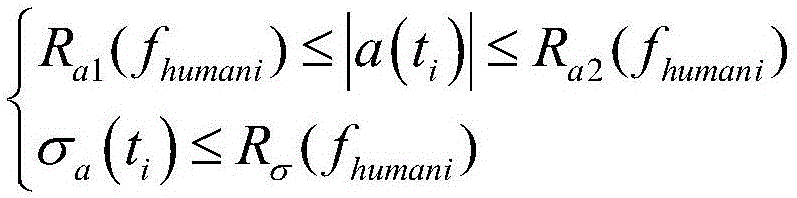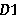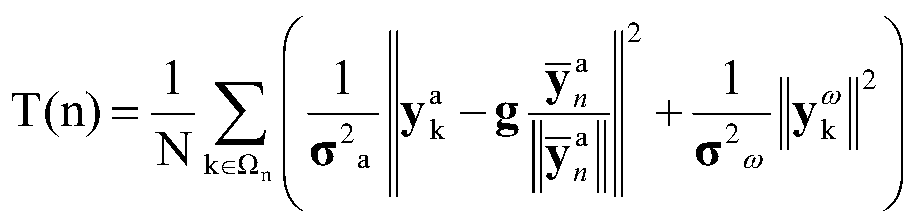Patents
Literature
44 results about "Pedestrian navigation system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
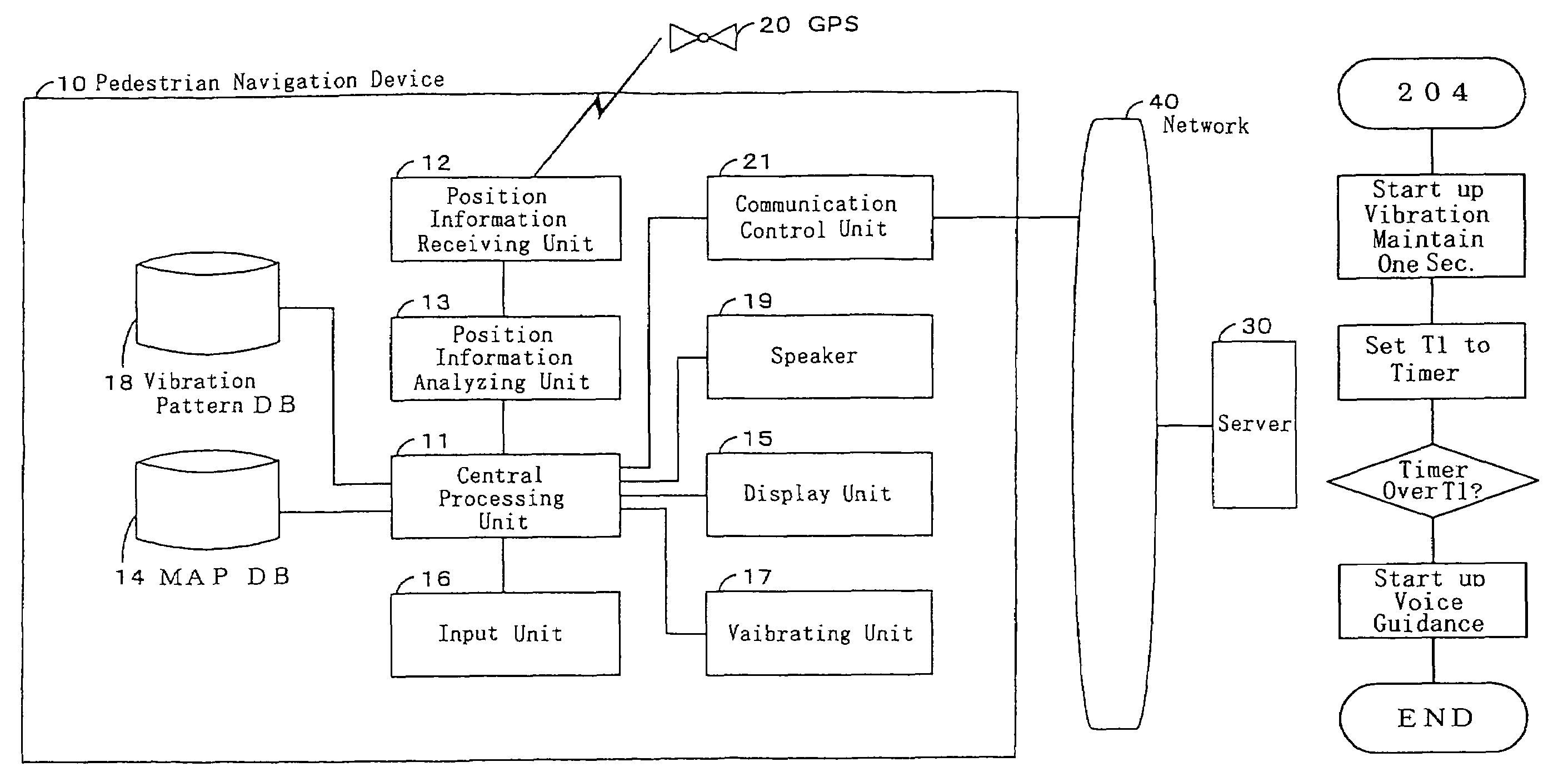
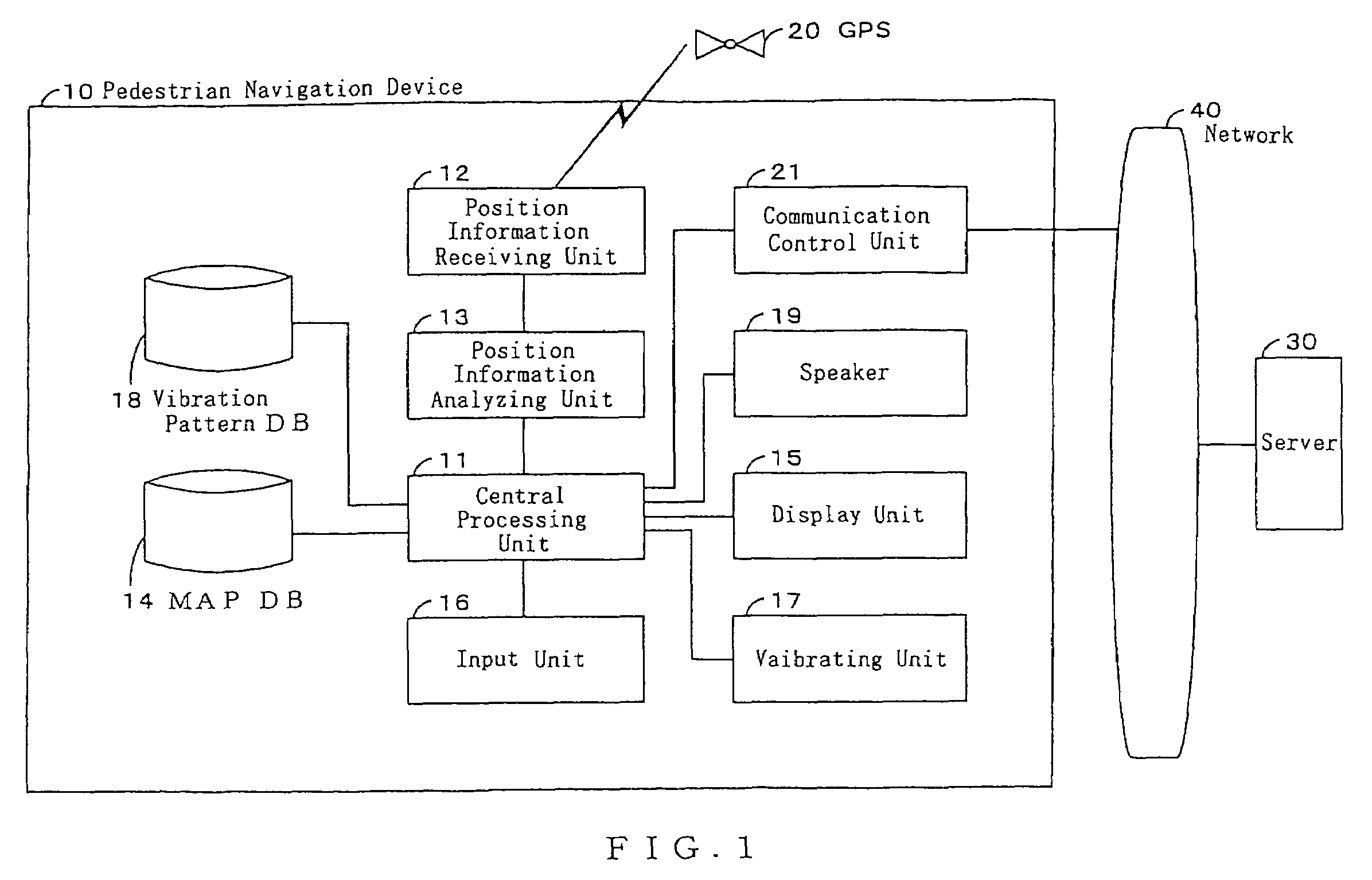
Pedestrian navigation device, pedestrian navigation system, pedestrian navigation method and program
ActiveUS20060190168A1Easy to watchImprove display qualityInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsPedestrian navigation systemSpeech sound
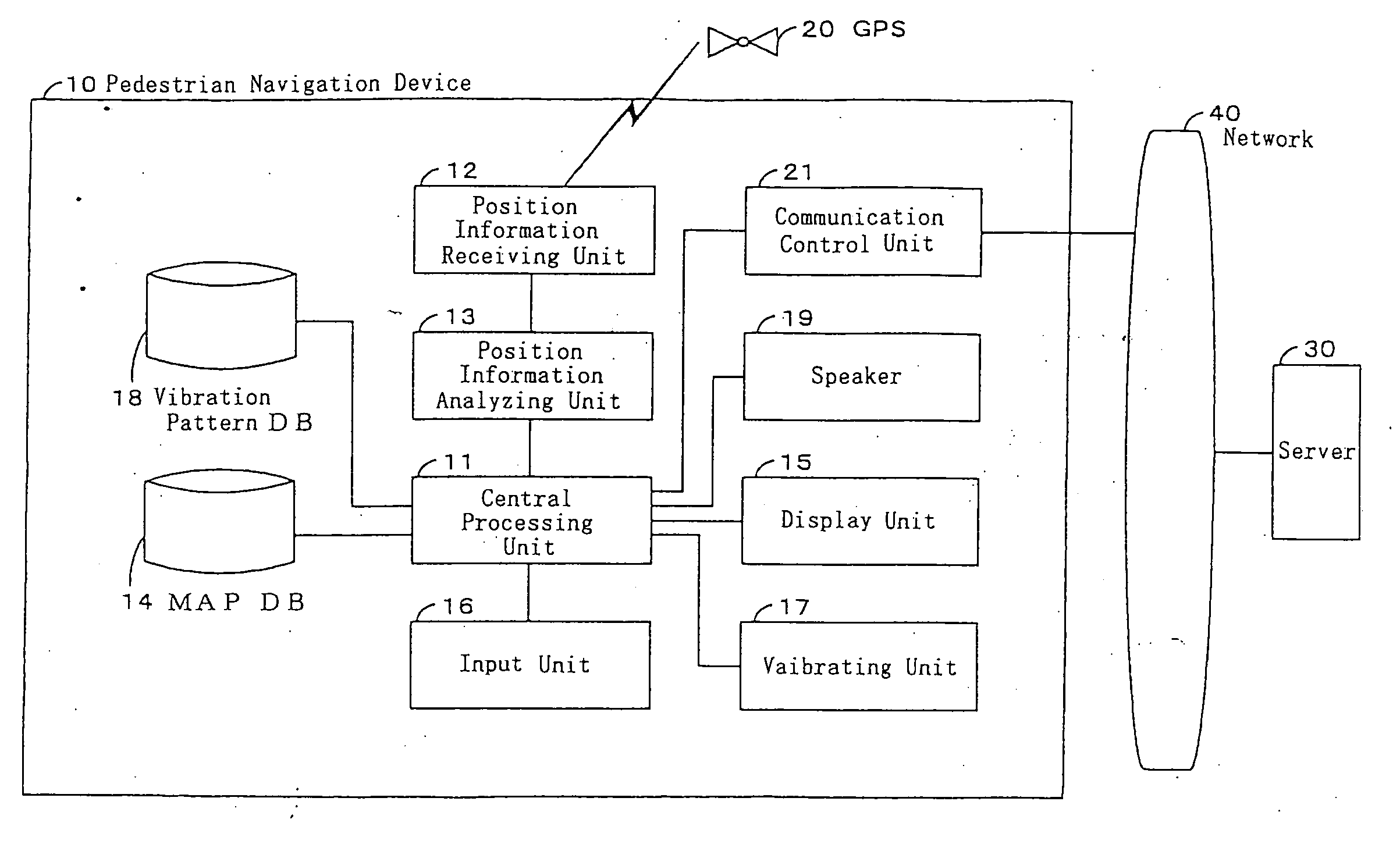
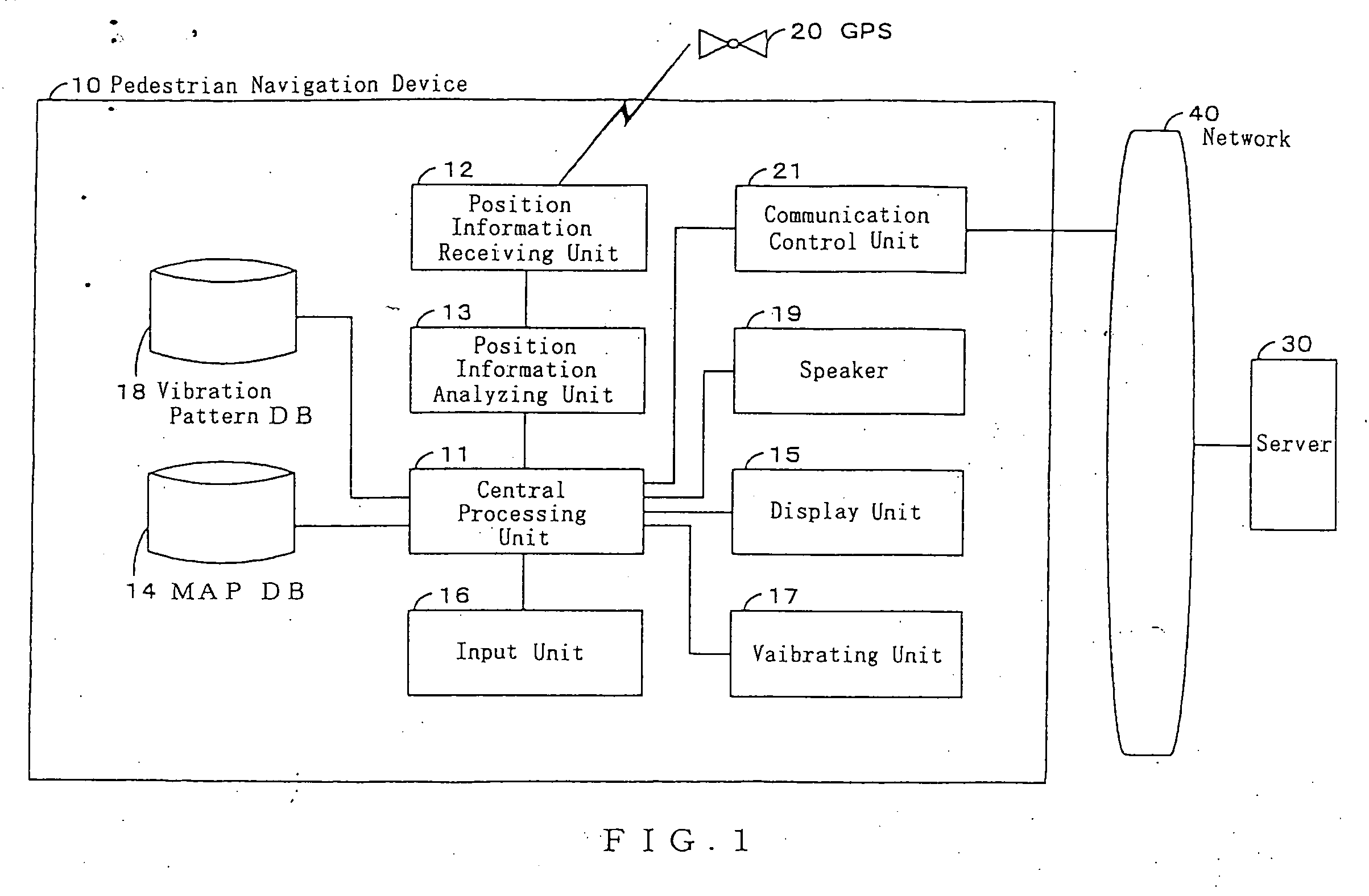
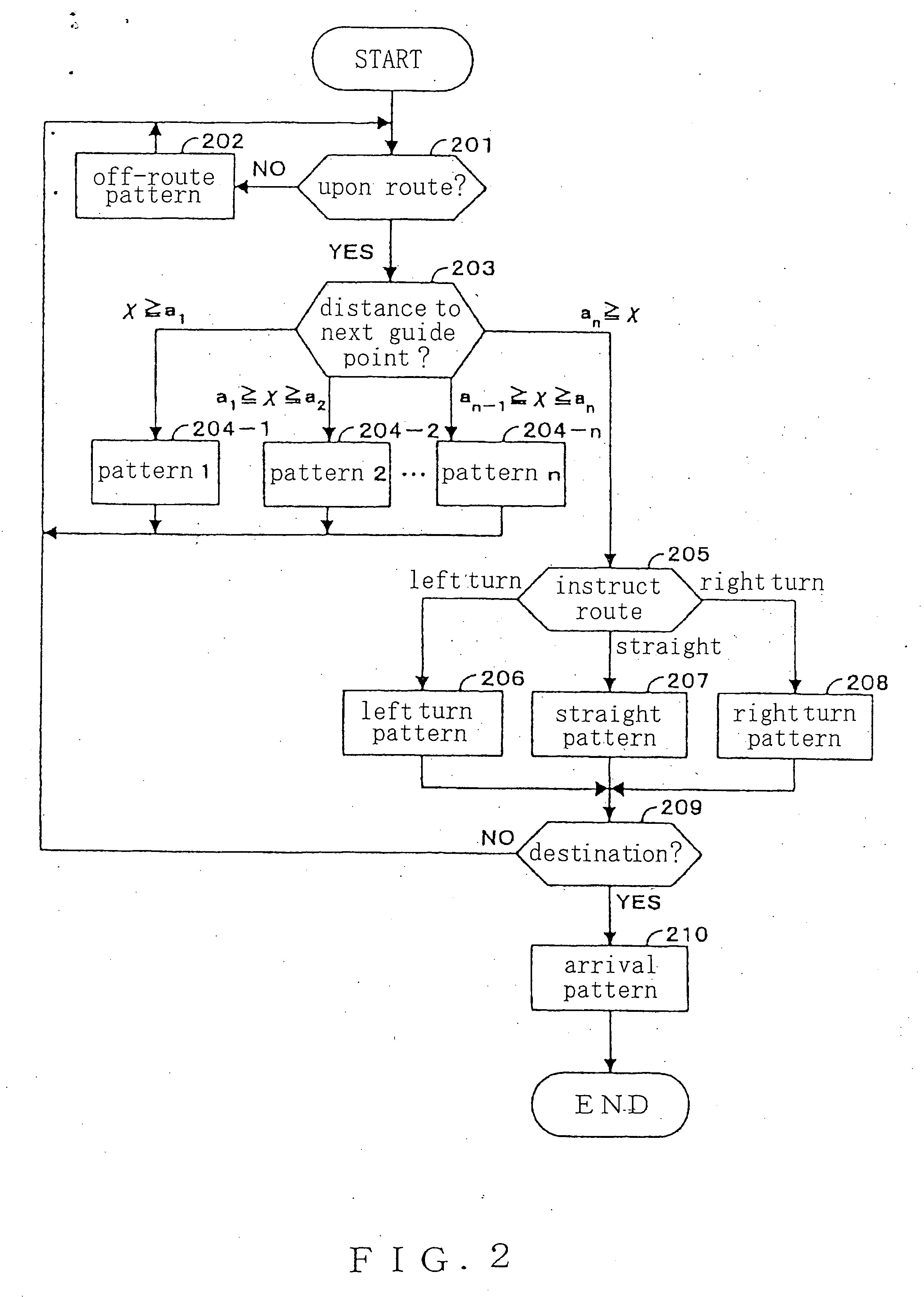
The present invention comprises a pedestrian navigation system for providing distance information and travel directions to a destination, comprising a pedestrian navigation device 10 for navigating a pedestrian's route by means of a vibration, a server 30 for offering navigation information to the pedestrian navigation device 10, a network 40 for connecting the pedestrian navigation device 10 with the server 30 to permit communication between each other, and a GPS 20 for offering position information to the pedestrian navigation device 10. Further, the pedestrian navigation device 10 can be constructed to comprise a speaker 19 for outputting a guide voice based on the user's present position information, so as to start a voice guide after generating vibration, thereby facilitating verification of the guidance information provided.
Owner:NAVITIME JAPAN CO LTD
Traveling Direction Measuring Apparatus and Traveling Direction Measuring Method
InactiveUS20090143972A1High positioning accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsControl with pedestrian guidance indicatorData setClassical mechanics
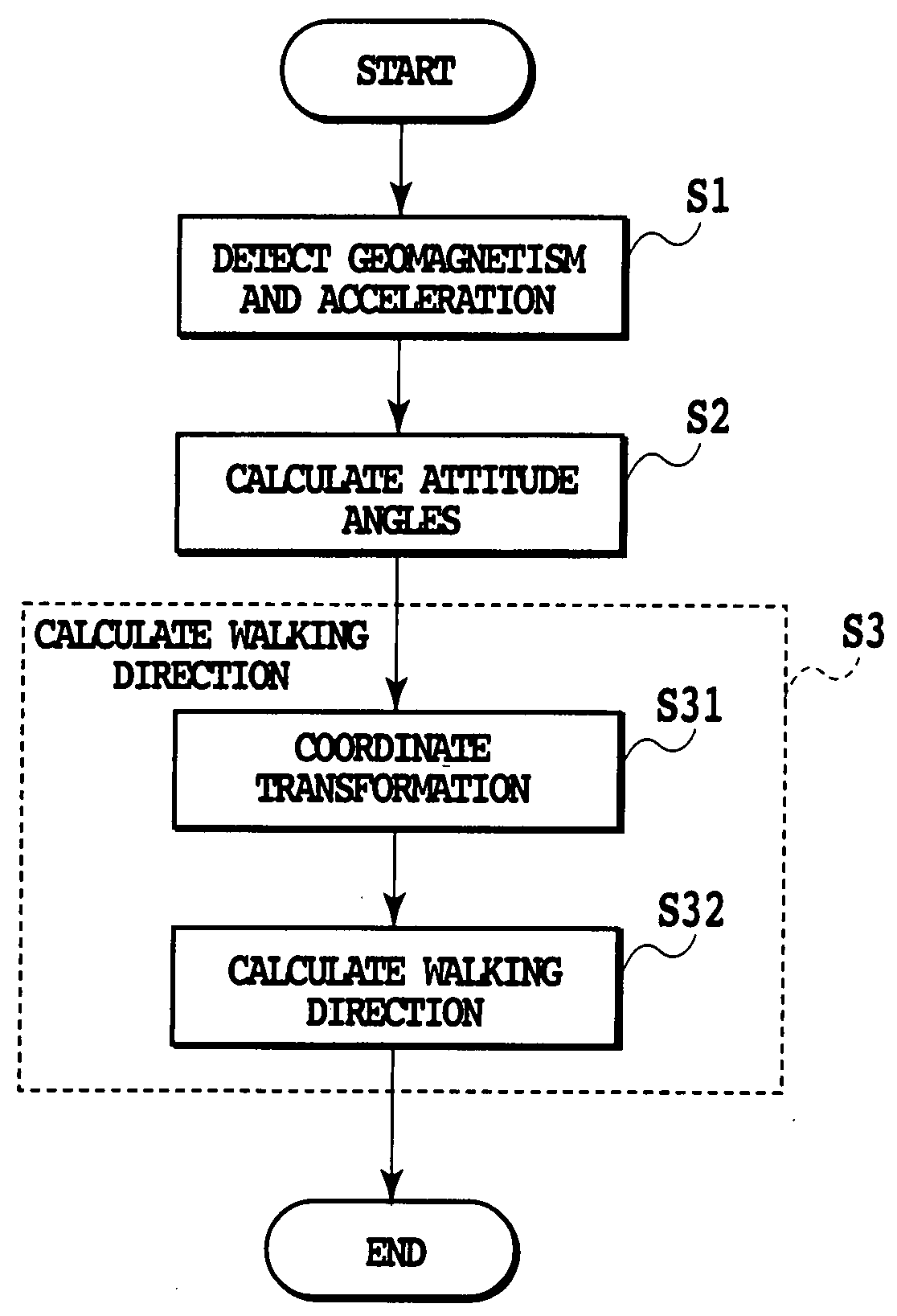
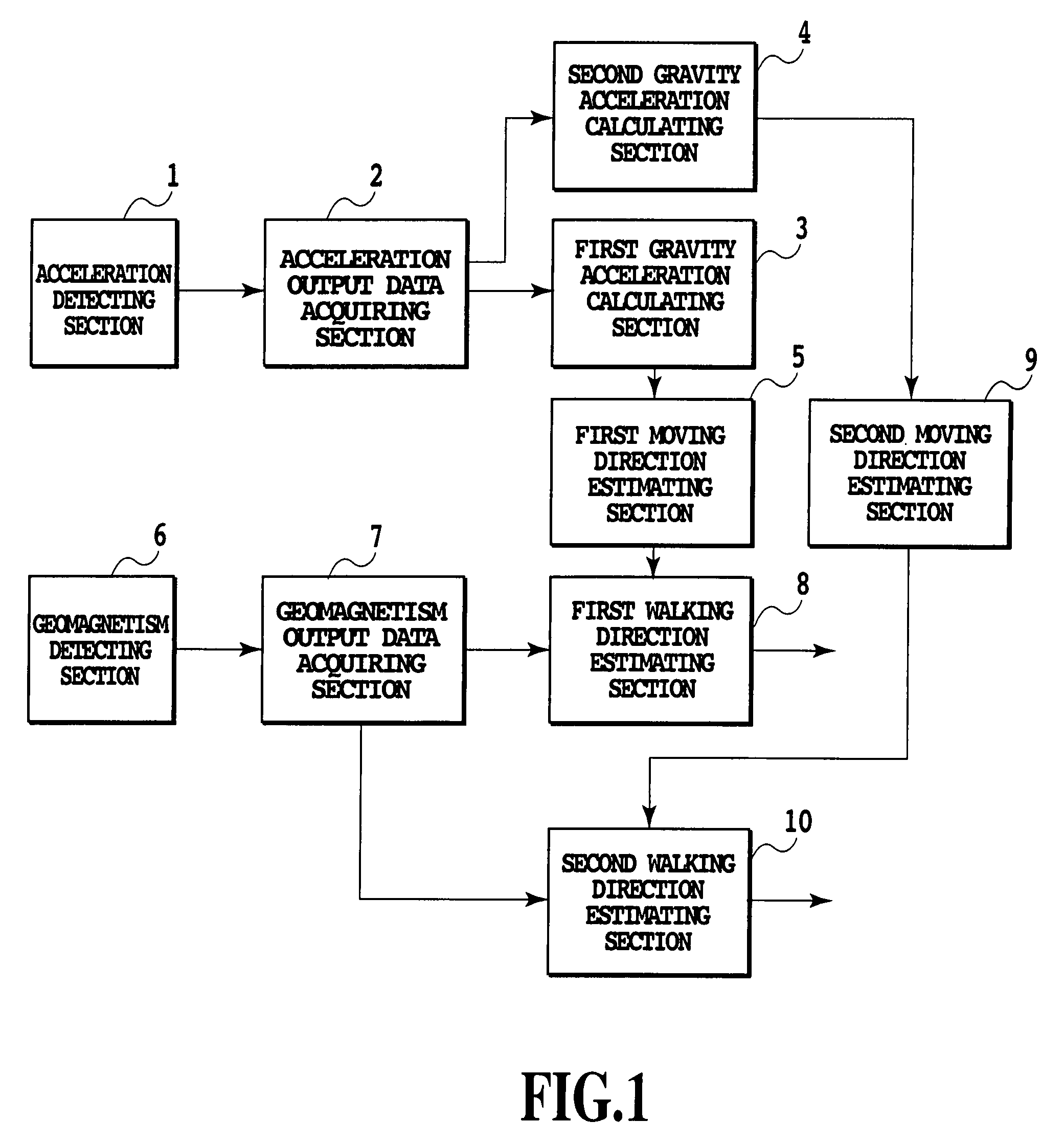
The present invention relates to a traveling direction measuring apparatus usable as a pedestrian navigation system in locations where it is difficult to obtain high positioning accuracy such as inside buildings or around multistory buildings where a GPS cannot be used. An acceleration detecting section (1) detects 3-axes acceleration of the traveling direction measuring apparatus, which varies with the walking of the pedestrian. An acceleration data acquiring section (2) obtains 3-axes acceleration data repeatedly by the number of prescribed times or more, said 3-axes acceleration data varies with the walking of the pedestrian. A first gravity acceleration calculating section (3) calculates, when the pedestrian is walking with holding the traveling direction measuring apparatus in a generally fixed attitude, gravity acceleration by averaging acceleration data sets during several steps obtained by the acceleration data acquiring section (2). A first moving direction estimating section (4) estimates the moving direction of the pedestrian from frequency components corresponding to the duration of one step of the acceleration data sets projected on a plane perpendicular to the gravity acceleration calculated by the first gravity acceleration calculating section (3).
Owner:ASAHI KASEI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Zero speed detecting method, zero speed detecting device, and pedestrian navigation method as well as pedestrian navigation system
ActiveCN104296750AEliminate the effects ofImprove reliabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPedestrian navigation systemAnalysis method
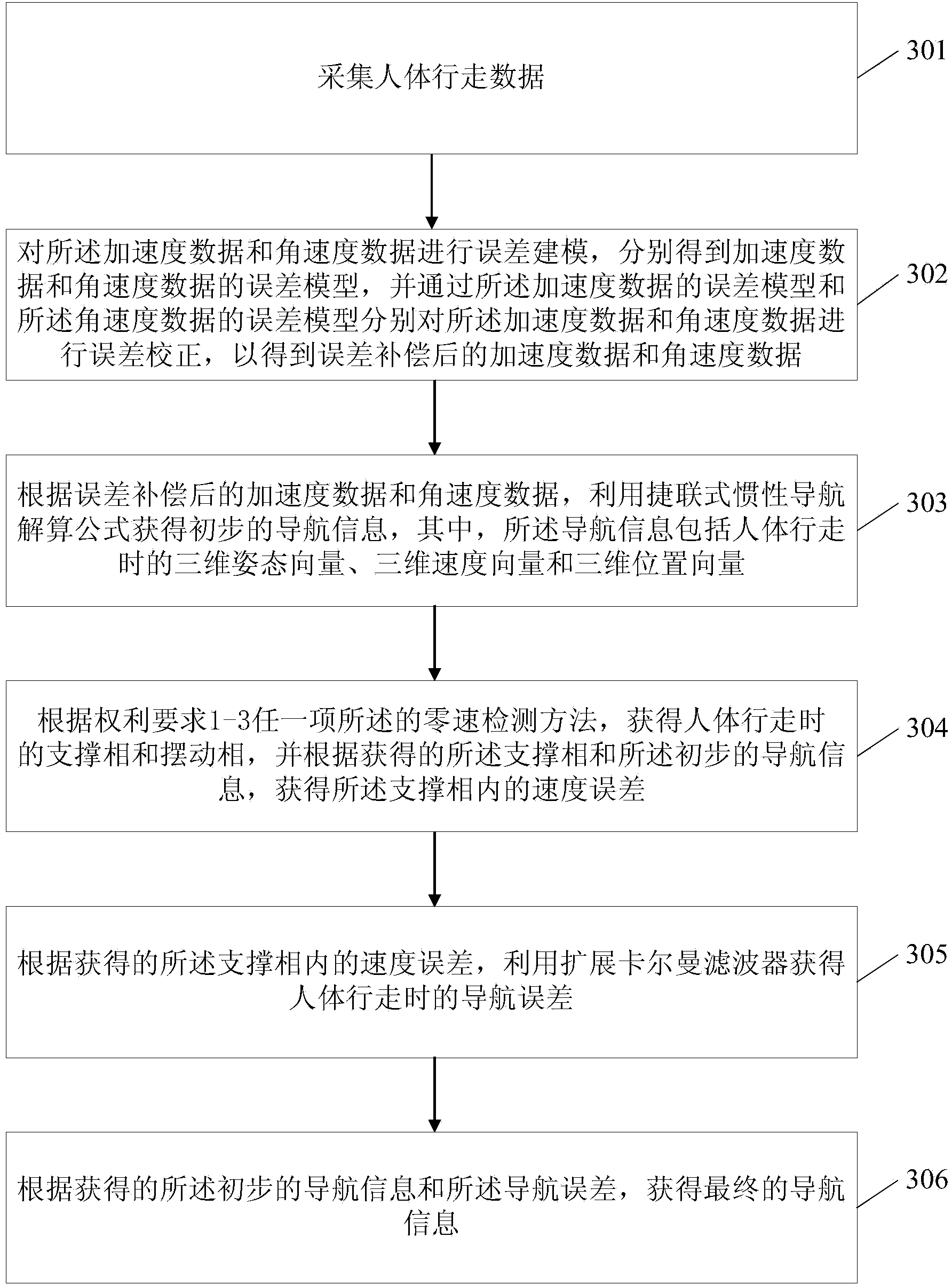
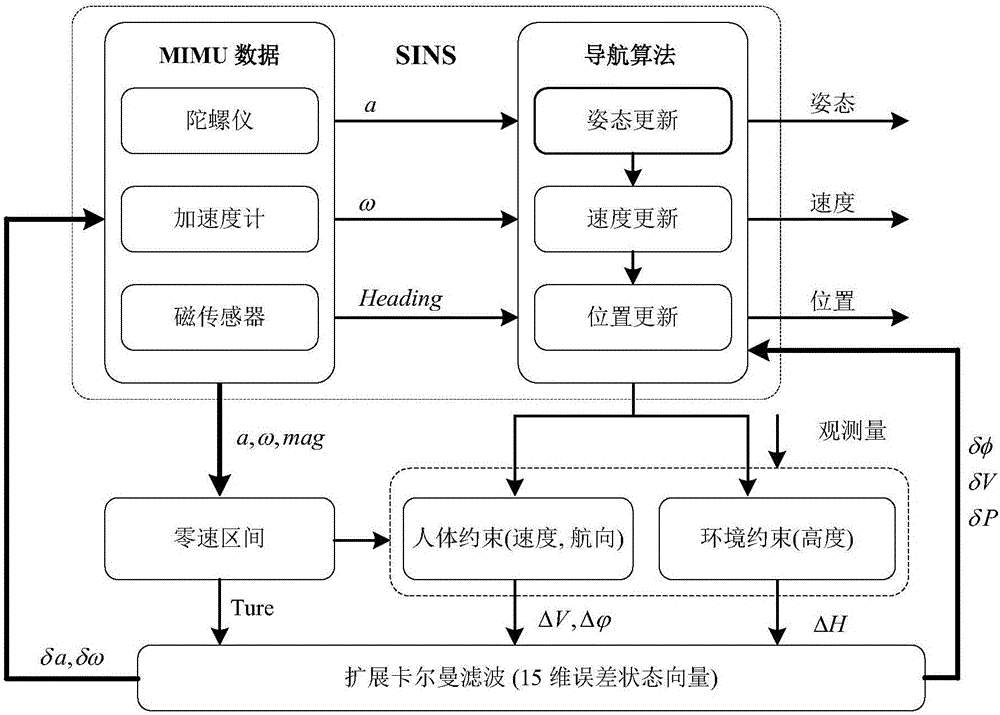
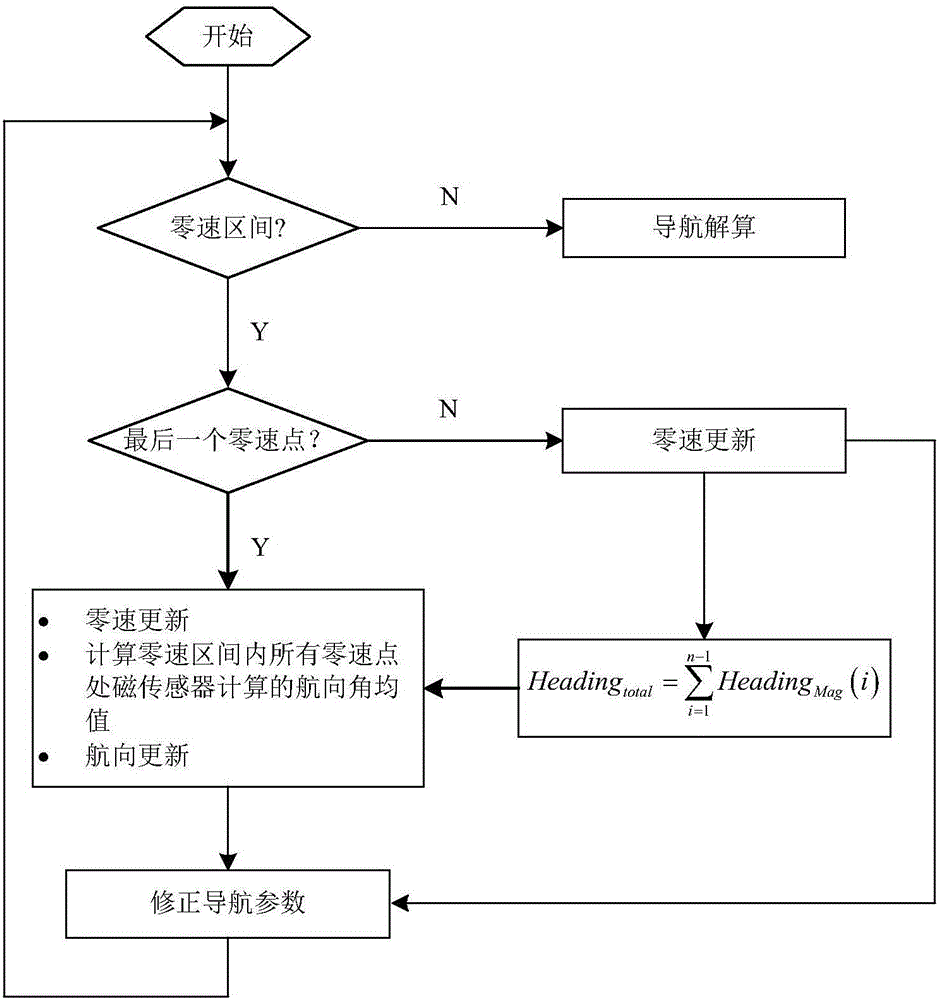
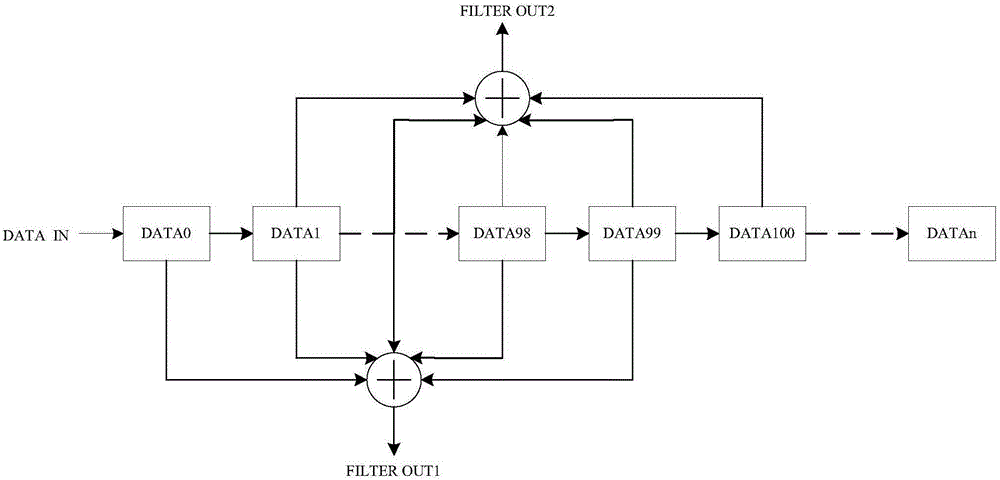
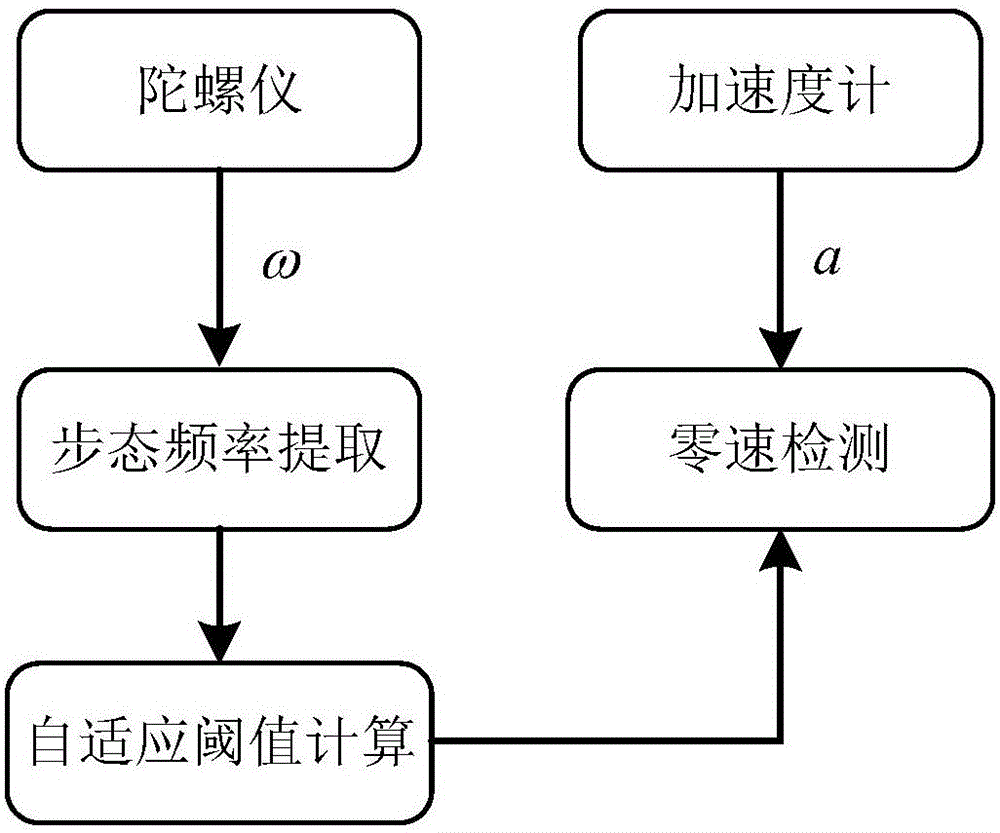
The invention relates to the technical field of pedestrian navigation and provides a zero speed detecting method, a zero speed detecting device, and a pedestrian navigation method as well as a pedestrian navigation system. The zero speed detecting method comprises the following steps: detection statistic is calculated by comprehensively utilizing acceleration data and angular speed data when a human body walks, wherein a threshold parameter is divided into a detection threshold and a correction threshold; the detection threshold is predetermined in advance and is used for roughly dividing a gait time phase; the correction threshold is used for finely dividing the gait time phase; the zero speed detecting statistic is compared with the predetermined detection threshold to roughly divide the gait time phase; a swinging amplitude of a swinging phase and time duration of a support phase in a primary division result are classified by a clustering analysis method; the correction threshold of fine division of the gait time phase is obtained by self adaption; and a rough division result of the gait time phase is compared with the correction threshold to finely divide the gait time phase. By virtue of the zero speed detecting method, the zero speed detecting device, and the pedestrian navigation method and the pedestrian navigation system, the accuracy and the reliability of the pedestrian navigation system can be improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
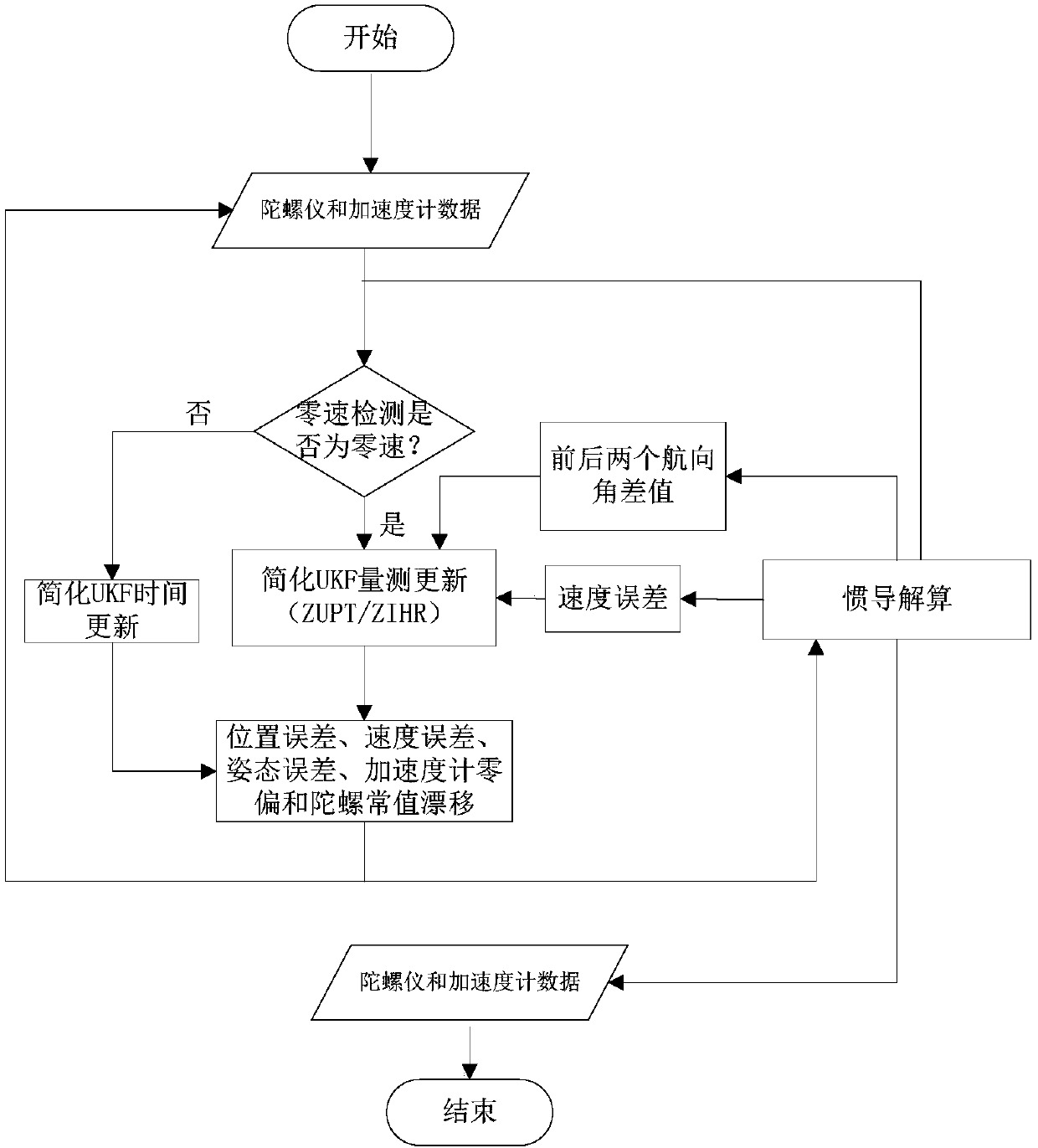
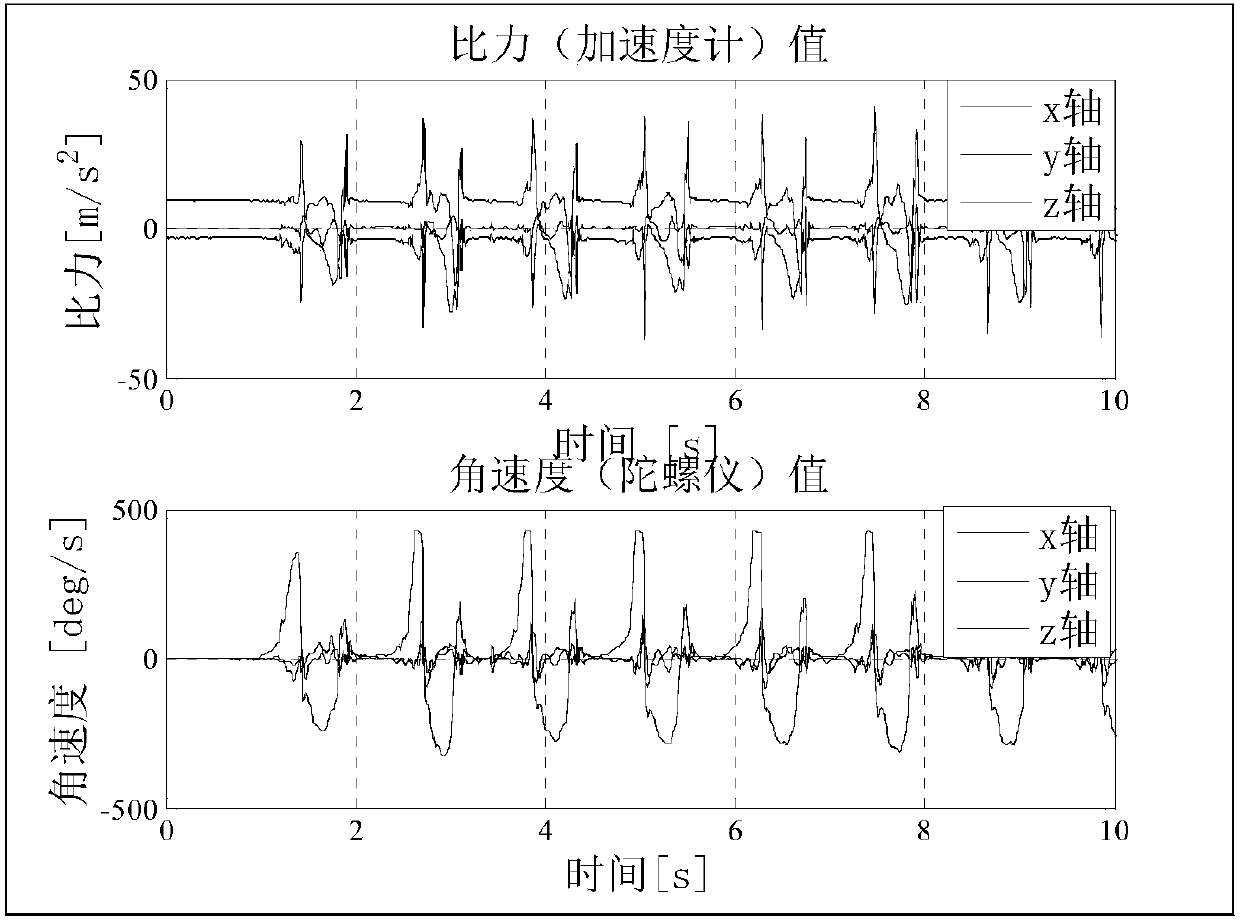
MEMS pedestrian navigation method based on ZIHR heading angle correction algorithm
InactiveCN108426574AAvoid divergenceExtended 1D measurementNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsCorrection algorithmAccelerometer
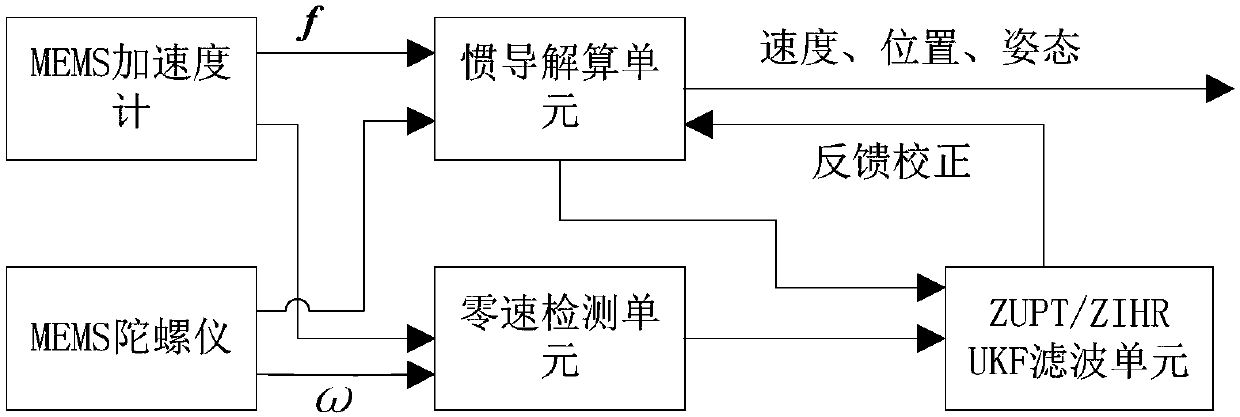
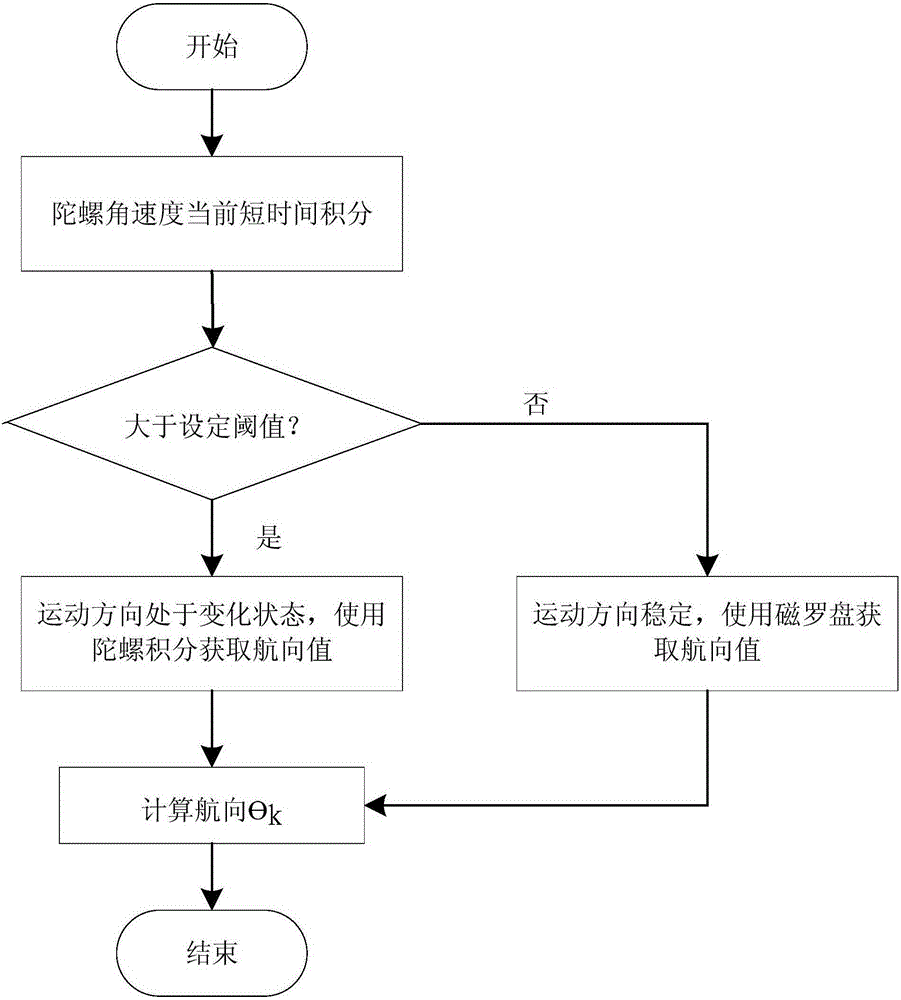
The invention provides an MEMS pedestrian navigation method based on ZIHR heading angle correction algorithm. The method includes: 1. conducting initial alignment on an MEMS pedestrian navigation system with an accelerometer and a magnetometer at a static moment; 2. working out an inertial navigation calculation equation and an error equation of the MEMS pedestrian navigation system; 3. conductingzero velocity state detection with the output values of a gyroscope and the accelerometer; 4. working out the relationship between the heading angle difference of adjacent moments under a zero velocity state, gyroscopic drift and a heading error angle in ZIHR (zero integrated heading rate) correction algorithm; and 5. establishing a simplified MEMS pedestrian navigation UKF filter model, and performing UKF filtering. The method provided by the invention maximumly utilizes the information of static moment, has uncomplicated calculation amount, and can well inhibit the divergence of the headingerror angle. Use of the UKF filter for real-time feedback correction at a zero velocity moment can well inhibit the problem of navigation parameter error divergence after long-time operation of a low-precision MEMS sensor, and improve the positioning precision of a pedestrian navigation system.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Pedestrian navigation device, pedestrian navigation system, pedestrian navigation method and program
ActiveUS7539576B2Convenient verificationInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsPedestrian navigation systemCelestial navigation
Owner:NAVITIME JAPAN CO LTD
Pedestrian autonomous navigation calculation algorithm based on MEMS-IMU
InactiveCN103776446AImprove the accuracy of useHigh precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAlgorithmPedestrian navigation system
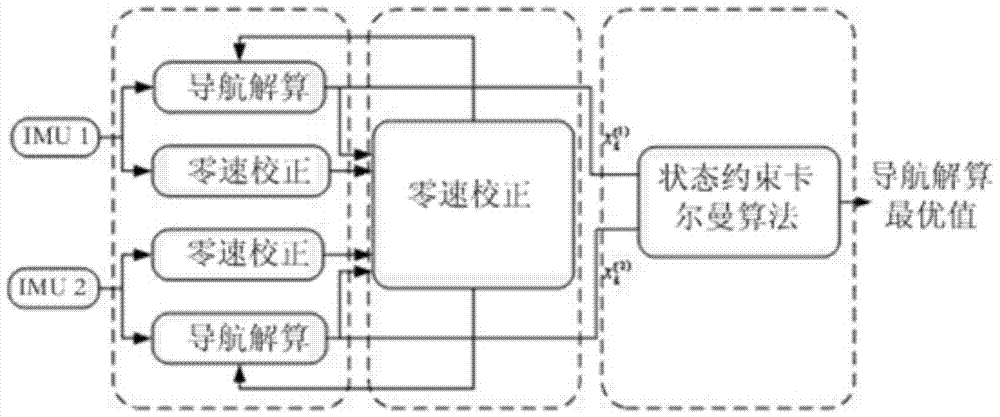
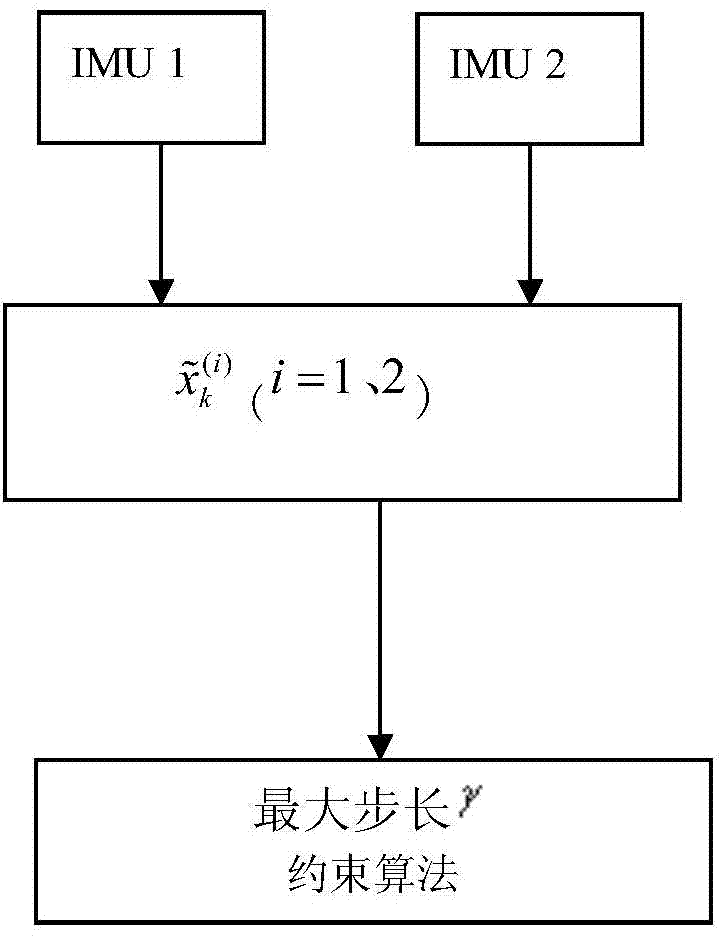
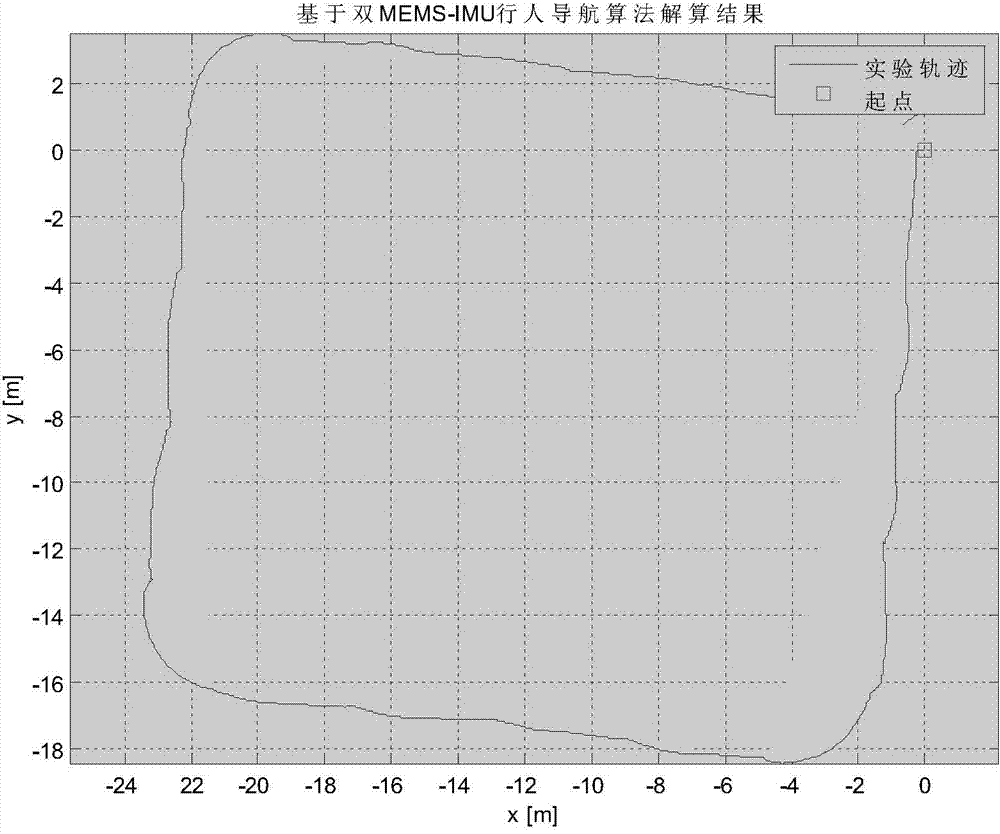
The invention discloses a pedestrian autonomous navigation calculation algorithm based on an MEMS-IMU. Two IMU systems are simultaneously and fixedly connected with the two feet of the user of a pedestrian navigation system; the two systems respectively perform a strapdown inertial navigation calculation algorithm and a zero-speed correcting algorithm on the basis of Kalman filtering, and then the positioning information of the two feet is fused; when the calculation distance between two feet exceeds the largest step size gamma between the two feet, inequality constraint is performed on navigation results of two IMUs by adopting a state constraint Kalman filtering algorithm, so that vague human physiological property problem is converted into a rigid mathematical problem, the optimal estimation of navigation results is achieved, and pedestrian navigational positioning function with higher accuracy is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Pedestrian navigation system three-dimensional spatial positioning method based on human/environment constraints
ActiveCN106017461AReduce missed detection rateHigh solution accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsData acquisitionGait
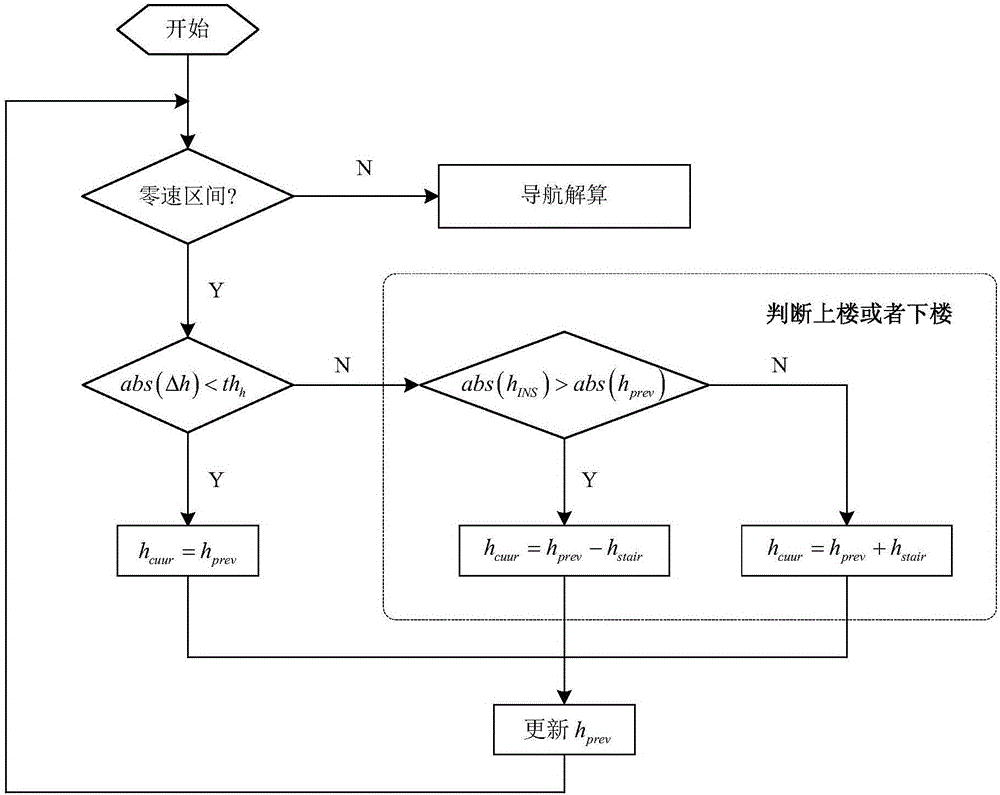
The invention relates to a pedestrian navigation system three-dimensional spatial positioning method based on human / environment constraints and solves the problem with high-precision positioning of a pedestrian navigation system in a three-dimensional space, wherein the system is designed based on a low-cost MEMS (micro-electromechanical system) inertial measurement unit; data collection and strap-down navigation calculation are performed by installing the MEMS inertial measurement unit on a shoe, and zero-speed ranges in pedestrian gaits are detected in connection with data output by a pressure sensor installed on a sole. A scheme is provided based on zero speed correction in connection with pedestrian motion characteristics and ambient building characteristics, the scheme is about constraining magnetic field abnormality in zero-speed ranges and constraining SINS (ship's inertial navigation system) height channel divergence, and an extended Kalman filter is designed to correct errors in navigation calculation results, thereby enabling high-precision positioning of pedestrians in the three-dimensional space.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
System and method for pedestrian navigation based on multiple sensors
InactiveCN105241454AOvercoming slow performance, unable to navigate properlyOvercoming positioningNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingAccelerometerGyroscope
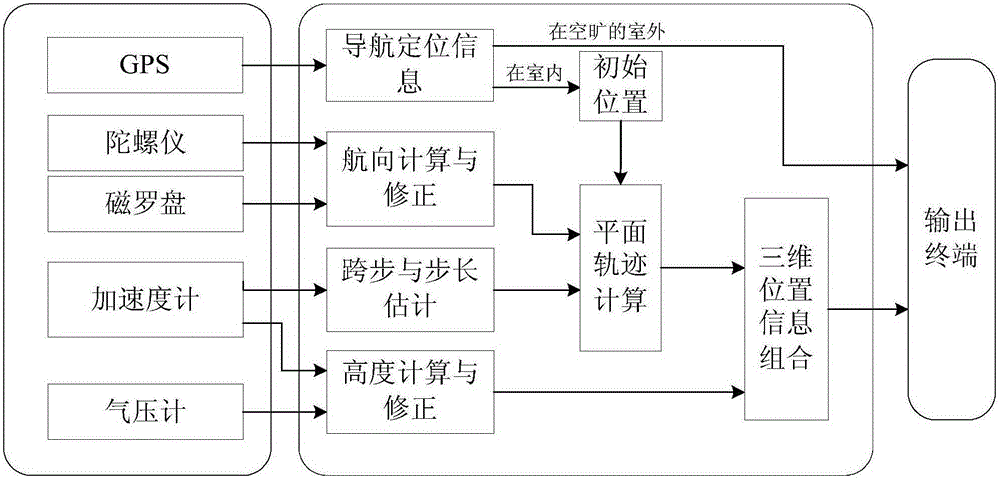
The invention discloses a system and method for pedestrian navigation based on multiple sensors. A sensor module comprises a GPS, an MEMS accelerometer, an MEMS gyroscope, a magnetic compass and a barometer. When the GPS is free of signal blockage, the GPS is adopted to perform navigation positioning. When GPS signal failure occurs, the MEMS accelerometer is utilized to collect and detect pedestrian's walking step number, the pedestrian walking course is calculated through data combination of the MEMS gyroscope and the magnetic compass, and a pedestrian's motion track in the plane is calculated according to the step number and navigation. A motion track of a pedestrian in the height direction is obtained by utilizing data obtained by the MEMS accelerometer and the barometer, and the positioning of a motion track of the pedestrian in a three-dimensional space is achieved. According to the system and method for pedestrian navigation based on the multiple sensors, the shortcoming that single GPS signals are lowered in performance when being indoors or being blocked out, and normal navigation and positioning cannot be performed is overcome, the requirements for small size and low cost of a personal navigating instrument are met, and the system and method for pedestrian navigation are more suitable for navigation of walking pedestrians.
Owner:SUZHOU R&D CENT OF NO 214 RES INST OF CHINA NORTH IND GRP
Pedestrian navigation system and navigation positioning method based on kinesiology model
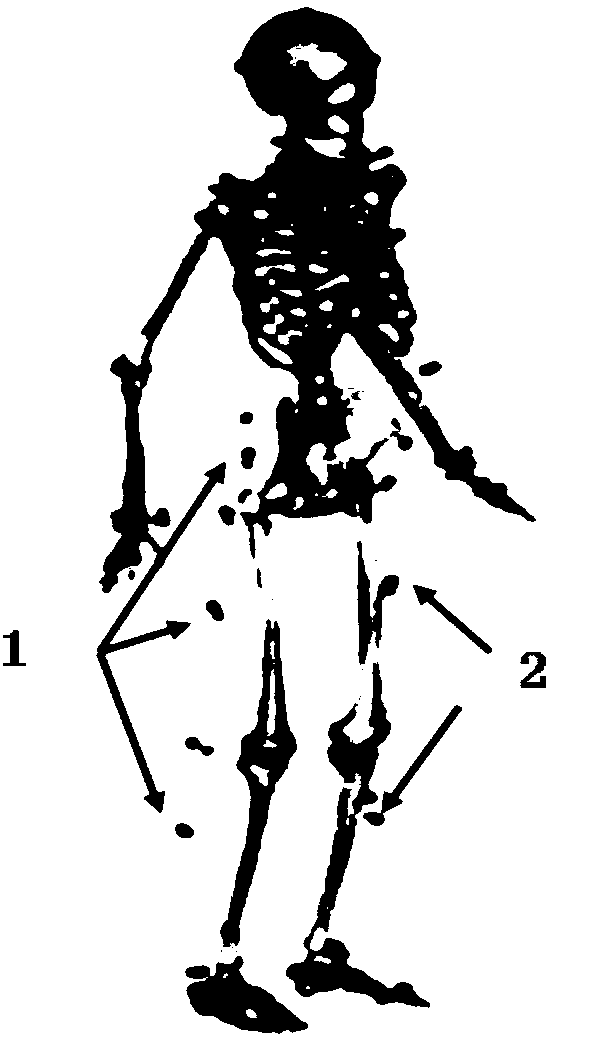
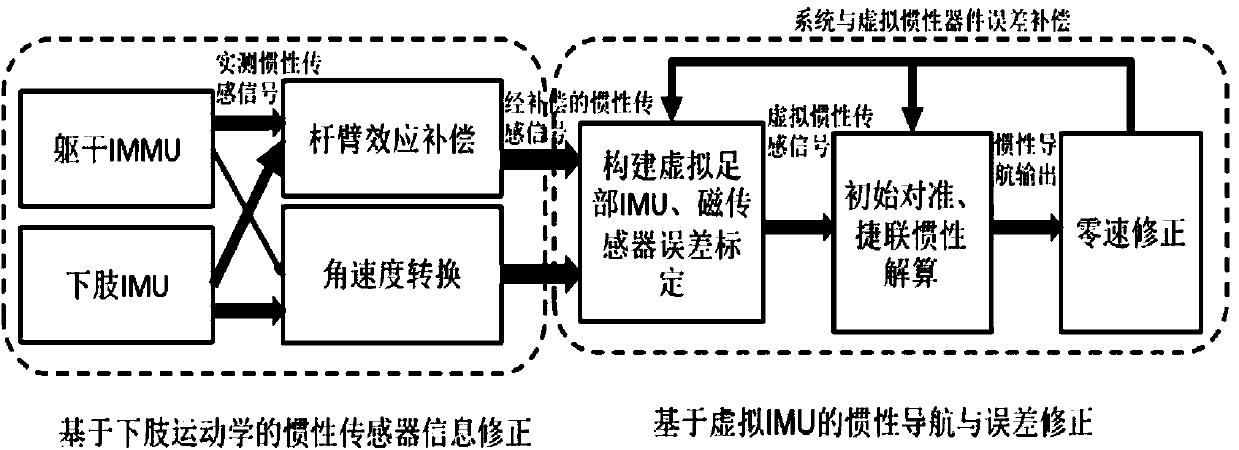
InactiveCN104613963ARealize precise navigation and positioningHigh real-time positioning performanceNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by terrestrial meansThighKinematics
The invention discloses a pedestrian navigation system and a navigation positioning method based on a kinesiology model, and belongs to the field of combination of biodynamics and inertial navigation. The navigation positioning method comprises the following steps: constructing a virtual inertial sensor component by using a kinematics law between lower limbs (including feet, calves, thighs and hips) in human movement and joints connecting the lower limbs, and correcting errors of the virtual inertial sensor component and the pedestrian navigation system in real time, so as to realize the accurate navigation positioning in human movement. In high-overload human movement, influences of measured information outrange, impact signals and the like on a navigation solution can be effectively overcome, and the real-time positioning performance is relatively high.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
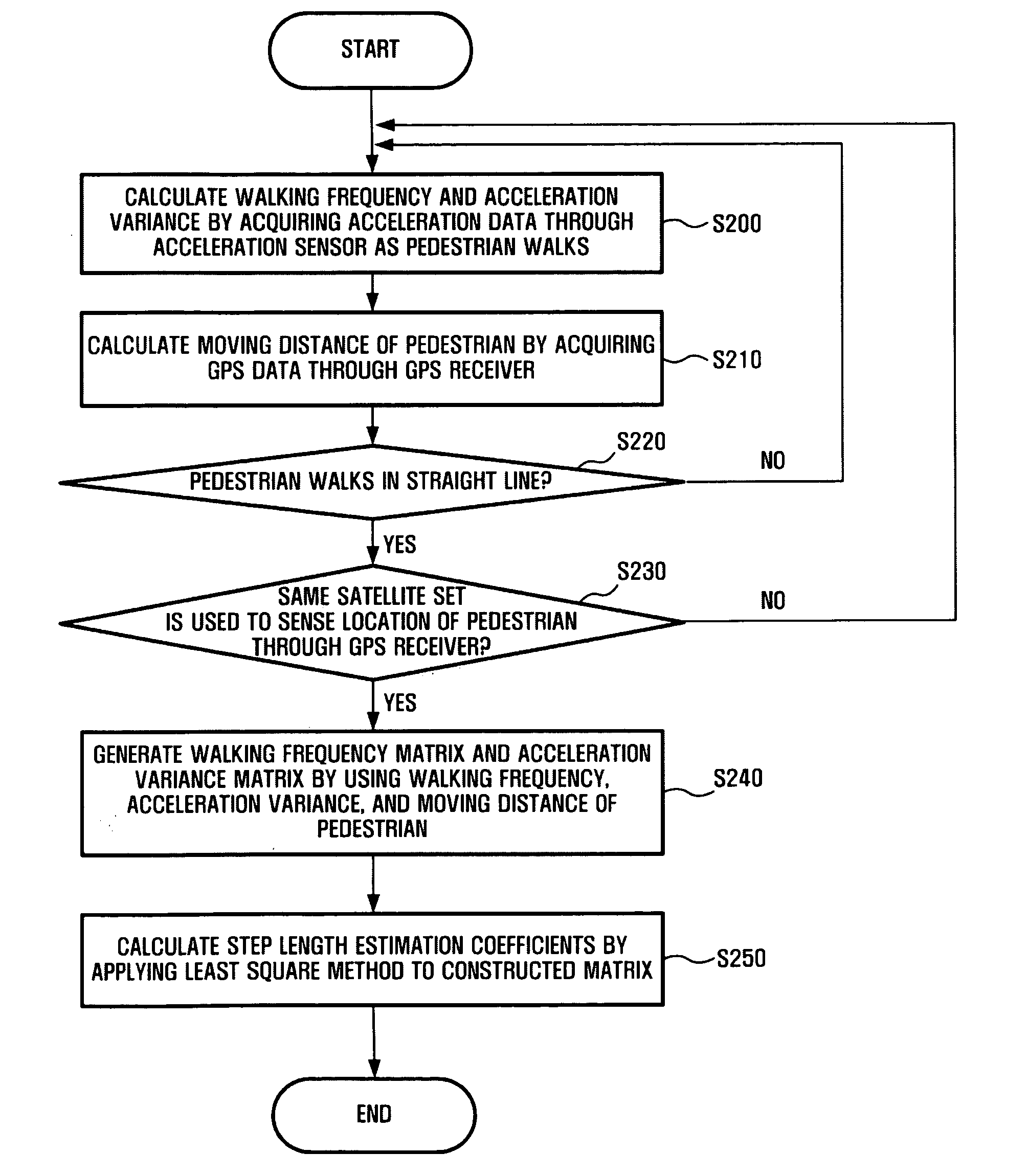
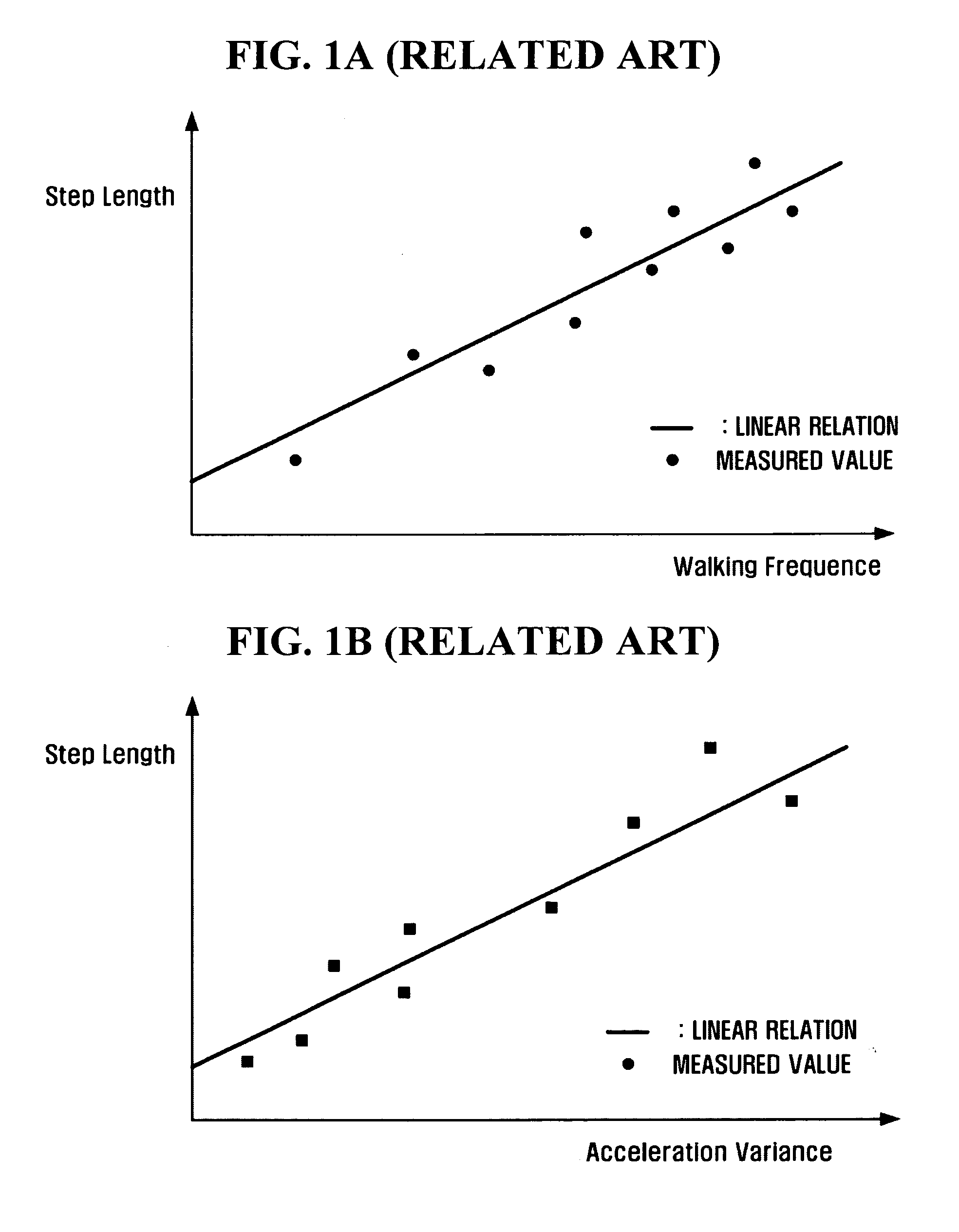
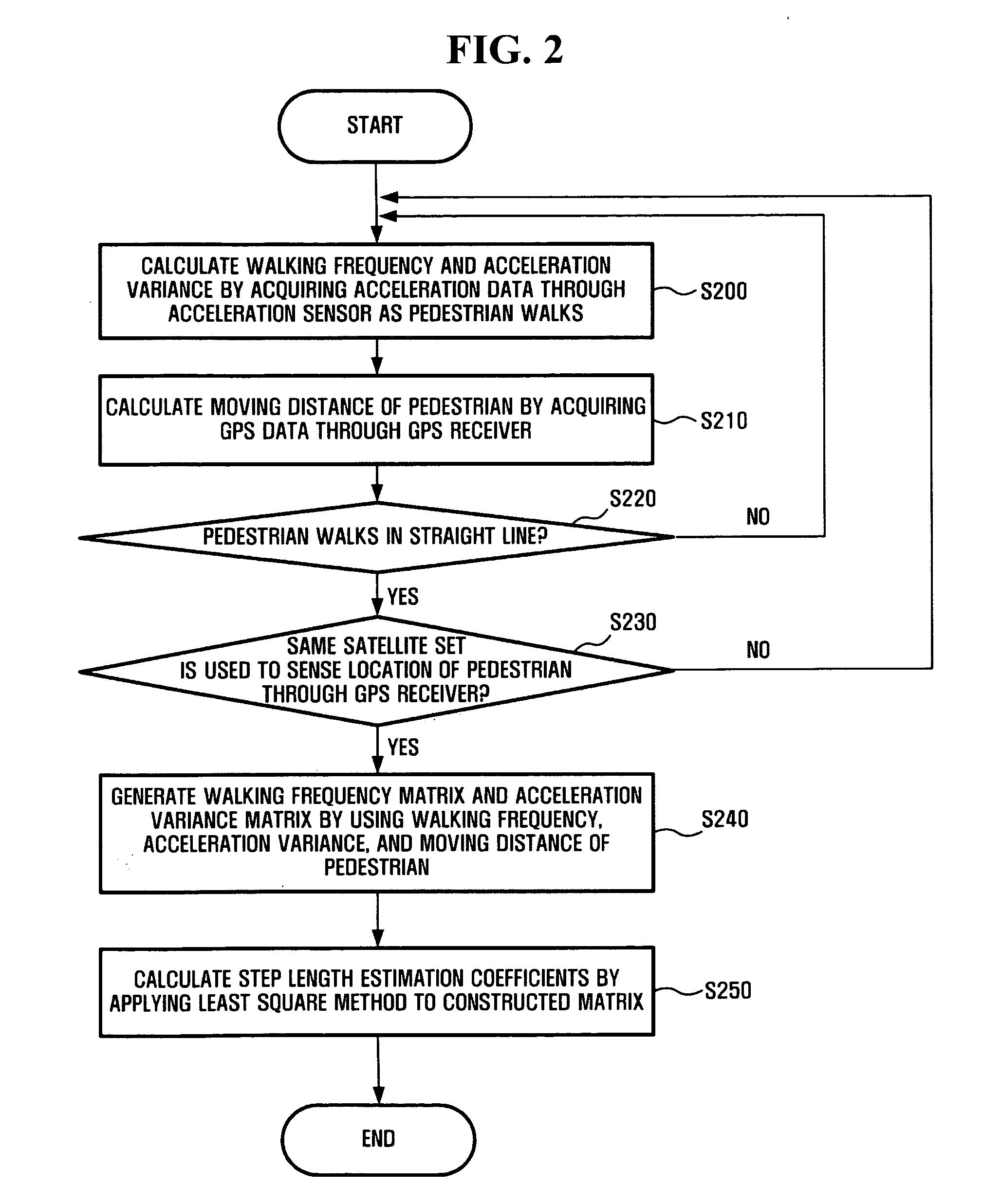
Method and system for estimating step length pedestrian navigation system
InactiveUS20090192708A1Position fixationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsWalking distanceGps receiver
A method and system for estimating a step length in a pedestrian navigation system is provided. The method of estimating a step length in a pedestrian navigation system includes calculating a walking frequency and an acceleration variance of a pedestrian by using acceleration data acquired from an acceleration sensor, calculating a walking distance of the pedestrian by using GPS data acquired from a GPS receiver, and estimating a step length of the pedestrian by using the calculated walking frequency, acceleration variance, and walking distance.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
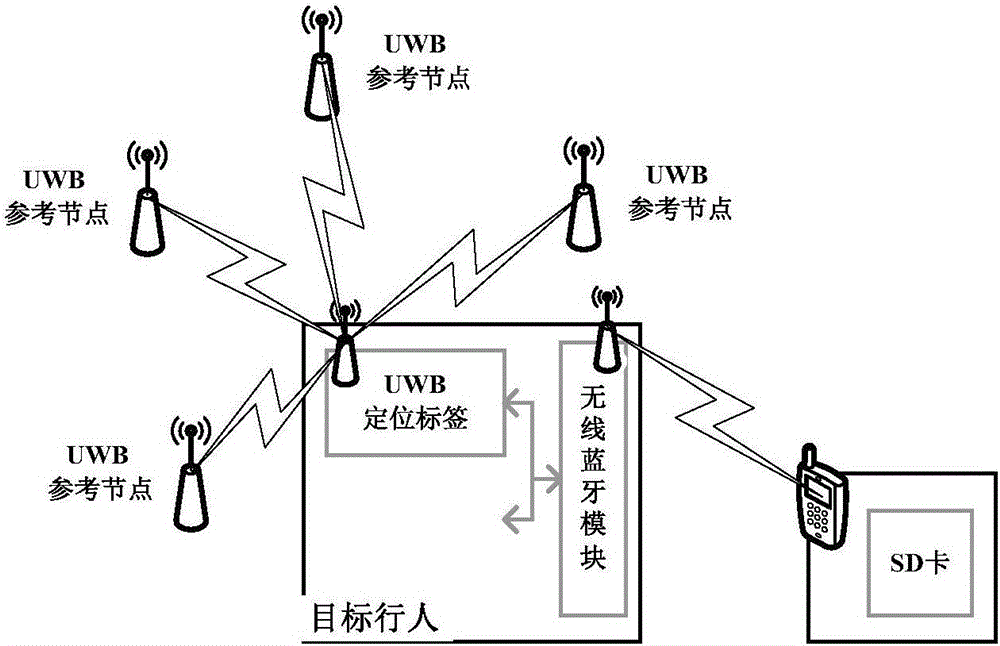
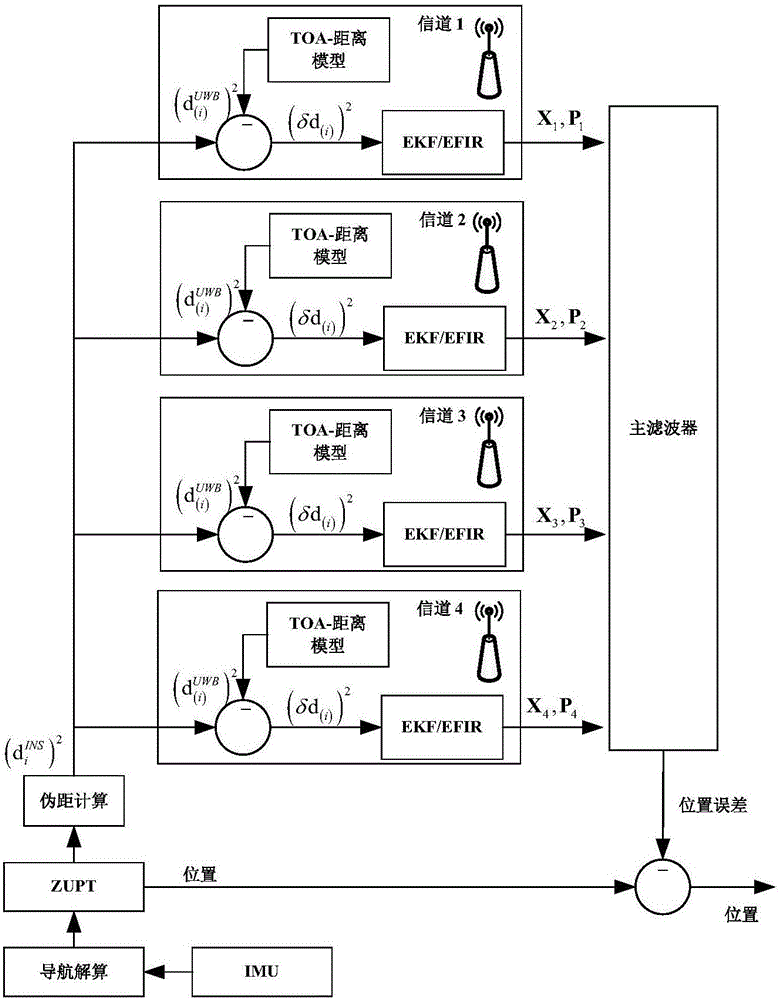
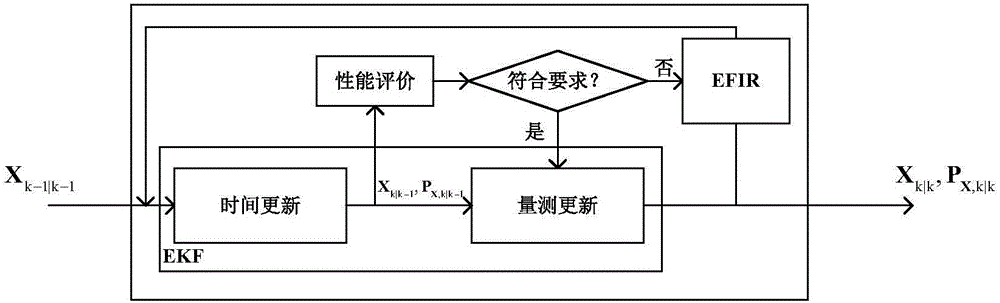
INS/UWB pedestrian navigation system and method based on distributed combined filter
PendingCN106680765AHigh precisionImprove robustnessNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosition fixationData processing systemWireless transmission
The invention relates to an INS / UWB pedestrian navigation system and method based on distributed combined filter. The system comprises an inertial navigation device, a pseudo distance detection unit, a wireless data transmission system and a data processing system. The inertial navigation device is used for measuring pedestrian navigation information; The pseudo distance detection unit is used for obtaining the pseudo distance information; The wireless data transmission system is used for transmitting the data collected by the inertial navigation device and the pseudo distance detection unit to the data processing system through wireless transmission, and transmitting the control command from the data processing system to the inertial navigation device; The data processing system has a distributed combined filter, and chooses one of the distributed combined filters according to the current communication quality of wireless communication channel, and data fusion estimation is made to the collected data, and then the system sends the control command to the inertial navigation device. The system and method can reduce the influence of indoor complex navigation environment on the accuracy of integrated navigation, and obtain the optimal prediction of the target pedestrian navigation information.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Pedestrian Navigation System, Information Delivery Server, and Program
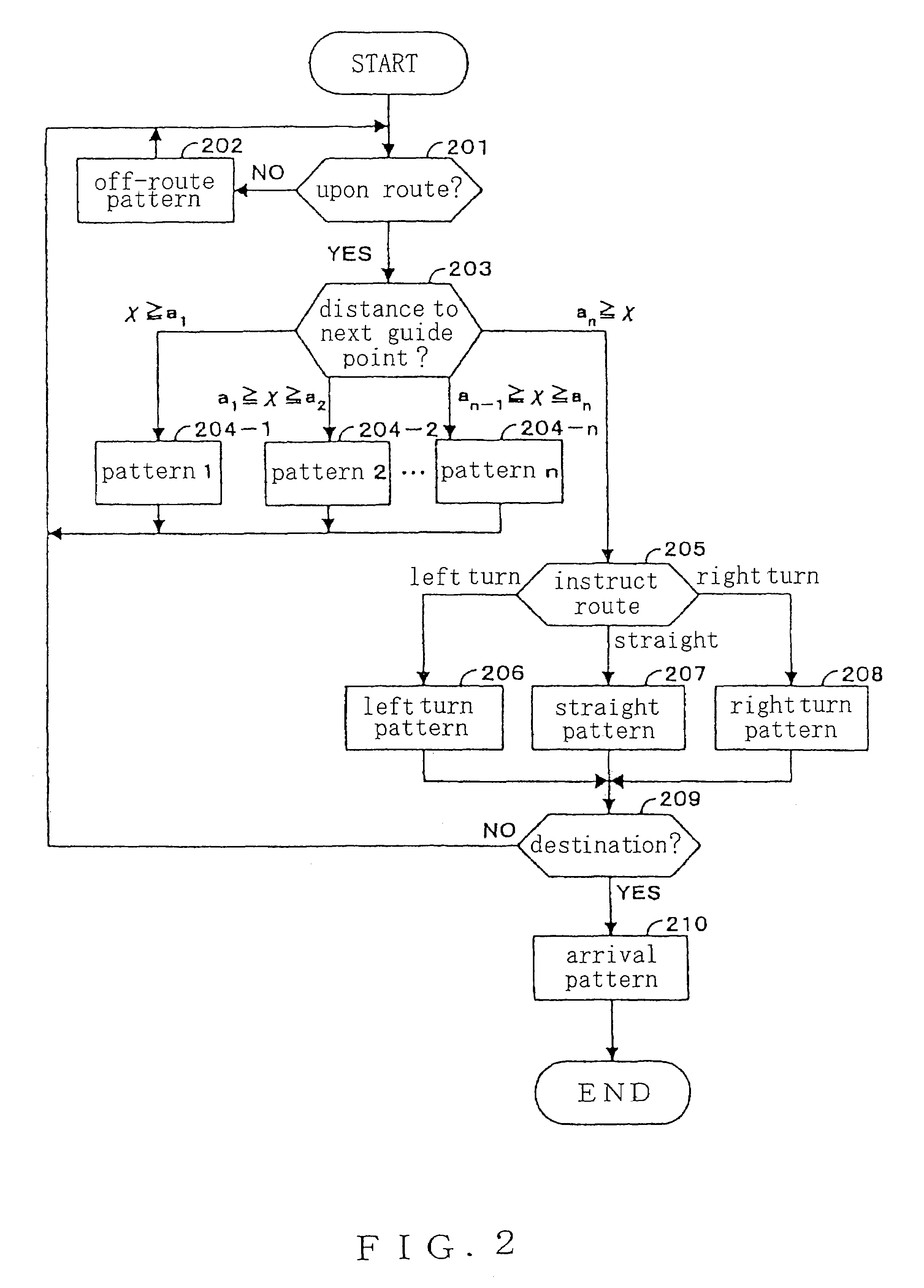
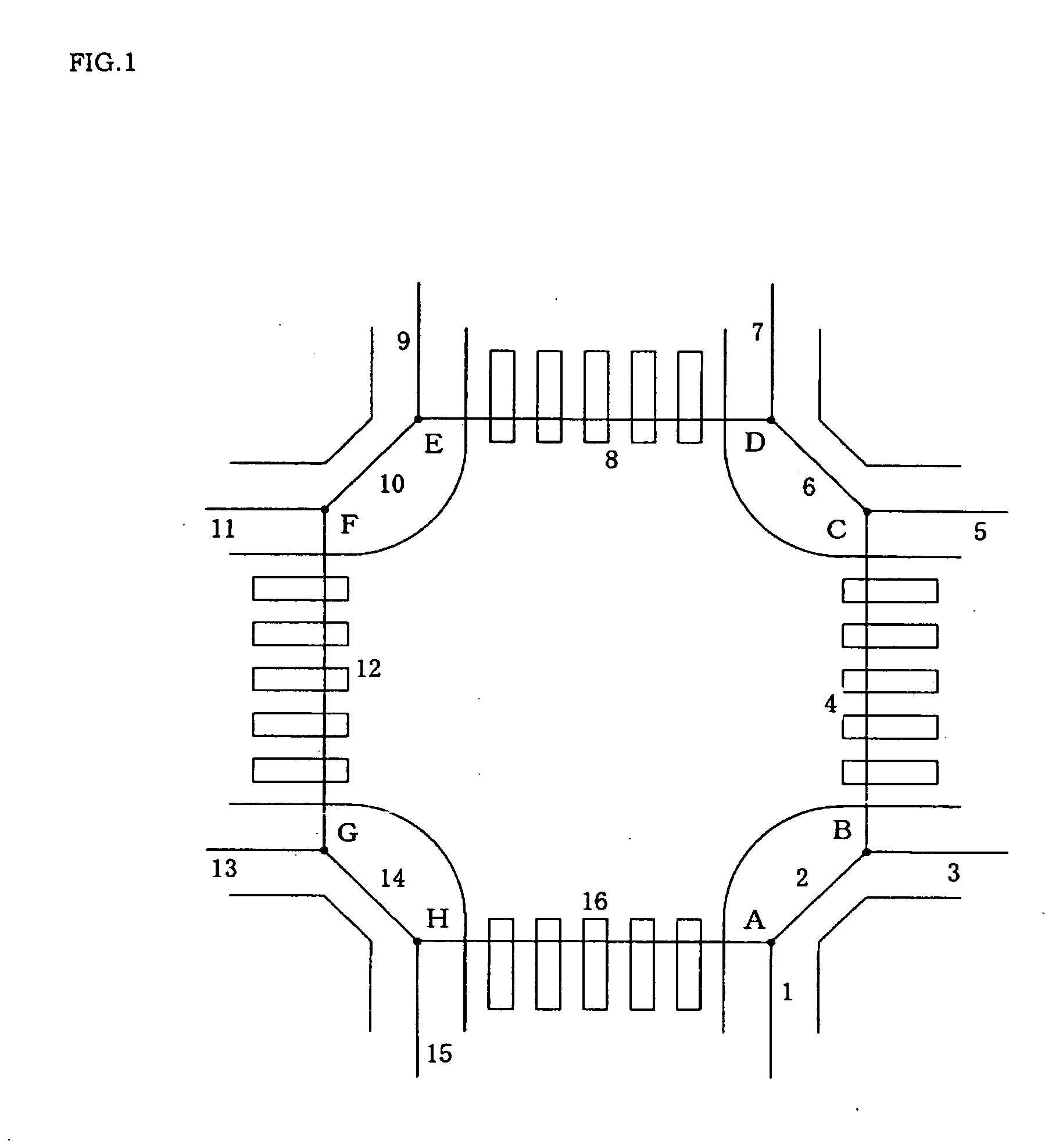
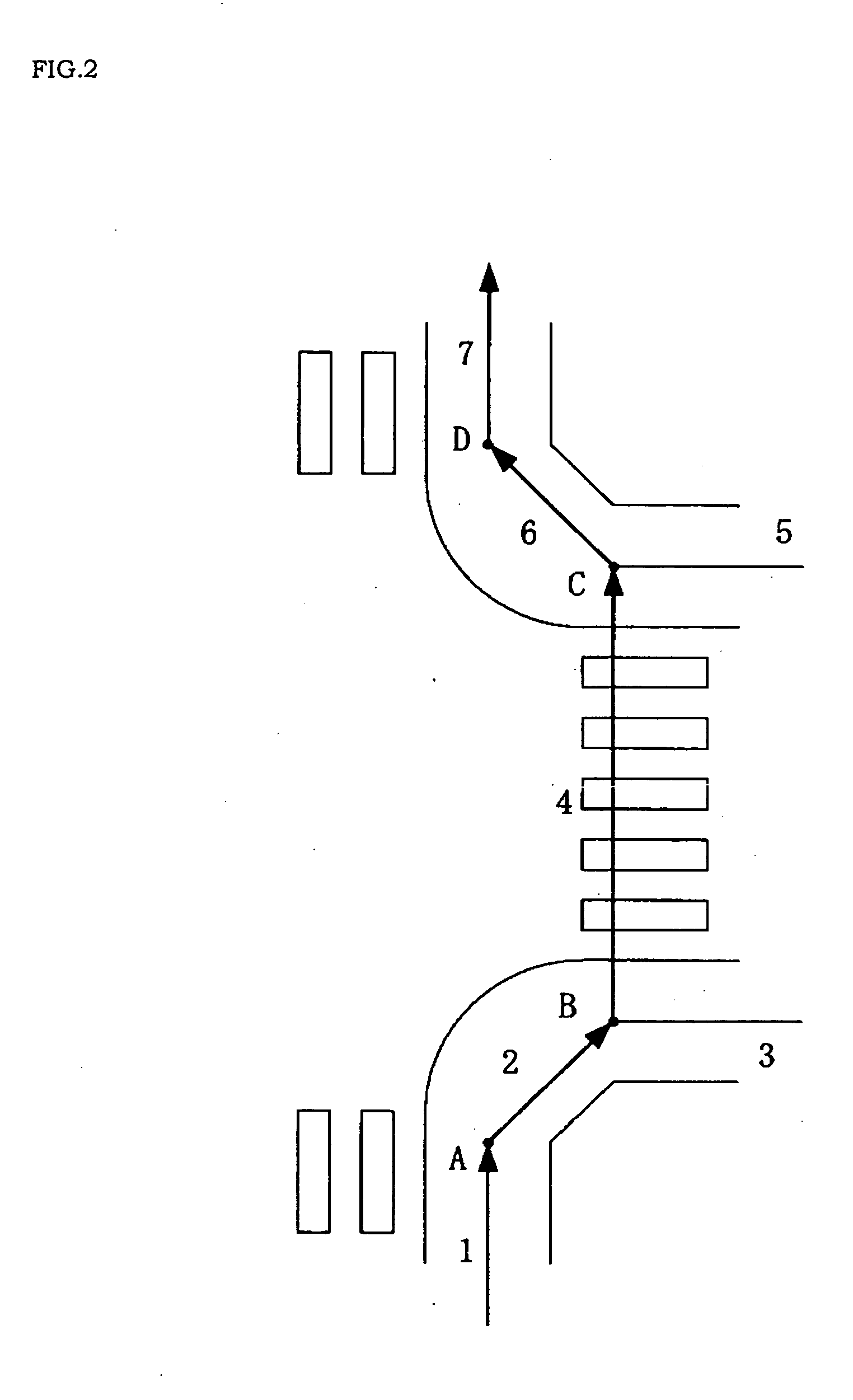
ActiveUS20070233372A1Easy for users to understandDetermined with easeInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsPedestrian navigation systemNavigation system
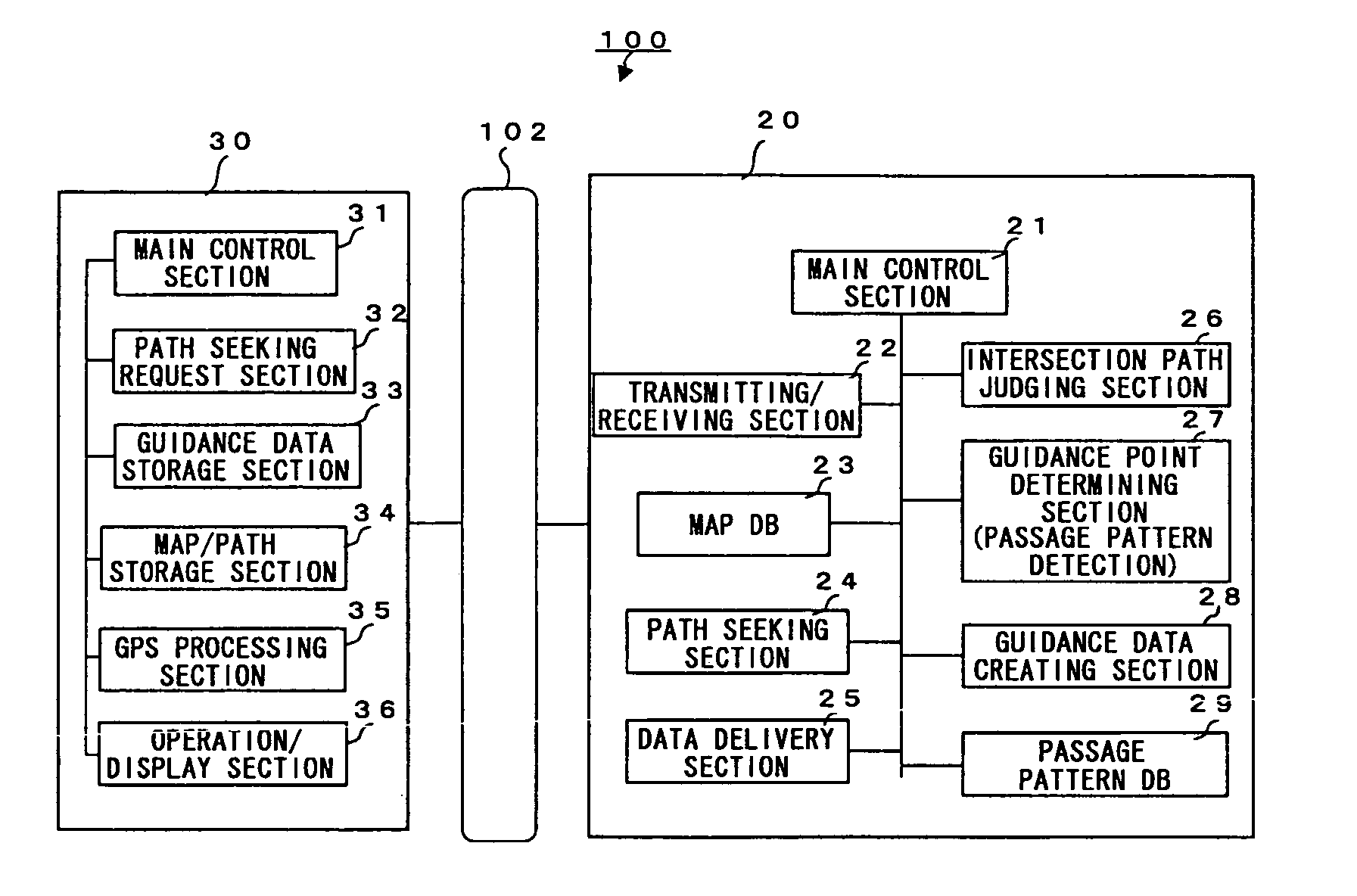
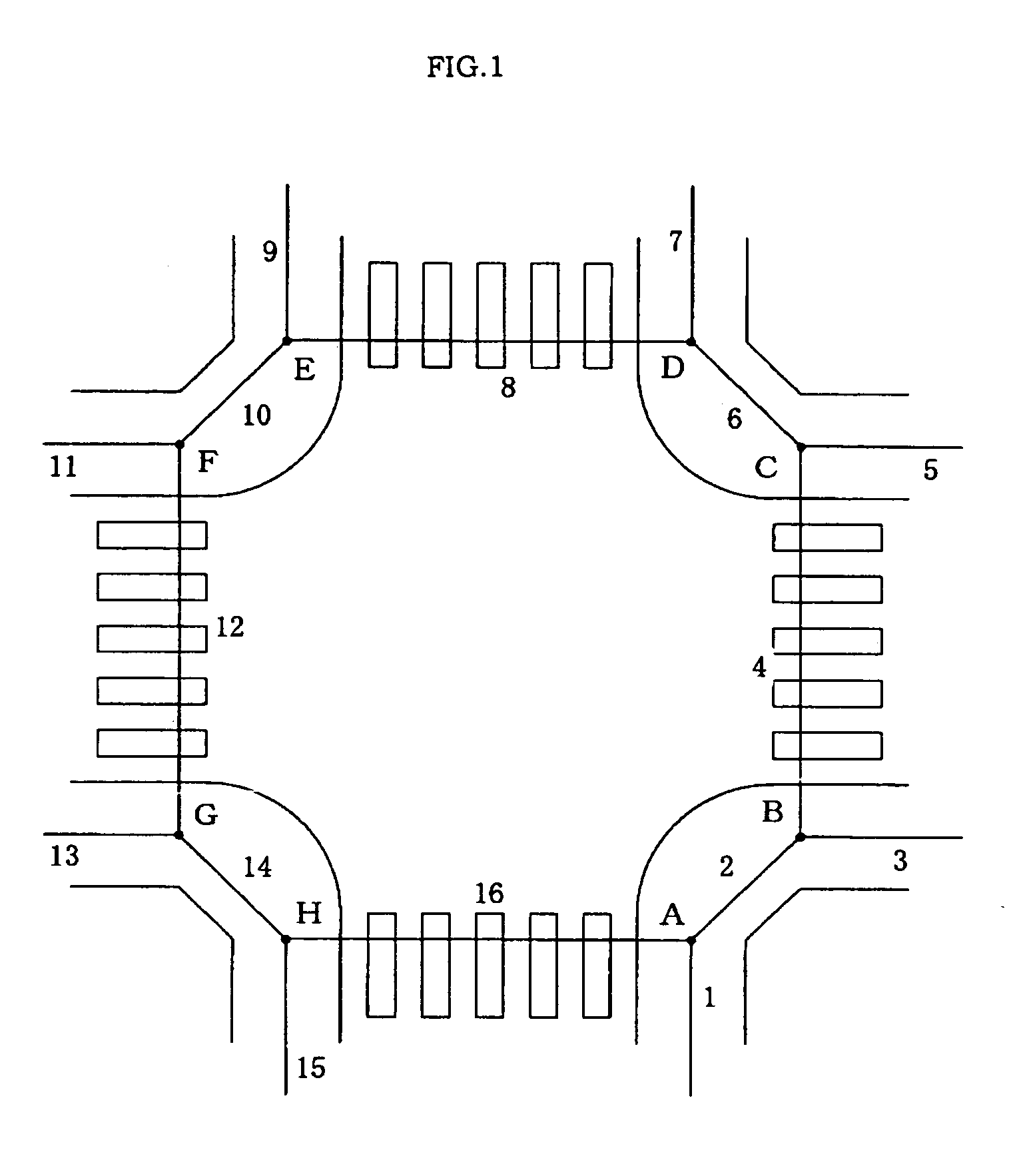
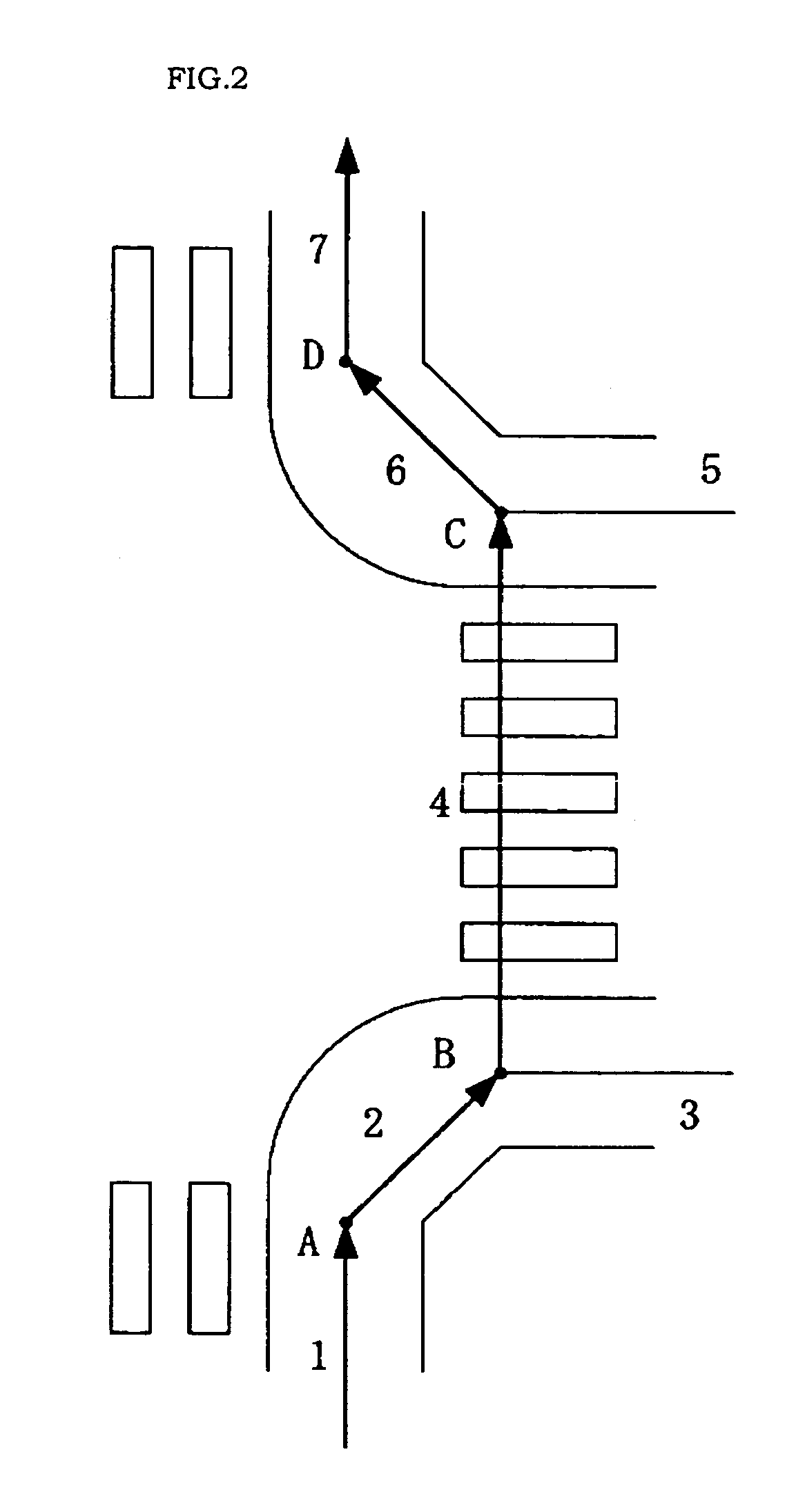
A pedestrian navigation system, an information delivery server, and a program for naturally guiding (such as speech-guiding) the user of a portable terminal at an intersection. An information delivery server (20) comprises a map database (23) containing data such as nodes including paths constituting intersections, links, and costs of the links, a path seeking section (24), an intersection path judging section (26) for detecting a path passing through an intersection from guidance paths which the path seeking section (24) has sought, a guidance point determining section (27) which determines a guidance point for path guidance, a guidance data creating section(28) which determines a guidance pattern of path guidance according to the guidance point, and a data delivering section (25) for delivering map data, guidance path data, and guidance data to a portable terminal. The guidance point determining section (27) selects a specific node out of all the nodes constituting intersections as a guidance point.
Owner:NAVITIME JAPAN CO LTD
Adaptive zero-speed interval detection method for pedestrian navigation system
ActiveCN106225786AEffective filteringAccurate detectionNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerGyroscope
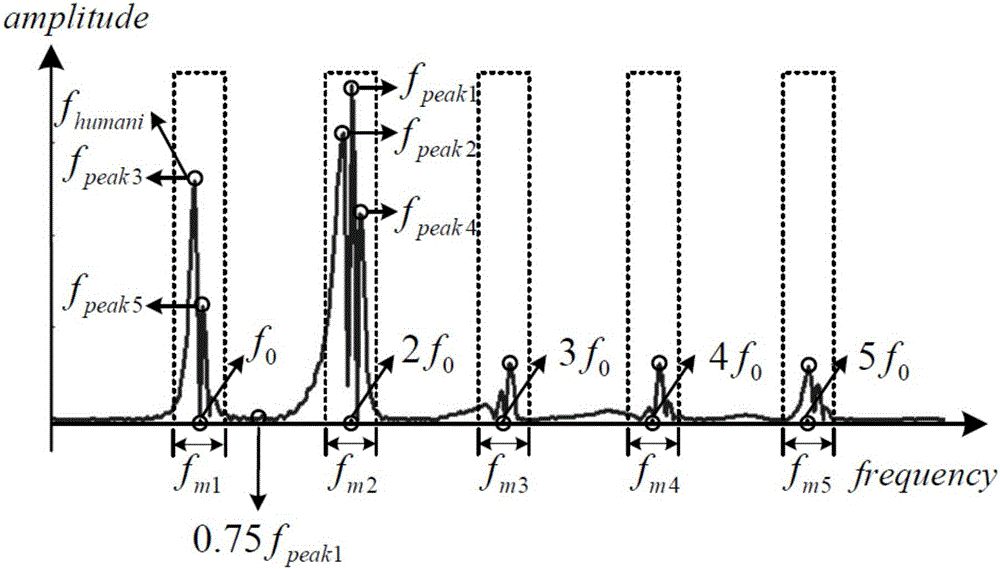
The invention discloses an adaptive zero-speed interval detection method for a pedestrian navigation system. According to a fixed threshold method, a zero-speed detection interval has the problems of false detection and missing detection under the walking condition with varying gait frequencies; by an adaptive threshold method, the relationship between a zero-speed interval detection threshold and the gait frequency of a pedestrian can be analyzed, so that the detection accuracy of a zero-speed interval is effectively improved. By carrying out a calibration experiment of a zero-speed point judging threshold under the condition with different gait frequencies, the functional relationship between a zero-speed detection threshold and the gait frequency is established, and the adaptive adjustment of the detection threshold and the accurate detection of a zero-speed point are achieved, so that the detection accuracy of the zero-speed interval is improved; by the adaptive zero-speed interval detection method, adaptive detection of the zero-speed interval can be achieved only by using output data of a gyroscope and three accelerometers in an inertial measurement unit, without needing to add or use other external sensors to assist the detection of the zero-speed interval, so that the detection method is simple and accurate.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Pedestrian navigation system, information delivery server, and program
ActiveUS7702457B2Easy to understandDetermined with easeInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsPedestrian navigation systemComputer science
A pedestrian navigation system, an information delivery server, and a program for naturally guiding (such as speech-guiding) the user of a portable terminal at an intersection are disclosed. An information delivery server includes a map database containing data such as nodes including paths constituting intersections, links, and costs of the links, a path seeking section, an intersection path judging section for detecting a path passing through an intersection from guidance paths which the path seeking section has sought, a guidance point determining section which determines a guidance point for path guidance, a guidance data creating section which determines a guidance pattern of path guidance according to the guidance point, and a data delivering section for delivering map data, guidance path data, and guidance data to a portable terminal. The guidance point determining section selects a specific node out of all the nodes constituting intersections as a guidance point.
Owner:NAVITIME JAPAN CO LTD
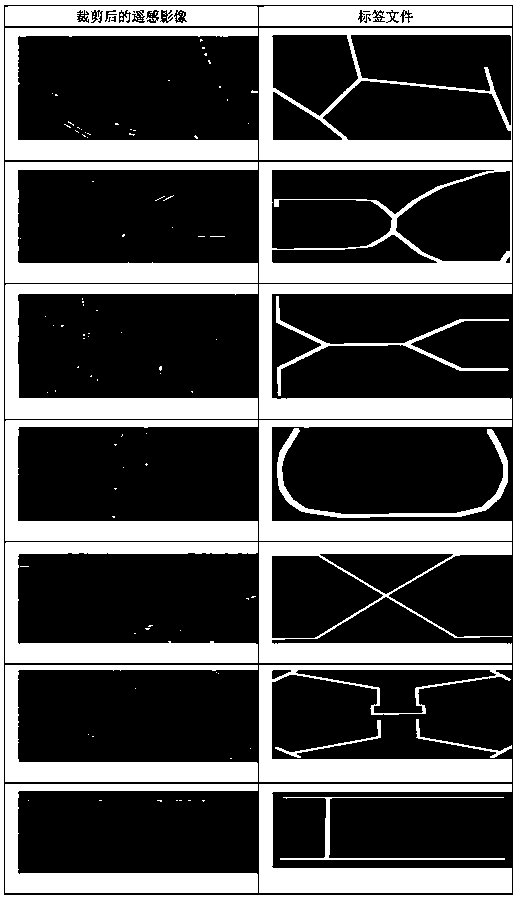
Deep learning method for extracting pedestrian foot-bridge by using OSM and remote sensing images
ActiveCN108921173AMake up for incomplete shortcomingsTaking into account the current situationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionTopology information
The invention discloses a deep learning method for extracting a pedestrian foot-bridge target by using OSM and remote sensing images. The deep learning method includes: firstly, automatically identifying and extracting a pedestrian foot-bridge from OSM data according to semantic information, topology information and shape information of the pedestrian foot-bridge in an Open Street Map (OSM); obtaining a contour of a pedestrian foot-bridge on by using a depth neural network model based on image semantic segmentation; performing structural modeling and vector mapping on the pedestrian foot-bridge; and finally updating pedestrian foot-bridge data in a pedestrian navigation system. The invention can automatically identify the pedestrian foot-bridge in the OSM, lower the subjectivity of the existing method, utilize the remote sensing image data to make up for the incompleteness of the OSM, take the timeliness and integrity of the data into account, and improve the identification efficiencyand accuracy of the pedestrian bridge.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
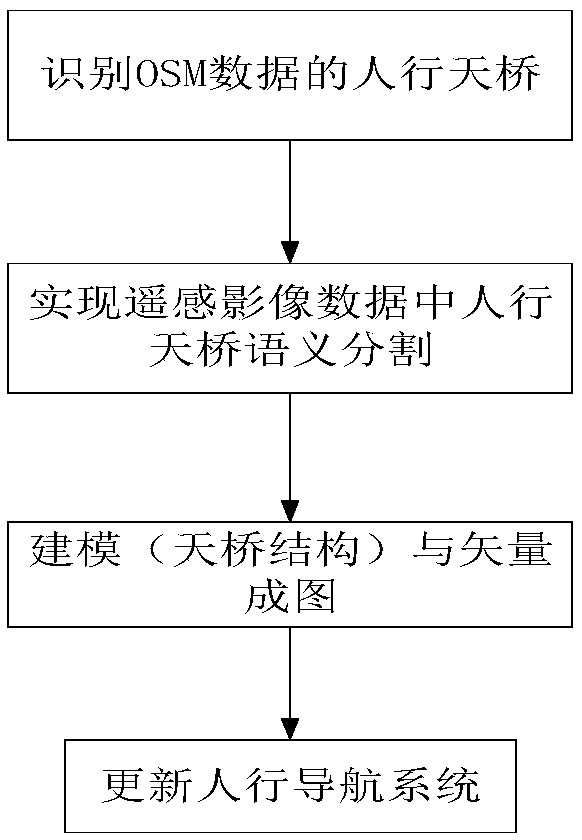
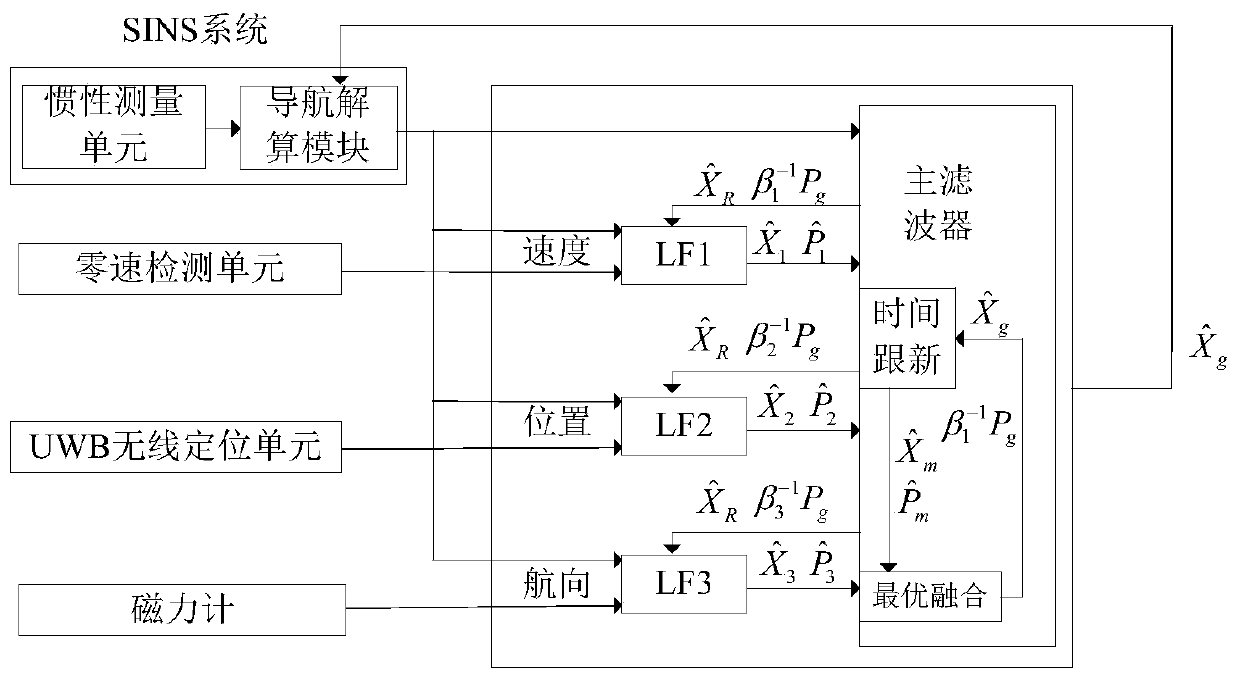
Combined indoor pedestrian navigation system and method based on UWB and SINS
ActiveCN109855621ARealize the positioning functionNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsUltra-widebandHuman motion
The invention discloses a combined indoor pedestrian navigation system and method based on UWB and SINS. The system comprises an inertial measurement unit, a navigation solution module, a zero velocity detection unit, a UWB wireless positioning unit, a magnetometer and a federated kalman filtering unit. The federated kalman filtering unit carries out data fusion on output signals of the navigationsolution module, the zero velocity detection unit, the UWB wireless positioning unit and the magnetometer to obtain error signals of human motion acceleration, course angle and position information and sends the error signals to the inertial measurement unit for correction. The method introduces a zero velocity correction technique on the basis of a conventional strapdown algorithm to detect zerovelocity moment; in an ultra-wideband signal region, position course angle is provided by utilizing the ultra wide band; in a non-ultra-wideband signal region, the course angle is provided by utilizing a magnetometer; and zero speed, position and course angle information are fused through federated kalman filtering to correct the speed, position and course of the navigation system, thereby realizing indoor personnel positioning.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD MAINTENANCE BRANCH
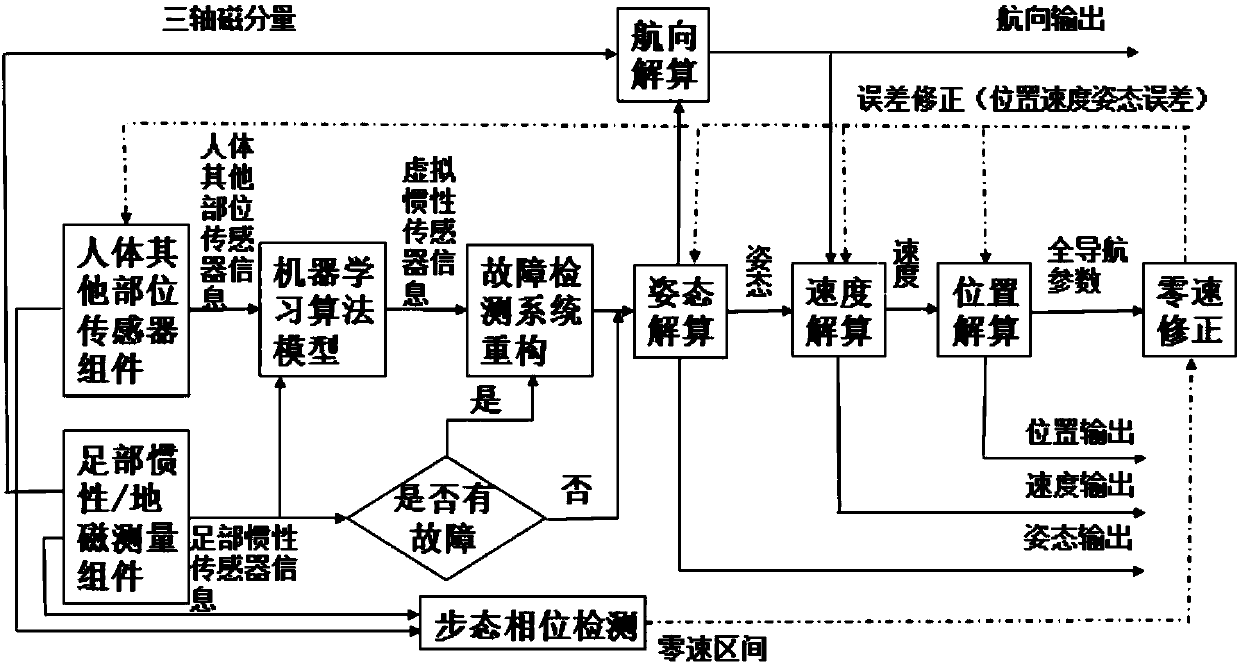
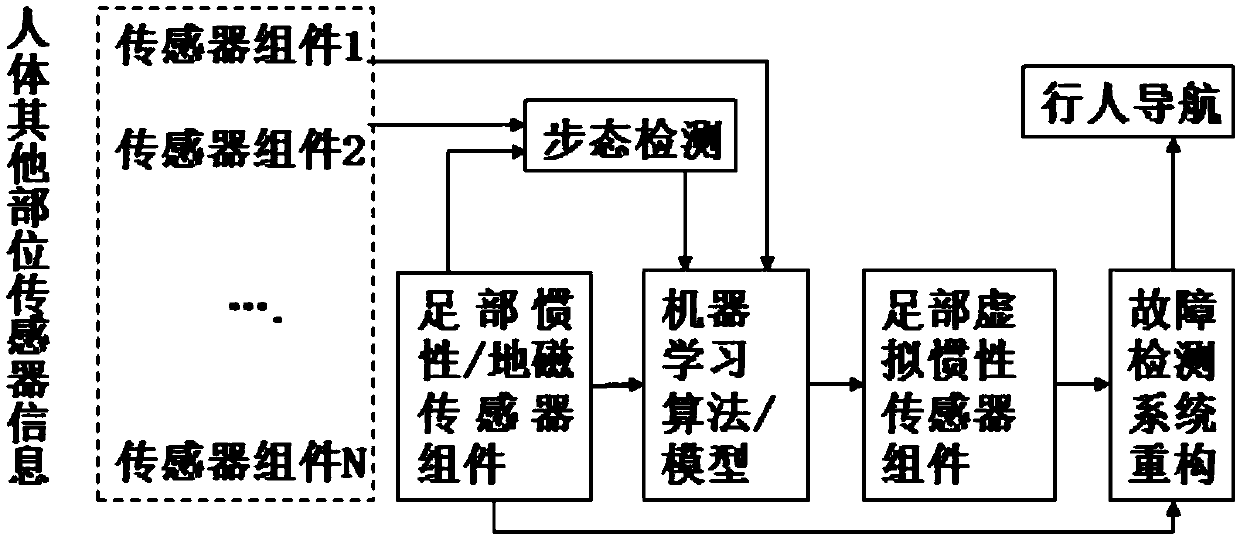
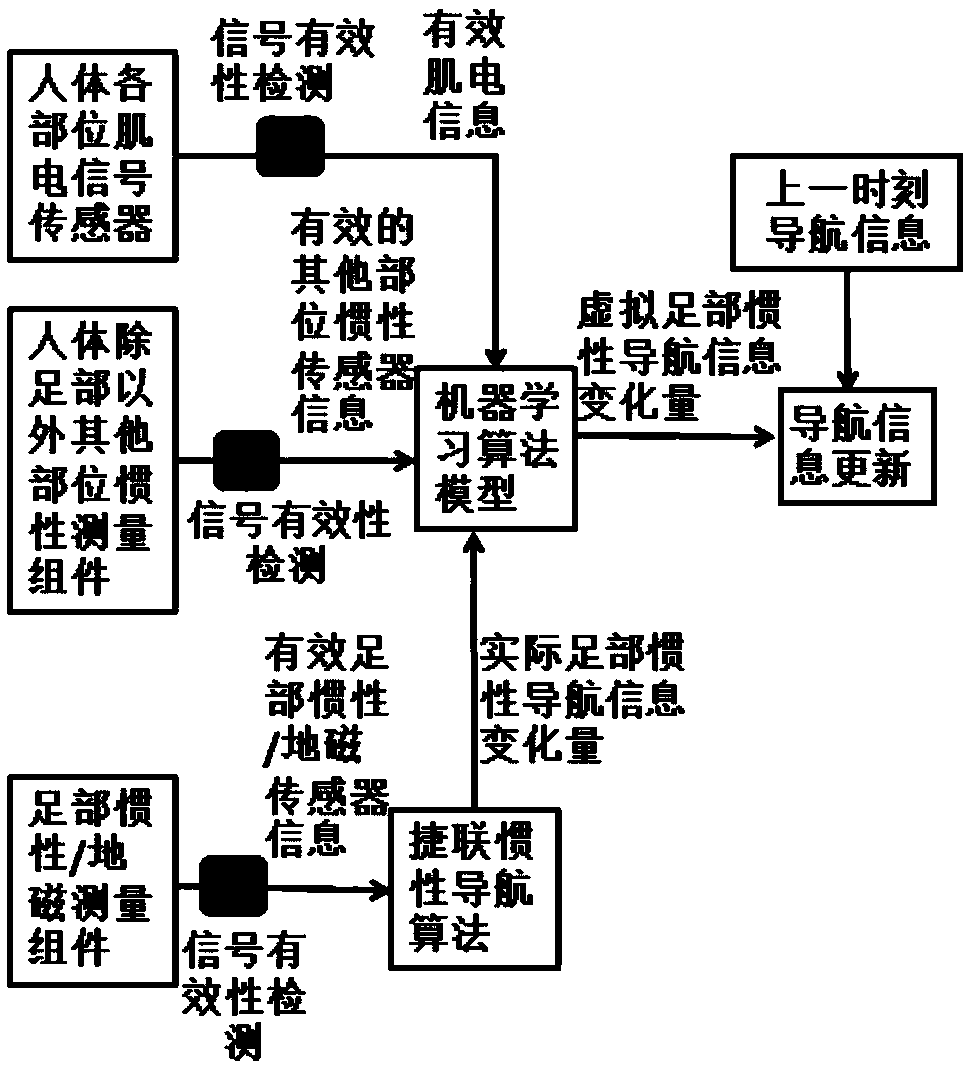
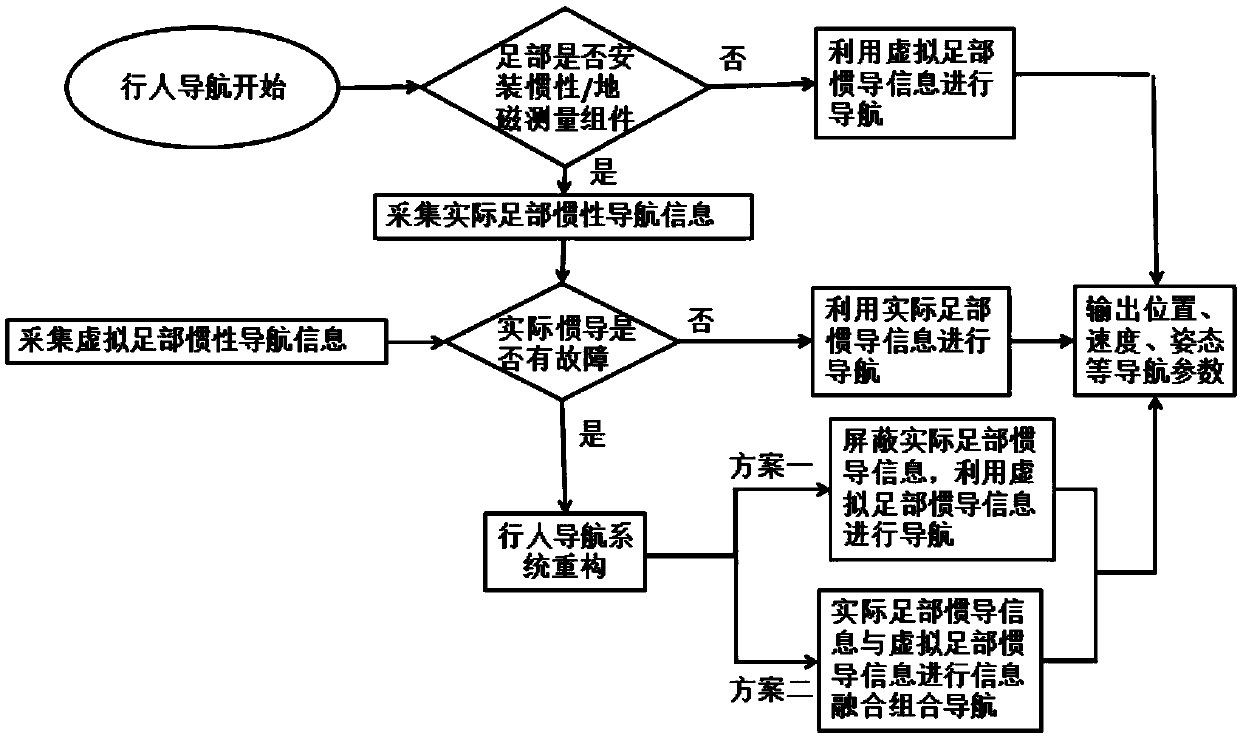
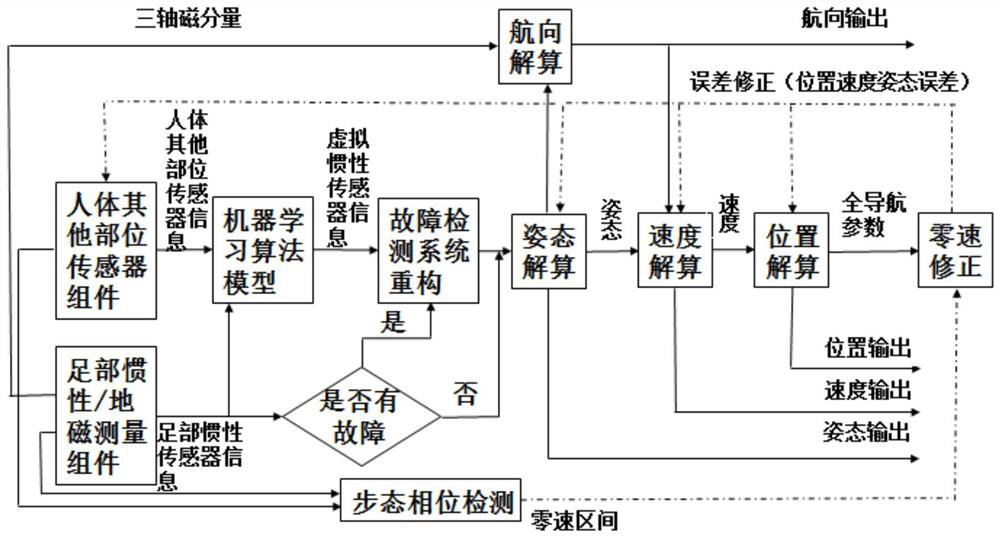
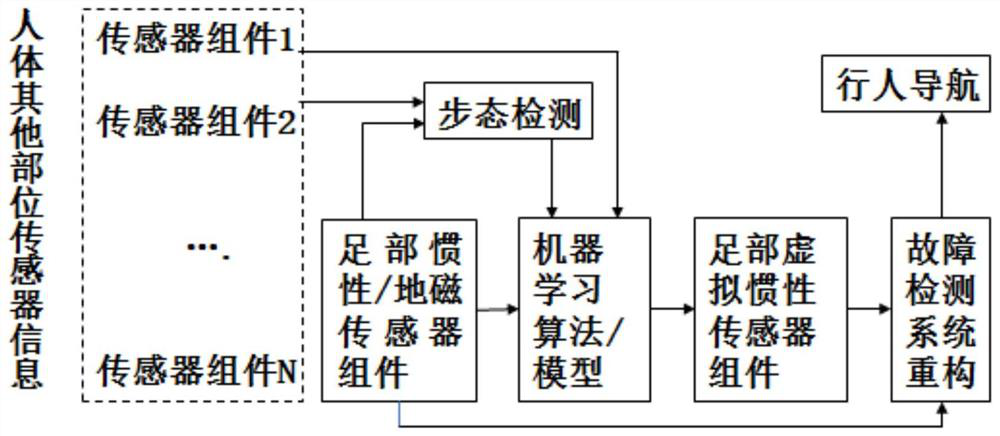
Pedestrian inertial navigation system and method assisted by machine learning algorithms and models
ActiveCN108168548ARealize inertial pedestrian navigation functionNavigation by terrestrial meansNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsHuman bodyPedestrian navigation system
The invention discloses a pedestrian inertial navigation system and method assisted by machine learning algorithms and models and belongs to the field of inertia and combined navigation and the fieldof artificial intelligence. The method recognizes different types of gait characteristics of a human body by inertial / geomagnetic sensor components arranged at the feet of the human body and sensor components arranged at the other parts of the human body in a concentrated or distributed manner. The pedestrian inertial navigation system and method disclosed by the invention have the beneficial effects that different machine learning algorithms and models are adopted in a self-adaptive manner to train sensor information of the feet and other parts and realize the purpose of simulating the inertial sensor information at the feet by the sensor information at the other parts, so that real-time fault detection can be carried out on the pedestrian navigation system, and prediction can be carriedout in one gait period before the inertial sensors at the feet are in outrange; then the pedestrian navigation system is constructed by the system reconstruction principle on the basis of one or morevirtual inertial sensor information at the feet, so that the inertial pedestrian navigation function under the conditions of faults and outrange is realized.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
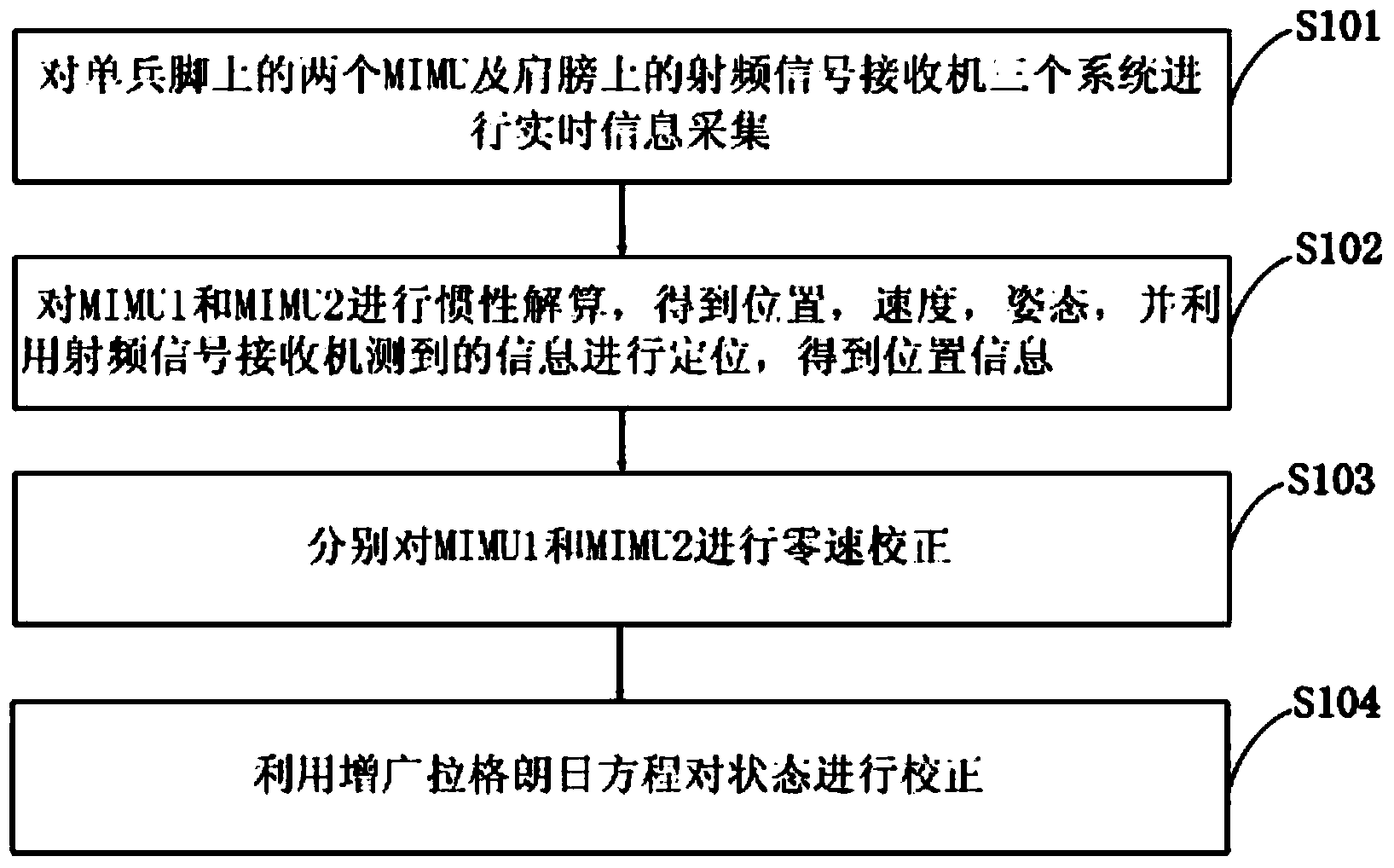
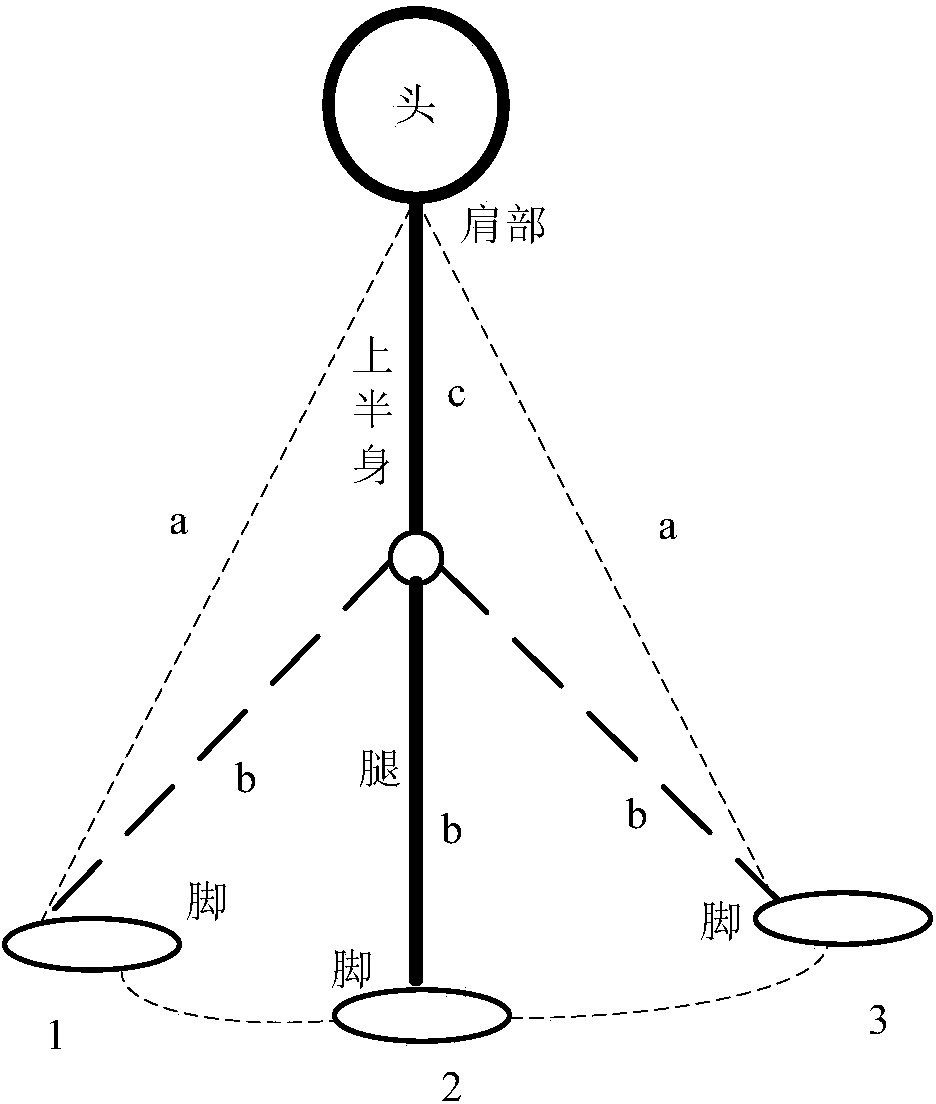
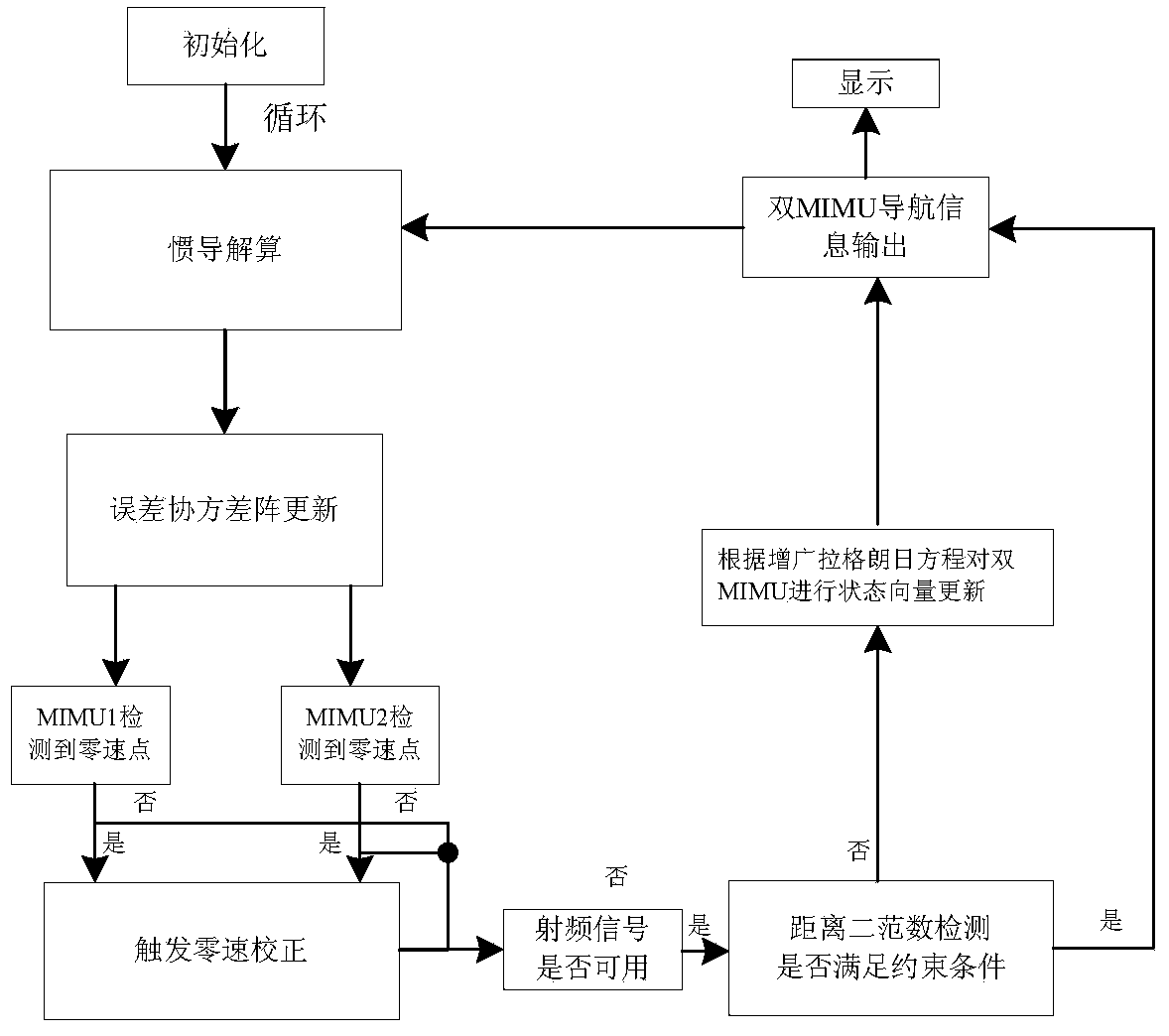
MIMU and GPS combined pedestrian navigation method based on augmented lagrangian condition
InactiveCN103900581AImprove usabilityCompensate for cumulative errorsInstruments for road network navigationRadio frequency signalPedestrian navigation system
The invention provides an MIMU and GPS combined pedestrian navigation method based on augmented lagrangian condition. A pedestrian navigation system is provided with a radio-frequency signal receiver and two MIMUs, wherein the radio-frequency signal receiver is fixed on the shoulder of a pedestrian, and the two MIMUs are respectively fixed on the tip of a toe and the heel of a foot, so that the system data can be acquired in real time; navigation calculation is carried out on the two MIMUs respectively, so that inertial navigation pedestrian position, speed and attitude information can be obtained; a radio-frequency signal is used for locating, so that the pedestrian position information can be obtained by the receiver; zero-speed correction is carried out on the two MIMUs respectively; a nonlinear equality constraint equation and a nonlinear inequality constraint equation are established; the constraint equations are combined with a kalman filter, and the state variable of the system is corrected by an augmented lagrangian equation, so that the problem of the location accuracy of the weak radio-frequency signal is lower can be solved. In the bad closed indoor navigation environment, the utilizability of the weak radio-frequency signal can be fully improved by the combined pedestrian navigation method.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
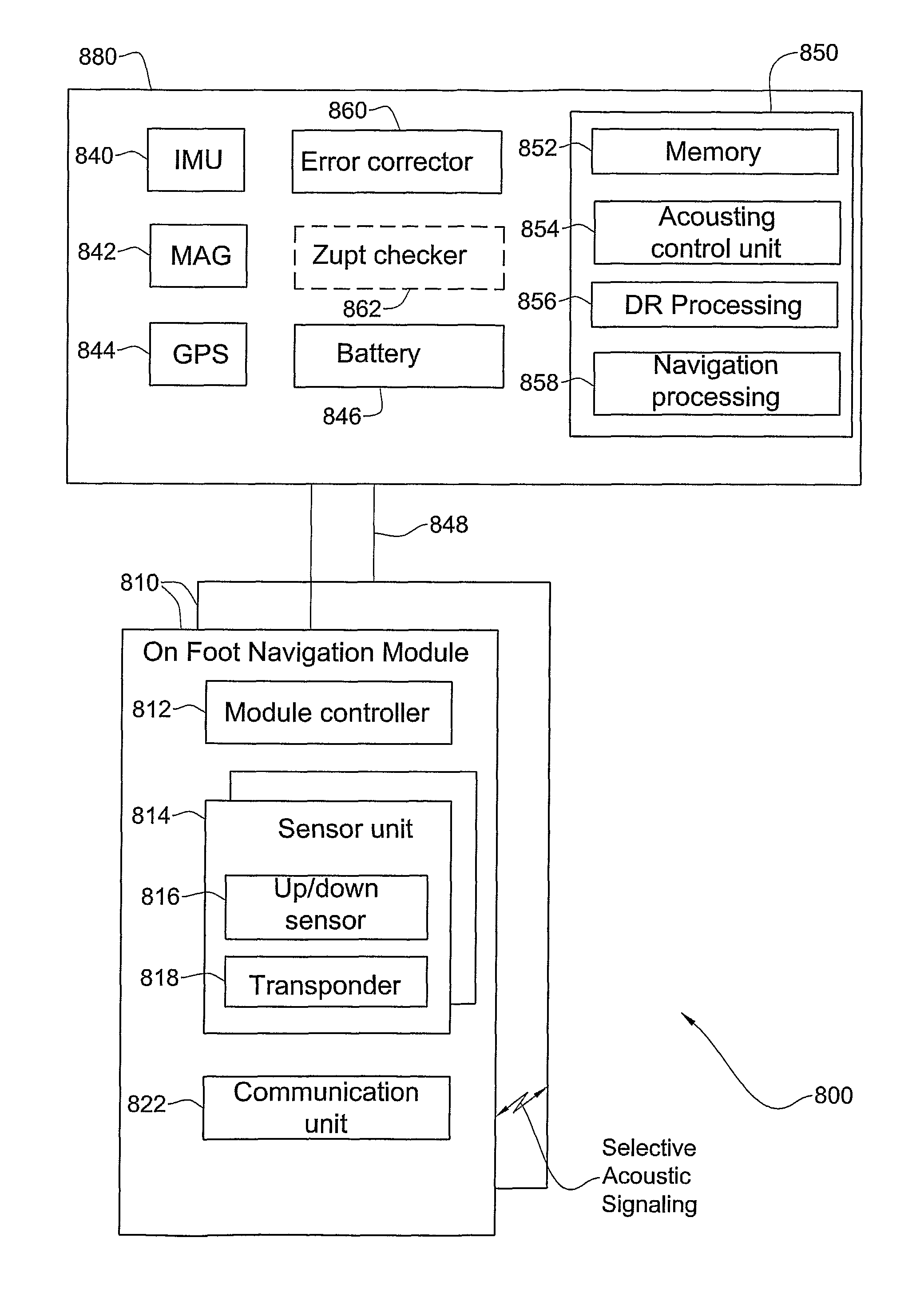
Pedestrian navigation system and method
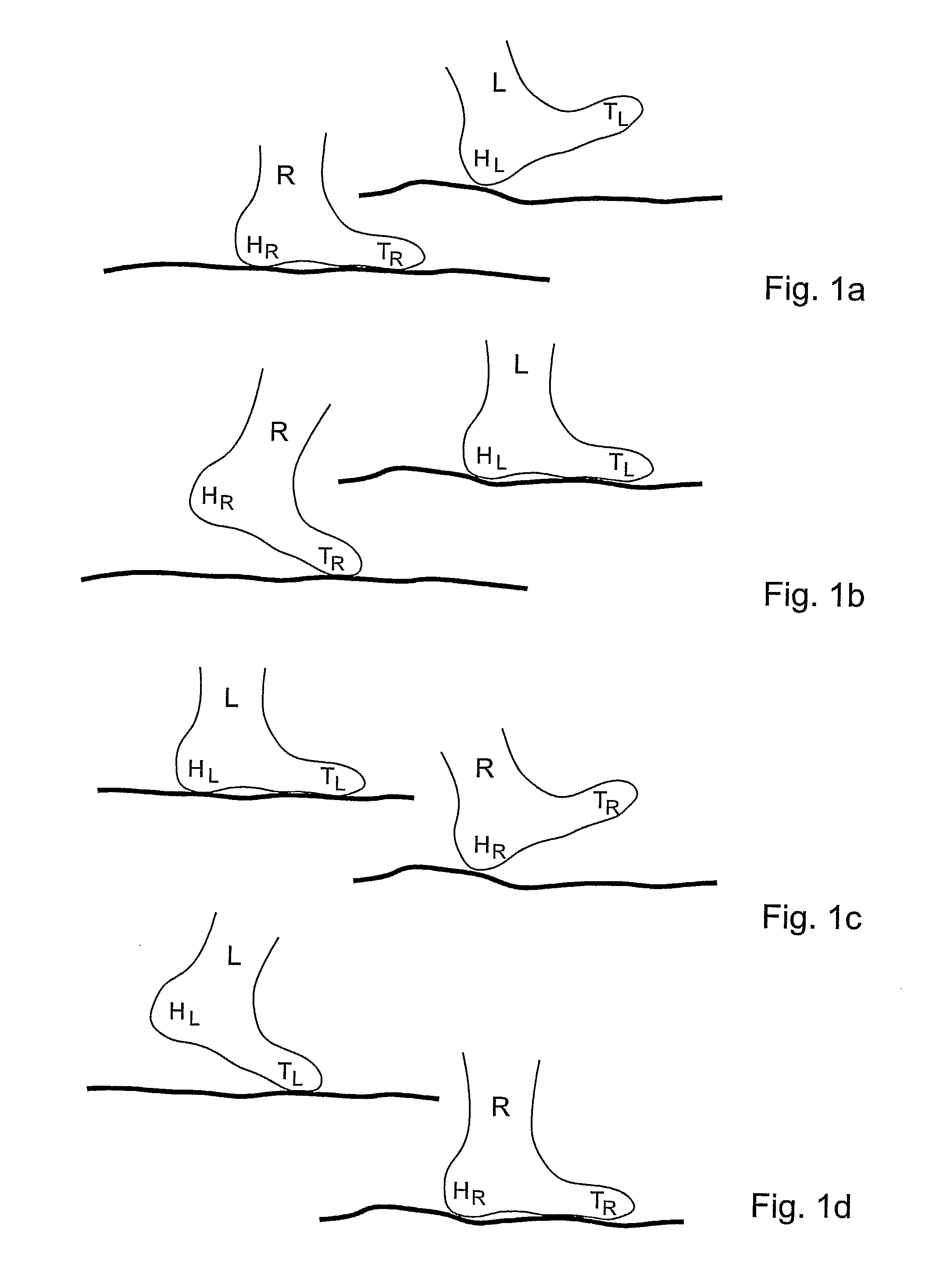
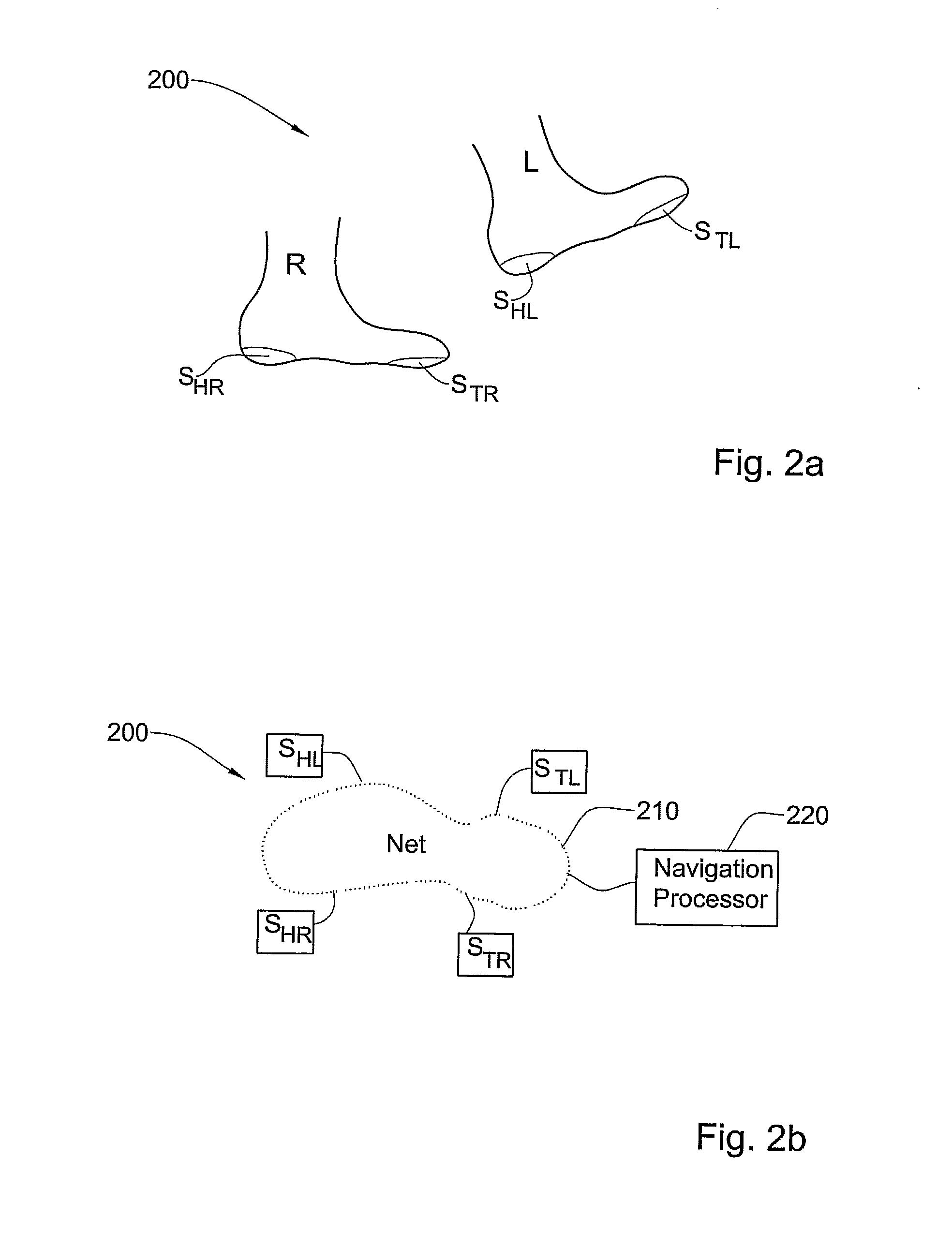
ActiveUS8355888B2Reduce accumulationImprove accuracyDigital data processing detailsUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansRelative displacementCommunication unit
An on-foot pedestrian navigation module useful for pedestrian navigation when operated with at least a control unit and another on-foot pedestrian navigation module, comprising (a) at least a first sensor unit and a second sensor unit, wherein each sensor unit including an up / down sensor adapted for sensing an ‘up’ condition and a ‘down’ condition associated with relative displacement of the module with respect to a surface, and a signal transmitter / receiver adapted, in response to an activation signal coming from a module controller, for generating a propagating signal (b) a module controller for controlling the operation of the module in response to a control signal coming from the control unit and (c) a communication unit for enabling said module to communicate with said at least the control unit and other module, thereby facilitating collecting motion data at the control unit and integrating the motion data with motion data coming from the other module, the motion data being indicative of a condition of each up / down sensor and receipt of the propagating signal by at least two sensor units of said other module, and wherein the motion data is useful for determining a momentary position of the pedestrian's foot during motion.
Owner:ISRAEL AEROSPACE IND
MEMS device zero offset correction method and device and storage medium
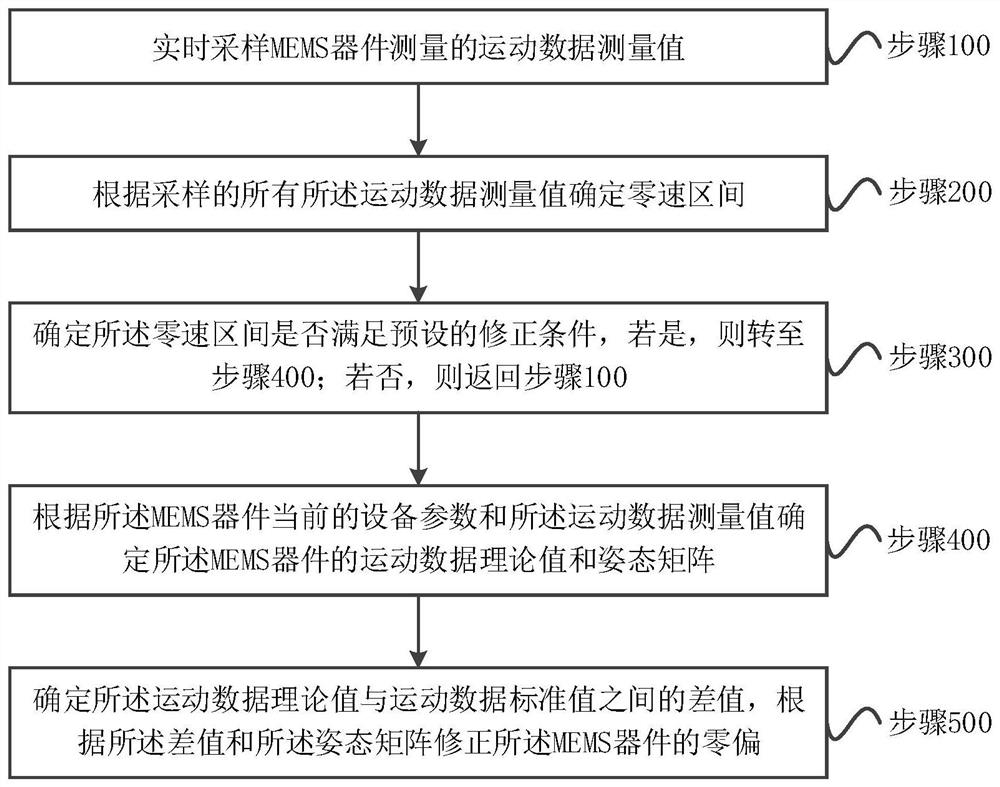
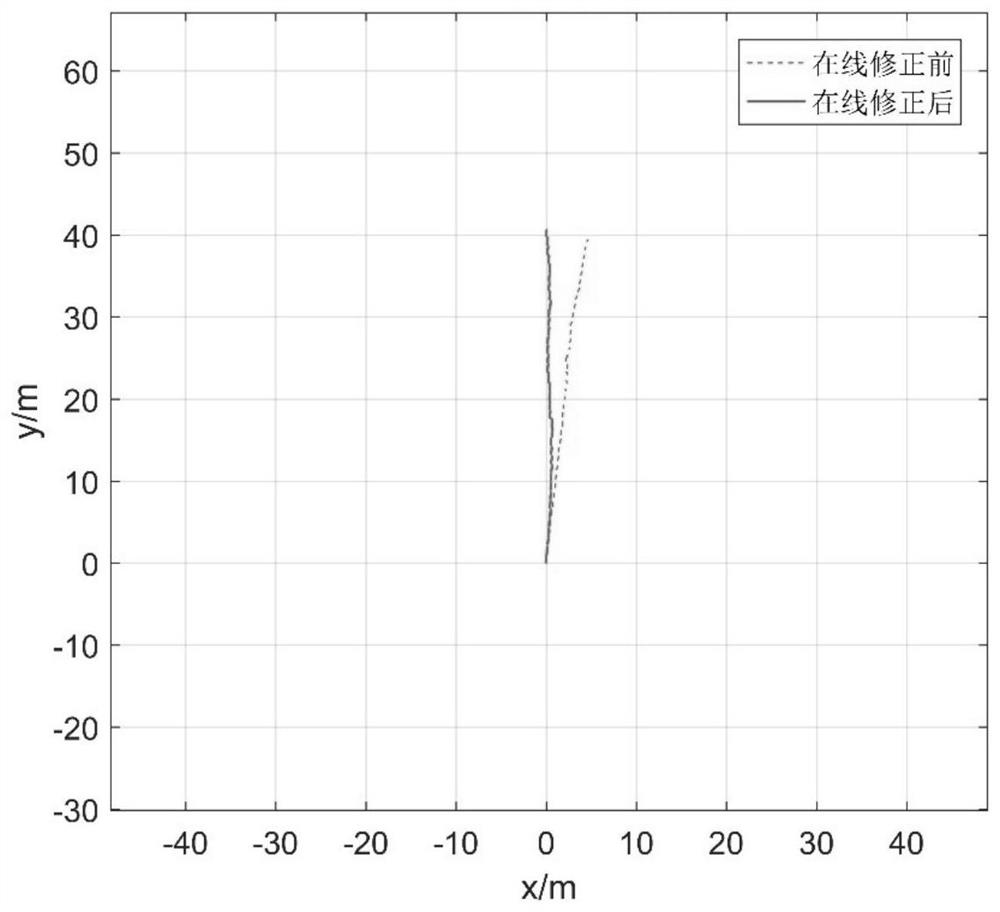
ActiveCN111721288AHigh positioning accuracyHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsClassical mechanicsPedestrian navigation system
The invention provides an MEMS device zero offset correction method and device and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of sampling a motion data measurement value measured by an MEMS device in real time; determining a zero-speed interval according to all the sampled motion data measurement values; determining whether the zero-speed interval meets a preset correction condition or not,and determining a motion data theoretical value and an attitude matrix of the MEMS device according to the current equipment parameters of the MEMS device and the motion data measurement value; and determining a difference value between the motion data theoretical value and a motion data standard value, and correcting the zero offset of the MEMS device according to the difference value and the attitude matrix. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the motion data theoretical value is determined by adopting the motion data measurement value sampled in real time, the zero offset ofthe MEMS device is corrected online in real time through the difference value between the motion data theoretical value and the motion data standard value, the precision is high, errors generated byzero offset accumulation can be avoided, and the positioning precision of a pedestrian navigation system is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for multi-source information self-adaption step number detection based on MEMS inertial measurement unit
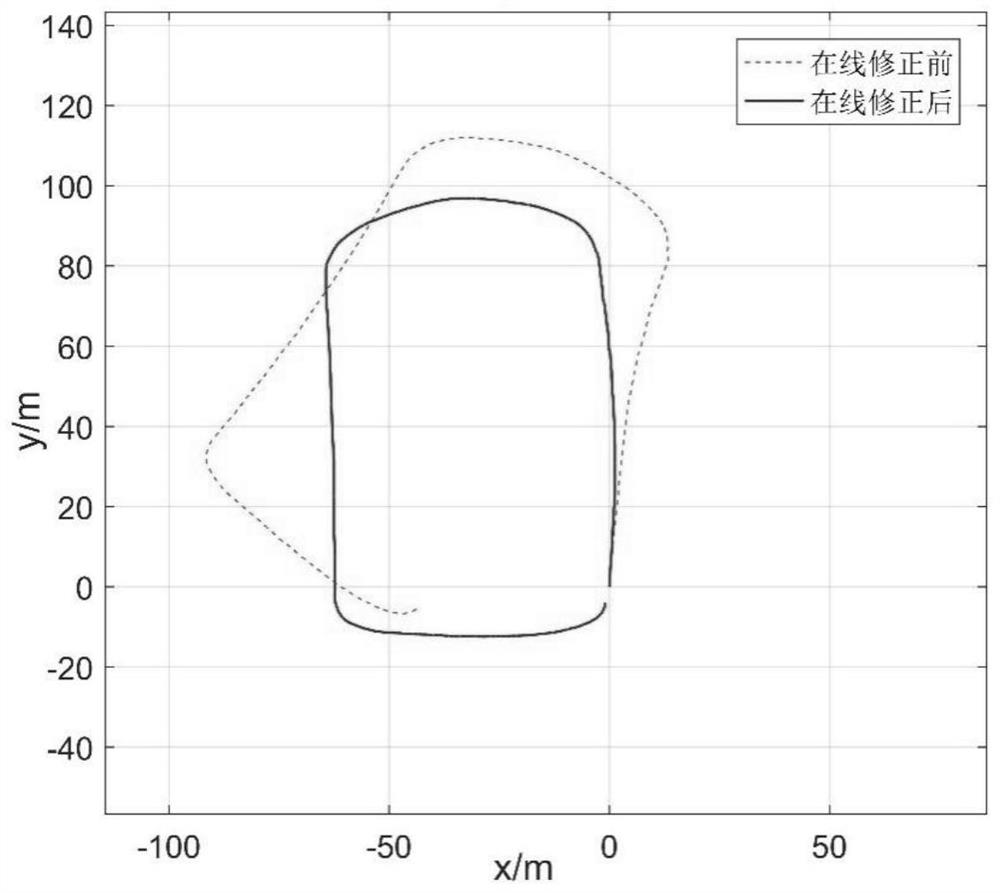
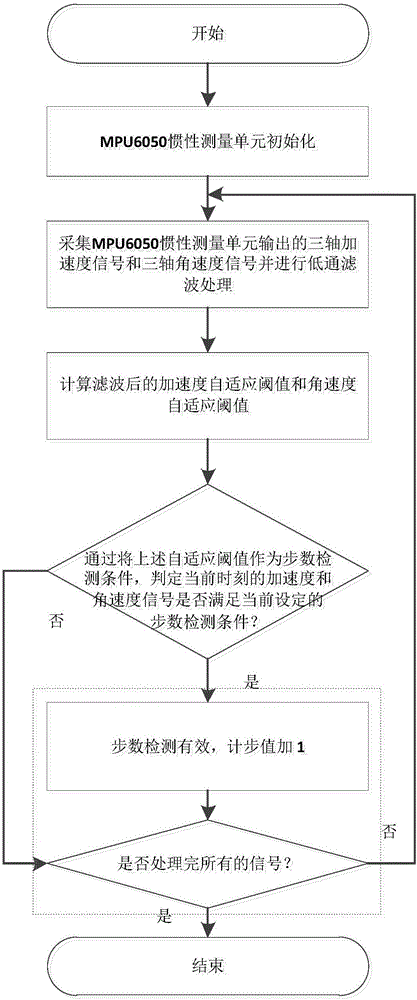
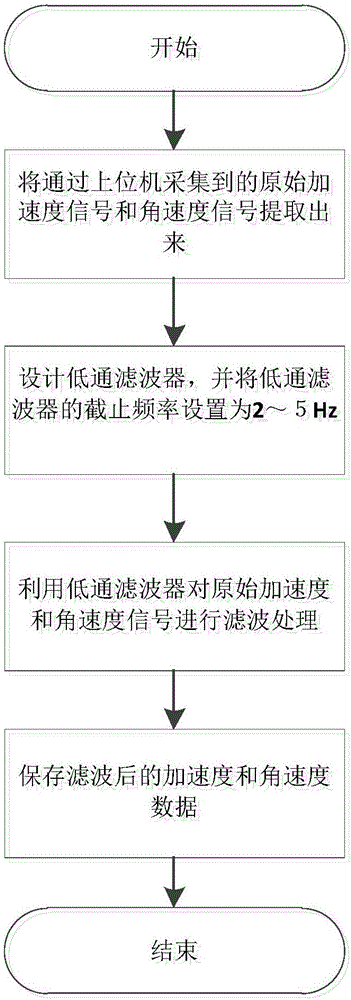
The invention discloses a method for multi-source information self-adaption step number detection based on an MEMS inertial measurement unit. According to the method, the low-cost MEMS inertial measurement unit is adopted to serve as a core component. The inertial measurement unit comprises a triaxial accelerometer and a three-axis gyroscope. First the inertial measurement unit is fixed to the foot under the conditions that users' normal walking is not affected, an upper computer is utilized to perform initial calibration on the measurement unit; the upper computer is utilized to collect acceleration and angular speed signals output by the measurement unit in the user's walking process, and performing low-pass filtering processing on the collected signals; gaining self-adaption thresholds for the filtered signals; and finally taking the self-adaption thresholds as conditions for step number detection to detect the step number. The pedestrian's step number is detected based on the low-cost MEMS inertial measurement unit, and the method is suitable for the field of personal health data monitoring and pedestrian navigation systems based on the MEMS inertial measurement unit.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Multiple data sources pedestrian navigation system
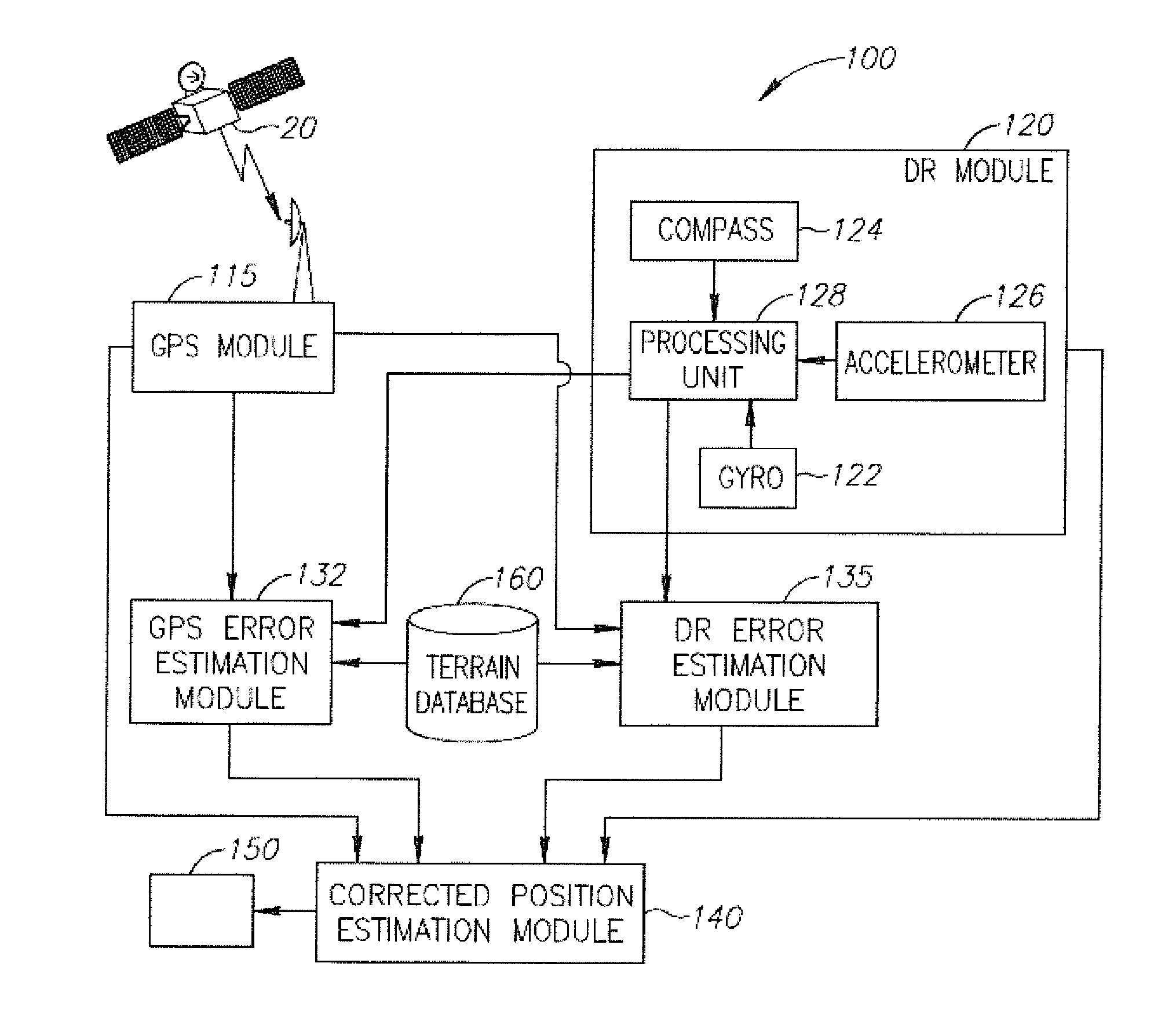
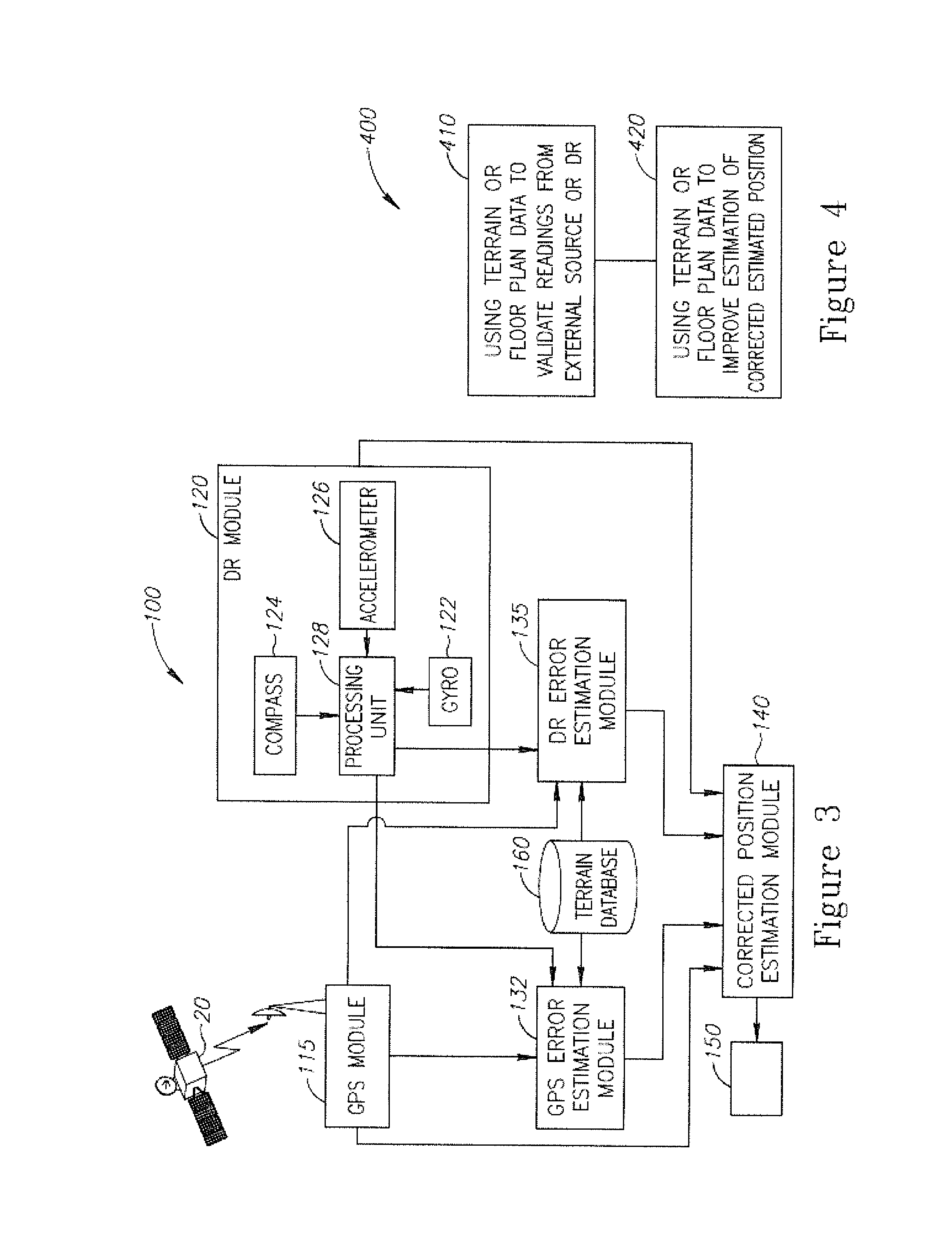
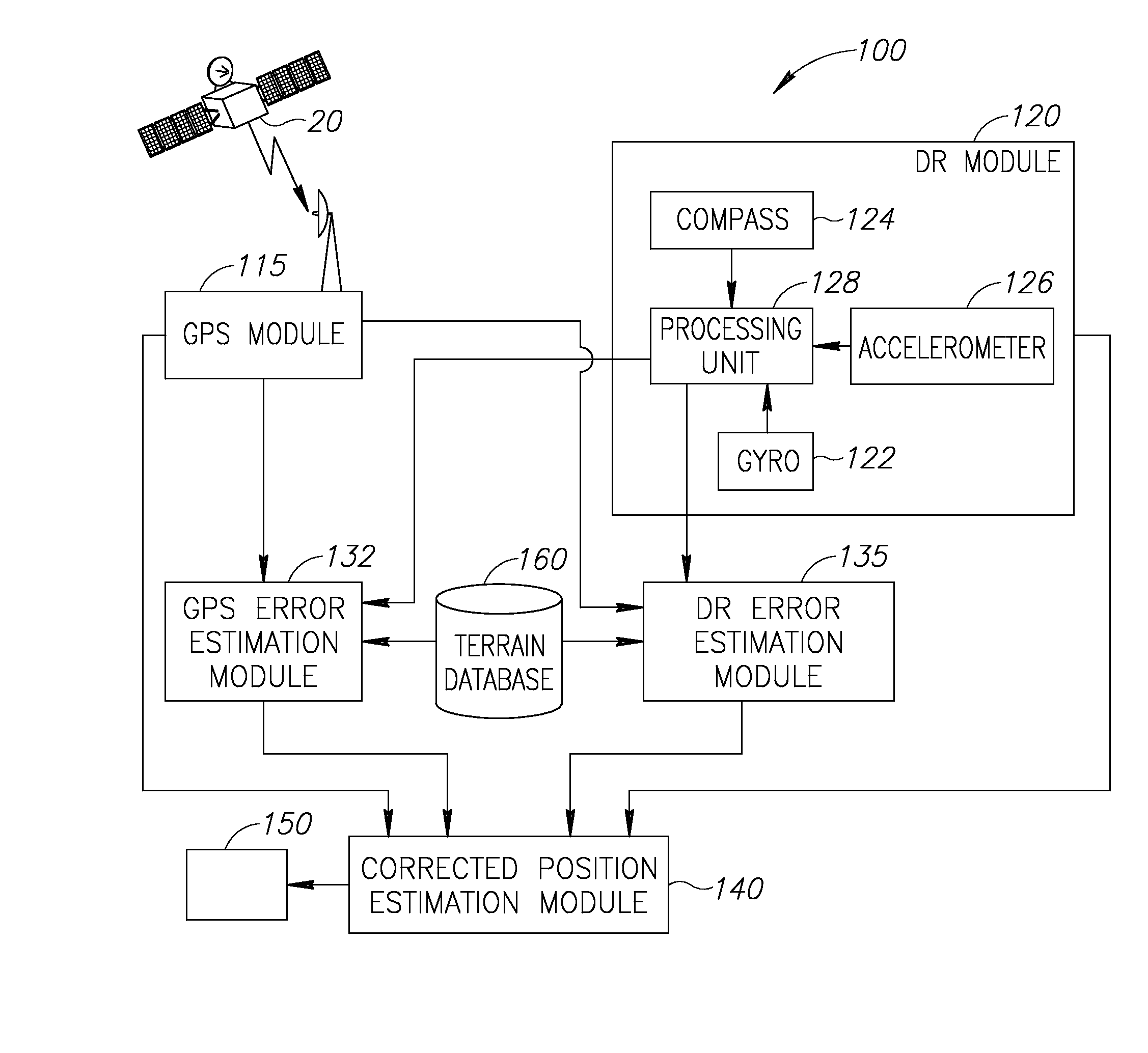
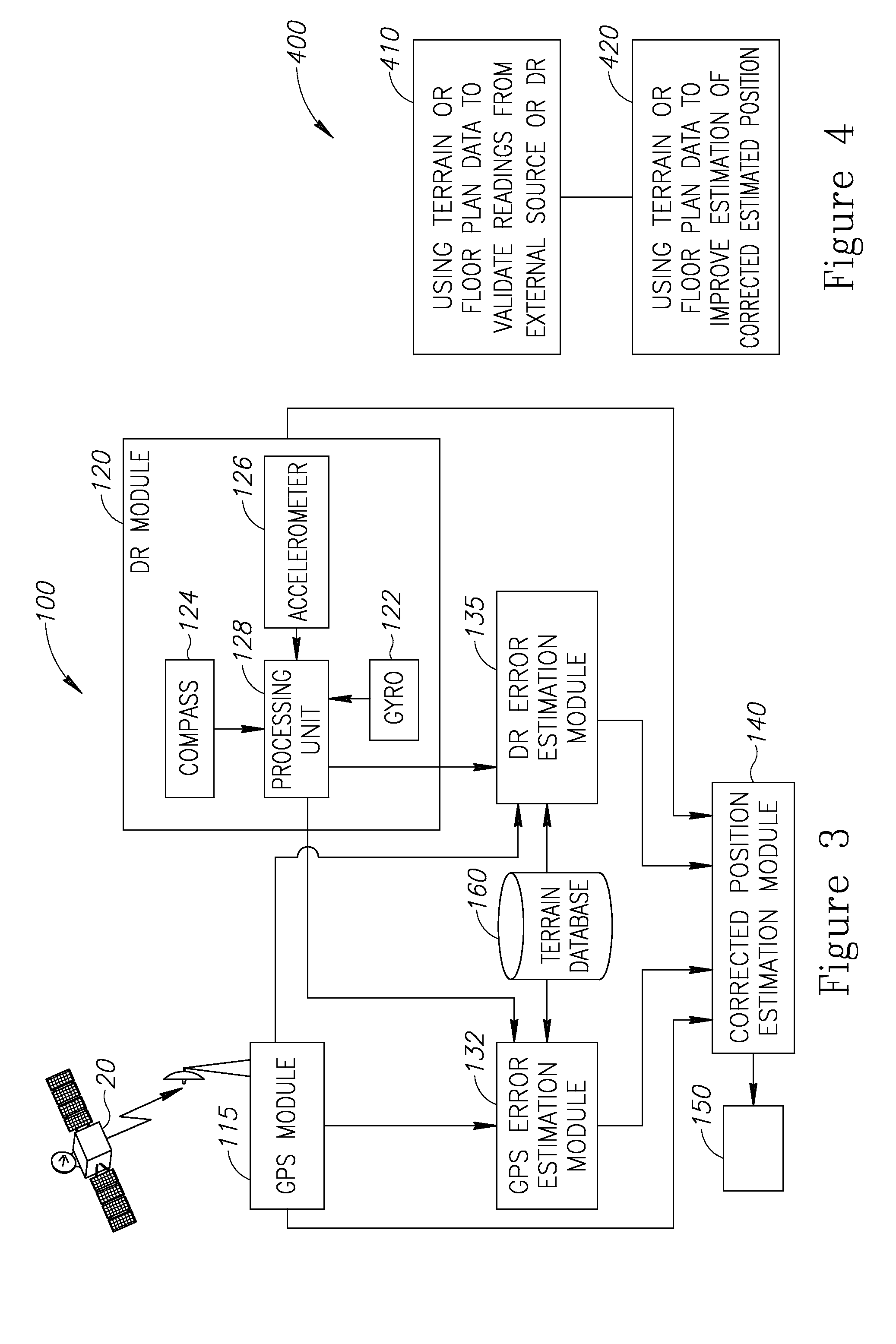
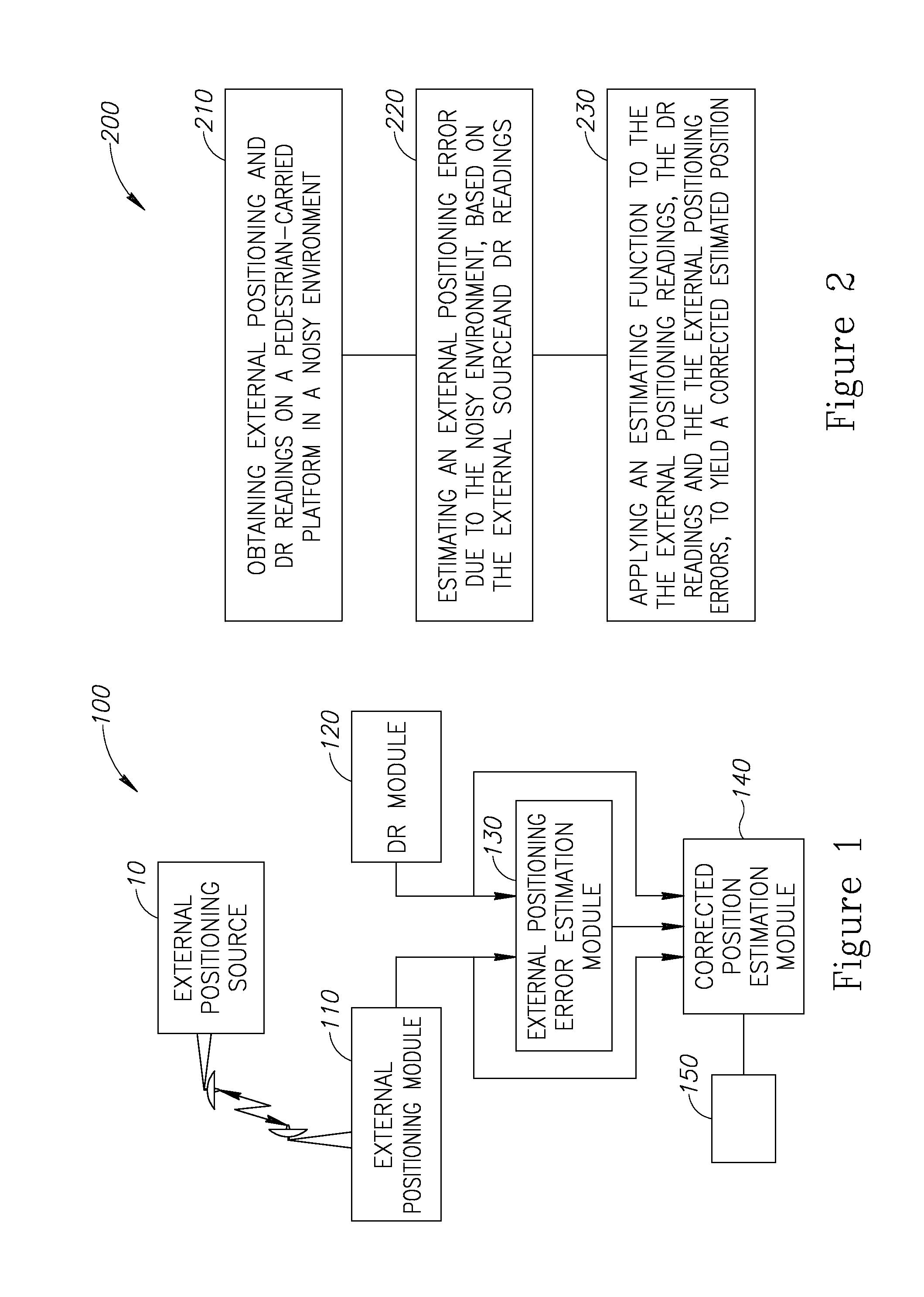
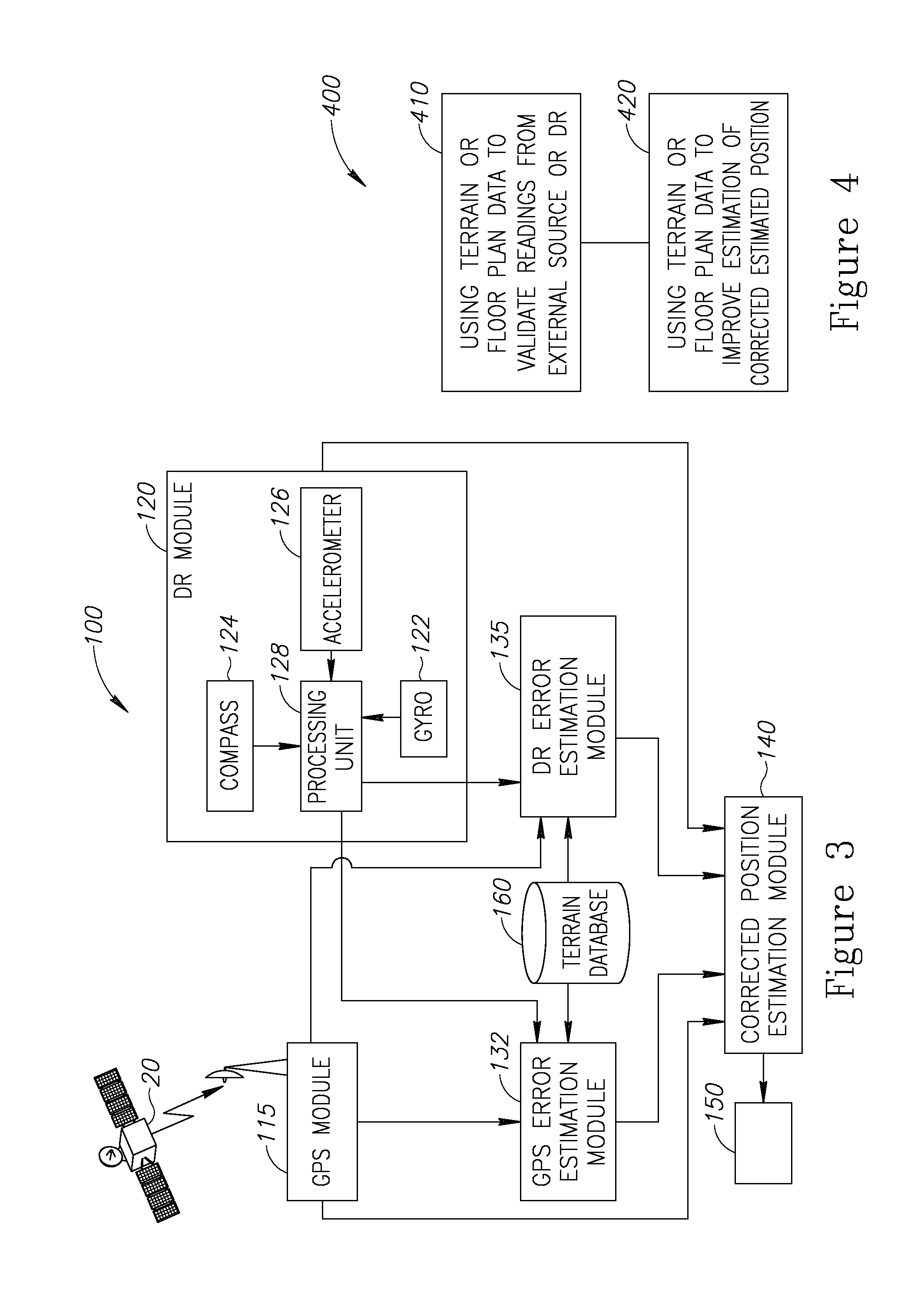
InactiveUS20160349057A1Navigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsComputer graphics (images)Data source
A method of pedestrian navigation based on an external positioning system and a Dead Reckoning (DR) system, us provided. The method includes: obtaining DR position readings from a plurality of pedestrian-carried platforms and external position readings from a remote source which is independent of the pedestrian-carried platforms, wherein the obtaining is repeated for a plurality of locations associated with the plurality of pedestrian-carried platforms; estimating, for each of the plurality of locations, an external positioning source error, based at least partially on the external position readings and the DR position readings; applying an estimation function to the external position readings, the DR position readings, and the external positioning source error, for the plurality of locations, to yield a corrected estimated position for each of the plurality of locations; and presenting the corrected estimated position for each of the plurality of locations to users of the pedestrian-carried platforms, respectively.
Owner:ELBIT SYST LTD
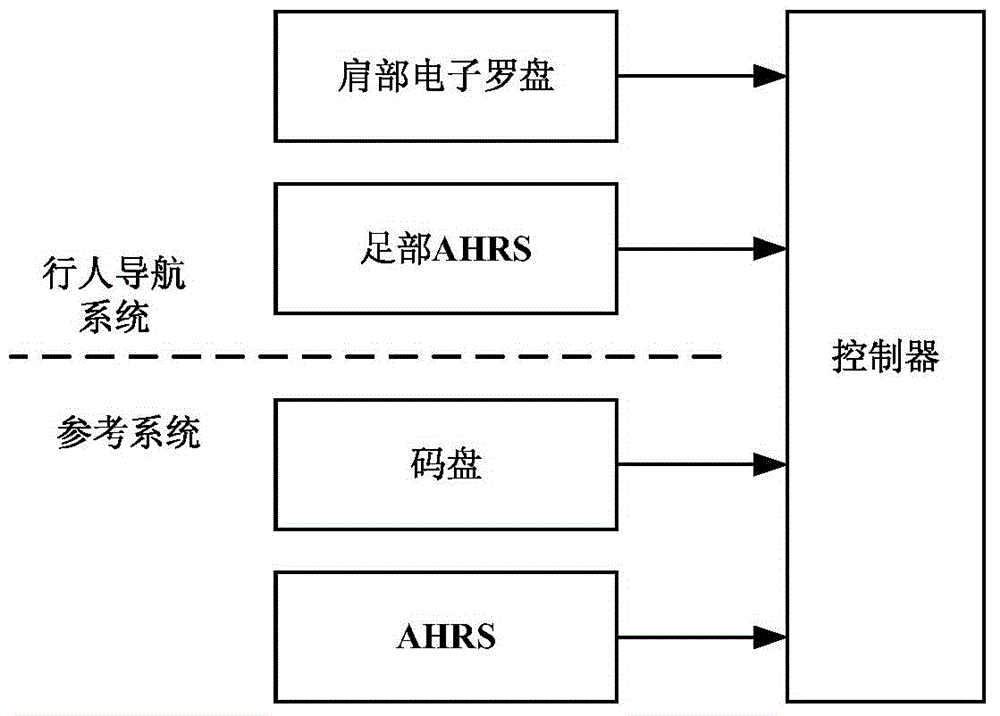
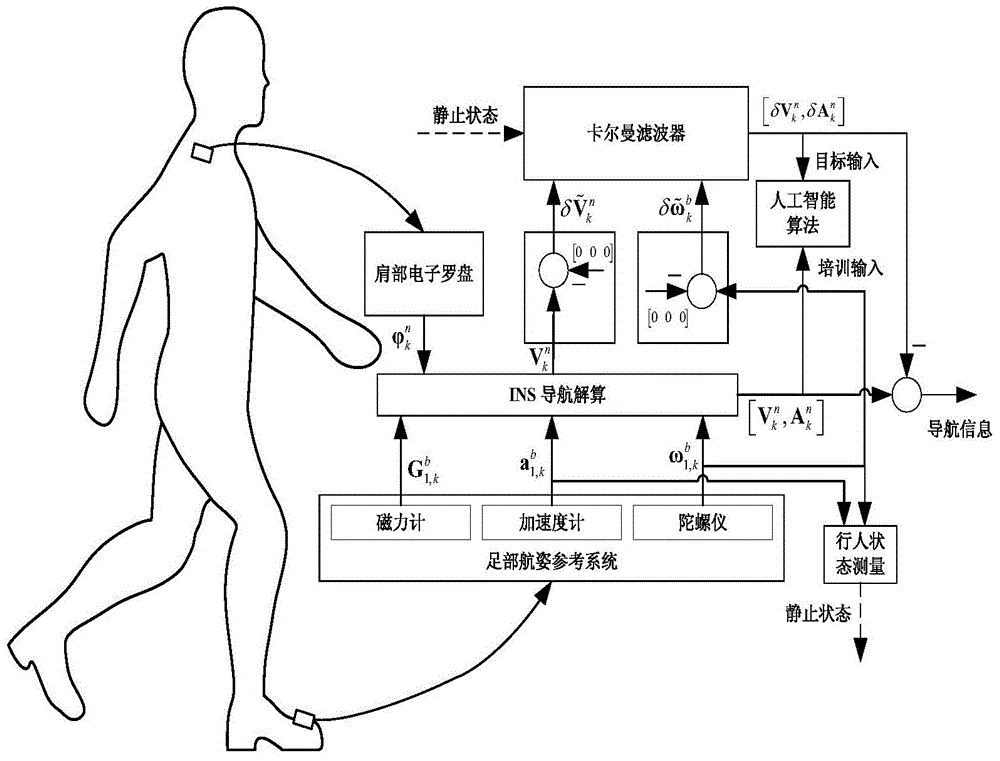
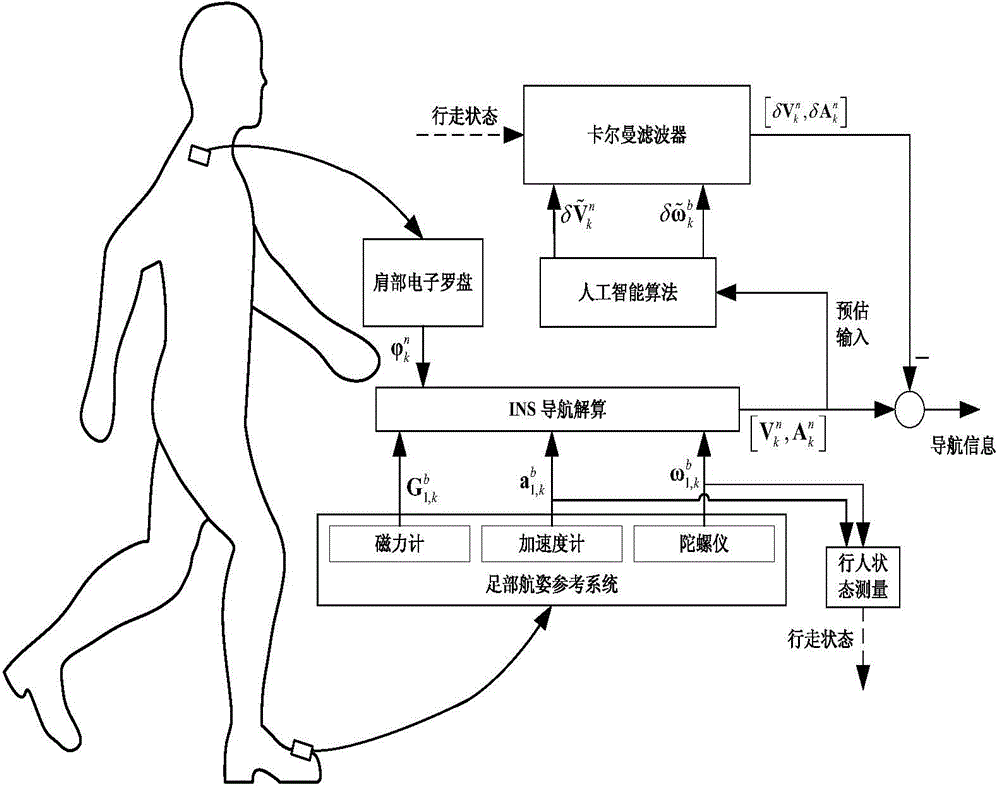
Personal navigation system and method based on foot attitude-heading reference and shoulder electronic compass
ActiveCN104897157AImprove calculation accuracyExcellent estimateNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAttitude and heading reference systemTransfer matrix
The invention discloses a personal navigation system and method based on foot attitude-heading reference and a shoulder electronic compass. A reference system comprises a coded disc and an AHRS (attitude and heading reference system) fixed on the coded disc. A pedestrian navigation system comprises a foot AHRS, the shoulder electronic compass and a controller. The foot AHRS is connected with the shoulder electronic compass. The reference system, the foot AHRS and the shoulder electronic compass are respectively connected to the controller. The shoulder electronic compass directly inputs measured pedestrian heading information to the foot AHRS to serve as the heading information required by the foot AHRS during attitude transfer matrix calculation. The foot AHRS calculates the track of a pedestrian through an accelerometer and a gyroscope carried thereon and the heading information provided by the electronic compass. The personal navigation system has the advantage that the pedestrian heading information measured by the shoulder electronic compass is introduced into the navigation information calculation process of the foot AHRS to increase the attitude transfer matrix calculation precision of the foot AHRS.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
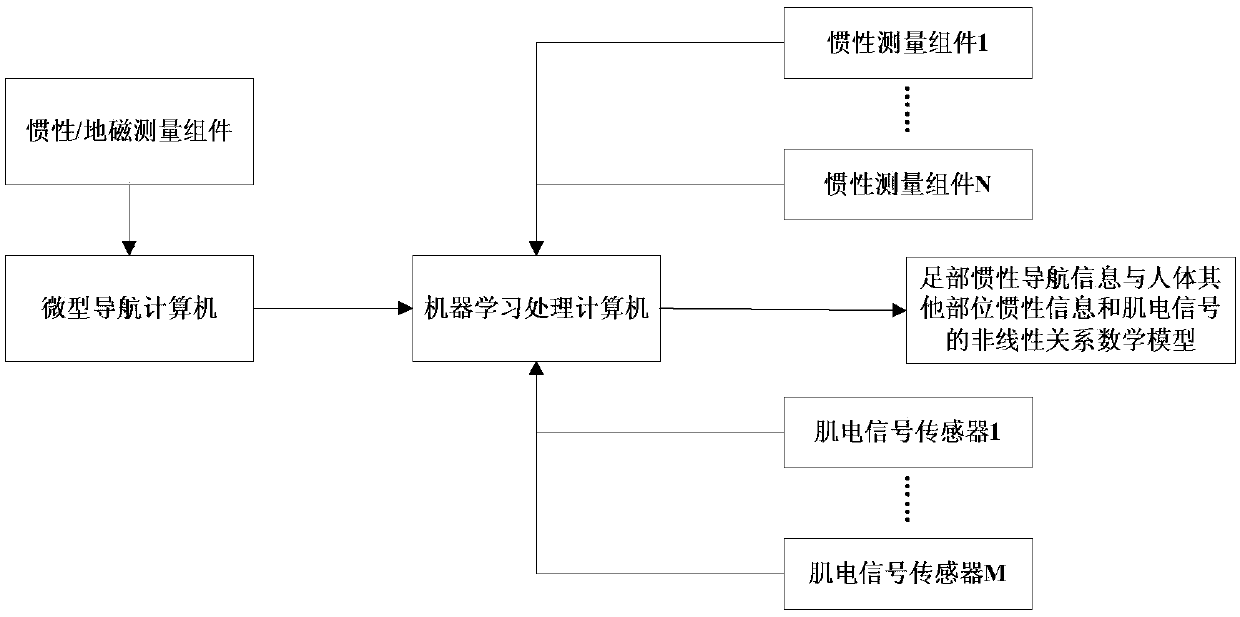
Pedestrian navigation system and method based on inertial and myoelectricity information and combined with machine learning
ActiveCN109059910AImprove reliabilityImprove stabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPedestrian navigation systemComputer vision
The invention discloses a pedestrian navigation system and method based on inertial and myoelectricity information and combined with machine learning. The pedestrian navigation system includes at least one set of inertial / geomagnetic measurement modules arranged at the feet of a pedestrian, a plurality of sets of inertial measurement modules arranged outside the feet of a human body, a plurality of sets of myoelectricity signal sensors arranged at various parts of the human body, and micro-navigation computers and machine learning processing computers arranged at any position of the human body. The inertial / geomagnetic measurement modules at the feet and the micro-navigation computers constitute a foot inertial navigation system, the effective data collected by each inertial measurement module and each myoelectricity signal sensor are used as input of a machine learning algorithm model, the variation of navigation information output by the foot inertial navigation system is used as output, and a model is built online and the pedestrian navigation is realized. When the inertial navigation system is not installed on the feet or part of the sensor devices distributed in the human bodyand the system fails, the pedestrian navigation and positioning can still be accurately realized, and the reliability and stability of the pedestrian navigation system are improved.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
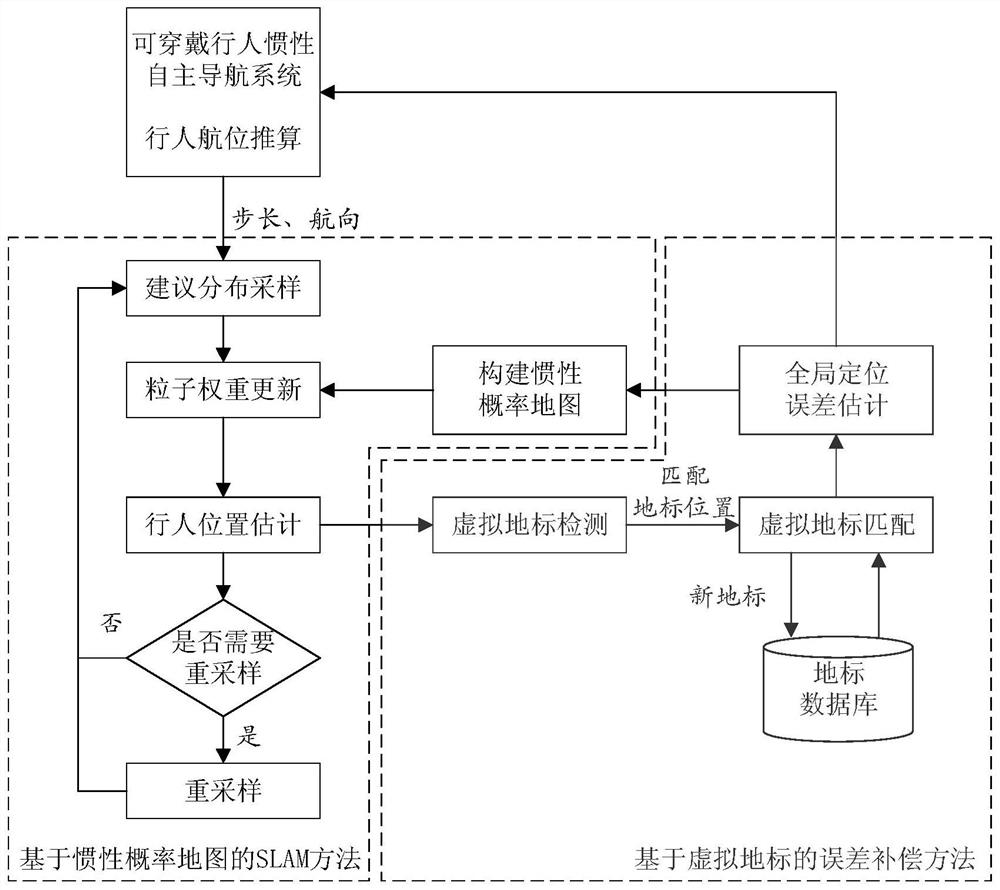
Pedestrian inertia SLAM method based on virtual landmark
ActiveCN112964257ASolve the problem of long-term navigation heading angle divergenceImprove navigation timeNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsComputer graphics (images)Odometer
The invention discloses a pedestrian inertia SLAM method based on a virtual landmark, and belongs to the technical field of pedestrian navigation methods. The pedestrian inertia SLAM method comprises the following steps of: firstly, identifying virtual landmark points in a pedestrian track according to information output by an inertial pedestrian odometer, performing error compensation on a position and a course by matching the virtual landmark points, then introducing an SLAM structure, constructing a hexagonal grid probability map and correcting position errors, and realizing simultaneous composition and positioning only based on an inertial sensor. According to the pedestrian inertia SLAM method, the problem that the course angle has accumulative errors when the pedestrian navigation system with a low-cost inertial sensor is used for estimating the course angle is solved, and high positioning precision is realized with small calculated amount.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Multiple data sources pedestrian navigation system
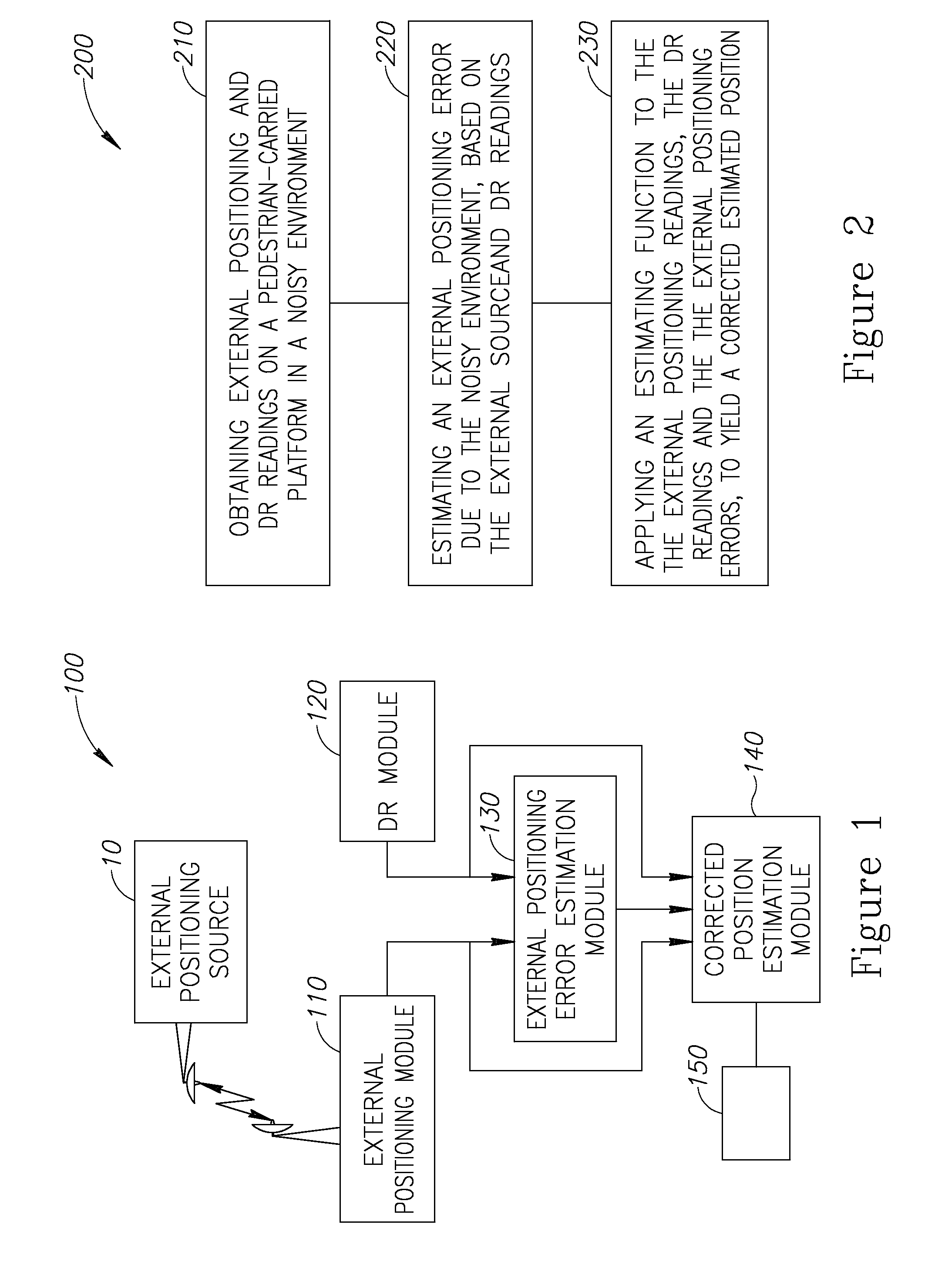
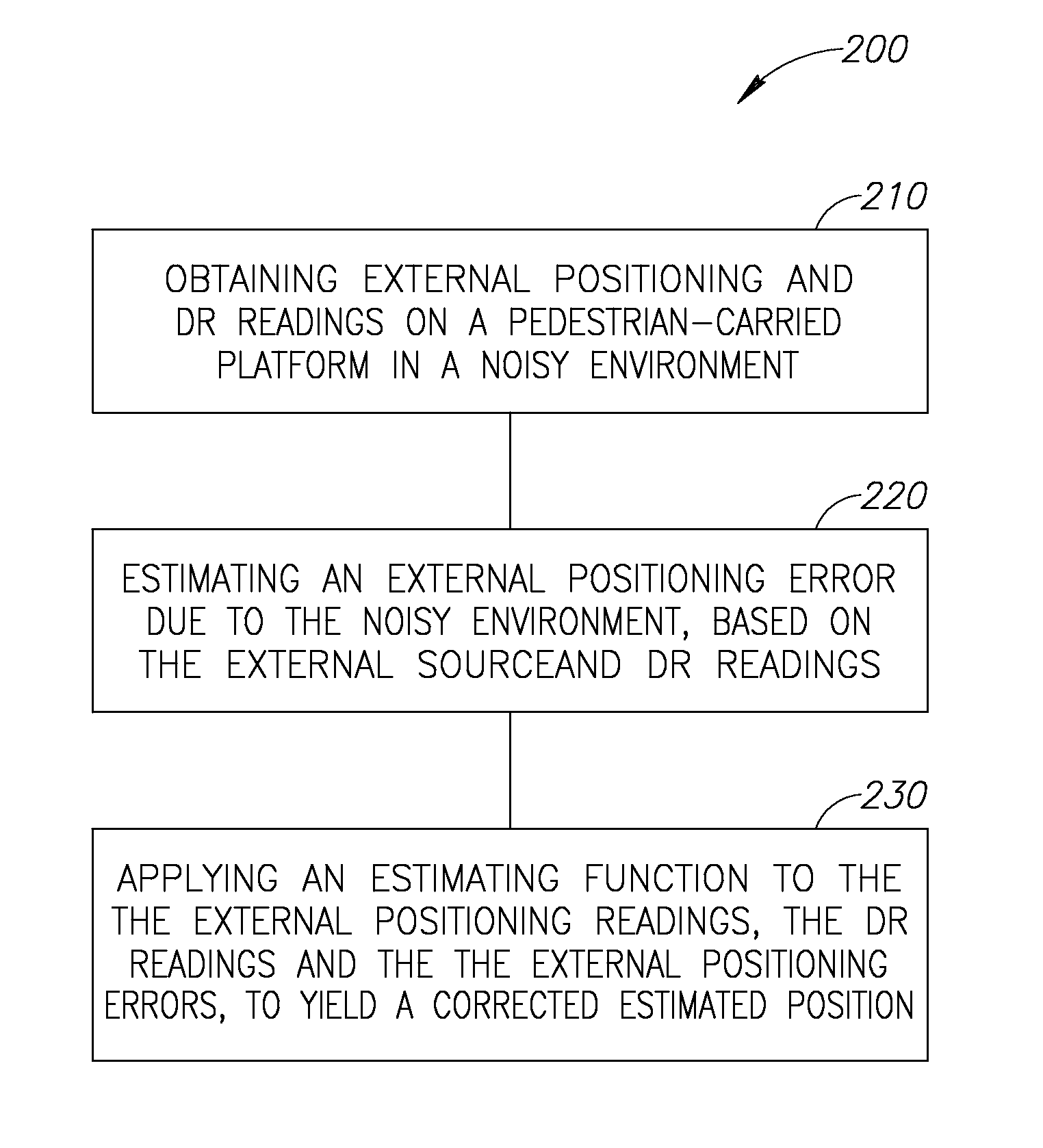
InactiveUS20130238237A1Road vehicles traffic controlNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPedestrian navigation systemComputer science
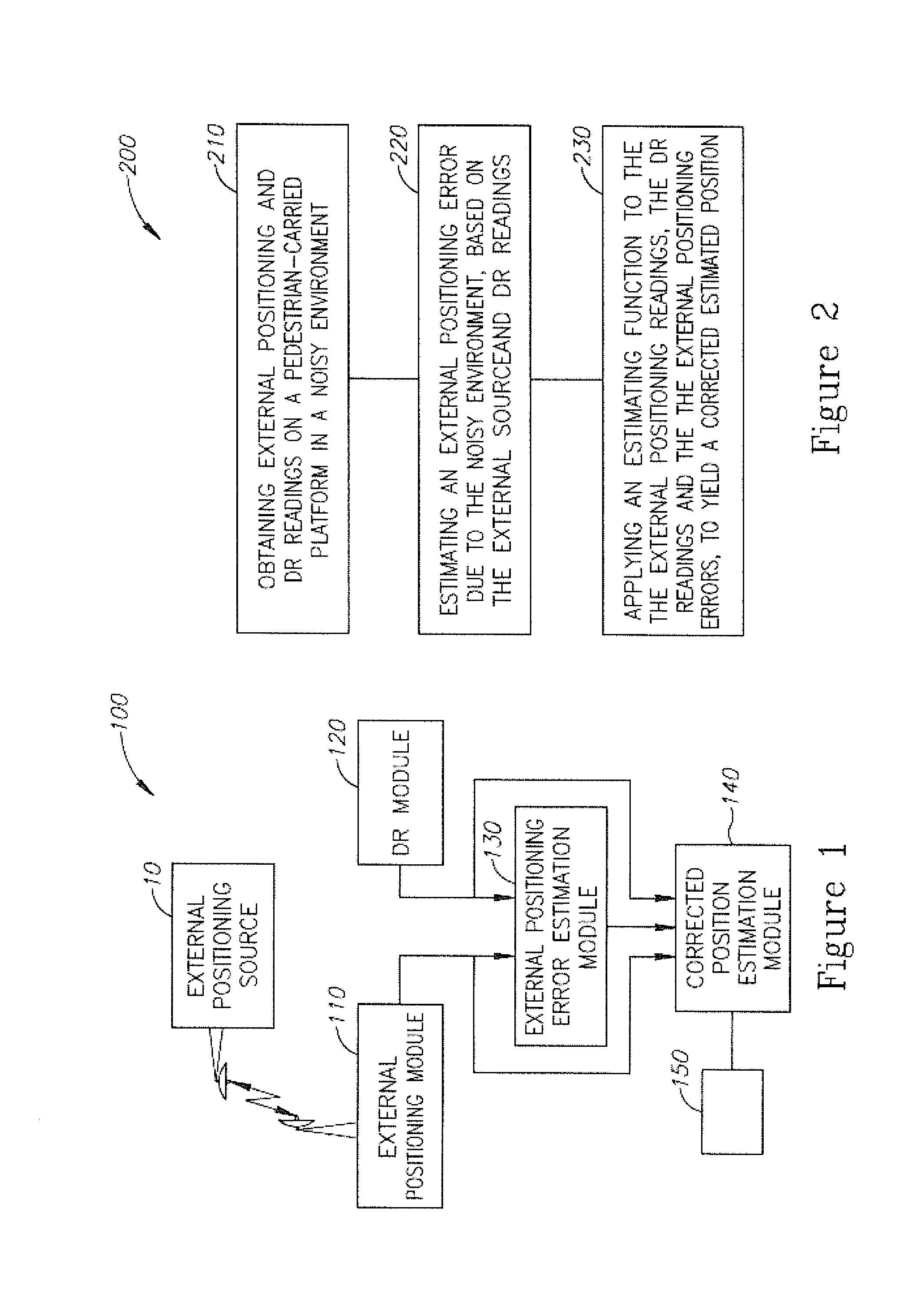
A method of pedestrian navigation, based on an external positioning system and a Dead Reckoning (DR) system is provided herein. The method may employ the following steps: obtaining external positioning readings from an external positioning source and DR position readings from a pedestrian-carried platform; estimating an external positioning error, based at least partially on the external positioning and the DR position readings; and applying an estimation function to the external position readings, the DR position readings, and the external positioning errors, to yield a corrected estimated position.
Owner:ELBIT SYST LTD
Multiple data sources pedestrian navigation system
InactiveUS20150204673A1Navigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDead reckoningPedestrian navigation system
A method of pedestrian navigation, based on an external positioning system and a Dead Reckoning (DR) system, is provided herein. The method may employ the following steps: obtaining external positioning readings from an external positioning source and DR position readings from a pedestrian-carried platform; estimating an external positioning error, based at least partially on the external positioning and the DR position readings; and applying an estimation function to the external position readings, the DR position readings, and the external positioning errors, to yield a corrected estimated position.
Owner:ELBIT SYST LTD
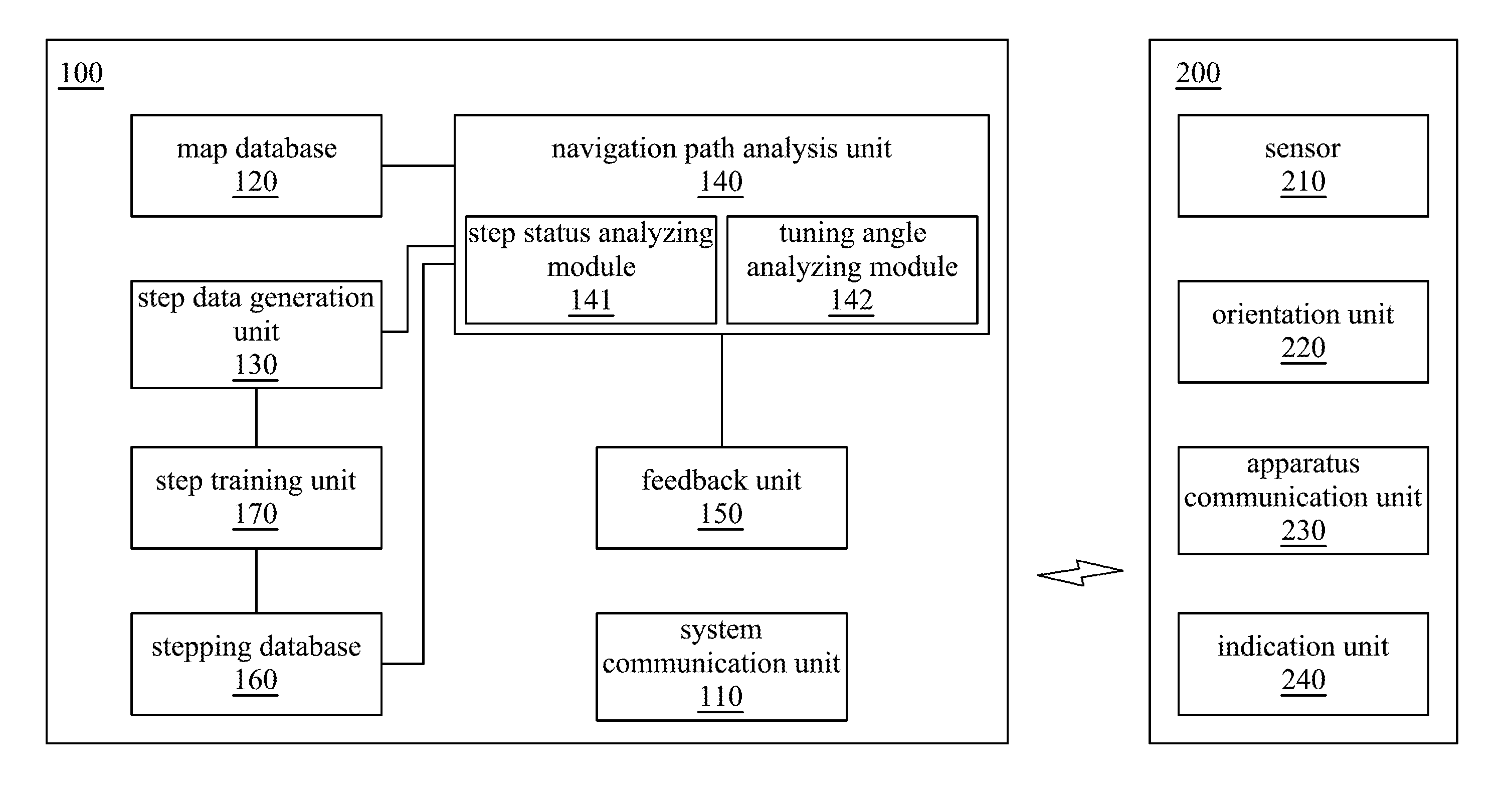
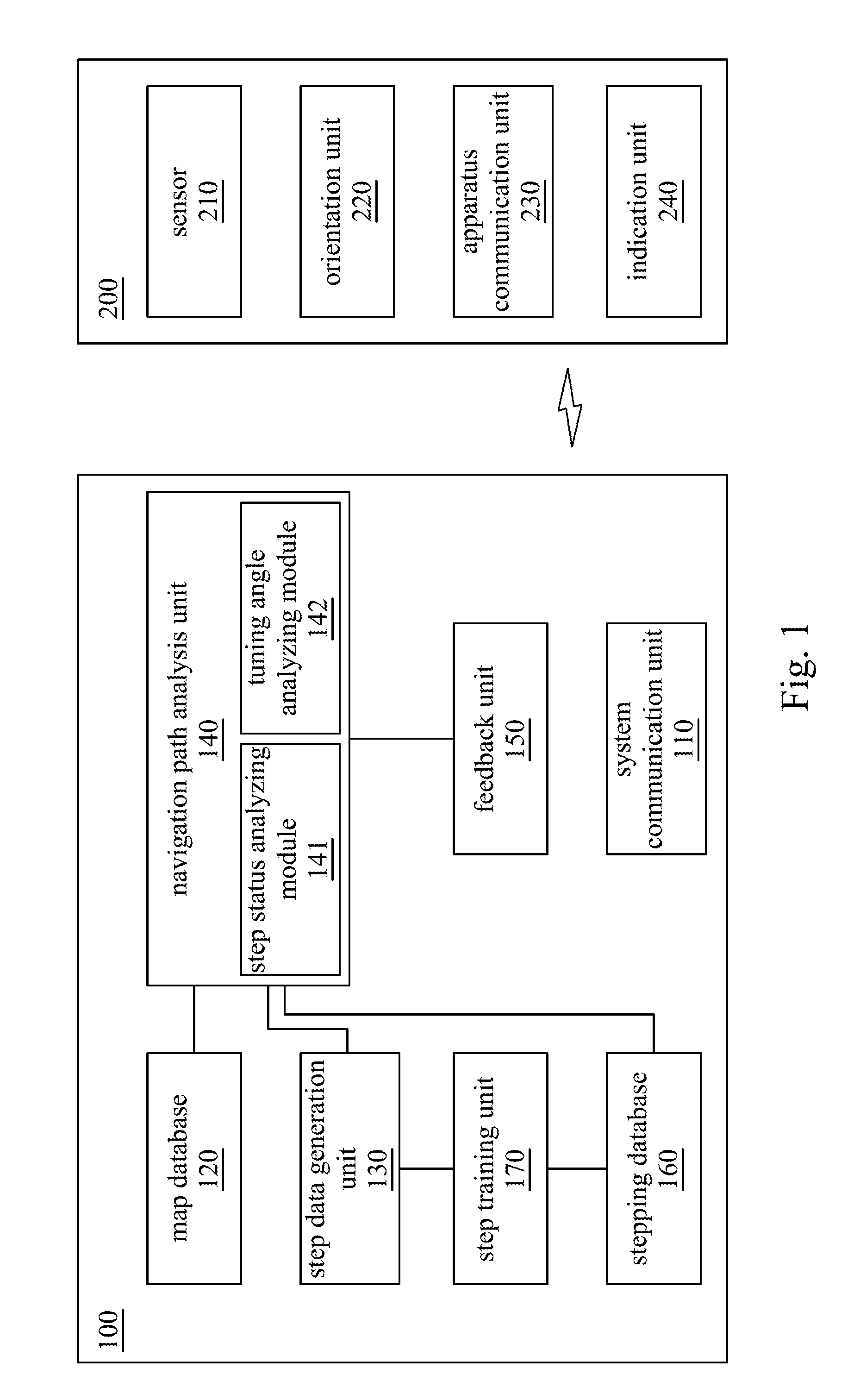
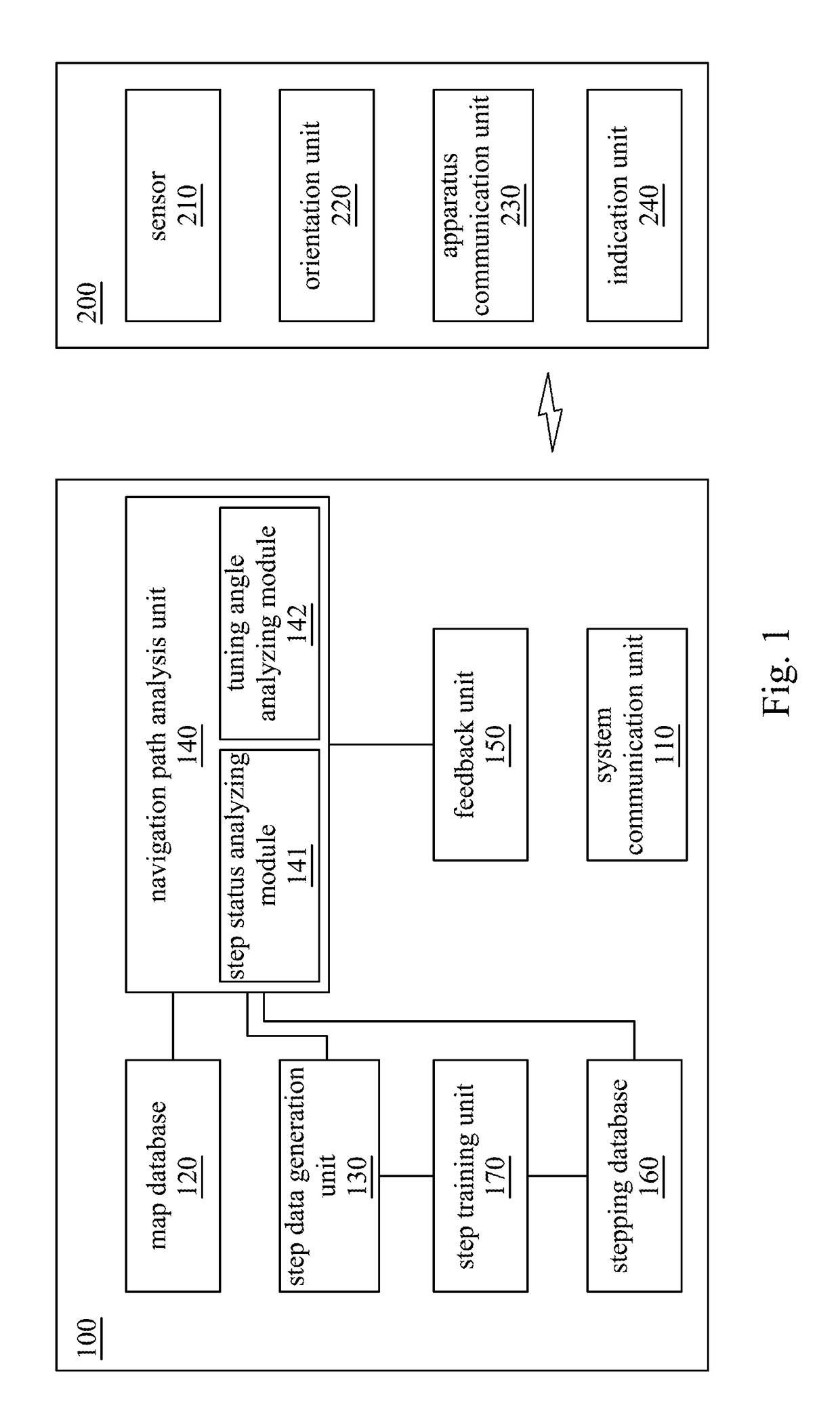
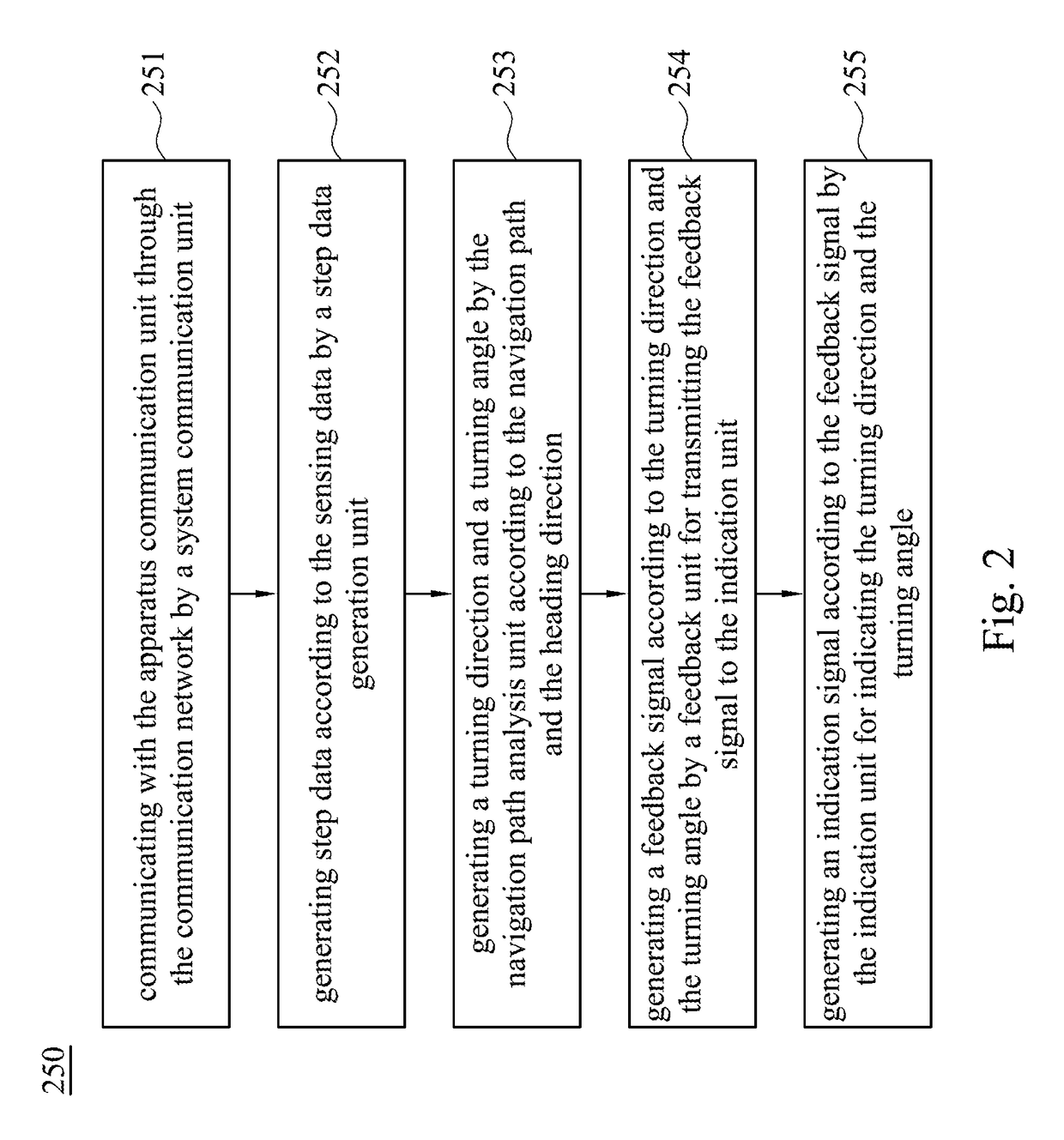
Pedestrian navigation system and method thereof
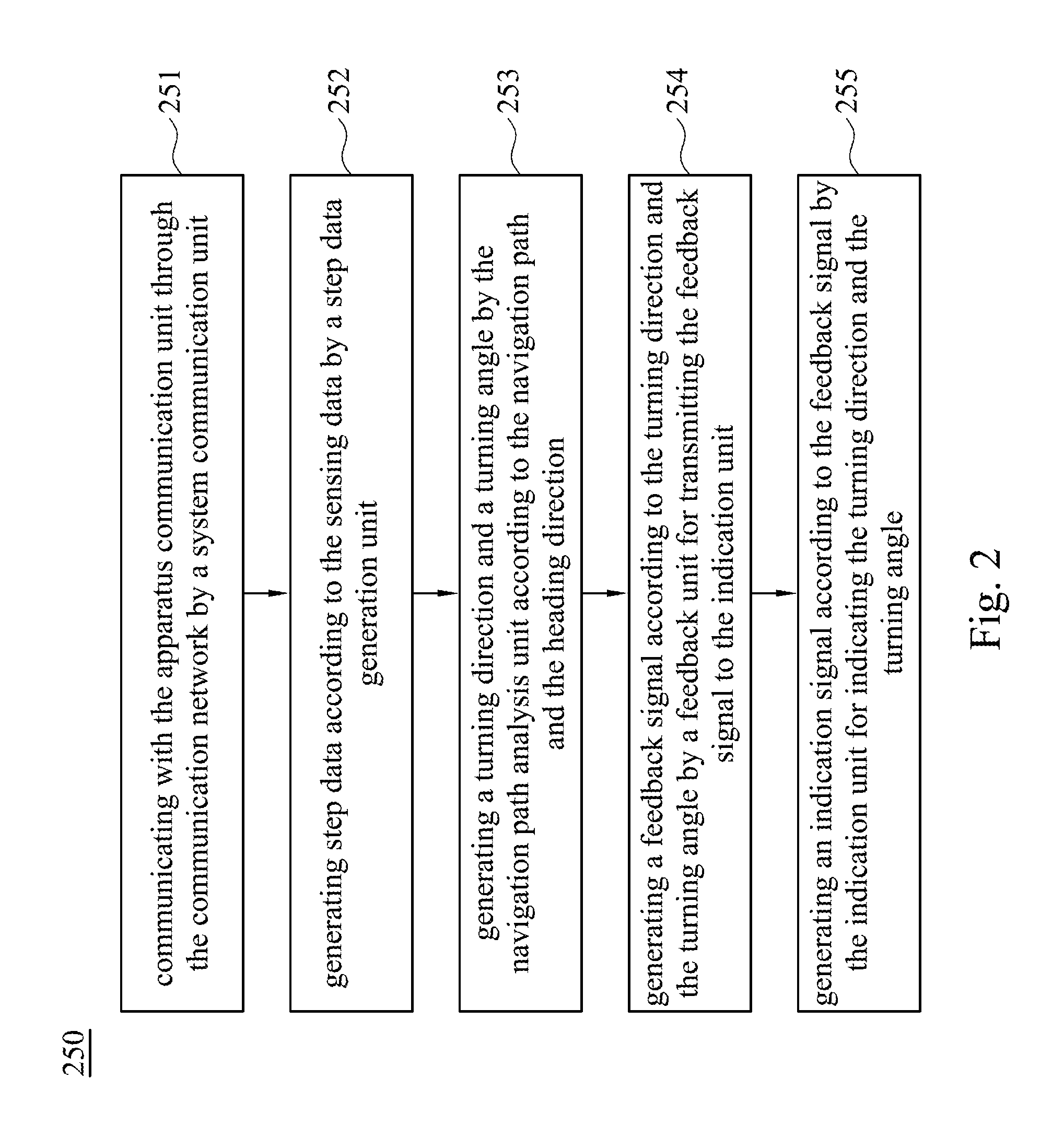
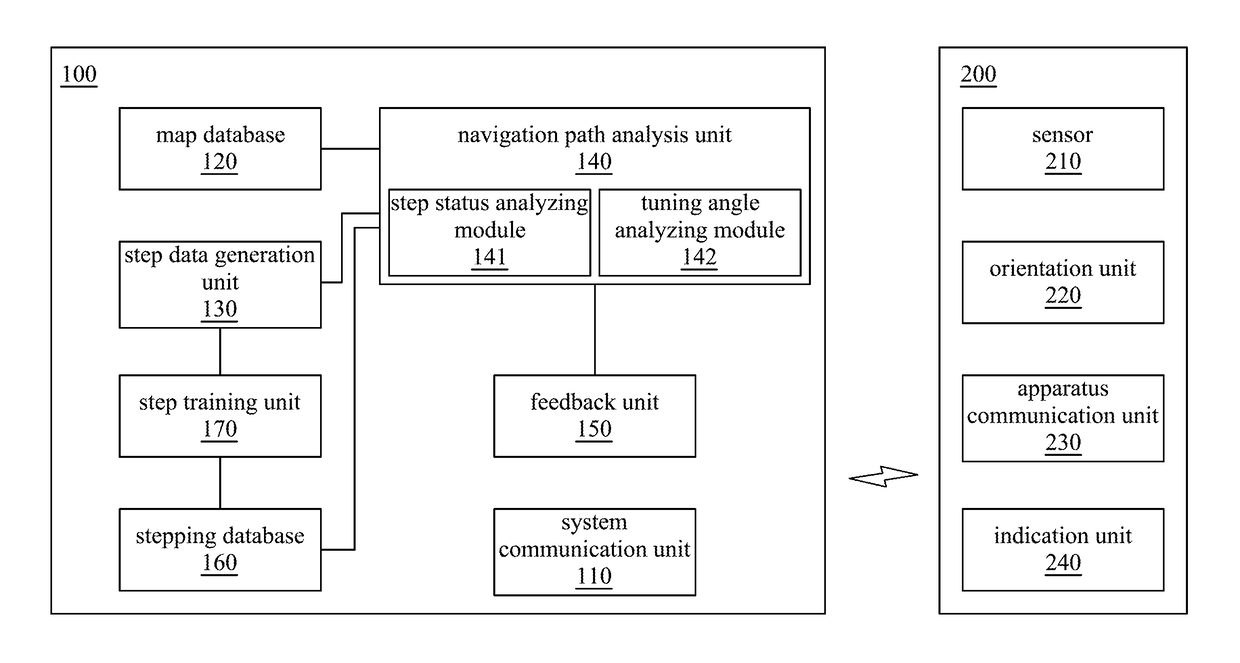
ActiveUS20160146609A1Complete responseInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlSensing dataTurn angle
A pedestrian navigation system for navigating a foot apparatus comprises a system communication unit, a map database, a step data generation unit, a navigation path analysis unit and a feedback unit. The system communication unit communicates with an apparatus communication unit of the foot apparatus. The step data generation unit generates step data according to the sensing data of the foot apparatus. The navigation path analysis unit determines a navigation path and determines a heading direction of the foot apparatus. A turning direction and a turning angle are generated according to the navigation path and the heading direction. The feedback unit receives the turning direction and the turning angle to generate a feedback signal. The indication unit generates an indication signal according to the feedback signal to indicate the turning direction and the turning angle.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
A pedestrian inertial navigation system and method assisted by machine learning algorithms and models
ActiveCN108168548BRealize inertial pedestrian navigation functionNavigation by terrestrial meansNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsHuman bodyAlgorithm
The invention discloses a pedestrian inertial navigation system and method assisted by a machine learning algorithm and a model, belonging to the field of inertial and integrated navigation and the field of artificial intelligence. The method recognizes different types of gait characteristics of the human body through inertial / geomagnetic sensor components installed on human feet, and sensor components installed centrally or distributed on other parts of the human body. Adaptively adopt different machine learning algorithms and models to train the sensor information of the foot and other parts, and realize the purpose of simulating the inertial sensor information of the foot through the sensor information of other parts, so that real-time fault detection can be performed on the pedestrian navigation system, and It can predict within a gait cycle before the foot inertial sensor exceeds the range, and then based on one or more virtual foot inertial sensor information generated by simulation, the pedestrian navigation system can be constructed through the principle of system reconstruction to realize fault and overshooting. Inertial Pedestrian Navigation Function in Range Conditions.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Pedestrian navigation system and method thereof
ActiveUS9613056B2Complete responseRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSensing dataTurn angle
A pedestrian navigation system for navigating a foot apparatus comprises a system communication unit, a map database, a step data generation unit, a navigation path analysis unit and a feedback unit. The system communication unit communicates with an apparatus communication unit of the foot apparatus. The step data generation unit generates step data according to the sensing data of the foot apparatus. The navigation path analysis unit determines a navigation path and determines a heading direction of the foot apparatus. A turning direction and a turning angle are generated according to the navigation path and the heading direction. The feedback unit receives the turning direction and the turning angle to generate a feedback signal. The indication unit generates an indication signal according to the feedback signal to indicate the turning direction and the turning angle.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com