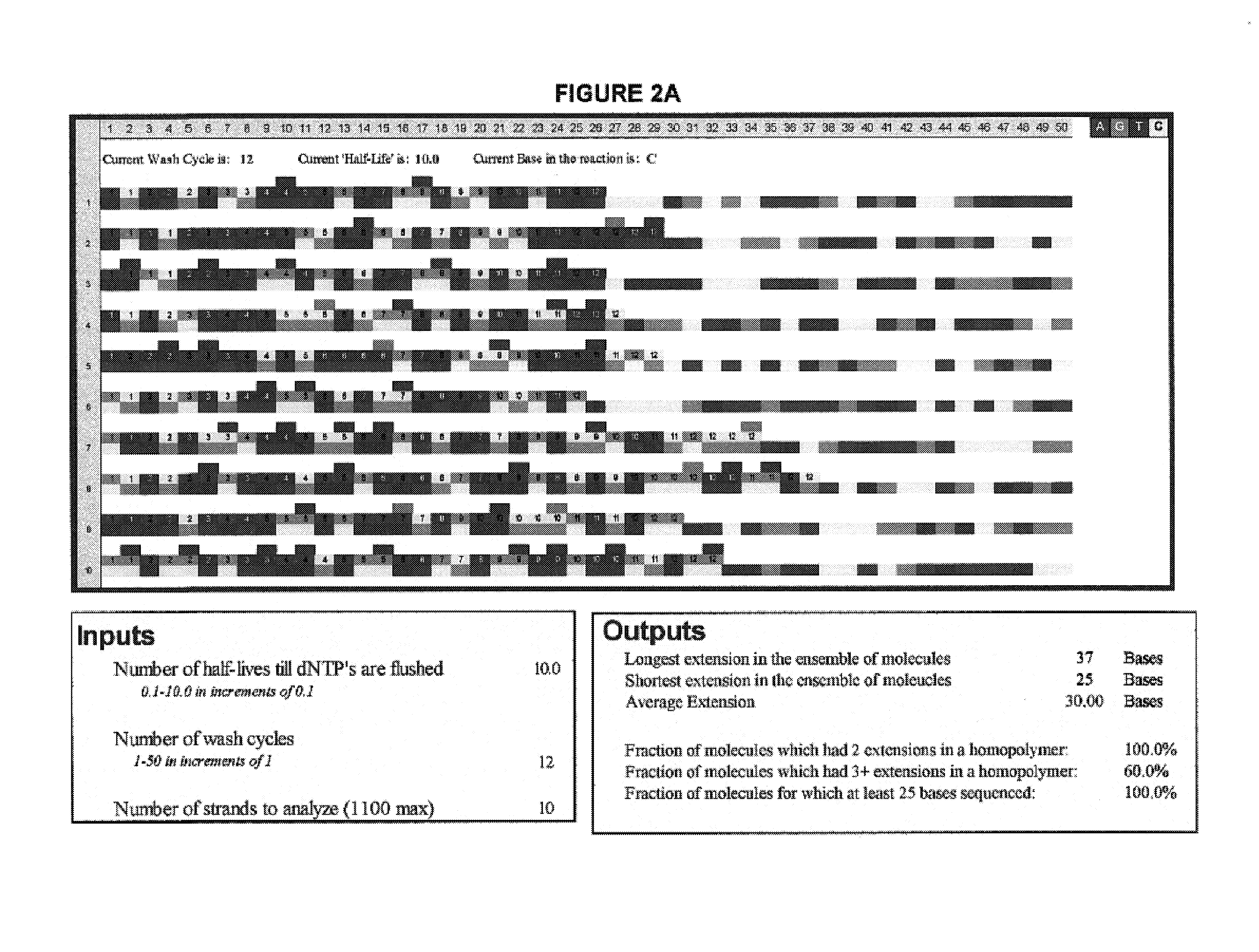
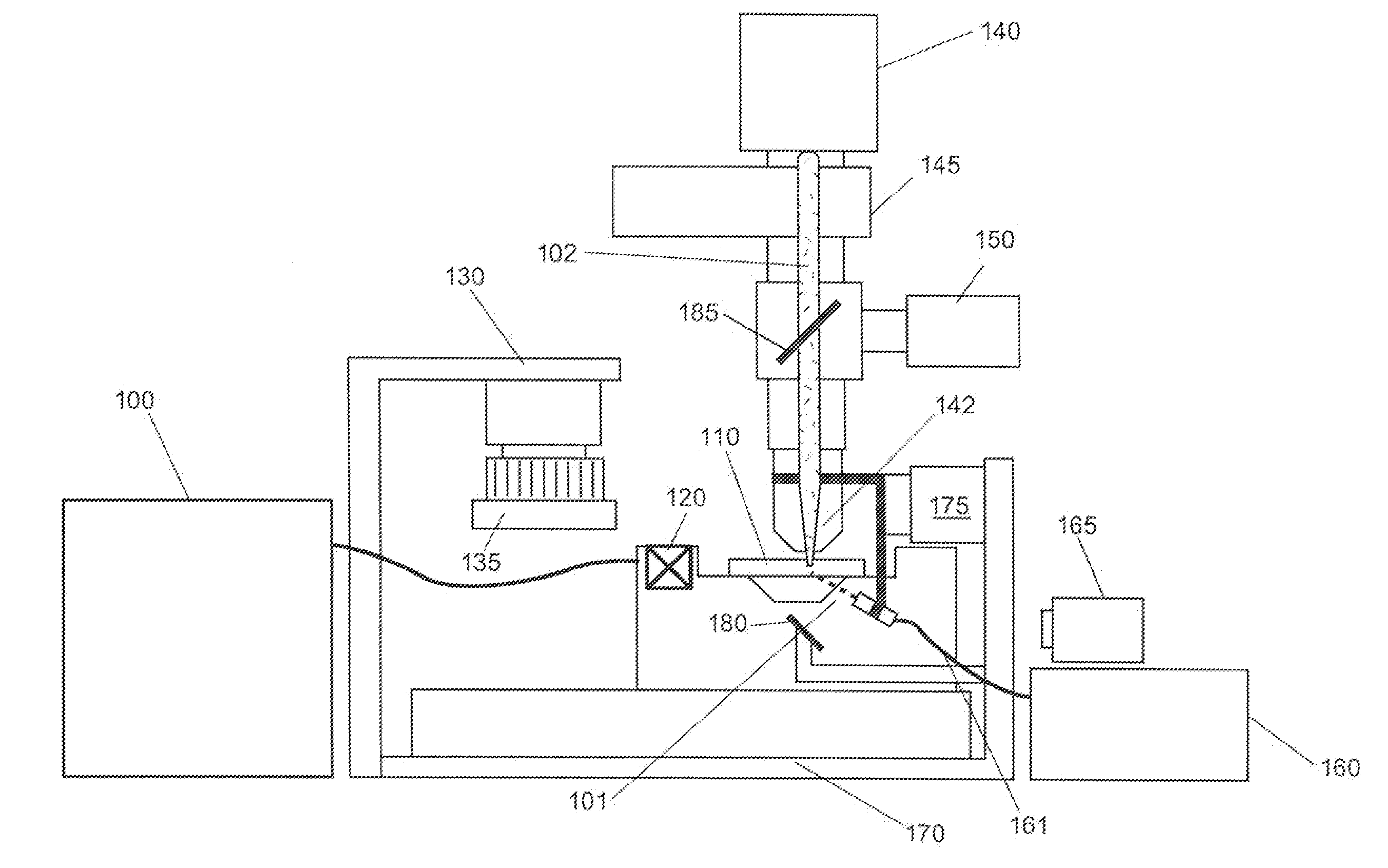
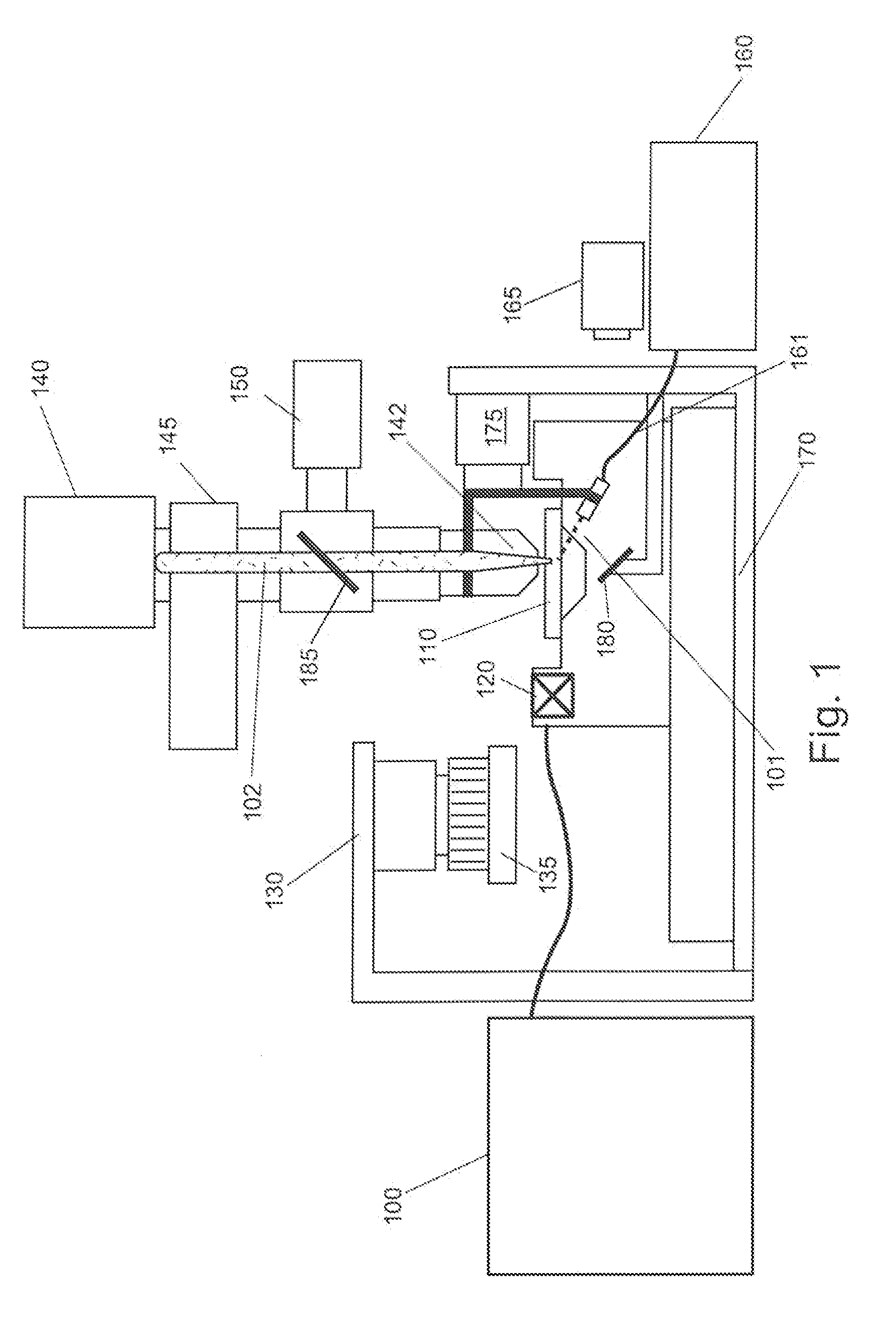
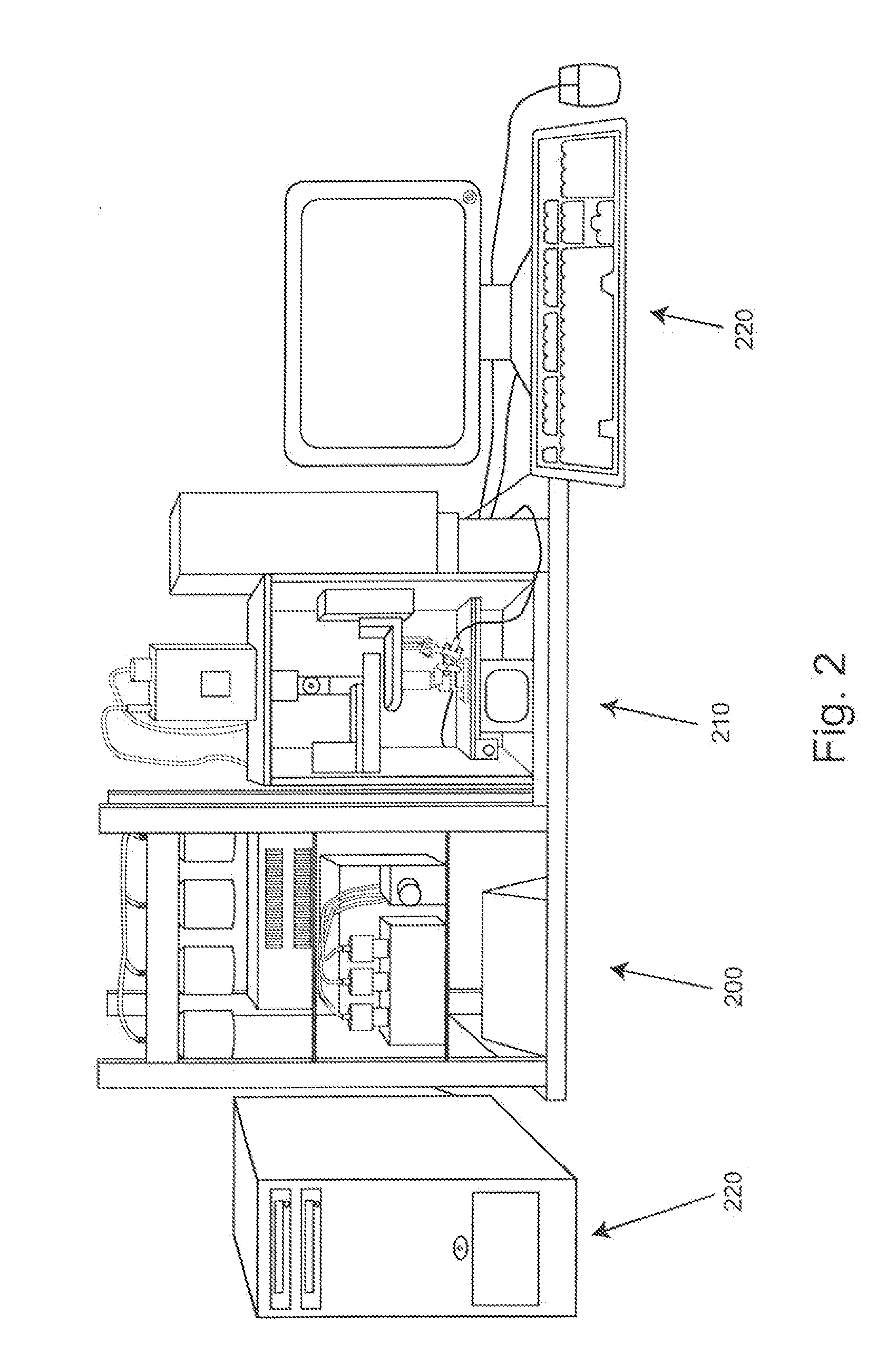
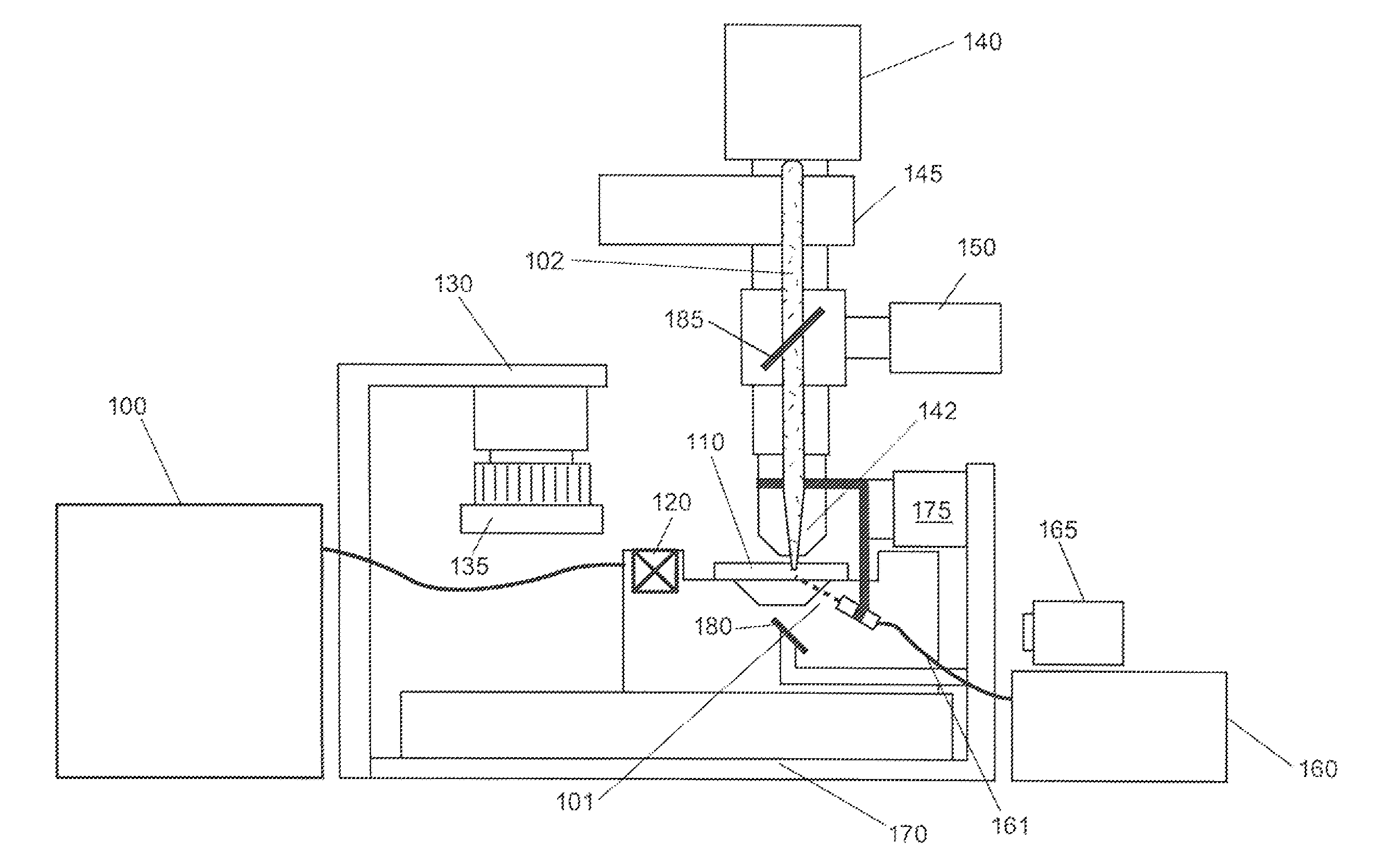
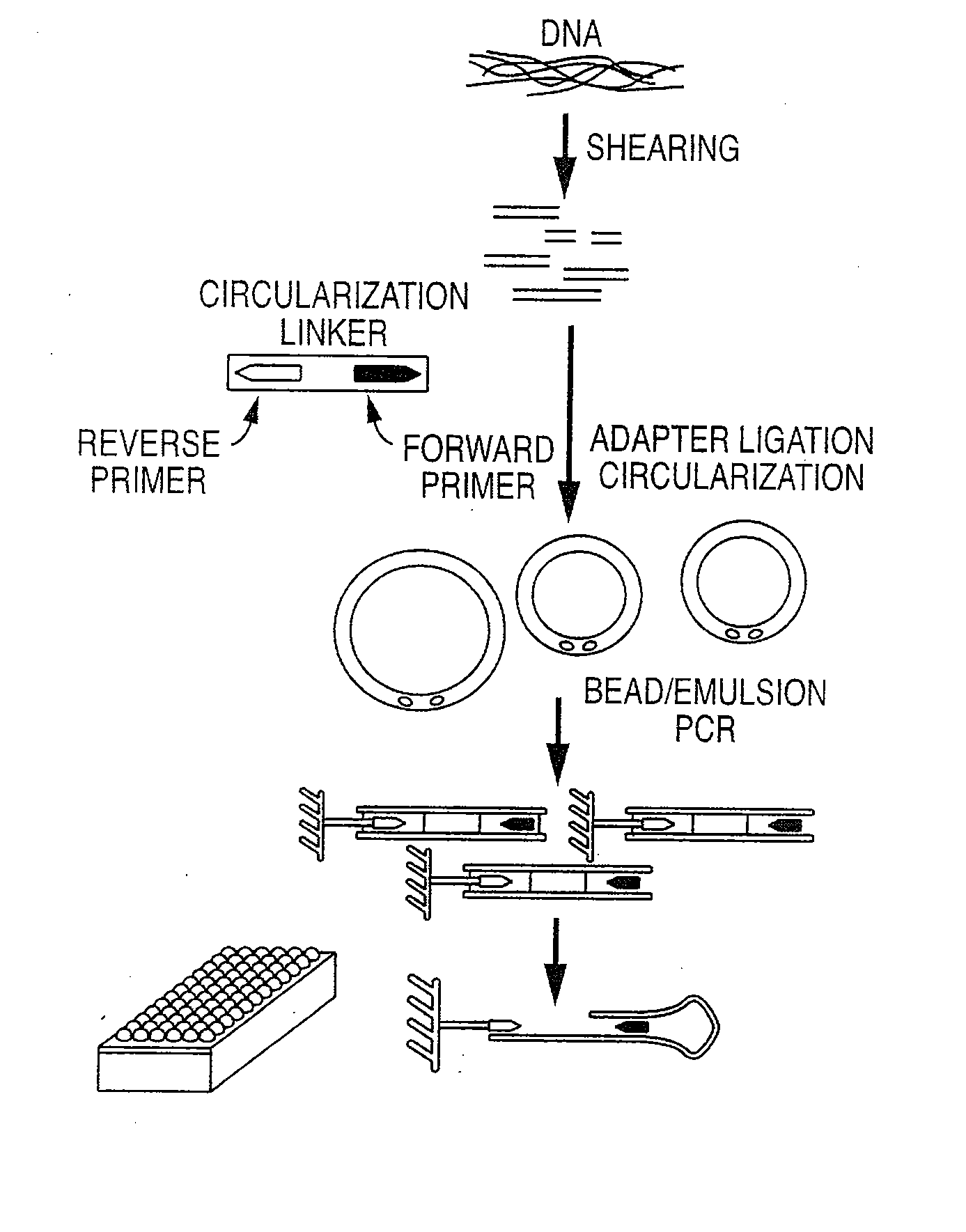
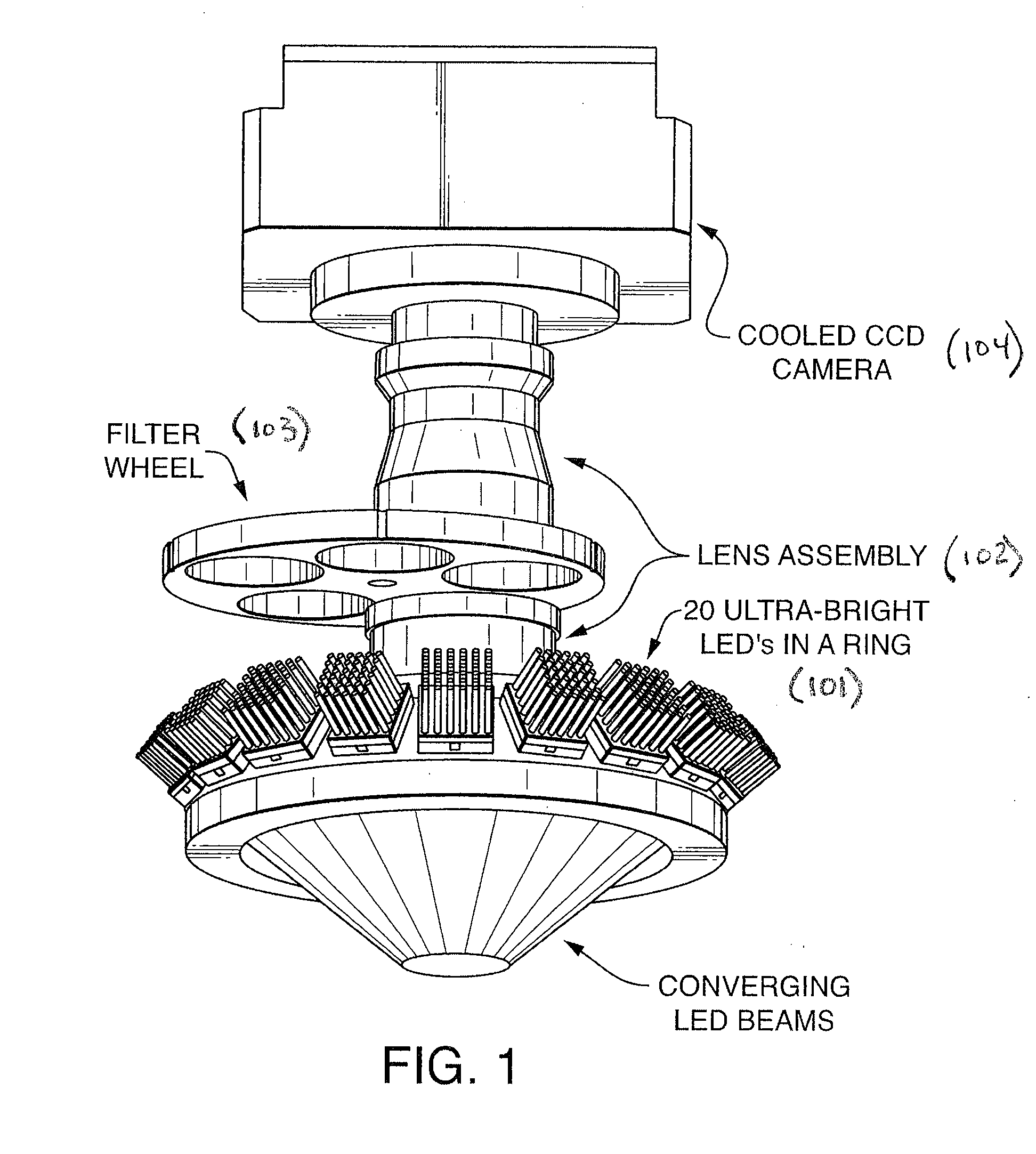
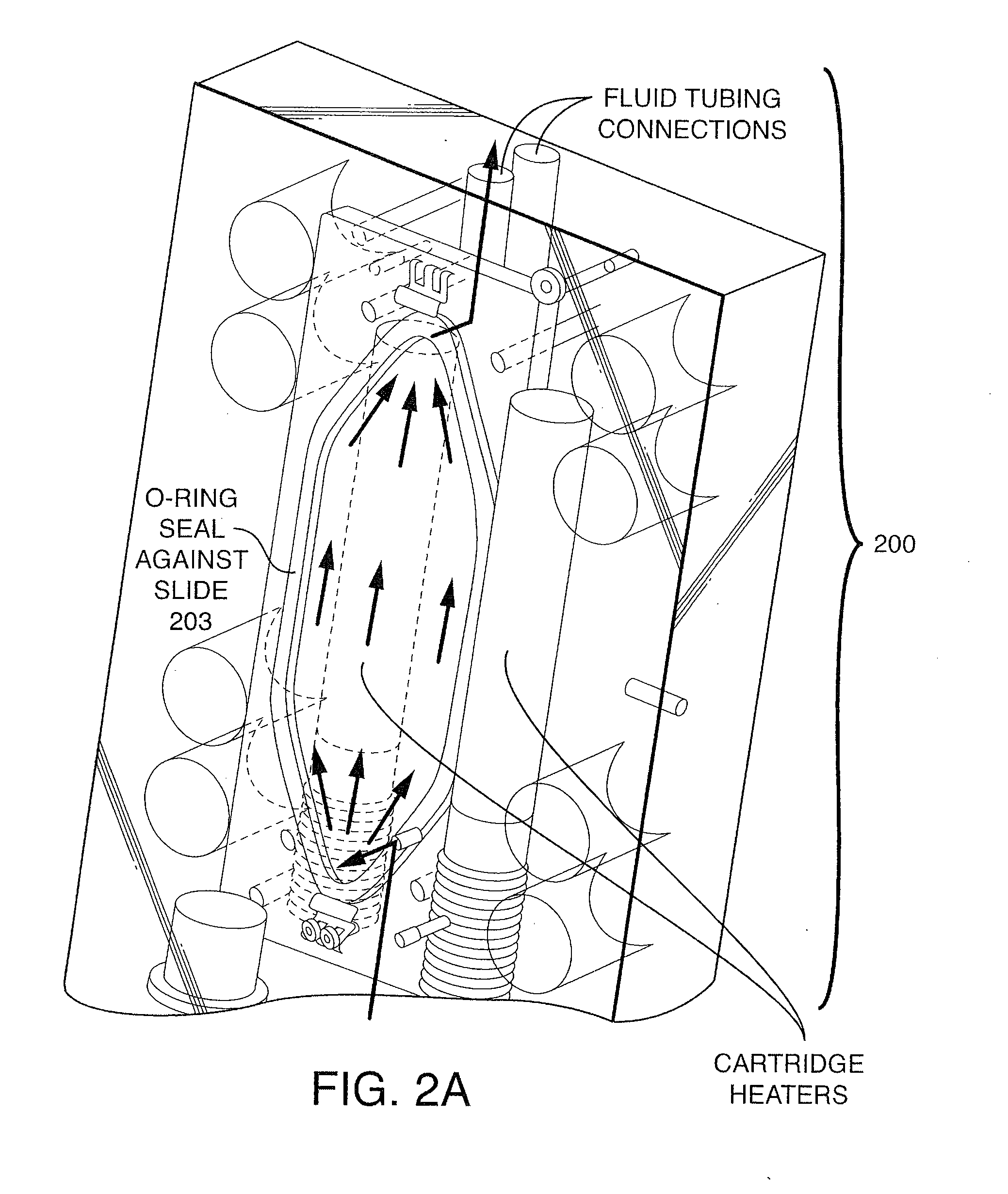
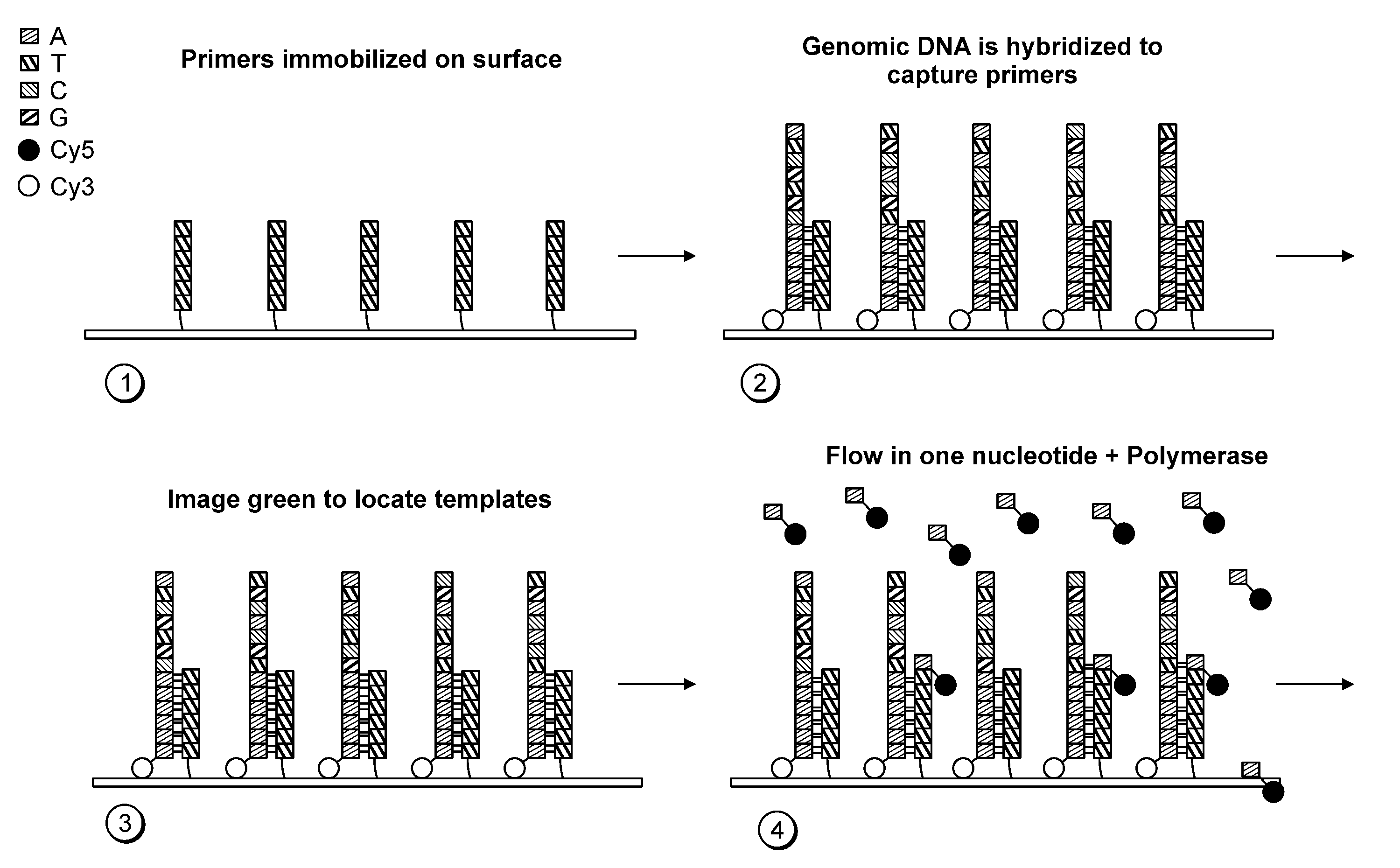
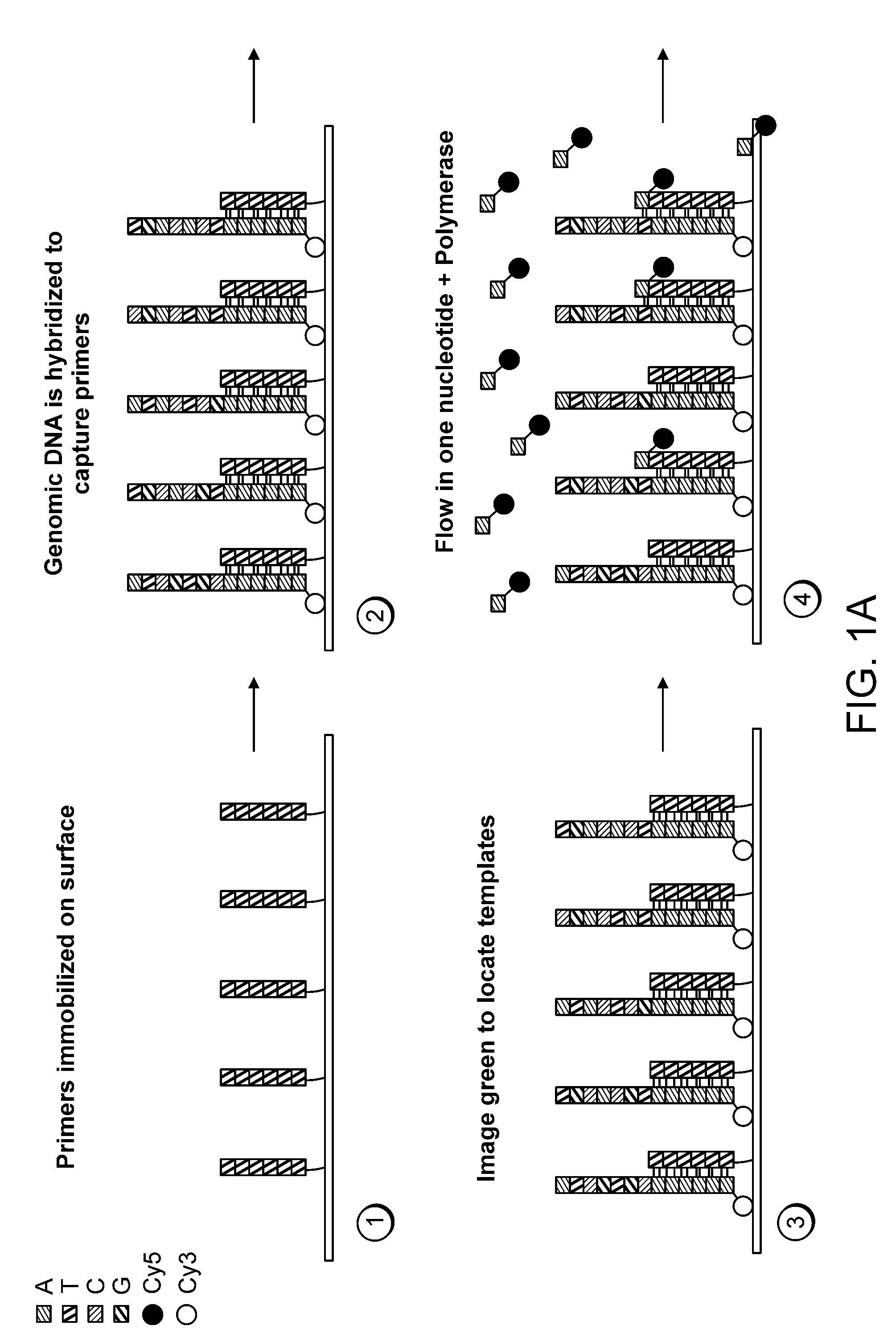
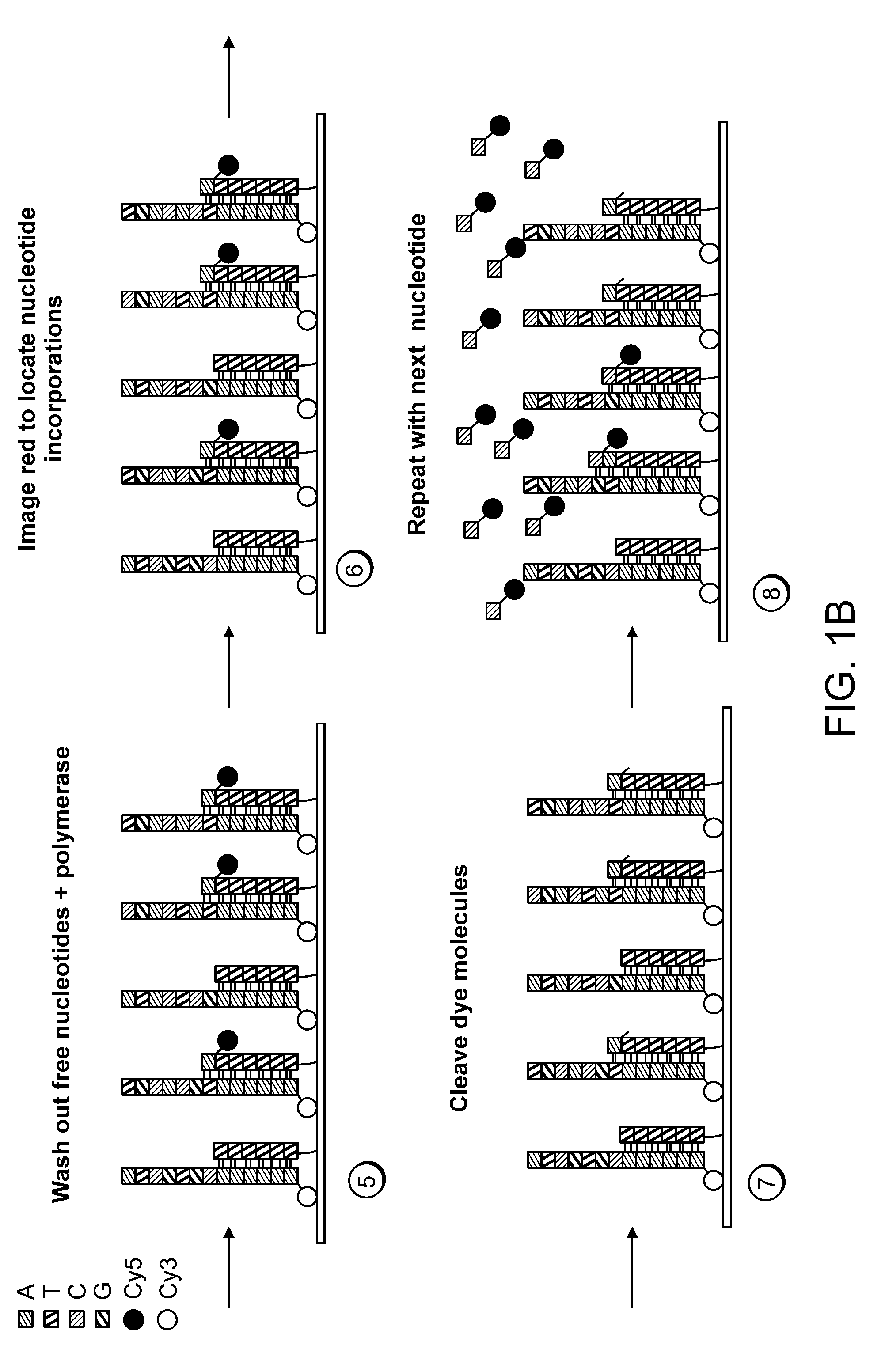
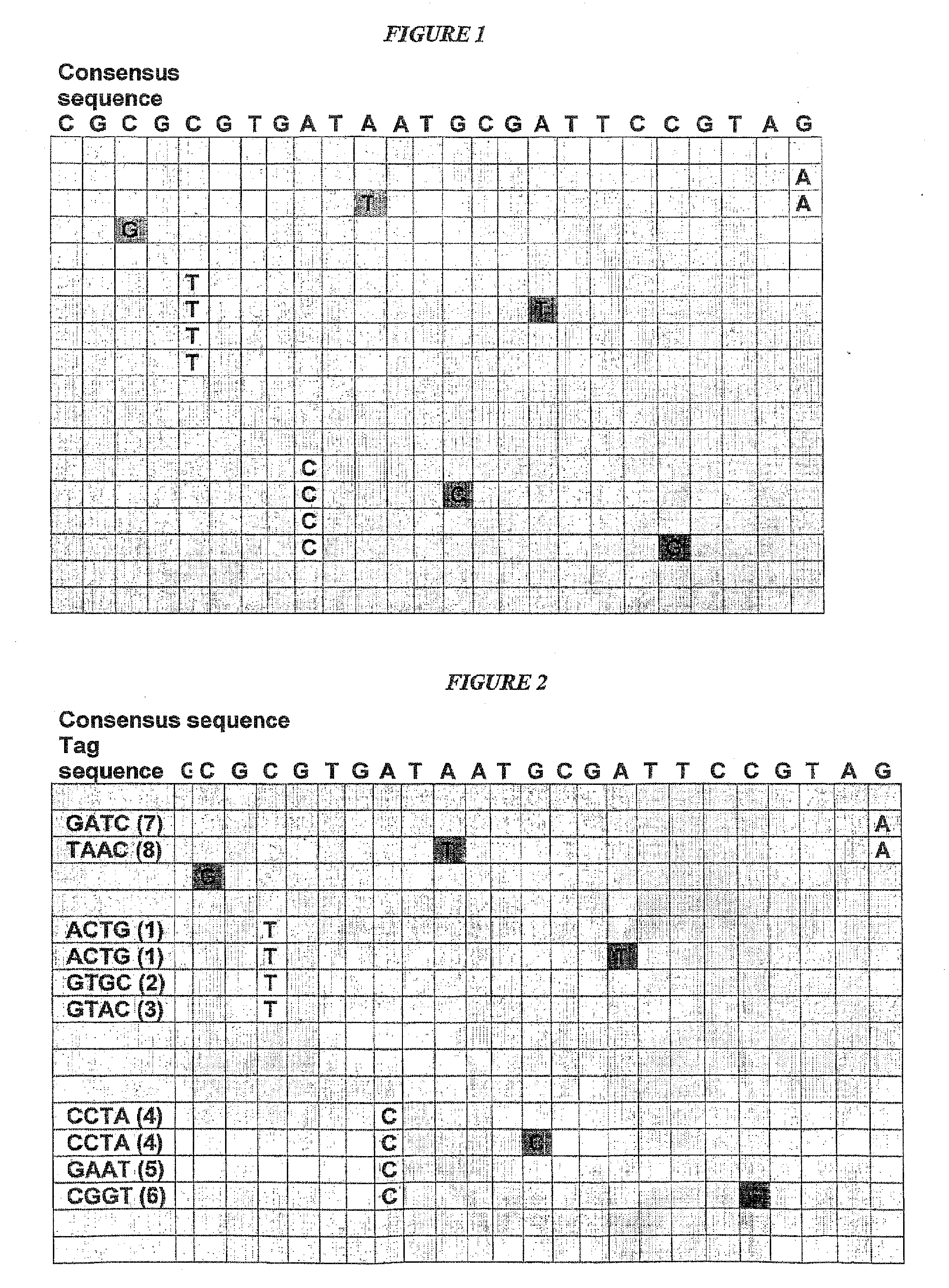
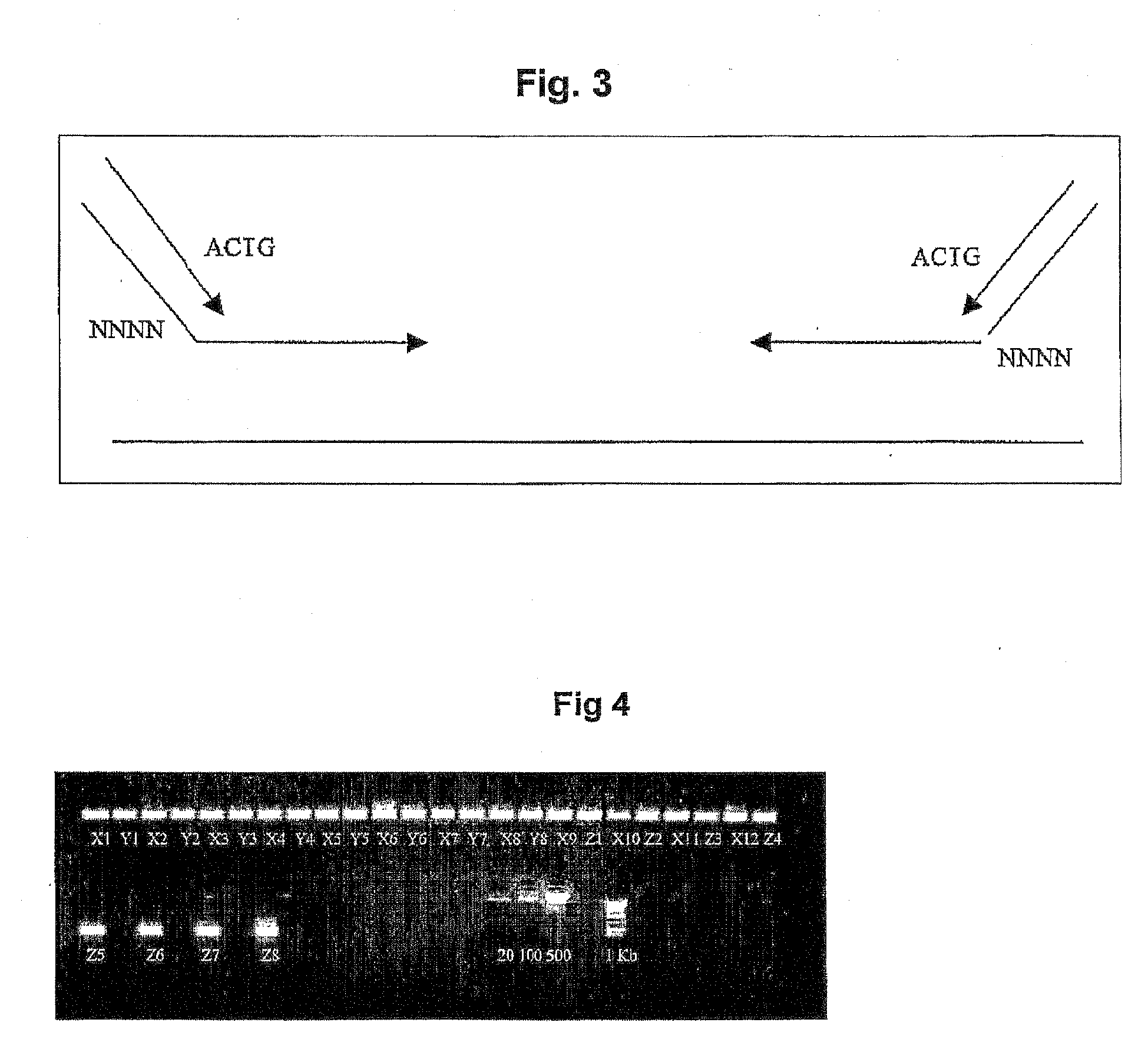
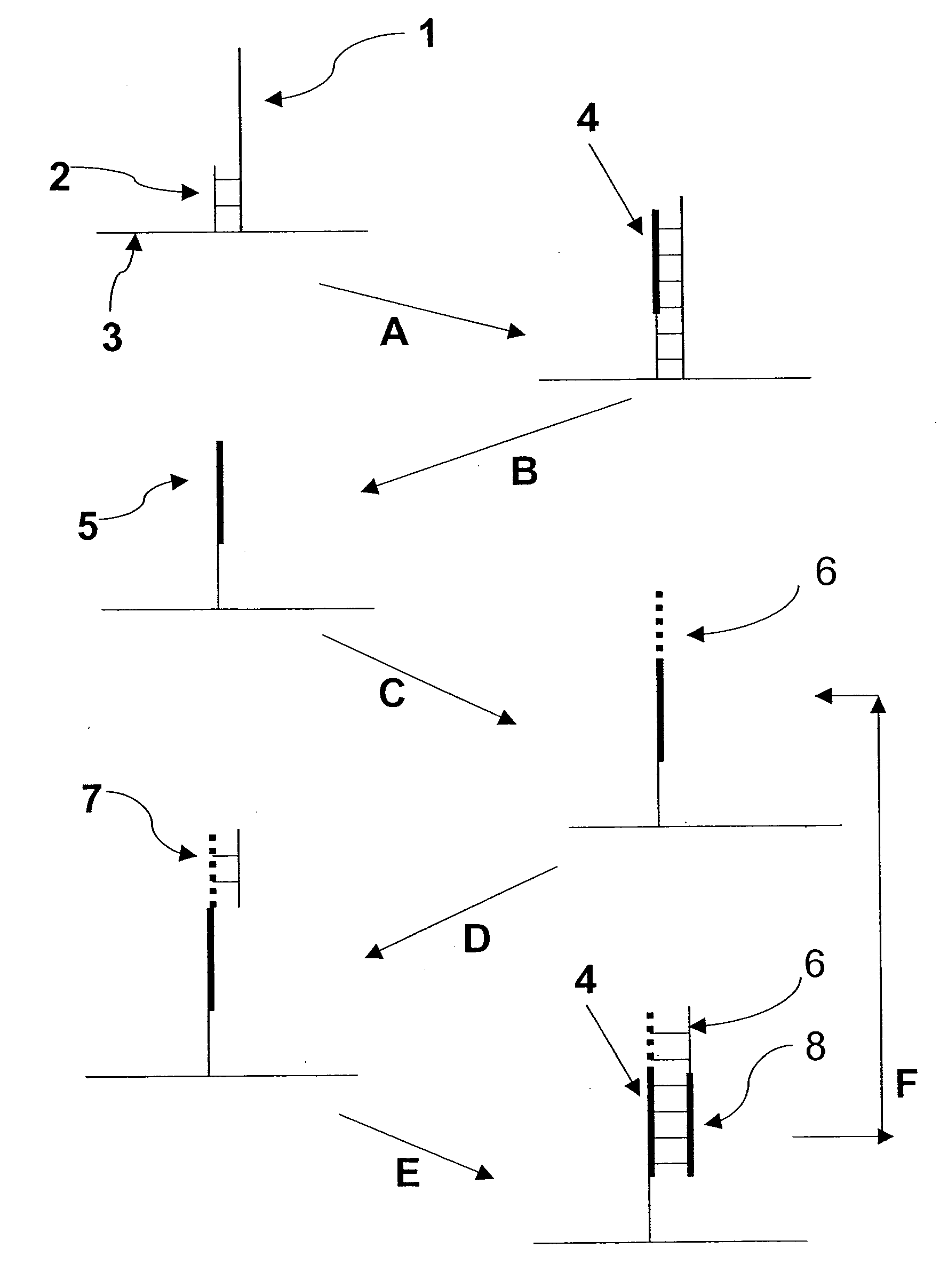
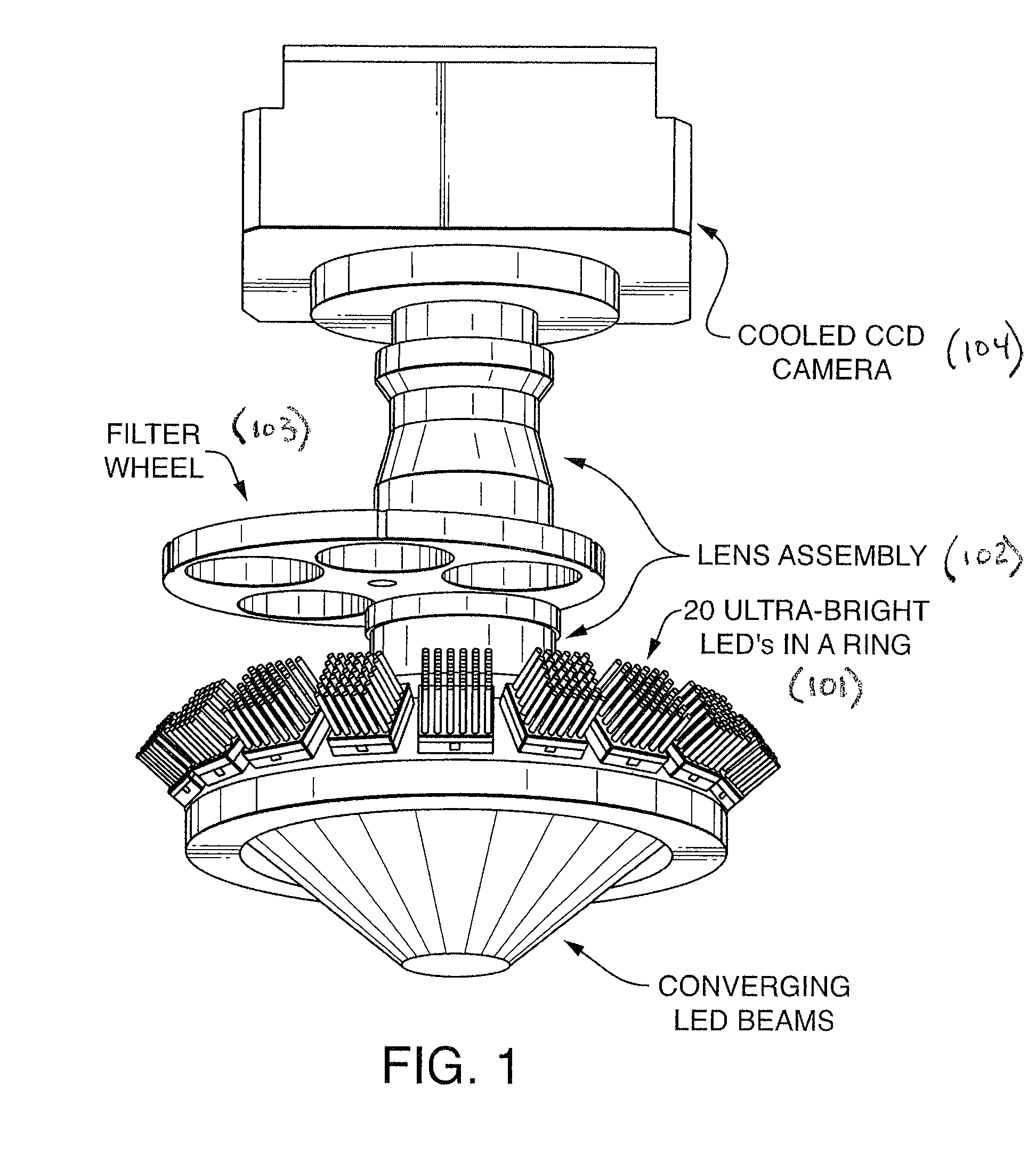
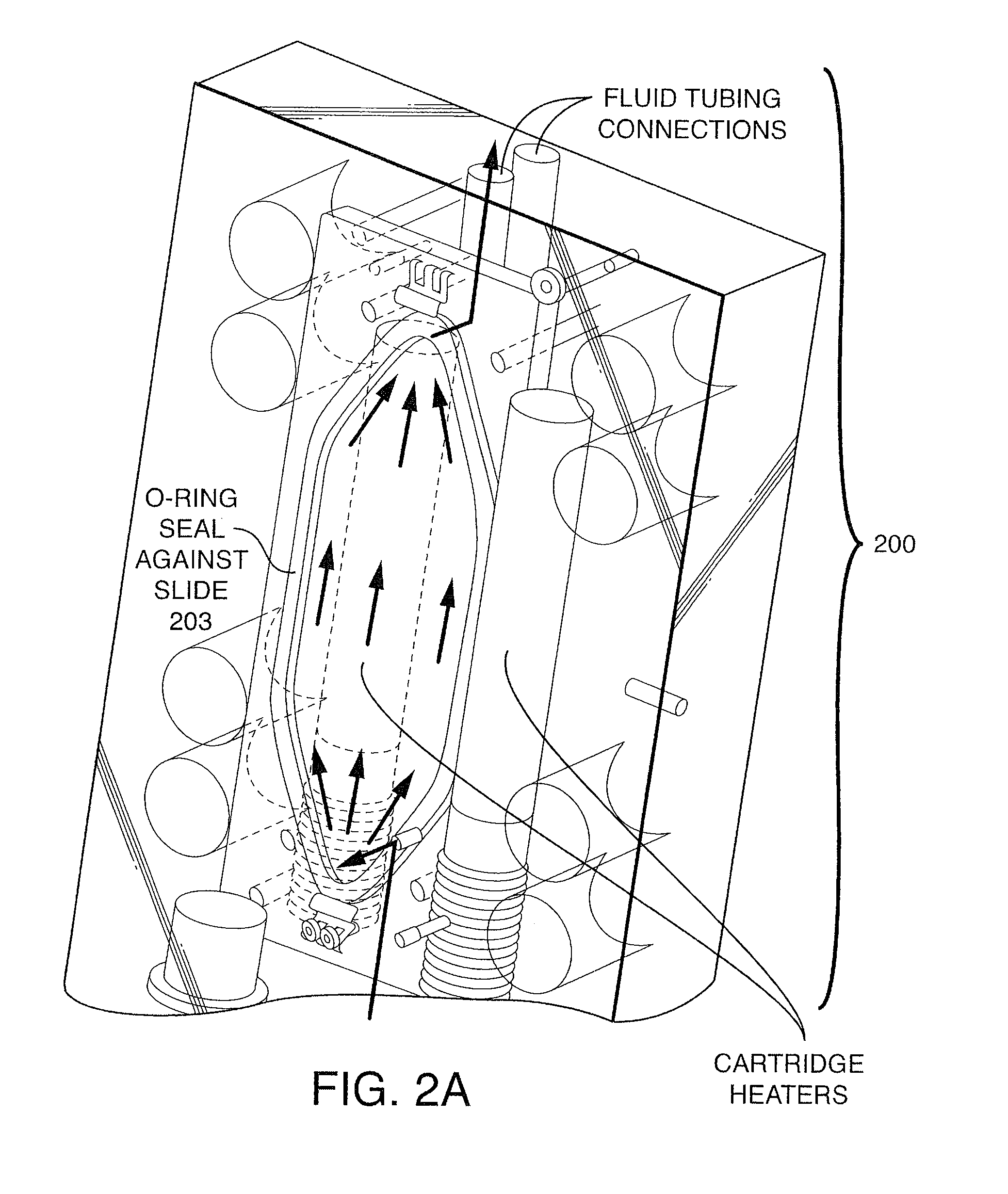
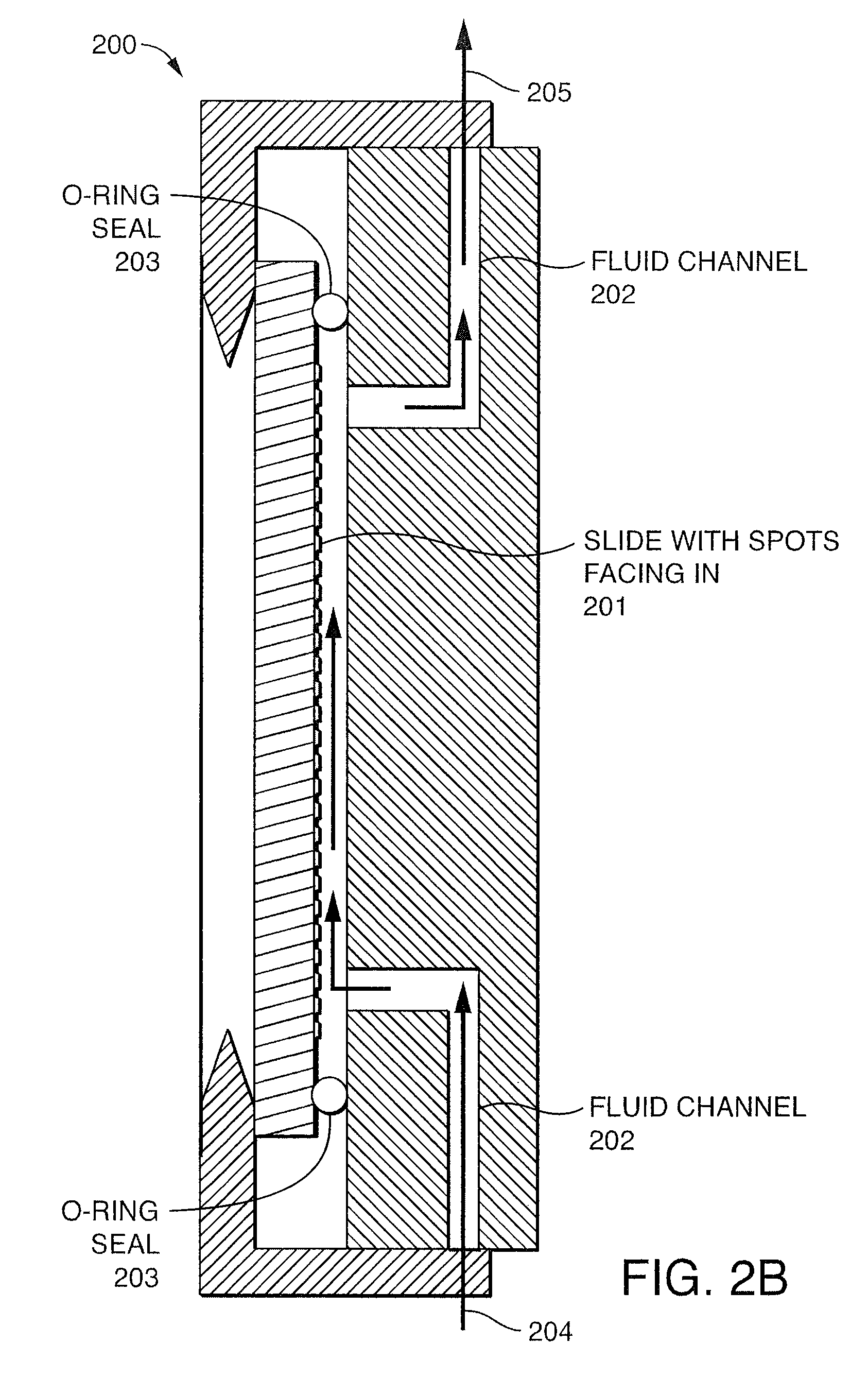
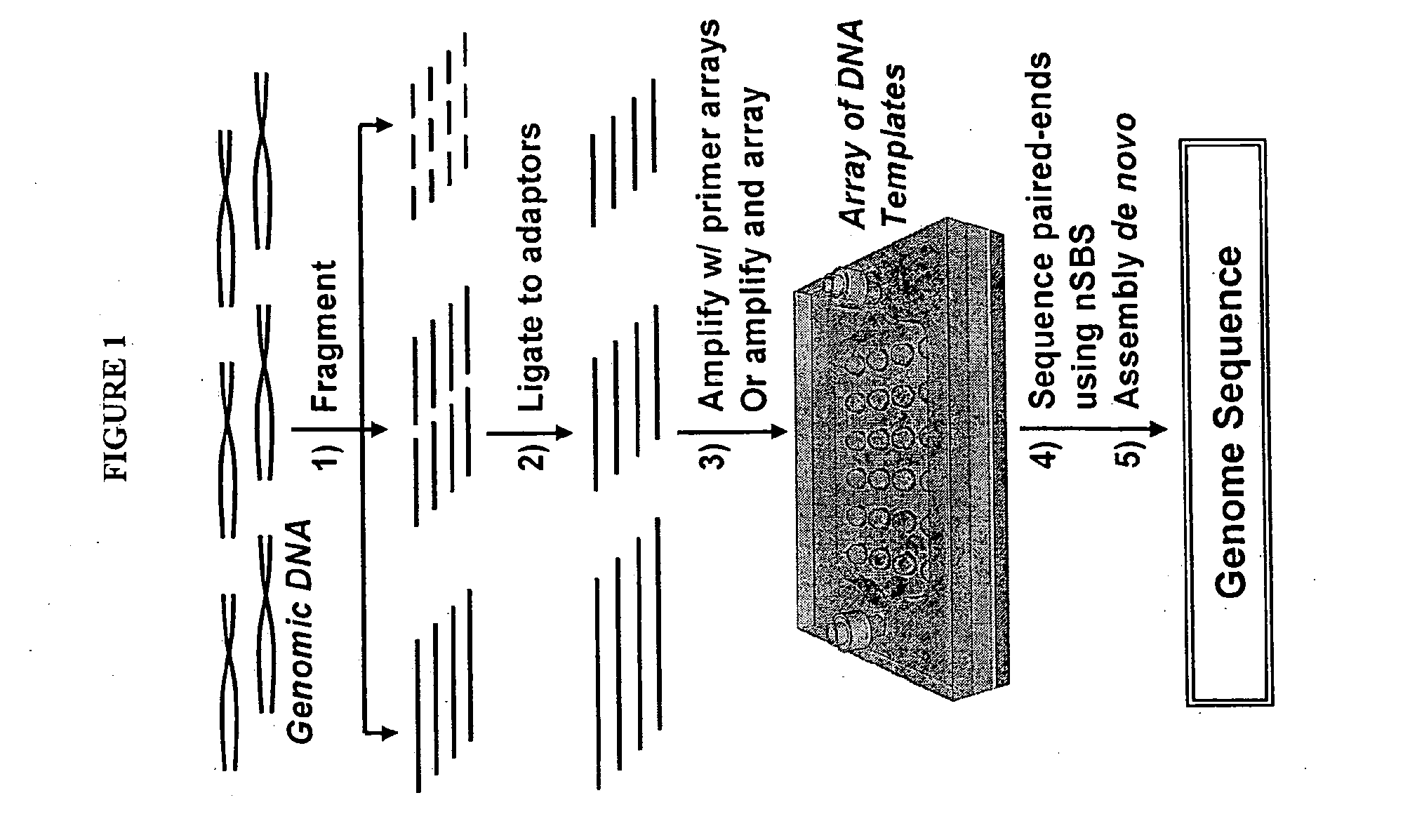
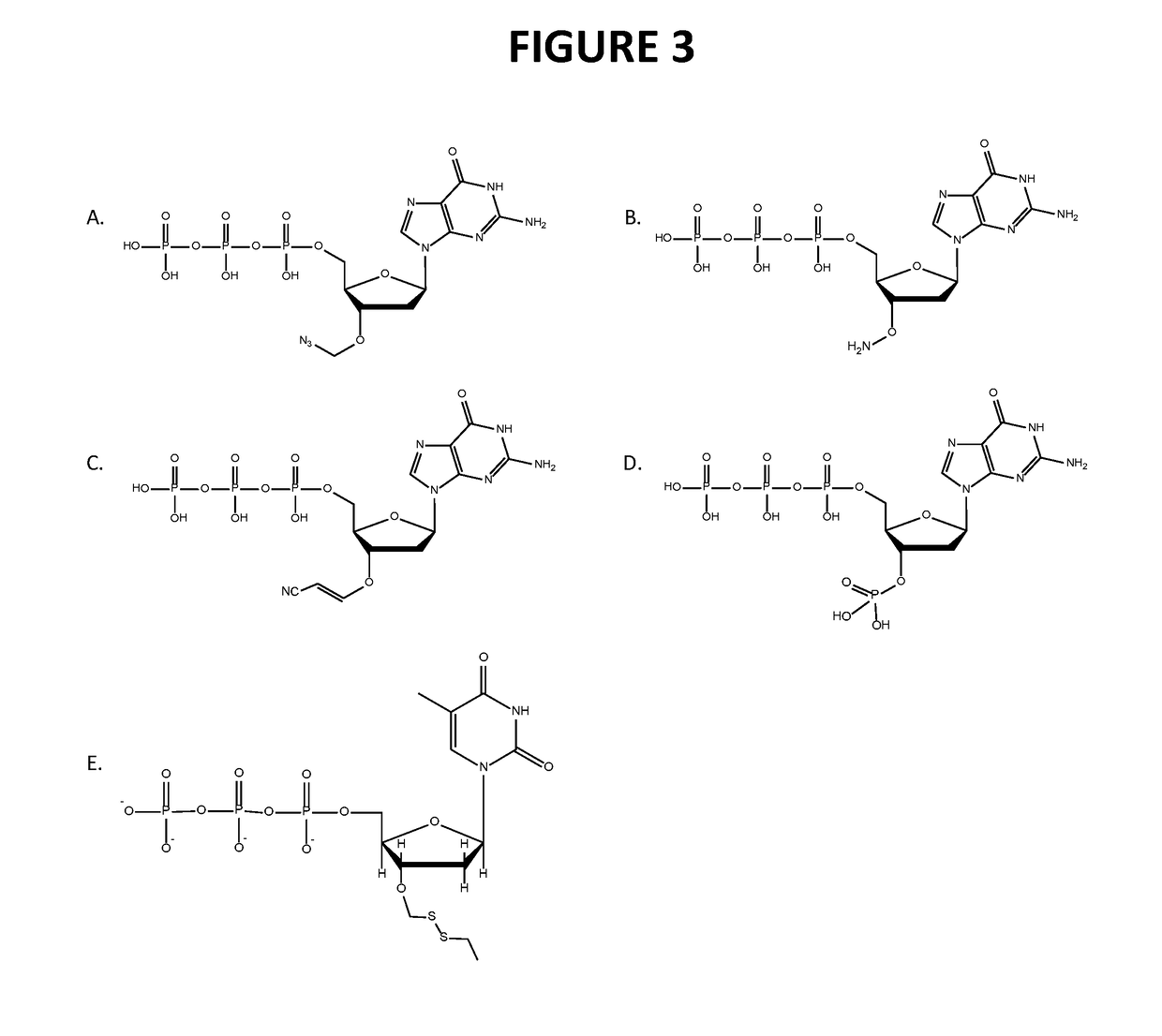
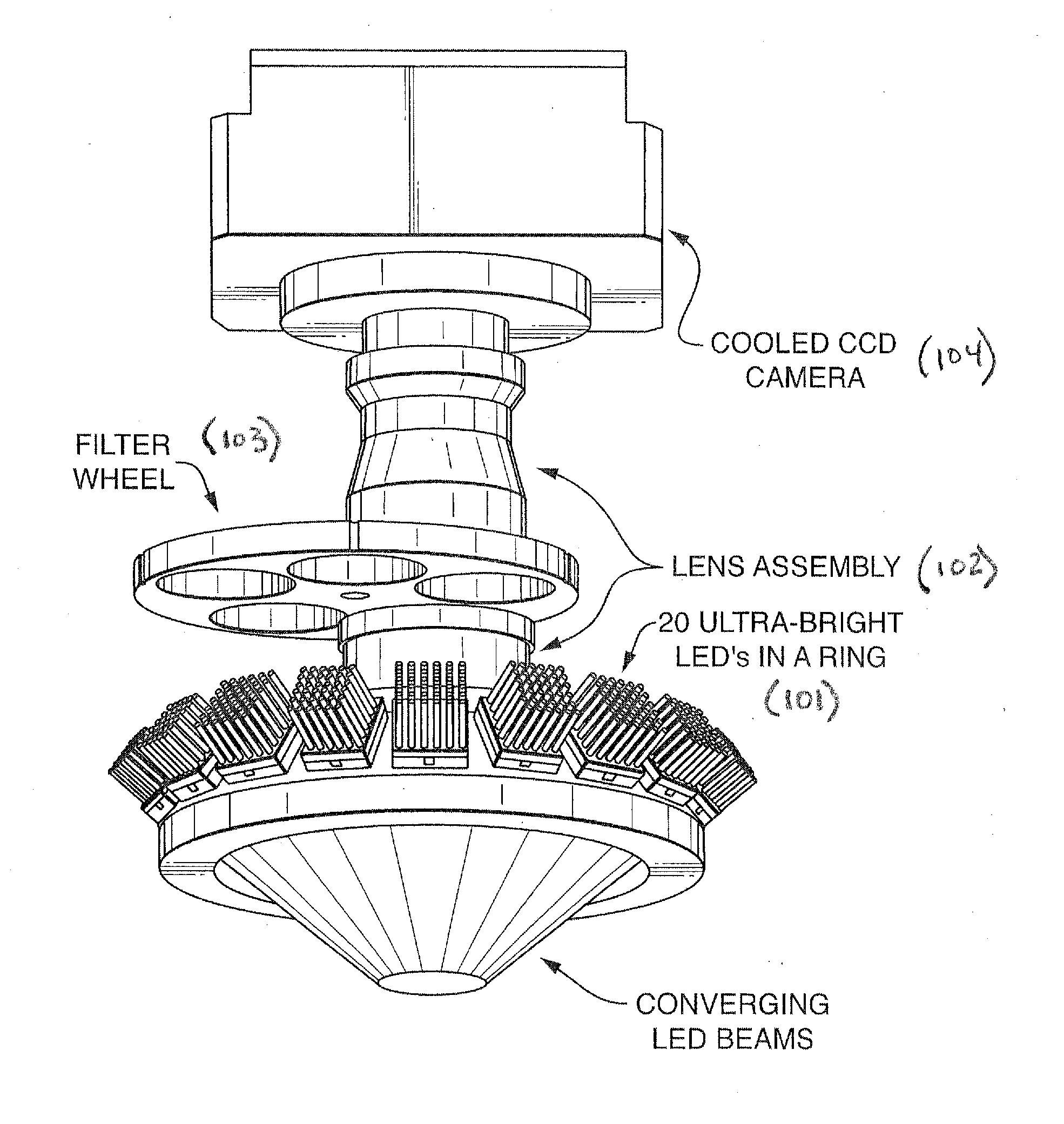
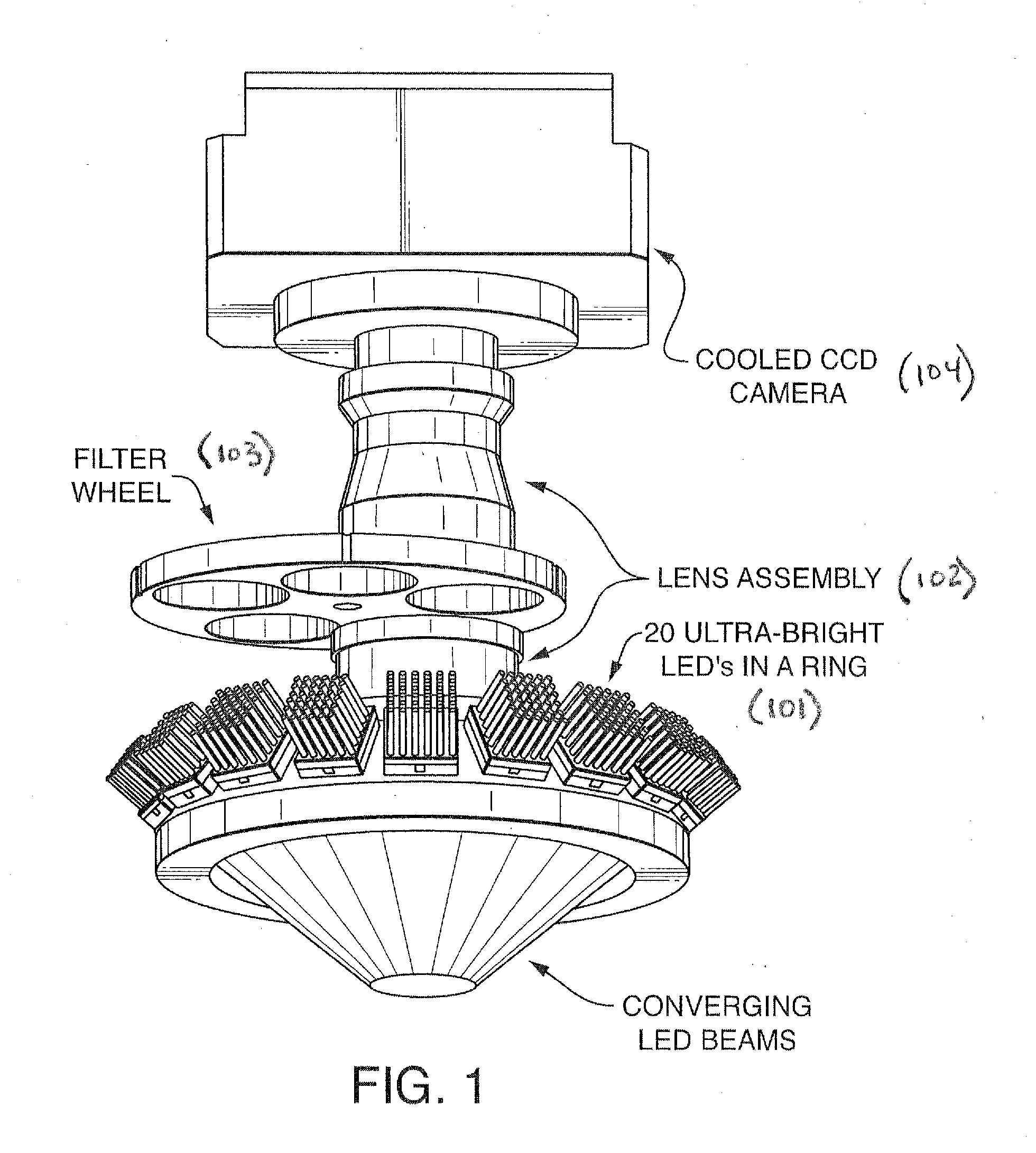
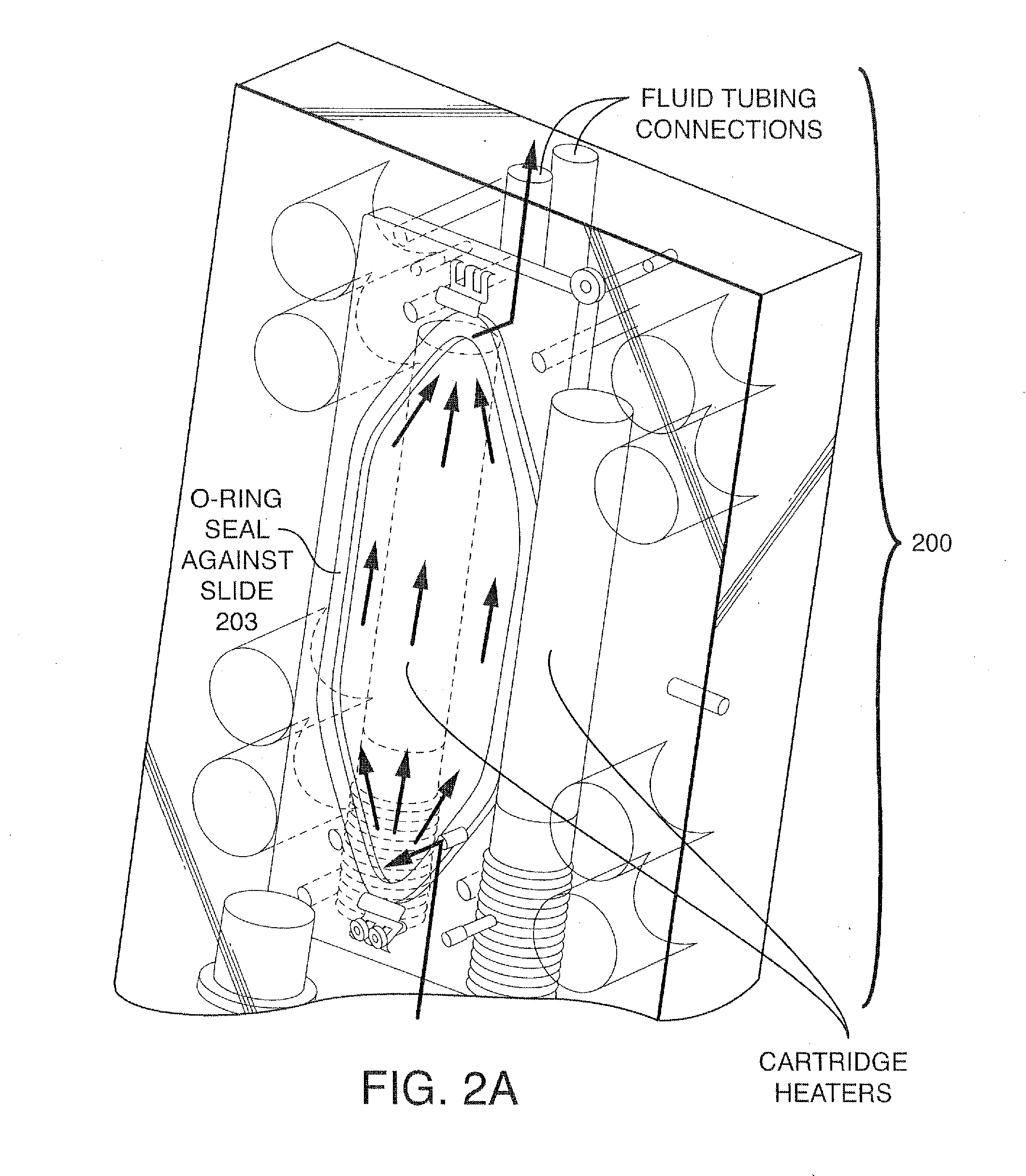
Patents
Literature
70 results about "Sequencing by synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
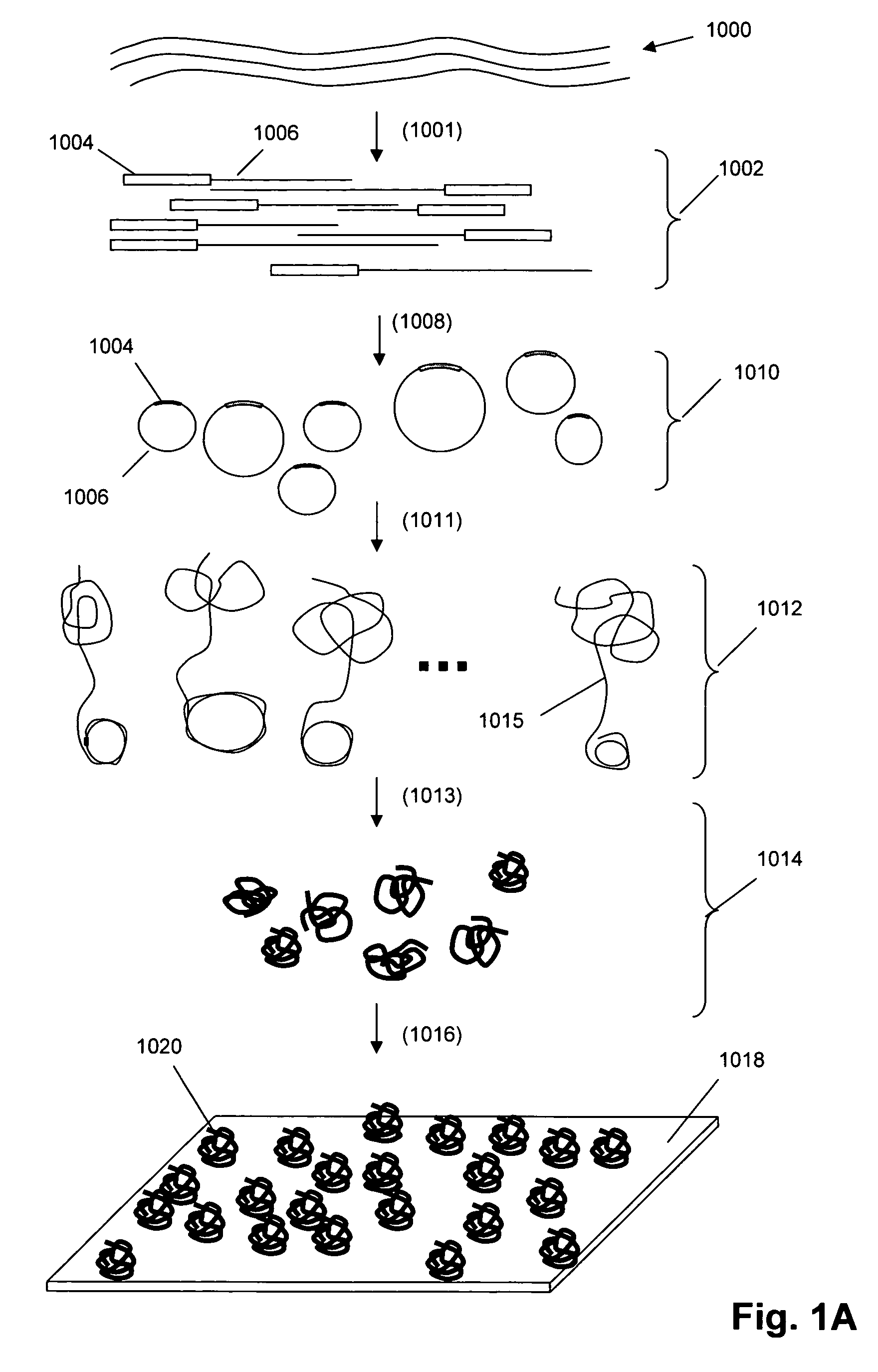
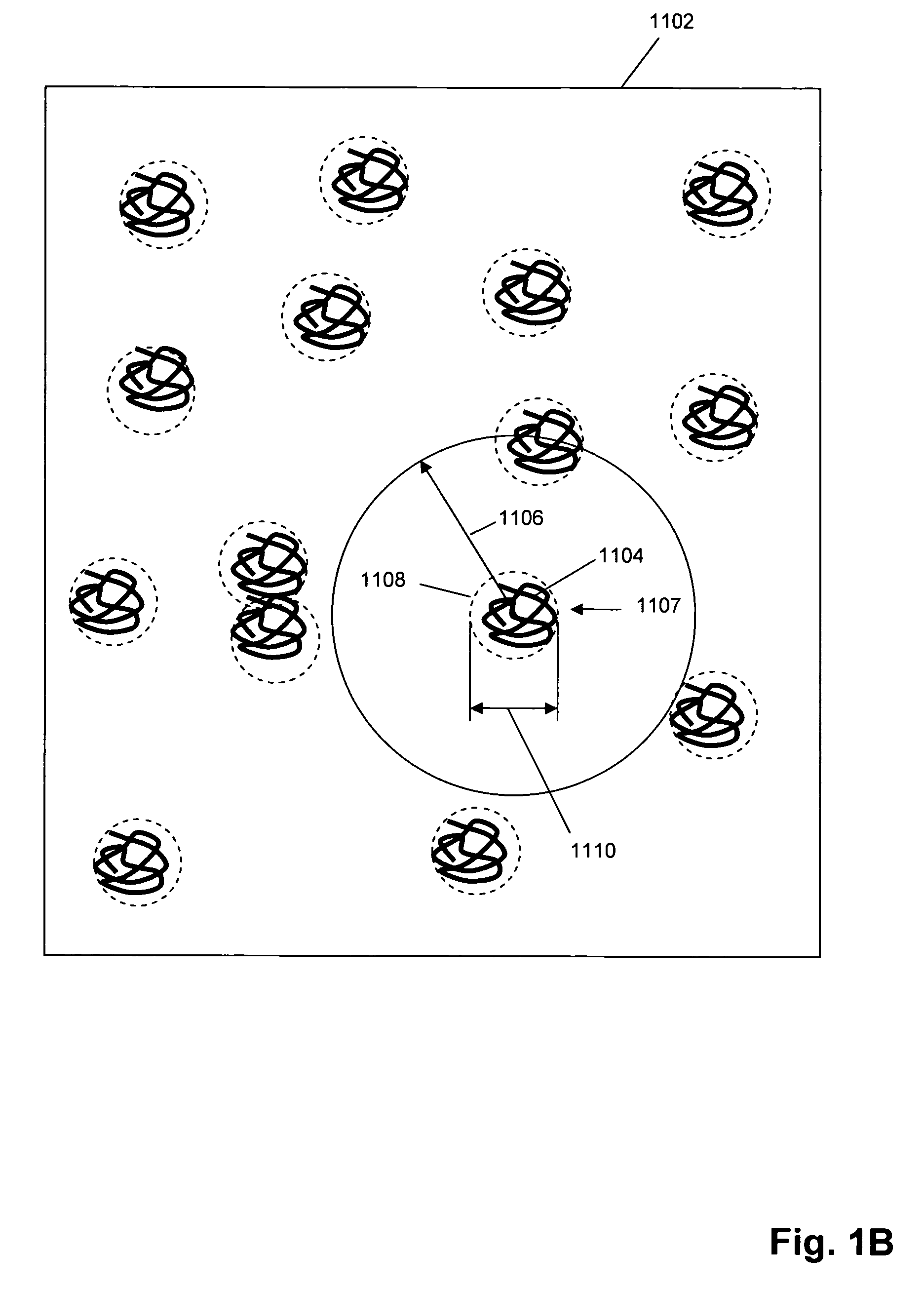
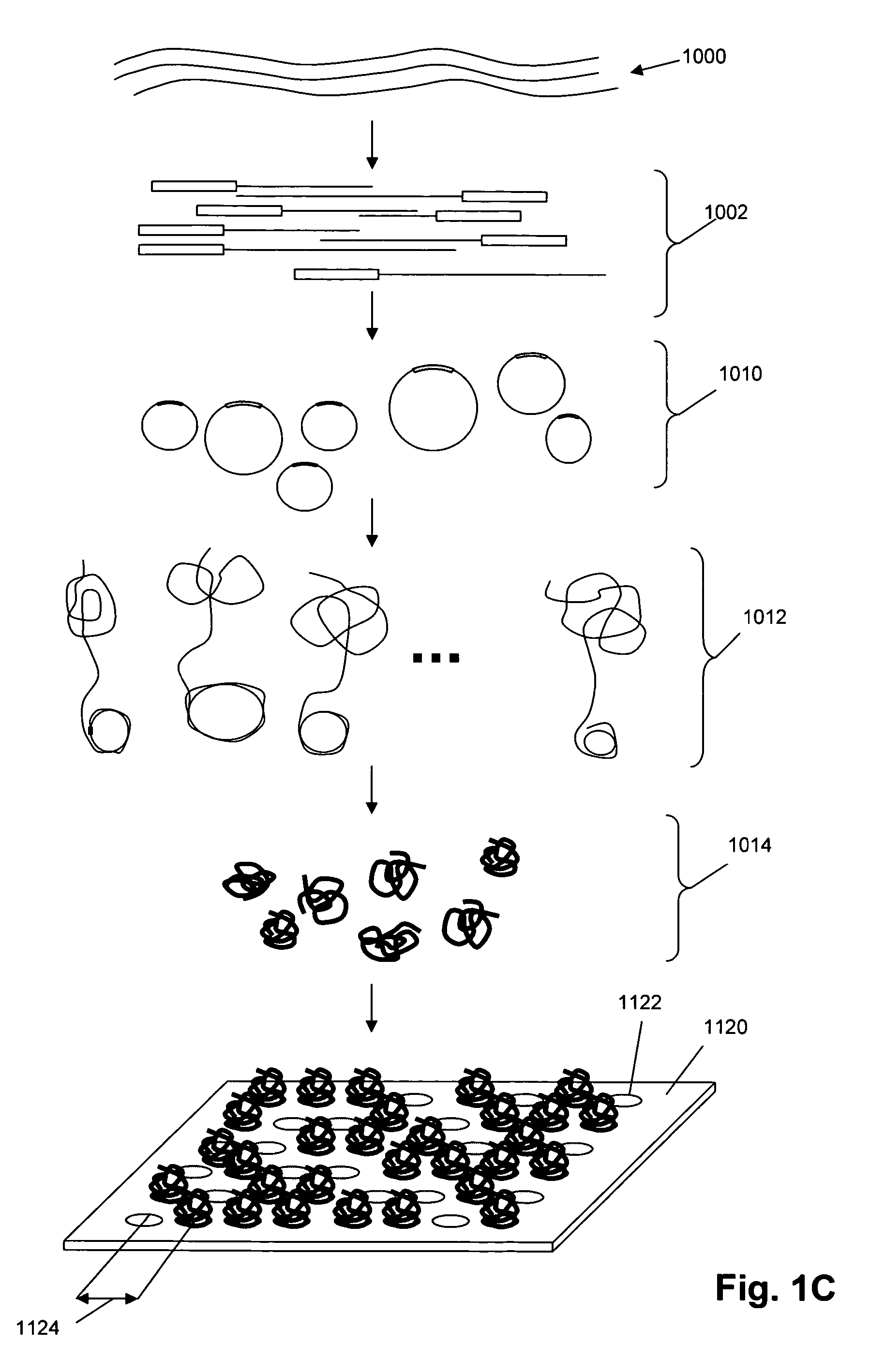
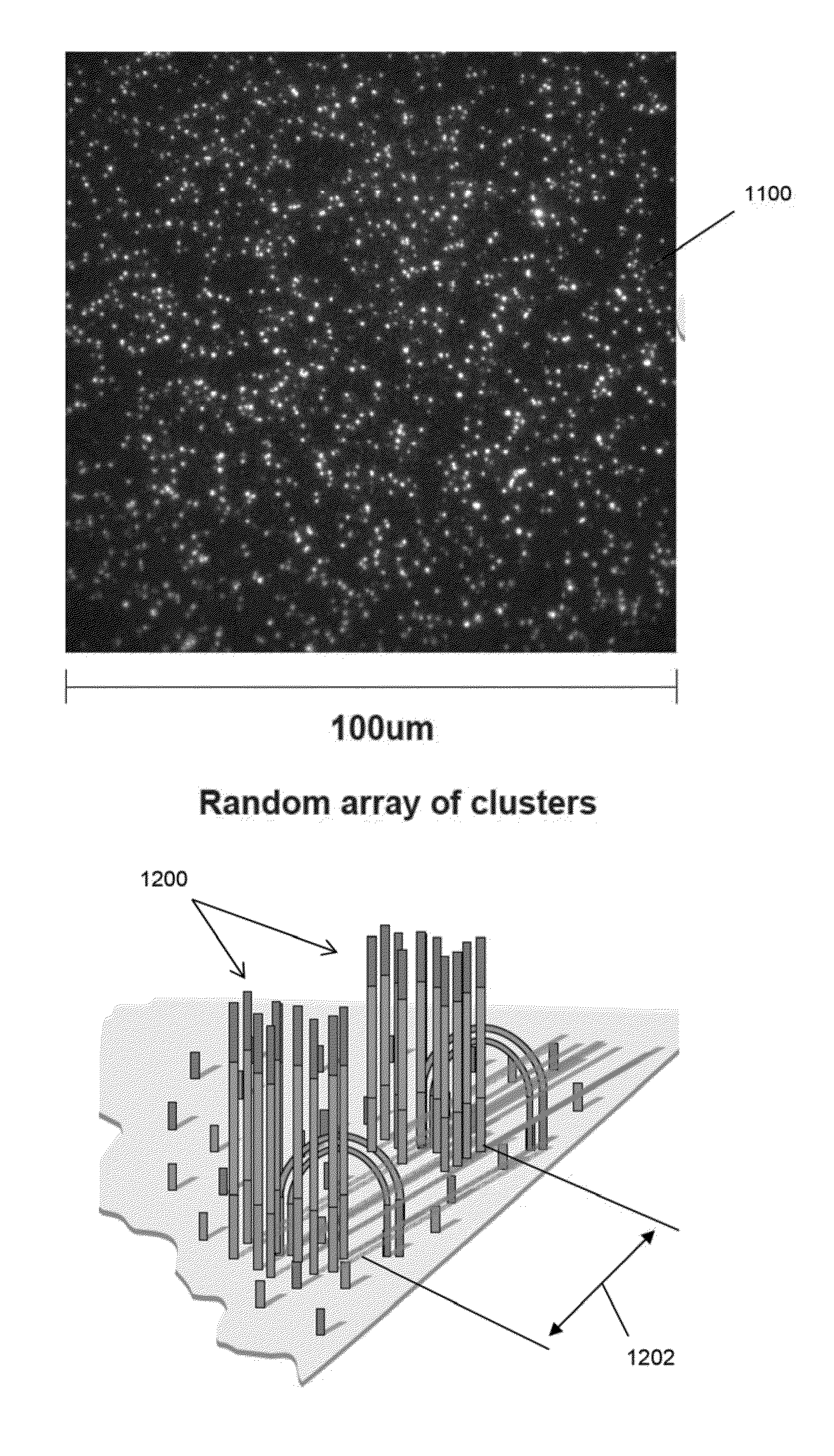
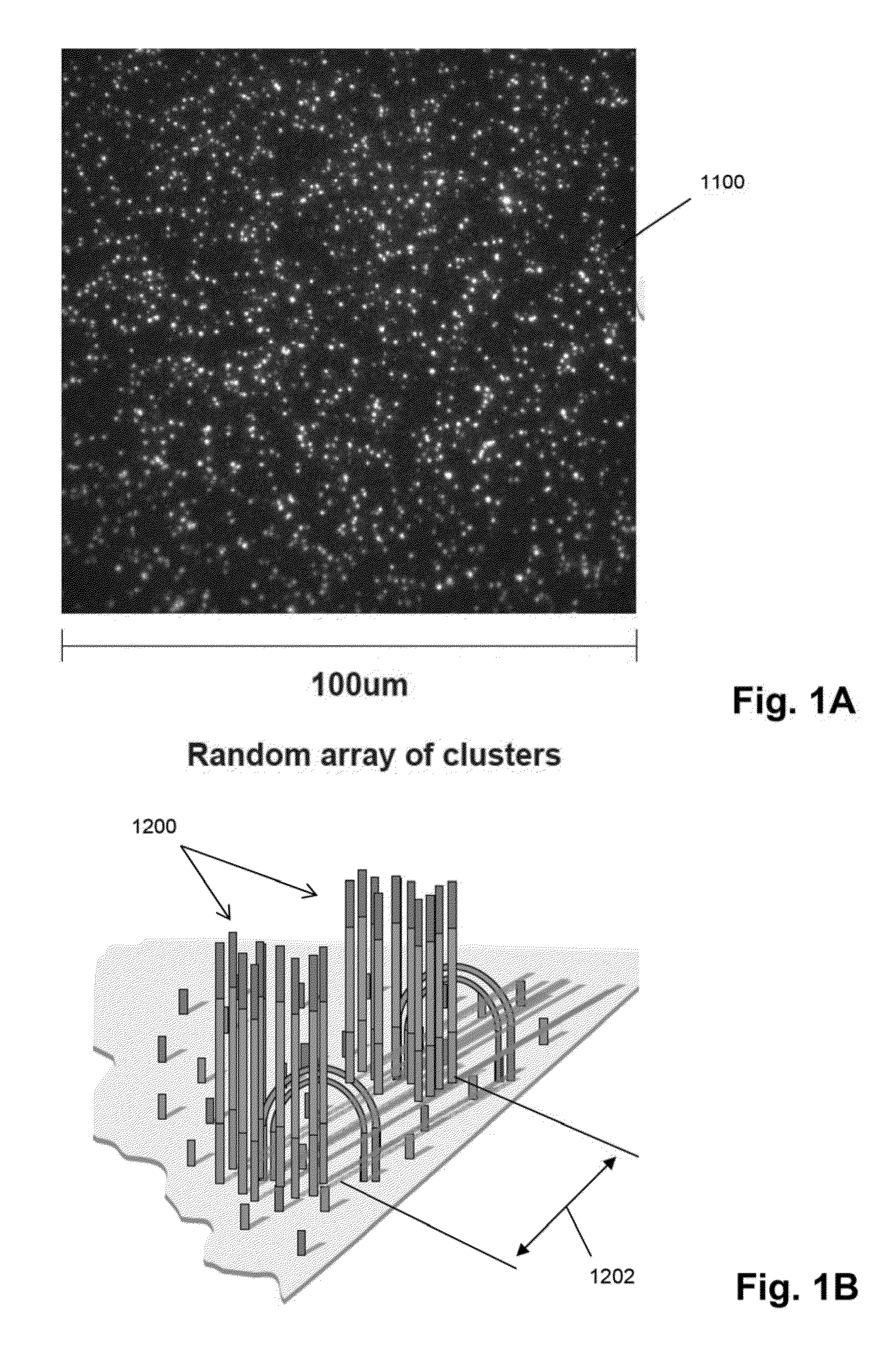
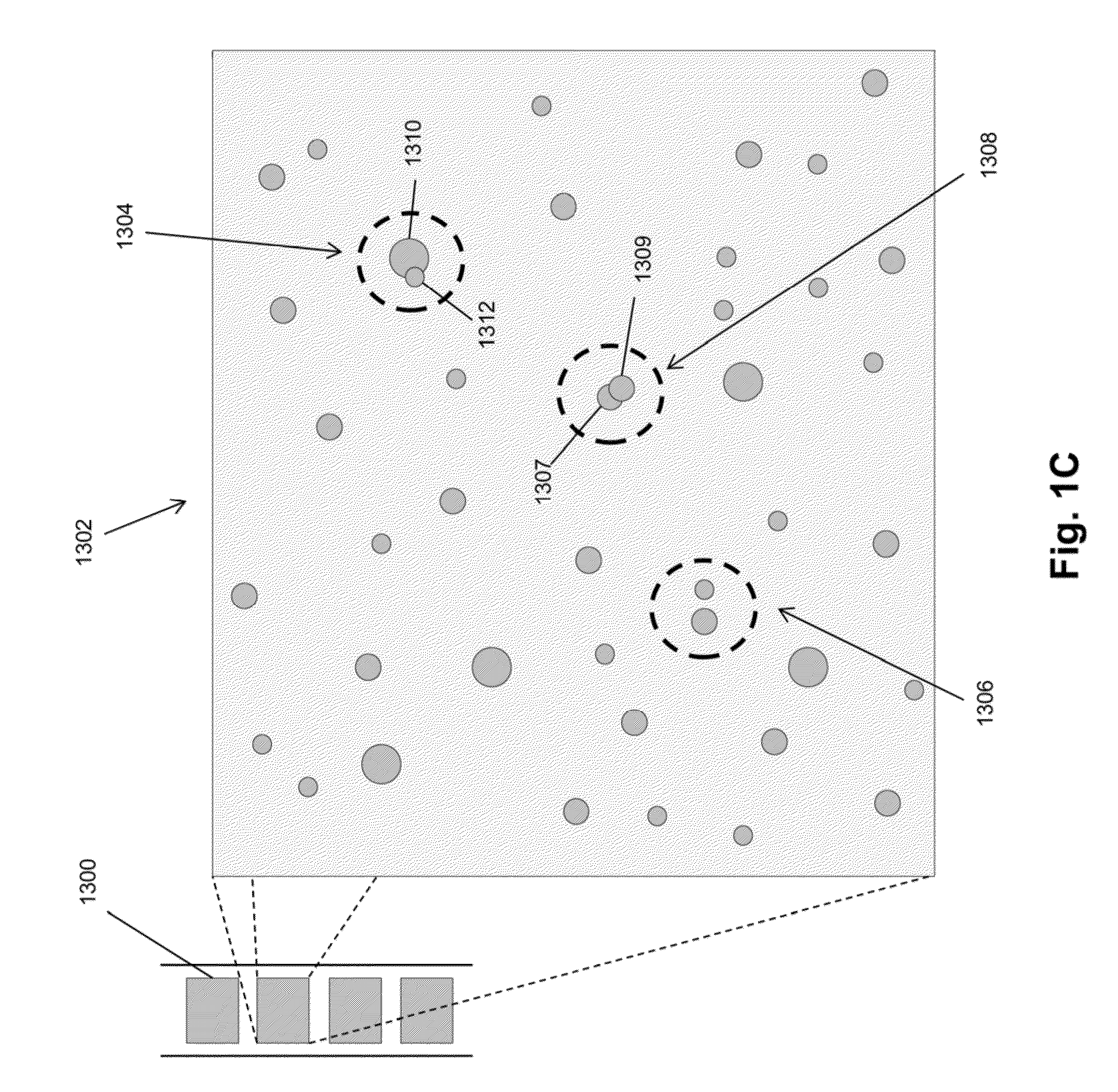
Single molecule arrays for genetic and chemical analysis
ActiveUS20070099208A1Efficient high resolution analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechImage resolutionRandom array
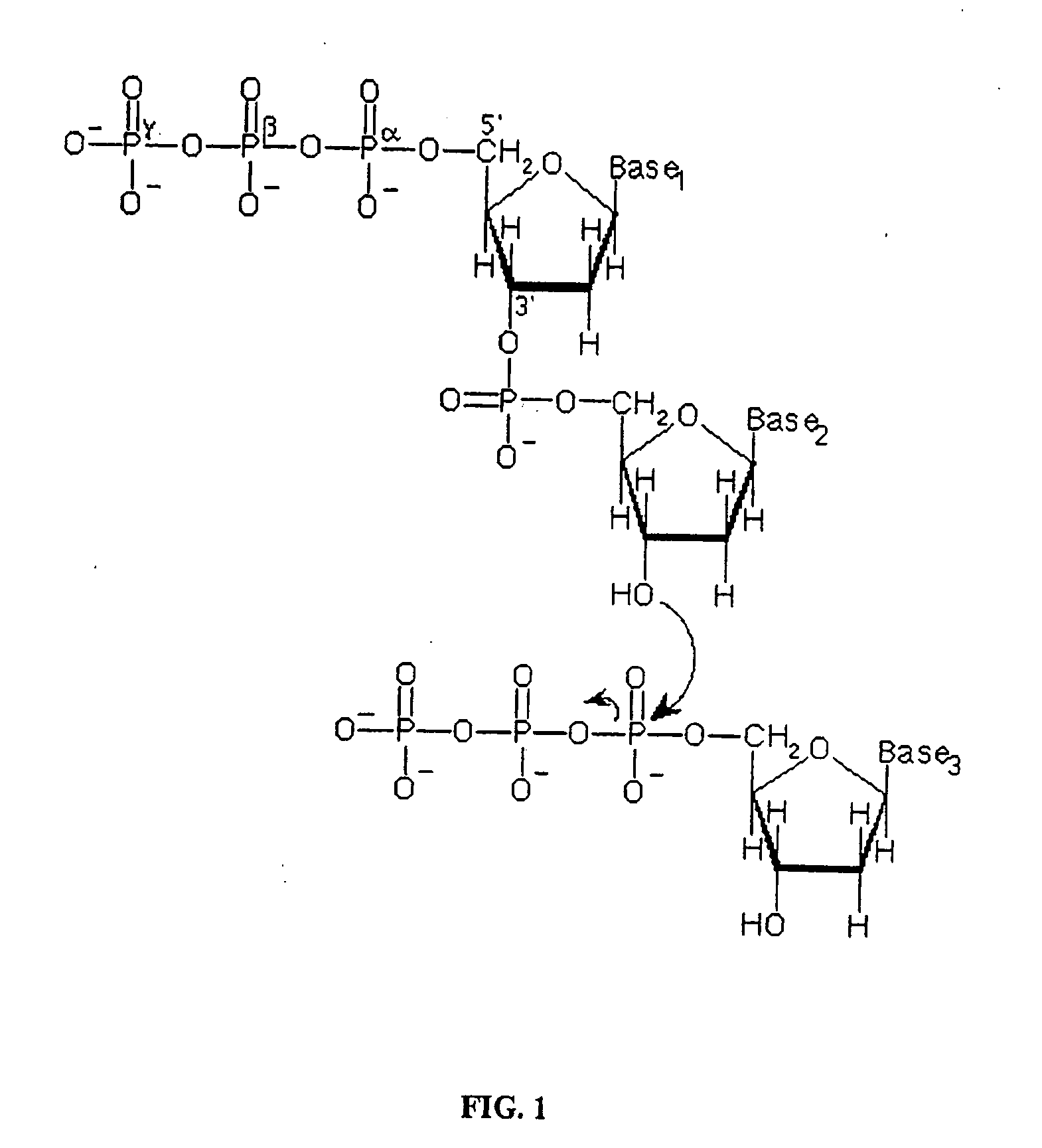
Random arrays of single molecules are provided for carrying out large scale analyses, particularly of biomolecules, such as genomic DNA, cDNAs, proteins, and the like. In one aspect, arrays of the invention comprise concatemers of DNA fragments that are randomly disposed on a regular array of discrete spaced apart regions, such that substantially all such regions contain no more than a single concatemer. Preferably, such regions have areas substantially less than 1 μm2 and have nearest neighbor distances that permit optical resolution of on the order of 109 single molecules per cm2. Many analytical chemistries can be applied to random arrays of the invention, including sequencing by hybridization chemistries, sequencing by synthesis chemistries, SNP detection chemistries, and the like, to greatly expand the scale and potential applications of such techniques.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
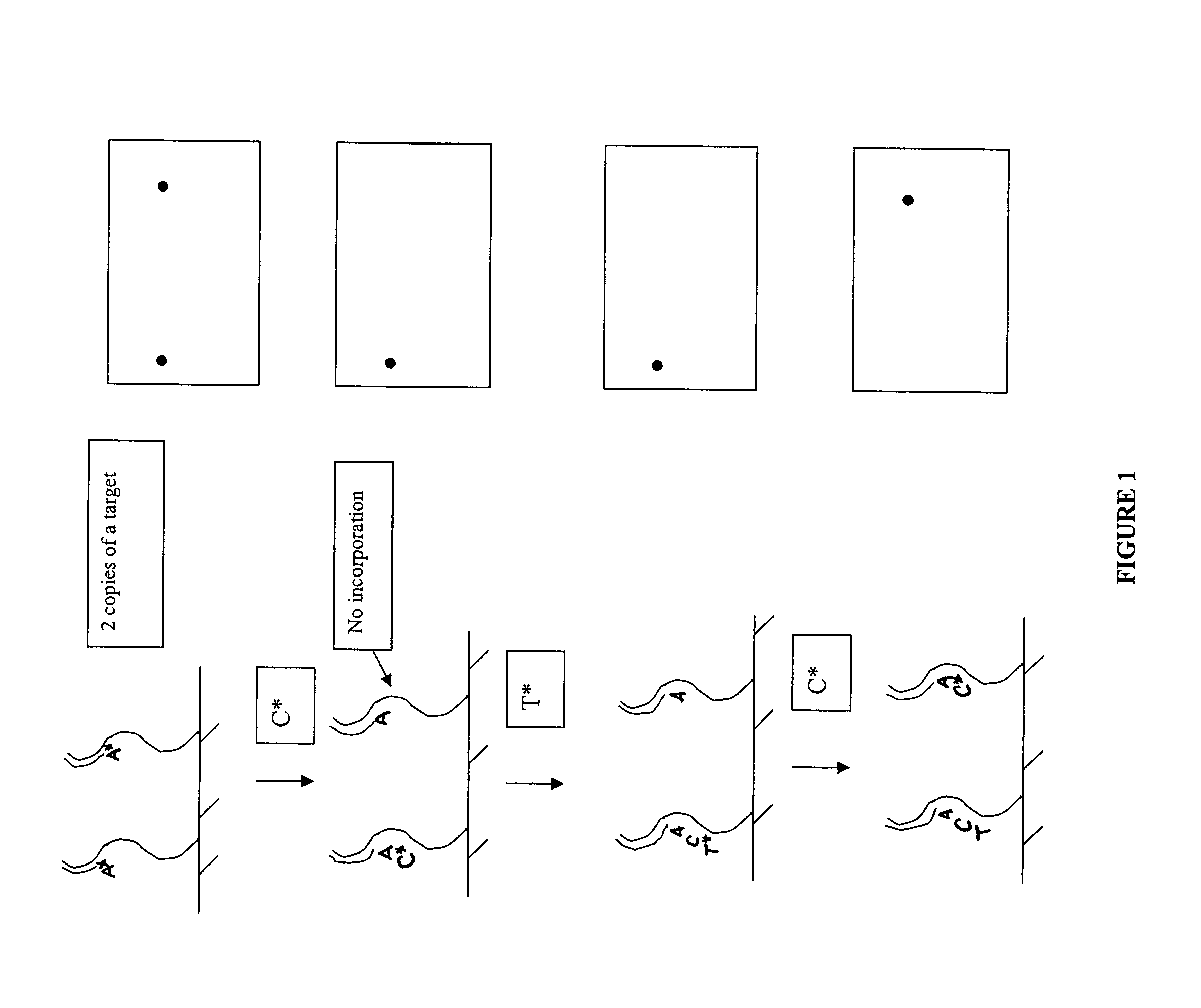
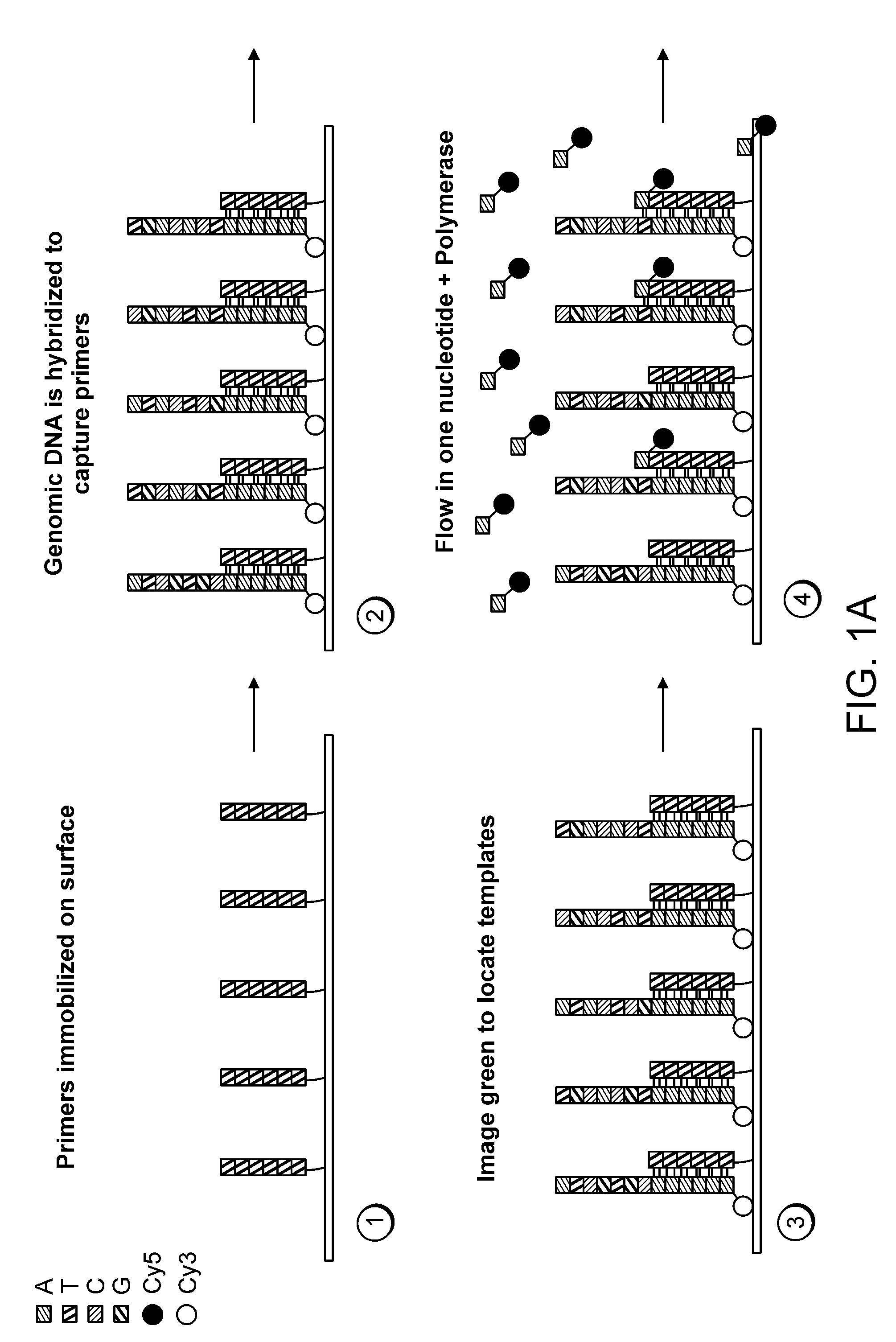
Short cycle methods for sequencing polynucleotides
InactiveUS7169560B2Increase resolution and reliabilityHigh throughput single molecule sequencingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolynucleotideComputational biology
The invention provides methods for sequencing a polynucleotide comprising stopping an extension cycle in a sequence by synthesis reaction before the reaction has run to near or full completion.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Systems and devices for sequence by synthesis analysis
ActiveUS20100111768A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNAComputational biology
The present invention comprises systems and devices for sequencing of nucleic acid, such as short DNA sequences from clonally amplified single-molecule arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods for increasing accuracy of nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS7282337B1Improve accuracyImprove Sequencing AccuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Short cycle methods for sequencing polynucleotides
InactiveUS20050100932A1High throughput single molecule sequencingImprove resolutionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolynucleotideComputational biology
The invention provides methods for sequencing a polynucleotide comprising stopping an extension cycle in a sequence by synthesis reaction before the reaction has run to near or full completion.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Systems and devices for sequence by synthesis analysis
ActiveUS8241573B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingDNA
The present invention comprises systems and devices for sequencing of nucleic acid, such as short DNA sequences from clonally amplified single-molecule arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods And Devices For Sequencing Nucleic Acids In Smaller Batches
ActiveUS20100323350A1Reducing spectral crosstalkHigh strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotide sequencingComputational biology
The invention provides methods and compositions, including, without limitation, algorithms, computer readable media, computer programs, apparatus, and systems for determining the identity of nucleic acids in nucleotide sequences using, for example, data obtained from sequencing by synthesis methods. A plurality of smaller flow cells is employed, each with a relatively small area to be imaged, in order to provide greater flexibility and efficiency.
Owner:ISOPLEXIS
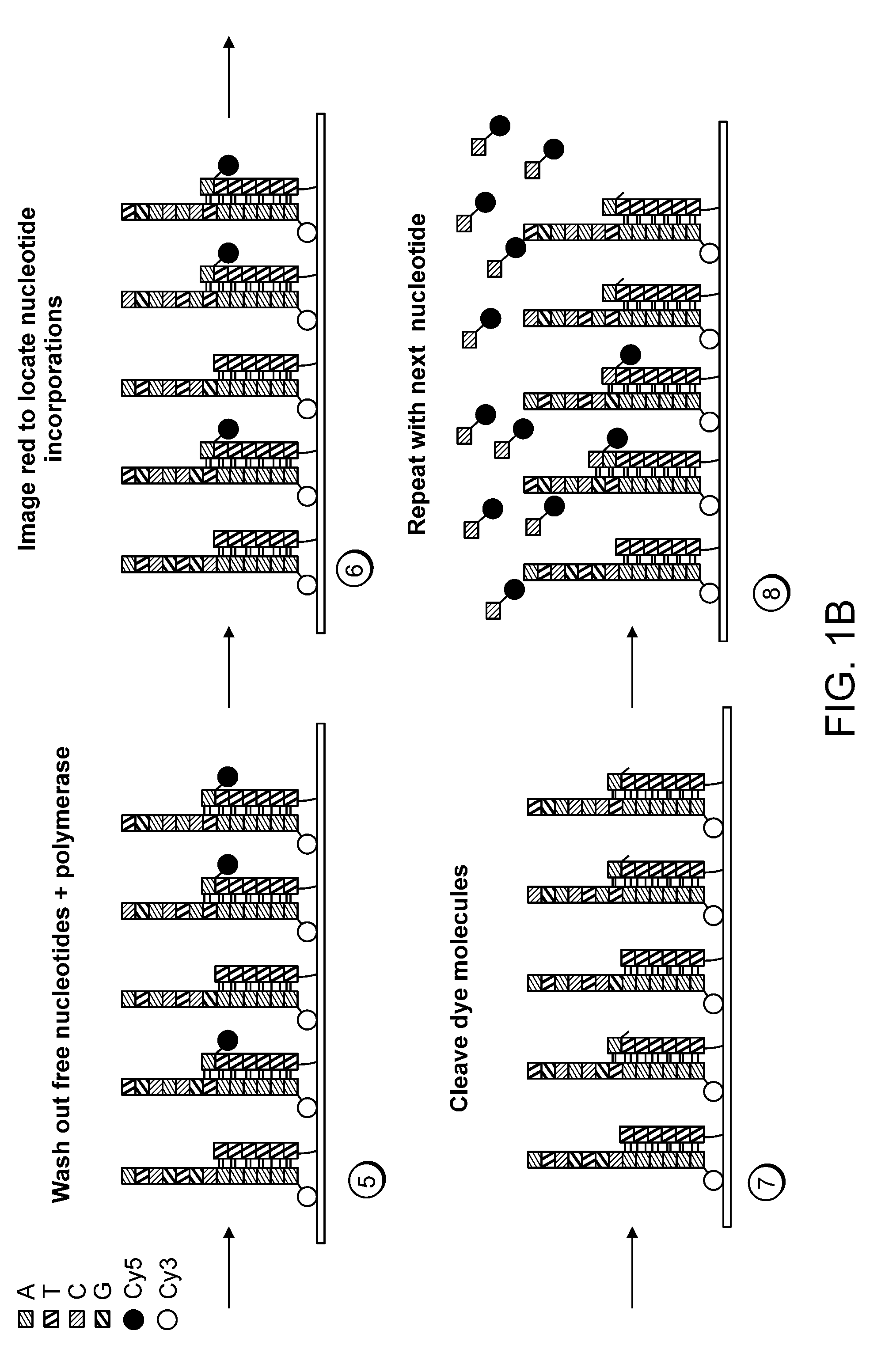
Paired-end reads in sequencing by synthesis
InactiveUS20090197257A1Yielding fewer sequencing errorsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRe sequencingShort read
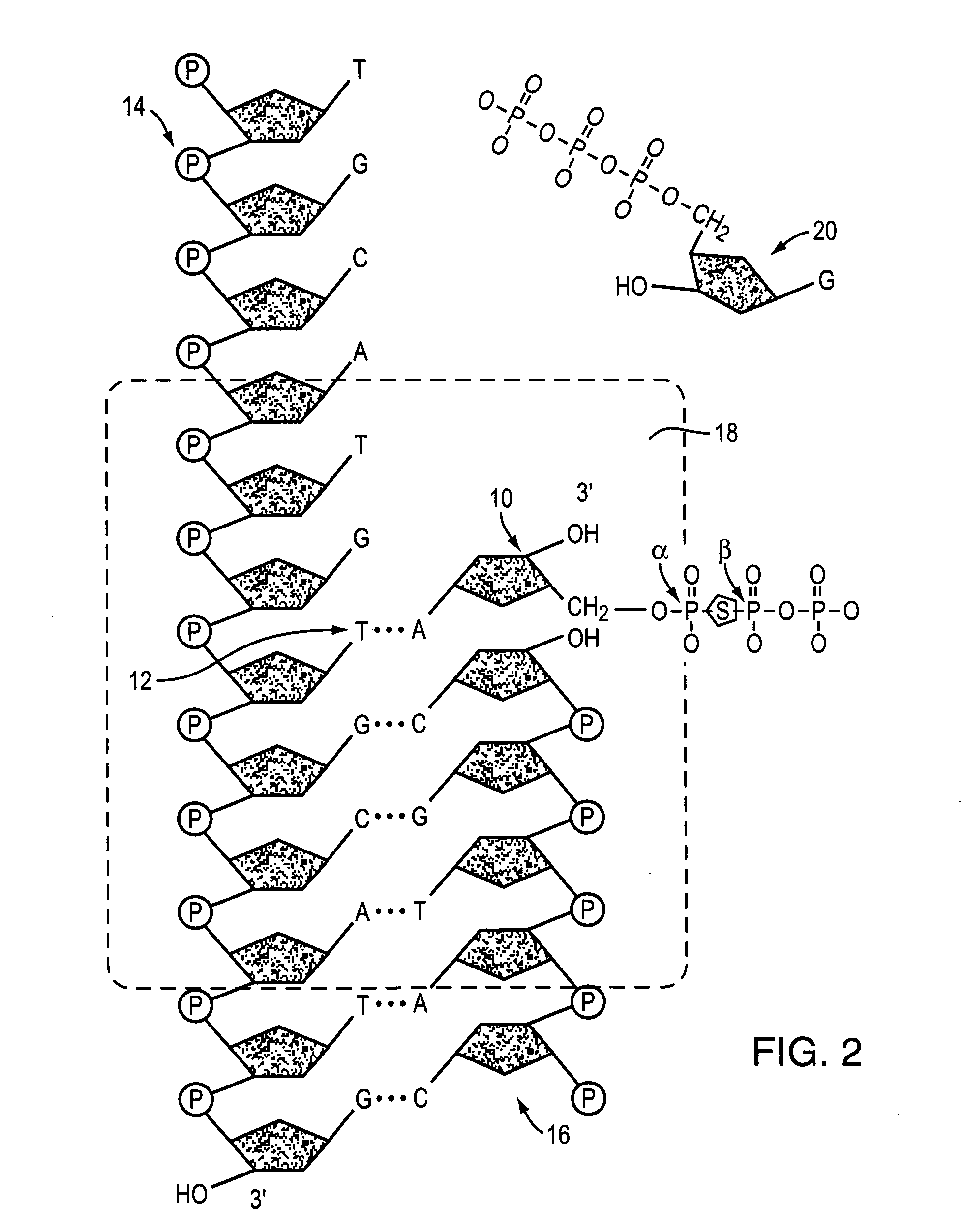
The disclosure provides methods of generating paired reads in sequencing-by-synthesis process, particularly, in systems with relatively short read lengths (e.g., 15-35 bases), such as for example, in single molecule sequencing by synthesis. Several implementations of the methods are provided. Of particular advantage are the methods that permit re-sequencing of the template, which yields lower error rates. The invention further provides methods of using paired reads, for example, for positioning them over repeats or for assembly into large sequences, including whole genome assembly.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
High throughput screening of mutagenized populations
InactiveUS20090170713A1Goal is achievedEfficient screeningSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsDNA
Efficient methods are disclosed for the high throughput identification of mutations in genes in members of mutagenized populations. The methods comprise DNA isolation, pooling, amplification, creation of libraries, high throughput sequencing of libraries, preferably by sequencing-by-synthesis technologies, identification of mutations and identification of the member of the population carrying the mutation and identification of the mutation.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Molecules and methods for nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20080103058A1Improve efficiencyImprove Sequencing AccuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingBiology
The invention provides molecules and methods for nucleic acid synthesis reactions useful in sequencing-by-synthesis processes.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Random array sequencing of low-complexity libraries
ActiveUS20130065768A1Vary numberMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationHigh densityRandom array
The invention is directed to a method of sequencing low-complexity amplicons randomly arrayed at high density on a surface. Methods of the invention include preparing amplicons for sequencing by a sets of primers that ensure initial signals front different amplicons on the surface will be evenly distributed among the different nucleotides being added in a sequencing by synthesis operation.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Paired-end reads in sequencing by synthesis
InactiveUS7767400B2Yielding fewer sequencing errorsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRe sequencingShort read
The disclosure provides methods of generating paired reads in sequencing-by-synthesis process, particularly, in systems with relatively short read lengths (e.g., 15-35bases), such as for example, in single molecule sequencing by synthesis. Several implementations of the methods are provided. Of particular advantage are the methods that permit re-sequencing of the template, which yields lower error rates. The invention further provides methods of using paired reads, for example, for positioning them over repeats or for assembly into large sequences, including whole genome assembly.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
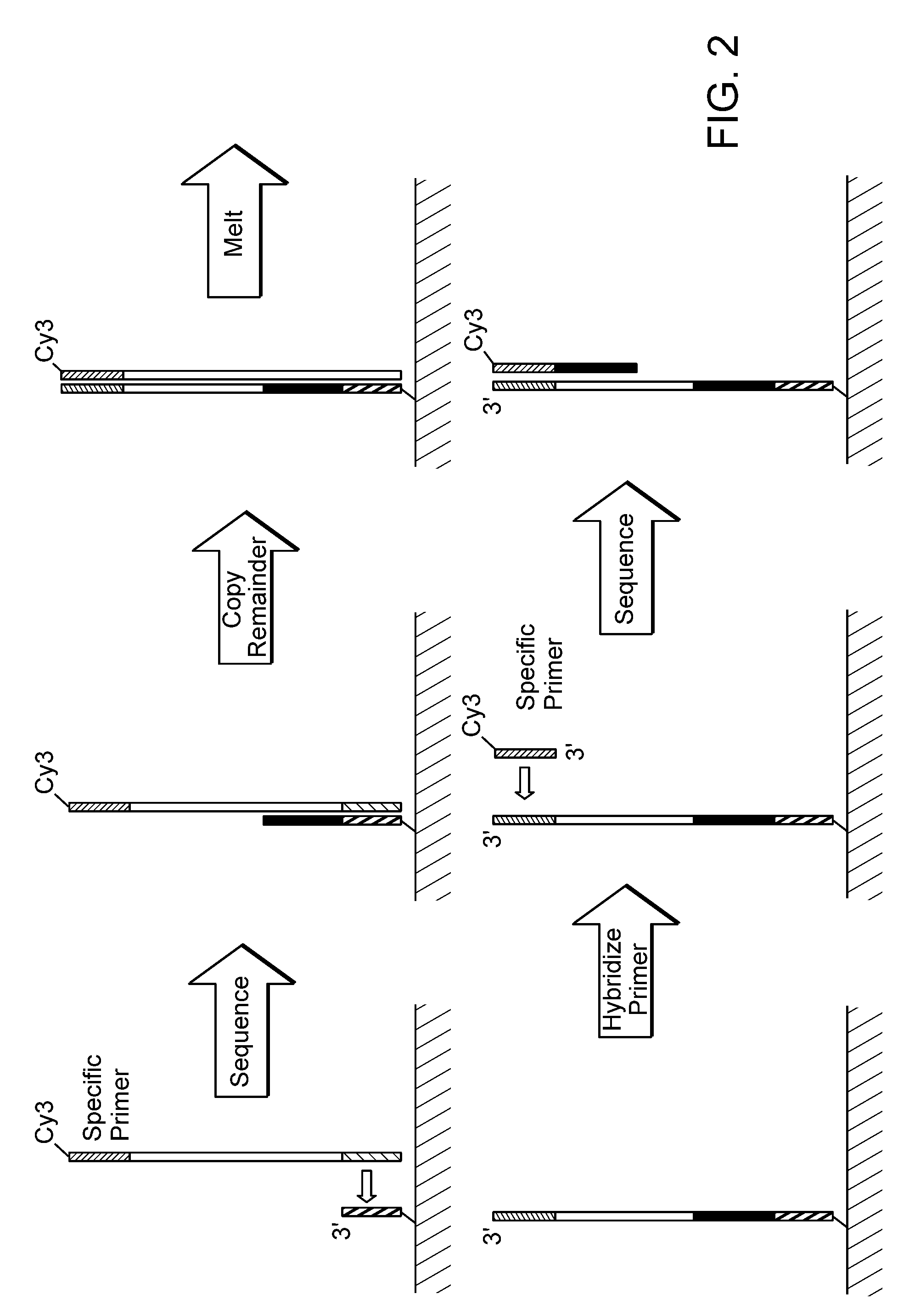
Two-primer sequencing for high-throughput expression analysis
InactiveUS20090163366A1Improve efficiencyImprove accuracySugar derivativesLibrary tagsBarcodePolynucleotide
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Methods for increasing accuracy of nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20090075252A1Improve accuracyAccuracy in determiningMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Methods for increasing accuracy of nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20090305248A1Improve accuracyAccuracy in determiningMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
The invention provides methods for improving the fidelity of a sequencing-by-synthesis reaction by resequencing at least a portion of a nucleic acid template.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Methods and devices for sequencing nucleic acids in smaller batches
ActiveUS8481259B2Good flexibilityCost-effective smaller runsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFlow cellNucleotide sequencing
Owner:ISOPLEXIS
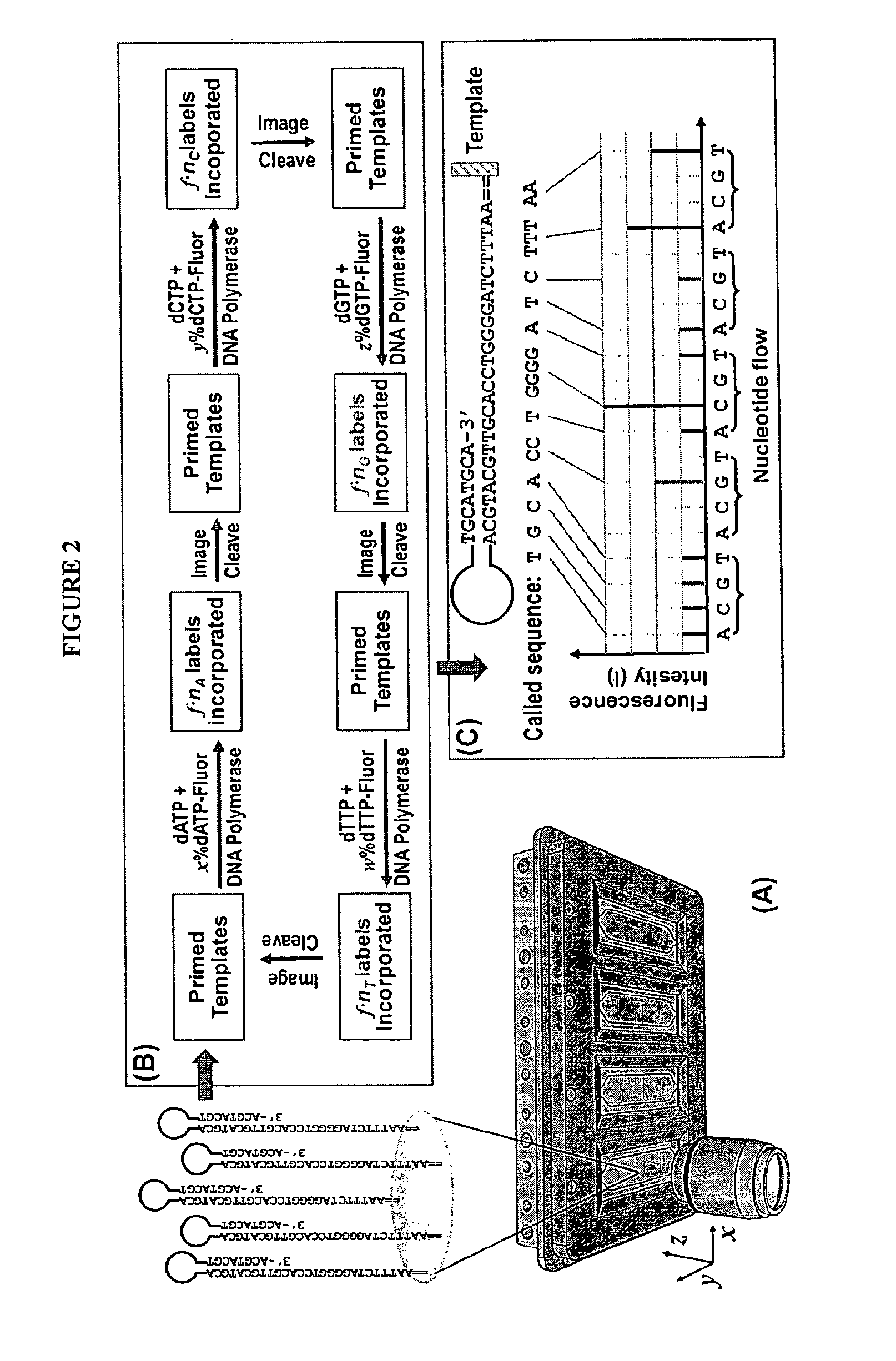
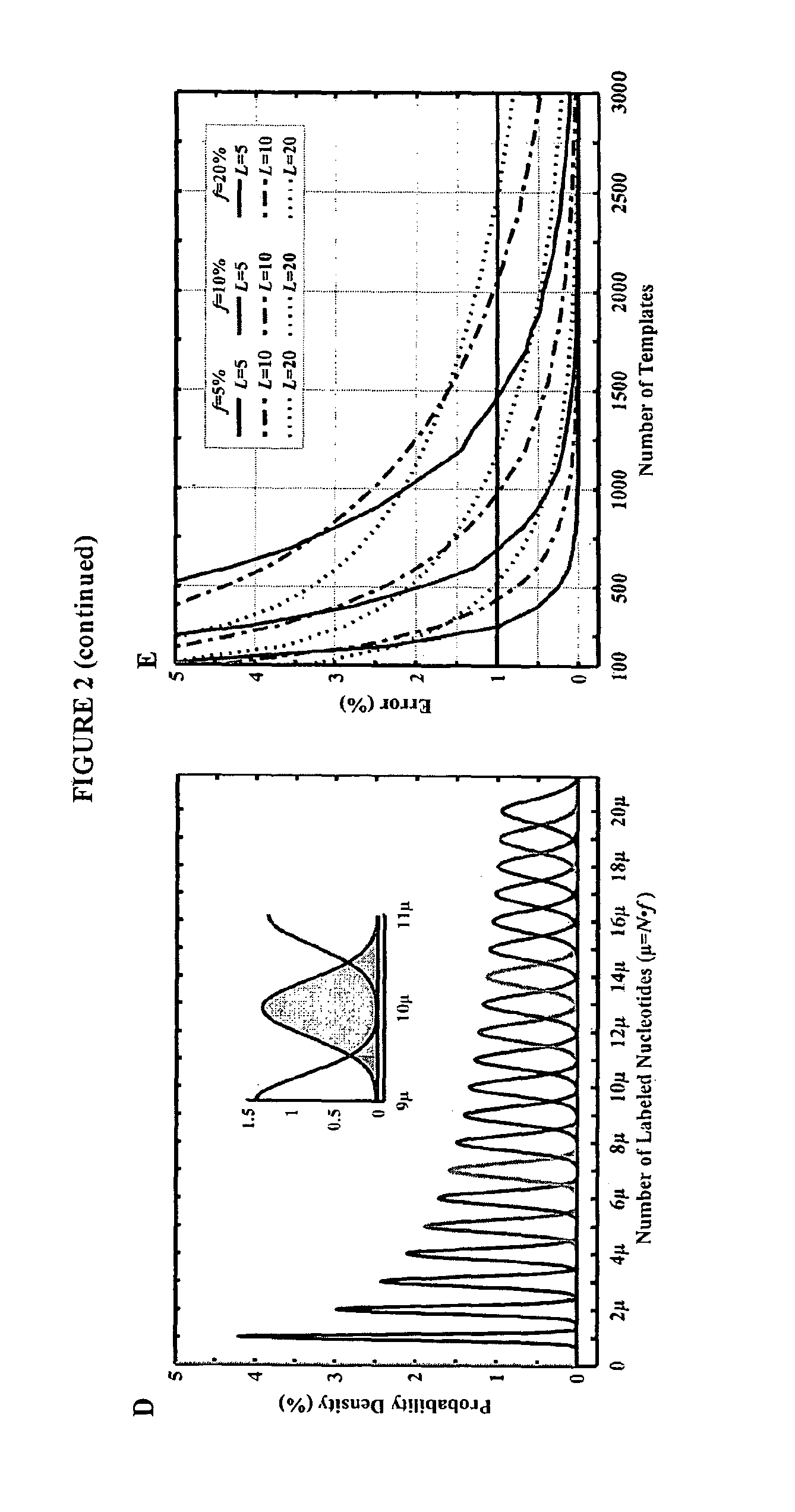
Mostly Natural DNA Sequencing by Synthesis
ActiveUS20120046177A1Rapid and inexpensive genome re-sequencingMaintain natural structureMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationBase JPolymerase
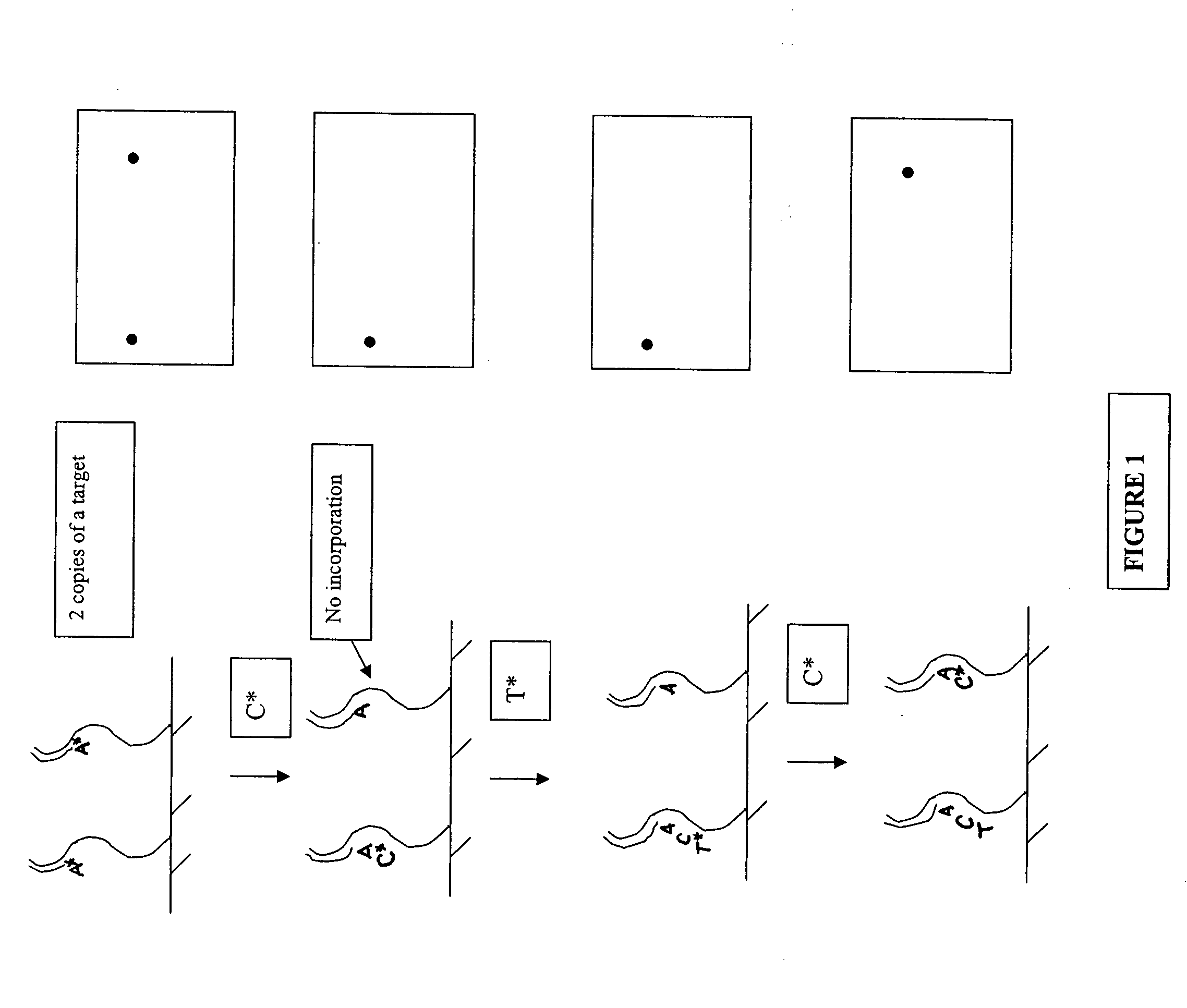
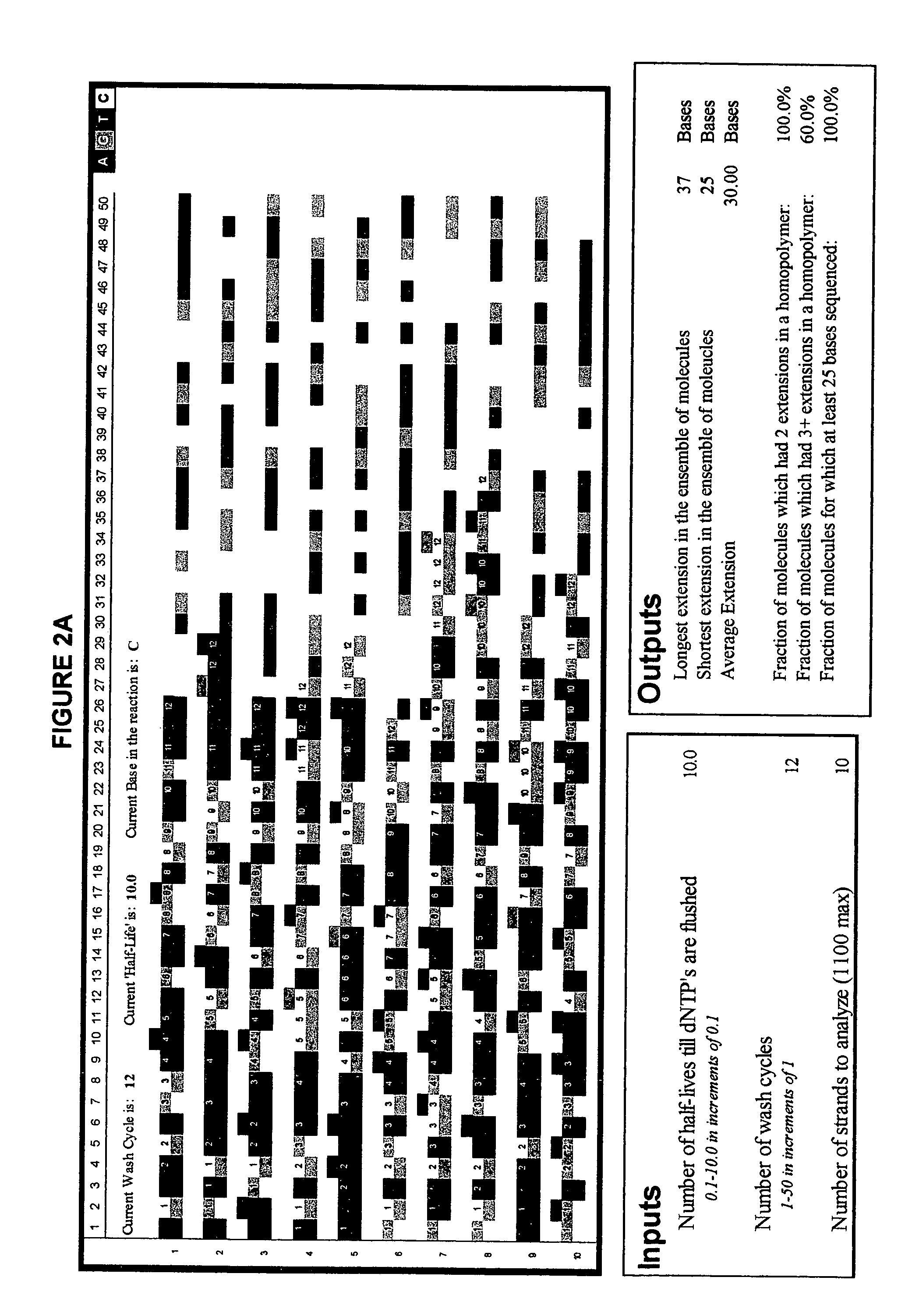
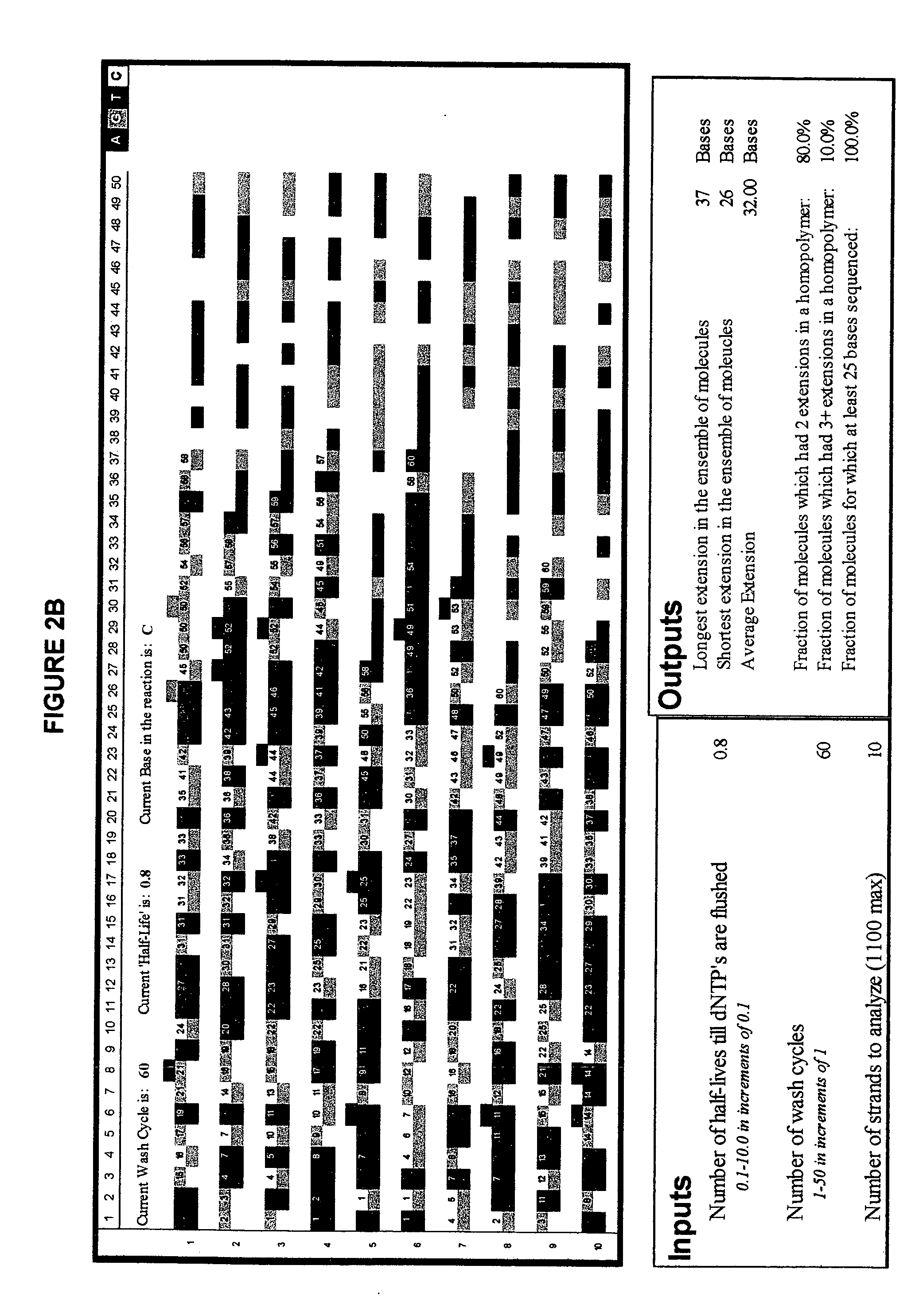
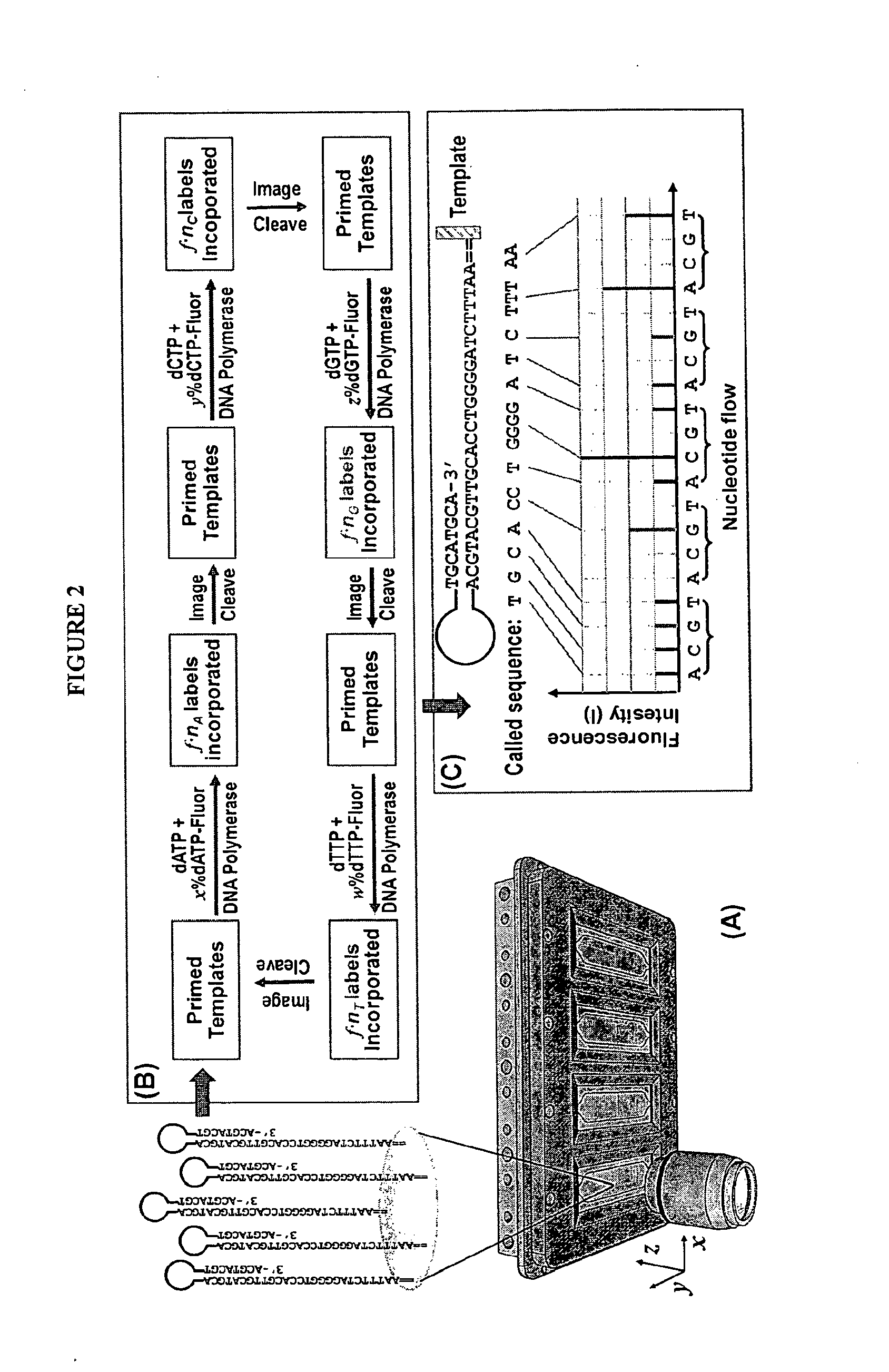
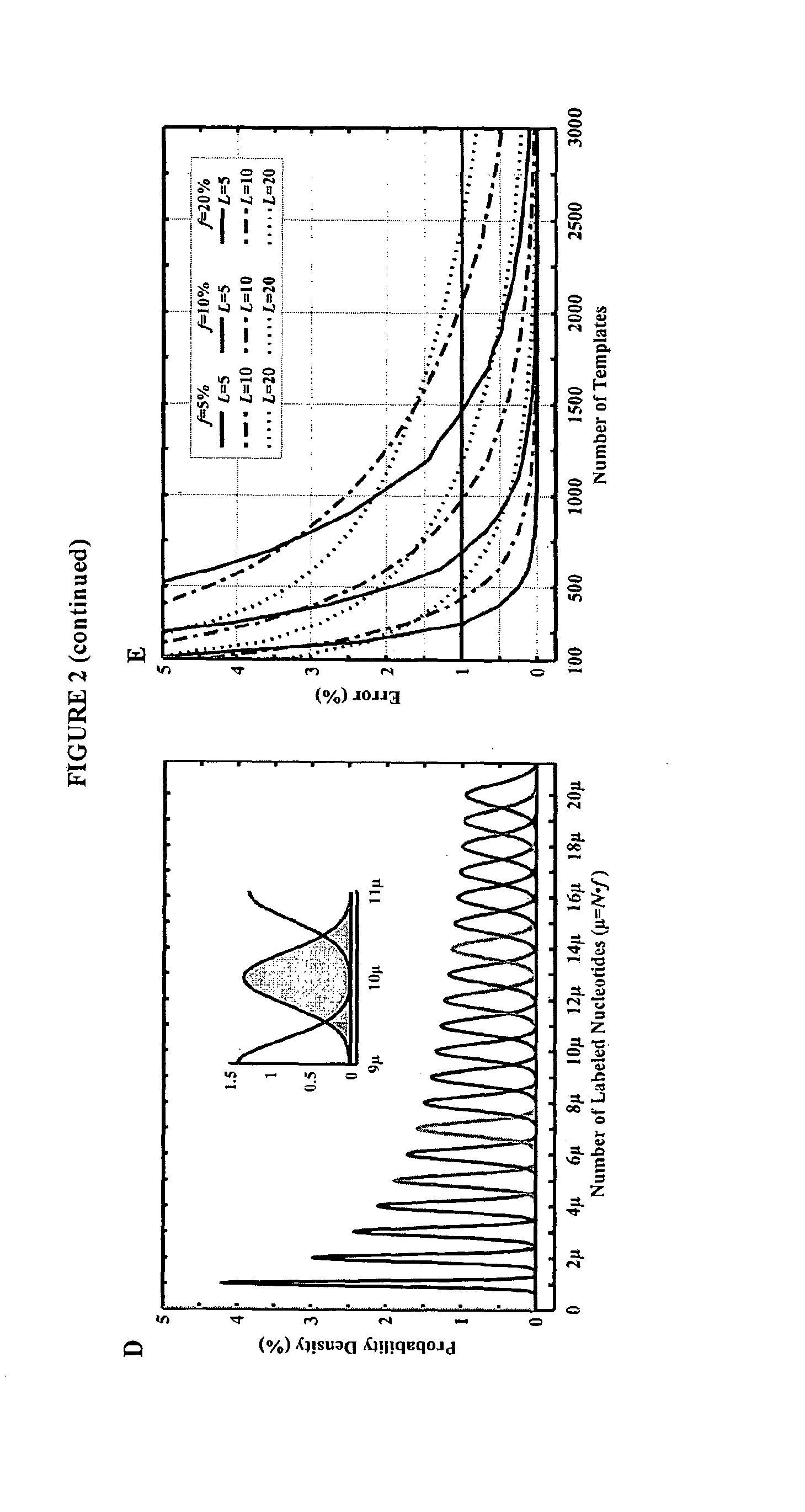
The invention provides a new method for DNA sequencing called “natural sequencing by synthesis” (nSBS). According to the method, DNA that includes a desired sequence is synthesized using a dNTP mix with a small percentage of fluorescently-labeled nucleotides. The fluorescent label is cleavable. In contrast to previous methods that utilize 100% labeled nucleic acids, use of a small percentage of labeled nucleic acids minimizes the distortion of the natural structure of the extending DNA strand and the DNA polymerase. Using the disclosed methods with less than 10,000 copies of template DNA and 10% of the nucleotides labeled, long homopolymer stretches up to 20 bases can be sequenced with high accuracy and Q20 (with 99% accuracy) read lengths of up to 1,000 bases can be achieved. A Q20 read length of greater than 100 bases can potentially be achieved, even if the sequencing is performed with 1,000 copies of a template and 10% of the nucleotides labeled.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
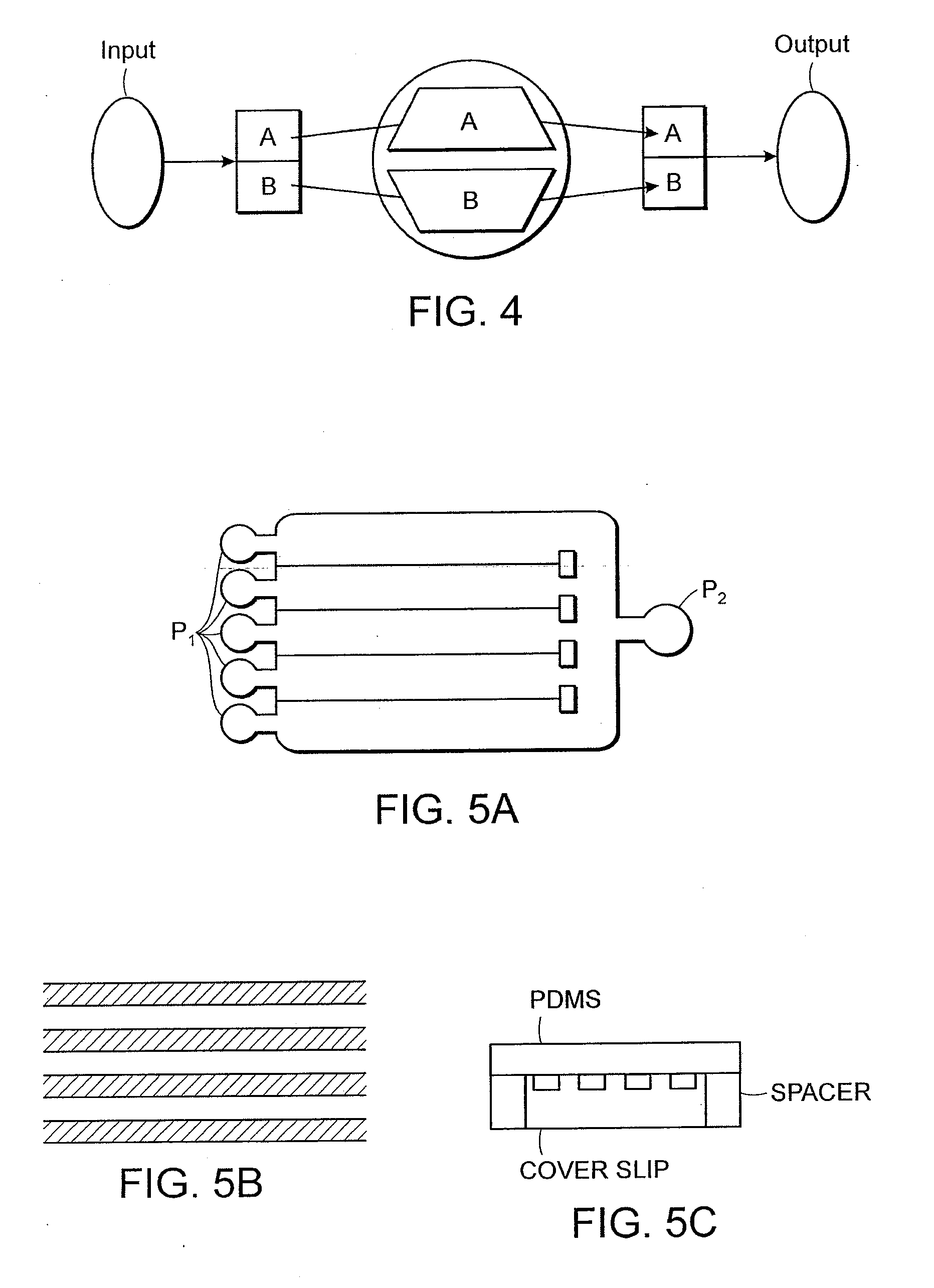
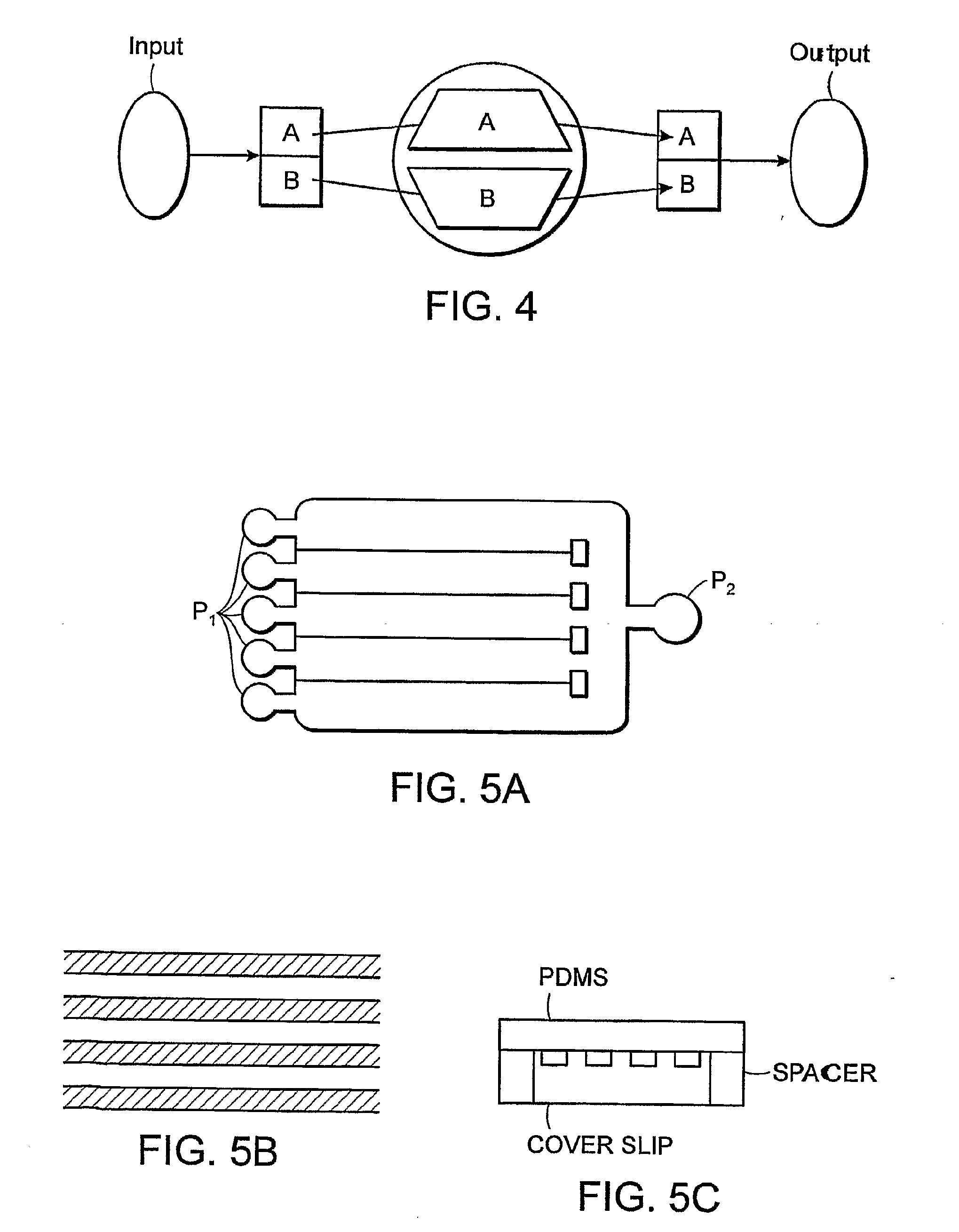
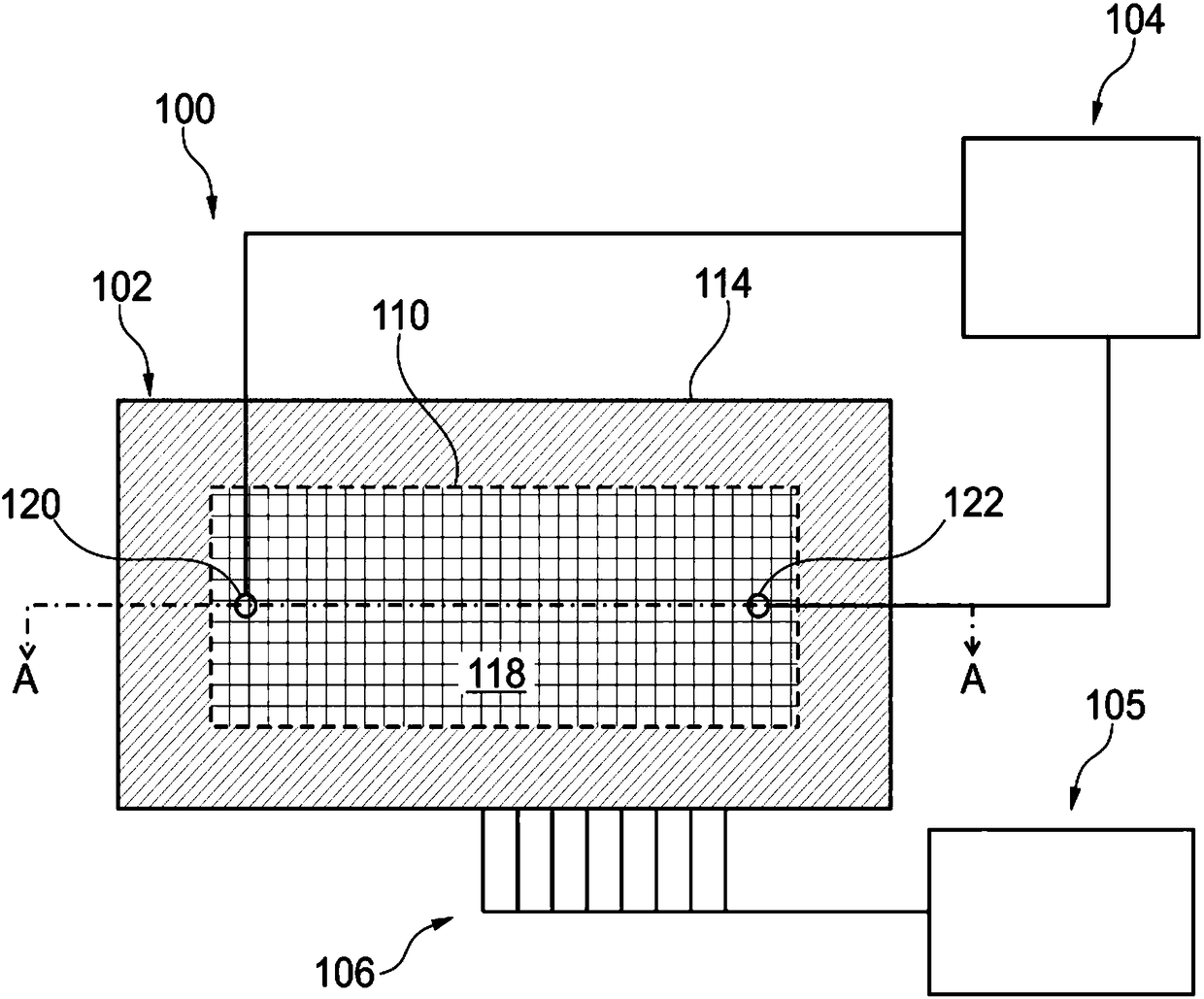
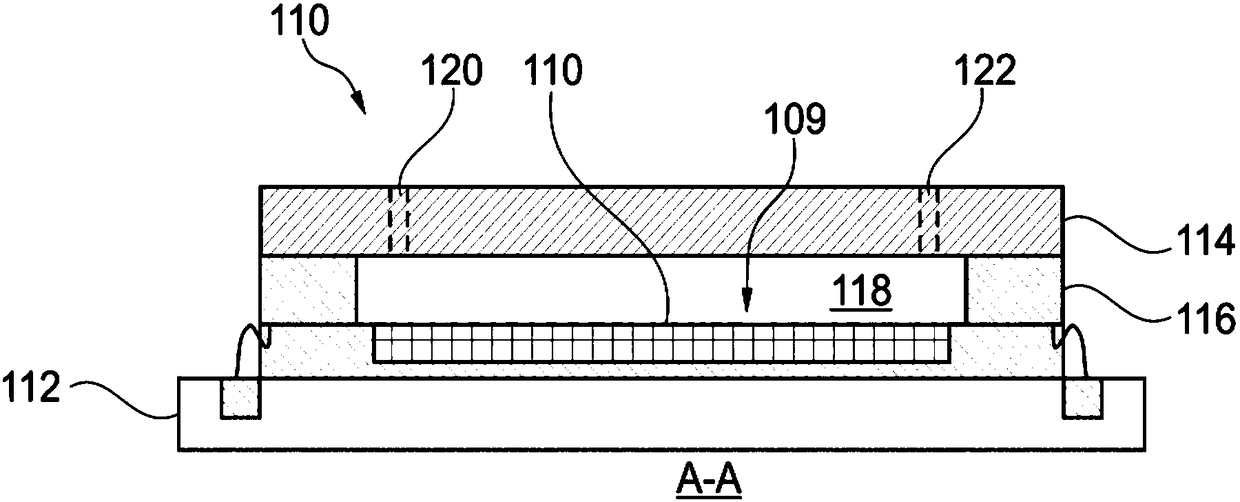
Multi-Channel Flow Cells
InactiveUS20080219888A1Avoid pollutionReduce cross contaminationMaterial analysis by optical meansLaboratory glasswaresFlow cellAnalyte
A multi-channel flow cell can allow for reduced cross-contamination in sample loading and the ability to observe activity within the flow cell once the channels are loaded. A multi-channel flow cell includes a plurality of independently-addressable channels sandwiched between a two substrates. Each of the channels can be coated with a layer that facilitates support-binding of an analyte. Each of the channels terminates on one end in an inlet and on the other end in an outlet. A loading block having inlet ports that match the inlets of the channels can be mated to the inlets of the channels, and an outlet block can be mated to the outlets of the channels. Analytes can be introduced into the channels via the inlet ports of the loading block and are pulled through the channels by capillary action or by vacuum. Once analyte has been introduced into each of the channels, the loading and outlet blocks can be removed and the device turned over. Such a flow cell can be used for streamlining the process of reaction and interrogation of biochemical assays at the microfluidic level. Reagents can be introduced into each of the channels of the flow cell for chemical reactions therein, excess reagent being washed out through the channel outlets. Observation of optically-detectable moieties is then conducted. With such a flow cell optical labels associated with incorporation in a sequencing-by-synthesis reaction can be observed.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Mostly natural DNA sequencing by synthesis
ActiveUS8772473B2Rapid and inexpensiveNot significantly perturbedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEthylene HomopolymersDistortion
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
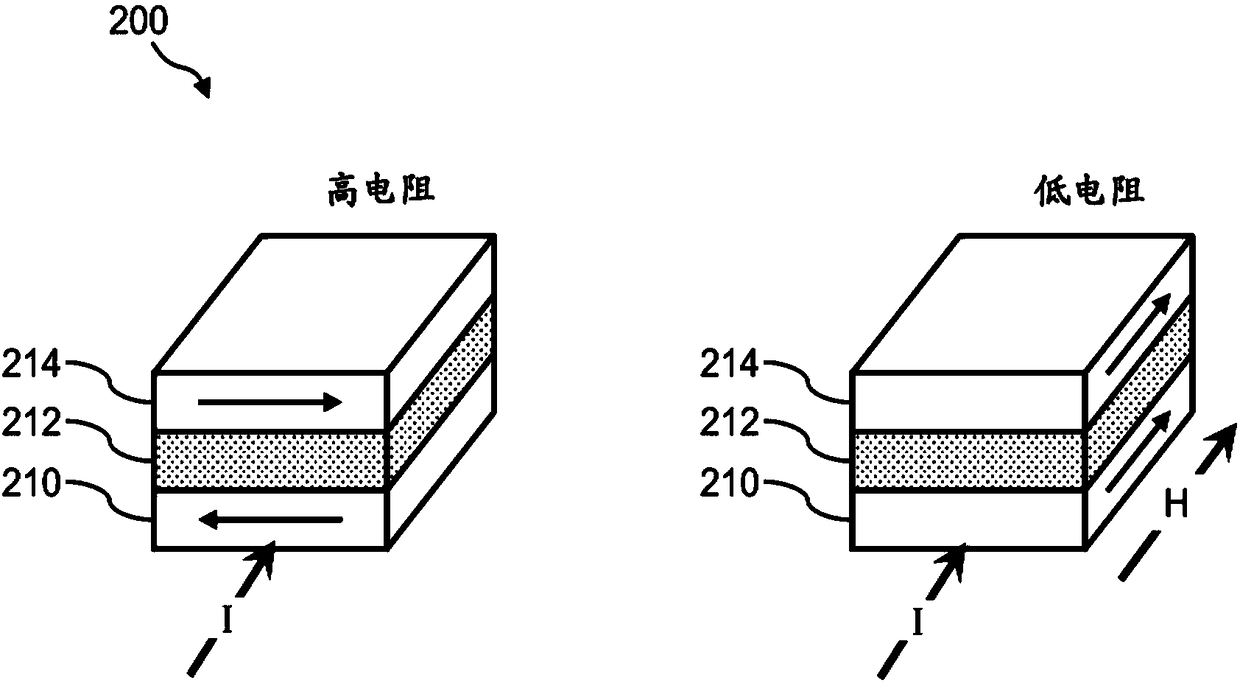
Systems and methods using magnetically-responsive sensors for determining a genetic characteristic
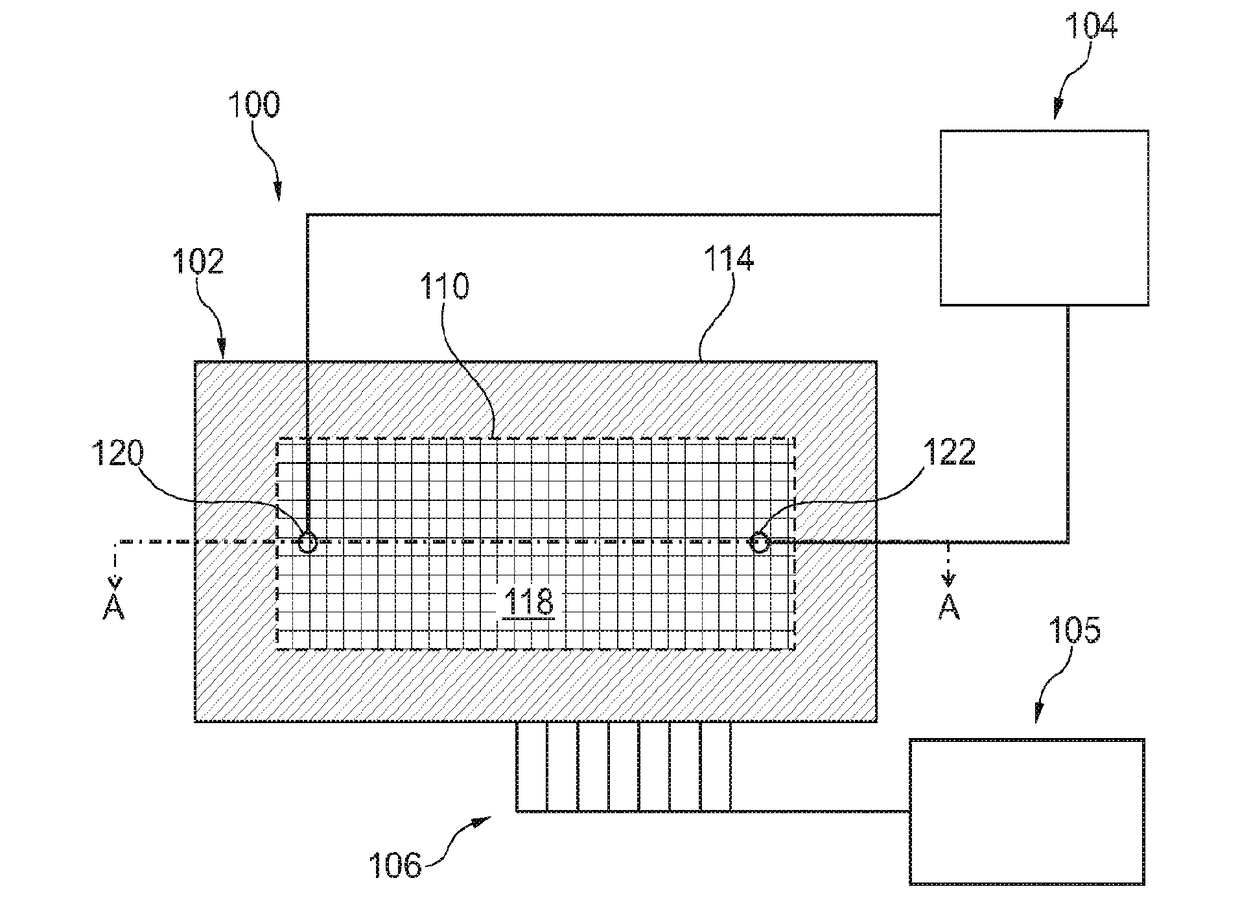
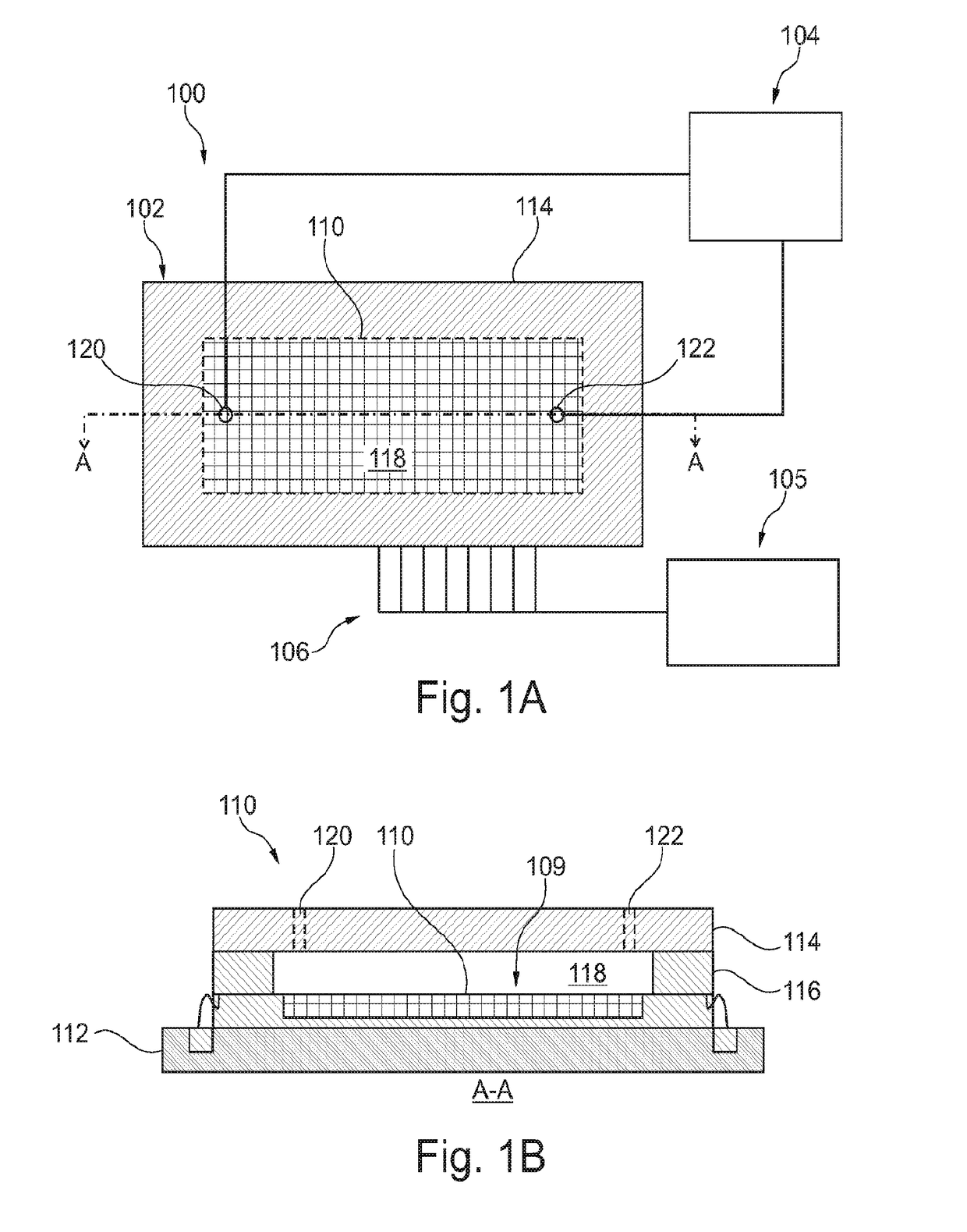
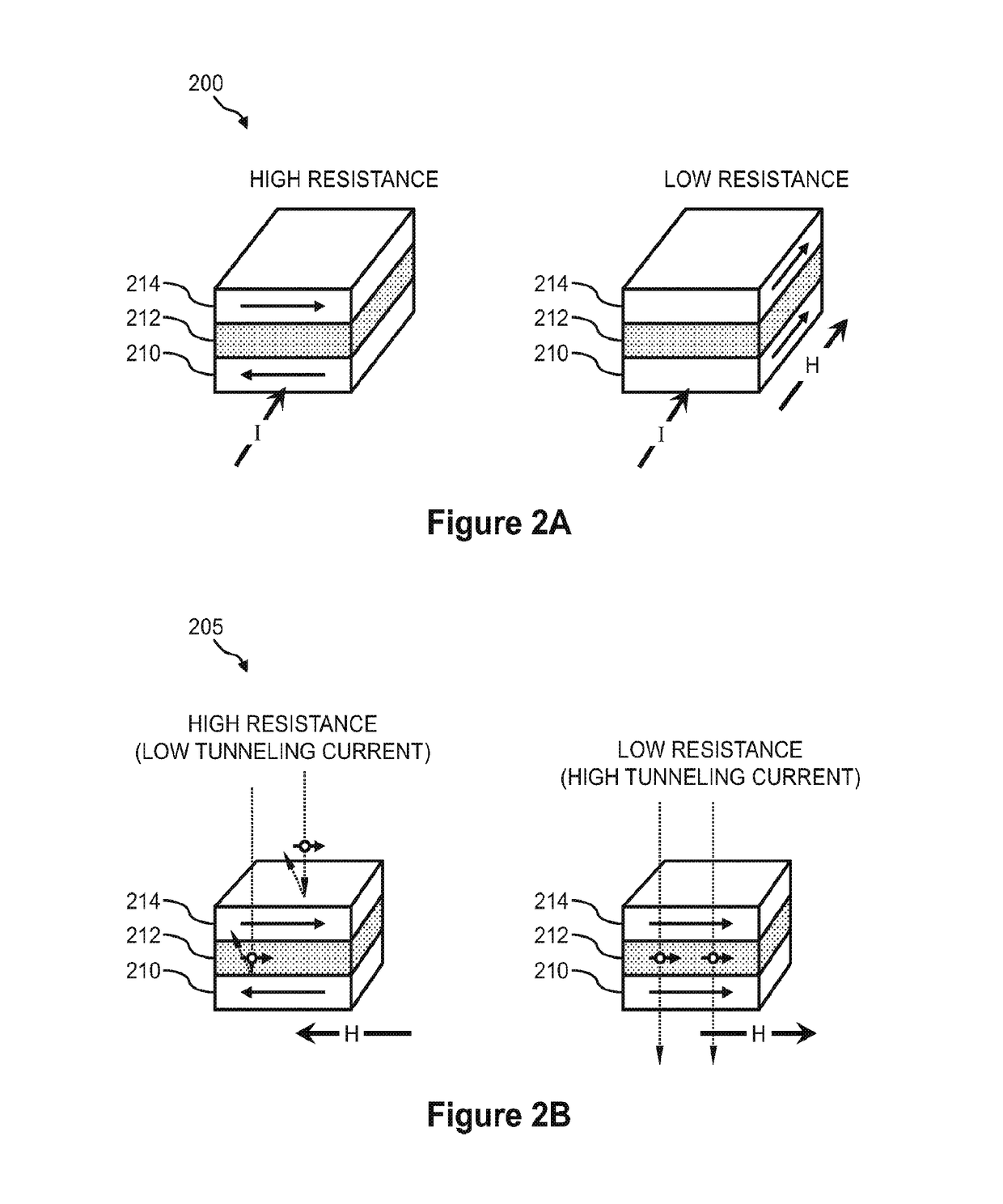
ActiveUS20180237850A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical resistance and conductanceBiology
Sequencing-by-synthesis (SBS) method is provided that includes providing a detection apparatus that includes an array of magnetically-responsive sensors. Each of the magnetically-responsive sensors is located proximate to a respective designated space to detect a magnetic property therefrom. The detection apparatus also includes a plurality of nucleic acid template strands located within corresponding designated spaces. The method also includes conducting a plurality of SBS events to grow a complementary strand by incorporating nucleotides along each template strand. At least some of the nucleotides are attached to corresponding magnetic particles having respective magnetic properties. Each of the plurality of SBS events includes detecting changes in electrical resistance at the magnetically-responsive sensors caused by the respective magnetic properties of the magnetic particles. The method also includes determining genetic characteristics of the complementary strands based on the detected changes in electrical resistance.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods and compositions for improving fidelity in a nucleic acid synthesis reaction
InactiveUS20060172313A1Improve fidelityInhibition formationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOrganic chemistryPolymerization
The invention provides methods and compositions for improving the fidelity of a sequencing-by-synthesis reaction by using a nucleotide derivative that forms a hydrogen bond with a complementary nucleotide on a template, but fails to form a phosphodiester bond with the 3′ hydroxyl group of a primer under conditions otherwise suitable for a polymerization reaction; thereby blocking incorporation of a mismatched nucleotide.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Multi-Channel Flow Cells
InactiveUS20090129980A1Avoid pollutionReduce loadMaterial analysis by optical meansLaboratory glasswaresFlow cellAnalyte
A multi-channel flow cell can allow for reduced cross-contamination in sample loading and the ability to observe activity within the flow cell once the channels are loaded. A multi-channel flow cell includes a plurality of independently-addressable channels sandwiched between a two substrates. Each of the channels can be coated with a layer that facilitates support-binding of an analyte. Each of the channels terminates on one end in an inlet and on the other end in an outlet. A loading block having inlet ports that match the inlets of the channels can be mated to the inlets of the channels, and an outlet block can be mated to the outlets of the channels. Analytes can be introduced into the channels via the inlet ports of the loading block and are pulled through the channels by capillary action or by vacuum. Once analyte has been introduced into each of the channels, the loading and outlet blocks can be removed and the device turned over Such a flow cell can be used for streamlining the process of reaction and interrogation of biochemical assays at the microfluidic level. Reagents can be introduced into each of the channels of the flow cell for chemical reactions therein, excess reagent being washed out through the channel outlets. Observation of optically-detectable moieties is then conducted. With such a flow cell optical labels associated with incorporation in a sequencing-by-synthesis reaction can be observed.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
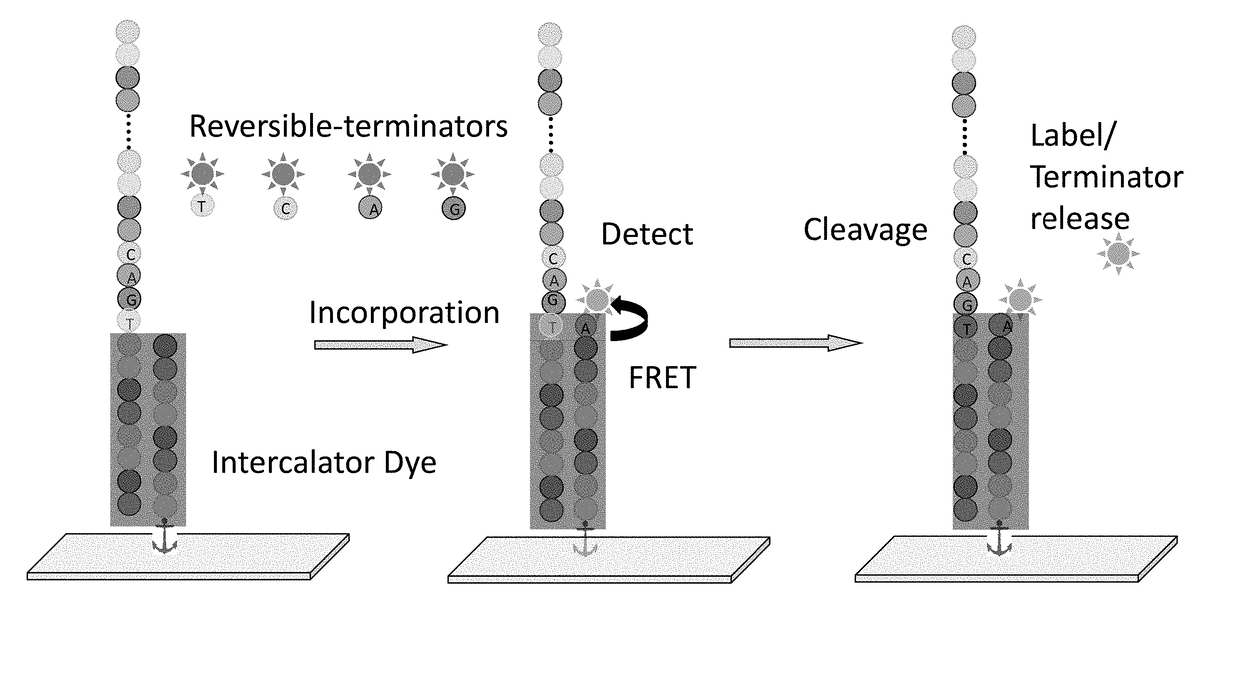
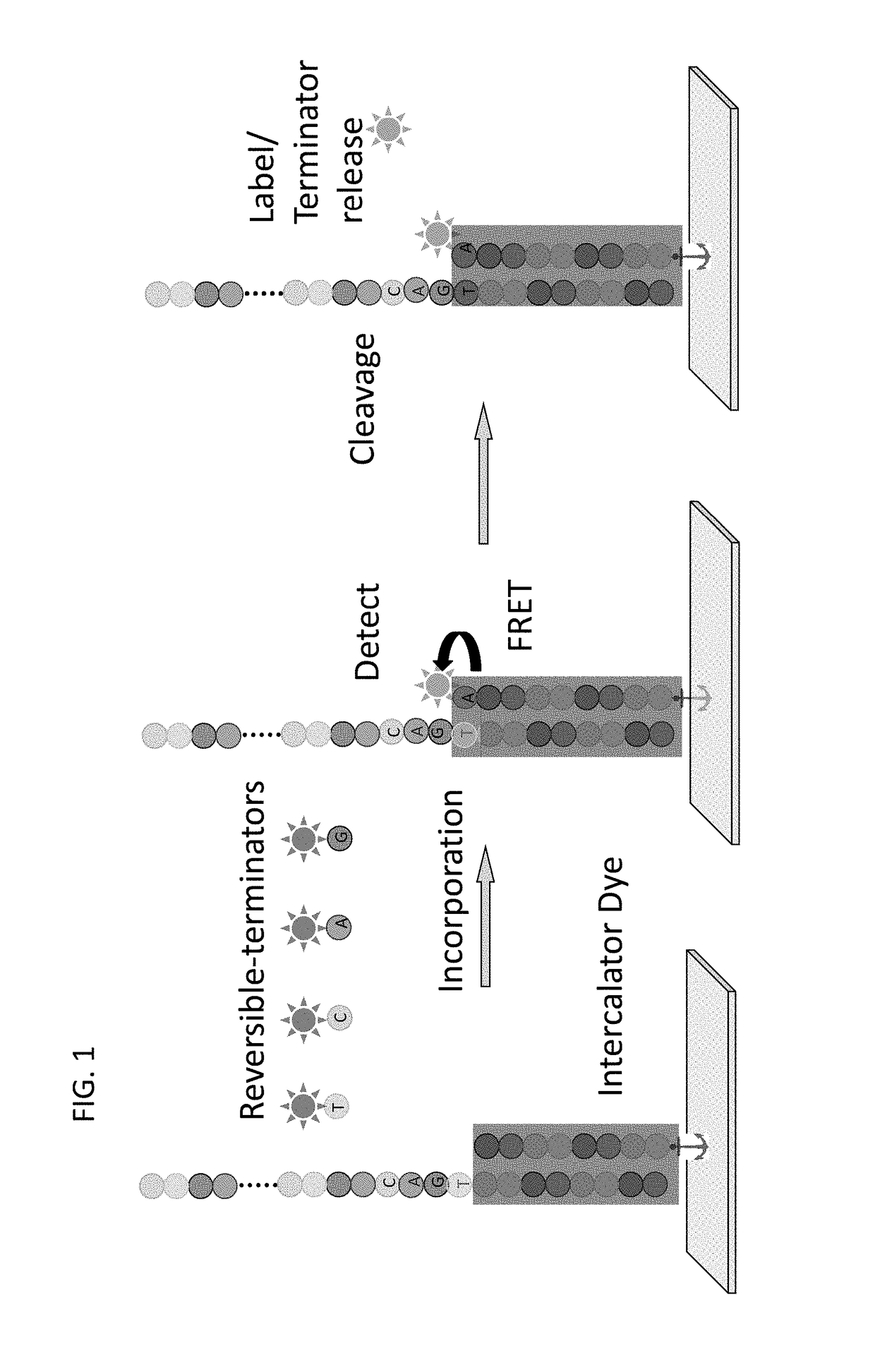
Super-Resolution Sequencing
ActiveUS20180327829A1Overcomes shortcomingMass numberMicrobiological testing/measurementDirect sequencingPolynucleotide
A method for template-directed sequencing-by-synthesis of an array of target polynucleotide can include:(a) providing an array of target polynucleotides in a fluidic vessel;(b) contacting the array of polynucleotides with a solution comprising (i) polymerization complex and (ii) reversibly terminating and differently labeled A,C,G, and T / U nucleotides;(c) incorporating one of the differently labeled nucleotides, using the polymerization complex, into a chain complementary to at least one of the array of polynucleotides;(d) binding imaging tags to the differently labeled nucleotides of step (c);(e) imaging and storing the identity and position of the imaging tags of step (d);(f) reversing termination (b)-(e);(g) repeating steps (b)-(e) and assembling a sequence for each of the array of target polynucleotides from the stored identity and position of the imaging tags, optionally as a homogeneous or one pot reaction. Additional methods of sequencing target polynucleotides are described herein.
Owner:MIR KALIM U
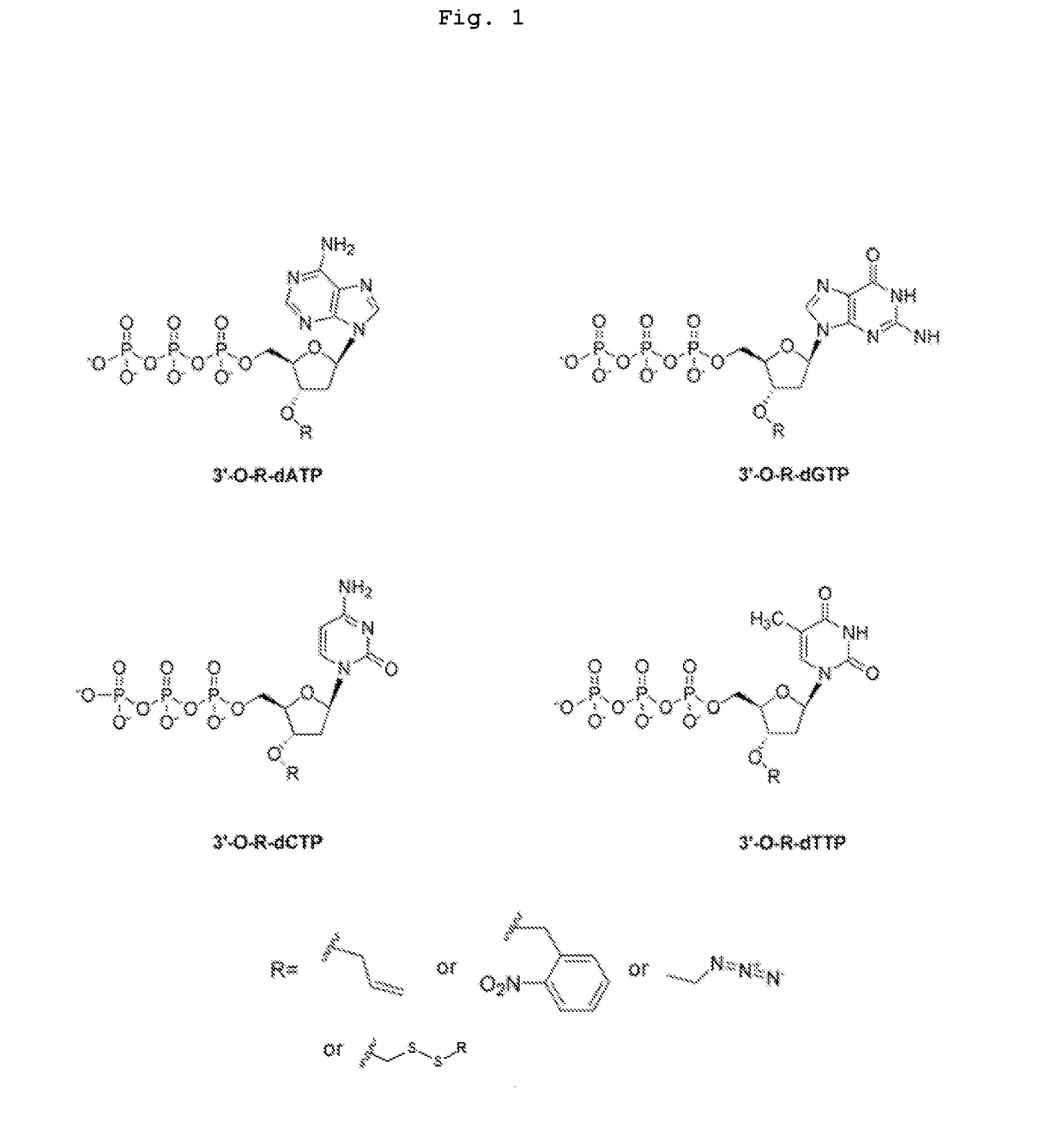
3'-o-fluorescently modified nucleotides and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110076679A1Improve efficiencyHigh yieldAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSugar derivativesFluorescenceA-DNA
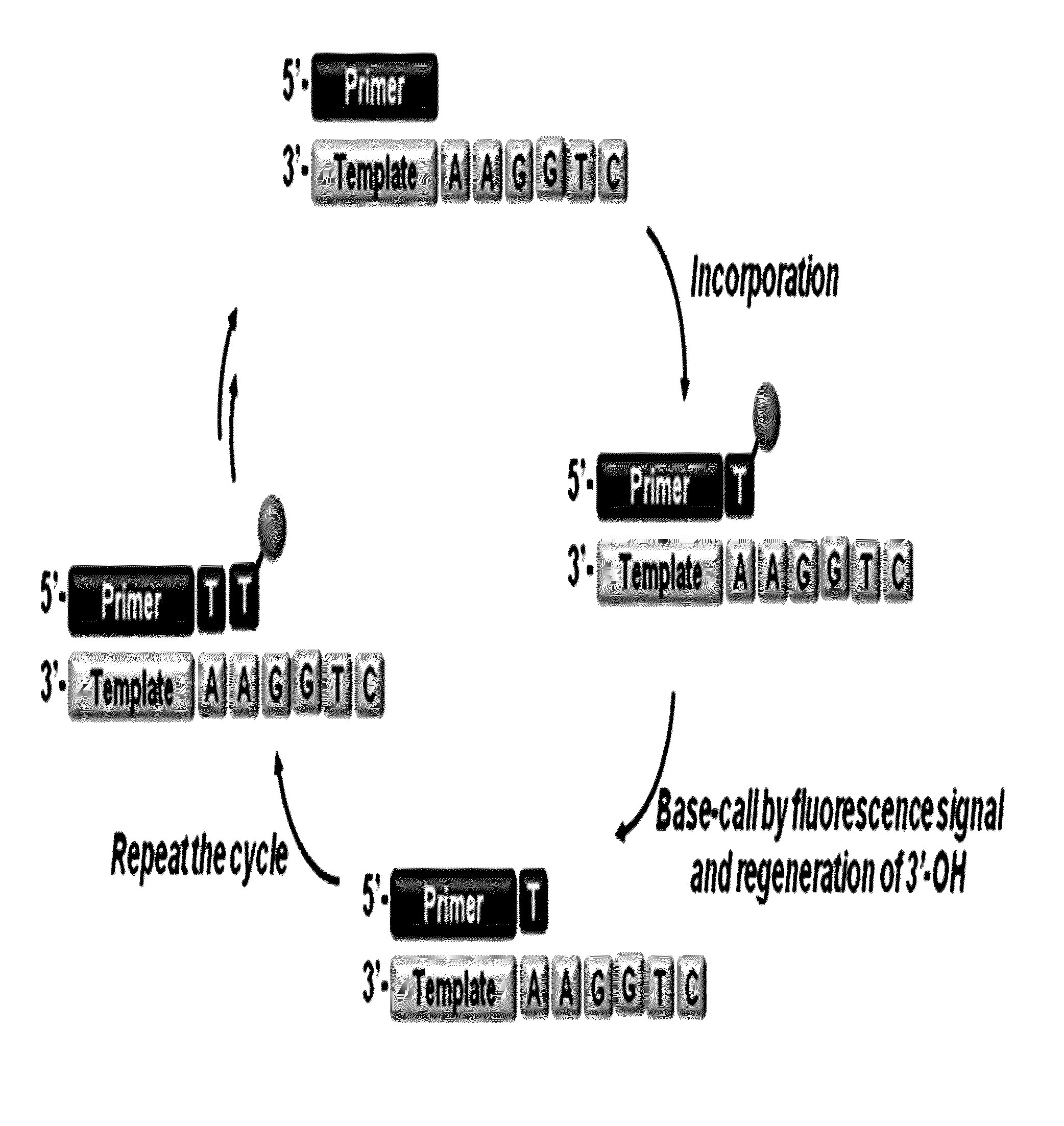
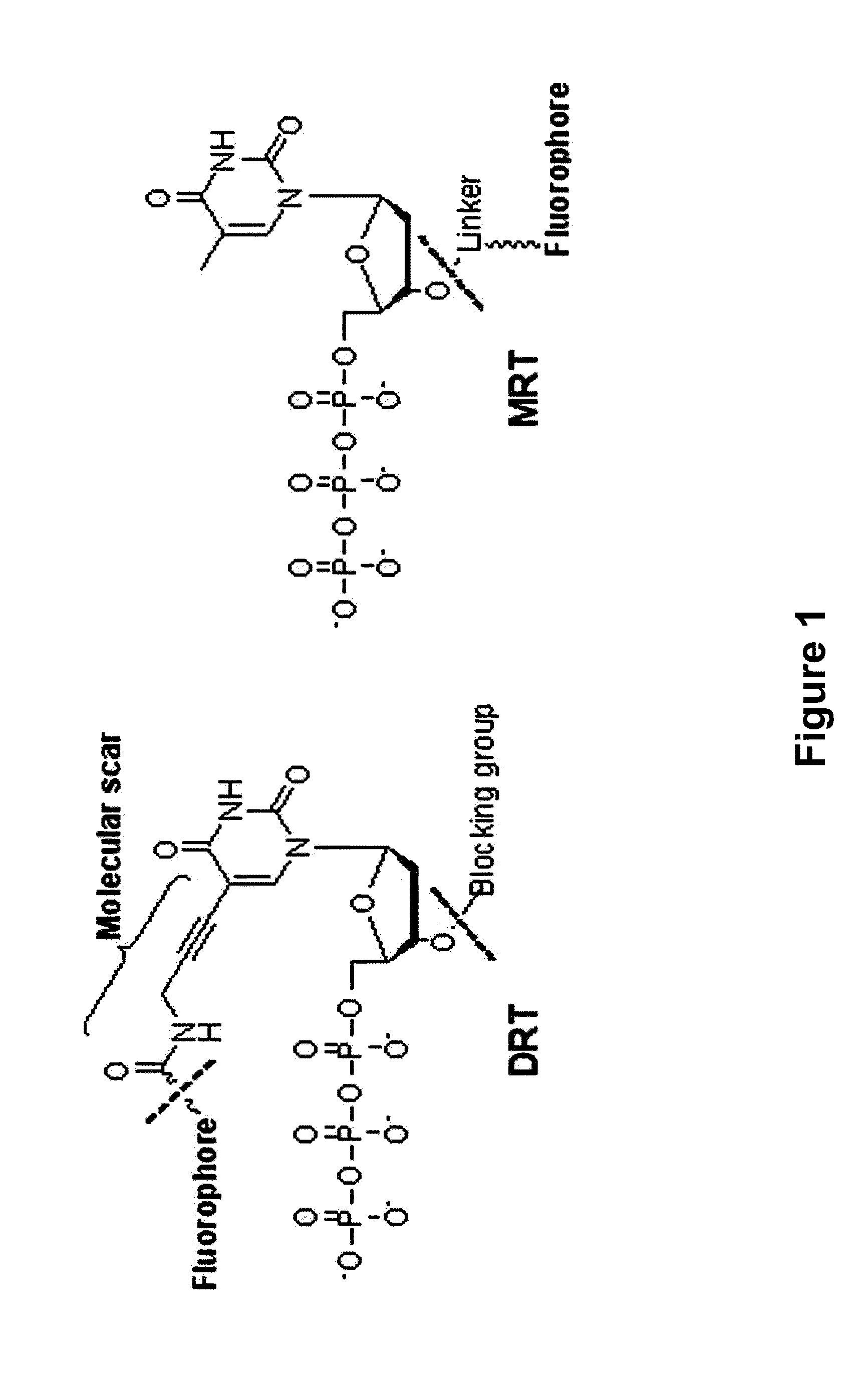
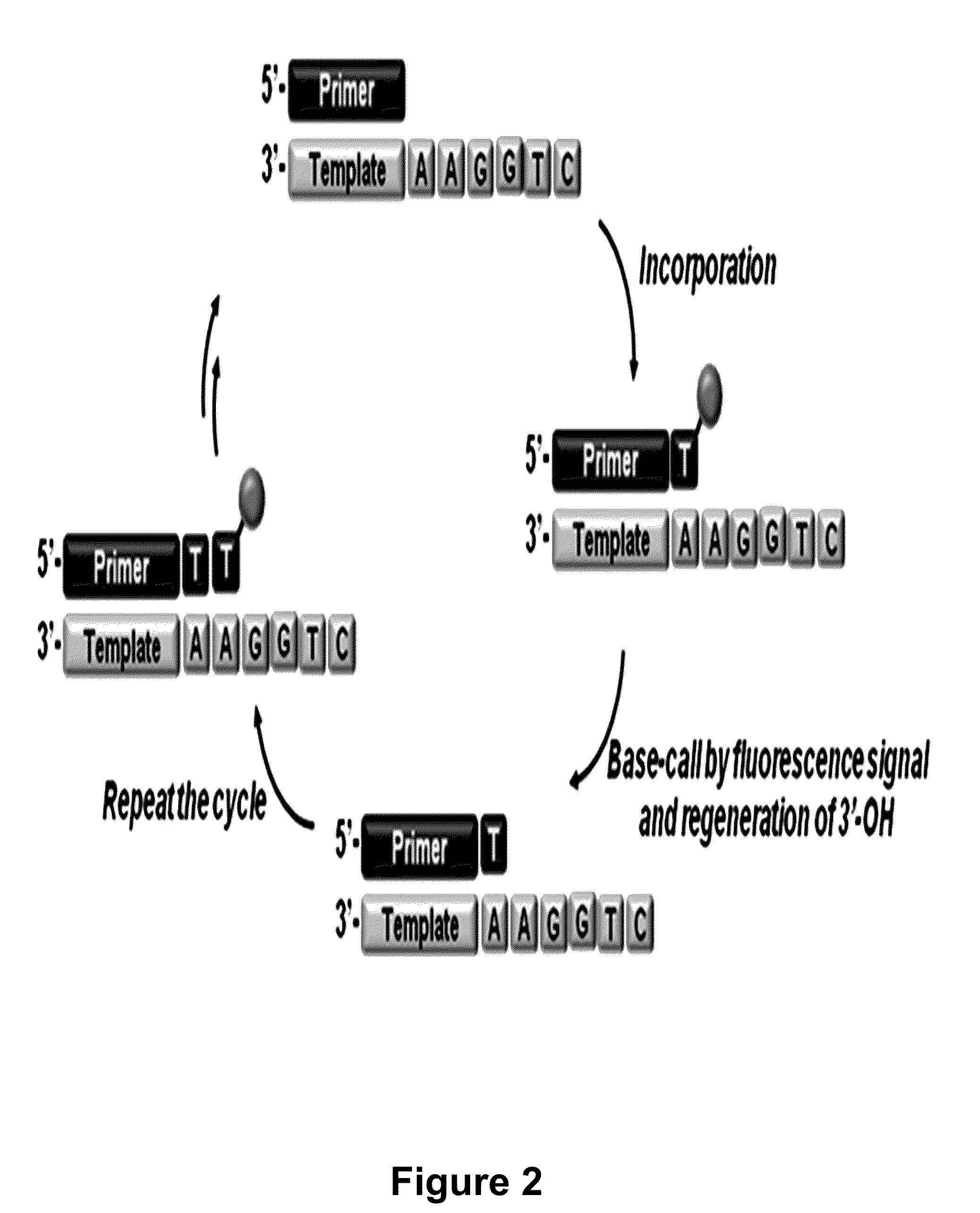
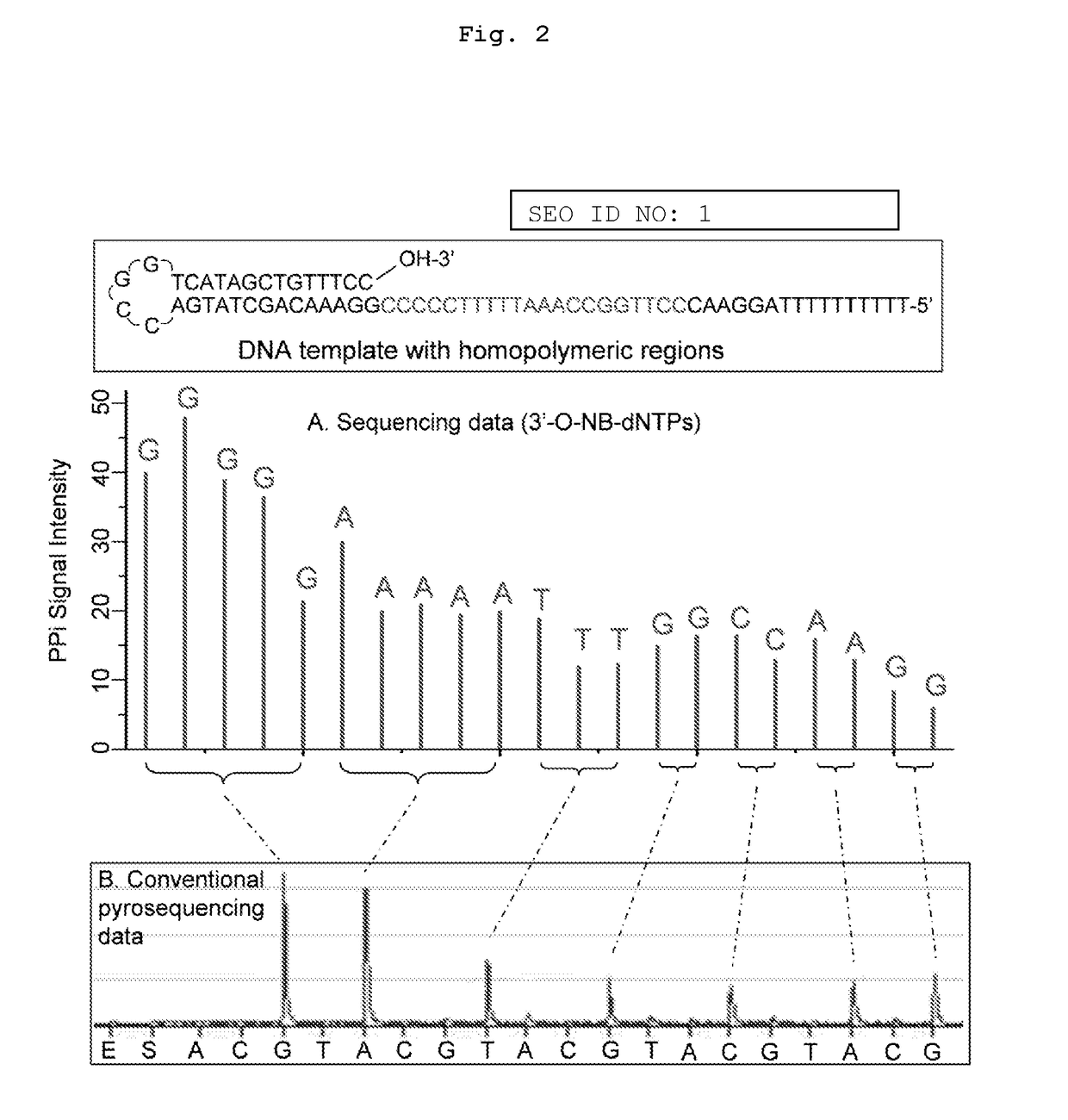
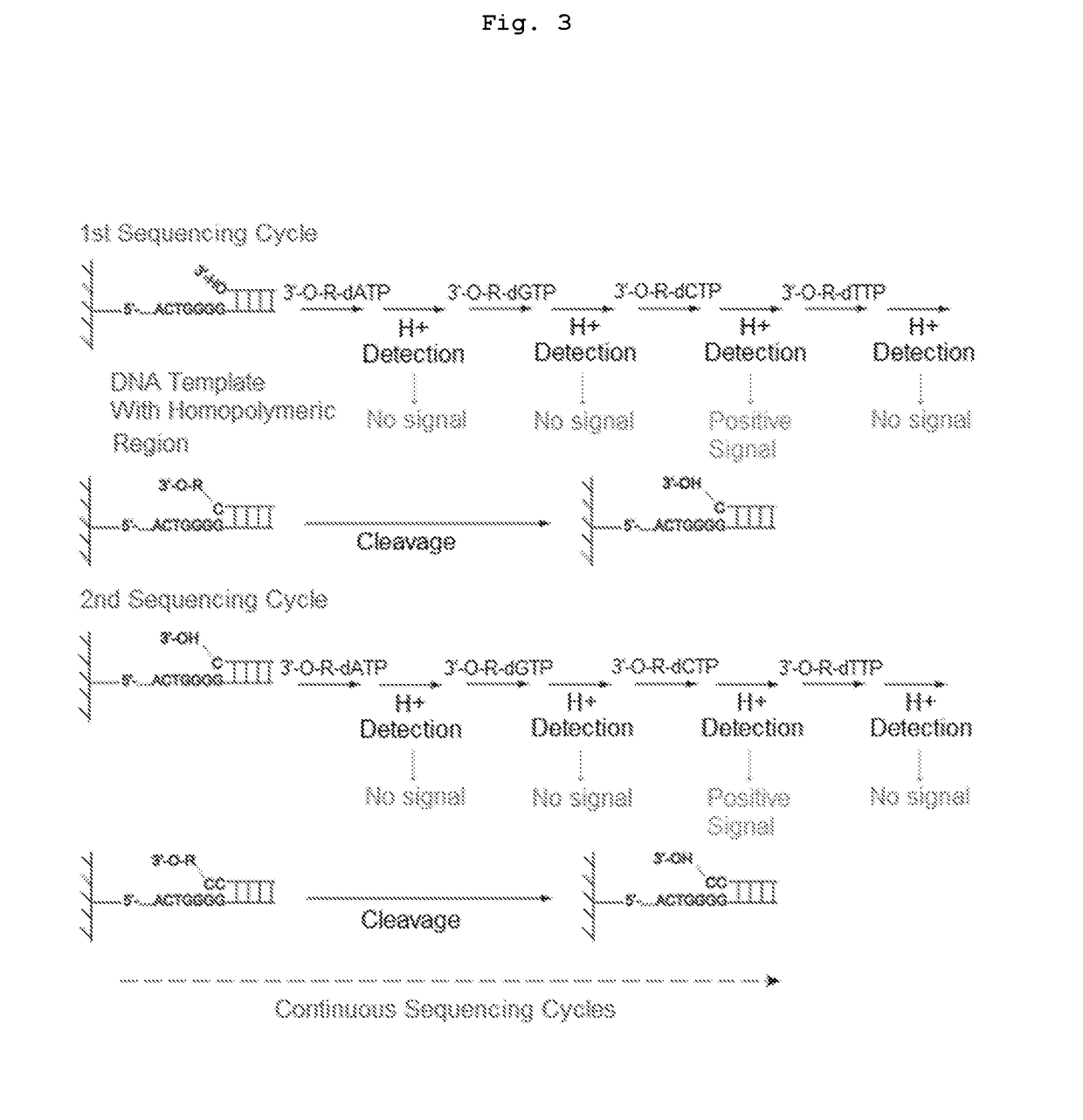
The present invention relates to a DNA sequencing method using a nucleoside triphosphate with a fluorescent blocking group on its 3′-OH end as a reversible terminator. Further, the present invention relates to sequencing-by-synthesis method using the mono-modified reversible terminator (MRT), the novel nucleotide monomer having a reversible fluorescent blocking group removable chemically or enzymatically at its 3′-OH end. The sequencing method of the present invention facilitates sequencing of bases inserted by terminating extension of a nucleotide chain by the nucleotide monomer and then detecting fluorescence signal from 3′-OH end. At this time, after analyzing the fluorescence signal, the blocking group conjugated to the 3′-OH end can be effectively removed, indicating that a free 3′-OH functional group can be successfully restored, so that the next monomer insertion is possible, making continuous sequencing possible.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Systems and methods using magnetically-responsive sensors for determining a genetic characteristic
ActiveCN108138229AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSensor arrayElectrical resistance and conductance
Sequencing-by-synthesis (SBS) method is provided that includes providing a detection apparatus that includes an array of magnetically-responsive sensors. Each of the magnetically-responsive sensors islocated proximate to a respective designated space to detect a magnetic property therefrom. The detection apparatus also includes a plurality of nucleic acid template strands located within corresponding designated spaces. The method also includes conducting a plurality of SBS events to grow a complementary strand by incorporating nucleotides along each template strand. At least some of the nucleotides are attached to corresponding magnetic particles having respective magnetic properties. Each of the plurality of SBS events includes detecting changes in electrical resistance at the magnetically-responsive sensors caused by the respective magnetic properties of the magnetic particles. The method also includes determining genetic characteristics of the complementary strands based on the detected changes in electrical resistance.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
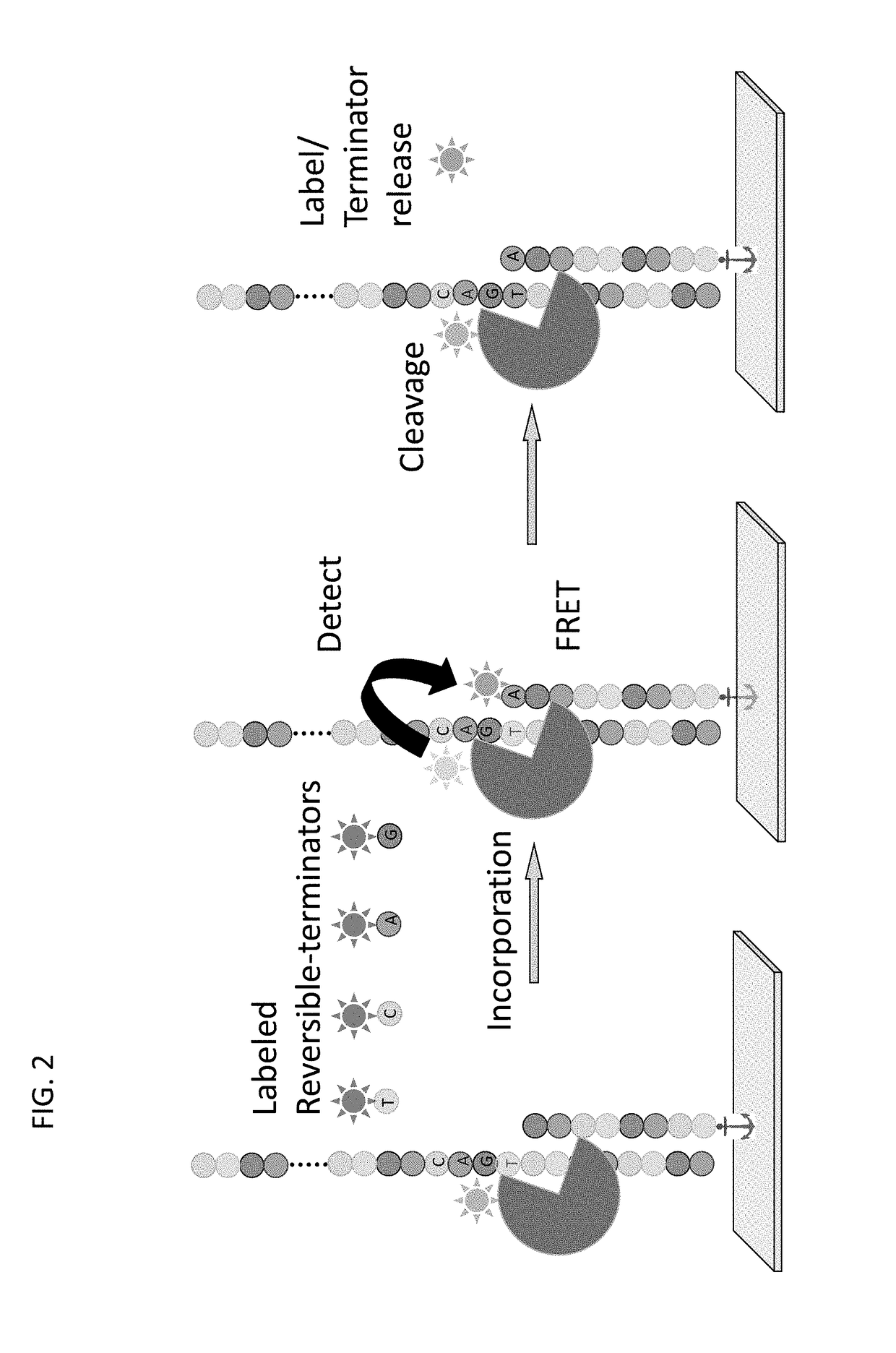
Stepwise sequencing by non-labeled reversible terminators or natural nucleotides
ActiveUS20180223358A1Low efficiencyStrong signalMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsPolymerase LBiology
The invention provides compositions and methods for sequencing nucleic acids and other applications. In sequencing by synthesis, unlabeled reversible terminators are incorporated by a polymerase in each cycle, then labeled after incorporation by binding to the reversible terminator a directly or indirectly labeled antibody or other affinity reagent.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Methods And Devices For Sequencing Nucleic Acids In Smaller Batches
ActiveUS20130316914A1Good flexibilityCost-effective smaller runsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFlow cellNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides methods and compositions, including, without limitation, algorithms, computer readable media, computer programs, apparatus, and systems for determining the identity of nucleic acids in nucleotide sequences using, for example, data obtained from sequencing by synthesis methods. A plurality of smaller flow cells is employed, each with a relatively small area to be imaged, in order to provide greater flexibility and efficiency.
Owner:ISOPLEXIS
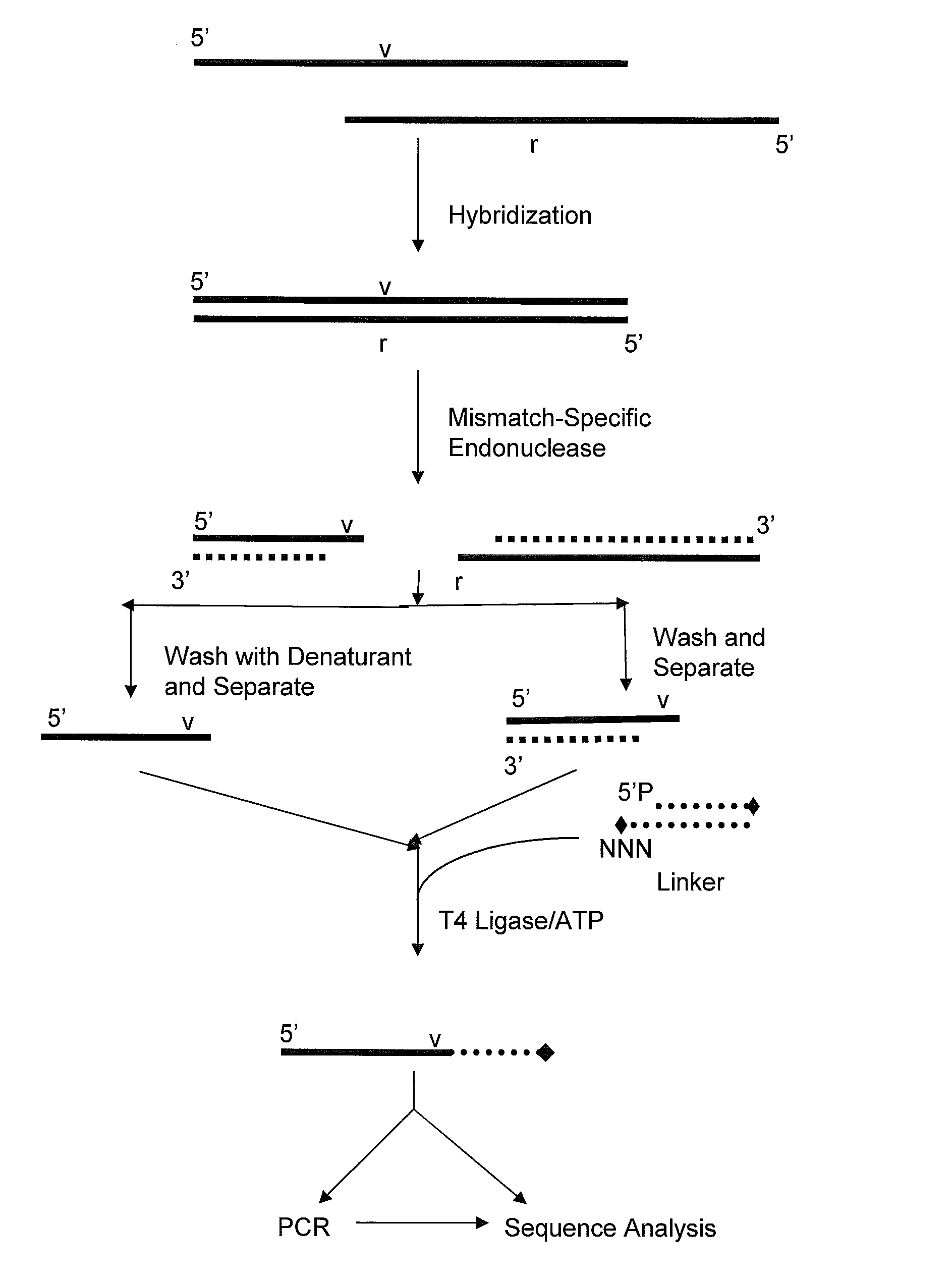
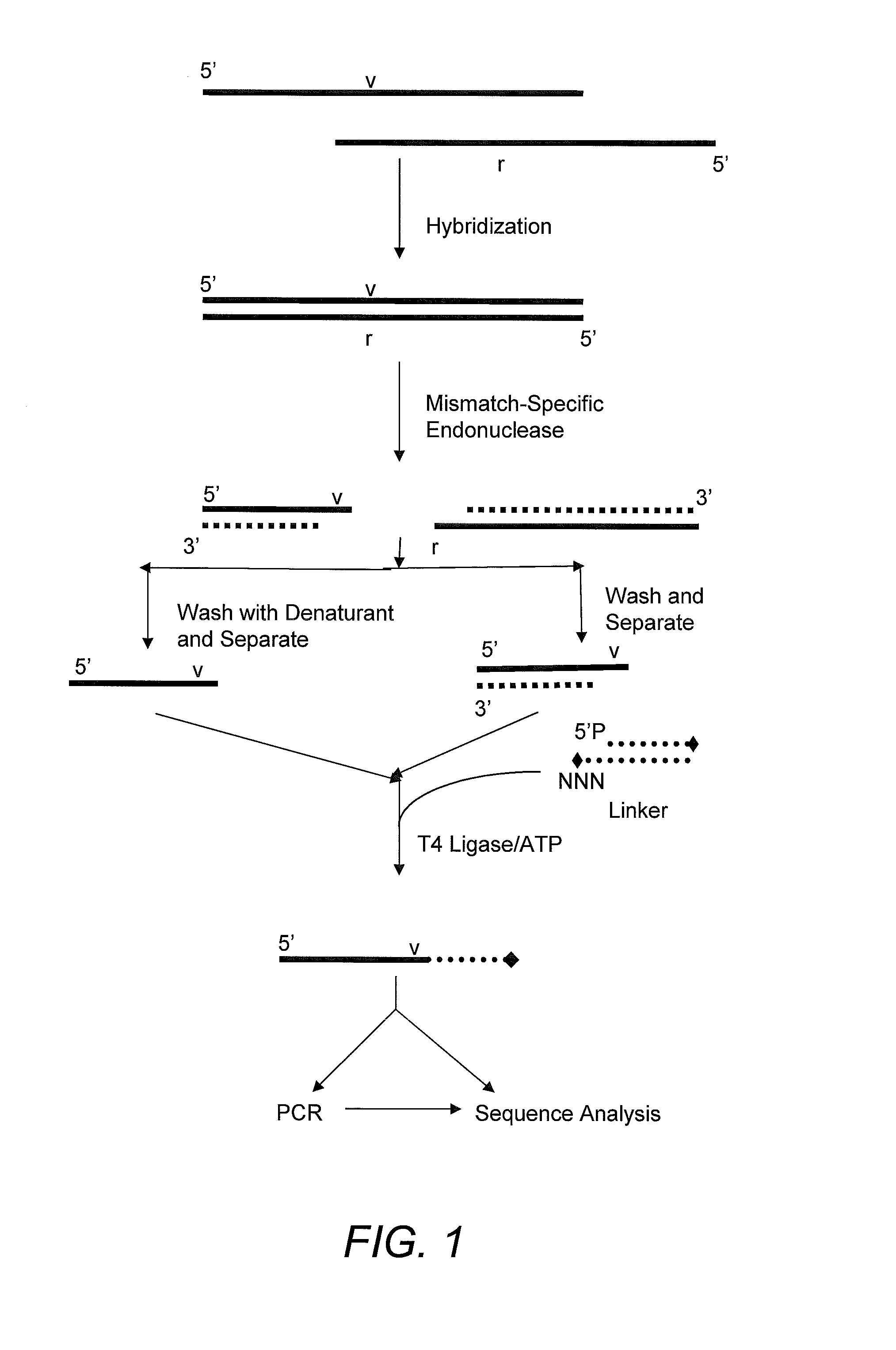
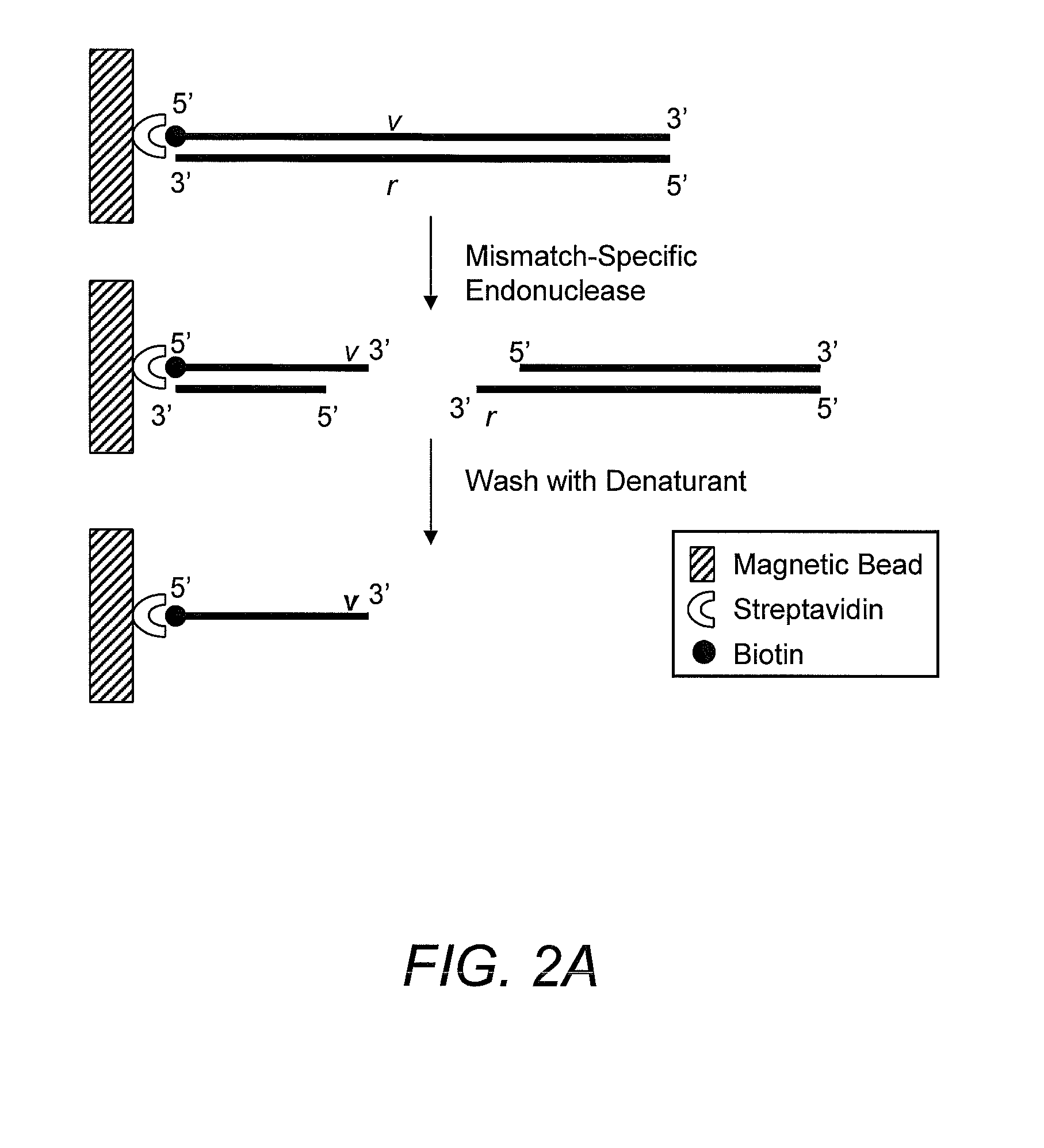
Method for identifying the sequence of one or more variant nucleotides in a nucleic acid molecule
InactiveUS20090068652A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDouble strandDNA Endonuclease
The invention relates to methods for identifying the sequence of one or more variant nucleotides in a nucleic acid molecule. The method involves cleaving a double-stranded nucleic acid molecule containing a mismatch with a mismatch-specific endonuclease which cleaves on the 3′ side of the mismatch, and preserving the integrity of the variant nucleotide by ligating a double-stranded linker with a 3′-overhang to said variant nucleotide. Because the variant nucleotide is immediately adjacent to the linker, PCR and / or sequence-by-synthesis analysis can be readily carried out.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
Ion sensor DNA and RNA sequencing by synthesis using nucleotide reversible terminators
InactiveUS20180327828A1Increase ion concentrationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequencing by synthesisSingle strand dna
This disclosure is related to a method for determining the identity of a nucleotide residue of a single-stranded DNA or RNA, or sequencing DNA or RNA, in a solution using an ion-sensing field effect transistor and reversible nucleotide terminators.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
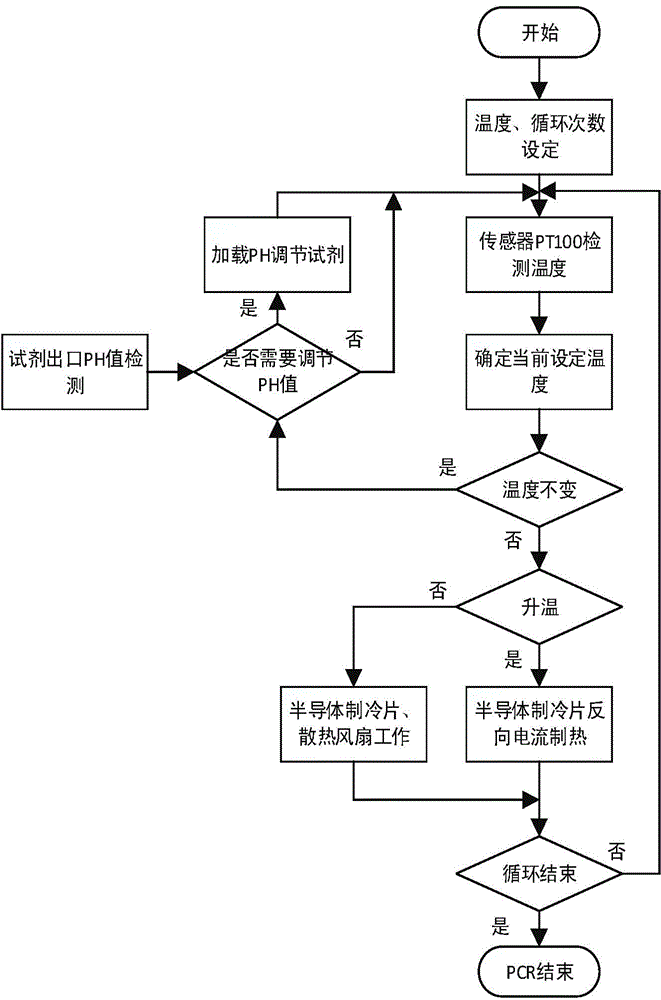
High-throughput gene sequencing dynamic dispatching control method and system device
InactiveCN104893972AIncrease temperature control reaction rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlFluorescence
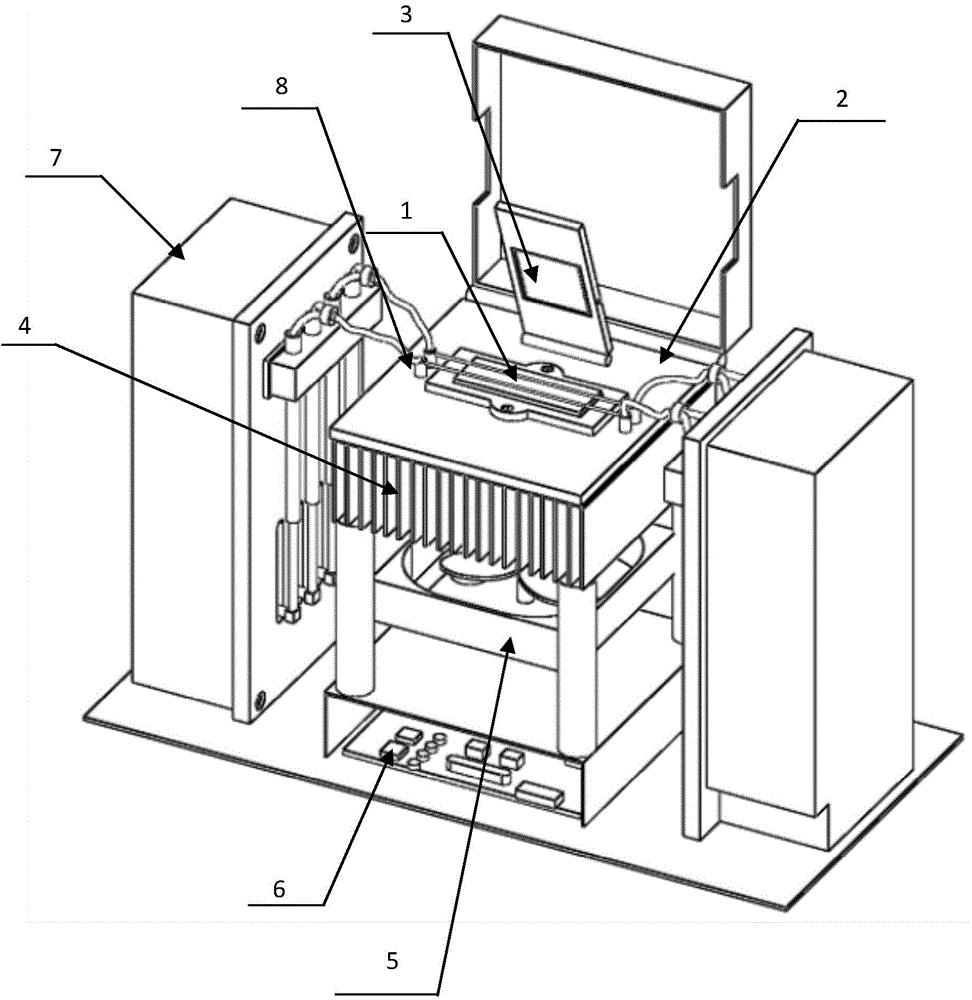
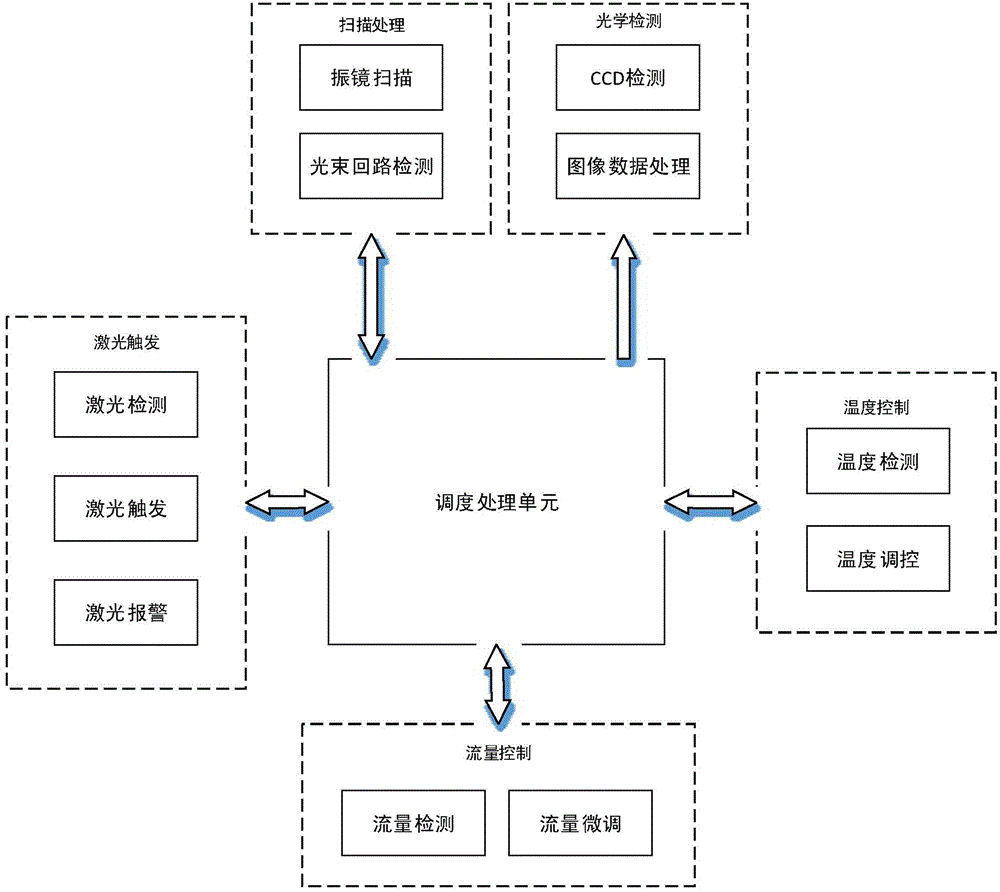
The invention relates to a high-throughput gene sequencing dynamic dispatching control method and system device. The system device comprises a temperature control system, a reagent control system, a laser trigger control system, a galvanometer scanning system and an optical acquisition system, wherein bridge-type PCR amplification is carried out for an interrupted to-be-tested fragment in a flow channel by virtue of the temperature and reagent control systems; the sequencing by synthesis (SBS) reaction is enabled to be successfully carried out by virtue of the temperature and reagent control systems; a fluorescent signal is captured and data is stored by virtue of laser triggering, galvanometer scanning and optical acquisition, so that an integrated control system of a high-throughput gene sequencing instrument is realized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com