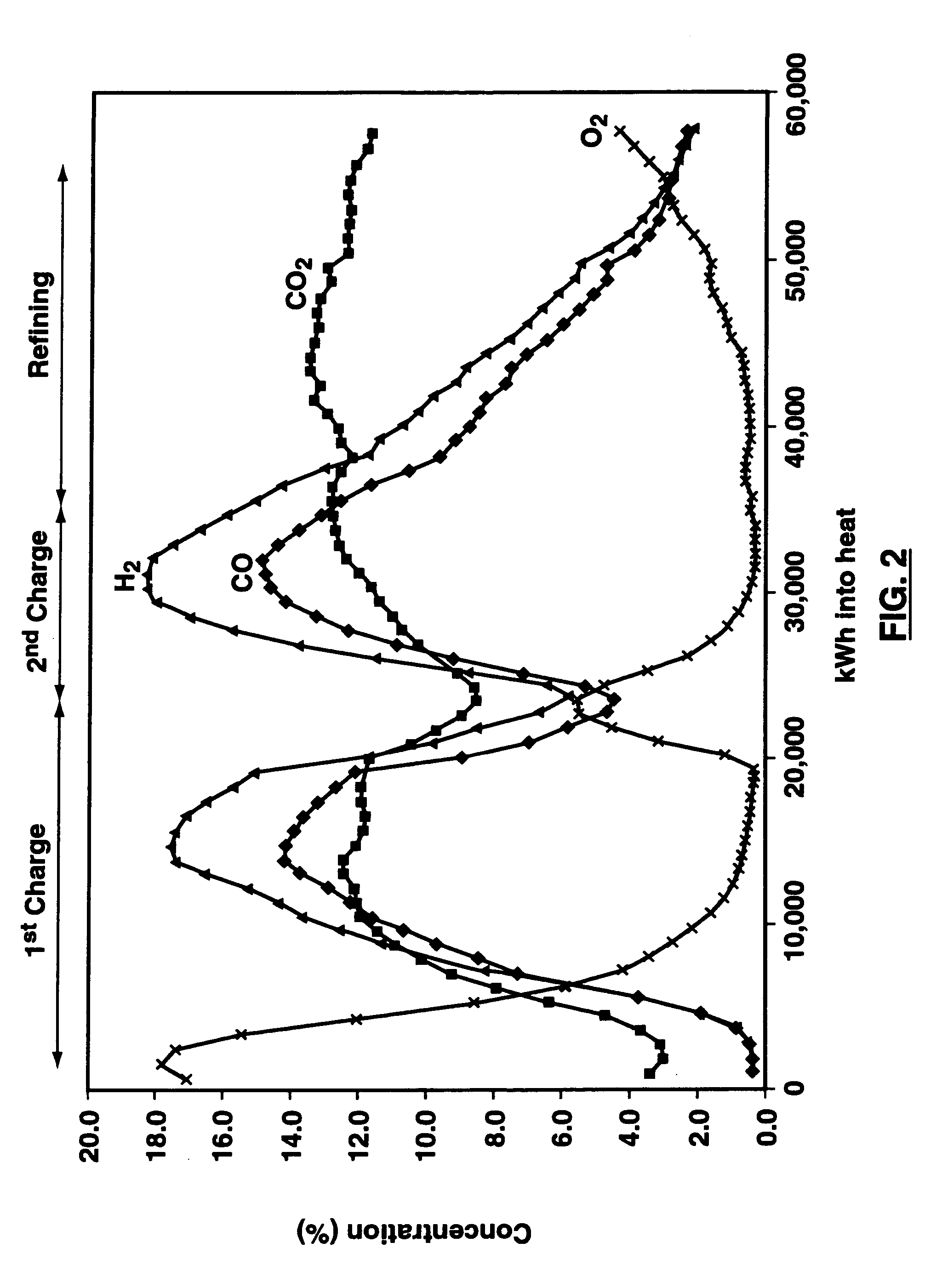
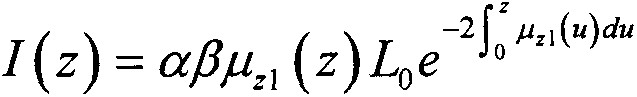Patents
Literature
174 results about "Infrared laser beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
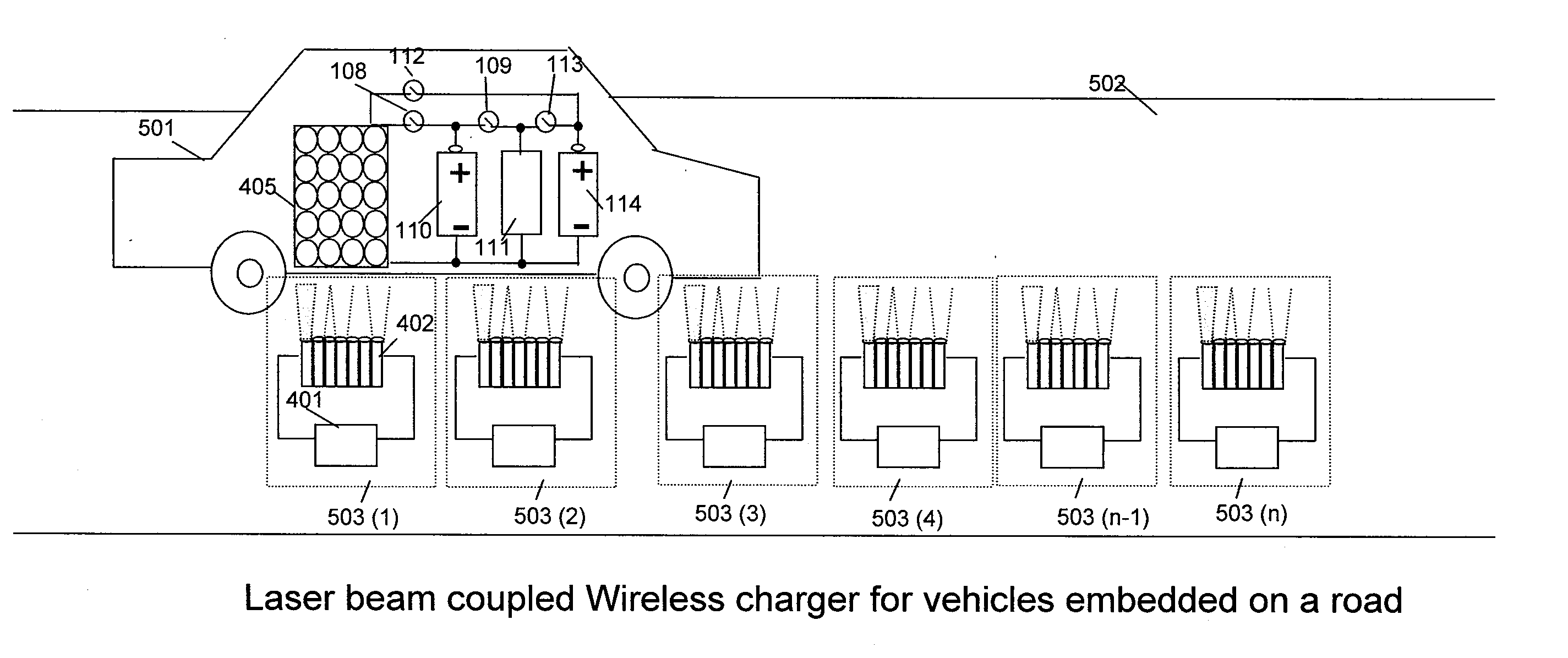
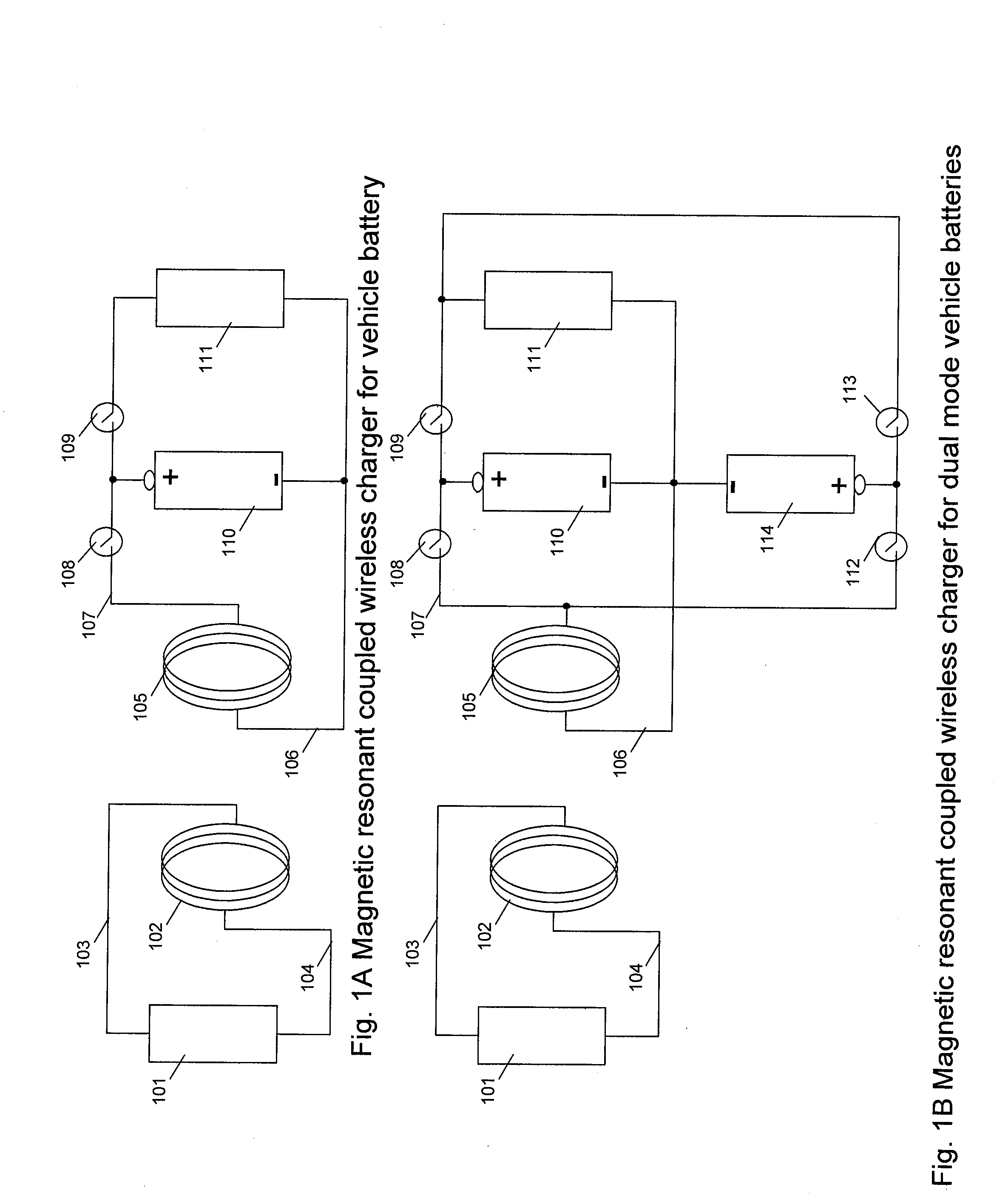
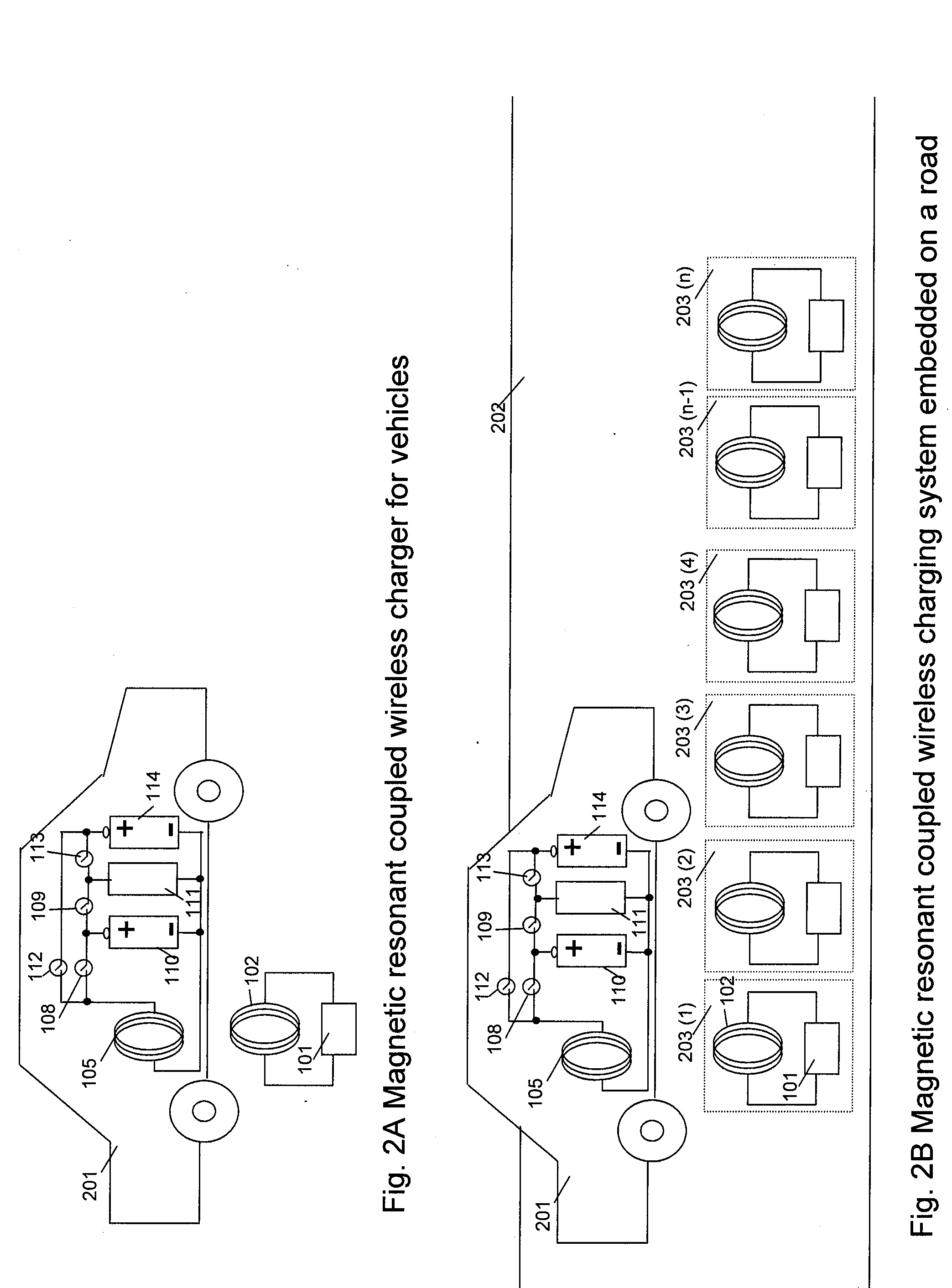
Wireless Charging System for Vehicles
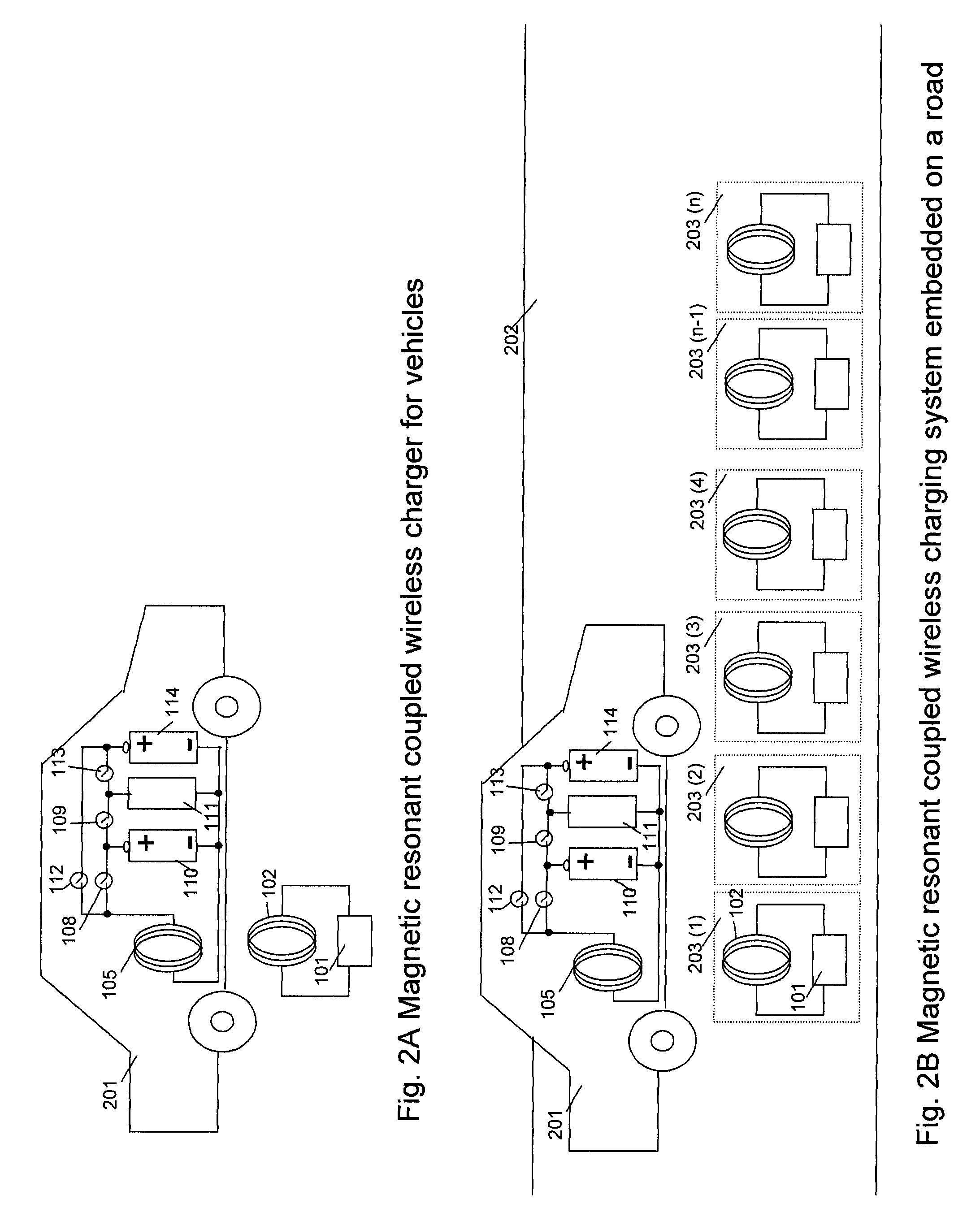
ActiveUS20090045773A1Eliminate needBatteries circuit arrangementsIn situ pavingsElectric power transmissionTransmitted power
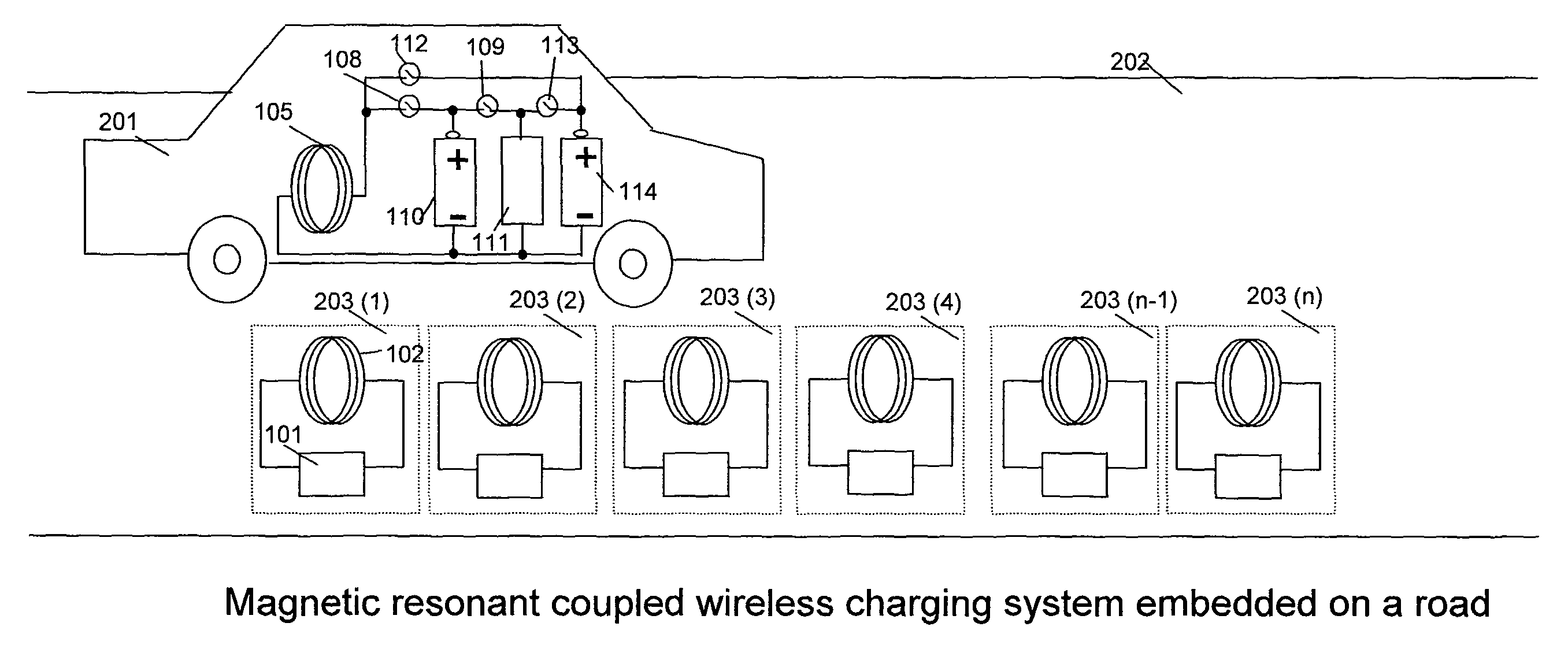
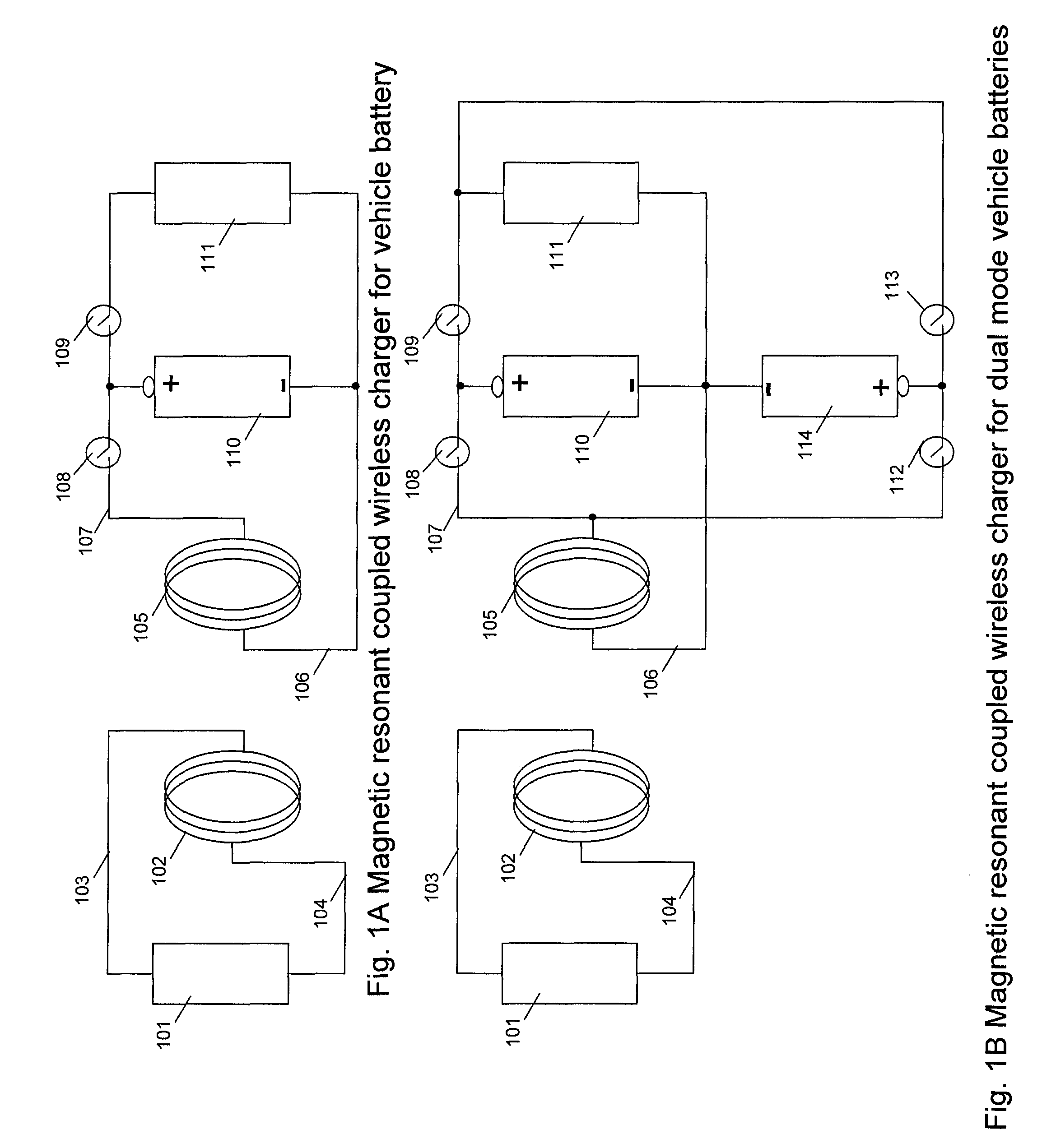
A system of energy storage and charging usable in vehicles and other applications that eliminate the battery capacity and automotive range issues is described. In our invention, vehicles are equipped with charging mechanisms to charge and recharge onboard batteries using wireless electricity and power transmission using magnetic resonant coupling between tuned electromagnetic circuits. The batteries may be charged using wireless charging systems installed along the roads while the vehicle is in use on the road. Charging system may optionally utilize infrared laser beam radiation to transmit power for charging the batteries on board a vehicle while it is in use as well. The onboard vehicle batteries may also be charged when the vehicle is not being driven either by plugging in the vehicle into wall electricity using wired power connection or may be wirelessly charged using the magnetic resonant coupling. By locating the charging circuits on roads, a continuous operation of electric-only mode of hybrid vehicles or pure electric-only vehicles can be accomplished and fully eliminate the need for gasoline usage
Owner:PANDYA RAVI A +1
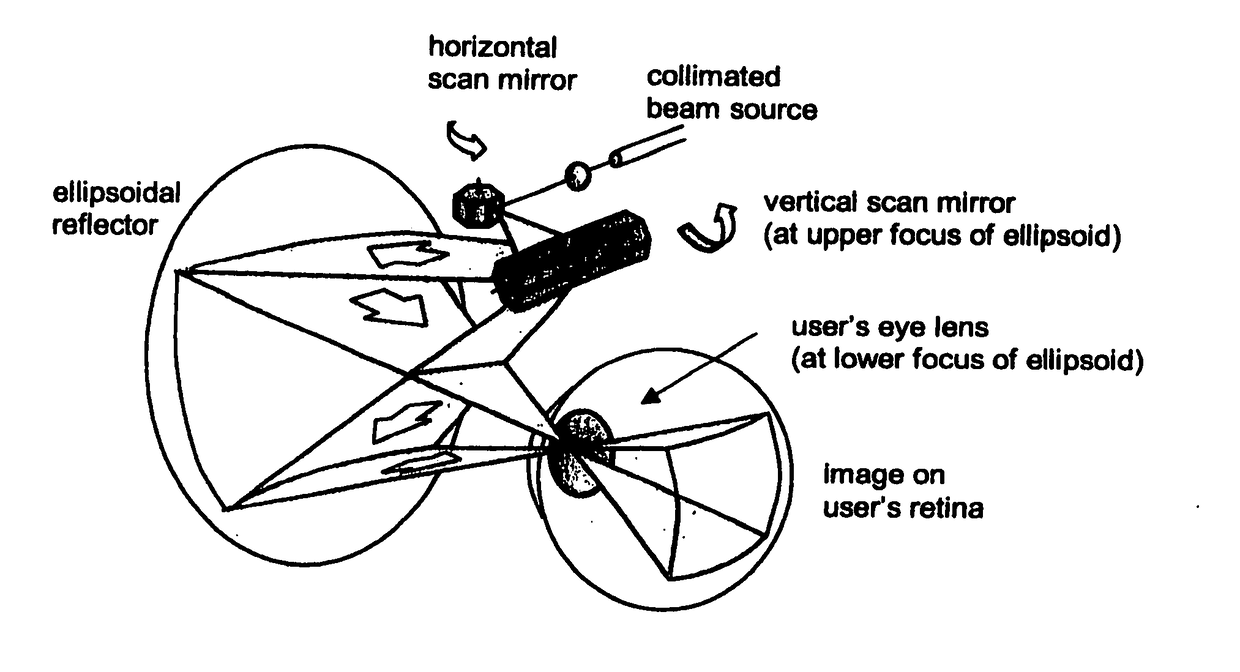
Dynamic foveal vision display
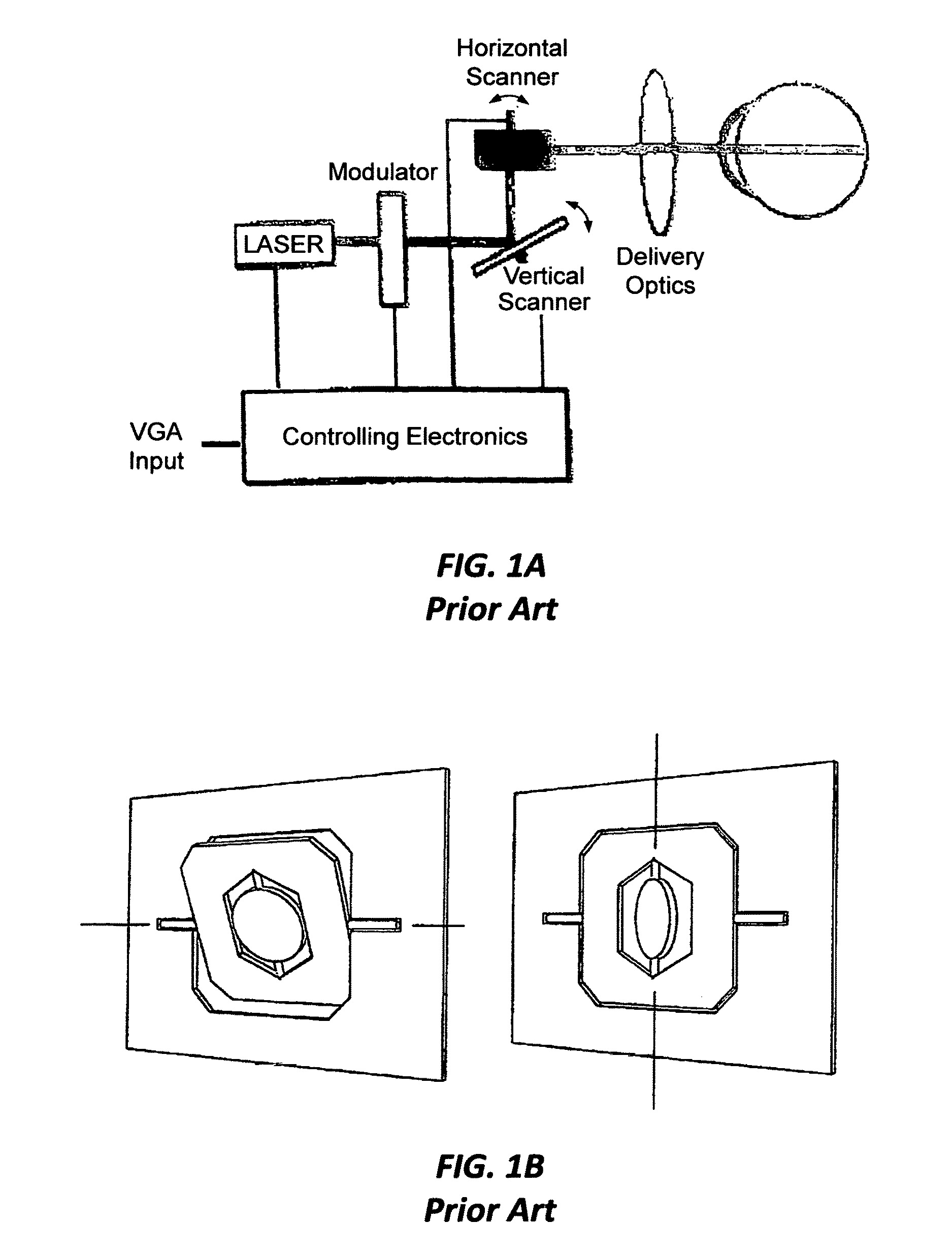
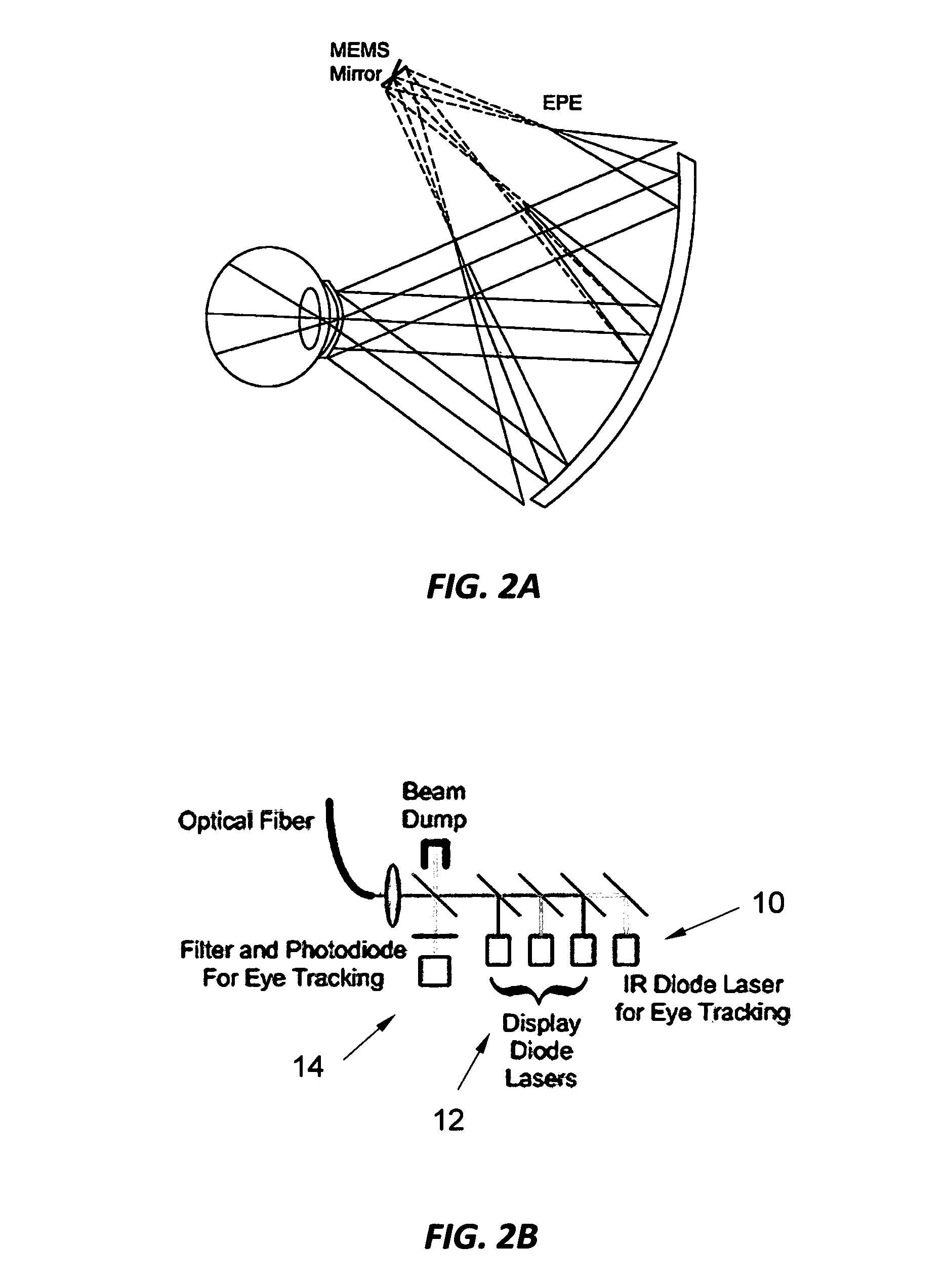
InactiveUS20120105310A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsOvercome limitationsCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsRetinaInfrared laser beam
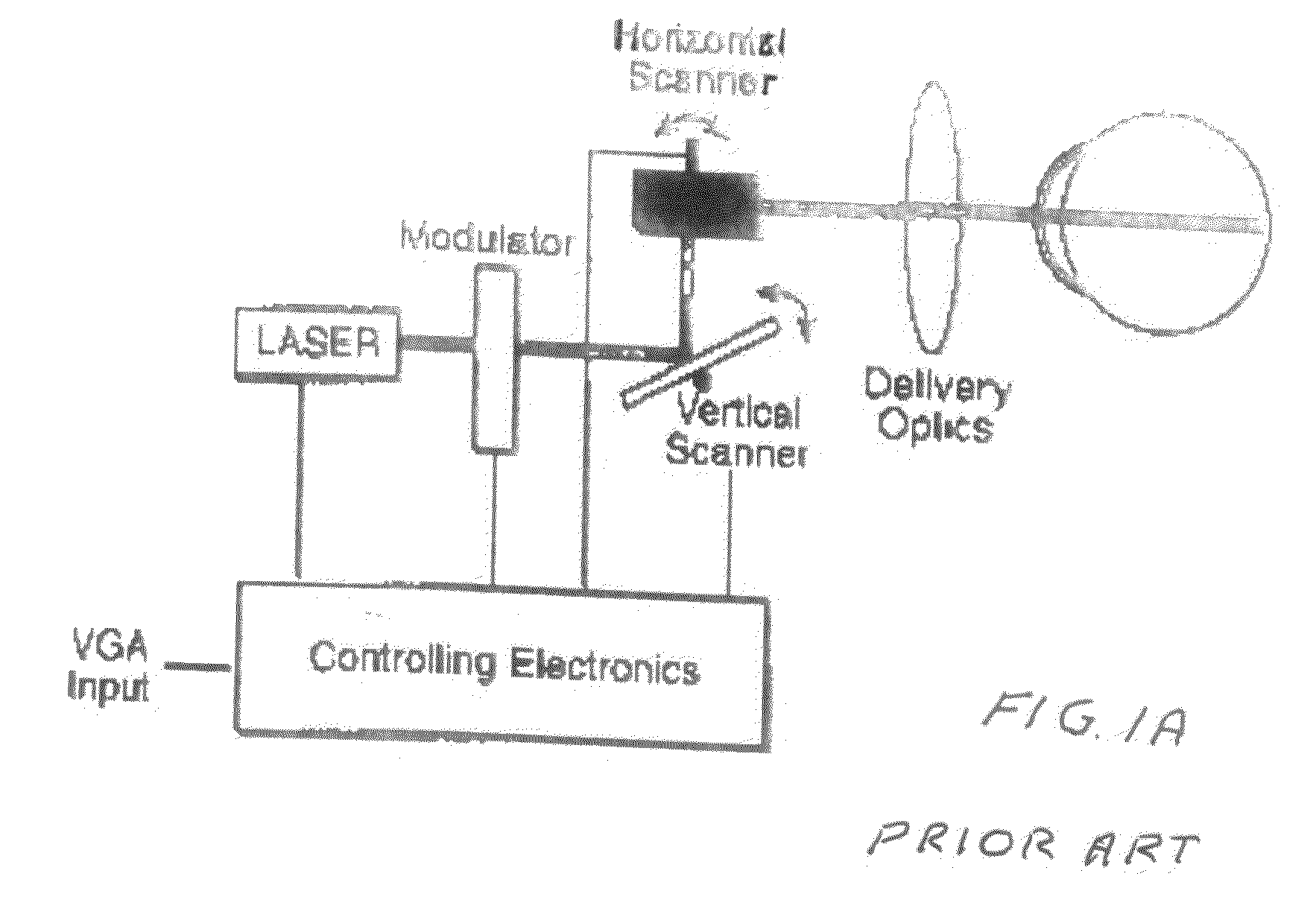
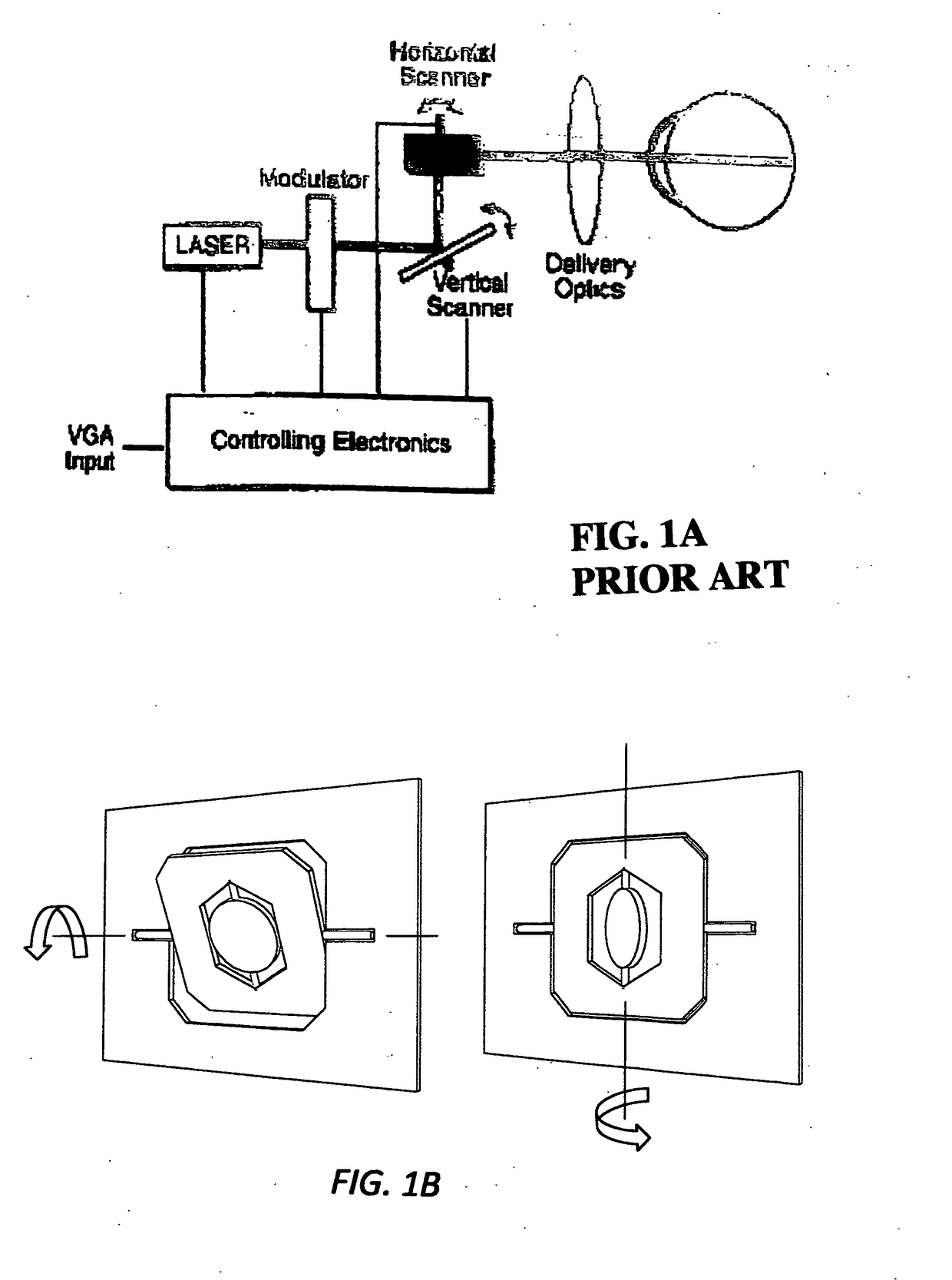
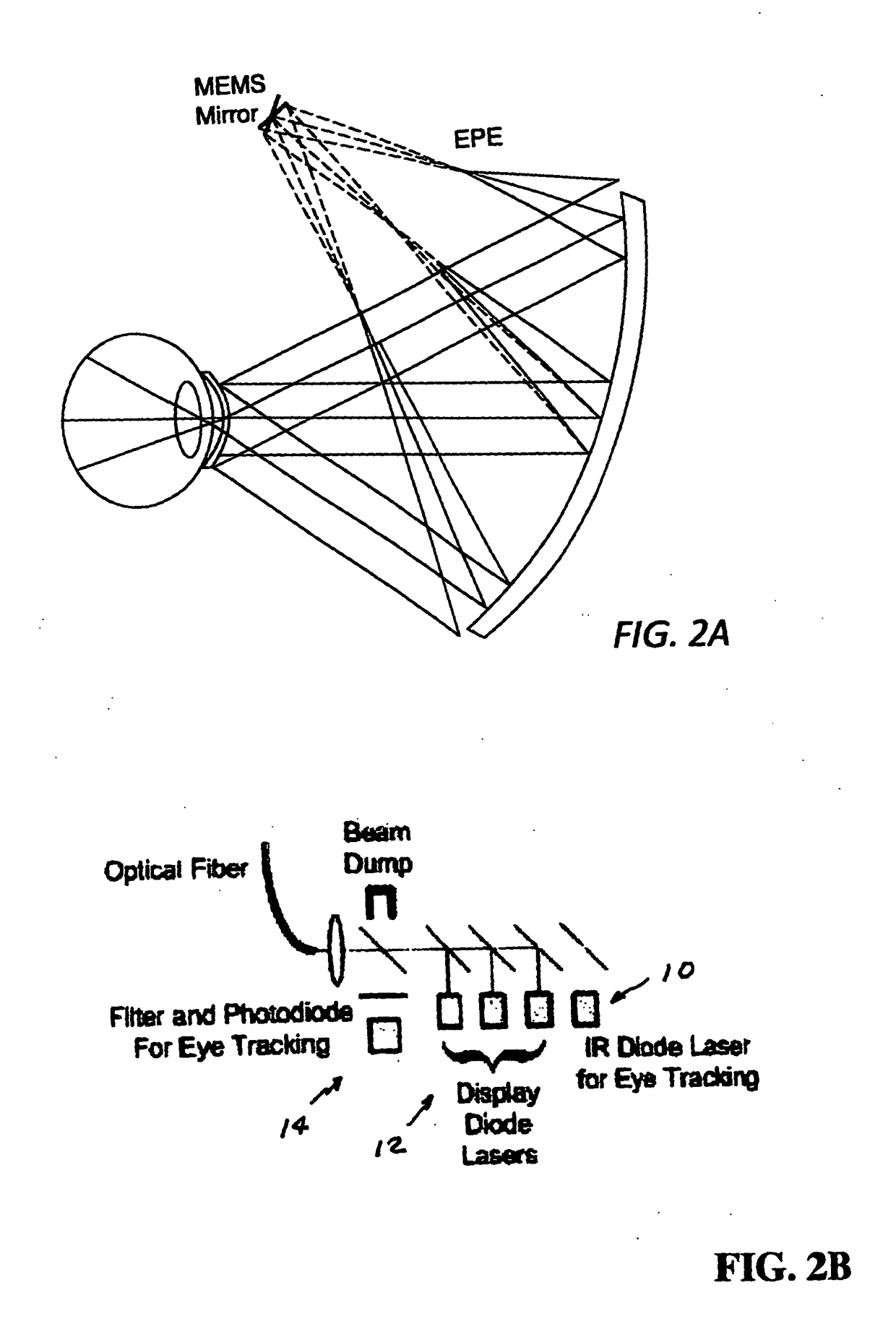
A head mounted display system with at least one retinal display unit having a curved reflector positioned in front of one eye or both eyes of a wearer. The unit includes a first set of three modulated visible-light lasers co-aligned and adapted to provide a laser beam with selectable color and a first scanner unit providing both horizontal and vertical scanning of the laser beam across a portion of the curved reflector in directions so as to produce a reflection of the color laser beam through the pupil of the eye onto a portion of the retina large enough to encompass the fovea. The unit also includes a second set three modulated visible-light lasers plus an infrared laser, all lasers being co-aligned and adapted to provide a color and infrared peripheral view laser beam, and a second scanner unit providing both horizontal and vertical scanning of the visible light and infrared laser beams across a portion of the curved reflector in directions so as to produce a reflection of the scanned color and infrared laser beams through the pupil of the eye onto a portion of retina corresponding to a field of view of at least 30 degrees×30 degrees.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Wireless charging system for vehicles
ActiveUS8030888B2Eliminate needBatteries circuit arrangementsIn situ pavingsElectric power transmissionOn board
A system of energy storage and charging usable in vehicles and other applications that eliminate the battery capacity and automotive range issues is described. In our invention, vehicles are equipped with charging mechanisms to charge and recharge onboard batteries using wireless electricity and power transmission using magnetic resonant coupling between tuned electromagnetic circuits. The batteries may be charged using wireless charging systems installed along the roads while the vehicle is in use on the road. Charging system may optionally utilize infrared laser beam radiation to transmit power for charging the batteries on board a vehicle while it is in use as well. The onboard vehicle batteries may also be charged when the vehicle is not being driven either by plugging in the vehicle into wall electricity using wired power connection or may be wirelessly charged using the magnetic resonant coupling. By locating the charging circuits on roads, a continuous operation of electric-only mode of hybrid vehicles or pure electric-only vehicles can be accomplished and fully eliminate the need for gasoline usage.
Owner:PANDYA RAVI A +1
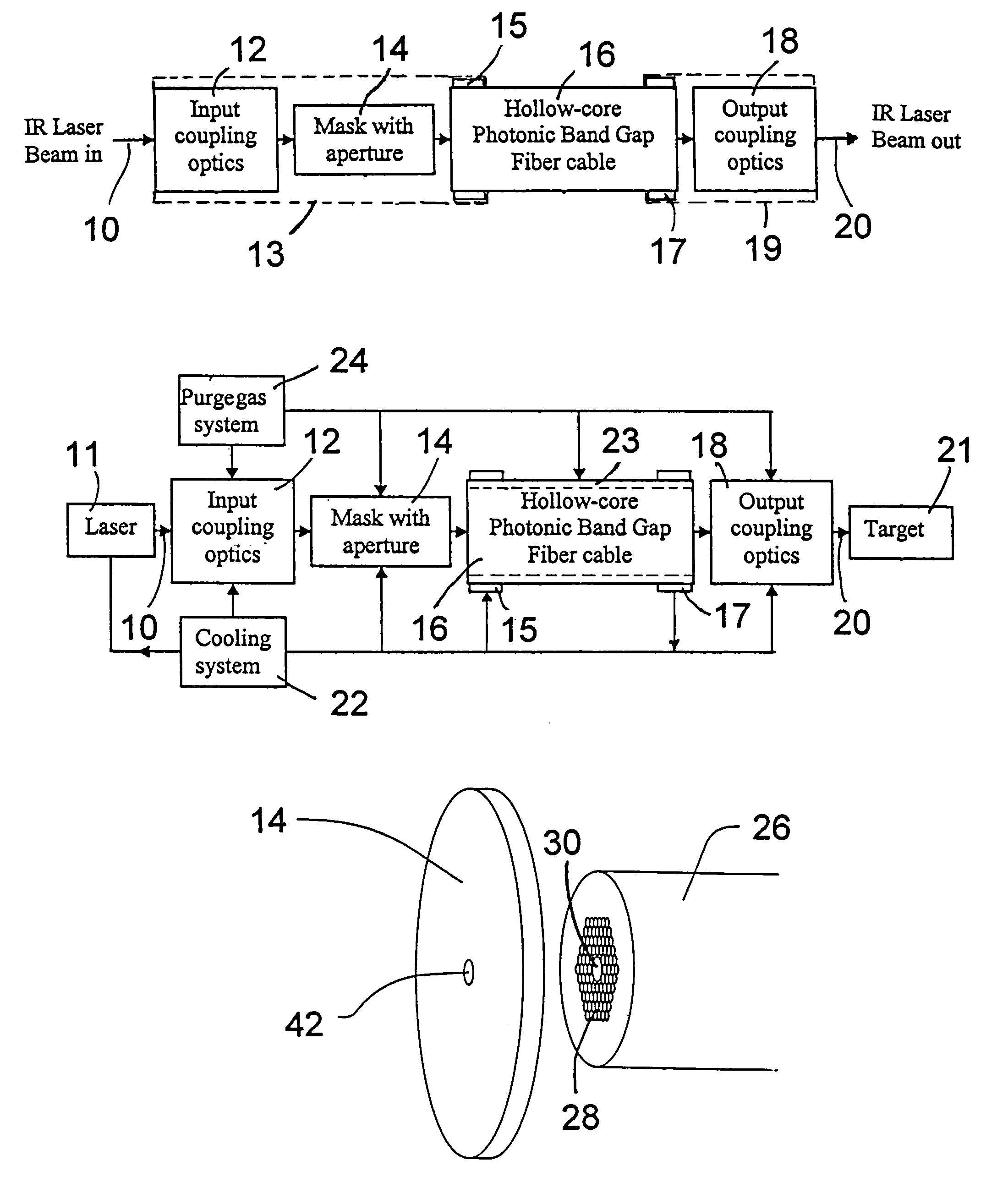
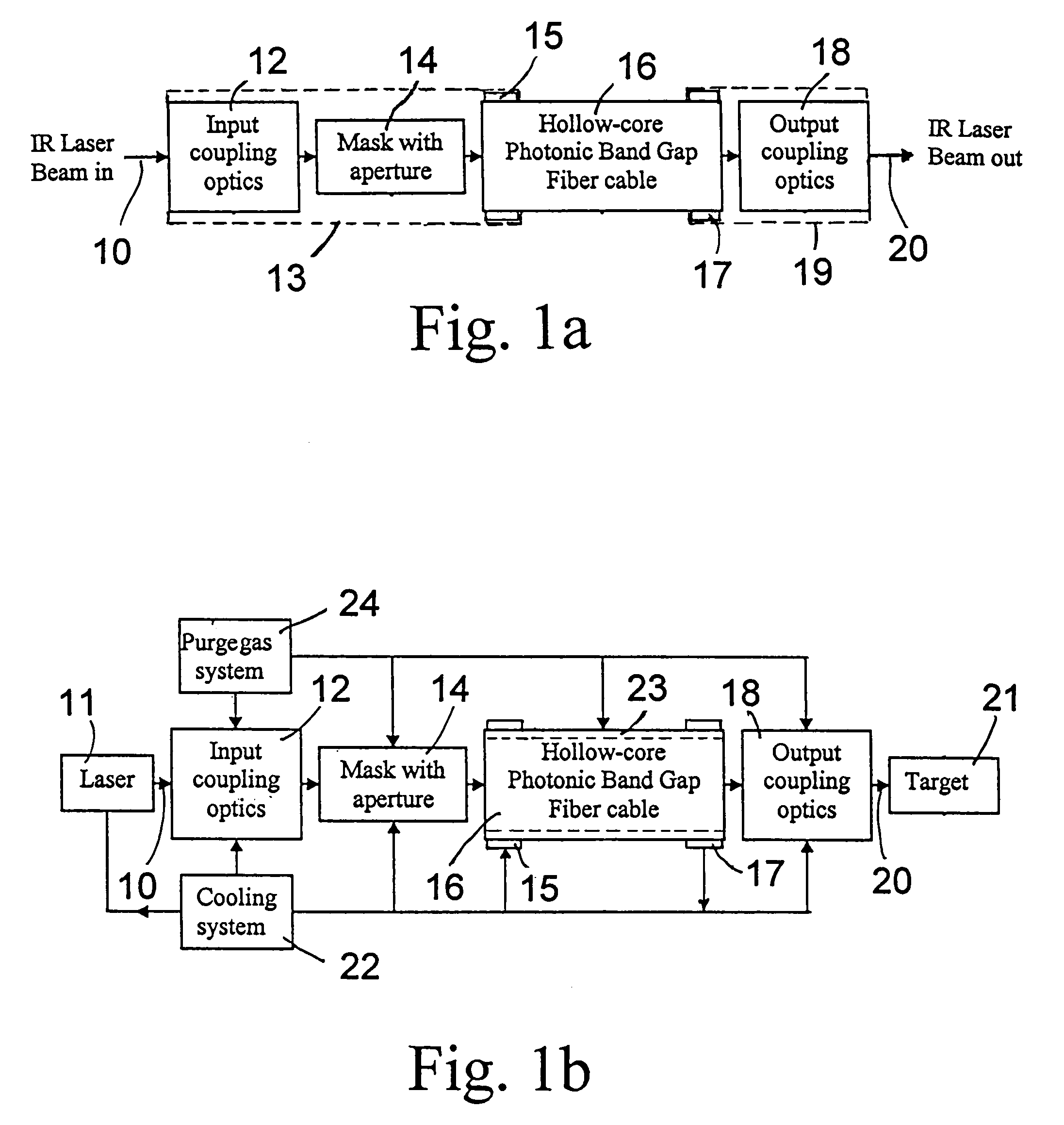
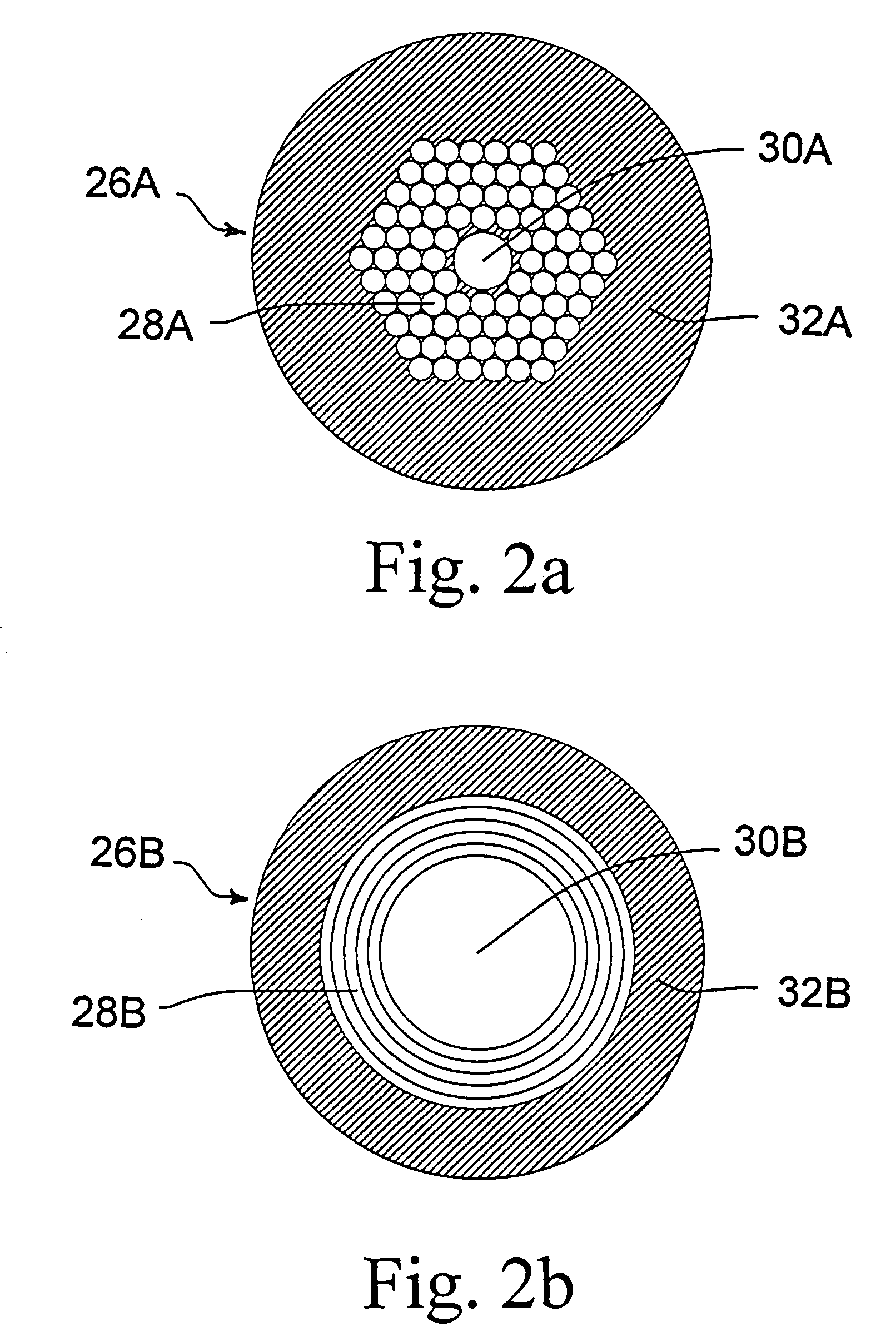
Fiber optic infrared laser beam delivery system
ActiveUS7099533B1Lower Level RequirementsAccurately heldOptical resonator shape and constructionCoupling light guidesFiberPhotonics
A laser beam delivery system is disclosed, which allows transmission of high-power infrared light through a hollow core photonic band gap (HC-PBG) fiber made of non-silica-based glass. In this system, the infrared beam first passes through input coupling optics which focus the beam onto the hollow core of the HC-PBG fiber. In front of the input end of the HC-PBG fiber, there is provided a mask with a hole aligned with the hollow core, and the infrared beam first passes through this hole before entering the hollow core of the HC-PBG fiber. This protects the photonic band gap structure from being damaged by the beam. After passing through the HC-PBG fiber, which may be from one to several hundred meters in length, the infrared beam exits at the output end of the fiber and passes through output coupling optics which collimate and focus the beam onto a desired target. The various components of the system may be water cooled during the operation or subjected to a gas purge to prevent condensation or gas ionization.
Owner:CHENARD FRANCOIS
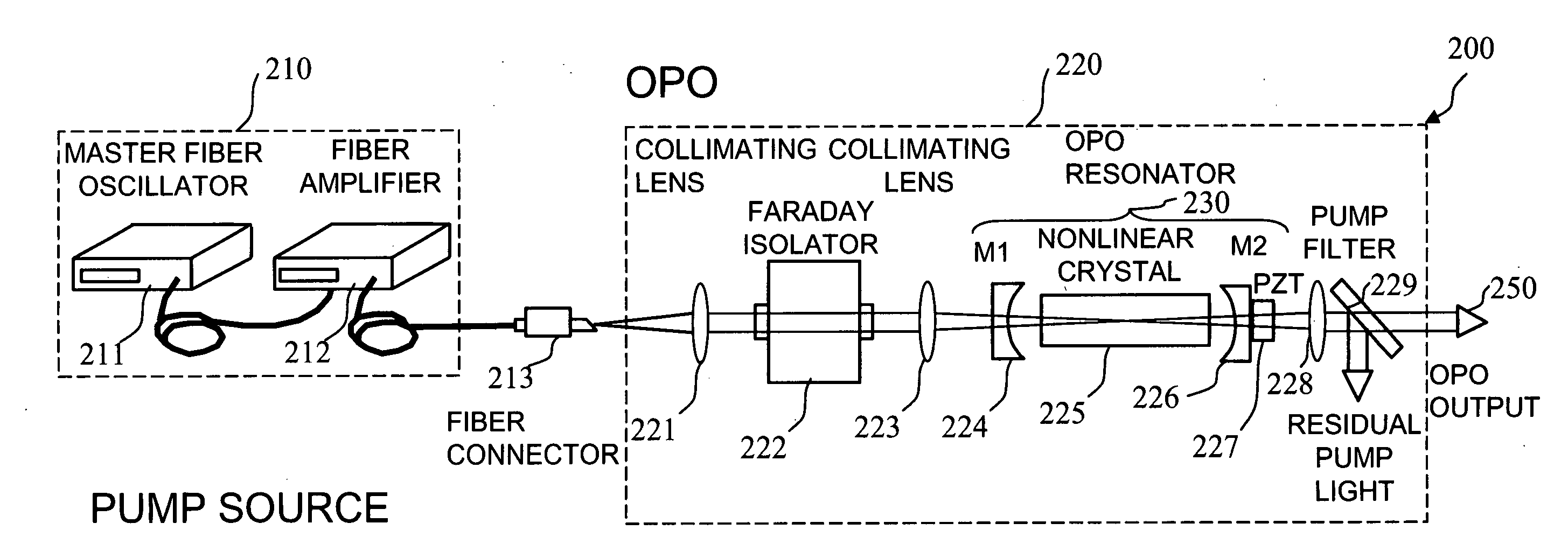
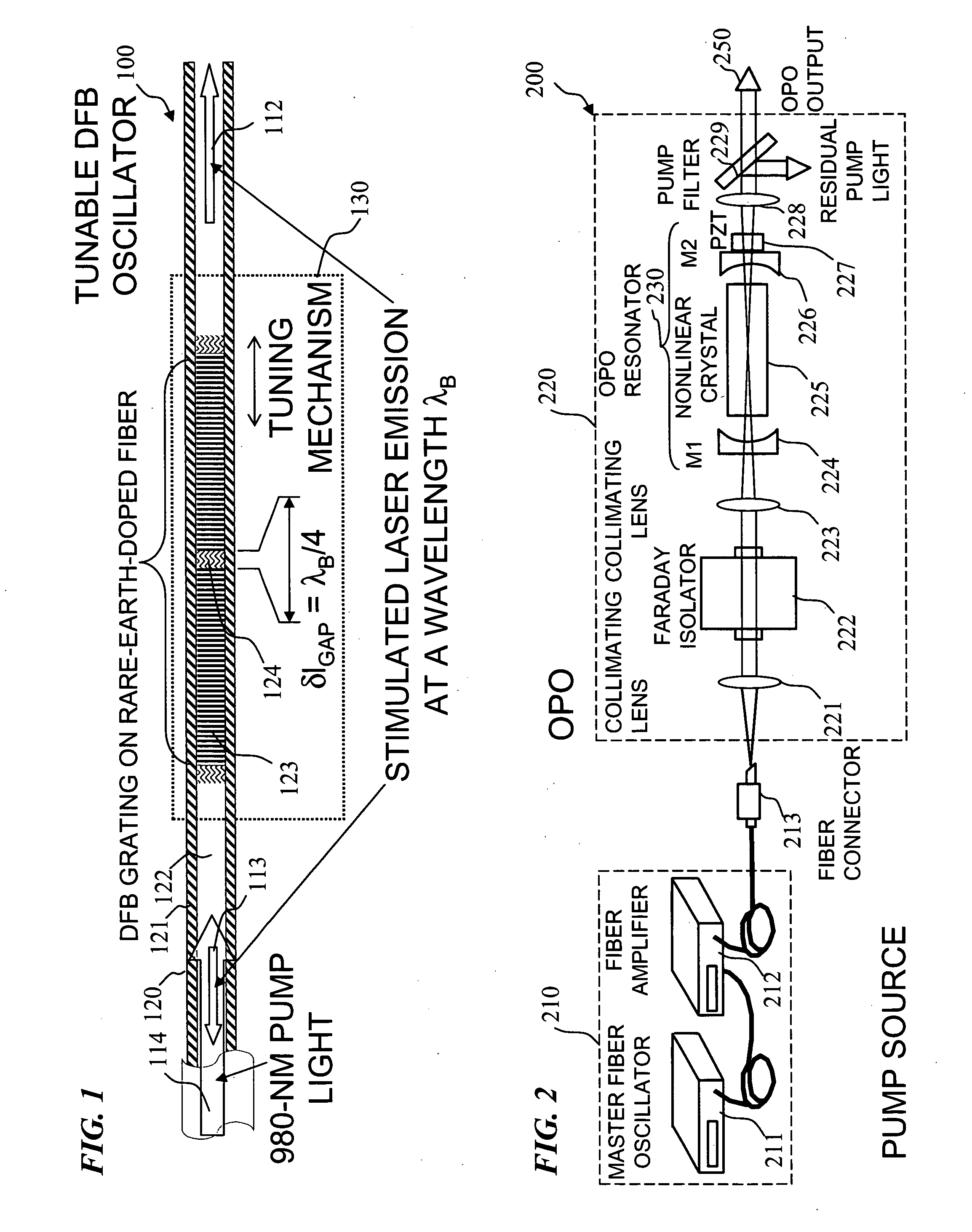
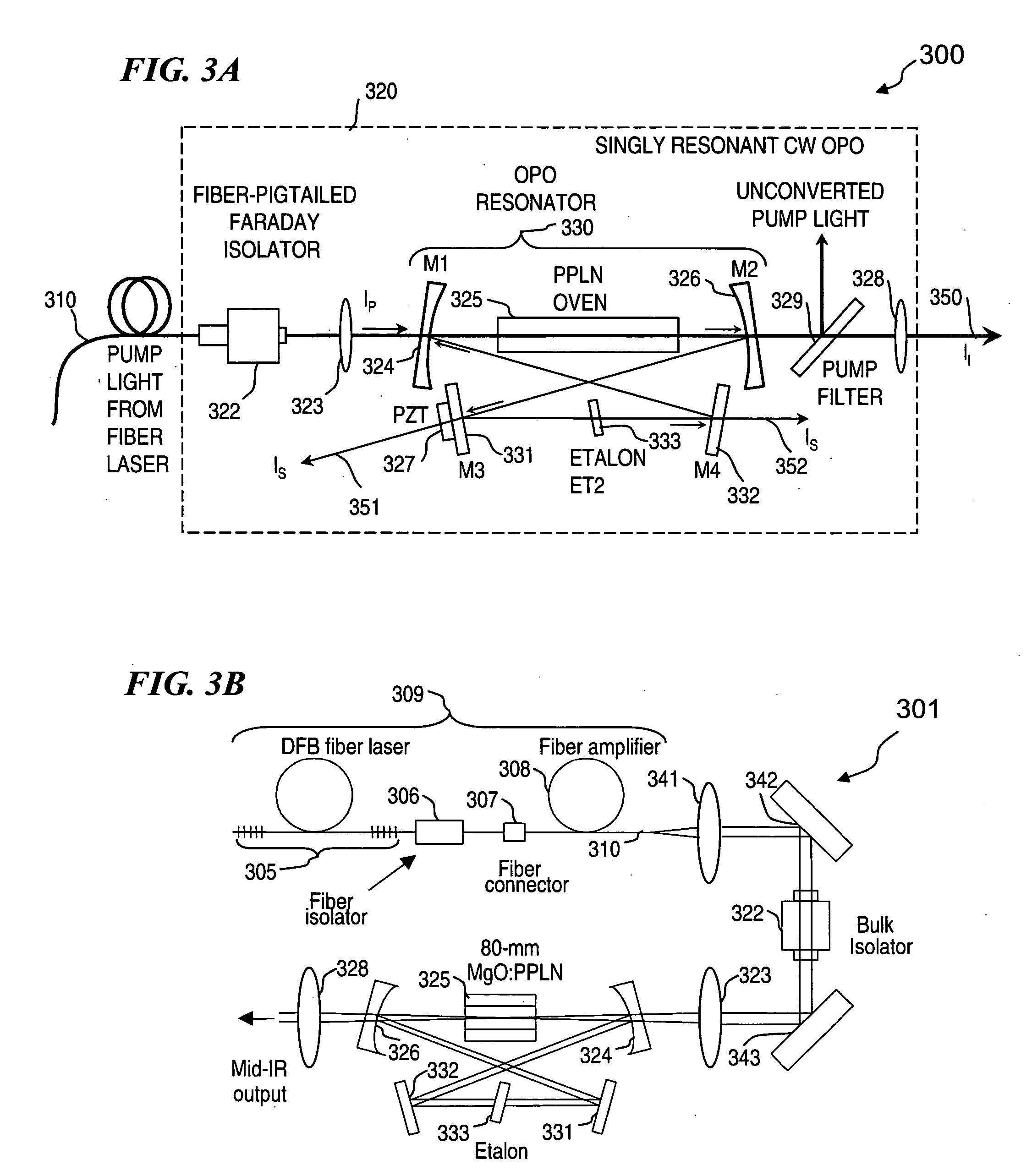
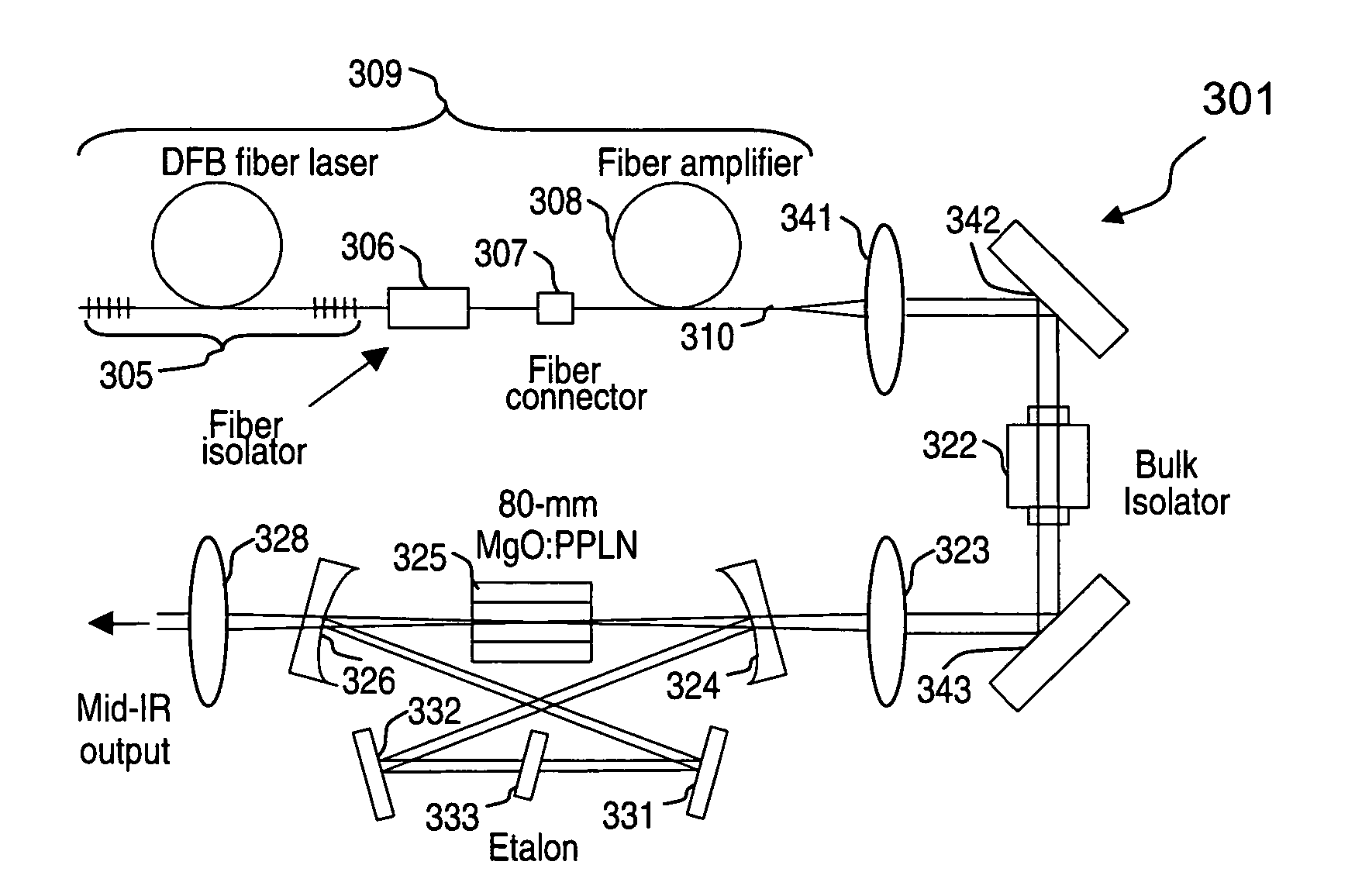
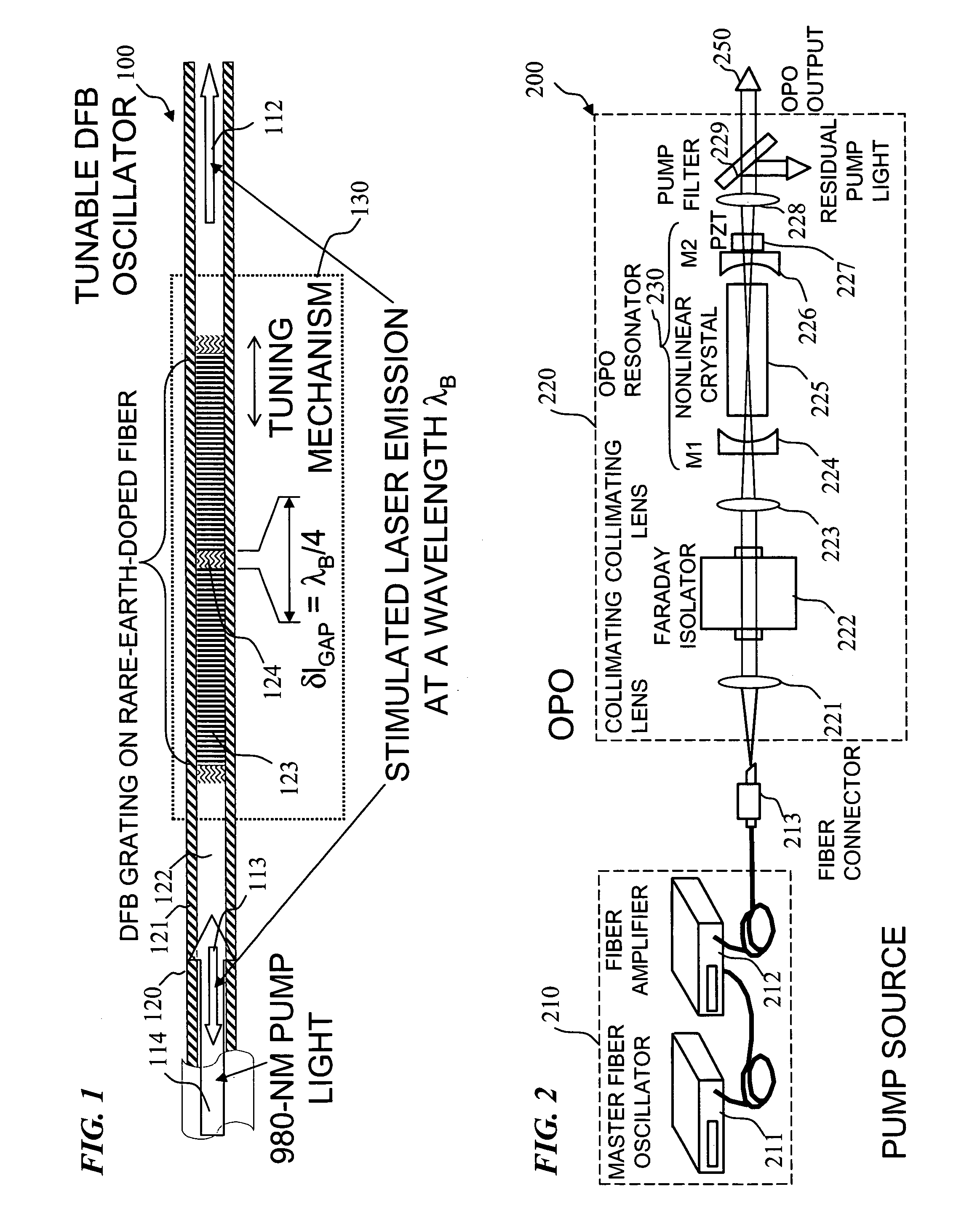
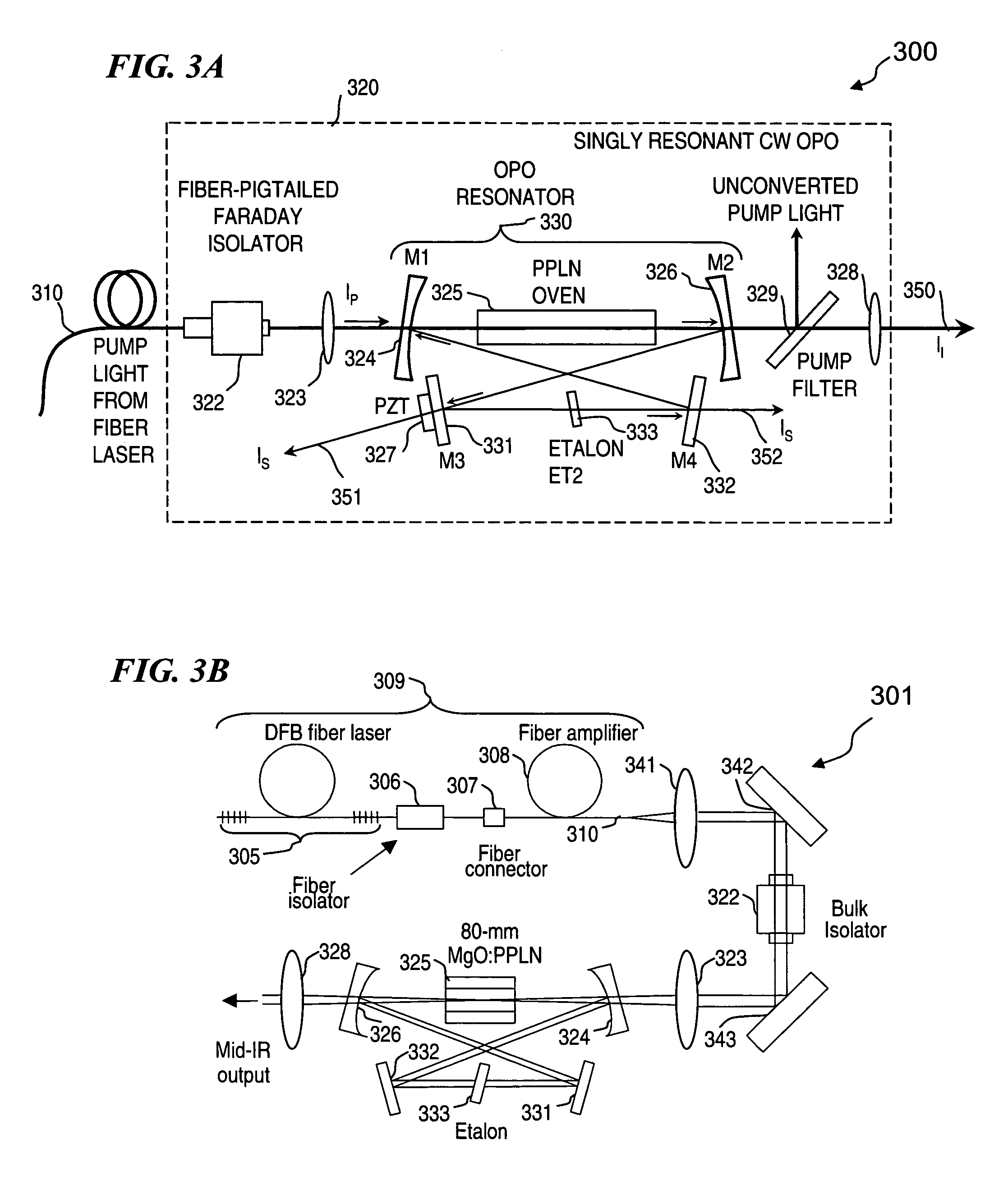
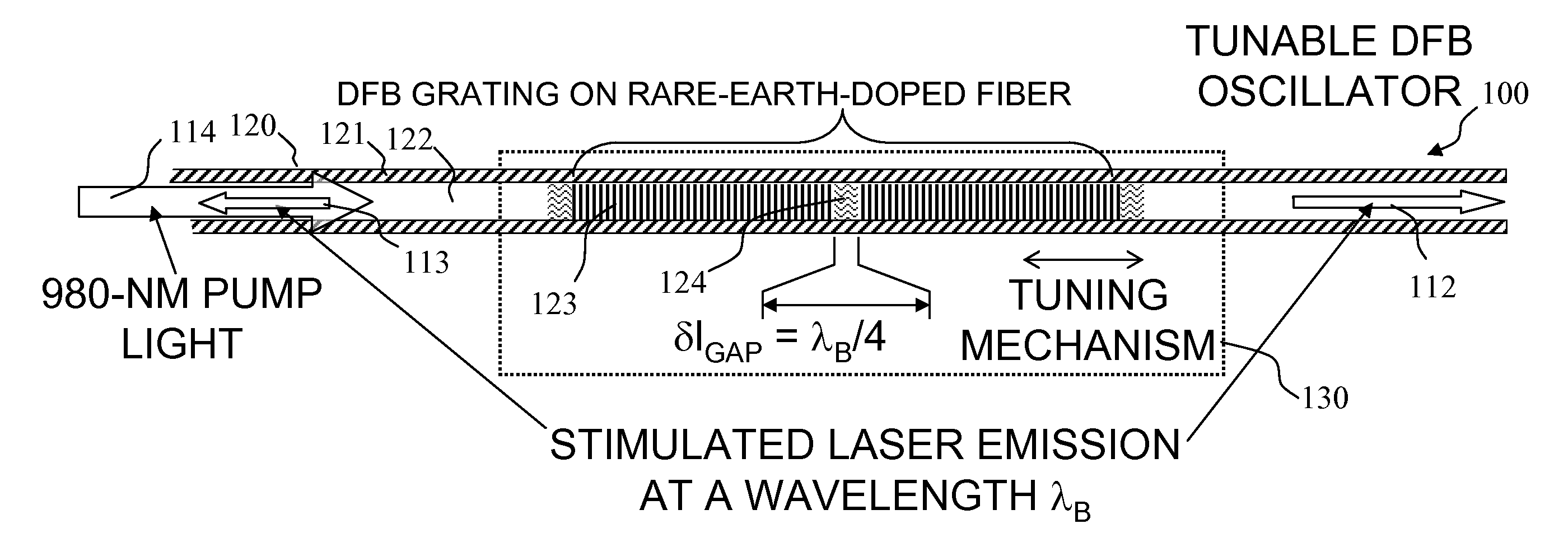
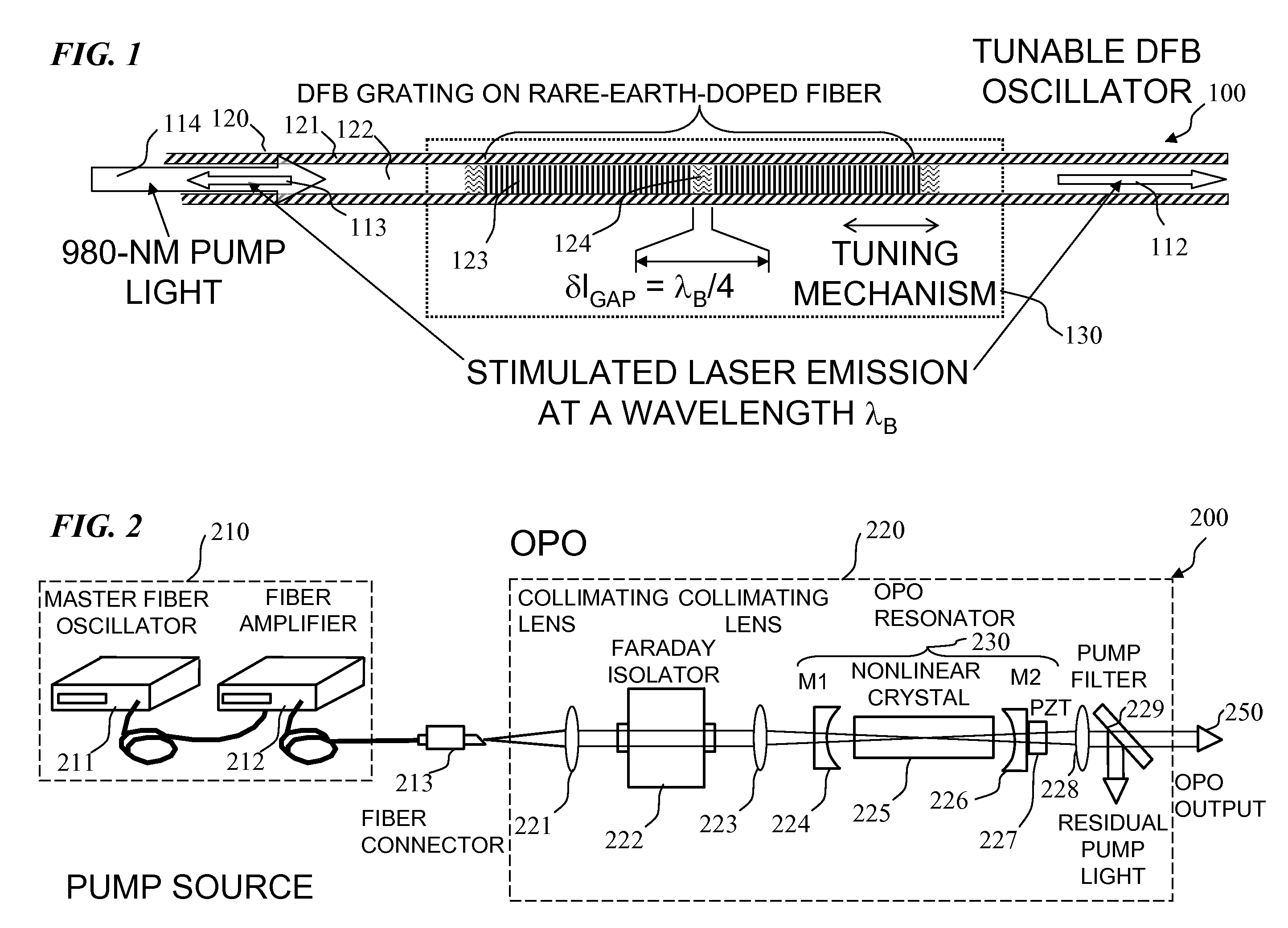
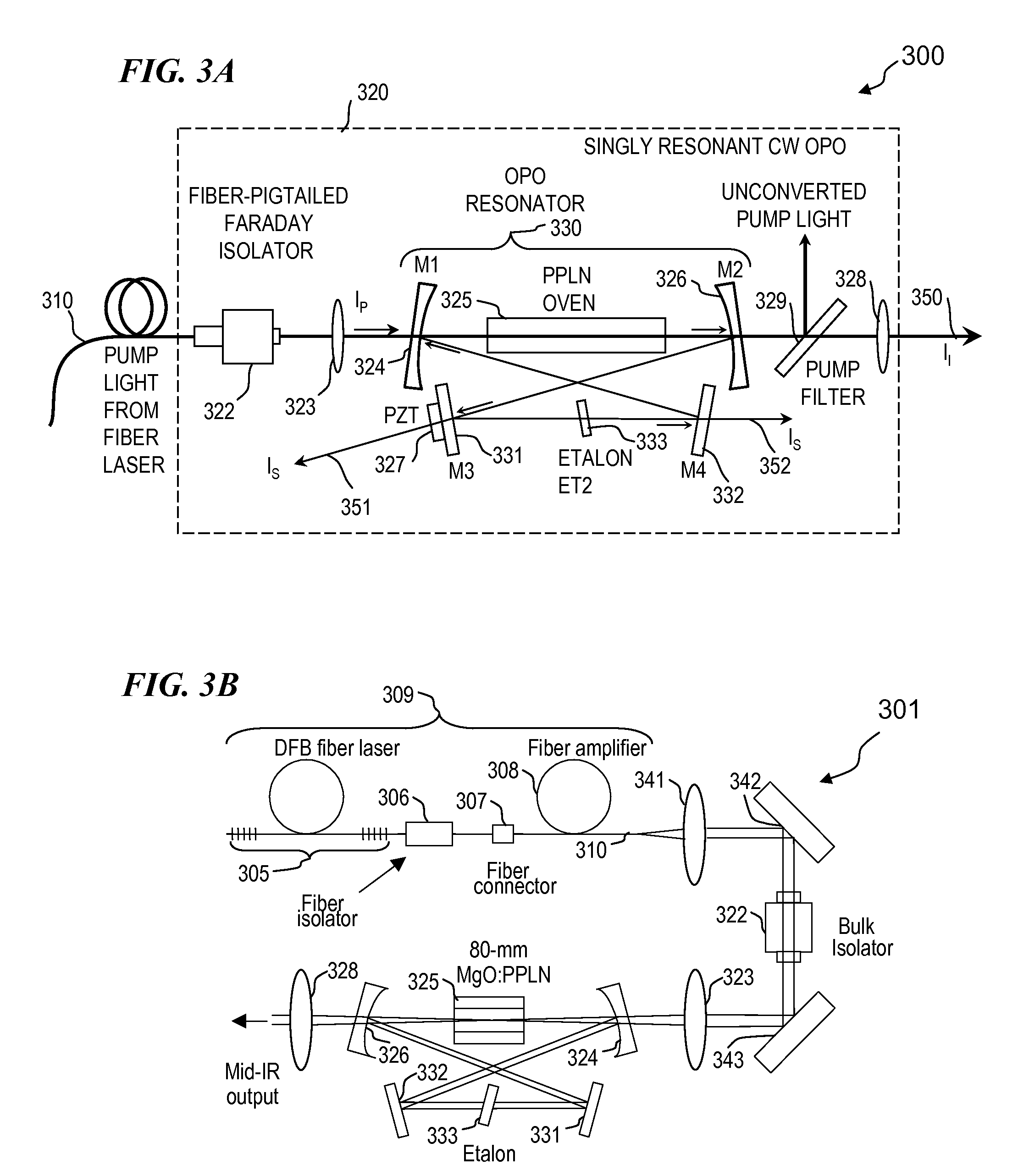
Apparatus and method for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using DFB fiber lasers
ActiveUS20070035810A1Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
An optical parametric oscillator (OPO) is described that efficiently converts a near-infrared laser beam to tunable mid-infrared wavelength output. In some embodiments, the OPO includes an optical resonator containing a nonlinear crystal, such as periodically-poled lithium niobate. The OPO is pumped by a continuous-wave fiber-laser source having a low-power oscillator and a high-power amplifier, or using just a power oscillator). The fiber oscillator produces a single-frequency output defined by a distributed-feedback (DFB) structure of the fiber. The DFB-fiber-laser output is amplified to a pump level consistent with exceeding an oscillation threshold in the OPO in which only one of two generated waves (“signal” and “idler”) is resonant within the optical cavity. This pump source provides the capability to tune the DFB fiber laser by straining the fiber (using an attached piezoelectric element or by other means) that allows the OPO to be continuously tuned over substantial ranges, enabling rapid, wide continuous tuning of the OPO output frequency or frequencies.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Head worn display with foveal and retinal display
InactiveUS20170285343A1Reduce the possibilityReduce bandwidth requirementsProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesDisplay deviceRetina
A head worn display system with at least one retinal display unit having a curved reflector positioned in front of one eye or both eyes of a wearer. The unit includes a first set of three modulated visible-light lasers co-aligned and adapted to provide a foveal laser beam with selectable color and a first scanner unit providing both horizontal and vertical scanning of the laser beam across a small portion of the curved reflector in directions so as to produce a reflection of the color laser beam through the pupil of the eye onto a portion of the retina large enough to encompass the fovea. The unit also includes a second set three modulated retinal visible-light lasers plus an infrared laser, all lasers being co-aligned and adapted to provide a color and infrared peripheral view laser beam, and a second scanner unit providing both horizontal and vertical scanning of the visible light and infrared laser beams across a portion of the curved reflector in directions so as to produce a reflection of the scanned color and infrared laser beams through the pupil of the eye onto a portion of retina corresponding to a field of view of at least 30 degrees×30 degrees.
Owner:BELENKII MIKHAIL +3
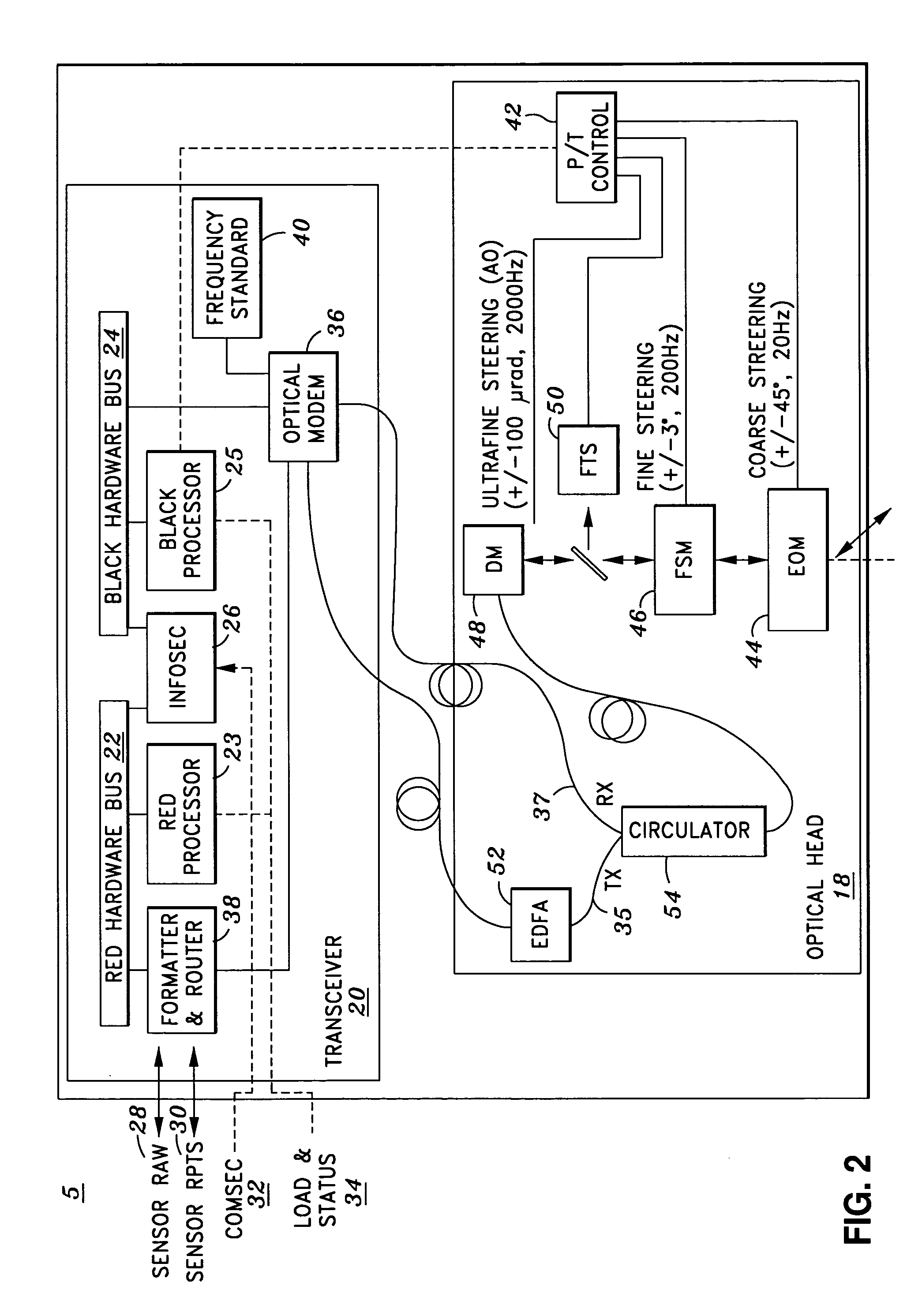
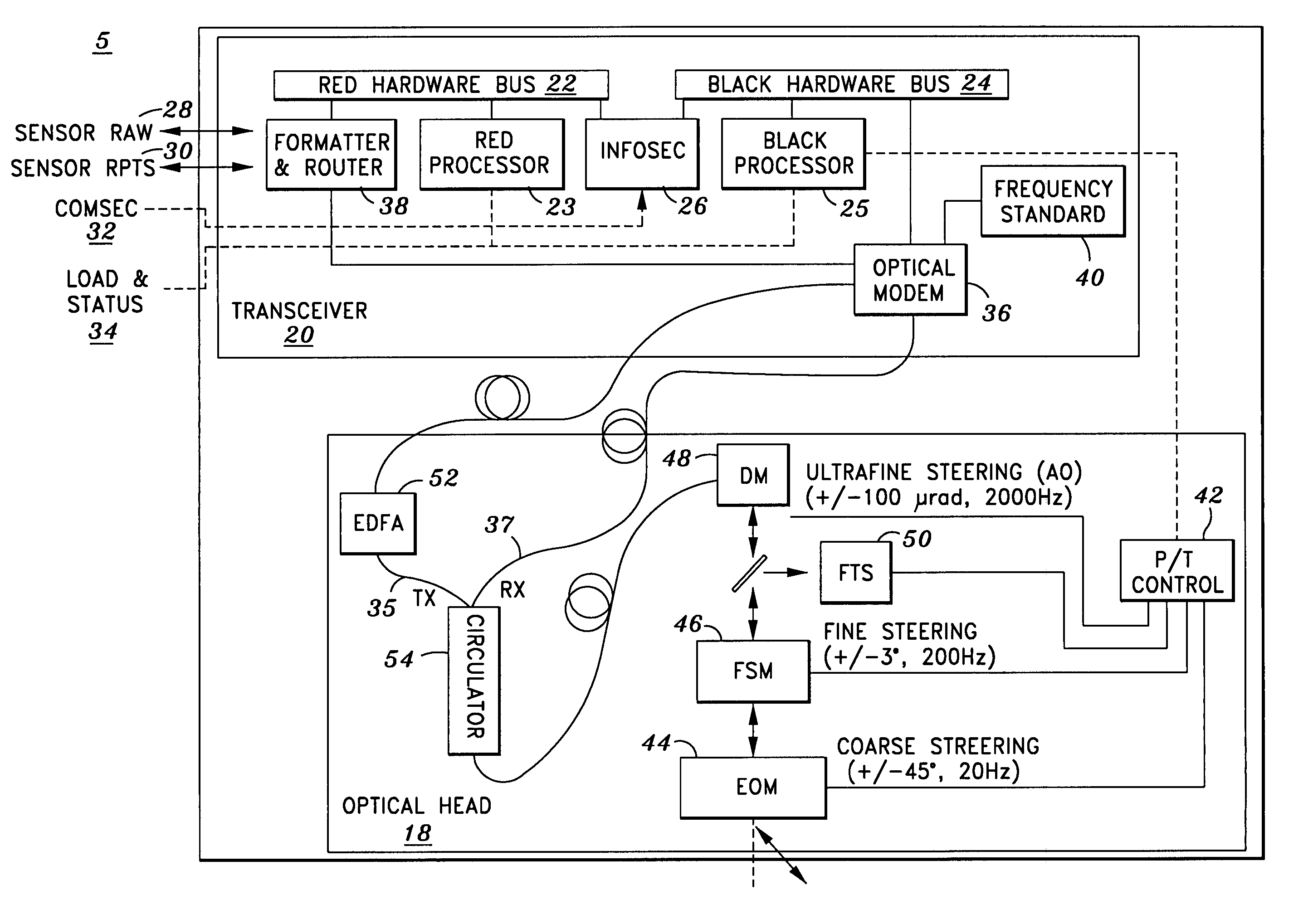
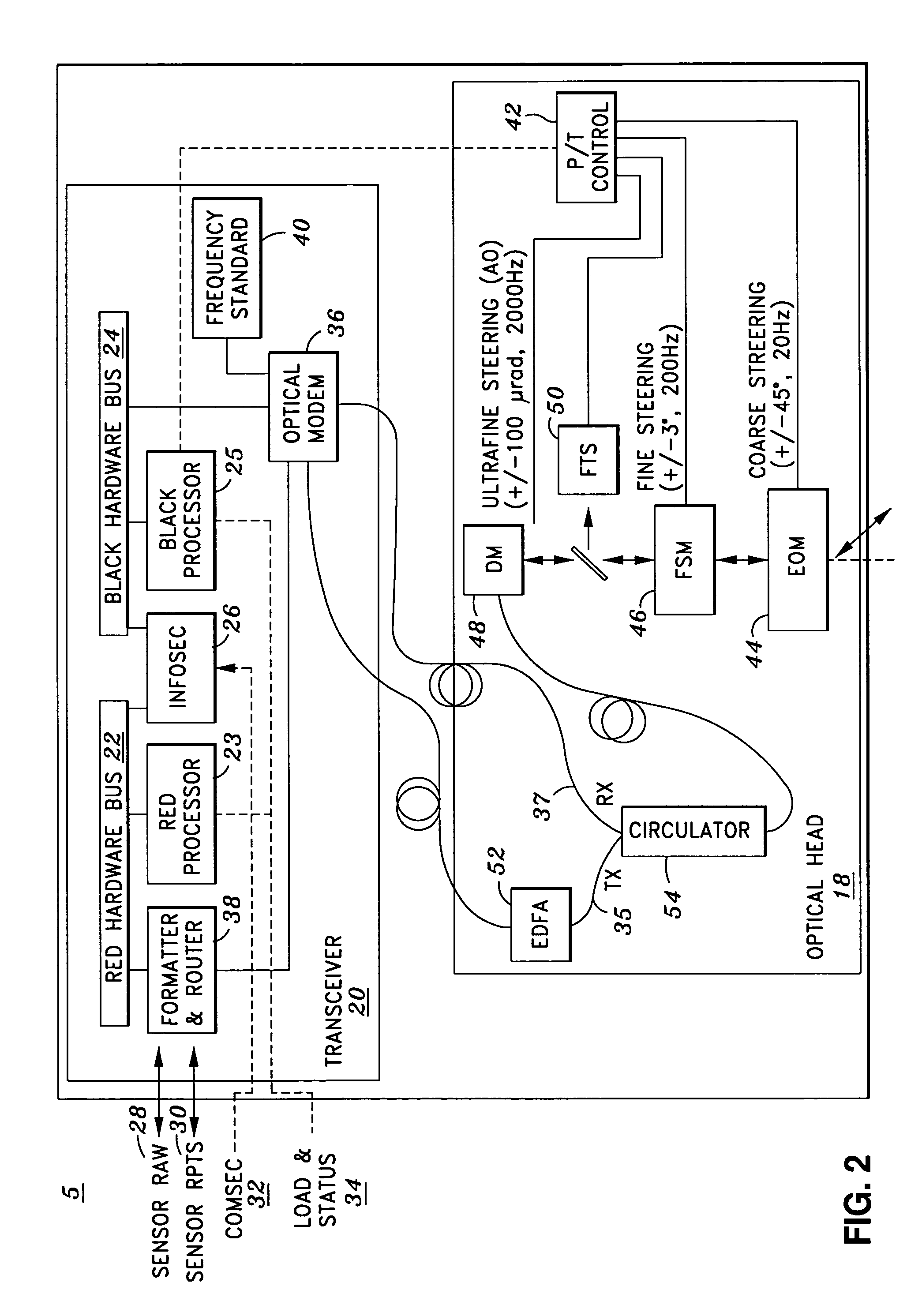
Airborne free-space-optical system utilizing three-tier, ultrafine steering
ActiveUS20050069325A1Mitigate vibration-inducedMitigate aero-optic-induced jitterSatellite communication transmissionRadio transmissionCommunications systemEngineering
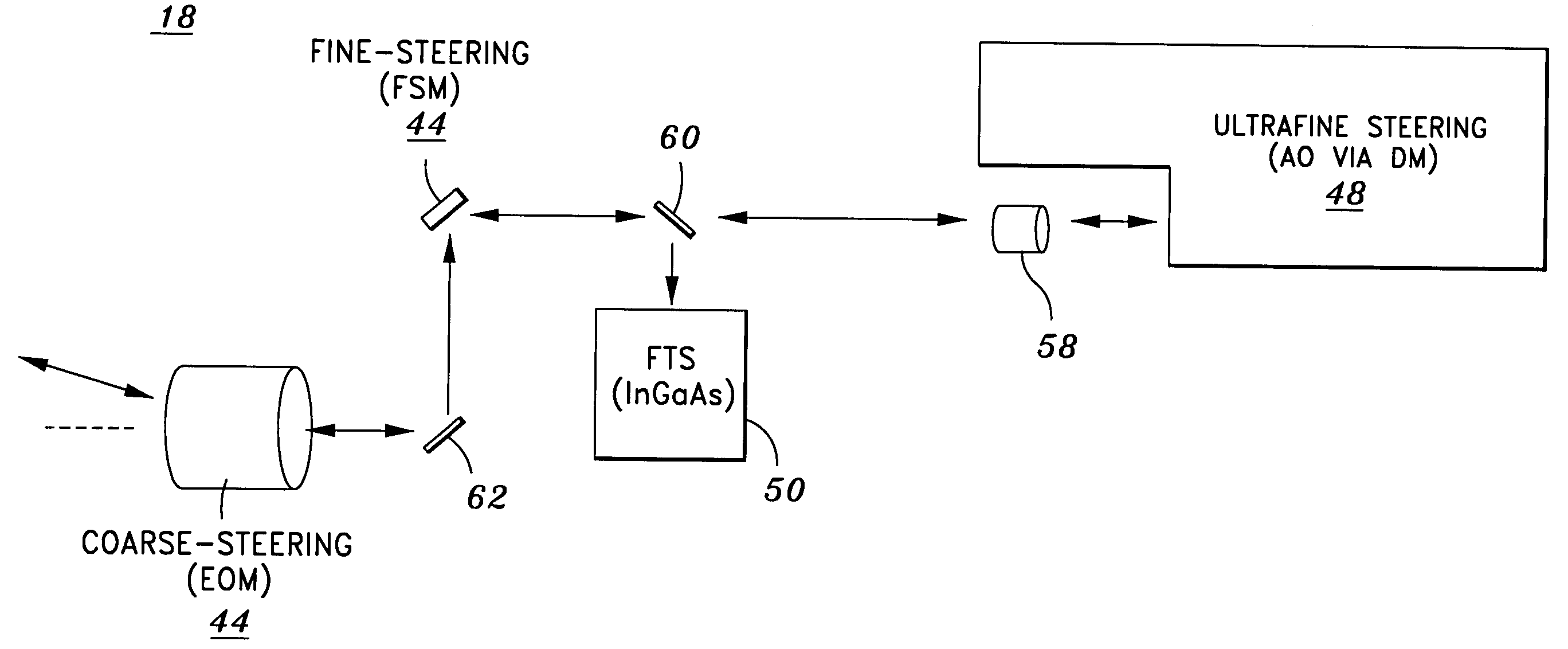
An optical head is provided for a free space optical communications system. The optical head is utilized for transmitting and receiving modulated infrared laser beams. The optical head includes an optical amplifier, a circulator, an ultrafine-steering element, a fine-steering element, a course-steering element, and a fine track sensor. Additionally, a method is provided for facilitating airborne free space optical communications between an airborne host platform and a link platform. Each platform has an optical head which transmits and receives data via modulated infrared laser beams, wherein the host includes at least an optical head having a fine, coarse, and ultrafine steering element configured in a cascaded three-tier steering element architecture.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
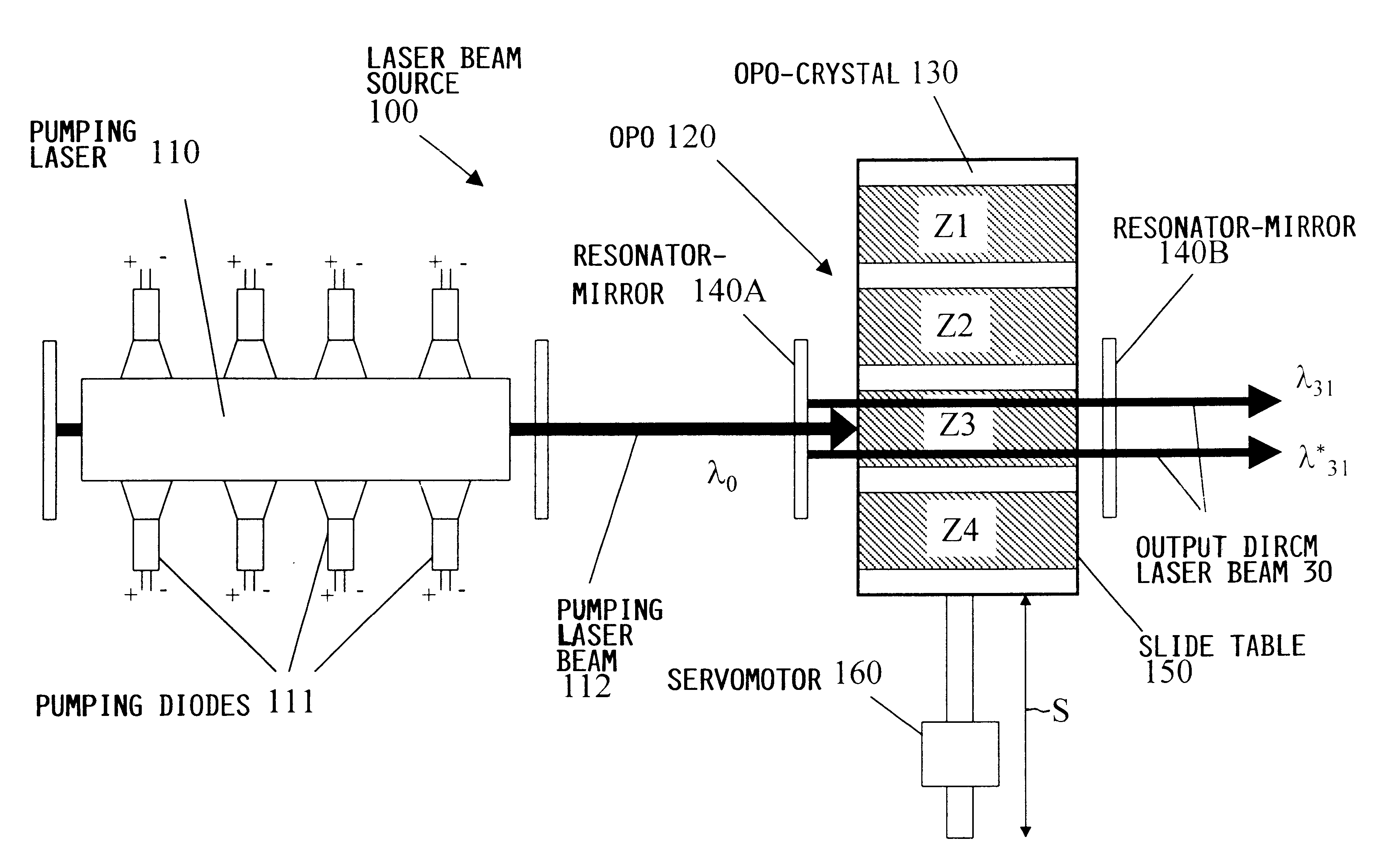
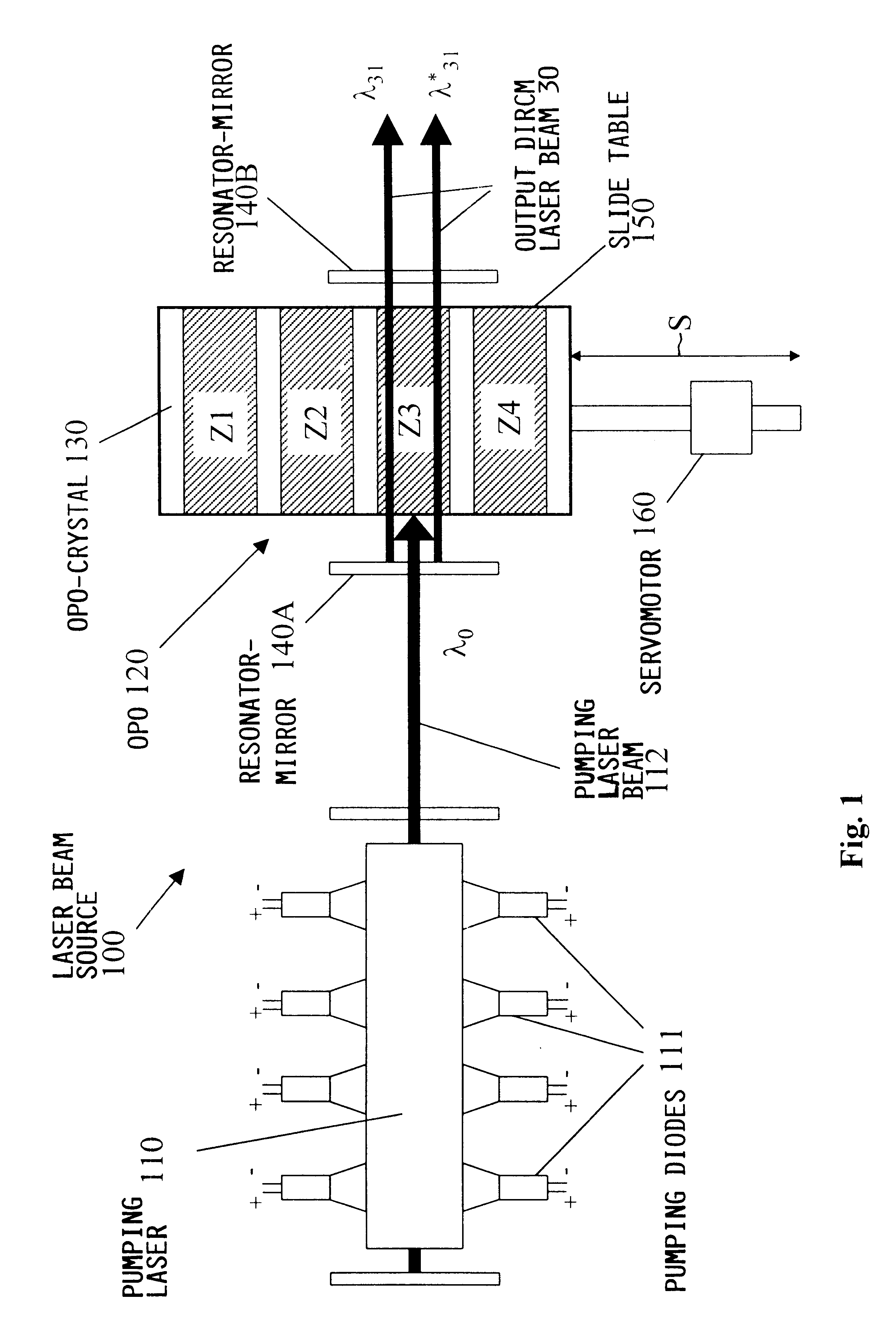
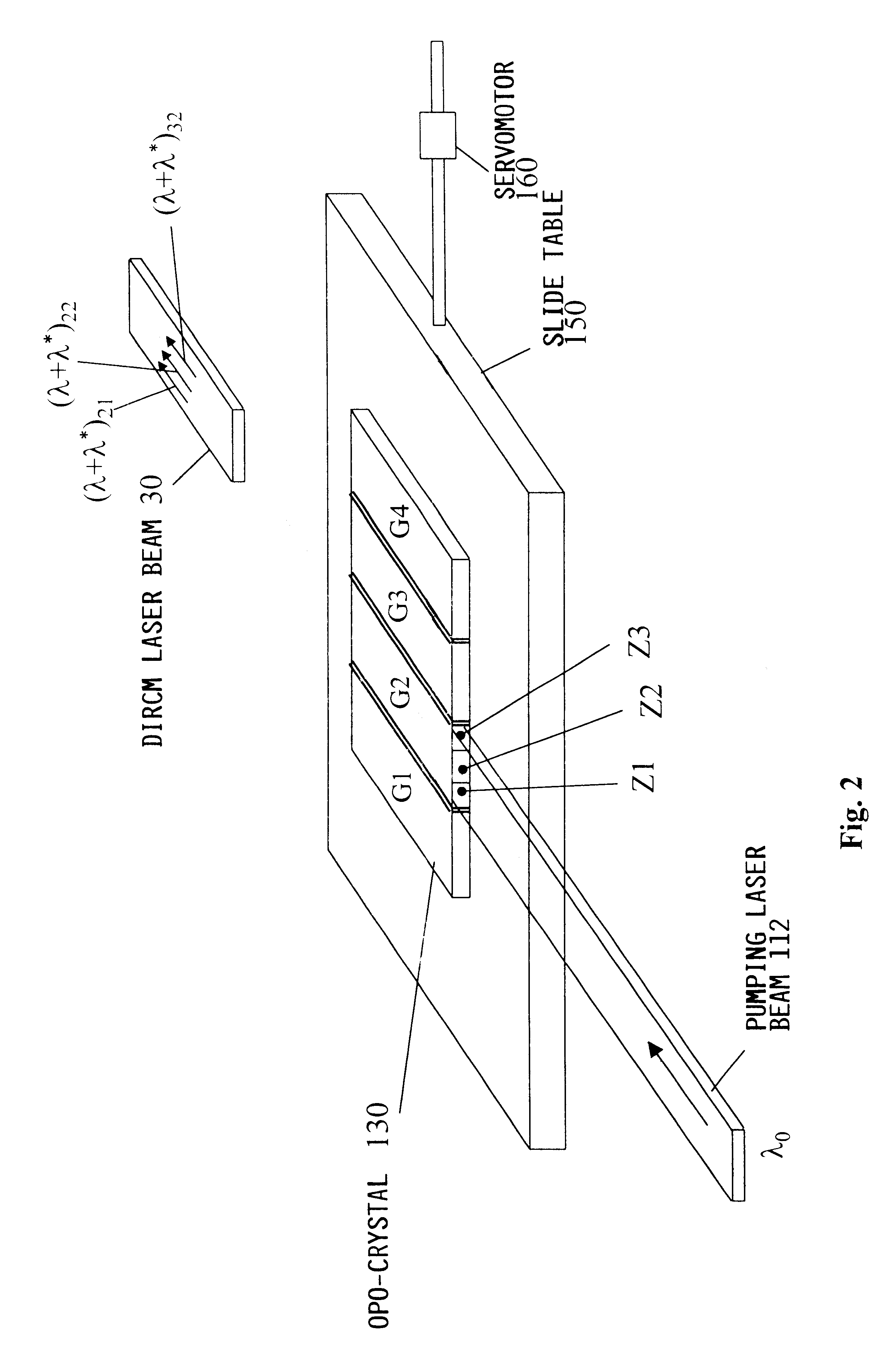
Laser beam source for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system
A laser beam source and an operating method thereof is provided for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system for defensively countering guided missiles having infrared seeking heads, by directing an infrared laser beam at the guided missile so as to disorient, saturate, or irreversibly destroy the IR detectors and circuitry arranged in the target seeking head. The power, pulse frequency and spectral composition of the laser beam is adjustable and selectable as required to adapt to any particular defensive engagement. To achieve this, the laser beam source comprises an Nd:YAG pumping laser and an optical parametric oscillator including an oscillator crystal arranged in a resonator cavity. The crystal includes a plurality of different periodically polarized crystal zones having different lattice constants. The adjacent zones can be grouped together into selectable crystal zone groups. The beam cross-section of the pumping laser beam corresponds to the cross-section of a single crystal zone or of a crystal zone group encompassing plural zones. The crystal is arranged on a slide table that is slidably displaceable by a servomotor, to move a selected crystal zone or group into the path of the pumping laser beam. Thereby the wavelength components and the relative intensities thereof of the output laser beam can easily be selectively adjusted.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
Apparatus and method for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using DFB fiber lasers
ActiveUS7620077B2Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
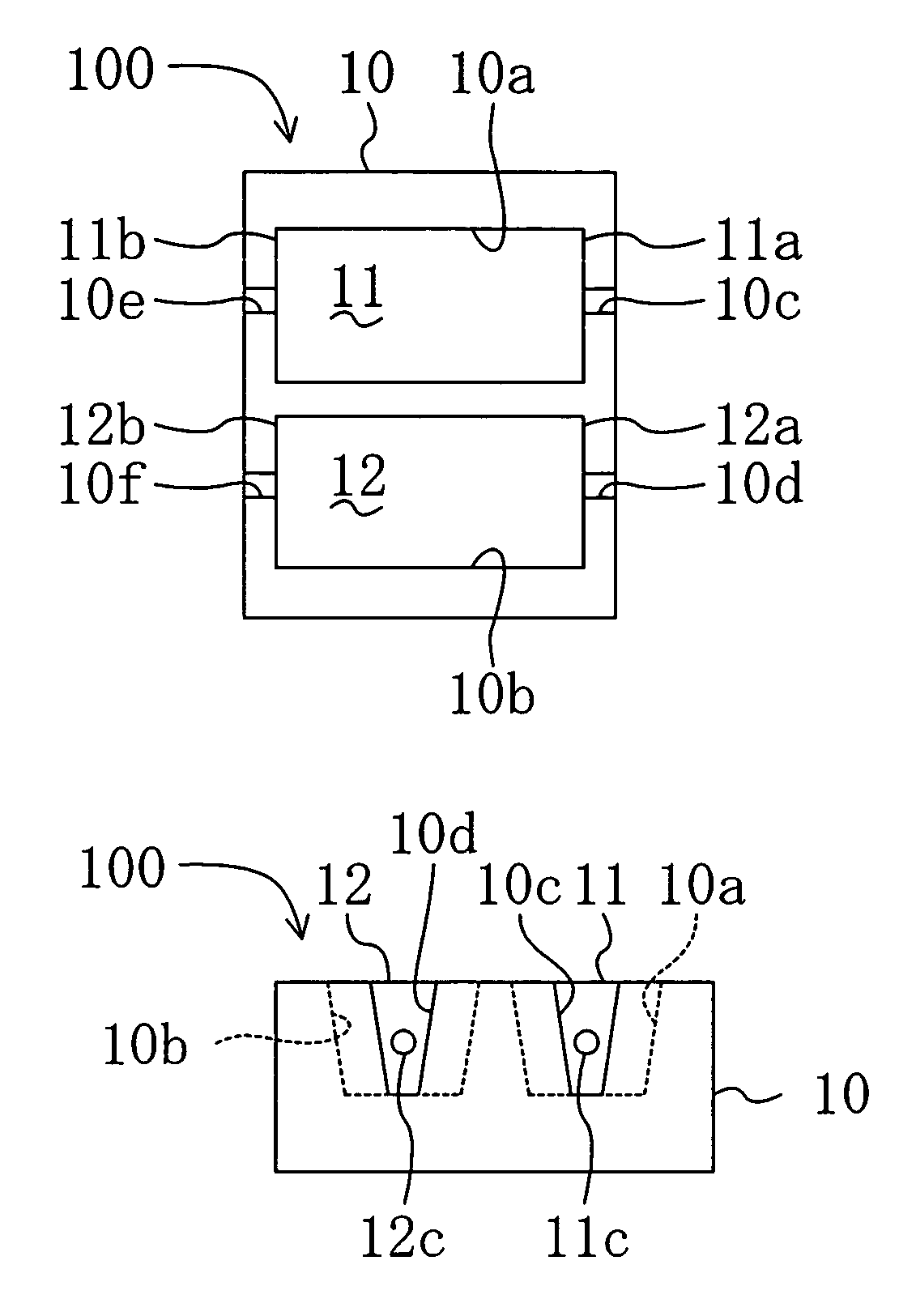
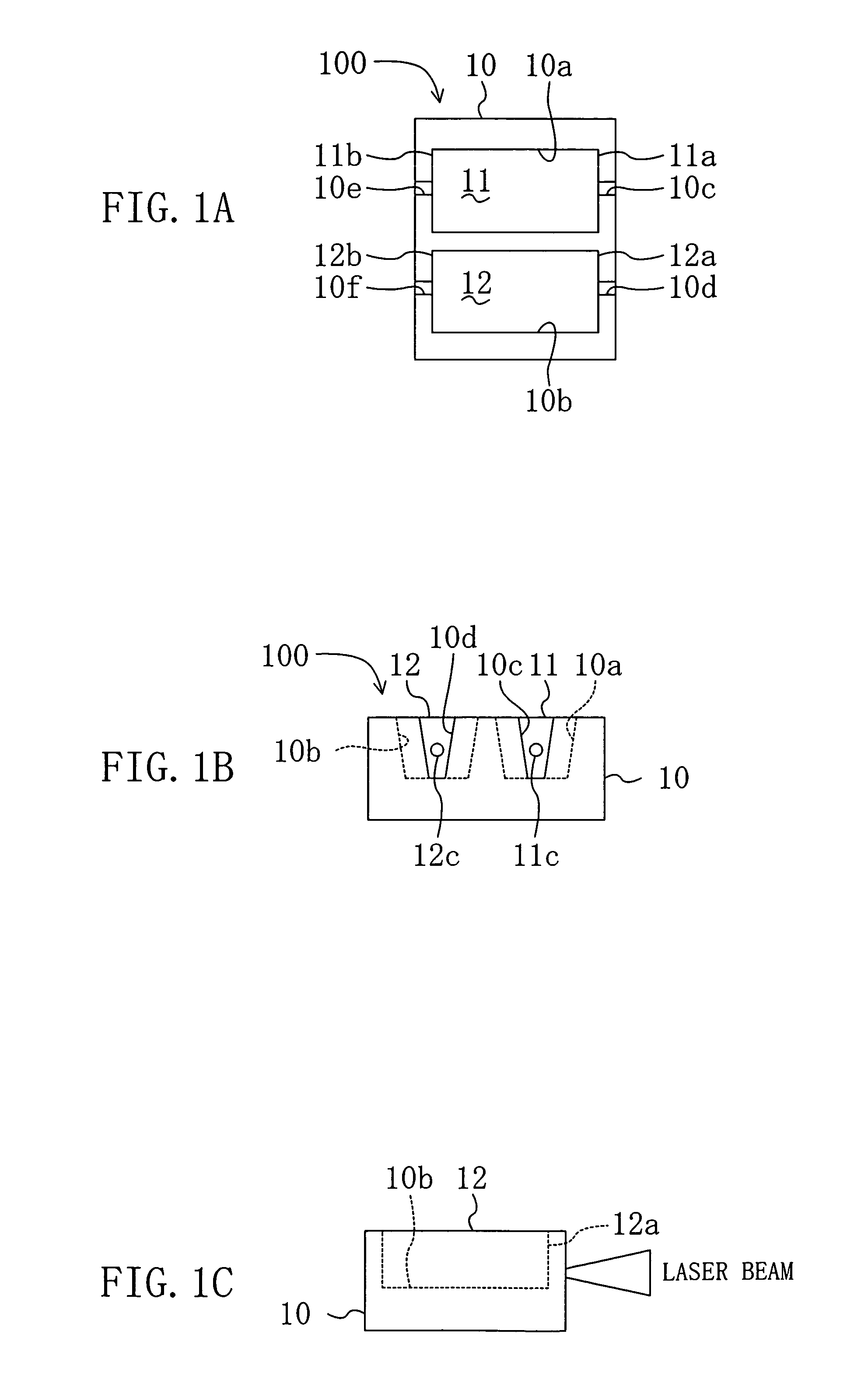
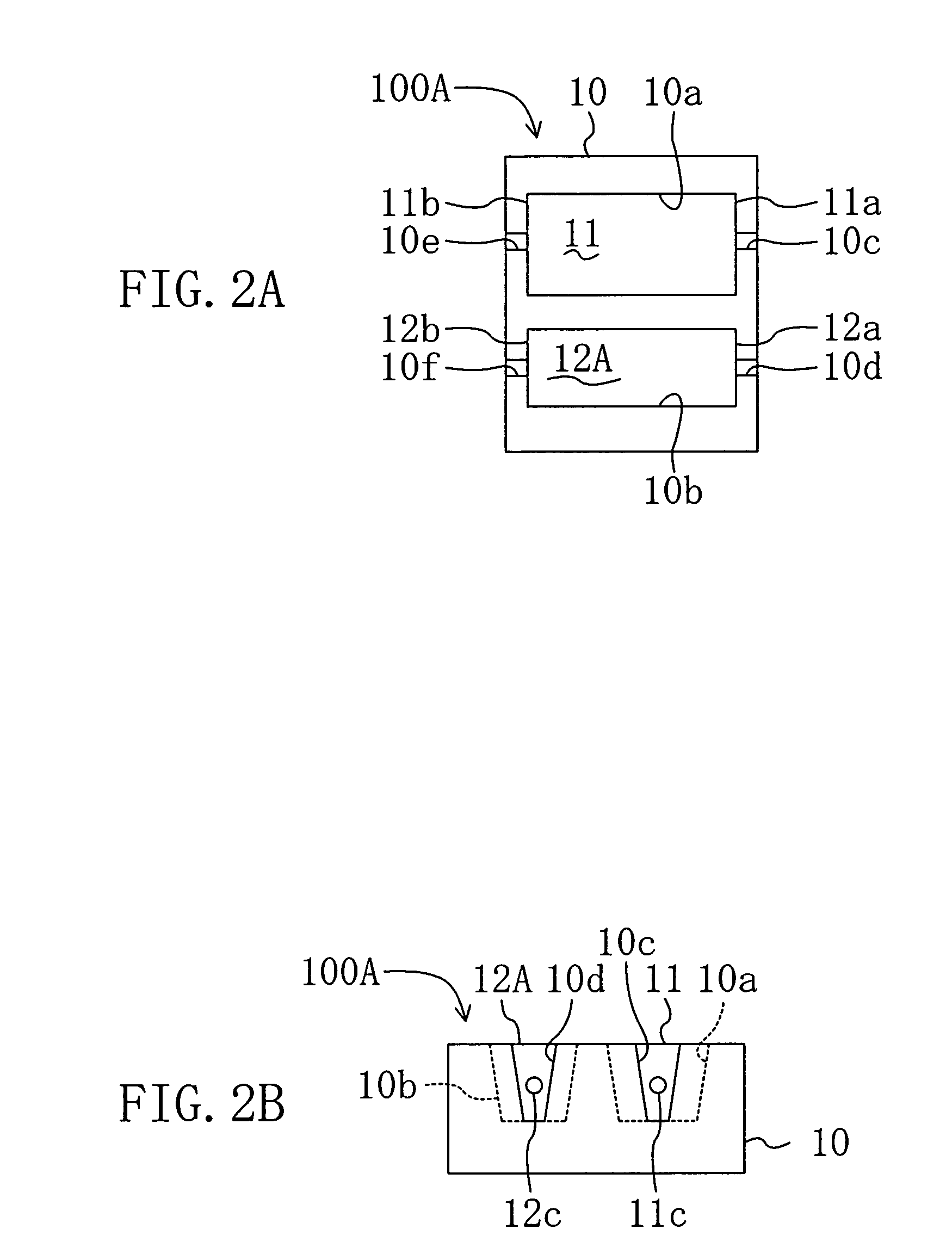
Semiconductor laser device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS7133431B2Reliably obtainedLimit distanceSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser structural detailsRed laserOptoelectronics
A semiconductor laser device includes a substrate which is made of, e.g., silicon and which has in its principal surface first and second recessed portions formed at a distance from each other. Disposed in the first recessed portion is a first semiconductor laser chip in the form of a function block, which emits an infrared laser beam. Disposed in the second recessed portion is a second semiconductor laser chip in the form of a function block, which emits a red laser beam.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
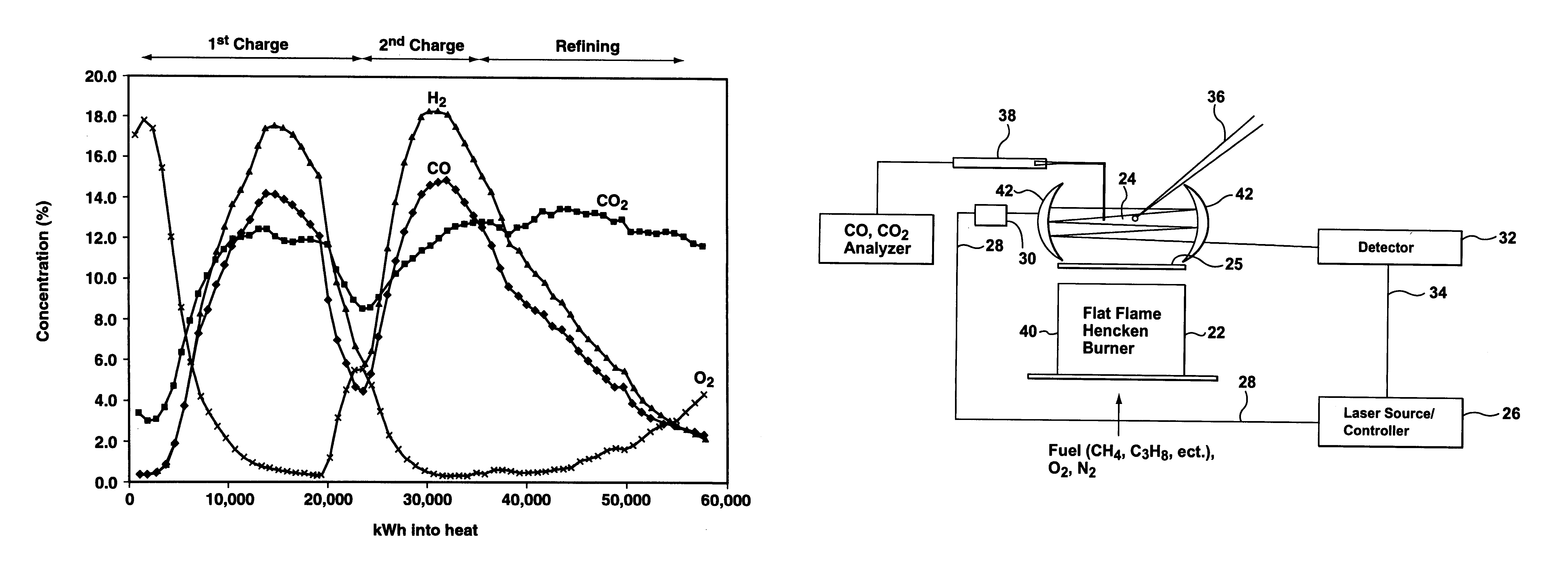
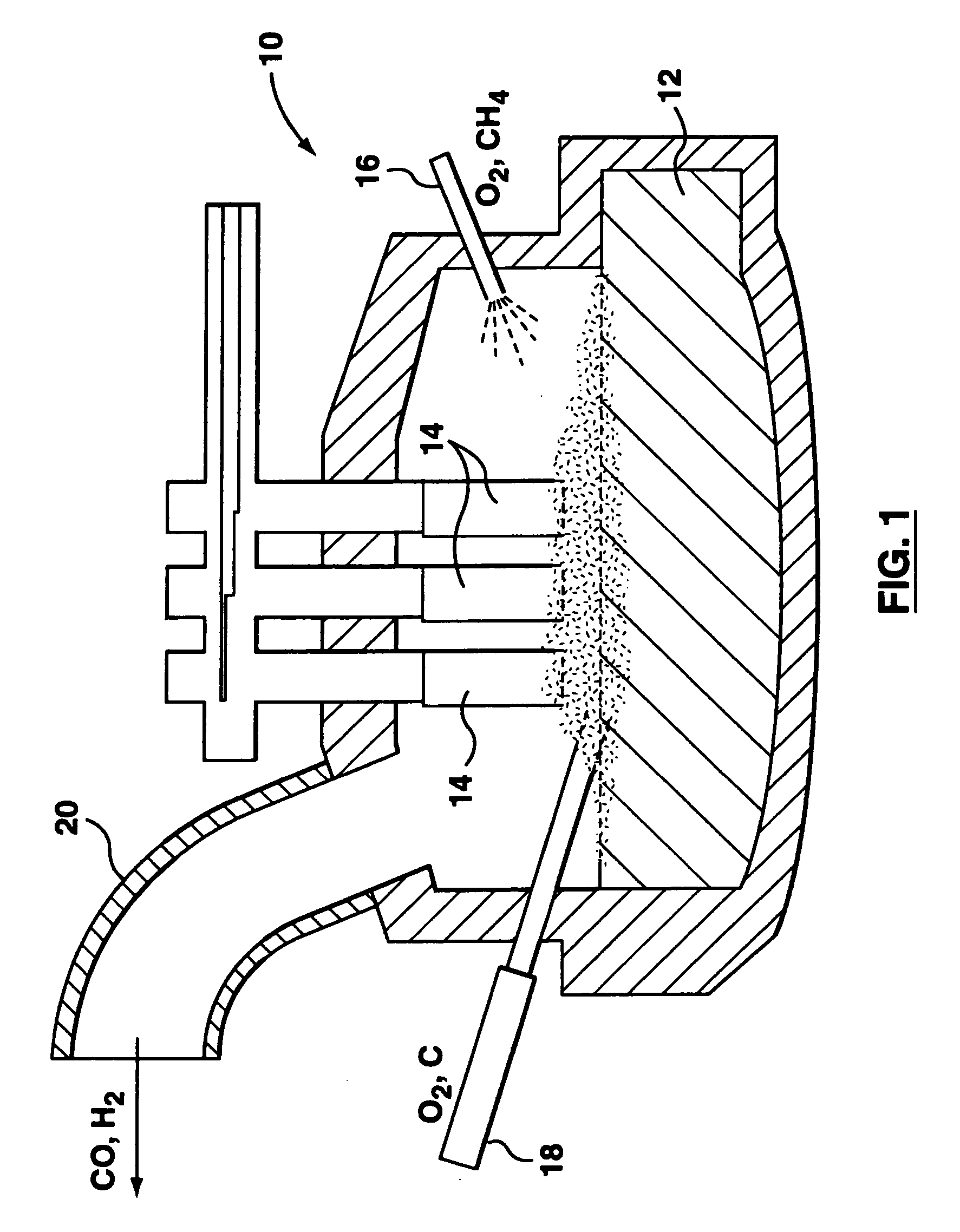
Method and apparatus for improved process control in combustion applications
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for improved process control in combustion applications, and particularly those relating to the steelmaking industry. An apparatus is provided for process control in a combustion application comprising a laser to transmit a near-infrared laser beam through off-gas produced by the combustion application, a detector to detect the transmitted laser beam and convert the detected laser beam to an electrical signal, and a control system for providing adjustment of select inputs to the combustion application in response to the electrical signal from the detector. The method of this invention comprises transmitting a near-infrared laser beam through off-gas produced by the combustion application, detecting the transmitted laser beam, and adjusting select inputs of the combustion application in response to the detected transmitted laser beam.
Owner:THOMSON MURRAY J +3
Compact solid-state laser
A compact optically-pumped solid-state laser designed for efficient nonlinear intracavity frequency conversion into desired wavelengths using periodically poled nonlinear crystals. These crystals contain dopants such as MgO or ZnO and / or have a specified degree of stoichiometry that ensures high reliability. The laser includes a solid-state gain media chip, such as Nd:YVO4, which also provides polarization control of the laser; and a periodically poled nonlinear crystal chip such as PPMgOLN or PPZnOLT for efficient frequency doubling of the fundamental infrared laser beam into the visible wavelength range. The described designs are especially advantageous for obtaining low-cost green and blue laser sources.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
Real-time temperature monitoring instrument for tunable semiconductor laser absorption spectrum
ActiveCN102183316AEliminate distractionsWill not measure the impactThermometers using physical/chemical changesAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyPhotovoltaic detectorsWater vapor
The invention discloses a temperature monitoring instrument for a tunable semiconductor laser absorption spectrum. Infrared laser beams penetrate through a zone to be temperature-measured, and the temperature of a measured zone is obtained in real time by utilizing a characteristic absorption spectrum of water vapor in the zone. Laser is transmitted and emitted through singlemode fibers, penetrates through the zone to be temperature-measured after being subjected to collimation and beam expansion, and is then received and coupled to multimode fibers; and the coupled laser is received by a photoelectric detector and converted to electric signals, and temperature is obtained by acquisition processing and inversion.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dynamic foveal vision display
InactiveUS9529191B2Reduce bandwidth requirementsHigh resolutionCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsRetinaInfrared laser beam
A head mounted display system with at least one retinal display unit having a curved reflector positioned in front of one eye or both eyes of a wearer. The unit includes a first set of three modulated visible-light lasers co-aligned and adapted to provide a laser beam with selectable color and a first scanner unit providing both horizontal and vertical scanning of the laser beam across a portion of the curved reflector in directions so as to produce a reflection of the color laser beam through the pupil of the eye onto a portion of the retina large enough to encompass the fovea. The unit also includes a second set three modulated visible-light lasers plus an infrared laser, all lasers being co-aligned and adapted to provide a color and infrared peripheral view laser beam, and a second scanner unit providing both horizontal and vertical scanning of the visible light and infrared laser beams across a portion of the curved reflector in directions so as to produce a reflection of the scanned color and infrared laser beams through the pupil of the eye onto a portion of retina corresponding to a field of view of at least 30 degrees×30 degrees.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
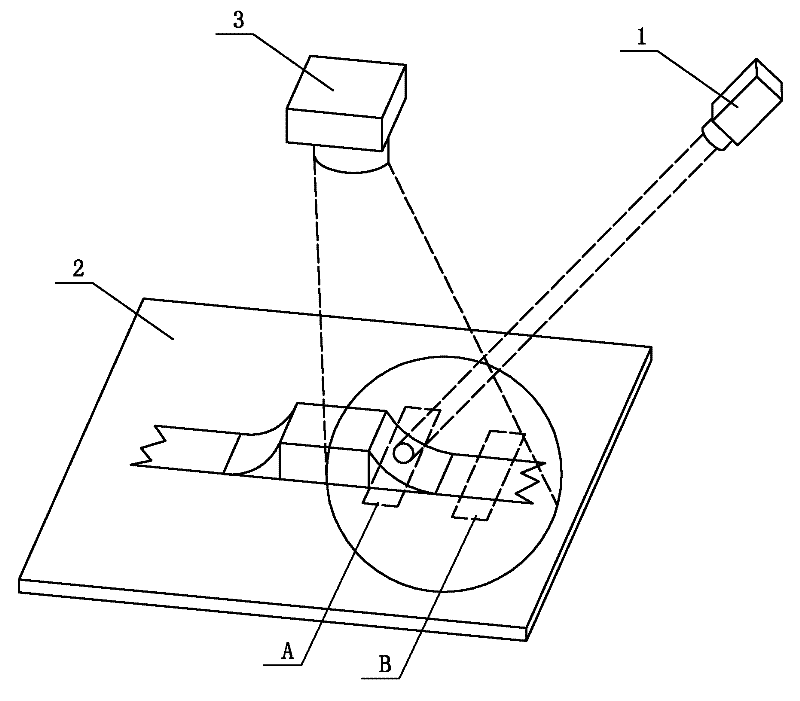
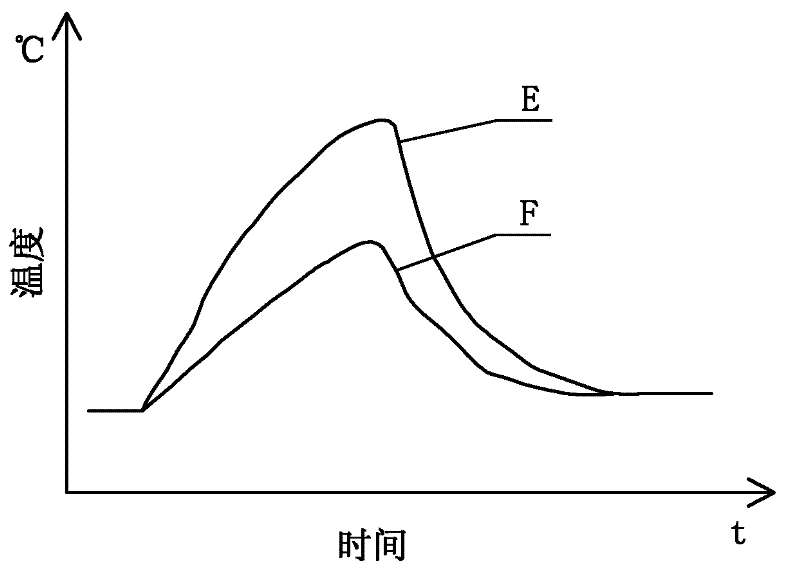
Infrared temperature measurement detection method for detecting solder joint reliability of circuit board
ActiveCN102183545AImprove reliabilitySimple methodMaterial flaws investigationThermodynamicsTwo temperature
The invention discloses an infrared temperature measurement detection method for detecting solder joint reliability of a circuit board, which belongs to the technical field of faulty soldering detection of solder joints and solves the problem that the prior method cannot detect the faulty solder point of which the appearance is normal. The infrared temperature measurement detection method comprises the following steps of: 1, concentrating an infrared laser beam emitted by an infrared laser device on a solder joint to be detected of the circuit board, using a thermal infrared imager to obtain a dynamic image of the solder joint to be detected and a dynamic image of a lead wire part of the solder joint to be detected, and getting temperature distribution curves of the solder joint to be detected and the lead wire part of the solder joint to be detected; 2, overlaying the temperature distribution curve of the solder joint with that of the lead wire part of the solder joint to be detected according to same proportion; 3, judging the overlaying result: when the two temperature distribution curves have same distribution trend, and the highest temperature points on the two temperature distribution curves are synchronous, judging that the solder joint to be detected is a qualified solder joint; otherwise, judging that the solder joint to be detected is unqualified. The infrared temperature measurement detection method is suitable for detecting the solder joint reliability of the circuit board.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Laser welded speaker and vibration plate thereof
InactiveUS20150208179A1Improve performanceQuality improvementSingle transducer incorporationMicrophonesEngineeringInfrared laser beam
A laser welded speaker, comprising a magnet, a voice coil disposed around the magnet, a vibration plate fixedly disposed on the voice coil, and a housing for accommodating the magnet, the voice coil and the vibration plate is provided. The vibration plate comprises a vibration plate top arc and a vibration plate edge, the vibration plate top arc is surrounded by the vibration plate edge and is laser welded to the vibration plate edge, one of the vibration plate top arc and the vibration plate edge is made of a first laser-penetrable material, and the other is made of a first laser-absorbable material, wherein the first laser-penetrable material contains a first organic pigment, the first laser-penetrable material containing the first organic pigment is capable of being penetrated by a first infrared laser beam, and wavelength of the first infrared laser beam ranges from 700 nm to 1600 nm.
Owner:MERRY ELECTRONICS SUZHOU
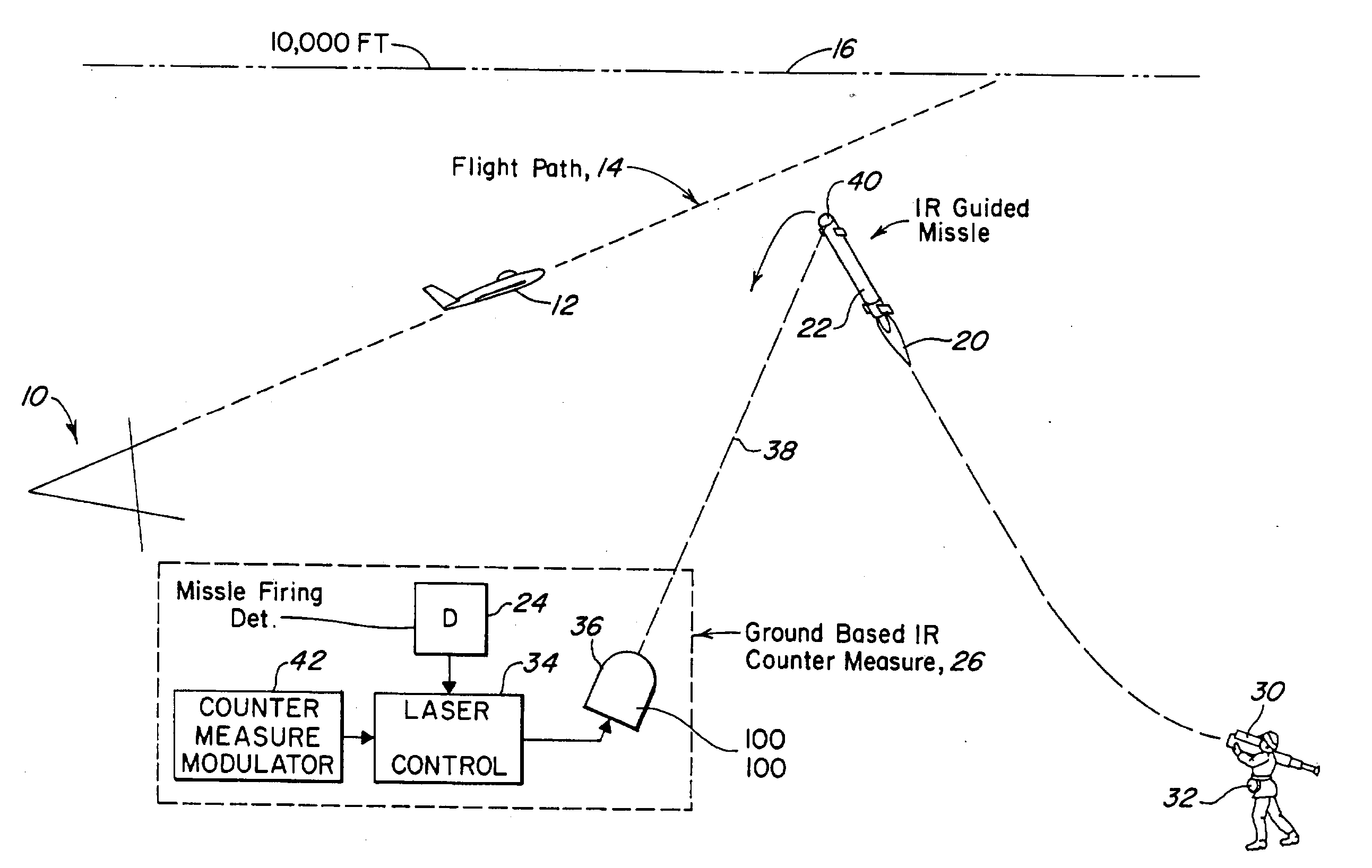
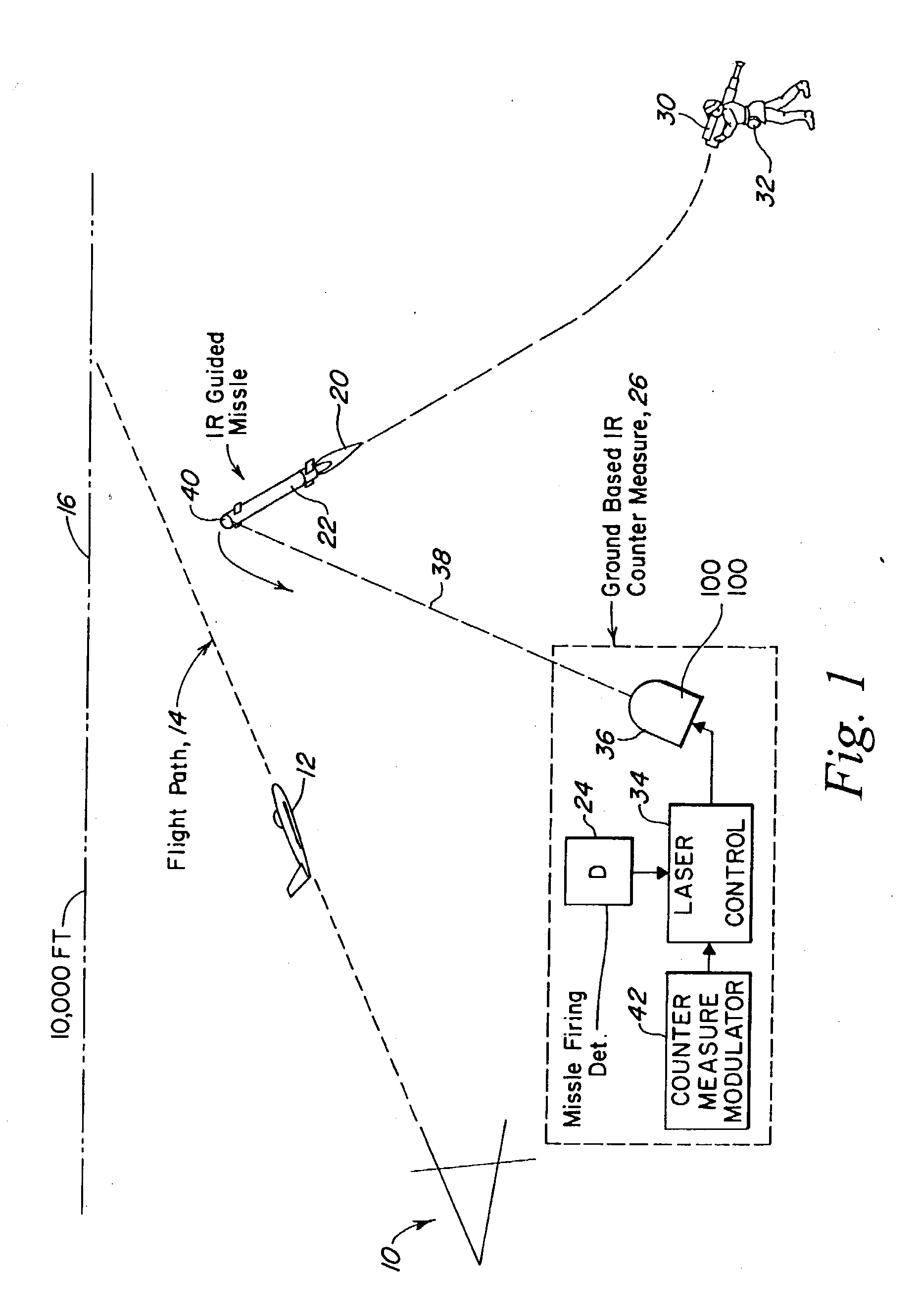
Back illumination method for counter measuring IR guided missiles
ActiveUS20090250634A1Obviating utilityEliminates perceptive problemAircraft componentsDefence devicesGuidance systemRefractive index
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Apparatuses and methods for laser processing
ActiveUS20180029919A1Glass severing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser processingLight beam
A workpiece may be laser processed by a method that may include forming a contour line in the workpiece, and directing an infrared laser beam onto the workpiece along or near the contour line to separate the workpiece along the contour line. The contour line may include defects in the workpiece. The infrared laser beam may have a beam profile such that a greater distribution of cumulated energy from the infrared laser beam is located in areas adjacent to the contour line than directly on the contour line.
Owner:CORNING INC
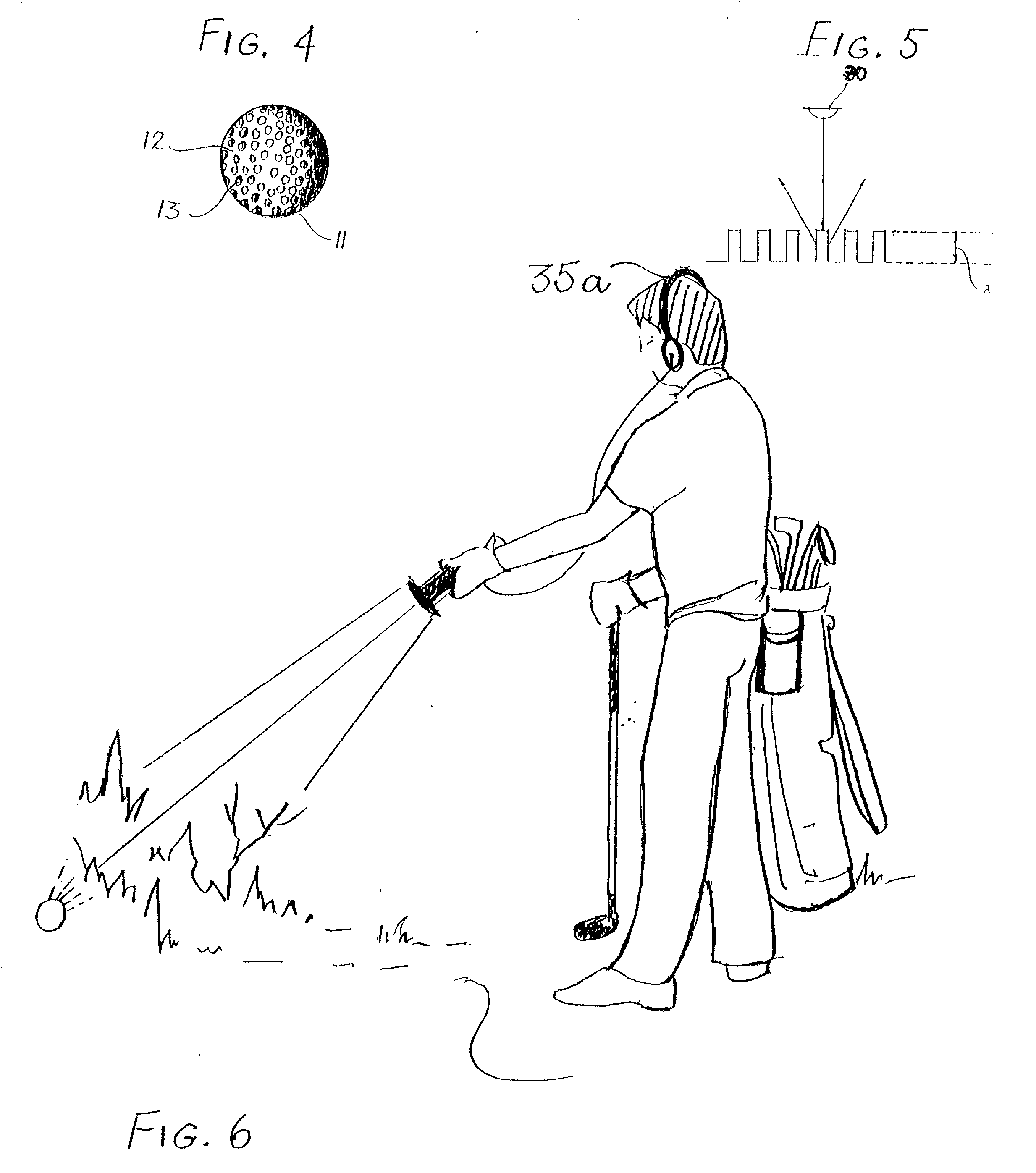
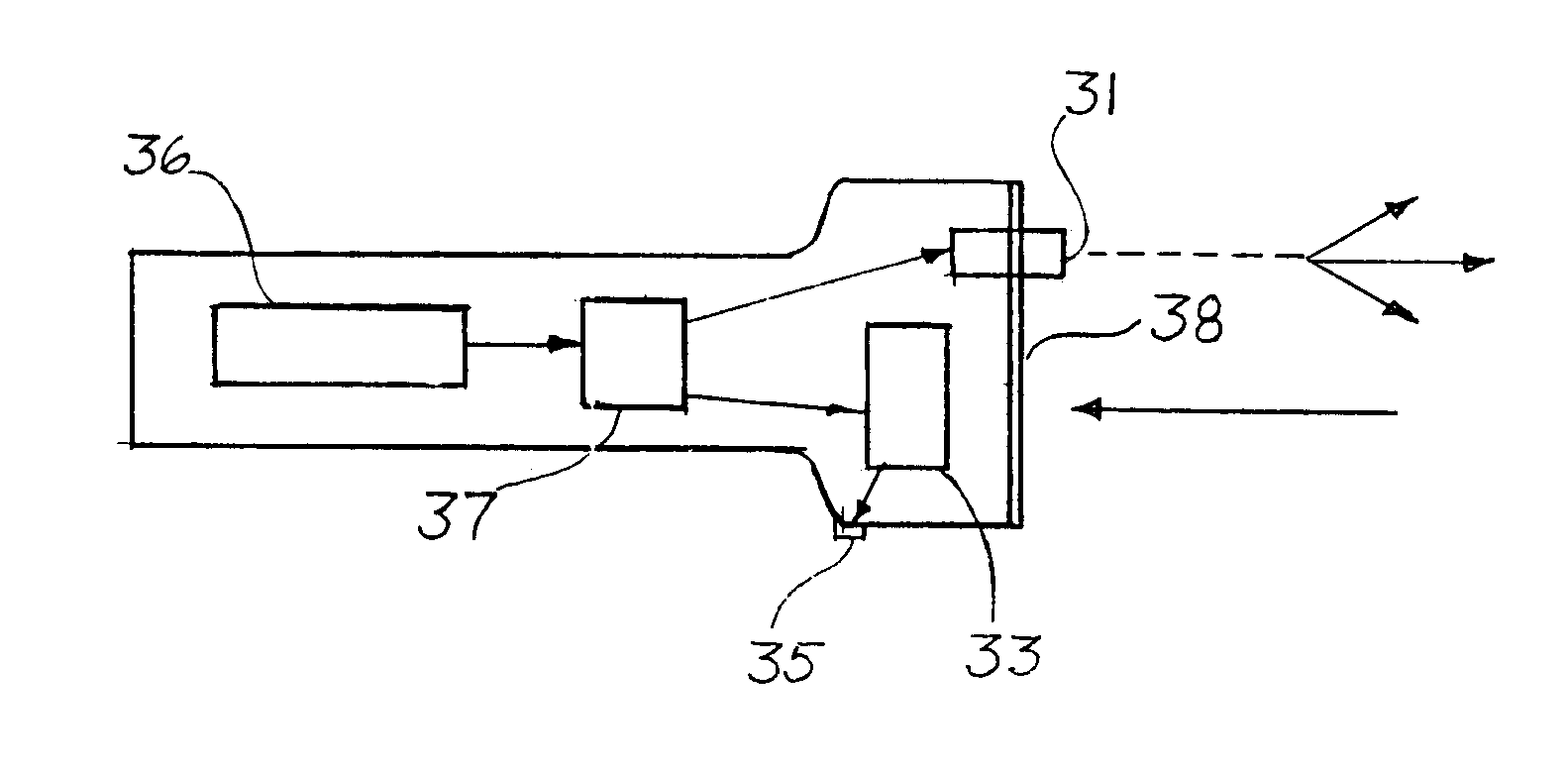
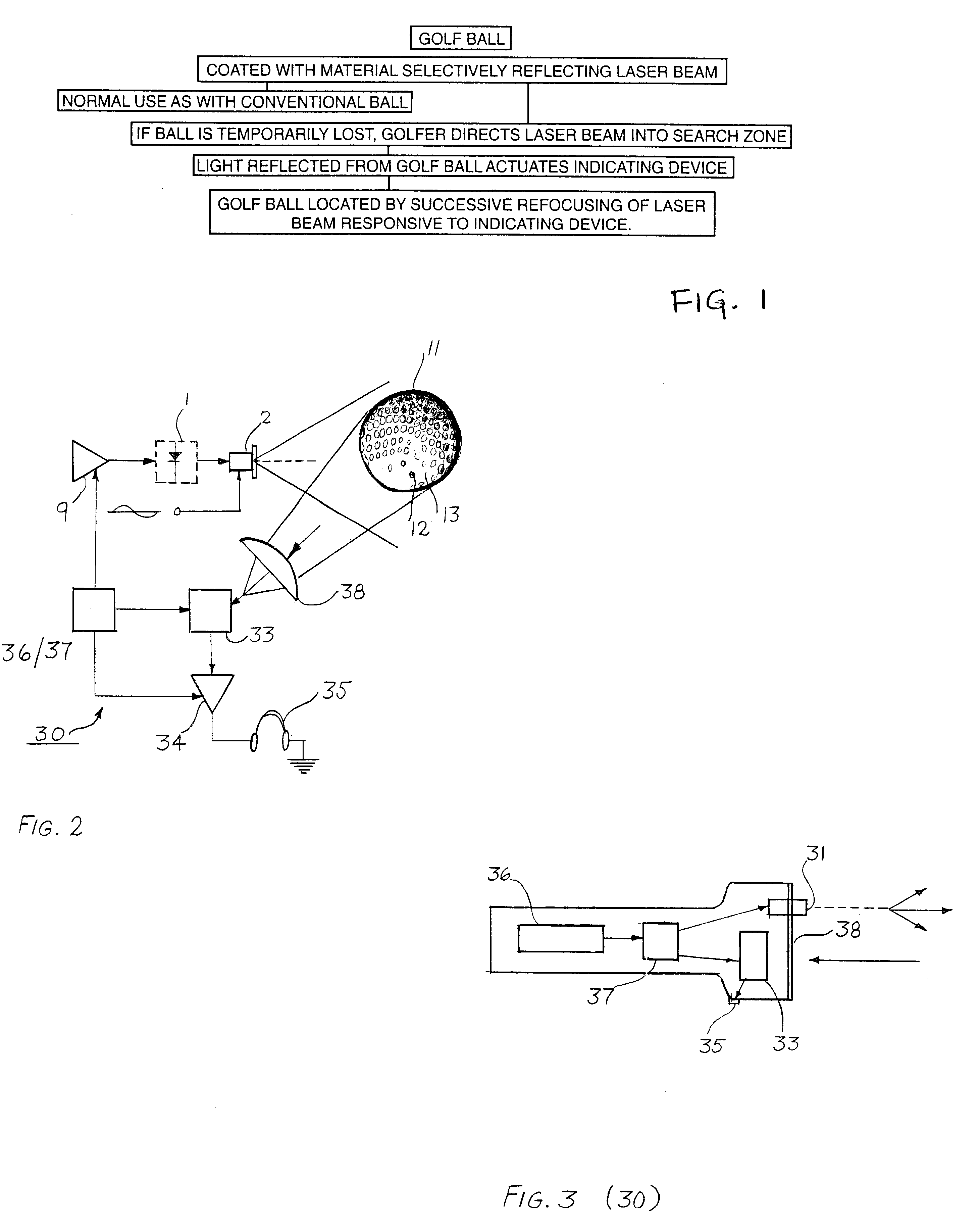
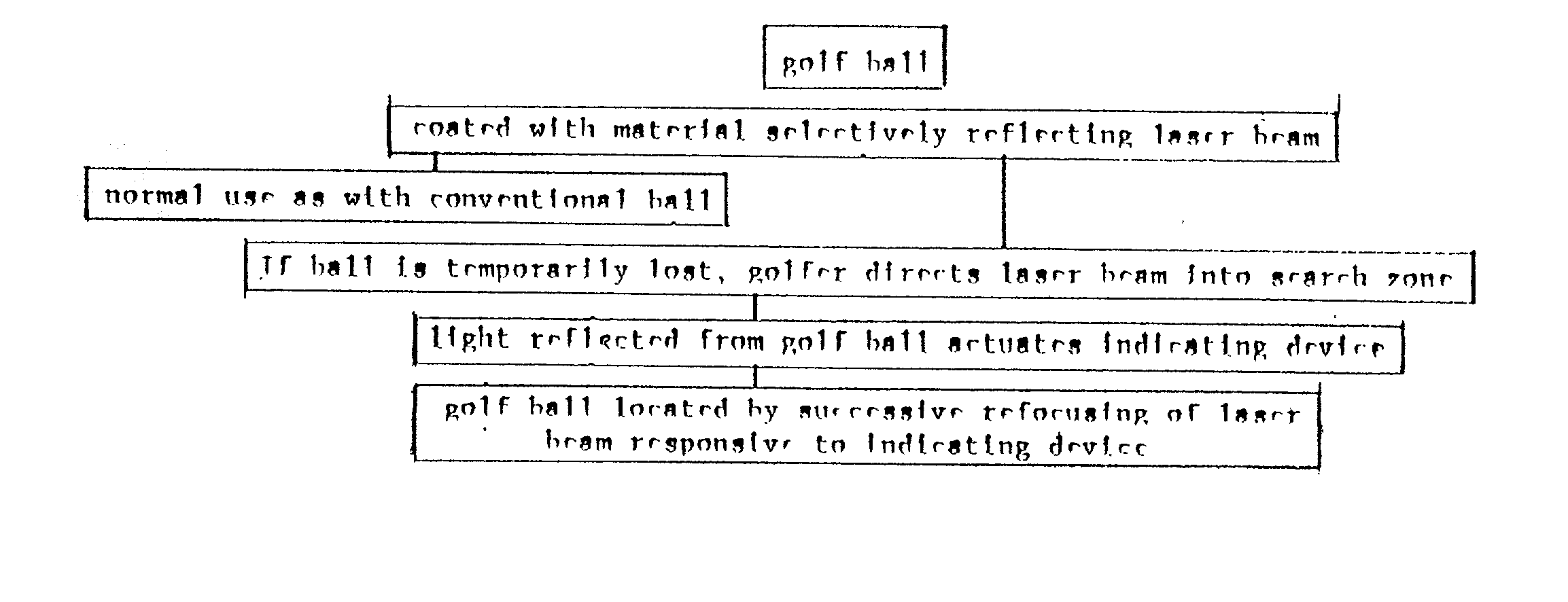
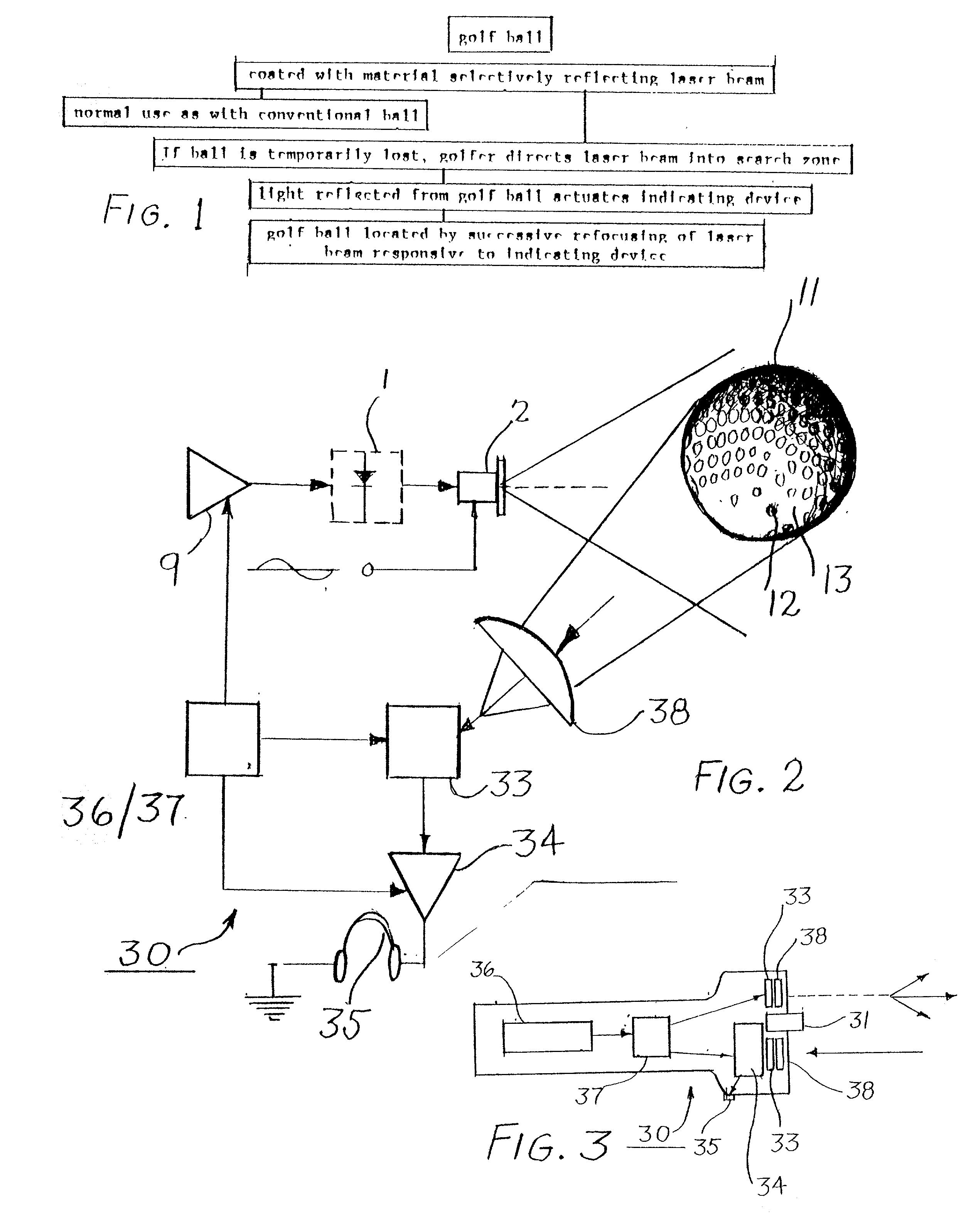
Infra-red laser device and method for searching for lost item
An ordinary golf ball is cleaned and then treated with an emulsion depositing in the dimples a hologram having the capacity to reflect a pre-selected wavelength of laser-beam. If a player temporarily looses such ball, a hand-held unit directs an infra-red laser beam of said pre-selected wavelength, desirably one not absorbed by atmospheric moisture, such as 1310 nm. Said hand-held unit contains an analyzer evaluating the light reflected back to such analyzer and attributable to such laser beam of said pre-selected wave-length. By evaluating the intensity of such reflected light, the golfer can target the location of the temporarily lost ball. Upon approaching the lost ball the angle at which the unit would be held would be modified for focusing on the lost ball. Earphones, meters, or other diagnostic equipment can monitor the intensity of the light reflected back from such laser beam. Such hand held analyzer of reflected light involves an investment which is small enough that a golf club can include the rental of such a unit as a part of the rental for a golf cart. Preliminary estimates indicated that any country club failing to utilize the present invention will encounter greater losses from lost balls than those practicing the present invention, because the cost of periodically regenerating the hologram for a ball represents such a small fraction of the cost of a replacement ball
Owner:LOST ITEM RETRIEVAL SYST
Method and apparatus for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using dfb fiber lasers
ActiveUS20100085632A1Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
An optical parametric oscillator (OPO) is described that efficiently converts a near-infrared laser beam to tunable mid-infrared wavelength output. In some embodiments, the OPO includes an optical resonator containing a nonlinear crystal, such as periodically-poled lithium niobate. The OPO is pumped by a continuous-wave fiber-laser source having a low-power oscillator and a high-power amplifier, or using just a power oscillator. The fiber oscillator produces a single-frequency output defined by a distributed-feedback (DFB) structure of the fiber. The DFB-fiber-laser output is amplified to a pump level consistent with exceeding an oscillation threshold in the OPO in which only one of two generated waves (“signal” and “idler”) is resonant within the optical cavity. This pump source provides the capability to tune the DFB fiber laser by straining the fiber (using an attached piezoelectric element or by other means) that allows the OPO to be continuously tuned over substantial ranges, enabling rapid, wide continuous tuning of the OPO output frequency or frequencies.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ACULIGHT CORP
Airborne free-space-optical system utilizing three-tier, ultrafine steering
ActiveUS7171126B2Facilitate high-pointing-resolutionMitigate vibration-induced and aero-optic-induced jitterSatellite communication transmissionRadio transmissionCommunications systemEngineering
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
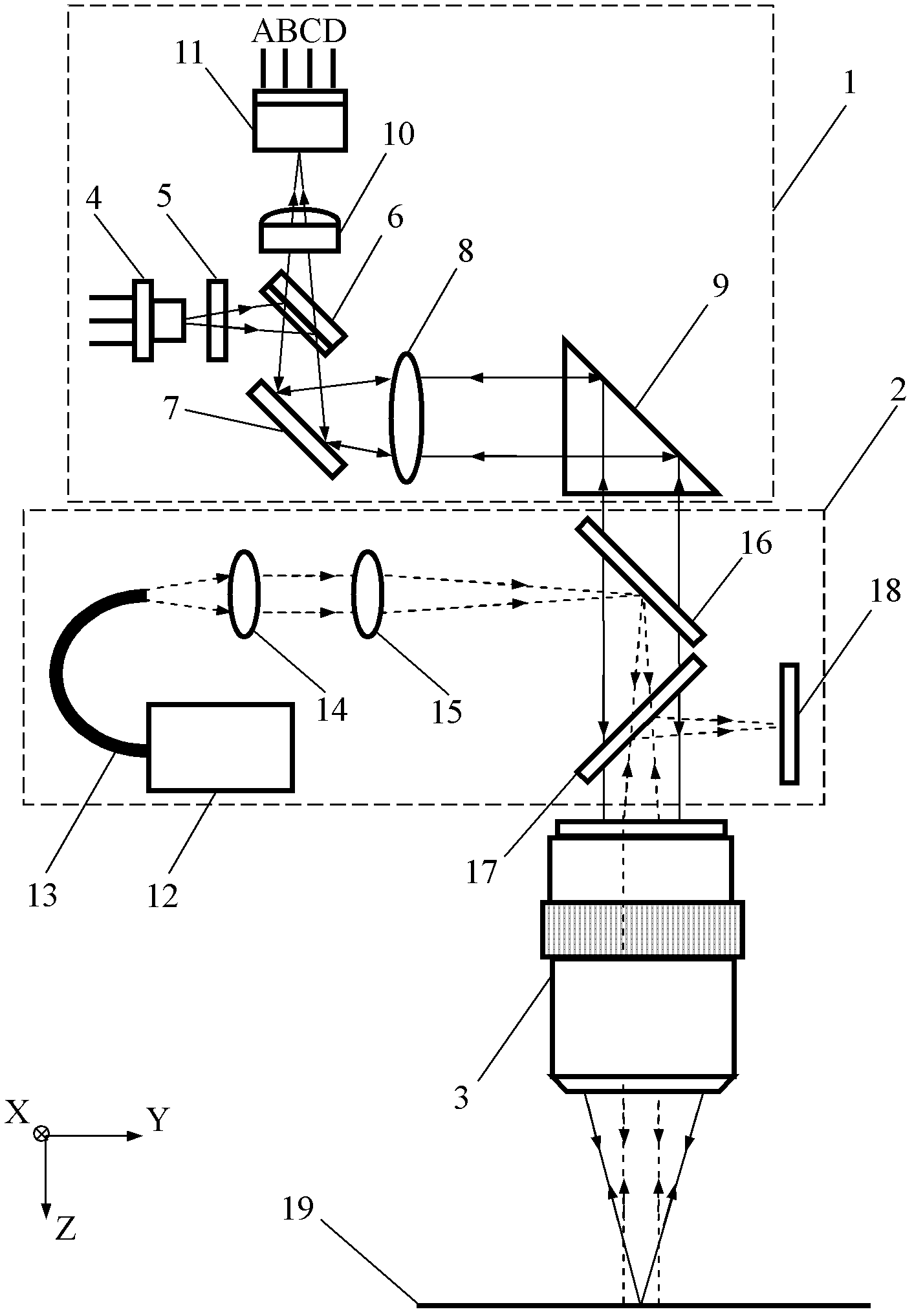
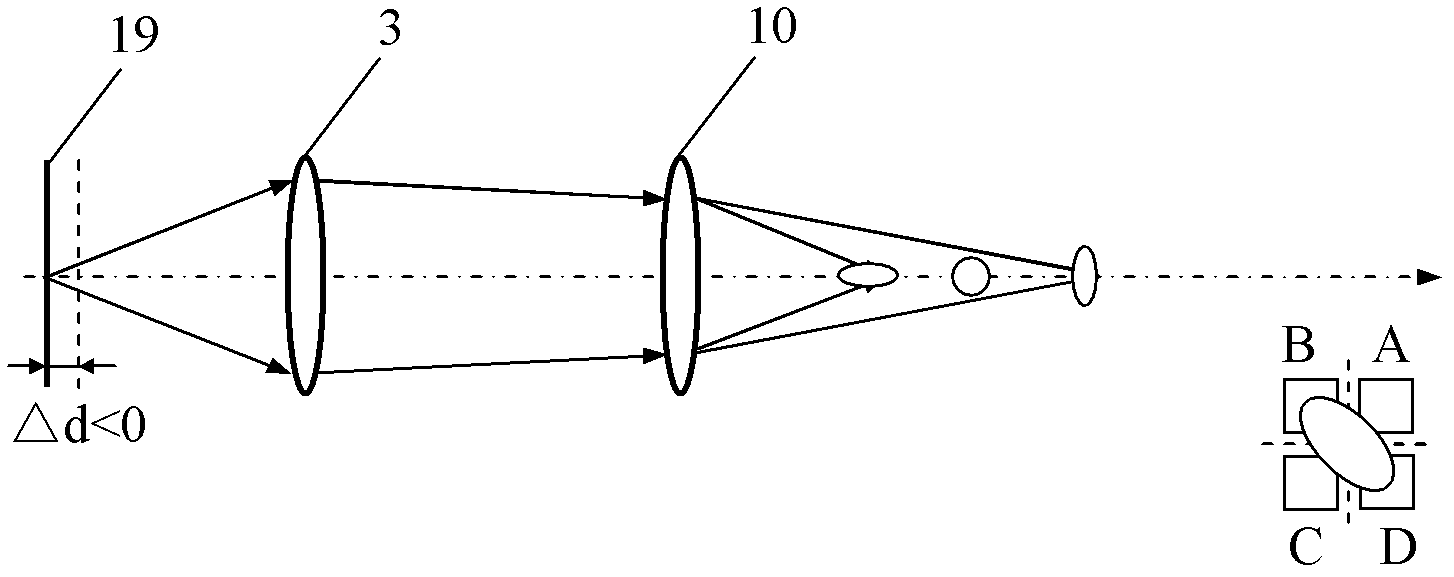
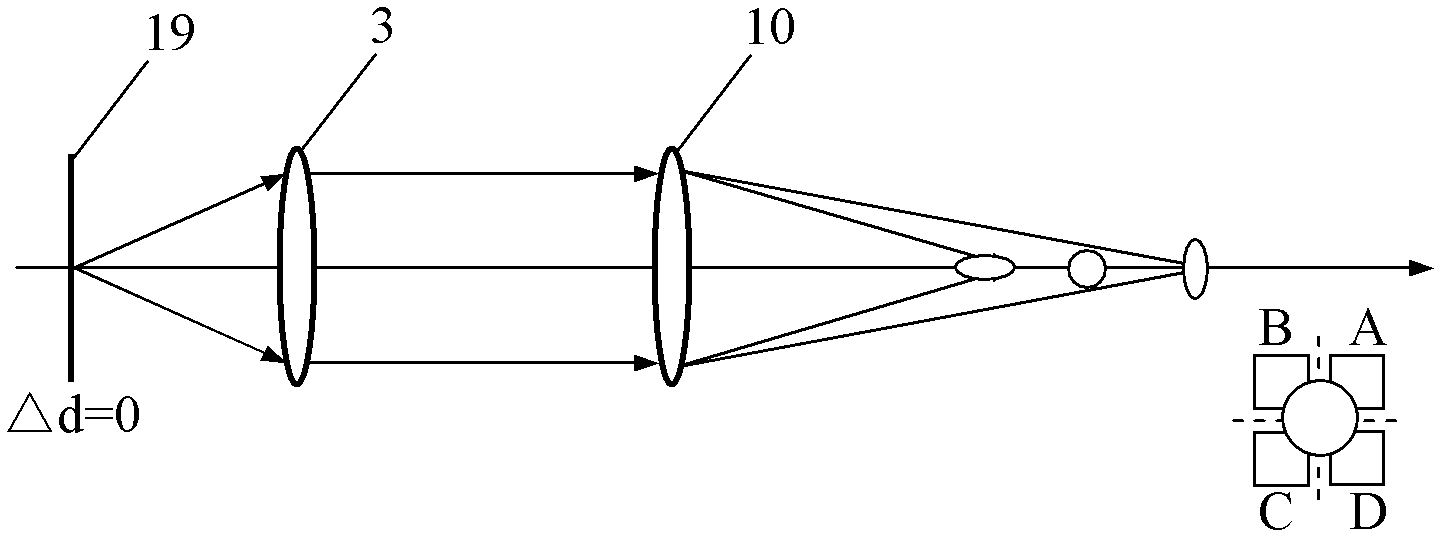
Normal displacement and angle sensing optical measuring head and measuring method thereof
The invention discloses a normal displacement and angle sensing optical measuring head and a measuring method thereof, optical measuring head laser light which is sent out by a semiconductor laser sequentially passes through a spectro-grating, a spectroscope and a reflecting mirror to be collimated into the collimated light beam, and the collimated light beam is reflected via a right-angle prism to enter a microobjective; the light beam which is reflected by an object to be measured returns back according to the same way to the spectroscope, and then is focused on a four-quadrant detector through an astigmatic lens; and laser light which is sent out by an infrared laser light source sequentially passes through a light guide optical fiber, a collimating lens and a focus lens to be focused on an infrared reflecting mirror to form a focus point which is superposed with the front focus of the microobjective, the infrared laser light is vertically reflected into the microobjective through the infrared reflecting mirror, the parallel infrared laser beam which is exited from the microobjective is reflected to the microobjective through the object to be measured, and an infrared beamsplitter reflects the returned infrared laser beam onto a two-dimensional phase-sensitive detector (PSD). The measuring head and the measuring method thereof can be effectively used for geometrical error measurement and calibration of the three freedom degrees of a linear guide rail, surface topographic reconstruction of a free-form surface and the like.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Compact solid-state laser with nonlinear frequency conversion using periodically poled materials
A compact optically-pumped solid-state laser designed for efficient nonlinear intracavity frequency conversion into desired wavelengths using periodically poled nonlinear crystals. These crystals contain dopants such as MgO or ZnO and / or have a specified degree of stoichiometry that ensures high reliability. The laser includes a solid-state gain media chip, such as Nd:YVO4, which also provides polarization control of the laser; and a periodically poled nonlinear crystal chip such as PPMgOLN or PPZnOLT for efficient frequency doubling of the fundamental infrared laser beam into the visible wavelength range. The described designs are especially advantageous for obtaining low-cost green and blue laser sources.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
Long-distance laser barrier clearing system
InactiveCN105977866ASolve the problem of focusing at a distanceImprove work efficiencyApparatus for overhead lines/cablesLight beamInfrared laser beam
The present invention discloses a long-distance laser barrier clearing system, belonging to the field of photoelectric technologies and being applied to fields of maintenance of overhead transmission lines, long-distance explosion, barrier clearing of toxic chemical environments, and so on. The long-distance laser barrier clearing system includes a support. An infrared laser is disposed above the support. A holder for adjusting a horizontal direction and a pitch angle of the infrared laser is disposed between the support and the infrared laser. An adjustable condenser lens is arranged at the front end of the infrared laser. The adjustable condenser lens is internally provided with a lens group for diffusing and focusing the infrared laser beam. An optical sighting telescope for observing sundry processing conditions is arranged above the tail end of the infrared laser. A visible light indicator is arranged above the front end of the optical sighting telescope. The infrared laser is connected with a power case by using a power line. Compared with the prior art, the long-distance laser barrier clearing system has the advantages of lowering labor intensity, reducing cost, and improving working efficiency and security.
Owner:济南舜风科技有限公司
Laser processing of display components for electronic devices
Electronic devices may be provided with display structures such as glass and polymer layers in a liquid crystal display. The glass layers may serve as substrates for components such as a color filter layer and thin-film transistor layer. The polymer layers may include films such as a polarizer film and other optical films. During fabrication of a display, the polymer layers and glass layers may be laminated to one another. Portions of the polymer layers may extend past the edges of the glass layers. Laser cutting techniques may be used to trim away excess portions of the polymer layer that do not overlap underlying portions of the glass layers. Laser cutting may involve application of an adjustable infrared laser beam.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method for manufacturing printed wiring board and copper foil for laser processing
ActiveCN104160792AFunction as a resistImprove absorption rateLight absorption dielectricsThin material handlingInfraredElectrical conductor
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of producing a printed wiring board which reduces production steps, is excellent in infrared laser processability, and is suitable for formation of an excellent wiring pattern; and to provide a copper foil for laser processing and a copper-clad laminate. In order to achieve the object, a method of producing a printed wiring board comprises: forming a via-hole for interlayer connection in a laminate in which a copper foil for laser processing comprises a copper foil and an easily soluble laser absorption layer provided on a surface of the copper foil which has a higher etching rate to a copper etchant than the copper foil and absorbs an infrared laser beam and another conductor layer is laminated through an insulating layer, directly irradiating the infrared laser beam on the easily soluble laser absorption layer; and removing the easily soluble laser absorption layer from the surface of the copper foil in a desmear step of removing a smear in a via-hole and / or a microetching step as a pretreatment of an electroless plating step is adopted.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
Infra-red laser device and method for searching for lost item
InactiveUS20020082120A1Selective reflectivitySufficient amountRadiation pyrometryIndoor gamesHand heldGolf Ball
An ordinary golf ball is cleaned and then heated with an emulsion depositing in the dimples a hologram having the capacity to reflect a pre-selected wavelength of laser-beam. If a player temporarily losses such ball, a hand-held unit directs an infra-red laser beam of said pre-selected wavelength, desirably one not absorbed by atmospheric moisture, such as 1310 nm. Said hand-held unit contains an analyzer evaluating the light reflected back to such analyzer and attributable to such laser bean of said pre-selected wave-length. By evaluating the intensity of such reflected light, the golfer can target the location of the temporarily lost ball. Upon approaching the lost ball the angle at which the unit would be held would be modified for focusing on the lost ball. Earphones, meters, or other diagnostic equipment can monitor the intensity of the light reflected back from such laser beam. Such hand held analyzer of reflected light involves an investment which is small enough that a golf club can include the rental of such a unit as a part of the rental for a golf cart. Preliminary estimates indicated that any country club failing to utilize the present invention will encounter greater losses from lost balls than those practicing the present invention, because the cost of periodically regenerating the hologram for a ball represents such a small fraction of the cost of a replacement ball.
Owner:LOST ITEM RETRIEVAL SYST
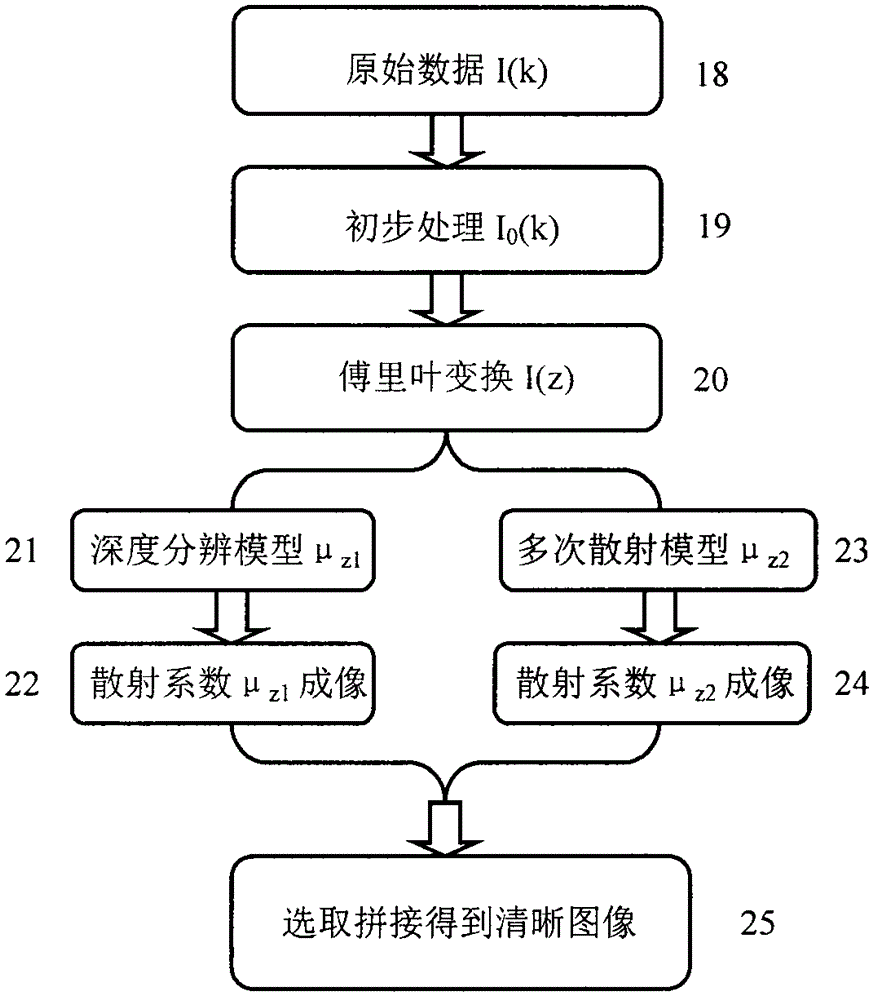
Method and system for measuring depth resolution attenuation coefficient of sample based on OCT
PendingCN105996999AImprove spatial resolutionOvercome the shortcomings of deep scattering coefficient image reconstruction blurDiagnostic signal processingDiagnostics using tomographyHigh spatial resolutionImage resolution
The invention discloses a method and a system for measuring the depth resolution attenuation coefficient of a sample based on OCT. According to the rule that the attenuation coefficient is different due to the fact that the concentration of the particle is different, the internal microstructure of medium space can be imaged by measuring the optical attenuation coefficient of the resolution of the medium space. Near-infrared laser beams adopt the single-time scattering manner when passing by a sample shallow layer area, and adopt the multi-time scattering manner when passing by a deep area. According to the method and the system, a single-time scattering model for depth resolution is adopted for measuring the scattering coefficient of the sample shallow layer area, and the scattering coefficient of the sample deep area is measured by adopting a multi-time scattering model based on the extended Huygens-Fresnel principle and combining with a segmentation fitting technology. Interference spectrum signals collected from the OCT system are subjected to data processing, the strength data of the OCT can be correspondingly converted into shallow layer and deep layer attenuation coefficient data, the reconstructed shallow layer high-spatial-resolution scattering coefficient image and deep layer high-measurement-accuracy scattering coefficient image are spliced, and the high-resolution and high-measurement-accuracy attenuation coefficient imaging of the sample can be realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Multilayered photosensitive material for flexographic printing plate
InactiveUS6897006B2Efficient processIncreased durabilityPhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical compoundCellulose compounds
The invention discloses a multilayered photosensitive material for processing into a flexographic printing plate by direct patterning with an infrared laser beam. The multilayered material comprises: (A) a substrate; (B) a photosensitive resinous layer having sensitivity to light excepting infrared light and comprising (b1) an elastomeric binder resin, (b2) a polymerizable monomeric compound and (b3) a polymerization initiator formed on the substrate (A); (C) a barrier layer of a composition comprising a resin such as a polyvinyl pyrrolidone and alkali-soluble cellulose compounds, which transmits light other than infrared light and is removable in the development treatment, formed on the photosensitive resinous layer (B); and (D) a masking layer of a composition comprising (d1) a film-forming binder resin, (d2) an infrared absorbing compound and (d3) a compound having no transmissivity to lights other than infrared light and removable by irradiation with an infrared laser beam, formed on the barrier layer (C).
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Semiconductor laser apparatus, method of manufacturing semiconductor laser apparatus, and optical pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20060227838A1Precise positioningLaser detailsSolid-state devicesOptical pickupBeam splitter
A monolithic red / infrared semiconductor laser device is joined to a blue-violet semiconductor laser device. The distance between a blue-violet emission point in the blue-violet semiconductor laser device and an infrared emission point in an infrared semiconductor laser device is significantly shorter than the distance between a red emission point in a red semiconductor laser device and the infrared emission point. A blue-violet laser beam, a red laser beam, and an infrared laser beam respectively emitted from the blue-violet emission point, the red emission point, and the infrared emission point are introduced into a photodetector after being incident on an optical disk by an optical system comprising a polarizing beam splitter, a collimator lens, a beam expander, a λ / 4 plate, an objective lens, a cylindrical lens, and an optical axis correction element.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com