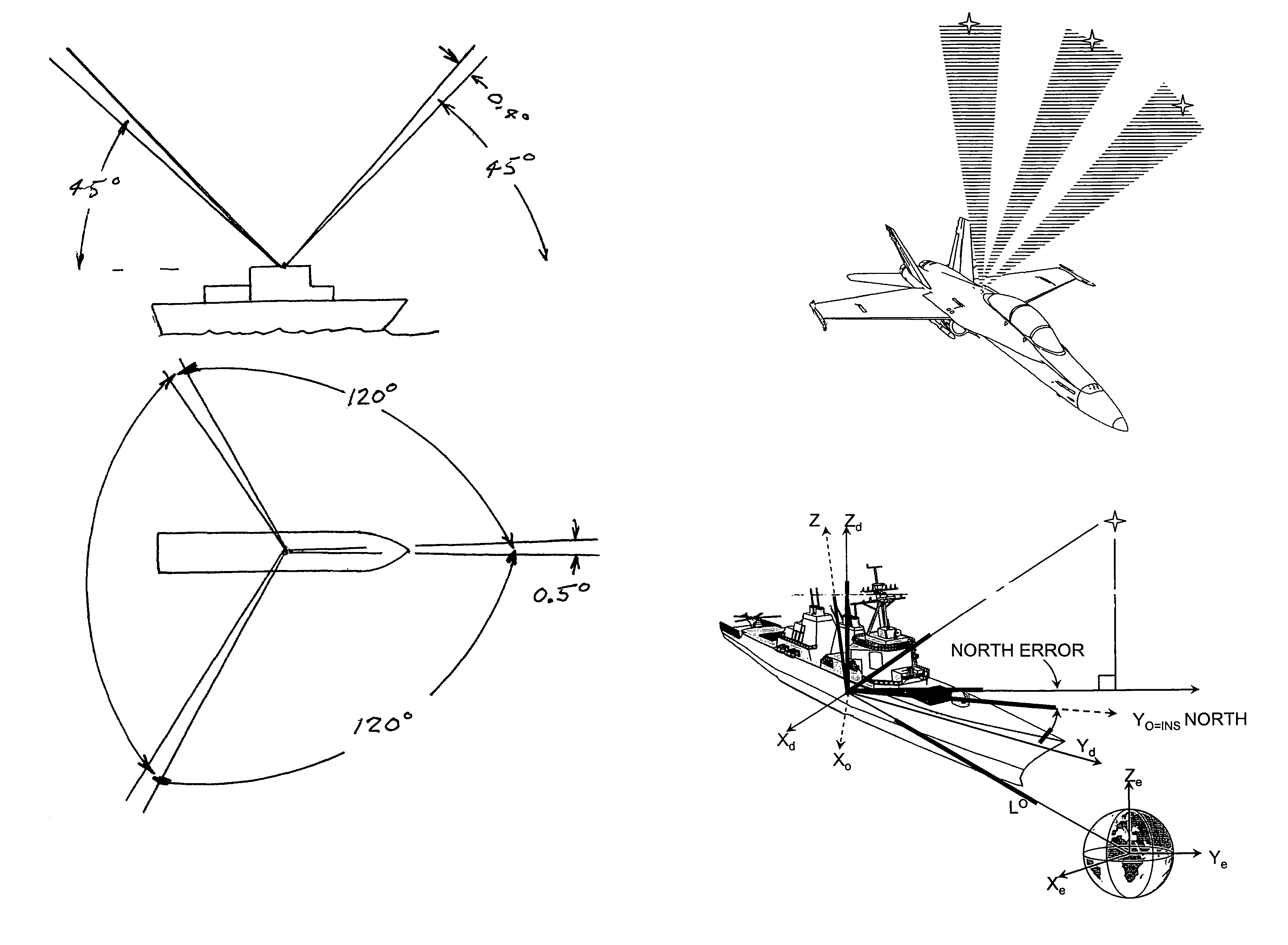
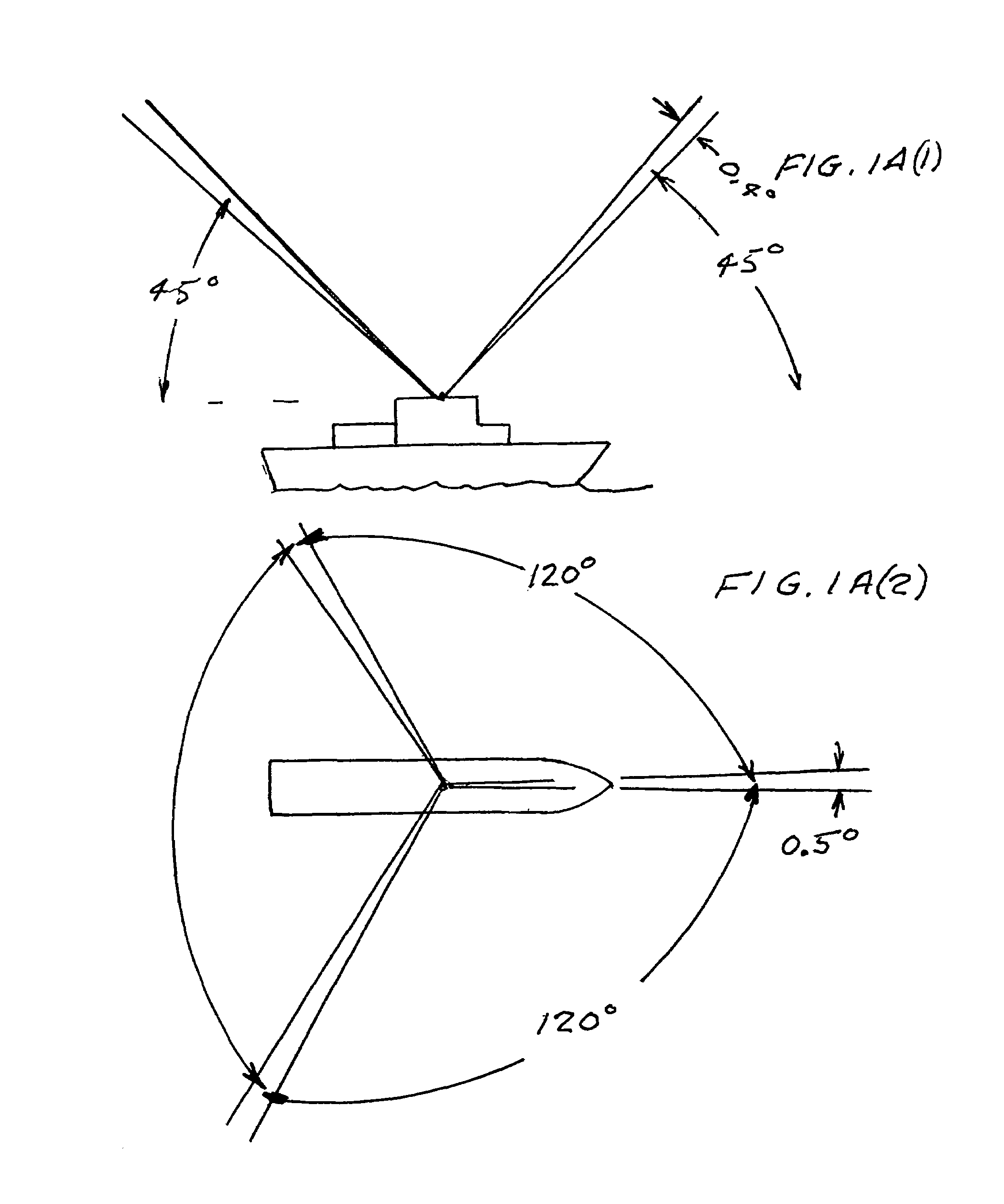
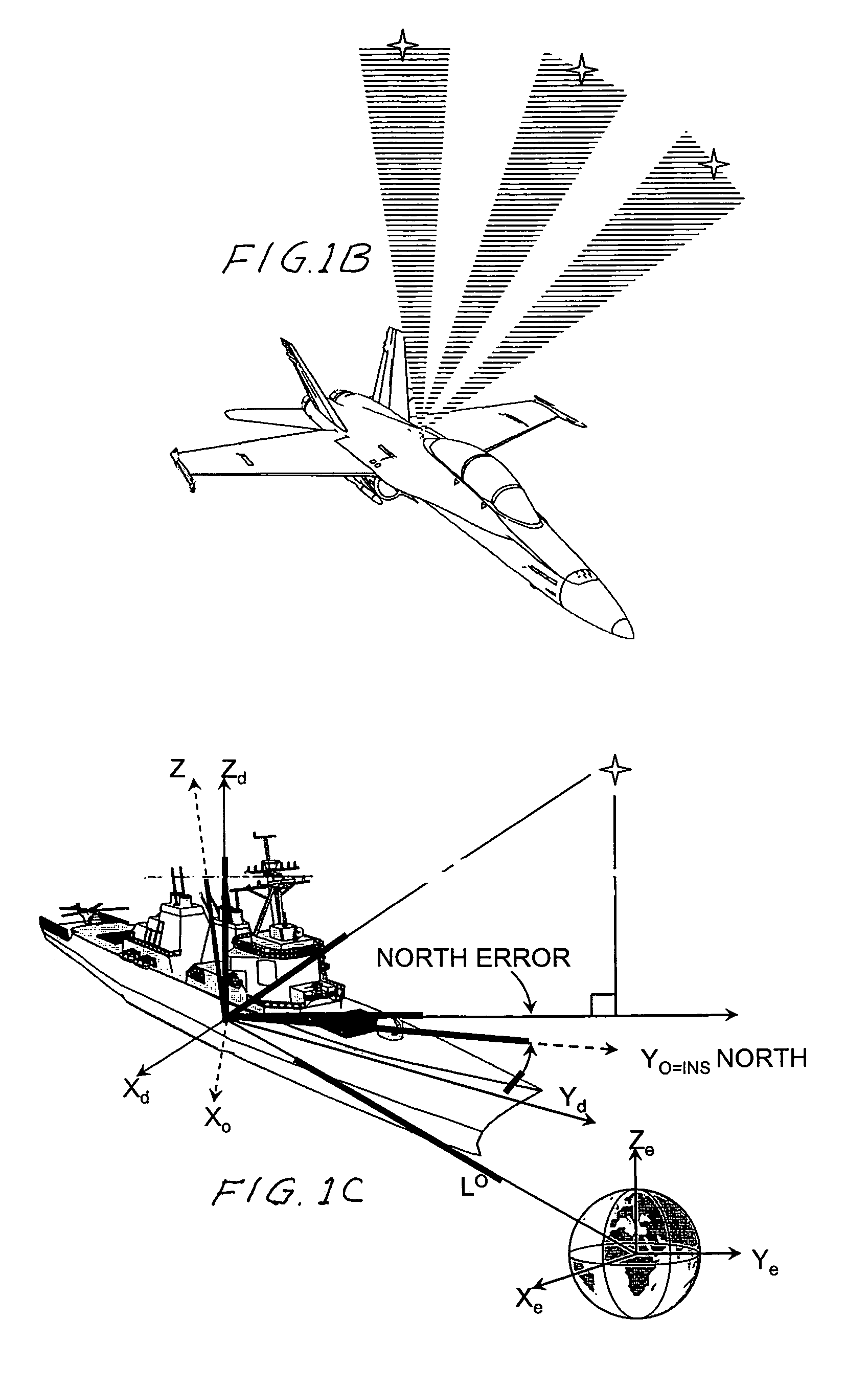
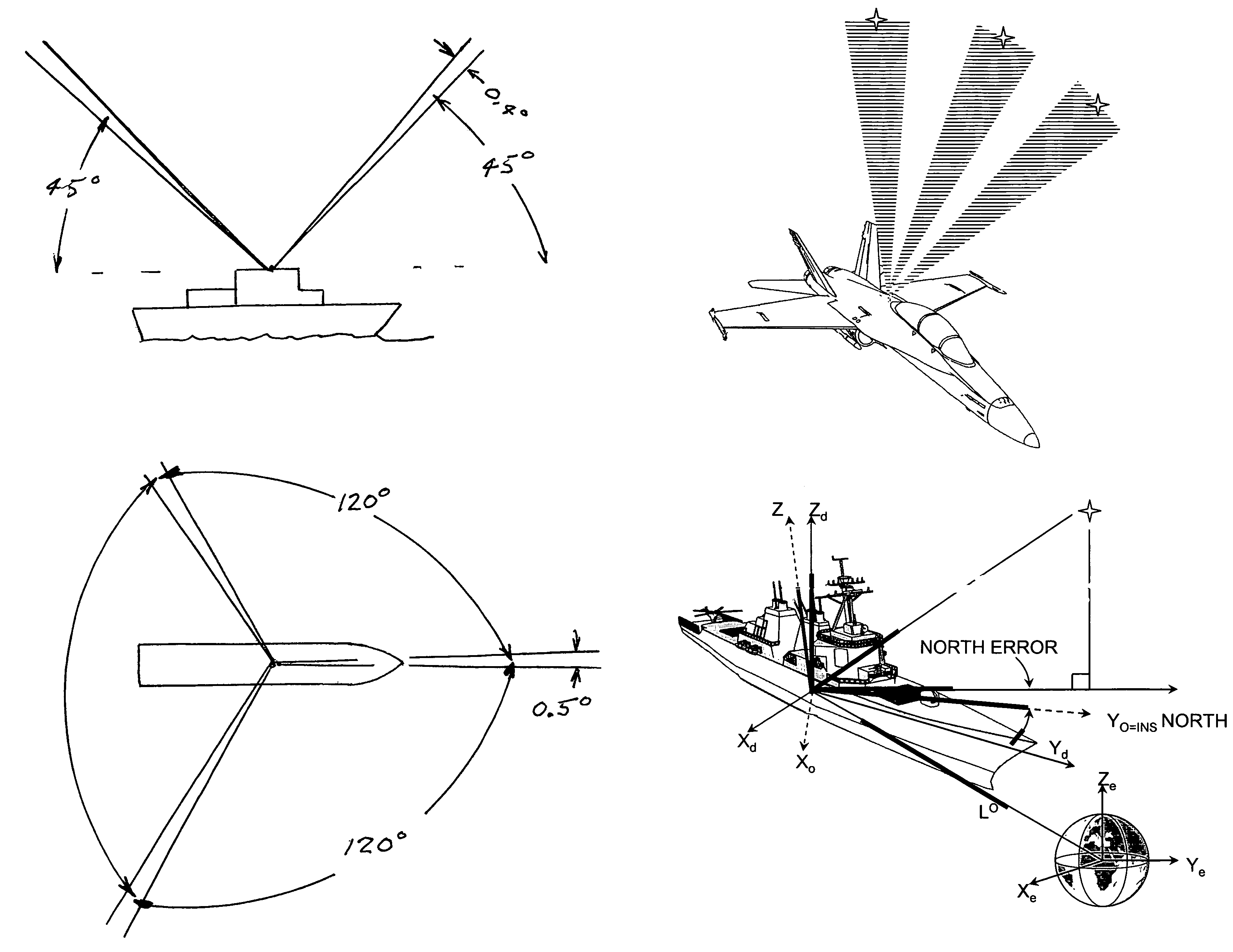
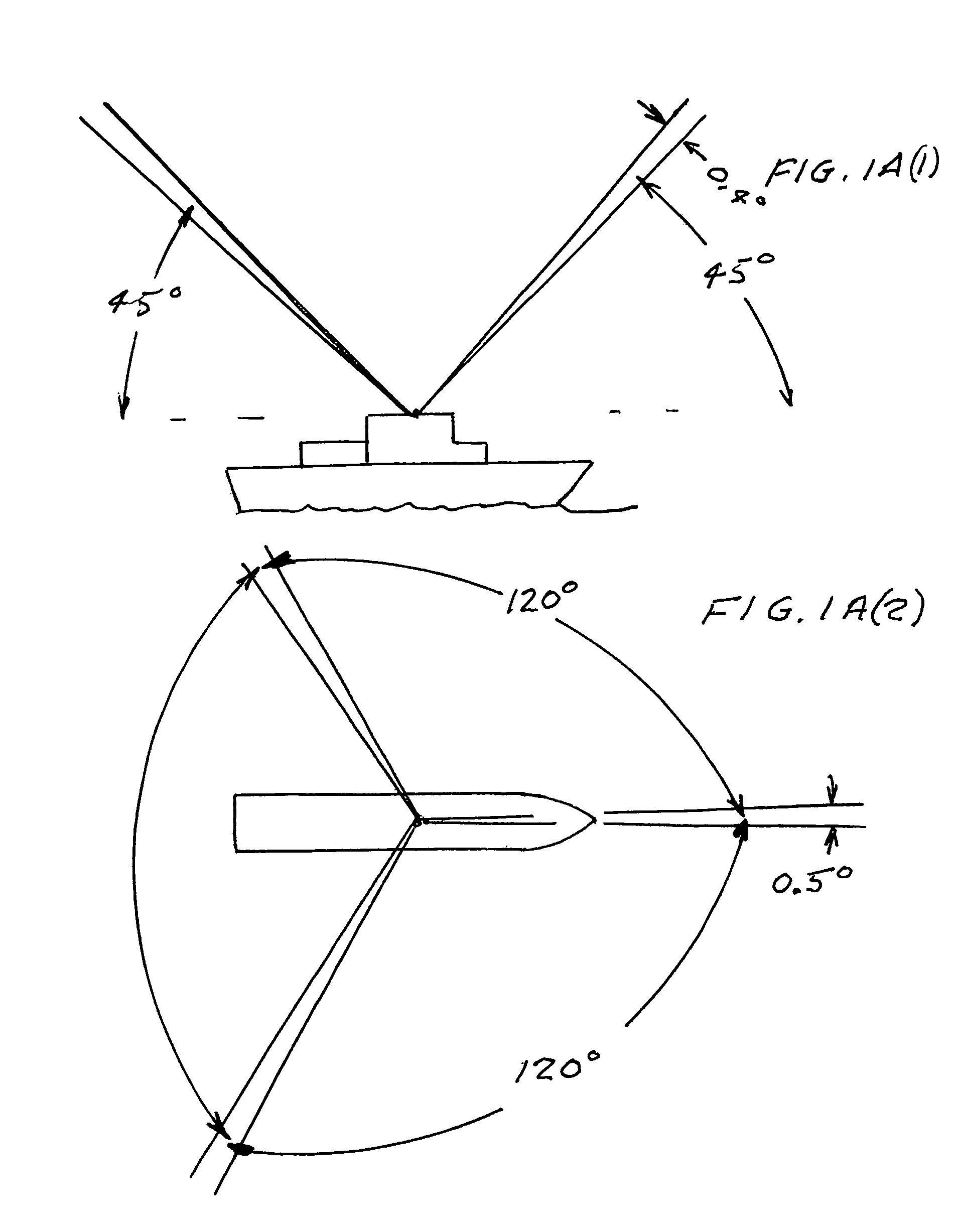
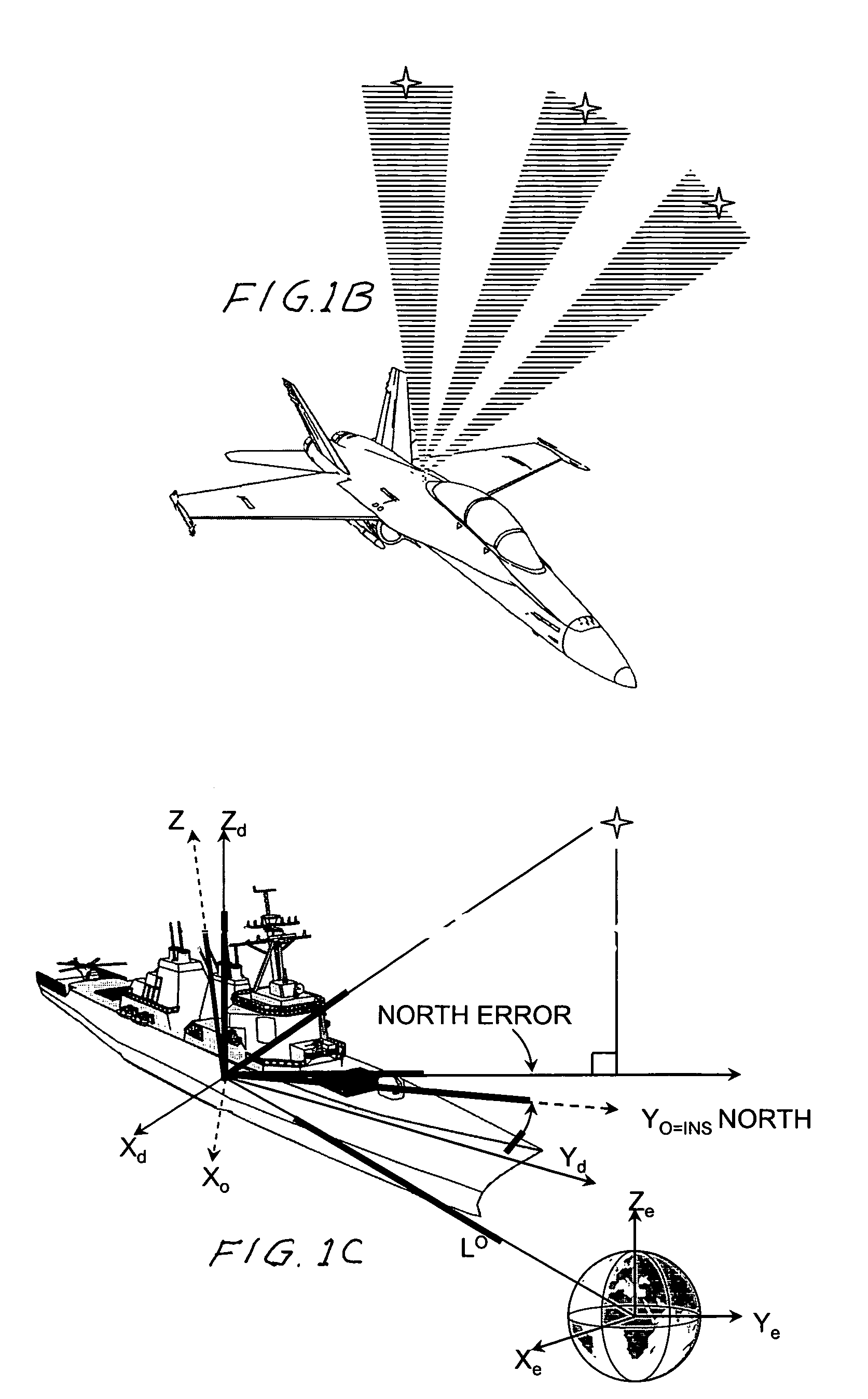
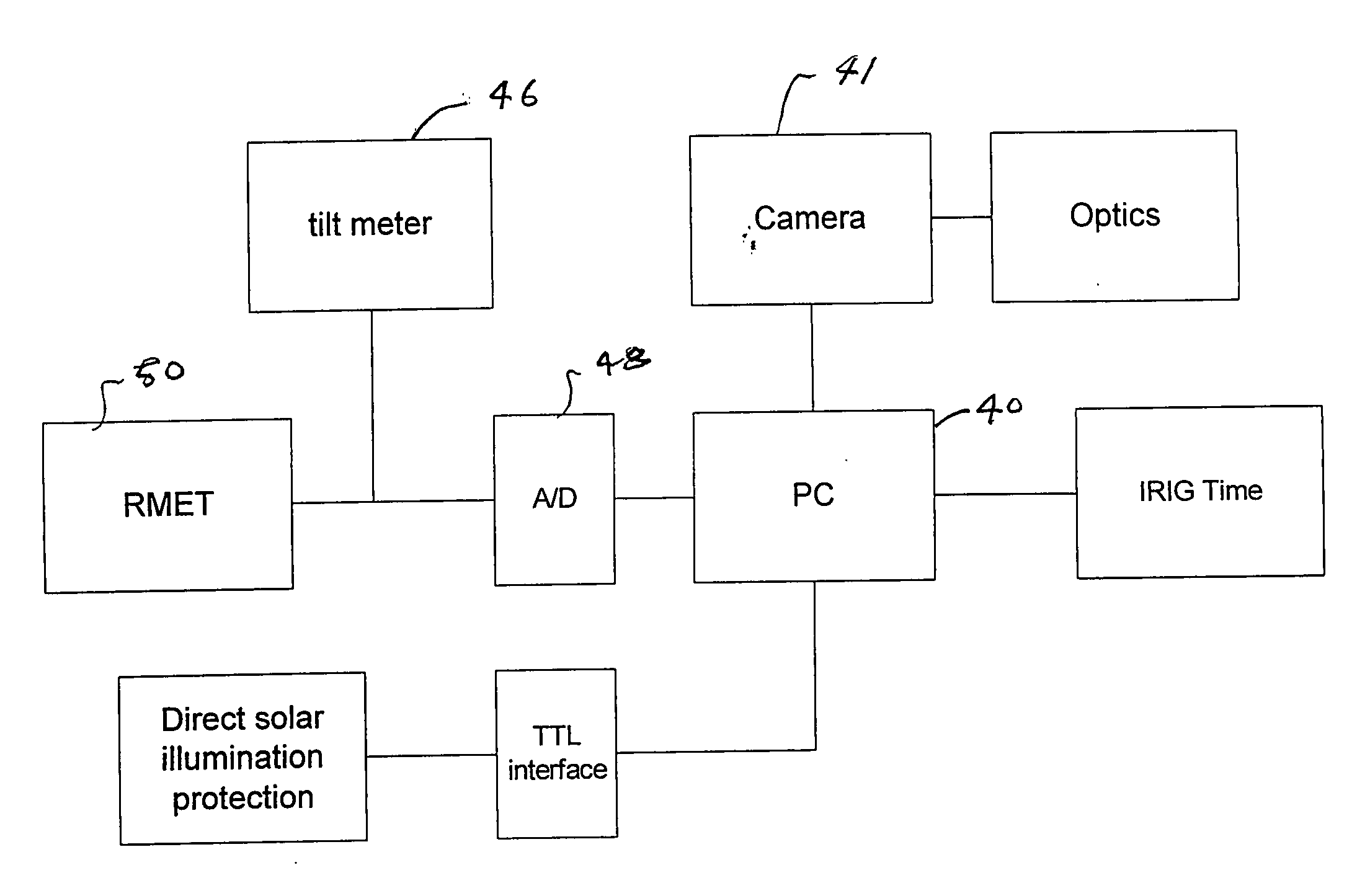
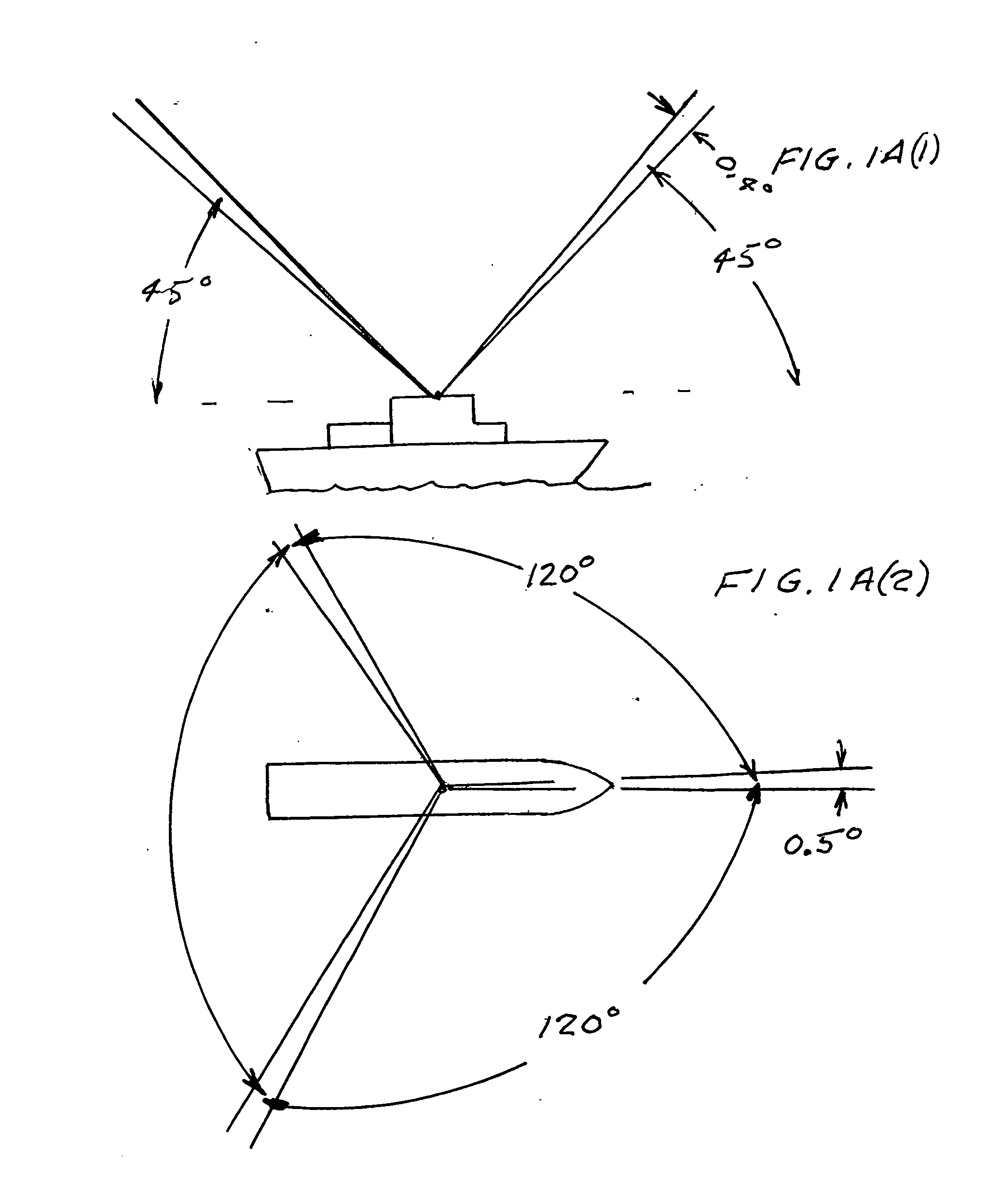
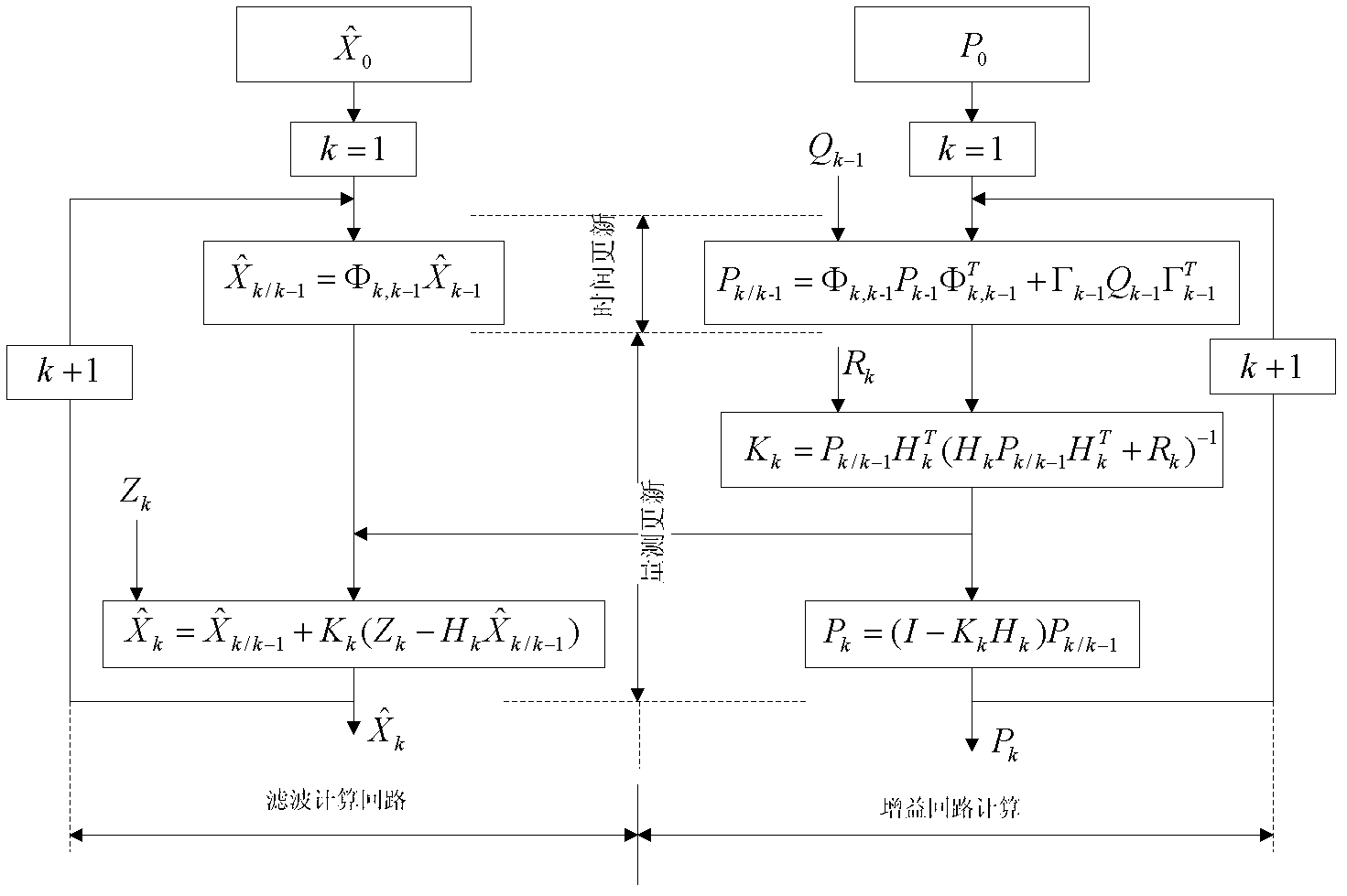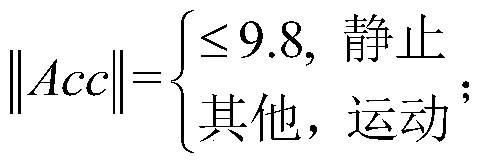Patents
Literature
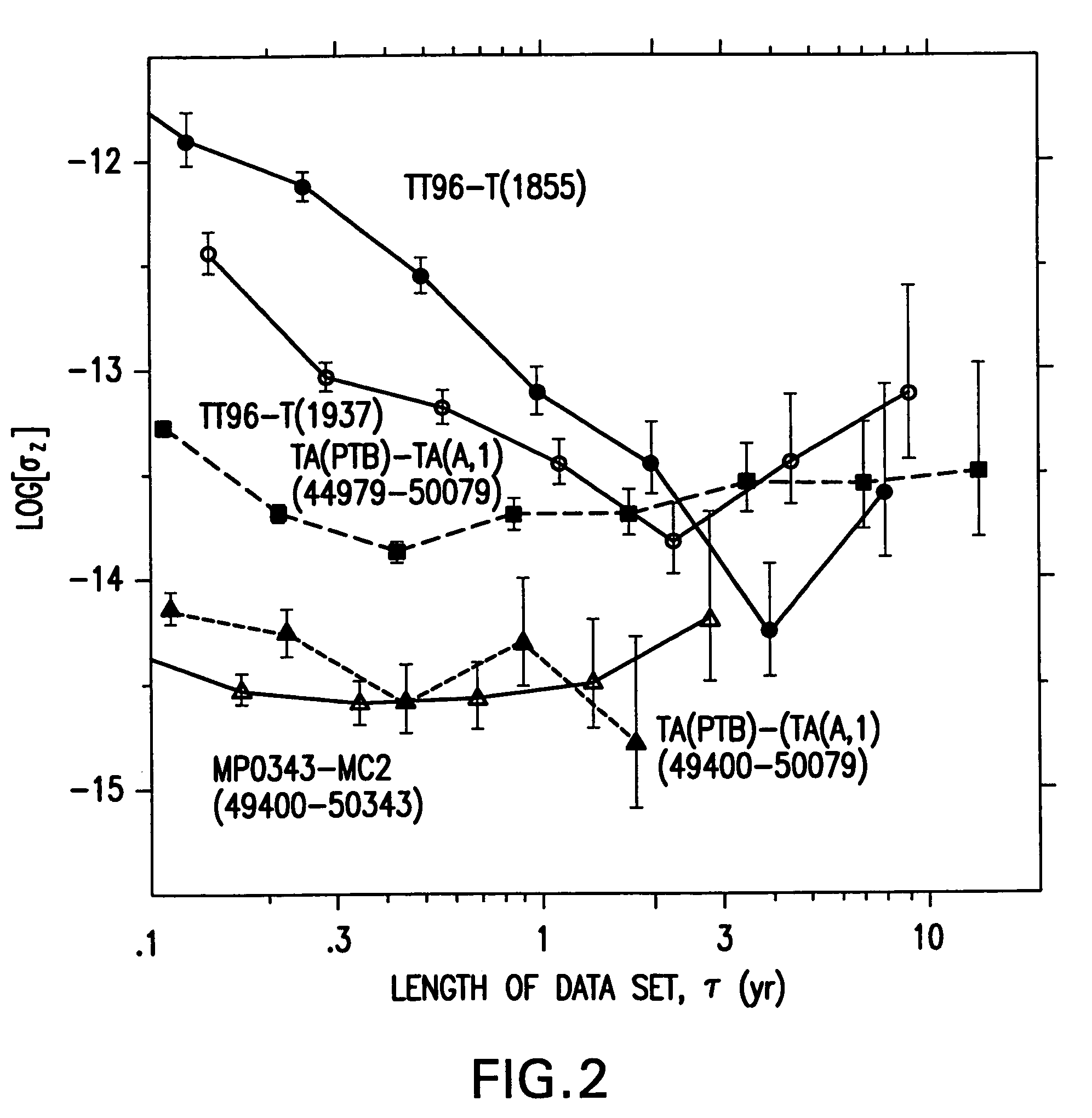
165 results about "Celestial navigation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
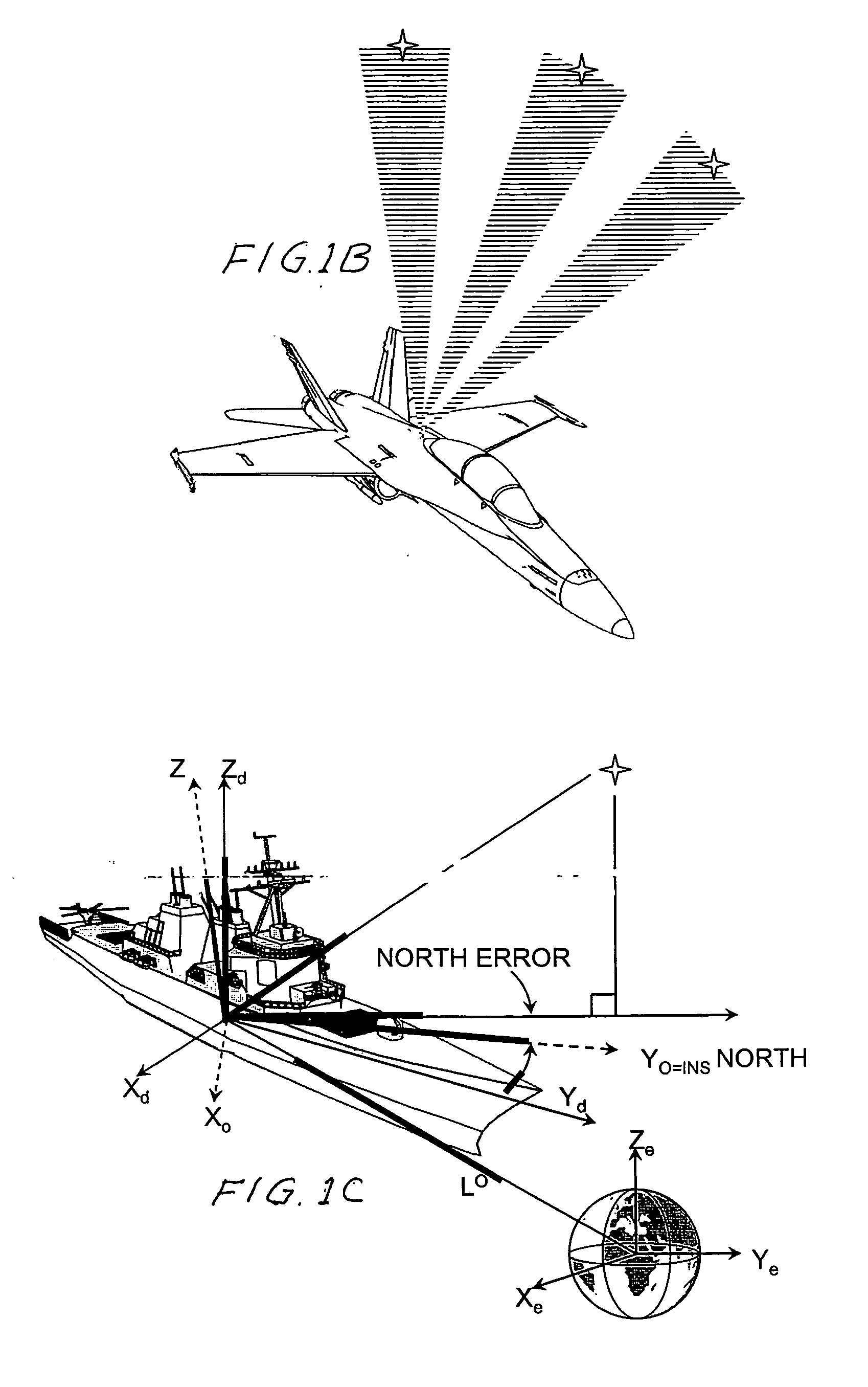
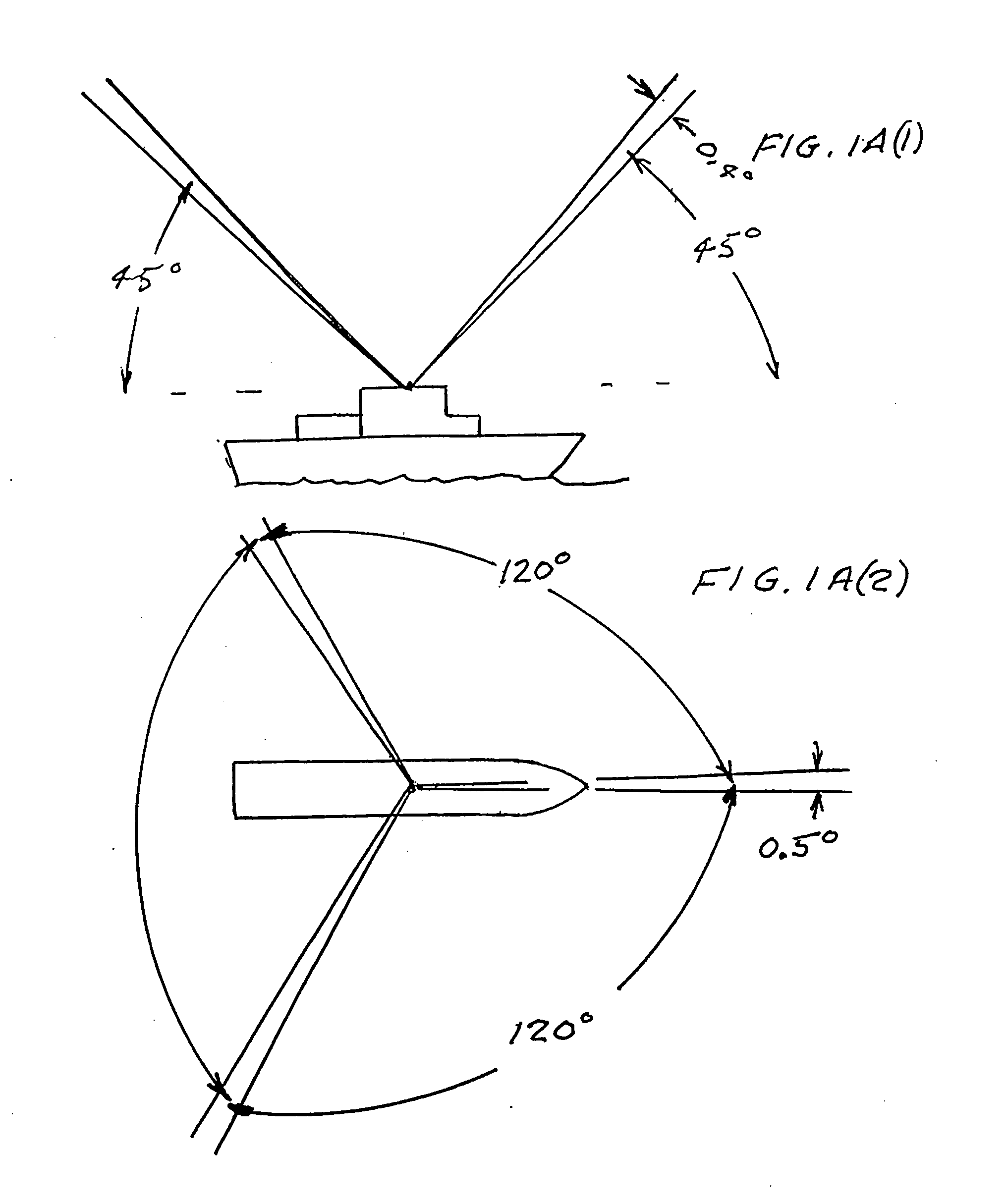
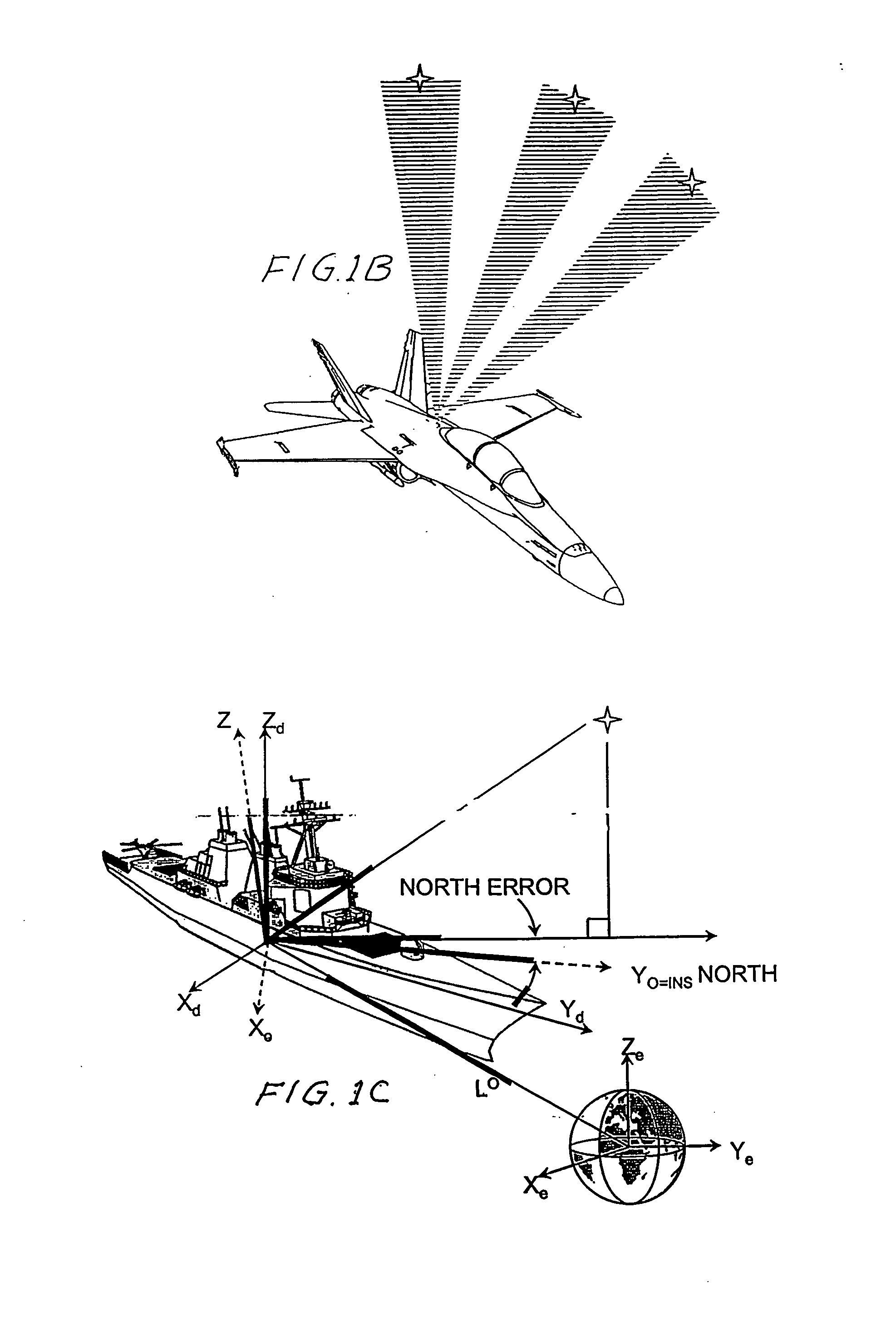
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the ancient and modern practice of [position fixing] that enables a navigator to transition through a space without having to rely on estimated calculations, or dead reckoning, to know their position. Celestial navigation uses "sights", or angular measurements taken between a celestial body (e.g. the Sun, the Moon, a planet, or a star) and the visible horizon. The Sun is most commonly used, but navigators can also use the Moon, a planet, Polaris, or one of 57 other navigational stars whose coordinates are tabulated in the nautical almanac and air almanacs.
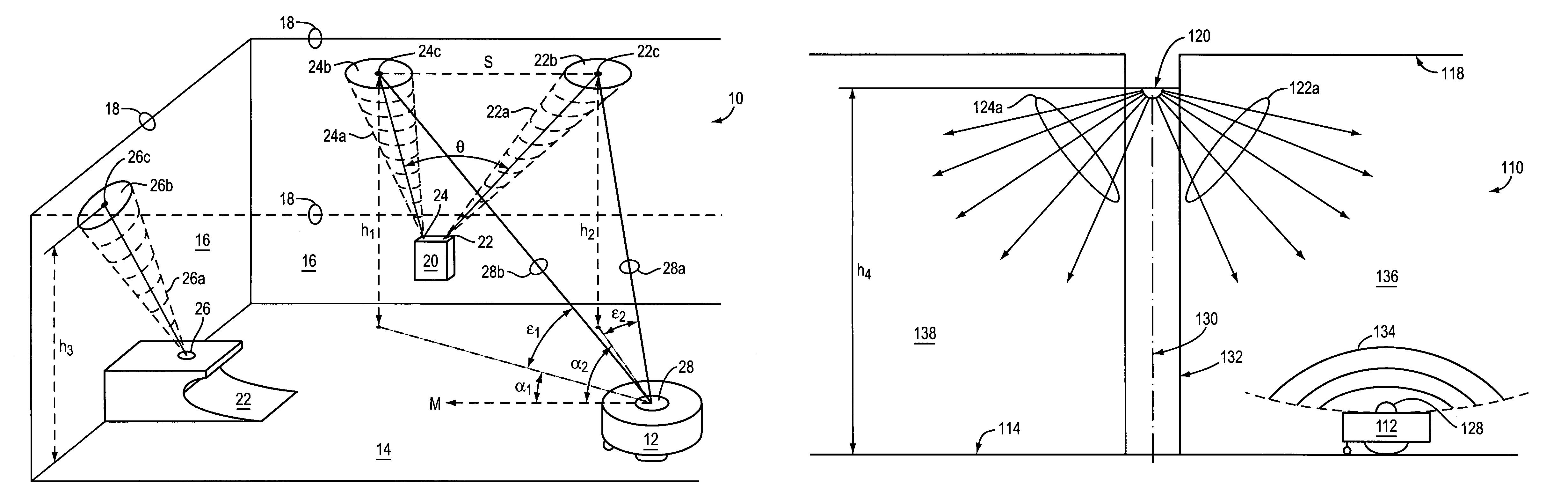
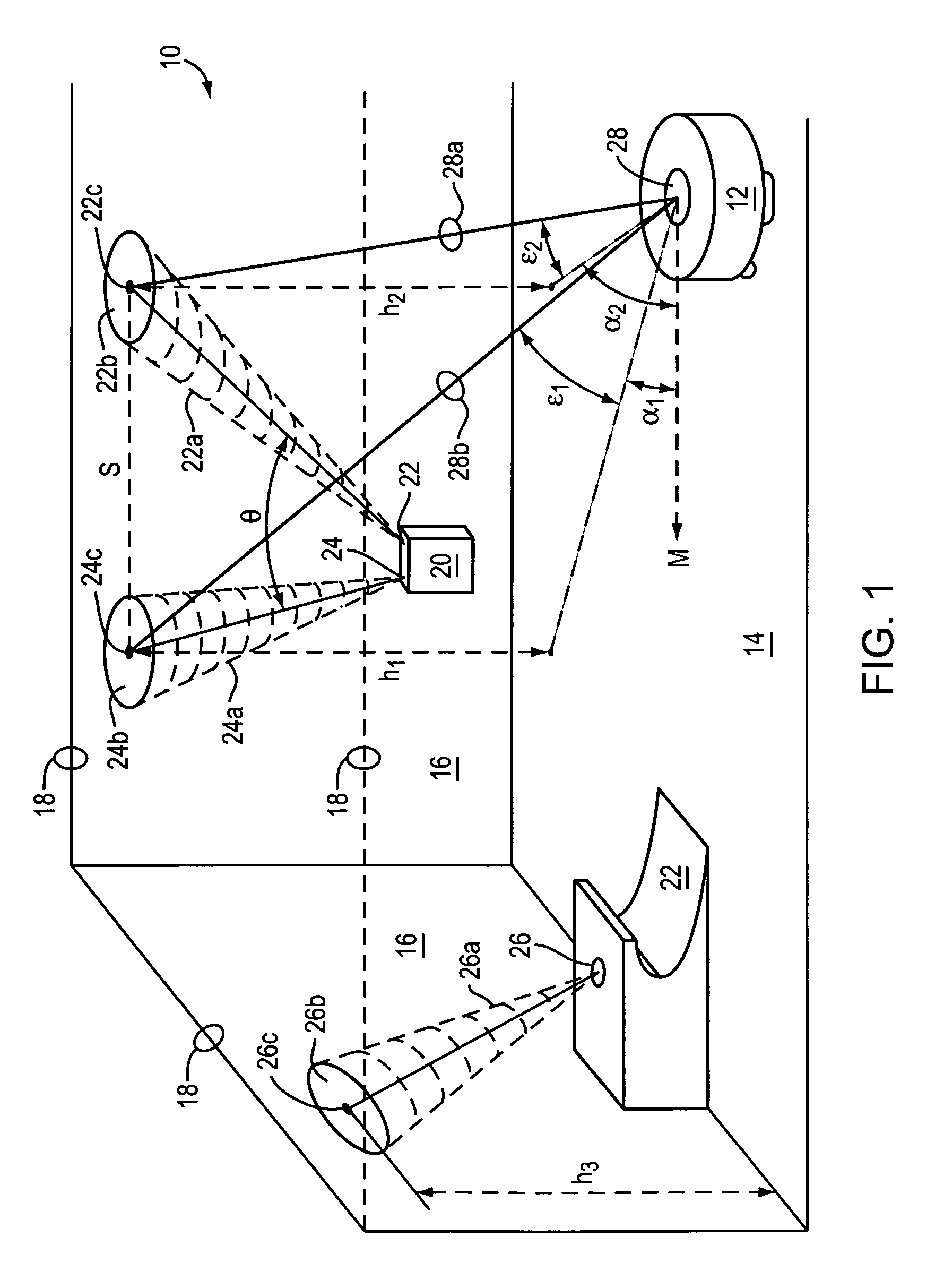
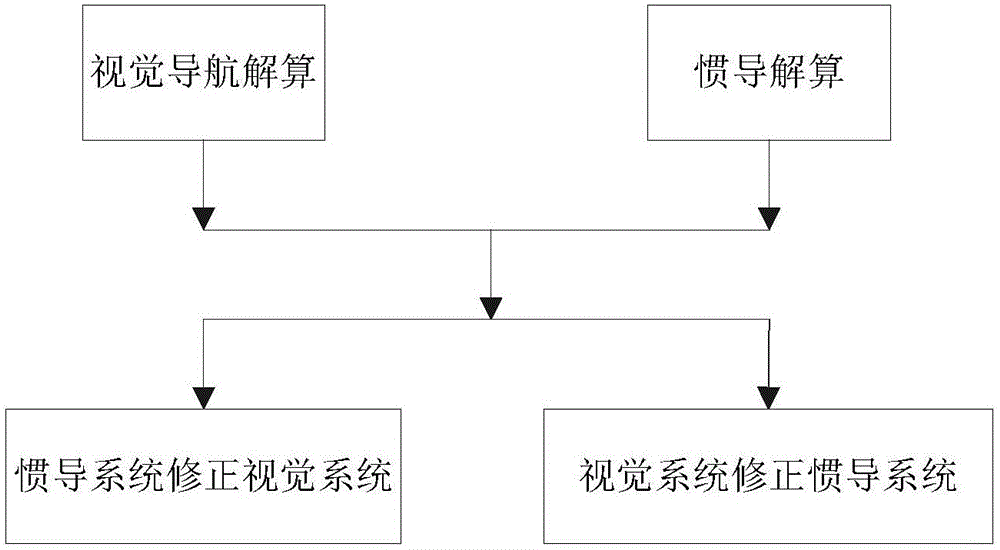
Celestial navigation system for an autonomous robot
A navigational control system for an autonomous robot includes a transmitter subsystem having a stationary emitter for emitting at least one signal. An autonomous robot operating within a working area utilizes a receiving subsystem to detect the emitted signal. The receiver subsystem has a receiver for detecting the emitted signal emitted by the emitter and a processor for determining a relative location of the robot within the working area upon the receiver detecting the signal.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
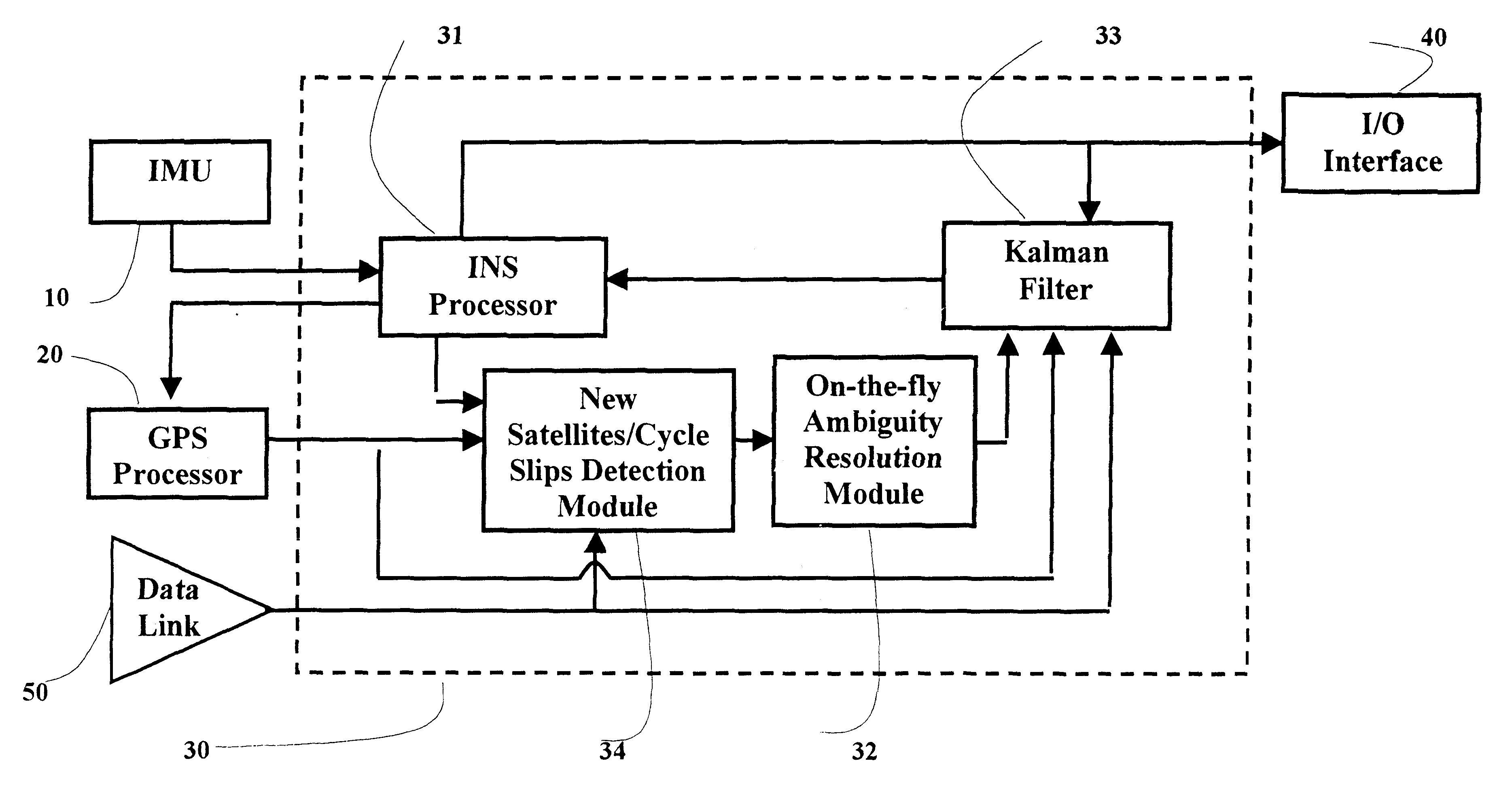
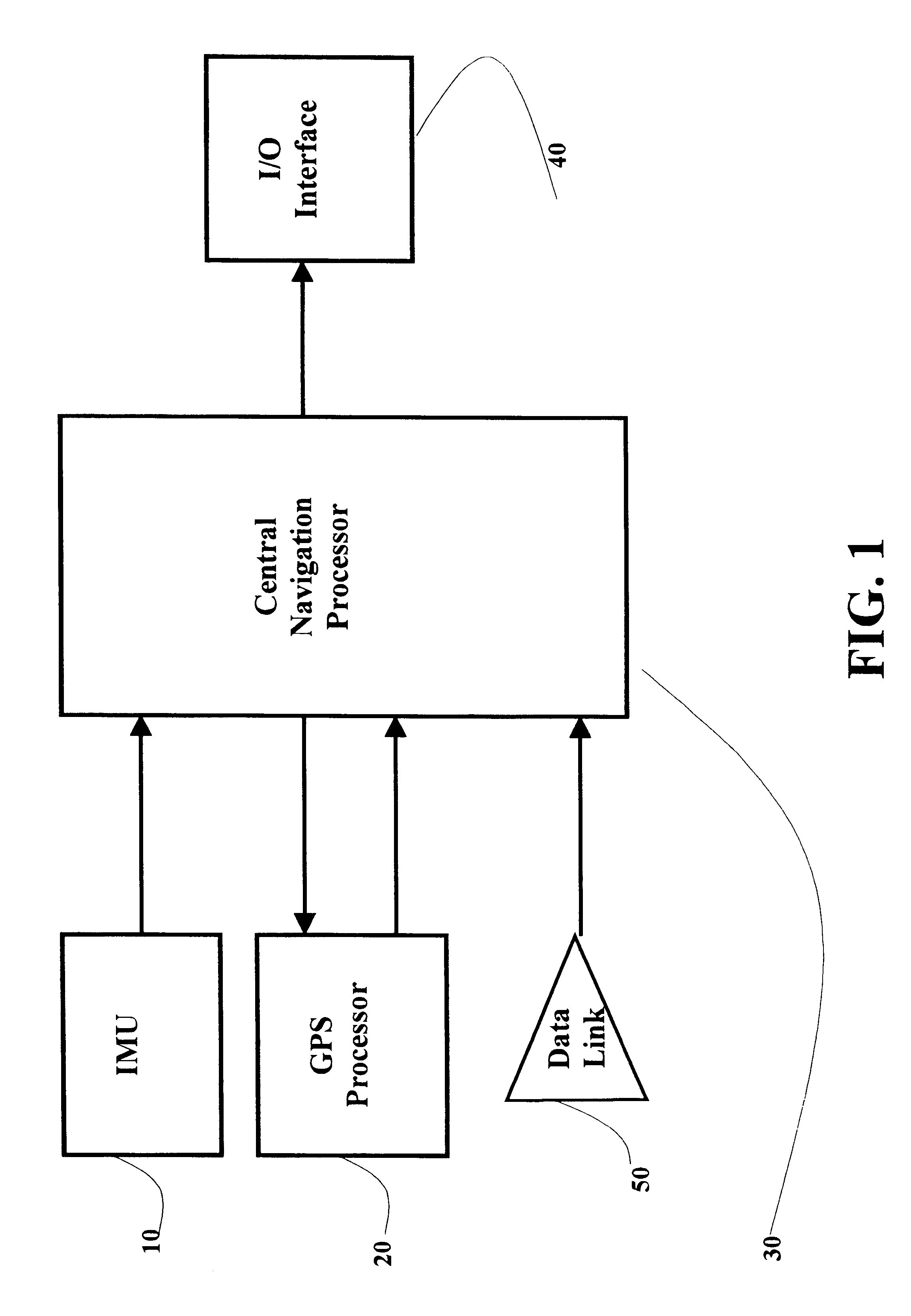
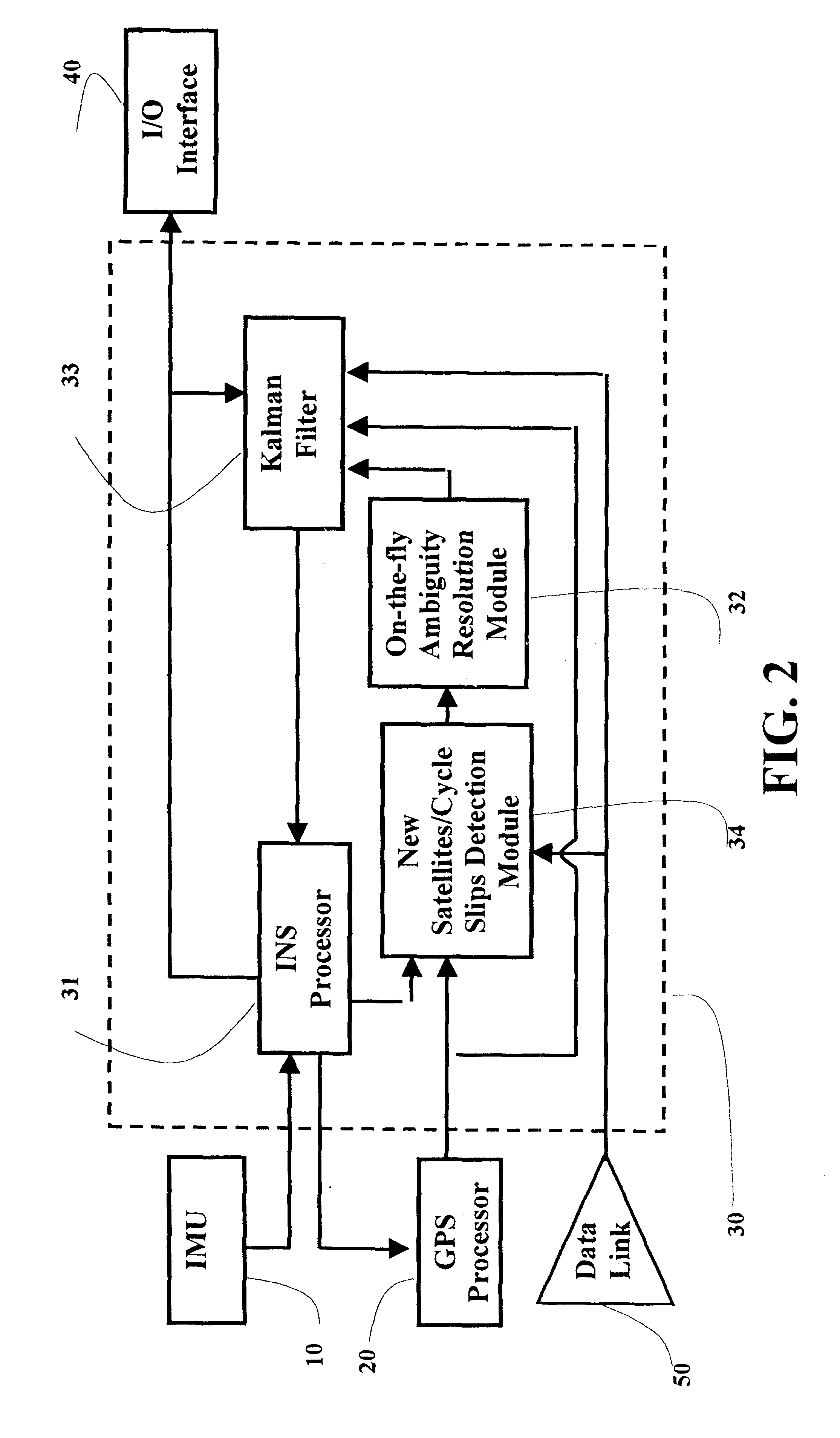
Real-time integrated vehicle positioning method and system with differential GPS
InactiveUS6496778B1Improve performanceLow costPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsDouble differenceFully coupled
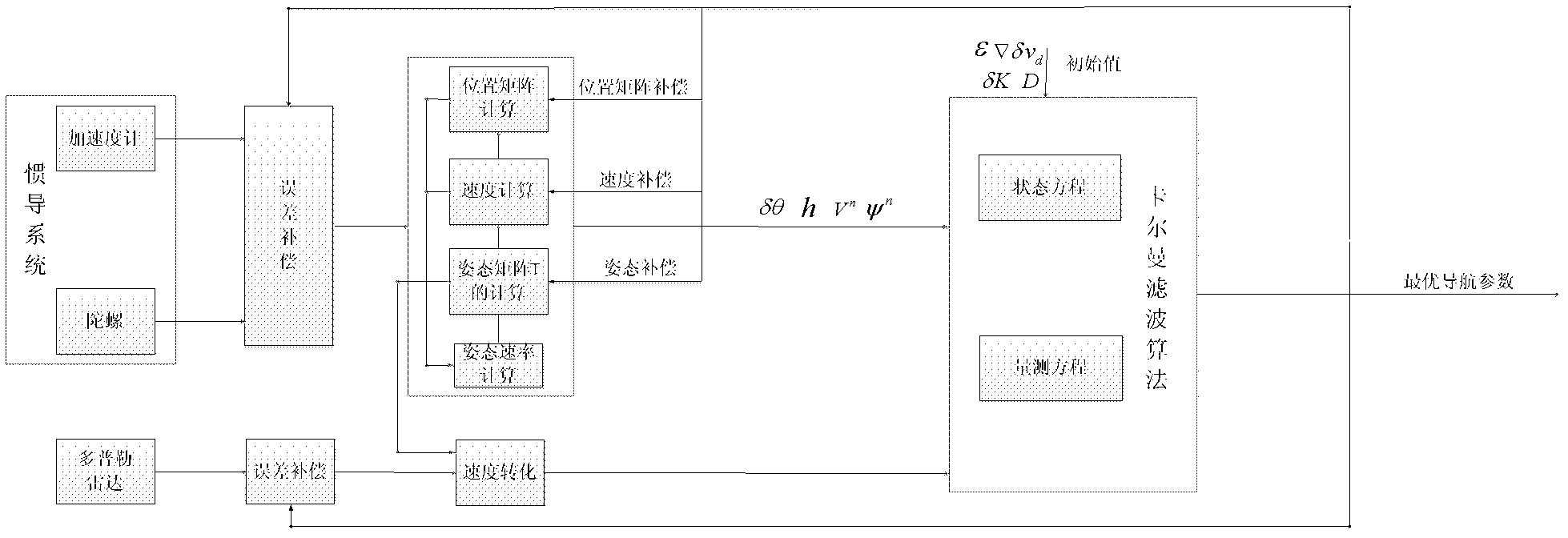
A real-time integrated vehicle positioning method and system with differential GPS can substantially solve the problems encountered in either the global positioning system-only or the inertial navigation system-only, such as loss of global positioning satellite signal, sensitivity to jamming and spoofing, and an inertial solution's drift over time. In the present invention, the velocity and acceleration from an inertial navigation processor of the integrated GPS / INS system are used to aid the code and carrier phase tracking of the global positioning system satellite signals, so as to enhance the performance of the global positioning and inertial integration system, even in heavy jamming and high dynamic environments. To improve the accuracy of the integrated GPS / INS navigation system, phase measurements are used and the idea of the differential GPS is employed. However, integer ambiguities have to be resolved for high accuracy positioning. Therefore, in the present invention a new on-the-fly ambiguity resolution technique is disclosed to resolve double difference integer ambiguities. The real-time fully-coupled GPS / IMU vehicle positioning system includes an IMU (inertial measurement unit), a GPS processor, and a data link which are connected to a central navigation processor to produce a navigation solution that is output to an I / O (input / output) interface.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
Remote high-precision independent combined navigation locating method
InactiveCN101270993AImprove drop point (hit) accuracyHigh resolutionInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSynthetic aperture radarNavigation system
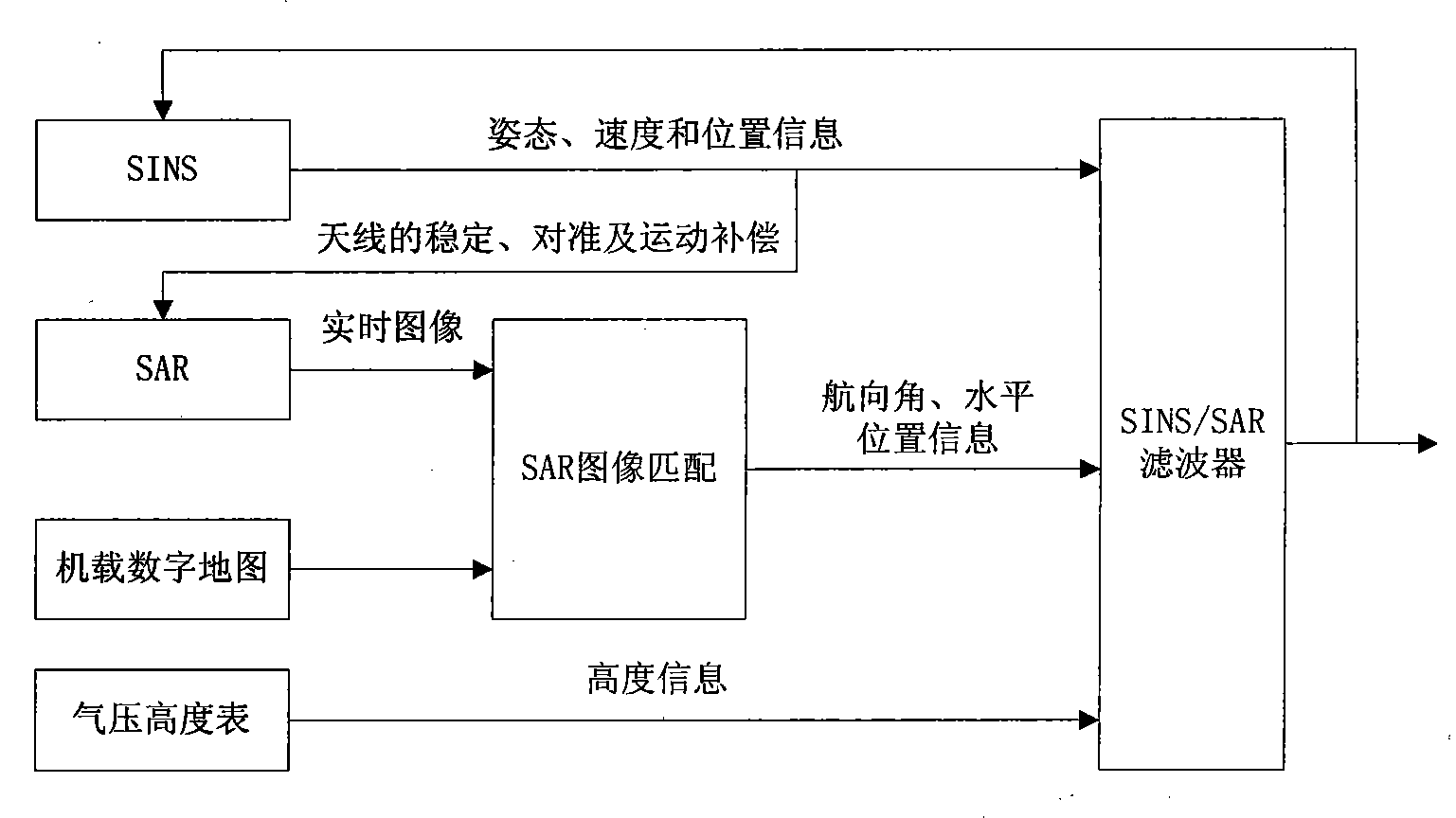
The invention relates to a remote high precision autonomous integrated navigation and positioning method, which is characterized in that a Strapdown Inertial Navigation System (SINS) is used as a main navigation system during the whole flight course of the aircraft, assisted by 3D high precision position and attitude angle information provided by celestial navigation system (CNS) based on the least square differential correction in boost phase (or middle segment). In reentry phase (terminal), using the characteristics of synthetic aperture radar (SAR), such as strong penetration capability, high resolving precision and all-weather, the SINS can be corrected through accurate location information and course information provided by SAR scene matching after motion compensation when the aircraft reentry into atmospheres, so the impact point (hit) accuracy of the aircraft can be increased and the invention has remarkable effects of eliminating or decreasing non-guidance error. The invention has advantages of autonomy and high precision, which can be used for improving remote ballistic missile, remote cruise missile, navigation and positioning accuracy of remote aircraft, such as long-endurance unmanned aerial vehicle, etc.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
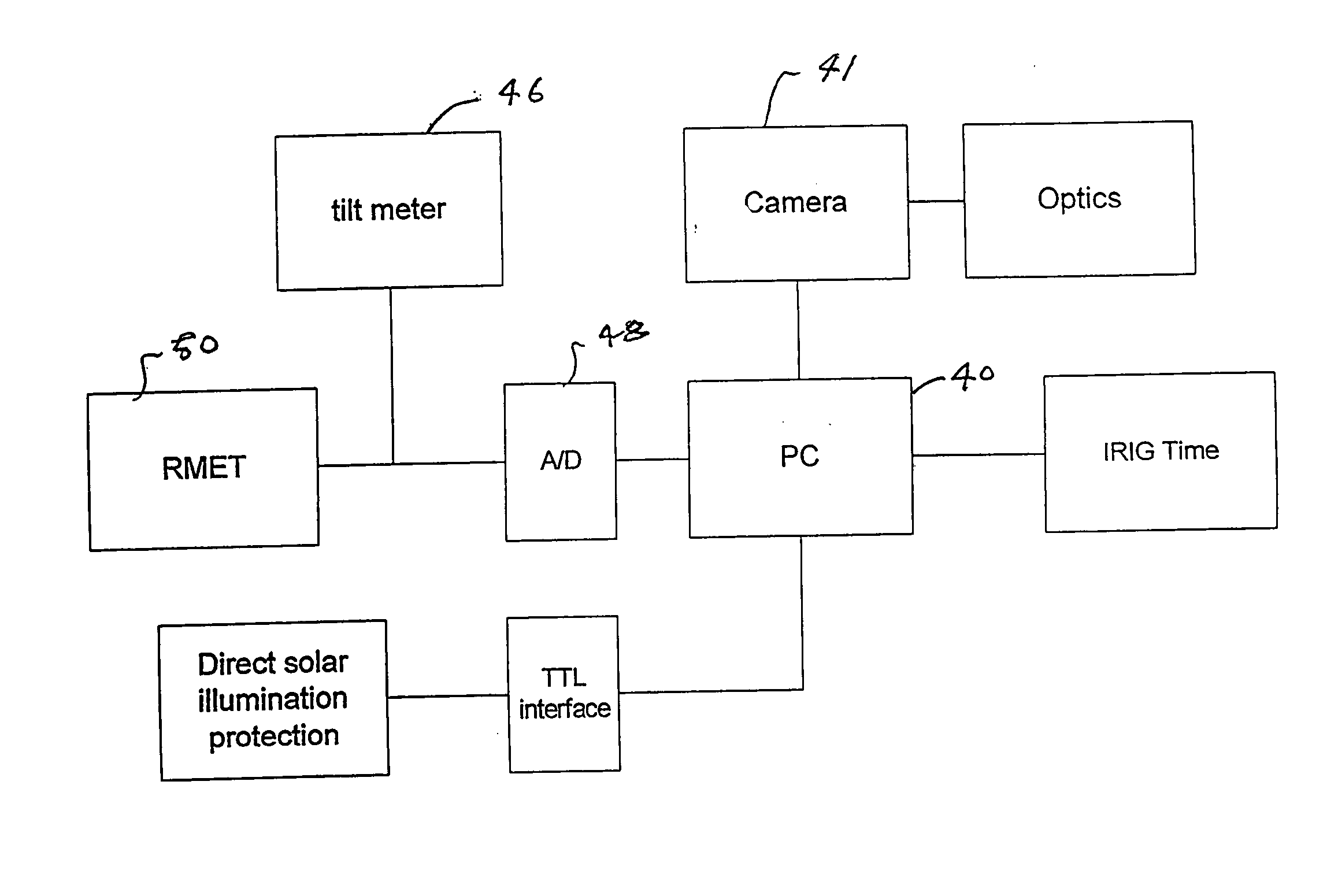
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS7349804B2Increase probabilityHighly preventive effectReactors manufactureNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDisplay deviceLongitude
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, inclination information from the inclinometer, time information from the timing device and the catalogued star charts information to determine positions of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to use this celestial position information to calculate latitude and longitude which may be displayed on a display device such as a monitor or used by a guidance control system. These embodiments are jam proof and insensitive to radio frequency interference. These systems provide efficient alternatives to GPS when GPS is unavailable and can be used for periodic augmentation of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS7349803B2Increase probabilityHighly preventive effectNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansJet aeroplaneSky
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. A preferred embodiment uses three telescopes with each of the three telescopes rigidly mounted with respect to each other and rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Telescope optics focuses, onto the pixel array of a sensor, H-band or K-band light from stars in the field of view of each telescope. The system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to cataloged infrared star charts.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Daytime stellar imager
InactiveUS20070038374A1Small and light systemAvoid star image blurCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsDisplay deviceLongitude
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes an inclinometer, an accurate timing device and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, inclination information from the inclinometer, time information from the timing device and the catalogued star charts information to determine positions of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to use this celestial position information to calculate latitude and longitude which may be displayed on a display device such as a monitor or used by a guidance control system. These embodiments are jam proof and insensitive to radio frequency interference. These systems provide efficient alternatives to GPS when GPS is unavailable and can be used for periodic augmentation of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Integrated navigation system applied to pilotless aircraft
InactiveCN101598557AImprove practicalityReduce mistakesInstruments for comonautical navigationAngular velocityNavigation system
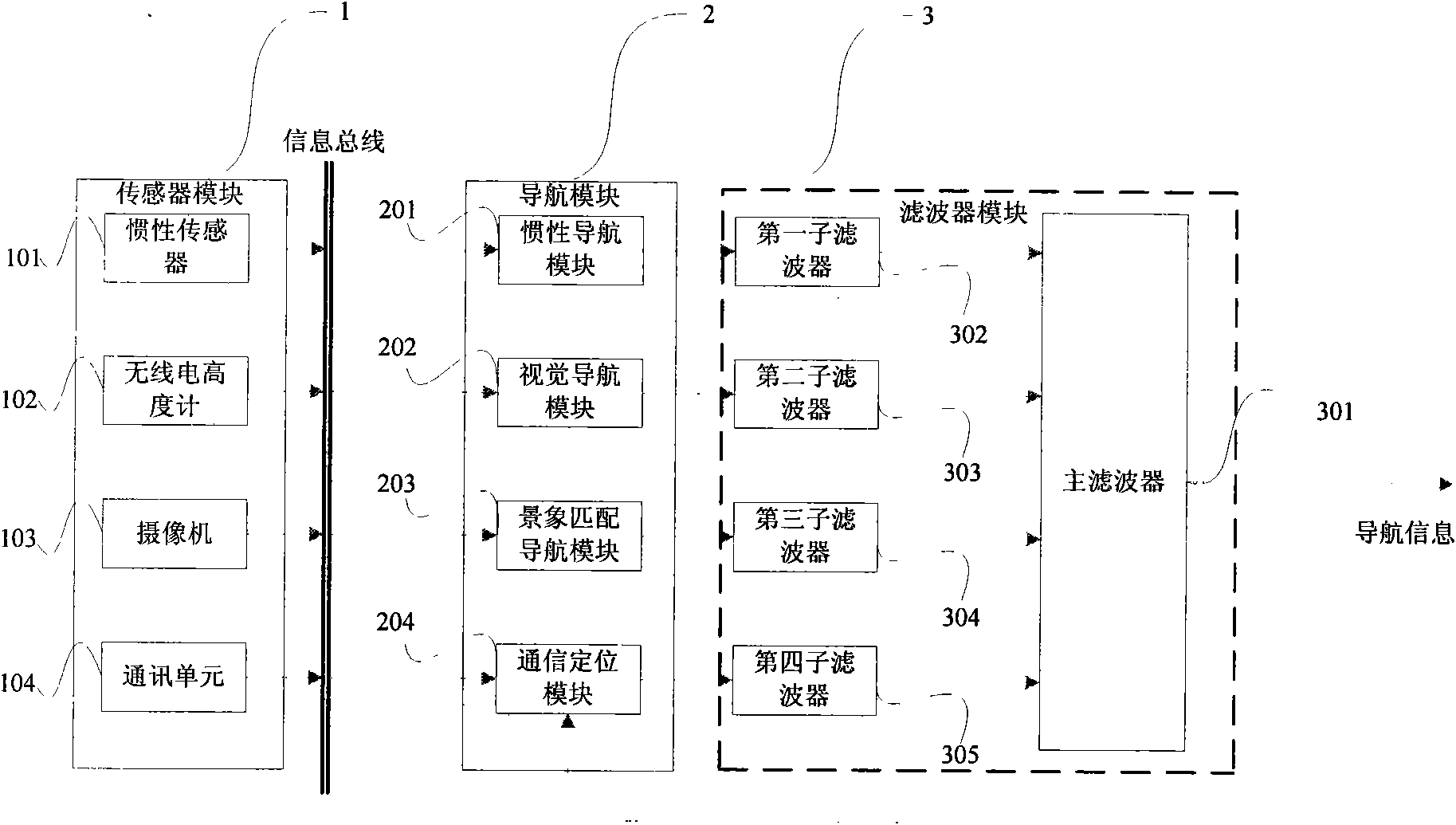
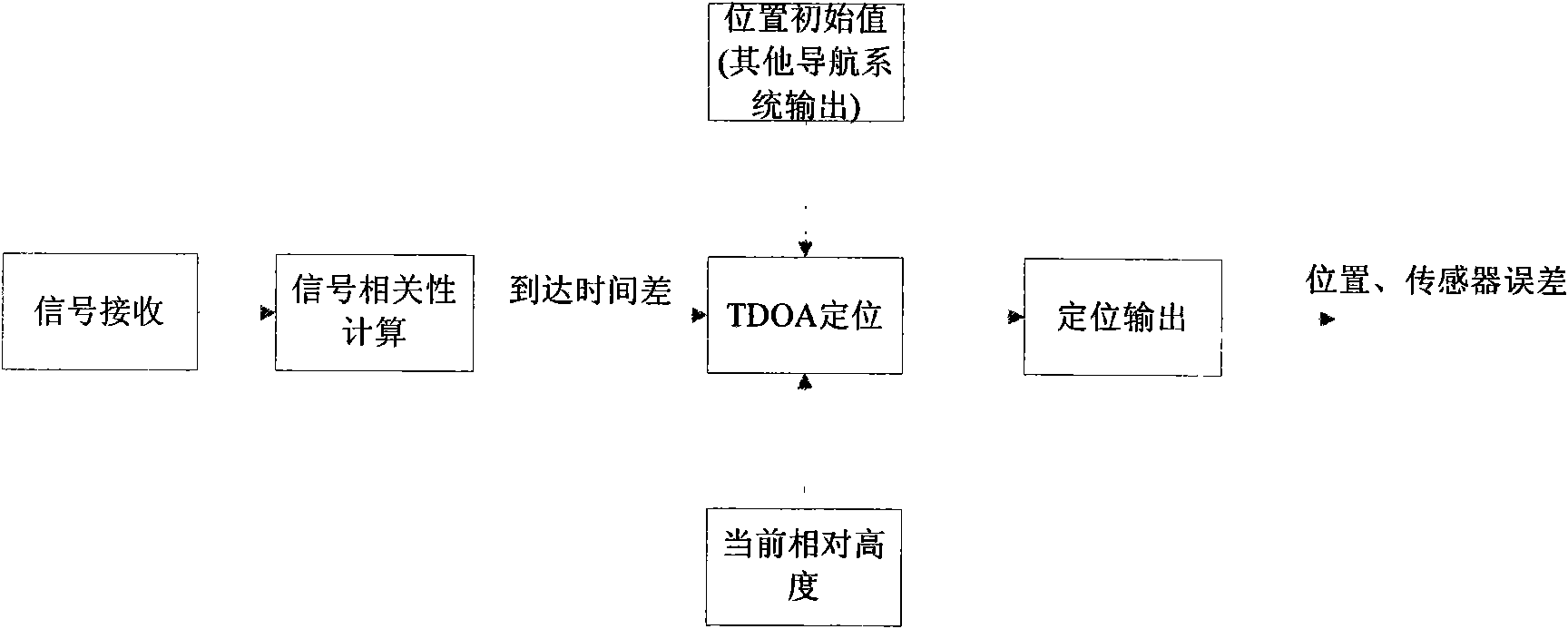
The invention discloses an integrated navigation system applied to a pilotless aircraft, which adopts a sensor comprising an inertial sensor, a radio altimeter, a communication module, a camera and the like, wherein the inertial sensor is used for acquiring motion acceleration and angular velocity of a carrier, and providing the motion acceleration and the angular velocity for an inertial navigation system and a vision navigation system in the unknown environment for setting up a system equation, thus further providing the current location information and matched trigger signals for scene matching navigation. The method integrates four combination ways which are inertial navigation, cellular wireless location navigation, vision navigation in the unknown environment and the scene matching navigation, and the four combination ways form each subsystem of the integrated navigation system and can be independently used for estimating the state of the aircraft; then, fault diagnosis and fusion estimation are carried out on the data output by the subsystems by a main filter, so that the accurate estimation of the state of the aircraft is obtained.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
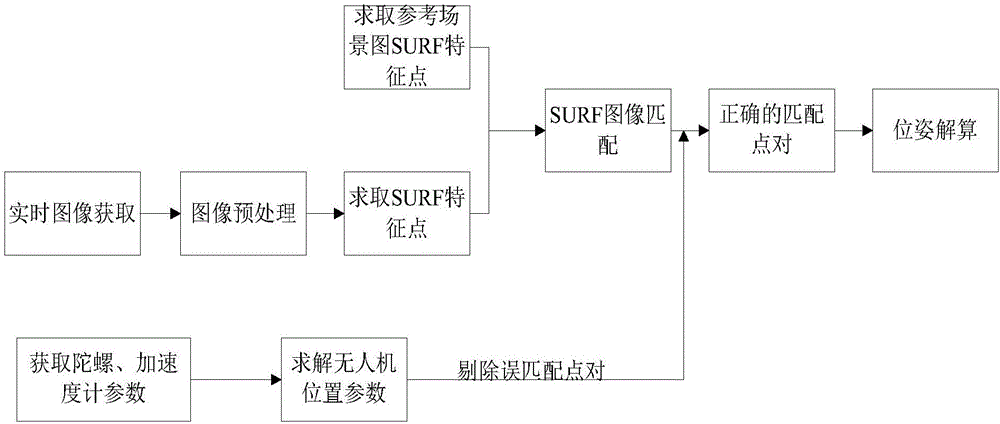
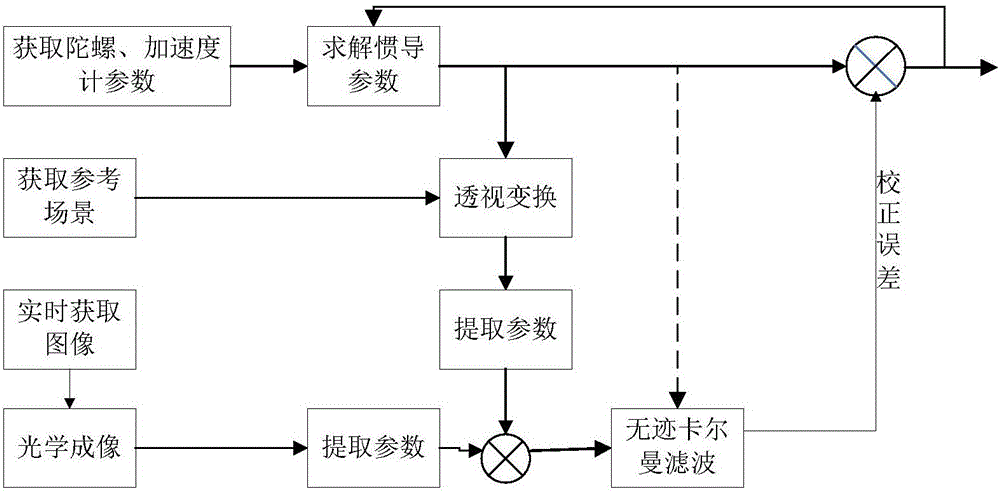
Autonomous landing method of unmanned aerial vehicle based on vision/inertial navigation
ActiveCN106708066AImprove real-time performanceQuick cullingNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPicture interpretationUncrewed vehicleReference image
The invention provides an autonomous landing method of an unmanned aerial vehicle based on vision / inertial navigation. The autonomous landing method comprises the following steps of firstly, utilizing a vision navigation algorithm to solve the location and poses of the unmanned aerial vehicle; then, utilizing the pose of the unmanned aerial vehicle solved by the vision navigation as an initial value of inertial navigation, and starting to solve the inertia navigation parameters; utilizing the parameters obtained from the adjacent period of inertial navigation to remove the false matching dot pairs of real-time images and reference images after SURF matching; finally, utilizing non-track Kalman filter combined with navigation parameters to adjust the poses of the unmanned aerial vehicle in real time to guide landing. The autonomous landing method has the advantages that the timeliness of the vision navigation algorithm is improved, and the vision system maintains high precision for a long time; the problem of failure to singly use the error dispersion of single inertial navigation is solved, and the carrier navigation parameters can be provided even if the vision navigation solution fails.
Owner:NO 20 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
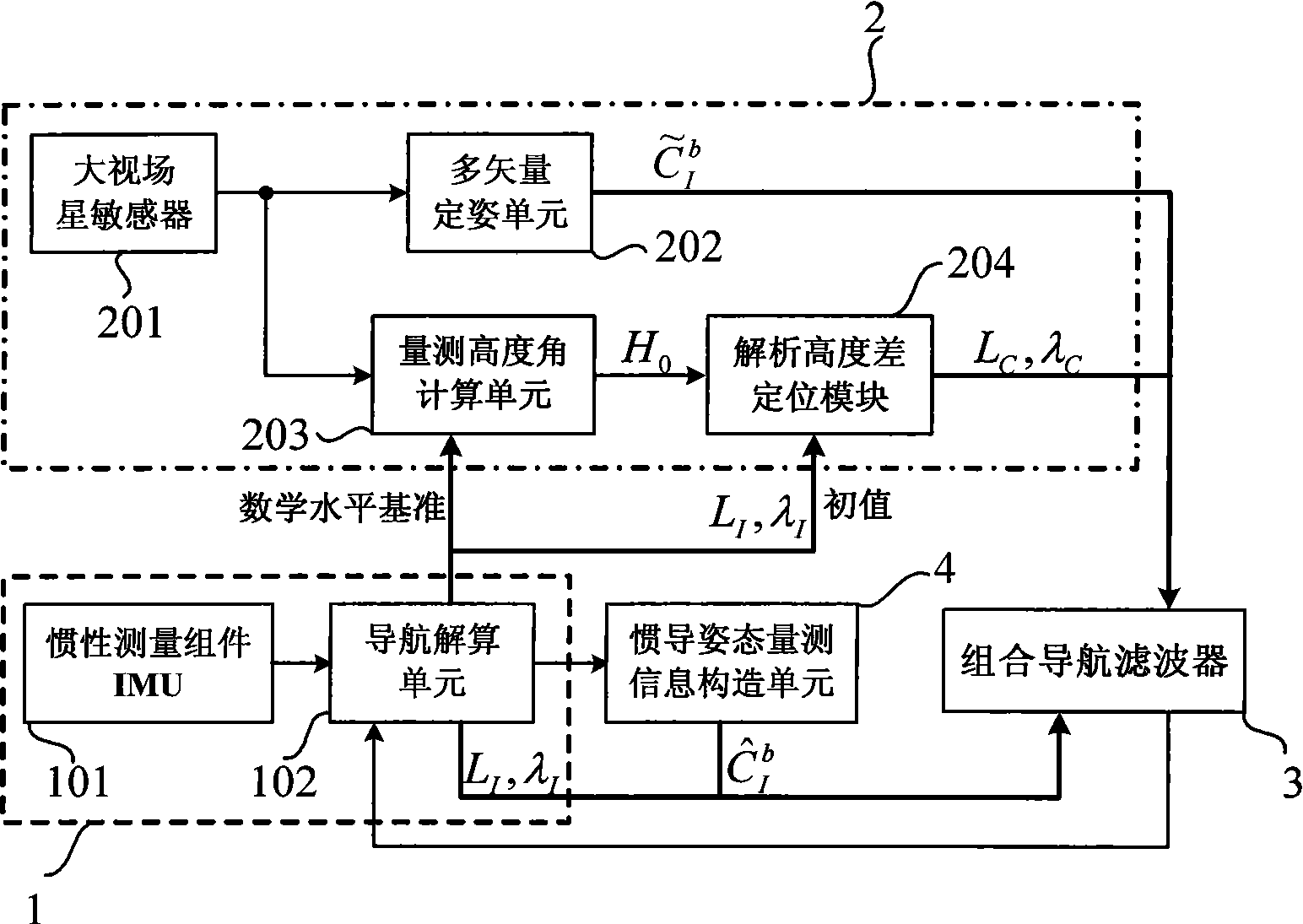
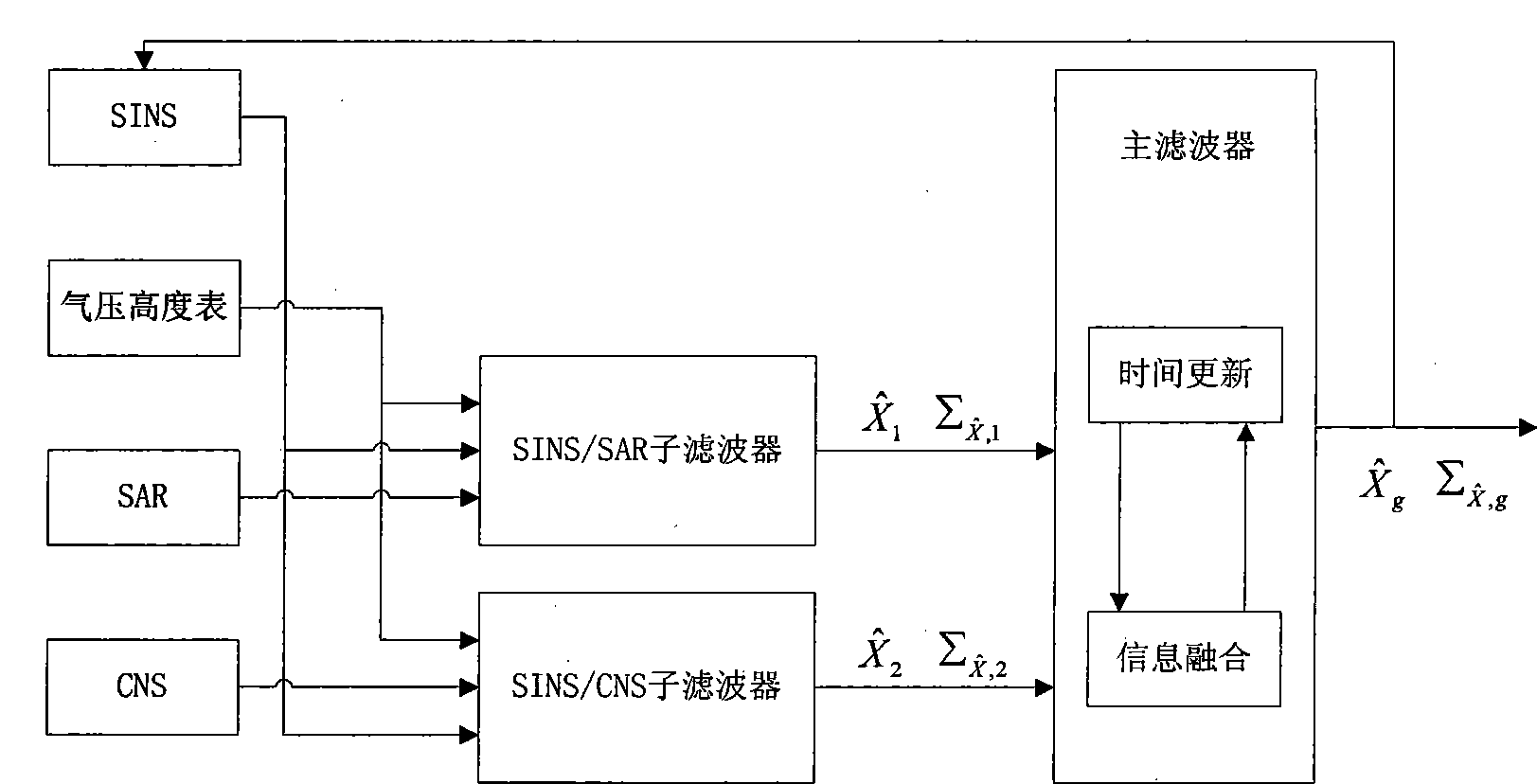
SINS/CNS deep integrated navigation system and realization method thereof
InactiveCN101788296AHigh precisionObserve and compensate drift in real timeNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDeep integrationNavigation system
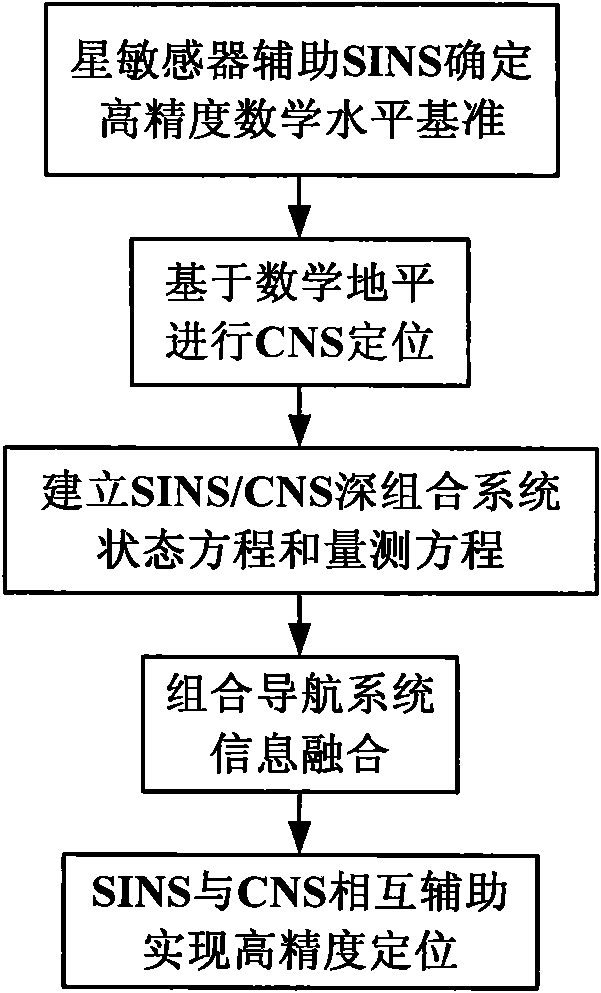
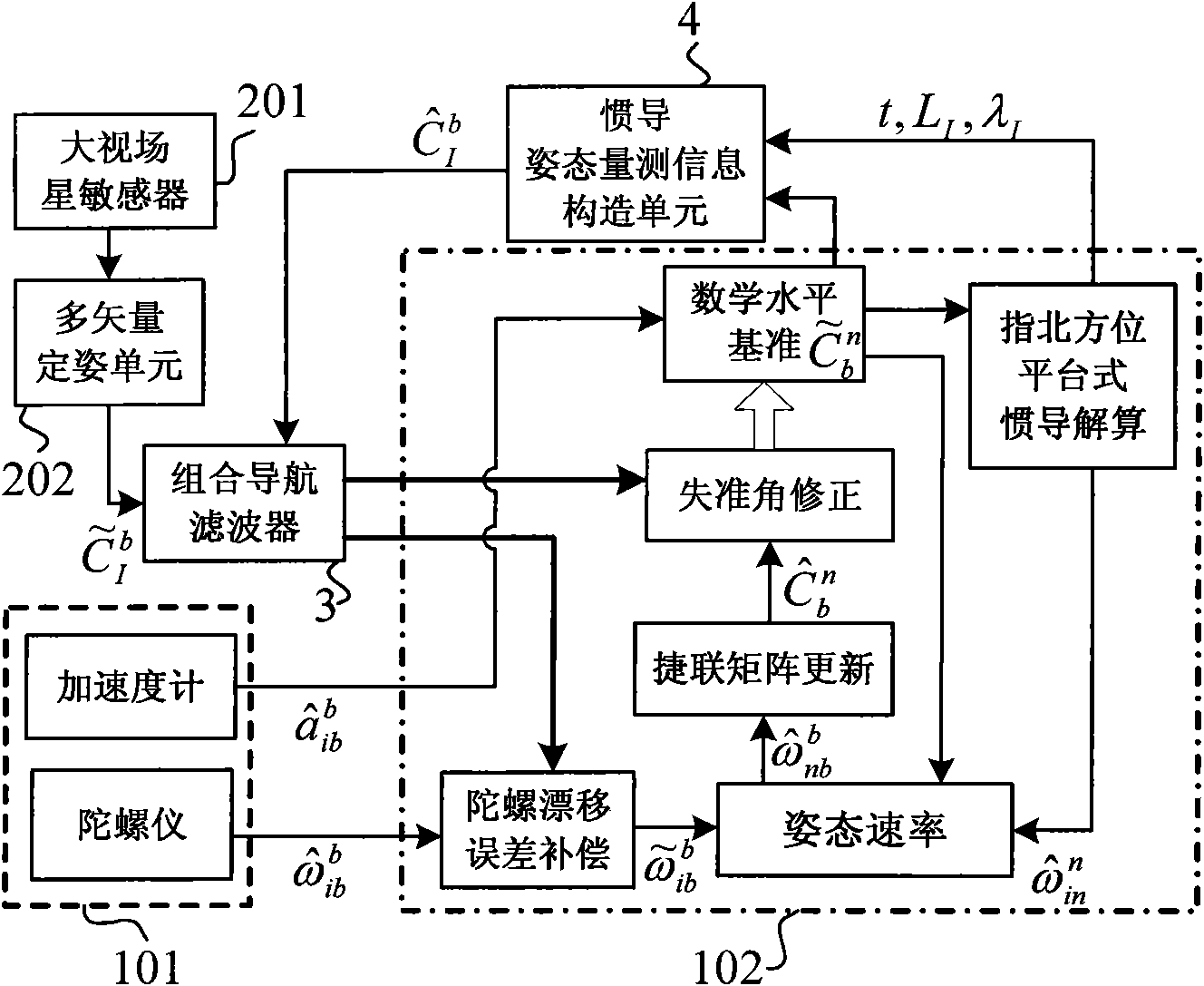
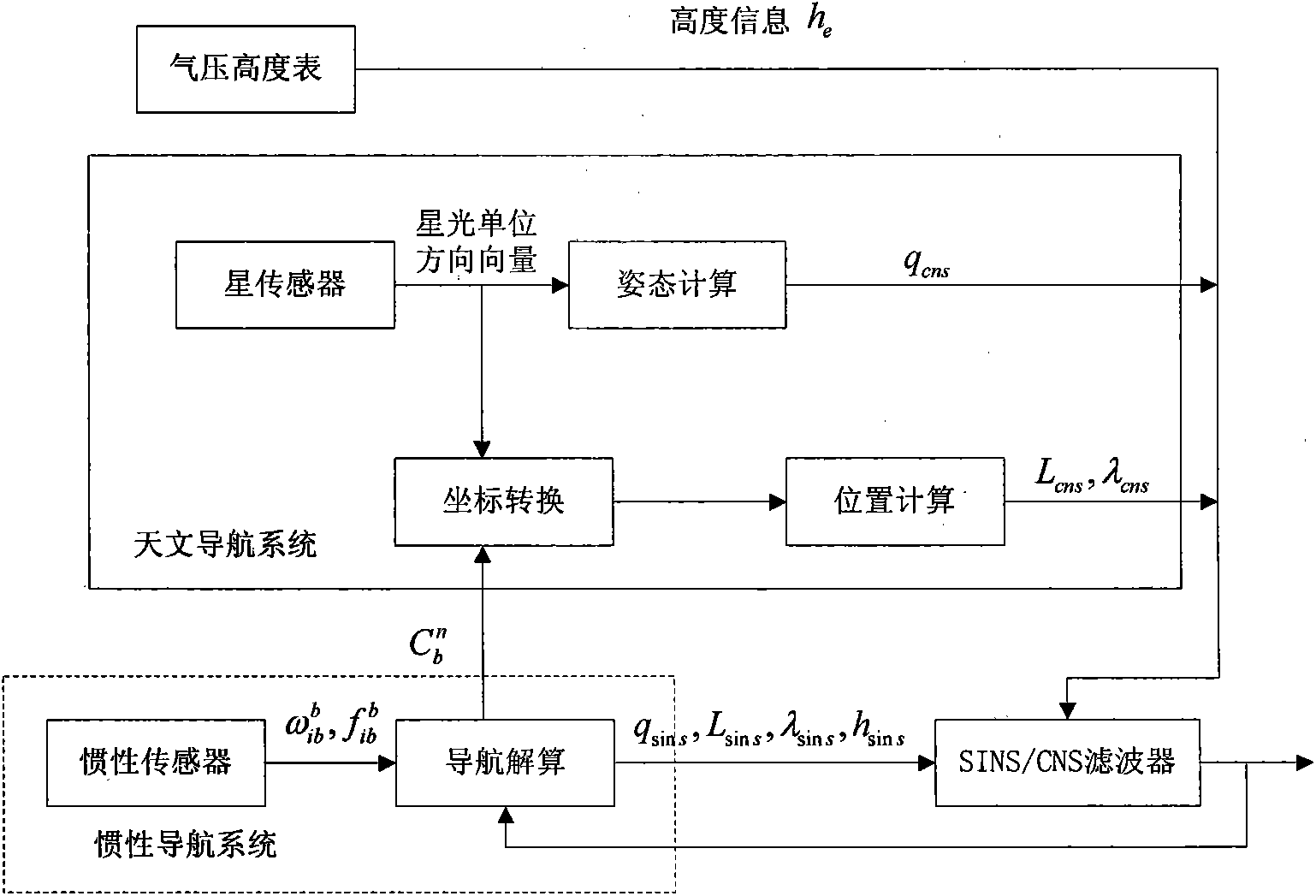
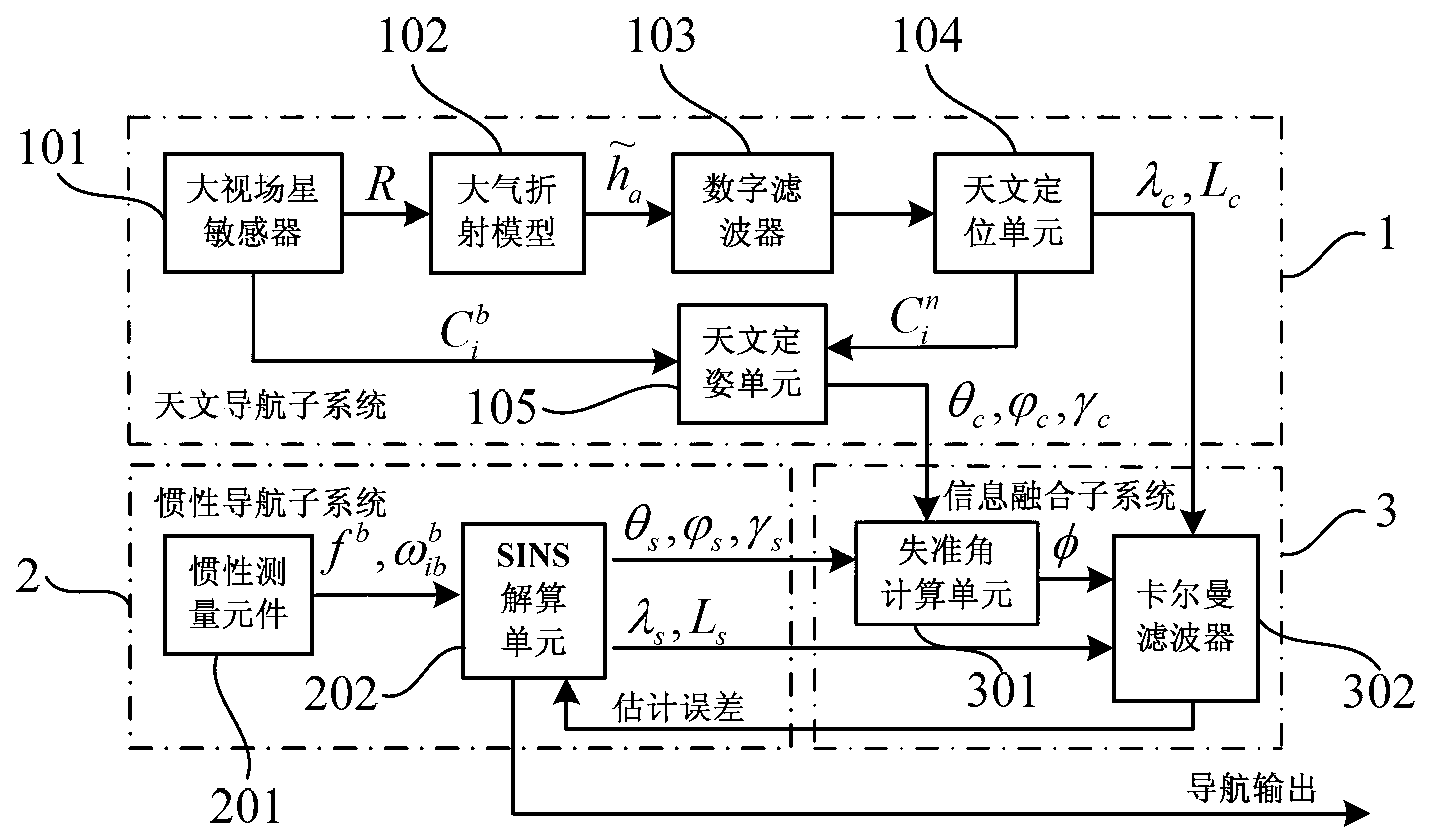
The invention discloses a SINS / CNS deep integrated navigation system and a realization method thereof. Wherein the navigation system comprises a strapdown inertial navigation system (SINS), a celestial navigation system (CNS), an integrated navigation filter, a inertial navigation posture measurement information structure unit; the realization unit comprises the following steps: 1. a large viewing field star sensor assists the strapdown inertial navigation system to obtain a high-precision mathematic horizontal reference; 2. CNS positioning is carried out based on the mathematic horizontal reference; 3. SINS / CNS deep integrated system model and measurement mode are established; 4. integrated navigation system information is fused; 5. the SINS and the CNS assists each other to realize high-precision positioning. In the invention, the star sensor high-precision posture information is employed to assist SINS to obtain high-precision SINS strapdown matrix which serves as the mathematic horizontal reference for CNS positioning, and on the basis, positions and postures of the CNS are employed to comprehensively calibrate the SINS, thus realizing SINS / CNS deep integration and finally achieving high-precision positioning and navigation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Autonomous integrated navigation system
InactiveCN103528587AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsSynthetic aperture radarCovariance
The invention relates to an autonomous integrated navigation system which belongs to the technical field of navigation systems. The SINS (Strapdown Inertial Navigation System) / SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) / CNS (Celestial Navigation System) integrated navigation system takes SINS as a main navigation system and SAR and CNS as aided navigation systems and is established by the following steps: firstly, designing SINS / SAR and SINS / CNS navigation sub-filters, calculating to obtain two groups of local optimal estimation values and local optimal error covariance matrixes of the integrated navigation system state, then transmitting the two groups of local optimal estimation values into a main filter by a federal filter technology for fusion to obtain an overall optimal estimation value and an overall optimal error covariance matrix, and finally, performing real-time correction on the error according to the overall optimal estimation value so as to obtain an optimal estimation fusion algorithm of the SINS / SAR / CNS integrated navigation system. The autonomous integrated navigation system, disclosed by the invention, is less in calculation amount and high in reliability, is applicable to aircrafts in near space, aircrafts flying back and forth in the aerospace, aircrafts for carrying ballistic missiles, orbit spacecrafts and the like, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Daytime stellar imager for attitude determination
InactiveUS20060085130A1Small and light systemAvoid star image blurInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationJet aeroplaneGuidance control
An automatic celestial navigation system for navigating both night and day by observation of K-band or H-band infrared light from multiple stars. In a first set of preferred embodiments three relatively large aperture telescopes are rigidly mounted on a movable platform such as a ship or airplane with each telescope being directed at a substantially different portion of sky. Embodiments in this first set tend to be relatively large and heavy, such as about one cubic meter and about 60 pounds. In a second set of preferred embodiments one or more smaller aperture telescopes are pivotably mounted on a movable platform such as a ship, airplane or missile so that the telescope or telescopes can be pivoted to point toward specific regions of the sky. Embodiments of this second set are mechanically more complicated than those of the first set, but are much smaller and lighter and are especially useful for guidance of aircraft and missiles. Telescope optics focus (on to a pixel array of a sensor) H-band or K-band light from one or more stars in the field of view of each telescope. Each system also includes a GPS sensor and a computer processor having access to catalogued infrared star charts. The processor for each system is programmed with special algorithms to use image data from the infrared sensors, position and timing information from the GPS sensor, and the catalogued star charts information to determine orientation (attitude) of the platform. Direction information from two stars is needed for locating the platform with respect to the celestial sphere. The computer is also preferably programmed to calculate further information which may be used by a guidance control system. These systems provide efficient alternatives to inertial navigation systems when such systems are too expensive and can be used for periodic augmentation and calibration of inertial navigation systems.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
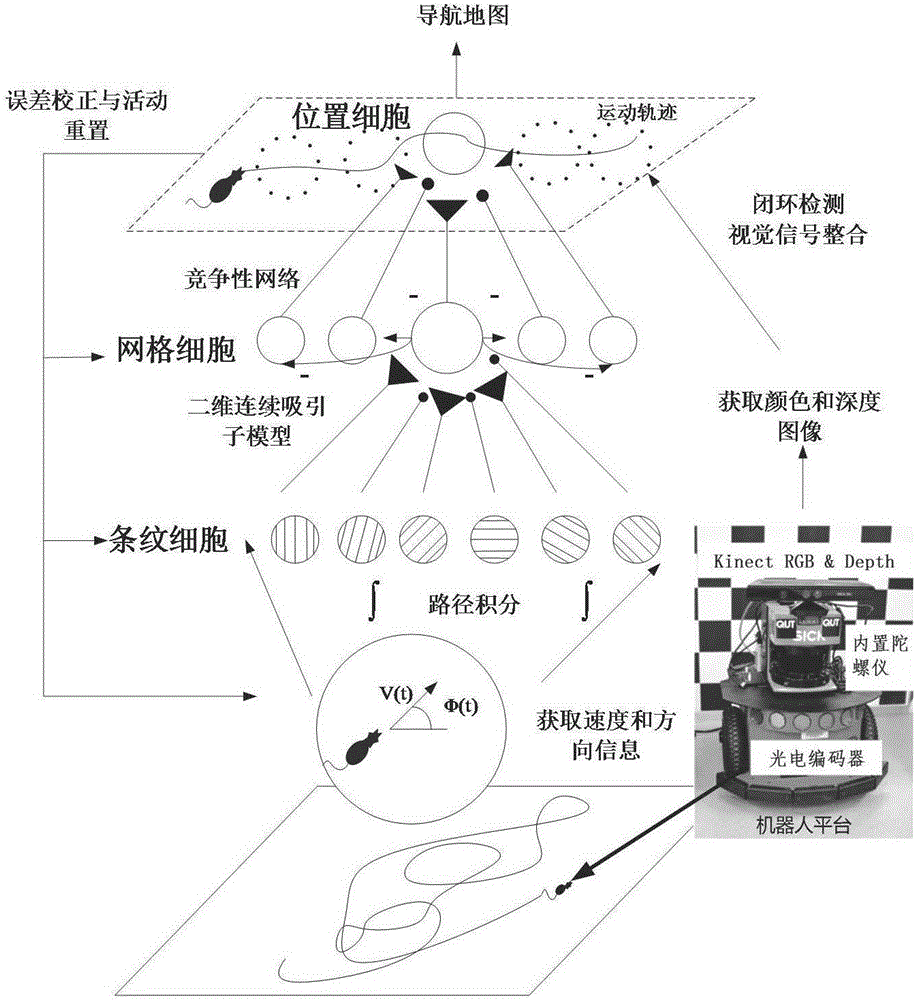
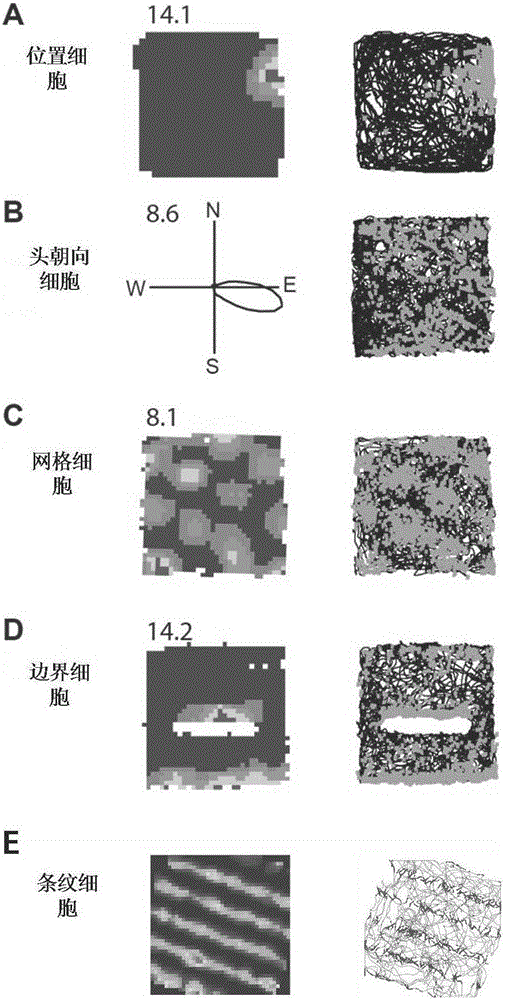
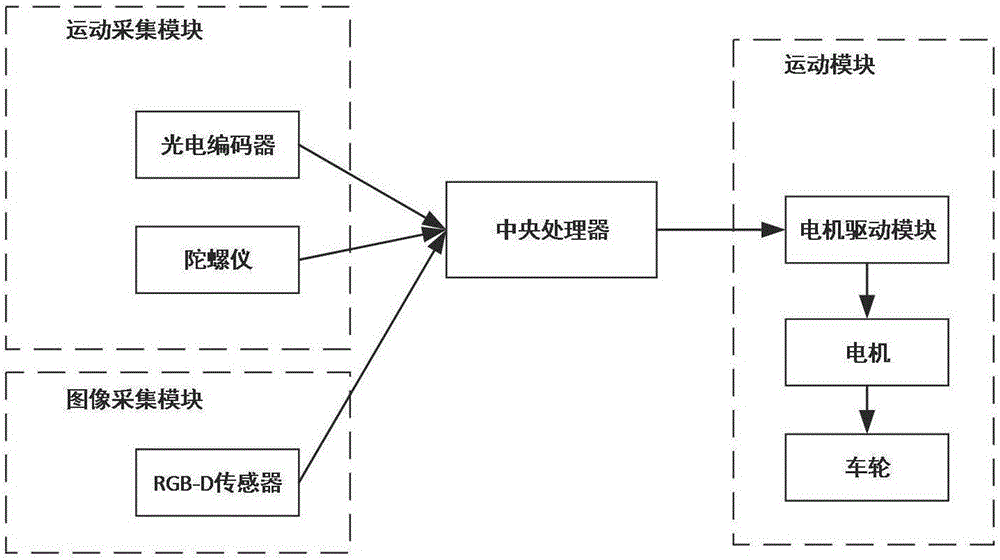
Robot navigation map construction method based on rat brain hippocampus spatial cells
The invention provides a robot navigation map construction method based on rat brain hippocampus spatial cells. According to an information transfer loop of spatial navigation related cells in a hippocampus structure of a mammal, a robot acquires a current autonomic movement clue and color depth image information through environment exploration. The autonomic movement clue progressively forms coding to the spatial environment through path integration and characteristic extraction of the spatial cells in the hippocampus structure. The place field of place cells is gradually formed in an exploration process and furthermore covers the whole spatial environment, thereby forming a cognitive map. Meanwhile, Kinect acquires color depth image information of a view scene right in front of the current position as an absolute reference for performing closed-loop detection on the path and correcting a path integration error. At a closed-loop point, a system resets spatial cell discharging activity and performs correction on the path integration error. Nodes on a final navigation map comprise place cell mass coding information, corresponding visual cues and place topological relationships.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
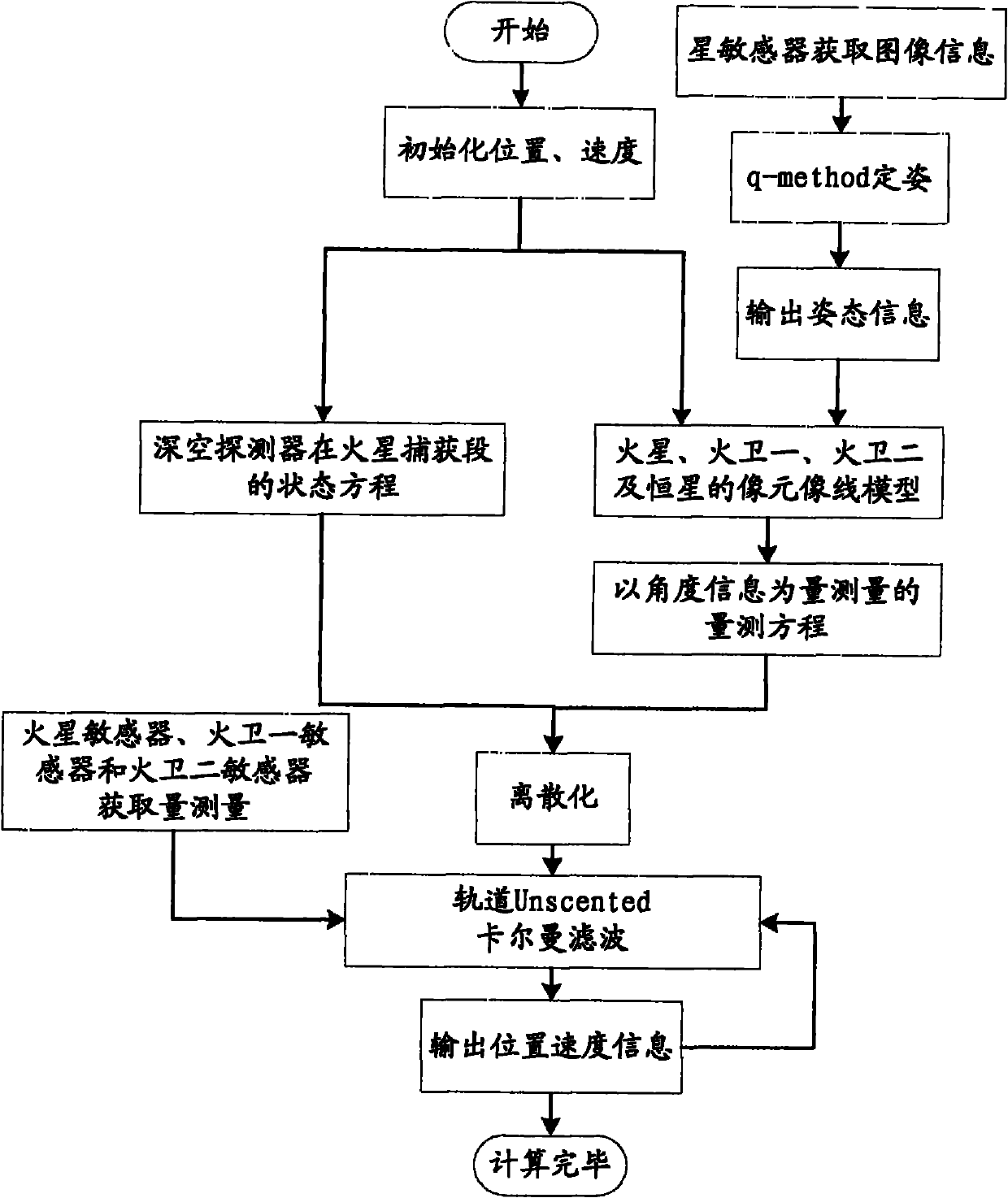
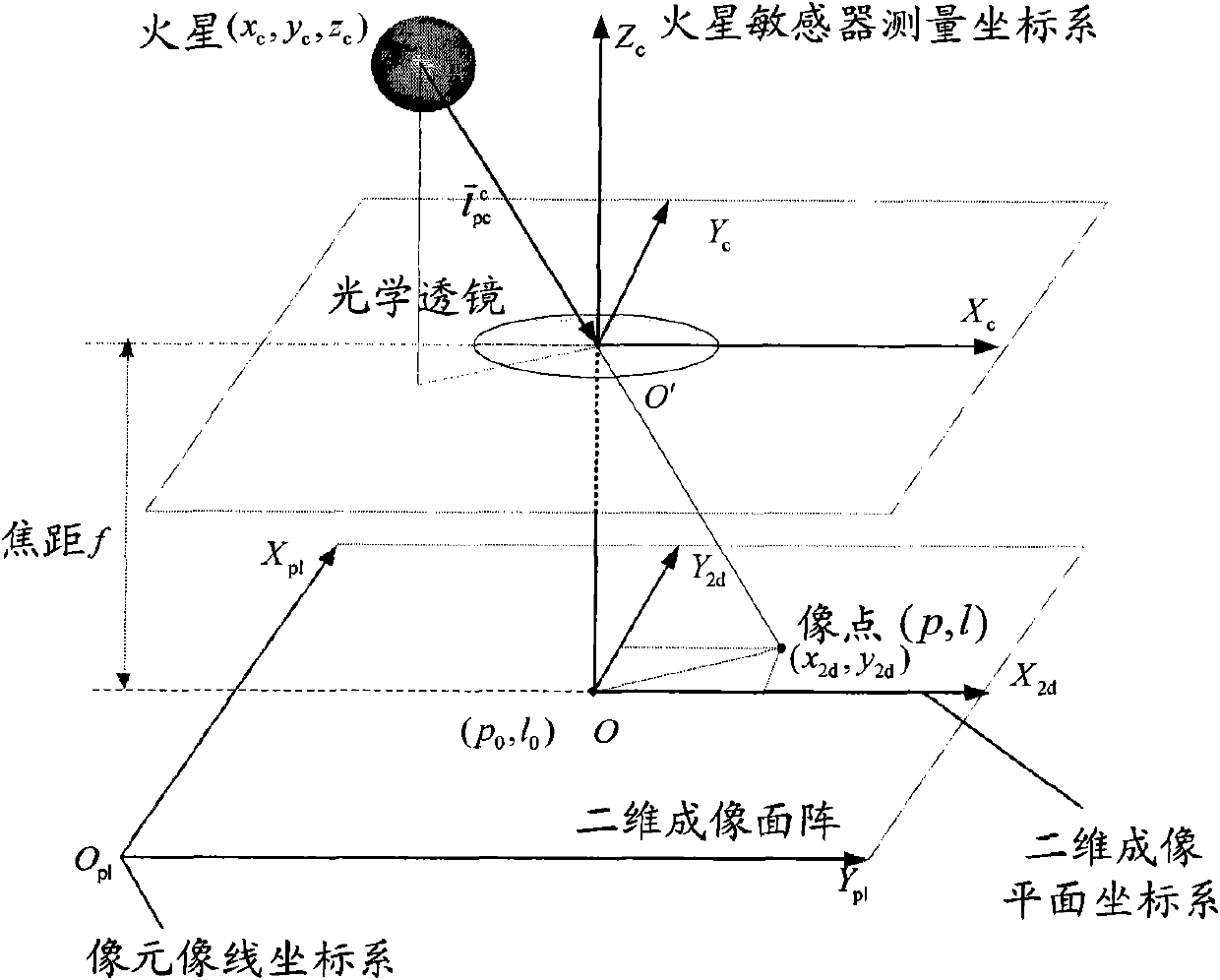
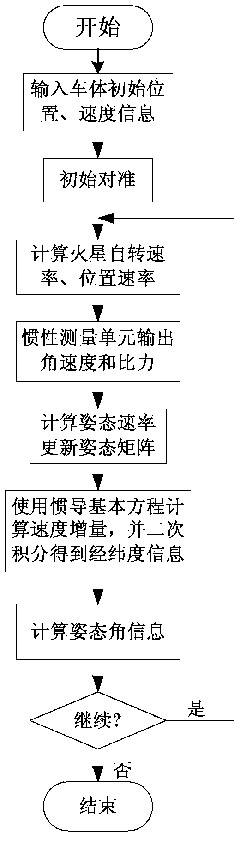
Independent celestial navigation method for Mars capturing section of deep space probe
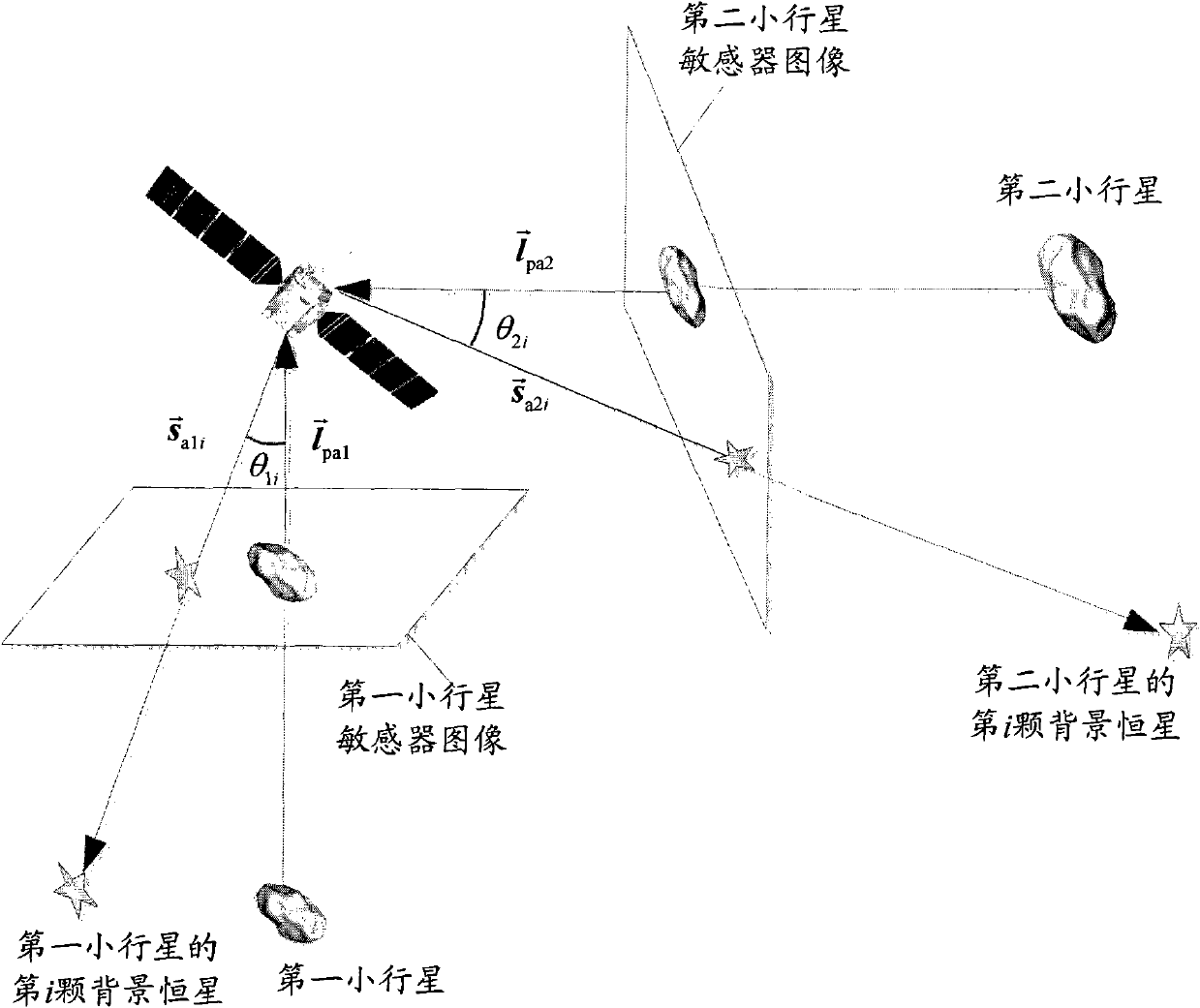
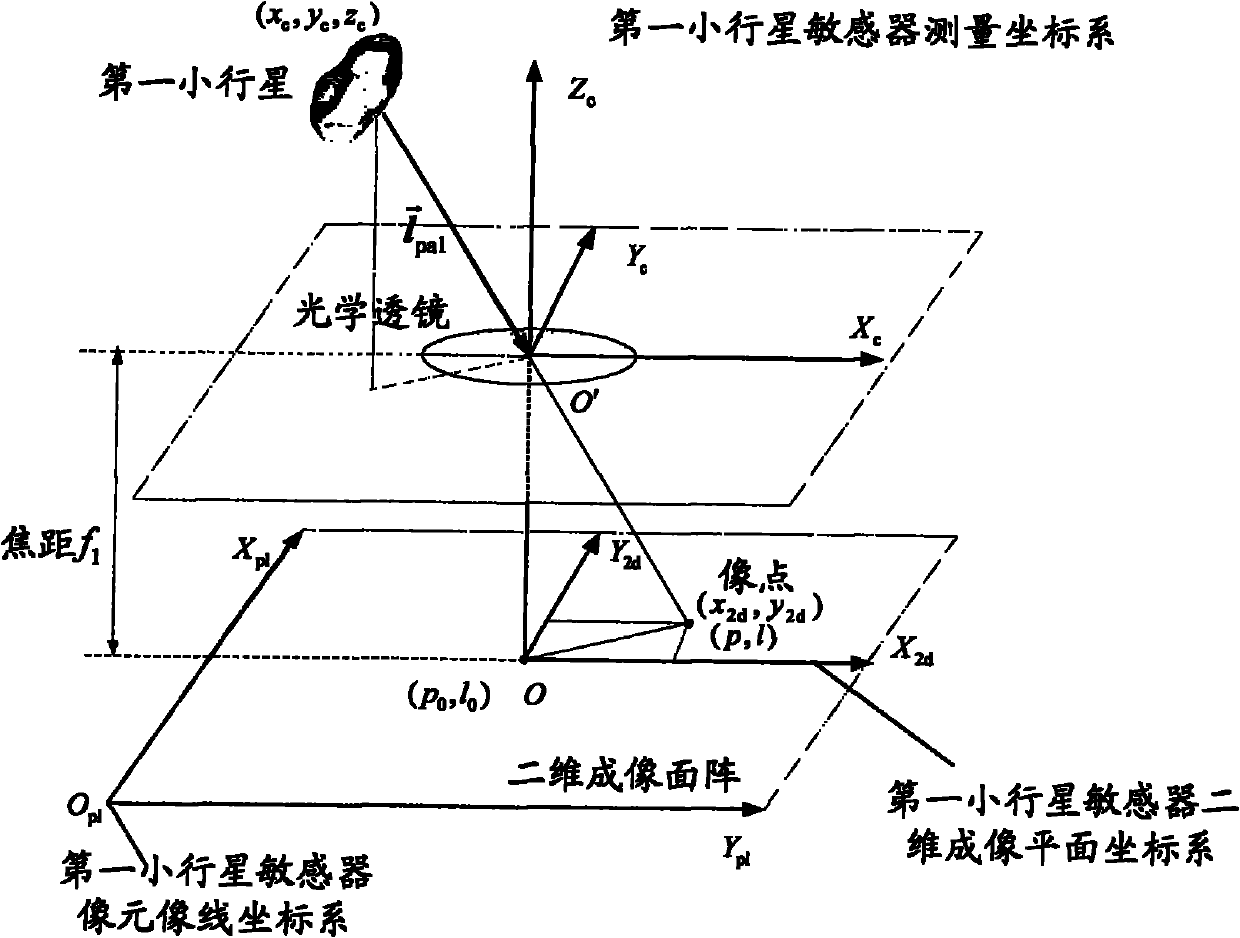
ActiveCN102168981AAvoid Accuracy ImpactImprove navigation accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationFixed starsDynamic models
The invention relates to an independent celestial navigation method for a Mars capturing section of a deep space probe. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a state model of the deep space probe according to a circular restrictive four-body track dynamics model; acquiring picture element and picture line information of Mars, Martian satellites and a background fixed star, converting the acquired picture element and picture line information into angle information of the Mars, the Martian satellites and the background fixed star and establishing an angle measuring model of the Mars, a Martian satellite I and a Martian satellite II; and estimating the attitude information of the probe by adopting a q-method and estimating the position and speed of the deep space probe in combination with Unscented Kallman filtering. The method has high estimation accuracy, and is very suitable for independent navigation of Mars capturing. The method belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation. By adopting the method, high-accuracy navigation parameters can be provided for Mars capturing of the deep space probe, and references can be provided for the design of an independent navigation system of the deep space probe.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
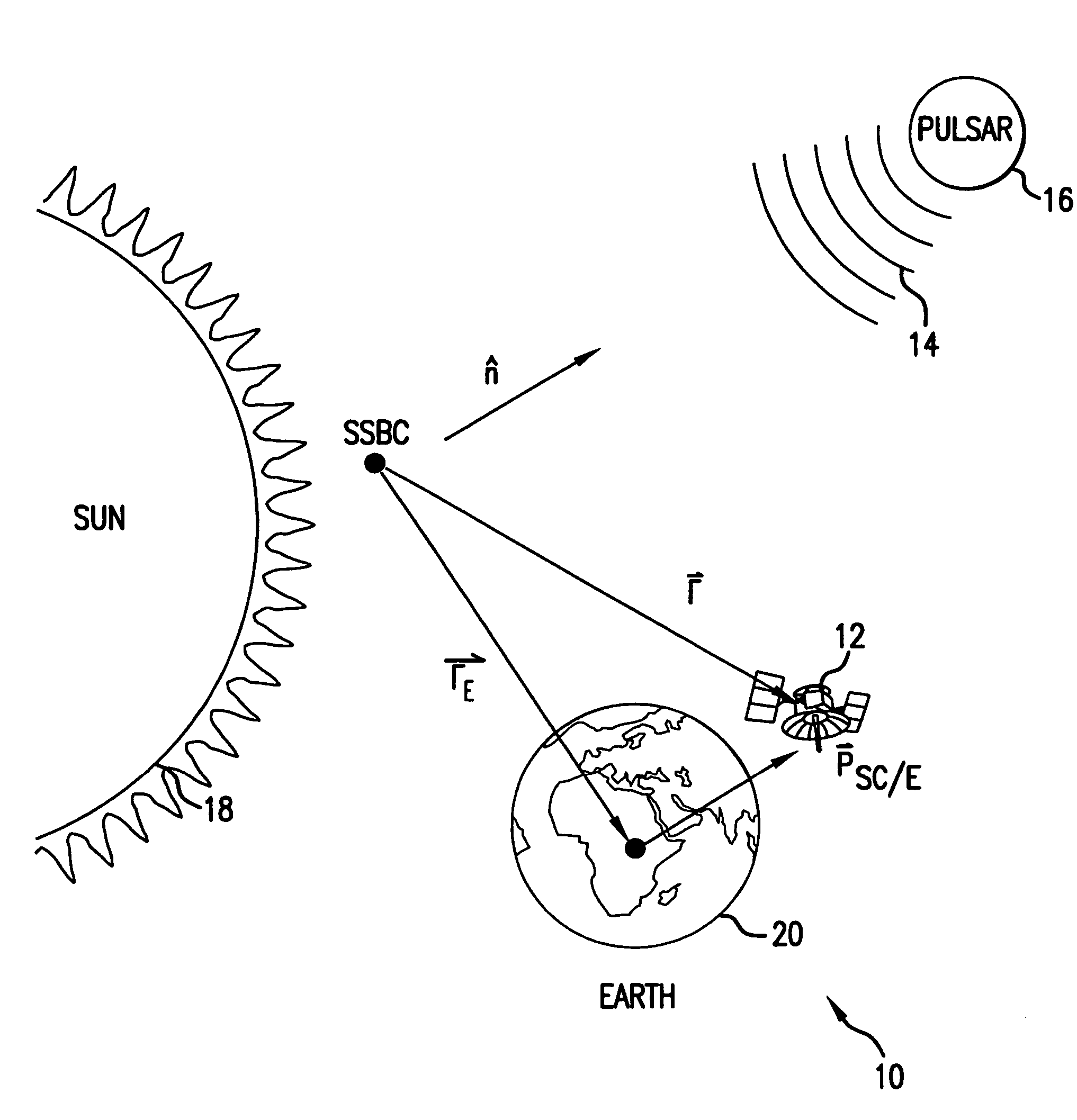
Navigational system and method utilizing sources of pulsed celestial radiation
A system and method for navigation utilizing sources of pulsed celestial radiation are provided. A spacecraft, satellite, or other vehicle (12) has a pulse sensor (22) mounted thereto for detecting signal pulses (14) generated by a plurality of pulsars or other celestial objects (16). The detected signal pulses (14) are synchronously averaged at the known period of the pulsar or other celestial object (16) with respect to a timer (24). Timer (24) measures the pulse time of arrival at the pulse sensor (22) by comparing the pulse signal (14) with a pulse shape template (52), and a processing means (30) calculates the offset time between the measured pulse time of arrival at sensor (22) with a calculated pulse time of arrival at the solar system barycenter (SSBC). The positions and pulse profile characteristics of the pulsars (16) are stored in a digital memory (34) and combining the calculated time offset with the known positions of pulsars (16), the navigational position, velocity, attitude and time of spacecraft (12) with respect to the SSBC can be calculated.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
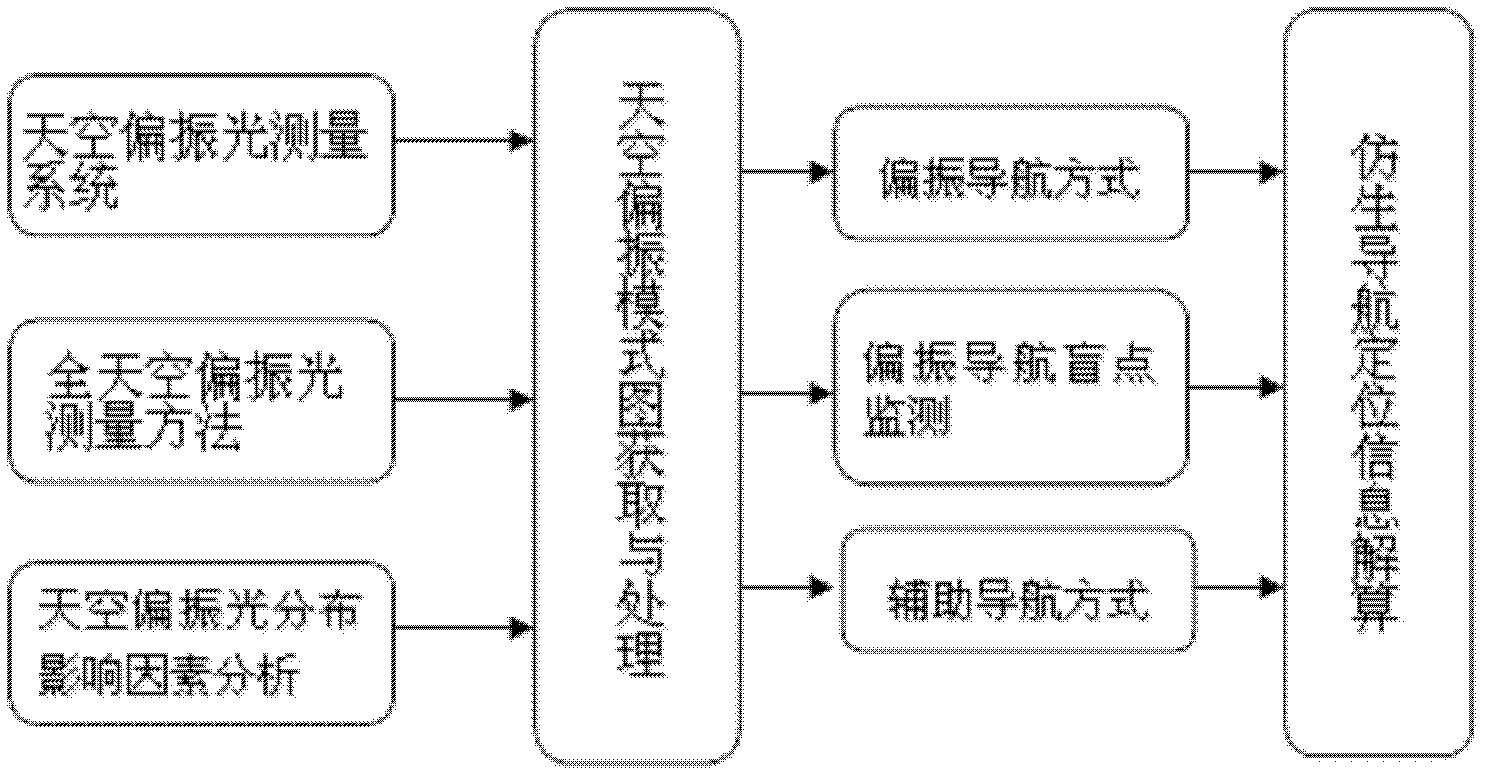
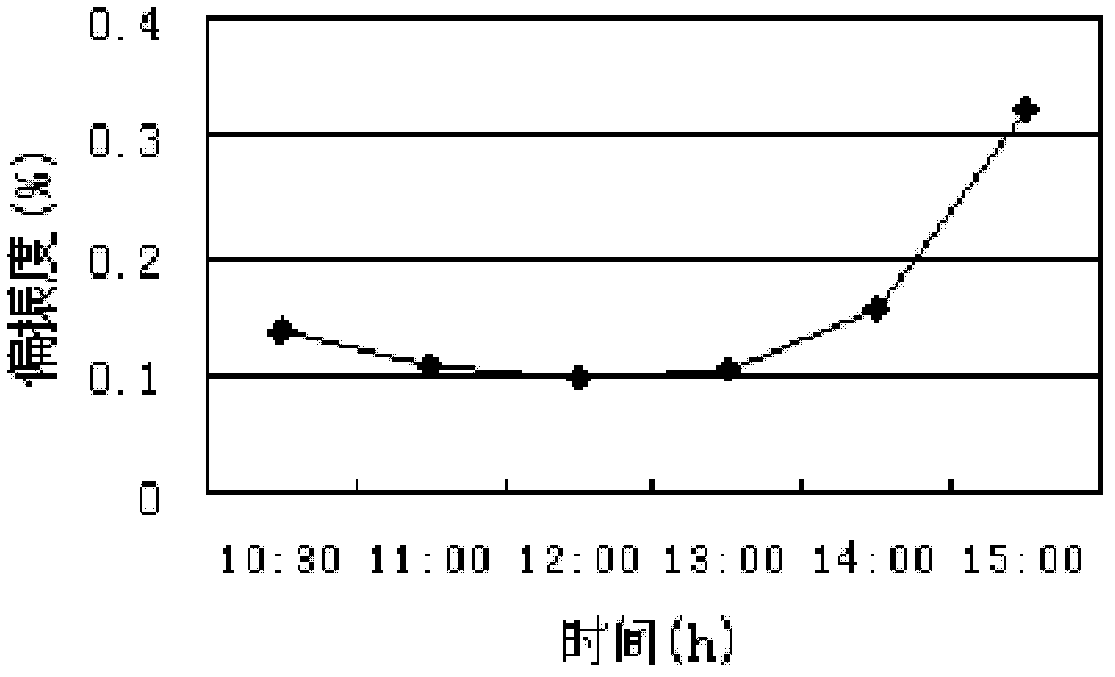
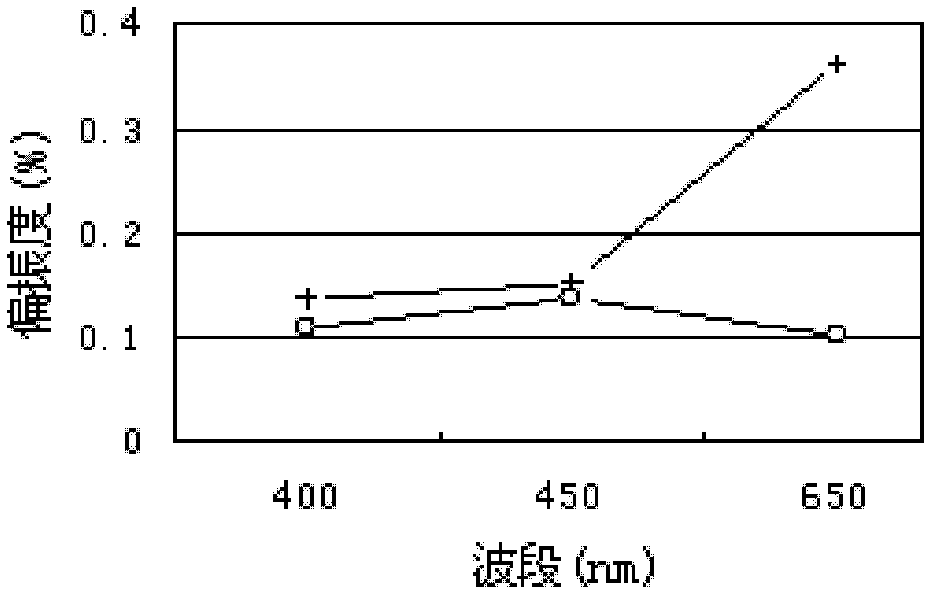
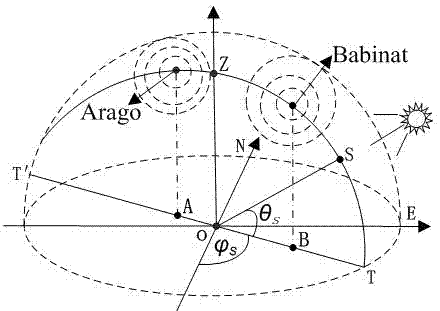
Bionic navigation method and navigation positioning system based on remote sensing sky polarization mode patterns
InactiveCN102538783AAvoid measurement time errorsGuaranteed accuracyNavigation instrumentsSkyGps navigation
The invention relates to a bionic navigation method and a navigation positioning system based on remote sensing sky polarization mode patterns. The method comprises the following steps: simultaneously measuring three images of light intensity of sky light by adopting a full-sky polarization remote sensing measurement method, and solving a polarization degree and a polarization azimuth angle which describe the polarization state of the sky light, thereby obtaining the remote sensing sky polarization mode patterns; analyzing each influence factor of the polarization degree and polarization azimuth angle in the remote sensing sky polarization mode patterns by adopting a full-sky polarization light measurement method, thereby obtaining the external conditions which are most suitable for polarization navigation; solving the sun azimuth angles at different time by combining celestial navigation theory knowledge, and amending the included angle between the sun meridian and a carrier by utilizing the sun azimuth angles, thereby obtaining a course angle taking geographical north and south as the reference directions; and processing the polarization navigation blind spot by adopting the combined navigation mode of a GPS (global positioning system) navigation mode and a polarization navigation mode. The bionic navigation method and navigation positioning system based on remote sensing sky polarization mode patterns can be widely applied to the measurement and research of navigation positioning under different conditions, and is a special new technology which enables the remote sensing observation image to serve the navigation positioning method and system by utilizing the bionic means.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
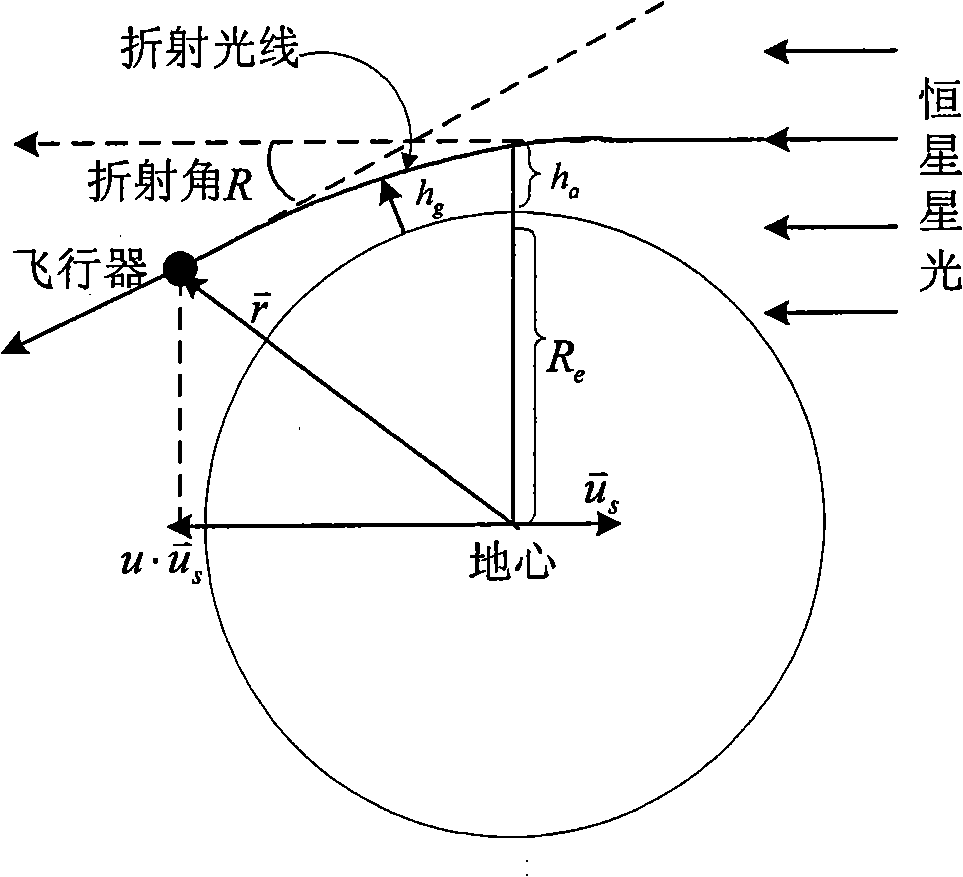
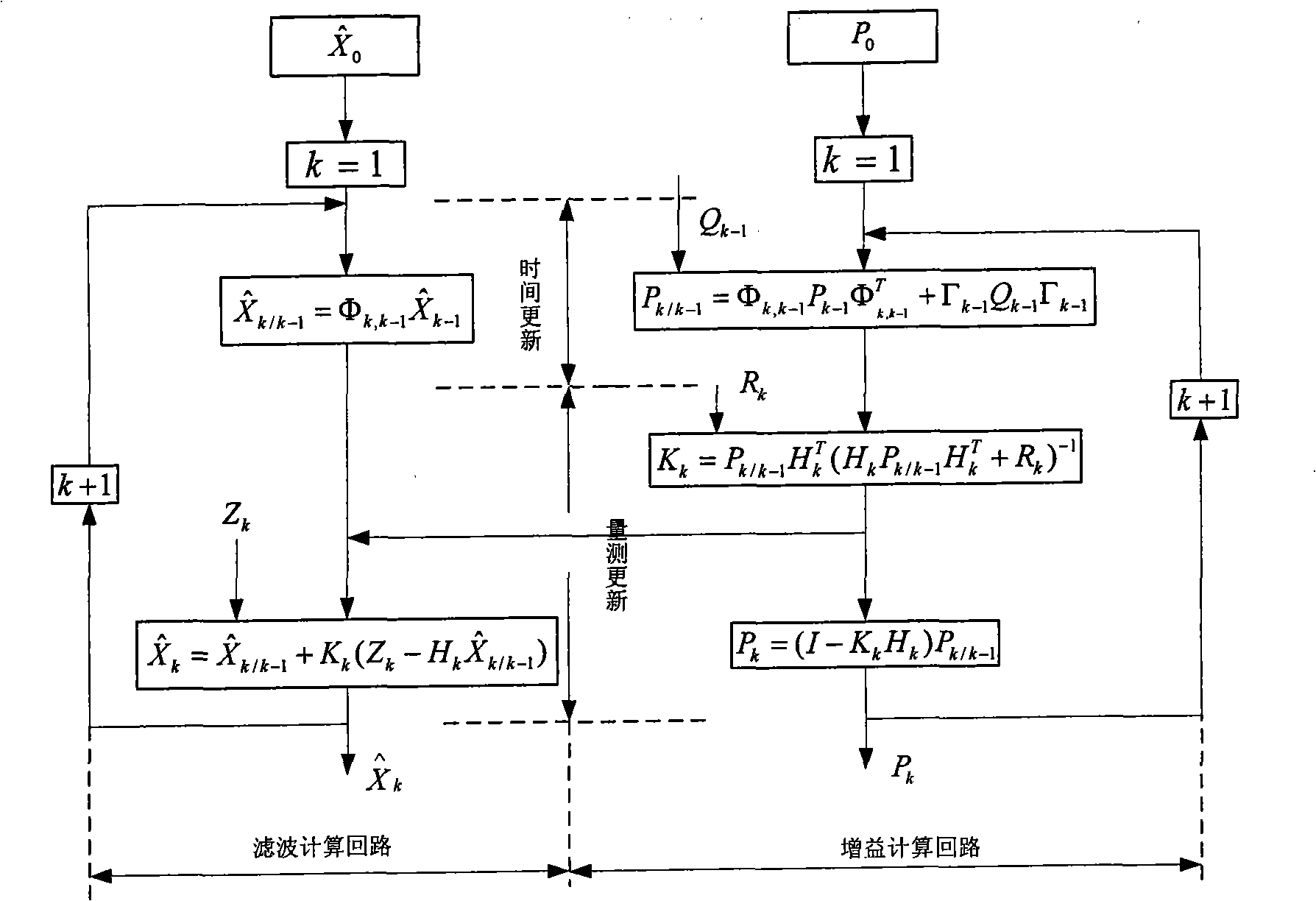
SINS/CNS integrated navigation system based on comprehensive optimal correction and navigation method thereof
InactiveCN103076015ARealize analytical astronomical positioningHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsHorizon
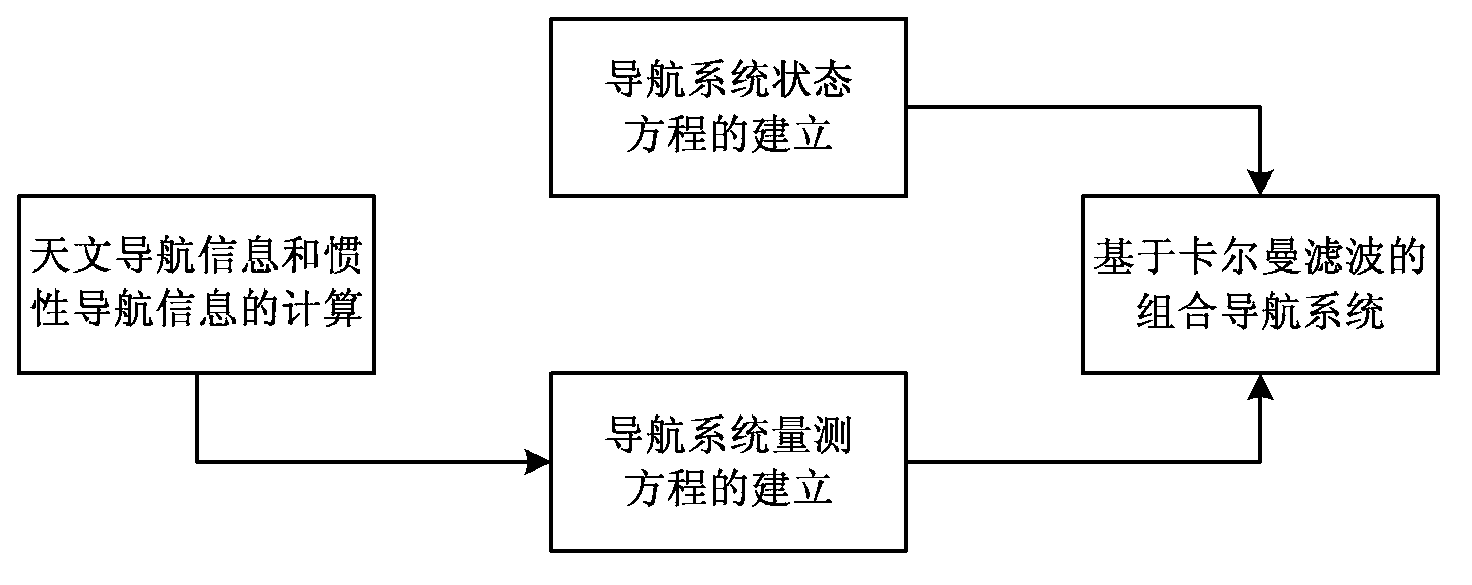
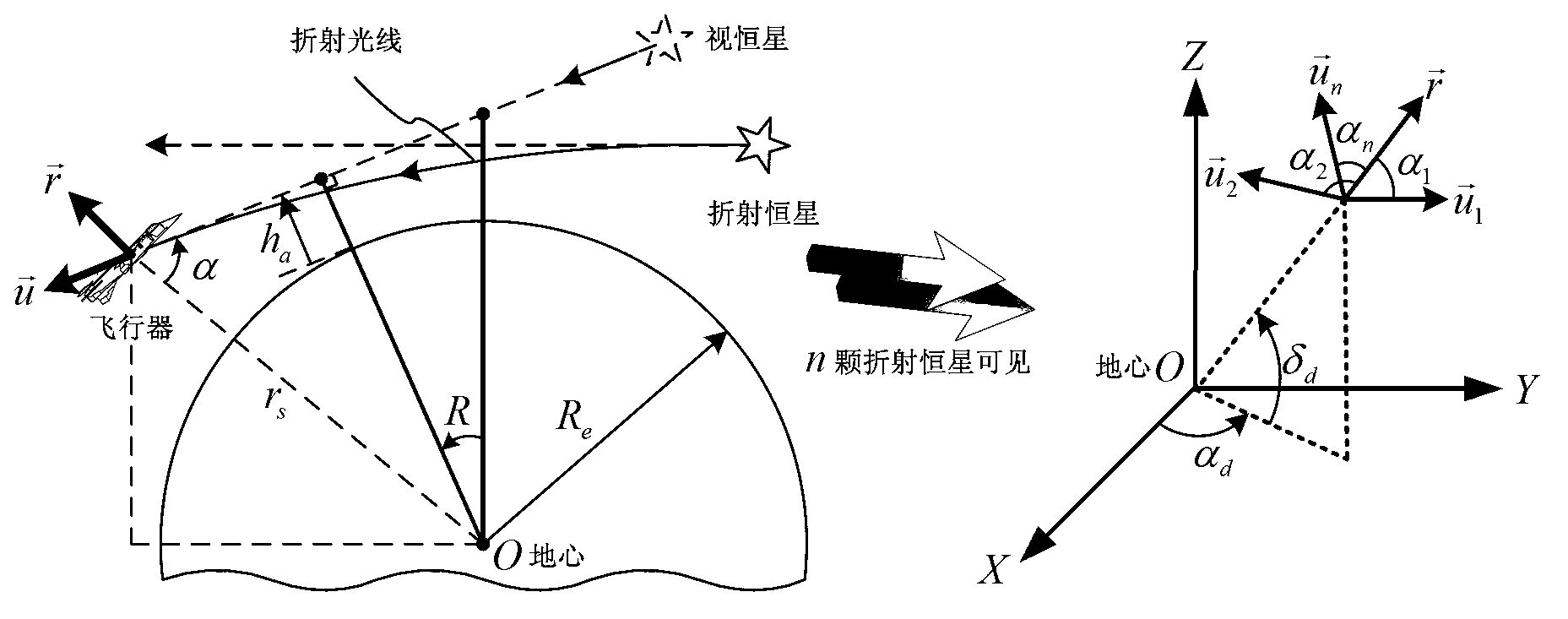
The invention provides an SINS / CNS integrated navigation system based on comprehensive optimal correction and a navigation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of integrated navigation. The integrated navigation system comprises an astronavigation subsystem, an inertia navigation subsystem and an information fusion subsystem. The navigation method comprises the following steps: analyzing celestial fix based on starlight refraction, building up navigation system state equations, building up navigation system measuring equations and performing information fusion of an integrated navigation system based on Kalman filtering. According to the invention, by utilizing the basic principle of starlight refraction indirection sensitive horizon and a large viewing field star sensor, the characteristics of a plurality of fixed stars can be observed at the same time, and the starlight refraction indirection sensitive horizon method is applied to aircrafts that do not fulfill track kinetics, so that the problem of high-precision autonomous horizon of the celestial navigation system is solved. According to the invention, position and posture information of the celestial navigation system are fully utilized to perform comprehensive optimal correction on the SINS deviation, so that the integrated navigation accuracy is significantly improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
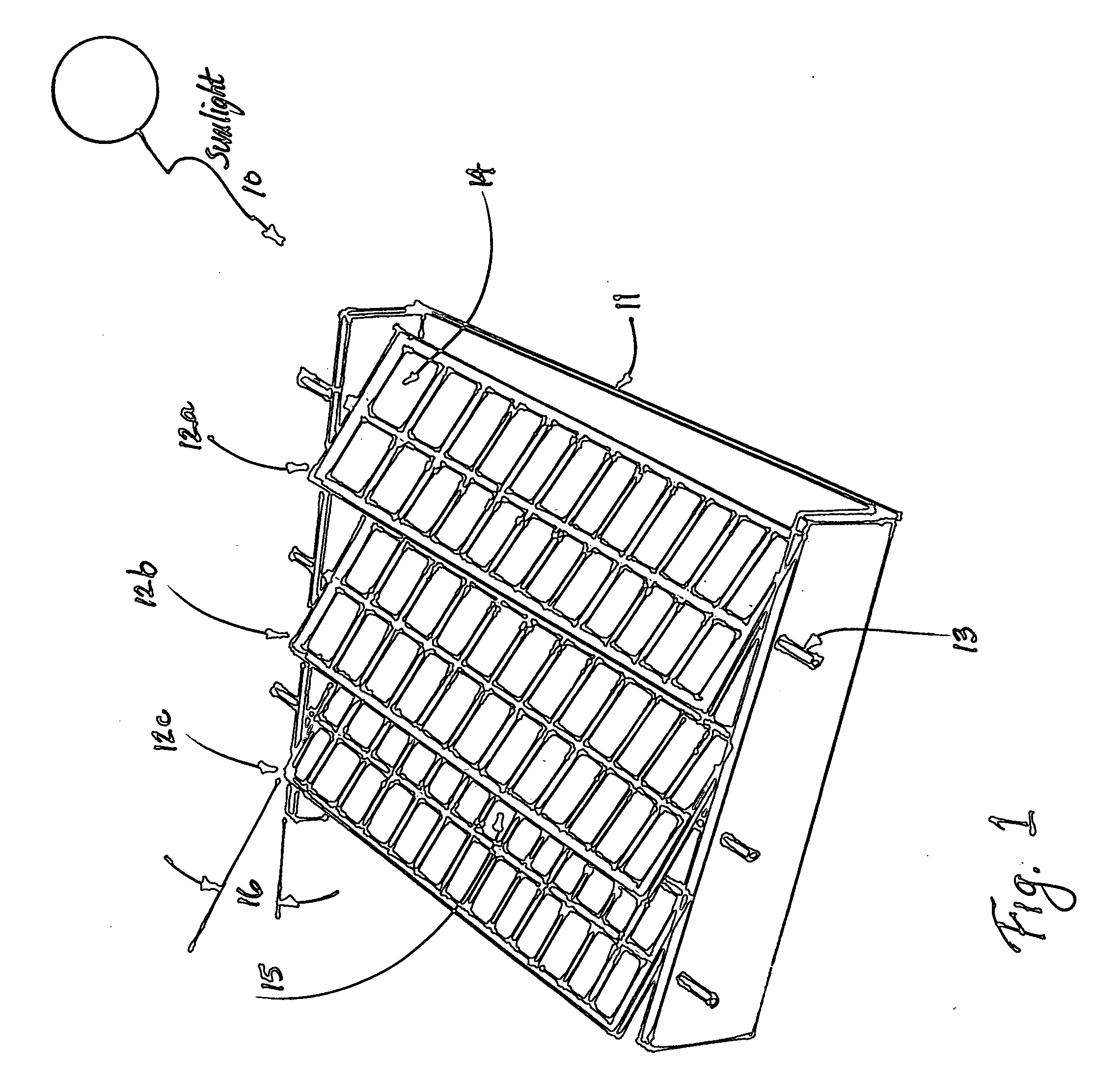
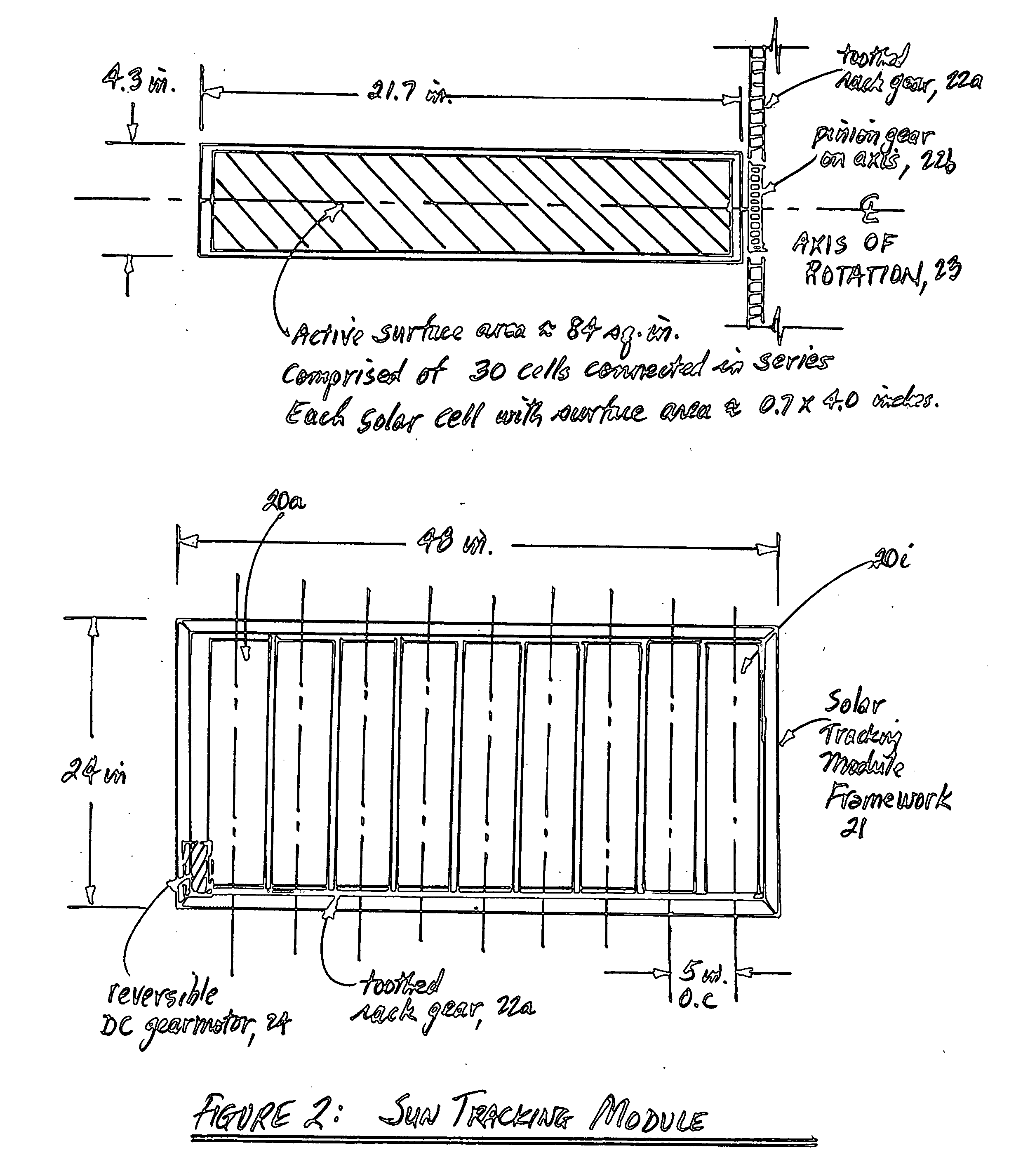
Method and apparatus for solar panel tracking
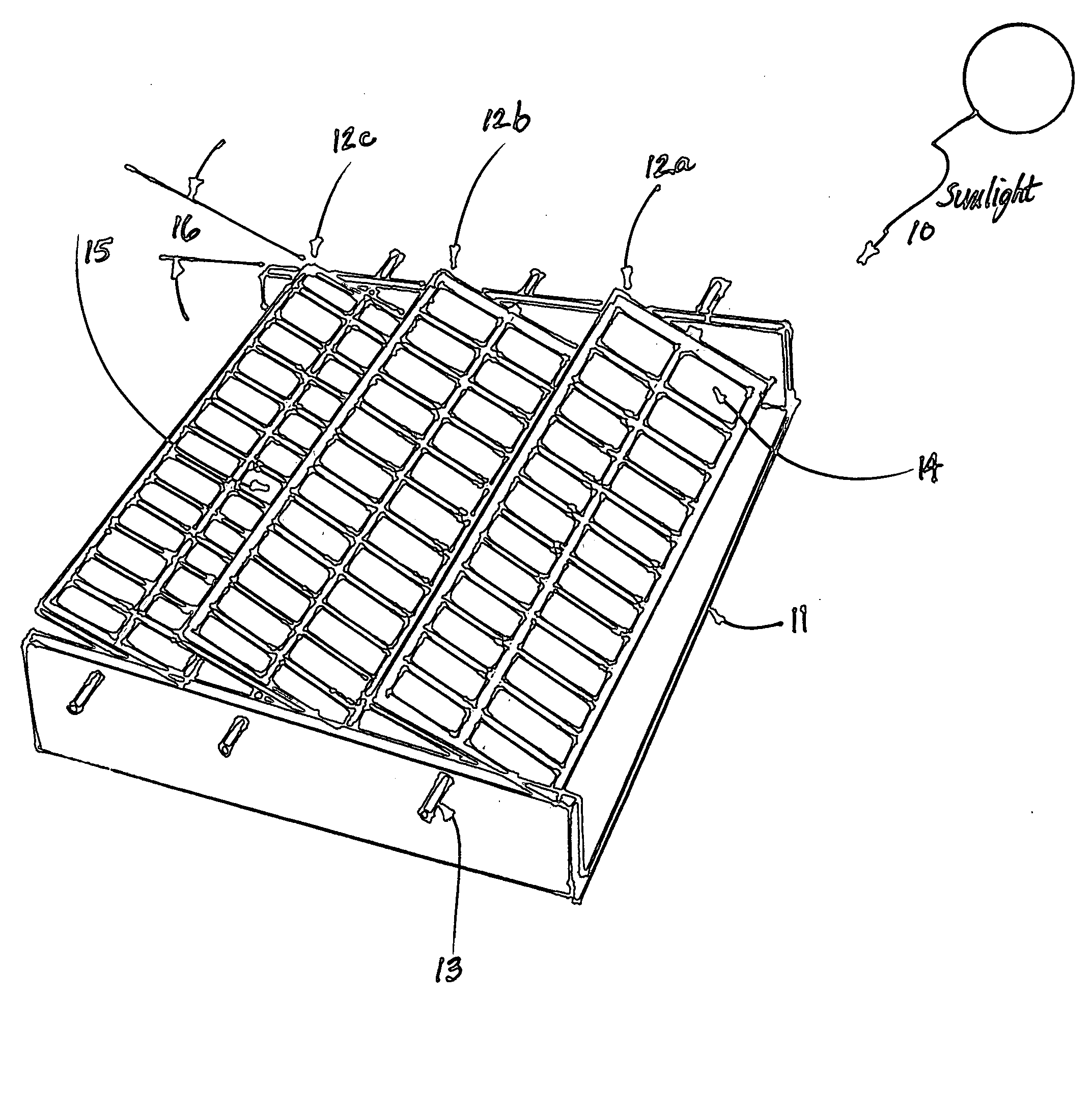
InactiveUS20110094503A1Improve and refine tracking abilityImprove accuracyPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringDaylight
A method for tracking the movement of the sun from East to West across the sky during daylight hours to enable solar photovoltaic (PV) panels or arrays of such panels to capture significantly more solar energy than fixed solar panels. Readily-available sun position data (taken from ephemeris or celestial navigation tables) can be programmed into read-only memory (ROM) chips. Date and time of day information can also be programmed into ROM chips powered by long-life, rechargeable batteries, such as lithium-ion batteries. Using such ROM chip data, a solar panel or an array of solar panels can track the sun position provided that during installation (with the panels aimed longitudinally towards the South), the solar panels are positioned upwards towards the noontime sun position to establish a starting point. This enables the sun tracking system of the present invention to track the sun without requiring a solar sensing device. Sun tracking provides an increase of from about 20% to 50% increased solar energy capture compared with fixed, non-tracking solar panels. Experimental data is also provided to illustrate the effectiveness of the present invention.
Owner:JONES DALE G +1
Information fusion method for airborne inertia/Doppler radar integrated navigation system
InactiveCN102608596ATroubleshoot navigation errorsHigh precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionClosed loop feedbackState variable
The invention discloses an information fusion method for an airborne inertia / Doppler radar integrated navigation system. The method comprises the following six major steps of: I, establishing an error model of an inertia device and a Doppler radar; II, determining a state variable based on the application of inertia / Doppler integrated navigation on an airborne fixed-wing aircraft; III, establishing an inertia / Doppler radar integrated navigation state equation; IV, establishing an inertia / Doppler radar integrated navigation measurement equation; V, discretizing a Kalman filtering continuous system; and VI, performing Kalman filtering data fusion resolving, obtaining the sub-optimal estimation related to navigation parameters through state estimation, and correcting the inertial navigation and Doppler radar in a closed-loop feedback mode at the same time. The method disclosed by the invention makes full use of the Doppler information and inertial navigation information, puts forward a data fusion scheme for airborne inertia / Doppler radar integrated navigation, effectively solves the problem of a navigation error caused by an imperfect error model, and improves the system precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Pedestrian navigation device, pedestrian navigation system, pedestrian navigation method and program
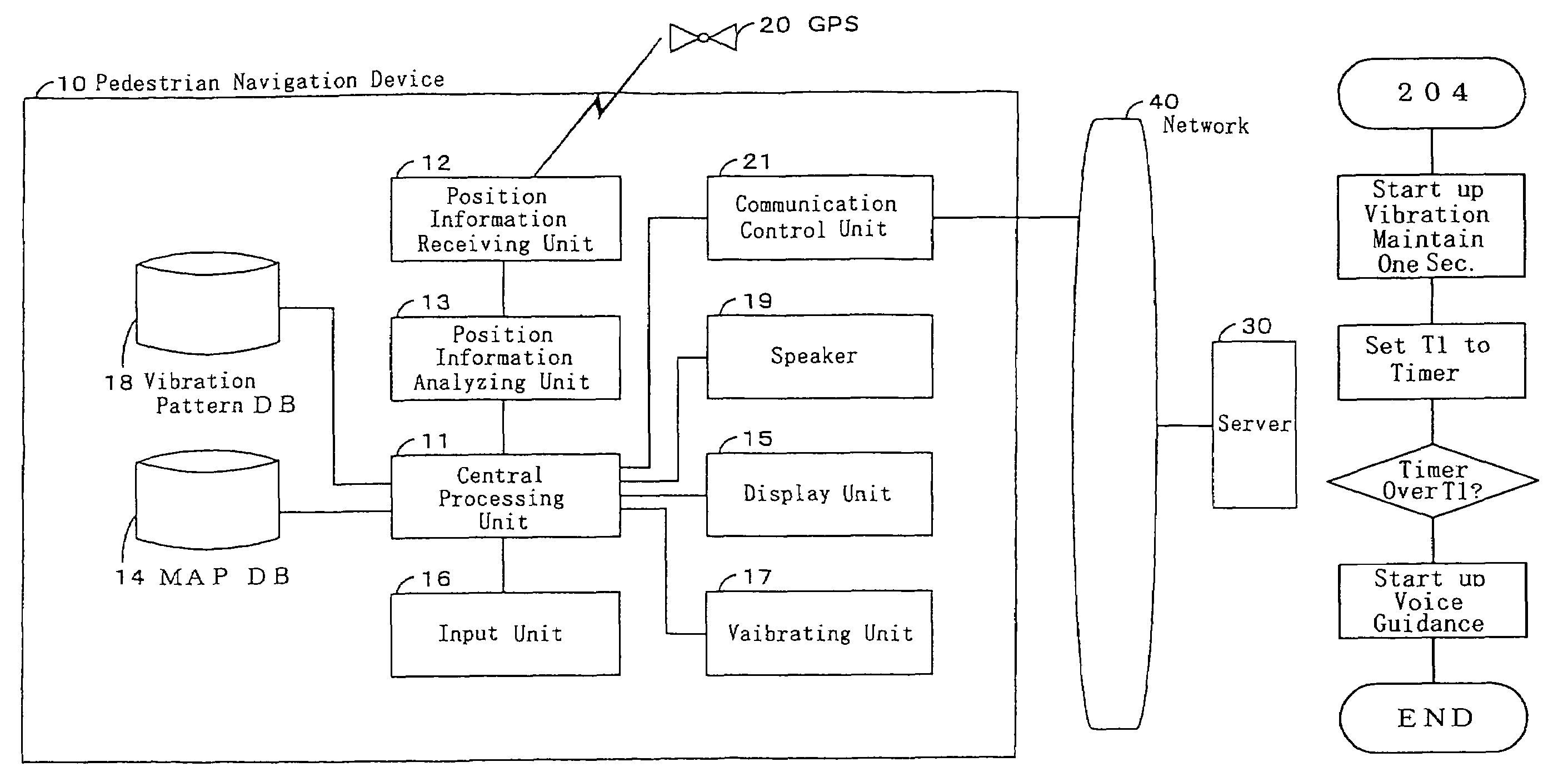
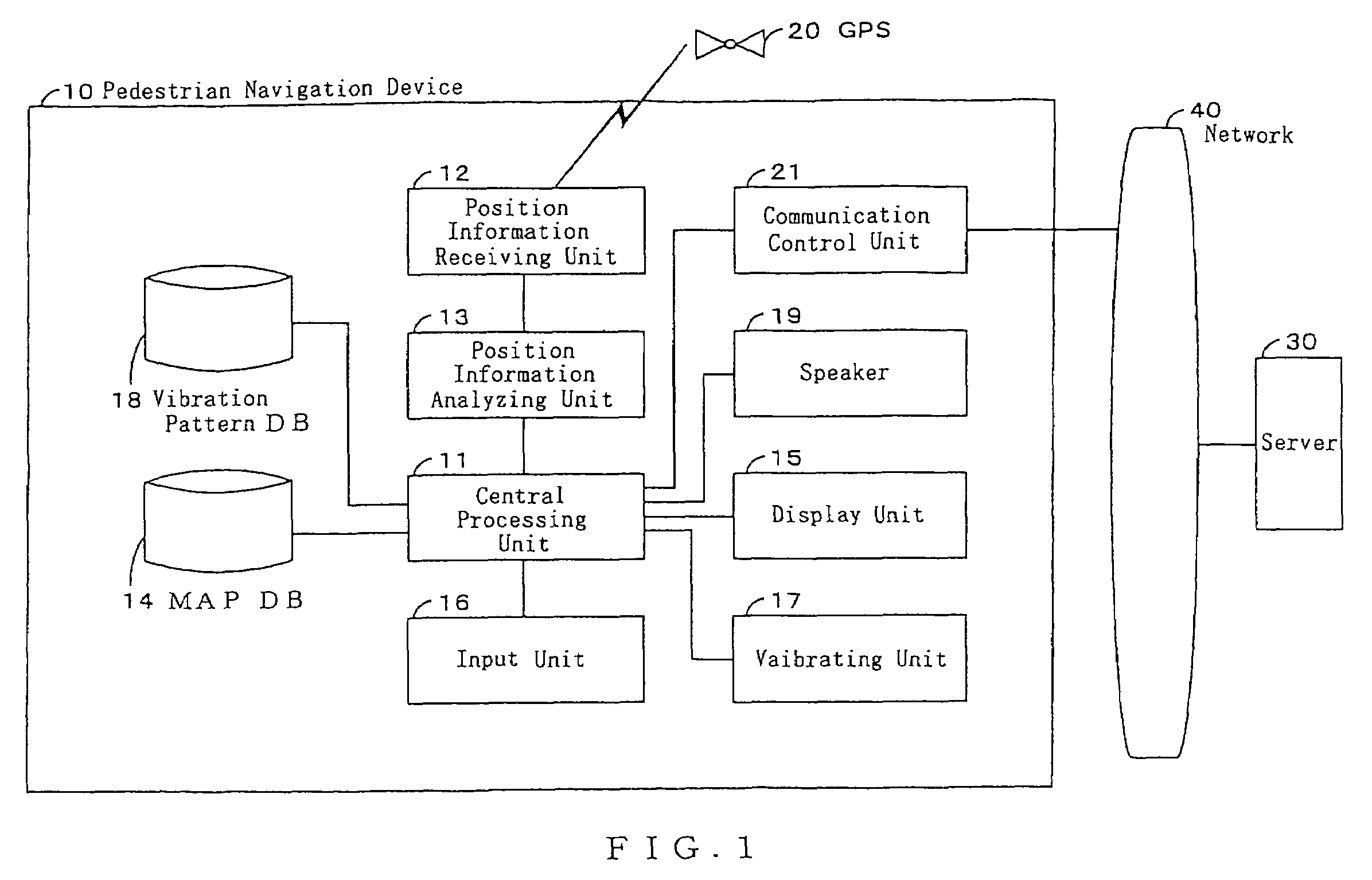
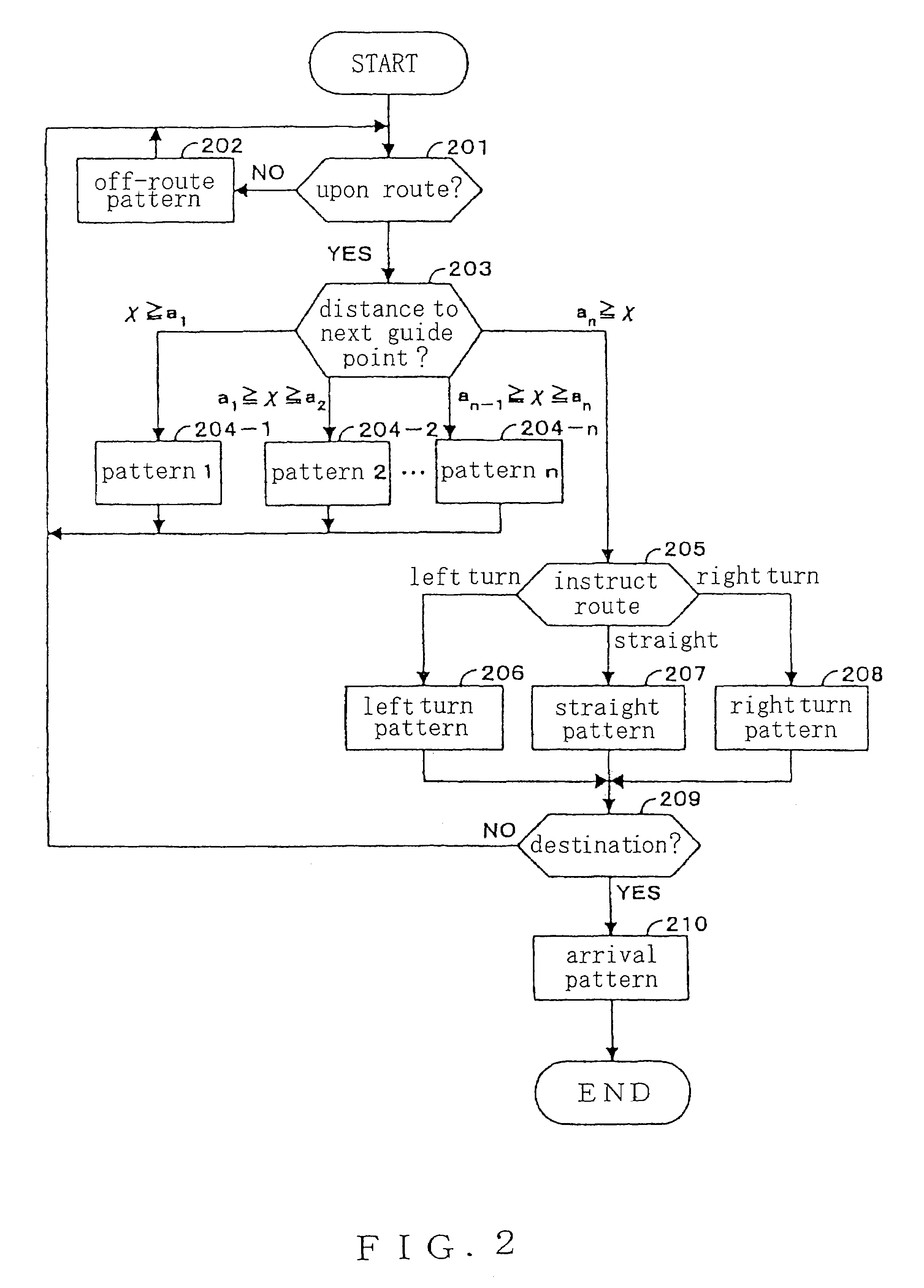
ActiveUS7539576B2Convenient verificationInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsPedestrian navigation systemCelestial navigation
Owner:NAVITIME JAPAN CO LTD
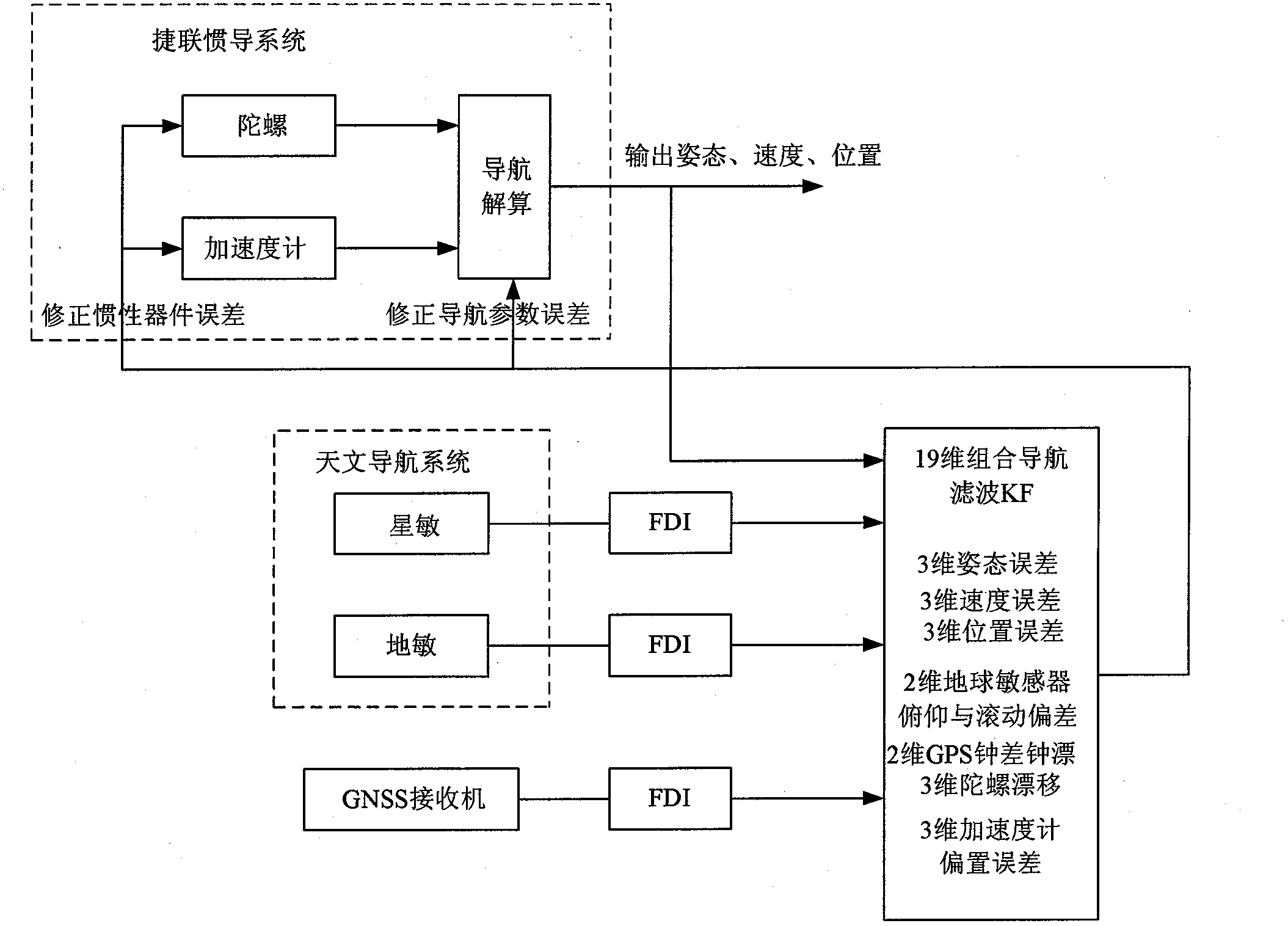
Integrated navigation system of strapdown inertial navigation system (SINS)/central nervous system (CNS)/global navigation satellite system (GNSS) of geostationary earth orbit (GEO) transfer vehicle
ActiveCN103134491AStrong autonomyHigh precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsTime errorClosed loop feedback
The invention provides an integrated navigation system of a strapdown inertial navigation system (SINS) / a central nervous system (CNS) / a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) of a geostationary earth orbit (GEO) transfer vehicle. The SINS serves as a core of the integrated navigation system. Navigation information of the GEO transfer vehicle is calculated and output by the SINS in real time, fault detection and isolation are conducted to data output by a GNSS receiver, a globe sensor and a star sensor by utilizing a residual error chi 2 detecting method improved by a kalman filter. Information fusion is conducted to output information of the globe sensor and the star sensor in a celestial navigation system, pseudorange measuring information output by the GNSS receiver and the navigation information output by the SINS. Navigation errors, inertial device errors, globe sensor errors and GNSS receiver time errors of the GEO transfer vehicle are evaluated in real time, and the navigation errors of the GEO transfer vehicle are corrected through a manner of closed loop feedback correction in real time so that in-orbit self navigation with high precision and high reliability of the GEO transfer vehicle is achieved, and therefore meaningful effects of good subjectivity, high precision, good robustness and high reliability are obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
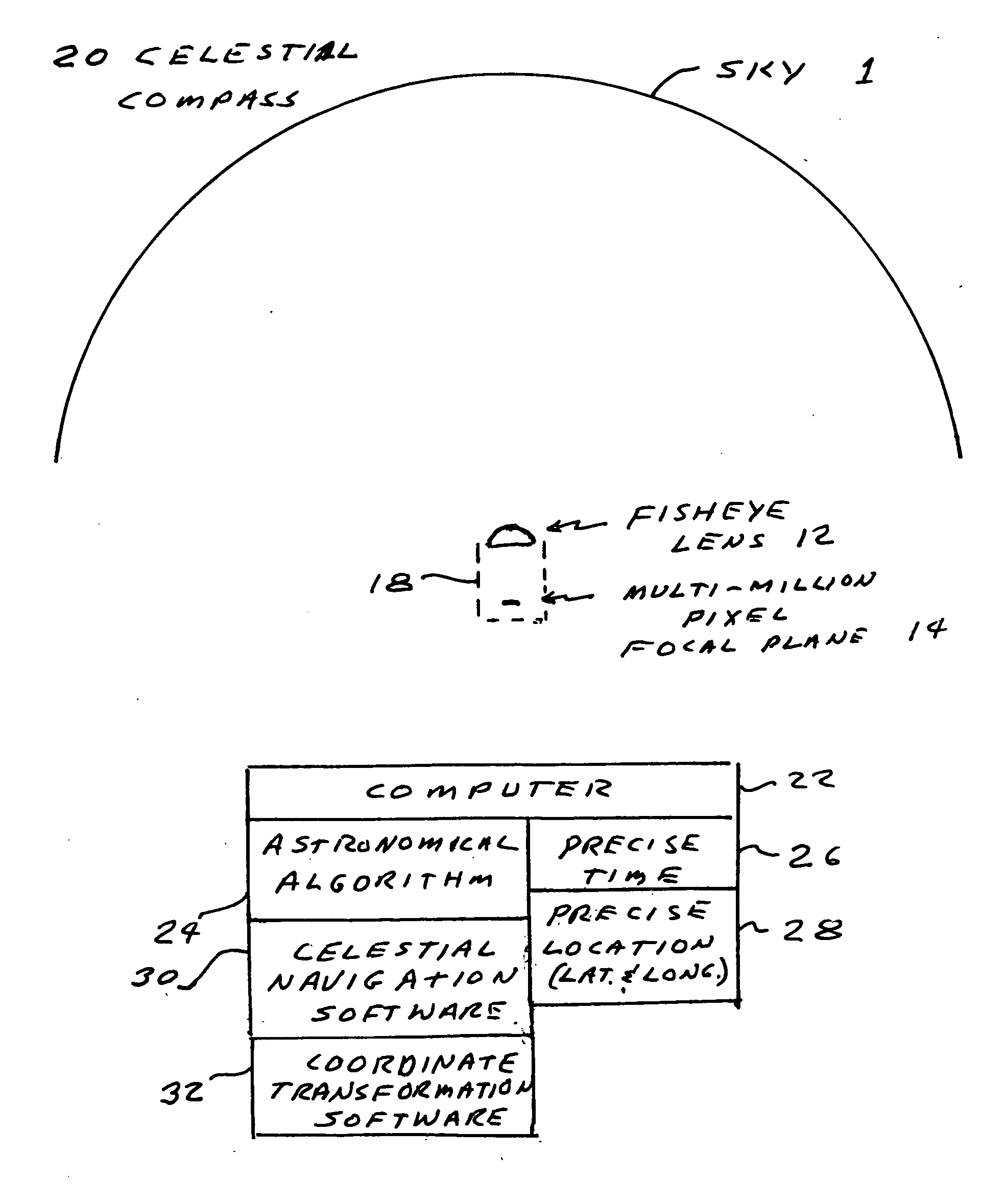
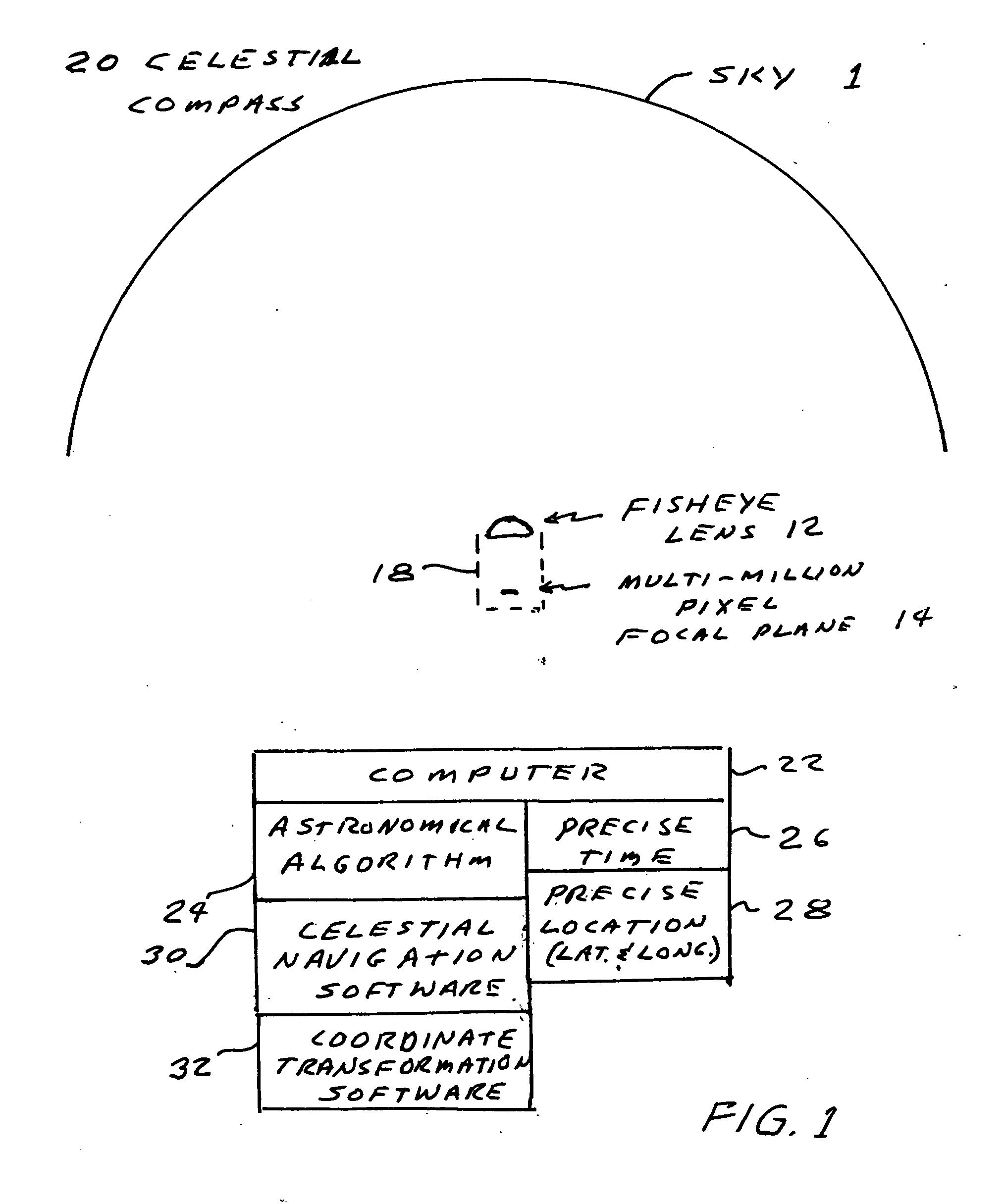
Celestial compass
A celestial compass. The celestial compass includes a camera with a wide angle lens suitable for viewing a large portion of the sky and a many-pixel sensor for collecting images of celestial objects such as stars, planets, the moon and the sun. The compass also includes a computer programmed with an (1) astronomical algorithm for providing the precise position of celestial objects based on precise input of time (date and time of day) and observation position (latitude and longitude), (2) celestial navigation software and (3) coordinate transformation software to correct distortion, convert pixel image data to astronomical coordinates and determine the instruments azimuth. The system includes provisions for the input of precise time and location information.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Strap-down inertial navigation system/visual odometer integrated navigation method
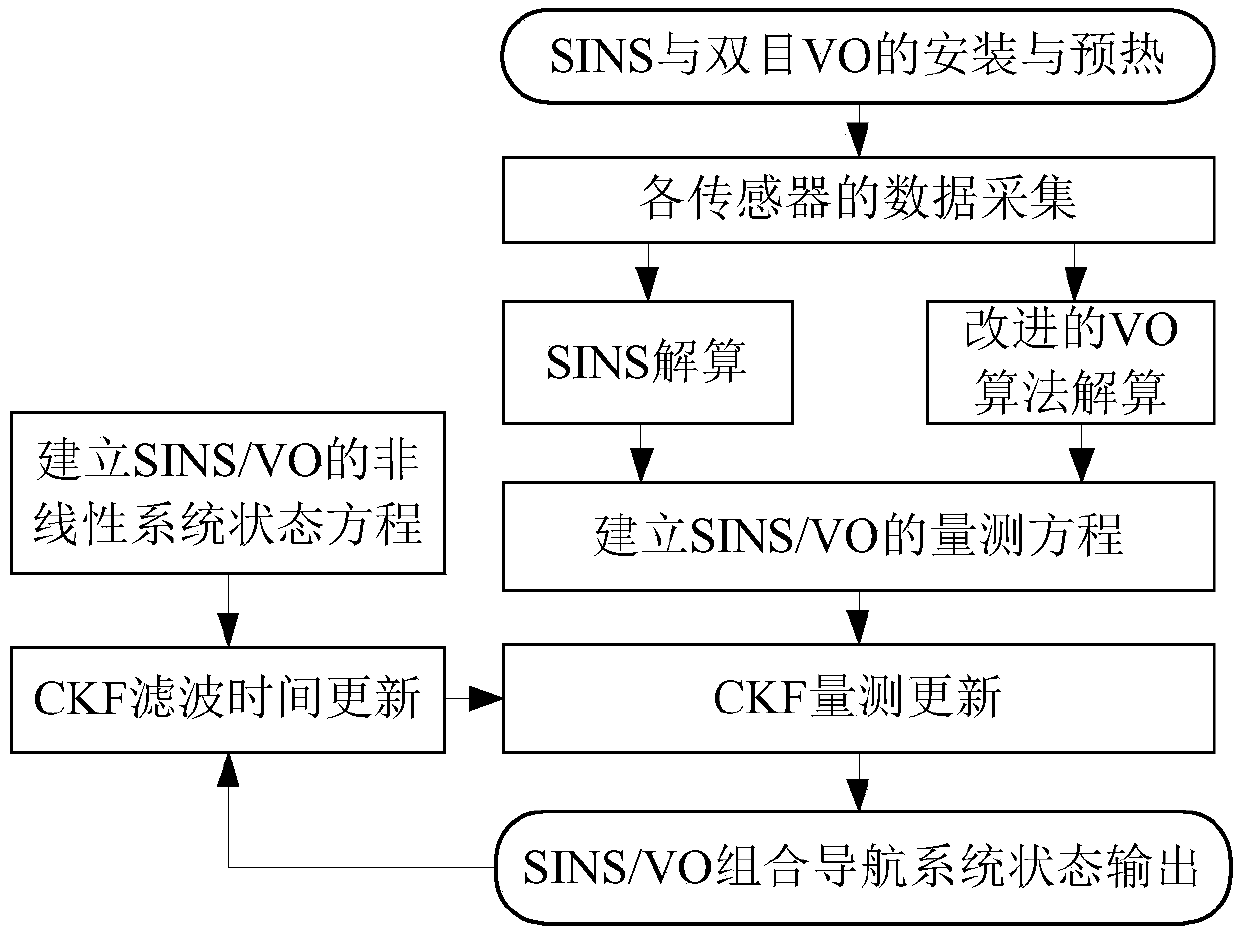
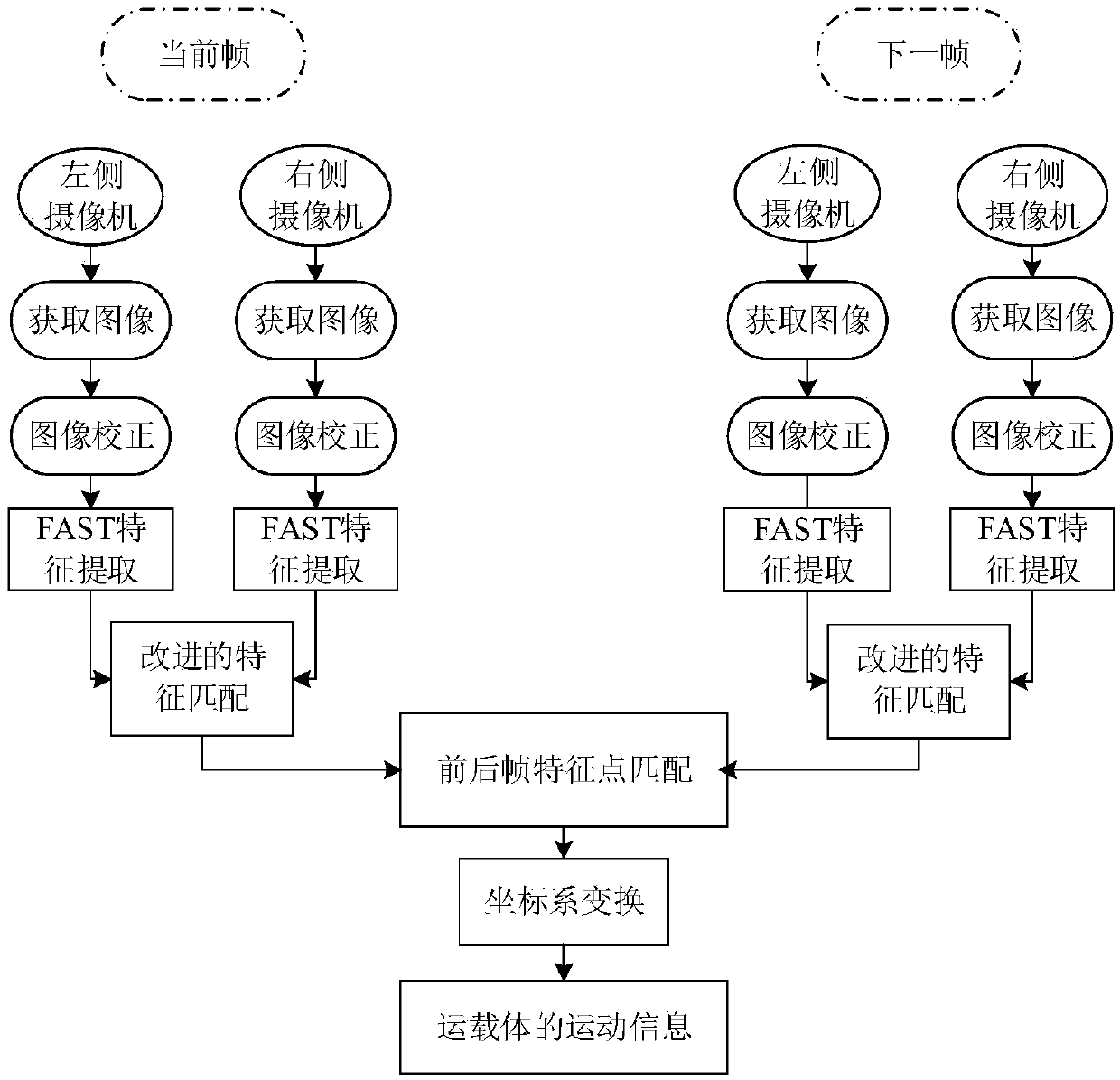
PendingCN107796391AHigh precisionImprove positioning accuracy and robustnessNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNonlinear filterCelestial navigation
The invention provides a strap-down inertial navigation system / visual odometer integrated navigation method which comprises the following steps: mounting a binocular visual odometer and a fiber-opticgyroscope inertial navigation system on a transporter and collecting data of all sensors; extracting features in an image sequence with an FAST method, completing feature matching with a feature matching method based on random sample consensus and calculating movement information of the transporter; establishing a nonlinear state equation and a measurement equation of a strap-down inertial navigation system / visual odometer integrated navigation system; and completing time update and measurement update of the strap-down inertial navigation system / visual odometer integrated navigation system with a volume Kalman filter of a nonlinear filter, and estimating the state of the system, so as to realize the navigation and location of the strap-down inertial navigation system / visual odometer integrated navigation system. According to the strap-down inertial navigation system / visual odometer integrated navigation method, a feature matching algorithm is optimized, and a nonlinear volume Kalman filter algorithm is utilized, so that the location accuracy and the robustness of the integrated navigation system are improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Multi-pulse star signal simulator
InactiveCN101644580AMeet the data requirements of the simulationHigh precisionInstruments for comonautical navigationCelestial navigationData reliability
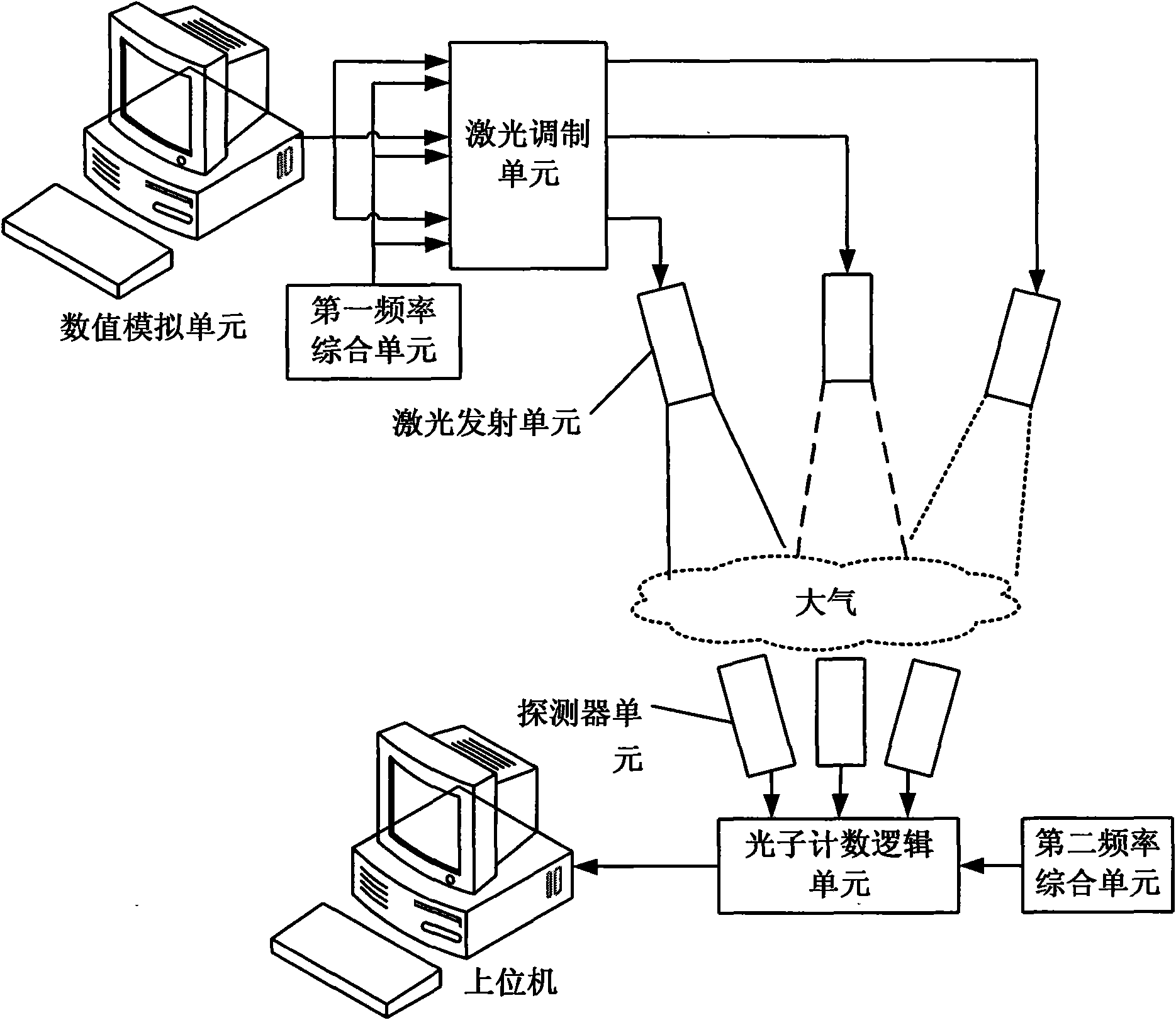
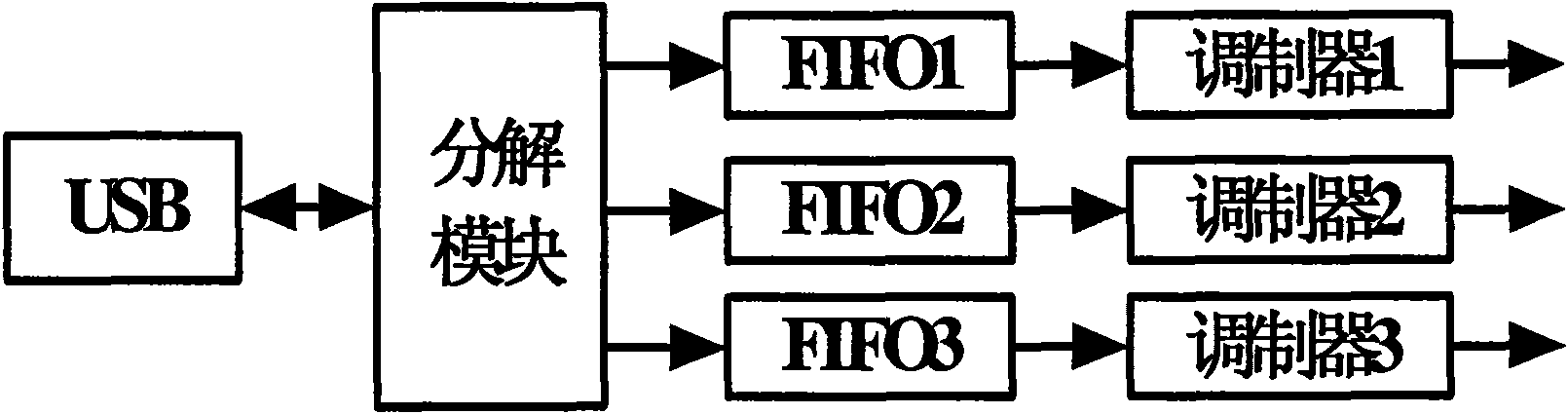
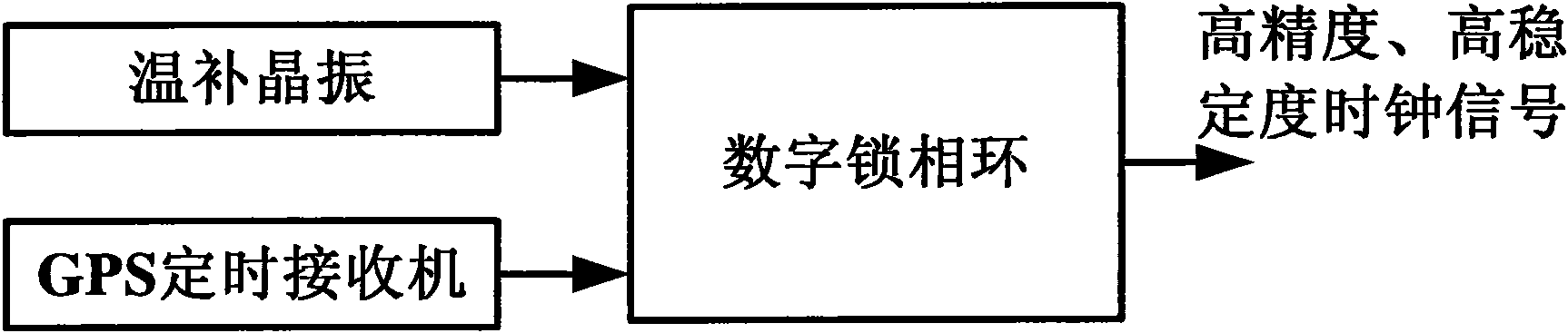
The invention discloses a multi-pulse star signal simulator comprising a numerical value simulation unit, a first frequency integration unit, a laser modulation unit, a laser emission unit, a detectorunit, a second frequency integration unit and a photon counting logical unit, wherein the numerical value simulation unit generates radiation signal data of a plurality of pulse stars by using a clock of the first frequency integration unit according to a signal numerical value model and sends the radiation signal data to the laser modulation unit; the laser modulation unit generates a current signal which can directly modulate a laser according to the clock of the first frequency integration unit; the laser emission unit converts the current signal of a laser modulator into a laser intensitysignal; the detector unit receives the laser signal, generates pulses and sends the pulses into the photon counting logical unit; and the photon counting logical unit counts the pulses according to aclock of the second frequency integration unit and sends a counting result to an upper computer. The invention has the advantages of high data reliability and coincidence of a signal generation and detection mechanism with the actual condition and is used for providing simulated data to the independent celestial navigation simulation of a spacecraft.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
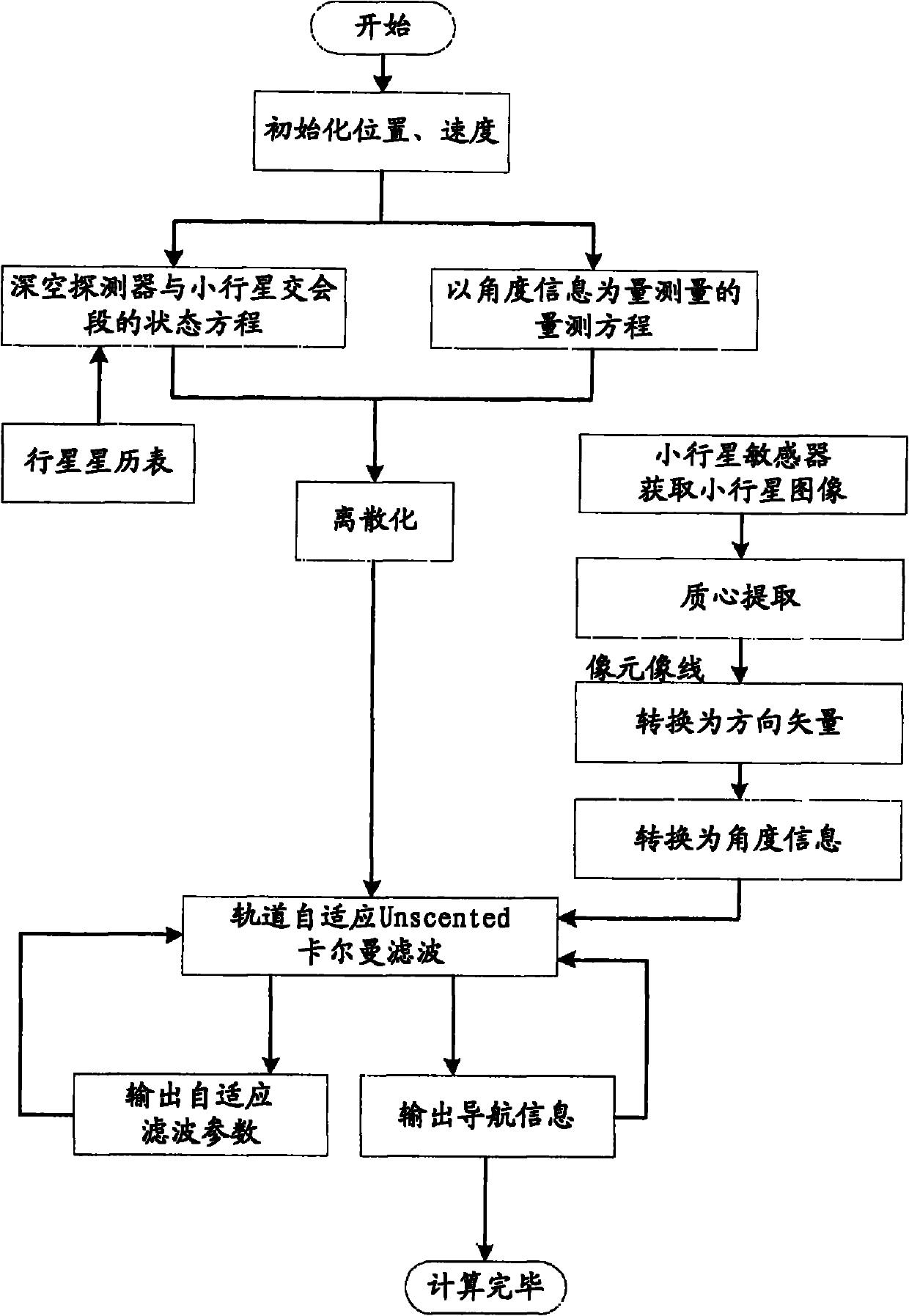
Independent celestial navigation method of deep space probe based on minor planet intersection
ActiveCN102168980AHigh precisionRealize high-precision navigationInstruments for comonautical navigationFixed starsAutonomous Navigation System
The invention relates to an independent celestial navigation method of a deep space probe based on minor planet intersection. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a state model of the deep space probe according to a circular restrictive track dynamics model; acquiring picture element and picture line information of minor planets and a background fixed star by using a sensor, converting the acquired picture element and picture line information into angle information of the minor planets and the background fixed star and establishing an angle measuring model of the minor planets; and estimating the position and speed of the deep space probe in combination with self-adaptive Unscented Kallman filtering. The method has high estimation accuracy, and is very suitable for independent navigation during minor planet intersection. The method belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation. By adopting the method, high-accuracy navigation parameters can be provided for the deep space probe, and references can be provided for the design of an independent navigation system of the deep space probe.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
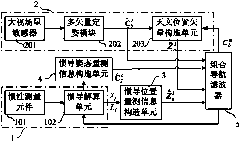
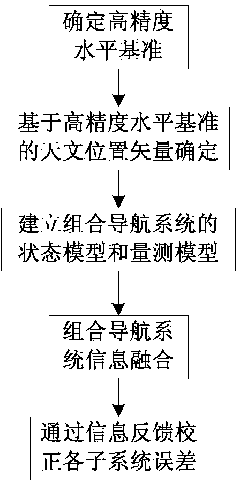
SINS (Ship's Inertial Navigation System)/CNS (Celestial Navigation System) deep integrated navigation system of mar rover, and realization method of system
InactiveCN103994763AHigh precisionImprove astronomical positioning accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsState modelLongitude
The invention provides an SINS (Ship's Inertial Navigation System) / CNS (Celestial Navigation System) deep integrated navigation system of a mar rover. The SINS / CNS deep integrated navigation system comprises an SINS, a CNS, an inertial navigation position unit, an inertial navigation posture unit and a filter, wherein the SINS provides a mathematic platform and a position matrix for the inertial navigation posture unit, and also provides longitude and latitude information for the inertial navigation position unit, the CNS transfers an inertial posture matrix to the filter, the inertial navigation posture unit inputs the constructed inertial posture matrix into the filter, the inertial navigation position unit inputs the constructed position vector information into the filter, and the filter provides posture and position estimation errors for a celestial navigation subsystem and a ship's inertial navigation subsystem respectively. The realization method comprises the following steps: I. helping the SINS to obtain high-precision level reference through a large-field-of-view star-sensor; II. confirming the high-precision level reference-based celestial position vector; III. establishing a state model and a measurement model of the integrated navigation system; IV. fusing information of the integrated navigation system; and V. correcting the errors of all the subsystems through information feedback.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
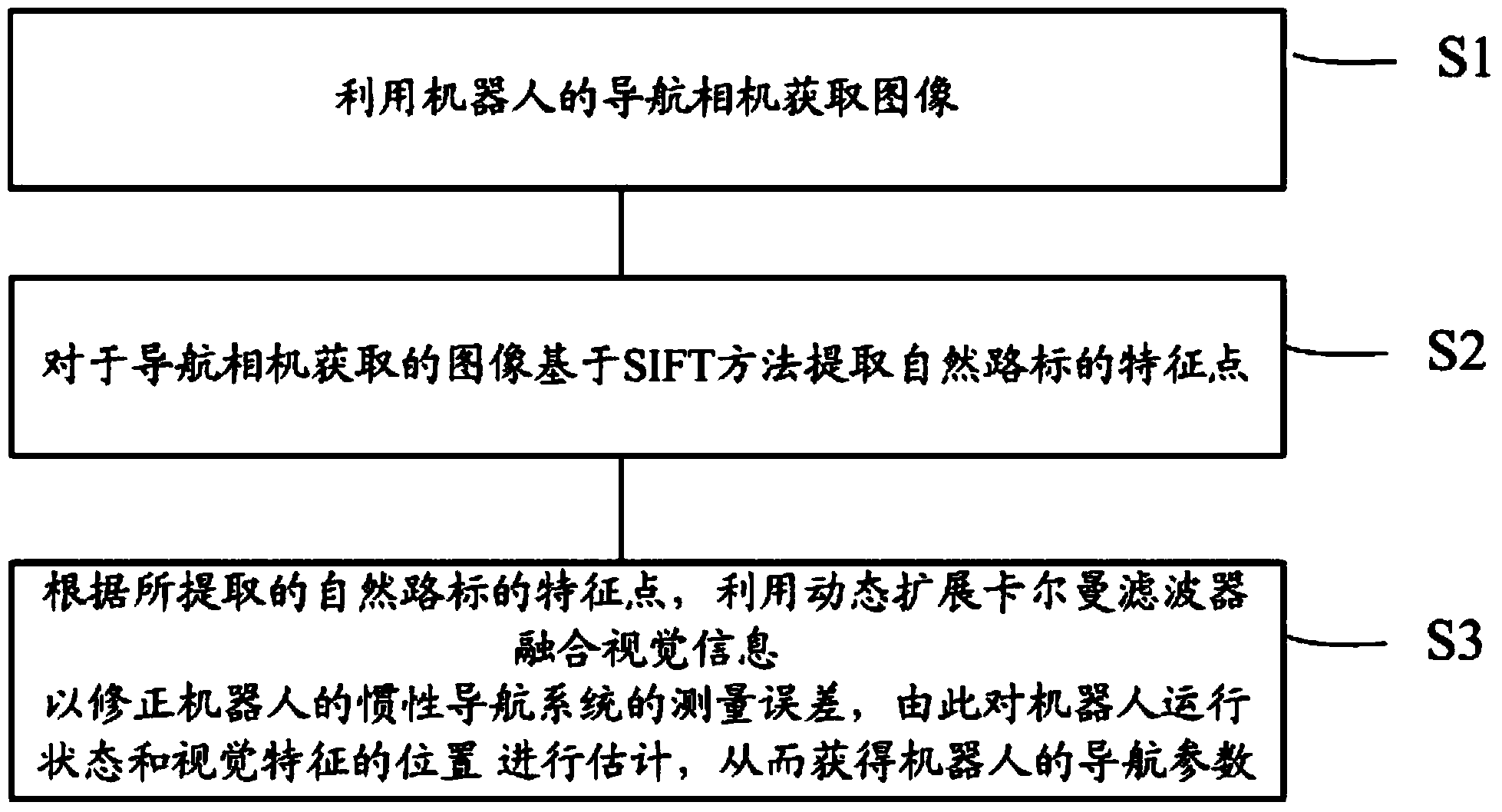
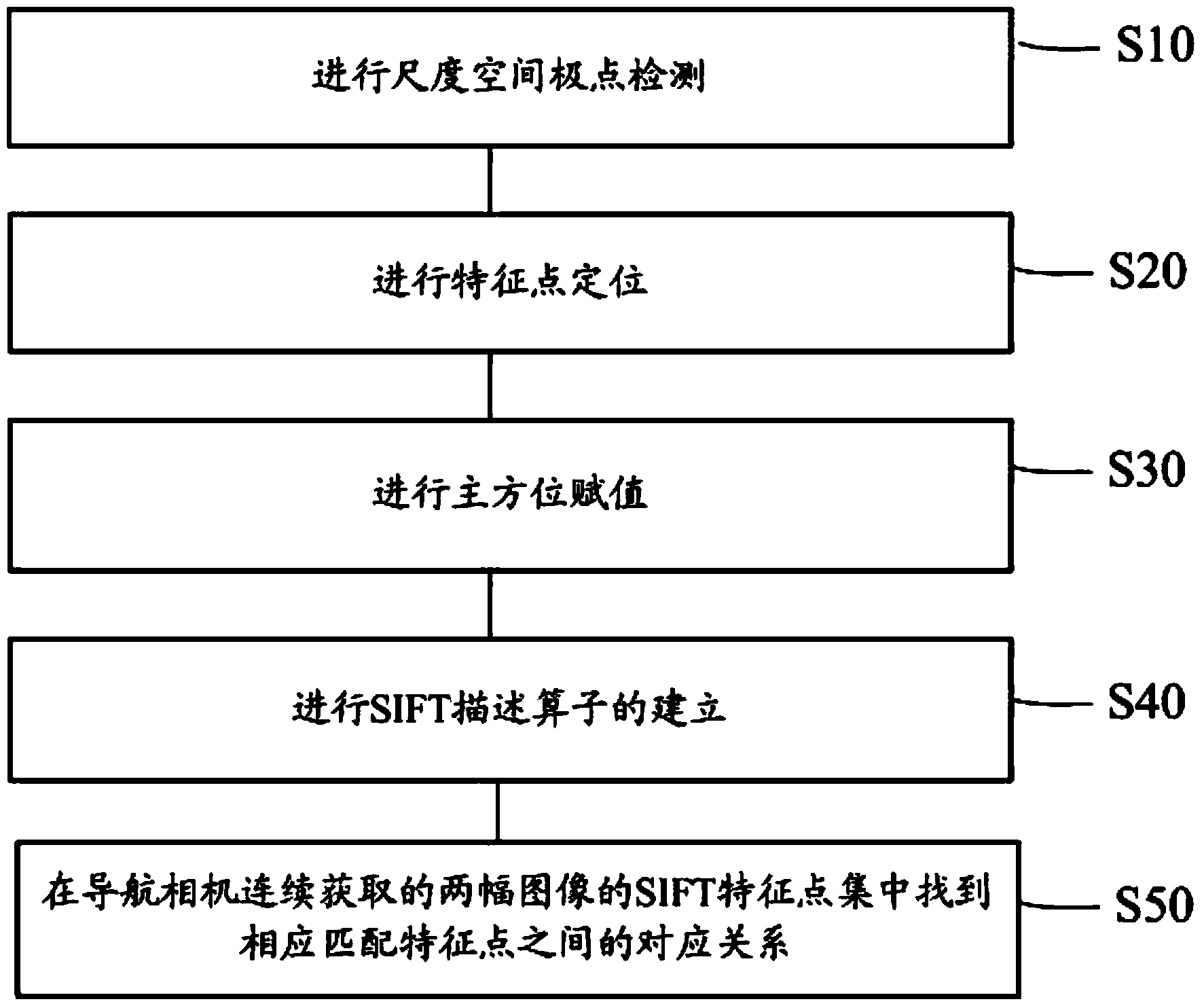
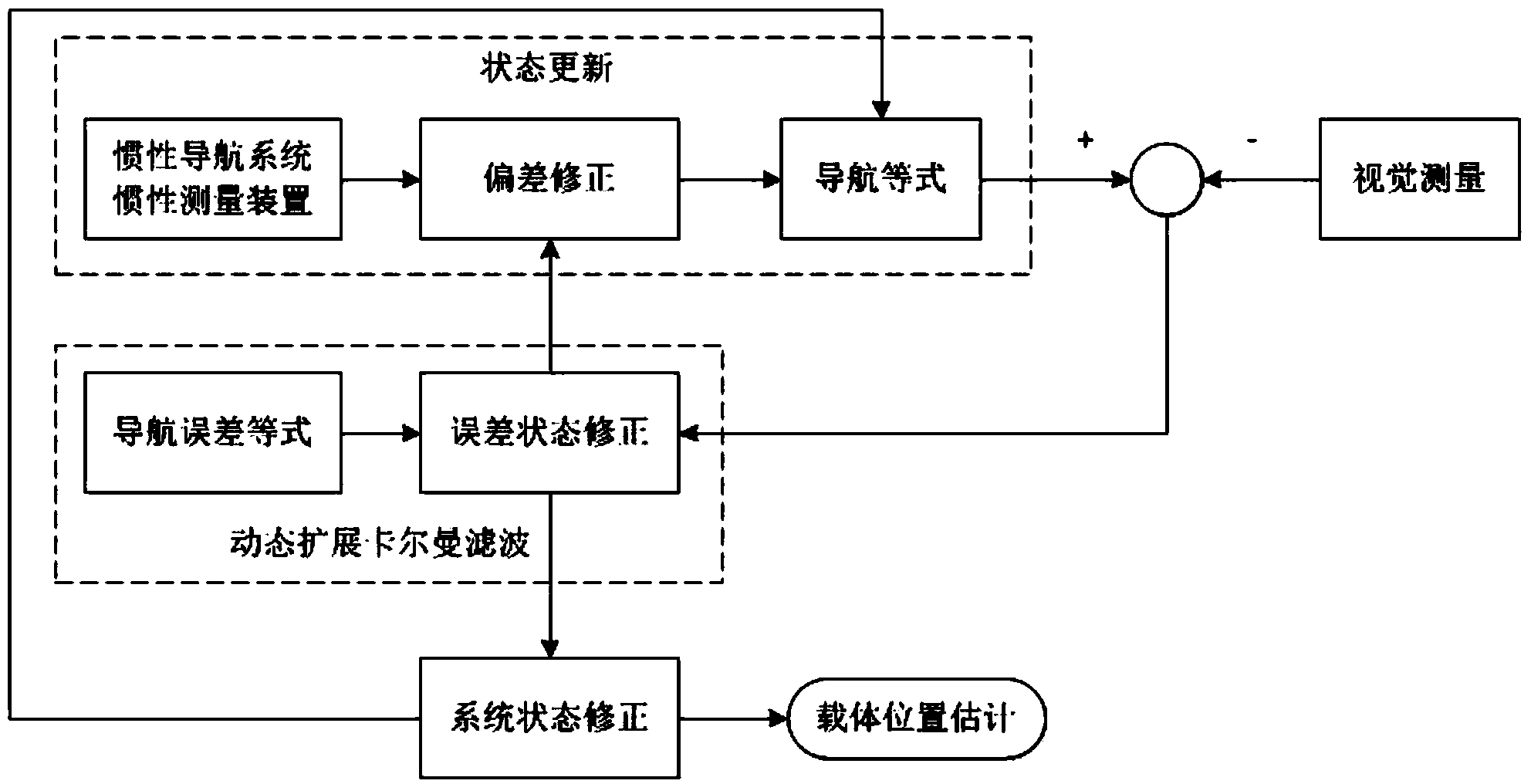
Visual navigation method based on SIFT (scale invariant feature transform) algorithm
InactiveCN103644904APrecise positioningMiniaturizationNavigational calculation instrumentsObservational errorKaiman filter
The invention provides a visual navigation method based on an SIFT (scale invariant feature transform) algorithm. The visual navigation method comprises the steps of 1, acquiring an image through a navigation camera of a robot; 2, extracting feature points of a natural landmark on the image acquired by the navigation camera by virtue of an SIFT method; and 3, correcting a measurement error of an inertial navigation system of the robot by using a dynamic extended Kalman filter and combining visual information according to the extracted feature points of the natural landmark, and estimating a running state of the robot and positions of visual features to obtain navigation parameters of the robot.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
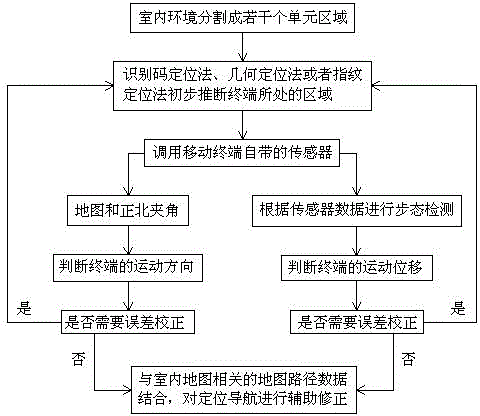
Indoor navigation method based on combination of region location, inertial navigation and map path
InactiveCN104596508AHigh precisionImprove accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsData aidedCelestial navigation
The invention discloses an indoor navigation method based on the combination of region location, inertial navigation and map path. The indoor navigation method comprises the following steps: S1, region identification location; S2, inertial navigation; S3, map path data aided navigation. According to the invention, the indoor navigation method heavily relies on sensor data and map path data of a terminal and less relies on wireless signals, so that the laying and maintenance costs are greatly reduced; meanwhile, the location and navigation technology for cooperating the sensor data, the map path data and the wireless signals greatly improve the accuracy of indoor location and navigation.
Owner:徐永鑫
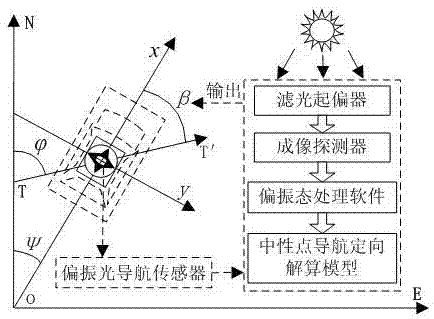
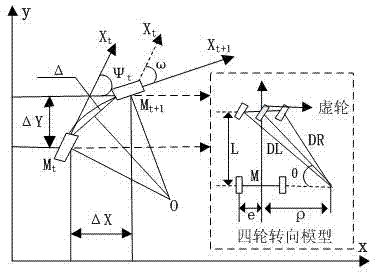
Autonomous vehicle navigation method for assisting orientation by applying omnimax neutral point
InactiveCN104713555AStrong autonomyImprove concealmentNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsVehicle dynamicsIn vehicle
The invention relates to an autonomous vehicle navigation method for assisting orientation by applying an omnimax neutral point. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a vehicle-mounted neutral point navigation orientation model, establishing an improved dynamic mathematical model of a vehicle, establishing a vehicle-mounted polarized light navigation / dynamic mathematical model / inertial navigation combined navigation system, establishing a vehicle-mounted combined navigation system state equation and establishing a vehicle-mounted combined navigation system measuring equation. According to the invention, atmospheric polarization characteristics, inertial navigation and vehicle dynamics / kinematics models are effectively combined, through research on an information fusion scheme and an information fusion method, a reasonable combination scheme is provided, the problem of atmospheric polarization navigation in vehicle-mounted application is solved, a passive navigation system with high autonomy, good hidden property and anti-interference is constructed, and precise reliable autonomous navigation positioning of a land fighting vehicle can be wholly realized.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
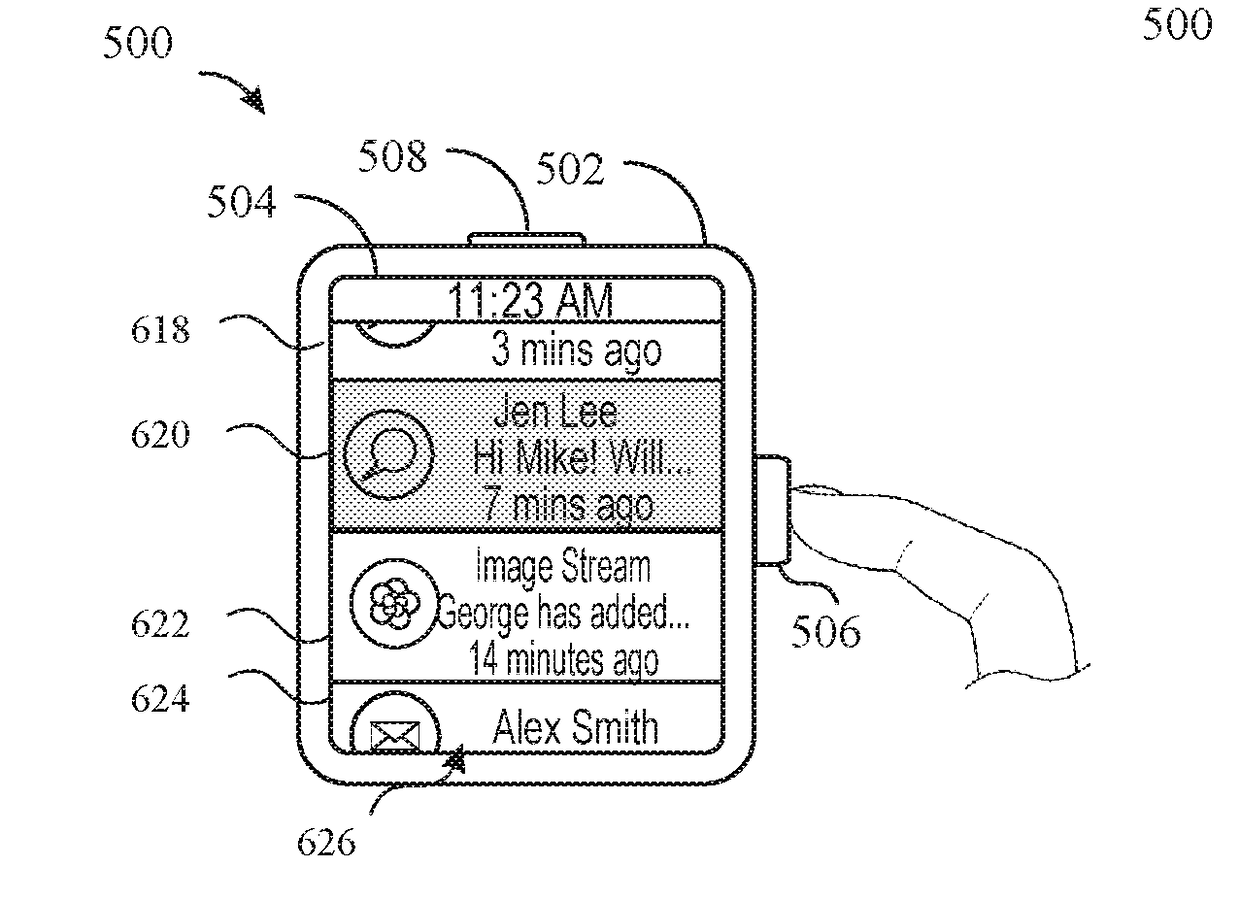
Gesture detection, list navigation, and item selection using a crown and sensors
ActiveUS20180081453A1Faster and efficient method and interfaceReduce cognitive loadDetails for portable computersInput/output processes for data processingElectronic documentReduced size
The present disclosure generally relates to methods and apparatuses for detecting gestures on a reduced-size electronic device at locations off of the display, such as gestures on the housing of the device or on a rotatable input mechanism (e.g., a digital crown) of the device, and responding to the gestures by, for example, navigating lists of items and selecting items from the list; translating the display of an electronic document; or sending audio control data to an external audio device.
Owner:APPLE INC
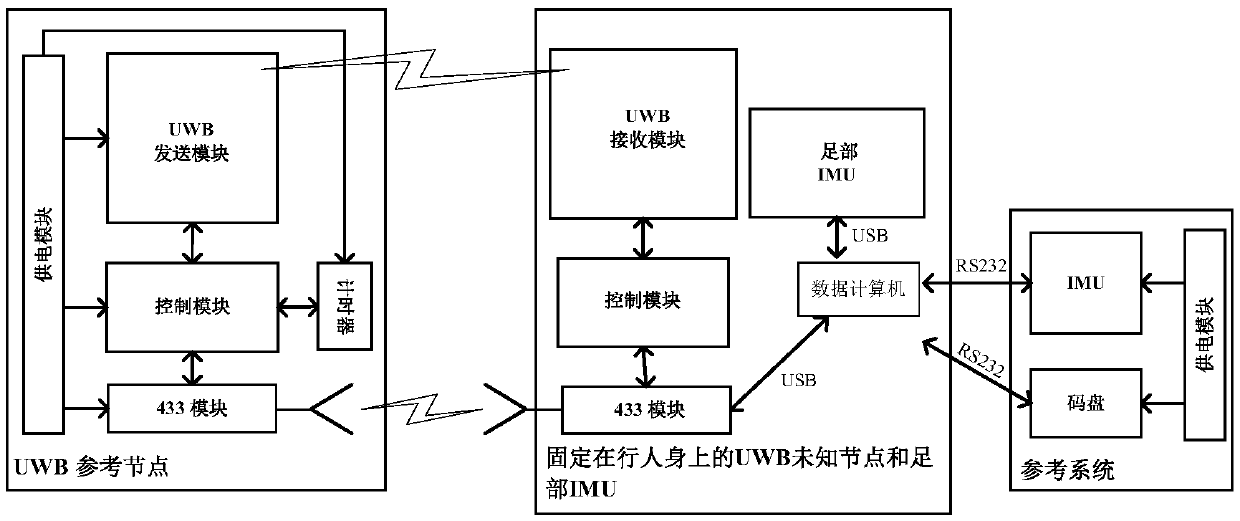
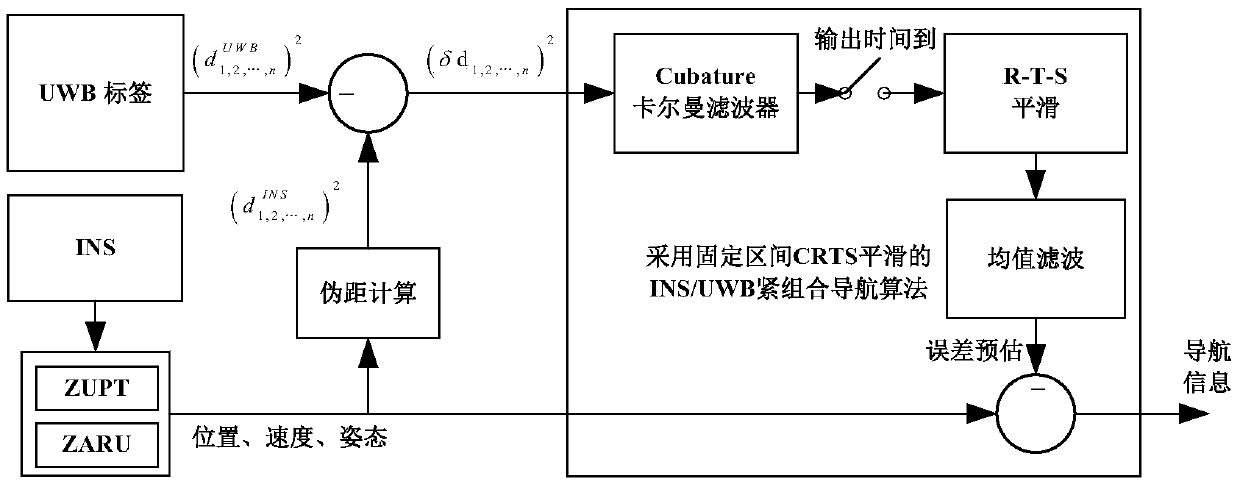
Tightly coupled INS/UWB integrated navigation system and method adopting fixed-interval CRTS smoothing
ActiveCN105509739ANavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsCubature kalman filterNavigation system
The invention discloses a tightly coupled INS / UWB integrated navigation system and method adopting fixed-interval CRTS smoothing. The navigation system comprises an inertial navigation system (INS), a UWB radio tag, UWB wireless reference nodes, a reference system and a data processing system, wherein the inertial navigation system (INS) and the UWB radio tag are arranged on shoes of a pedestrian; the UWB wireless reference nodes and the reference system are arranged at a set position; the inertial navigation system (INS), the UWB radio tag and the reference system are connected with the data processing system respectively; the data processing system comprises a local data fusion filter, a Cubature Kalman Filter (CKF), a pseudo-distance data processing module, an RTS smoothing module and an average filtering module. The tightly coupled INS / UWB integrated navigation system and method has the benefits that the possibility of introducing truncation errors due to omitting of higher terms of Taylor expansion in a conventional tightly coupled integrated navigation model is effectively decreased.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com