tilted upward to more broadly distribute the air. Such broad distribution might be particularly beneficial in cases where the fan is installed relatively low to avoid obstacles such as hanging lights, sprinkler heads and rafters. A low mounting position is possible, because the fan is suspended from a hanger of adjustable length. The fan includes several joints that are redundantly bolted and welded for safety. A continuous retaining ring provides additional safety. A resilient bushing enhances the flexibility of the fan blades and reduces strain where the fan blades connect to a central mounting hub. To more broadly distribute the airflow underneath the fan, each fan blade has a twisted geometry to provide an angle of attack that decreases from the root to the tip of the blade.
Owner:RITE HITE HLDG CORP +1
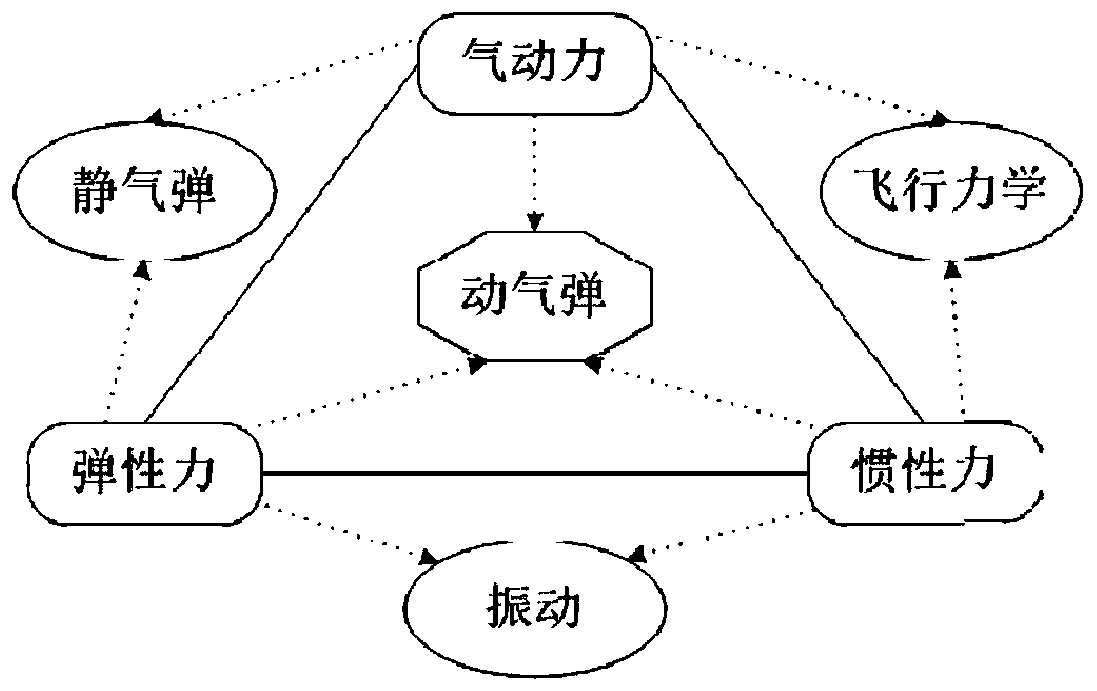
Simulation analysis method and system for gust response of elastic aircraft
ActiveCN110309579AReduce design investmentShorten the design cycleGeometric CADSustainable transportationAnalysis methodAngle of attack
The invention belongs to the technical field of aircraft simulation, and particularly relates to a simulation analysis method and system for gust response of an elastic aircraft. The method comprisesthe steps of according to the dynamics and the structure correspondence of the elastic aircraft under gust excitation, firstly, modeling an aircraft six-degree-of-freedom system, the atmospheric turbulence, the gust excitation and the aerodynamic force data according to the flight state; secondly, under the condition of static elasticity, analyzing the deformation of the aircraft wing under the aerodynamic force load and the change of an angle of attack and the influence of the angle of attack on an aerodynamic coefficient, correcting the aerodynamic coefficient to enable the aerodynamic coefficient to better conform to the real flight state of the elastic aircraft, and finally, connecting all the modules into a system to realize the corresponding analysis under the excitation of gust of the elastic aircraft. The system achieves a good effect in cases of a general aircraft and a civil large-scale passenger plane.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Multi-function air data sensor
InactiveUS7490510B2Fluid speed measurement using pressure differenceIndication/recording movementEngineeringAngle of attack
An air data sensor that determines a body's angle of attack, static air pressure, total air pressure, mach number, static air temperature and true air speed in one device using pressure and temperature readings. The air data sensor includes a probe that protrudes into an airflow to collect data, a base plate for attaching the probe to a body, and an electronics housing including electronics for interpreting the data collected from the probe.
Owner:AMETEK INC
Zero Transition Vertical Take-Off and Landing Aircraft
InactiveUS20140158815A1Stable levelOptimize both vertical and forward flightAircraft navigation controlVertical landing/take-off aircraftsNacelleLevel flight
A zero transition vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft, which is stable in all levels of flight, especially the transition phase from vertical to horizontal flight. The zero transition VTOL aircraft is capable of achieving both vertical and horizontal flight without changing the positioning of thrusters, such as through the use of tiltable or rotatable nacelles or wings. Rather a front thruster assembly and a rear thruster assembly are positioned at specific angles in relation to each other along at least one fuselage in order to generate the desired ratio of vertical to horizontal thrust. At least one wing is also positioned at a specific wing angle in order to achieve a desired angle of attack when in horizontal flight. The attitude of the zero transition VTOL aircraft can be controlled through the use of differential thrust alone, or in conjunction with control surfaces.
Owner:RENTERIA JOSEPH RAYMOND
High efficiency turbine and method of generating power
ActiveUS20090129928A1Efficient use ofImprove efficiencyPropellersWind motor controlRadial spokeTurbine
The present invention is directed to a turbine comprising a plurality of blades that rotate in a single direction when exposed to fluid flow, wherein the plurality of blades are joined to the central shaft by a plurality of radial spokes disposed substantially perpendicular to the central shaft such that the rotating plurality of blades causes the shaft to rotate. The plurality of blades has a uniform airfoil-shaped cross section, where the airfoil cross section presents a non-zero angle of attack to the current. The plurality of blades wind in a spiral trajectory, rotating around the central shaft and having a variable radius along the length of the central shaft such that a distance measured from the plurality of blades to the center shaft is greater near the center of the turbine than at either end.
Owner:OCEAN RENEWABLE POWER COMPANY
Method for correcting influence of high-speed wind tunnel model afterbody distortion on lateral-directional aerodynamic characteristics
The invention provides a method for correcting the influence of high-speed wind tunnel model afterbody distortion on lateral-directional aerodynamic characteristics. A test model contains a freely-replaceable real afterbody and a distortion afterbody model; the test model pre-deviates to a given sideslip angle through a sideslip angle-varying blade belly supporting device; a wind tunnel test is performed on the real afterbody model and the distortion afterbody model according to the same test conditions; interpolation is performed on lateral-directional aerodynamic coefficients according to the same angle of attack sequence; subtraction is performed on two kinds of interpolated lateral-directional aerodynamic coefficients, so that an obtained difference value of the two kinds of interpolated lateral-directional aerodynamic coefficients is the influence of the afterbody distortion on the aerodynamic characteristics of the test model. The method can be used for correcting the influence of the afterbody distortion on the lateral-directional aerodynamic characteristics of the model test under the given sideslip angle.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com