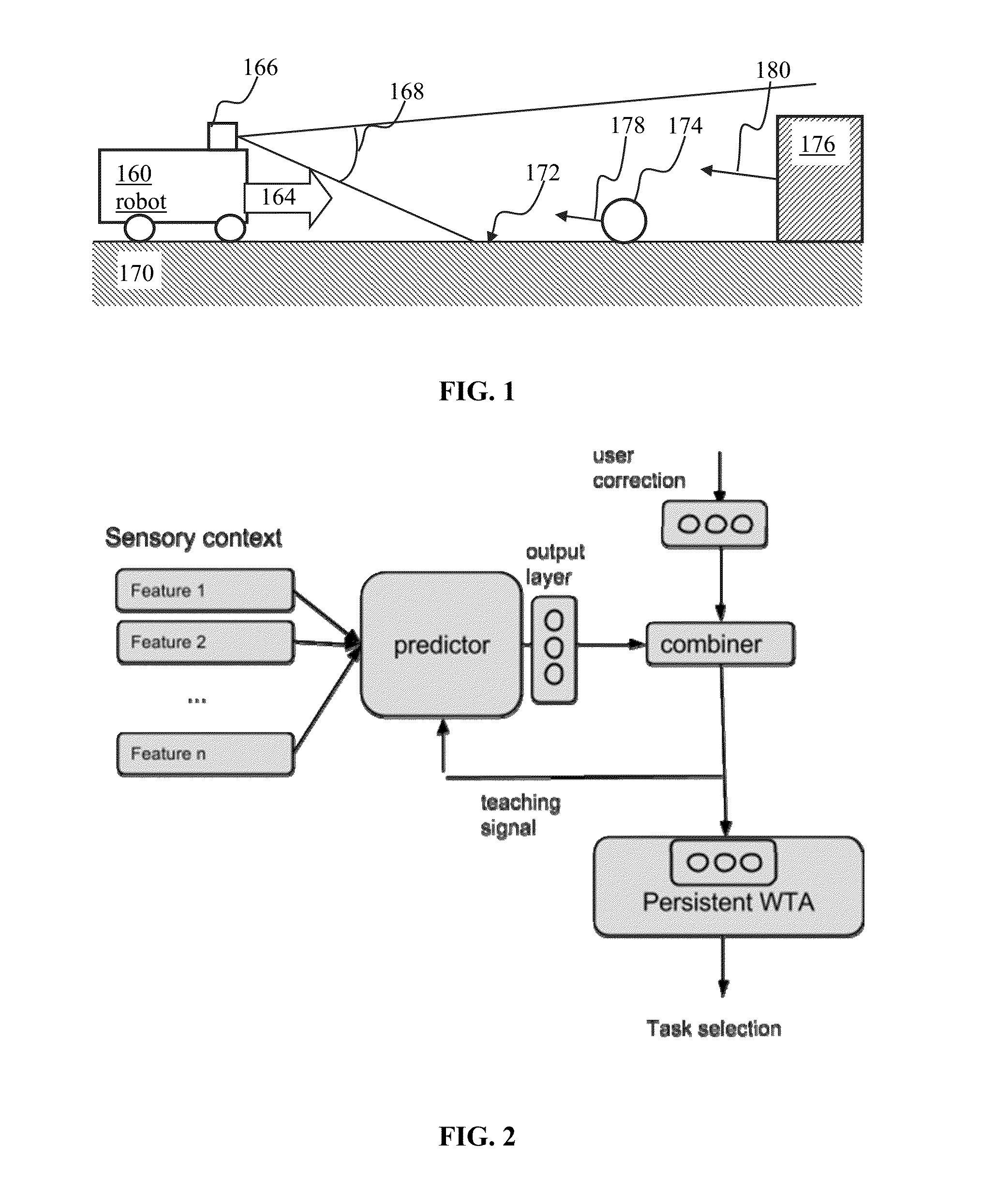
Patents
Literature
2301 results about "Near neighbor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Single molecule arrays for genetic and chemical analysis
ActiveUS20070099208A1Efficient high resolution analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechImage resolutionRandom array
Random arrays of single molecules are provided for carrying out large scale analyses, particularly of biomolecules, such as genomic DNA, cDNAs, proteins, and the like. In one aspect, arrays of the invention comprise concatemers of DNA fragments that are randomly disposed on a regular array of discrete spaced apart regions, such that substantially all such regions contain no more than a single concatemer. Preferably, such regions have areas substantially less than 1 μm2 and have nearest neighbor distances that permit optical resolution of on the order of 109 single molecules per cm2. Many analytical chemistries can be applied to random arrays of the invention, including sequencing by hybridization chemistries, sequencing by synthesis chemistries, SNP detection chemistries, and the like, to greatly expand the scale and potential applications of such techniques.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
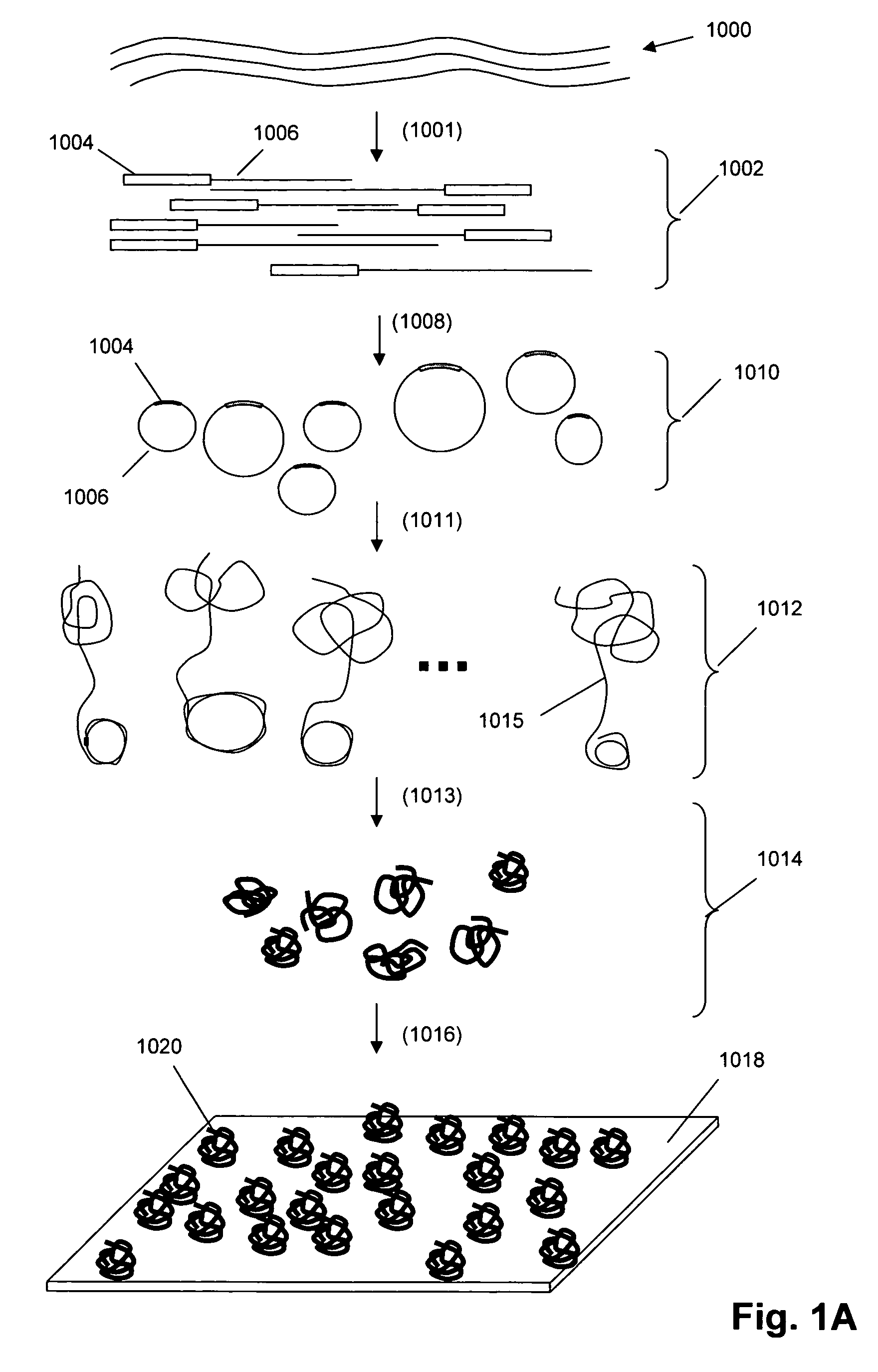
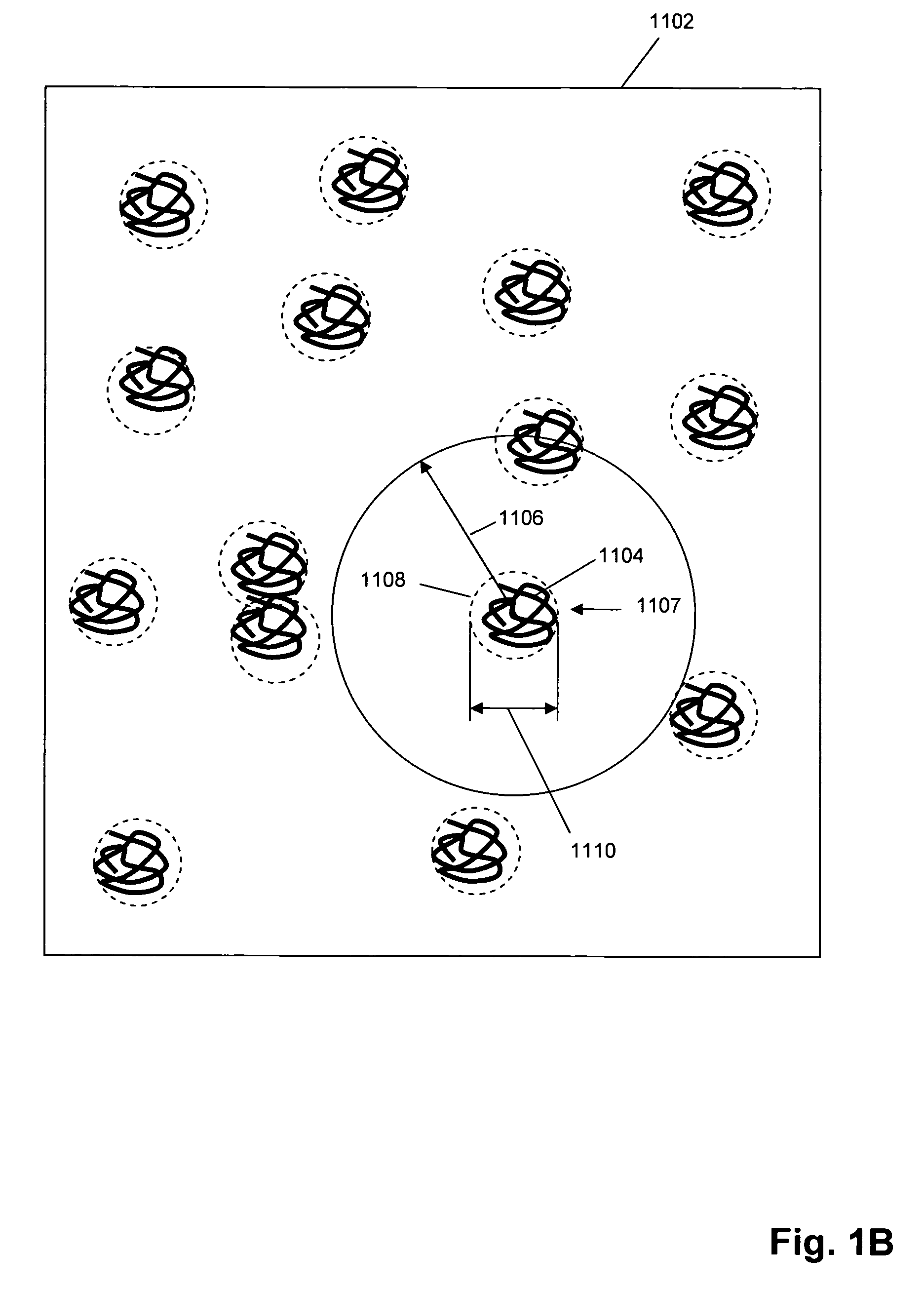
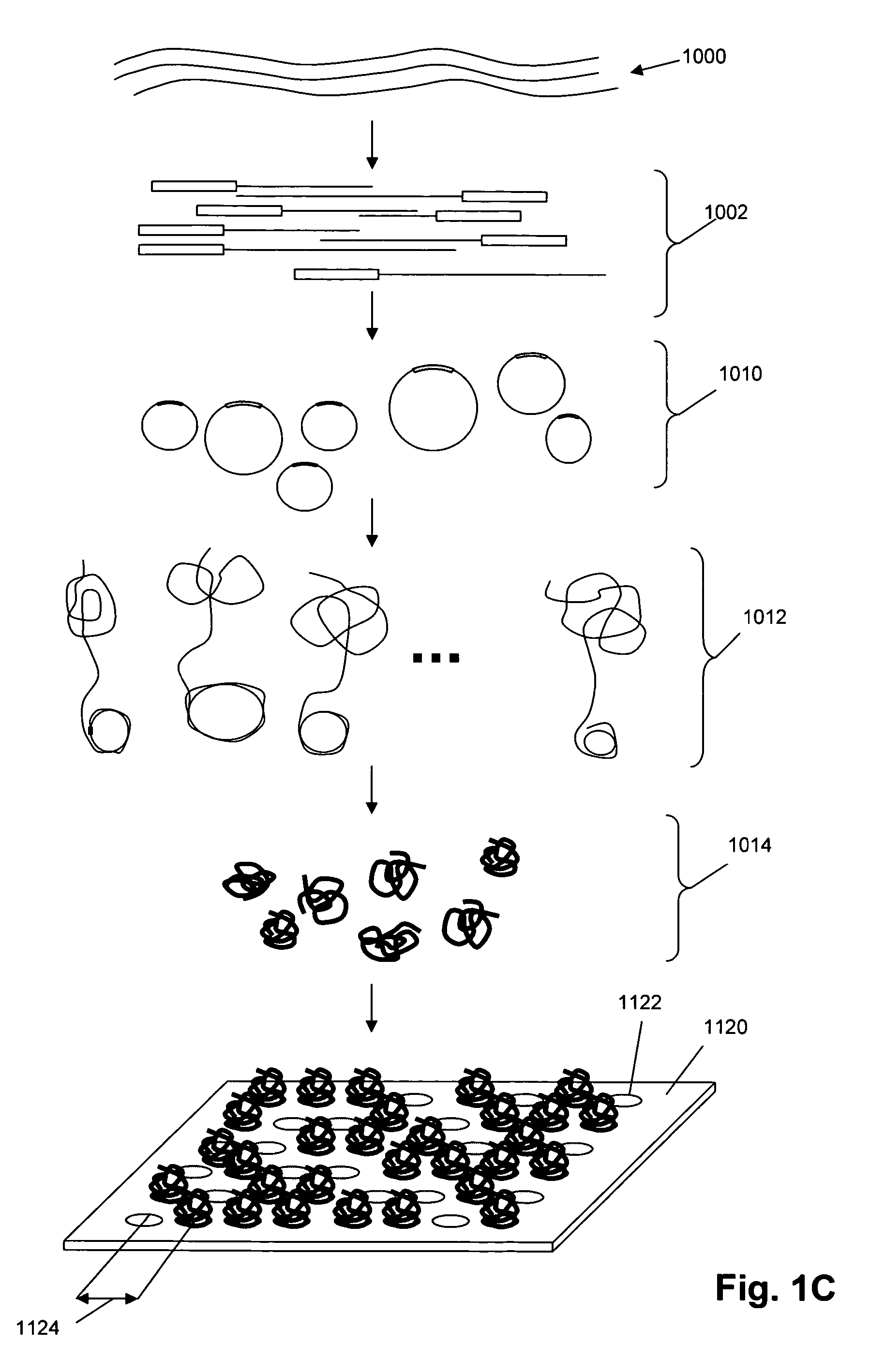
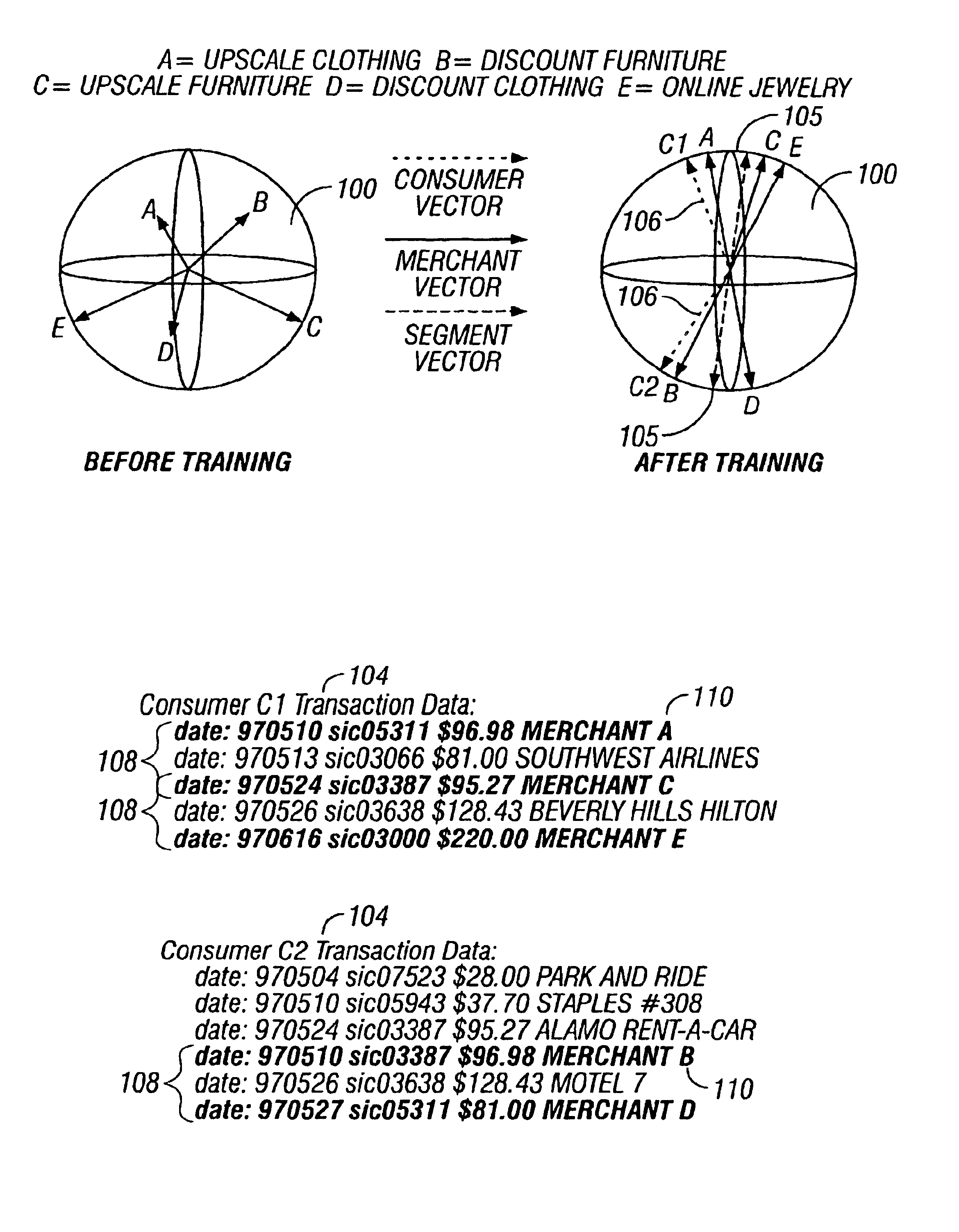
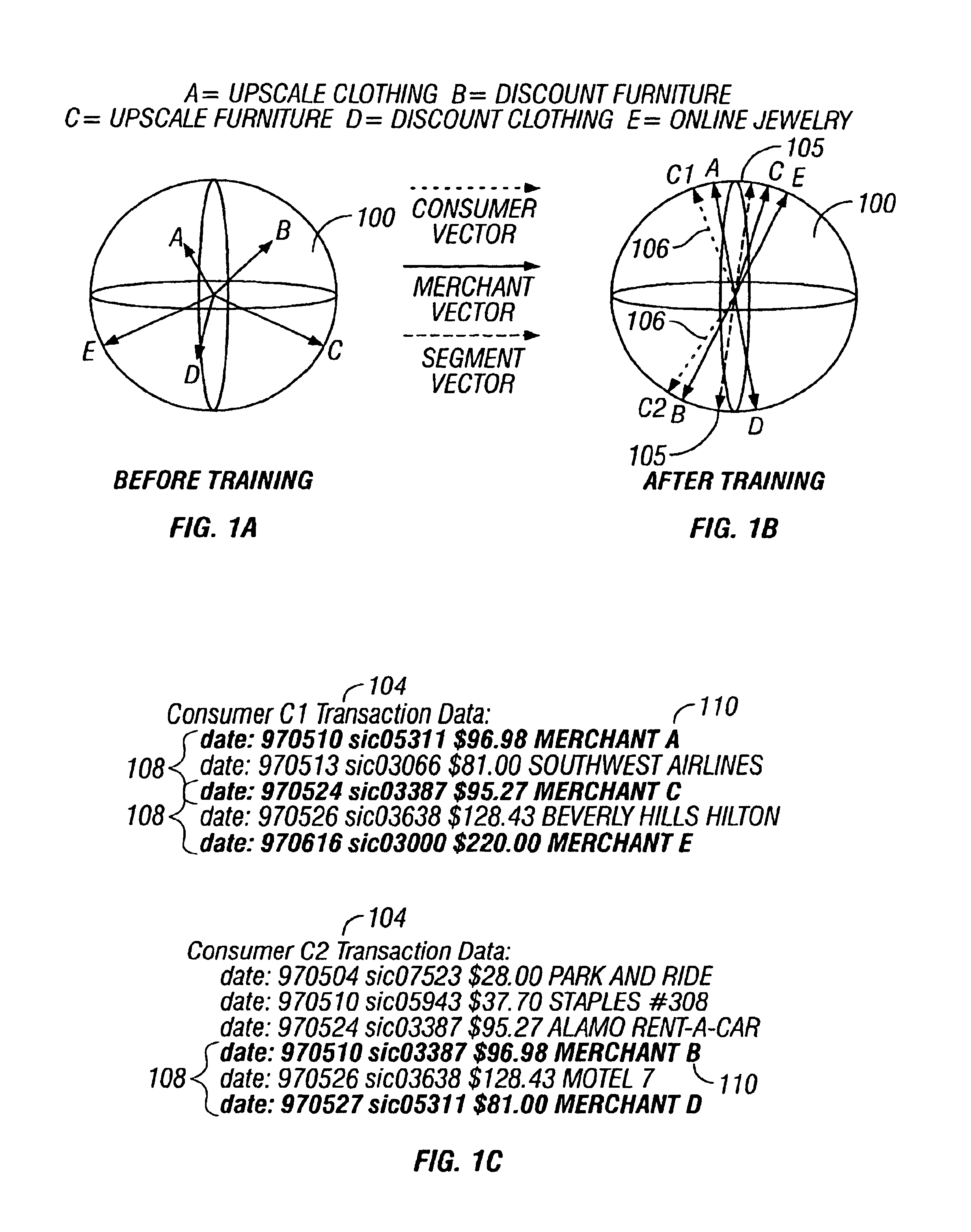
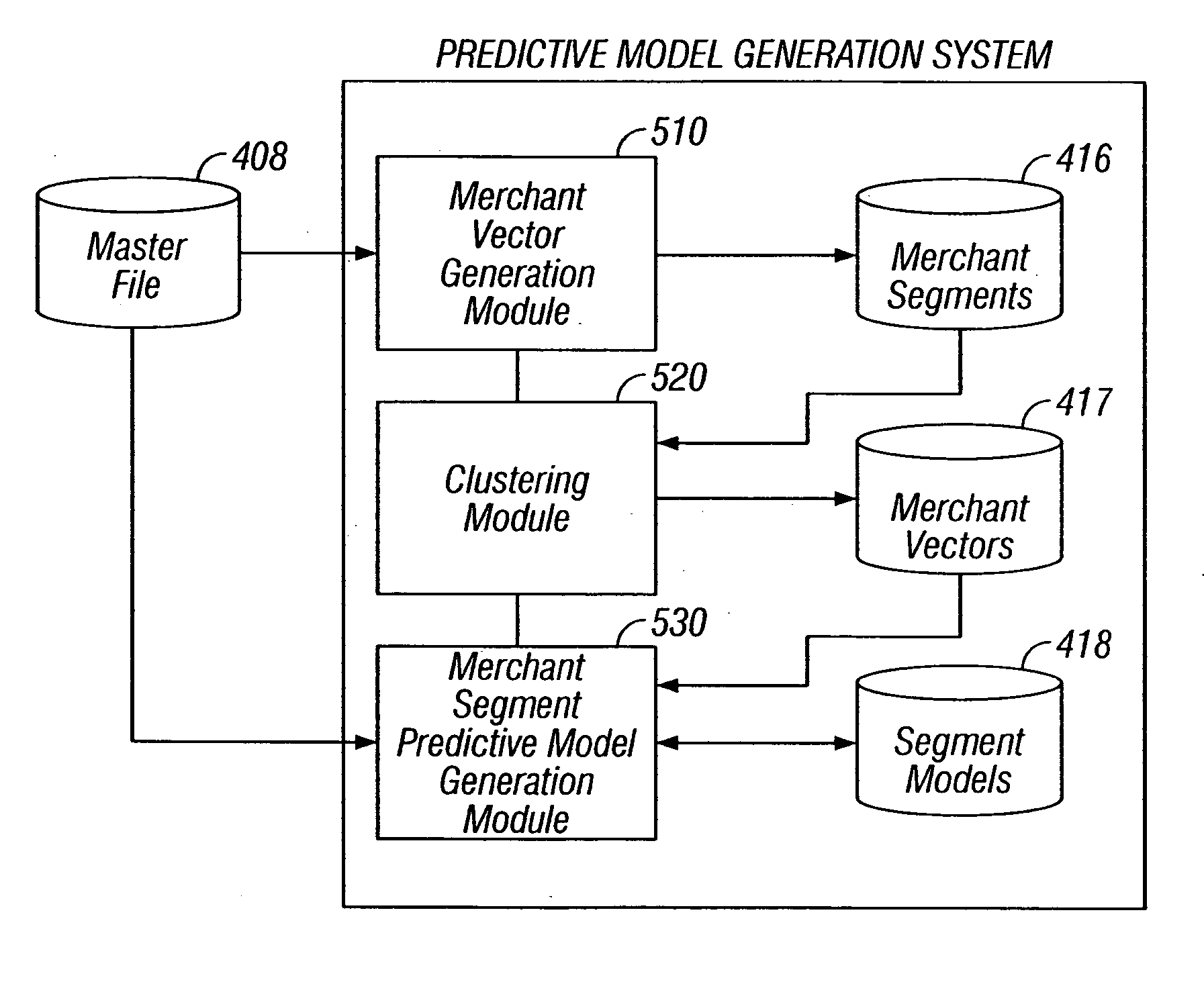
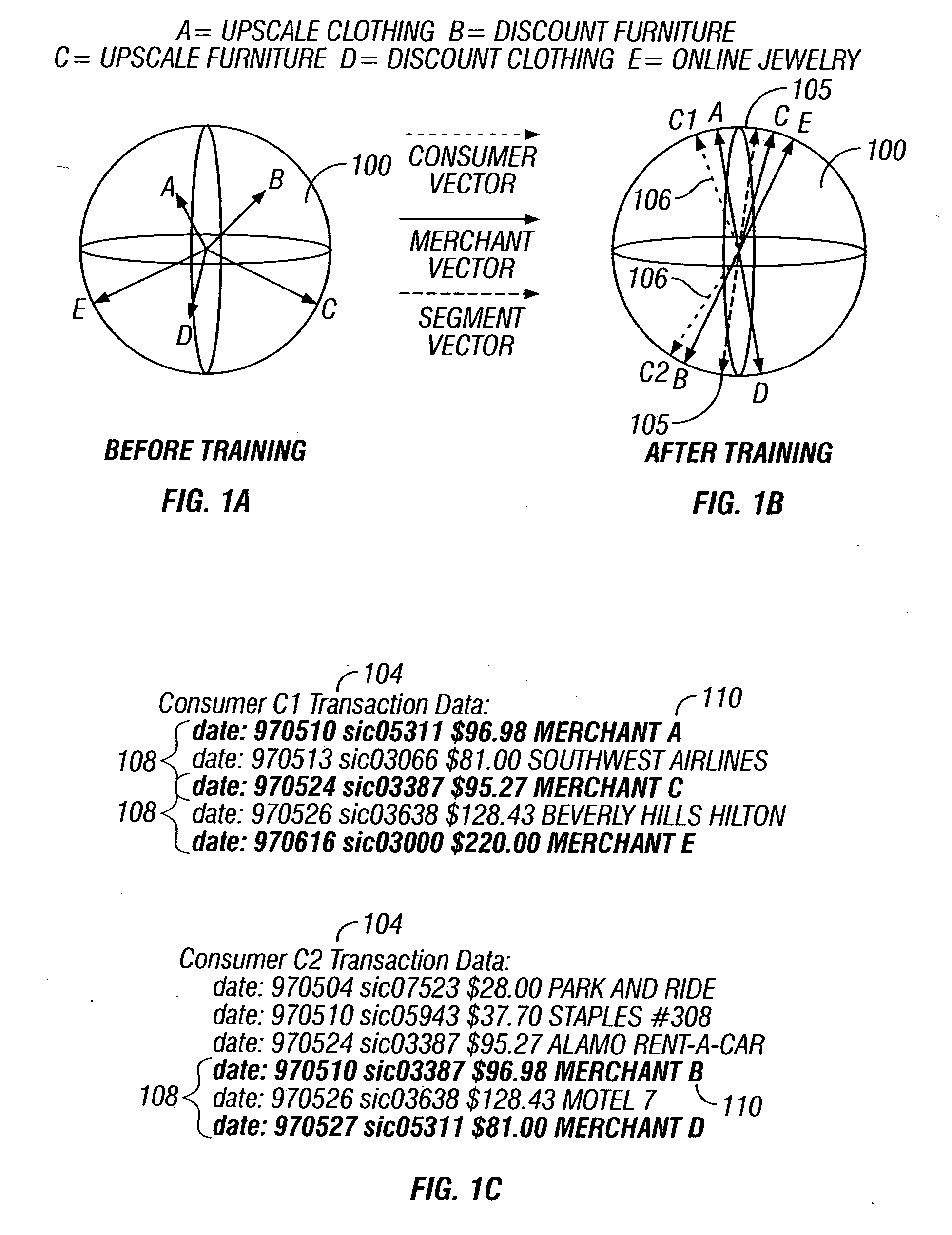
Predictive modeling of consumer financial behavior using supervised segmentation and nearest-neighbor matching
InactiveUS6839682B1Specific accurate targetingIncrease valueDiscounts/incentivesDigital computer detailsPredictive modellingAlgorithm
Predictive modeling of consumer financial behavior, including determination of likely responses to particular marketing efforts, is provided by application of consumer transaction data to predictive models associated with merchant segments. The merchant segments are derived from the consumer transaction data based on co-occurrences of merchants in sequences of transactions. Merchant vectors represent specific merchants, and are aligned in a vector space as a function of the degree to which the merchants co-occur more or less frequently than expected. Consumer vectors are developed within the vector space, to represent interests of particular consumers by virtue of relative vector positions of consumer and merchant vectors. Various techniques, including clustering, supervised segmentation, and nearest-neighbor analysis, are applied separately or in combination to generate improved predictions of consumer behavior.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
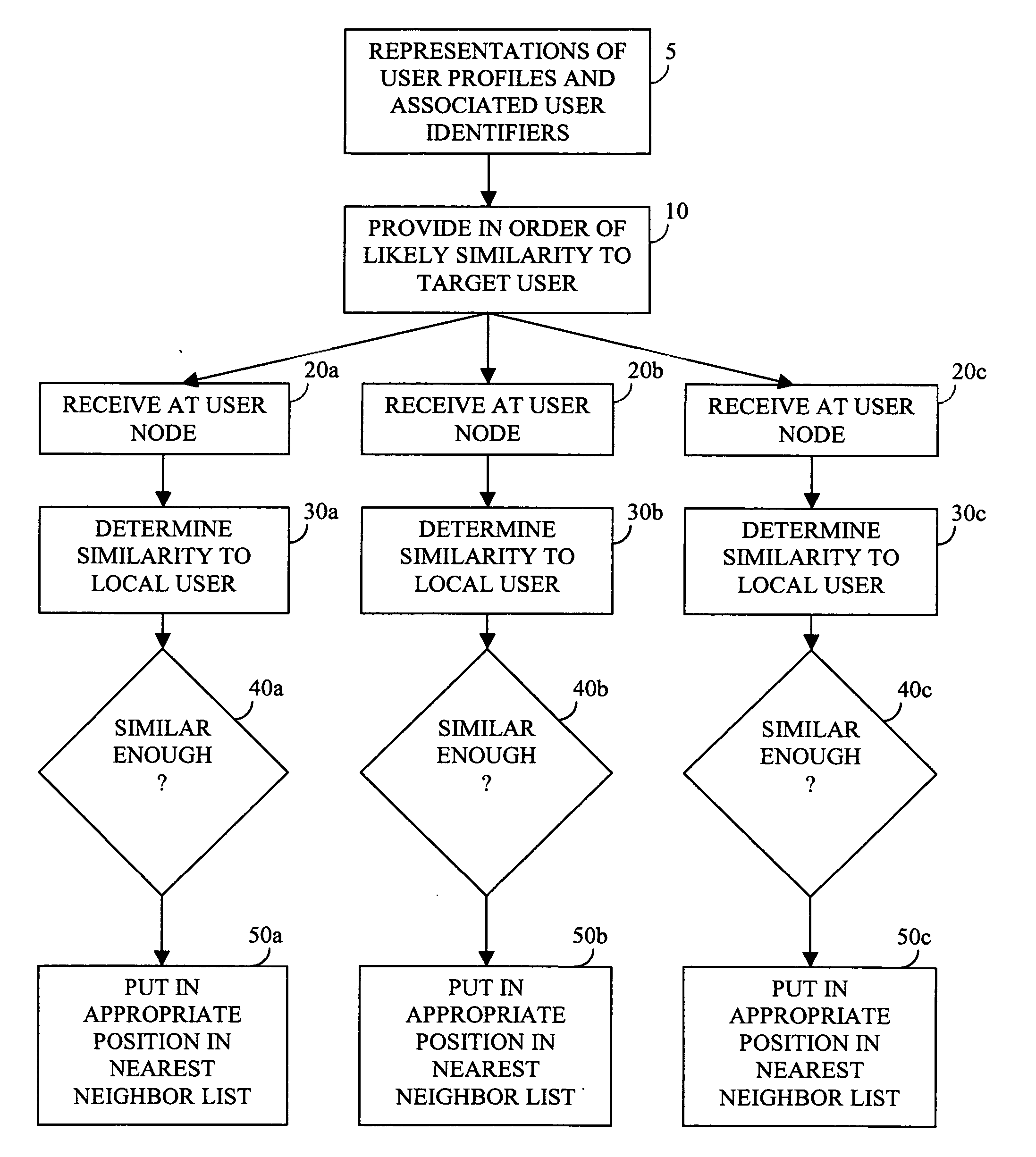
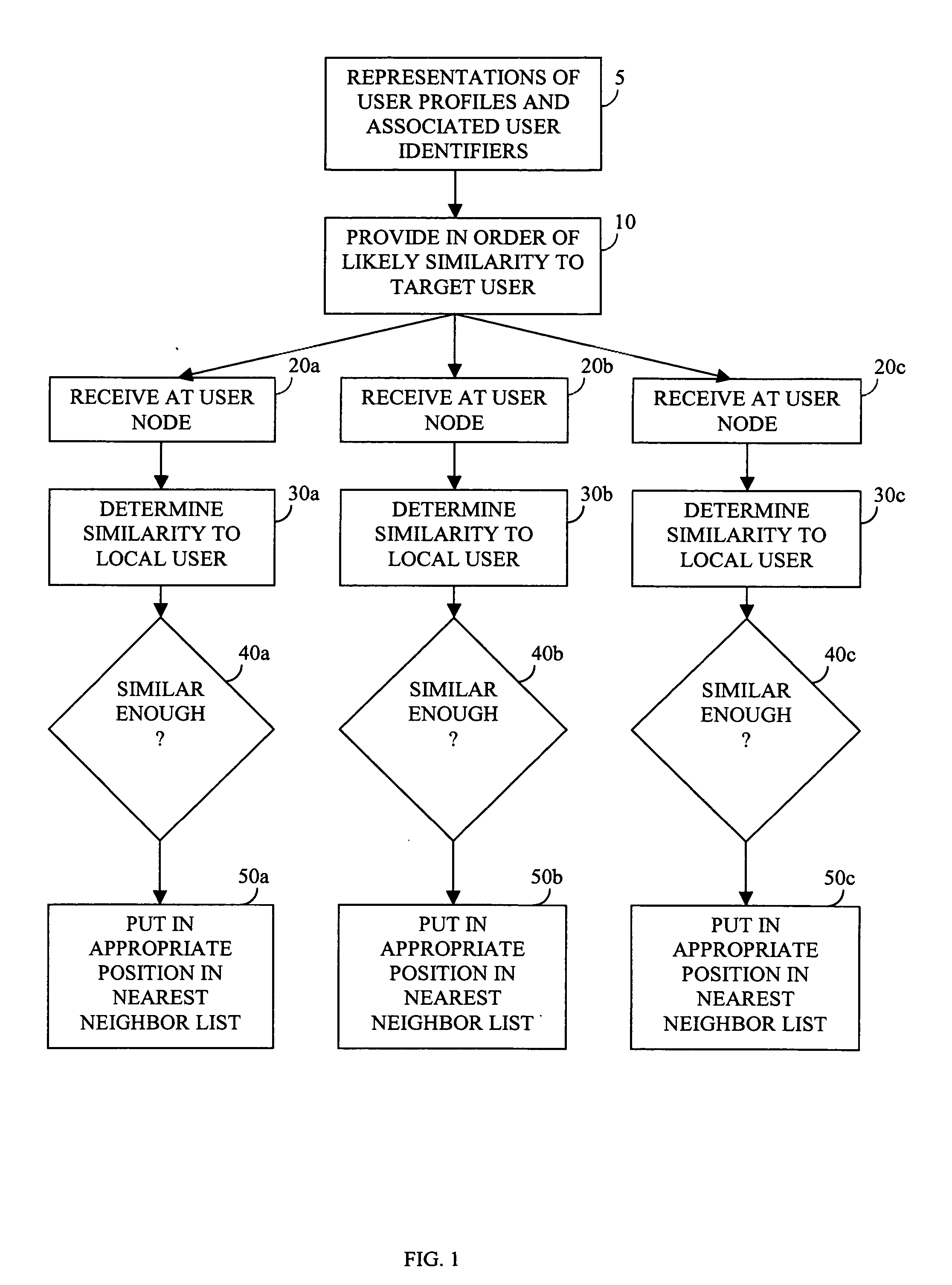
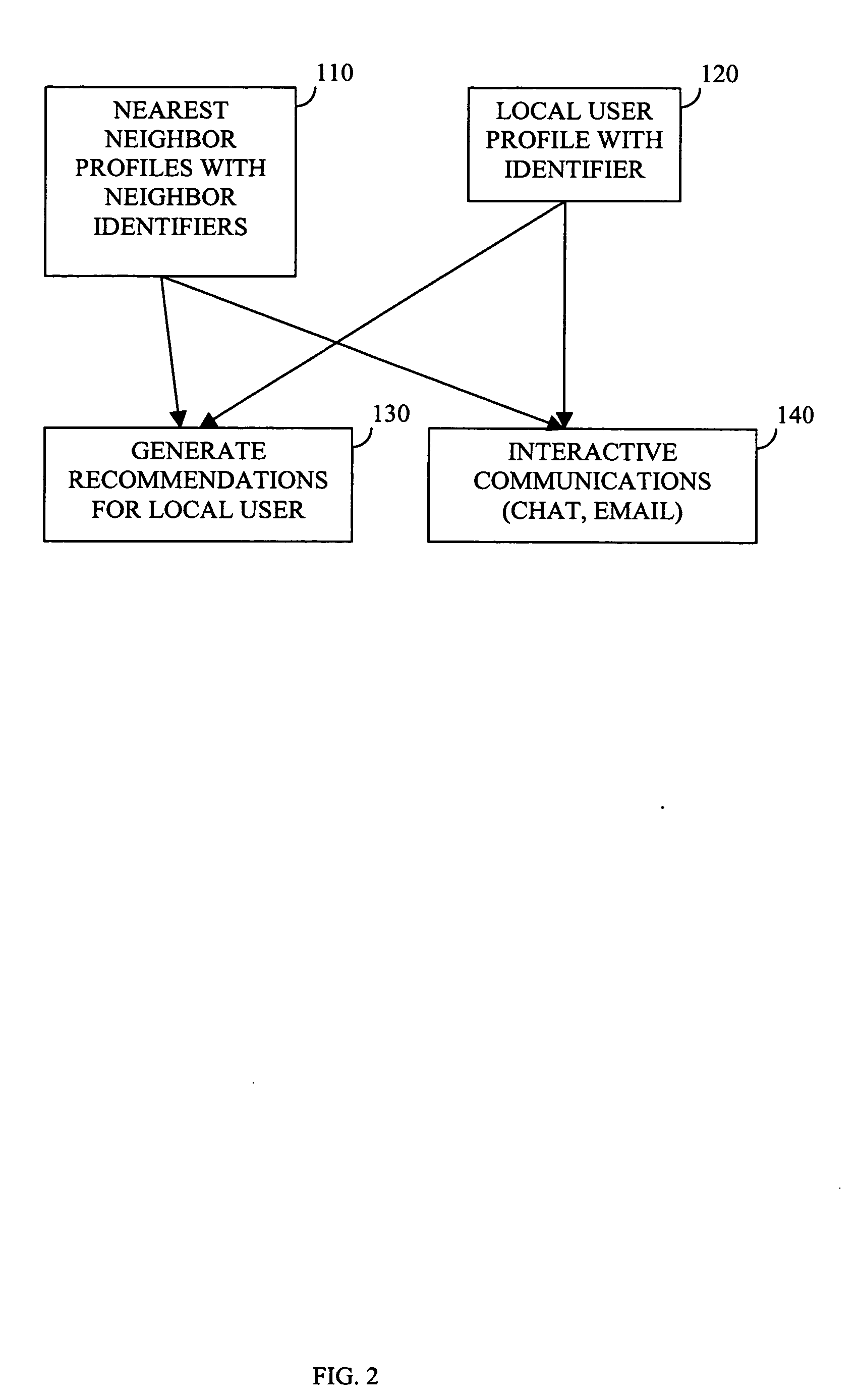
Enabling recommendations and community by massively-distributed nearest-neighbor searching
InactiveUS20060020662A1Reason to have confidenceGreat extremityMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksNear neighborEnd user
The computer associated with each of a potentially large number of end users is harnessed to provide a massively-distributed mechanism for finding the nearest neighbors of each user, according to tastes and / or interests. Once these nearest neighbors are determined, there taste or and / or interest profiles are leveraged for highly accurate recommendations, and their online addresses are leveraged for community purposes.
Owner:EMERGENT MUSIC
Predictive modeling of consumer financial behavior using supervised segmentation and nearest-neighbor matching
InactiveUS20050159996A1Improve efficiencyDiscounts/incentivesSpecial data processing applicationsPredictive modellingCo-occurrence
Predictive modeling of consumer financial behavior, including determination of likely responses to particular marketing efforts, is provided by application of consumer transaction data to predictive models associated with merchant segments. The merchant segments are derived from the consumer transaction data based on co-occurrences of merchants in sequences of transactions. Merchant vectors represent specific merchants, and are aligned in a vector space as a function of the degree to which the merchants co-occur more or less frequently than expected. Supervised segmentation is applied to merchant vectors to form the merchant segments. Merchant segment predictive models provide predictions of spending in each merchant segment for any particular consumer, based on previous spending by the consumer. Consumer profiles describe summary statistics of each consumer's spending in the merchant segments, and across merchant segments. The consumer profiles include consumer vectors derived as summary vectors of selected merchants patronized by the consumer. Predictions of consumer behavior are made by applying nearest-neighbor analysis to consumer vectors, thus facilitating the targeting of promotional offers to consumers most likely to respond positively.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
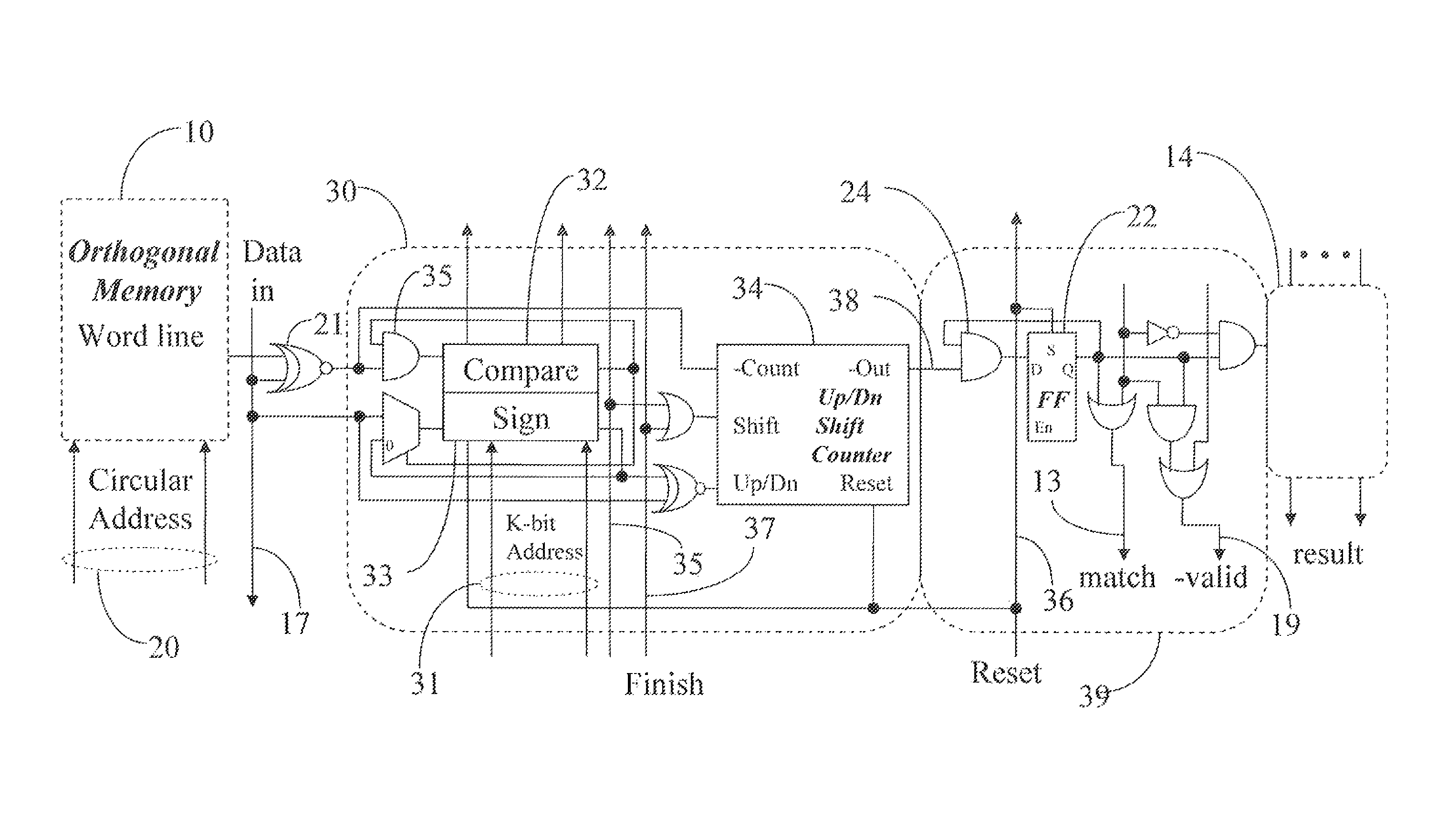
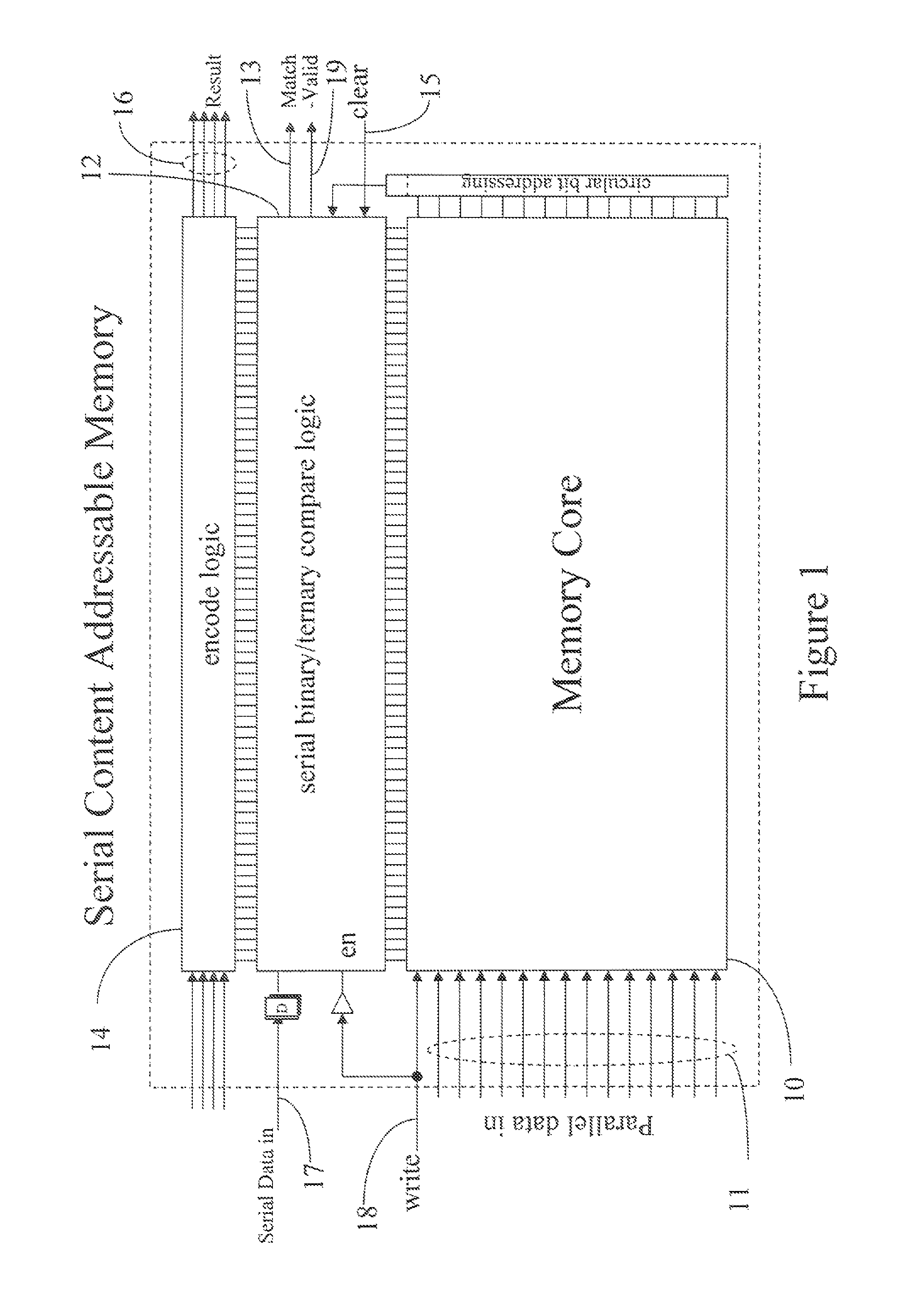
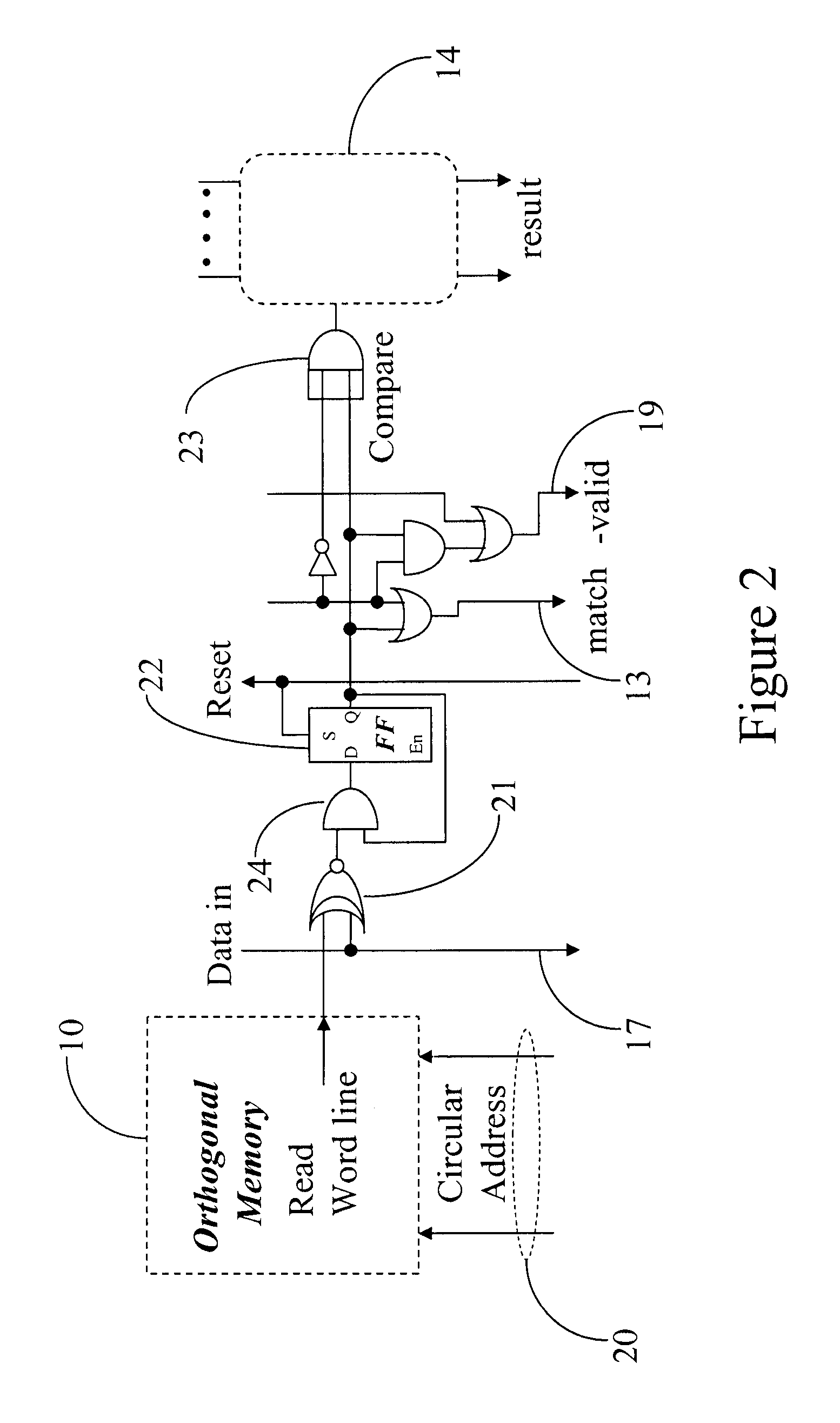
Nearest neighbor serial content addressable memory
A digital design and technique may be used to implement a Manhattan Nearest Neighbor content addressable memory function by augmenting a serial content addressable memory design with additional memory and counters for bit serially accumulating in parallel and subsequently comparing in parallel all the Manhattan distances between a serially inputted vector and all corresponding vectors resident in the CAM. Other distance measures, besides a Manhattan distance, may optionally be used in conjunction with similar techniques and designs.
Owner:COOKE LAURENCE H
Analog processor comprising quantum devices
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
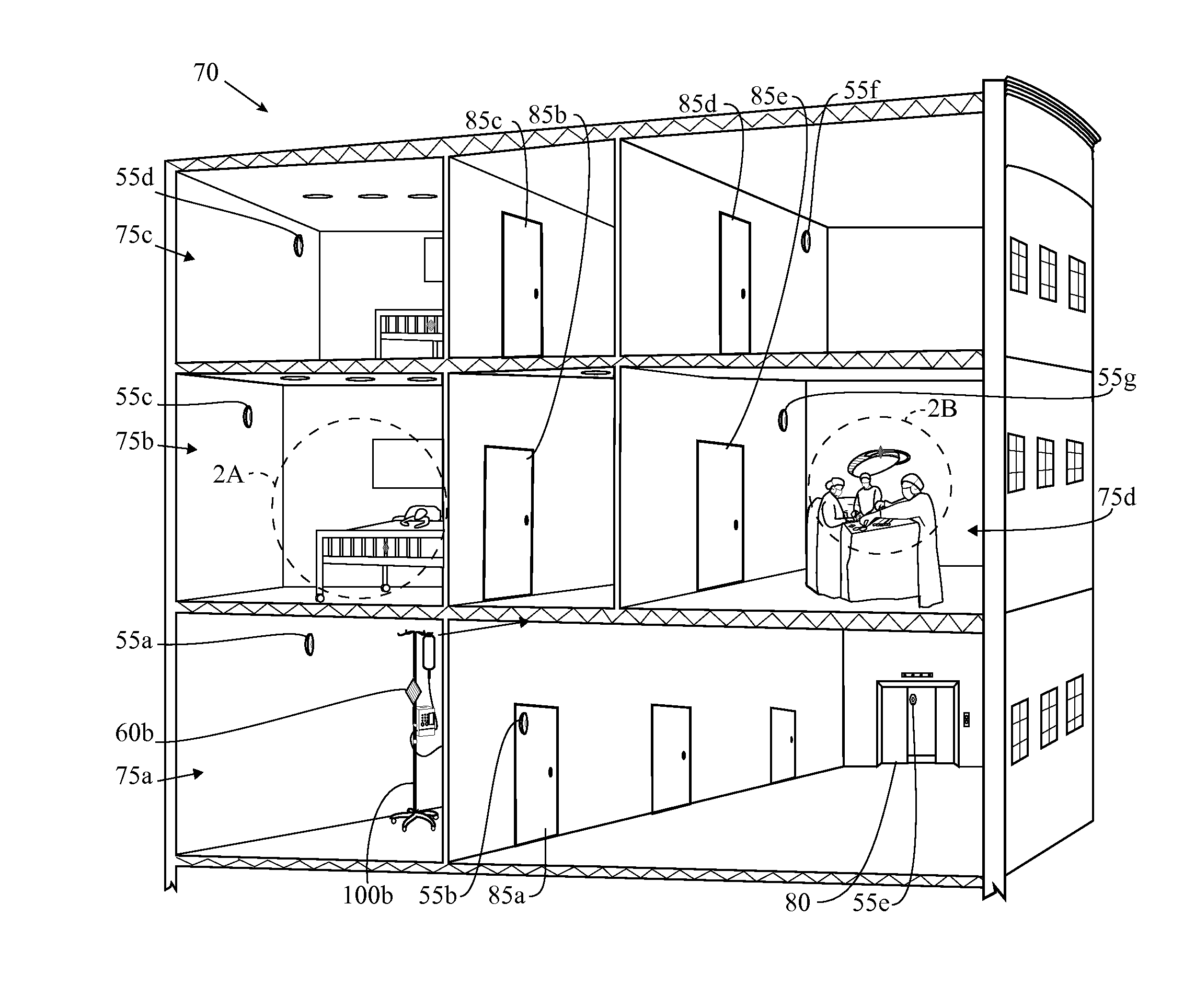
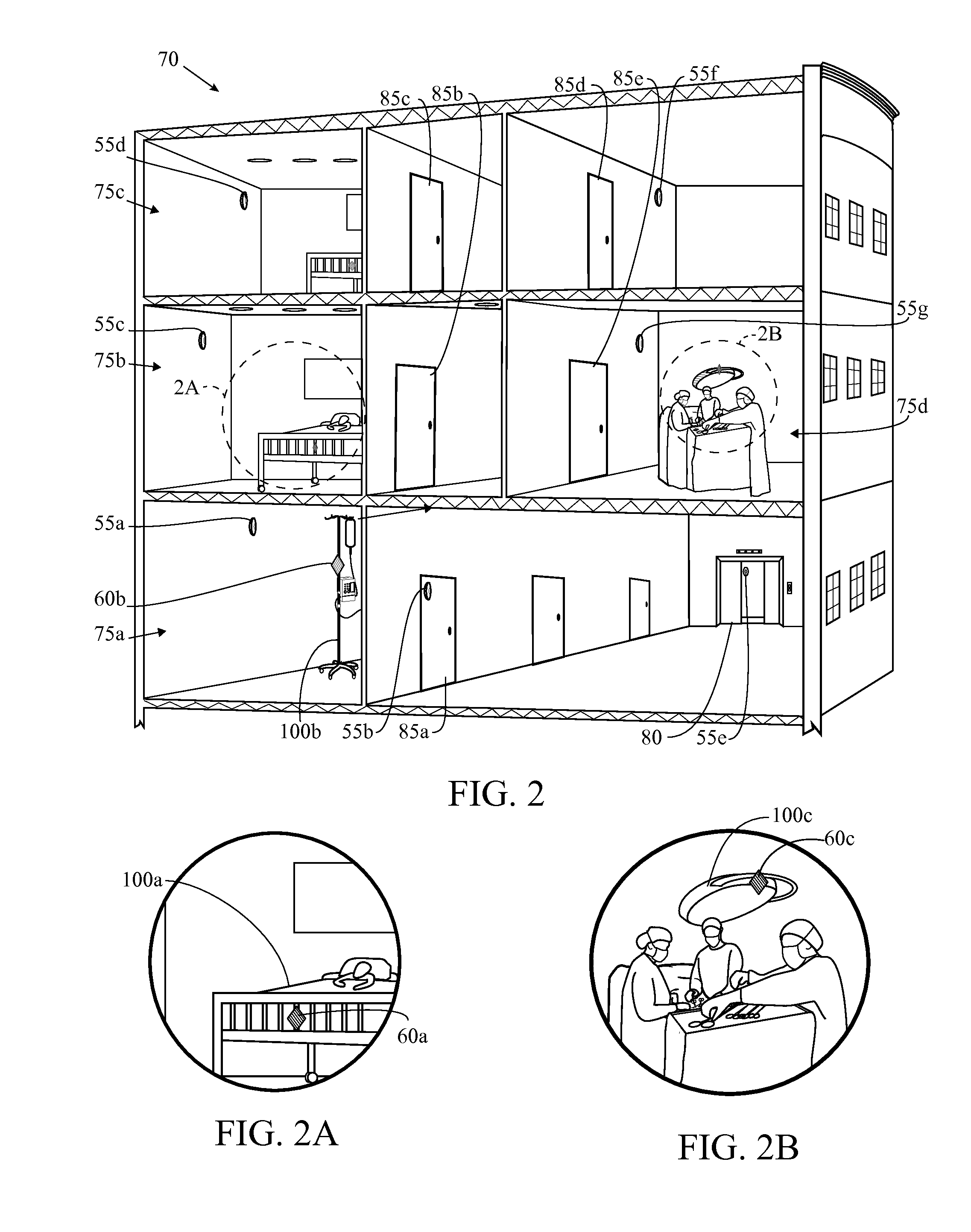
Wireless tracking system and method utilizing multiple location algorithms
The present invention provides a solution to mistaken location calculations based on multipath effects. The present invention determines a real-time location of an object in a facility using a combination of location algorithms, with a signal characteristic for a wireless signal from a communication device attached to the object received at a sensor of a mesh network. The location algorithms preferably include at least two of a proximity algorithm, a radial basis function algorithm, a maximum likelihood algorithm, a genetic algorithm, a minimum mean squared error algorithm, a radiofrequency fingerprinting algorithm, a multilateration algorithm, a time difference of arrival algorithm, a signal strength algorithm, a time of arrival algorithm, an angle of arrival algorithm, a spatial diversity algorithm, and a nearest neighbor algorithm.
Owner:CENTRAK INC
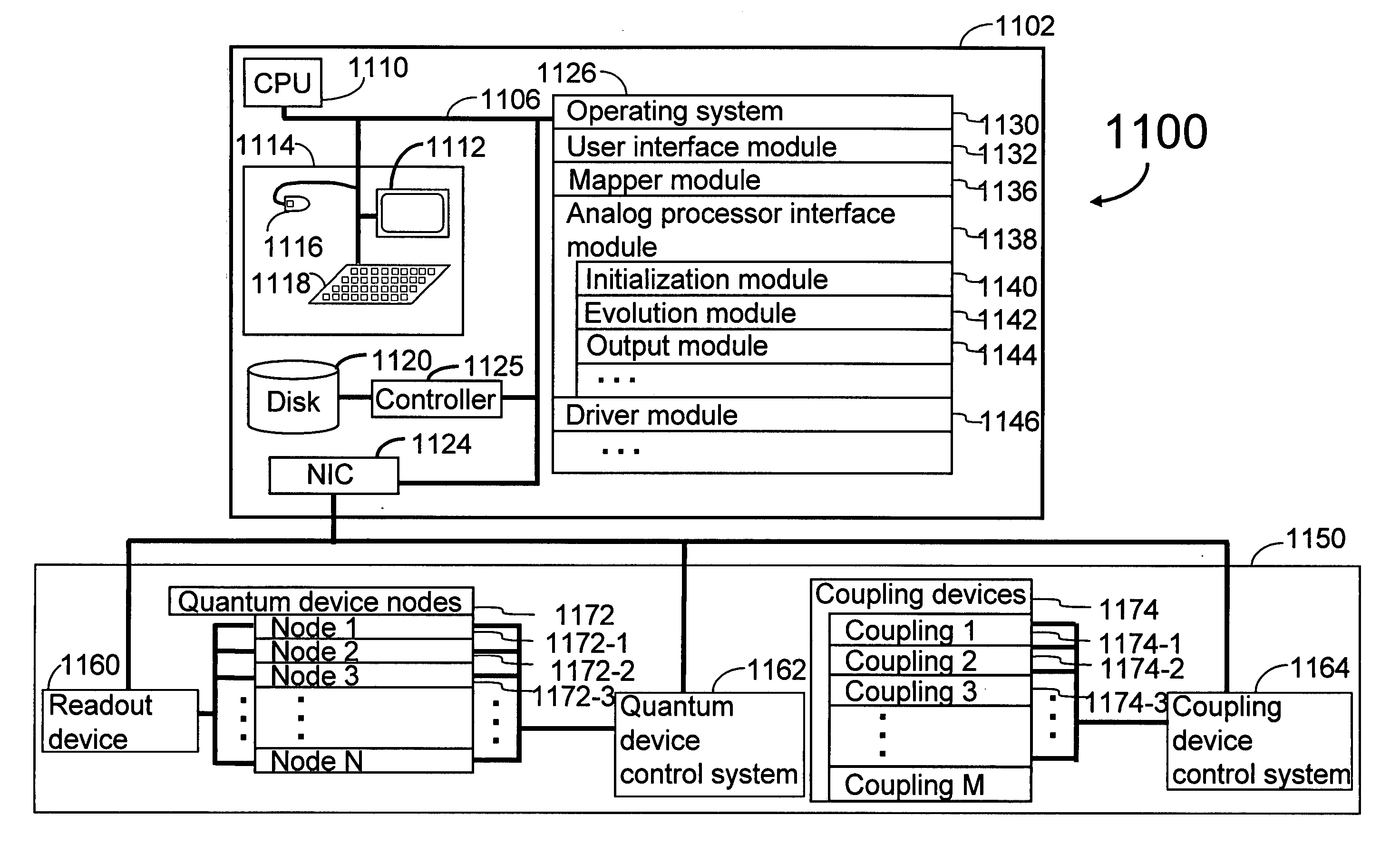
Analog processor comprising quantum devices
Analog processors for solving various computational problems are provided. Such analog processors comprise a plurality of quantum devices, arranged in a lattice, together with a plurality of coupling devices. The analog processors further comprise bias control systems each configured to apply a local effective bias on a corresponding quantum device. A set of coupling devices in the plurality of coupling devices is configured to couple nearest-neighbor quantum devices in the lattice. Another set of coupling devices is configured to couple next-nearest neighbor quantum devices. The analog processors further comprise a plurality of coupling control systems each configured to tune the coupling value of a corresponding coupling device in the plurality of coupling devices to a coupling. Such quantum processors further comprise a set of readout devices each configured to measure the information from a corresponding quantum device in the plurality of quantum devices.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Audio spatialization and environment simulation
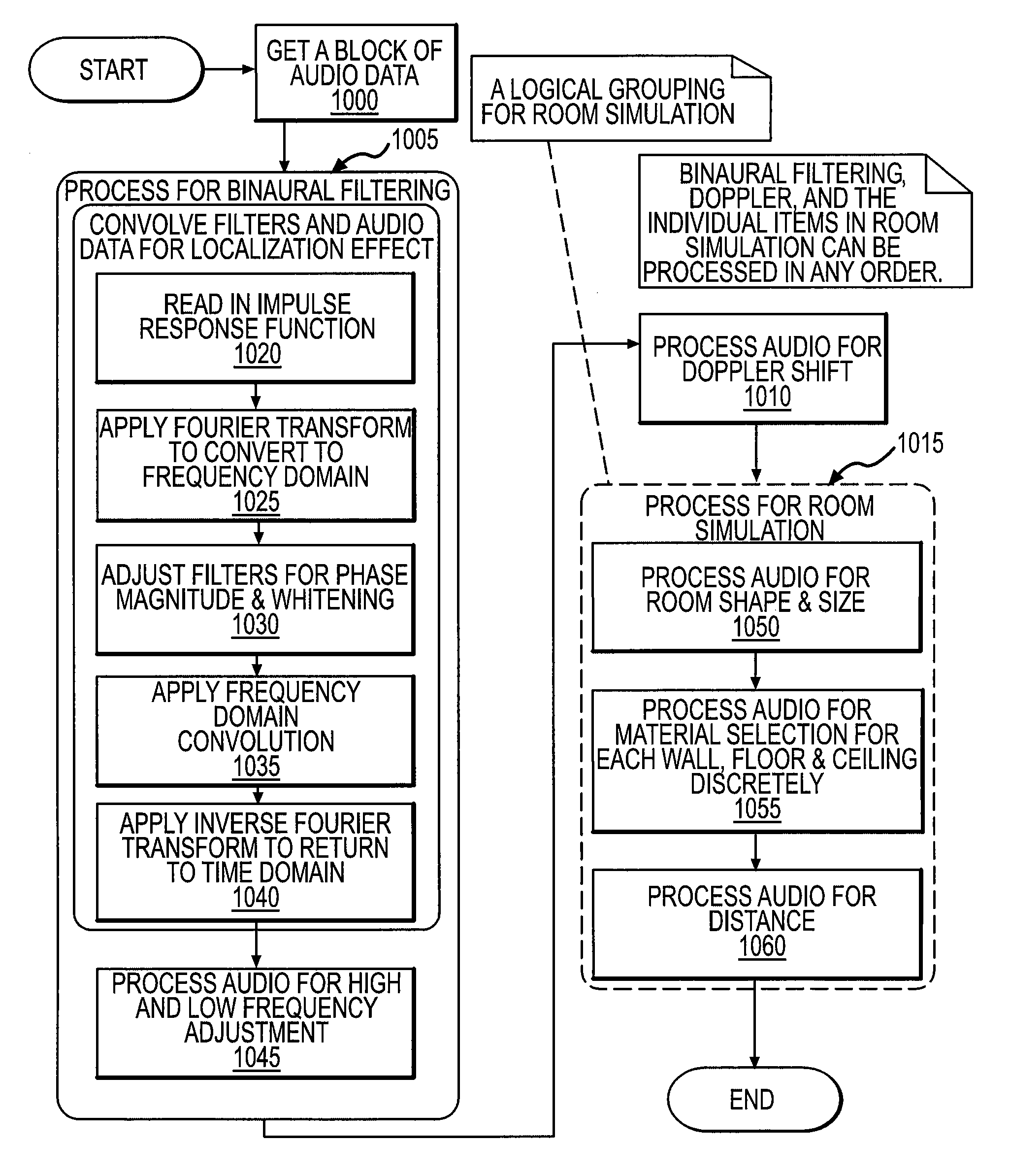
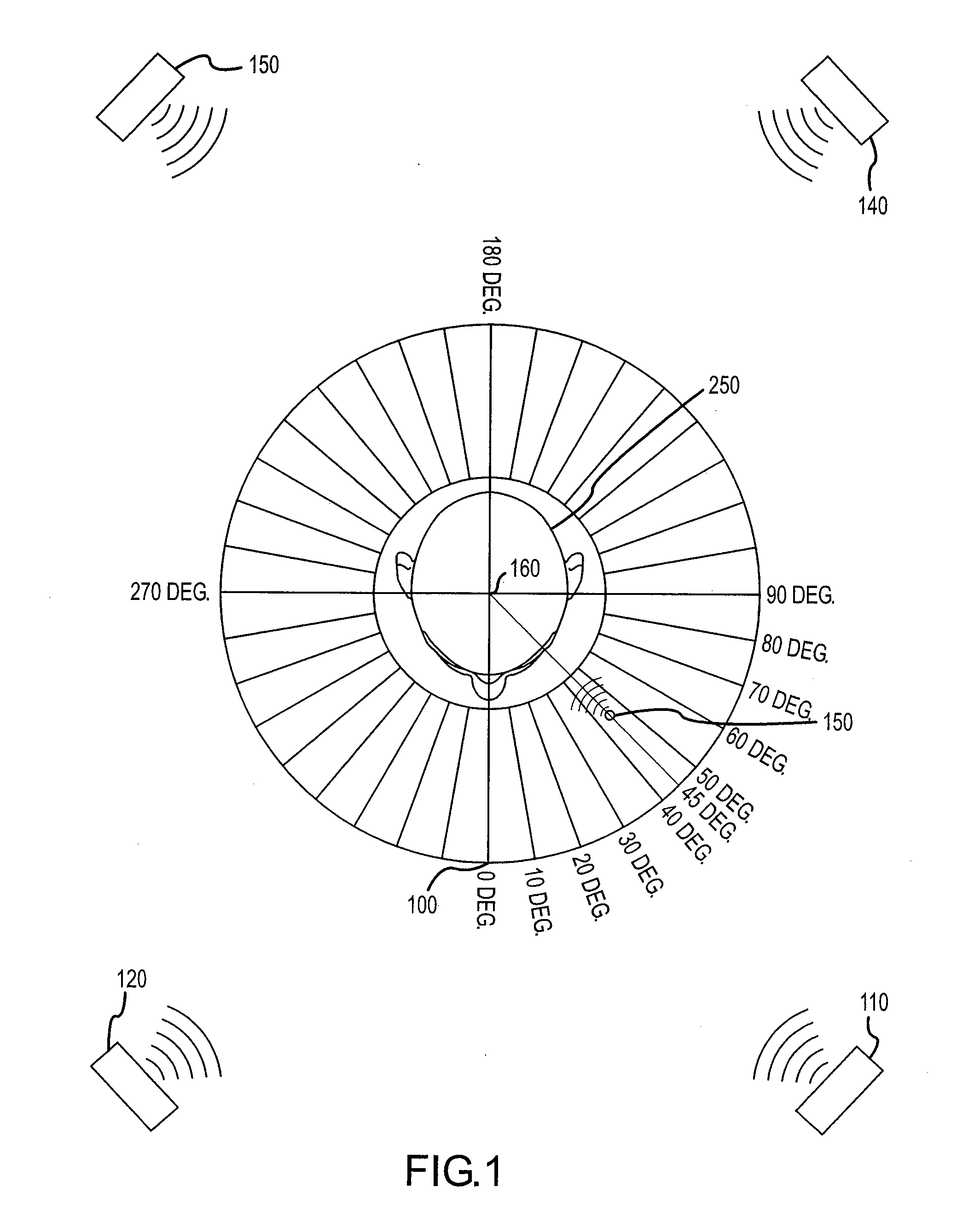
InactiveUS20090046864A1Accurate audio spatializationAccurate transfer functionHeadphones for stereophonic communicationStereophonic circuit arrangementsSound sourcesTime segment
A method and apparatus for processing an audio sound source to create four-dimensional spatialized sound. A virtual sound source may be moved along a path in three-dimensional space over a specified time period to achieve four-dimensional sound localization. A binaural filter for a desired spatial point is applied to the audio waveform to yield a spatialized waveform that, when the spatialized waveform is played from a pair of speakers, the sound appears to emanate from the chosen spatial point instead of the speakers. A binaural filter for a spatial point is simulated by interpolating nearest neighbor binaural filters chosen from a plurality of pre-defined binaural filters. The audio waveform may be processed digitally in overlapping blocks of data using a Short-Time Fourier transform. The localized sound may be further processed for Doppler shift and room simulation.
Owner:GENAUDIO
Digital camera system containing a VLIW vector processor
InactiveUS6879341B1Material nanotechnologyTelevision system detailsCrossbar switchArithmetic logic unit
A digital camera has a sensor for sensing an image, a processor for modifying the sensed image in accordance with instructions input into the camera and an output for outputting the modified image where the processor includes a series of processing elements arranged around a central crossbar switch. The processing elements include an Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) acting under the control of a writeable microcode store, an internal input and output FIFO for storing pixel data to be processed by the processing elements and the processor is interconnected to a read and write FIFO for reading and writing pixel data of images to the processor. Each of the processing elements can be arranged in a ring and each element is also separately connected to its nearest neighbors. The ALU receives a series of inputs interconnected via an internal crossbar switch to a series of core processing units within the ALU and includes a number of internal registers for the storage of temporary data. The core processing units can include at least one of a multiplier, an adder and a barrel shifter. The processing elements are further connected to a common data bus for the transfer of a pixel data to the processing elements and the data bus is interconnected to a data cache which acts as an intermediate cache between the processing elements and a memory store for storing the images.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and system for communicating with and tracking RFID transponders
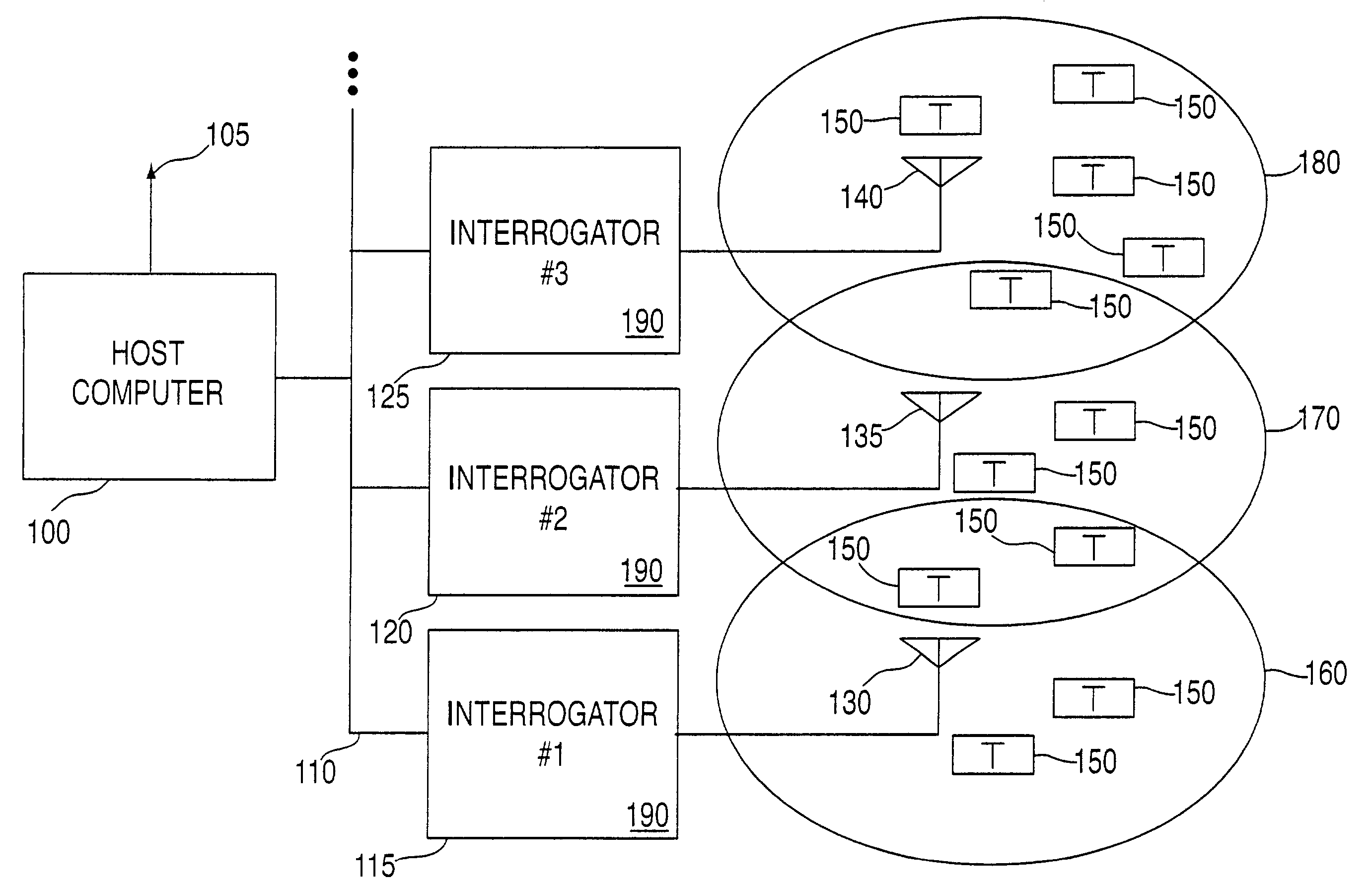
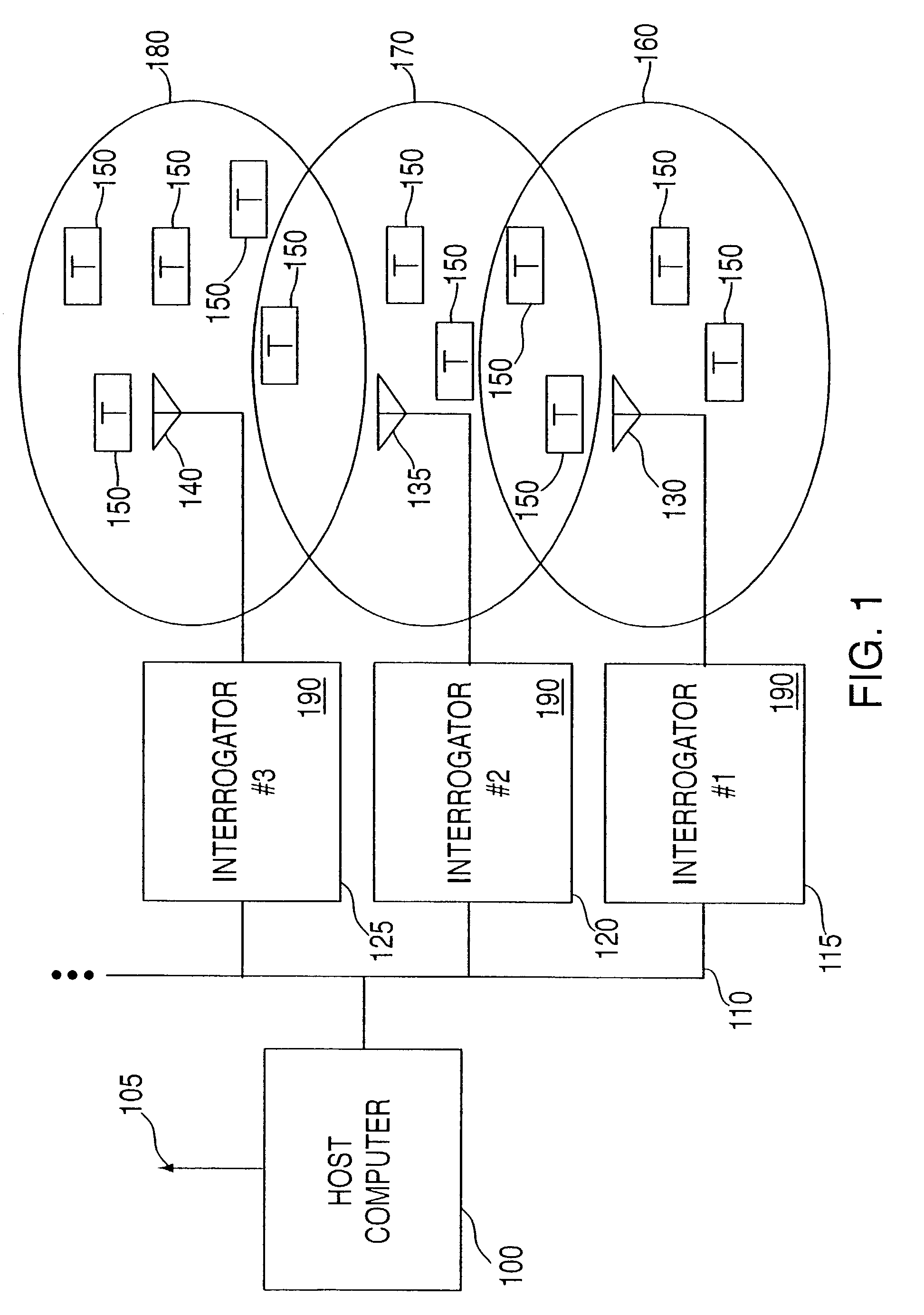
ActiveUS7253717B2Reduce the valueMemory record carrier reading problemsCo-operative working arrangementsNear neighborNumber generator
An RFID system and method for communicating between a host computer, one or more interrogators connected to the host computer, and a large body of transponders distributed within an area covered by the interrogators. Each transponder originally has a common identification code, and upon initialization by the host computer internally generates a unique identification code based upon an internally generated random number. The host, through the interrogators, reads each of the identification codes associated with each transponder by iteratively transmitting a read identification code command along with a controlled variable. Each transponder compares the received controlled variable to an internally generated random number, and selectively transmits its identification code based upon the outcome of this comparison. After the completion of each read identification code iteration, the host adjusts the controlled variable based upon the responses received in the previous iteration. Preferably, communications between the interrogators and the transponders are DSSS signals in TDMA format, and the transponders use the random number generator to assign a time slot for transmission of their response. Each interrogator includes an antenna system utilizing a switch matrix to connect multiple antennas having different polarizations, which ensures that all transponders within the range of the interrogator receive the signals from the interrogator. In a further aspect, the interrogators are arranged in groups, each group in nearest neighbor format, to reduce the time for reading the transponders and the emissions generated when more than one interrogator is active at the same time.
Owner:TERRESTRIAL COMMS LLC
Multi-image feature matching using multi-scale oriented patches
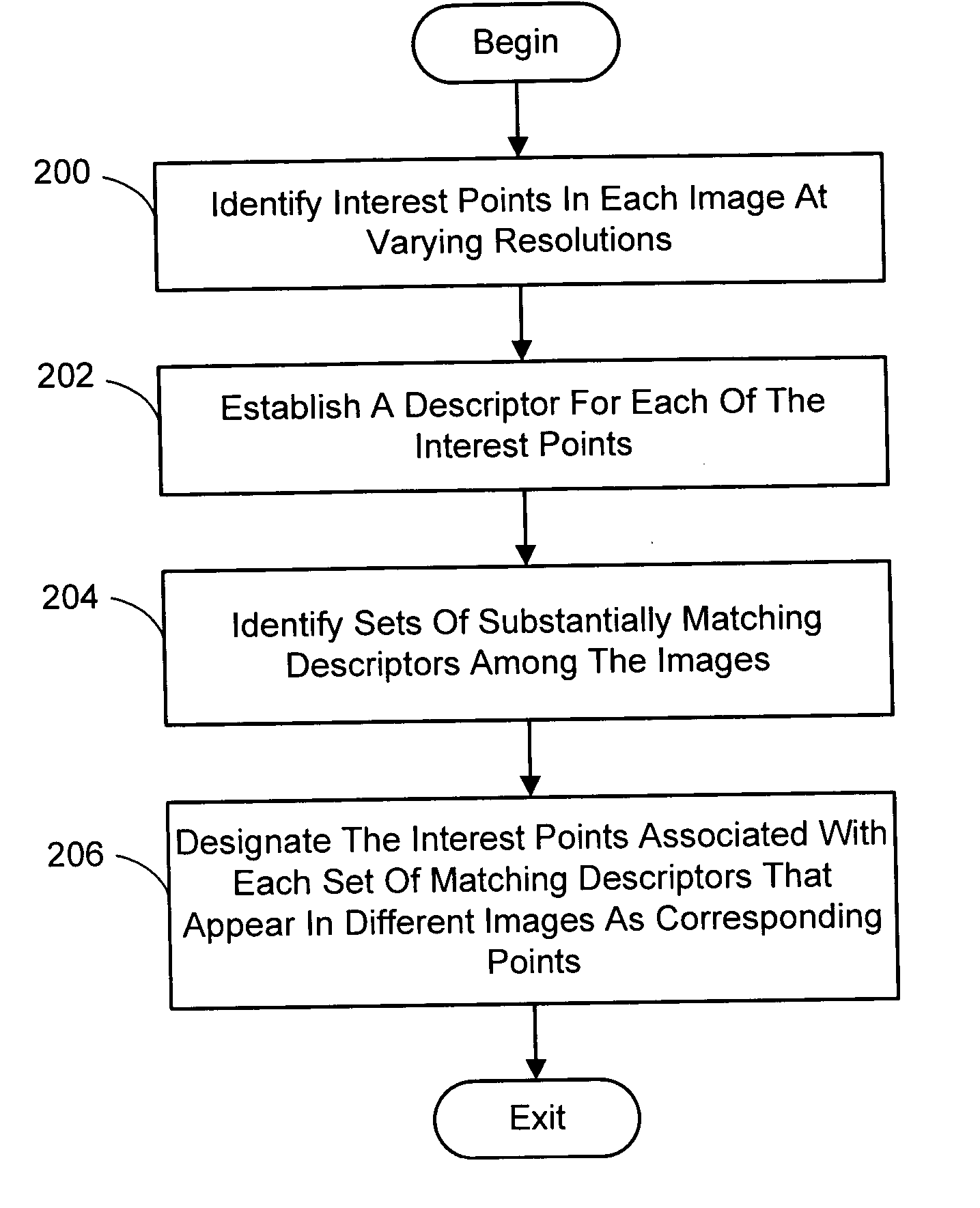
InactiveUS20050238198A1Quick extractionEasy to liftConveyorsImage analysisPattern recognitionNear neighbor
A system and process for identifying corresponding points among multiple images of a scene is presented. This involves a multi-view matching framework based on a new class of invariant features. Features are located at Harris corners in scale-space and oriented using a blurred local gradient. This defines a similarity invariant frame in which to sample a feature descriptor. The descriptor actually formed is a bias / gain normalized patch of intensity values. Matching is achieved using a fast nearest neighbor procedure that uses indexing on low frequency Haar wavelet coefficients. A simple 6 parameter model for patch matching is employed, and the noise statistics are analyzed for correct and incorrect matches. This leads to a simple match verification procedure based on a per feature outlier distance.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
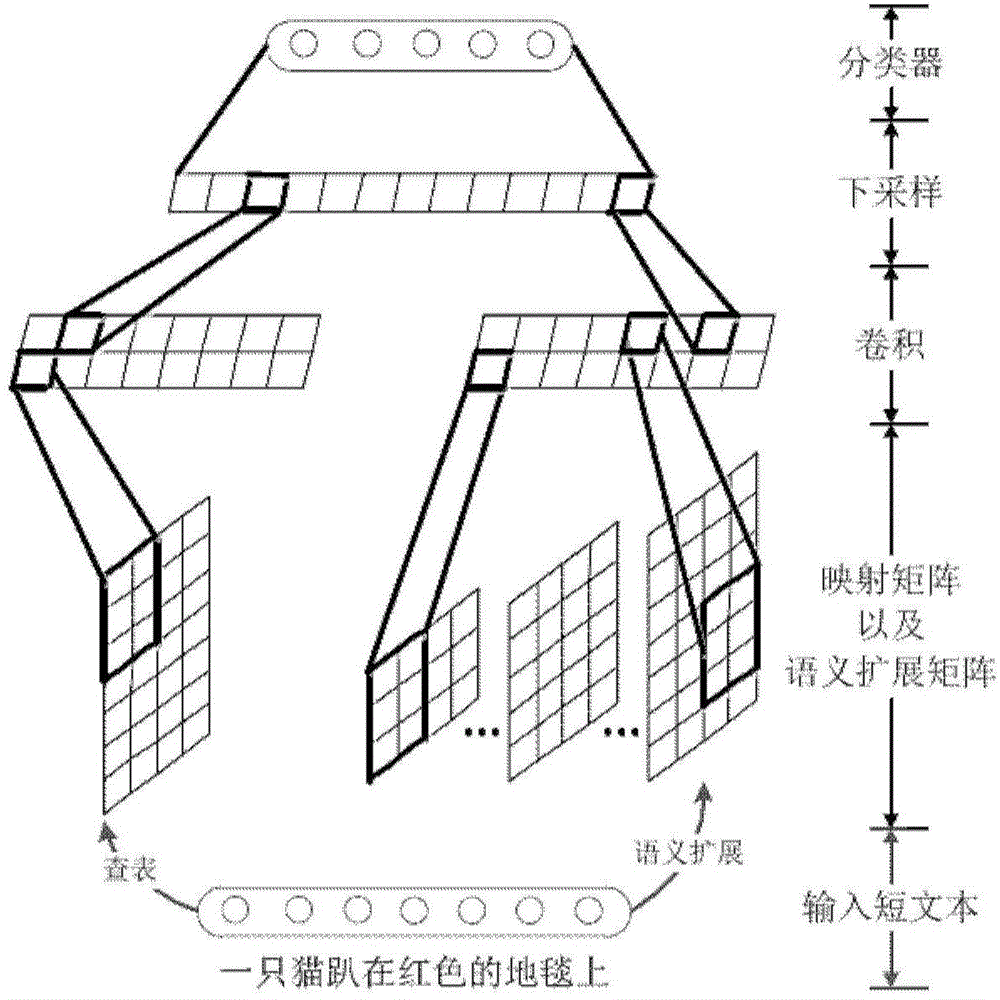
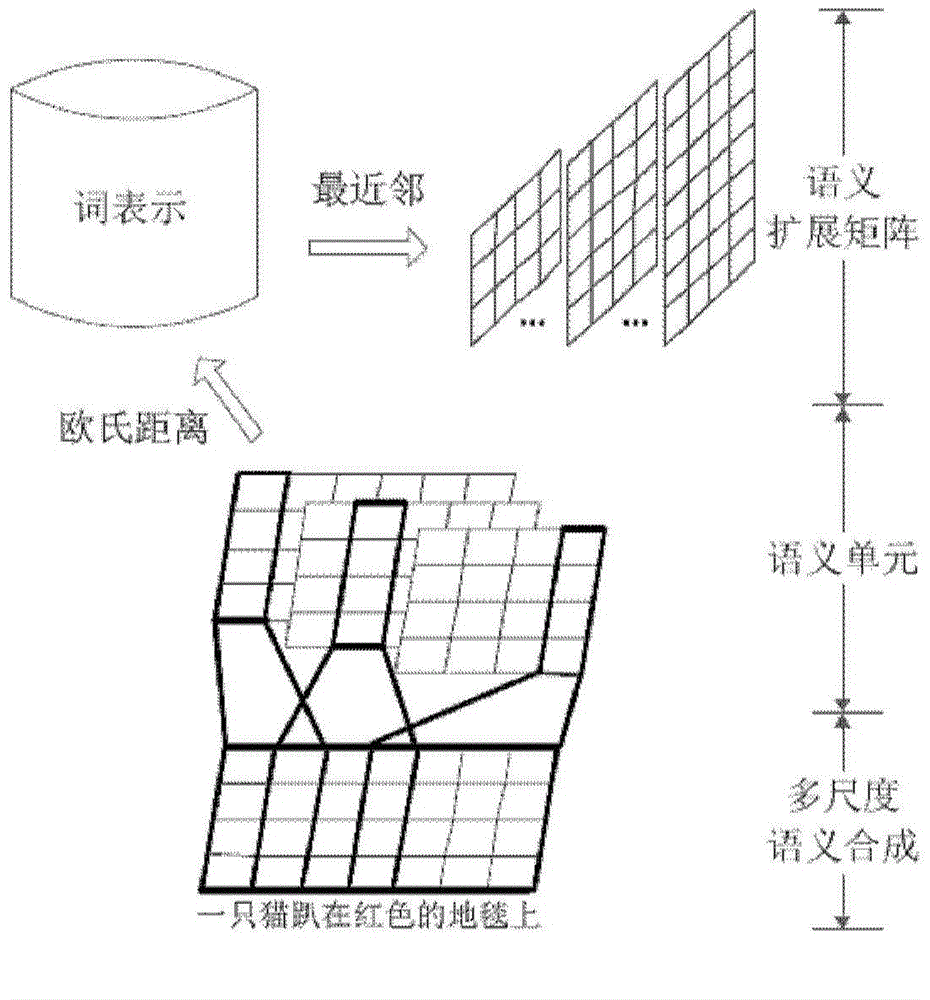
Short text classification method based on convolution neutral network
ActiveCN104834747AImprove semantic sensitivity issuesImprove classification performanceInput/output for user-computer interactionBiological neural network modelsNear neighborClassification methods
The invention discloses a short text classification method based on a convolution neutral network. The convolution neutral network comprises a first layer, a second layer, a third layer, a fourth layer and a fifth layer. On the first layer, multi-scale candidate semantic units in a short text are obtained; on the second layer, Euclidean distances between each candidate semantic unit and all word representation vectors in a vector space are calculated, nearest-neighbor word representations are found, and all the nearest-neighbor word representations meeting a preset Euclidean distance threshold value are selected to construct a semantic expanding matrix; on the third layer, multiple kernel matrixes of different widths and different weight values are used for performing two-dimensional convolution calculation on a mapping matrix and the semantic expanding matrix of the short text, extracting local convolution features and generating a multi-layer local convolution feature matrix; on the fourth layer, down-sampling is performed on the multi-layer local convolution feature matrix to obtain a multi-layer global feature matrix, nonlinear tangent conversion is performed on the global feature matrix, and then the converted global feature matrix is converted into a fixed-length semantic feature vector; on the fifth layer, a classifier is endowed with the semantic feature vector to predict the category of the short text.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Automatic labeling of unlabeled text data
InactiveUS6697998B1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsNearest neighbour algorithmNear neighbor
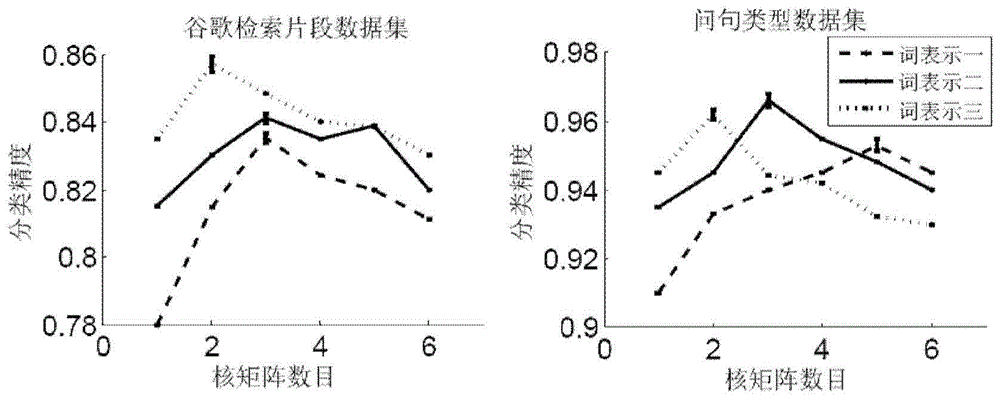
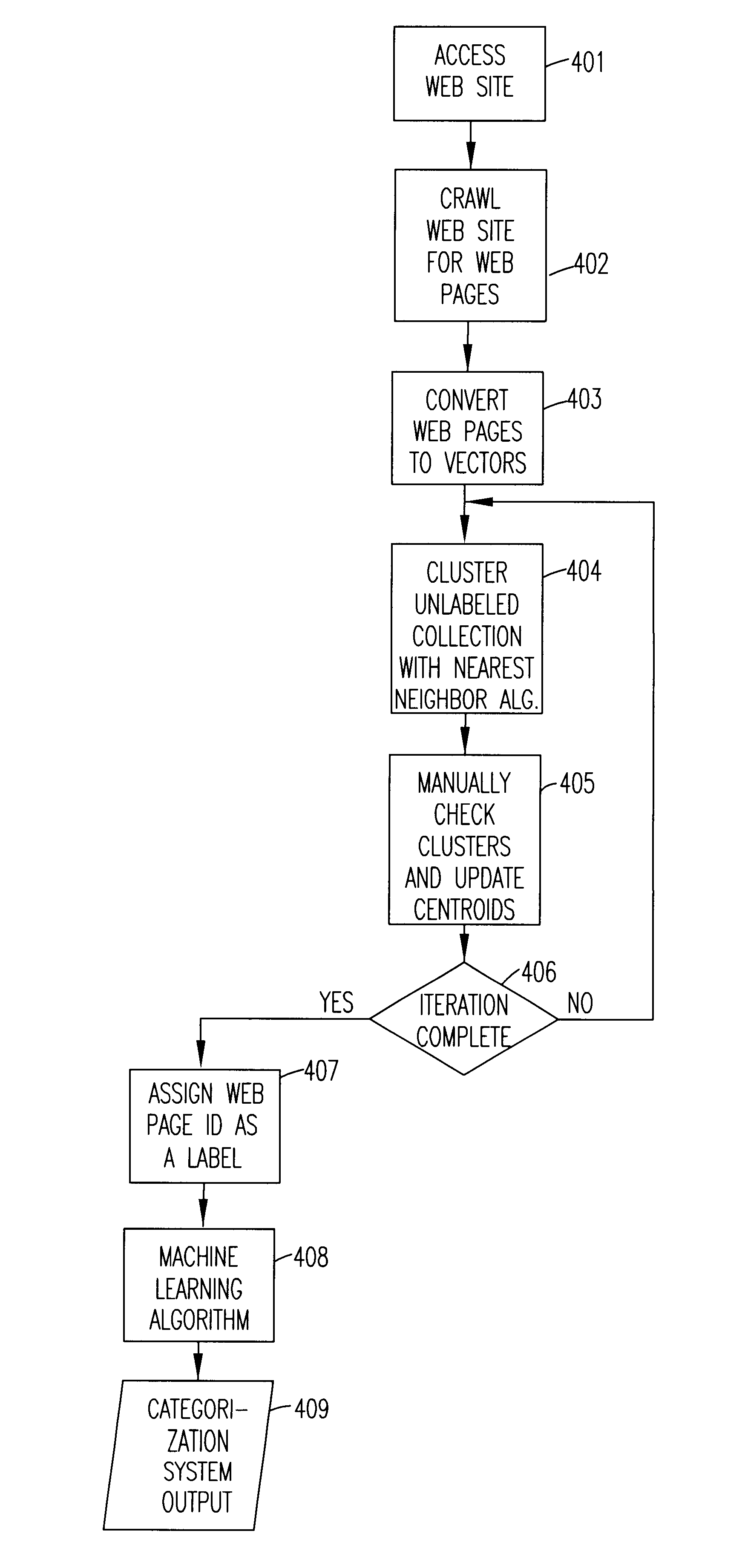
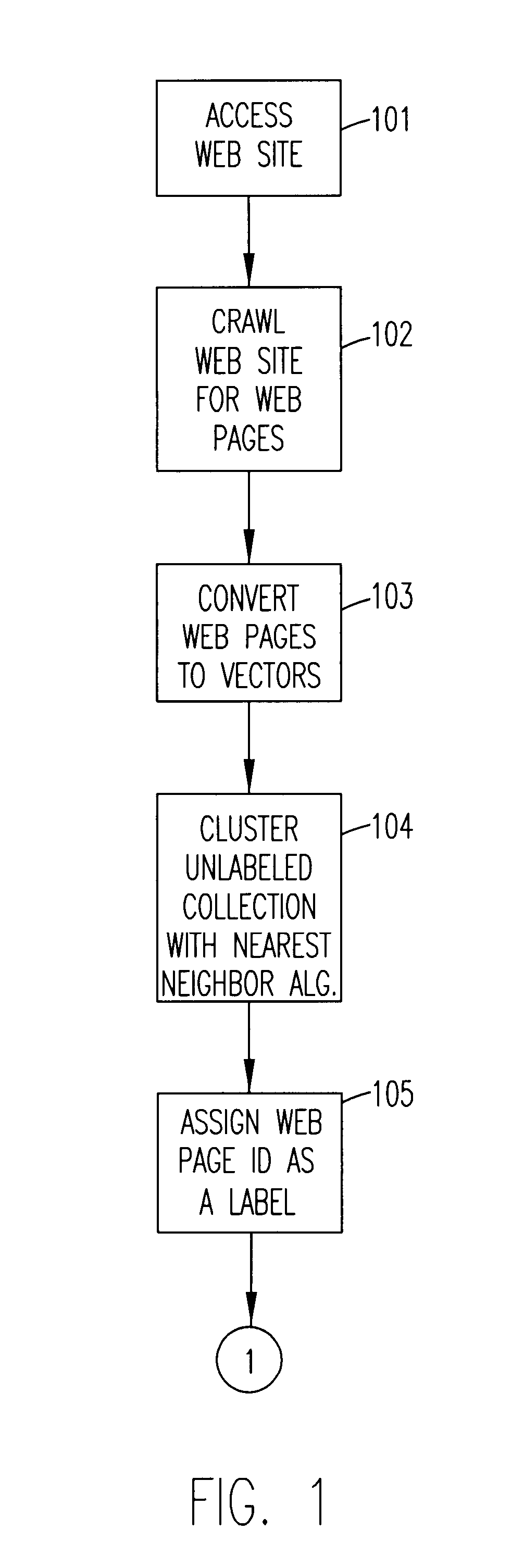
A method of automatically labeling of unlabeled text data can be practiced independent of human intervention, but that does not preclude manual intervention. The method can be used to extract relevant features of unlabeled text data for a keyword search. The method of automated labeling of unlabeled text data uses a document collection as a reference answer set. Members of the answer set are converted to vectors representing centroids of unknown groups of unlabeled text data. Unlabeled text data are clustered relative to the centroids by a nearest neighbor algorithm and the ID of the relevant answer is assigned to all documents in the cluster. At this point in the process, a supervised machine learning algorithm is trained on labeled data, and a classifier for assigning labels to new text data is output. Alternatively, a feature extraction algorithm may be run on classes generated by the step of clustering, and search features output which index the unlabeled text data.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Multi-resolution graph-based clustering
InactiveUS6295504B1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingCharacter and pattern recognitionReference sampleData set
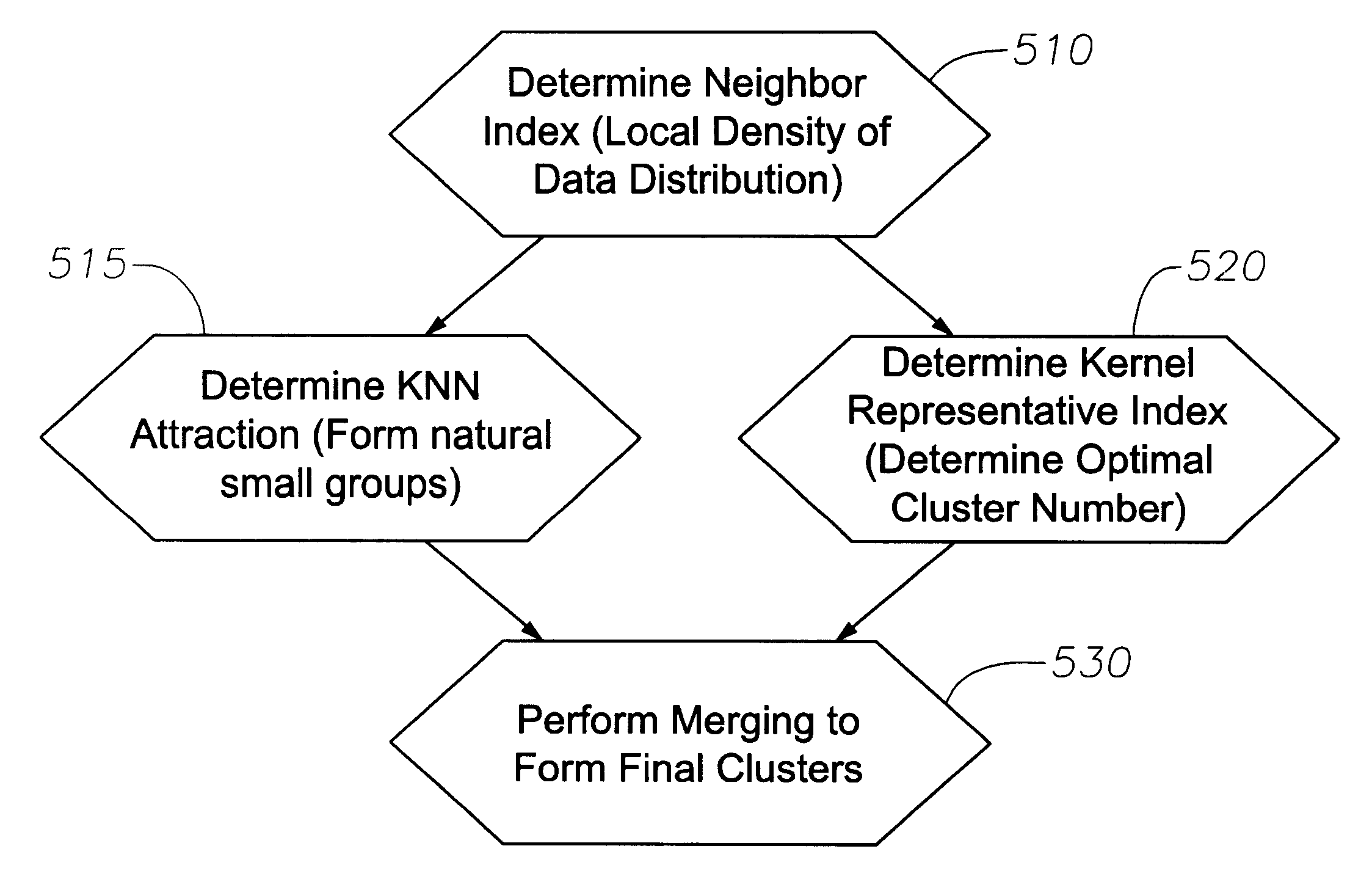
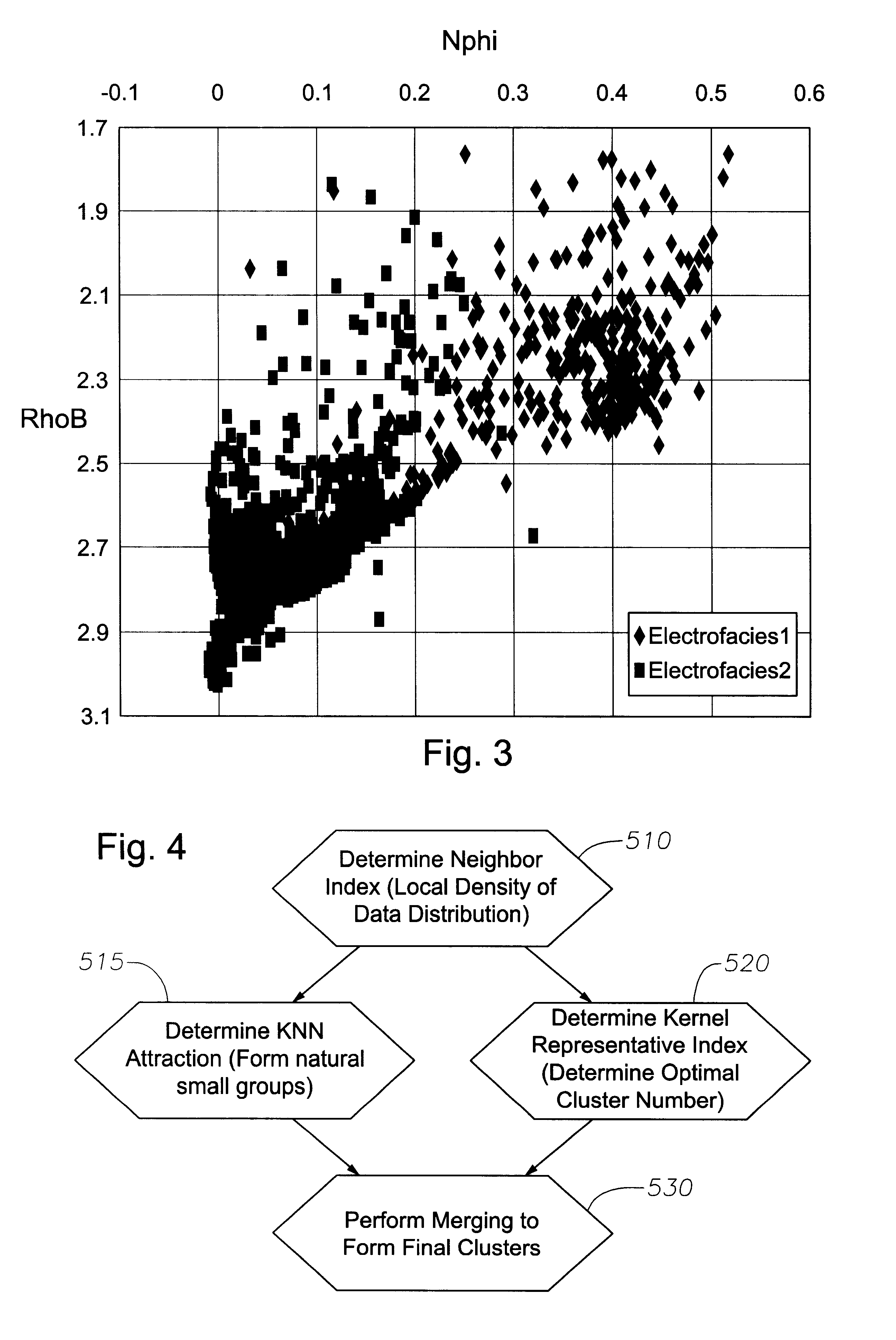
An apparatus and method for obtaining facies of geological formations for identifying mineral deposits is disclosed. Logging instruments are moved in a bore hole to produce log measurements at successive levels of the bore hole. The set of measurements at each such level of the bore hole interval is associated with reference sample points within a multidimensional space. The multidimensional scatter of sample points thus obtained is analyzed to determine a set of characteristic modes. The sample points associated with characteristic modes are grouped to identify clusters. A facies is designated for each of the clusters and a graphic representation of the succession of facies as a function of the depth is thus obtained. To identify the clusters, a "neighboring index" of each log measurement point in the data set is calculated. Next, small natural groups of points are formed based on the use of the neighboring index to determine a K-Nearest-Neighbor (KNN) attraction for each point. Independently of the natural group formation, an optimal number of clusters is calculated based on a Kernel Representative Index (KRI) and based on a user-specified resolution. Lastly, based on the data calculated from the prior steps, final clusters are formed by merging the smaller clusters.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
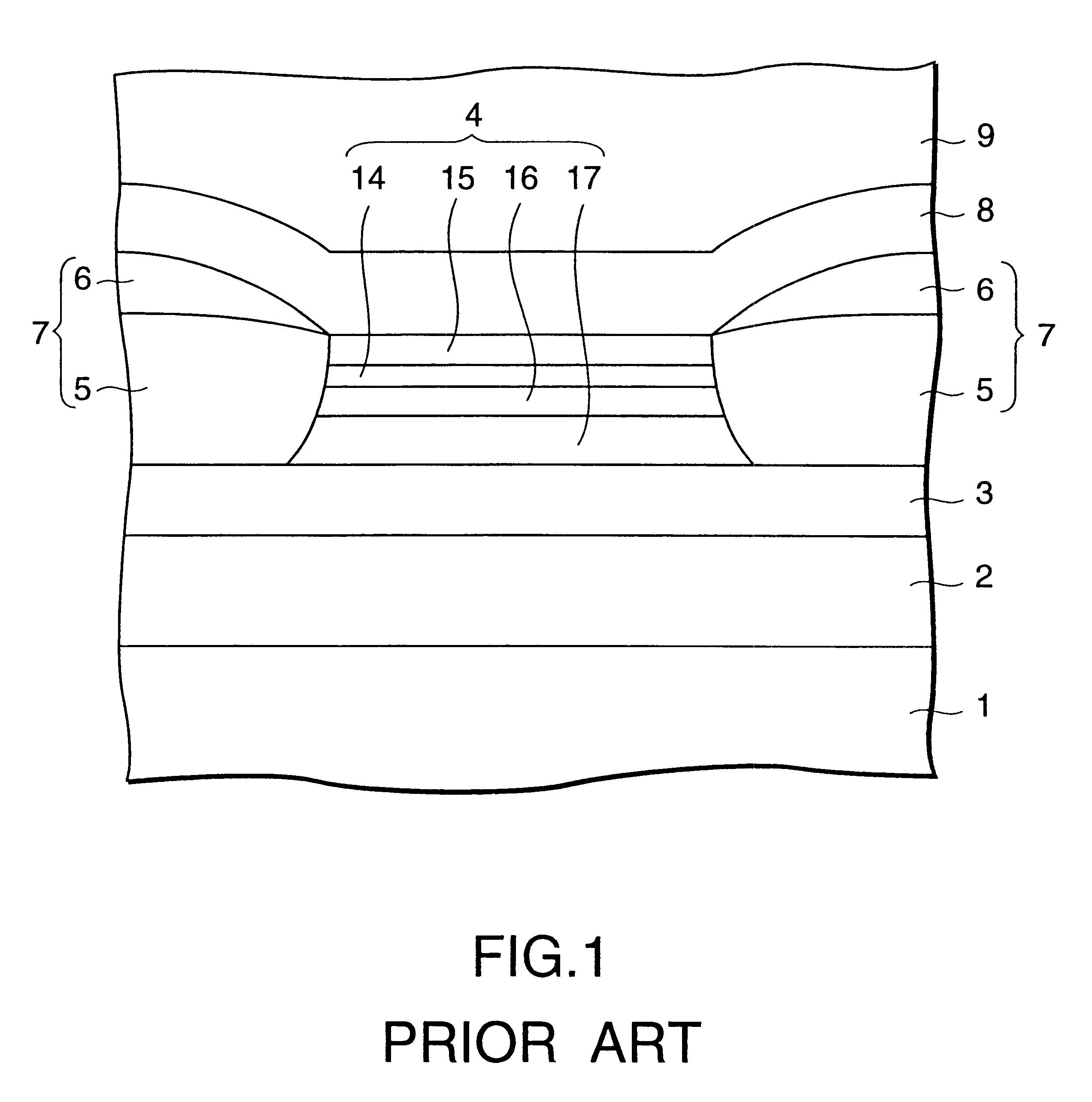
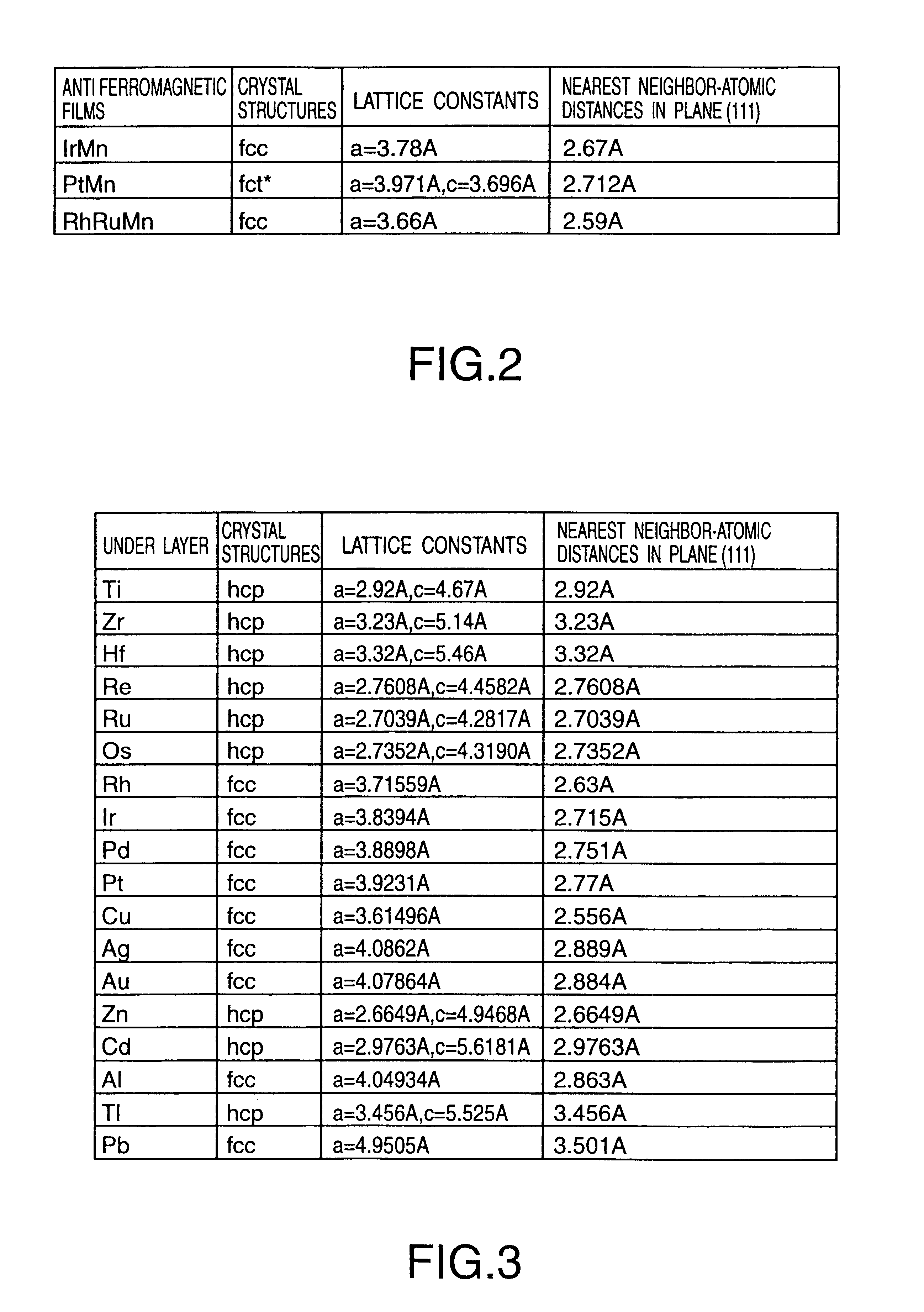
Laminated magnetorestrictive element of an exchange coupling film, an antiferromagnetic film and a ferromagnetic film and a magnetic disk drive using same
InactiveUS6313973B1Stable output voltageRaise the ratioNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsGiant magnetoresistanceCoupling
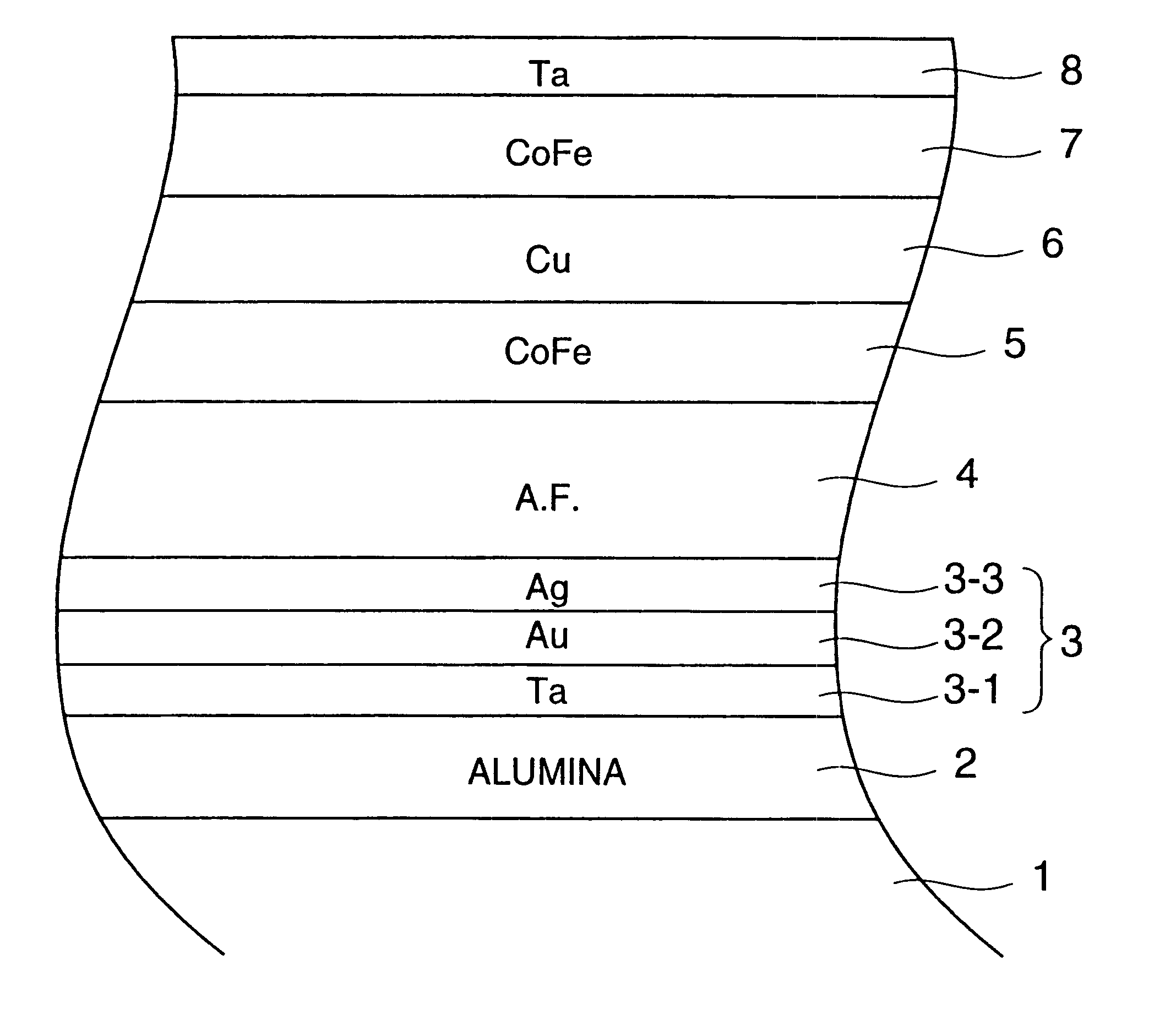
A magnetoresistive element comprises an exchange coupling film having a under layer, an antiferromagnetic film and a ferromagnetic film, which are laminated in that order, the under layer including a metal having a face centered cubic crystal structure or hexagonal closest packing crystal structure which have a longer nearest neighbor atomic distance than that of the antiferromagnetic film. With this construction, it is possible to improve the exchange coupling field and to satisfy a stable output over a long period of time. A magnetoresistive element having a dual spin valve structure has a magnetization adjusting layer, which is antiferromagnetically connected to a pinned layer via an anti-parallel connection layer, to adjust the value of the product of the saturation magnetization of each of the magnetization adjusting layer and the pinned layer by the thickness thereof. Moreover, a magnetoresistance head use a giant magnetoresistance effect, and has at least one pair of pinned layer and free layer arranged via a non-magnetic spacer layer. The pinned layer has a pair of ferromagnetic layers which have different compositions and different coercive forces and which are antiferromagnetically connected to each other via a connection layer, so that the effective exchange coupling field of the pinned layer is 200 Oe or more.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
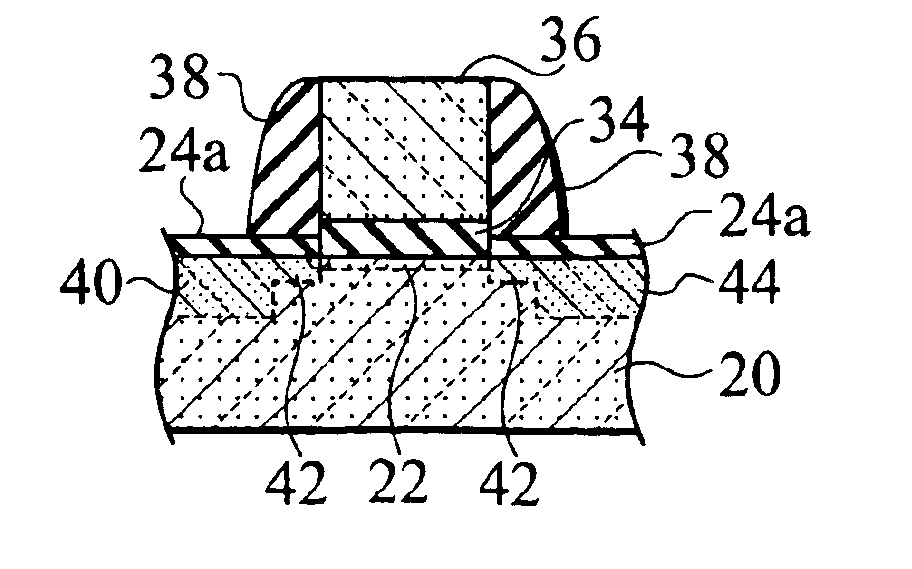
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS6930360B2High activation rateSuppress DiffuseTransistorSolid-state devicesNear neighborSite location
A semiconductor device having a semiconductor layer, includes: a first impurity atom having a covalent bond radius larger than a minimum radius of a covalent bond of a semiconductor constituent atom of a semiconductor layer; and a second impurity atom having a covalent bond radius smaller than a maximum radius of the covalent bond of the semiconductor constituent atom; wherein the first and second impurity atoms are arranged in a nearest neighbor lattice site location and at least one of the first and second impurity atoms is electrically active.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
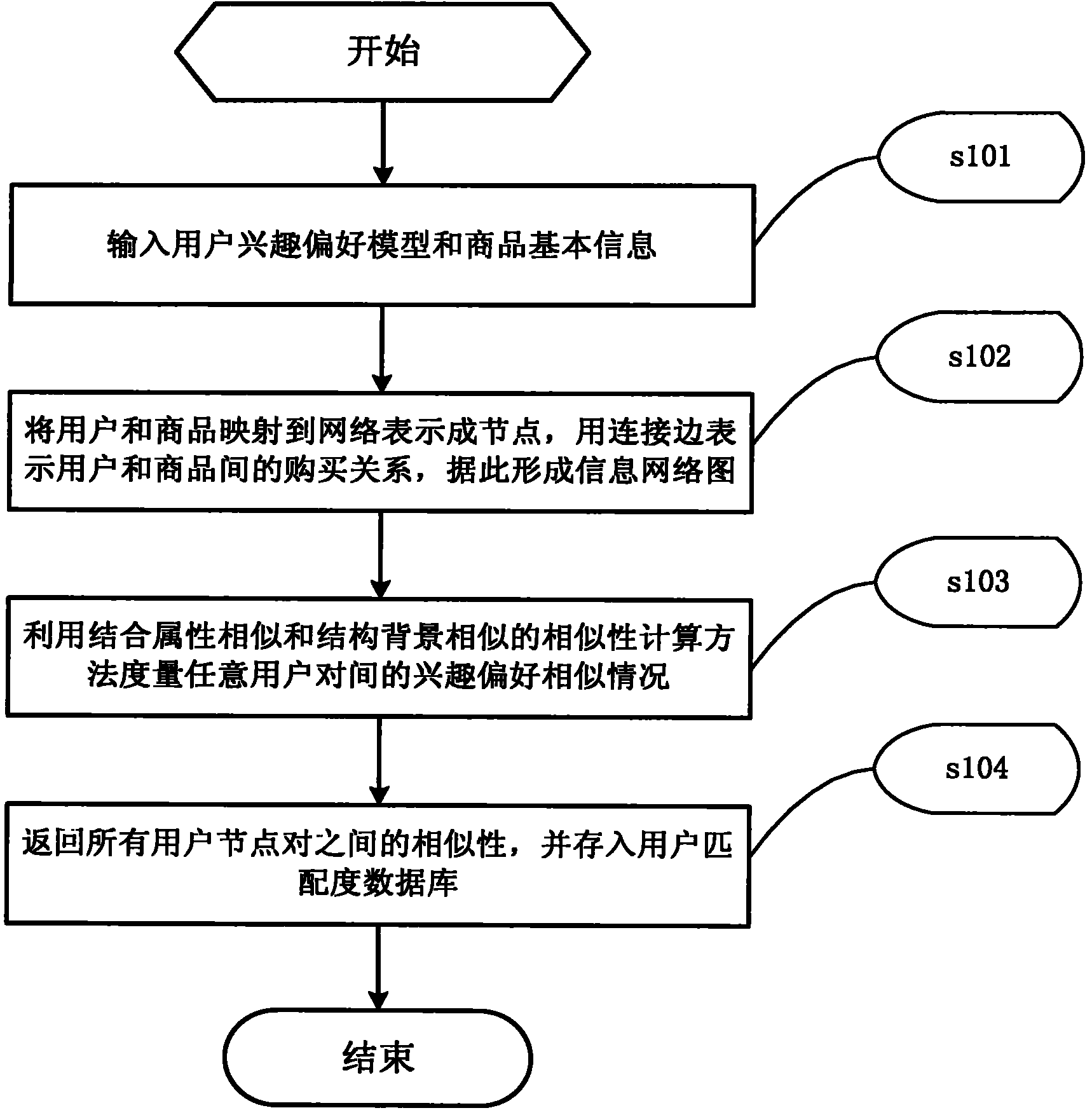
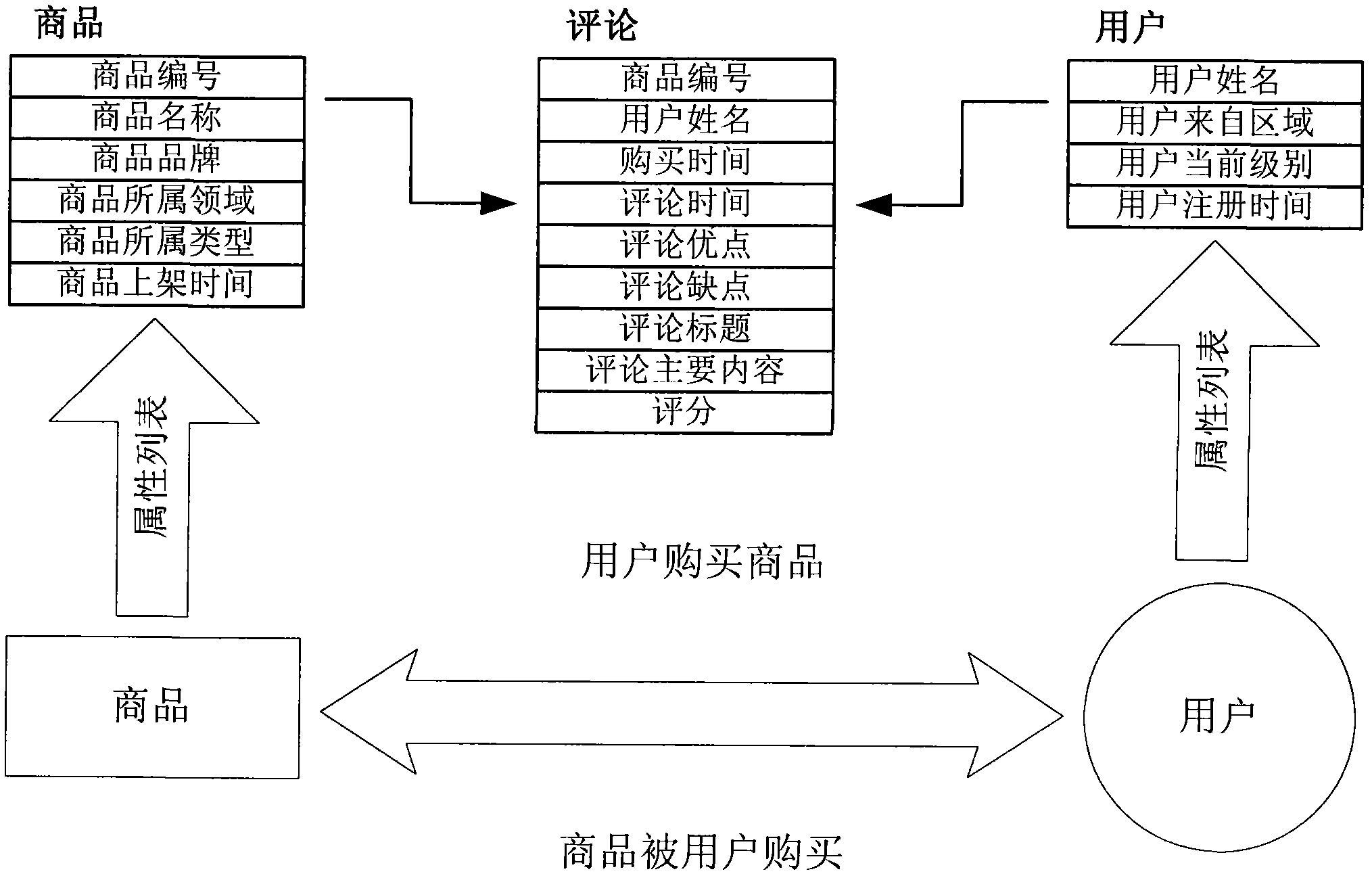
Personalized commodity recommending method and system which integrate attributes and structural similarity
InactiveCN102254028AQuick referral requests in real timeRespond to referral requestsCommerceSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationNear neighbor
The invention discloses a personalized commodity recommending method which integrates attributes and structural similarity. In the method, users and commodities are used as nodes with characteristic information to be mapped to a network by integrating the attribute information and structural similarity information, and an information network chart is established according to the purchasing relation between customers and the commodities; and interests and preference among user node pairs are measured by the integrated attributes and structural similarity in the information network chart, and the nearest neighbor is selected by the interests and the preference to improve the accuracy of recommending. On the basis of the recommending method, the invention also discloses a personalized commodity recommending method which integrates the measurement of the attributes and the structural similarity. In the system, the interests and the preference of the users are measured accurately by a computing method of integrating the similarity of the attributes and the similarity of node structure backgrounds in the information network chart, and the generation efficiency of the nearest neighbor is improved by utilizing clustering technology. The method and the system can be applied to electronic commerce, and provide personalized commodity recommending for the users.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Optimizing layout of an application on a massively parallel supercomputer
InactiveUS20060101104A1Shorten the timeMinimize cost functionDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsMarkov chainSupercomputer
A general computer-implement method and apparatus to optimize problem layout on a massively parallel supercomputer is described. The method takes as input the communication matrix of an arbitrary problem in the form of an array whose entries C(i, j) are the amount to data communicated from domain i to domain j. Given C(i, j), first implement a heuristic map is implemented which attempts sequentially to map a domain and its communications neighbors either to the same supercomputer node or to near-neighbor nodes on the supercomputer torus while keeping the number of domains mapped to a supercomputer node constant (as much as possible). Next a Markov Chain of maps is generated from the initial map using Monte Carlo simulation with Free Energy (cost function) F=Σi,jC(i,j)H(i,j)—where H(i,j) is the smallest number of hops on the supercomputer torus between domain i and domain j. On the cases tested, found was that the method produces good mappings and has the potential to be used as a general layout optimization tool for parallel codes. At the moment, the serial code implemented to test the method is un-optimized so that computation time to find the optimum map can be several hours on a typical PC. For production implementation, good parallel code for our algorithm would be required which could itself be implemented on supercomputer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Peer-to-peer enterprise storage
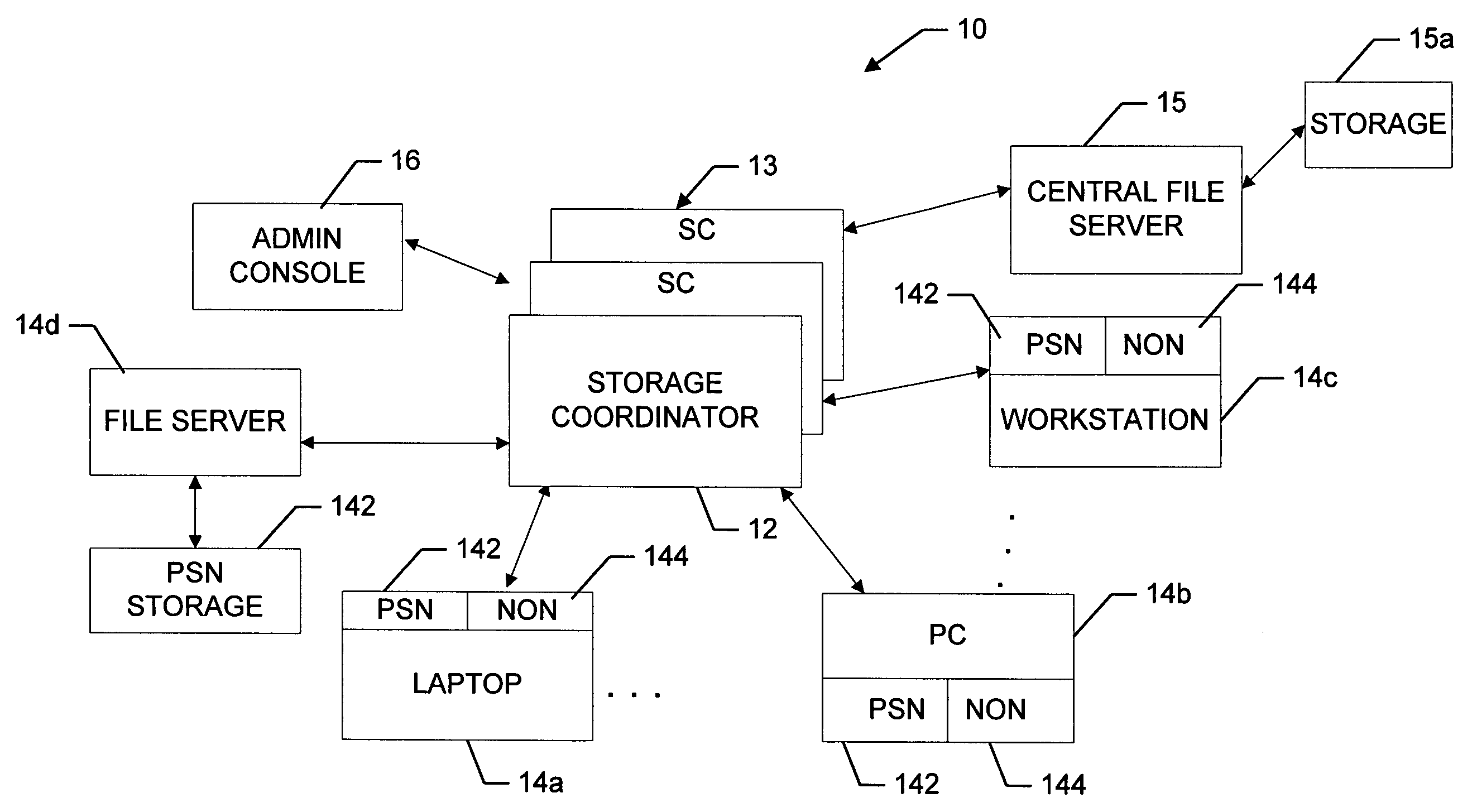
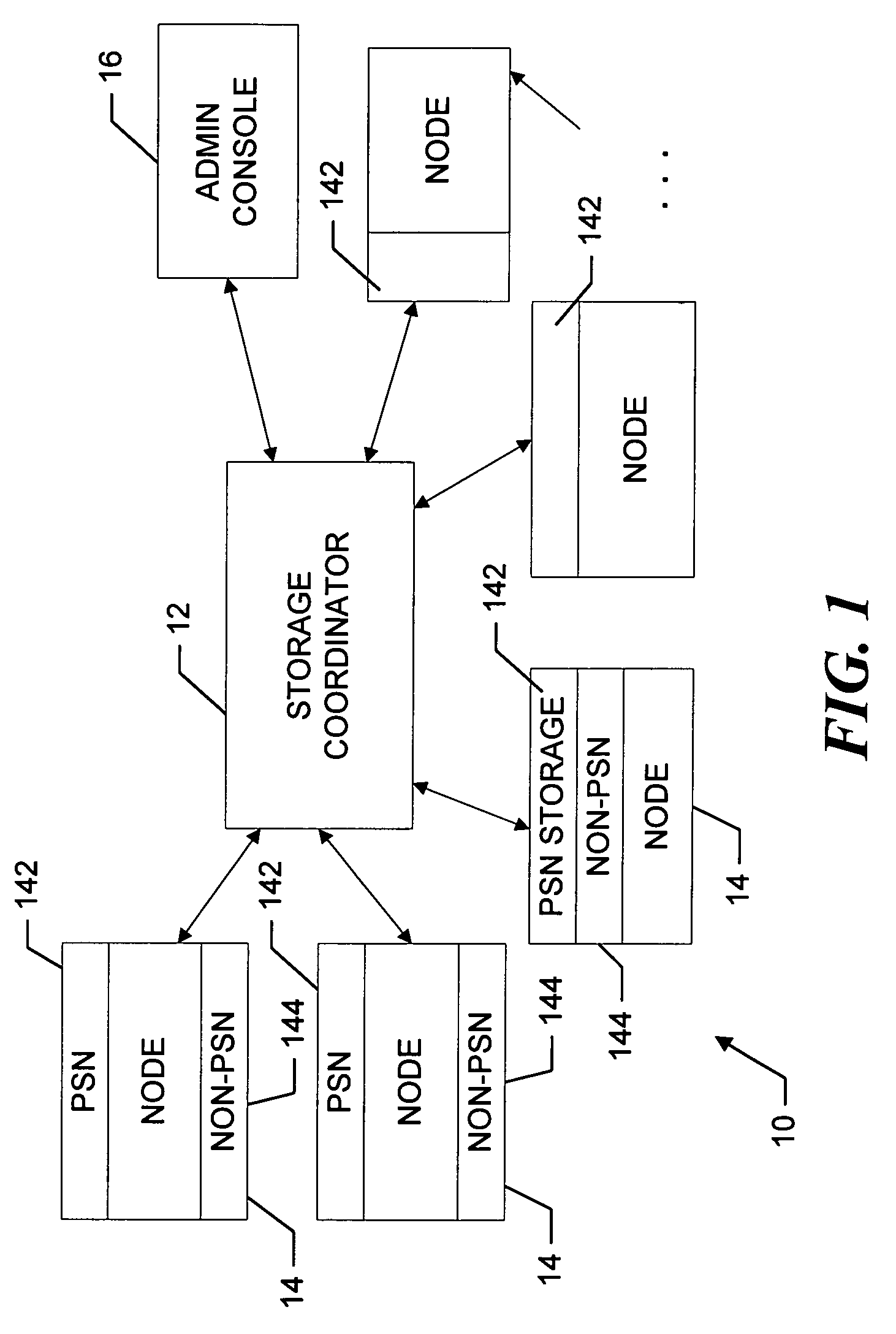
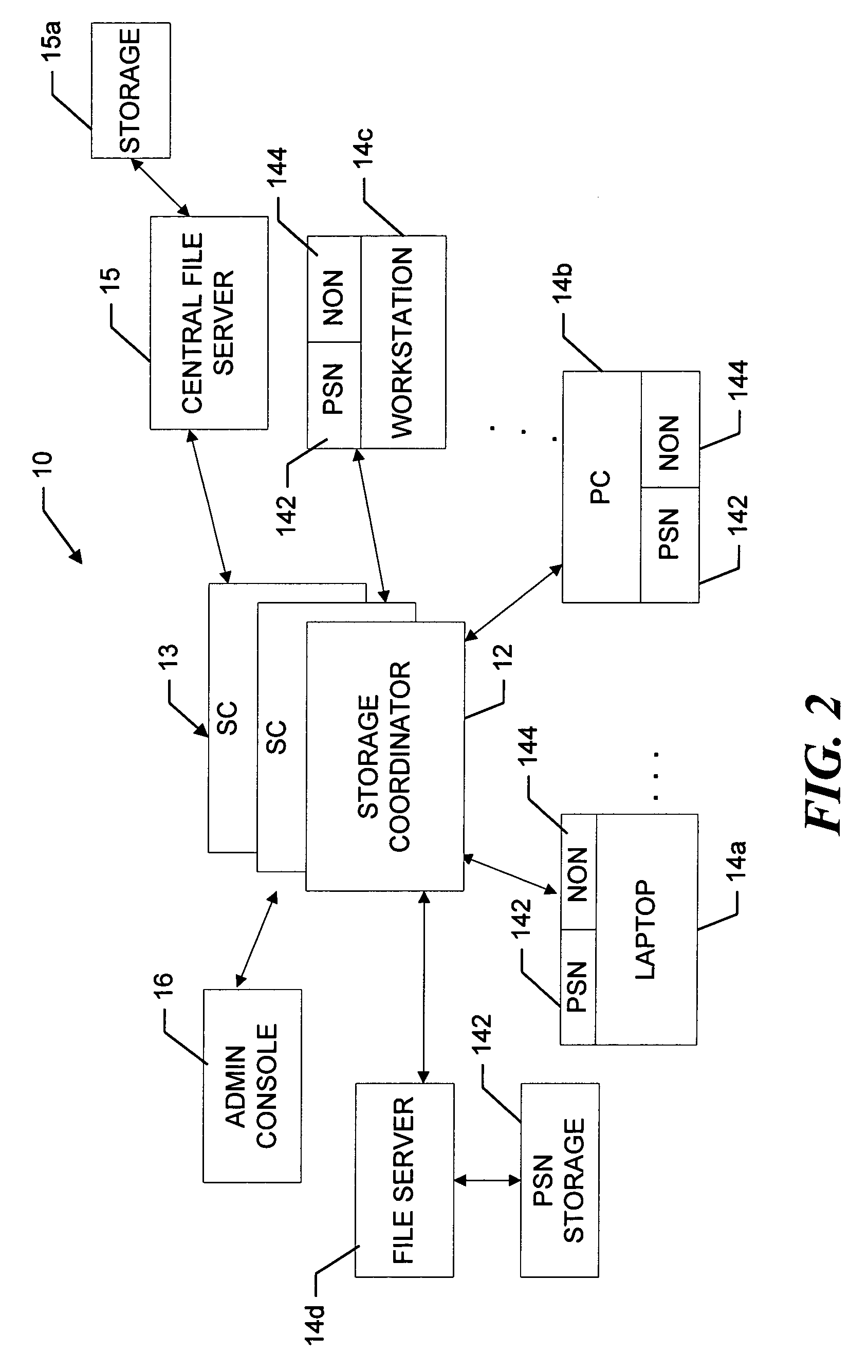
InactiveUS7069295B2Quantity minimizationMaximize rangeDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationFile replicationNear neighbor
A peer-to-peer storage system includes a storage coordinator that centrally manages distributed storage resources in accordance with system policies administered through a central administrative console. The storage resources, or “nodes,” are otherwise unused portions of storage media, e.g., hard disks, that are included in the devices such as personal computers, workstations, laptops, file servers, and so forth, that are connected to a corporate computer network, and are thus otherwise available only individually to the respective devices. The storage coordinator assigns the nodes to various “replication groups” and allocates the storage resources on each of the nodes in a given group to maintaining dynamically replicated versions of the group files. The storage nodes in a given group perform dynamic file replication and synchronization operations by communicating directly, that is, peer-to-peer, using a message-based protocol. The storage coordinator also manages distributed searches of file content on the network by selecting one node from each group to search through the associated group files. The selected nodes report the search results back to the storage coordinator, which organizes the results and provides them to the user. Thereafter, in response to a request for various files by the user, the storage coordinator instructs the nodes that are near neighbors of the user to provide the requested files. The storage coordinator thus ensures that the amount of the network bandwidth consumed by the search operation is minimized.
Owner:ESCHER GROUP
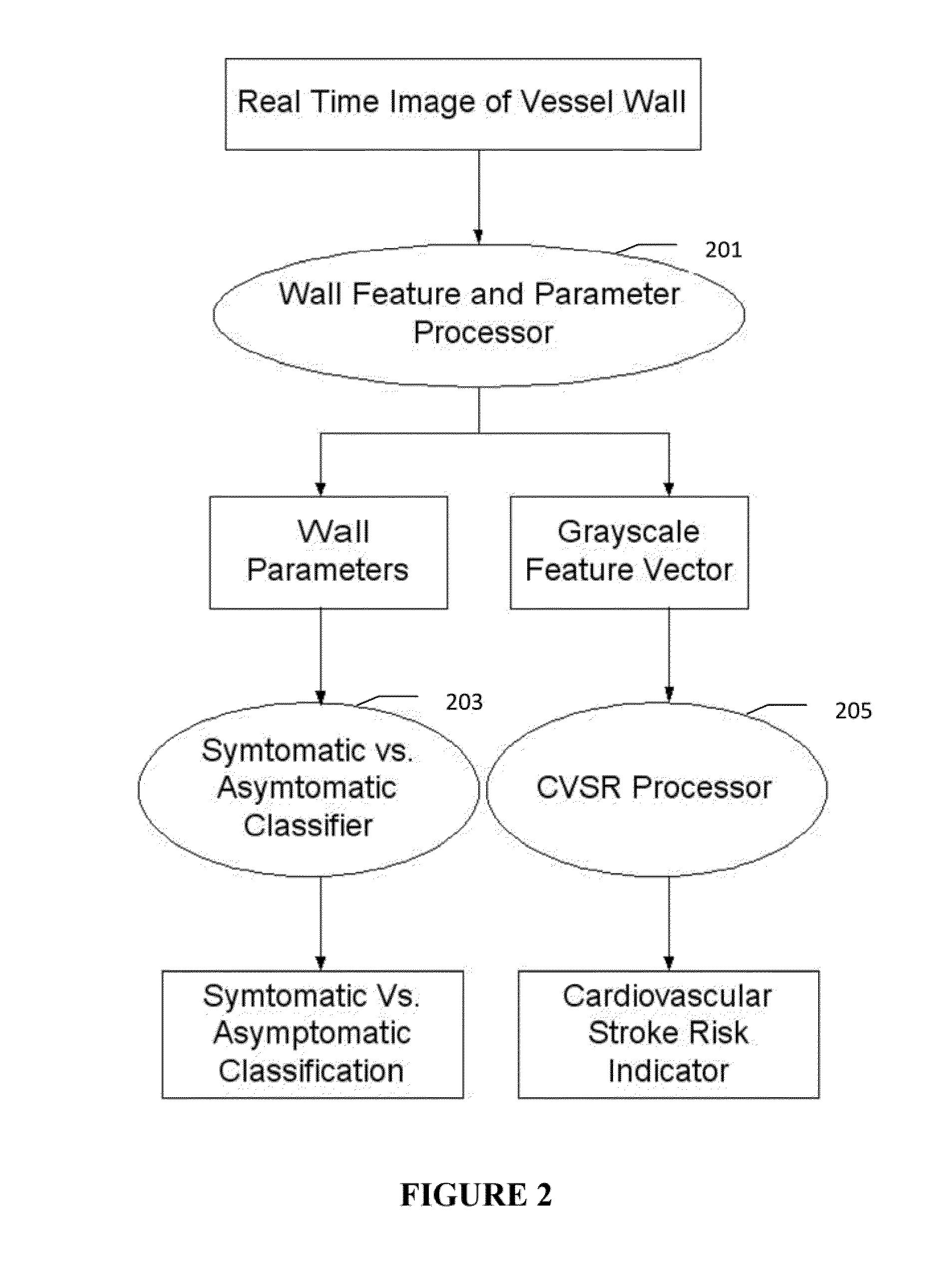
Imaging based symptomatic classification and cardiovascular stroke risk score estimation
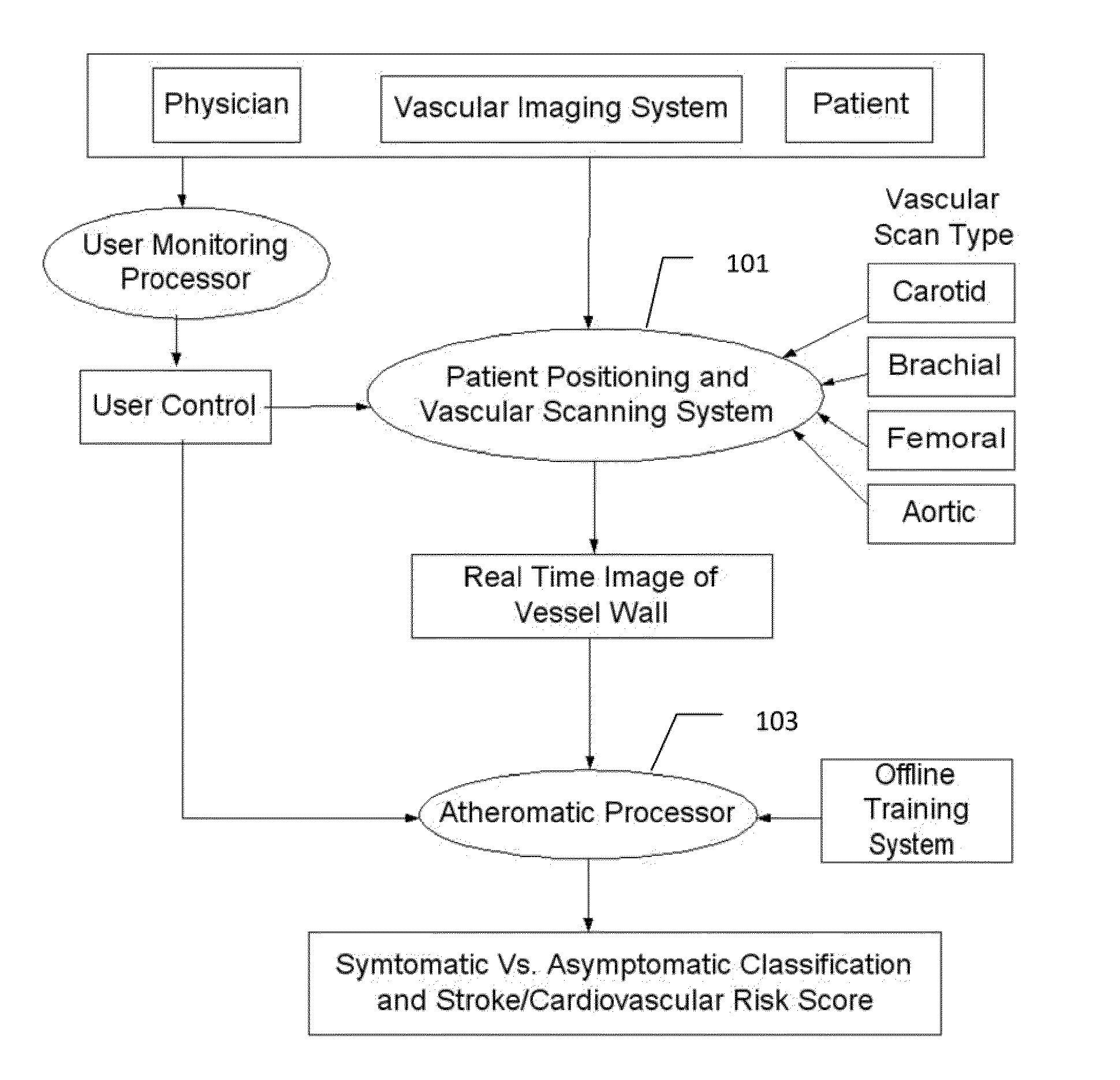
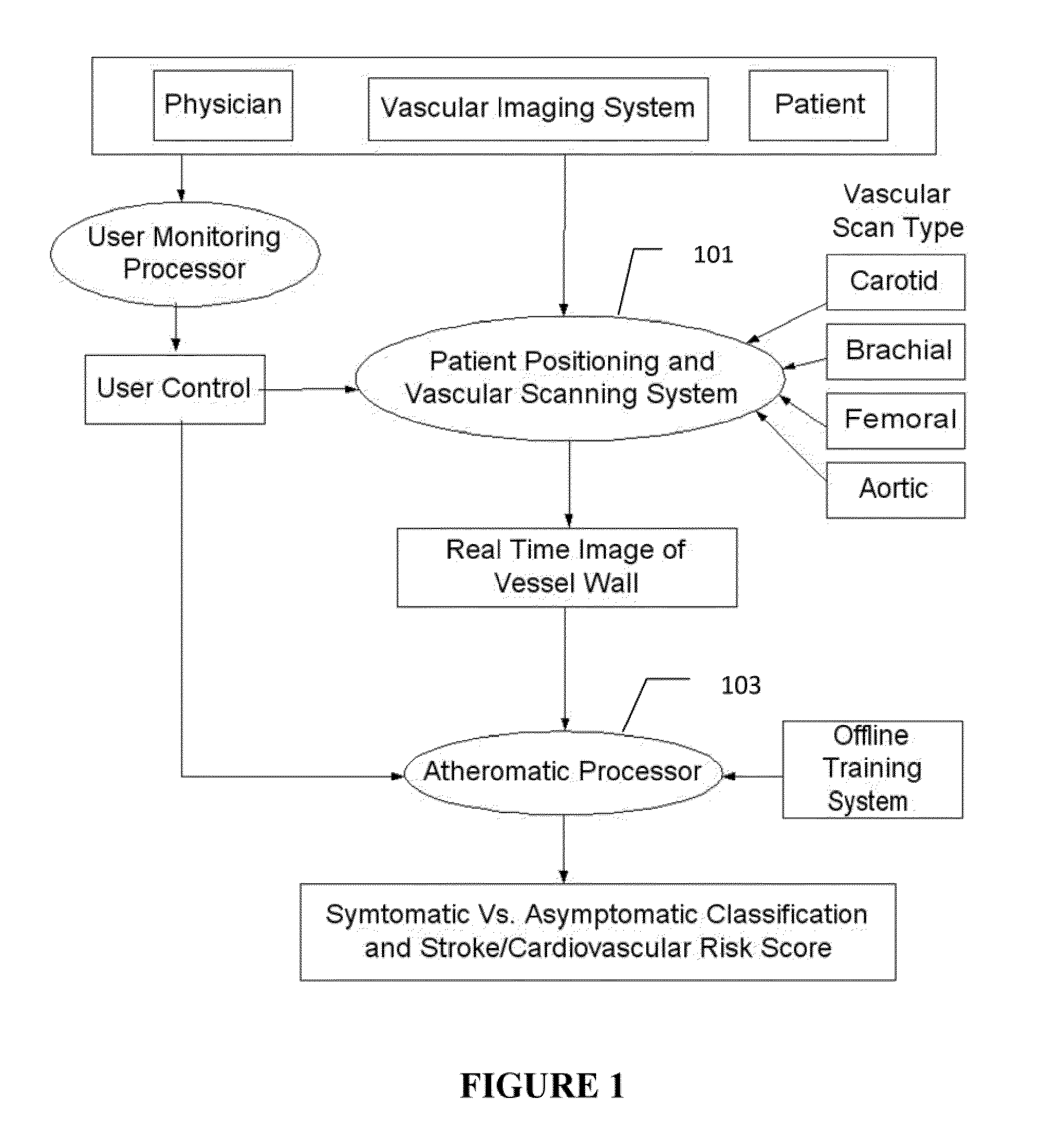
InactiveUS20110257545A1Improve accuracyMaximum accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementGround truthCross modality
Characterization of carotid atherosclerosis and classification of plaque into symptomatic or asymptomatic along with the risk score estimation are key steps necessary for allowing the vascular surgeons to decide if the patient has to definitely undergo risky treatment procedures that are needed to unblock the stenosis. This application describes a statistical (a) Computer Aided Diagnostic (CAD) technique for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification of carotid ultrasound images and (b) presents a cardiovascular stroke risk score computation. We demonstrate this for longitudinal Ultrasound, CT, MR modalities and extendable to 3D carotid Ultrasound. The on-line system consists of Atherosclerotic Wall Region estimation using AtheroEdge™ for longitudinal Ultrasound or Athero-CTView™ for CT or Athero-MRView from MR. This greyscale Wall Region is then fed to a feature extraction processor which computes: (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability. The output of the Feature Processor is fed to the Classifier which is trained off-line from the Database of similar Atherosclerotic Wall Region images. The off-line Classifier is trained from the significant features from (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability, selected using t-test. Symptomatic ground truth information about the training patients is drawn from cross modality imaging such as CT or MR or 3D ultrasound in the form of 0 or 1. Support Vector Machine (SVM) supervised classifier of varying kernel functions is used off-line for training. The Atheromatic™ system is also demonstrated for Radial Basis Probabilistic Neural Network (RBPNN), or Nearest Neighbor (KNN) classifier or Decision Trees (DT) Classifier for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification. The obtained training parameters are then used to evaluate the test set. The system also yields the cardiovascular stroke risk score value on the basis of the four set of wall features.
Owner:SURI JASJIT S
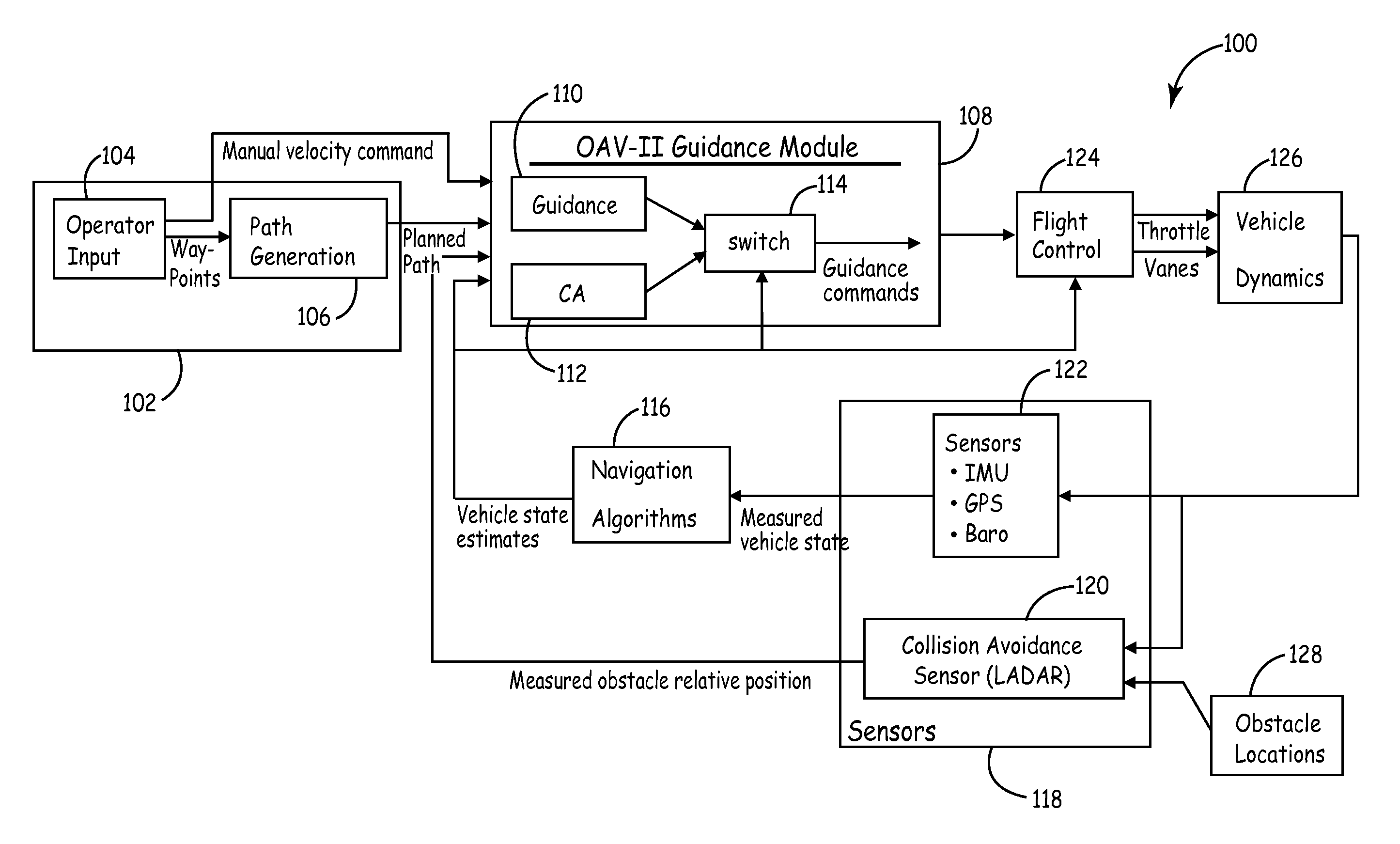
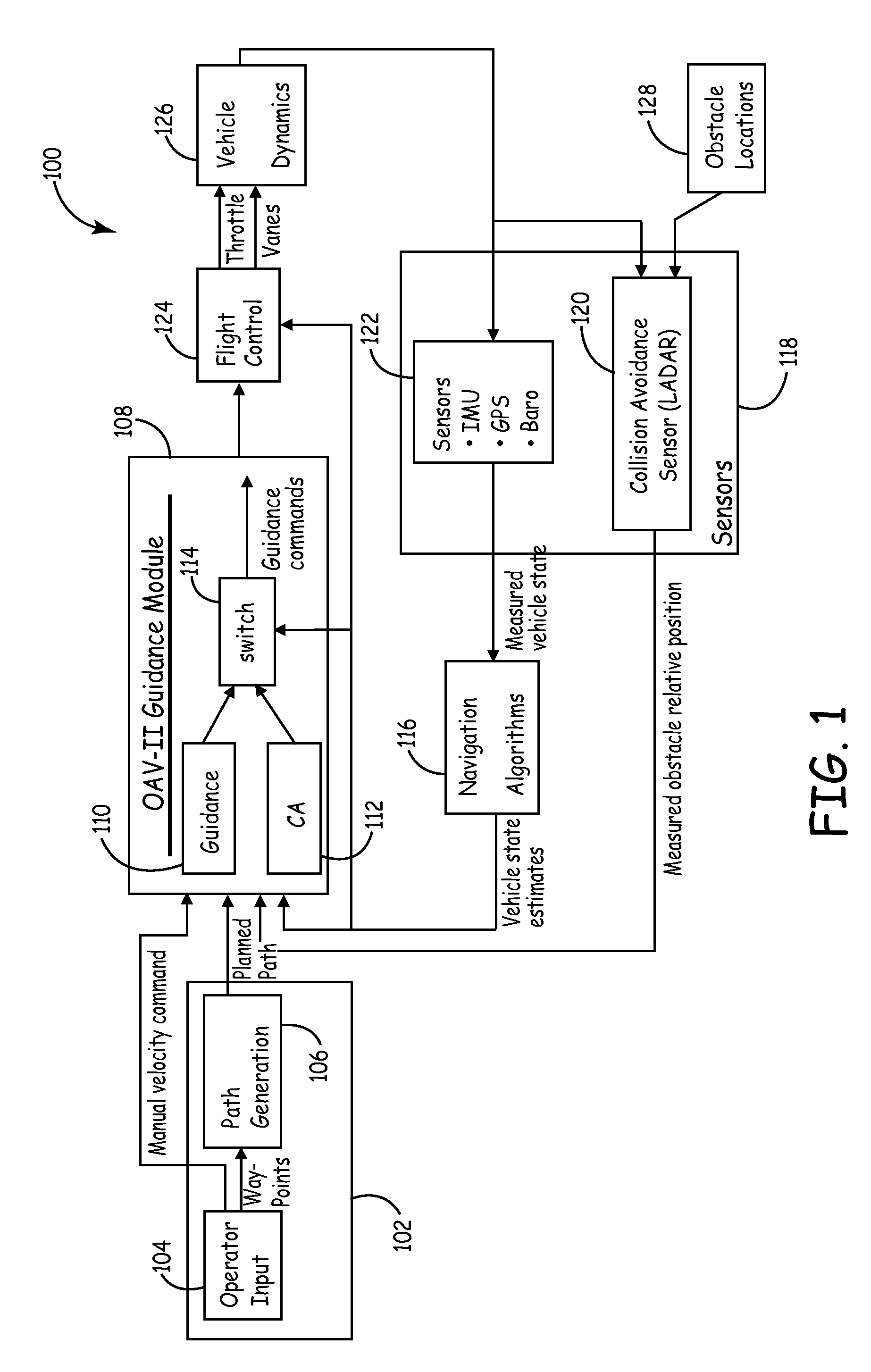
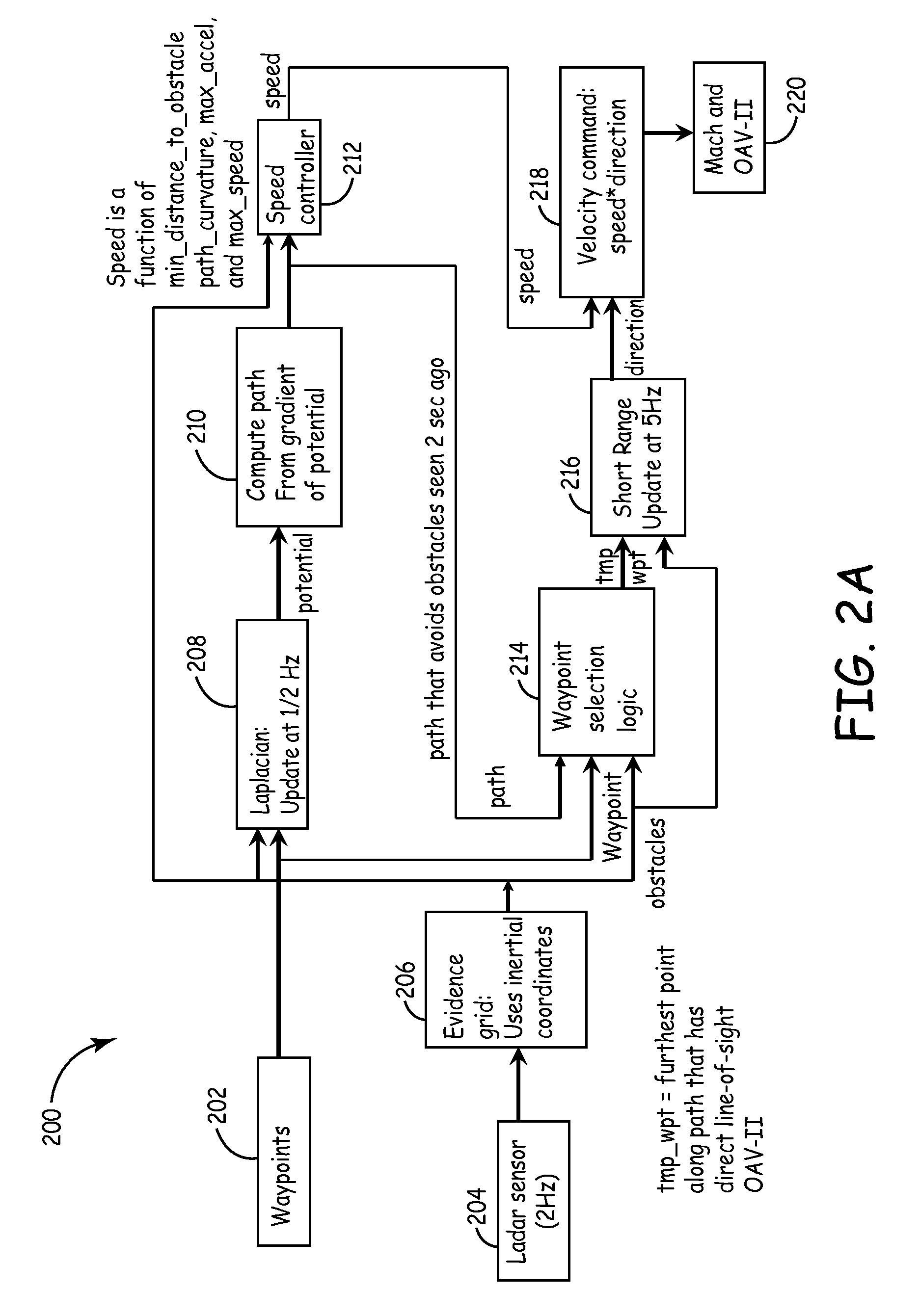
Method and system for automatic path planning and obstacle/collision avoidance of autonomous vehicles
InactiveUS20090088916A1Instruments for road network navigationVehicle position/course/altitude controlNear neighborA domain
Method and systems of traversing through a domain is provided. One method comprises getting a set of widely spaced waypoints, assigning the next waypoint to be the goal, then using a Laplacian path planner to construct a desired finely detailed path towards the goal, through the domain that avoids boundaries and objects in the domain. Assigning a potential value of v(r)=0 for r on boundaries and obstacles. Assigning a potential value of v(r)=−1 for r on a goal region, wherein the goal is a point on a planned path. Obtaining a numerical solution to the desired path with a Laplace's equation by gridding up the domain with a multi-sized cell grid, wherein the cells near an object are denser then the cells away from the objects. Iteratively setting a potential at each interior point equal to the average of its nearest neighbors and following the numerical solution provided by the Laplace's equation to the goal region.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Clustering techniques for large, high-dimensionality data sets
ActiveUS8363961B1Digital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionHigh dimensionalityData set
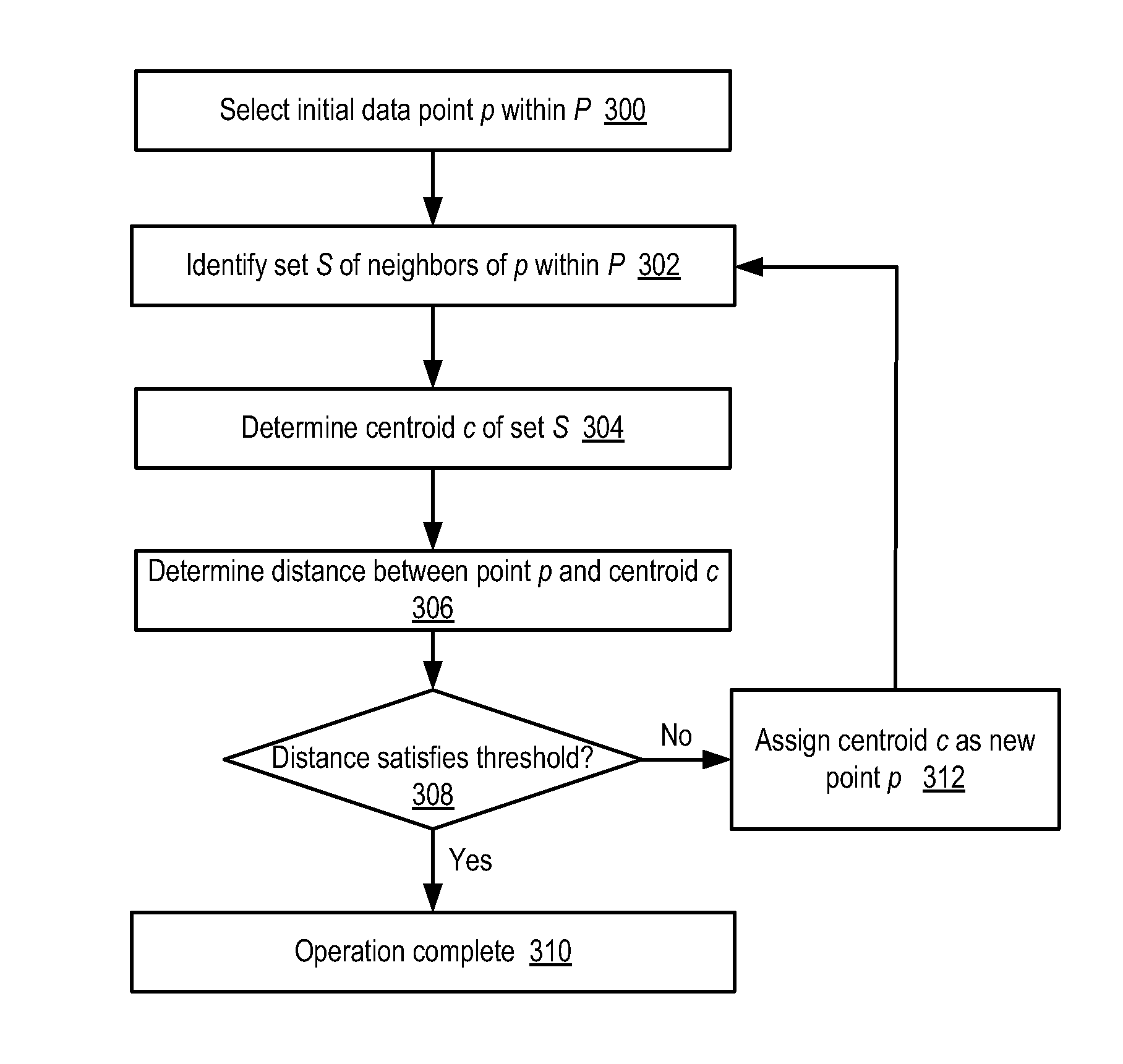
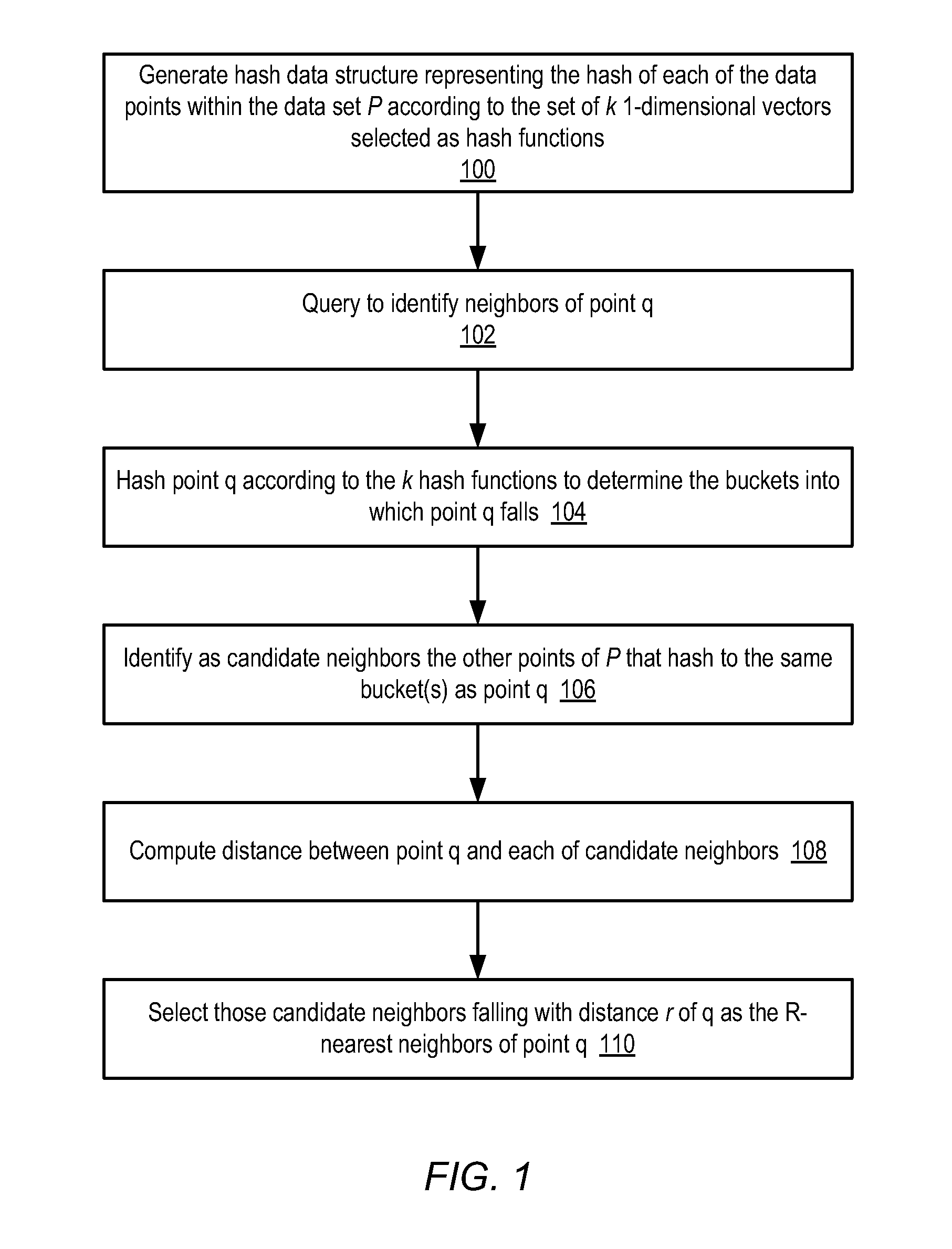
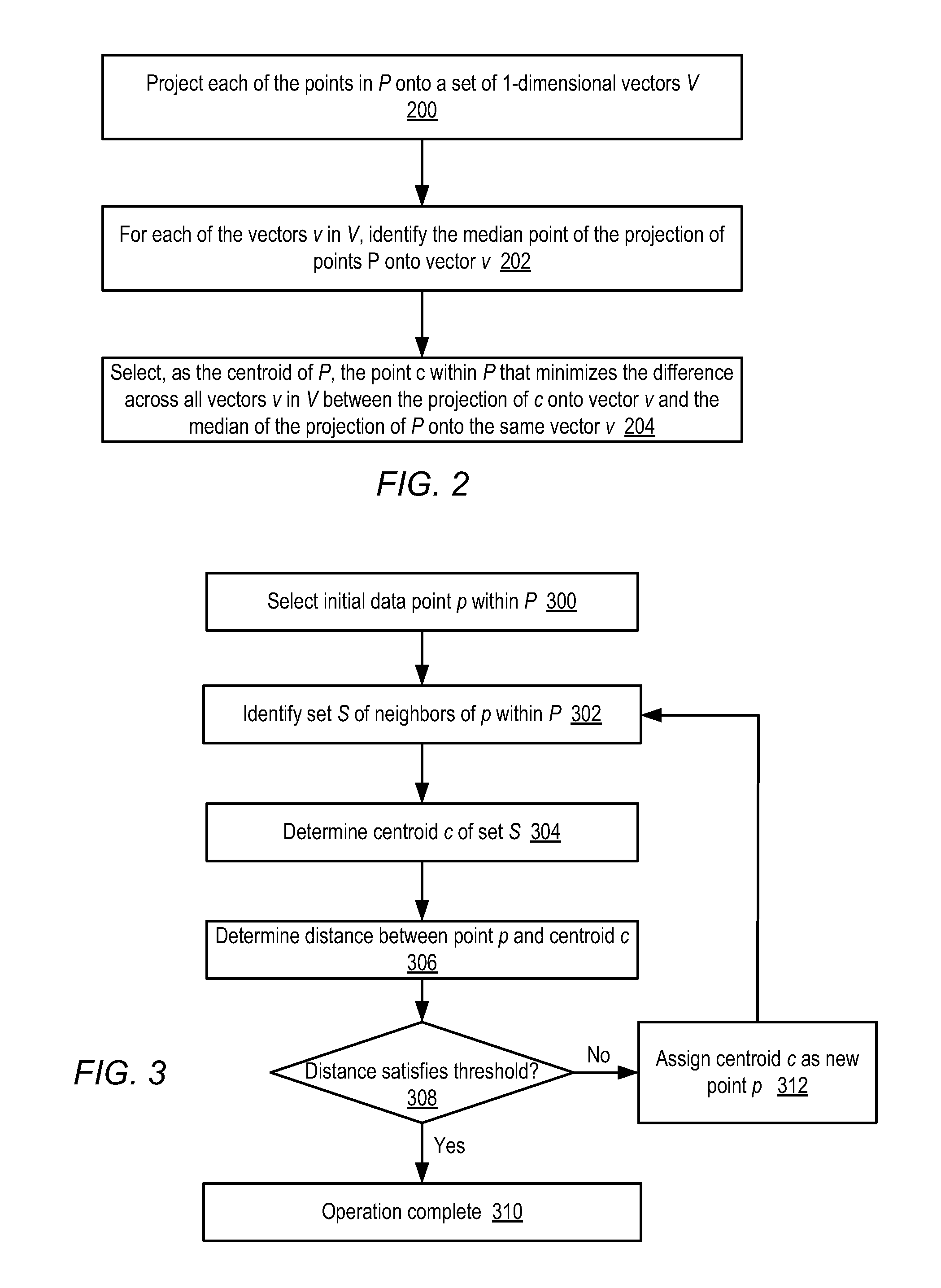
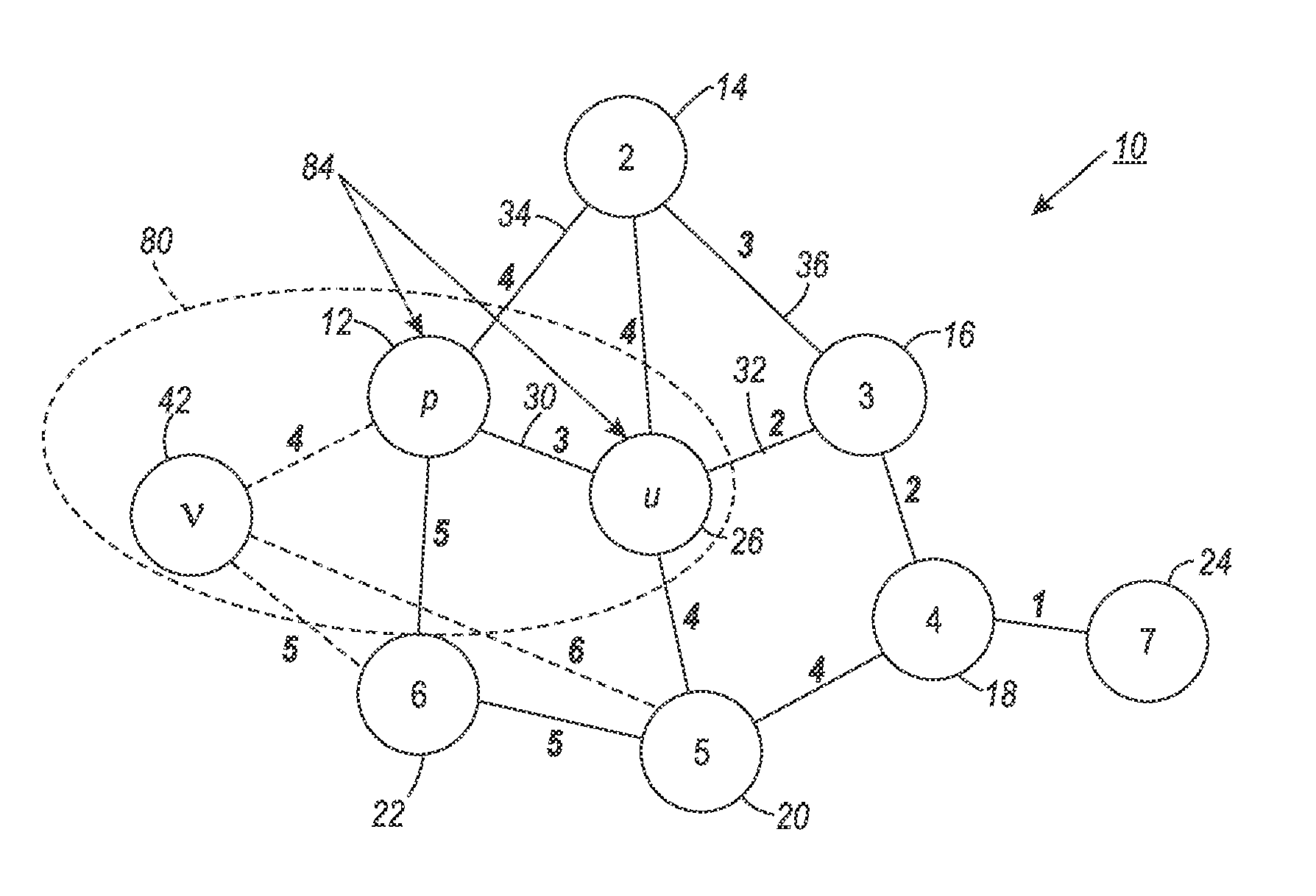
A clustering method for high-dimensionality data includes identifying a set of nearest neighbors of a point in a multidimensional space and determining the centroid of the set of nearest neighbors, where the centroid is a member of the set of nearest neighbors. The method is then repeated using the neighbors identified around the computed centroid. In one embodiment, the method may terminate when the computed centroid becomes stationary over successive iterations. The resulting centroid may be returned as a mode of the data set. Points of the data set having common modes may be assigned to the same cluster.
Owner:ADOBE INC
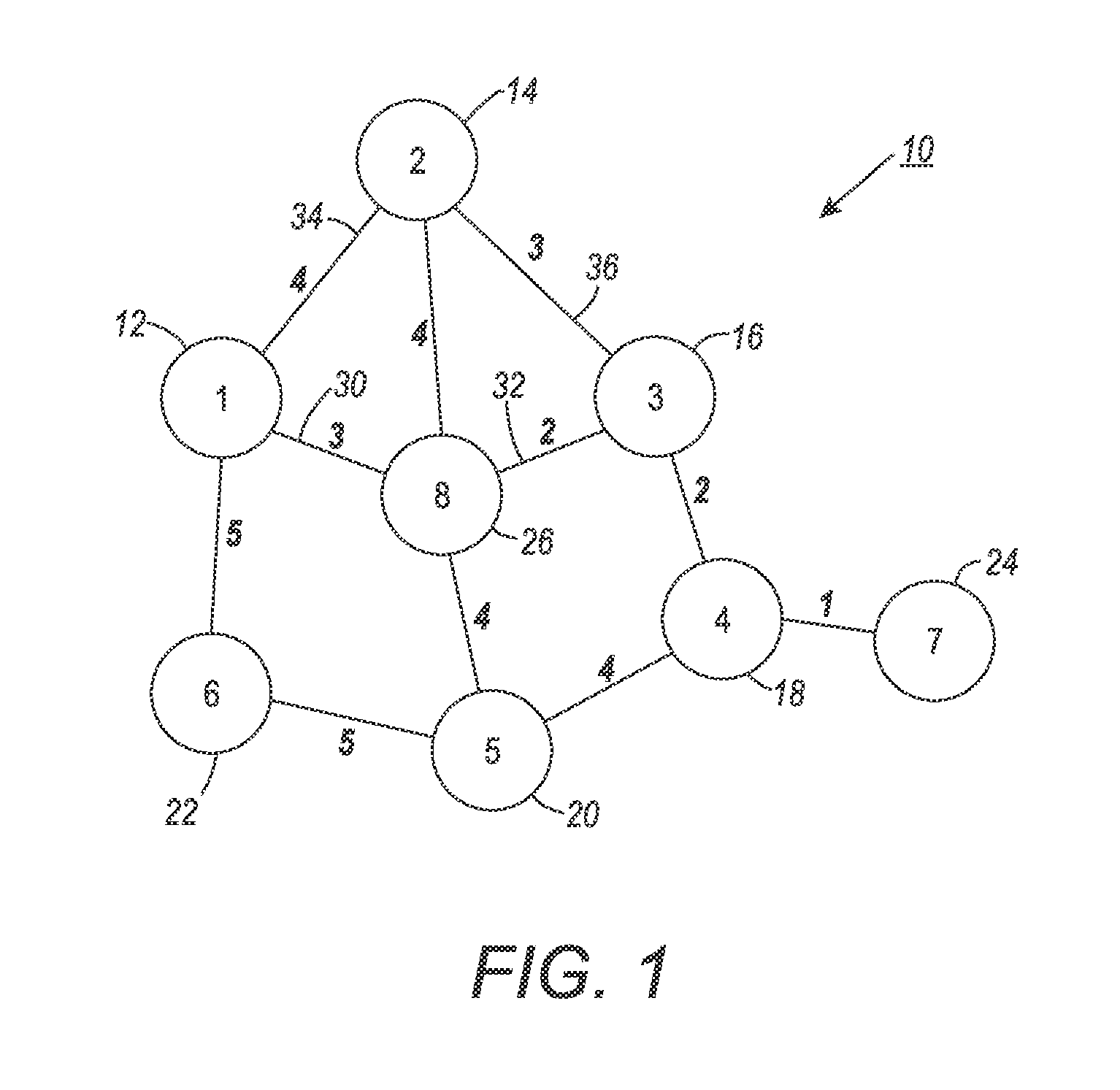
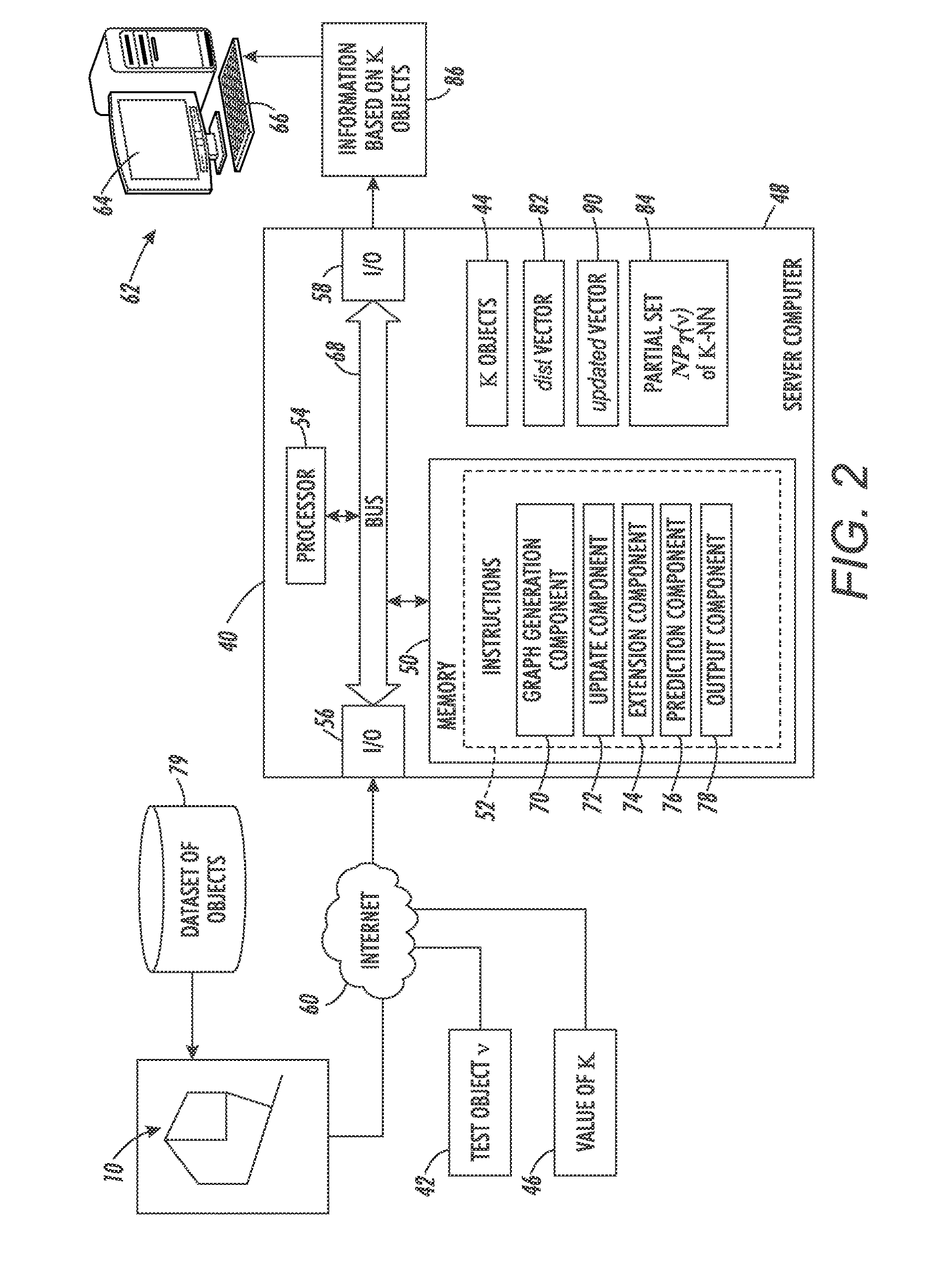
System and method for performing k-nearest neighbor search based on minimax distance measure and efficient outlier detection
A system and method enable a set of dataset objects that are K-nearest neighbors (K-NN), based on their Minimax distances to a test object, to be identified without computing the all-pair Minimax distances directly. A pairwise distance between the test object and each dataset object is computed. Iteratively, one of the dataset objects is selected to add to a K-NN set until the K-NN set includes a predefined number of nearest neighbors. The selected dataset object at each iteration is the one for which there is no other unselected dataset object which has a smaller pairwise distance to any of a current subset of objects than the selected dataset object. The current subset of objects includes the test object and the dataset objects currently in the K-NN set. After the K-NN set is identified it may be output or used to generate other information, such as a test object label.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
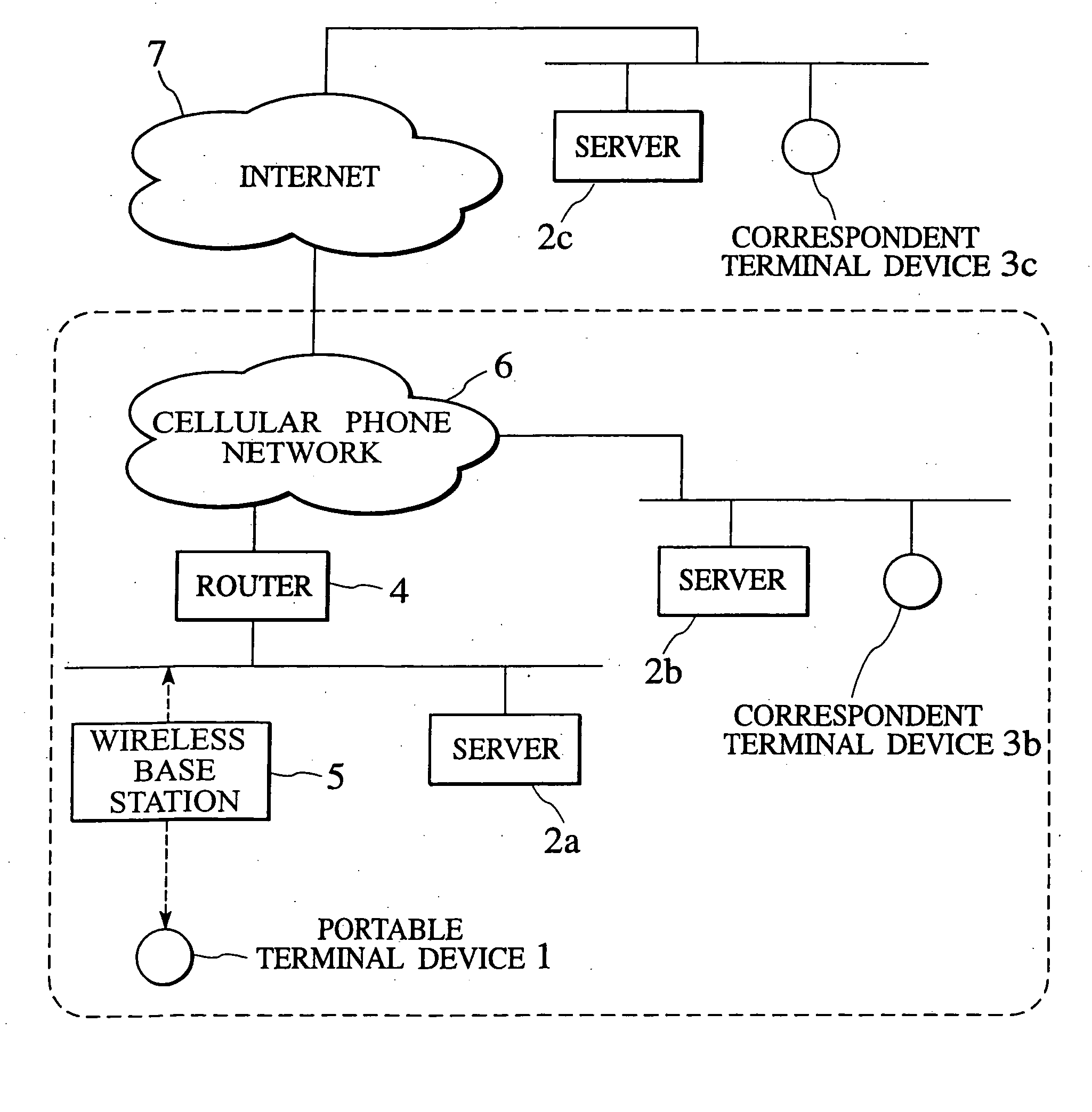
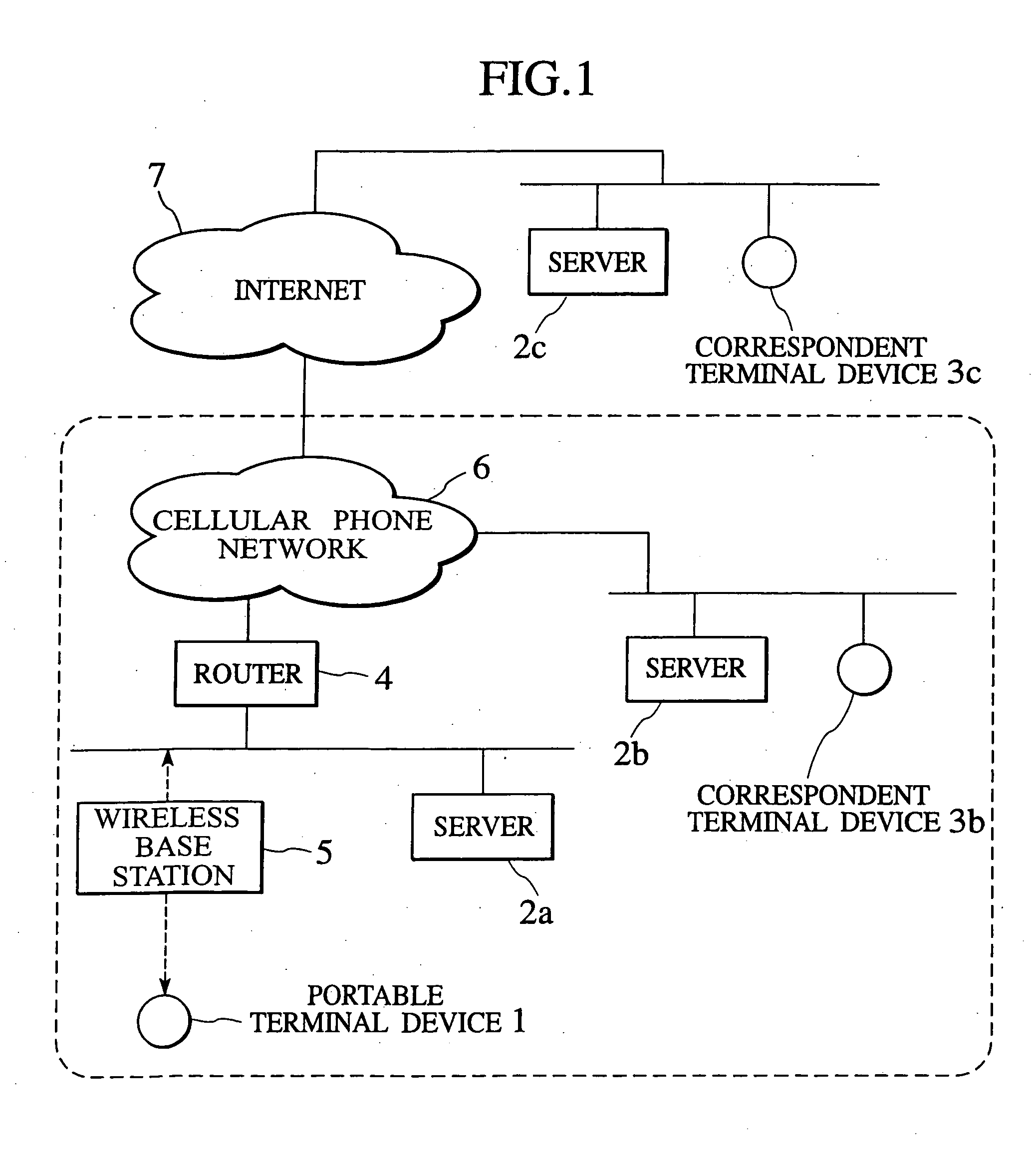
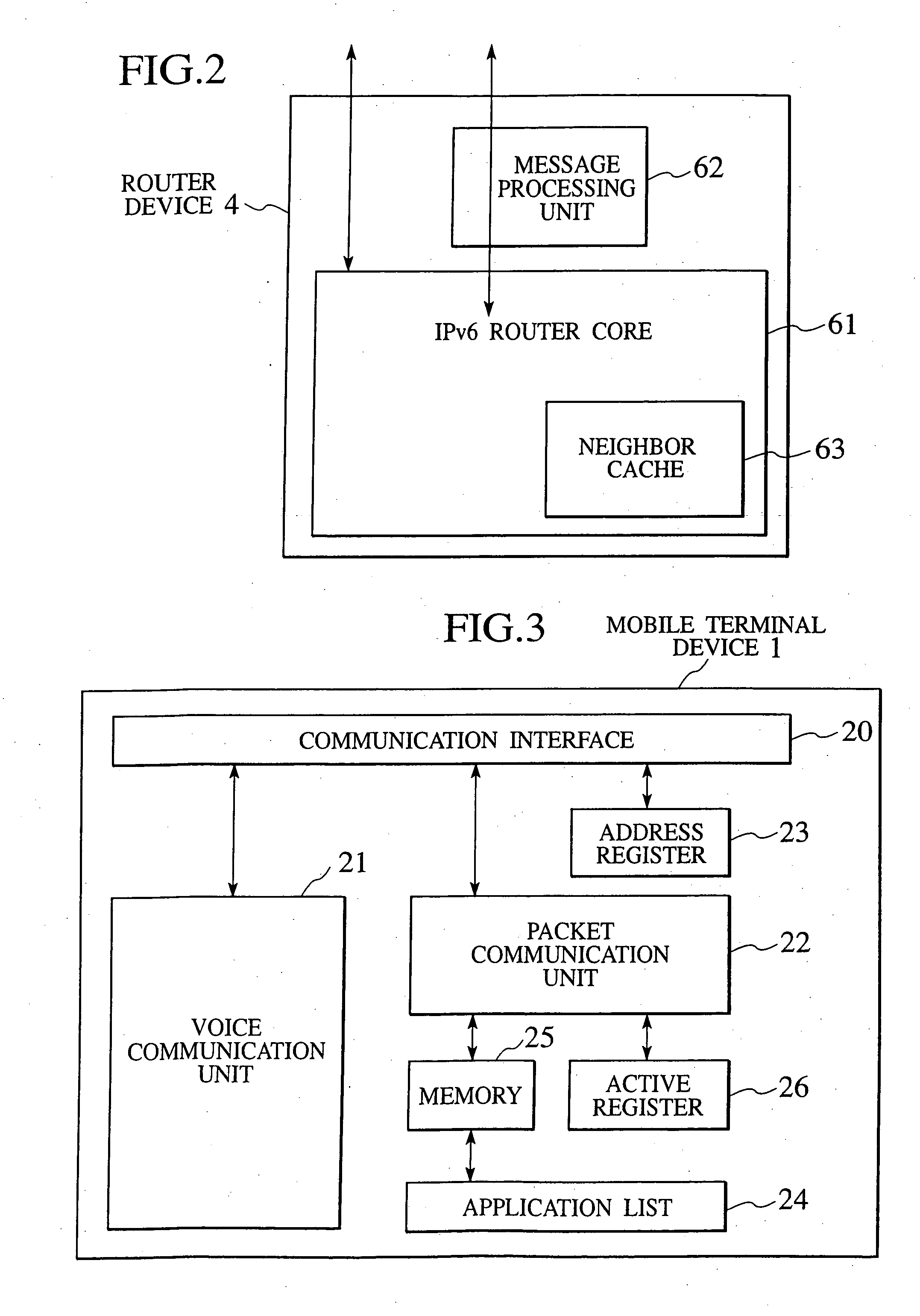
Packet transfer scheme using mobile terminal and router for preventing attacks using global address
In a mobile communication network providing an Internet service, the arrived packets are delivered from the nearest neighbor router device to the mobile terminal device according to the need such as when a prescribed application is activated or when a prescribed packet has arrived, by using message exchanges between the nearest neighbor router device and the mobile terminal device, so that it becomes possible to prevent the unnecessary packet attacks from the global Internet.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
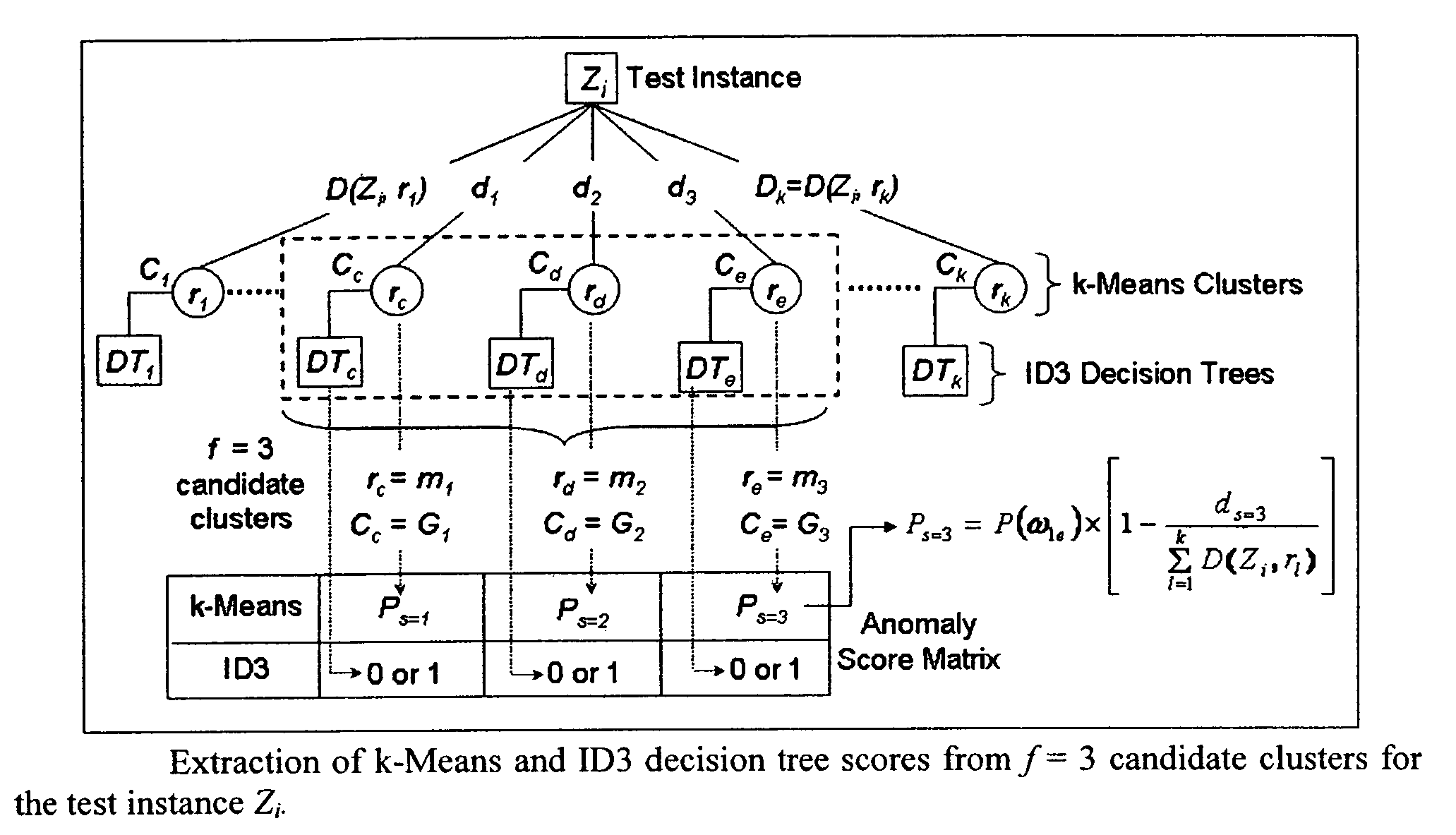
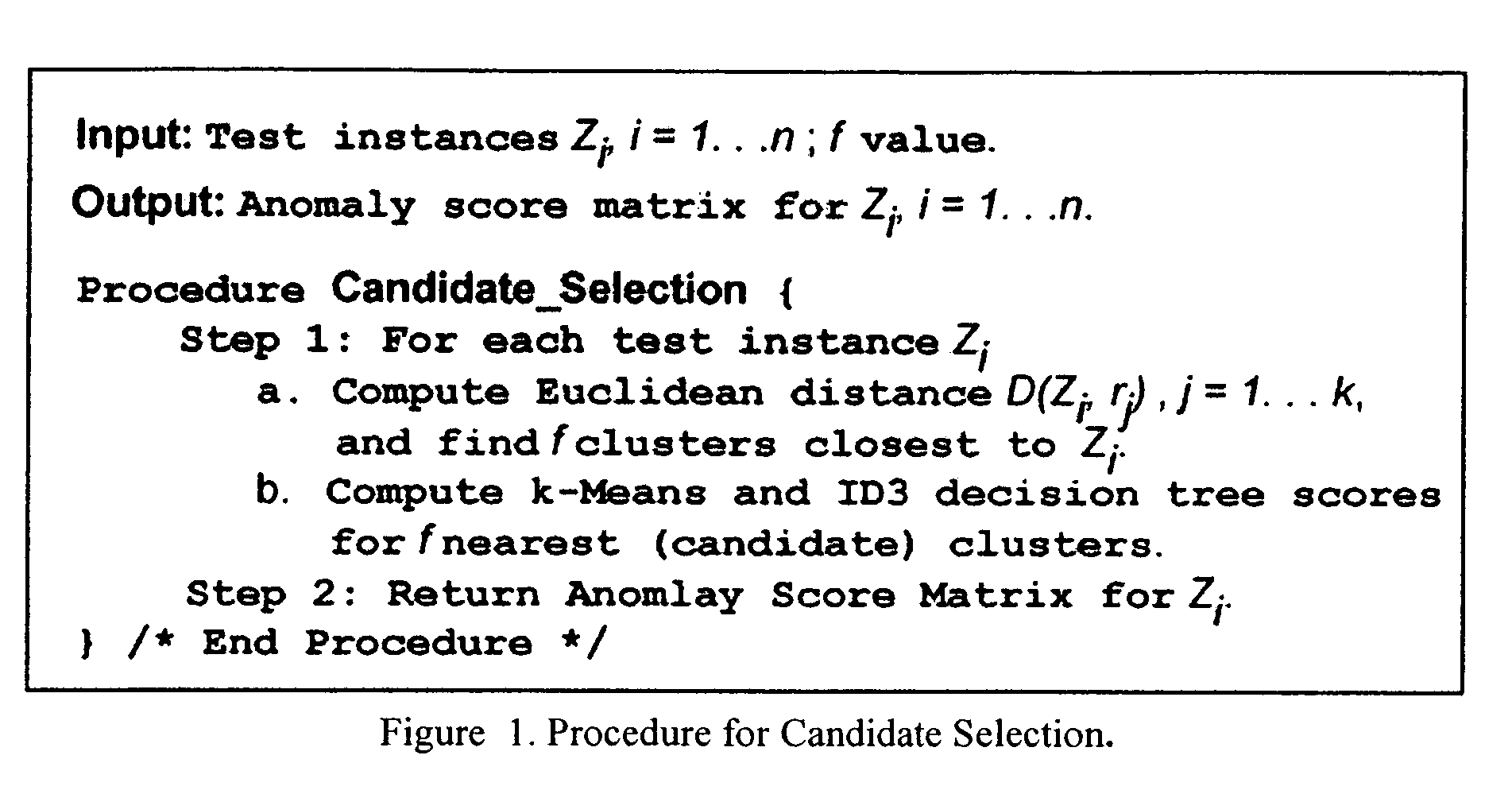
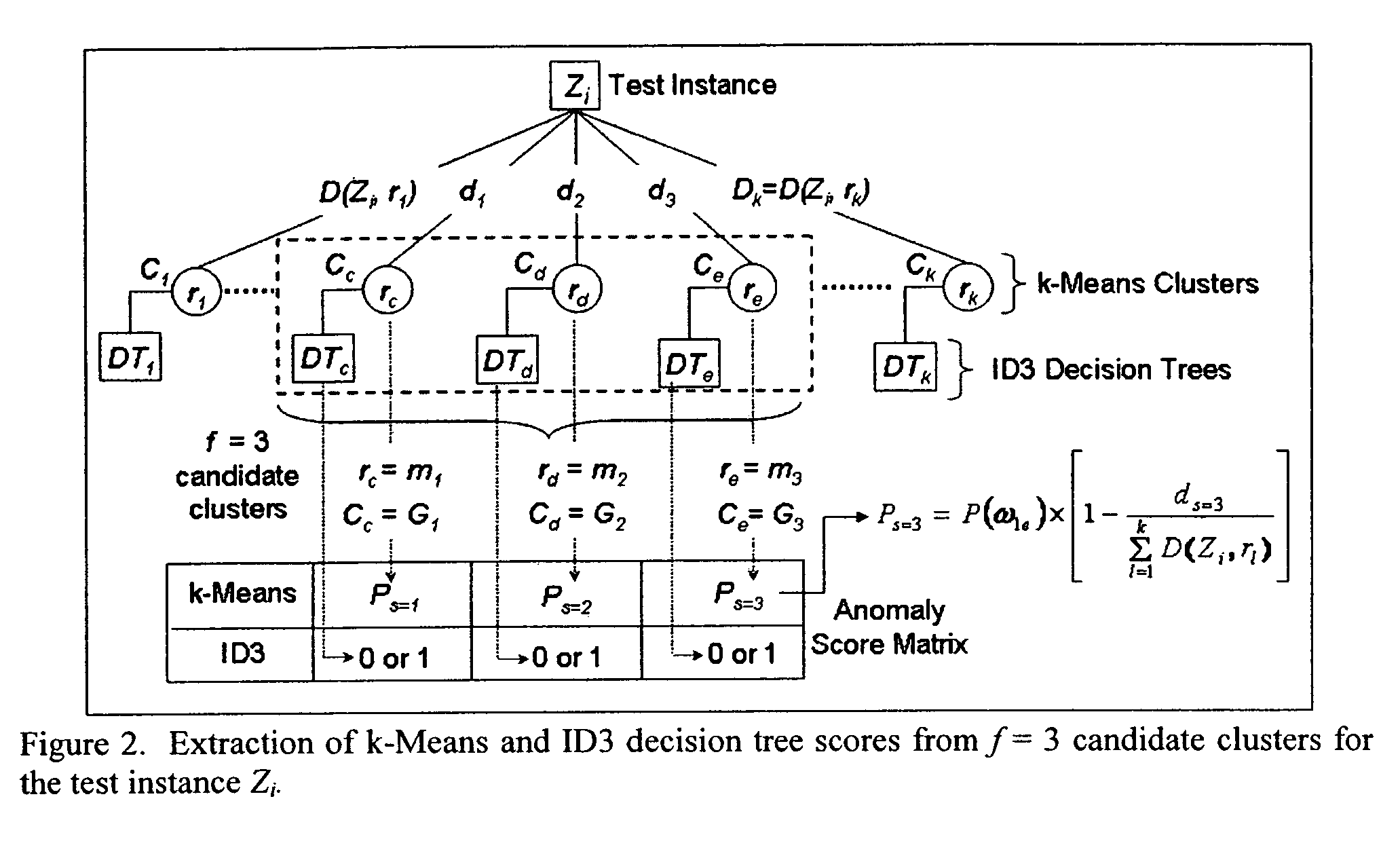
Method to indentify anomalous data using cascaded K-Means clustering and an ID3 decision tree
The invention is a computer implemented technique for id entifying anomalous data in a data set. The method uses cascaded k-Means clustering and the ID3 decision tree learning methods to characterize a training data set having data points with known characterization. The k-Means clustering method first partitions the training instances into k clusters using Euclidean distance similarity. On each training cluster, representing a density region of normal or anomaly instances, the invention builds an ID3 decision tree. The decision tree on each cluster refines the decision boundaries by learning the sub-groups within the cluster. A test data point is then subjected to the clustering and decision trees constructed form the training instances. To obtain a final decision on classification, the decisions of the k-Means and ID3 methods are combined using rules: (1) the Nearest-neighbor rule, and (2) the Nearest-consensus rule.
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH RES CORP
Determining User Preference of Items Based on User Ratings and User Features
ActiveUS20100250556A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsNear neighborCollaborative filtering
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Apparatus and methods for training of robots
ActiveUS20160096272A1Programme-controlled manipulatorAutonomous decision making processVision basedCharacteristic space
A random k-nearest neighbors (RKNN) approach may be used for regression / classification model wherein the input includes the k closest training examples in the feature space. The RKNN process may utilize video images as input in order to predict motor command for controlling navigation of a robot. In some implementations of robotic vision based navigation, the input space may be highly dimensional and highly redundant. When visual inputs are augmented with data of another modality that is characterized by fewer dimensions (e.g., audio), the visual data may overwhelm lower-dimension data. The RKNN process may partition available data into subsets comprising a given number of samples from the lower-dimension data. Outputs associated with individual subsets may be combined (e.g., averaged). Selection of number of neighbors, subset size and / or number of subsets may be used to trade-off between speed and accuracy of the prediction.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
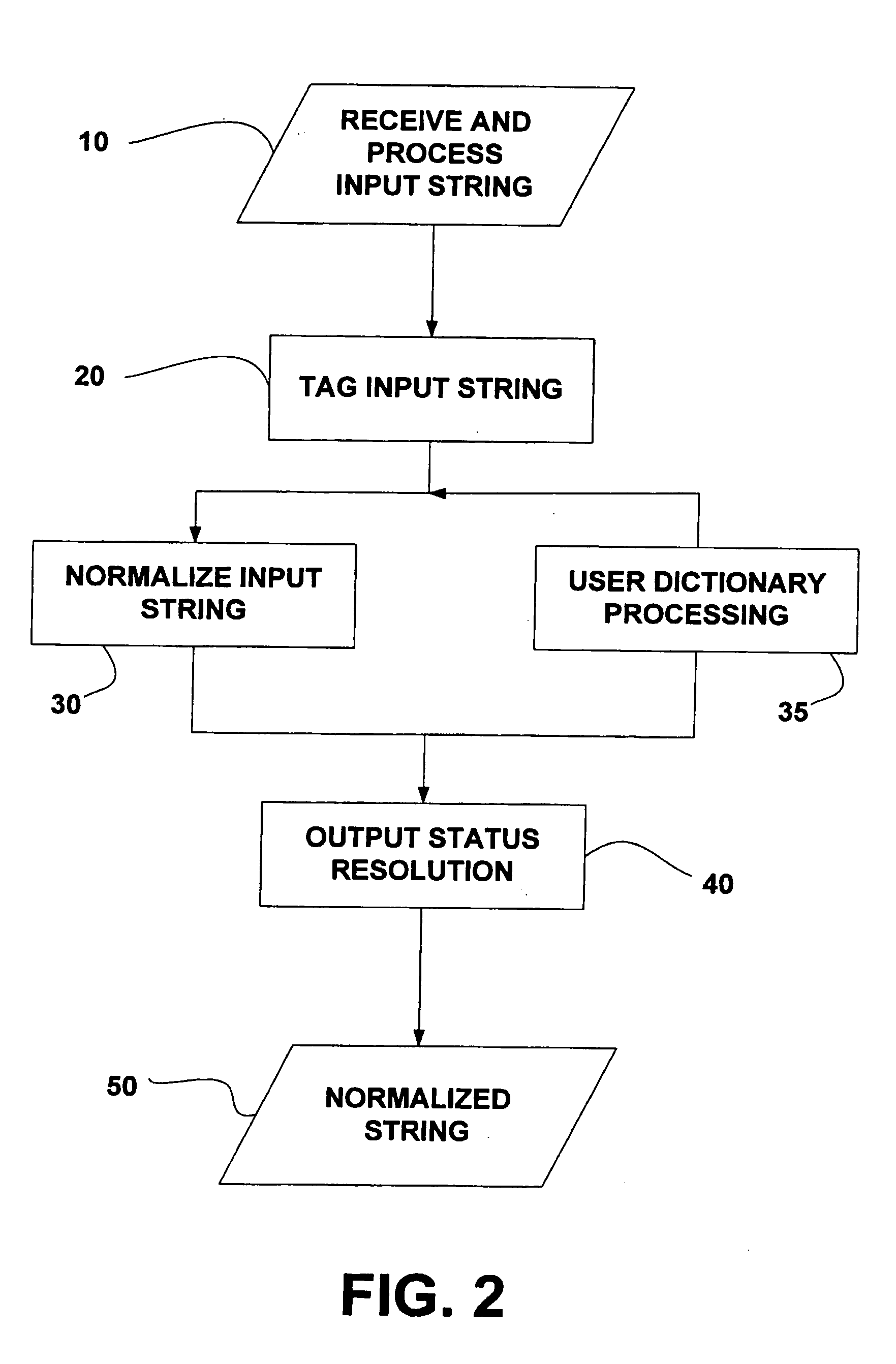
System and method for normalization of a string of words
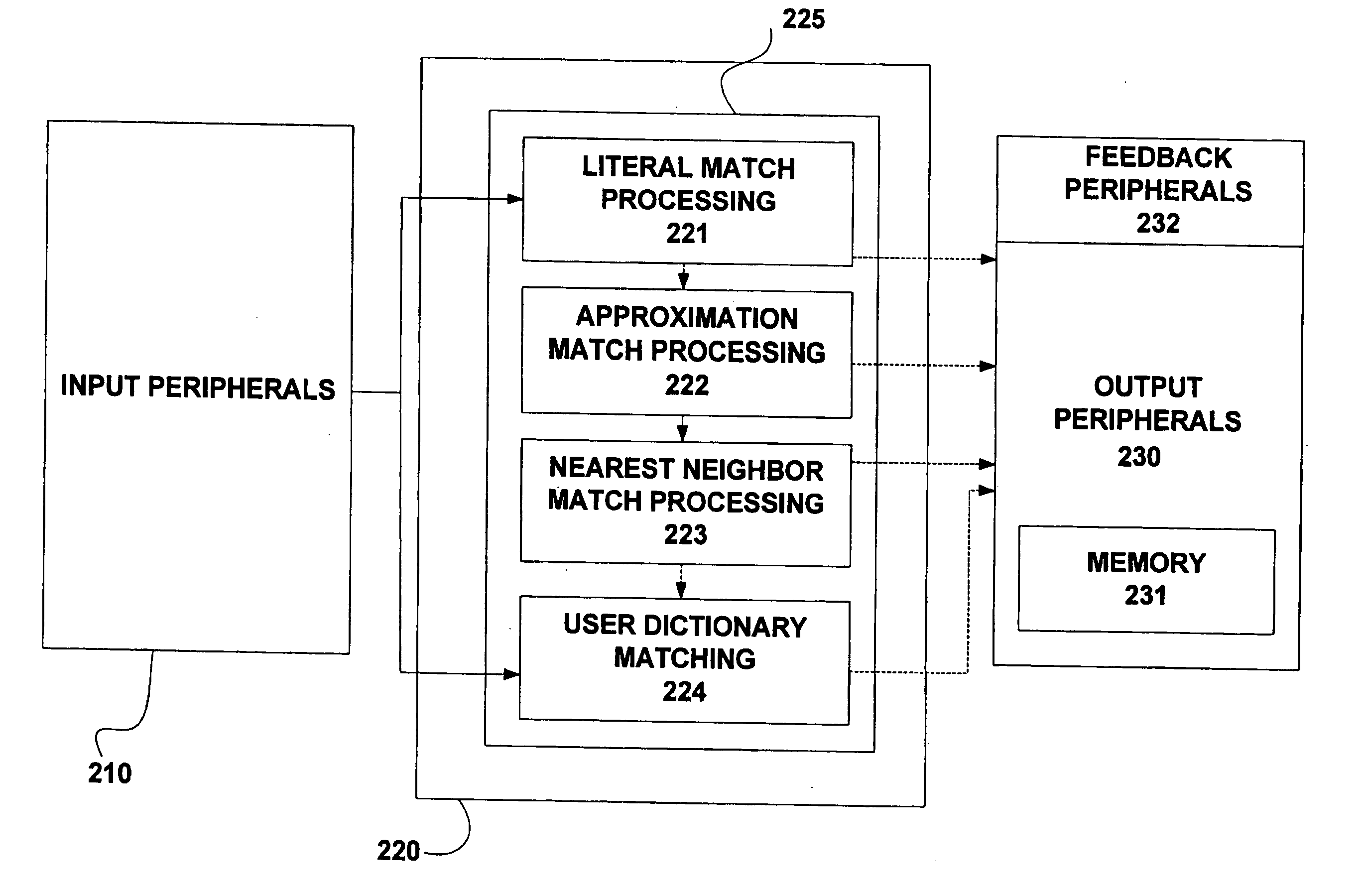
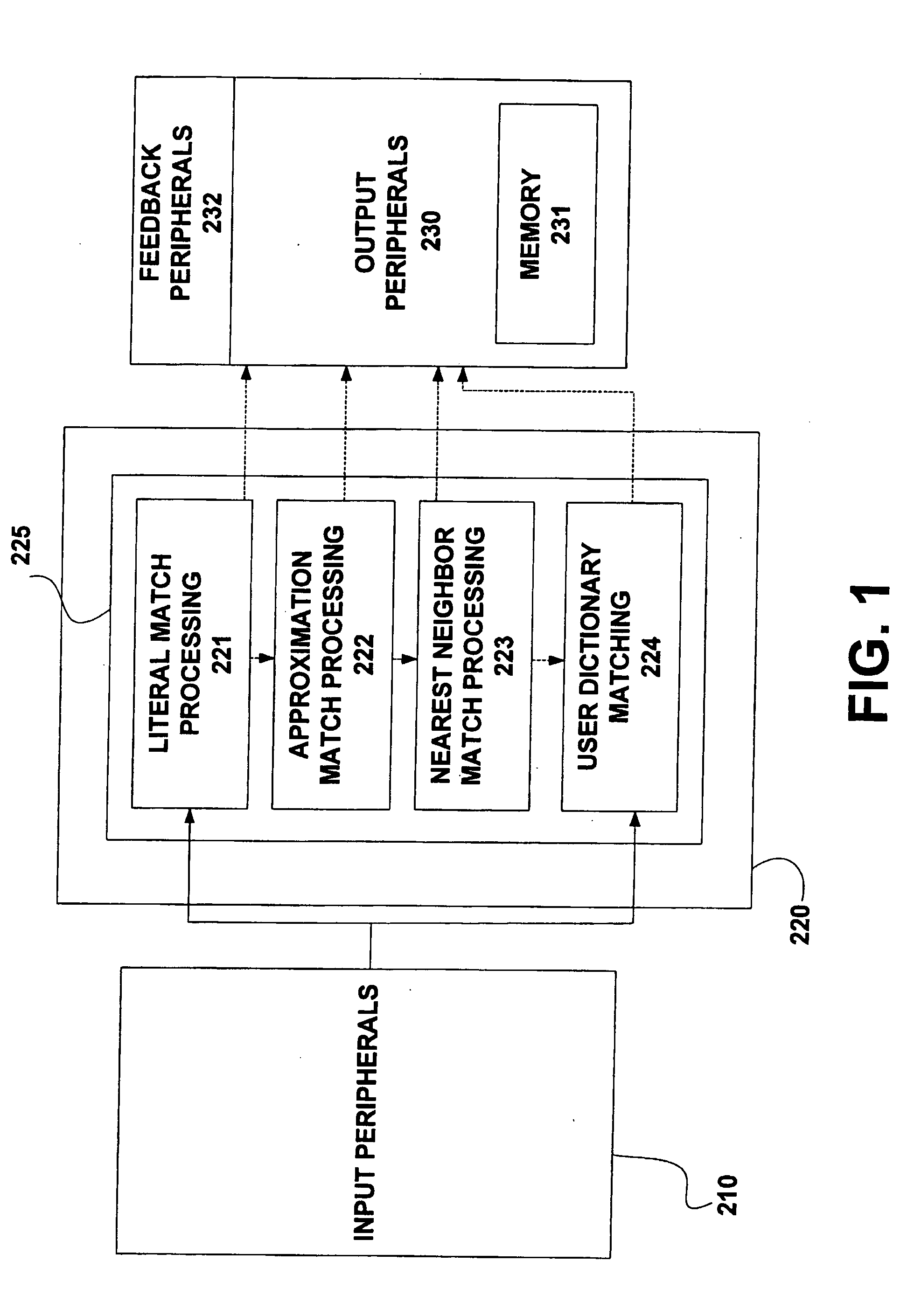
The present invention relates generally to a system and method for categorization of strings of words. More specifically, the present invention relates to a system and method for normalizing a string of words for use in a system for categorization of words in a predetermined categorization scheme. A method for adaptive categorization of words in a predetermined categorization scheme may include receiving a string of text, tagging the string of text, and normalizing the string of text. Normalization may be performed with a three-stage algorithm including a literal match processing stage, an approximation match processing stage, and a nearest neighbor match processing stage. The normalized string of text can be compared to a number of sequences of text in the predetermined categorization scheme.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
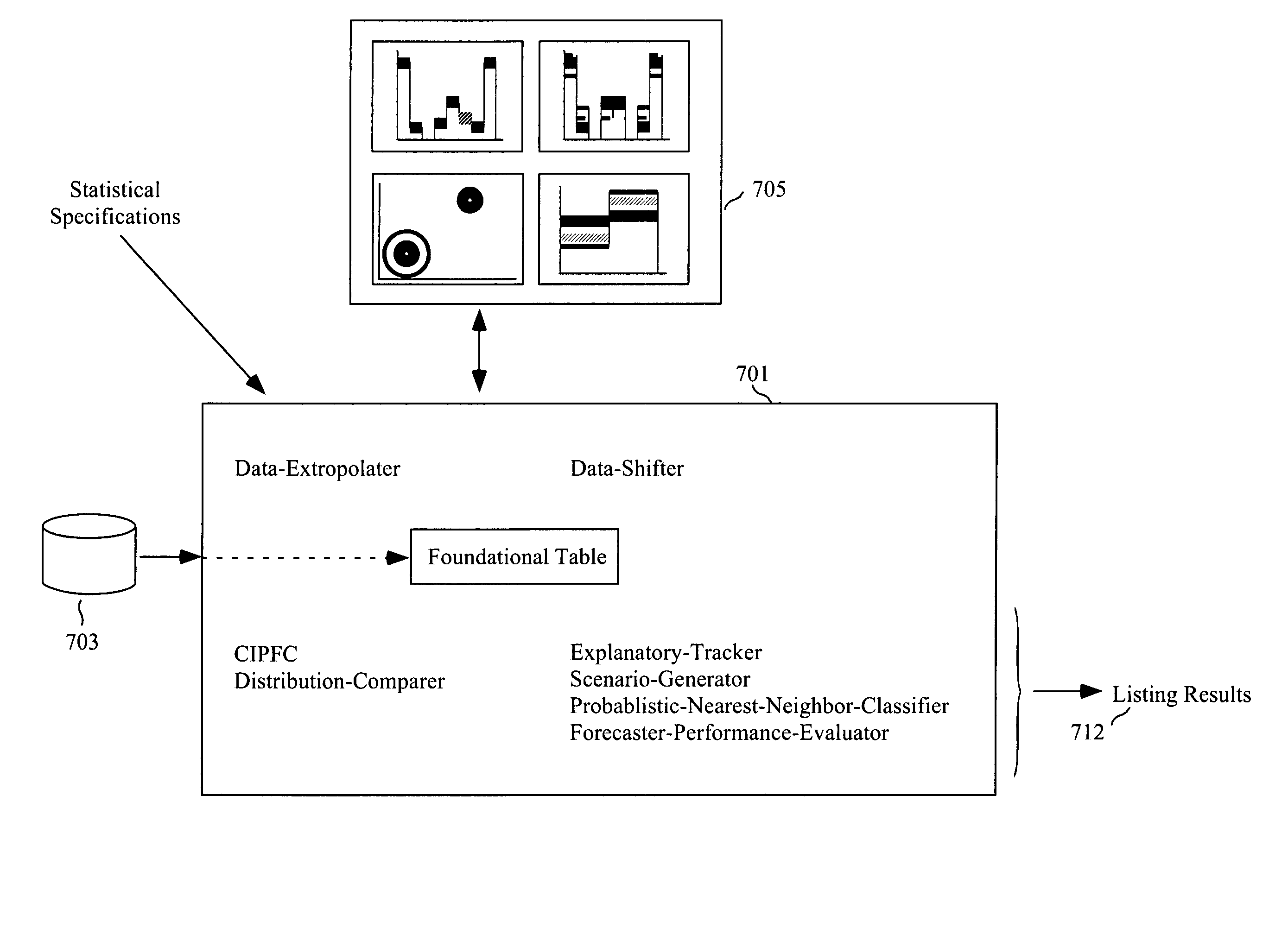
Optimal scenario forecasting, risk sharing, and risk trading
An integrated and unified method of statistical-like analysis, scenario forecasting, risking sharing, and risk trading is presented. Variates explanatory of response variates are identified in terms of the "value of the knowing." Such a value can be direct economic value. Probabilistic scenarios are generated by multi-dimensionally weighting a dataset. Weights are specified using Exogenous-Forecasted Distributions (EFDs). Weighting is done by a highly improved Iterative Proportional Fitting Procedure (IPFP) that exponentially reduces computer storage and calculations requirements. A probabilistic nearest neighbor procedure is provided to yield fine-grain pinpoint scenarios. A method to evaluate forecasters is presented; this method addresses game-theory issues. All of this leads to the final component: a new method of sharing and trading risk, which both directly integrates with the above and yields contingent risk-contracts that better serve all parties.
Owner:JAMESON JOEL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com