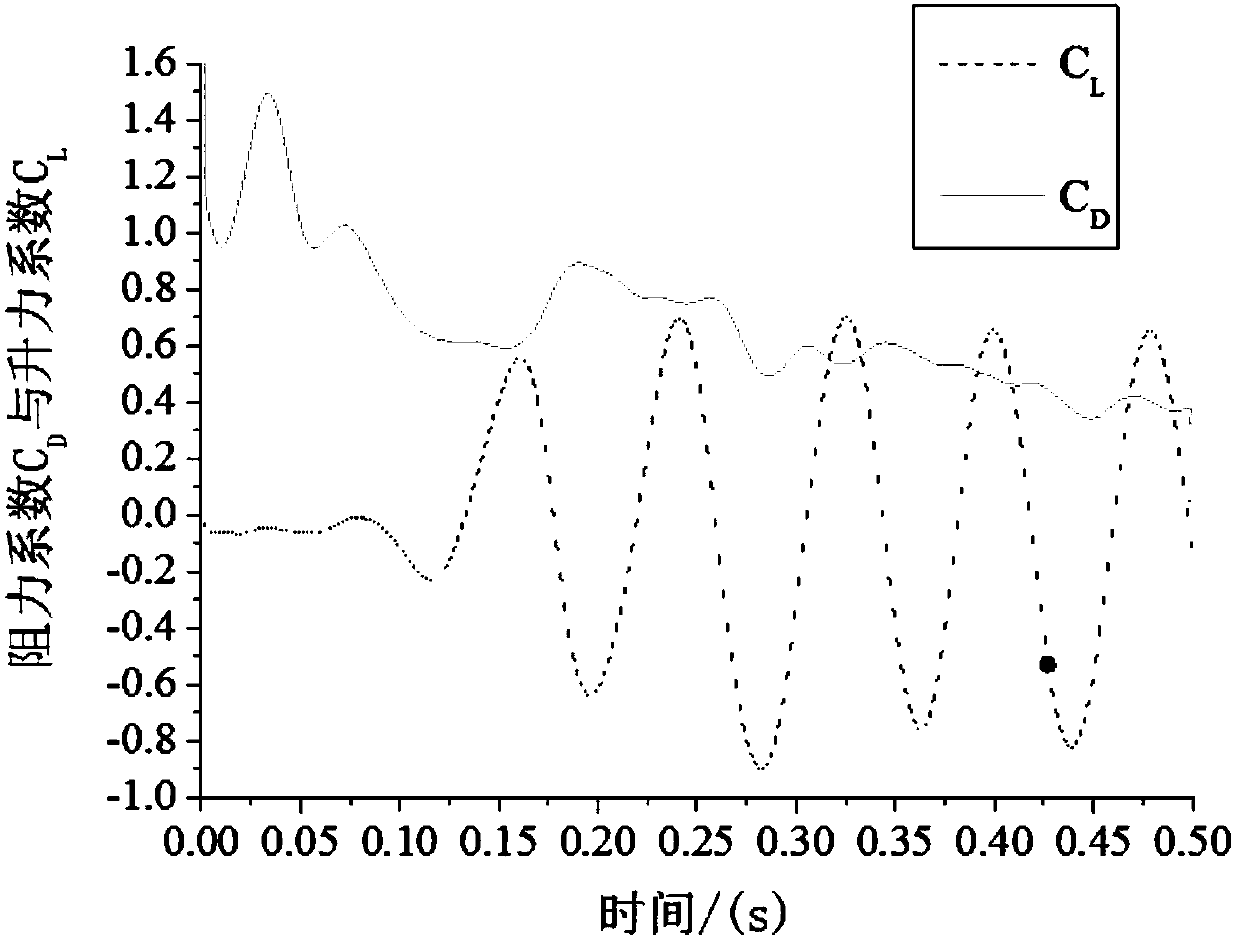
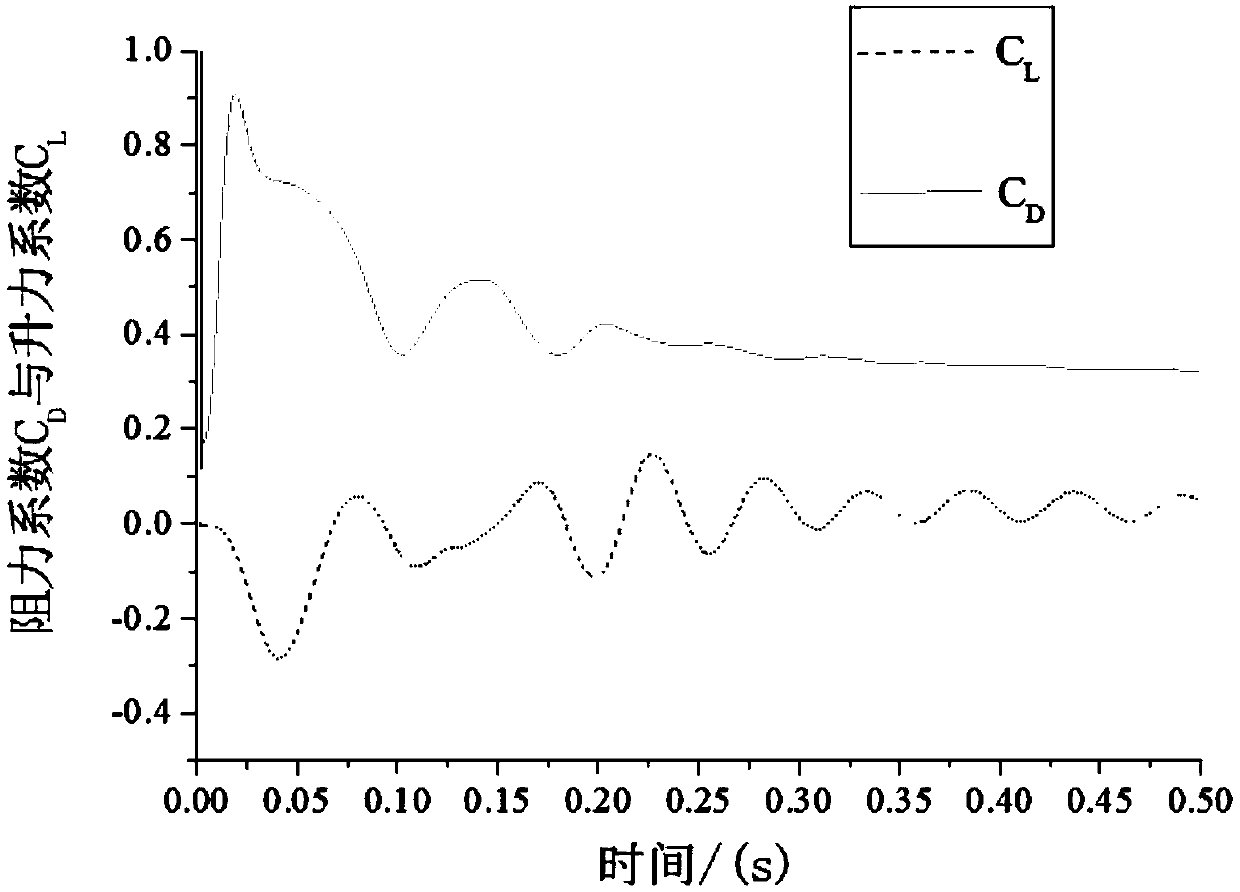
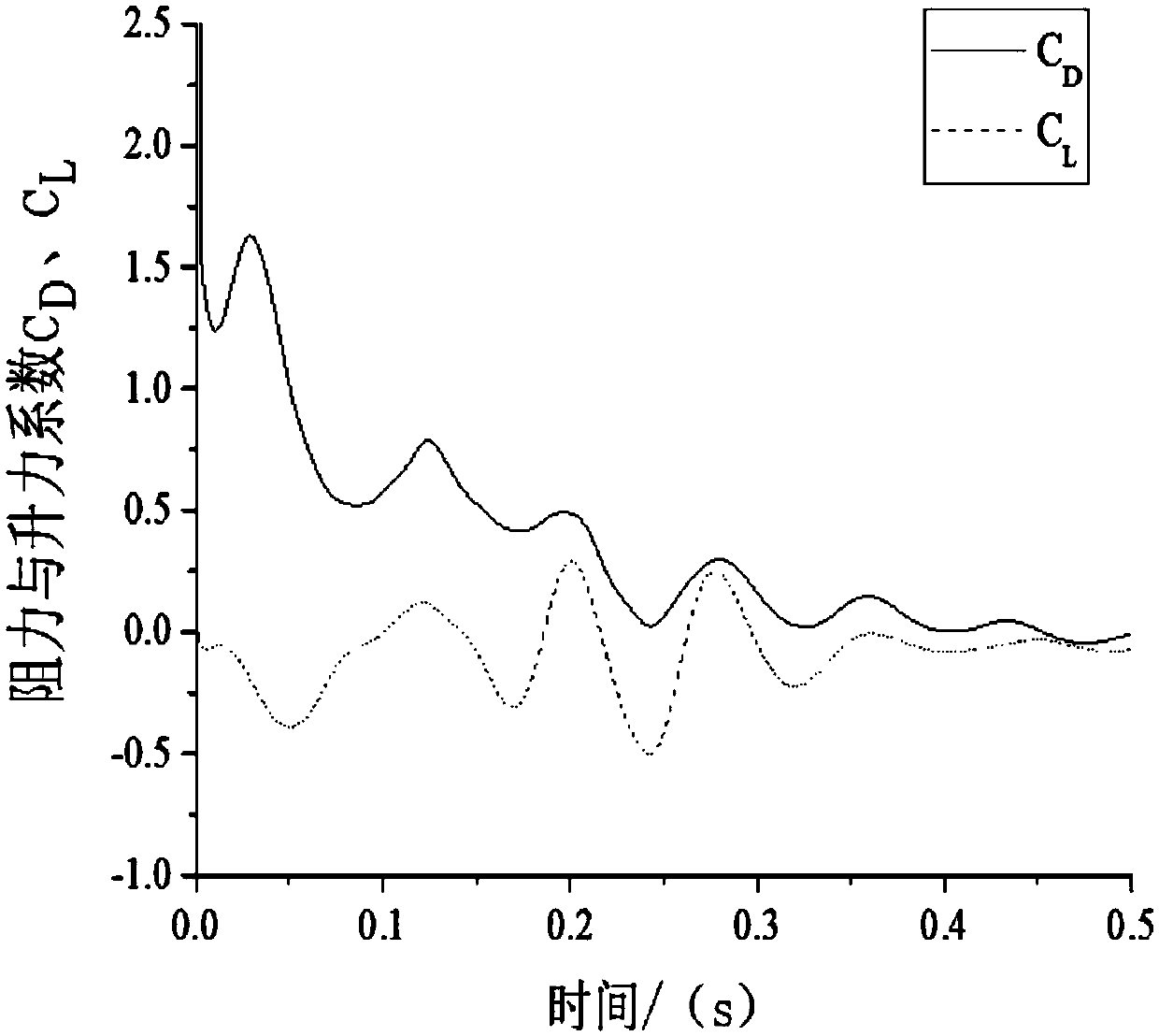
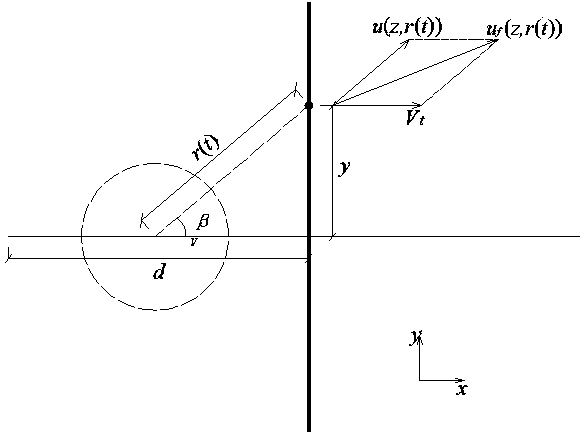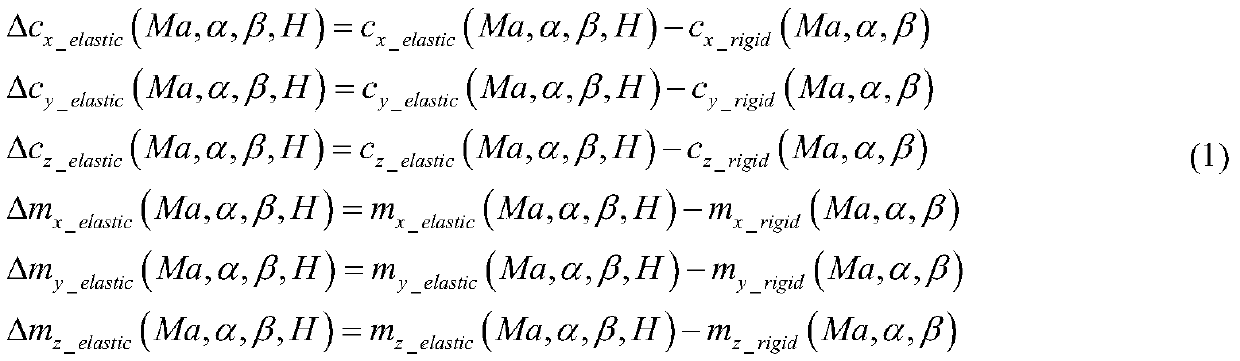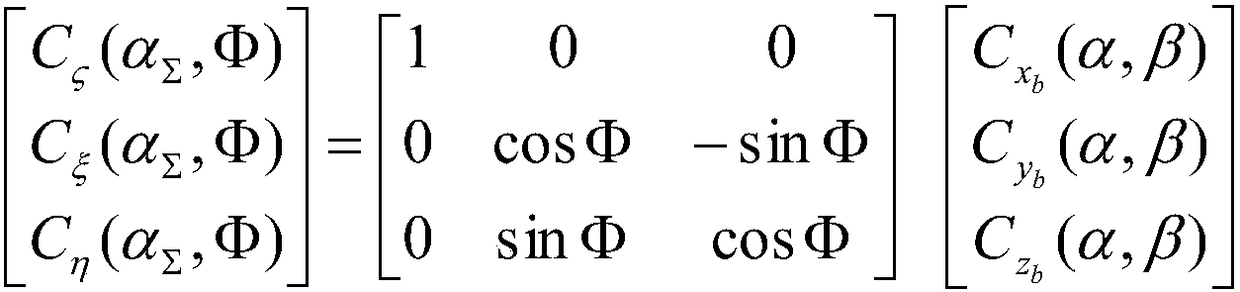Patents
Literature
119 results about "Aerodynamic coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
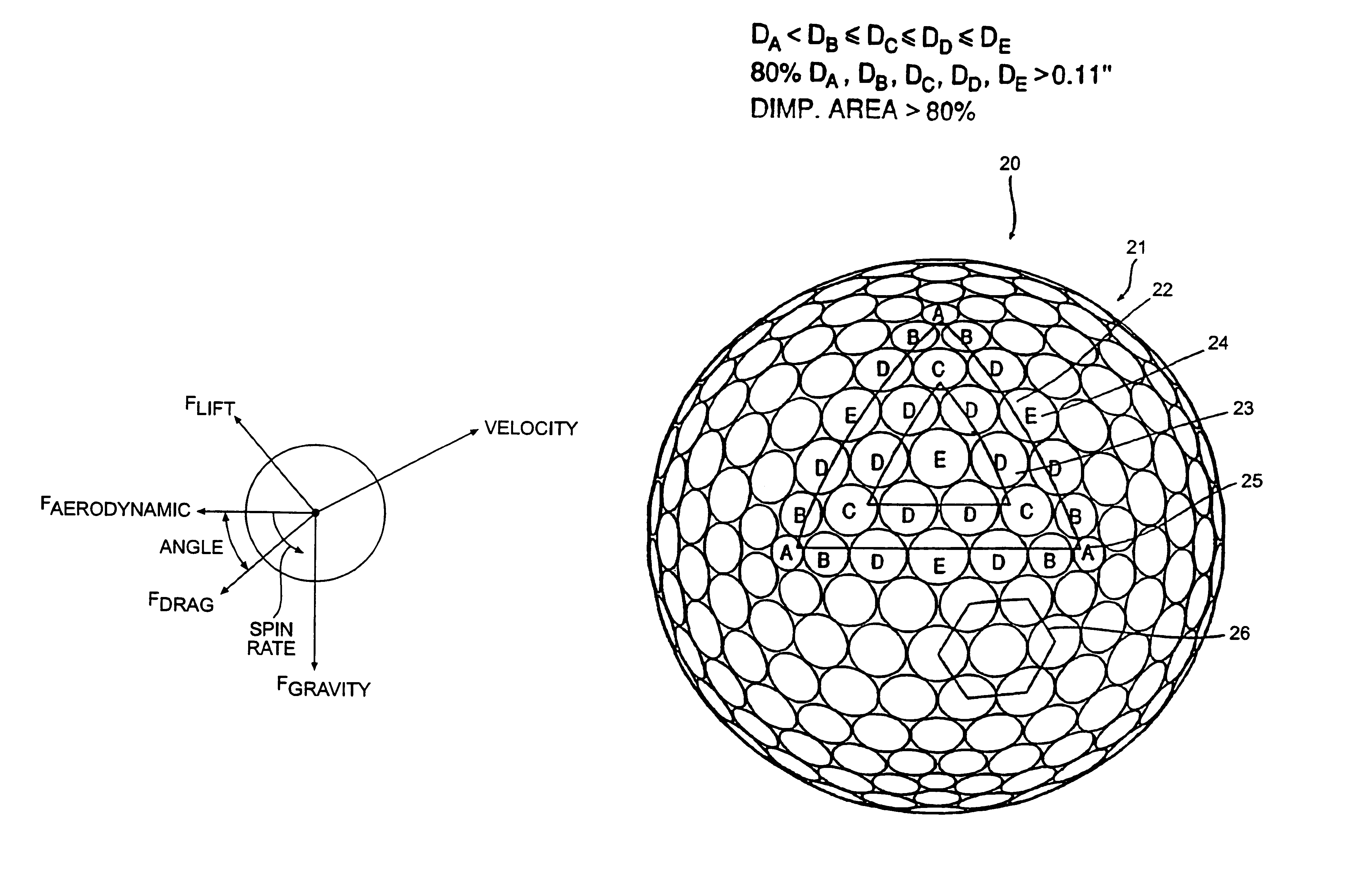
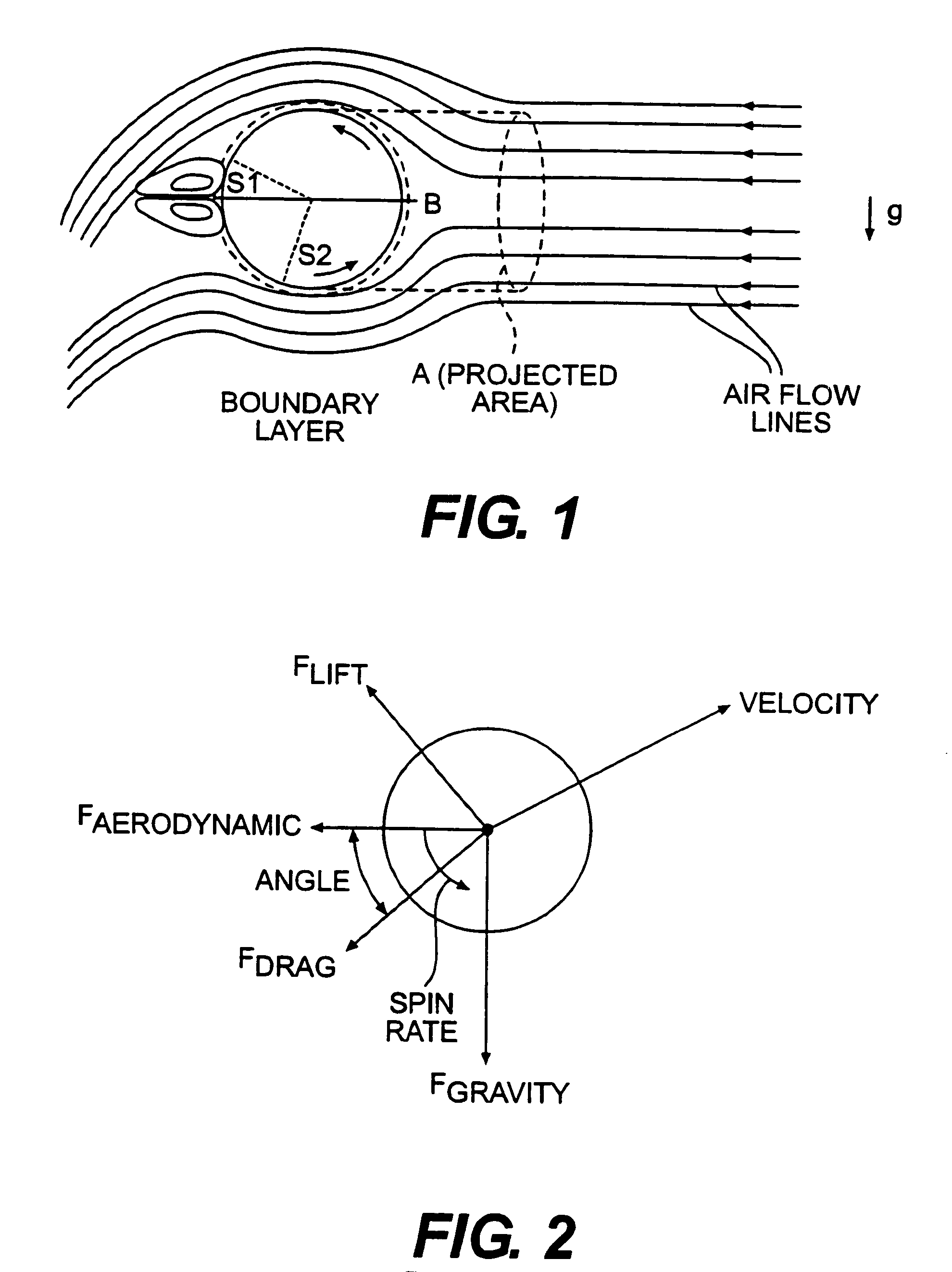
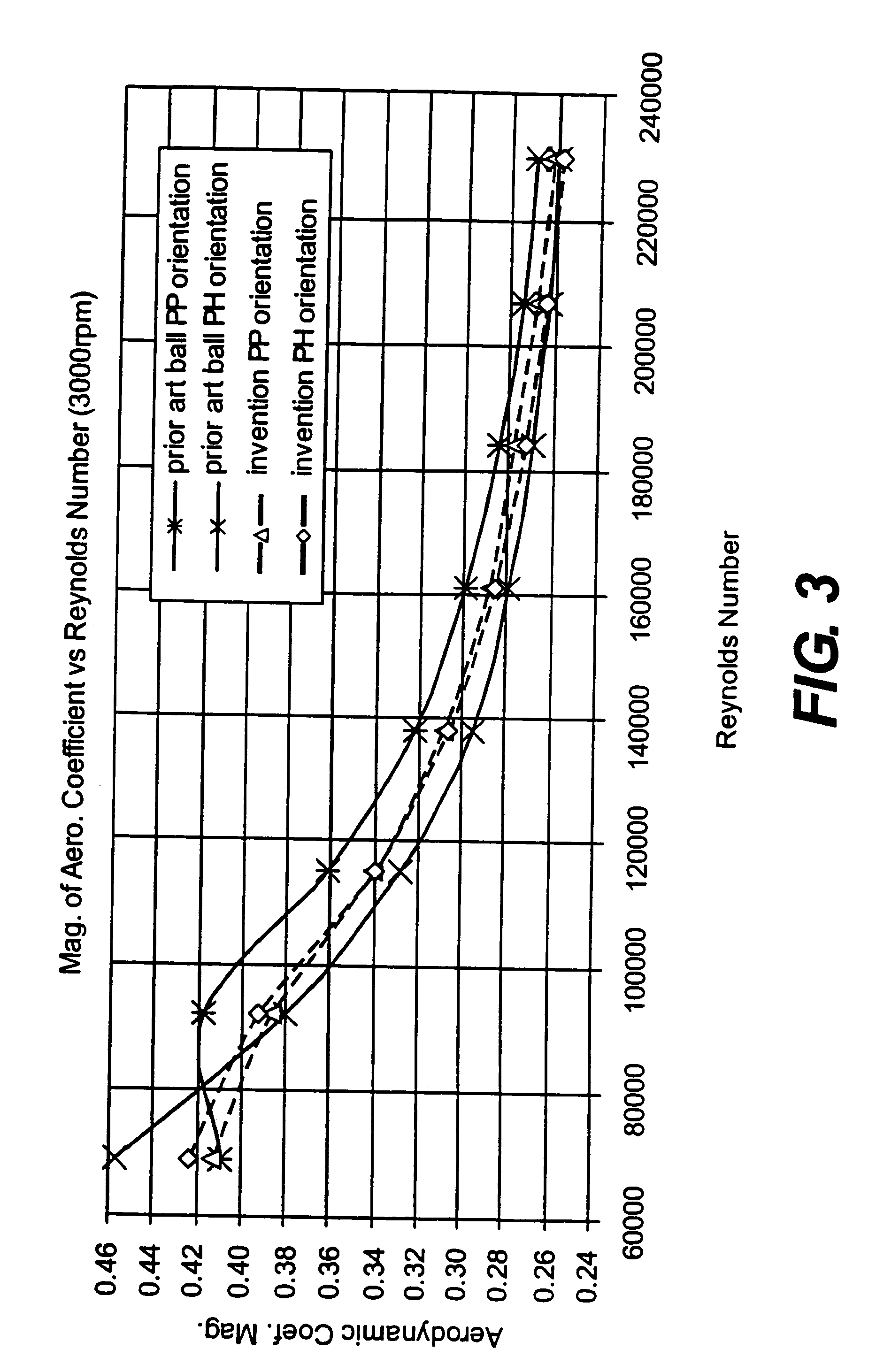
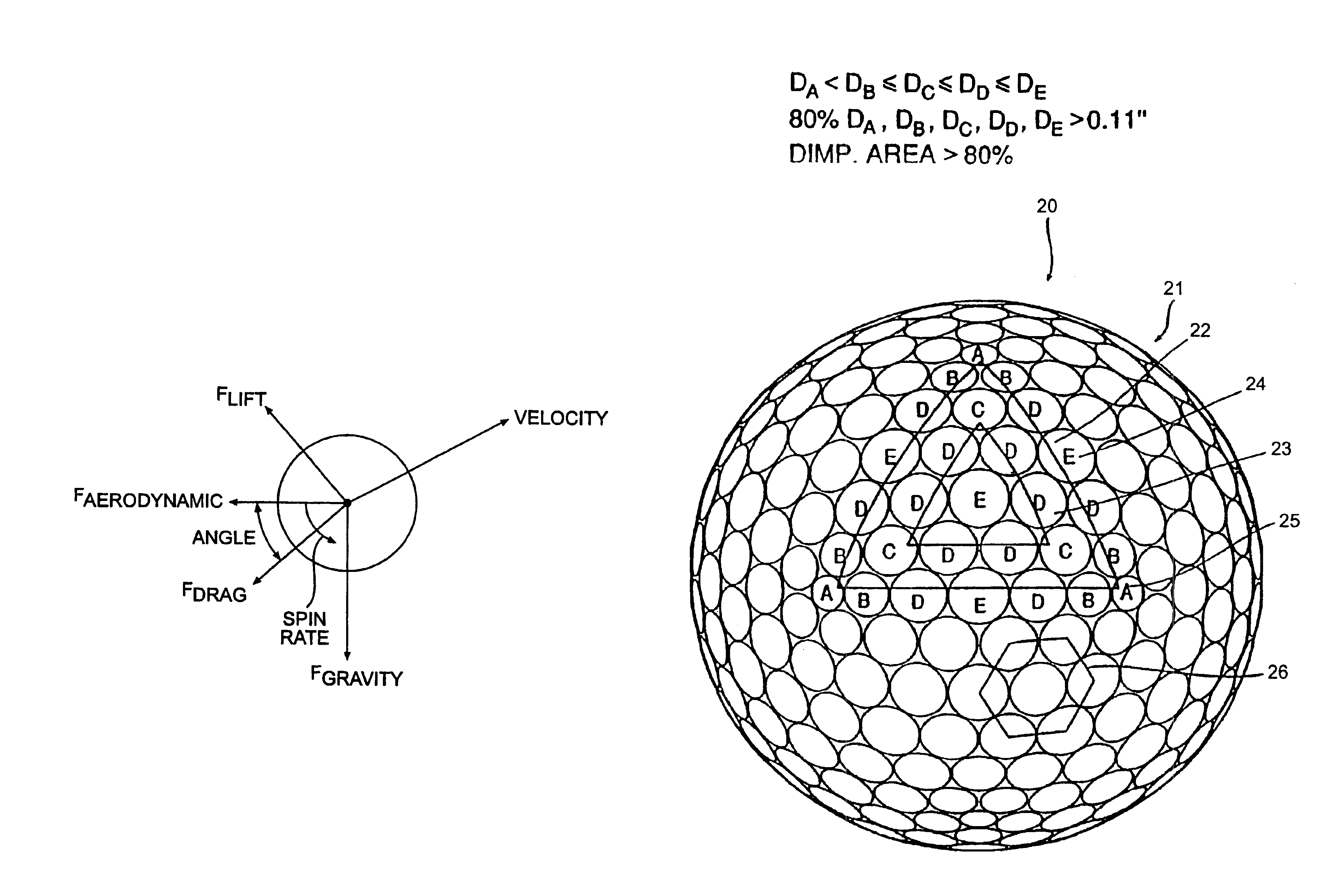
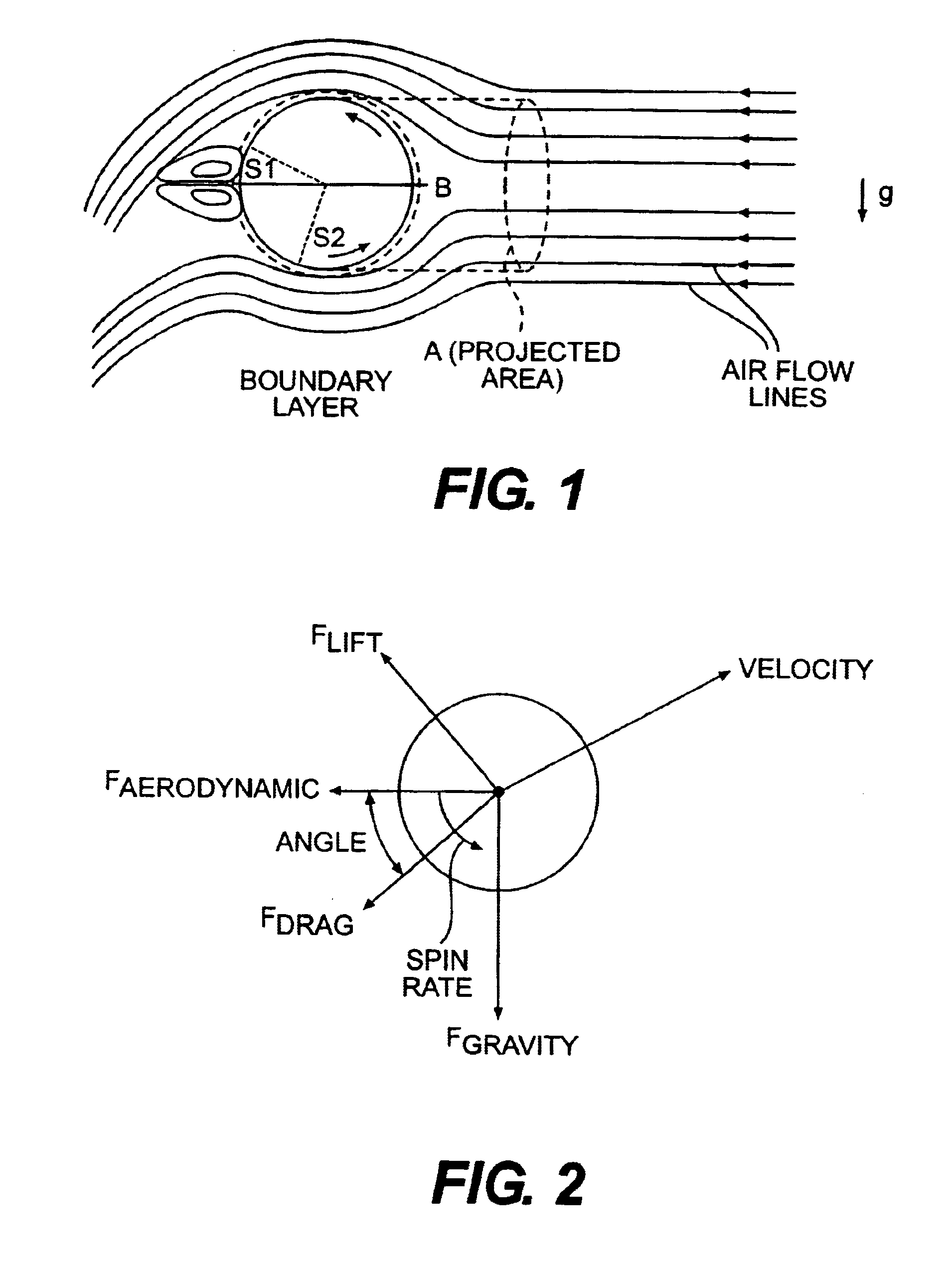
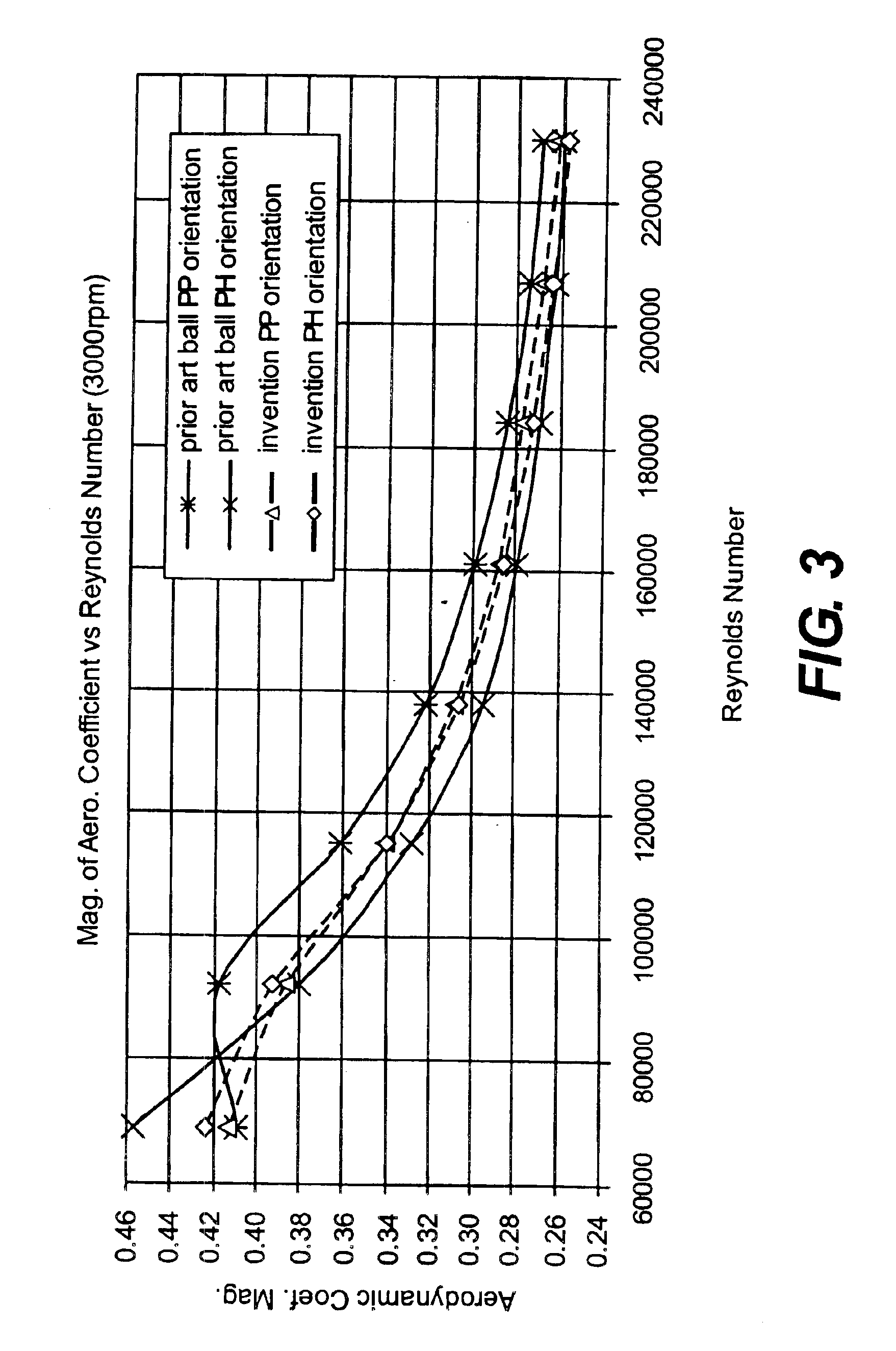
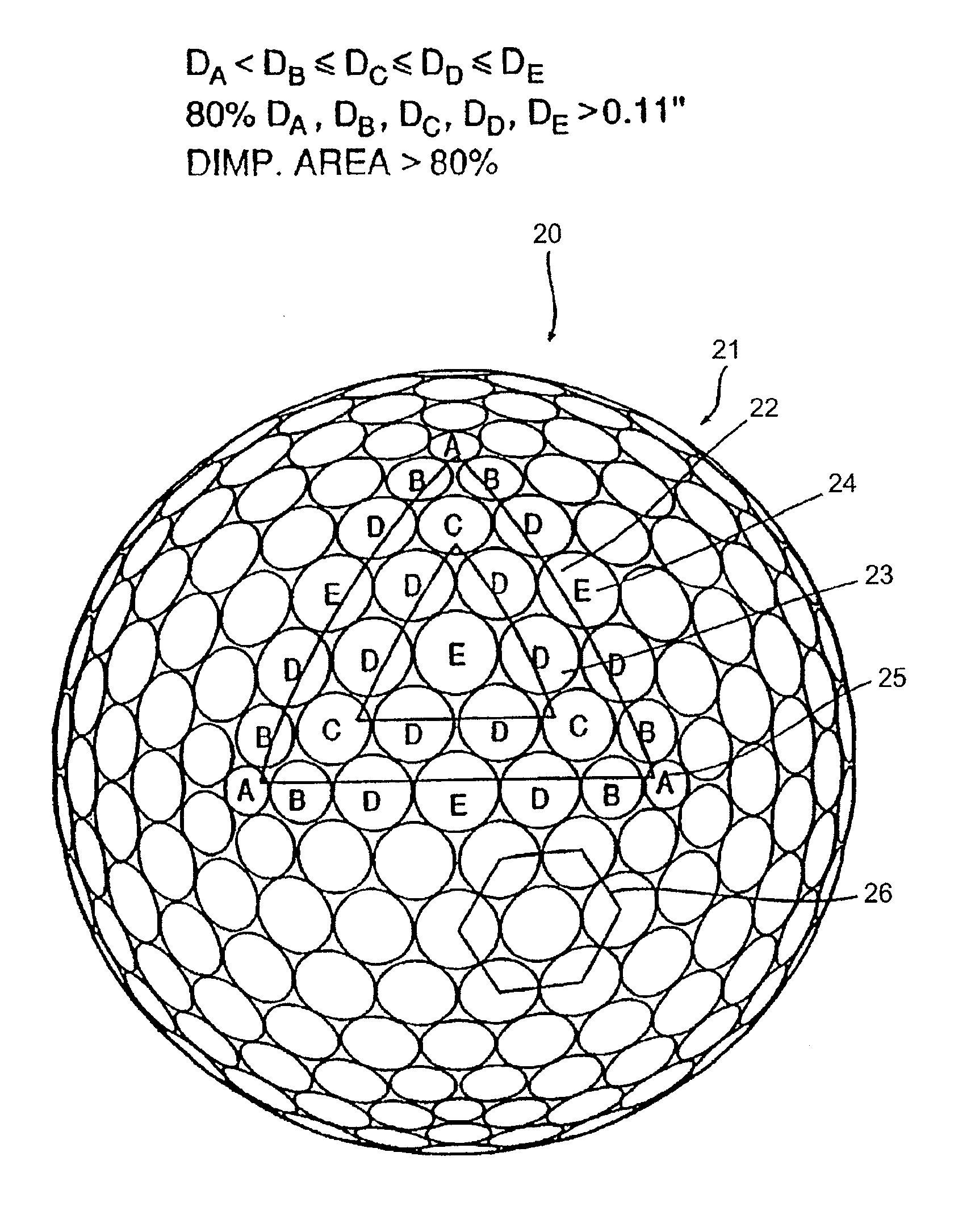
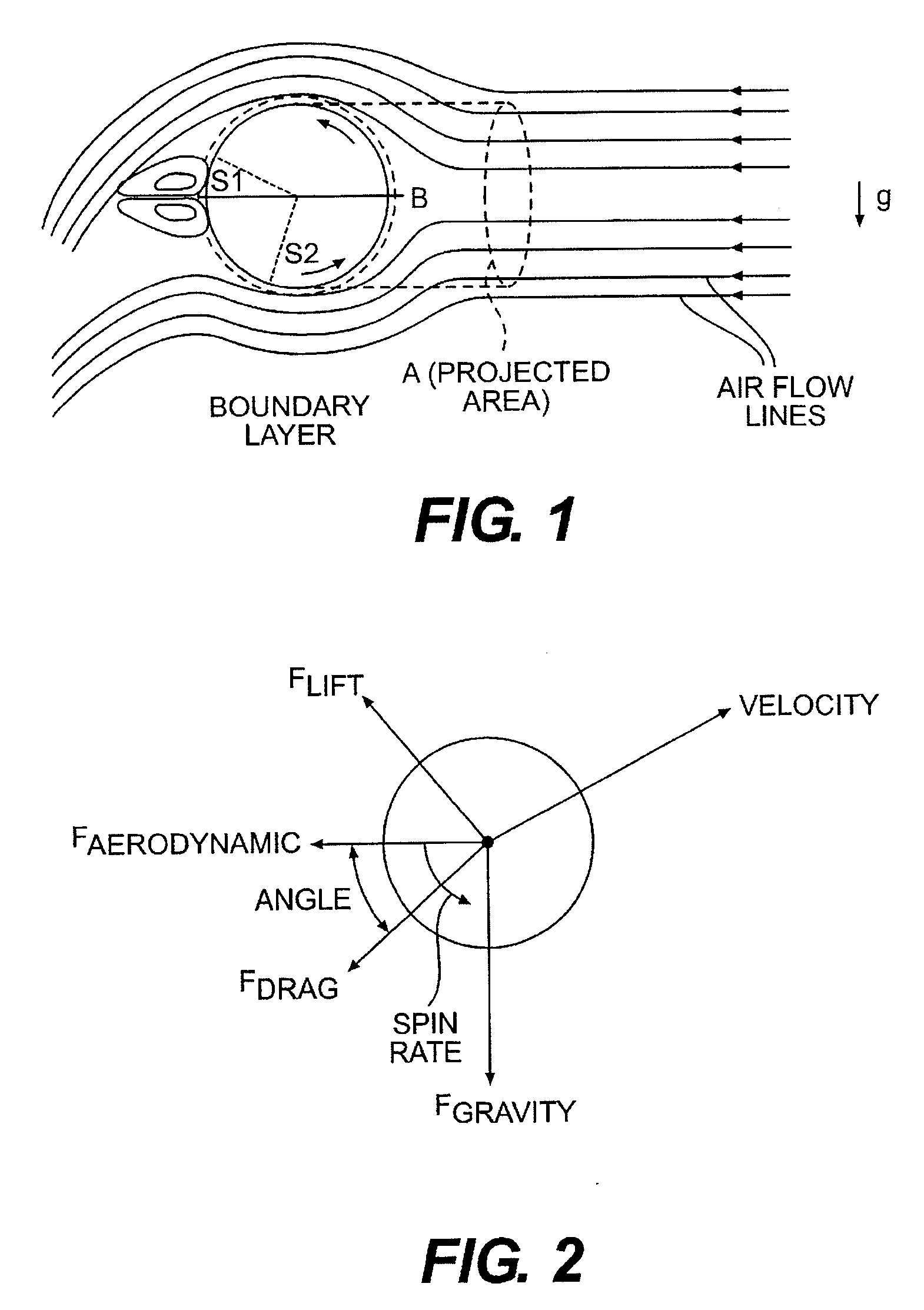
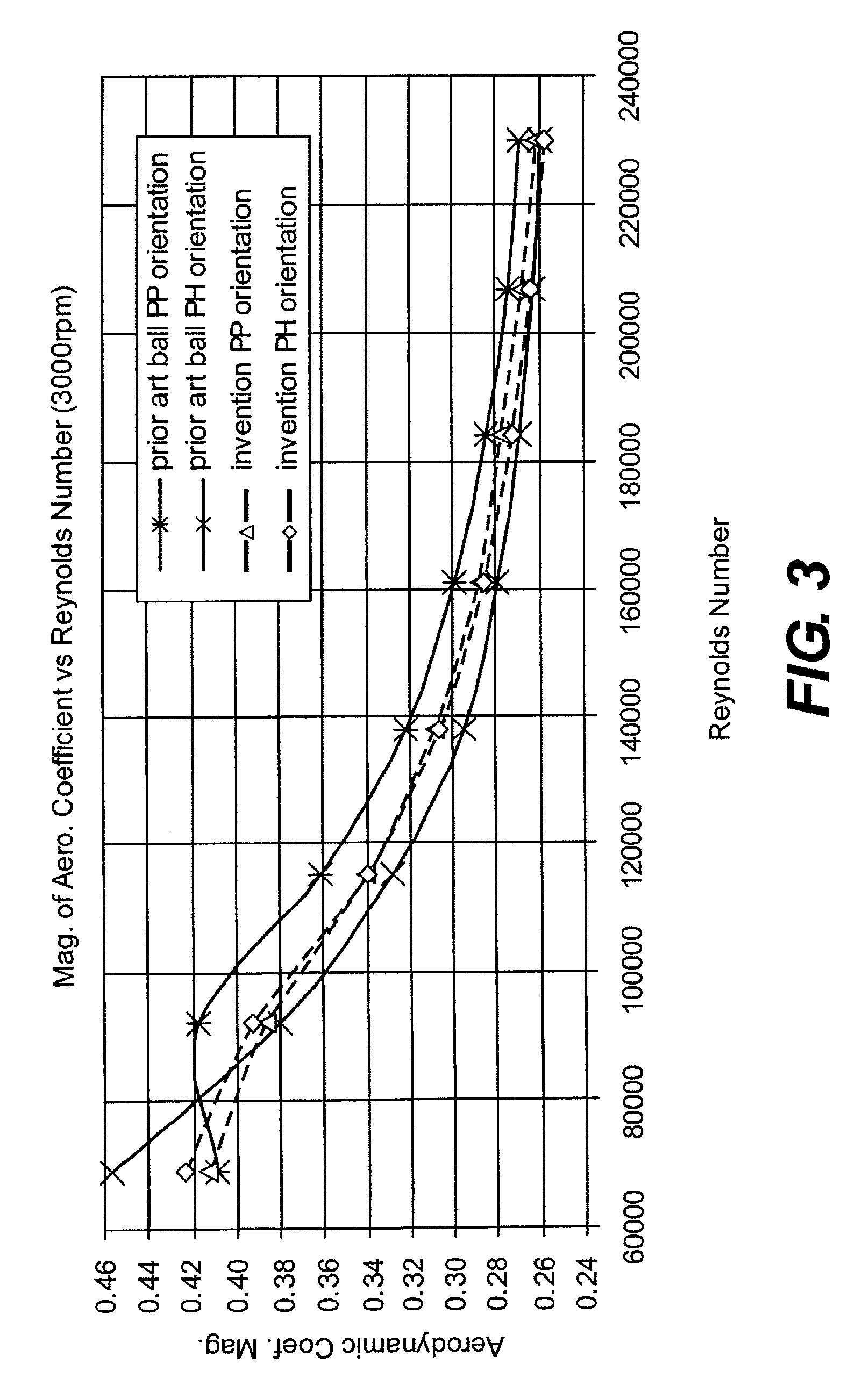
Golf ball with improved flight performance
InactiveUS7156757B2Increase percentageBetter dimple packingGolf ballsSolid ballsEngineeringGolf Ball
A golf ball with aerodynamic coefficient magnitude and aerodynamic force angle, resulting in improved flight performance, such as increased carry and flight consistency regardless of ball orientation. In particular, the present invention is directed to a golf ball having increased flight distance as defined by a set of aerodynamic requirements at certain spin ratios and Reynolds Numbers, and more particularly the golf ball has a low lift coefficient at a high Reynolds Number.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
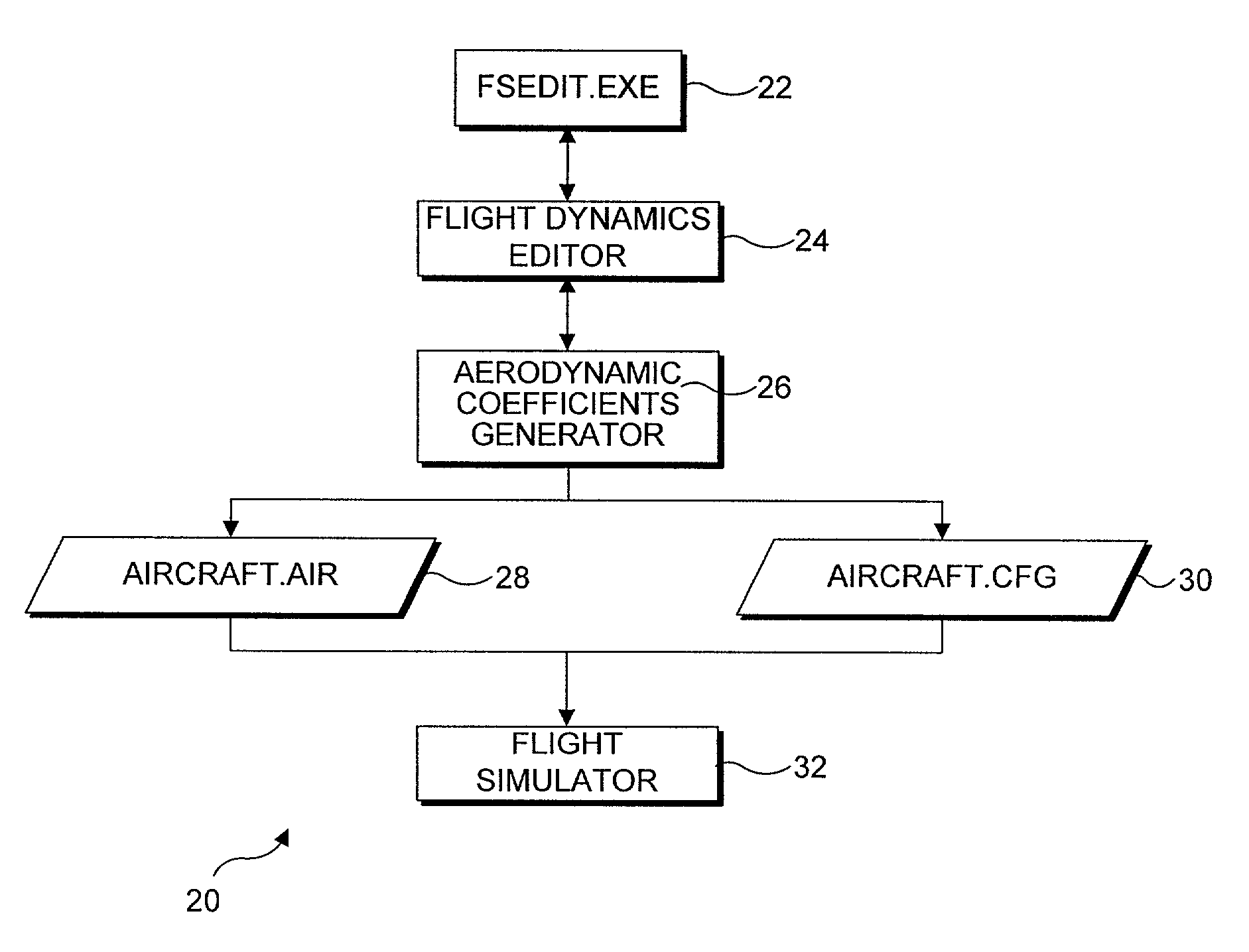
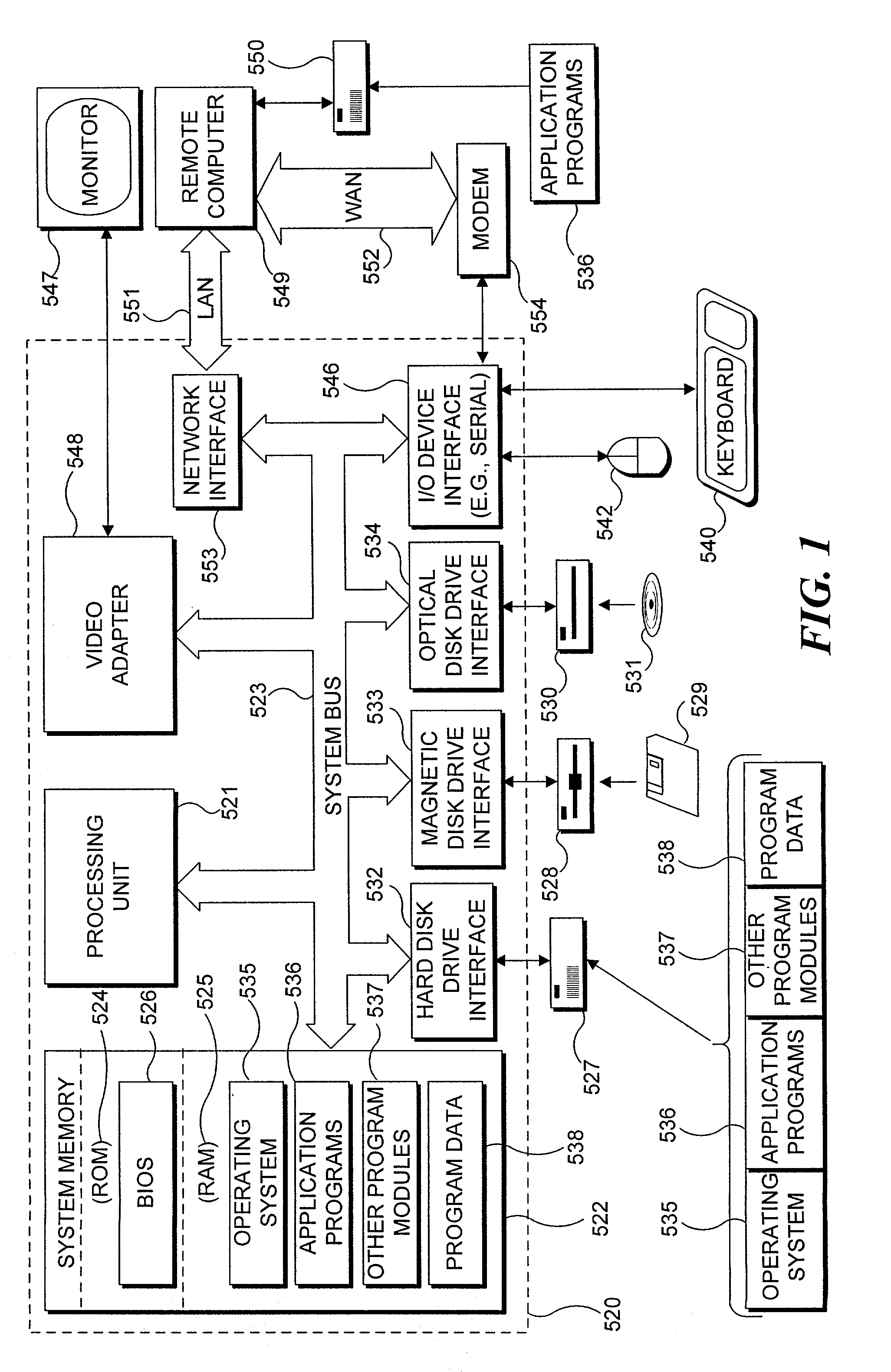
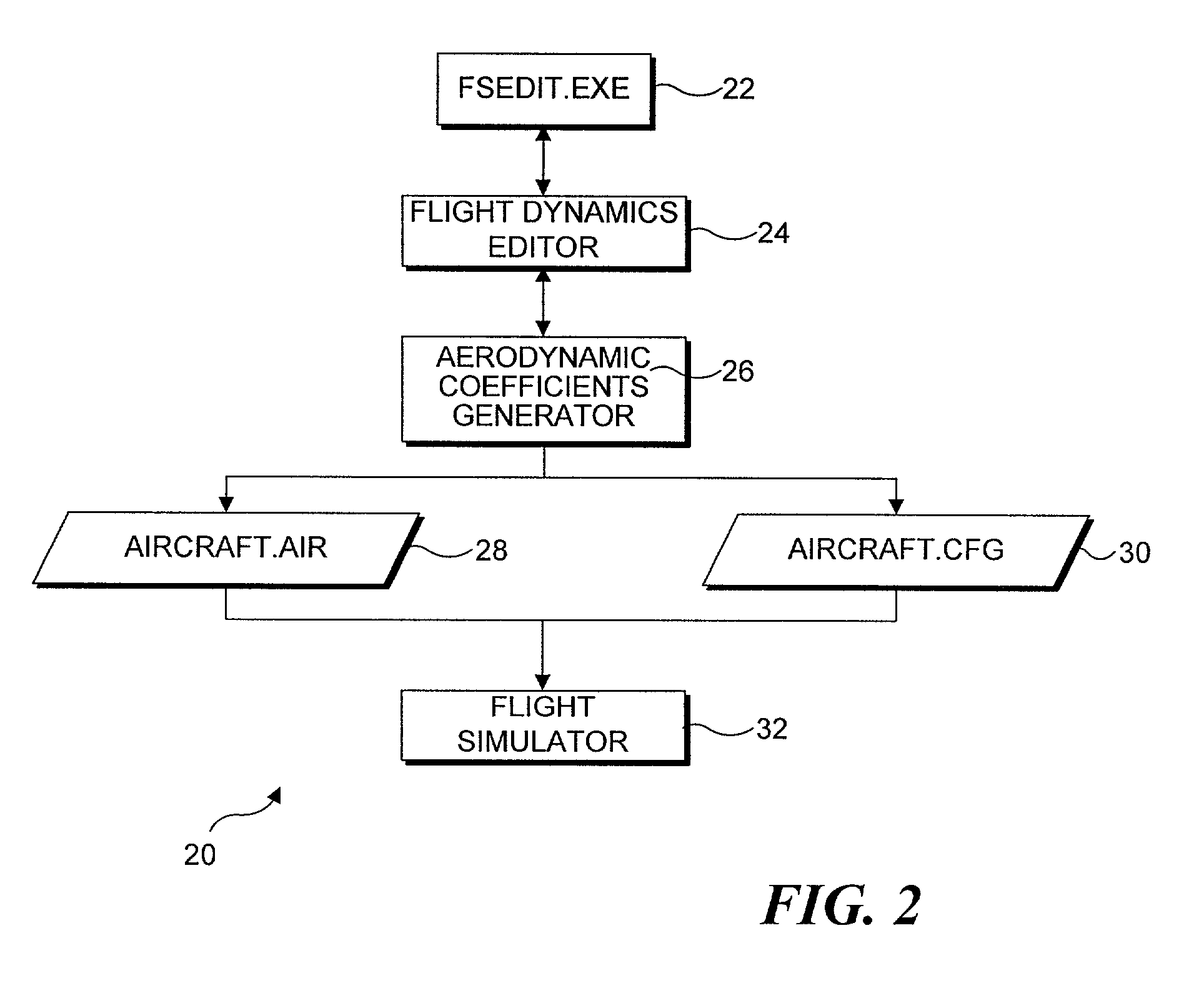
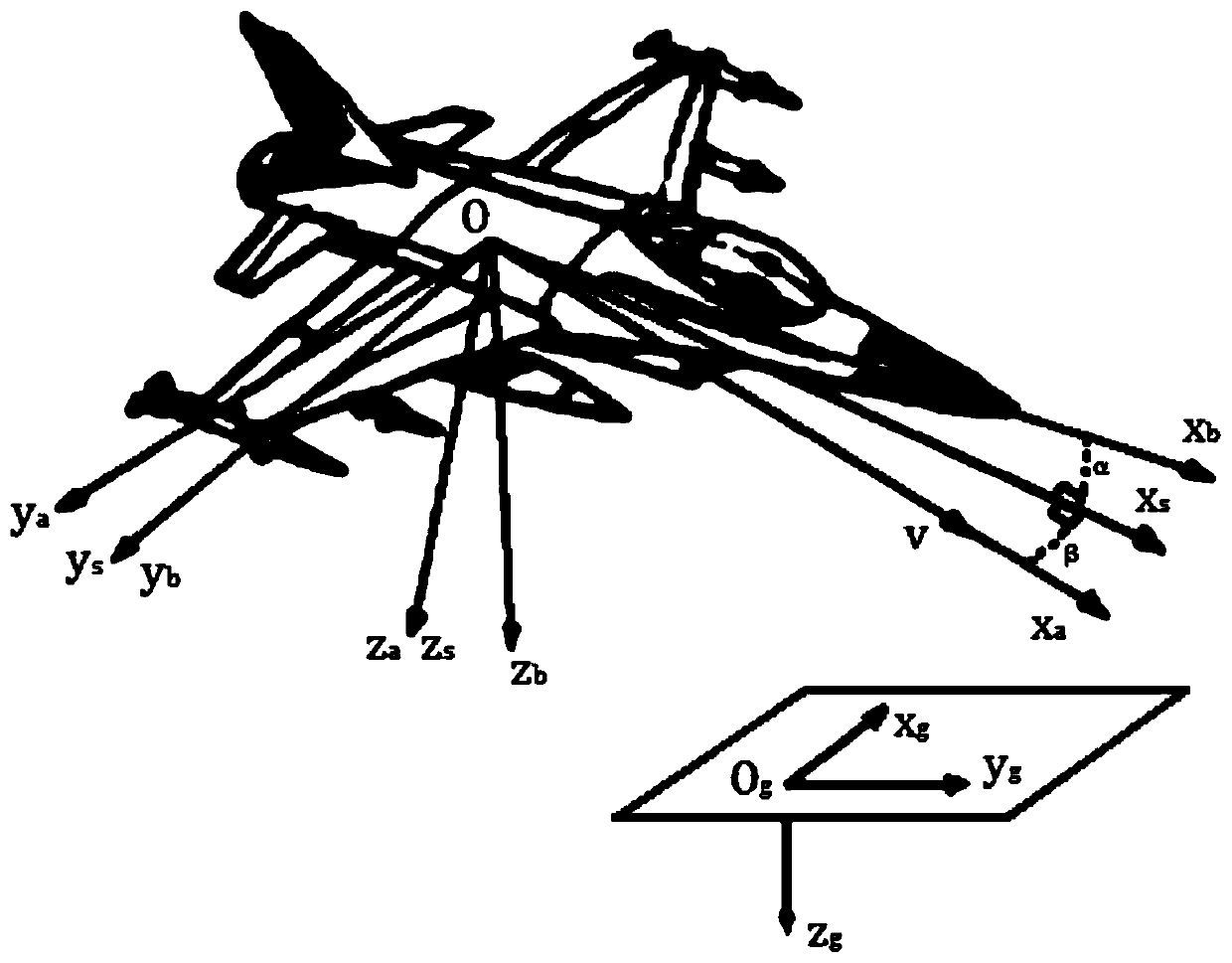
Integrated aircraft flight dynamics prediction and simulation
In a flight simulator program, a flight dynamics editing module enables the user to input parameters for modifying an existing aircraft design or creating an aircraft design. Starting with the type and purpose of aircraft, the user is able to specify parameters defining the configuration, and various other aspects of the aircraft, including the number and type of engines, properties of the flight controls, type of landing gear, etc. Once the user has input the parameters, an aerodynamic coefficients generator module included with the flight simulation program determines aerodynamic coefficients for the aircraft design, using classical formulas and determining the coefficients in an appropriate order. The aerodynamic coefficients and certain parameters input by the user are then output as two flight model data files, in a format usable by the flight simulator program, so that the user can evaluate the aircraft design by flying it within the simulation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
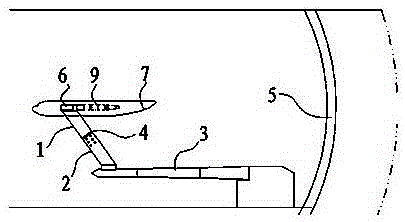
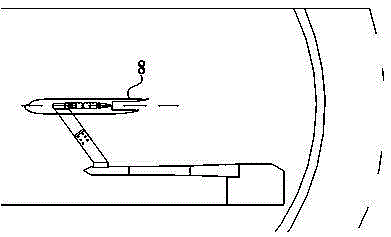
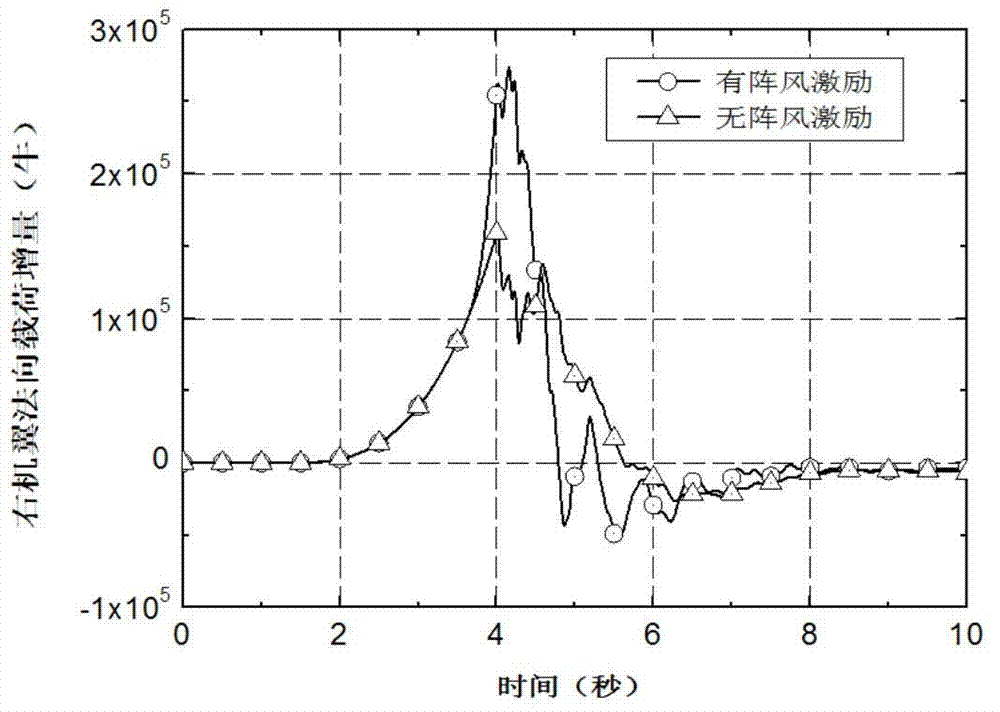
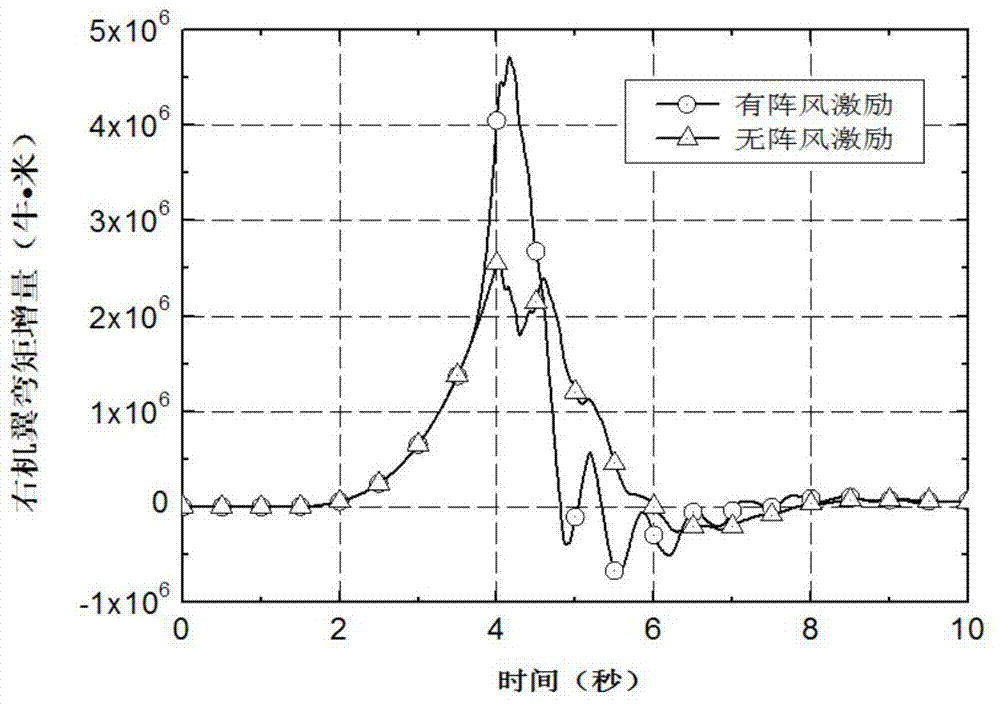
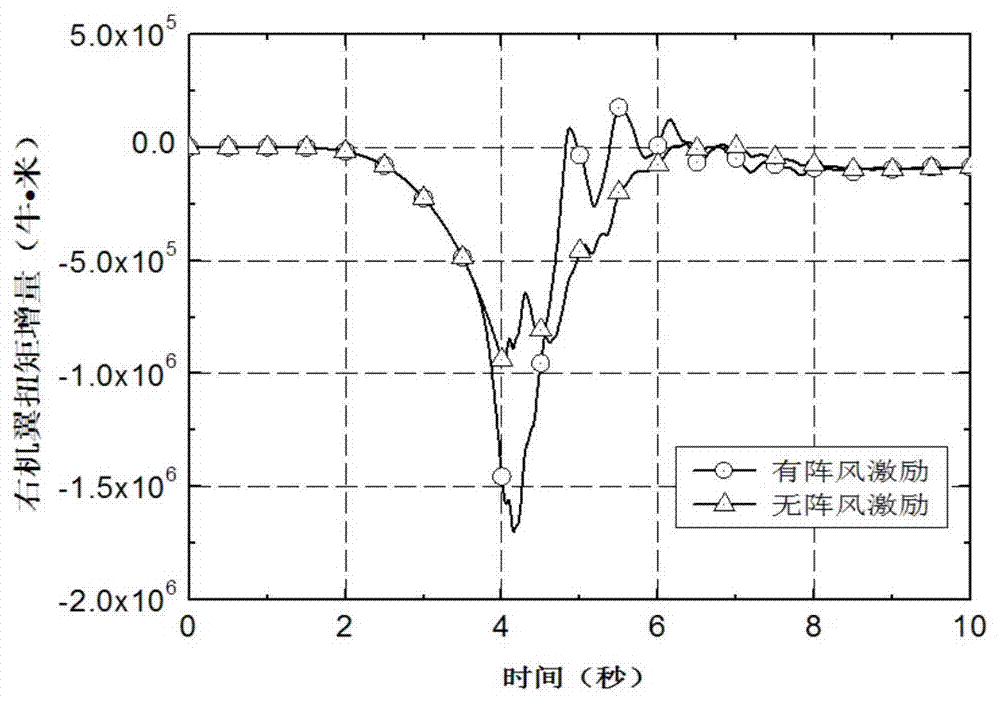
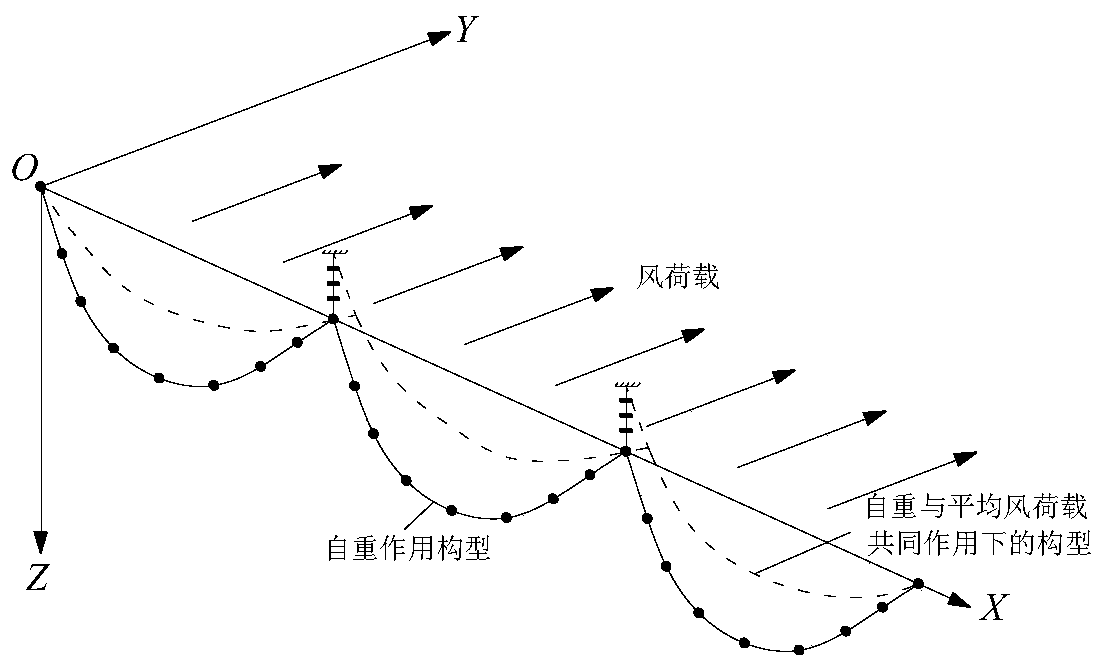
Simulation analysis method and system for gust response of elastic aircraft
ActiveCN110309579AReduce design investmentShorten the design cycleGeometric CADSustainable transportationAnalysis methodAngle of attack
The invention belongs to the technical field of aircraft simulation, and particularly relates to a simulation analysis method and system for gust response of an elastic aircraft. The method comprisesthe steps of according to the dynamics and the structure correspondence of the elastic aircraft under gust excitation, firstly, modeling an aircraft six-degree-of-freedom system, the atmospheric turbulence, the gust excitation and the aerodynamic force data according to the flight state; secondly, under the condition of static elasticity, analyzing the deformation of the aircraft wing under the aerodynamic force load and the change of an angle of attack and the influence of the angle of attack on an aerodynamic coefficient, correcting the aerodynamic coefficient to enable the aerodynamic coefficient to better conform to the real flight state of the elastic aircraft, and finally, connecting all the modules into a system to realize the corresponding analysis under the excitation of gust of the elastic aircraft. The system achieves a good effect in cases of a general aircraft and a civil large-scale passenger plane.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Golf ball with improved flight performance
A golf ball with aerodynamic coefficient magnitude and aerodynamic force angle, resulting in improved flight performance, such as increased carry and flight consistency regardless of ball orientation. In particular, the present invention is directed to a golf ball having increased flight distance as defined by a set of aerodynamic requirements, at particular spin ratios and Reynolds Numbers. The invention is also directed toward golf balls with dimple diameters of greater than 6.5 percent of the ball diameter and dimples with a profile defined by a catenary curve.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
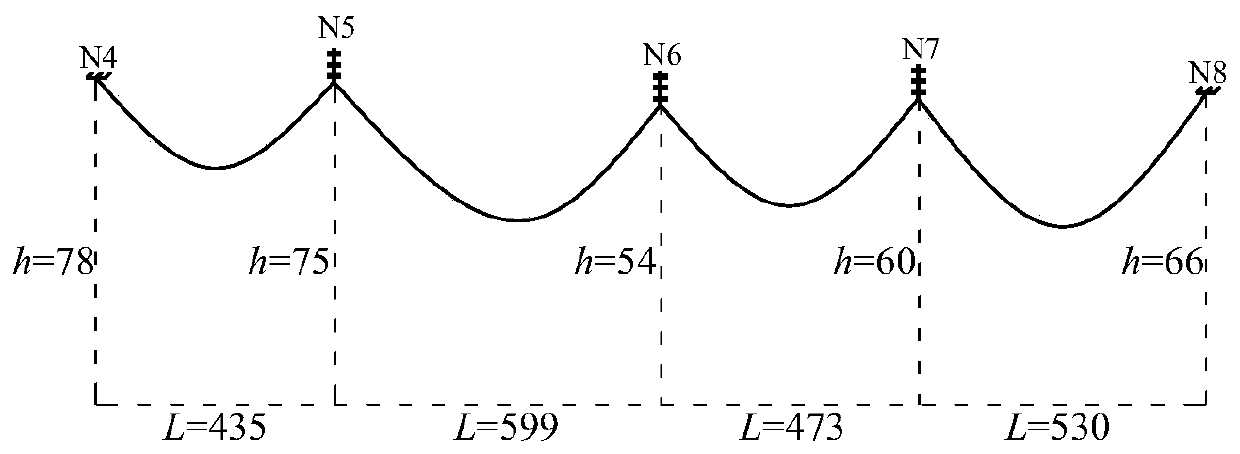
Method for correcting influence of high-speed wind tunnel model afterbody distortion on lateral-directional aerodynamic characteristics
The invention provides a method for correcting the influence of high-speed wind tunnel model afterbody distortion on lateral-directional aerodynamic characteristics. A test model contains a freely-replaceable real afterbody and a distortion afterbody model; the test model pre-deviates to a given sideslip angle through a sideslip angle-varying blade belly supporting device; a wind tunnel test is performed on the real afterbody model and the distortion afterbody model according to the same test conditions; interpolation is performed on lateral-directional aerodynamic coefficients according to the same angle of attack sequence; subtraction is performed on two kinds of interpolated lateral-directional aerodynamic coefficients, so that an obtained difference value of the two kinds of interpolated lateral-directional aerodynamic coefficients is the influence of the afterbody distortion on the aerodynamic characteristics of the test model. The method can be used for correcting the influence of the afterbody distortion on the lateral-directional aerodynamic characteristics of the model test under the given sideslip angle.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Method for determining wing structure load when transportation aircraft drops goods
ActiveCN103577648AEnsure flight safetyEnsure safetySpecial data processing applicationsDesign loadImproved method
The invention belongs to the technical field of aircraft flying load design, and relates to the improvement on a method for determining a wing structure load when a transportation aircraft drops goods. The method for determining the wing structure load is characterized by comprising the step of initializing aircraft air-dropping goods parameters, the step of analyzing aircraft limited element modals, the step of calculating an aircraft non-steady aerodynamic coefficient matrix, the step of calculating an aircraft air-dropping goods dynamic response, the step of calculating a wing structure load dynamic response, and the step of determining the design load of the wing structure in the process of air-dropping. By means of the improved method for determining the wing structure load when the transportation aircraft drops the goods, the determining precision of the wing structure load is improved, and the safety of the wing structure and the flying safety of the aircraft are guaranteed.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Airfoil robust optimization design method based on non-probability interval analysis model
ActiveCN105718634ASmall drag coefficientGuarantee safety and reliabilityGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmGenetic algorithm
The present invention discloses an airfoil robust optimization design method based on a non-probability interval analysis model, and belongs to the technical field of optimization design. According tothe method disclosed by the present invention, an indefinite factor in airfoil design is fully considered, and in the case that a probability density of an indefinite parameter is unknown, quantifiedcharacterization of the indefinite parameter is implemented by using an interval vector. By means of a sample point experiment, a mapping relationship among an airfoil design variable, the indefiniteparameter and an aerodynamic coefficient is established. On this basis, upper and below interval boundaries of the airfoil aerodynamic coefficient are obtained by using a non-probability interval analysis model. Robust optimization model is established, then airfoil optimization design is implemented by using genetic algorithm. As numerical prediction indicates, on the premise of maintaining an airfoil lift coefficient and a geometric shape constraint, the method disclosed by the present invention reduces a resistance coefficient of a designed airfoil, reduces a variation range of the resistance coefficient and provides a new idea for airfoil optimization design.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
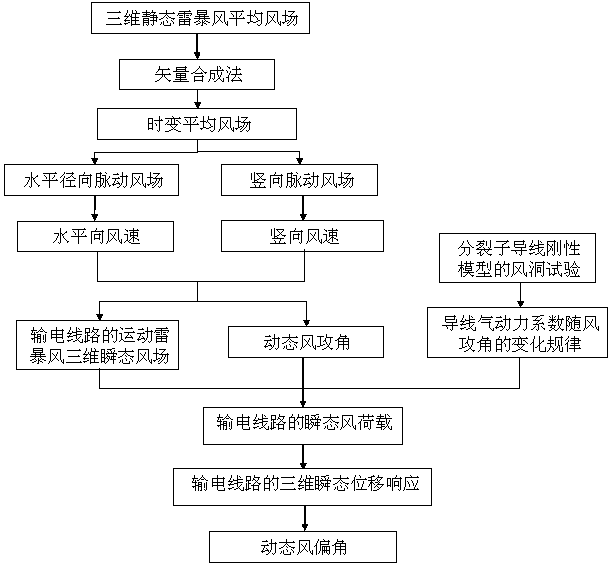
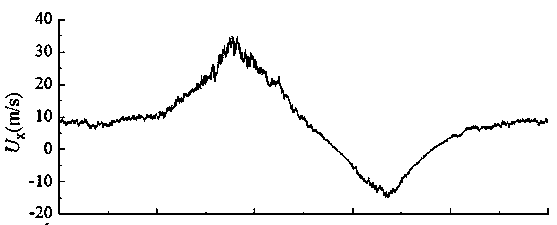
Method for electric transmission line windage yaw transient analysis under action of moving thunderstorm wind
ActiveCN103683086AImprove computing efficiencyWide coverage of resultsCable installation apparatusTime domainSpatial correlation
The invention discloses a method for electric transmission line windage yaw transient analysis under action of moving thunderstorm wind. The method comprises the steps that the vertical wind speed is considered in simulation of a moving thunderstorm wind field and the spatial correlation and the pulsation effect are synchronously considered; when the wind load is determined, a transient wind attack angle and a corresponding divided conductor aerodynamic coefficient are introduced, and the wind speed and change of the direction are considered in a time domain; in the analysis process of a wind deflection angle, displacement, caused by the asymmetric load, in the direction of a line is considered, the largest wind deflection angle of part of the electric transmission line is calculated under the condition of the extreme wind load, design work of windproof measures of the electric transmission line is directed, and the power supply reliability of the electric transmission line is improved.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Golf ball with improved flight performance
ActiveUS20100075776A1Improve flight performanceEasy to flyGolf ballsSolid ballsGolf BallFlight distance
A golf ball with aerodynamic coefficient magnitude and aerodynamic force angle, resulting in improved flight performance, such as increased carry and flight consistency regardless of ball orientation. In particular, the present invention is directed to a golf ball having increased flight distance as defined by a set of aerodynamic requirements, at particular spin ratios and Reynolds Numbers. The invention is also directed toward golf balls having high spin decay rates during the first second of flight that yields improved flight performance and longer ball flight
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
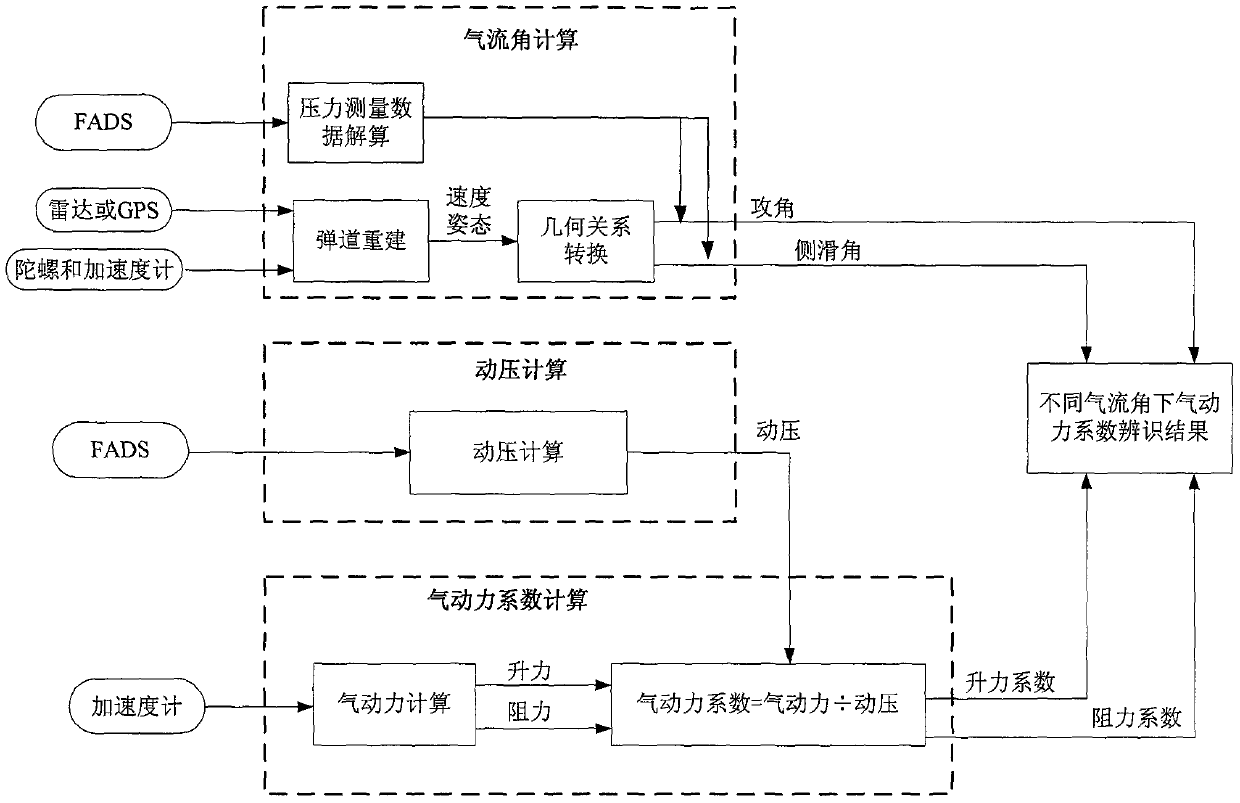
Aerodynamic parameter measurement method for aircraft
The invention provides an aerodynamic parameter measurement method for an aircraft, which is used for measuring key data in three aspects of an airflow angle, dynamic pressure and an aerodynamic force. The method comprises the following steps: the airflow angle is calculated, the airflow angle is acquired through an embedded atmospheric data sensing system or a trajectory reconstruction mode, andthe above two modes are in mutual backup; the dynamic pressure is calculated, data are outputted according to pressure sensors configured by the embedded atmospheric data sensing system on the aircraft, the dynamic pressure is calculated and input is provided for calculating an aerodynamic coefficient; and the aerodynamic coefficient is calculated, the output is measured by using accelerometers, the aerodynamic force, that is, the lift force and the drag force, is calculated, and in combination of the dynamic pressure data, an aerodynamic calculation formula is used to directly determine the lift force coefficient and the drag force coefficient of the aircraft. The embedded atmospheric data sensing system is equipped with two sets of pressure sensors and multiple sets of accelerometers andgyroscopes. A hardware redundancy design and an algorithm redundancy design are adopted, and the aerodynamic parameter measurement reliability is improved.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
System and method for processing dynamic force measurement wind tunnel test data of rotary aircraft
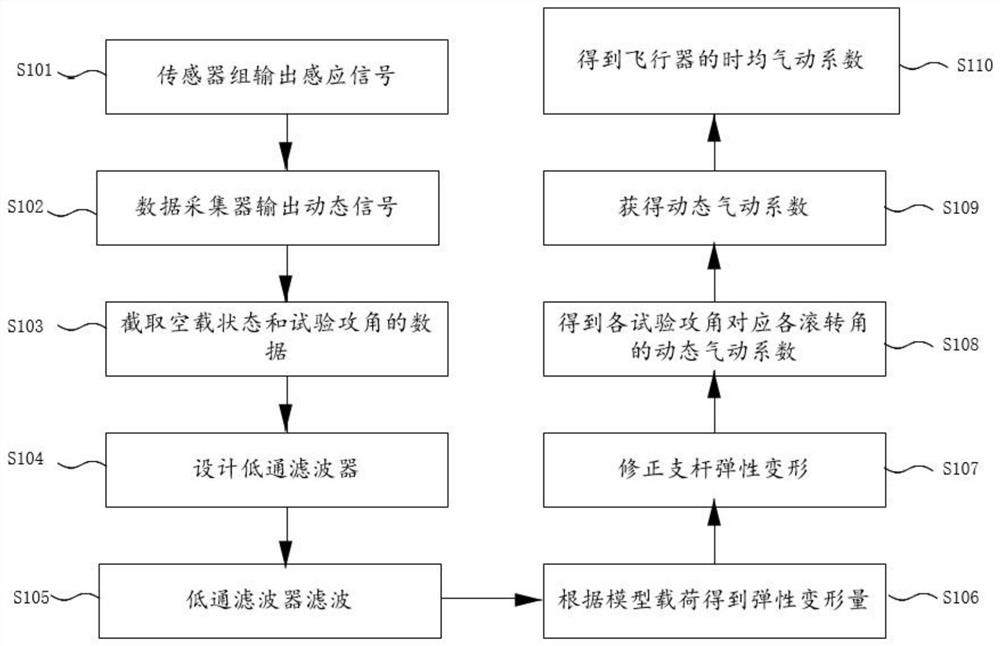
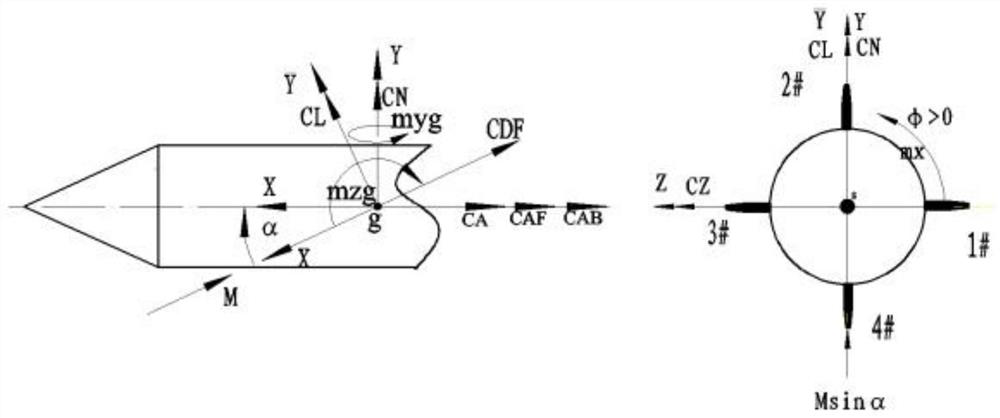
ActiveCN112595487ADynamic aerodynamic coefficient correctionAerodynamic testingFlight vehicleData acquisition
The invention provides a method and a system for processing dynamic force measurement wind tunnel test data of a rotary aircraft. The method comprises: outputting an induction signal through a sensorgroup; outputting a dynamic signal through a data collector; calculating a model attack angle and a roll angle and segmenting a dynamic signal; obtaining a low-pass filtering cut-off frequency throughspectrum law analysis, and designing a low-pass filter; obtaining an elastic deformation amount to correct elastic deformation of the strut; calculating aerodynamic coefficients of the no-load stateand the test attack angle; obtaining a dynamic aerodynamic coefficient of each test attack angle corresponding to each roll angle; correcting the dynamic aerodynamic coefficient under each test attackangle and obtaining an available dynamic aerodynamic coefficient; and calculating the average value of the dynamic aerodynamic coefficients as the time-average aerodynamic characteristics of the aircraft. The method for processing dynamic force measurement wind tunnel test data of the rotary aircraft improves the problem that the dynamic aerodynamic coefficient from the original signal of the dynamic force measurement wind tunnel test to the aircraft cannot be analyzed and processed in the prior art.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Direct force and aerodynamic force composite control method and forward-direction interception guidance method
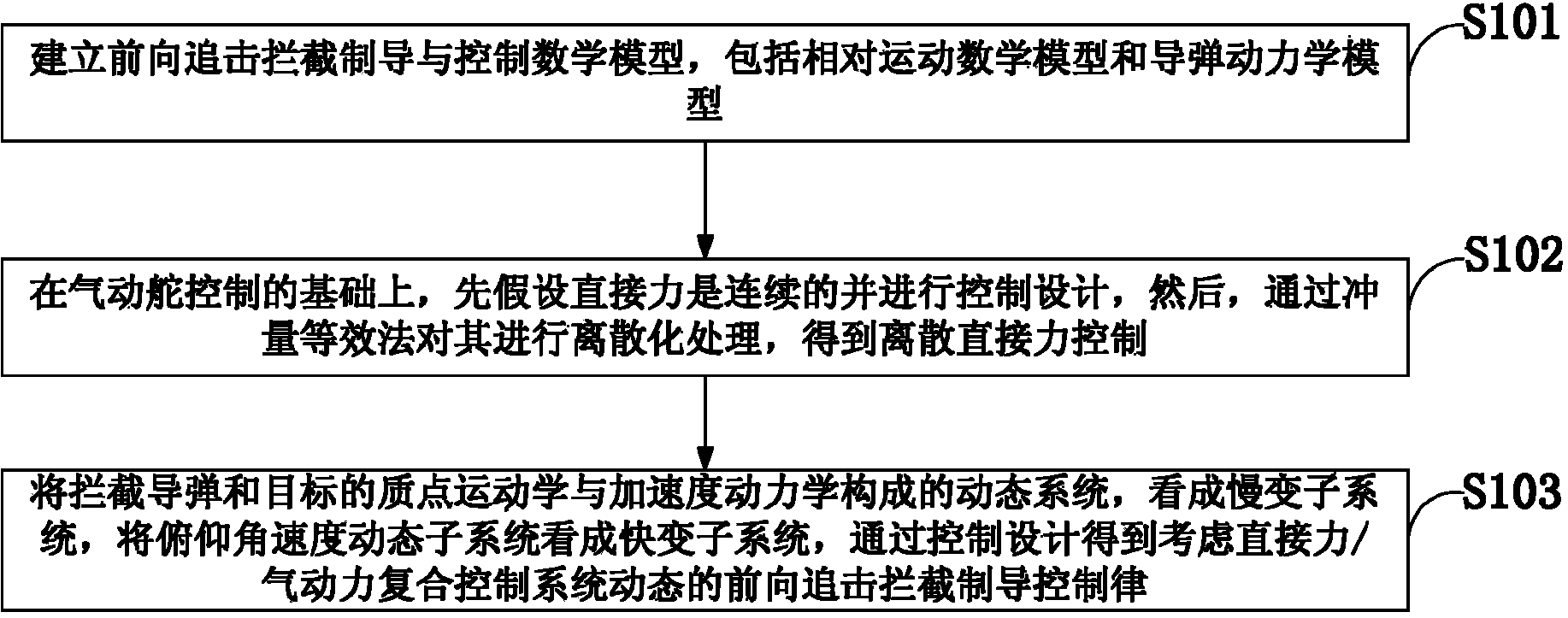
InactiveCN104019701AAvoid Control Assignment ProblemsMeet needsDefence devicesSelf-propelled projectilesKinematicsControl system
The invention discloses a direct force and aerodynamic force composite control method and a forward-direction interception guidance method, and provides a direct force design method which carrying out discretization through an impulse equivalence method on the basis of considering characteristics of continuous aerodynamic force and characteristics of discrete direct force, so that a complex control distribution problem is solved. According to a two-dimensional forward-direction interception guidance motion model and an interceptor missile kinetic model and by means of time scale separation, a dynamical system formed by a particle kinematics and accelerated speed slow subsystem of an interceptor missile and a target is regarded as a slow subsystem, a pitch angle speed dynamic subsystem is regarded as a fast subsystem, and a forward-direction interception guidance rule with dynamic conditions of a direct force / aerodynamic force composite control system taken into account is obtained through tracking control design of a pitch angle speed instruction. According to the direct force and aerodynamic force composite control method and the forward-direction interception guidance method, the complex control distribution problem is solved, the dynamic conditions and characteristics of composite control are conveniently taken into account through the design of the forward-direction interception guidance rule, interpolation calculation can be carried out through nominal values of aerodynamic coefficients conveniently, and practical application is convenient.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
Non-linear optimization algorithm for rational approximation of unsteady aerodynamic minimum state
ActiveCN105046021AHigh precisionImprove computing efficiencySustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainAlgorithm
The invention discloses a non-linear optimization algorithm for rational approximation of a unsteady aerodynamic minimum state. According to the non-linear optimization algorithm, key model lines of a matrix D are initialized; then, each column of a matrix E and the rest of lines of the matrix D are sequentially solved; function value information at a current sequential solving method on each column of matrix E and other lines of matrix D; and the function iteration point is sufficiently utilized, so that approximate precision of the inverse Hessian matrix is effectively improved, and the efficiency of an outer-layer non-linear optimization algorithm is improved. According to the non-linear optimization algorithm, fitting precision of elements in the key model lines of a general aerodynamic matrix is effectively improved, so that the precision of time-domain flutter analysis results and the gust response analysis results is increased in a facilitated mode. A discrete unsteady aerodynamic coefficient matrix in the frequency domain is extended to the Laplace-domain in the form of an MS algorithm; and the computing efficiency and the precision of the key model can be effectively improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
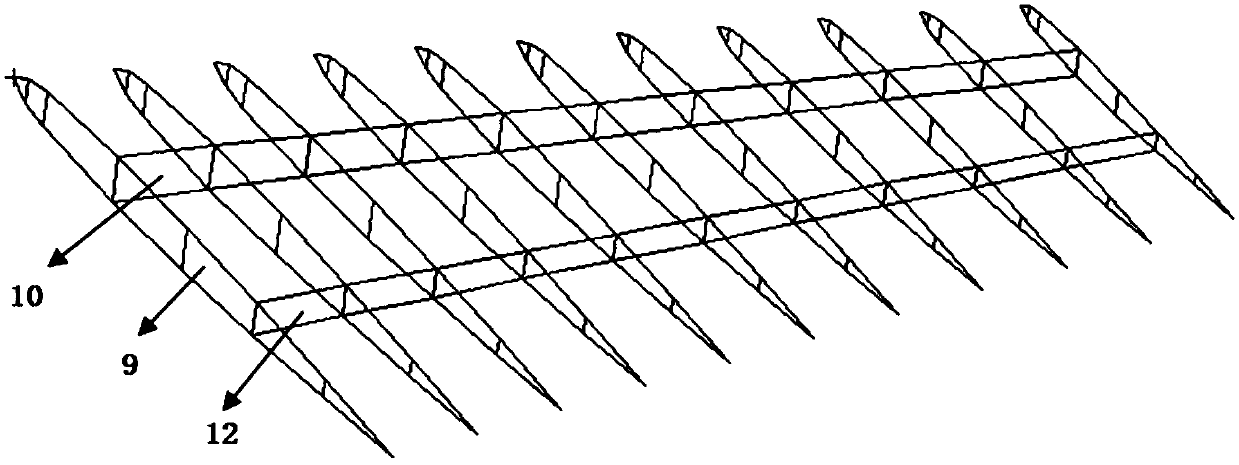
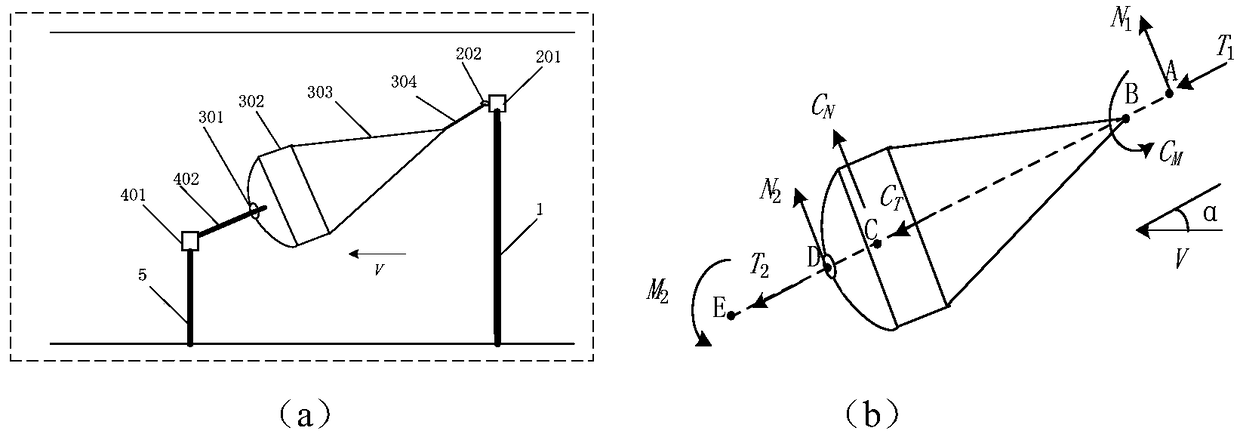
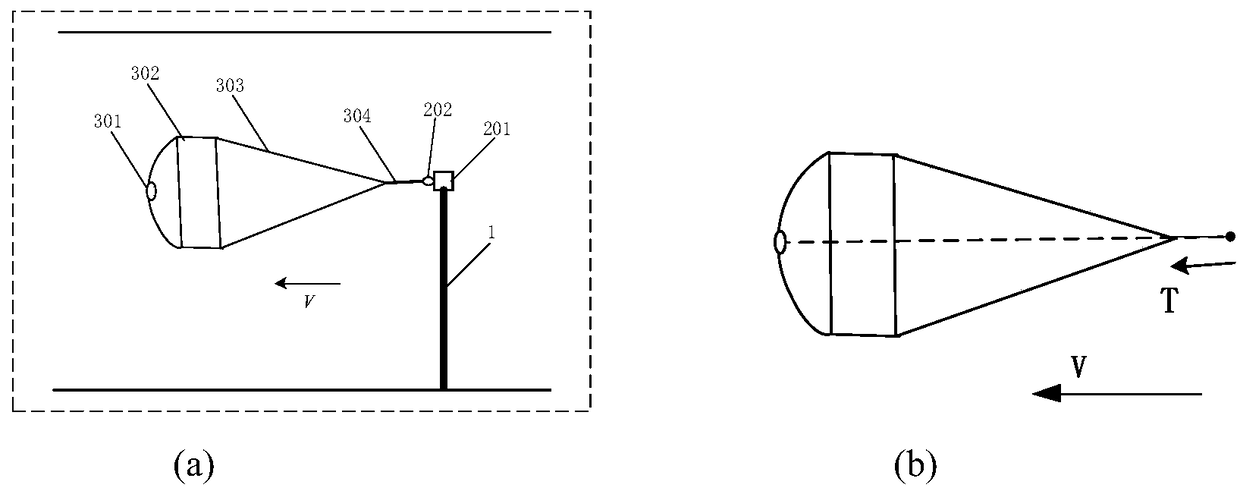
Parachute aerodynamic coefficient and moment coefficient calculation method and system
ActiveCN109141805AThe dynamic pressure is close to the actualExact aerodynamic coefficientAerodynamic testingData simulationAxial force
The invention provides a parachute aerodynamic coefficient and moment coefficient calculation method and system. The method comprises wind tunnel test measurement, numerical simulation correction andtheoretical calculation. Firstly the axial force, the normal force, the moment and the resistance of the connected parachute are measured by the front and back balance through the wind tunnel test under the given incoming flow condition; the wind tunnel test condition is simulated and data simulation of the approximate actual working condition and the actual working condition is performed under the same inflow condition so as to obtain the aerodynamic force of the parachute; the wall influence coefficient k1 and the bracket influence coefficient k2 of the wind tunnel are calculated according to the load on the parachute; and the aerodynamic coefficient and the moment coefficient of the parachute are calculated according to the axial force, the normal force, the moment and the resistance ofthe connected parachute measured by the front and back balance and the wall influence coefficient k1 and the bracket influence coefficient k2 of the wind tunnel. According to the method, the aerodynamic coefficient and the moment coefficient of the parachute can be simultaneously obtained through the test, and the test data can be corrected by using numerical simulation so that the obtained result is more accurate.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
A simplified calculation method for dynamic windage yaw of an iced conductor
InactiveCN109902351AAccurately account for pulsation effectsDoes not increase the amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainCalculation error
The invention discloses a simplified calculation method for dynamic windage yaw of an iced conductor. The simplified calculation method comprises the following steps: solving an equivalent static windload of the iced conductor based on a gust load envelope line method (GLE); instroducing A height difference correction coefficient, so that the problem that a rigid straight rod method is inaccuratein gravity load estimation when the height difference of a line hanging point is large is solved; Taking the circular-section ice-coated wire as an example, carrying out verification and parametric analysis on the effectiveness of the simplified calculation method by adopting a time domain method to obtain a change rule of the windage yaw angle of the ice-coated wire along with wind speed, ice coating density and ice coating thickness. According to the calculation method, the pulsation effect of the wind load can be accurately considered, excessive calculated amount cannot be increased, calculation errors of the gravity load of the wire caused by large height difference of line hanging points are avoided, and the calculation method is suitable for batch analysis of multiple parameters such as the icing shape, density, thickness and aerodynamic coefficient of the wire.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
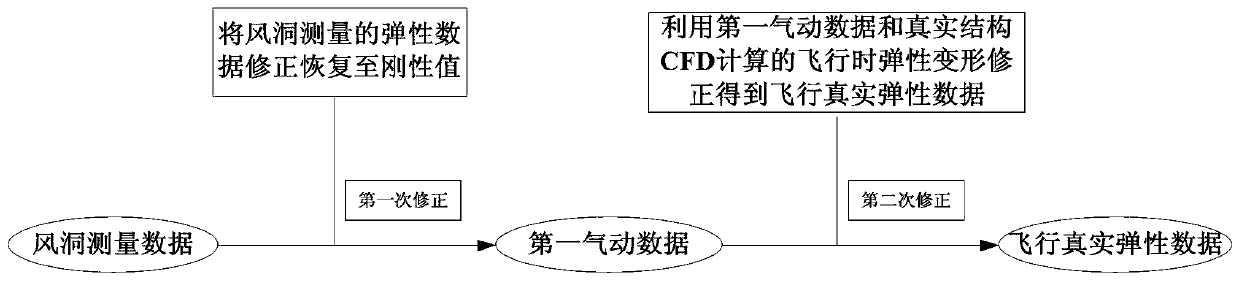
CFD method based precise acquisition method for elastic pneumatic data
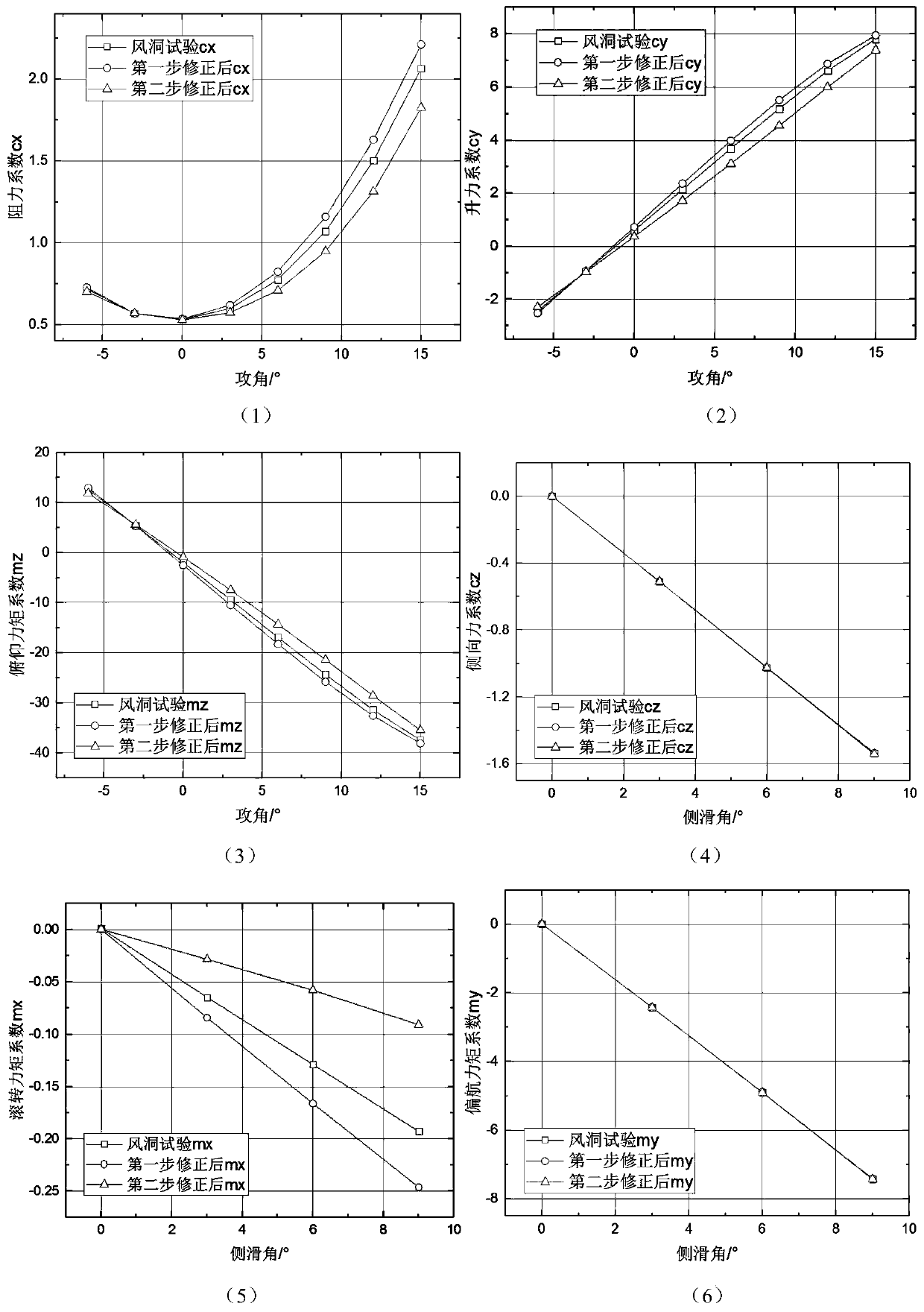
ActiveCN110155363AHigh precisionImprove the accuracy of aerodynamic data designAircraft components testingEngineeringTwo step
The invention provides a CFD method based precise acquisition method for elastic pneumatic data. The method comprises the following steps: 1, establishing a wind tunnel model and a real model of an aircraft; 2, conducting pneumatic elastic property estimation for the wind tunnel model and the real model, and entering the step 3 as the elastic pneumatic data based on the wind tunnel model and the real model is judged to be corrected; 3, carrying out first-time elastic correction: measuring an aerodynamic coefficient of the wind tunnel model by means of a wind tunnel test; calculating the aerodynamic coefficient change amount before and after deformation of the wind tunnel model by adopting the CFD method; subtracting the wind tunnel deformation data and the aerodynamic coefficient change amount to obtain first pneumatic data; and 4, carrying out second-time elastic correction: calculating the aerodynamic coefficient change amount before and after deformation of the wind tunnel model byadopting the CFD method and superposing the aerodynamic coefficient change amount with the first pneumatic data. The two-step elastic pneumatic data precise correction method is established, and the precision of the acquired flying elastic pneumatic data is improved greatly.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Transonic limit cycle flutter analysis method
InactiveCN103310060AModerate amount of calculationEasy to masterSustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsEquivalent linearizationAnalysis method
The invention provides a transonic limit cycle flutter analysis method. The transonic limit cycle flutter analysis method comprises the following steps: through equivalent linearization of a describing function, processing nonlinear characteristics of a transonic aerodynamic force; substituting a frequency-domain aerodynamic coefficient after the equivalent linearization into a flutter equation; obtaining a flutter speed and a flutter frequency by a frequency-domain flutter solving method; and for different limit cycle amplitudes, calculating to obtain different flutter speeds and flutter frequencies to form limit cycle characteristics of a transonic nonlinear flutter. The equivalent linearization is performed on the nonlinear characteristics of the transonic aerodynamic force through the aerodynamic describing function, the flutter equation is solved within a frequency domain, so that the flutter speed and the flutter frequency at a given limit cycle amplitude can be accurately predicted; and the transonic limit cycle flutter analysis method is moderate in computation amount, easy to master and very good in robustness.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for acquiring aerodynamic coefficients of guided missile
ActiveCN106228014ACost savingsSave time and costSustainable transportationAerodynamic testingRectangular coordinatesAngular acceleration
The invention relates to a method for acquiring the aerodynamic coefficients of a guided missile. The method solves the problem that a polar coordinate system aerodynamic coefficient can not be used under a rectangular coordinate system. The method includes the steps that firstly, after the step of acquiring the aerodynamic coefficient under the polar coordinate system of the guided missile through a wind tunnel test, guided missile ballistic parameters are acquired, and guided missile aerodynamic parameters are obtained through resolving according to the guided missile ballistic parameters, wherein the guided missile ballistic parameters include the flight speed with the symbol shown in the description and the flight attitude angle, and the guided missile aerodynamic parameters include the flight attack angle alpha and the flight sideslip angle beta; then, the total attack angle alpha sigma and the roll angle phi under the polar coordinate system are obtained according to the flight attack angle alpha, the flight sideslip angle beta and a conversion formula; then, the interpolation polar coordinate aerodynamic coefficient is obtained through interpolation according to the total attack angle alpha sigma and the roll angle phi; then, the rectangular coordinate system aerodynamic coefficient is obtained according to the interpolation polar coordinate aerodynamic coefficient and a conversion formula; accordingly, the acceleration and the angular acceleration of the guided missile are obtained; finally, the ballistic parameters including the flight speed with the symbol shown in the description and the flight attitude angle of the guided missile at the next moment are obtained.
Owner:JIANGXI HONGDU AVIATION IND GRP
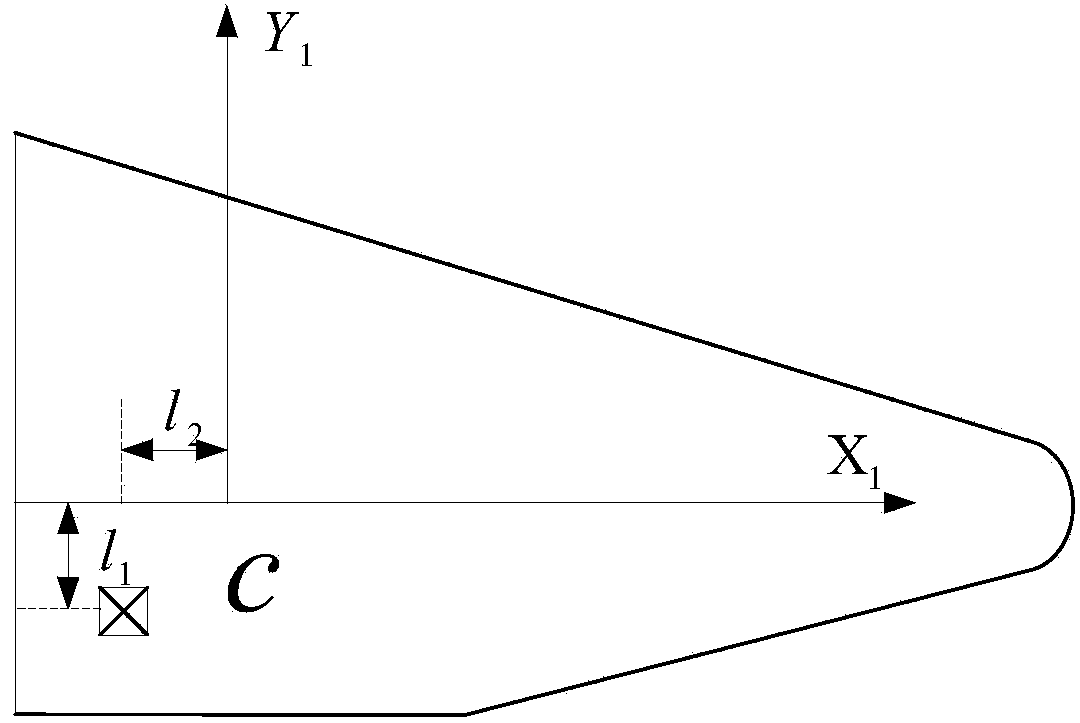
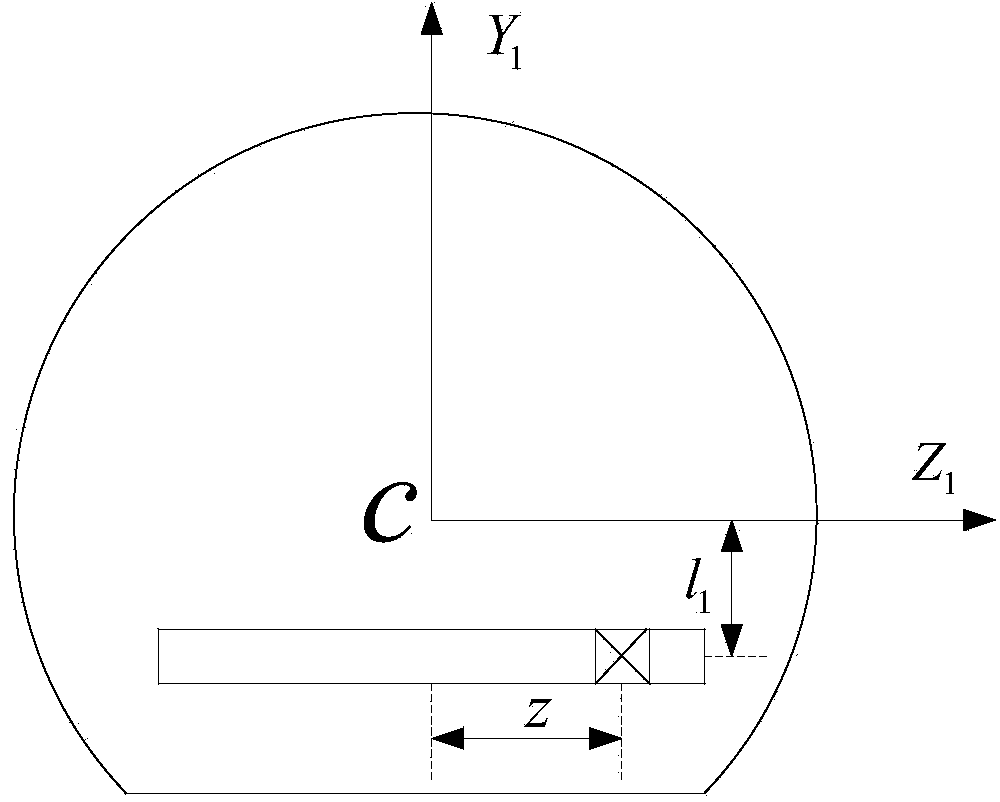
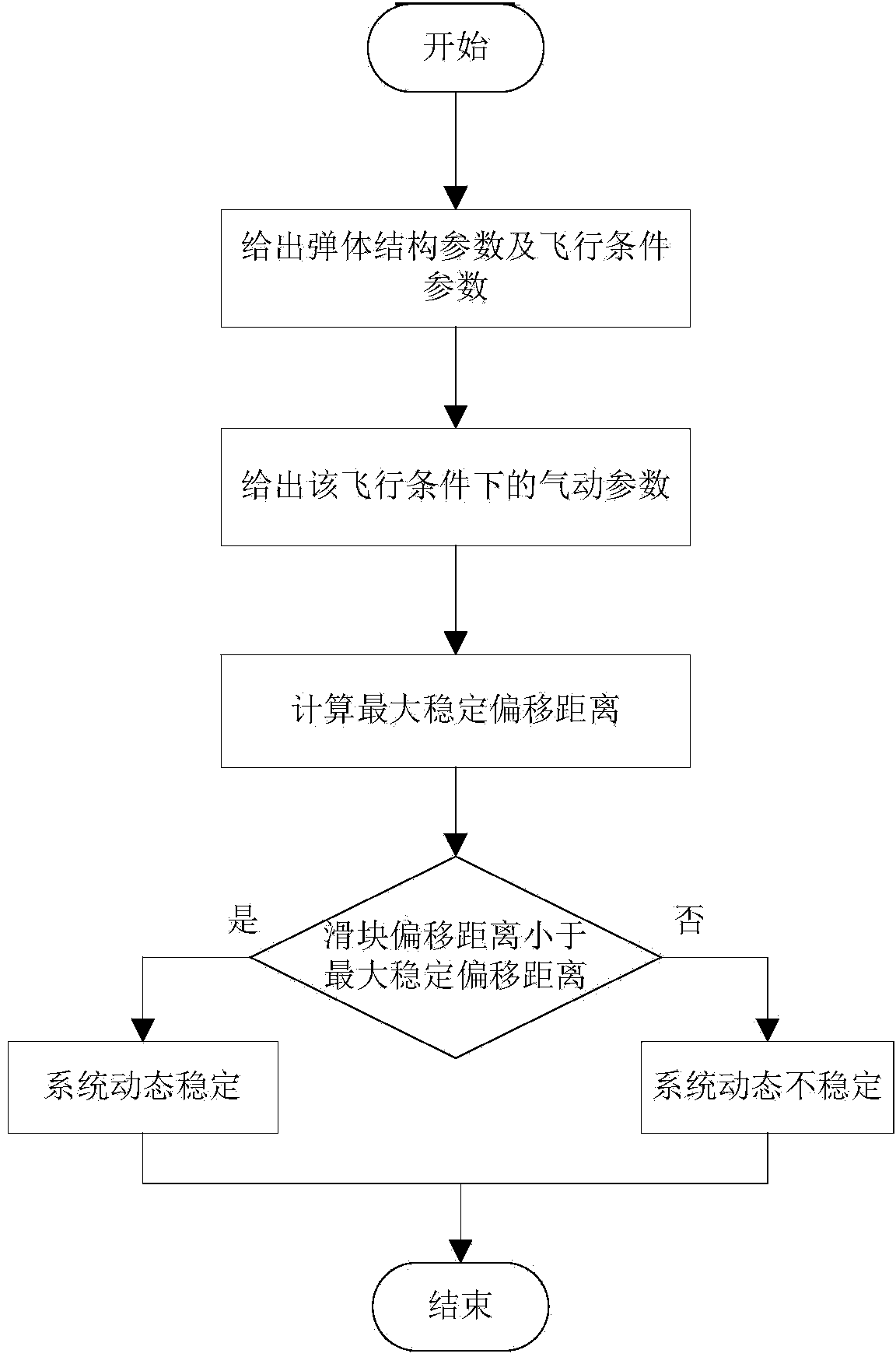
Dynamic stability judgment method of single-slider variable-mass-center control aircraft
InactiveCN104166348AJudgment stabilityWell formedAttitude controlAdaptive controlOffset distanceNutation
The invention provides a dynamic stability judgment method of a single-slider variable-mass-center control aircraft. Dynamic stability of a system under different slider offset distances can be judged. The method includes the steps that first, projectile body parameters and flight condition parameters of a reentry vehicle to be analyzed are obtained; second, the aerodynamic coefficient of the aircraft under the flight condition is obtained through aerodynamic analysis software or a wind tunnel test; third, the maximum stable offset distance zm is calculated according to the obtained parameters and the aerodynamic coefficient; fourth, whether the slider offset distance is smaller than the maximum stable offset distance obtained in the third step obtained in the third step or not is judged, if the slider offset distance meets the formula that |z|< zm, the system is stable in terms of attitude dynamics, and nutation movement of the aircraft can converge to a balance point; if |z|>= zm, the system is unstable in terms of attitude dynamics, and at the moment, the nutation angle of the aircraft tends to diverge along with time.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
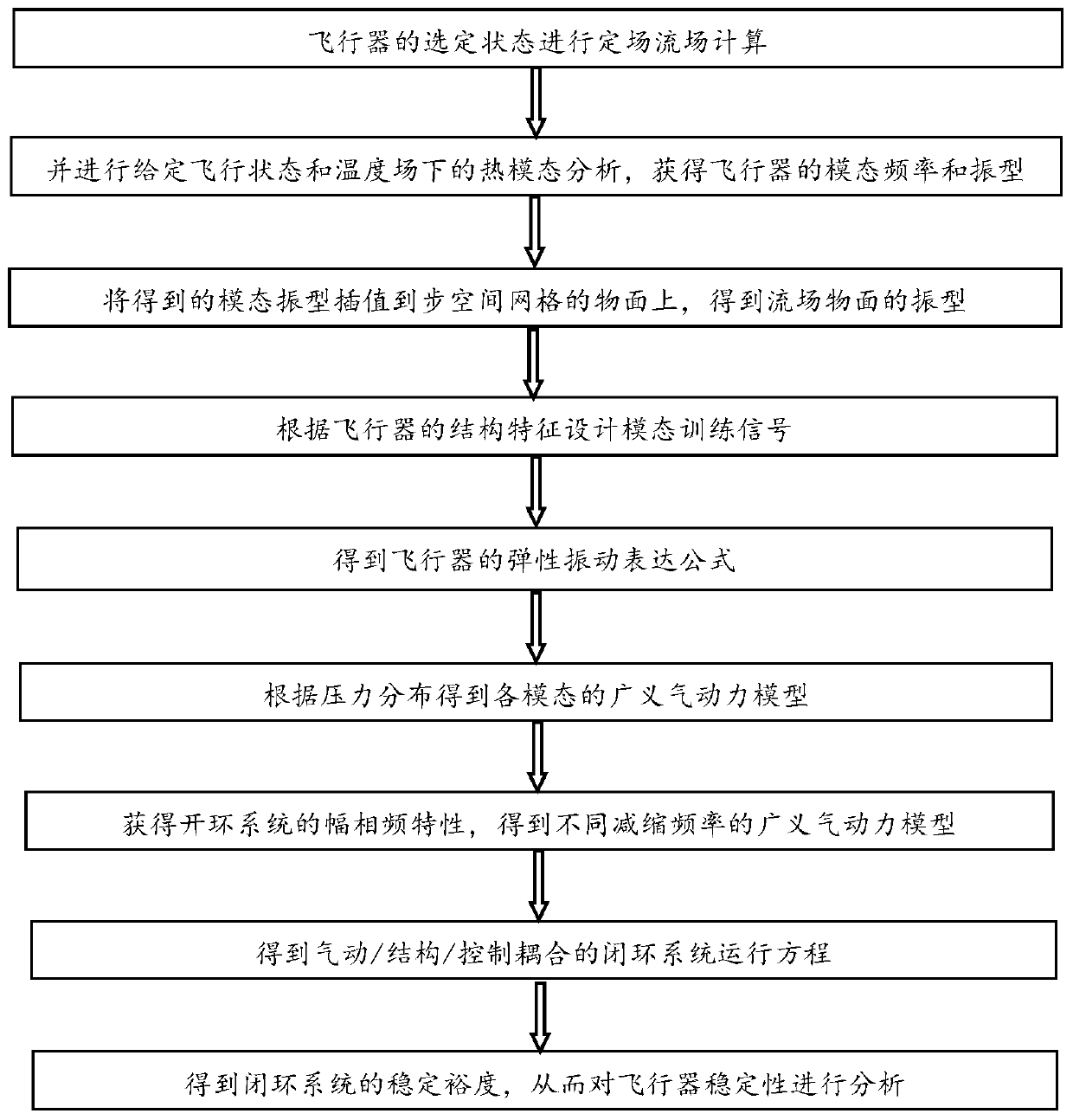
Aircraft stability analysis method
The invention provides an aircraft stability analysis method which comprises the following steps: establishing a space grid according to the appearance of an aircraft, and carrying out steady flow field calculation on a selected state of the aircraft to obtain an aerodynamic coefficient and a coefficient matrix; acquiring modal frequency and vibration mode of the aircraft; calculating the vibration mode of the flow field object plane; designing a modal training signal according to the structural characteristics of the aircraft; obtaining an elastic vibration expression formula of the aircraft; obtaining a generalized aerodynamic model of each mode; obtaining an aerodynamic state equation in the discrete space; extracting generalized aerodynamic models with different reduction frequencies; obtaining a pneumatic / structural / control coupled closed-loop system operation equation; and converting the closed-loop system operation equation into a transfer function, and carrying out stability analysis, thereby analyzing the stability of the aircraft. According to the method, the elastic deformation of the aircraft enters the influence on the control system, and the stability analysis accuracy of the control system is improved.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
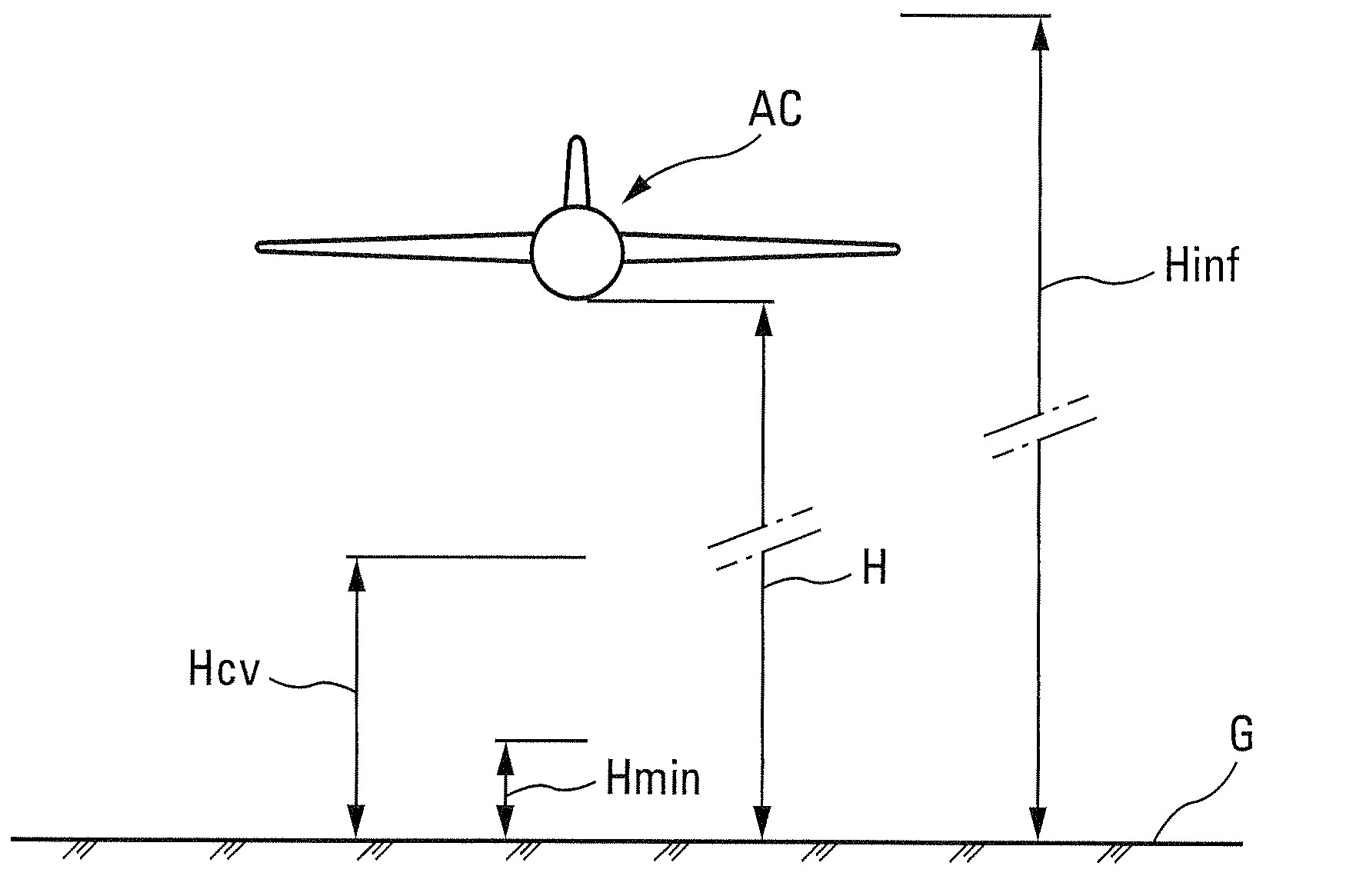
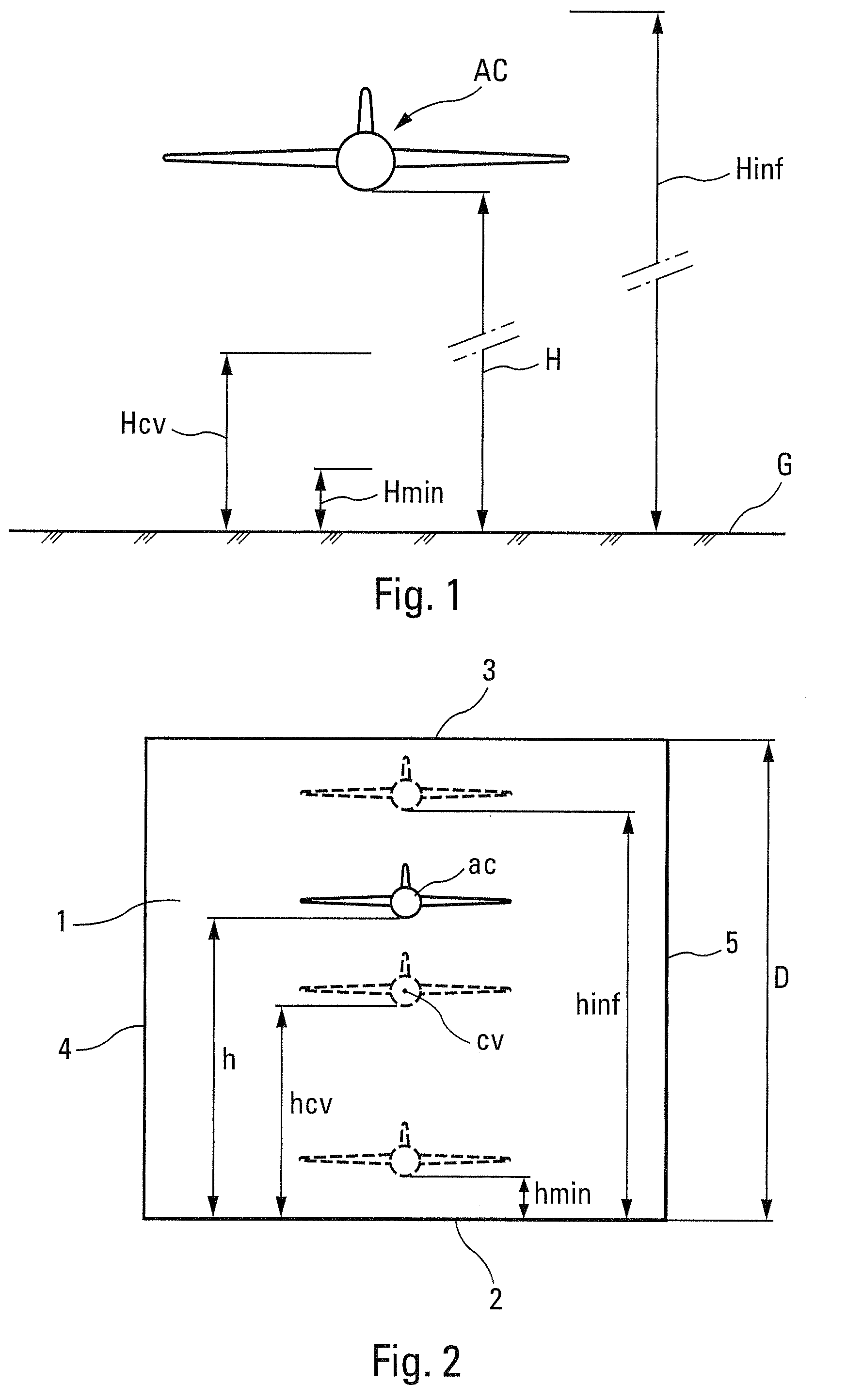
Hybrid method for estimating the ground effect on an aircraft
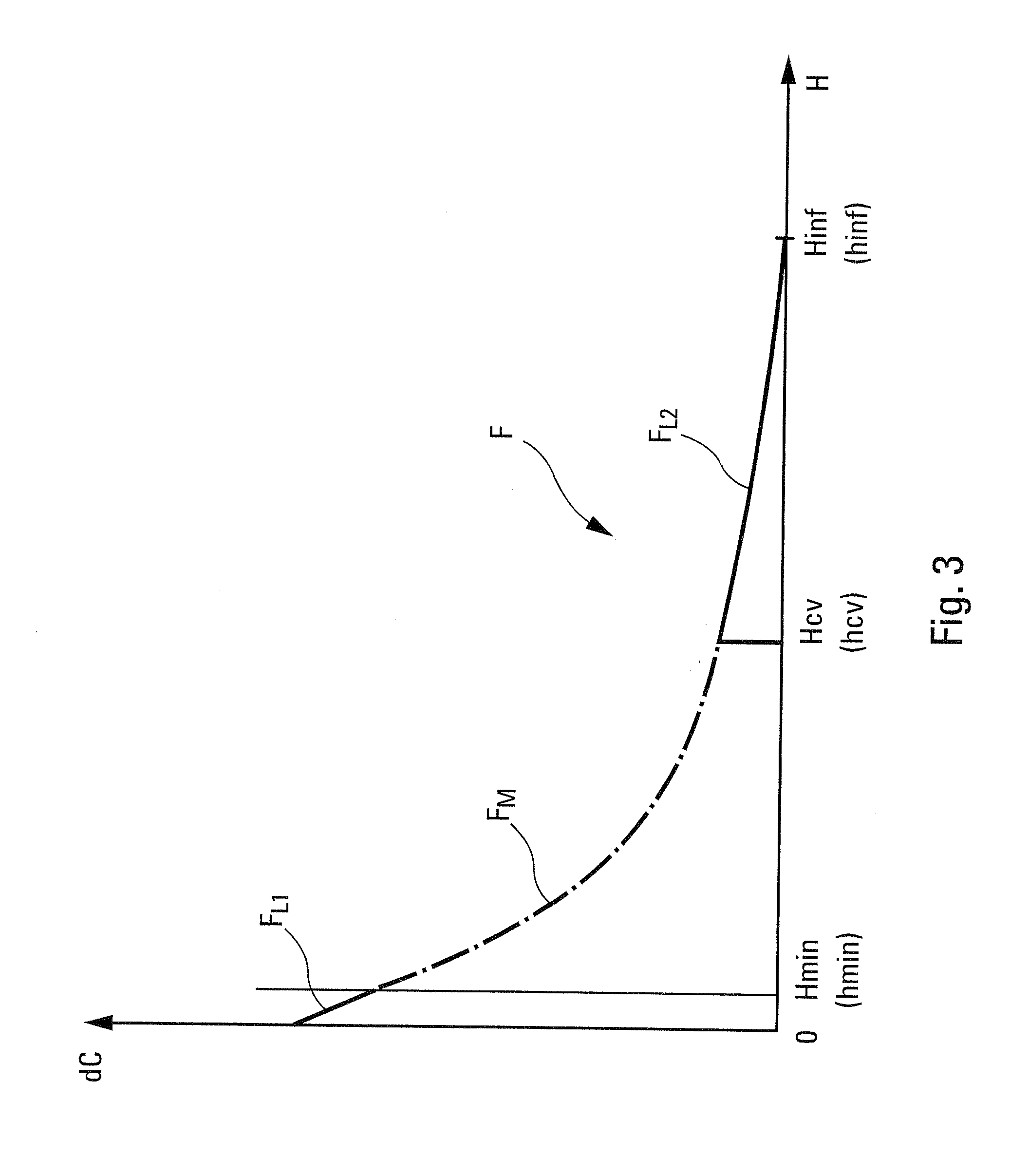
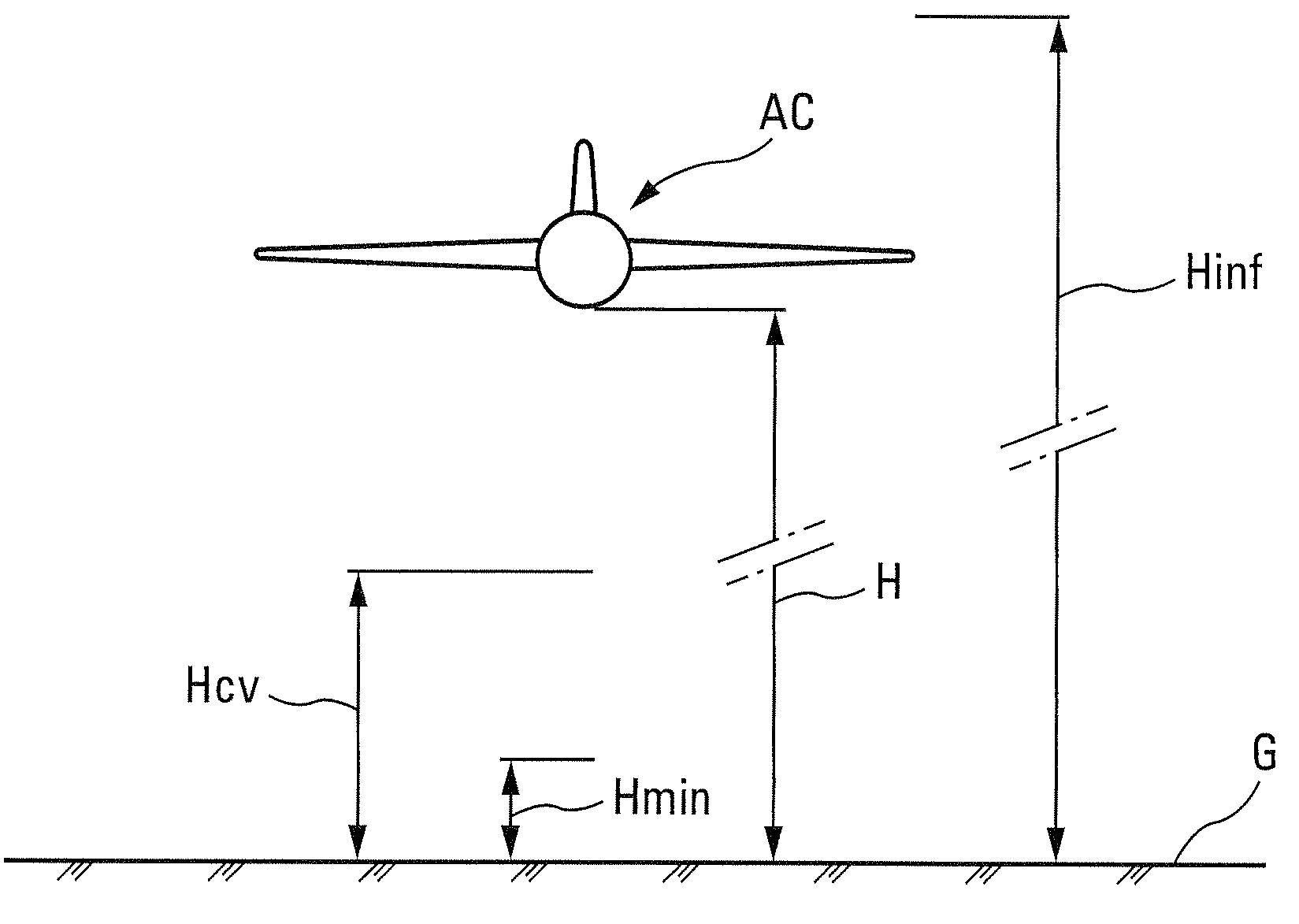
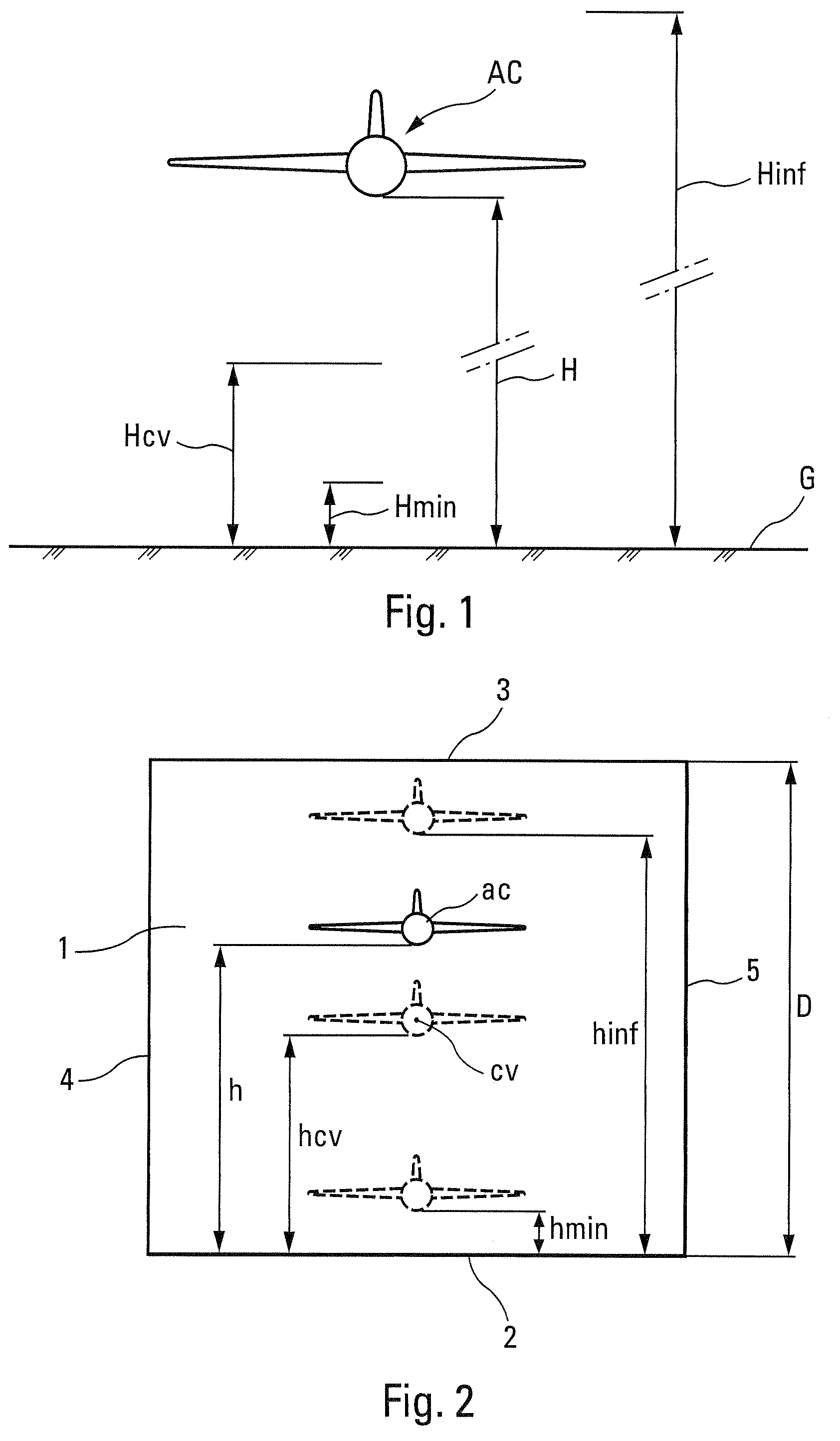
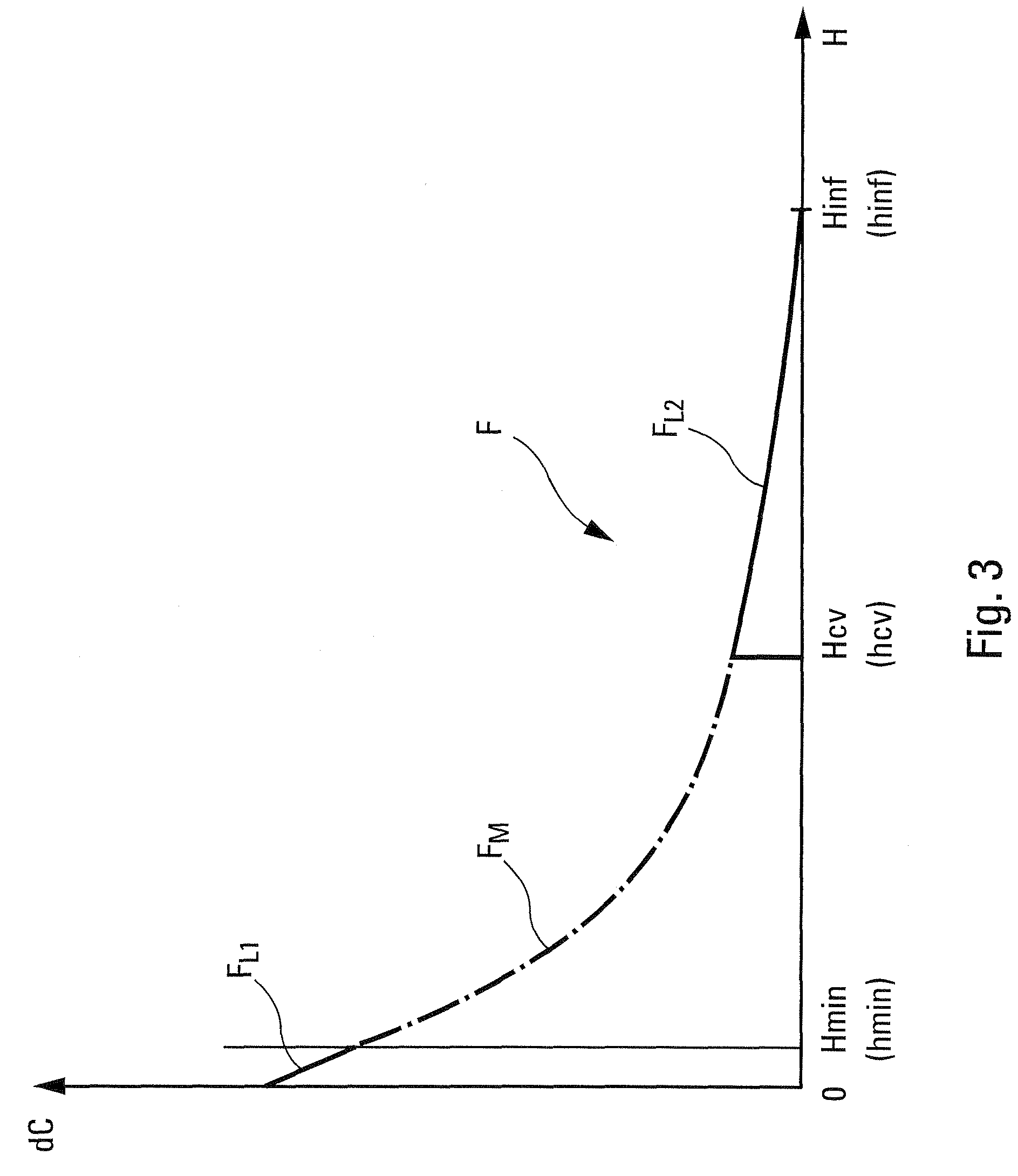
A method for assessing the aerodynamic ground effects on an aircraft. The method includes determining the variation of at least one aerodynamic coefficient of the aircraft as a function of the height for a range of heights extending from an aerodynamically infinite height to a zero height. In the method, (i) the range of heights is subdivided into at least two consecutive sets of heights; (ii) for one of the sets of heights, the variation of said aerodynamic coefficient is determined by wind tunnel tests using a model of the aircraft; and (iii) for the other of the sets of heights, the variation of said aerodynamic coefficient is determined by digital simulation reproducing by computation the physical reality of the air flow around said aircraft.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Streamline body and equipment for restraining vibration of enclosure structure and tower barrel hoisting method
ActiveCN107620680ASolve the damageSolve hidden dangersEngine fuctionsWind motor assemblyEngineeringFront edge
The invention discloses a streamline body and equipment for restraining vibration of an enclosure structure and a tower barrel hoisting method. The streamline body surrounds the enclosure structure and is provided with a streamline-shaped front edge. The front edge can face towards an upwind direction incoming flow, so that the upwind direction incoming flow forms a positive attack angle and / or anegative attack angle. According to the scheme, the streamline body surrounds the enclosure structure, when the upwind direction incoming flow flows around the enclosure structure to make contact withthe streamline body, the aerodynamic shape is changed, the aerodynamic coefficient C is decreased, and vibration is reduced; and the air flow direction and the path are changed, correlation of an upwind direction air flow around the streamline body is damaged, the consistency of the vortex shedding frequency of the streamline body and air flows in other positions is disrupted, thus the combined action of the streamline body and the air flows is weakened, vortex-induced vibration response during around-flow body shedding of the outer surface boundary layer of the enclosure structure is reducedor prevented, and namely, vortex-induced vibration of the enclosure structure is prevented.
Owner:BEIJING GOLDWIND SCI & CREATION WINDPOWER EQUIP CO LTD
Method for researching influence of double-cable spacing and icing on double-cable wake galloping
InactiveCN108052766AImprove reliabilityImprove applicabilityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCable stayedEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of bridges, and discloses a method for researching the influence of double-cable spacing and icing on double-cable wake galloping. The method includes thefollowing steps that a double-cable three dimensional model is established, and wind load is applied to the double-cable three dimensional model through a numerical simulation method; through a finiteelement solution method, a lift coefficient time-history curve and a resistance coefficient time-history curve of the double-cable three dimensional model, an aerodynamic coefficient curve of an omnidirectional-angle double-cable three dimensional model and a galloping force coefficient curve of the omnidirectional-angle double-cable three dimensional model are calculated, wherein the double-cable three dimensional model includes a first cable-spacing icing cable-stayed double-cable model, a second cable-spacing icing cable-stayed double-cable model, a third cable-spacing icing cable-stayed double-cable model and a second cable-spacing icing-free cable-stayed double-cable model. The invention provides a method for researching the influence of double-cable spacing and icing on double-cablewake galloping, and the result is high in applicability.
Owner:WUHAN OPTICS VALLEY BEIDOU HLDG GRP
Wind and rain vibration simulation experiment device for transmission conductor
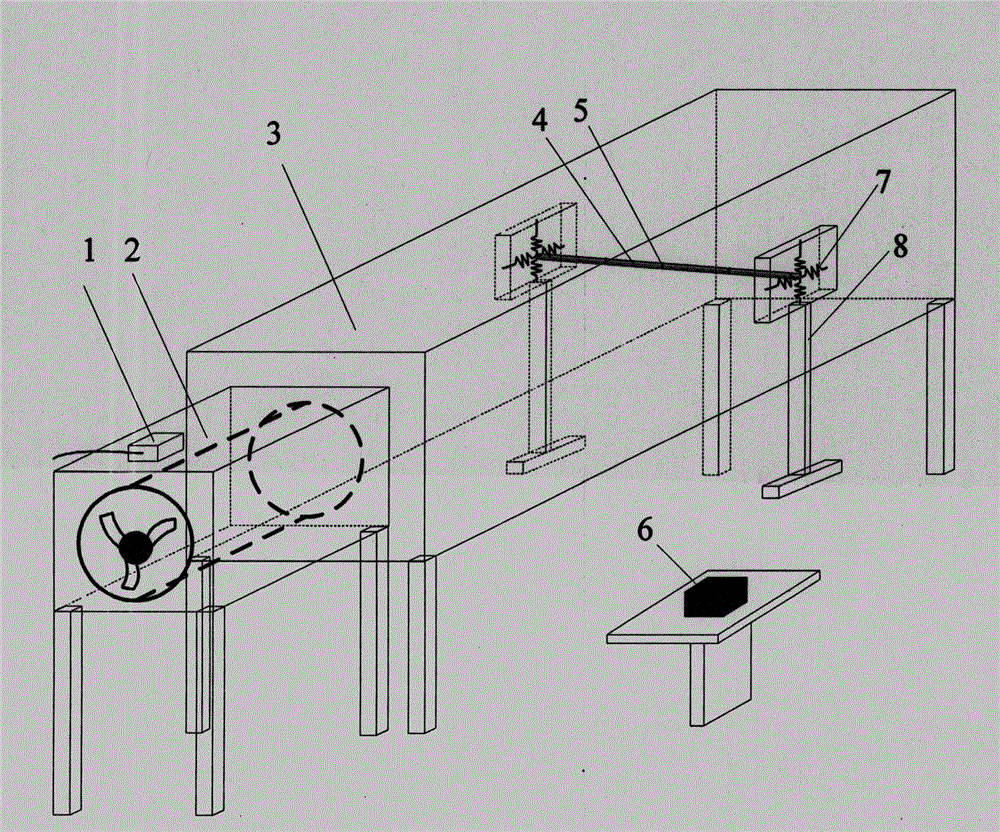
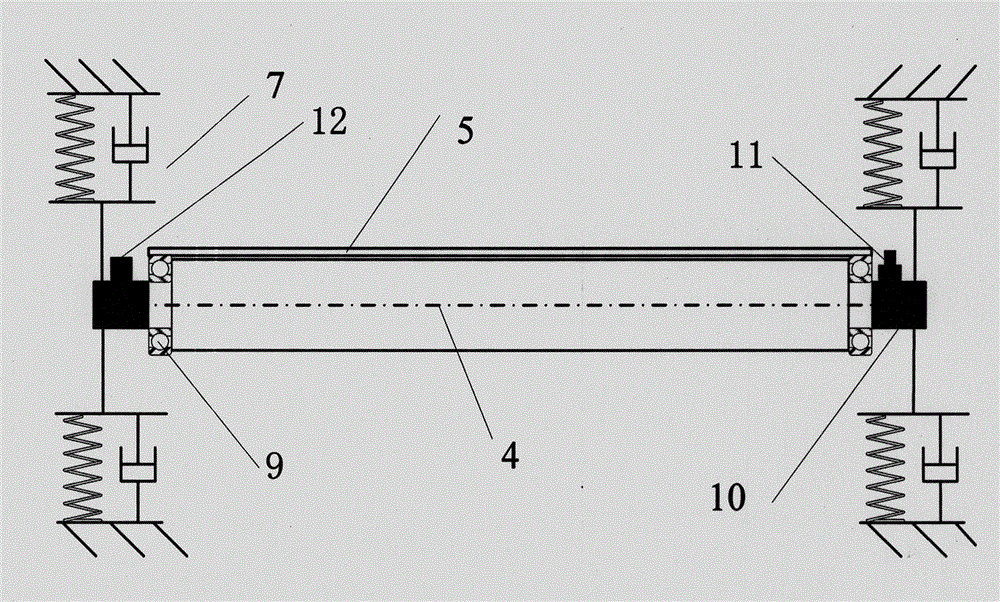
InactiveCN104599568ACompact structureAvoid affecting aerodynamic parametersEducational modelsWater sourceSprayer
The invention discloses a wind and rain vibration simulation experiment device for a transmission conductor. The device is used for researching wind and rain vibration possibly induced by the wind and rain coupling function of the transmission conductor and comprises a test bench body structure, a rainfall simulation device, a wind speed simulation system, a conductor frame structure and a conductor position adjusting and testing device. A sprayer of the rainfall simulation device can horizontally move along with a pipeline support to adjust the distance between the sprayer and an air outlet. A device water source comes from a water tank and is supplied by a side water pump. Rainfall simulated by the sprayer passes a diversion trench and then is recovered to a water tank, so that water is recycled. A conductor frame is arranged on two sides of a middle experiment area, has two height adjustment stages and comprises a support, a rough adjustment screw and a fine adjustment screw, the rough adjustment screw and the fine adjustment screw are arranged at the joint of the support and the base, and the transmission conductor is hung in a rectangular frame of the conductor frame through a spring. In addition, a pressure sensor, a displacement sensor, a speed sensor and an acceleration sensor are arranged at two ends of the transmission conductor respectively and used for measuring aerodynamic coefficient, vibration displacement, displacement speed and acceleration.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
A method for obtaining aerodynamic coefficients
PendingCN109492237ACost savingsSave time and costGeometric CADSustainable transportationRectangular coordinatesFlight velocity
A method for obtaining aerodynamic coefficients includes obtaining aerodynamic coefficients of an aircraft; solving to obtain the aerodynamic parameters; calculating the angle of attack alpha and theangle of sideslip beta; and obtaining the interpolation rectangular coordinates aerodynamic coefficients. The aerodynamic coefficients of the polar coordinate system are obtained. Obtaining acceleration and angular acceleration of the aircraft; the flight velocity (as shown in the description) and attitude angle of the aircraft at the next time are obtained; and calculating the aerodynamic coefficients of the vehicle at the next time. The method of the invention saves the development cost and time cost of CFD calculation, wind tunnel test.
Owner:JIANGXI HONGDU AVIATION IND GRP
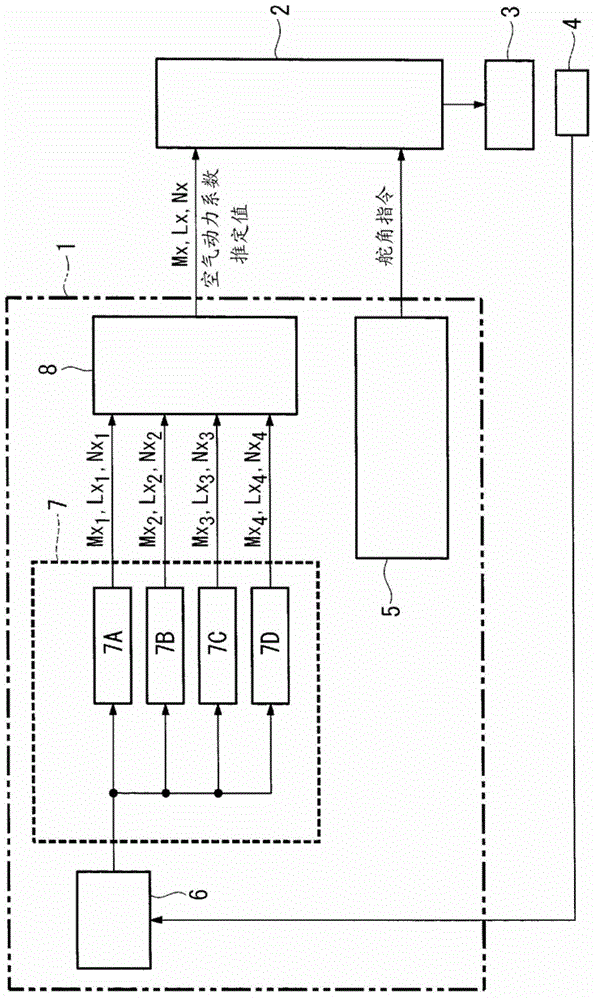
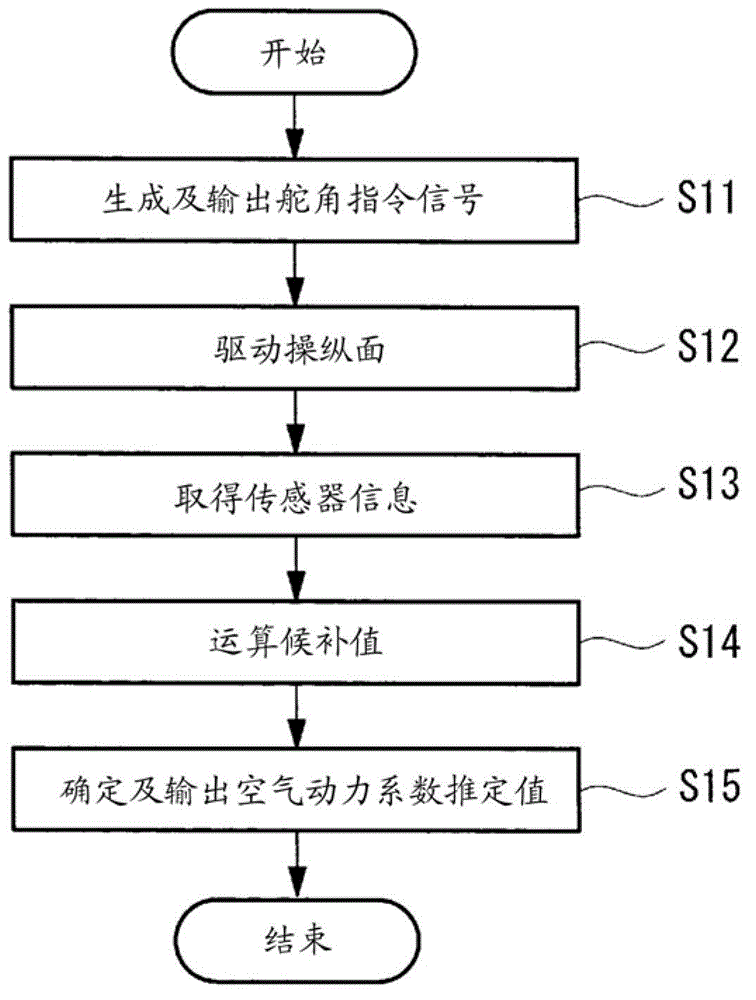
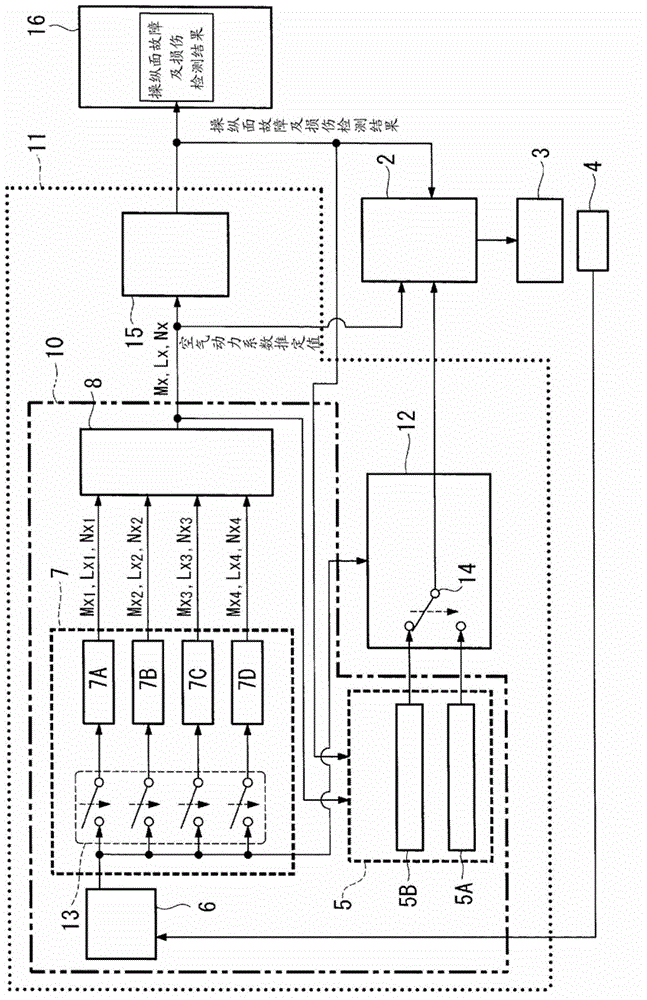
Aerodynamic coefficient estimation device and control surface failure/damage detection device
InactiveCN102753435AReduce the burden onAircraft health monitoring devicesAircraft controlEstimation methodsEngineering
The disclosed device can compute a high-reliability estimate of aerodynamic coefficients, allowing accurate detection of failure of or damage to control surfaces while reducing the burden on passengers. Said device is provided with: a control-angle command-signal generation means (5) that generates a control-angle command signal for estimating aerodynamic coefficients that indicate the aerodynamic characteristics of an airframe; a kinetic state quantity acquisition means (6) that acquires kinetic state quantities for the airframe, resulting from control surfaces provided on the airframe being driven on the basis of the control-angle command signal; a candidate-value computation means (7) that uses at least two different estimation methods to compute, from the kinetic state quantities, candidate values for estimating the aforementioned aerodynamic coefficients; and an aerodynamic coefficient estimate determination means (8) that determines aerodynamic coefficient estimates on the basis of the candidate values.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Hybrid method for estimating the ground effect on an aircraft
ActiveUS7926340B2Reduce weightAerodynamic testingIndication/recording movementPhysical realityEngineering
A method for assessing the aerodynamic ground effects on an aircraft. The method includes determining the variation of at least one aerodynamic coefficient of the aircraft as a function of the height for a range of heights extending from an aerodynamically infinite height to a zero height. In the method, (i) the range of heights is subdivided into at least two consecutive sets of heights; (ii) for one of the sets of heights, the variation of said aerodynamic coefficient is determined by wind tunnel tests using a model of the aircraft; and (iii) for the other of the sets of heights, the variation of said aerodynamic coefficient is determined by digital simulation reproducing by computation the physical reality of the air flow around said aircraft.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Simulation method for determining aerodynamic coefficients of an aircraft
ActiveUS9317633B2Detailed analysisIncrease familiarityGeometric CADAerodynamic testingComputer methodsComputer science
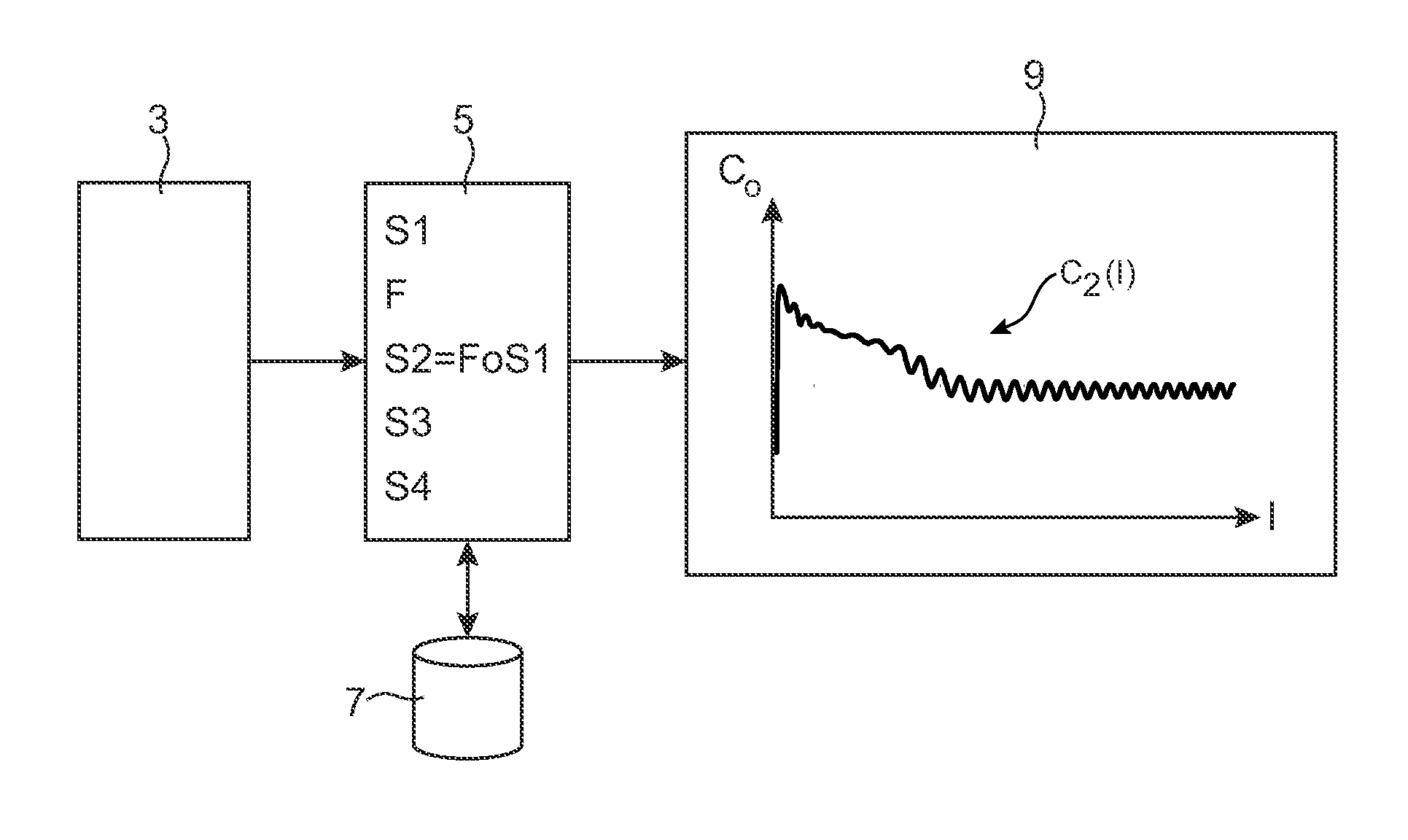
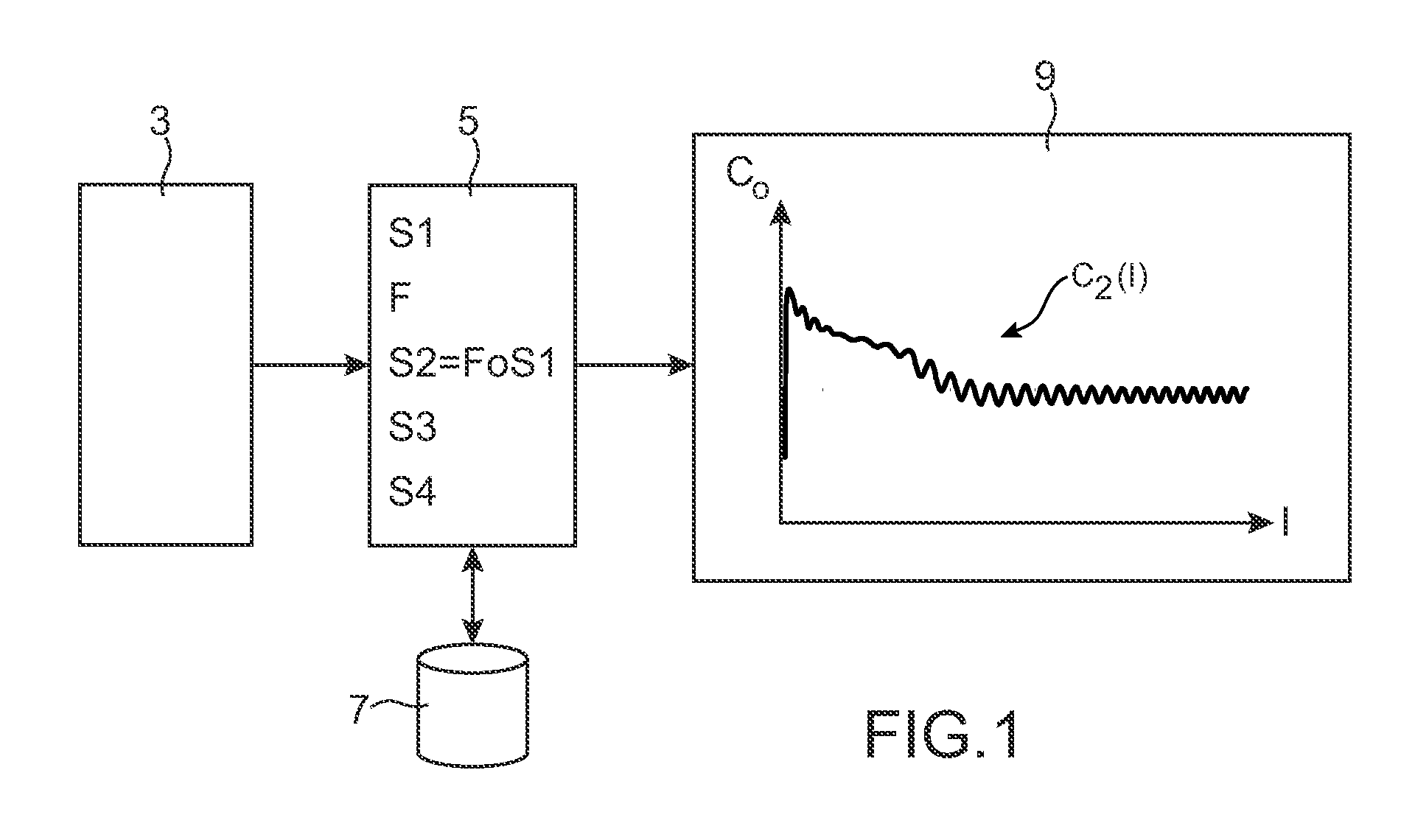
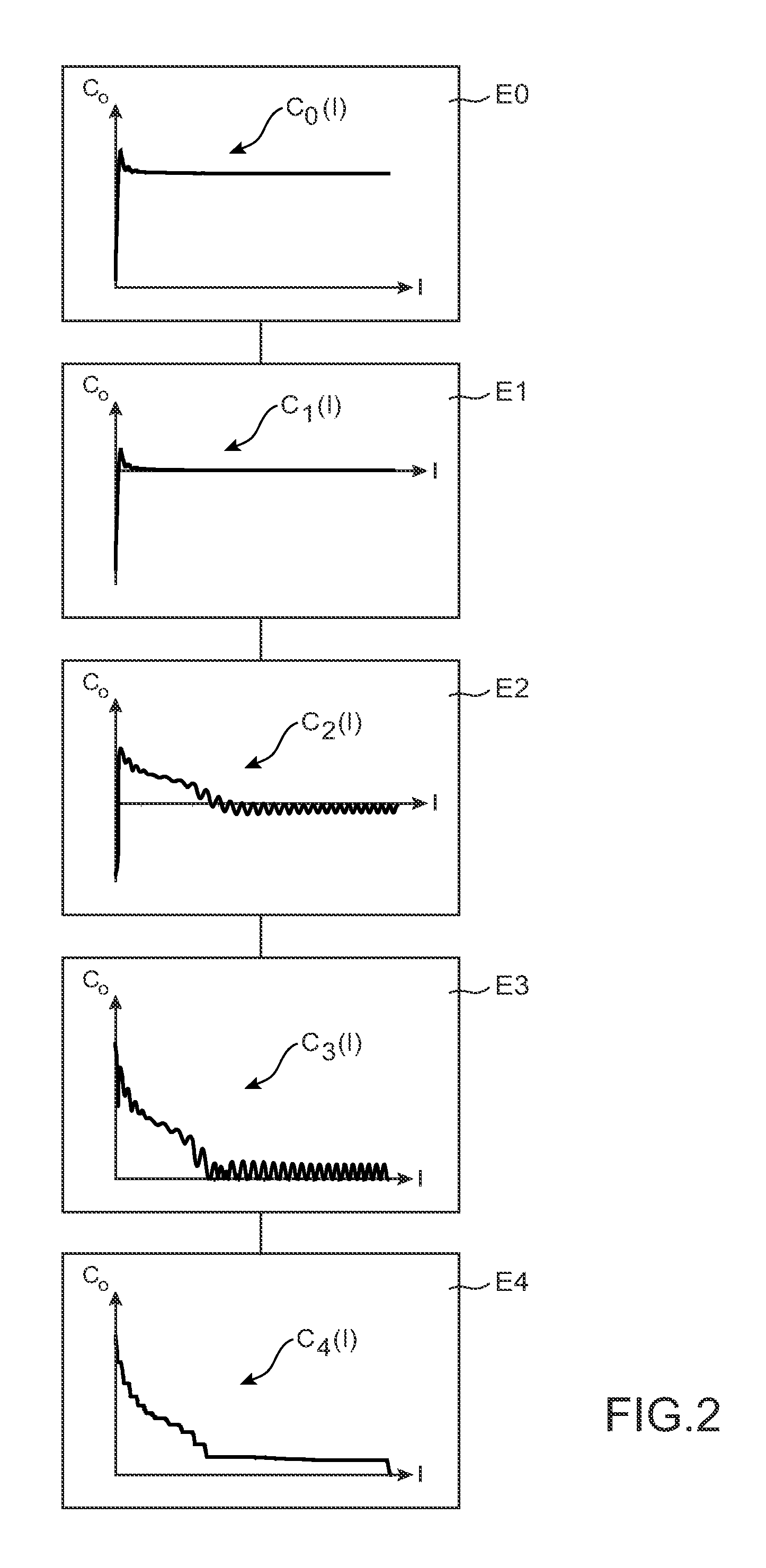
A computer method of simulating a fluid flow in an aircraft environment to determine at least one aerodynamic coefficient, comprising obtaining a first series of values of the aerodynamic coefficient. The method also includes defining a criterion for convergence of said aerodynamic coefficient, selecting a determined set of terms belonging to said first series, defining a monotonic function configured to make a relatively expanding transformation in said determined set relative to the complement of said set, applying said monotonic function on said first series to form a second series of values of the aerodynamic coefficient, determining said aerodynamic coefficient by plotting a variation curve representative of said second series of values of the aerodynamic coefficient, and displaying said variation curve including an intrinsic zoom of the convergence zone of said aerodynamic coefficient.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
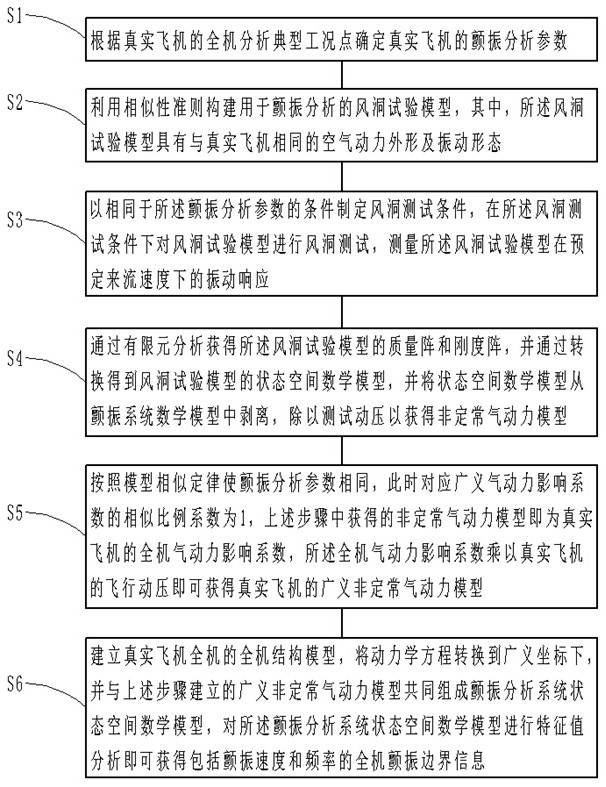
Aerodynamic modeling and full-aircraft flutter analysis method based on wind tunnel test response
ActiveCN111950079AImprove economyConfidence in Flutter Analysis ResultsGeometric CADSustainable transportationClassical mechanicsTest response
The invention provides an aerodynamic modeling and full-aircraft flutter analysis method based on wind tunnel test response, and belongs to the technical field of aircraft design. According to the method, an unsteady aerodynamic model is identified through wind tunnel test data, the unsteady aerodynamic model is obtained, an unsteady aerodynamic coefficient of a scaling wind tunnel model is converted to the full-aircraft model through the similarity law, and flutter analysis is made on the full-aircraft model by using a converted aerodynamic model so as to obtain a flutter boundary. Compared with flutter analysis by using flight test data in the prior art, aerodynamic modeling is performed by using the response data of the wind tunnel test model, and since sensors are relatively easy to embed in the wind tunnel test, more effective data can be obtained based on the test data of the wind tunnel, the aerodynamic model is more accurate, and the reliability of the aerodynamic model is improved. Thus, the flutter analysis result is more credible, especially aerodynamic modeling of a transonic interval.
Owner:CHINA AIRPLANT STRENGTH RES INST
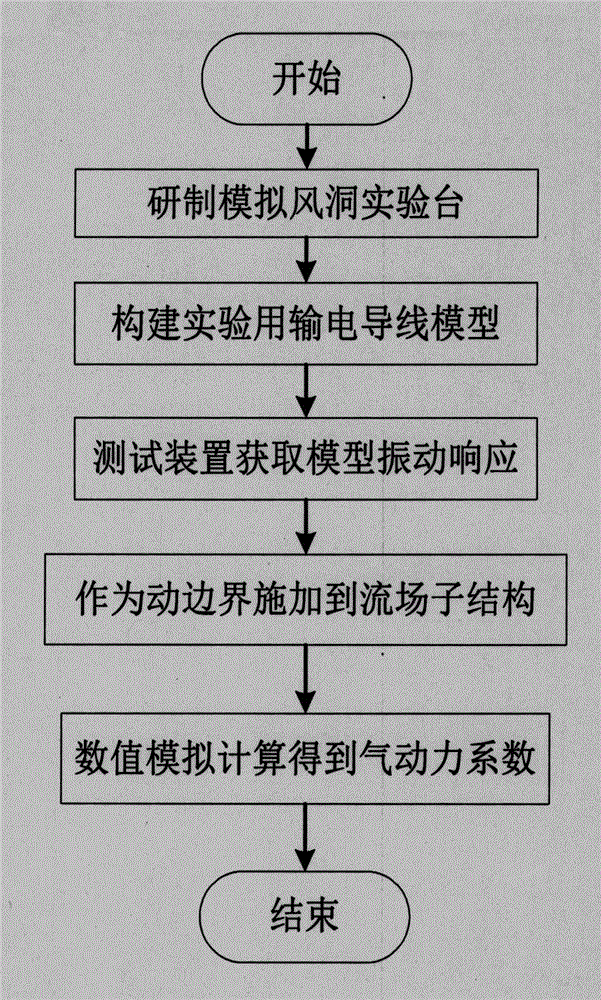
Method for calculating unsteady aerodynamic coefficient of wind and rain induced vibration of power transmission line
InactiveCN104964808AImprove computing efficiencyHigh precisionAerodynamic testingVibration amplitudeEngineering
The invention provides a method for calculating an unsteady aerodynamic coefficient of wind and rain induced vibration of a power transmission line, that is, an experiment and CFD numerical simulation hybrid substructure method. The method comprises the steps of (1) developing a simulation wind tunnel experiment bench; (2) constructing an experimental power transmission line model; (3) acquiring the amplitude and the frequency inside and outside the surface of the model by a measuring device; (4) using model vibration response acquired by the experiment to act a moving boundary and applying the moving boundary to a CFD flow field substructure; and (5) only carrying out CFD numerical simulation calculation on a circumferential flow field of the moving boundary so as to acquire the unsteady aerodynamic coefficient of the line vibration. The method provided by the invention does not need to carry out finite element calculation or data exchange of the structure, so that the calculation efficiency of the wind-induced vibration of the structure can be greatly improved; and meanwhile, the vibration of the structure is acquired by a physical test, so that a numerical calculation result of circumferential flow field characteristics is high in precision.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com