Patents
Literature
3949 results about "Missile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
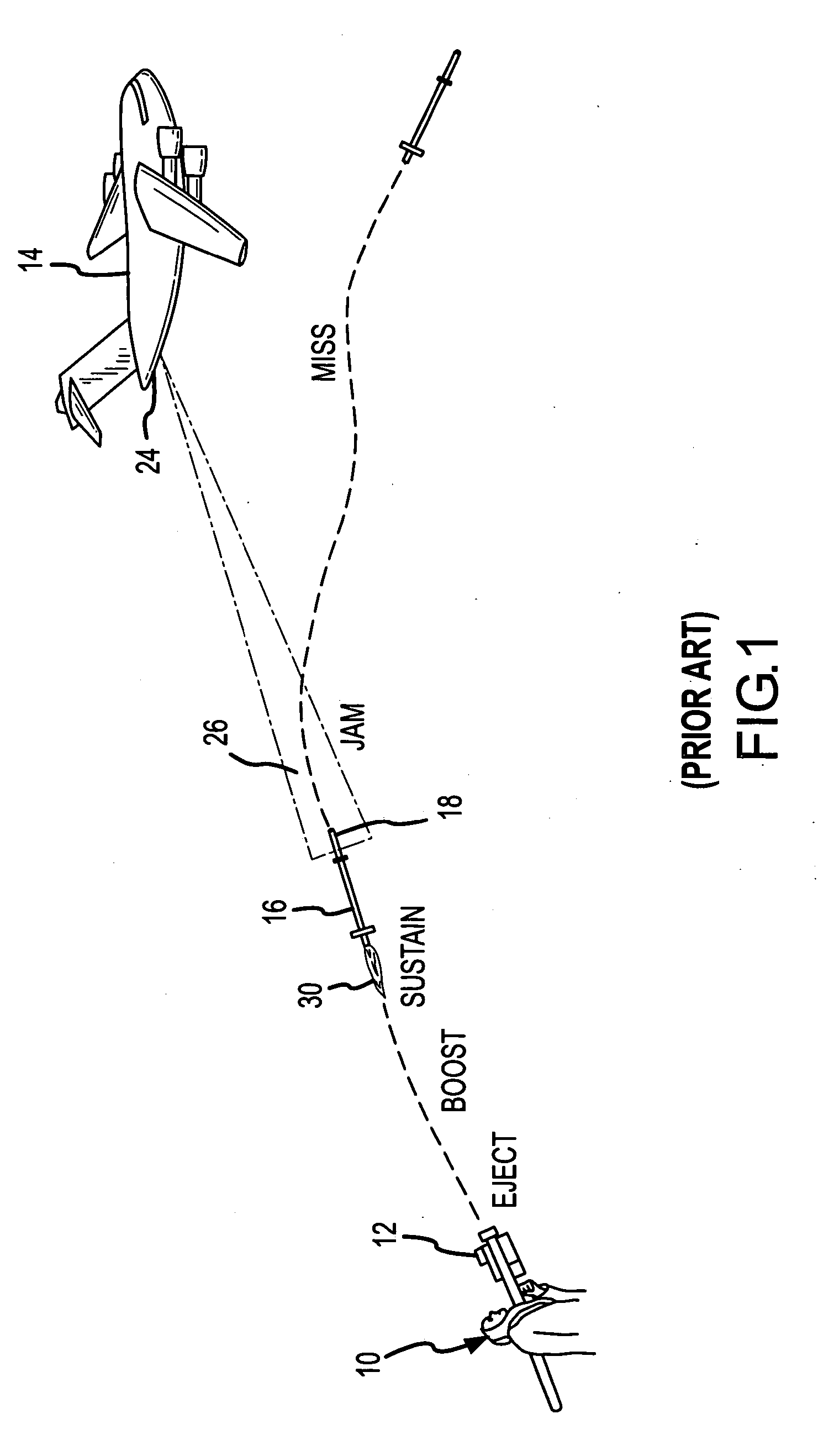
In military language, a missile, also known as a guided missile, is a guided self-propelled flying weapon usually propelled by a jet engine or rocket motor. This is in contrast to an unguided self-propelled flying munition, referred to as a rocket (although these too can also be guided). Missiles have four system components: targeting or missile guidance, flight system, engine, and warhead. Missiles come in types adapted for different purposes: surface-to-surface and air-to-surface missiles (ballistic, cruise, anti-ship, anti-tank, etc.), surface-to-air missiles (and anti-ballistic), air-to-air missiles, and anti-satellite weapons. Non-self-propelled airborne explosive devices are generally referred to as shells and usually have a shorter range than missiles. In ordinary language the word means an object which can be thrown, shot, or propelled toward a target.
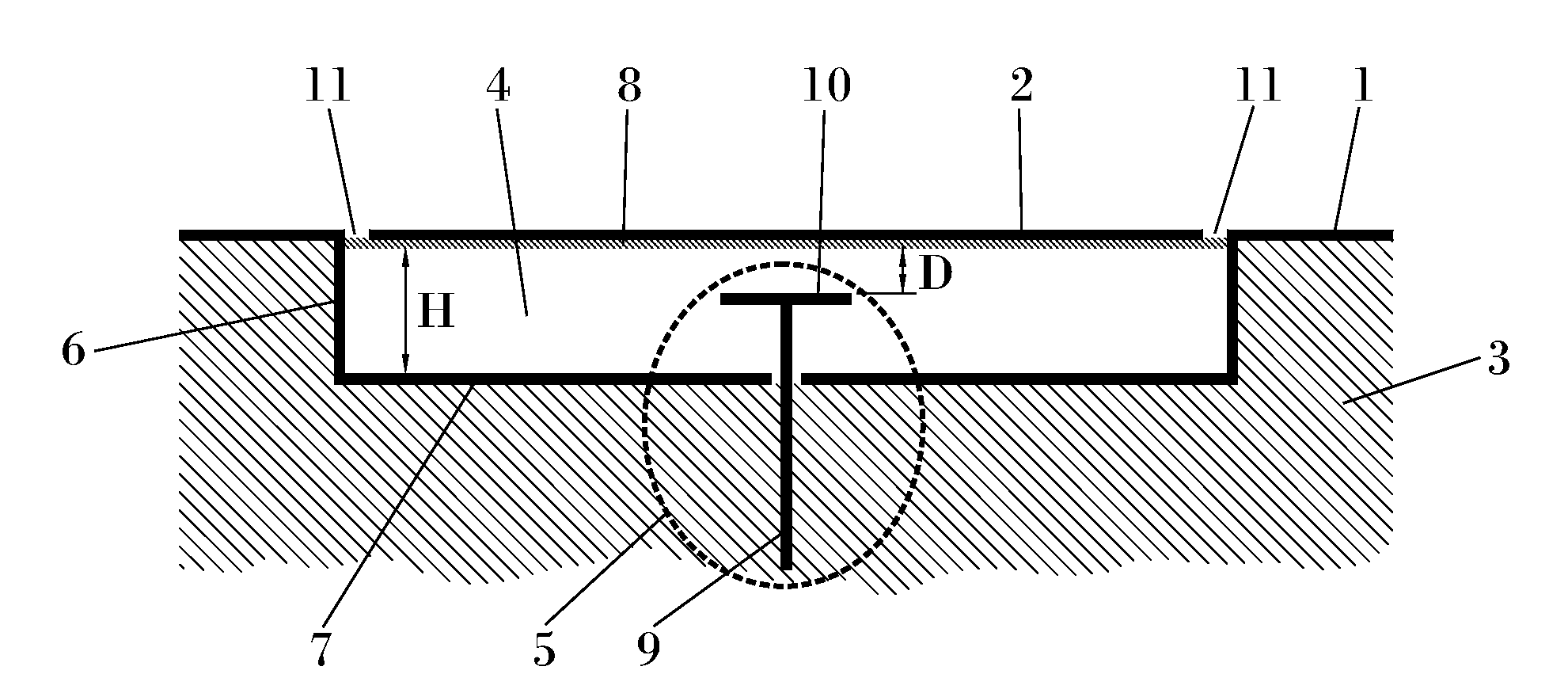
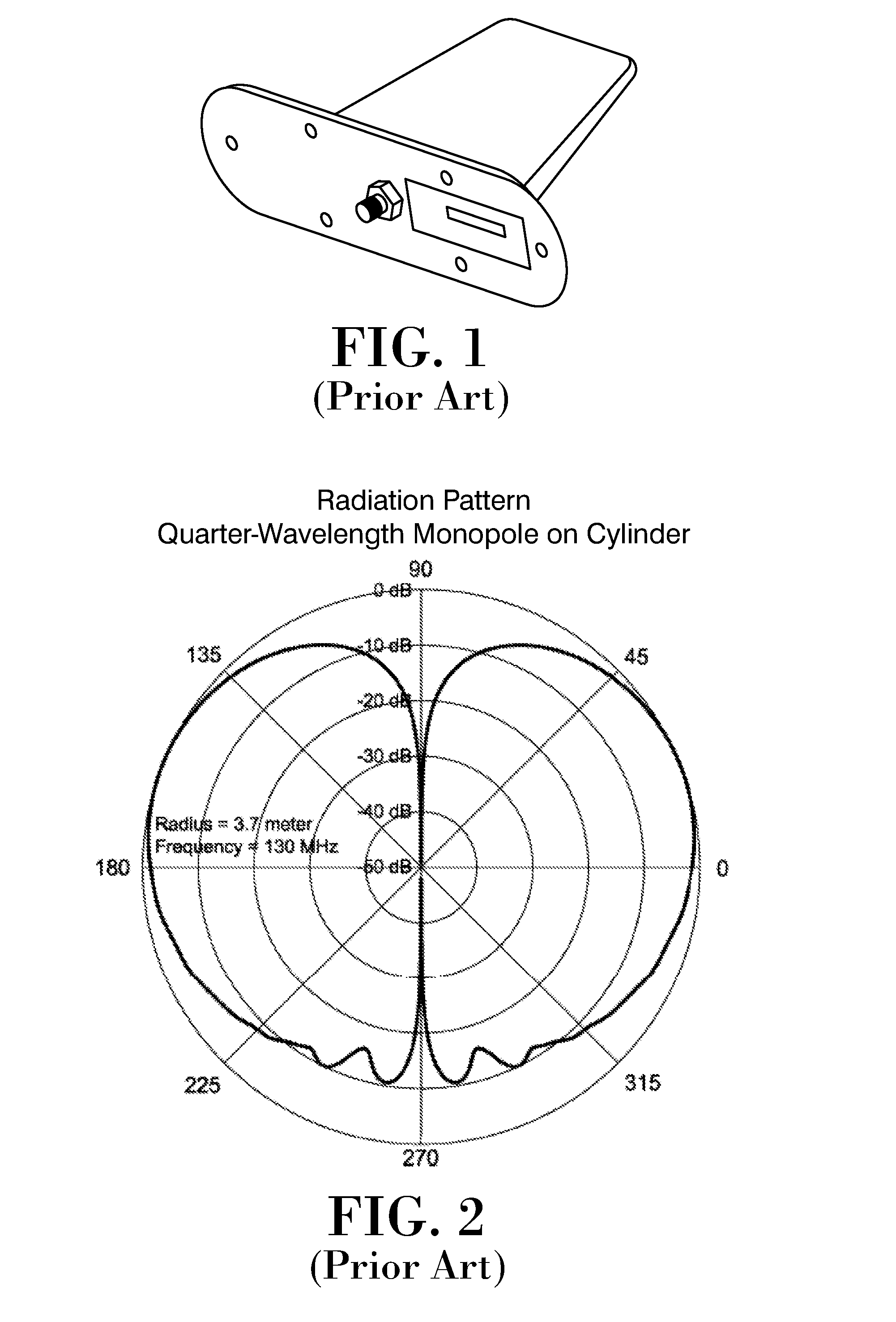
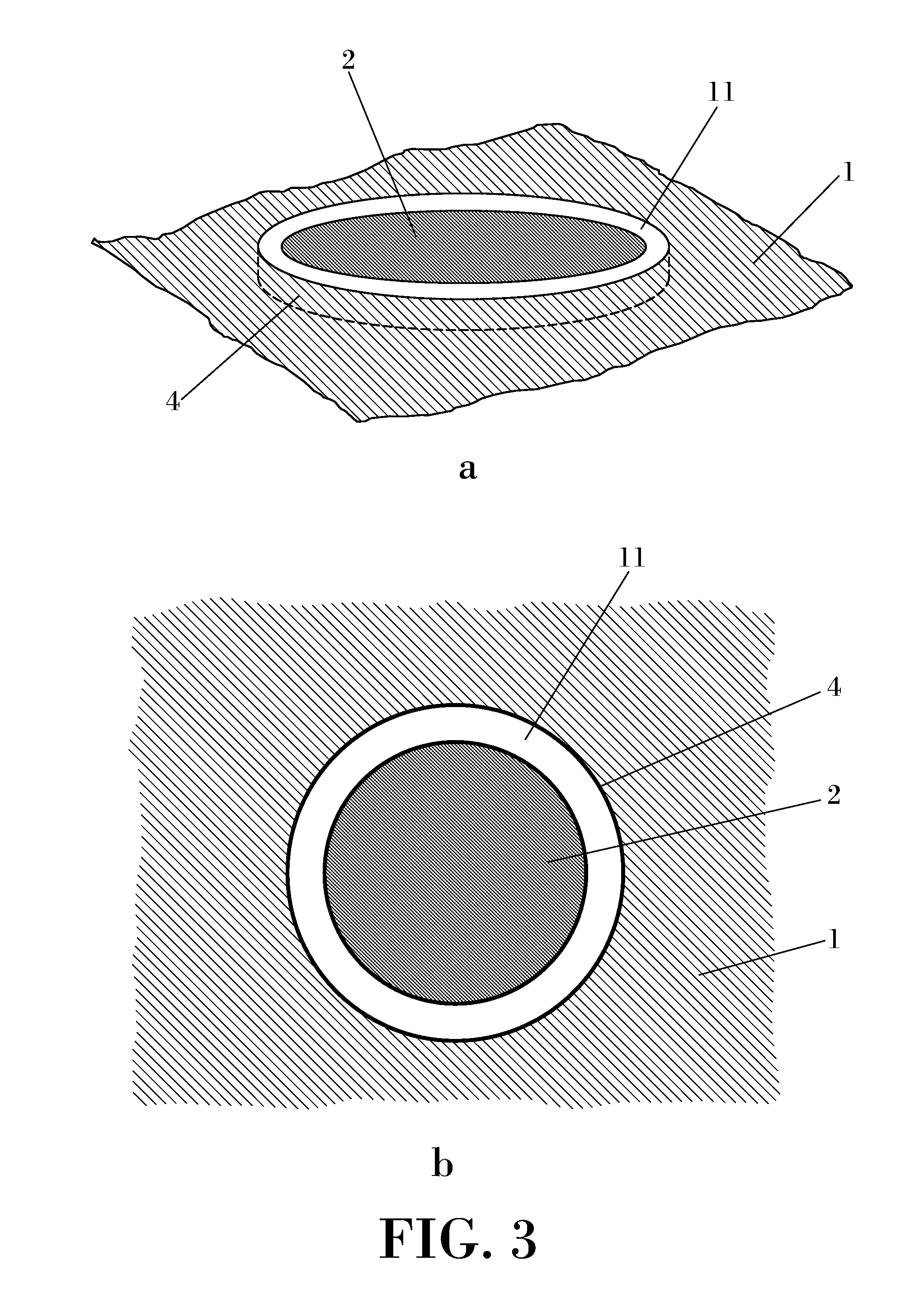
Flush-mounted low-profile resonant hole antenna
ActiveUS20120038525A1Low profileAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating element housingsClassical mechanicsConductive materials
The invention relates to a flush-mounted aircraft, UAV or missile antenna system, which is an integral part of the fuselage (3) of an aircraft, UAV or missile. The antenna system comprises a surface (3) made of a conductive material and a resonant recess (4) formed in said conducting surface, wherein said recess is conformed to provide a resonant behaviour in a selected operating frequency, the antenna system further comprising a radiating element (2) located within said recess and a feeding element (5) within said recess coupled to said radiating element.
Owner:ADVANCED AUTOMOTIVE ANTENNAS
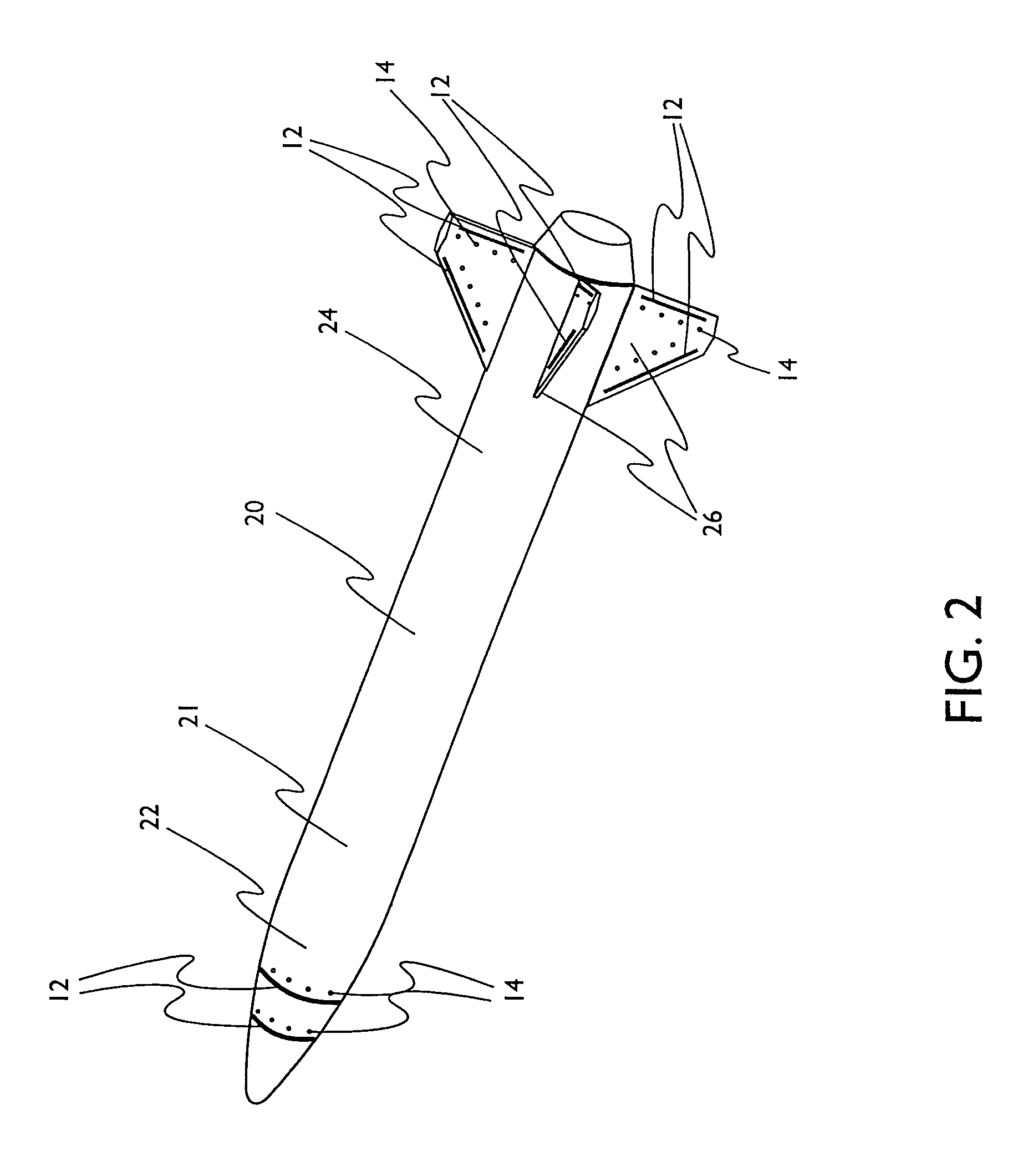
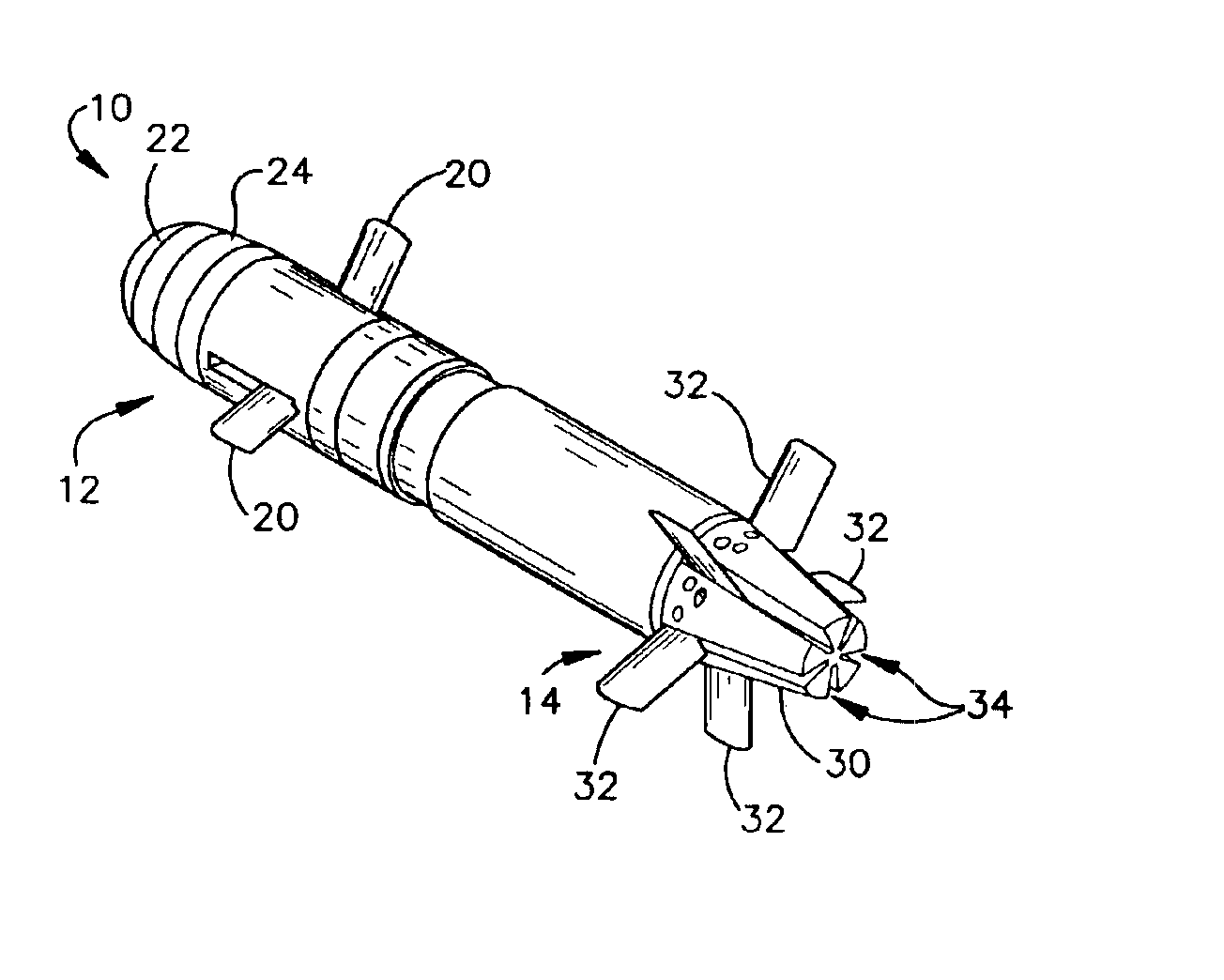
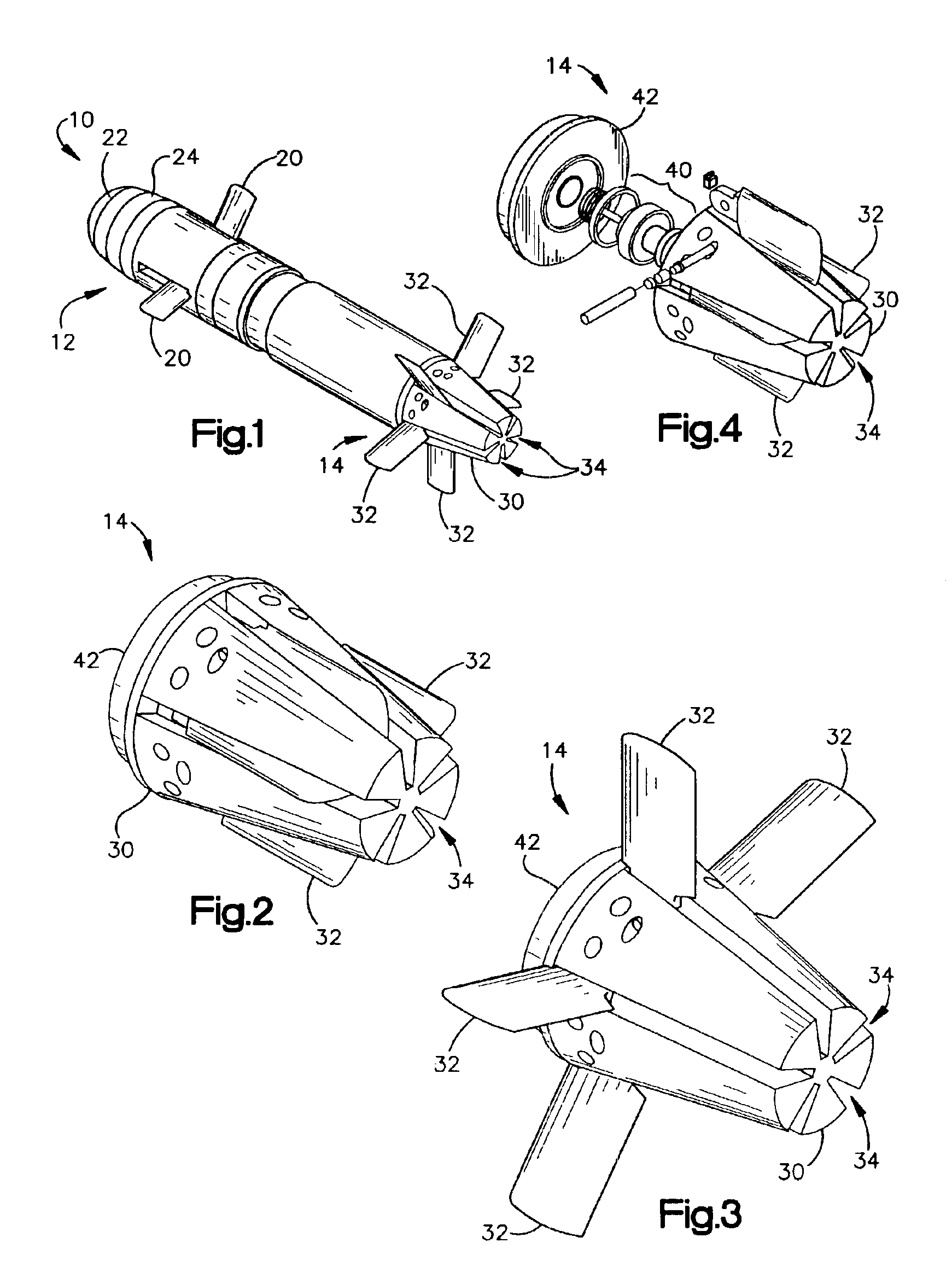
Apparatus and methods for variable sweep body conformal wing with application to projectiles, missiles, and unmanned air vehicles
InactiveUS6923404B1Improve aerodynamic efficiencyImprove aerodynamic performanceAircraft stabilisationUnmanned aerial vehiclesBody axisUncrewed vehicle
An unmanned air vehicle (“UAV”) apparatus is configured to have a body and a body-conformal wing. The body-conformal wing is configured to variably sweep from a closed position to a fully deployed position. In the closed position, the body-conformal wing span is aligned with the body axis and in the fully deployed position the body-conformal wing span is perpendicular to the axial direction of the body. Delivery of the UAV comprises the steps of: positioning the span of a body conformal wing in alignment with the axis of the body of the UAV; initiating the flight of the UAV; and adjusting the sweep angle of the body-conformal wing as a function of the current speed, altitude, or attack angle of the UAV, with the adjustment starting at a 0 degree position and varying between a closed position and a fully deployed position. The UAV also has a control mechanism configured to variably adjust the sweep of the body-conformal wing to achieve a high lift over drag ratio through out the flight path of the UAV.
Owner:ZONA TECH
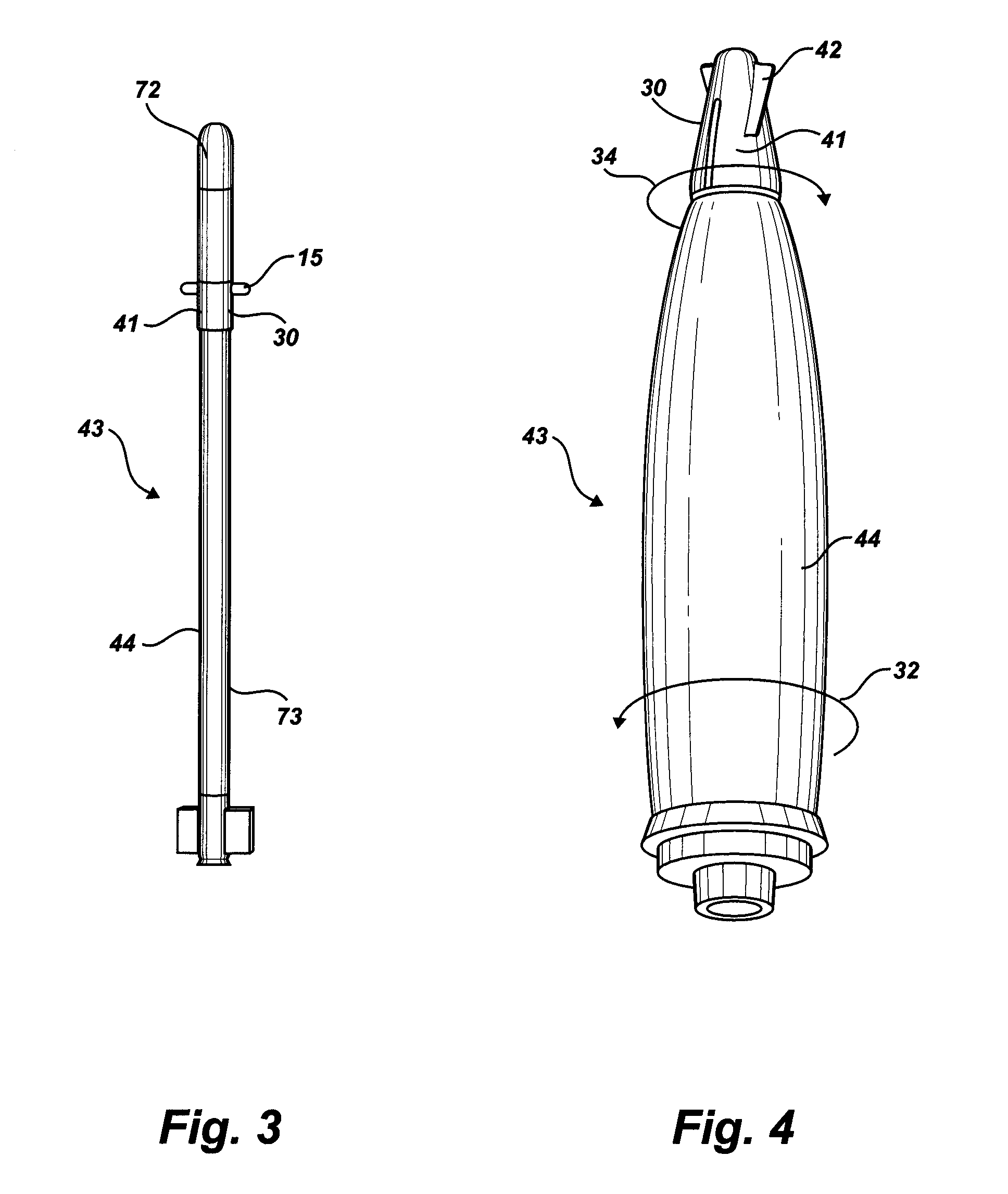
Cover ejection and fin deployment system for a gun-launched projectile
InactiveUS6880780B1Control rateSufficient velocityWing adjustmentsSelf-propelled projectilesActuatorCam
A fin cover release and deployment system designed for high G forces of gun-launched missiles. In one embodiment, a pyrotechnic actuator drives actuator arms to first release and eject the fin slot covers, followed by deployment of the fins radially outward to the steering position. Following complete ejection of the covers, the fins are driven outwardly by cam surfaces along the latch arms, followed by a spring and wedge mechanism installed interiorly of the fin steering shaft to lock the fins in the fully deployed state. In another embodiment, a motor and rotating threaded shaft replace the pyrotechnic actuator.
Owner:GEN DYNAMICS ORDNANCE & TACTICAL SYST +1
Music teaching device and method
InactiveUS7030307B2Simple technologyEasy to FeedbackElectrophonic musical instrumentsMusicTime rangeDisplay device
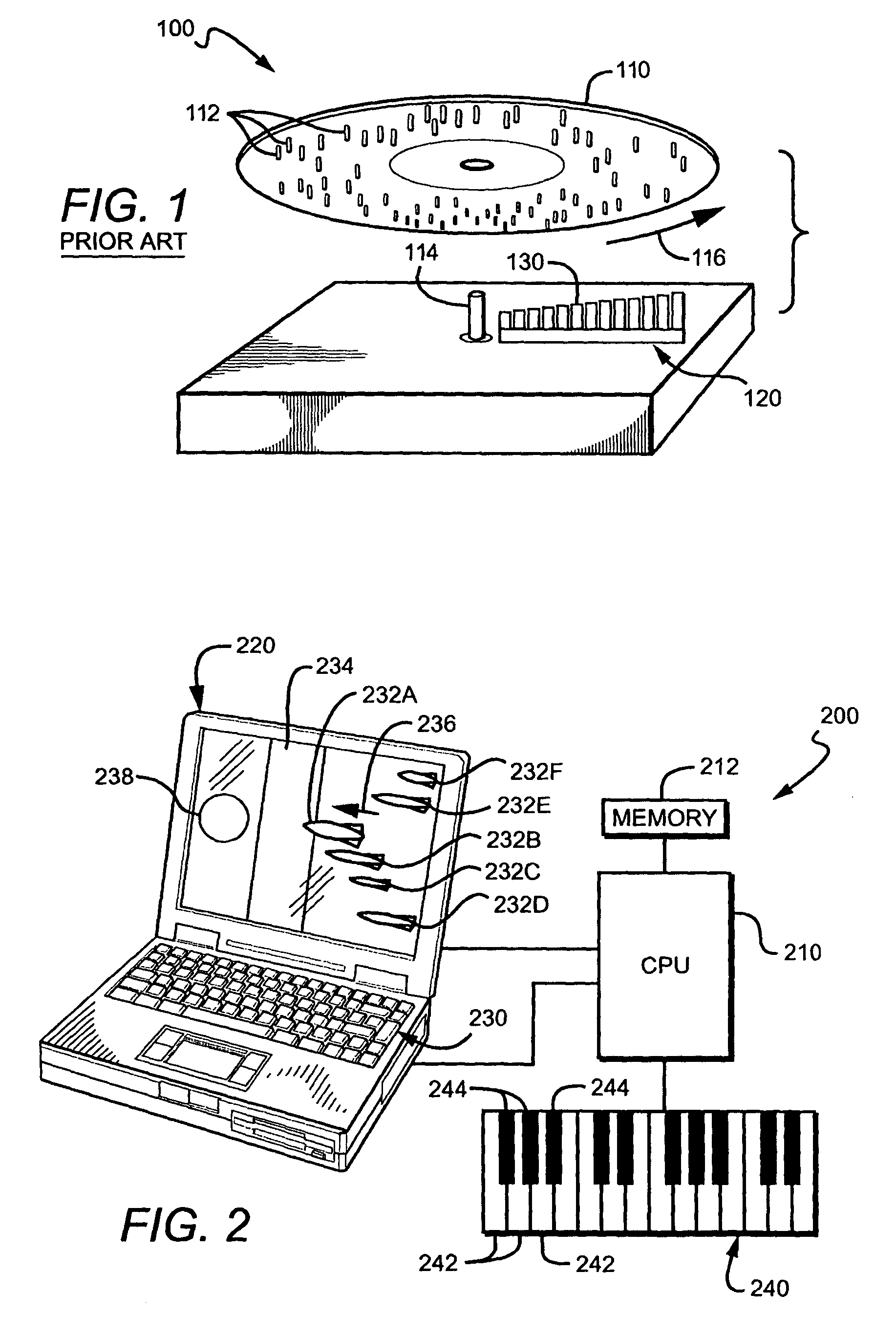
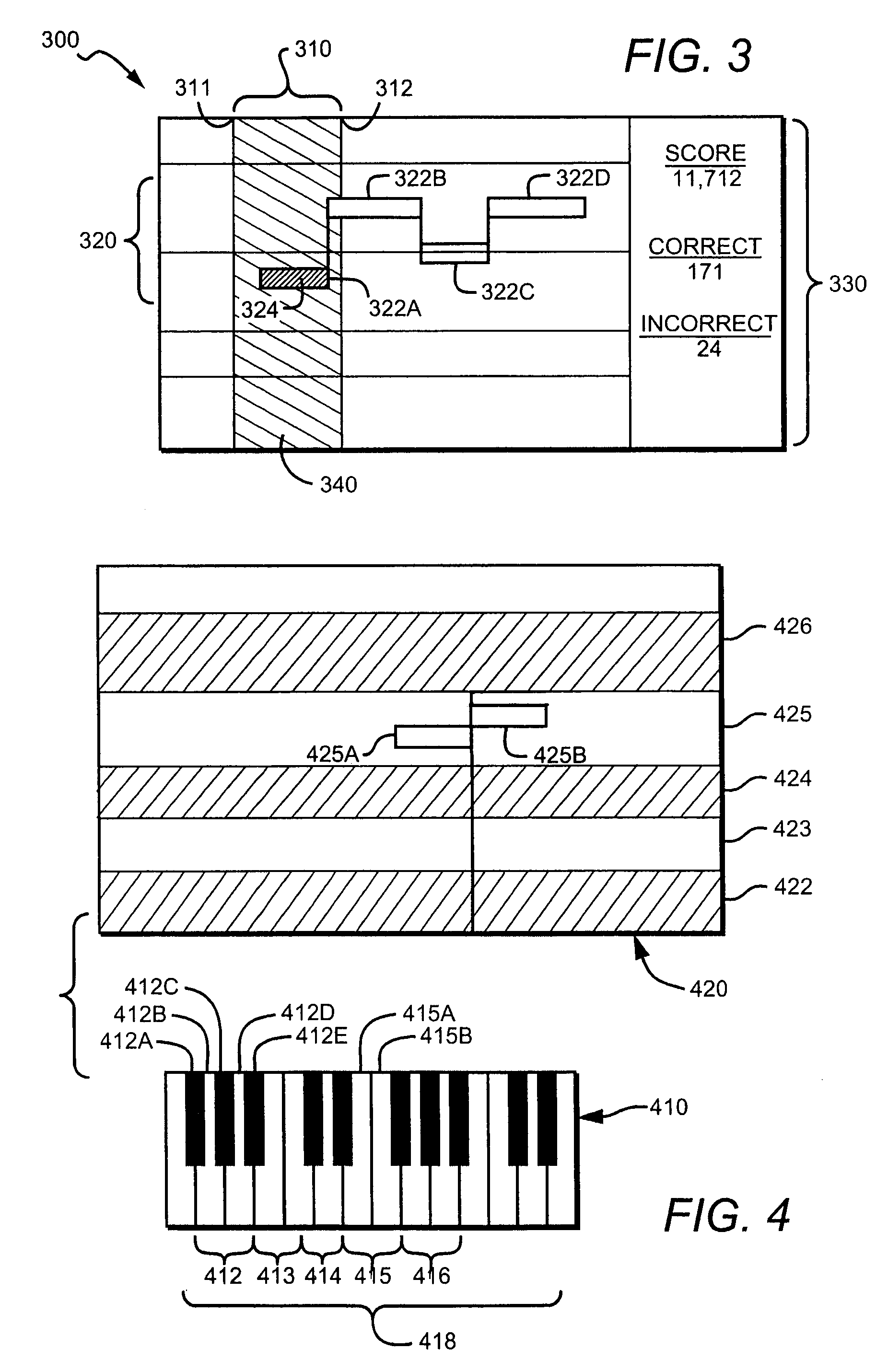
Methods and apparatus are provided that help users learn to play one or more instruments by employing simplified note recognition techniques, improved feedback, and a simplified keyboard tablature. In one aspect, users are encouraged to play specified notes within a specified time frame. The pitch and duration can be represented in any suitable manner, but are advantageously displayed together as a single icon (232A–232F). Preferably, the icon has an elongated shape in which the horizontal length correlates with duration of the note, and its vertical position on a display correlates with a pitch of the note. Notes can thus be represented by elongated lines, bars, ellipses, or even missiles or arrows. In another aspect, an improved musical tablature effectively clusters juxtaposed black keys (412A, 412C, 412E) and white keys (412B, 412D) on a display for easier visualization.
Owner:WEDEL DOUGLAS
High-resolution polarization-sensitive imaging sensors
An apparatus and method to determine the surface orientation of objects in a field of view is provided by utilizing an array of polarizers and a means for microscanning an image of the objects over the polarizer array. In the preferred embodiment, a sequence of three image frames is captured using a focal plane array of photodetectors. Between frames the image is displaced by a distance equal to a polarizer array element. By combining the signals recorded in the three image frames, the intensity, percent of linear polarization, and angle of the polarization plane can be determined for radiation from each point on the object. The intensity can be used to determine the temperature at a corresponding point on the object. The percent of linear polarization and angle of the polarization plane can be used to determine the surface orientation at a corresponding point on the object. Surface orientation data from different points on the object can be combined to determine the object's shape and pose. Images of the Stokes parameters can be captured and viewed at video frequency. In an alternative embodiment, multi-spectral images can be captured for objects with point source resolution. Potential applications are in robotic vision, machine vision, computer vision, remote sensing, and infrared missile seekers. Other applications are detection and recognition of objects, automatic object recognition, and surveillance. This method of sensing is potentially useful in autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance systems in automobiles and automated manufacturing and quality control systems.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
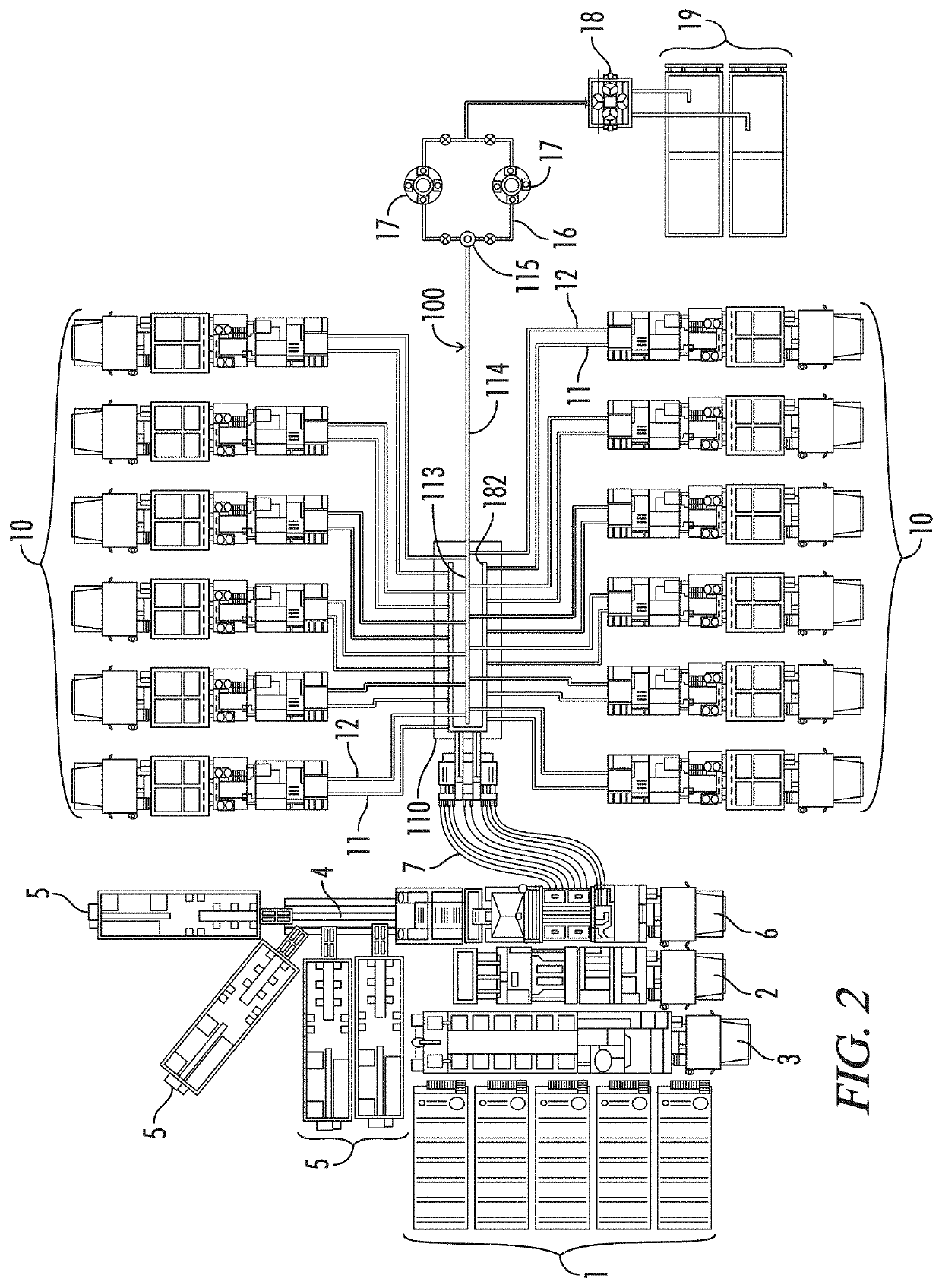
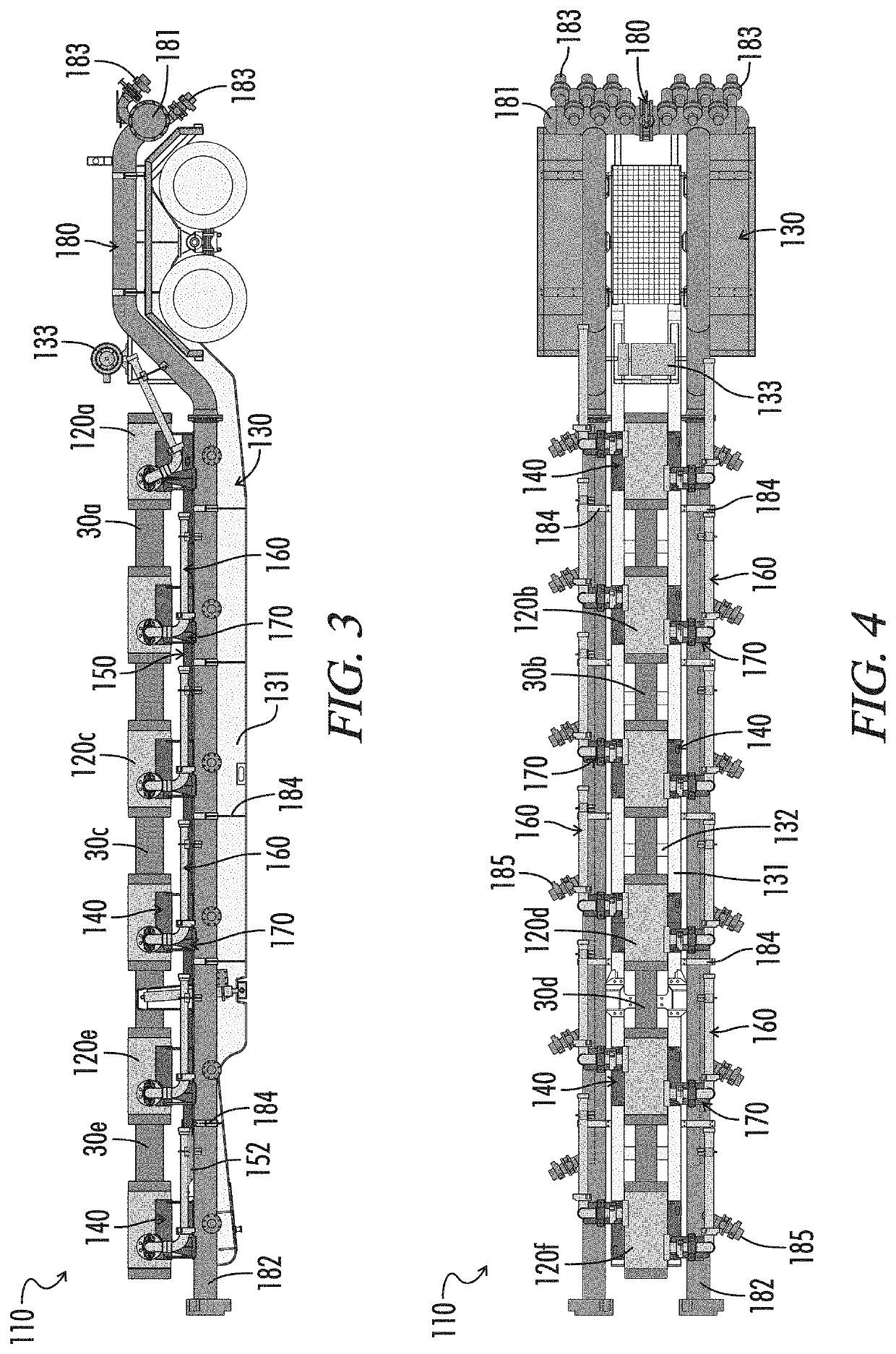
Frac manifold missile and fitting
A missile flow line is assembled in a frac manifold to manifold the discharge from a plurality of pumps. The missile comprises at least two junction fittings joined by a flange union to at least one spooled pipe to form a conduit. The junction fittings comprise a fitting body having a primary bore and at least two feed bores. The primary bore extends axially through the body between primary union faces adapted for connection to a flowline component by a flange union. The feed bores extend radially through the body from a feed union face to an intersection with the primary bore. The feed union faces are adapted for connection to pump discharge lines by a flange union. The intersections of the feed bores with the primary bore are offset axially from each other along the primary bore.
Owner:KHOLLE MAGNOLIA 2015 LLC
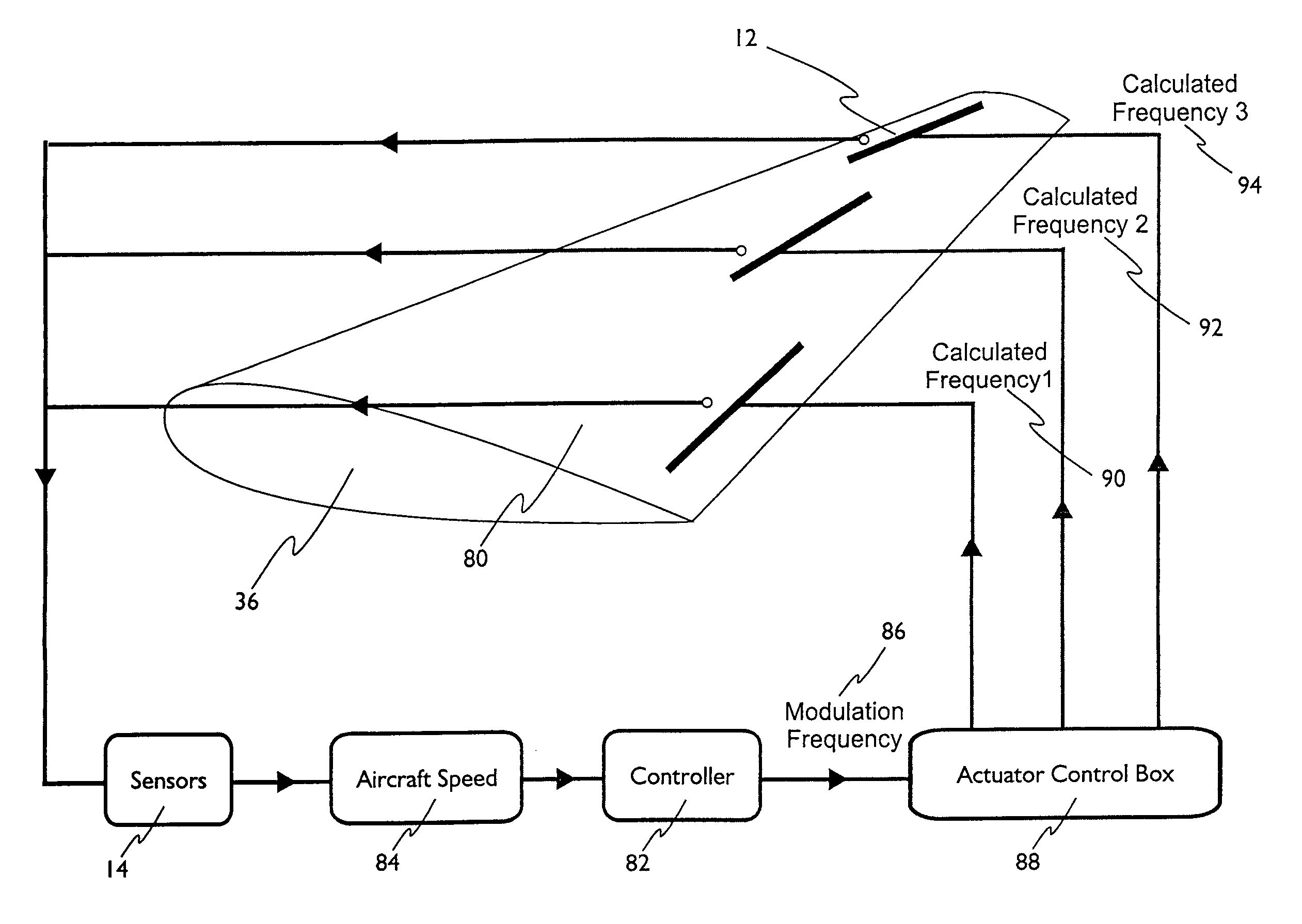
Method of controlling aircraft, missiles, munitions and ground vehicles with plasma actuators
ActiveUS7624941B1Improve efficiencyReduced Power RequirementsDirection controllersBoundary layer controlsJet aeroplanePlasma actuator
The present invention relates to a method of controlling an aircraft, missile, munition or ground vehicle with plasma actuators, and more particularly to controlling fluid flow across their surfaces or other surfaces, which would benefit from such a method. The method includes the design of an aerodynamic plasma actuator for the purpose of controlling airflow separation over a control surface of a aircraft, missile, or a ground vehicle, and more particularly to the method of determining a modulation frequency for the plasma actuator for the purpose of fluid flow control over these vehicles. The various embodiments provide the steps to increase the efficiency of aircraft, missiles, munitions and ground vehicles. The method of flow control provides a means for reducing aircraft, missile's, munition's and ground vehicle's power requirements. These methods also provide alternate means for aerodynamic control using low-power hingeless plasma actuator devices.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC +1
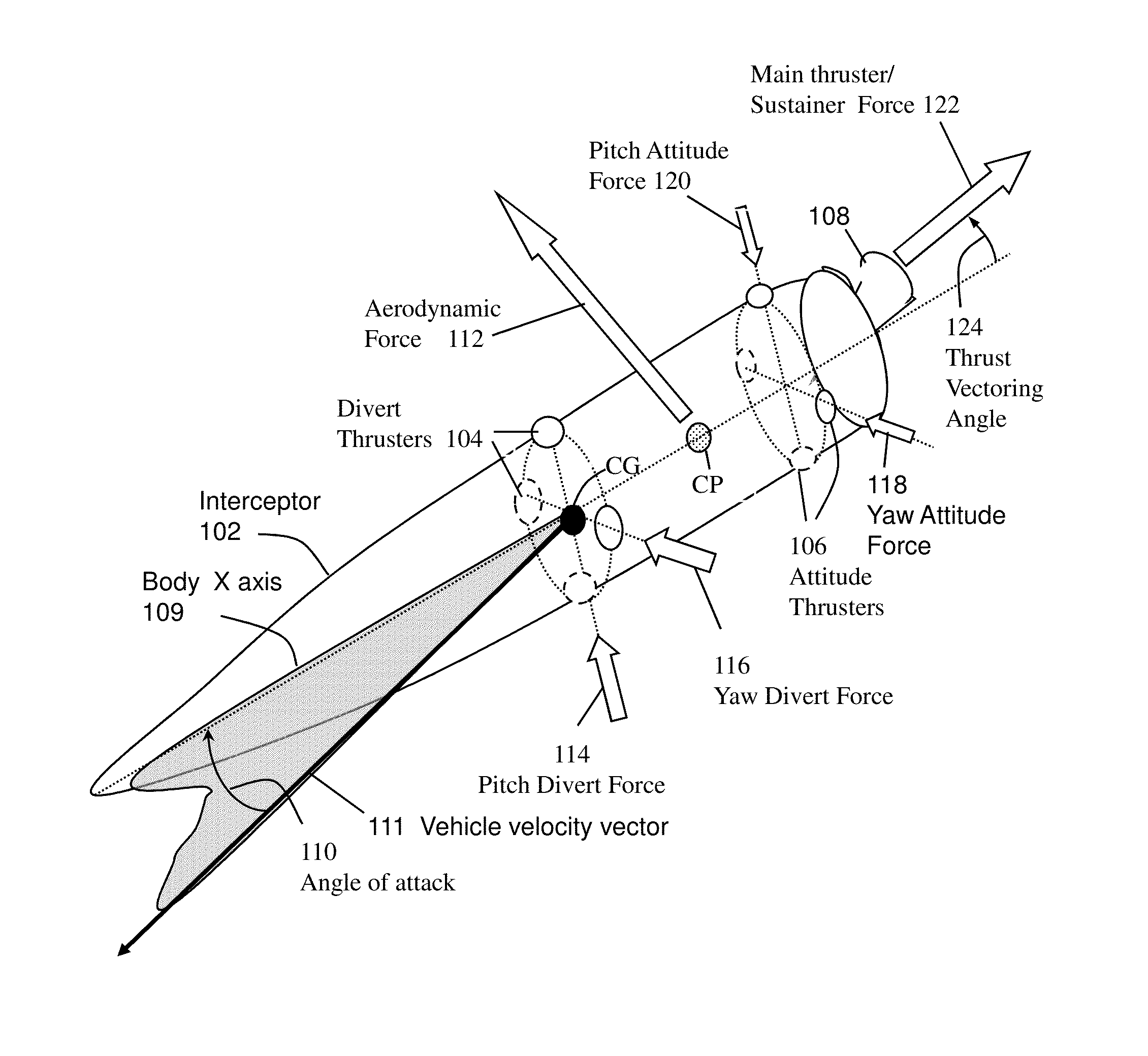
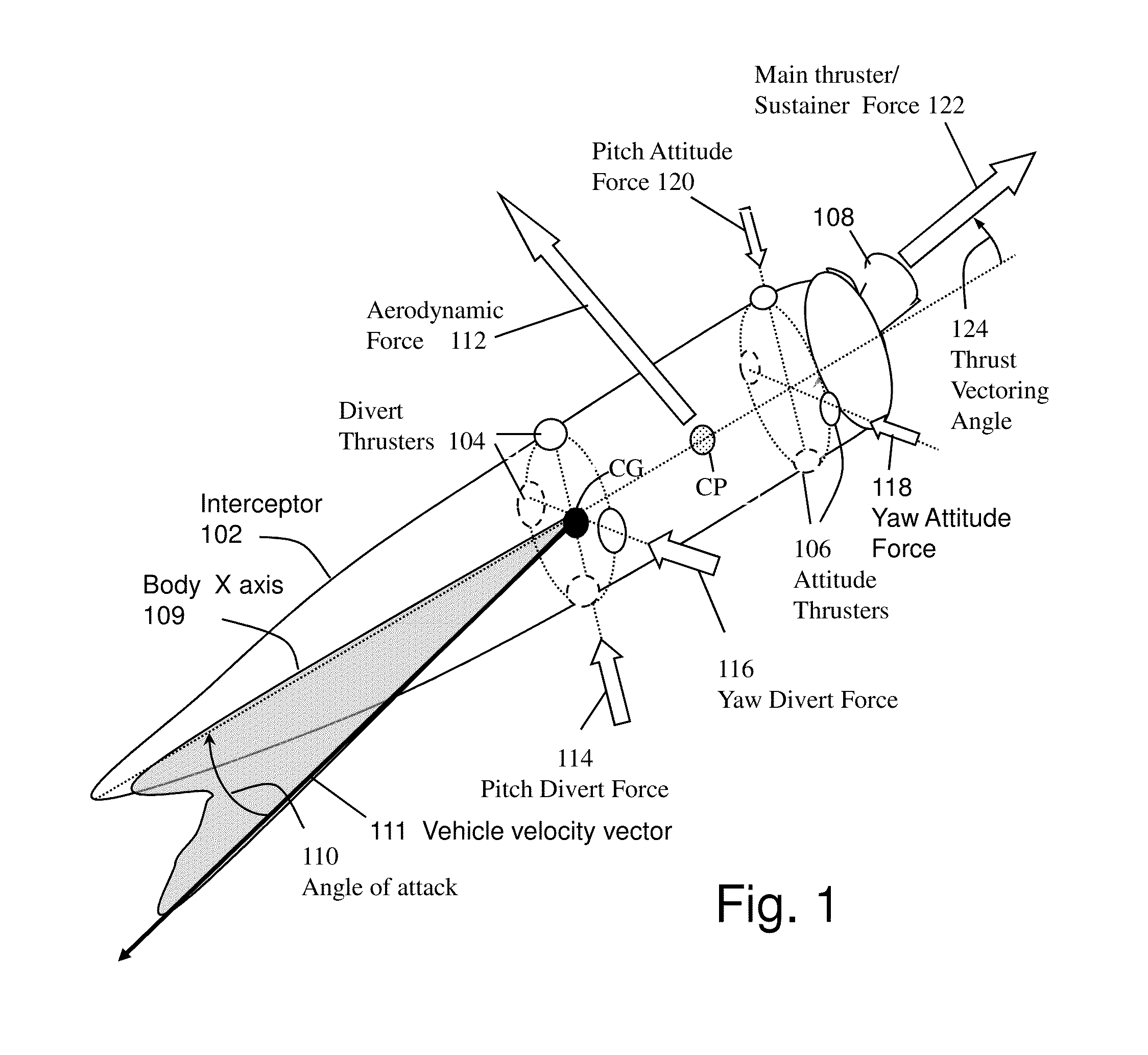
System and method for guiding and controlling a missile using high order sliding mode control
ActiveUS20130092785A1Reduce needPromote resultsDirection controllersTarget-seeking controlCouplingQuaternion
Higher Order Sliding Mode (HOSM) control techniques are applied to the Guidance Control (G&C) of interceptor missile in which velocity may be steered by combination of main thrust, aerodynamic lift and lateral on-off divert thrusters, and attitude may be steered by continuous or on-off actuators. Methods include the pointing of the seeker, its associated estimation processes, a guidance law that uses concurrent divert mechanisms, and an attitude autopilot. The insensitivity of the controller to matched disturbances allows the concurrent usage of the divert mechanisms without adverse effect on the accuracy. The controller also allows the de-coupling of the control of roll, pitch and yaw channels, and usage quaternions to represent body attitude and it provides control perfect robustness. While it conceivable to design separately the components of the G&C method, it is widely accepted that designing them in an integrated fashion usually produces a better result.
Owner:DAVIDSON TECH
Shock initiation devices including reactive multilayer structures
The invention provides shock initiation devices comprising multilayer structures with constituent layers that undergo an exothermic self-propagating reaction once initiated by shock. The multilayer structures may be used as components in shaped charges, EFP devices, warheads, munition casings, interceptors, missiles, bombs, and other systems. The reactive layer materials may be selected based on required structural properties, density and reaction temperature.
Owner:SURFACE TREATMENT TECH INC
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS7349804B2Increase probabilityHighly preventive effectReactors manufactureNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDisplay deviceLongitude
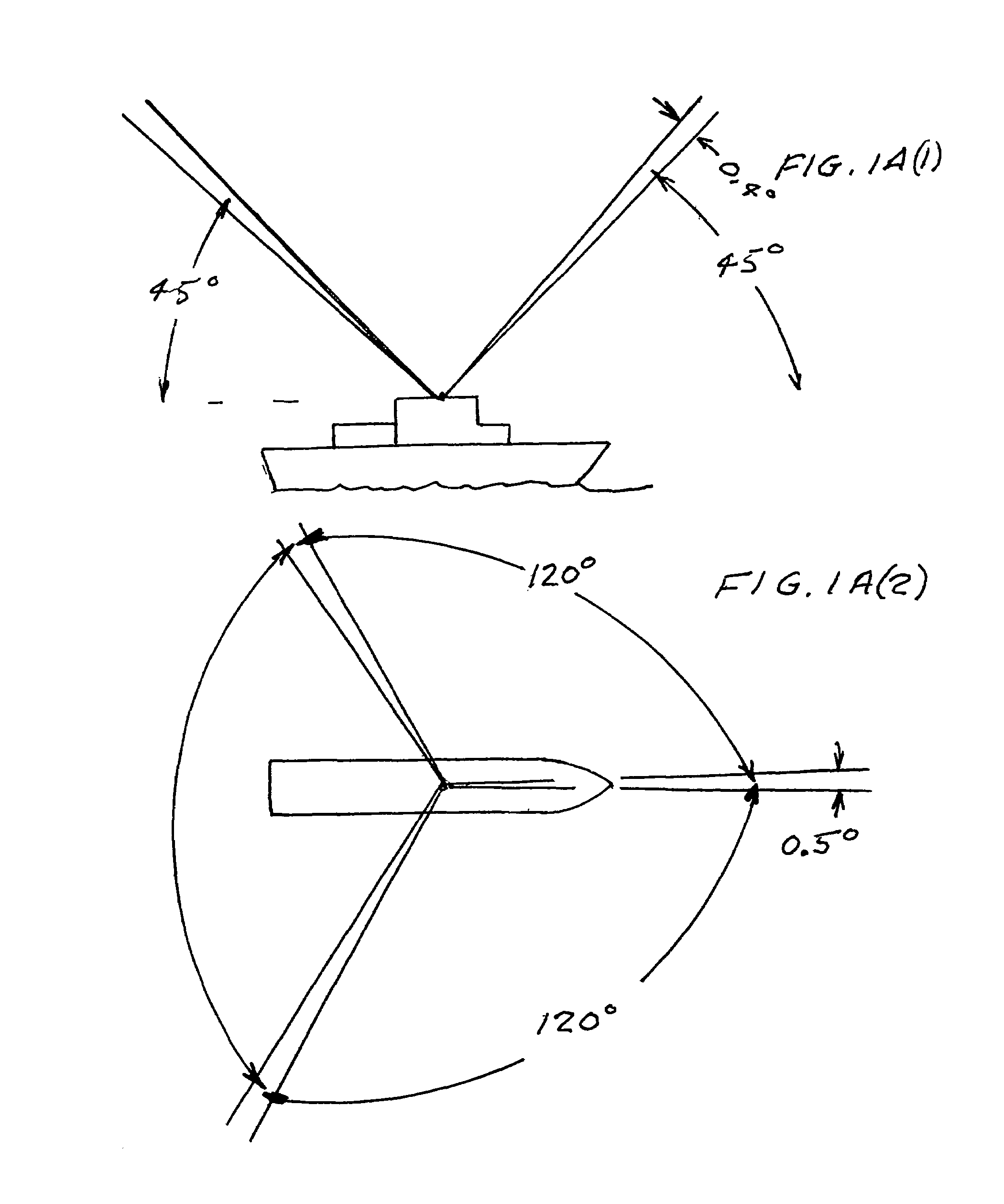
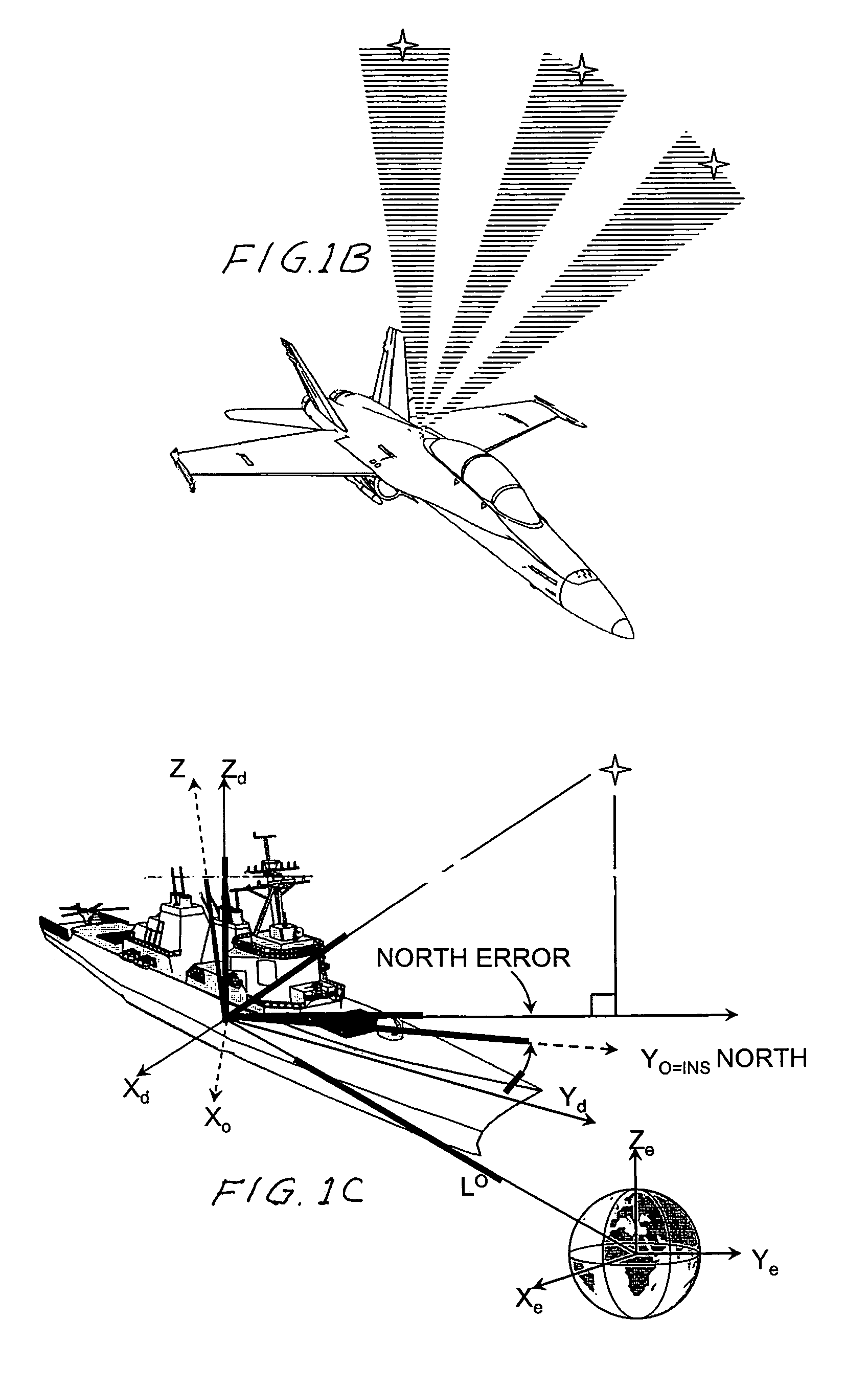
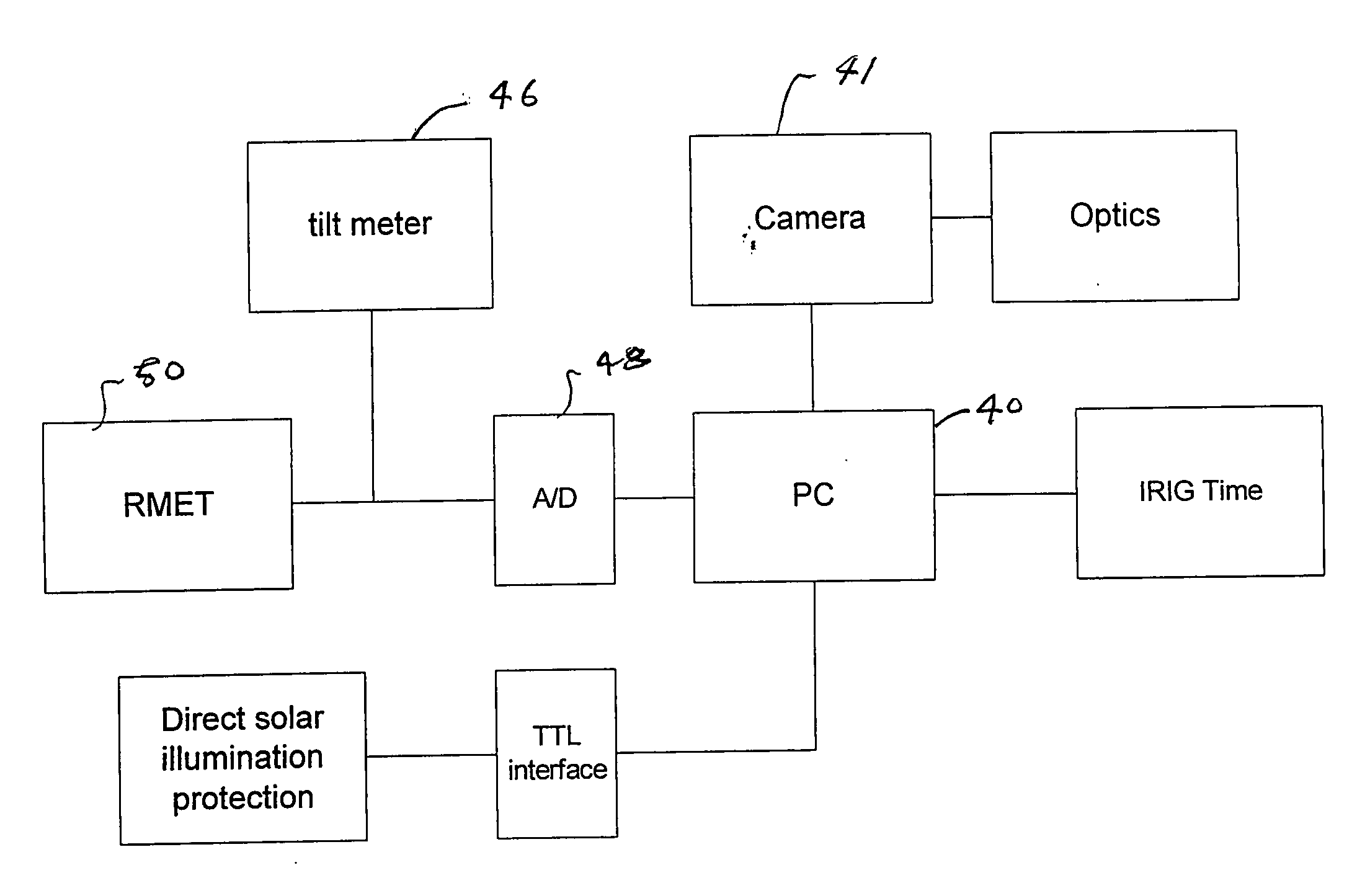
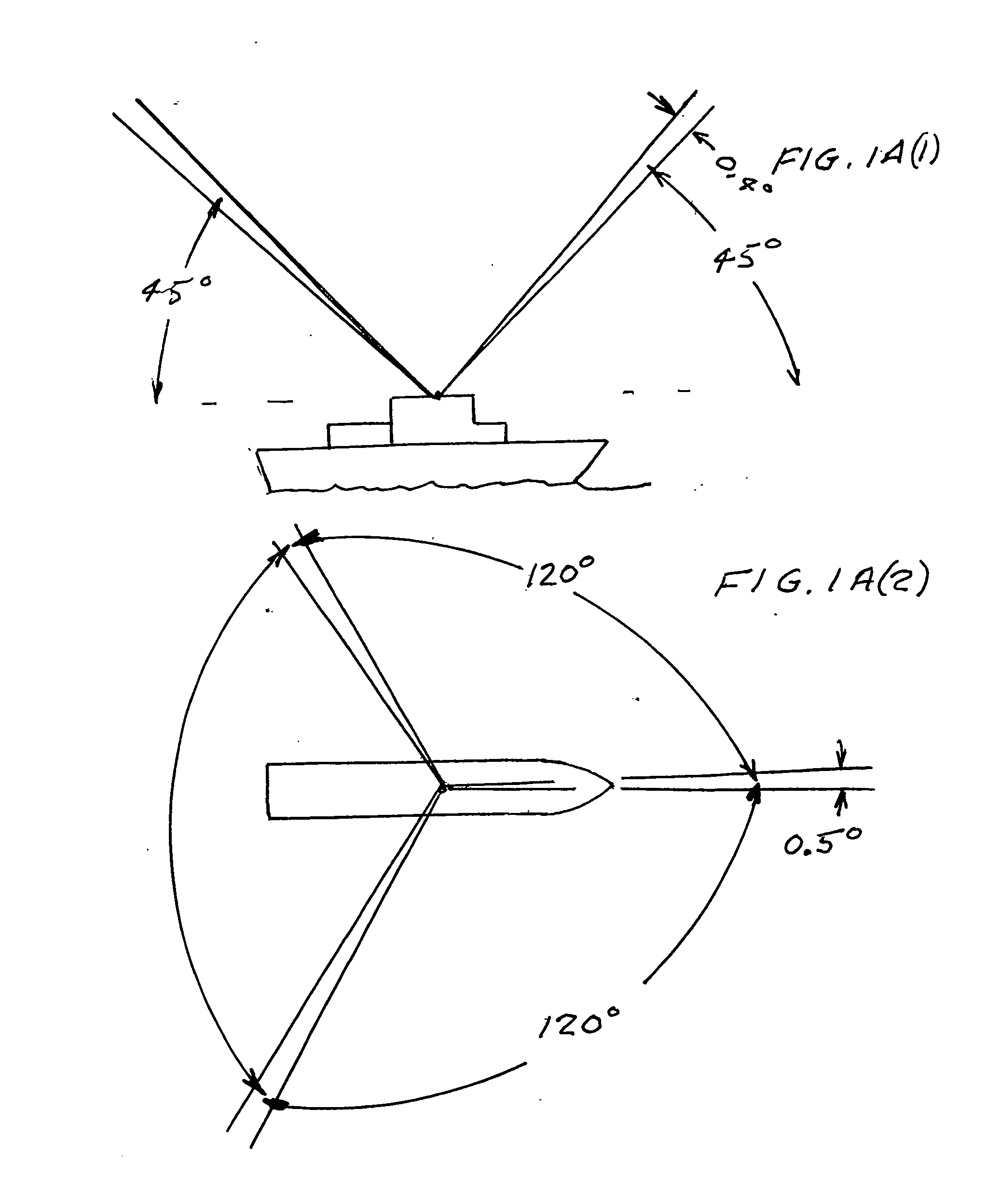
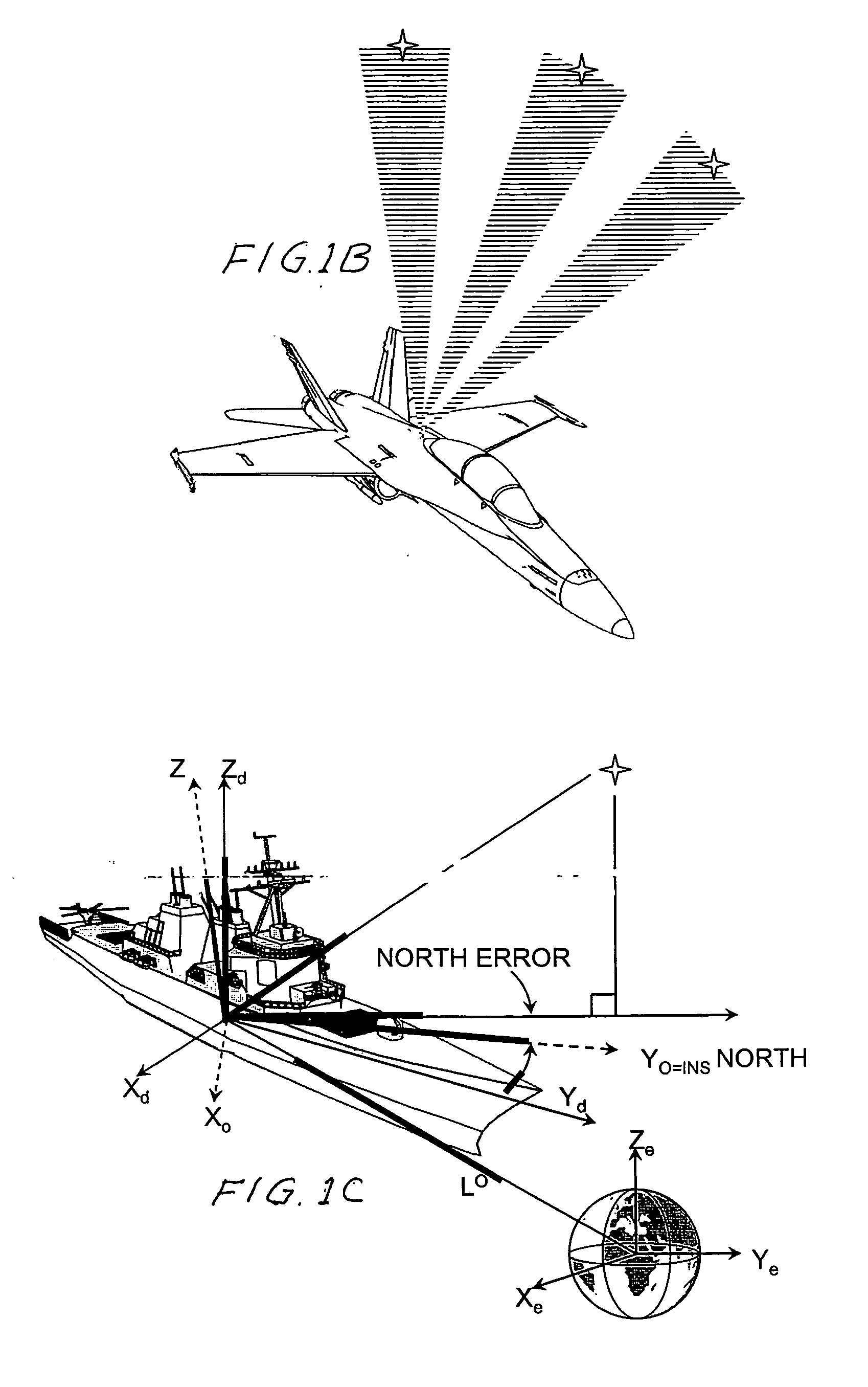
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, inclination information from the inclinometer, time information from the timing device and the catalogued star charts information to determine positions of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to use this celestial position information to calculate latitude and longitude which may be displayed on a display device such as a monitor or used by a guidance control system. These embodiments are jam proof and insensitive to radio frequency interference. These systems provide efficient alternatives to GPS when GPS is unavailable and can be used for periodic augmentation of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
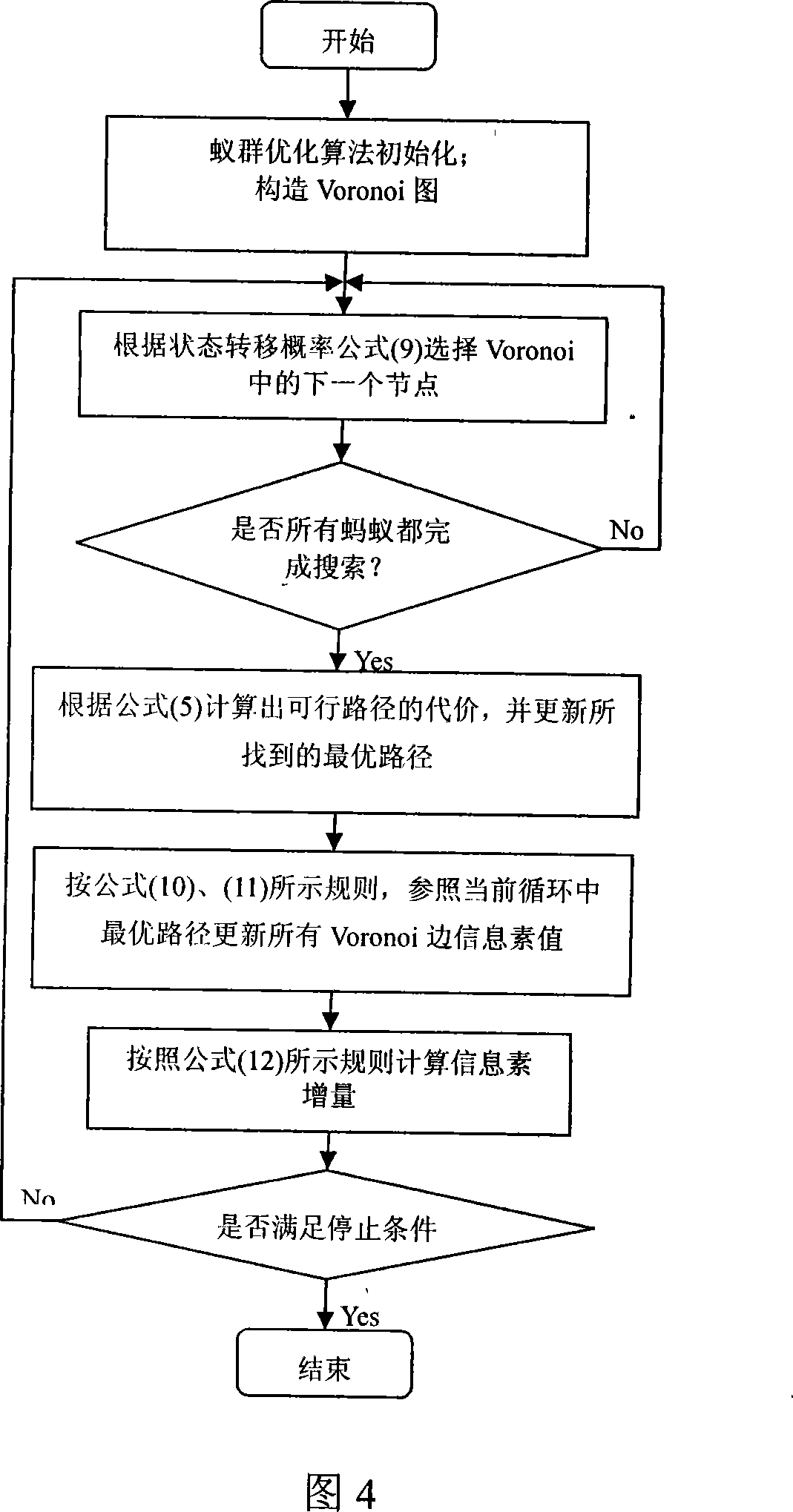
Un-manned plane fairway layout method based on Voronoi graph and ant colony optimization algorithm
InactiveCN101122974ASolve planning problemsEffective technical solutionsEnergy saving arrangementsBiological modelsNODALRadar
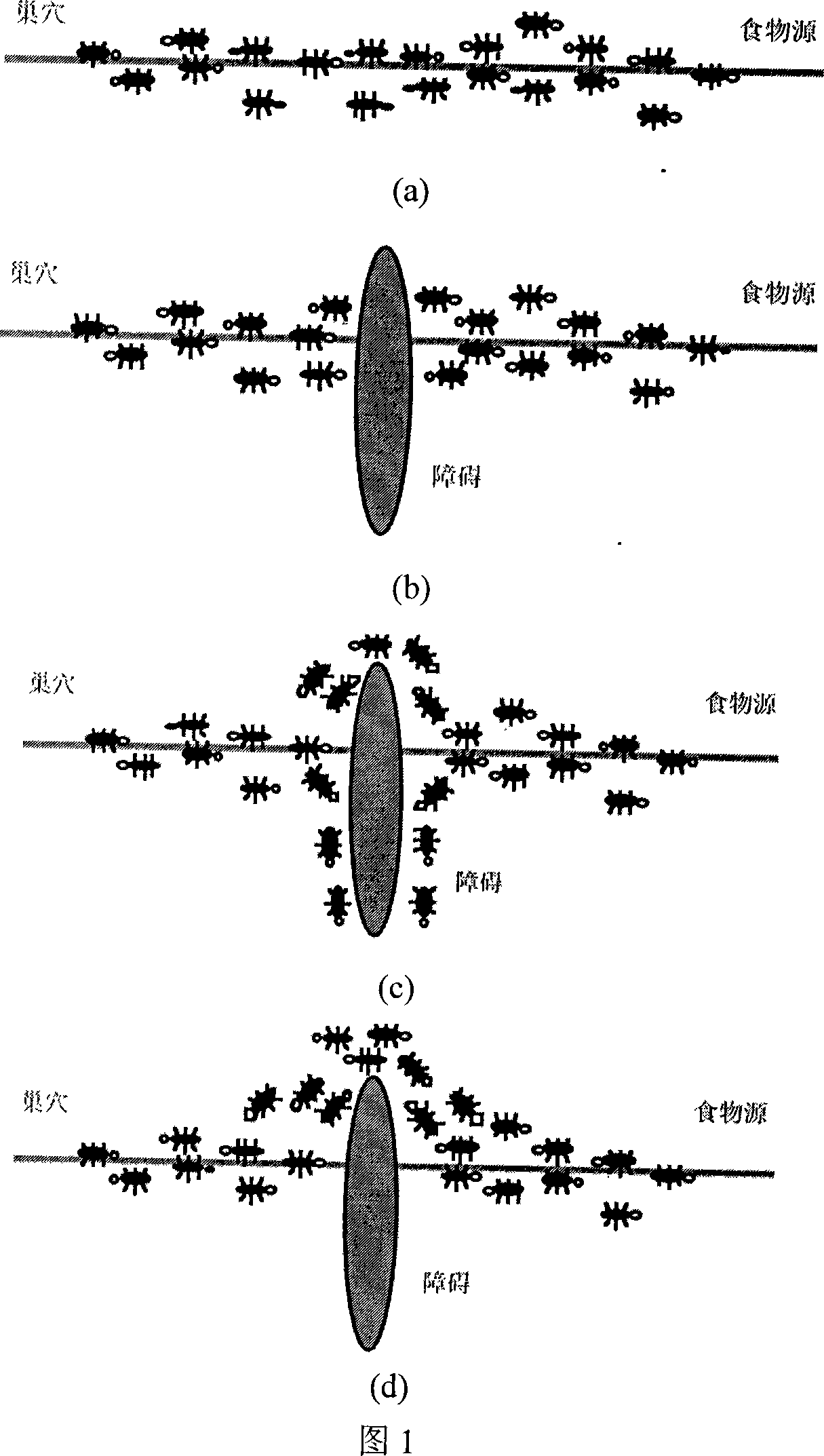
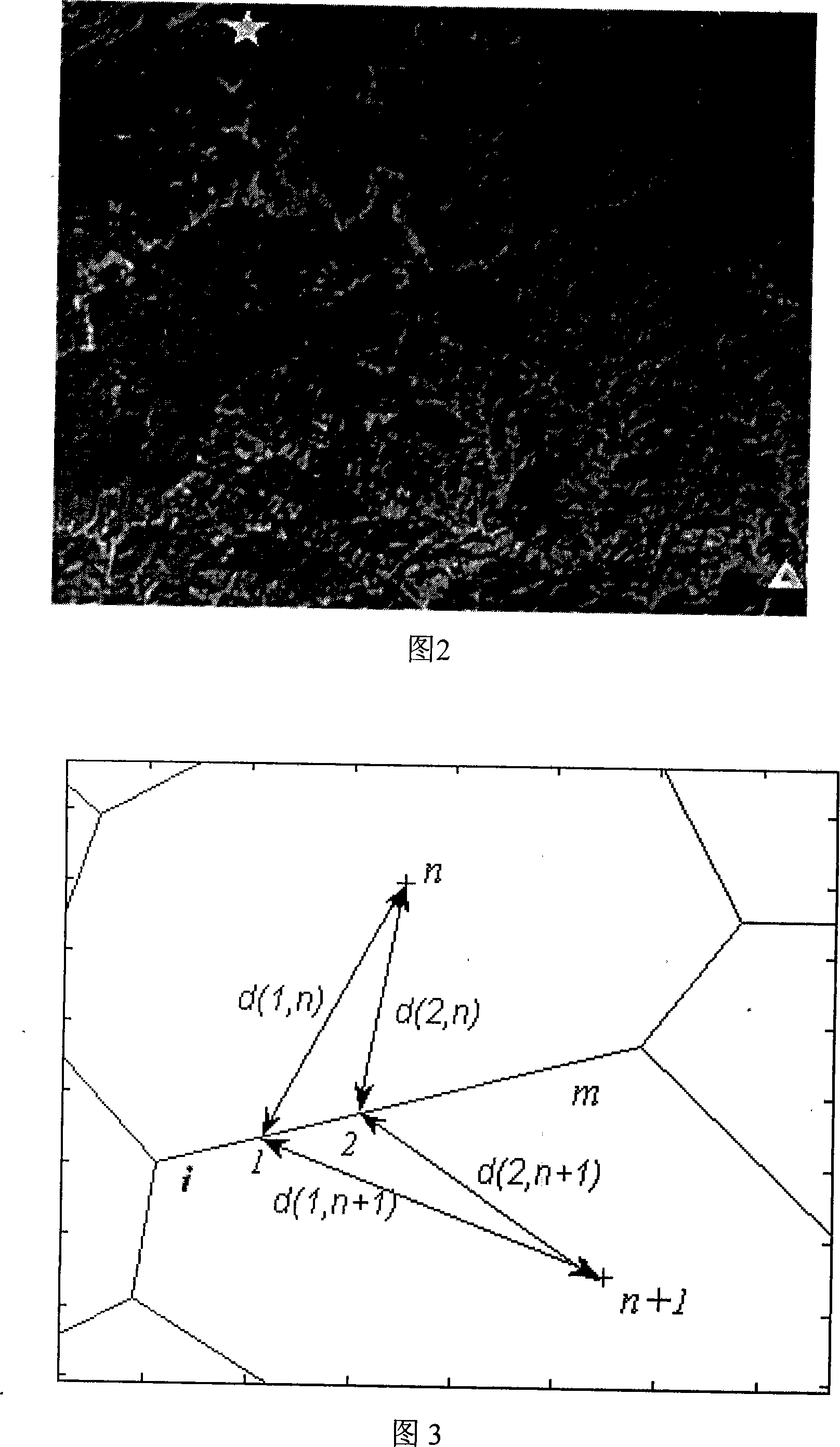
The invention provides an unmanned aircraft route planning method based on combination of Voronoi diagram and ant group optimizing algorithm. Firstly a model is established in accordance with properties of various threaten sources, e. g. landform, radar, missile and anticraft gun, and the unmanned aircraft route cost includes threaten costs and fuel oil costs; then initial pheromone values are given to each edge of the Voronoi diagram, enabling an ant to begin the search from the Voronoi node nearest to the start point. The marching Voronoi edge is selected based ob the status shift rule, then the search at the Voronoi node nearest to the target point is finished; And when all the ants have finished their own candidate route selection, the pheromones at each edge of the Voronoi diagram are updated in accordance with the improving and updating rules, wherein the pheromones at edges with no ant passing by are evaporated, and the process is repeated until an optimal unmanned aircraft route is found out. The method is characterized by good real-time and high-speed performance, and the found route is closer to the actual optimal unmanned aircraft route.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
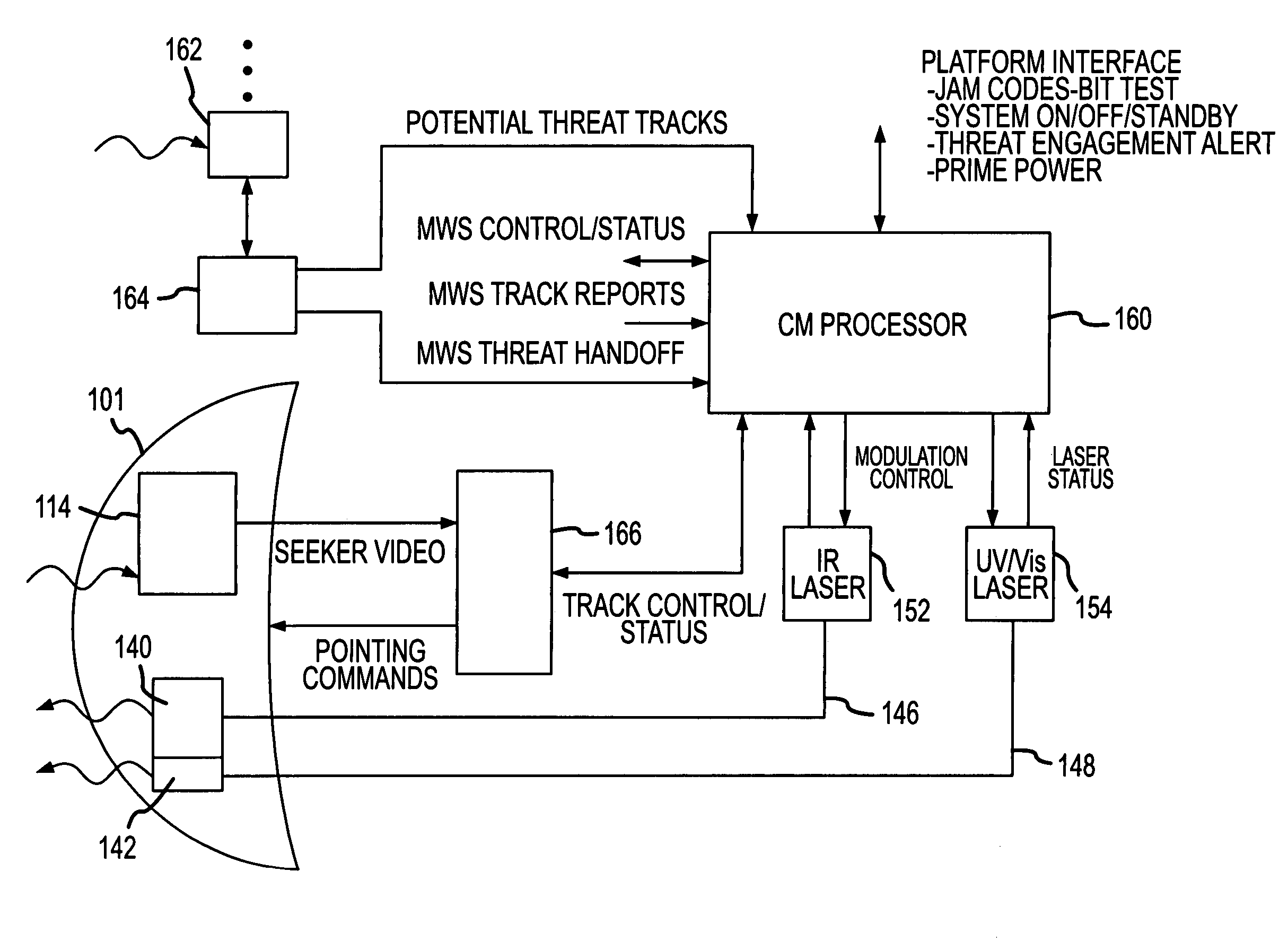
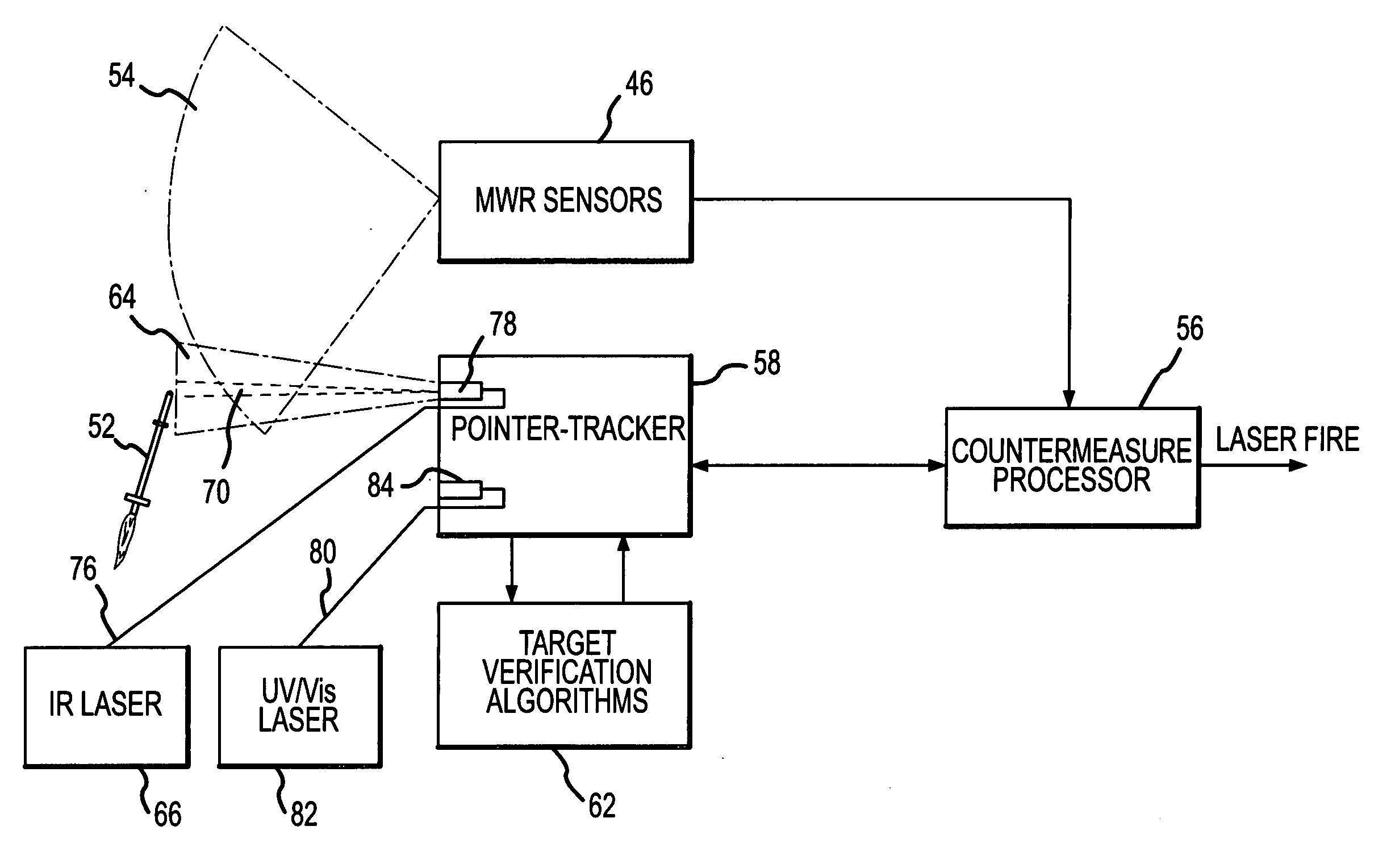
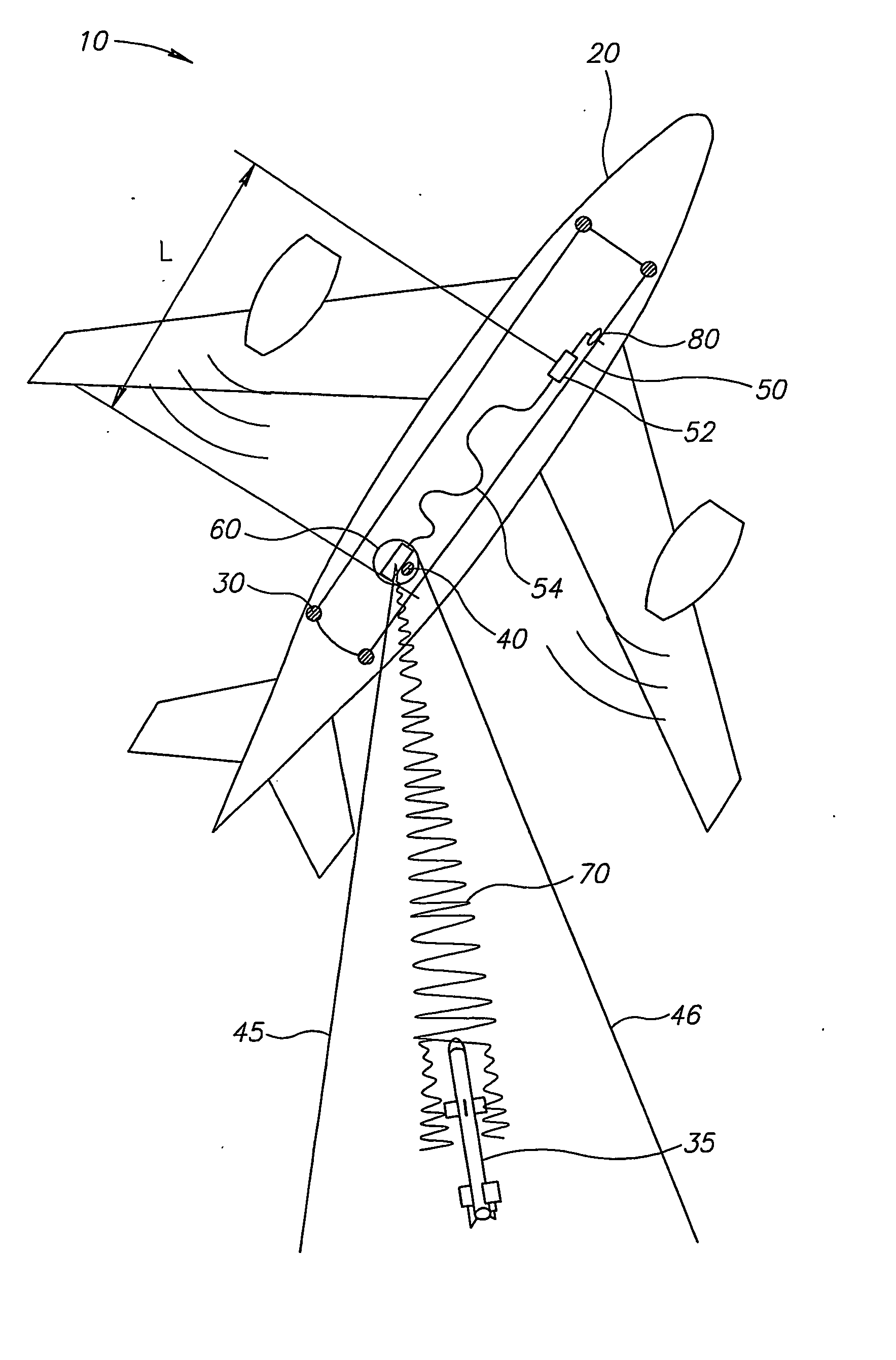
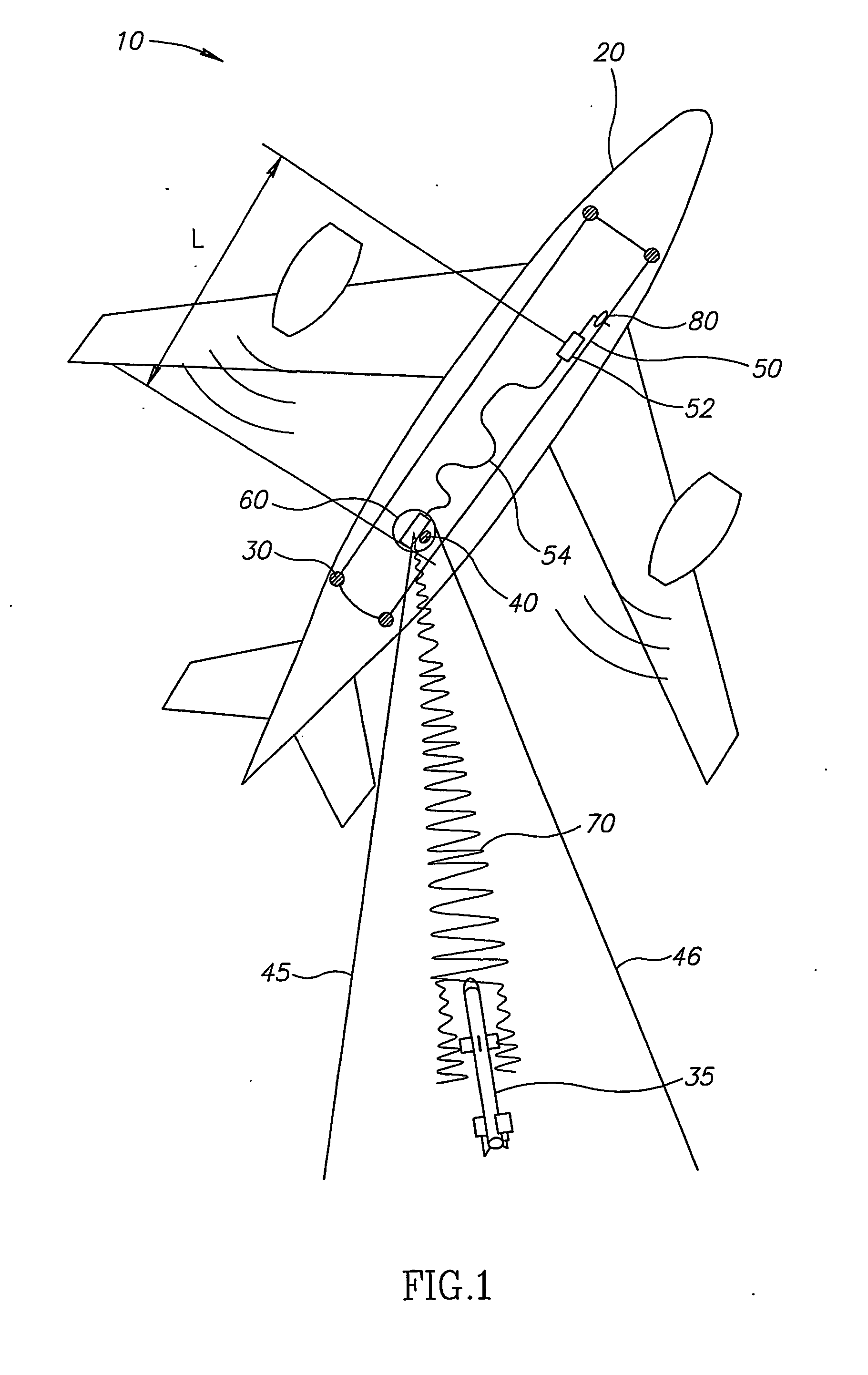
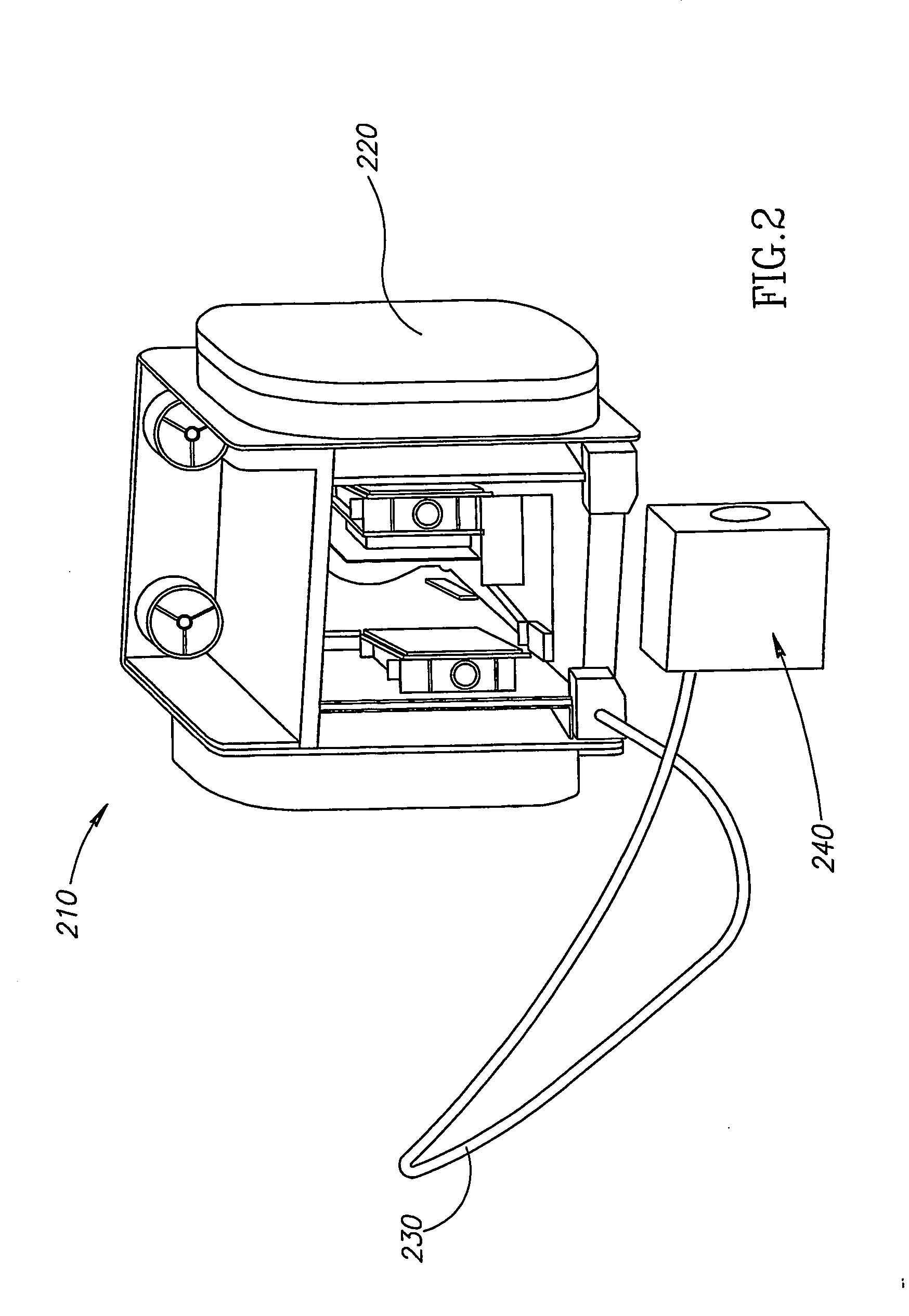
Directed infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) system and method
ActiveUS7378626B2Easy to liftAgile and high-power and reliableWave based measurement systemsDirection controllersMulti bandCountermeasure
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
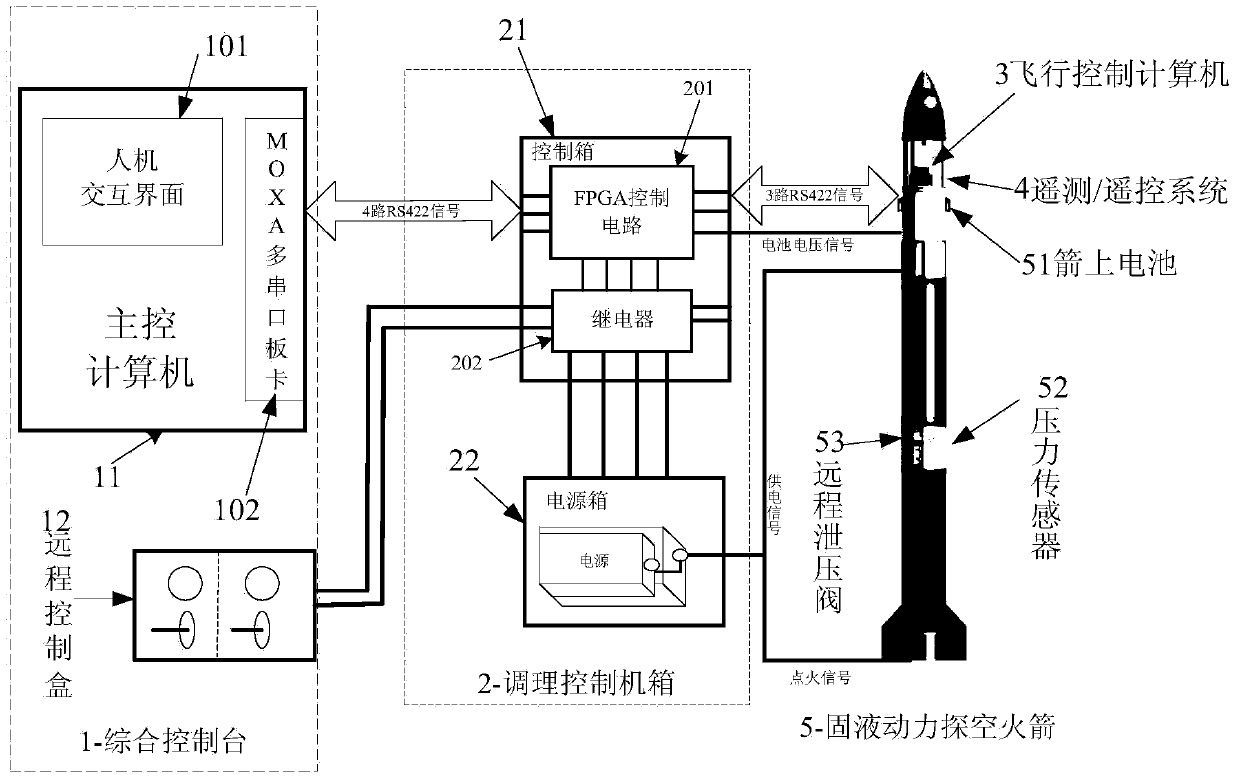
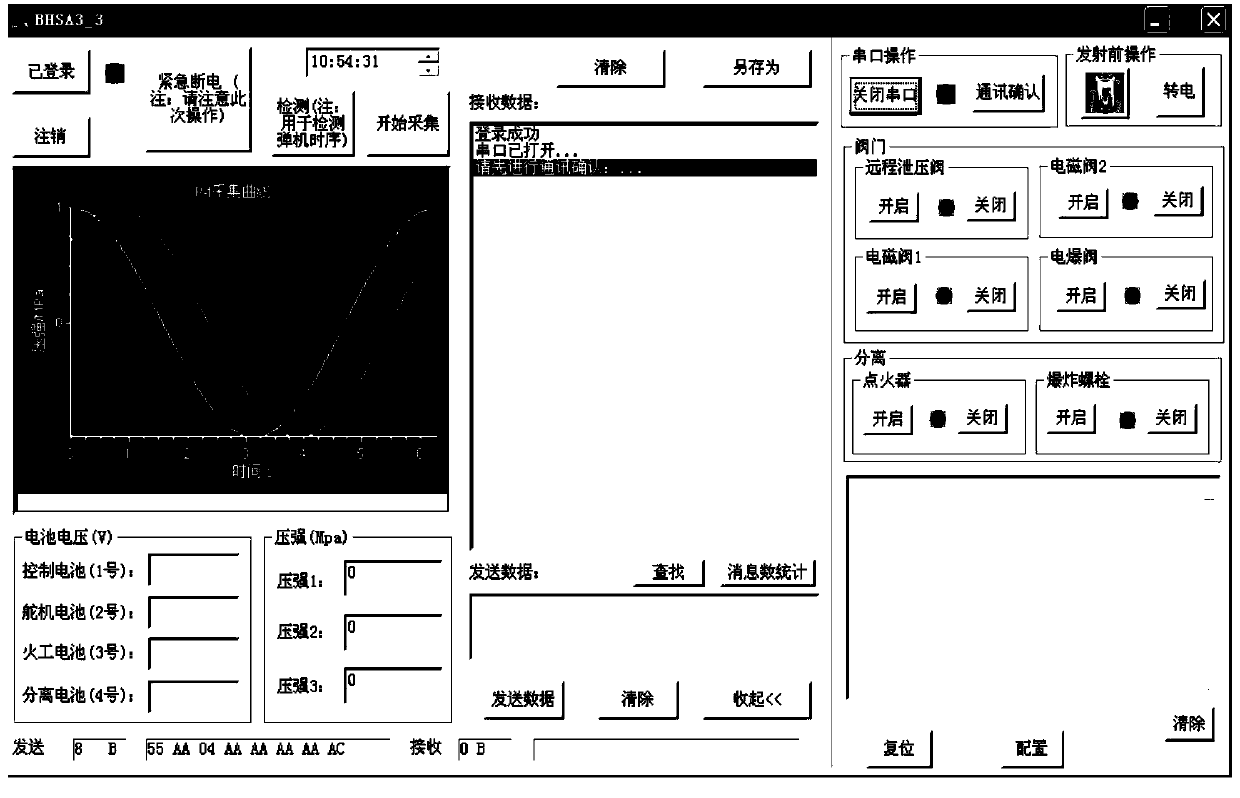
Solid-liquid power air vehicle ground test and launch control system of 422 bus
ActiveCN103558838ASafe and Efficient Ground Test Launch ControlRealize long-distance transmissionElectric testing/monitoringInteraction interfaceControl data
The invention relates to a solid-liquid power air vehicle ground test and launch control system of a 422 bus. The system comprises a ground integrated console, an adjusting control machine box, a flying control computer and a telemetering / telecontrol system. A main control computer of the ground integrated console uses a human-computer interaction interface, a CP-134U-I / DB9M board card of MOXA is used as a 422 node, orders are received and sent, and state information is displayed. The adjusting control machine box carries out ground and missile-borne power supply and distribution, signal forwarding, signal state monitoring and testing. The flying control computer receives orders sent by the main control computer and feeds the state information of an air vehicle back to the ground. According to the system, ground testing of the whole system, missile-borne system self detecting, result back transmitting, flying control data stapling, important parameter real-time detecting and system information back reading can be completed, and comprehensive monitoring of bus information, data real-time storage and displaying and safe protecting integration design are achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Methods and apparatus for high performance structures
ActiveUS7710347B2Additive manufacturing apparatusAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesEngineeringRadome
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
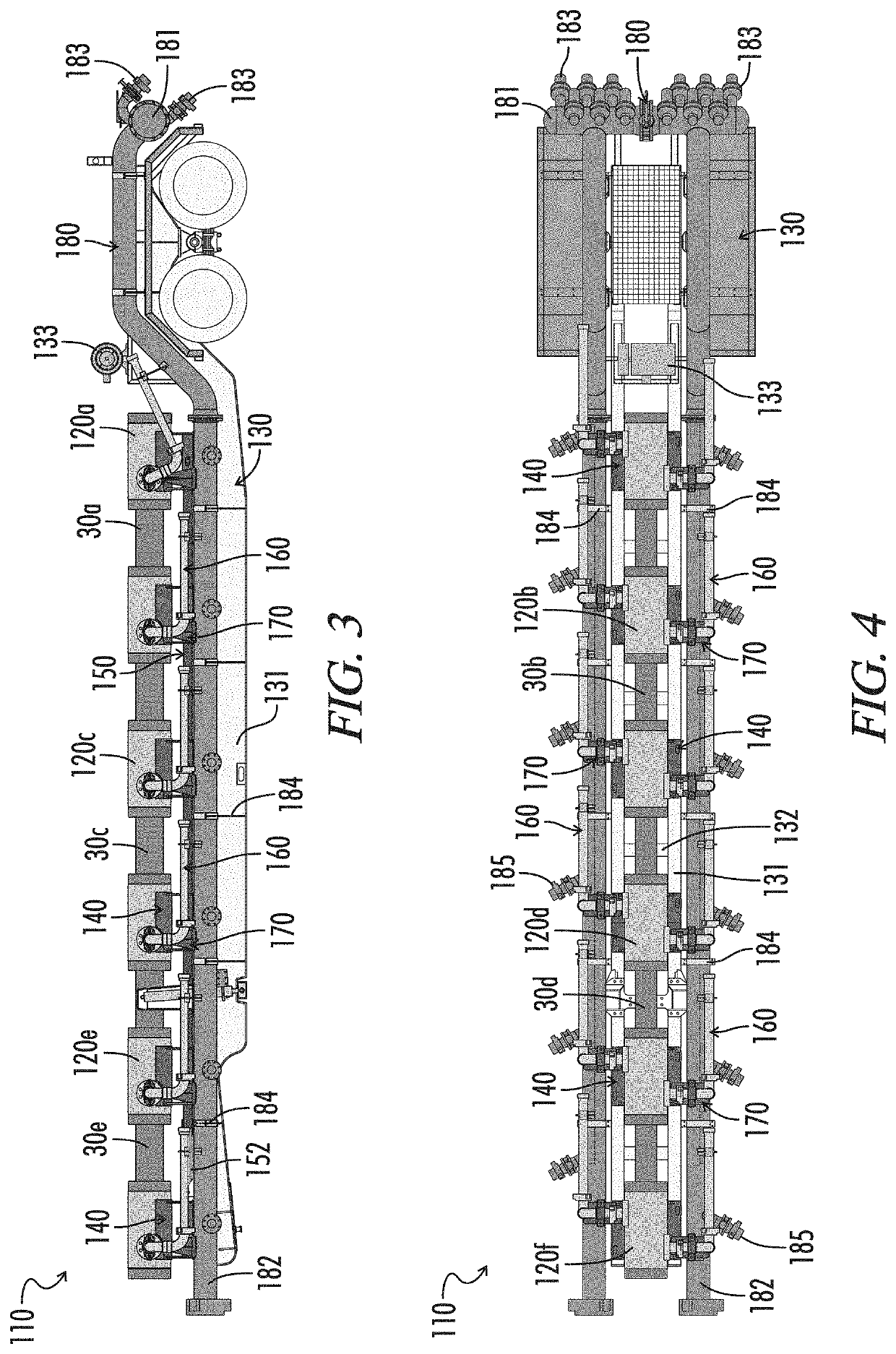
Flowline junction fittings for frac systems
ActiveUS10662749B1Limiting transverse movementPipe supportsFlanged jointsClassical mechanicsStructural engineering
Flowline junction fittings are assembled to missiles of frac manifolds. The fittings have a body with a primary bore, at least four secondary bores, and a tertiary bore. The bores extend from union faces adapted for connection to flowline components by a flange union. The tertiary bore intersects with the primary bore at an angle of approximately 90°. Goat head fittings are assembled to well heads. The goat heads have a body with a primary bore and at least four secondary bores. The bores extend from union faces adapted for connection to flowline components by a flange union. The intersections between the secondary bores and the primary bore have an interior angle of substantially less than 90°.
Owner:KHOLLE MAGNOLIA 2015 LLC
Directed infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) system and method
ActiveUS20070075182A1Easy to liftAgile and high-power and reliableWave based measurement systemsDirection controllersMulti bandCountermeasure
An agile, high-power, reliable DIRCM system that is easily extended to address sophisticated UV or UV-visible capable multi-band threats includes a missile warner having missile warning receivers (MWRs), one or two-color suitably in the mid-IR range, that detect likely missile launch and pass the threat coordinates to a pointer-tracker having a Roll / Nod gimbal on which the IR laser transmitter is mounted. The pointer-tracker slews the gimbal to initiate tracking based on the threat coordinates and then uses its detector to continue to track and verify the threat. If the threat is verified, the pointer-tracker engages the laser to fire and jam the missile's IR seeker. By slewing the gimbal based on unverified threat coordinates to initiate tracking the system is highly agile and can respond to short and near simultaneous MANPADS shots.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
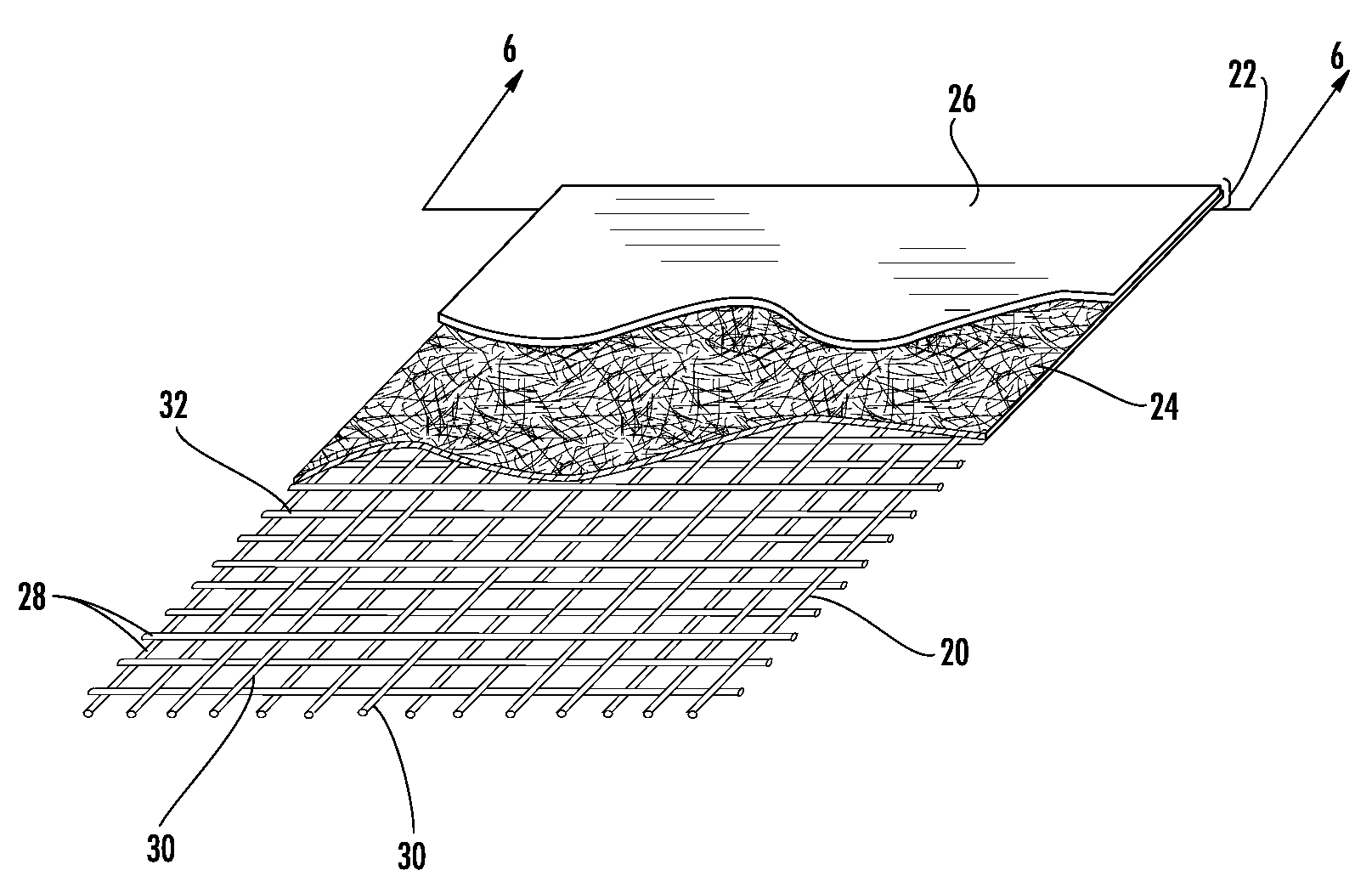
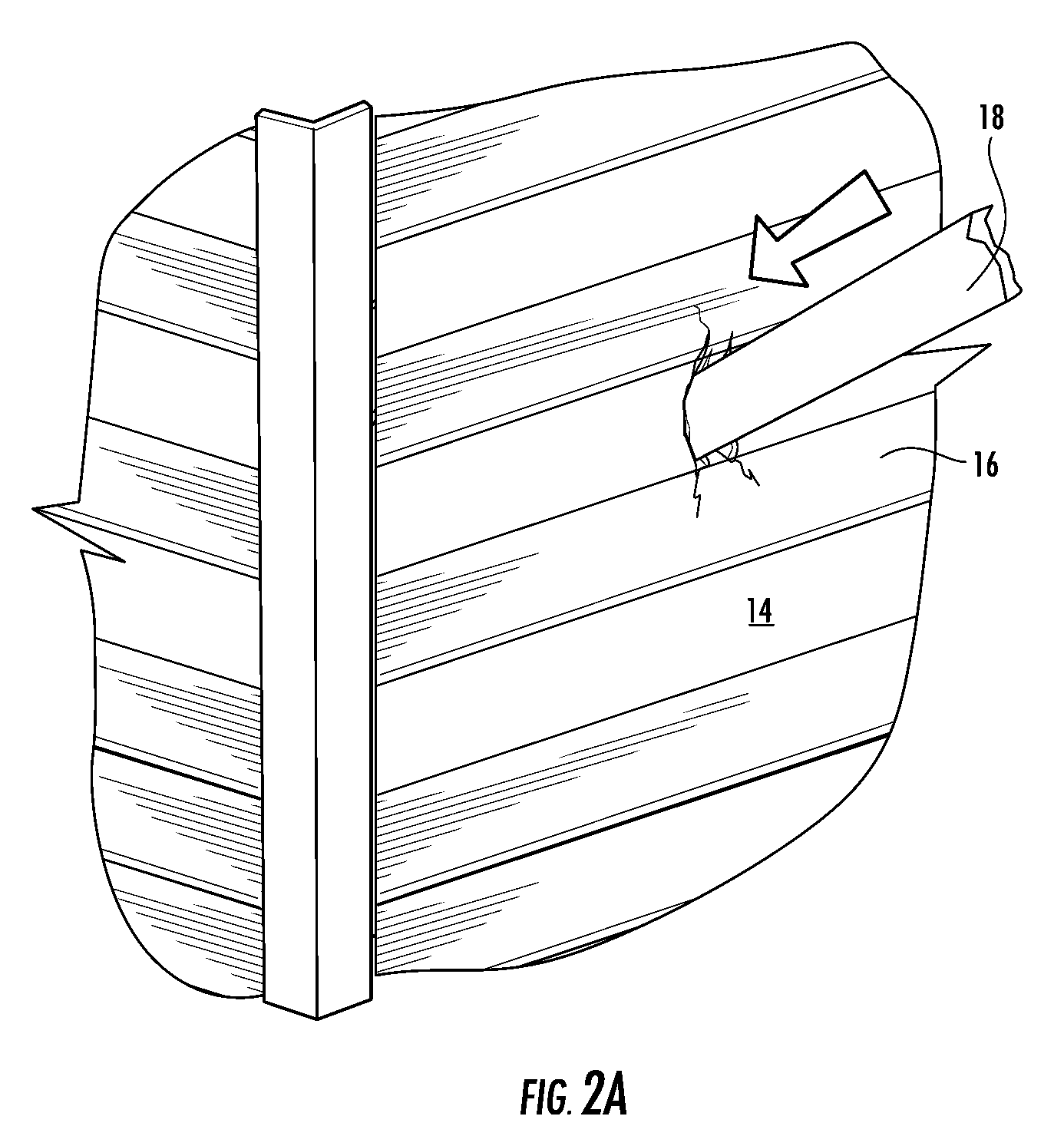
Impact Resistant Sheet Material
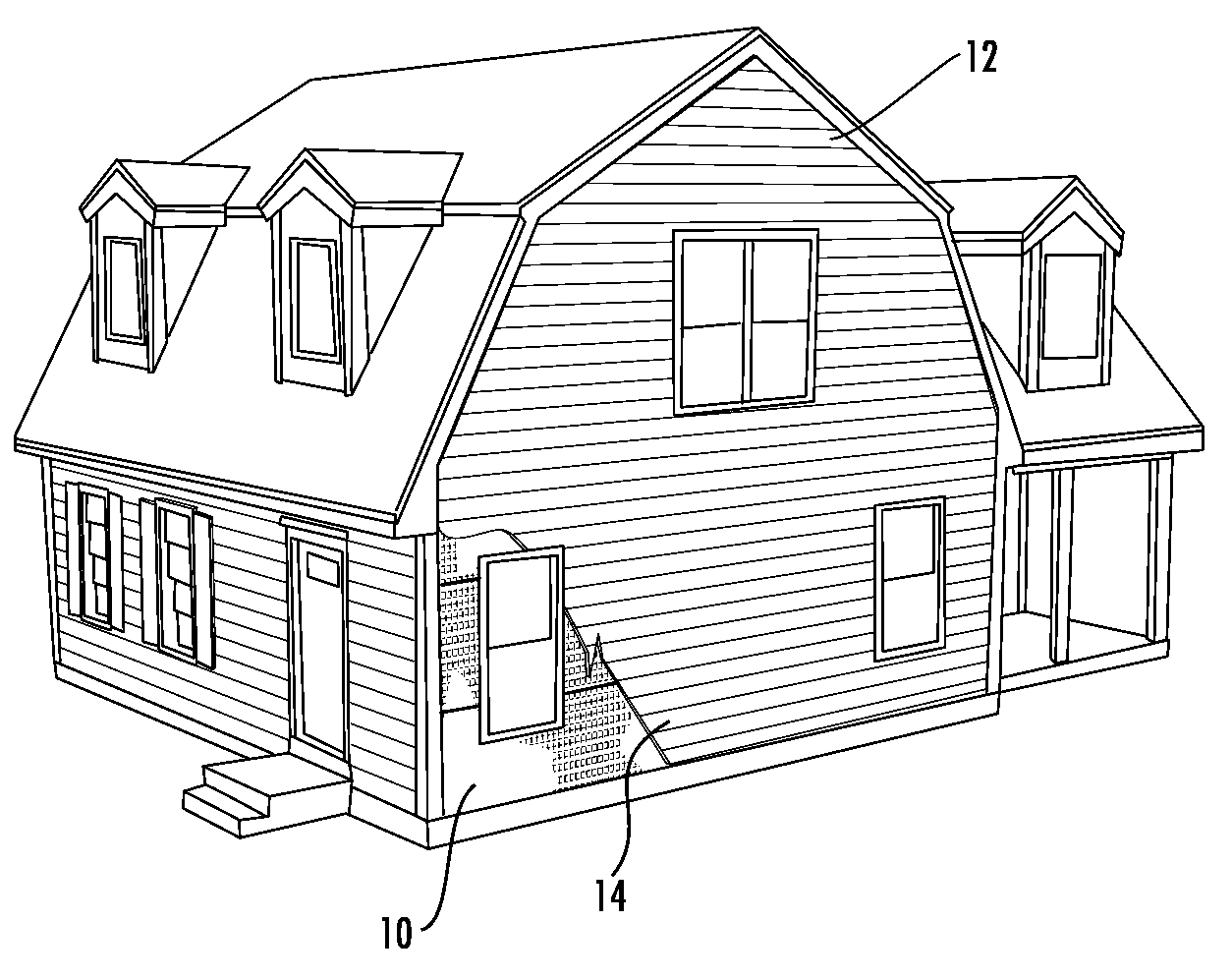
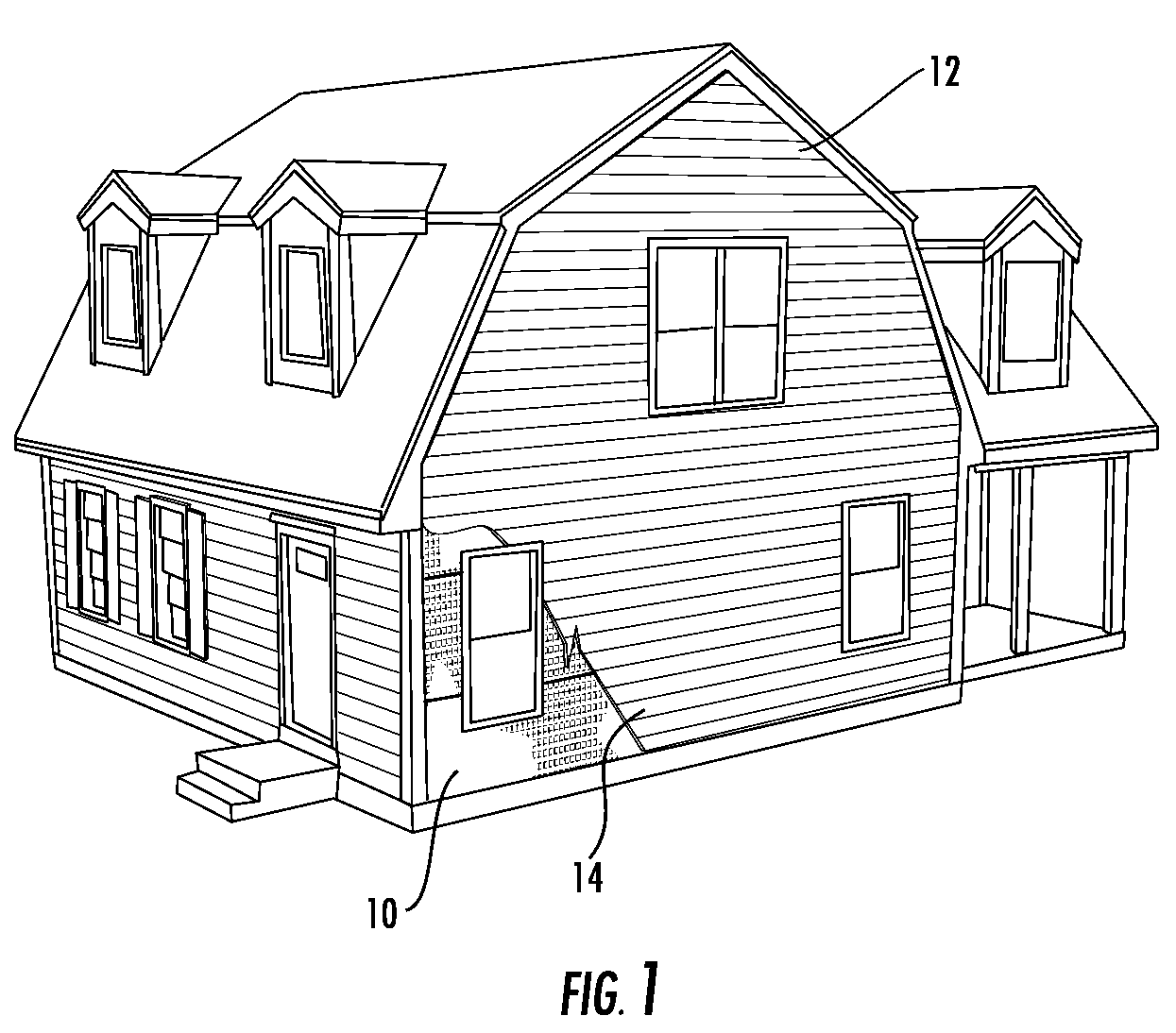
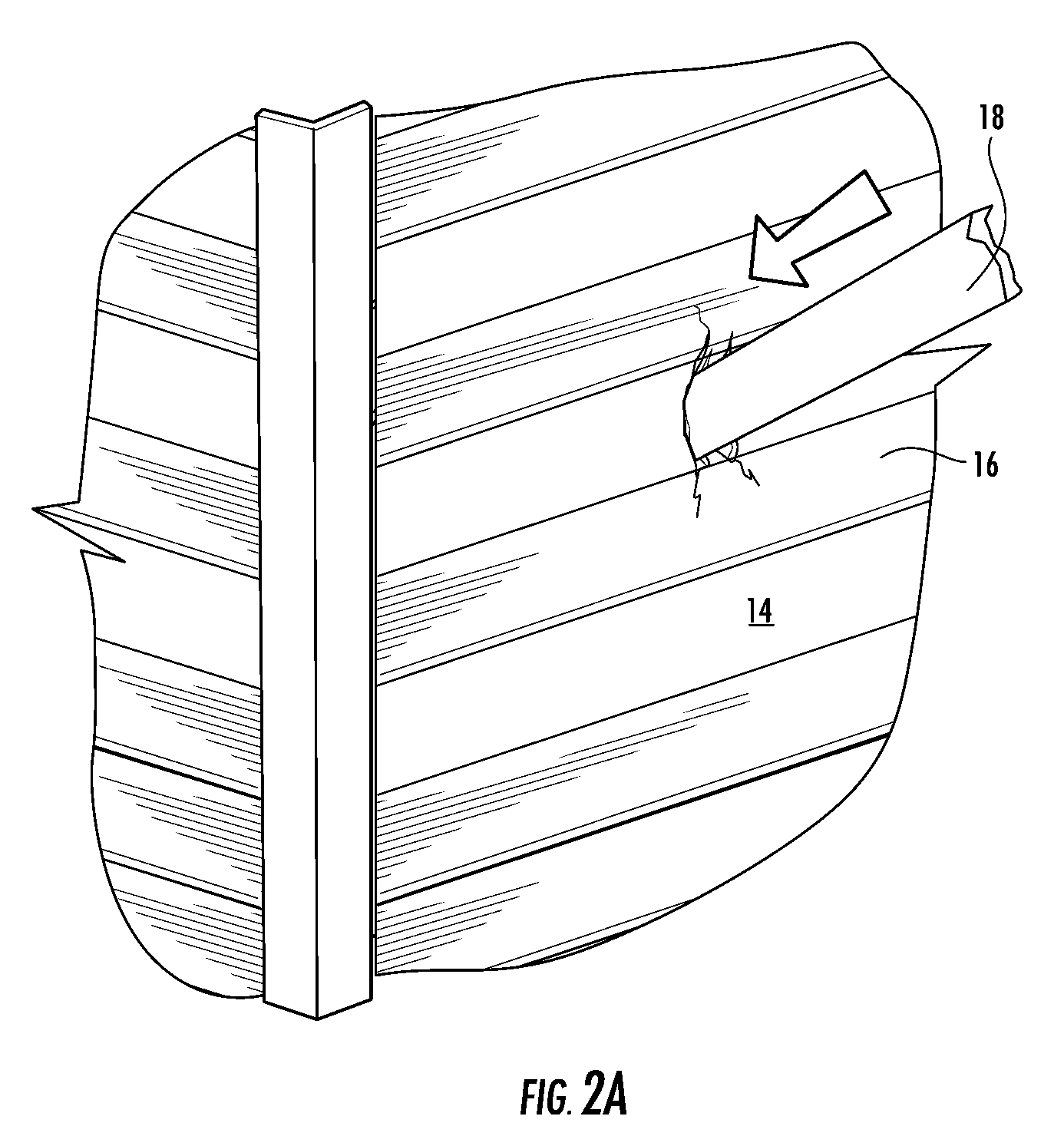
The present invention provides an impact resistant sheet material that helps provide exterior walls of a building with resistance to impacts so that the building structure can meet building standards, such as the Miami-Dade County Large Missile Impact Test, for resisting impacts in high wind areas. In one embodiment, sheet material comprises an impact resistant layer that attached to fibrous substrate. The impact resistant layer provides impact resistance to the sheet material so that a wall structure employing the sheet material is able to successfully withstand an impact from a projectile comprising a 9 pound, 7 foot two-by-four (“2×4”) traveling at a speed of at least 34 miles per hour. The impact resistant sheet material may comprise a moisture vapor permeable, water-impermeable barrier layer having a hydrohead of at least 55 cm and a moisture vapor transmission rate of at least 35 g / m2 / day. Such a sheet material is particularly useful in barrier applications, such as a house wrap.
Owner:FIBERWEB LLC
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS20070038374A1Small and light systemAvoid star image blurCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsDisplay deviceLongitude
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, inclination information from the inclinometer, time information from the timing device and the catalogued star charts information to determine positions of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to use this celestial position information to calculate latitude and longitude which may be displayed on a display device such as a monitor or used by a guidance control system. These embodiments are jam proof and insensitive to radio frequency interference. These systems provide efficient alternatives to GPS when GPS is unavailable and can be used for periodic augmentation of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Three-dimensional multi-missile cooperative guidance method and system with finite time convergence
ActiveCN106843265AGuaranteed Line of Sight Angular RateGuaranteed convergenceAiming meansPosition/course control in three dimensionsThree-dimensional spaceAngular velocity
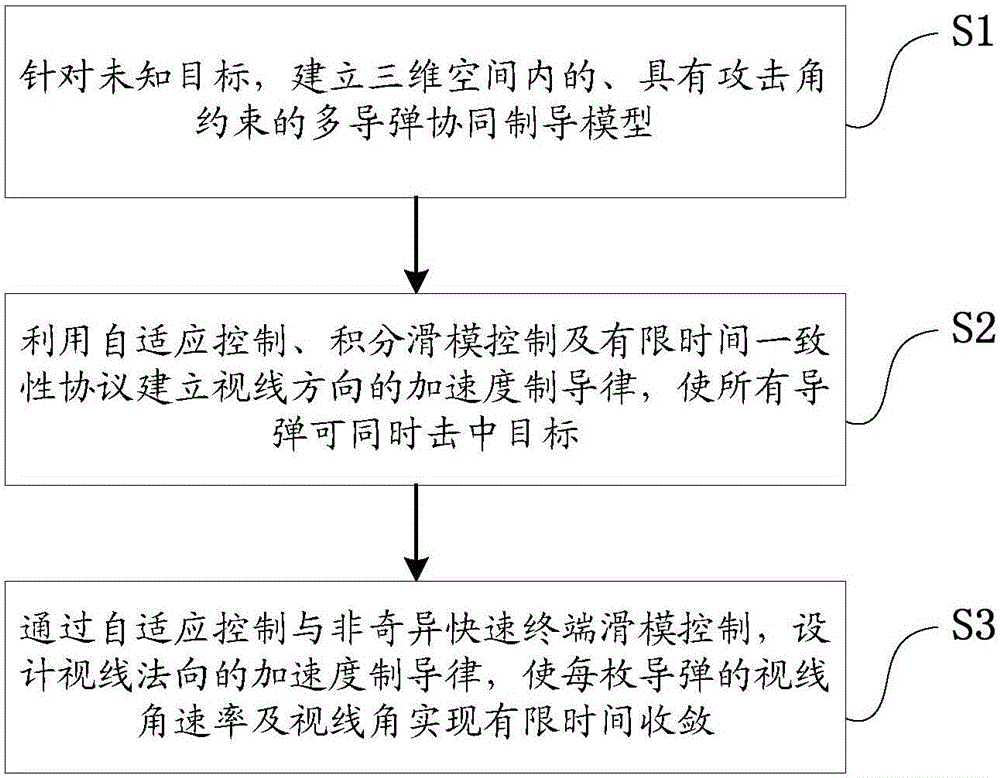
The invention discloses a three-dimensional multi-missile cooperative guidance method with finite time convergence. The method comprises the steps that for an unknown target, a multi-missile cooperative guidance model with attacking angle constraint in three-dimensional space is established; by adaptive control, integral sliding model control and a finite time consistency protocol, an acceleration guidance law in the sight direction is established to make all missiles hit the target at the same time; through the adaptive control and non-singular fast terminal sliding model control, and the acceleration guidance law in the sight direction is designed to make the finite time convergence of a sight angular velocity rate and a sight angle of each missile achieved. According to the three-dimensional multi-missile cooperative guidance method with the finite time convergence, all the missiles can hit the target at a desired angle at the same time on condition that no maneuvering information of the target is known, and at the same time the occurrence of buffeting is avoided.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Near field probe
InactiveUS6940264B2Improve reliabilityReduce outputMeasurement using dc-ac conversionElectric devicesSystem under testElectromagnetic radiation
A near field probe for testing installed components of an electromagnetic radiating system on a missile. The probe design comprises a diode antenna with a balun. The probe utilizes a dual diode arrangement which provides approximately twice the output voltage as the previous probe. The probe may then be placed further away from the radiating system under test.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Impact resistant sheet material
The present invention provides an impact resistant sheet material that helps provide exterior walls of a building with resistance to impacts so that the building structure can meet building standards, such as the Miami-Dade County Large Missile Impact Test, for resisting impacts in high wind areas. In one embodiment, sheet material comprises an impact resistant layer that attached to fibrous substrate. The impact resistant layer provides impact resistance to the sheet material so that a wall structure employing the sheet material is able to successfully withstand an impact from a projectile comprising a 9 pound, 7 foot two-by-four (“2×4”) traveling at a speed of at least 34 miles per hour. The impact resistant sheet material may comprise a moisture vapor permeable, water-impermeable barrier layer having a hydrohead of at least 55 cm and a moisture vapor transmission rate of at least 35 g / m2 / day. Such a sheet material is particularly useful in barrier applications, such as a house wrap.
Owner:FIBERWEB LLC
Extended range, light weight laser target designator
InactiveUS6926227B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce false alarm rateDirection controllersPosition fixationLaser targetCountermeasure
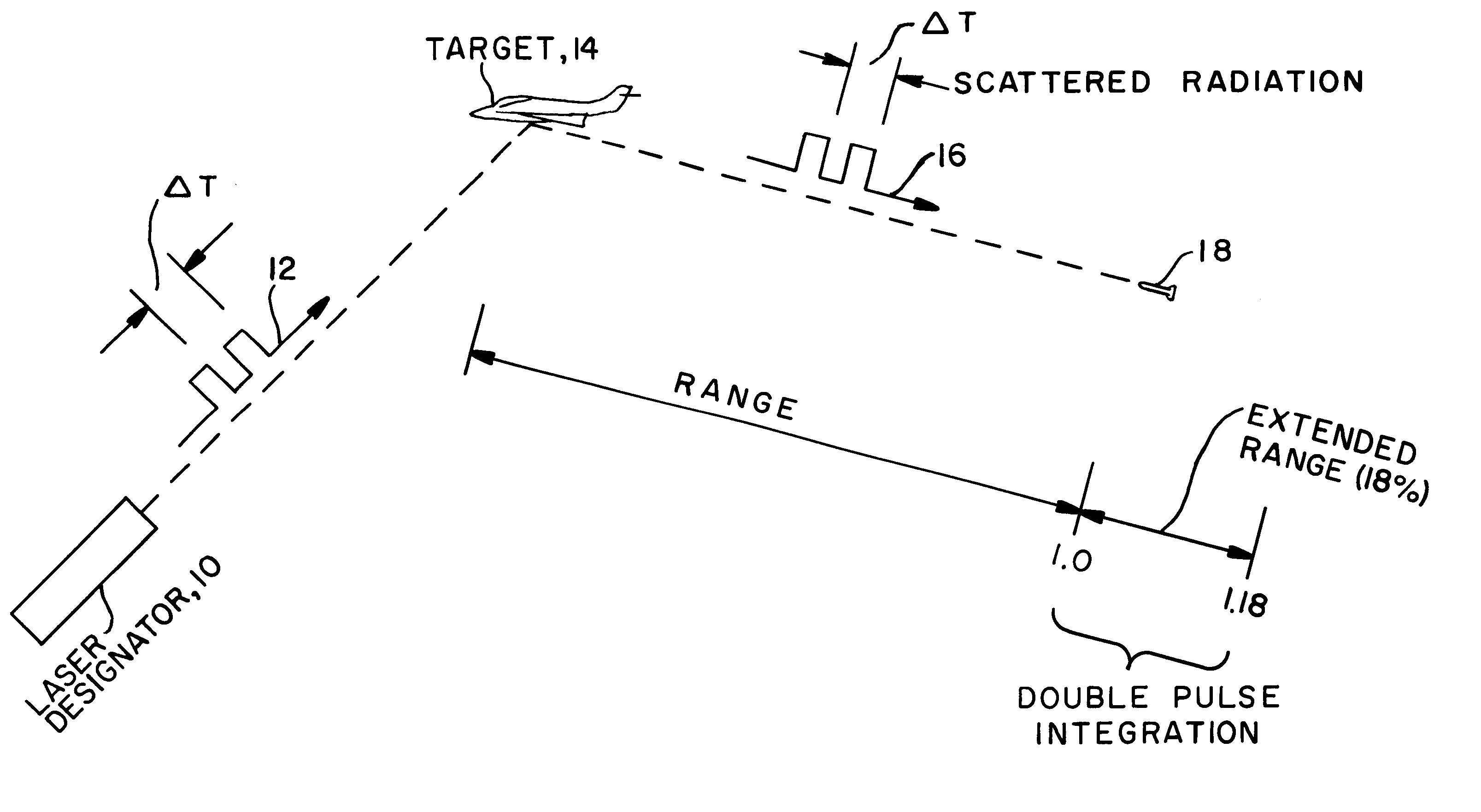
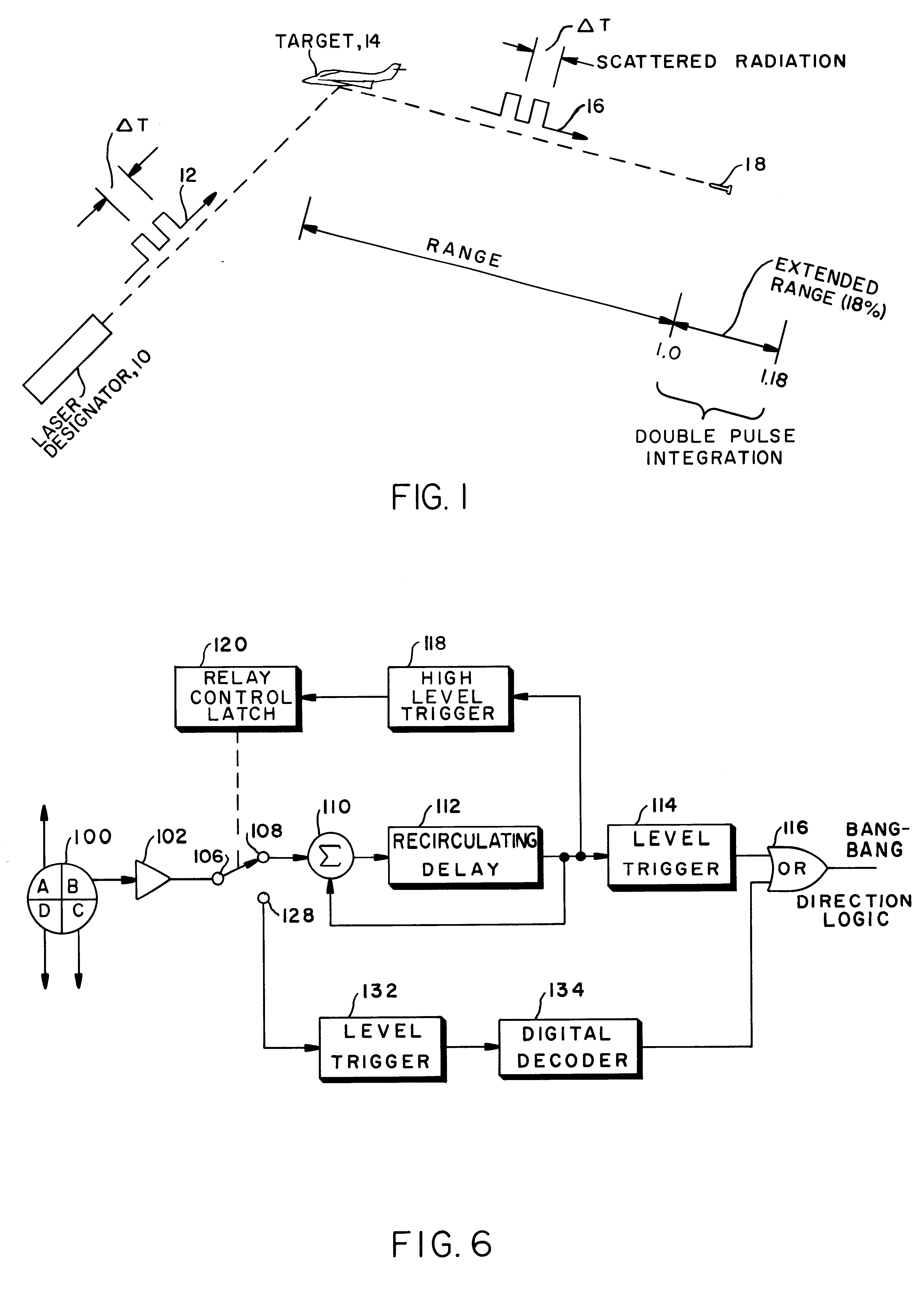
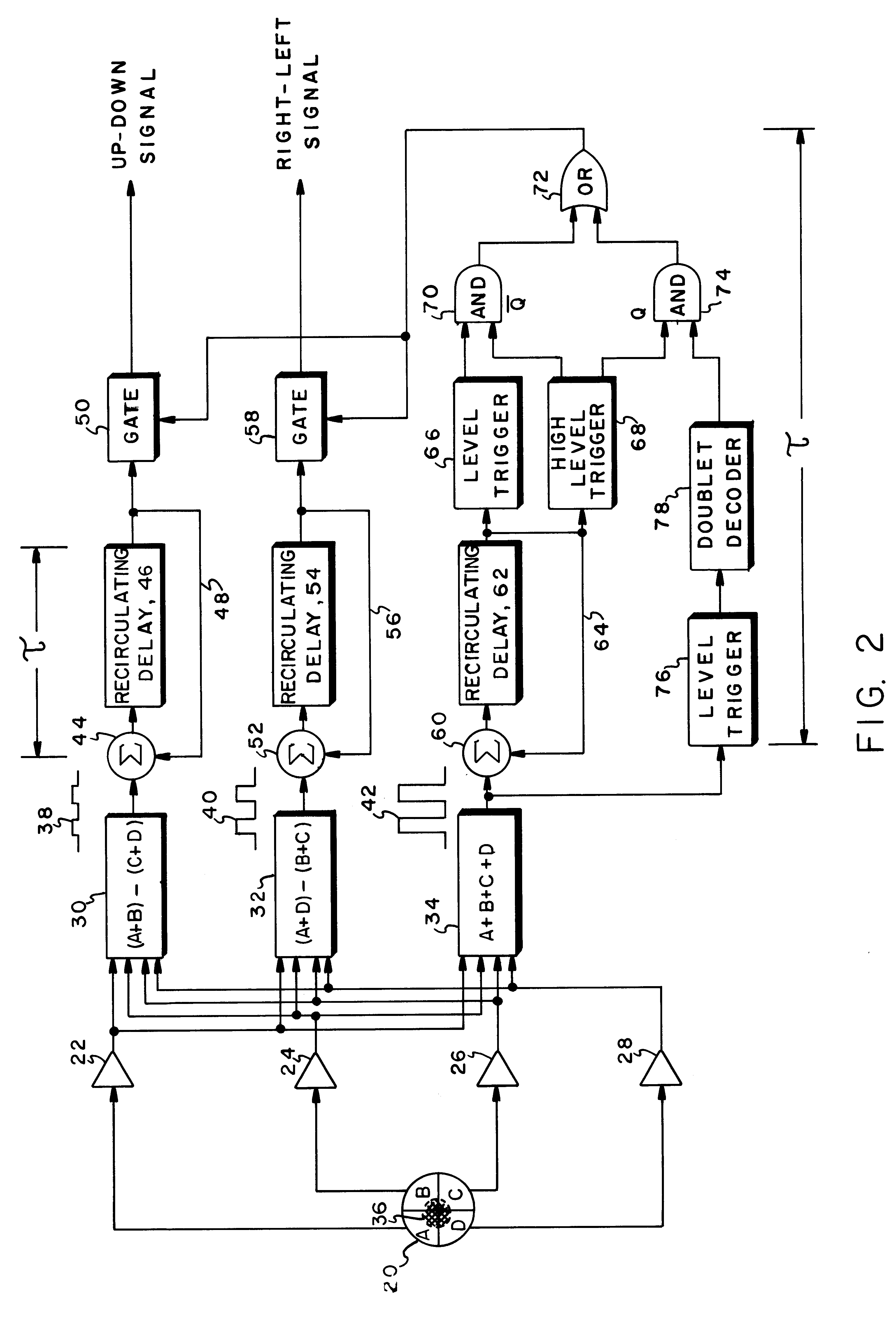
Pulse integration is utilized on board an optically guided missile or other ordinance device used as a part of a target designation system for extending the lock-on range of the missile by approximately 18%, when a double pulse laser is utilized to illuminate and designate the target. Pulse integration is accomplished with a recirculating delay unit which superimposes the first pulse on the second pulse, such that while the pulses add coherently, noise does not add in phase. The pulse integration technique therefore enhances the signal-to-noise ratio when the missile is at the outer limits of its operating range. When the missile is sufficiently close to the target, doublet decoding is actuated to offer countermeasure resistance. At this point, pulse integration may proceed in lieu of doublet decoding or may be dispensed with in view of the increased signal-to-noise ratio due to the close range of the missile to the target.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC +1
Projectile trajectory control system
ActiveUS7354017B2Reduce time and energyReduce weightAmmunition projectilesDirection controllersAviationVehicle frame
Trajectory is controlled by a control system having fins that de-spin a section of the control system relative to a projectile or missile. The control system also includes aero-surfaces that produce a lift when brought to rotation speed of about 0 Hz relative to a reference frame and a brake that couples the guidance package to the rotational inertia of the projectile or missile. In one example, no electric motor is used in the trajectory control system, saving weight and increasing reliability.
Owner:GEN DYNAMICS ORDNANCE & TACTICAL SYST
Missile with odd symmetry tail fins
InactiveUS6869044B2Free spinsDirection controllersSelf-propelled projectilesFree rotationRadio frequency
A missile, either a powered missile or an unpowered projectile, includes a freely-rolling tail assembly having an odd number of fins. Having an odd number of fins may reduce oscillations caused by the rotation of the freely-rotating tail. This may make a more stable platform for a seeker, such as an uncooled focal point array or other imaging infrared (IIR) or millimeter wave radio frequency (MMW) seeker, in the body of the missile. Also, minimizing oscillation by using an odd number of fins may facilitate control of the missile.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Sport novelty missile
InactiveUS7727097B2Increase and enhances individual 's enjoymentHollow inflatable ballsHollow non-inflatable ballsEngineeringAmbient air
Owner:SIEGEL MICHAEL L +2
Conformal airliner defense (CAD) system
InactiveUS6929214B2OptimizationQuickly “ role fitted ”Wave based measurement systemsMilitary adjustmentCountermeasureCad system
A conformal air defense (CAD) system is provided which is adapted to be attached externally to an aircraft as an appendage. The CAD system includes a conformal mounting adapter having an aircraft-to-adapter interface and upper adapter side. A mounting structure is provided which has an adapter interface and a mounting side, wherein the adapter interface is attached to the upper adapter side. A missile countermeasures system is mounted on the mounting side of the mounting structure. And a cover substantially encloses the countermeasures system, wherein the cover is removably fastened to the mounting side of the mounting structure.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Fiber laser based directional infrared countermeasure (dircm) system
ActiveUS20070206177A1Improve operating characteristicsImprove efficiencyDefence devicesAmmunition projectilesCountermeasureData system
A DIRCM (Direct IR Counter Measures) system includes a detection and warning apparatus for detecting a missile that might pose a threat on the platform to which said system is allocated, and for generating a warning of its existence. The warning may include data that enable the calculation of the expected direction from which the missile is approaching. The DIRCM system may also include an acquisition device for performing acquisition of the approaching missile in accordance with the data provided by the detection and warning apparatus, and issuing data that may enable the calculation in real time of the updated position of the missile, a fiber laser for generating a laser beam, and a motion and aiming enabled turret, coupled with the laser, for directing the laser beam onto the approaching missile. The laser beam may be generated in accordance with the missile's updated position as calculated based on data received from the acquisition device, and processing means, linked to the detection and warning apparatus and also to the acquisition device, the laser and the turret.
Owner:EL OP ELECTRO OPTICS INDS
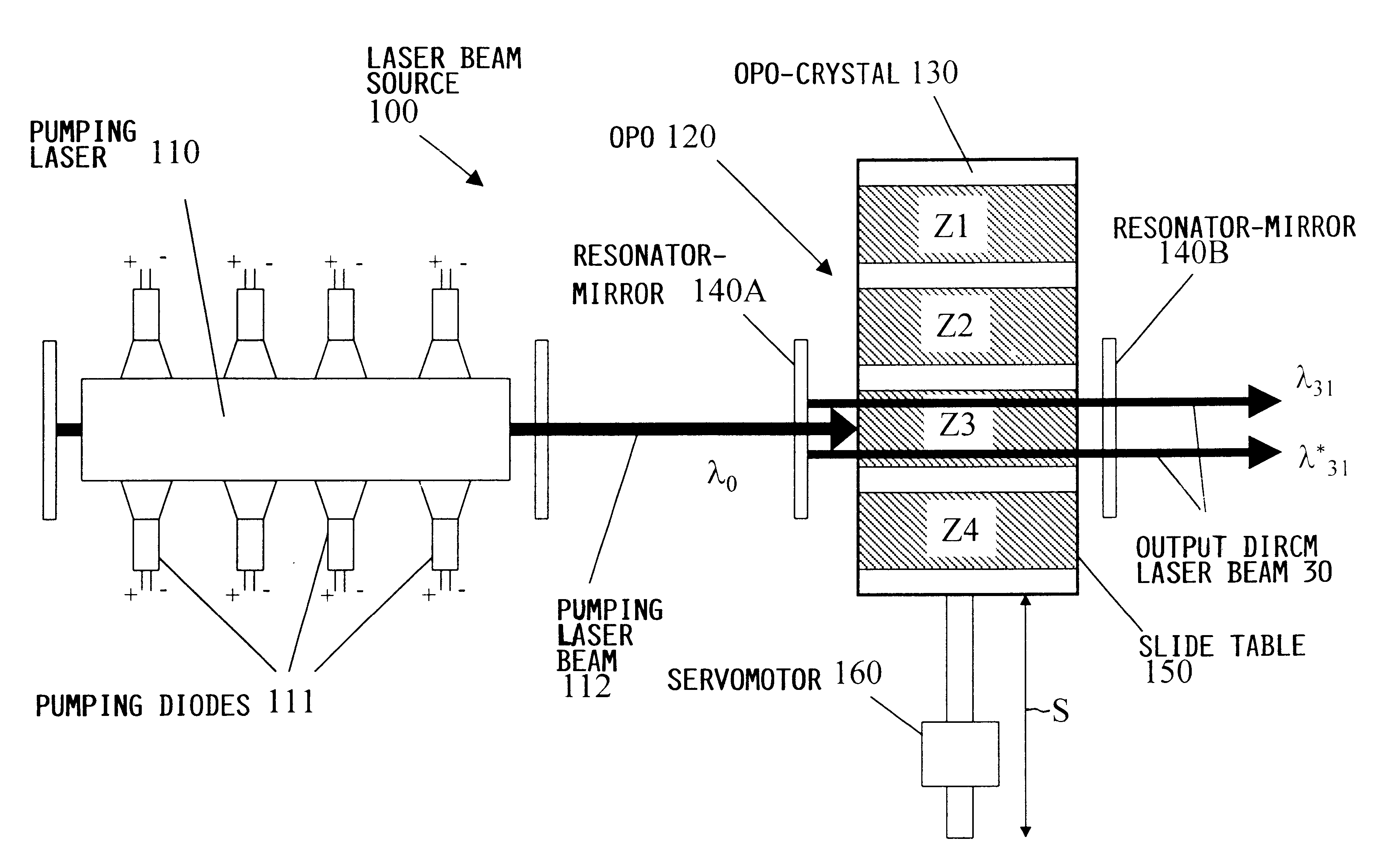
Laser beam source for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system
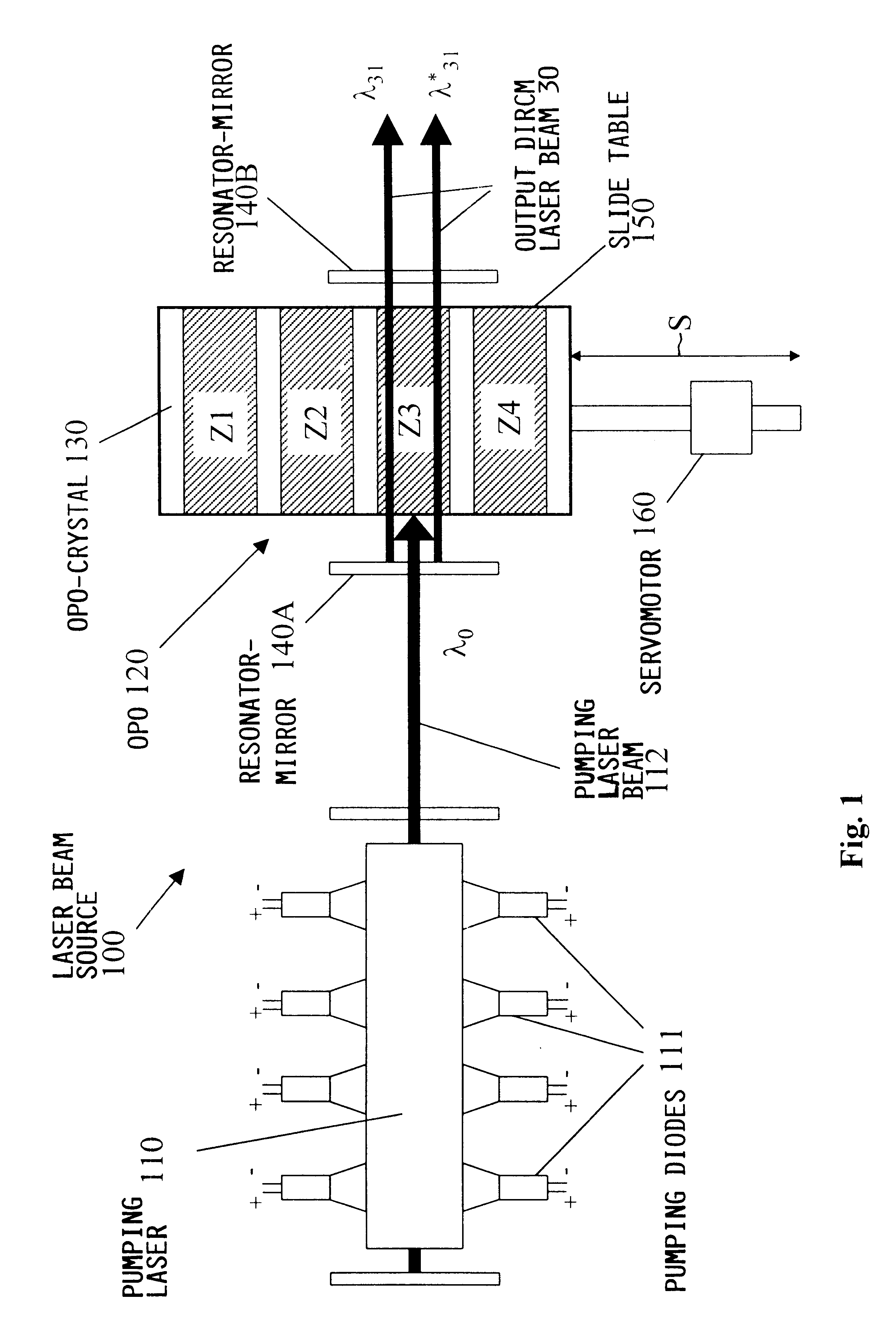
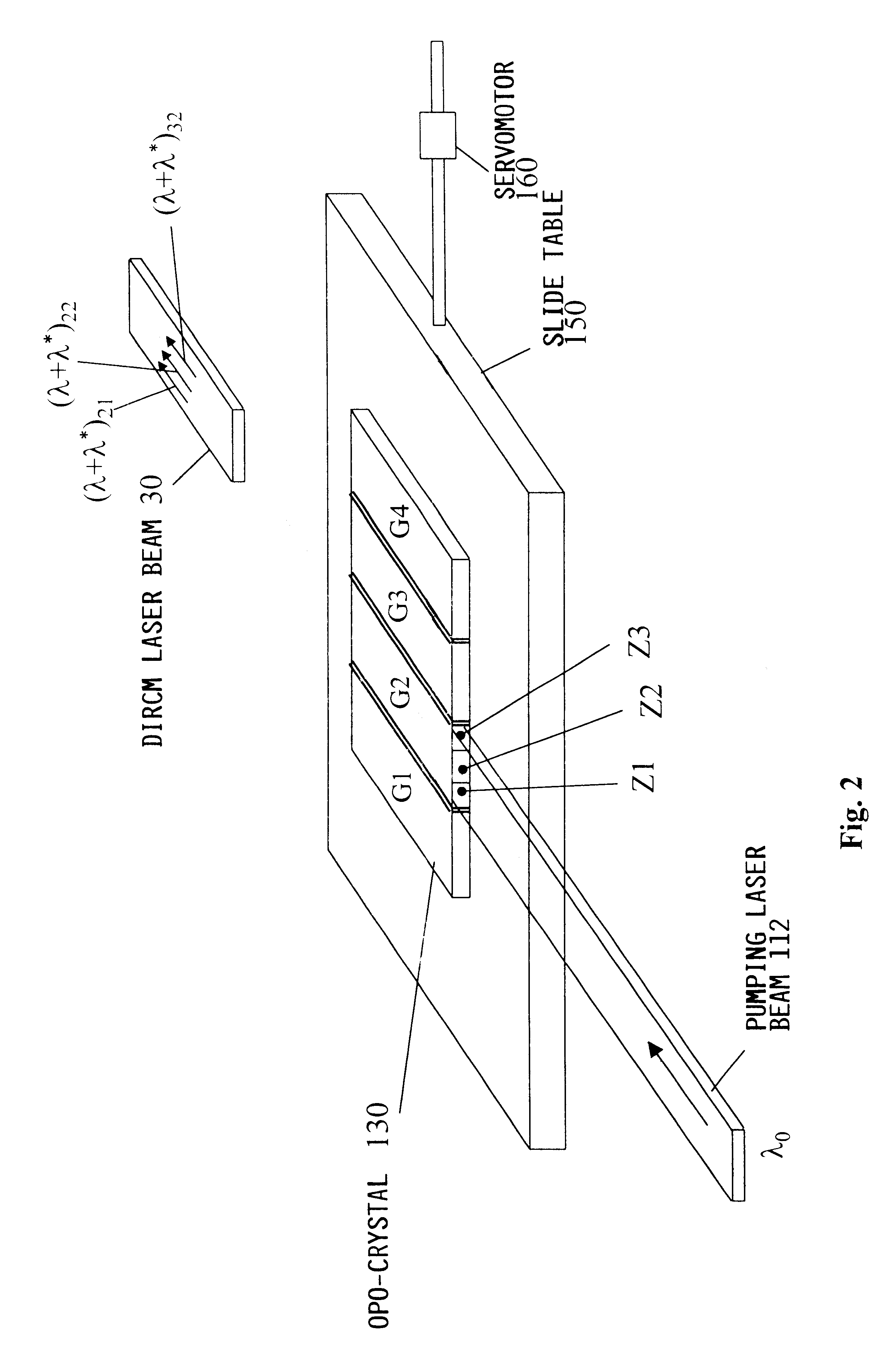
A laser beam source and an operating method thereof is provided for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system for defensively countering guided missiles having infrared seeking heads, by directing an infrared laser beam at the guided missile so as to disorient, saturate, or irreversibly destroy the IR detectors and circuitry arranged in the target seeking head. The power, pulse frequency and spectral composition of the laser beam is adjustable and selectable as required to adapt to any particular defensive engagement. To achieve this, the laser beam source comprises an Nd:YAG pumping laser and an optical parametric oscillator including an oscillator crystal arranged in a resonator cavity. The crystal includes a plurality of different periodically polarized crystal zones having different lattice constants. The adjacent zones can be grouped together into selectable crystal zone groups. The beam cross-section of the pumping laser beam corresponds to the cross-section of a single crystal zone or of a crystal zone group encompassing plural zones. The crystal is arranged on a slide table that is slidably displaceable by a servomotor, to move a selected crystal zone or group into the path of the pumping laser beam. Thereby the wavelength components and the relative intensities thereof of the output laser beam can easily be selectively adjusted.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
Flight control actuation system
InactiveUS7007897B2Reduce loadAircraft stabilisationWithout power ampliicationFly controlFlight control surfaces
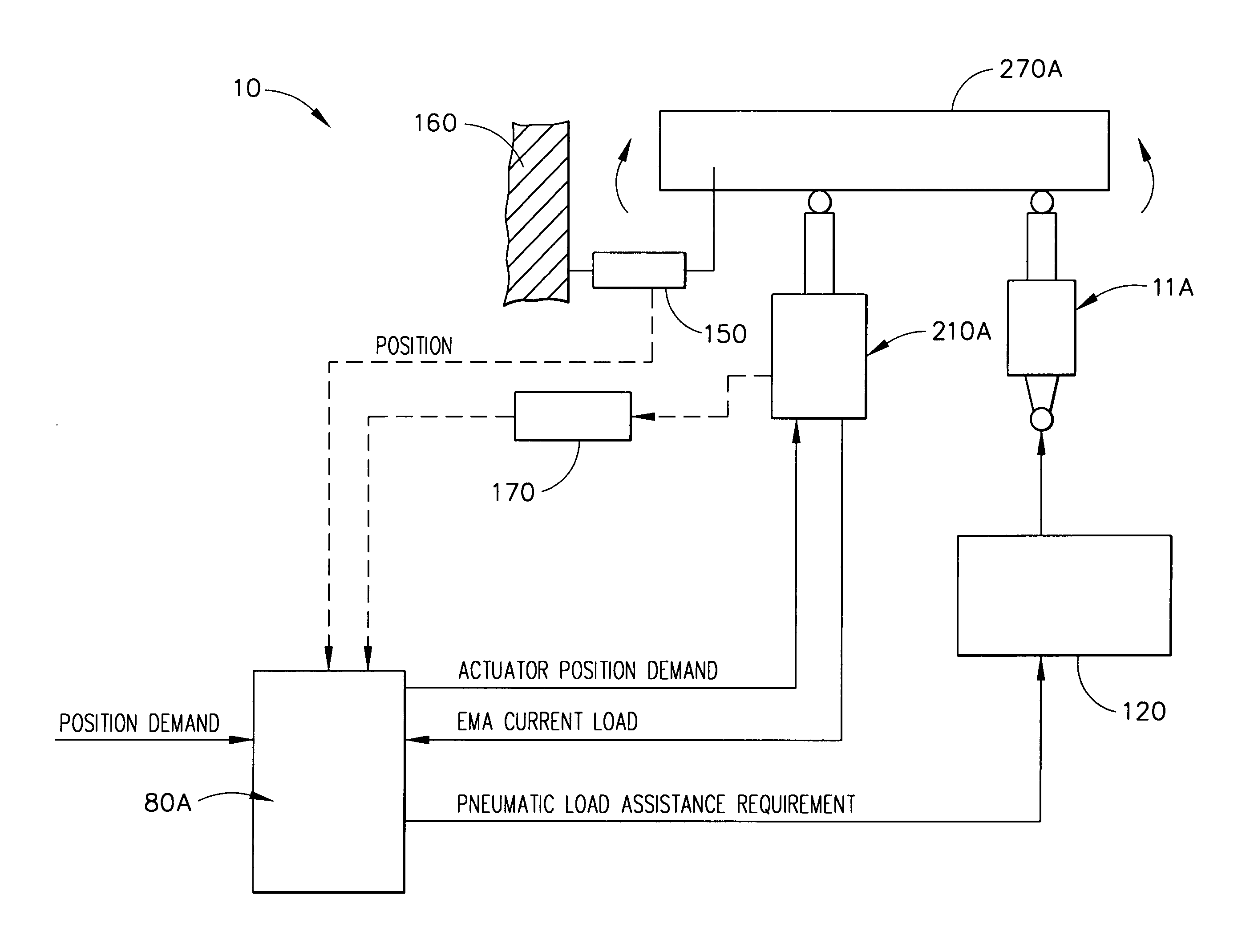
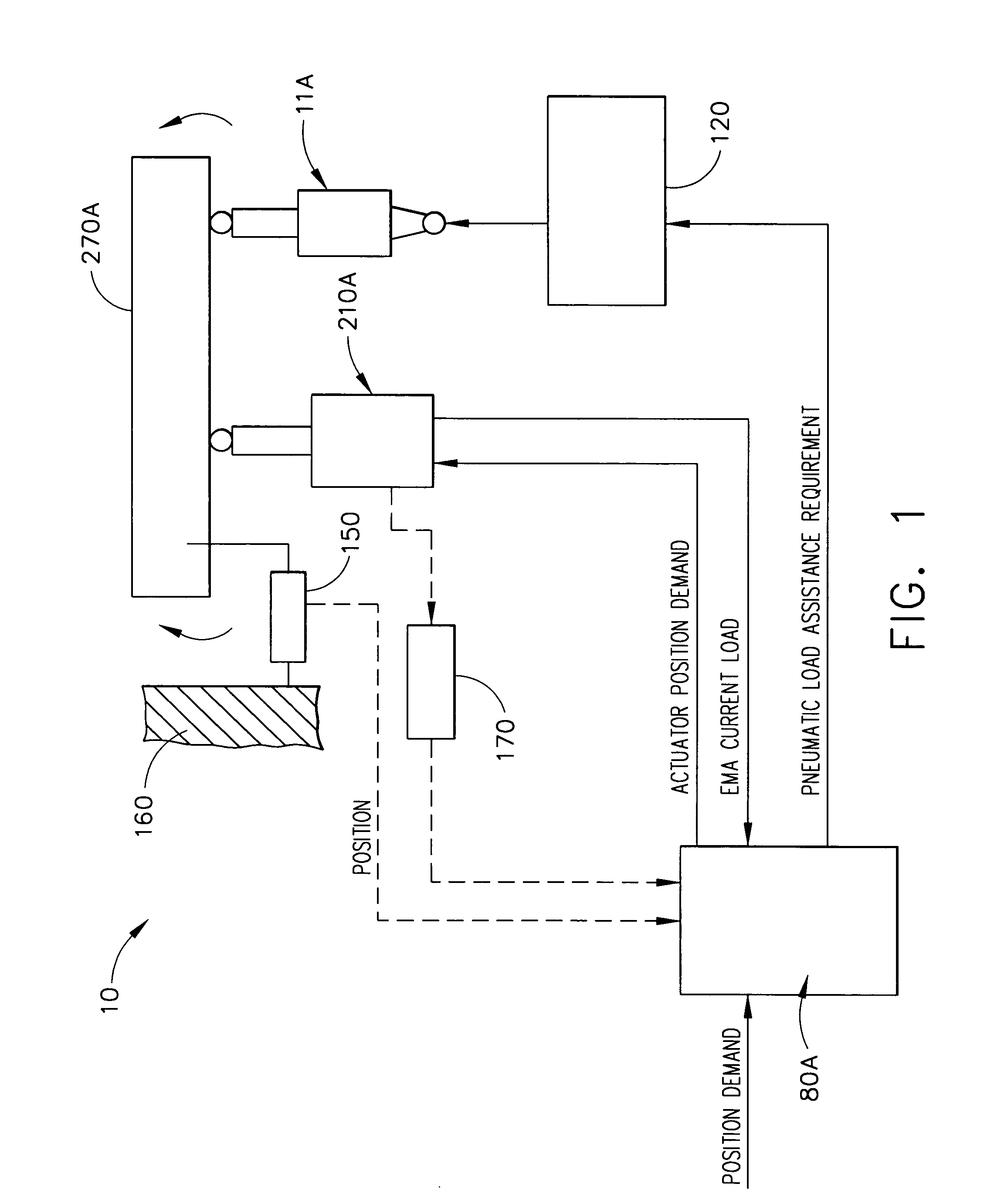
A flight control actuation system comprises a controller, electromechanical actuator and a pneumatic actuator. During normal operation, only the electromechanical actuator is needed to operate a flight control surface. When the electromechanical actuator load level exceeds 40 amps positive, the controller activates the pneumatic actuator to offset electromechanical actuator loads to assist the manipulation of flight control surfaces. The assistance from the pneumatic load assist actuator enables the use of an electromechanical actuator that is smaller in size and mass, requires less power, needs less cooling processes, achieves high output forces and adapts to electrical current variations. The flight control actuation system is adapted for aircraft, spacecraft, missiles, and other flight vehicles, especially flight vehicles that are large in size and travel at high velocities.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Electron beam directed energy device and methods of using same
InactiveUS7282727B2Avoid excessive distanceLess detectableDefence devicesThermometer detailsX-rayEnergy device
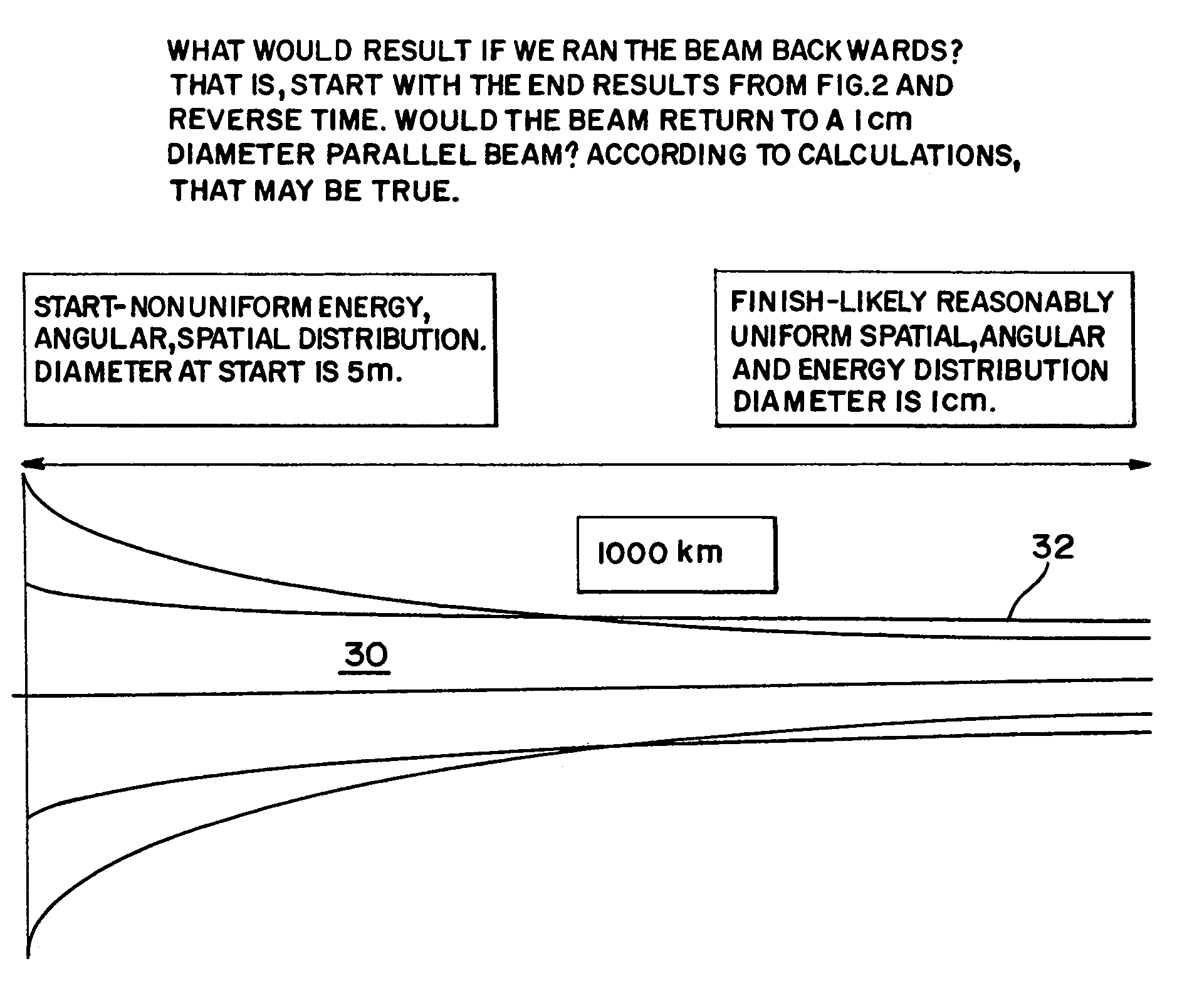
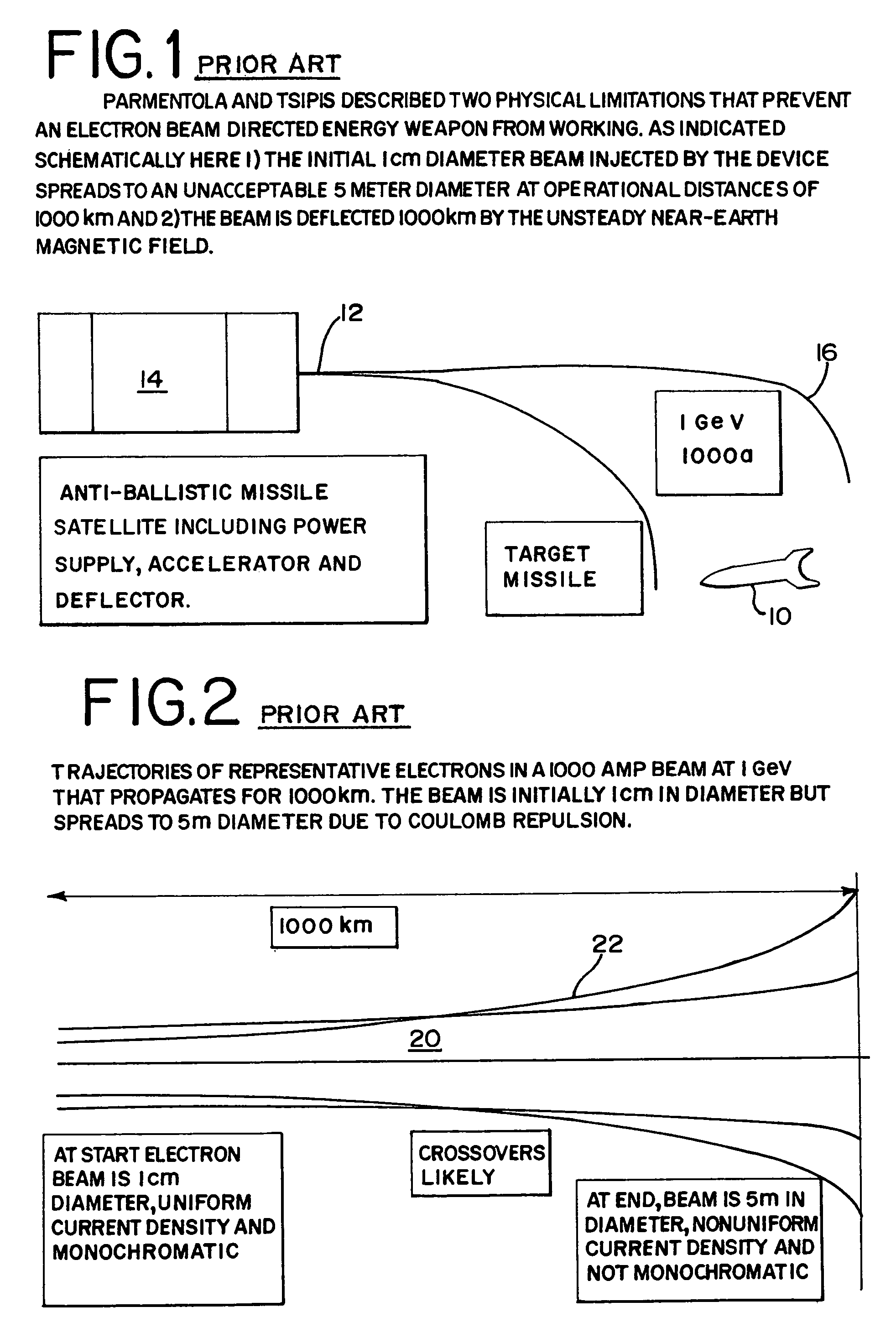
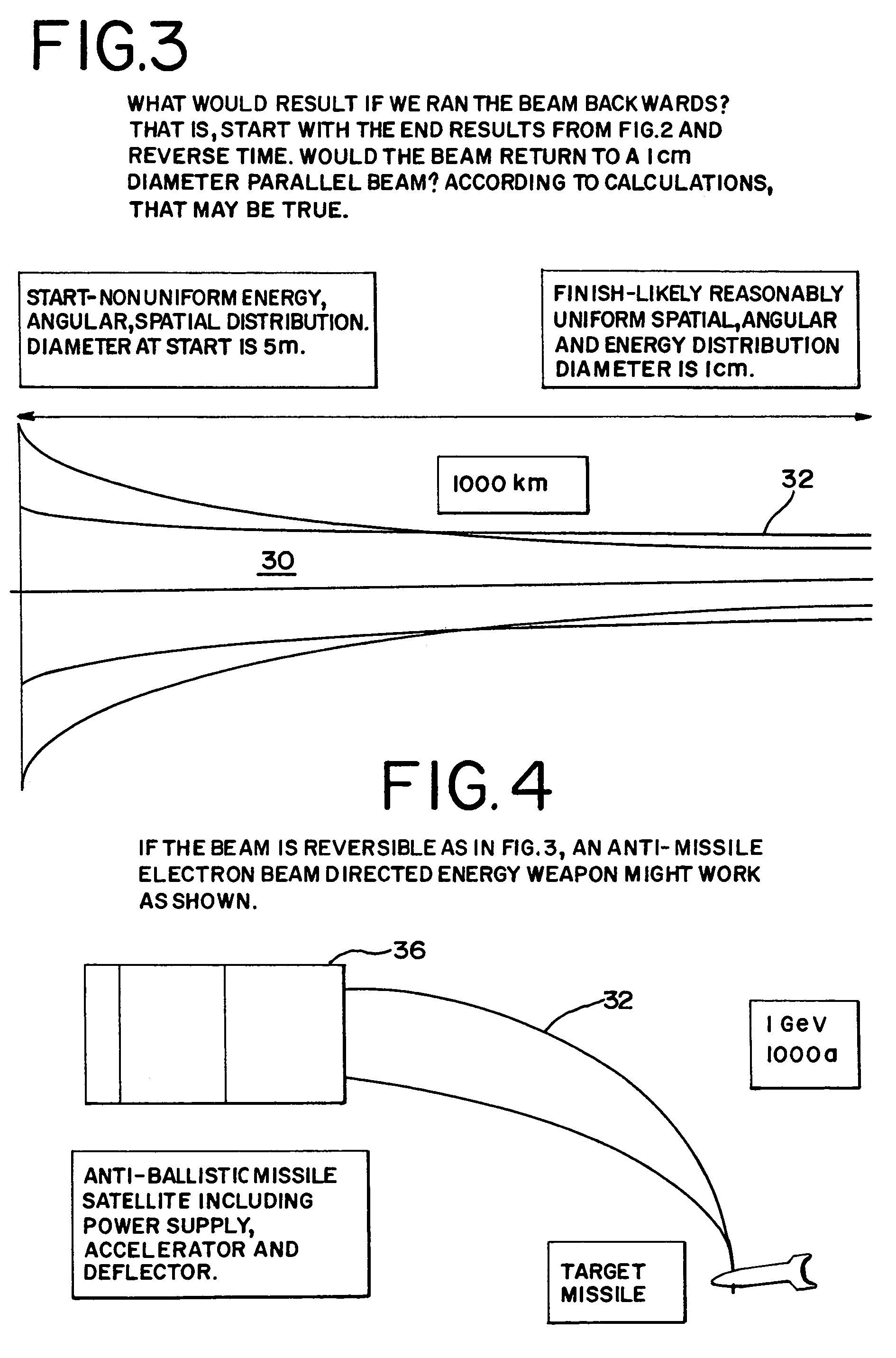
A method and apparatus is disclosed for an electron beam directed energy device. The device consists of an electron gun with one or more electron beams. The device includes one or more accelerating plates with holes aligned for beam passage. The plates may be flat or preferably shaped to direct each electron beam to exit the electron gun at a predetermined orientation. In one preferred application, the device is located in outer space with individual beams that are directed to focus at a distant target to be used to impact and destroy missiles. The aimings of the separate beams are designed to overcome Coulomb repulsion. A method is also presented for directing the beams to a target considering the variable terrestrial magnetic field. In another preferred application, the electron beam is directed into the ground to produce a subsurface x-ray source to locate and / or destroy buried or otherwise hidden objects including explosive devices.
Owner:RETSKY MICHAEL W
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com