Patents
Literature
4719 results about "Telescope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A telescope is an optical instrument that makes distant objects appear magnified by using an arrangement of lenses or curved mirrors and lenses, or various devices used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. The first known practical telescopes were refracting telescopes invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century, by using glass lenses. They were used for both terrestrial applications and astronomy.
Surgical instruments and method for creating anatomic working space in minilaparotomy procedure
InactiveUS6878110B2Minimize invasive procedureEasy to useSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSubject matterEngineering
A method for creating an anatomic working space in a body for a minilaparotomy procedure includes forming a minilaparotomy opening in the body, forming a trocar opening in the body, inserting a trocar into the trocar opening, introducing a telescope through the trocar to observe a first tissue to be surgically treated, inserting at least one first piercing retractor into the body through the opening, wherein the piercing retractor has first and second end portions, puncturing a wall of the body by the first end portion of the first piercing retractor, and lifting the wall of the body and moving around by using the first piercing retractor until a desirable anatomic working space is created in the body. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:YANG SEUNG CHOUL +1
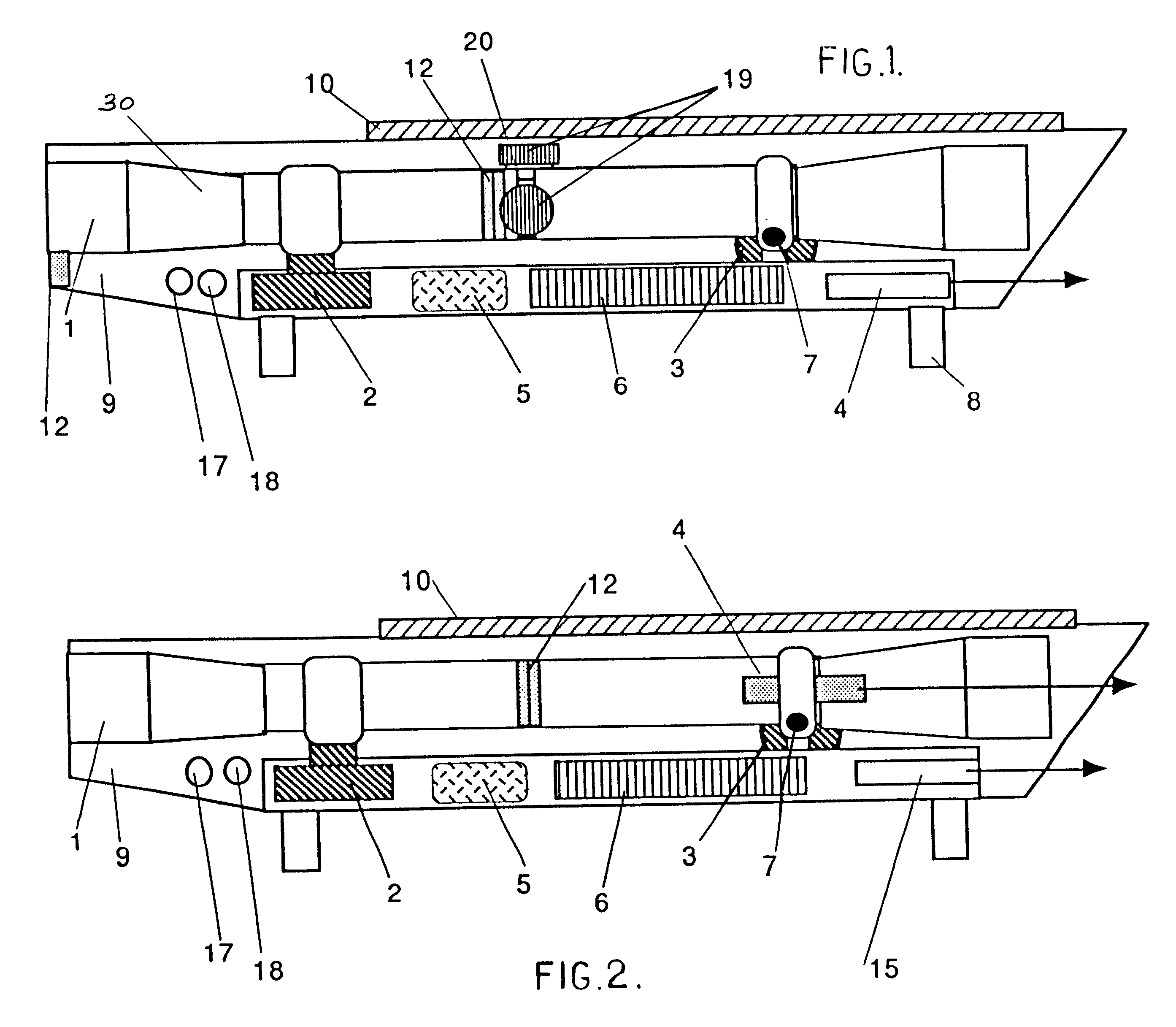
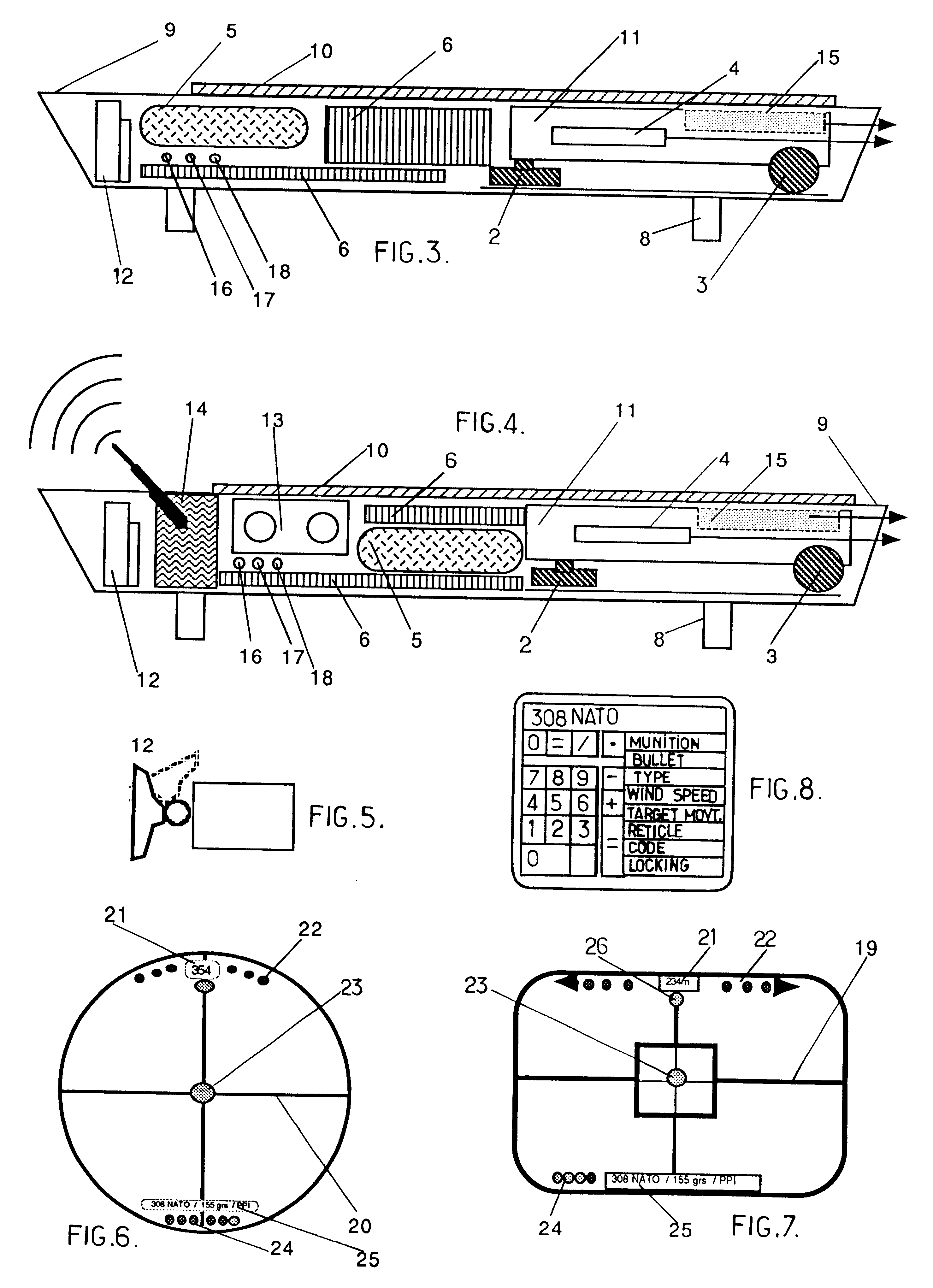
Telescopic sight for individual weapon with automatic aiming and adjustment
The invention concerns a telescopic rifle sight for individual weapon equipped with at least one step micro-motor designed to vary the angle of the sight relative to the axis of the weapon and the initial axis of aim, thereby adequately varying the whole sight assembly and thus varying the original position of the sight reticle from the original point of aim to the required point of aim.
Owner:GUARY GABRIEL +1
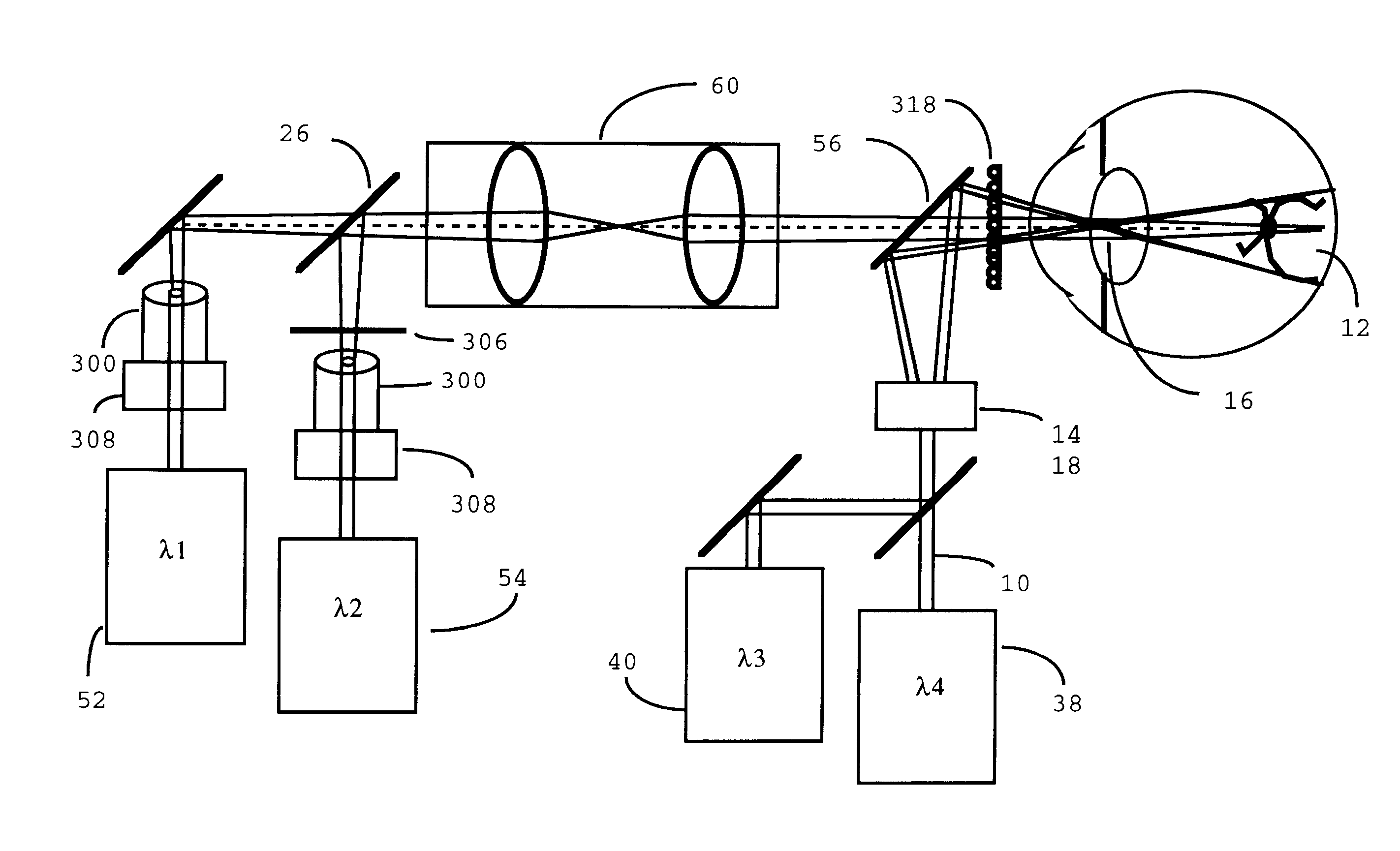
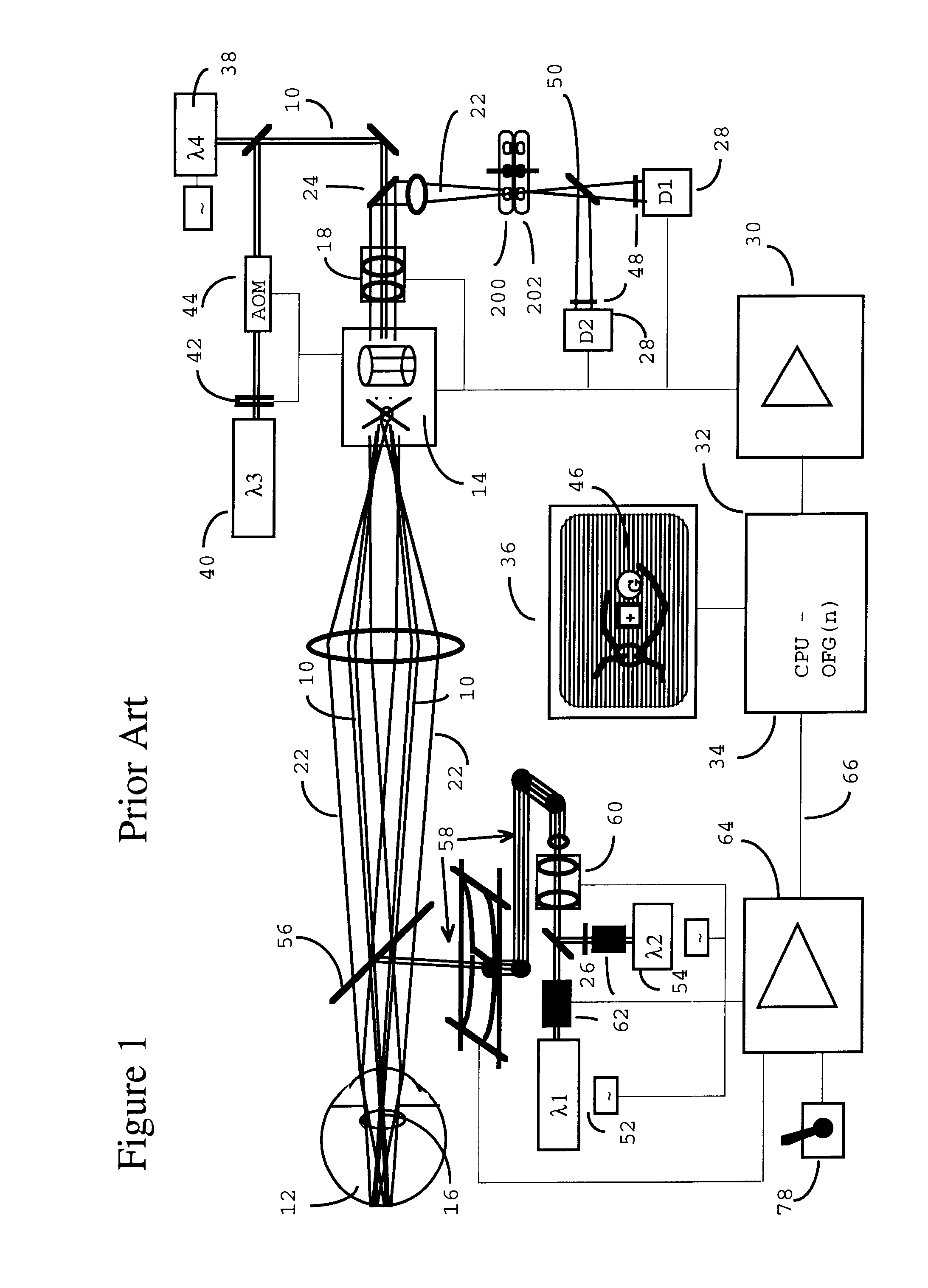
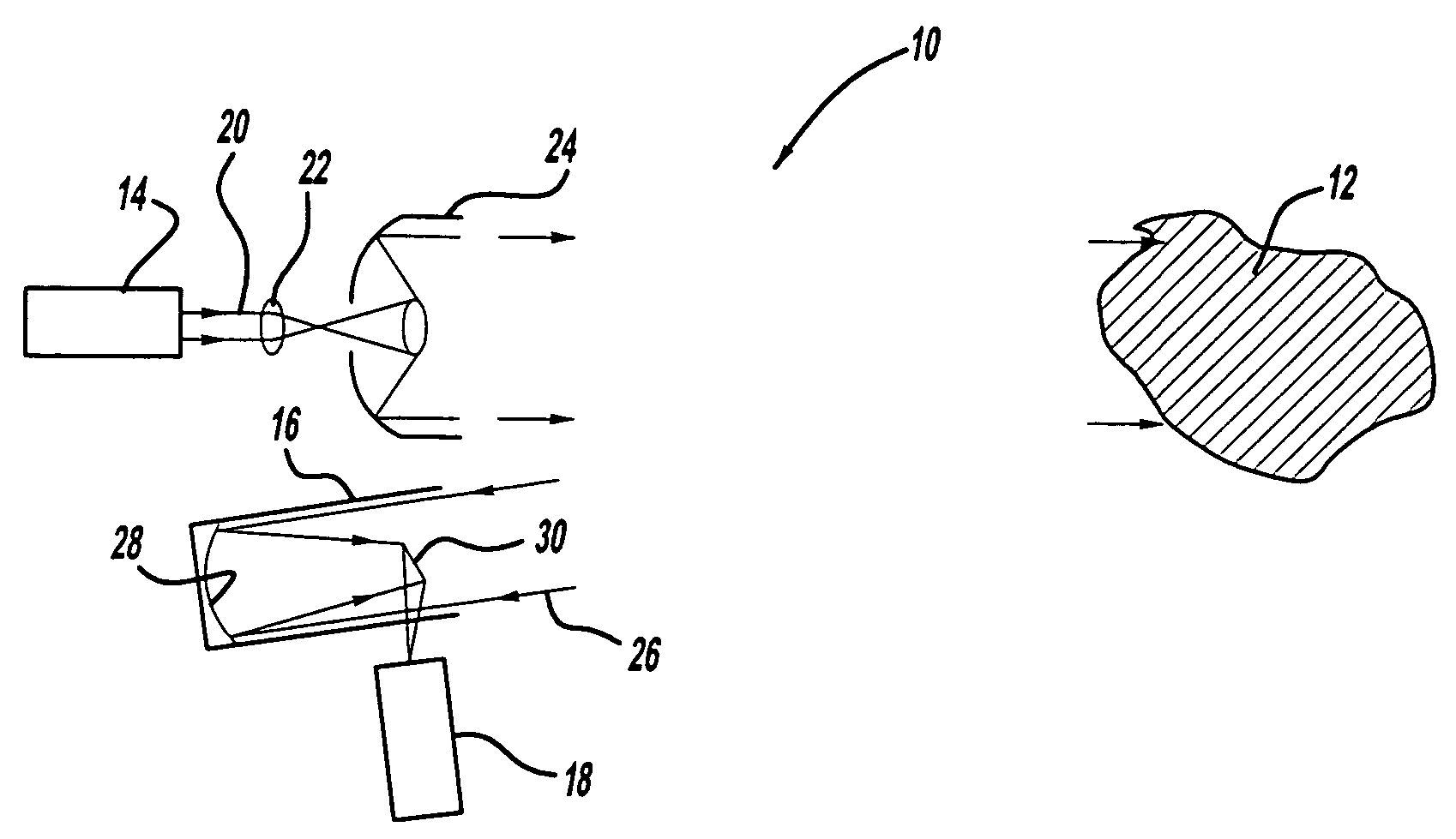
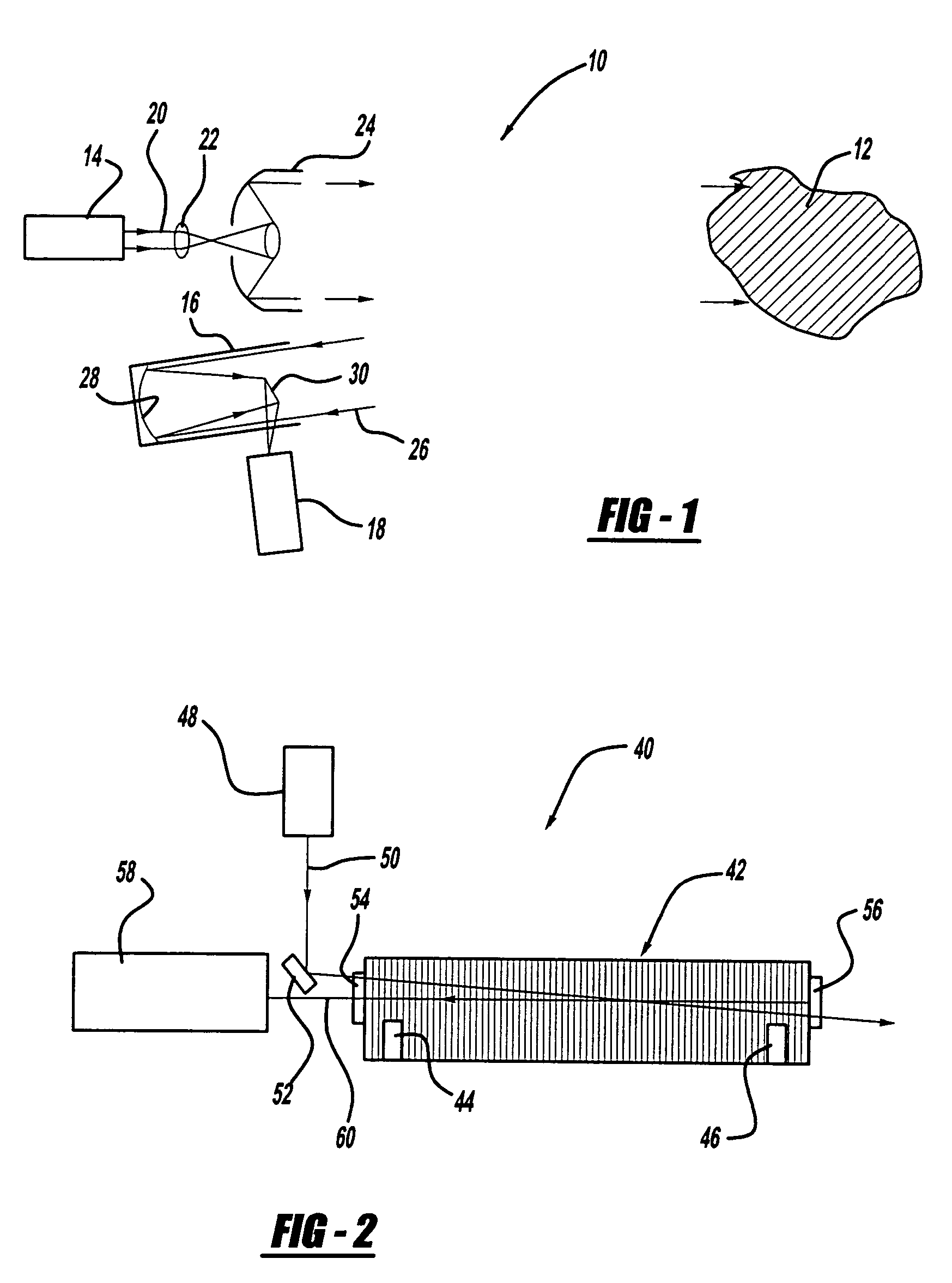
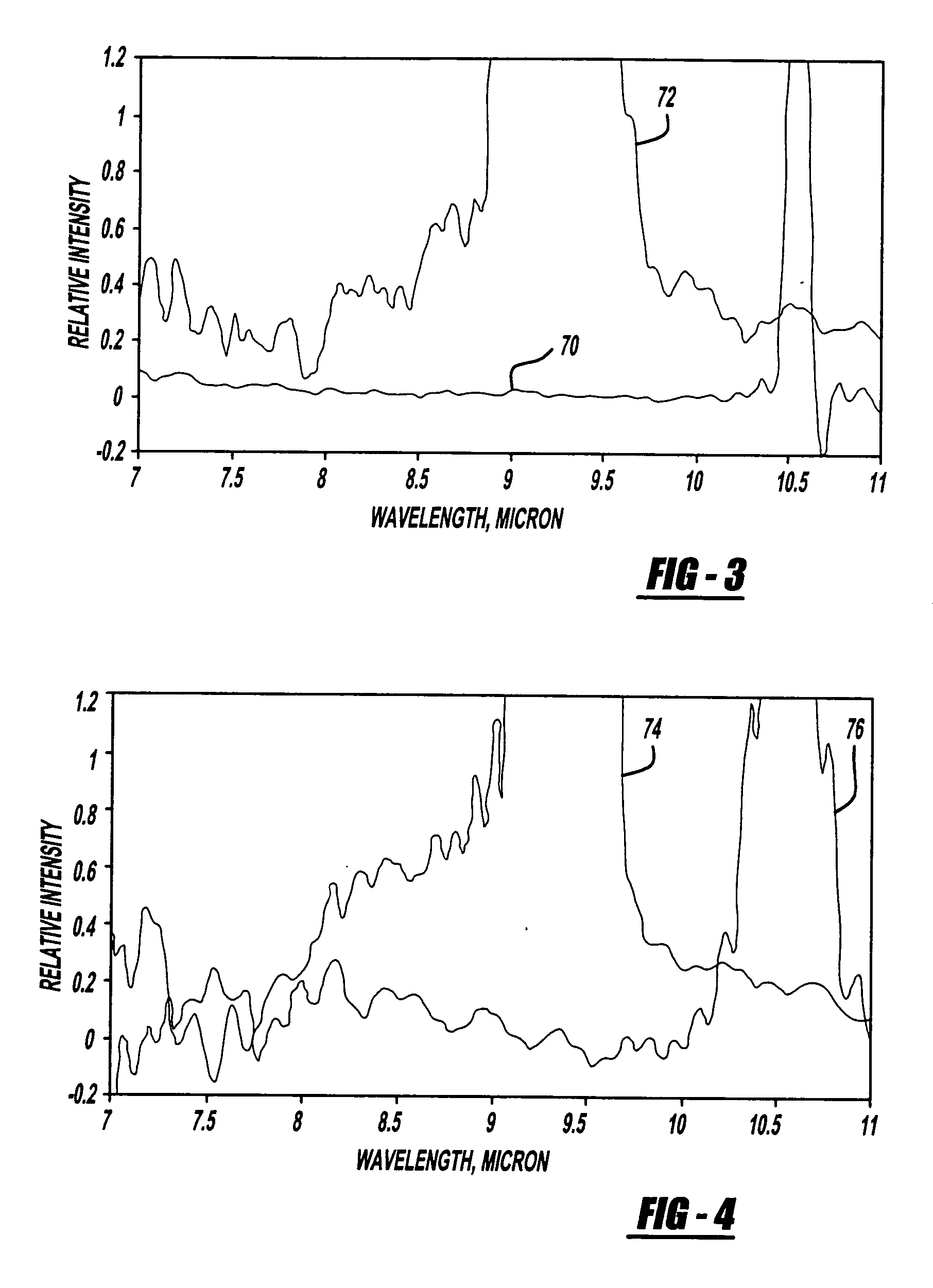
Scanning laser ophthalmoscope for selective therapeutic laser
A combination of a scanning laser ophthalmoscope and external laser sources (52) is used for microphotocoagulation and photodynamic therapy, two examples of selective therapeutic laser. A linkage device incorporating a beamsplitter (56) and collimator-telescope (60) is adjusted to align the pivot point (16) of the scanning lasers (38, 40) and external laser source (52). A similar pivot point minimizes wavefront aberrations, enables precise focusing and registration of the therapeutic laser beam (52) on the retina without the risk of vignetting. One confocal detection pathway of the scanning laser ophthalmoscope images the retina. A second and synchronized detection pathway with a different barrier filter (48) is needed to draw the position and extent of the therapeutic laser spot on the retinal image, as an overlay (64). Advanced spatial modulation increases the selectivity of the therapeutic laser. In microphotocoagulation, an adaptive optics lens (318) is attached to the scanning laser ophthalmoscope, in proximity of the eye. It corrects the higher order optical aberrations of the eye optics, resulting in smaller and better focused applications. In photodynamic therapy, a spatial modulator (420) is placed within the collimator-telescope (60) of the therapeutic laser beam (52), customizing its shape as needed. A similar effect can be obtained by modulating a scanning laser source (38) of appropriate wavelength for photodynamic therapy.
Owner:VAN DE VELDE JOZEK F
Apparatus and method for calculating aiming point information
InactiveUS20050021282A1Precise positioningEasy to adjustSighting devicesDigital computer detailsComputer architectureTarget acquisition
The present invention relates to target acquisition and related devices, and more particularly to telescopic gunsights and associated equipment used to achieve shooting accuracy at, for example, close ranges, medium ranges and extreme ranges
Owner:HVRT CORP
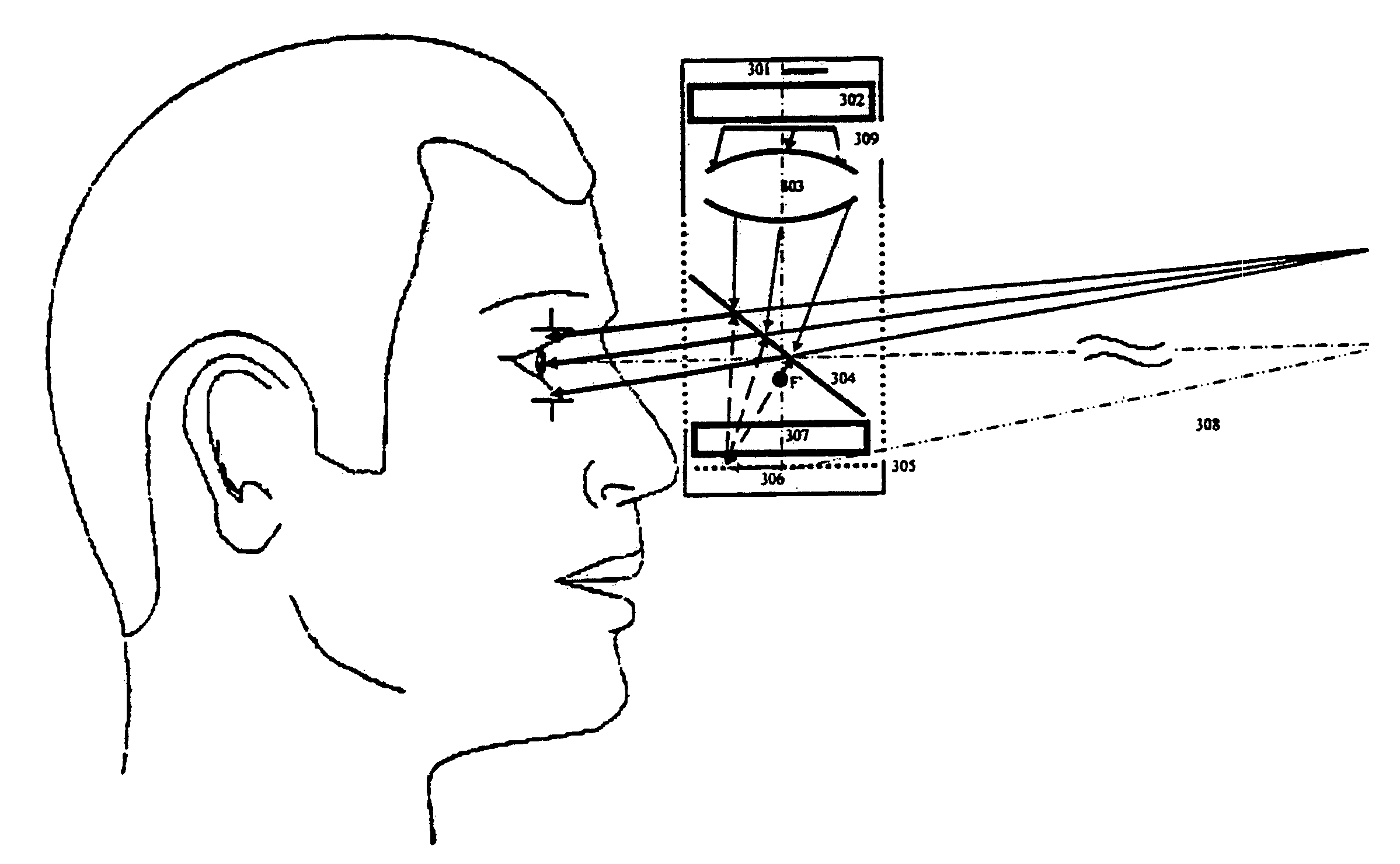
Ophthalmic instrument with adaptive optic subsystem that measures aberrations (including higher order aberrations) of a human eye and that provides a view of compensation of such aberrations to the human eye
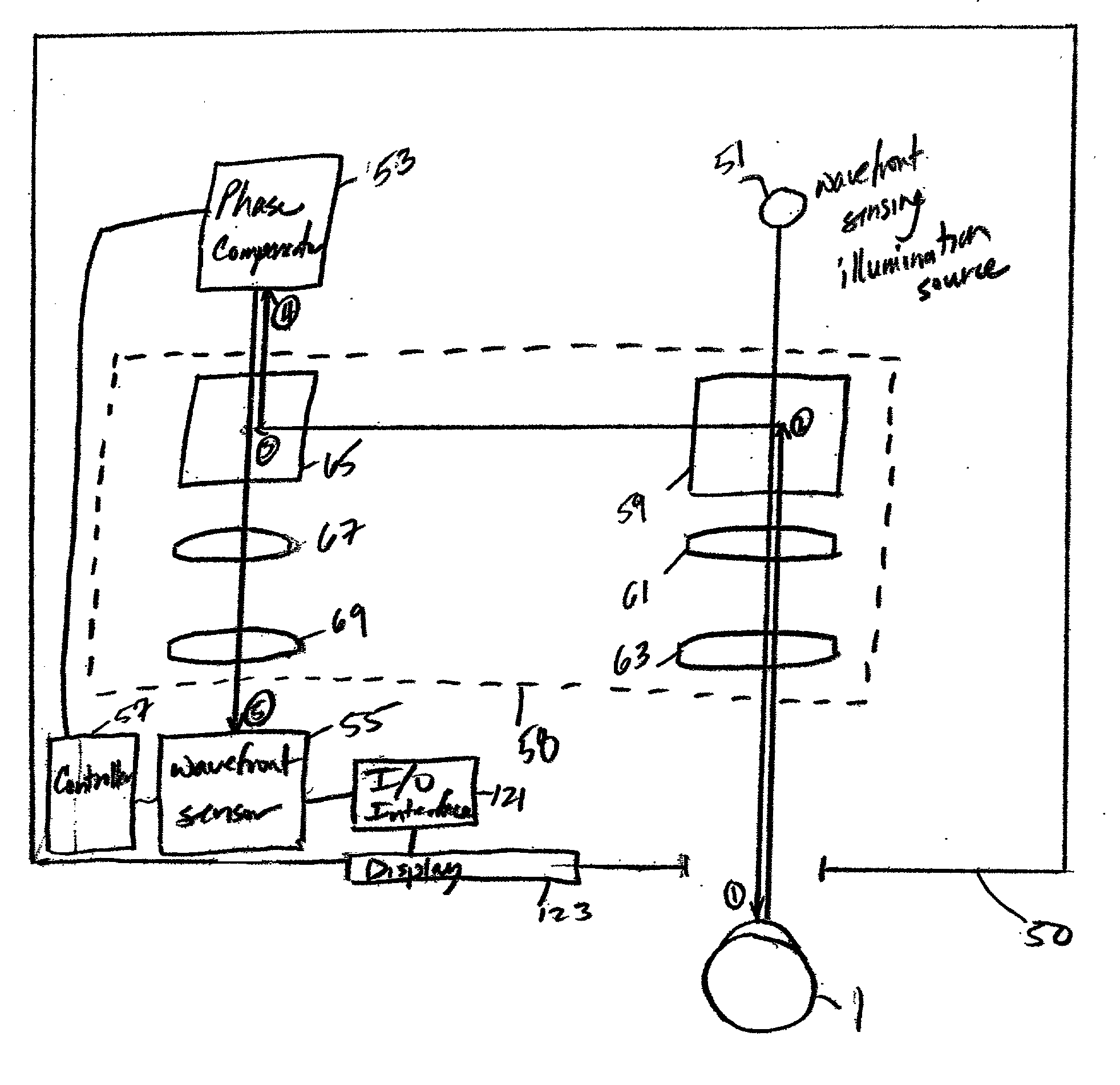
An improved ophthalmic instrument for in-vivo examination of a human eye including a wavefront sensor that estimates aberrations in reflections of the light formed as an image on the retina of the human eye and a phase compensator that spatially modulates the phase of incident light to compensate for the aberrations estimated by the wavefront sensor Optical elements create an image of a fixation target at the phase compensator, which produces a compensated image of the fixation target that compensates for aberrations estimated by the wavefront sensor. The compensated image of the fixation target produced by the phase compensator is recreated at the human eye to thereby provide the human eye with a view of compensation of the aberrations the human eye as estimated by the wavefront sensor. The phase compensator preferably comprises a variable focus lens that compensates for focusing errors and a deformable mirror that compensates for higher order aberrations. The optical elements preferably comprise a plurality of beam splitters and a plurality of lens groups each functioning as an afocal telescope. In addition, instruments and systems are provided that exploit these capabilities to enable efficient prescription and / or dispensing of corrective optics (e.g., contact lens and glasses).
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
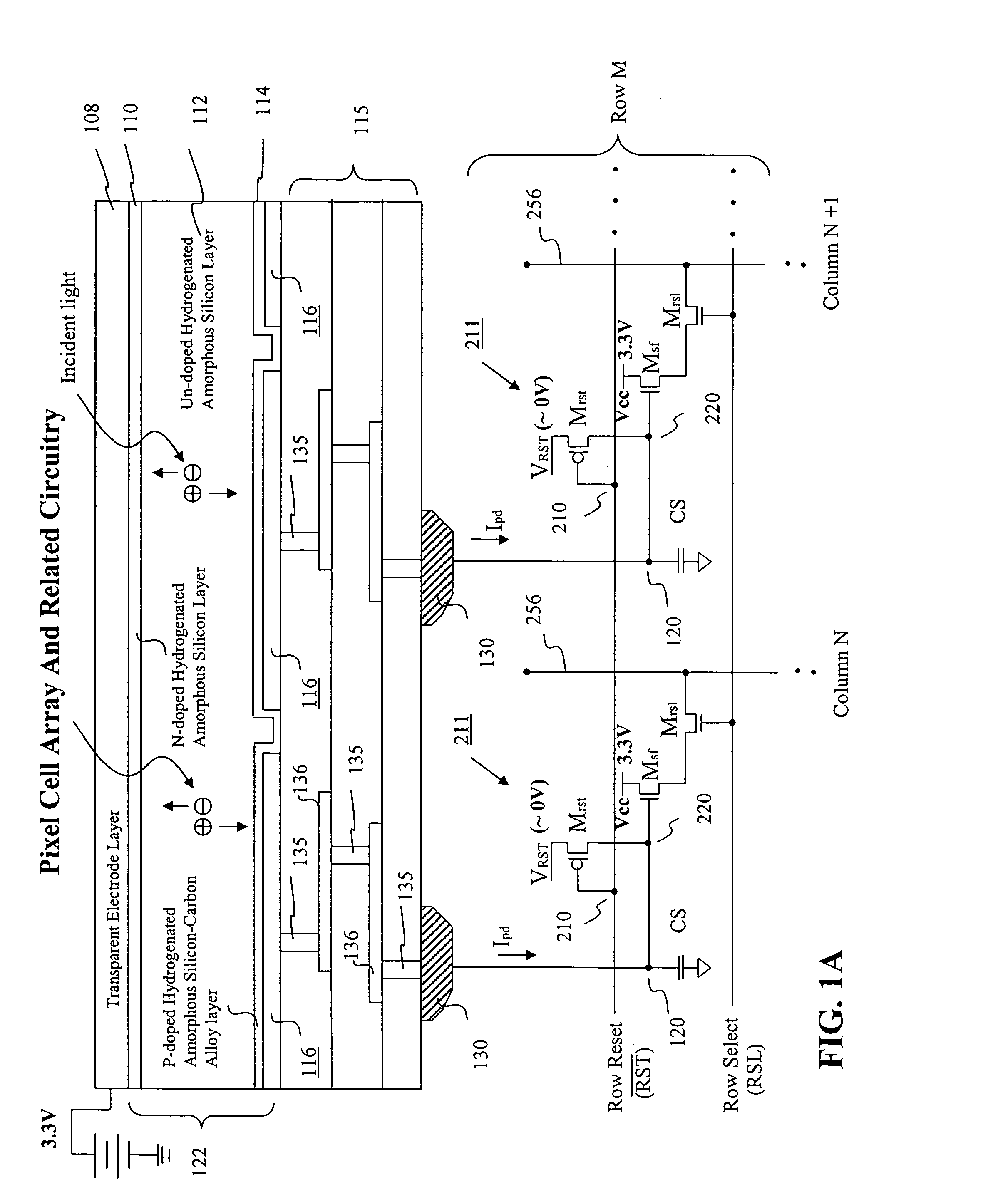
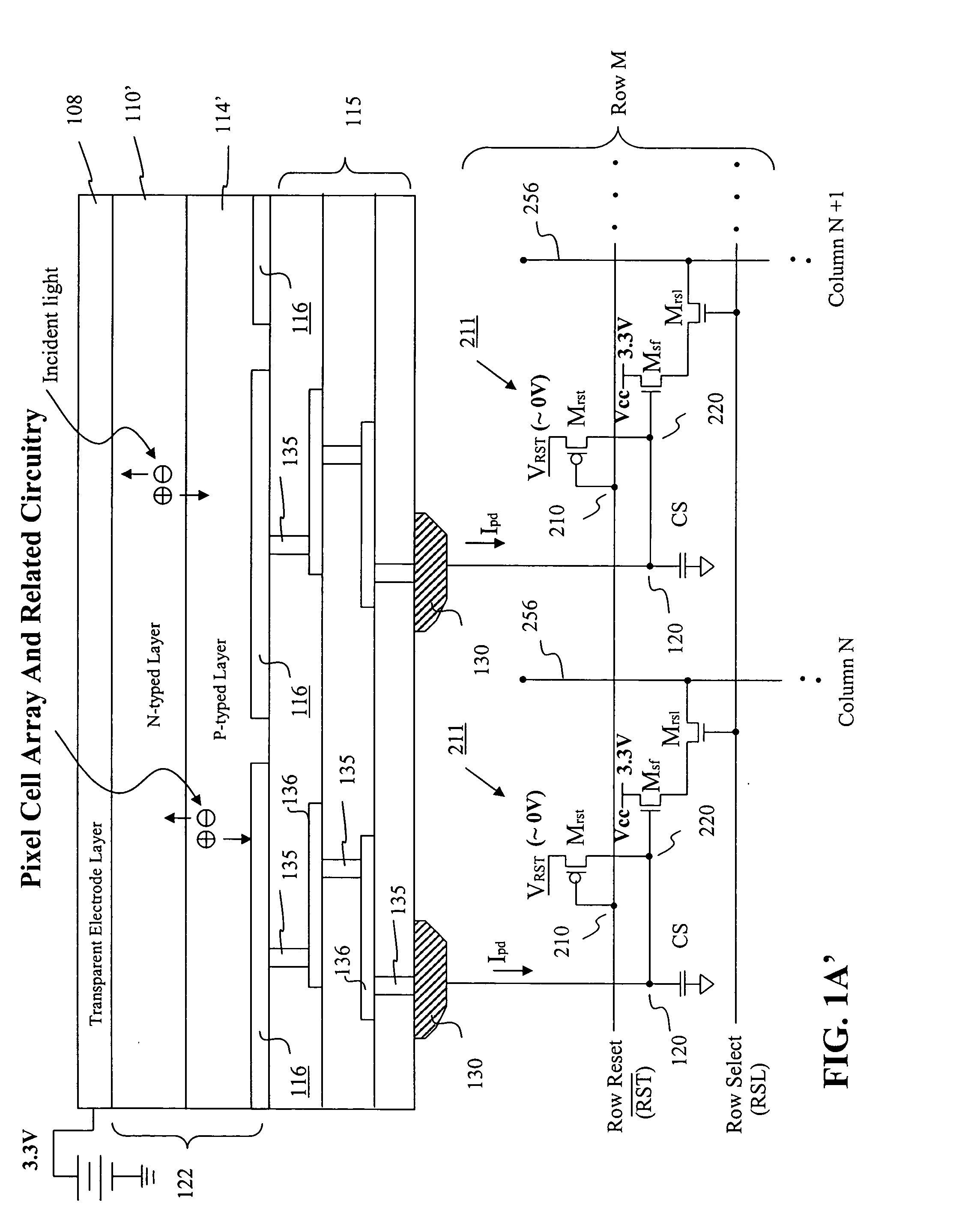
Visible/near infrared image sensor
InactiveUS20050104089A1Improve performanceHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow earth orbitBeam steering
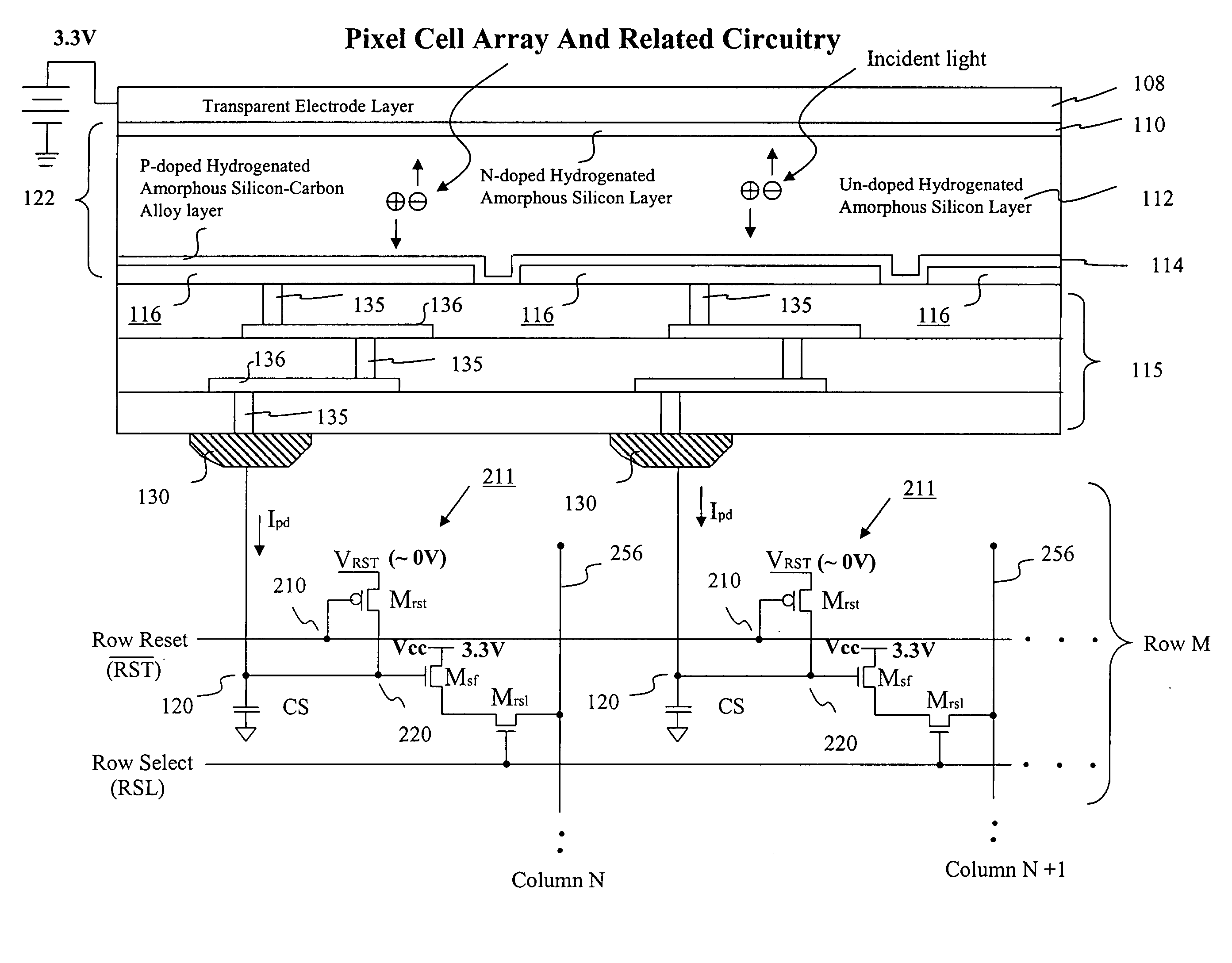
A MOS or CMOS sensor for high performance imaging in broad spectral ranges including portions of the infrared spectral band. These broad spectral ranges may also include portions or all of the visible spectrum, therefore the sensor has both daylight and night vision capabilities. The sensor includes a continuous multi-layer photodiode structure on a many pixel MOS or CMOS readout array where the photodiode structure is chosen to include responses in the near infrared spectral ranges. A preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline copper indium diselenide / cadmium sulfide photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. An alternate preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline silicon germanium photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. Each of these embodiments provides night vision with image performance that greatly surpasses the GEN III night vision technology in terms of enhanced sensitivity, pixel size and pixel count. Further advantages of the invention include low electrical bias voltages, low power consumption, compact packaging, and radiation hardness. In special preferred embodiments CMOS stitching technology is used to provide multi-million pixel focal plane array sensors. One embodiments of the invention made without stitching is a two-million pixel sensor. Other preferred embodiments available using stitching techniques include sensors with 250 million (or more) pixels fabricated on a single wafer. A particular application of these very high pixel count sensors is as a focal plane array for a rapid beam steering telescope in a low earth orbit satellite useful for tracking over a 1500-meter wide track with a resolution of 0.3 meter.
Owner:C PHOCUS
System and method for 3D photography and/or analysis of 3D images and/or display of 3D images
InactiveUS20050053274A1Generate efficientlySolve the real problemProjectorsCharacter and pattern recognitionScale model3d image
When 3D viewing means become much more available and common, it will be very sad that the many great movies that exist today will be able to be viewed in 3D only through limited and partial software attempts to recreate the 3D info. Films today are not filmed in 3D due to various problems, and mainly since a normal stereo camera could be very problematic when filming modern films, since for example it does not behave properly when zooming in or out is used, and it can cause many problems when filming for example smaller scale models for some special effects. For example, a larger zoom requires a correspondingly larger distance between the lenses, so that for example if a car is photographed at a zoom factor of 1:10, the correct right-left disparity will be achieved only if the lenses move to an inter-ocular distance of for example 65 cm instead of the normal 6.5 cm. The present invention tries to solve the above problems by using a 3D camera which can automatically adjust in a way that solves the zoom problem, and provides a solution also for filming smaller models. The angle between the two lenses is preferably changed according to the distance and position of the object that is at the center of focus, and changing the zoom affects automatically both the distance between the lenses and their angle, since changing merely the distance without changing the convergence angle would cause the two cameras to see completely different parts of the image. The patent also shows that similar methods can be used for example for a much better stereoscopic telescope with or without a varying zoom factor. In addition, the patent shows various ways to generate efficiently a 3D knowledge of the surrounding space, which can be used also for example in robots for various purposes, and also describes a few possible improvements in 3d viewing.
Owner:MAYER YARON +1
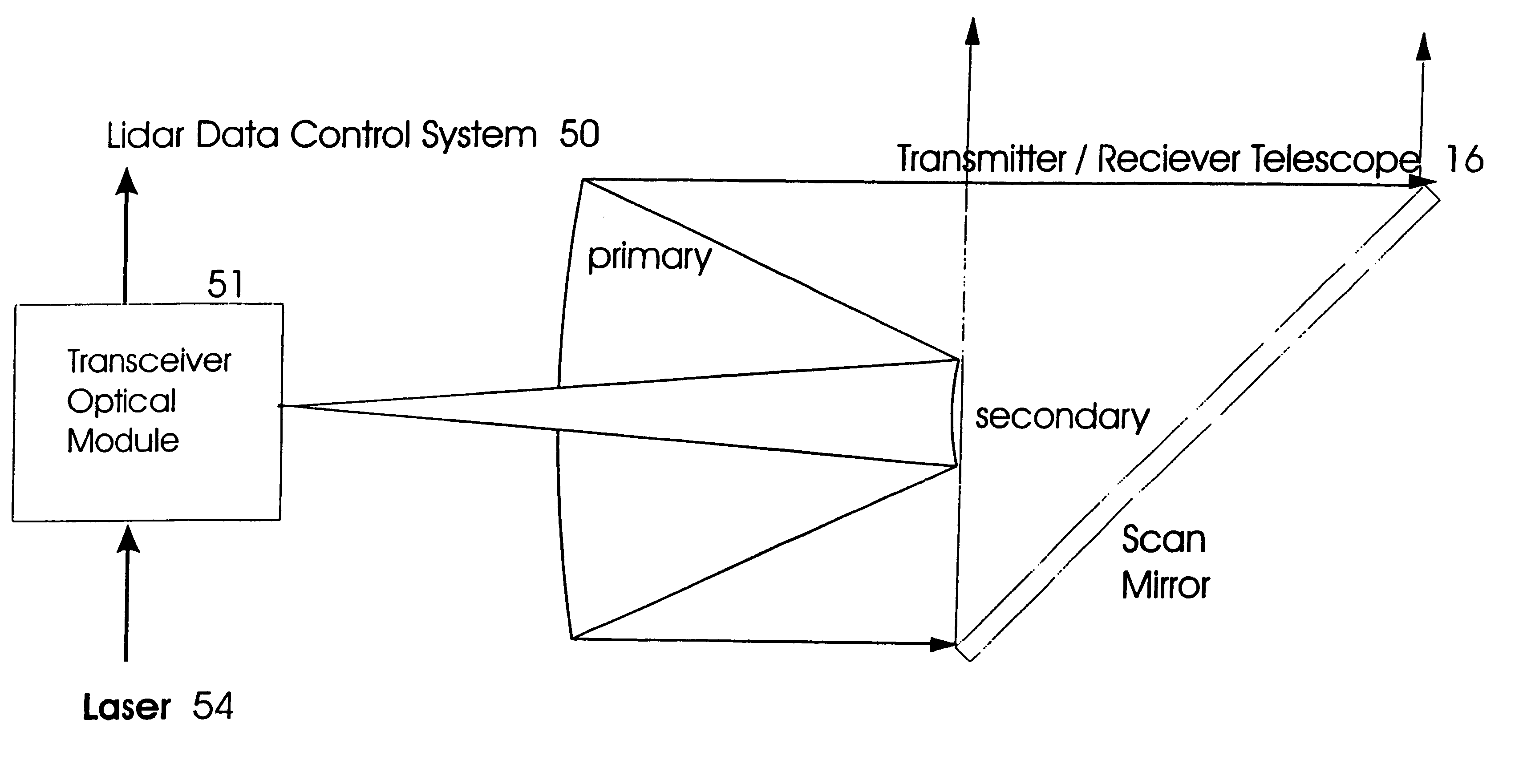
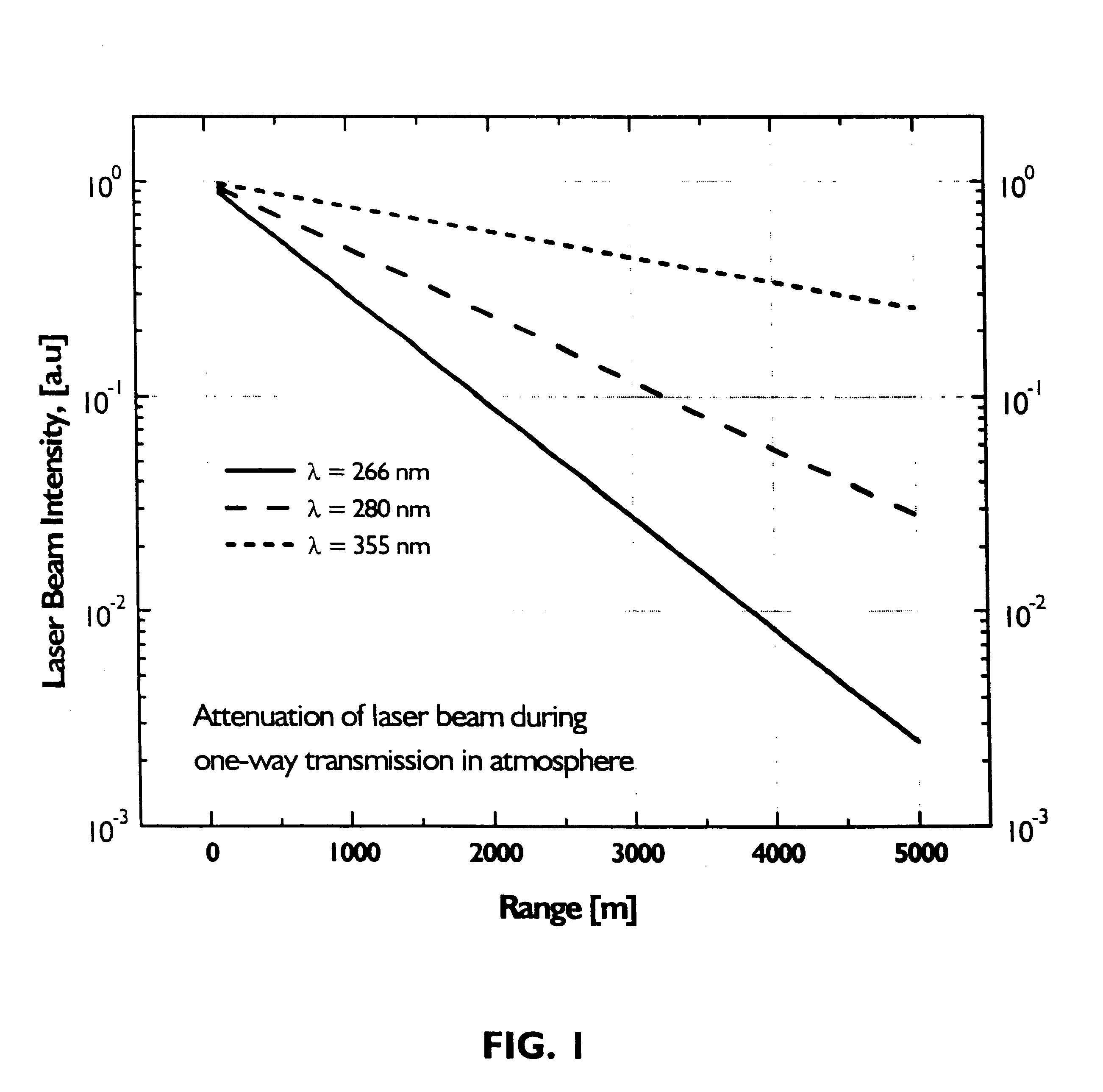
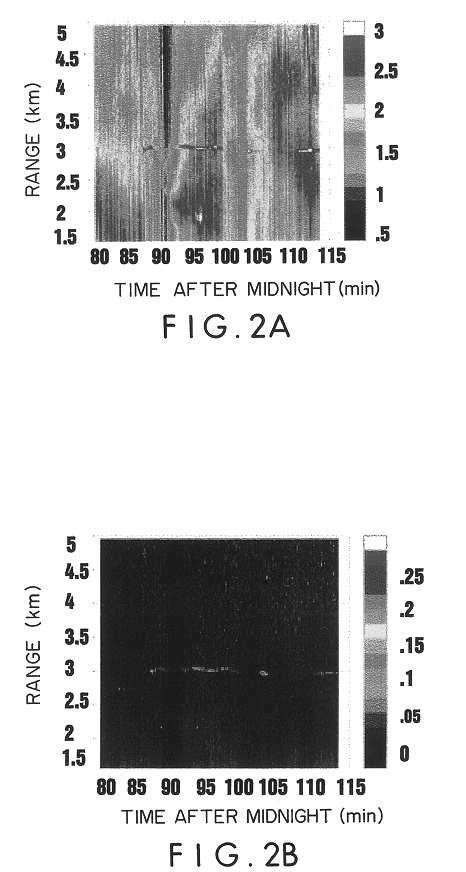
Enhanced portable digital lidar system
InactiveUS20060231771A1Easy to set upEasy maintenancePhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansSpectral bandsFluorescence
A system for detecting airborne agents. The system can include a laser source that provides laser pulses of at least two wavelengths, a transmitter that transmits the laser pulses, and a coupling mechanism configured to remotely couple the laser pulses between the laser source and the transmitter. The system can include a receiver receives both elastically backscattered signals from airborne agents and fluorescence signals from the airborne agents. The system can include a telescope both transmits a collimated laser beam of the laser pulse from the transmitter to a far field and receives the elastically backscattered signals and the fluorescence signals from the far field. The system can include a detection system having at least one of a backscatter optical detector that detects the elastically backscattered signals and one or more fluorescence optical detectors that detect the fluorescence signals in selected spectral band(s) from the airborne agents.
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
Digital focus lens system
Owner:BATCHKO ROBERT G
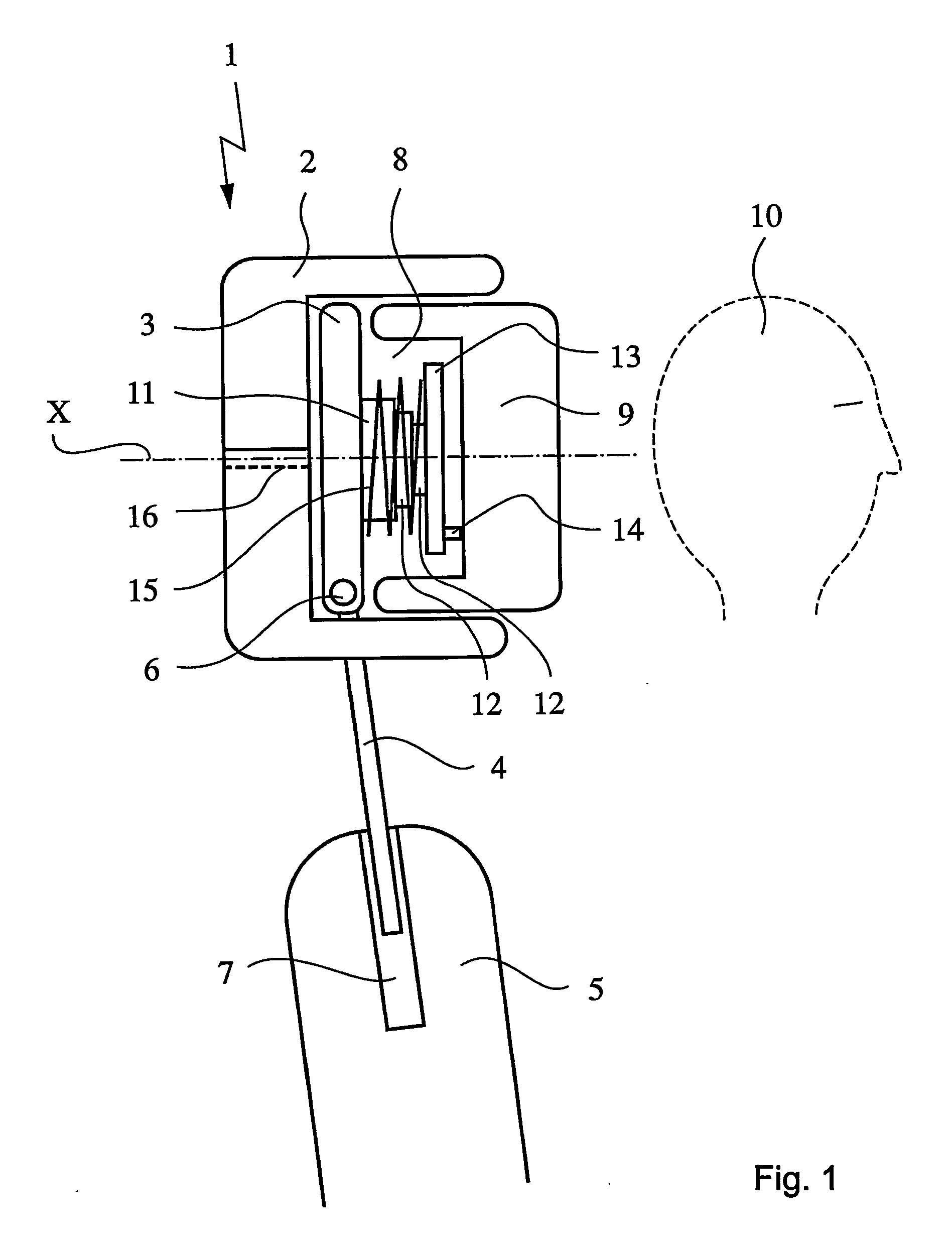
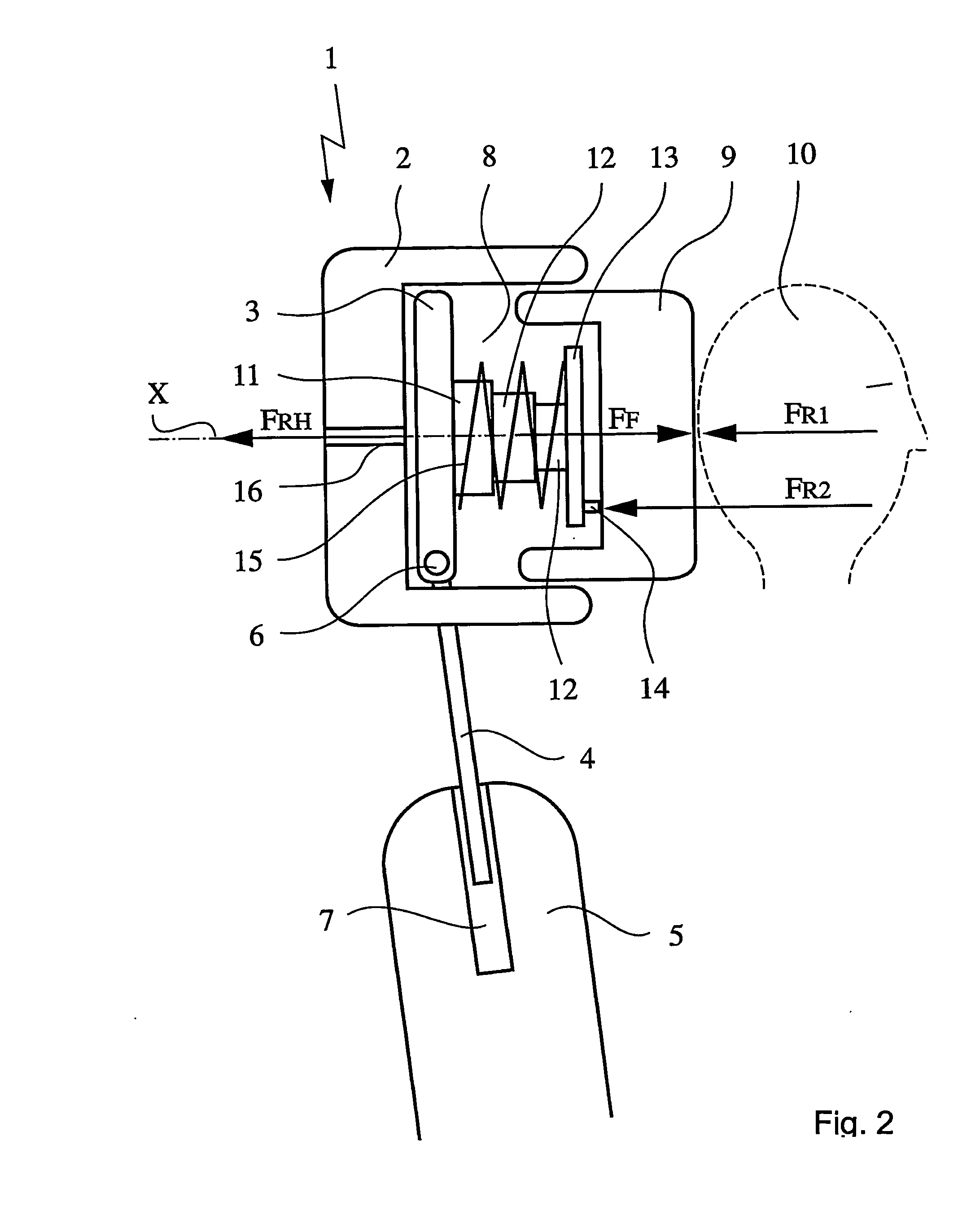
Head rest for the seat of a vehicle
InactiveUS20050077762A1Little effortComfortable environmentVehicle seatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementControl theoryMechanical engineering
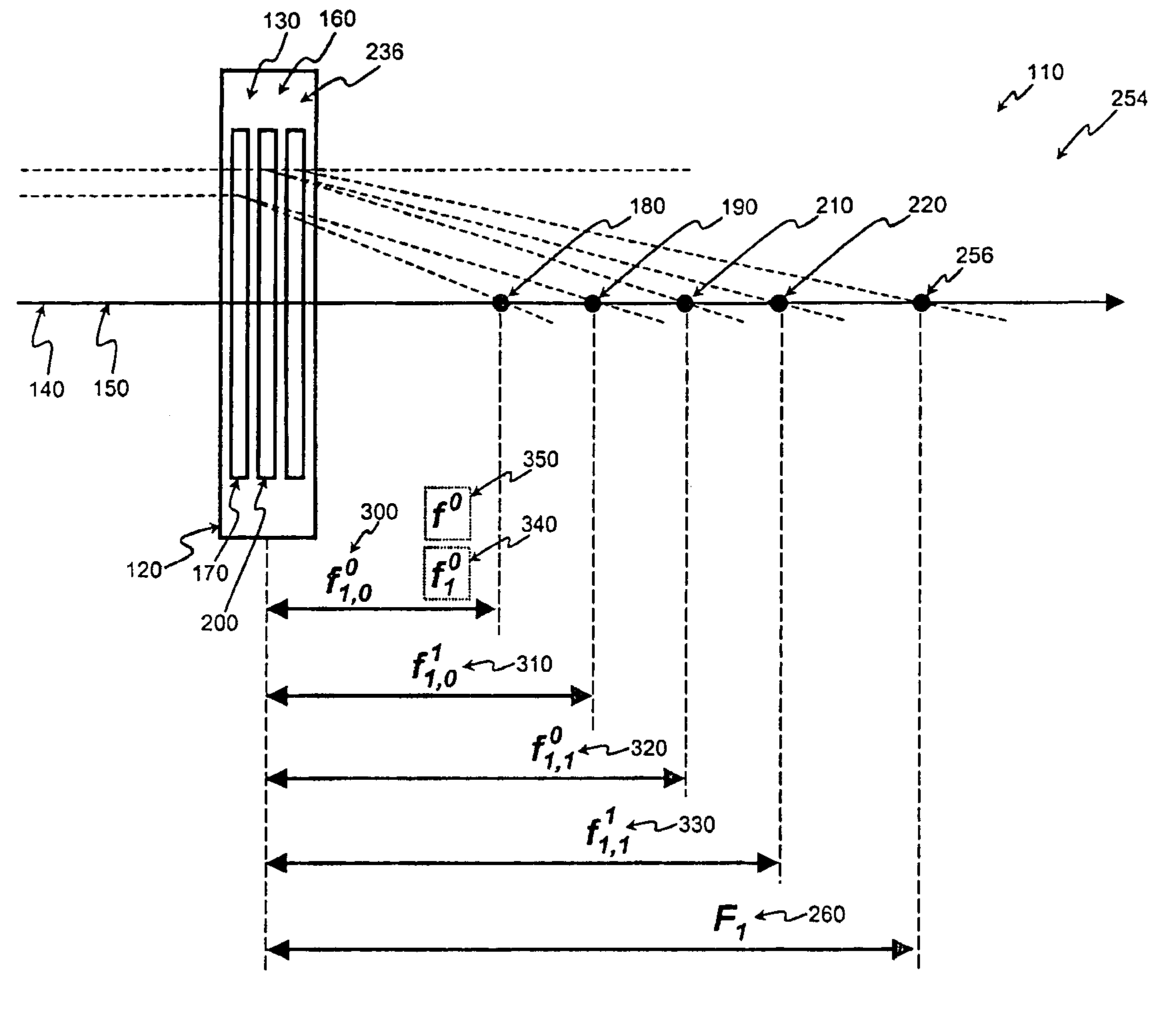
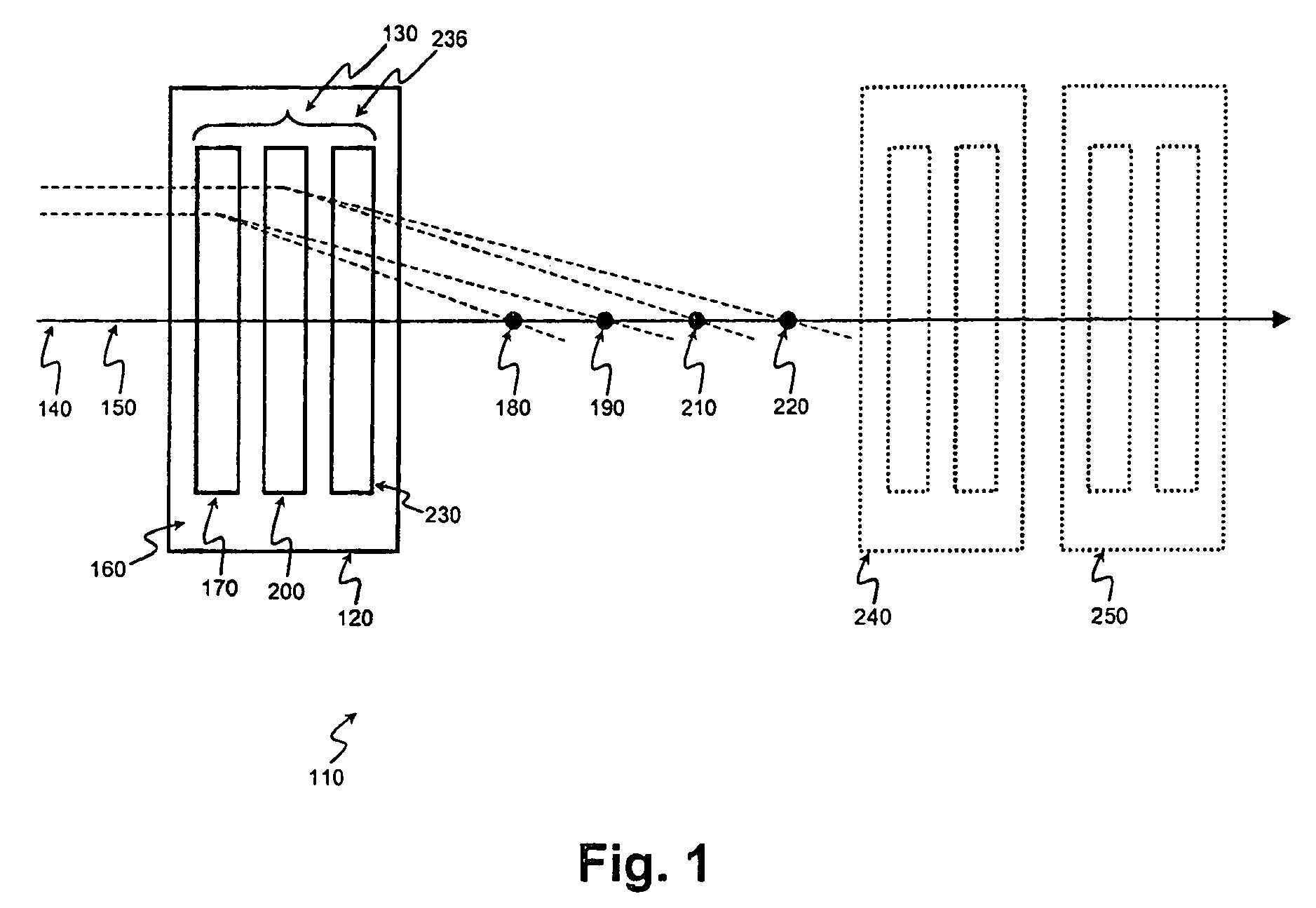
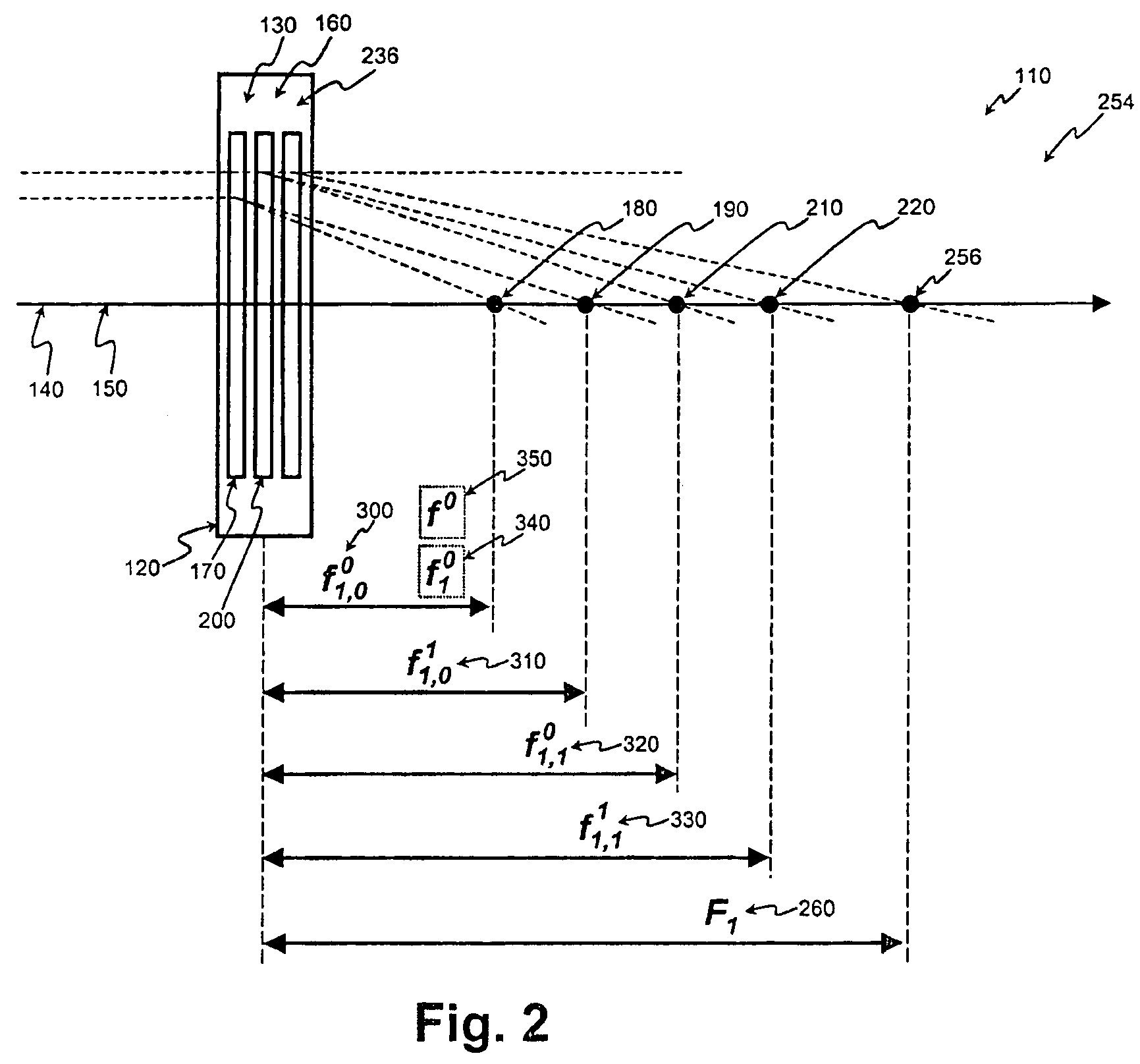
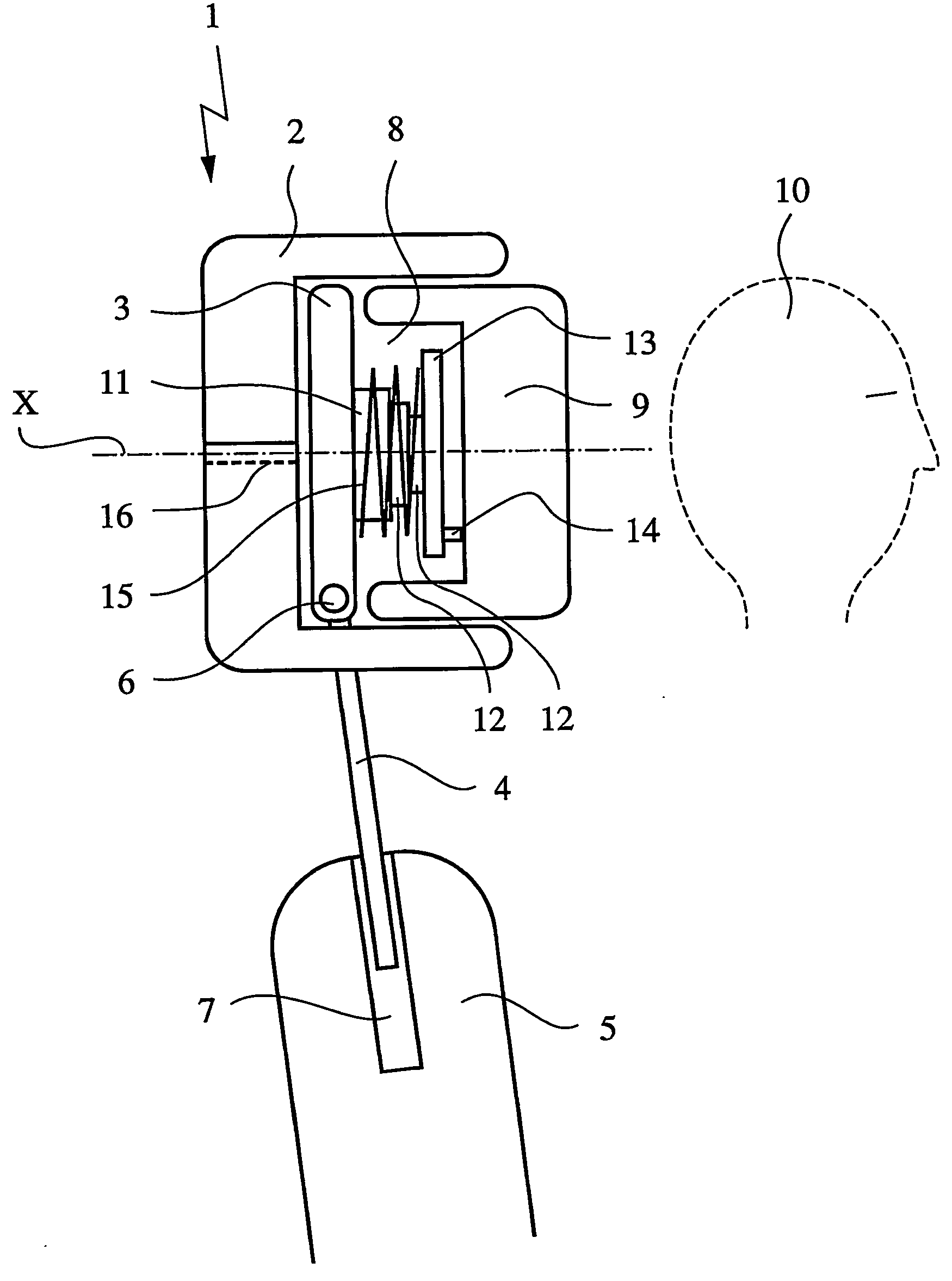
In the case of a head restraint which is connected to the backrest (5) of a vehicle seat, a padded segment (9) which can be changed in position relative to the basic body (1) of the head restraint can be shifted, in the event of an accident, under the action of a force-generating device from the use position toward the seat occupant's head (10) into a safety position and can be locked therein by means of a fixing device. According to the invention, the fixing device comprises a telescope (11) which, on the one hand, is supported on the basic body (1) and, on the other hand, is connected to the shiftable padded segment (9), it being possible for the resetting forces (FR) which act on the padded element to be introduced into the telescope in a direction deviating from the telescope axis (X).
Owner:DZHONSON KONTROLZ GMBKH
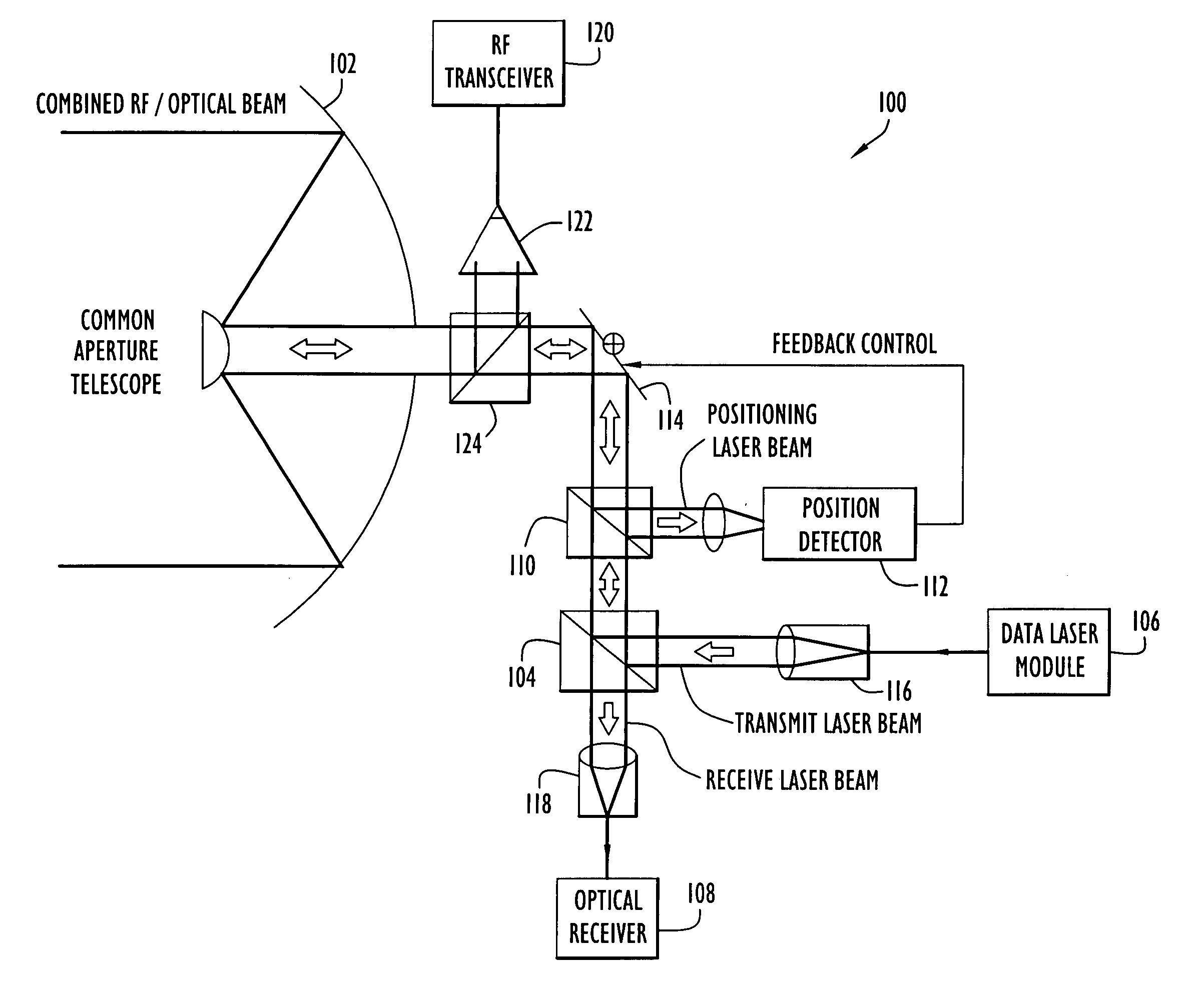
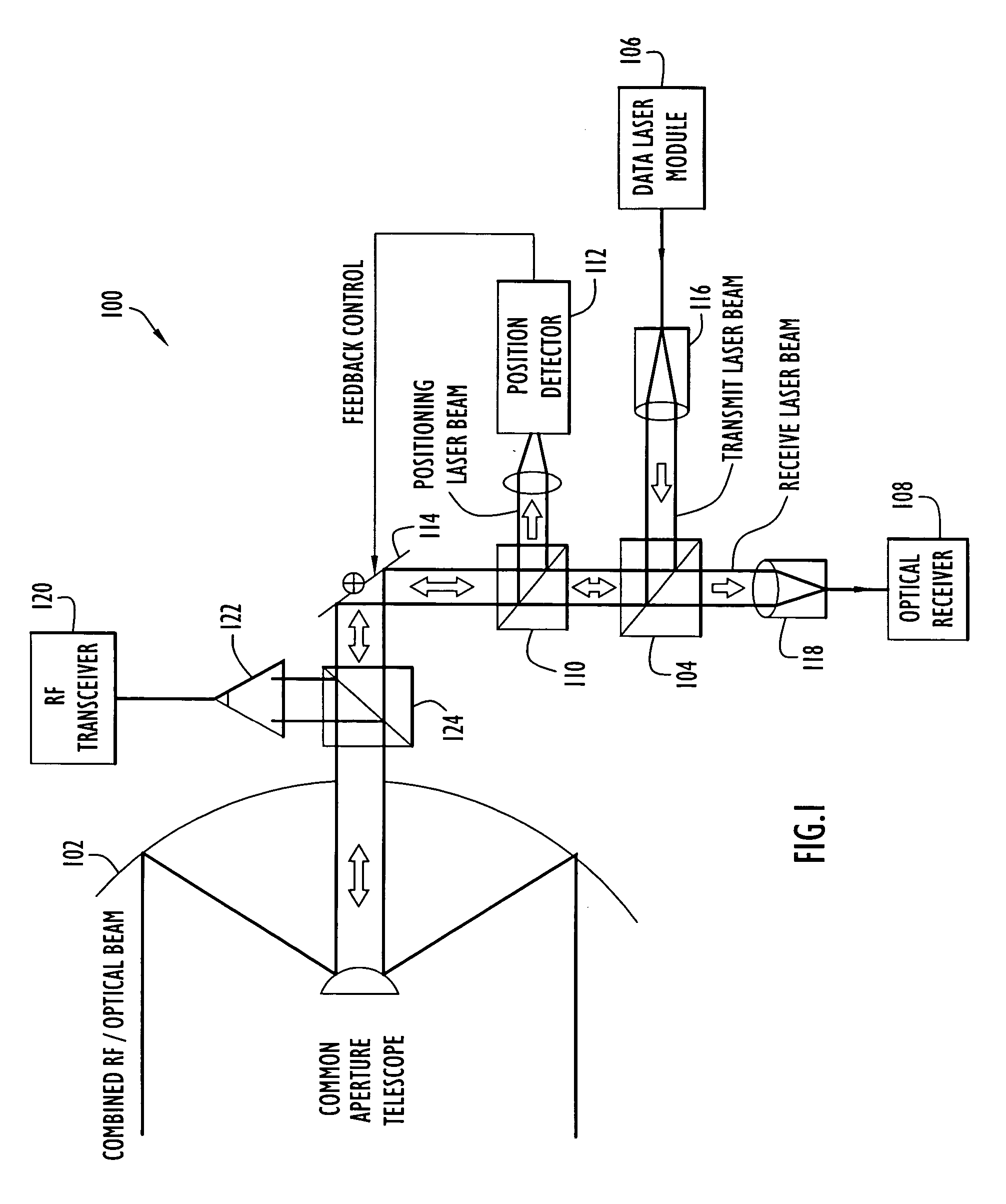
Communication transceiver architecture
ActiveUS20070031150A1Reduce sensitivitySimplifies the transceiver architectureSatellite communication transmissionRadio transmissionLaser transmitterOptical axis
A free-space communication transceiver includes a telescope for transmitting and receiving laser beams, a tunable laser transmitter for generating a transmit laser beam modulated with data, a tunable optical receiver for processing a receive laser beam received from the telescope to recover data, and a tunable beamsplitter that directs the transmit laser beam to the telescope and directs the receive laser beam from the telescope to the optical receiver. Between the telescope and beamsplitter, the transmit and receive laser beams travel along a common optical axis as collinear collimated free-space beams. The transmit and receive laser beams operate at different wavelengths that can be interchanged, thereby support full-duplex operation. The beamsplitter employs a tunable etalon filter whose wavelength-dependent transmission characteristics are adjusted according to the transmit and receive wavelengths. Optionally, RF signals can additionally be couple to the common optical axis and transmitted and received by the telescope.
Owner:PERATON INC
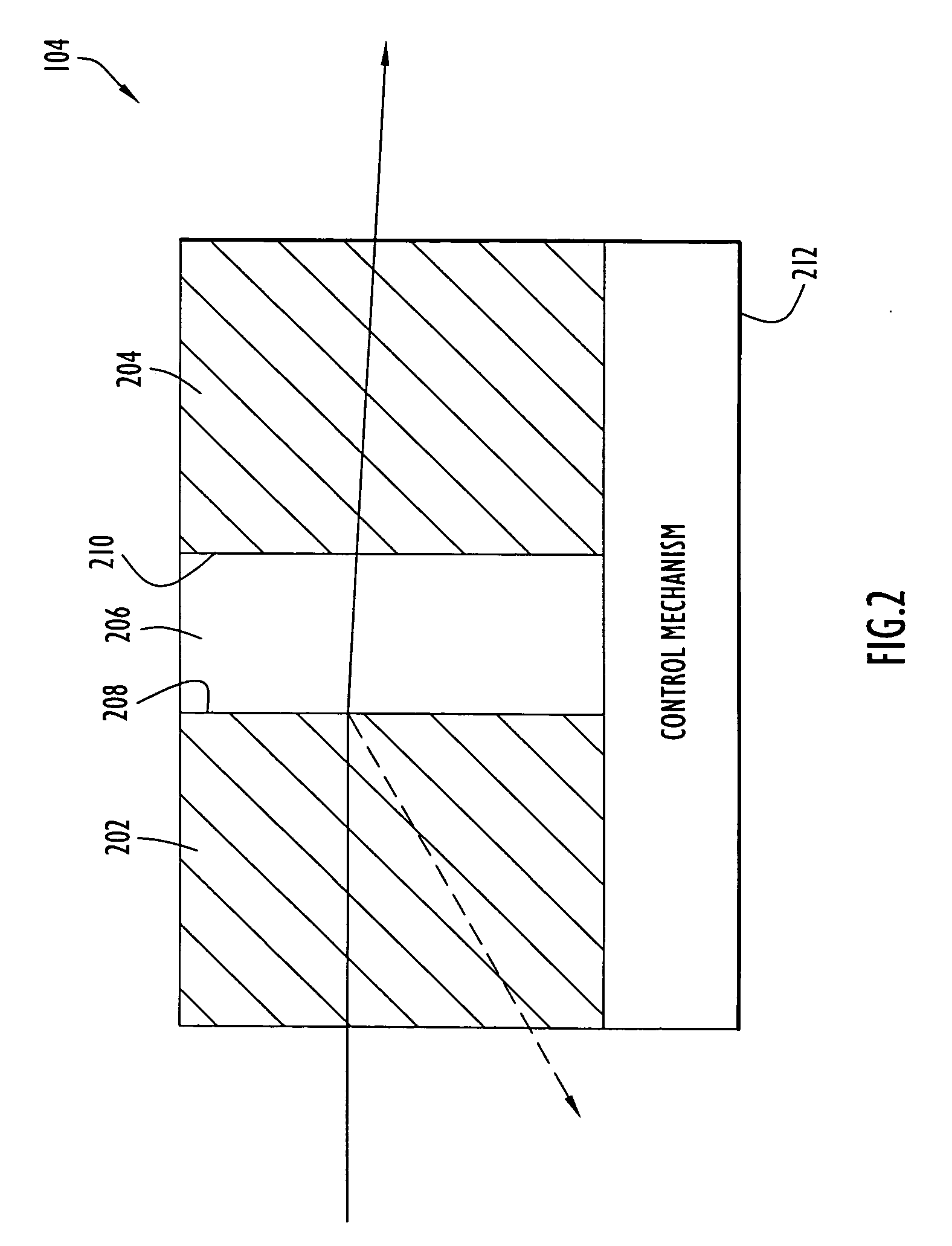
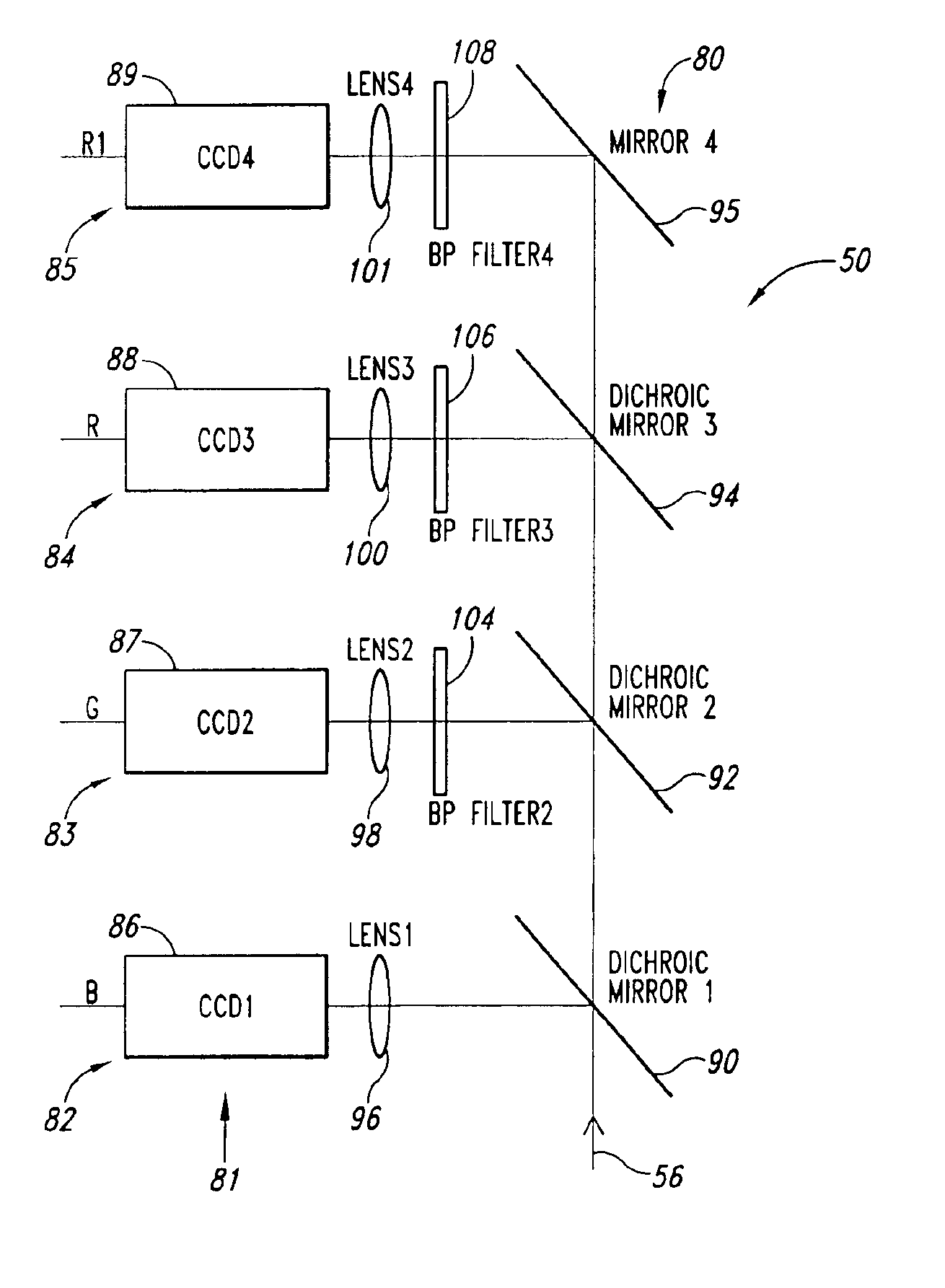
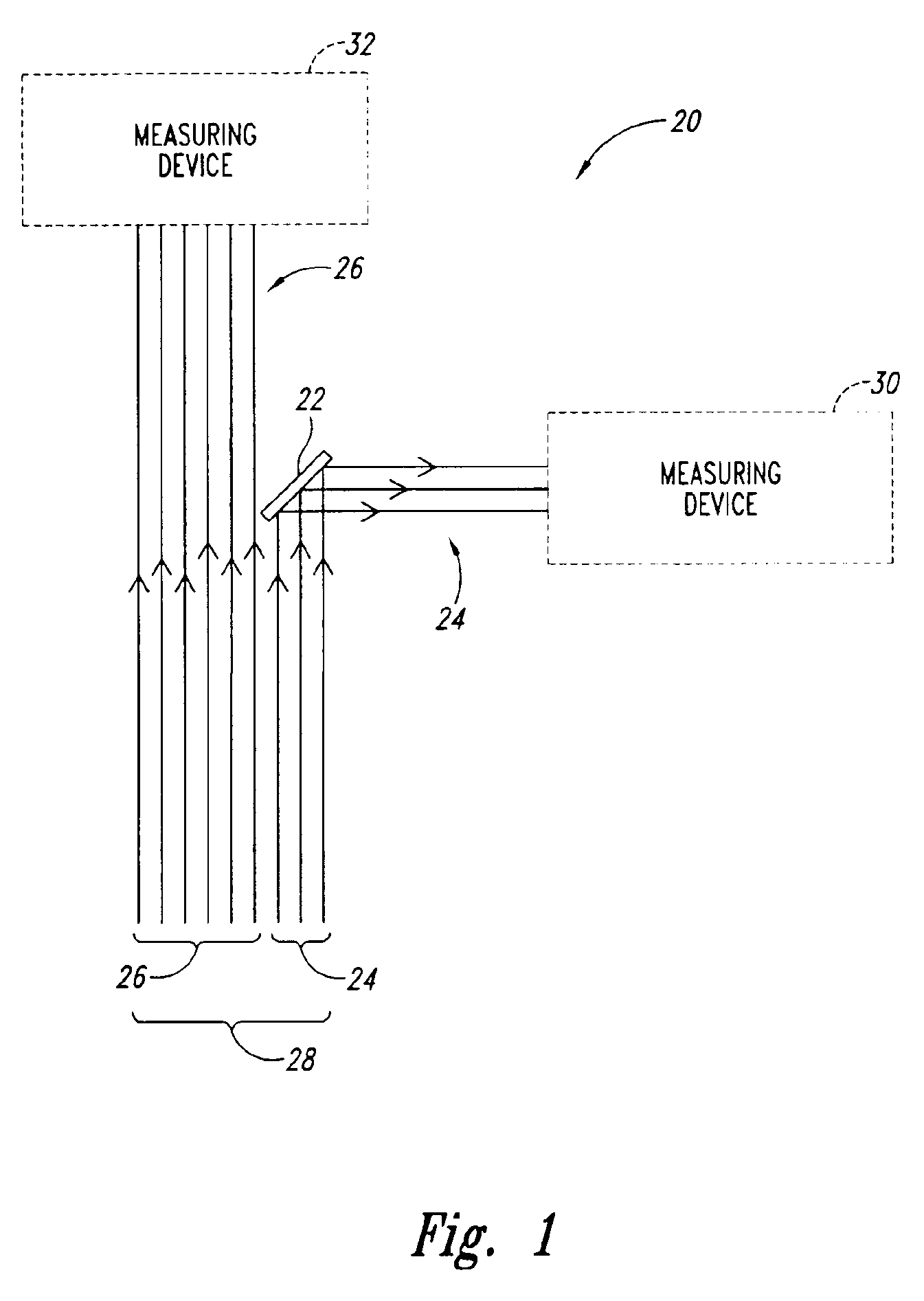
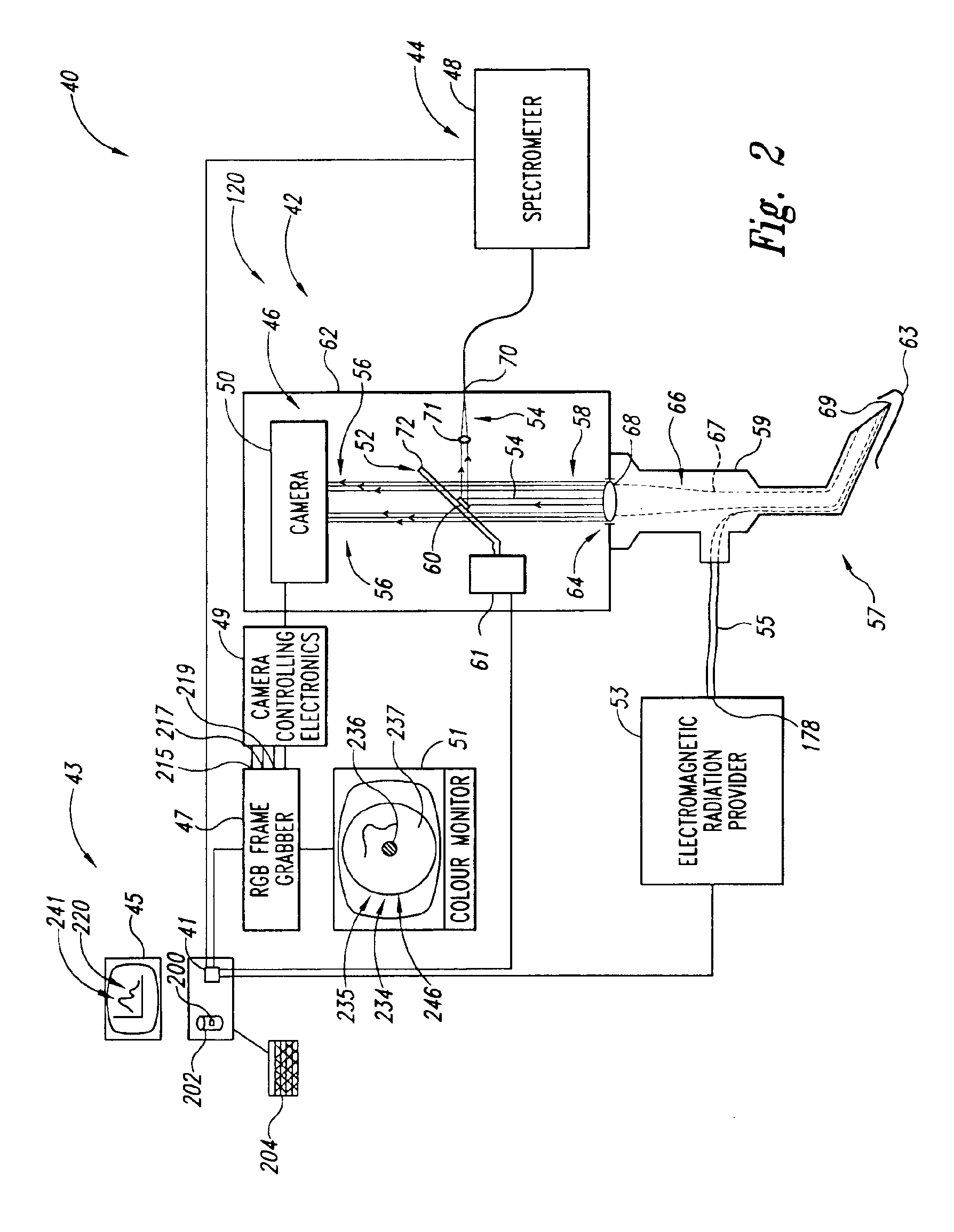
Methods and apparatus for fluorescence and reflectance imaging and spectroscopy and for contemporaneous measurements of electromagnetic radiation with multiple measuring devices
InactiveUS6898458B2Improve abilitiesEasy to measureRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMeasurement deviceFluorescence
Optical systems that provide for simultaneous images and spectra from an object, such as a tissue sample, an industrial object such as a computer chip, or any other object that can be viewed with an optical system such as a microscope, endoscope, telescope or camera. In some embodiments, the systems provide multiple images corresponding to various desired wavelength ranges within an original image of the object, as well as, if desired, directional pointer(s) that can provide both an identification of the precise location from which a spectrum is being obtained, as well as enhancing the ability to point the device.
Owner:VERISANTE TECH
Continuous flow single sheath for endoscope
InactiveUS20060041186A1Maintaining distentionHigh hydraulic diameterSurgeryEndoscopesMedicineContinuous flow
Owner:VANCAILLIE THIERRY G
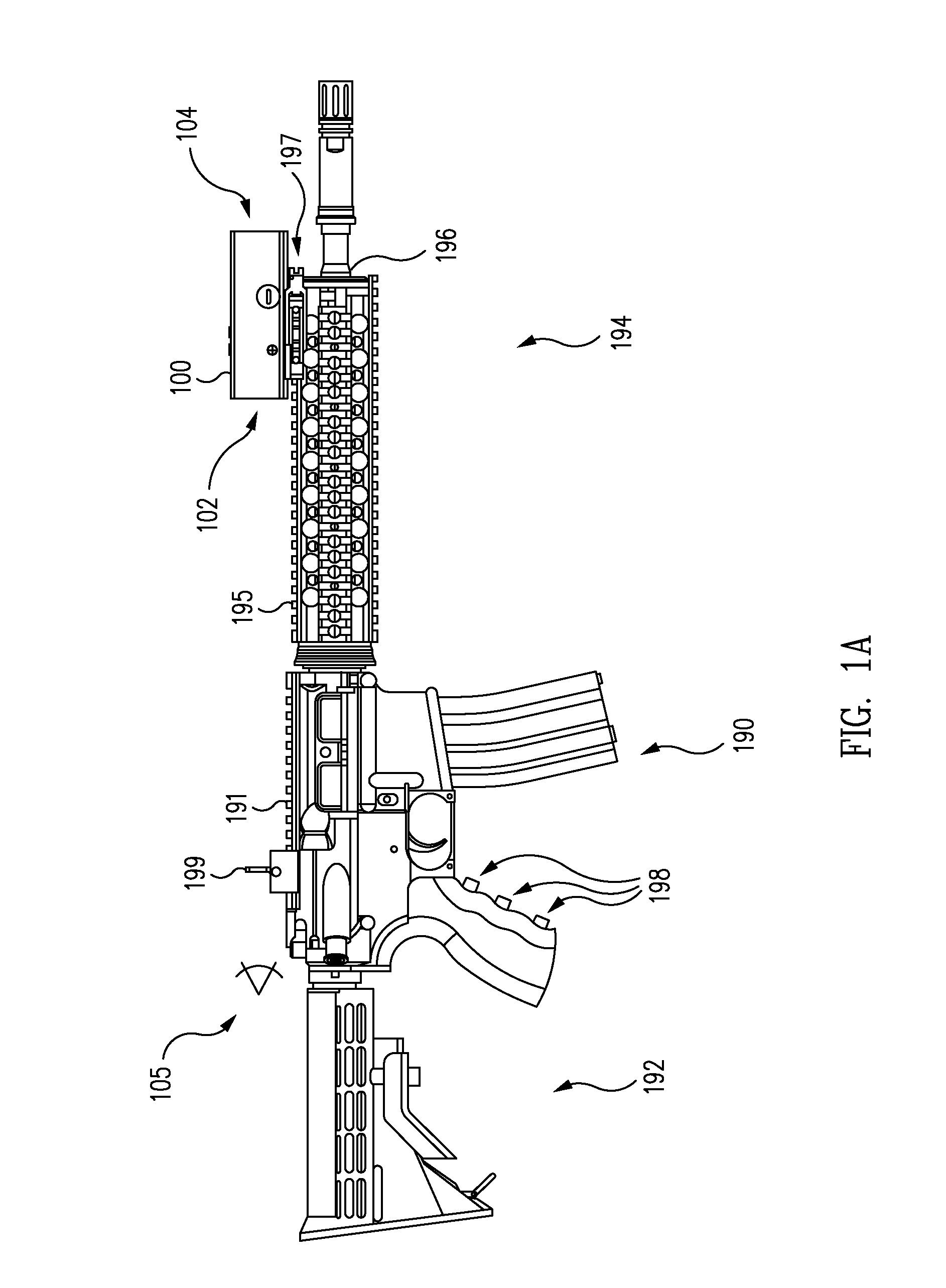
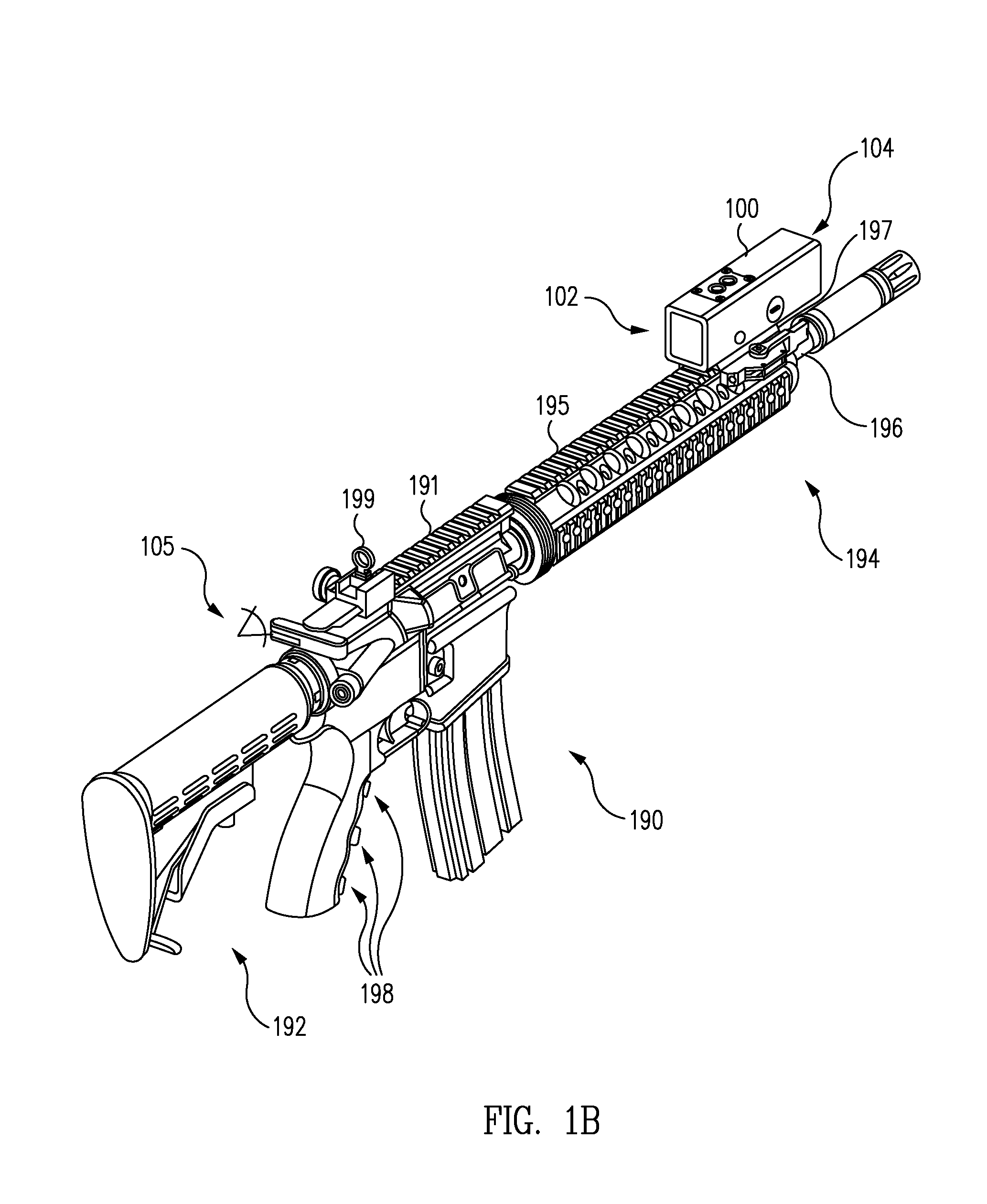
Sight system
ActiveUS20120106170A1Effectively sightWithout compromising situational awarenessOptical rangefindersNon-optical adjunctsDisplay deviceEngineering
A sight system is provided which may be selectively used in a variety of different ways. In one example, the sight system may be positioned on a rifle to provide a rifle sight system. In this example, the sight system may be positioned on the rifle barrel a substantial distance away from a user's eye. Advantageously, such an implementation may permit a user to effectively sight the rifle without compromising situational awareness. In another example, the sight system may be used to provide a telescopic sight with a reticle (e.g., a dot, crosshair, mark, or other appropriate shape) superimposed on an image (e.g., a zoomed or non-zoomed image) displayed from a camera. In another example, the sight system may be used to provide an occluded sight in which a camera and / or display of the sight system is disabled. As a result, a reticle may be displayed over an opaque background.
Owner:SUREFIRE LLC
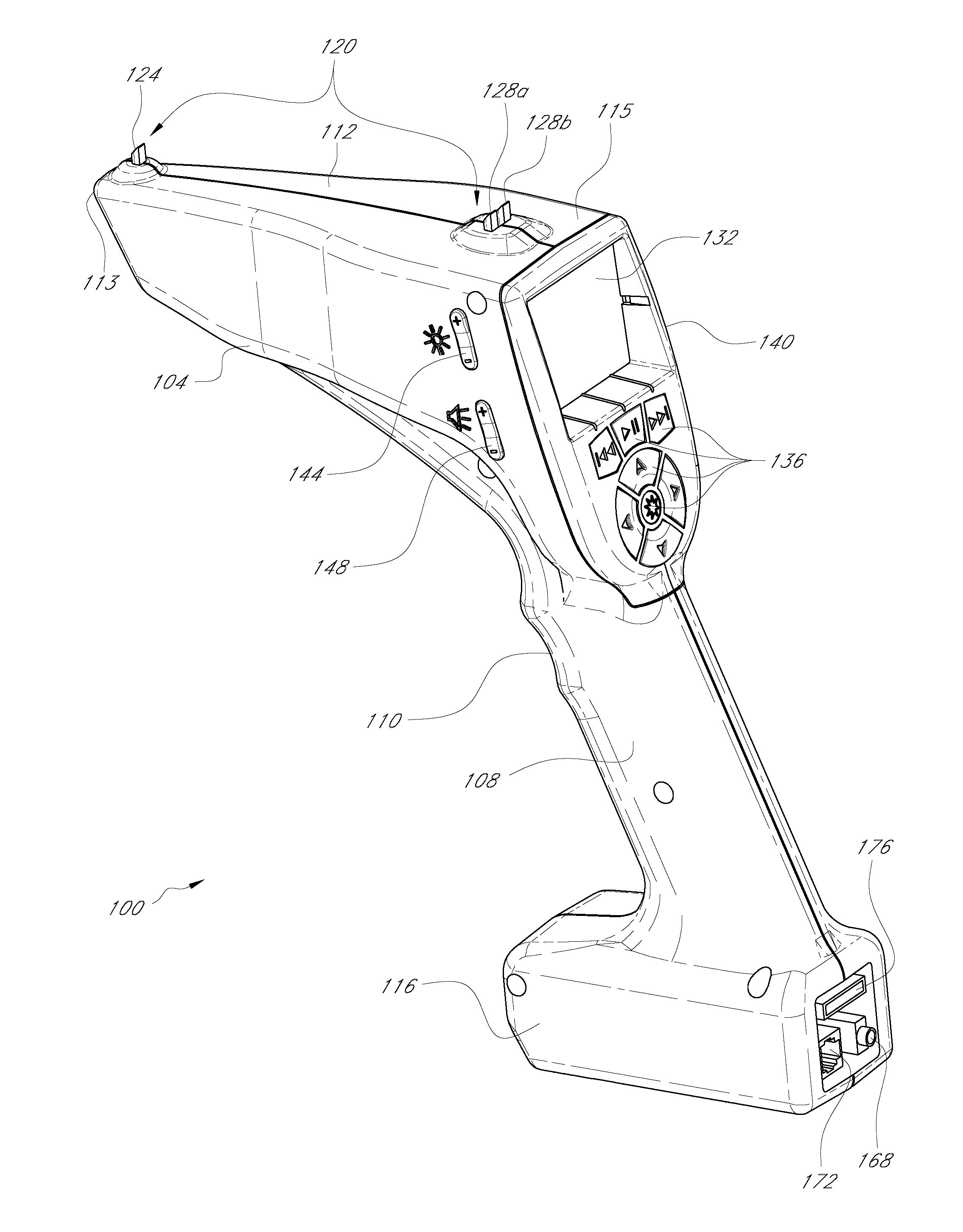
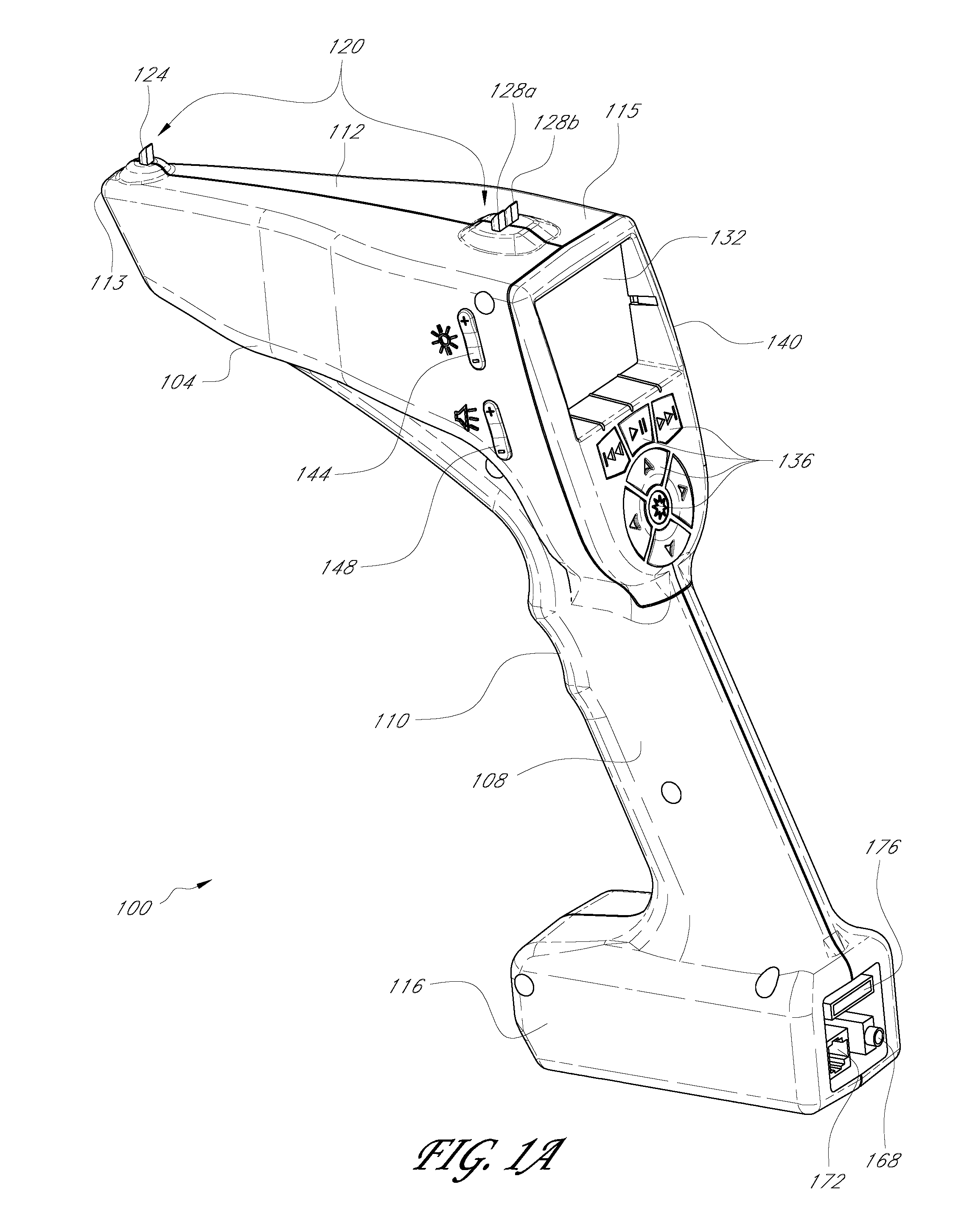
Apparatus and methods for locating and identifying remote objects
A sighting device may be used to identify and / or locate remote celestial and / or terrestrial objects. The device may include one or more gravity sensors and one or more magnetic sensors that are used to determine the direction in which the device is aimed. Once the aiming direction is determined, a device control system may be used to access an object database and determine a likely candidate object on or near the aiming direction. The device may include capability to output audiovisual information related to the object. The device may be configured to provide audiovisual commands that direct the user to point the device toward a desired or target location, thereby allowing the user to locate objects with unknown positions. The device may be used as a control system for telescopes and other optical devices.
Owner:MEADE INSTRUMENTS
Mounting bracket for scope of a gun
A mounting bracket for a scope of a gun is disclosed. The mounting bracket is used to mount night scopes or telescopic scopes onto the barrel of a gun rapidly. The bracket comprises a seat body having a securing jaw, an actuating jaw and a triggering block, and the actuating jaw is pivotally mounted at the seat body and, together with the securing jaw, correspondingly grips the barrel of the gun. Further, the triggering block is pivotally mounted at the seat body, and the triggering block correspondingly urges or releases the actuating jaw. The user can rapidly disassemble the mounting bracket and the barrel of the gun. The direction of action of the triggering block is perpendicularly intersected with the vibration direction of the barrel and therefore the mounting bracket will not be dislocated in the course of shooting.
Owner:THE 401ST PLANT MATERIEL PRODION CENT ARMAMENTS BUREAU M N D
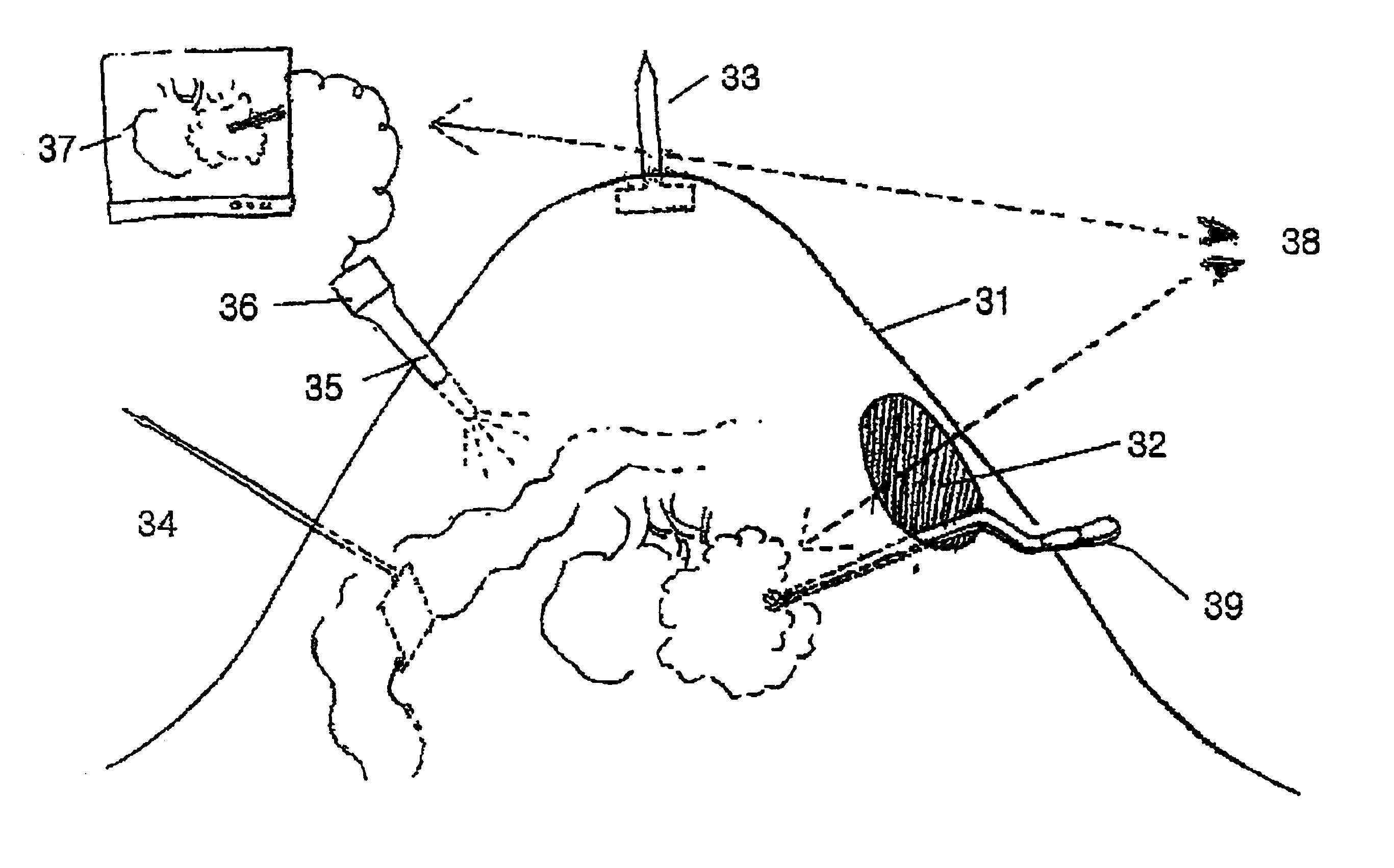
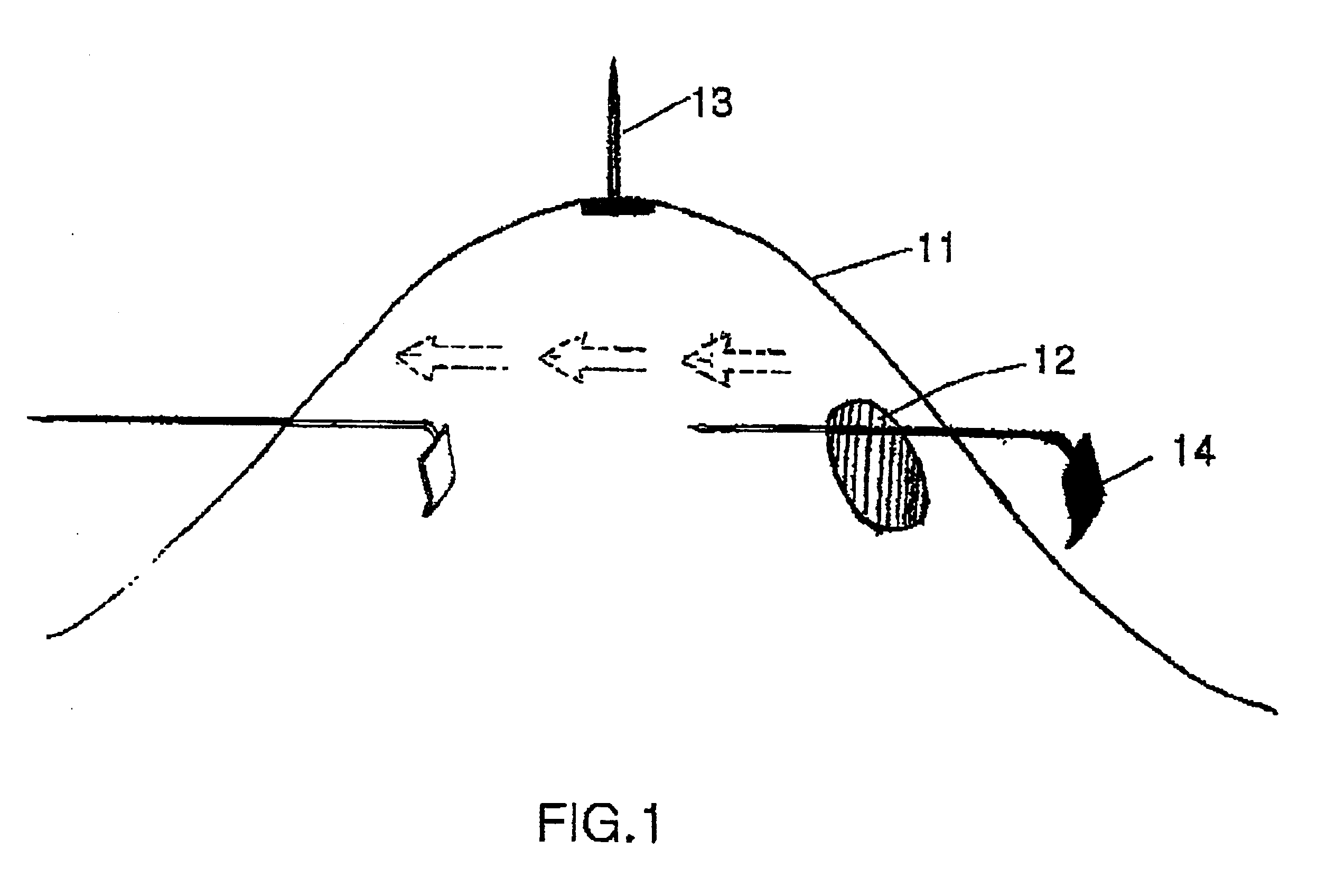
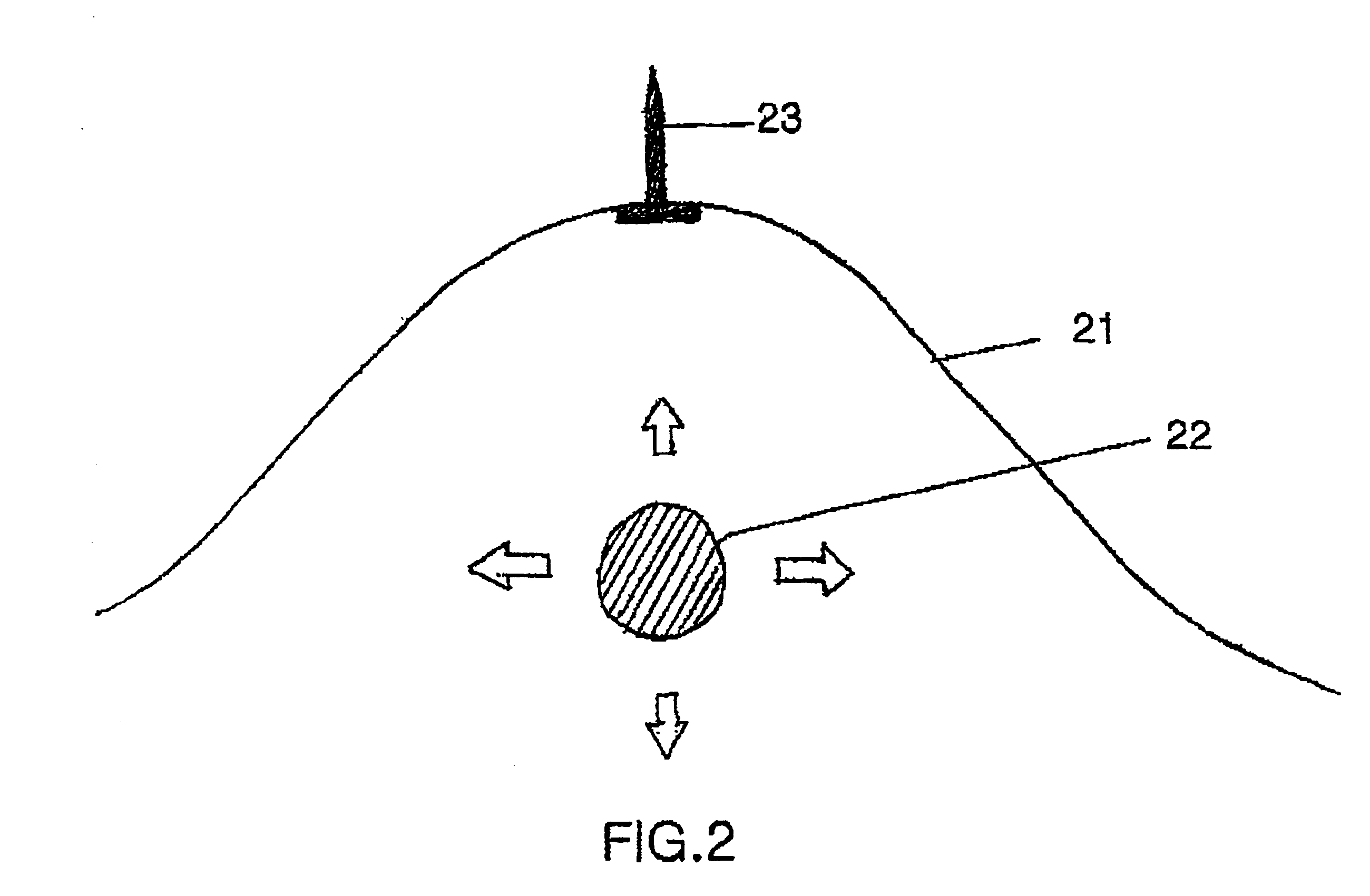
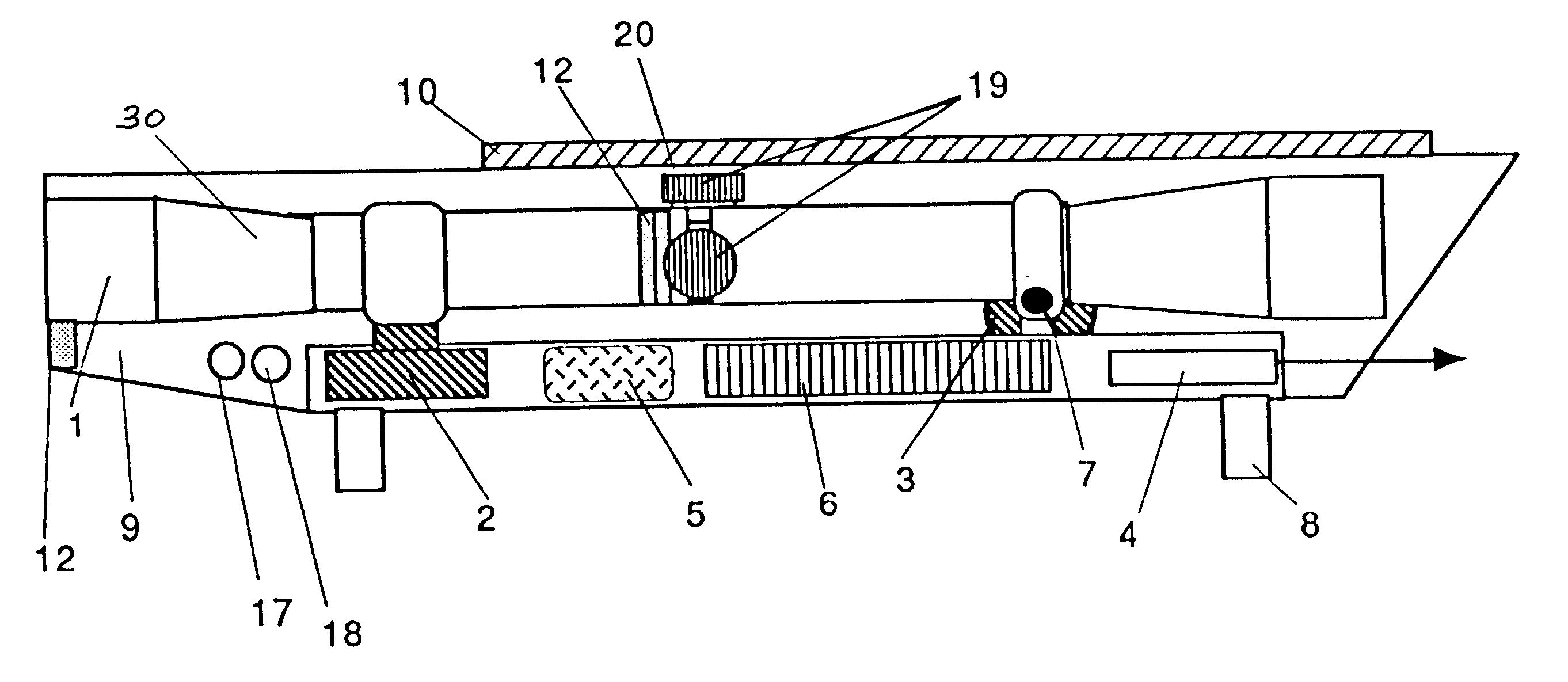
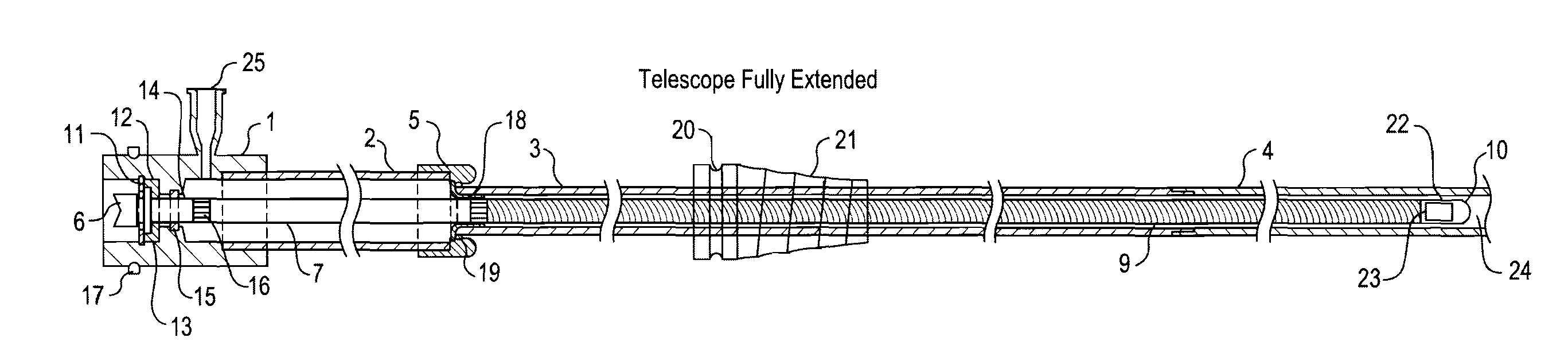
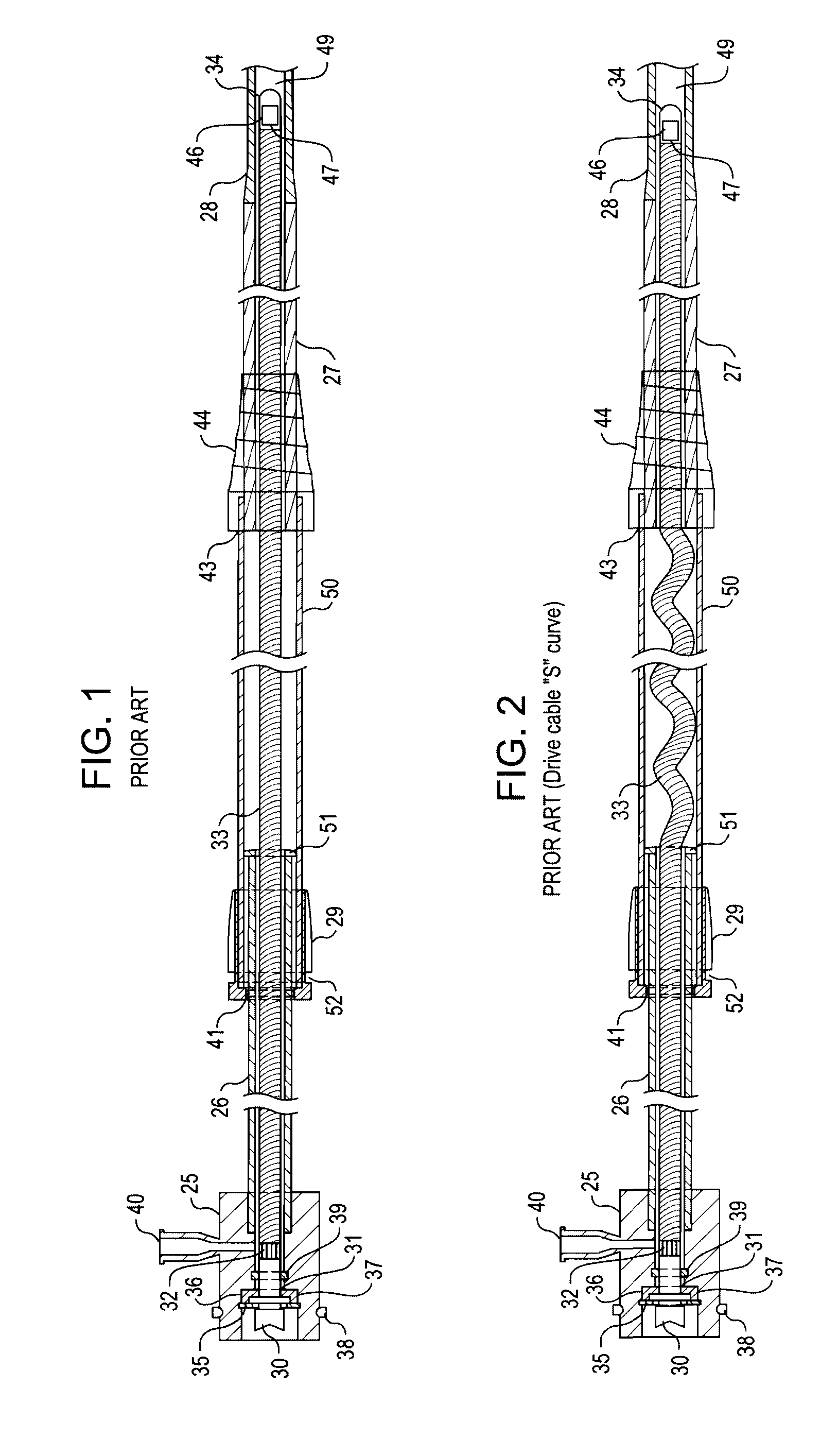
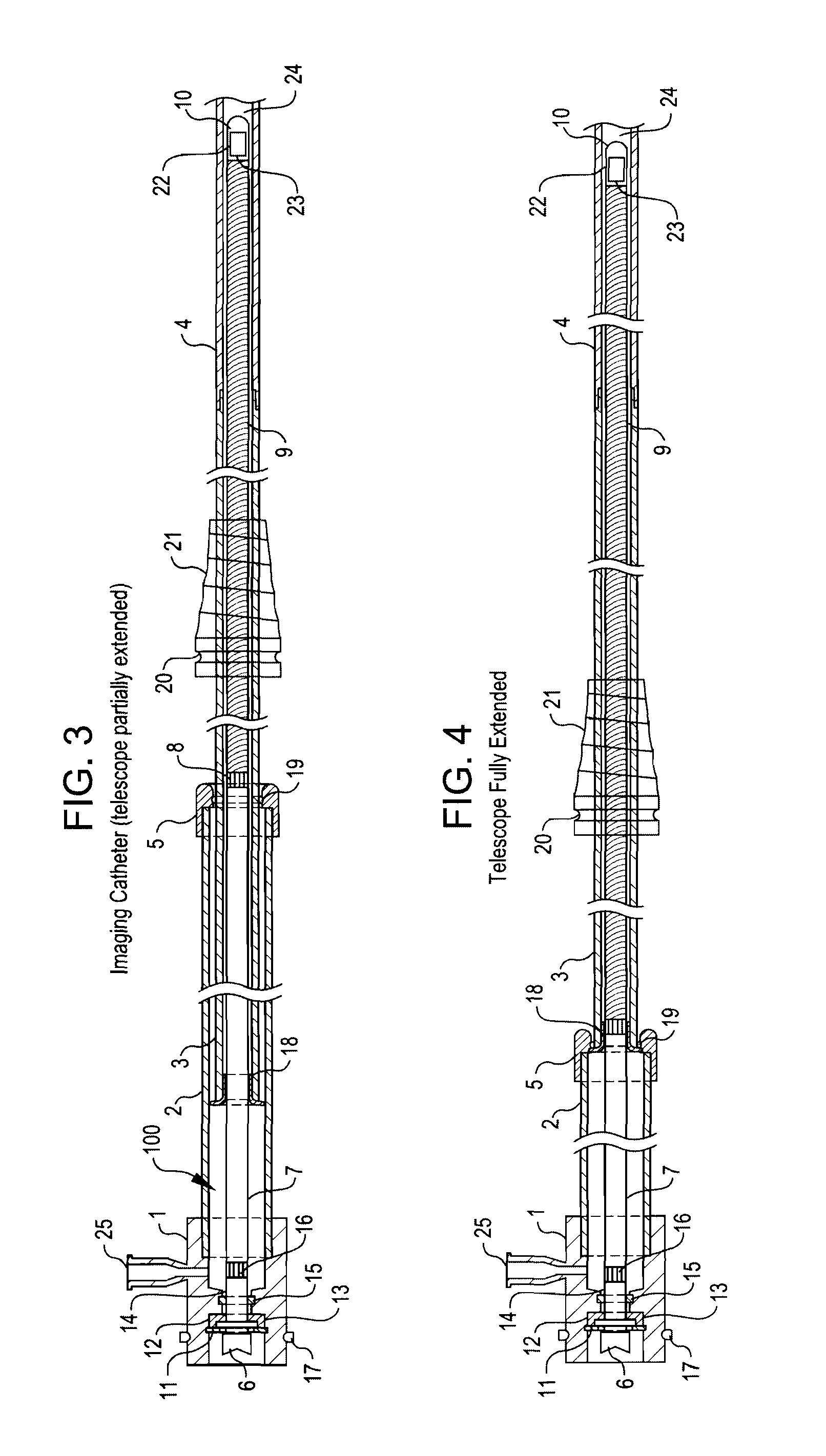
Telescope for an imaging catheter
A catheter has a proximal end and a distal end and comprises an outer tube having a proximal end, an inner sheath slidingly received within the outer tube and extending distally from the outer tube, and a rotatable shaft extending from the proximal end of the outer tube to within the inner sheath. The rotatable shaft is axially fixed with respect to the outer tube and axially moveable within and with respect to the inner sheath. The rotatable shaft includes a proximal substantially rigid section and a distal flexible section. The catheter further includes a working element carried on the distal flexible section of the rotatable shaft.
Owner:ACIST MEDICAL SYST
Remote detection and analysis of chemical and biological aerosols
InactiveUS20050026276A1Quickly thermalizedEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEmission spectroscopyElectromagnetic radiationOxygen
A system for detecting and analyzing chemical and biological aerosols. A beam of radiation is used to radiate a target cloud including the aerosol. The radiation energy that is absorbed by the cloud is thermalized by collisional energy transfer between the molecules that absorb the radiation to generate heat. The wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation is selected to be in resonance with the absorption lines of water or oxygen molecules in the cloud, or to be in resonance with absorption lines of known target molecules in the cloud to generate the heat. An increase in the cloud temperature increases the emission intensity of the molecules against the background, resulting in improved detection of the target molecules in the aerosol. A tracking telescope collects the thermal emissions generated by the radiation beam. A spectrometer receives the emissions from the cloud and generates an emission spectrum.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
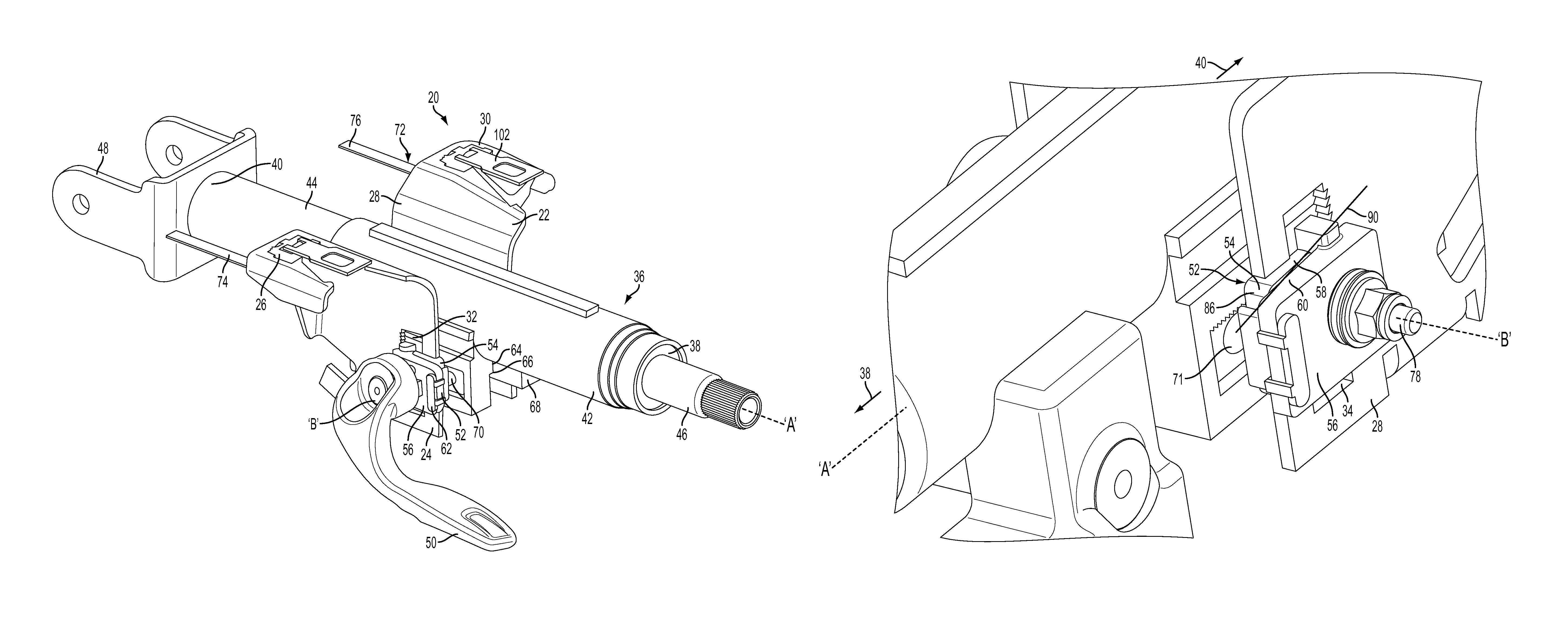
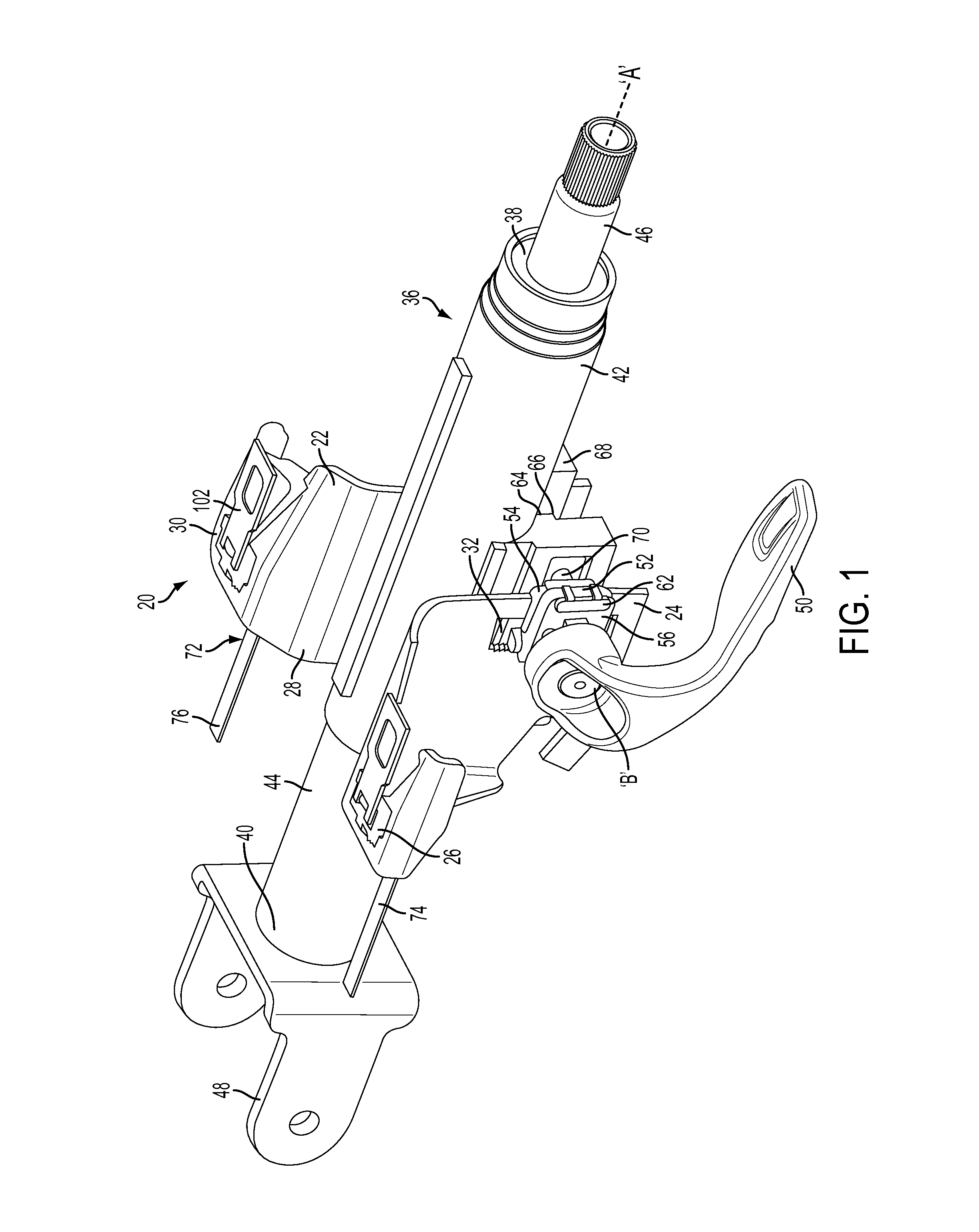
Crash release mechanism for automotive steering column
An adjustable steering column for a vehicle is provided. The adjustable steering column includes a mounting bracket configured to be secured to an adjacent vehicle component, a compression bracket movably positioned relative to the mounting bracket, and a column jacket extending along a first axis and having an upper jacket and a lower jacket telescopically coupled to one another. The adjustable steering column further includes a locking mechanism movable between a locked position and an unlocked position configured to selectively restrict adjustment of the upper jacket in a telescope direction, and at least one release mechanism configured to allow telescoping movement of the upper jacket with the locking mechanism in the locked position in response to an excessive axial force applied to the column jacket. At least one energy absorbing mechanism is configured to absorb energy during telescoping movement of the upper jacket with the locking mechanism in the locked position.
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG
Portable digital lidar system
A light detecting and ranging system and method for detecting airborne agents in which the system includes a laser which provides laser pulses of at least two wavelengths, a transmitter which transmits the laser pulses, a receiver which receives both elastically backscattered signals from airborne agents and fluorescence signals from the airborne agents, a common telescope which both focuses a laser beam transmission of the laser pulse from the transmitter to a far field and receives the elastically backscattered signals and the fluorescence signals from the far field, a digital detection system having at least one of a backscatter optical detector which detects the elastically backscattered signals and a fluorescence optical detector which detects the fluorescence signals from the airborne agents.
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
System and method for remote sensing and/or analyzing spectral properties of targets and/or chemical species for detection and identification thereof
A method and a low-cost, robust and simple system for remote sensing and analyzing spectral properties of targets as a means to detect and identify them is introduced. The system can be highly portable but is usable in fixed locations or combination thereof. An aspect of the method and system includes the capability to distribute, modulate, aperture and spectrally analyze radiation emitted or absorbed by a volumetric target chemical species (solid, liquid or gas) or a target surface. Radiation is first collected by a single light gathering device, such as a lens, telescope, or mirror, and then distributed to multiple detectors through spectrally discriminating components and if desired through apertures to achieve this desired detection and identification.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Multi-target-tracking optical sensor-array technology
ActiveUS7551121B1Highly accurate positional metricWide field-of-viewDirection controllersWeapon control systemsSensor arrayAviation
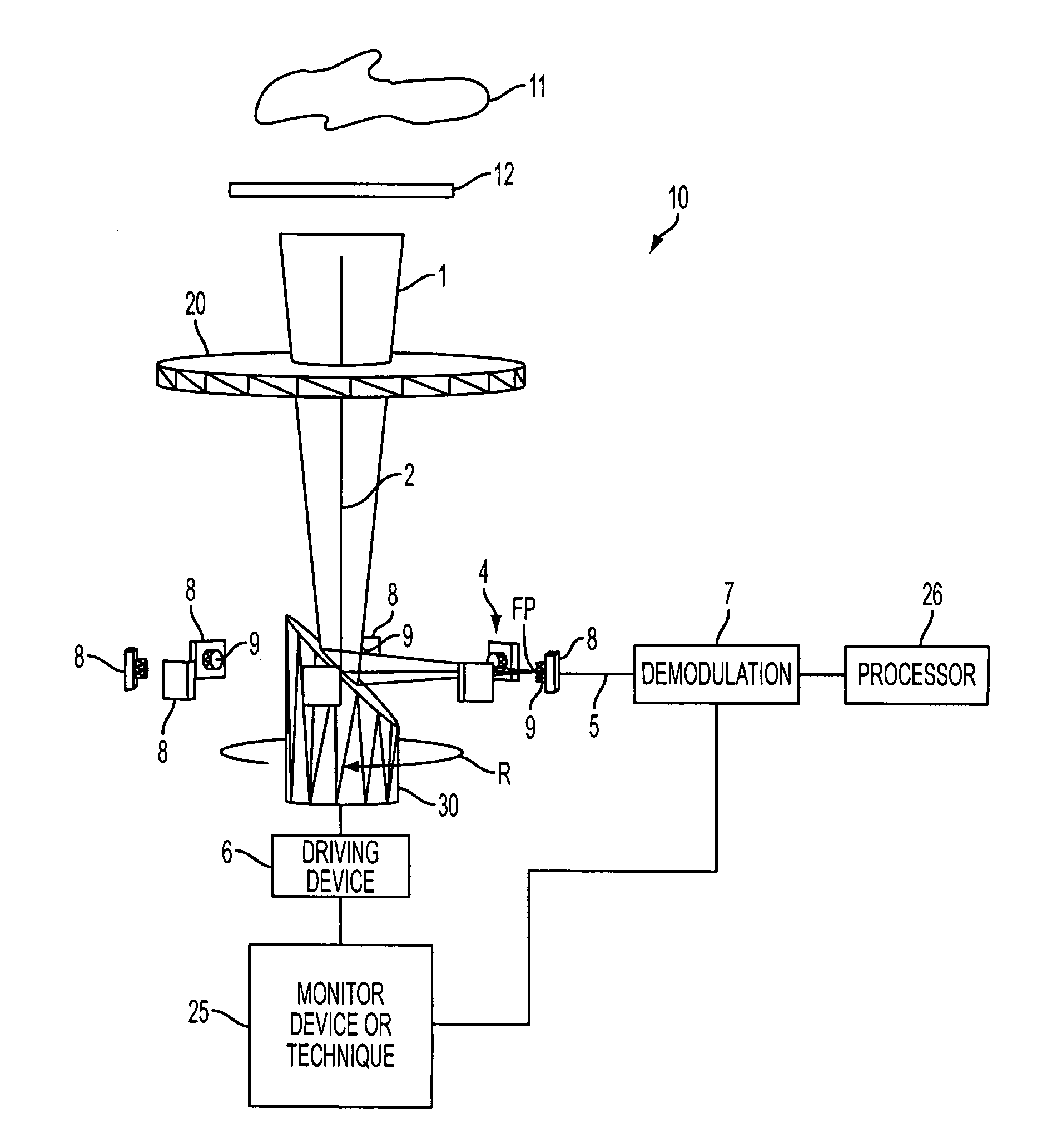
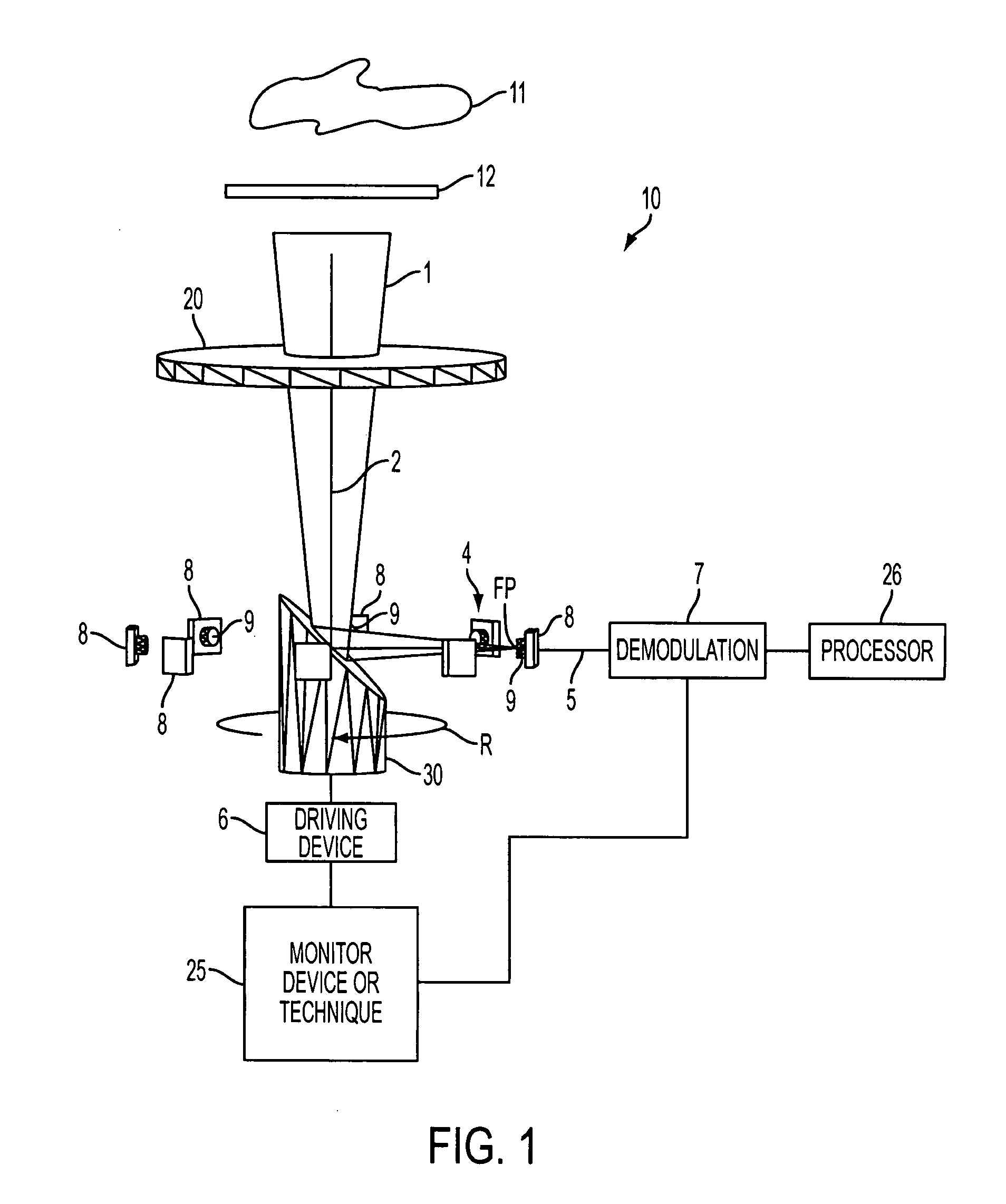
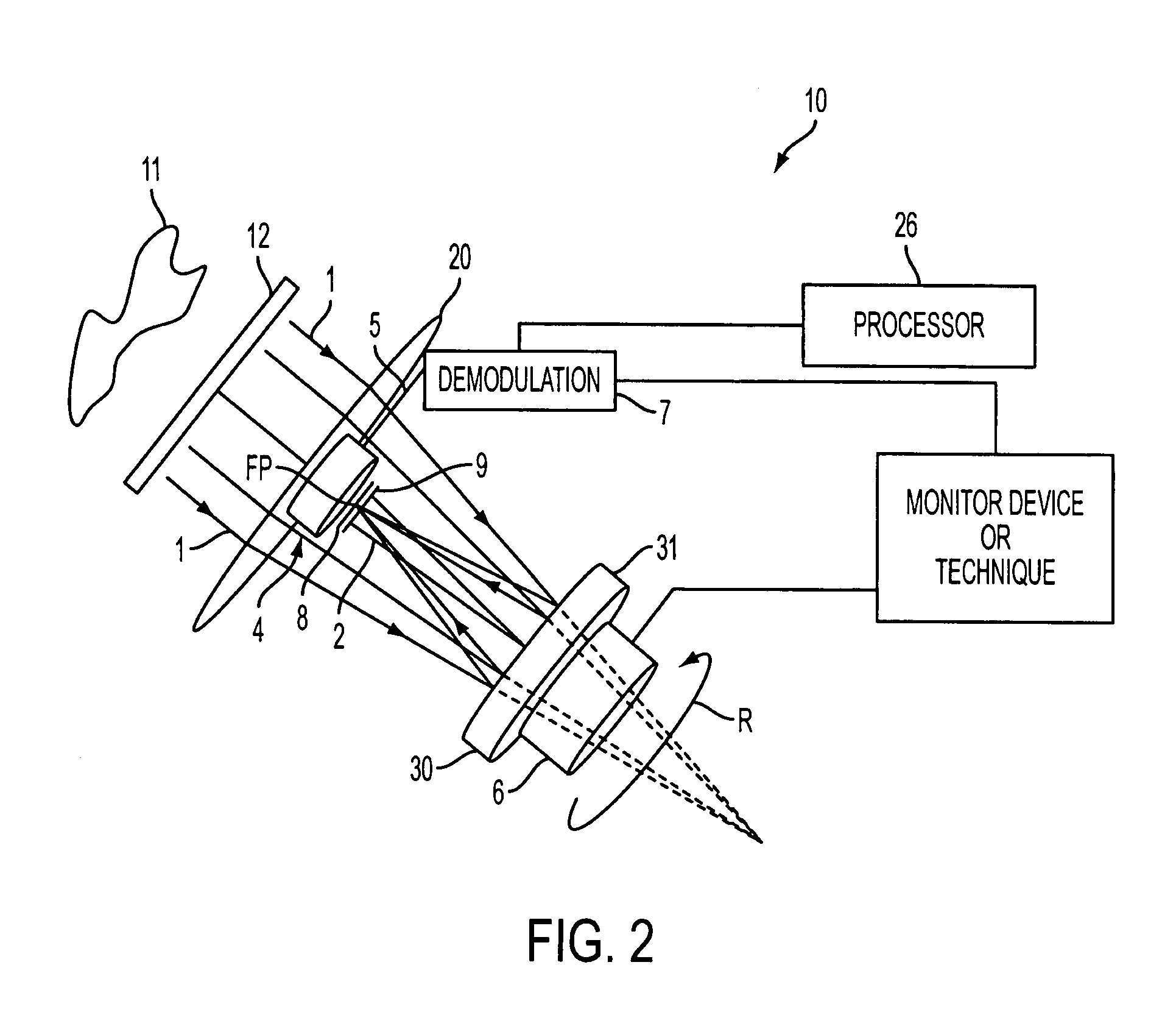
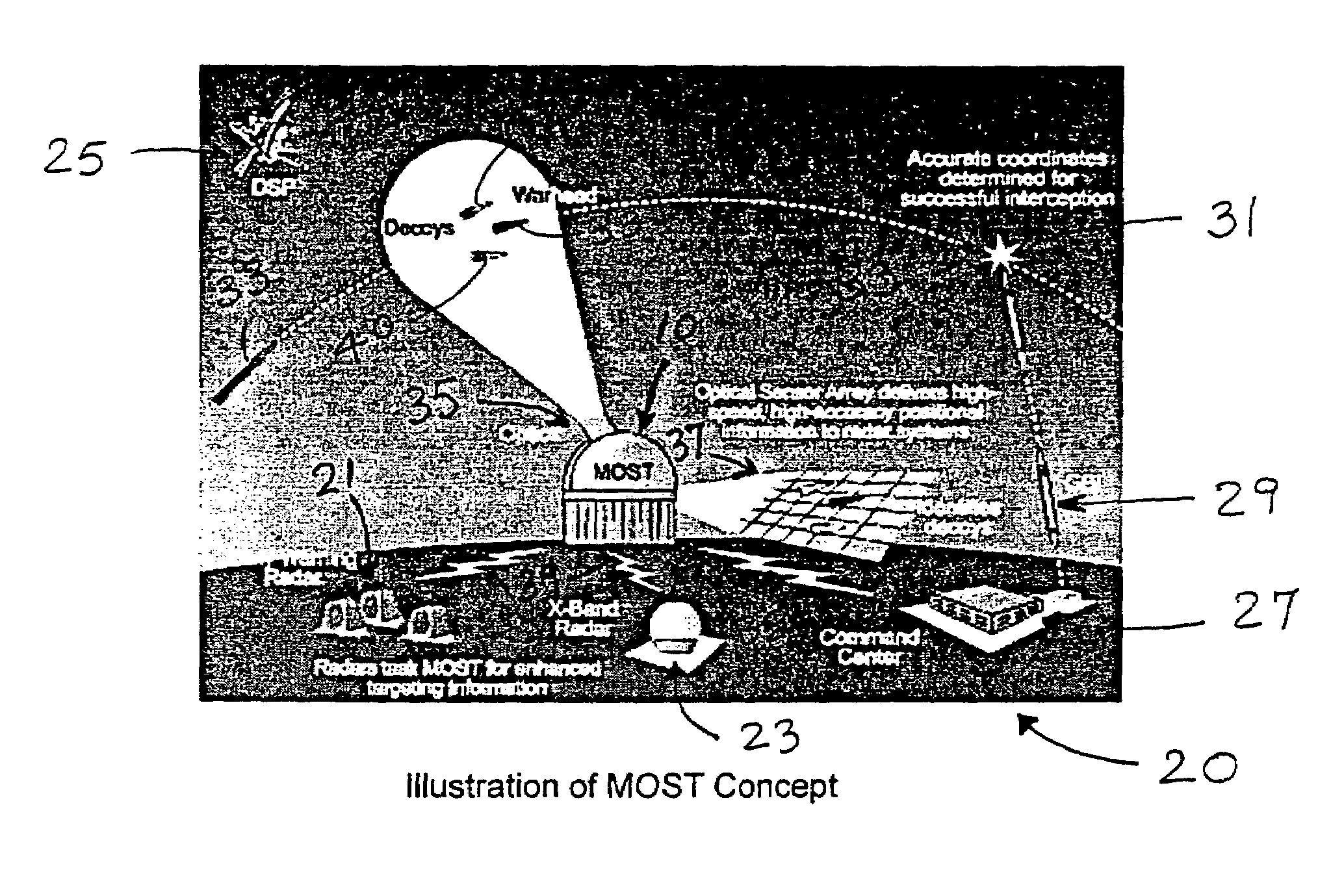
The multi-target tracking and discrimination system (MOST) fuses with and augments existing BMDS sensor systems. Integrated devices include early warning radars, X-band radars, Lidar, DSP, and MOST which coordinates all the data received from all sources through a command center and deploys the GBI for successful interception of an object detected anywhere in space, for example, warheads. The MOST system integrates the optics for rapid detection and with the optical sensor array delivers high-speed, high accuracy positional information to radar systems and also identifies decoys. MOST incorporates space situational awareness, aero-optics, adaptive optics, and Lidar technologies. The components include telescopes or other optical systems, focal plane arrays including high-speed wavefront sensors or other focal plane detector arrays, wavefront sensor technology developed to mitigate aero-optic effects, distributed network of optical sensors, high-accuracy positional metrics, data fusion, and tracking mounts. Field applications include space monitoring, battlefield artillery, battlefield management, ground defense, air defense, space protection, missile defense, gunfire detection, and the like.
Owner:OCEANIT LAB
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS7349804B2Increase probabilityHighly preventive effectReactors manufactureNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDisplay deviceLongitude
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, inclination information from the inclinometer, time information from the timing device and the catalogued star charts information to determine positions of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to use this celestial position information to calculate latitude and longitude which may be displayed on a display device such as a monitor or used by a guidance control system. These embodiments are jam proof and insensitive to radio frequency interference. These systems provide efficient alternatives to GPS when GPS is unavailable and can be used for periodic augmentation of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Method and device for extracting objects from the body
A device for extracting objects from the body, such as urinary stones, using a low pressure inflatable toroidal balloon that serves to engulf the object during extraction while dilating and protecting the passageway. The balloon loads onto an ureteroscope prior to insertion, rather than through the ureteroscope as do existing balloons. The toroidal balloon is a simple and unique device that may be applied external to the extracting telescope and does not interfere with existing methods for stone manipulation such as laser lithotripsy, irrigation and basket extraction in the case of urinary stone manipulation.
Owner:MASSICOTTE J MATHIEU +1
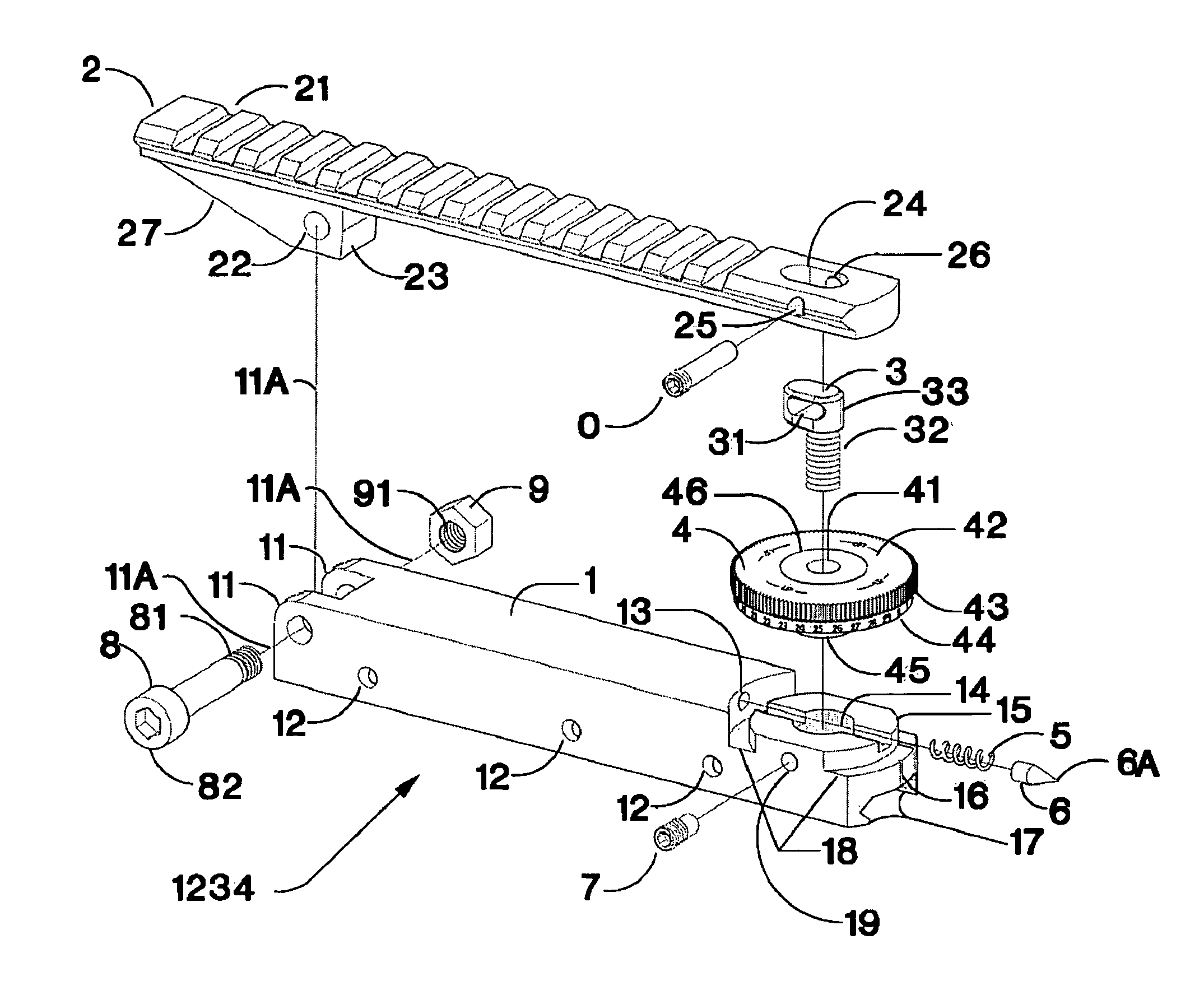
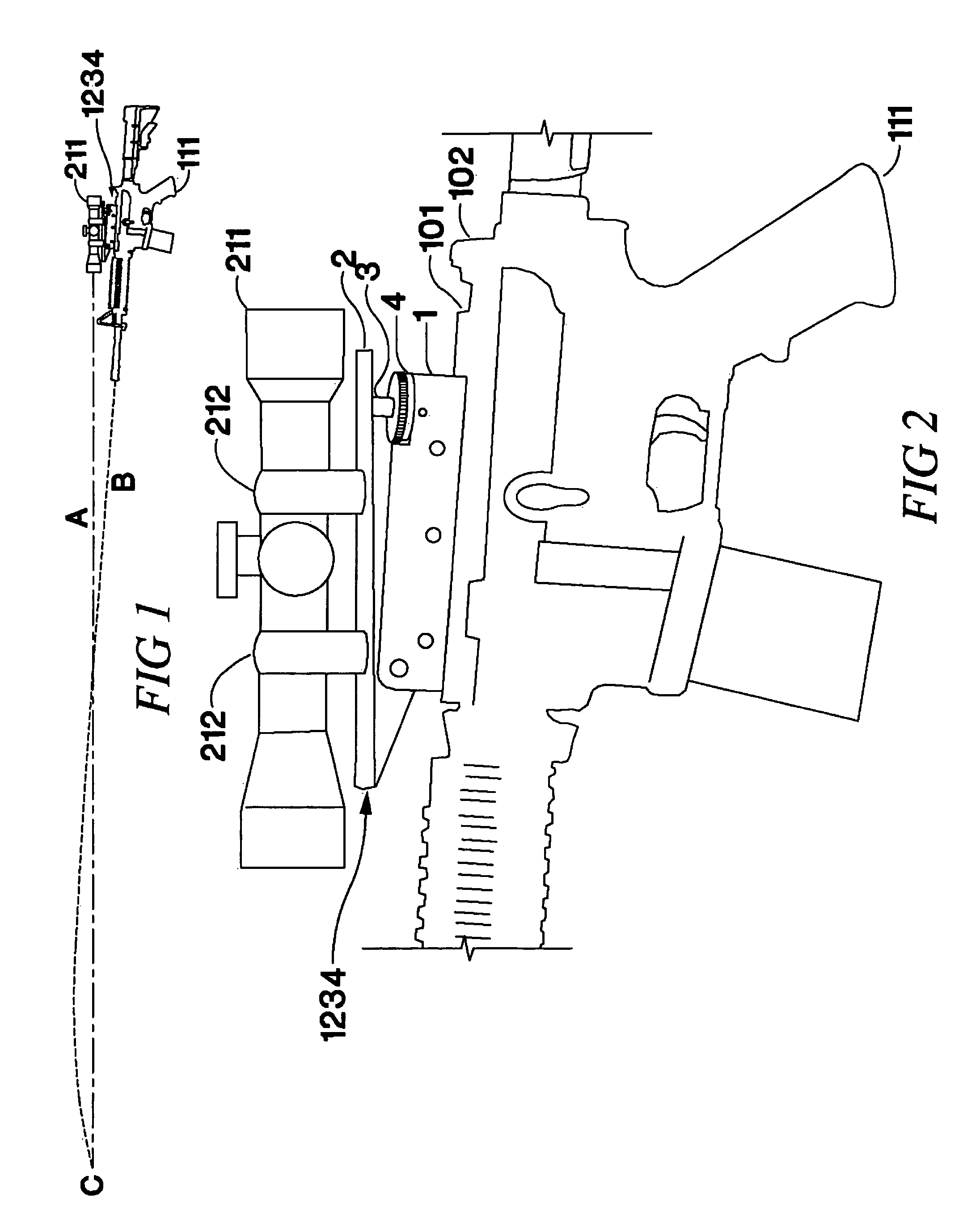
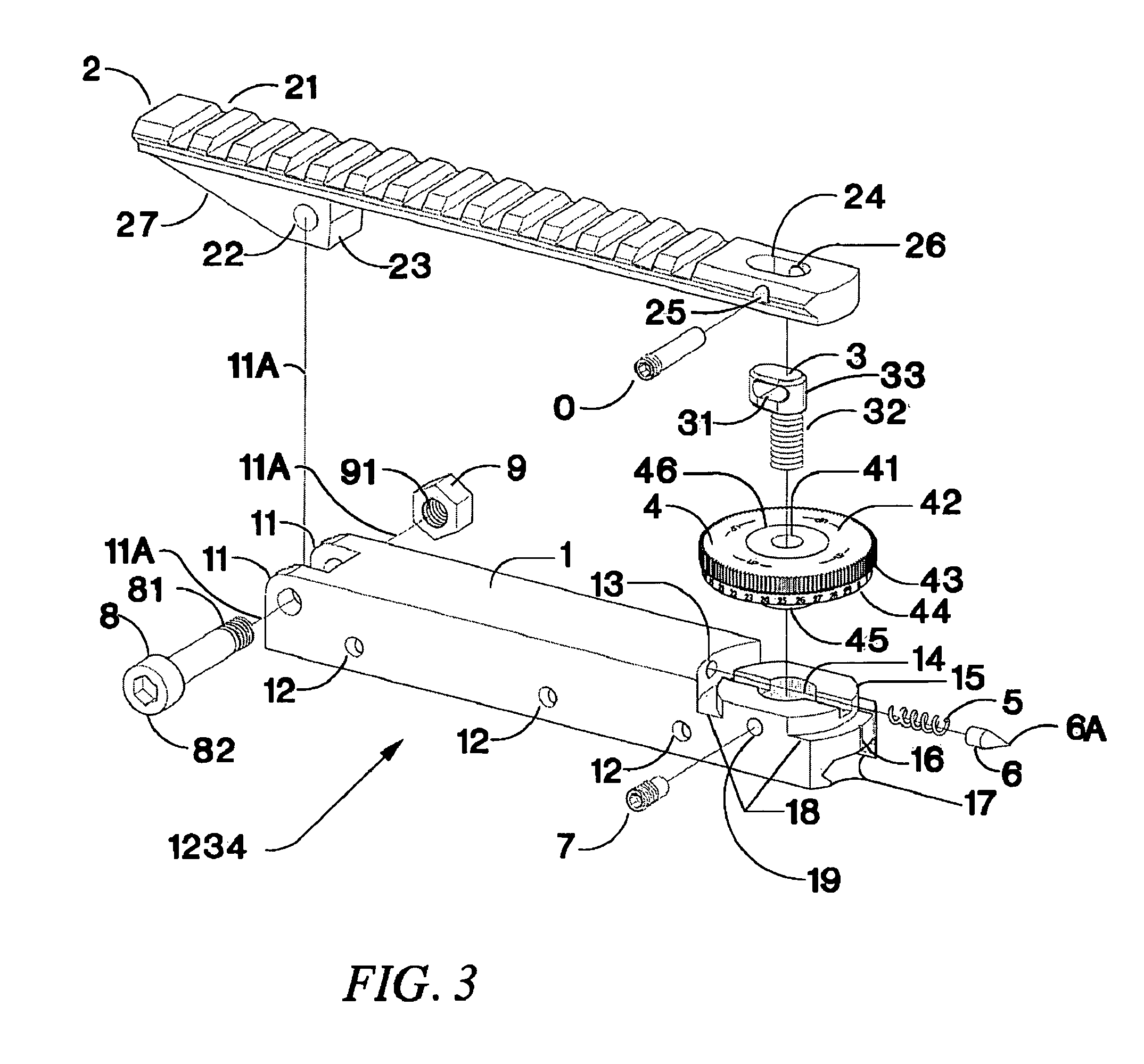
Adjustable bases for sighting devices
ActiveUS8240075B1Good long-term durabilityLarge range of motionSighting devicesButtsEngineeringTelescope
An adjustable base for attaching a sighting device such as a telescopic sight to a rifle or other ballistic projectile launcher, comprising upper and lower rails pivotally attached at the muzzle ends thereof, is disclosed. Adjustments are provided for altering the angle between the sight and the weapon's boreline or similar axis in elevation in increments of minutes of arc or fractions thereof.
Owner:COLD SHOT LLC
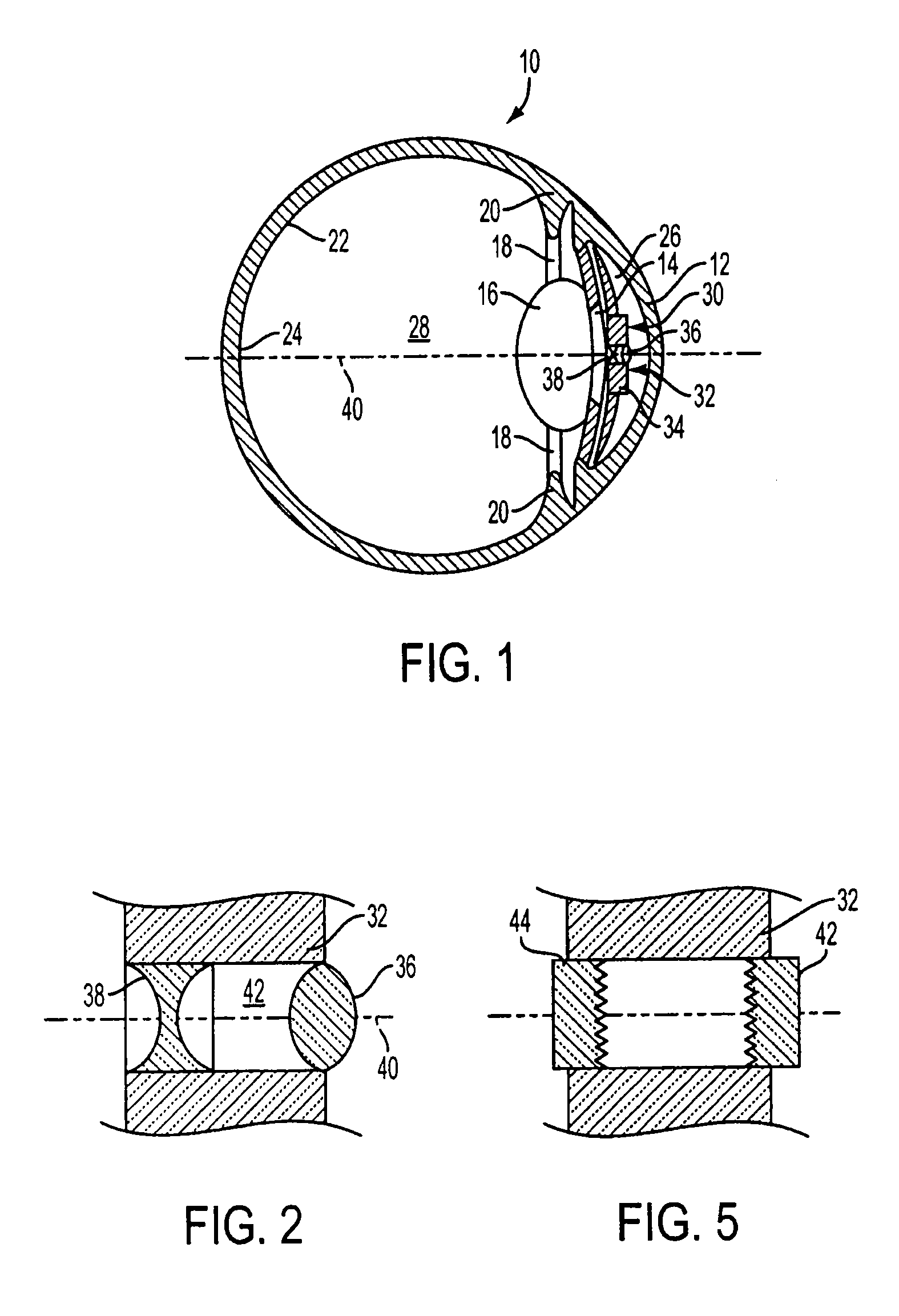
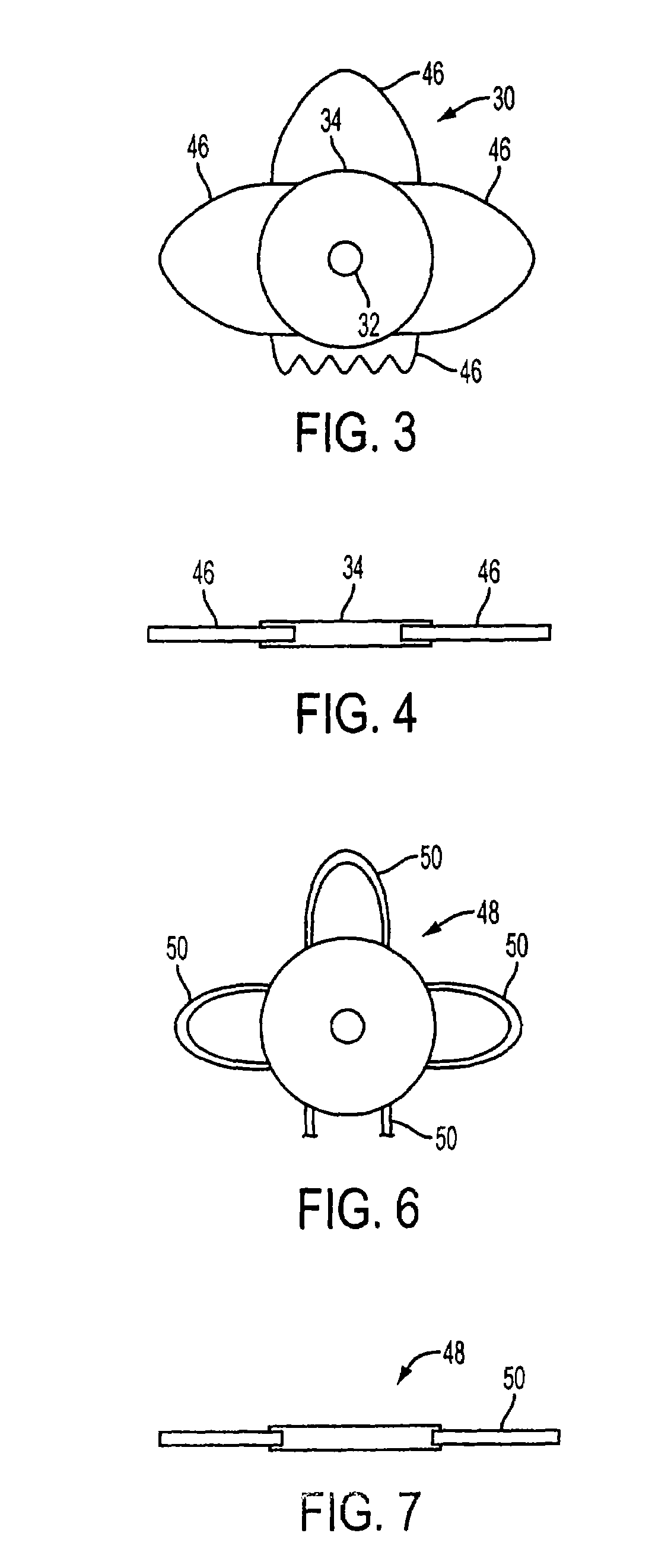
Bifocal intraocular telescope for low vision correction
InactiveUS7186266B2Provide bifocal correction to the eyeIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical axis
Owner:TELEDIOPTIC LENS SYST
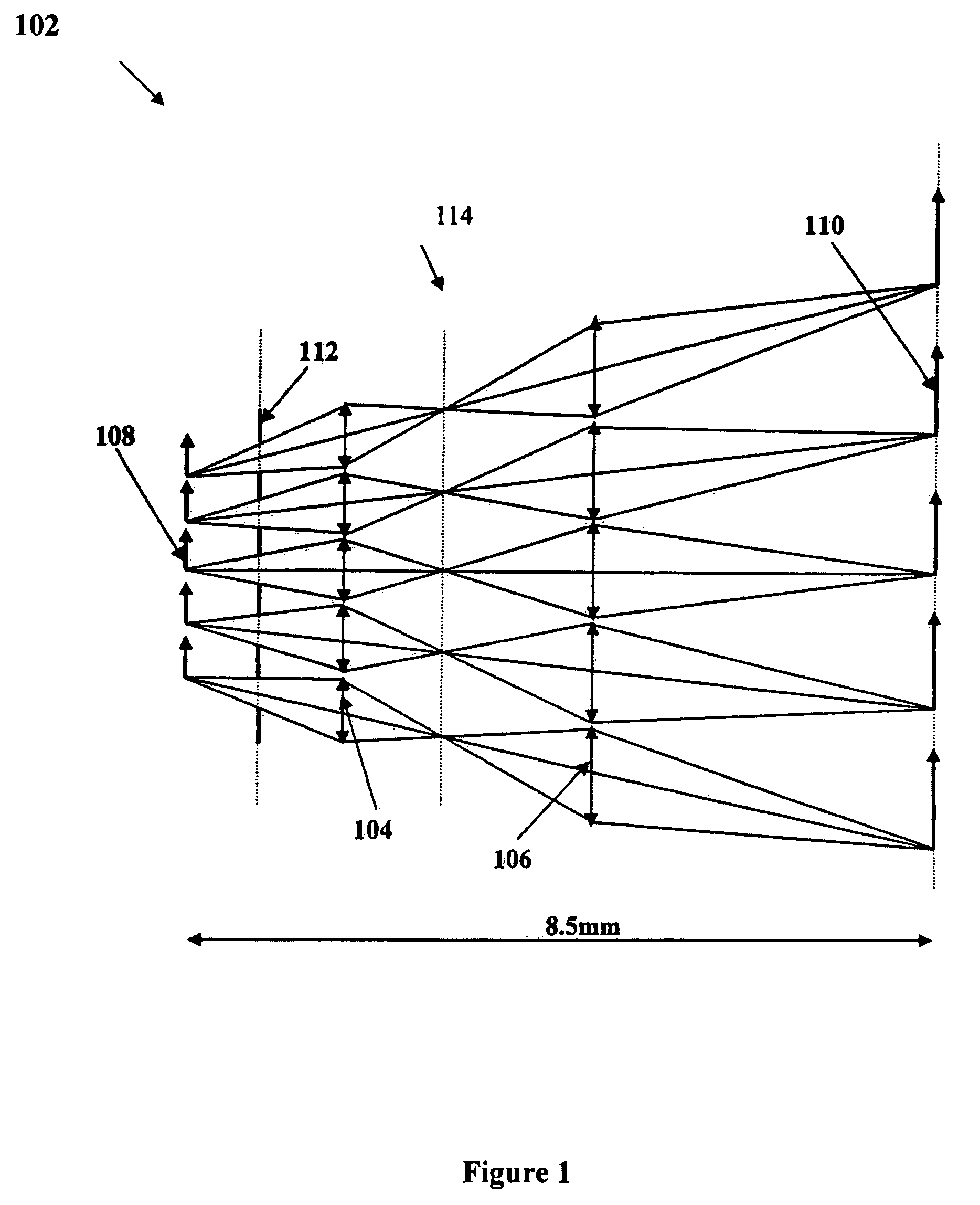
Compact microlenslet arrays imager
InactiveUS7009773B2More compactIncrease appearance sizeCathode-ray tube indicatorsDiffraction gratingsDisplay deviceMagnification
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
General laying-out and recovering system for submersible
The invention relates to a universal launching process system which can launch a plurality of diving devices and includes an A-shaped frame which can swing; the two sides of the A-shaped frame are hinged with a swing telescope oil cylinder; the upper end of the A-shaped frame is hinged with a swing frame; the system is characterized in that the lower end of the swing frame is provided with a connection seat; the middle part of the connection seat is provided with a hinging pin roll; the two sides of the connection seat are hinged with a damper which resists transverse swinging; the connection seat is connected with the guide joint of the diving device or the guide pulley of a depth sea towed system; a lifting winch and an umbilical cord guide pulley are respectively arranged above the swing frame. The launching process device can be used for launching various underwater vehicles since the guide joint of the device is replaced, thereby improving the operating factor of the voyage of a mother ship to a large extent. The system has a compact and reasonable structure and strong functions as well as is convenient to be used and operated. Besides, the state of supporting diving device is stable; under the effect of the damper which resists transverse swinging, the system has better vibration-stopping swinging-resistance effects, thereby improving the applicable sea situations of the diving devices.
Owner:CHINA SHIP DEV & DESIGN CENT
Weaponry camera sight
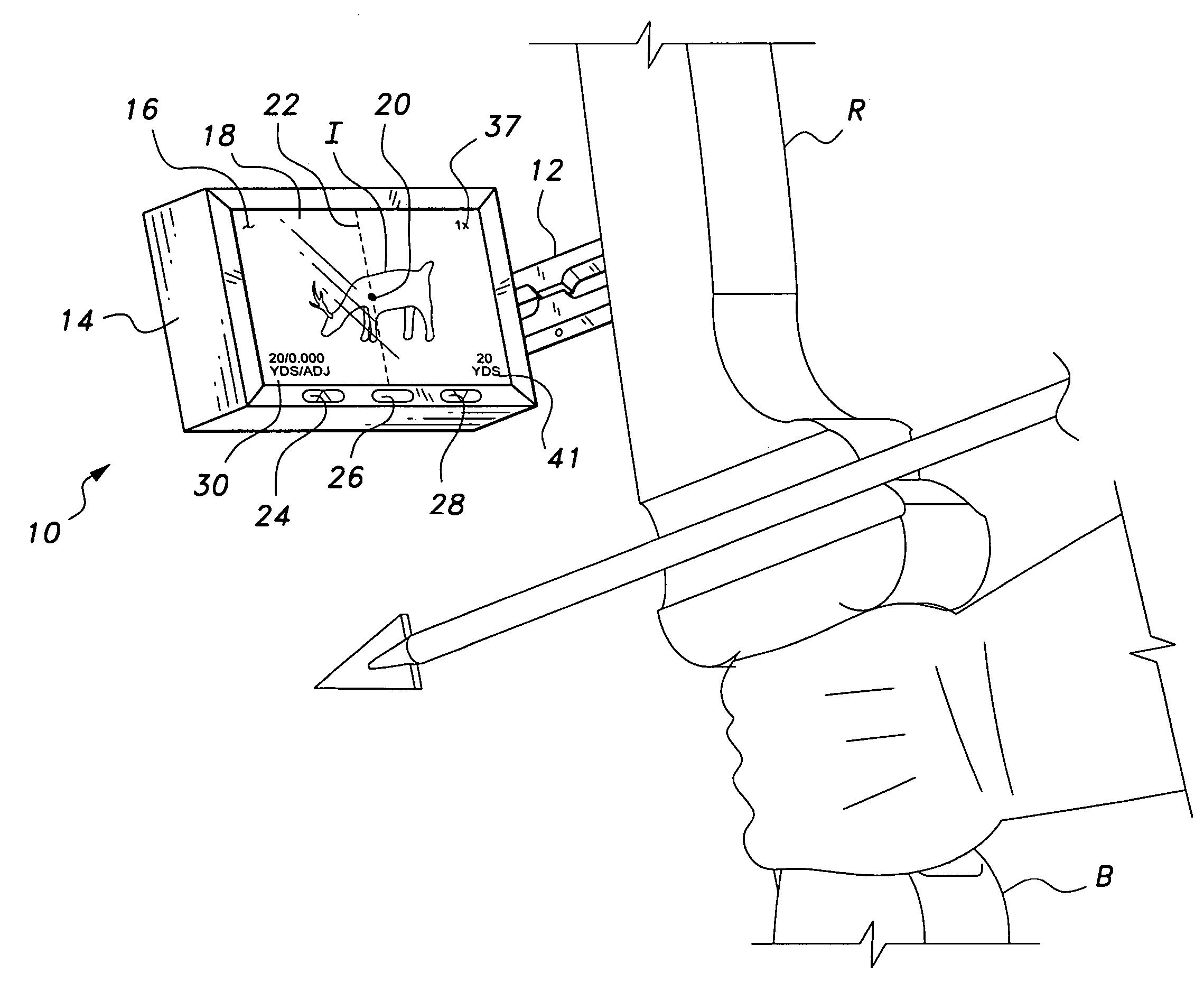
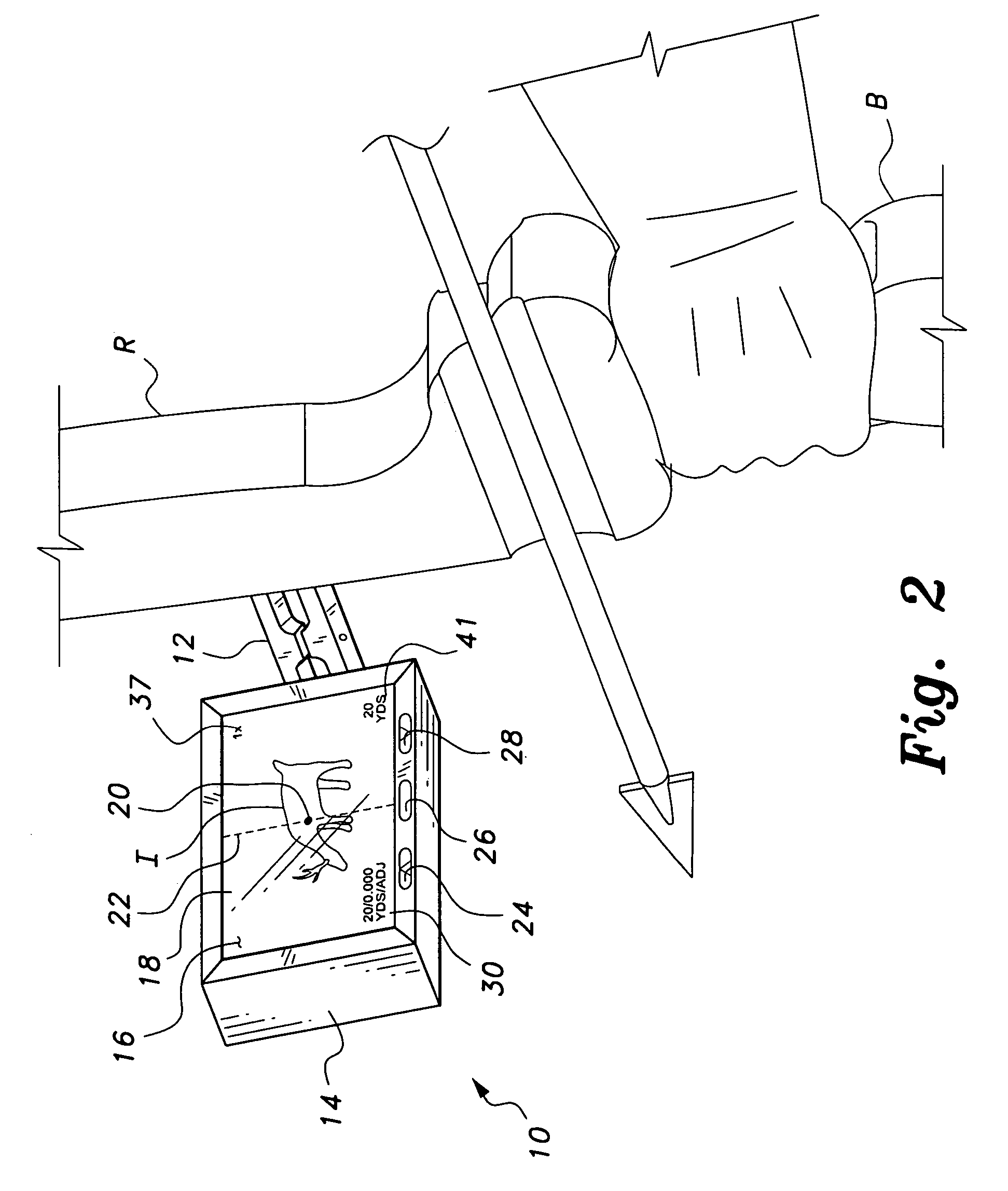
InactiveUS7255035B2Eliminate needOptical rangefindersBows/crossbowsComputer graphics (images)Display device
The weaponry camera sight has a digital electronic display of the sight picture for the shooter. The display may be magnified as desired, thereby eliminating need for a scope sight. The device may also include a range finding device, with range information being provided on screen. The camera may also be used to record the image viewed on screen, if so desired. Remotely situated controls may be provided for operating the zoom magnification and recording feature, thereby allowing the shooter to operate the present camera sight without need to move his or her hands on the weapon. The present camera sight is particularly well suited for use with an archery bow, but may be used with a firearm if so desired.
Owner:MOWERS MICHAEL S
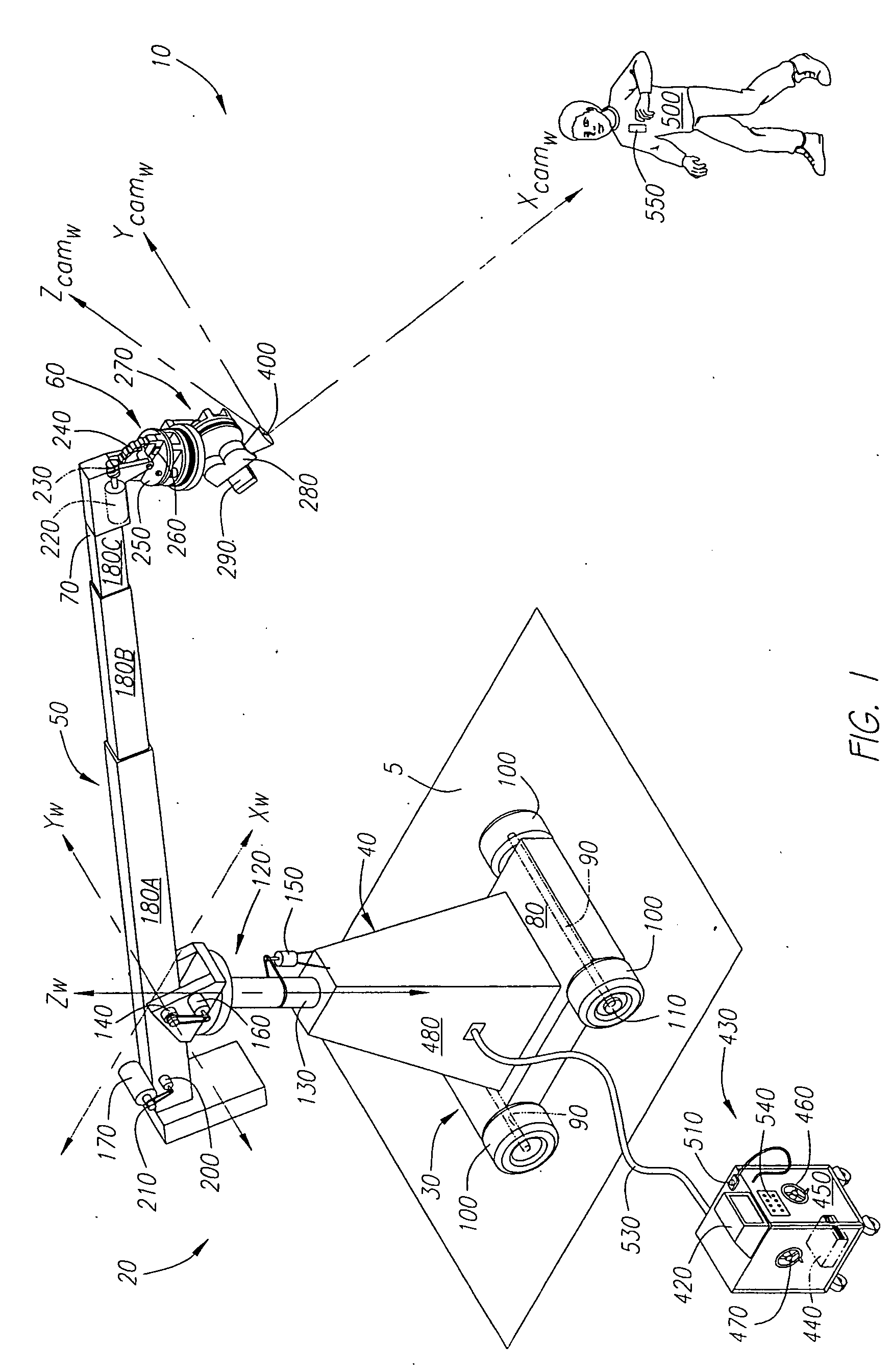
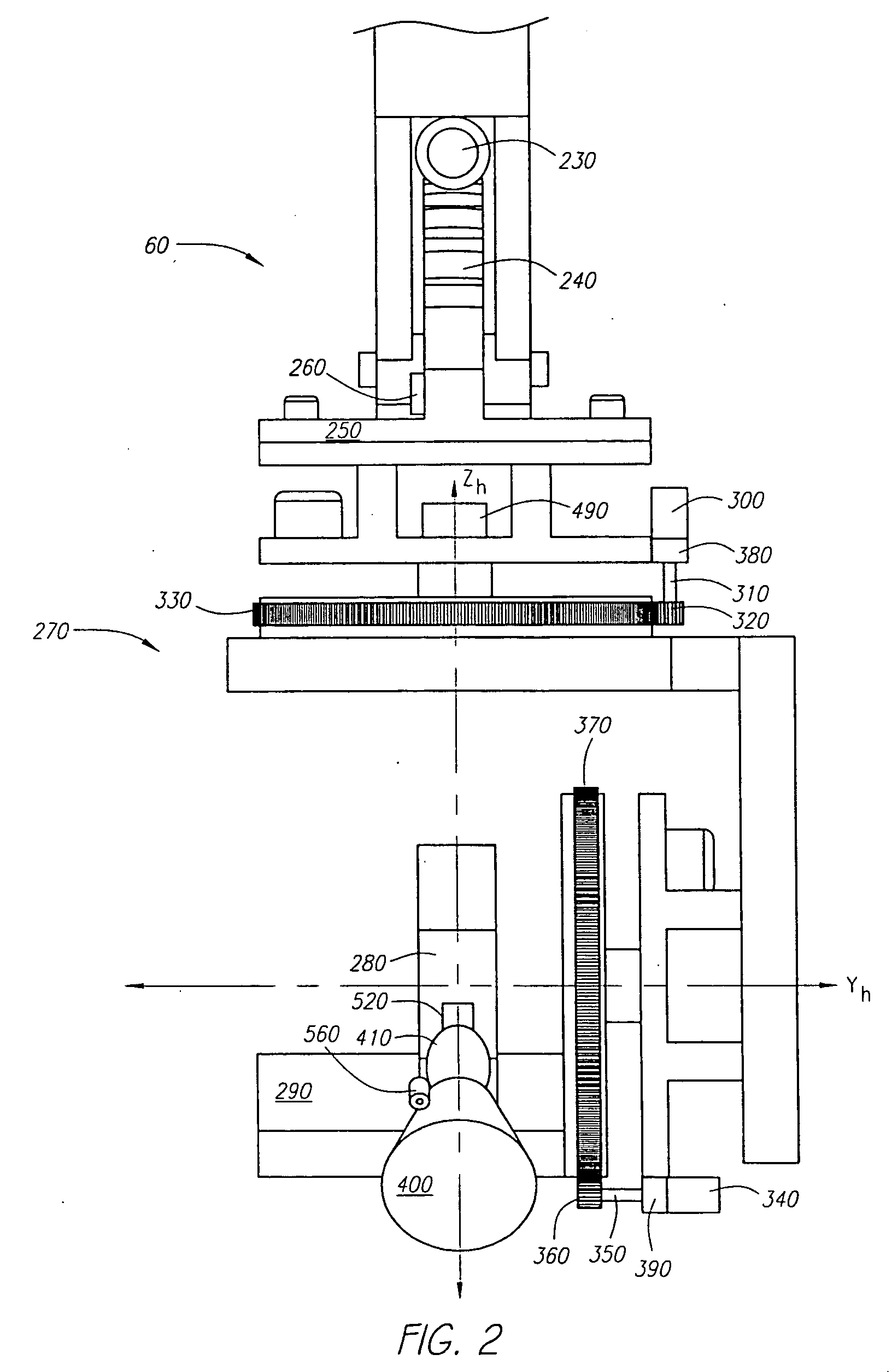
Automatic pan and tilt compensation system for a camera support structure
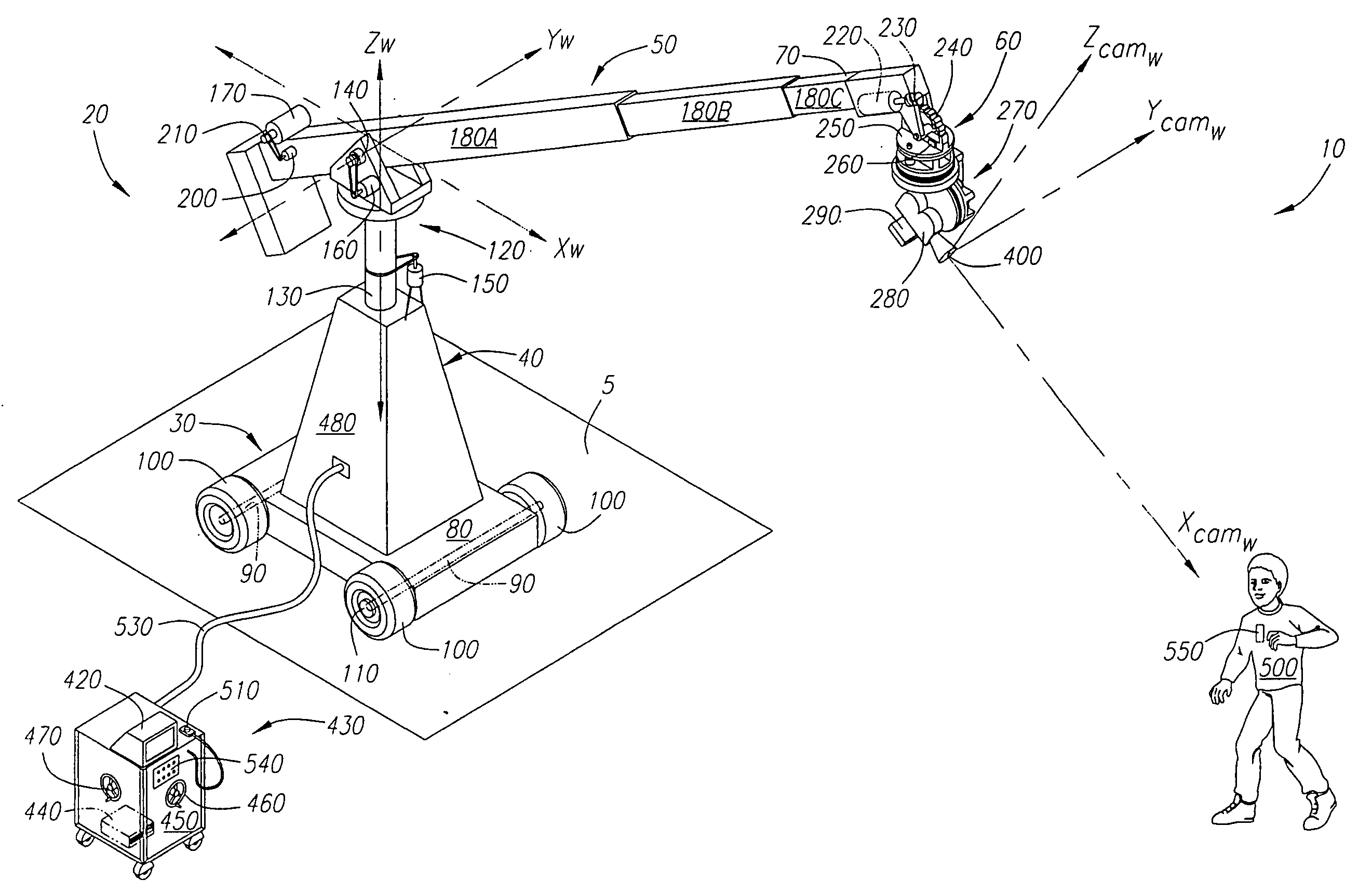
An automated system for compensating the pan and tilt of a camera head for the movements of a camera support structure and / or a subject matter. A processing system receives signals relating to the movement of the camera support structure, such as the swing, boom and telescope of the crane arm, the movements of a dolly, and preferably the movements of a subject matter. The system employs these inputs to determine the position of the camera and subject matter in a defined world coordinate system and sends signals to compensate the pan and tilt of the camera head so that the field of view of the camera is generally centered on the subject matter being filmed as defined within the system.
Owner:PANAVISION INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com