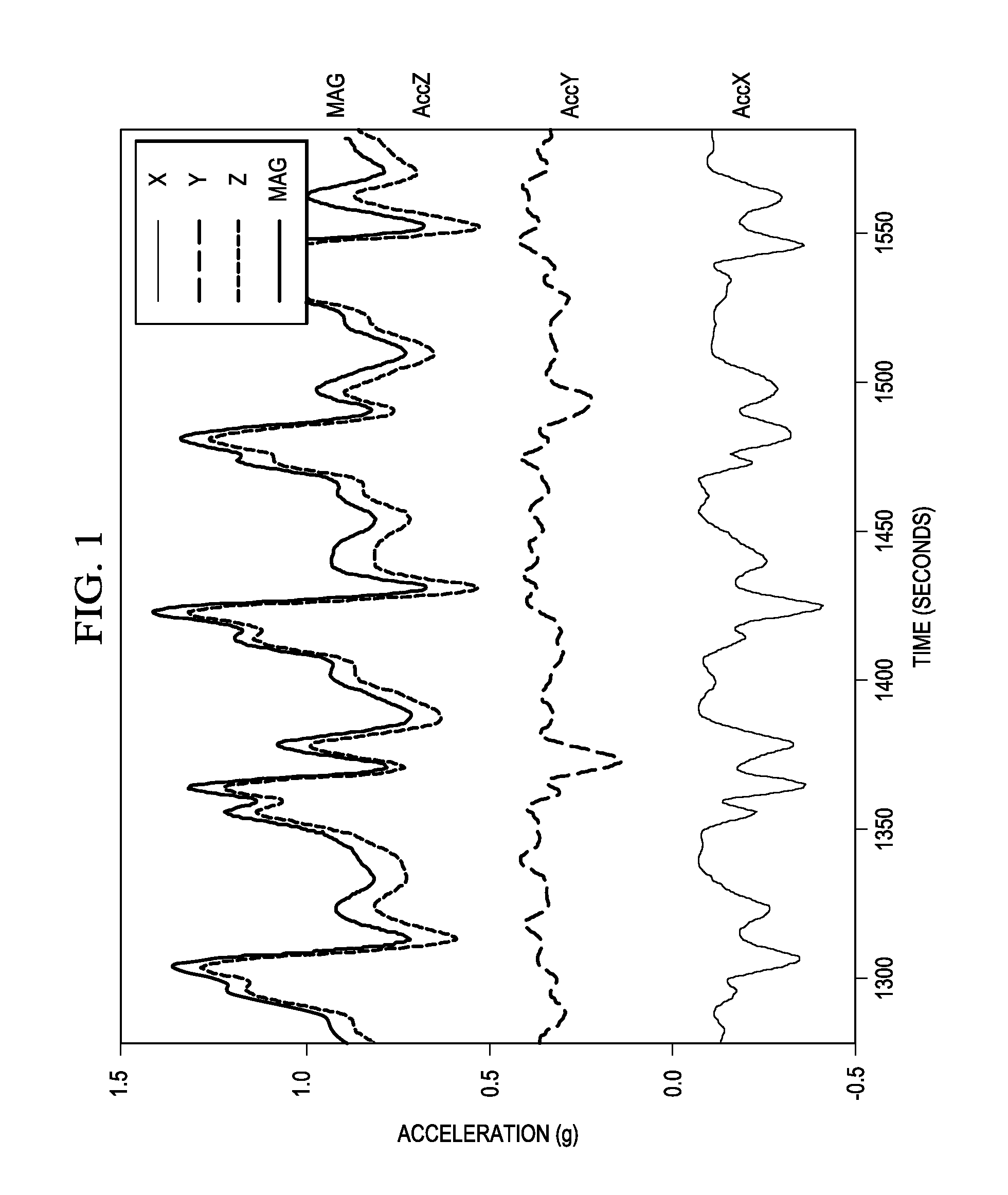
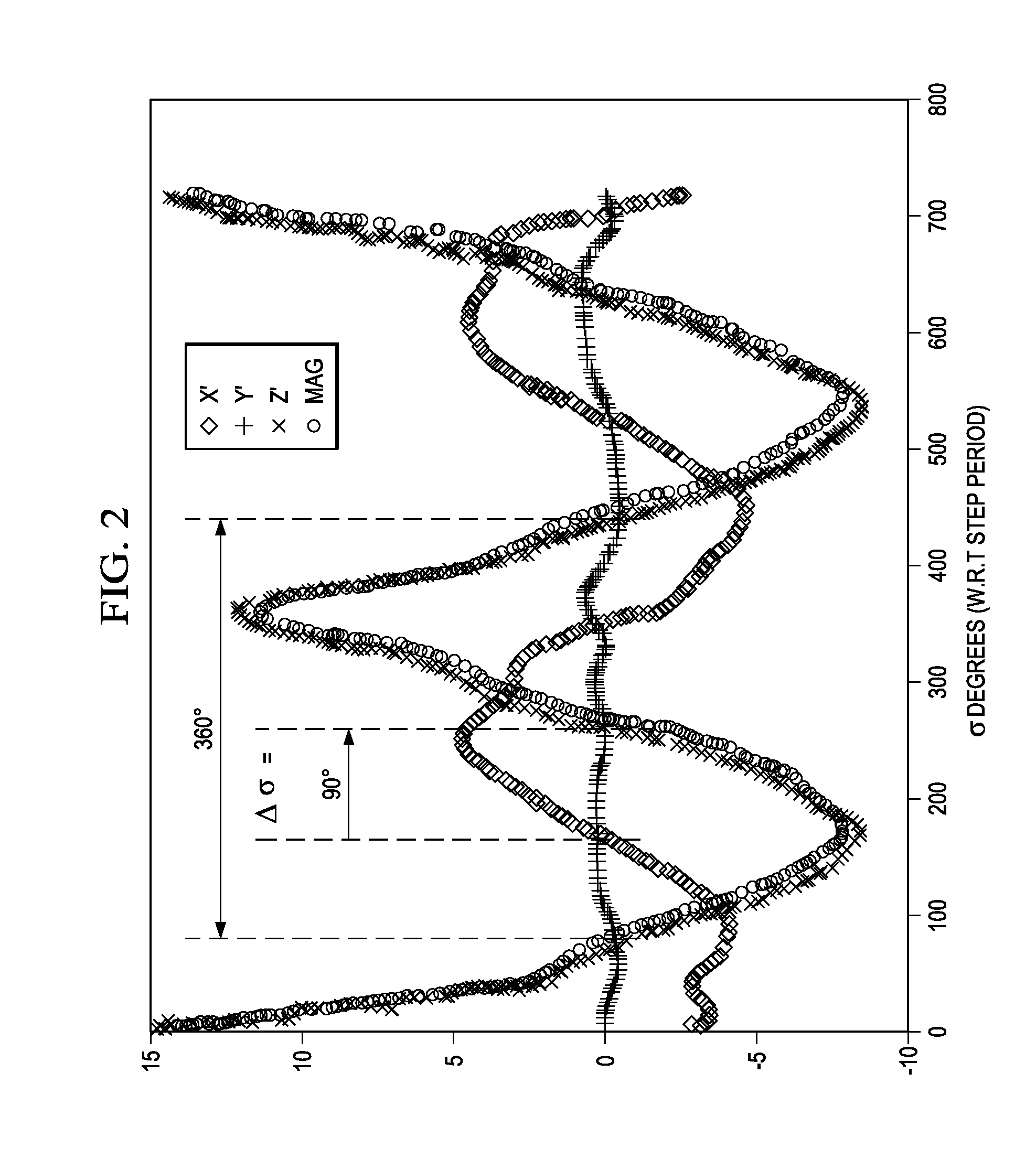
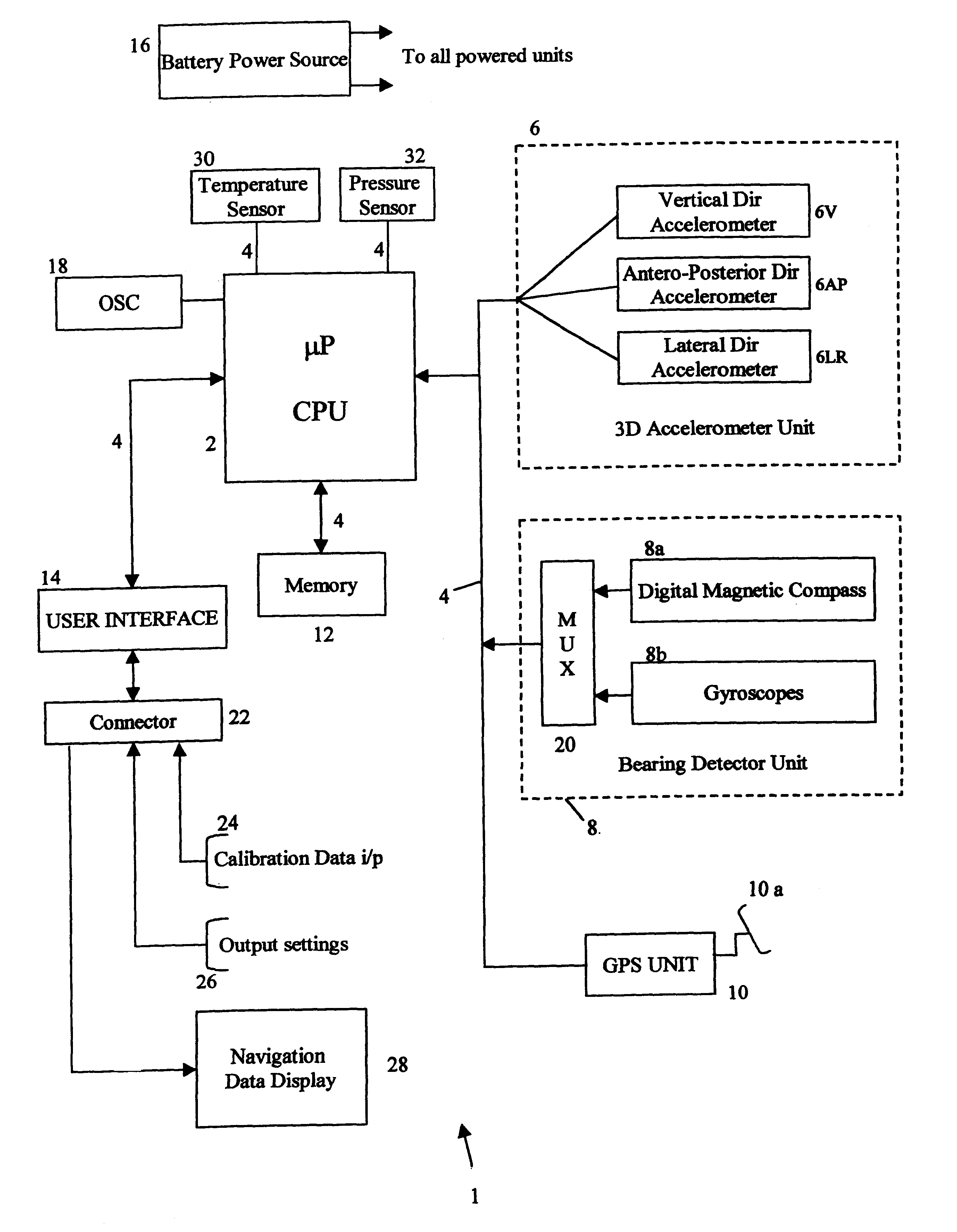
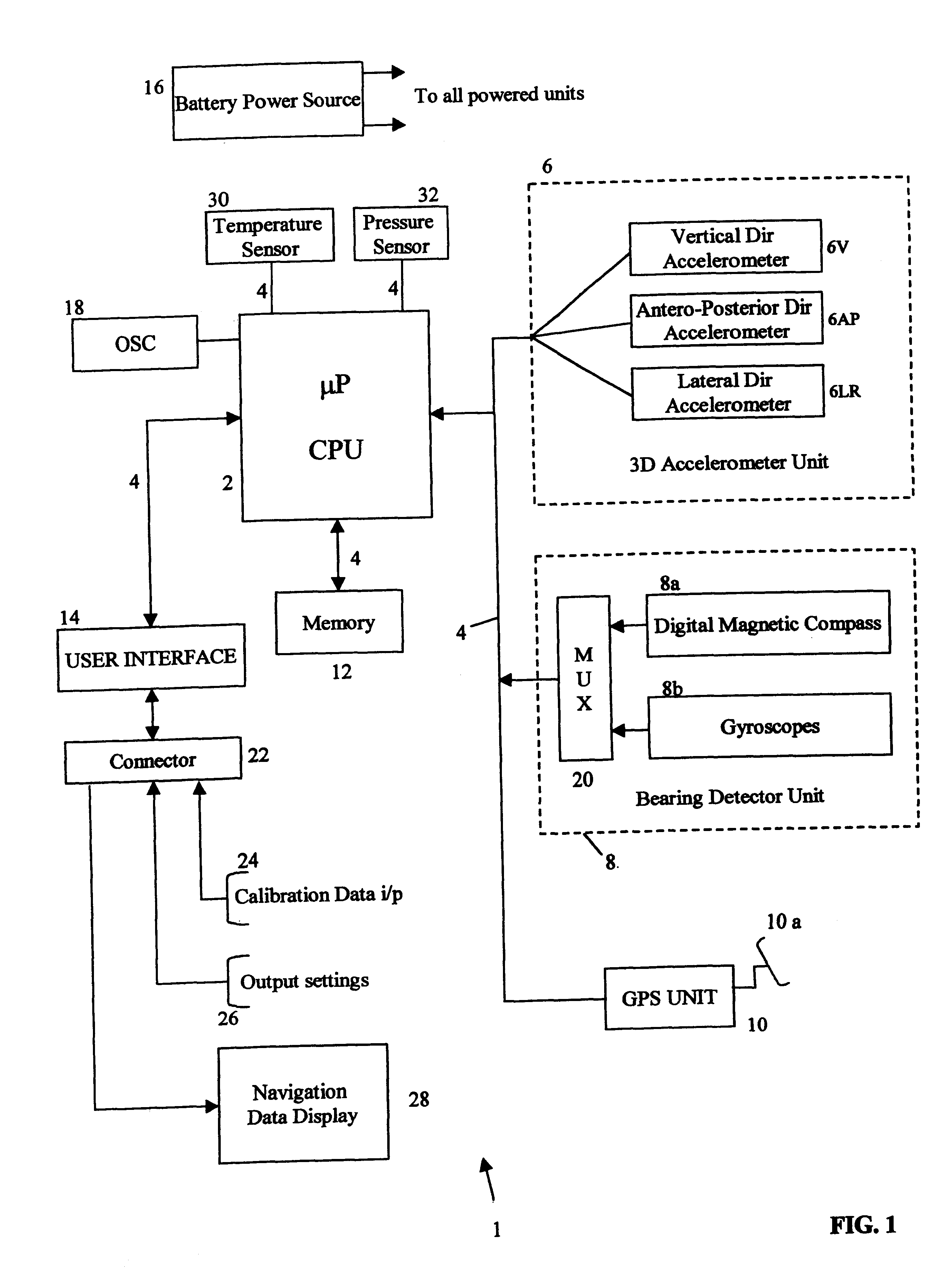
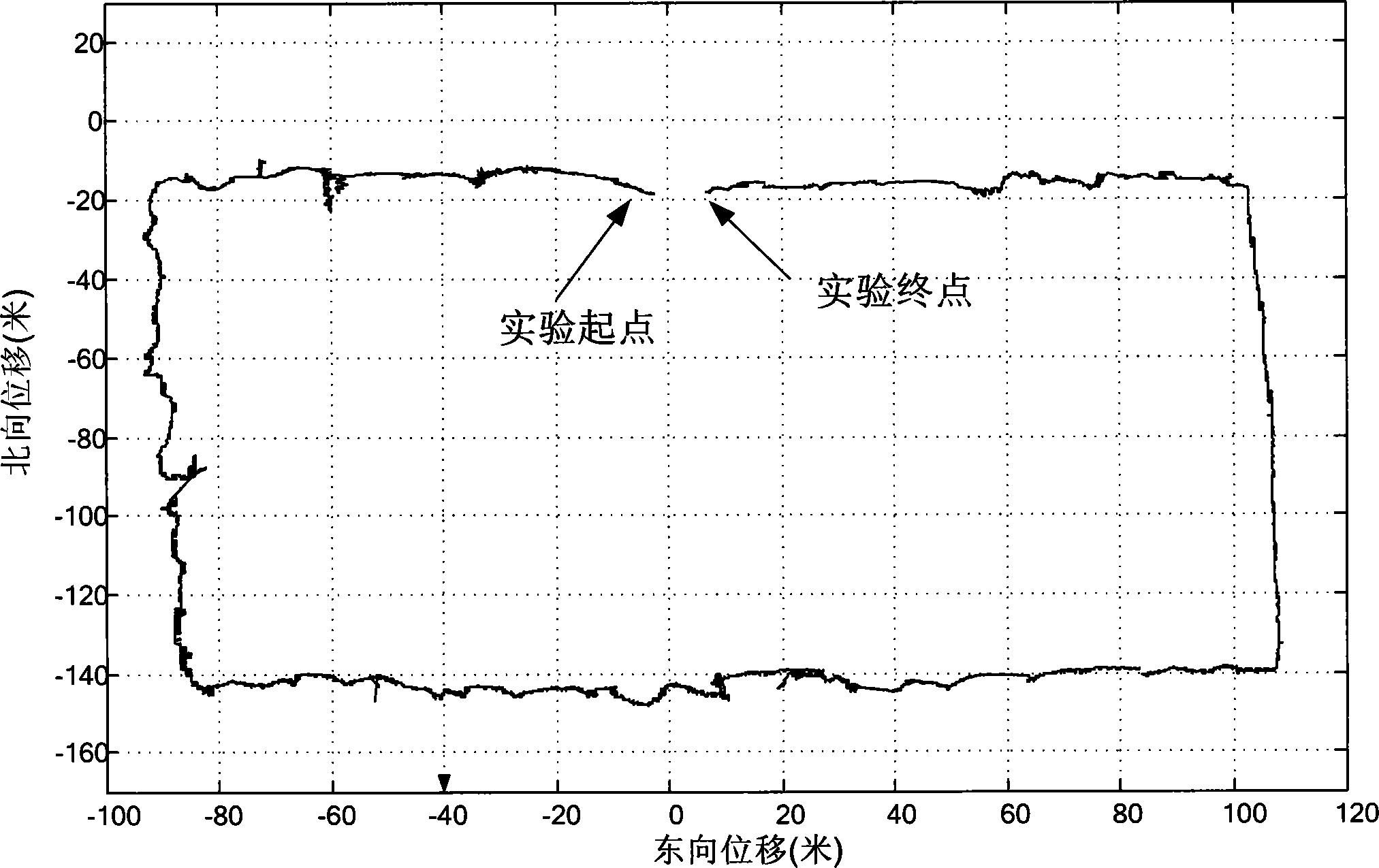
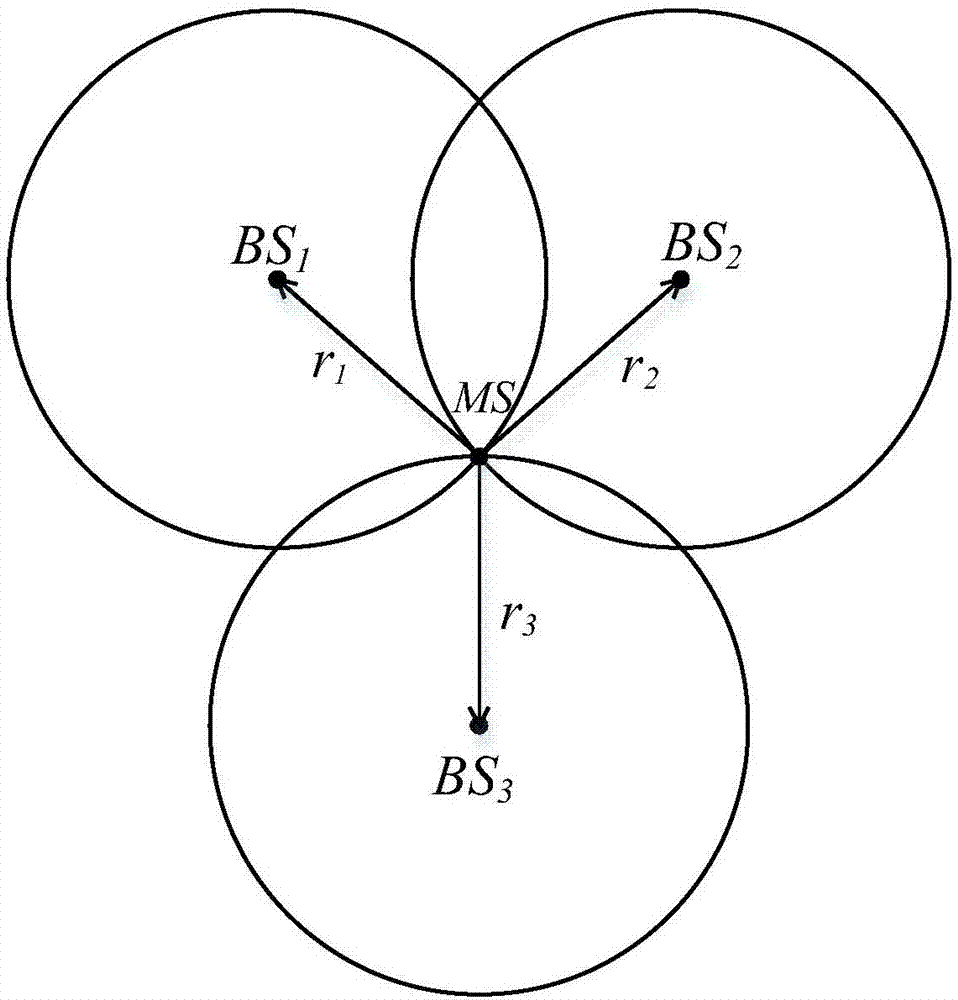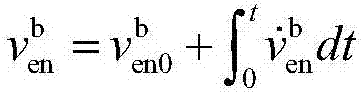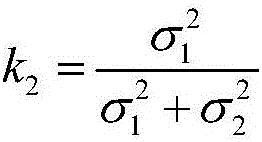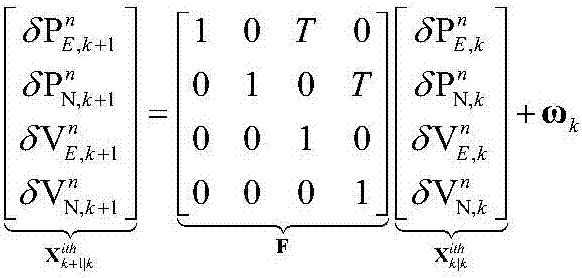Patents
Literature
138 results about "Pedestrian navigation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Wearable augmented reality computing apparatus
InactiveUS20120050144A1Improve image qualityDevices with GPS signal receiverDevices with sensorDisplay deviceInput device
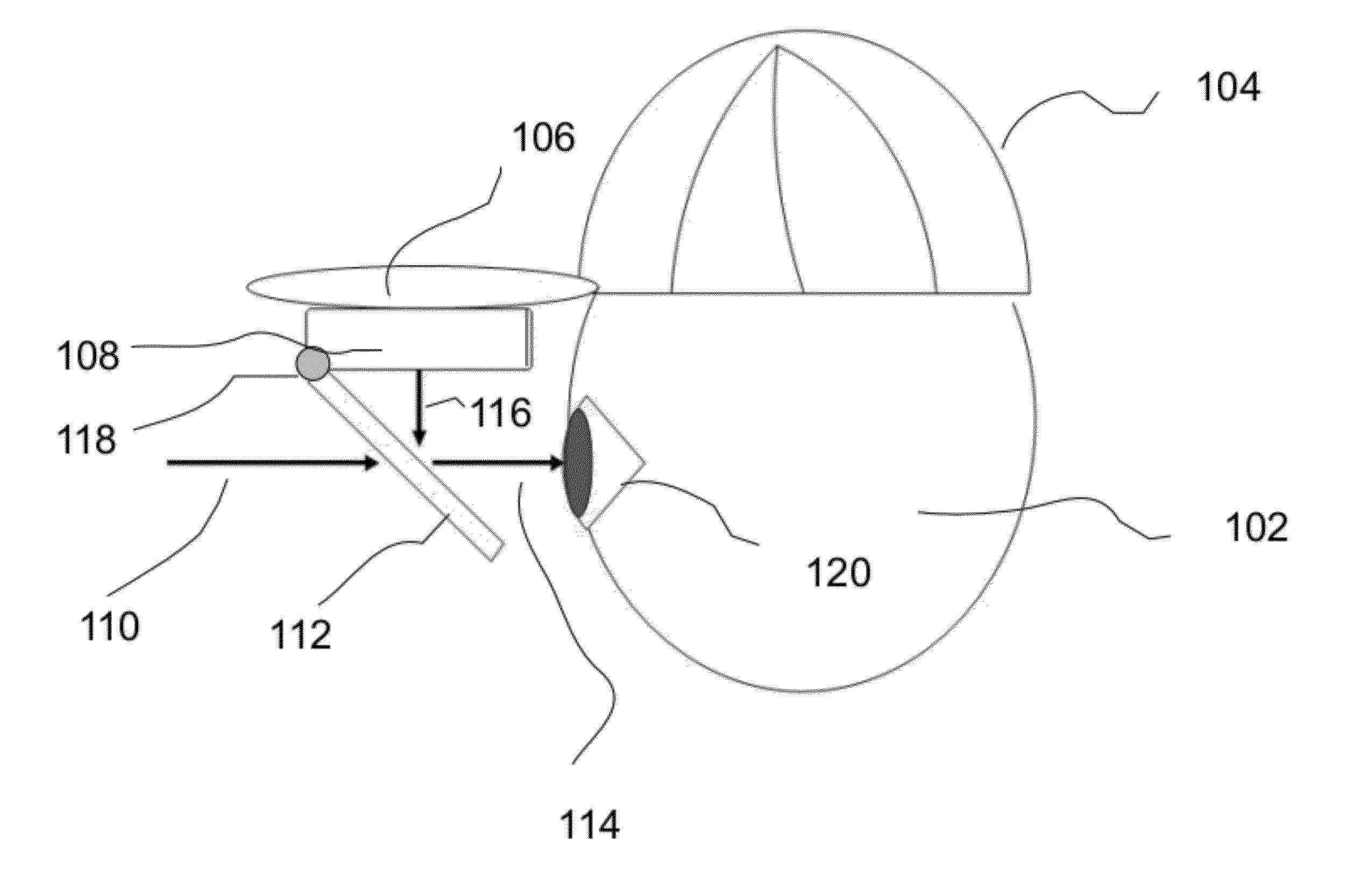
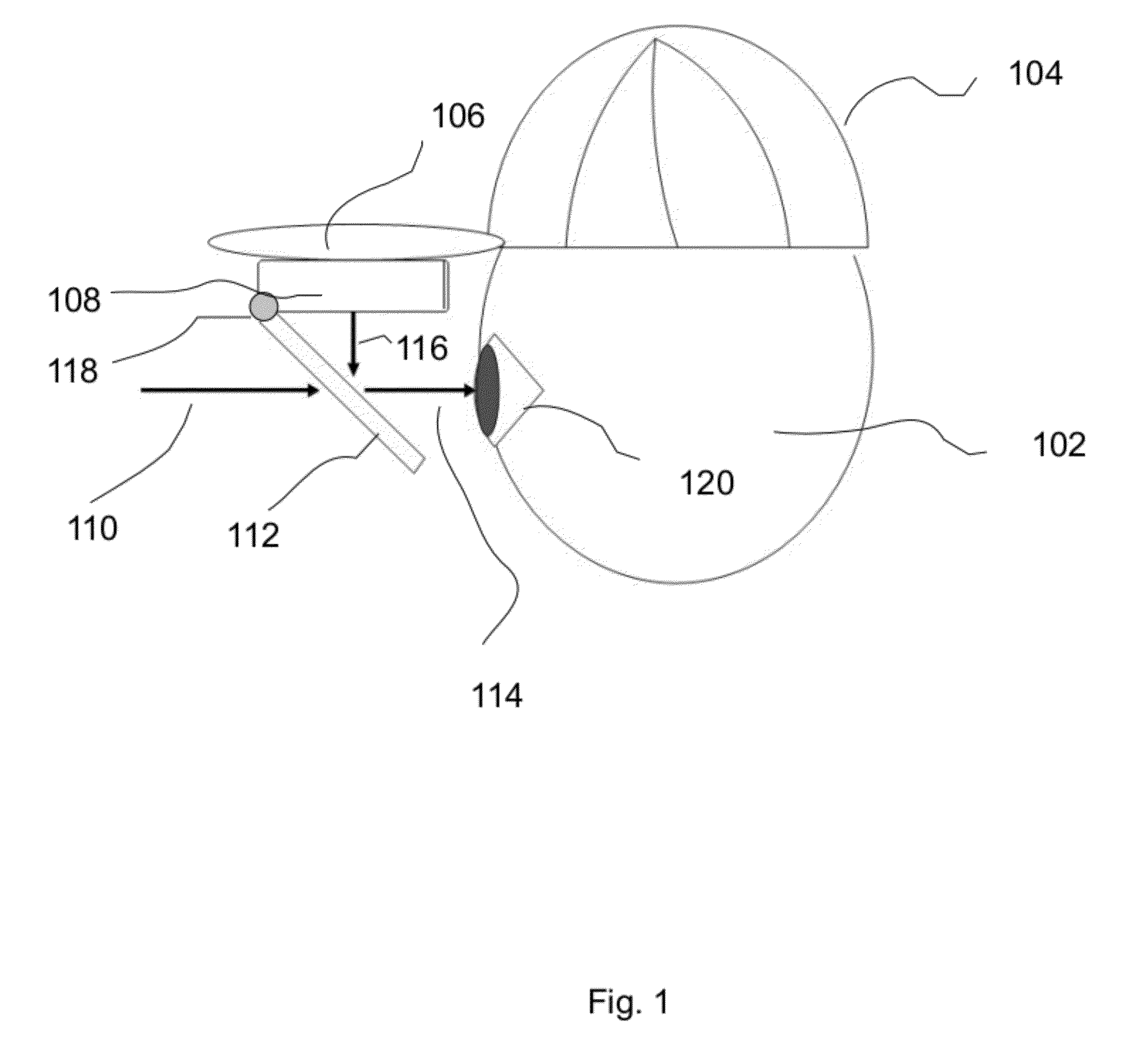
A wearable augmented reality computing apparatus with a display screen, a reflective device, a computing device and a head mounted harness to contain these components. The display device and reflective device are configured such that a user can see the reflection from the display device superimposed on the view of reality. An embodiment uses a switchable mirror as the reflective device. One usage of the apparatus is for vehicle or pedestrian navigation. The portable display and general purpose computing device can be combined in a device such as a smartphone. Additional components consist of orientation sensors and non-handheld input devices.
Owner:MORLOCK CLAYTON RICHARD
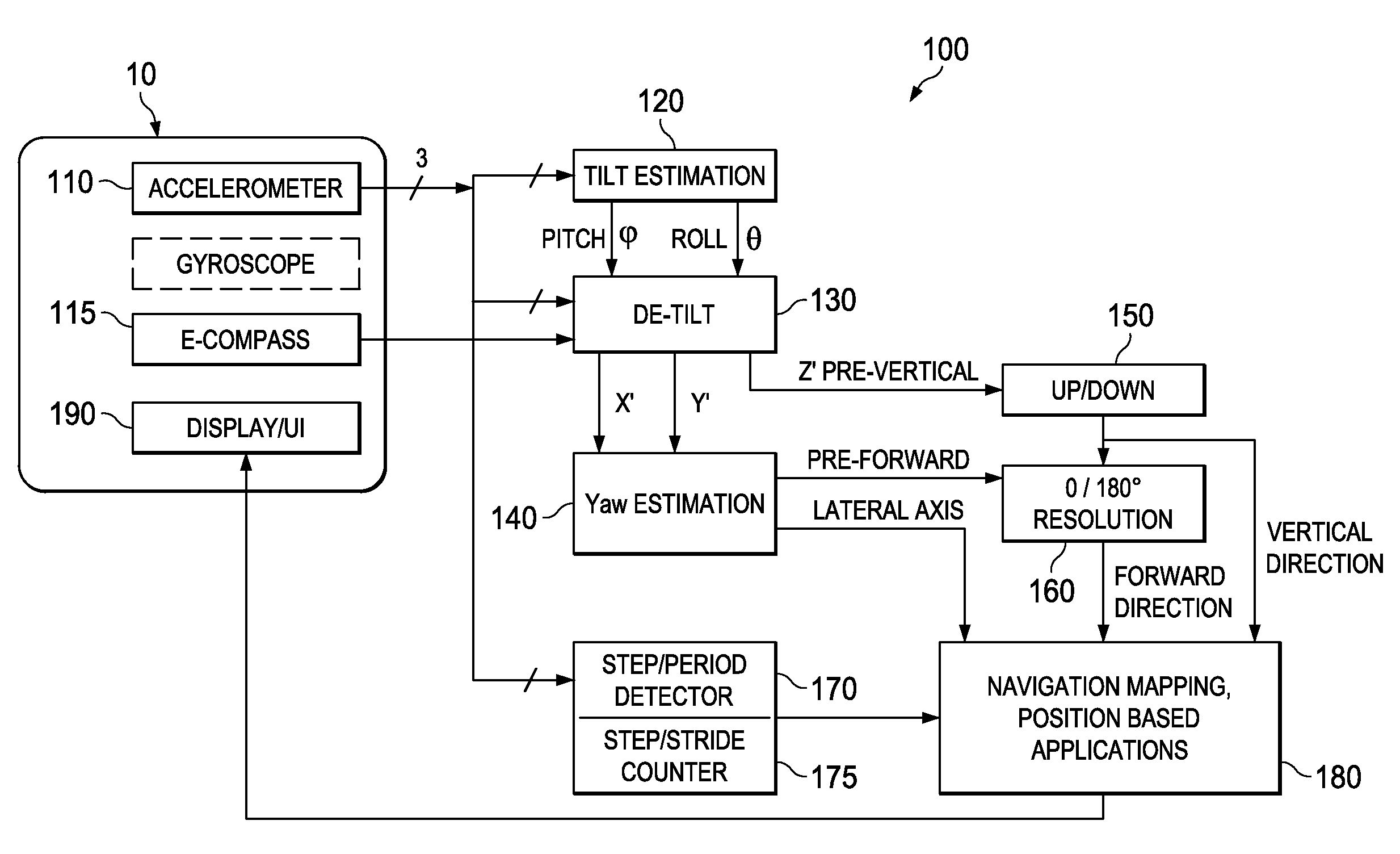
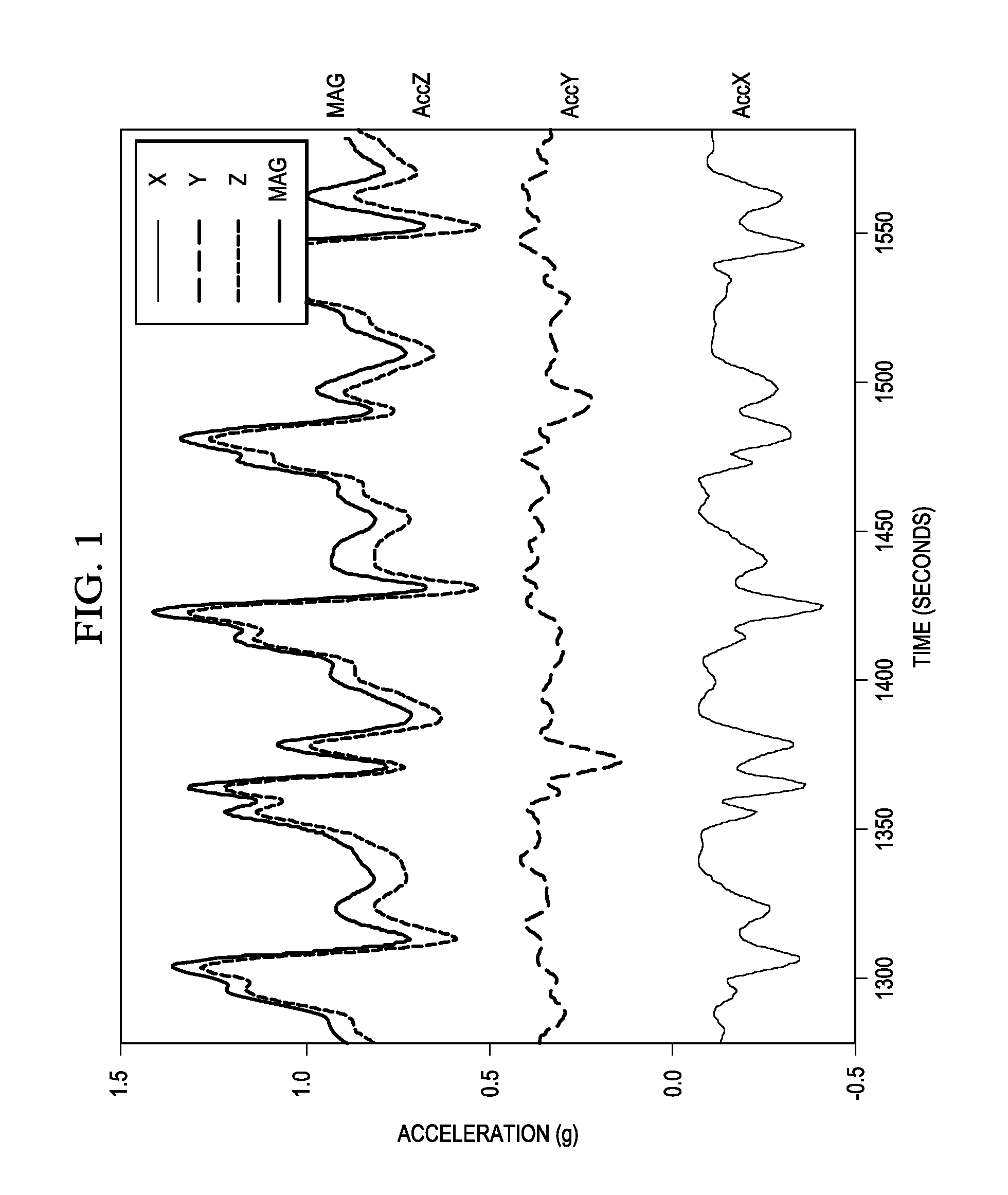
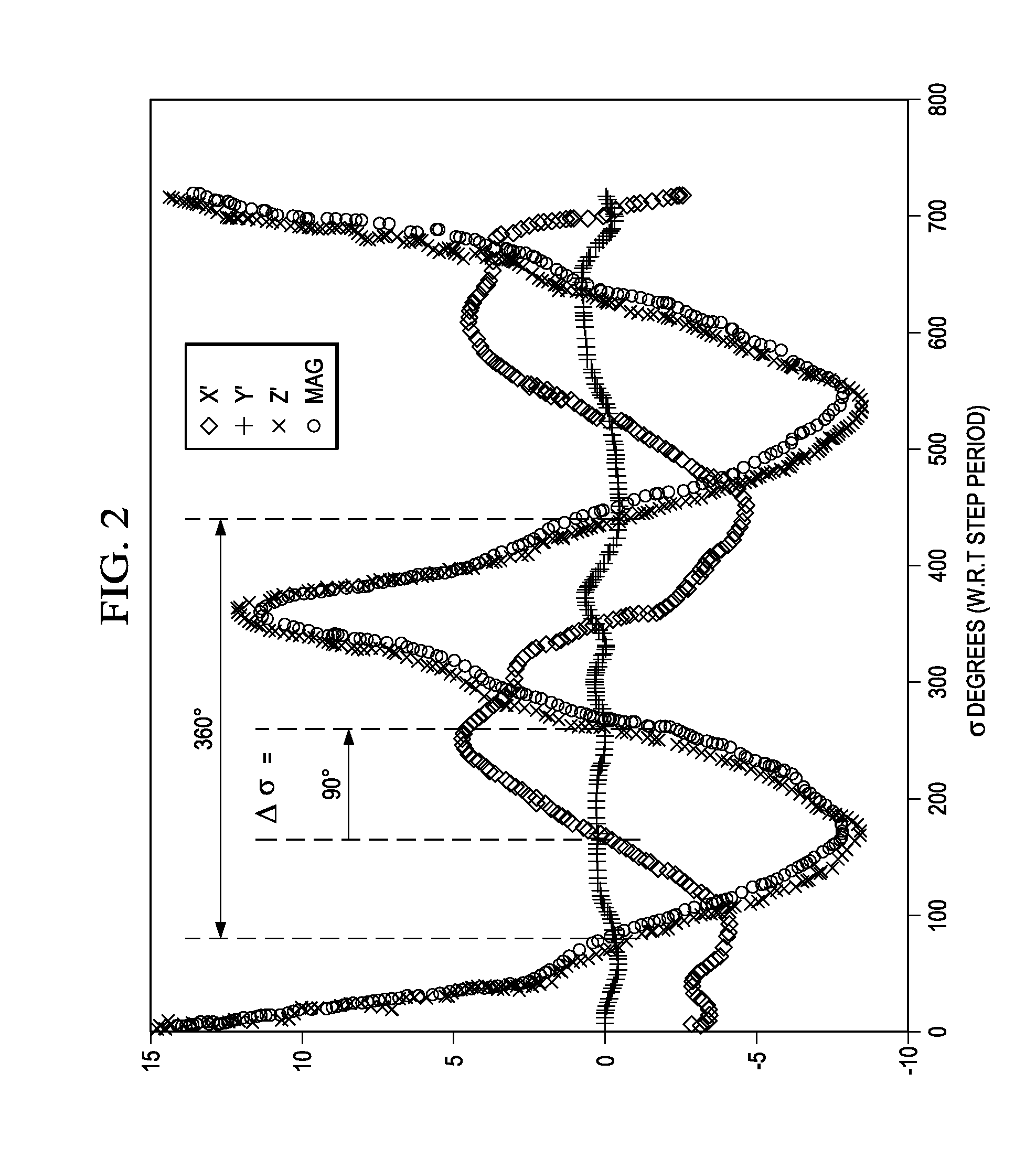
Attitude estimation for pedestrian navigation using low cost MEMS accelerometer in mobile applications, and processing methods, apparatus and systems
ActiveUS20120136573A1Navigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerControl engineering
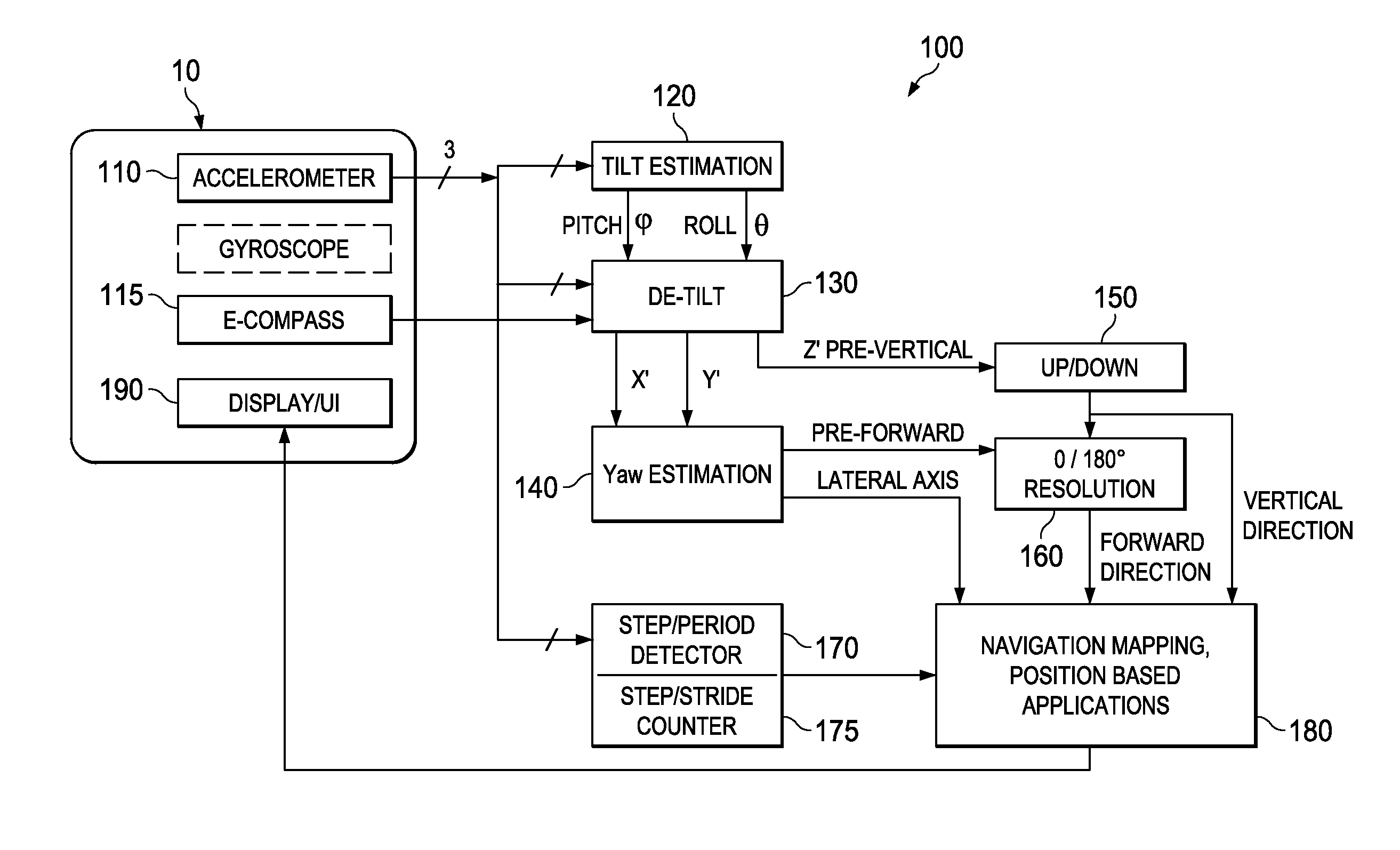
A user-heading determining system (10) for pedestrian use includes a multiple-axis accelerometer (110) having acceleration sensors; a device-heading sensor circuit (115) physically situated in a fixed relationship to the accelerometer (110); an electronic circuit (100) operable to generate signals representing components of acceleration sensed by the accelerometer (110) sensors, and to electronically process at least some part of the signals to produce an estimation of attitude of a user motion with respect to the accelerometer, and further to combine the attitude estimation (750, α) with a device heading estimation (770, ψ) responsive to the device-heading sensor circuit, to produce a user heading estimation (780); and an electronic display (190) responsive to the electronic circuit (100) to display information at least in part based on the user heading estimation. Other systems, circuits and processes are also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Pedestrian navigation method and apparatus operative in a dead reckoning mode
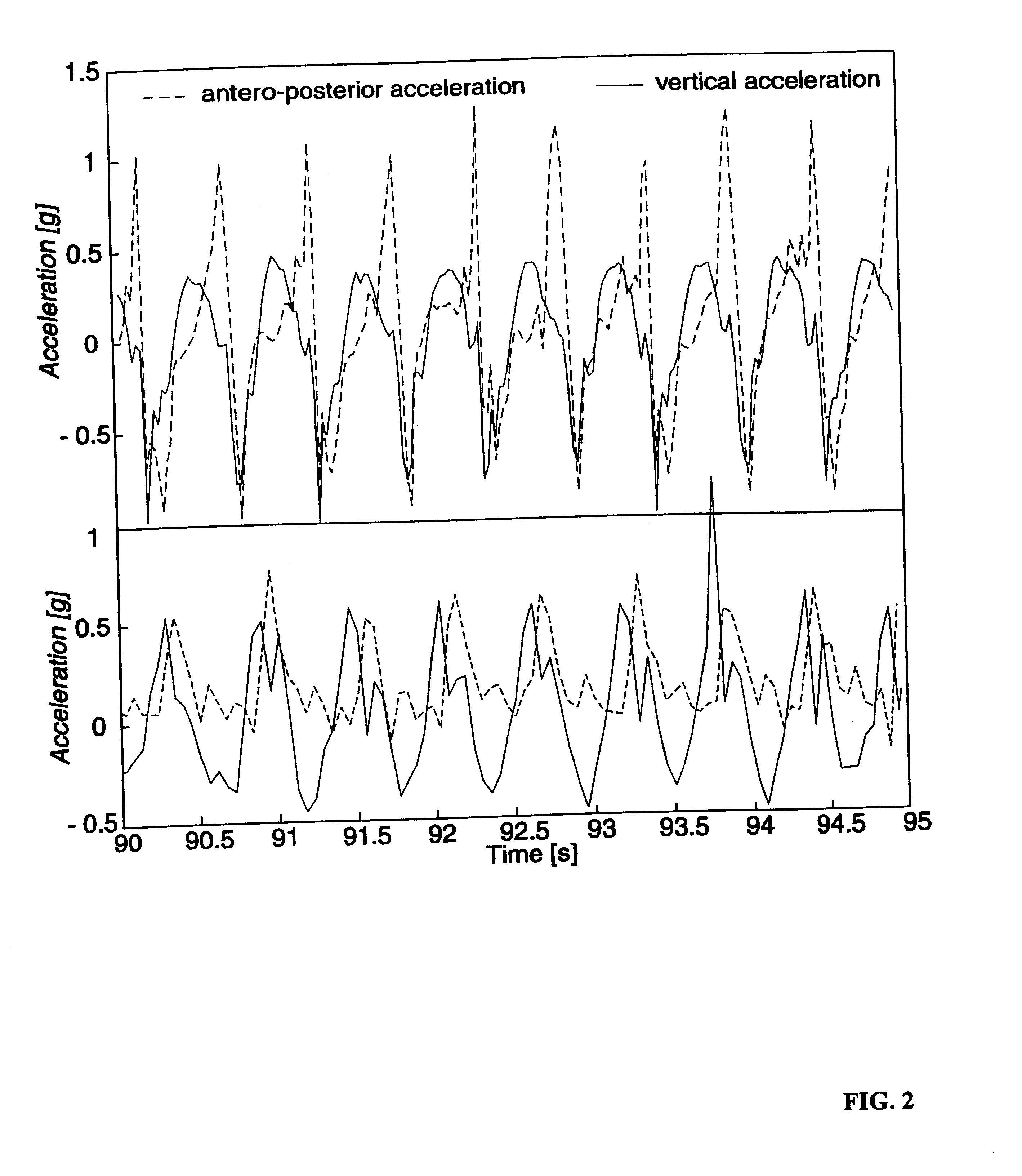
A displacement of a pedestrian is determined from his or her accelerations by detecting accelerations which is substantially non vertical, determining a characteristic feature in the detected accelerations correlated with a step frequency, determining the displacement on the basis of said determined characteristic.The acceleration data can be submitted to waveform analysis to determine an actualized time interval of an occurring feature, such a maximum values, from which it is determined whether the actualized time period falls within determined limit values. The currently detected characteristic feature is then determined as corresponding to a displacement step if the actualized time period falls within said determined limit value.By using non-vertical acceleration measurements, the invention can make it possible to distinguish between forward, backward, left and right stepping movements and take these into account for the navigation.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
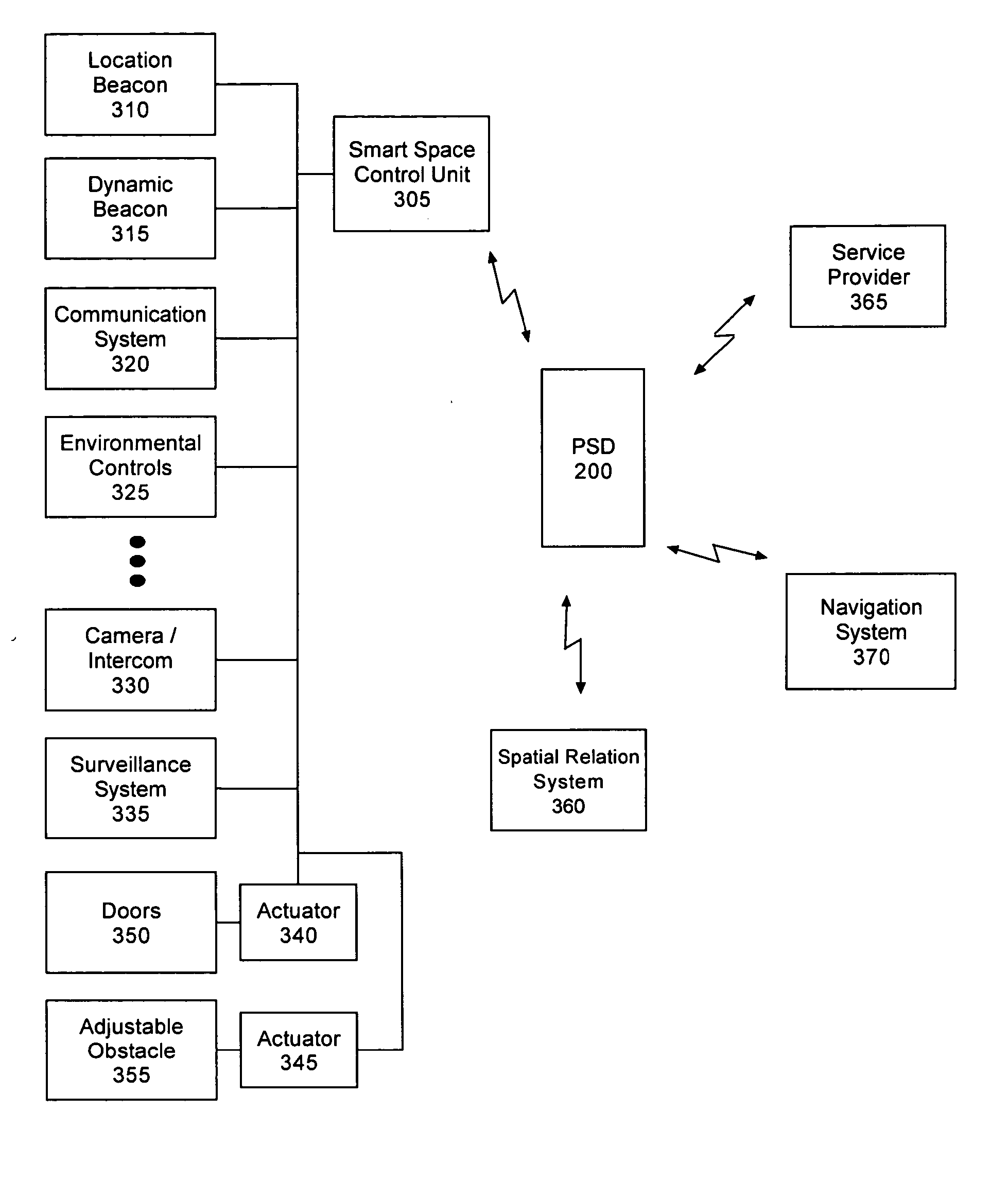
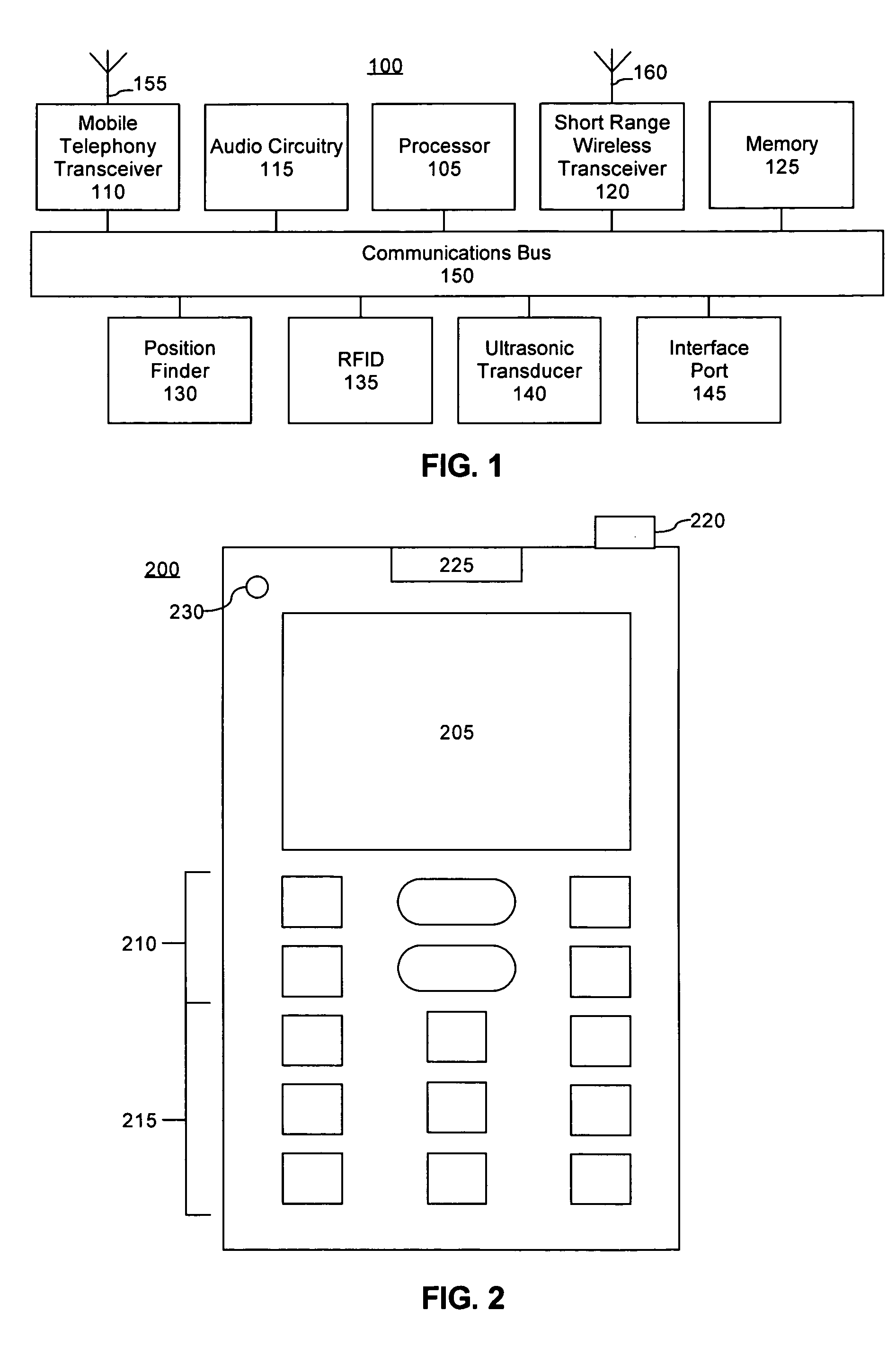
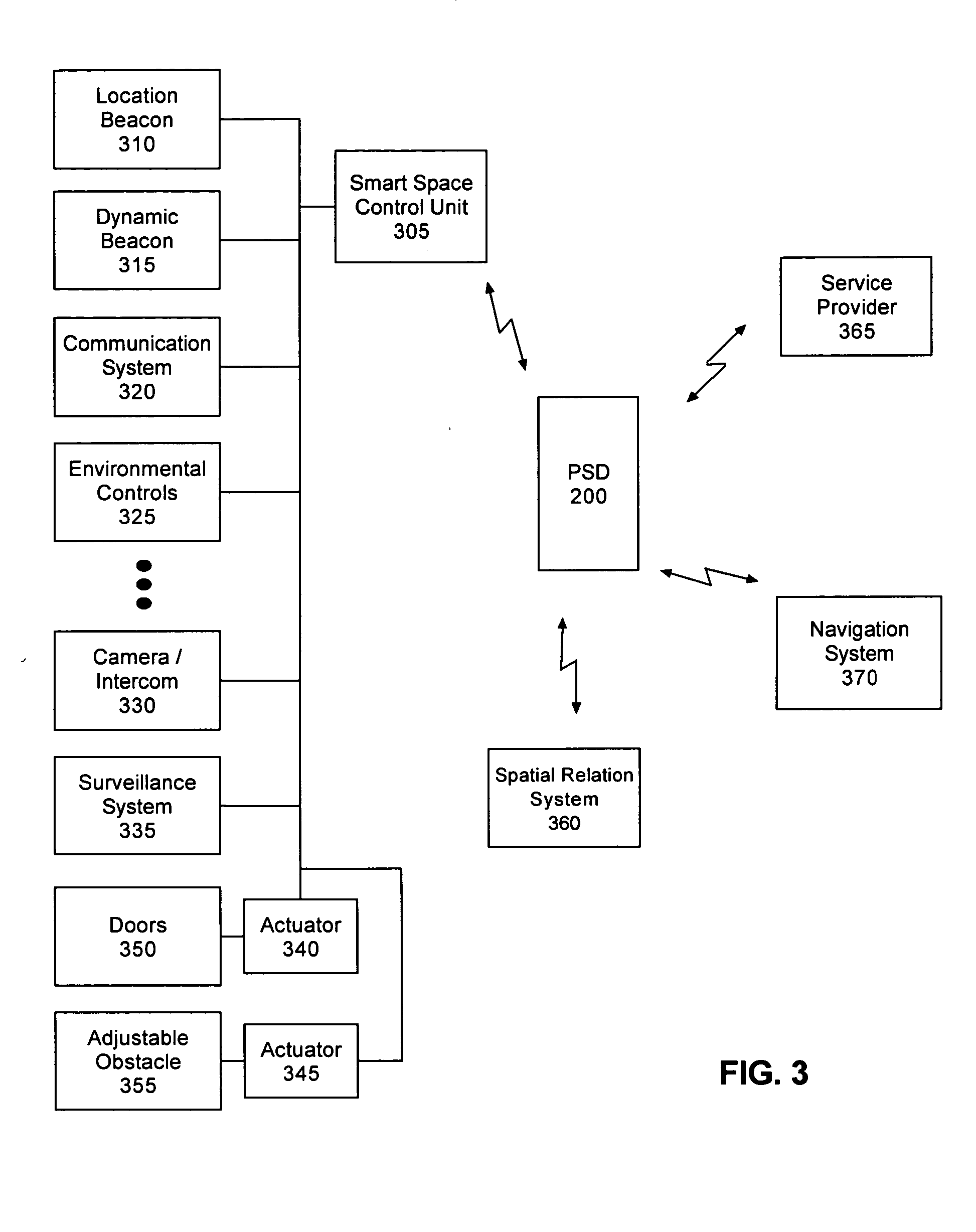
Pedestrian navigation and spatial relation device
InactiveUS20050060088A1Avoid obstaclesDevices with sensorRespiratory organ evaluationUser deviceSpatial relation
A pedestrian navigation and spatial relation device including a position finder, a spatial relationship sensor, an input mechanism, and an output mechanism. The position finder can be configured to determine a geographic position of the device based upon received wireless signals. The spatial relationship sensor can provide data used to detect a position of at least one obstacle relative to the device. The input mechanism can specify a destination location. The output mechanism can present device output to a user. The device output can include sensory indicators for at least one of guiding a pedestrian to the destination location and warning a pedestrian about the detected obstacles.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
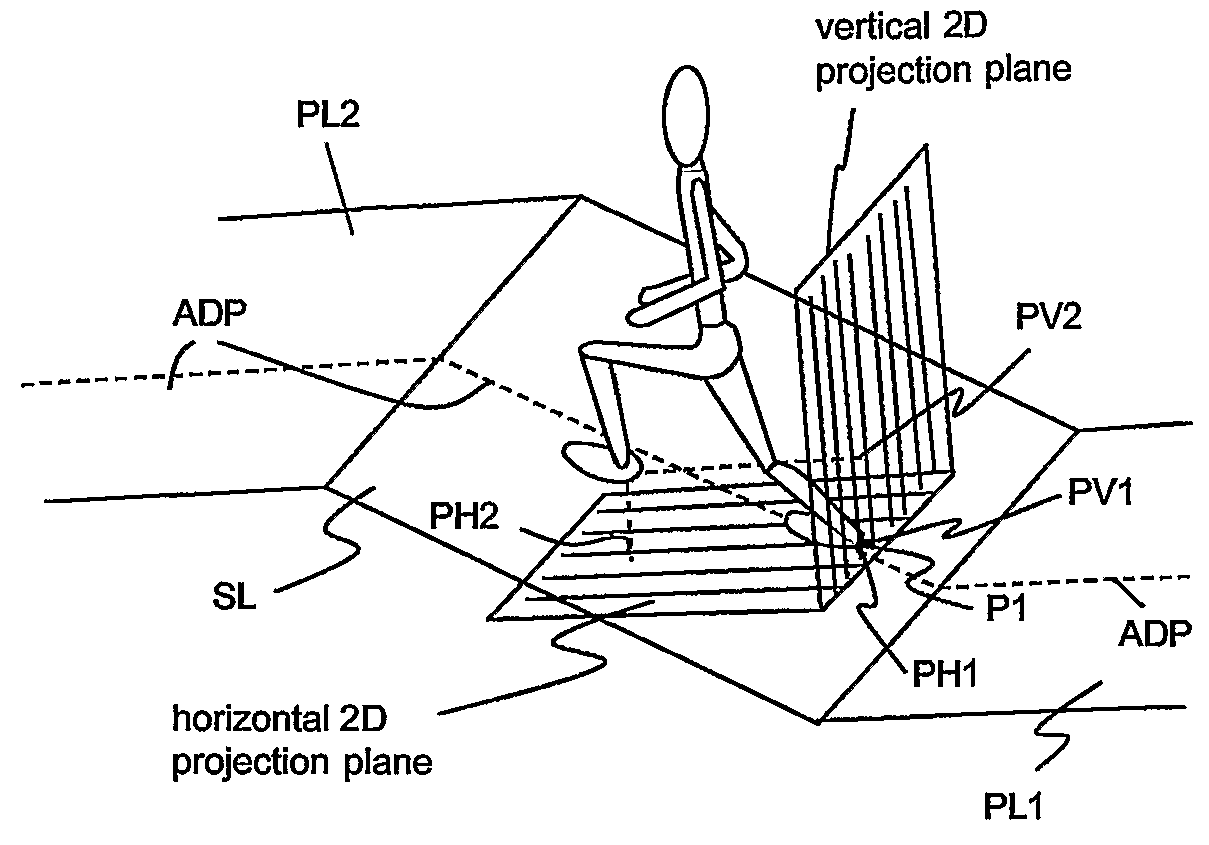
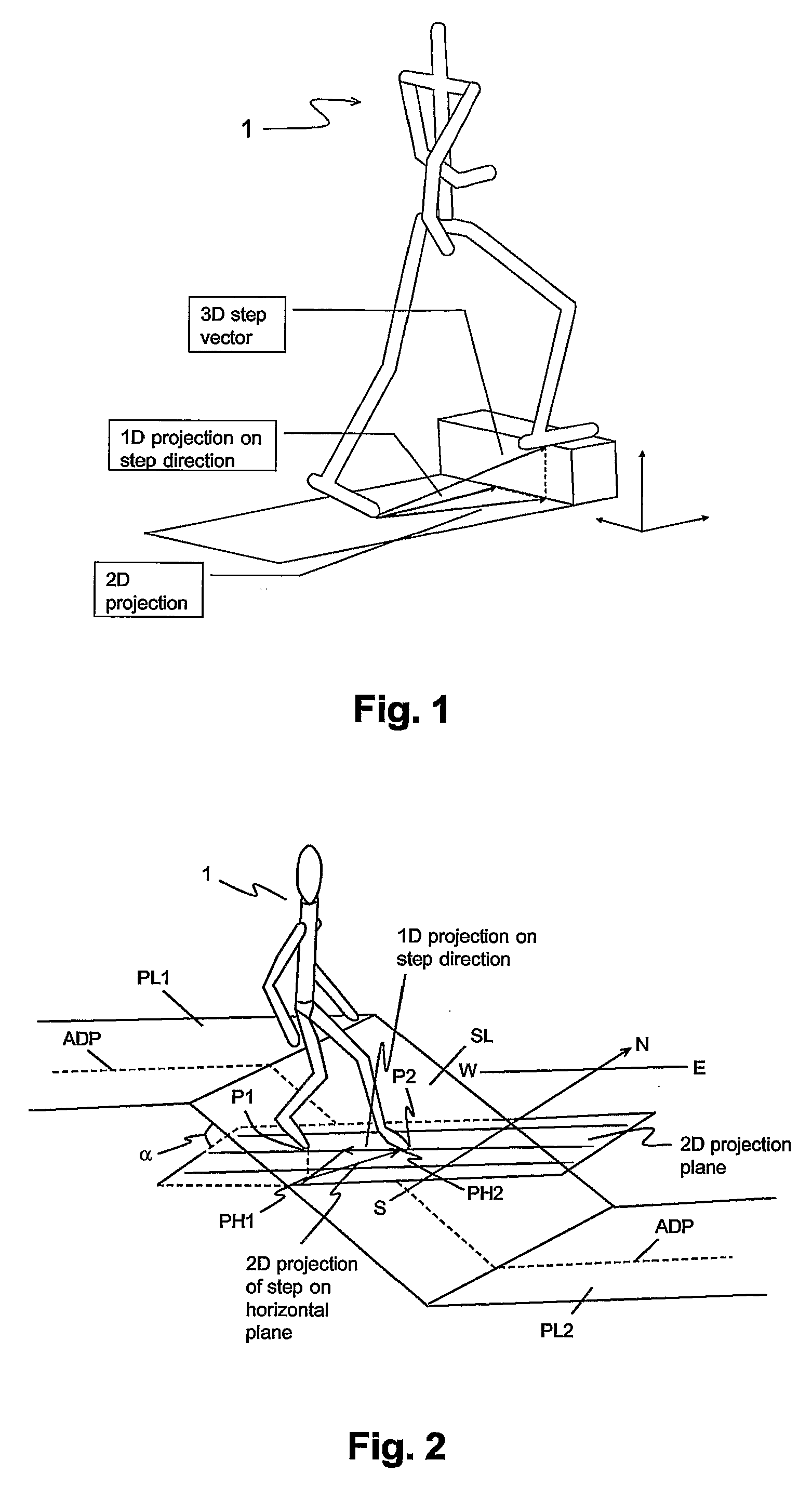
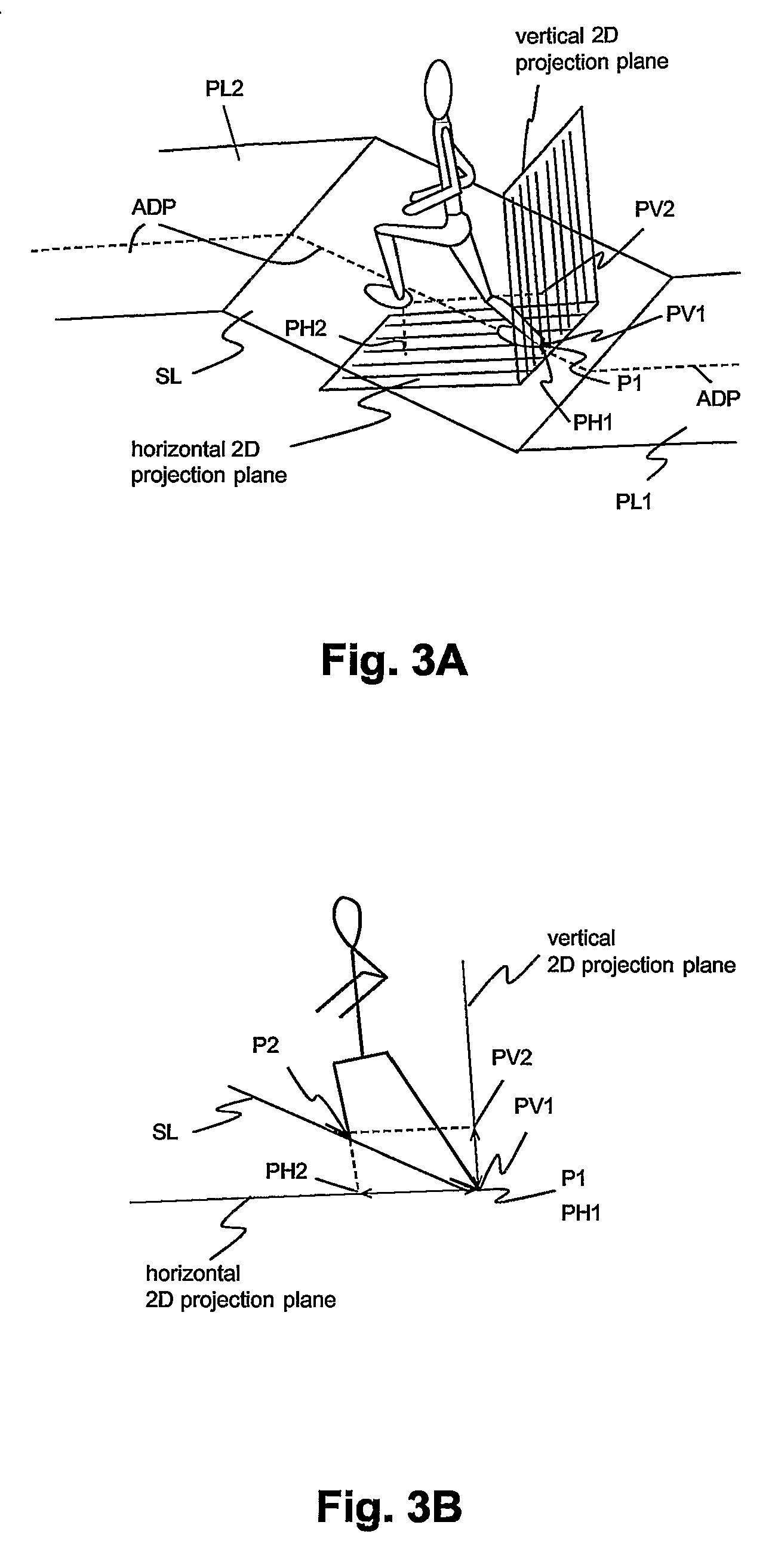
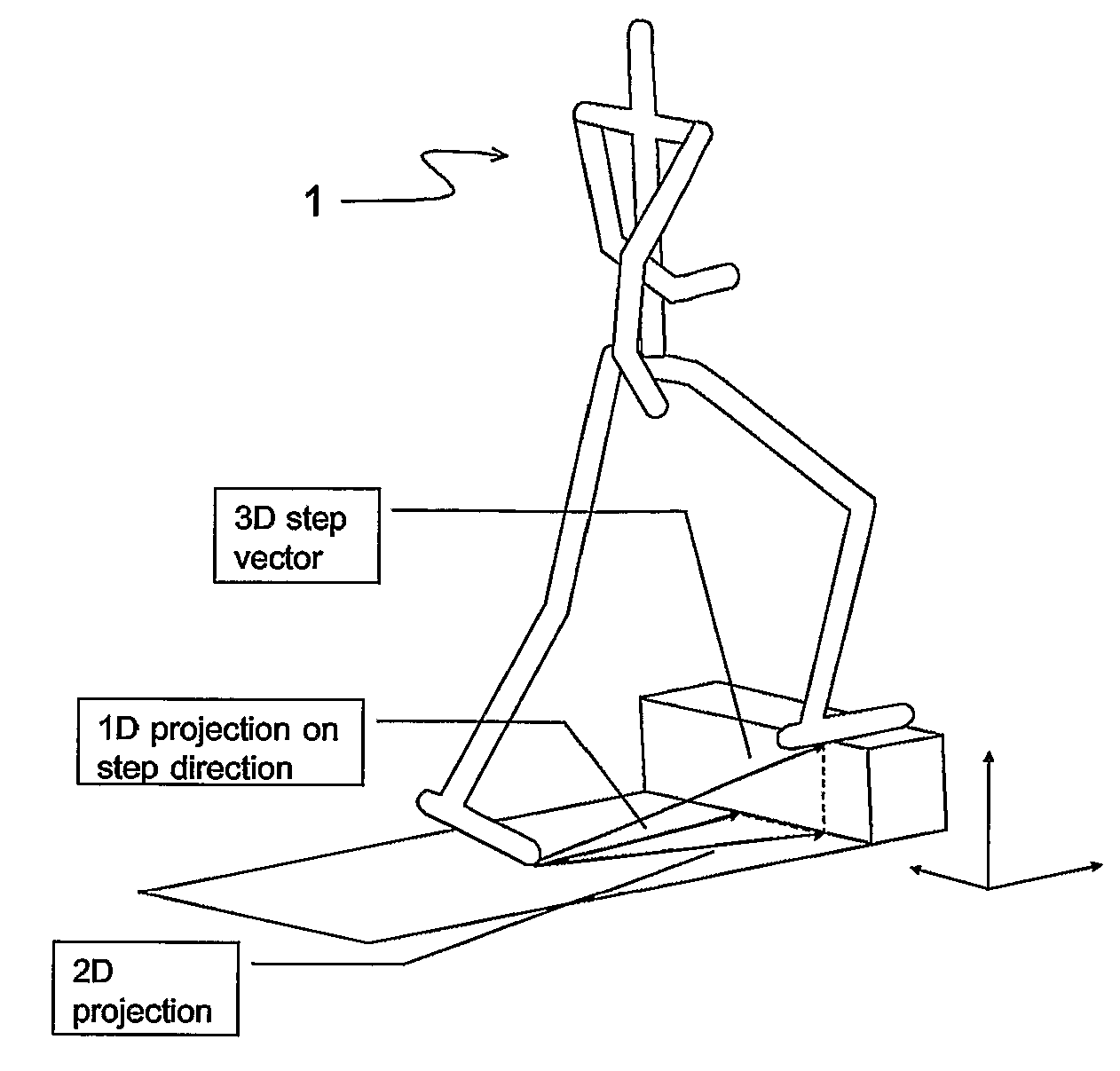
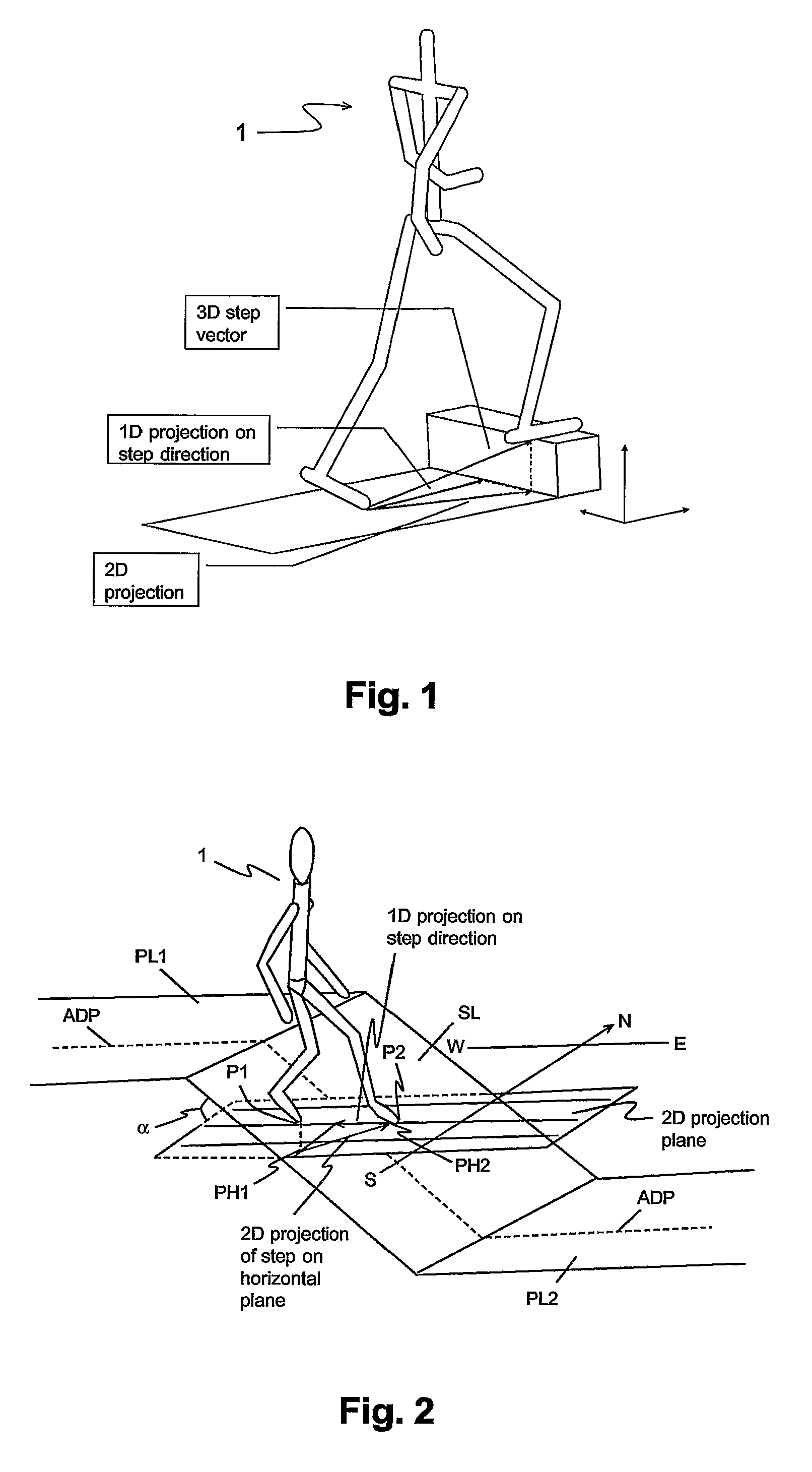
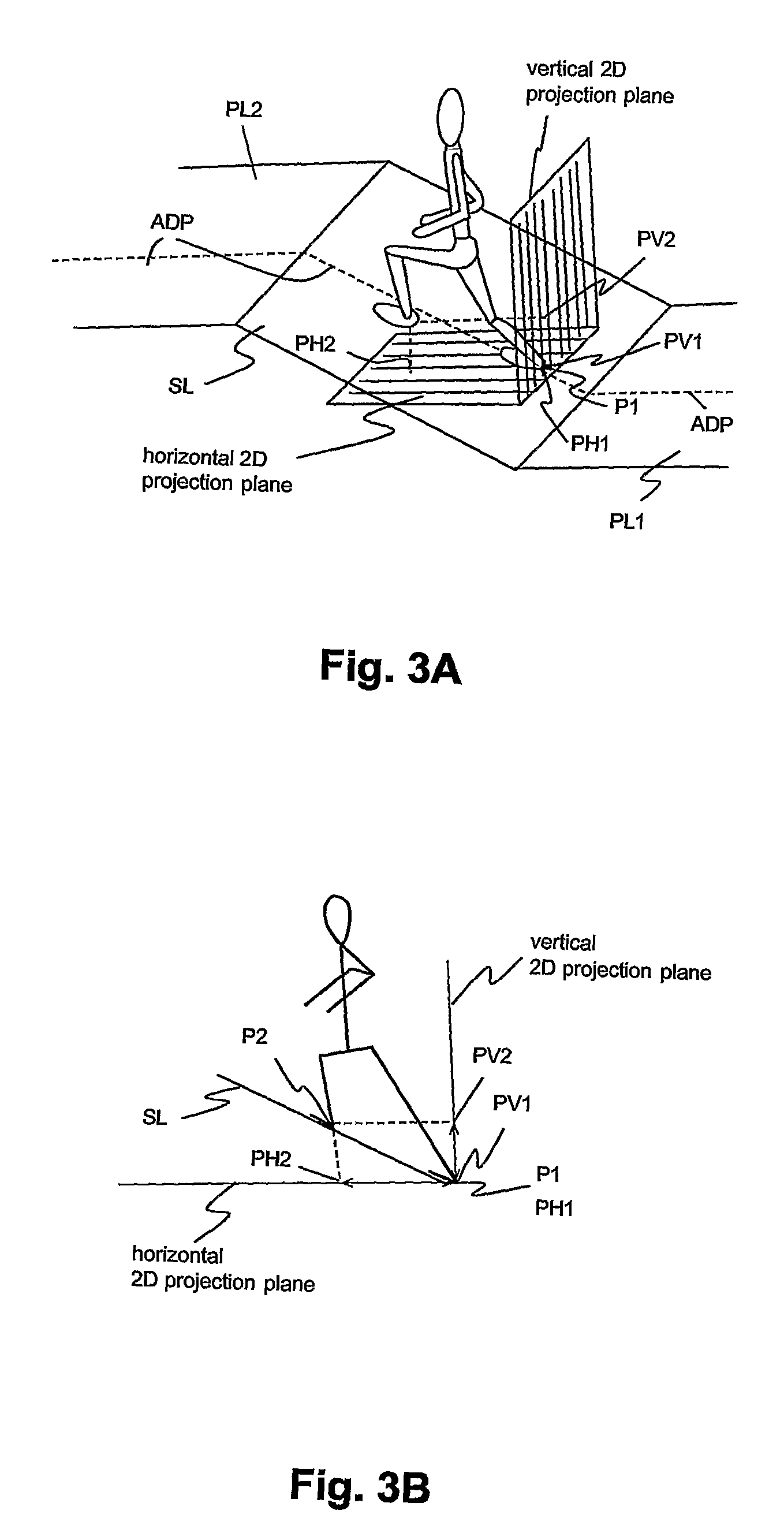
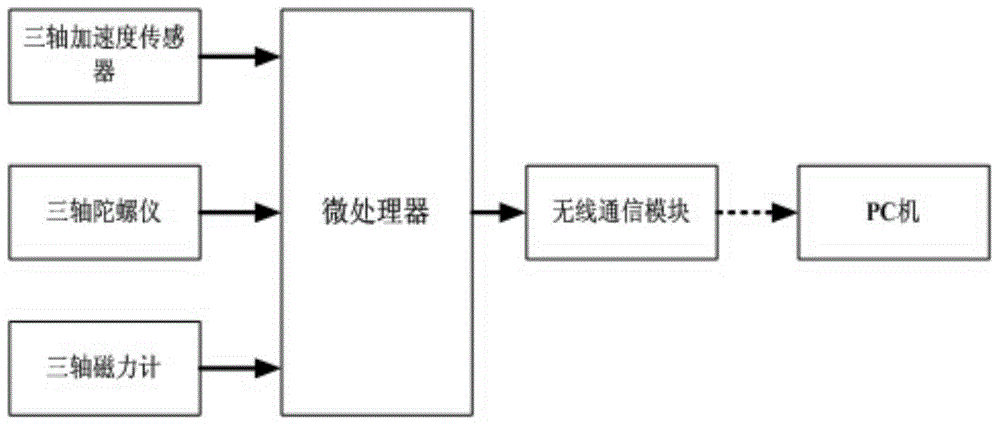
Pedestrian Navigation Apparatus and Method
ActiveUS20070260418A1Improve accuracyInput/output for user-computer interactionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsComputer graphics (images)Computer vision
The motion of a pedestrian is evaluated by determining at least one position of at least one identified portion of the pedestrian, projecting the positions(s) on at least one plane, and deriving the motion from the position(s) projected on the at least one plane. Typically the position(s) are determined in three-dimensions, e.g. of the feet. It is possible to project on two different planes to provide three-dimensional navigation information.
Owner:VECTRONIX AG
Systems, methods and apparatuses for continuous in-vehicle and pedestrian navigation
InactiveUS20070156337A1Easy to useSimplifies and minimizes processingInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationAccelerometerIn vehicle
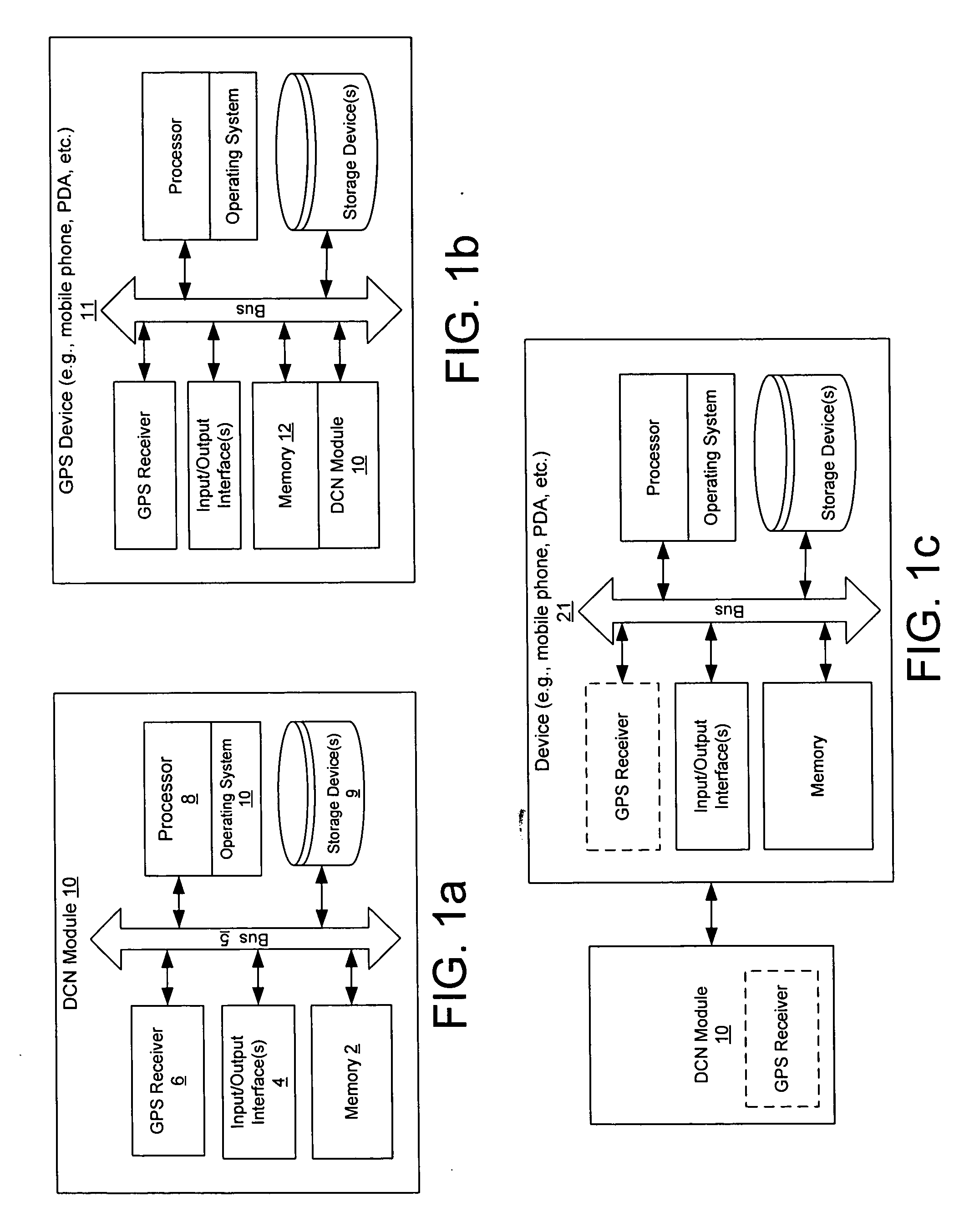
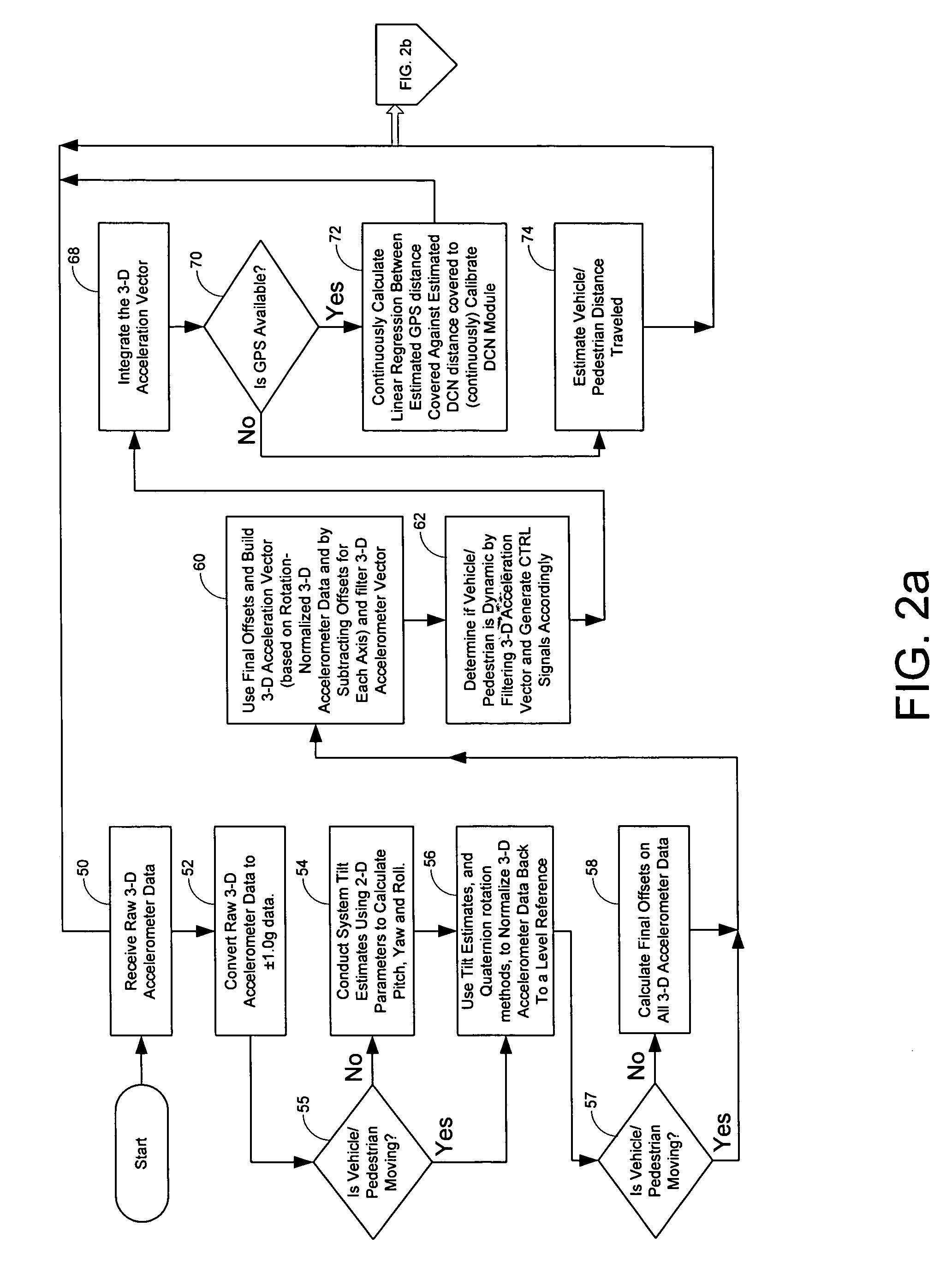
Accelerometers are used to provide acceleration data in 3 dimensions, from which vehicle distance traveled may be calculated during GPS outage using a one step integration of a 3-D pseudo acceleration vector. Magnetometers may also be used in combination with the accelerometers to calculate direction of travel. The system may be utilized for combined in-vehicle navigation and pedestrian navigation applications, and the same hardware is utilized for both system applications.
Owner:INTRINSYC SOFTWARE INT
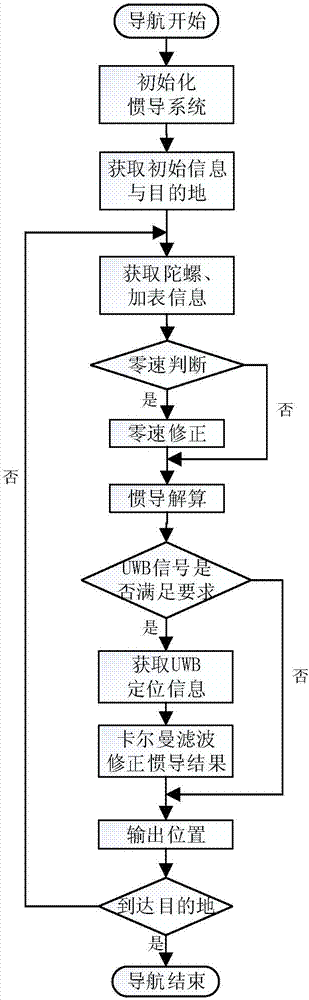
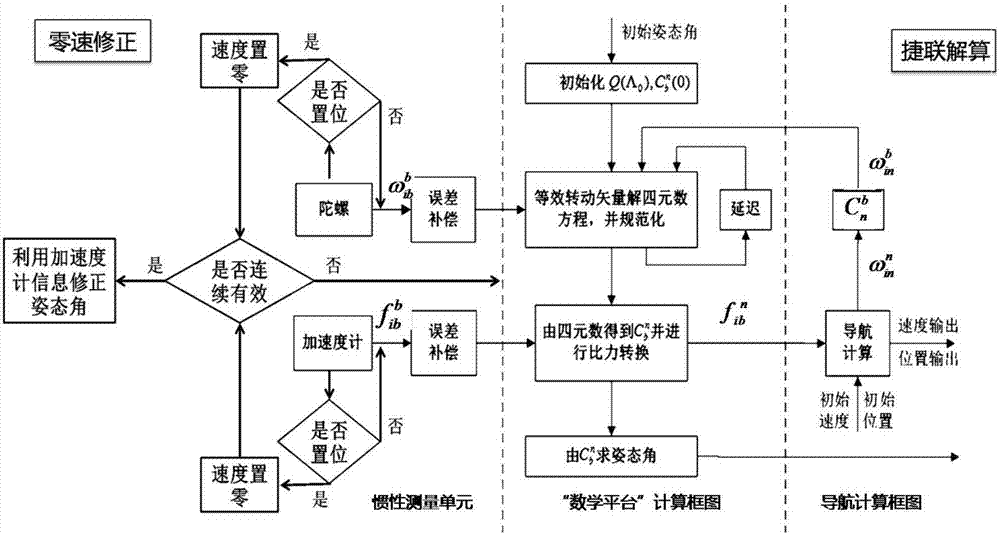
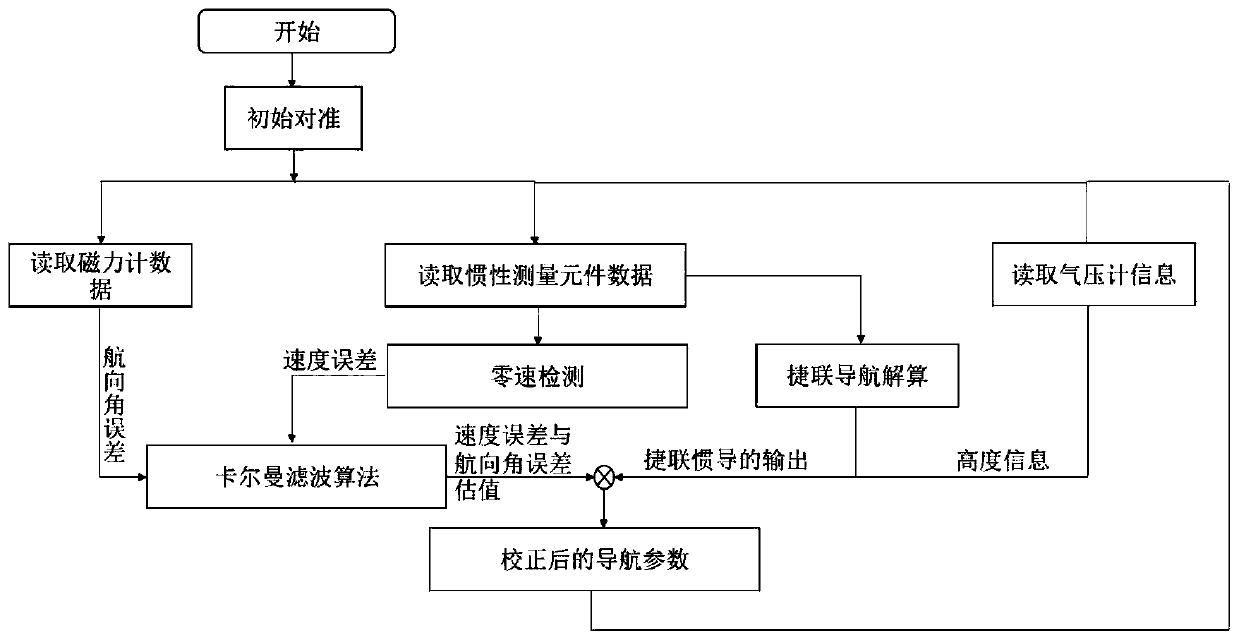
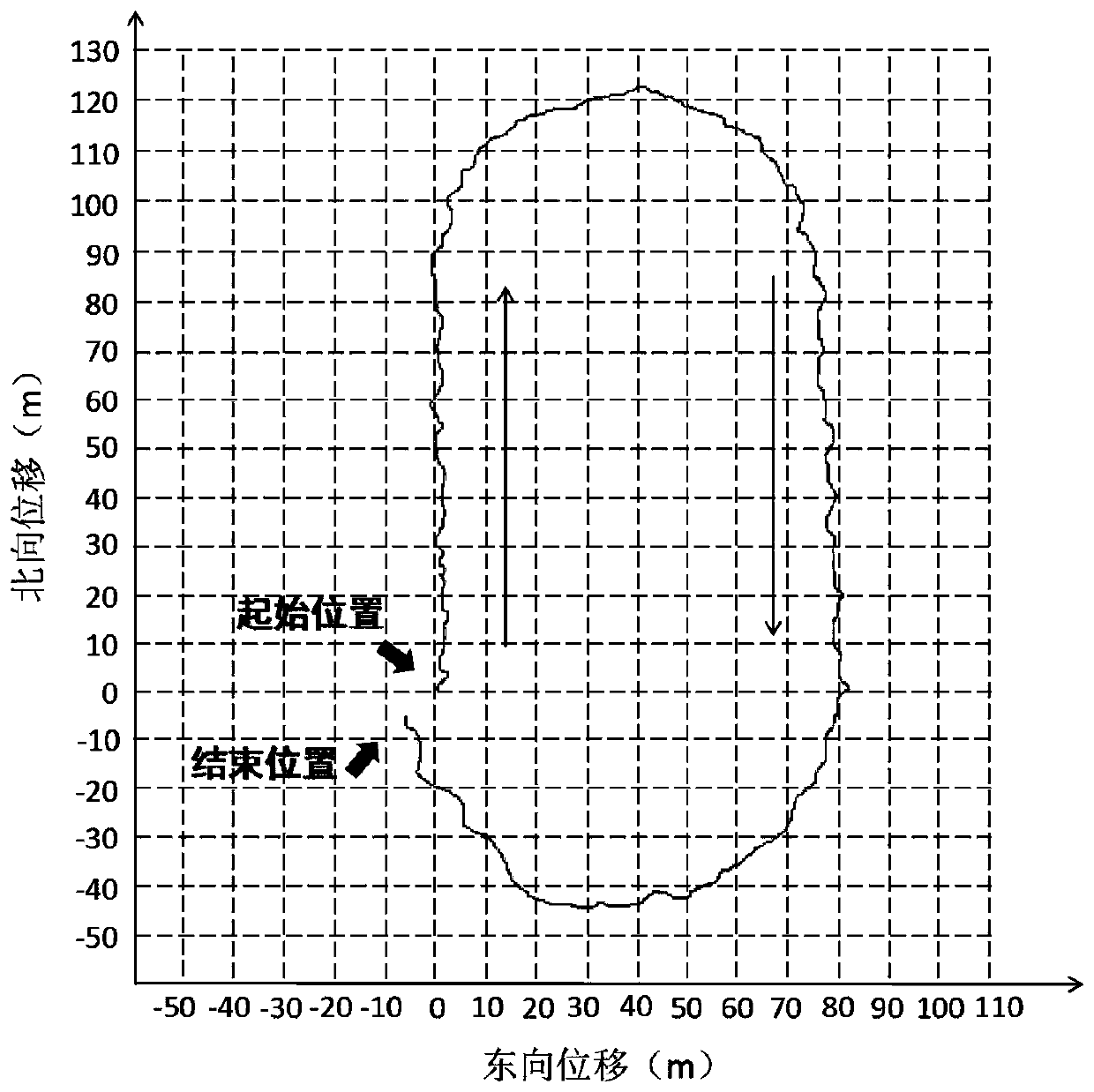
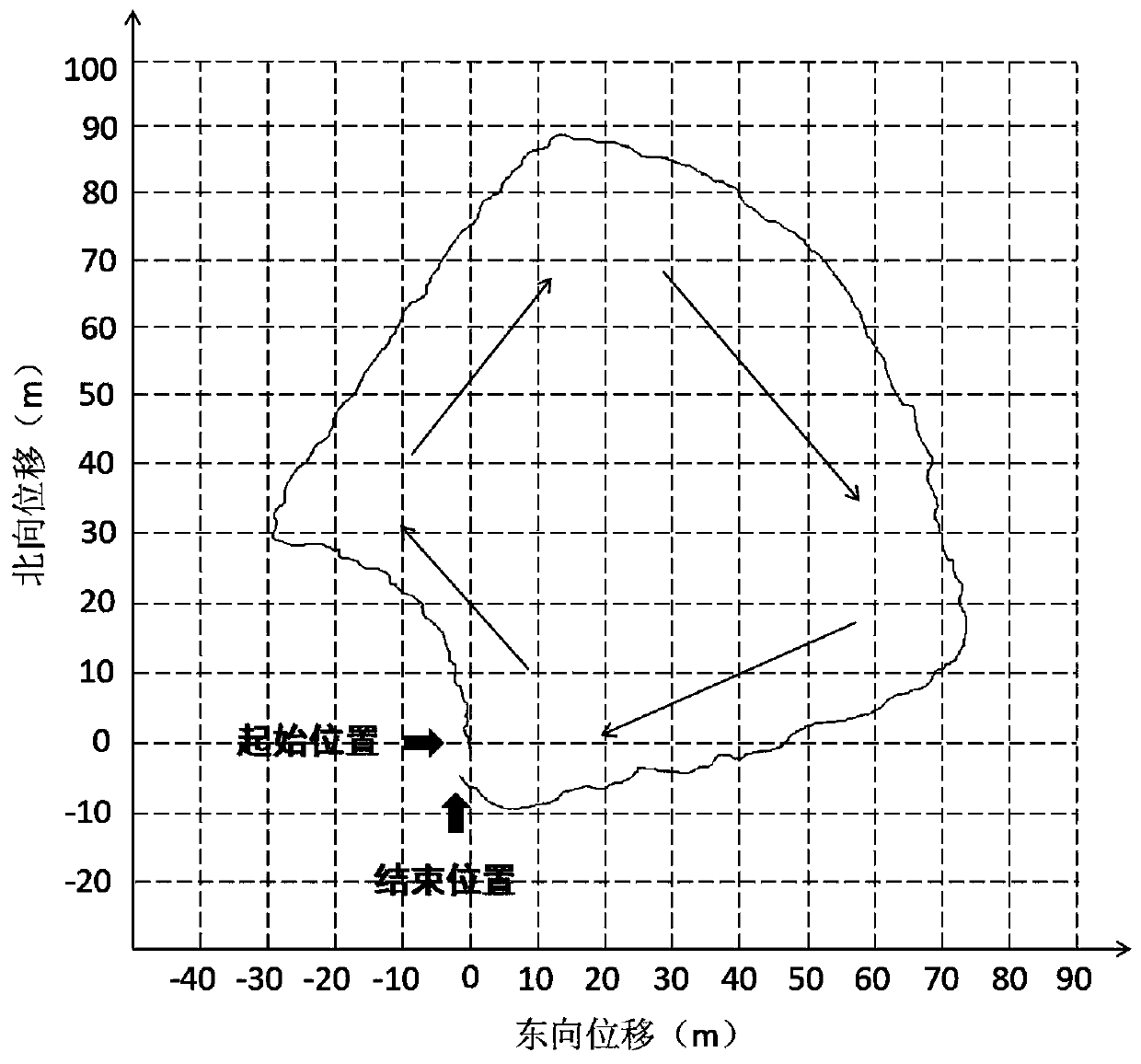
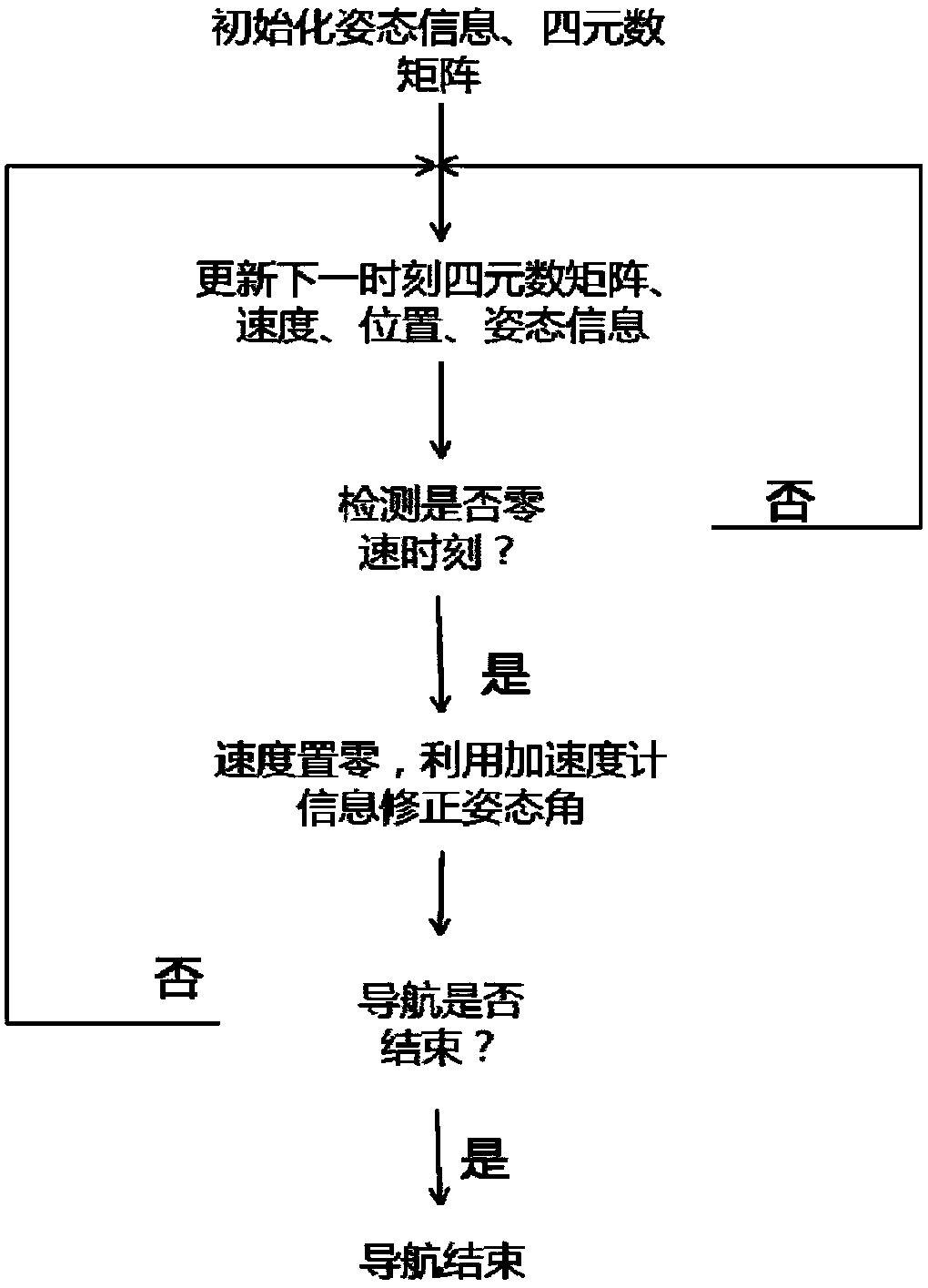
Autonomous navigation system positioning method based on strapdown inertial navigation resolving and zero-speed correction
InactiveCN103616030AHigh precisionImprove the accuracy of useInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsAutonomous Navigation SystemAccelerometer
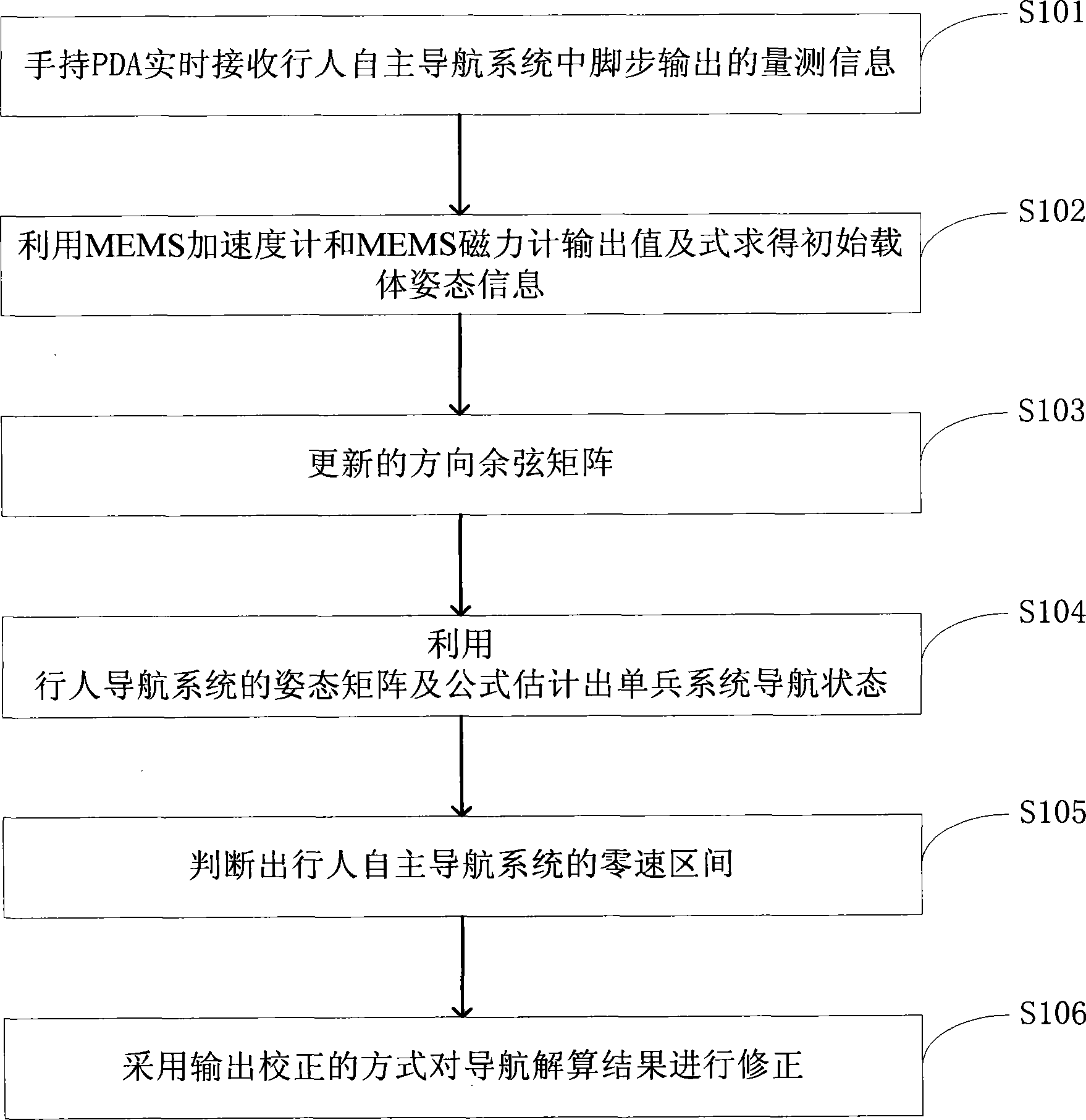
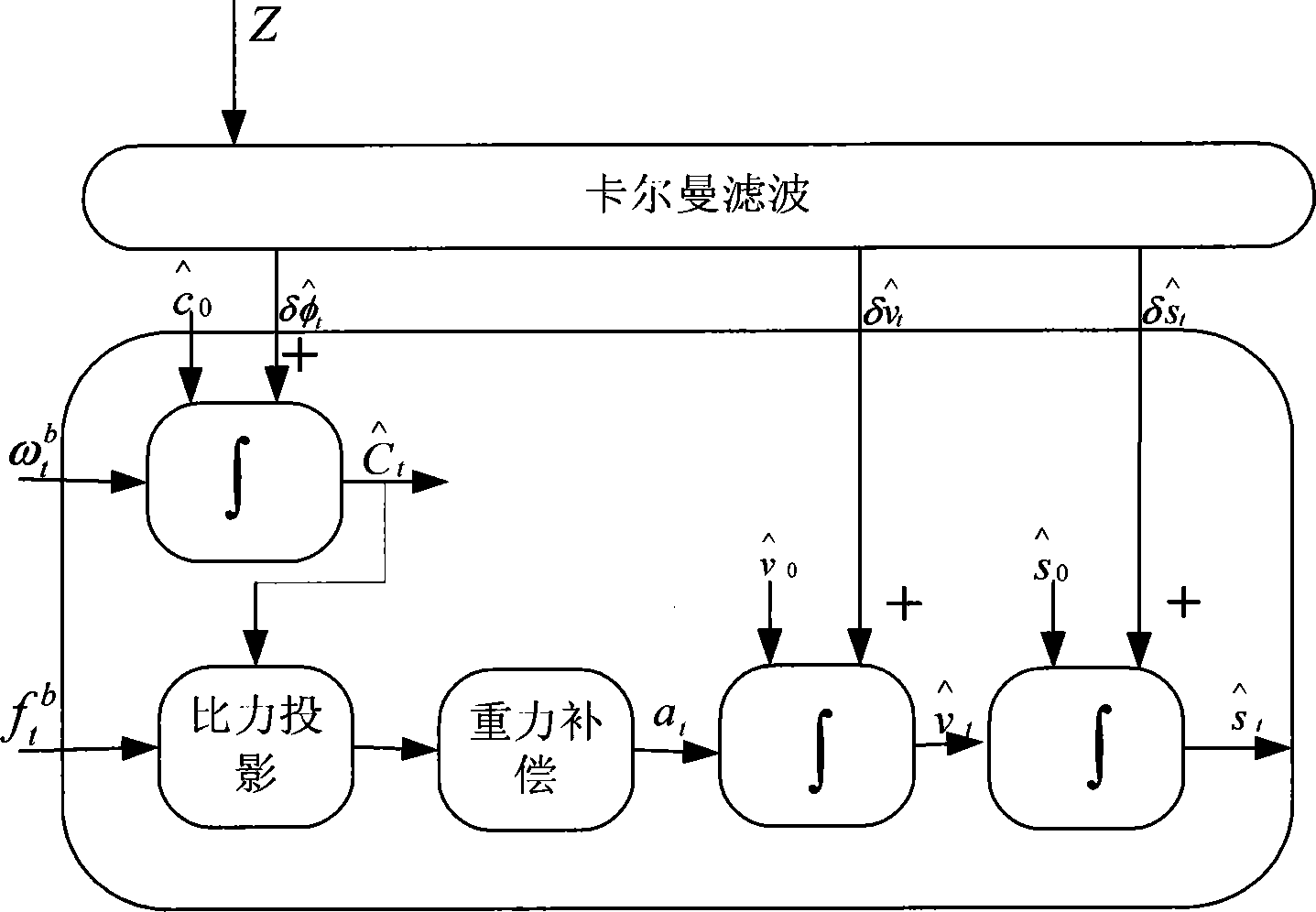
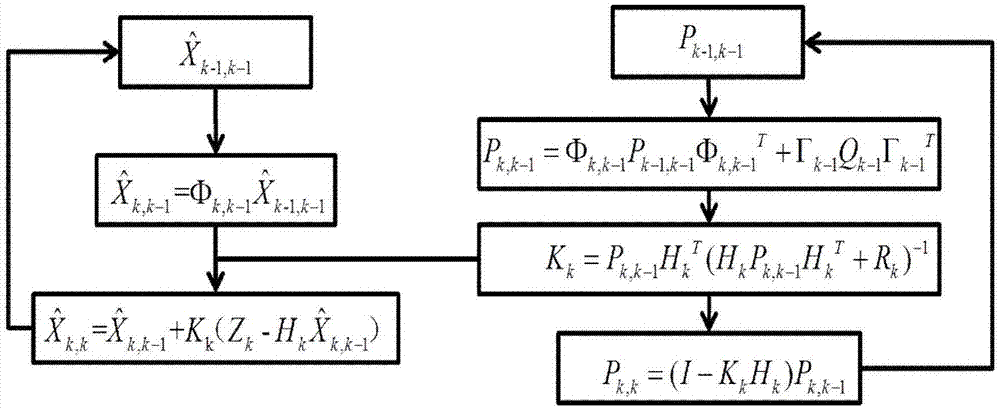
The invention discloses an autonomous navigation system positioning method based on strapdown inertial navigation resolving and zero-speed correction. According to the autonomous navigation system positioning method, output data of an MEMS (Micro-electromechanical Systems) accelerometer and an MEMS magnetometer in a pedestrian autonomous navigation system is used for carrying out initial alignment on the system; a strapdown inertial navigation resolving algorithm is used for estimating the state of the pedestrian autonomous navigation system; when a static detecting algorithm detects that pedestrian footsteps are stopped, a zero-speed correction error compensator based on Kalman filtering is designed and a navigation resolving result of the pedestrian autonomous navigation system is corrected by adopting a manner of outputting correction; the defects that an MEMS inertia measurement device is low in precision and has a great positioning error when being used for long time are overcome; a high-precision positioning function of the pedestrian autonomous navigation system is realized under the condition of not increasing external cost. The autonomous navigation system positioning method is simple and high in stability and reliability; the use precision of a single-pawn autonomous navigation system is improved effectively; the autonomous navigation system positioning method has important meanings of realizing autonomous pedestrian navigation and positioning with the high positioning precision.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Attitude estimation for pedestrian navigation using low cost mems accelerometer in mobile applications, and processing methods, apparatus and systems
ActiveUS8694251B2Navigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerMedicine
A user-heading determining system (10) for pedestrian use includes a multiple-axis accelerometer (110) having acceleration sensors; a device-heading sensor circuit (115) physically situated in a fixed relationship to the accelerometer (110); an electronic circuit (100) operable to generate signals representing components of acceleration sensed by the accelerometer (110) sensors, and to electronically process at least some part of the signals to produce an estimation of attitude of a user motion with respect to the accelerometer, and further to combine the attitude estimation (750, α) with a device heading estimation (770, ψ) responsive to the device-heading sensor circuit, to produce a user heading estimation (780); and an electronic display (190) responsive to the electronic circuit (100) to display information at least in part based on the user heading estimation. Other systems, circuits and processes are also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
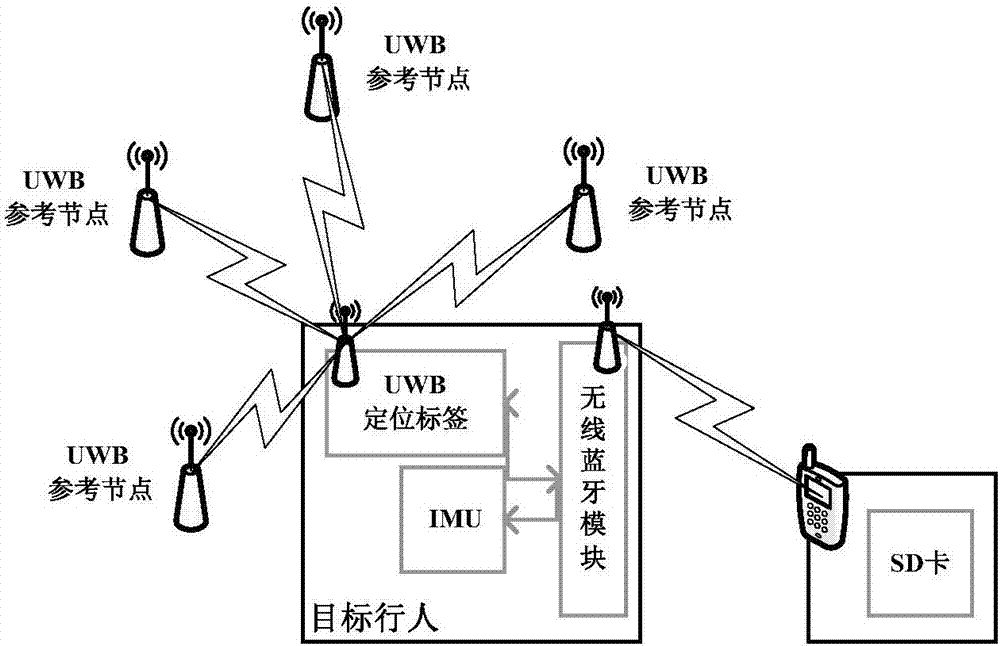
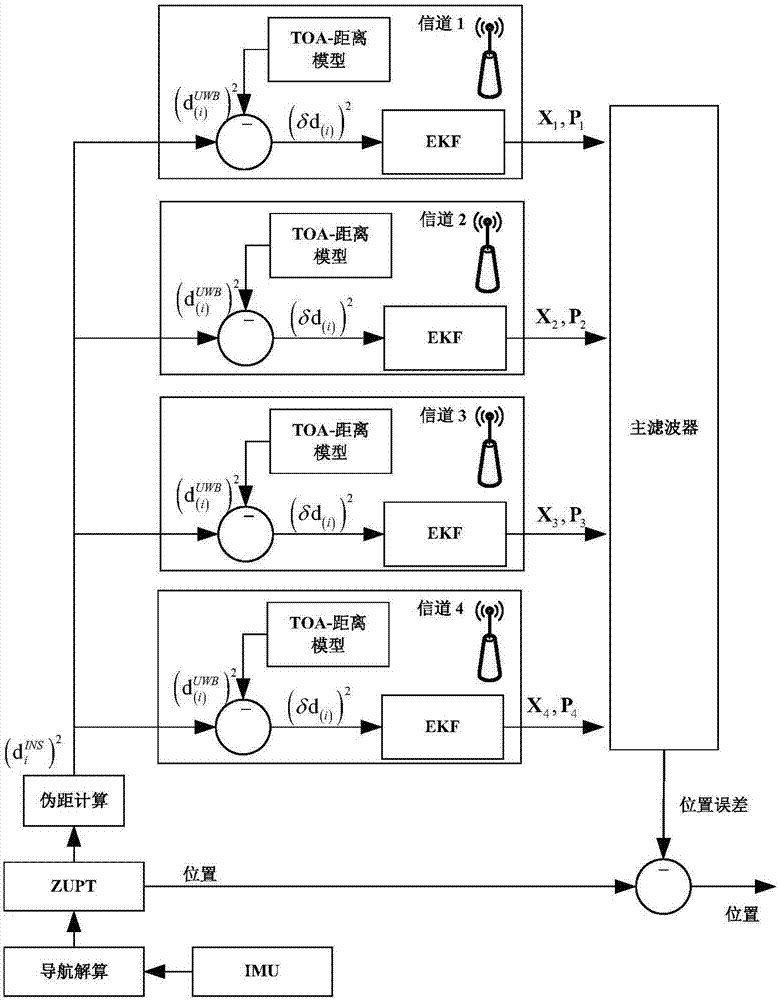
UWB-technology-based indoor pedestrian navigation method
The invention discloses a UWB-technology-based indoor pedestrian navigation method. An inertial navigation system based on zero-velocity correction is used to carry out navigation, thereby suppressing divergency of an inertial navigation positioning error with time. A UWB base station is configured at a key node in the area in an optimized manner; and Kalman filtering is carried out by using UWB positioning data and zero-velocity-correction-based inertial navigation positioning data, thereby realizing correction of an inertial navigation positioning result effectively. The UWB-technology-based indoor pedestrian navigation method is suitable for position monitoring of the special crowd, for real-time positioning of the staff in a special industry like the fire-fighting and security industries, and for navigation positioning of common pedestrians in an area with no satellite signal coverage.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Pedestrian navigation apparatus and method
ActiveUS7747409B2Input/output for user-computer interactionDigital computer detailsComputer scienceMarine navigation
The motion of a pedestrian is evaluated by determining at least one position of at least one identified portion of the pedestrian, projecting the positions(s) on at least one plane, and deriving the motion from the position(s) projected on the at least one plane. Typically the position(s) are determined in three-dimensions, e.g. of the feet. It is possible to project on two different planes to provide three-dimensional navigation information.
Owner:VECTRONIX AG
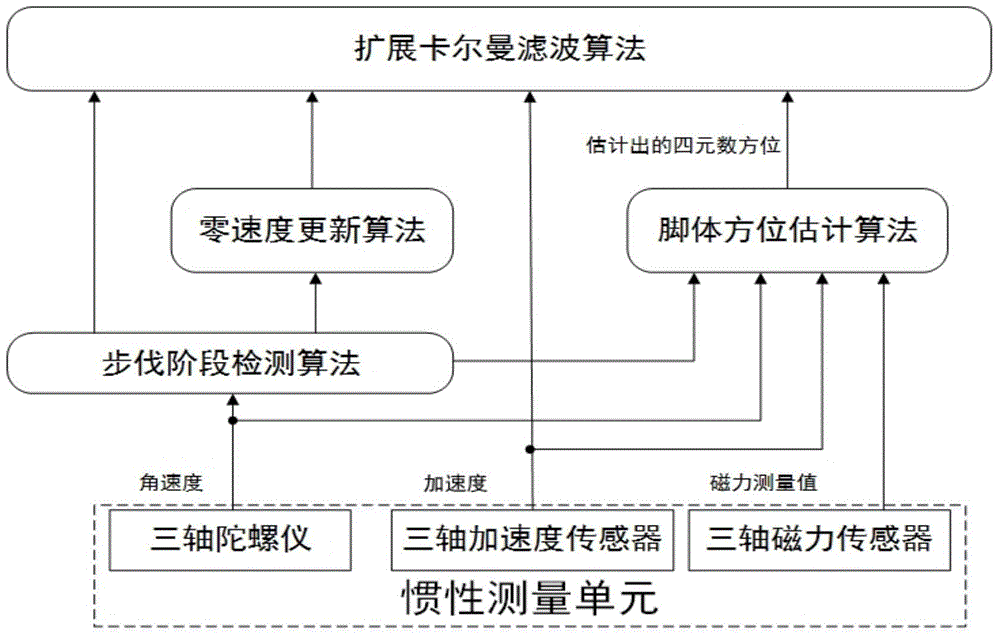
Pedestrian navigation device and pedestrian navigation method based on inertial sensor
ActiveCN104406586AMake up for the inability to workHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopePersonal computer
The invention discloses a pedestrian navigation device based on an inertial sensor. The pedestrian navigation device comprises a microprocessor, a three-axis acceleration sensor, a three-axis gyroscope, a three-axis magnetometer and a wireless communication module, wherein the three-axis acceleration sensor, the three-axis gyroscope, the three-axis magnetometer and the wireless communication module are respectively connected with the microprocessor; the microprocessor is used for receiving data collected by the three-axis acceleration sensor, the three-axis gyroscope and the three-axis magnetometer and uploading the data to a PC (Personal Computer) through the wireless communication module. The invention further discloses a pedestrian navigation method based on the pedestrian navigation device. The pedestrian navigation method comprises a step stage detection algorithm, a foot and body orientation estimation algorithm and an extended Kalman filter algorithm. The complexity of calculation is greatly reduced while the accuracy is guaranteed, and a condition that the requirement of timeliness can be met is guaranteed without consuming a large amount of hardware power consumption in a practical environment.
Owner:JIANGSU TOYOU RES INST OF INFORMATION INTELLIGENCE & TECH
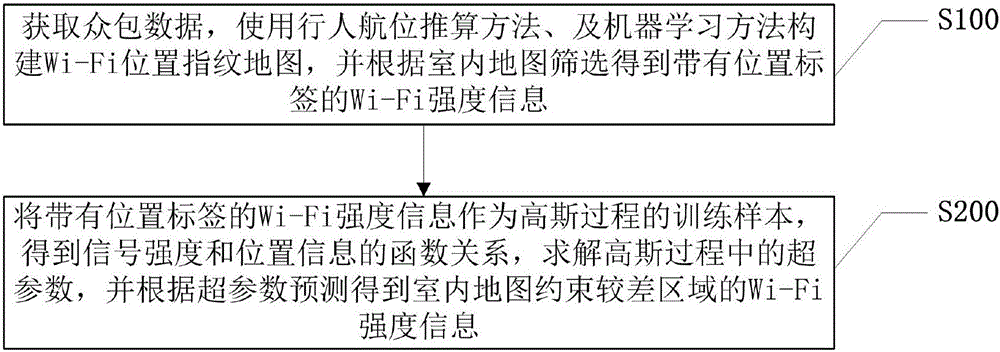
Auto building method and system of Wi-Fi position fingerprint map
ActiveCN106714110AImplement automatic buildLocation information based serviceWide areaPattern recognition
The present invention discloses an auto building method and system of a Wi-Fi position fingerprint map. The method comprises the steps of acquiring crowdsourcing data, building the Wi-Fi position fingerprint map by using a pedestrian navigation reckoning method and a machine learning method, and screening according to an indoor map to obtain Wi-Fi strength information with a position tag; and using the Wi-Fi strength information with the position tag as a training sample of a Gaussian process, so as to obtain a function relationship between the signal strength and the position information, resolving a super parameter in the Gaussian process, and predicting according to the super parameter so as to obtain Wi-Fi strength information of a poor constraint area of the indoor map. Regression is performed by using the Gaussian process, the Wi-Fi position fingerprint of a wide area is predicted based on the Wi-Fi position fingerprint information of a high constraint area of the map, so that the Wi-Fi position fingerprint map of the whole indoor area is built automatically.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Wearable pedestrian navigational positioning method and equipment based on human motion model aid
InactiveCN107218938AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsHuman motionBluetooth
The invention discloses a wearable pedestrian navigational positioning method and equipment based on a human motion model aid. The method comprises the following steps of (1) analyzing a gait during human motion and inertial sensor output under different motion modes; (2) building a zero-speed correction and discrimination model based on the human motion model aid; (3) building a strapdown inertial navigation calculation course angle error model based on a geomagnetism aid; (4) building a strapdown inertial navigation calculation height error model based on a barometric altimeter aid. The equipment comprises an IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) inertial sensor device, a posture calculation module, a bluetooth module and a button, which can be used for realizing the method. According to the wearable pedestrian navigational positioning method and the equipment based on the human motion model aid provided by the invention, the accuracy and the reliability of pedestrian navigational positioning without GPS (Global Positioning System) and wireless communication signals are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
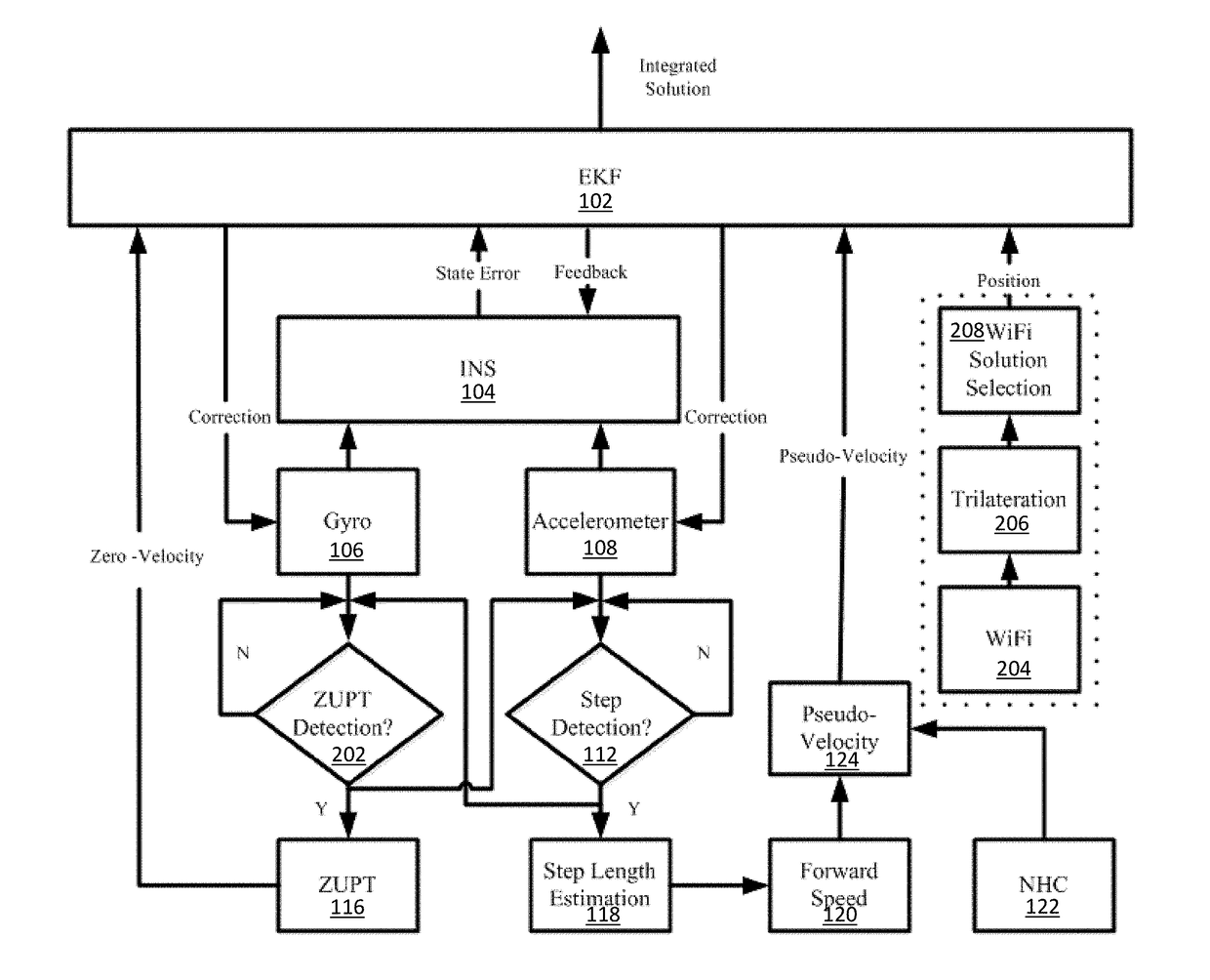
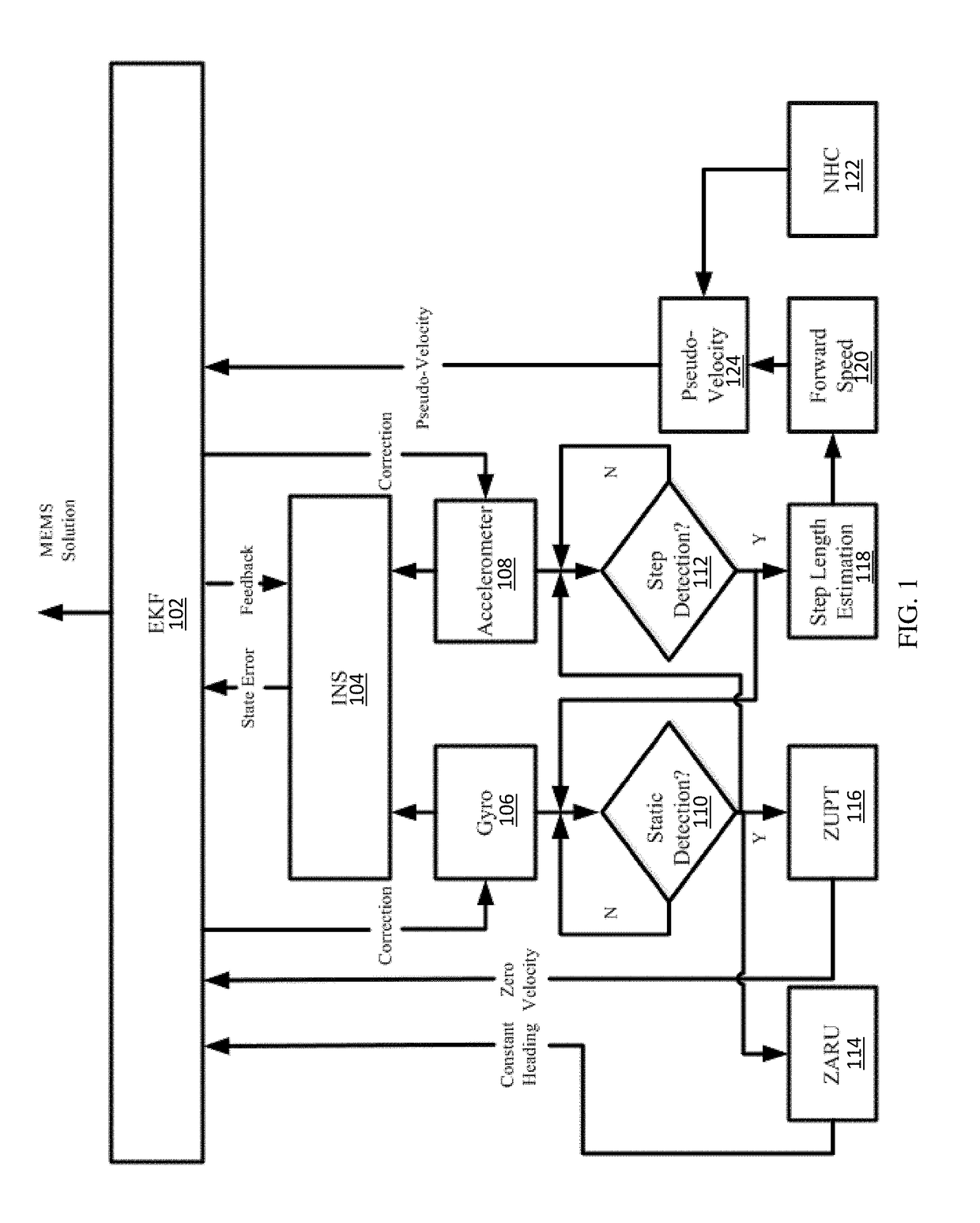
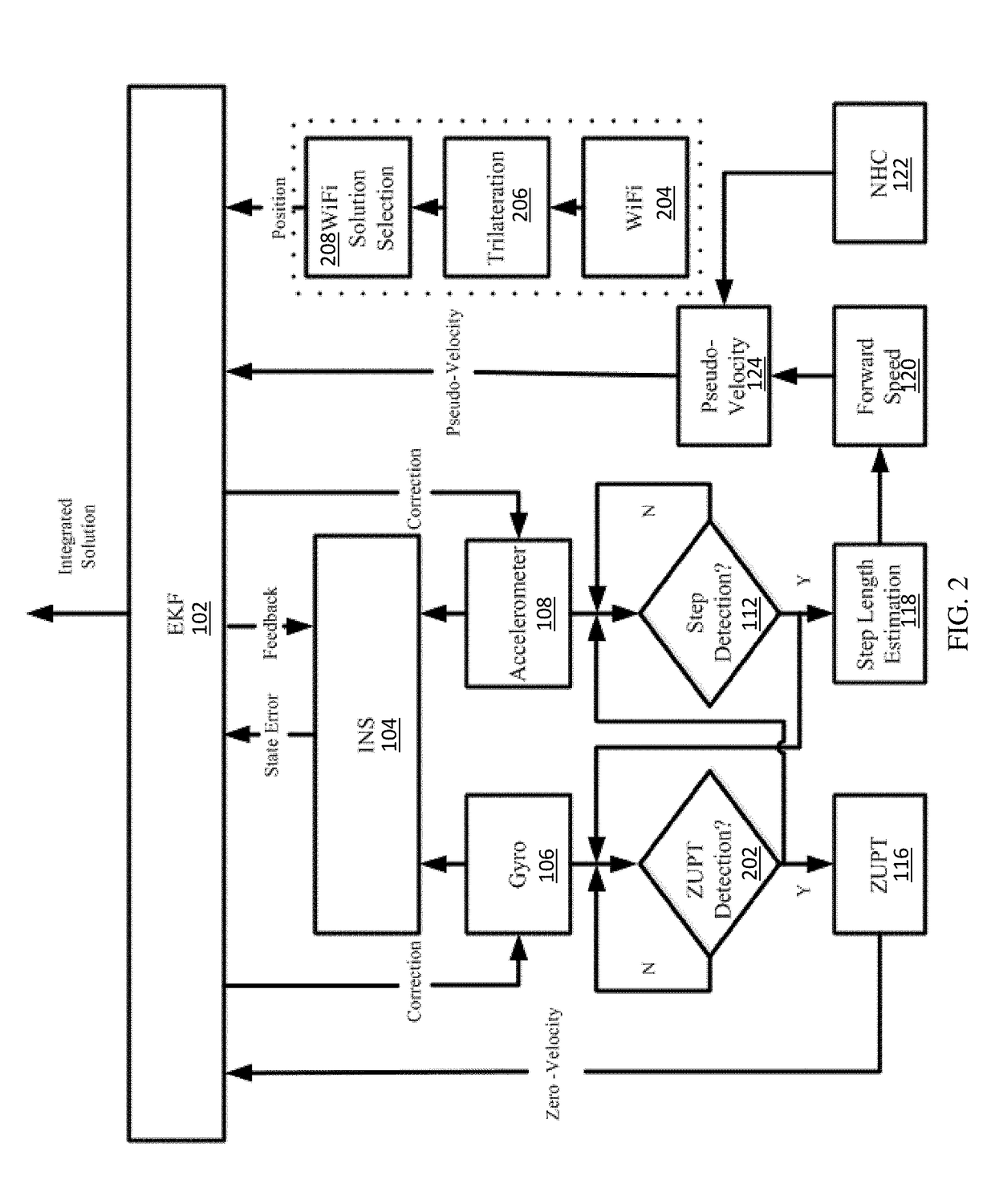
Method and apparatus for enhanced pedestrian navigation based on WLAN and MEMS sensors
Methods, systems and apparatuses for enhanced Microelectromechanical (MEMS)-based navigation in a mobile device are disclosed. In an embodiment, a method includes receiving navigation data from one or more navigation sensors on board the mobile device. The method may also include calculating, using a processing device, position, velocity, and attitude (PVA) values in response to the navigation data using an Inertial Navigation System (INS) mechanization. Additionally, the method may include calculating, using the processing device, Pedestrian Dead Reckoning (PDR) values in response to the navigation data. Also, the method may include determining, using the processing device, one or more navigation values in response to a combination of the PVA values calculated by the INS mechanization and the PDR values.
Owner:PROFOUND POSITIONING INC
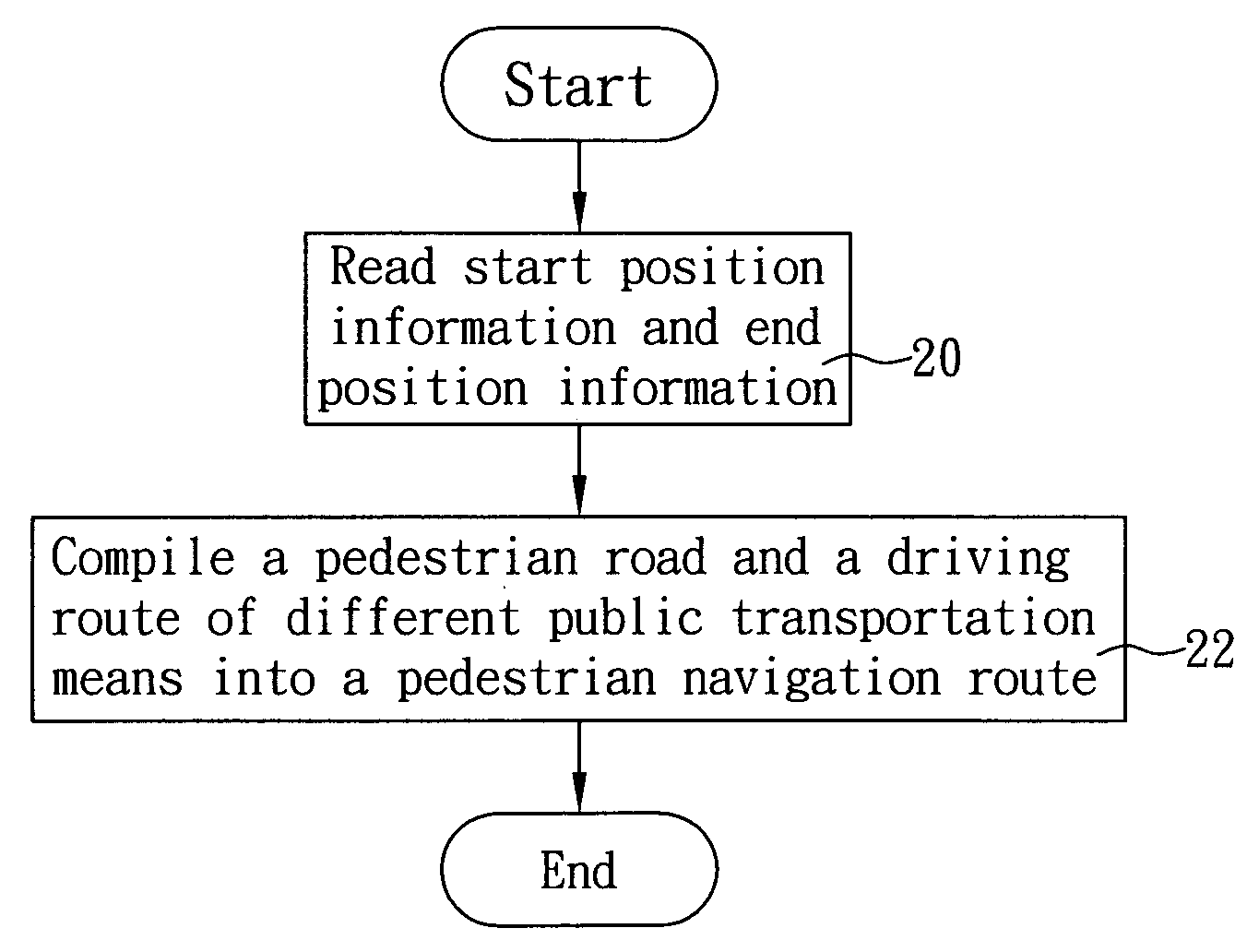
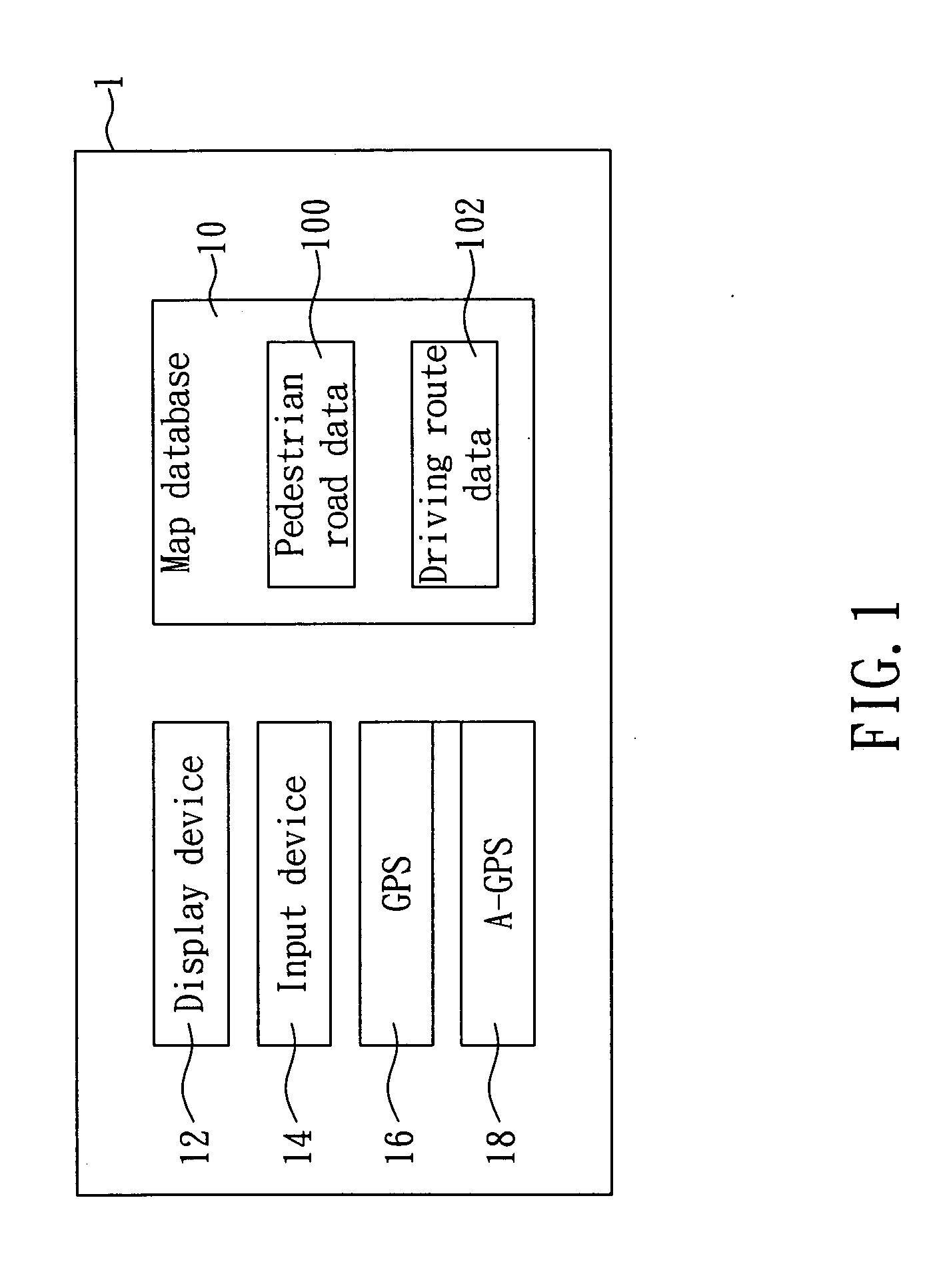
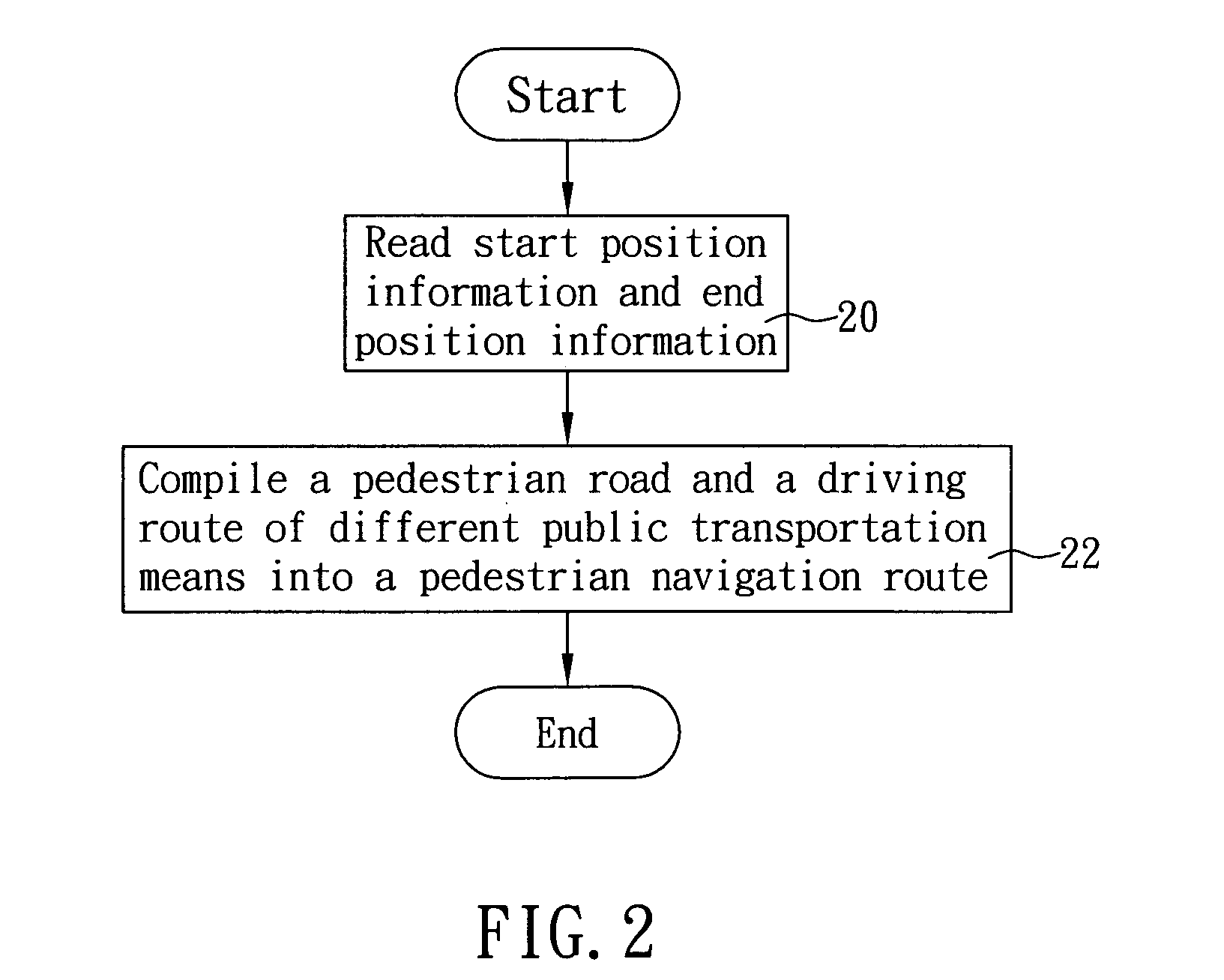
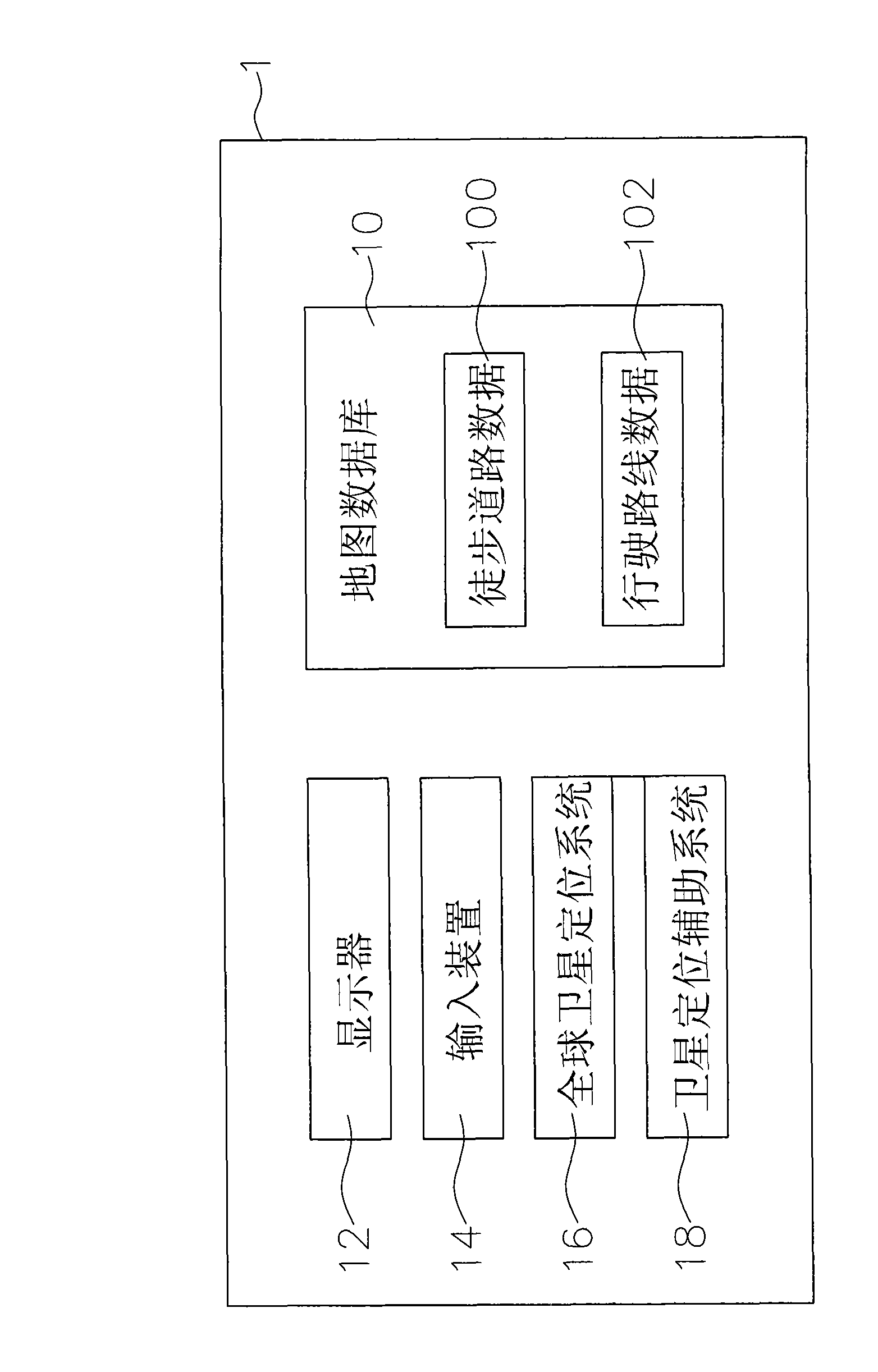
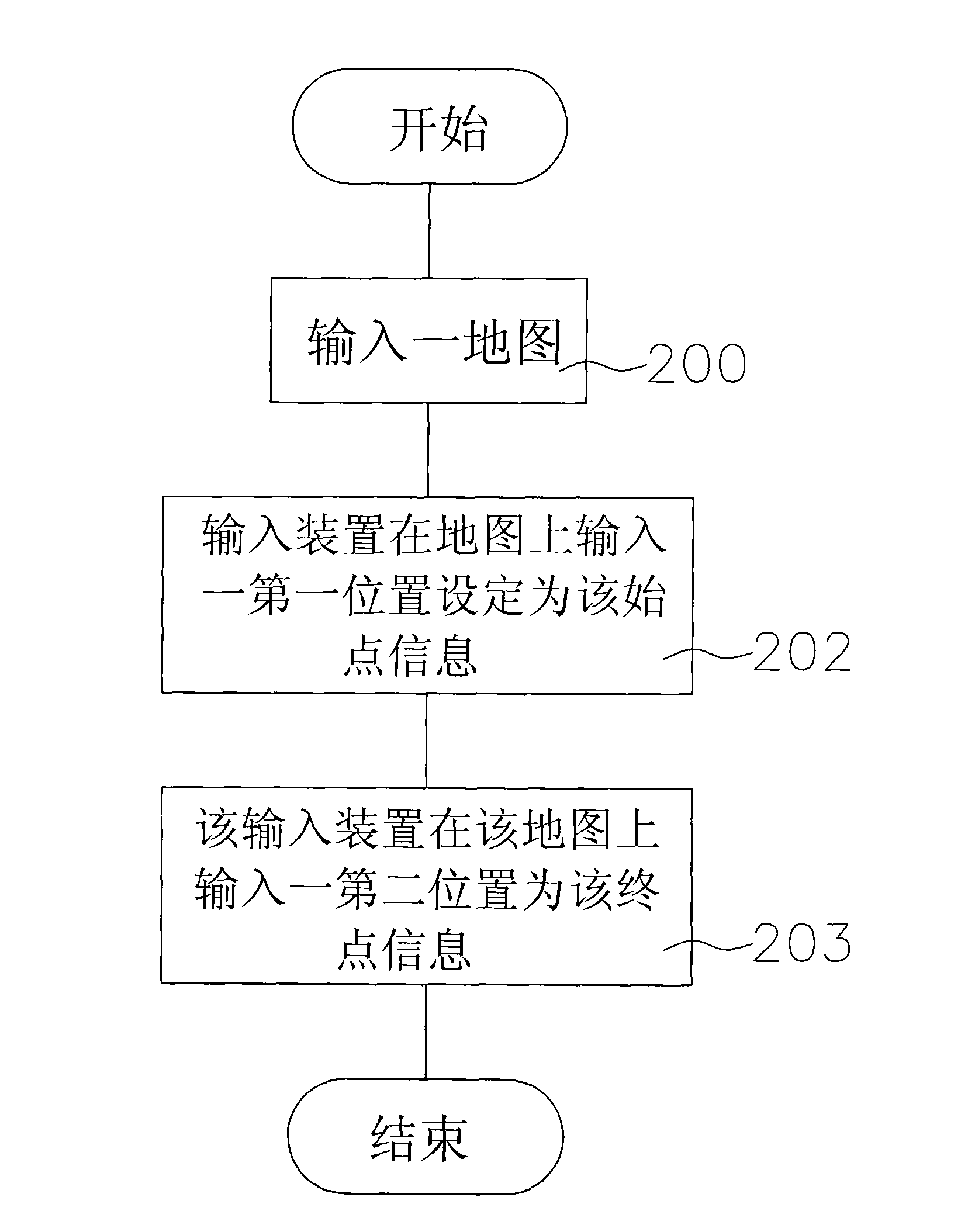
Method of planning pedestrian navigation route
InactiveUS20090177387A1Instruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsComputer sciencePublic transport
The present invention discloses a method of planning a pedestrian navigation route, and the method is applied to a pedestrian navigation device. The pedestrian navigation device includes a map database having a pedestrian road data and a driving route data of at least one public transportation means. In the method, when the pedestrian navigation device is planning a pedestrian navigation route, the pedestrian navigation device reads start position information and end position information, plans a pedestrian road and a driving route of different public transportation means between a start position and an end position according to a pedestrian road data and a driving route data, and then compiles the same into a pedestrian navigation route. The invention allows a pedestrian to reach an end position (or destination) selectively by walking along the planned pedestrian road or taking a ride of the selected public transportation means.
Owner:MITAC INT CORP
Indoor positioning method based on particle filtering algorithm
ActiveCN108632761AImprove robustnessHigh positioning accuracyParticular environment based servicesLocation information based serviceAlgorithmNear neighbor
The invention discloses an indoor positioning method based on a particle filtering algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: by fusing pedestrian navigation position information of a user after the user walks N steps, WiFi signal strength information and a geomagnetic signal three-dimensional sequence, determining an initial point region through WiFi and determining coordinates of an initial position through geomagnetic accurate positioning; and then verifying the initial point region and the coordinates of the initial position by using the independence of positioning results of a WiFi-based nearest neighbor matching algorithm, a WiFi and PDR (Pedestrian Dead Reckoning)-based particle filtering algorithm and a geomagnetism and PDR-based particle filtering algorithm, so as to keep tracking the positioning to improve the robustness of positioning. On the premise of obtaining accurate pedestrian navigation position information (including step counting and pedestrian directions), the method disclosed by the invention is applicable to four mobile phone placement modes, namely holding steady, swinging, pocketing and backpacking, and is high in positioning precision.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Wearable autonomous navigation system for pedestrian and navigation method thereof
InactiveCN106595653AImprove navigation accuracyImplement positioning and navigation servicesTransmission systemsNavigational calculation instrumentsMicrocontrollerGyroscope
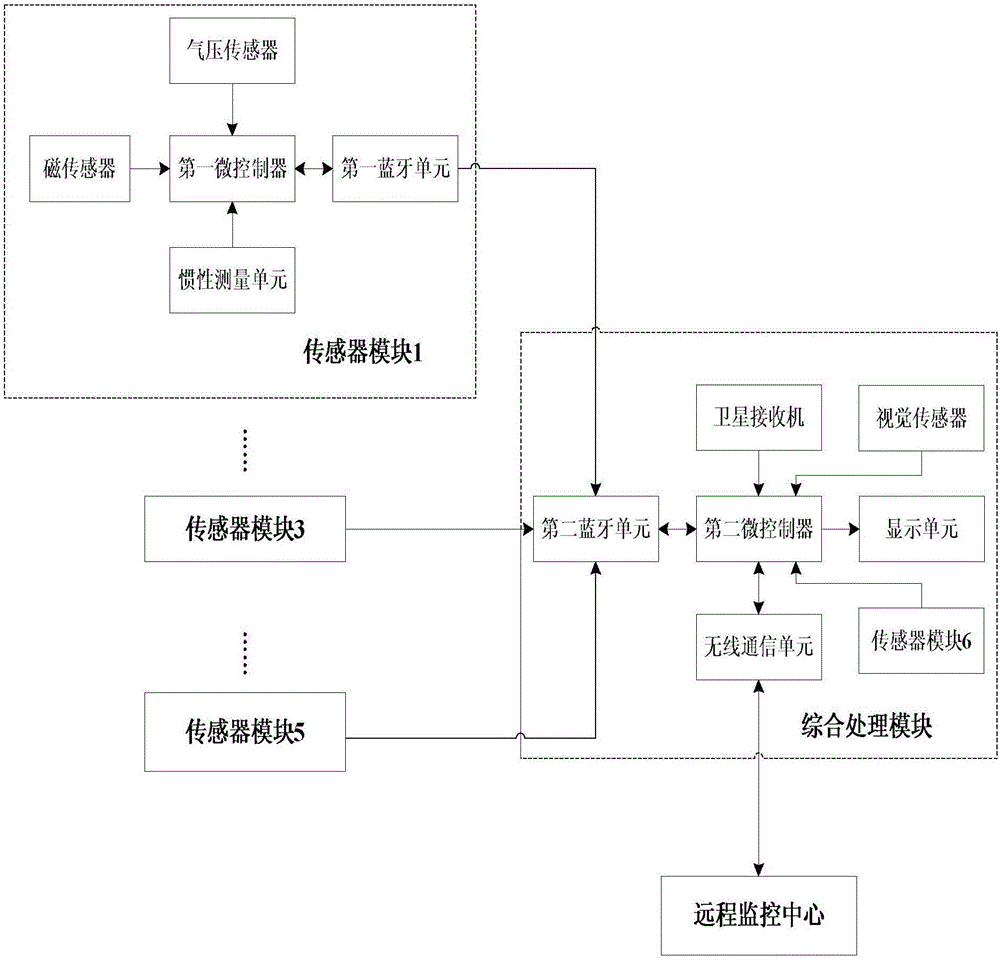
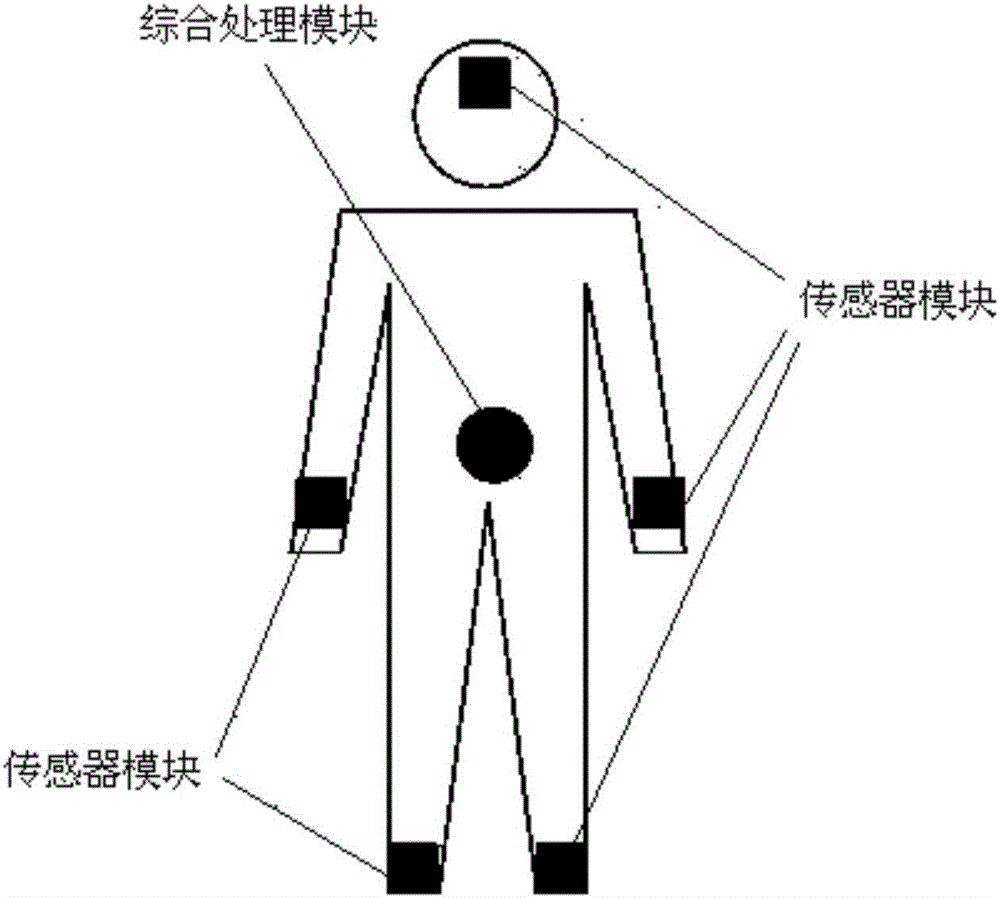
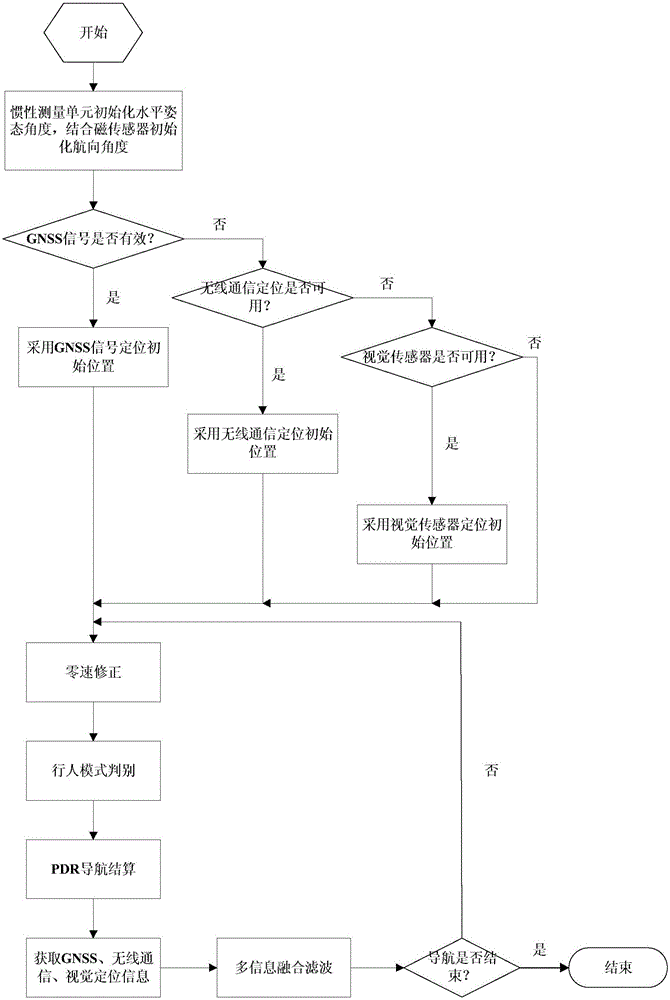
The invention discloses a wearable autonomous navigation system for a pedestrian and a navigation method thereof. The wearable autonomous navigation system comprises five sensor modules and one comprehensive processing module, wherein the five sensor modules are arranged on the head, arms and feet of the pedestrian respectively; each sensor module comprises a first microcontroller, and an inertial measurement unit, a magnetic sensor, a gas pressure sensor and a first Bluetooth unit which are connected with the first microcontroller respectively; the inertial measurement unit comprises a triaxial accelerometer and a triaxial gyroscope; comprehensive processing module comprises a second microcontroller, and a wireless communication unit, a visual sensor, a satellite receiver, a second Bluetooth unit and a display unit which are connected with the second microcontroller respectively. The five sensor modules acquire a variety of navigation information and transmit the navigation information to the comprehensive processing module, and the variety of navigation information are fused to solve out a navigation result. Based on distributed wearable multi-point information acquisition, data fusion and data filtering are performed according to an inertial navigation method and other navigation methods, so that the pedestrian navigation performance is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Zero-speed correction method based on sole pressure detection in pedestrian navigation
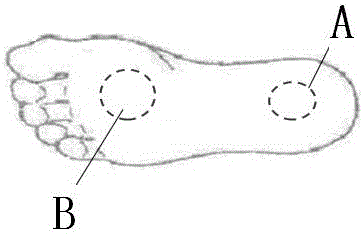
ActiveCN106482733ADetection helpsImprove accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterEngineering
The invention provides a zero-speed correction method based on sole pressure detection in pedestrian navigation. Static sections are judged through the combination of the sole pressure value, the acceleration value and the angular speed value during motion, the speed values in the static sections serve as quantities of a Kalman filter to be measured, and error parameters are estimated and speed, position and posture errors are corrected through Kalman filtering. By setting multiple static section threshold values and judgment conditions, the accuracy of detecting the static sections is improved, detection of the static sections under high dynamic is promoted, meanwhile, the errors are corrected through the Kalman filter, and the positioning precision of pedestrian navigation is improved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Low cost MEMS/GPS integrated navigation system and low cost MEMS/GPS integrated navigation method for pedestrian navigation
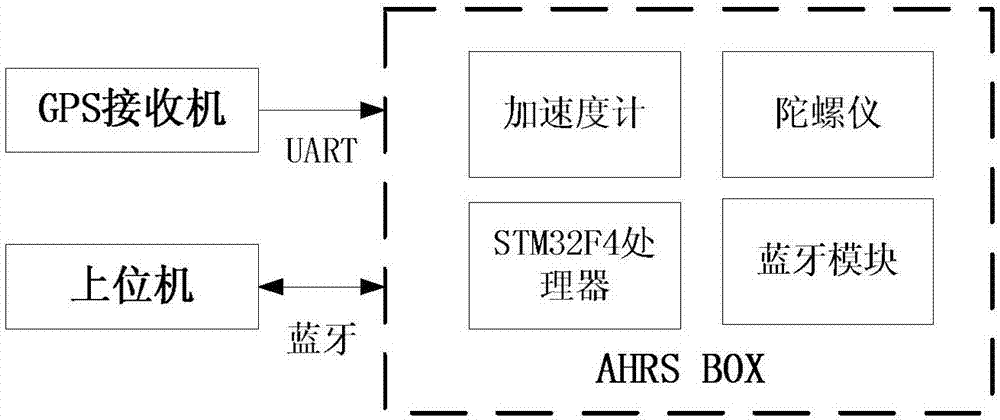
InactiveCN106949889AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsTablet computerAccelerometer
The invention discloses a low cost MEMS / GPS integrated navigation system for pedestrian navigation. The low cost MEMS / GPS integrated navigation system comprises a STM32F4 processor, a Bluetooth module, a low cost accelerometer, a gyroscope, a low cost GPS module and a tablet computer, wherein the STM32F4 processor and the tablet computer perform data exchange through the Bluetooth module, and the output terminals of the low cost accelerometer, the gyroscope and the low-cost GPS module are respectively connected to the STM32F4 processor. The invention further discloses a low cost MEMS / GPS integrated navigation method for pedestrian navigation. The low cost MEMS / GPS integrated navigation method comprises: carrying out modeling on an integrated navigation system inertial navigation error state quantity equation; establishing an SINAP / GPS loosely integrated navigation system state equation; carrying out modeling on an integrated navigation system measurement equation; and carrying out Kalman filtering according to the state equation and the measurement equation. With the technical scheme of the present invention, the strapdown inertial navigation and the Kalman filter solution can be efficiently achieved, and the high-precision and high-reliability navigation result can be obtained; and the effective support can be provided for the engineering achievement and the application of the MEMS / GPS integrated navigation for pedestrian navigation, and the outstanding practical value is provided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Pedestrian navigation device and method based on novel multi-sensor fusion technology
ActiveCN106017454AEasy to useHigh precisionInstruments for road network navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsOriginal dataIntelligent equipment
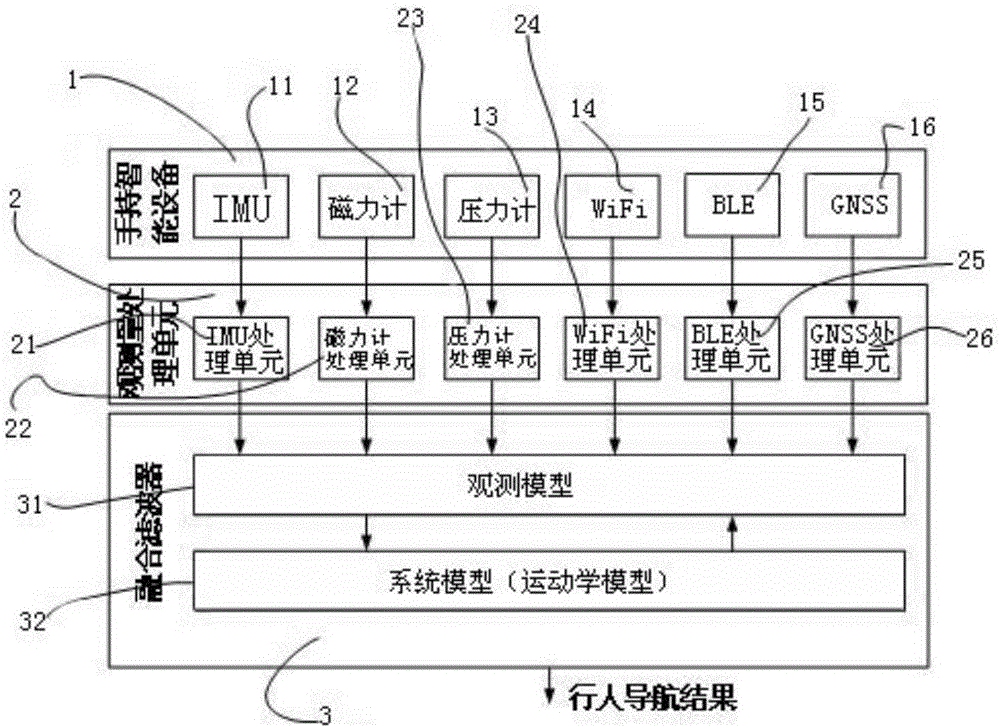
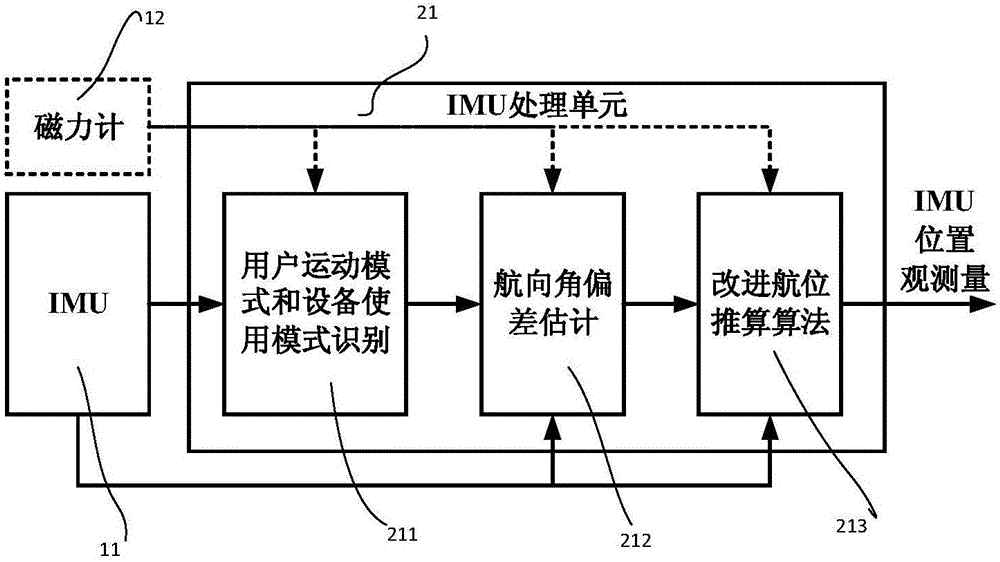
The invention discloses a pedestrian navigation device and method based on a novel multi-sensor fusion technology. The device comprises a handheld intelligent equipment platform, an observed quantity processing unit and a fusion filter. The method comprises the following steps that 1, handheld intelligent equipment utilizes hardware for obtaining original data of IMU, a magnetometer, a pressure meter, WiFi, BLE, GNSS and the like; 2, the observed quantity processing unit processes the original data provided by the handheld intelligent equipment so as to provide the observed quantity such as the position or speed for the fusion filter; 3, the fusion filter utilizes a kinetic model as a system model, an observation model is built according to a result of the observed quantity processing unit, and a pedestrian navigation result is finally obtained through processing of the fusion filter. According to the pedestrian navigation device and method, the defect that on the condition that no other auxiliary system exists, navigation errors are rapidly accumulated is overcome; an IMU processing module considers various modes of the handheld intelligent equipment and breaks through the limit of a traditional multi-sensor fusion IMU and carrier fixation; the pedestrian navigation accuracy is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
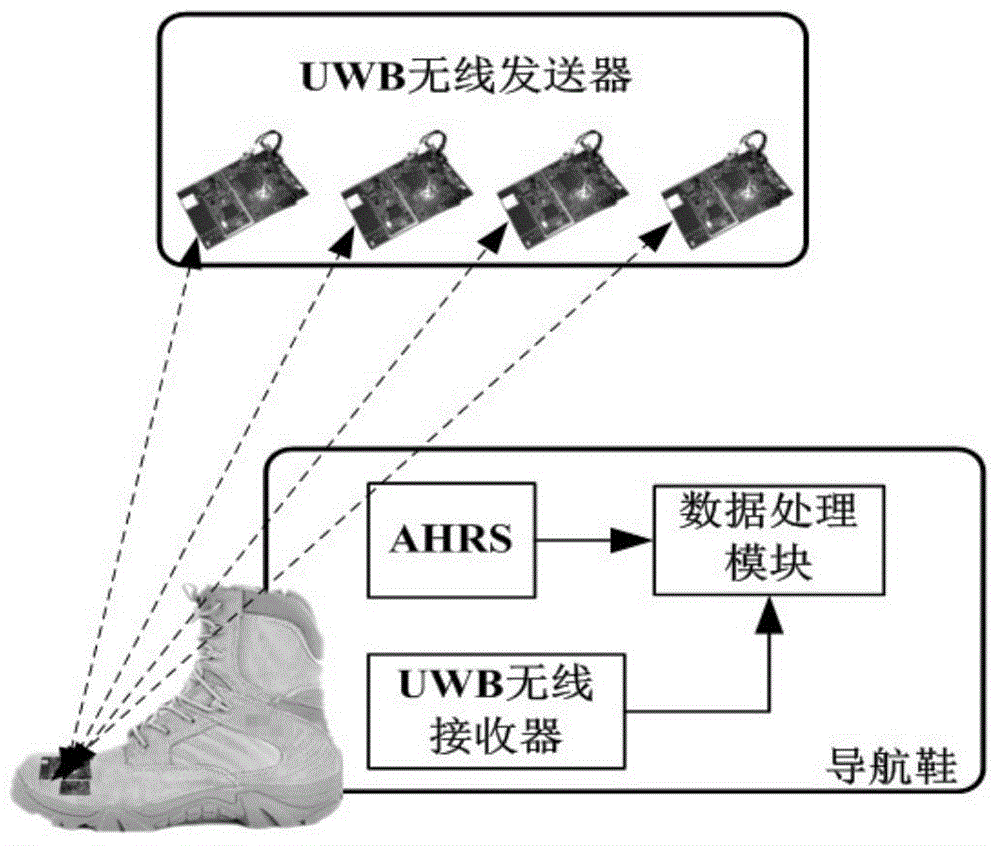
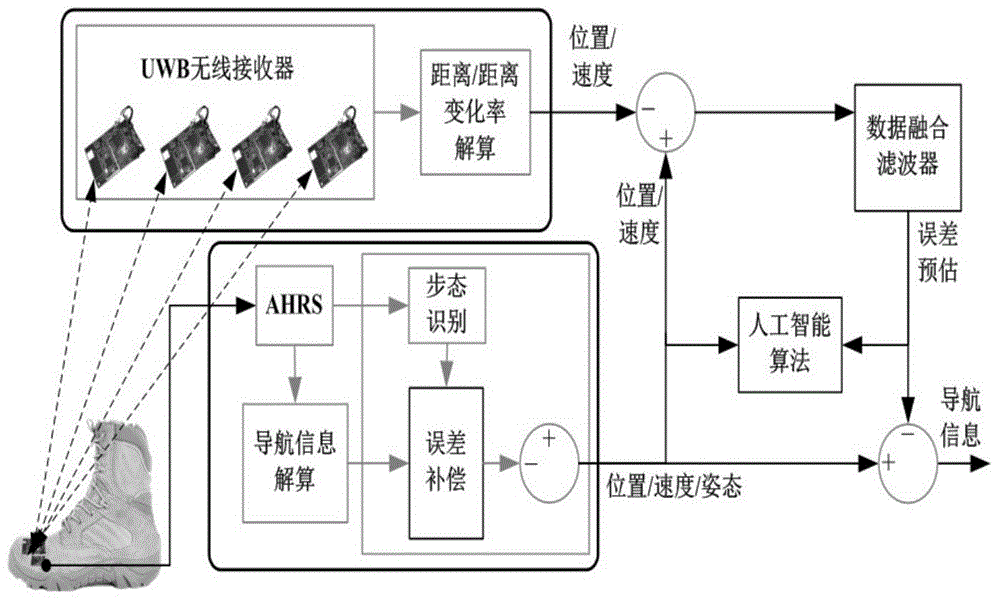
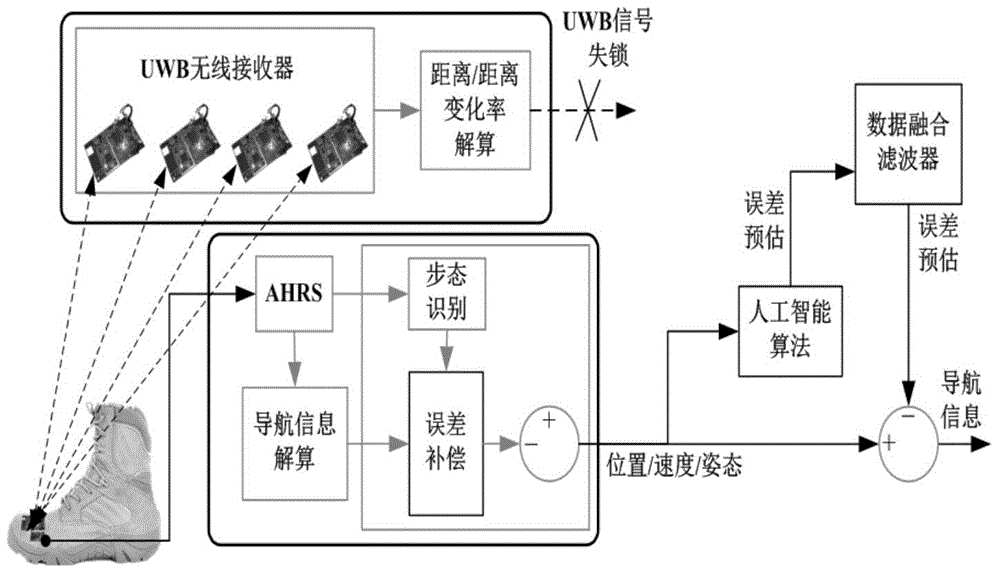
Indoor pedestrian navigation-oriented AHRS/UWB (attitude and heading reference system/ultra-wideband) seamless integrated navigation method
ActiveCN104864865AHigh precisionGuaranteed to workNavigational calculation instrumentsUltra-widebandAttitude and heading reference system
The invention discloses an indoor pedestrian navigation-oriented AHRS / UWB (attitude and heading reference system / ultra-wideband) seamless integrated navigation method. The method comprises the following steps: dividing the overall navigation method into a training stage and a prediction stage; adopting a difference value between the position and speed information collected by an AHRS and the position and speed information collected by a UWB as observed quantity of a main data fusion filter under the condition that a UWB signal is normal, and predicting the optimal position, speed and attitude error at the current moment; once the UWB signal is unlocked, conveying the position, speed and attitude information output in the AHRS into an artificial intelligence algorithm as prediction input; through the built mapping relationship, predicting an observation vector of the unlocked main data fusion filter, and ensuring normal working of the main data fusion filter, so that seamless navigation of an overall navigation system is ensured.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
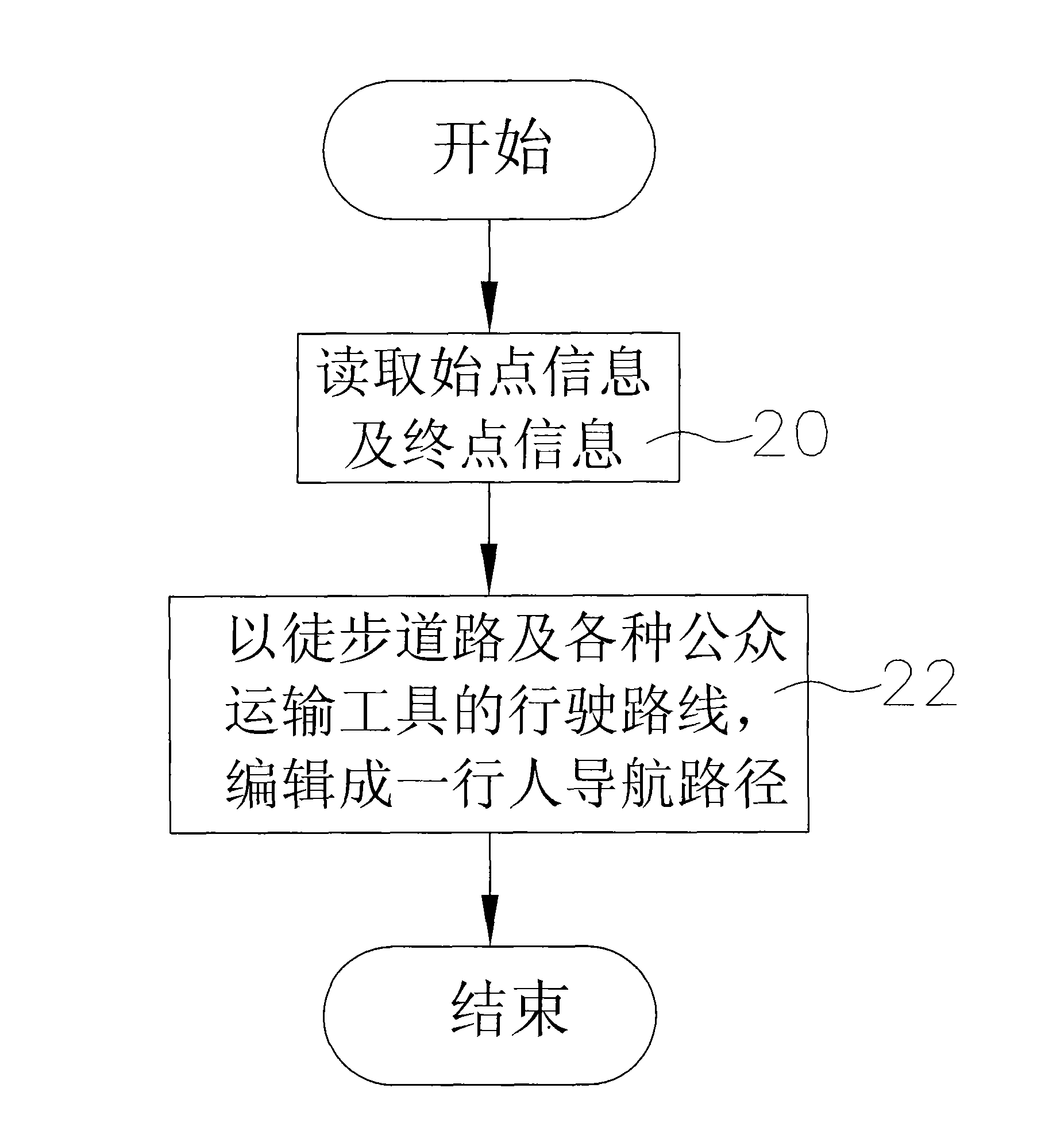
Method for programming pedestrian navigation path
The invention relates to a method for programming a pedestrian navigation path, which is applied to a pedestrian navigation device. A map database of the pedestrian navigation device at least comprises walking road data and running route data of at least one public transportation tool. The method comprises that when the pedestrian navigation device is used for programming the pedestrian navigation path, the pedestrian navigation device reads the information of an initial point and an end point, and the method programs running routes of walking roads and various public transportation tools between the initial point and the end point according to the walking road data and the running route data to edit the pedestrian navigation path. The method solves the problem that the prior navigation device programs the pedestrian navigation path only by the walking roads, and achieves the aim that a pedestrian reaches the end point by selectively walking on the walking roads or taking the public transportation tools.
Owner:MITAC COMP (SHUN DE) LTD
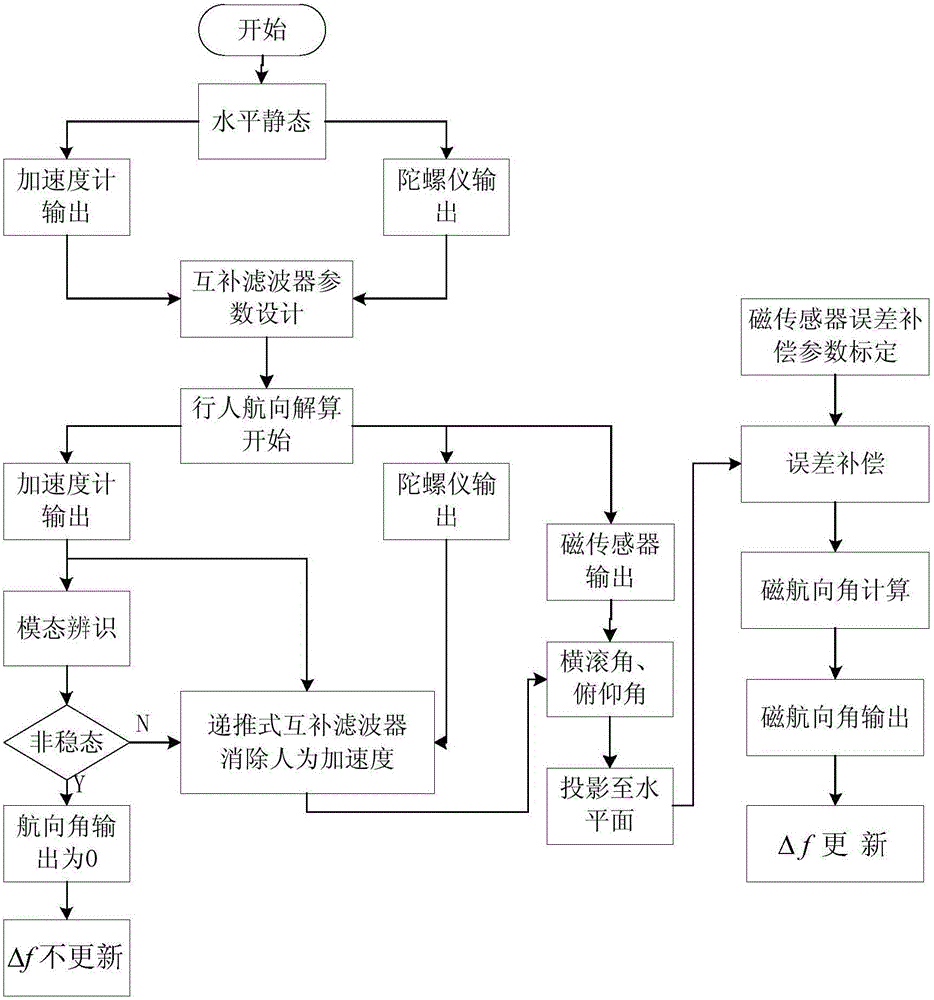
Magnetic course resolving method for indoor pedestrian navigation based on improved complementary filter
ActiveCN106123900AHigh precisionPracticalNavigational calculation instrumentsTime domainComplementary filter
The invention discloses a magnetic course resolving method for indoor pedestrian navigation based on an improved complementary filter. Parameters of a complementary filter are designed in a view of a time domain; an improved complementary filter algorithm model is established; a pedestrian movement mode identification algorithm model is established; and two-dimensional elliptical calibration of a magnetic sensor is utilized for resolving a magnetic course angle of an indoor pedestrian in real time. A low-precision consumer-grade MEMS sensor chip is adopted for ensuring high accuracy of indoor and outdoor course angle and is high in practicability. The MEMS sensor chip is installed in a non-fixed connection manner, is high in installation flexibility, and is not limited by the use environment. The MEMS sensor chip is suitable for a wide scene, is simple and convenient in use method, and ensures high-precision output in a short time.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Distributed type INS/UWB tightly-coupled navigation system and method
InactiveCN106871893AReduced impact of integrated navigation accuracyHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsData processing systemWireless transmission
The invention discloses a distributed type INS / UWB tightly-coupled navigation system and method. The system comprises an inertial navigation device, a pseudorange detection unit, a wireless data transmission system and a data processing system; the inertial navigation device is used for measuring the navigation information of pedestrian, wherein the navigation information includes position, speed and posture information; the pseudorange detection unit is used for acquiring pseudorange information; the wireless data transmission system is connected with the inertial navigation device and the pseudorange detection unit, and used for transmitting the data, acquired by the inertial navigation device and the pseudorange detection unit, into the data processing system through wireless transmission, and transmitting a control command, sent by the data processing system, to the inertial navigation device; and the data processing system is used for performing data integration estimation on collected data by adopting a distributive type data integration estimation unit, and sending the control command to the inertial navigation device. According to the distributed type INS / UWB tightly-coupled navigation system and the method, influence of the interior complicated navigation environment on the integrated navigation precision can be reduced so as to obtain the optimal pre-estimation on the navigation information of target pedestrian.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
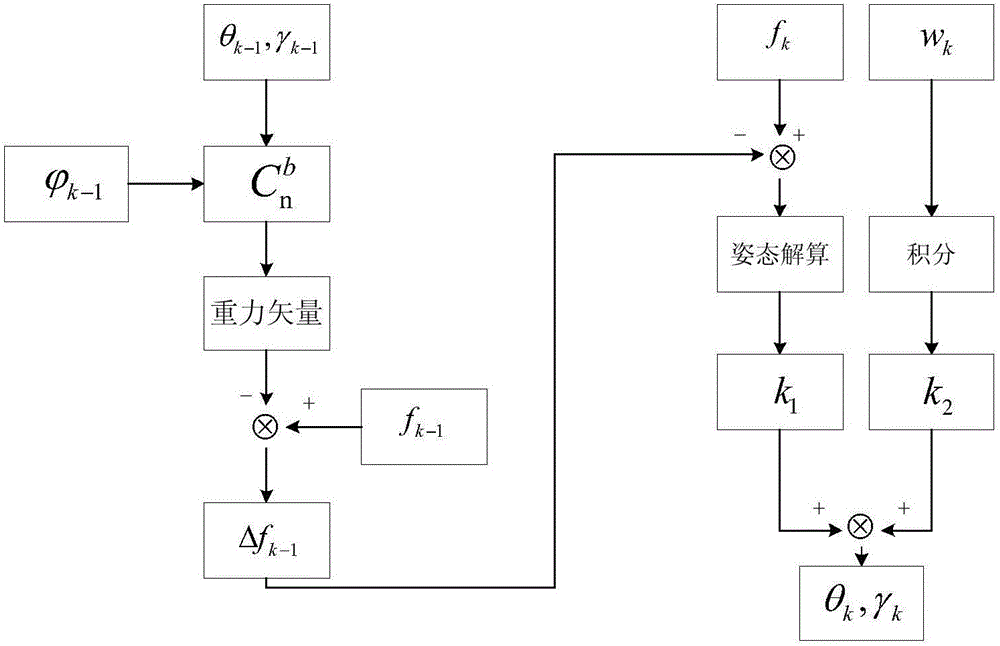
Pedestrian navigation method based on inertia, magnetic heading and zero-speed correction
ActiveCN110553646AOptimal Estimation of Navigation ErrorNavigation by terrestrial meansNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsLinear motionErrors and residuals
The invention discloses a pedestrian navigation method based on inertia, magnetic heading and zero-speed correction, which comprises the following steps: (1) measuring linear motion information and angular motion information of a pedestrian by adopting an inertia measurement element, and resolving to obtain attitude, speed and position information of the pedestrian; calculating the three-axis magnetic component measured by a magnetometer to obtain the heading information of the pedestrian; and (2) obtaining a zero-speed state in a walking process through a zero-speed interval detection algorithm, updating an observed quantity of a speed error in the state, establishing a Kalman filtering equation to carry out error correction on pedestrian navigation output in combination with the observedquantity of a course angle error, and finally completing output of corresponding navigation information. Therefore, the magnetic heading angle is calculated by utilizing the three-axis magnetic induction data, and the defects of an inertial navigation system are overcome. In the process, a zero-speed interval is judged by utilizing measurement data of an inertia measurement element, a system error model and a Kalman filtering equation are established, a proper observed quantity is selected, and a state error is estimated.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
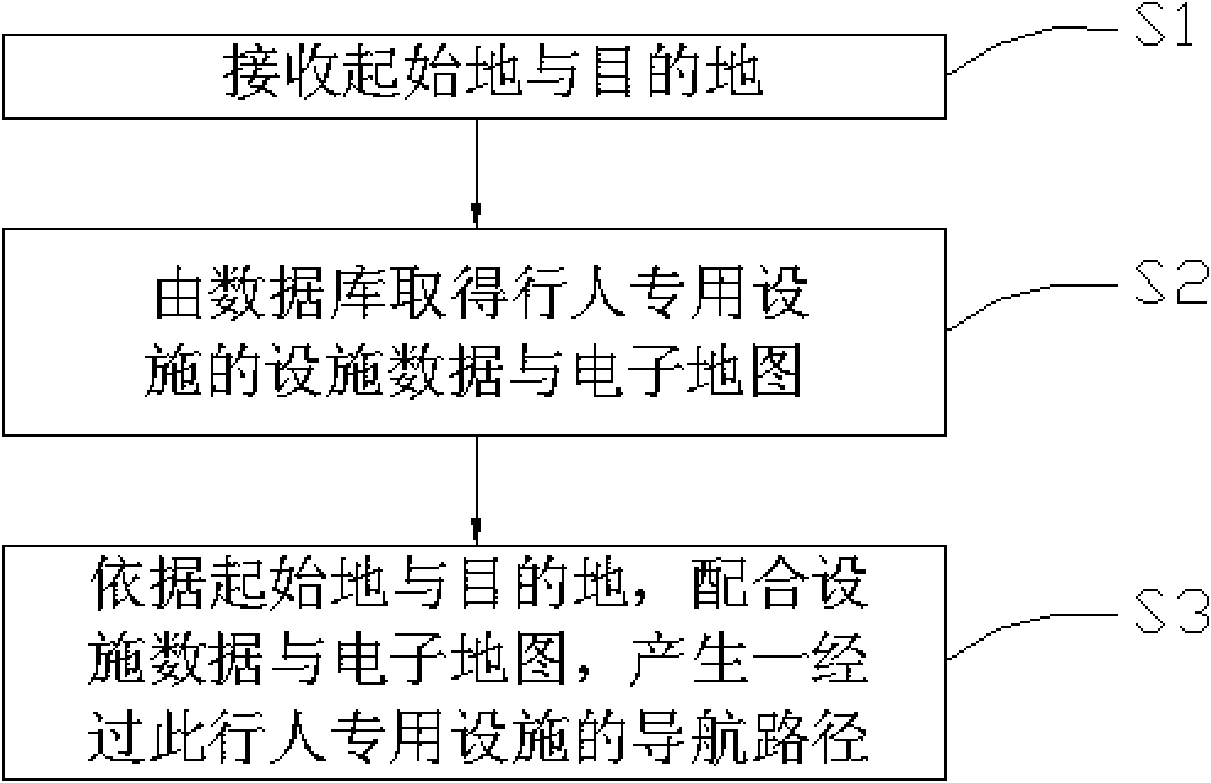
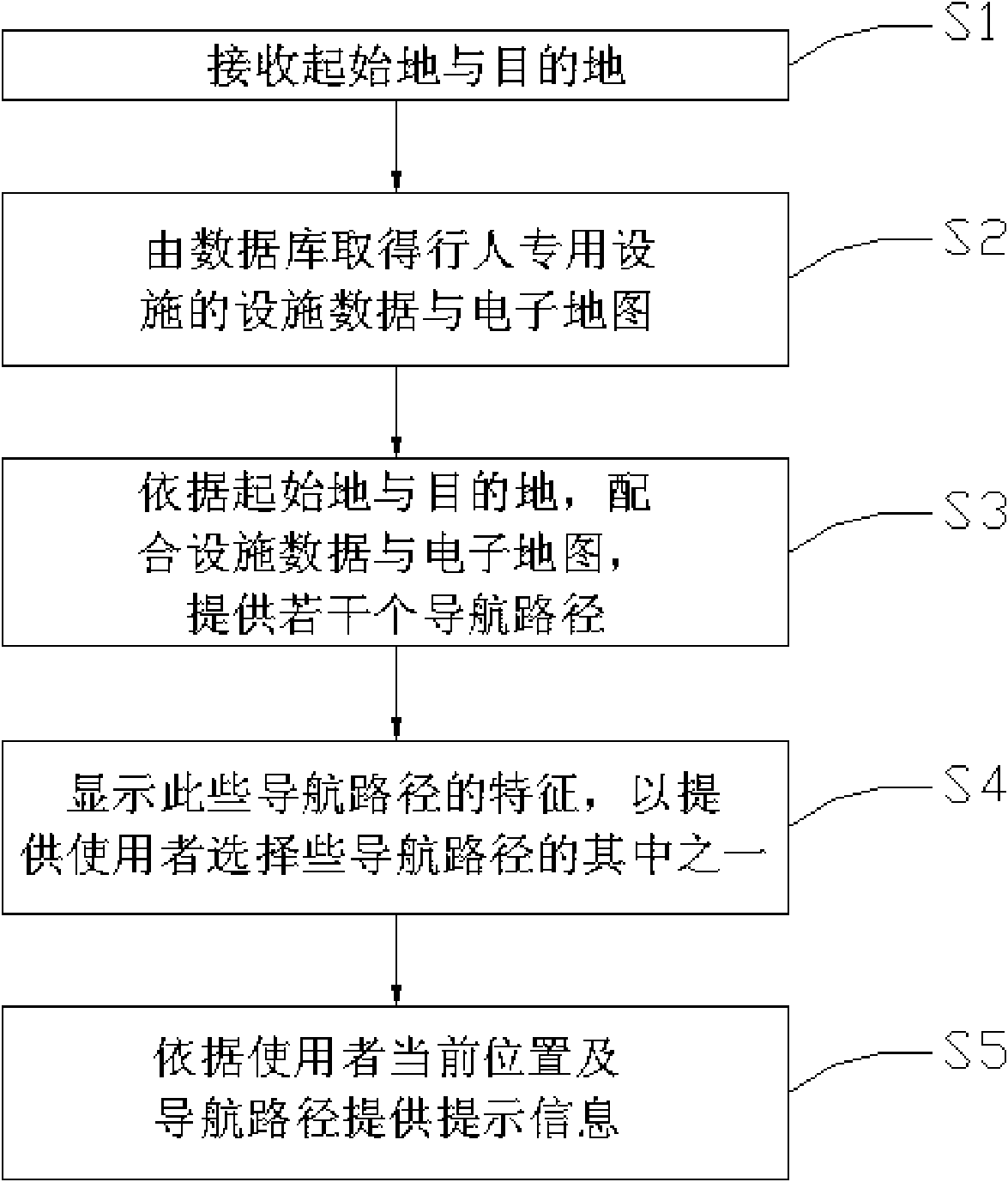
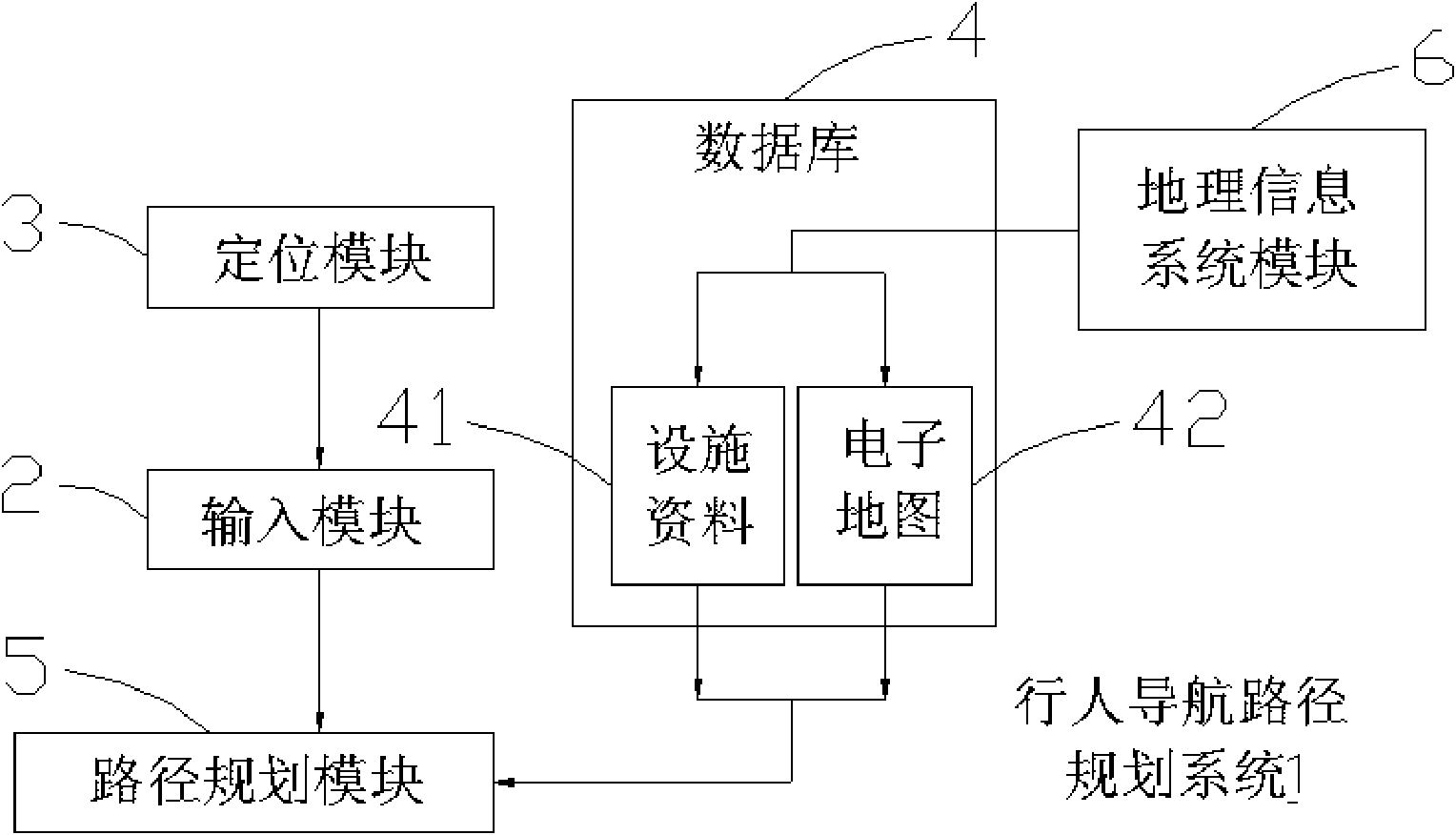
Pedestrian navigation path planning method and system thereof
The invention discloses a pedestrian navigation path planning method and a system thereof. The invention is characterized by based on an electronic map with the pedestrian private facilities, the received initial position and the destination, making a plan of the navigation path by coordinating with the navigation path of the pedestrian private facilities on the road such as zebra crossing, overline bridge or underpasses and combining the electronic map, thereby enabling a user to correctly arrive the destination under the condition of according with the safe and traffic regulation. Additionally, in an embodiment, when the pedestrian position is close to the pedestrian private facilities, a prompt message is send out to remind the pedestrian of walking on the safer pedestrian private facilities to go across the road.
Owner:MITAC COMP (SHUN DE) LTD
Indoor pedestrian navigation method based on self-backtracking algorithm
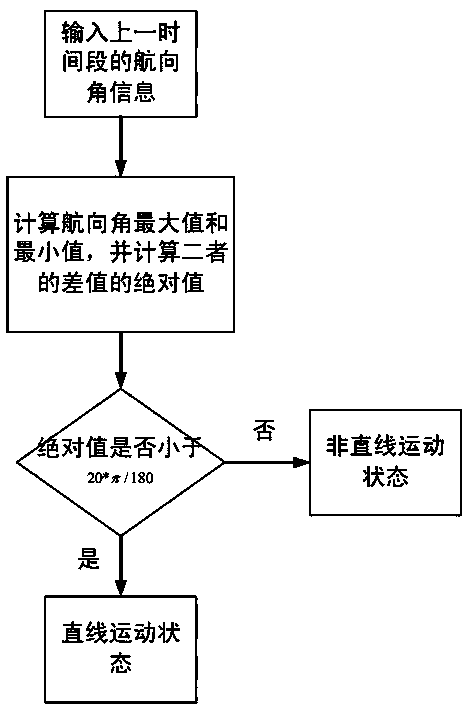
ActiveCN109855620AImprove the accuracy of positioning and attitude determinationAccurate and effective walking constraintsNavigational calculation instrumentsGyroscopeAccelerometer
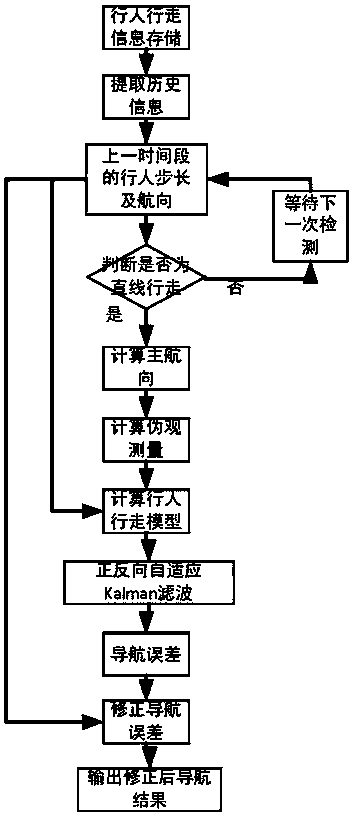
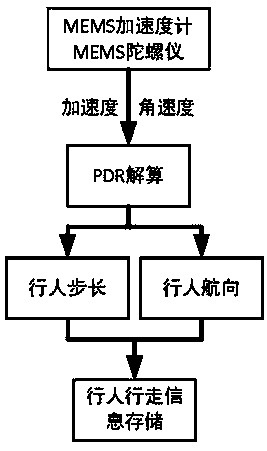
The invention discloses an indoor pedestrian navigation method based on a self-backtracking algorithm. A pedestrian being navigated wears an MEMS sensor. The navigation method comprises the followingsteps: carrying out pedestrian dead reckoning according to an MEMS gyroscope and an MEMS accelerometer to obtain pedestrian walking information during a period of time; carrying out straight line detection on the walking information in the period of time to judge whether the walking route of the pedestrian in the period of time is a straight line; if determining that the pedestrian walks in a straight line, constructing pseudo observed quantity according to heading angle information; carrying out navigation error detection and correction compensation through a forward and backward adaptive kalman filtering algorithm; and outputting a pedestrian indoor navigation and positioning result. By fully exploring the gait characteristics of the pedestrian when walking, the method carries out navigation error estimation and compensation on pedestrian position and attitude information by utilizing walking constraint conditions, thereby realizing a purpose of improving position and posture determination accuracy of the indoor pedestrian navigation scheme based on the motion sensor.
Owner:湖南兵器科技研究院有限责任公司 +1
Indoor pedestrian navigation attitude estimation method based on foot-worn inertia measurement unit
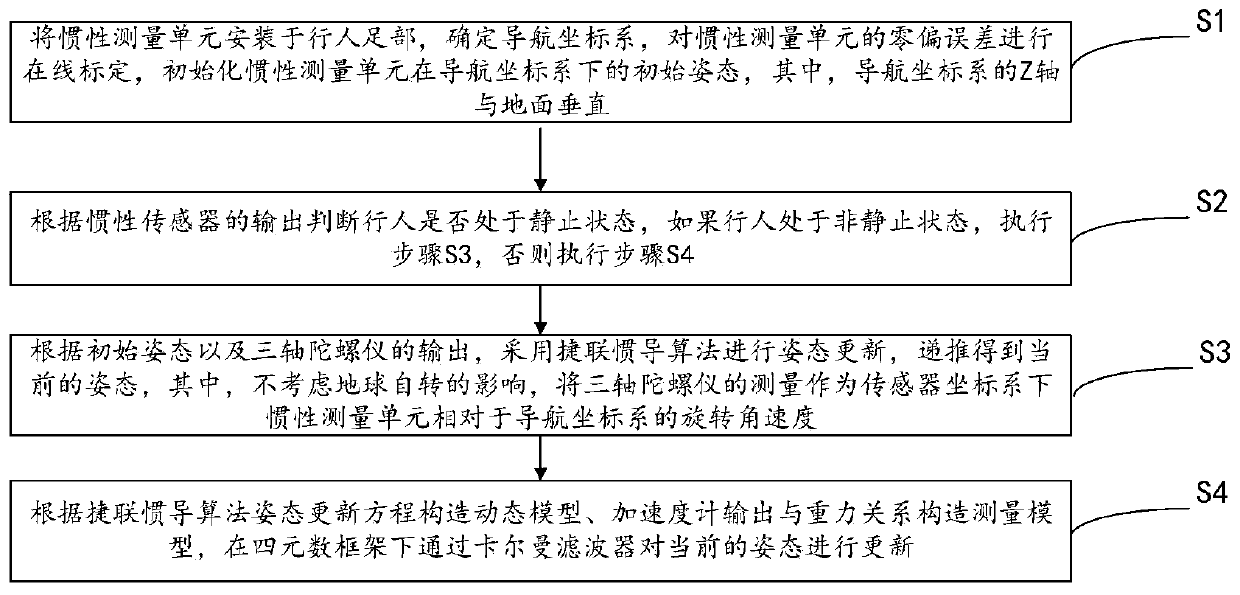
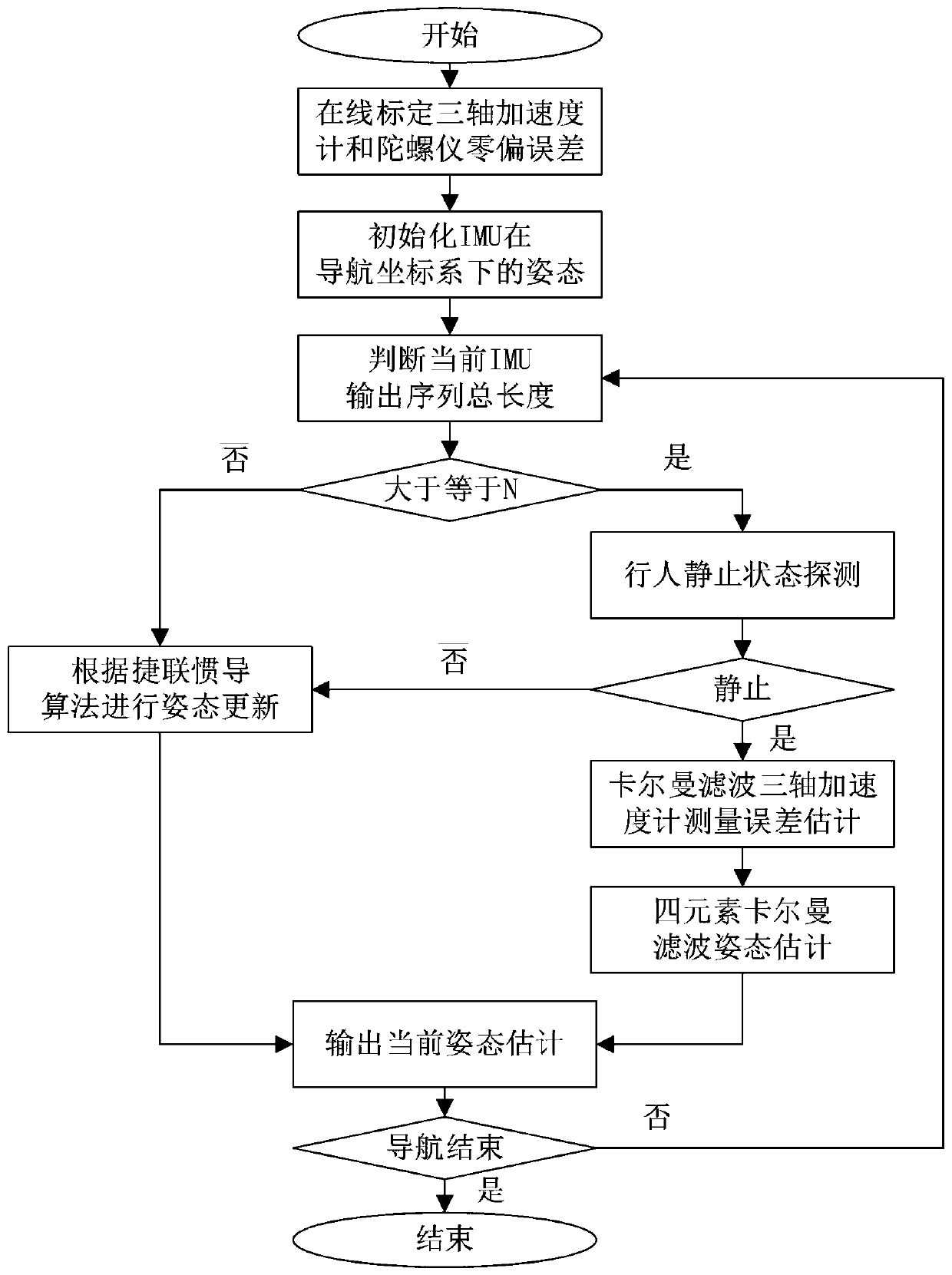
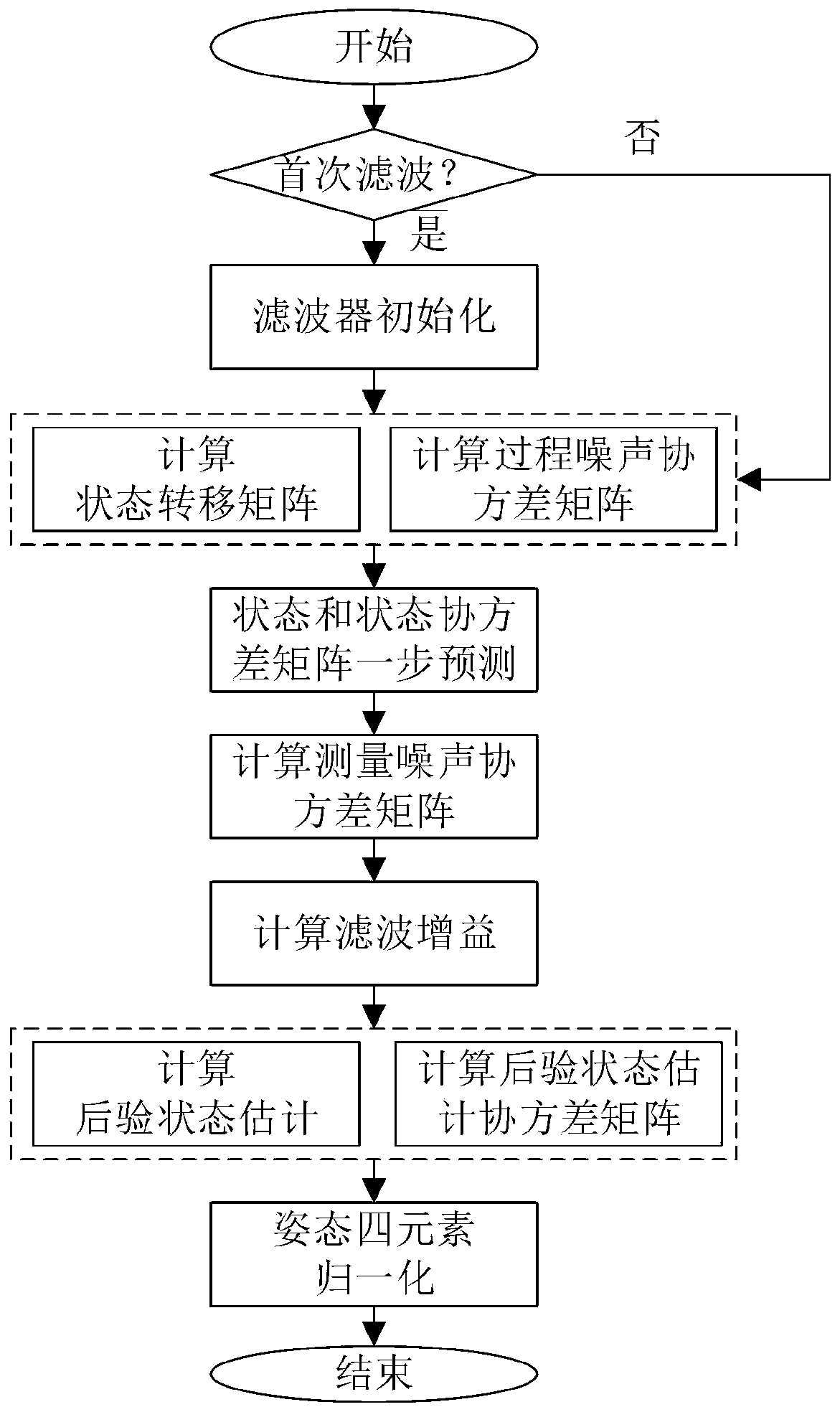
ActiveCN110398245ASolve technical problems that are difficult to provide accurate attitude informationNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerDynamic models
The invention provides an indoor pedestrian navigation attitude estimation method based on a foot-worn inertia measurement unit. The method comprises the following steps: firstly mounting an inertia measurement unit on the foot of the pedestrian, initializing an initial attitude of an inertia measurement unit under a navigation coordinate system, and then judging whether the pedestrian is in a static state according to the output of the inertia sensor; when the pedestrian is in the non-static state, performing attitude updating by adopting the strap-down inertial navigation algorithm, recursing to obtain the current attitude; when the pedestrian is in the static state, constructing a dynamic model, accelerometer output and gravity relation construction measurement model according to the strap-down inertia navigation algorithm attitude updating equation, and updating the current attitude through a Kalman filter under a quaternion frame. The observed quantity is estimated by utilizing the measurement construction attitude of the accelerometer at the static moment, the precise attitude information can be obtained by executing data fusion through the Kalman filter under the quaternionframe, and the technical effect of providing the precise attitude information is provided.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Walker navigation device, walker navigation method, and program
InactiveUS7428461B2Precise NavigationNavigational calculation instrumentsControl with pedestrian guidance indicatorInformation analysisRoute search
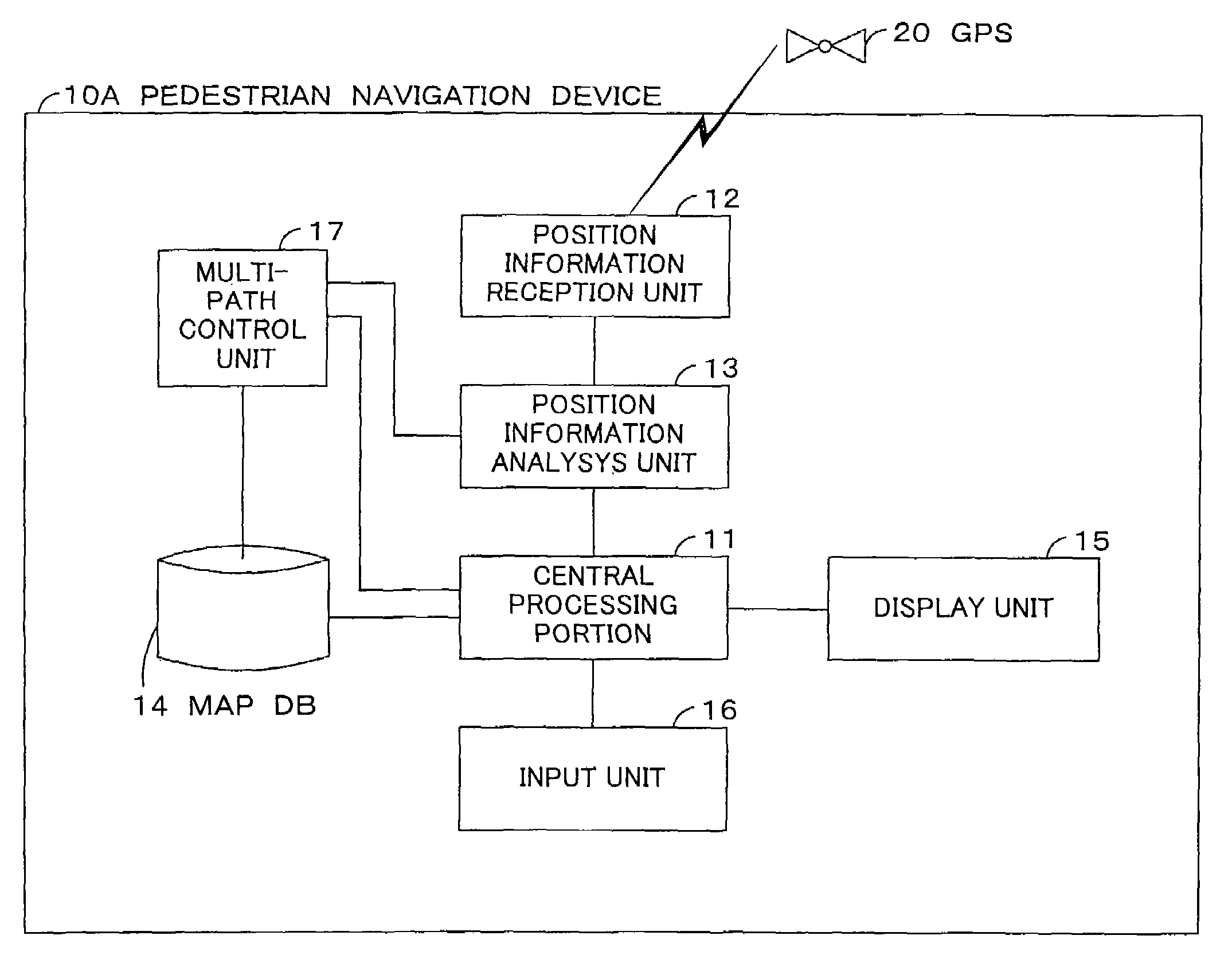
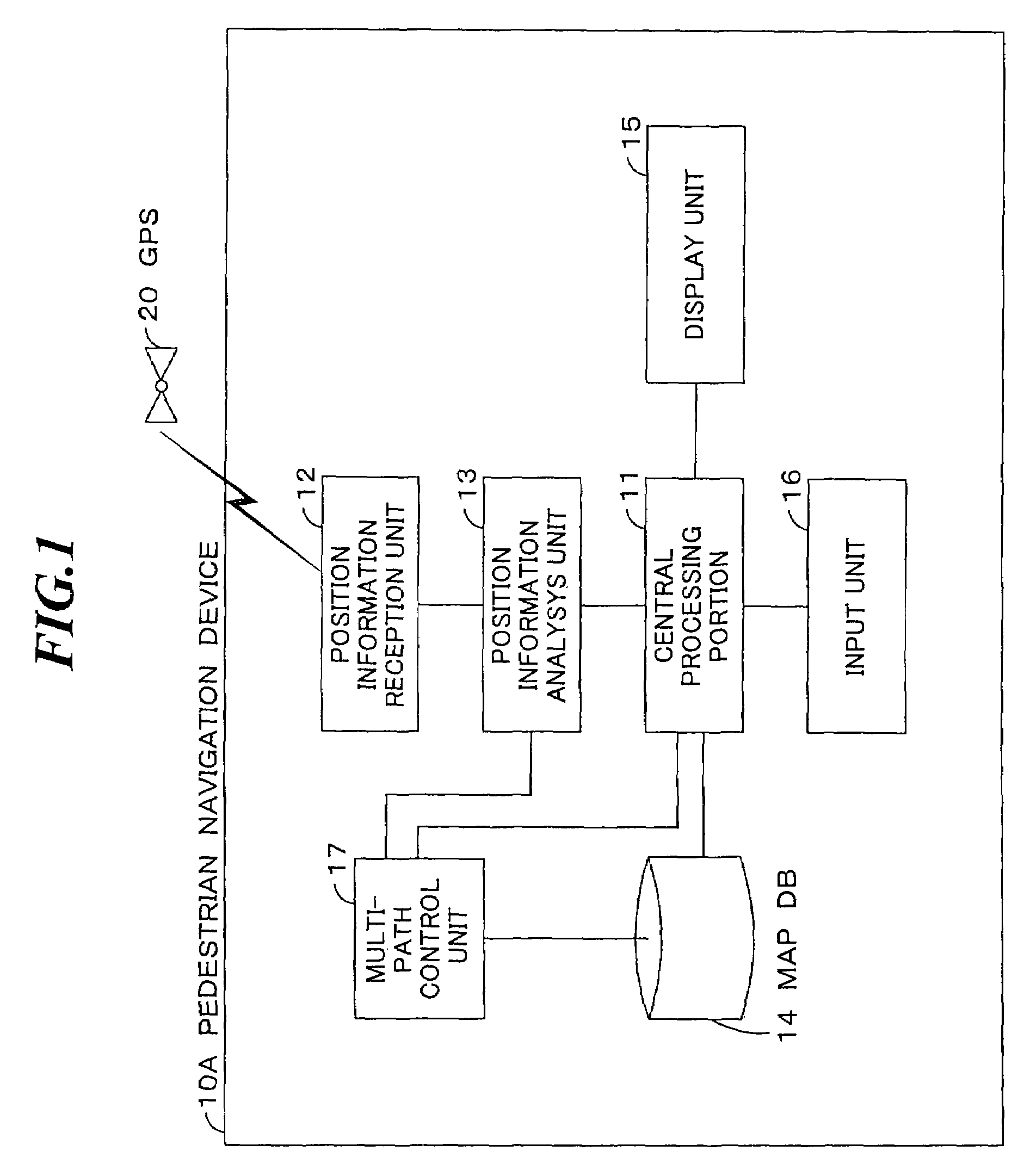
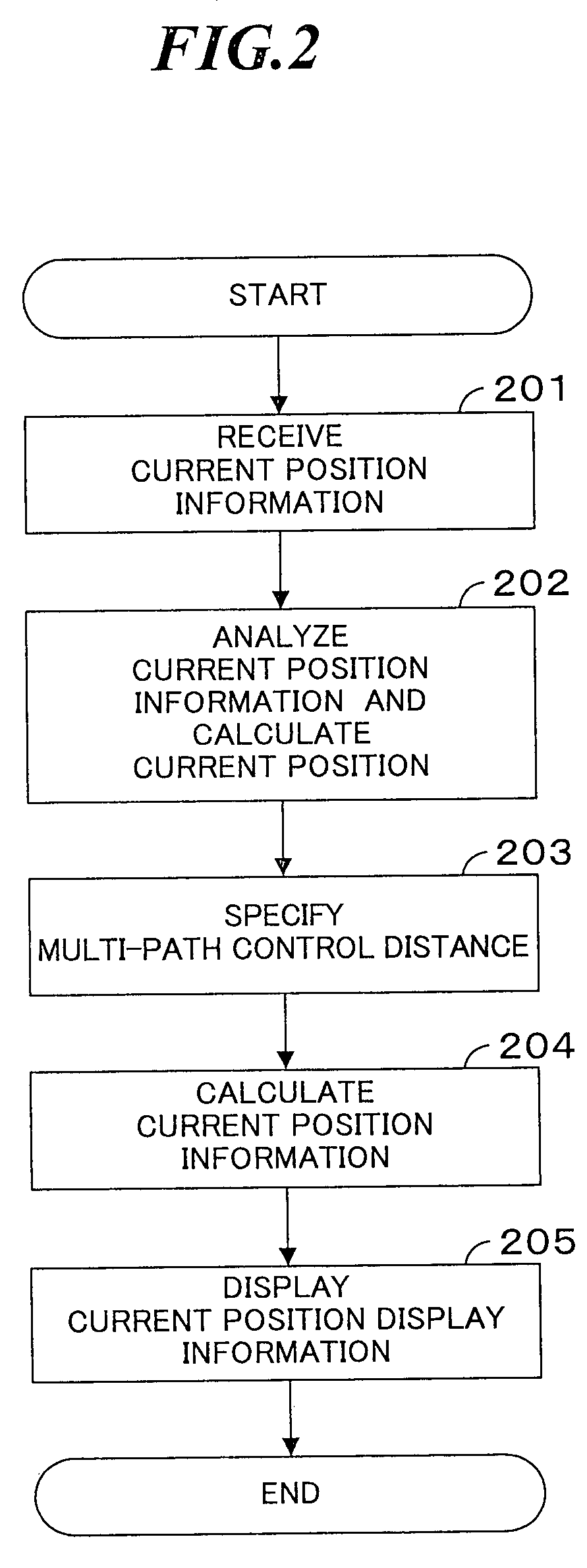
A pedestrian navigation device (10A) of this invention has a position information reception unit (12), which obtains current position information from a GPS (20); a position information analysis unit (13), which calculates the current position by analyzing received current position information; a MAPDB (Map Data Base) (14), which stores map information; a multi-path control unit (17), which specifies a multi-path control distance to control multi-path interference; a central processing portion (11), which calculates current position display information, based on the current position calculated by the position information analysis unit (13), on map information stored in the MAPDB (14), and on the multi-path control distance specified by the multi-path control unit (17); a display unit (15), which displays current position display information; and an input unit (16), which inputs distance specification value and route search conditions and issues instructions to begin navigation. By this means, a pedestrian navigation device is provided, which enables to accurately navigate the route of a pedestrian by appropriately correcting the multi-path interference.
Owner:NAVITIME JAPAN CO LTD
Self-adaptive zero velocity update pedestrian navigation method based on MEMS sensor
InactiveCN107843256AChange the zero-speed discrimination threshold in real timeImprove adaptabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDiscrimination thresholdMems sensors
The invention discloses a self-adaptive zero velocity update pedestrian navigation method based on a MEMS sensor. By analyzing gait during people multidirectional movement, based on output of the MEMSsensor under different motion modals, a zero velocity update discrimination algorithm combines with strapdown inertial navigation resolving for correcting information radiated with time of speed position resolved by correction resolution; a self-adaptive zero velocity correction model is established according to practical motion characteristic of pedestrians, and zero velocity discrimination threshold can be changed with real time. The method better solve the radiation problem of speed position of different pedestrians under different motion modals under pure inertia resolving, and self-adaptability and reliability of pedestrian navigation positioning during people multidirectional movement is increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com